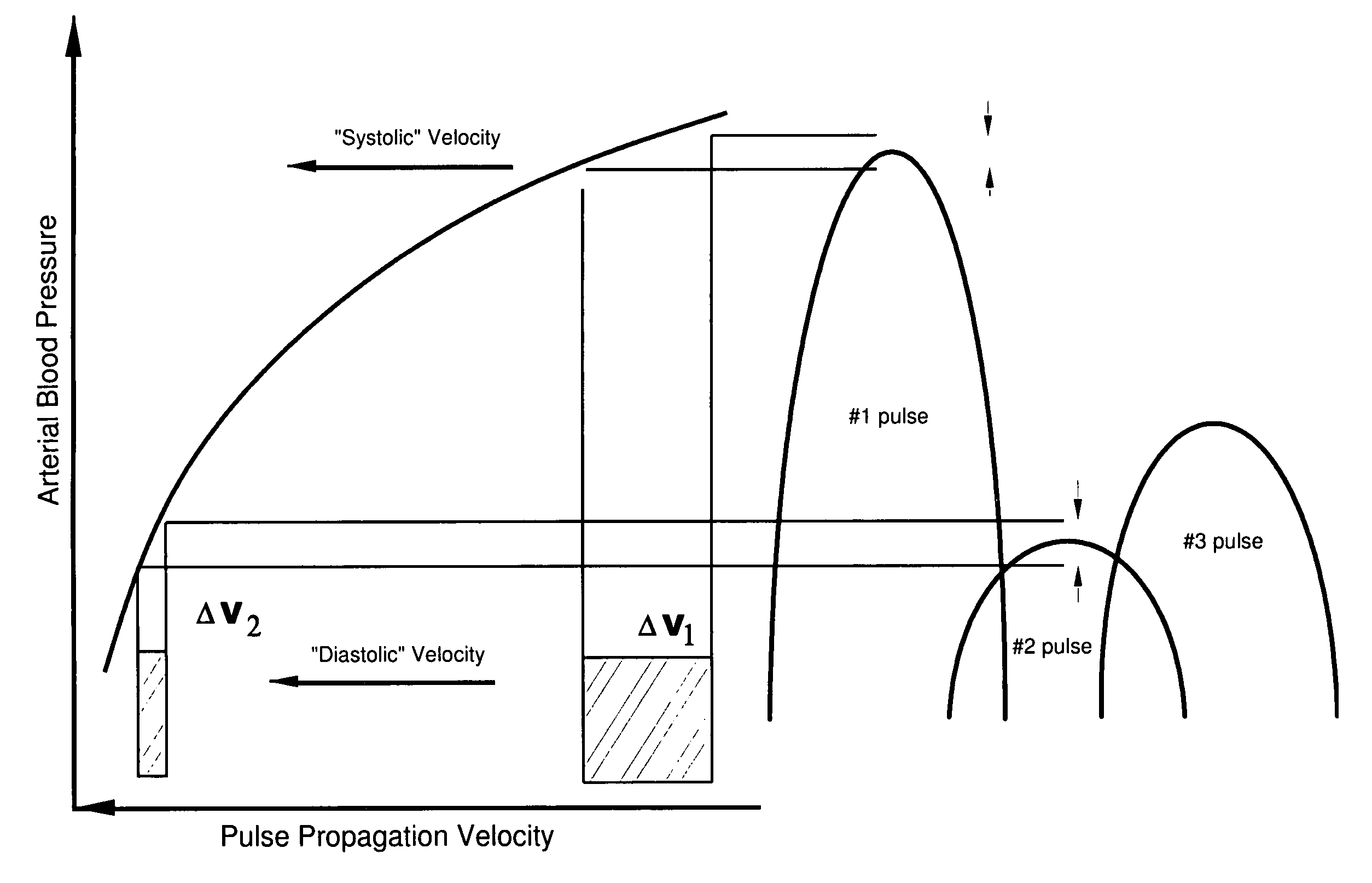
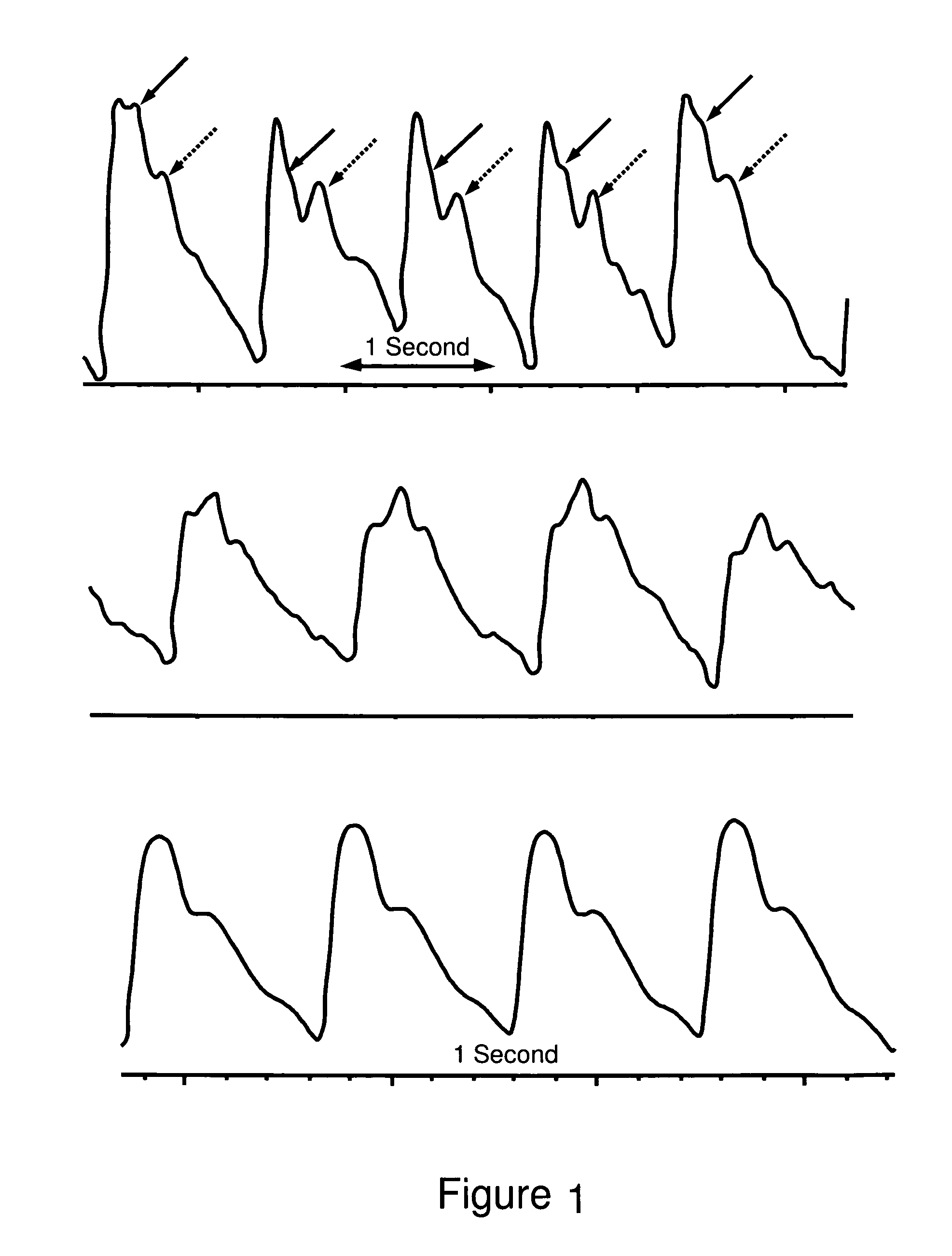
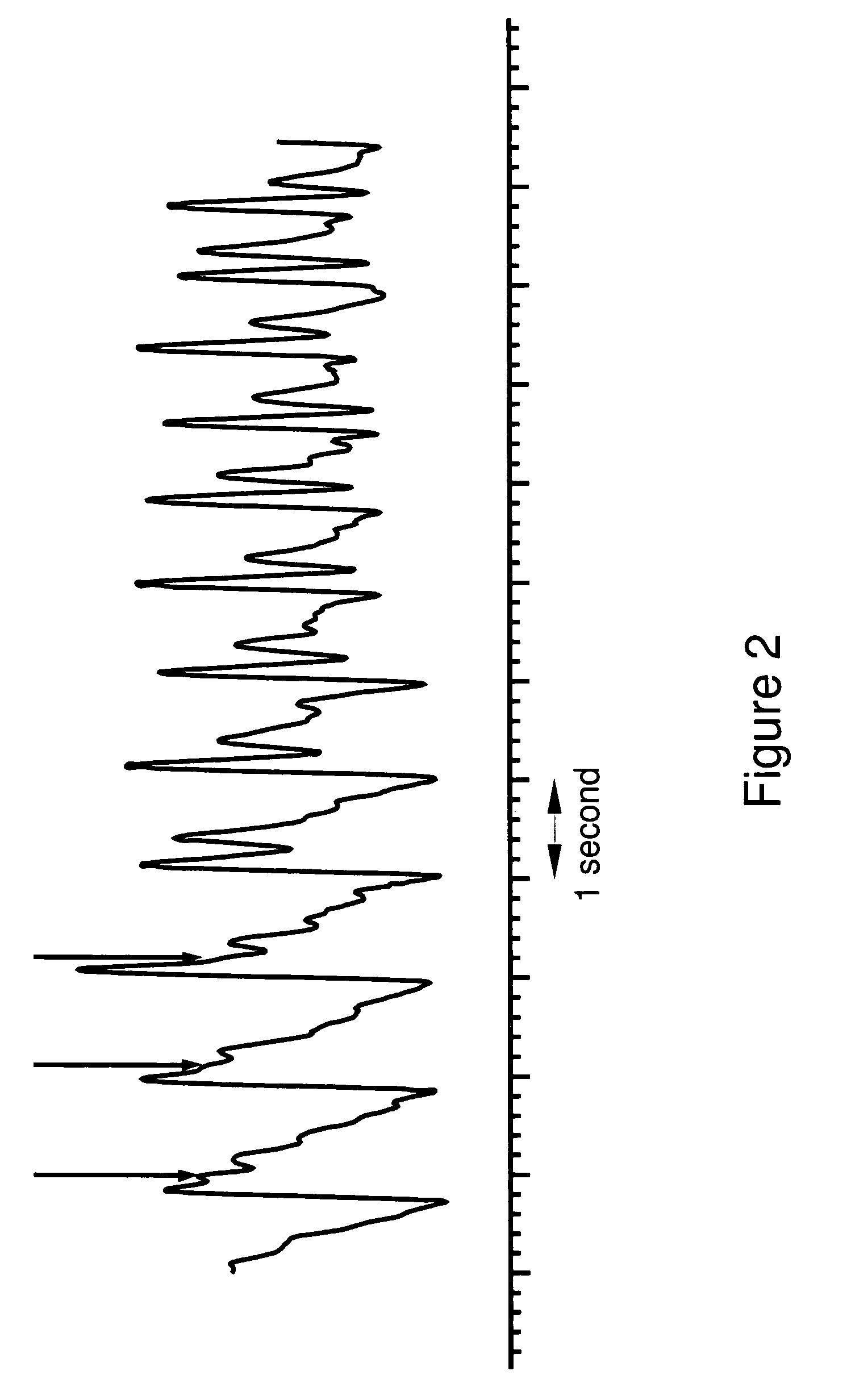
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
127 results about "Arterial pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arterial pulse. In medicine, a person's pulse is the throbbing of their arteries as an effect of the heart beat. It can be felt at the neck (carotid artery), at the wrist (radial artery), behind the knee (popliteal artery), on the inside of the elbow (brachial artery), near the ankle joint (posterior tibial artery), and a few other places.
Active-pulse blood analysis system
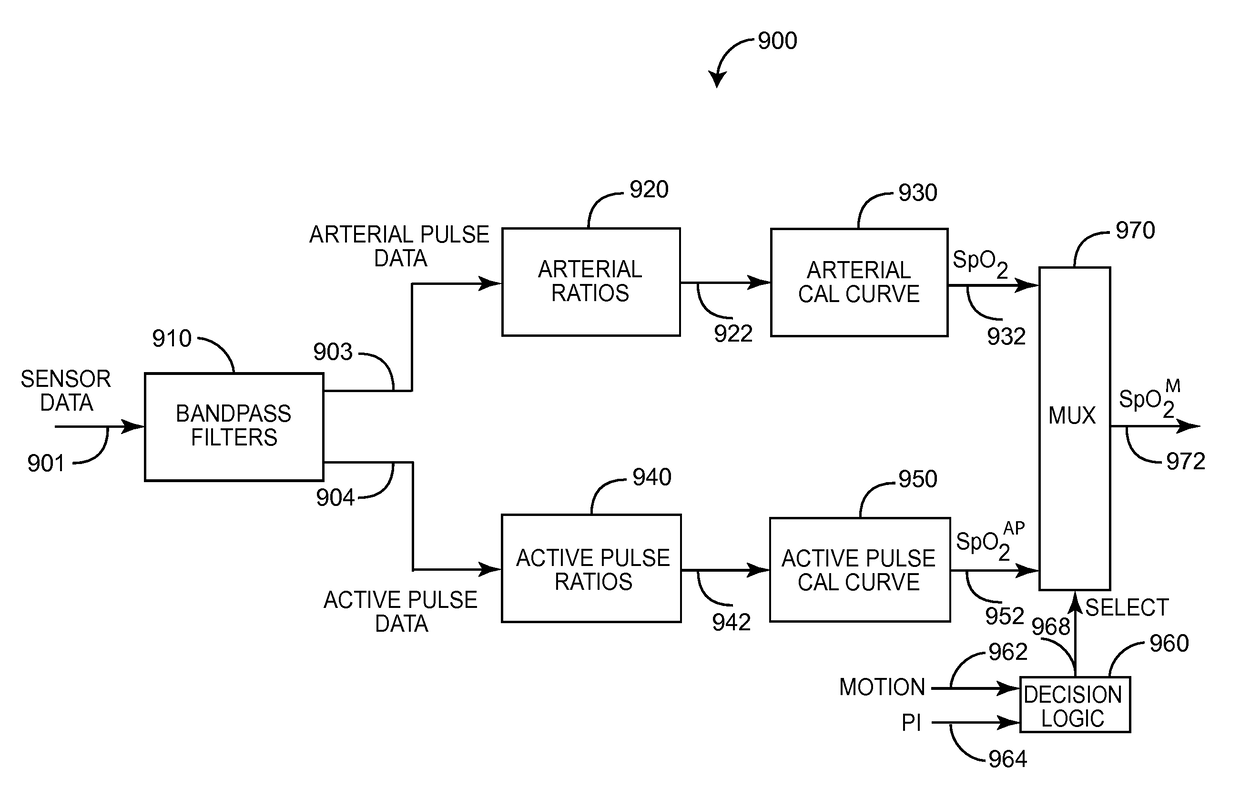
An active-pulse blood analysis system has an optical sensor that illuminates a tissue site with multiple wavelengths of optical radiation and outputs sensor signals responsive to the optical radiation after attenuation by pulsatile blood flow within the tissue site. A monitor communicates with the sensor signals and is responsive to arterial pulses within a first bandwidth and active pulses within a second bandwidth so as to generate arterial pulse ratios and active pulse ratios according to the wavelengths. An arterial calibration curve relates the arterial pulse ratios to a first arterial oxygen saturation value and an active pulse calibration curve relates the active pulse ratios to a second arterial oxygen saturation value. Decision logic outputs one of the first and second arterial oxygen saturation values based upon perfusion and signal quality.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Active-pulse blood analysis system
An active-pulse blood analysis system has an optical sensor that illuminates a tissue site with multiple wavelengths of optical radiation and outputs sensor signals responsive to the optical radiation after attenuation by pulsatile blood flow within the tissue site. A monitor communicates with the sensor signals and is responsive to arterial pulses within a first bandwidth and active pulses within a second bandwidth so as to generate arterial pulse ratios and active pulse ratios according to the wavelengths. An arterial calibration curve relates the arterial pulse ratios to a first arterial oxygen saturation value and an active pulse calibration curve relates the active pulse ratios to a second arterial oxygen saturation value. Decision logic outputs one of the first and second arterial oxygen saturation values based upon perfusion and signal quality.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Method and apparatus for measuring pulsus paradoxus
InactiveUS6869402B2Accurate measurementReliable measurementCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringTime domainPulsus paradoxus
A method and apparatus are disclosed of utilizing a source of arterial and / or arteriolar pulse waveform data from a patient for the purpose of measuring pulsus paradoxus. The arterial pulse waveform data source described is a pulse oximeter plethysmograph but can be any similar waveform data source, including intra-arterial transducer, blood pressure transducer, or plethysmograph. Through incorporation of the measurements of values, such as the area under the pulse waveform curve, that are time-domain functions of a change in height of the pulse waveform over at least a partial duration of the waveform, embodiments of the present invention represent a significant improvement upon previously described methods of measuring pulsus paradoxus and, further, produce improved accuracy in measurement of the multiple contributing variables generating pulsus paradoxus, in particular the contribution of diastolic events, to the extent that the physical signs so measured can be regarded as “Revised Pulsus Paradoxus.”
Owner:PRECISION PULSUS
Diagnostic apparatus for analyzing arterial pulse waves
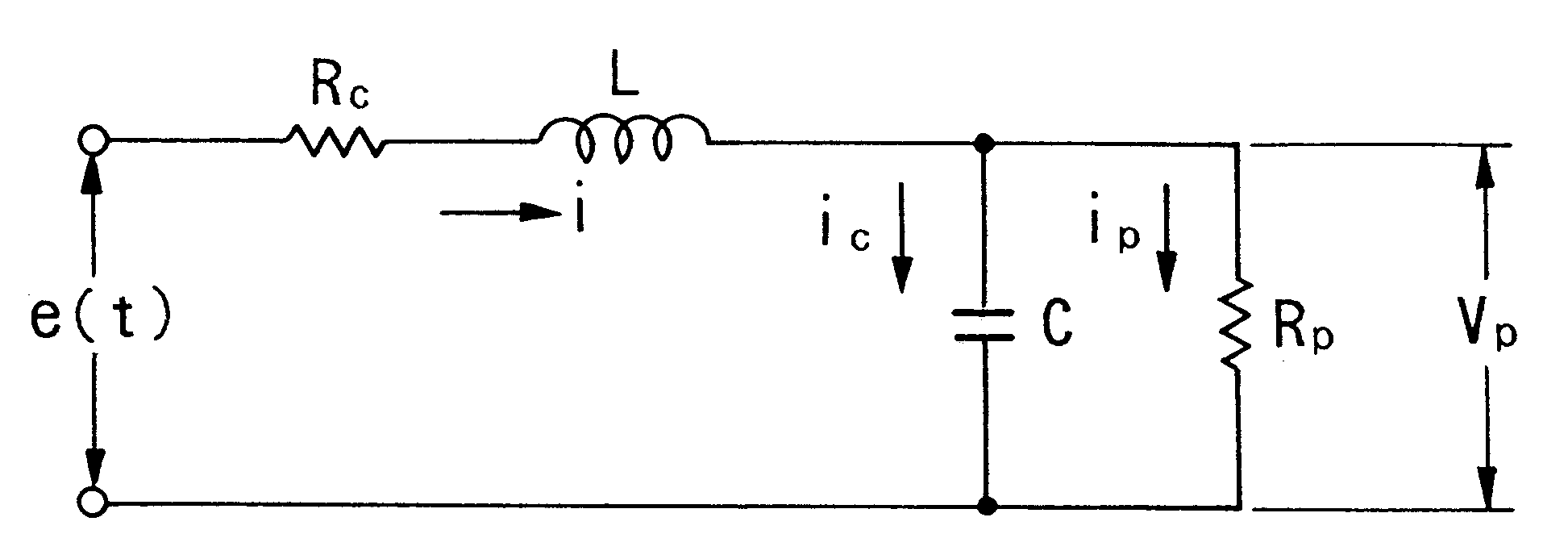
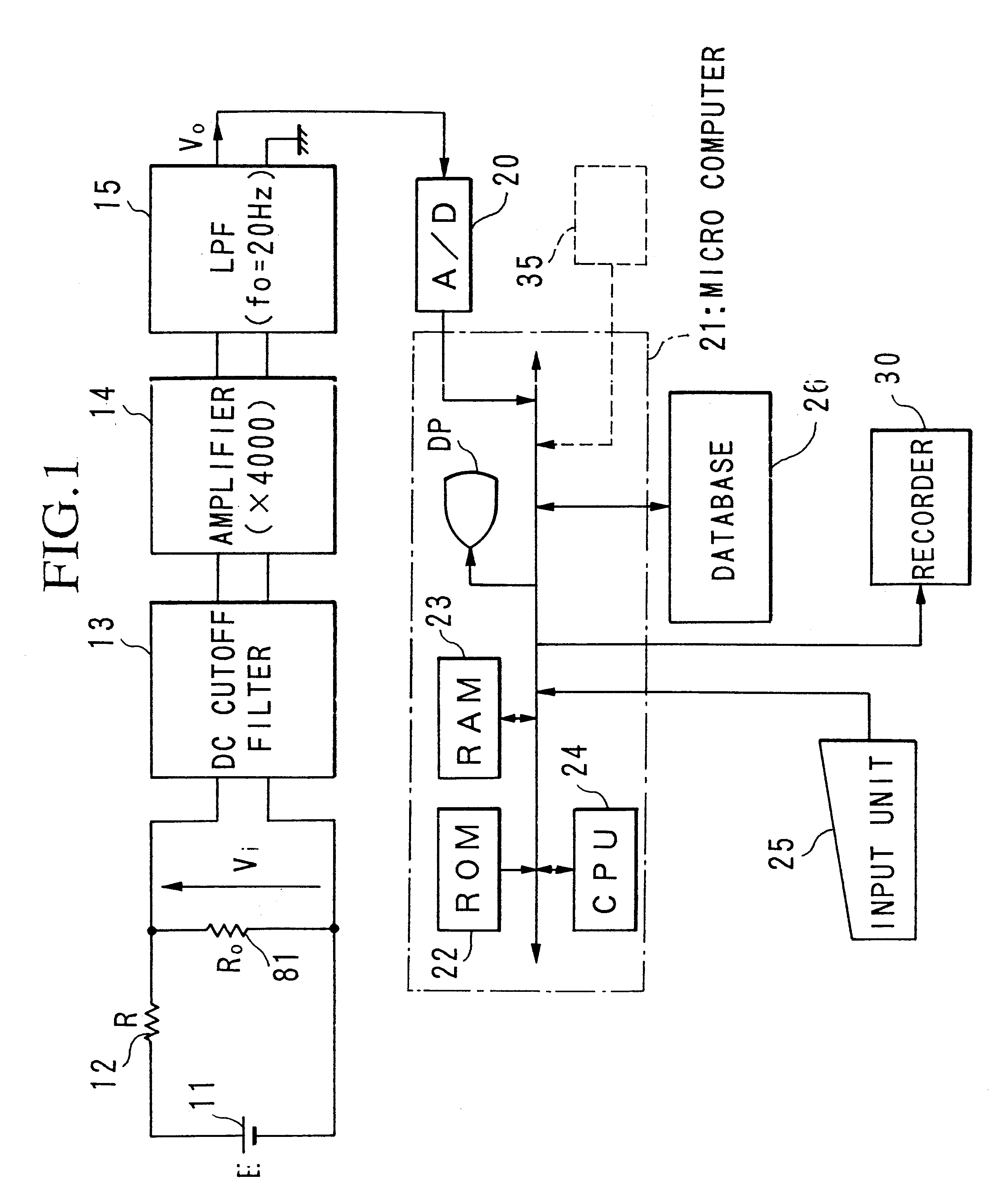
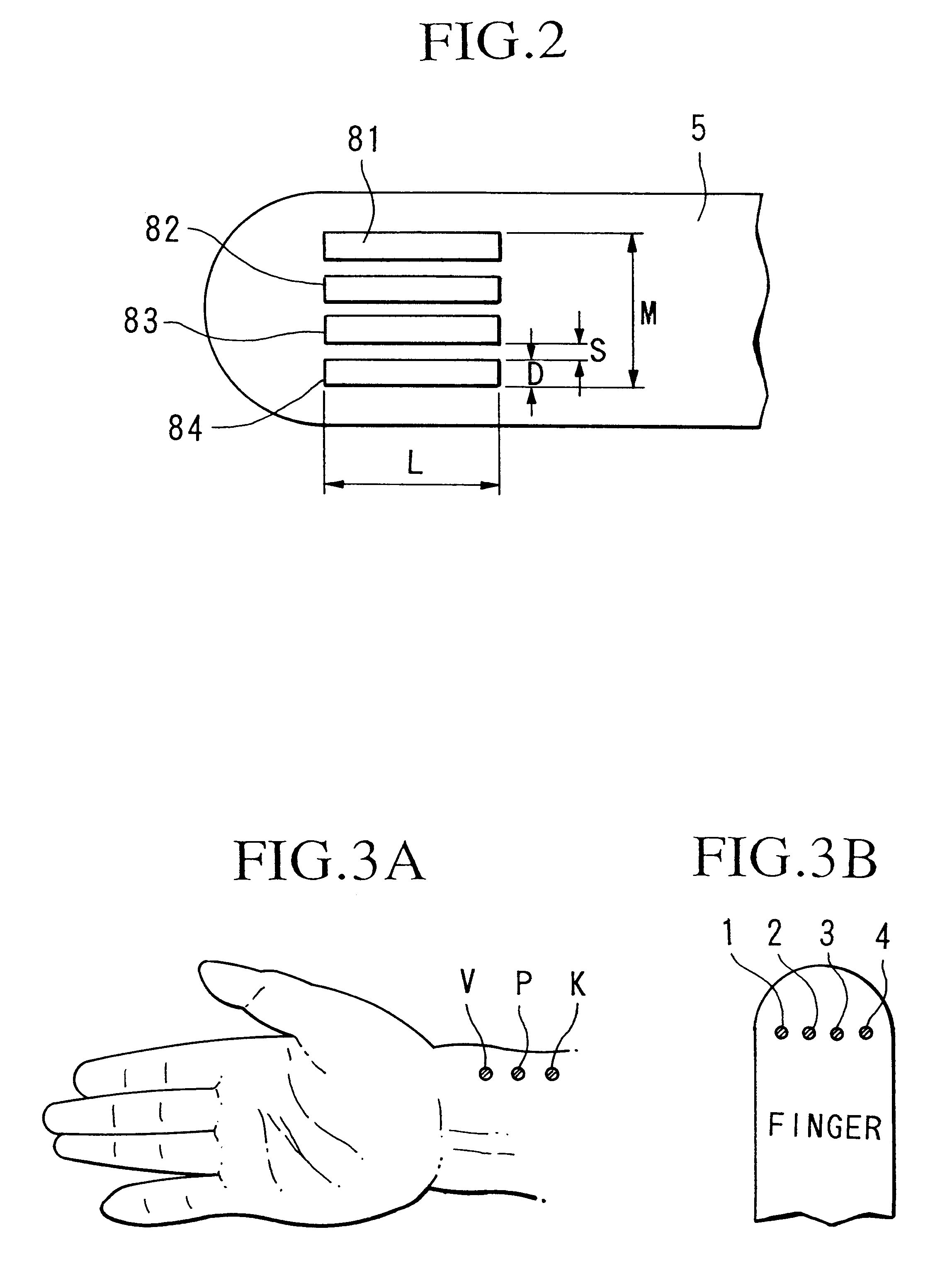
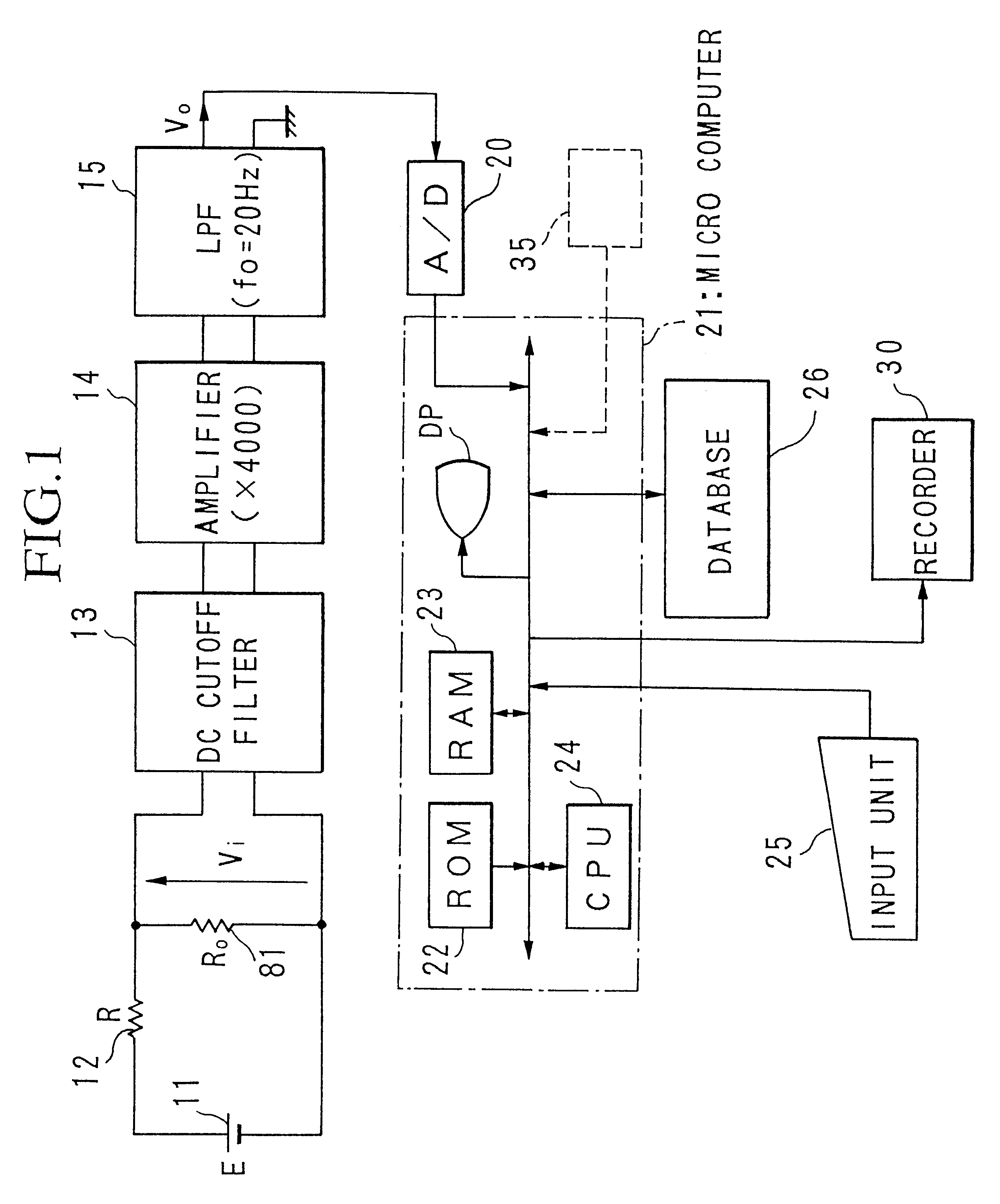
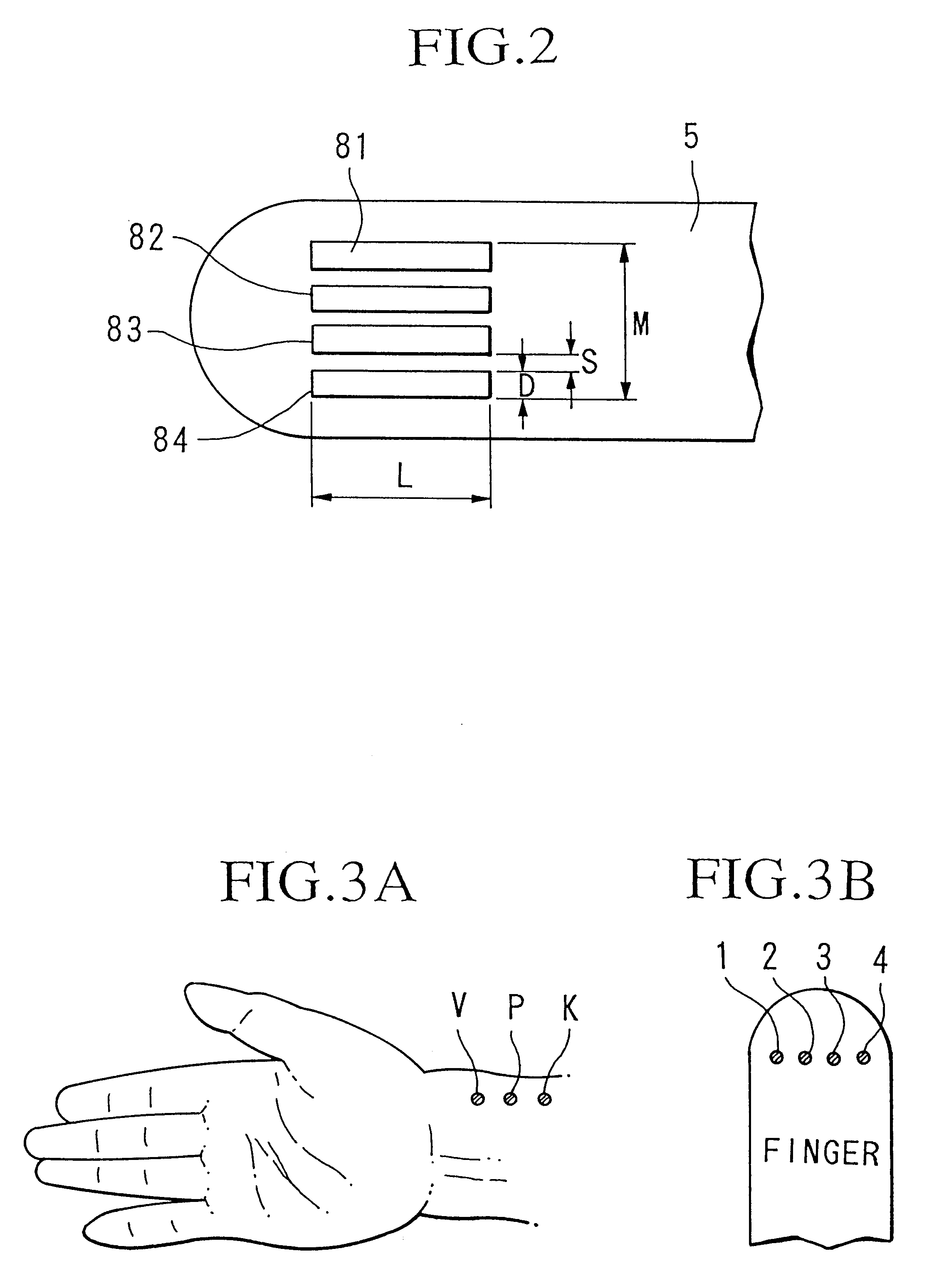
The present invention relates to a diagnosis apparatus for analyzing arterial pulse waves comprising a database 26 in which is stored data showing the relationship between data representing a pulse wave of a living body and teaching data representing conditions of the living body; and a micro-computer 21 for outputting teaching data corresponding to the pulse wave detected from the living body in the teaching data on the basis of the pulse wave detected from the living body and the stored data inside database 26. As a result, it becomes possible to perform diagnoses equivalent to a skilled doctor.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method of improving reproducibility of non-invasive measurements
InactiveUS6411832B1Improve accuracyDiagnostics using lightScattering properties measurementsNon invasivePhysical therapy
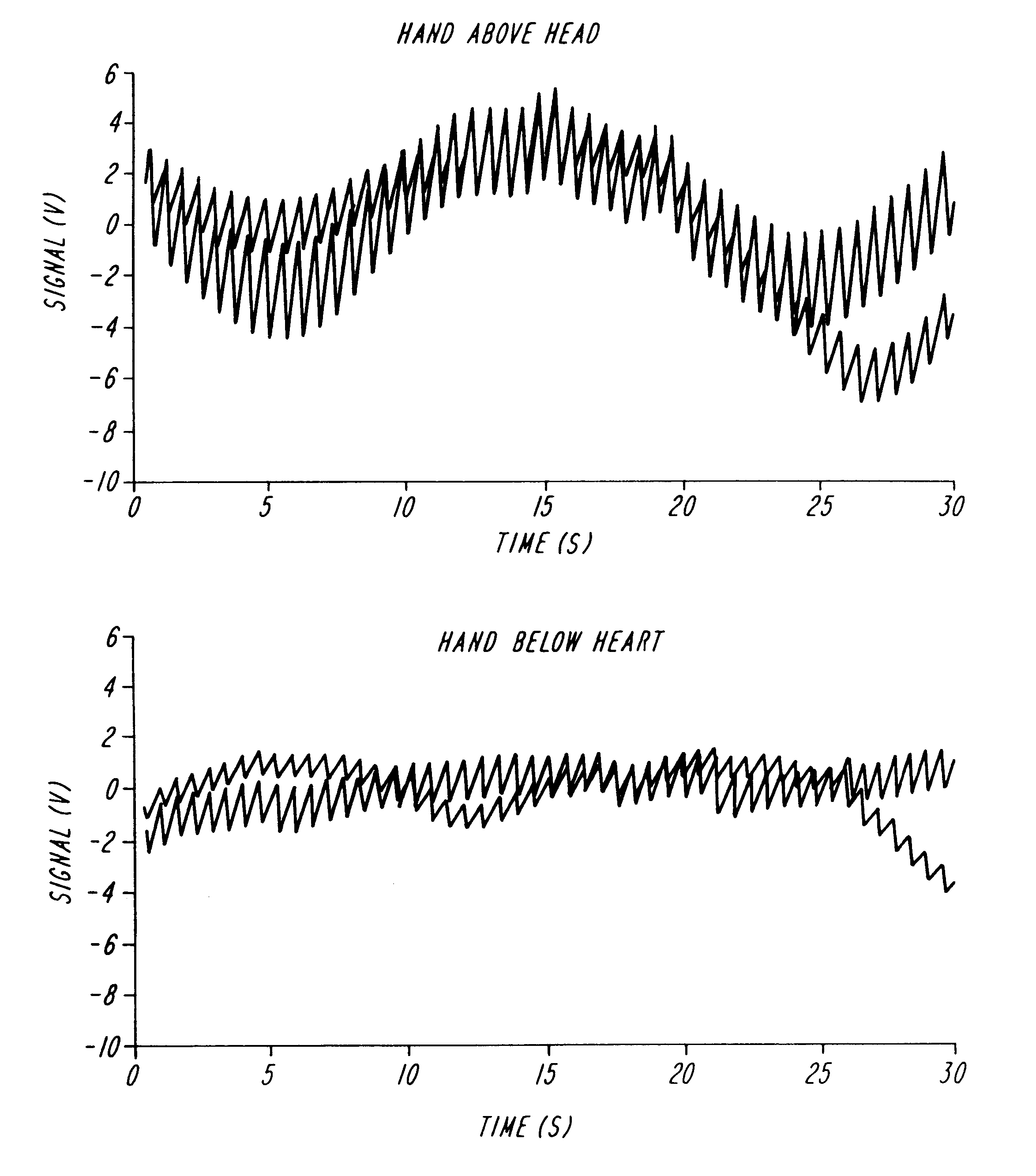
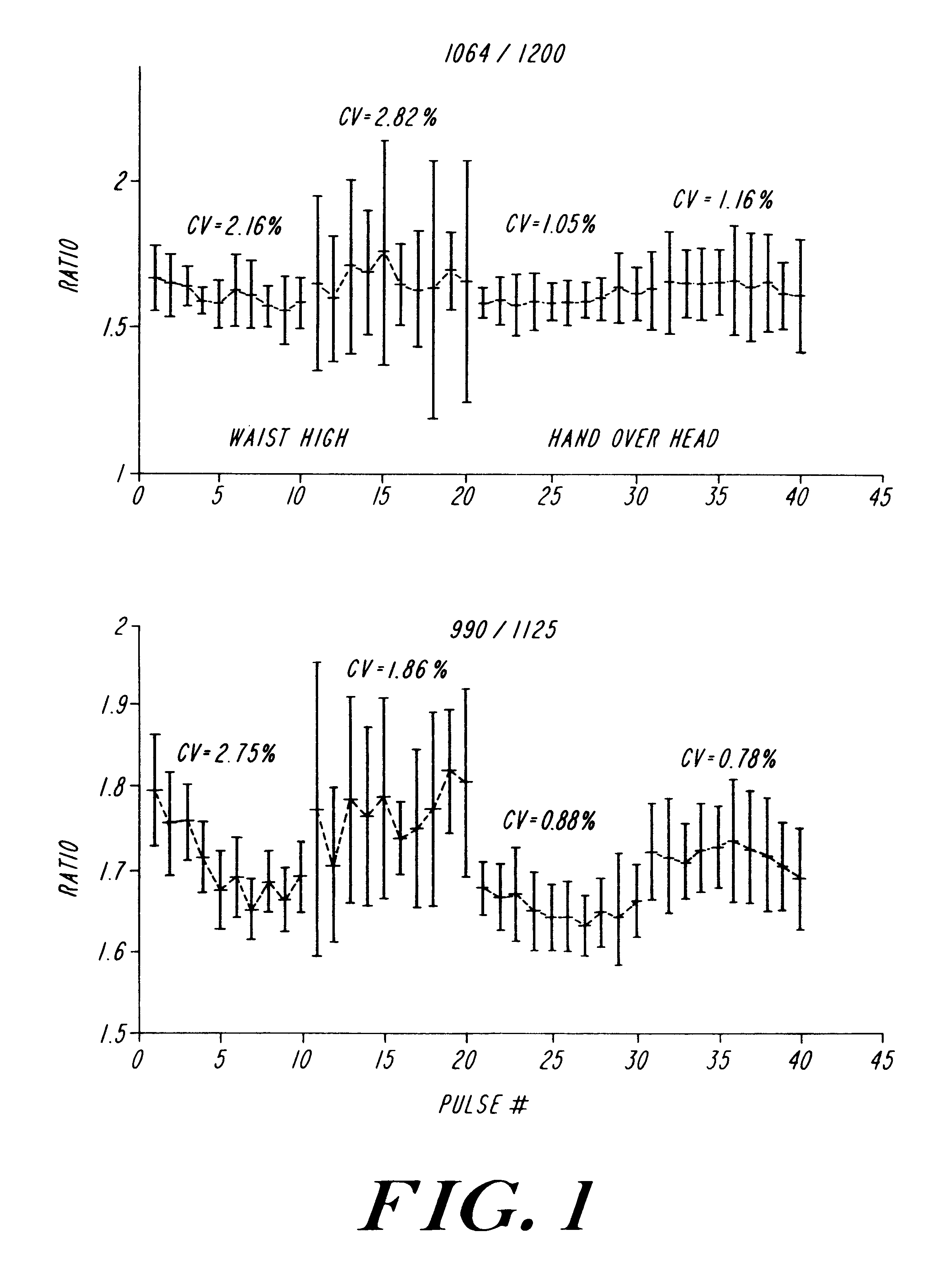
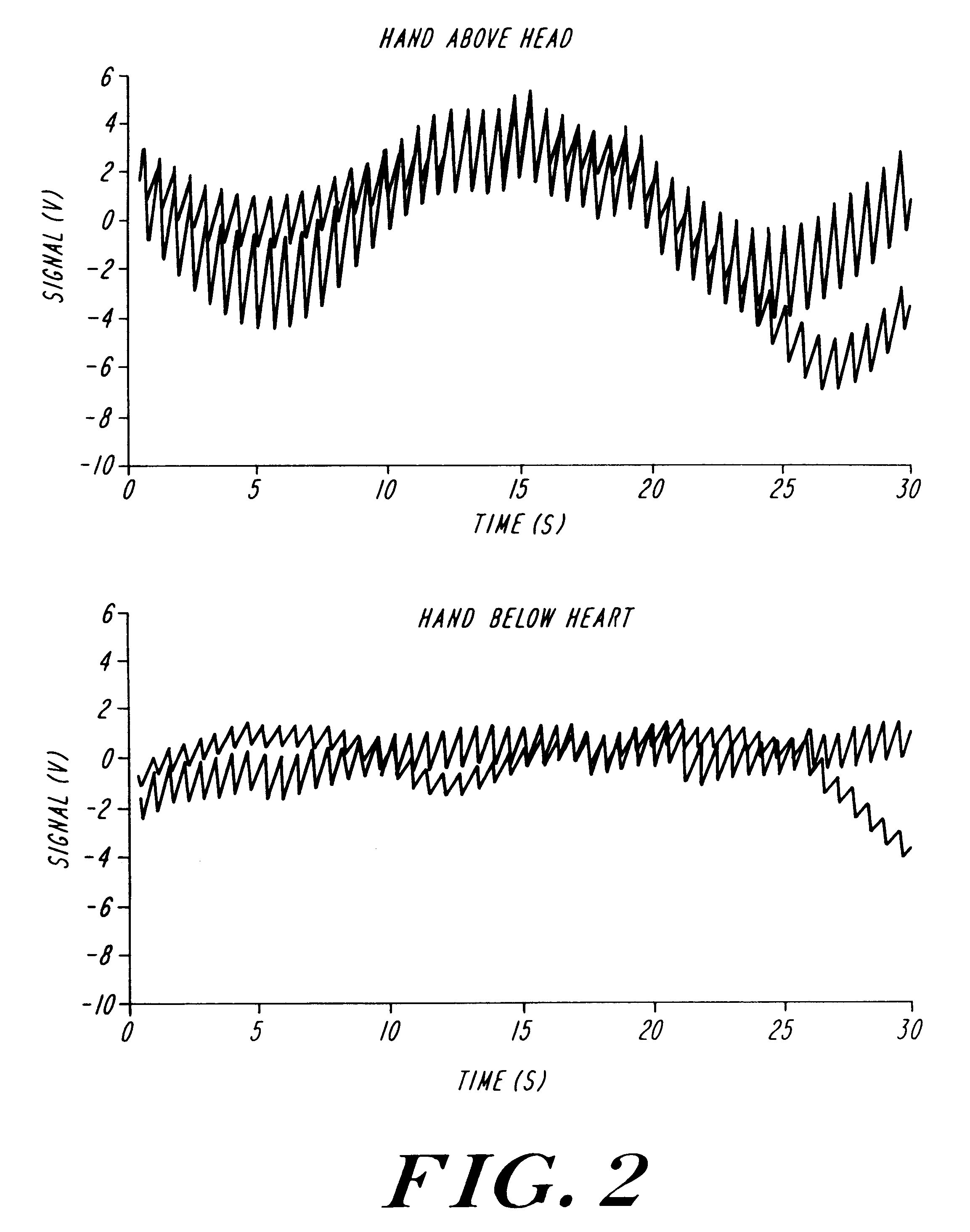
A method of improving the accuracy and reproducibility of non-invasive measurements of a concentration of a constituent of interest carried in a body part has been developed. The method relies on elevating the body part during the measurement cycle so that the body part is maintained above the heart during the measurement cycle. Measurements of the constituent during an arterial pulse leads to improved intra-run and run-to-tun determinations.
Owner:OPTIX
Hypothenar sensor
InactiveUS20100292589A1Good acquisitionDiagnostic signal processingElectrocardiographyHypothenar regionBiomedical engineering
A device having an arterial pulse sensor that is adhered to the hypothenar region of a palm using an adhesive patch. The patch has an adhesive surface that is covered by a removable film with an outer portion and a central portion. Also disclosed is a method of detecting an arterial pulse by providing an arterial pulse sensor, placing the sensor on the hypothenar region of the palm of a hand, and receiving an arterial pulse signal from the sensor.
Owner:GOODMAN JESSE BRUCE
Apparatus and method for sensing radial arterial pulses for noninvasive and continuous measurement of blood pressure and arterial elasticity
InactiveUS20100210956A1Improve accuracyEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterContinuous measurementReflected waves
Provided is a radial arterial pulse sensing apparatus for noninvasive and continuous measurement of blood pressure and arterial elasticity. The apparatus includes two pressure sensor for detecting radial arterial pulses, two cuffs that are disposed under the respective pressure sensors and expandable by application of external pressure, a motor unit for providing proper pressure to expandable pouches under the respective pressure sensors in a state where a wrist band having the pressure sensors is put on a wrist, a pulse wave velocity calculating unit that calculates a pulse wave transfer velocity to attain a blood pressure value using an output from the pressure sensors, and an augmentation index calculating unit that estimates the blood pressure value by finding a time point of a reflective wave of the pulses using the outputs from the pressure sensors.
Owner:GRAMPION GRP
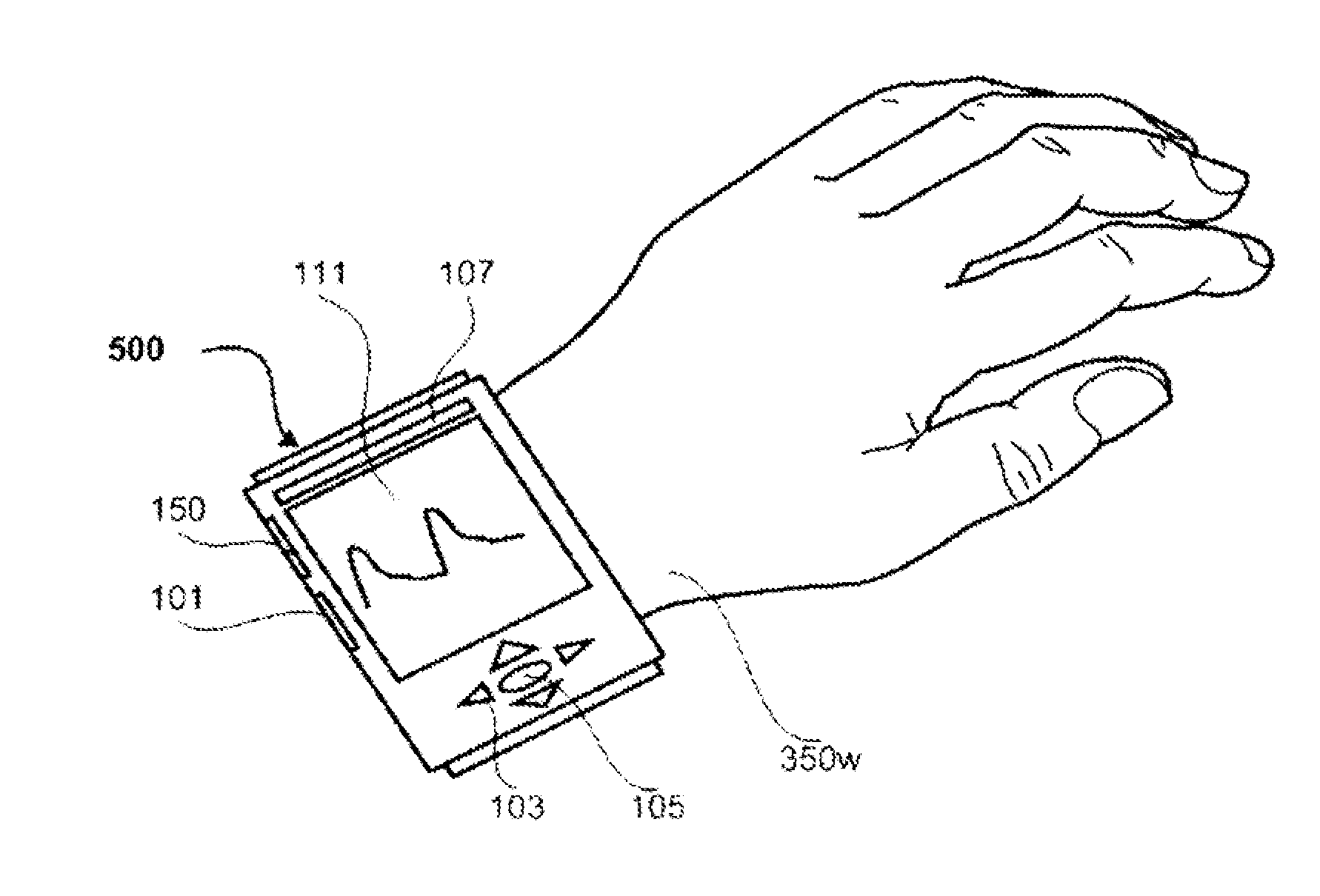
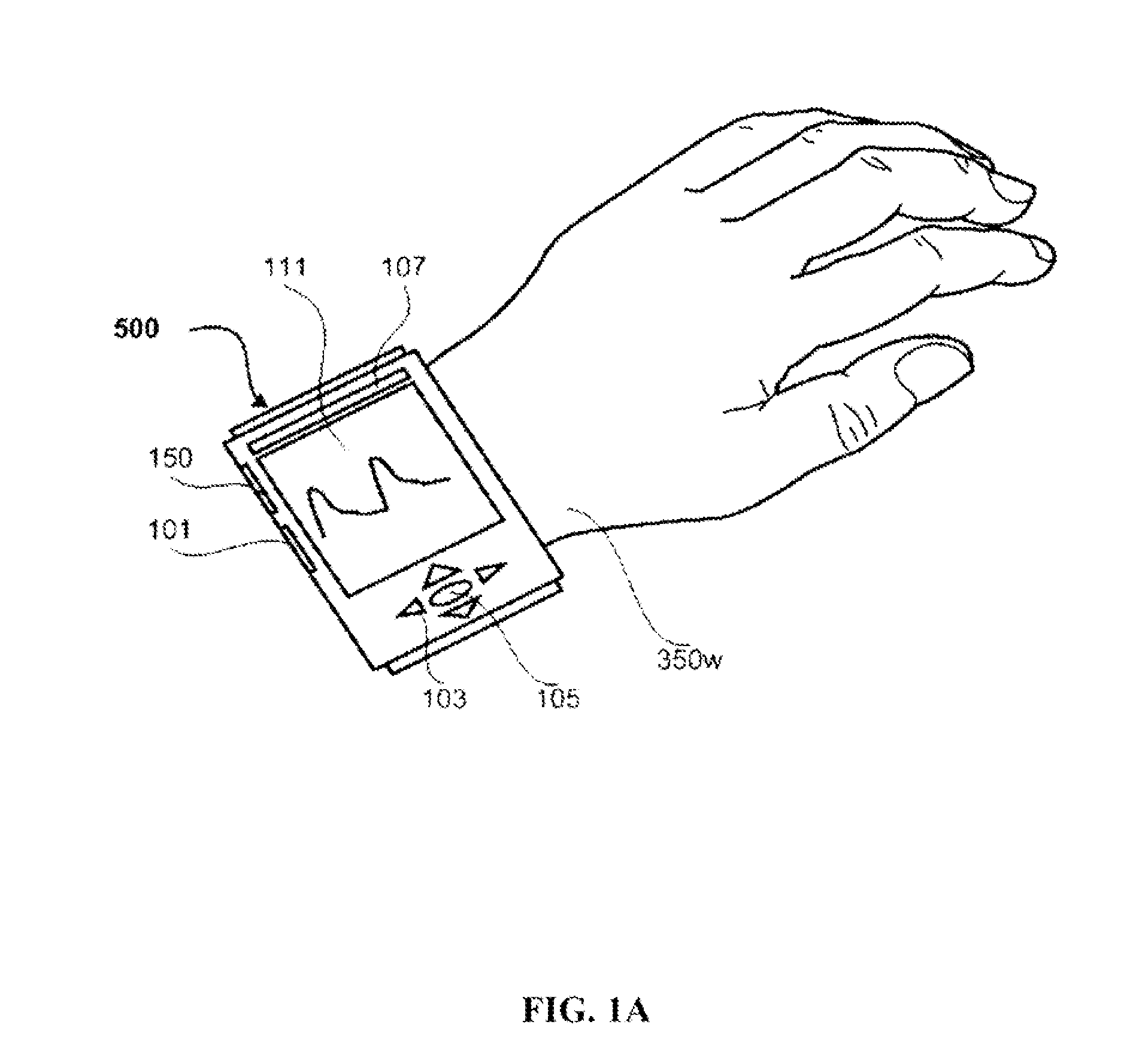
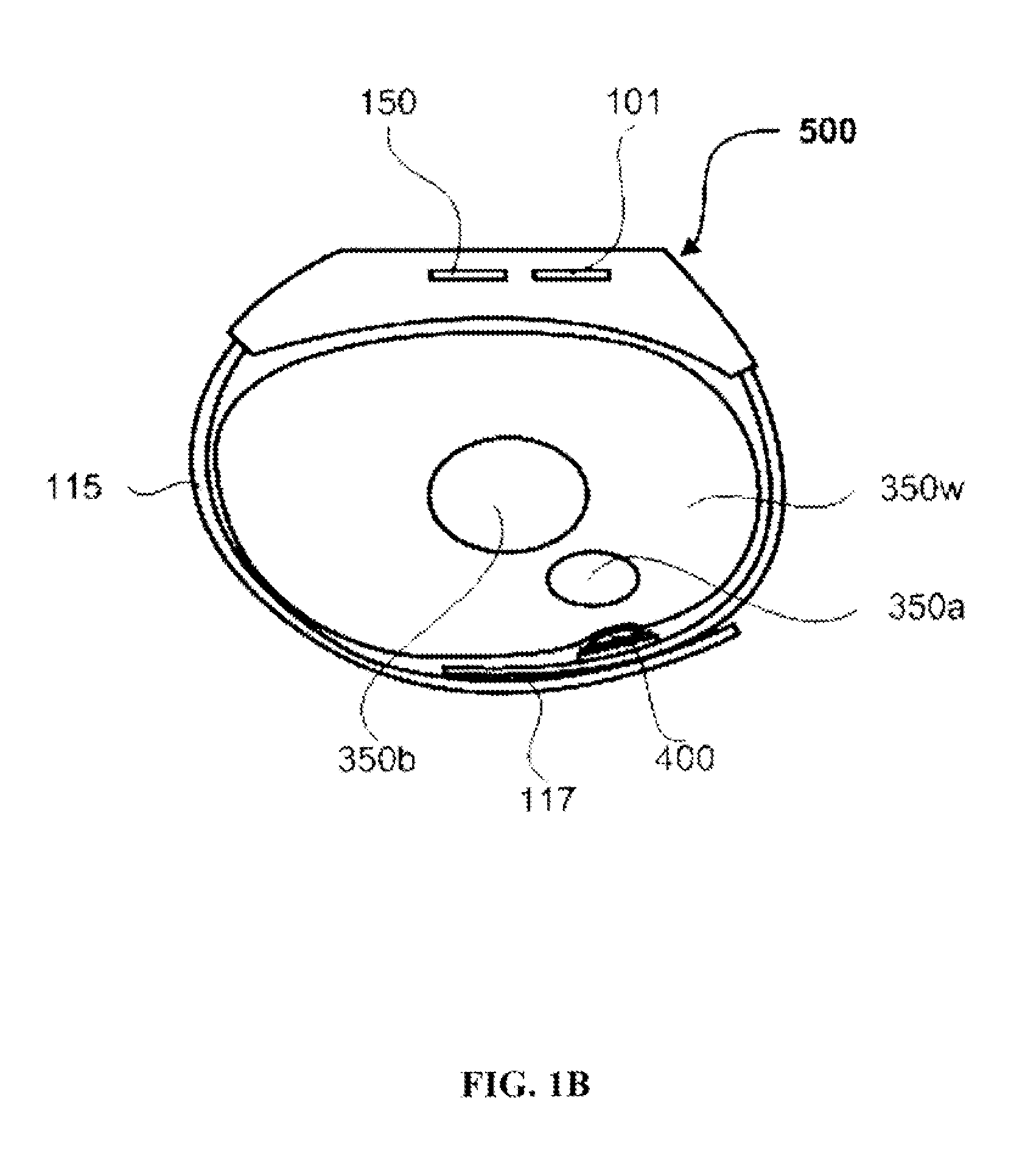
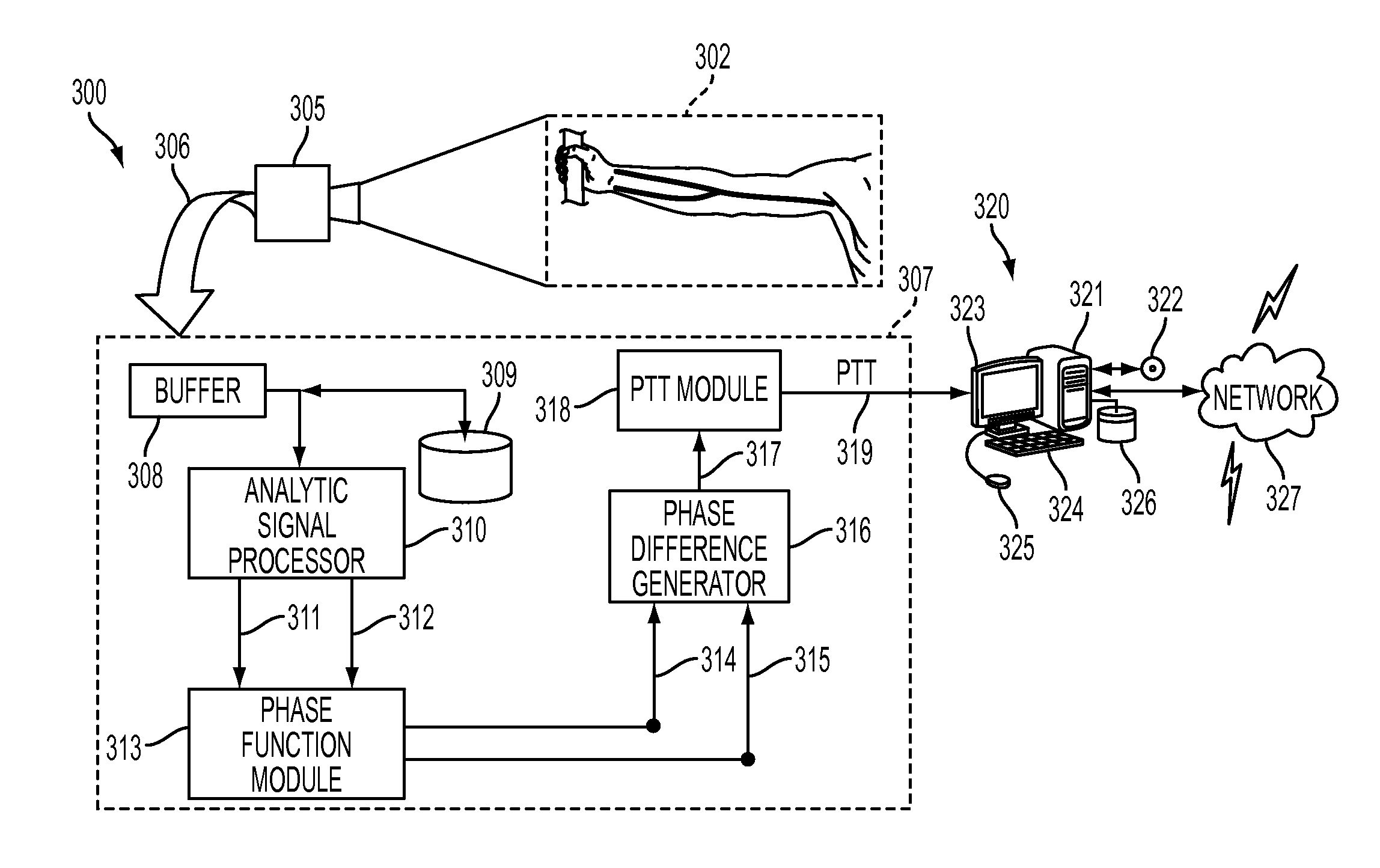
Determining arterial pulse transit time from time-series signals obtained at proximal and distal arterial sites
What is disclosed is a system and method for determining arterial pulse transit time (PTT) for a subject. In one embodiment, time-series signals are received for each of a proximal and distal arterial site of a subject's body which represent blood volume changes in the microvascular tissue at each site. A proximal and distal analytic signal is obtained which has a first component being a waveform of the respective time-series signal and a second component being a transform of the respective waveform. A phase function is determined for the first and second components of each analytic signal. The phase function obtained for the proximal waveform is then subtracted from the phase function obtained for the distal waveform to get a phase difference. The phase difference is analyzed with the subject's heart rate to determine an arterial pulse wave transit time between the two proximal and distal sites.
Owner:XEROX CORP
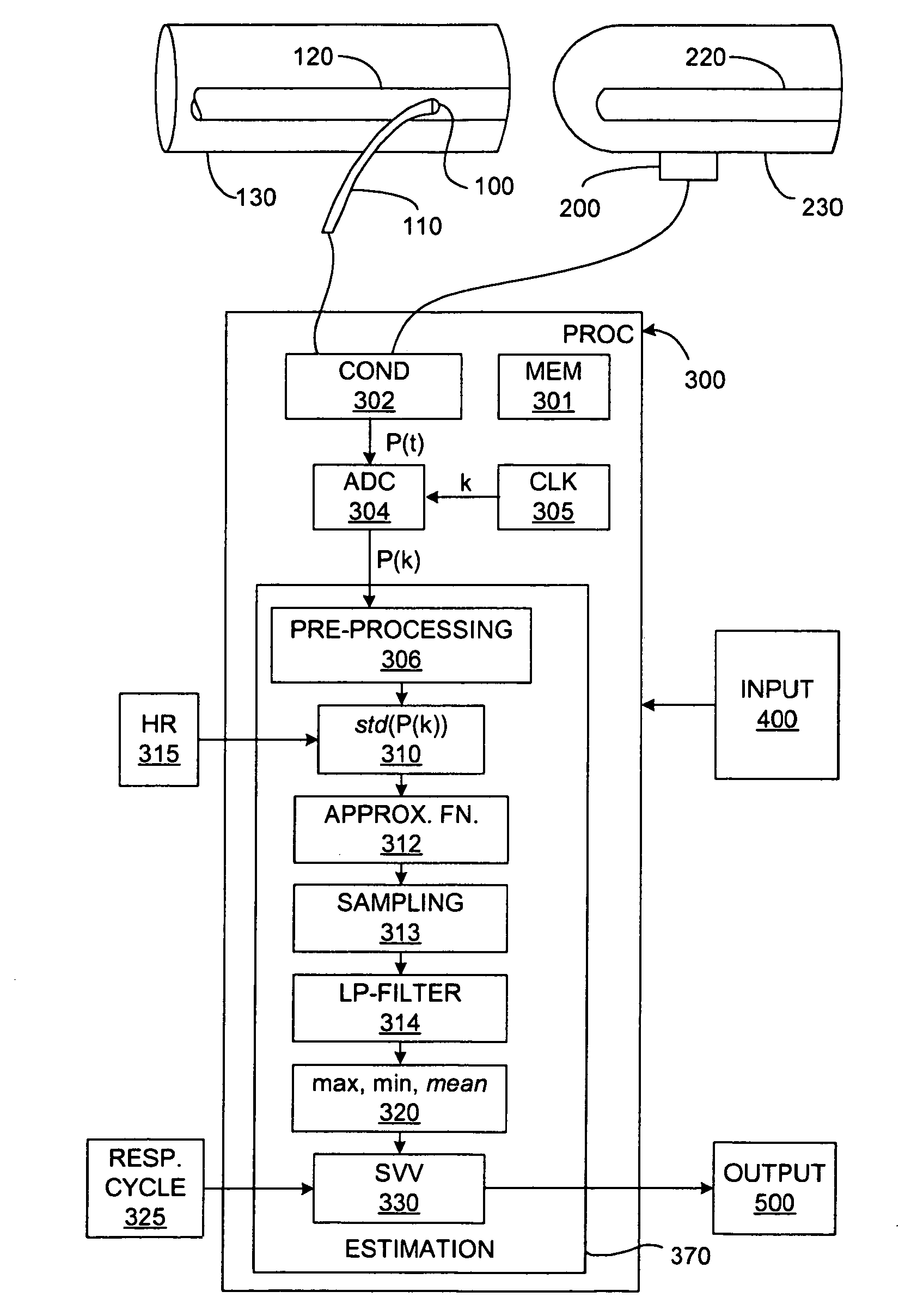
Real-time measurement of ventricular stroke volume variations by continuous arterial pulse contour analysis
Ventricular stroke volume variation (SVV) is estimated as a function of the standard deviation of arterial blood pressure value measured over each of at least two cardiac cycles, preferably over each of the cardiac cycles in a computation interval covering a full respiratory cycle. In one embodiment, maximum and minimum standard deviation values are determined over the computation interval. SVV is then estimated proportional to the ratio of the difference between the maximum and minimum standard deviation values and the mean of the standard deviation values. In another embodiment, SVV is then estimated proportional to the ratio of the standard deviation of the standard deviation values and the mean standard deviation over the entire computation interval. A pre-processing arrangement for improving reliability of estimates of more general cardiac or hemodynamic parameters is also disclosed and involves smoothing with an approximating function, and sampling and low-pass filtering at an adjustable rate.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Brain assessment monitor
InactiveUS6887199B2Easy to transportCharacteristic is differentSurgeryEvaluation of blood vesselsMedicineNon invasive
A non-invasive brain assessment monitor is disclosed. An embodiment of the monitor includes a head-mounted brain sensor which passively senses acoustic signals generated from pulsing blood flow through a patient's brain. A reference sensor may be mounted at another location on the patient's body to sense an arterial pulse, and the signals from the brain sensor and reference sensor may be compared. Another embodiment includes transmitters which generate acoustic signals in the brain which are also detected by the brain sensor. The brain assessment monitor may be used to detect conditions such as head trauma, stroke and hemorrhage.
Owner:ACTIVE SIGNAL TECH
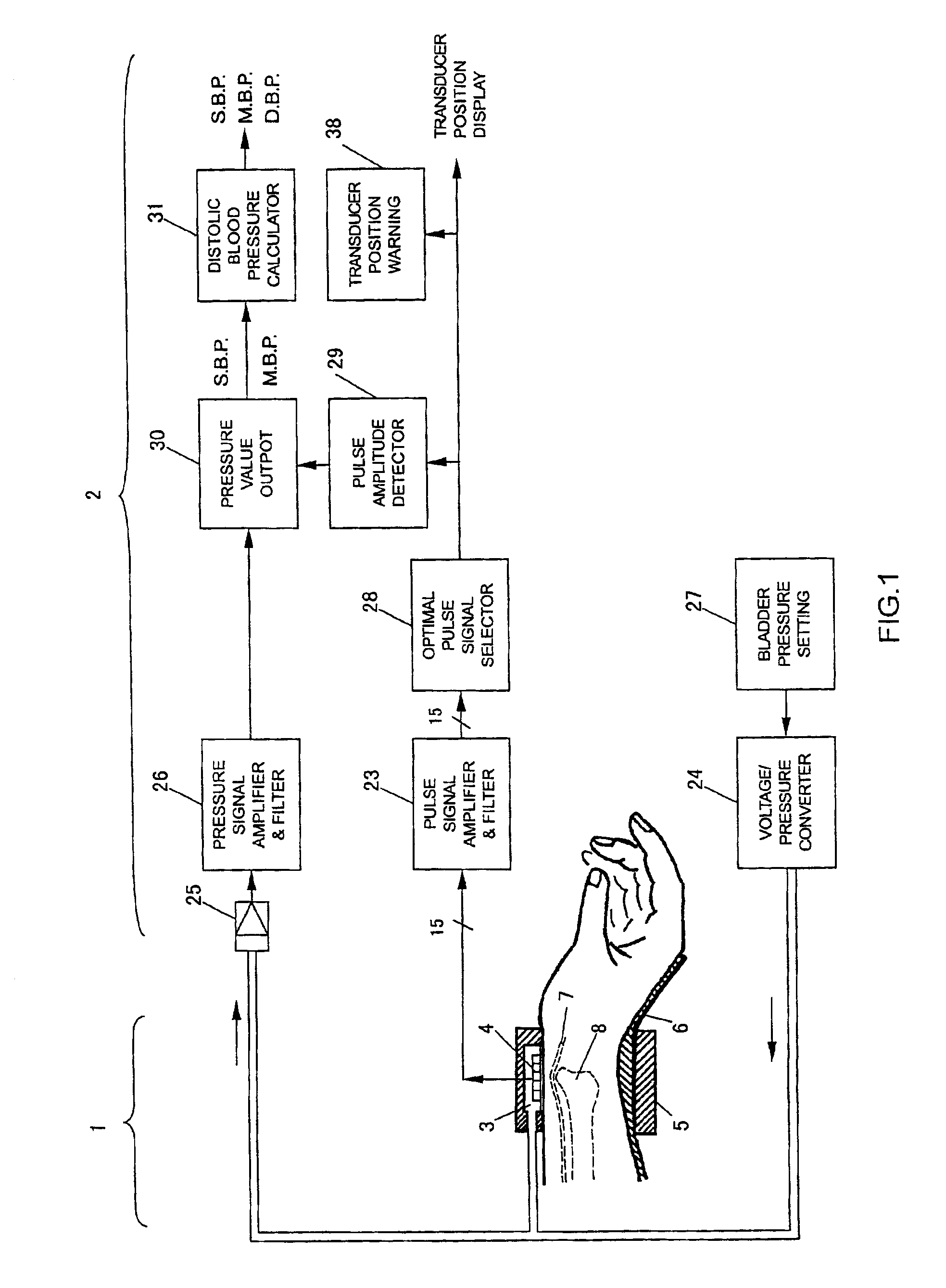
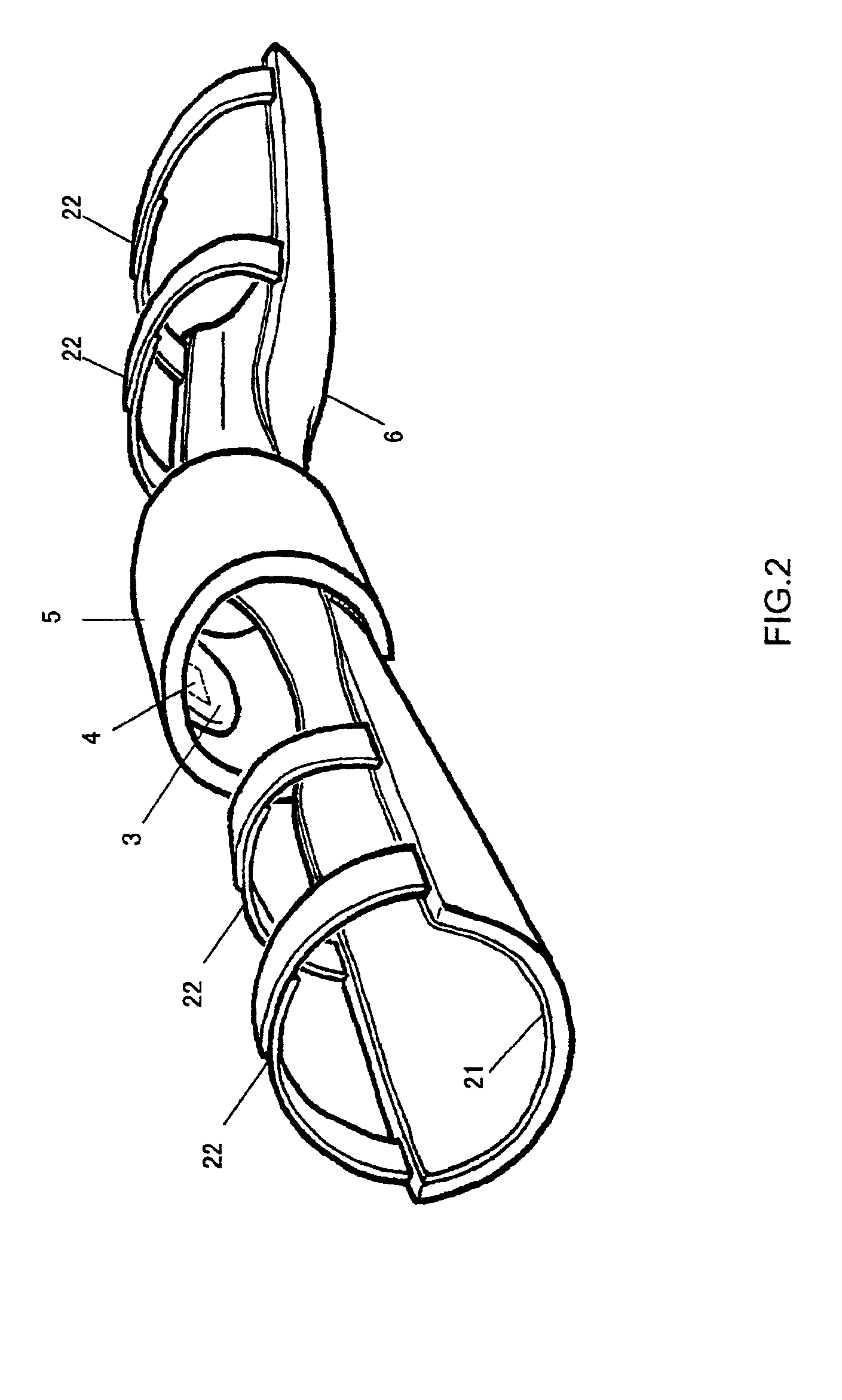
Noninvasive blood pressure measuring method and apparatus
InactiveUS6932772B2Exclusion from blood circulationEliminate circulationEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterTurn angleUlnar artery
A method and a device for non-invasive blood pressure measurement wherein the angle between the hand and the wrist, and the turning angle of the wrist relative to the middle part of the forearm, are kept to the most suitable degree for measuring the blood pressure of the radial artery. At least one pressure bladder and one arterial pulse transducer array are placed on the skin over the radial artery of the wrist to apply the external pressure to the artery and to detect the change of the arterial pulse signals. This method and device can correctly measure the intermittent or continuous blood pressure of the radial artery or the ulnar artery based on the principles of oscillation method and volume compensation method, and effectively eliminate the influence on the measurement due to body movement and the influence on blood circulation and neural function of the hand caused by long-term blood pressure measurement.
Owner:XIAN LIBANG MEDICAL ELECTRONICS
System and method for a non-invasive medical sensor
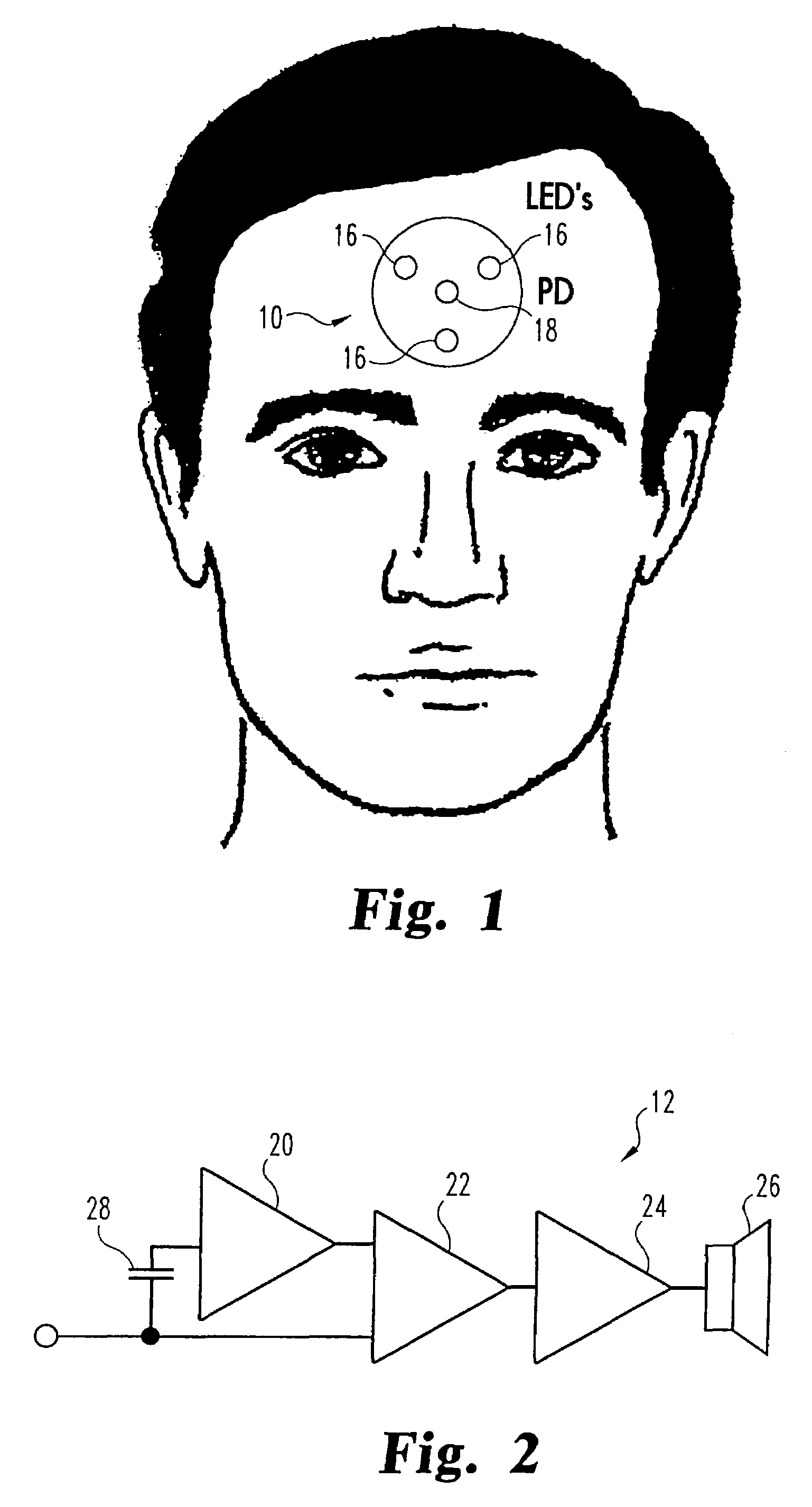
A sensor is disclosed having one or more light sources, and one or more light detectors. At least one of the detectors produces an output in response to received light. Also, electrical circuitry in response to the output generates a pulse waveform proportional to the arterial and venous pulse of a human body, wherein the pulse waveform is used to synchronize an arterial-pulse measurement of the absorption or reflectance of one or more coherent light sources.
Owner:BIOINTELLISENSE INC
Apparatus and method for electrocardiogram-assisted blood pressure measurement
InactiveUS20120283583A1Reduce noiseReduce transmission noiseEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterPatient managementNon invasive
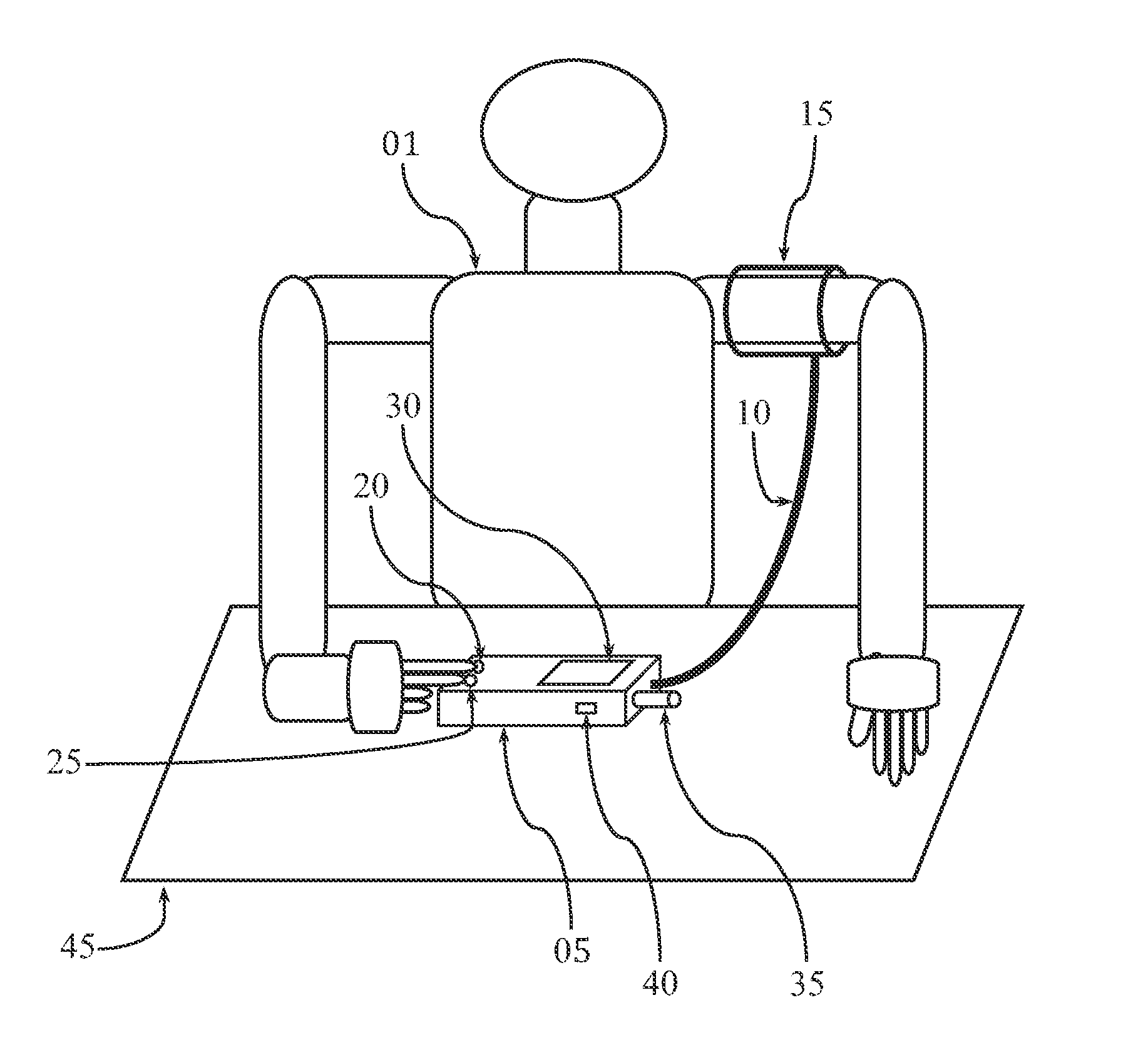
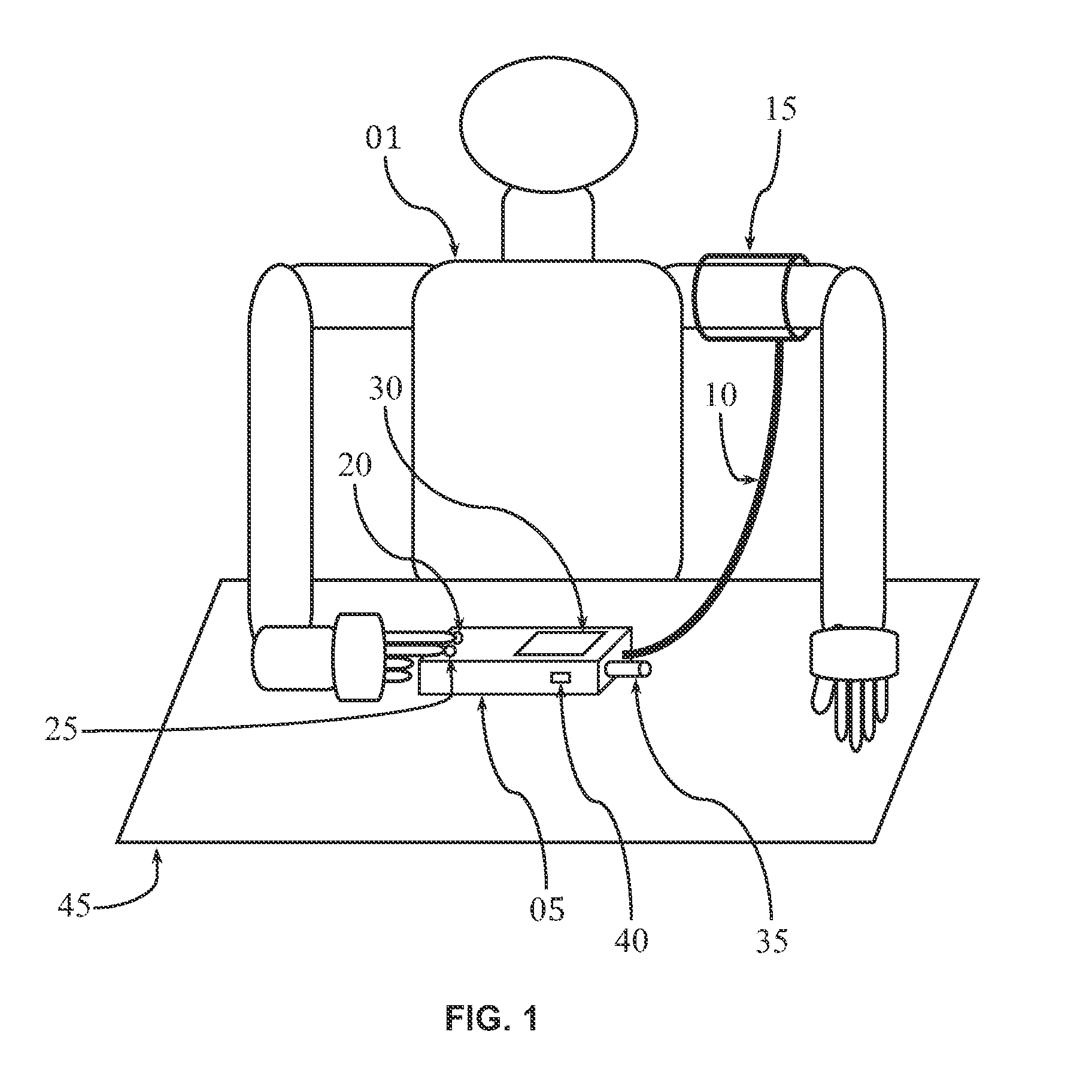
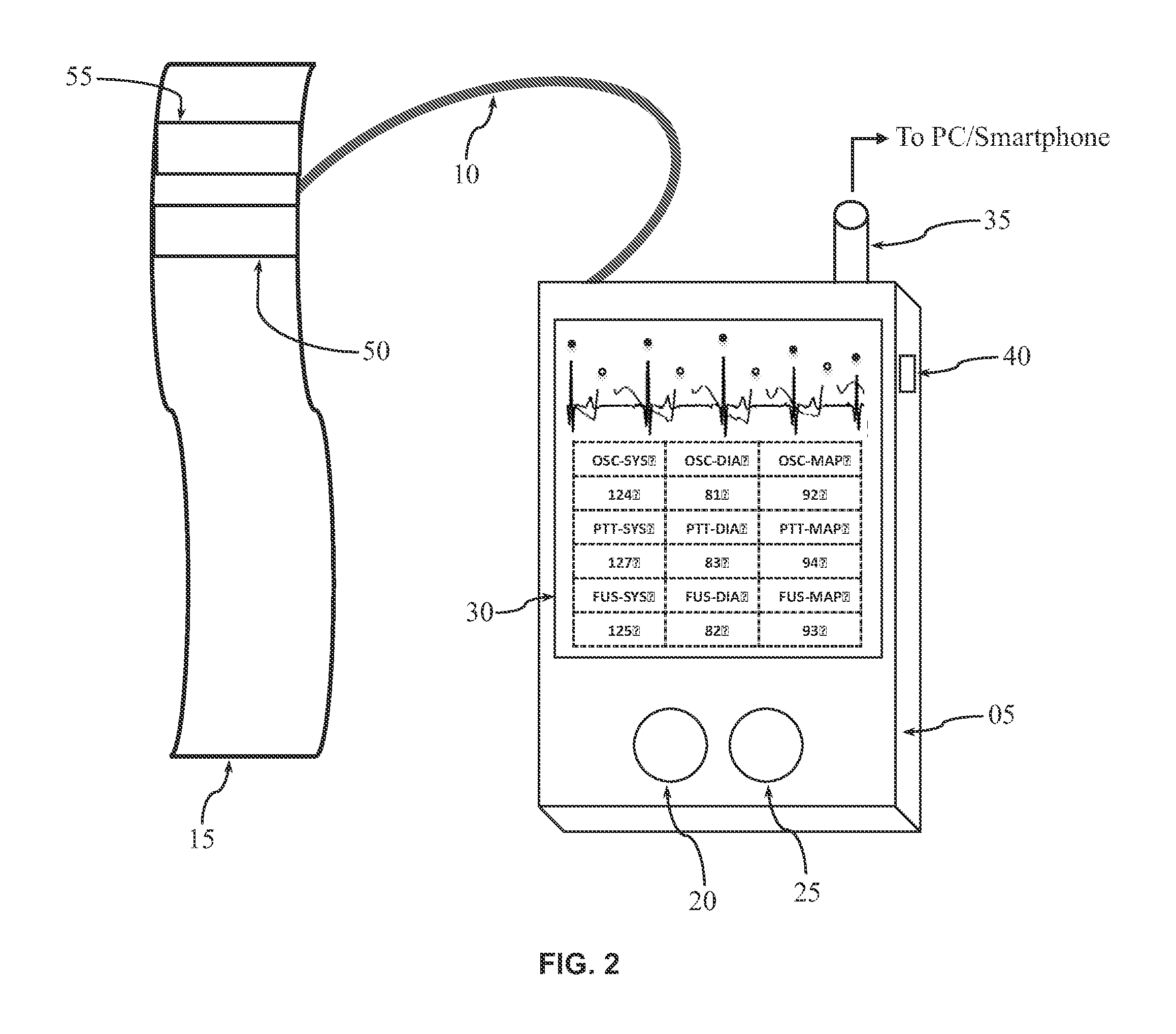
Apparatus, method, and software for electrocardiogram-assisted non-invasive arterial blood pressure d stiffness measurement is disclosed including brachial cuff with flexible electrodes, control box with rigid electrodes, and associated hardware / software. Cuff is wrapped around upper arm while electrodes on device are touched with fingers of other hand. Device acquires simultaneous ECG / oscillometric data during cuff deflation. Processing unit determines ECG R-peak positions to isolate arterial pulses and calculate pulse transit time. Change in pulse amplitude as function of cuff pressure is used for constructing oscillometric envelope and calculating blood pressure using empirical coefficients. Change in pulse transit time as function of cuff pressure is used independently for constructing pulse transit time envelopes and finding blood pressure with / without empirical coefficients. Fusion algorithm combines results for robust blood pressure and vessel stiffness evaluation. Device sends physiological information to personal computer / smartphone wirelessly, for further analysis. Computer / smartphone transmits information to third party for patient management.
Owner:BATKIN IZMAIL +5
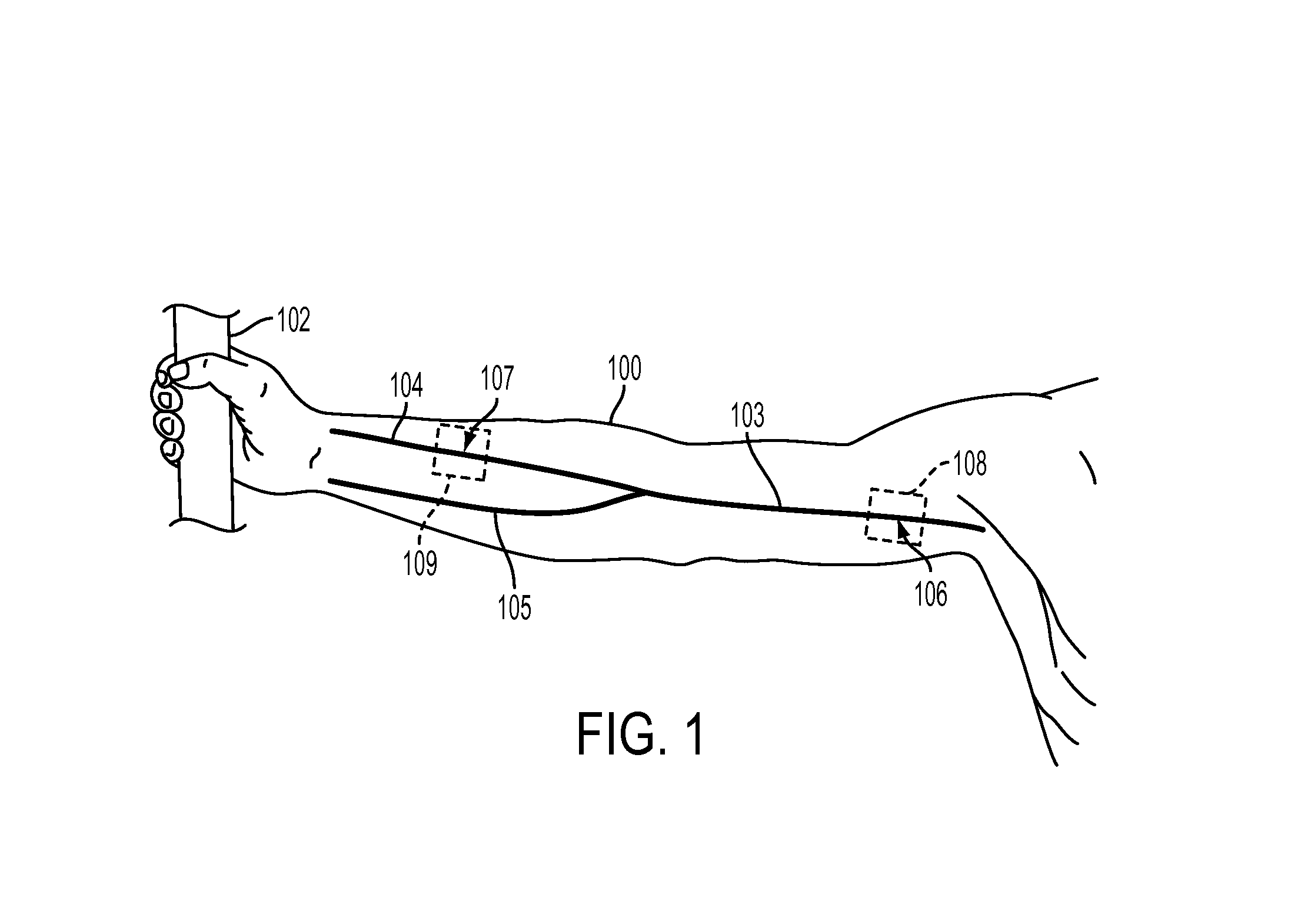
Deriving arterial pulse transit time from a source video image
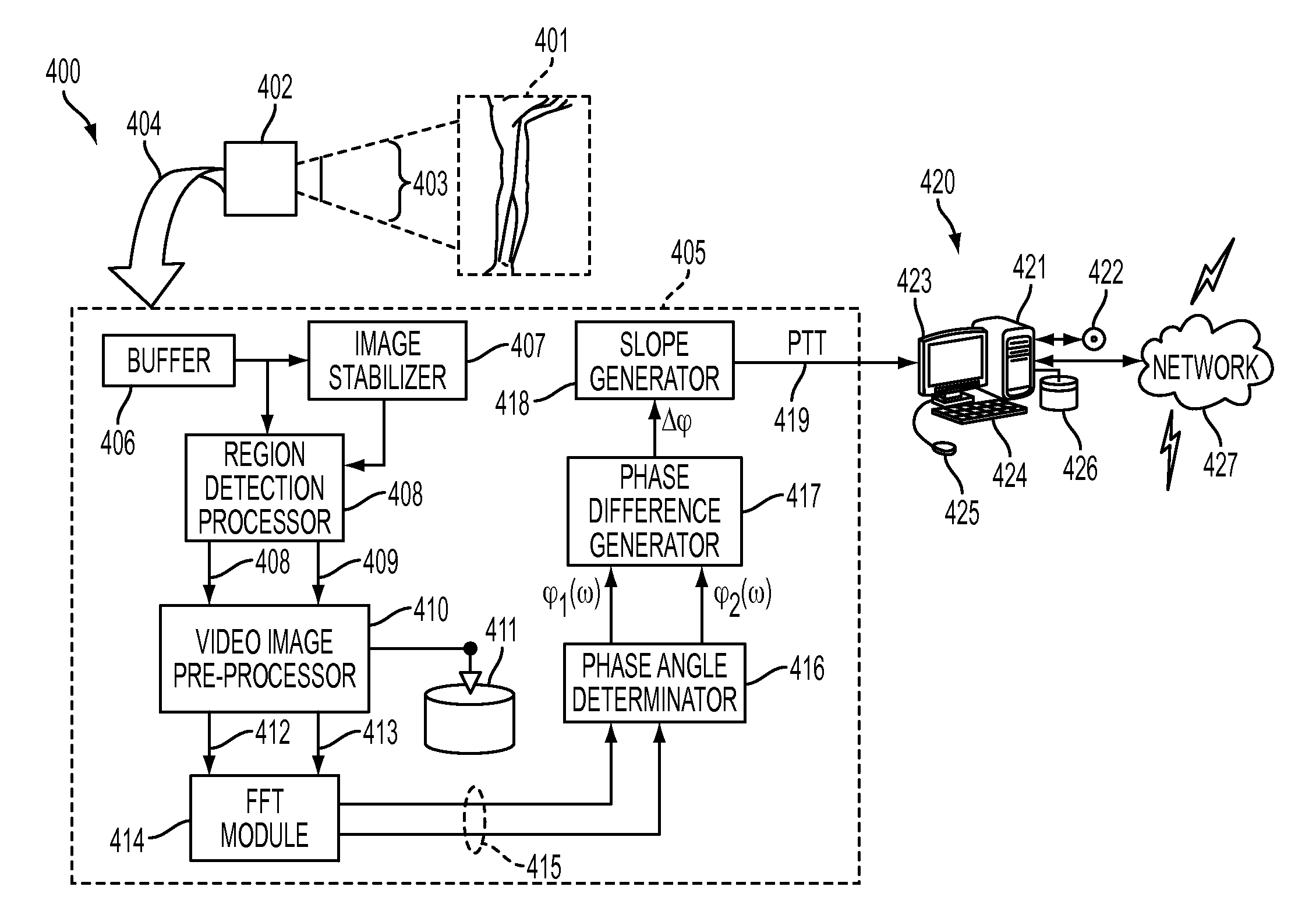
ActiveUS20130218028A1Readily apparentImage enhancementImage analysisVascular obstructionPhase difference
What is disclosed is a system and method for determining an arterial pulse transit time of a subject of interest in a remote sensing environment. A video imaging system is used to capture a time varying source images of a proximal and distal region of a subject intended to be analyzed for arterial pulse transit time. A time series signal for each of the proximal and distal regions is extracted from the source images and a phase of each of the extracted time series signals is computed. A difference is then computed between these phases. This phase difference is a monotonic function of frequencies in the signals. From the monotonic function, an arterial pulse transit time of the subject is extracted. The subject's arterial pulse transit time is then communicated to a computer system. The computer system determines blood pressure, blood vessel blockage, blood flow velocity, or a peripheral neuropathy.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method For Detecting Physiology At Distance Or During Movement For Mobile Devices, Illumination, Security, Occupancy Sensors, And Wearables
InactiveUS20150148624A1Implementation more simply and inexpensivelyDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyConfocalOxygenated Hemoglobin
An improved sensor (102) for physiology monitoring in mobile devices, wearables, security, illumination, photography, and other devices and systems uses broadband light (114) transmitted to a target (125) such as the ear, face, or wrist of a living subject. Some of the scattered light returning from the target to detector (141) is passed through narrowband spectral filter set (155) to produce multiple detector regions, each sensitive to a different wavelength range. Data from the detected light is spectrally analyzed to computationally partition the analyzed data into more than one compartment of different temporal or physiological characteristics (such as arterial bloodstream, venous bloodstream, skin surface, and tissue), and into more than one component compound (such as oxygenated hemoglobin, water, and fat), allowing a measure of physiology of the subject to localized to one compartment, thereby reducing the effects of body motion, body position, and sensor movement that can be localized to other physiological compartments or components. In one example, variations in components of the bloodstream over time such as oxyhemoglobin and water are determined based on the detected light, and localized to remove skin surface scattering and reflection, and to minimize changes in the venous bloodstream caused by impact and motion, resulting in an arterial bloodstream signal with an improved signal to noise for the cardiac arterial pulse. The same sensor can provide identifying features of type or status of a tissue target, such as heart rate or variability, respiratory rate, calories ingested or expended, hydration status, or even confirmation that the tissue is alive. Monitoring devices and systems incorporating the improved sensor, and methods for analysis, are also disclosed.
Owner:J FITNESS LLC
Diagnostic apparatus for analyzing arterial pulse waves
The present invention relates to a diagnosis apparatus for analyzing arterial pulse waves comprising a database 26 in which is stored data showing the relationship between data representing a pulse wave of a living body and teaching data representing conditions of the living body; and a micro-computer 21 for outputting teaching data corresponding to the pulse wave detected from the living body in the teaching data on the basis of the pulse wave detected from the living body and the stored data inside database 26. As a result, it becomes possible to perform diagnoses equivalent to a skilled doctor.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Monitoring apparatus of arterial pulses and method for the same
A monitoring apparatus includes an antenna board including a transmission antenna for transmitting an ultra wideband electromagnetic wave to an arterial blood vessel and a reception antenna for receiving the ultra wideband electromagnetic wave scattered by the arterial blood vessel, an analog board with a plurality of electronic devices for acquiring analog signals representing the arterial pluses of the arterial blood vessel, a digital board with a plurality of electronic devices for digitalizing the analog signal, and a display device for showing the arterial pulses. The method for acquiring arterial pulses first radiates an ultra wideband electromagnetic wave to an arterial blood vessel, and measures the phase difference between the ultra wideband electromagnetic wave scattered by the arterial blood vessel and the reference ultra wideband electromagnetic wave. Finally, the arterial pulses are acquired based on the variation of the phase difference.
Owner:MARCOTT INT INVESTMENT
Apparatus and method for noninvasively detecting the quality of cardiac pumping
InactiveUS7569018B1Evaluate the effectiveness of each chest compressionHeart defibrillatorsCatheterPhotodetectorLoudspeaker
An auditory pulse monitor for noninvasively detecting the amplitude of arterial pulses on a beat-by-beat basis. A light-weight optical sensor including a light source and photodetector is adapted for application to the skin surface of a subject over a tissue bed containing an arterial supply. The photodetector generates an output signal proportional to the amplitude of an arterial pulse, and an electronic circuit connected to the photodetector generates a signal having a frequency proportional to the photodetector output signal level. A speaker or other audio indicator connected to the electronic circuit generates an audible tone indicating the amplitude of the arterial pulse. Another aspect of the invention is an improvement in automated or automatic external defibrillators (AEDs). An AED is disclosed which optically detects arterial pulses after delivering a defibrillation shock and signals the need for CPR if it detects inadequate cardiac pumping following successful defibrillation.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
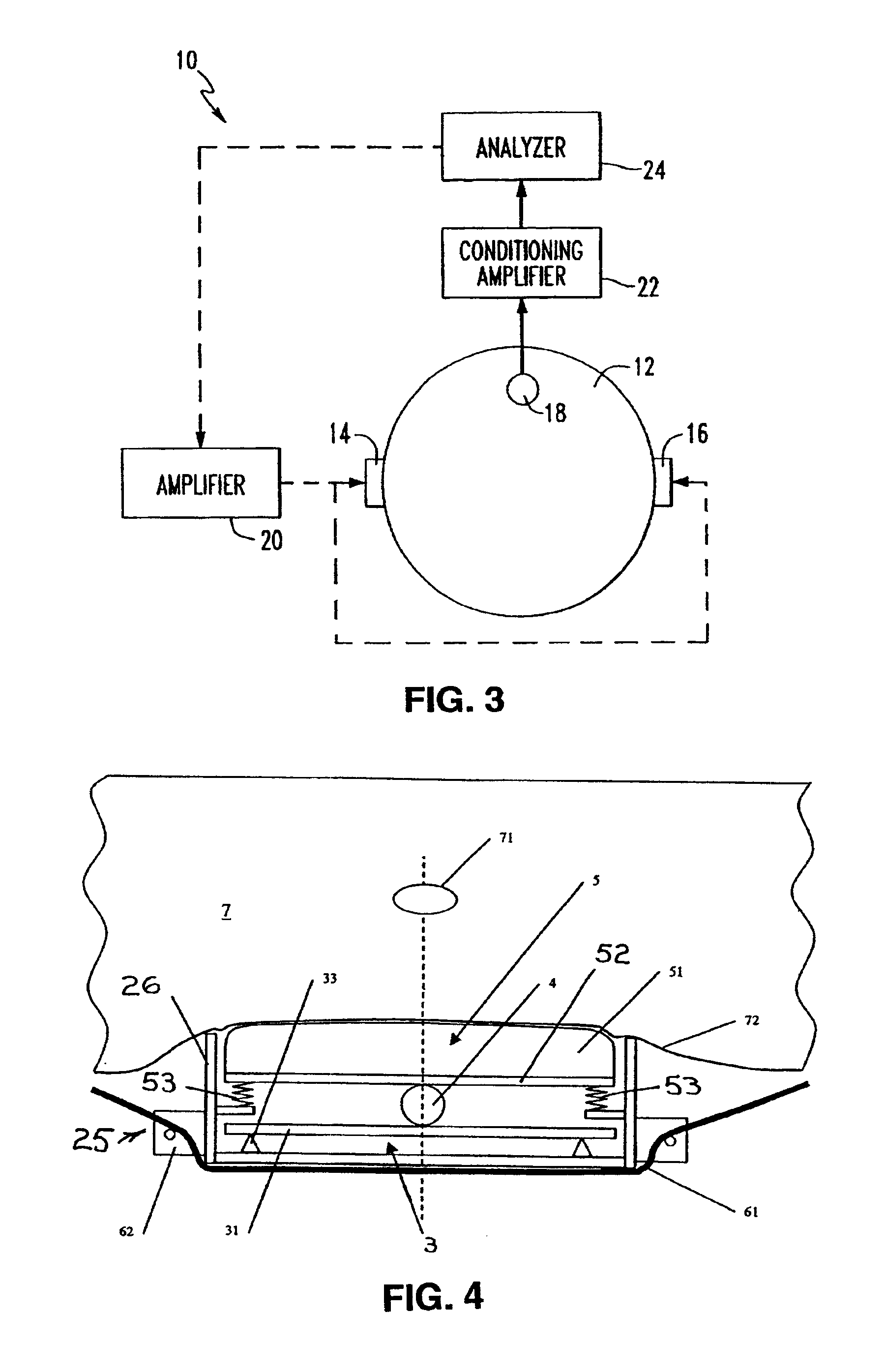
Sensor for non-invasive and continuous determination of the duration of arterial pulse waves
InactiveUS6200270B1Improve the sensor knownAvoiding any discomfort to the patientFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsCatheterEngineeringNon invasive
A sensor for non-invasive and continuous determination of the duration of arterial pulse waves is provided in which at least two spaced apart piezoelectric pressure sensors are disposed in succession in the flow direction of the artery, with the sensor being provided with pressure sensitive surfaces and being integrated in a casing. The piezoelectric pressure sensors are provided with a pressure-sensitive, strip-shaped surface, with the strips each being disposed in their longitudinal extension perpendicular to the flow direction of the artery. The casing is provided with at least two recesses adapted to the contours of the strip-shaped surfaces into which the pressure-sensitive, strip-shaped surfaces of the pressure sensors are disposed flush to the surface of the casing.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Blood flow rate imaging device
InactiveUS20100056936A1Suppress noiseObserve clearlyVolume/mass flow measurementCatheterRed blood cellVenous pulse
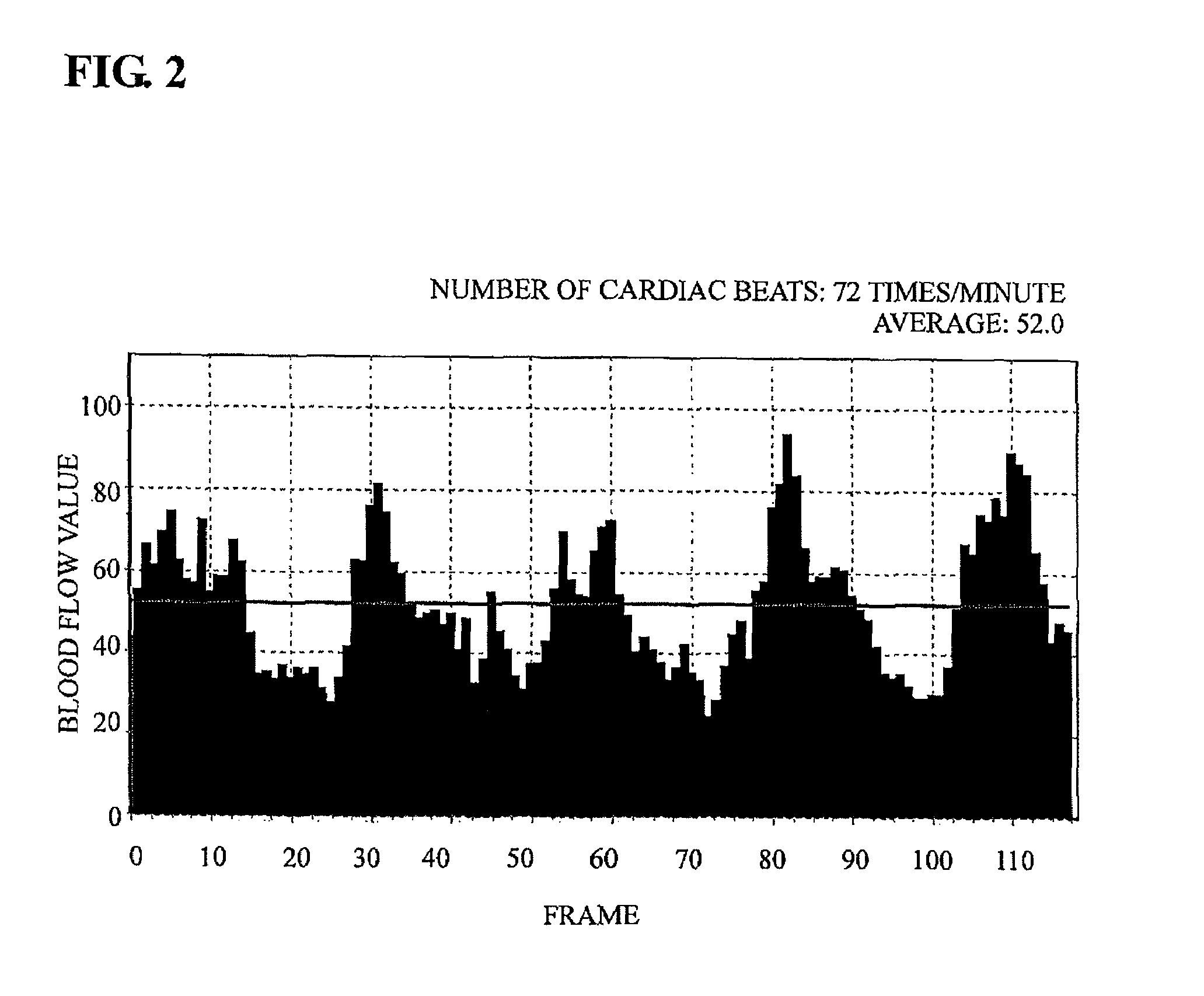
Provided is a blood flow rate imaging device that can automatically distinguish an artery and a vein from a blood flow rate obtained on a time series blood flow map. A blood flow rate imaging device of the present invention includes a laser beam irradiation system (1) that irradiates a laser beam to a biological tissue that has a blood cell, a light receiving system (2) that has a light receiver (5) including many pixels that detect reflected light from the biological tissue, an image capture section (12) that continuously captures a plurality of images for a predetermined time of one or more cardiac beats on the basis of signal from the light receiver (5), an image storage section (15) that stores a plurality of images, and an arithmetic section (16) that calculates a blood flow rate within a biological tissue from the time variation of the output signal of each pixel corresponding to a plurality of stored images, wherein the above arithmetic section has a detecting section that detects an artery and a vein from a plurality of images of the above one or more cardiac beats and displays an arterial pulse part and a venous pulse part on the blood flow map.
Owner:SANGAKU RENKEI KIKO KYUSHU KK
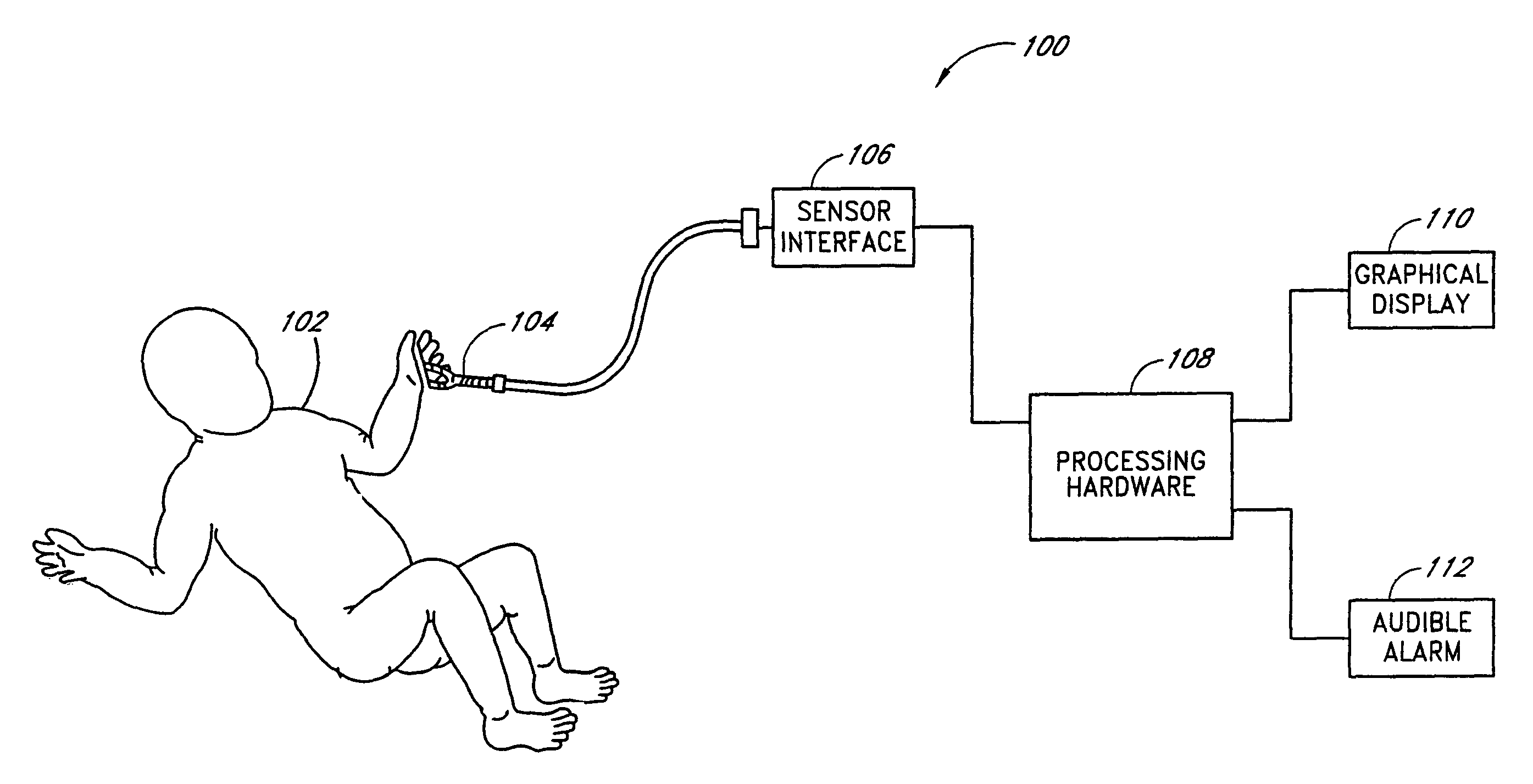
Arterial pulse decomposition analysis for vital signs determination
Determining physiological life signs, with a sensor that is in contact with the surface of a patient's skin at point proximate an artery, and measuring arterial blood vessel displacement and / or blood pressure changes. A data stream of measurements of is collected and a set of parameters from the collected data, a number of physiological life signs parameters, is extracted from the data. The physiological life signs that can be extracted include heart rate, breathing rate, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure.
Owner:BARUCH MARTIN
Systems, apparatuses and methods for determining blood pressure
ActiveUS20160345845A1Flexible configurationElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsTransceiverRadiology
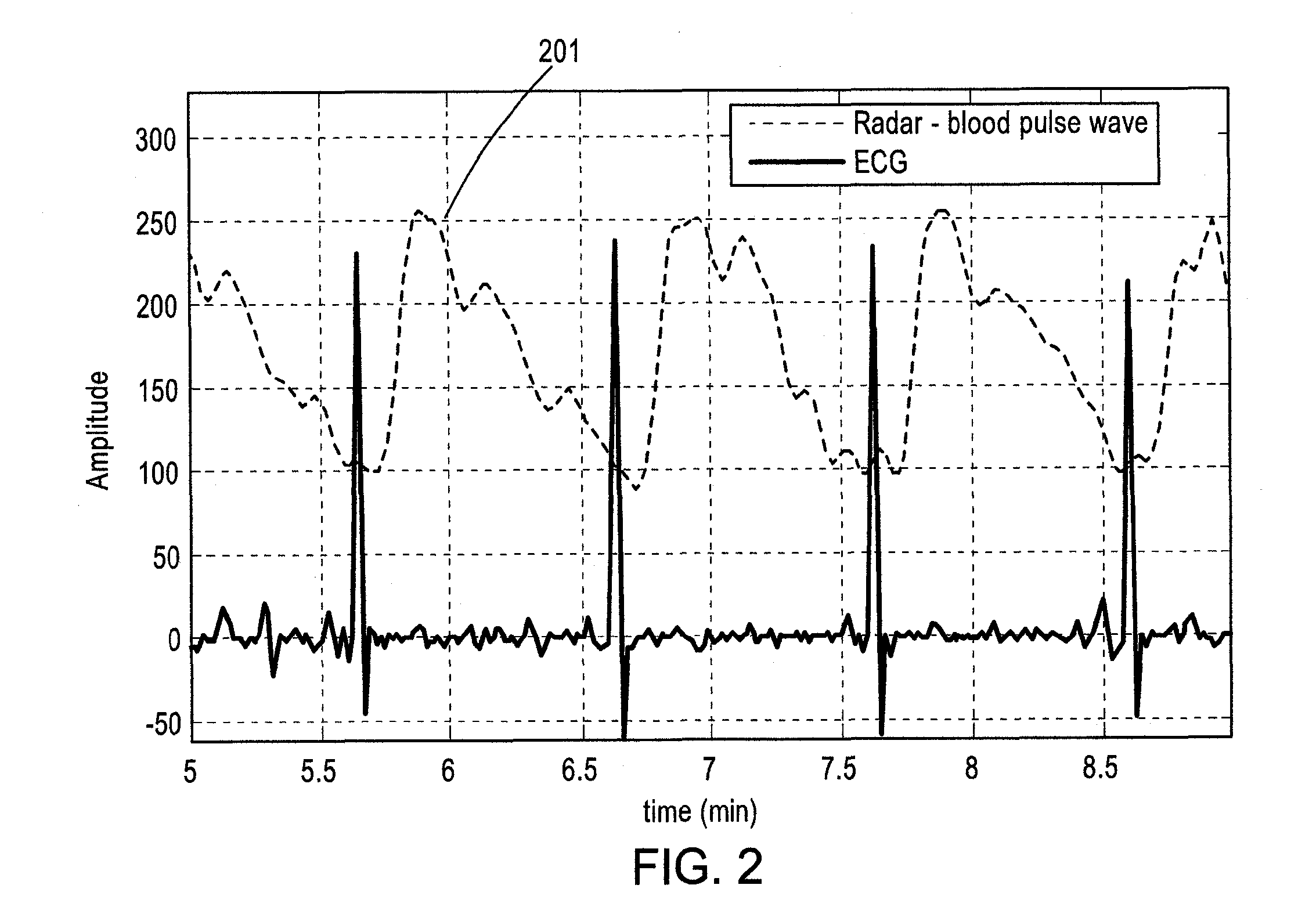
The present disclosure is directed to apparatuses, systems and methods for measuring time-varying radar cross section (RCS) of an artery of a patient, which may be used to determine blood pressure of a patient. In some embodiments, an apparatus is provided which comprises a radio-frequency (RF) transceiver for generating RF waves, and at least one sensor configured for positioning on or adjacent the skin of a patient, and at least one of transmitting the RF waves into tissue of the patient and receiving RF wave reflections from at least one artery located within the tissue. The apparatus may further comprise a processor having computer instructions operating thereon configured to cause the processor to determine an RF arterial pulse waveform based on the received RF wave reflections. The time-varying radar cross section (RCS) comprises the RF arterial pulse waveform. This may be in turn correlated to blood pressure of the patient.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL ISRAEL LTD
Apnea detection system
A method and apparatus are described for utilizing a source of vascular pulse waveform data from a patient for the purpose of measuring pulsus paradoxus. The arterial pulse waveform data source described is a pulse oximeter plethysmograph but can be any similar waveform data source, including an intra-arterial transducer, external blood pressure transducer, or plethysmograph. Through incorporation of measurements of values, such as an area under a pulse waveform curve, that are time-domain functions of a change in amplitude of the pulse waveform over a duration of the waveform, embodiments of the present invention represent a significant improvement upon previously described methods of measuring pulsus paradoxus.
Owner:PRECISION PULSUS
Real-time blood pressure measuring device and measuring method
ActiveCN105708431AImprove convenienceImprove accuracyDiagnostics using lightEvaluation of blood vesselsMeasurement deviceCardiac cycle
The invention relates to a real-time blood pressure measuring device. The real-time blood pressure measuring device comprises a first pulse wave sensor module, a second pulse wave sensor module and a signal processing module, wherein the first pulse wave sensor module is used for acquiring a first pulse wave signal of an aorta in each cardiac cycle, and the first pulse wave signal is a pressure pulse wave; the second pulse wave sensor module is used for acquiring a second pulse wave signal of a capillary artery adjacent to the aorta in each cardiac cycle, and the second pulse wave signal is a volume pulse wave; and the signal processing module is used for acquiring the first pulse wave signal at the aorta and the second pulse wave signal of the capillary artery adjacent to the aorta, acquiring transmission time difference between the first pulse wave signal and the second pulse wave signal, obtaining peripheral arterial pulse wave transmission characteristic time and obtaining arterial blood pressure in each cardiac cycle according to relation between the peripheral arterial pulse wave transmission characteristic time and blood pressure. The invention further relates to a blood pressure measuring method.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
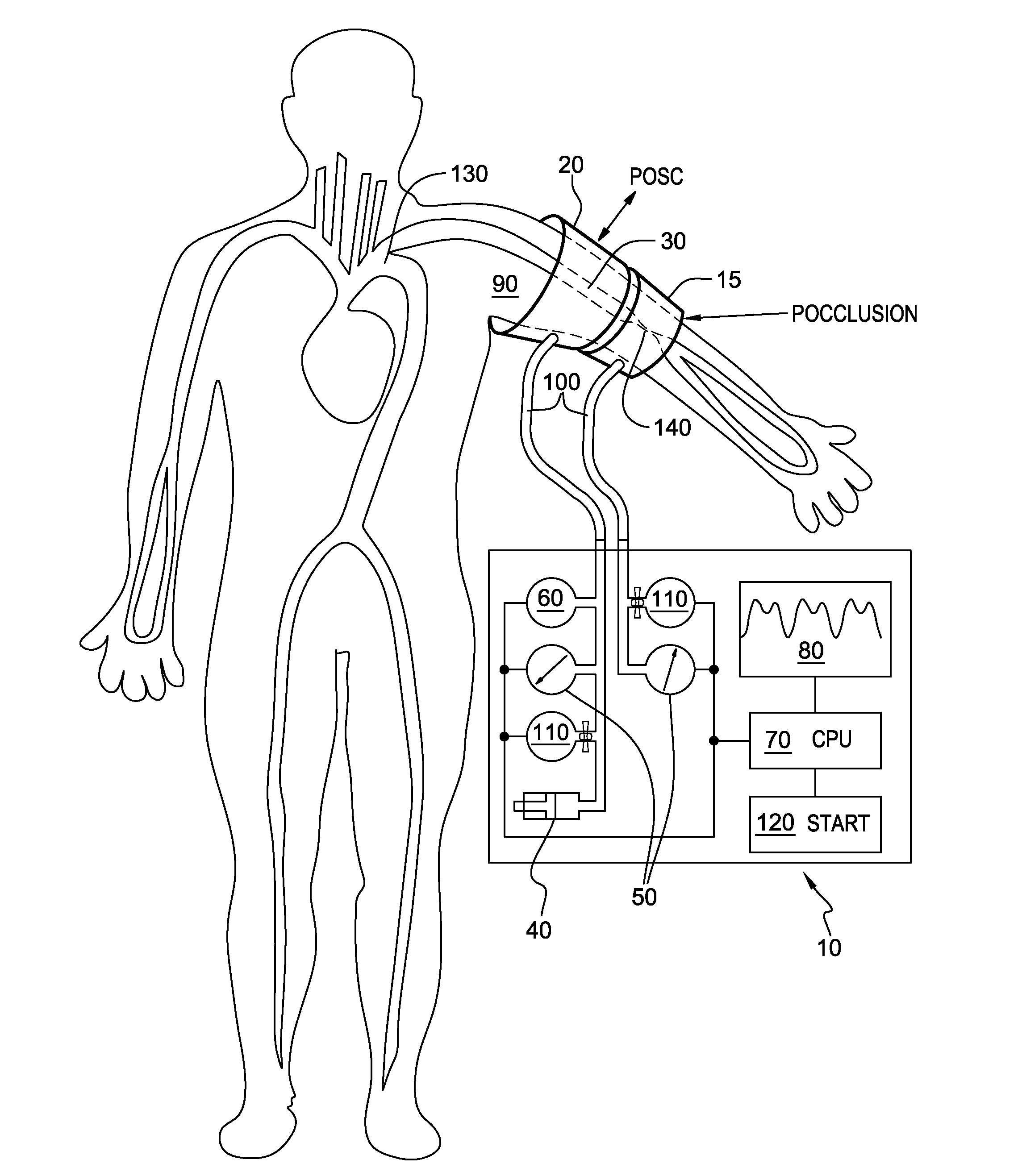
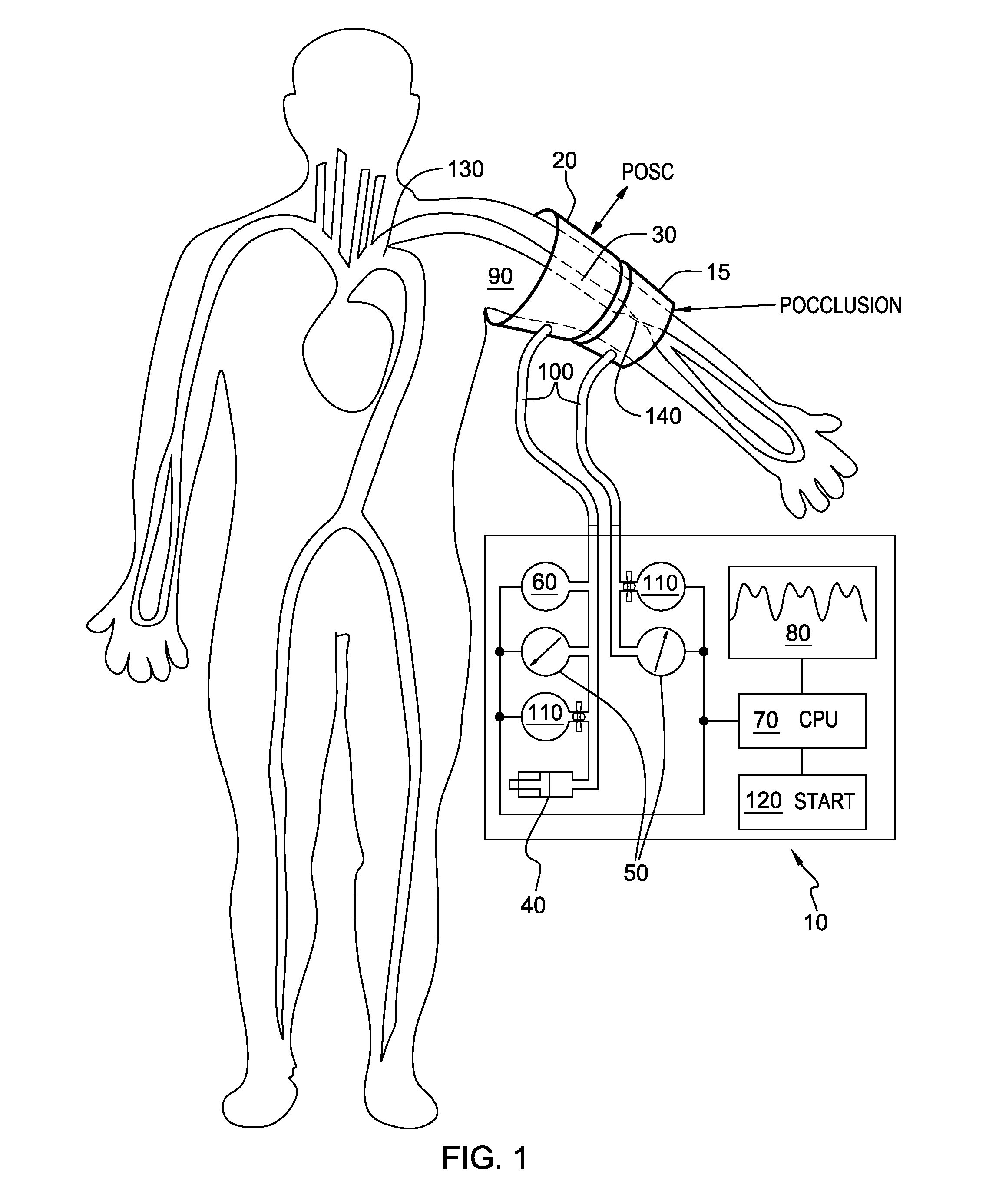
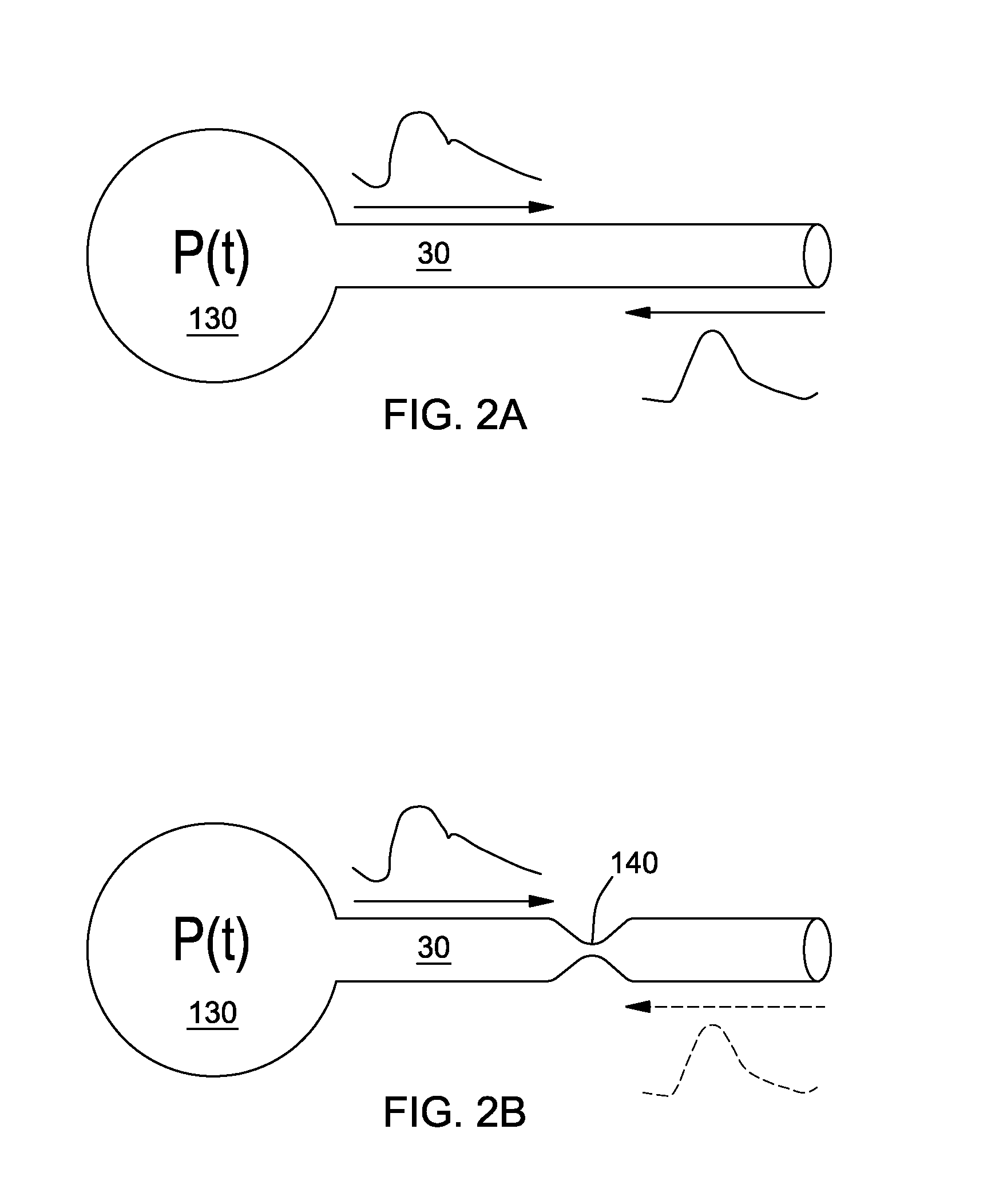
Noninvasive method and apparatus to measure central blood pressure using extrinsic perturbation
InactiveUS20140135634A1Pressure dropDrop reflectionDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsVenous stasisArterial occlusions
Method to obtain continuous recording of the central arterial blood pressure waveform noninvasively utilizes dual (distal occlusion and proximal) brachial artery occlusion cuffs and dual external osculation. The distal arterial occlusion cuff eliminates venous stasis artifact and flow related gradient from aorta to the brachial artery. The proximal cuff measures, and delivers, dual external oscillation. The dual external oscillation allows measurement of the arterial compliance at a multitude of transmural pressure values during each cardiac cycle. Transmural pressure / arterial compliance and arterial pressure curves are subsequently reconstructed using dual external oscillation. The curves consist of two parts, rapid and slow parts, both at the frequency higher than the arterial pulse.
Owner:PRANEVICIUS OSVALDAS +2
Monitoring pulse transmissions using radar
ActiveUS20170105622A1Improving biometric dataDigital data authenticationElectronic input selection/mixingBiometric dataRadar
A method for improving biometric data by using a plurality of wearable devices on a network includes making a first measurement at a first wearable sensor at a first location on a body, making a second measurement at a second wearable sensor positioned at a second location on the body, and detecting an arterial pulse wave transmit time using the first measurement and the second measurement.
Owner:BRAGI
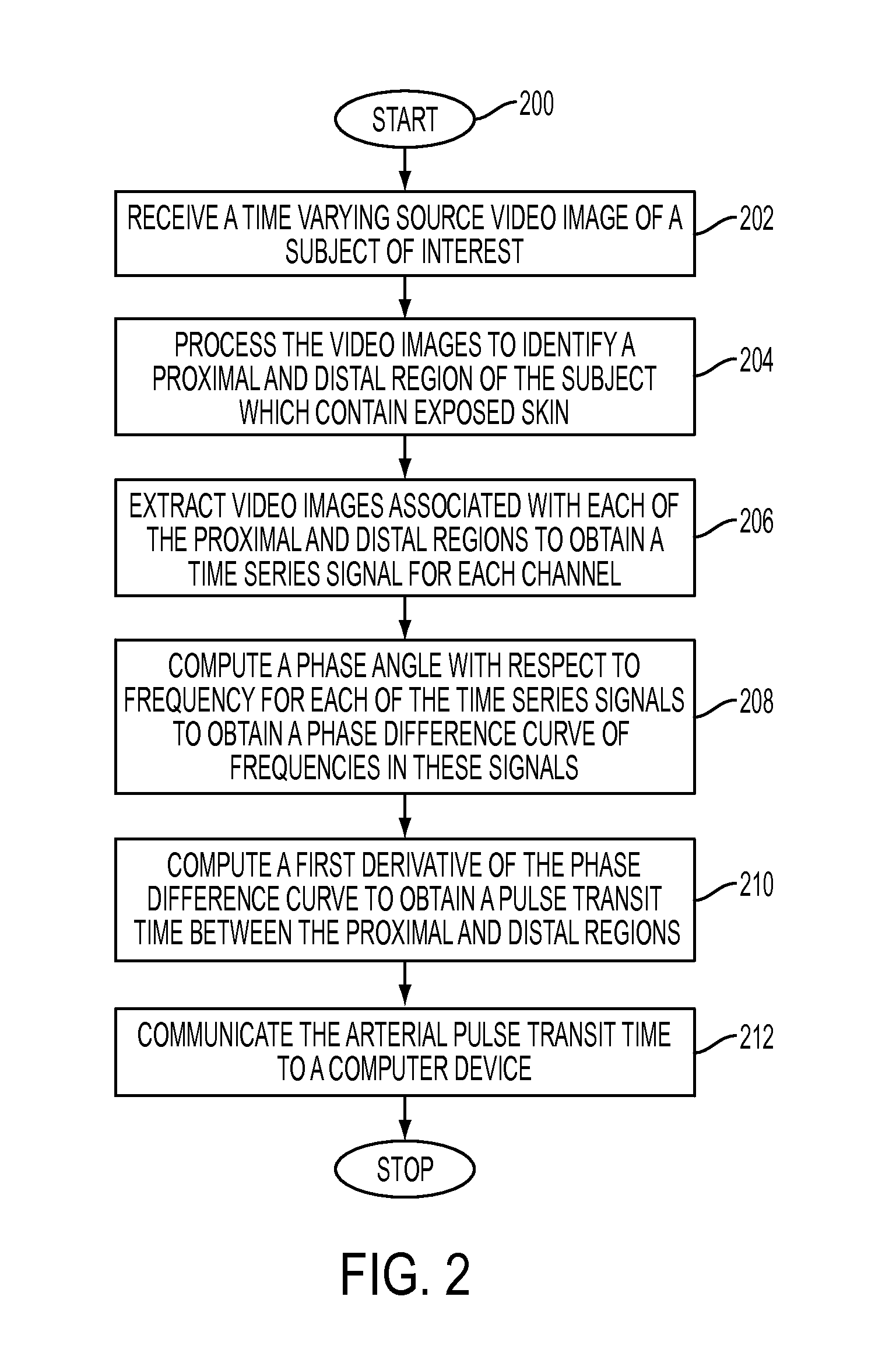
System and method for determining video-based pulse transit time with time-series signals
What is disclosed is a system and method for determining a subject of interest's arterial pulse transit time from time-varying source signals generated from video images. In one embodiment, a video imaging system is used to capture a time-varying source signal of a proximal and distal region of a subject of interest. The image frames are processed to isolate localized areas of a proximal and distal region of exposed skin of the subject. A time-series signal for each of the proximal and distal regions is extracted from the source video images. A phase angle is computed with respect to frequency for each of the time-series signals to produce respective phase v / s frequency curves for each region. Slopes within a selected cardiac frequency range are extracted from each of the phase curves and a difference is computed between the two slopes to obtain an arterial pulse transit time for the subject.
Owner:XEROX CORP
System and method for monitoring cardiac output, flow balance, and performance parameters
InactiveUS20150025328A1Improved design and performanceElectrotherapyDialysis systemsBlood flowVenous pulse
A system for measuring of cardiac output and cardiac performance parameters based on a cardiac blood flow balance parameter between a right chamber of the heart and a left chamber of the heart, includes a sensor device for measuring one of blood pressure and blood flow rate and blood constituent concentration of a patient so as to generate an arterial pulse signal. A processing unit is responsive to the arterial pulse signal for generating a full arterial pulse signal, an arterio-venous pulse signal, and a balance parameter. A computational device is responsive to the balance parameter for further generating cardiac output and a set of cardiac performance parameters. A display station device is responsive to the set of physiological parameters from the computational device for displaying meaningful information.
Owner:KHAIR MOHAMMAD
Electric air pressure tourniquet
ActiveCN102178554AMeasurement has no effectShort measurement timeEvaluation of blood vesselsTourniquetsSurgical operationWave detection
The invention relates to an electric air pressure tourniquet applicable to the hemostasis operation in surgery and intravenous local narcotherapy. The electric air pressure tourniquet comprises a hemostasis loop, a hemostasis loop tube, a pump tube, a pump and a pressure control valve, wherein the hemostasis is bound on the hemostasis part of a living body; the pump offers power by the pressure control valve to tighten or loosen the hemostasis loop; a pressure sensor is used for measuring the pressure of the hemostasis loop; a static pressure filtering circuit for measuring the compression pressure in the pressure of the hemostasis loop and an arterial pulse wave detection circuit for measuring the arterial pulse wave in the pressure of the hemostasis loop are respectively connected with the pressure sensor; a static pressure A / D (Analog to Digital) converter and an arterial pulse wave A / D converter respectively convert and then transmit the signals detected in the static pressure filtering circuit and the arterial pulse wave detection circuit to an electronic control device; and the electronic control device controls the start and close of the pump, as well as the start and close of the pressure control valve.
Owner:杭州迈迪克仪器有限公司
Fully-automatic multi-functional integrated puncture training computer dummy
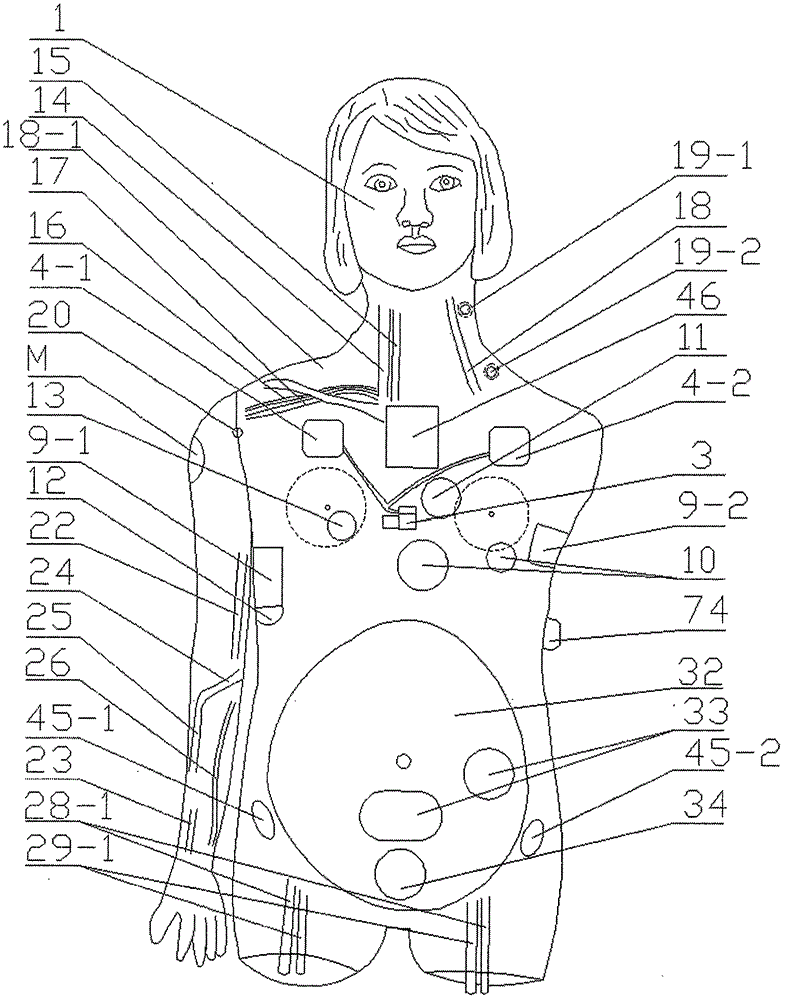
ActiveCN107437362ANovel ideaReasonable designCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsAutomatic controlHydrothorax
The invention belongs to the medical teaching equipment technical field and relates to a fully-automatic multi-functional integrated puncture training computer dummy. The fully-automatic multi-functional integrated puncture training computer dummy comprises a high-simulation human body model, a position-automatic changing experimental table, puncture cavities, modules, arteriovenous veins, a liquid injection automatic control device, a fully-automatic arterial pulse simulator and a microcomputer controller. The dummy is characterized in that the high-simulation human body model is installed on the position-automatic changing position experimental table and is provided with various puncture cavities / modules such as pneumothorax, hydrothorax and abdominocentesis modules which are all connected with the microcomputer controller and / or a micro water pump / air pump; double-layer metal mesh electrodes are distributed on the neck, thoracic puncture and lumbar puncture positions of the dummy; the dummy is further provided with kidney, bladder, lymph gland and bone marrow puncture cavities / modules as well as a variety of puncturable central veins and peripheral veins; and arteries are connected with a fully-automatic blood circulation simulator. With the dummy adopted, dozens of puncture items can be provided; puncture position change, liquid injection, gas injection and artery pulsing are completely automated; and sound-light alarms can be given out automatically; life-like simulation effects can be realized; and teaching effects can be significantly improved.
Owner:营口市贵东医疗器械制造有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com