Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1075 results about "Transit time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
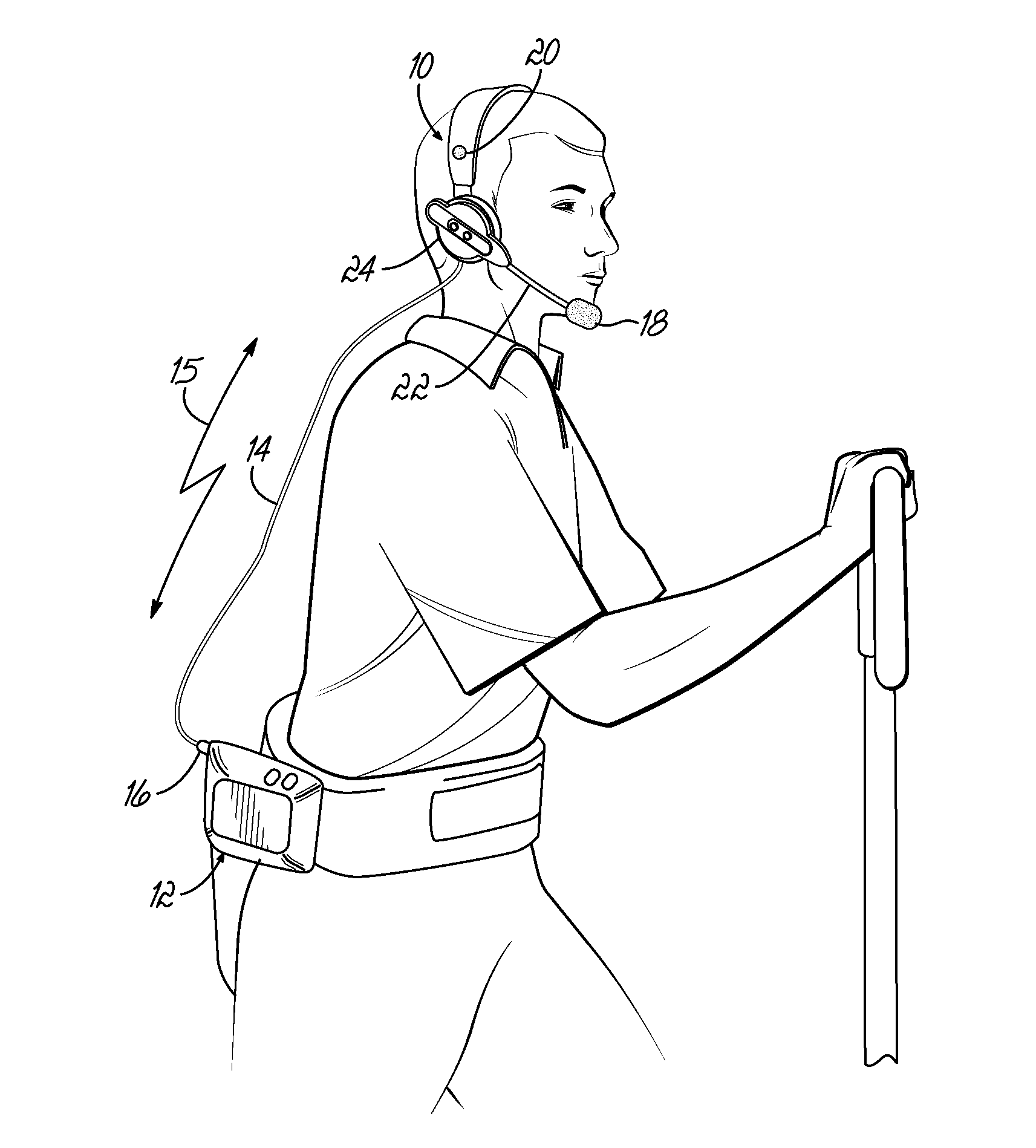
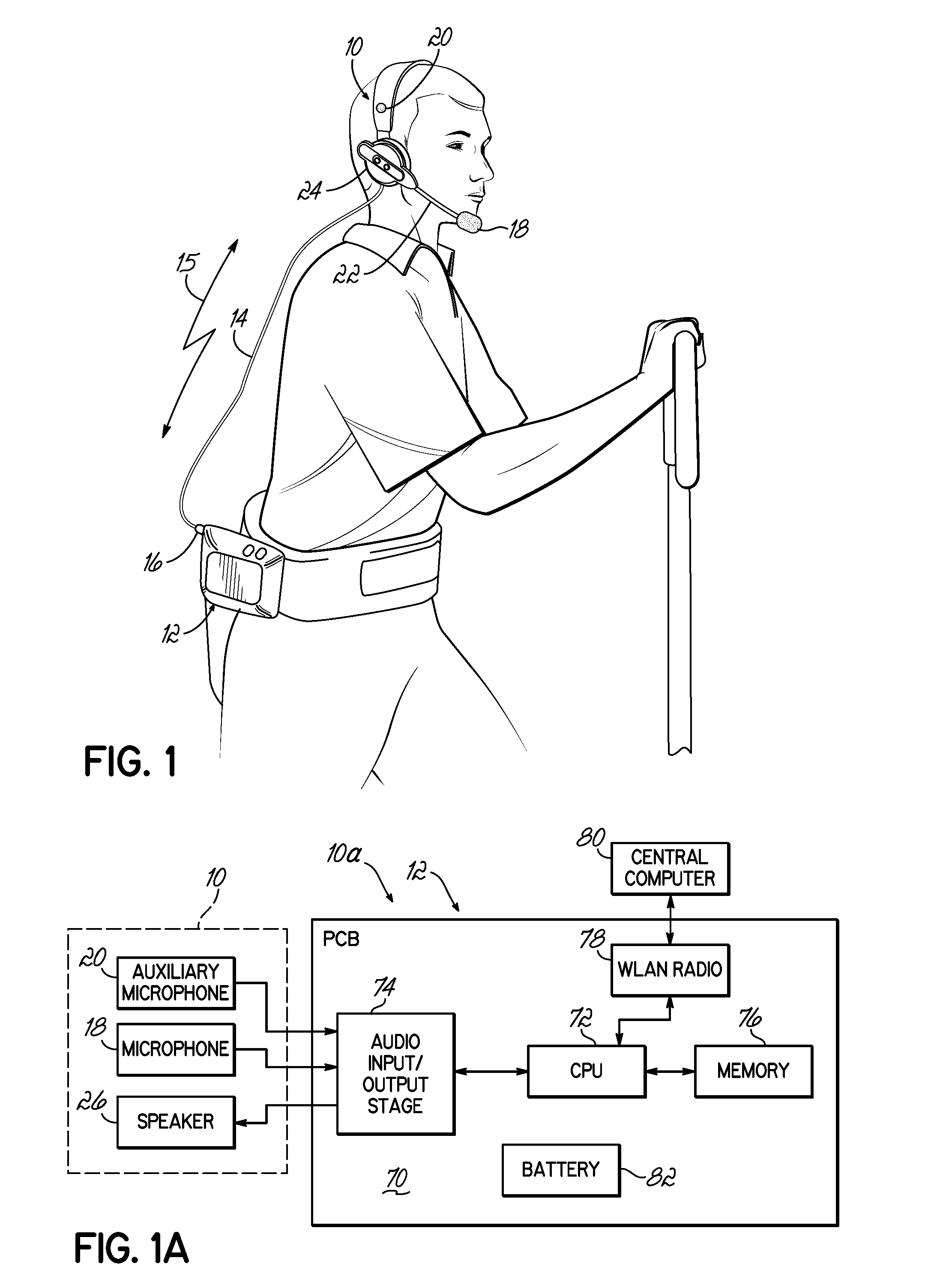
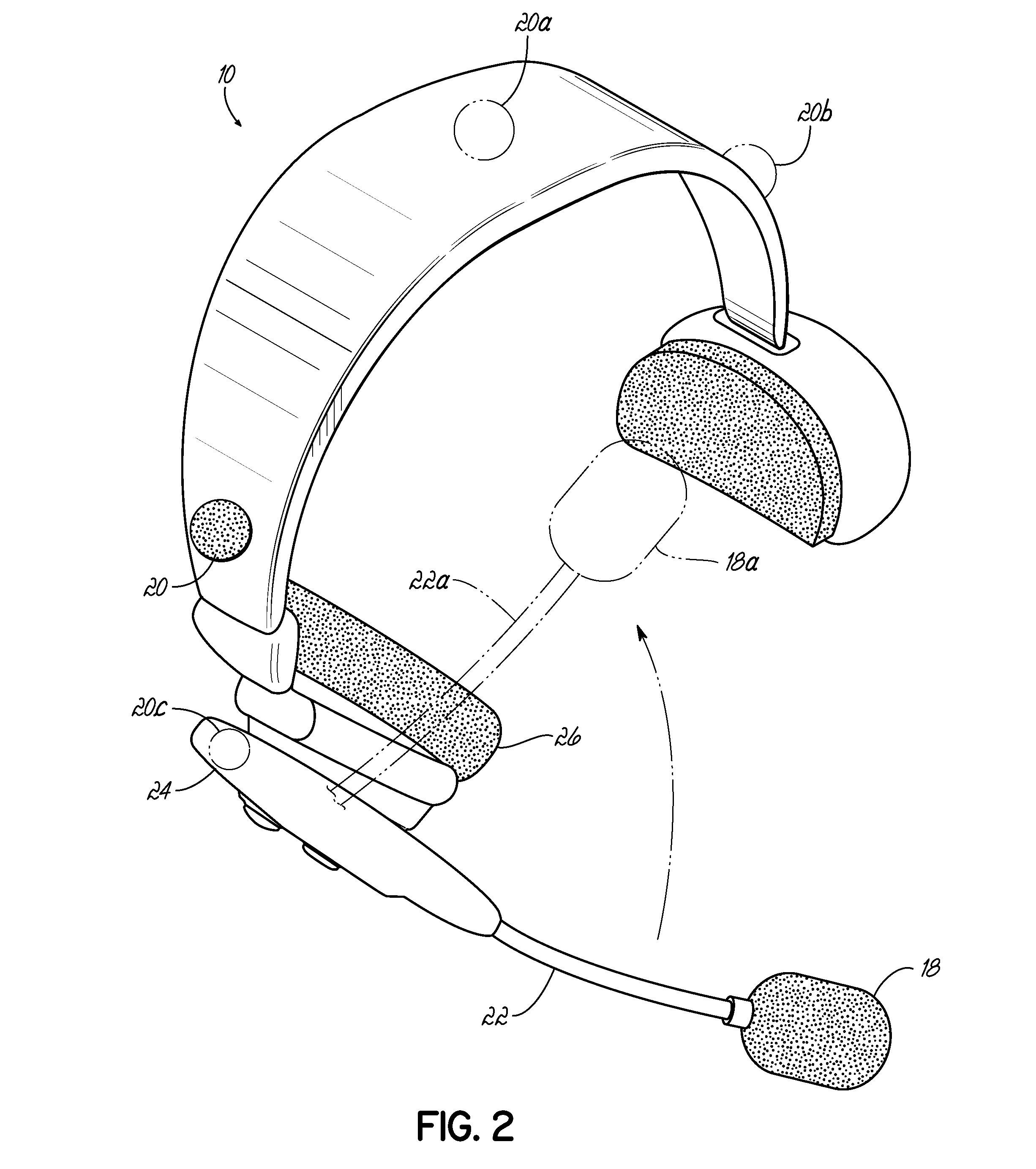
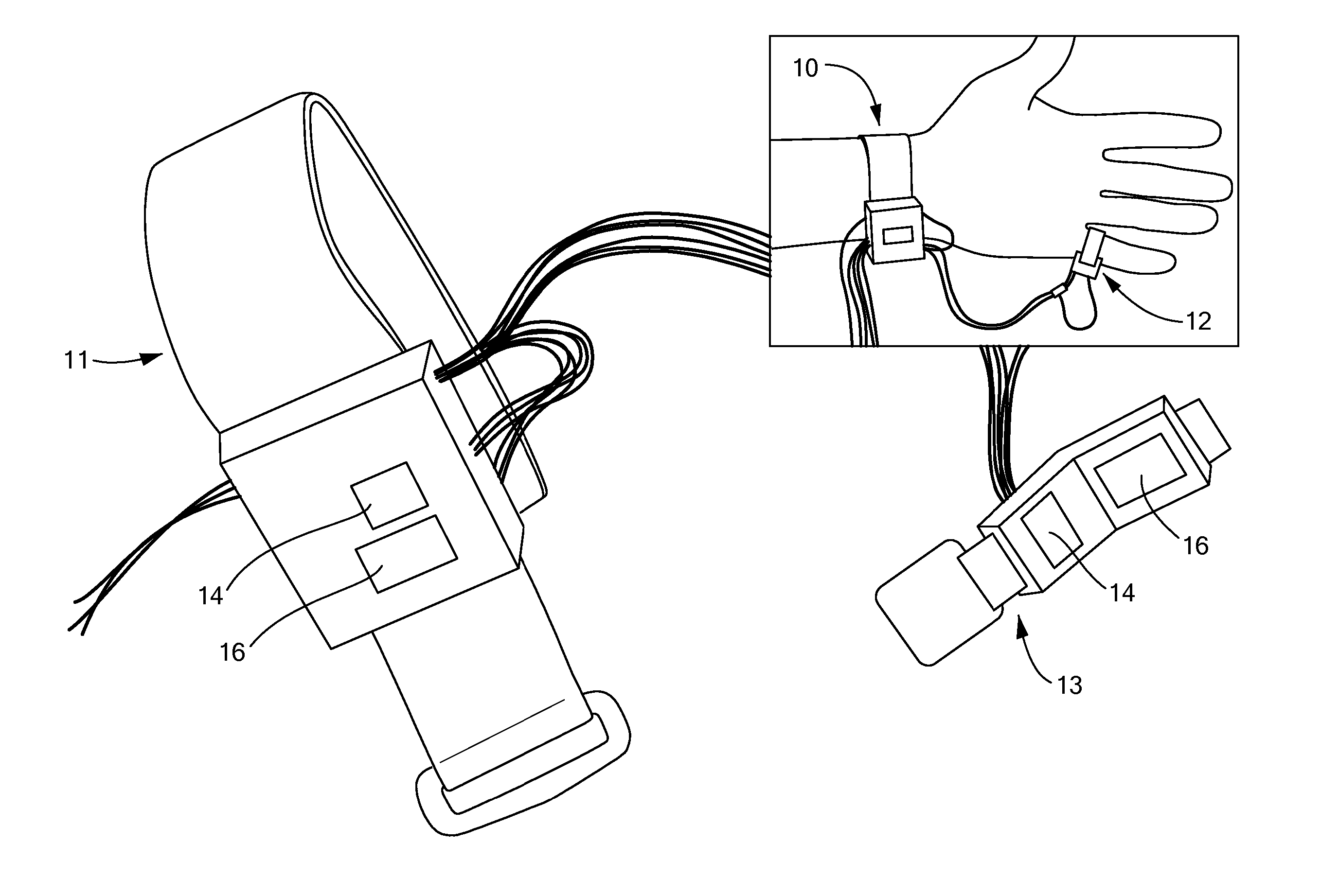
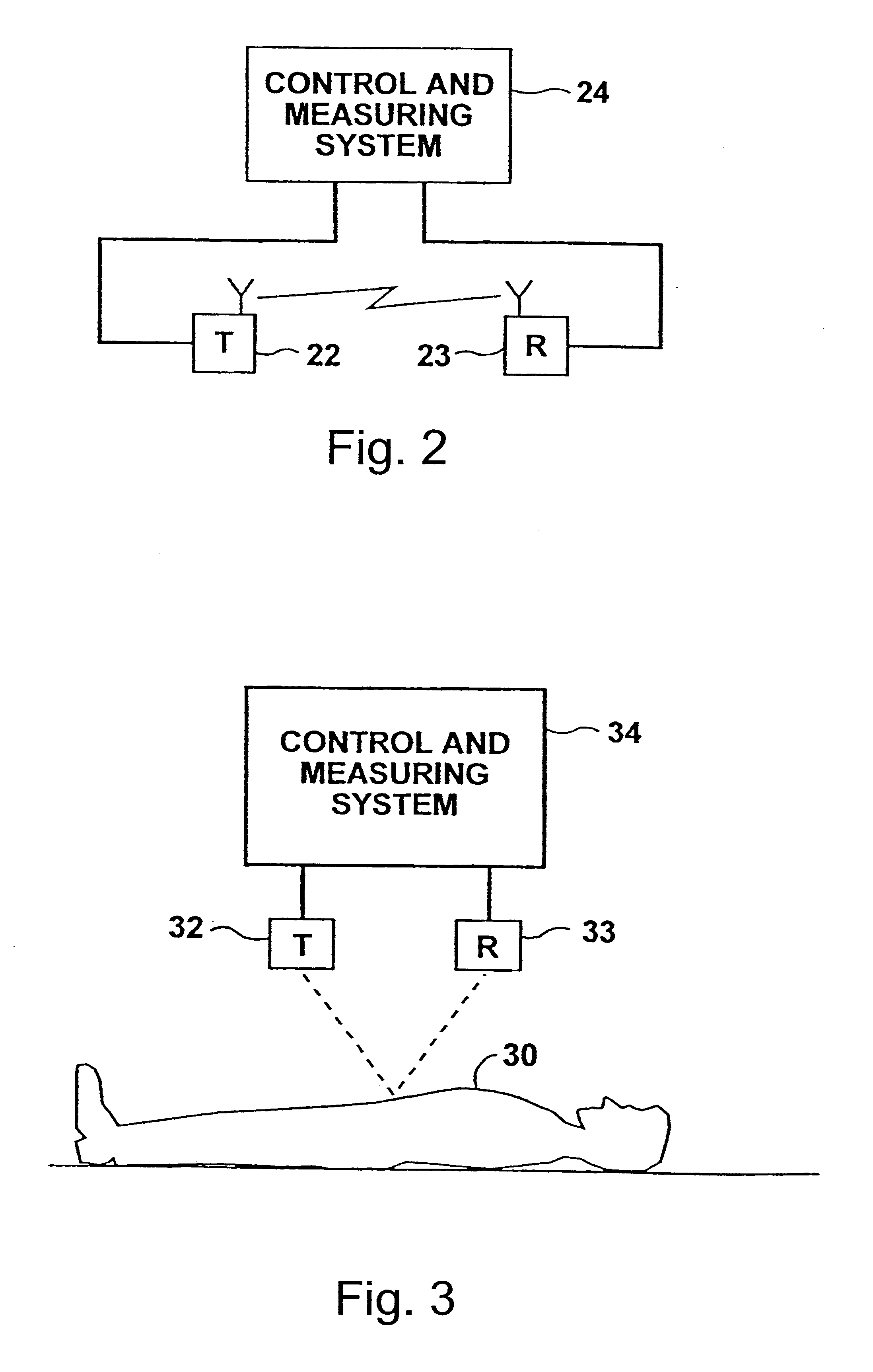
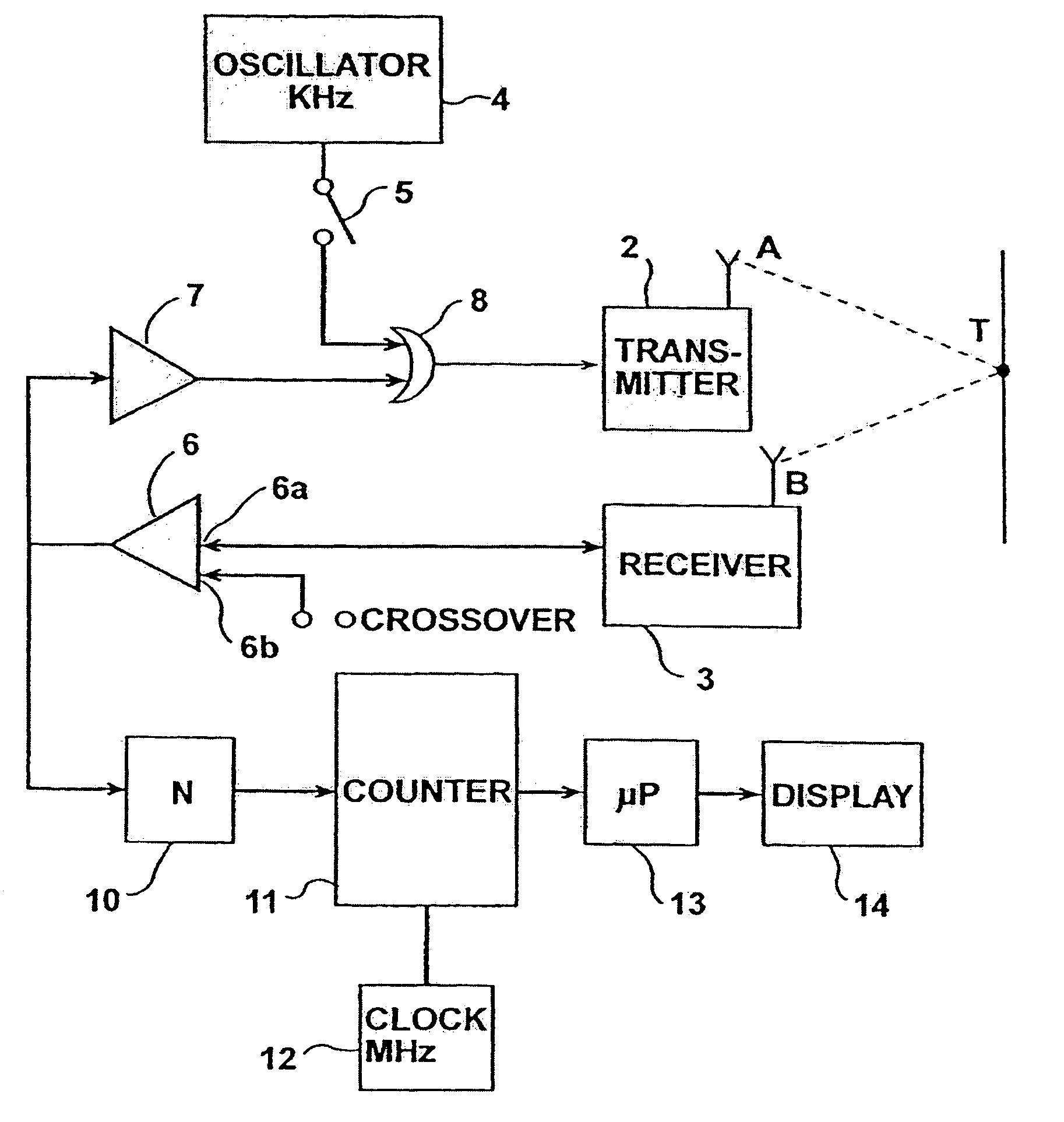
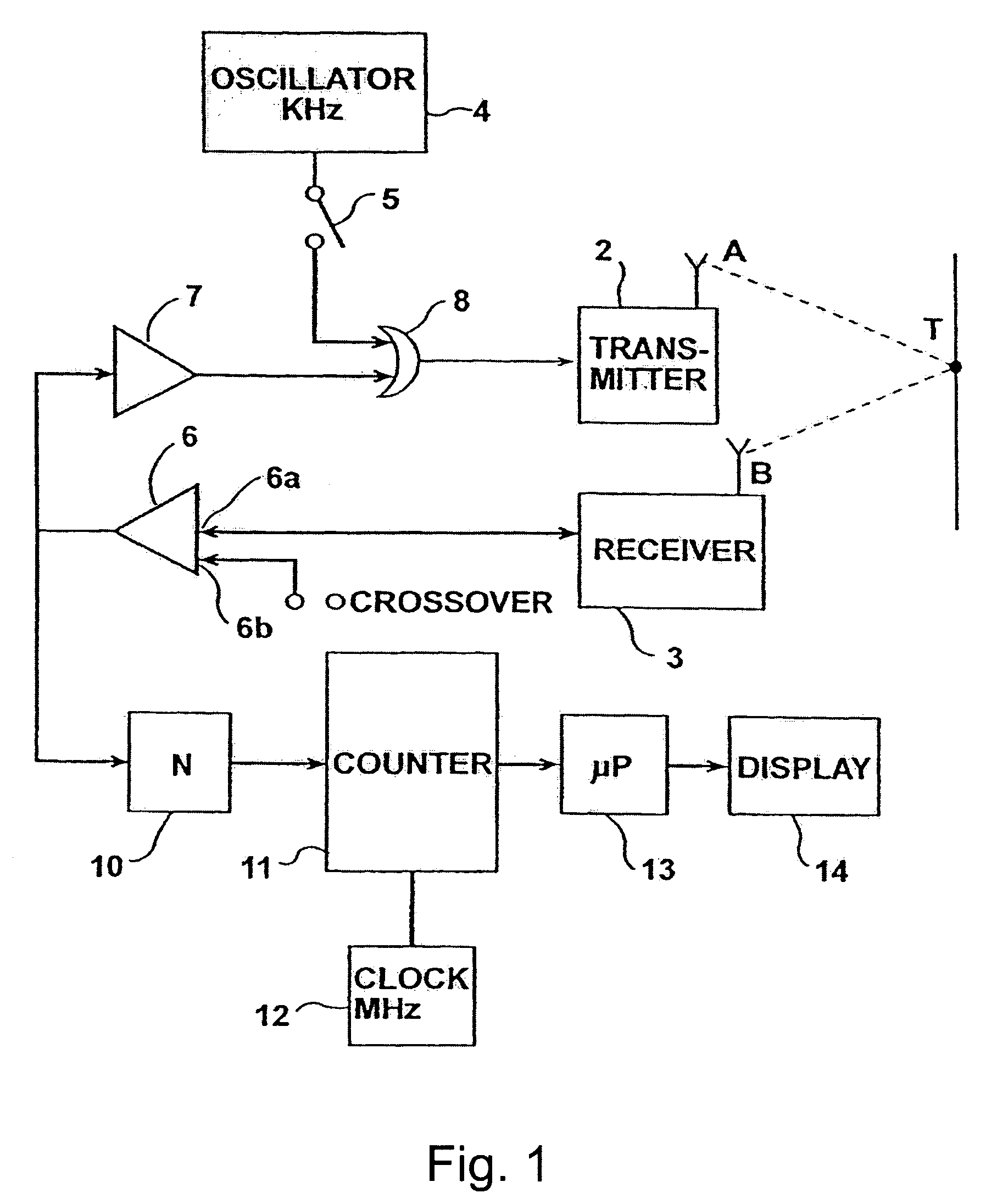
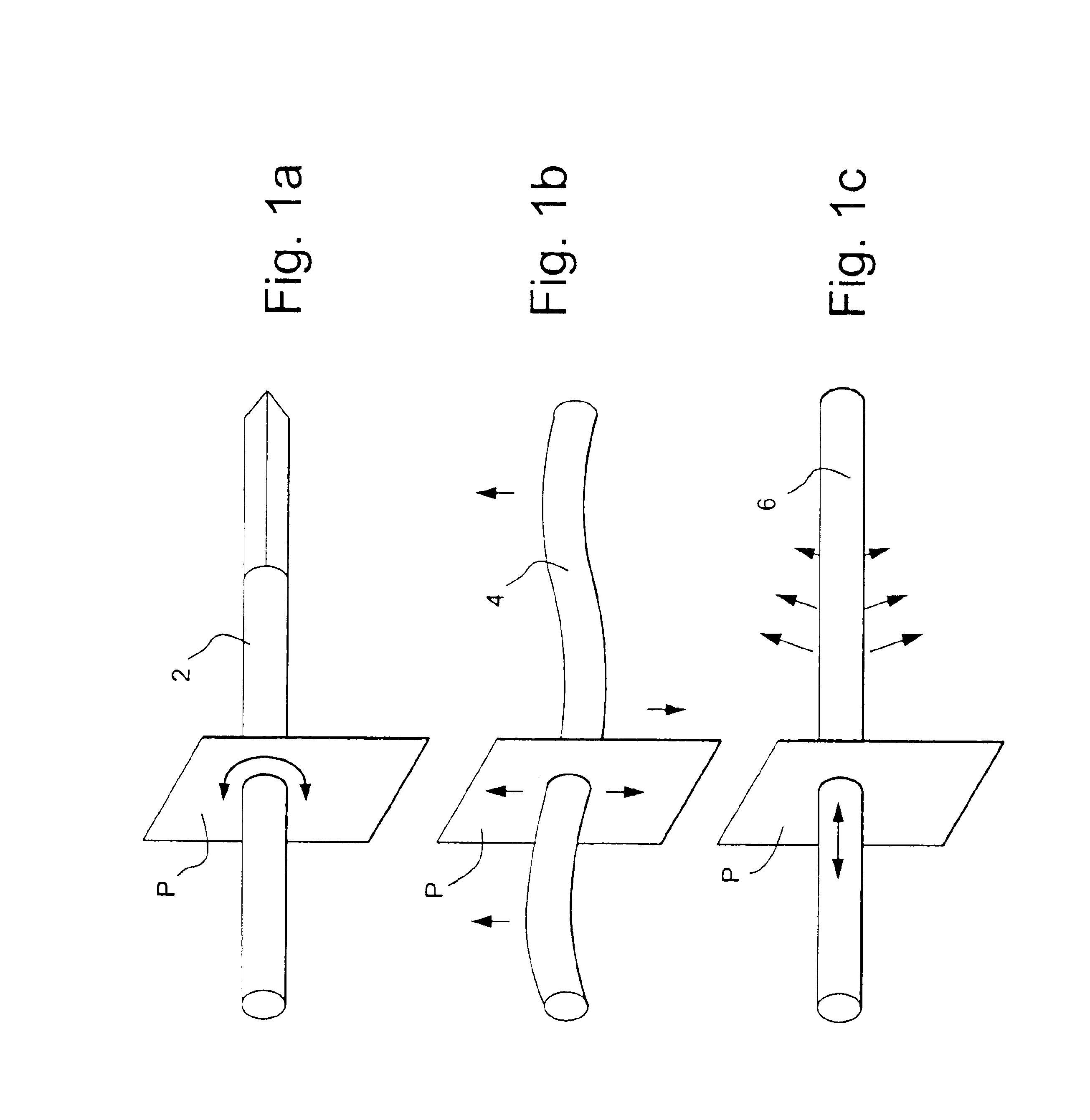
System and method for improving speech recognition accuracy in a work environment
Apparatus and method that improves speech recognition accuracy, by monitoring the position of a user's headset-mounted speech microphone, and prompting the user to reconfigure the speech microphone's orientation if required. A microprocessor or other application specific integrated circuit provides a mechanism for comparing the relative transit times between a user's voice, a primary speech microphone, and a secondary compliance microphone. The difference in transit times may be used to determine if the speech microphone is placed in an appropriate proximity to the user's mouth. If required, the user is automatically prompted to reposition the speech microphone.
Owner:VOCOLLECT
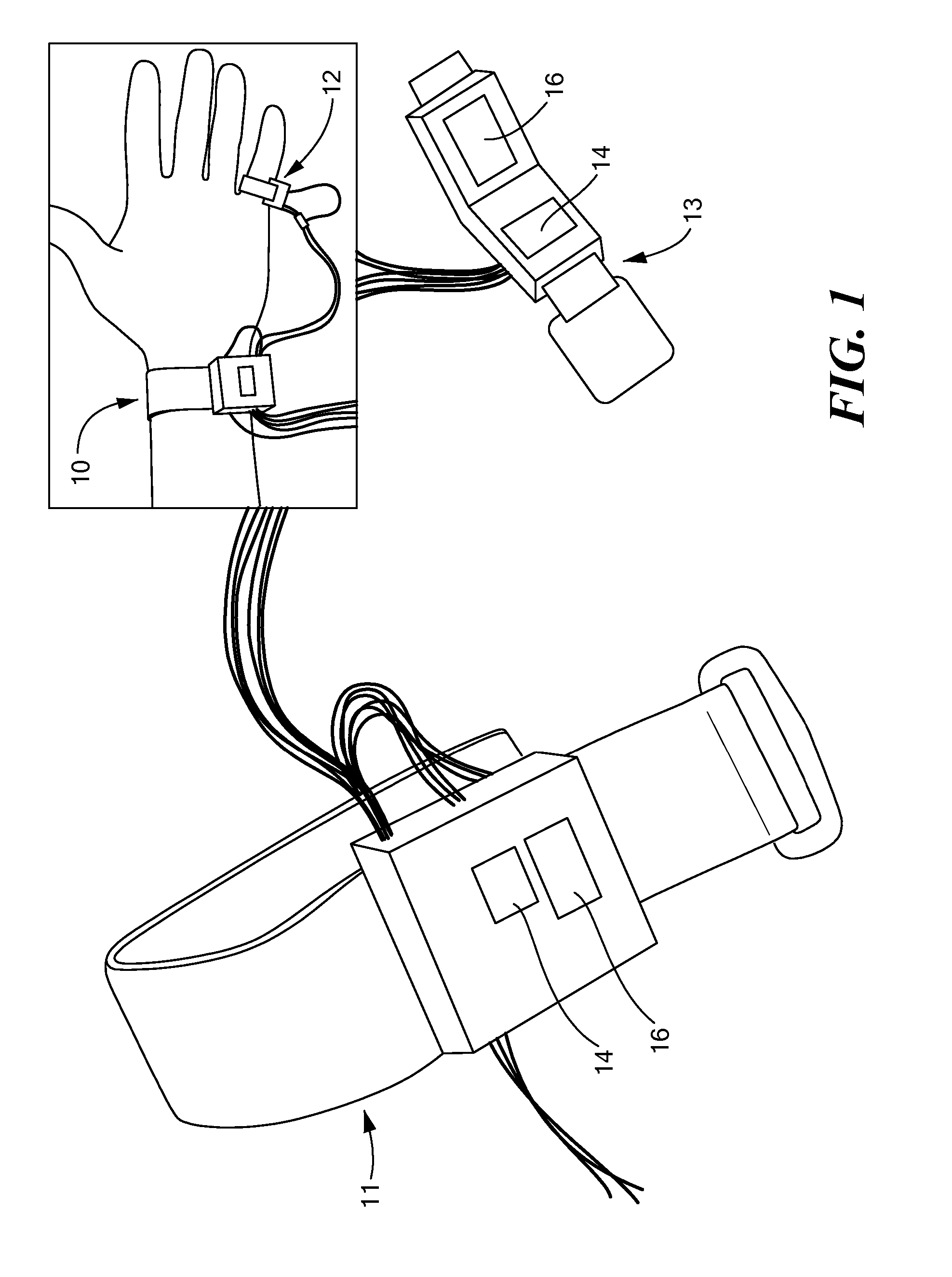
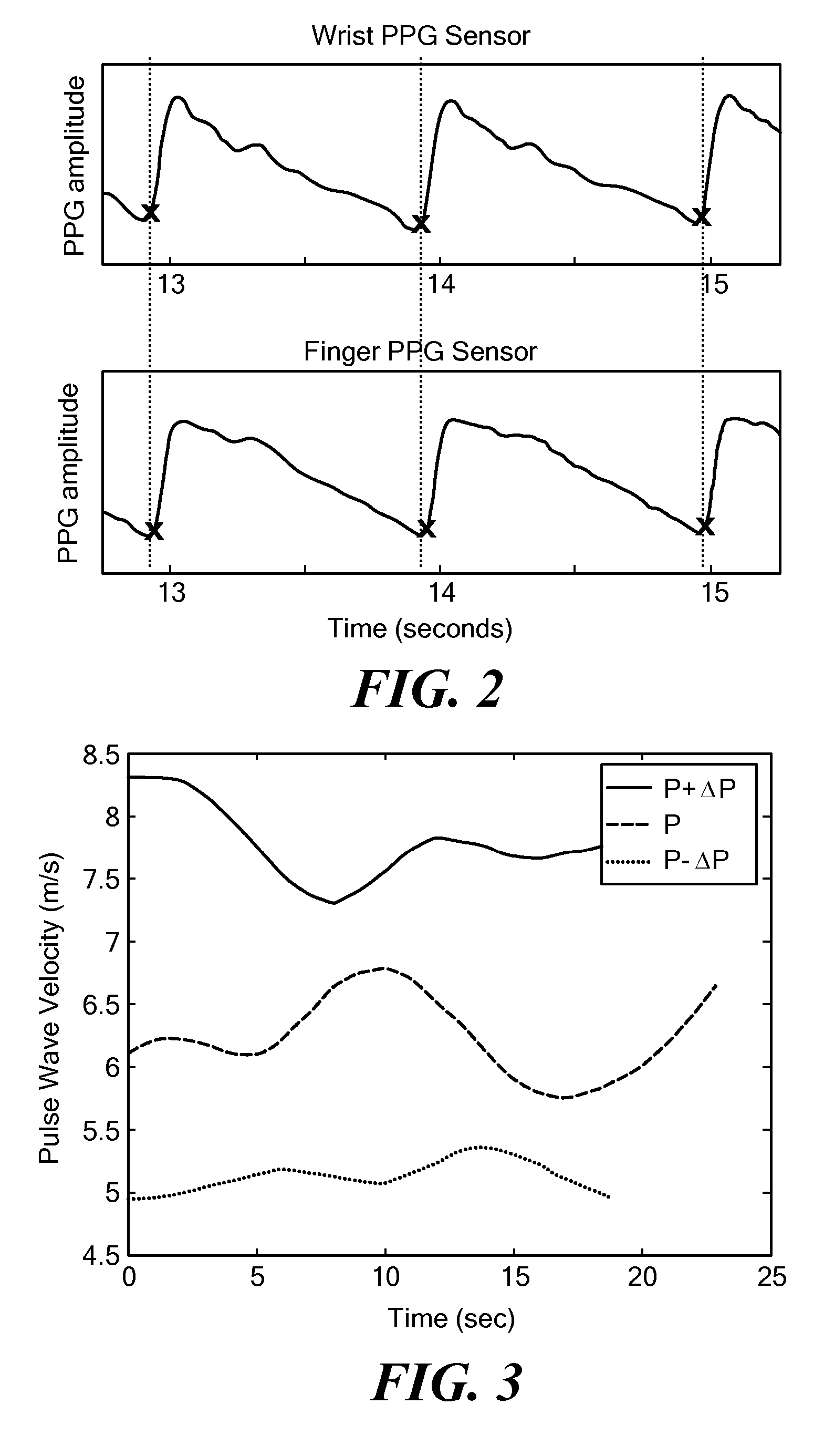
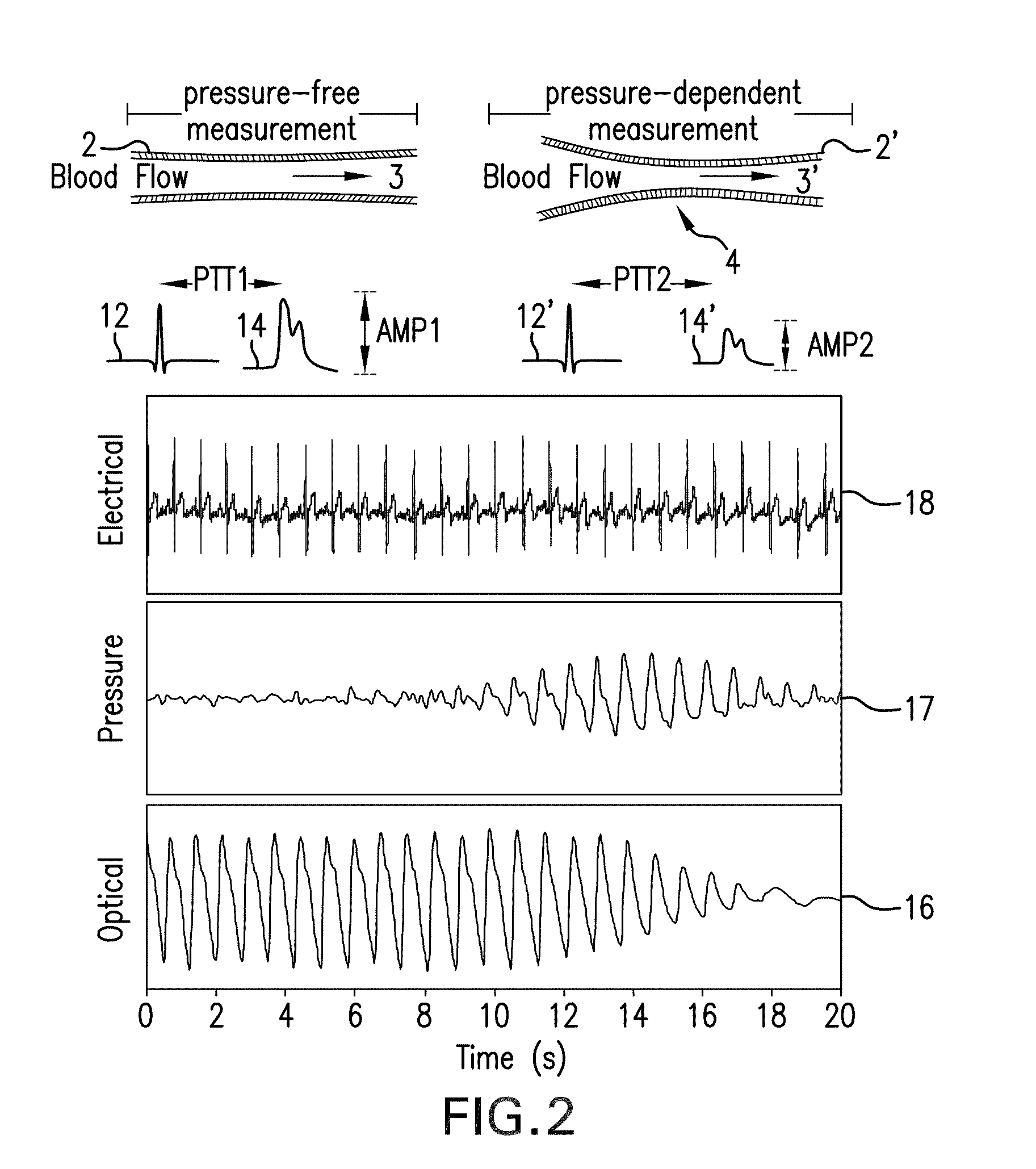
Wearable Pulse Wave Velocity Blood Pressure Sensor and Methods of Calibration Thereof
An apparatus and methods for performing a circulatory measurement on an extremity, such as a hand, of a subject. The circulatory measurement results in the derivation of an output circulatory metric that may encompass blood pressure or various other circulatory metrics. An indicator of an input circulatory metric at a locus on the extremity is measured, such as a pulse transit time. To determine the pulse transit time, a first plethysmographic signal may be obtained at a first position on the extremity, while a second plethysmographic signal may be obtained at a second position on the extremity of the subject. A transit time characterizing a circulatory pressure wave is calculated based on the first and second plethysmographic signals, leading to derivation of a wave speed. A calibration is then applied to provide the circulatory measurement based at least on the derived wave speed and a measured indicator of a hydrostatic component of blood pressure. Calibration is provided, in certain described embodiments, by derivation of two calibration parameters, a gain and a pulse transit time at zero pressure. Methods for deriving the calibration parameters include performing measurements under distinct hydrostatic pressure conditions, and based upon a measured derivative with respect to pressure of the pulse wave velocity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
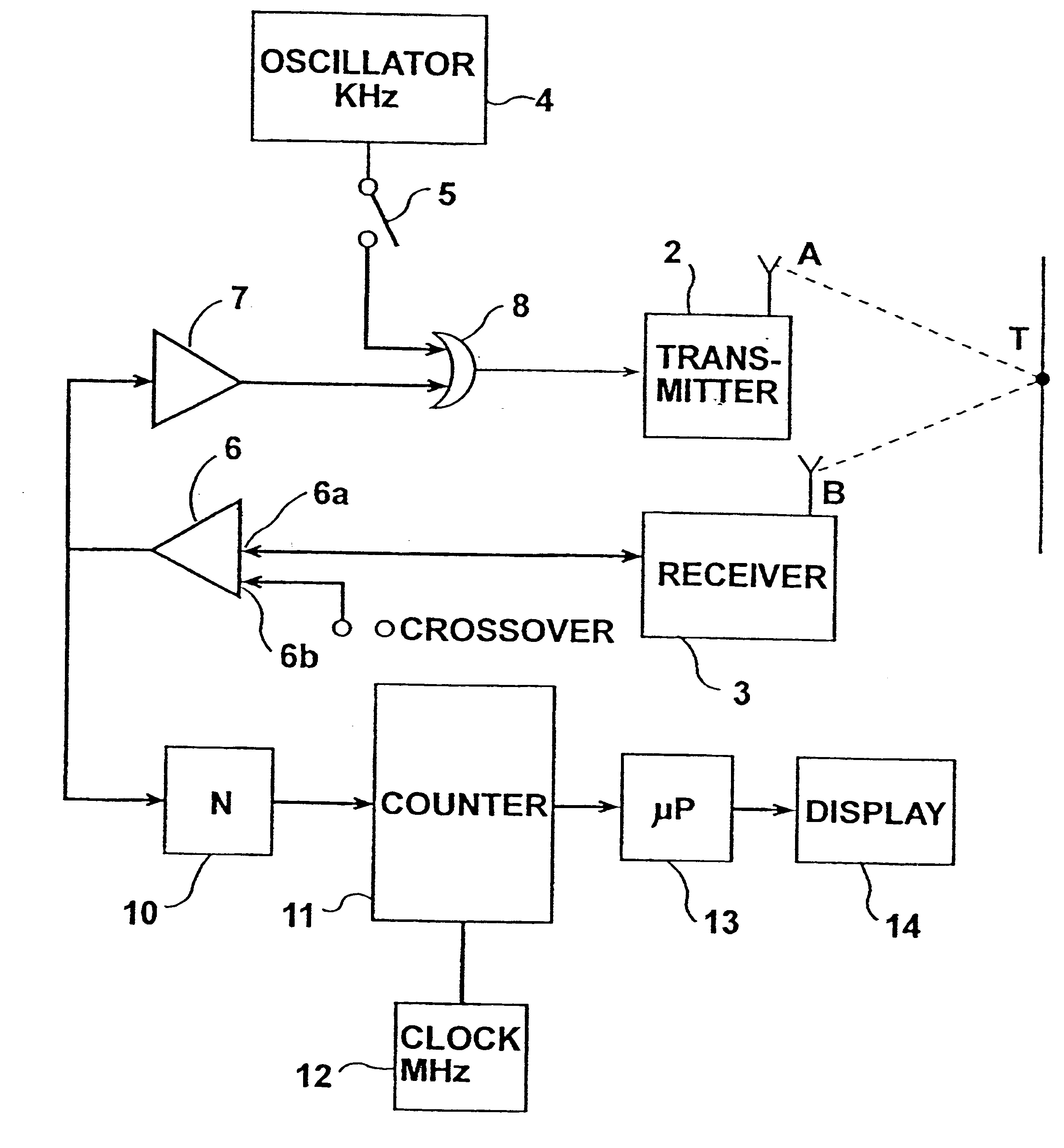
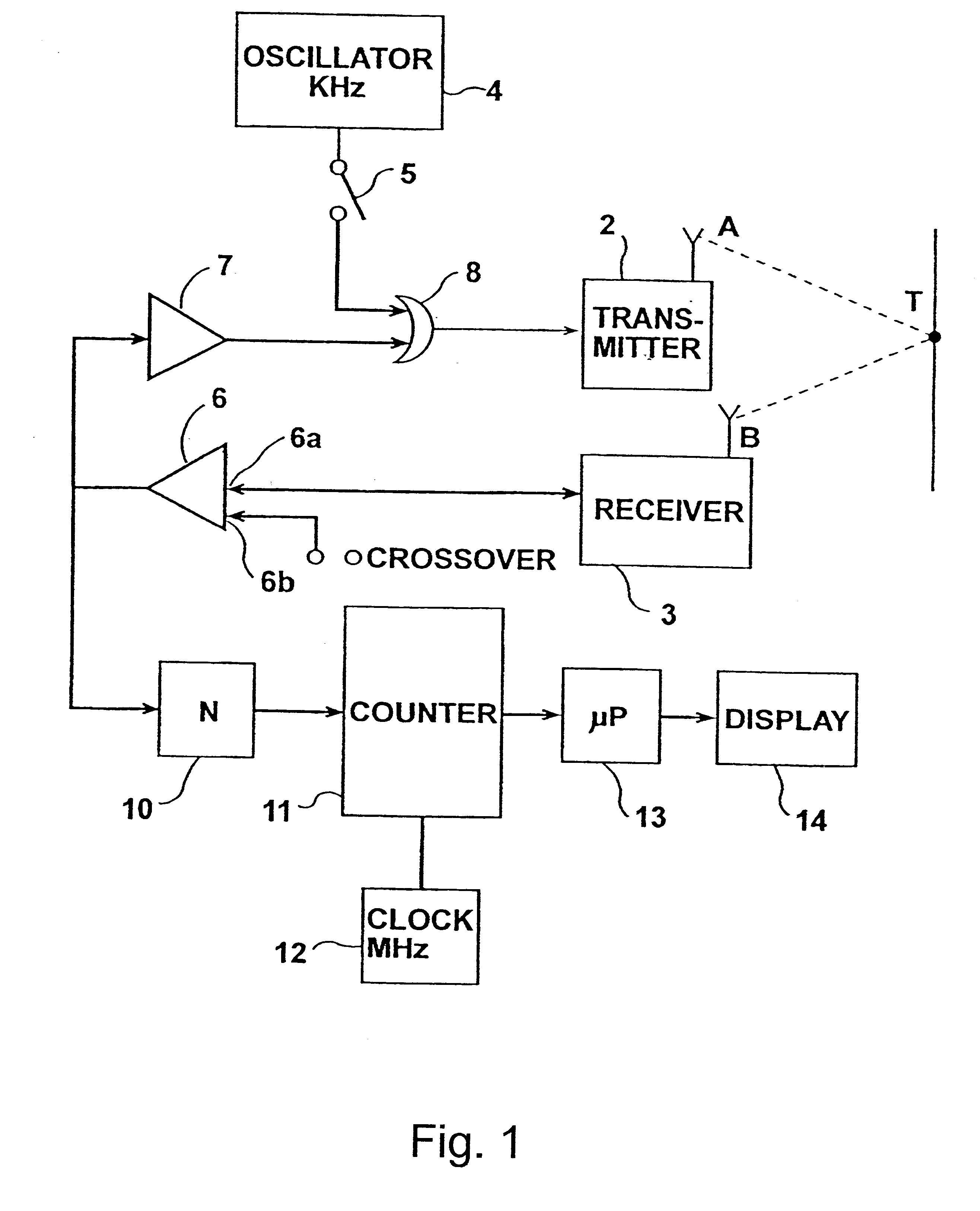
High-precision measuring method and apparatus
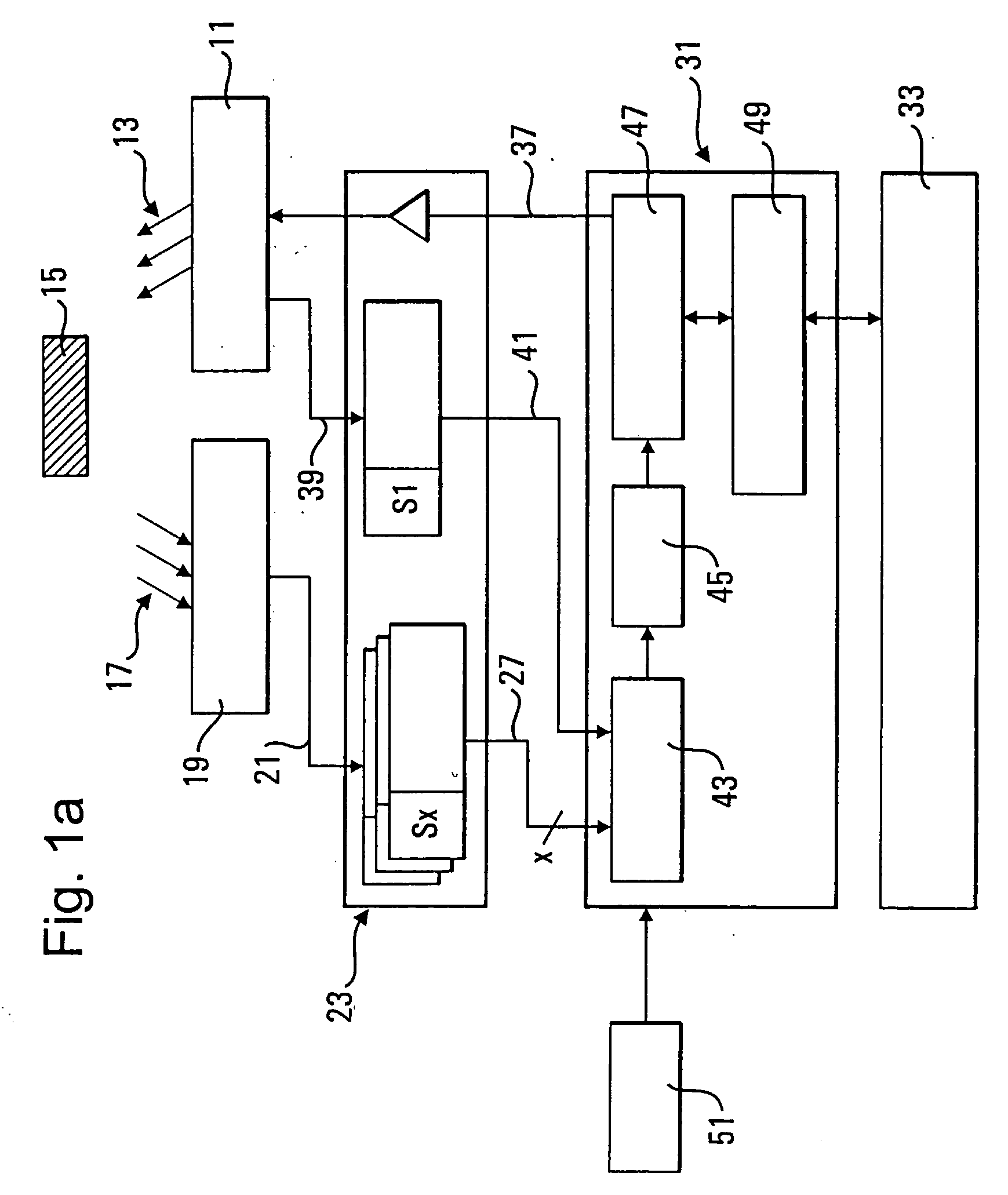
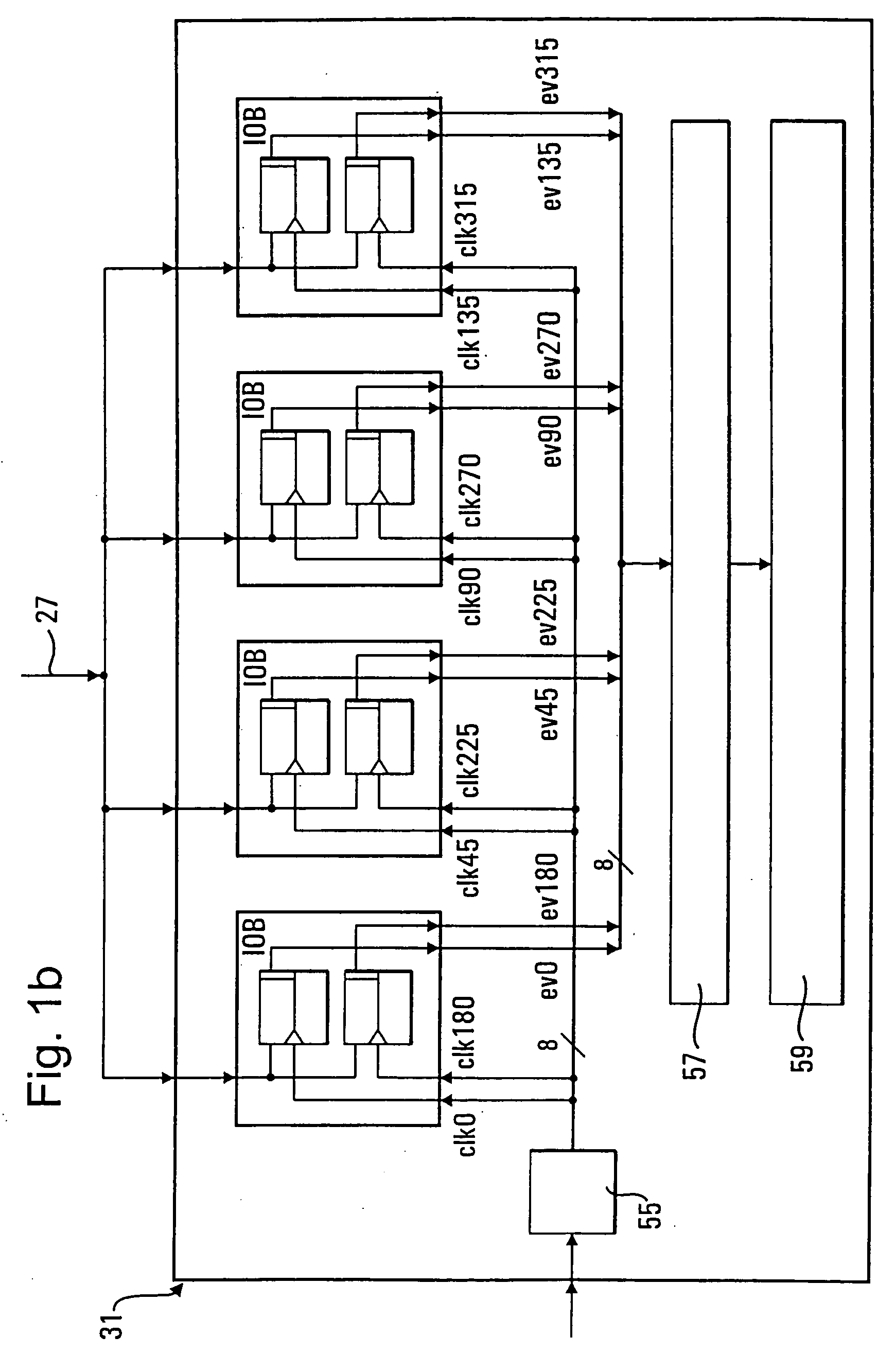
InactiveUS6621278B2Low-cost equipmentHigh precisionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringFiducial points
A method and apparatus of measuring a predetermined parameter having a known relation to the transit time of movement of an energy wave through a medium, by transmitting from a first location in the medium a cyclically-repeating energy wave; receiving the cyclically-repeating energy wave at a second location in the medium; detecting a predetermined fiducial point in the cyclically-repeating energy wave received at the second location; continuously changing the frequency of transmission of the cyclically-repeating energy wave from the first location to the second location in accordance with the detected fiducial point of each received cyclically-repeating energy wave received at the second location such that the number of waves received at the second location from the first location is a whole integer; and utilizing the change in frequency to produce a measurement of the predetermined parameter.
Owner:NEXENSE
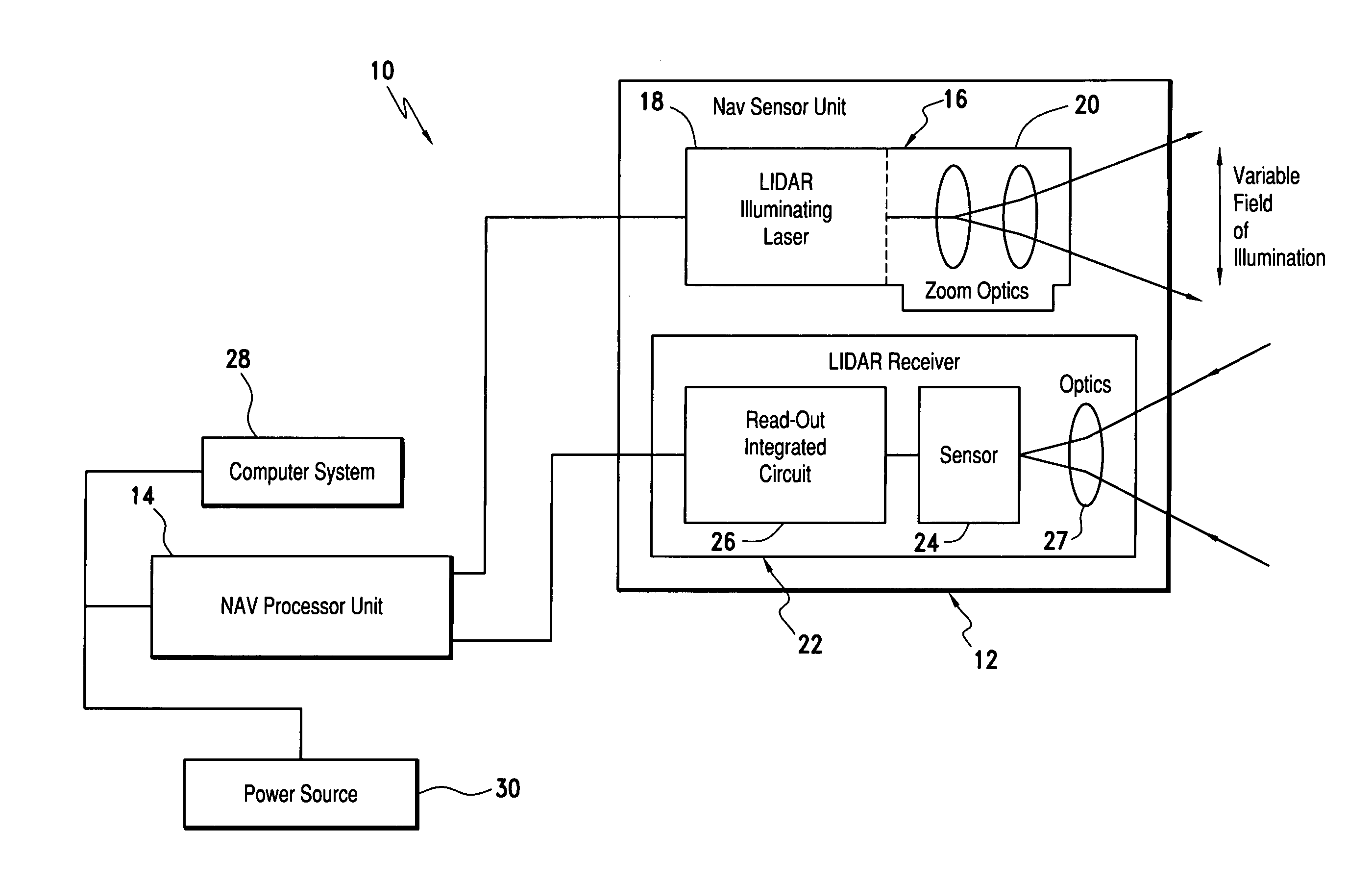
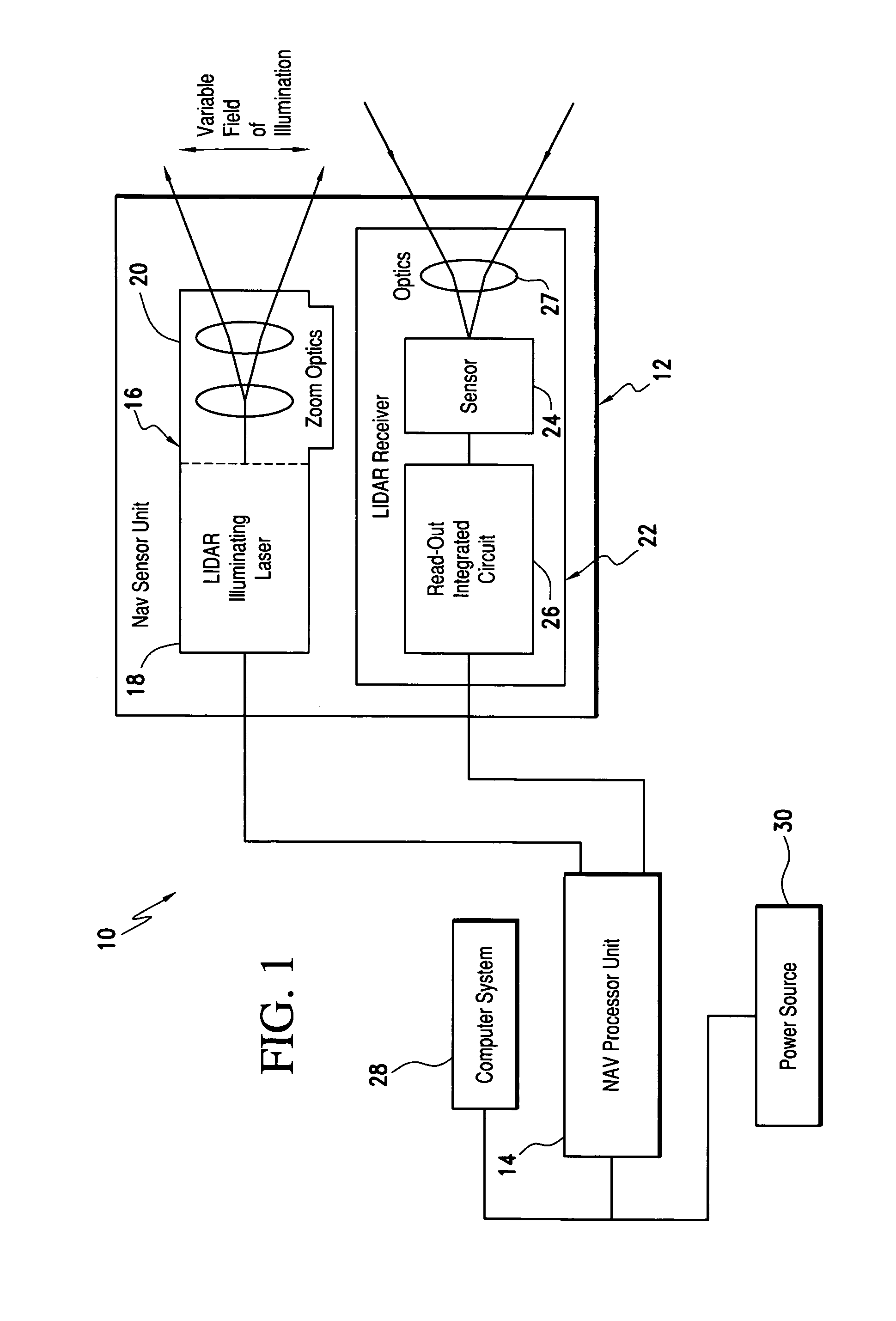
Laser range finding system using variable field of illumination flash lidar
ActiveUS8072581B1Reduce areaReduce resolutionOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingImage resolution
The laser range finding system includes a light detection and ranging (LIDAR) sensor unit (SU) and a LIDAR processor unit (PU). The LIDAR SU is for transmitting light pulses and receiving resulting input light signals reflected from objects within the field of view of the SU. The LIDAR SU includes a flash LIDAR illuminating laser source for transmitting light pulses. The LIDAR illuminating laser source includes an illuminating laser and zoom optics operatively associated with the laser. A LIDAR receiver receives resulting input light signals reflected from the objects. The LIDAR receiver includes a sensor; and, a flash readout integrated circuit (IC). The flash readout IC measures the transit time of the light pulses. The LIDAR processor unit (PU) is operatively associated with the LIDAR SU and it utilizes flash LIDAR ranging. A power source is operatively coupled to the LIDAR PU. Zooming of the transmitted light pulses results in the received resulting input light signals illuminating a relatively reduced area of the frame. Thus, a flash LIDAR image of relatively reduced resolution but enhanced range is provided by utilization of the transit time measurements.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
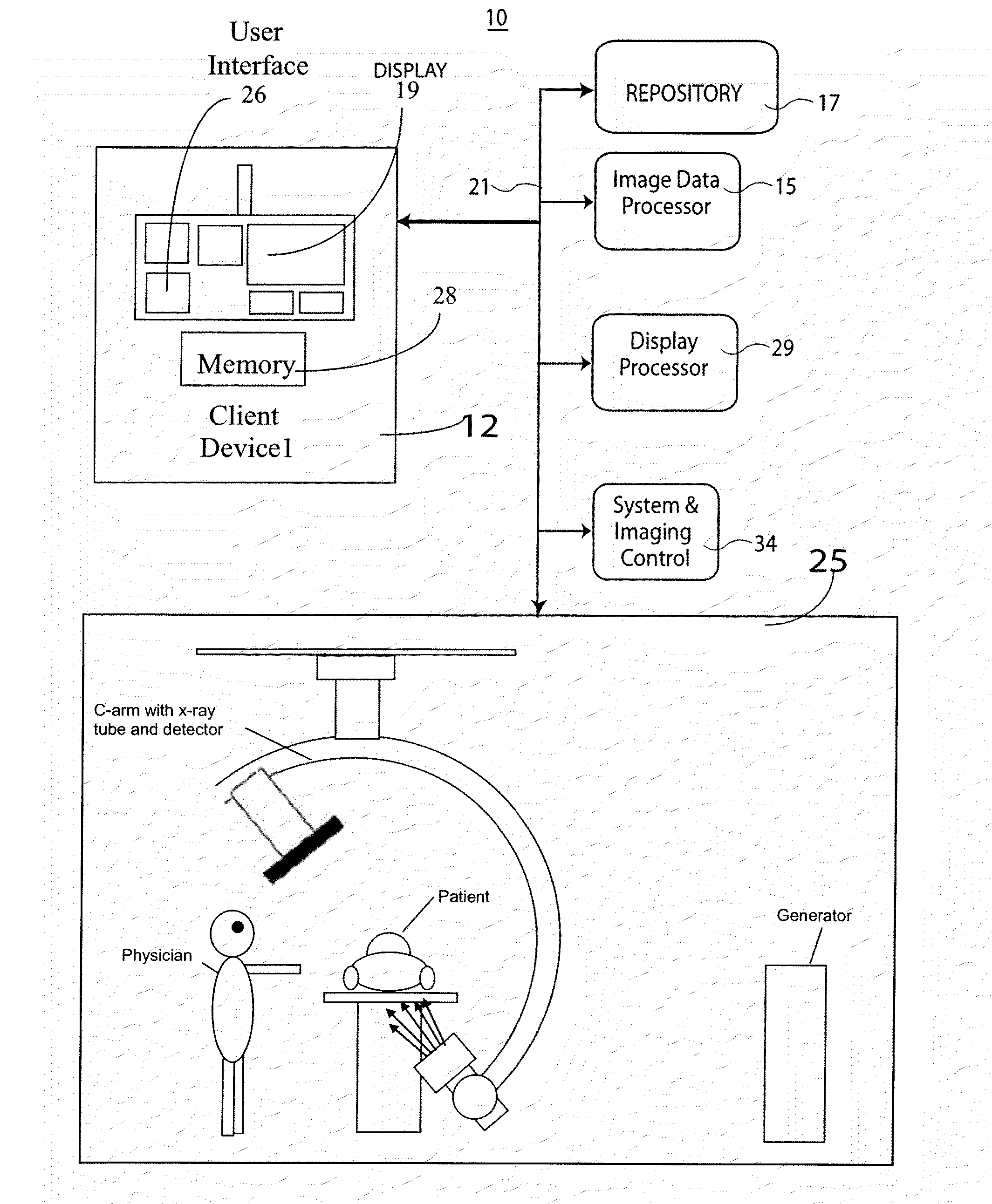
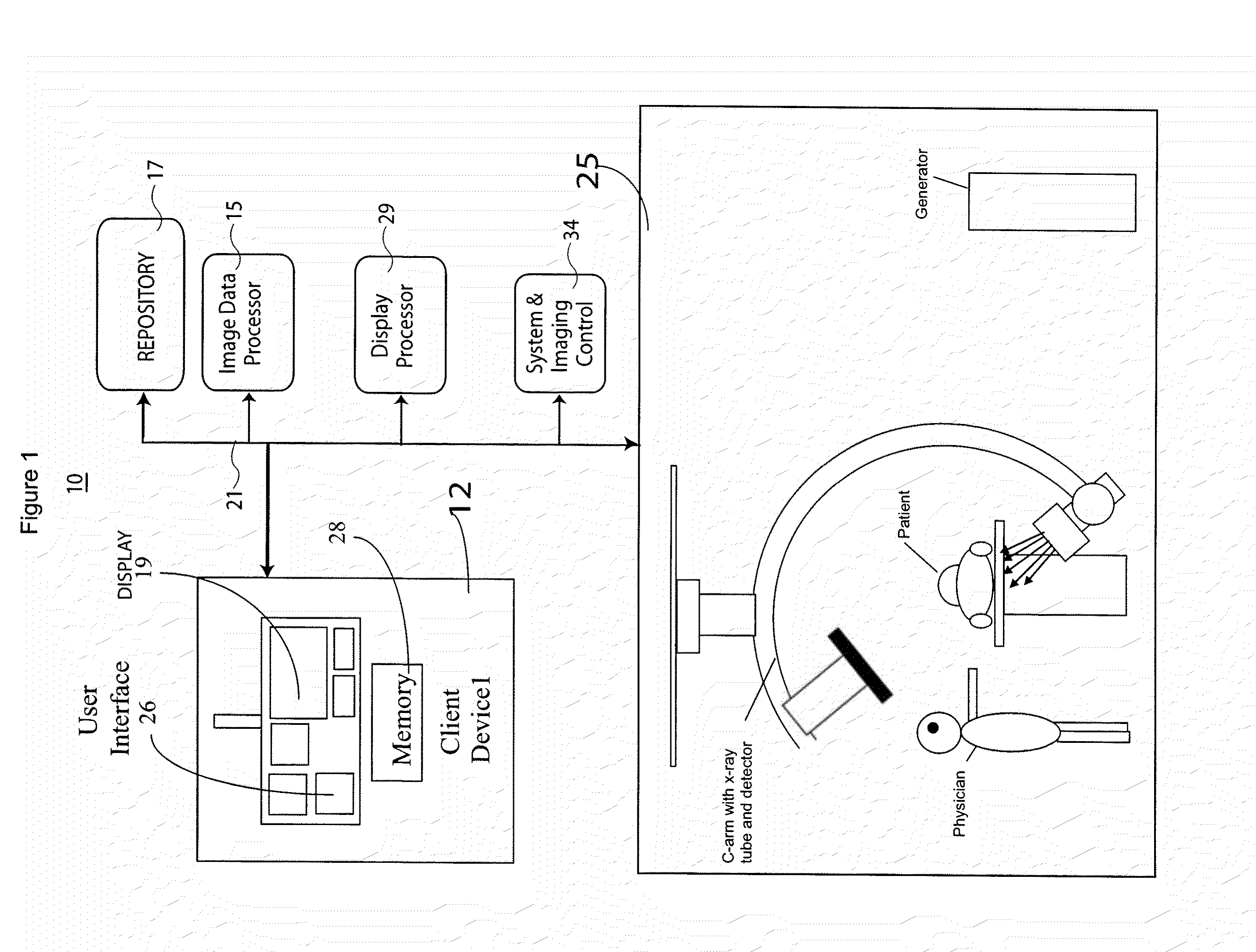
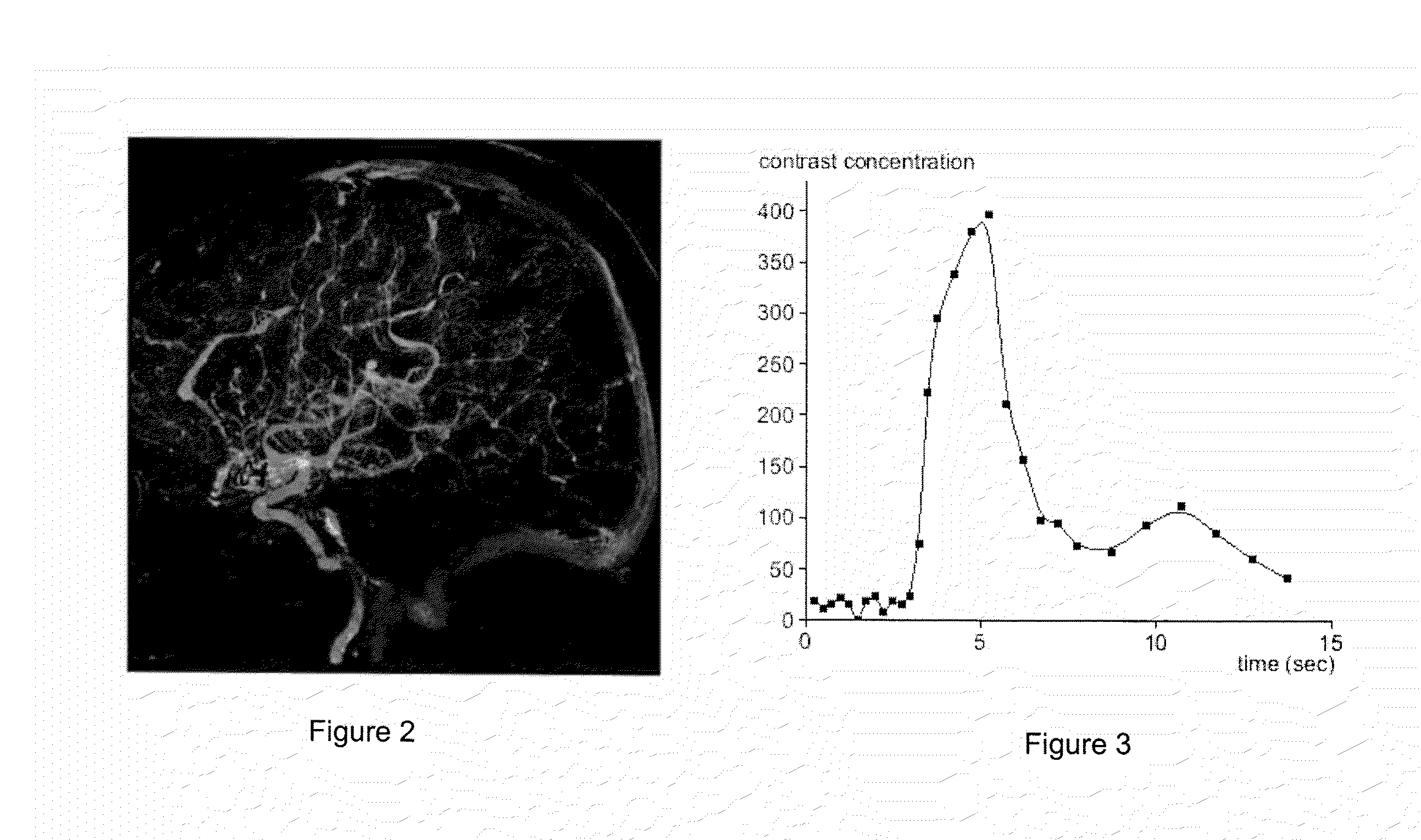
System for Processing Medical Image data to Provide Vascular Function Information
A system creates a visually (e.g., color) coded 3D image that depicts 3D vascular function information including transit time of blood flow through the anatomy. A system combines 3D medical image data with vessel blood flow information. The system uses at least one repository for storing, 3D image data representing a 3D imaging volume including vessels, in the presence of a contrast agent and 2D image data representing a 2D X-ray image through the imaging volume in the presence of a contrast agent. An image data processor uses the 3D image data and the 2D image data in deriving blood flow related information for the vessels. A display processor provides data representing a composite single displayed image including a vessel structure provided by the 3D image data and the derived blood flow related information.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
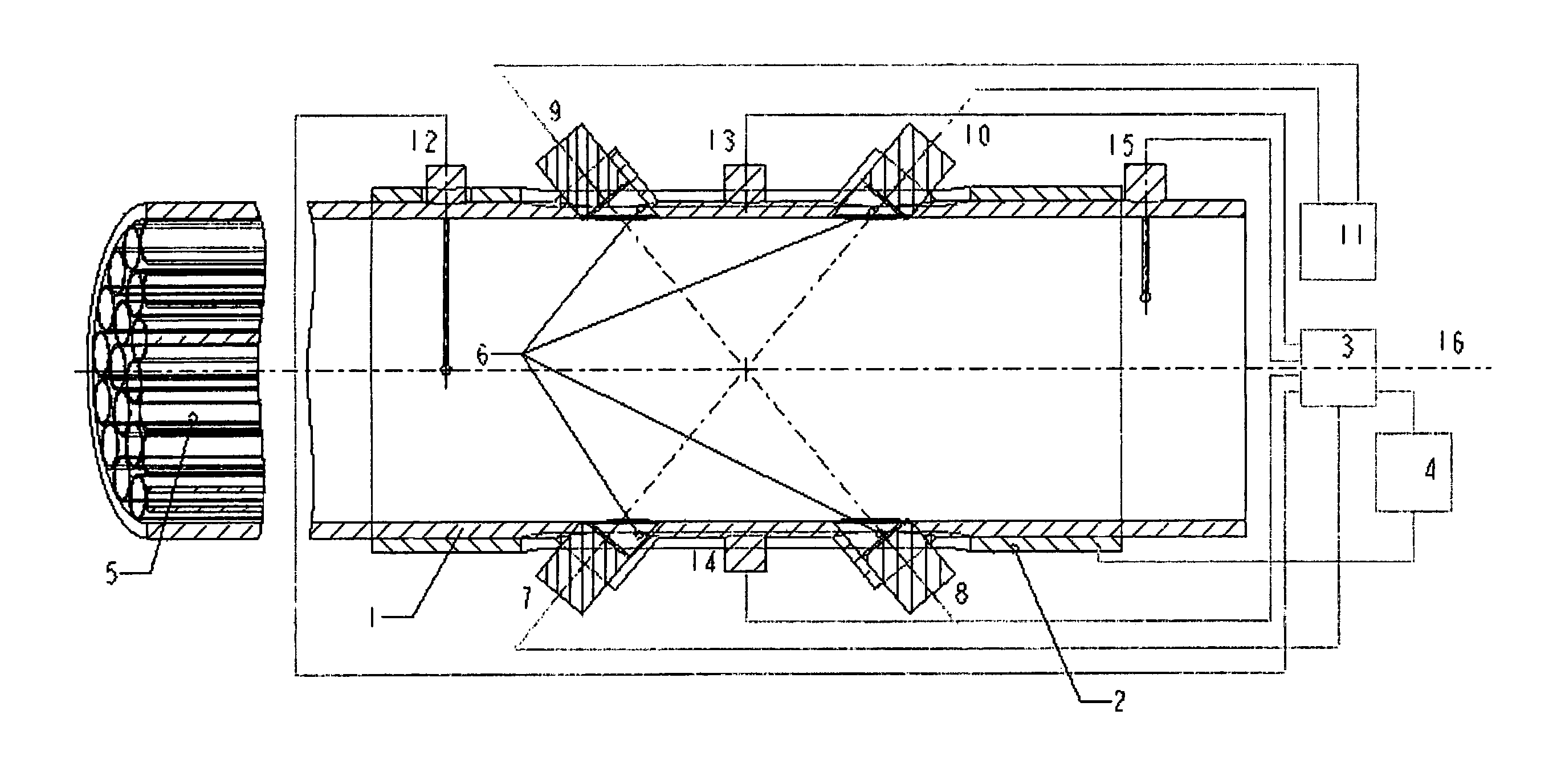
3-D imaging multiple target laser radar
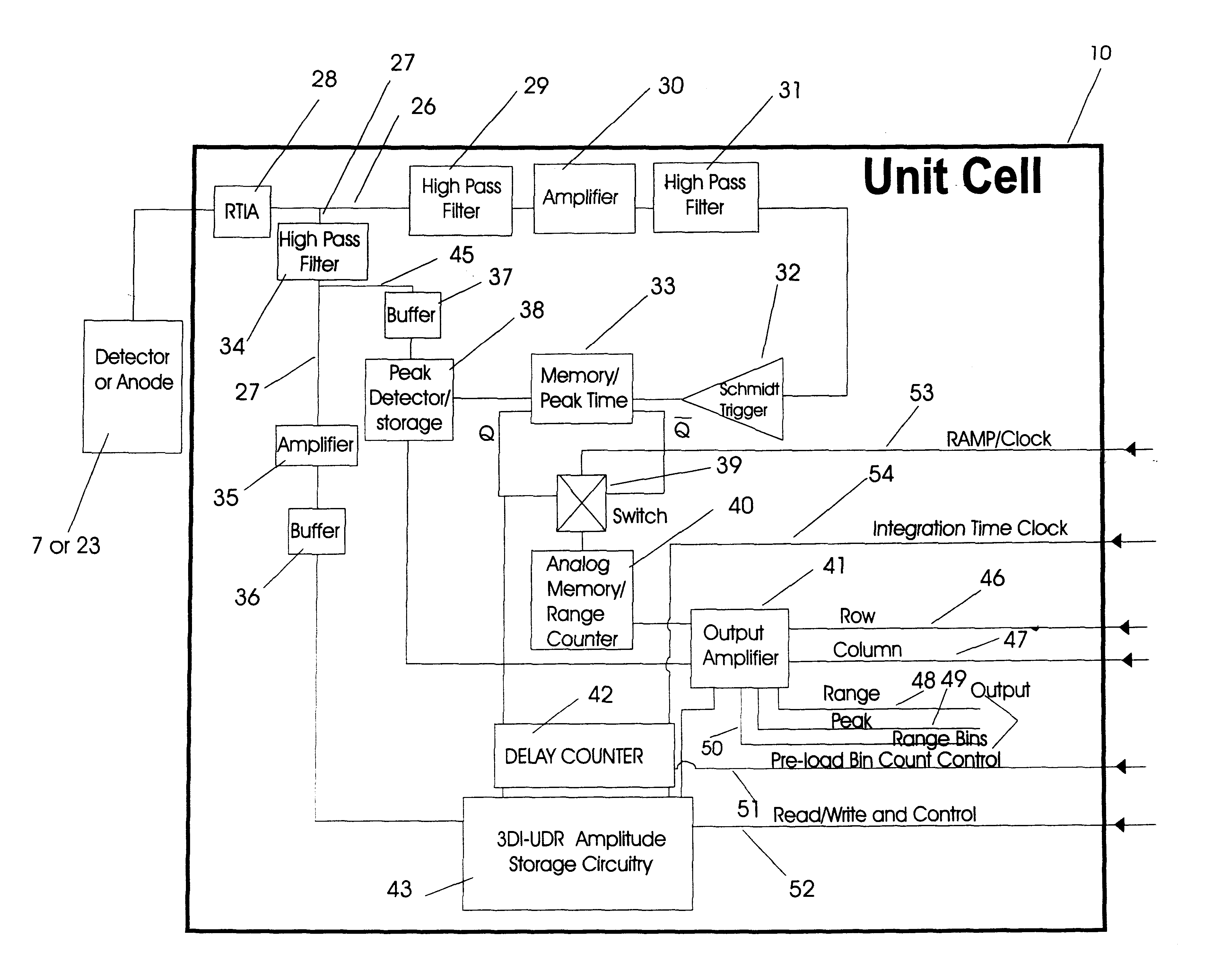
InactiveUS6414746B1Accurately determineOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesElectronIntegrated circuit
A three dimensional imaging device is presented which uses a single pulse from a pulsed light source to detect objects which are obscured by camouflage, fog or smoke but otherwise enveloped by a light-transmitting medium. The device simultaneously operates in two modes, light reflected from the nearest object is processed to form a three-dimensional image by an array of pixels. This first image is based upon the light-pulse transit time recorded in each pixel. Each pixel also contains a high-speed analog memory that sequentially stores reflected signals at a repeated time interval. The first reflection acts as a time base that controls when the analog memory begins or ends the storage sequence. The first return could be from a camouflage net and the amplitudes of the return signals, after the first return, would then be from objects behind the net. Computer processing these amplitudes reveals the three-dimensional nature of the obscured objects.The device consists of the pulsed light source, optics for collecting the reflected light, a sensor for detecting the light and converting it to electrical data, drive and output electronics for timing and signal conditioning of data generated by the sensors and a computer for processing the sensor data and converting it to a three dimensional image. The sensor collects and processes the light data in a unique manner, first converting it to electricity by a number of alternate detector technologies and then using integrated circuit chips which consist of a two dimensional array of electronic pixels also called unit cells. The two dimensional array defines two dimensions of the image. Stored within each unit cells is data associated with the third dimension, ranges of targets, and amplitudes of target reflections. This data is read out of the integrated circuit chip in the time interval between laser pulses to a processing computer. The processing computer corrects the data and, by means of computer algorithms specific to the device, converts the data to a three-dimensional image of one or more targets. This image may be viewed or processed electronically to isolate targets.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
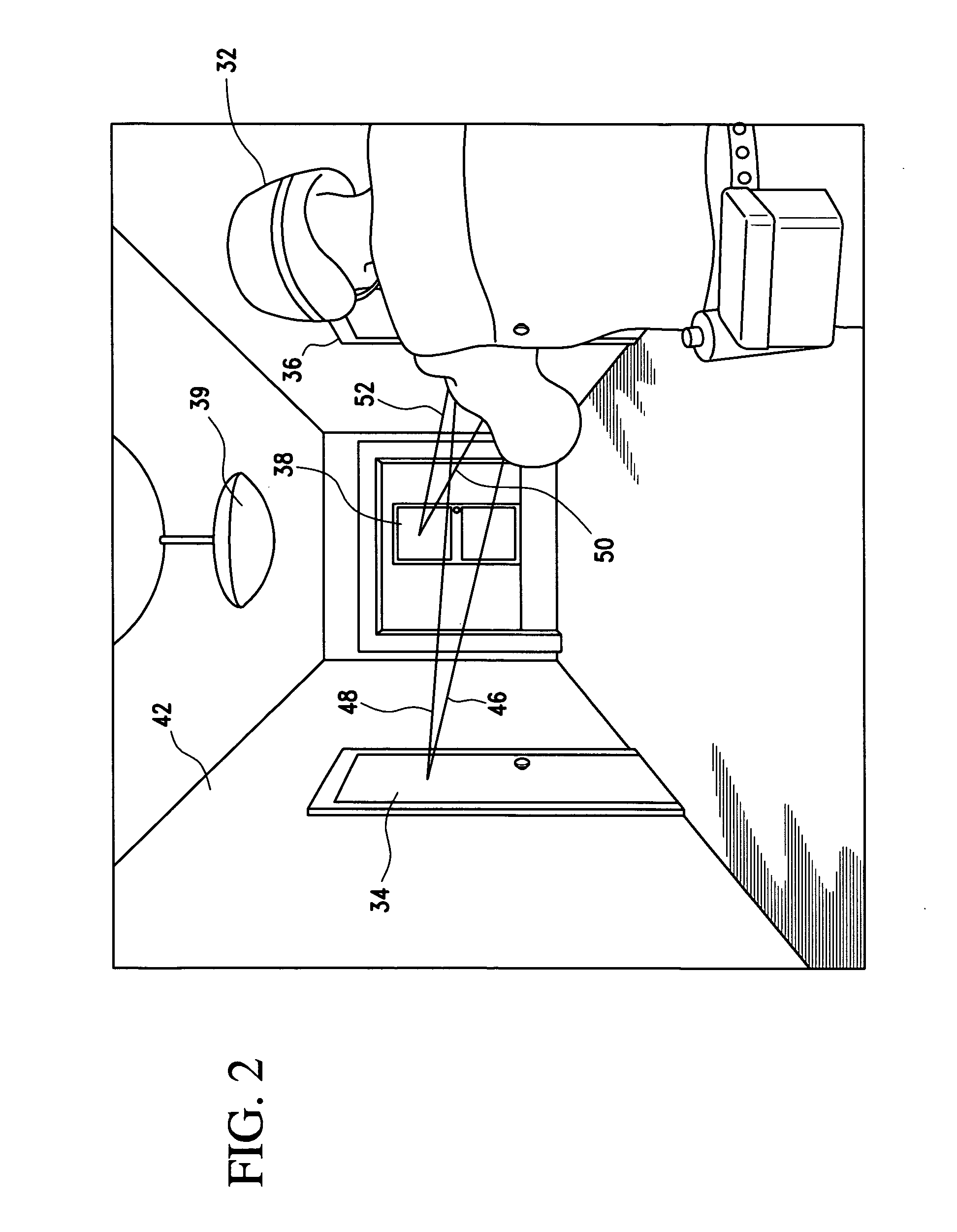
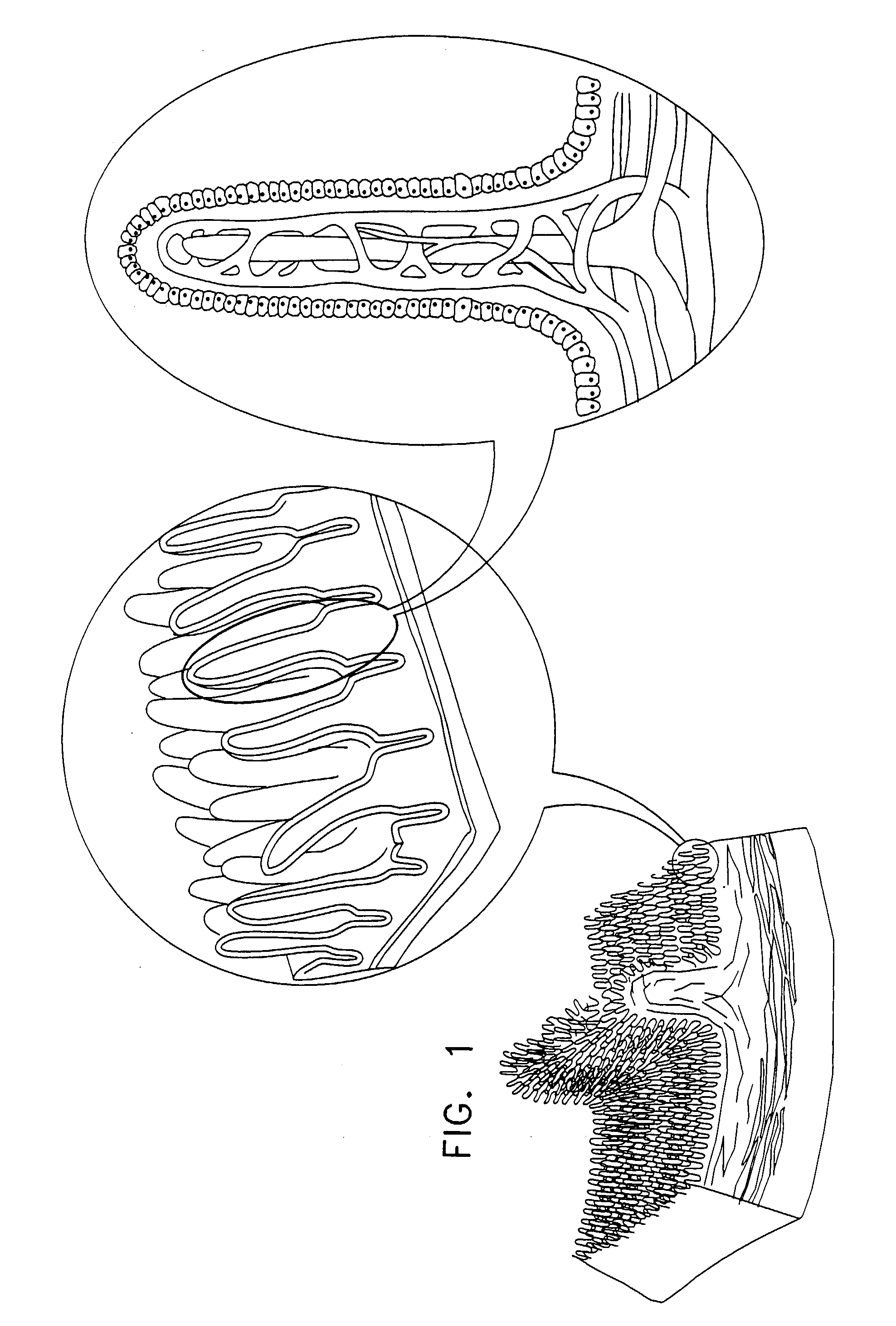
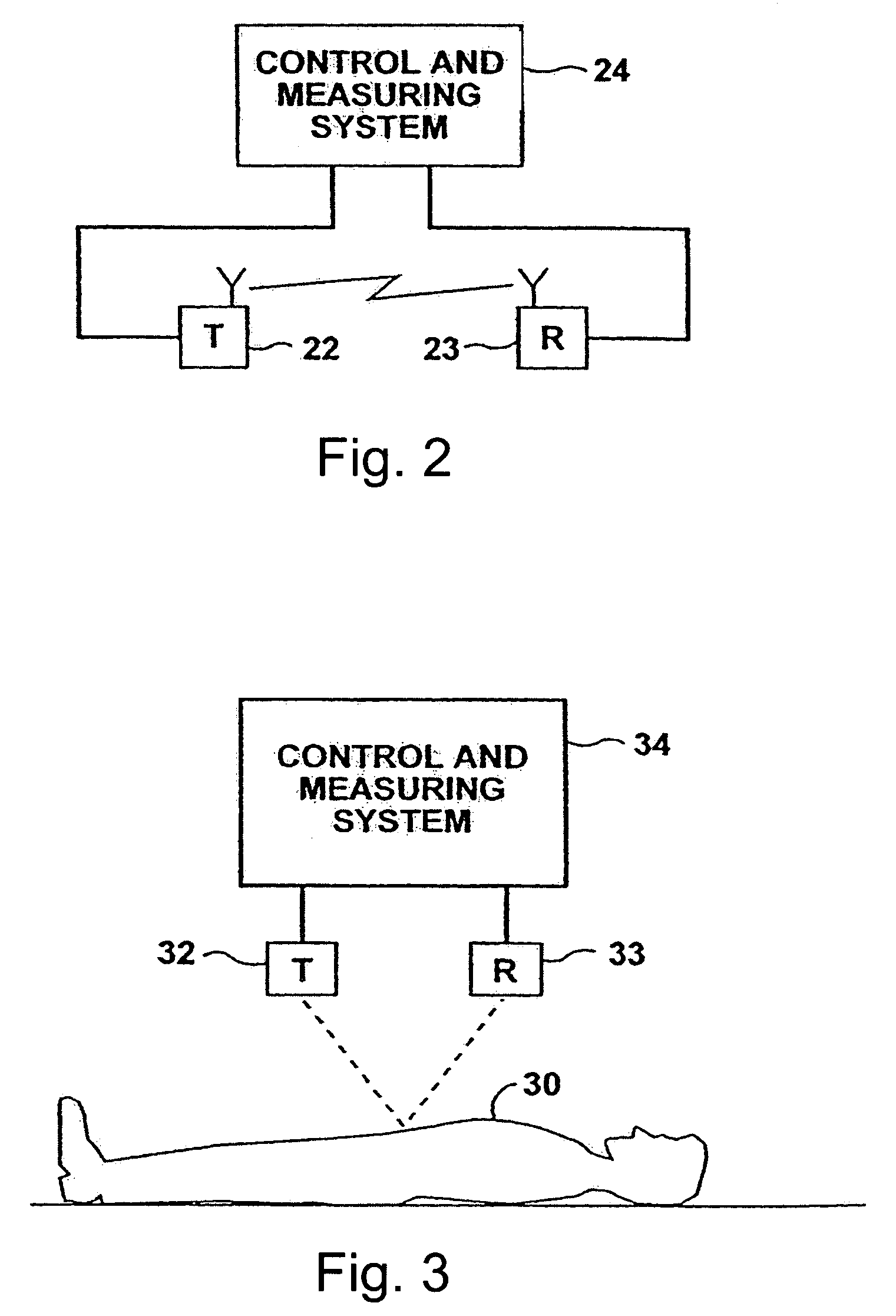
System and method of evaluating a subject with an ingestible capsule
A computerized method of analyzing measurements obtained from the gastrointestinal tract of subject comprising the steps of providing an ingestible capsule (20) having a sensor (22, 23, 24) for measuring a parameter of the gastrointestinal tract of a subject, having a subject ingest (118) the capsule, recording (130) measurements from the sensor as the capsule passes through the gastrointestinal tract of the subject, transmitting (131, 122) the measurements to a processor (31), conditioning (132) the measurements to provide data as a function of a time interval, plotting (133) the data on a display (32), providing a query (205, 216, 234), on the display, receiving input (207, 218, 237) from a user in response to the query, setting a marker (50-53) on the plot (40) at a location as a function of the input, and determining (238) a capsule transit time for a selected portion of the gastrointestinal tract as a function of the location of the marker.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
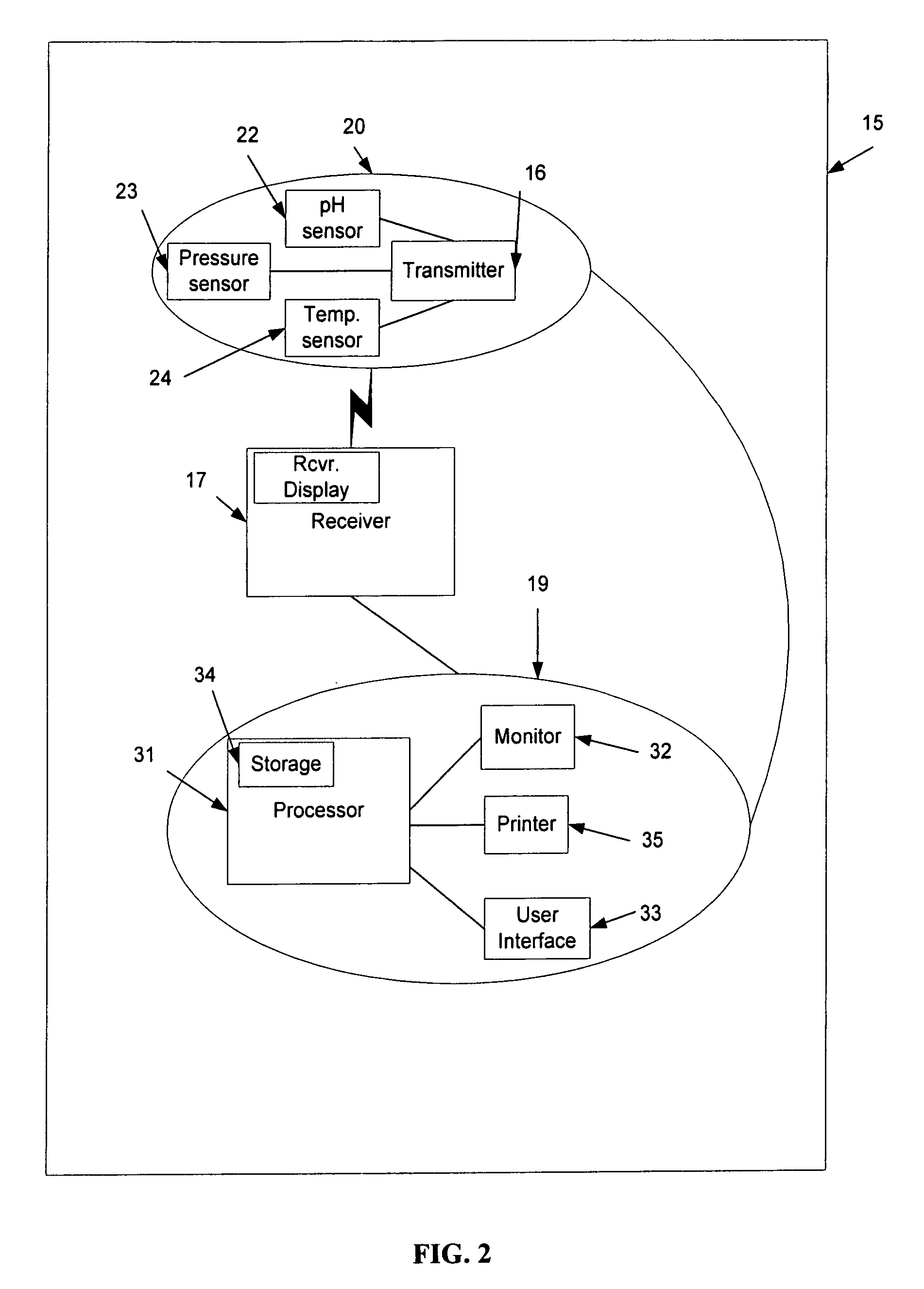
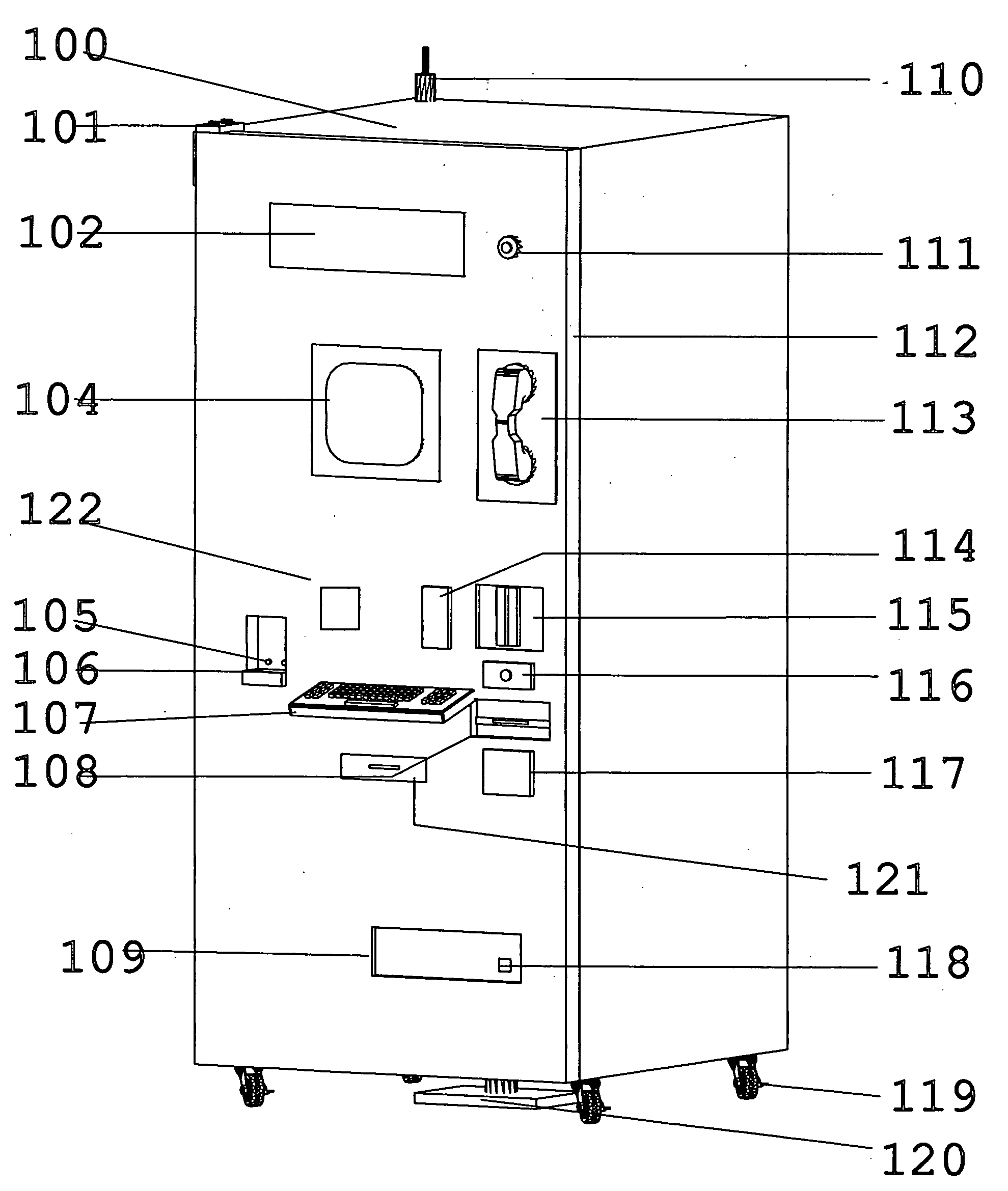
Inventory control and prescription dispensing system
ActiveUS20070043469A1Ensure integrityEnsure safetyDrug and medicationsCoin-freed apparatus detailsEngineeringPatient registration
An inventory control and prescription management and dispensing system including a dispensing vault for storing and dispensing prescriptions, the dispensing vault in communication with a central computer system that, in turn, communicates with prescription providers, insurance companies, and other third parties; the dispensing vault including robotic means for randomly accessing pre-filled prescriptions within the vault, with the vault further including RFID, bar code, and other means for verifying the content and internal location of pre-filled prescriptions; a customer interface that uses customer biometrics to ID a customer to ensure that prescriptions are only dispensed to the correct person; a patient registration system in communication with the central computer system for collecting insurance, doctor, biometric, and other information to facilitate transactions; a labeling system for labeling pre-filled prescriptions with customer specific information upon dispensing; transport container that integrate into the dispensing vault and provide secure transportation from a pharmaceutical manufacturer or repackager to the dispensing vault, security provided through RFID tags which communicate with the central computer to verify that the transport container contains the correct formulary and that the integrity of the container (temperature range, time in transit, tampering) has not been compromised; a payment system integral to the dispensing vault that is in communication with third party banks and pharmacy billing management systems, credit agencies and the central computer; a verification system for ensuring that pre-filled bottles received from the manufacturer (before they are placed into the storage locations inside the vault) have not had their integrity compromised, with this system evaluating each container's weight, size, moisture content, shape, velocity change, color, pattern, and physical integrity (all comparisons made against standards stored in the central computer).
Owner:DRAPER LONNIE
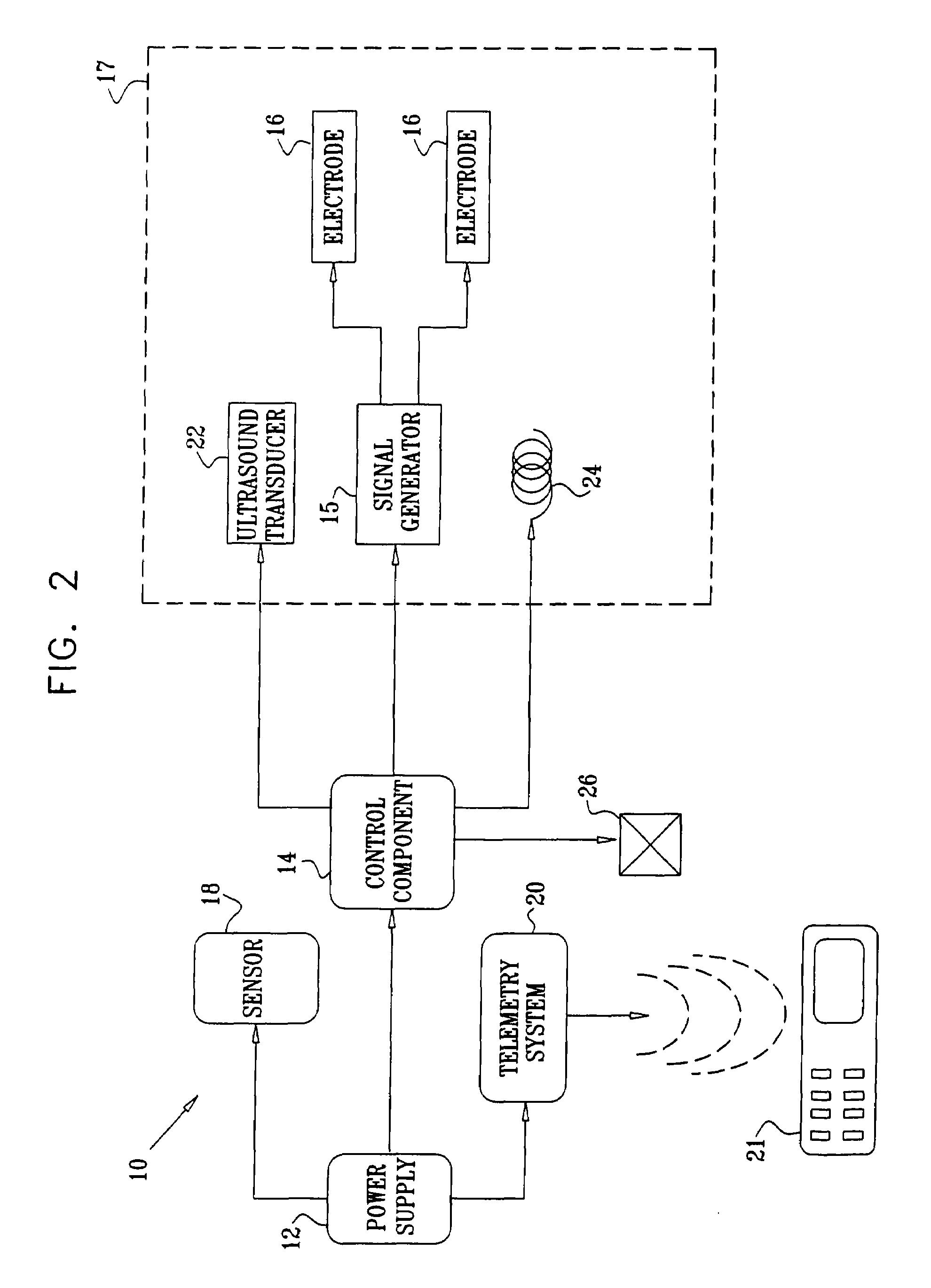
Prolonged Transit Time of Permeability-Enhancing Drug Eluting Pill
InactiveUS20080275430A1Promote absorptionShorten speedMedical devicesMicromachined deliveryPower flowMedicine
Apparatus is provided for drug administration. The apparatus includes an ingestible capsule, which includes a drug, stored by the capsule. The apparatus also includes an environmentally-sensitive mechanism, adapted to change a state thereof responsively to a disposition of the capsule within a gastrointestinal (GI) tract of a subject; one or more drug-passage facilitation electrodes; and a control component, adapted to facilitate passage of the drug, in response to a change of state of the environmentally-sensitive mechanism, by driving the drug-passage facilitation electrodes to apply an electrical current. The apparatus further includes a velocity-reduction element adapted to reduce a velocity of the capsule through the GI tract for at least a portion of the time that the control component is facilitating the passage of the drug. Additional embodiments are also described.
Owner:E PILL PHARMA
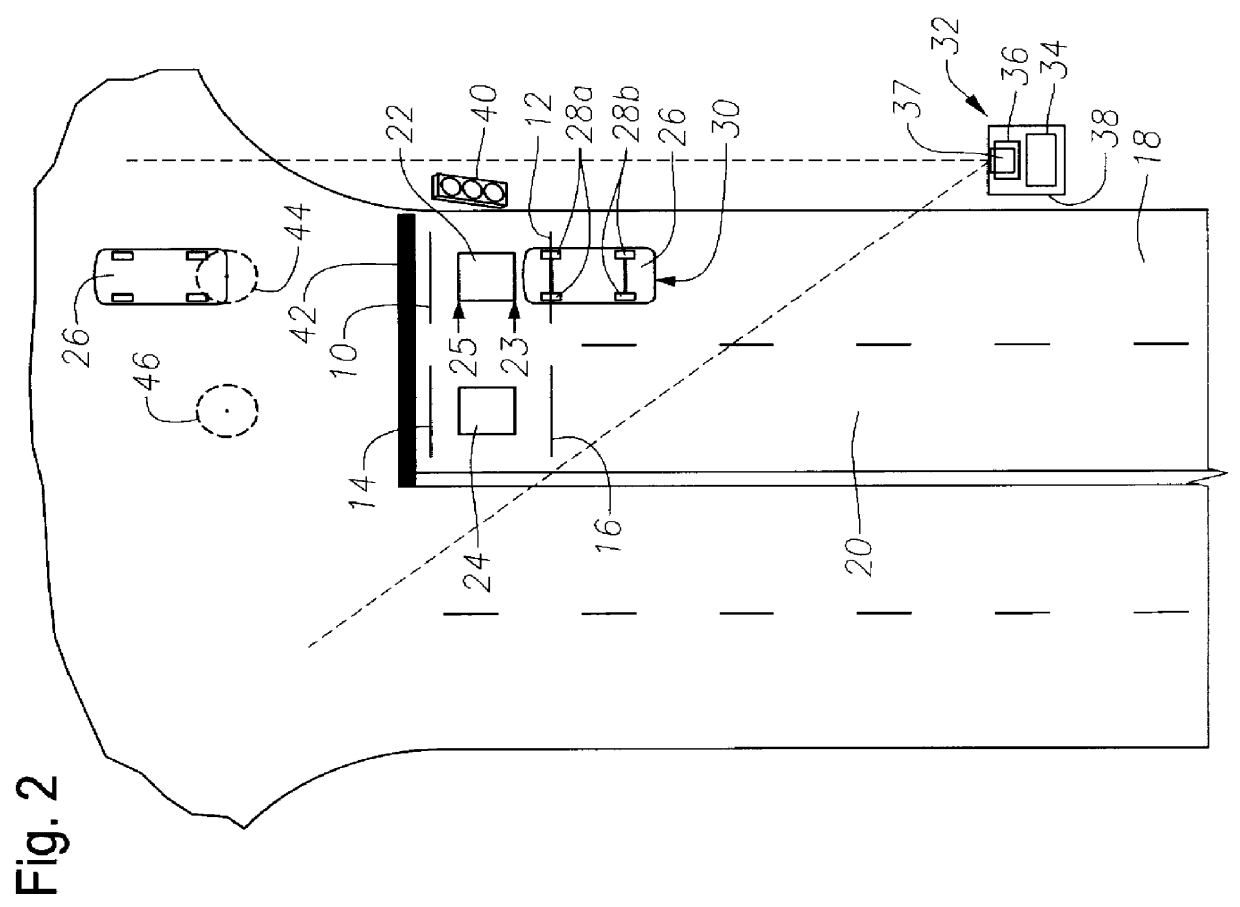
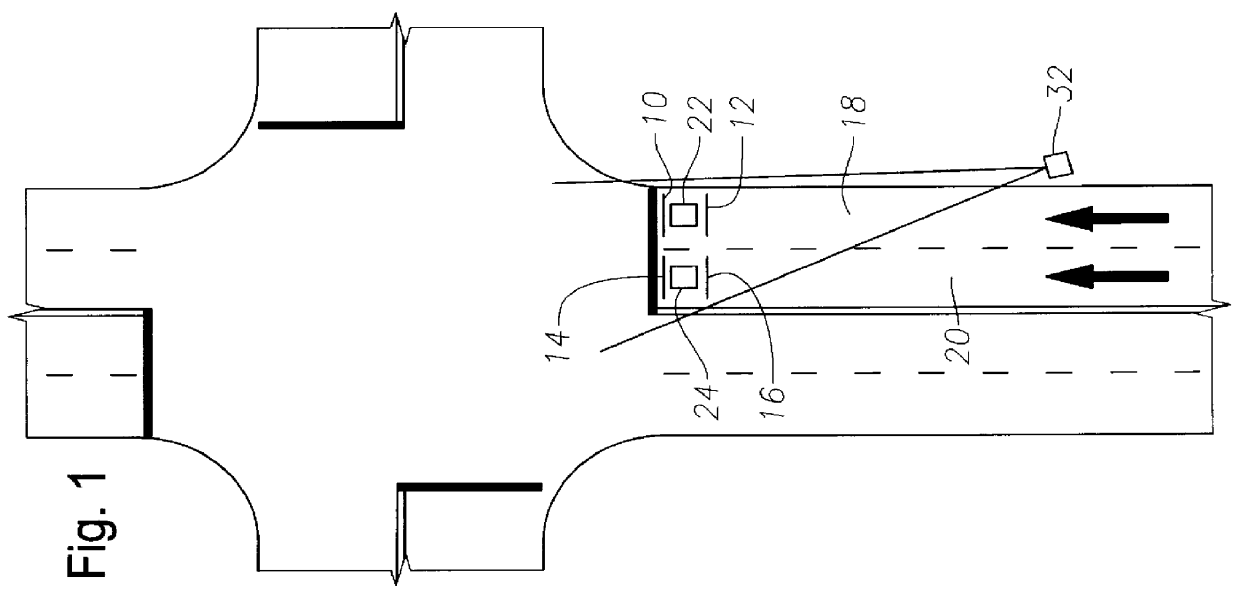
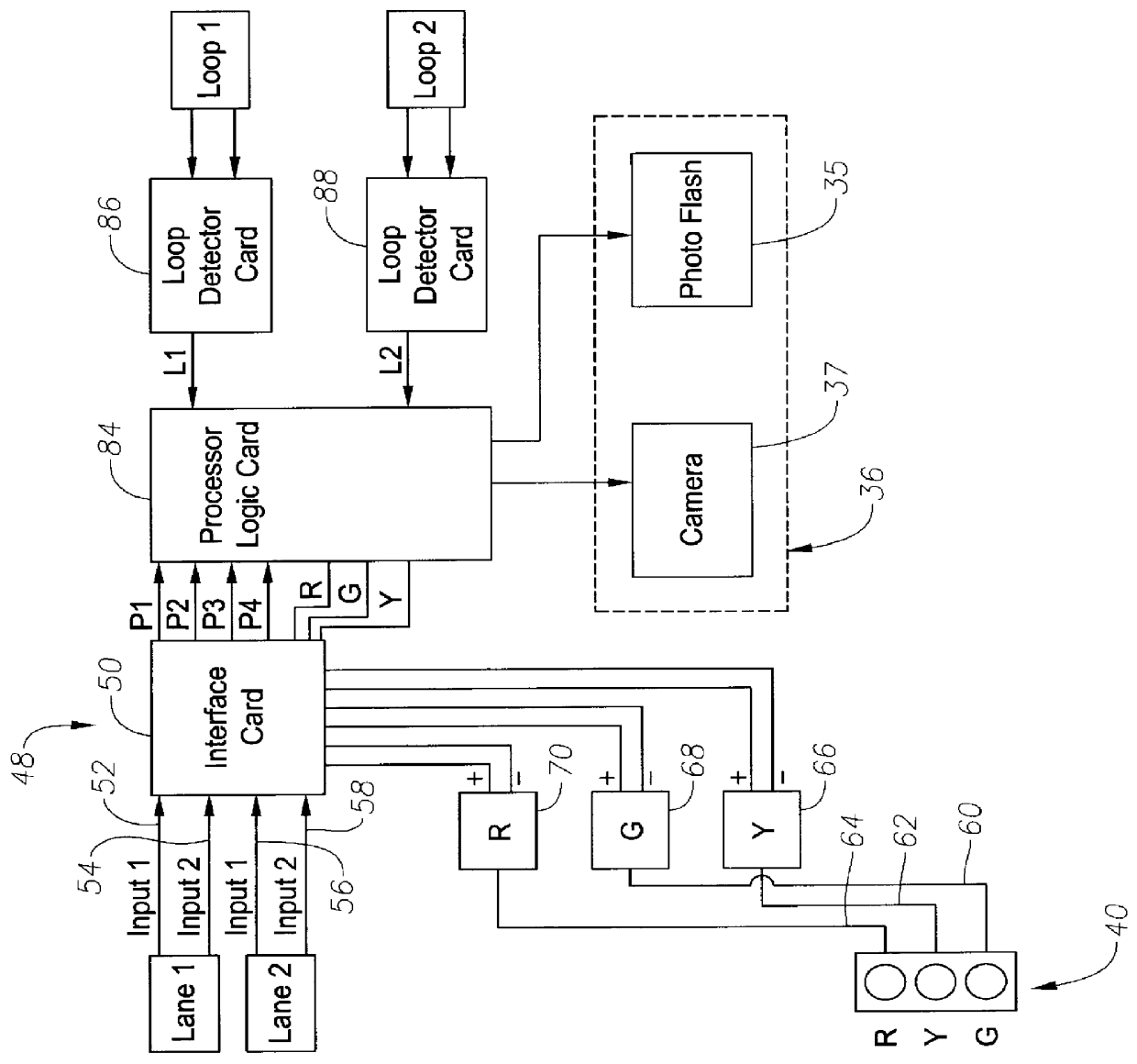
Method and apparatus for photographing traffic in an intersection
InactiveUS6111523AAccurately and reliably photographedShoot accuratelyAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficMobile vehicleSensor array
An apparatus of the invention includes a device for triggering a camera to photograph a vehicle within a traffic intersection, where the triggering of the camera is dependent on the speed of the vehicle before entering the intersection and may also be dependent on presence information. The device includes a sensor system (or "sensor array") to transmit signals corresponding to a moving vehicle and a control system for processing the signals and triggering the camera. The signals preferably include "position signals" from which a transit time can be calculated, and "presence signals," from which presence information can be obtained, particularly the location of the rear of the vehicle or the location of the rear wheels of the vehicle. A trigger time for taking a picture of the vehicle may be calculated from the transit time. A method of the invention includes the step of transmitting signals to a control system in response to the vehicle passing over a first traffic sensor and corresponding to the speed of the vehicle. The method may also include the steps of transmitting presence signals to the control system, preferably corresponding to the presence of the vehicle in a known presence zone outside the intersection, and photographing the vehicle in response to those signals. The system preferably uses a first set of signals (reflecting vehicle speed or transit time) and a second set of signals (reflecting the presence of the vehicle) to determine when to trigger the photograph of the vehicle in the intersection zone.
Owner:TRANSCORE
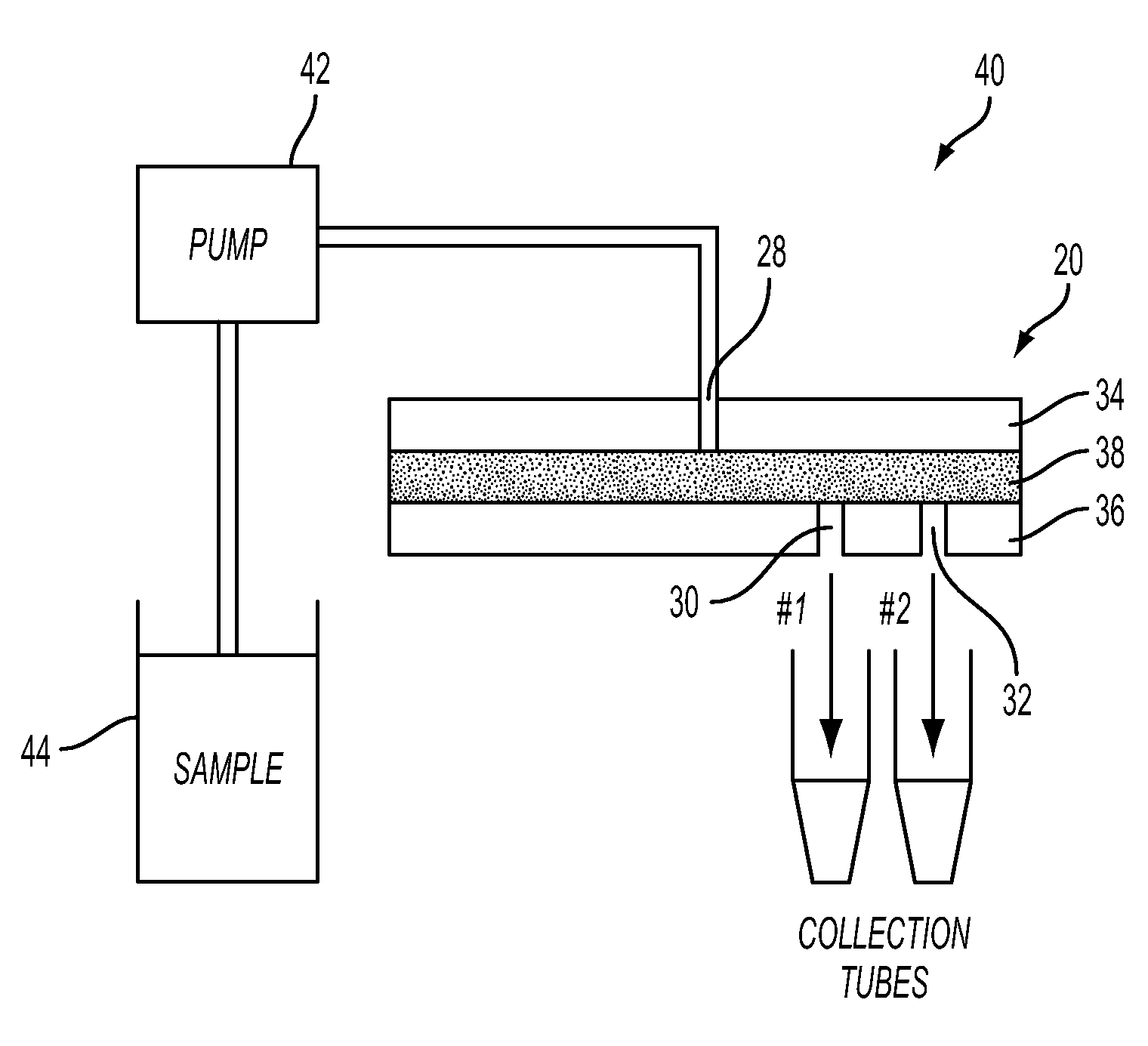
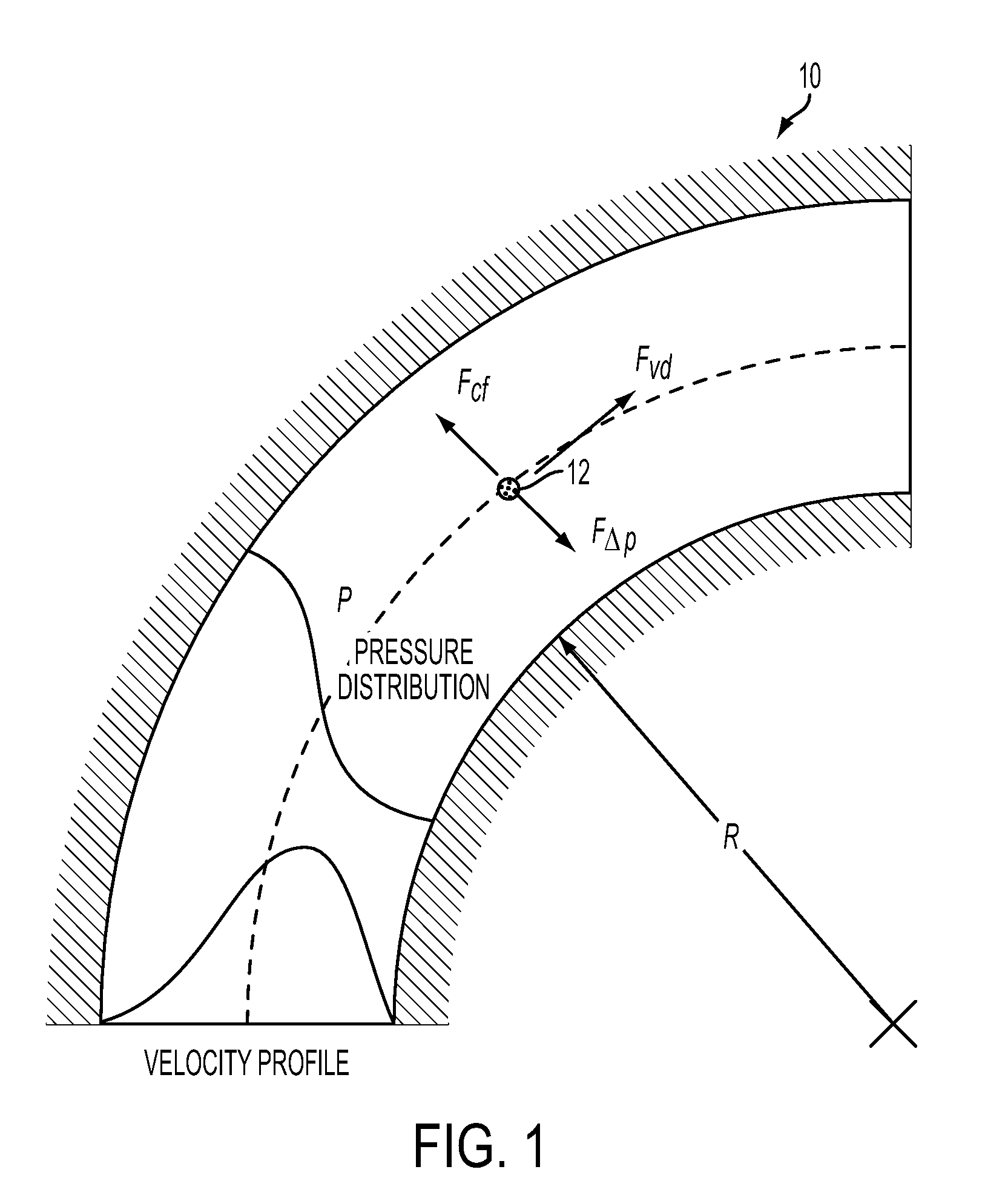
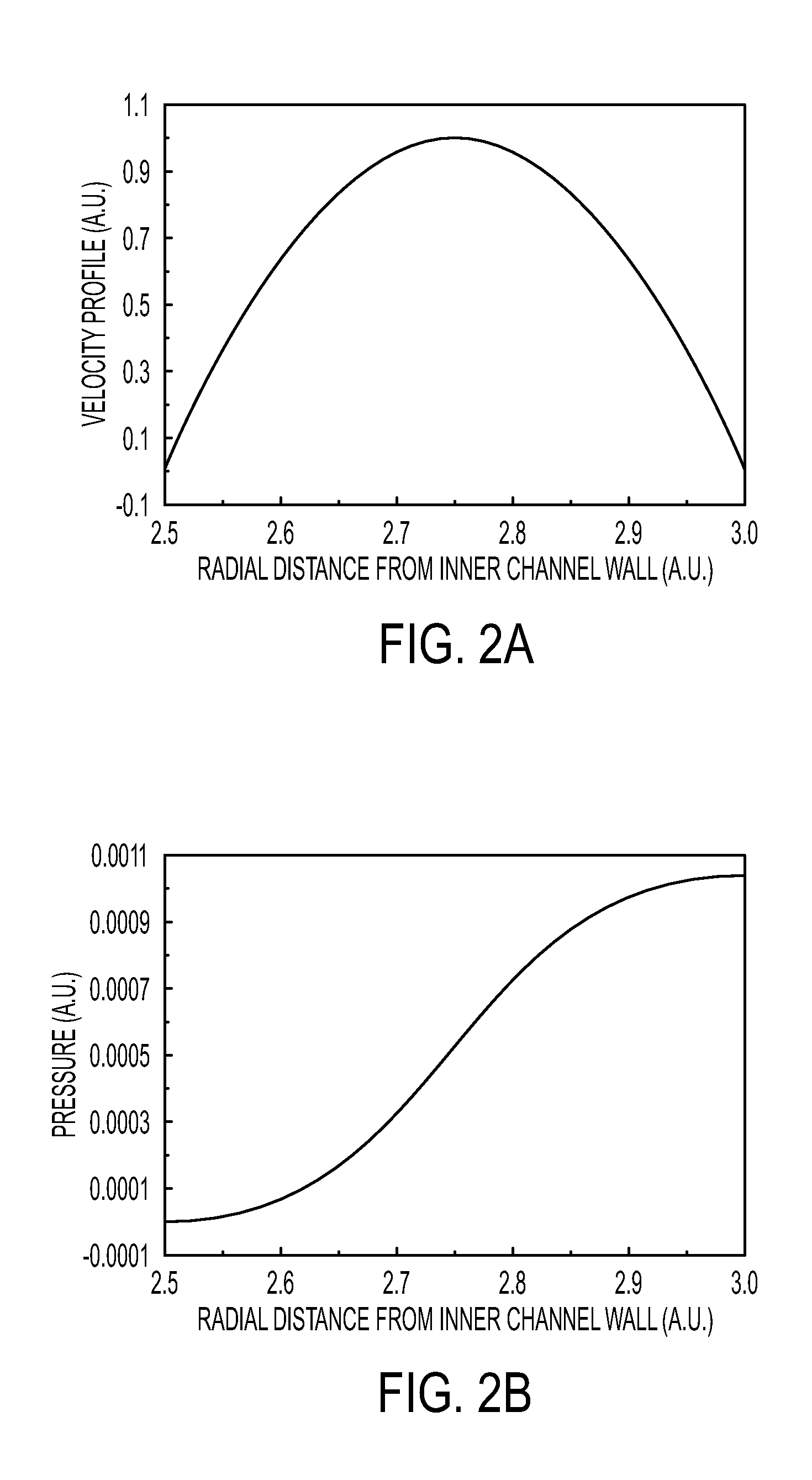
Particle separation and concentration system
This invention is based on size and mass separation of suspended particles, including biological matter, which are made to flow in a spiral channel. On the spiral sections, the inward directed transverse pressure field from fluid shear competes with the outward directed centrifugal force to allow for separation of particles. At high velocity, centrifugal force dominates and particles move outward. At low velocities, transverse pressure dominates and the particles move inward. The magnitudes of the two opposing forces depend on flow velocity, particle size, radius of curvature of the spiral section, channel dimensions, and viscosity of the fluid. At the end of the spiral channel, a parallel array of outlets collects separated particles. For any particle size, the required channel dimension is determined by estimating the transit time to reach the side-wall. This time is a function of flow velocity, channel width, viscosity, and radius of curvature. Larger particles may reach the channel wall earlier than the smaller particles which need more time to reach the side wall. Thus a spiral channel may be envisioned by placing multiple outlets along the channel. This technique is inherently scalable over a large size range from sub-millimeter down to 1 μm.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Ultrasonic tracking and locating system
ActiveUS20060013070A1Improve data transfer performanceDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationUltrasonic sensorSonification
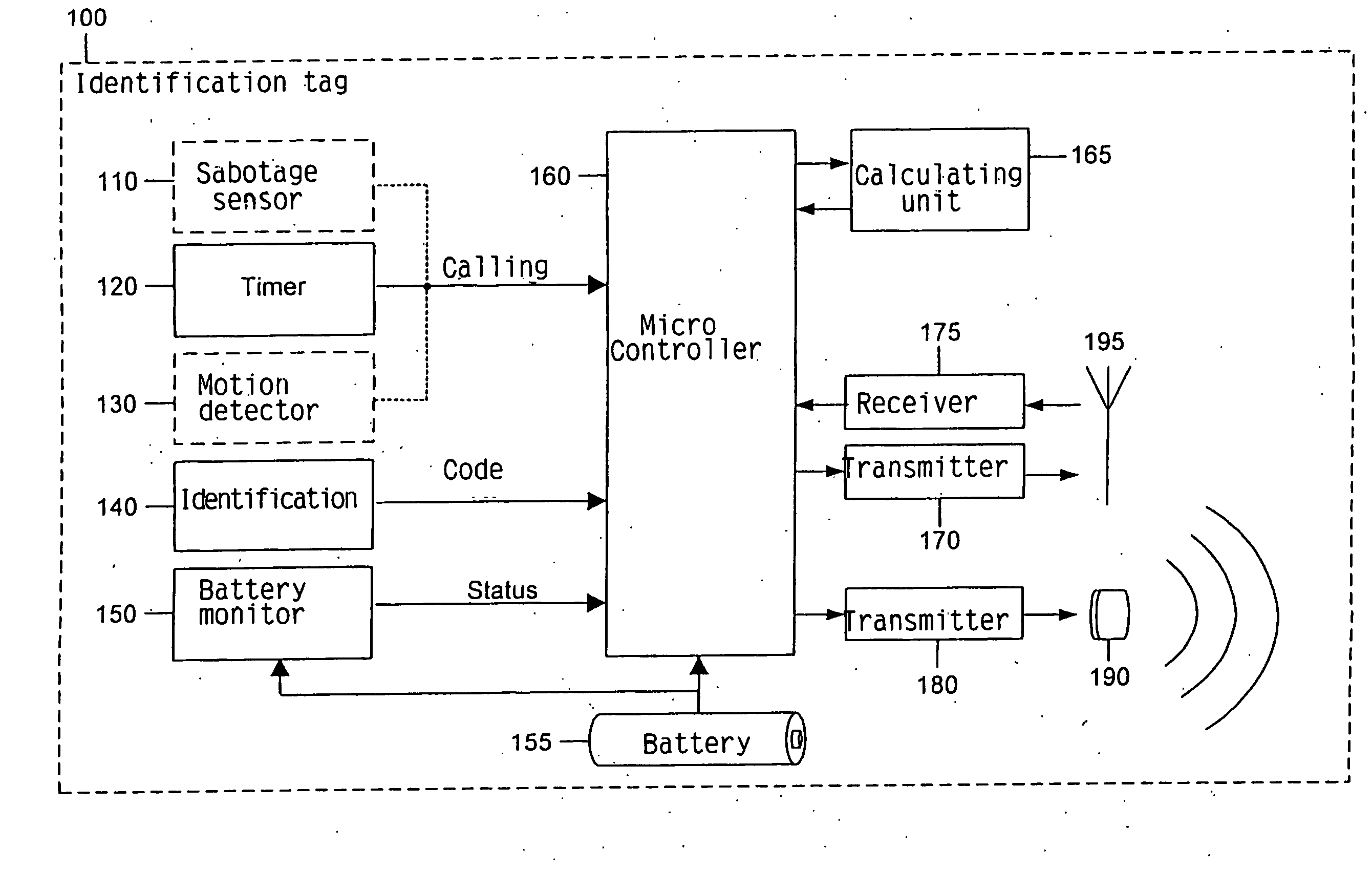
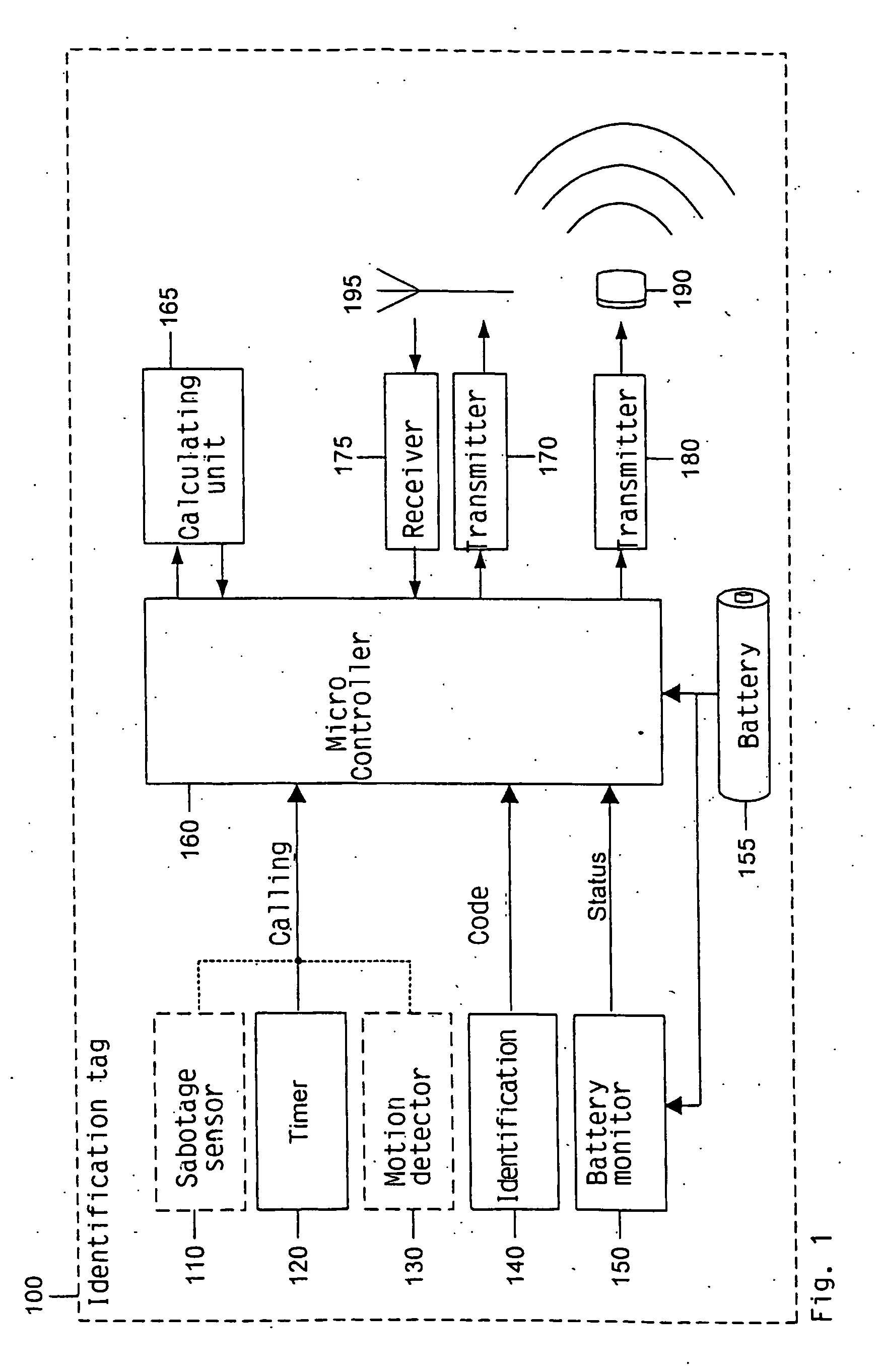
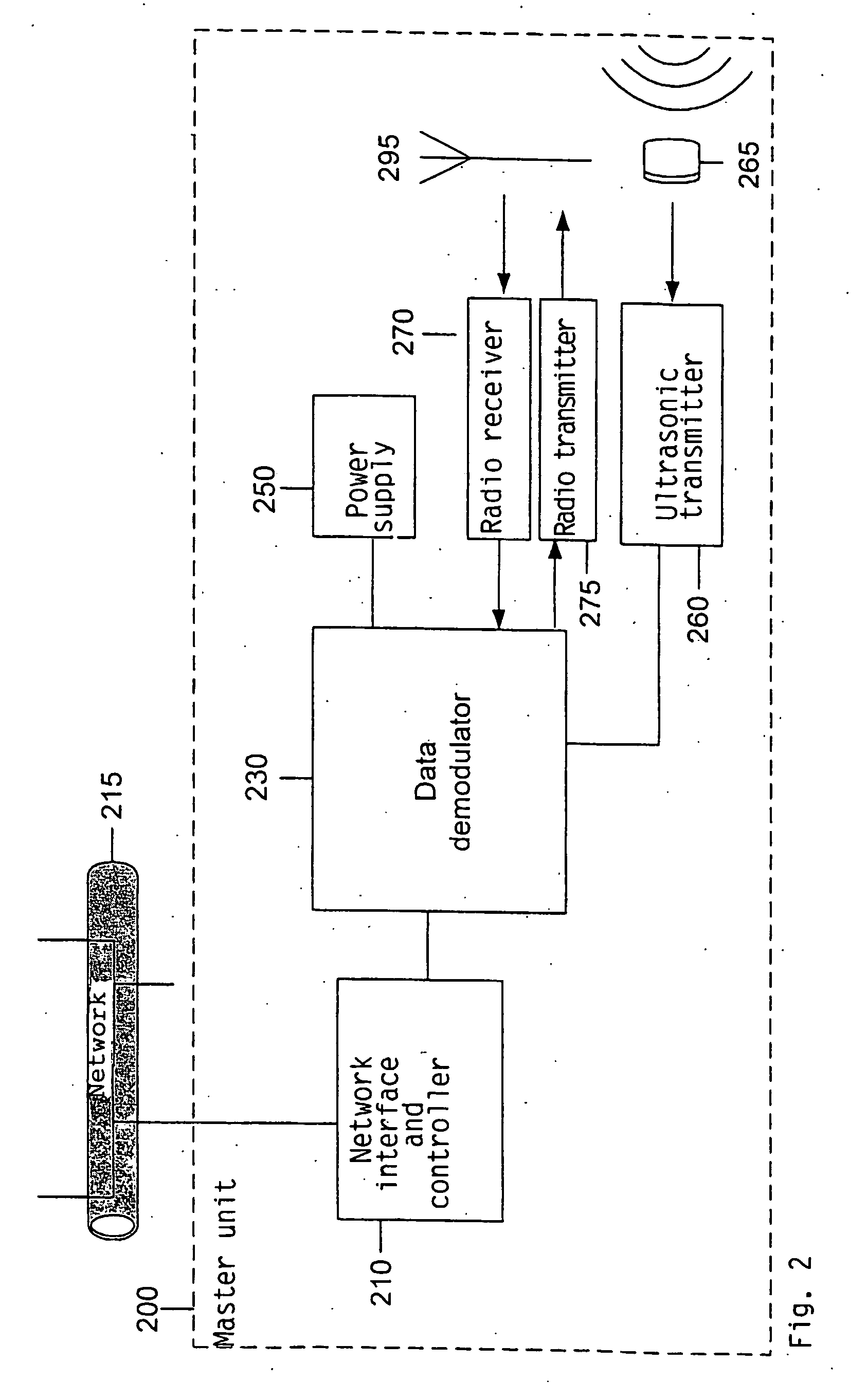
The invention relates to a method and a system for monitoring and position determination of objects and / or living beings within an area, such as, e.g. a room in a building. The system comprises a plurality of electronic units, called identification tags, which are attached to the objects that have to be monitored. Each identification tag has its own identification code (ID code) and is equipped with an ultrasonic transmitter, radio transmitter and radio receiver. The ultrasonic signals are recieved by one or more master and slave units which calculate transit time differences of ultrasonic pulses. This information together with the identification tags' ID code, identification of the room in which it is located, and any additional information are transmitted to a central processing unit which calculates the identification tag's position and presents it to a user of the system.
Owner:SONITOR TECH
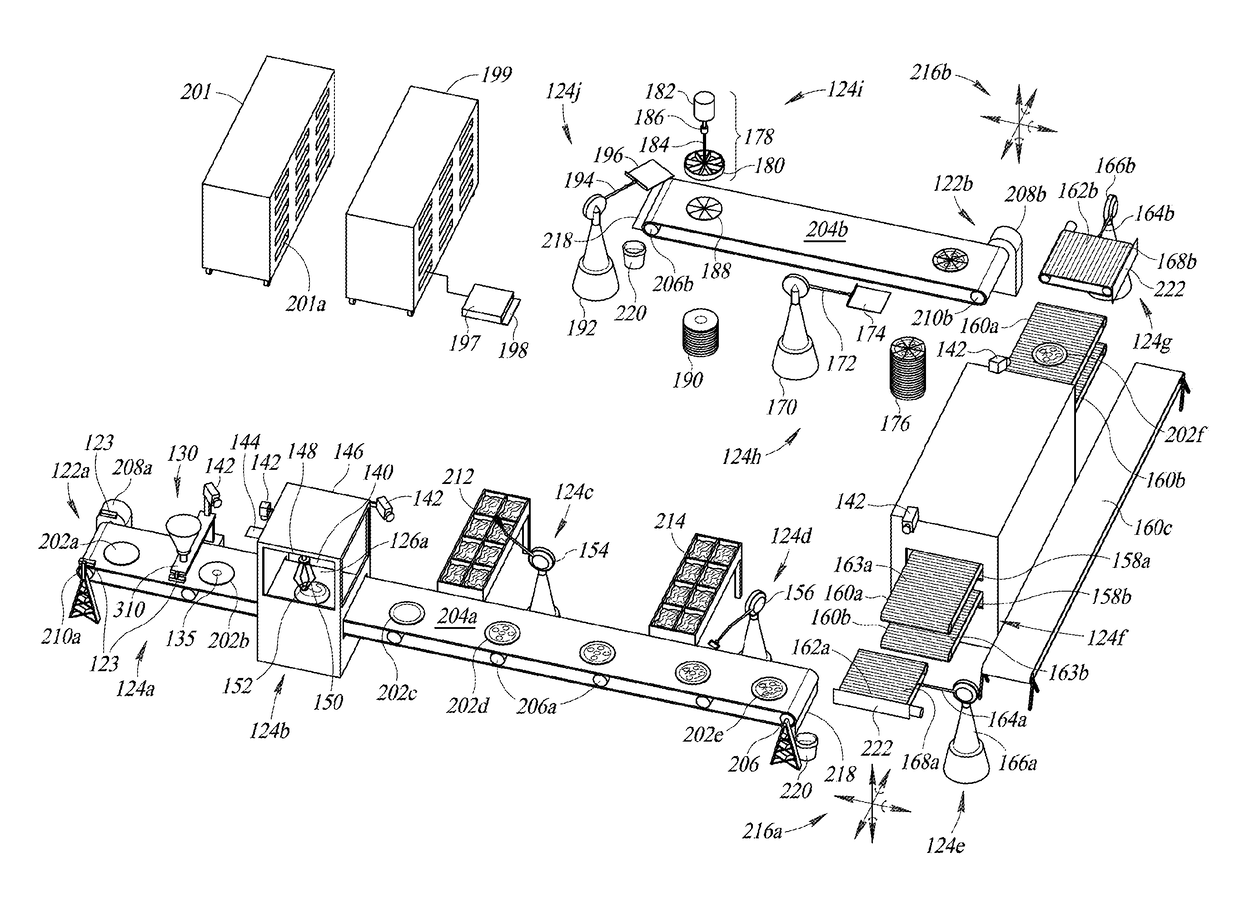
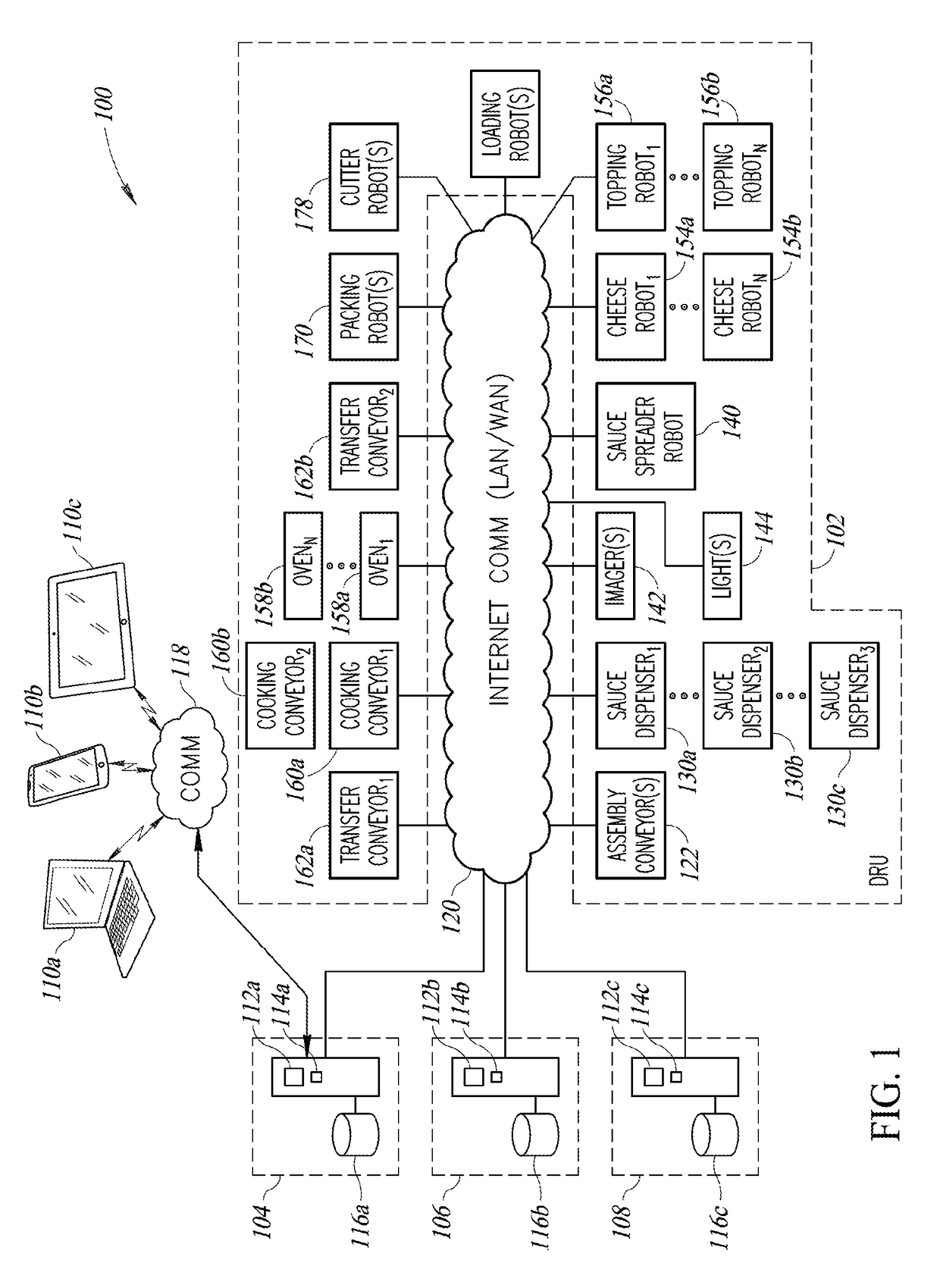
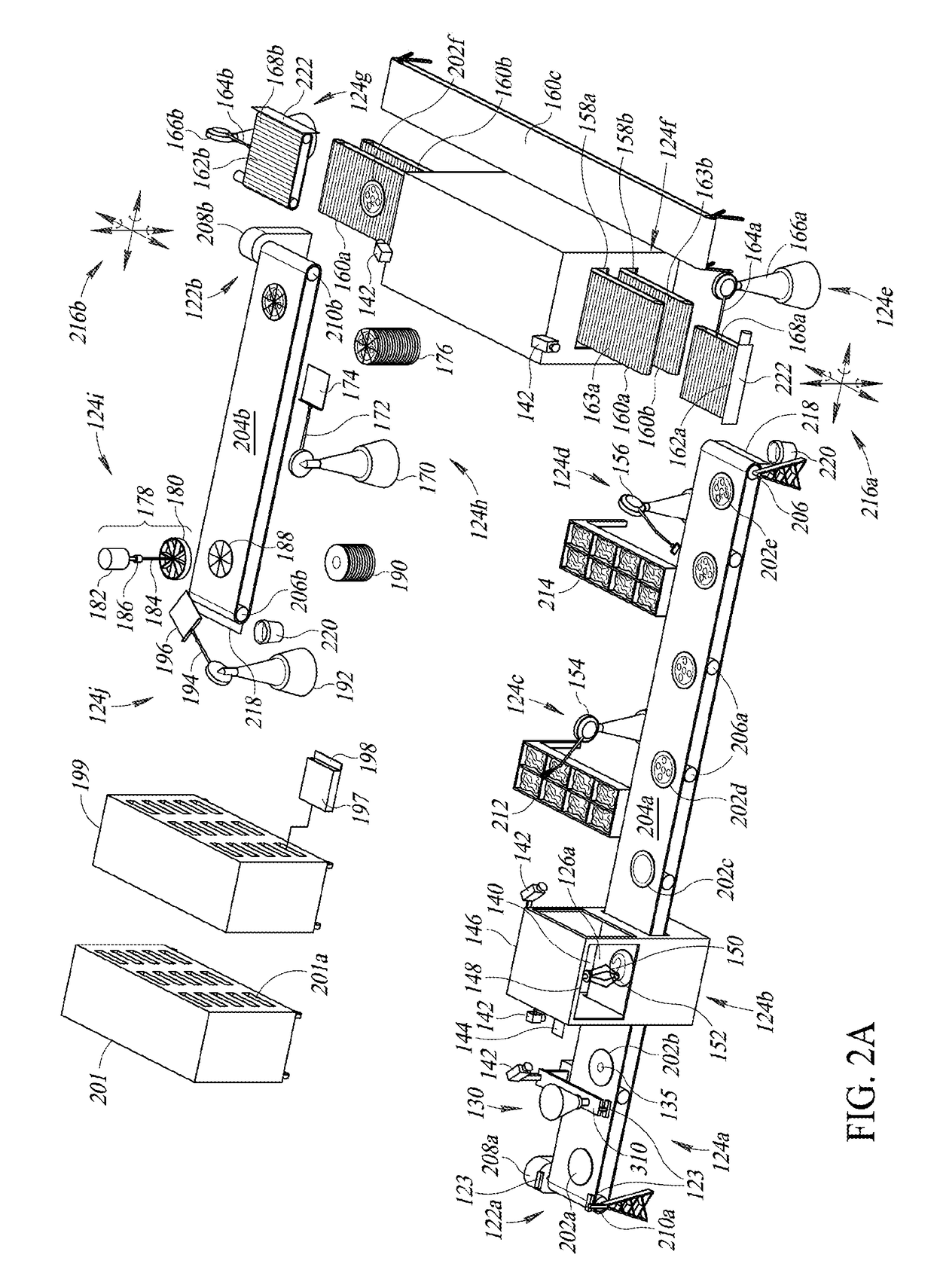
On-demand robotic food assembly and related systems, devices and methods
An on-demand robotic food assembly line can include one or more conveyors and one or more robots, operable to assemble food items in response to received orders for food items, and one or more ovens operable to, for example, partially cook assembled food items. The on-demand robotic food assembly line can optionally package the assembled and partially cooked food items in packaging, and optionally load the packaged partially cooked food items into portable cooking units (e.g., ovens) that are optionally loaded into racks that are, in turn, optionally loaded into delivery vehicles, where the food items are individually cooked under controlled conditions while en route to consumer destinations, such the cooking of each food item is completed just prior to arrival at the consumer destination location. A dynamic fulfillment queue for control of assembly is maintained based at least in part on estimated transit time for orders.
Owner:ZUME INC
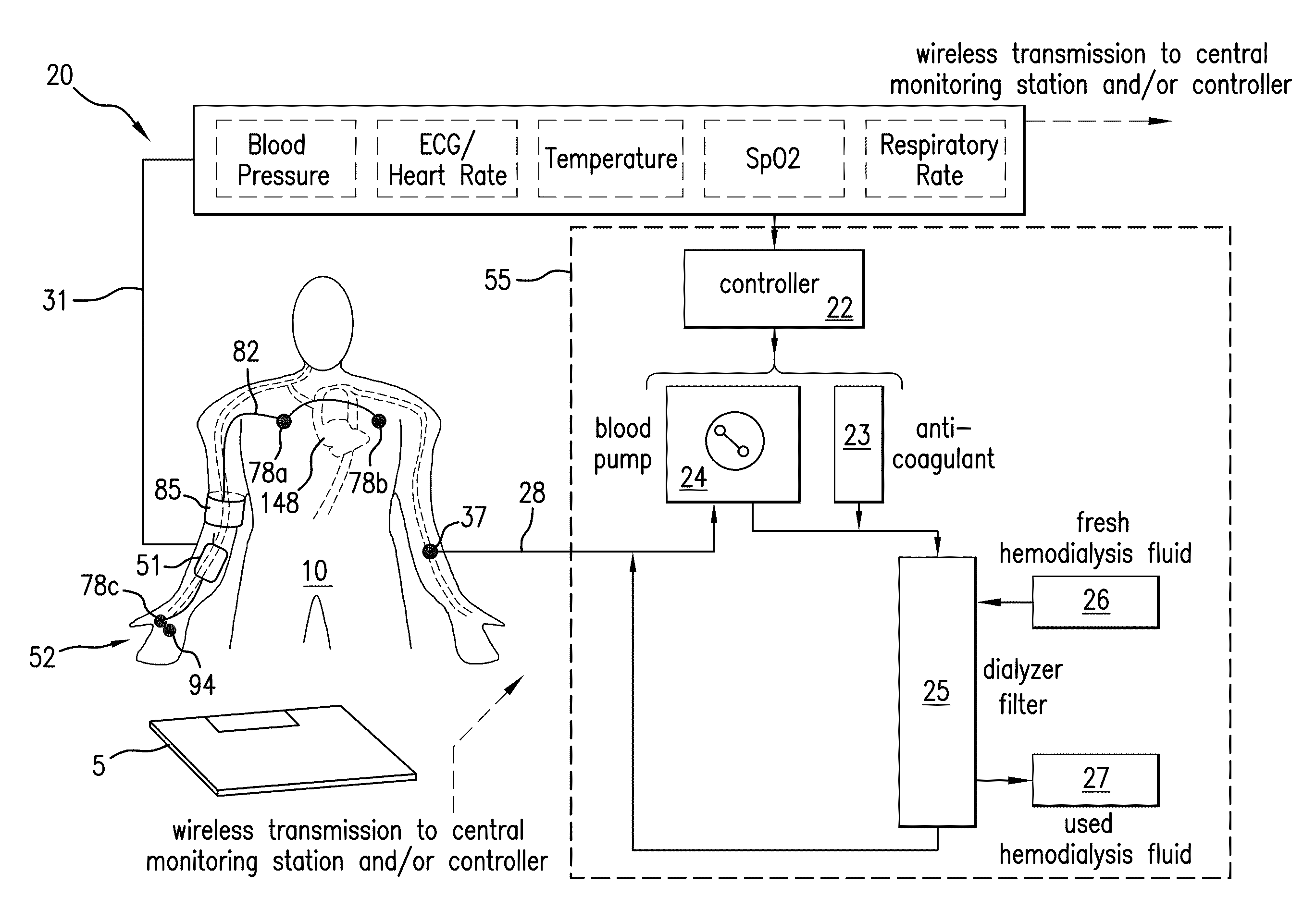
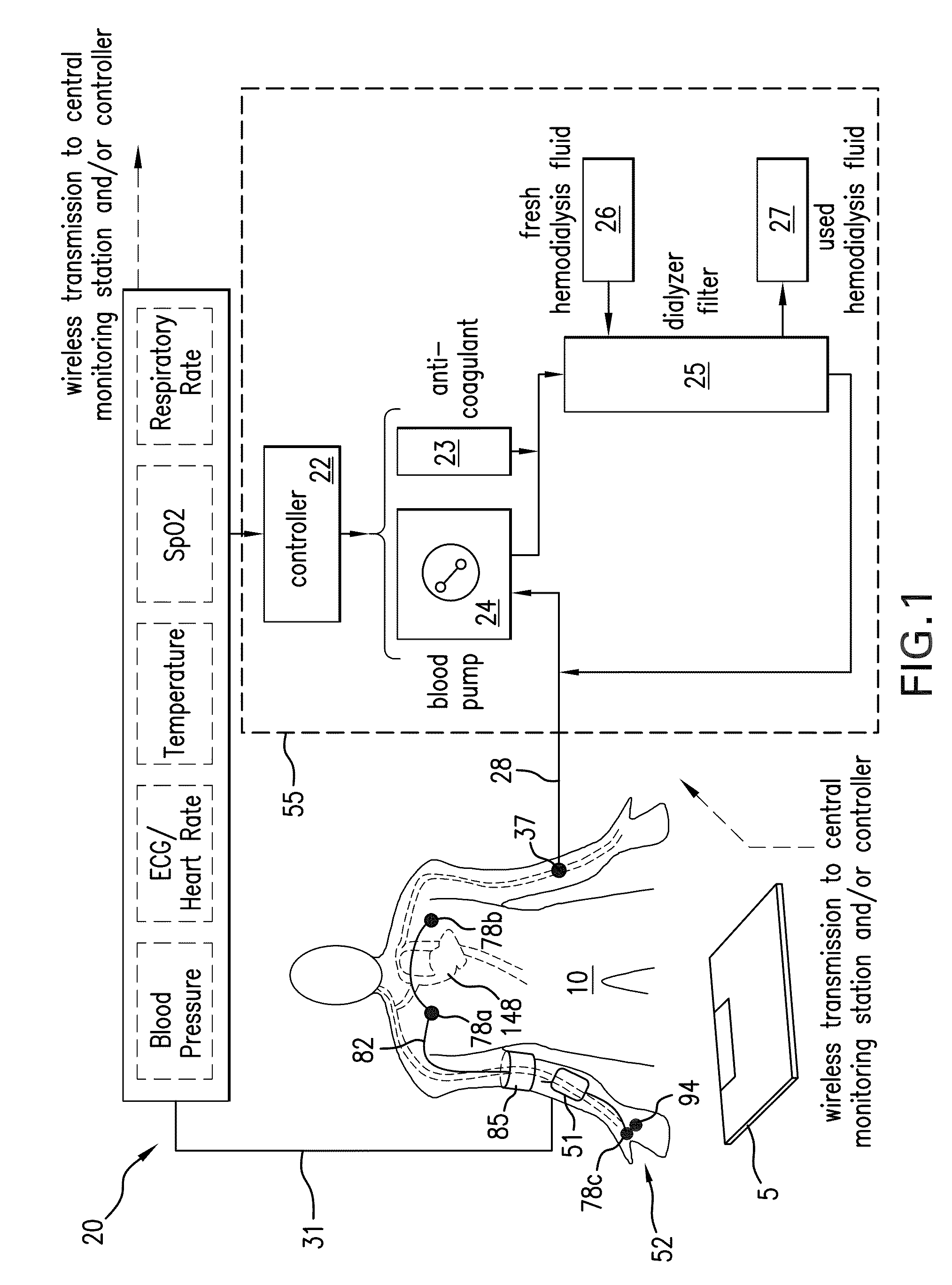
System for measuring vital signs during hemodialysis
ActiveUS20110066006A1Simplifies and expedites applicationEfficient detectionElectrocardiographyMedical devicesHemodialysisBlood pressure
The invention provides a system for continuously monitoring a patient during hemodialysis. The system includes a hemodialysis machine for performing the hemodialysis process that features a controller, a pump, a dialyzer filter, a lumen, and an interface to a body-worn monitor. A patient attaches to the dialysis machine through the lumen, and wears a body-worn monitor for continuously measuring blood pressure. The monitor includes an optical system for measuring an optical waveform, an electrical system for measuring an electrical waveform, and a processing component for determining a transit time between the optical and electrical waveforms and then calculating a blood pressure value from the transit time. The body-worn monitor features an interface (e.g. a wired serial interface, or a wireless interface) to transmit the blood pressure value to the controller within the hemodialysis machine. The controller is configured to receive the blood pressure value, analyze it, and in response adjust the dialysis process.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
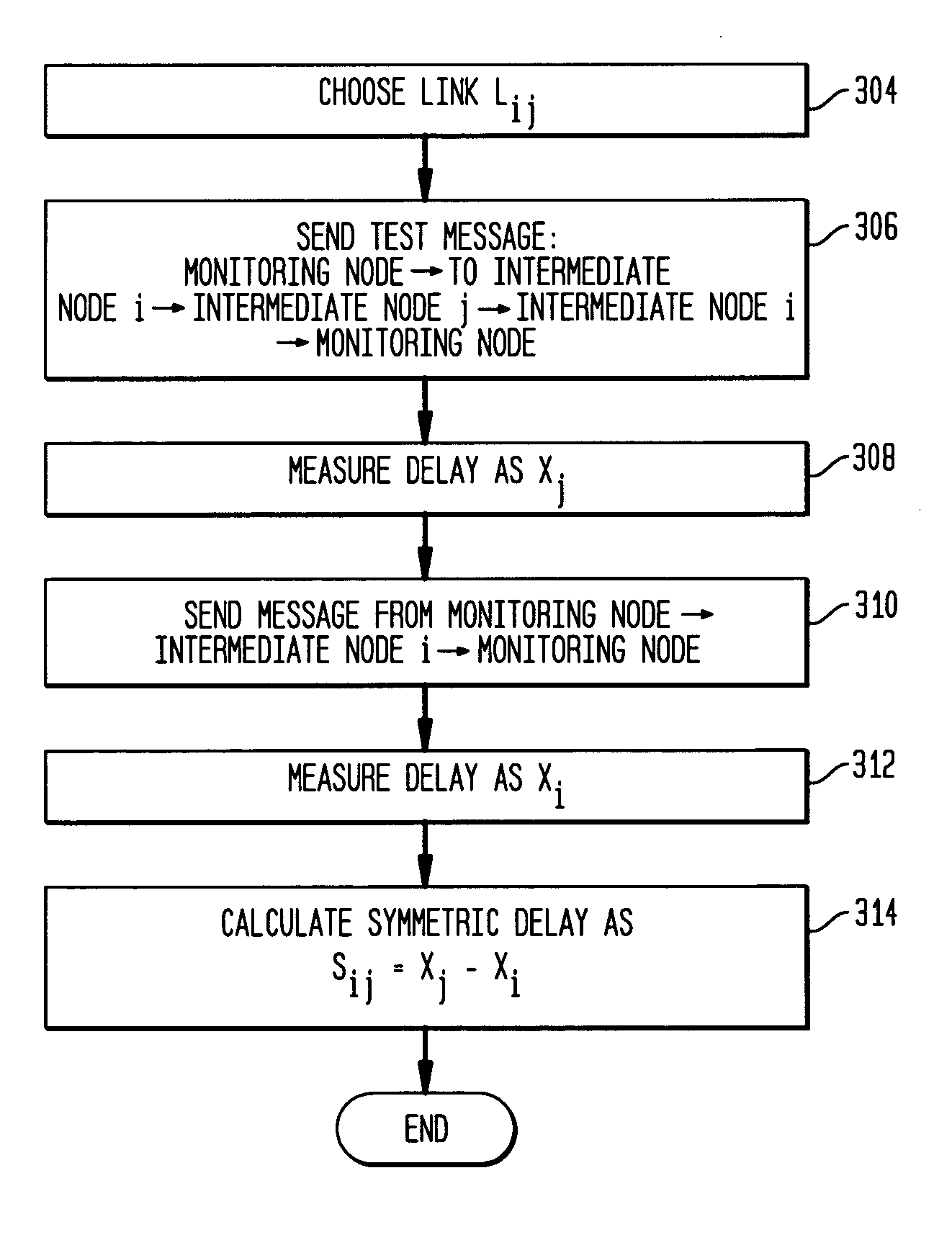
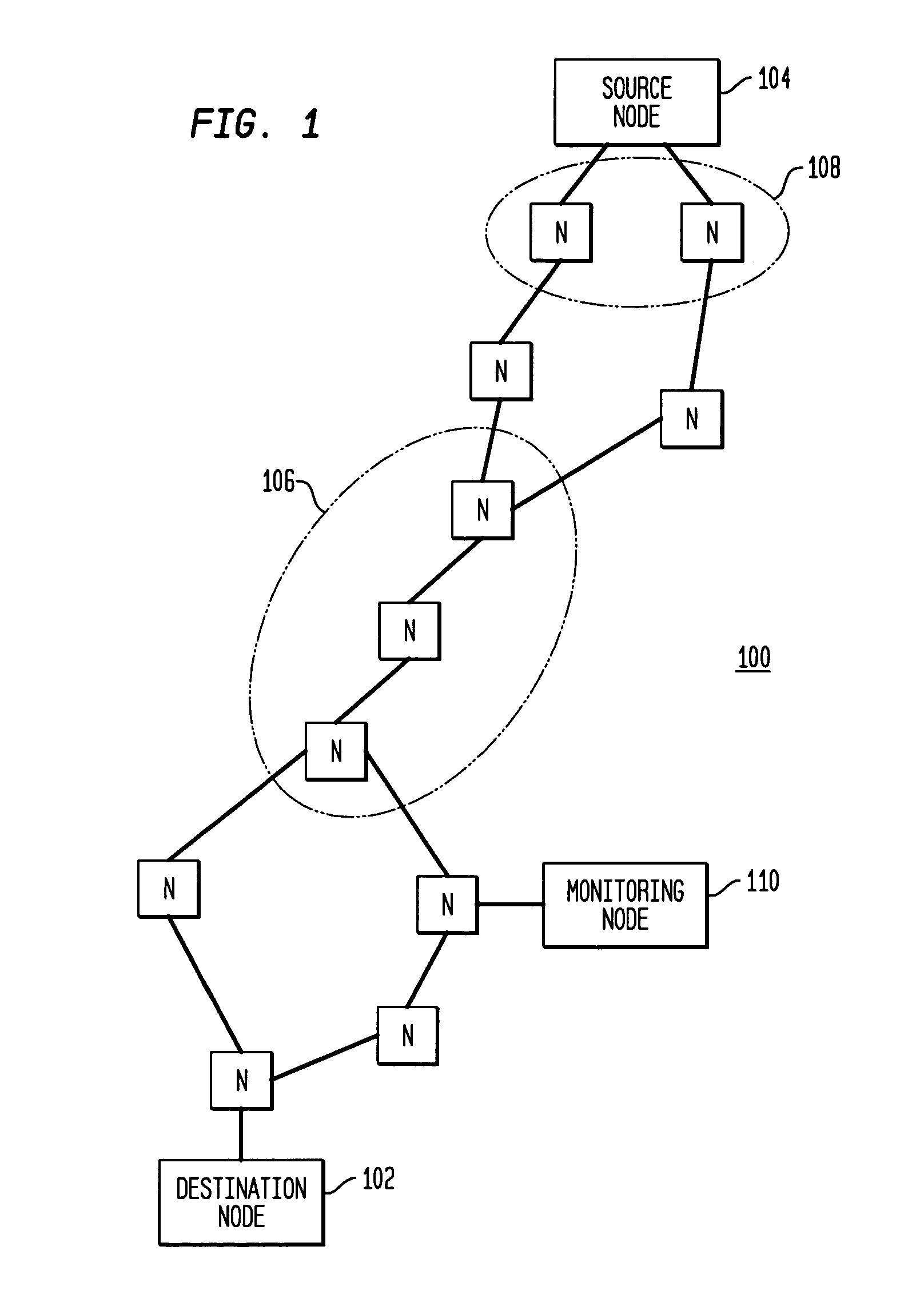
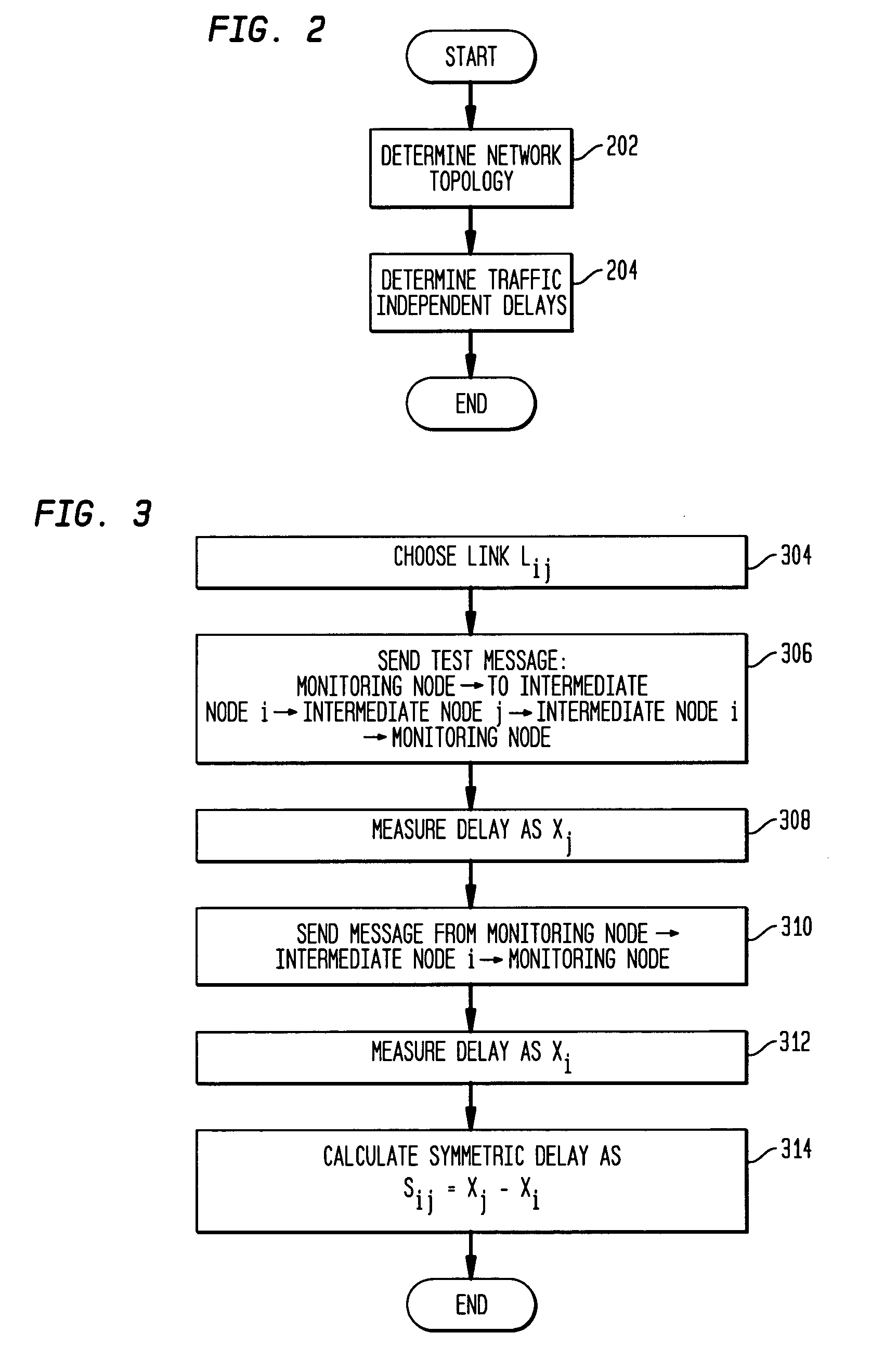
Remote estimation of round-trip delays in a data network
ActiveUS20060092850A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting tableNetwork topology
Disclosed is a technique for data network congestion diagnosis using remote estimation of round-trip delays. A monitoring node transmits test messages between network nodes and measures the transit times between when the test messages are transmitted from, and when they return to, the monitoring node. A path delay between network nodes is determined based on the measured time delays. The techniques for determining network path delay are also utilized in conjunction with a three phase test procedure for diagnosing network congestion problems. Due to various network topologies and routing tables, certain confirmatory checks may be required to determine whether the procedures of the first or second phase test procedures are appropriate for particular path segments. Further, queuing delays may be determined by subtracting traffic independent delays from the measured transit times of the test messages, and such queuing delays may be used to determine the path delays. Such traffic independent delays may be determined during periods of low network traffic.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Ultrasonic liquid flow controller
ActiveUS20050288873A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesFlow propertiesTime domainSonification
An ultrasonic flow meter includes a conduit, a first ultrasonic transducer, a second ultrasonic transducer, and a controller. The first ultrasonic transducer is disposed at a first position about a first portion of the conduit to transmit a first ultrasonic signal and to receive a second ultrasonic signal. The second ultrasonic transducer is disposed at a second position about a second portion of the conduit that is spaced apart from the first position along a length of the conduit to transmit the second ultrasonic signal and to receive the first ultrasonic signal. The controller is configured to cross-correlate the first and second received ultrasonic signals and generate a resulting time-domain signal, analyze the resulting time-domain signal to determine a difference in transit time between the first and second received ultrasonic signals, and calculate a rate of flow of a fluid in the conduit based upon the determined difference.
Owner:BROOKS INSTRUMENT
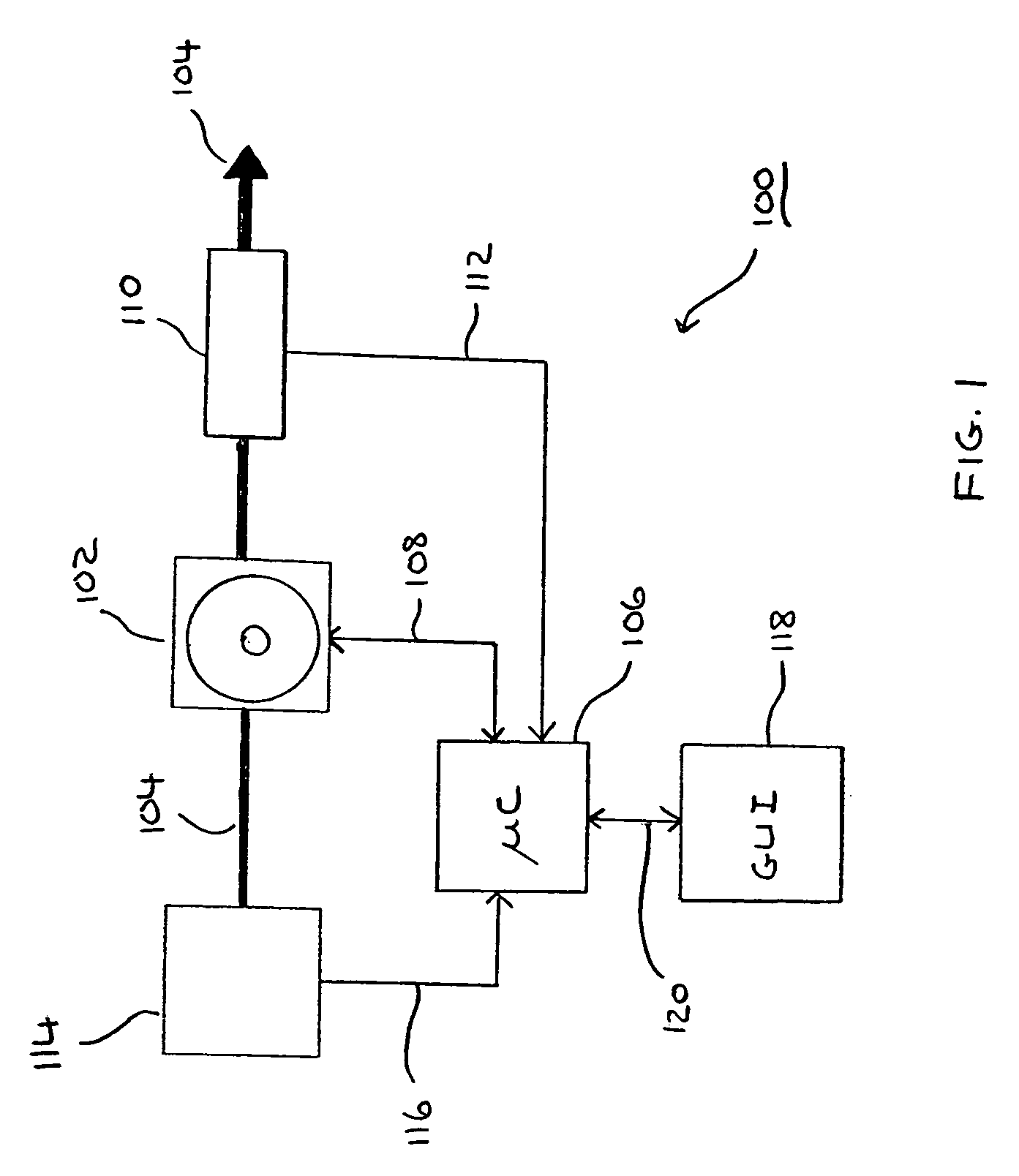
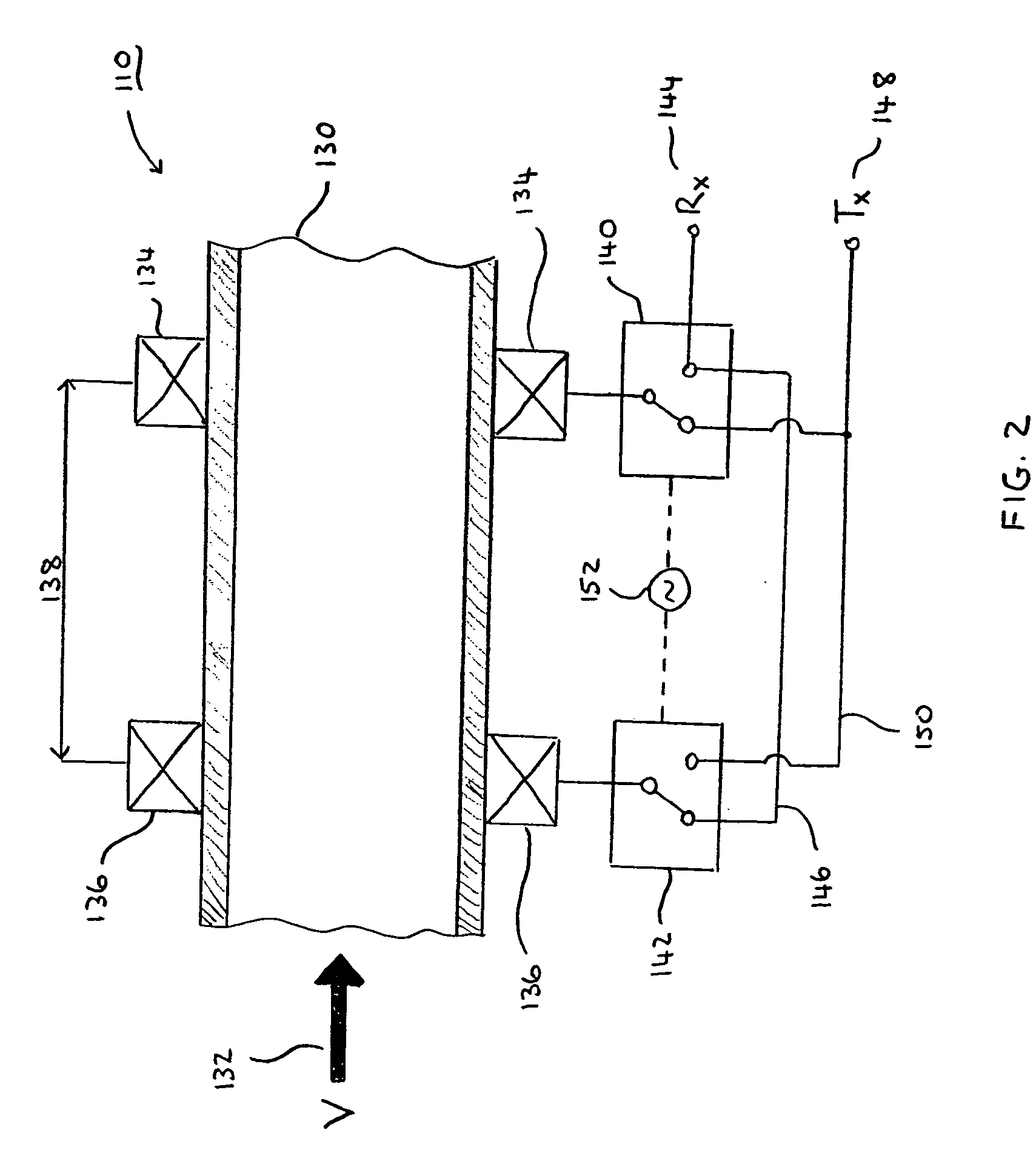
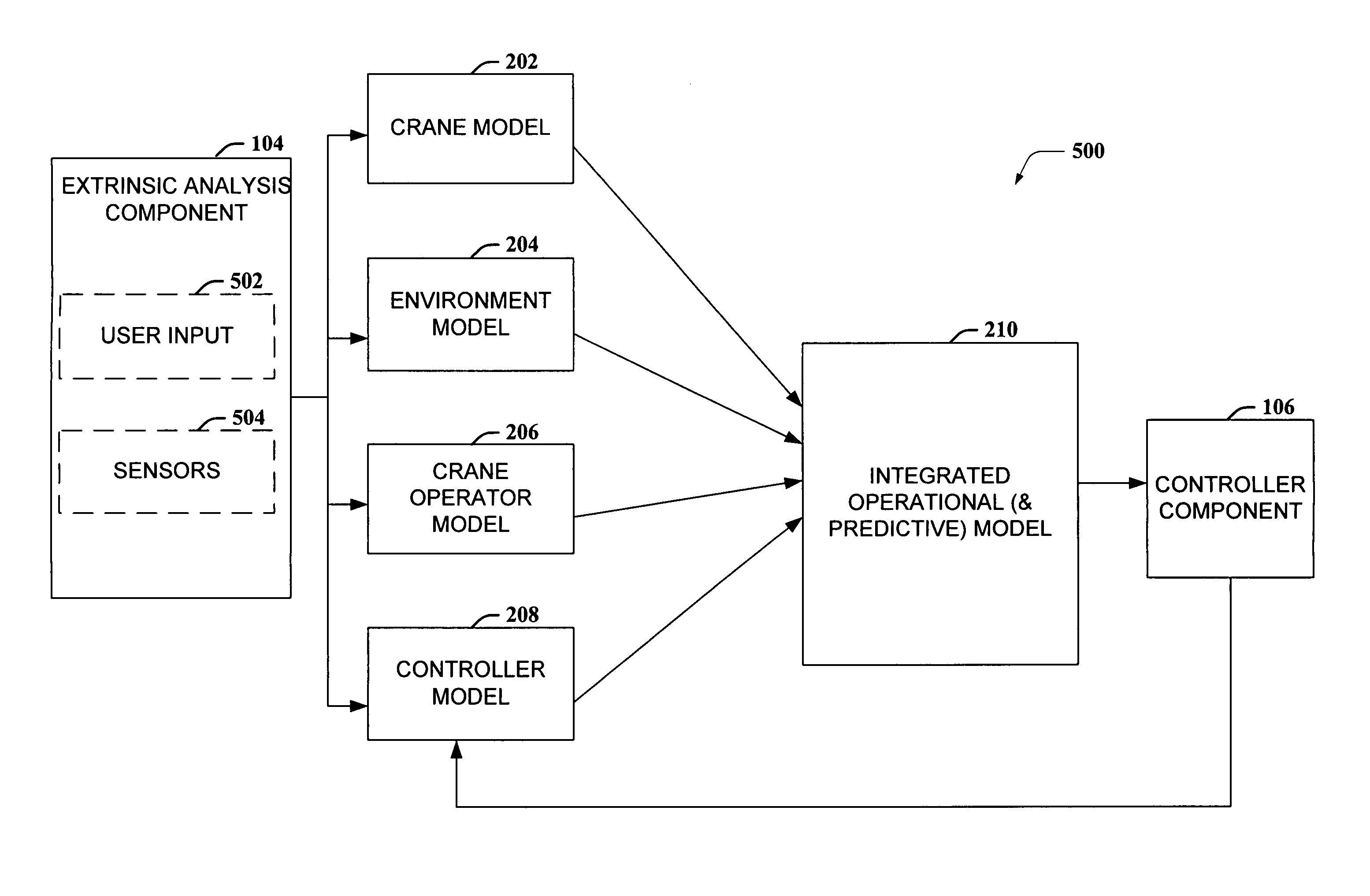
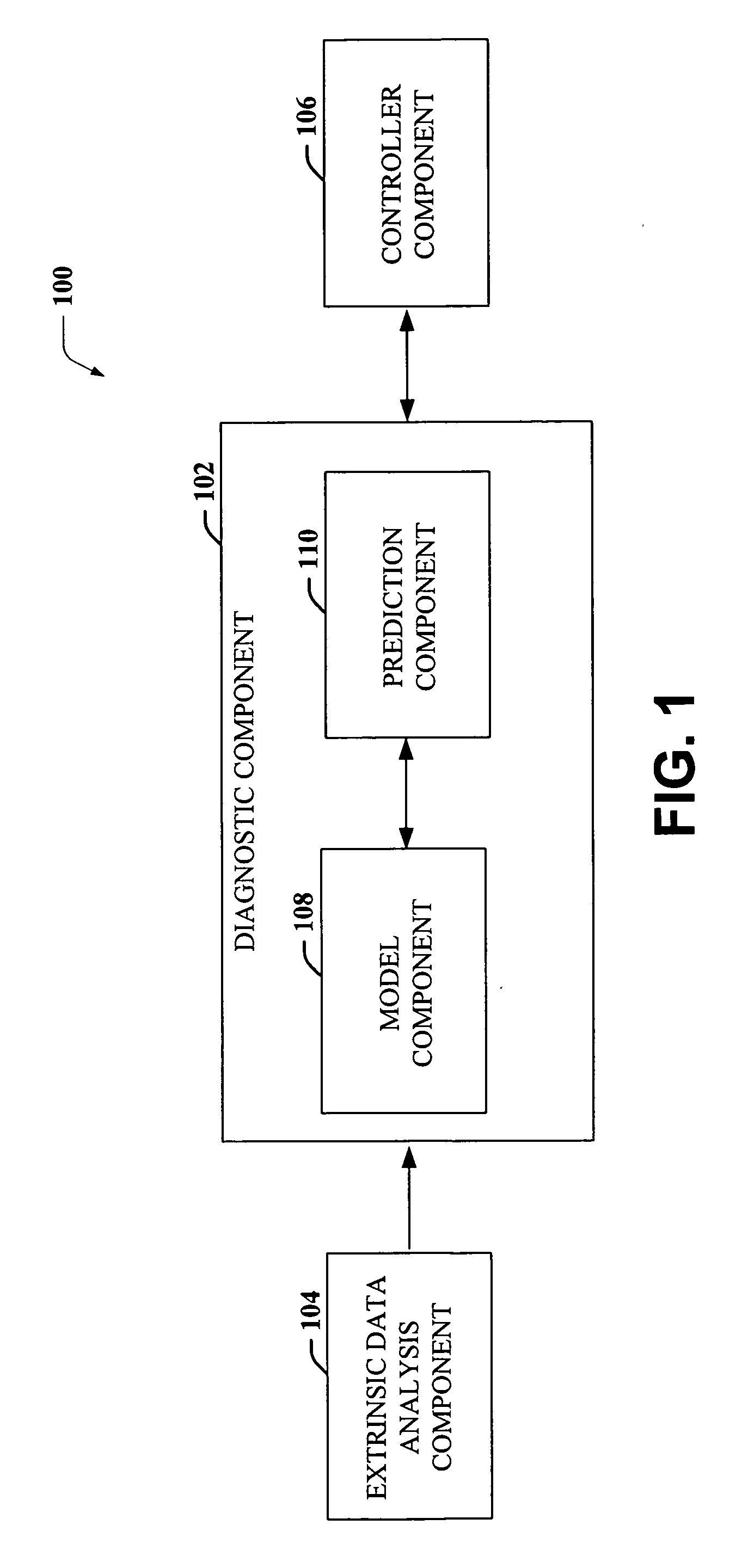
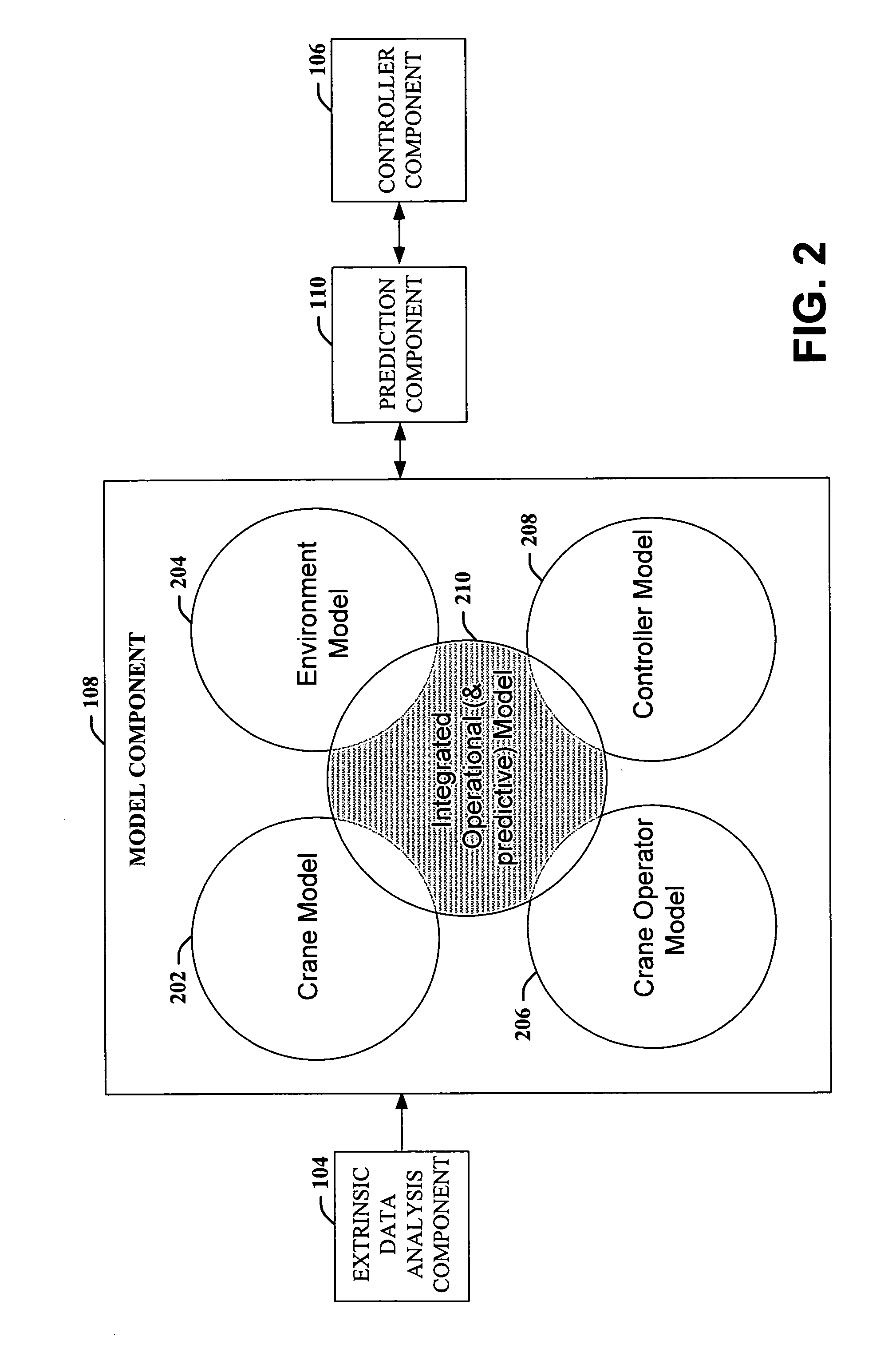
Model-based control for crane control and underway replenishment
ActiveUS20070050115A1Easy to controlMitigates container swayAnalogue computers for trafficTrolley cranesTransport timeExternal data
Crane control and anti-sway are facilitated utilizing a diagnostic component that includes a model component and a control component. The diagnostic component interfaces with an extrinsic data analysis component and a controller component. The diagnostic component receives operating condition information from the extrinsic data analysis component and performs predictive modeling, based on a current status and stored information. Further, the diagnostic component predicts the affect of the operating conditions on a crane and implements and / or recommends actions to mitigate the affect of the existing and / or predicted operating conditions. The diagnostic component further mitigates crane sway and / or induces crane sway to reduce container transit time. Intelligent agents are employed to provide trajectory planning and execution and / or to detect potential component failure.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Network latency analysis packet and method
ActiveUS20070274227A1Efficient methodAttenuation bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsTimestampNetwork packet
A packet and a method for analyzing network latency are disclosed. The disclosed systems and methods measure the latency between nodes in a network and do so while using less bandwidth and processing than traditional methods by using a packet to traverse a network and collect timestamps at various nodes so that the delay in transit time between nodes can be calculated when the packet returns to a server.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
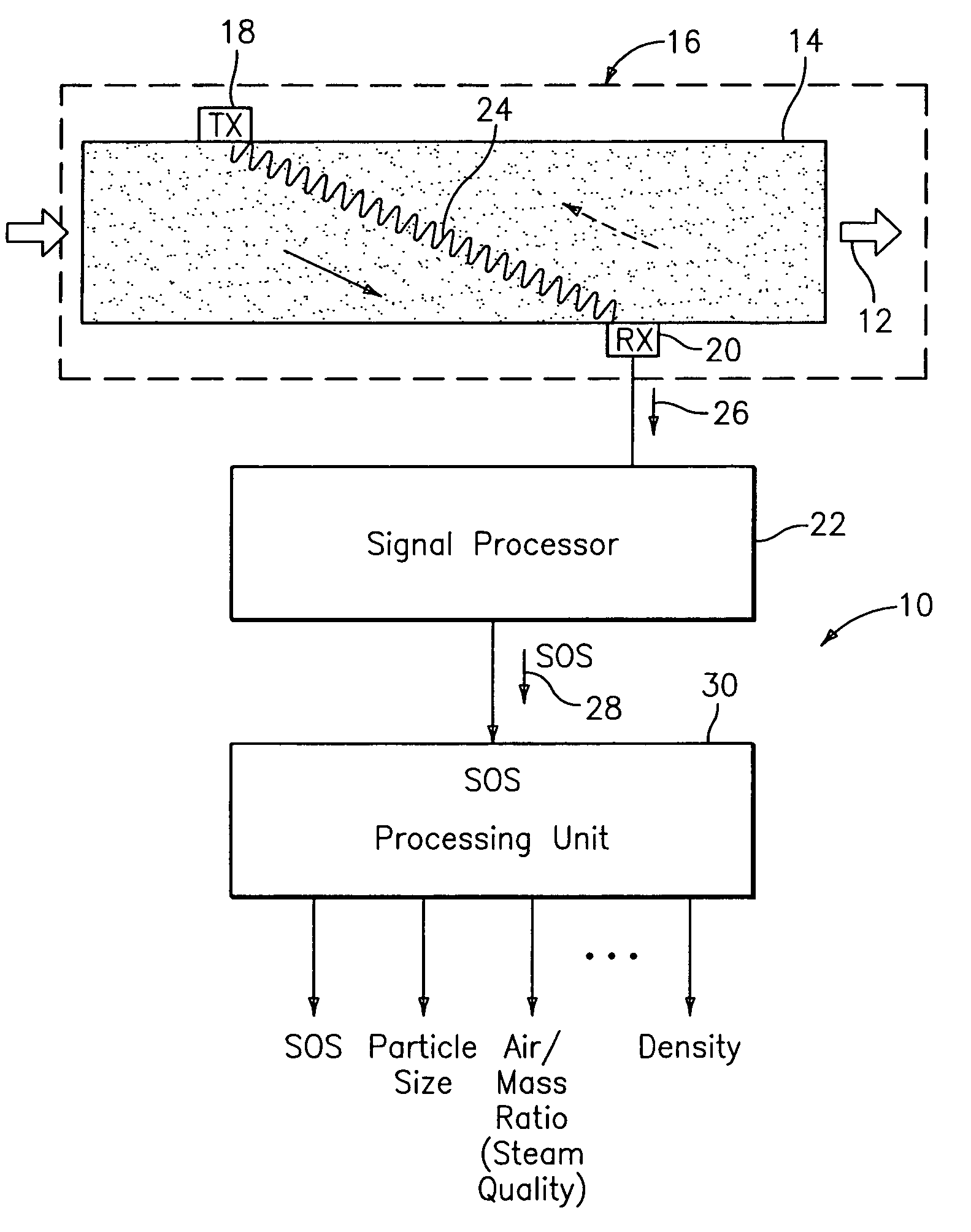
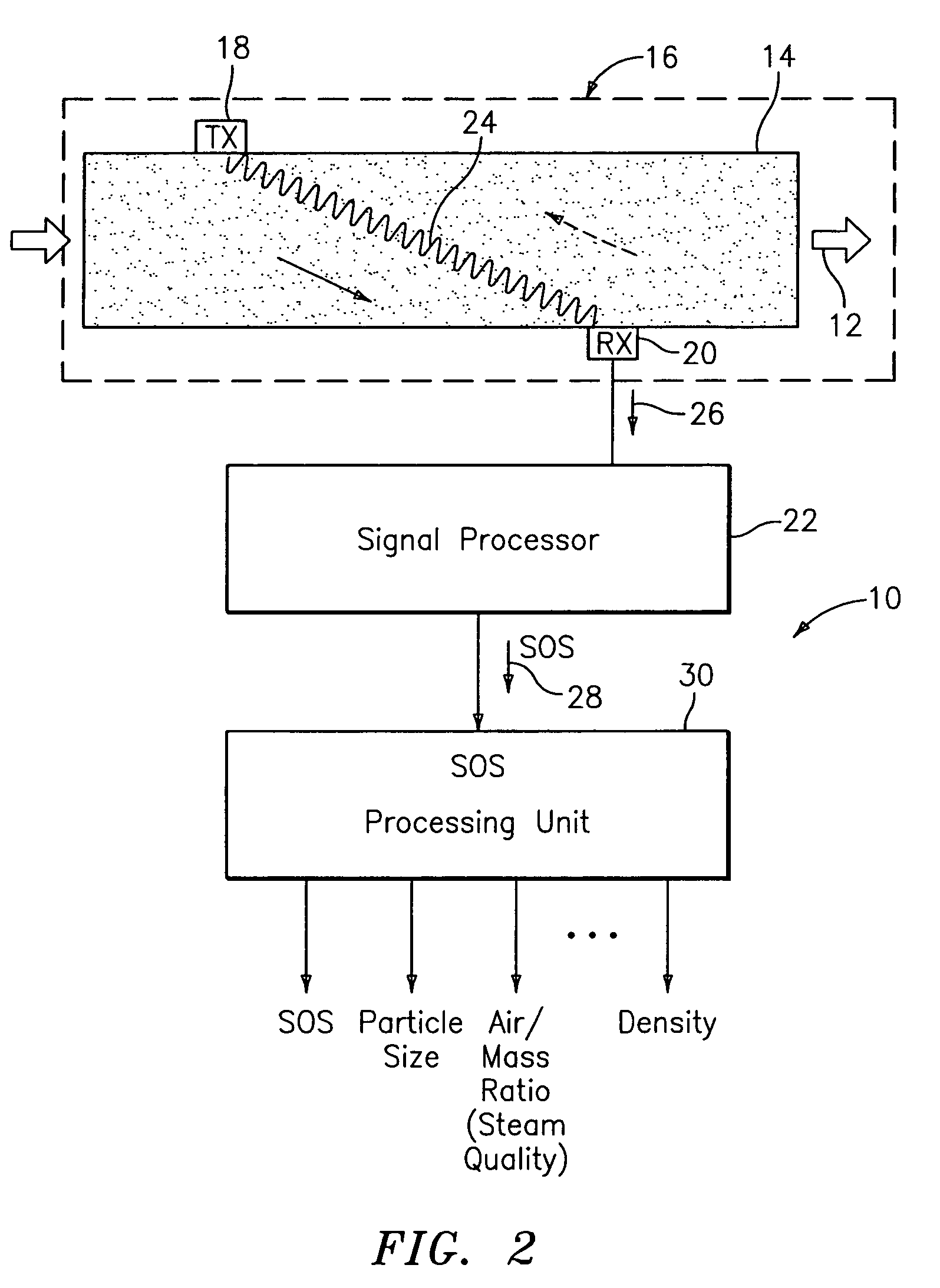
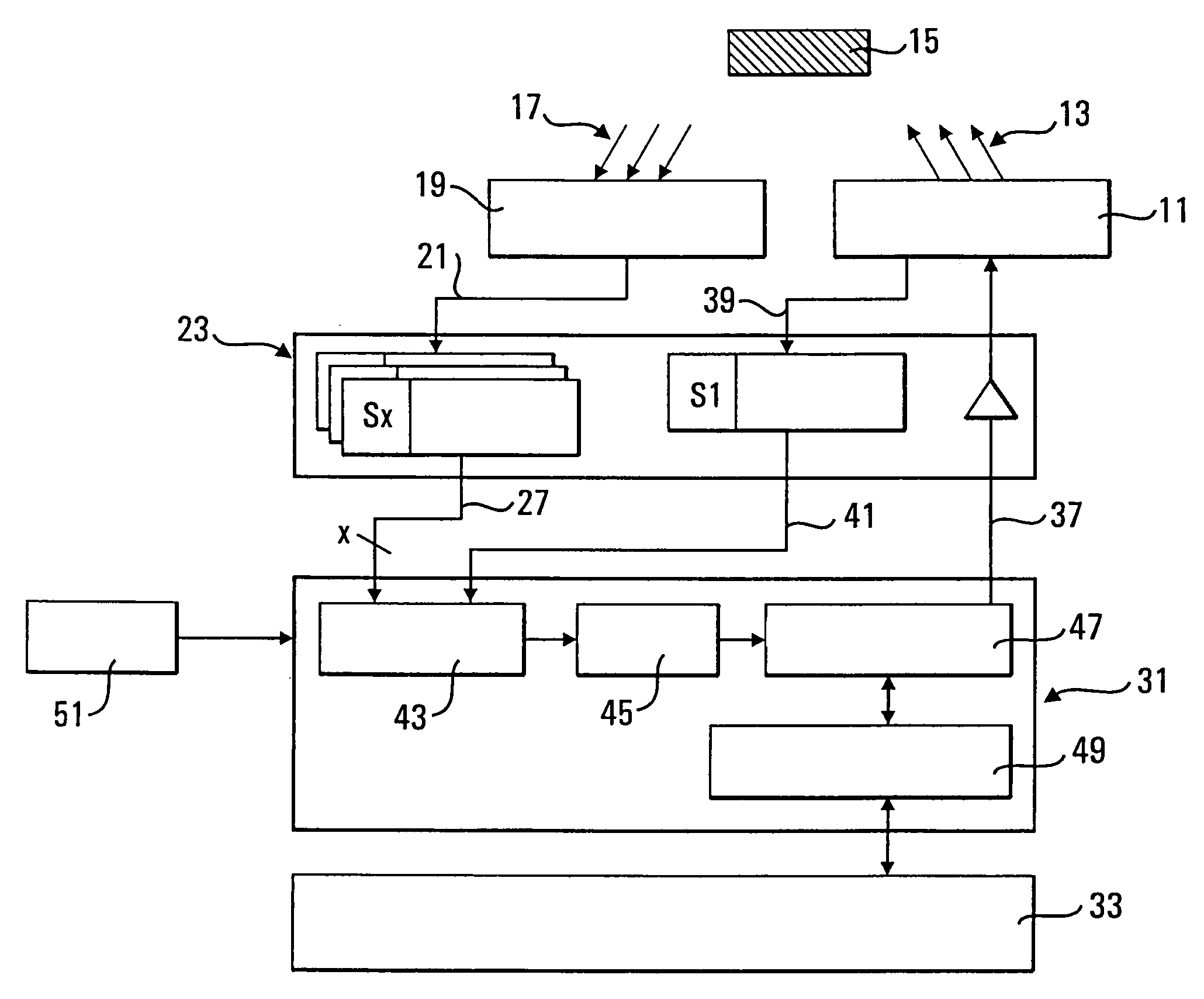
Apparatus for measuring parameters of a flowing multiphase mixture
ActiveUS7096719B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorMass ratio
An apparatus 10 is provided that measures the speed of sound propagating in a multiphase mixture to determine parameters, such as mixture quality, particle size, vapor / mass ratio, liquid / vapor ratio, mass flow rate, enthalpy and volumetric flow rate of the flow in a pipe or unconfined space, for example, using acoustic and / or dynamic pressures. The apparatus includes a pair of ultrasonic transducers disposed axially along the pipe for measuring the transit time of an ultrasonic signal to propagate from one ultrasonic transducer to the other ultrasonic transducer. A signal process, responsive to said transit time signal, provides a signal representative of the speed of sound of the mixture. An SOS processing unit then provides an output signal indicative of at least one parameter of the mixture flowing through the pipe. The frequency of the ultrasonic signal is sufficiently low to minimize scatter from particle / liquid within the mixture. The frequency based sound speed is determined utilizing a dispersion model to determine the at least one parameter of the fluid flow and / or mixture.
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
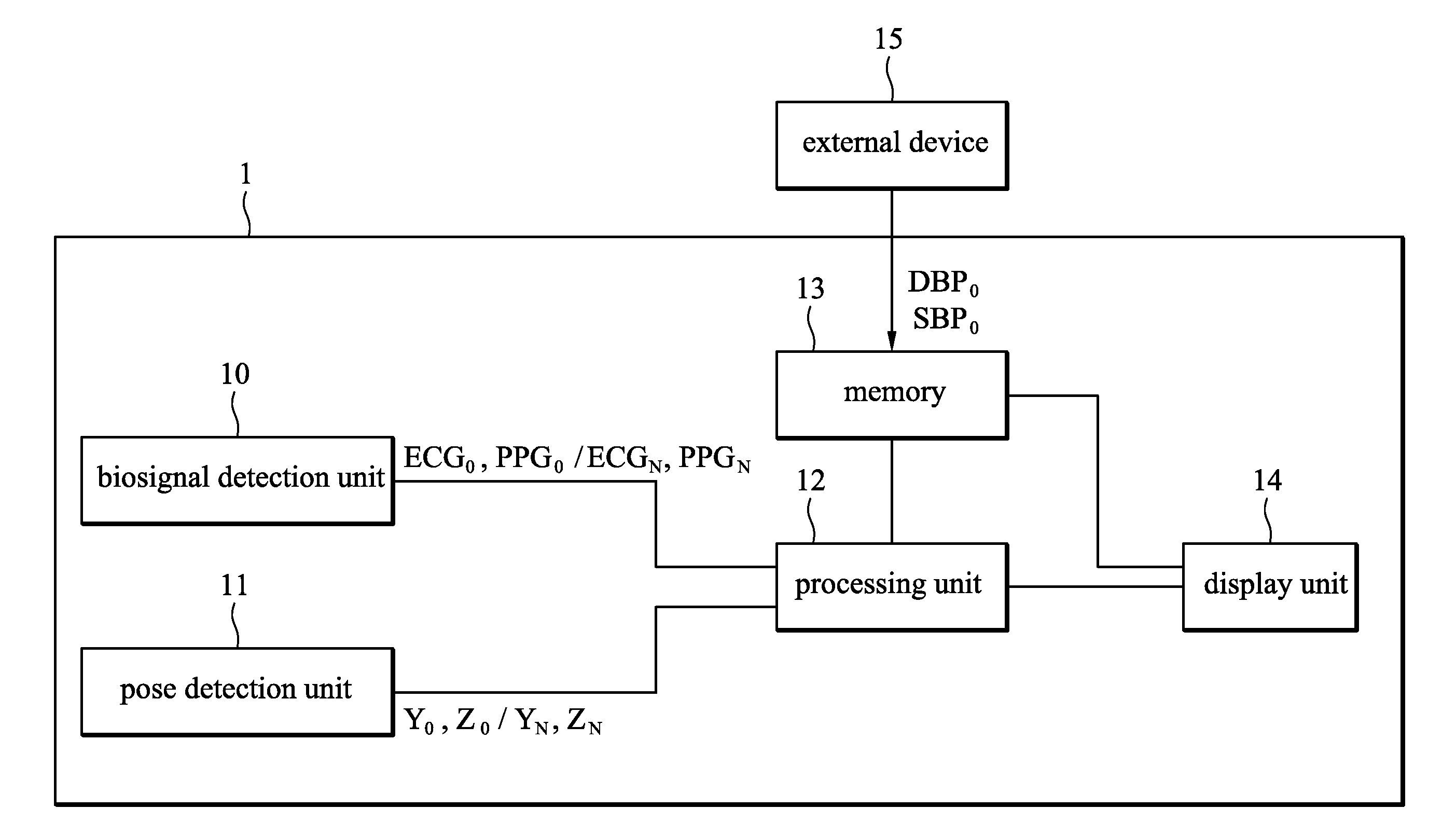
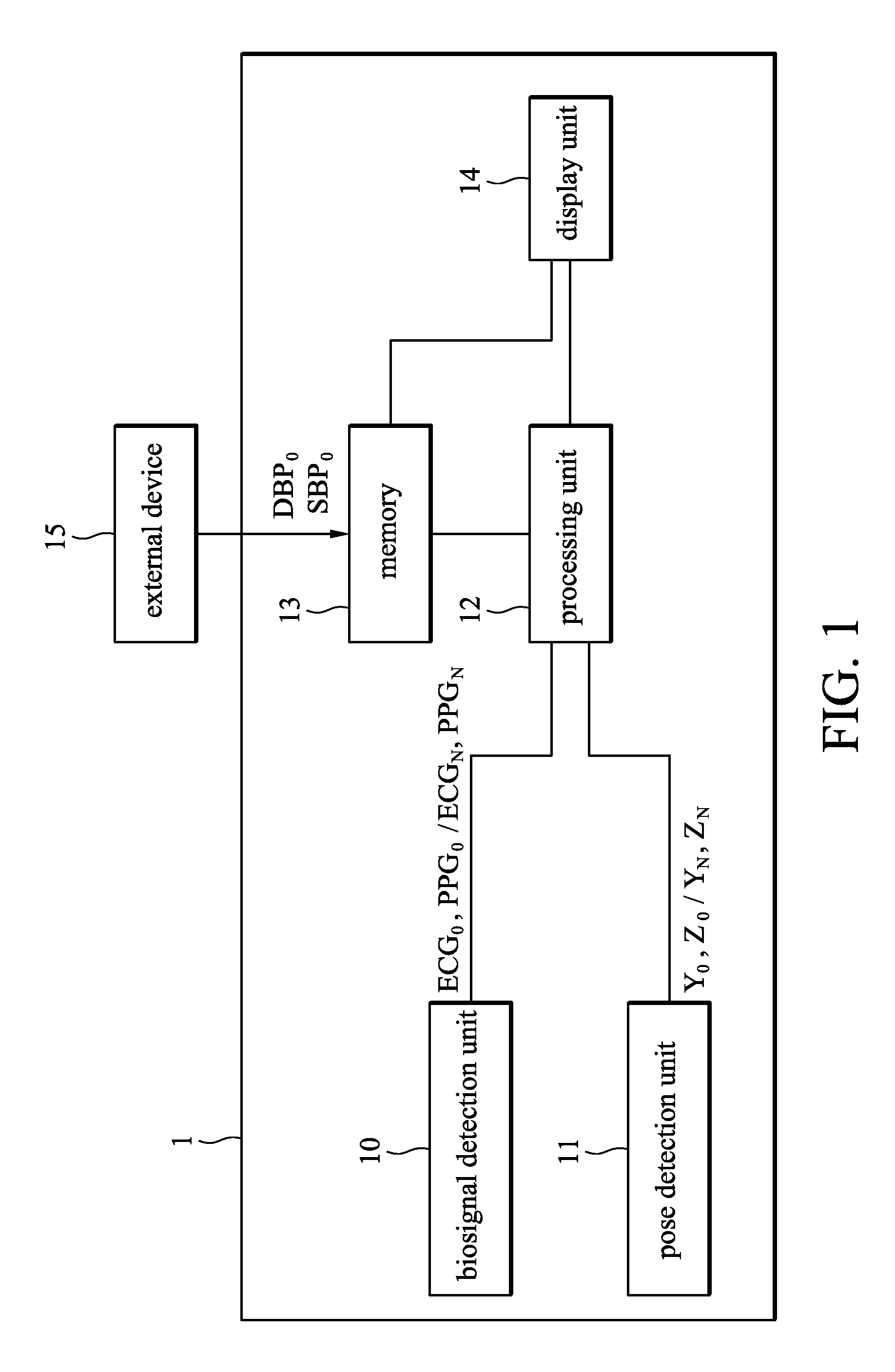
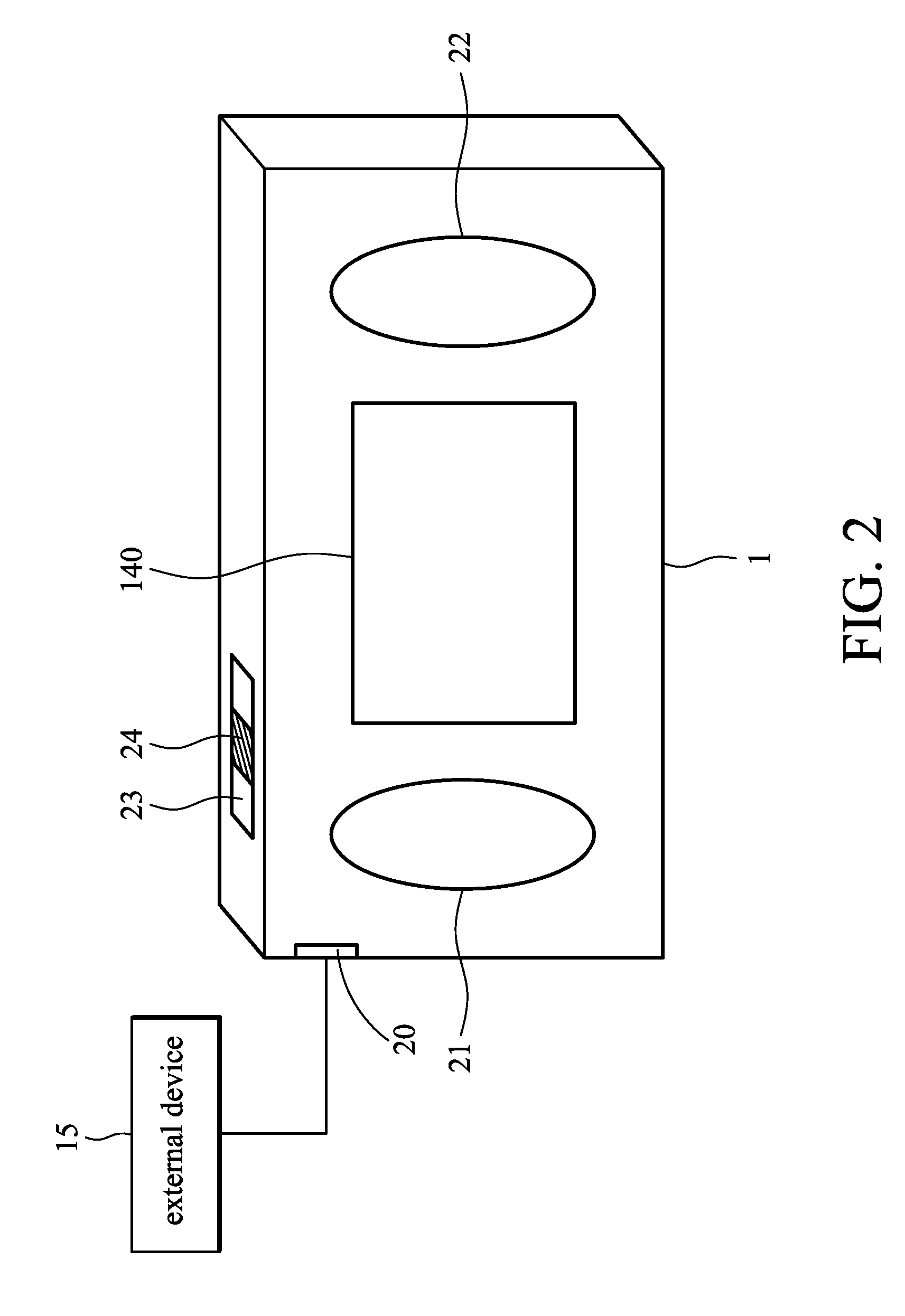
Biosignal measurement modules and methods
ActiveUS20100160793A1ElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsHeight differencePostural orientation
A biosignal measurement module is provided and includes a biosignal measurement unit, a pose detection unit, and a processing unit. The biosignal measurement unit measures an electrocardiogram signal and a pulse signal of a subject. The pose detection unit detects a position of the biosignal measurement module and outputs position signals. The processing unit receives the electrocardiogram signal, the pulse signal, and the position signals. The processing unit generates a height variation parameter, which indicates the height difference between the position of the biosignal measurement module and a reference position, according to the position signals. The processing unit calculates a current pulse transit time according to the electrocardiogram signal and the pulse signal and compensates for the current pulse transit time according to the height variation parameter to obtain a compensated pulse transit time. The processing unit obtains a blood pressure signal according to the compensated pulse transit time.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Ultrasonic gas flowmeter as well as device to measure exhaust flows of internal combustion engines and method to determine flow of gases
ActiveUS7093502B2Level gas temperature profileMinimize impactVolume/mass flow measurementVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusUltrasonic sensorDischarge measurements
An ultrasonic gas flowmeter includes a measuring pipe with flowing gas, transmitting and receiving sound transducers, transmission and reception electronics, and evaluation electronics. The sound transducers (7, 8, 9, 10) are designed as capacitive electro-acoustic ultrasonic transducers to construct a flowmeter with improved capacity, especially in view of temperature stability and the reduction and consideration of a temperature profile. Devices (5, 6) are provided to level the gas temperature profile and to minimize the influence of the temperature profile on the flow measurement. A more accurate and dependable detection of the volume flow or the mass flow of gases is to be achieved, especially in highly dynamic flows, for the method of determining the flow of gases whereby the mean flow velocity is determined and the flowing gas quantity is determined with highly synchronized resolution from the two transit times of two acoustic signals. In addition, an assessed value is computed (35) for the flow after the determination of the transit times and the assessed value is corrected at least by means of a characteristic temperature of the gas and the temperature of the wall of the measuring pipe (36).
Owner:AVL LIST GMBH
Non-invasive tranducers for ultrasonic transit time flow meters
An ultrasonic flow meter permitting easy insertion and removal of a tube or conduit. A partial ring transducer or partial cylinder transducer is used to permit easy insertion and removal of a flexible tube in an ultrasonic flow meter for measuring fluid flow. In another embodiment a split ring or split cylinder transducer is used to facilitate easy removal and insertion of a tube or conduit in which fluid flow is to be measured. In another embodiment a clamping system is used to securely hold and couple a tube or conduit within the ultrasonic flow meter system. The present invention is conveniently adapted to hold flexible tubes and in particular disposable flexible tubes often used in the medical industry.
Owner:STRAIN MEASUREMENT DEVICES
Method and apparatus for determining the flow parameters of a streaming medium
ActiveUS20100095782A1Avoid interferenceHigh measurement accuracyVolume/mass flow measurementVolume meteringLongitudinal waveTransducer
According to the method longitudinal waves are generated in a transducer used only as a transmitter connected from outside to a conduit. These waves are transmitted along two diagonal paths through the streaming medium in an upstream and a downstream direction, and received by two transducers used only as receivers which are located in a diagonal upstream and downstream position and on an opposite side relative to the transducer used as a transmitter, also connected to the conduit. A transit time value of the waves between the transducer used as a transmitter and each of the transducers used as receivers is determined. A difference value on the basis of the determined transit time values is generated and the flow parameters are determined on the basis of said difference value. This measuring method is highly independent of the propagation velocity of the wave in the medium streaming in the conduit therefore also independent of the temperature and humidity of a gaseous medium. An apparatus and a conduit for use in the apparatus for performing the method is also suggested. The conduit used in the apparatus comprises a first location for receiving a transmitter in a middle region of the measuring area and two second locations for receiving receivers in a border region of the measuring area opposite to the first location. The wall of the conduit is dimensioned so that the longitudinal waves can pass through it with minimal loss and maximum efficiency. The inner wall of the conduit forms a uniform and continuos surface for the transmission of the longitudinal waves between the transmitter and the receivers and for blocking the passage of any organic or inorganic material. In medical applications the apparatus and its housing is configured to receive, hold and release a sterile conduit.
Owner:USCOM
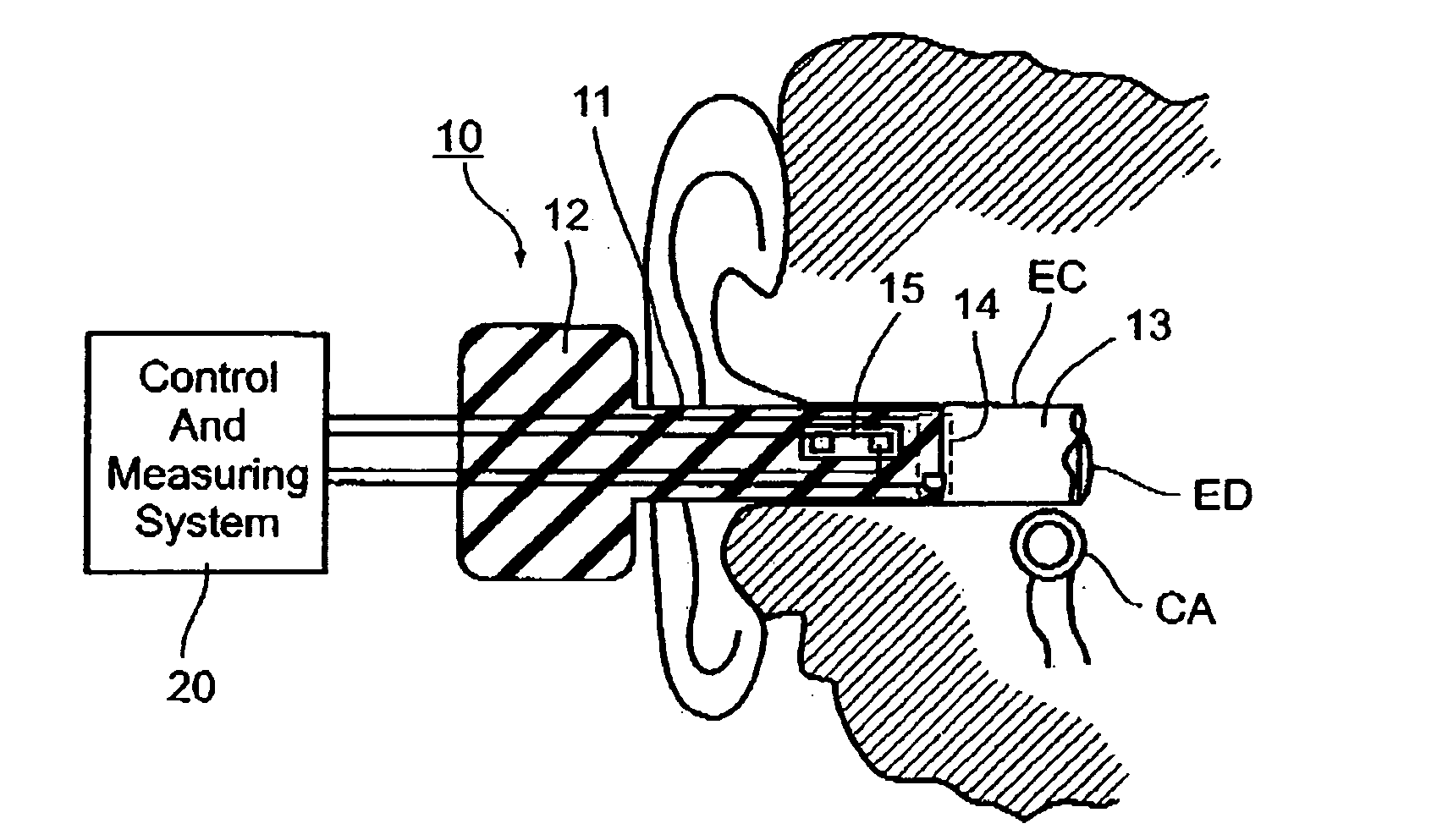
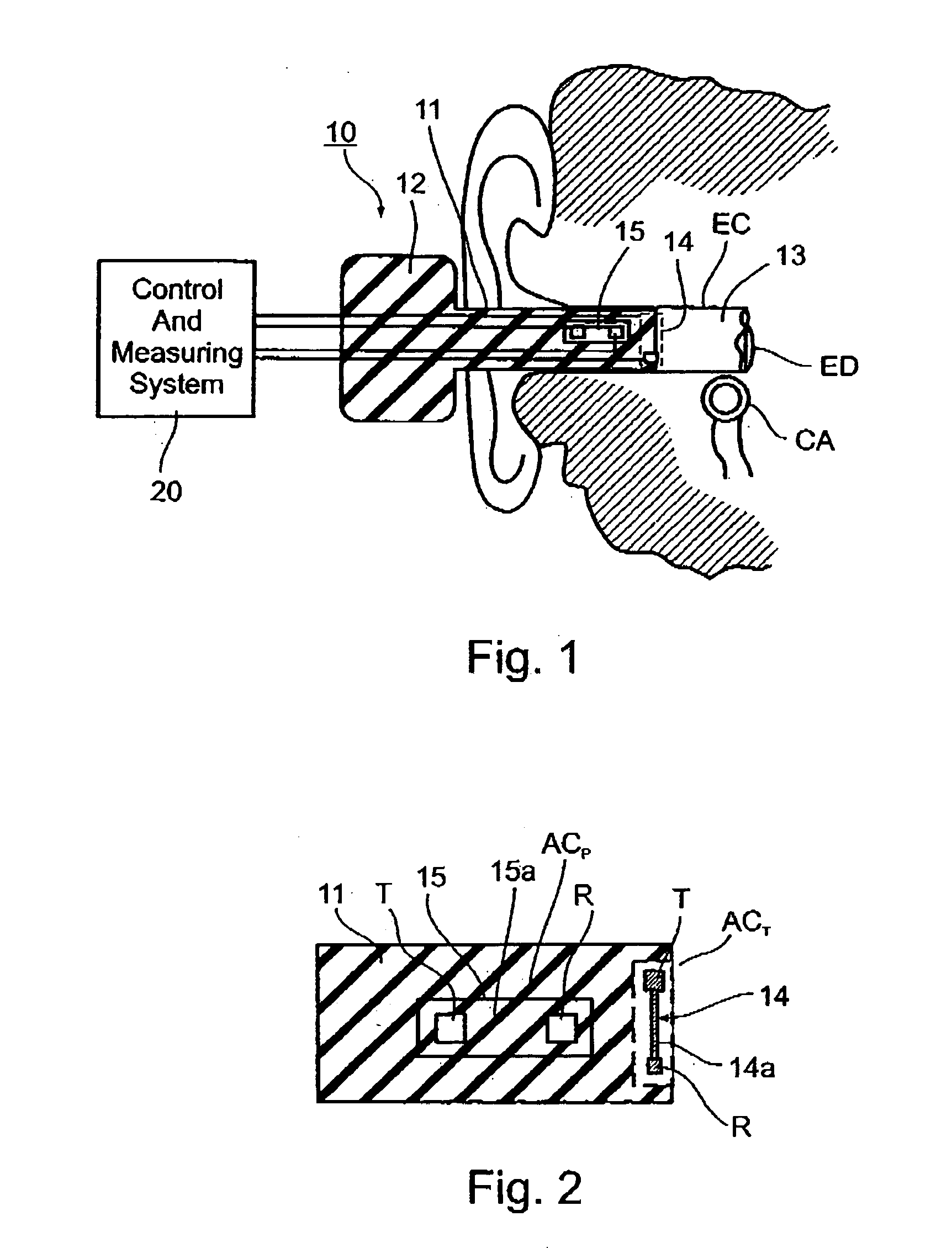
Ear probe particularly for measuring various physiological conditions particularly blood pressure, temperature and/or respiration
InactiveUS20060206014A1Accurate and non-invasive measurementAccurate measurementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBody temperature measurementMedicineBlood pressure
An ear probe for detecting and / or measuring at least one predetermined physiological condition of a subject, includes: an earplug shaped and dimensioned for insertion into an ear of the subject; and a sensor carried by the earplug for sensing the predetermined physiological condition of the subject; the sensor including: an acoustical transmitter and an acoustical receiver spaced from the transmitter and defining an acoustical channel therebetween; and a processor for monitoring changes in the transit time, caused by the predetermined physiological condition, of an acoustical wave transmitted from the transmitter to the receiver through the acoustical channel.
Owner:NEXENSE
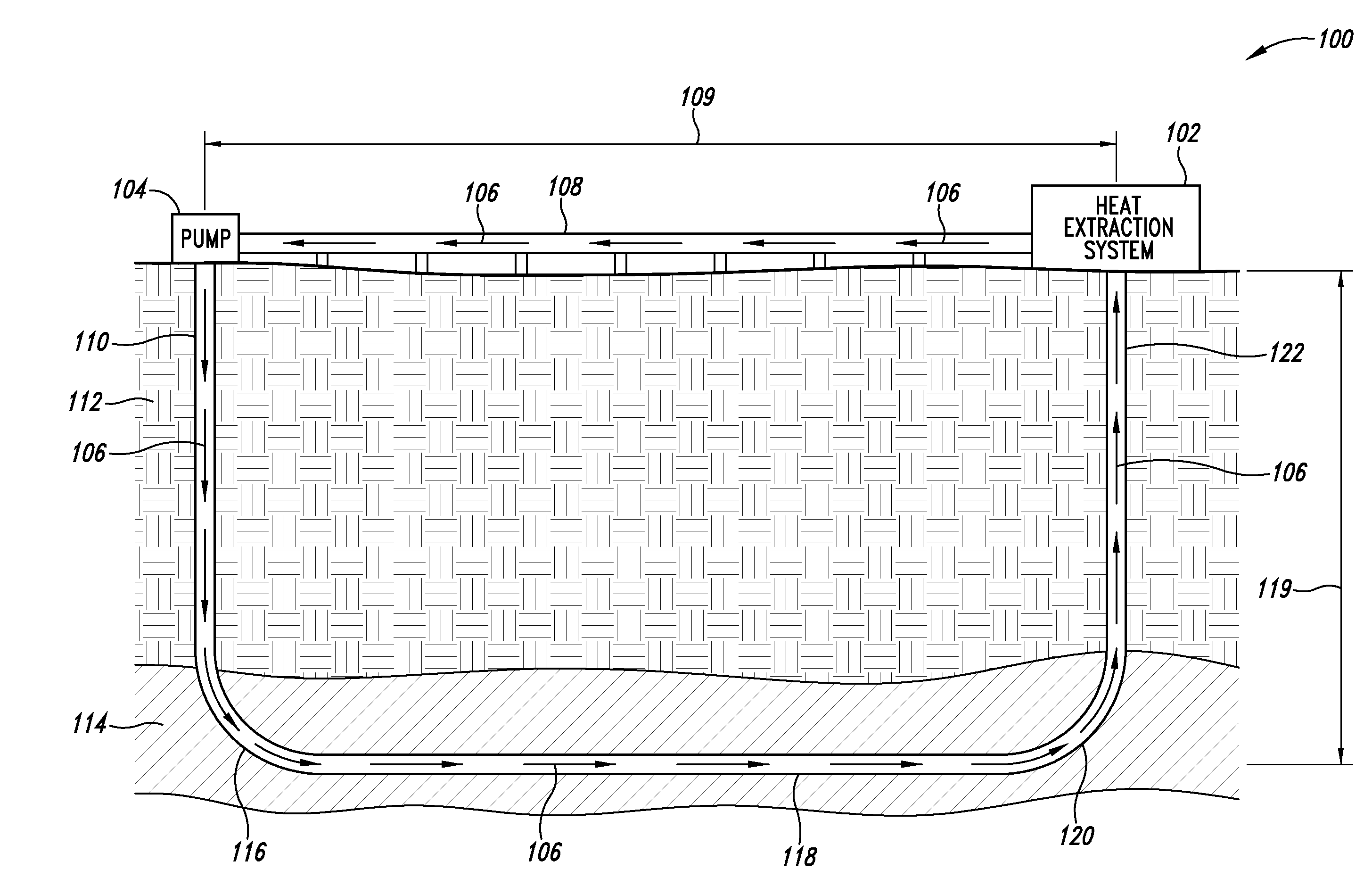
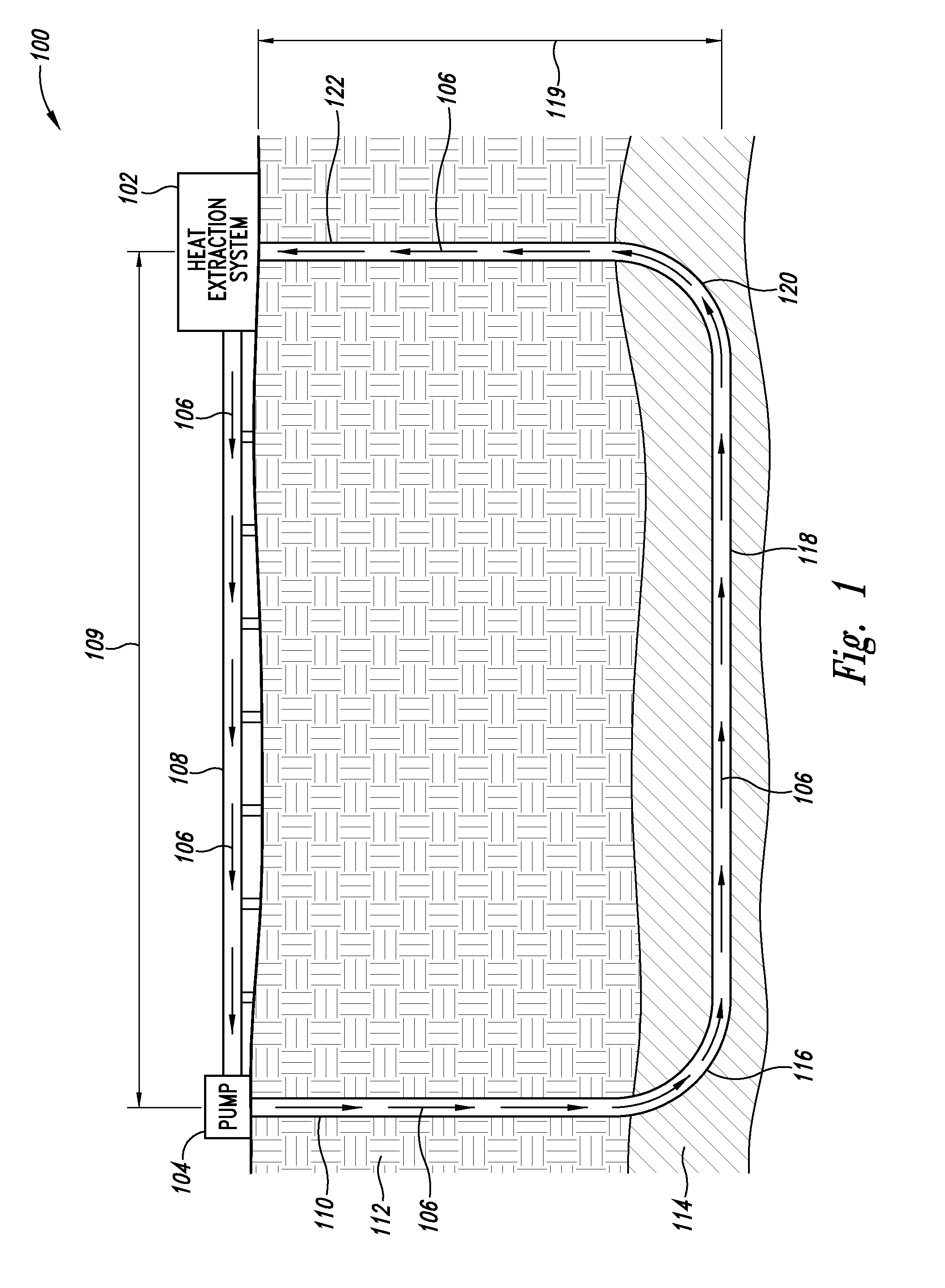
Directional geothermal energy system and method
InactiveUS20070245729A1Collector components/accessoriesGeothermal energy generationMultiple injectionTransport time
A directional geothermal energy system and method helps to increase control in paths to be taken by geo-fluid flow through hot rock to create engineered geothermal reservoirs and networks to mine heat from hot rock resources. The system uses directional drilling techniques to create a spanning borehole extending between an injection borehole and a production borehole. The spanning borehole typically extends through hot rock for a distance on the order of kilometers to allow the geo-fluid flowing through the spanning borehole adequate transit time and surface contact to obtain sufficient heat given a certain flow rate for the geo-fluid. In some implementations, multiple injection boreholes can supply geo-fluid to a single production borehole. Individual geo-fluid networks can be so sized, shaped, and located with respect to one another to form a collection of geo-fluid networks to mine heat from very large hot rock resources.
Owner:MICKLESON D LYNN
Method of creating map data comprising transit times for intersections
ActiveUS20110112760A1Accurate timingImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationMaps/plans/chartsComputer scienceTransit time
A computerised method is disclosed of creating map data from position data derived from the positions of at least one vehicle over a period of time, the map data including a plurality of navigable segments representing segments of a navigable route in the area covered by the map and the map data also including intersections between navigable segments representing intersections in the navigable route. In at least one embodiment, the method includes using a processing circuitry to perform the following: i. processing the position data; ii. calculating from the processing of the position data a transit time or set of transit times for at least some of the intersections in the map data; and iii generating further map data, which for at least some of the intersections therein, contains the calculated transit time or set of transit times associated with the intersection for which the calculation was made.
Owner:TOMTOM GLOBAL CONTENT
High-precision measuring method and apparatus
InactiveUS7080554B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhase locked loop circuitTransmission channel
Owner:NEXENSE
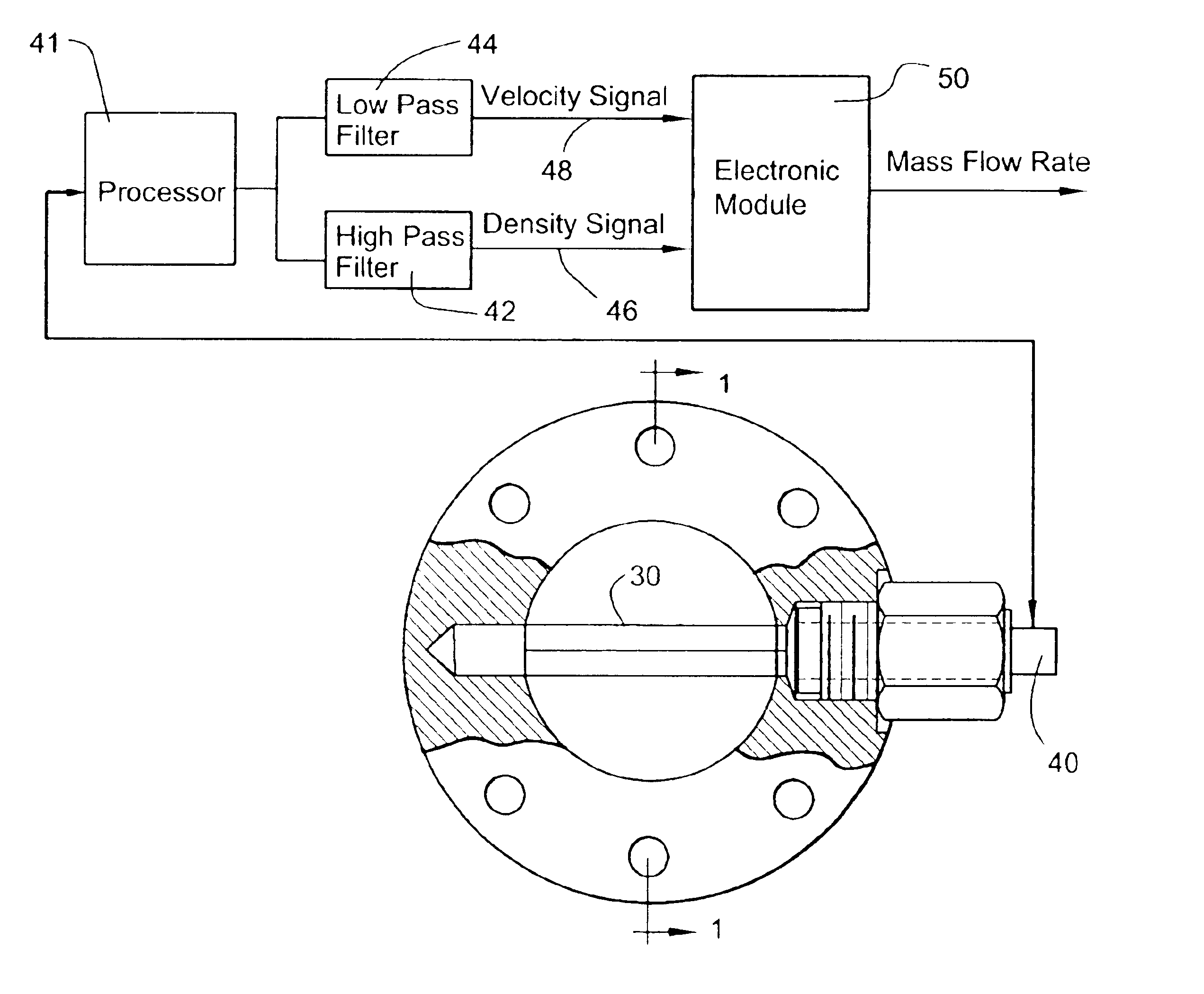
Mass flow sensor and methods of determining mass flow of a fluid
ActiveUS6912918B1Prevent leakageAvoid radiationVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectSpecific gravity measurementSonificationUltrasonic beam
The mass flow rate sensor includes a waveguide disposed in a flow passage having a bluff body facing in an upstream direction. Waves are pulsed along the waveguide for interaction with the fluid. A receiver is coupled to the waveguide to detect a propagated wave and provides a first output signal proportional to the transit time of the propagated wave for determining fluid density. The receiver also provides a second output signal proportional to the shedding frequency of vortices from the waveguide to determine velocity. An electronics module calculates mass flow rate from the velocity times density times area of the flow passage and a constant. In other forms, the velocity is ascertained by transmitting an ultrasonic beam through the shedding vortices to determine vortex frequency which is proportional to velocity.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
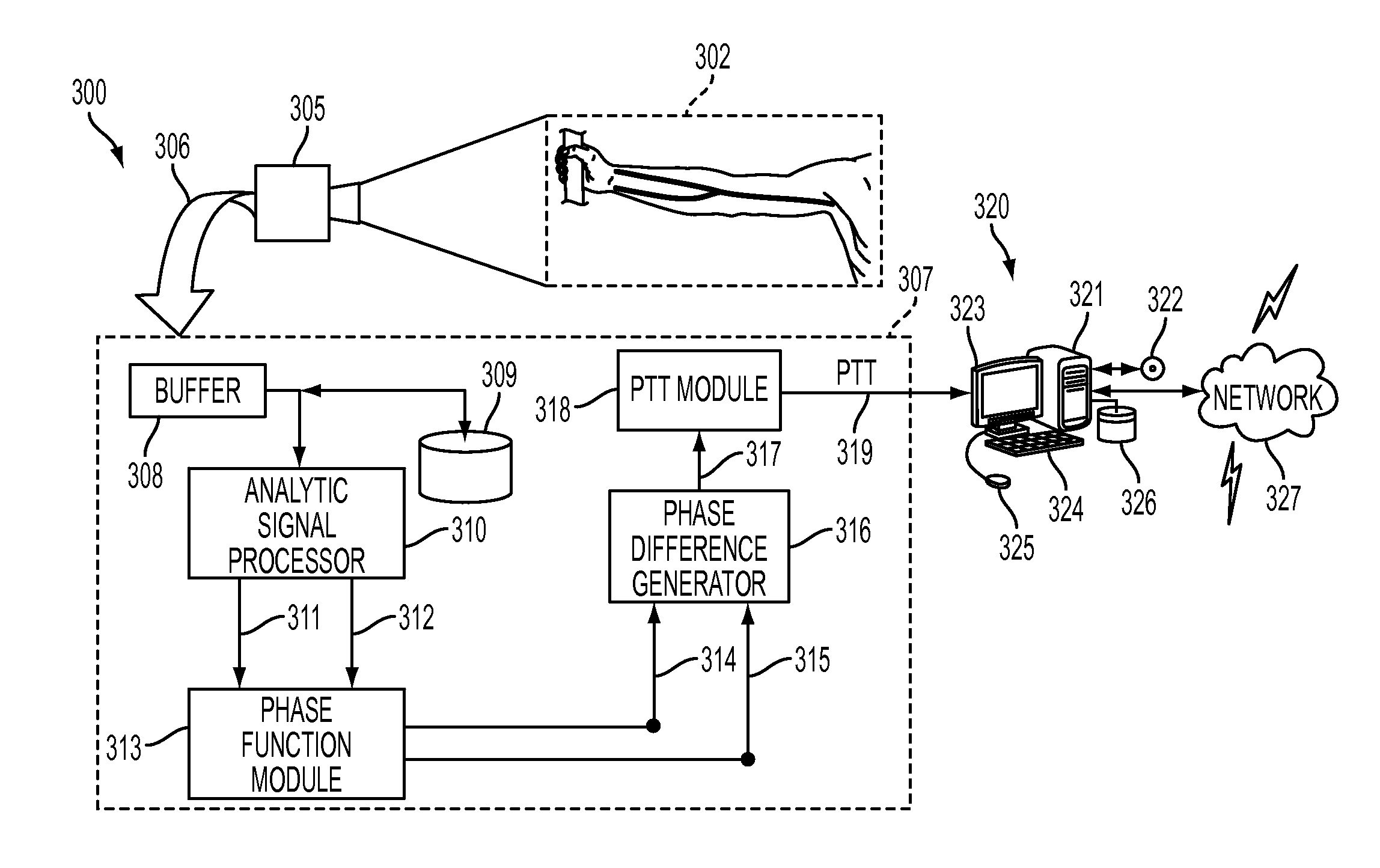
Determining arterial pulse transit time from time-series signals obtained at proximal and distal arterial sites
What is disclosed is a system and method for determining arterial pulse transit time (PTT) for a subject. In one embodiment, time-series signals are received for each of a proximal and distal arterial site of a subject's body which represent blood volume changes in the microvascular tissue at each site. A proximal and distal analytic signal is obtained which has a first component being a waveform of the respective time-series signal and a second component being a transform of the respective waveform. A phase function is determined for the first and second components of each analytic signal. The phase function obtained for the proximal waveform is then subtracted from the phase function obtained for the distal waveform to get a phase difference. The phase difference is analyzed with the subject's heart rate to determine an arterial pulse wave transit time between the two proximal and distal sites.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and an apparatus for distance measurement
InactiveUS20050248749A1Cancel noiseClosely placedBeacon systemsDevices using optical meansAnalog signalElectromagnetic radiation
The invention relates to a method for distance measurement by determining the pulse transit time, in which pulsed electromagnetic radiation is transmitted using at least one transmitter and signal pulses reflected at objects are detected using at least one receiver, wherein at least one received logic signal containing logic signals is generated from the received analog signal containing the signal pulses, in particular by means of a threshold circuit, and is evaluated with respect to the transit times of the logic signals, and wherein the received logic signal is read into a programmable logic circuit by means of a clocked data reading device and is mapped onto a time pattern in the logic circuit, in that instantaneous values of the received logic signal are stored in logic units of the logic circuit associated with the time windows for time windows of the time pattern corresponding to at least one clock pulse of the data reading device. The invention moreover relates to an apparatus for distance measurement.
Owner:IBEO AUTOMOBILE SENSOR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com