Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
706 results about "Path delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
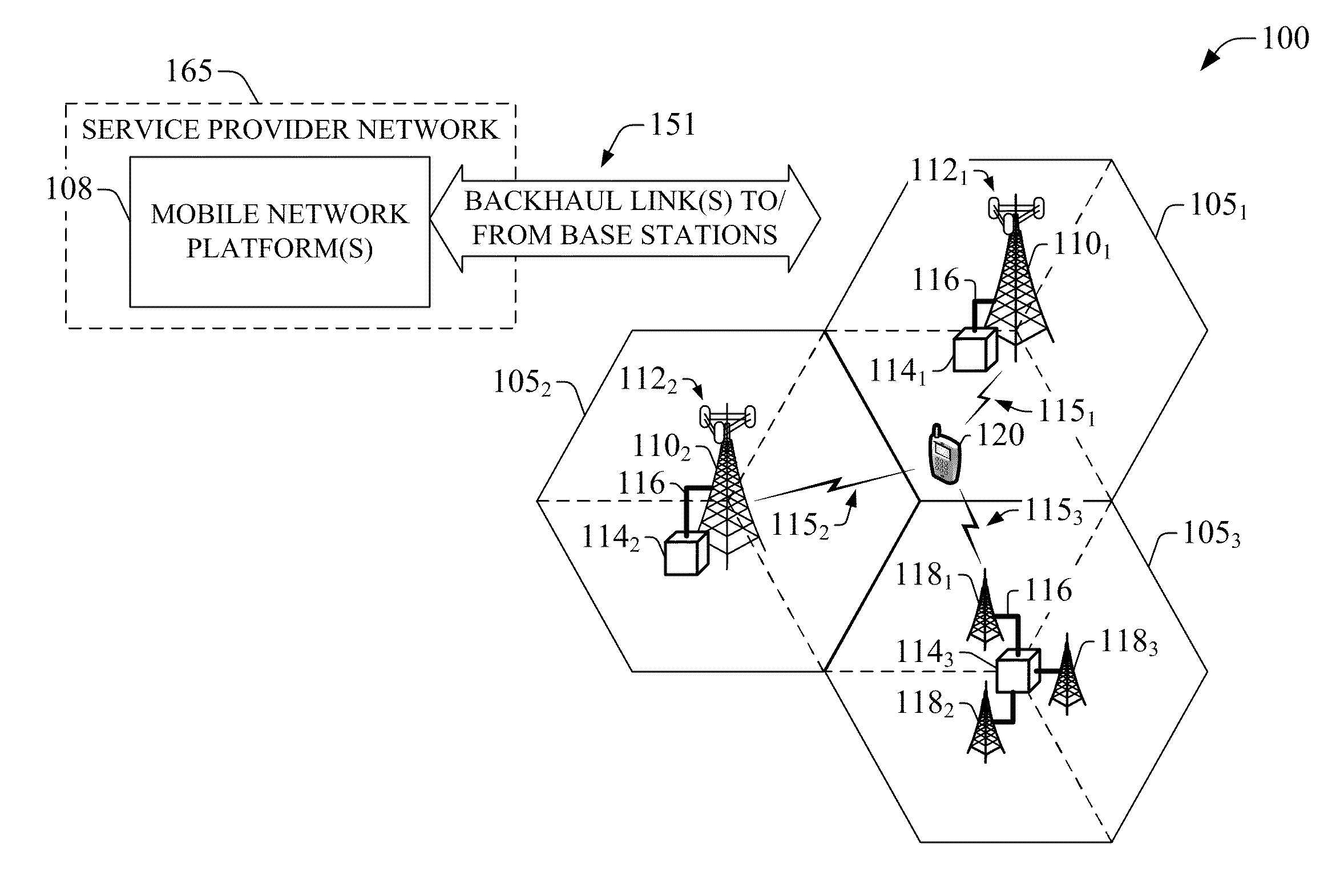
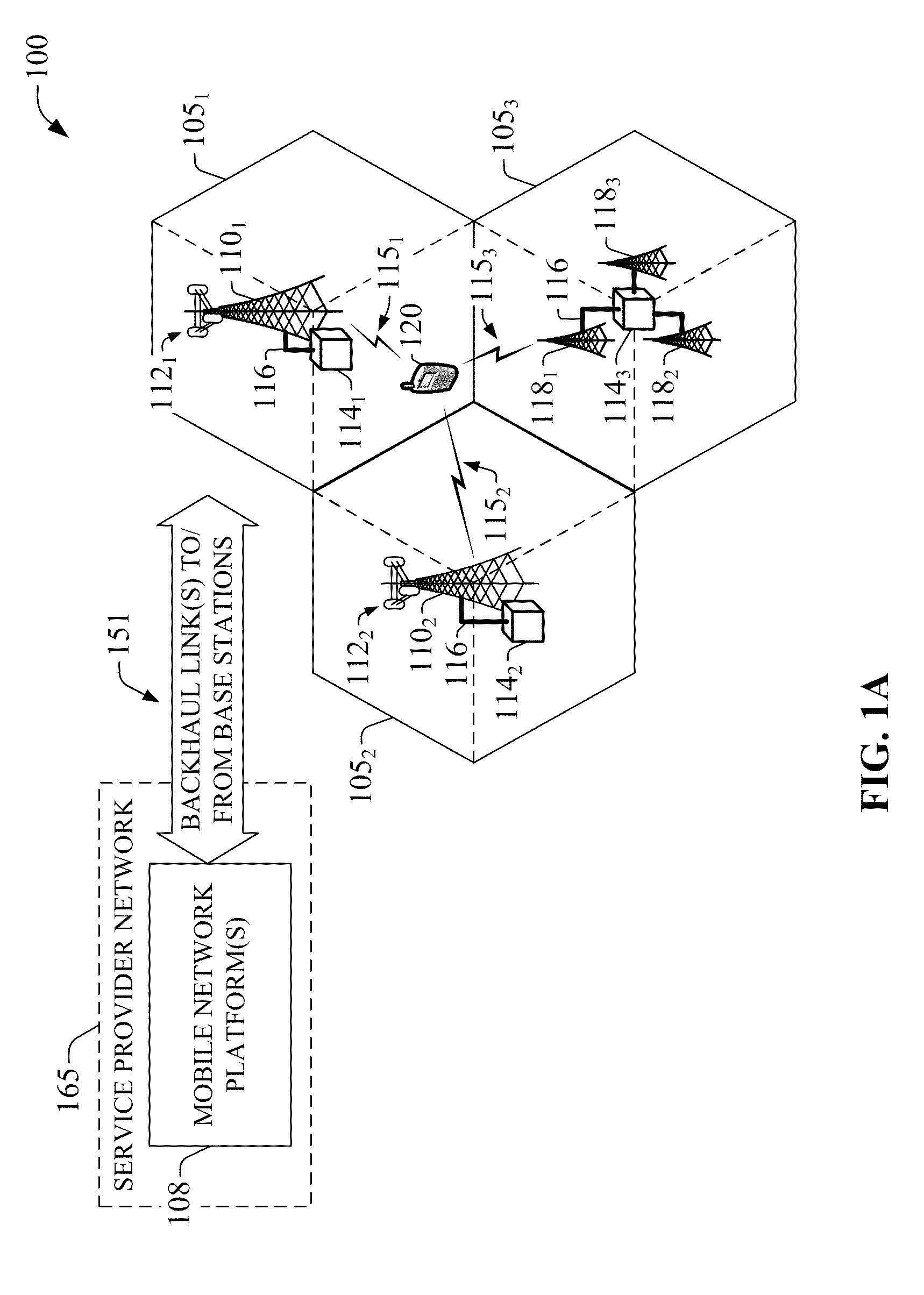
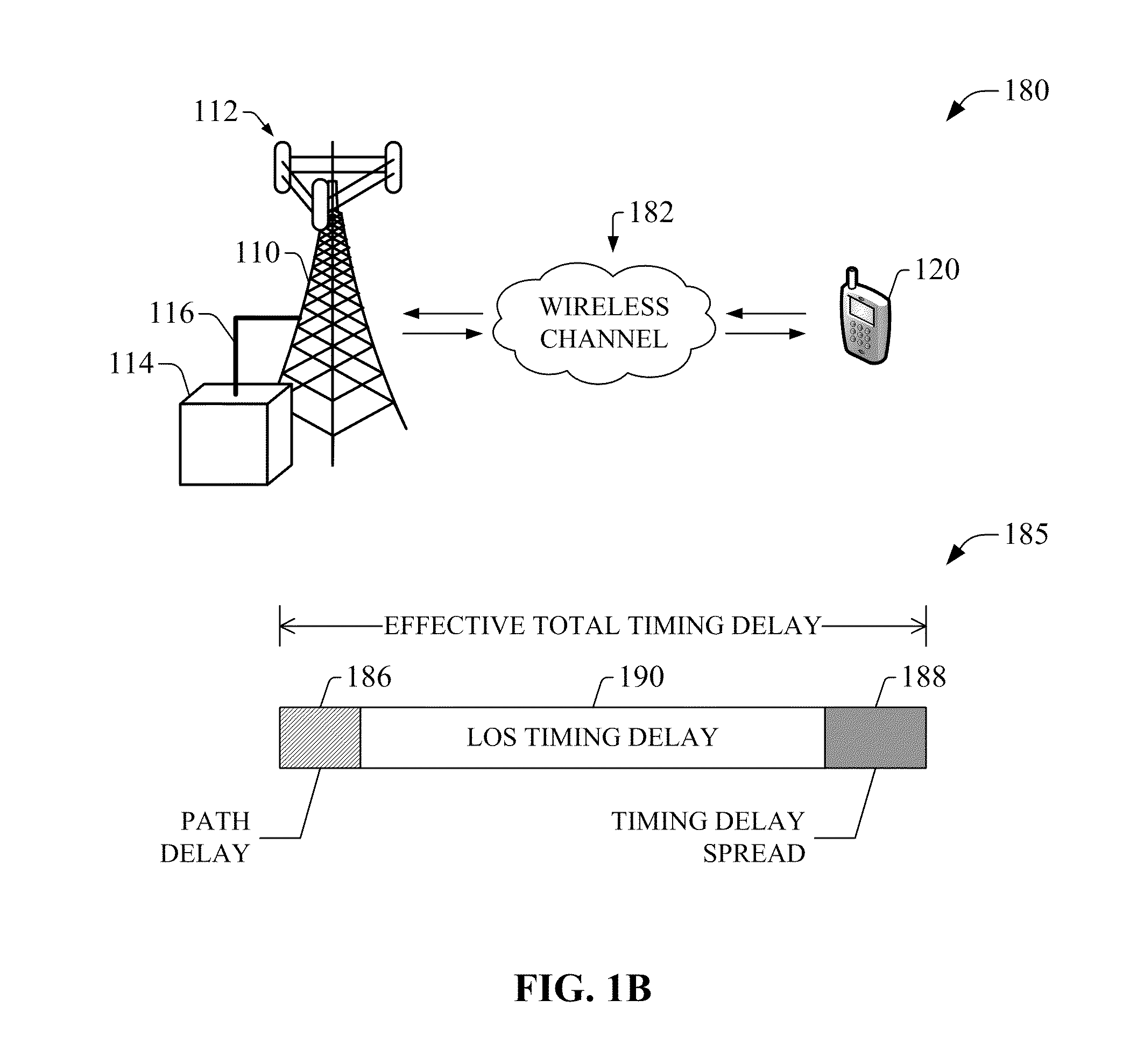
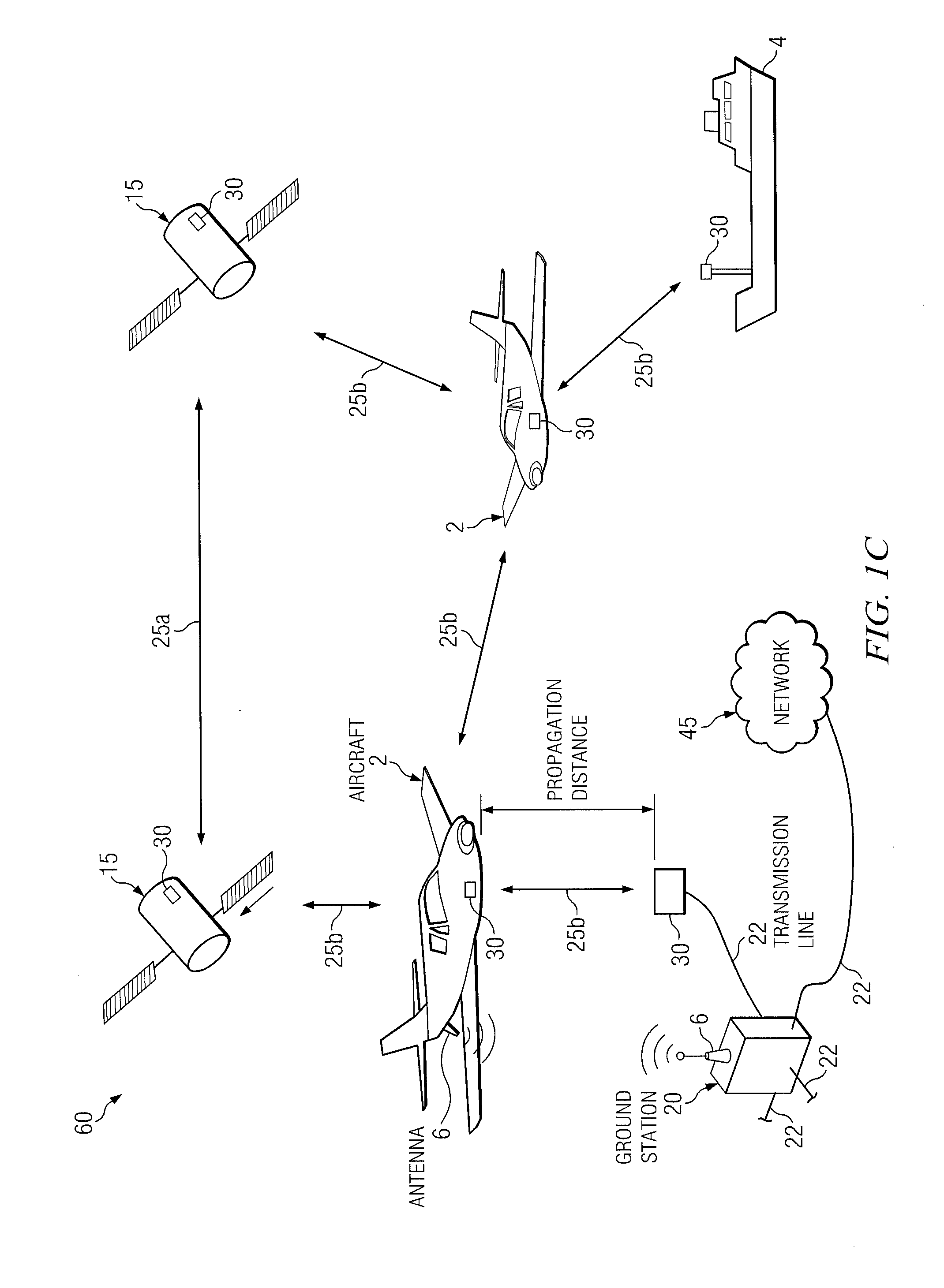
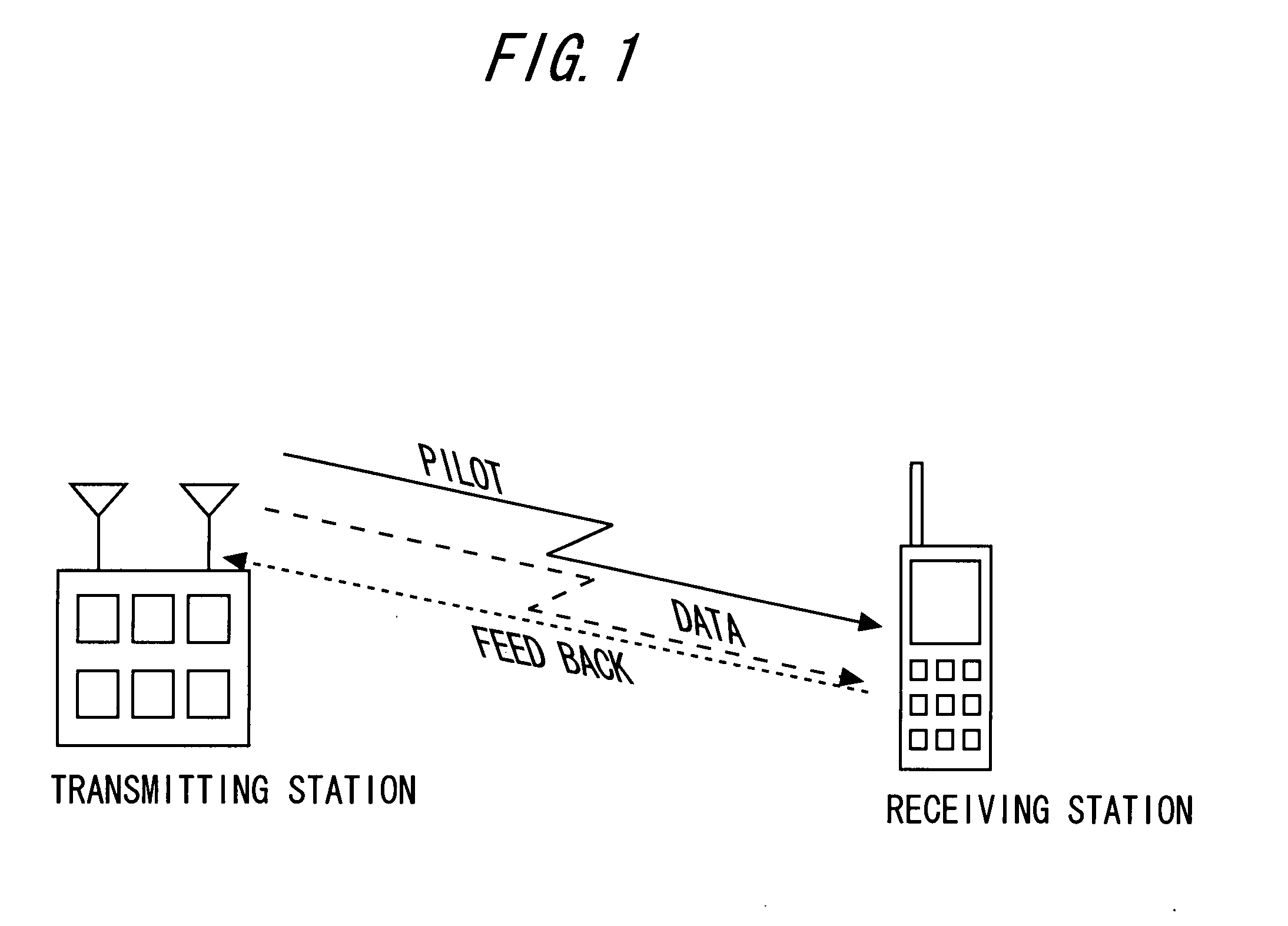
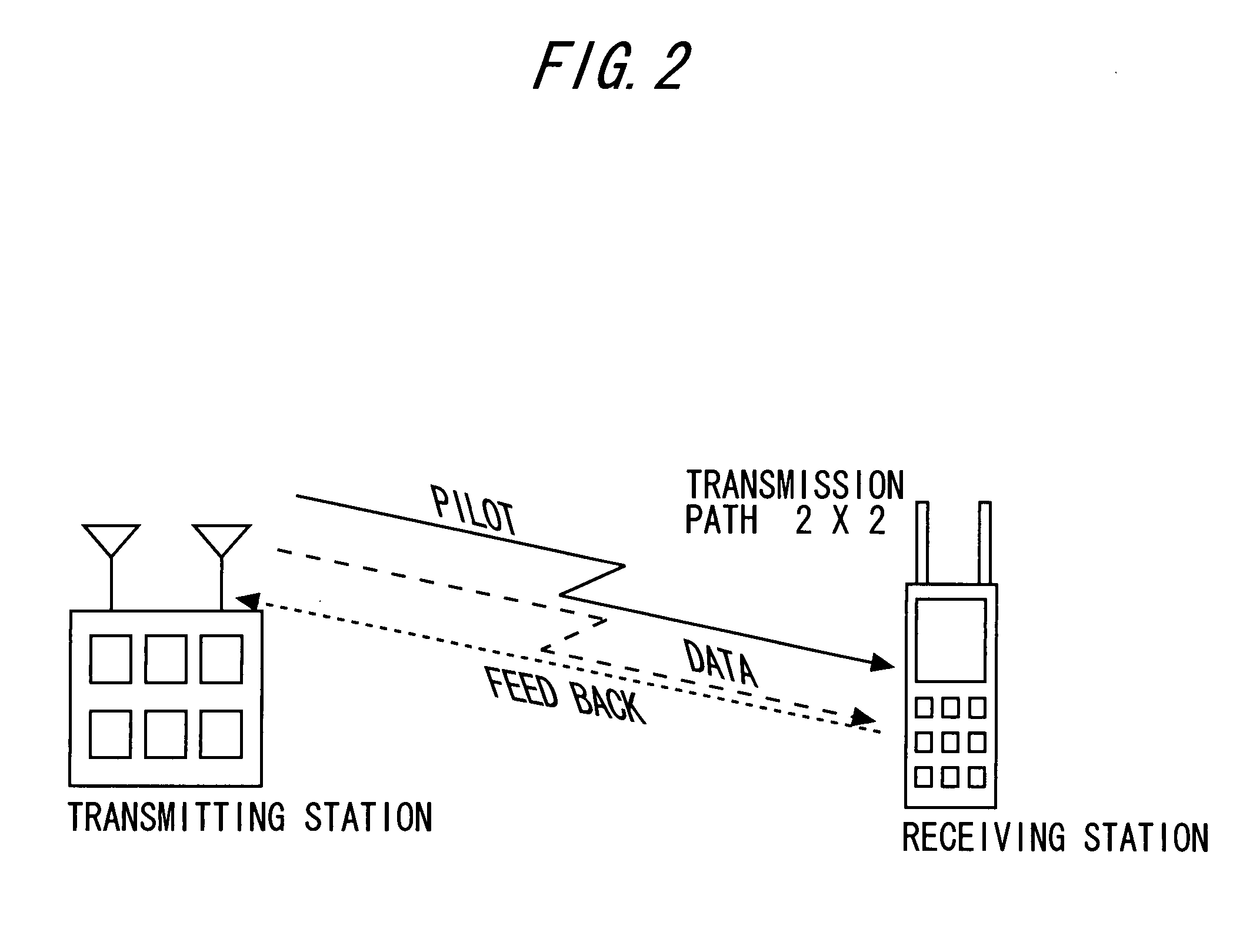
Compensation of propagation delays of wireless signals
ActiveUS20100190509A1Weakening rangeImprove accuracySynchronisation arrangementLocation information based servicePropagation delayRadio networks
System(s) and method(s) for compensation of propagation delay offsets of wireless signals. Compensation is accomplished through determination of an effective wireless signal propagation delay that accounts for signal path delay and propagation delay over the air. Such determination is based at least in part on statistical analysis of accurate location estimates of reference positions throughout a coverage sector or cell, and location estimates of the reference positions generated through time-of-flight (TOF) measurements of wireless signals. Determination of propagation or signal path delay offset also is attained iteratively based at least in part on reference location estimates and TOF location estimates. High-accuracy location estimates such as those obtained through global navigation satellite systems are employed as reference location estimates. Position of probes or wireless beacons, deployed throughout a sector or cell, also are employed as reference locations. Compensation of propagation delay offset improves accuracy of conventional TOF location estimates and radio network performance.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
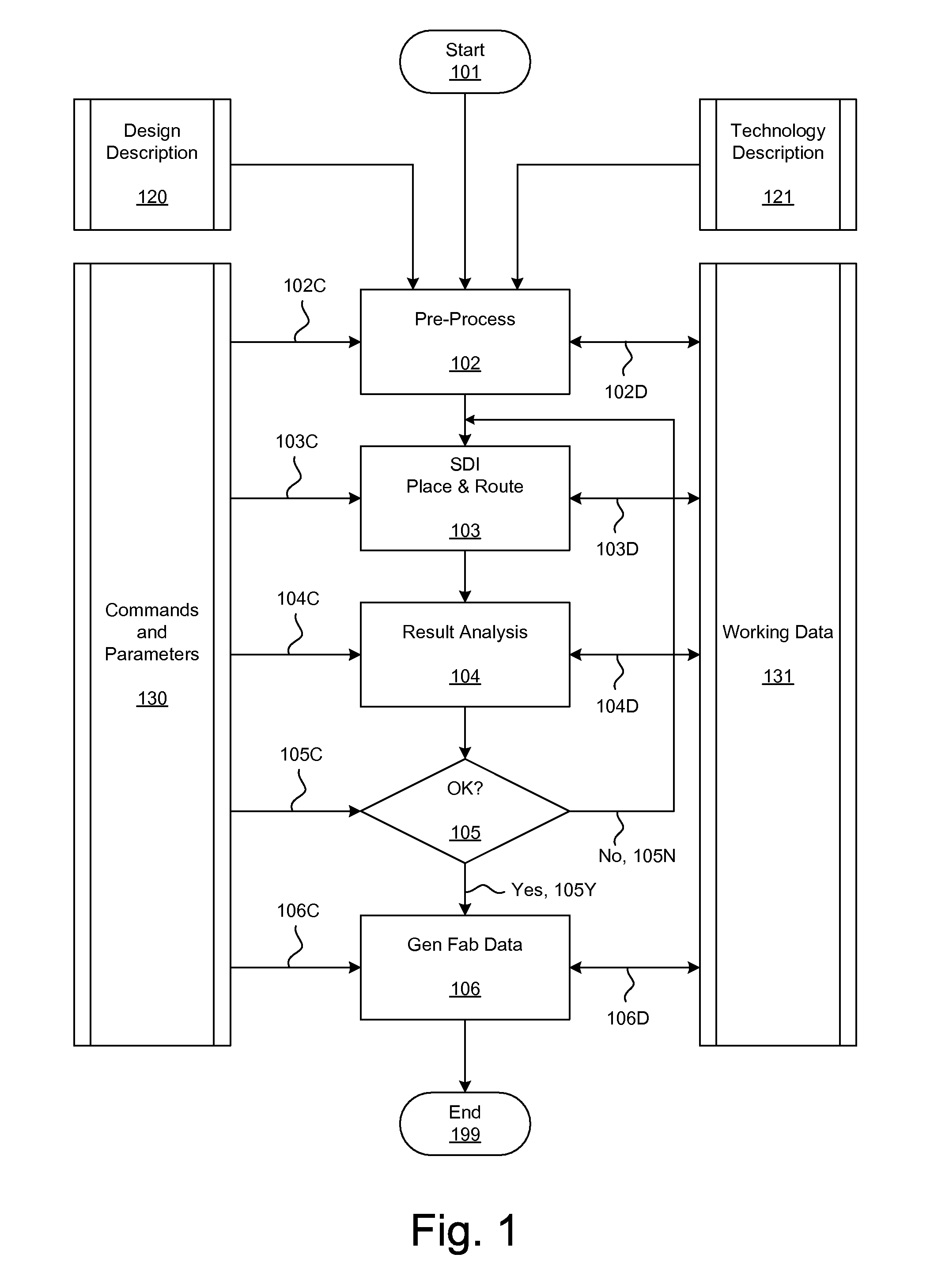
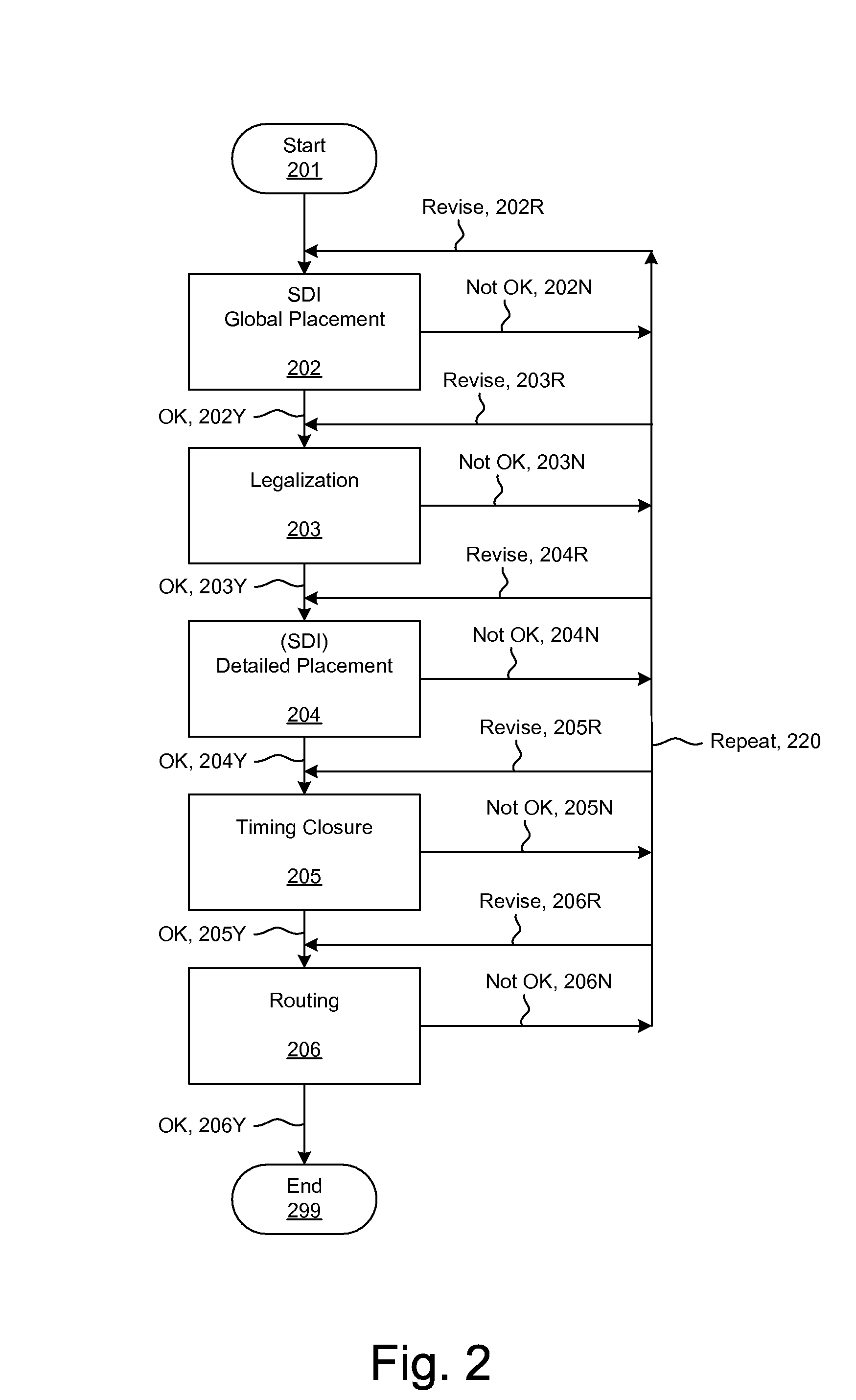
Methods and systems for placement and routing
ActiveUS20090254874A1Influence optimizeImprove performanceCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
Techniques for placement of integrated circuit elements include global placement, detailed placement, timing closure, and routing. The integrated circuit is described by a netlist specifying interconnections of morphable devices. The detailed placement uses, for example, Simultaneous Dynamical Integration, wherein the morphable-devices correspond to nodes influenced by forces, including timing forces. The timing forces are derived, for example, from a timing graph; path delay; slack; and drive resistance of the elements. The timing closure uses timing-driven buffering and timing-driven resizing to reduce maximum delay and / or transition time, and / or to fix hold time. Nets having high capacitance and / or fanout, and timing critical nets are preferentially processed. Timing-driven buffering applies buffering solutions to segments of route trees, combines solutions of adjoining segments, and prunes sets of solutions. Timing-driven resizing morphably replaces selected elements with upsized versions thereof.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Location-assisted wireless communication
InactiveUS20050136943A1Improve wireless communication performanceEasy to receiveReceivers monitoringRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime delaysPath delay
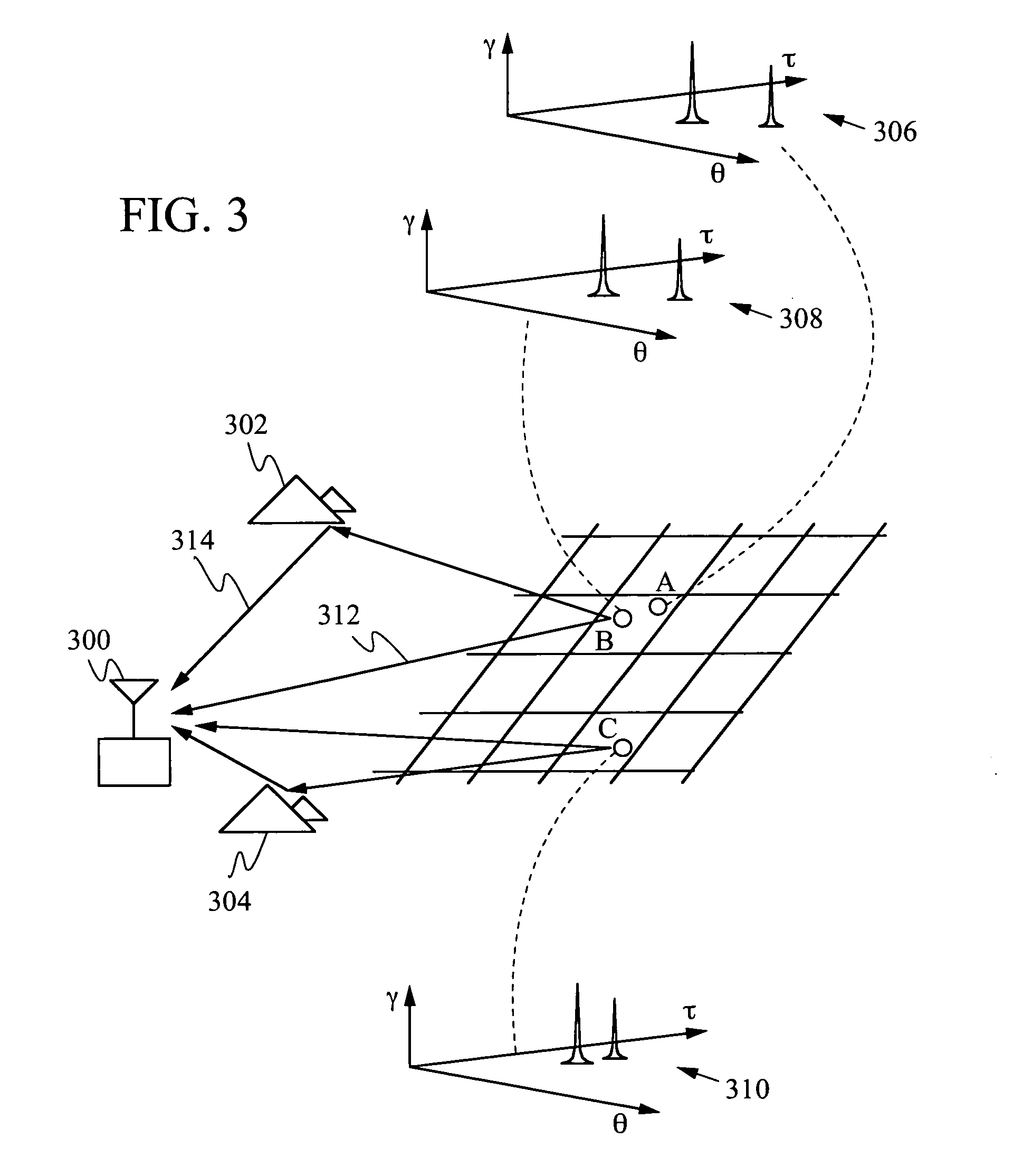
Techniques for location-assisted wireless communication use real-time location(s) of wireless transceiver(s) together with stored location-indexed channel information to improve communication over a wireless channel between the transceiver(s). The stored channel information includes channel characteristics (e.g., average power, angle-of-arrival, and time delay of multipath components) that are substantially constant in time but vary gradually as a function of location. Current transceiver location(s) are obtained and used to retrieve stored channel characteristics corresponding to the location(s). The channel information may be used at either or both transceiver(s) to improve reception and / or transmission of signals propagating over the wireless channel. For example, reception may be improved by using path angle information to perform spatially structured reception, or using path delay information to perform temporally structured reception, e.g., to assign fingers to multipath components in a RAKE receiver and / or to track time delays of multipath components.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Multipath interference reduction for a CDMA system
InactiveUS6865218B1Improve receiver performanceReduce multipath interferenceRadio transmissionMultipath interferenceRake receiver
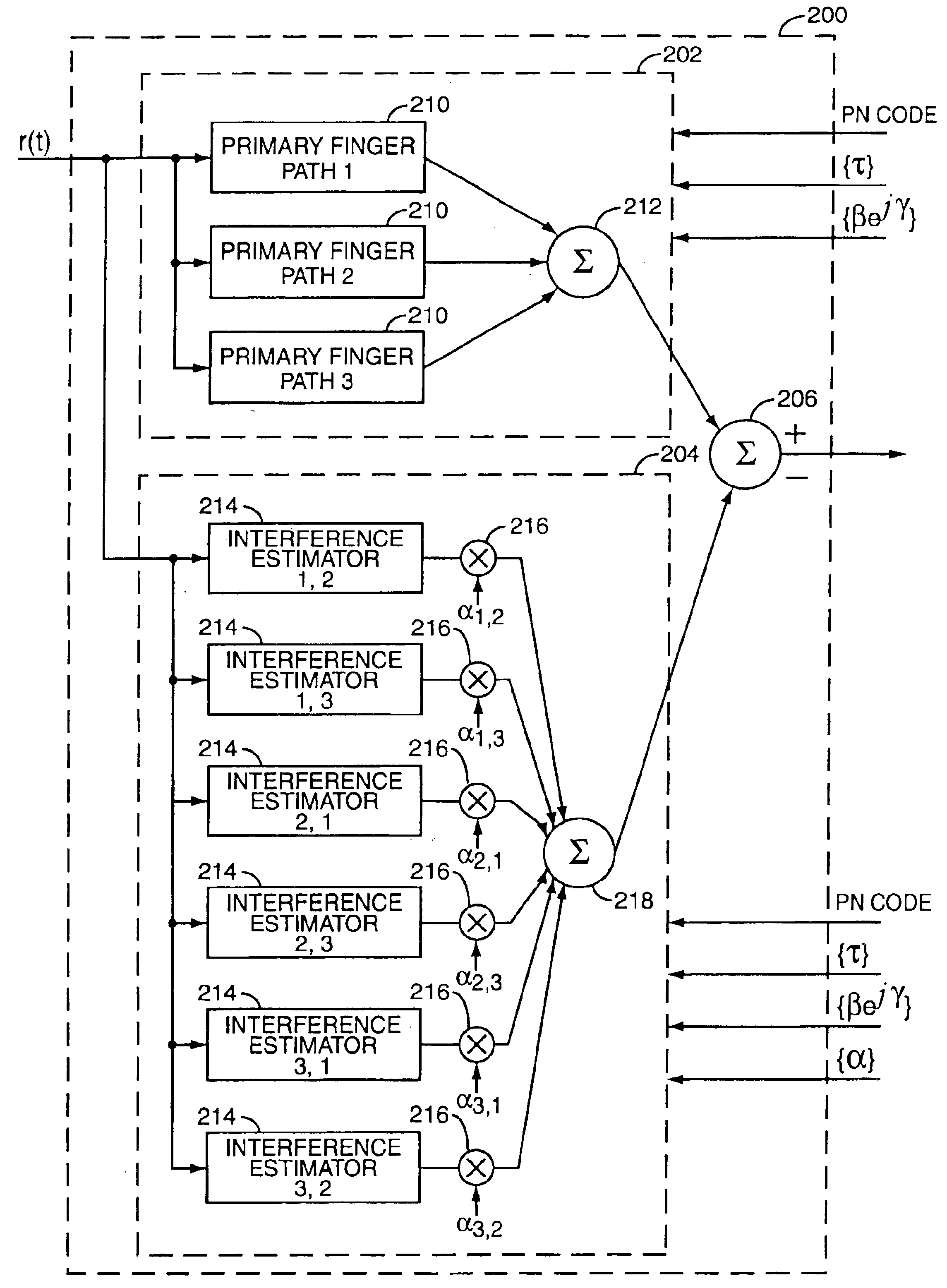
A method and system reduce multipath signal interference in a CDMA receiver. The CDMA receiver including parallel first and second RAKE receivers receives a multipath signal. The first RAKE receiver includes a number of individual RAKE fingers, each operating with a defined finger delay matched to a propagation path delay. The output signal from each RAKE finger includes multipath interference. The second RAKE receiver includes a group of RAKE fingers corresponding to each RAKE finger in the first RAKE receiver. Each group of RAKE fingers is configured to produce an estimate of the multipath interference in the output signal generated by the corresponding RAKE finger in the first RAKE receiver. The estimated multipath interference signals are scaled, and then subtracted from the RAKE finger outputs from the first RAKE receiver to reduce multipath interference. Scaling coefficients are adjusted to ensure that such subtraction effectively reduces multipath interference.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
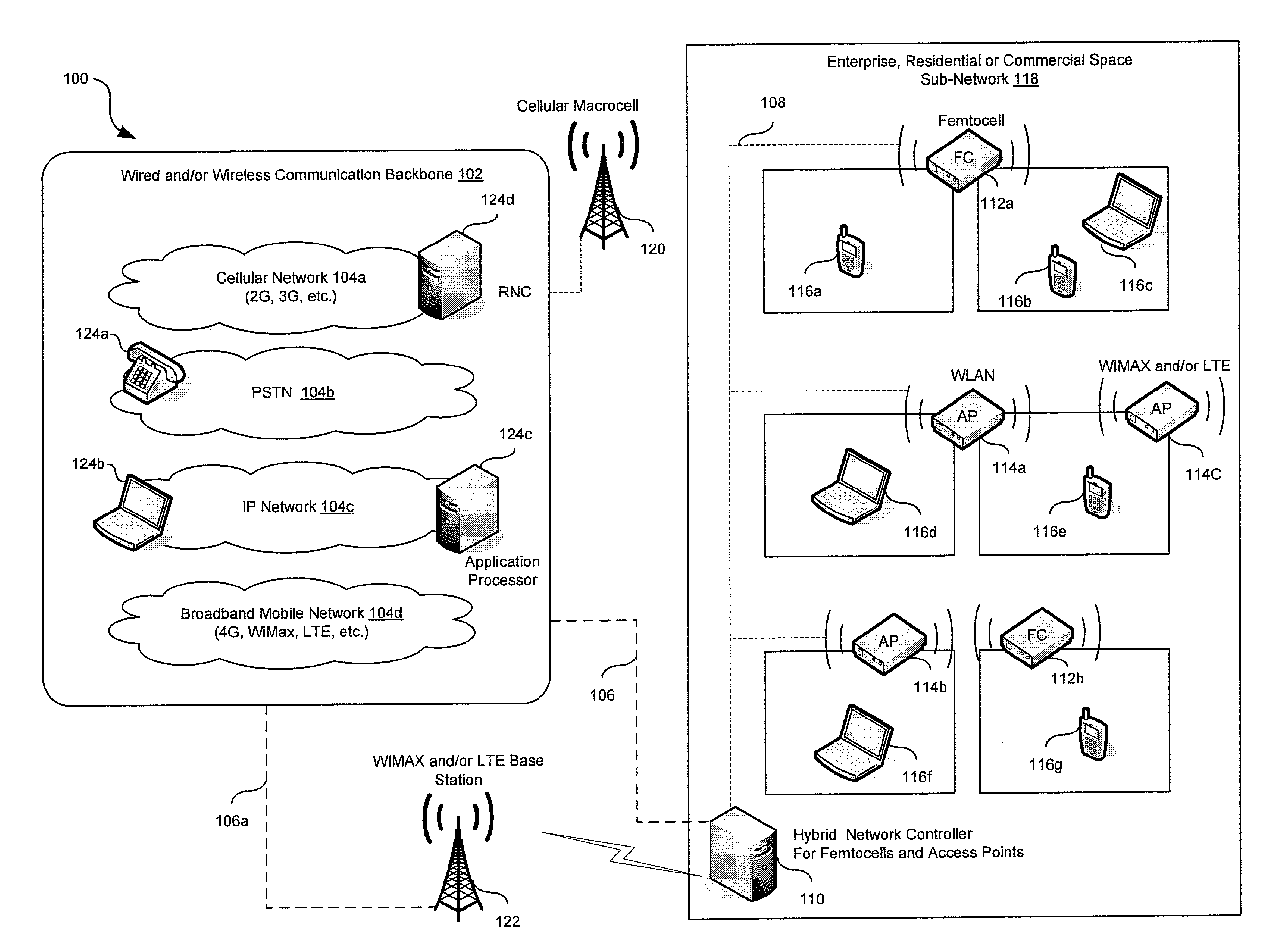
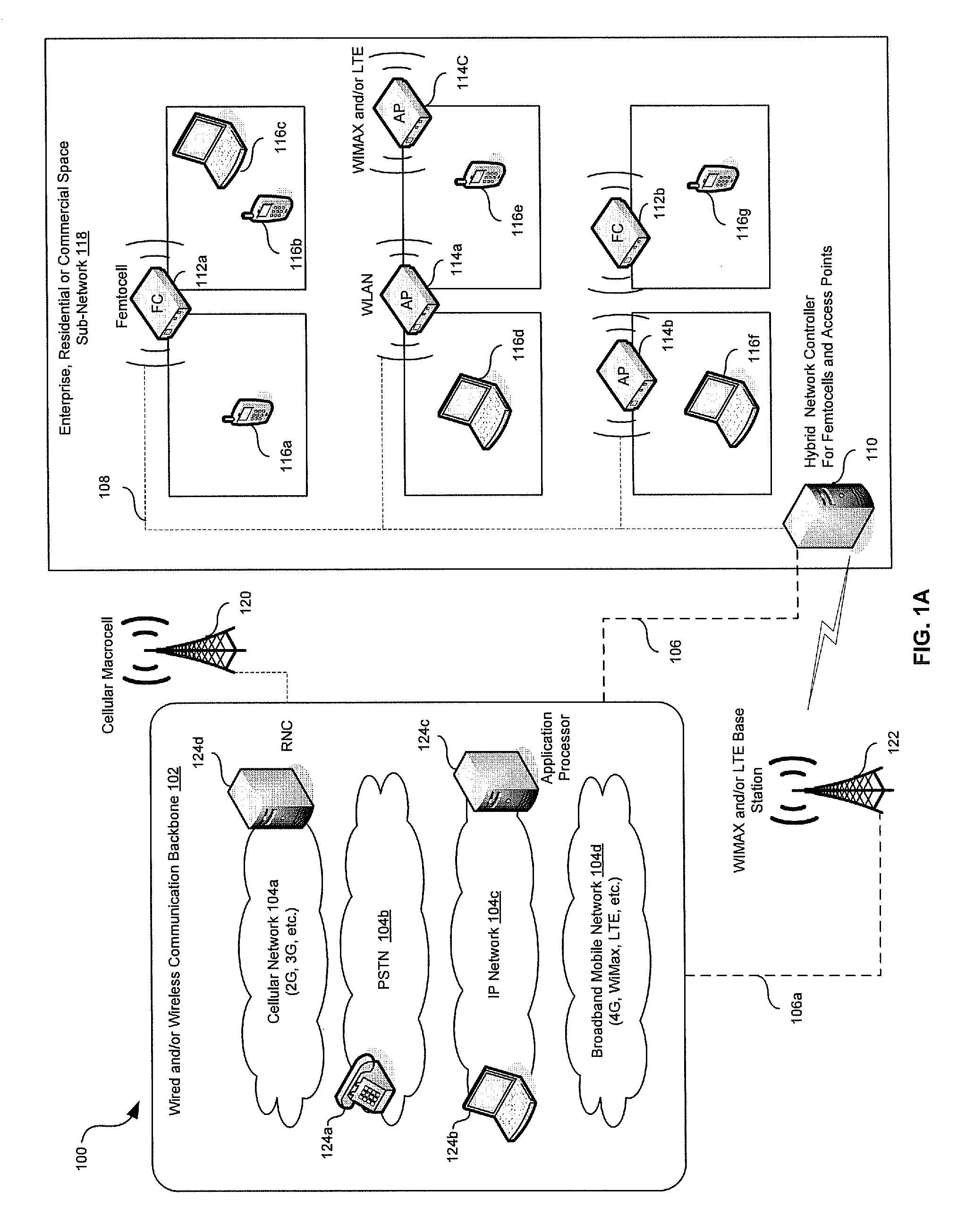
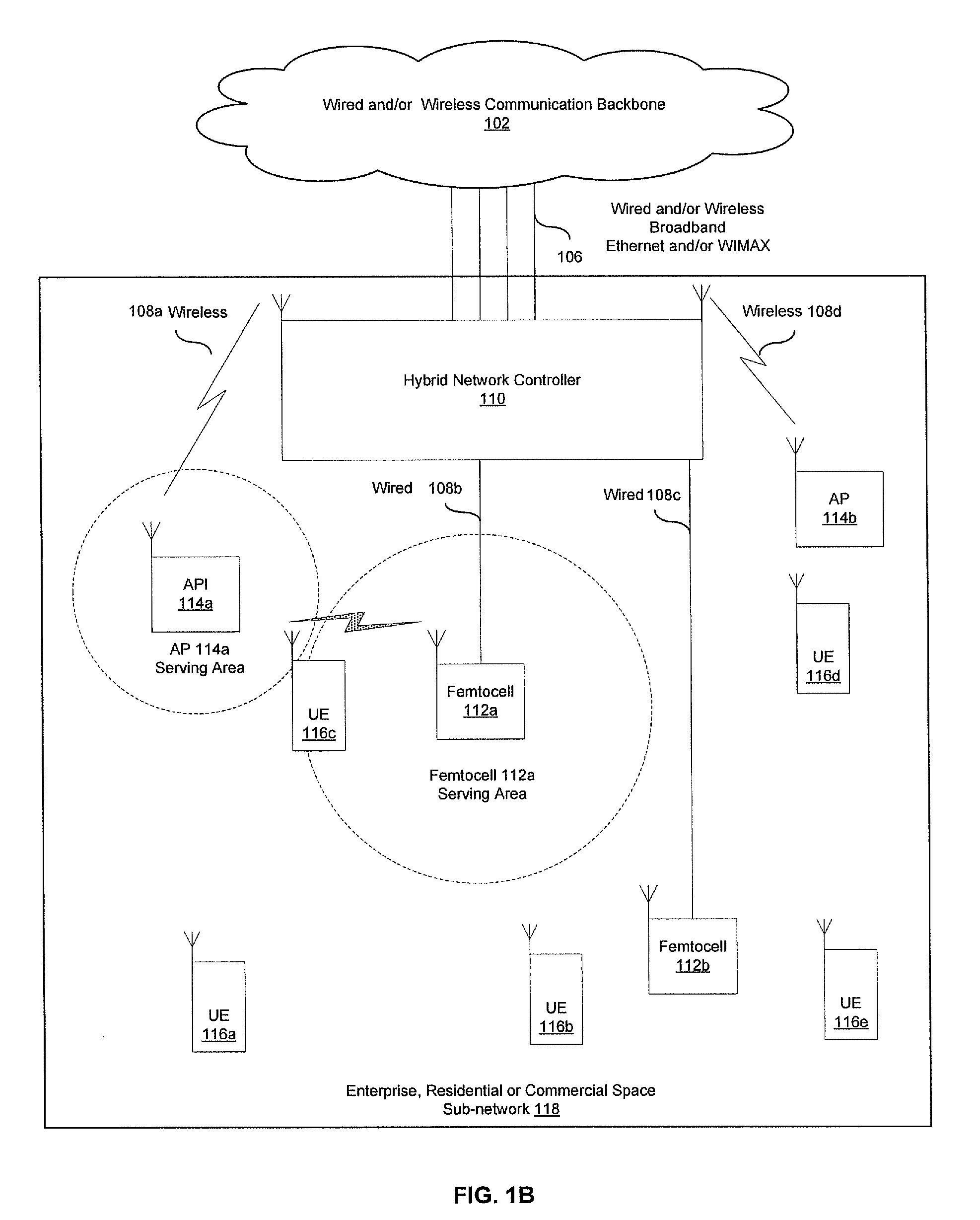
Traffic management in a hybrid femtocell/wlan wireless enterprise network
A hybrid network controller may determine and / or communicate traffic management information for enabling setup and / or handoff of call and / or communication session among femtocells, access points and / or end-point devices. Traffic management information may comprise set-up instructions, handoff instructions, transmit power, neighbor list information, signal quality thresholds, frequency assignments, transmission time, code assignments and / or antenna pattern assignments. The hybrid network controller and / or an end-point device may control handoffs between a communication device external to the communication system and the femtocells, access points and / or end-point devices. Received signal strength, interference levels, SNR, signal path delay, power consumption, traffic loads, bandwidth usage and / or radio resource availability may be monitored and / or analyzed by the hybrid network controller. The hybrid network controller may assign time slots, codes, antenna patterns as well as a serving femtocell and / or AP for a set up and / or a handoff. The information may be communicated via wired, optical and / or wireless interfaces.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
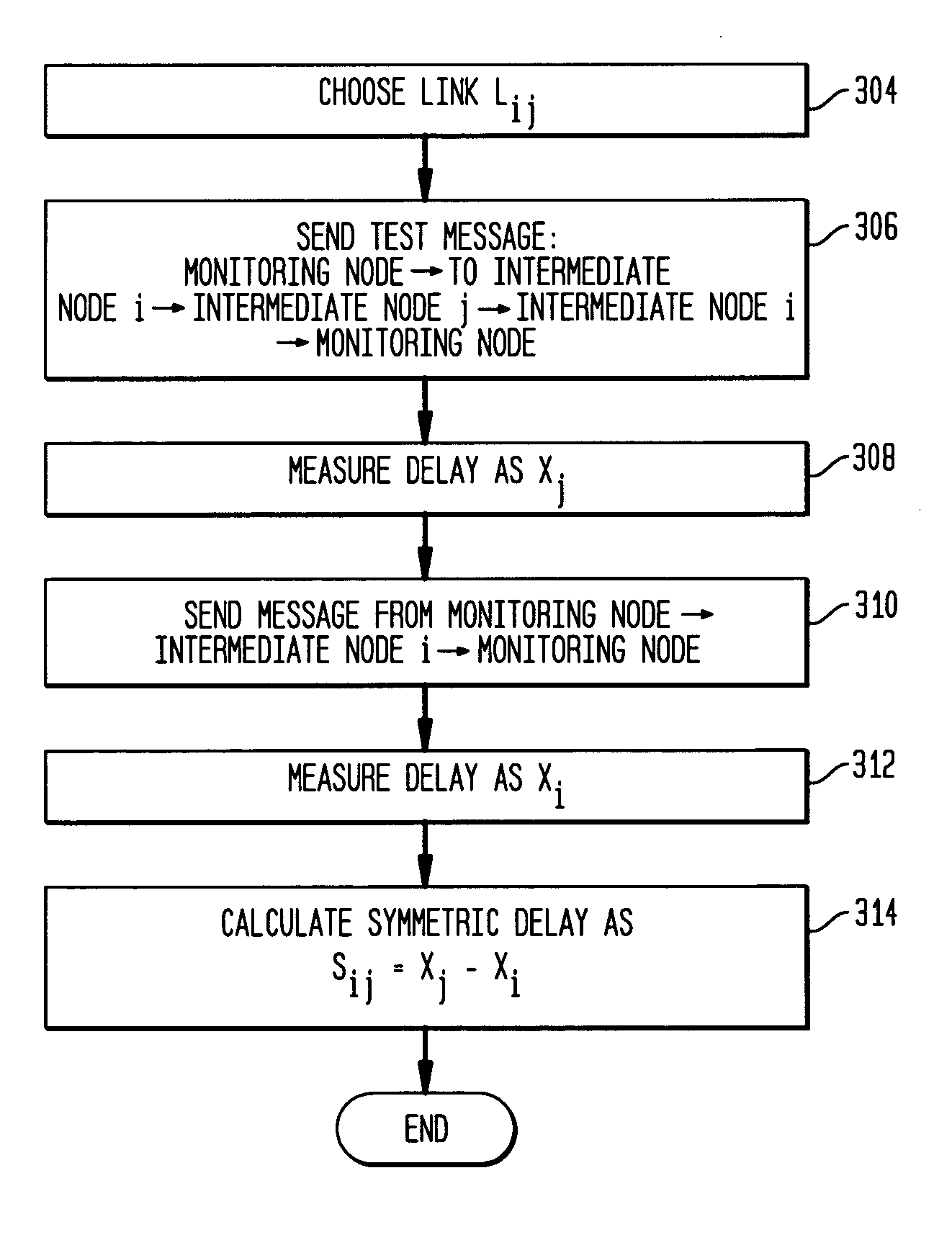
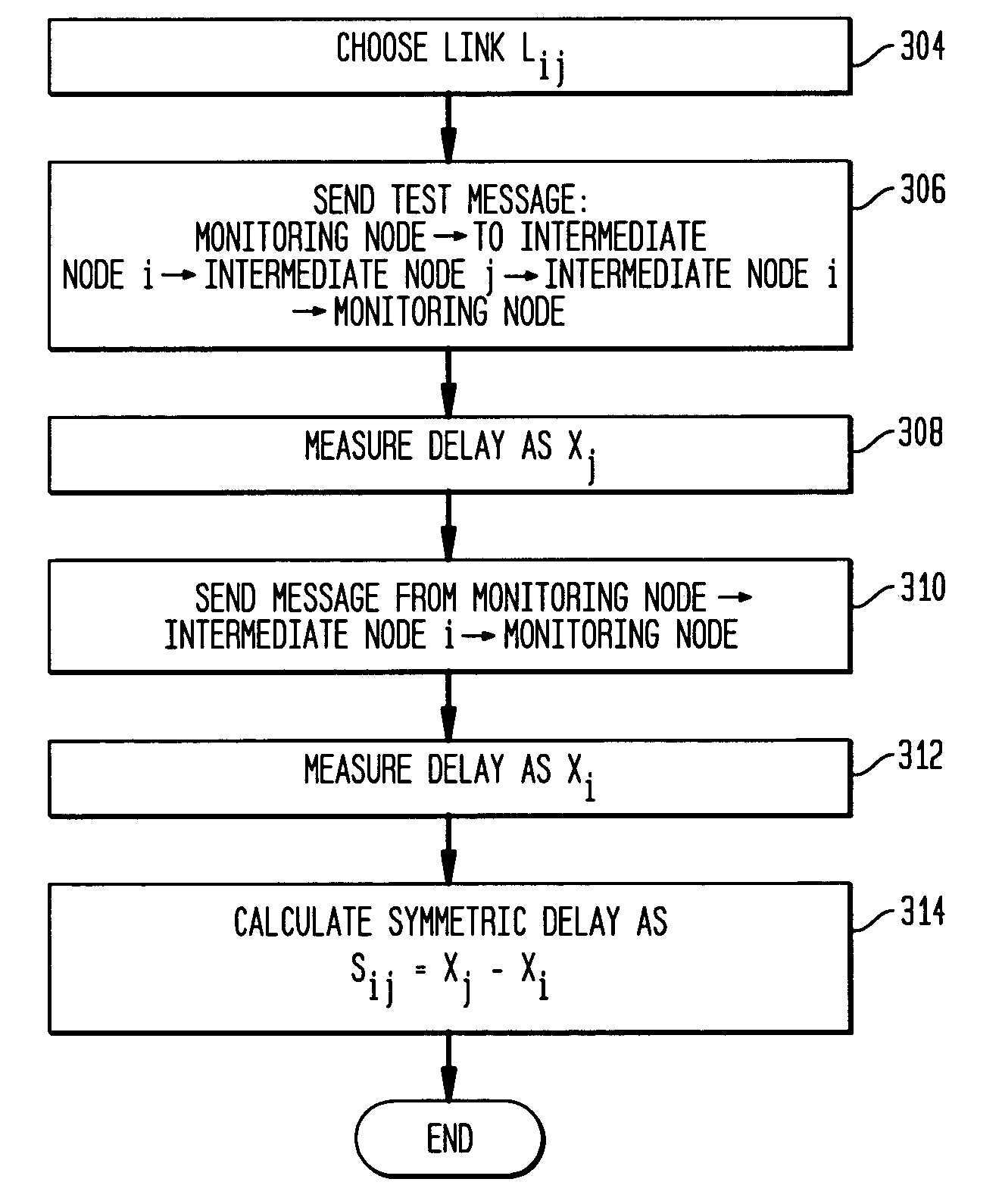
Remote estimation of round-trip delays in a data network
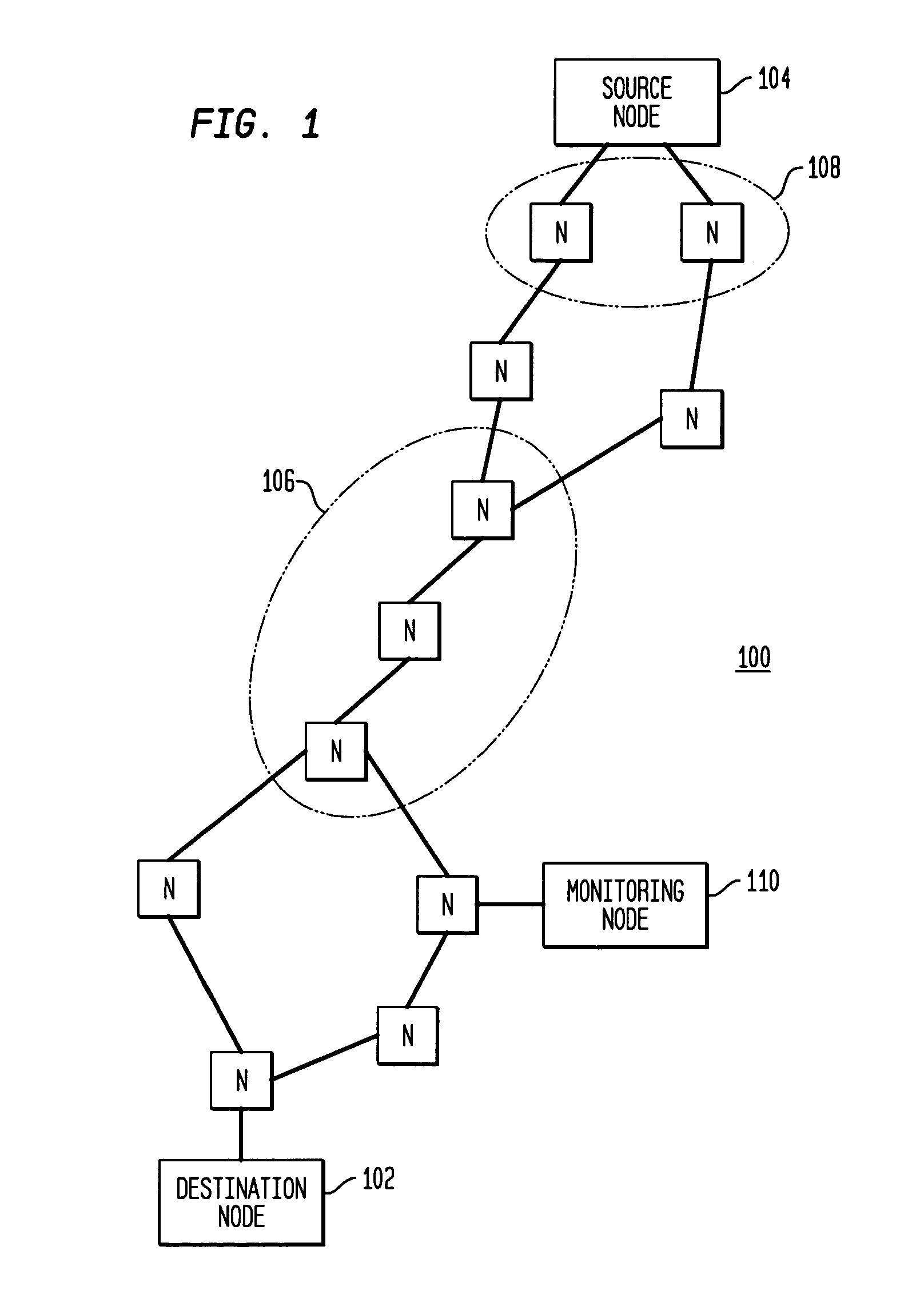
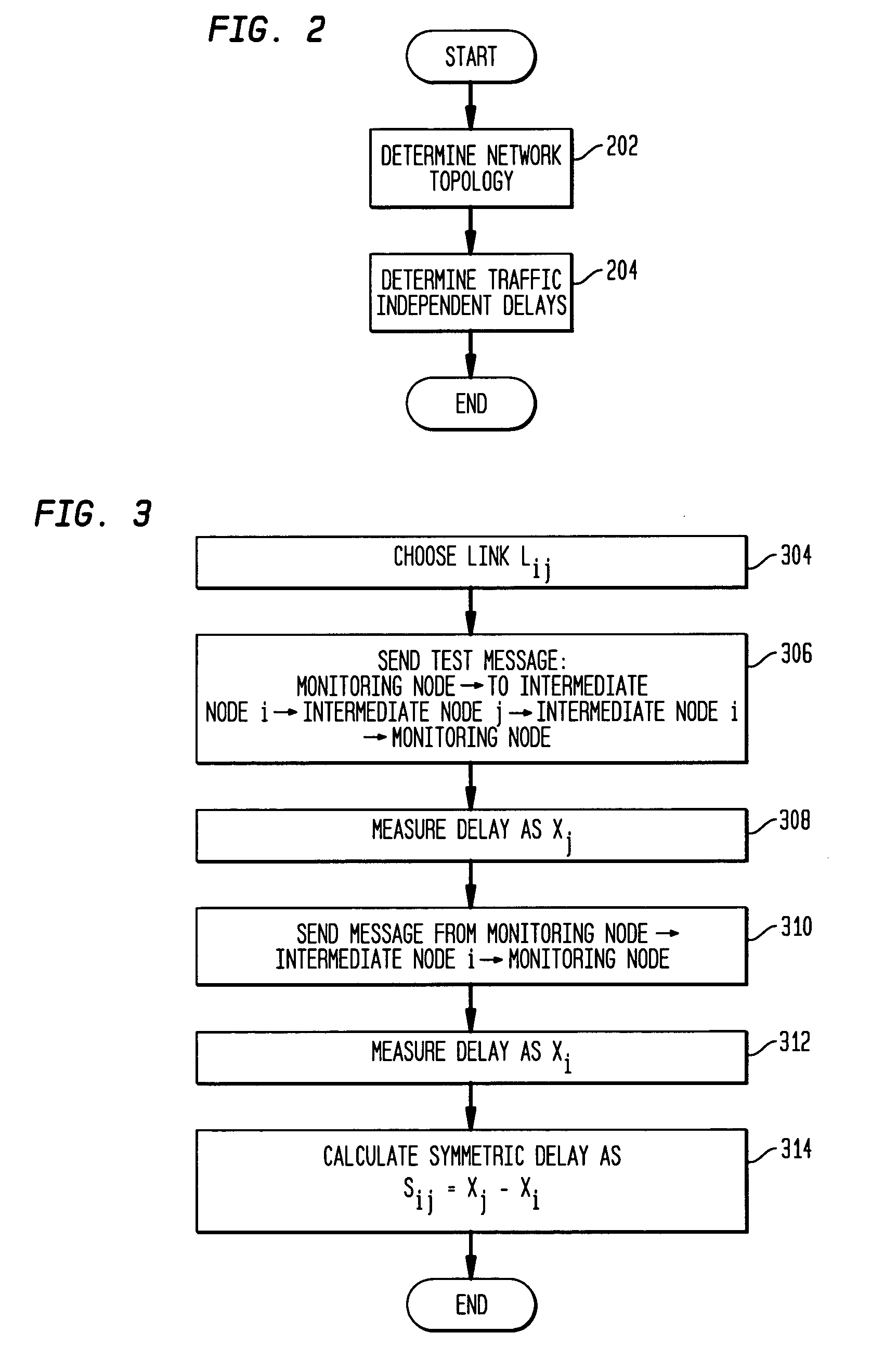
ActiveUS20060092850A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting tableNetwork topology
Disclosed is a technique for data network congestion diagnosis using remote estimation of round-trip delays. A monitoring node transmits test messages between network nodes and measures the transit times between when the test messages are transmitted from, and when they return to, the monitoring node. A path delay between network nodes is determined based on the measured time delays. The techniques for determining network path delay are also utilized in conjunction with a three phase test procedure for diagnosing network congestion problems. Due to various network topologies and routing tables, certain confirmatory checks may be required to determine whether the procedures of the first or second phase test procedures are appropriate for particular path segments. Further, queuing delays may be determined by subtracting traffic independent delays from the measured transit times of the test messages, and such queuing delays may be used to determine the path delays. Such traffic independent delays may be determined during periods of low network traffic.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
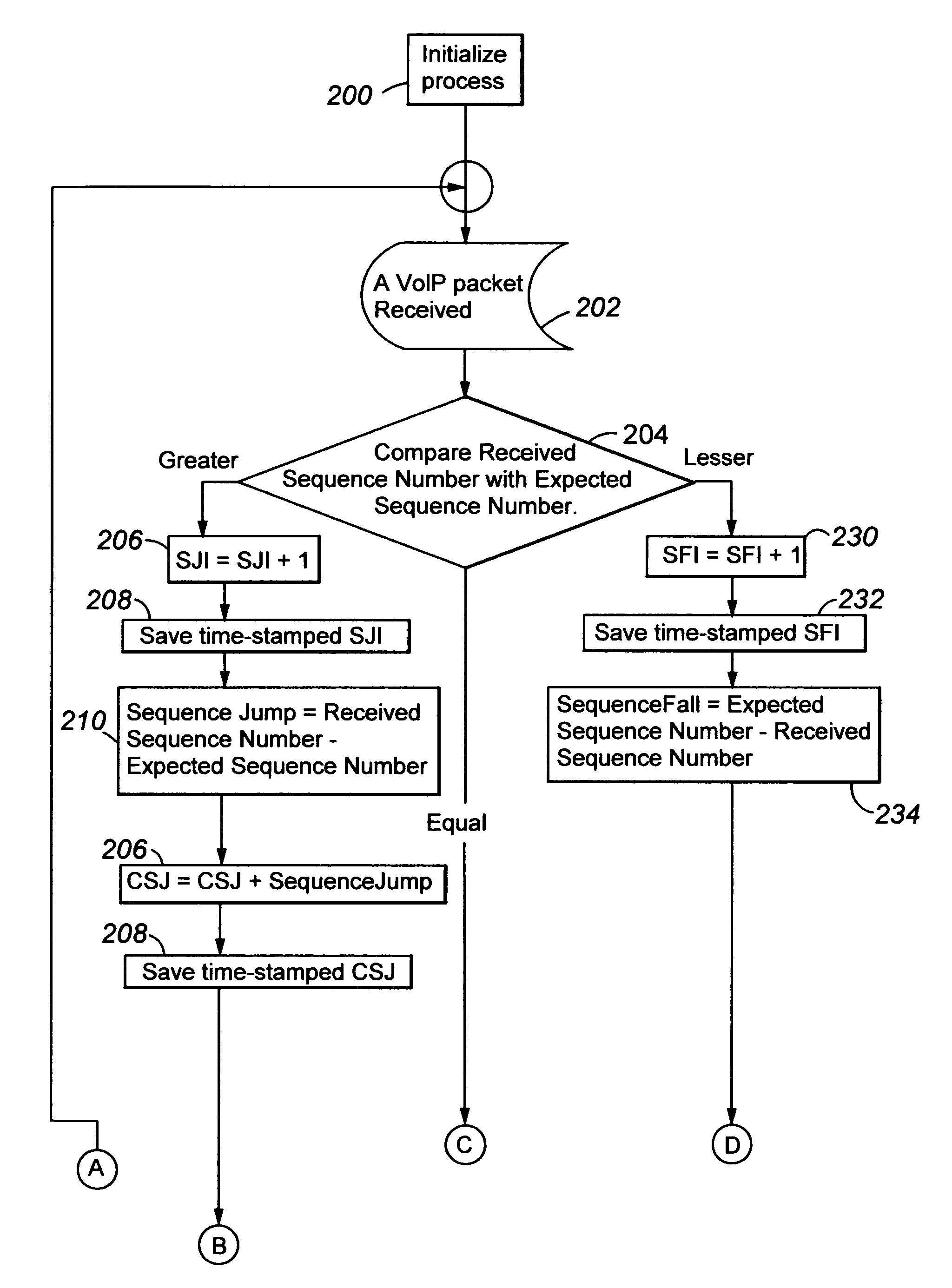
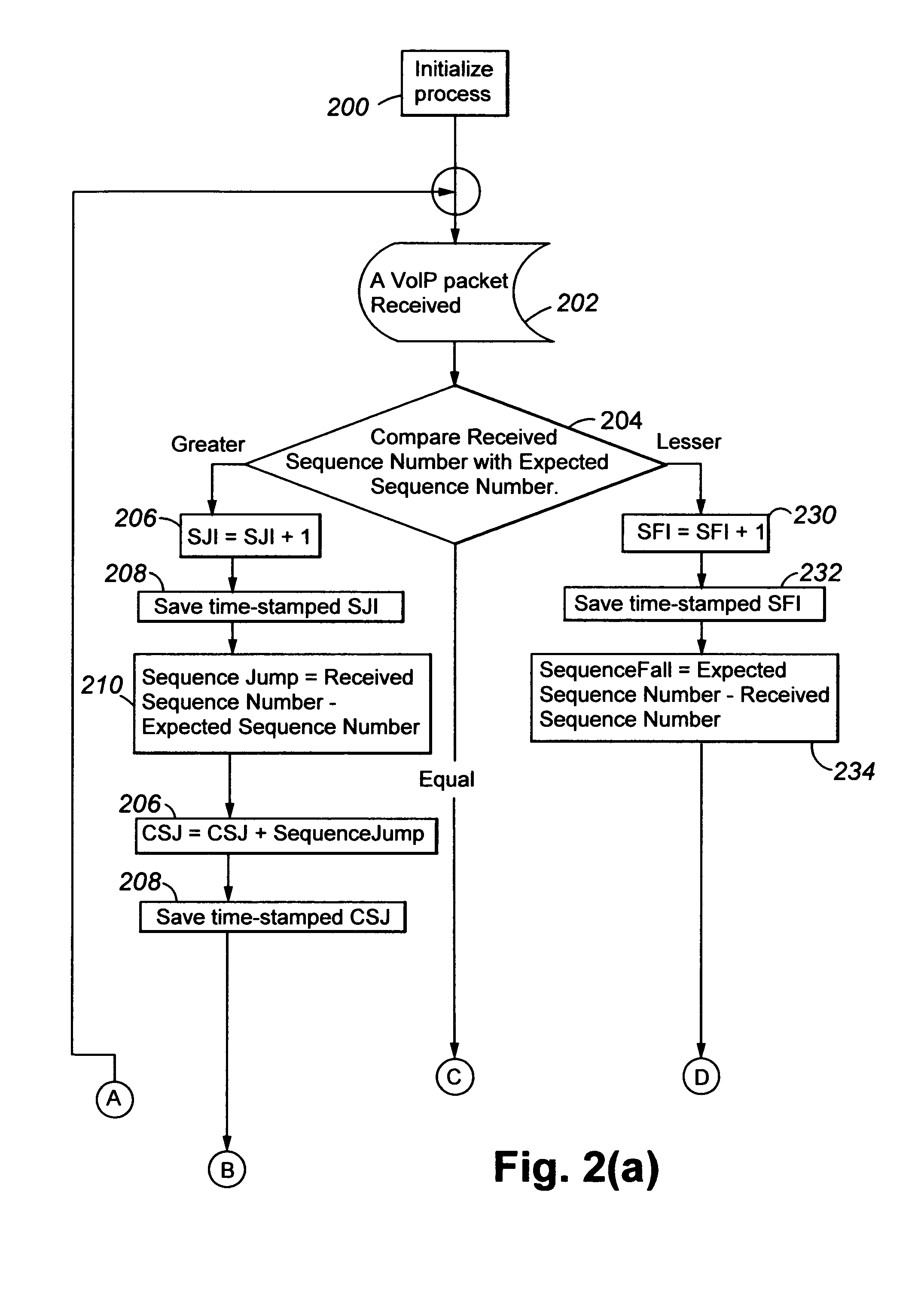
Network quality estimation
Disclosed are new calculations of packet loss bursts, packet re-ordering, and an indication of relative alternate network path delay metrics, based upon differences between received and expected packet sequence numbers, for determining packet network performance.
Owner:AVAYA INC
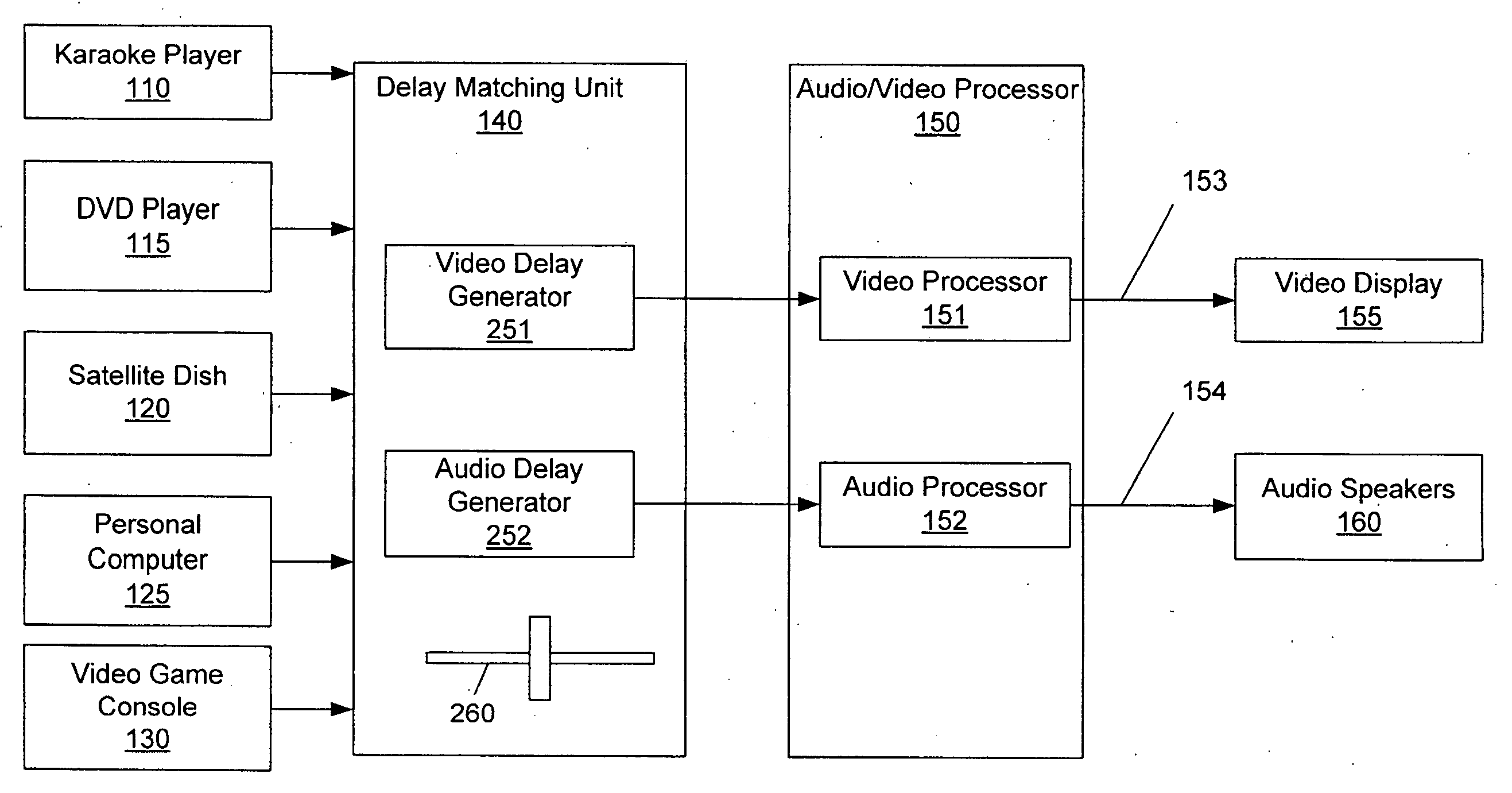
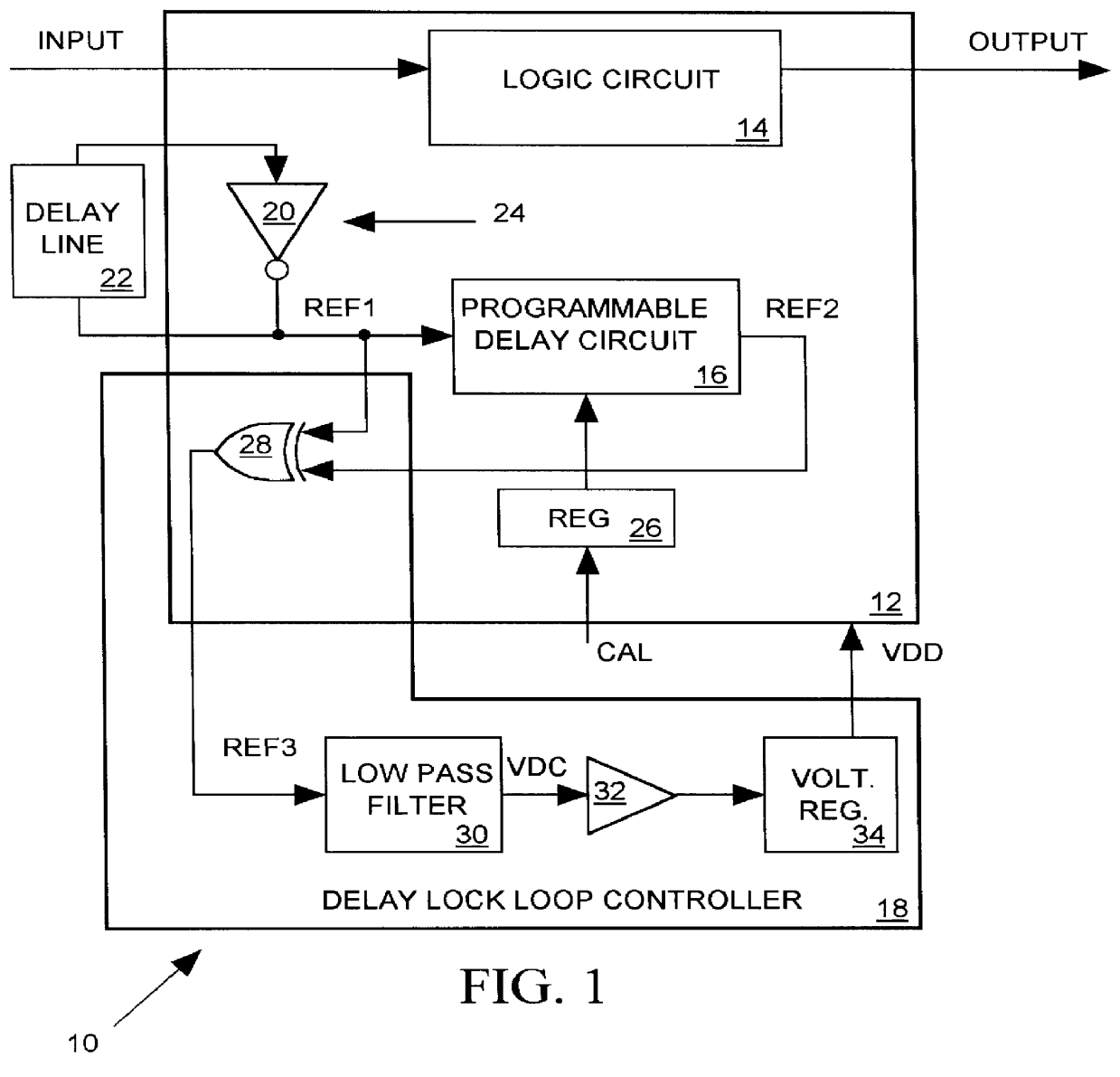
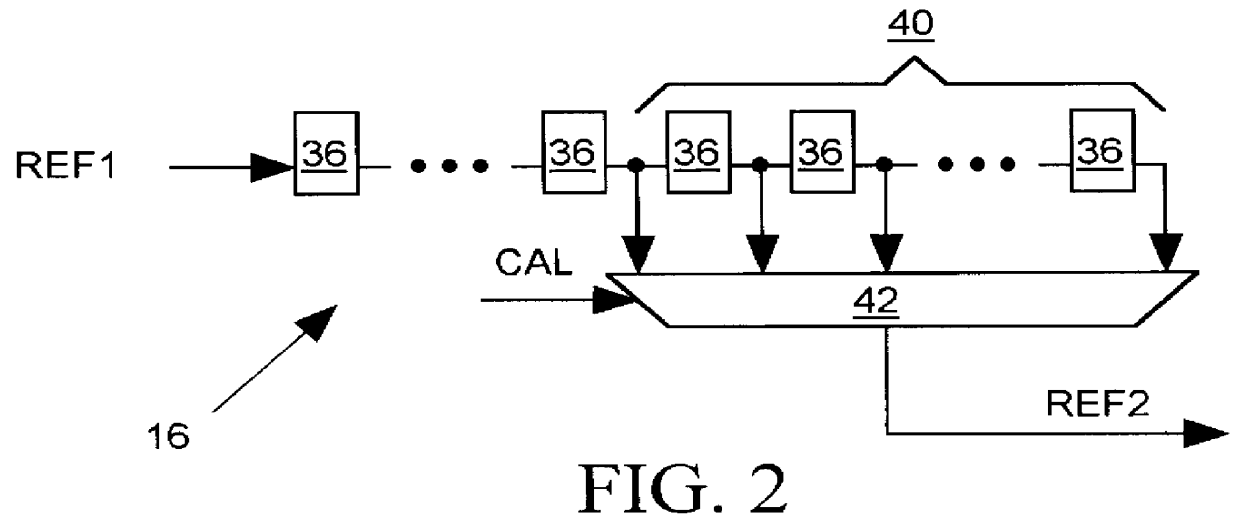
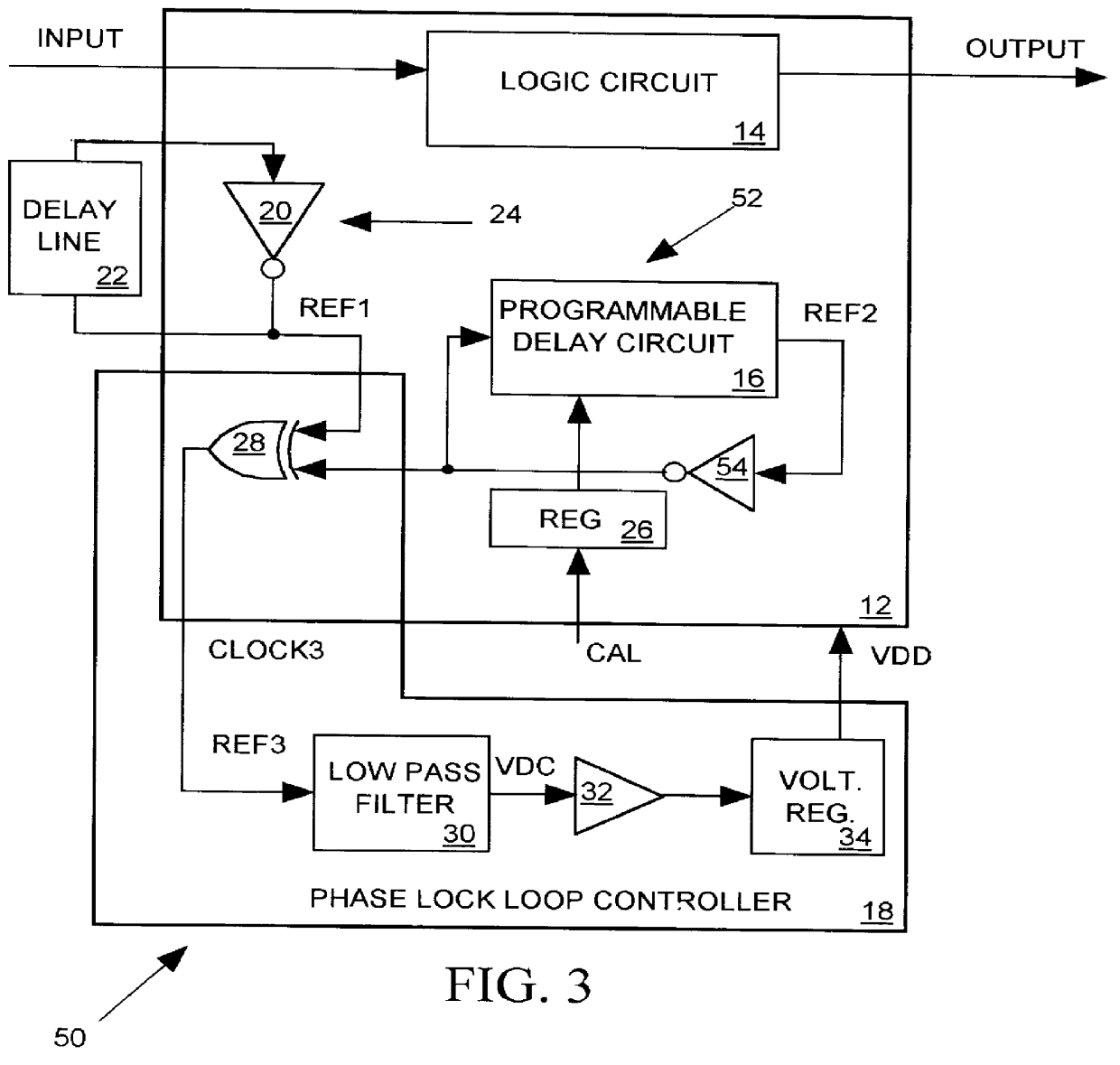
Delay matching in audio/video systems
ActiveUS20060290810A1Increase delayTelevision system detailsDifferential synchronisation source lockingComputer scienceAudio frequency
An audio / video system comprises an audio signal processing path having an audio path delay and a video signal processing path having a video path delay. The audio path delay may be different from the video path delay. The audio path delay and / or the video path delay may change, for example because of replacement of a component within the audio signal processing path or the video signal processing path. Delay matching (synchronization) in the audio / video system comprises adjusting the audio path delay to be substantially equal to the video path delay. Matching the audio path delay to the video path delay generally includes adding delay to the signal processing path with the lesser delay.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
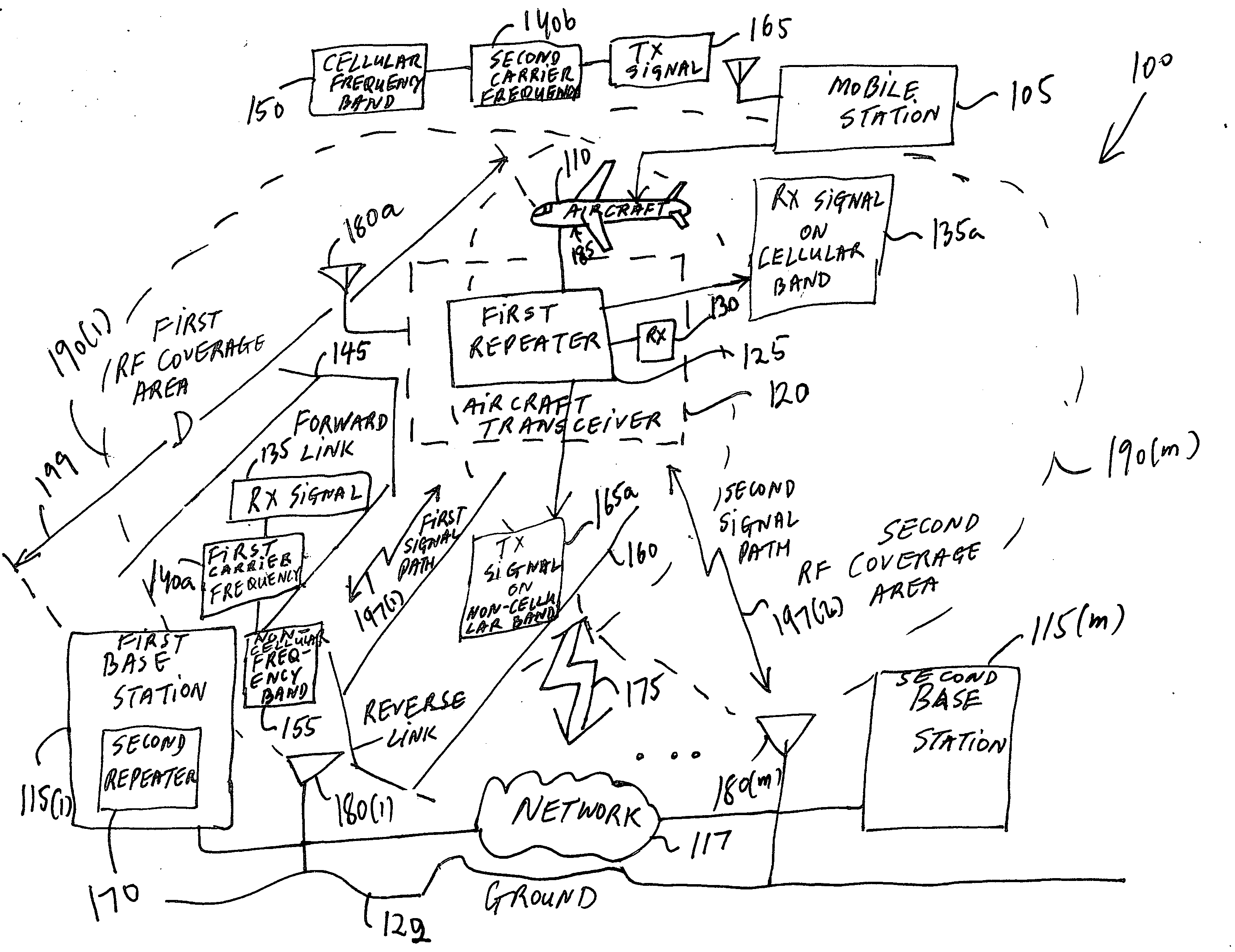
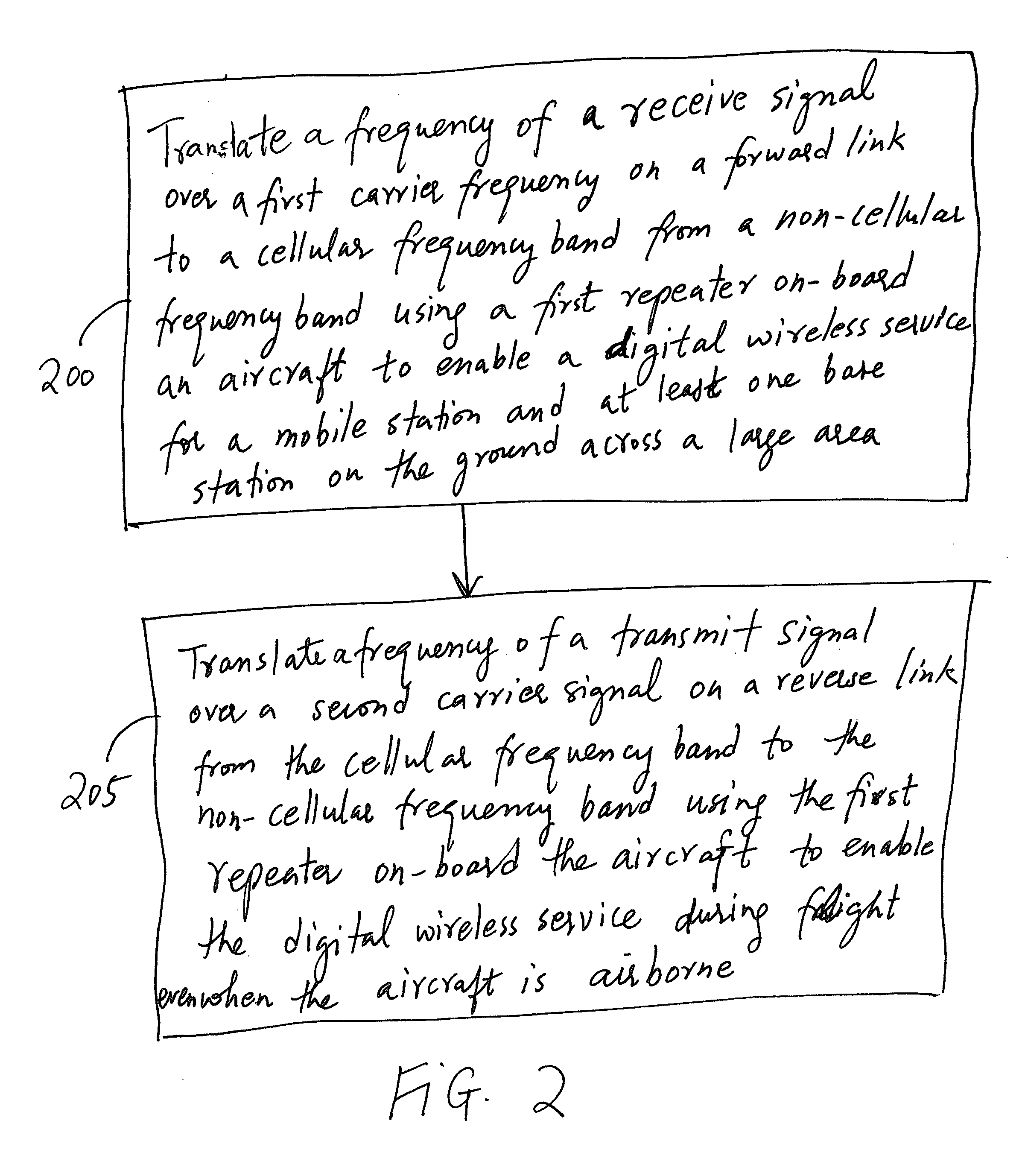
Enabling a digital wireless service for a mobile station across two different wireless communications environments
A method and an apparatus for enabling a digital wireless service across a first and a second wireless communications environment is provided. The method comprises translating a receive signal carried on a forward link and having a first carrier frequency in the first wireless communications environment from a first frequency band to a second frequency band different from the first frequency band. The method further comprises translating a transmit signal carried on a reverse link and having a second carrier frequency in the first wireless communications environment from the second frequency band to the first frequency band. In this way, a digital wireless service may be provided between a mobile station and at least one base station on the ground across two different wireless communications environments. The method further comprises compensating Doppler shift separately for individual beams directed at a plurality of terrestrial base stations. The method further comprises injecting an additional path delay to insure that the terrestrial base stations receive reverse link signals at substantially similar round trip time offsets and to reduce search windows for the terrestrial base stations. In this way, a wireless communication system may enable in-flight use of a mobile station to communicate with one or more base stations on the ground.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
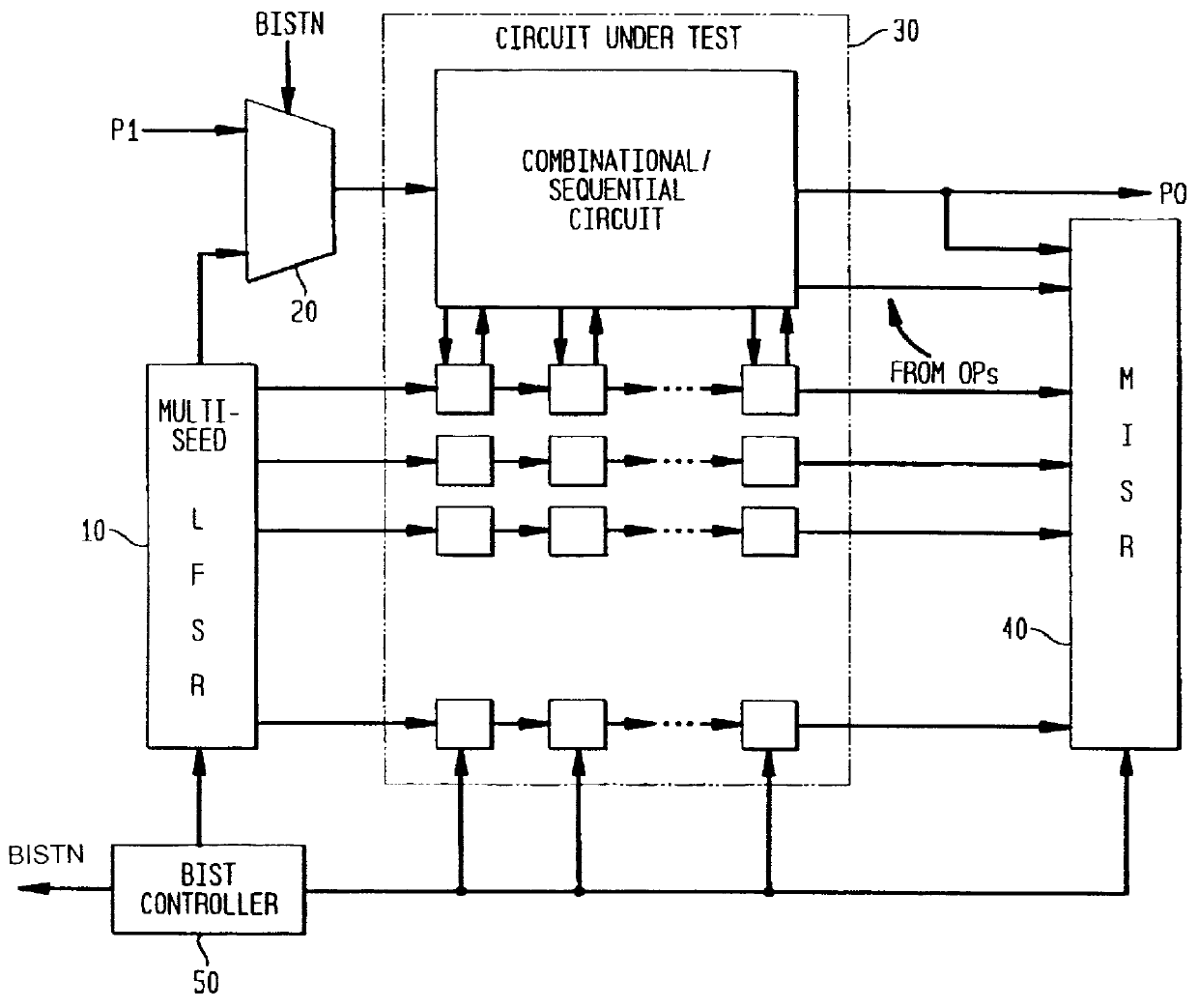
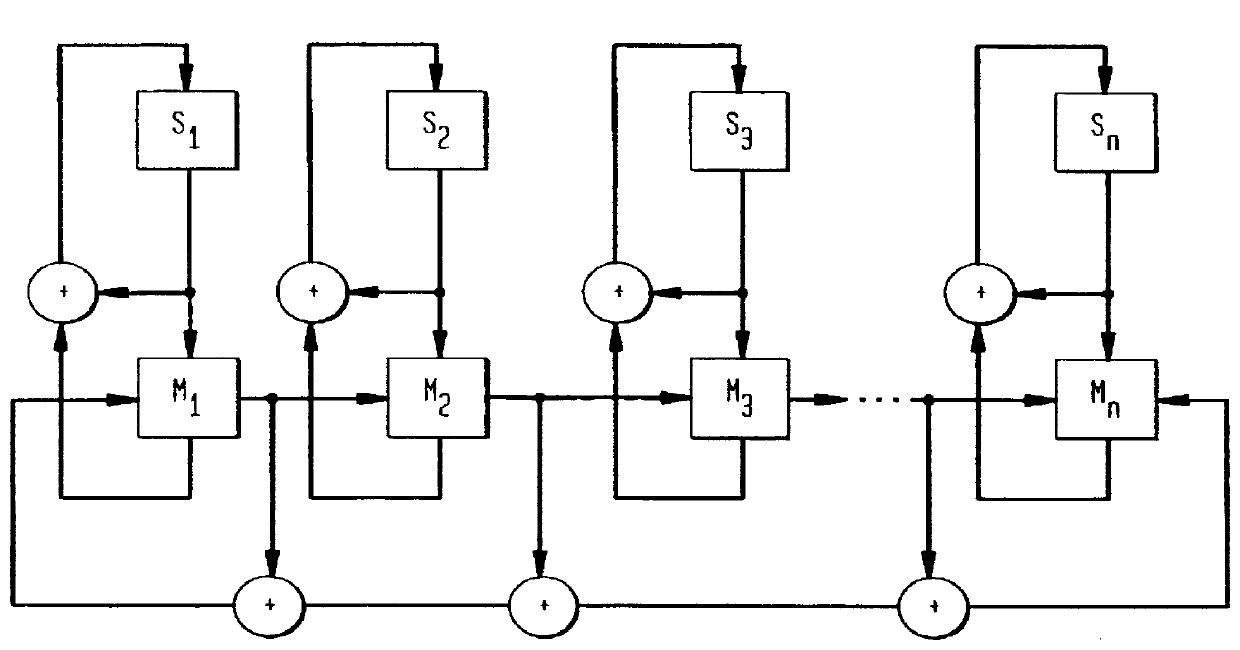
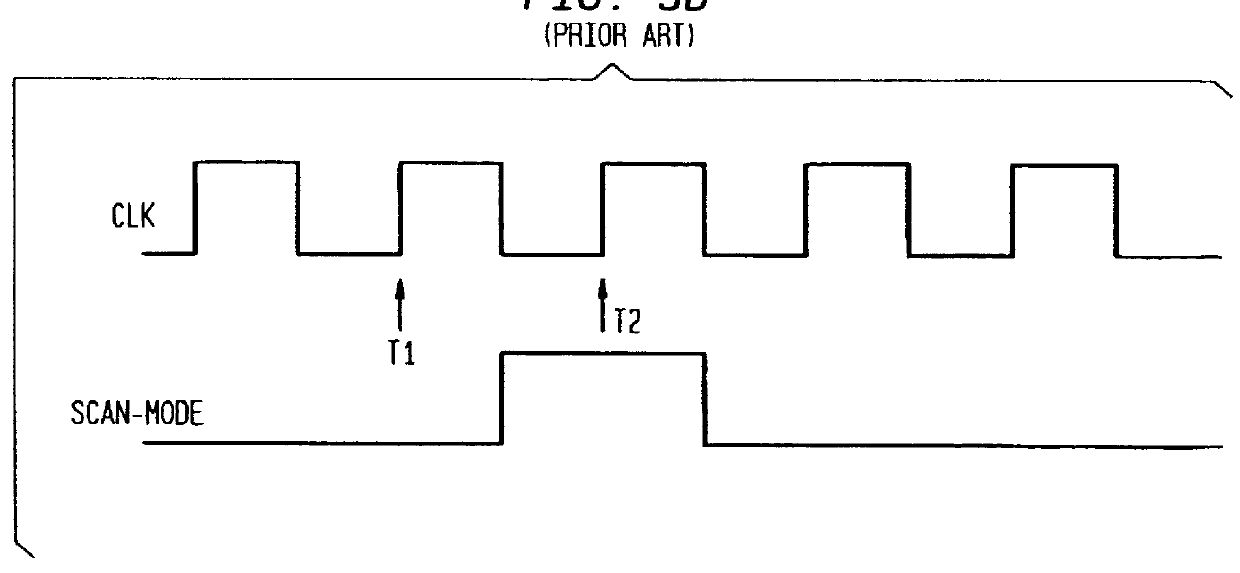
Bist architecture for detecting path-delay faults in a sequential circuit
A scan-based BIST architecture for detecting path-delay faults in a sequential circuit converted to a combinational circuit or a less complex sequential circuit including a combinational portion and a plurality of scan flip-flops. The BIST structure includes a test pattern generator for generating two test patterns and a controller for generating a clock signal and an extended scan mode signal which is held high for two clock cycles while the output response of the combinational portion to the first and second test vectors is latched into the scan flip-flops in order to detect a signal transition. The invention is further directed to a method for detection of path-delay faults using this scan-based BIST architecture. To improve the fault coverage for path-delay faults, observation points may be inserted at the inputs of selected scan flip-flops. A predetermined number of scan flip-flops having the highest activation frequency are selected as the observation points.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
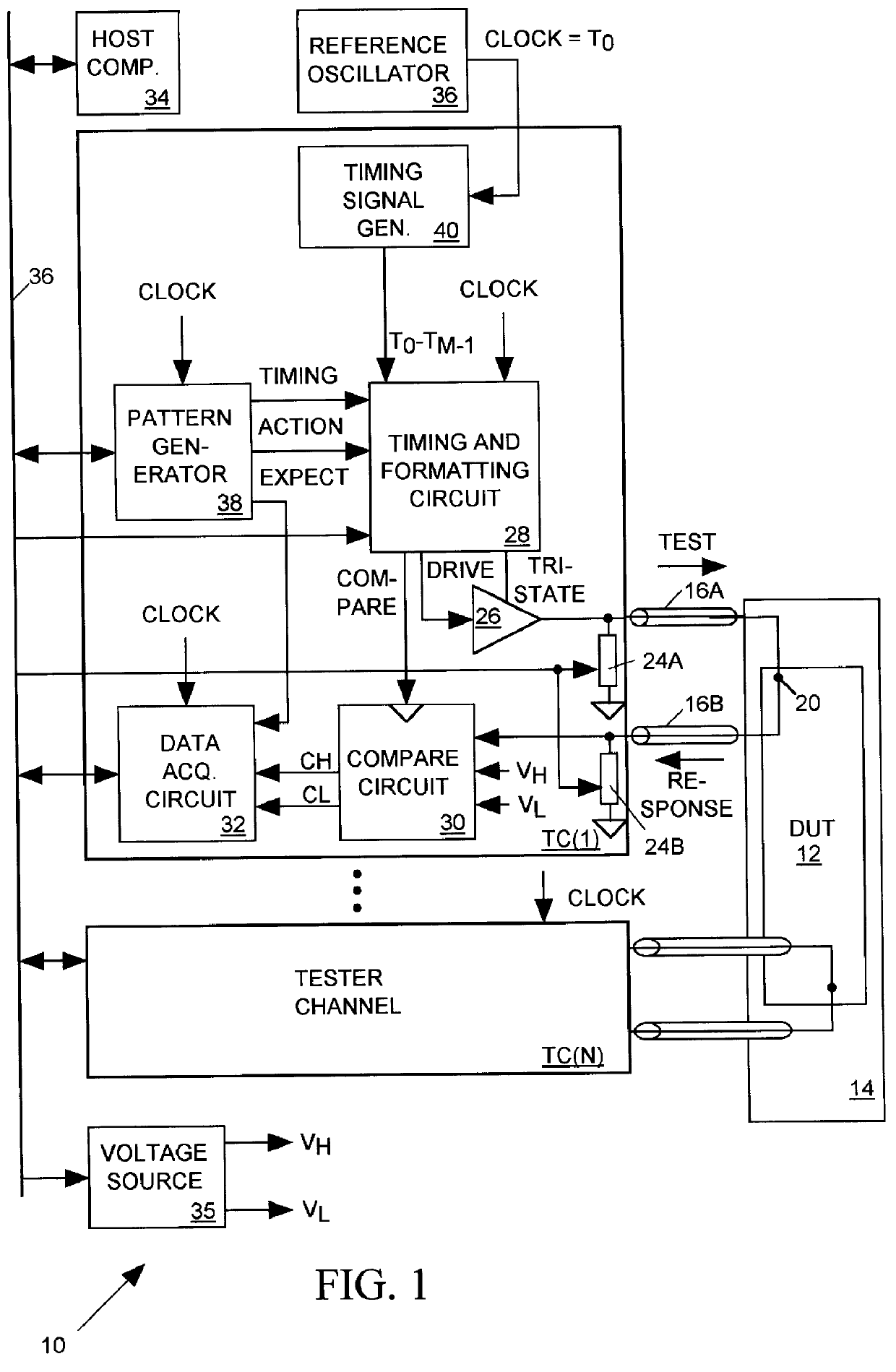
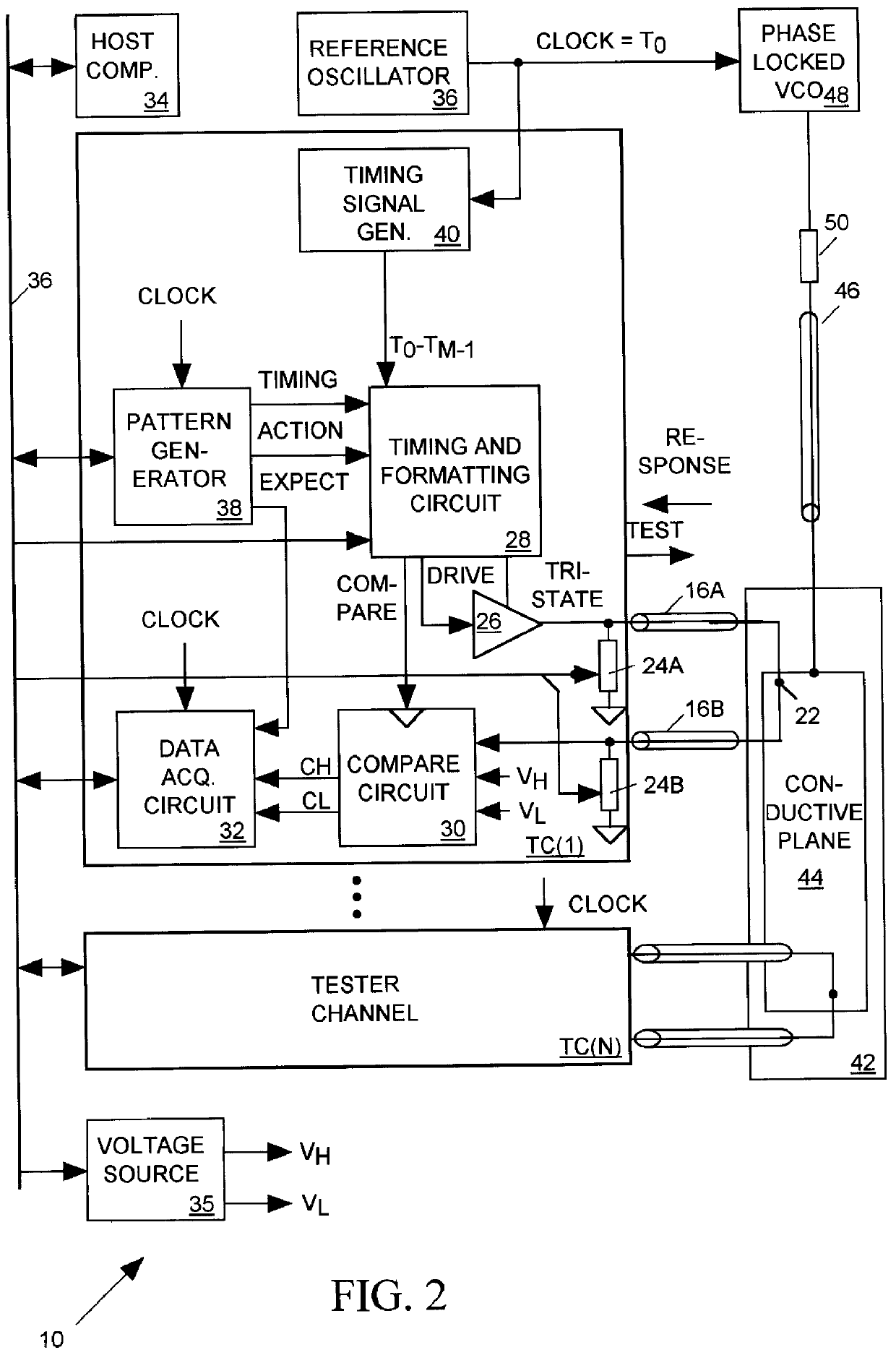
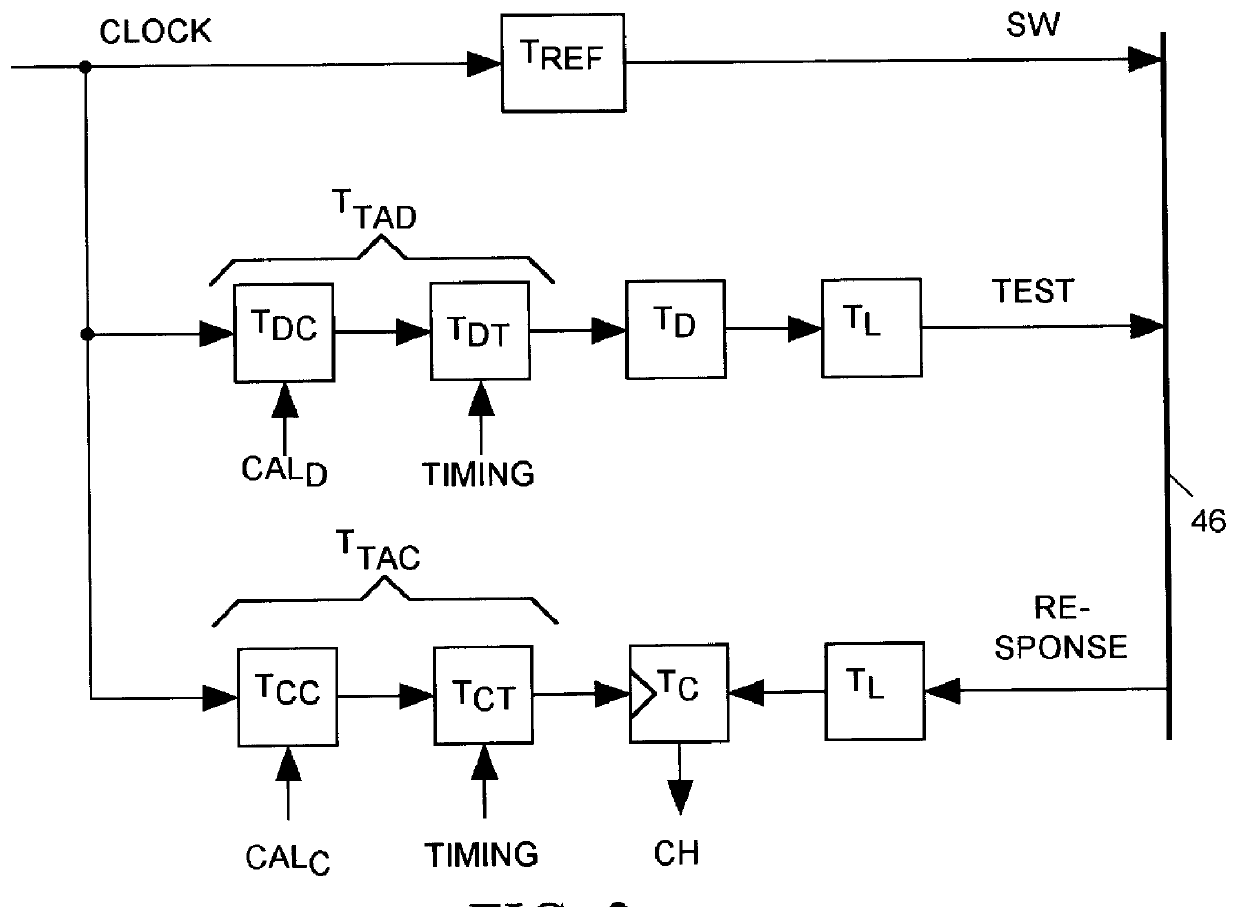
Salphasic timing calibration system for an integrated circuit tester
InactiveUS6105157AQuickly and easily calibratingDigital circuit testingError detection/correctionTester deviceEngineering
An integrated circuit tester produces an output TEST signal following a pulse of a reference CLOCK signal with a delay that is a sum of an inherent drive delay and an adjustable drive delay. The tester also samples an input RESPONSE signal following a pulse of the reference CLOCK signal with a delay that is a sum of an inherent compare delay and an adjustable compare delay. The inherent drive and compare signal path delays within an integrated circuit tester are measured by first connecting a salphasic plane to transmission lines that normally convey signals between the tester and terminals of an integrated circuit device under test. A standing wave signal appearing on that salphasic plane is phase locked to the CLOCK signal so that a zero crossing of the standing wave occurs at a fixed interval after each pulse of the CLOCK signal. Each transmission line concurrently conveys the standing wave to the tester to provide timing references for measuring the inherent drive and compare signal path delays within the tester. Transmission line signal paths are also measured. Delays are added to the drive and compare signal paths to compensate for the measured inherent drive, compare and transmission line delays.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
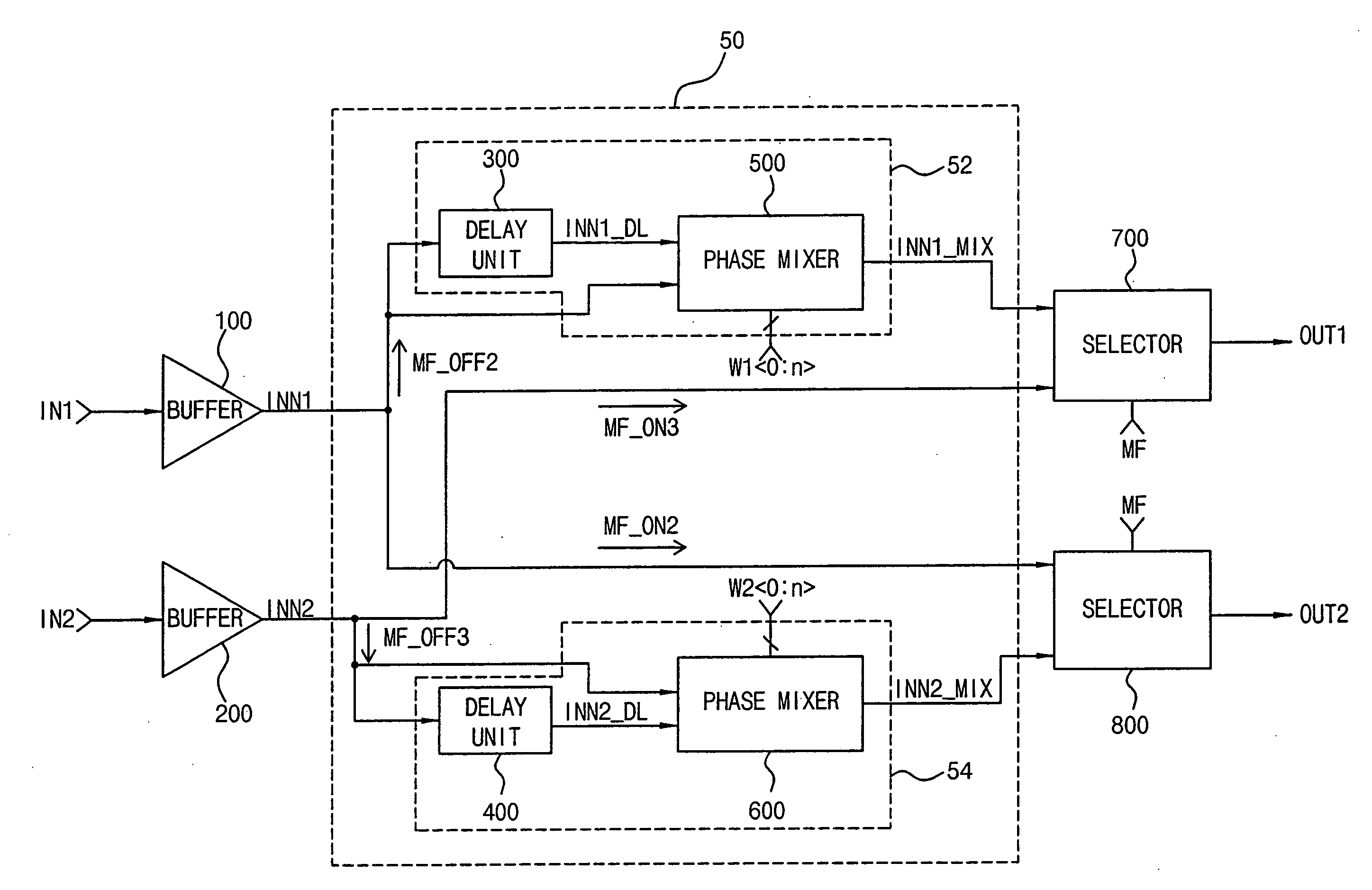
Semiconductor memory device with mirror function module and using the same
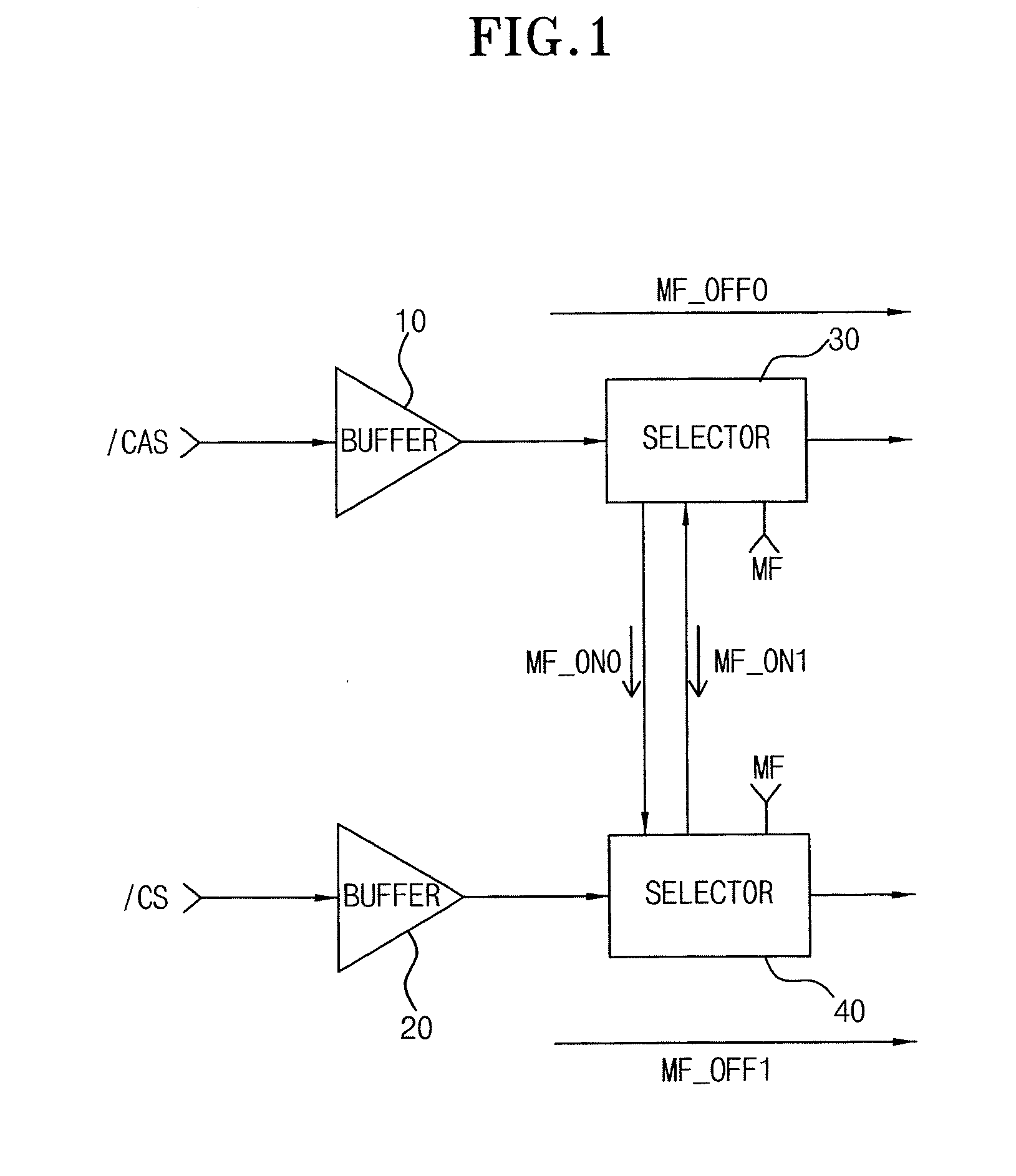
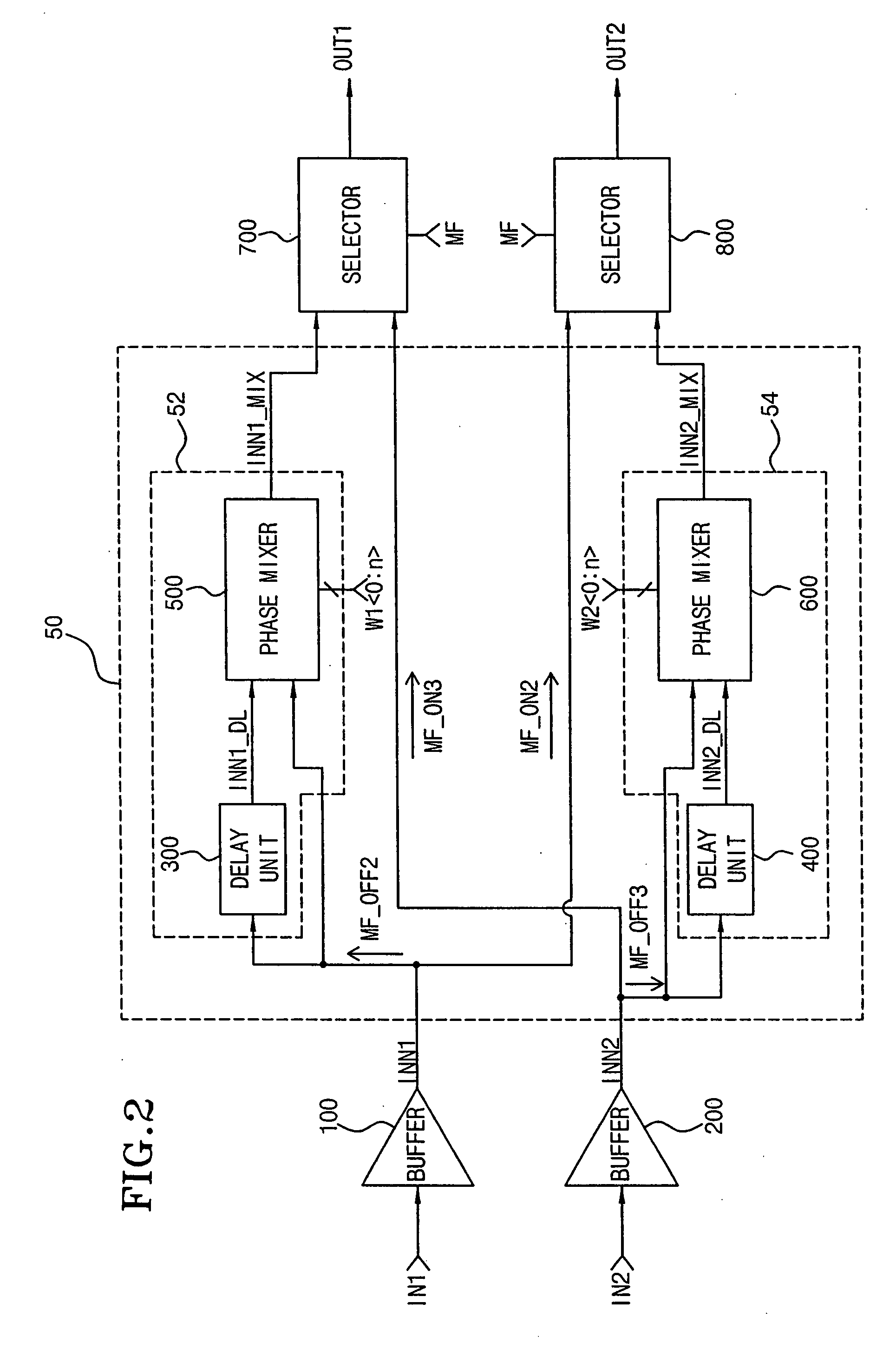
A semiconductor memory device with a mirror function enables two memory devices such as two DRAMs to share the same address and control signals. A pair of semiconductor memory devices are mounted on both sides of a substrate to be symmetrical to each other. A mirror function transfers a first transmission signal and a second transmission signal input on respective pads to any one of a mirror “on” path and a mirror “off” path. The mirror function can vary or reduce path delay differences between the mirror function “on” path and the mirror function “off” path by means of the delay and the mixture of phases in the semiconductor memory device, and reduce skew occurred in the operation of the mirror function.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
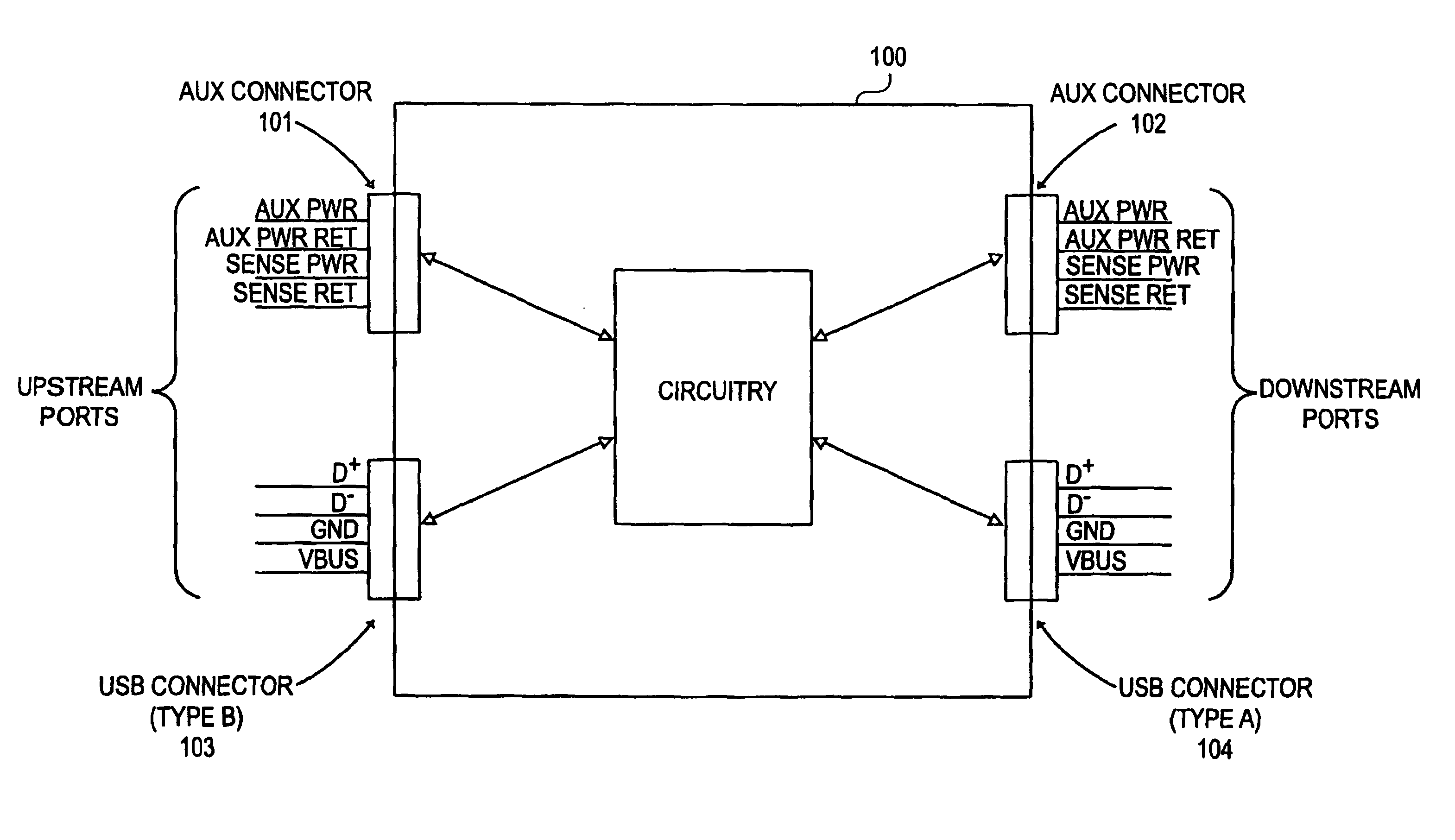
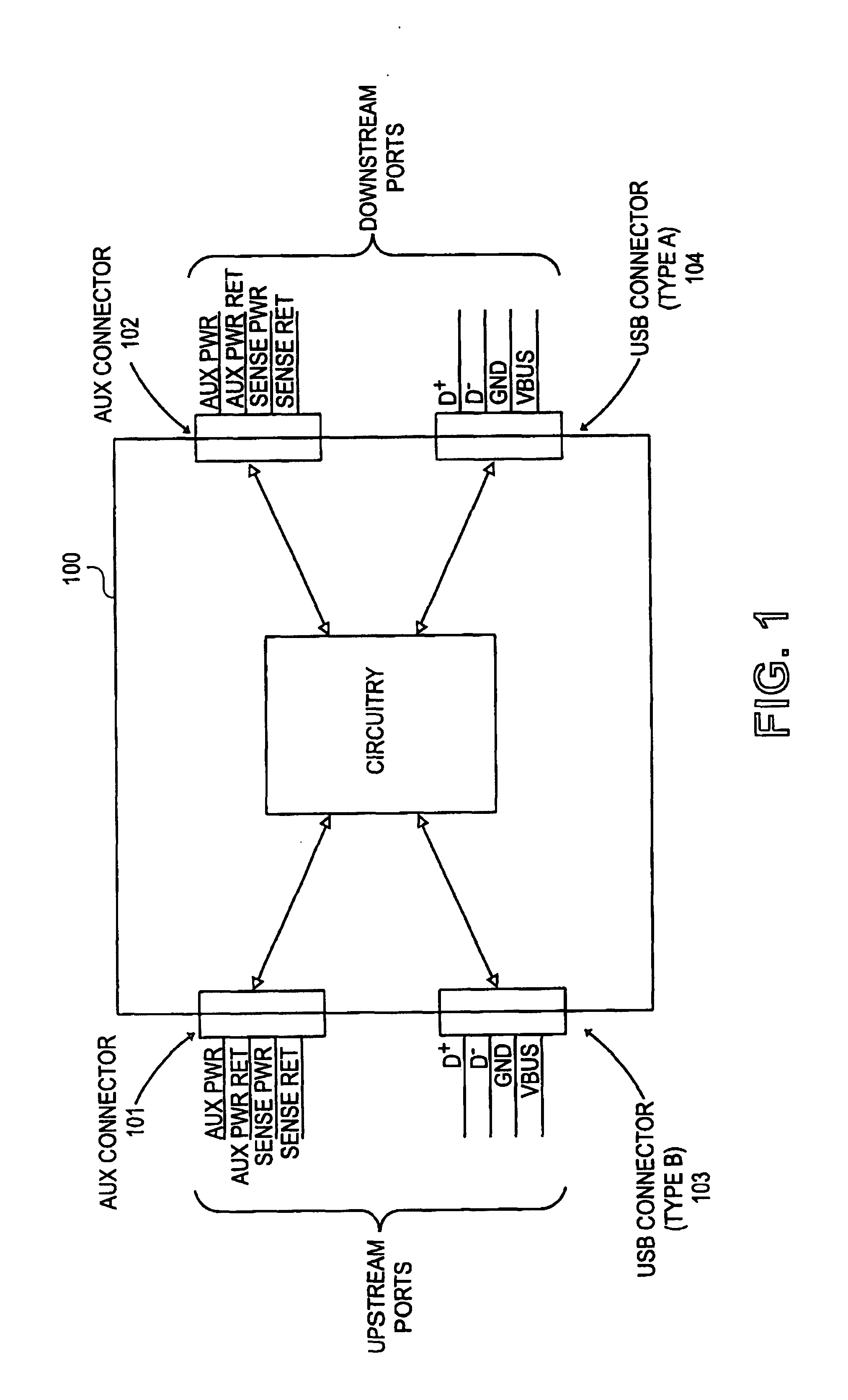
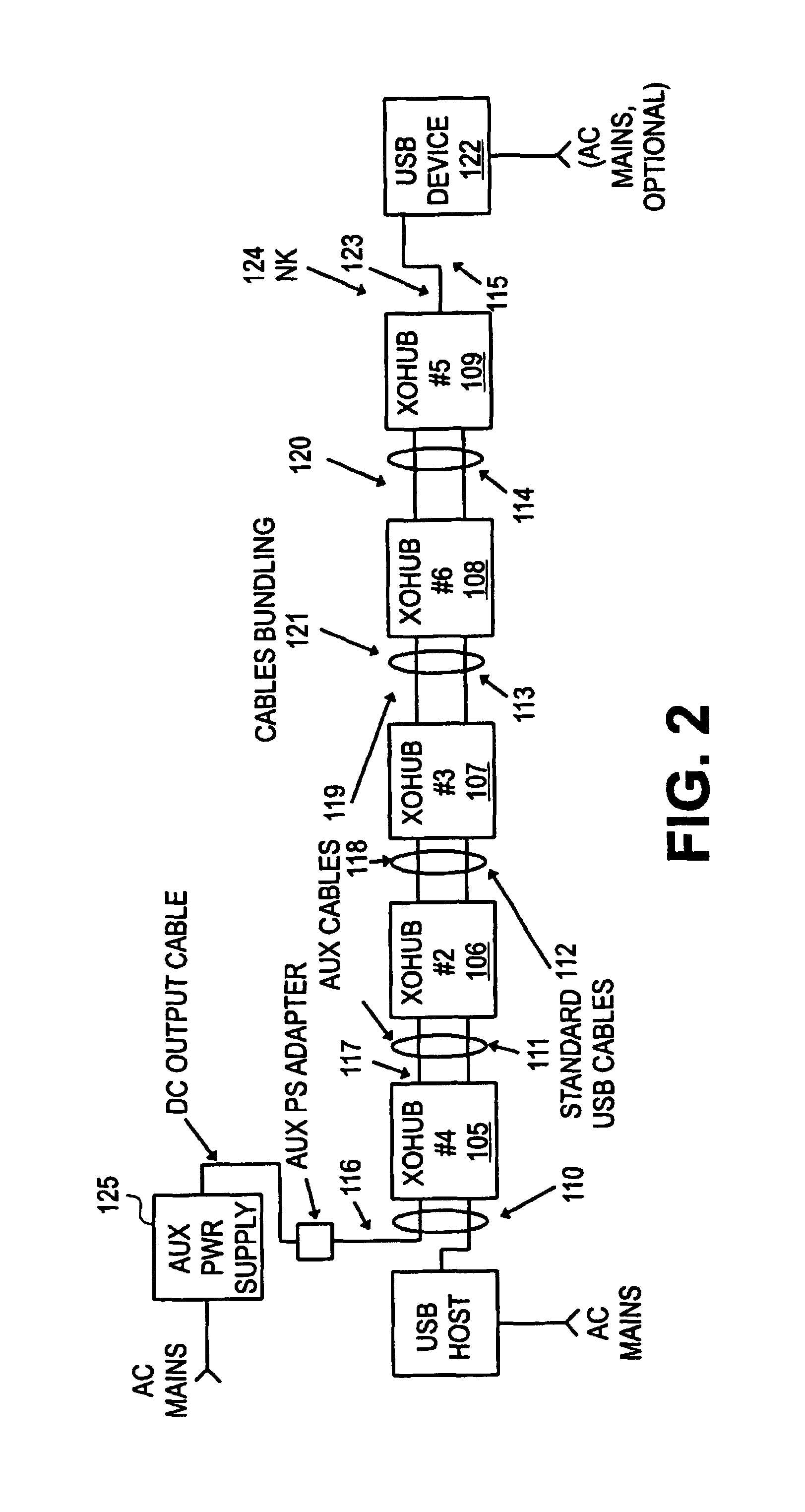
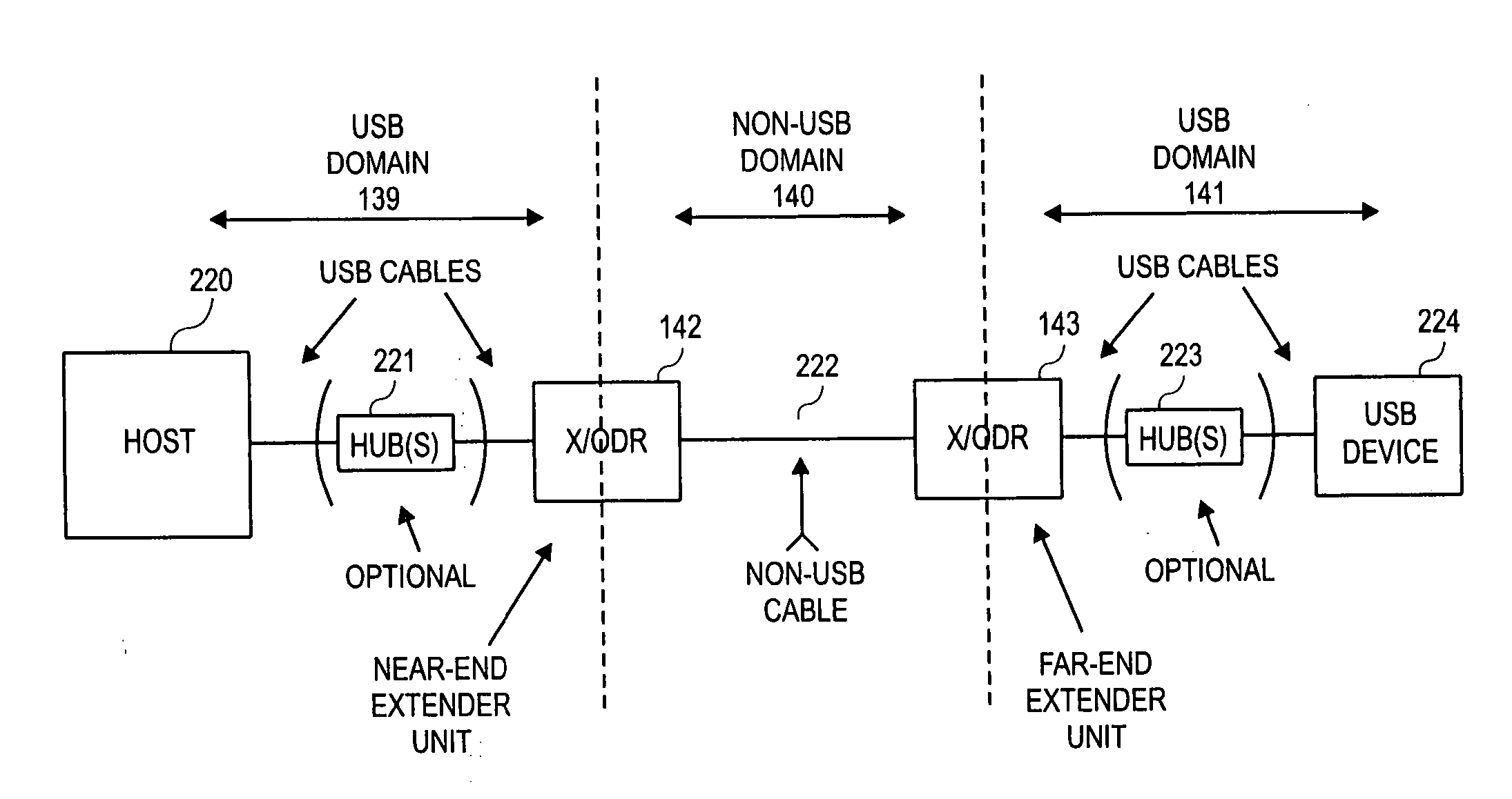
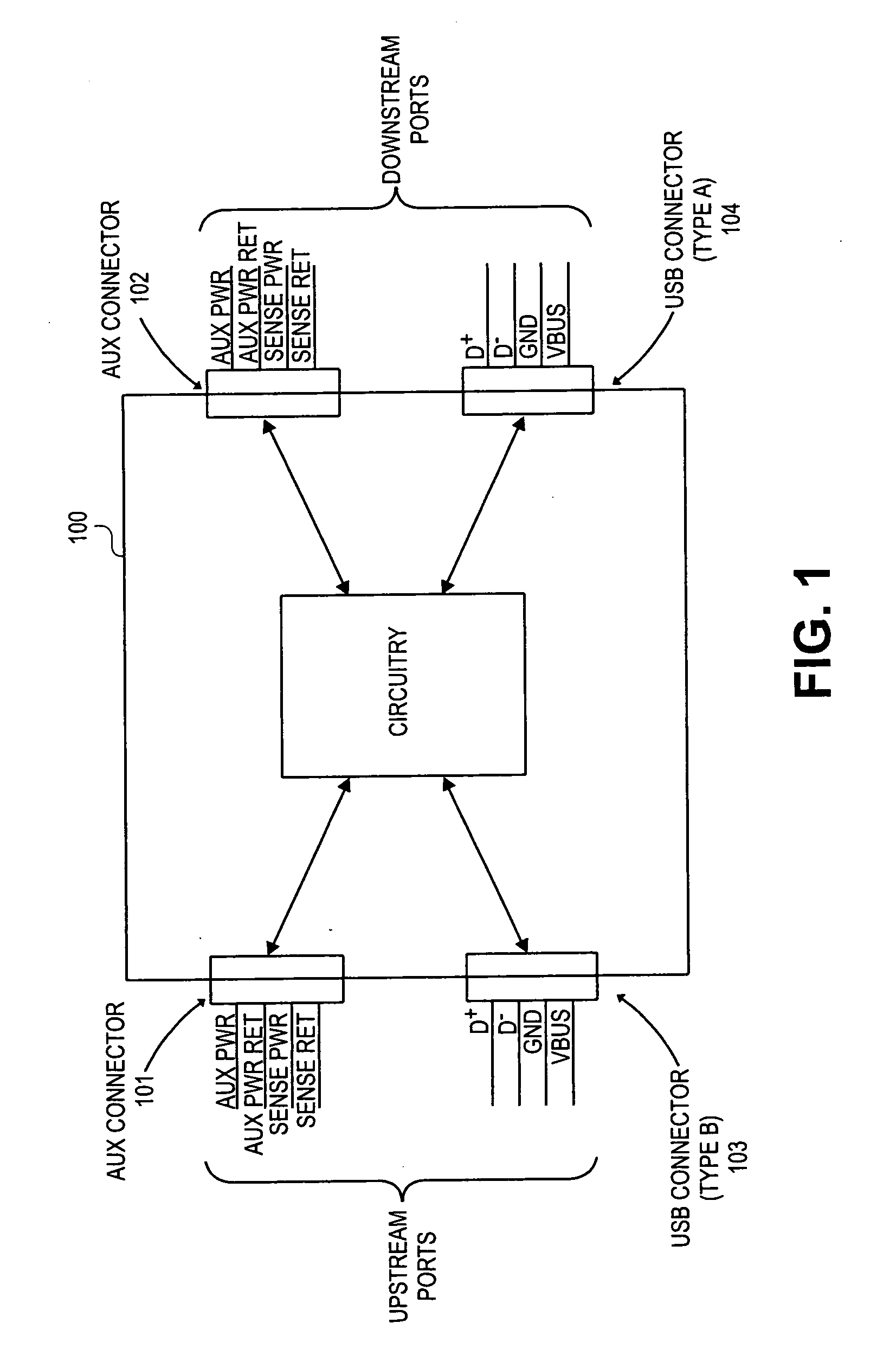
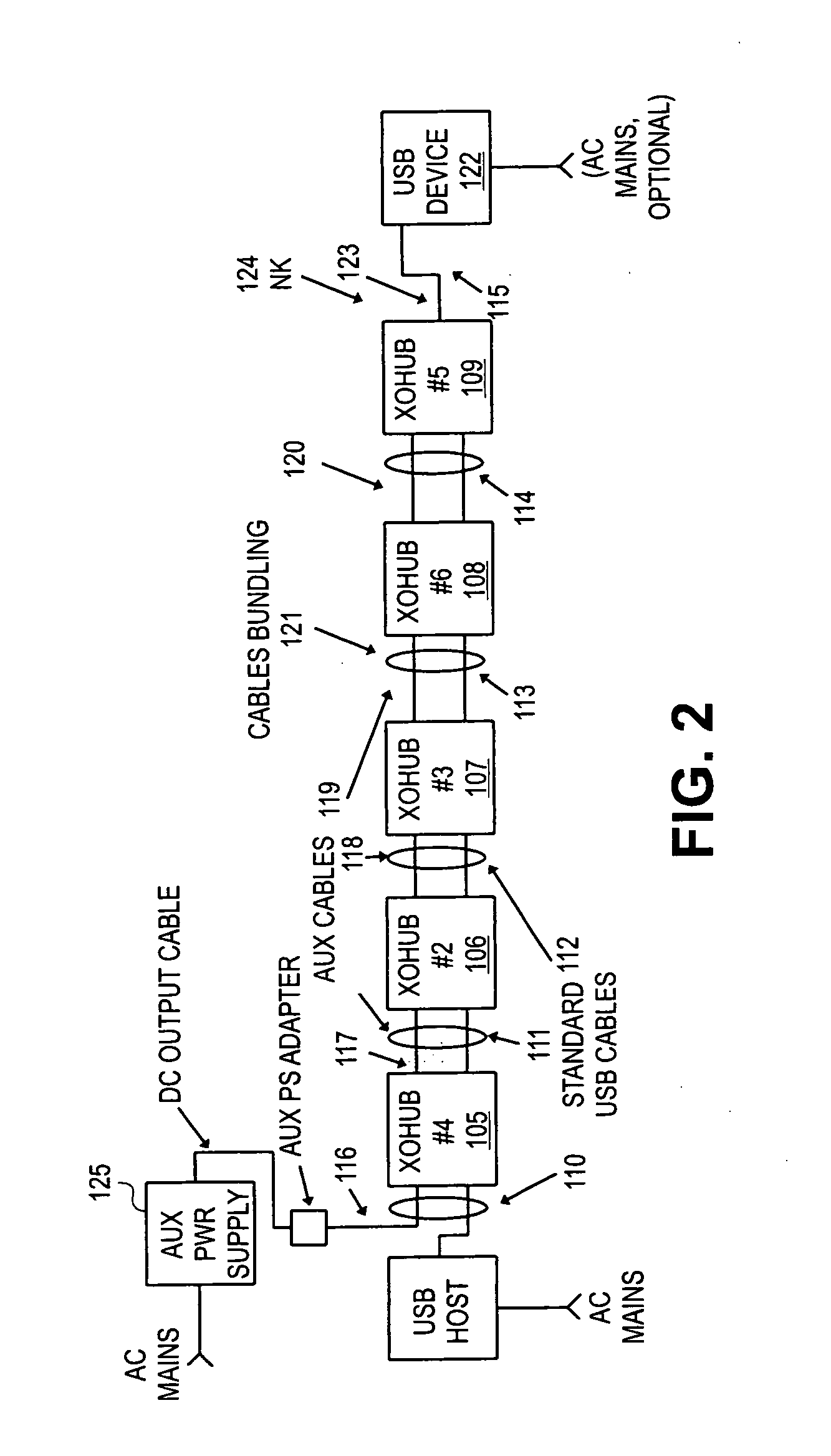
Method and apparatus for extending communications over USB
Method and apparatus are described for improving information transfer over USB. In one approach, hub-based extension is realized wherein power is distributed using auxiliary wiring distinct from signal and power wiring present in conventional USB cabling. Additional signals allow optimization of power distribution for powering attached devices, and for detecting and handling illegal connection configurations.In another approach, improvements are realized through use of alternative signaling techniques which eschew reflective and high-speed common-mode signaling. Described are various configuration, media and signal-protocol combinations, including implementations containing embedded hubs. Methods ensuring reliable system behavior are also described, including determination of extension path delay and use of topology-enforcement hubs.In other approaches, further improvements are realized by allowing information exchanges to take longer than the nominal timeout period, or by allowing host requests to be delayed for transmission until the extended bus is available for use.
Owner:INTEL CORP
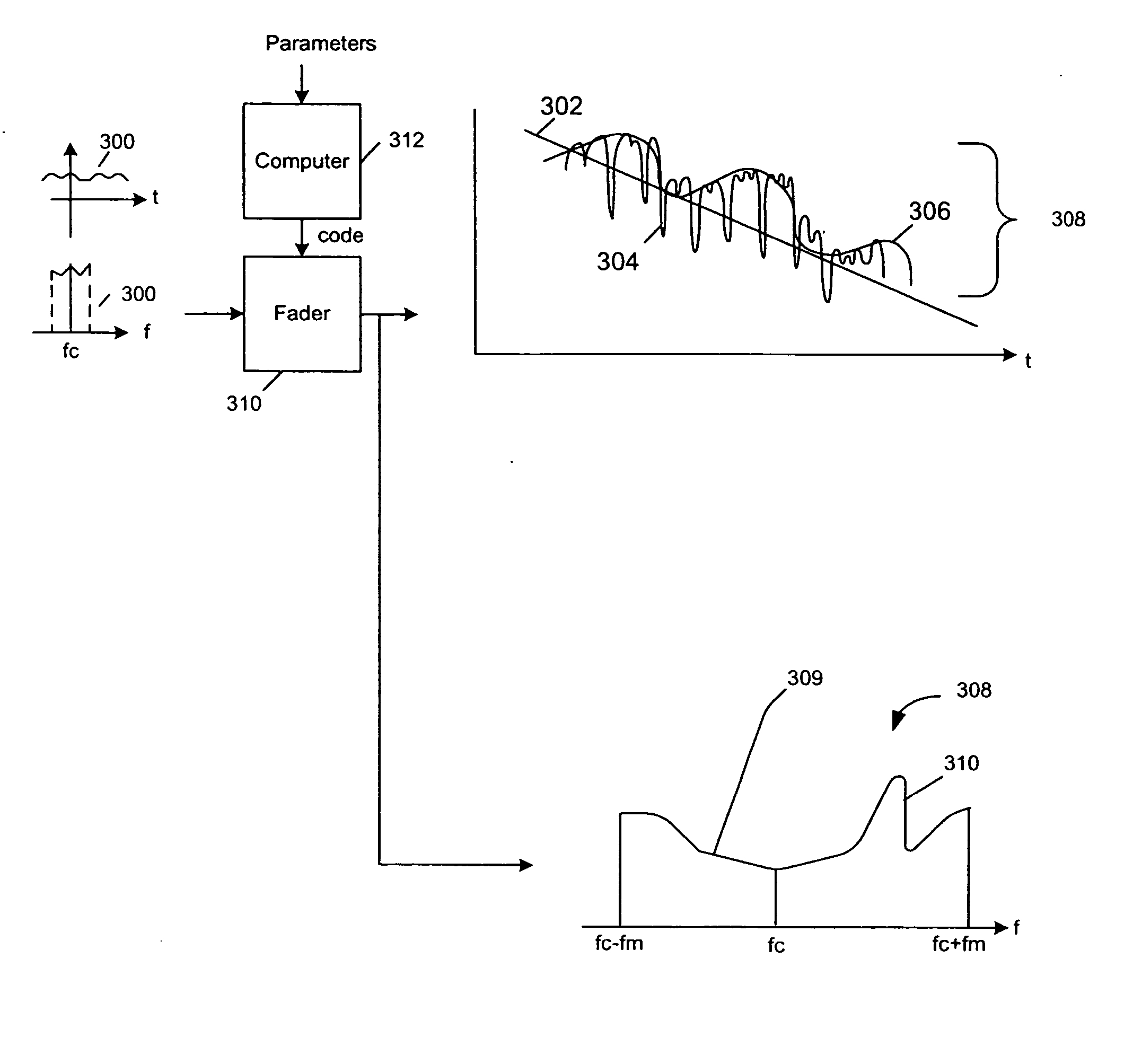
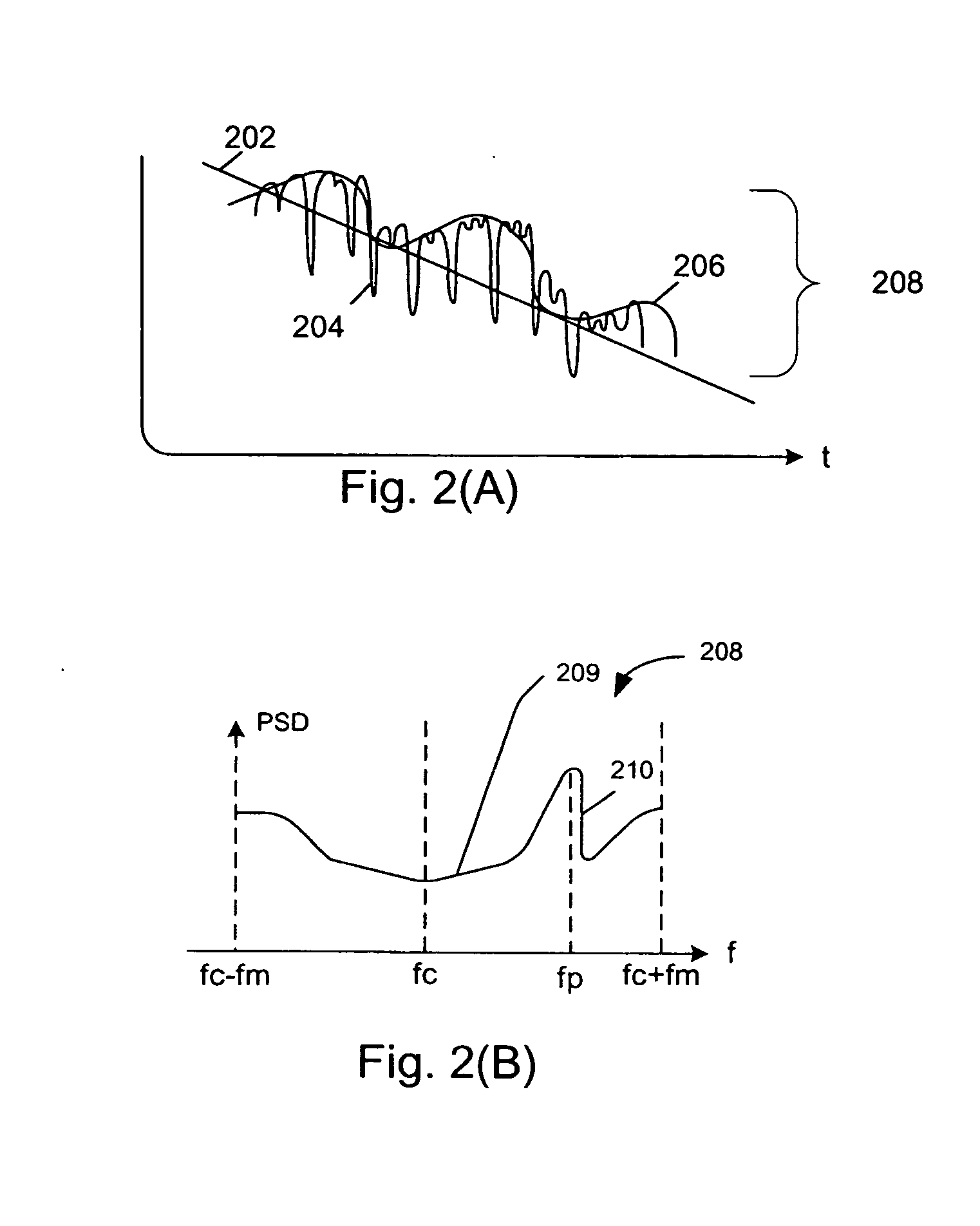
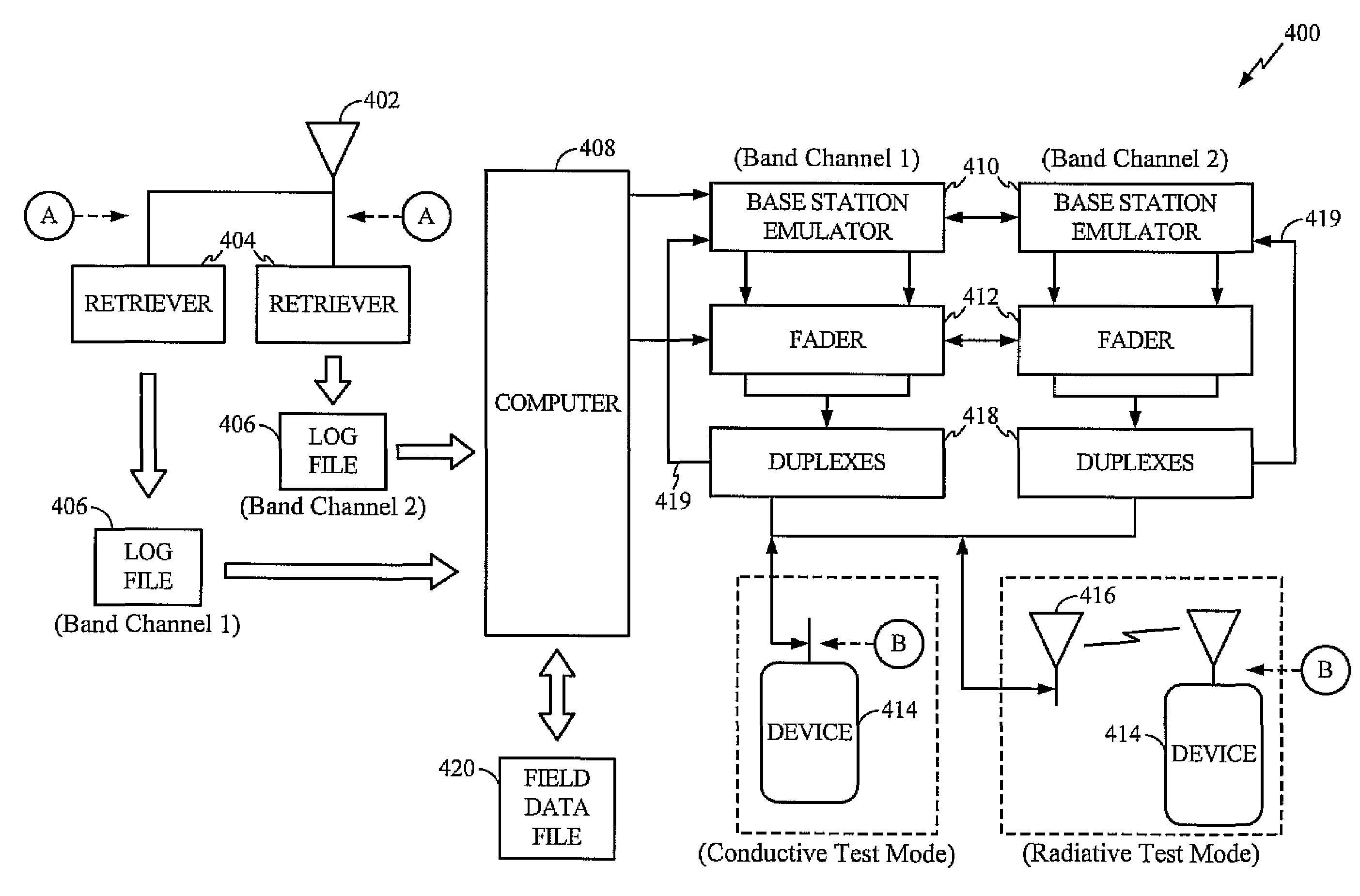
Systems and methods for testing the performance of and simulating a wireless communication device
InactiveUS20070127559A1Exact reproductionMaintain optimum performancePolarisation/directional diversityTransmission monitoringControl signalData file
A system abstracts channel information from field data gathered in actual wireless communication system environments. The abstracted data is then transformed into control signals or programming codes that can be used to control channel simulators so as to recreate the field conditions, including path loss, slow fading, fast fading, path delay, fading power spectral density with and without line-of-sight (LOS), and different kind of handoff scenarios, such as soft, softer, intra-band hard, inter-band hard handoffs. The system thus can accurately simulate a realistic wireless communication link originated from multiple signal sources in different band channels and formed by multipath signal propagation. The simulated realistic wireless communication link can be condensed by selecting the most useful scenarios from its original field data files or modified by tuning its parameters as desired.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Delay stabilization system for an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6157231AEasy to adjustPrecise processReliability increasing modificationsPulse automatic controlPhase differenceEngineering
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
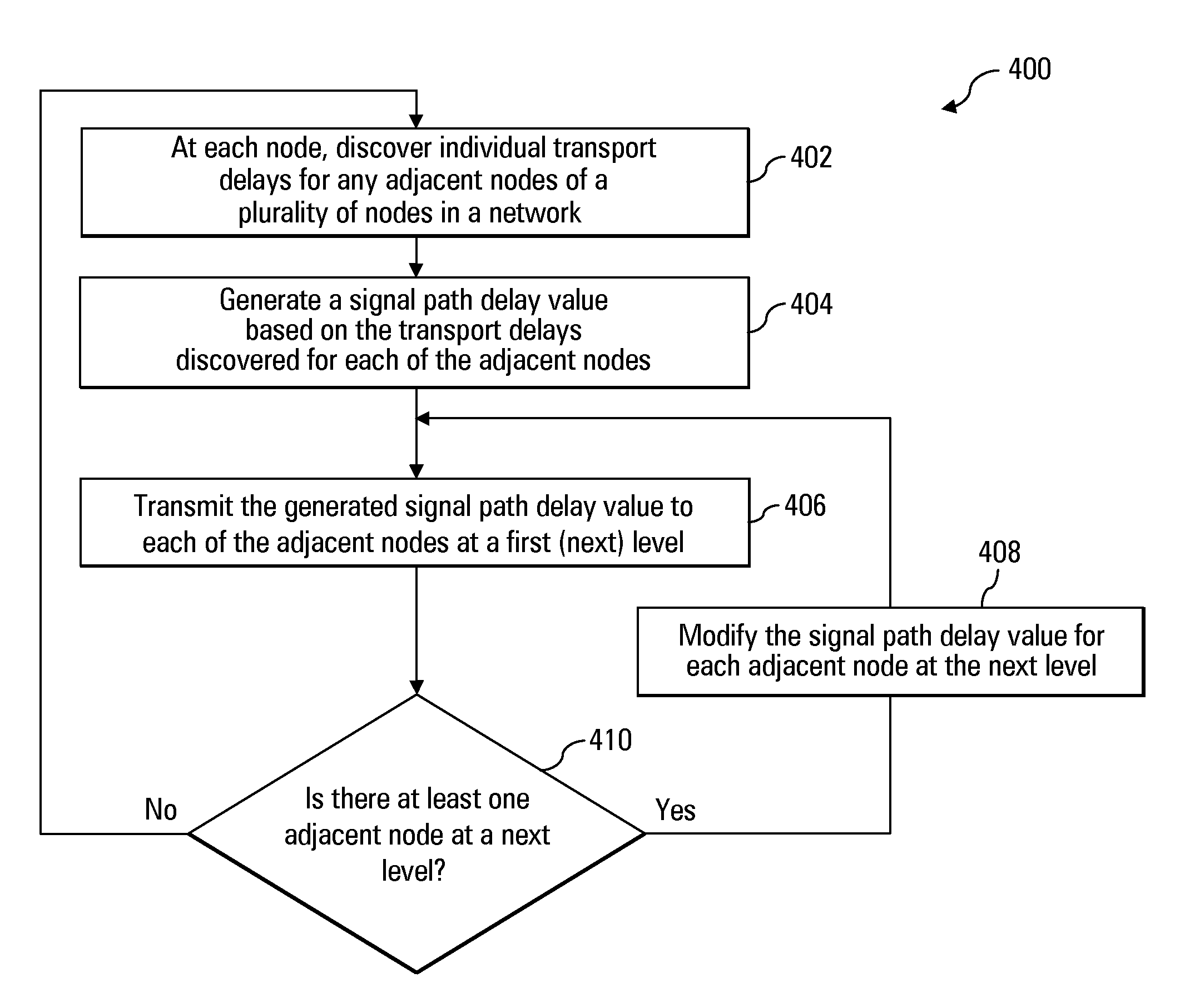
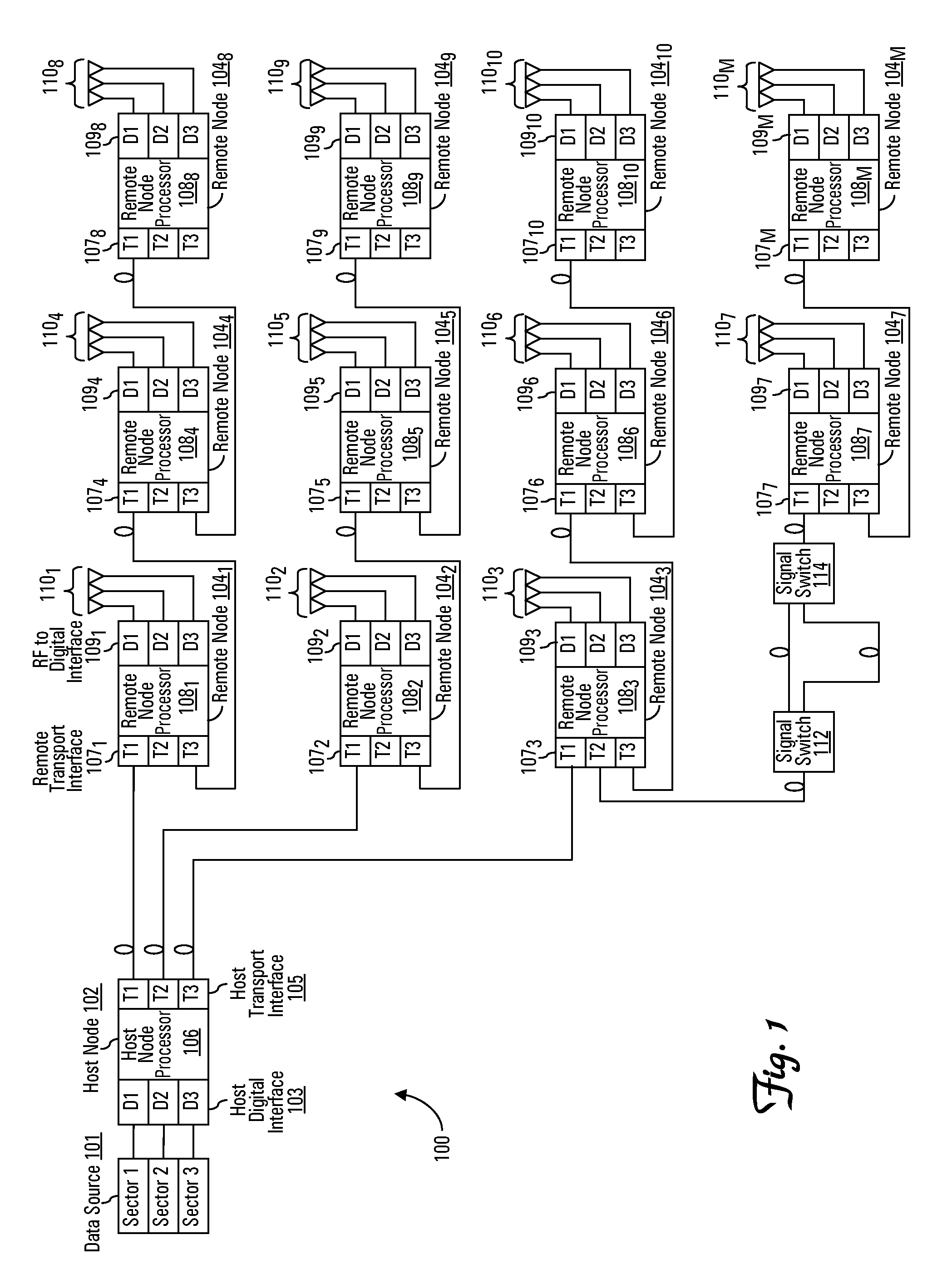
Delay management for distributed communications networks
A method for programming the delay for a node in a communication system is disclosed. The node receives a selected delay value and a signal path delay value indicating a delay for signals communicated to the node. The signal path delay comprises an aggregation of transport delays calculated by each node for segments of the communication system between the node and a host node. The method further calculates an additional delay necessary to meet the selected delay value.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for phase shift keyed optical communications
ActiveUS20110274429A1High data rateConstructionsModulated-carrier systemsTransceiverOptical communication
A burst-mode differential phase shift keying (DPSK) communications system according to an embodiment of the present invention enables practical, power-efficient, multi-rate communications between an optical transmitter and receiver. An embodiment of the system utilizes a single interferometer in the receiver with a relative path delay that is matched to the DPSK symbol rate of the link. DPSK symbols are transmitted in bursts, and the data rate may be varied by changing the ratio of the burst-on time to the burst-off time. This approach offers a number of advantages over conventional DPSK implementations, including near-optimum photon efficiency over a wide range of data rates, simplified multi-rate transceiver implementation, and relaxed transmit laser line-width requirements at low data rates.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
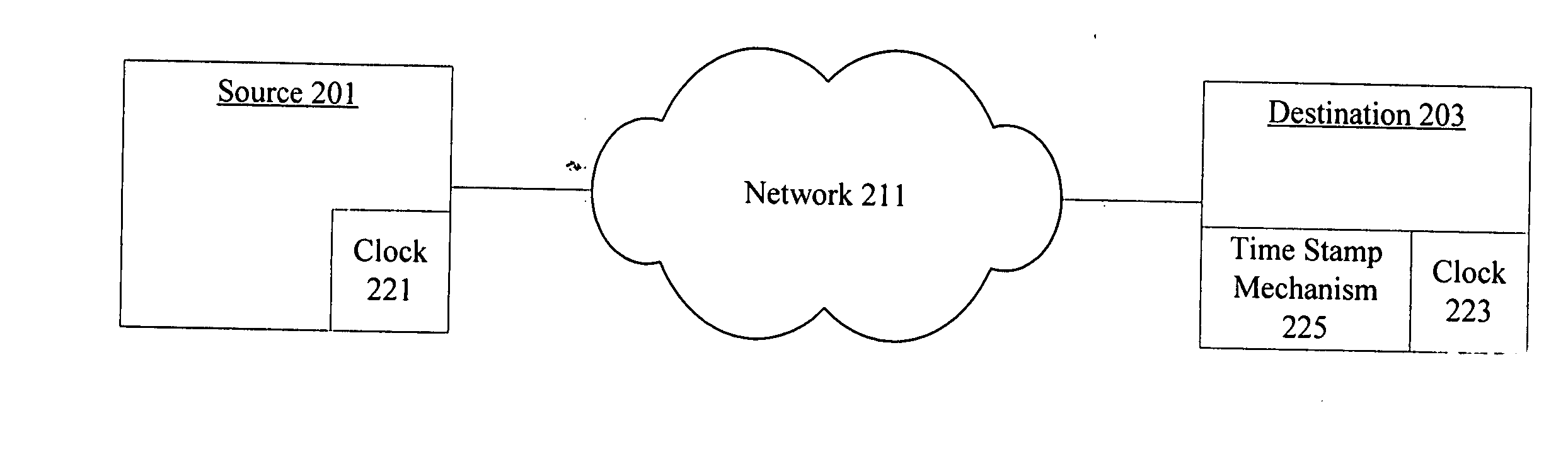
Methods and apparatus for determining reverse path delay
According to the present invention, methods and apparatus are provided for determining components of a round trip time (RTT). A source node sends data to a destination node. The destination node inserts a timestamp into an acknowledgment and sends the acknowledgment back to the source node. The source node determines the RTT from its own measurements and estimates reverse path delay by comparing timestamps to expected timestamps. Considerations for destination node timestamp speed differences are provided.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
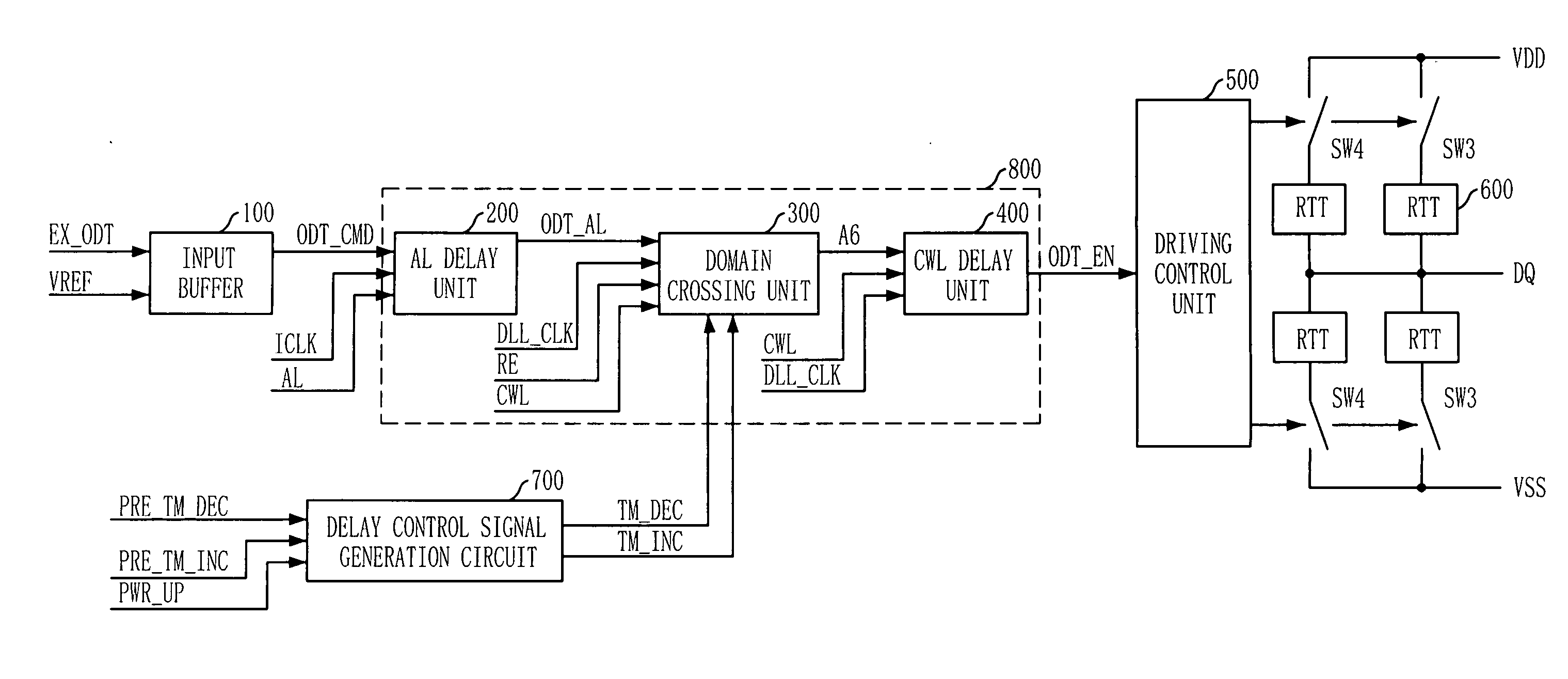
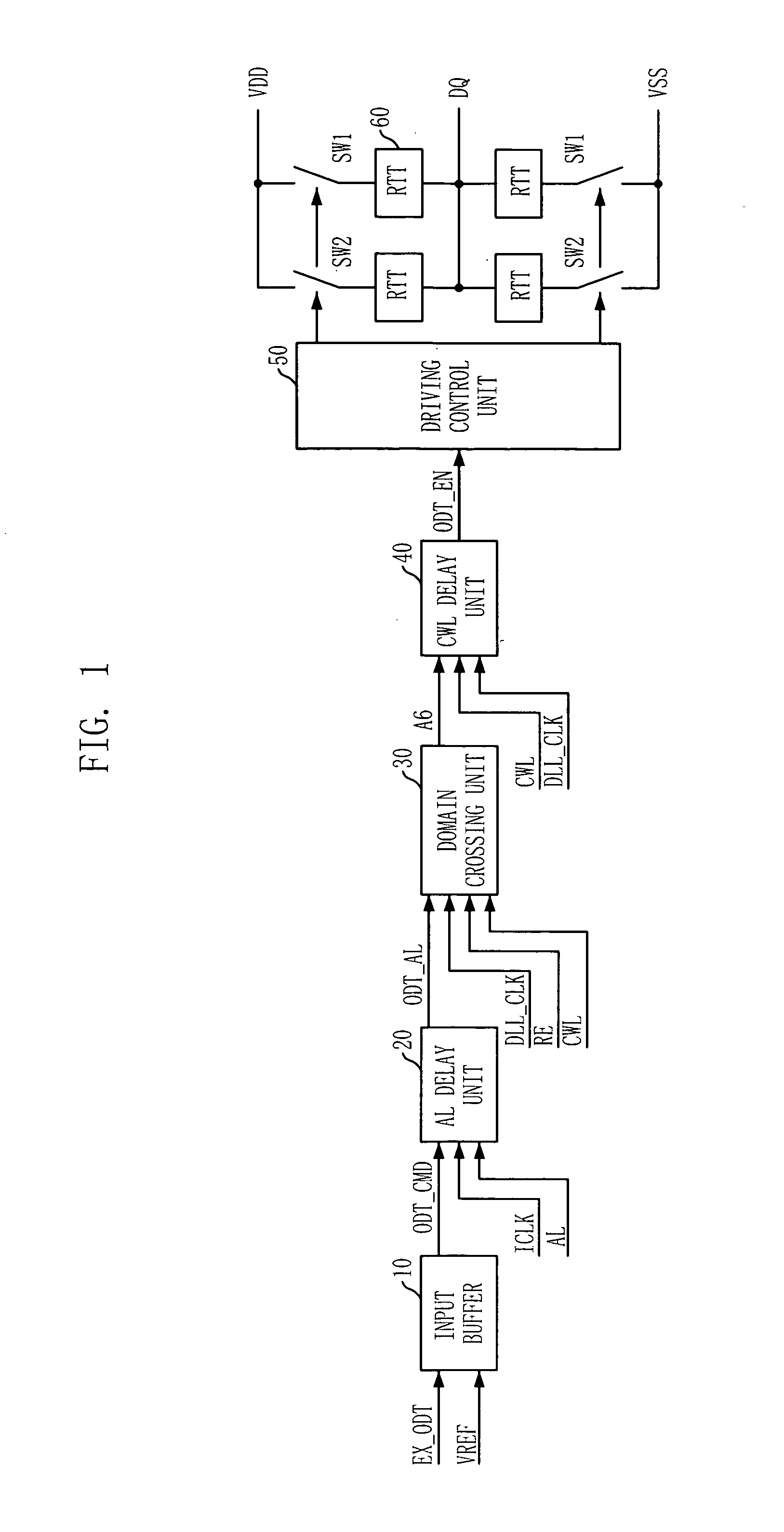
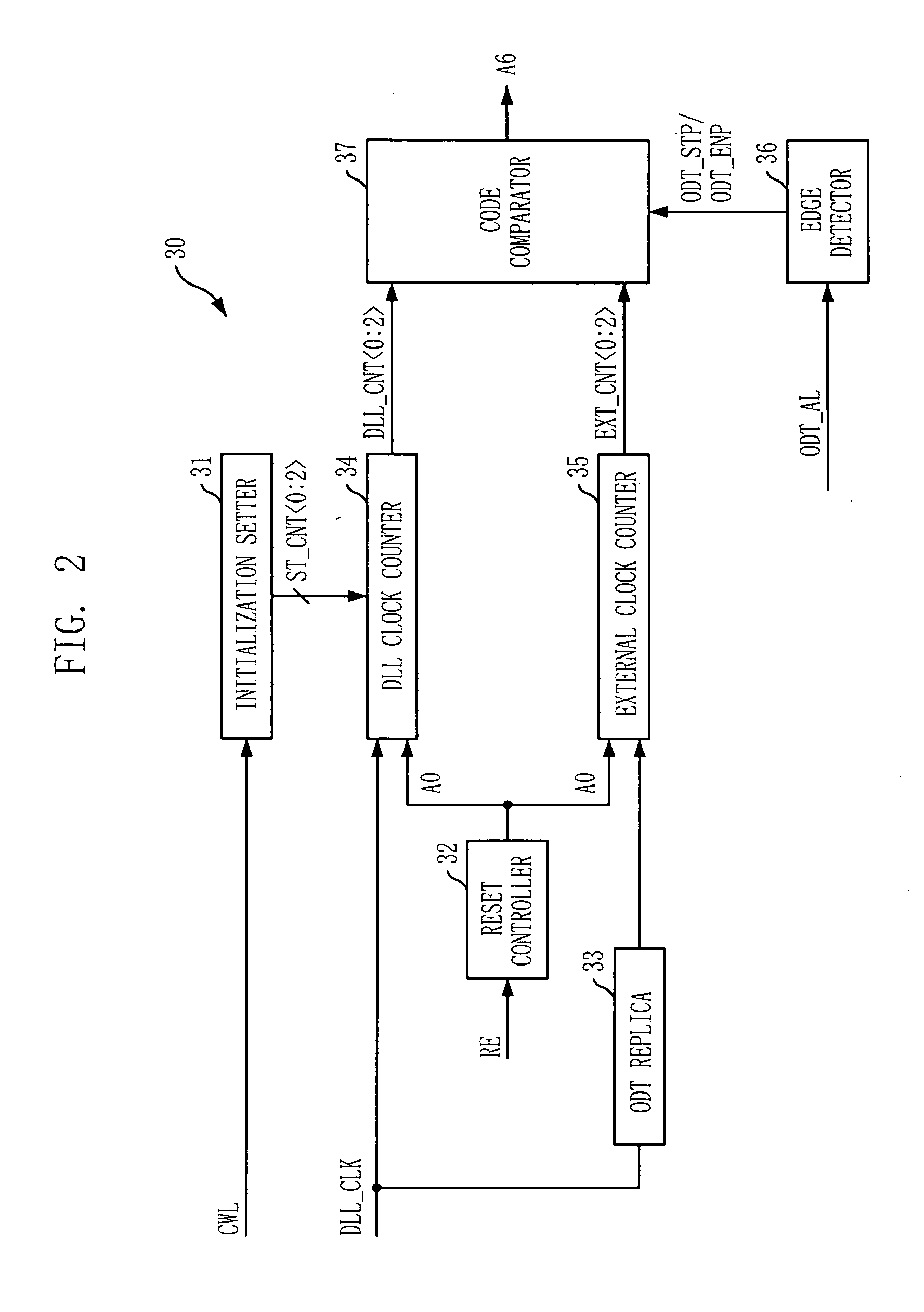
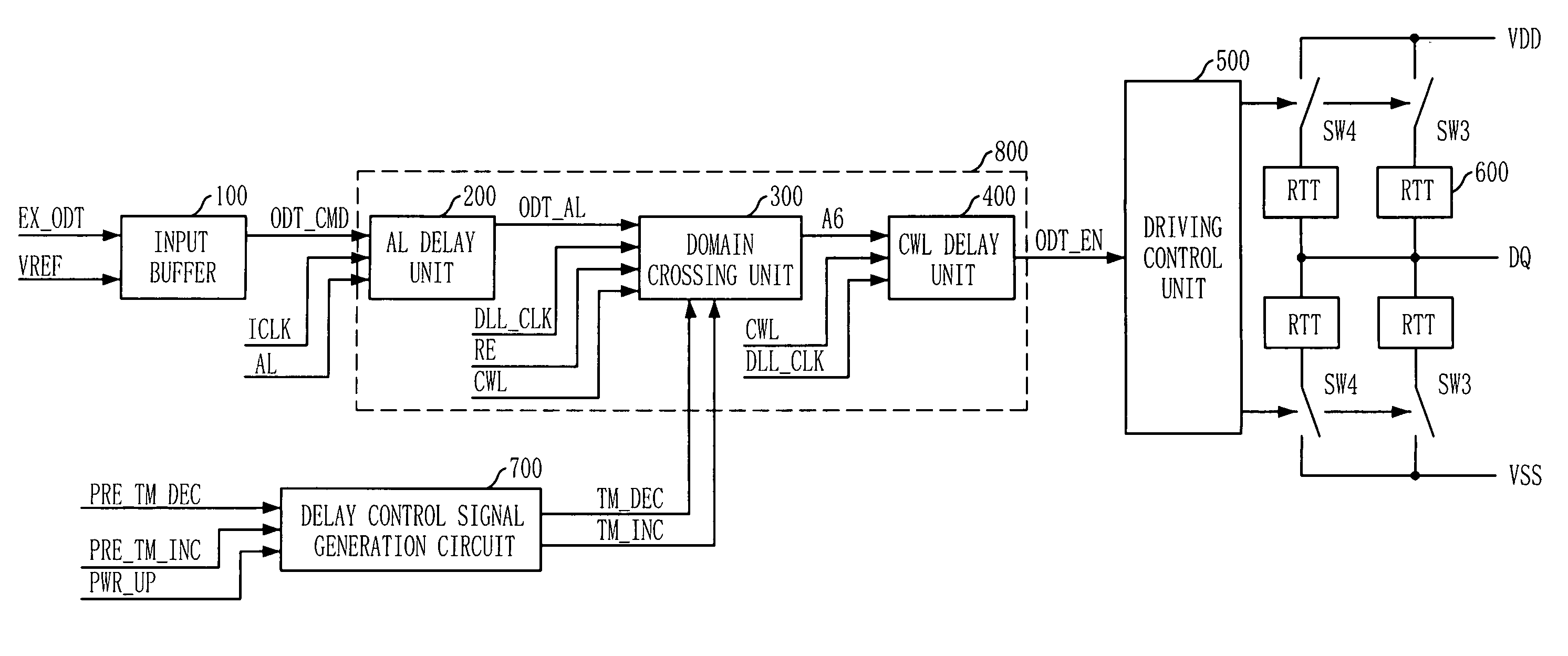
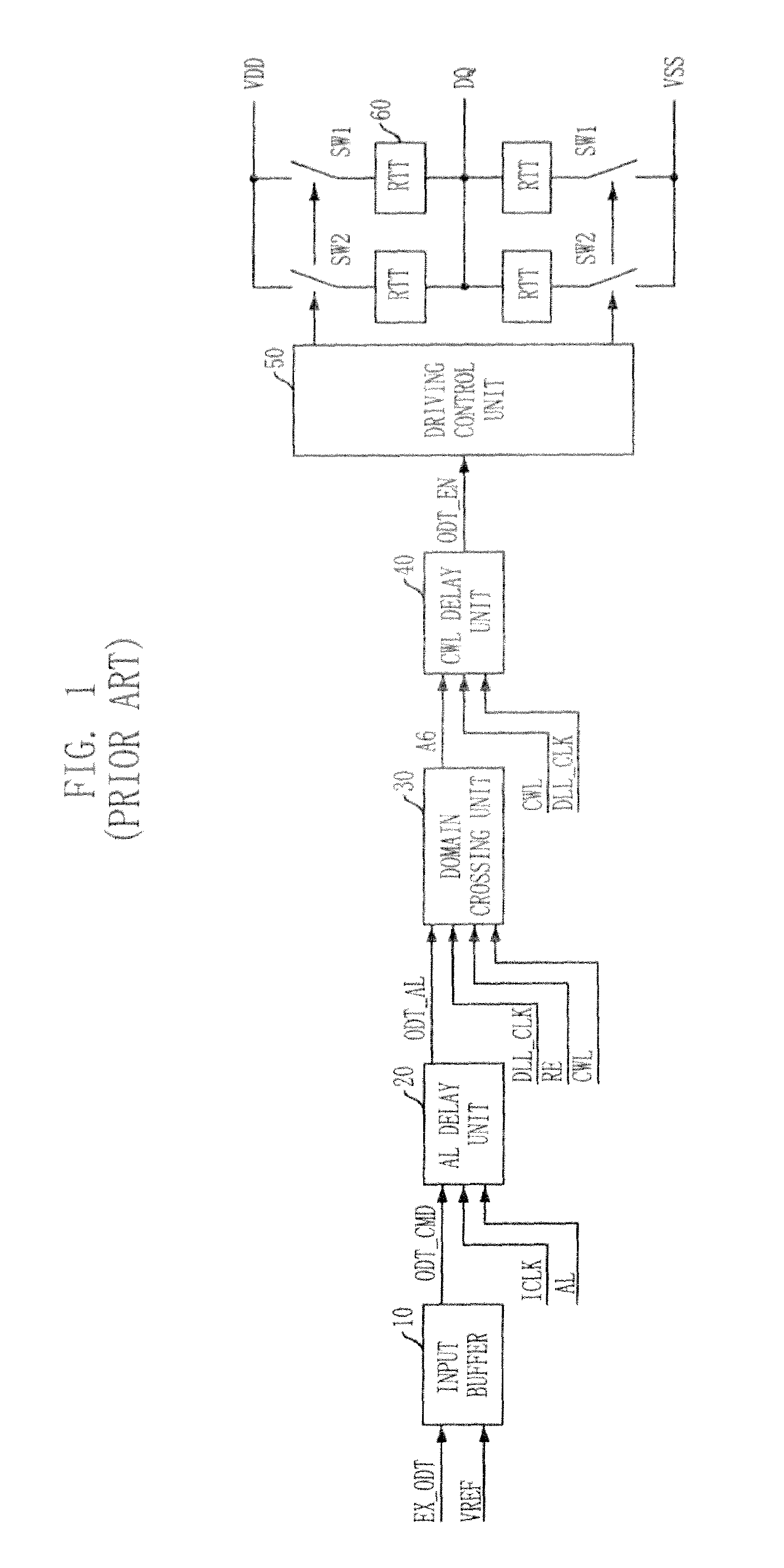
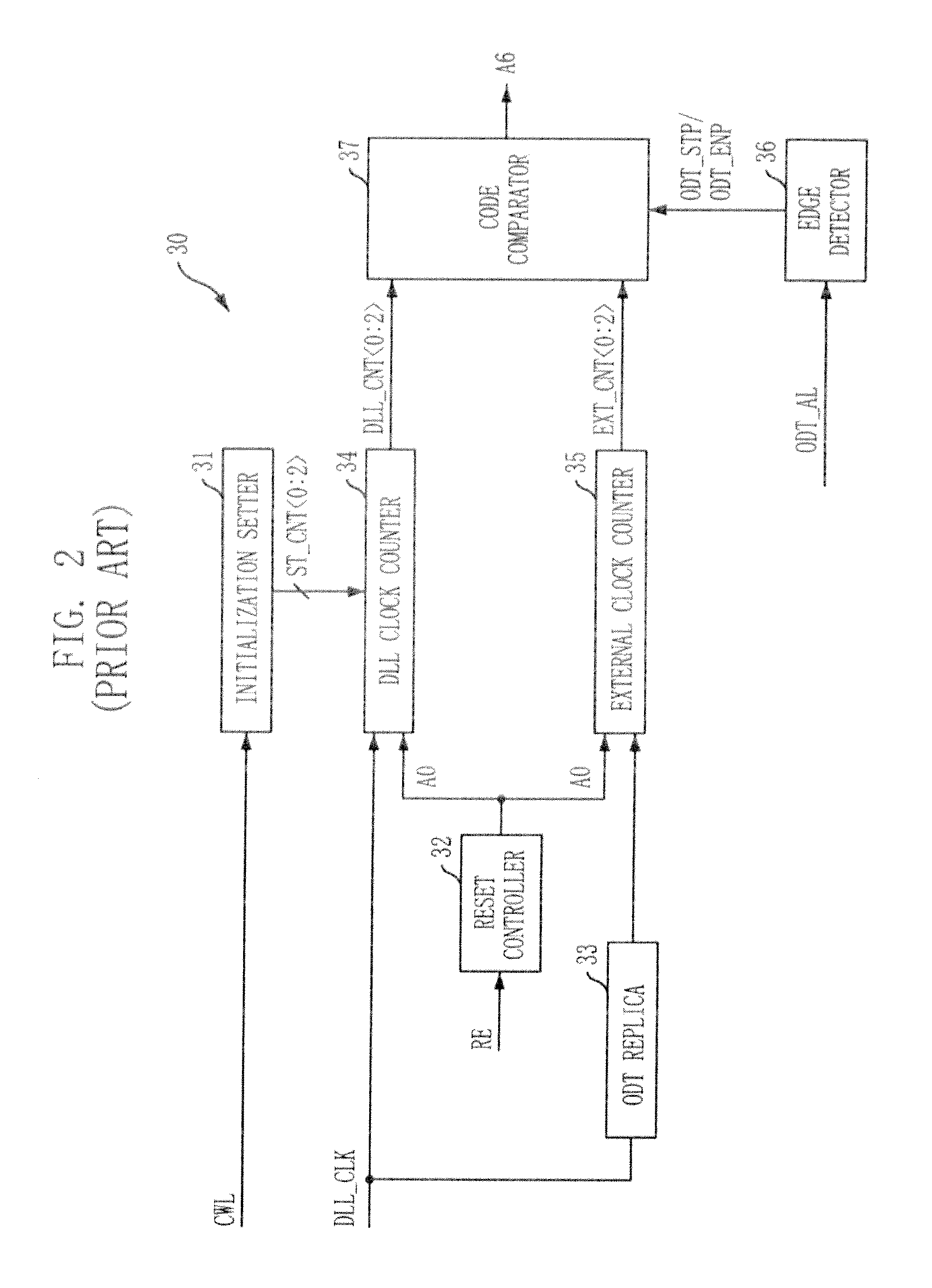
Semiconductor memory device having on-die-termination device and operation method thereof
ActiveUS20090016124A1Easy to fixLogic circuit coupling arrangementsDigital storageControl signalDelay-locked loop
A semiconductor memory device is capable of stably securing an on-die-termination (ODT) latency in spite of PVT variations and various operating speeds. The semiconductor memory device includes a plurality of termination resistors connected to an output pad in series and parallel, a drive controller, a delay path, and a delay control signal generator. The drive controller activates / inactivates the plurality of termination resistors in response to a driving control signal. The delay path delays a termination command by a delay time corresponding to an on-die-termination (ODT) latency to output the driving control signal, wherein the termination command is converted into a delay locked loop (DLL) clock domain signal. The delay control signal generator controls a conversion point of the termination command into the DLL clock domain signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method and apparatus for extending communications over USB
InactiveUS20060020736A1Long processEnergy efficient ICTMultiplex communicationEngineeringSignaling protocol
Method and apparatus are described for improving information transfer over USB. In one approach, hub-based extension is realized wherein power is distributed using auxiliary wiring distinct from signal and power wiring present in conventional USB cabling. Additional signals allow optimization of power distribution for powering attached devices, and for detecting and handling illegal connection configurations. In another approach, improvements are realized through use of alternative signaling techniques which eschew reflective and high-speed common-mode signaling. Described are various configuration, media and signal-protocol combinations, including implementations containing embedded hubs. Methods ensuring reliable system behavior are also described, including determination of extension path delay and use of topology-enforcement hubs. In other approaches, further improvements are realized by allowing information exchanges to take longer than the nominal timeout period, or by allowing host requests to be delayed for transmission until the extended bus is available for use.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Centralized synchronization for wireless networks
InactiveUS7324559B2Undo distortion effectAccurate samplingSynchronisation arrangementFrequency-division multiplex detailsRadio networksDigital radio
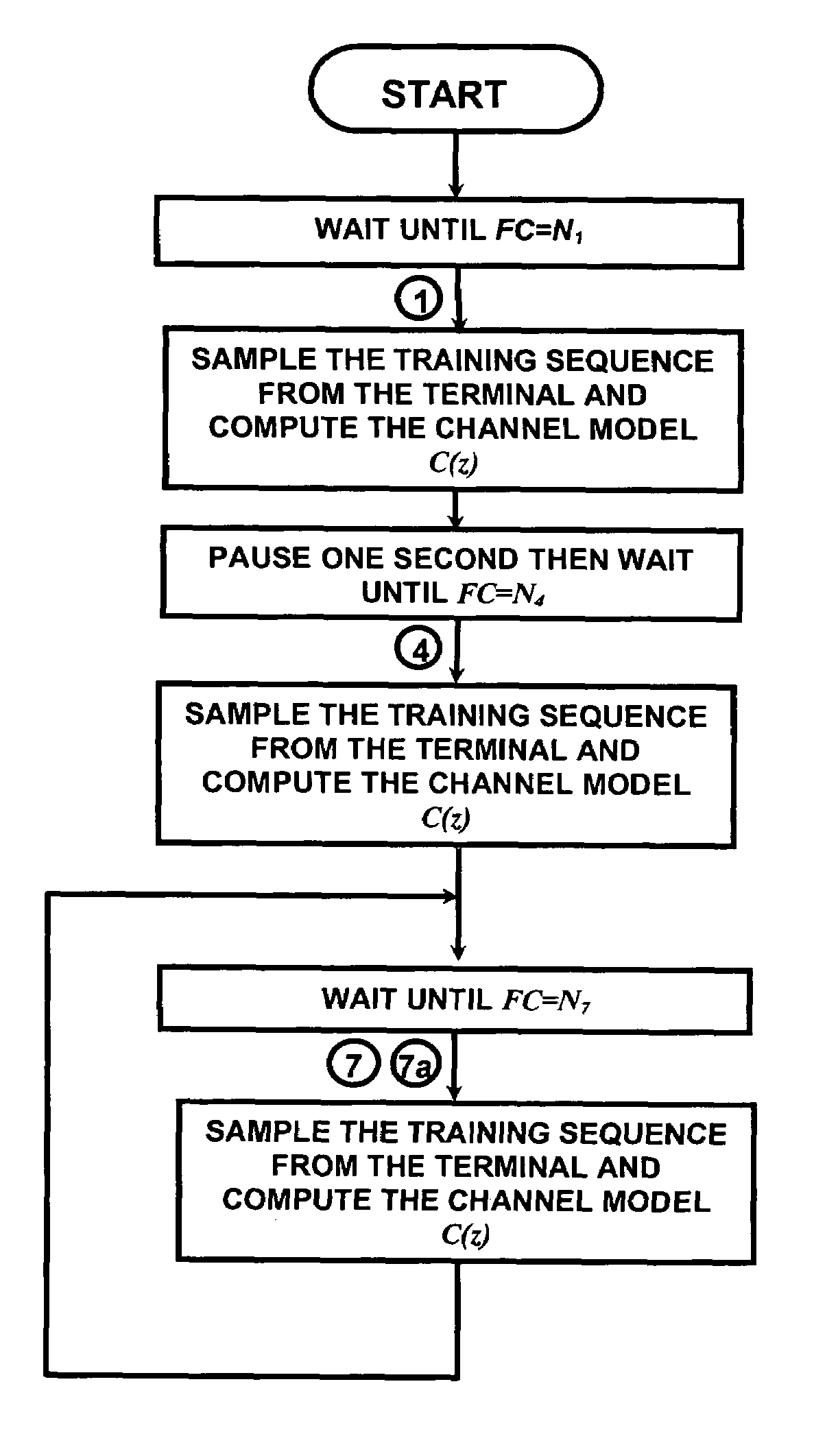
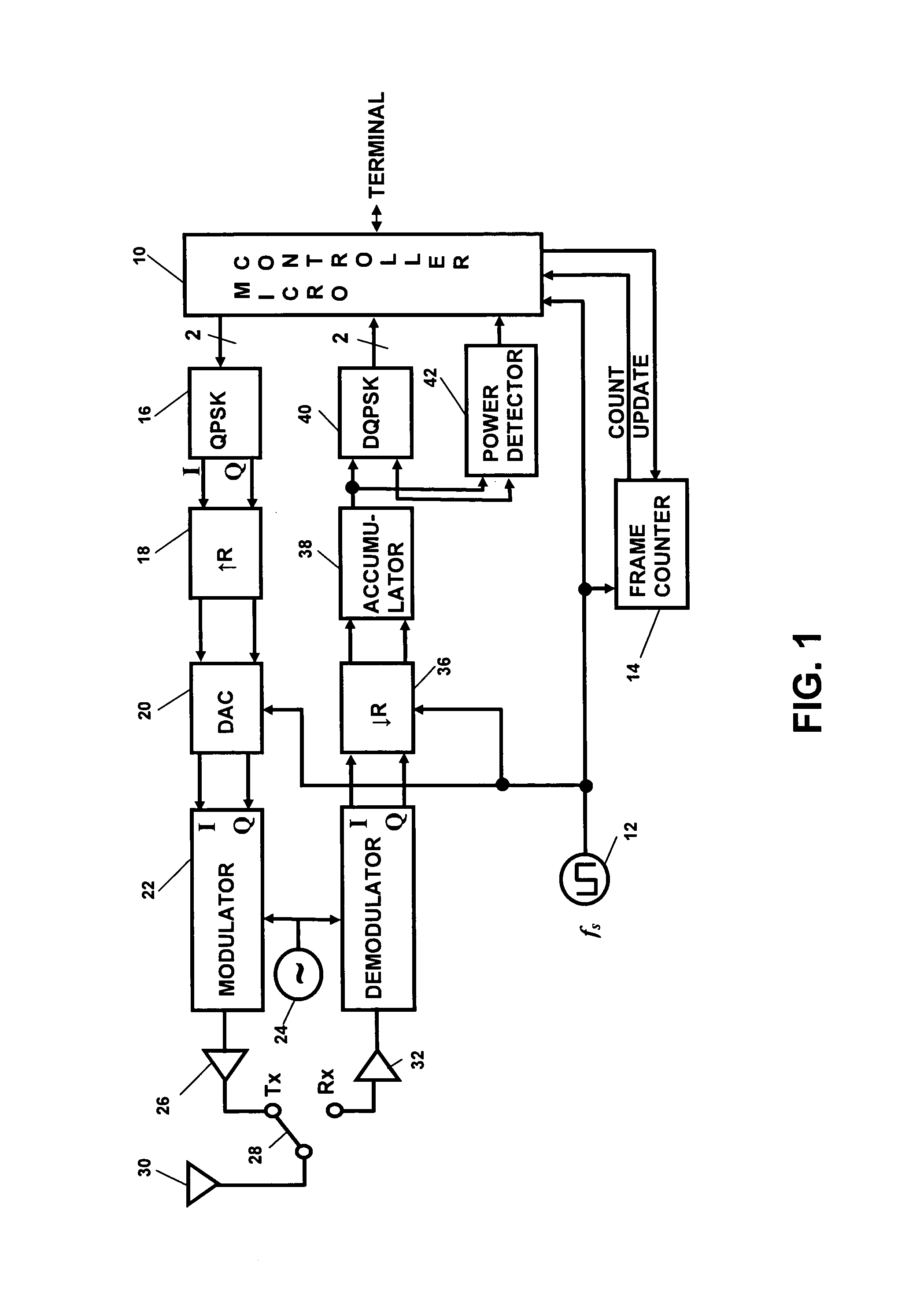
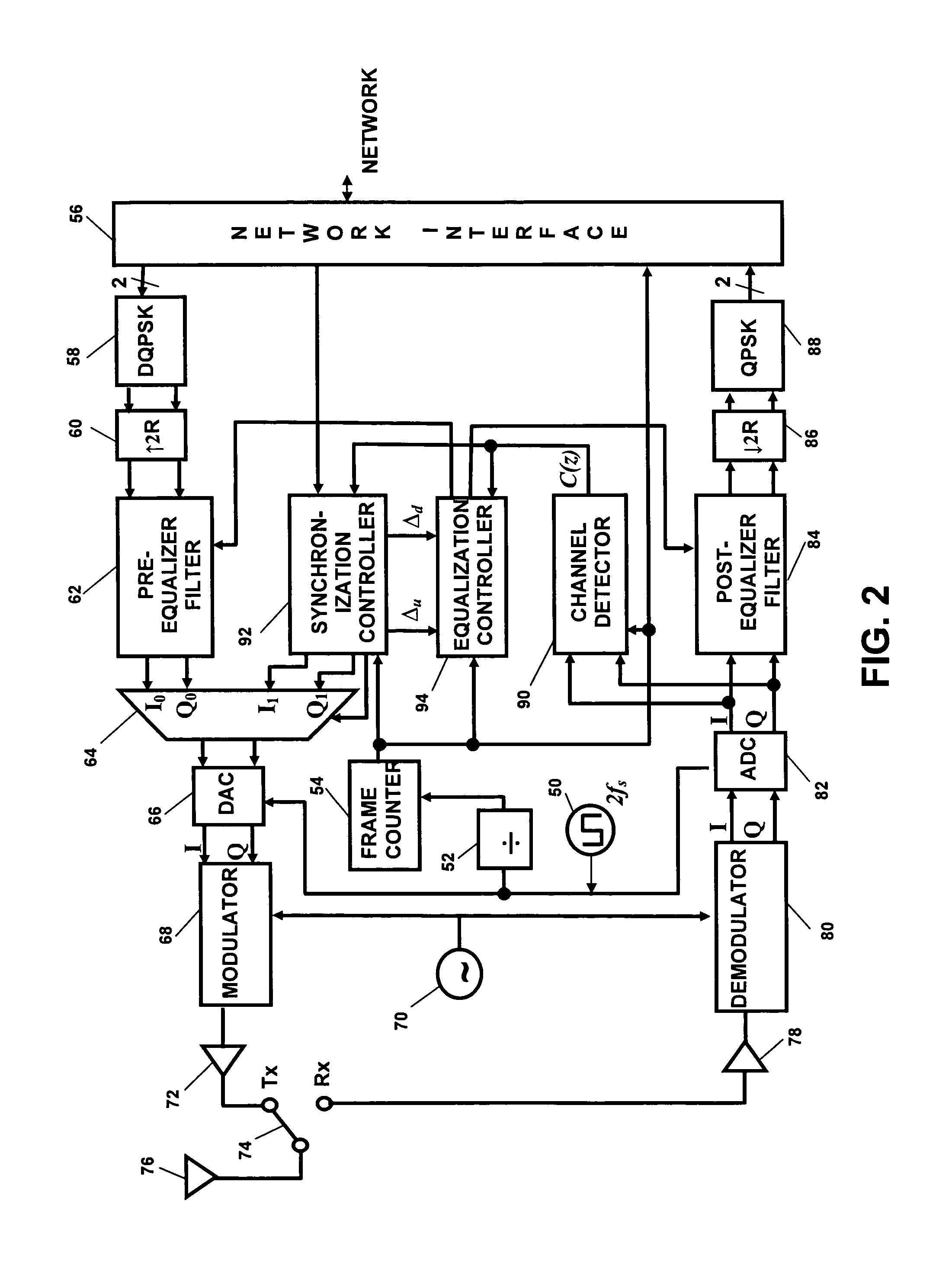
This invention synchronizes the sample clocks of an entire wireless network from a single central base station. Unlike a conventional digital radio network where every terminal must have a synchronization circuit in its receiver to adjust the sample clock, each of the radio terminals in this network is clocked from an independent free-running oscillator. For each terminal, the base station learns the frequency and phase of the oscillator by exchanging a special set of signals: first a vernier signal to determine the initial time and frequency offset, and then an early-late signal to track changes in the oscillator. Once the base station is synchronized to the terminal's oscillator, it can determine the absolute path delay between itself and the terminal and correct for the delay using an equalizer. Signals received from the terminal are corrected after the signal arrives at the base station. Signals sent to the terminal are corrected within the base station before they are transmitted so they arrive at the terminal at the precise time that the terminal's free running oscillator takes a sample.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
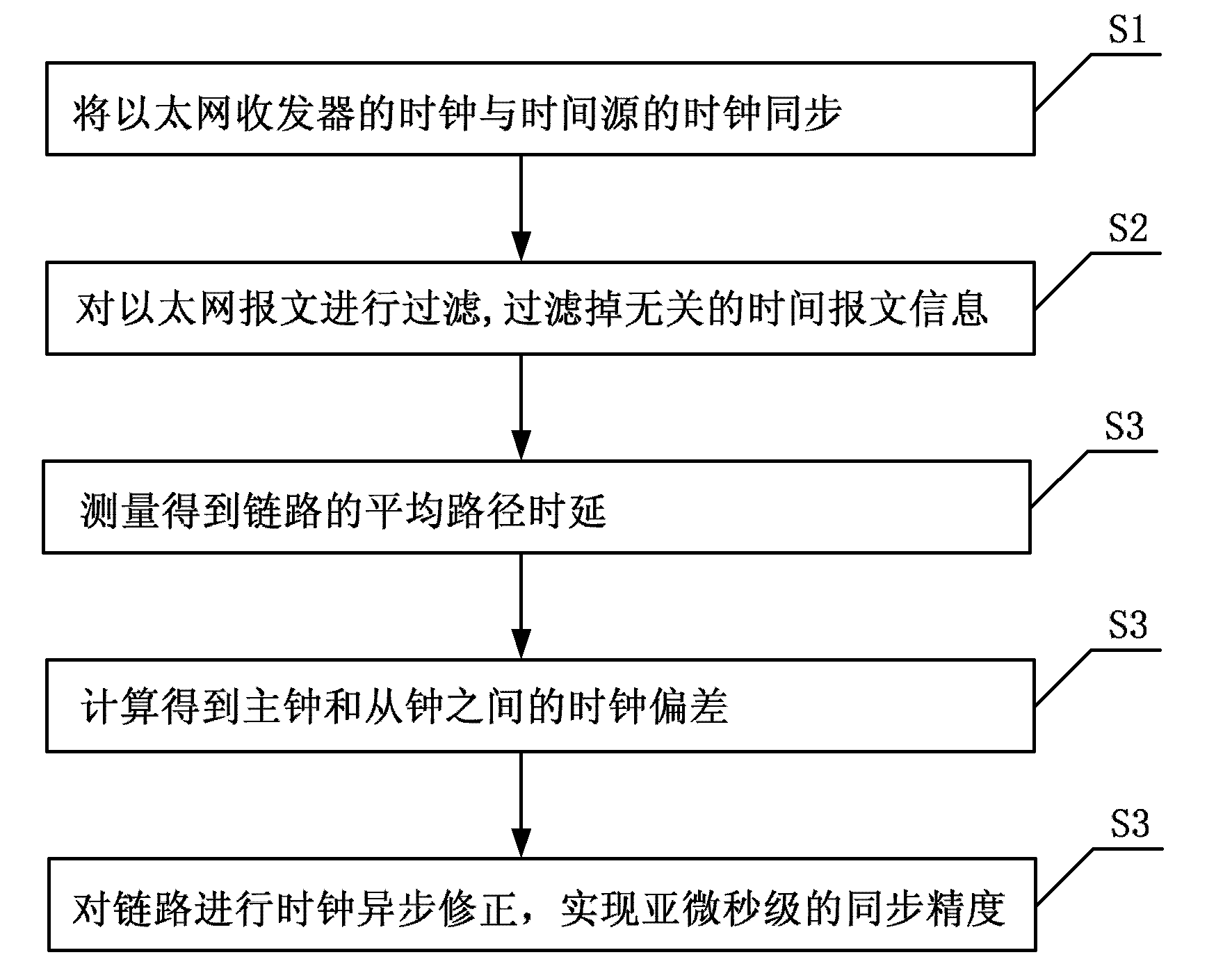
Method for realizing sub-microsecond synchronization accuracy based on PTP (Precision Time Protocol)
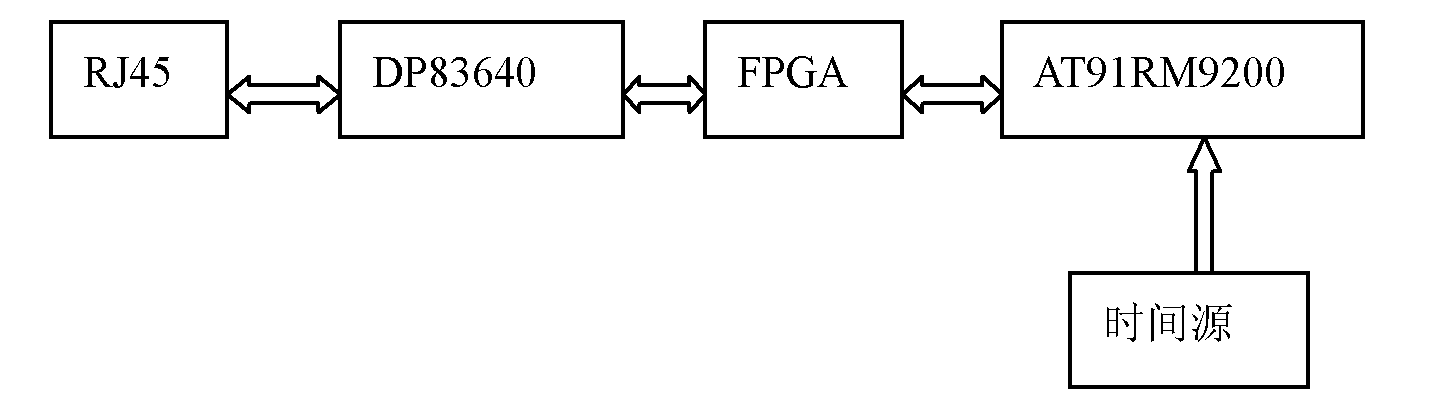
The invention relates to a method for realizing sub-microsecond synchronization accuracy based on a PTP (Precision Time Protocol), belonging to the technical field of communication; in order to obtain high-accuracy synchronization efficiency and save hardware investment cost, the method comprises the following steps: before a master time sends synchronization messages, synchronizing a clock and a clock source of an Ethernet transceiver; obtaining average path delay of links by a delay request information packet delay measuring mechanism or measuring a waiting delay information packet delay measuring mechanism; and performing asynchronous correction on the links so as to realize sub-microsecond synchronization accuracy. In the method, the DP83640 Ethernet transceiver is adopted, network message time stamp can be exactly obtained, the PTP protocol on an AT91RM9200 platform is realized, and sub-microsecond synchronization accuracy can be realized. Via test, the synchronization accuracy can be up to 100ns; and the whole system is low in cost, excellent in openness and expandability, and easy to implement.
Owner:GZH BEIDOU TECH GRP
Systems and methods for testing the performance of and simulating a wireless communication device
InactiveUS7508868B2Exact reproductionTest accuratePolarisation/directional diversitySupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsControl signalData file
A system abstracts channel information from field data gathered in actual wireless communication system environments. The abstracted data is then transformed into control signals or programming codes that can be used to control channel simulators so as to recreate the field conditions, including path loss, slow fading, fast fading, path delay, fading power spectral density with and without line-of-sight (LOS), and different kind of handoff scenarios, such as soft, softer, intra-band hard, inter-band hard handoffs. The system thus can accurately simulate a realistic wireless communication link originated from multiple signal sources in different band channels and formed by multipath signal propagation. The simulated realistic wireless communication link can be condensed by selecting the most useful scenarios from its original field data files or modified by tuning its parameters as desired.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
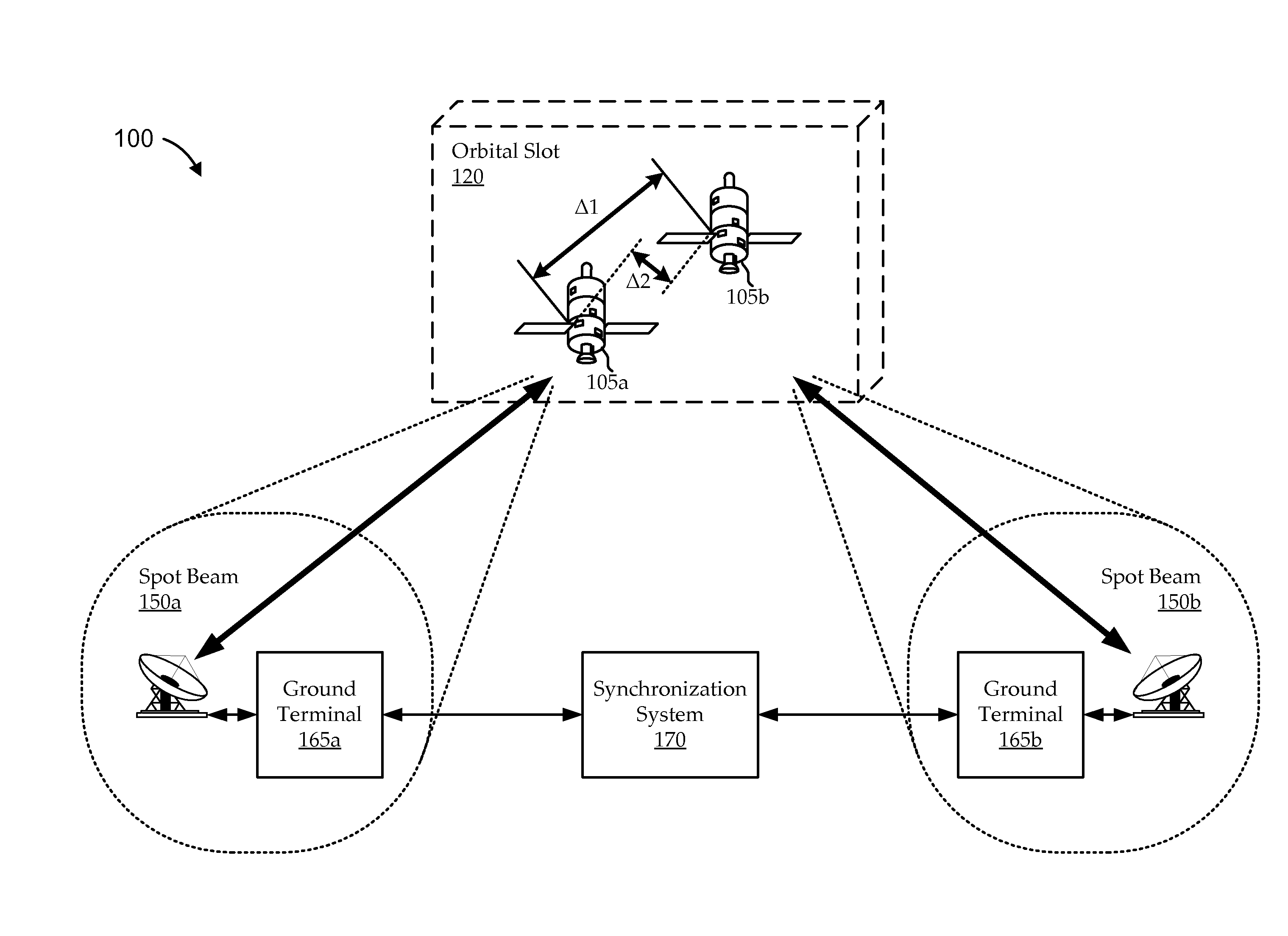
Tandem satellite frame synchronization
Systems and methods are described synchronizing communications frames and their respective time slots for satellite communications architectures having multiple satellites in the same orbital slot in such a way that addresses inter-satellite inter-beam interference. In some embodiments, the first and second satellites communicate with a respective number of ground terminals (e.g., gateway and user terminals) according to first and second satellite time slots, respectively. The satellites maintain relative positions in their orbital slot to manifest a maximum path delay difference between first and second path delays, the first path delay being between the first ground terminals and the first satellite, and the second path delay being between the first ground terminals and the second satellite. A synchronization system can offset the first satellite time slots from the second satellite time slots as a function of the maximum path delay difference.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Semiconductor memory device having on-die-termination device and operation method thereof
ActiveUS7663946B2Easy to fixLogic circuit coupling arrangementsDigital storageControl signalDelay-locked loop
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
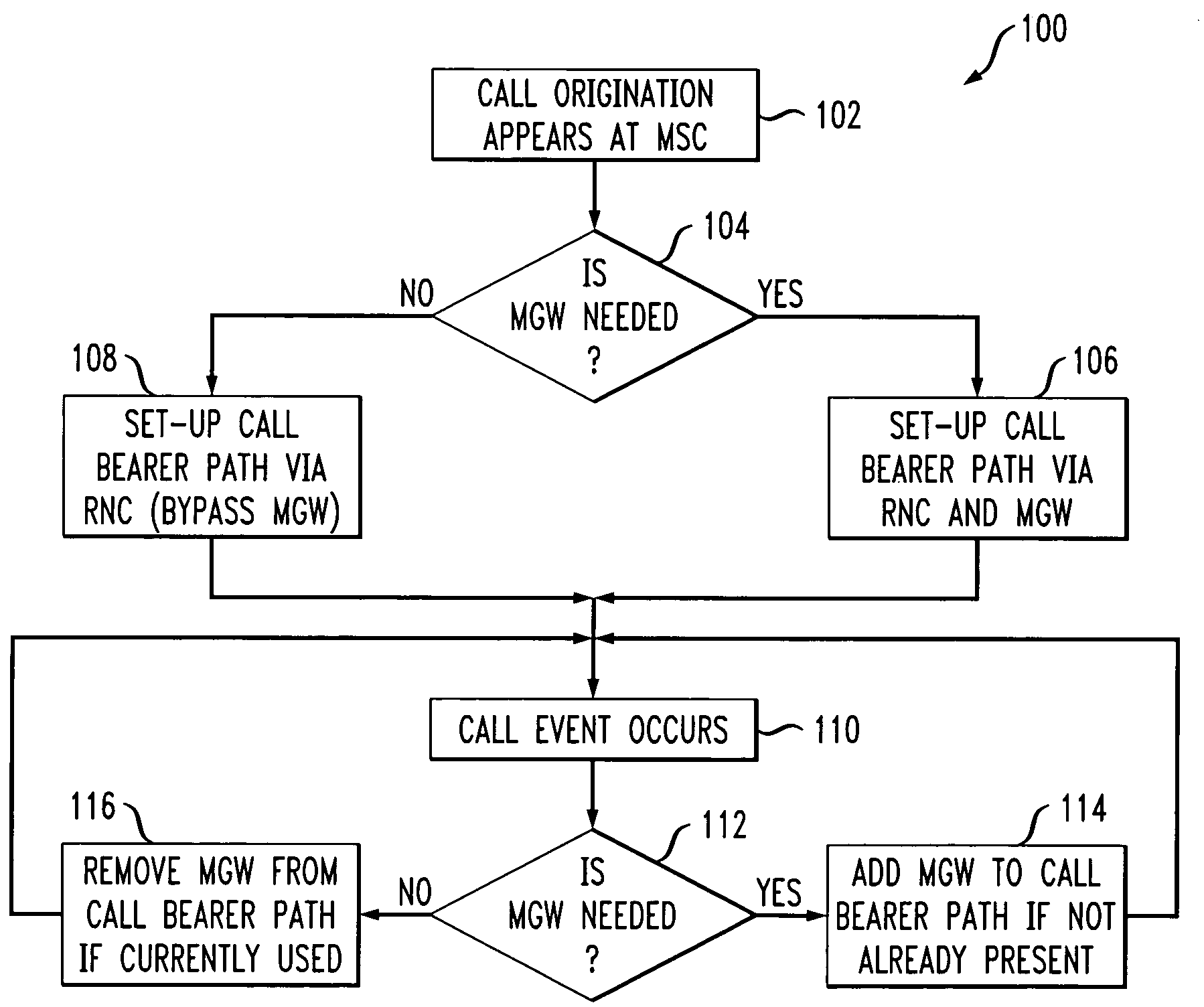
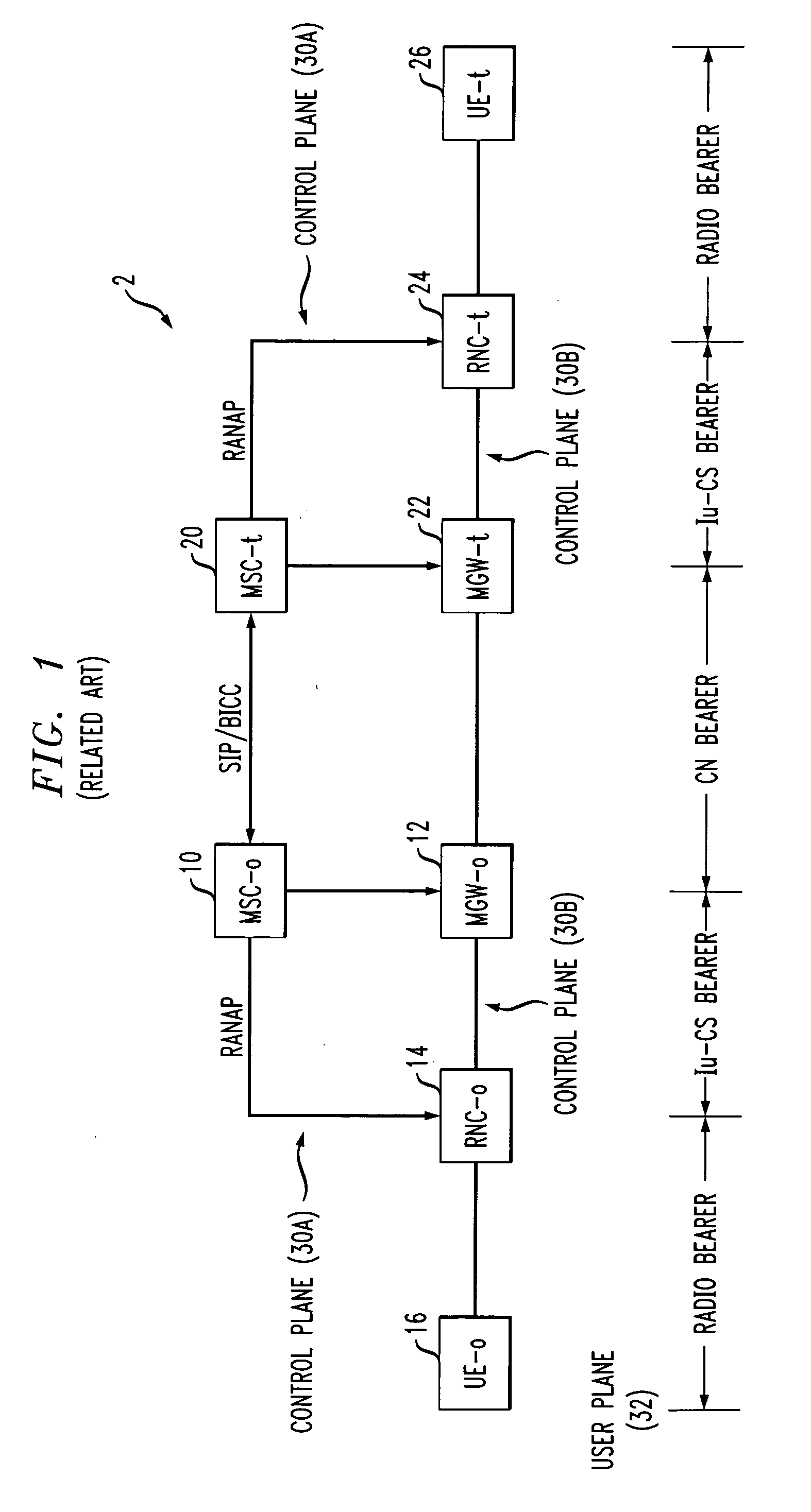
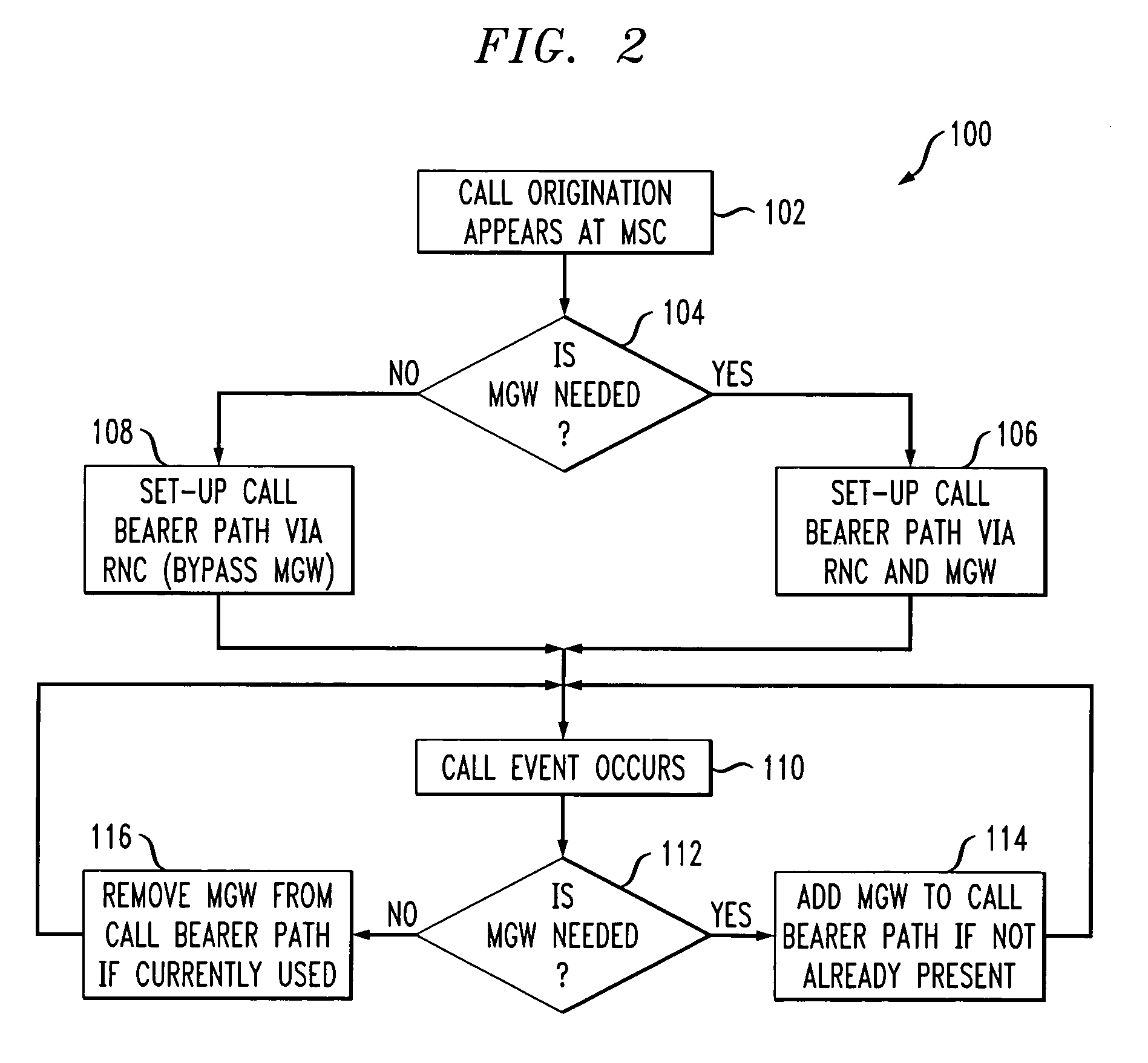
Method and system for bypassing media gateways in wireless networks
ActiveUS20080146208A1Low costControl is neededMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersWireless mesh networkComputer science
A call processing method and system in which the use of the MGW between the RNC and the peer party is limited to only certain situations. This invention uses RFC 3267 (AMR / IETF) on the RNC. This will avoid inserting a MGW context for framing conversion only. This invention provides an optimization that sets up calls from the RNC, thus avoiding the need for a MGW in the path for basic calls. With this optimization, the usage of DSP and packet resources and the number of MGW chassis, as well as bearer path delay, are all reduced.
Owner:RPX CORP
Communication device and communication method
InactiveUS20080008276A1Preferable communicationModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityTime correlationEngineering
There is provided a radio communication device having a high quality and accuracy regardless of fluctuation degree of the transmission path characteristic. The radio communication device estimates the fluctuation speed of the transmission path characteristic from the time correlation of the reception signal, judges the diversity technique used between the communication devices from the estimated value, and feeds back the judgment information so as to switch the diversity between the communication devices, thereby increasing the diversity gain. The feedback information is minimized by defining a correspondence table. Moreover, diversity switching is performed at a timing considering a control delay and a propagation path delay so as to prevent an instantaneous disconnection of the communication.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Remote estimation of round-trip delays in a data network
Disclosed is a technique for data network congestion diagnosis using remote estimation of round-trip delays. A monitoring node transmits test messages between network nodes and measures the transit times between when the test messages are transmitted from, and when they return to, the monitoring node. A path delay between network nodes is determined based on the measured time delays. The techniques for determining network path delay are also utilized in conjunction with a three phase test procedure for diagnosing network congestion problems. Due to various network topologies and routing tables, certain confirmatory checks may be required to determine whether the procedures of the first or second phase test procedures are appropriate for particular path segments. Further, queuing delays may be determined by subtracting traffic independent delays from the measured transit times of the test messages, and such queuing delays may be used to determine the path delays. Such traffic independent delays may be determined during periods of low network traffic.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
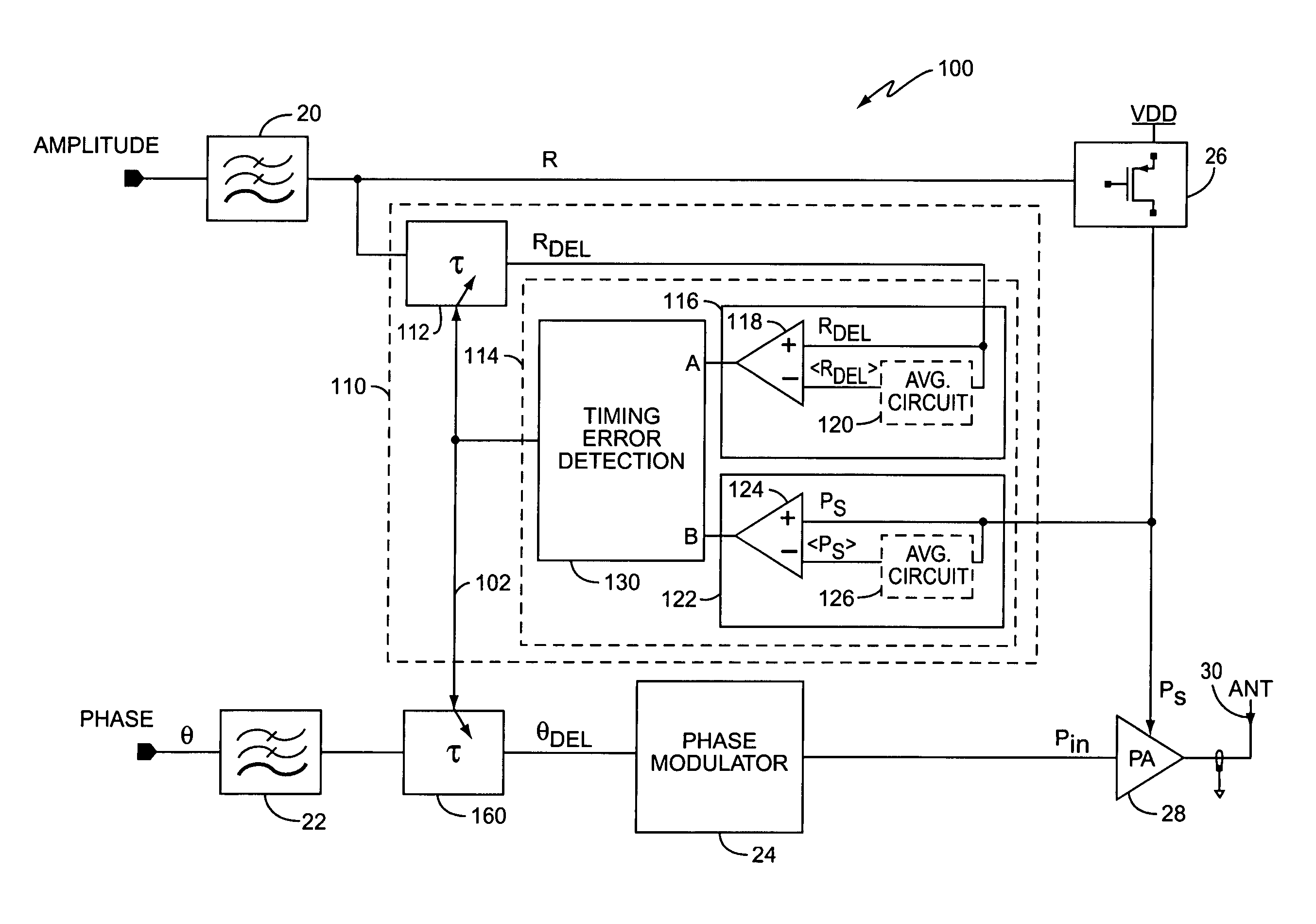
Delay calibration in polar modulation transmitters
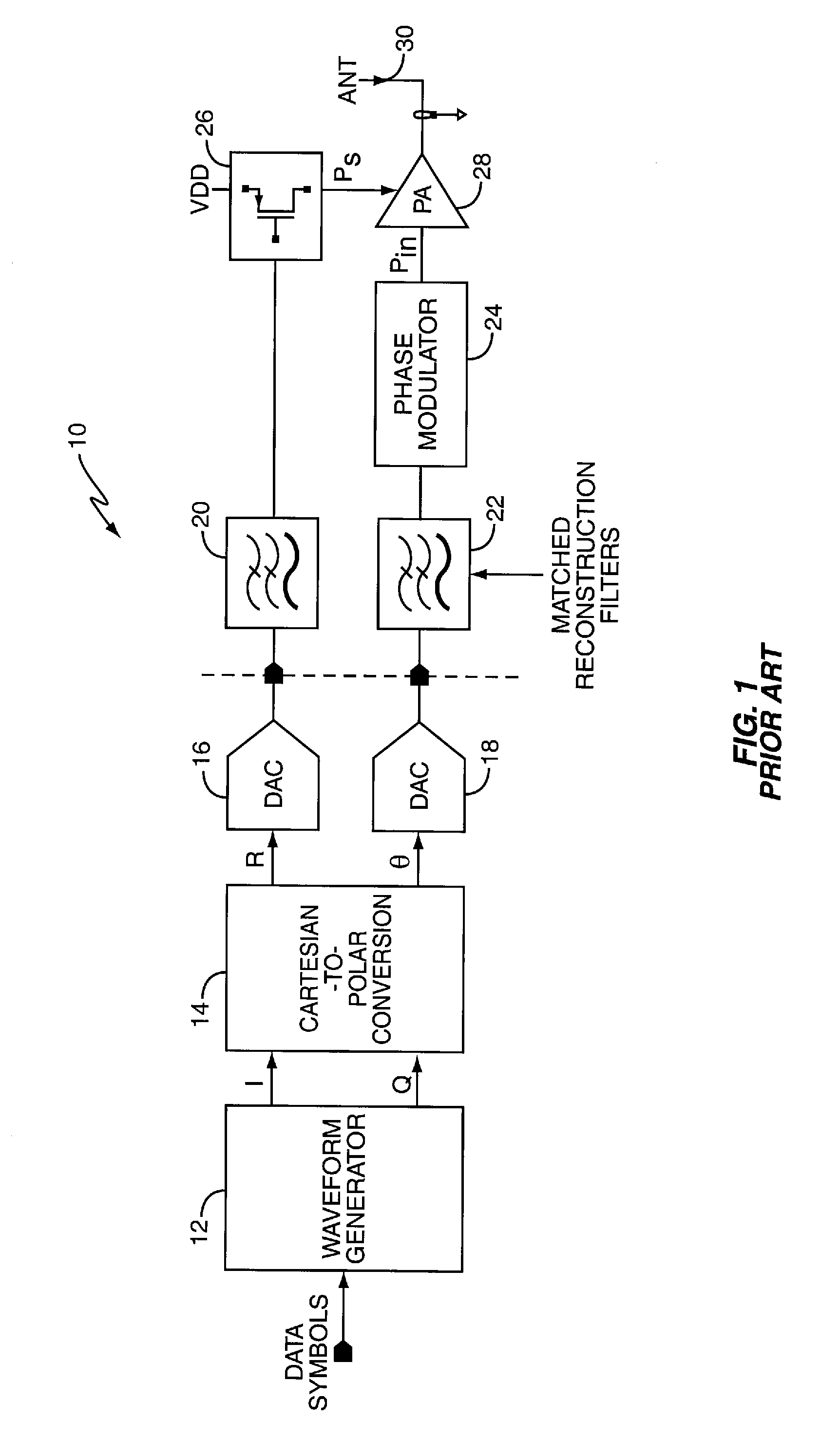
ActiveUS7359680B2Modulated-carrier systemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierEngineering
A method and apparatus for dynamically compensating for delay mismatch between a supply signal and an input signal of a power amplifier in polar modulation transmitters. One exemplary polar modulation transmitter according to the present invention comprises a power amplifier, a phase modulator, a regulator, a delay tracking circuit, and a delay circuit. The phase modulator derives the amplifier input signal responsive to one or more phase signals, while the regulator derives the amplifier supply signal responsive to an amplitude signal. Based on the amplitude signal and the amplifier supply signal, the delay tracking circuit tracks an observed amplitude path delay. The delay circuit adjusts a path delay associated with the phase signal, responsive to the observed amplitude path delay, to compensate for the delay mismatch.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
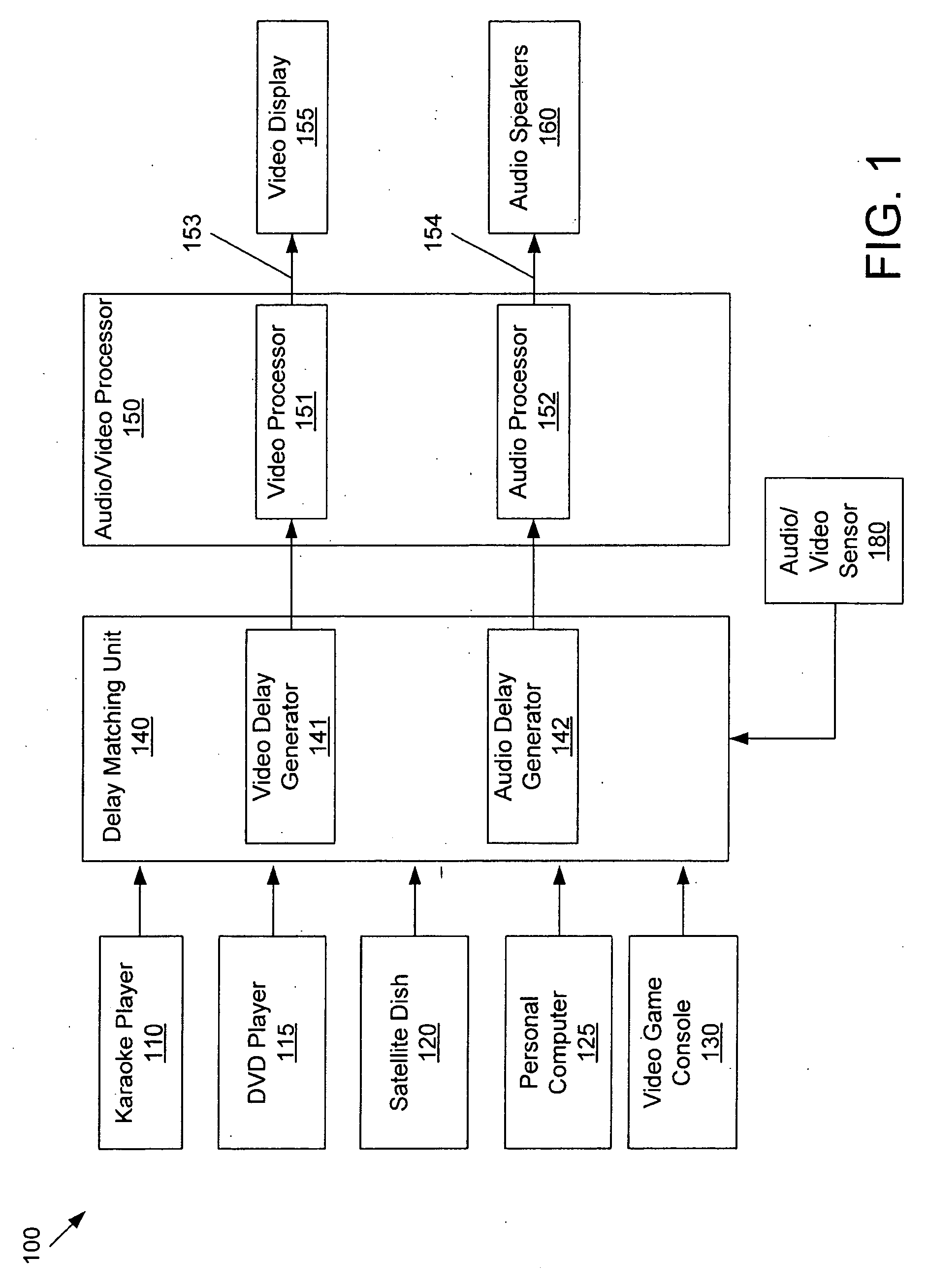
Delay matching in audio/video systems
ActiveUS7636126B2Television system detailsDifferential synchronisation source lockingAudio frequencyComputer science
An audio / video system comprises an audio signal processing path having an audio path delay and a video signal processing path having a video path delay. The audio path delay may be different from the video path delay. The audio path delay and / or the video path delay may change, for example because of replacement of a component within the audio signal processing path or the video signal processing path. Delay matching (synchronization) in the audio / video system comprises adjusting the audio path delay to be substantially equal to the video path delay. Matching the audio path delay to the video path delay generally includes adding delay to the signal processing path with the lesser delay.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com