Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
462results about "Logic circuit coupling arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
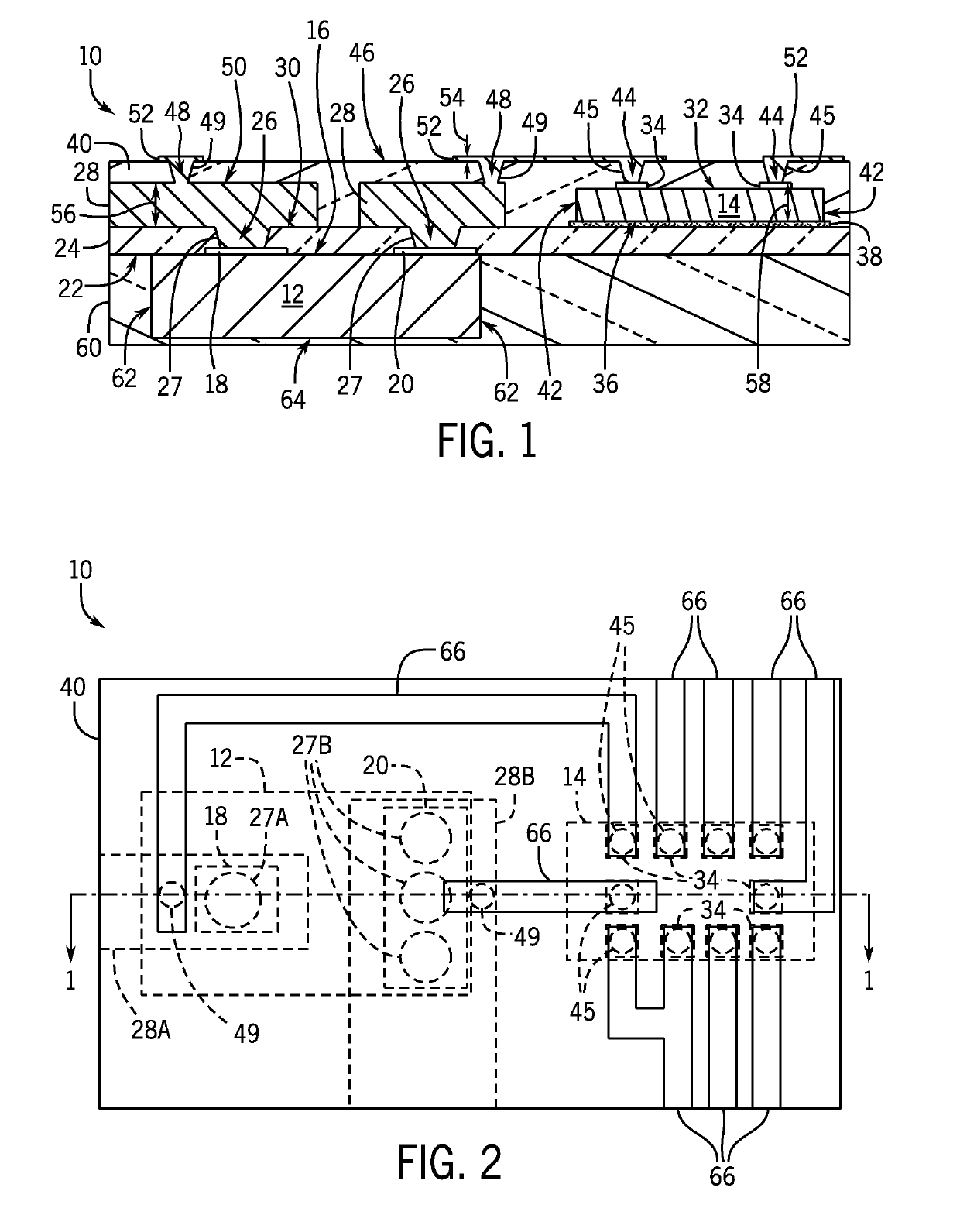
Embedded electronics package with multi-thickness interconnect structure and method of making same
An embedded electronics package and method of manufacture includes a support substrate, a power semiconductor component coupled to a first side of the support substrate, and a logic semiconductor component coupled to a second side of the support substrate, opposite the first side. A first insulating material surrounds the logic semiconductor component. A logic interconnect layer is electrically coupled to the logic semiconductor component by at least one conductive micro-via extending through a portion of the first insulating material. A power interconnect layer is electrically coupled to the power semiconductor component by at least one conductive macro-via extending through a thickness of the support substrate. The power interconnect layer is thicker than the logic interconnect layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
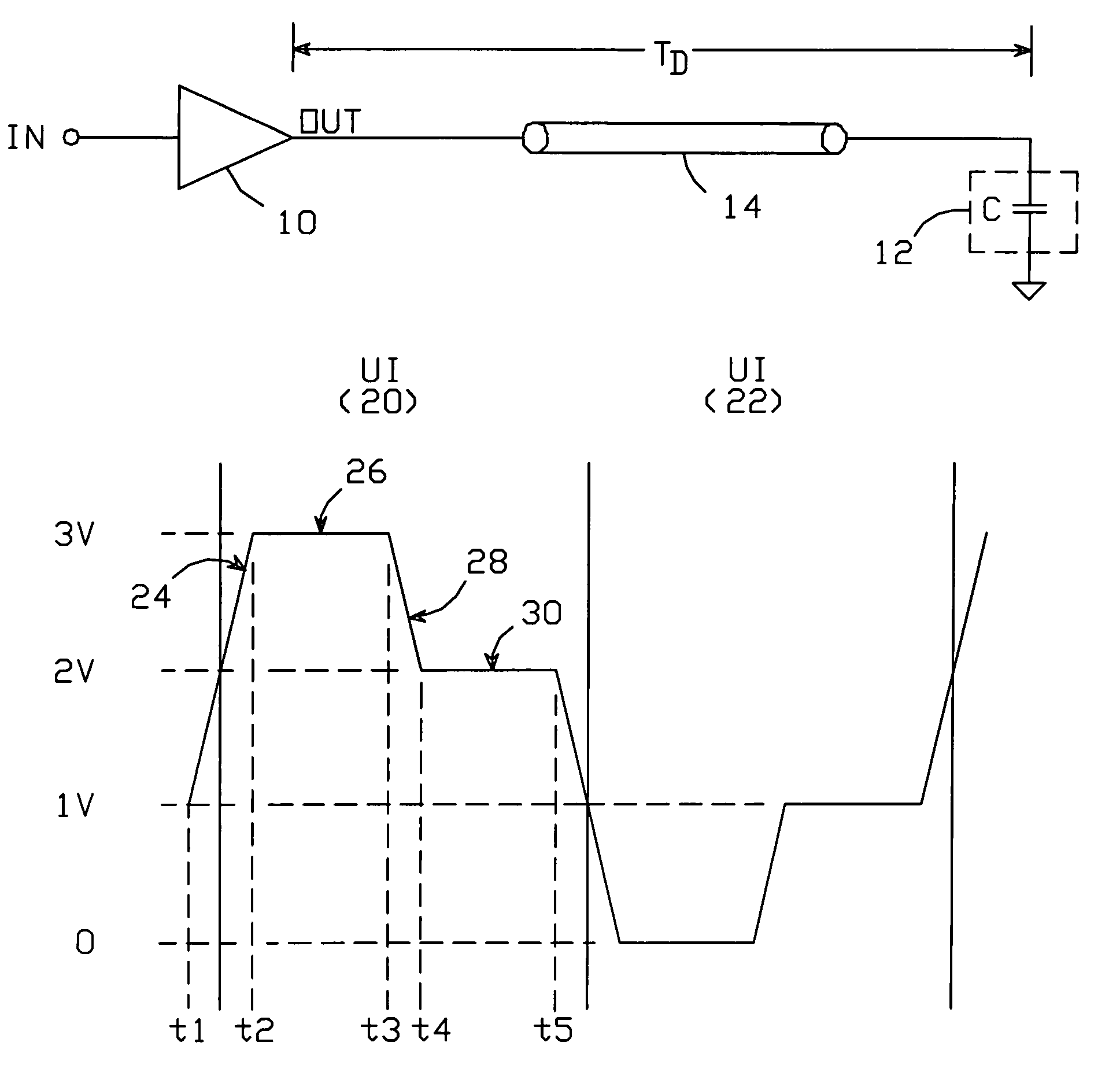
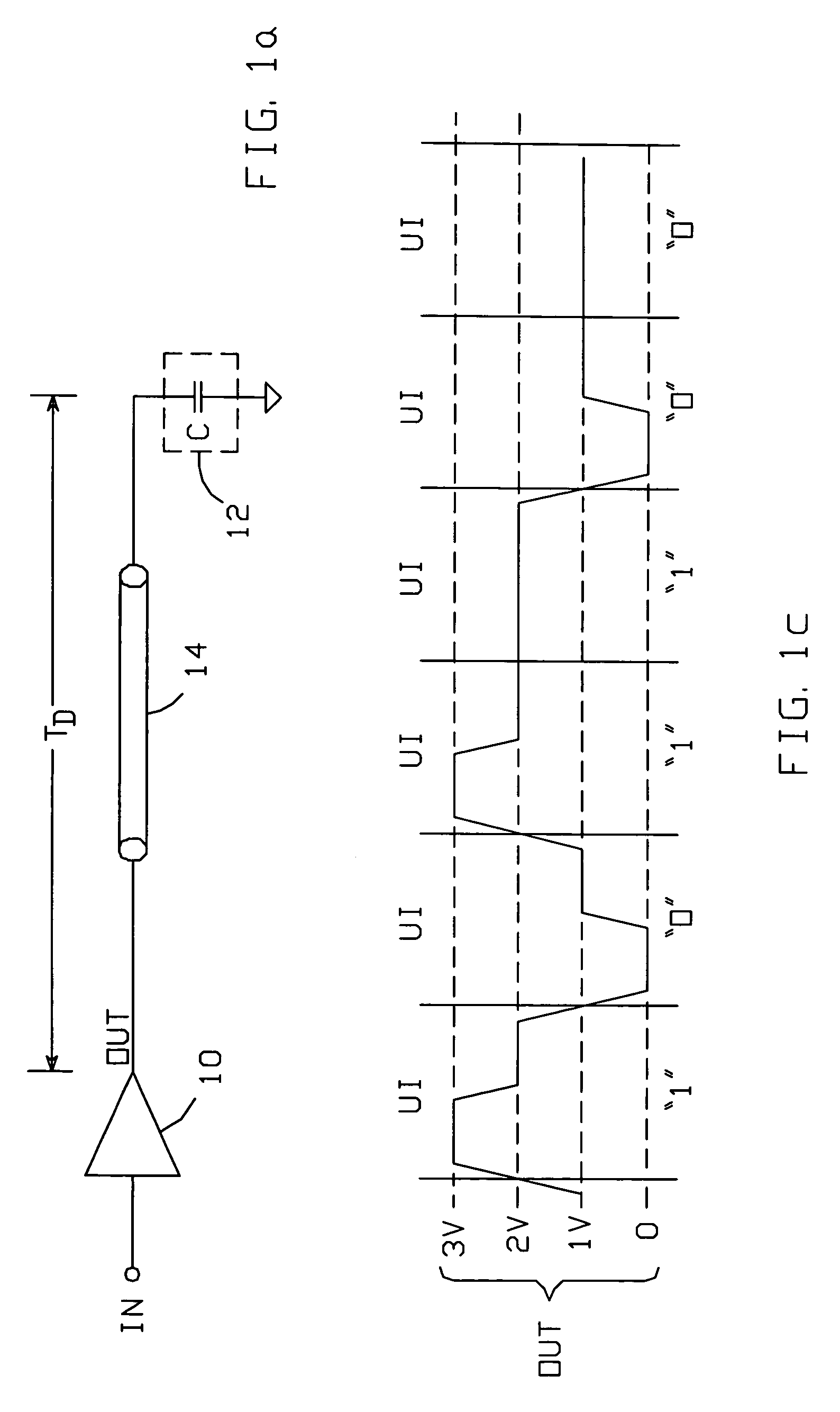
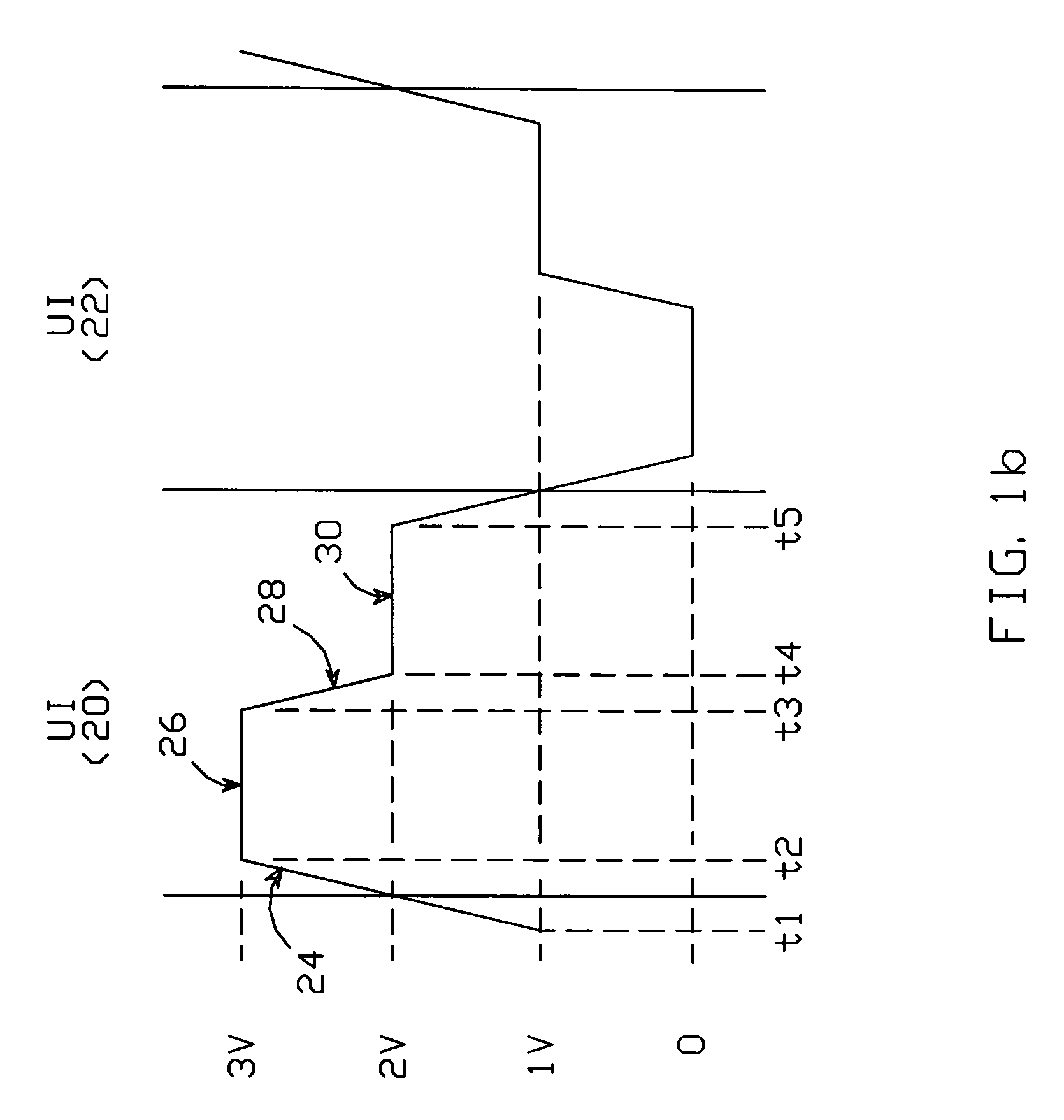
Output buffer with time varying source impedance for driving capacitively-terminated transmission lines
ActiveUS6980021B1Reduce impactFast chargingReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuit coupling arrangementsEngineeringLogic state
An output buffer for driving a capacitively-terminated transmission line produces a waveform which comprises a first portion during which the waveform transitions from a voltage V1 to a voltage V2; a second portion during which it remains fixed at V2; a third portion during which it transitions to a voltage V3; and a fourth portion during which it remains fixed at V3. The waveform is created within a unit interval whenever successive data bits transition between logic states. The first and second portions are generated with circuitry arranged such that V2 is maximized by reducing the buffer's output impedance. The fourth portion is generated with circuitry which has a non-zero output impedance preferably equal to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, to absorb transitions reflected back to the source circuitry by the capacitive termination.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
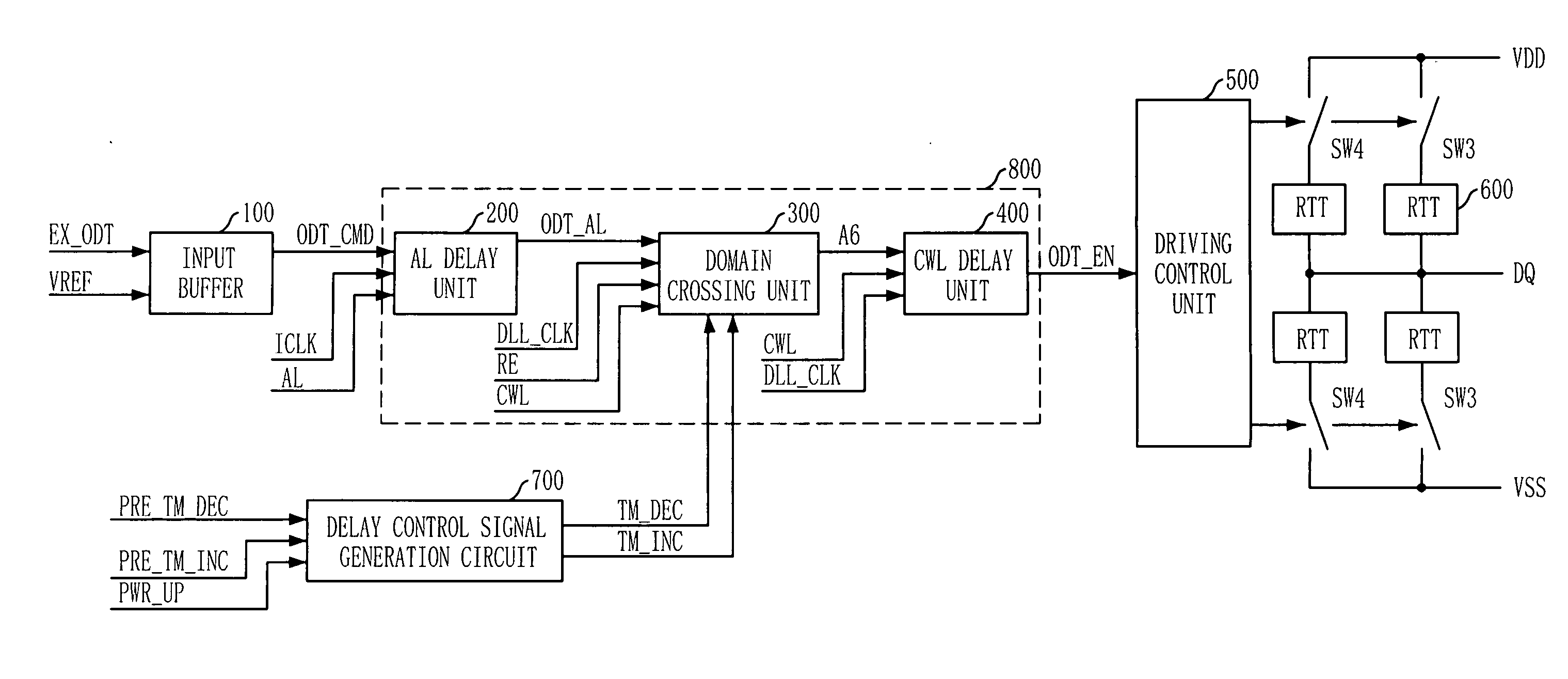
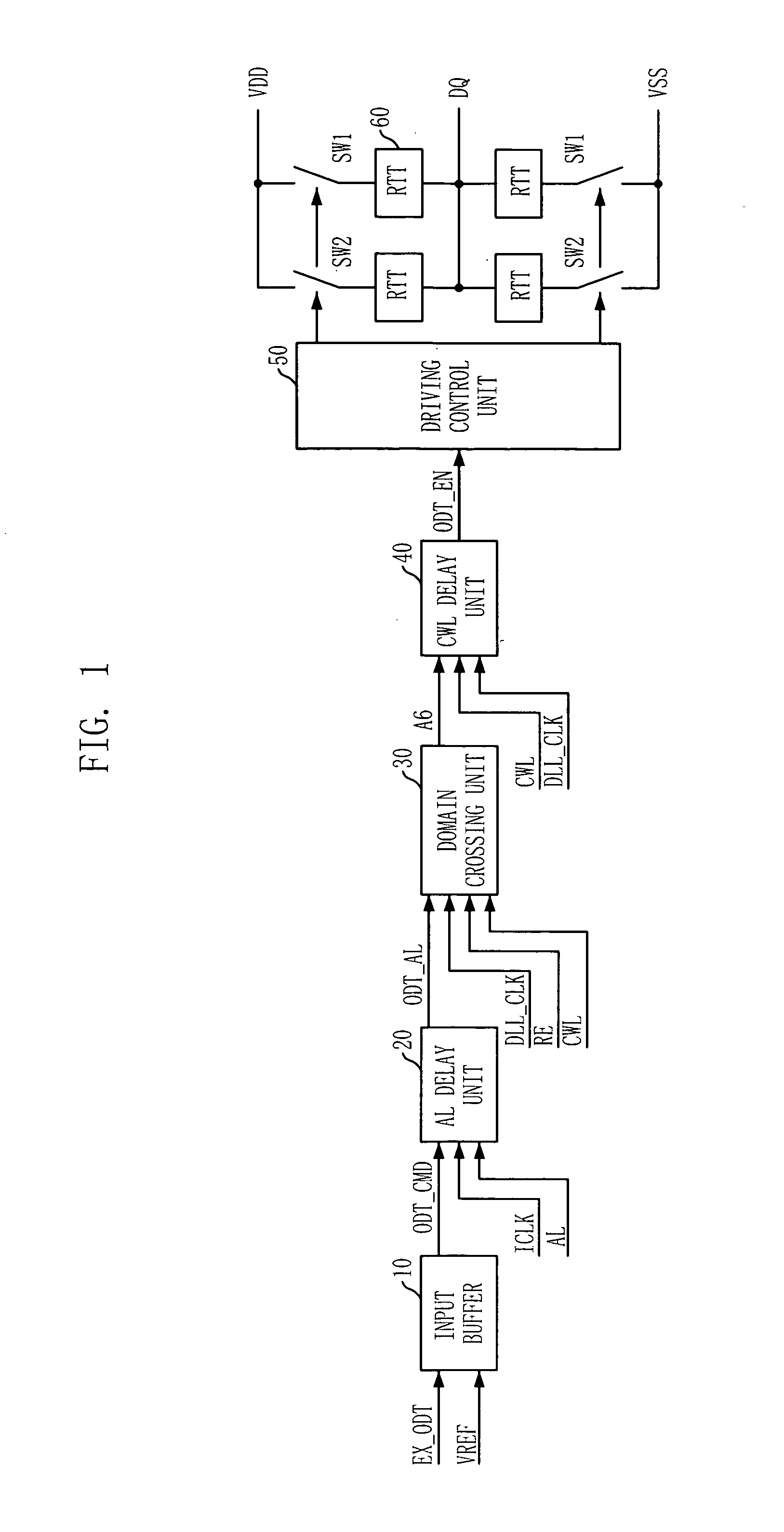
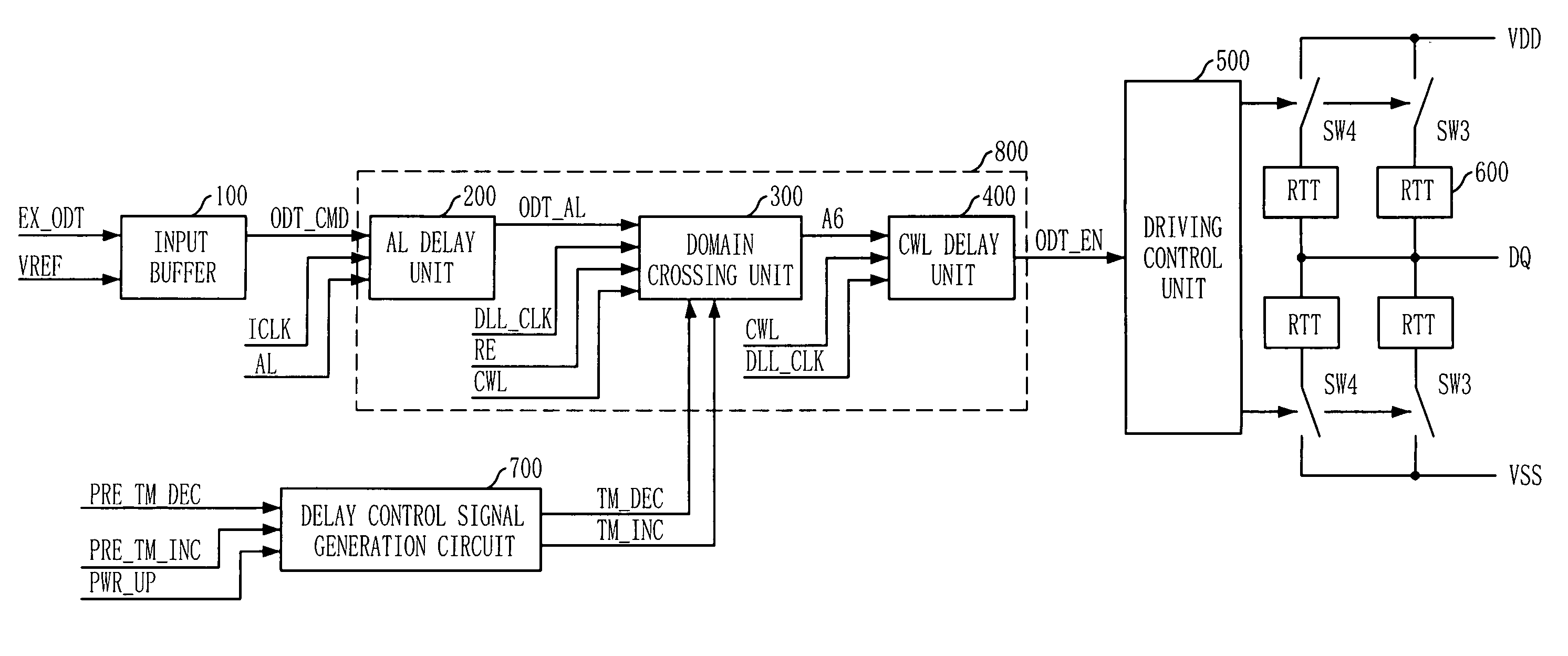
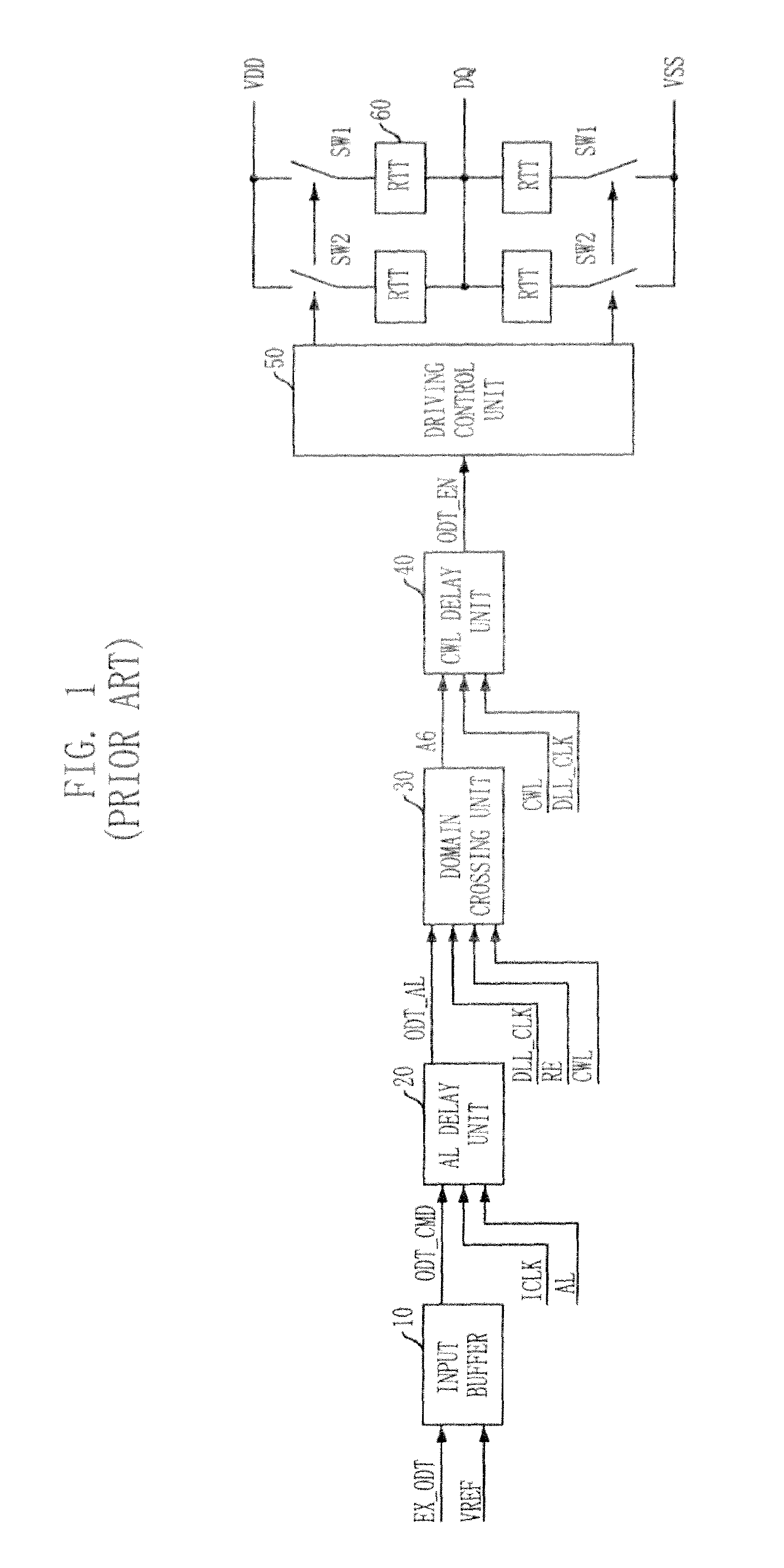
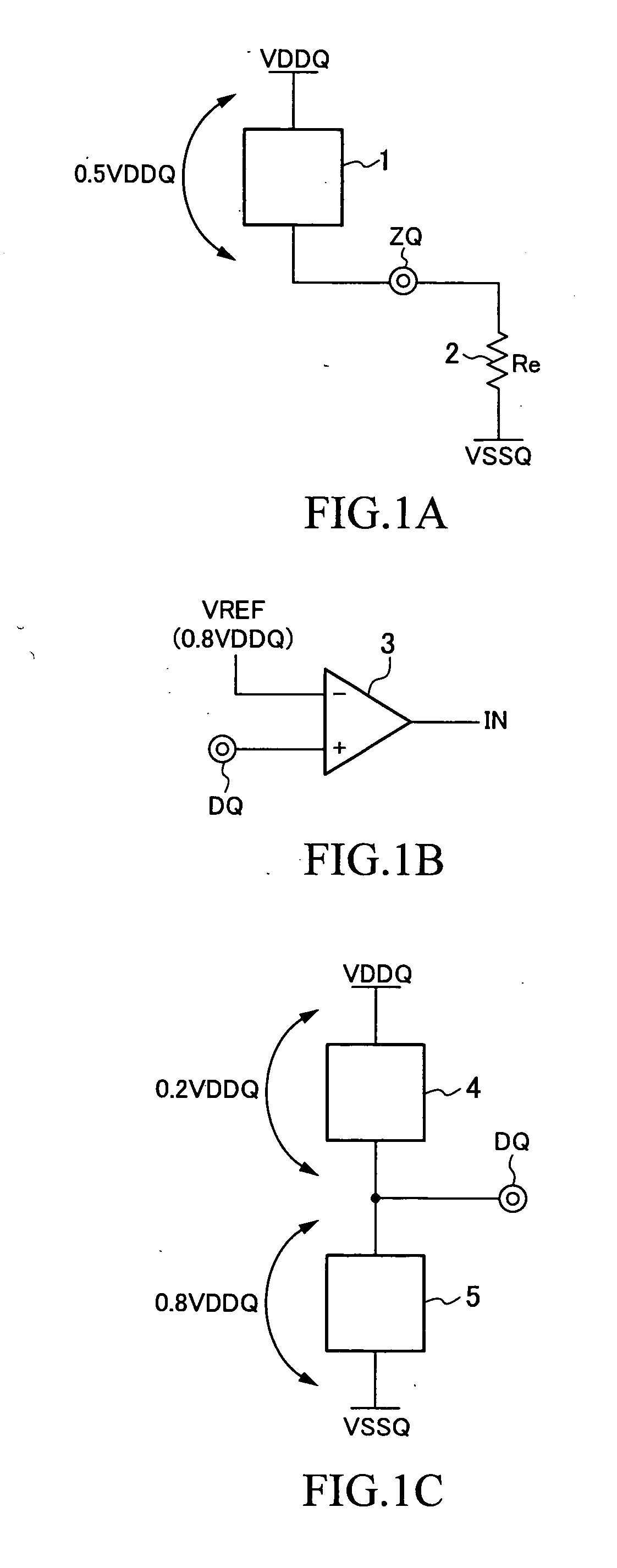
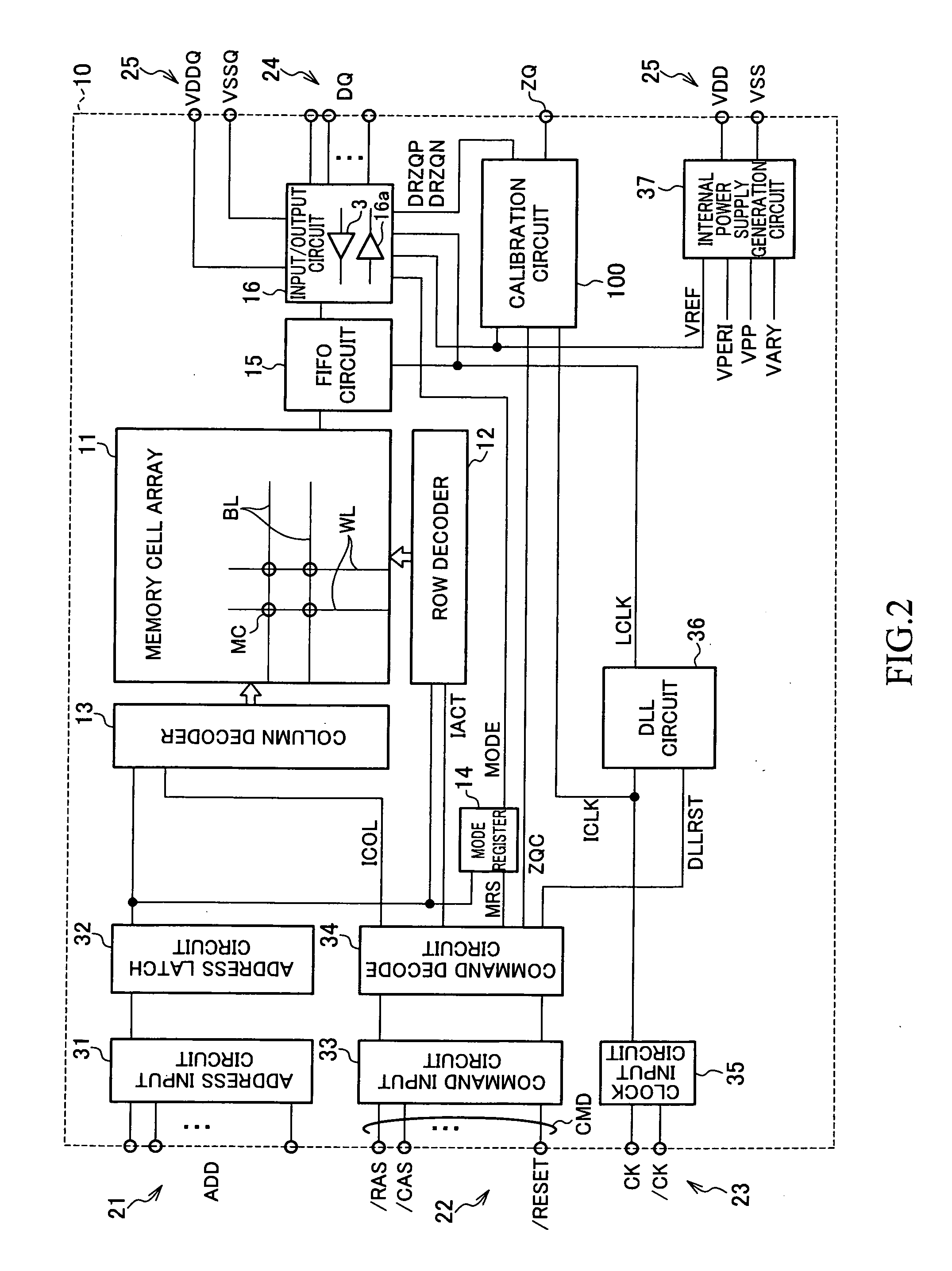
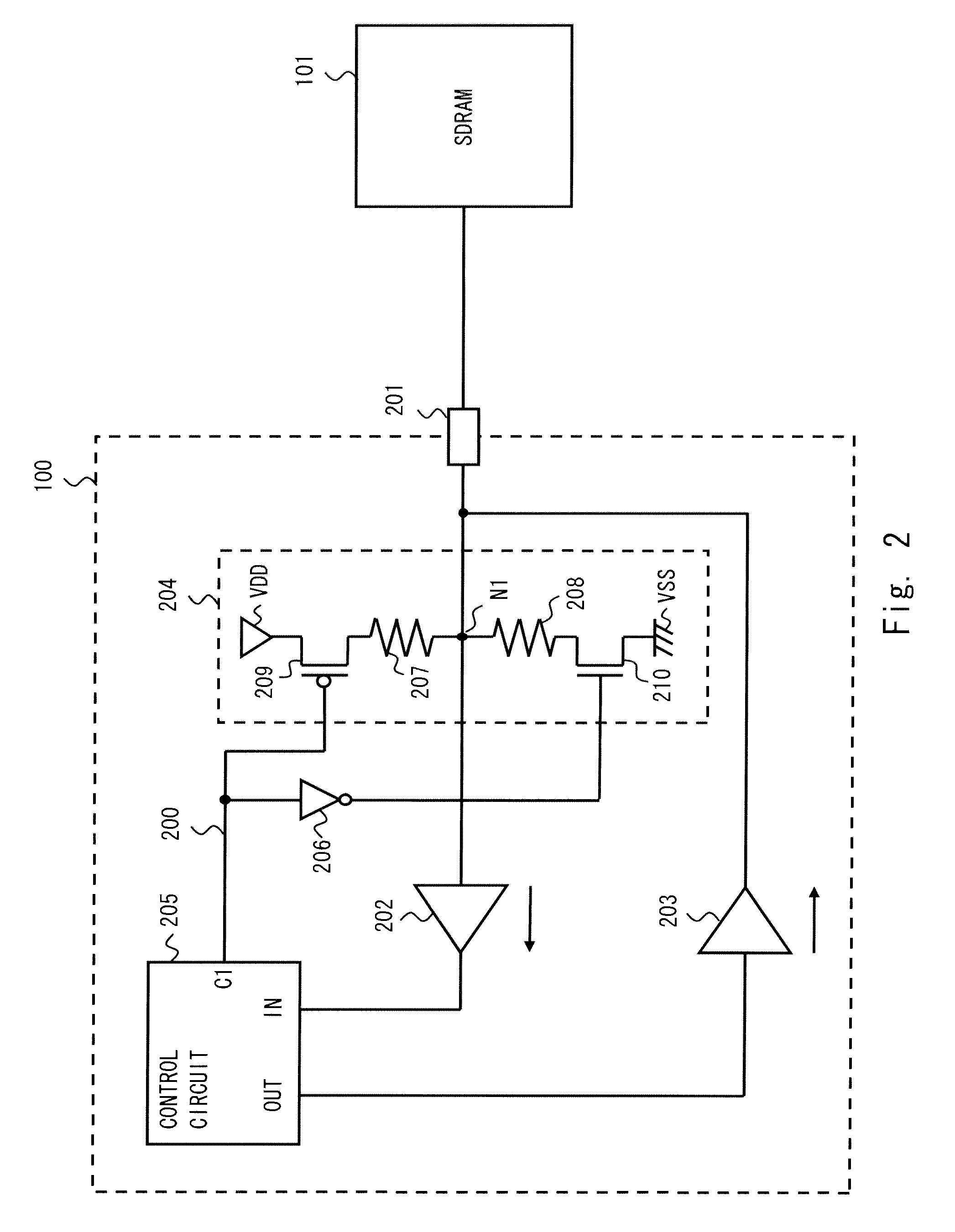
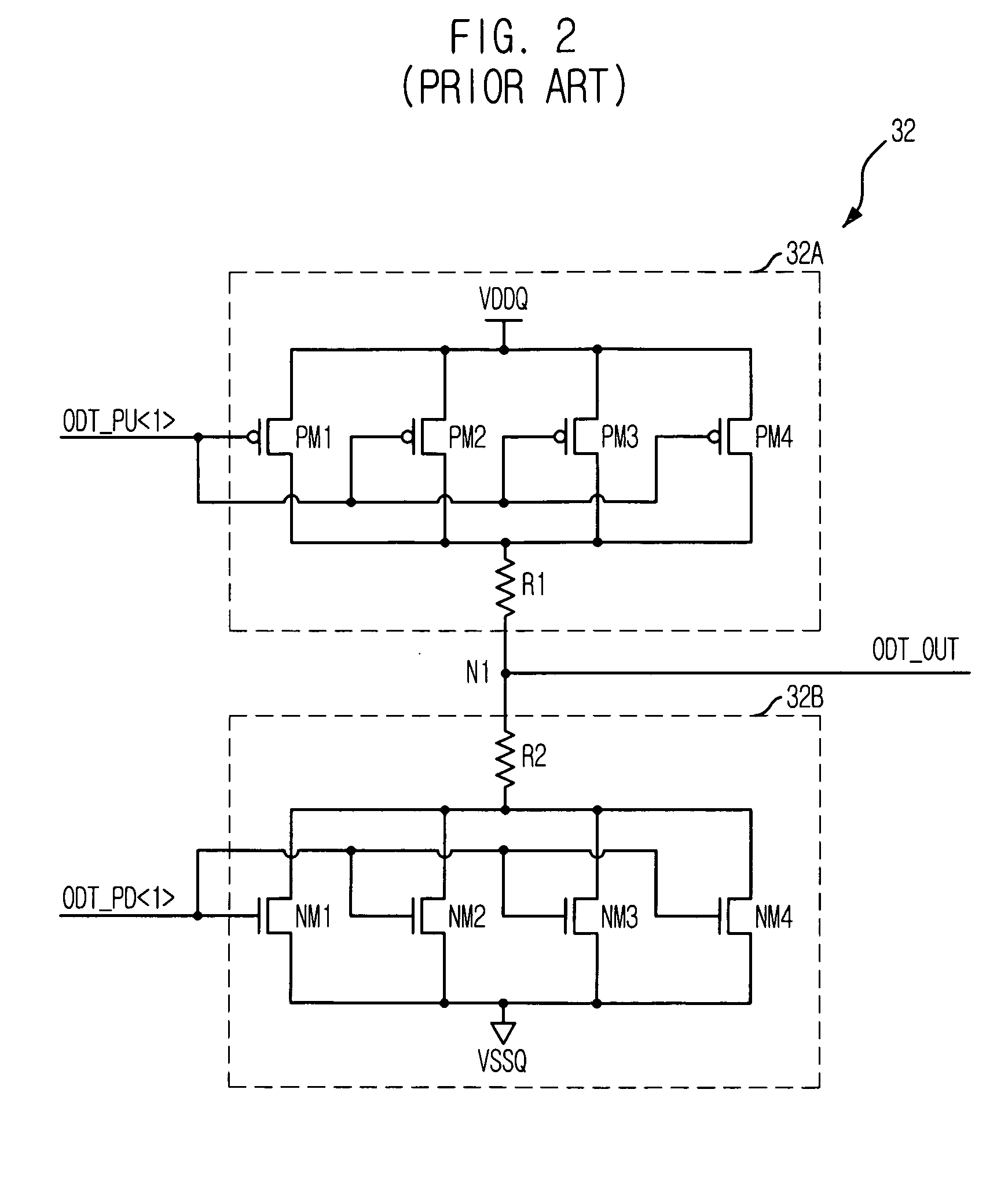
Semiconductor memory device having on-die-termination device and operation method thereof
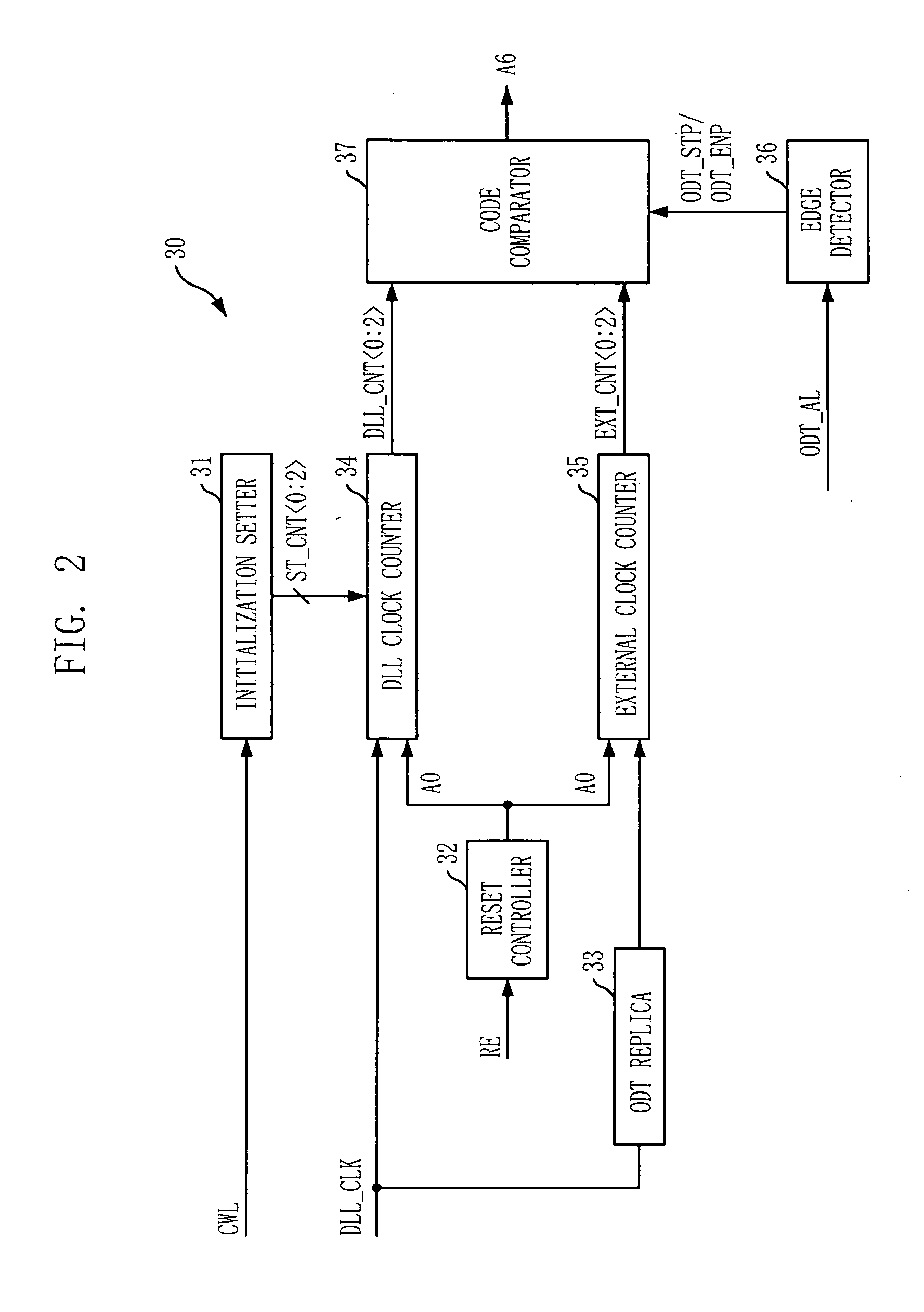
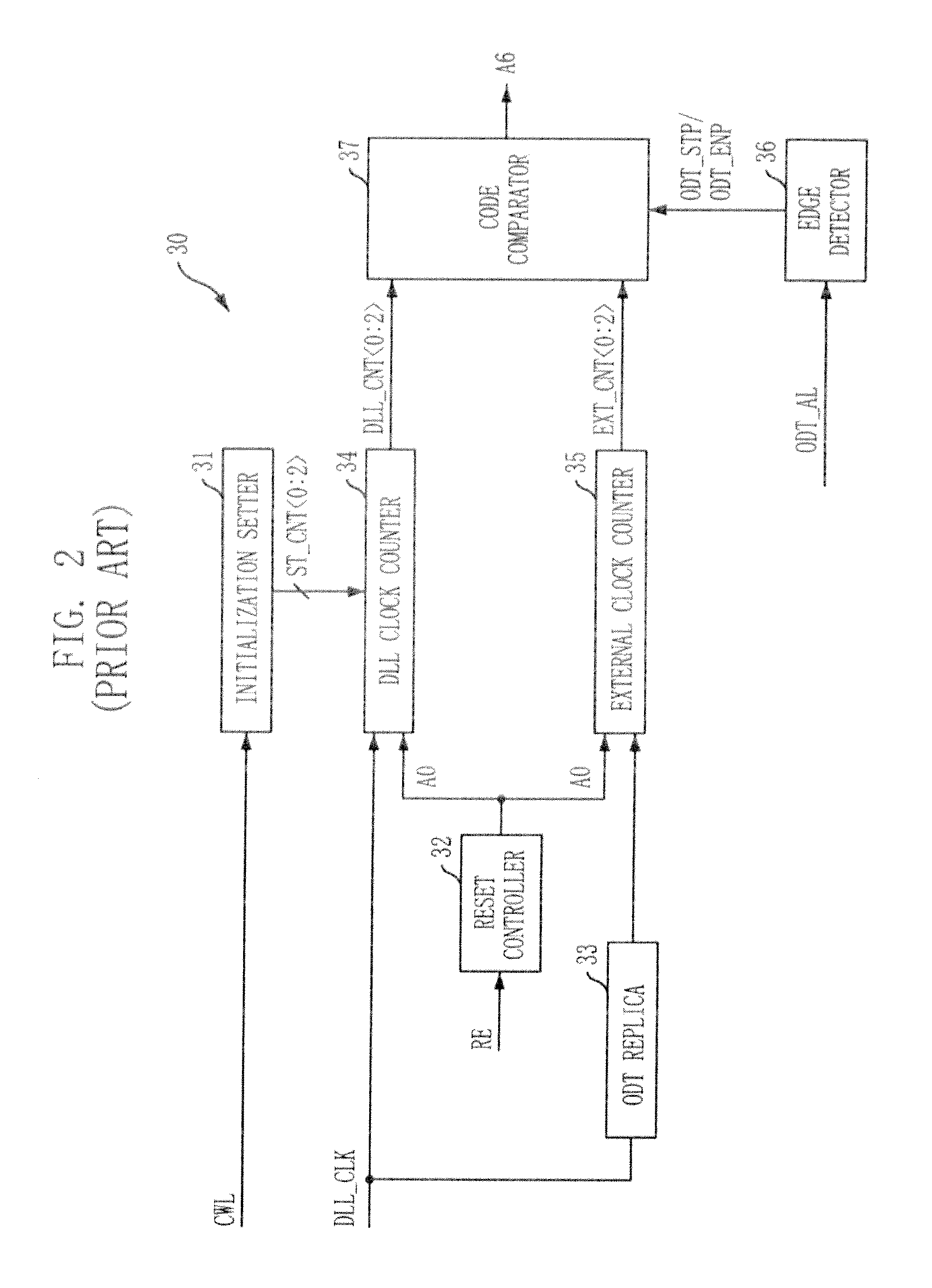
ActiveUS20090016124A1Easy to fixLogic circuit coupling arrangementsDigital storageControl signalDelay-locked loop
A semiconductor memory device is capable of stably securing an on-die-termination (ODT) latency in spite of PVT variations and various operating speeds. The semiconductor memory device includes a plurality of termination resistors connected to an output pad in series and parallel, a drive controller, a delay path, and a delay control signal generator. The drive controller activates / inactivates the plurality of termination resistors in response to a driving control signal. The delay path delays a termination command by a delay time corresponding to an on-die-termination (ODT) latency to output the driving control signal, wherein the termination command is converted into a delay locked loop (DLL) clock domain signal. The delay control signal generator controls a conversion point of the termination command into the DLL clock domain signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor memory device having on-die-termination device and operation method thereof
ActiveUS7663946B2Easy to fixLogic circuit coupling arrangementsDigital storageControl signalDelay-locked loop
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
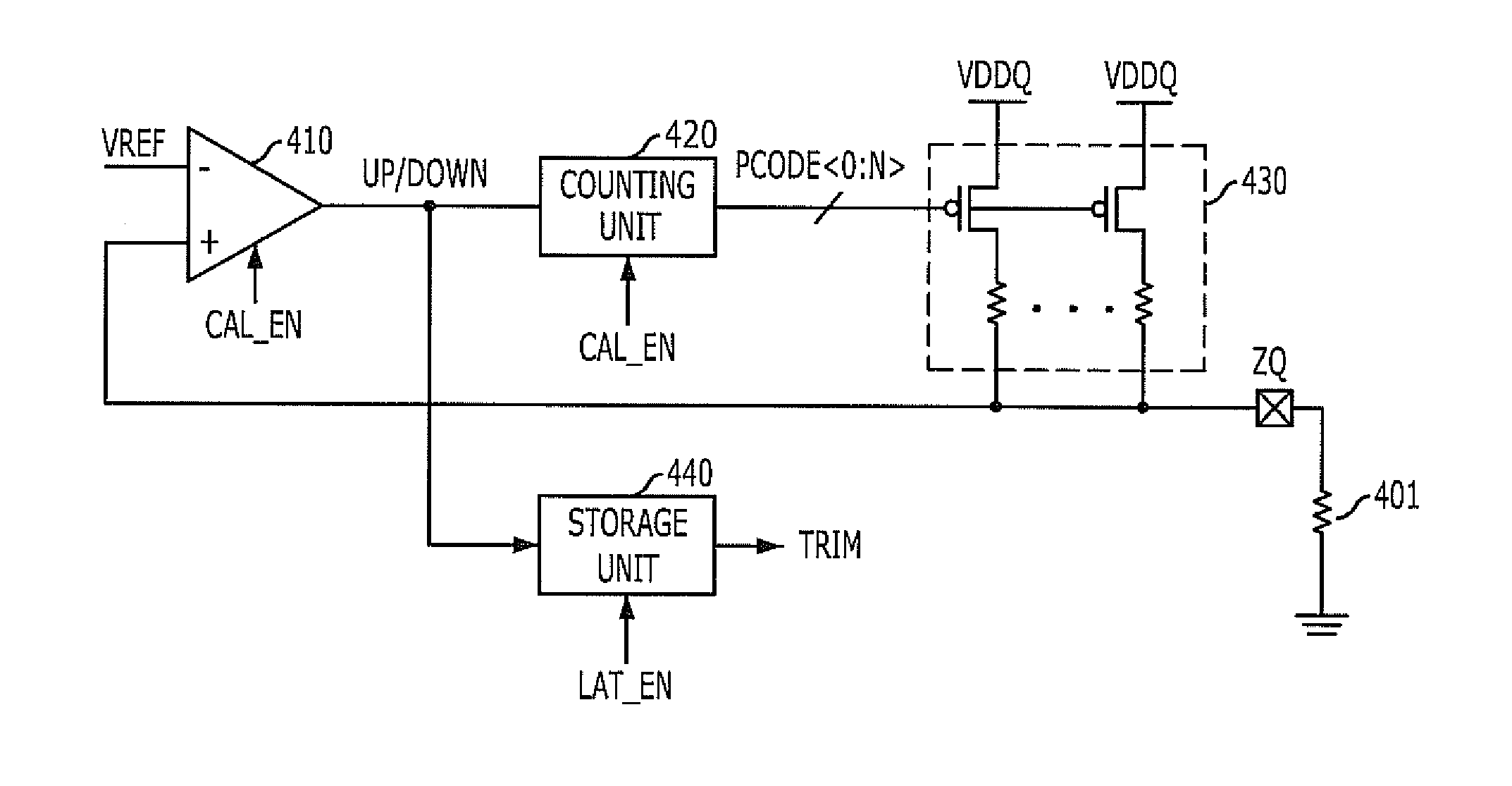
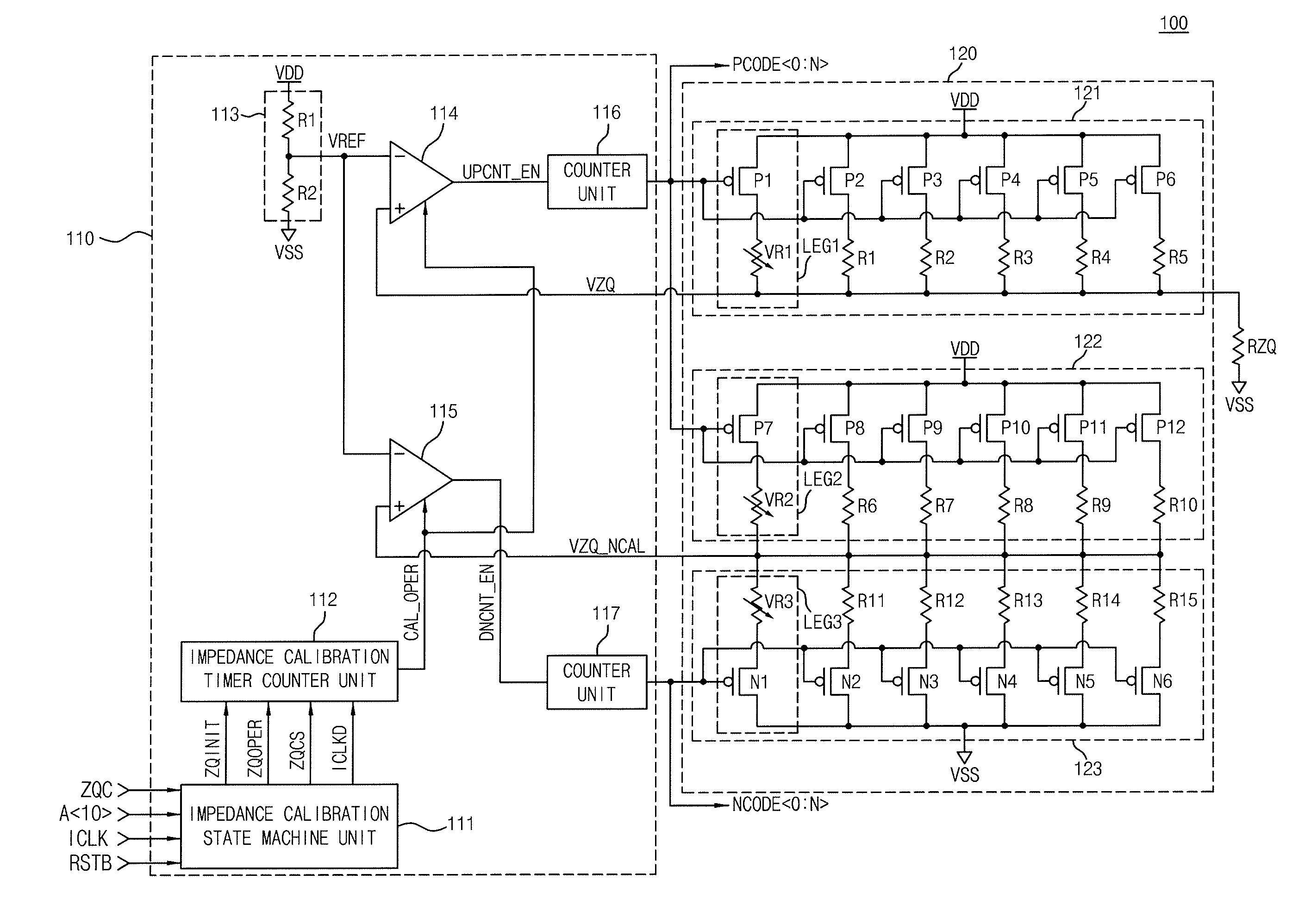
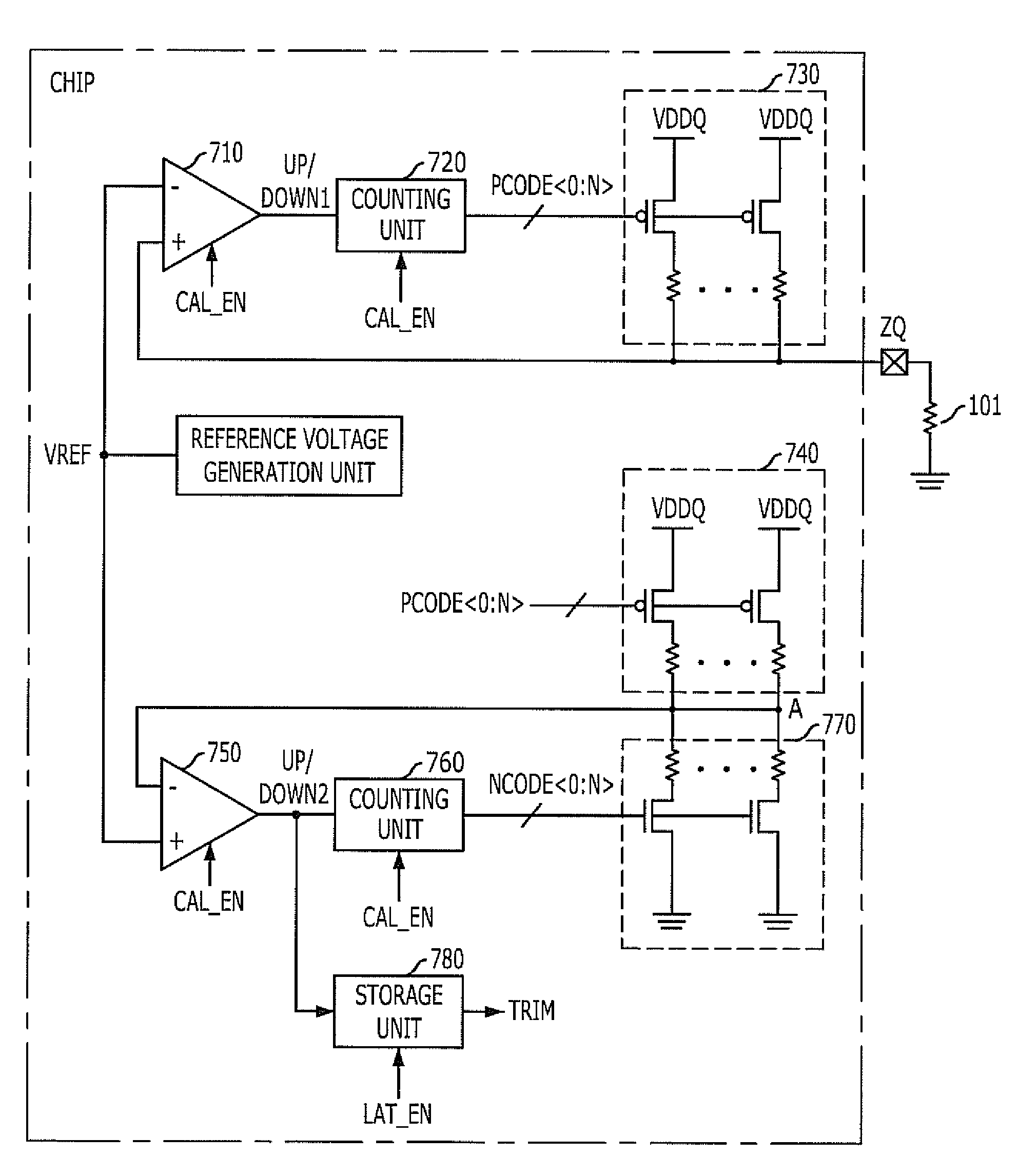
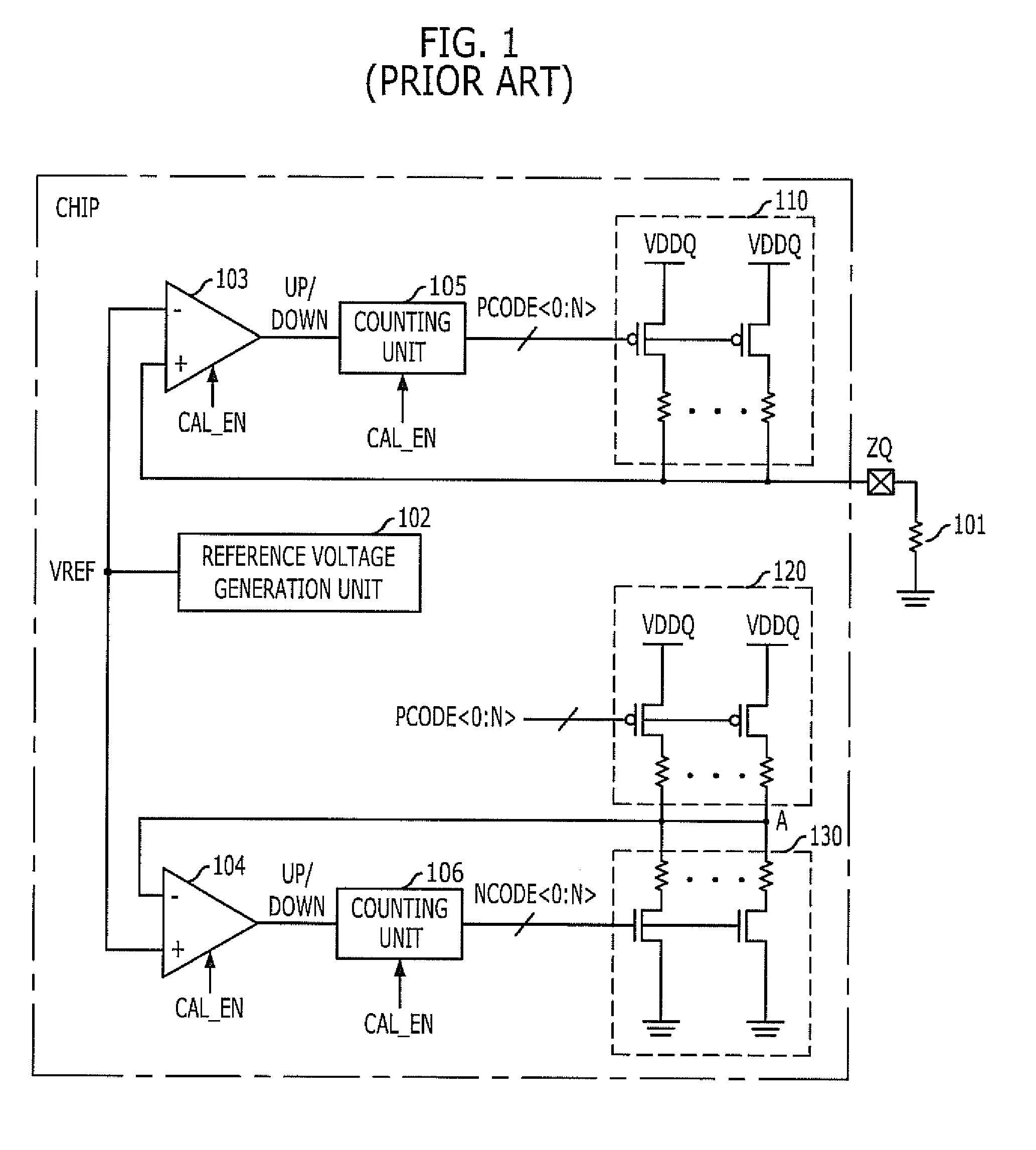
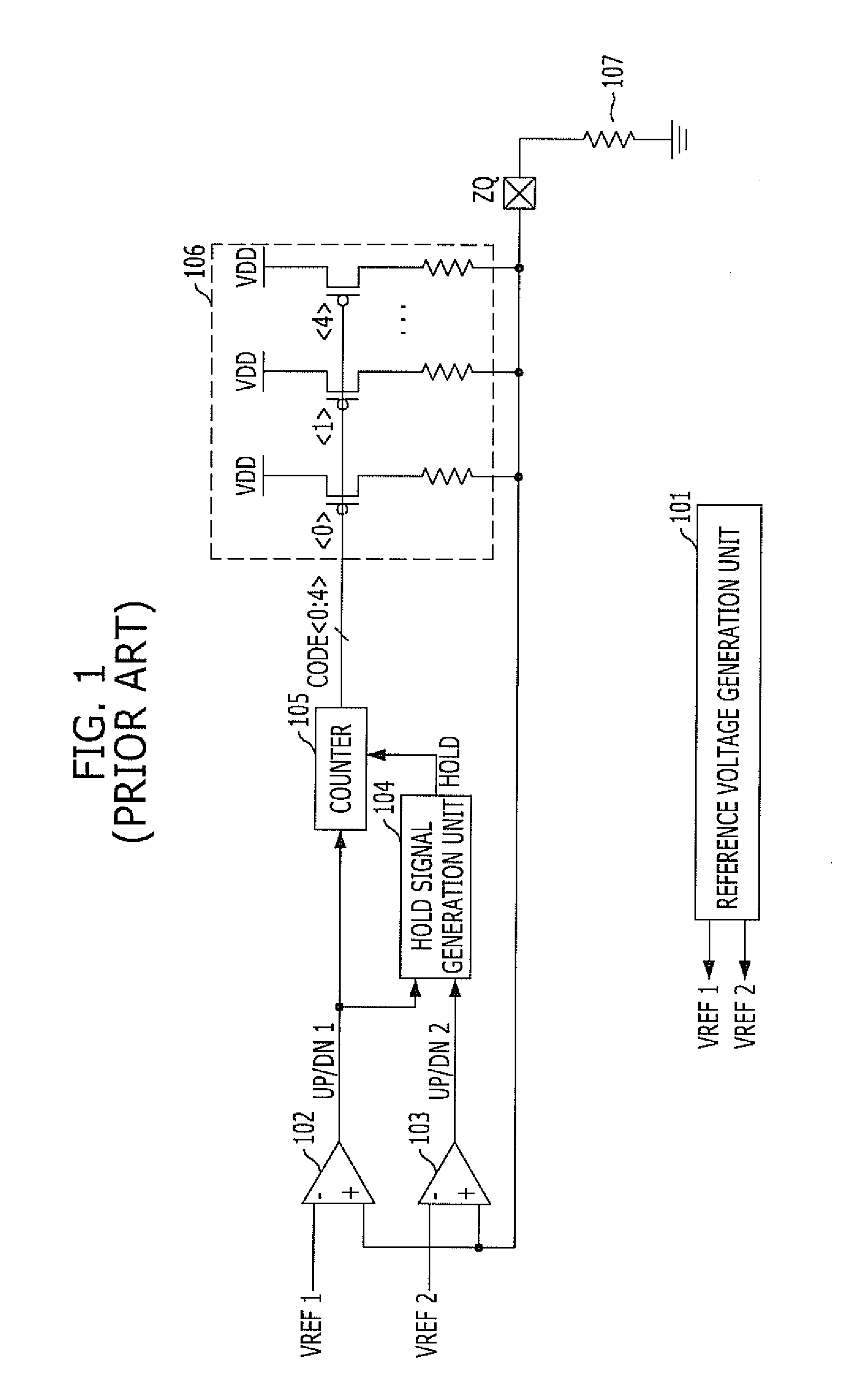
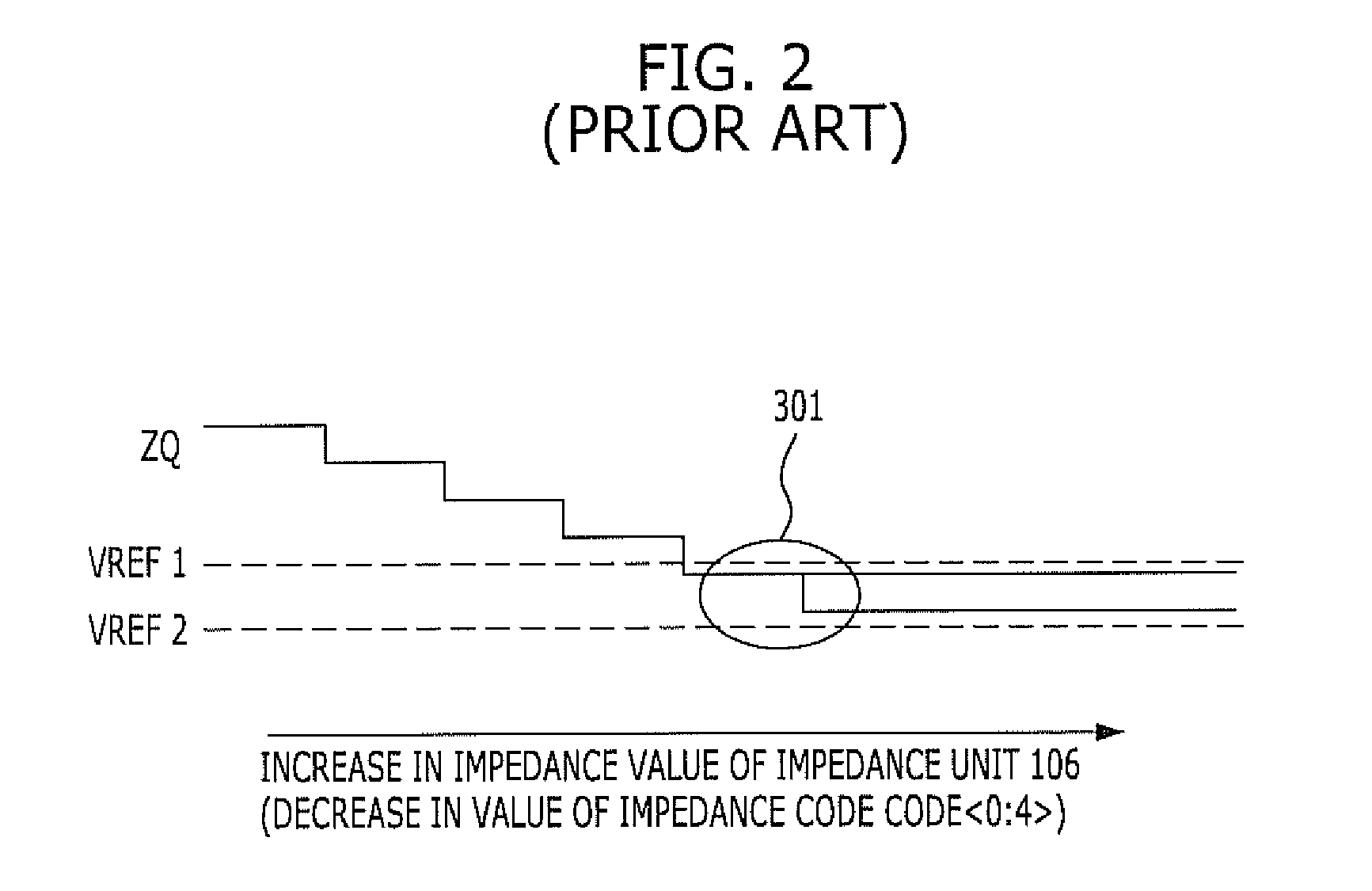
Impedance adjusting device
InactiveUS20110128038A1Easy CalibrationIncreasing of terminationReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuit coupling arrangementsEngineeringVoltage reference
An impedance adjusting device includes: a calibration node; a comparison unit configured to compare a reference voltage with a voltage of the calibration node; a counting unit configured to generate an impedance code according to a comparison result of the comparison unit; a reference impedance unit having an impedance value according to the impedance code and connected to the calibration node; a storage unit configured to store the comparison result of the comparison unit upon the generation of the impedance code being completed; an interface node; and a termination unit configured to terminate the interface node, the termination unit including a plurality of parallel resistors configured to be turned on / off according to the impedance code, and a parallel resistor configured to be turned on / off according to a value stored in the storage unit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor device having impedance calibration function to data output buffer and semiconductor module having the same
ActiveUS20130088257A1Impedance can be adjustedInput/output impedence modificationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsData terminalSemiconductor
Disclosed herein is a semiconductor device that includes a first transistor unit coupled to the data terminal, and a plurality of second transistor units coupled to the calibration terminal. The first transistor unit includes a plurality of first transistors having a first conductivity type connected in parallel to each other so that an impedance of the first transistor unit is adjustable. Each of the second transistor units includes a plurality of second transistors having the first conductivity type connected in parallel to each other so that an impedance of each of the second transistor units is adjustable. The semiconductor device further includes an impedance control circuit that reflects the impedance of each of the second transistor units to the first transistor unit.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS20110057720A1Reduce power supply noiseAccurate reception of dataInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsControl signalEngineering
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Device for controlling on die termination
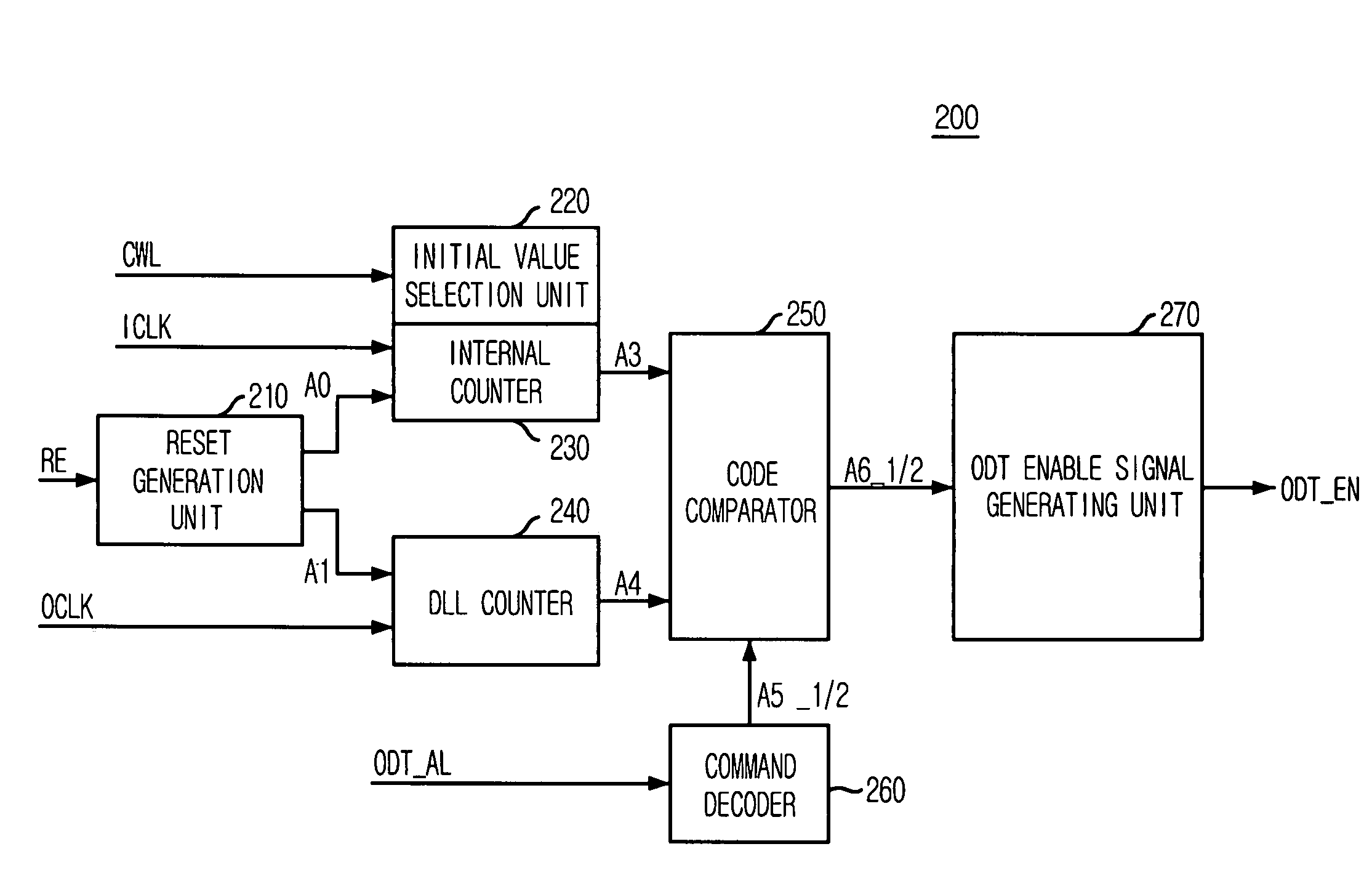
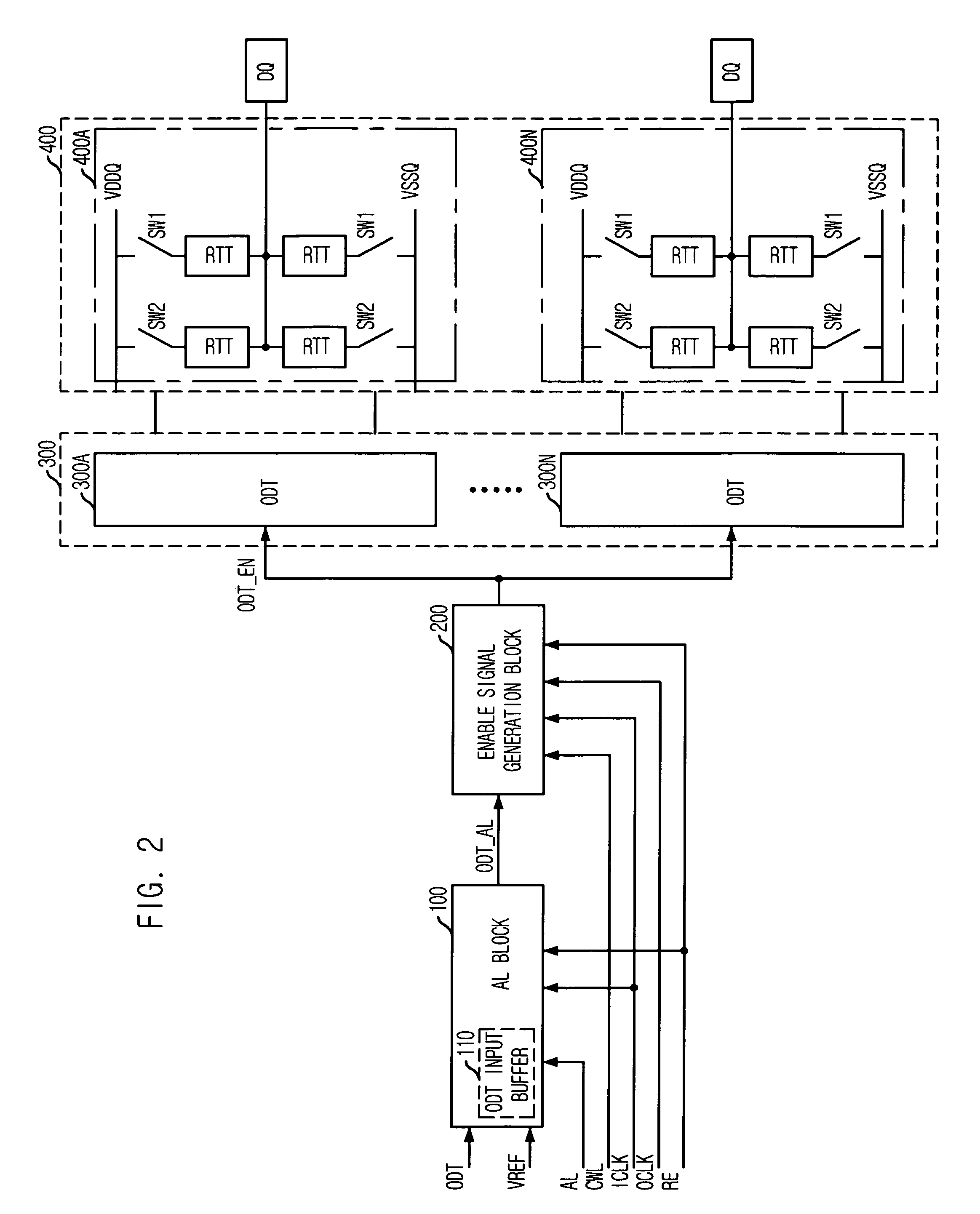
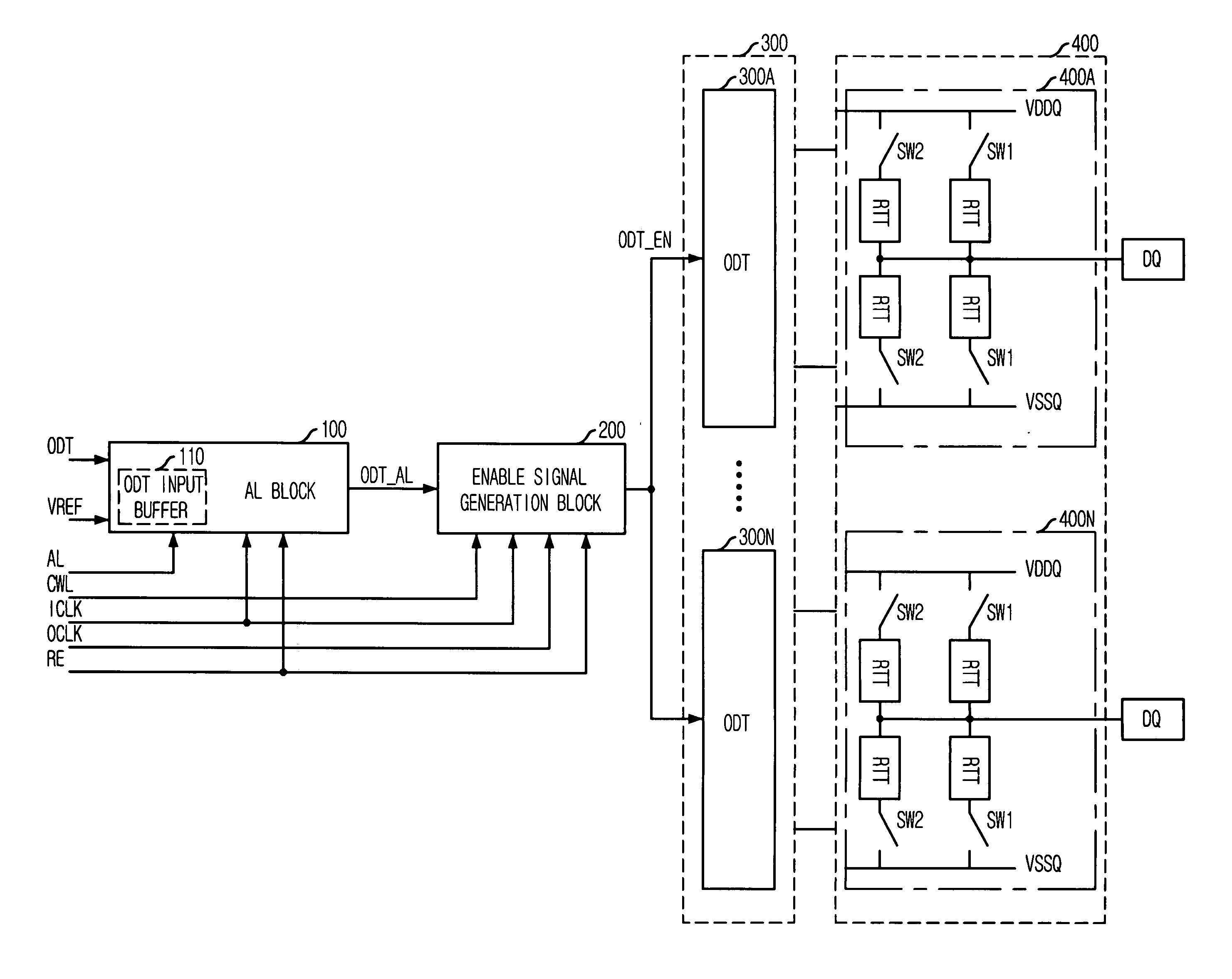
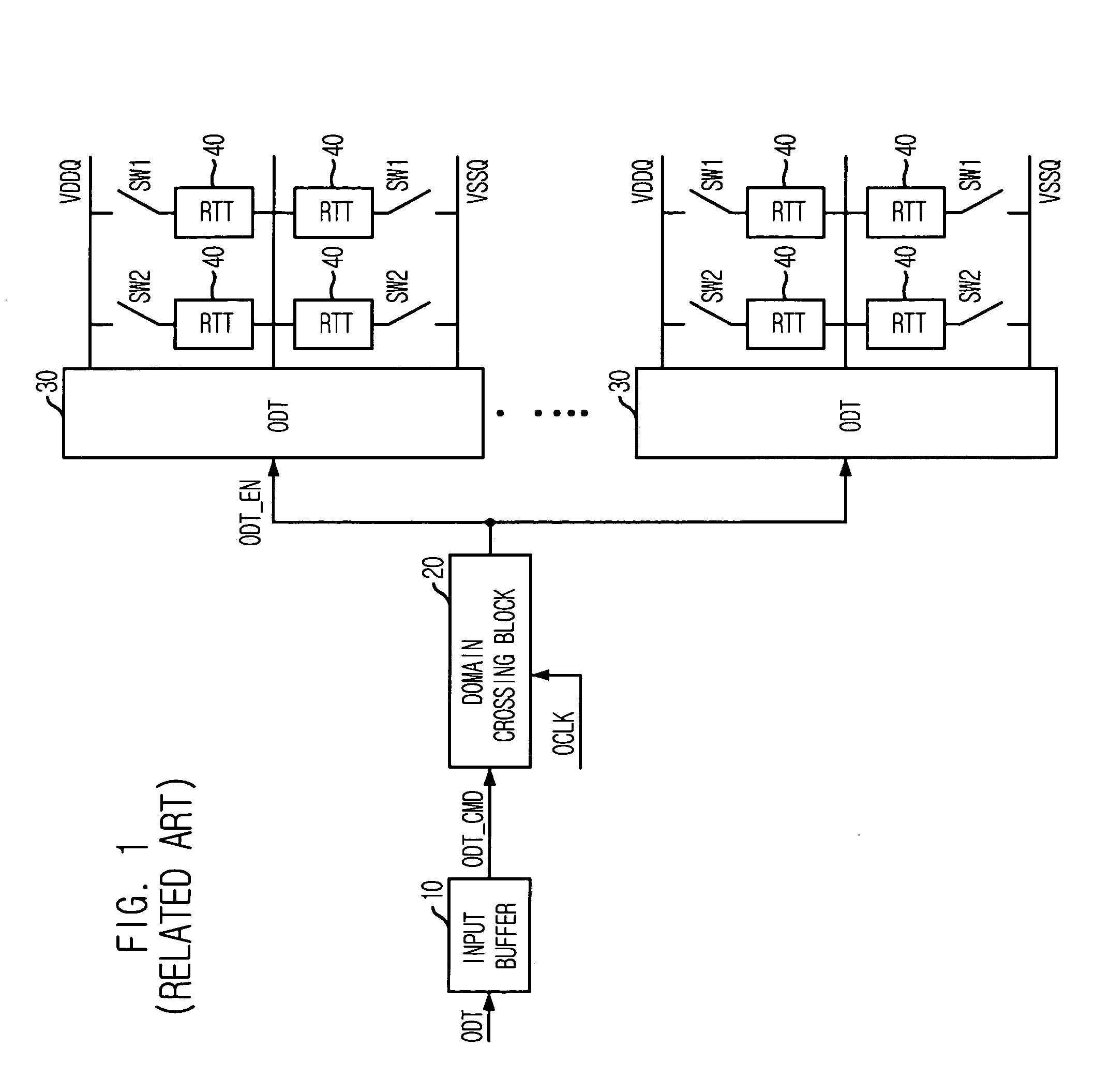
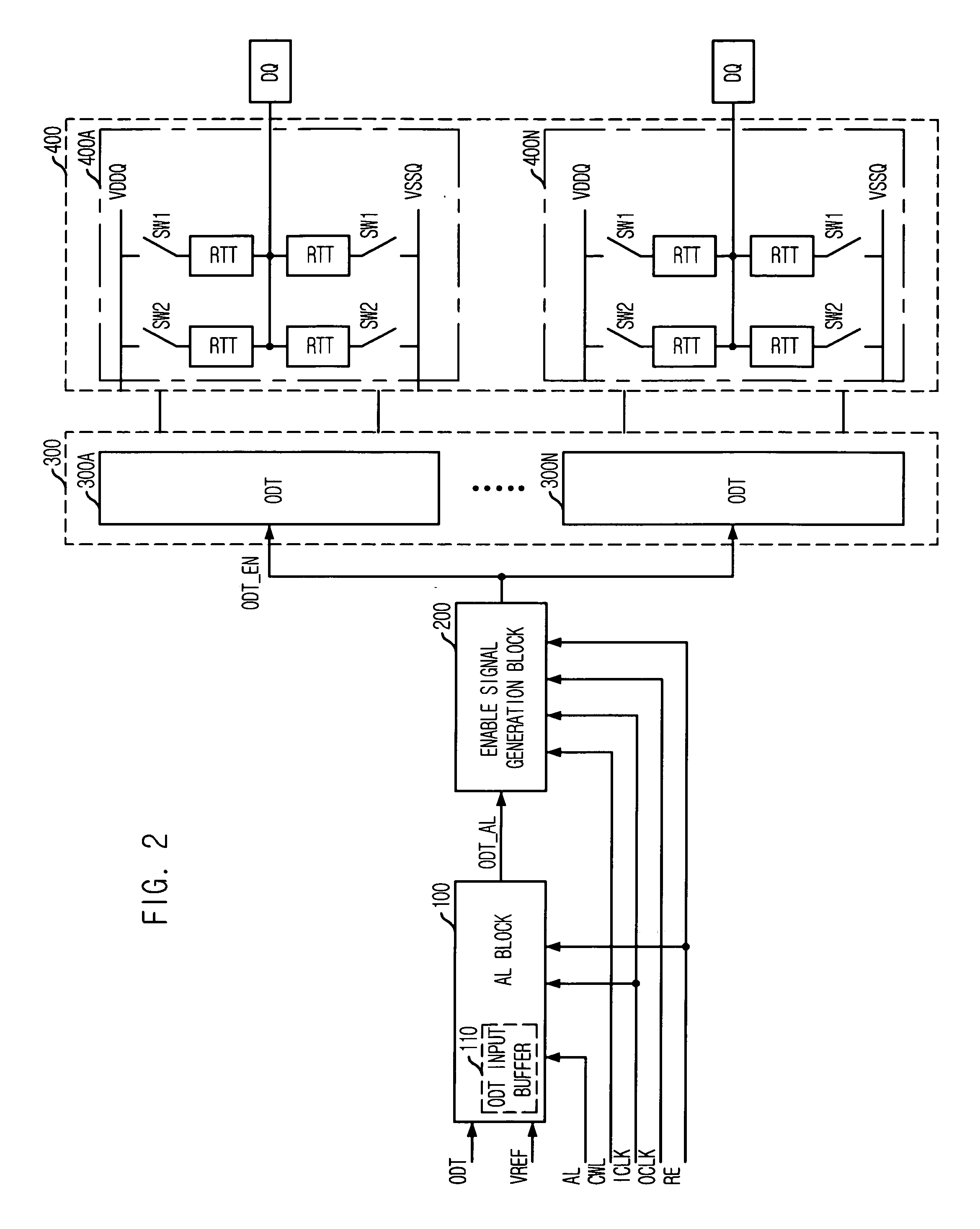
ActiveUS7342412B2Control impedanceLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsControl signalComputer science
An on die termination (ODT) control device includes a latency block for buffering an ODT control signal to output a latency control signal by selecting one of a plurality of intermediate control signals, which are generated by sequentially delaying the buffered ODT control signal in synchronization with an internal clock, based on first latency information; an enable signal generation block for comparing a first control signal with a second control signal in response to the latency control signal to thereby produce an ODT enable signal based on the compared result; and an ODT block for controlling a termination impedance based on the ODT enable signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Device for controlling on die termination
ActiveUS20070126468A1Flexible controlControl impedanceReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuit coupling arrangementsControl signalComputer science
An on die termination (ODT) control device includes a latency block for buffering an ODT control signal to output a latency control signal by selecting one of a plurality of intermediate control signals, which are generated by sequentially delaying the buffered ODT control signal in synchronization with an internal clock, based on first latency information; an enable signal generation block for comparing a first control signal with a second control signal in response to the latency control signal to thereby produce an ODT enable signal based on the compared result; and an ODT block for controlling a termination impedance based on the ODT enable signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
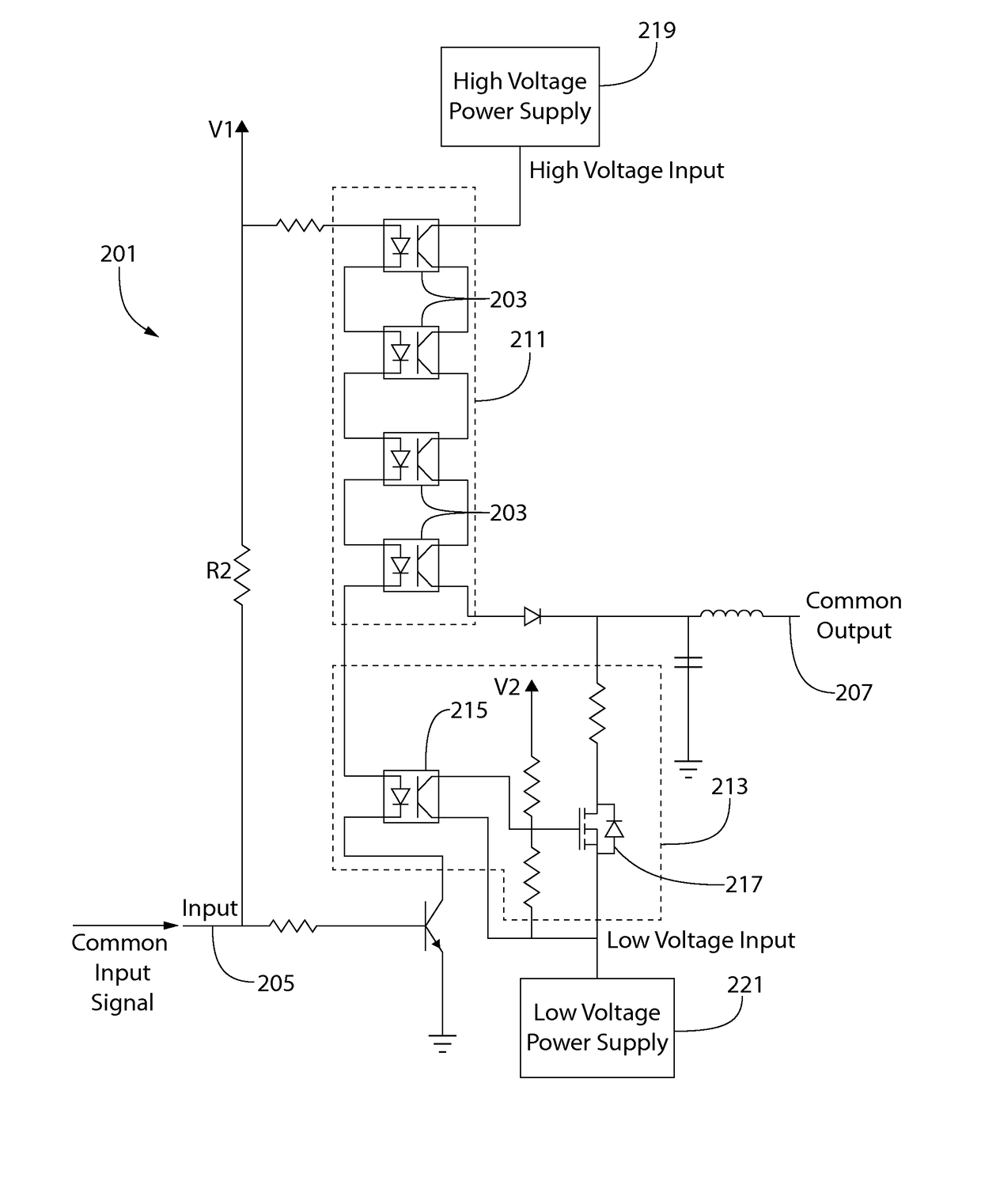
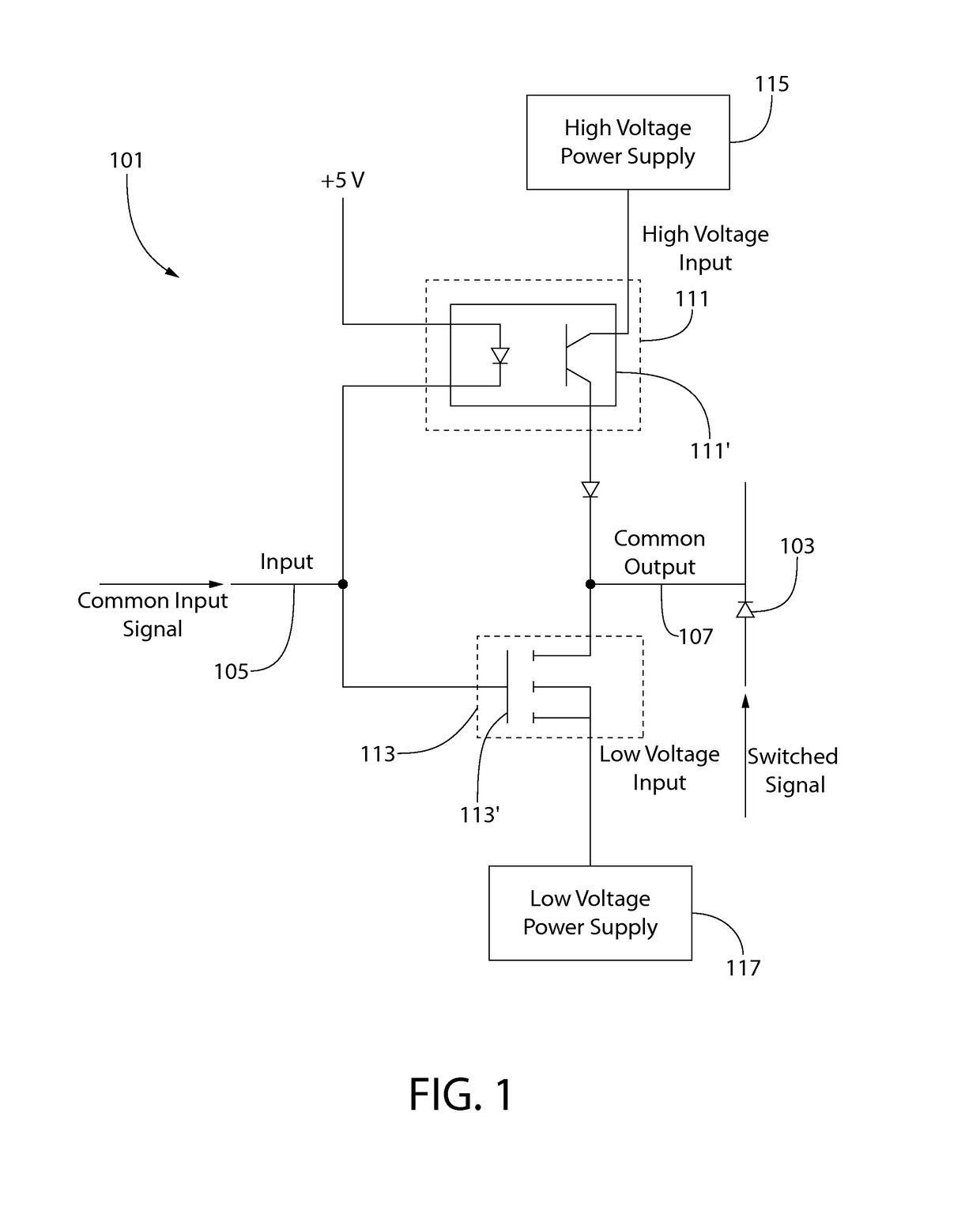
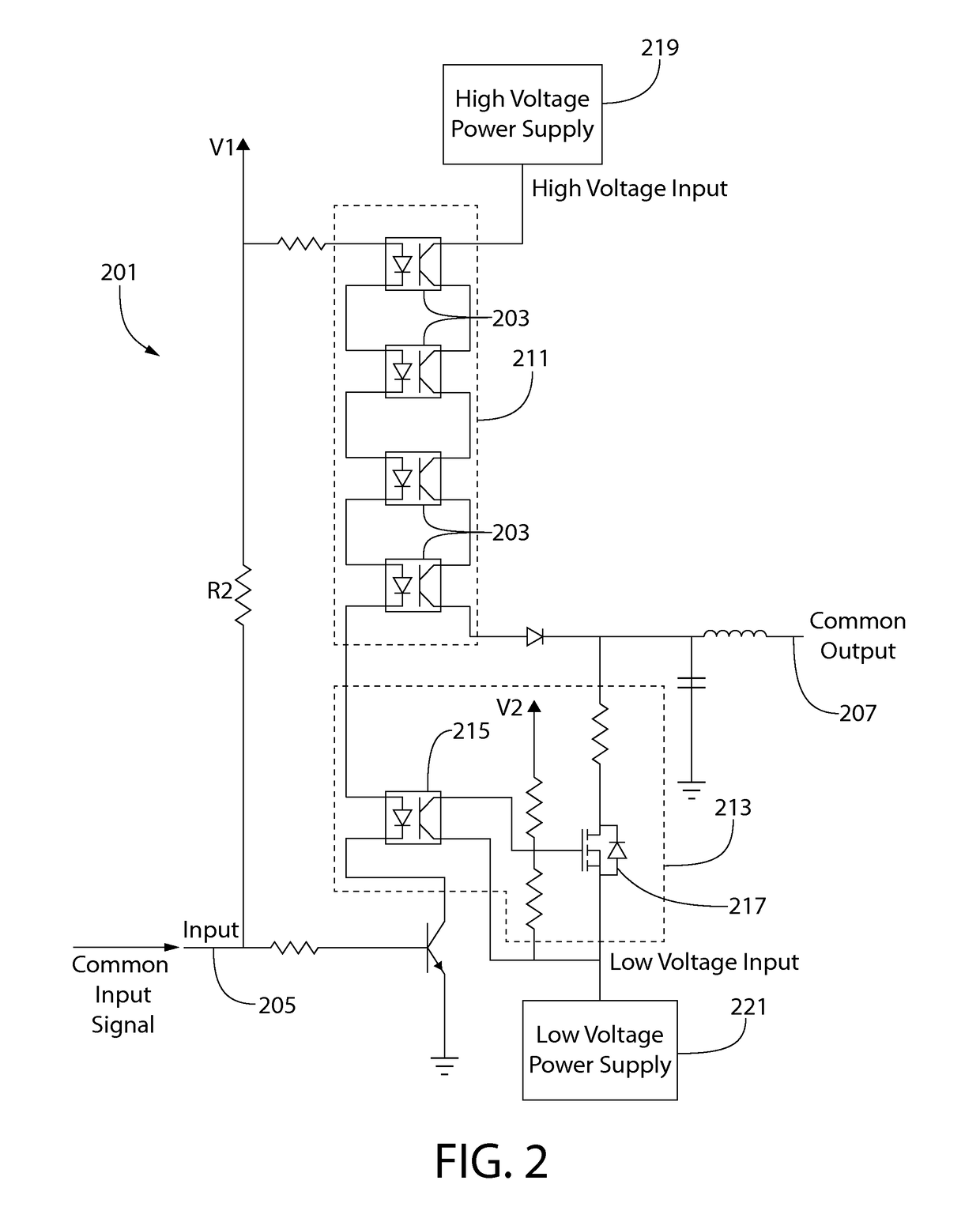
High speed high voltage switching circuit
ActiveUS9755641B1Logic circuit coupling arrangementsElectronic switchingPower switchingElectronic switch
A control circuit for an electronic switch includes a first power switch receiving a common input signal and a first voltage input and a second power switch receiving the common input signal and a second voltage input. The first and second power switches switchably connect the first voltage input and the second voltage input, respectively, to a common output in response to the common input signal. The second voltage input is opposite in polarity to the first voltage input, and the first power switch and the second power switch are configured to asynchronously connect the first voltage input and the second voltage input, respectively, to the common output in response to the common input signal, the electronic switch being switched according to the first voltage input or the second voltage input being connected to the common output.
Owner:RENO TECH
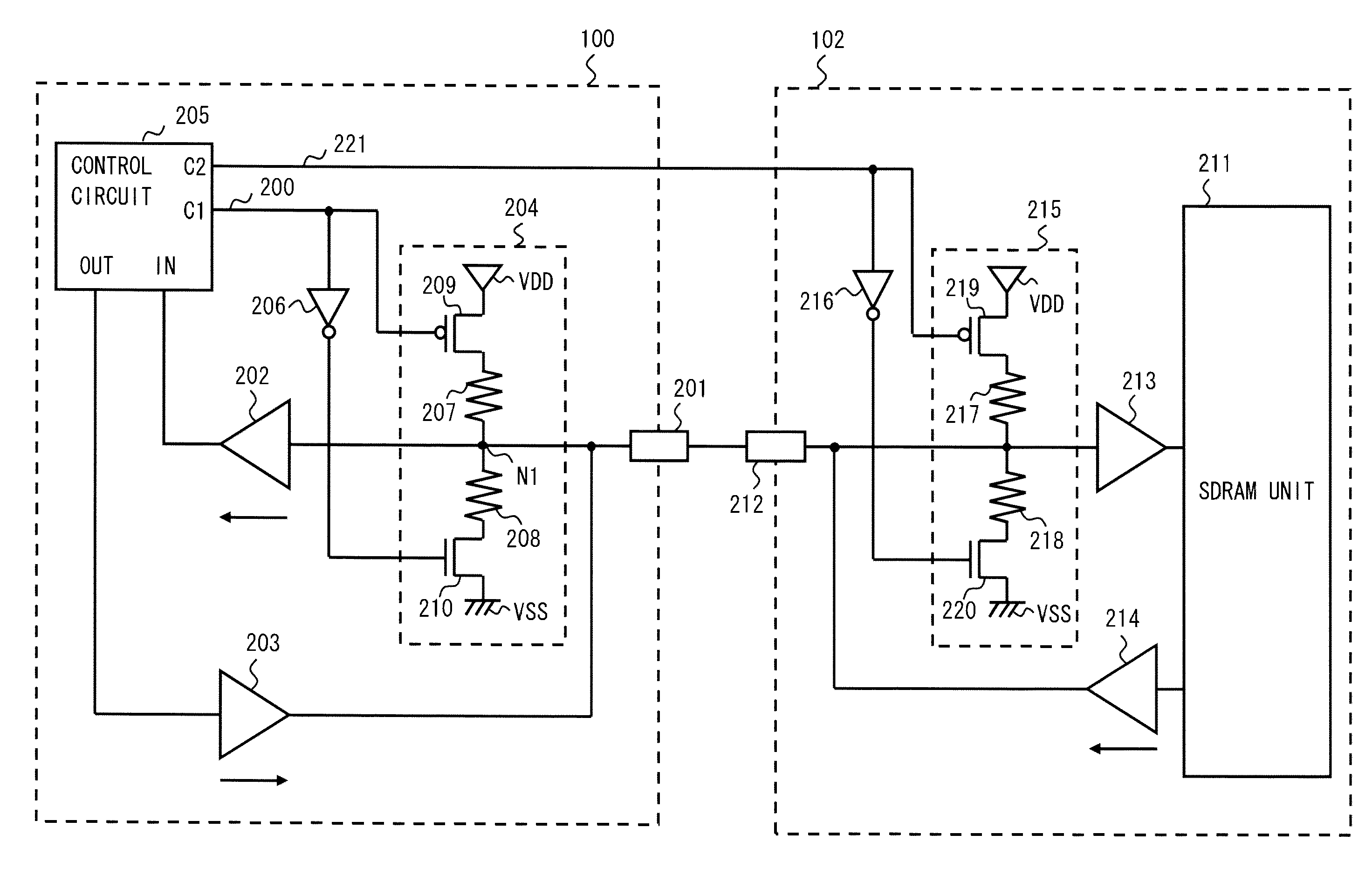
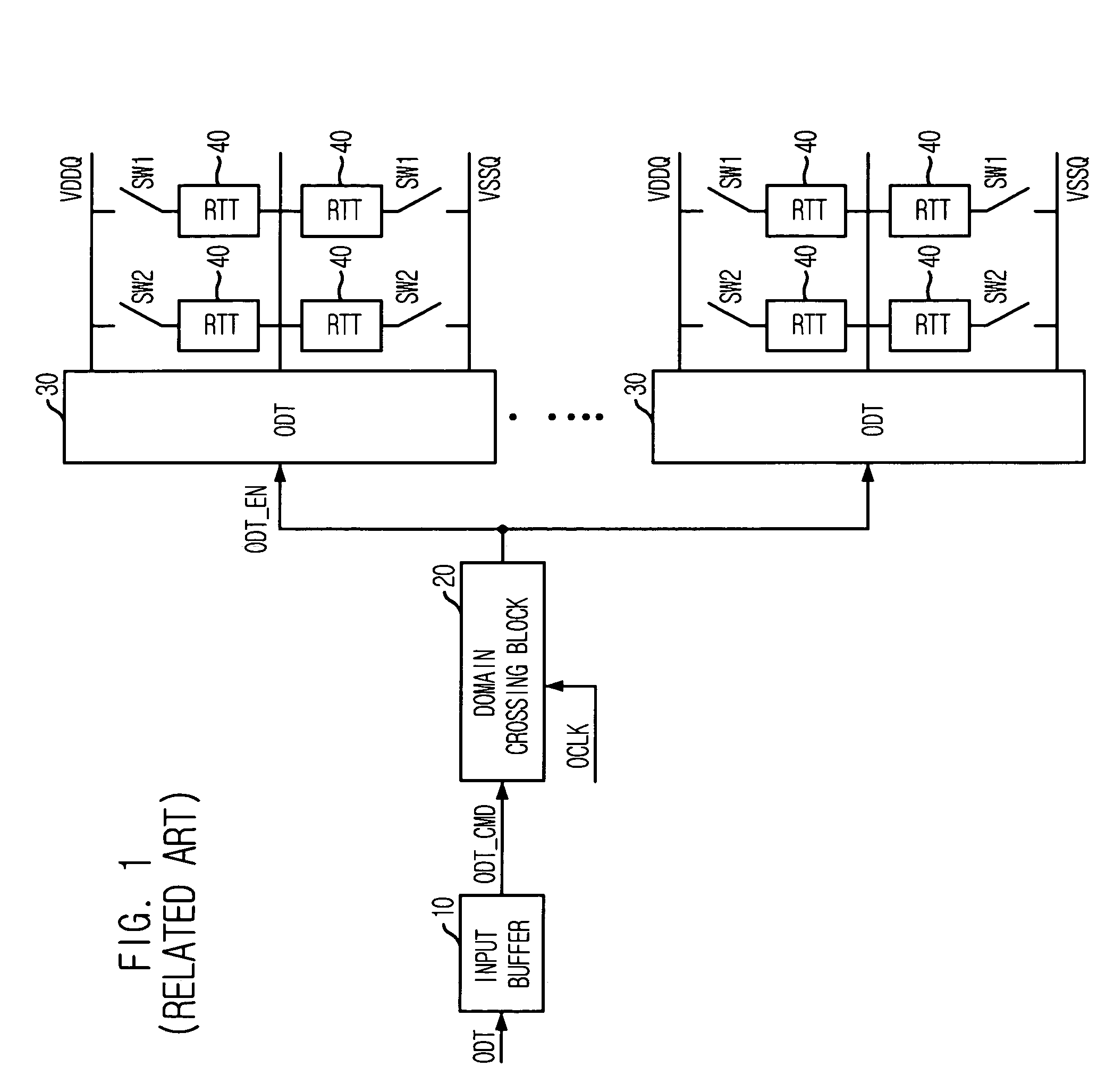
Memory systems, on-die termination (ODT) circuits, and method of ODT control
InactiveUS7786752B2Latency of operationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsPower modeDelay-locked loop
According to one aspect, an on-die termination (ODT) circuit is controlled during transition from a first power mode to a second power mode of a memory device. The transition from an asynchronous ODT circuit path to a synchronous ODT circuit path is delayed to compensate for an operational latency of a delay locked loop (DLL) circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Termination circuit and impedance matching device including the same
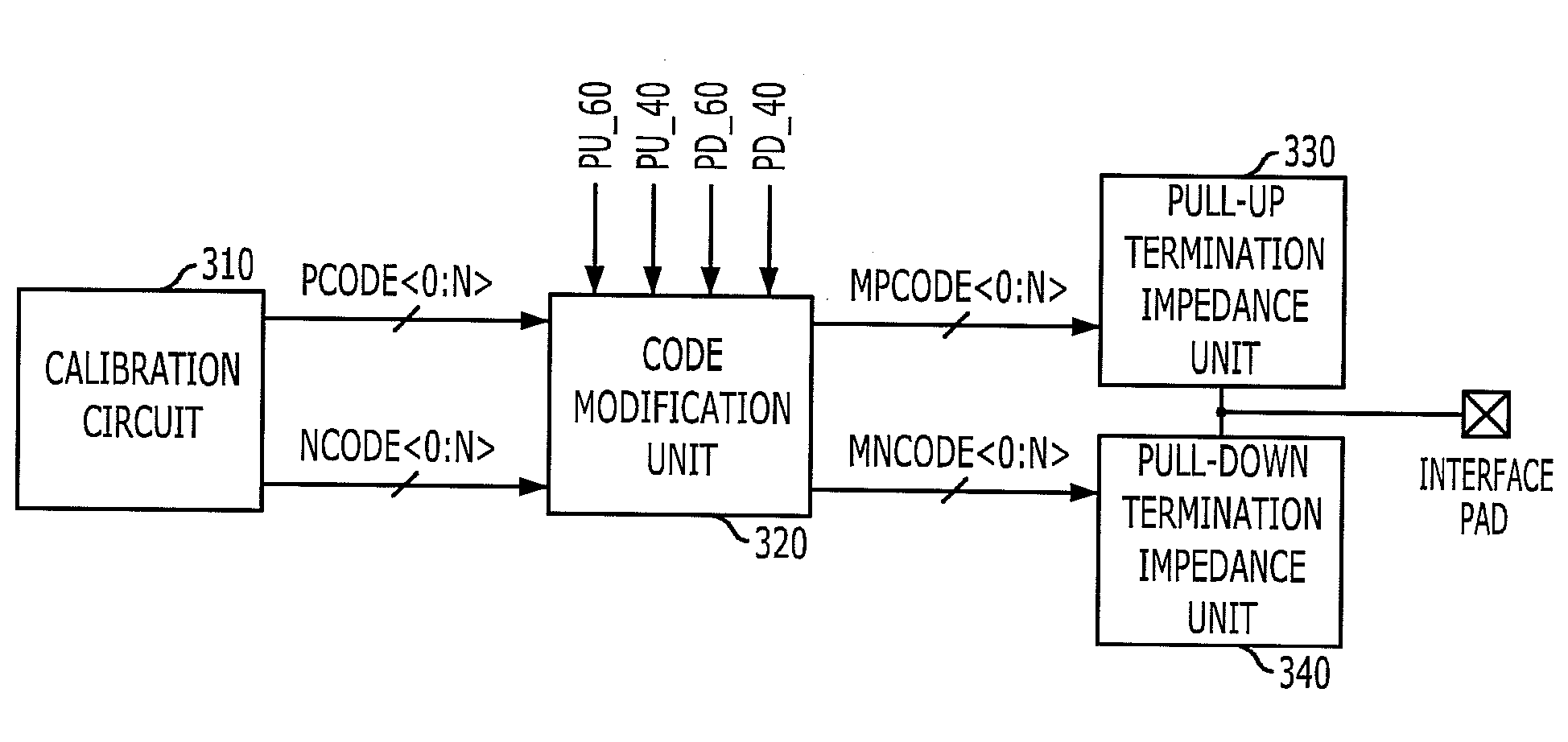
An impedance matching device includes a calibration circuit configured to generate impedance calibration codes for modification of impedance; a code modification unit configured to modify the impedance calibration codes according to impedance setting information and output modified impedance calibration codes; and a termination impedance unit configured to terminate an interface node with impedance determined according to the modified impedance calibration codes.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
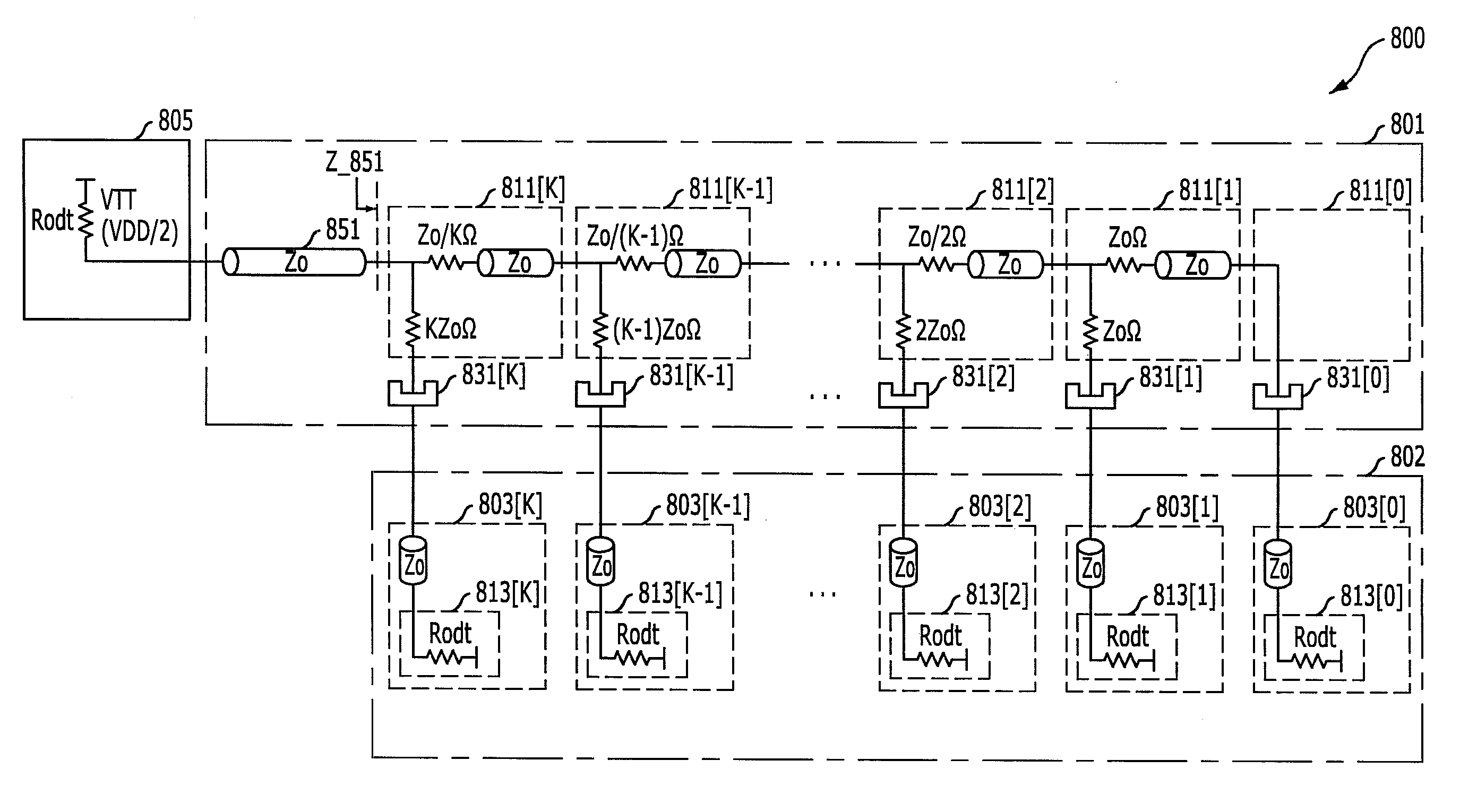
On-die system and method for controlling termination impedance of memory device data bus terminals
ActiveUS20080284465A1Logic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceControl memory
A system for controlling the termination impedance of memory device data bus terminals is fabricated on the same die as the memory device. The system includes a termination resistor connected to each data bus terminal, which is connected in parallel with several transistors that are selectively turned on to adjust the termination impedance. The transistors are controlled by a circuit that determines the resistance of the termination resistor and turns on the correct number of transistor to properly set the termination impedance. In one example, the resistance of the termination resistor is determined by directly measuring a resistor of the same type as the termination resistor. In another example, the resistance of the termination resistor is determined indirectly by measuring parameters that affect the resistance of the termination resistor. In either case, the system can maintain the termination impedance of the data bus terminals constant despite changes in the termination resistor.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
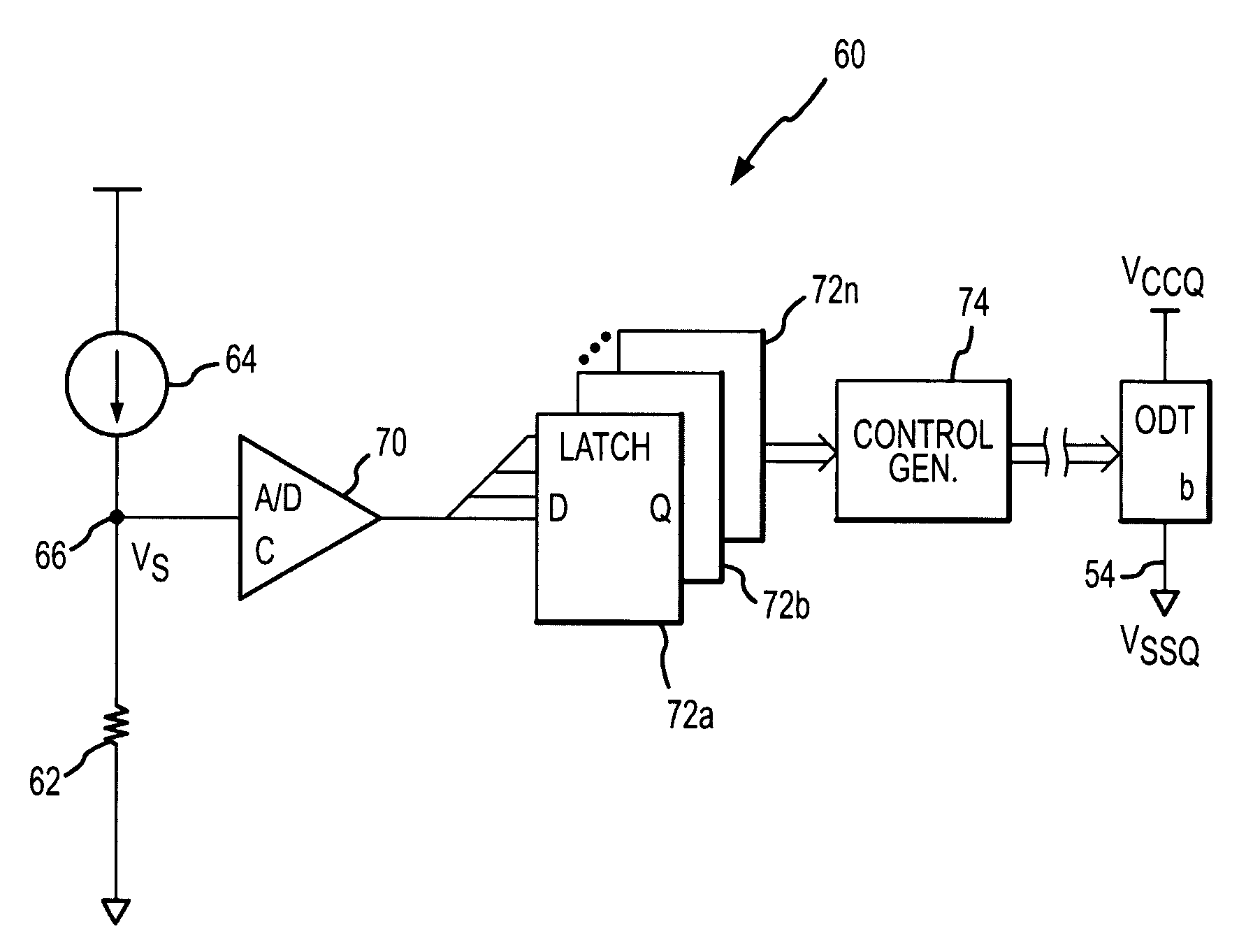
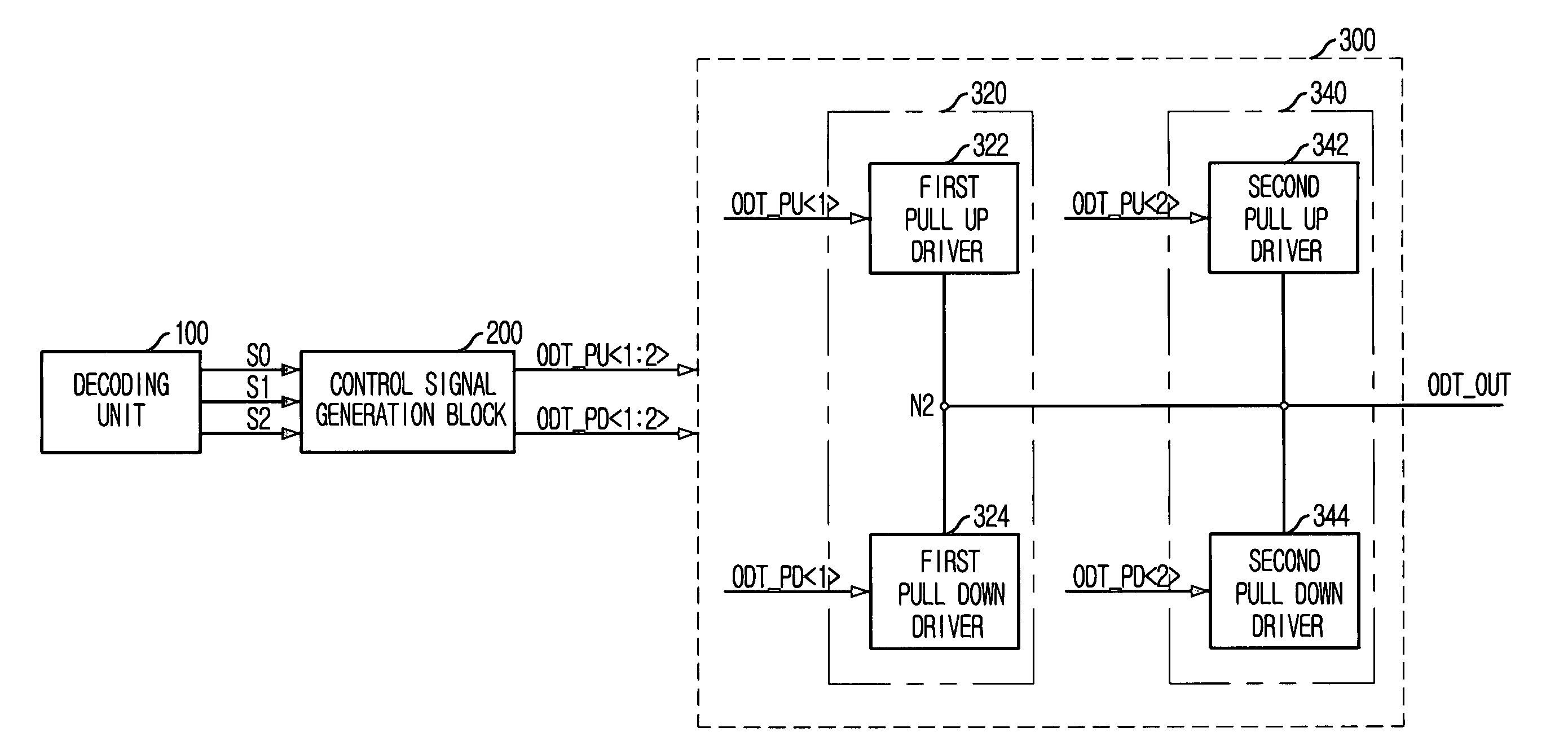
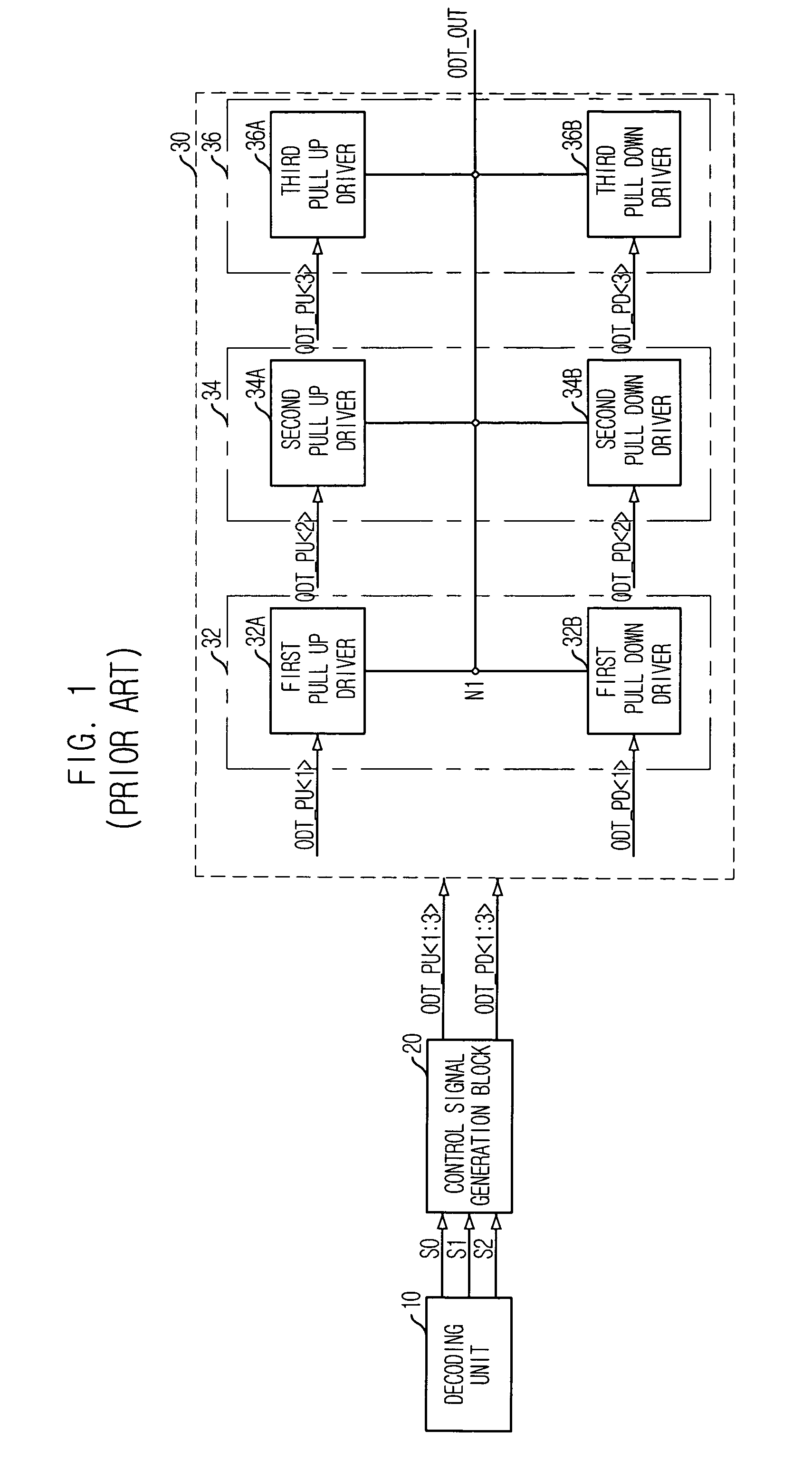
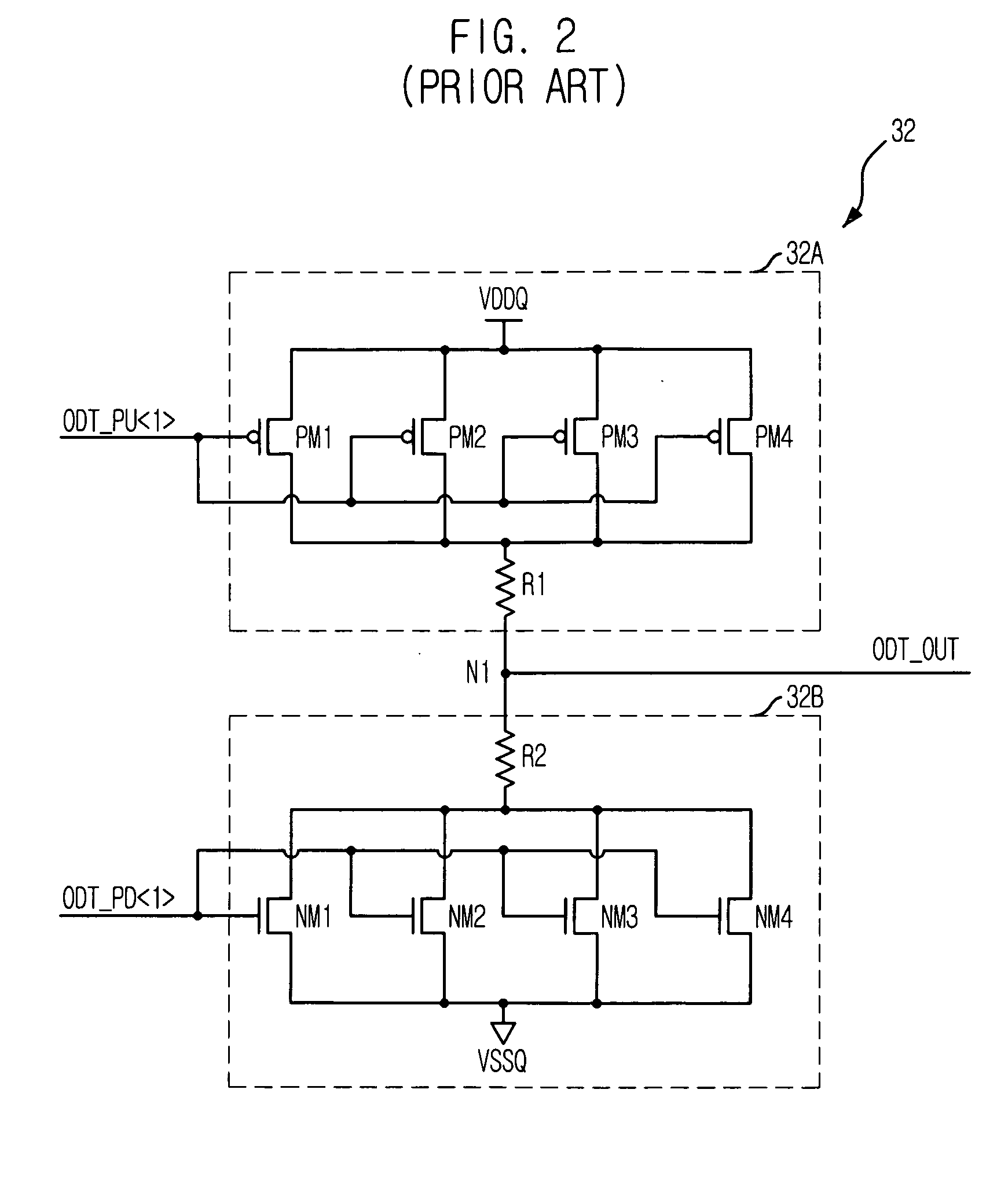
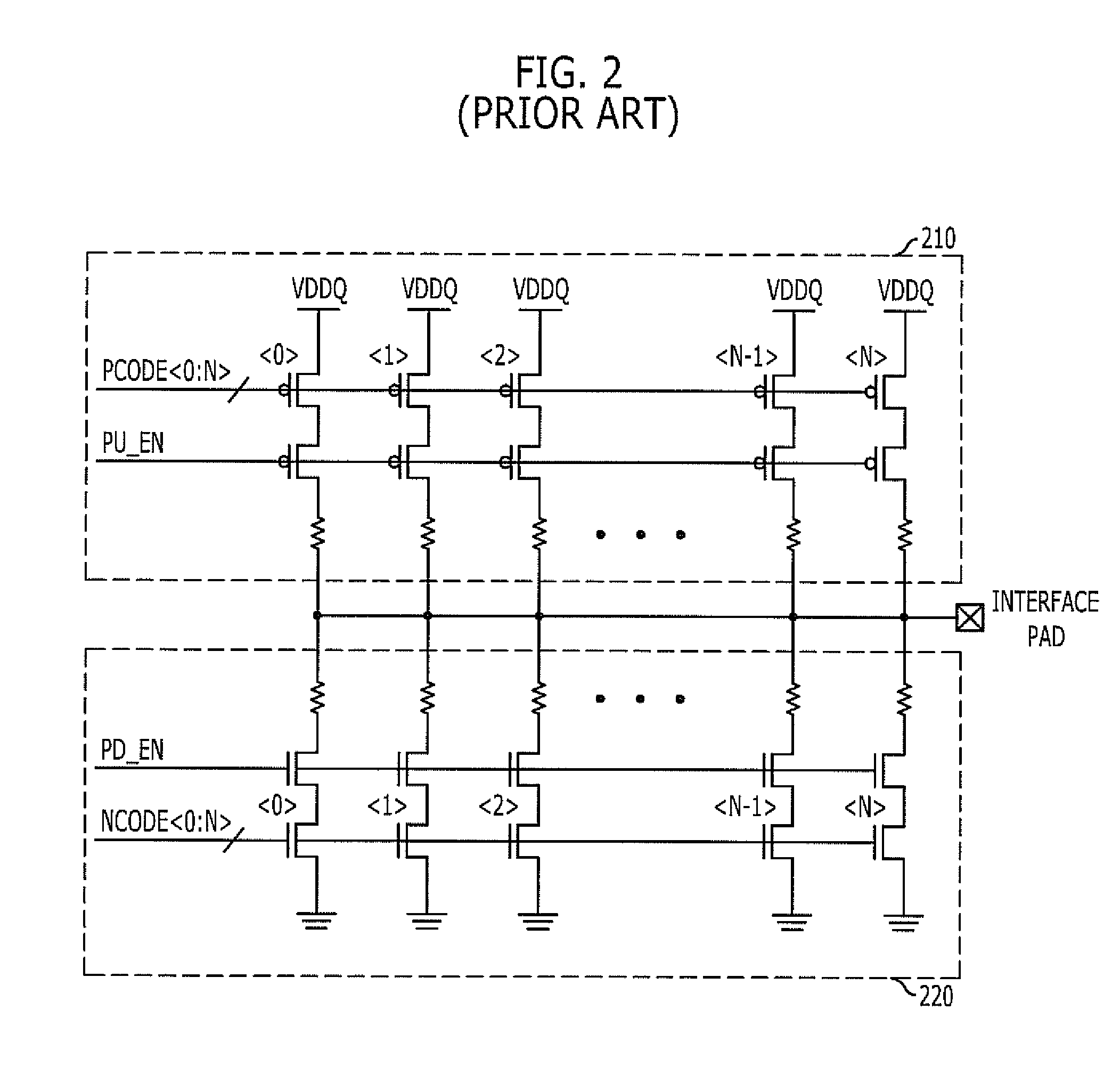
Semiconductor memory device with on-die termination circuit
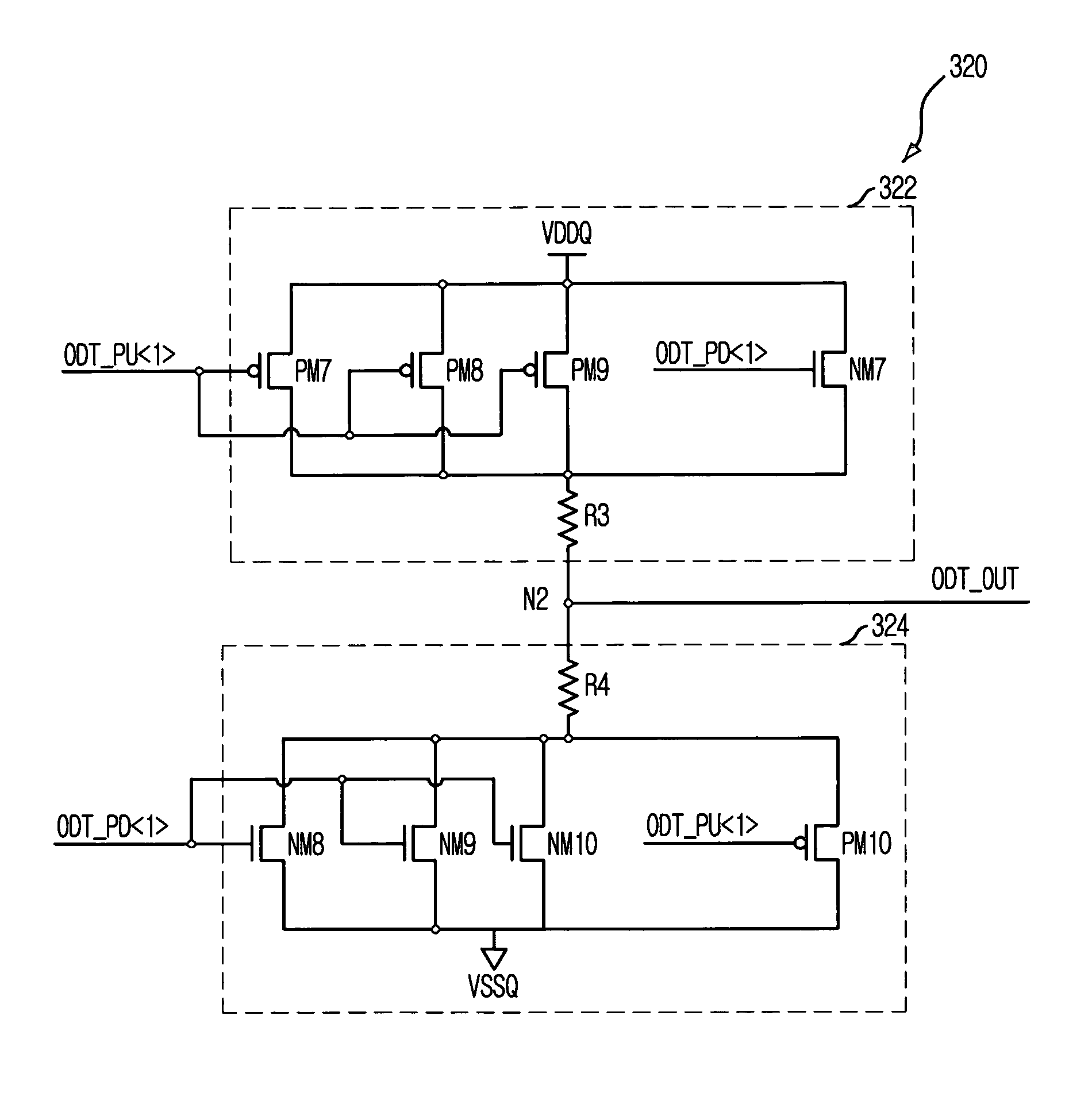
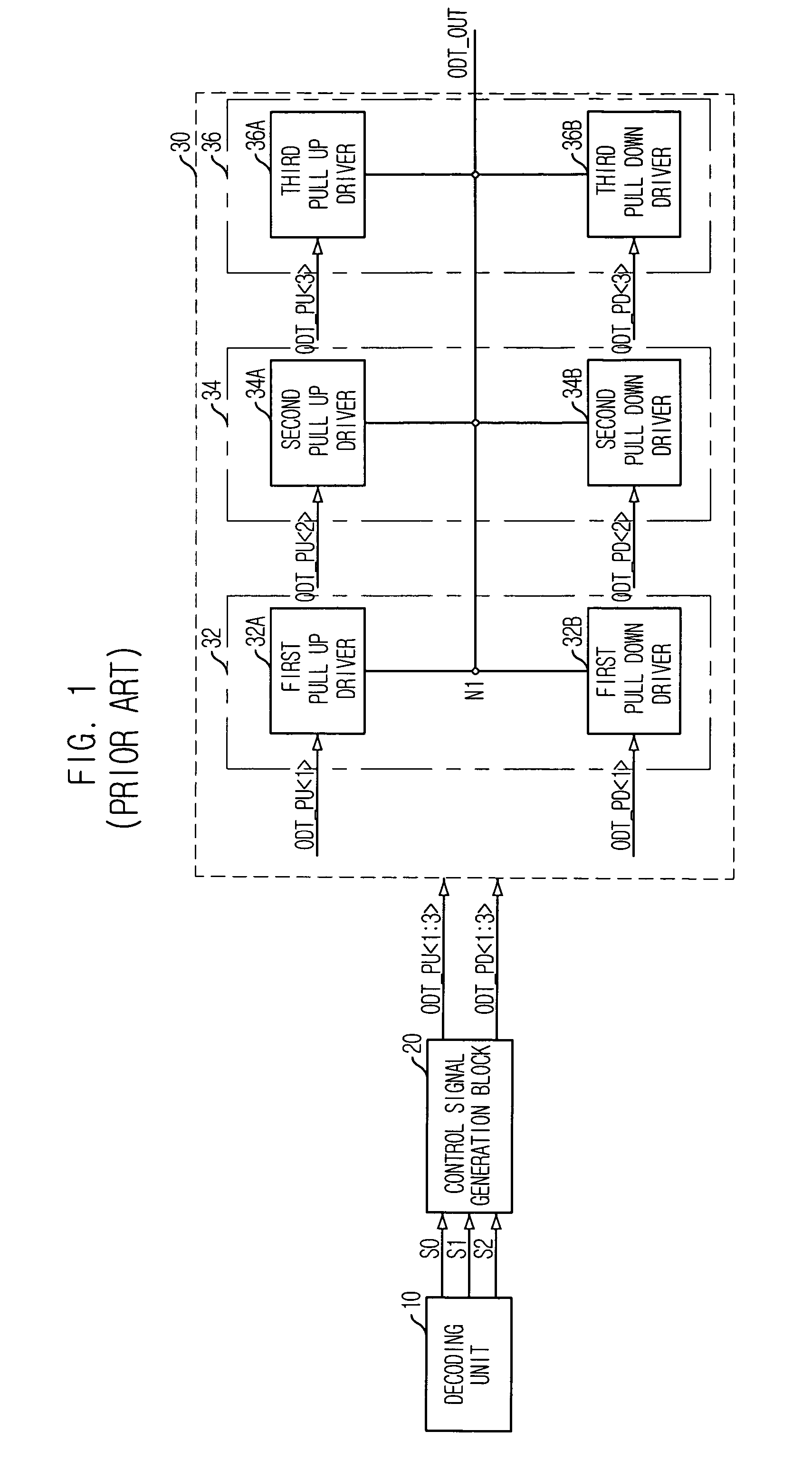
ActiveUS20060091901A1Stable effective termination resistance valueEffective valueLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsControl signalProcessor register
An on-die termination circuit with a stable effective termination resistance value and stabilized impedance mismatching. The on-die termination circuit includes: a decoding unit for decoding set values of an extended mode register set; an ODT output driver block including a plurality of output driver units connected in parallel with an output node for outputting an output signal and assigned with different resistance values; and a control signal generation block for generating a plurality of pull up and pull down control signals for turning on / off the plurality of output driver units in response to output signals of the decoding unit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
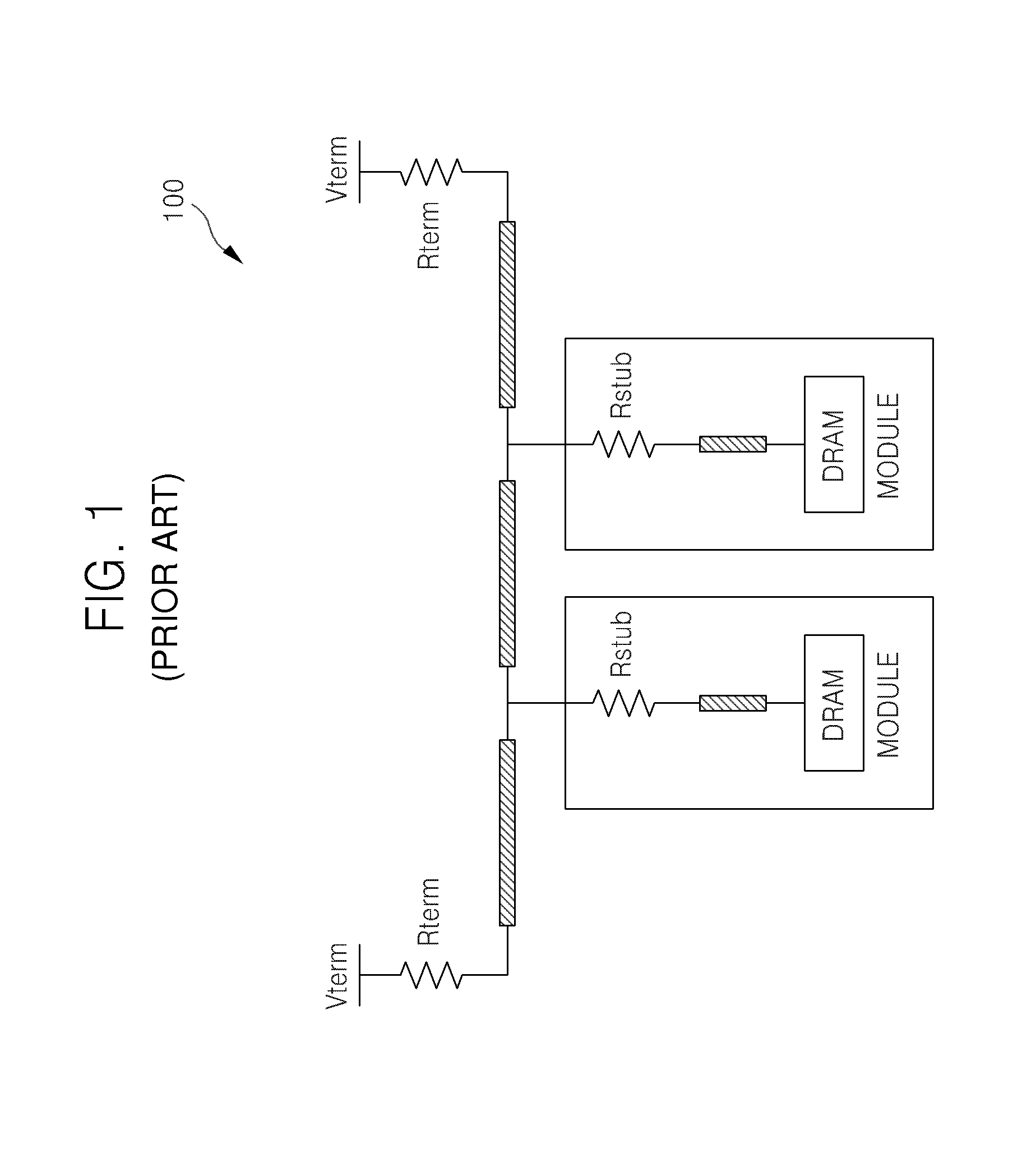
Bi-directional multi-drop bus memory system
ActiveUS20090313410A1Logic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsMultidrop busEngineering
A bus system includes a plurality of stubs; a plurality of connectors, each of which is serially coupled between a corresponding one of the stubs and a corresponding one of memory modules; a plurality of first serial loads, each of which is serially coupled to a corresponding one of the connectors; and a plurality of second serial loads, each of which is serially coupled to characteristic impedance of a transmission line of a corresponding one of the stubs, wherein the first and the second serial loads are determined to be impedance matched at each transmission line terminal of the stubs.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC +1
Reduced power differential type termination circuit
ActiveUS7750666B2Reduce power consumptionImprove integrityInput/output impedence modificationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsVoltage generatorTransmission gate
A reduced power differential type termination circuit for use in SSTL, HSTL and other transmission line systems reduces power consumption. A differential type termination circuit may comprise first and second nodes for coupling, respectively, to first and second transmission lines; a first impedance coupled between the first transmission line and a third node; a second impedance coupled between the second transmission line and the third node; and a low direct current reference voltage generator for generating a reference voltage applied to the third node. The first and second transmission lines may transmit complimentary signals. The first and second impedances may be symmetric or asymmetric. The first impedance may match the second impedance. The first and second impedances may, respectively, match the impedances of the first and second transmission lines. The first and / or second impedances may include a bidirectional switch, such as a transmission gate, to enable and disable the termination circuit.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
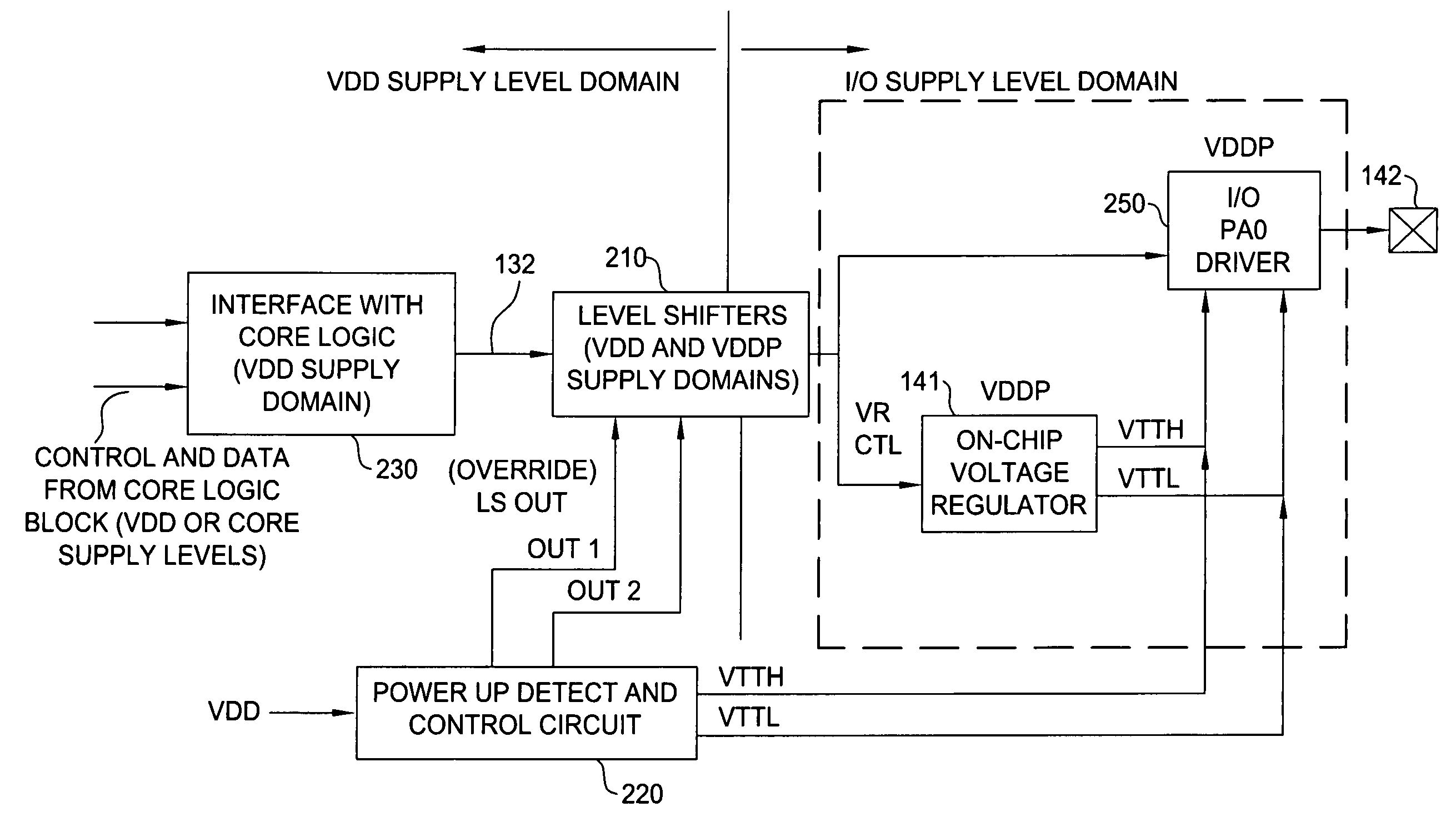
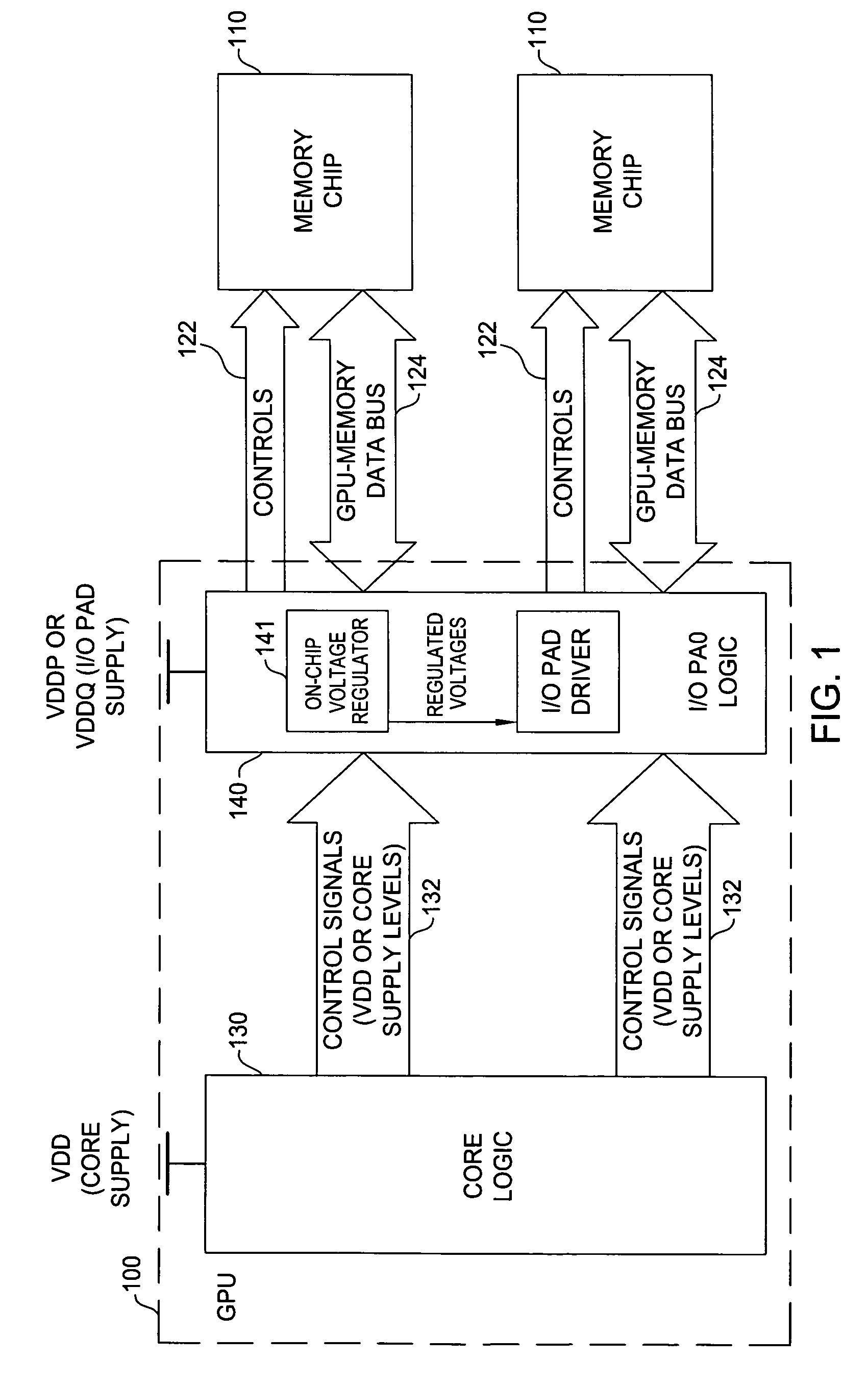
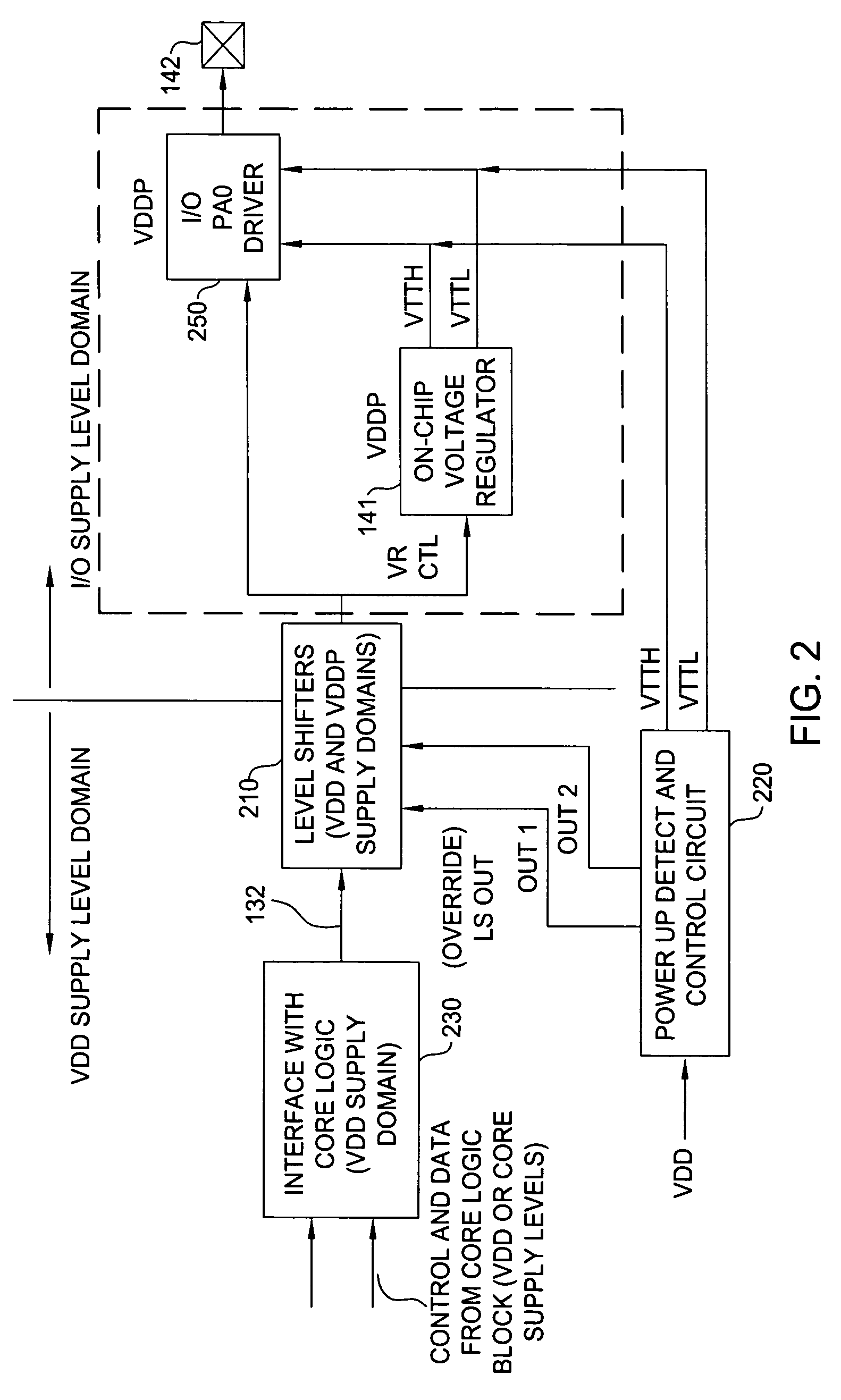
Circuit technique to prevent device overstress
ActiveUS7619444B1Avoid applicationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsPulse automatic controlControl signalVoltage regulation
Techniques and circuits for ensuring one or more circuit components are not subjected to voltage levels above their rated voltage tolerance due to core logic and I / O logic supply voltages reaching final voltage levels at different times are provided. According to some embodiments, an internal voltage supply sense circuit may monitor a level of a voltage supply that powers core logic that generates control signals used to program a voltage regulator. In response to determining the core logic voltage supply is below a predetermined level, the sense circuit may generate one or more regulated voltage signals to override regulated voltage signals generated by the voltage regulator.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
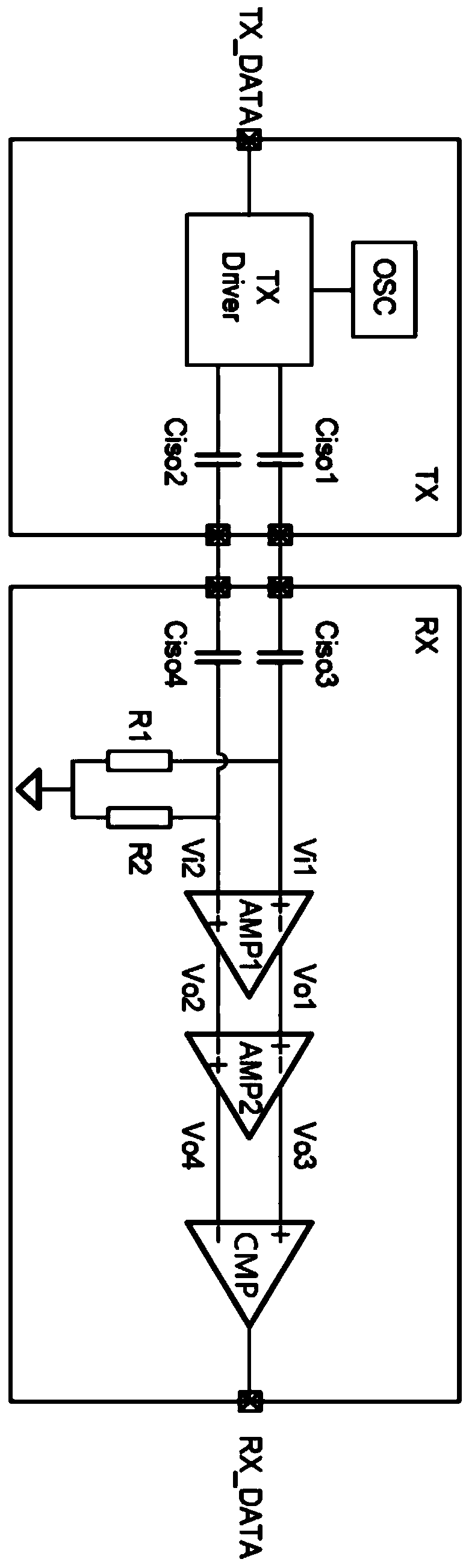
Differential signal amplification circuit, digital isolator, and digital receiver
ActiveCN111446935ASuppresses abnormal signal transmissionLogic circuit coupling arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceIsolatorSoftware engineering
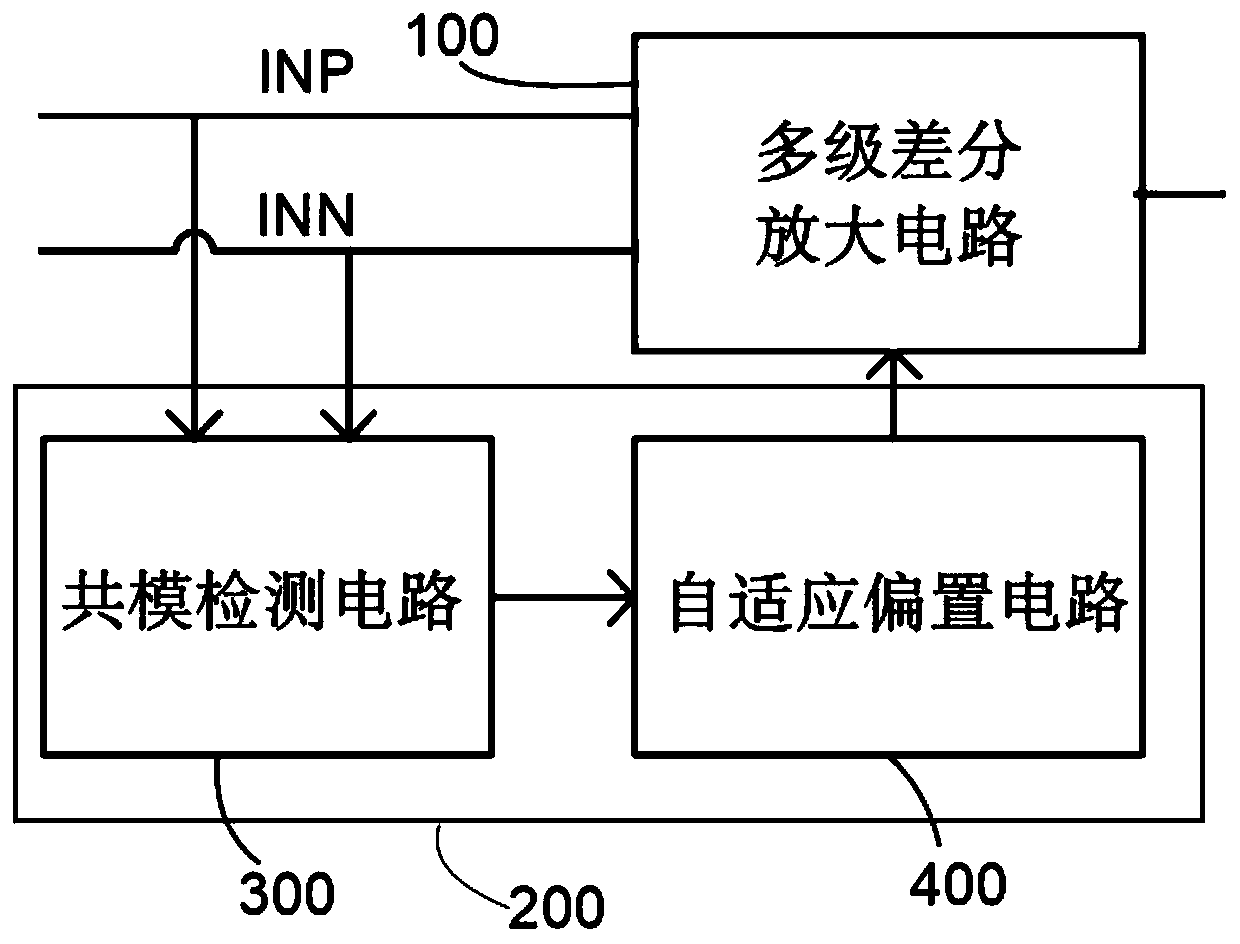
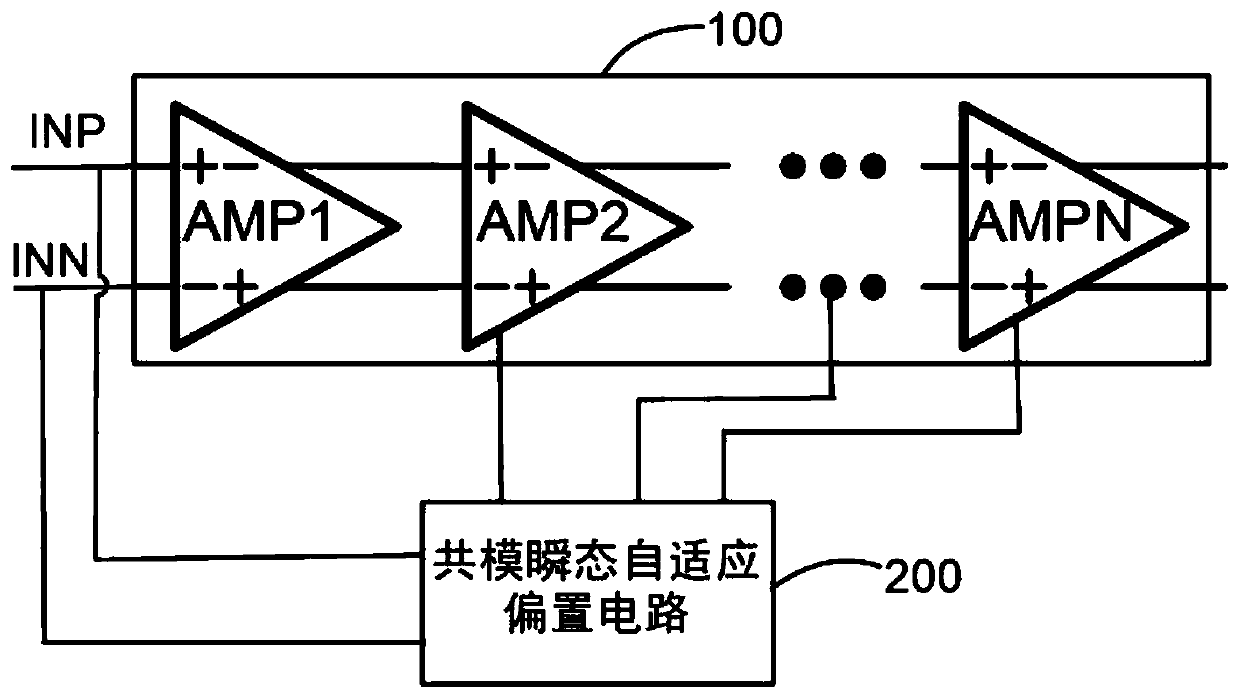
The invention discloses a differential signal amplification circuit, and a digital isolator and a receiver using the differential signal amplification circuit. The differential signal amplifying circuit comprises a multi-stage differential amplifier and a common-mode transient self-adaptive biasing circuit; and the common-mode transient adaptive bias circuit is used for detecting positive or negative common-mode transient interference signals of the positive input end and the negative input end and providing bias current of at least one stage of differential amplifier above the second stage when the positive or negative common-mode transient interference signals are detected. According to the technical scheme, abnormal signal transmission caused by common-mode interference signals can be suppressed.
Owner:SUZHOU NOVOSENSE MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device with on-die termination circuit
ActiveUS7282955B2Effective valueLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsControl signalProcessor register
An on-die termination circuit with a stable effective termination resistance value and stabilized impedance mismatching. The on-die termination circuit includes: a decoding unit for decoding set values of an extended mode register set; an ODT output driver block including a plurality of output driver units connected in parallel with an output node for outputting an output signal and assigned with different resistance values; and a control signal generation block for generating a plurality of pull up and pull down control signals for turning on / off the plurality of output driver units in response to output signals of the decoding unit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
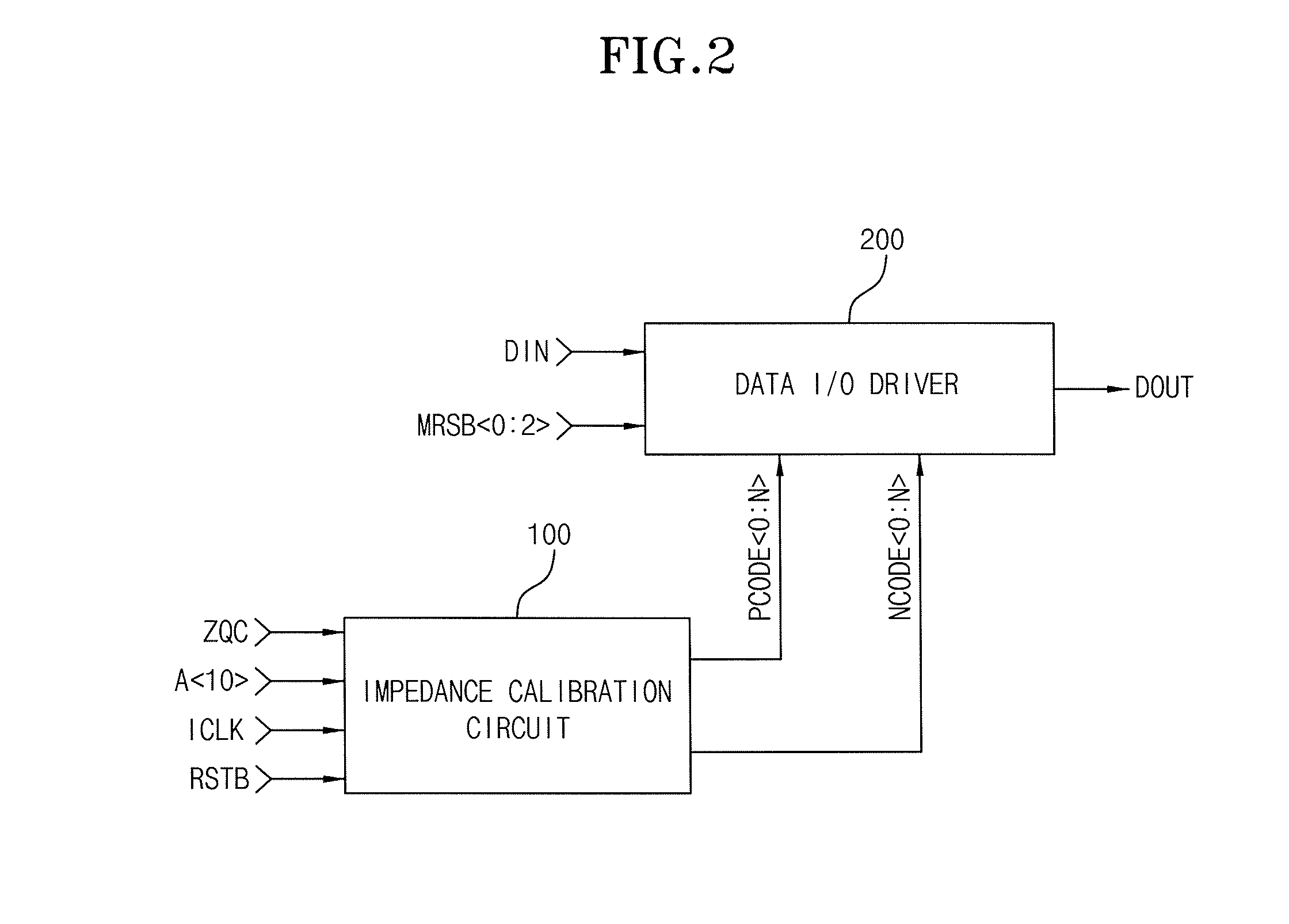
Impedance calibration circuit, semiconductor memory device with the impedance calibration circuit and layout method of internal resistance in the impedance calibration circuit
InactiveUS20090289658A1Easily impedance mismatchEasy to adjustInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsInternal resistanceEngineering
An impedance calibration circuit for impedance matching between a semiconductor memory device and an external device includes a driving circuit and a comparing circuit. The driving circuit has a plurality of internal resistances, with one or more of the internal resistances being a variable resistance. The driving circuit compares the impedance of the internal resistances to the input / output impedance of the external device in order to provide a calibration voltage. The comparing circuit compares the calibration voltage to a reference voltage and provides a code signal for calibrating the impedance corresponding to output data with the input / output impedance of the external device. The impedance calibration circuit calibrates an impedance mismatch between the impedance calibration circuit and a data input / output driver by adjusting the impedance of the impedance calibration circuit through the variable resistance.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Electronic Switch for Electronic Fuse
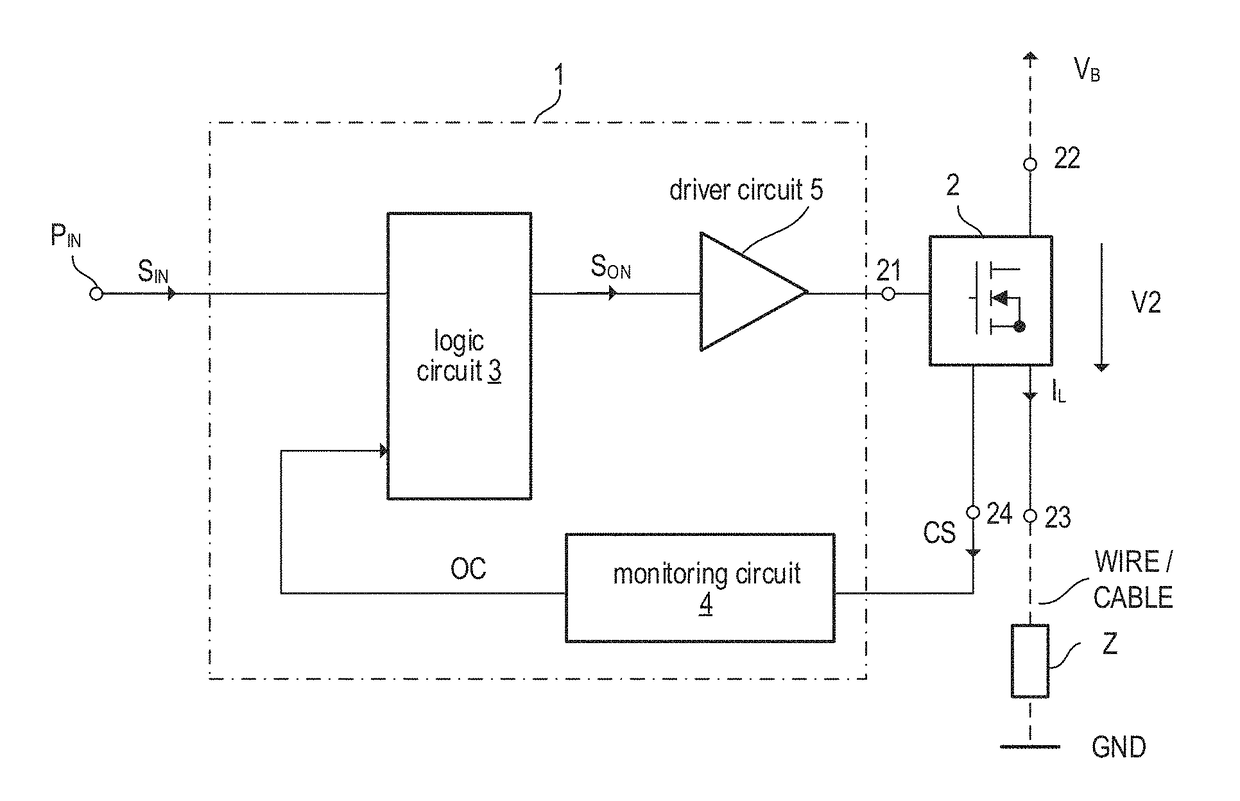
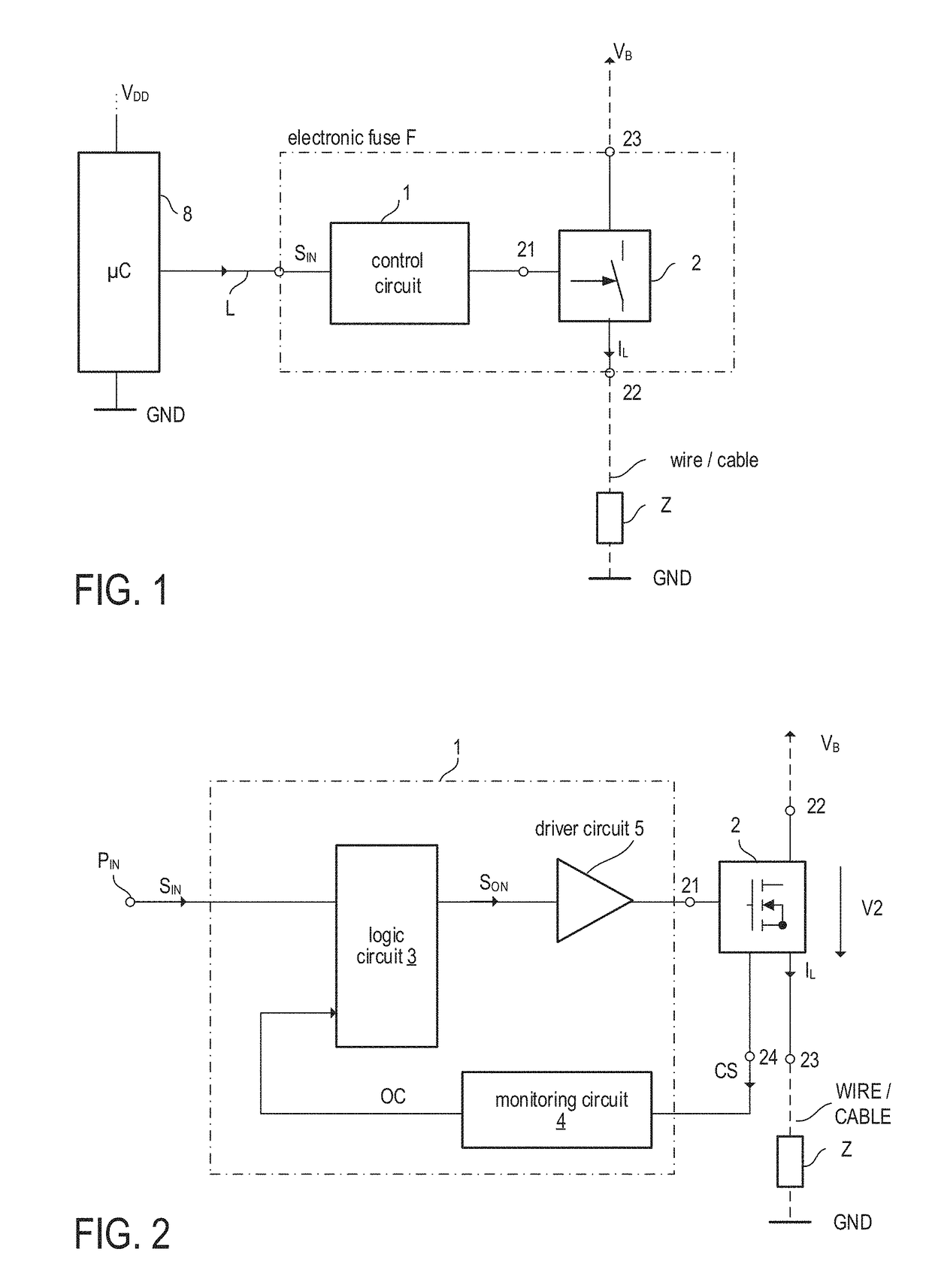
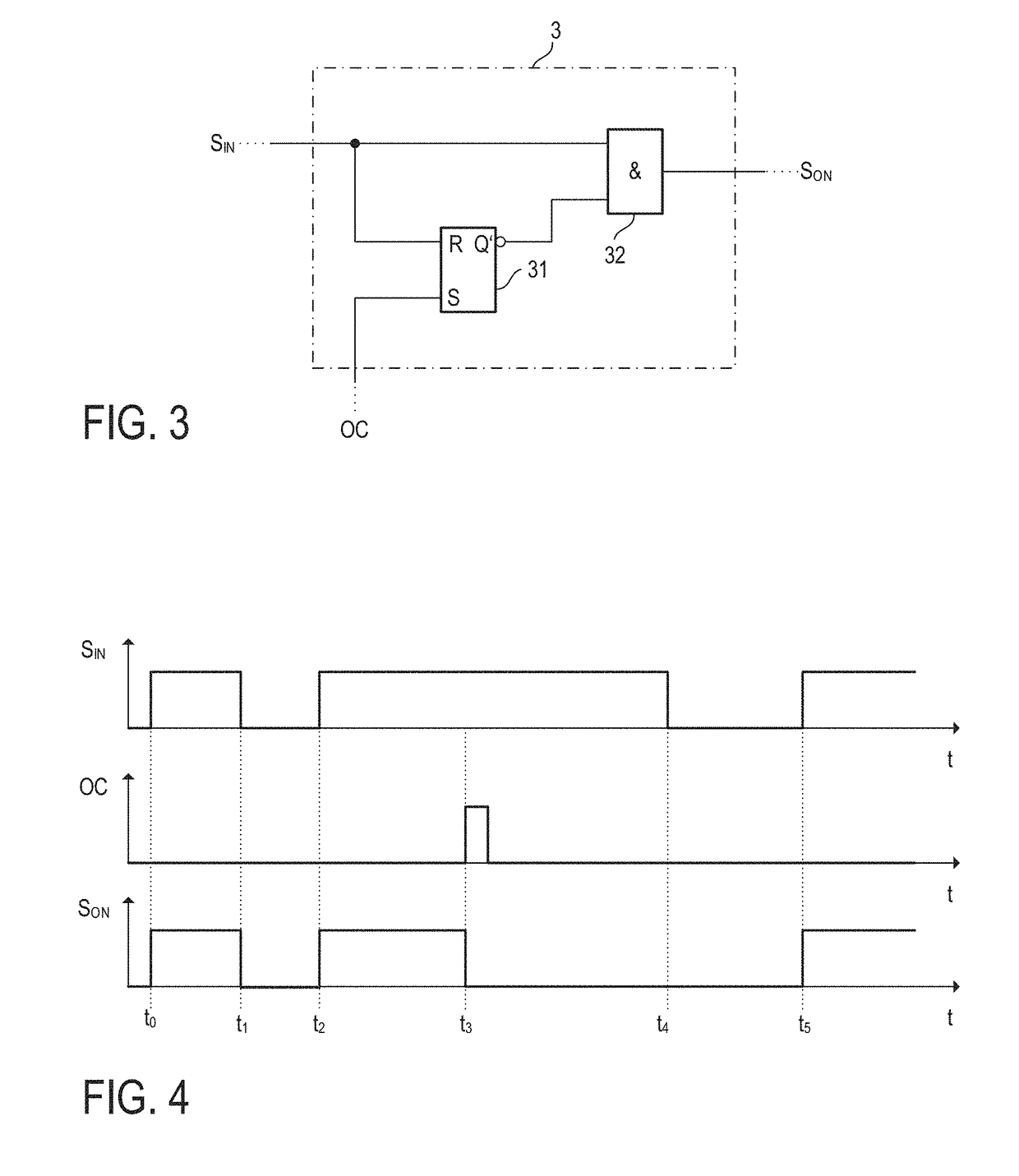
In accordance with one example, the electronic switch has a load current path operably coupled to a load via a wire; the electronic switch is configured to connect or disconnect a load current supply node and the load via the wire dependent on a drive signal. Further, the electronic fuse circuit includes a monitoring circuit configured to receive a current sense signal representing the load current passing through the wire and to determine a first protection signal based on the current sense signal and at least one wire parameter. The first protection signal is indicative of whether to disconnect the load current supply node from the load. Moreover, the electronic fuse circuit includes a logic circuit configured to receive at least one selection signal and to set the at least one wire parameter based on the at least one selection signal.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
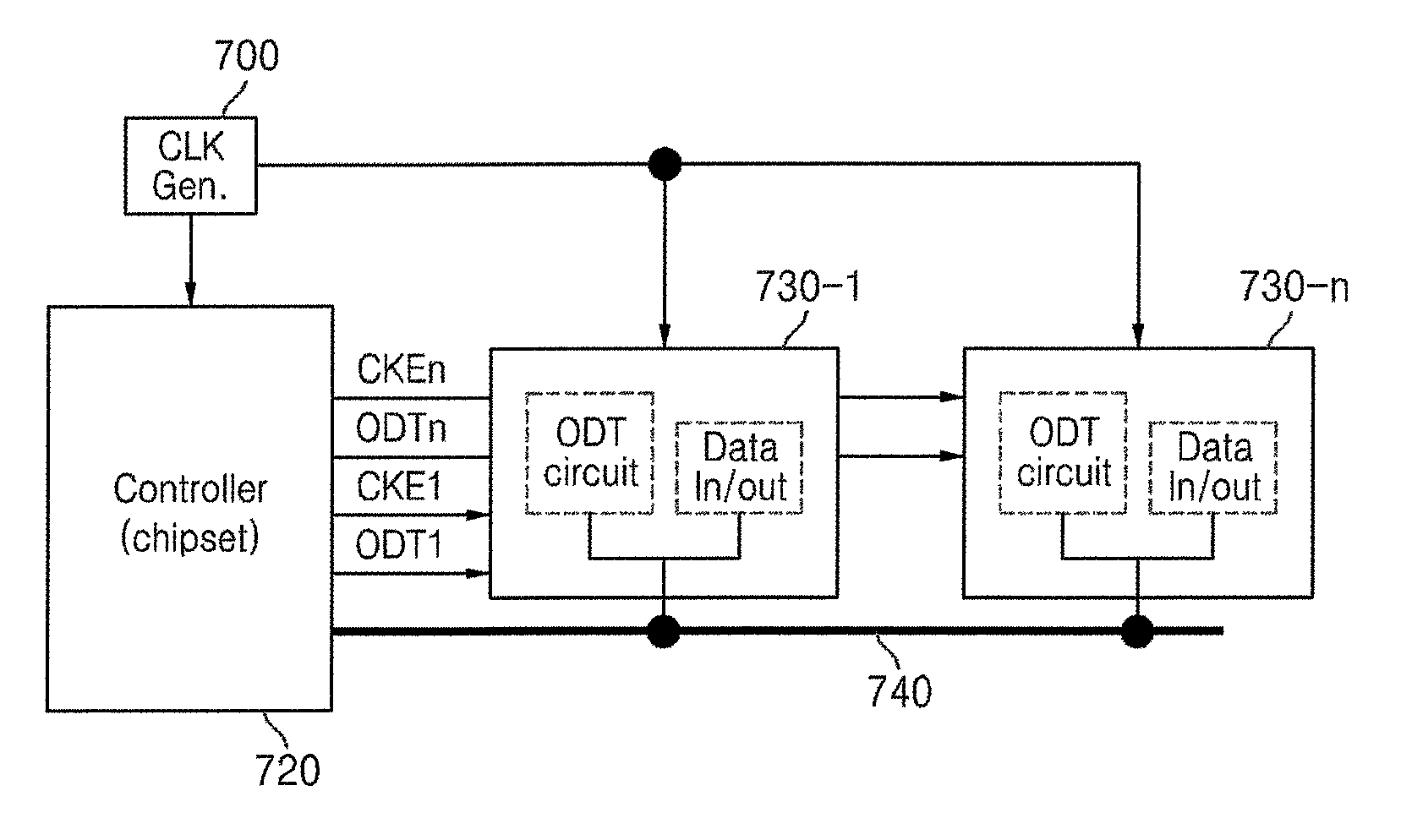
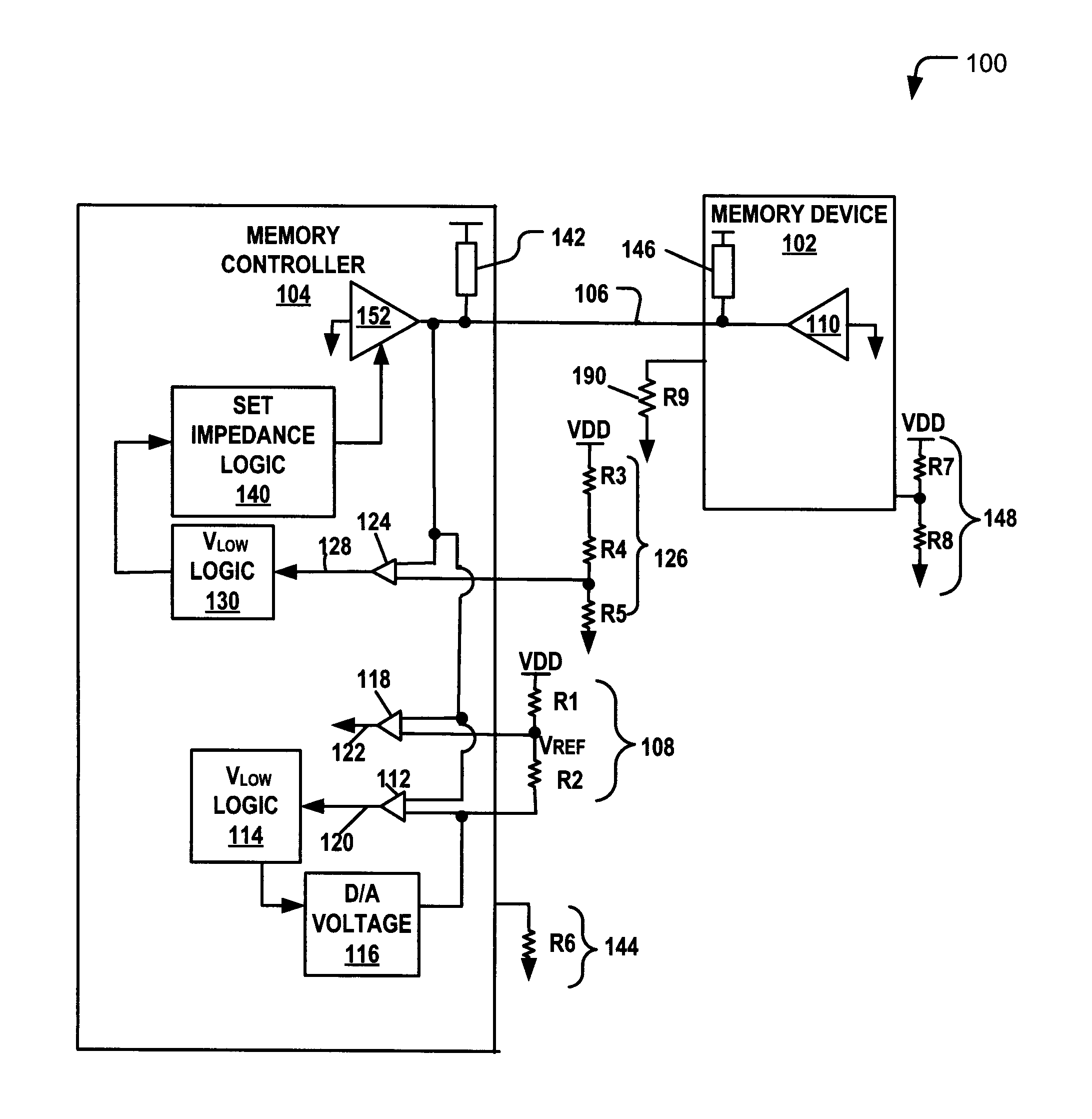
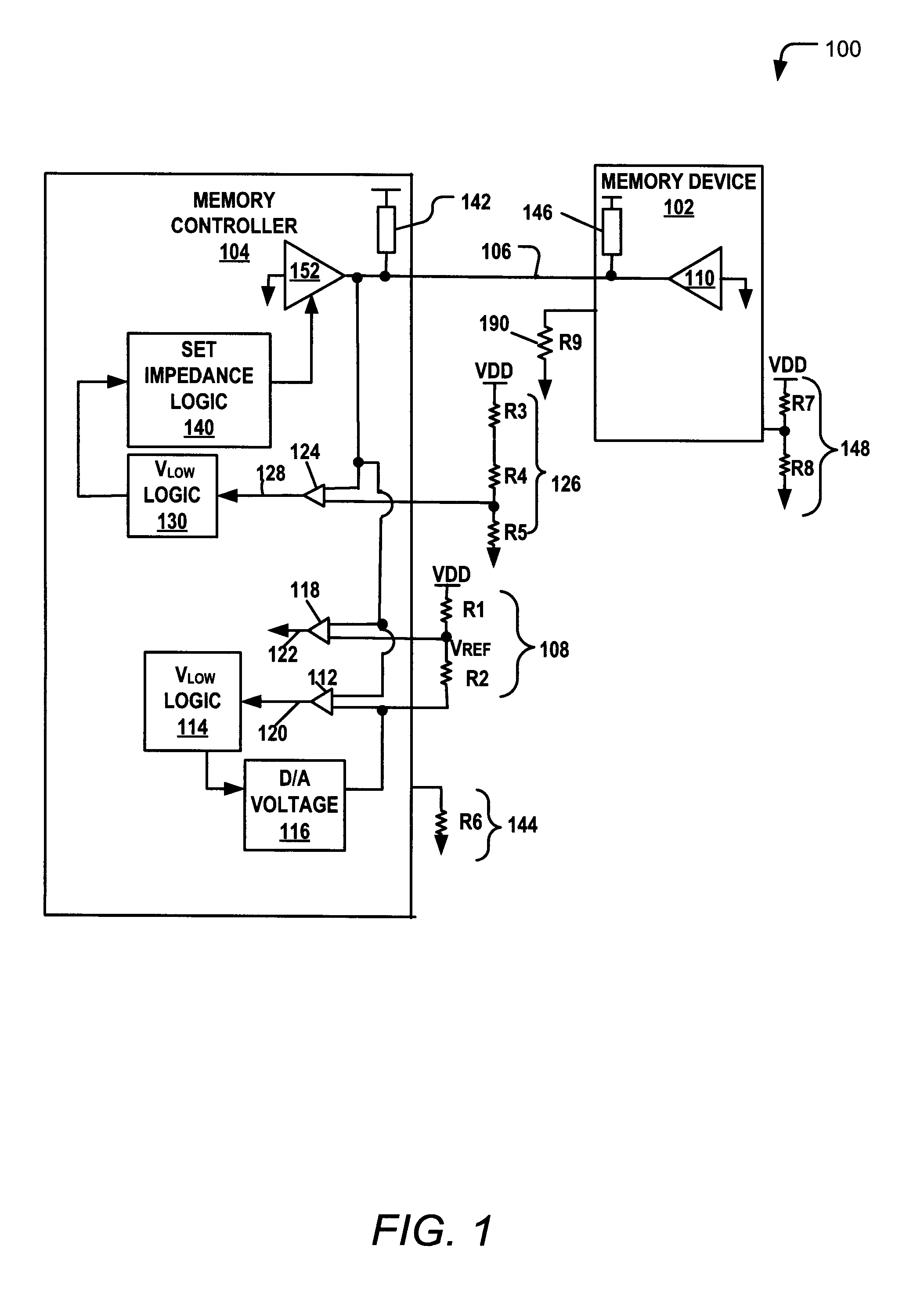
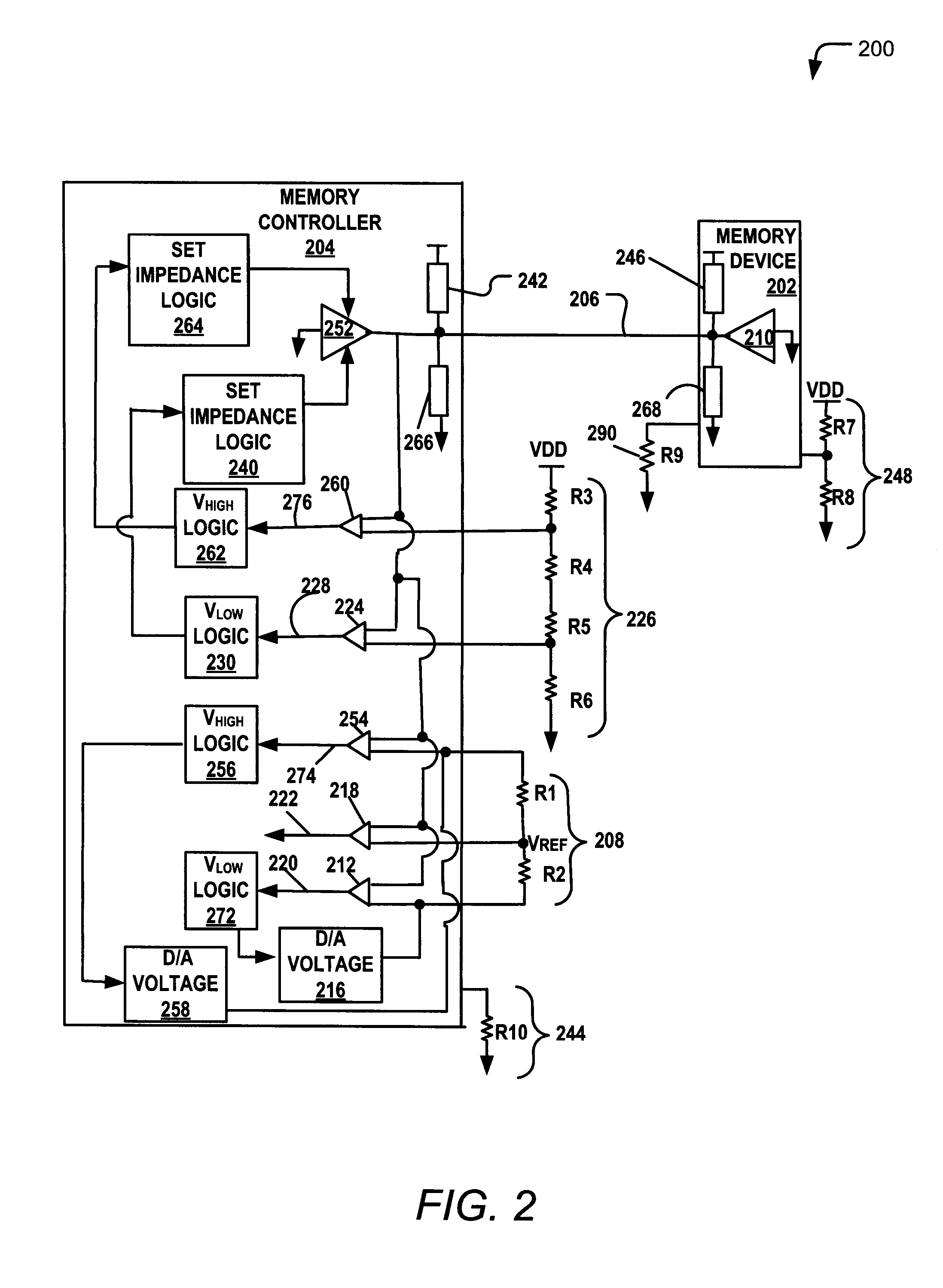
Training a Memory Controller and a Memory Device Using Multiple Read and Write Operations
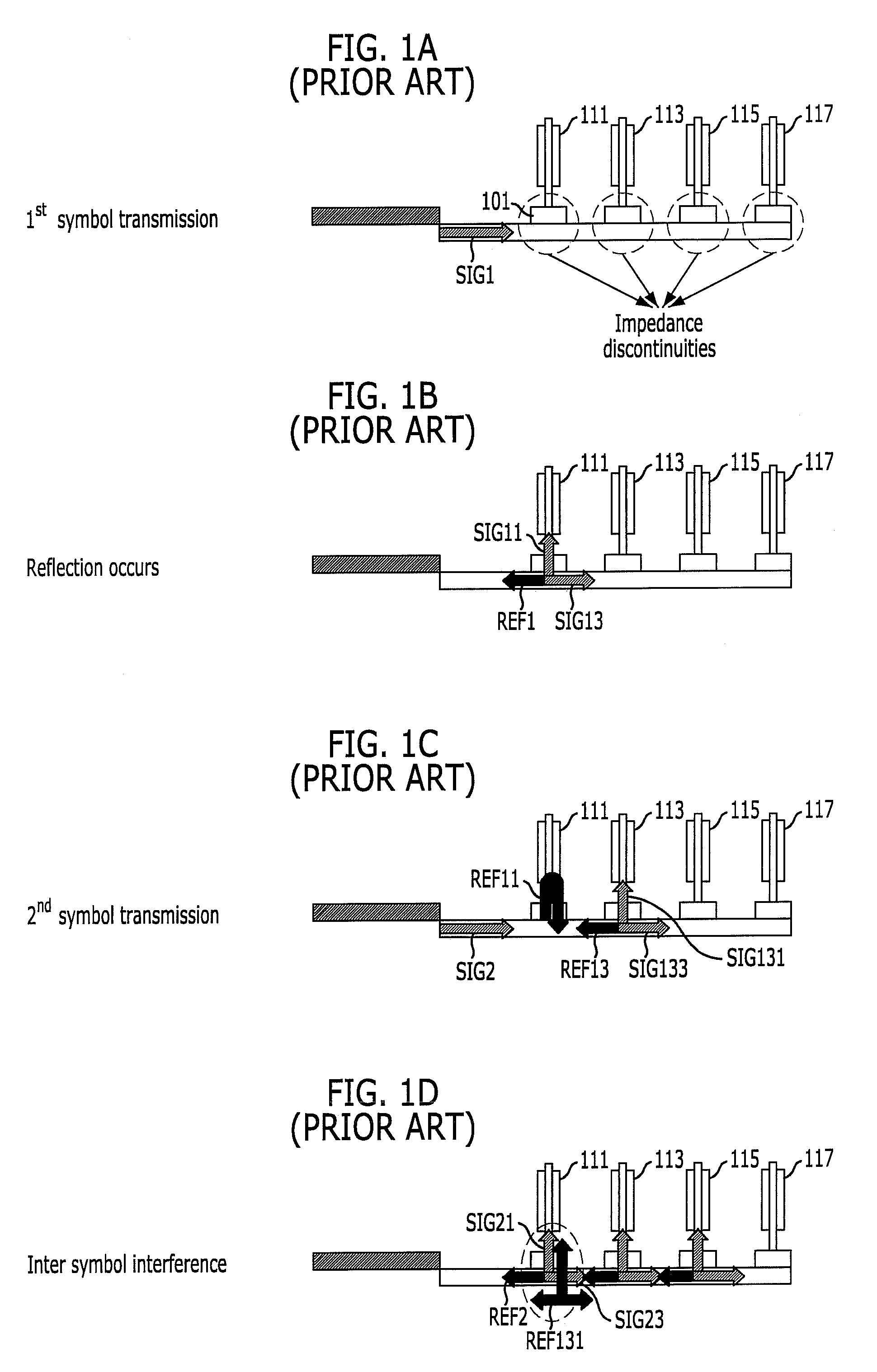
InactiveUS20110307671A1Reduce Signal ErrorSpeedLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsControl storeMemory controller
Systems and methods to set a voltage value associated with a communication bus that includes memory controller coupled to a memory device are disclosed. A particular method may include performing a first calibration operation associated with first data written from a memory controller to a memory device. A second calibration operation may be associated with second data read at the memory controller from the memory device. The operating parameter may be set based on a result of at least one of the first and the second calibration operations at the memory device or the memory controller.
Owner:IBM CORP
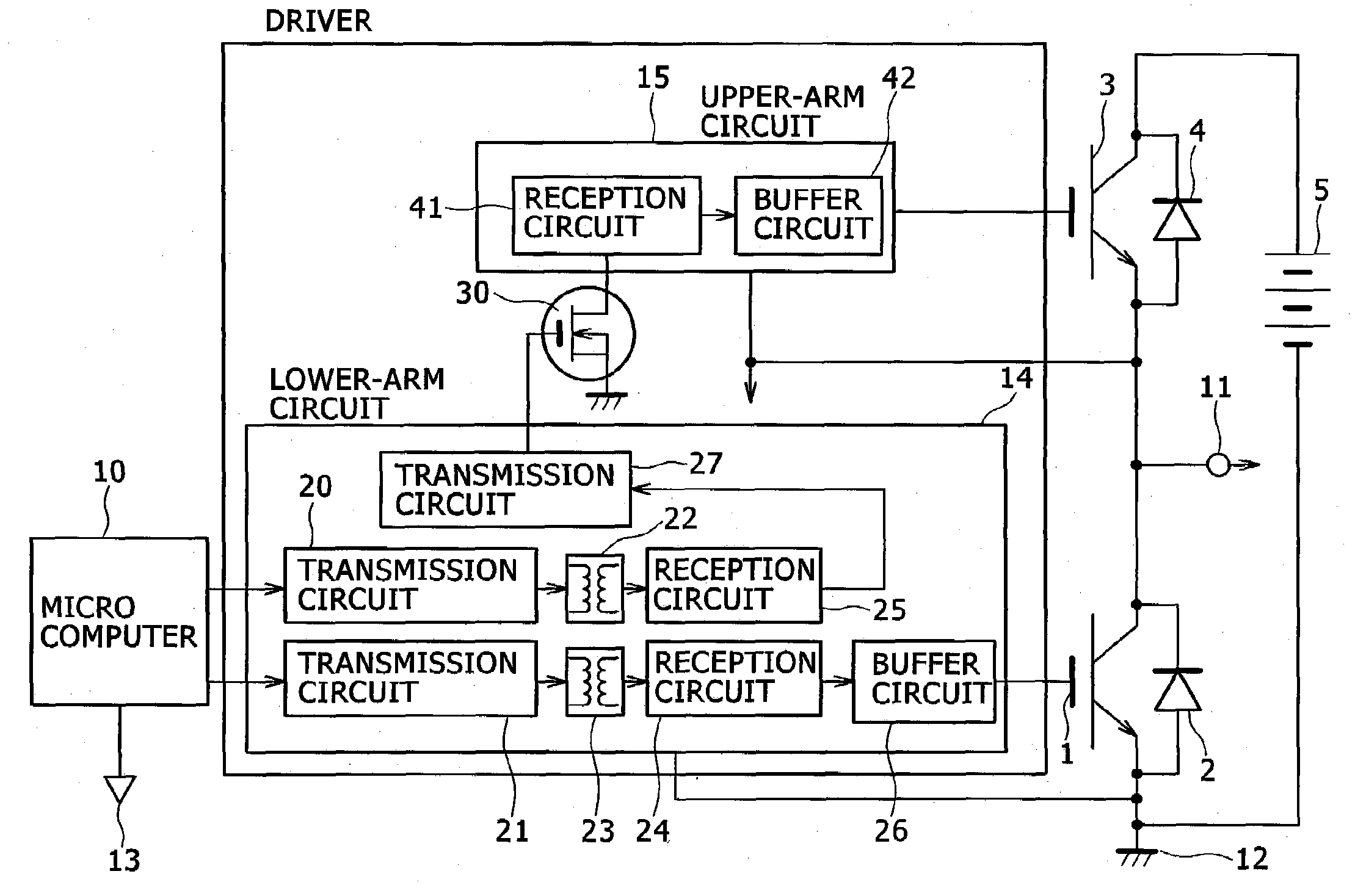
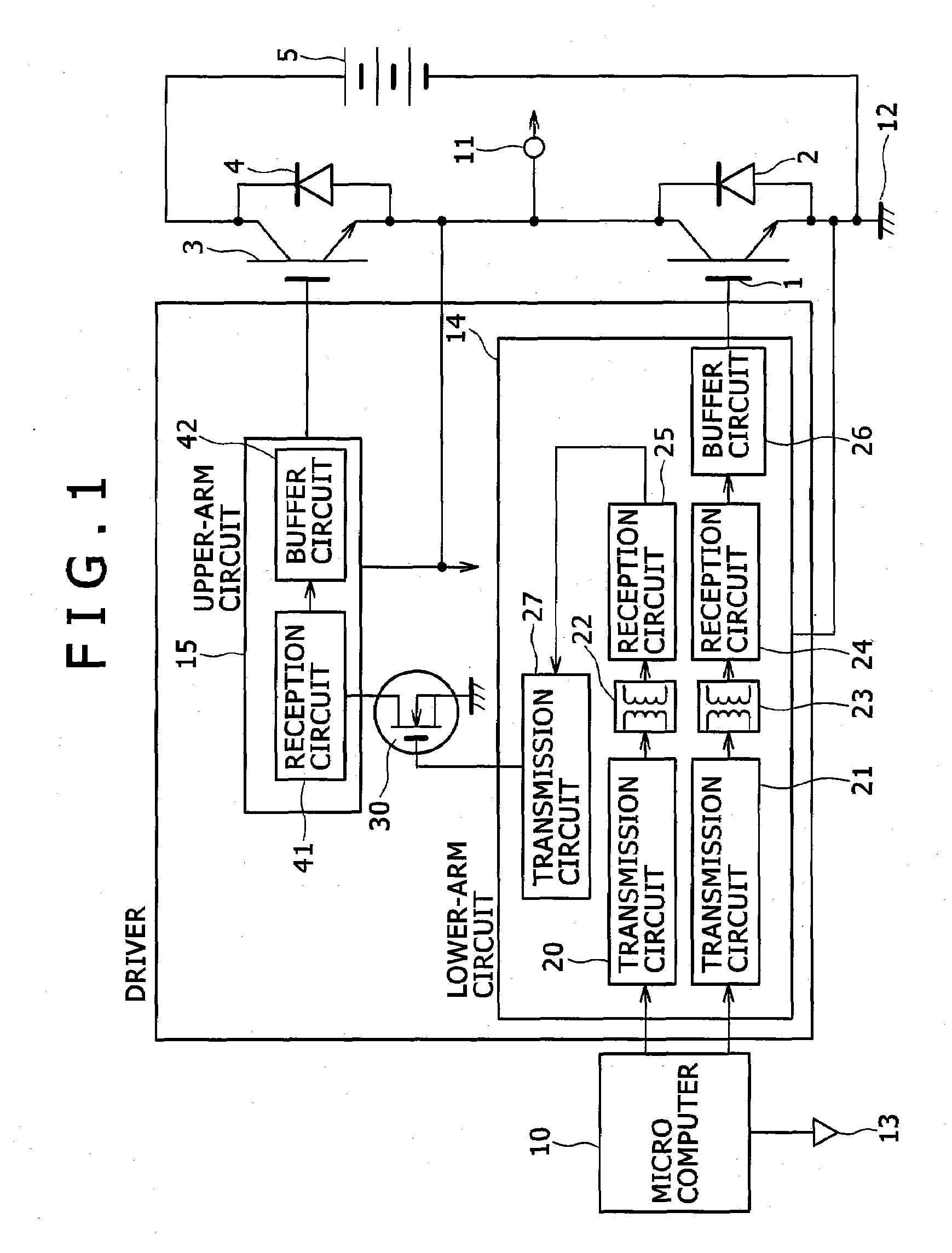
Electric Power Conversion Apparatus
InactiveUS20090230938A1Reduce deterioration in insulationReduce deteriorationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsAc-dc conversionControl signalEngineering
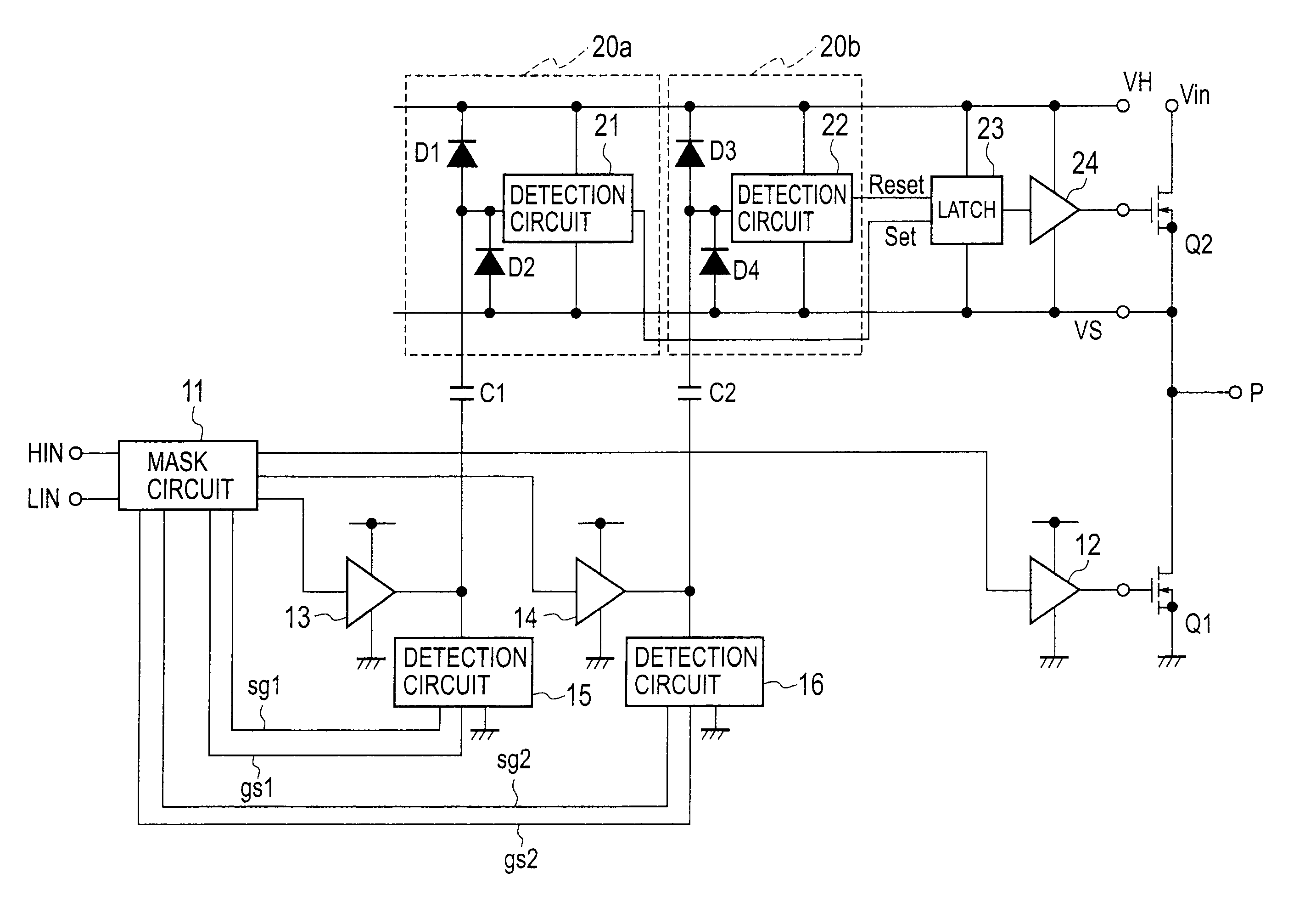
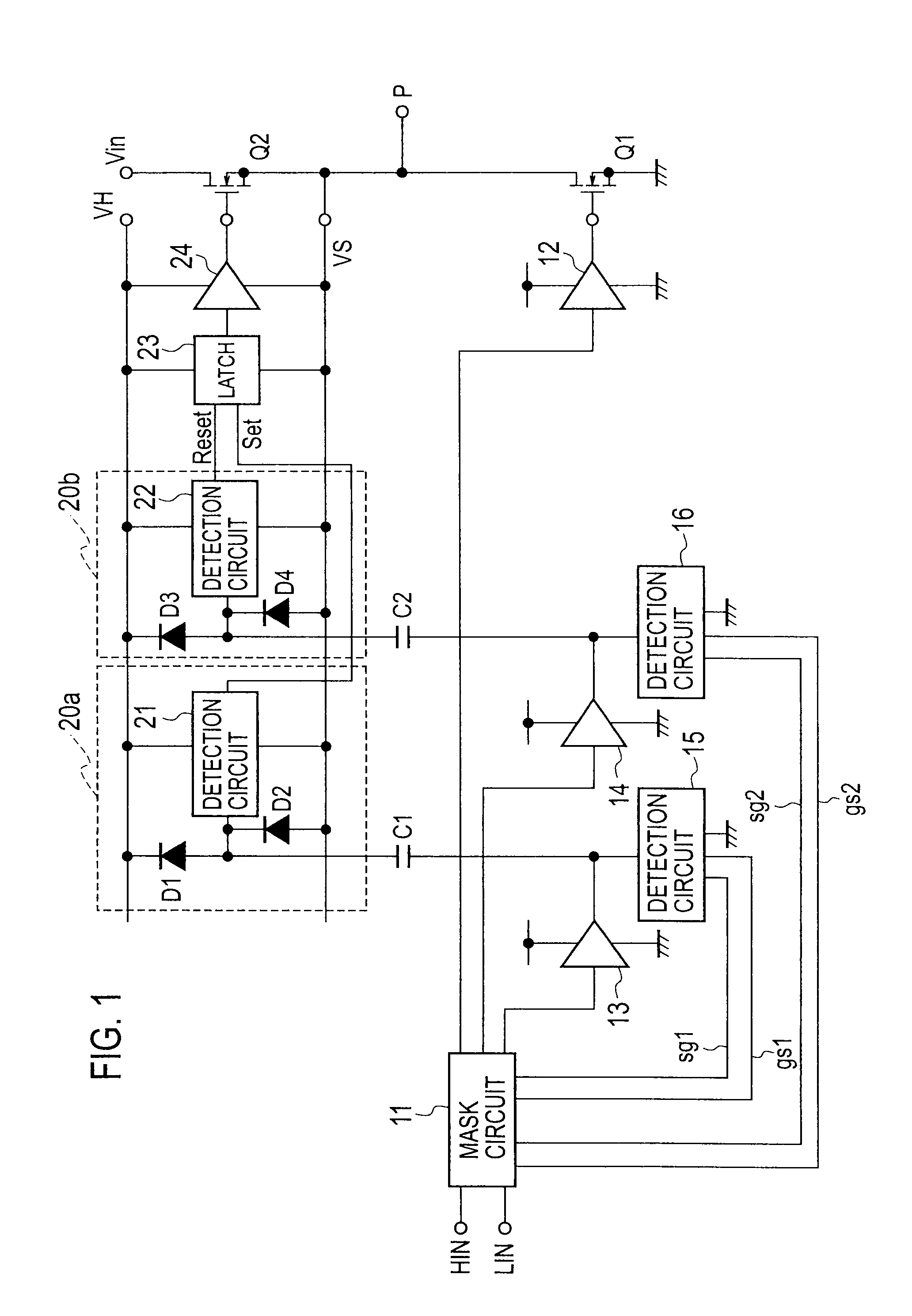
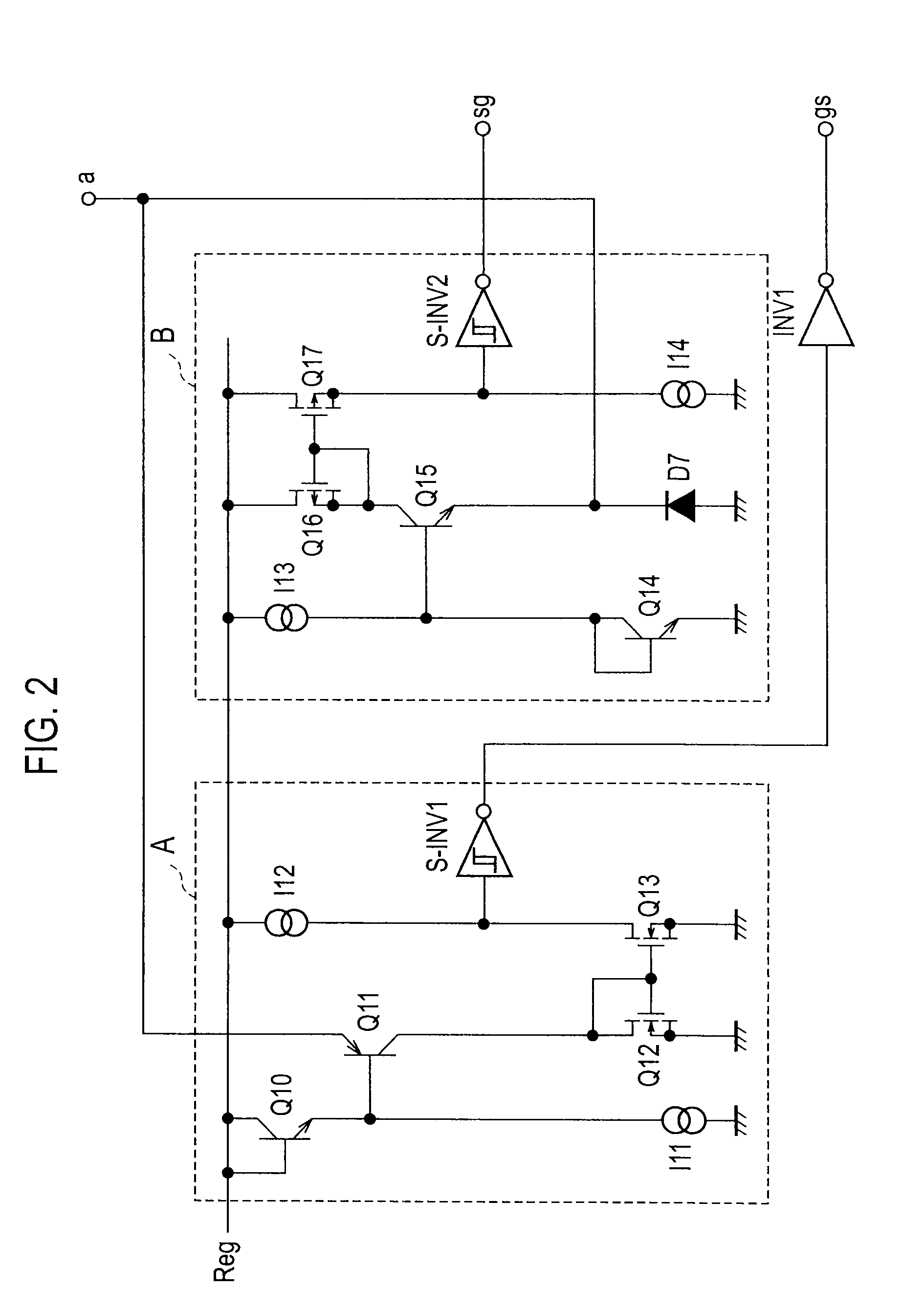
In an electric power conversion apparatus, there is reduced deterioration in insulation of a means which is provided inside an IC chip and transmits a signal from a low electric potential system to a high electric potential system. The electric power conversion apparatus includes a lower-arm circuit 14 which transmits control signals from a micro computer 10 through the pulse transformers 22 and 23 provided inside an IC chip and outputs the control signal transmitted through the pulse transformer 23 to a lower-arm IGBT 1, a high-voltage nMOS 30 which converts the electric potential of the control signal for an upper-arm IGBT 3 transmitted through the pulse transformer 22 of the lower-arm circuit 14 and an upper-arm circuit 15 which outputs the control signal of which the electric potential is converted by the high-voltage nMOS 30 to the upper-arm IGBT 3.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
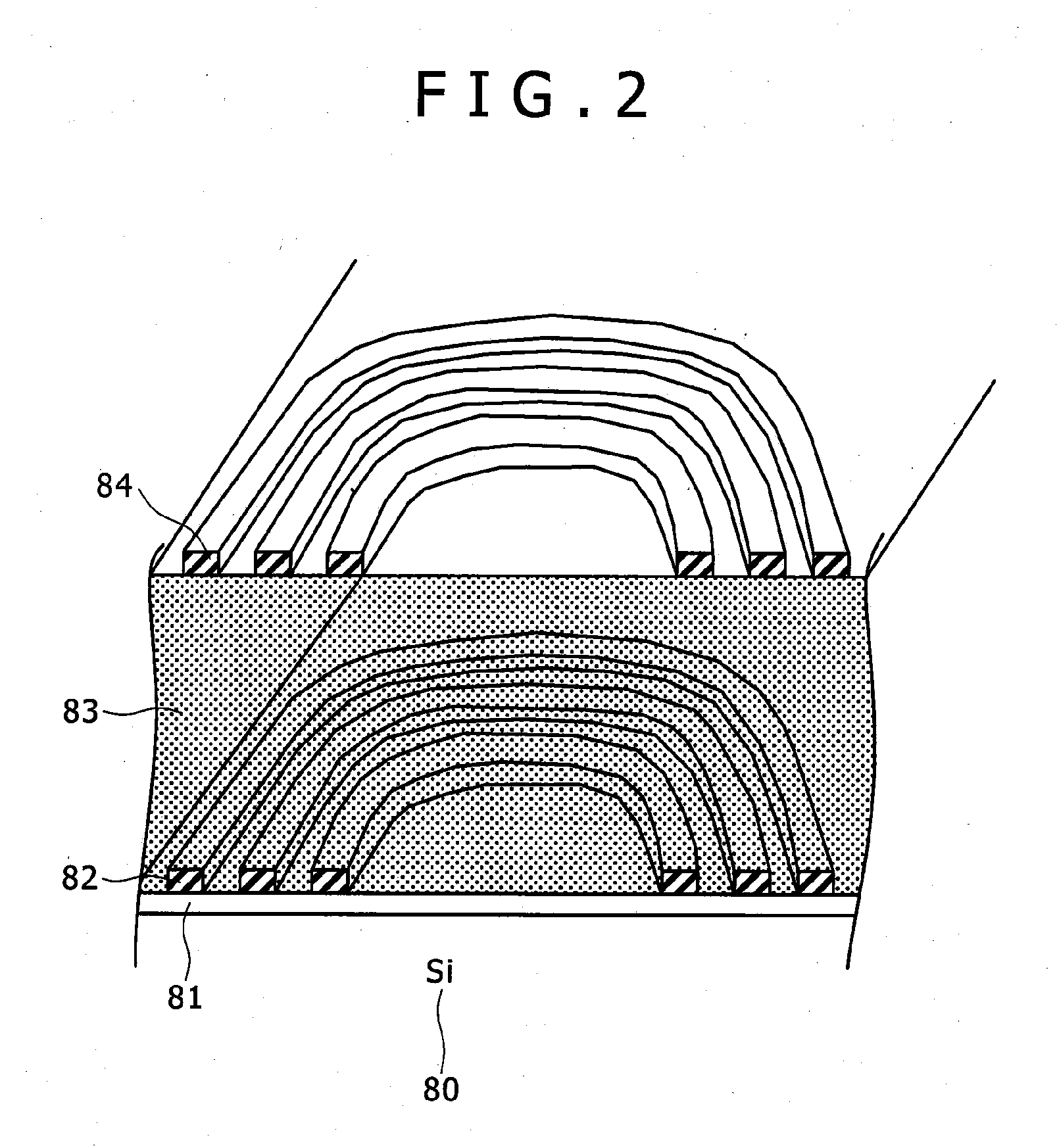
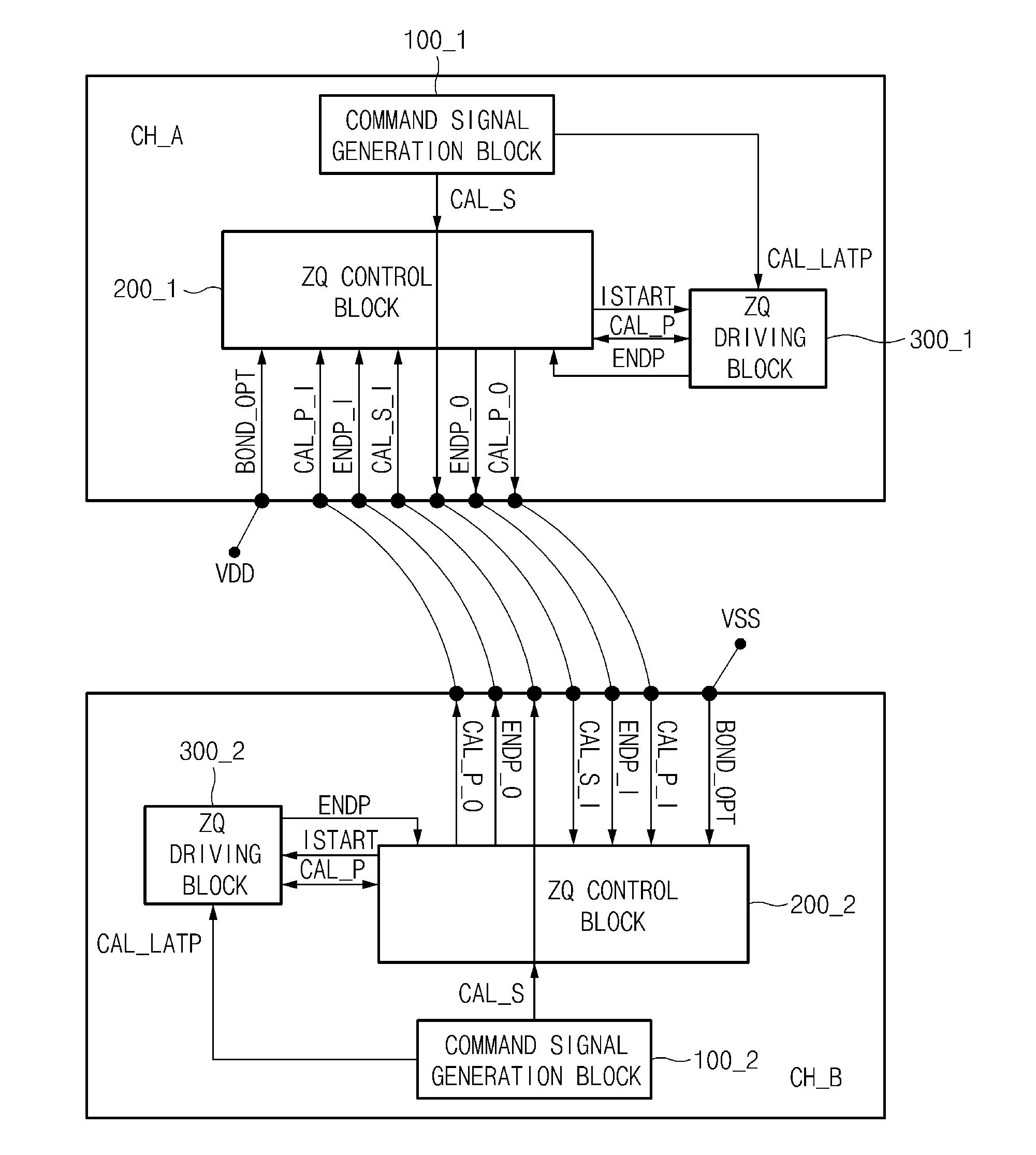
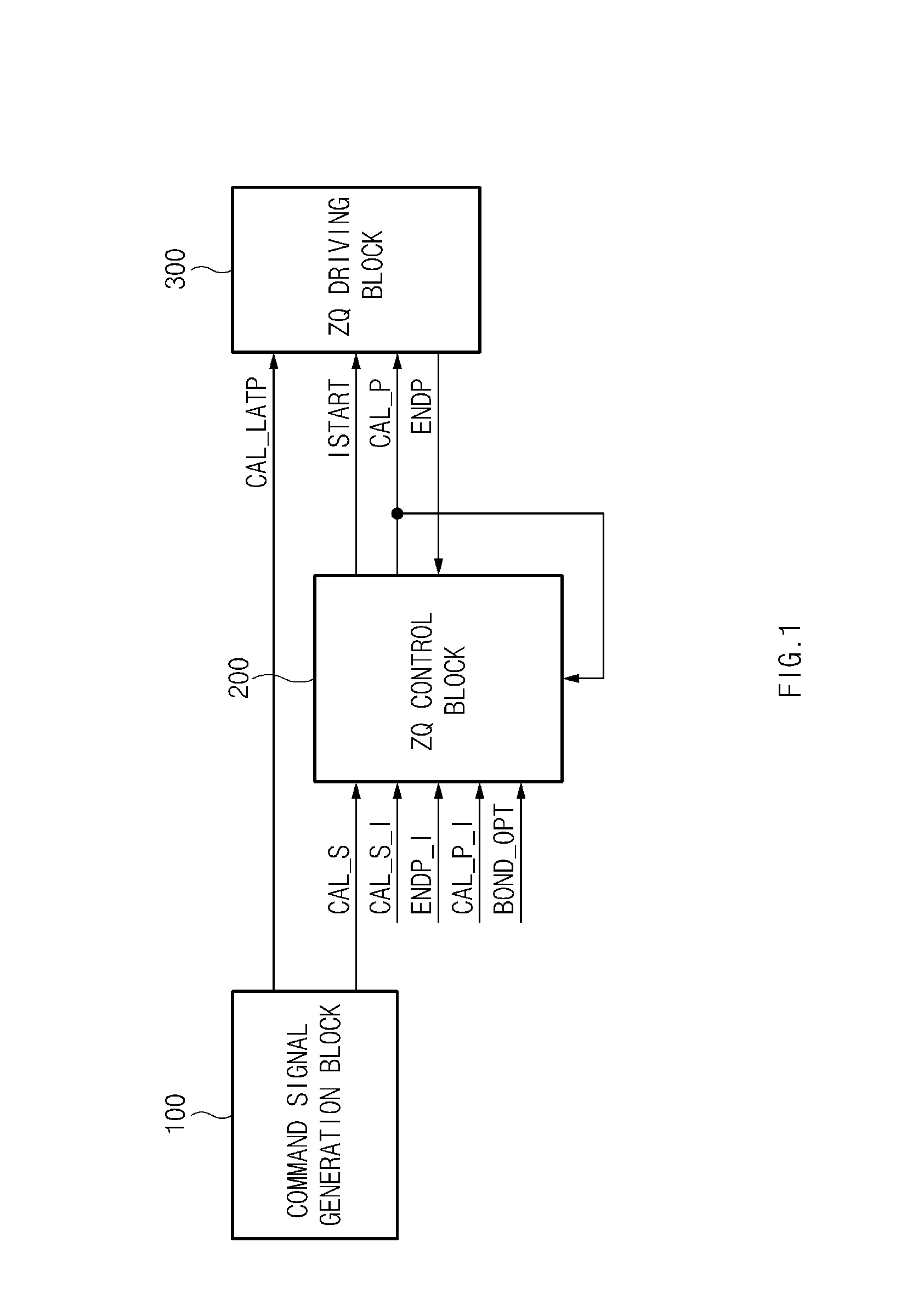
Semiconductor device
A semiconductor device may include a first channel provided in a first die. The semiconductor device may include a second channel provided in a second die and disposed adjacent to the first channel, and configured to exchange signals and data with the first channel. The first channel and the second channel may receive and output calibration-related signals from and to each other through bonding, and may share calibration start signals. The calibration start signal may be respectively generated in the first channel and the second channel.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Impedance adjusting device
InactiveUS7961001B1Easy CalibrationIncreasing of terminationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsVoltage referenceTerminal unit
An impedance adjusting device includes: a calibration node; a comparison unit configured to compare a reference voltage with a voltage of the calibration node; a counting unit configured to generatean impedance code according to a comparison result of the comparison unit; a reference impedance unit having an impedance value according to the impedance code and connected to the calibration node; a storage unit configured to store the comparison result of the comparison unit upon the generation of the impedance code being completed; an interface node; and a termination unit configured to terminate the interface node, the termination unit including a plurality of parallel resistors configured to be turned on / off according to the impedance code, and a parallel resistor configured to be turned on / off according to a value stored in the storage unit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
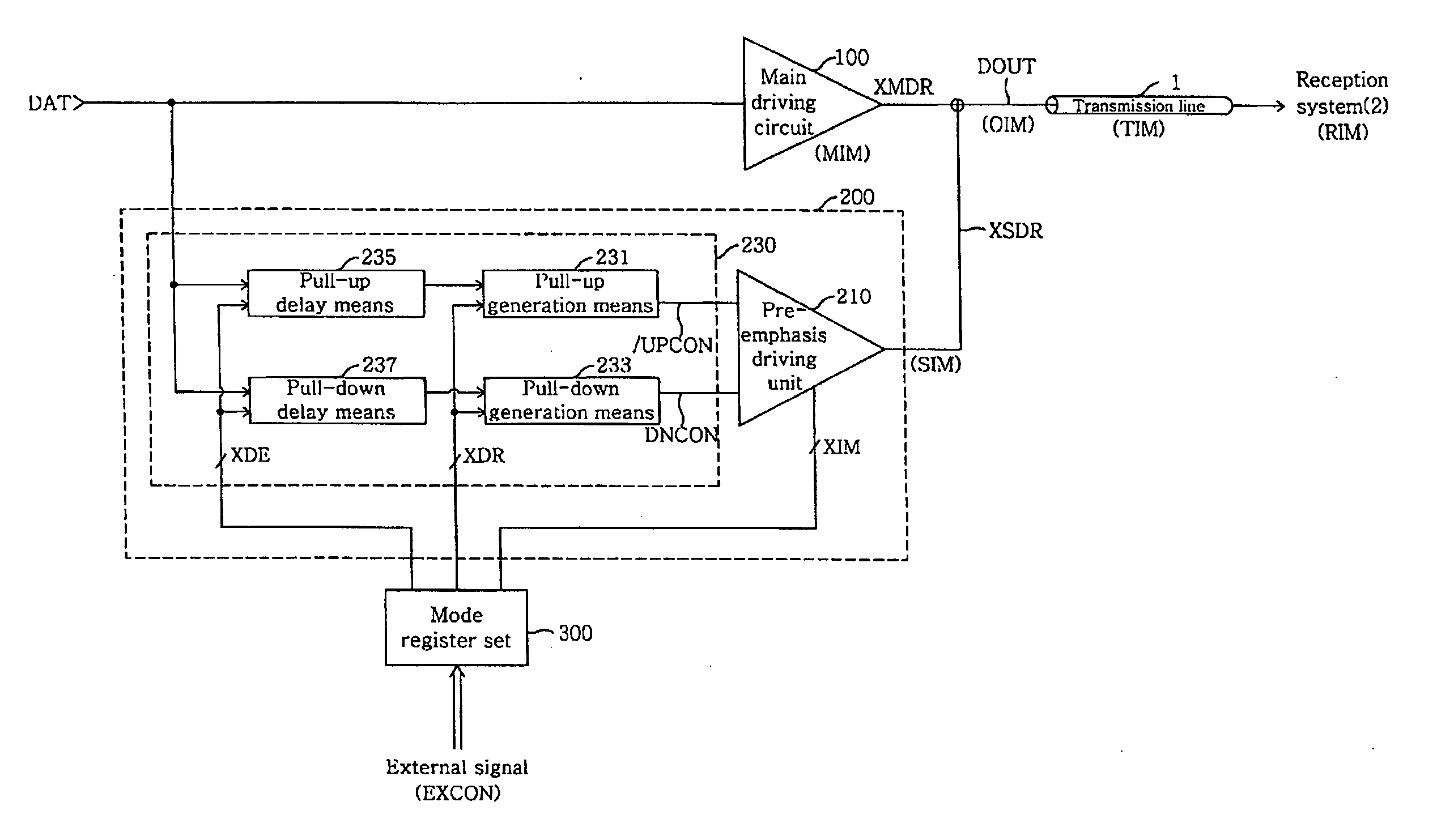
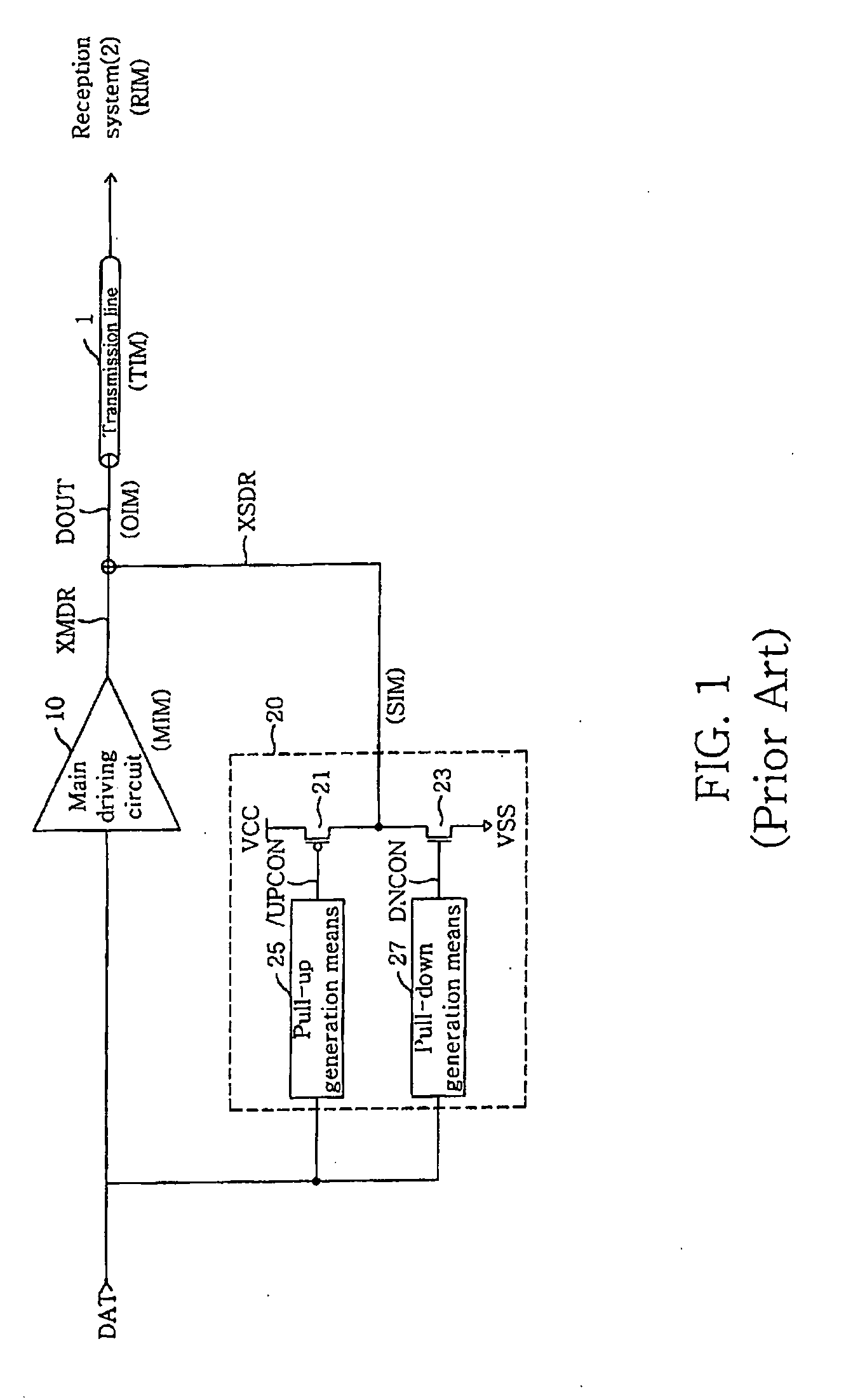
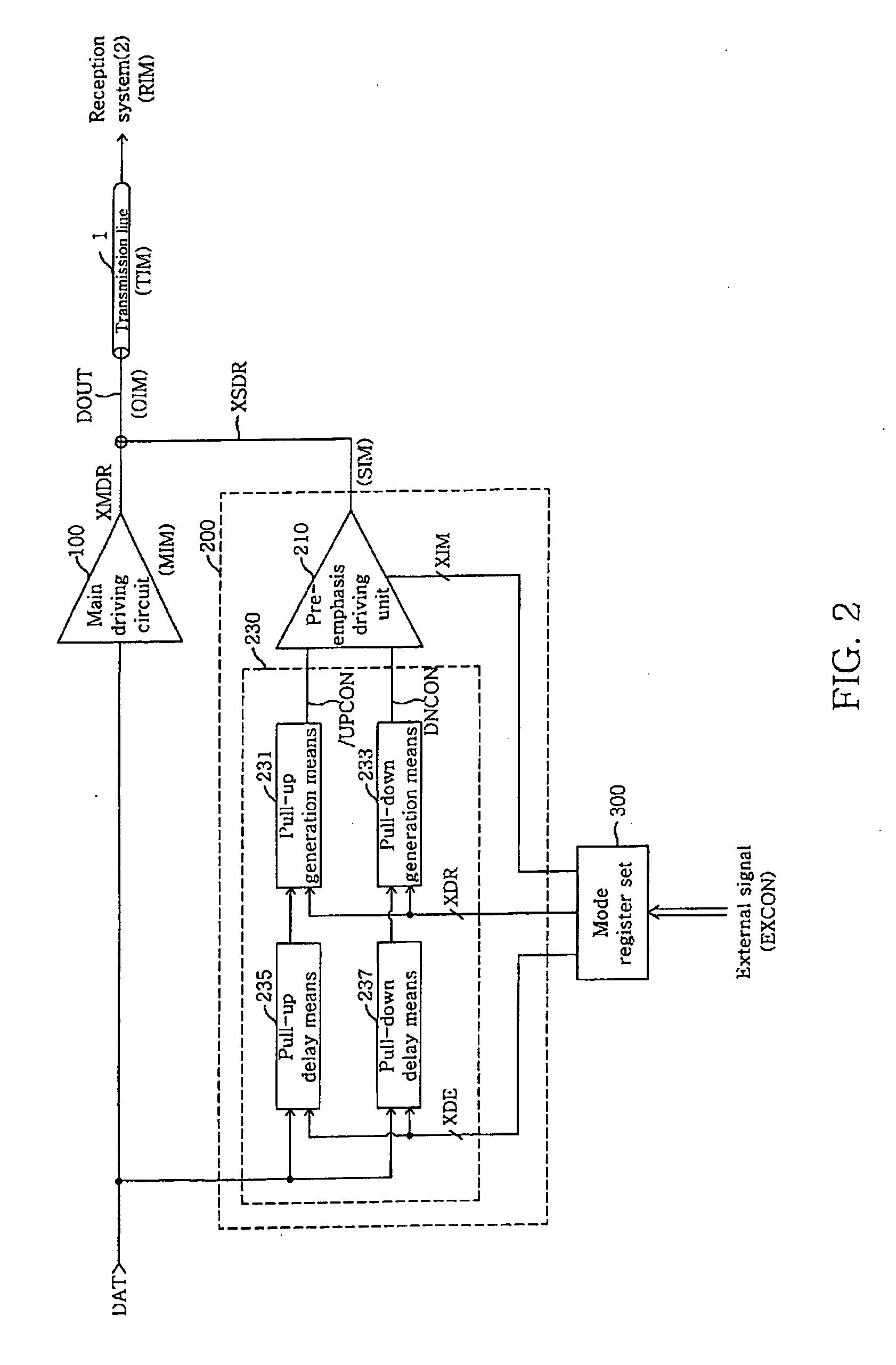
Output driver for controlling impedance and intensity of pre-emphasis driver using mode register set
ActiveUS20070075745A1Efficient receptionEfficiently match output impedanceLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitControl signal
An output driver controls impedance using a mode register set. The output driver includes a main driving circuit that outputs and drives a main signal based on a data signal to a predetermined transmission line, an auxiliary driving circuit that outputs and drives an auxiliary signal to the transmission line, and a mode register set. The mode register set generates an impedance control signal group, a driving width control signal group and a delay control signal group. The amount of an auxiliary impedance (SIM), and the driving width and driving time point of an auxiliary signal (XSDR) can be controlled using the impedance control signal group, the driving width control signal group and the delay control signal group. Therefore, in accordance with the output driver of the present invention, the amount of output impedance (OIM), a pre-emphasis width and a pre-emphasis time point can be readily controlled, and the efficiency of the transmission of an output signal to a reception system is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
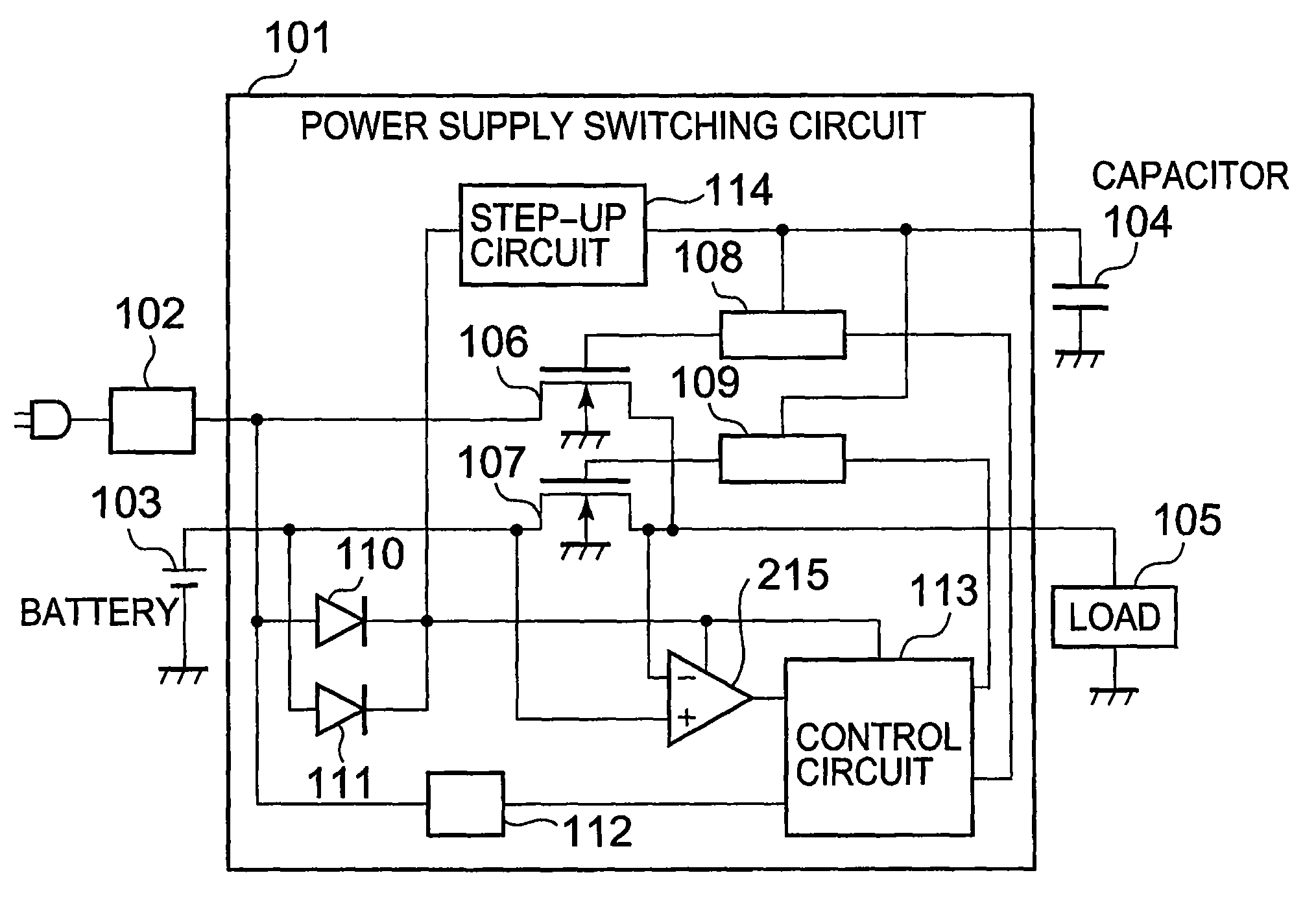
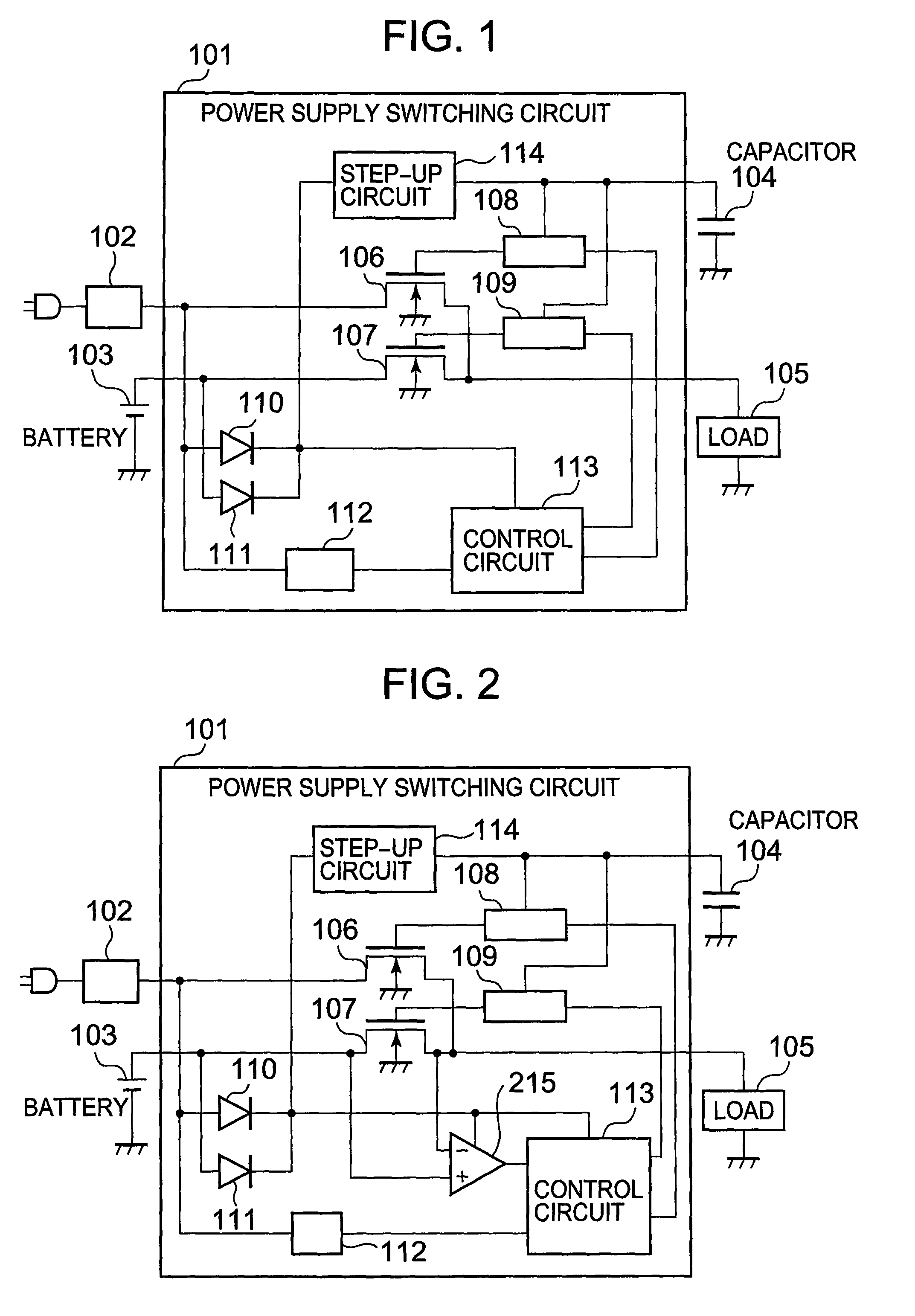
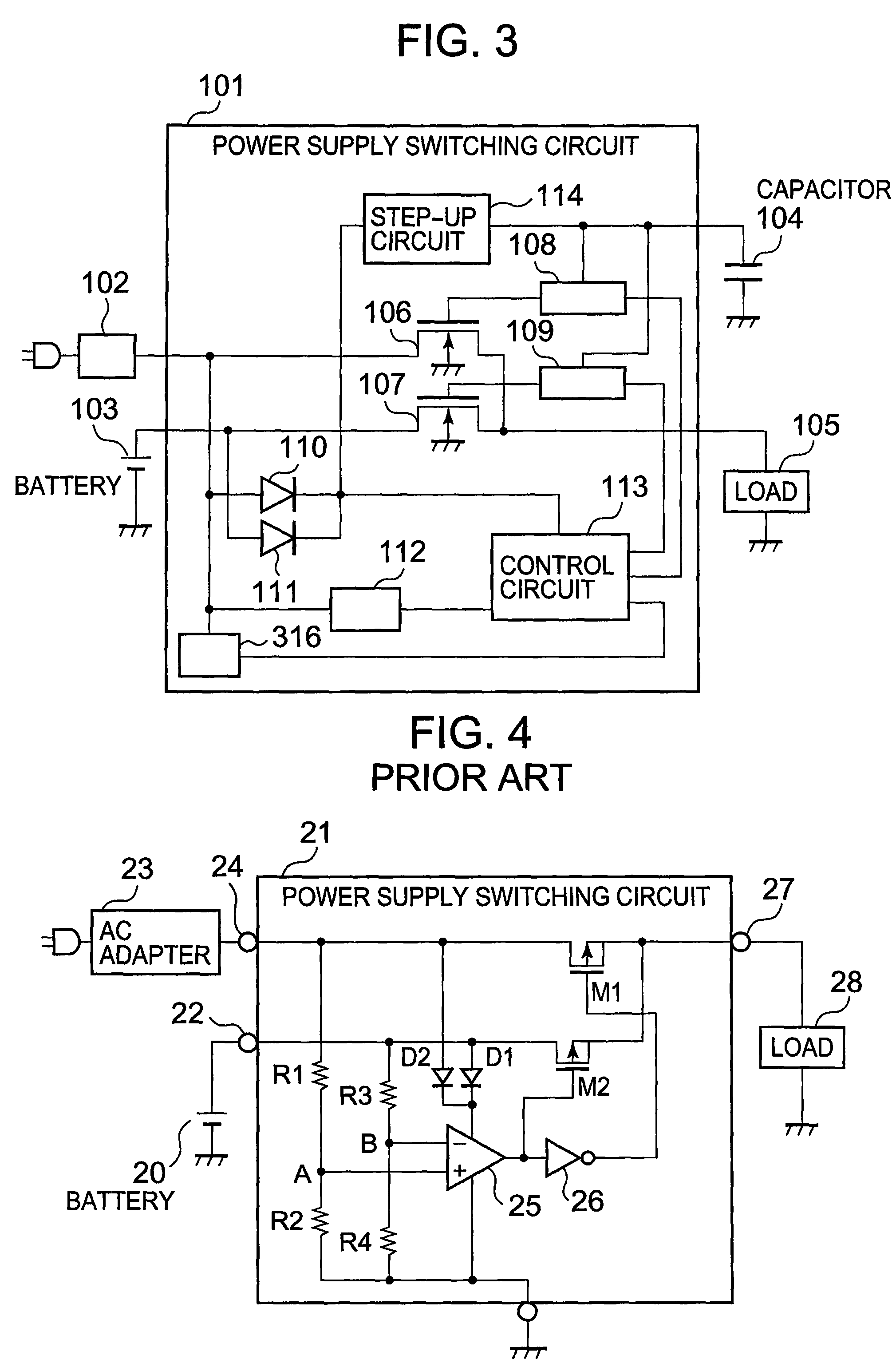
Power supply switching circuit
InactiveUS7800433B2Efficient supplyLogic circuit coupling arrangementsElectronic switchingAC adapterPower switching
Owner:ABLIC INC
Level-shift circuit
InactiveUS20100123479A1Prevent unreliable signal transmissionReliable signal transmissionLogic circuit coupling arrangementsElectronic switchingDriver circuitEngineering
A level-shift circuit converts a first voltage level into a second voltage level different from the first voltage level. The level-shift circuit includes a first high-side signal detection circuit, a second high-side signal detection circuit, a drive circuit and electric current detection circuits. The first high-side signal detection circuit sets a logical voltage state of the second voltage level via a first capacitor. The second high-side signal detection circuit resets the logical voltage state of the second voltage level via a second capacitor. The drive circuit on-off drives a high-side switch connected to a low-side switch in series by a set signal of the first high-side signal detection circuit and a reset signal of the second high-side signal detection circuit. The electric current detection circuits detect an electric current flowing into or from the first and / or second capacitors.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
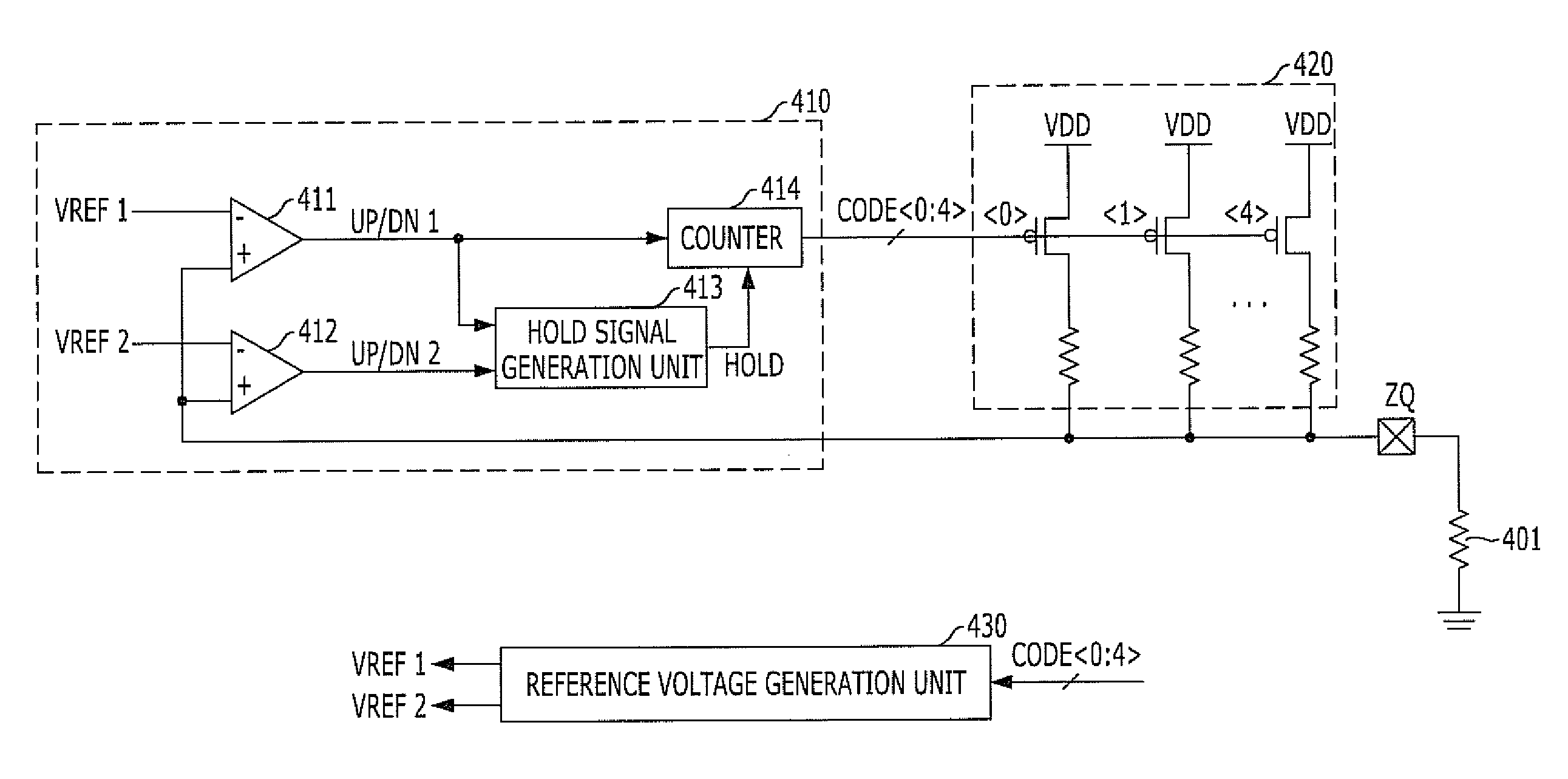
Impedance code generation circuit and integrated circuit including the same
ActiveUS20120092039A1Input/output impedence modificationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsEngineeringVoltage reference
An impedance code generation circuit includes an impedance unit configured to drive a calibration node to a first level by using an impedance value determined by an impedance code, a code generation unit configured to generate the impedance code so that a voltage of the calibration node has a voltage level between a first reference voltage and a second reference voltage, and a reference voltage generation unit configured to generate the first reference voltage and the second reference voltage in response to the impedance code.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
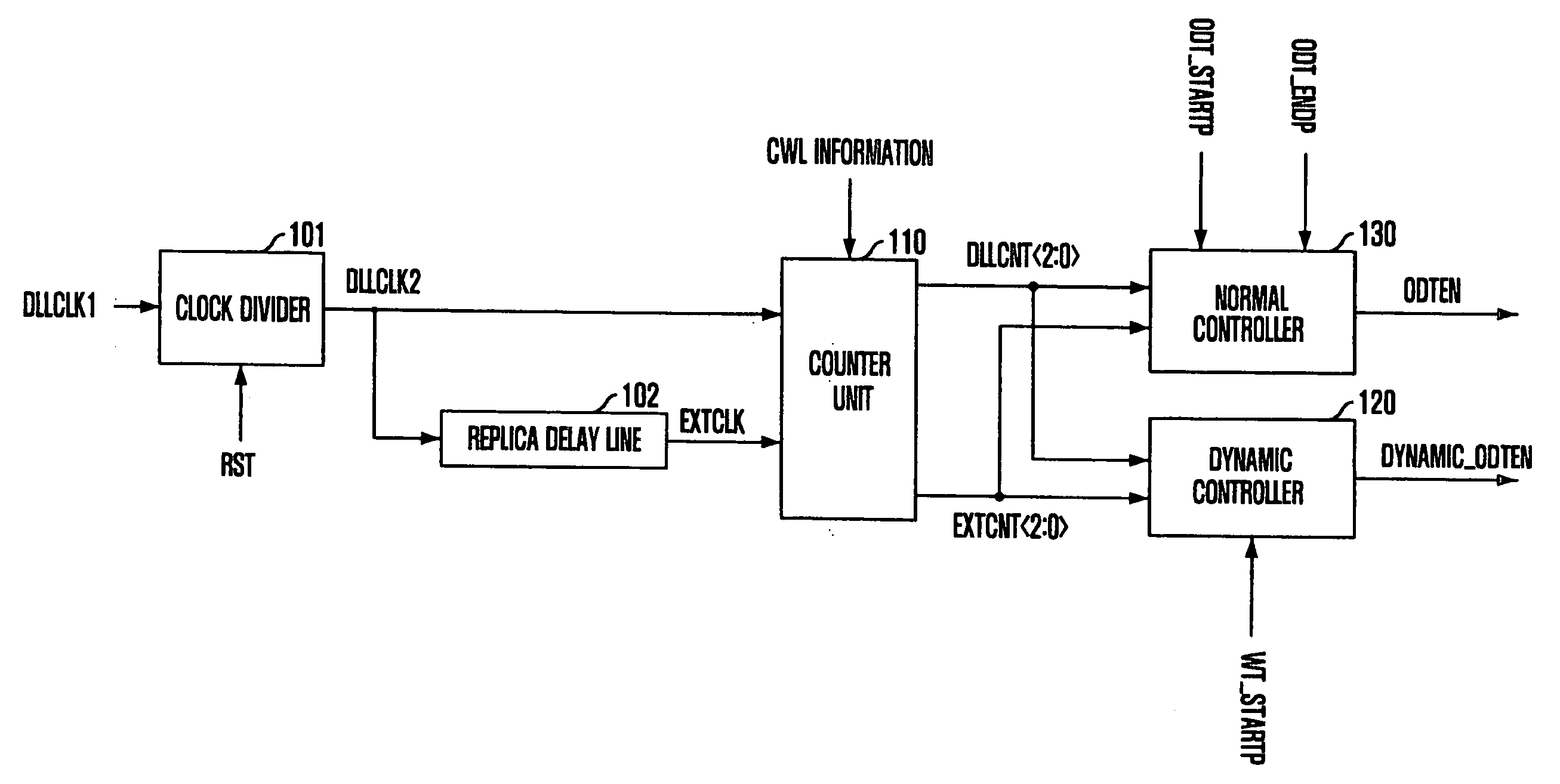
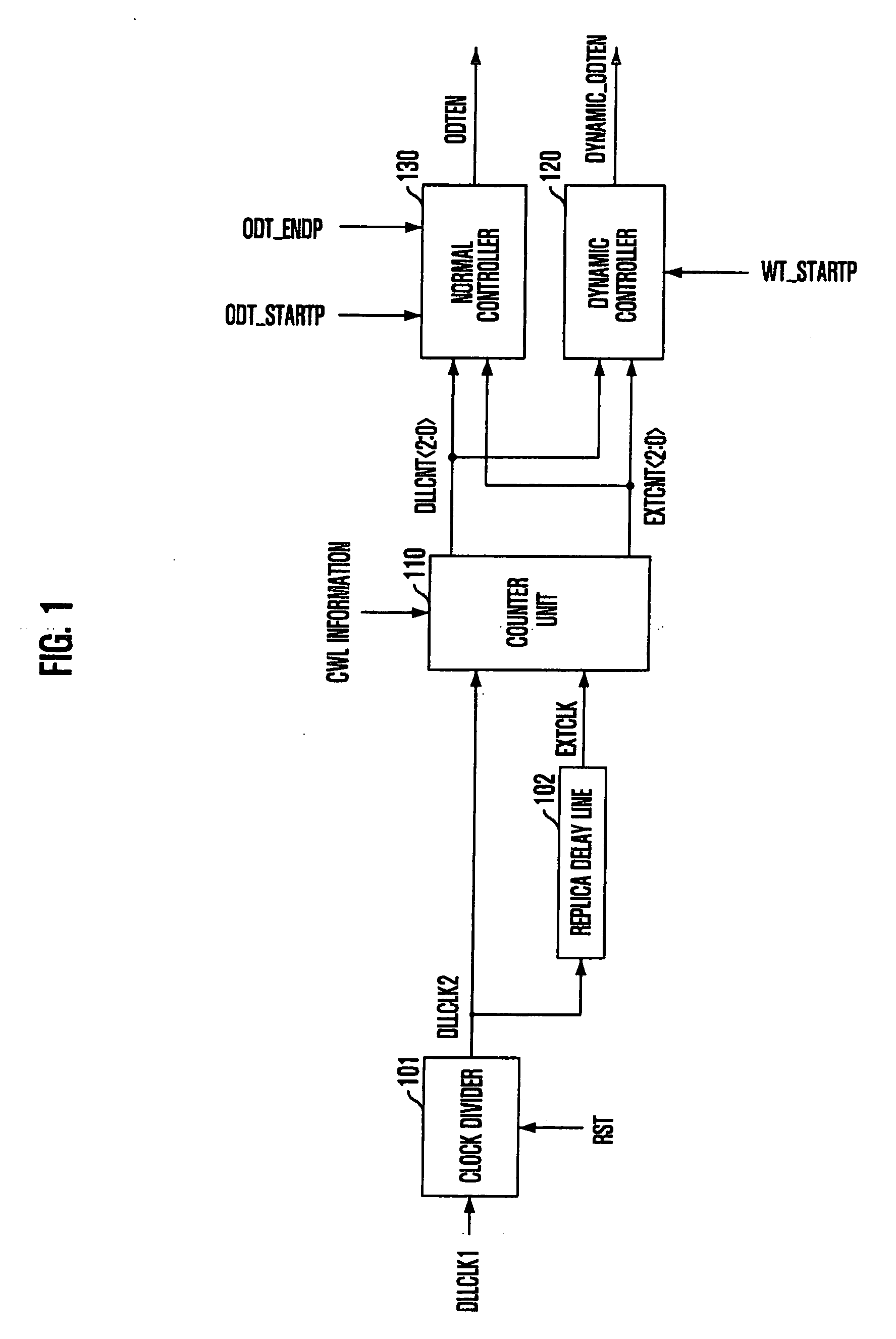
Circuit and method for controlling termination impedance
ActiveUS20090115450A1Easily marginInput/output impedence modificationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsControl circuitSemiconductor
A termination impedance control circuit is capable of controlling a dynamic ODT operation in a DDR3-level semiconductor memory device. The termination impedance control circuit includes a counter unit configured to count an external clock and an internal clock to output a first code and a second code, respectively, and a dynamic controller configured to enable a dynamic termination operation by comparing the first code with the second code in response to a write command and disable the dynamic termination operation after a predetermined time, determined according to a burst length, has lapsed after the dynamic termination operation is enabled.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com