Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2153 results about "Terminal unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A terminal unit is an outlet in ductwork to allow air delivery to an environment like a room. The terminal unit taps into the ducts with a fan to push air out of the ductwork at varying speeds to control the environment. Terminal units may also have built in heating and cooling coils, depending on the installation.
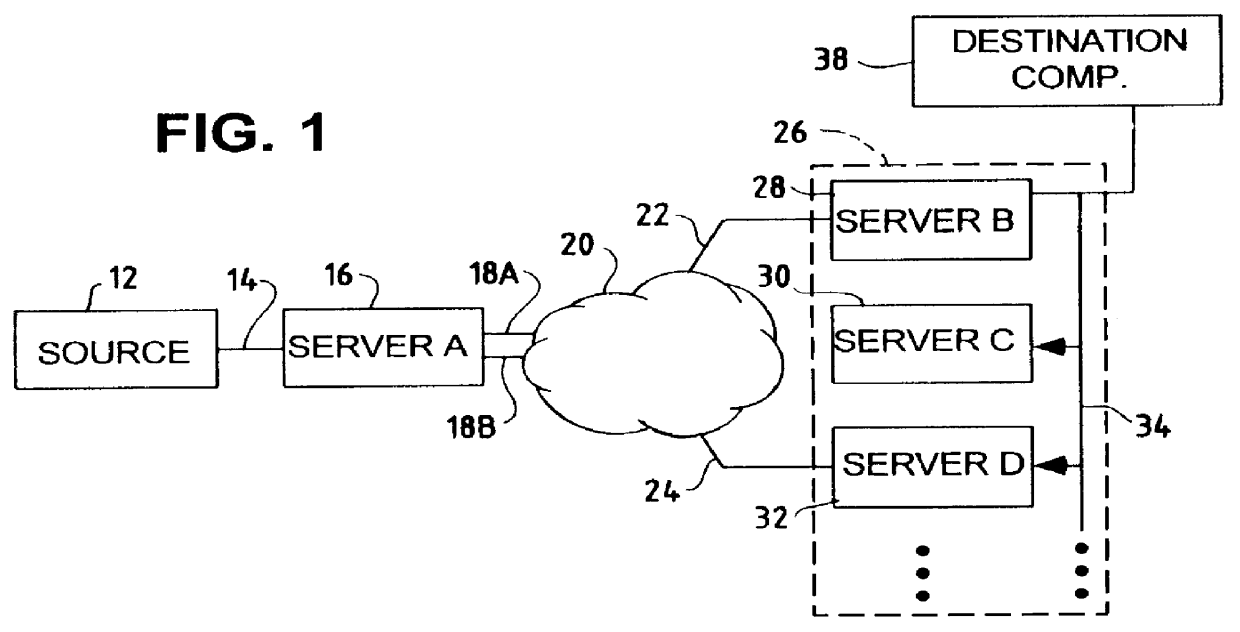
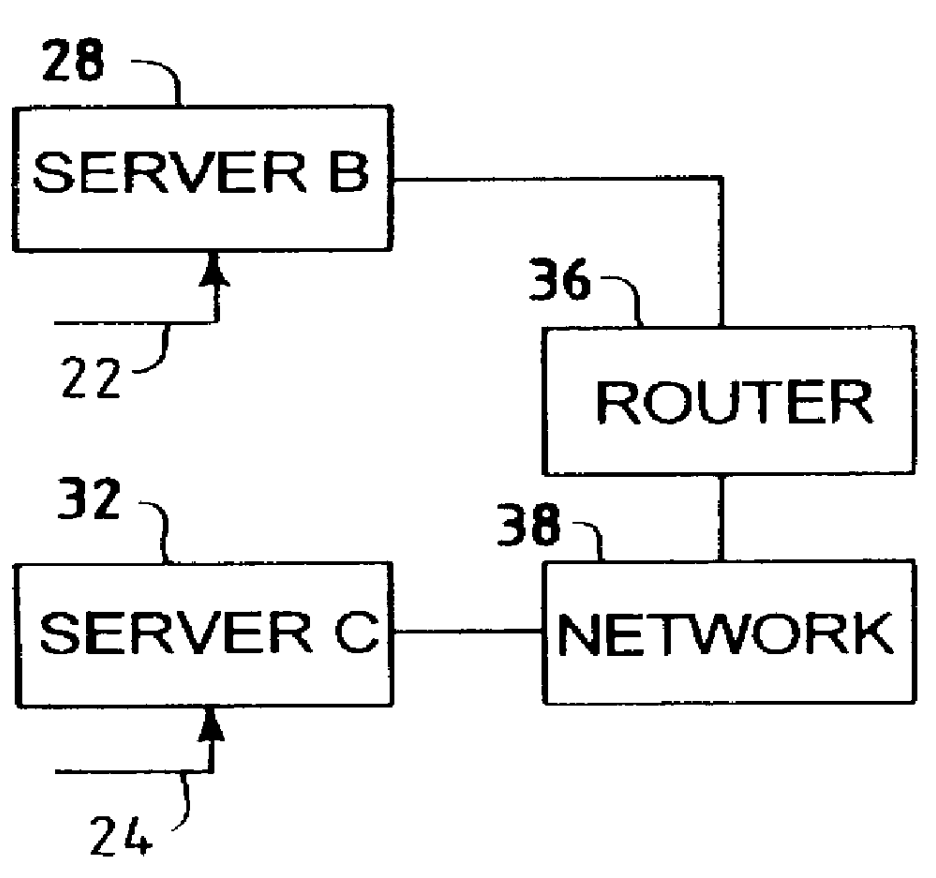
Multi-channel support for virtual private networks in a packet to ATM cell cable system
InactiveUS6917614B1Avoid compromiseExtension of timeBroadband local area networksFrequency-division multiplexQuality of serviceScheduling function
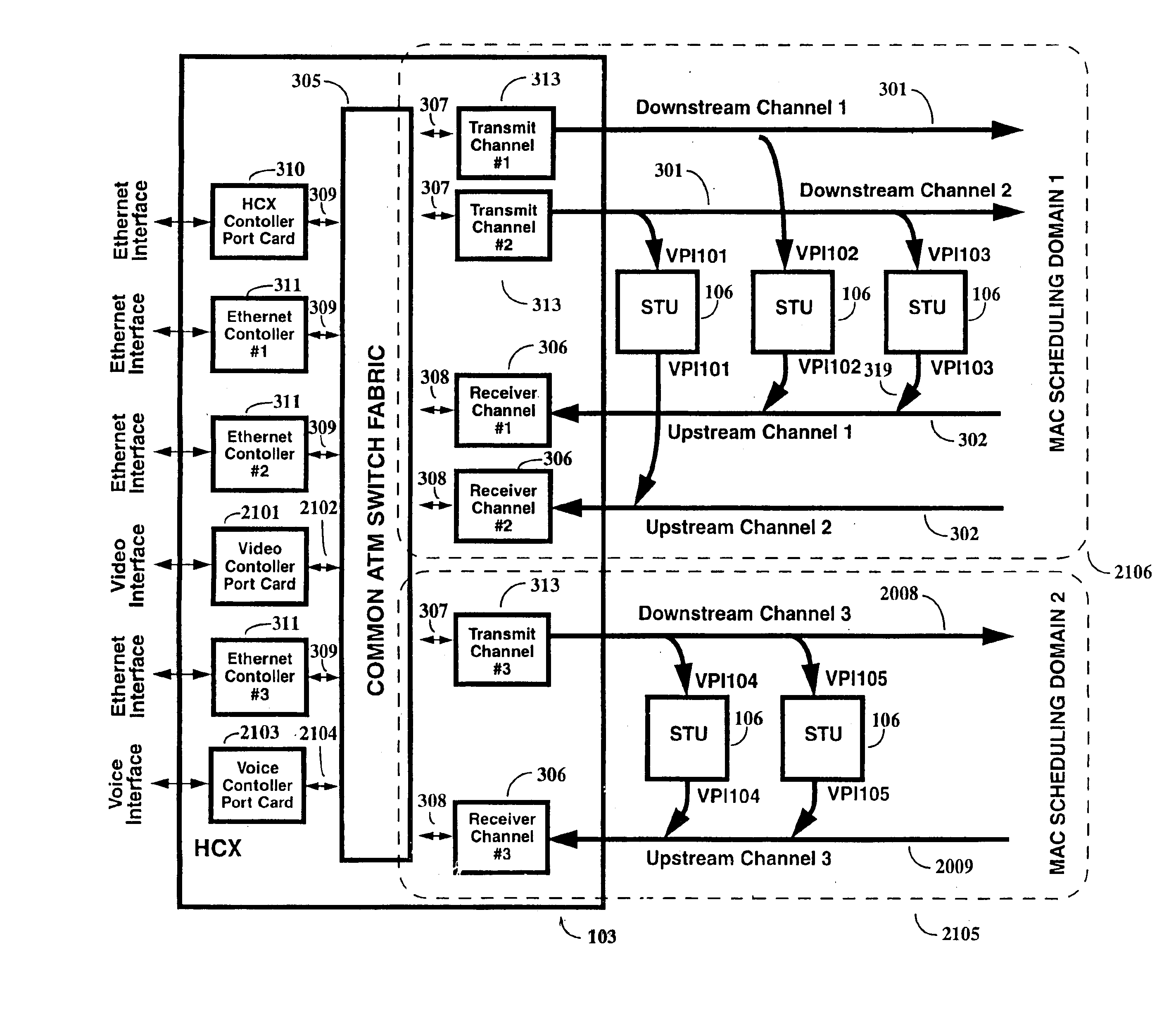
A two-way cable network offering high-speed broadband communications delivered via virtual private networks over a multi-channel shared media system. Bi-directional transmission of packet to ATM cell based communications is established between a head end communication controller and a number of subscriber terminal units, whereby individual cells are prioritized and routed according to a virtual connection. Virtual connections are organized to support multiple virtual private networks in a shared media CATV system. The virtual private network to which a particular STU belongs is user selectable and has the flexibility of handling multi up / downstream channels with different MAC domains. The present invention can also handle non-ATM MAC domains via the same common ATM switch. To overcome the limited number of addresses inherent to common ATM switches, a mapping / remapping function is implemented in the port cards. Furthermore, downstream as well as upstream traffic are filtered at each STU. In one embodiment, information pertaining to downstream traffic is used to implement predictive scheduling in order to improve the timing associated with the request / grant cycle. In another embodiment, a user has the ability to select a quality of service that best suits the needs of the current application. In a further embodiment, the scheduling function is associated with each of the receivers in order to provide improved scalability.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Billing system, and device constituting same
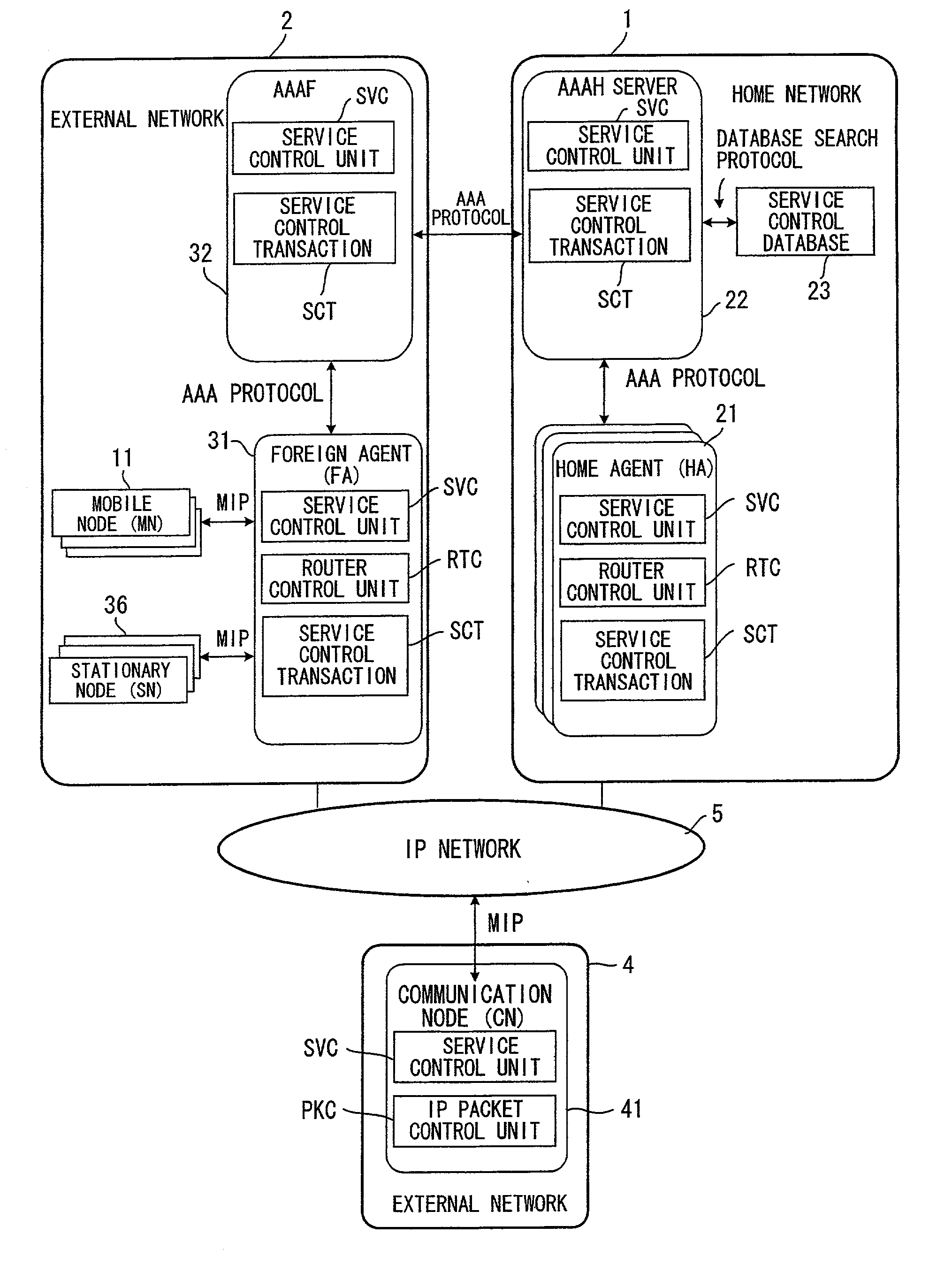
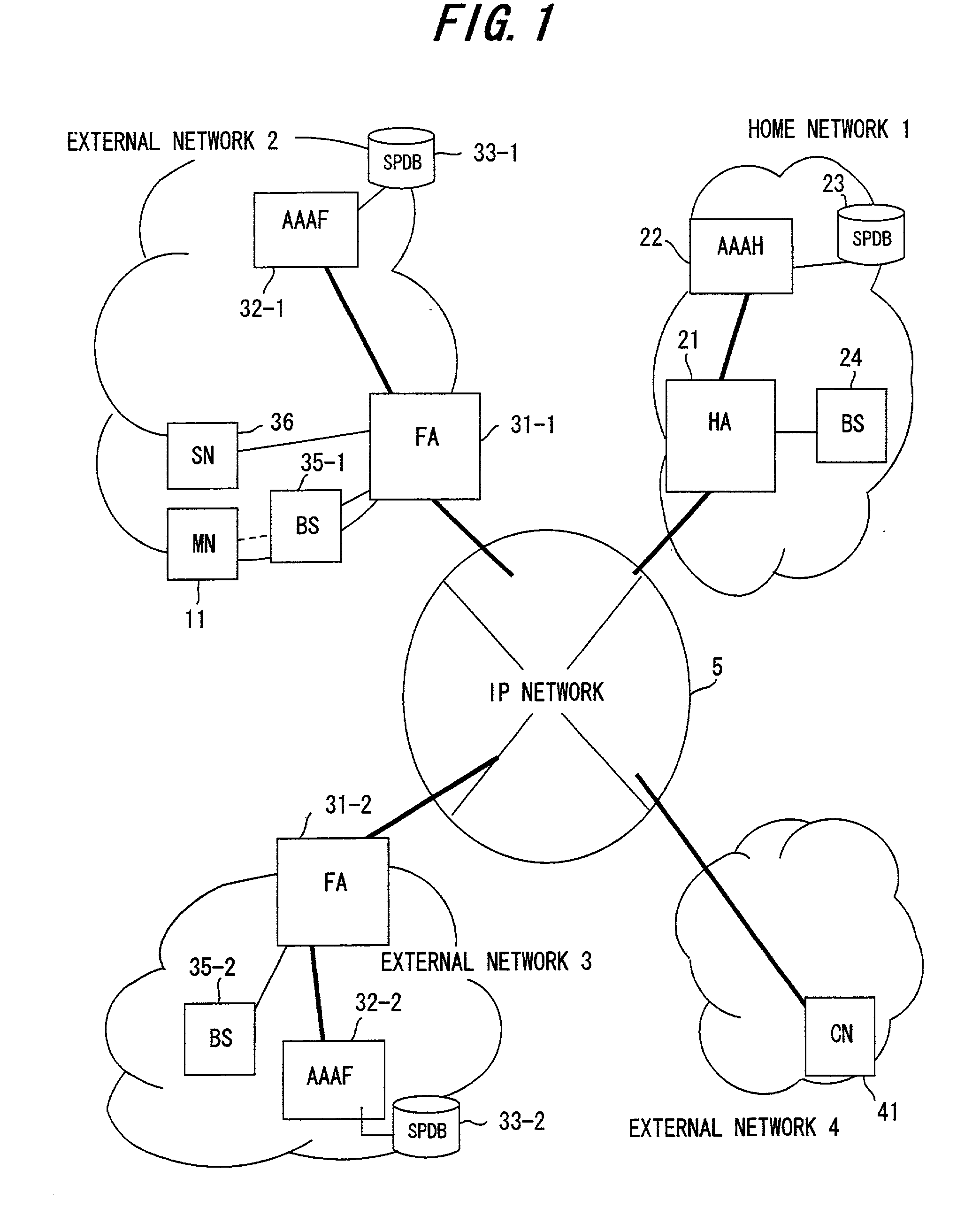
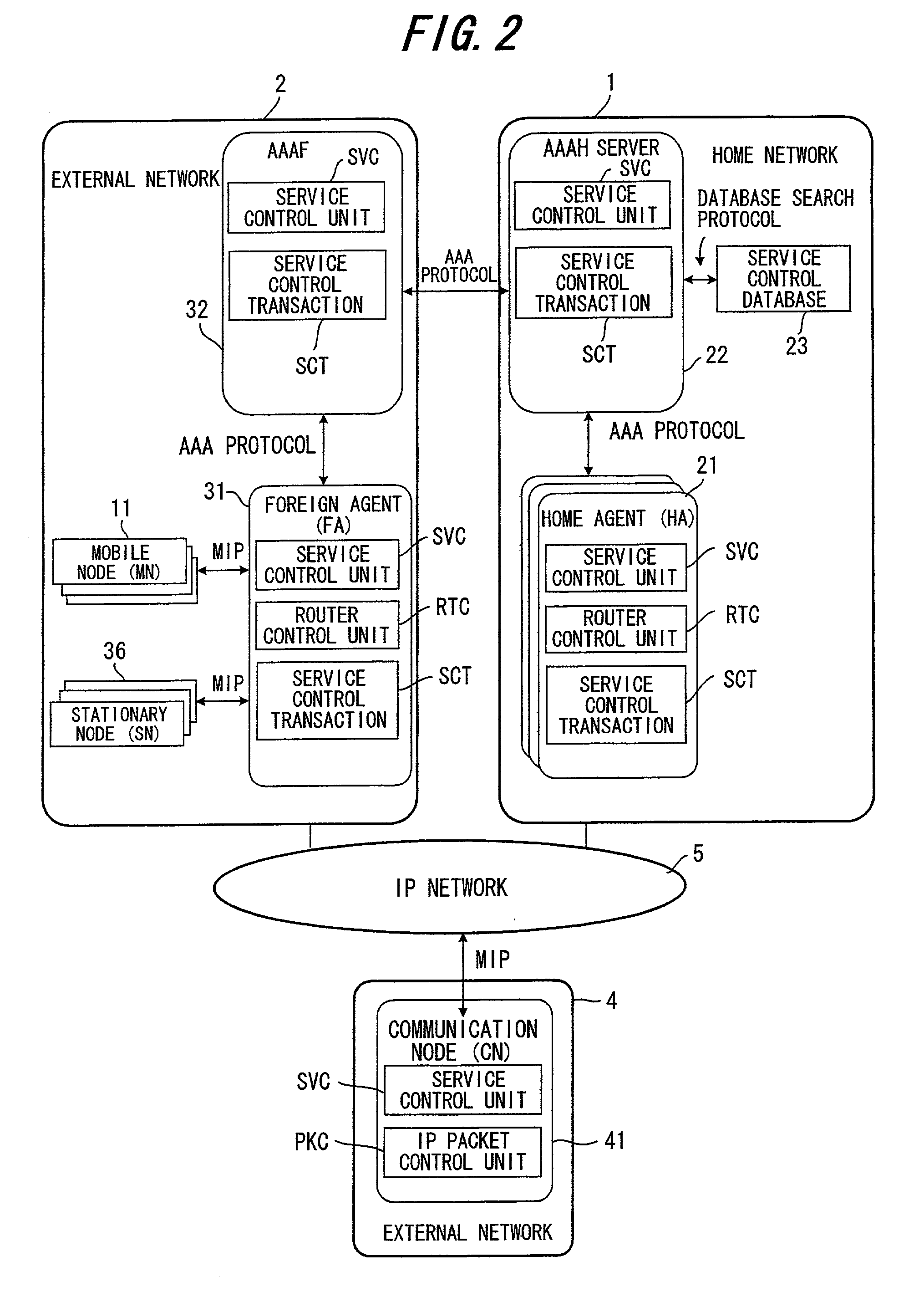
InactiveUS20020188562A1Complete banking machinesMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsForeign agentTerminal unit
A billing system is disclosed which performs processing in order to provide service to user terminals, and which performs billing for the service provided to the user terminals. In this billing system, user billing profiles UBP are stored in a user billing profile registration unit, by service type and in user terminal units; a billing condition generation unit within a service provider server compares the user billing profile UBP corresponding to a specified service type and to a user terminal with a server billing profile SBP to generate billing conditions, and a billing condition setting unit of a foreign agent sets the billing conditions in a billing unit; and based on the billing conditions thus set, the billing unit executes billing processing for each user terminal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Web-based television system and method for enabling a viewer to access and display HTML-encoded documents located on the World Wide Web (WWW) by reading bar code symbols printed in a WWW-site guide using a wireless bar-code driven remote control device
InactiveUS6321991B1Digital data information retrievalTransmission systemsTelecommunications linkInternet information services
A Web-based television system for enabling an operator to access and display HTML-encoded documents located on the WWW. The system comprises one or more Internet information servers, an Internet terminal unit, and television set having a wireless remote control device and an audio-visual monitor. The Internet information servers store a plurality of HTML-encoded documents at a plurality of storage locations specified by a plurality of Uniform Resource Locators (URLs). The Internet terminal unit is operably connected to the infrastructure of the Internet and embodies a GUI-based Internet browser program, supporting the TCP / IP networking protocol. The television set is operably connected to the Internet terminal unit. The wireless remote control device includes a bar code symbol reader for reading bar code symbols, and an IR-based communication circuit for establishing a wireless communication link with the Internet terminal unit. A WWW-site guide is provided to television viewers. On the guide, a plurality of bar code symbols are preprinted along with a plurality of Web-site descriptions. Each preprinted bar code symbol is encoded with information related to one of the plurality of URLs. The bar code symbol reader is programmed for reading the bar code symbols in the WWW-site guide. In response to reading each bar code symbol, the bar code symbol reader produces information related to one of the URLs, and this information is transmitted, over the wireless information communication link, to the Internet terminal unit. Thereupon, the GUI-based Internet browser uses the TCP / IP networking standard and the produced information to automatically access the HTML-encoded document specified by the related URL, and automatically display the accessed HTML-encoded document on the audio-visual monitor of the television set, for viewing purposes.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Portable radio terminal unit
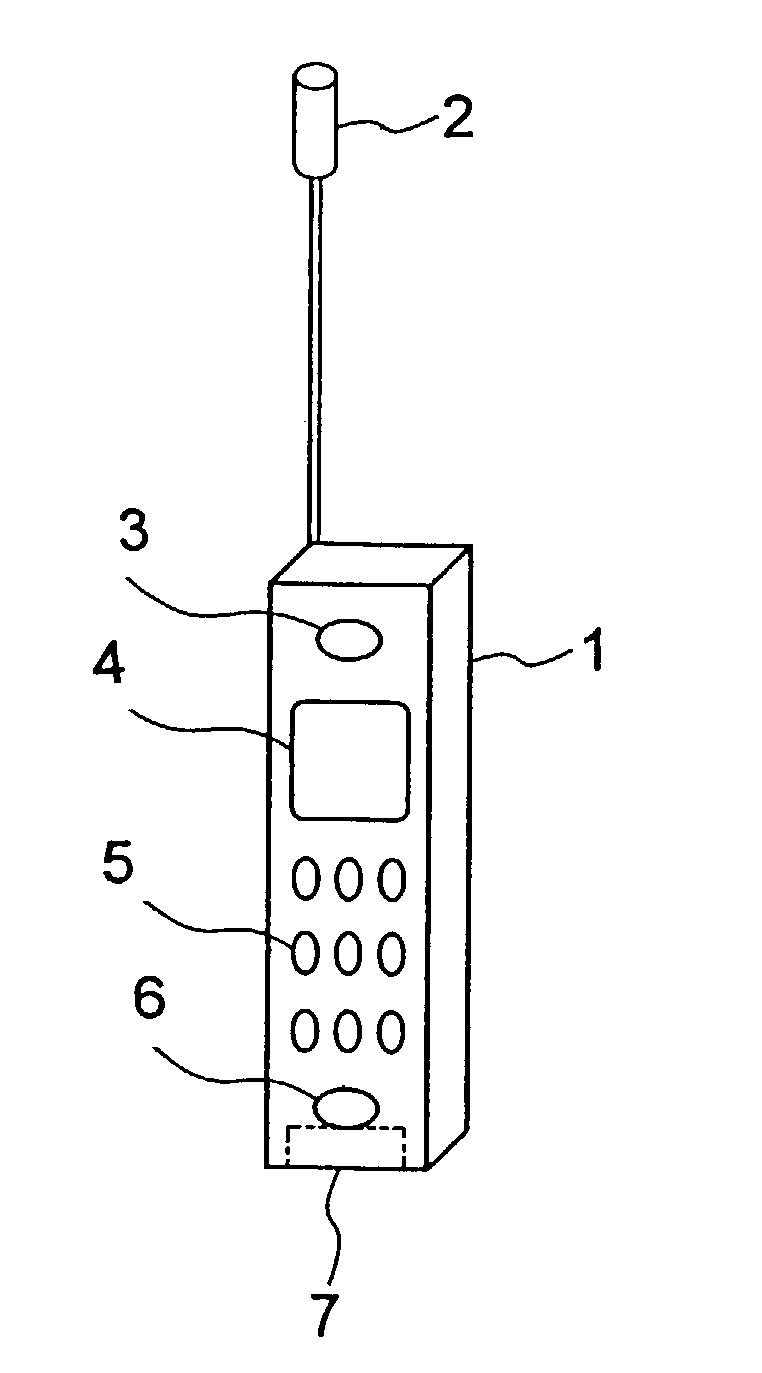
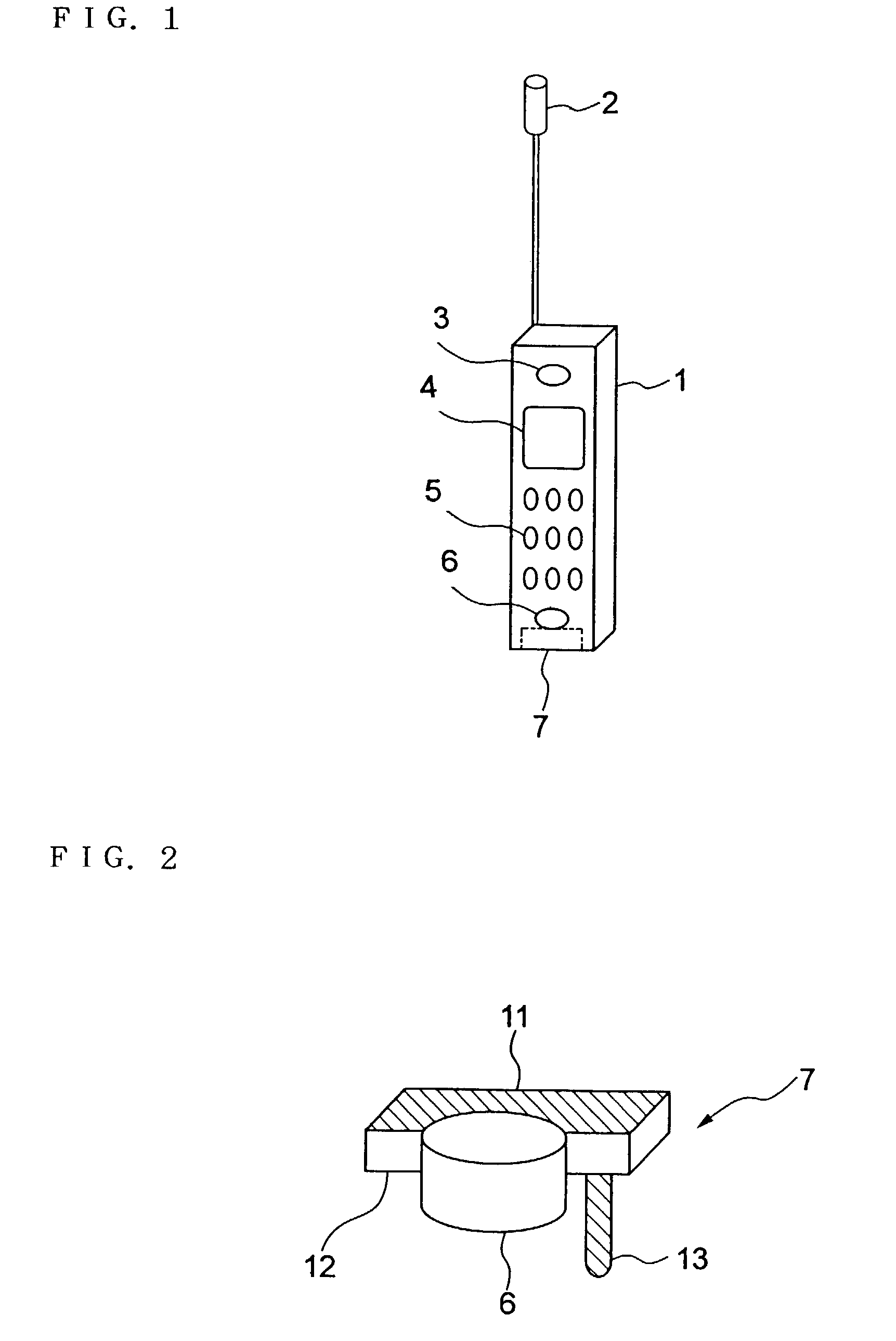
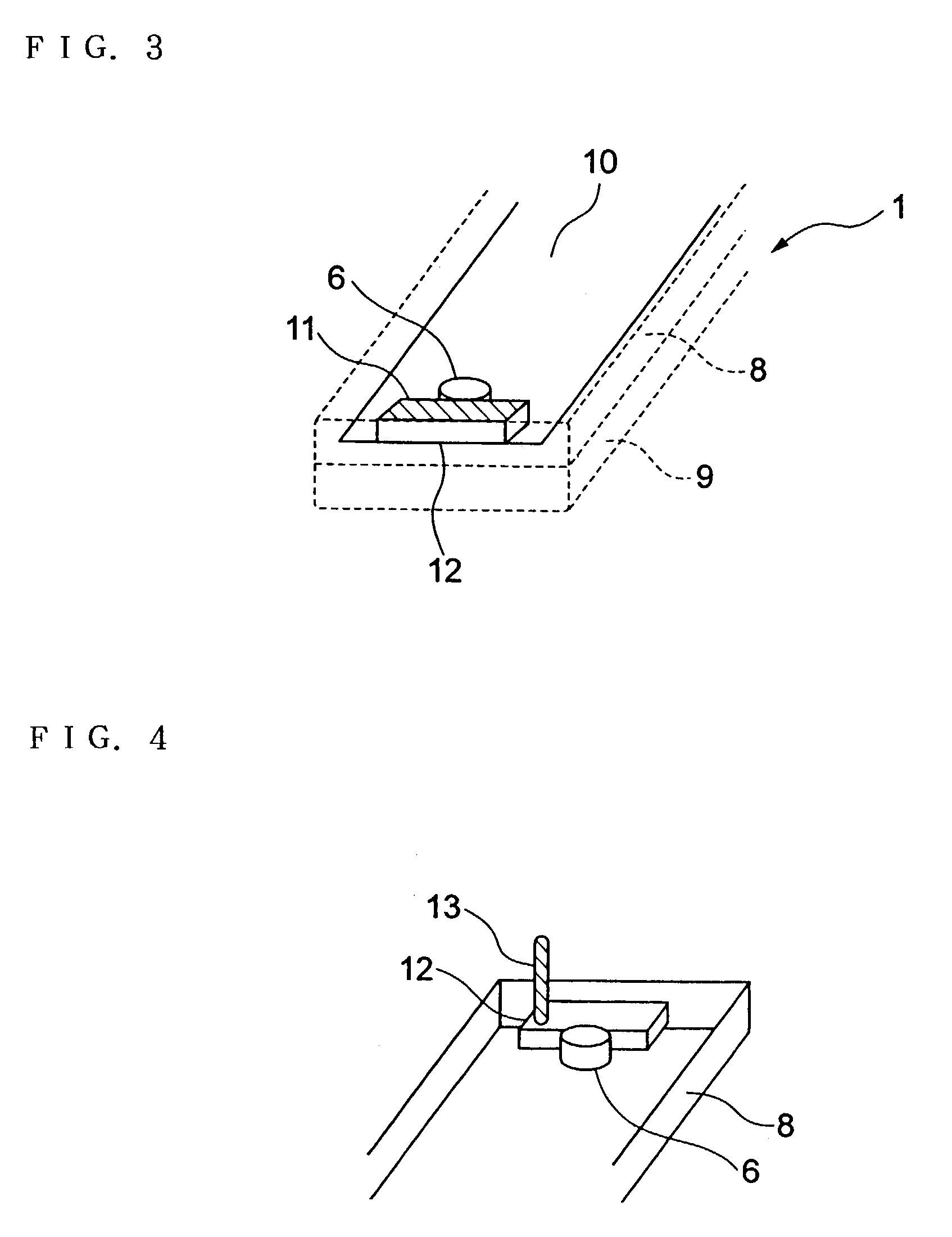
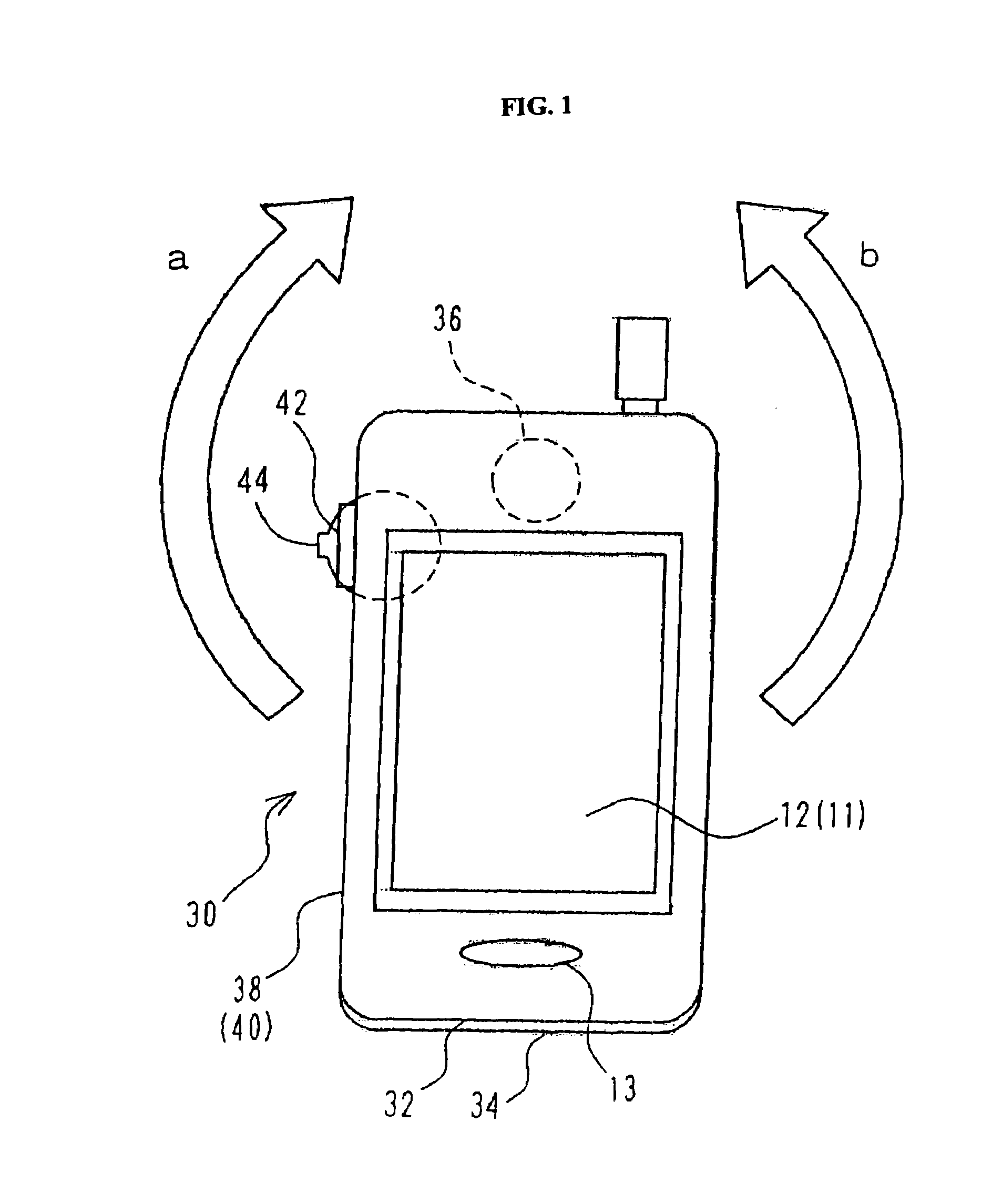
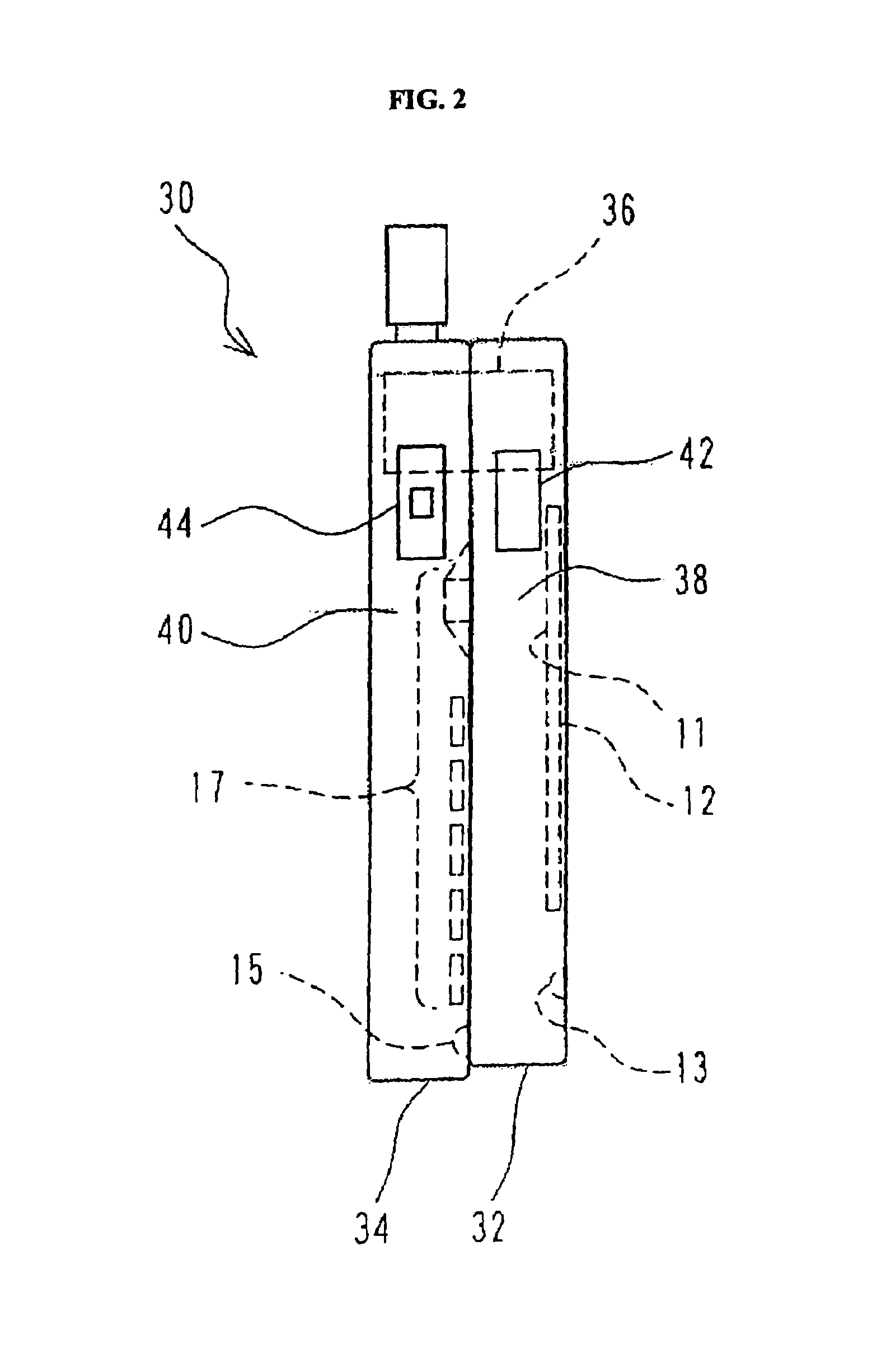
InactiveUS7082322B2Reduce deteriorationIncrease contactAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsTerminal unitMicrophone
In a portable radio terminal unit, when a built-in antenna is provided, influence of user's body is to be reduced as small as possible to prevent deterioration of antenna characteristics. The built-in antenna is arranged in contact with a microphone unit positioned at lower portion of a unit casing. The microphone unit is mounted on a front casing forming the casing. Therefore, the built-in antenna is also mounted on the front casing. Thus, even during calling and browsing display, the built-in antenna may not contact with a user's head or may not be covered by the user's hand to reduce deterioration of the antenna characteristics for maintaining more stable communication characteristics.
Owner:NEC CORP
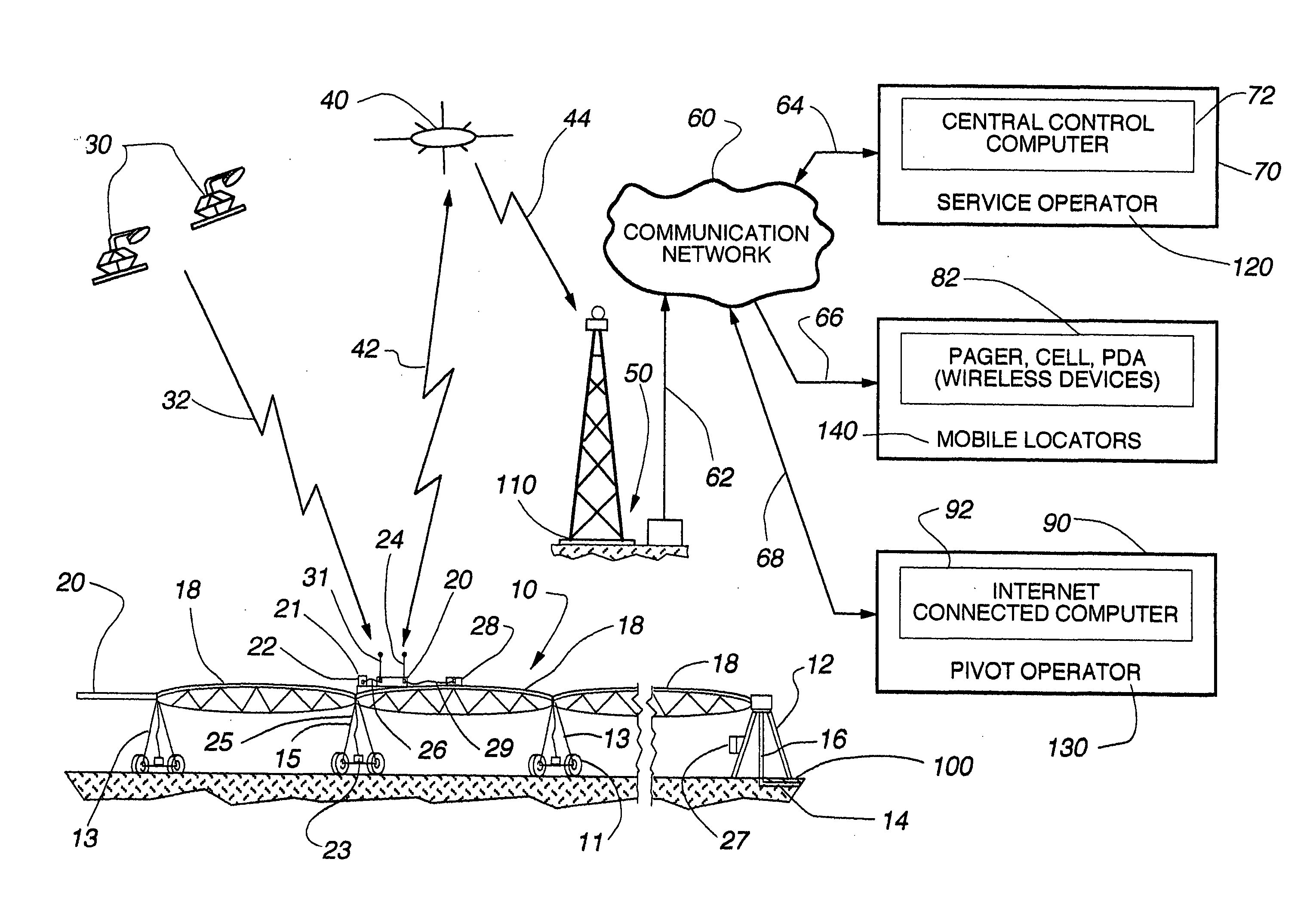
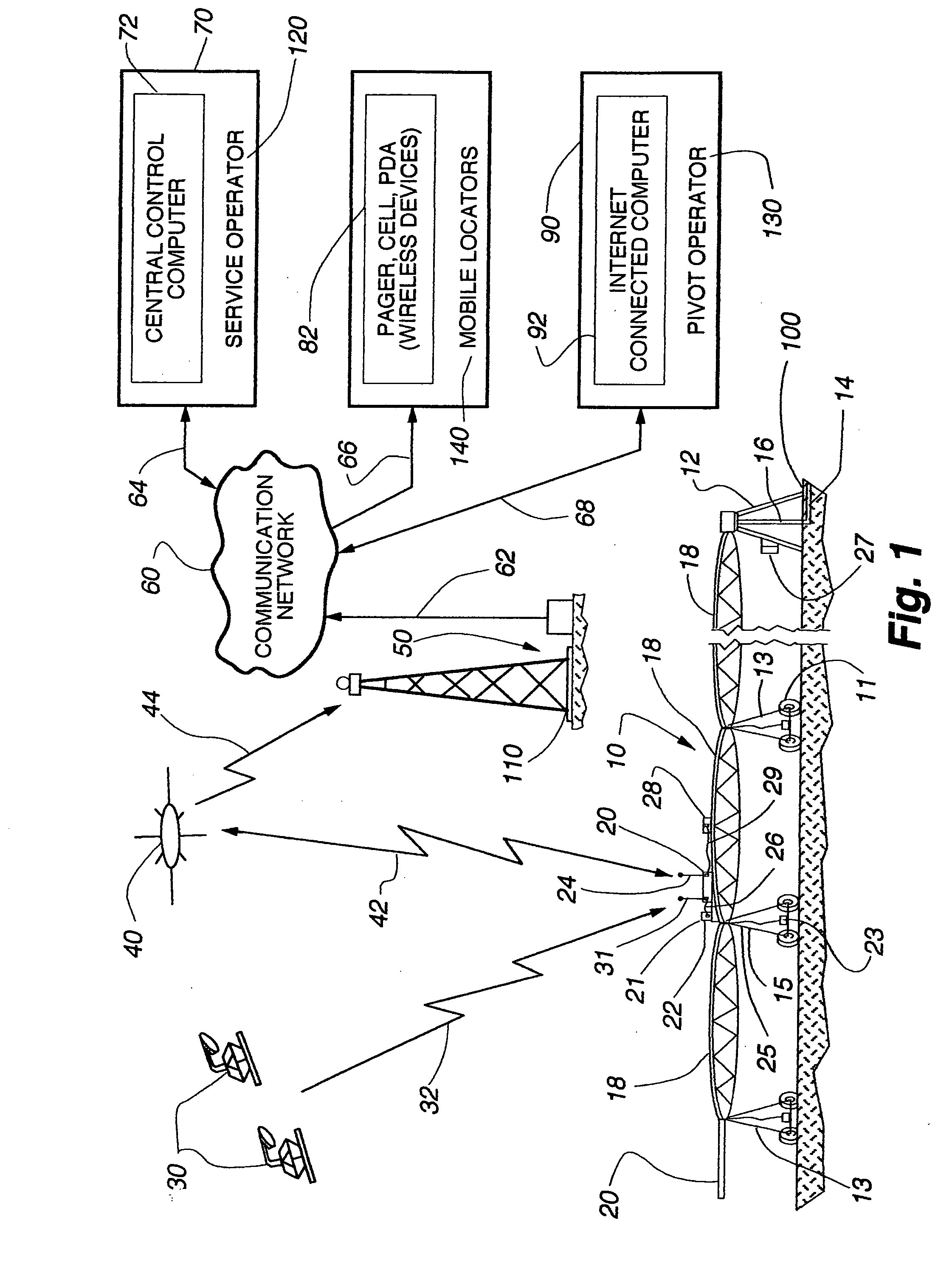
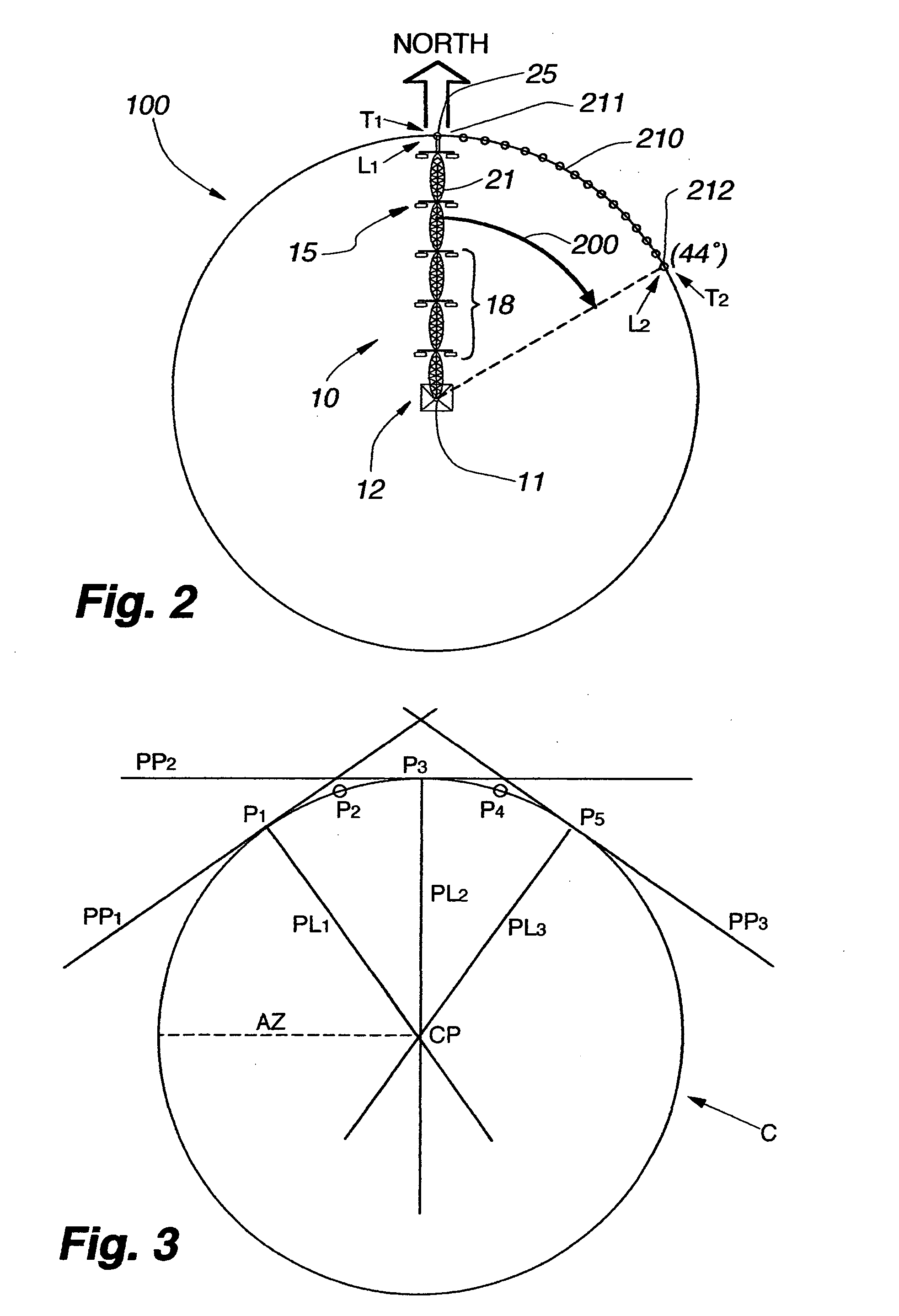
Remote current sensor monitoring system and GPS tracking system and method for mechanized irrigation systems
ActiveUS20060027677A1Low costImprove reliabilitySelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesTransceiverCurrent sensor
A wireless interface remote monitoring system for self-propelled irrigation systems (center pivot and lateral move sprinklers) includes a remote terminal unit (RTU) mounted on an outer drive tower of the irrigation system. The RTU includes a radio transceiver capable of sending and receiving data packets over a satellite or terrestrial telemetry backbone to and from a central control computer. The RTU further includes a current sensor and a GPS receiver both for detecting movement or non-movement of the sprinkler, a microprocessor with nonvolatile memory for storing current data and GPS coordinate data from readings taken in series over time, and a pressure or flow sensor for detecting the presence or absence of water flow at the outer drive tower of the sprinkler. The current sensor connected between the RTU and a tower drive motor, allows the RTU to calculate the “movement” or “non-movement” of the irrigation system over a specified time period. Redundantly, the GPS receiver records changes in position to indicate movement or non-movement within the GPS error tolerance. Once a change from movement to non-movement or vice-versa is determined, the RTU transmits the data by satellite or radio telemetry to a central control computer which logs the movement or non-movement of the monitored drive tower, the GPS coordinate data and the water status readings, all with time and date stamp. The central control computer creates “page message” and “text message” updates as necessary on the status of individual irrigation systems and “groups” of irrigation systems that are in turn delivered to wireless devices and computers for sprinkler operators.
Owner:HAALAND KARLYLE
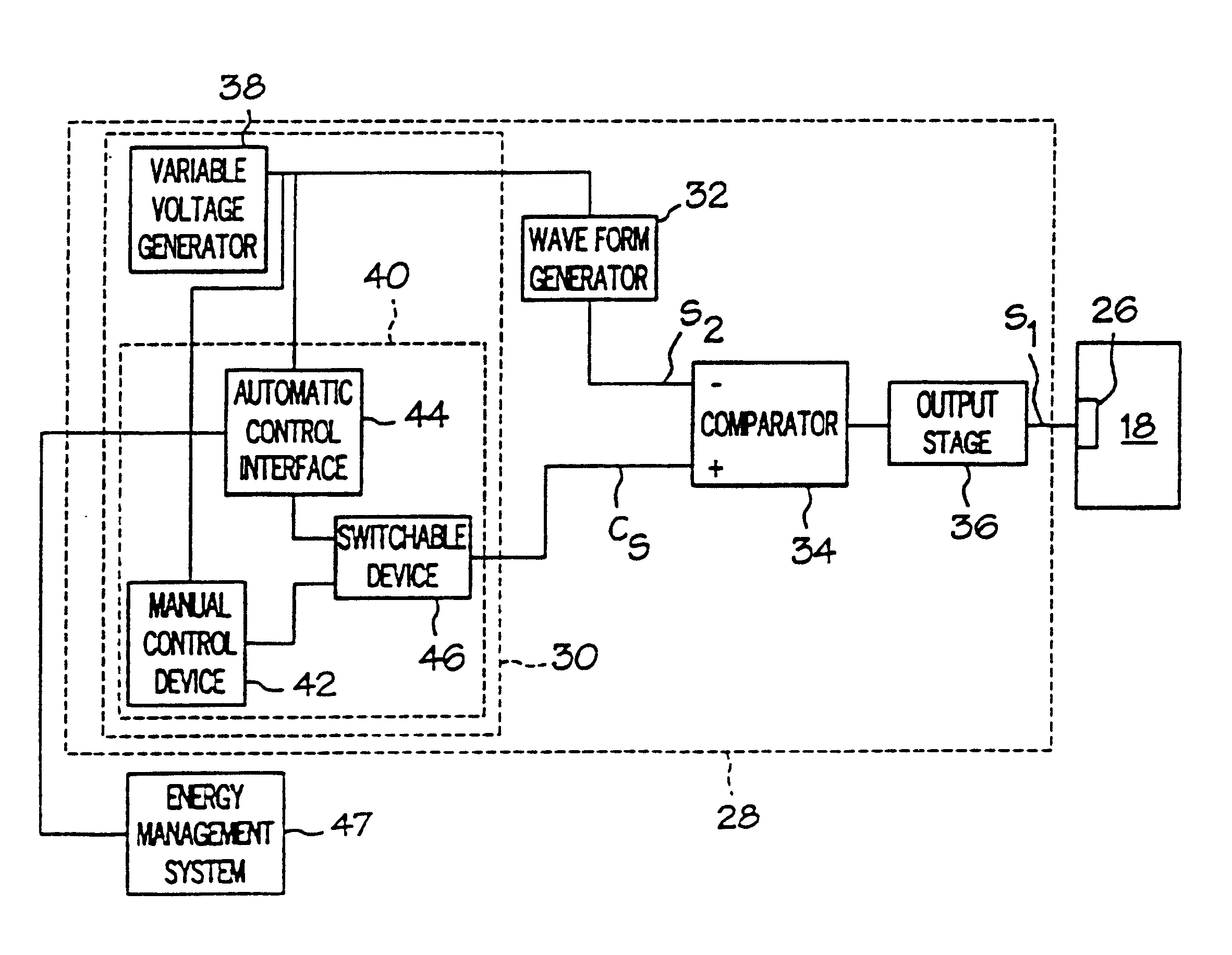
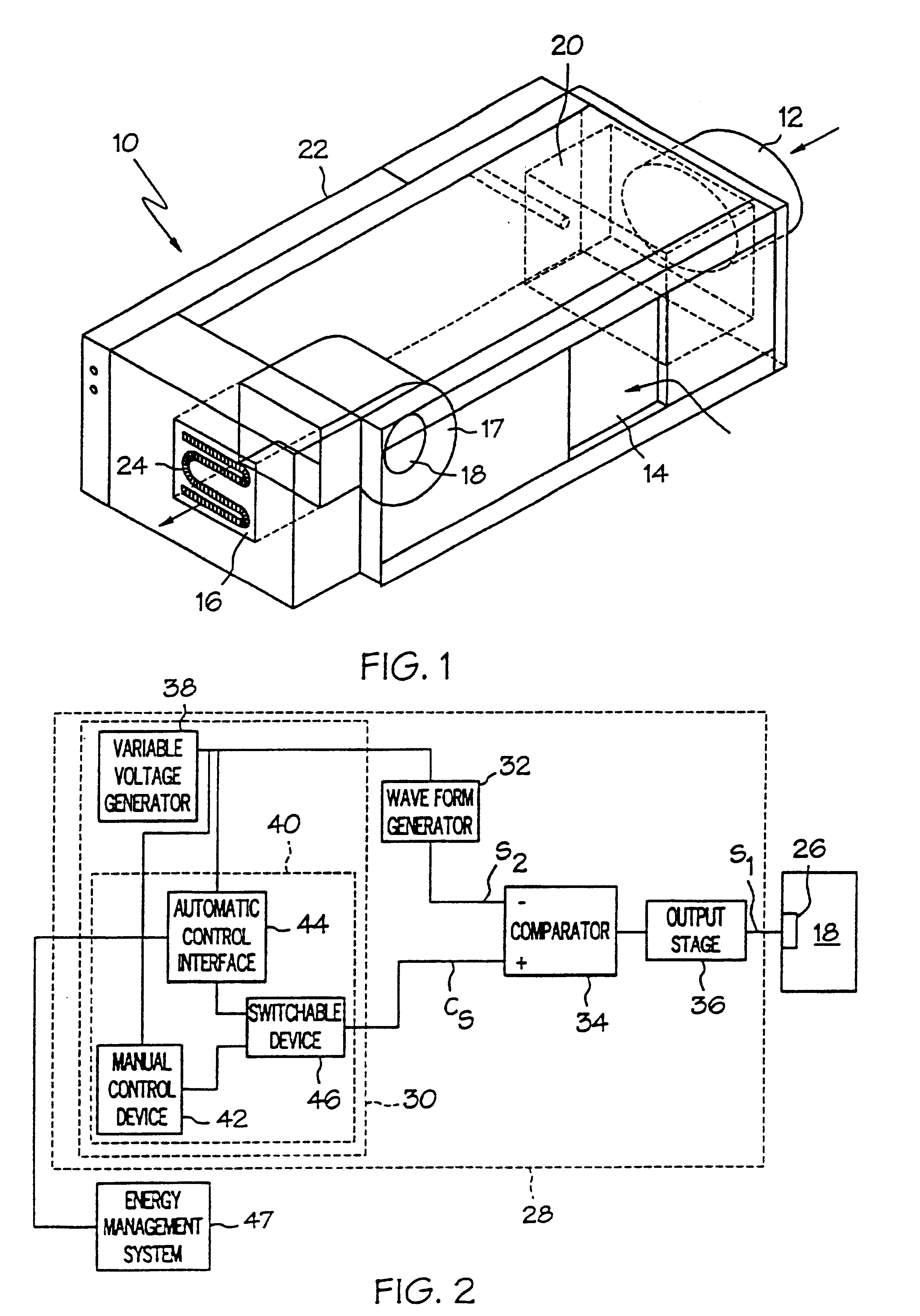
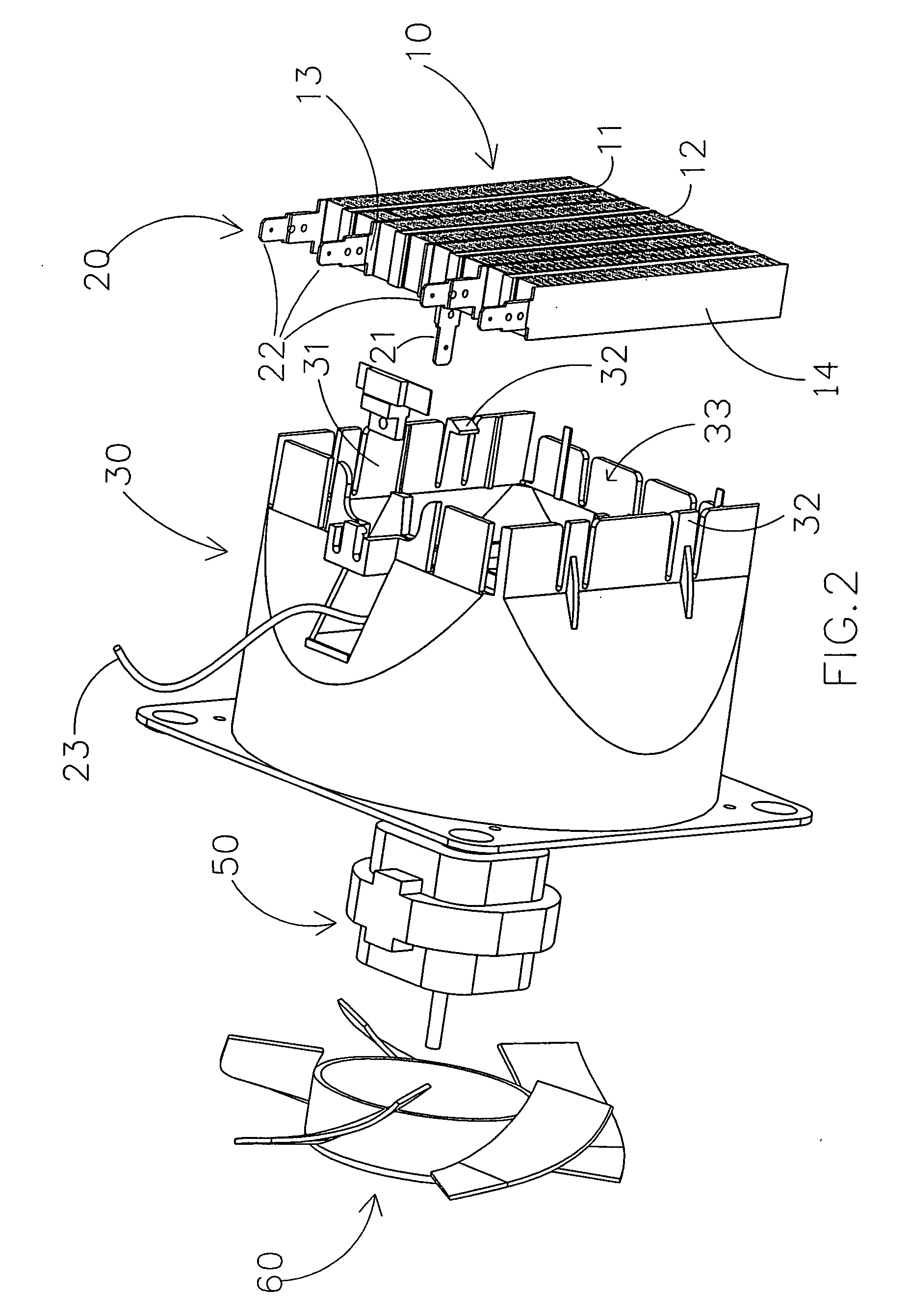
HVAC fan-powered terminal unit having preset fan CFM
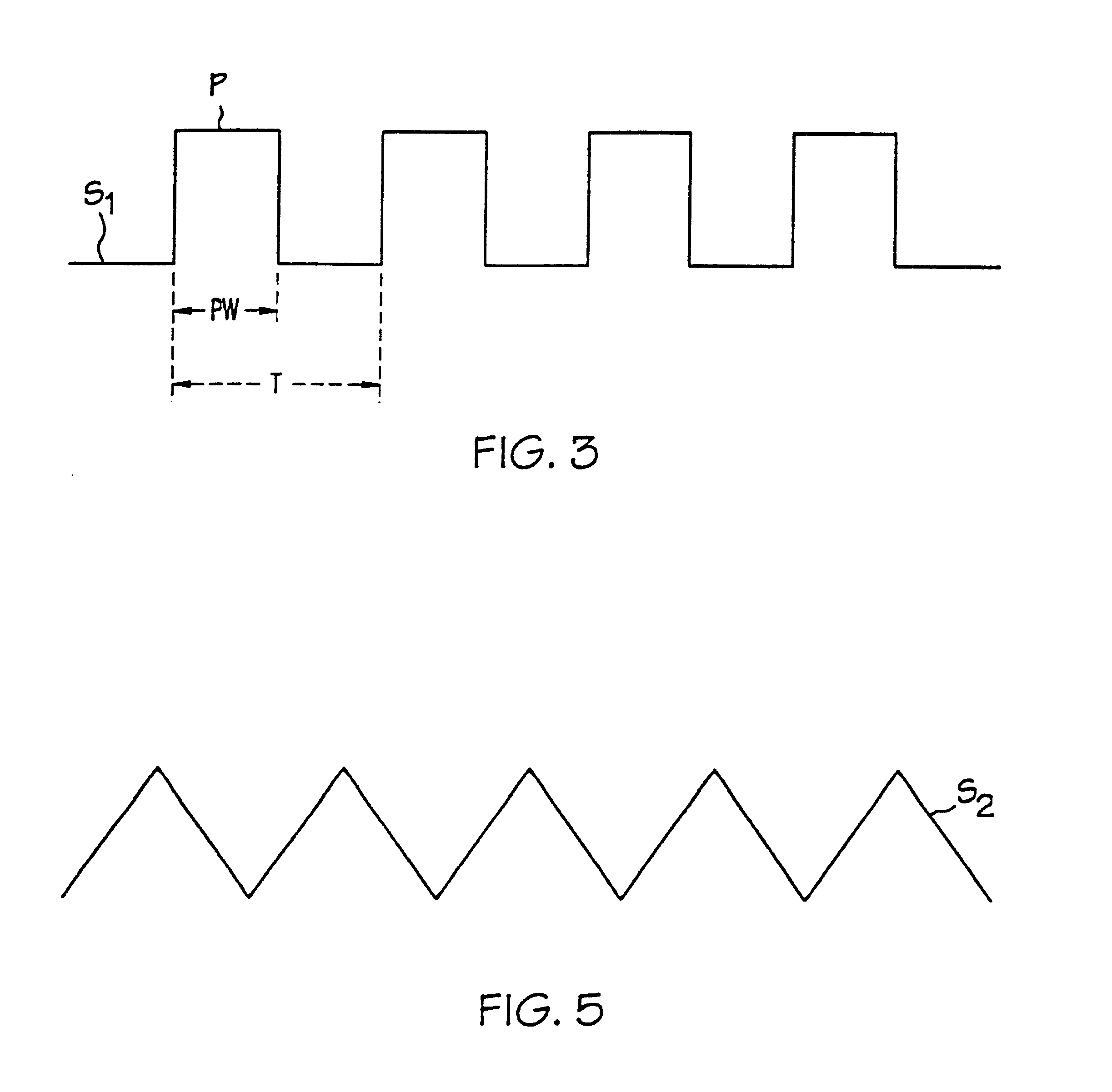
InactiveUSRE38406E1Mechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsVoltmeterEngineering
An arrangement is disclosed for controlling fan motors in fan-powered terminal units which permit the air flow of the terminal units to be factory preset and reset using a voltmeter. The fan motor is responsive to the pulse width of pulses of a pulse width modulated signal to provide an air flow which is proportional to the pulse width. By adjusting the pulse width, the air flow may be set as desired. A pulse width modulated signal having pulses with a set amplitude and frequency is generated. The dc voltage of the pulse width modulated signal is measured using a voltmeter. As the pulses have a set amplitude and frequency, the pulse width of the pulses may be adjusted by controlling the dc voltage of the pulse width modulated signal. The fan motor is programmed to deliver the set air flow over a range of static pressures.
Owner:NAILOR INDS OF TEXAS
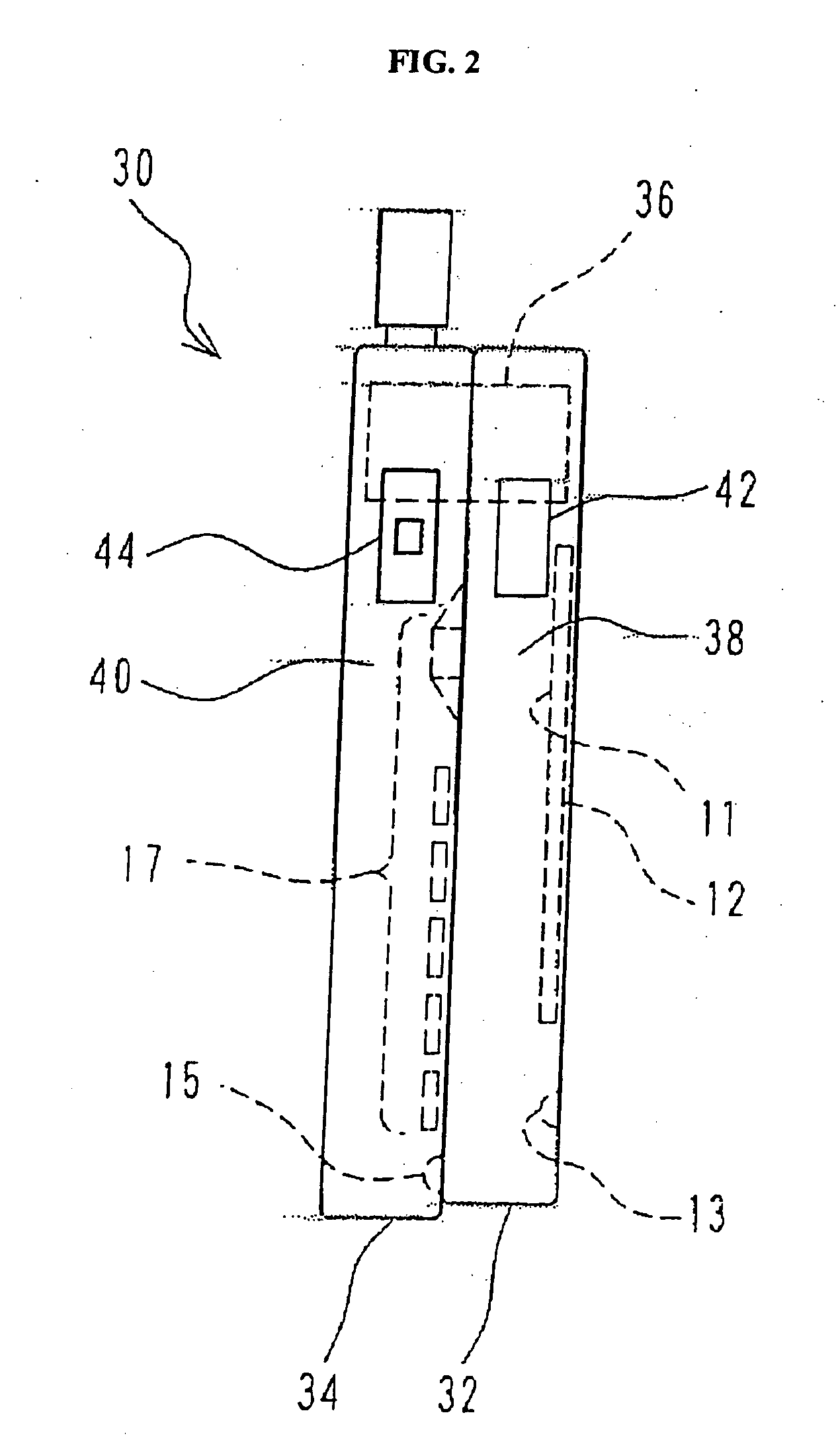
Portable terminal unit
InactiveUS20050130715A1Easy to operateClear distinctionInterconnection arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCouplingTerminal equipment
A overlapping type portable terminal unit is in a closed state such that a first housing and a second housing face in the same direction and are overlapping each other. These housings are coupled at their ends by a coupling section having a shaft which passes through the both housings. The unit is in an opened state in the case that the first housing is rotated from the closed state in a clockwise direction or a counterclockwise direction. A control section selects a screen so that a first screen is displayed in the display section when the first housing is rotated in relation to the second housing clockwise from the closed state, and so that a second screen is displayed in the display section when the first housing is rotated in relation to the second housing counterclockwise.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Mobile terminal unit, display method, display program, and recording medium
ActiveUS20090051830A1Efficient use ofEffective displayTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceComputer terminal
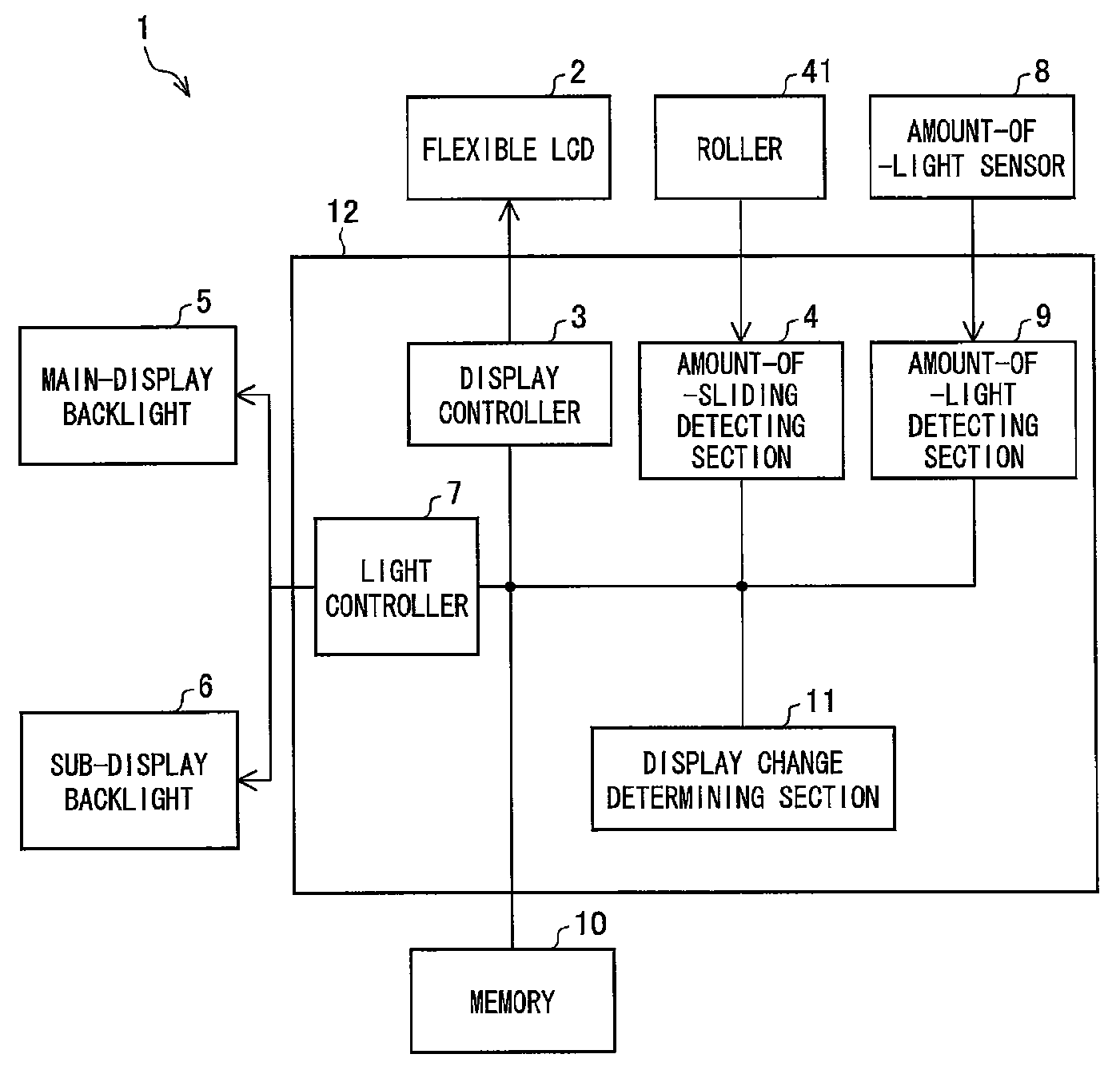
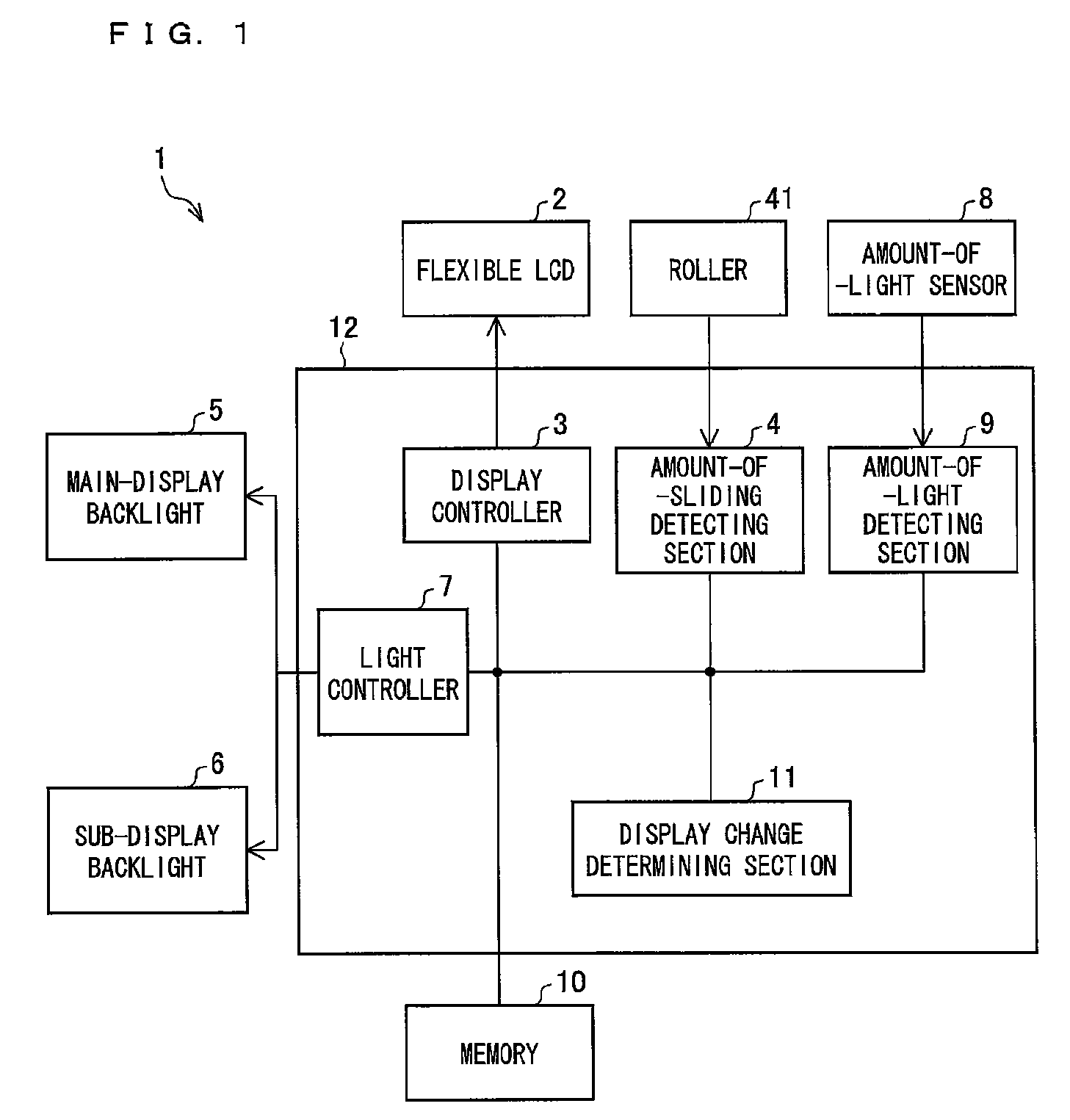
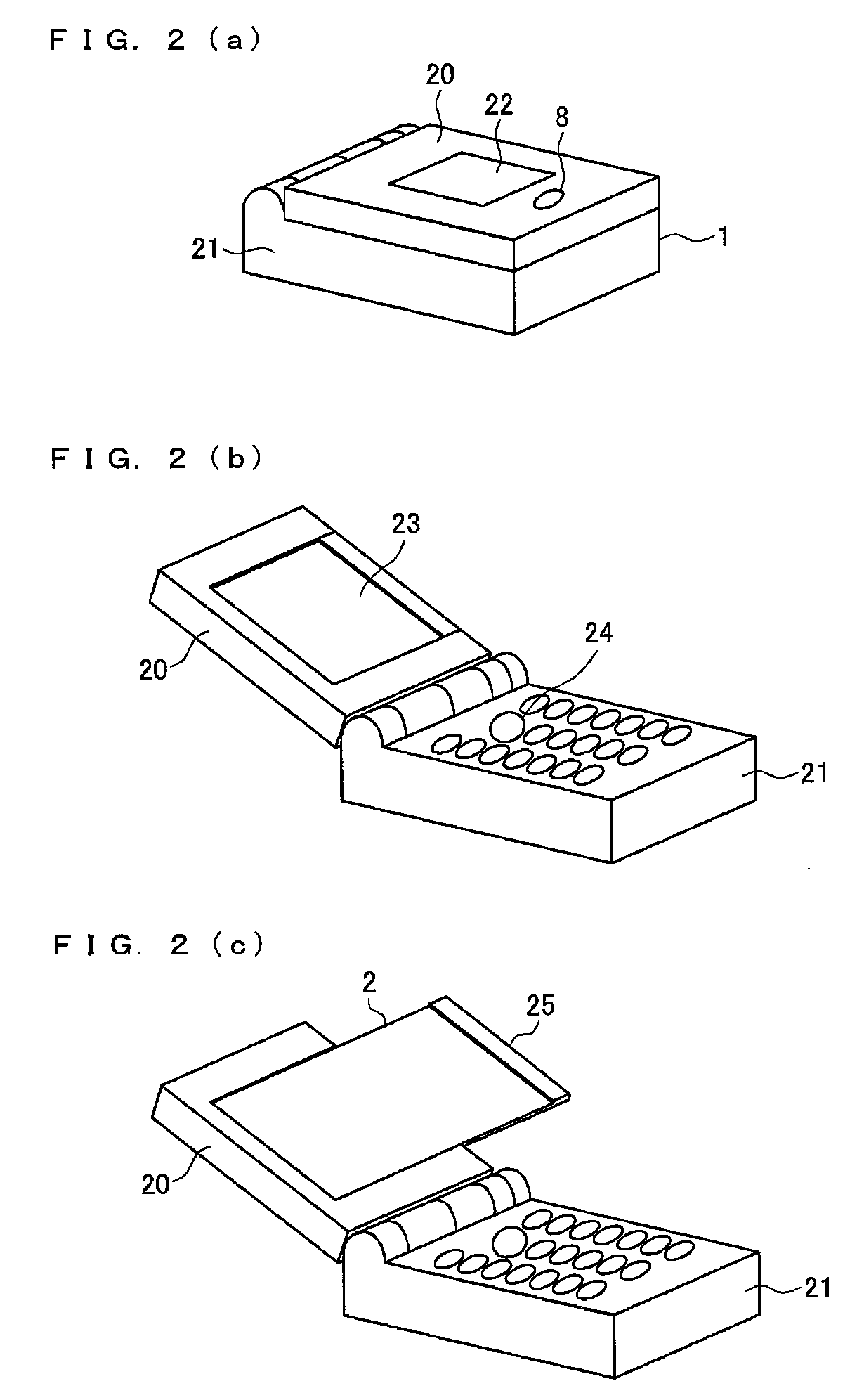
A flexible LCD (2) is a flexible display. The flexible LCD (2) is pulled out from an upper cabinet to change a display area of the flexible LCD (2). An amount-of-sliding detecting section (4) measures the pullout amount (amount of sliding) of the flexible LCD (2) when the flexible LCD (2) is pulled out from a mobile terminal unit (1) or is retracted into the mobile terminal unit (1). A display controller (3) causes the flexible LCD (2) to display in a manner responsive to the amount of sliding that is measured by the amount-of-sliding detecting section (4). The foregoing makes it possible to utilize effectively the display having a display area that is revealed when the display is pulled out.
Owner:UNIFIED INNOVATIVE TECH
Method and system for coordination and control of data streams that terminate at different termination units using virtual tunneling
InactiveUS6157649ATime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork access serverData stream
A method for coordinating and controlling multiple data streams representing a data transmission session that terminate in different termination units (such as network access servers) using a virtual data stream tunnel is presented. The data streams are transmitted over two or more links, collectively forming a "bundle. One of the termination units that receives a data stream is designated as the termination unit to receive and reconstruct a call. The designated termination unit is the "owner" of the bundle. A termination unit that is a not a bundle owner creates a virtual tunnel to the termination unit that is the bundle owner, and sends data streams through the virtual tunnel to the bundle owner to reconstruct the call. The designated termination unit reconstructs the data streams for the bundle and directs the bundle to a destination.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
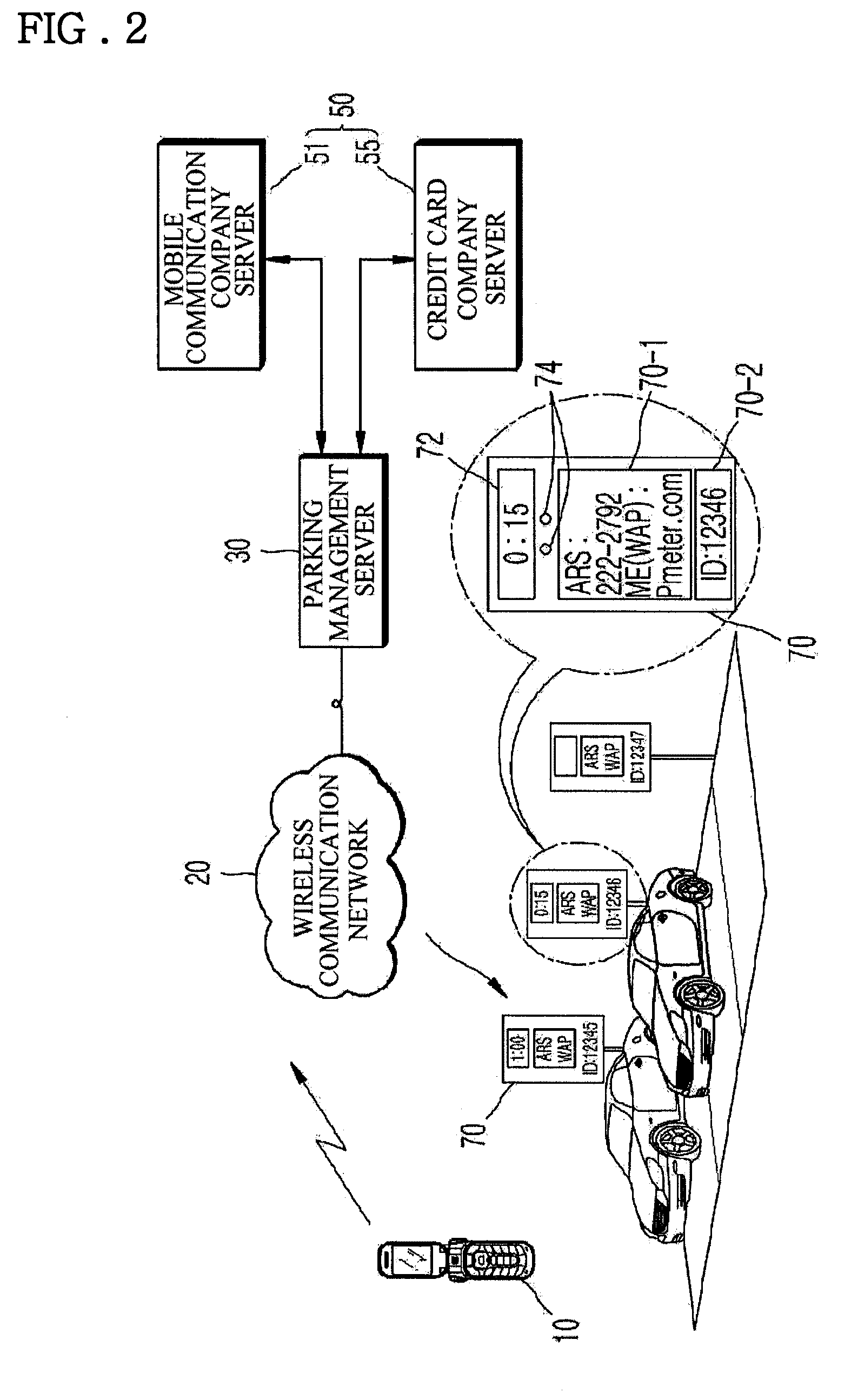
Parking count control system using parking management server and method thereof
InactiveUS20090109062A1The process is convenient and fastCarry-out conveniently and efficientlyTicket-issuing apparatusParking metersParking areaVoice communication
Provided is a parking count control system using a parking management server which is a parking management control system using a driver terminal unit, the system including: a mobile driver terminal unit capable of performing voice communication or / and wireless Internet; a parking management server receiving parking information about an identifier (ID) of a parking area and a parking time from the driver terminal unit when the parking management server has an access to the driver terminal unit to perform settlement and counting a parking time according to a parking area to notify the driver terminal unit of a parking completion message; a parking terminal unit installed in the parking area or in a plurality of parking areas, receiving parking-related information transmitted from the parking management server to count and display a parking remaining time; and a settlement server connected to the parking management server and processing and authenticating parking-related small amount or credit settlement by request of the parking management server.
Owner:AN IK SONG
System And Method For Tracking And Displaying Equipment Operations Data
InactiveUS20140095114A1Digital computer detailsData acquisition and loggingTerminal unitComputer science
A maintenance terminal unit is provided with a processor and a computer readable medium coupled to the processor. The computer readable medium is non-transitory and local to the processor. The computer readable medium stores computer executable instructions, that when executed by the processor cause the processor to: (1) receive equipment operations parameter data indicative of an operating status of a plurality of equipment, wherein separate equipment operations parameter data is received for at least two of the plurality of equipment; (2) translate the equipment operations parameter data relative to at least one threshold level into management operations data; (3) generate indicia of logs for the plurality of equipment; (4) generate indicia of log entries for the plurality of equipment; and (5) display indicia of the logs and log entries. The equipment can be wellsite equipment located at a wellsite.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Display device, display method, and display control program
InactiveUS20070074262A1Complicated operationTelevision system detailsSpecific information broadcast systemsDisplay deviceTerminal equipment
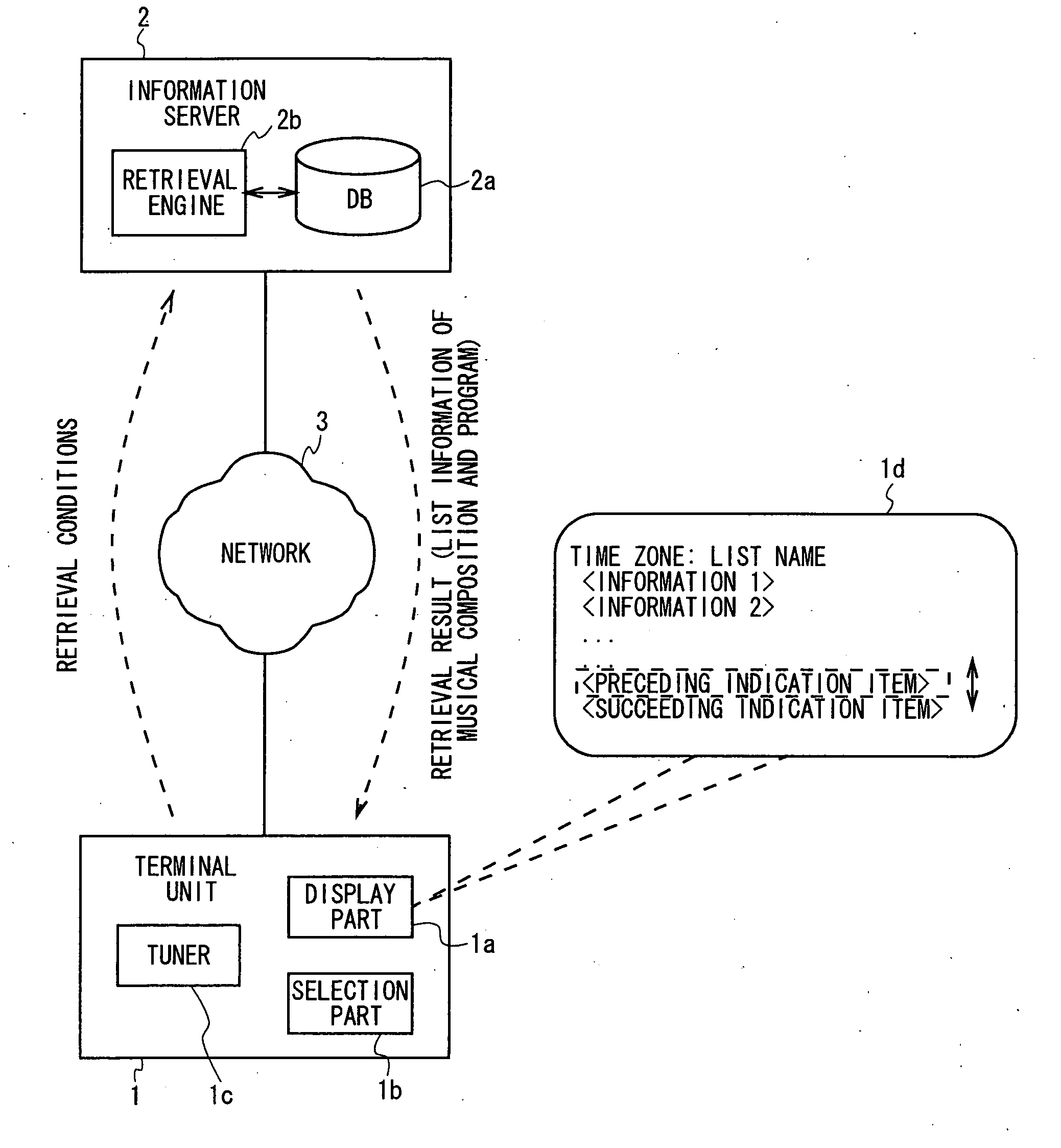
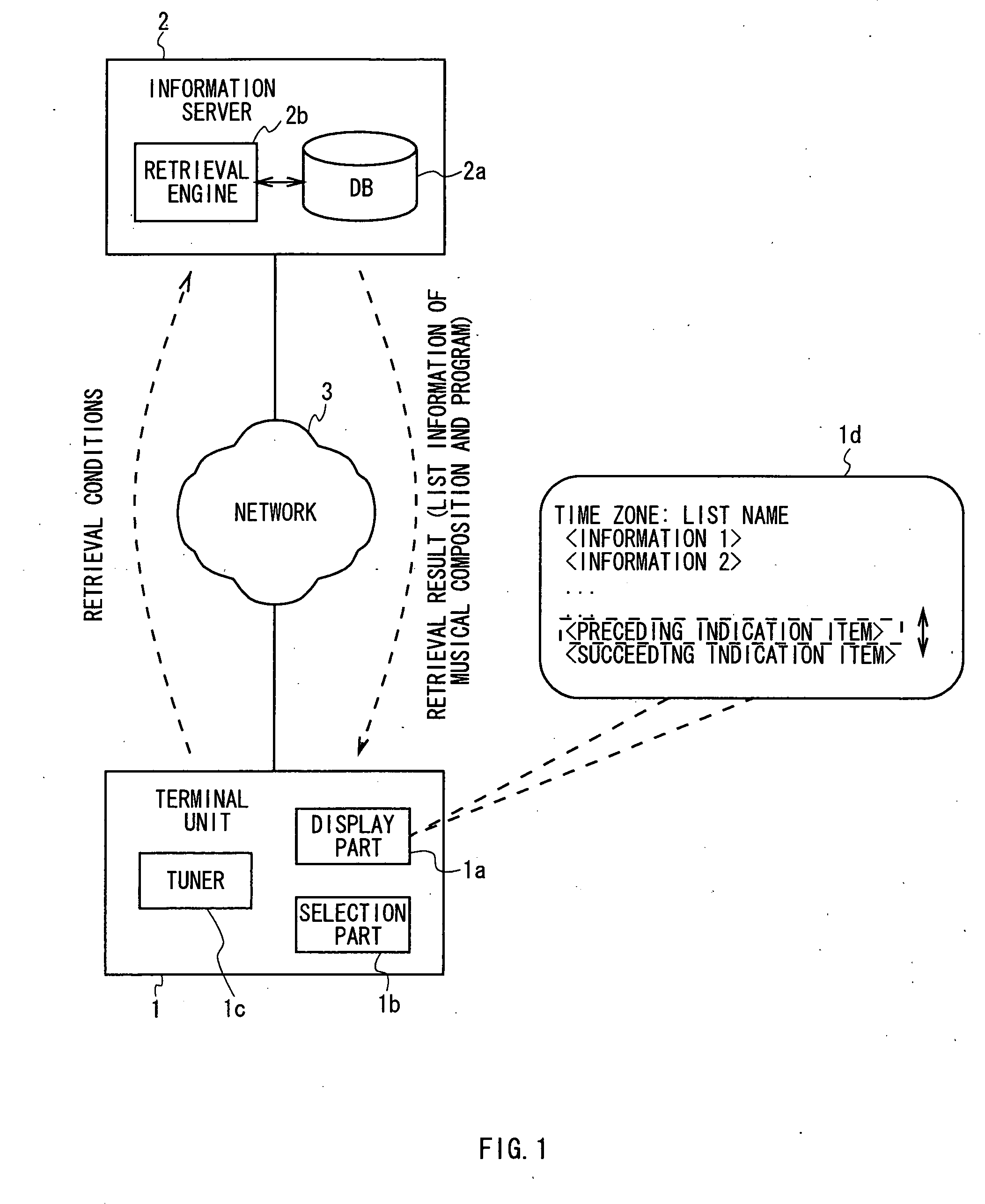
The present invention provides a display device for retrieving and displaying the list information regarding the broadcast contents in which the list information corresponding to the program broadcast before or after can be displayed without making the complicate key operations. An information server 2 transmits a list of musical compositions broadcast in a designated time zone to a terminal unit 1, based on a retrieval key such as date and time zone from the terminal unit 1. The terminal unit 1 displays the received list of musical compositions on a display part 1a. At this time, the directive items for displaying the list of musical compositions broadcast before and after are displayed, together with the received list of musical compositions. The user is allowed to display the list of musical compositions broadcast in a preceding or succeeding time zone only by selecting a directive item by performing an operation in series with a selection operation for a musical composition within the list of musical compositions, without returning to other screen, or re-specifying the retrieval conditions.
Owner:SONY CORP
Portable terminal unit
InactiveUS7409059B2Easy to operateInterconnection arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer terminalTerminal unit
To provide a superposition type portable terminal unit in which functions other than opening and closing functions are added to opening and closing operations thereby to improve the operating performance of the portable terminal unit. In a superposition type portable terminal unit in which a first housing having at least a display section and a second housing having at least an operation section, in a close state where the display section and the operation section face in the same direction and the housings are superimposed on each other so that the operation section of the second housing is covered with the first housing, are coupled at their ends by a coupling part having an axis in a direction where the both housings are pierced, the unit is put in an open state in case that the first housing is turned about the axis from the close state in any of a clockwise direction and a counterclockwise direction; and a control unit is provided, which selects a screen so that a first screen is displayed in the display section in case that the first housing is turned in relation to the second housing clockwise from the close state, and so that a second screen is displayed in the display section in case that the first housing is turned in relation to the second housing counterclockwise.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
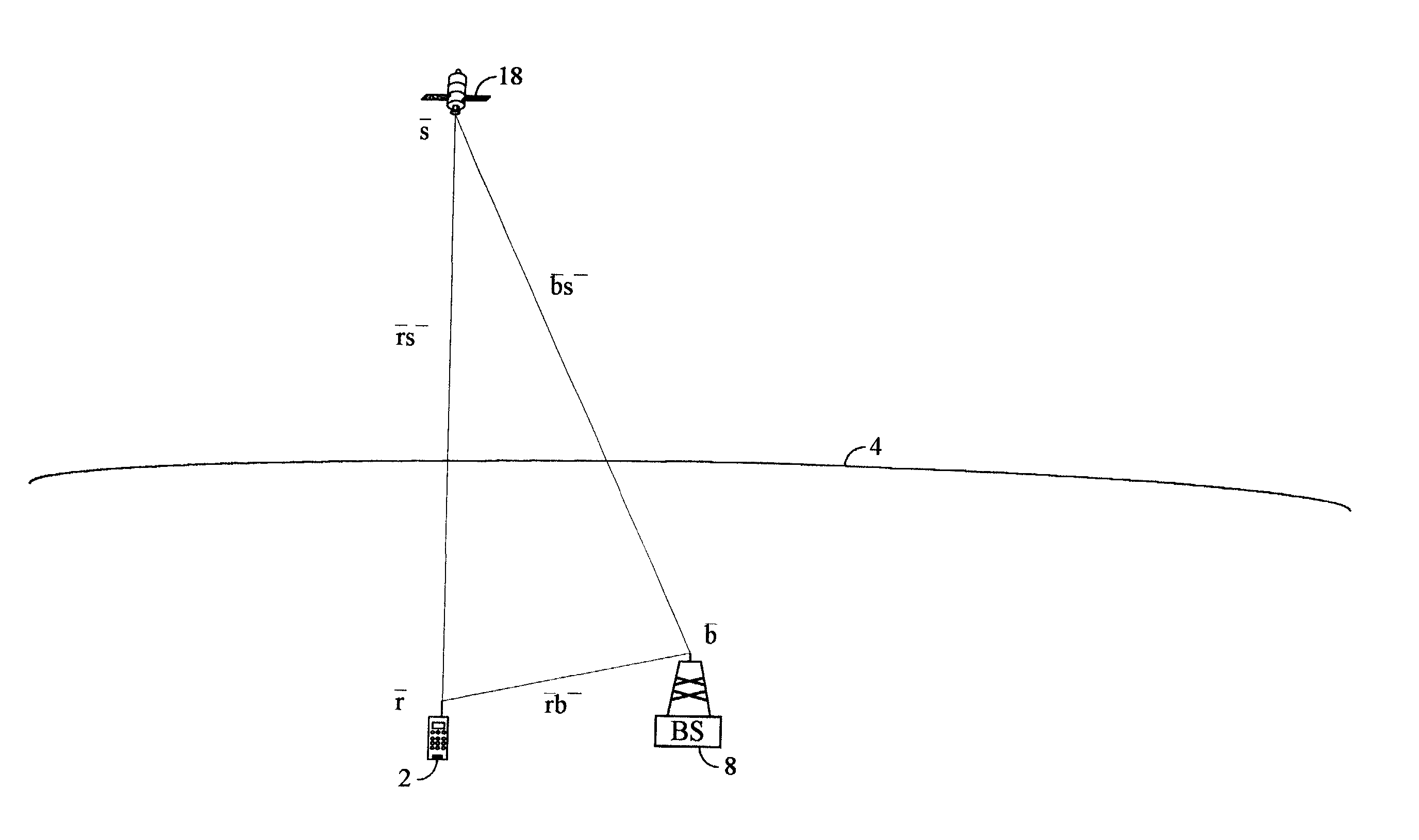
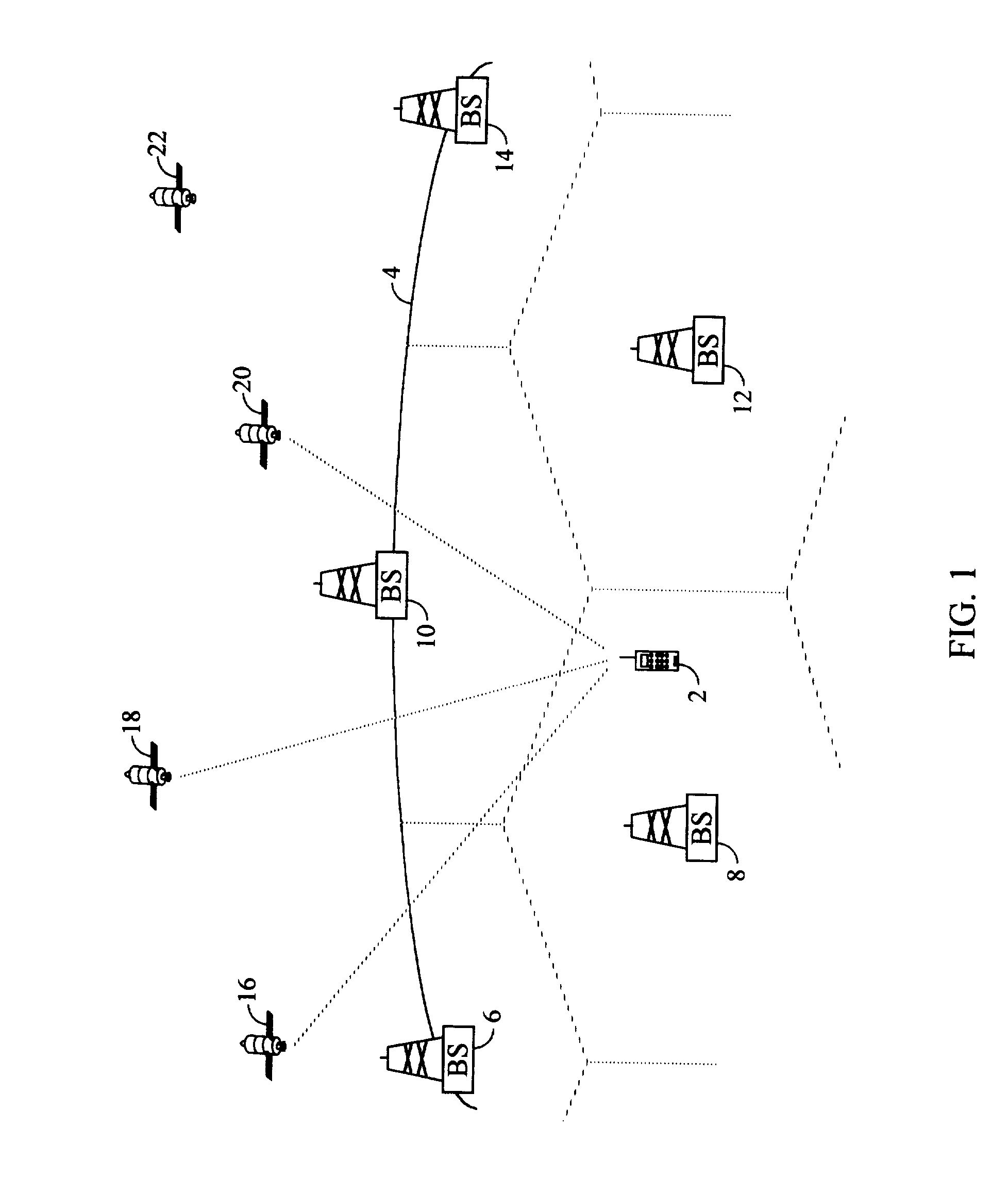
GPS satellite signal acquisition assistance system and method in a wireless communications network
InactiveUS20020123352A1Telephonic communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime delaysGeolocation
A system and method for assisting an integrated GPS / wireless terminal unit in acquiring one or more GPS satellite signals from the GPS satellite constellation. The invention includes a method for narrowing the PN-code phase search. That is, by accounting for the variables in geographic location and time delay relative to GPS time, the systems and methods of the present invention generate a narrow code-phase search range that enables the terminal unit to more quickly acquire and track the necessary GPS satellites, and thereby more quickly provide accurate position information to a requesting entity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
HDMI connector
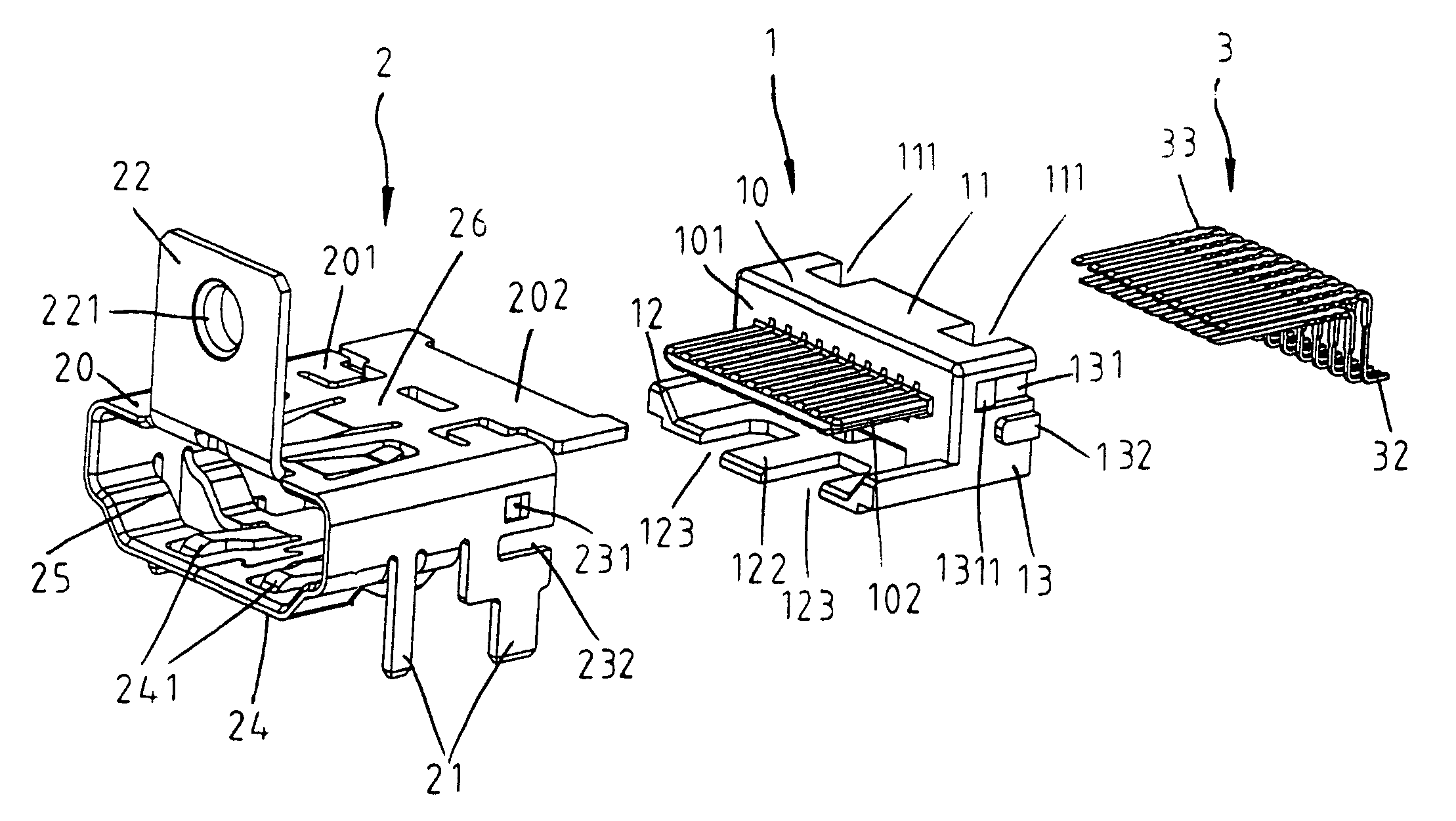
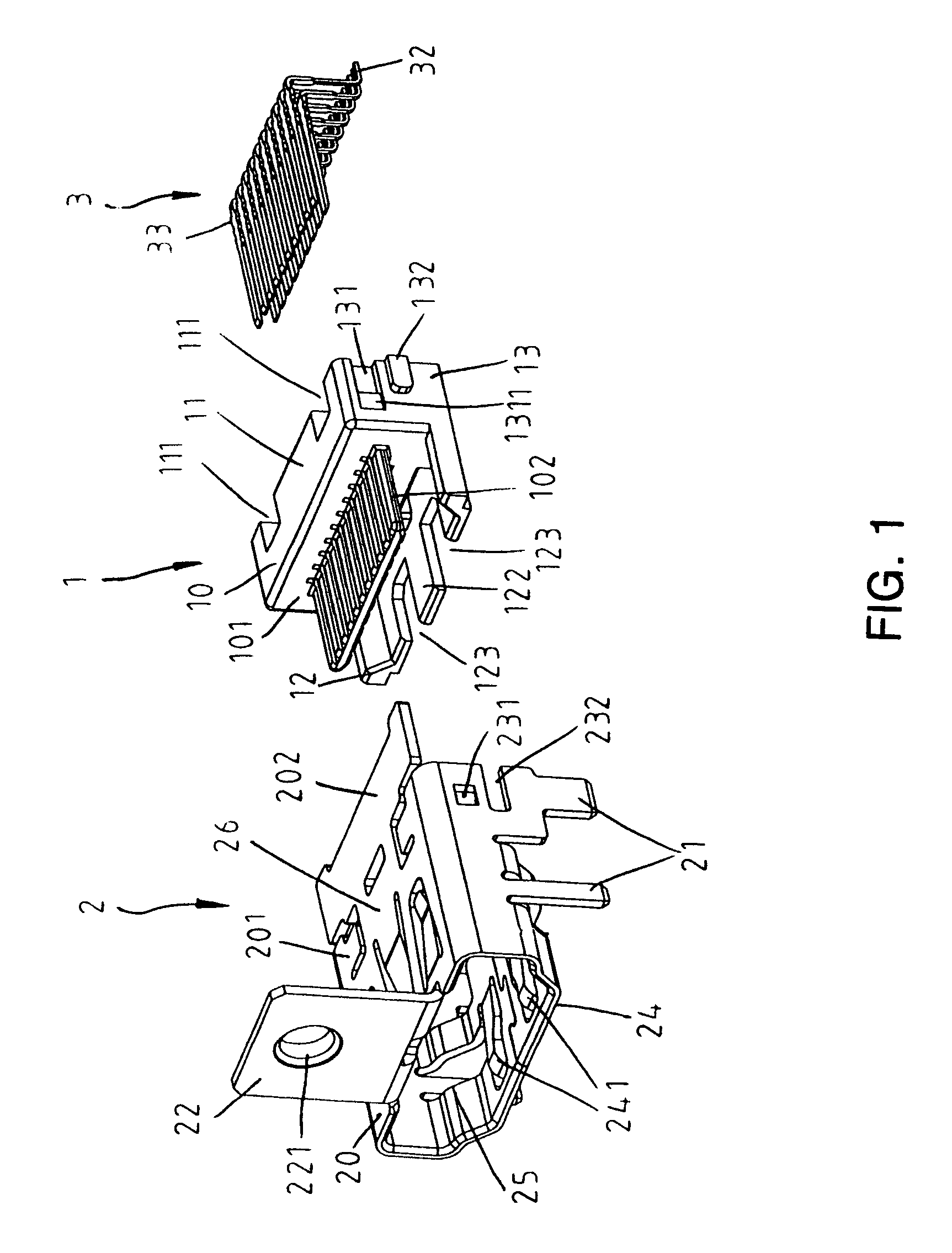
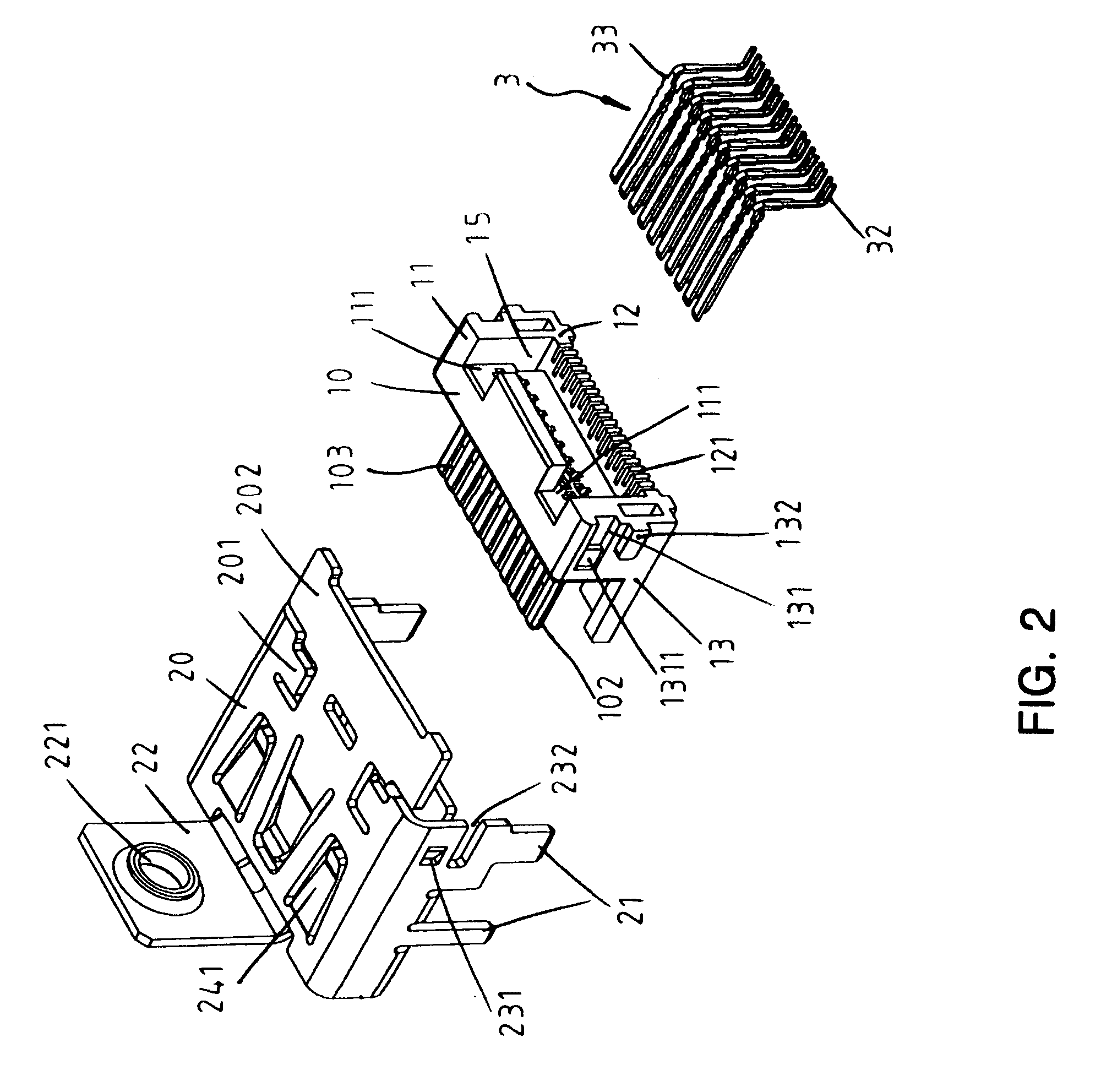
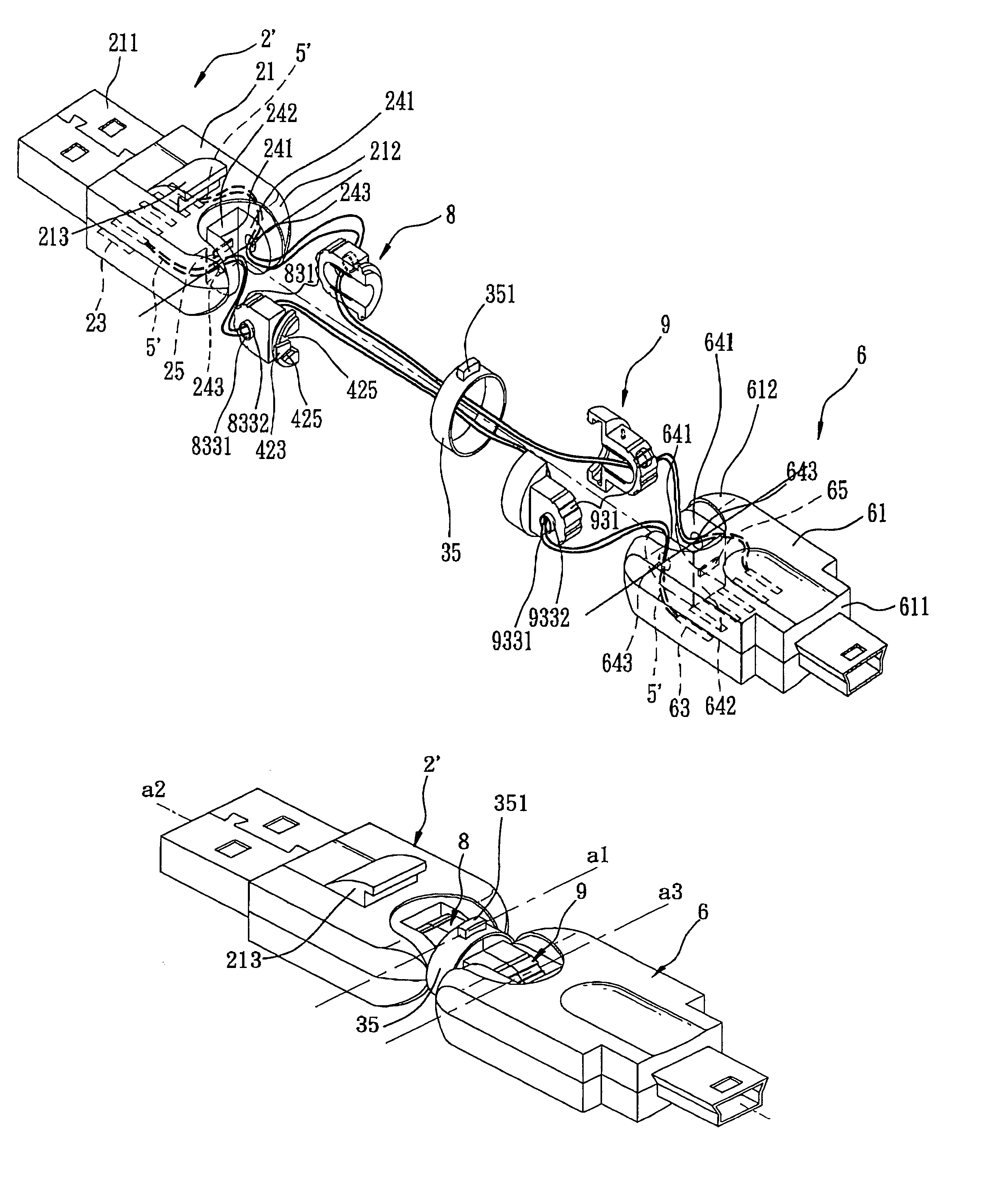
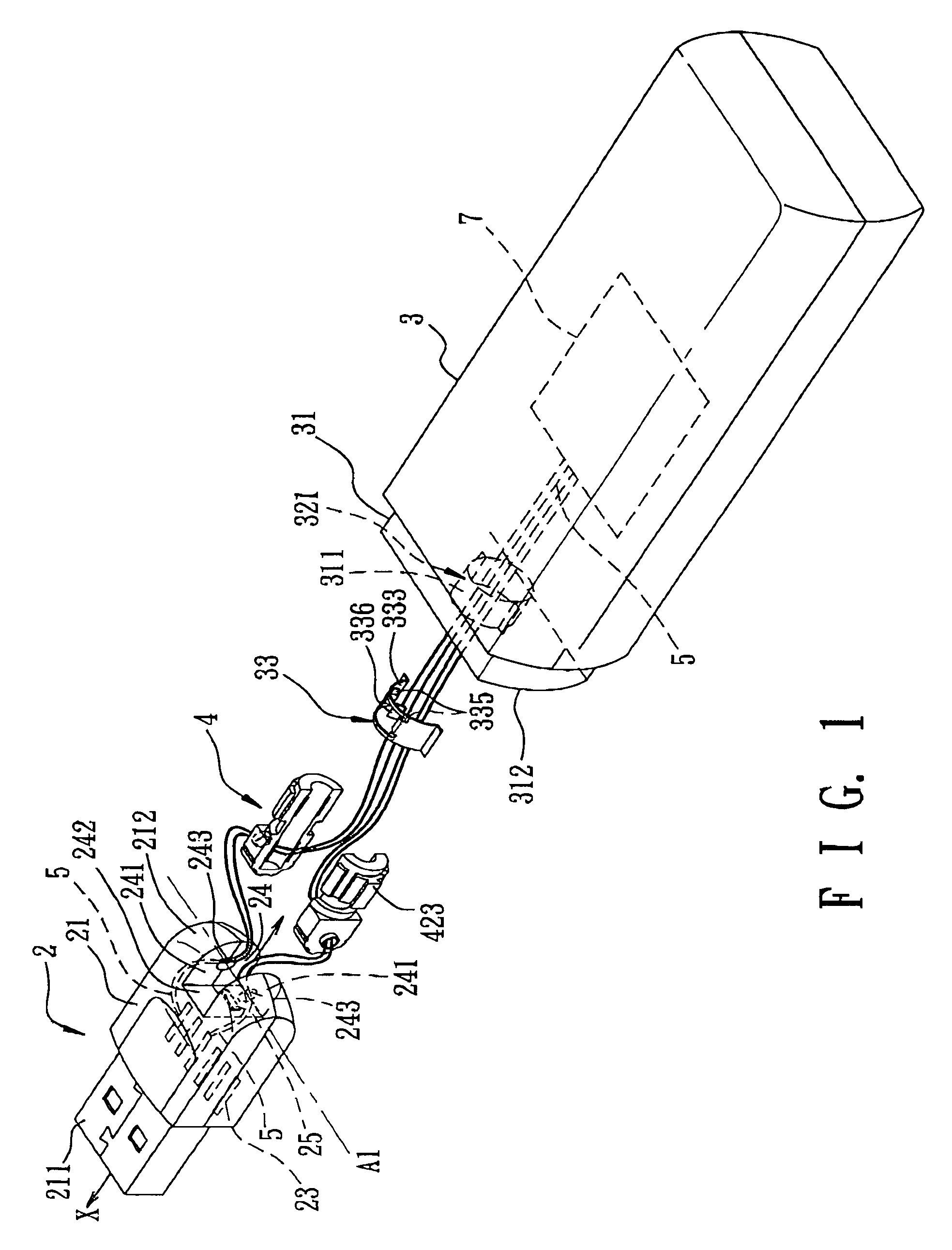
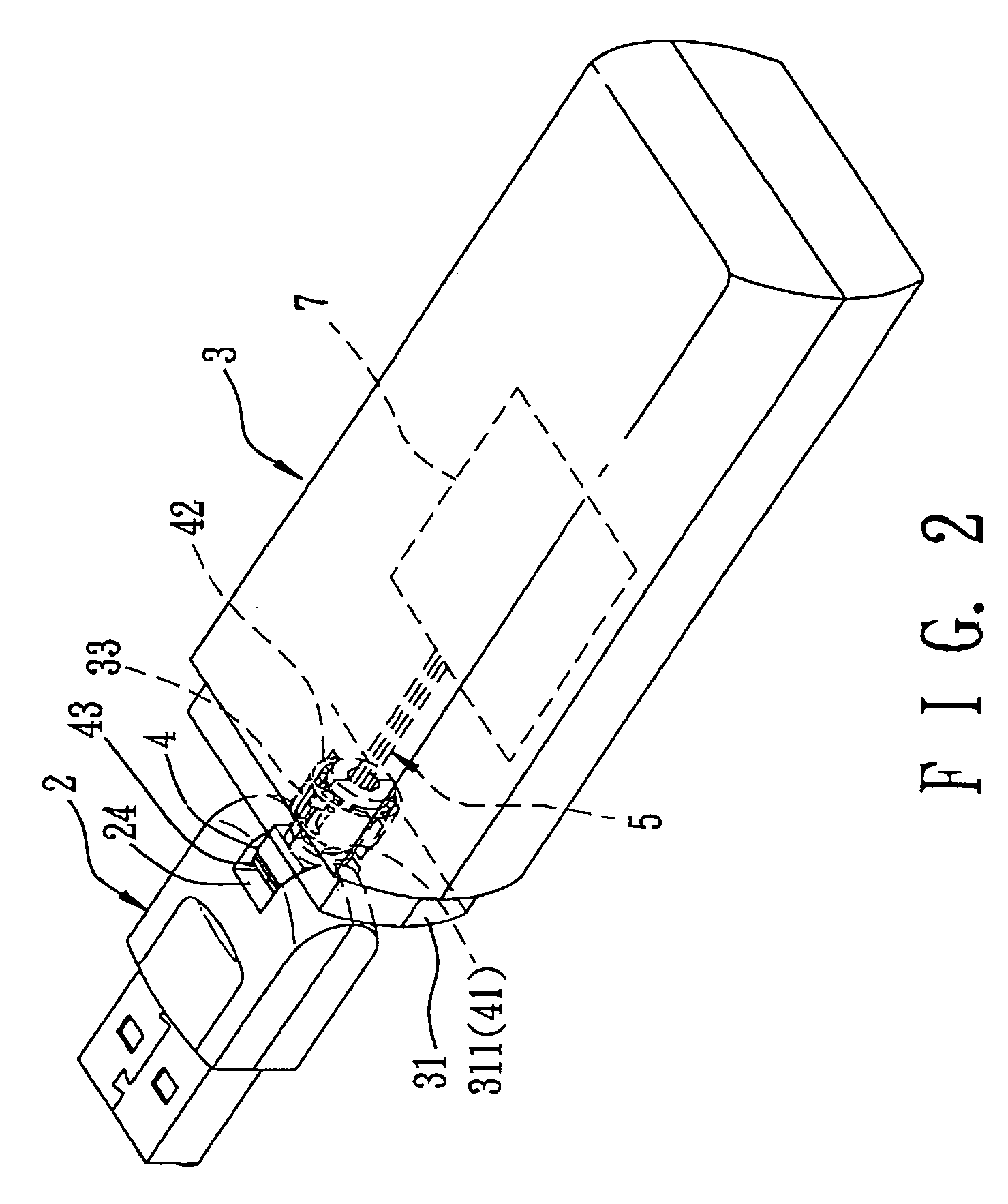
InactiveUS6986681B2Two-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsHDMITerminal unit
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
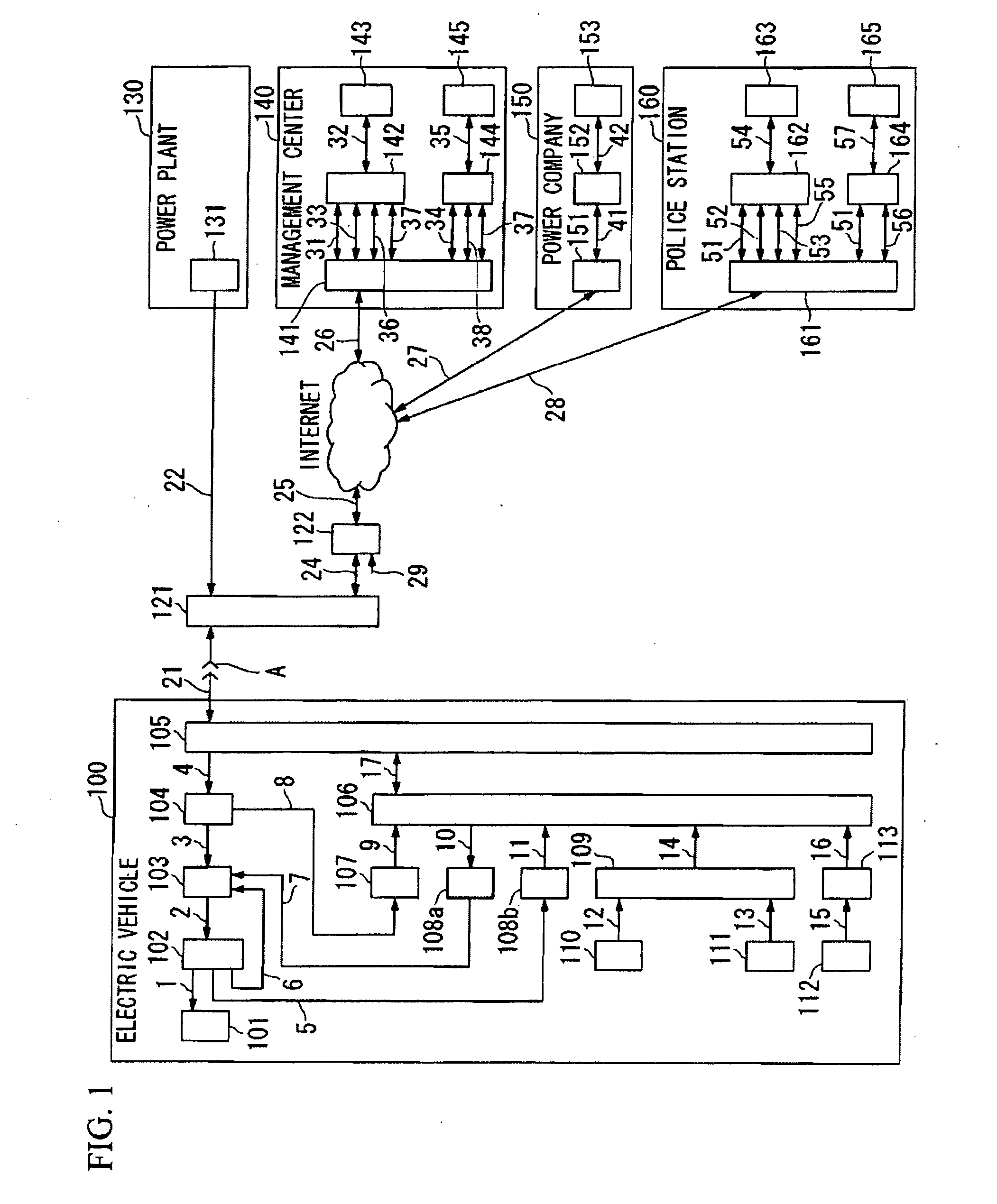
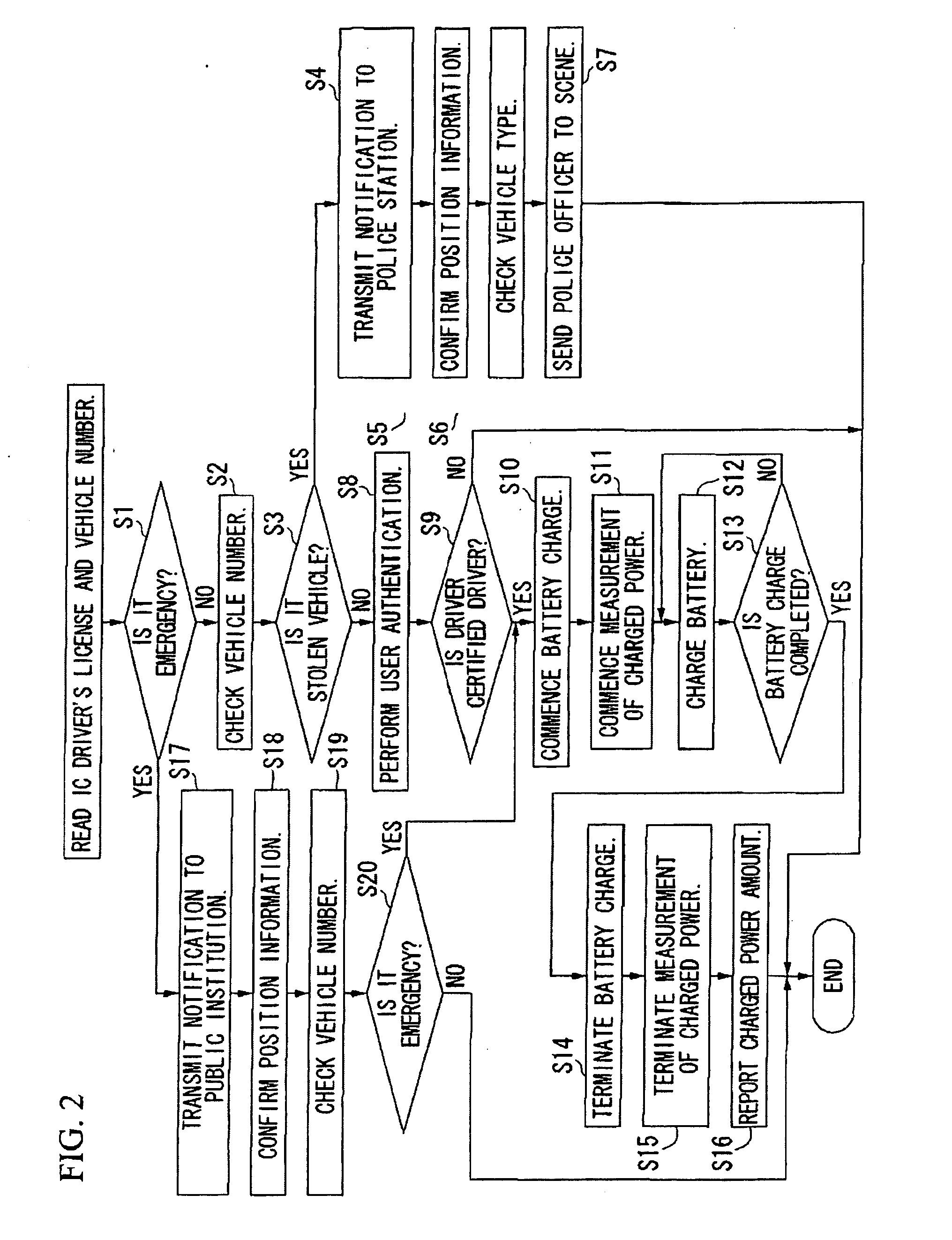
Battery charging system for electric vehicle
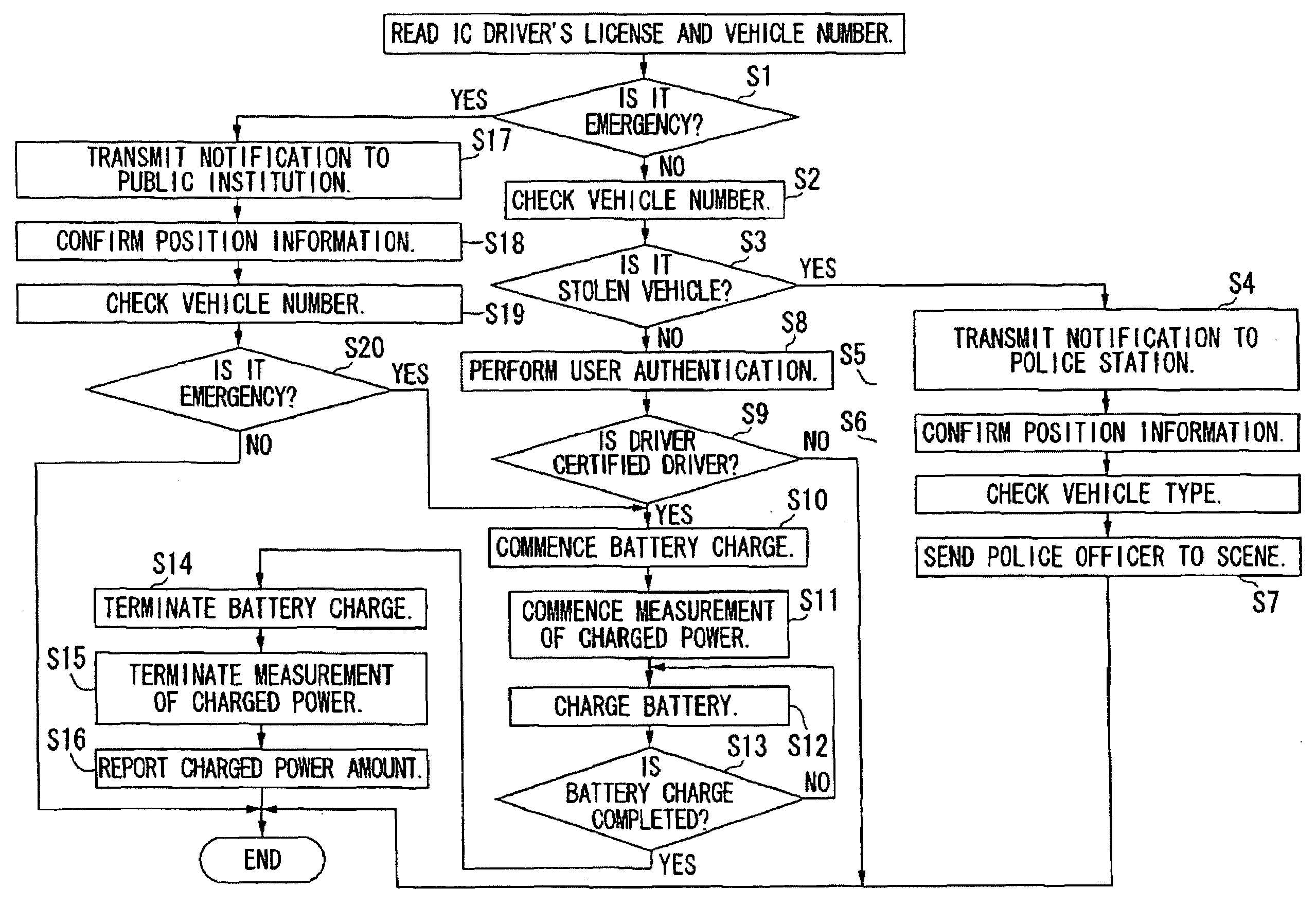
ActiveUS20090251300A1Quick searchDigital data processing detailsAnti-theft devicesNetwork terminationBattery charge
A battery charging system includes: an electric vehicle; a network termination unit connectable to the electric vehicle through a power line cable for supplying electric power to the electric vehicle; and a first server that transmits a control signal indicative of permission or forbiddance of power supply from the network termination unit to the electric vehicle to the electric vehicle through the network termination unit. The electric vehicle transmits identification information for identifying the electric vehicle and the user thereof to the first server through the network termination unit. The network termination unit transmits position information concerning the position of the network termination unit to the first server. The first server determines permission or forbiddance of the power supply based on the identification information and the position information.
Owner:NEC CORP
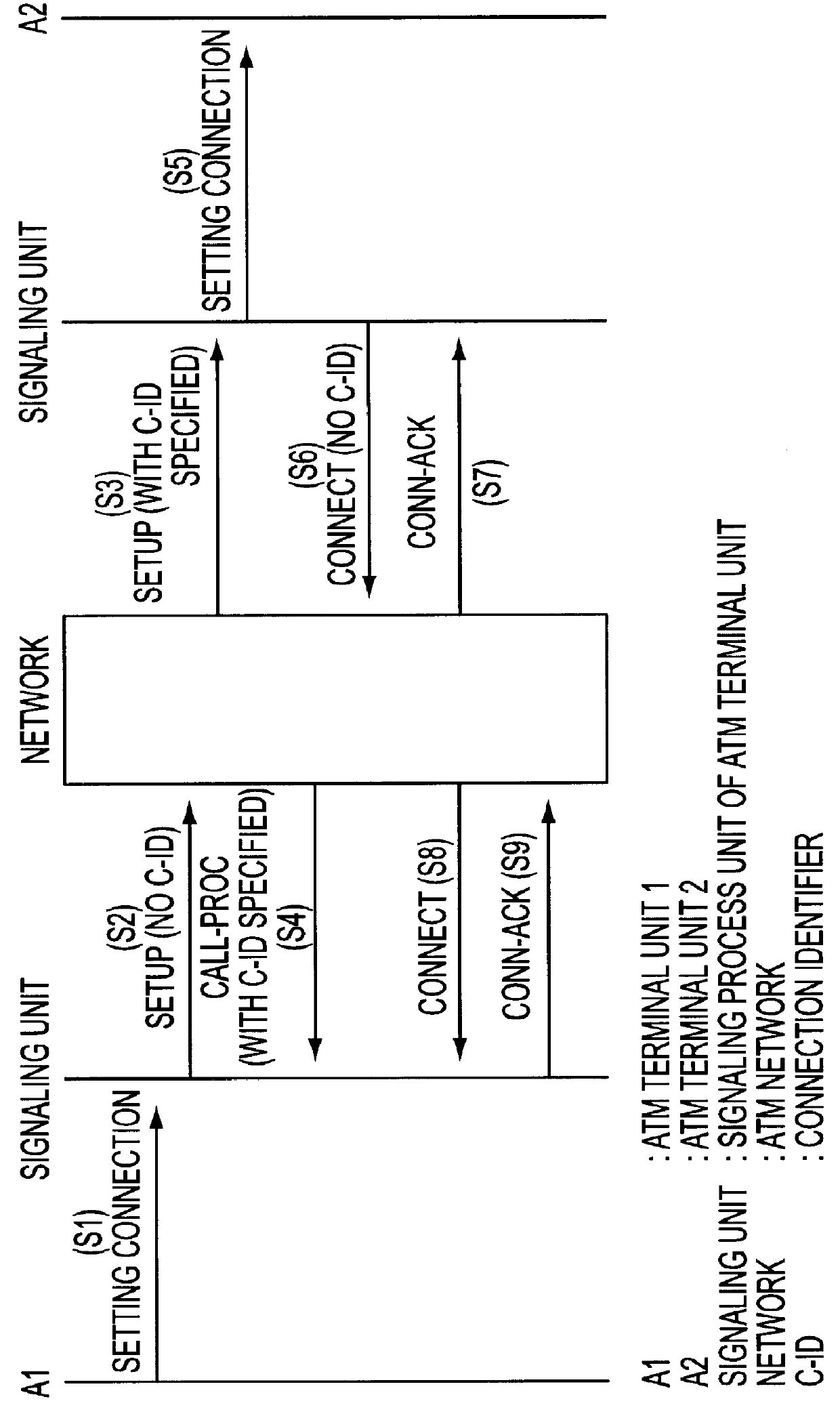
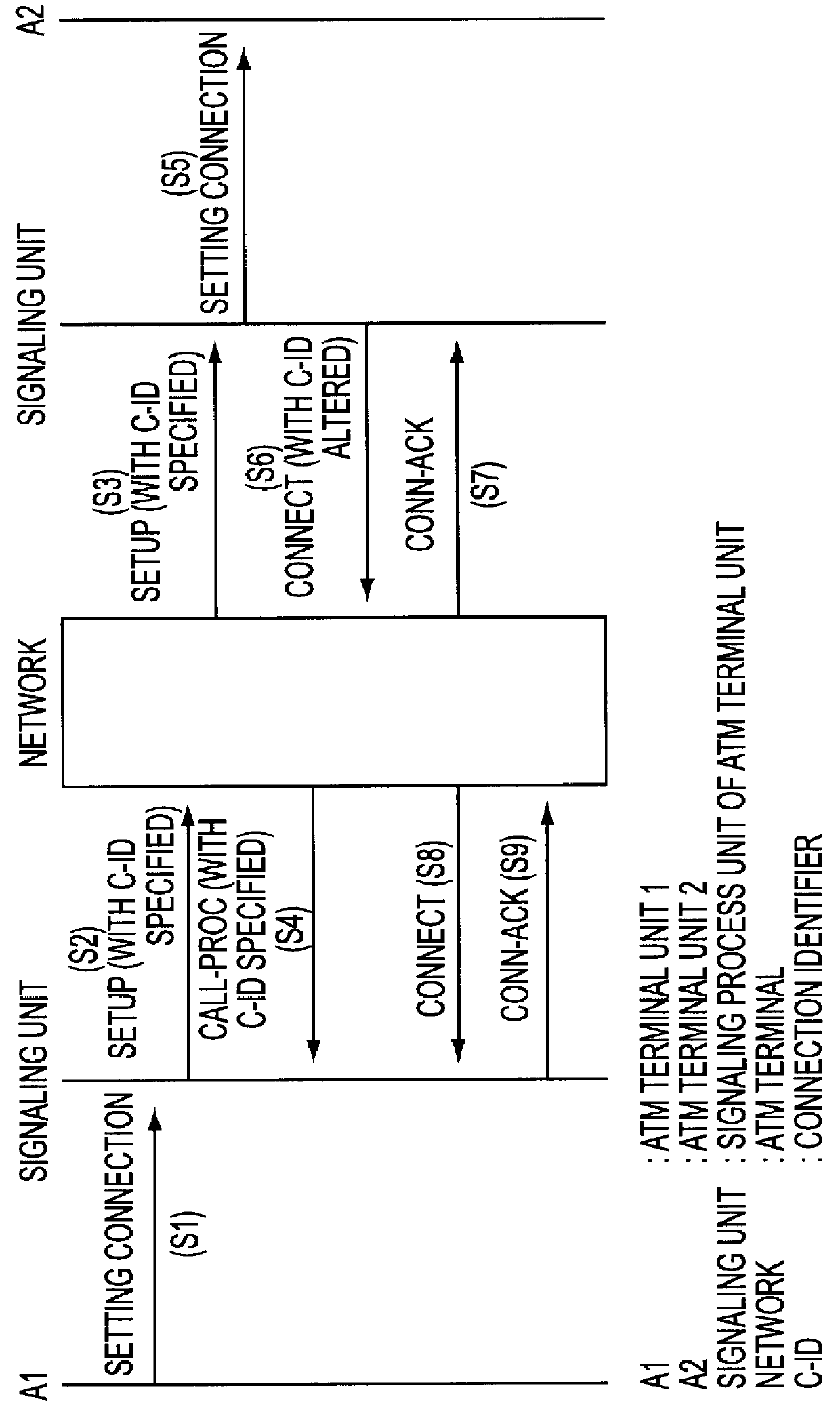
Method and apparatus for negotiating connection identifier
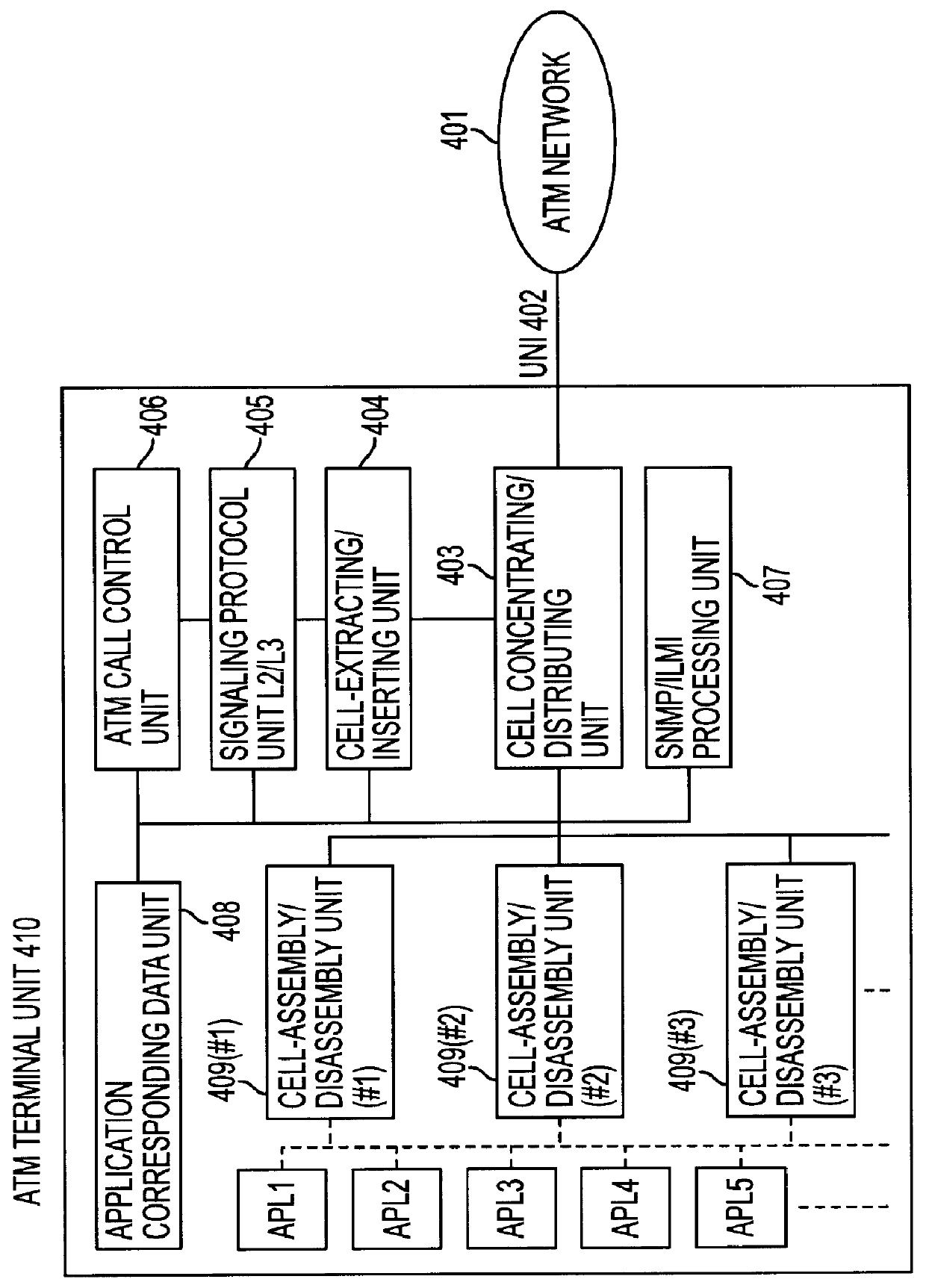
InactiveUS6028863ATime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTerminal unitElectric power
A device at the terminal unit and a device at the network support an interim local management (ILMI) protocol. When the power is applied to the device at the terminal unit, it notifies the device at the network of support range information about a VPI / VCI of the device at the terminal unit. The device at the network assigns a VPI / VCI to the device at the terminal unit according to the support range information about the VPI / VCI received in a cold start trap message from the device at the terminal unit when a signal is received from the device at the terminal unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Data processing apparatus, data processing method, terminal unit, and transmission method of data processing apparatus
InactiveUS20040218214A1Avoid dataDigital data processing detailsRead-only memoriesMass storageComputer terminal
A data processing apparatus is disclosed, that comprises a large capacity memory means for storing a plurality of files, a memory means for storing move / copy history when a particular file is moved / copied from the large capacity memory means to a non-volatile memory, a reference menas for referencing the history information stored in the memory means when the particular file is moved / copied from the large capacity memory means to the non-volatile memory, and a control means for prohibiting the particular file from being moved / copied from the large capacity memory means to the non-volatile memory when the reference means has detected that the history information is stored in the memory means.
Owner:SONY CORP
Electronic device having a pivotable electrical connector, and electrical connector assembly
InactiveUS7172428B2Prevent rotationCoupling device connectionsRotary current collectorEngineeringTerminal unit
Owner:HUANG YEA YEN
Satellite signal splitter
InactiveUS6023603AReduce component countSimple working processTelevision system detailsSpatial transmit diversitySwitching signalTerminal unit
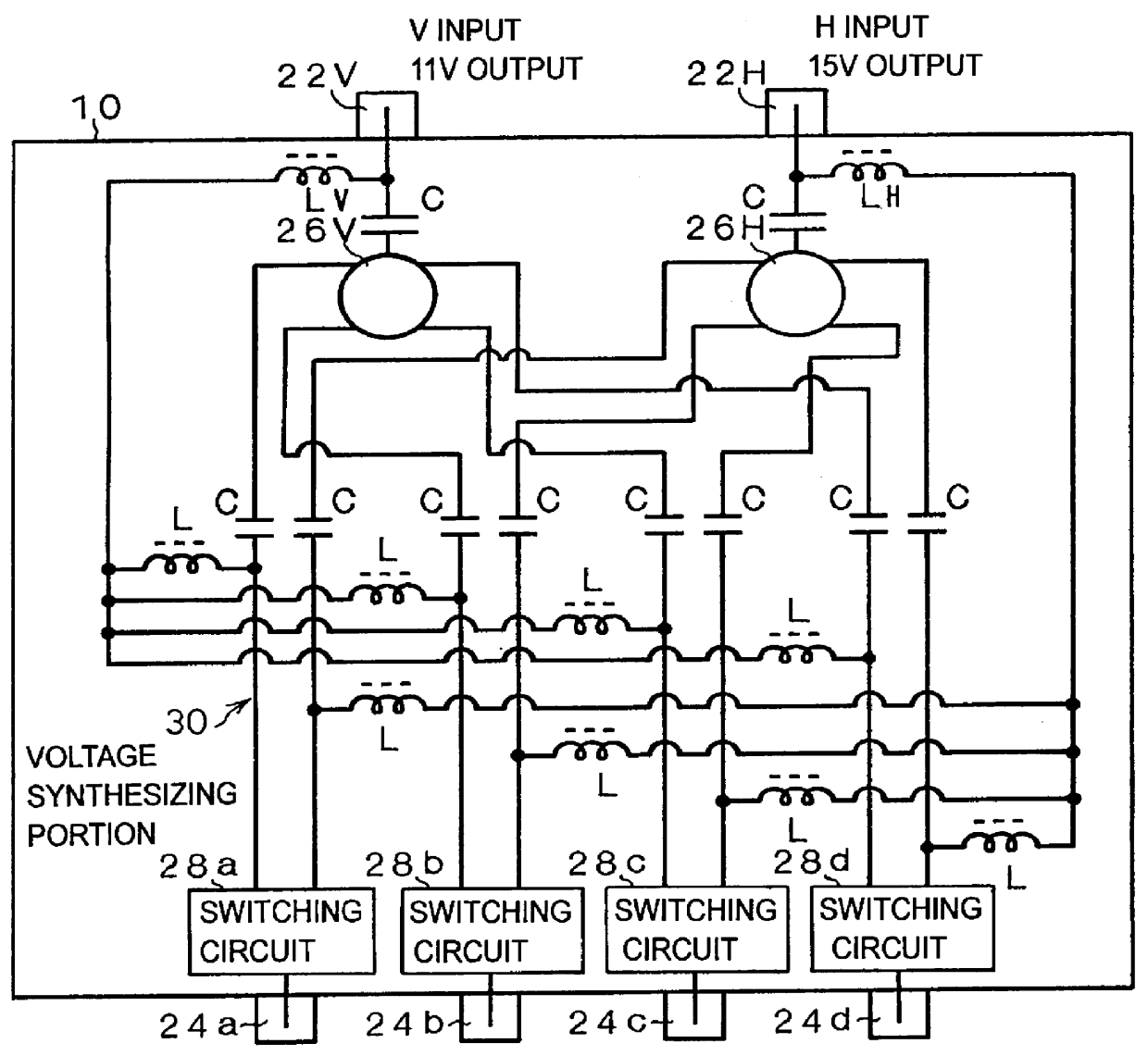
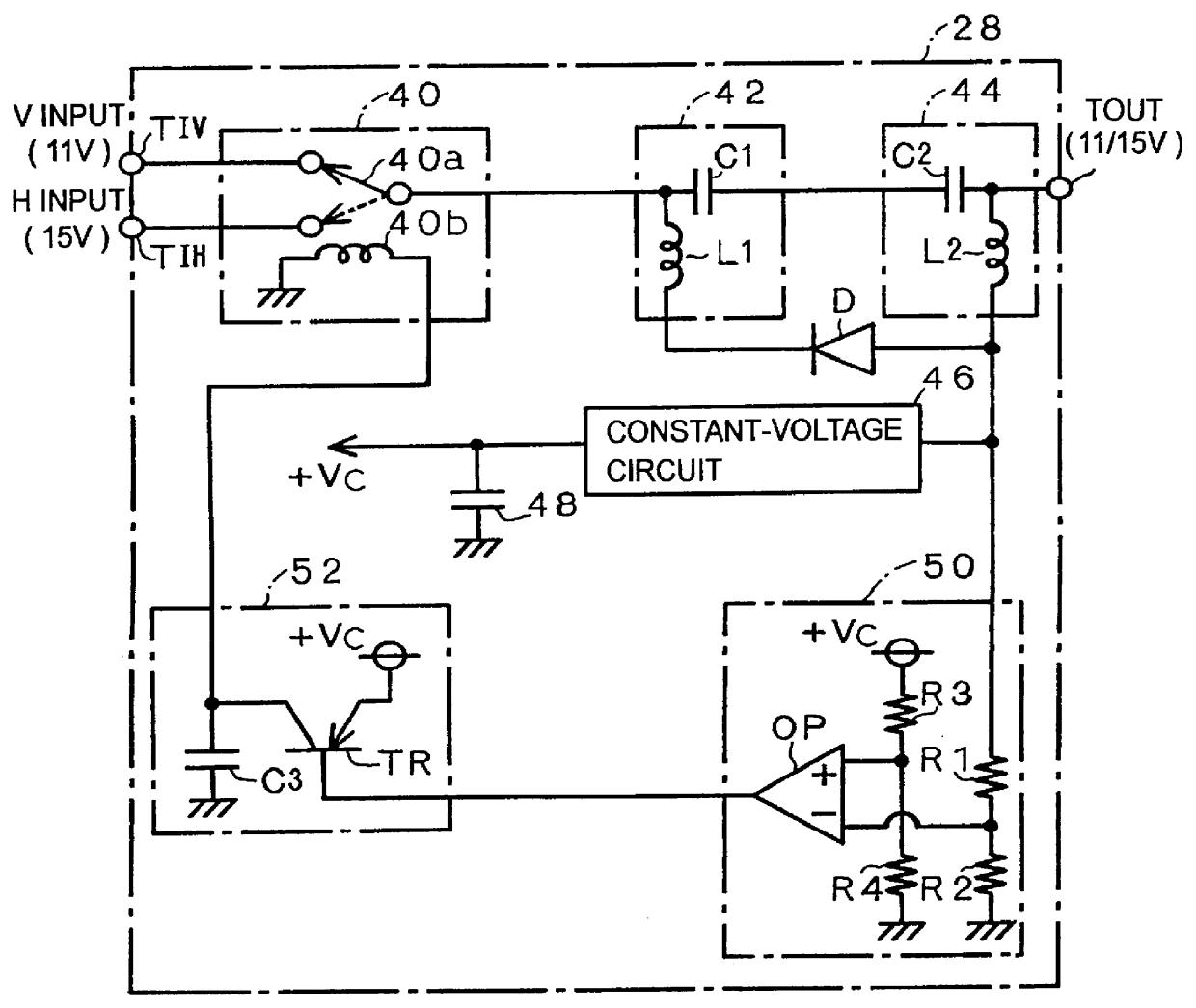
A satellite signal splitter is proposed which can transmit a received signal of a desired polarized wave with one cable to each terminal side when transmitting to plural terminal sides the received signals from a satellite receiving antenna which emits the received signals of a vertically polarized wave and a horizontally polarized wave. The vertically and horizontally polarized-wave received signals transmitted to input terminals 22V and 22H are split into four by splitting circuits 26V and 26H, respectively. The four split signals are transmitted to switching circuits 28a to 28d. In the switching circuits 28a to 28d, in accordance with a voltage level (11V or 15V) of a polarized-wave switching signal transmitted from terminal units connected to output terminals 24a to 24d, either the vertically or horizontally polarized-wave signal is selected and emitted from the output terminals 24a to 24d. Also, the polarized-wave switching signal (11V or 15V) is transmitted via a voltage synthesizing portion 30, choke coils LV, LH and the like from the input terminals 22V and 22H to a corresponding receiving portion of a receiving antenna.
Owner:MASPRODENKOH KK
PTC airflow heater
InactiveUS20080124060A1Small sizeSpace minimizationAir heatersControl of fluid heatersElectricityElectrical connection
An airflow heater includes a housing, a control arrangement supported at an upper portion of the housing, an air source for generating a flow of air, a PTC heat generator for generating heat, and a terminal unit including an upward terminal connector upwardly extended from the PTC heat generator to align with the control arrangement and a sideward terminal connector rearwardly extended from the PTC heat generator to minimize a distance between the terminal unit and the control arrangement for electrical connection. The upward terminal connector and the sideward terminal connector are electrically connected to the control arrangement. The air source and the PTC heat generator are activated by the control arrangement for generating the air towards the PTC heat generator and for generating the heat respectively, such that when the air passes through the PTC heat generator, the air is heated up before exiting the housing.
Owner:GAO TIANYU
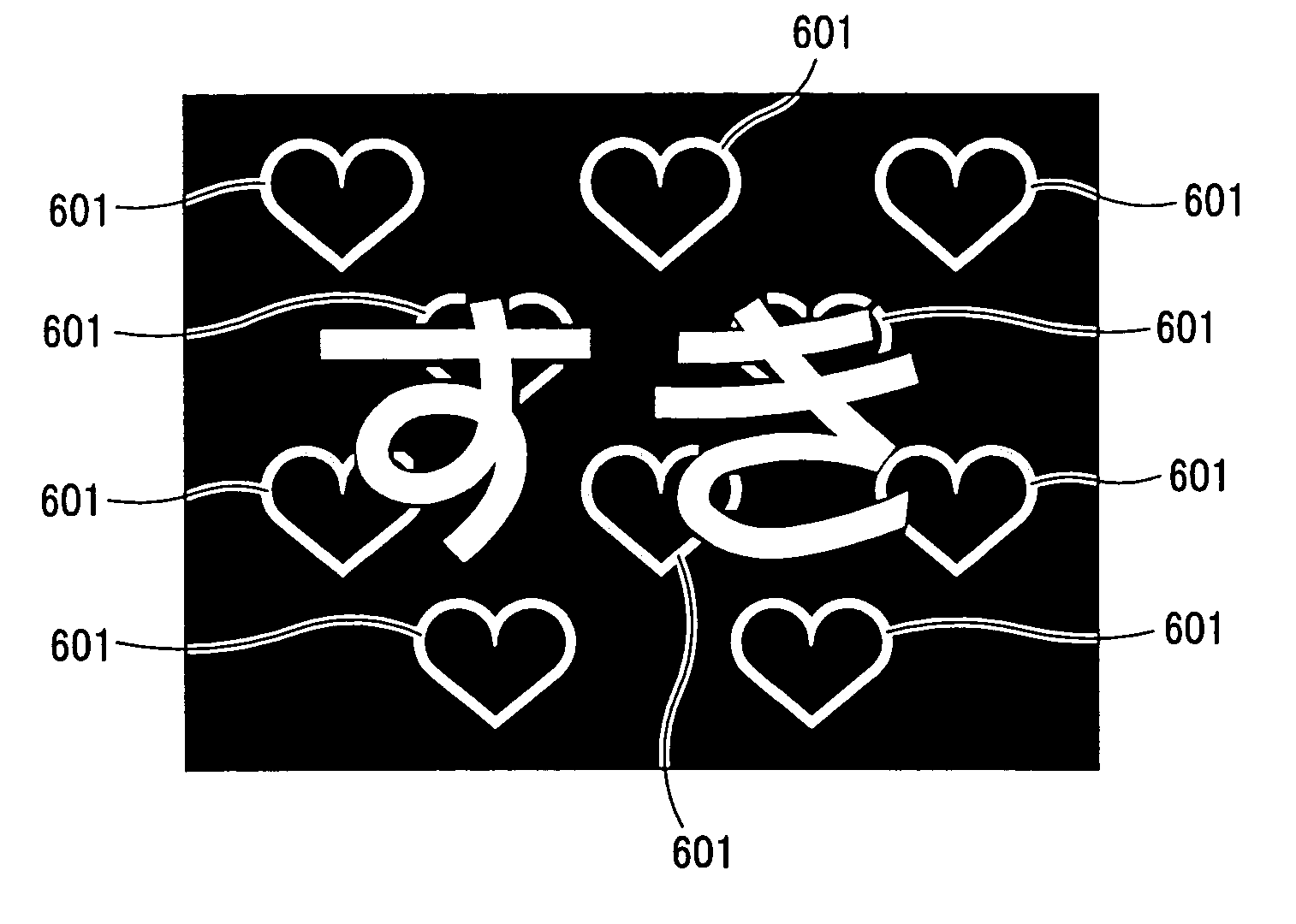
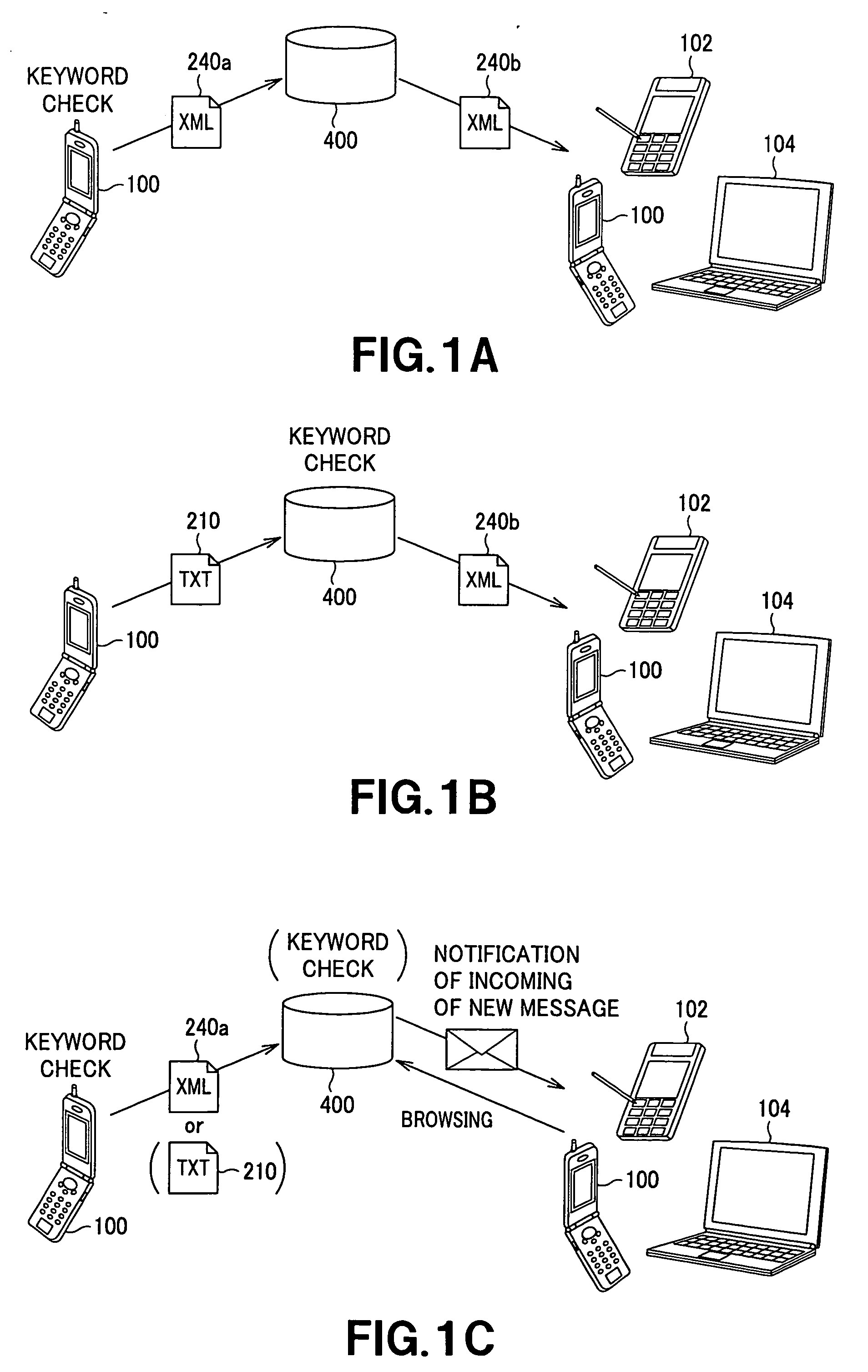
Text display terminal device and server
ActiveUS20050156947A1Drawback can be obviatedCathode-ray tube indicatorsNatural language data processingText displayUser input
This invention is relative with a text displaying terminal unit used for preparation, transmission / reception and display of a text message. A text message entered by a user is collated to a keyword and, if there is a keyword in the text, displaying attributes of the text and / or the background image are added to the text to send the resulting text added by the displaying attributes to a server (400). Alternatively, the server may collate the text to the keyword to add the displaying attributes of the text and / or the background image to the text. A receiving side terminal unit receives an XML document (240b), added by the displaying attributes, from the server to display the XML document added by the displaying attributes as a motion text message. This motion text message may also be provided by the server to the user as the Web information.
Owner:SONY ELECTRONICS INC +2
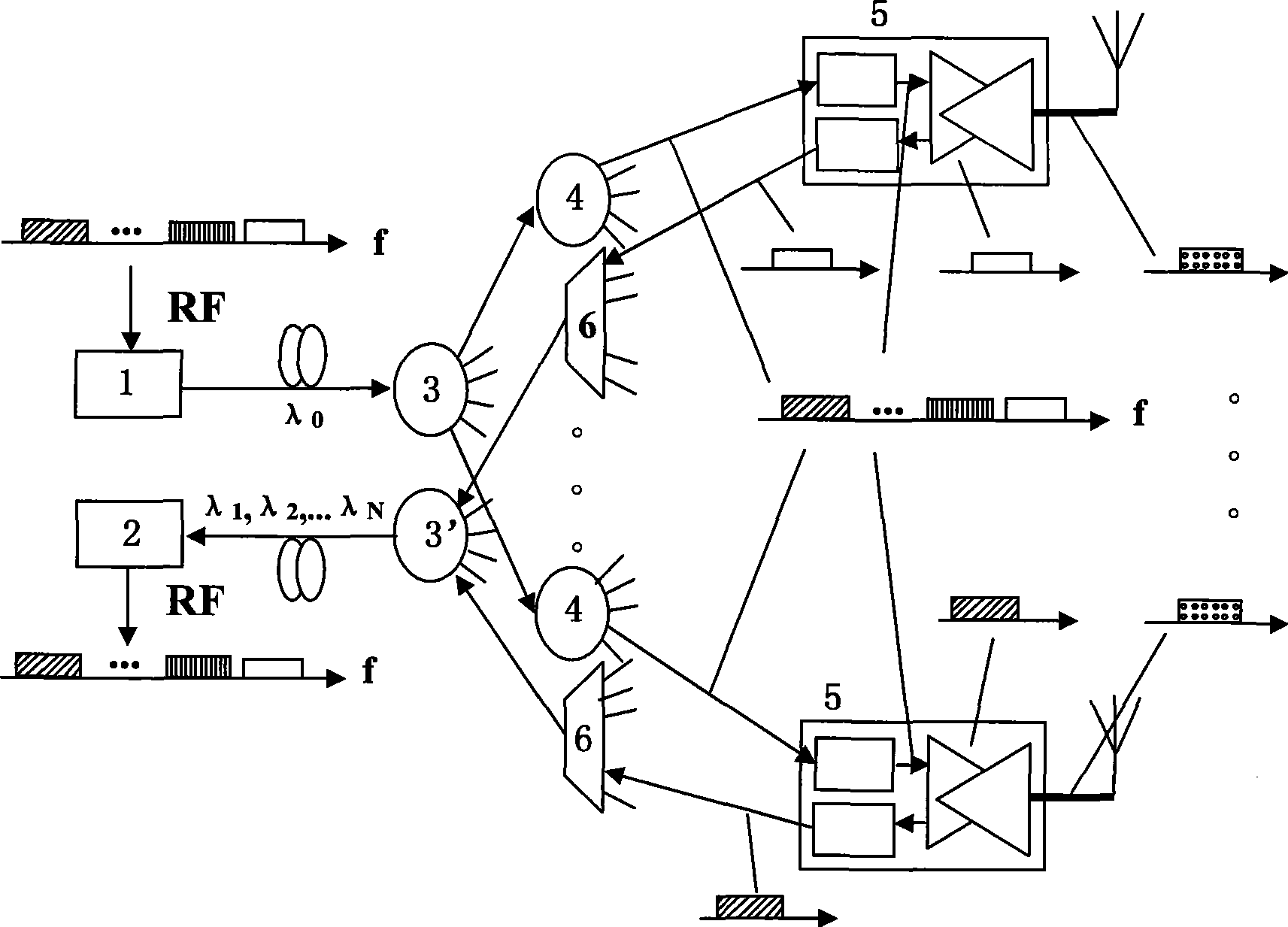
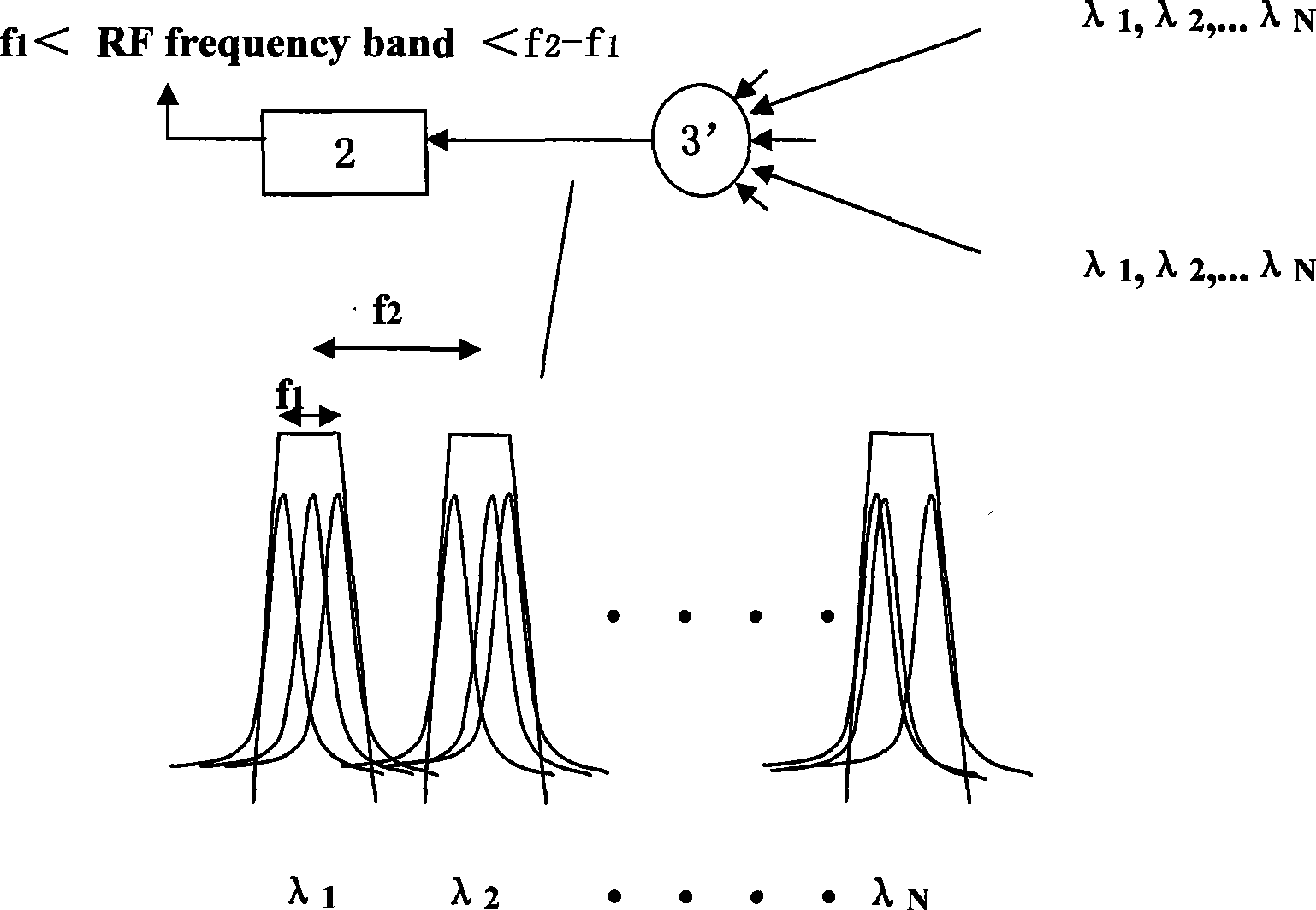
Broadband wireless signal covering network based on passive optical network structure
The invention relates to a broadband wireless signal covering network based on a passive optical network structure. The network comprises a first fiber power divider / wave combiner, a plurality of user terminal units, an optical wavelength multiplexing / de-multiplexing device, a second fiber power divider / wave combiner and a broadband photoreceiver, wherein the first fiber power divider / wave combiner allocates light carrier signals of a light emitter to a plurality of fiber power dividers; a plurality of the user terminal units correspondingly receive the light carrier signals of the fiber power dividers, emit the light carrier signals to air and receive user uplink RF signals through antennas; the optical wavelength multiplexing / de-multiplexing device collects user uplink optical signals of a plurality of the user terminal units and transmits the signals to the uplink direction; the second fiber power divider / wave combiner collects the user uplink optical signals and transmits the signals to the uplink direction; and the broadband photoreceiver converts the received multi-wavelength user uplink optical signals into multi-bandwidth broadband RF signals and sends the signals to upper layer equipment. The broadband wireless signal covering network solves the problem of realizing broadband wireless communication for large-scale indoor multiuser, strengthens the adaptability to the horizontal dynamic change of uplink optical signal power and can adapt to the functional requirement of various wireless communication systems.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Remote wireless communication device
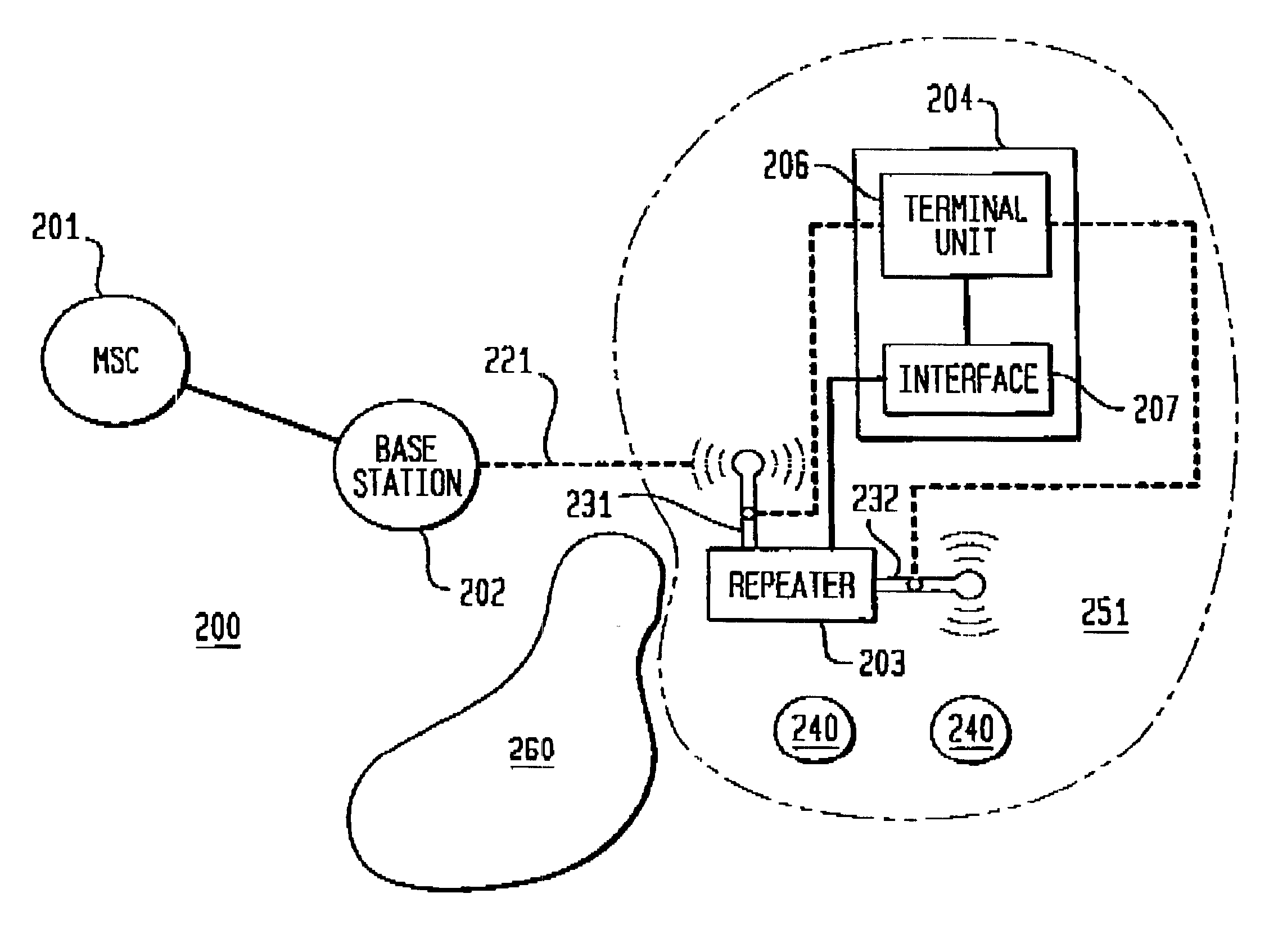
A device is disclosed for facilitating communication with a remote apparatus. The remote apparatus has control functionality and is located within a wireless network. The device comprises a terminal unit having means for transmitting a signal and receiving a signal. The transmitted signal includes an identification of the terminal unit. Additionally, the device includes a control interface operatively connected between the terminal unit and the apparatus. The control interface interfaces signals of the terminal unit with the control functionality of the apparatus.< / PTEXT>
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Common subscriber managing apparatus and method based on fuctional modeling of a common subscriber server for use in an ALL-IP network
InactiveUS20020003789A1Hybrid switching systemsCommmunication supplementary servicesQuality of serviceSecurity association
A common subscriber managing apparatus and method for use in an all Internet Protocol network integrating a circuit network for voice and a packet network for data. The apparatus comprises a portable user terminating unit satisfying media standards supported in the network, a wireless interfacing unit controlling wireless resources of the user terminating unit and wireless traffic, controlling handoff, realigning data from and to the packet network upon interface request of the user terminating unit, providing realigned data to the user terminating unit and transferring media to another user terminating unit, a call controlling unit controlling a call between the wireless interfacing unit and common subscriber managing unit, and common subscriber managing unit for providing Security Association setup function for voice processing and commonly managing mobility management, Quality of Service, authentication and authorization management, accounting management and service management functions for the user terminating unit through a common subscriber database.
Owner:PANTECH CORP
Method and system for dynamically organizing audio-visual items stored in a central database
InactiveUS20070156697A1Easy to changeLarge degree of independenceMultimedia data browsing/visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationGraphics
Embodiments of a method and a system are disclosed for remotely and dynamically managing, sequencing and retrieving audio-visual items from a central database in order to generate a customized digital audio-visual data stream. The content of this stream is associated to the selected items and can be visualized and / or stored in a storing device for a later use. An embodiment of this method is carried out via a central content database, central rights database and any number of rules databases (“Filters”) which can reflect changing parameters and rules of the system, which can pertain to evolving digital rights and permissions, marketing and other system goals and rules pertaining to information exchange between users. An example of a graphic and user-friendly interface is presented on a user terminal unit which can dynamically reflect both user and system generated changes, and dynamically present customized audio-visual streams (playlists) based on user selection and personalized preferences, system objectives and eventual play-list sharing between users.
Owner:TRANSMEDIA COMM
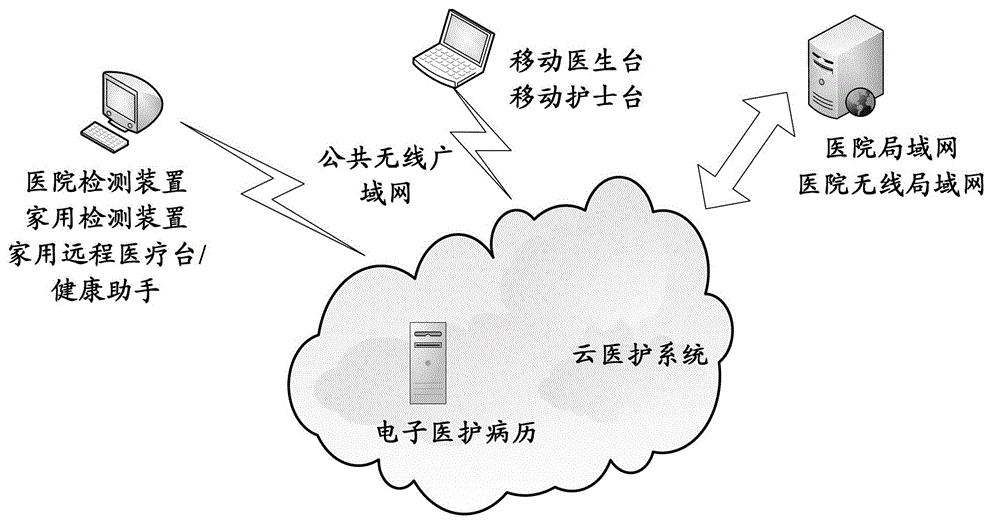
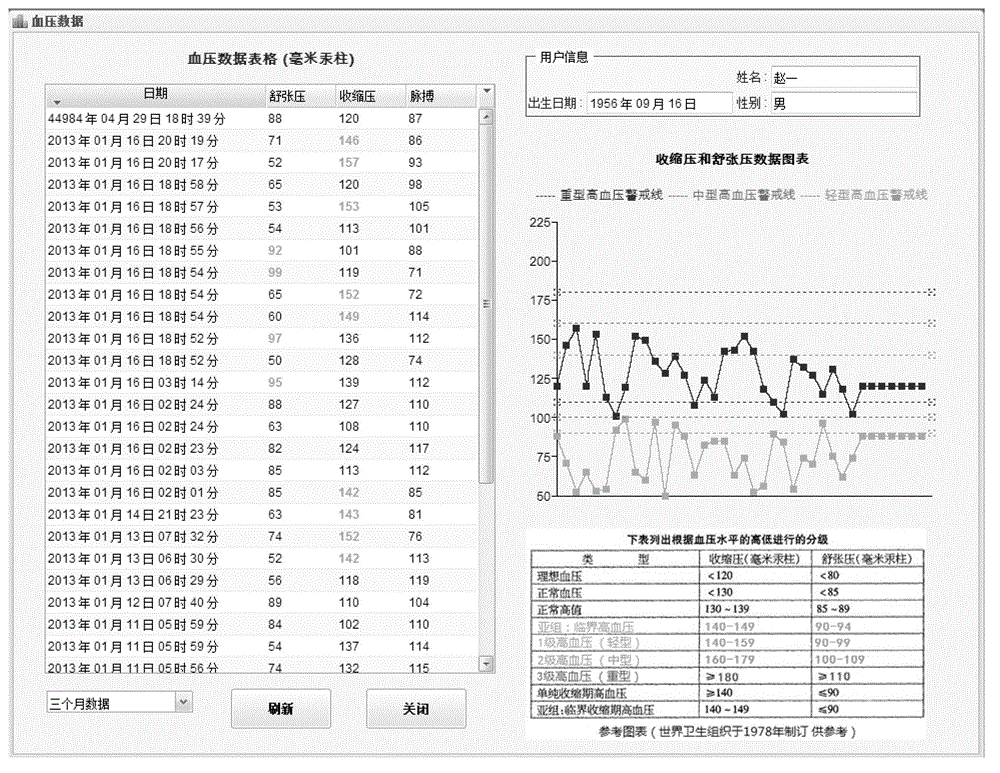
Telemedicine service system based on cloud platform and telemedicine service control method
InactiveCN103942402ASimple structureAchieve maintenanceTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsMedical recordMedical equipment
The invention relates to a telemedicine service system based on a cloud platform and a telemedicine service control method and belongs to the technical field of medical equipment. The system comprises a cloud server, a medical care subject terminal unit and a doctor diagnosis terminal unit. The cloud server is used for storing self-measured vital sign information and doctor diagnosis information of a medical care subject and generating medical record information according to the diagnosis information. The medical care subject terminal unit is used for acquiring the vital sign information of the medical care subject and uploading the vital sign information to the cloud server and can also be used for downloading the diagnosis information and the medical record information so that the information can synchronize with the information of the cloud server. The doctor diagnosis terminal unit is used for downloading the vital sign information of the medical care subject and uploading the corresponding diagnosis information to a cloud server terminal so that a doctor can perform online diagnosis according to the self-collected vital sign information of the medical care subject by means of the doctor diagnosis terminal unit of the system to achieve telemedicine. The cloud server can achieve cloud storage and maintenance of medical records so as to facilitate consultation and downloading, and thus the medical care subject can share the medical record with the family and a service institution.
Owner:江苏睿博信息科技股份有限公司
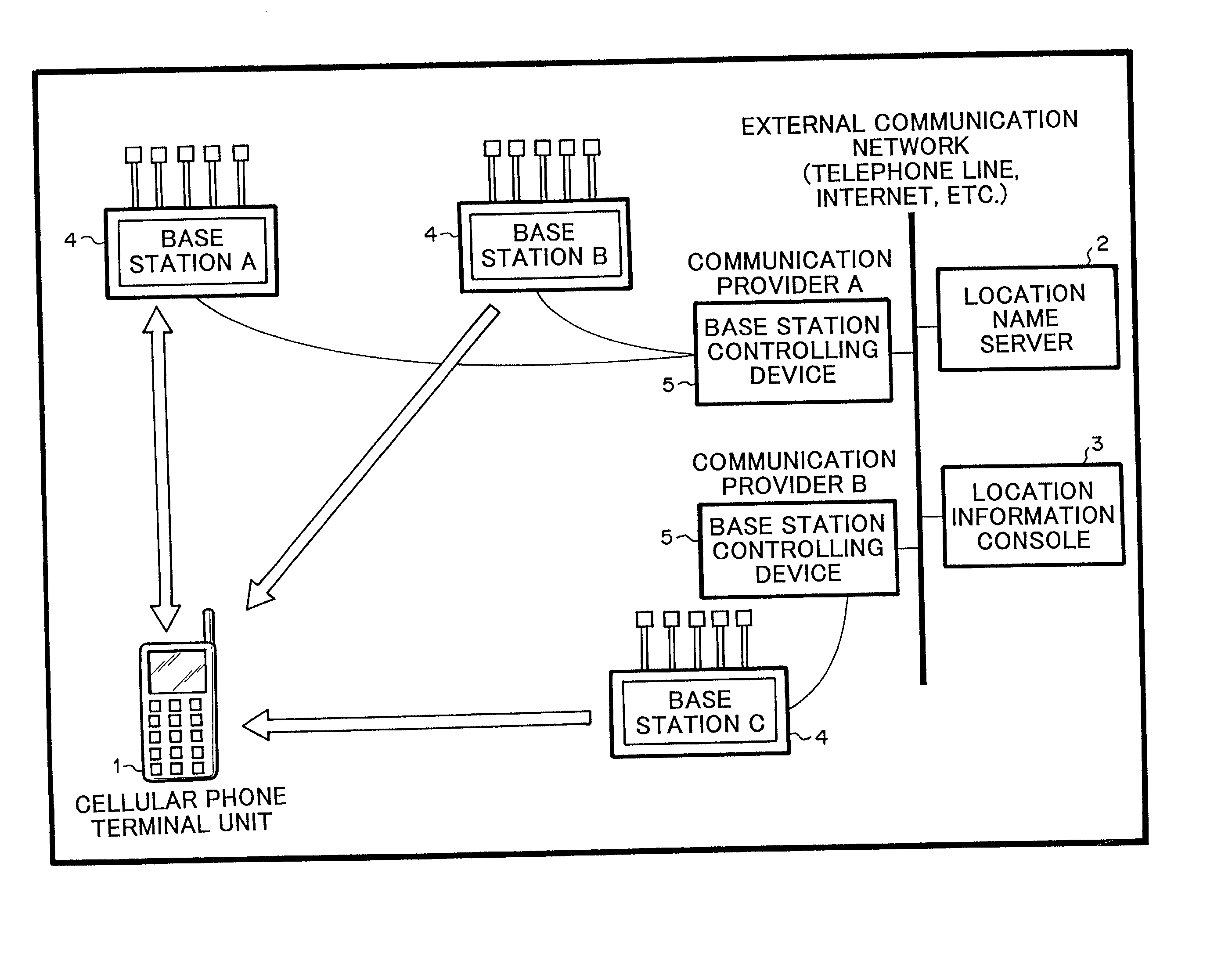
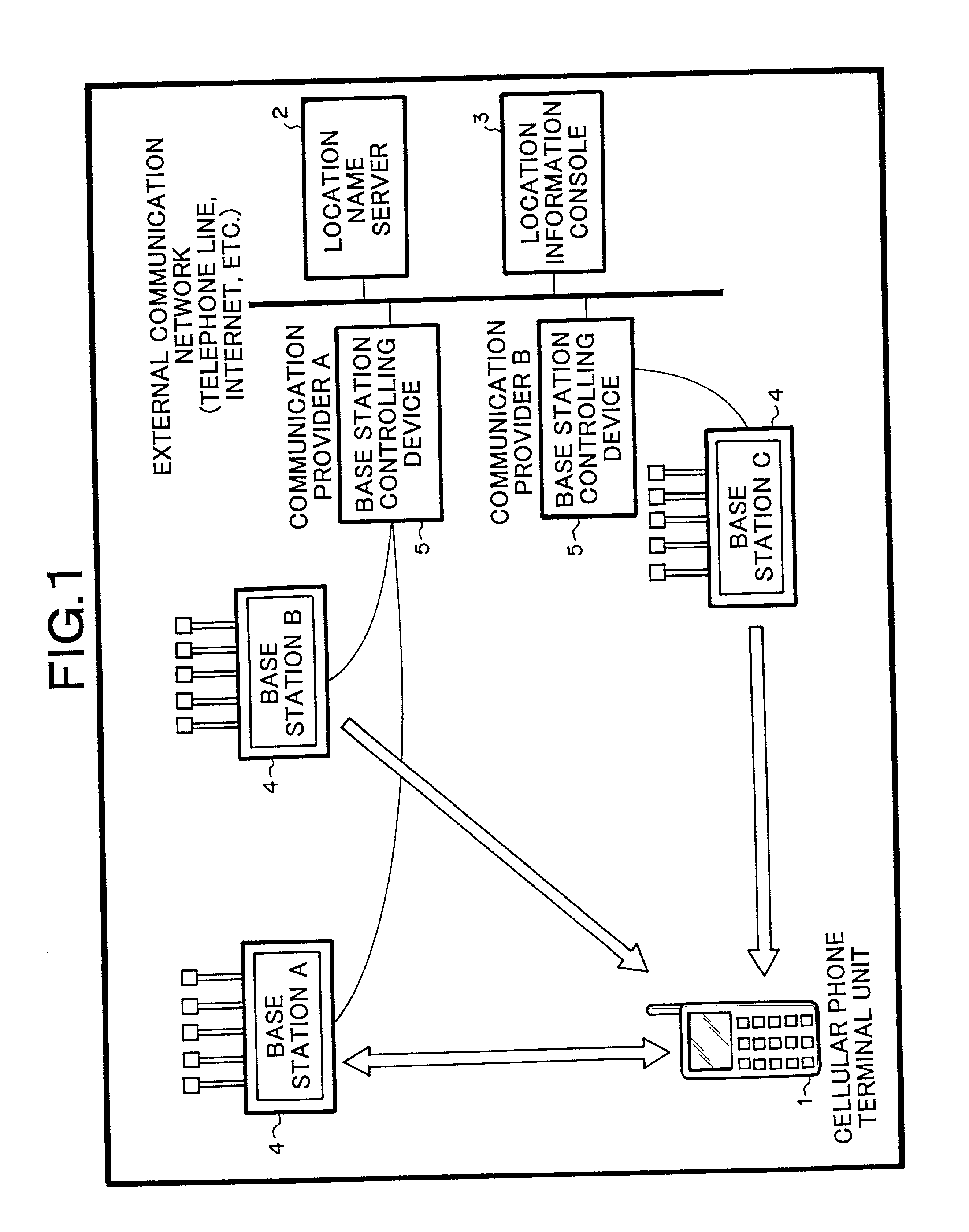
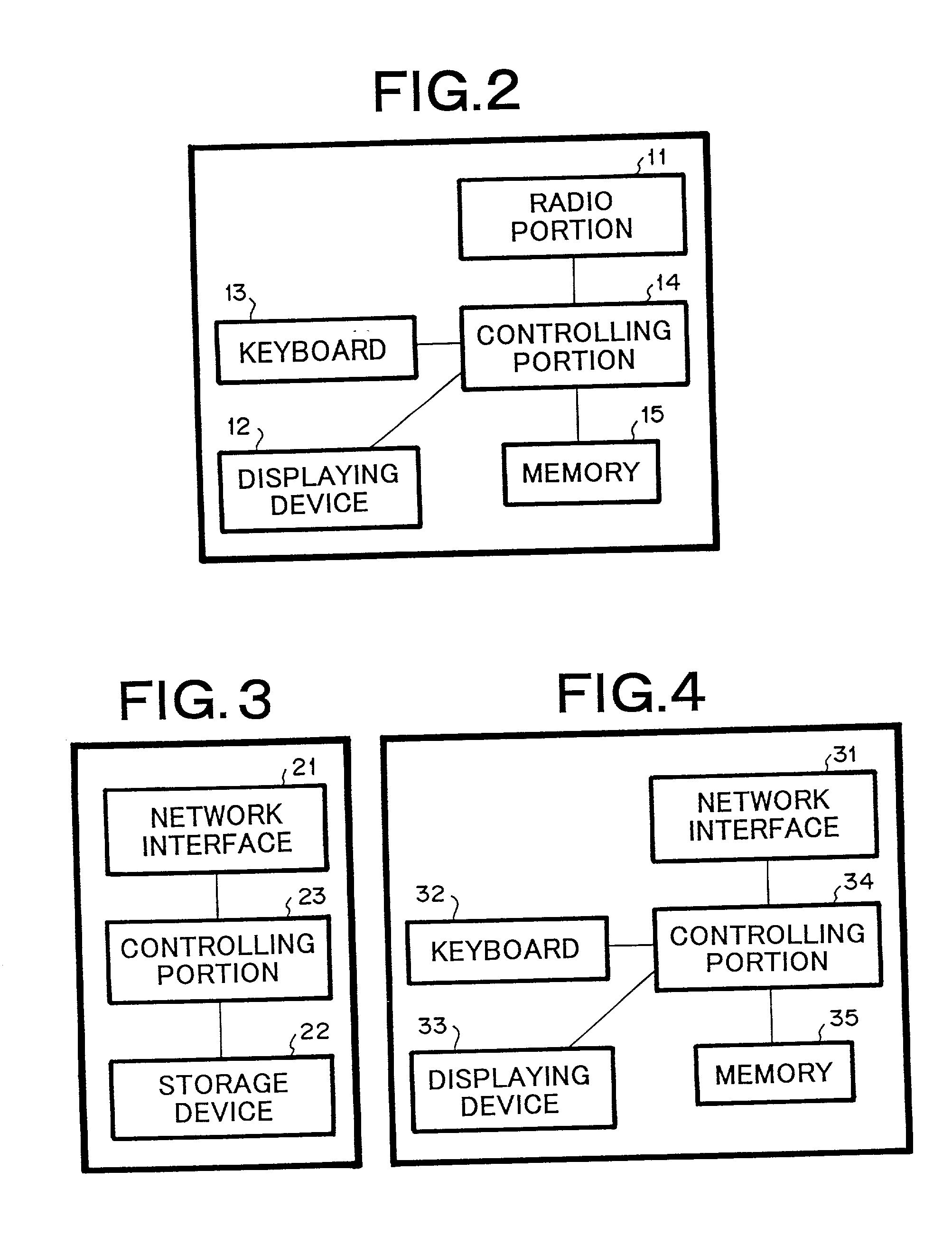
System for providing name of location at which cellular phone terminal unit
ActiveUS20020032036A1Low costDirection finders using radio wavesSpecial service for subscribersName serverTerminal unit
A location name server is disclosed, that comprises a database for storing peripheral information and location names that have been correlated each other as a plurality of sets, a means for transmitting a request for peripheral information to an objective cellular phone terminal unit when a request for the name of a location at which the object cellular phone terminal unit is located is received, a means for searching the database for the name of the location corresponding to peripheral information received from the objective cellular phone terminal unit corresponding to the request for the peripheral information, and a means for transmitting the obtained name of the location to a transmission source of the request therefor.
Owner:APPLE INC
Battery pack
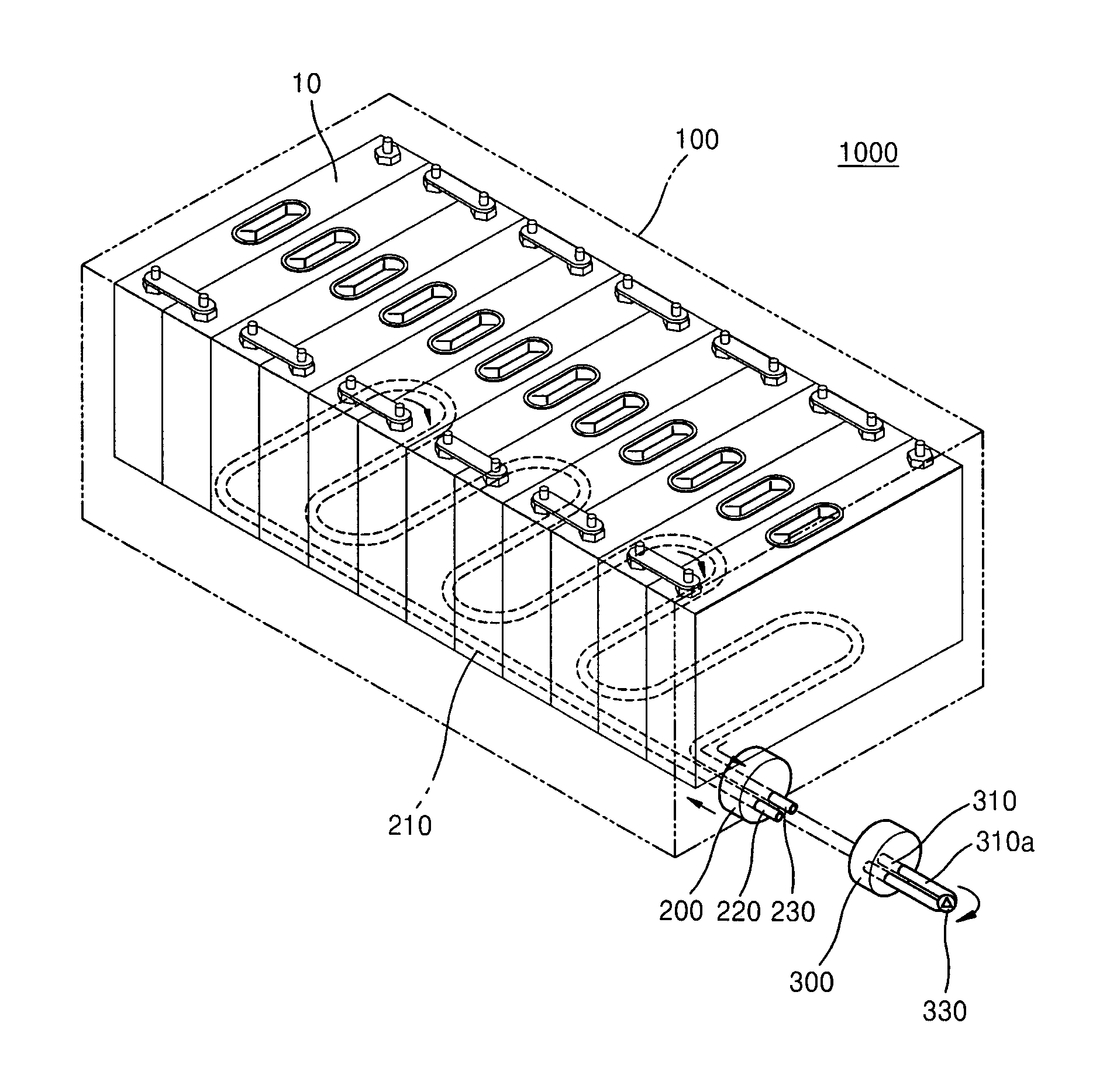
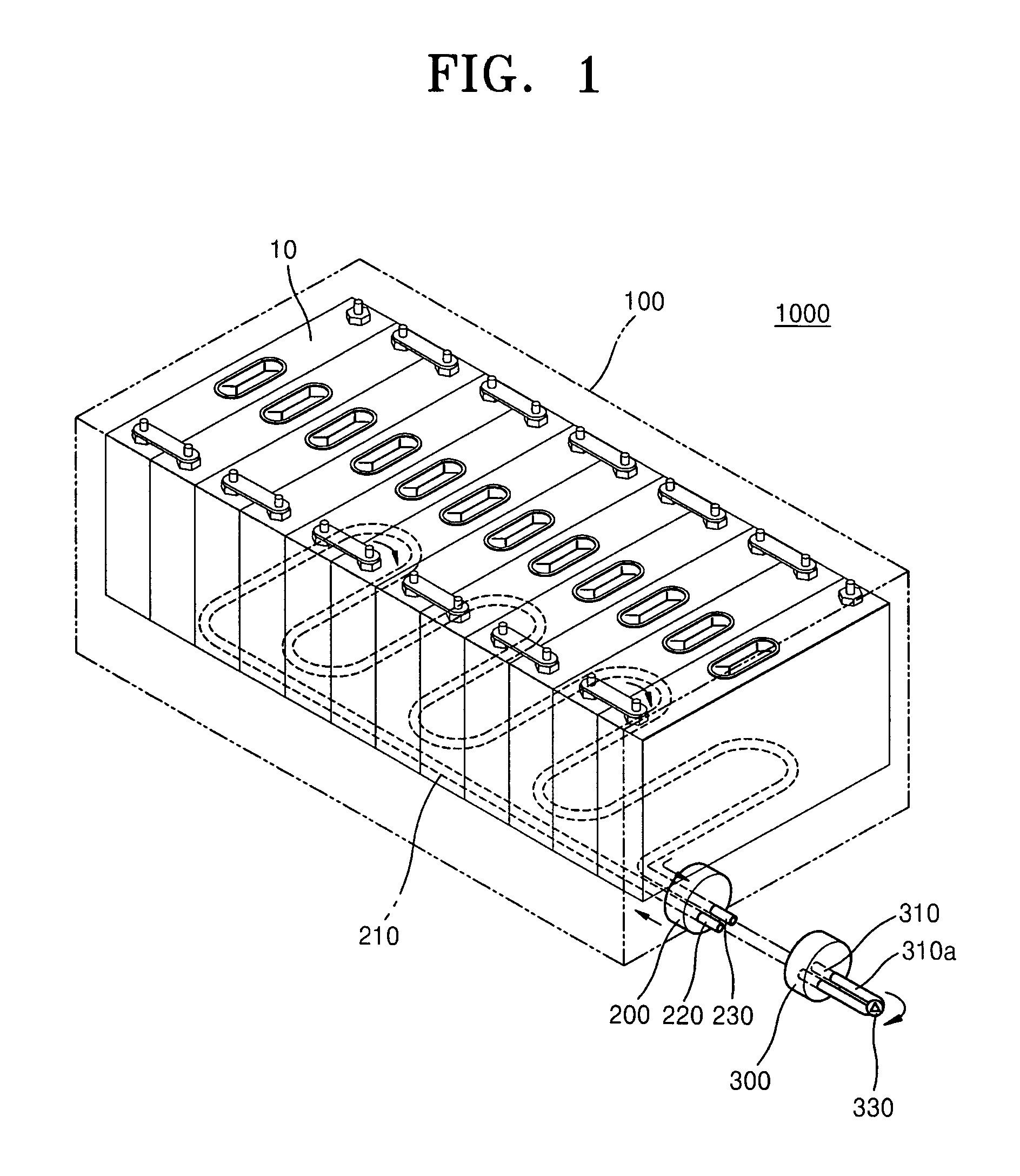
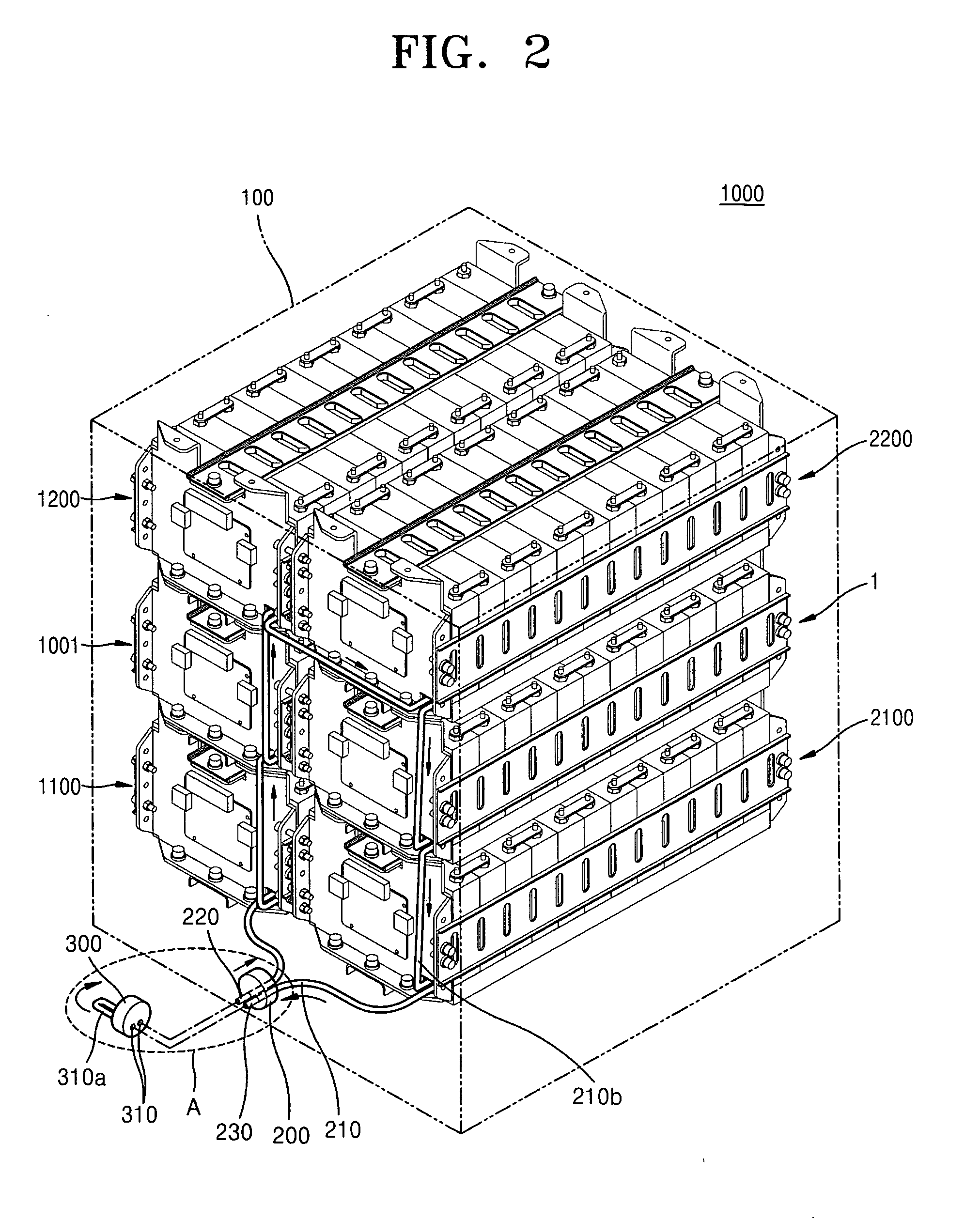
ActiveUS20110293974A1Large-sized flat cells/batteriesCell component detailsElectrical batteryEngineering
A battery pack including a housing for accommodating a plurality of secondary batteries; a cooling unit for cooling the secondary batteries, the cooling unit including an inlet through which a cooling fluid flows in and an outlet through which the cooling fluid flows out; and a terminal unit detachably connectable to the cooling unit, the terminal unit including a first terminal for circulating the cooling fluid.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
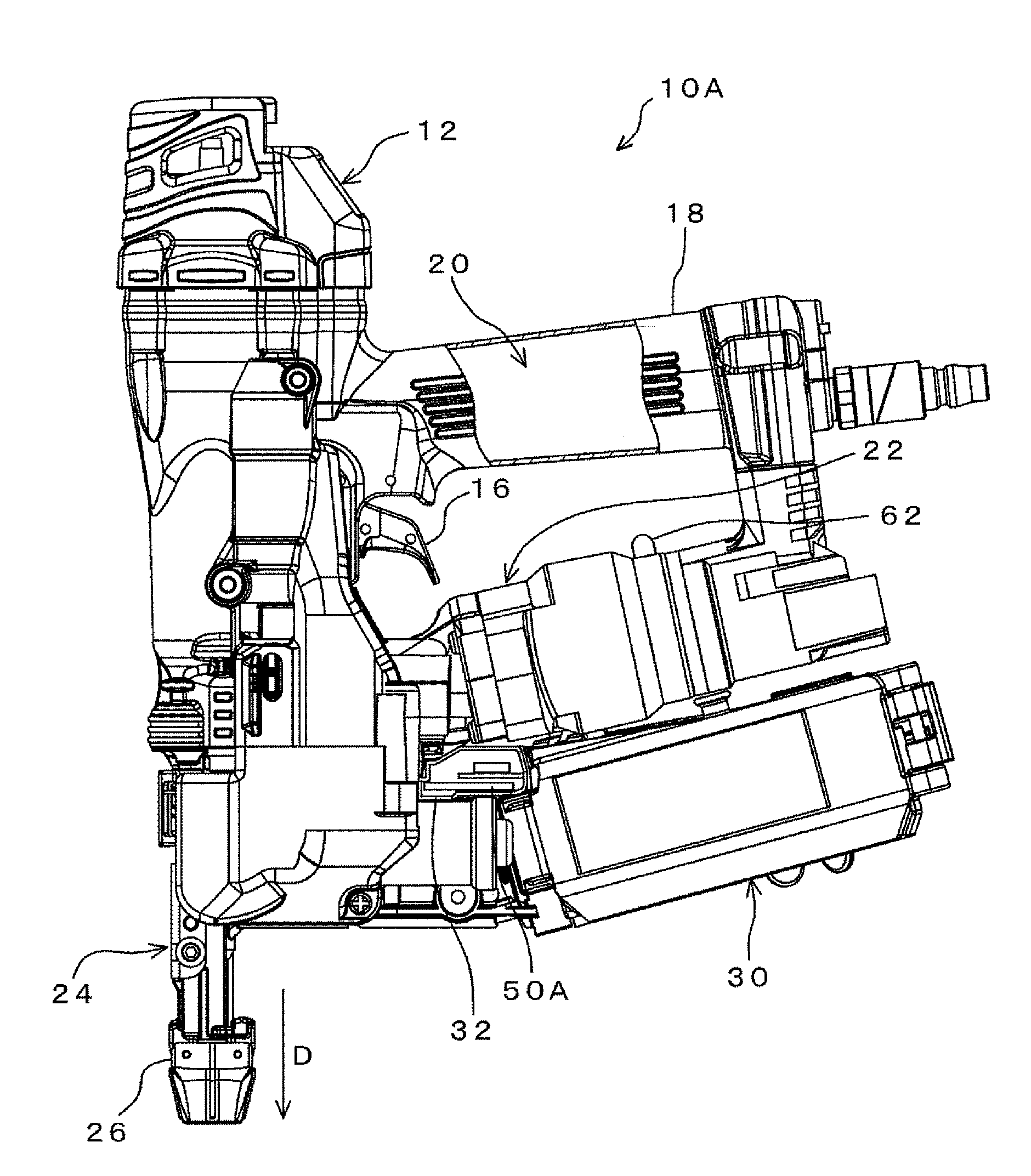
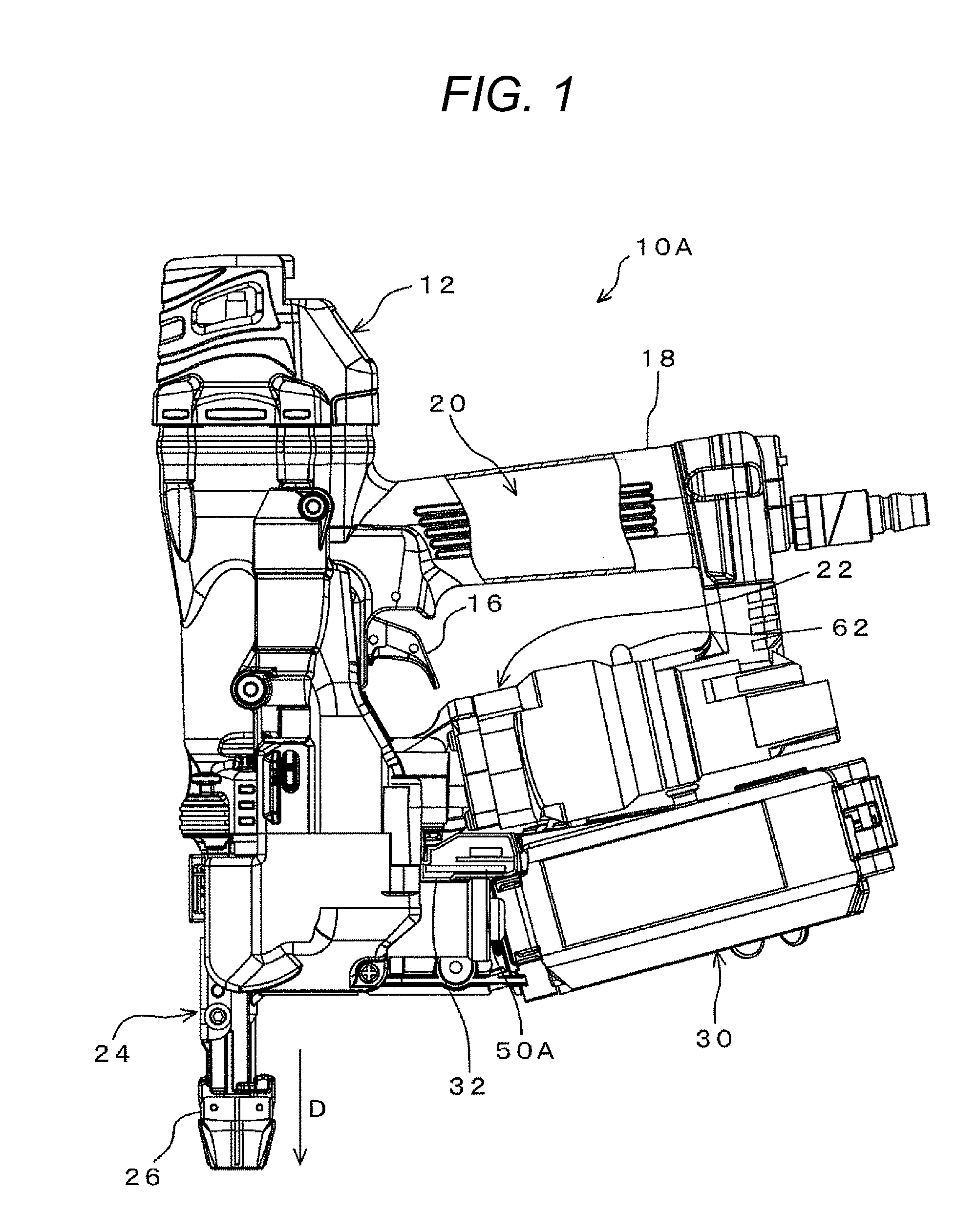
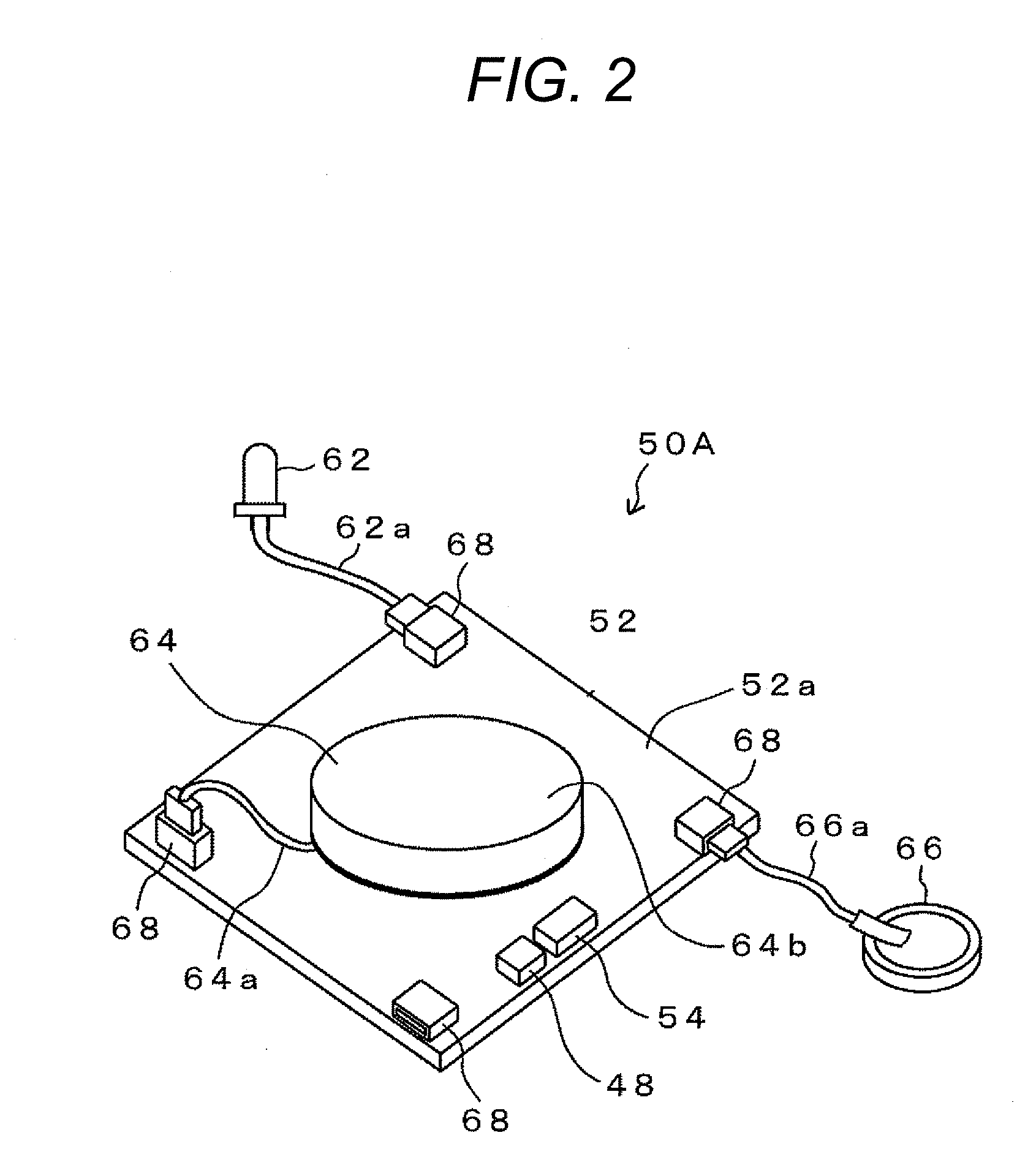
Tool, information processing unit, terminal unit, and management system
A sensor part detects an actual driving signal in the driving time by a pneumatic tool. A control part, based on the detected actual driving signal, makes an addition to the actual driving number which has already stored in a memory part to updates the actual driving number, and compares the updated accumulative actual driving number with the previously set basic maintenance number. As a result of the comparison, in case the accumulative actual driving number exceeds the basic maintenance number, it is determined that maintenance is necessary for the pneumatic tool. A light emitting part emits the light and blinks by an instruction from the control part, thereby to warn a user that the pneumatic tool is into the maintenance time. Hereby, the user can grasp the maintenance time of the tool surely and exactly.
Owner:MAX CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com