Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2778results about How to "Easy Calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
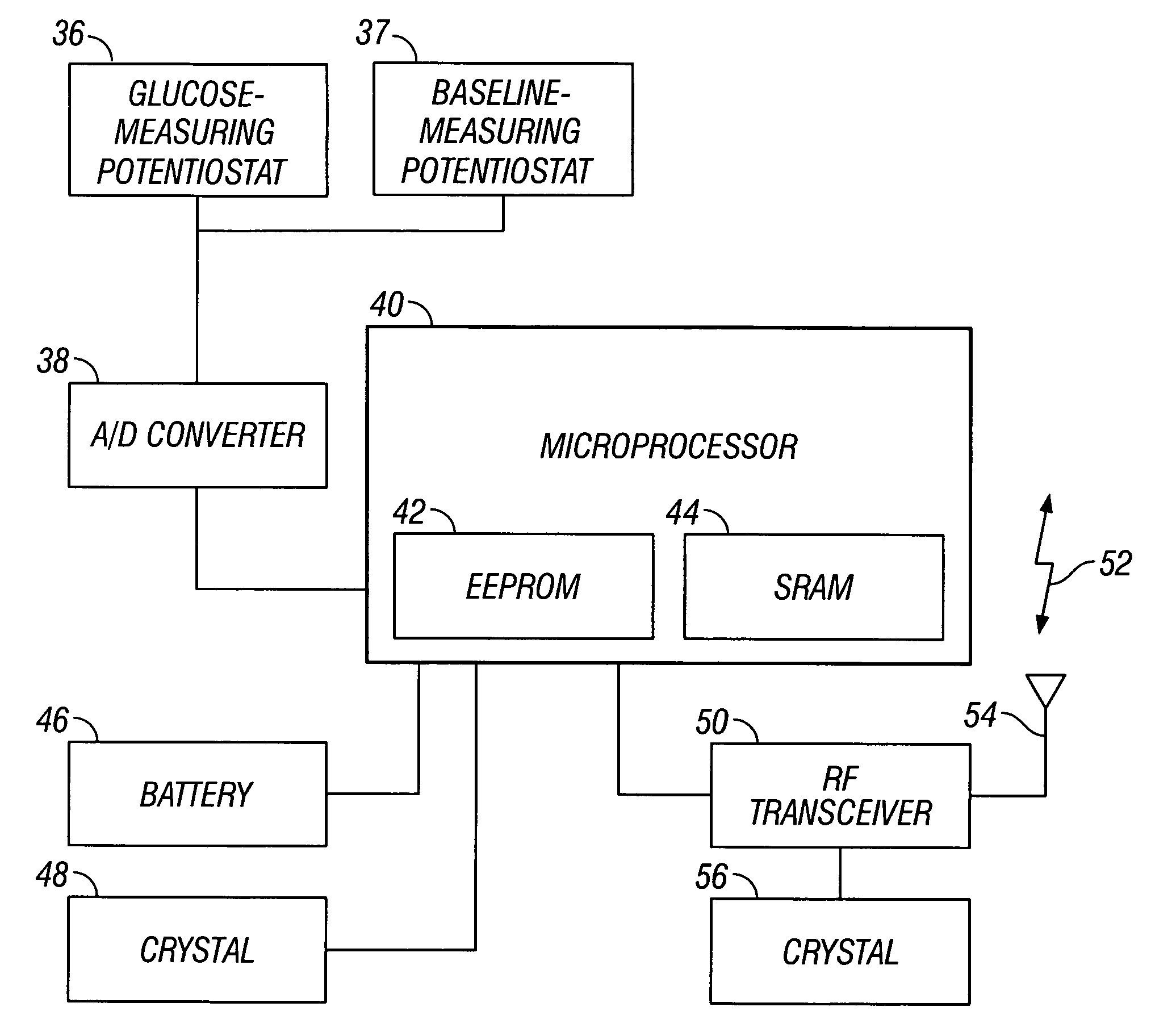
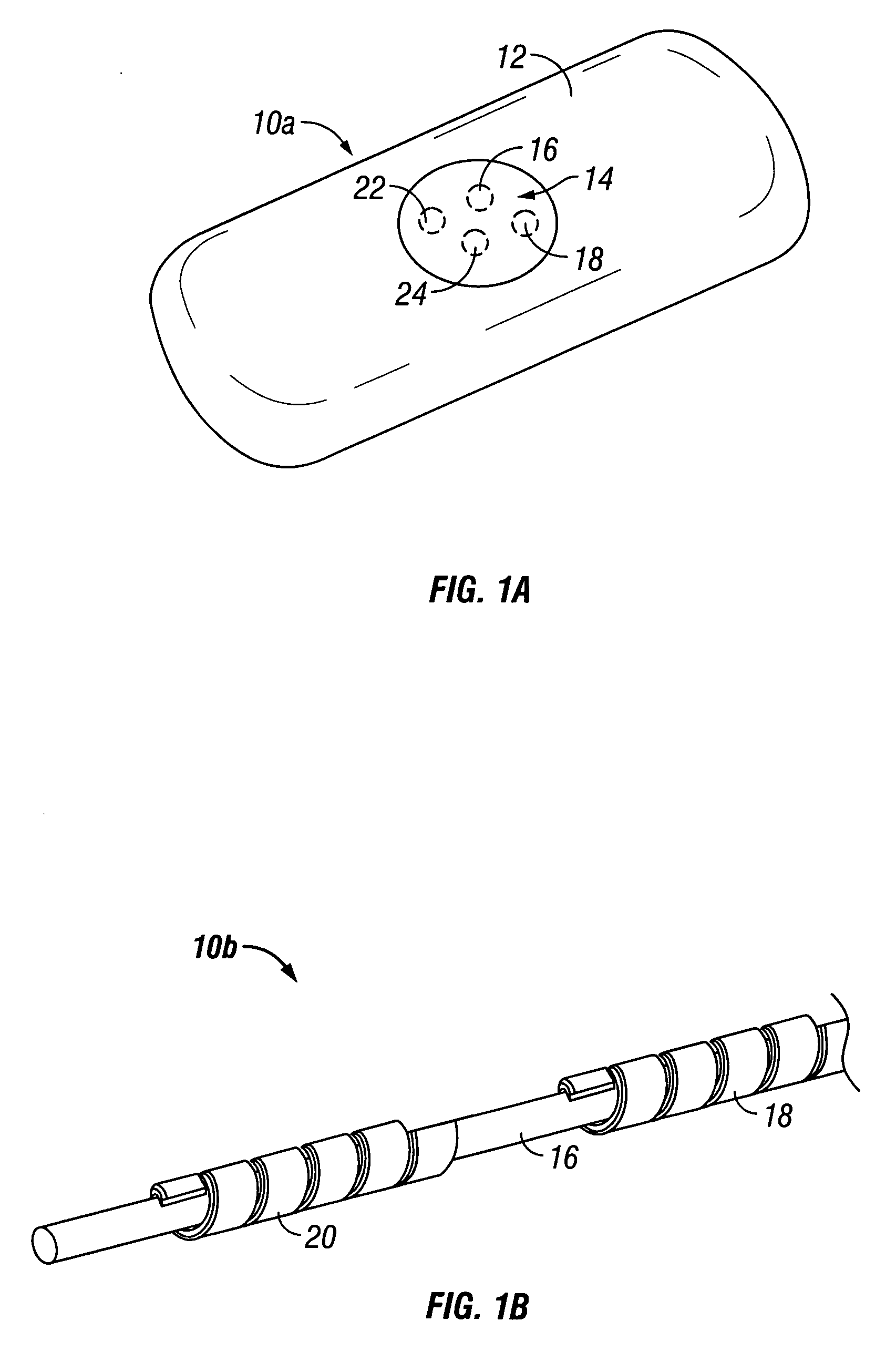
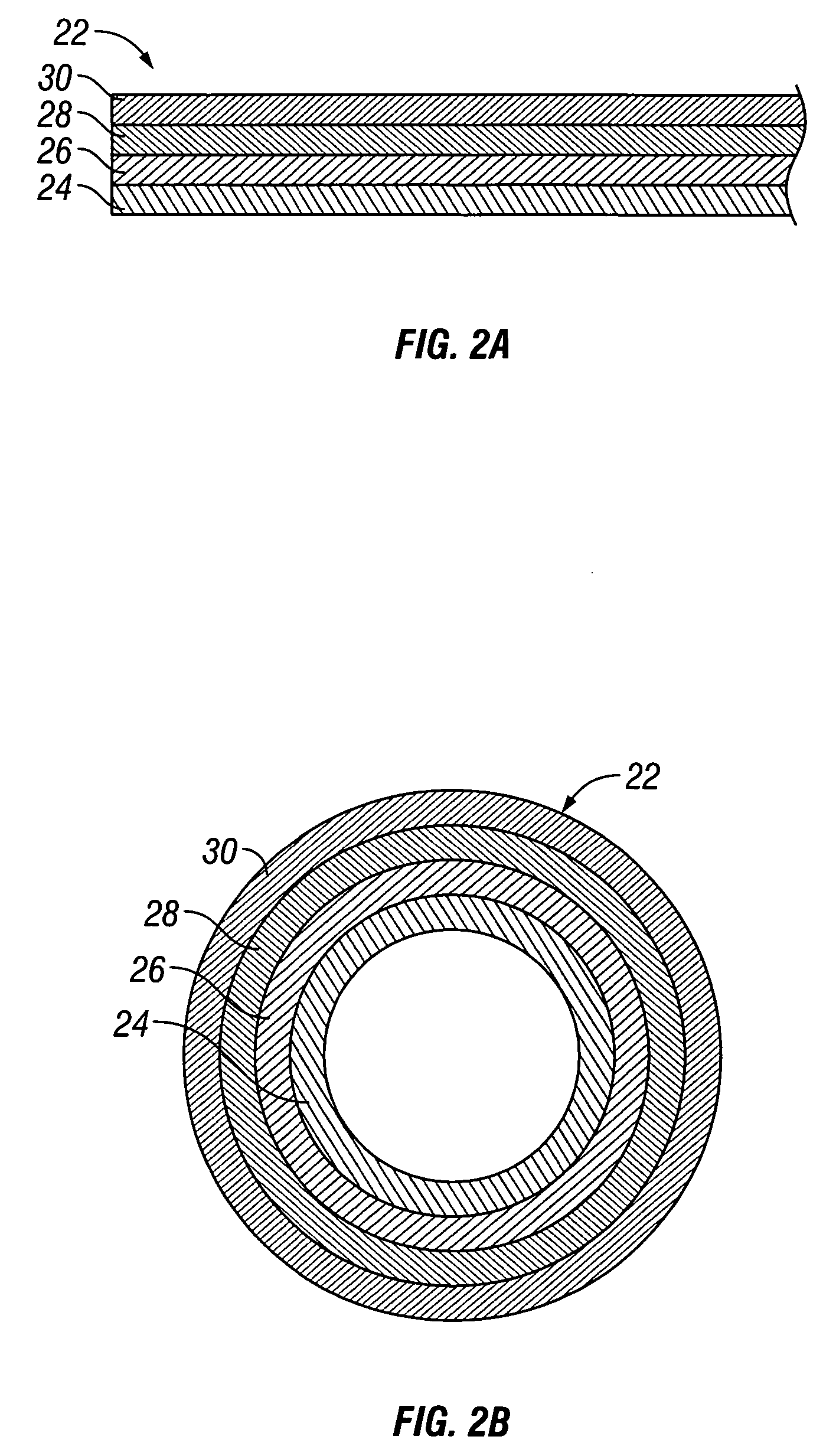
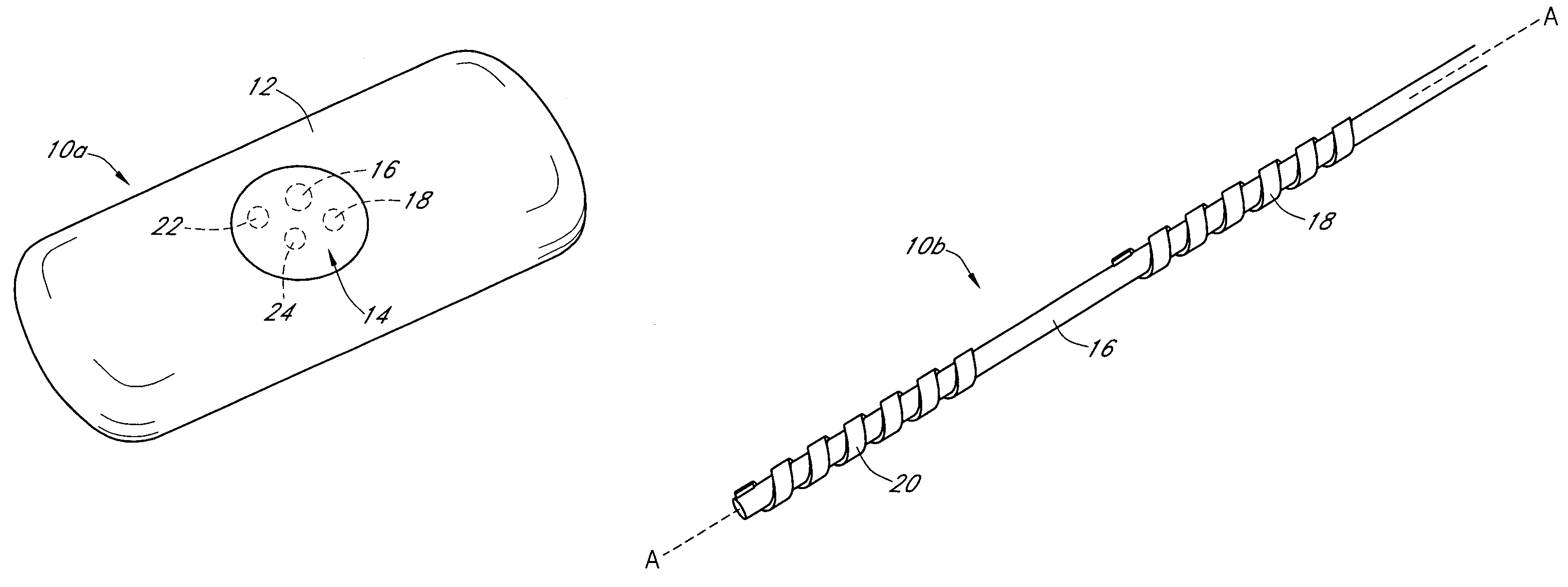
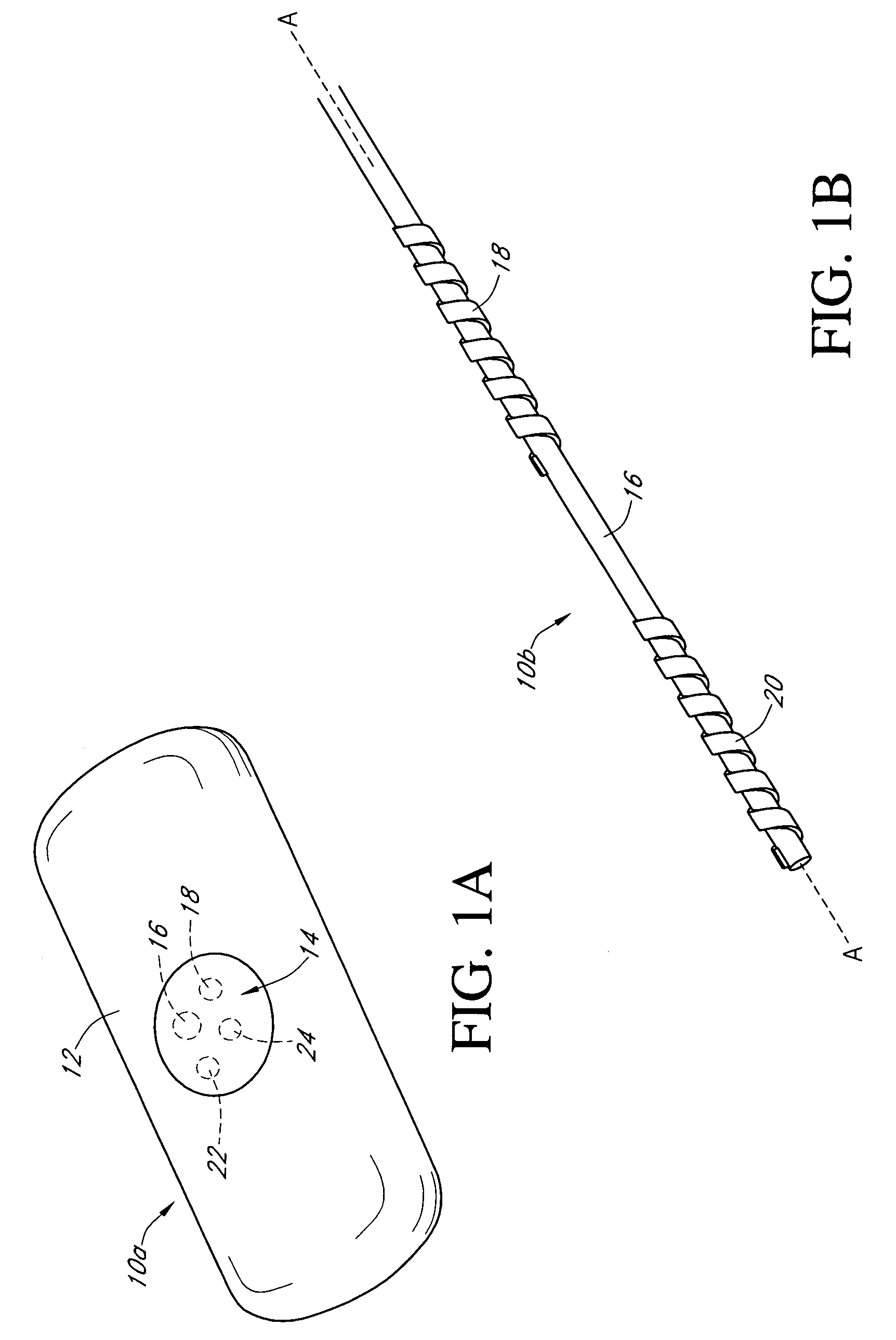
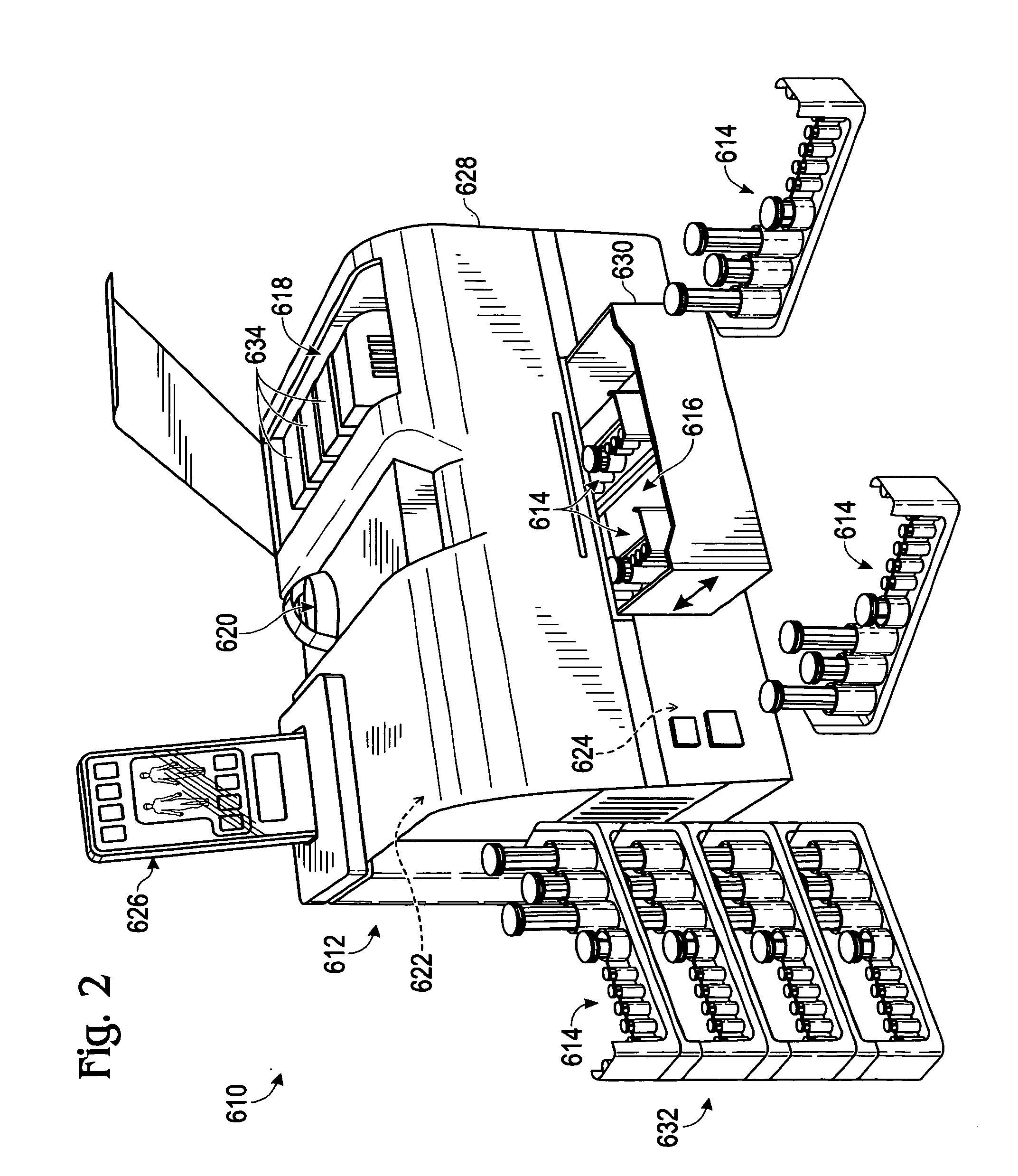
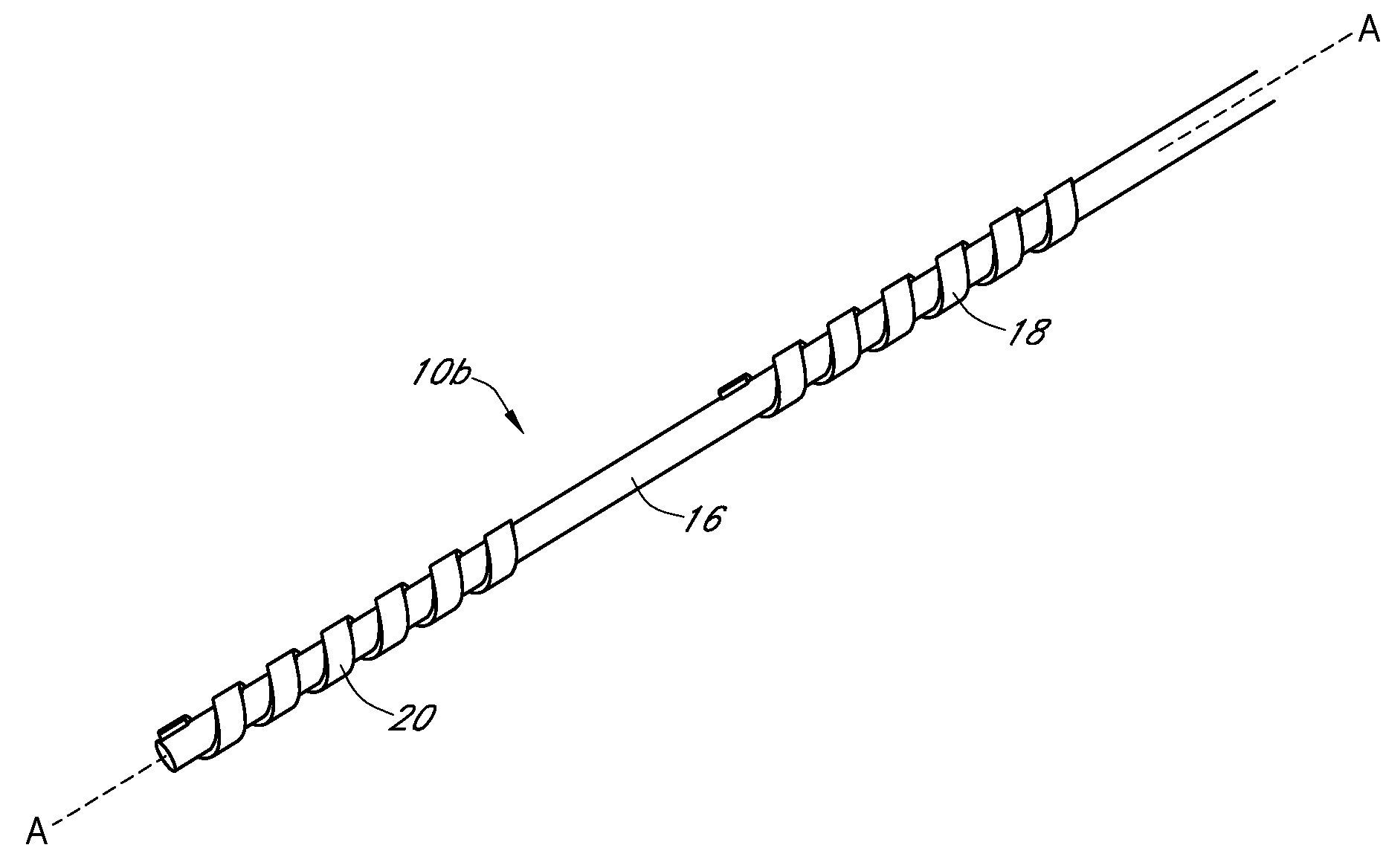
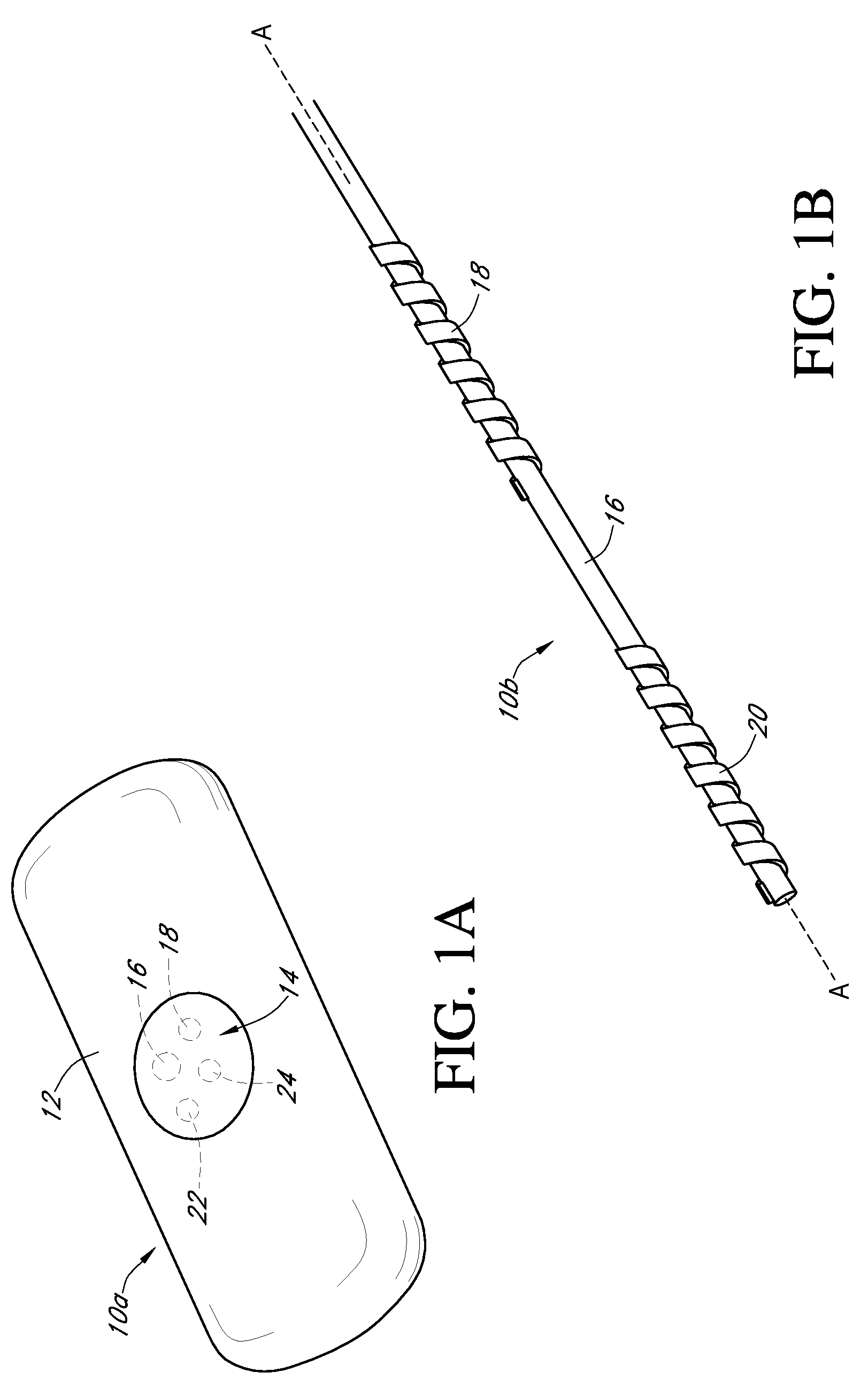
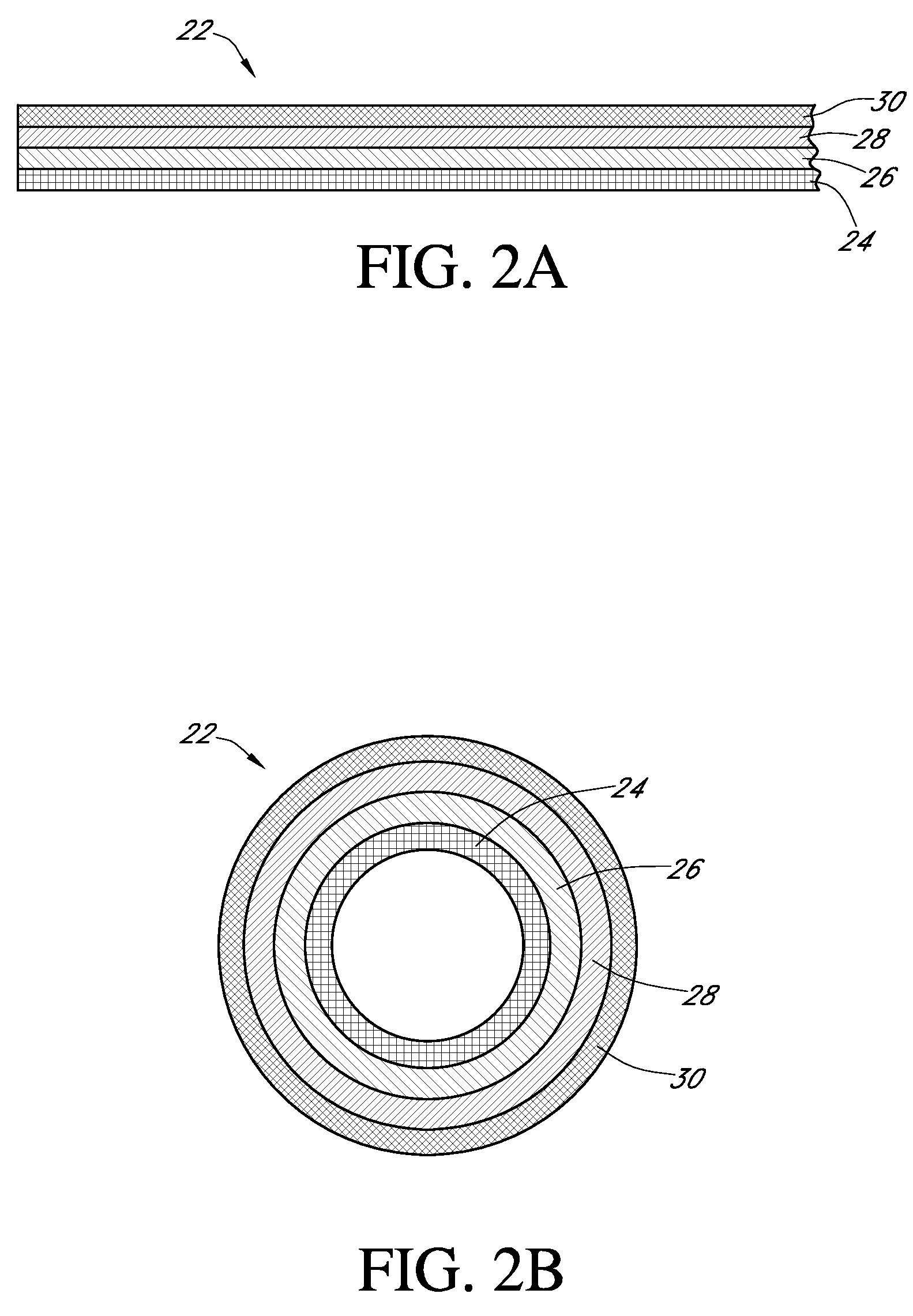
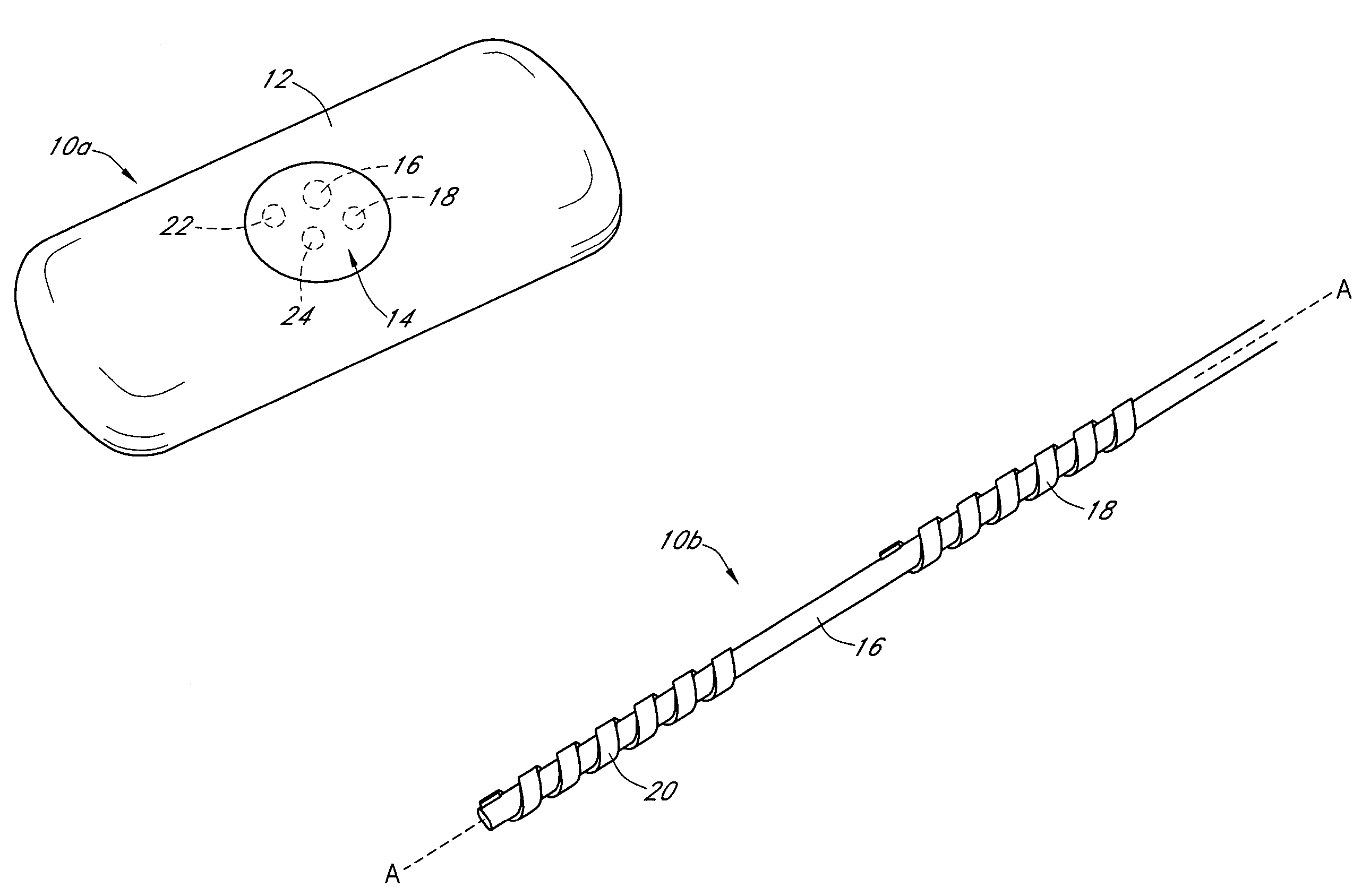
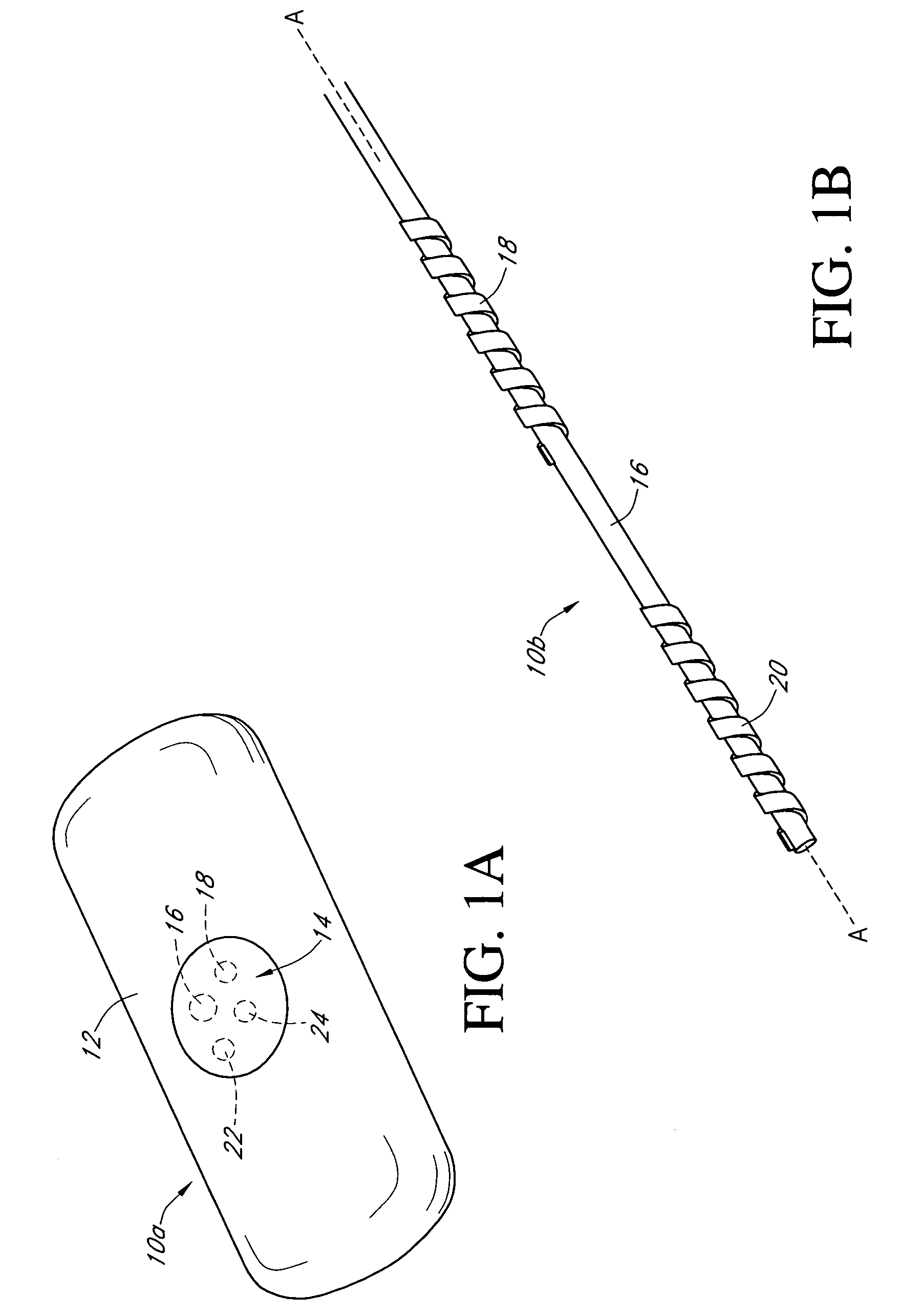
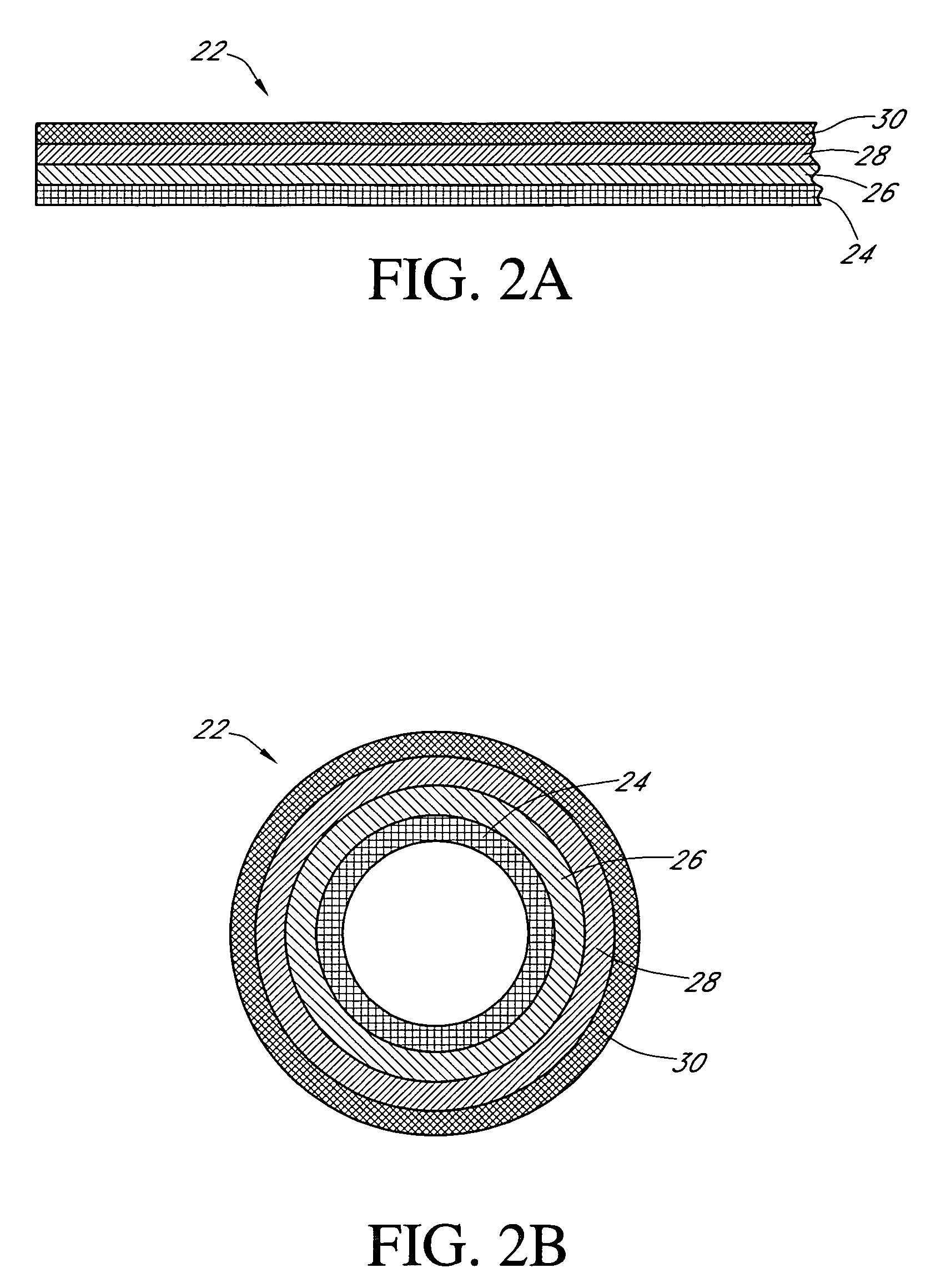
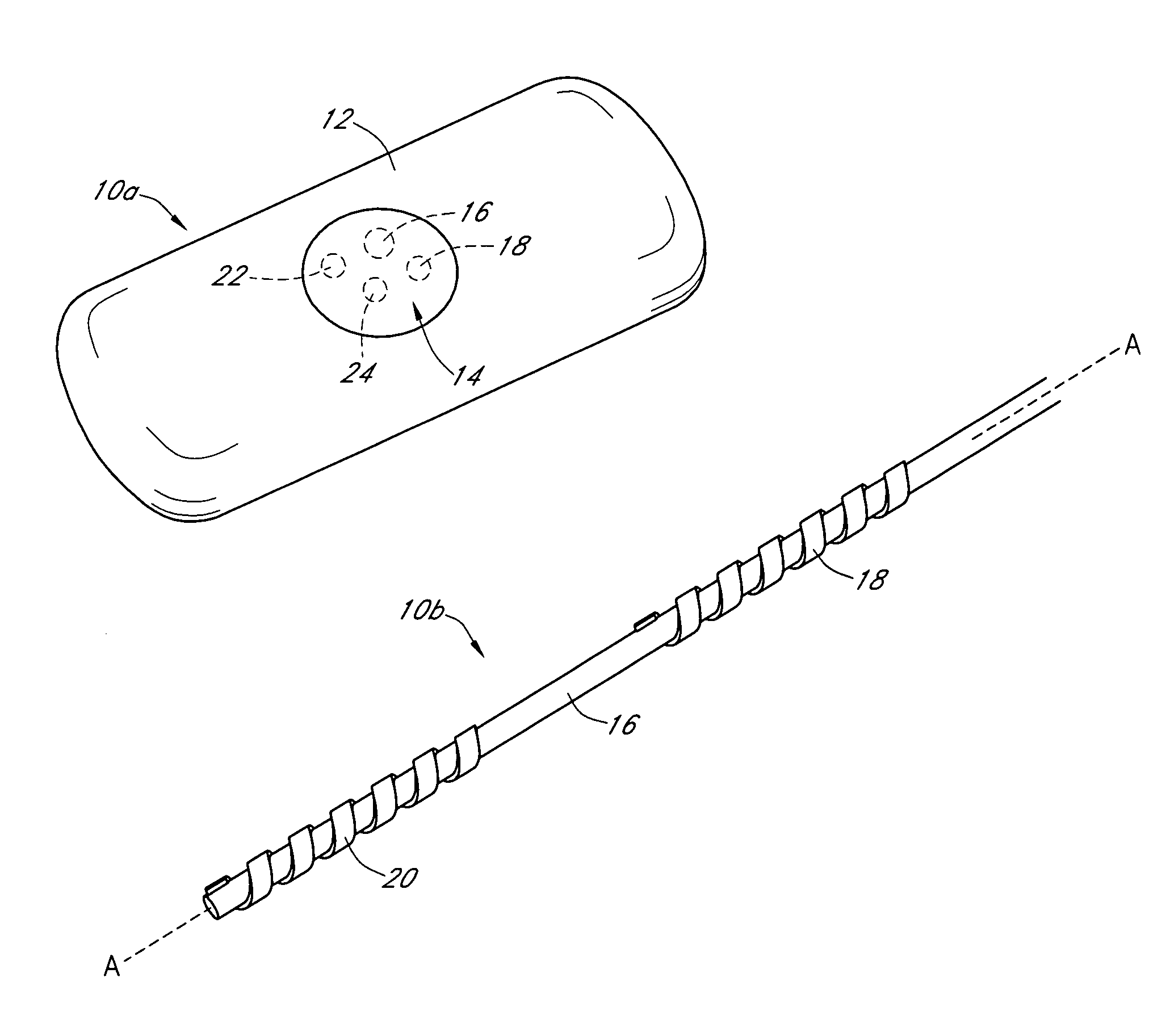
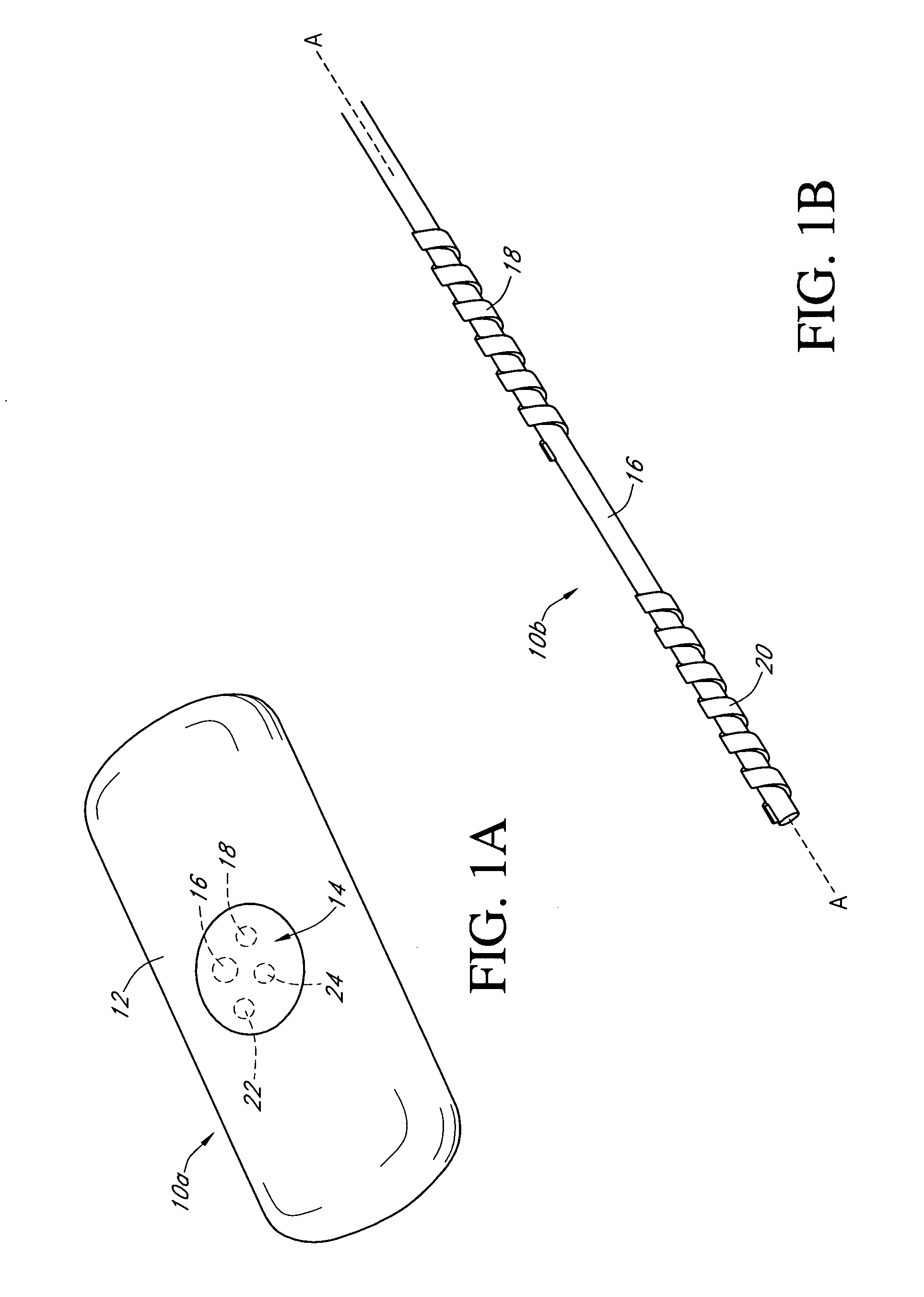
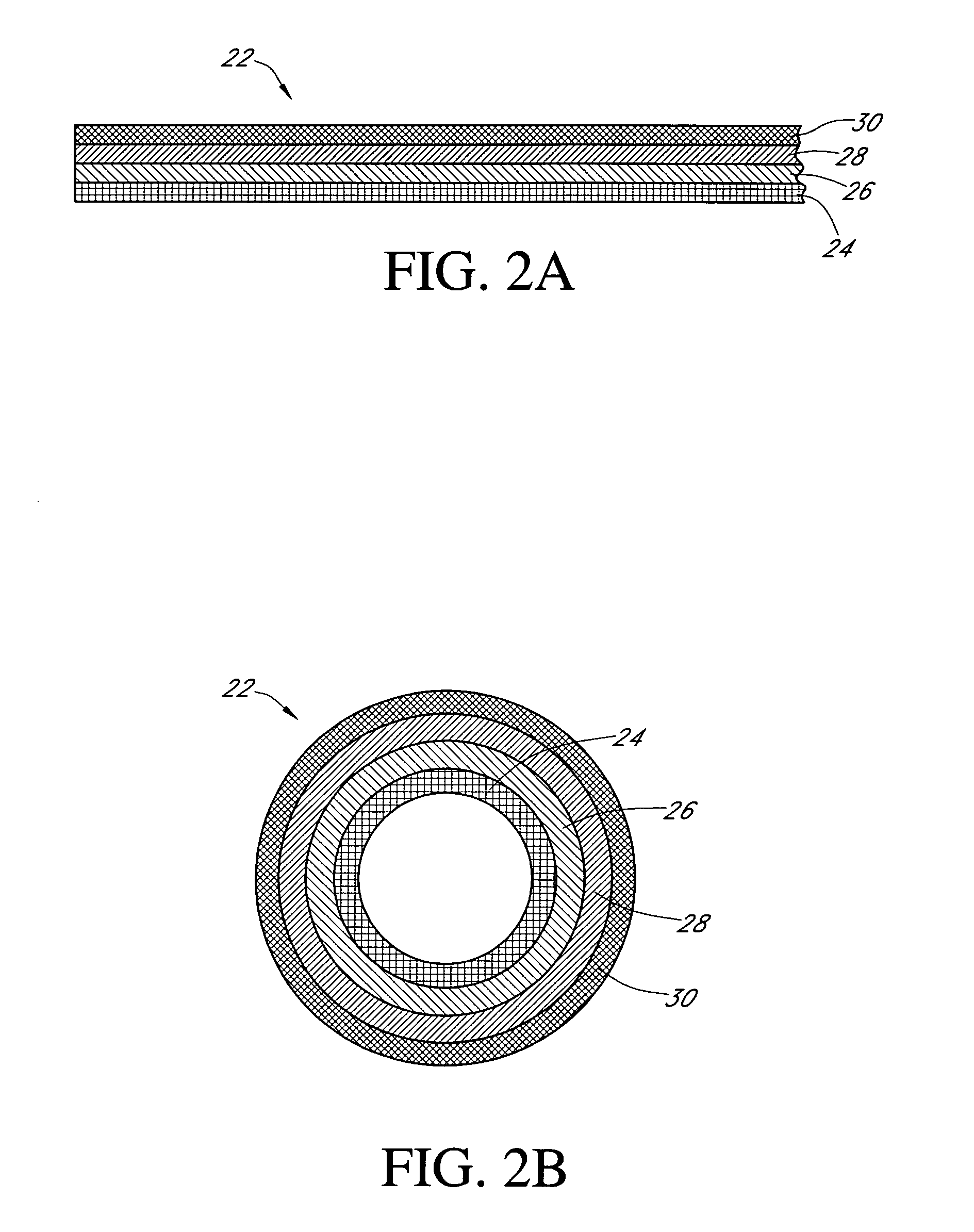
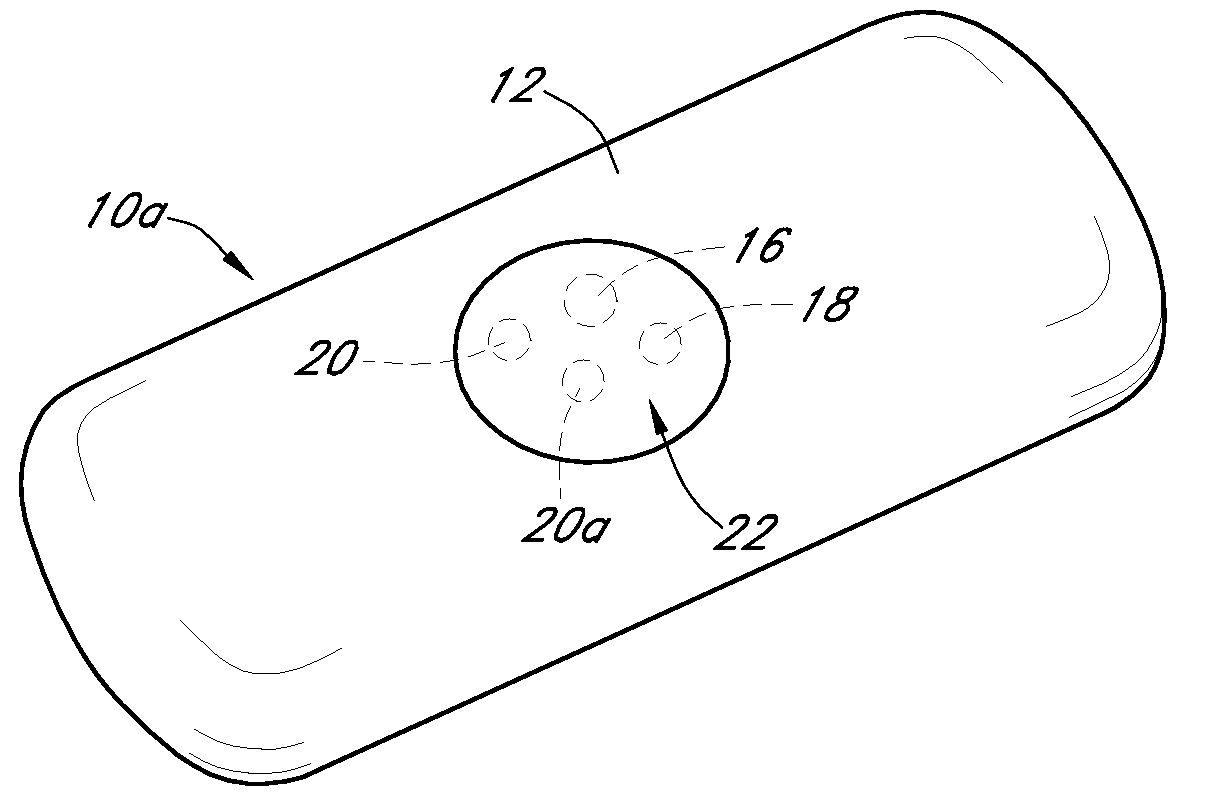
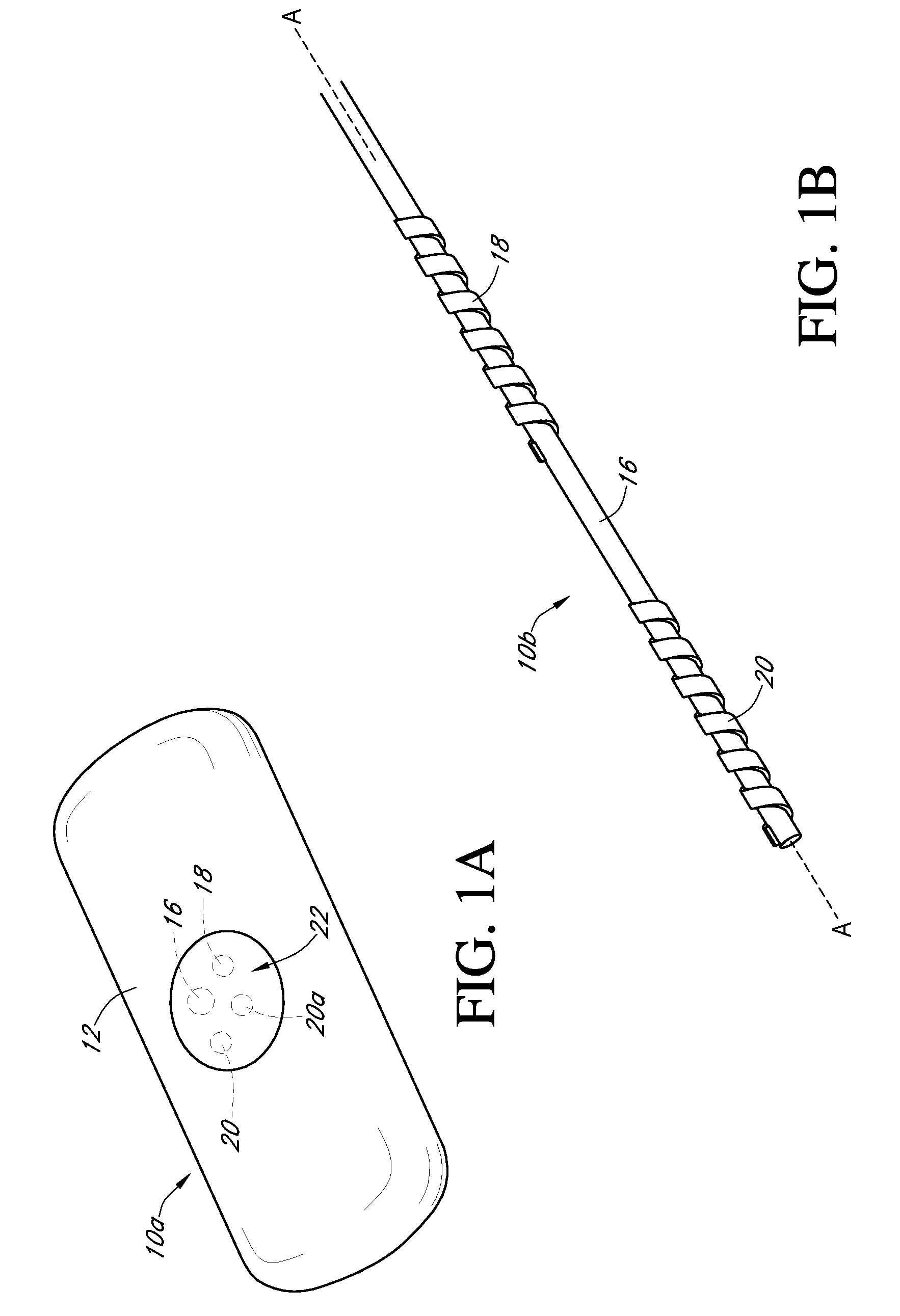
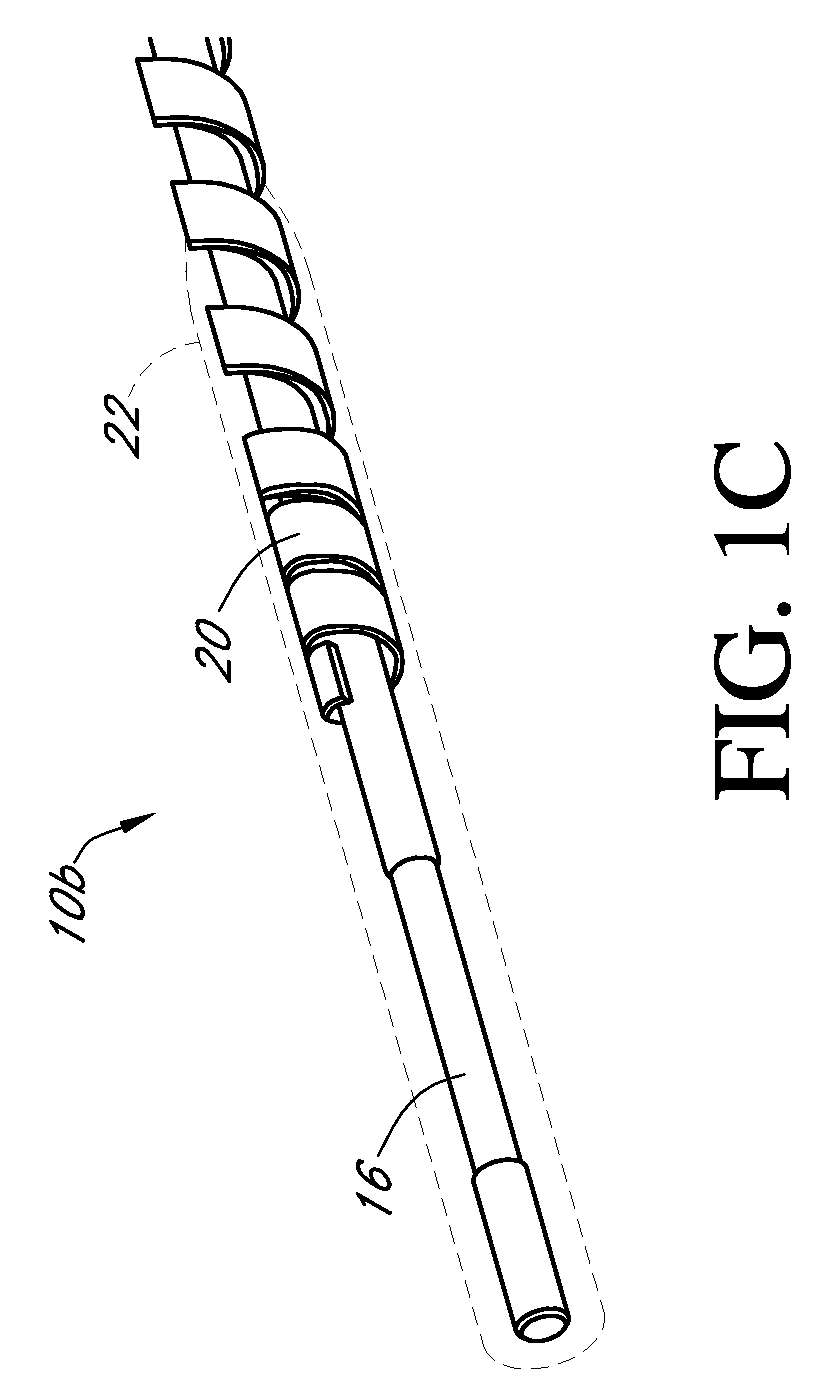
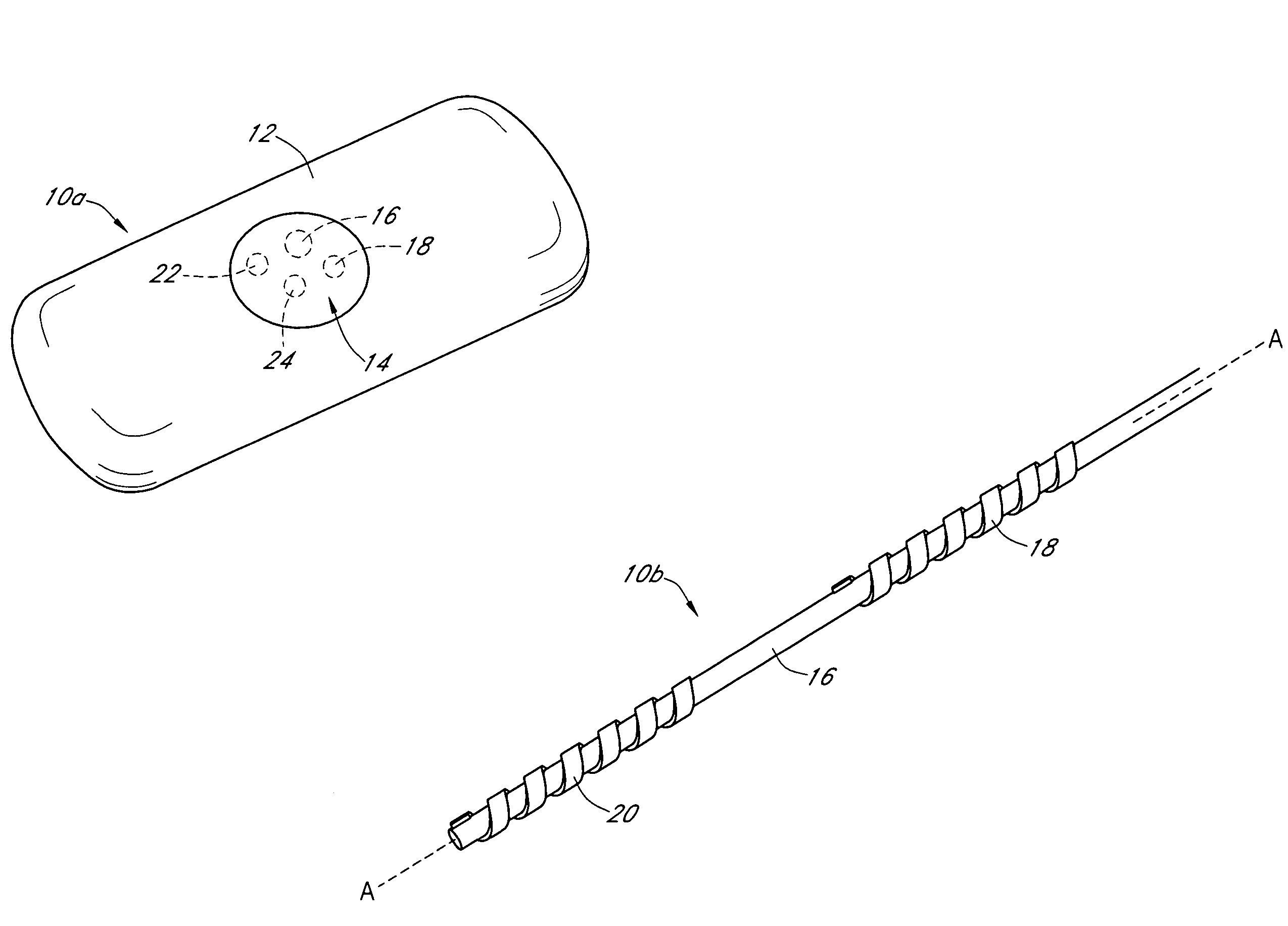
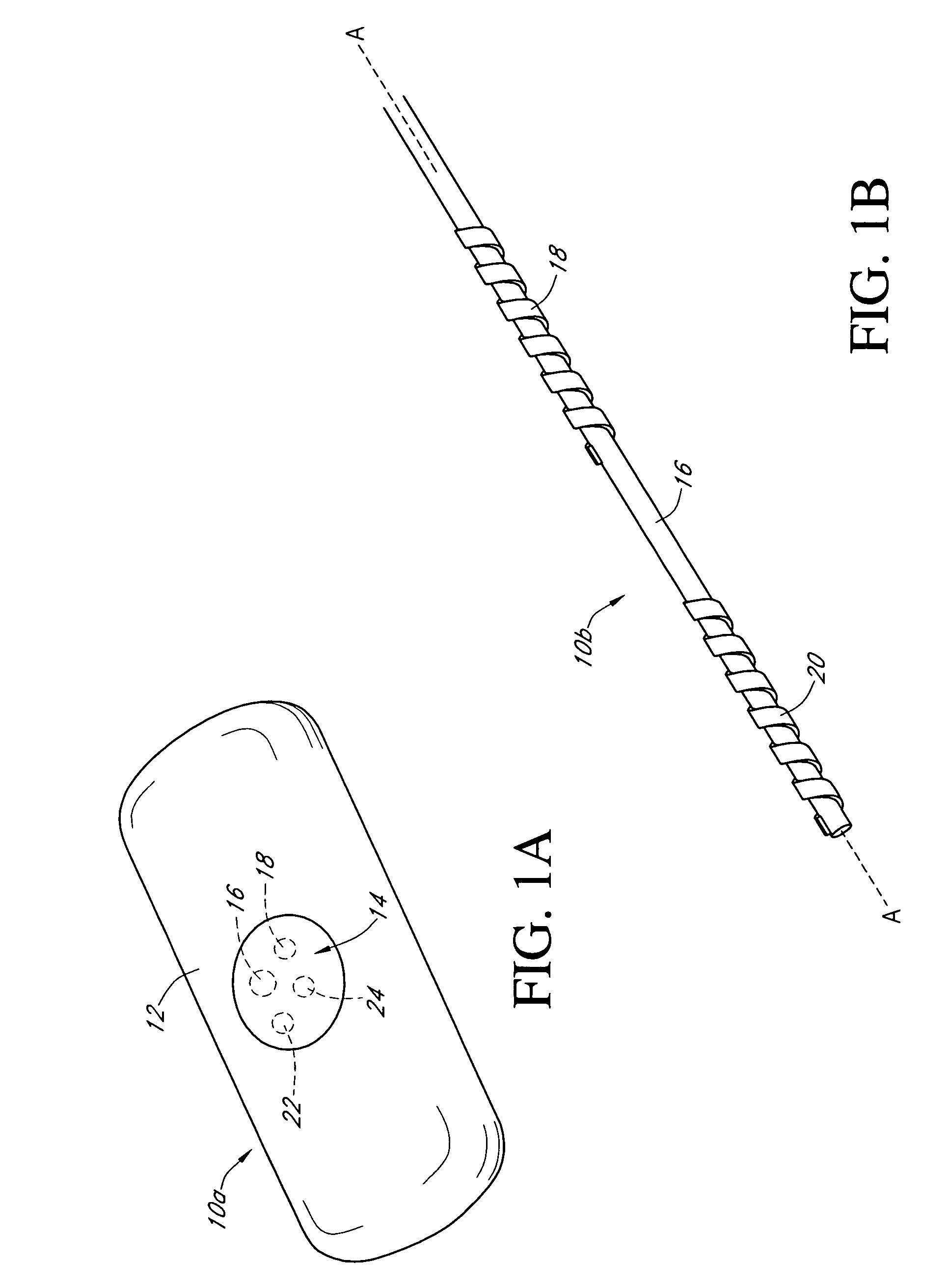
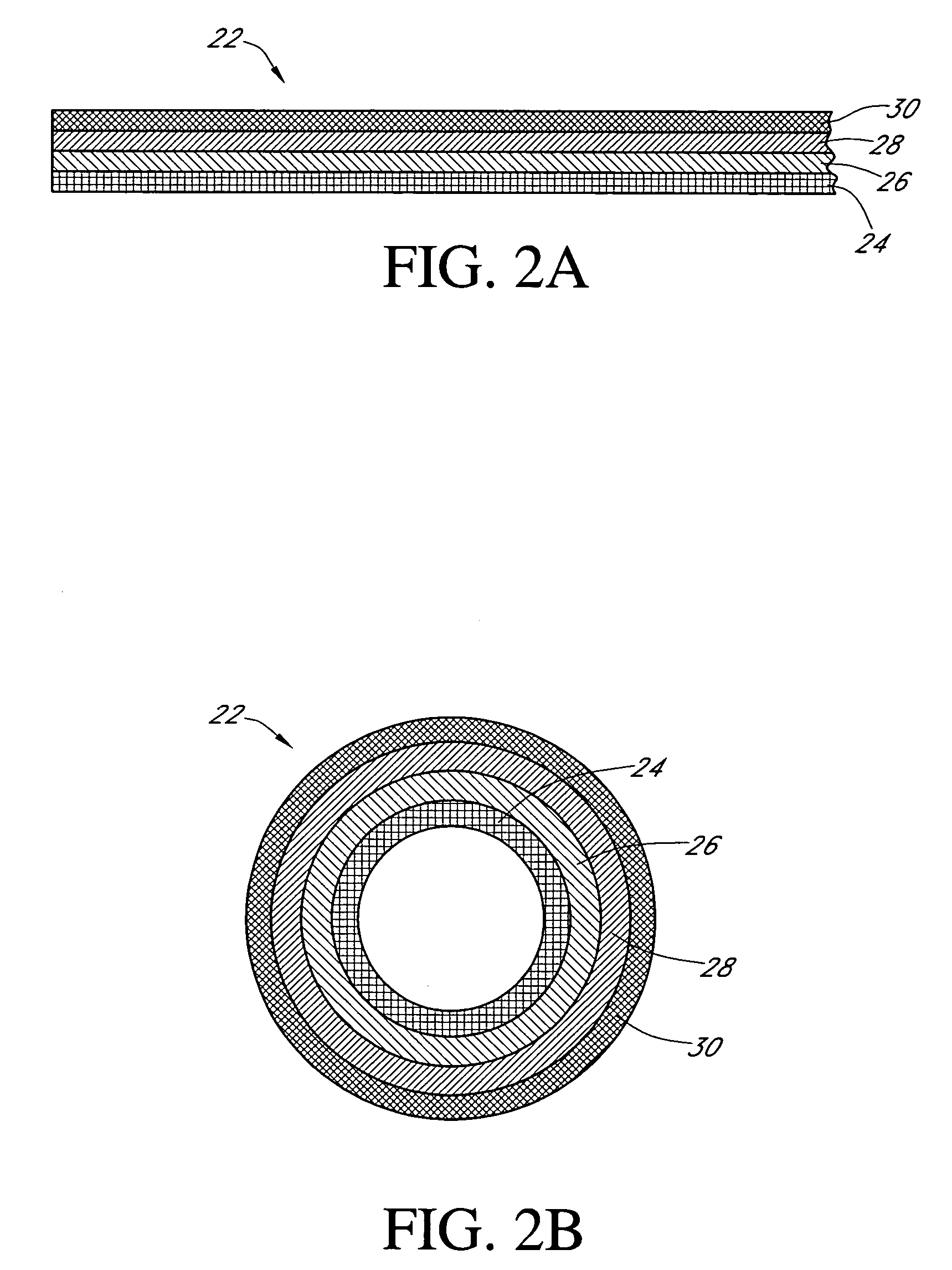
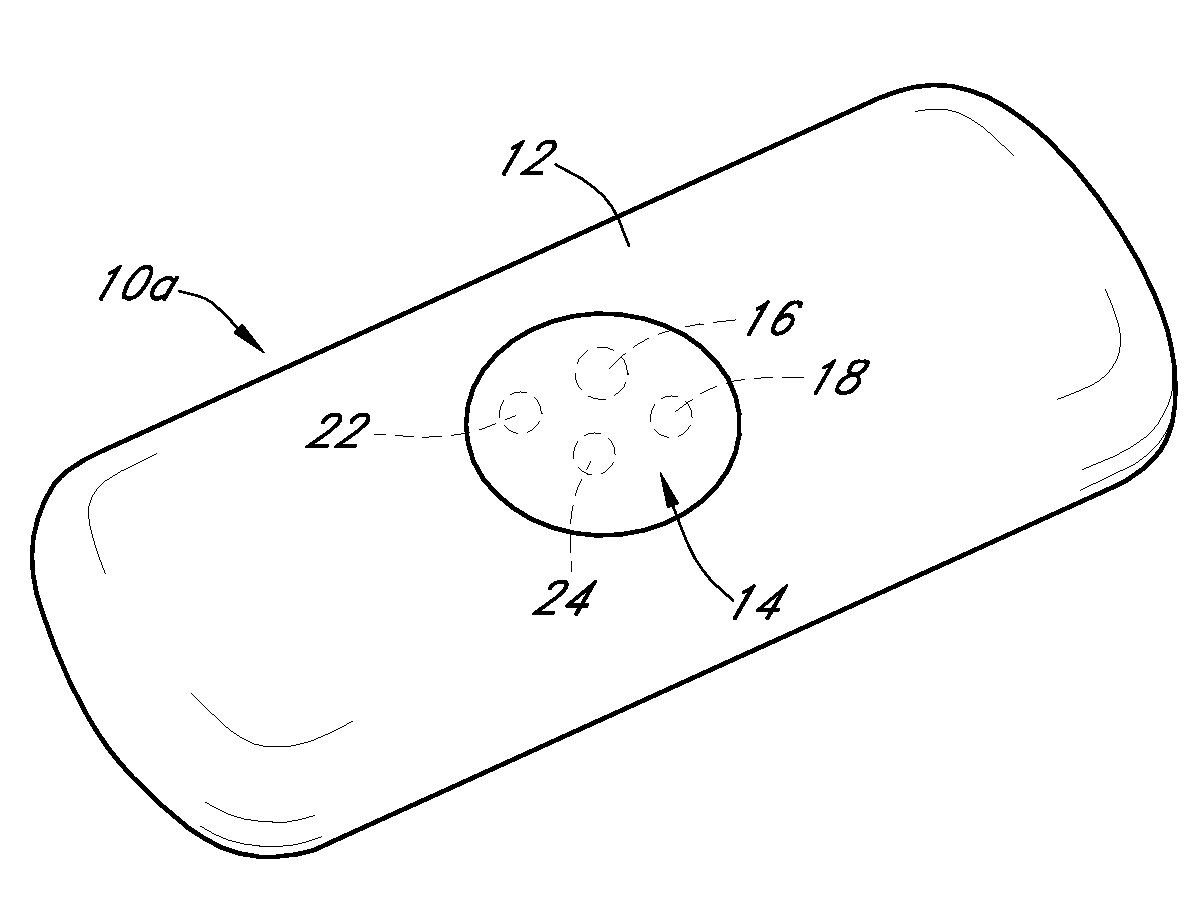
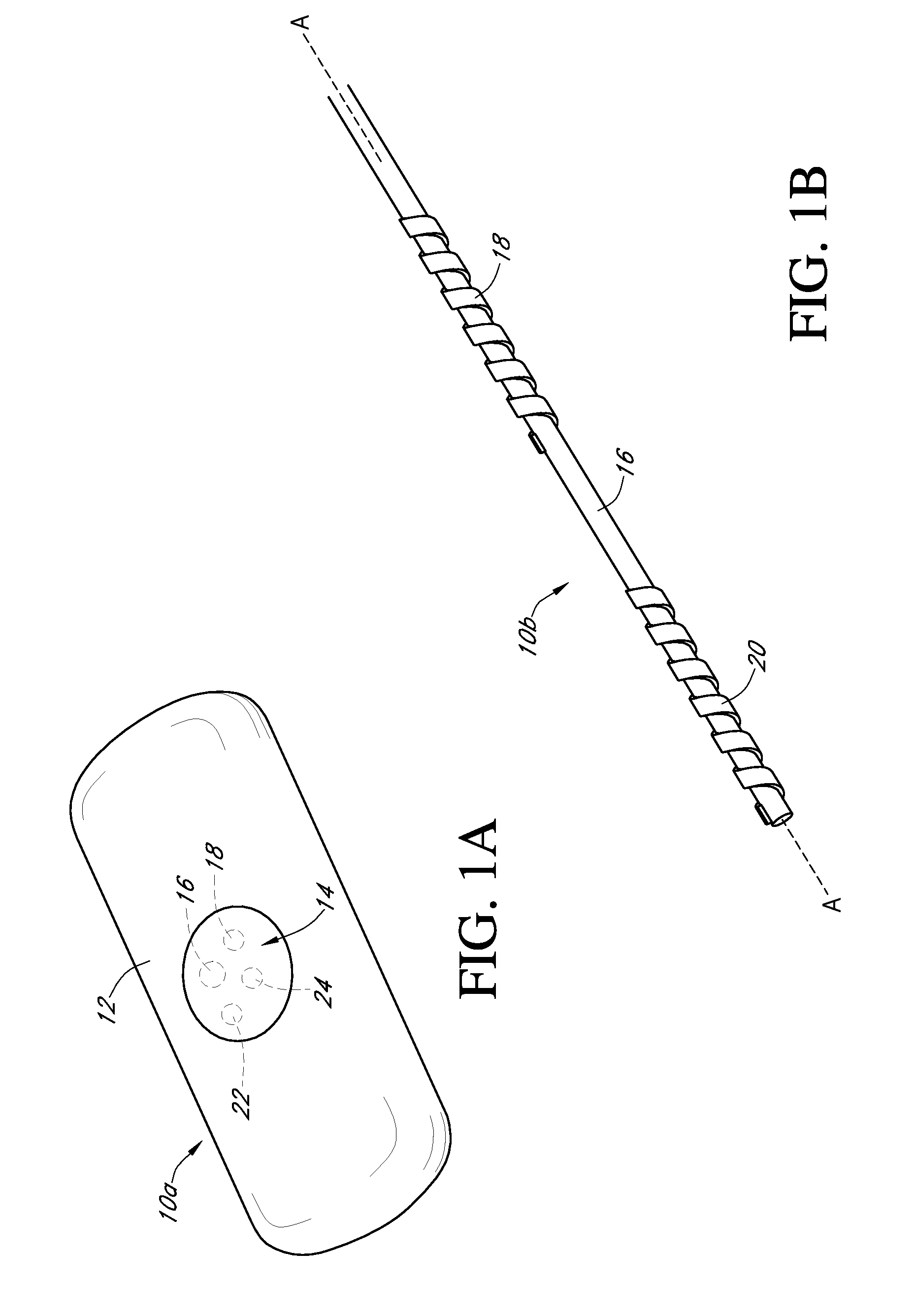
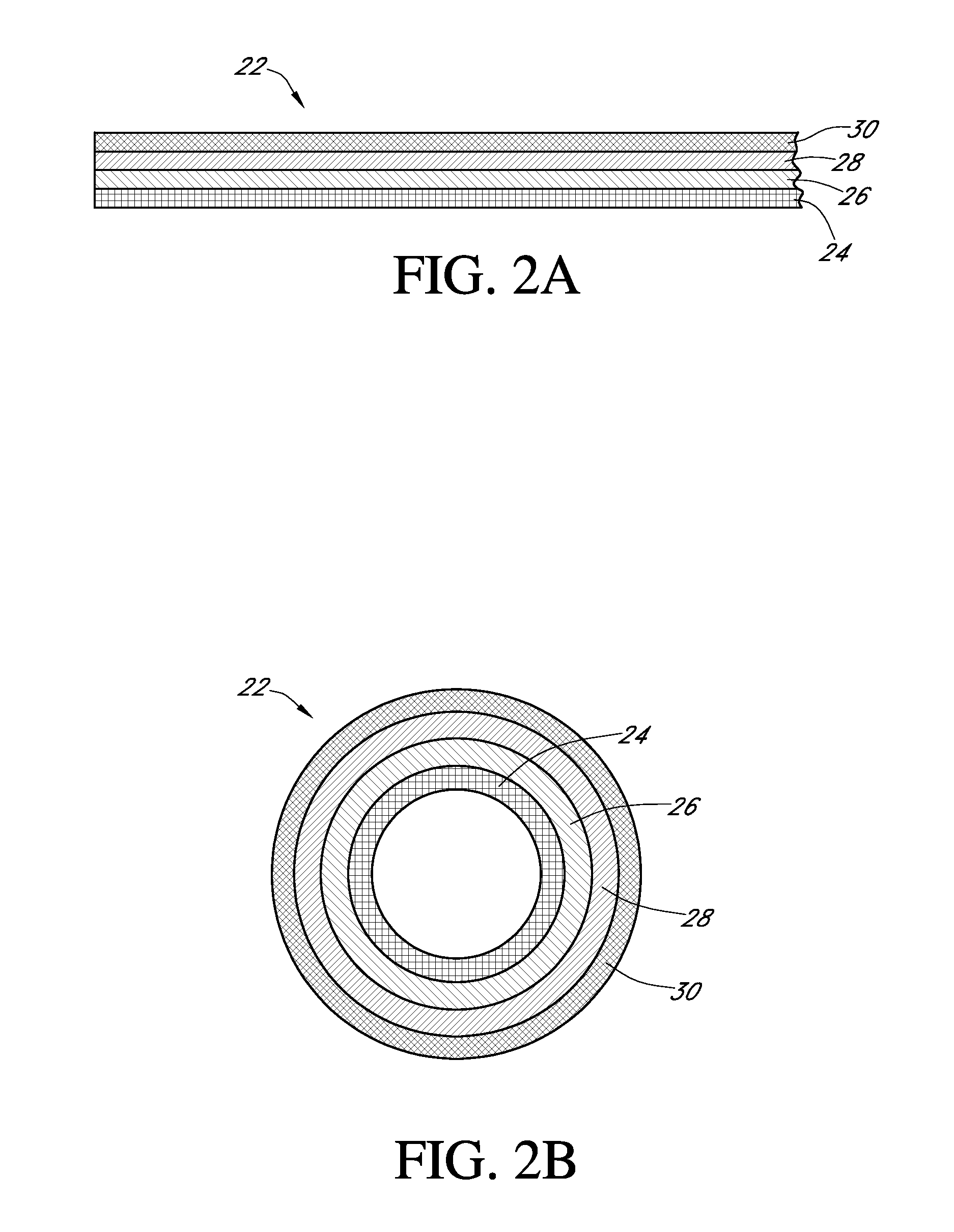
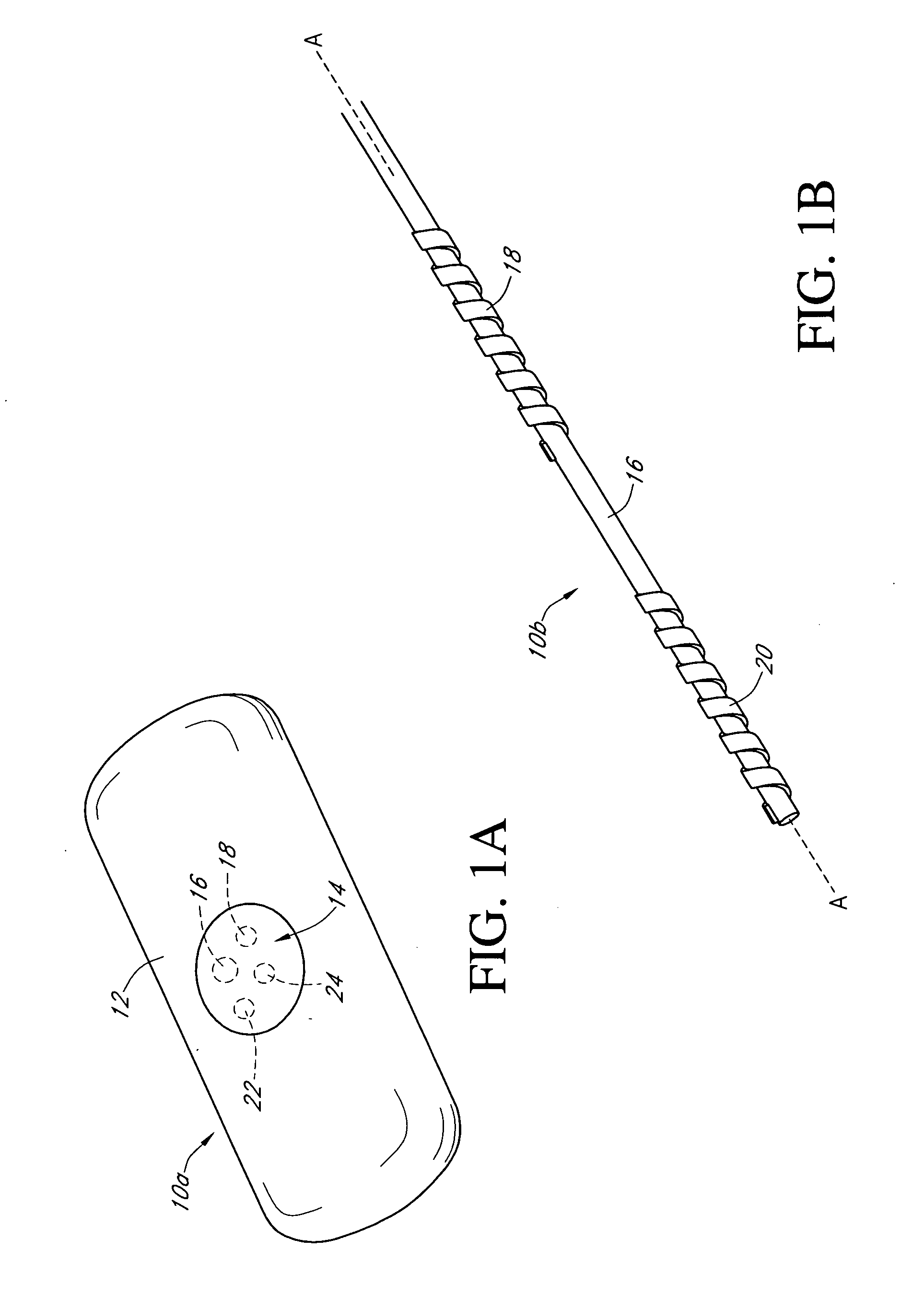
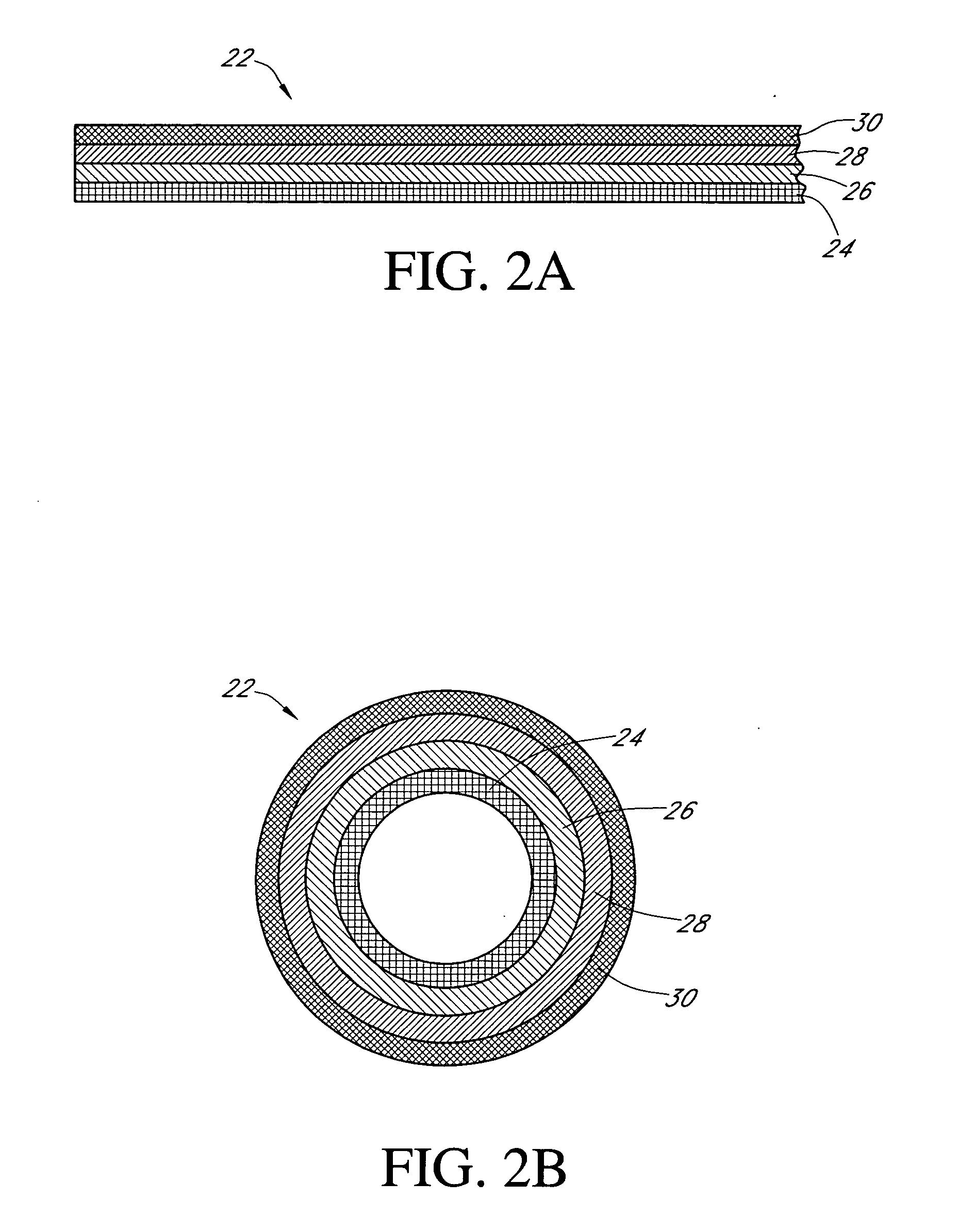
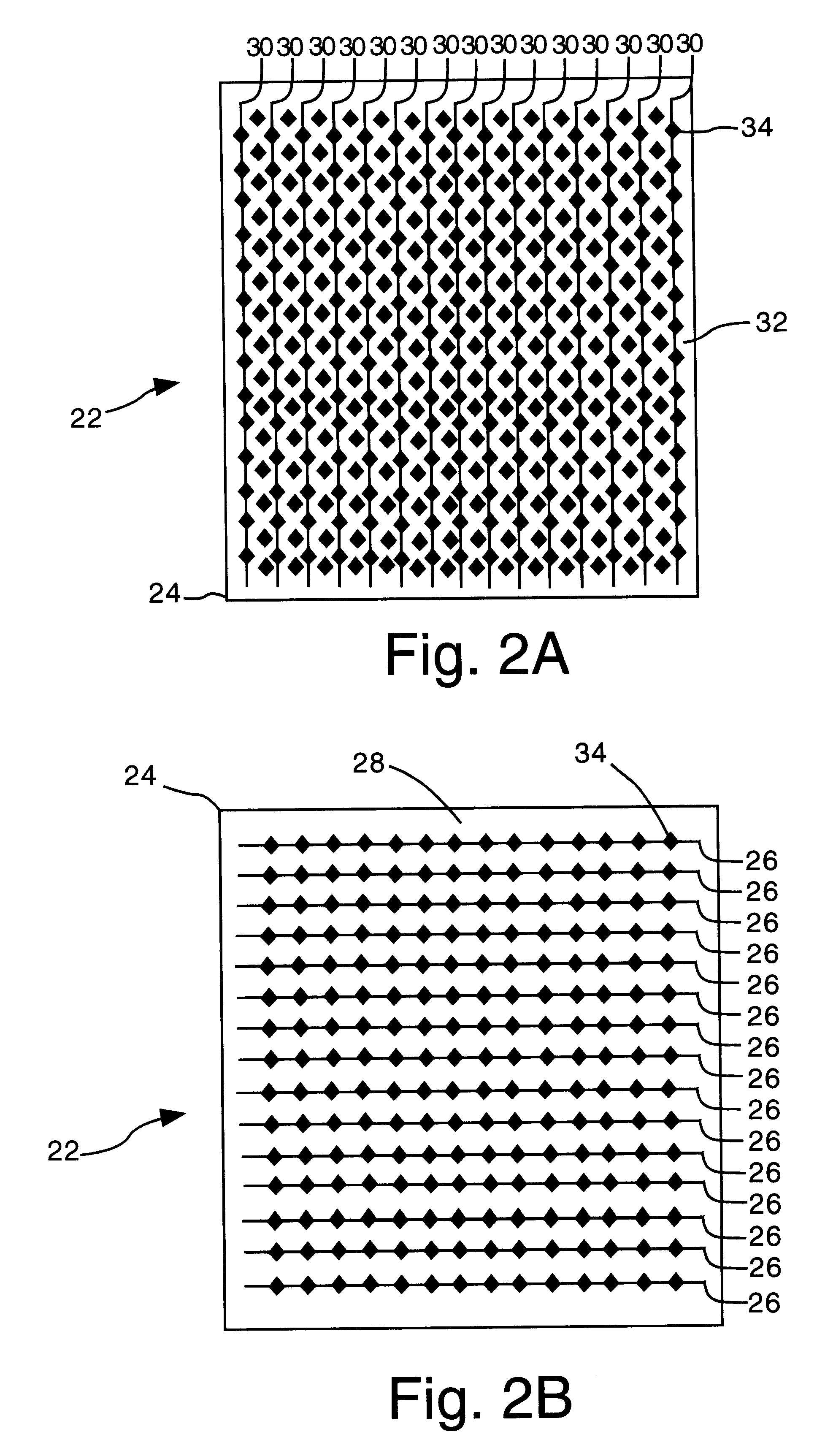
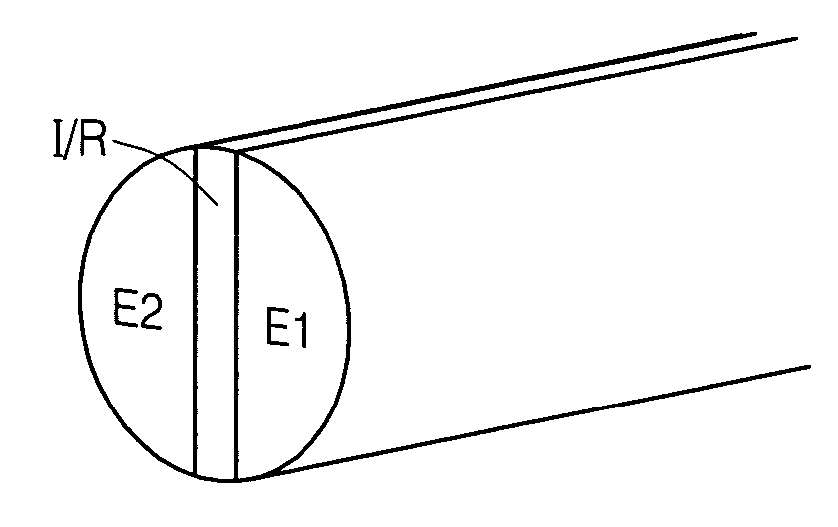
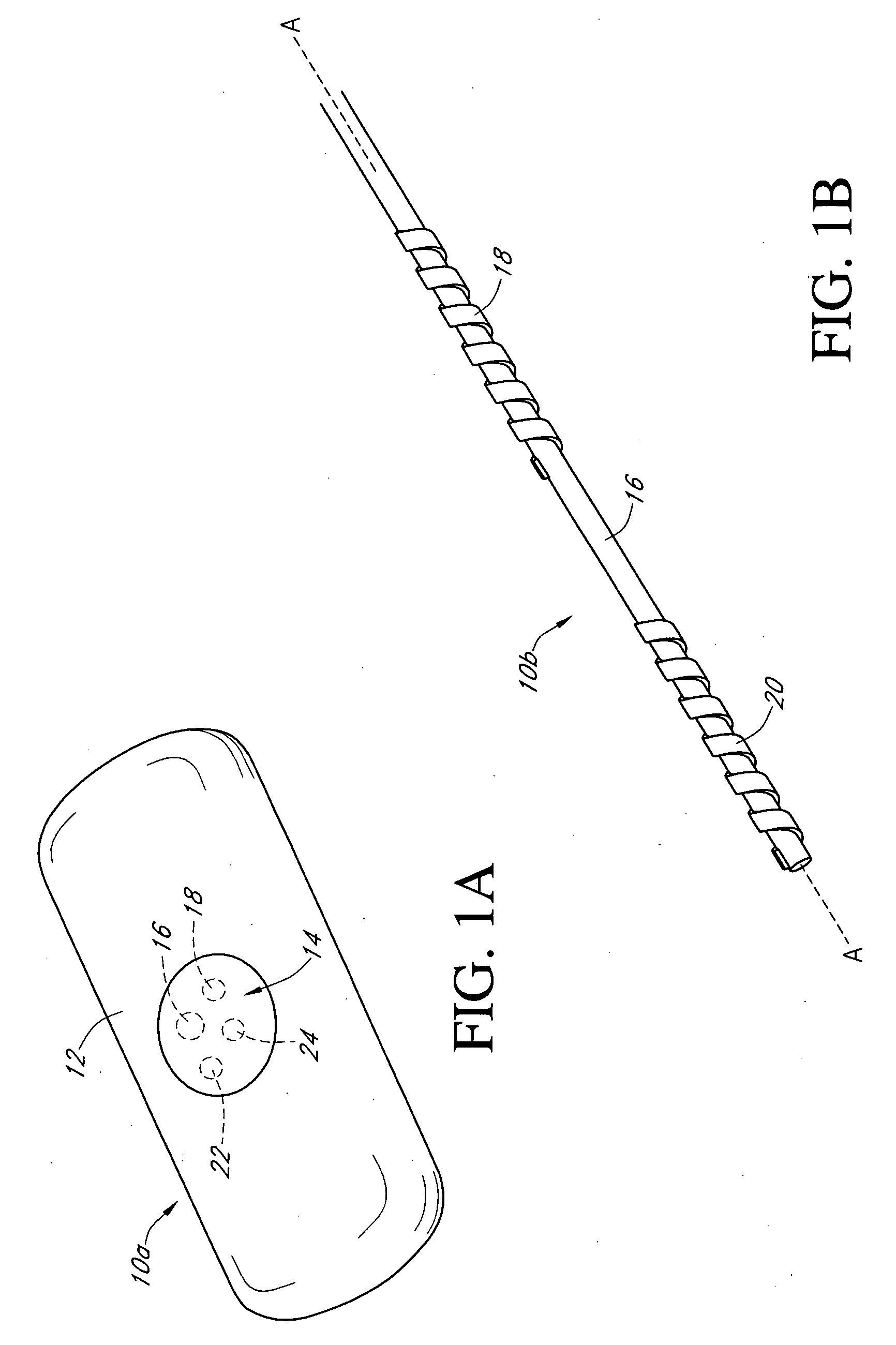
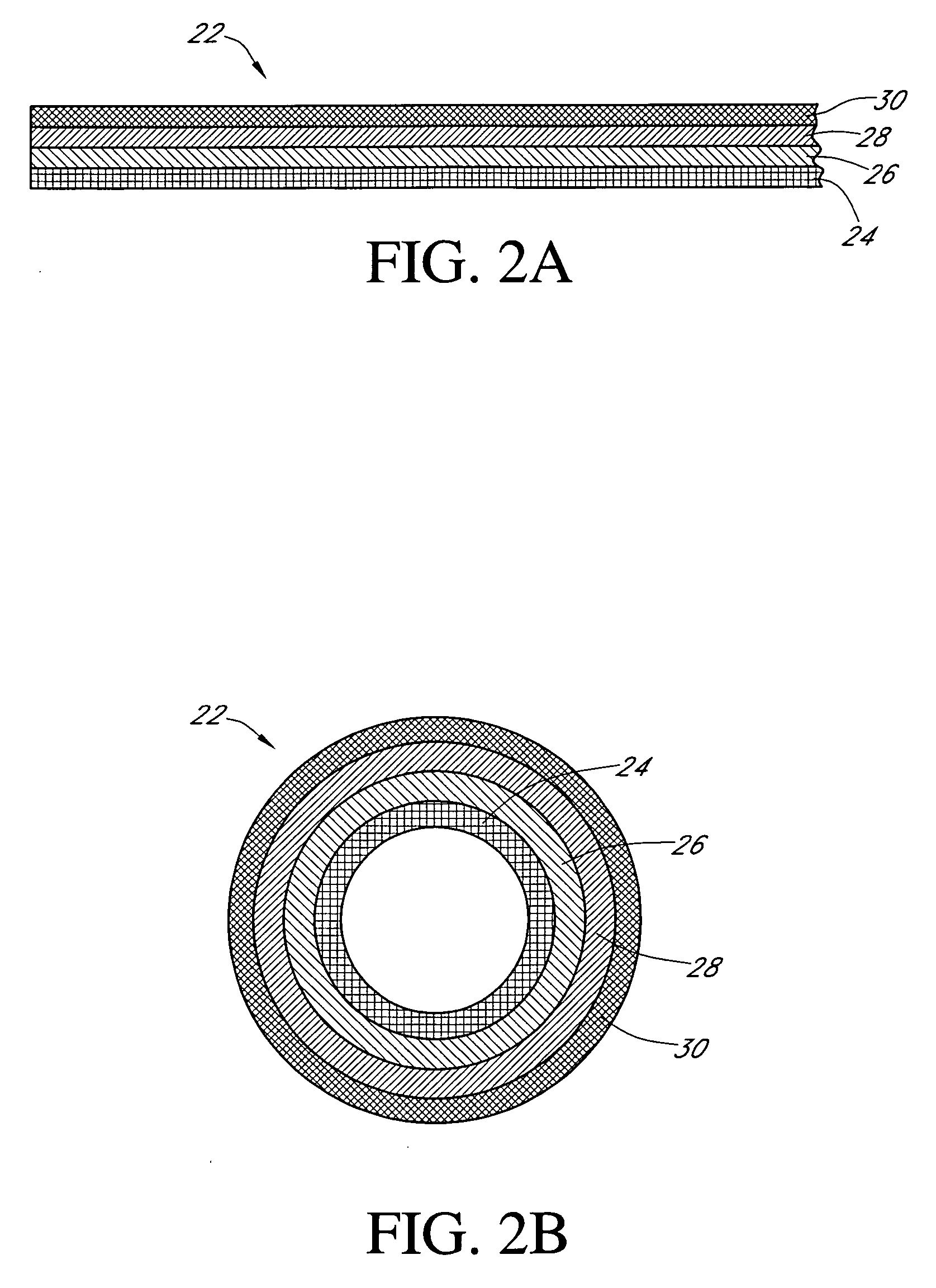
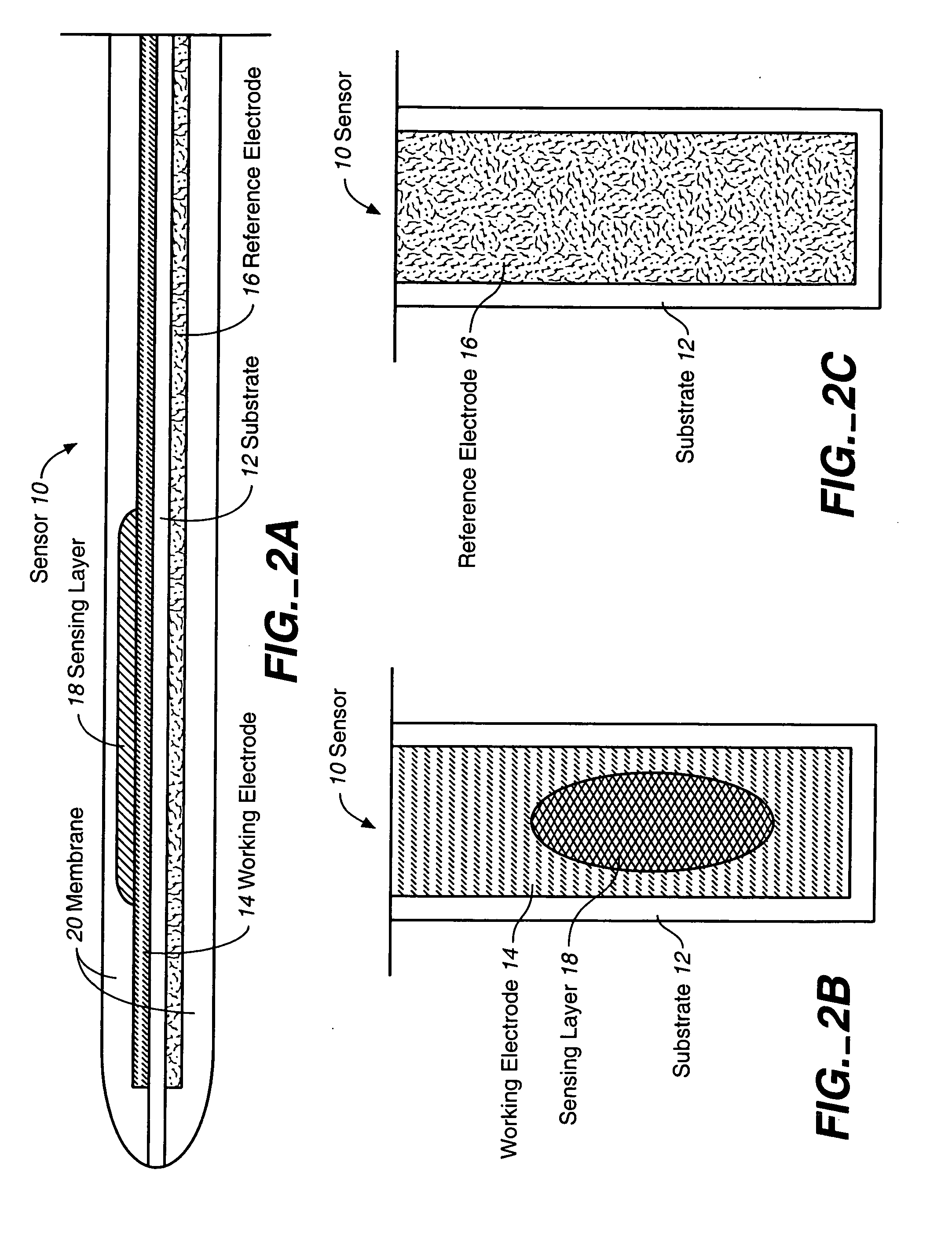
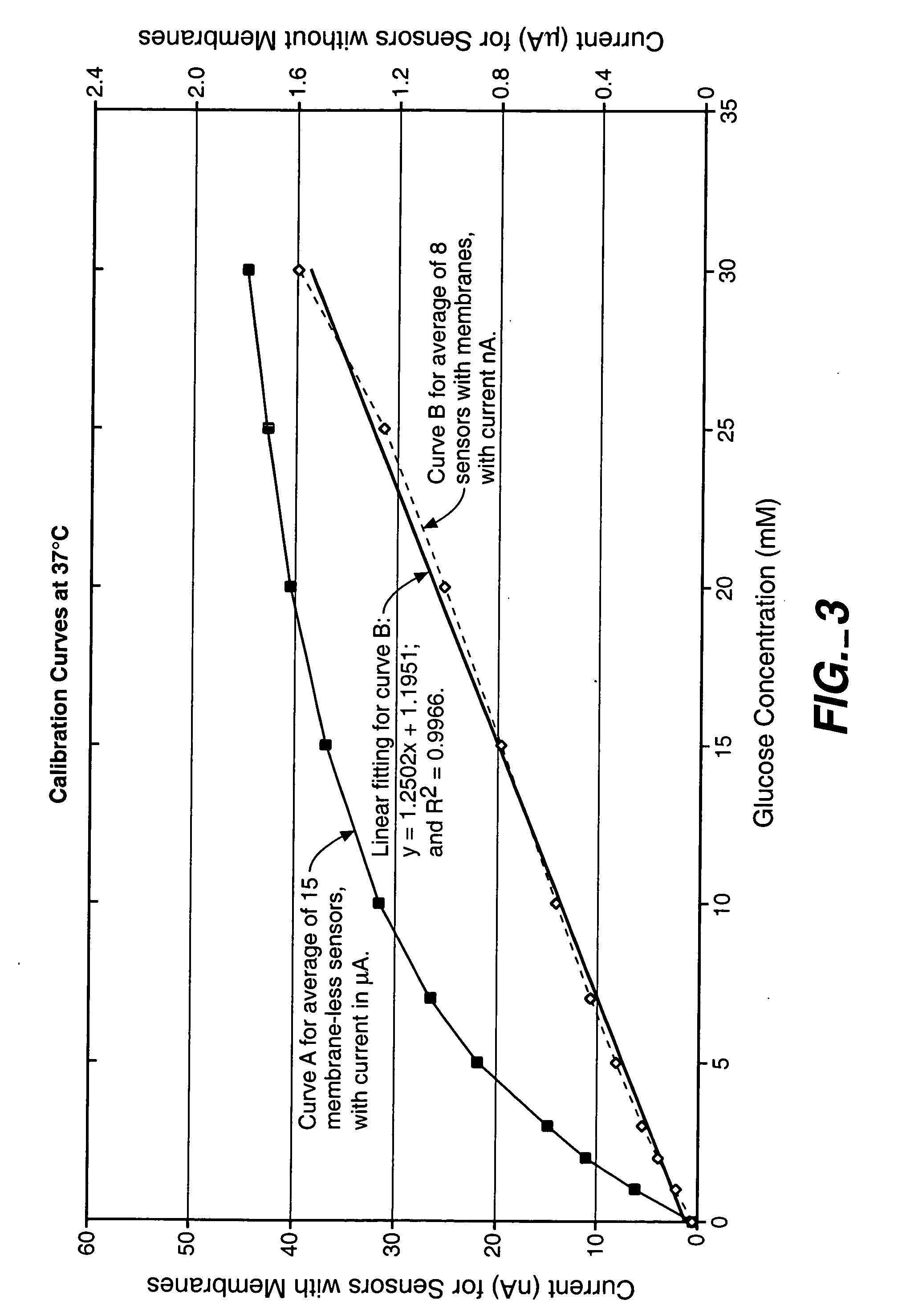
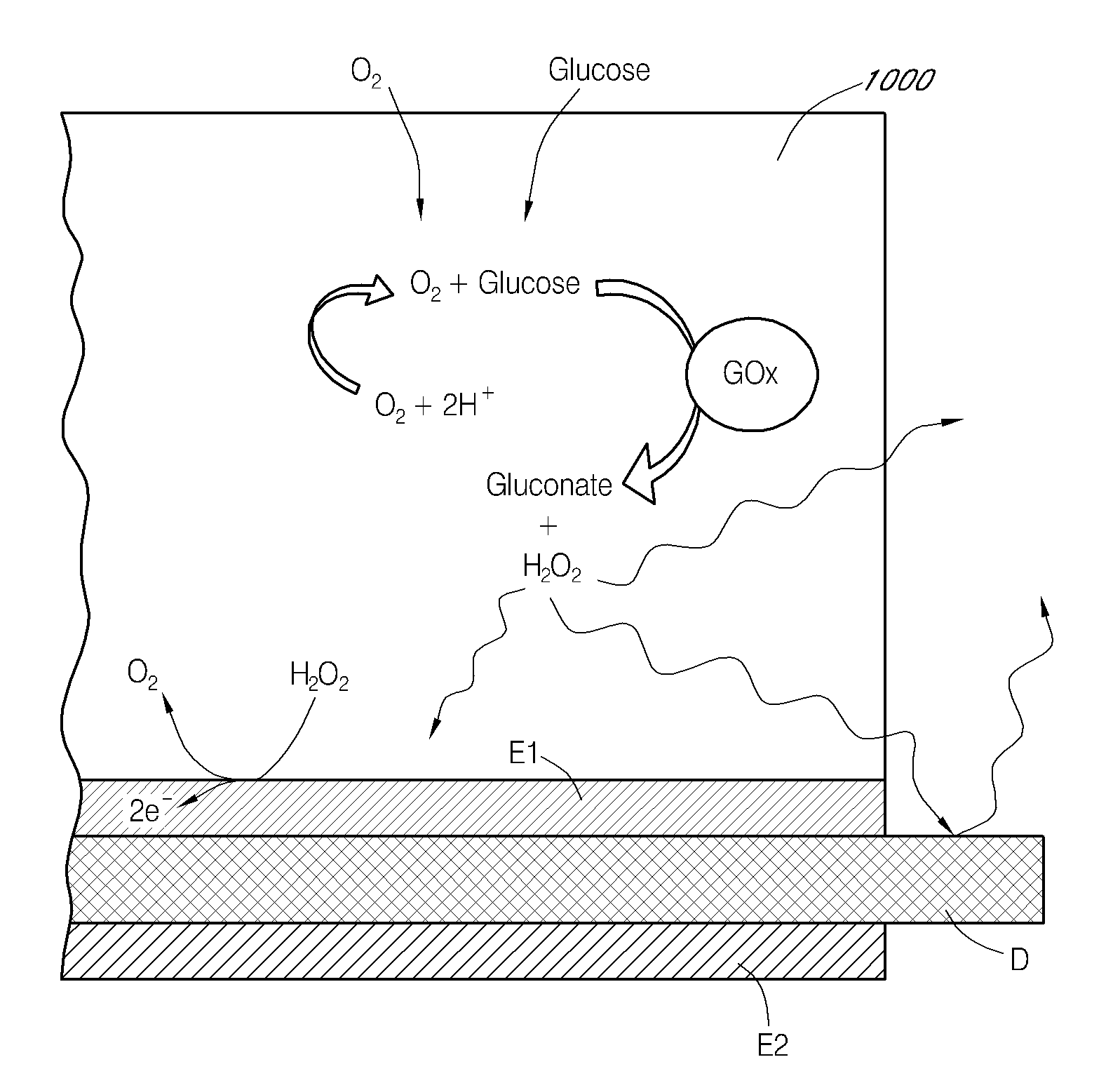
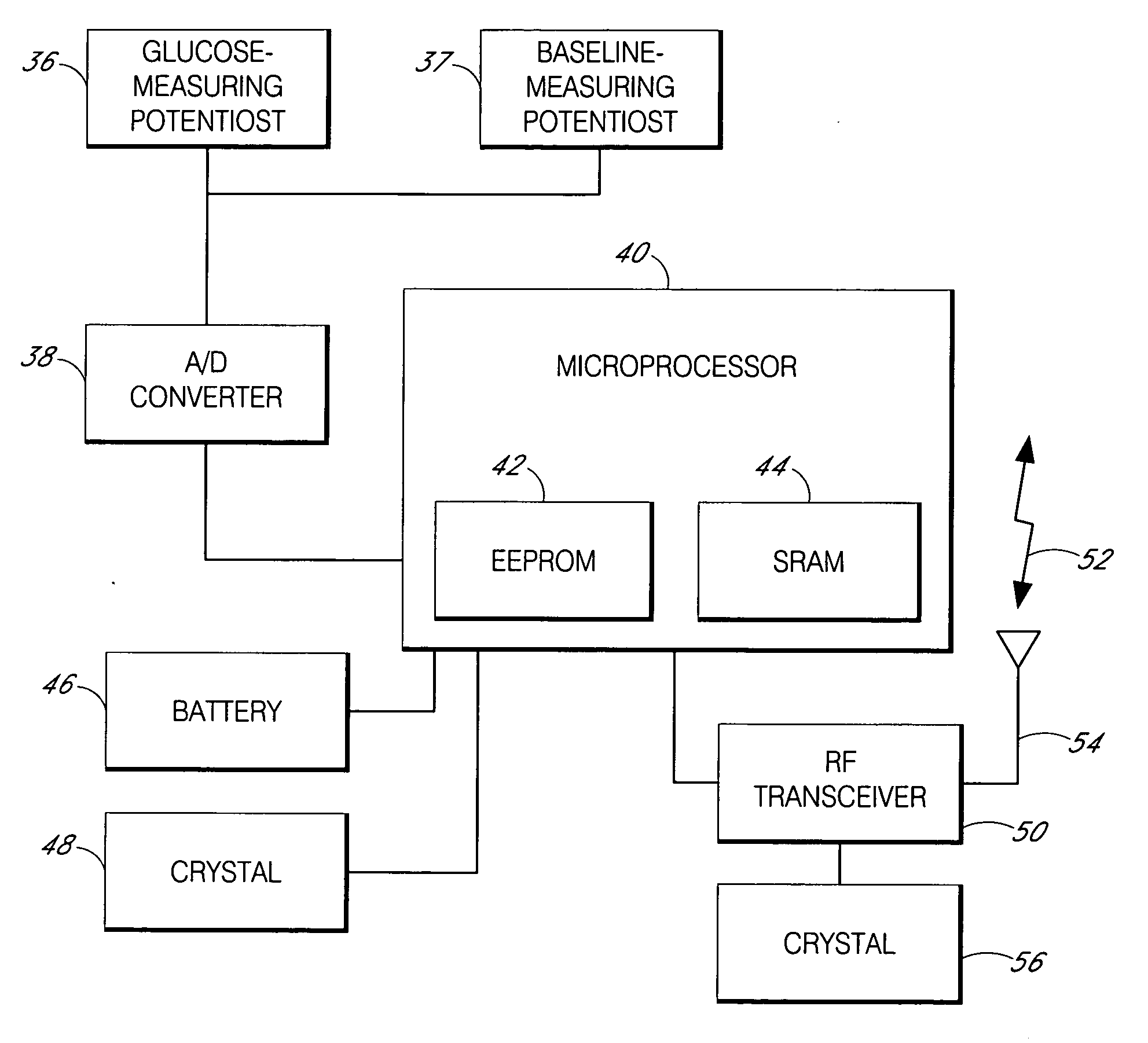
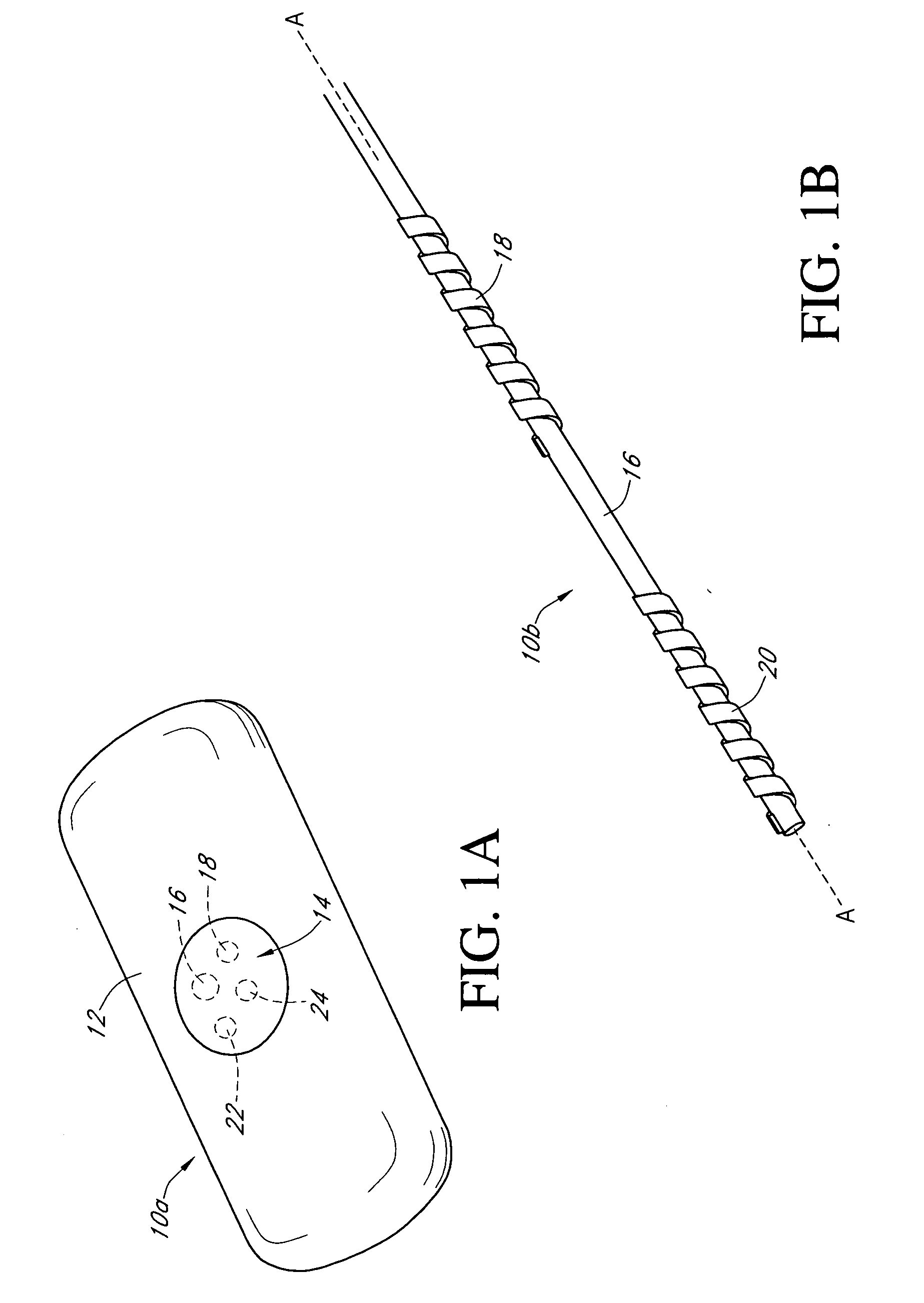
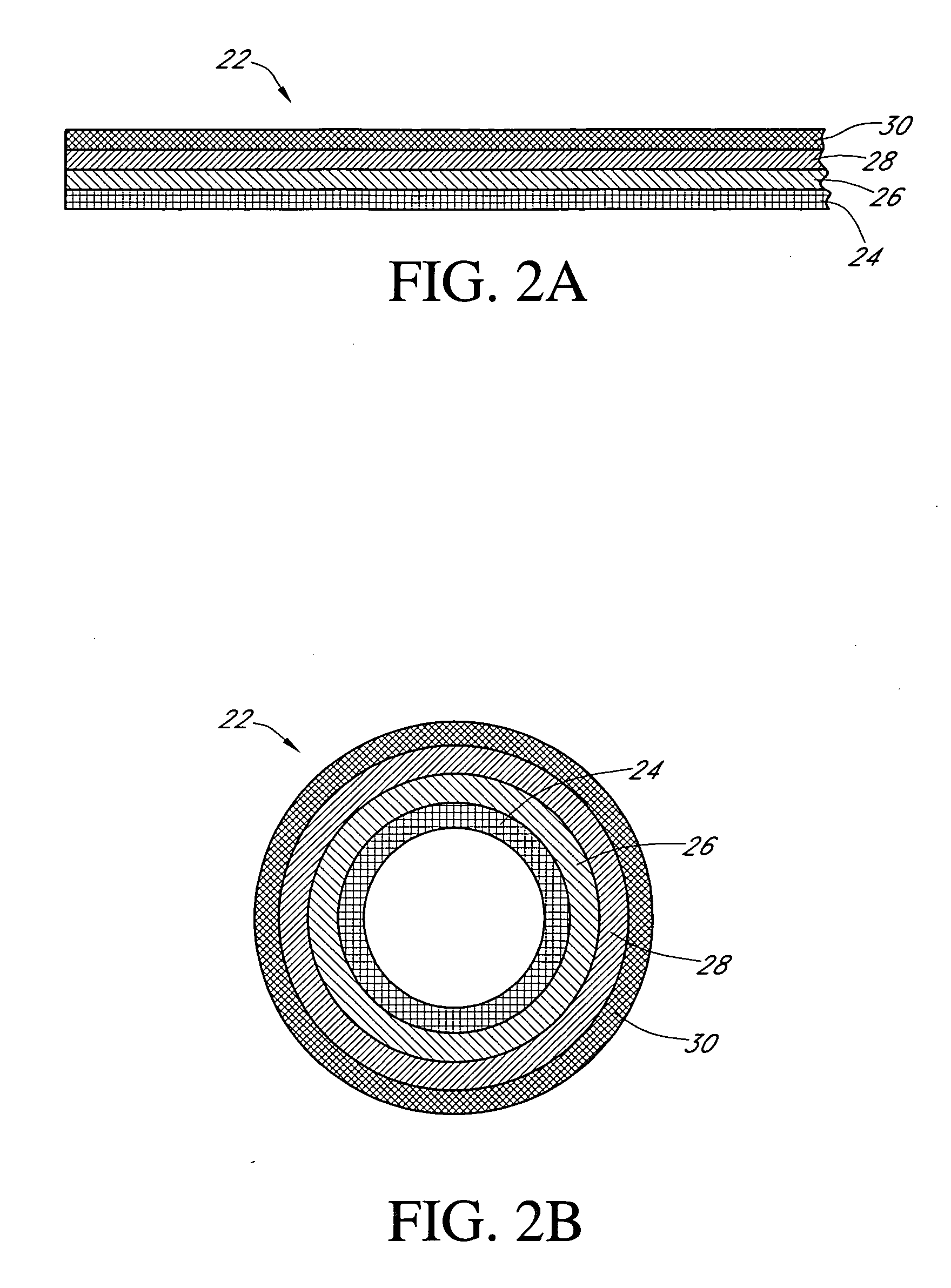
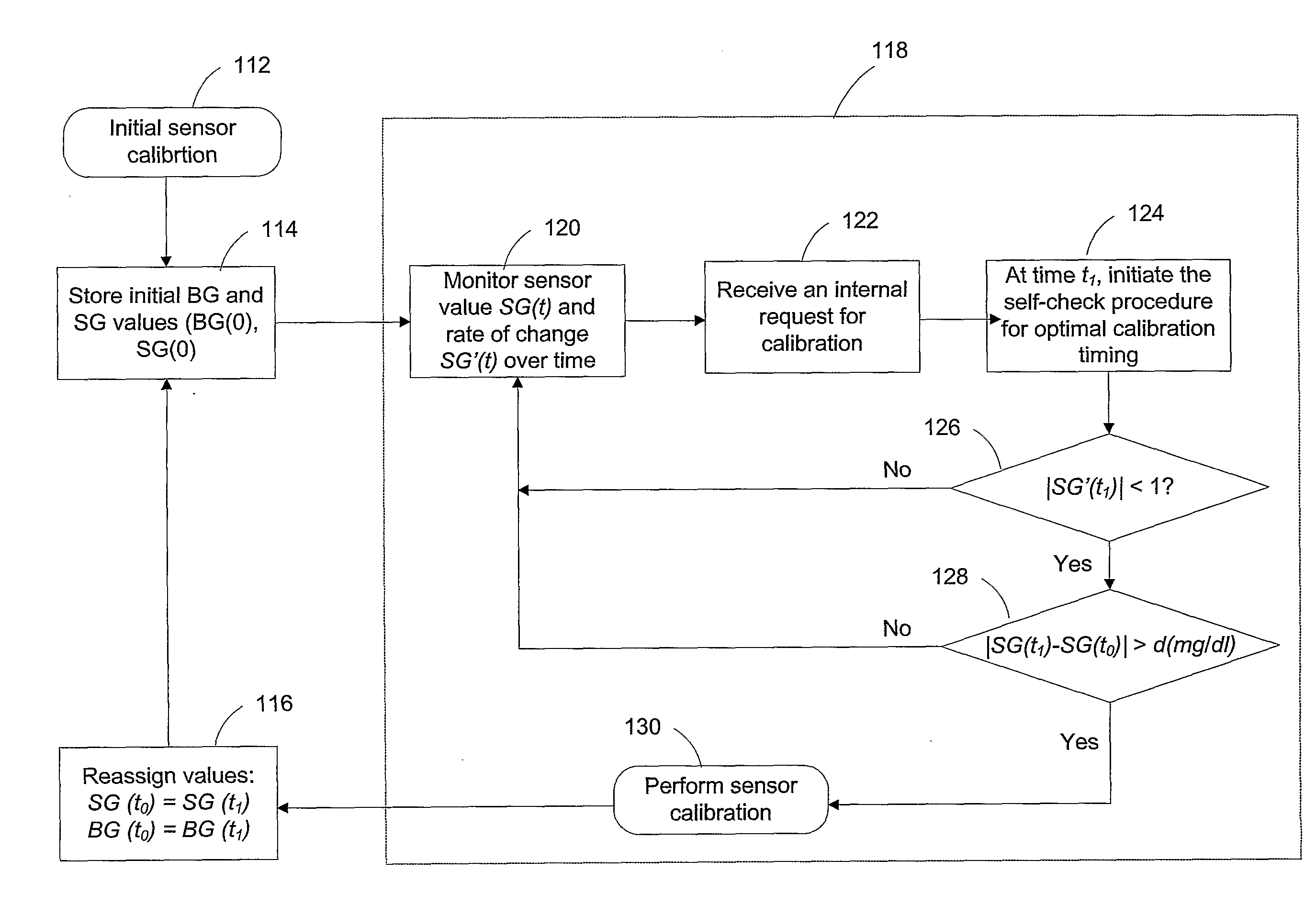
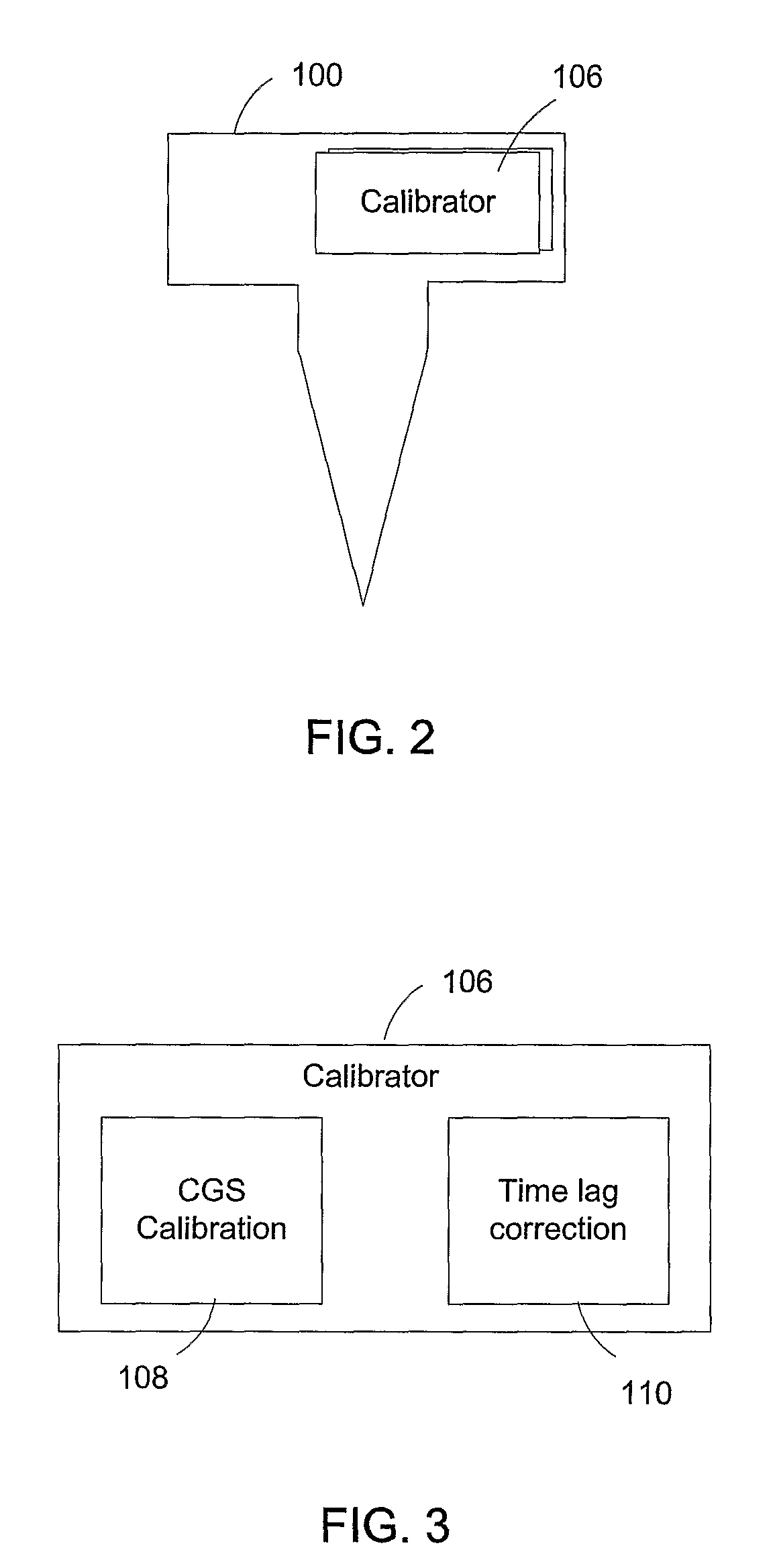
Calibration techniques for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20050143635A1Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCatheterAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for calibrating a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes one or more electrodes to measure an additional analyte. Such measurements may provide a baseline or sensitivity measurement for use in calibrating the sensor. Furthermore, baseline and / or sensitivity measurements may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
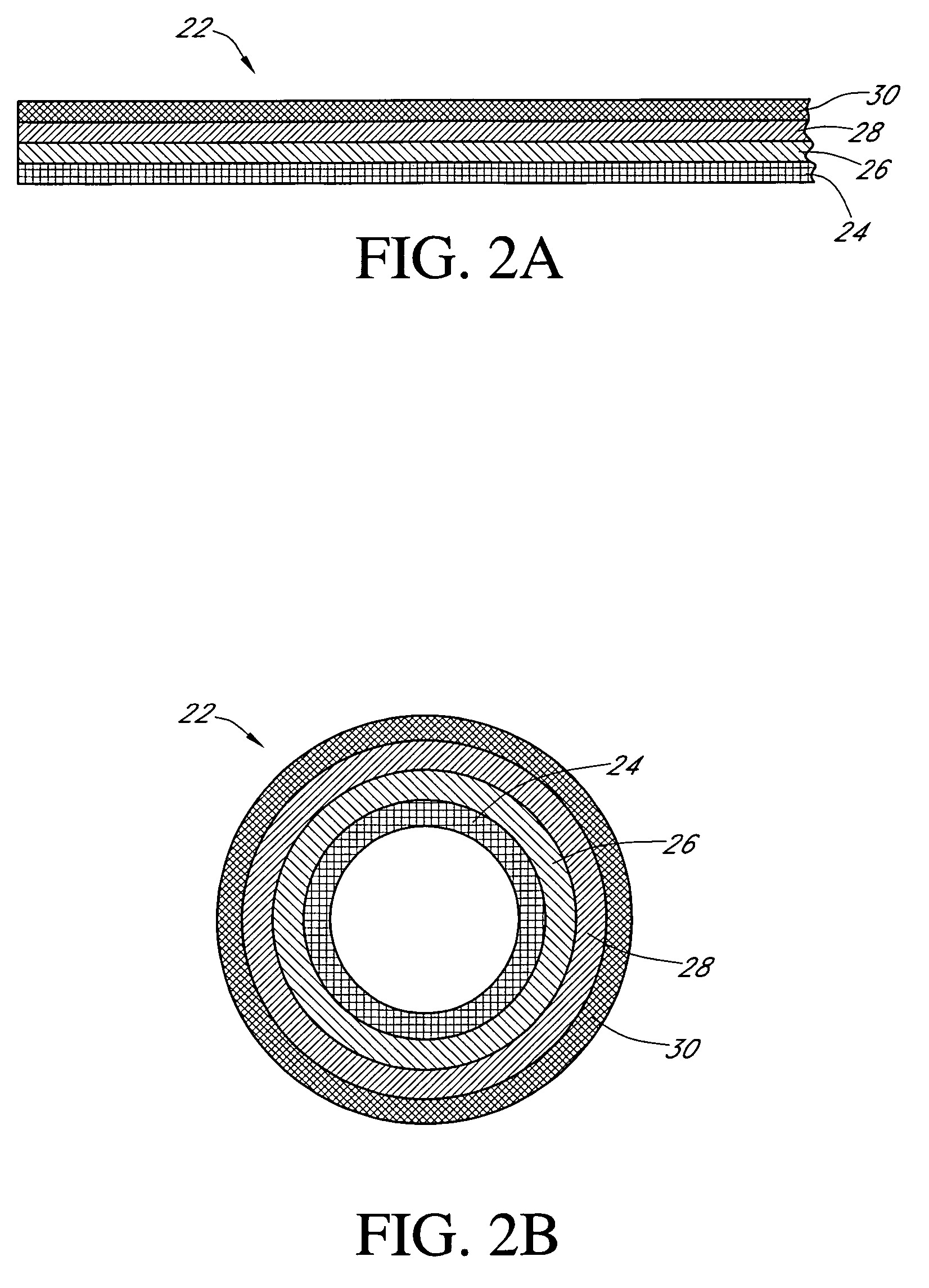
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS7366556B2Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
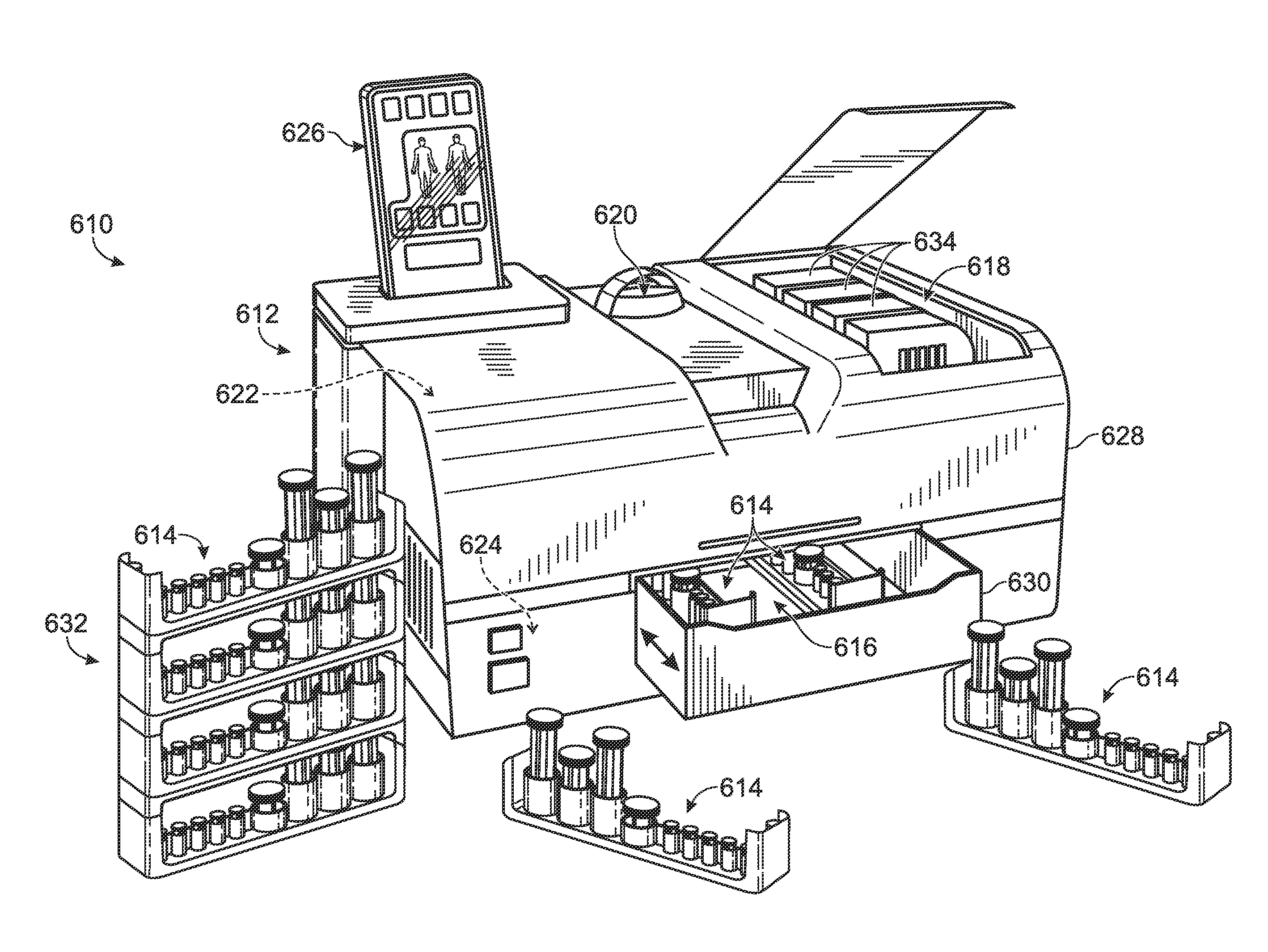
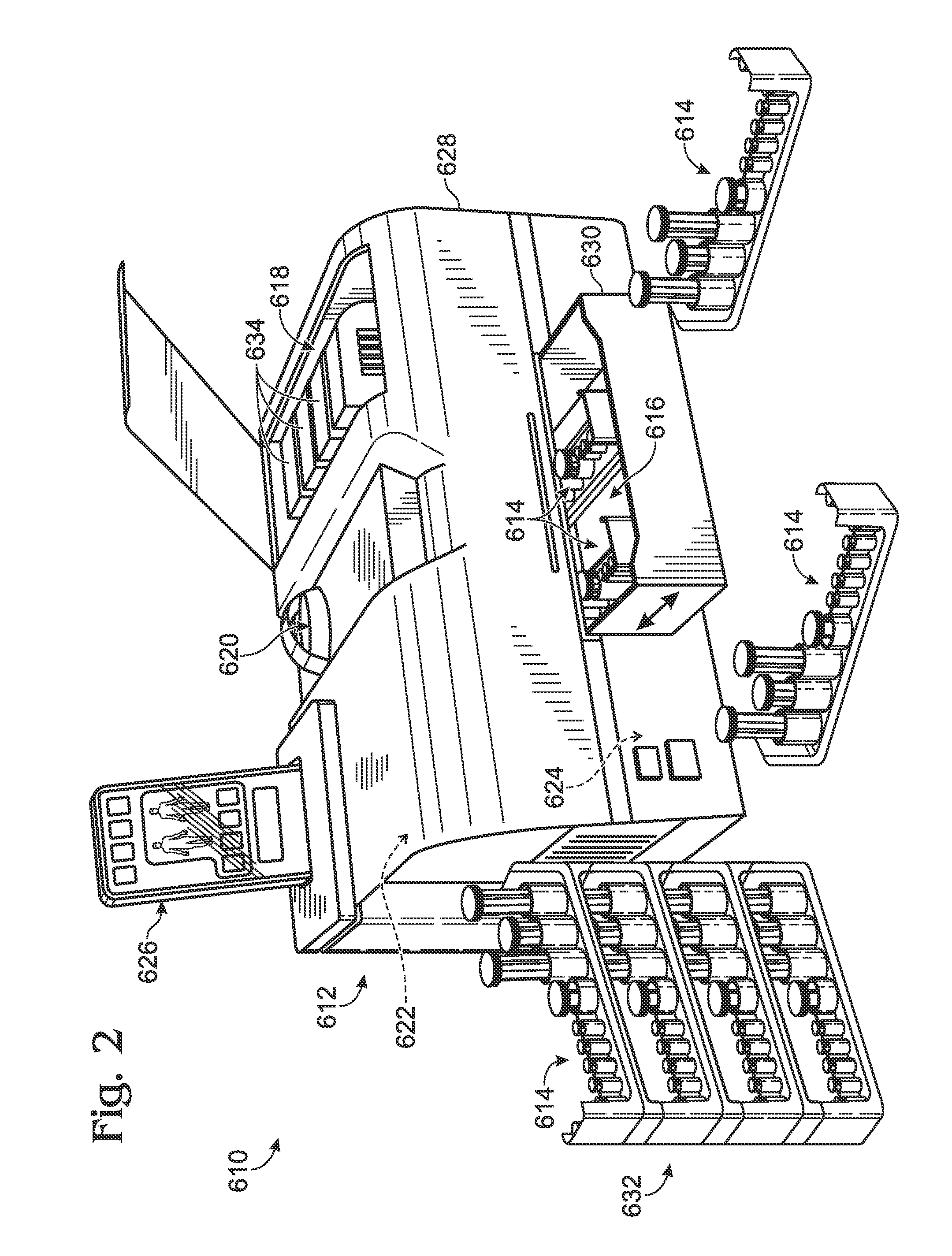
Droplet-based assay system
ActiveUS20100173394A1Easy CalibrationImprove accuracy and reliabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayBiology
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20090099436A1Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCatheterAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS7467003B2Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS7460898B2Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS7424318B2Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20080214918A1Cancel noiseImprove convenienceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20070027385A1Cancel noiseImprove convenienceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
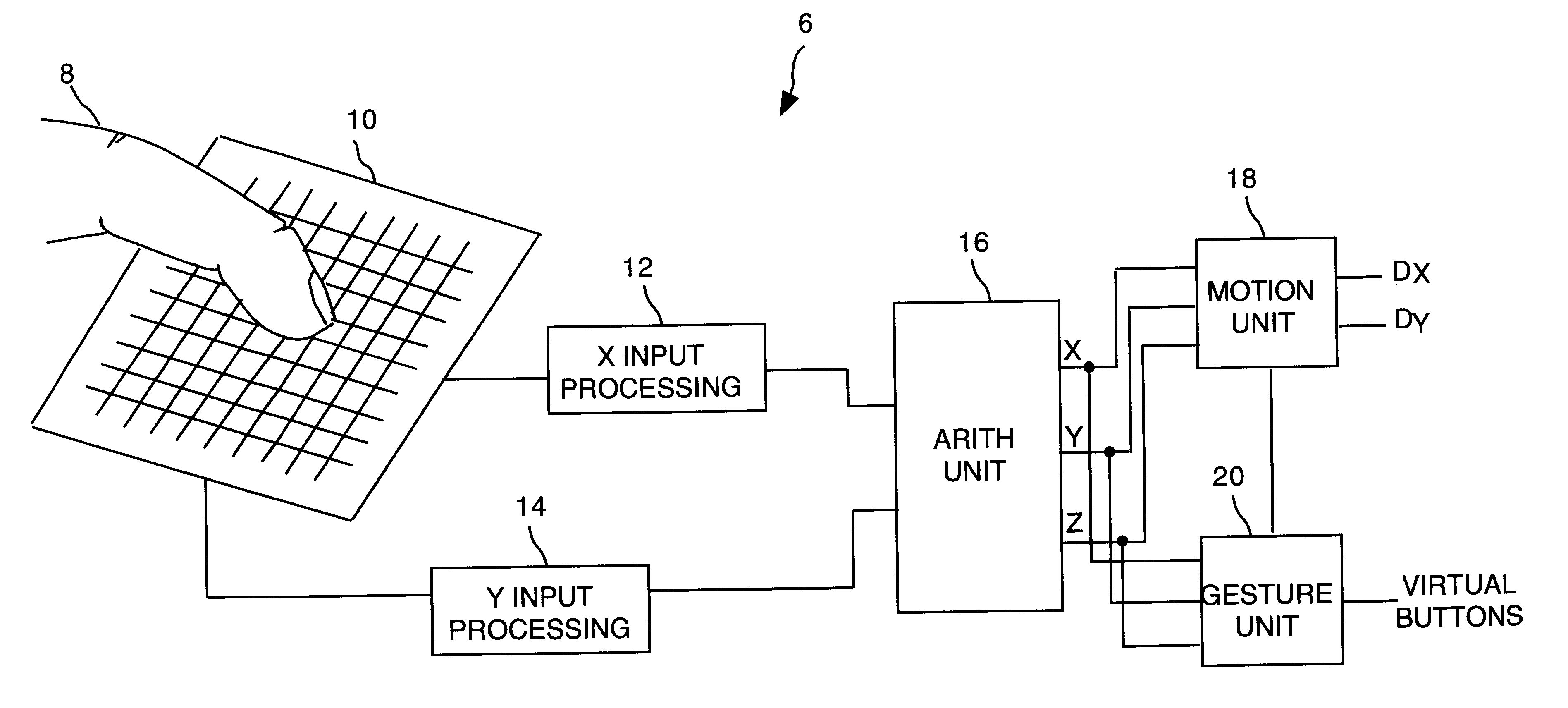
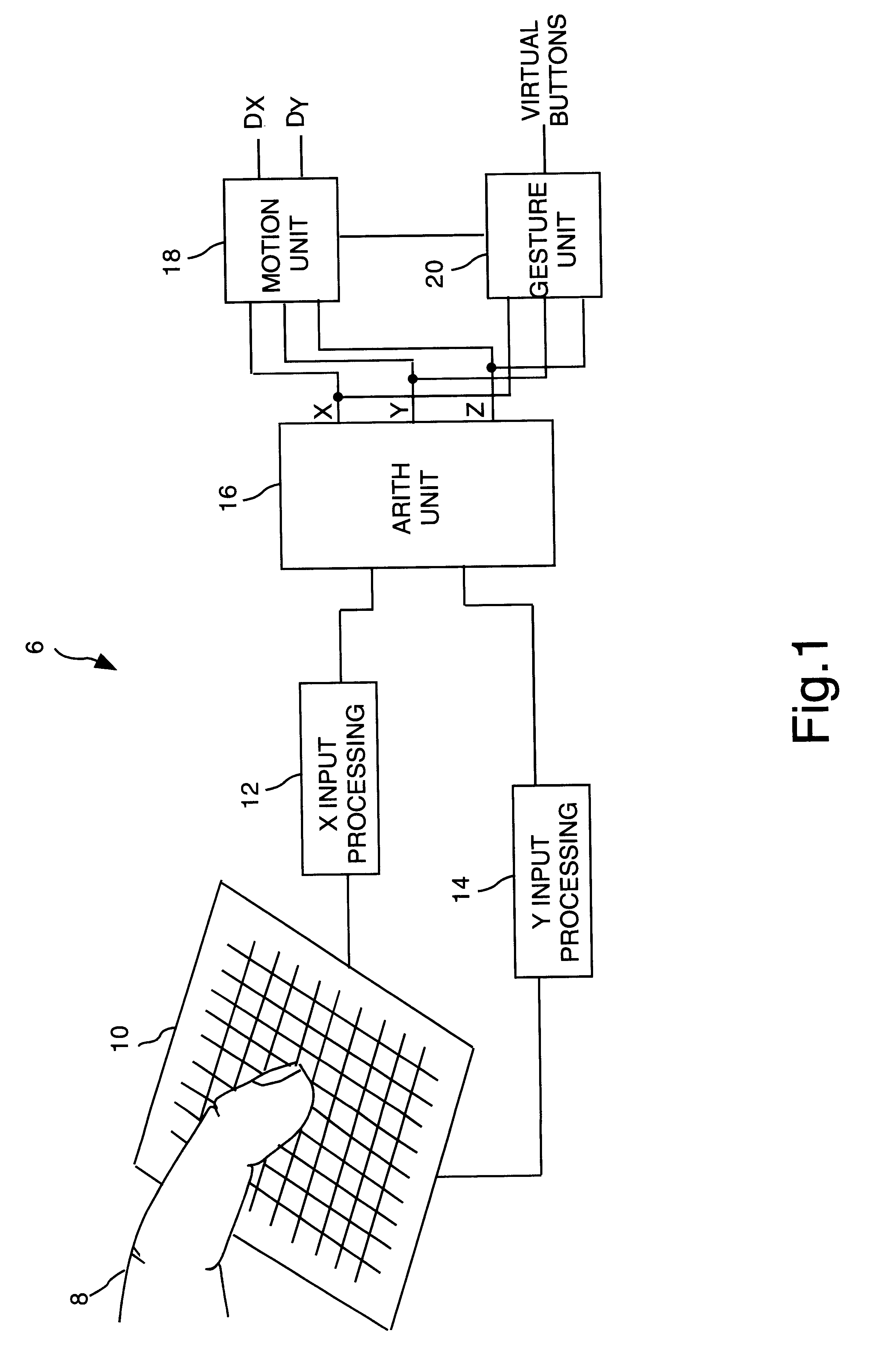
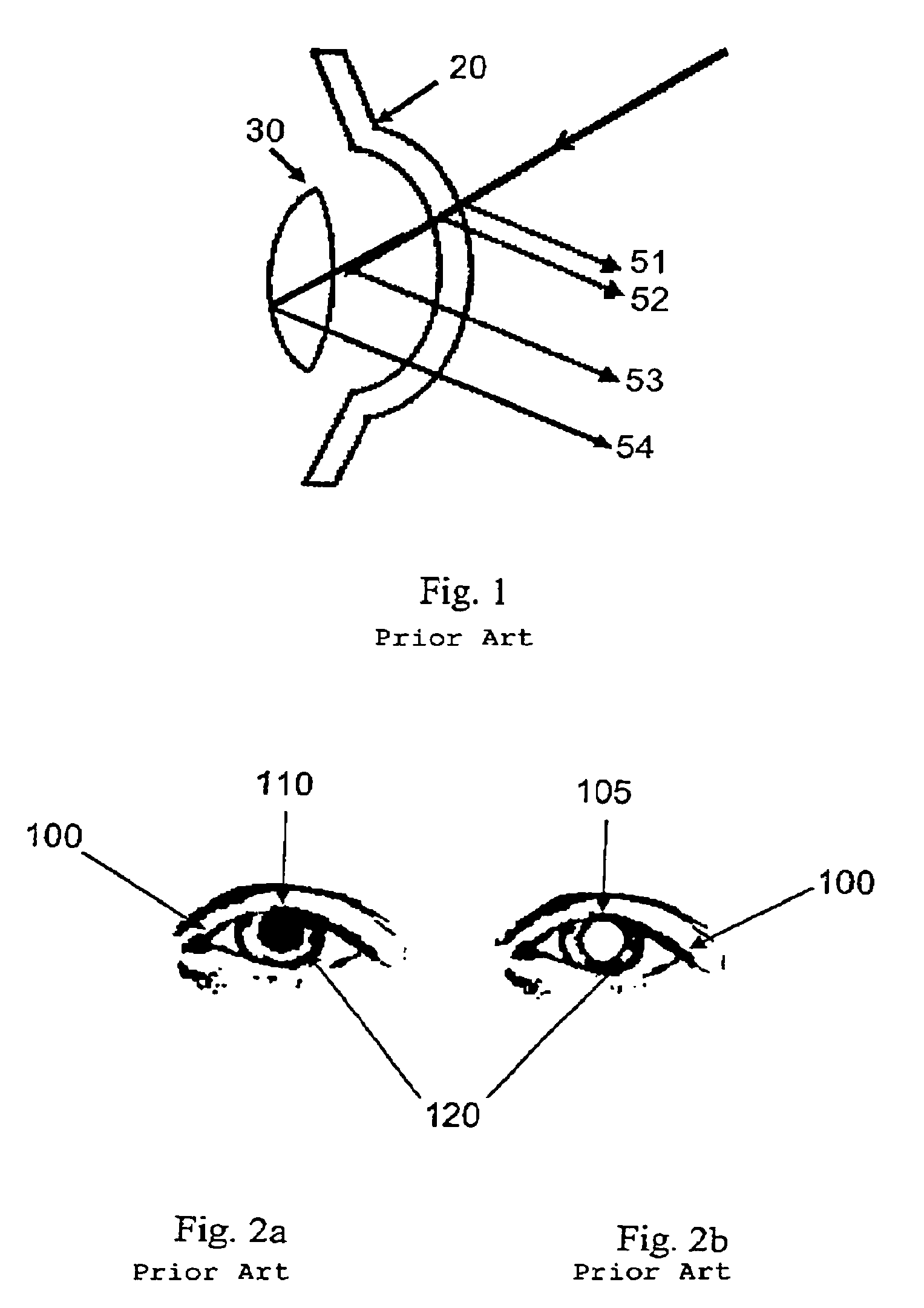
Object position detector with edge motion feature and gesture recognition
InactiveUS6380931B1Easy CalibrationEasy to implementTransmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionGlyphComputer vision
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20070032717A1Cancel noiseImprove convenienceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Biosensor membranes composed of polymers containing heterocyclic nitrogens
InactiveUS20050241957A1Easy CalibrationConsider sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteNitrogen
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
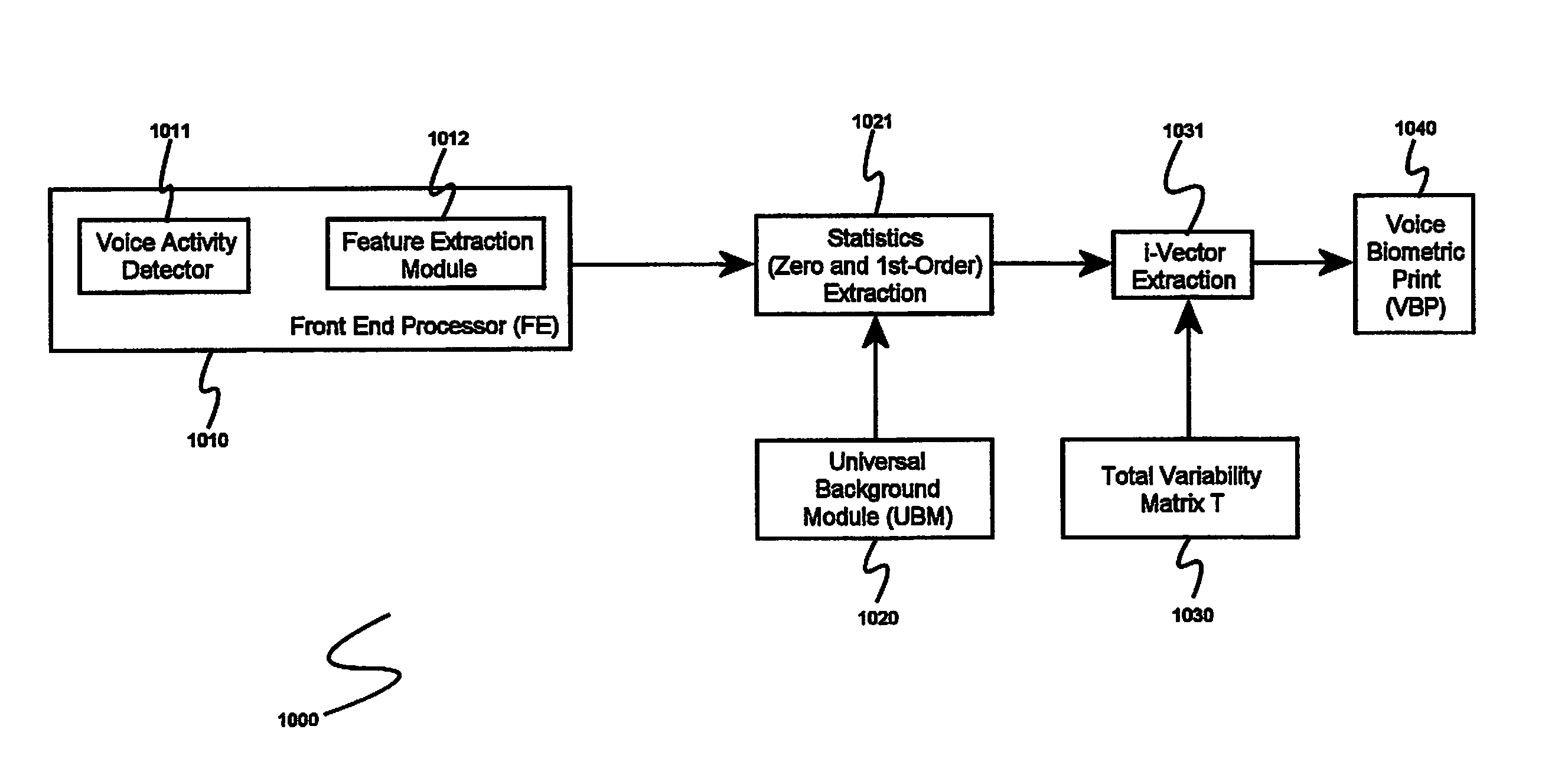
System and method for speaker recognition on mobile devices
InactiveUS20130225128A1Reduce storageReduce processUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsSpeaker recognition systemMobile device
A speaker recognition system for authenticating a mobile device user includes an enrollment and learning software module, a voice biometric authentication software module, and a secure software application. Upon request by a user of the mobile device, the enrollment and learning software module displays text prompts to the user, receives speech utterances from the user, and produces a voice biometric print. The enrollment and training software module determines when a voice biometric print has met at least a quality threshold before storing it on the mobile device. The secure software application prompts a user requiring authentication to repeat an utterance based at least on an attribute of a selected voice biometric print, receives a corresponding utterance, requests the voice biometric authentication software module to verify the identity of the second user using the utterance, and, if the user is authenticated, imports the voice biometric print.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Object position detector with edge motion feature and gesture recognition
InactiveUS6028271AEasy CalibrationEasy to implementTransmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionComputer science
Methods for recognizing gestures made by a conductive object on a touch-sensor pad and for cursor motion are disclosed. Tapping, drags, pushes, extended drags and variable drags gestures are recognized by analyzing the position, pressure, and movement of the conductive object on the sensor pad during the time of a suspected gesture, and signals are sent to a host indicating the occurrence of these gestures. Signals indicating the position of a conductive object and distinguishing between the peripheral portion and an inner portion of the touch-sensor pad are also sent to the host.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
InactiveUS20100185071A1Noise-free signalImprove convenienceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteGlucose sensors
Owner:DEXCOM
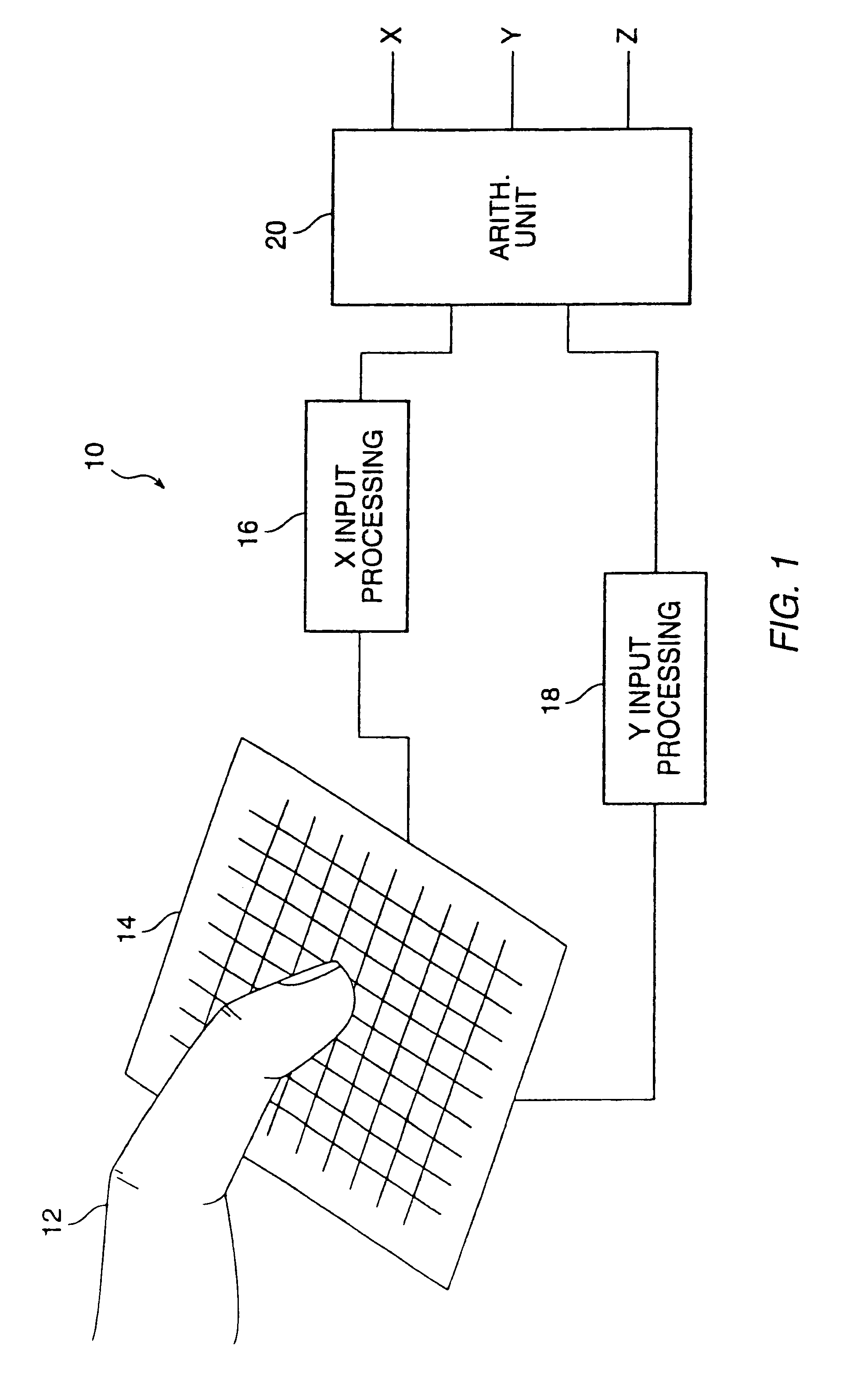
Object position detection system and method
InactiveUS6239389B1Effective positioningEasy CalibrationTransmission systemsDigital data processing detailsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A proximity sensor system includes a sensor matrix array having a characteristic capacitance on horizontal and vertical conductors connected to sensor pads. The capacitance changes as a function of the proximity of an object or objects to the sensor matrix. The change in capacitance of each node in both the X and Y directions of the matrix due to the approach of an object is converted to a set of voltages in the X and Y directions. These voltages are processed by digital circuitry to develop electrical signals representative of the centroid of the profile of the object, i.e, its position in the X and Y dimensions. Noise reduction and background level setting techniques inherently available in the architecture are employed.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
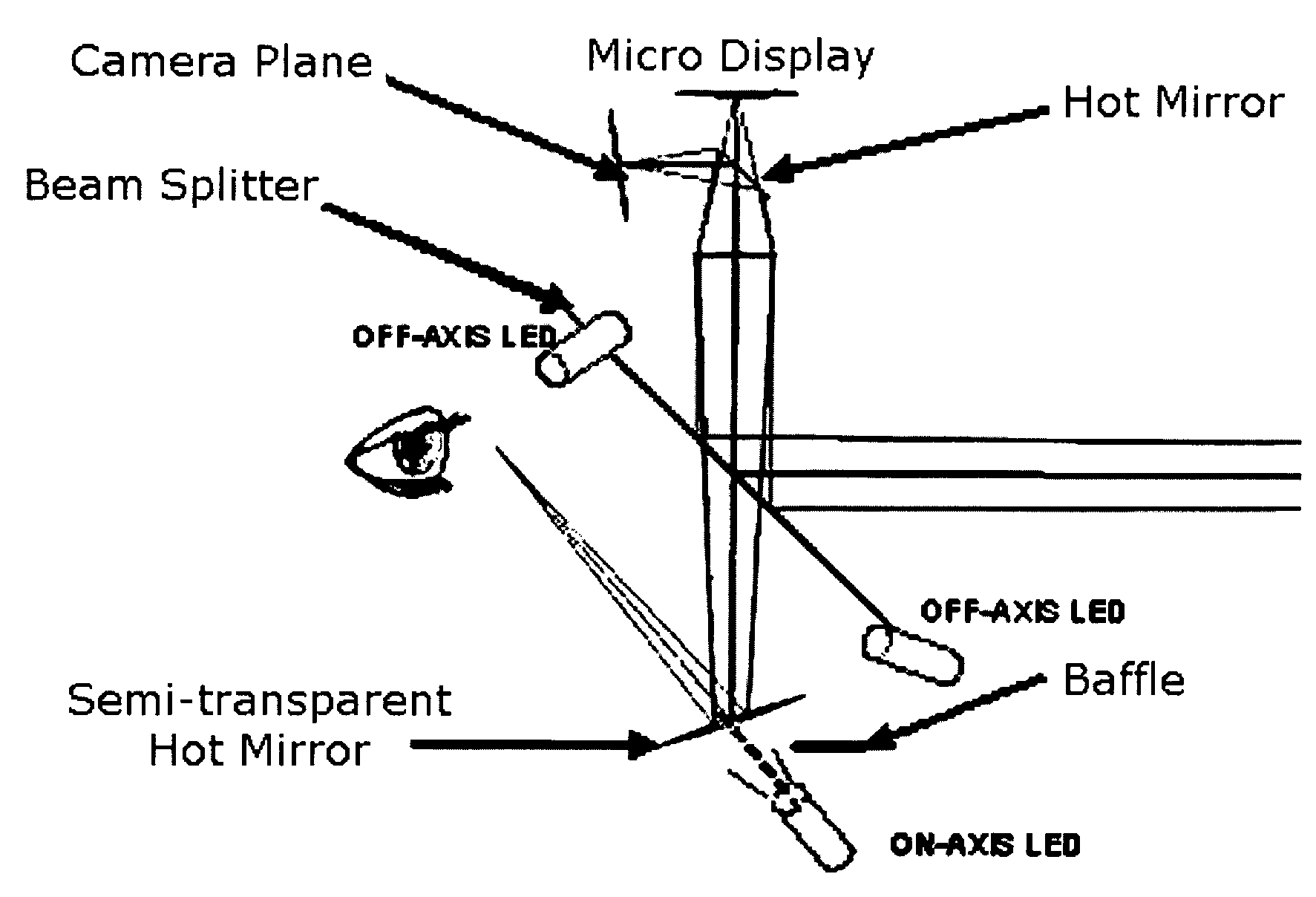
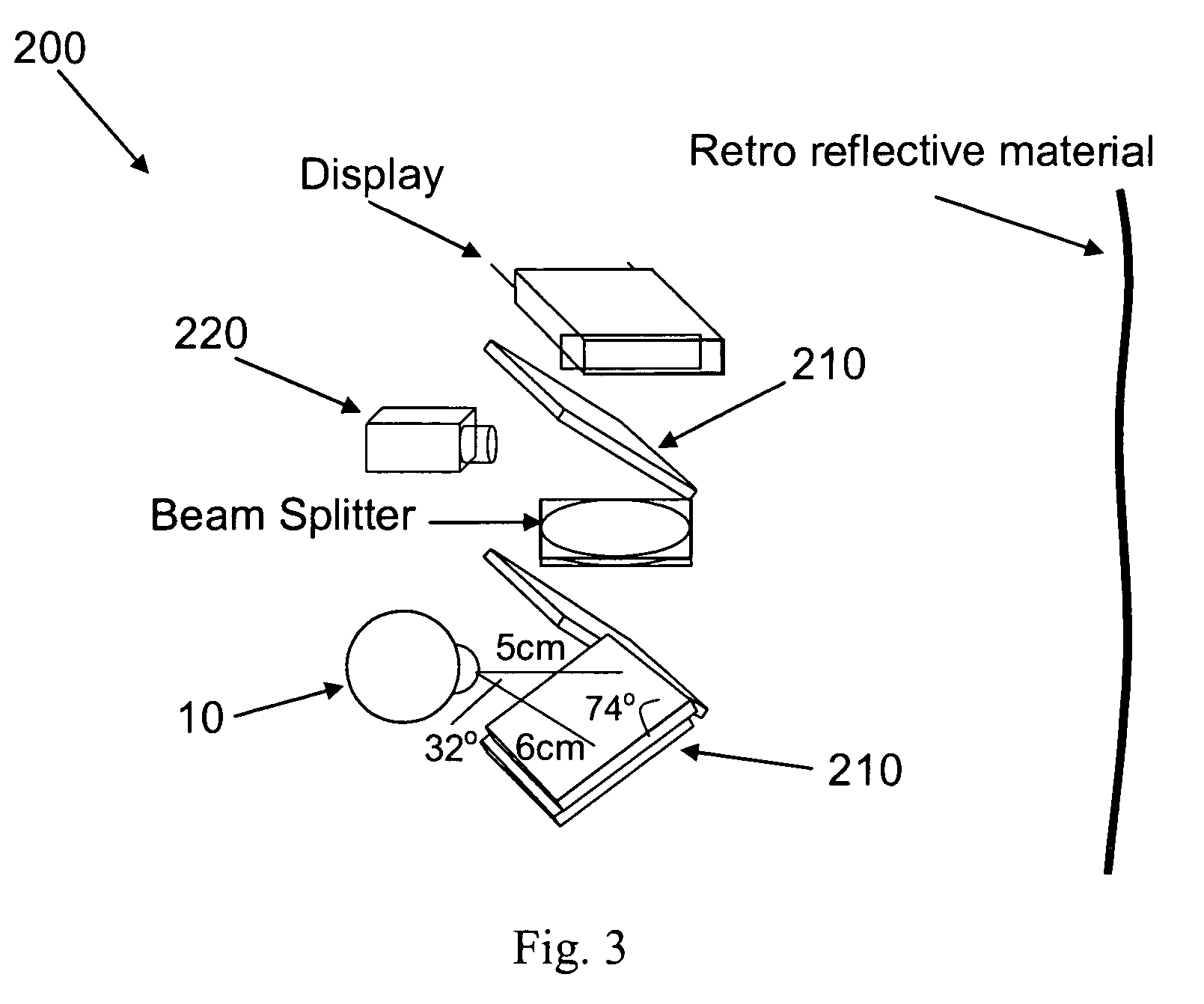
Projection-based head-mounted display with eye-tracking capabilities
ActiveUS7522344B1Reduce weightImprove balanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingOptical pathHead worn display
Methods, systems, apparatus and devices for the lens design of an HMPD with eye-tracking capabilities. The integration uses a low-level optical configuration in order to achieve a compact, comfortable, easy-to-use system. The optical system is further designed and optimized for sharing of the optical path between the HMD and the Eye-Tracker with minimal performance loss for both tasks.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20070027384A1Cancel noiseImprove convenienceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
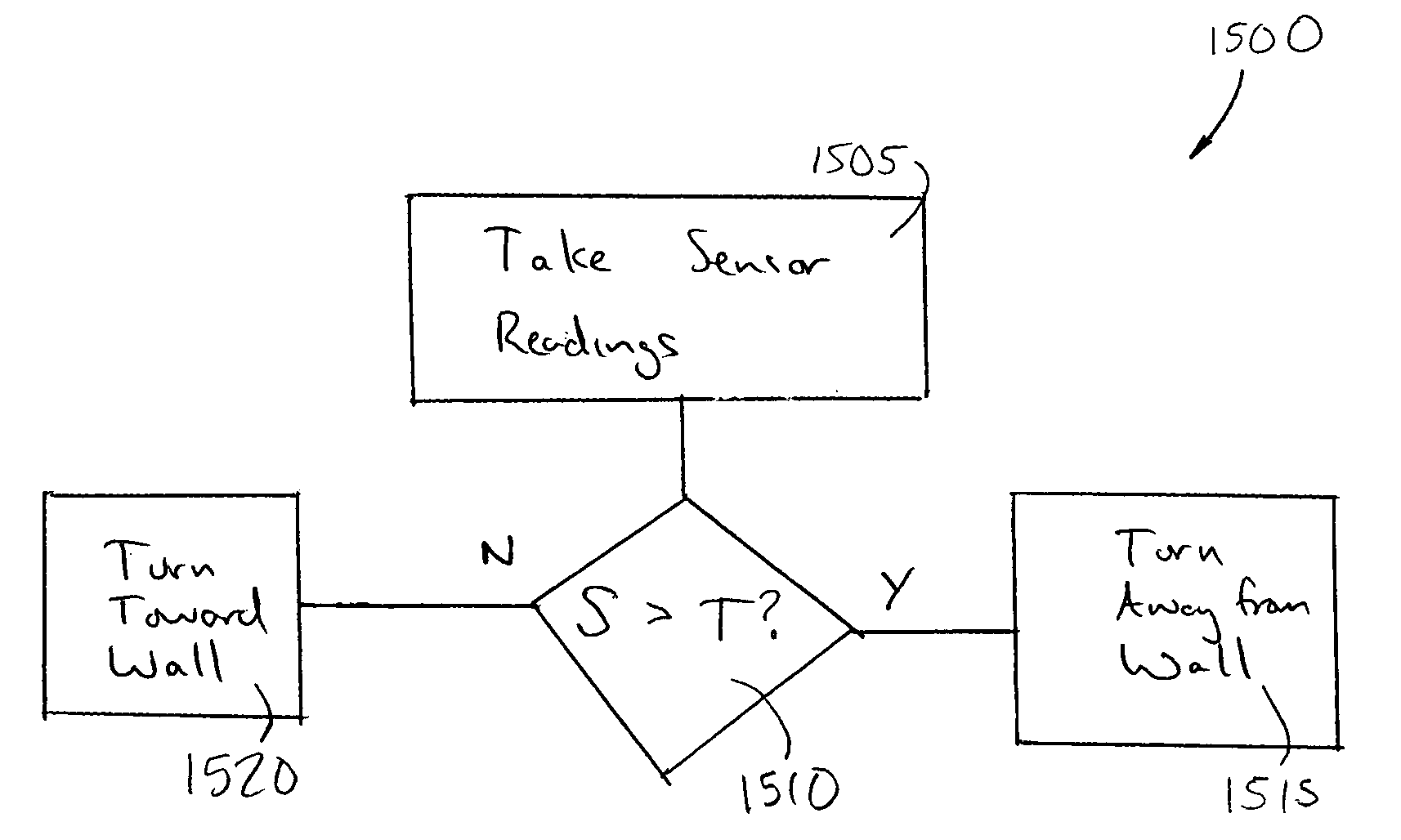
Obstacle following sensor scheme for a mobile robot
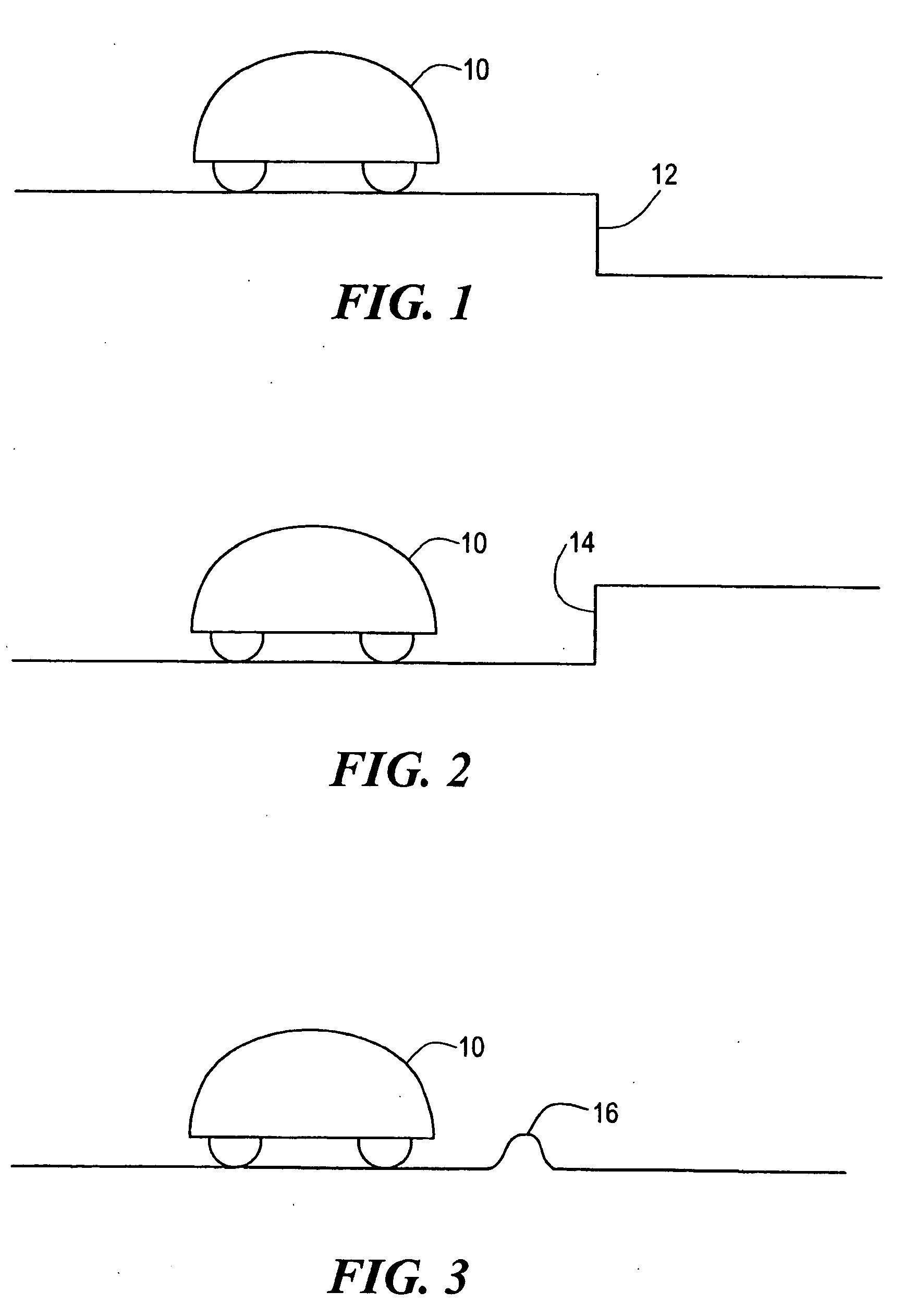
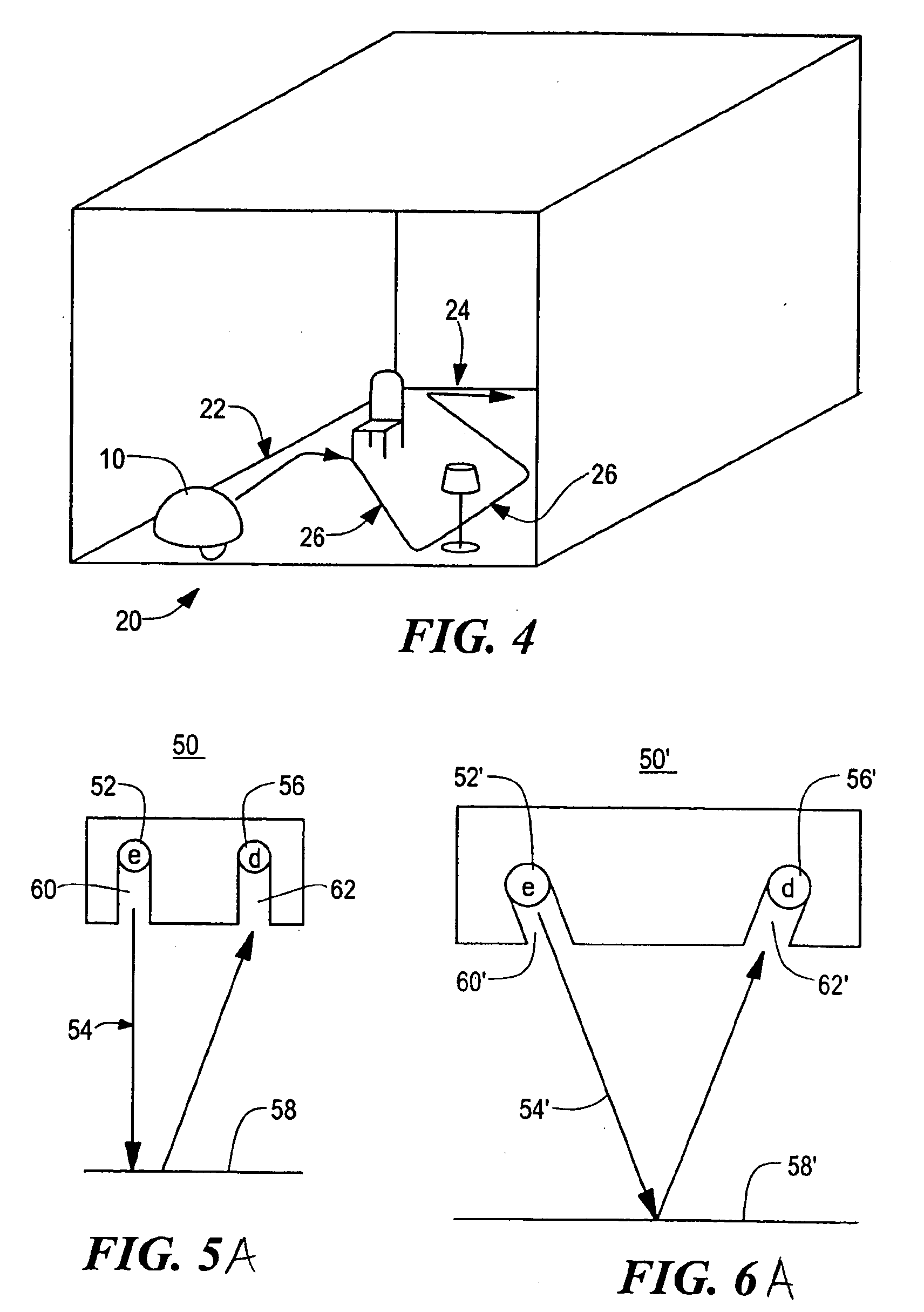
ActiveUS20050251292A1Simple designLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutomatic obstacle detectionProximateEngineering
A robot obstacle detection system including a robot housing which navigates with respect to a surface and a sensor subsystem aimed at the surface for detecting the surface. The sensor subsystem includes an emitter which emits a signal having a field of emission and a photon detector having a field of view which intersects the field of emission at a region. The subsystem detects the presence of an object proximate the mobile robot and determines a value of a signal corresponding to the object. It compares the value to a predetermined value, moves the mobile robot in response to the comparison, and updates the predetermined value upon the occurrence of an event.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
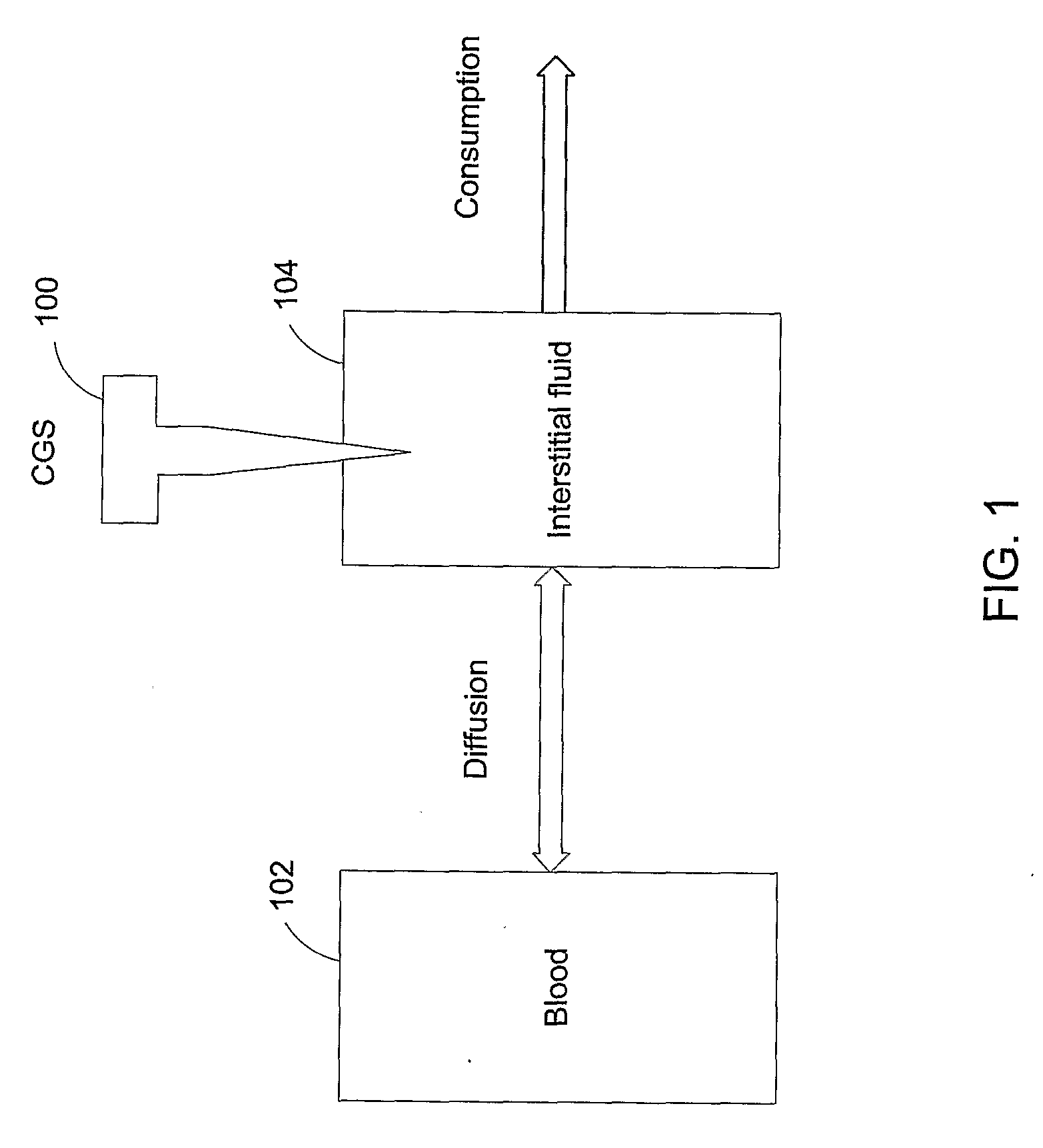
Accuracy of Continuous Glucose Sensors
InactiveUS20080314395A1Improve accuracy and reliabilityEasy CalibrationSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsComputer science
A method, apparatus, and a kit are capable of improving accuracy of CGS devices using dynamic outputs of continuous glucose sensors.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20070093704A1Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Modular hybrid snake arm
ActiveUS20080302200A1Reduced arm manufacturing costImprove work performanceMechanical apparatusJointsModularitySimulation
An intelligent modular hybrid robot arm system is usable with mobile robots, and is applicable to stationary industrial arms. The intelligent modular hybrid robot arm system provides a large work envelope and a controlled and directed rotational movement for a flexible snake robot arm. The intelligent modular hybrid robot arm system has the ability to change end effector tools and sensors. The platform computers have the ability to interact with other subsystems for coordinated as well as independent tasks. The flexibly snake robot arm can be covered with a flexible sensor network, or “skin”. The intelligent modular hybrid robot arm system can manage its energy use, stores the arm in a compact shape and uses a central support tube offering unobstructed arm access to all sectors of its working envelope.
Owner:CYCOGS
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS7831287B2Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Automatic object extraction
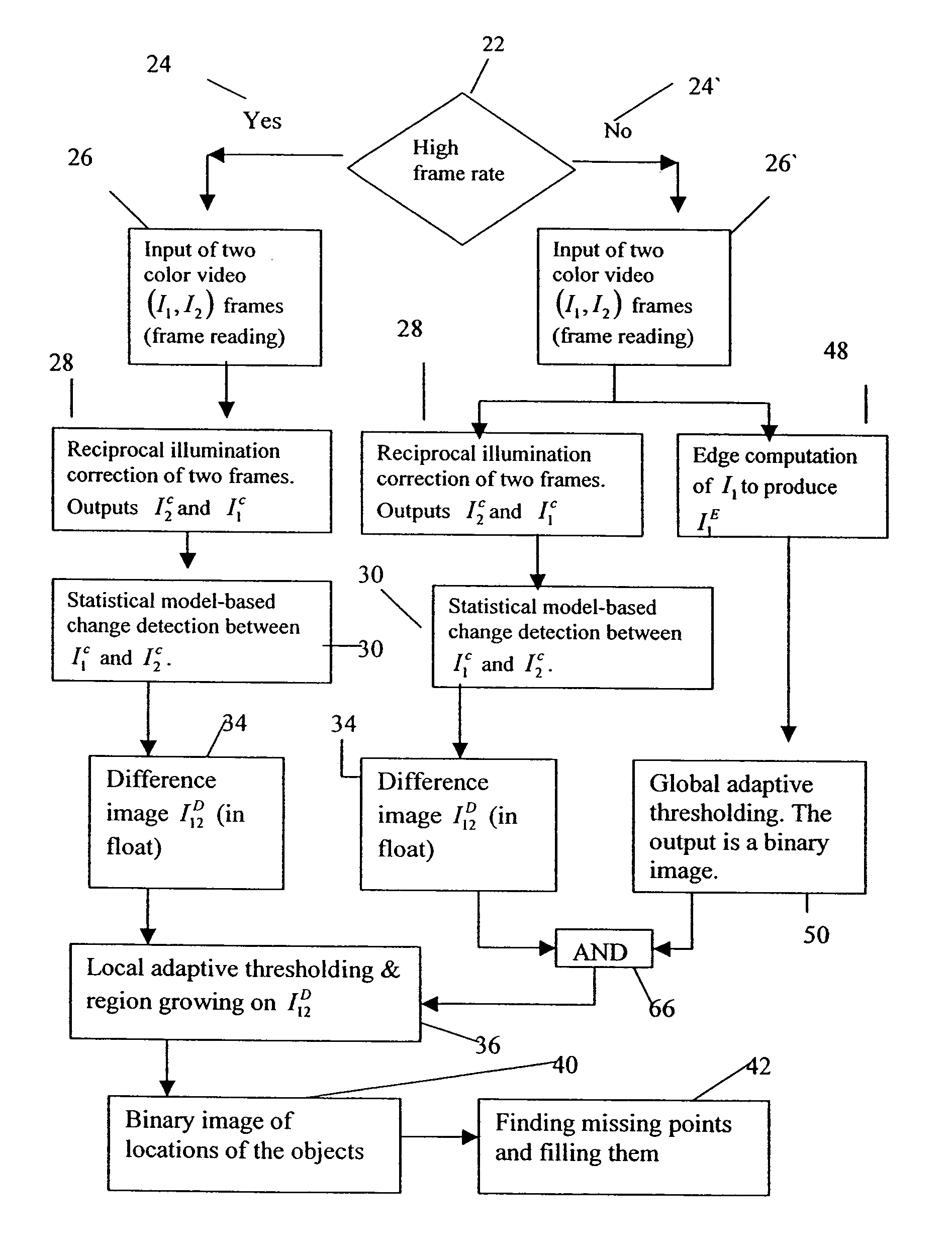
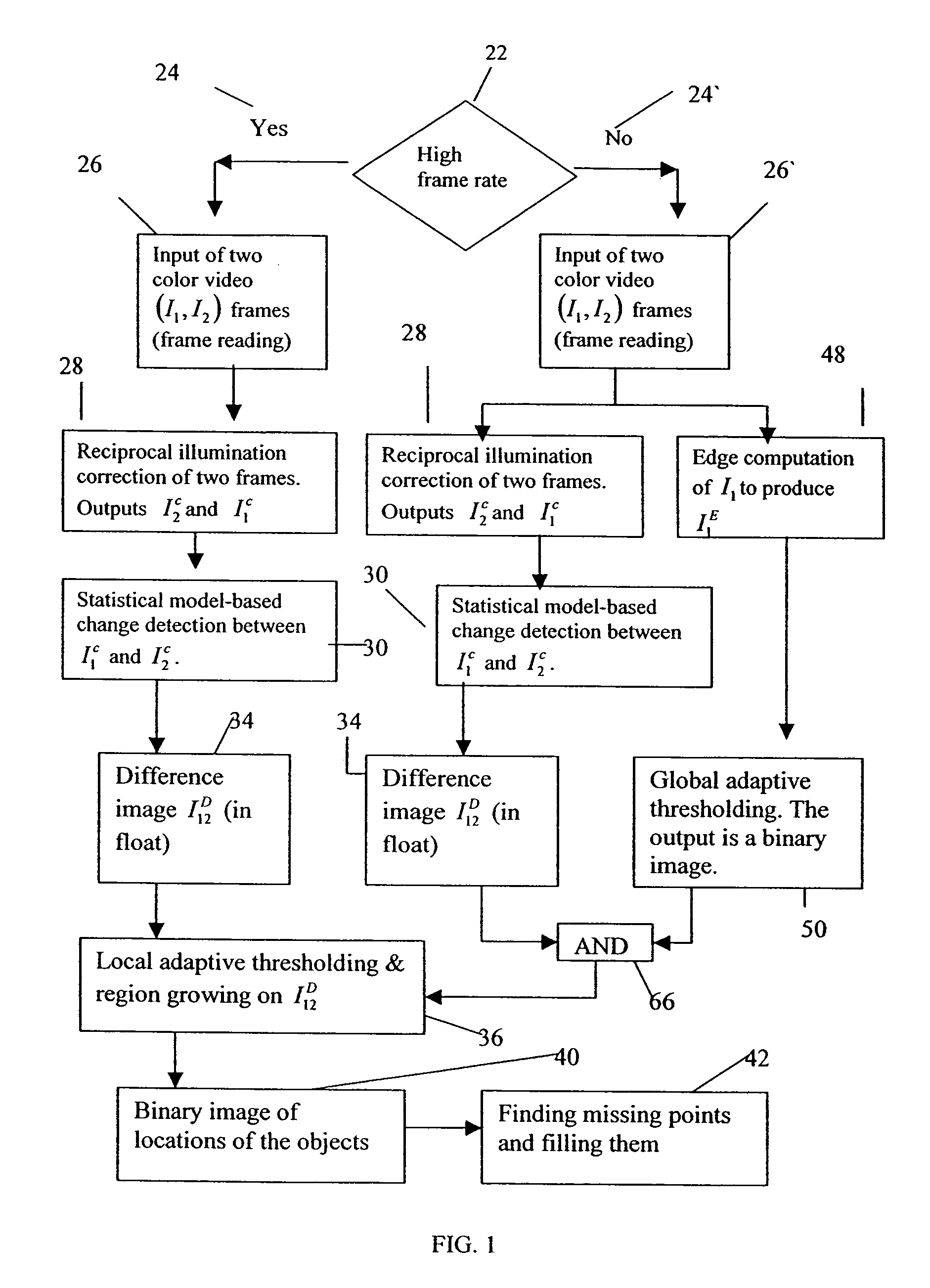
ActiveUS7085401B2Poor exposureQuality degradationImage enhancementImage analysisHigh rateBinary image
A method for automatic, stable and robust object extraction of moving objects in color video frames, achieved without any prior knowledge of the video content. For high rate video, the method includes providing at least a first and a second high frame rate video frames, performing a reciprocal illumination correction of the first and second video frames to yield respective first and second smoothed frames, performing a change detection operation between the first and second smoothed frames to obtain a difference image, and performing a local adaptive thresholding operation on the difference image to generate a binary image containing extracted objects, the local thresholding operation using a weight test to determine a boundary of each of the extracted objects. For an extracted object with a fragmented boundary, the method further comprises re-unifying the boundary. For low rate video, additional steps include: an edge correction applied on the first image to yield a first edge-corrected image, a global thresholding applied to the first edge-corrected image to yield a first binary edge image, and an ANDing operation on the difference image and the first binary edge image to generate a second binary image which is fed to the local adaptive thresholding operation.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
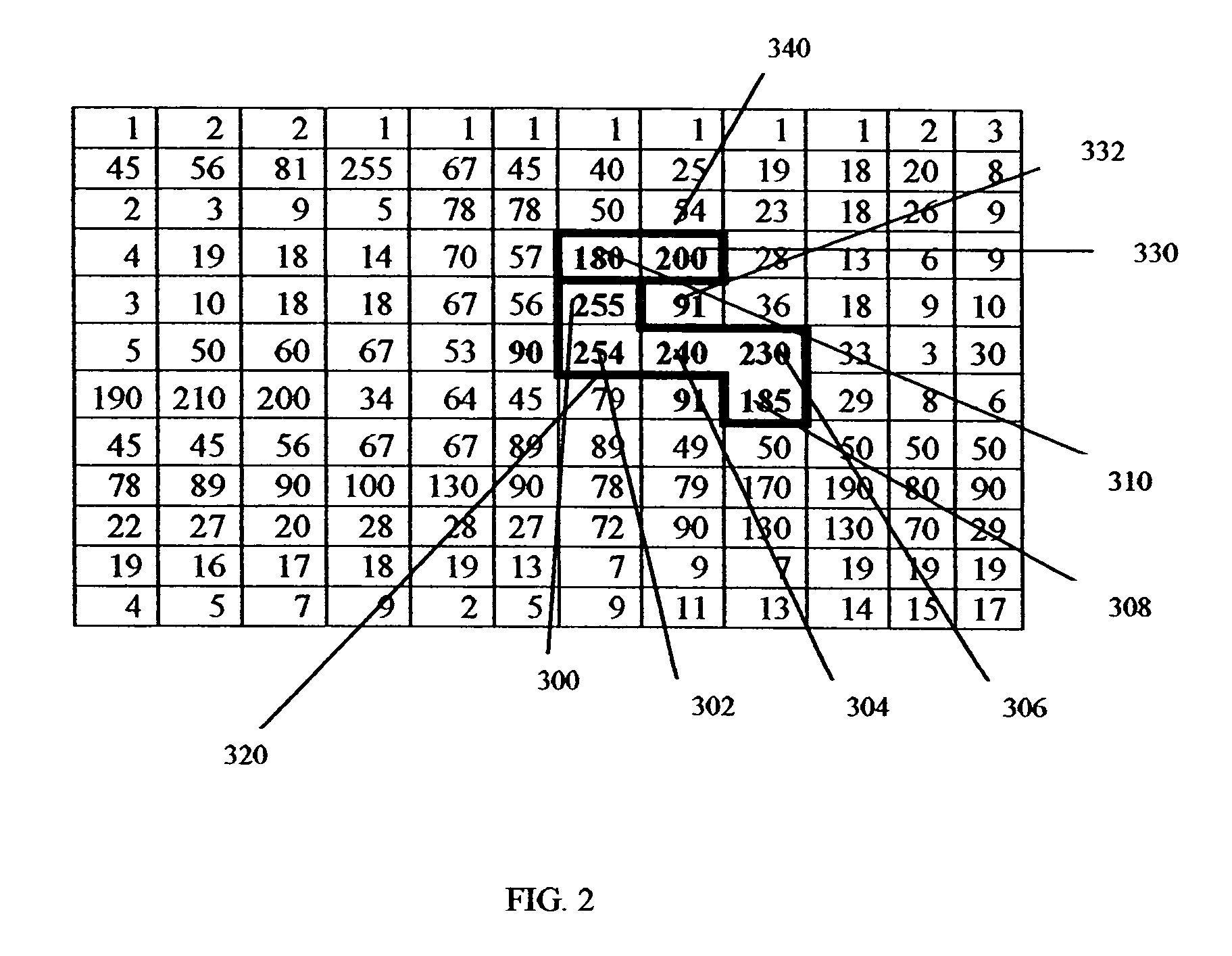
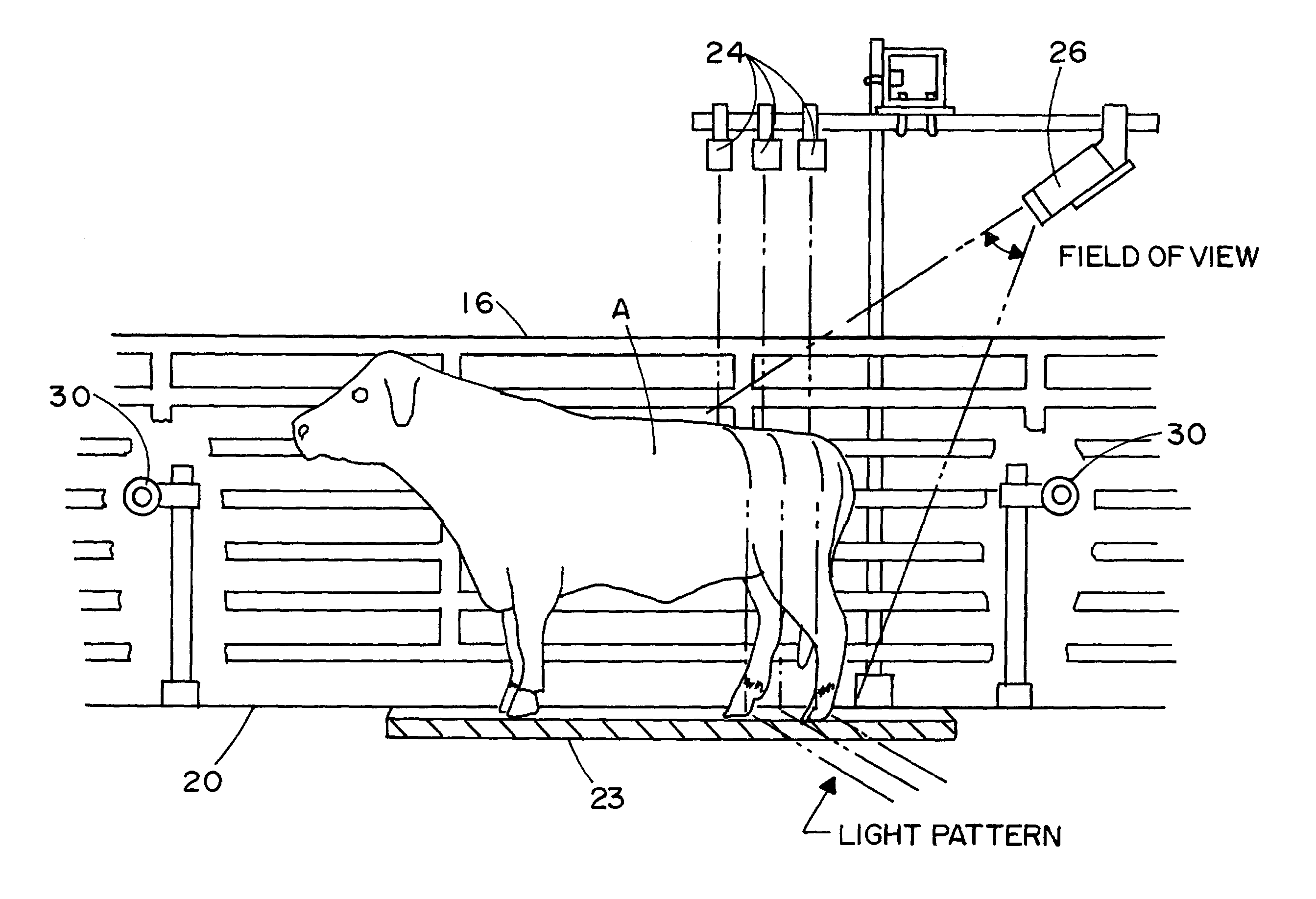
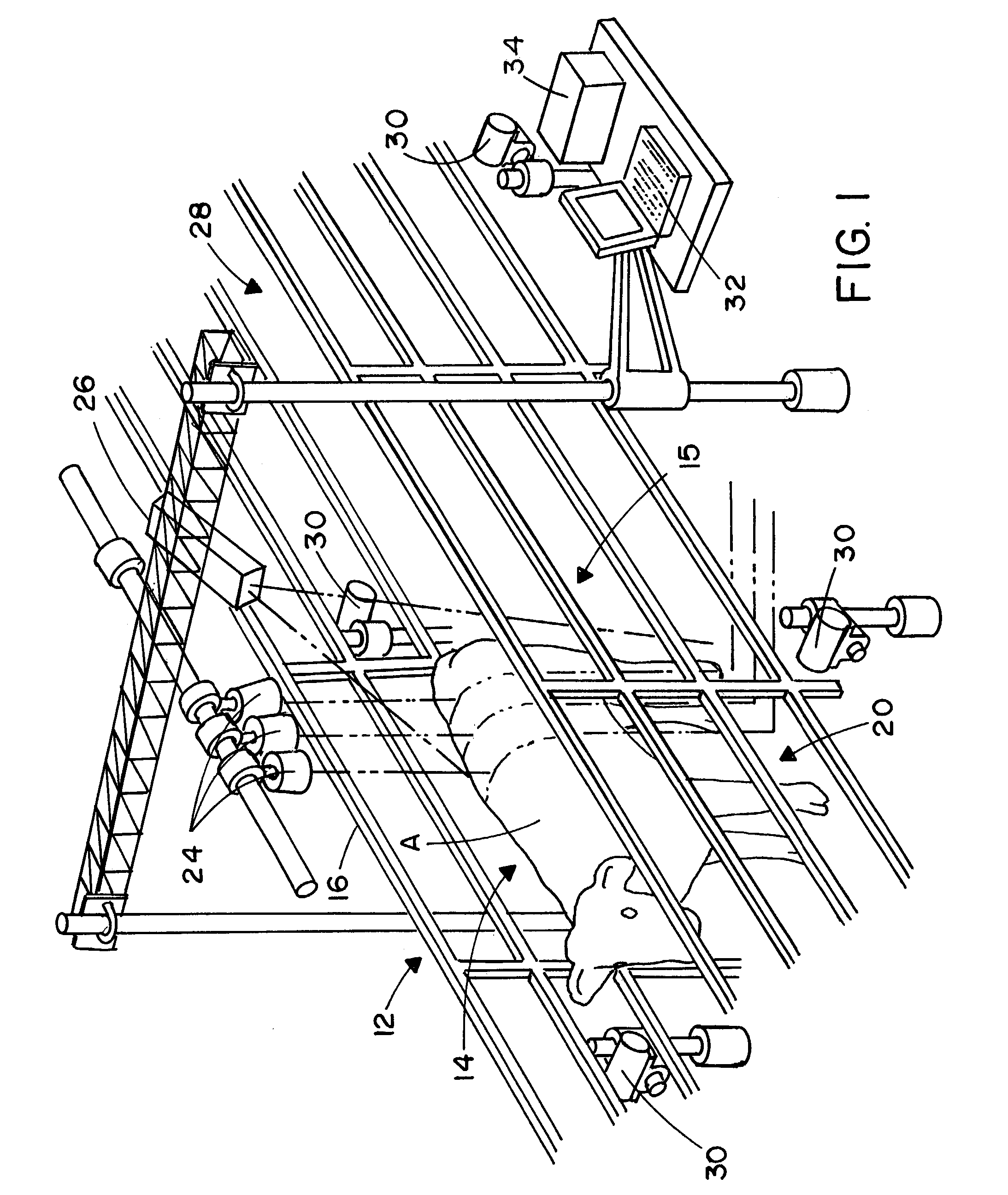
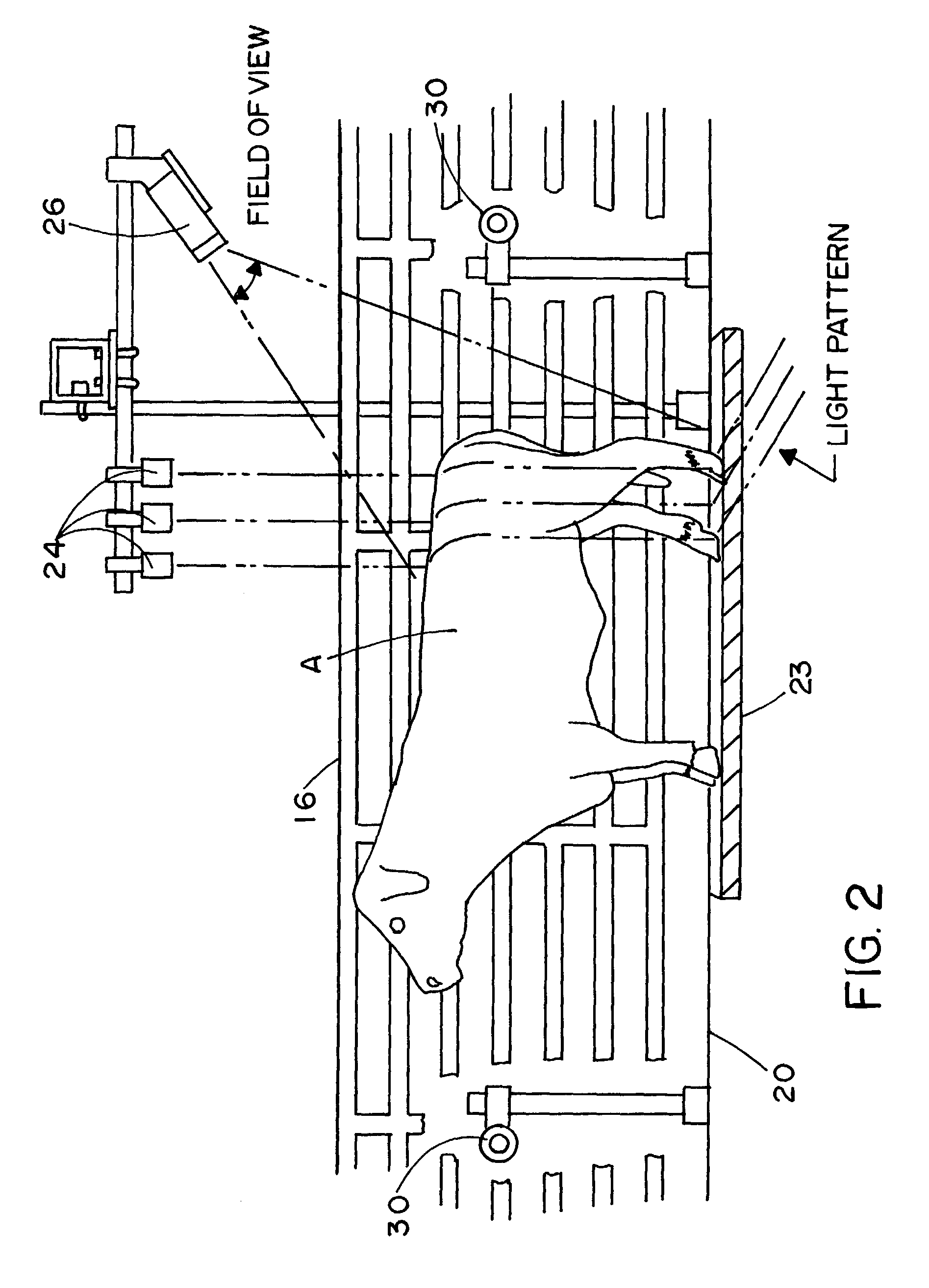
Methods and apparatus for the dimensional measurement of livestock using a single camera
ActiveUS7039220B2Increase speedImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansBiologyLivestock
A method and apparatus for measuring target animals, including livestock animals and full carcasses, and more specifically livestock animals such as cattle and hogs using a single camera system. More particularly, the method of the invention is directed toward obtaining key measurements of the target animal, such as animal weight, animal hip height and animal hip width.
Owner:KALLINA
System for forming an array of emulsions
ActiveUS20110086780A1Easy CalibrationImprove accuracy and reliabilityHeating or cooling apparatusTransportation and packagingEmulsionEngineering
A system, including method and apparatus, for forming an array of emulsions. The system may include a plate providing an array of emulsion production units each configured to produce a separate emulsion and each including a set of wells interconnected by channels that intersect to form a site of droplet generation. Each set of wells, in turn, may include (1) at least one first input well to receive a continuous phase, (2) a second input well to receive a dispersed phase, and (3) an output well configured to receive from the site of droplet generation an emulsion of droplets of the dispersed phase disposed in the continuous phase.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Obstacle following sensor scheme for a mobile robot
InactiveUS7430455B2Simple designLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutomatic obstacle detectionEngineeringField of view
A robot obstacle detection system including a robot housing which navigates with respect to a surface and a sensor subsystem aimed at the surface for detecting the surface. The sensor subsystem includes an emitter which emits a signal having a field of emission and a photon detector having a field of view which intersects the field of emission at a region. The subsystem detects the presence of an object proximate the mobile robot and determines a value of a signal corresponding to the object. It compares the value to a predetermined value, moves the mobile robot in response to the comparison, and updates the predetermined value upon the occurrence of an event.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
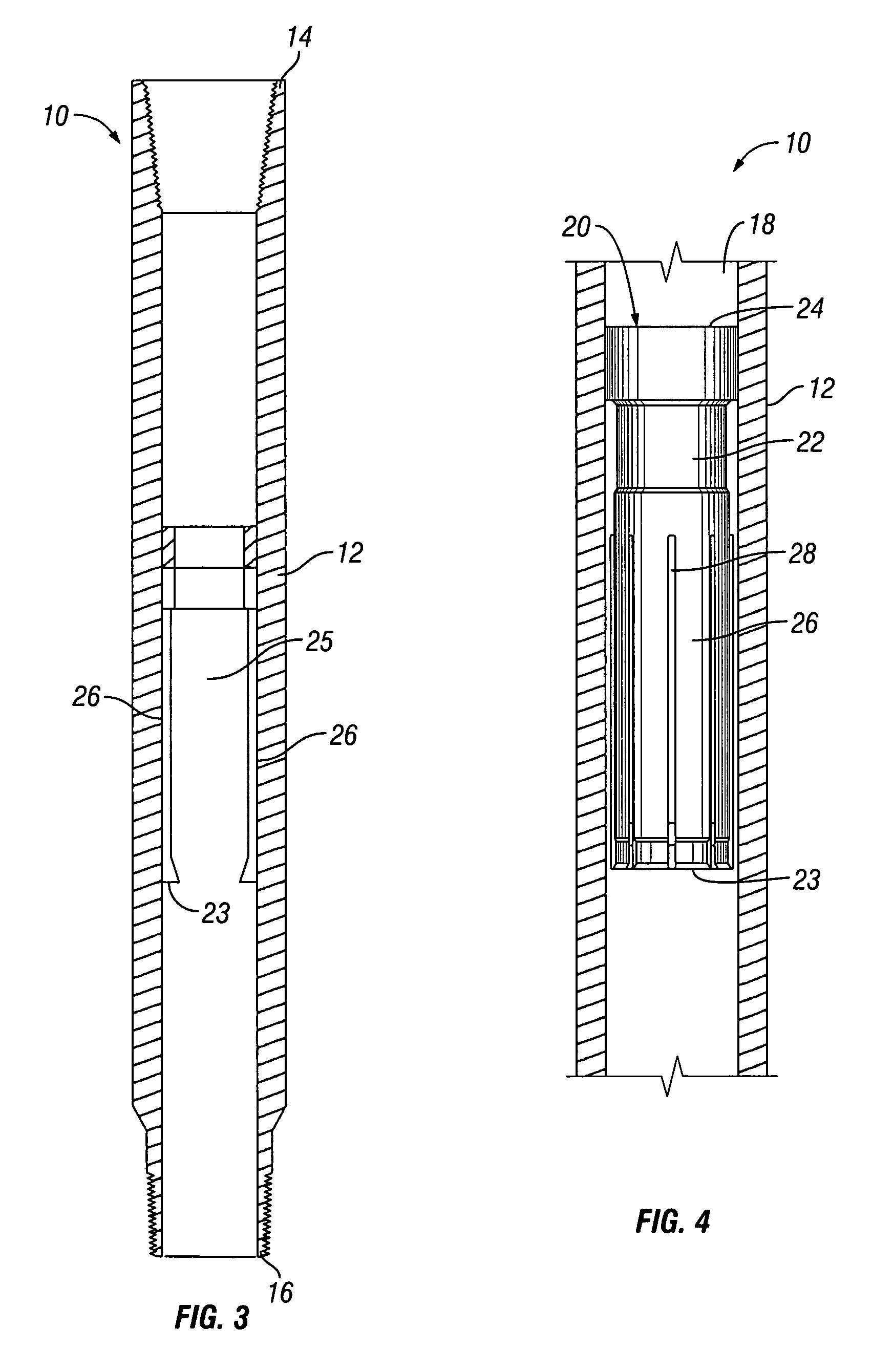
Retractable ball seat having a time delay material
ActiveUS7464764B2Easy CalibrationPromote sportsFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsTime delaysTime segment
Retractable ball seats having a housing, a seat, and a plug such as a ball are disclosed. The seat has a retracted position that prohibits the ball from passing through the passageway and an expanded position that permits the ball to pass through the passageway. A time delay material, such as a dissolvable material, maintains the seat in the retracted position. The time delay material disintegrates, degrades, or dissolves within a known period of time such that the retractable ball seat can be placed in a desired location in the wellbore and the ball will be released through the passageway within a known period of time.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com