Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10582results about "Well/borehole valve arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
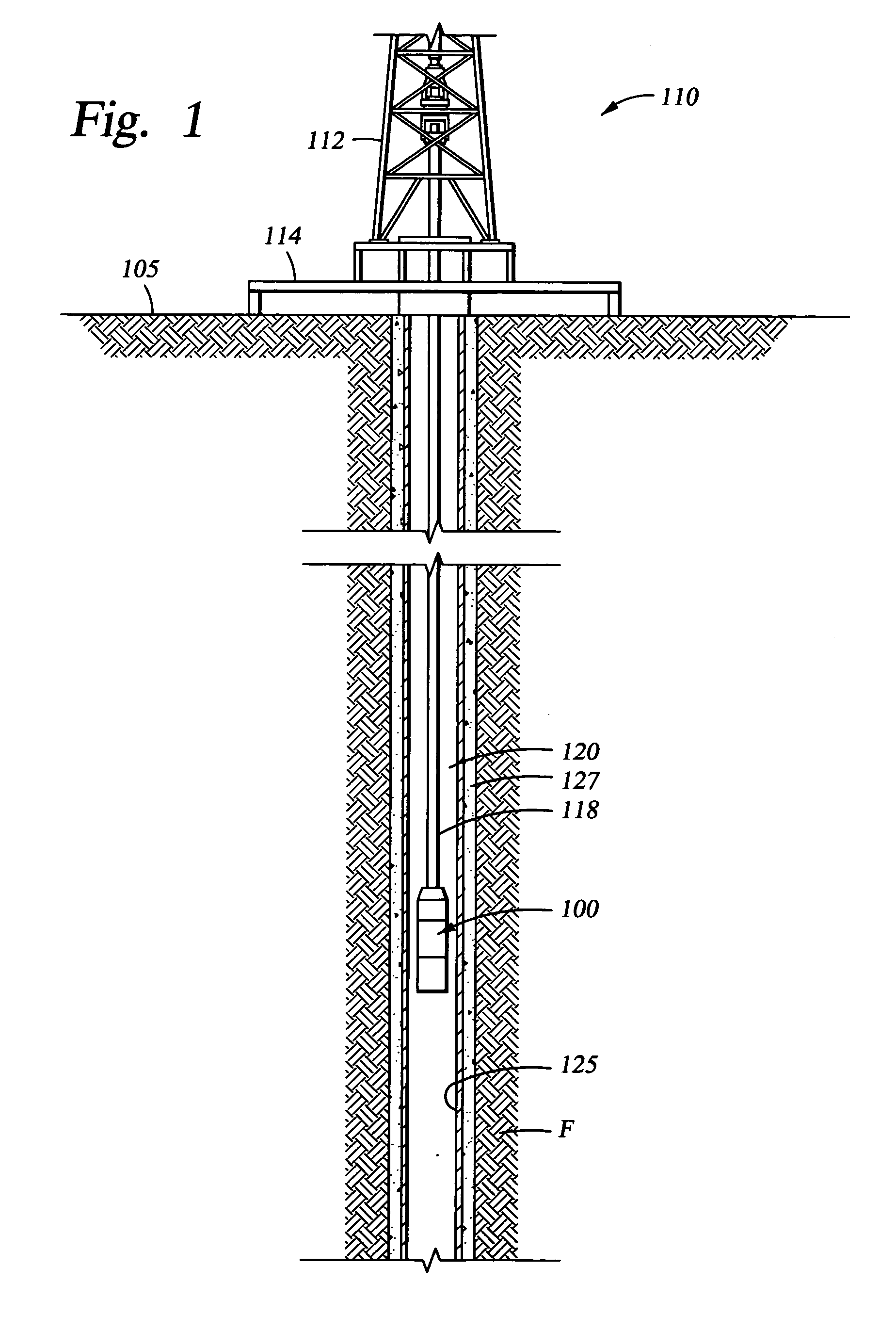
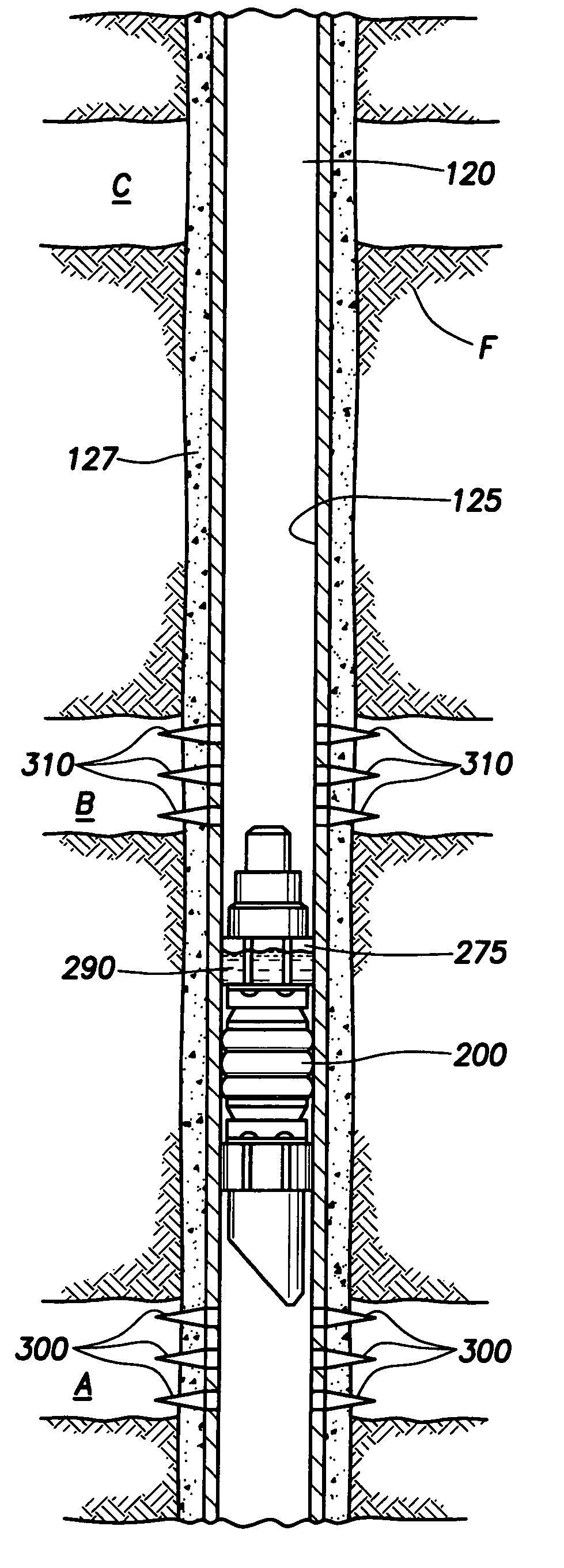
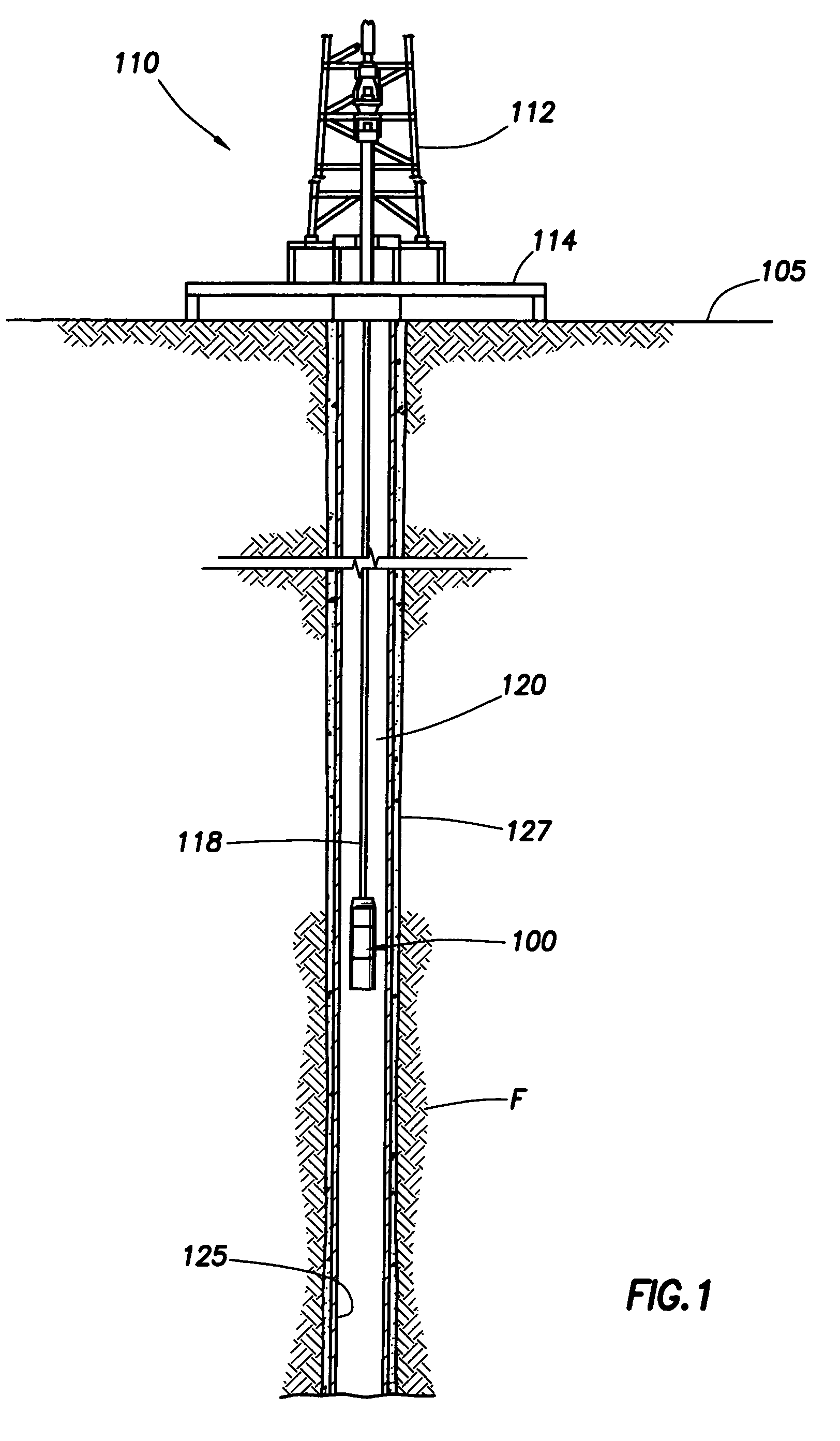
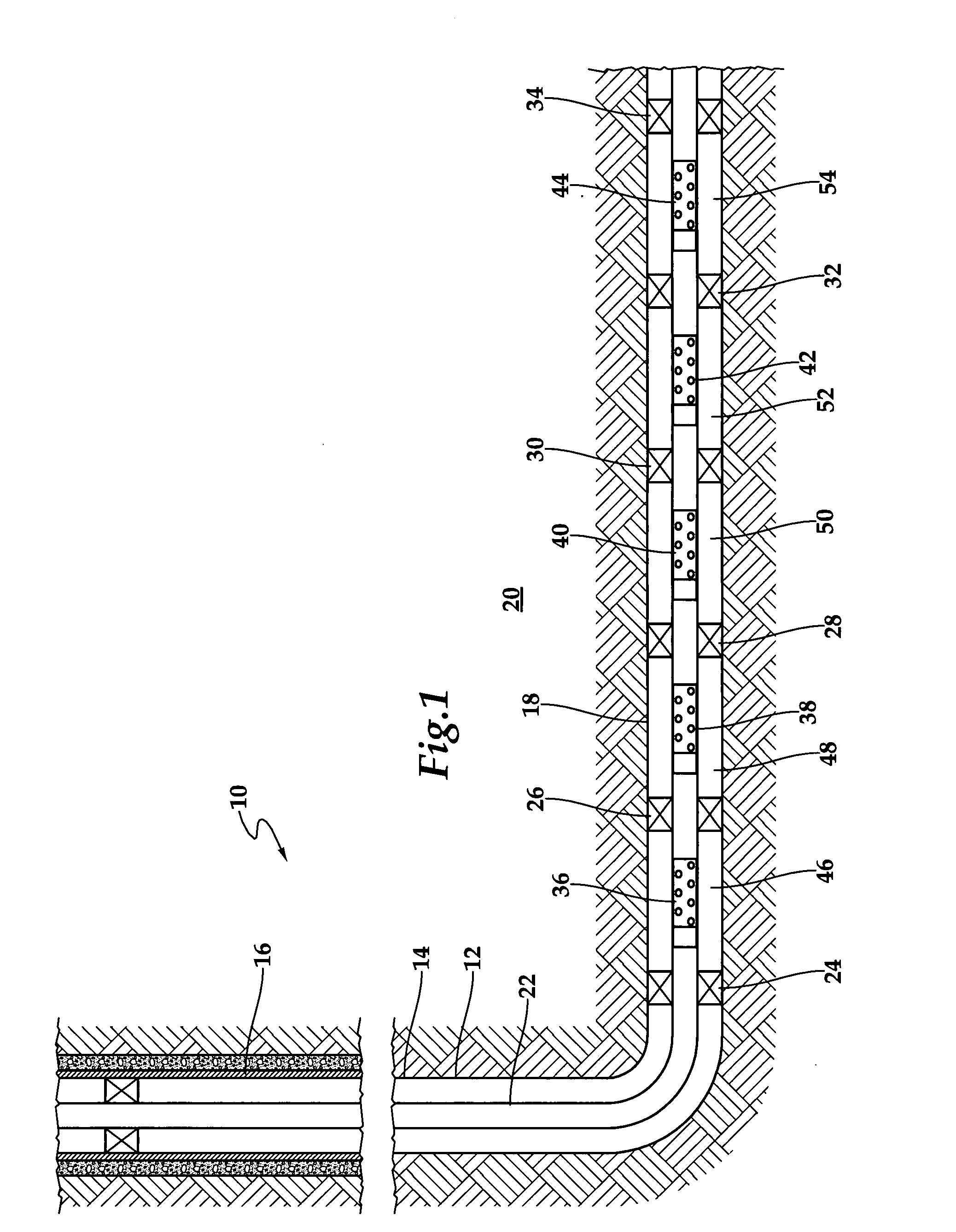
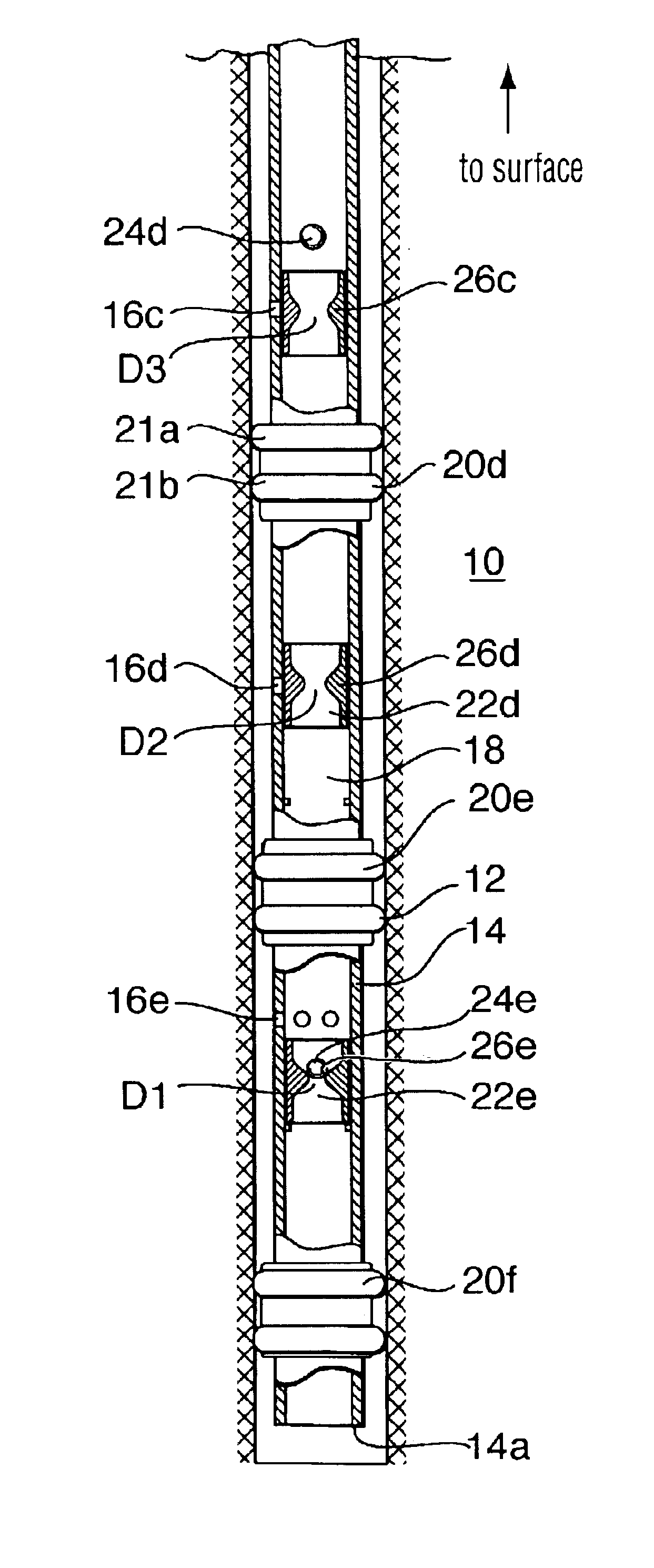
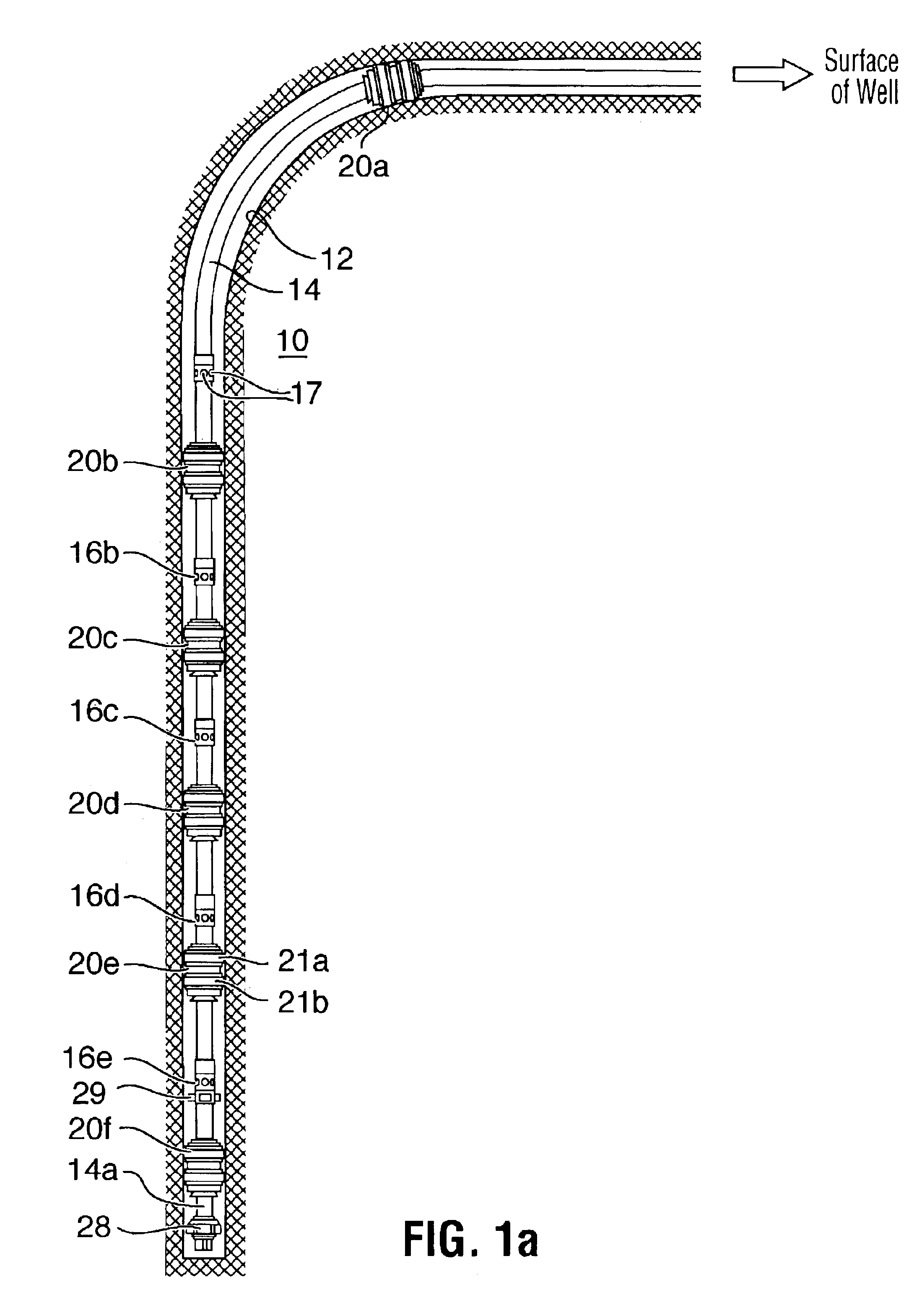
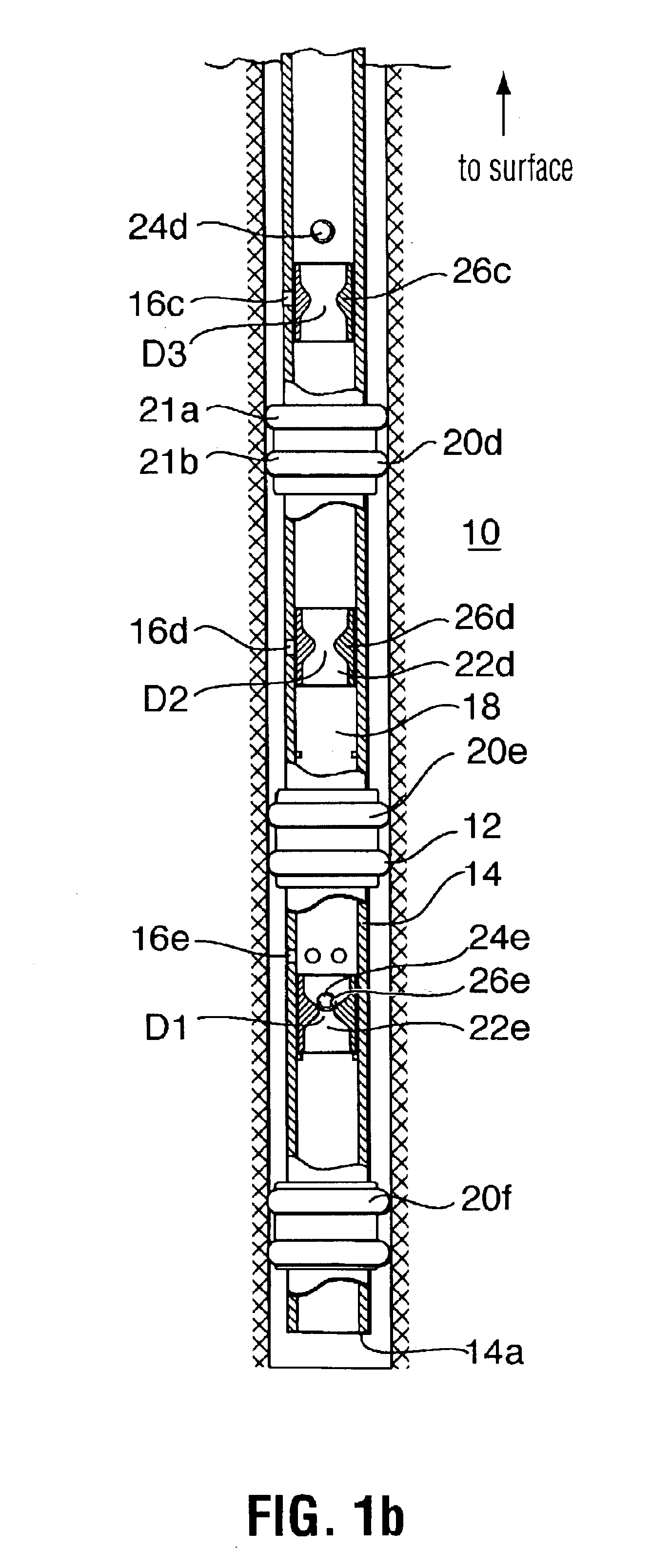
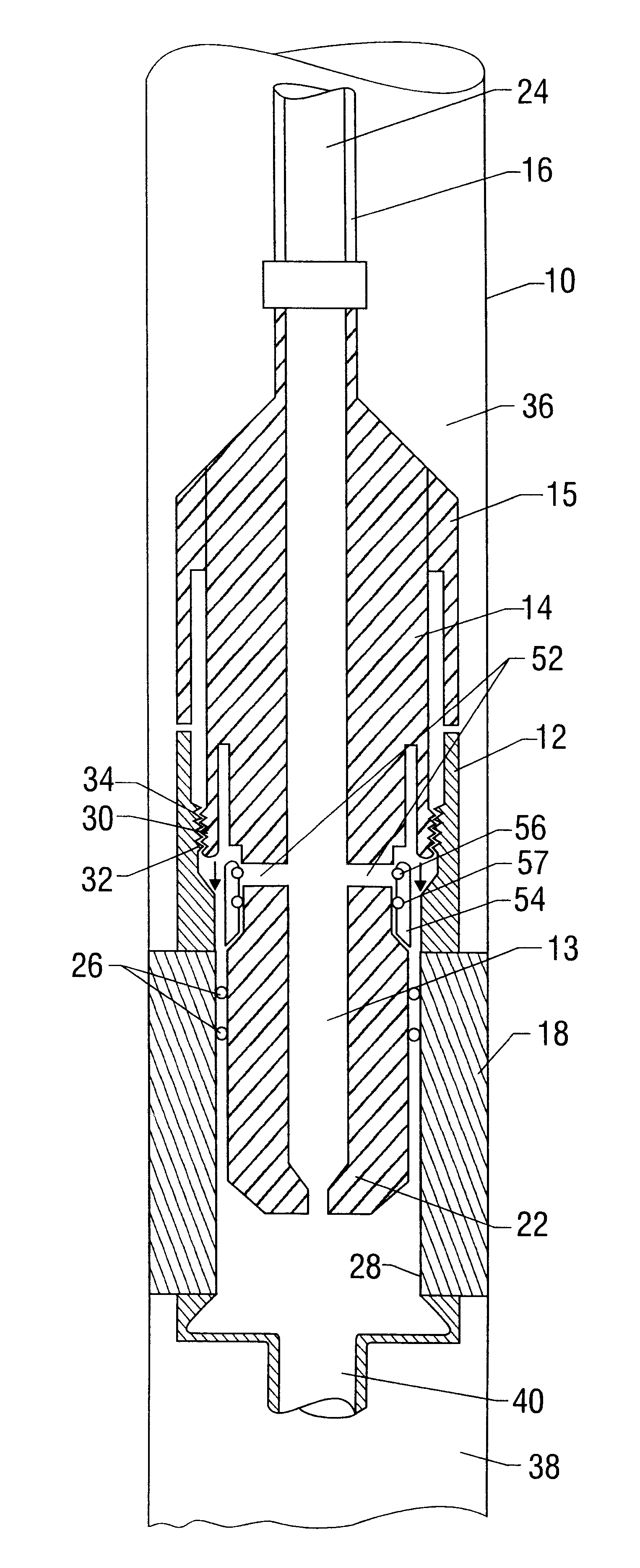
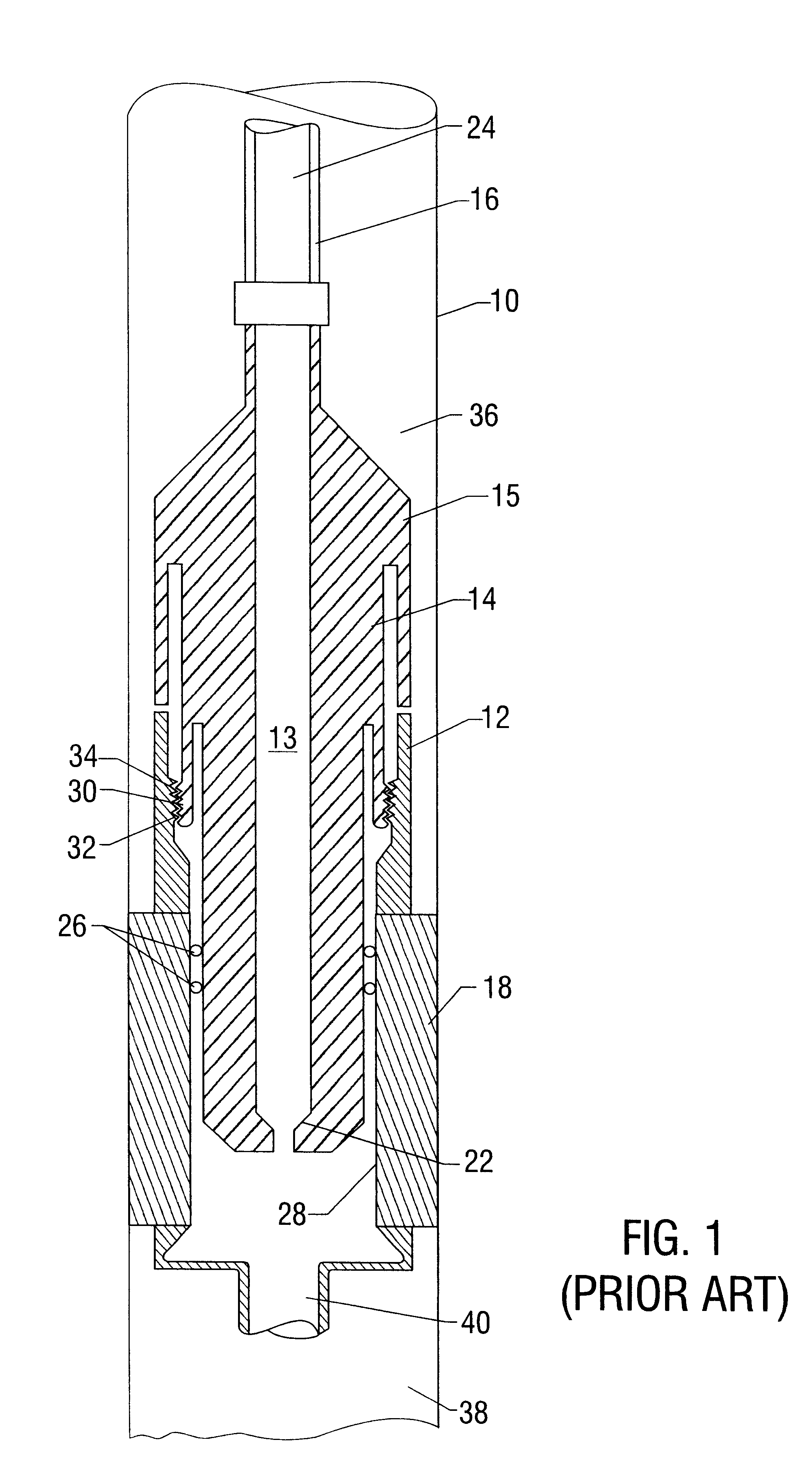
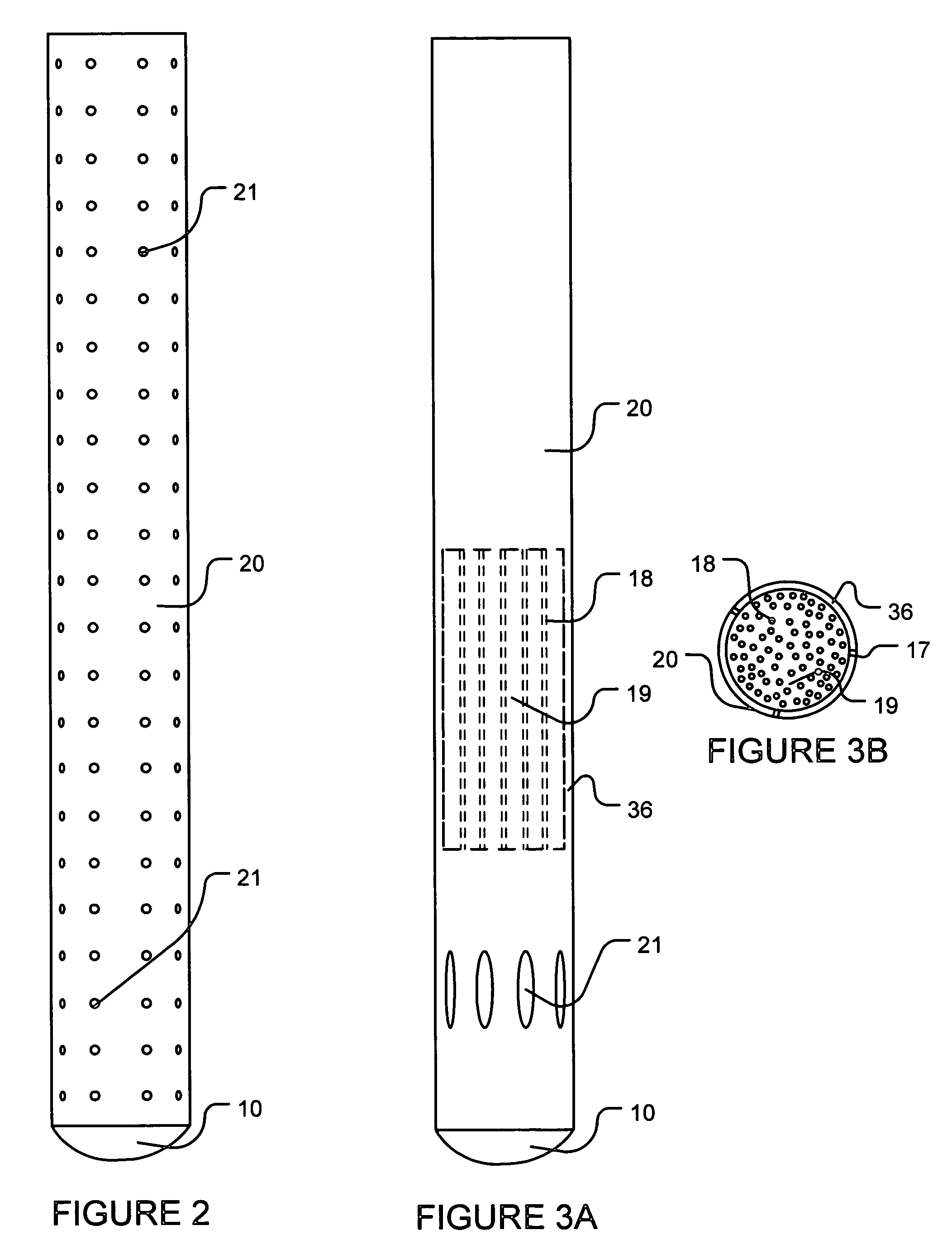
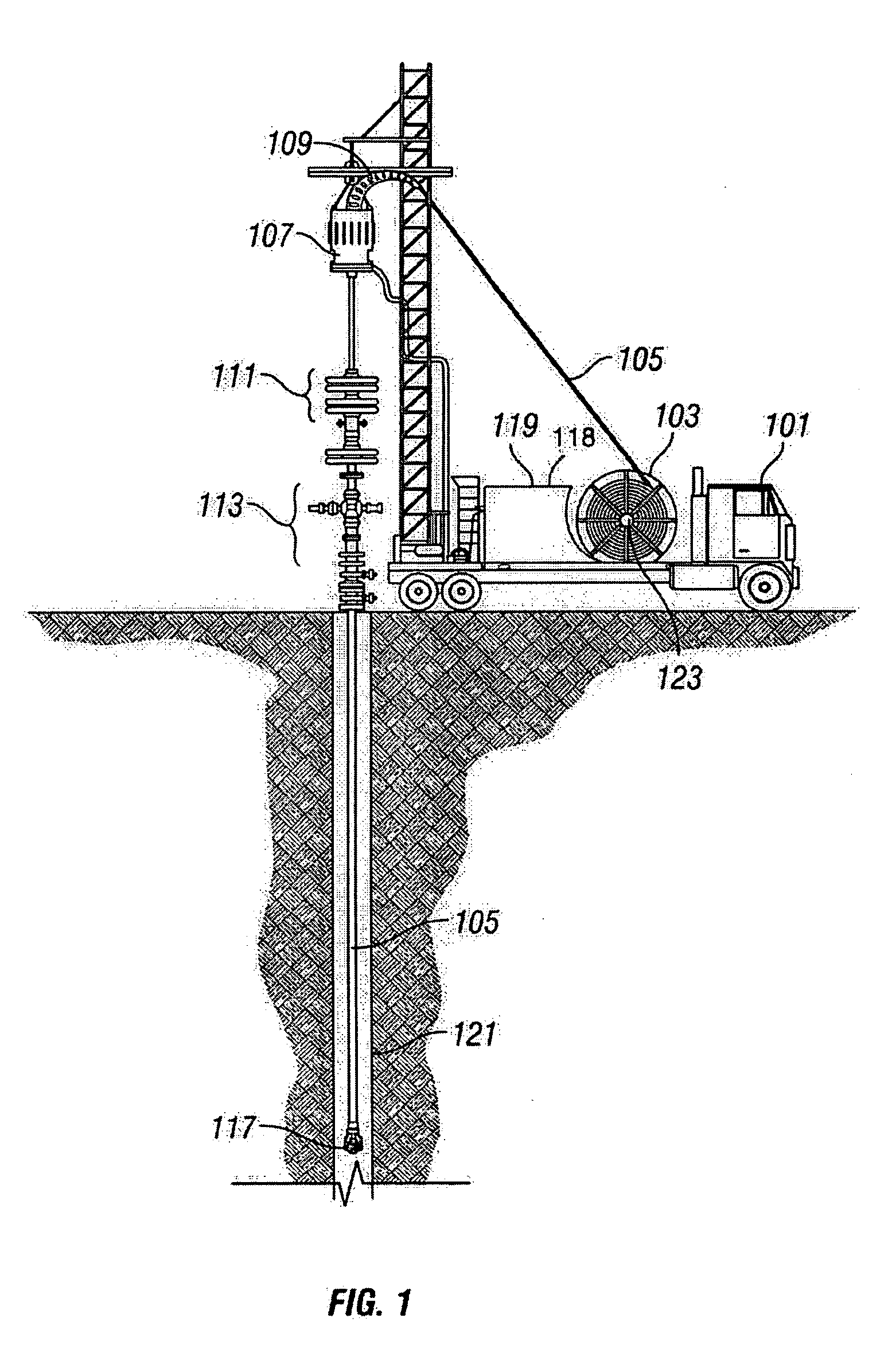
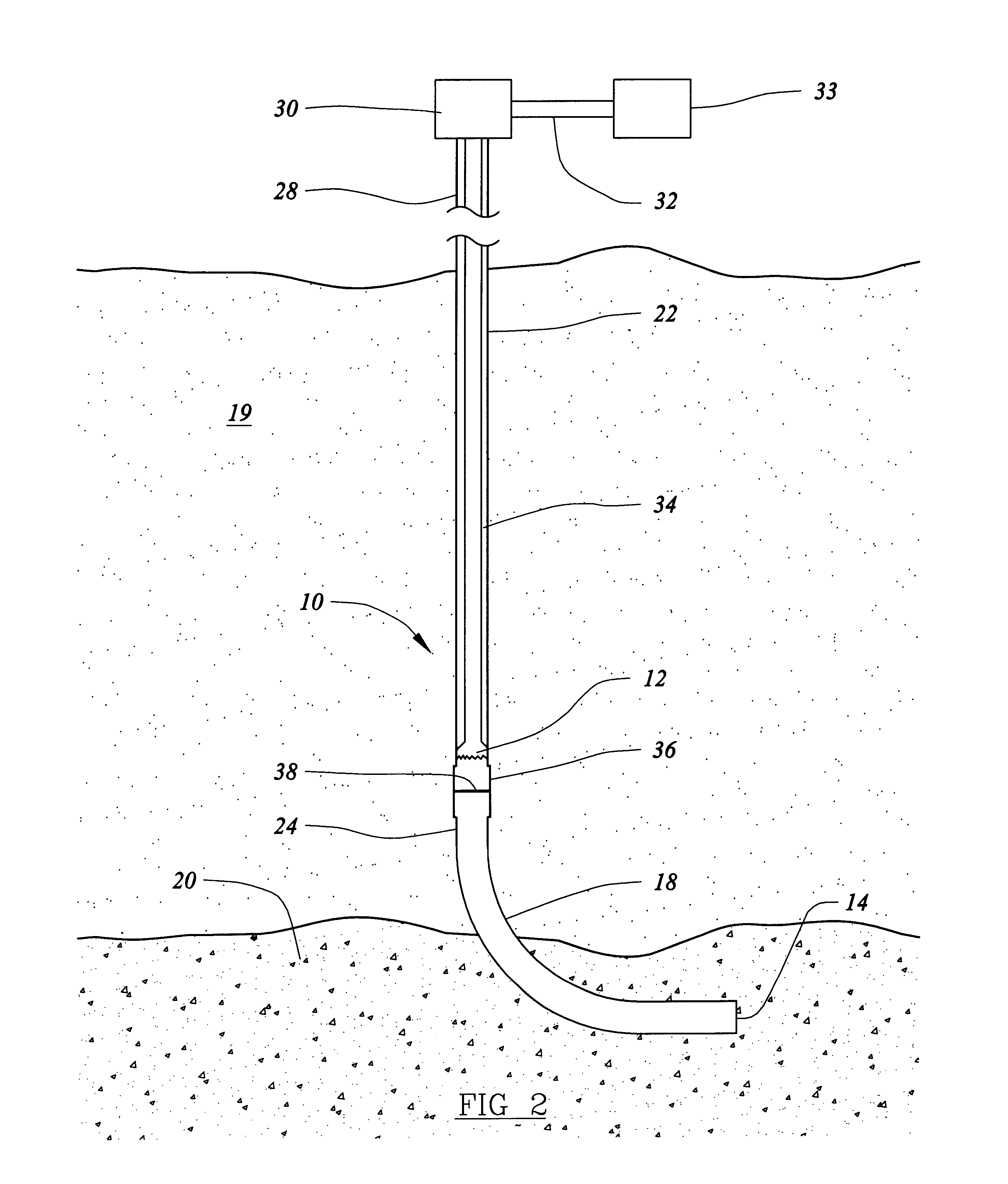
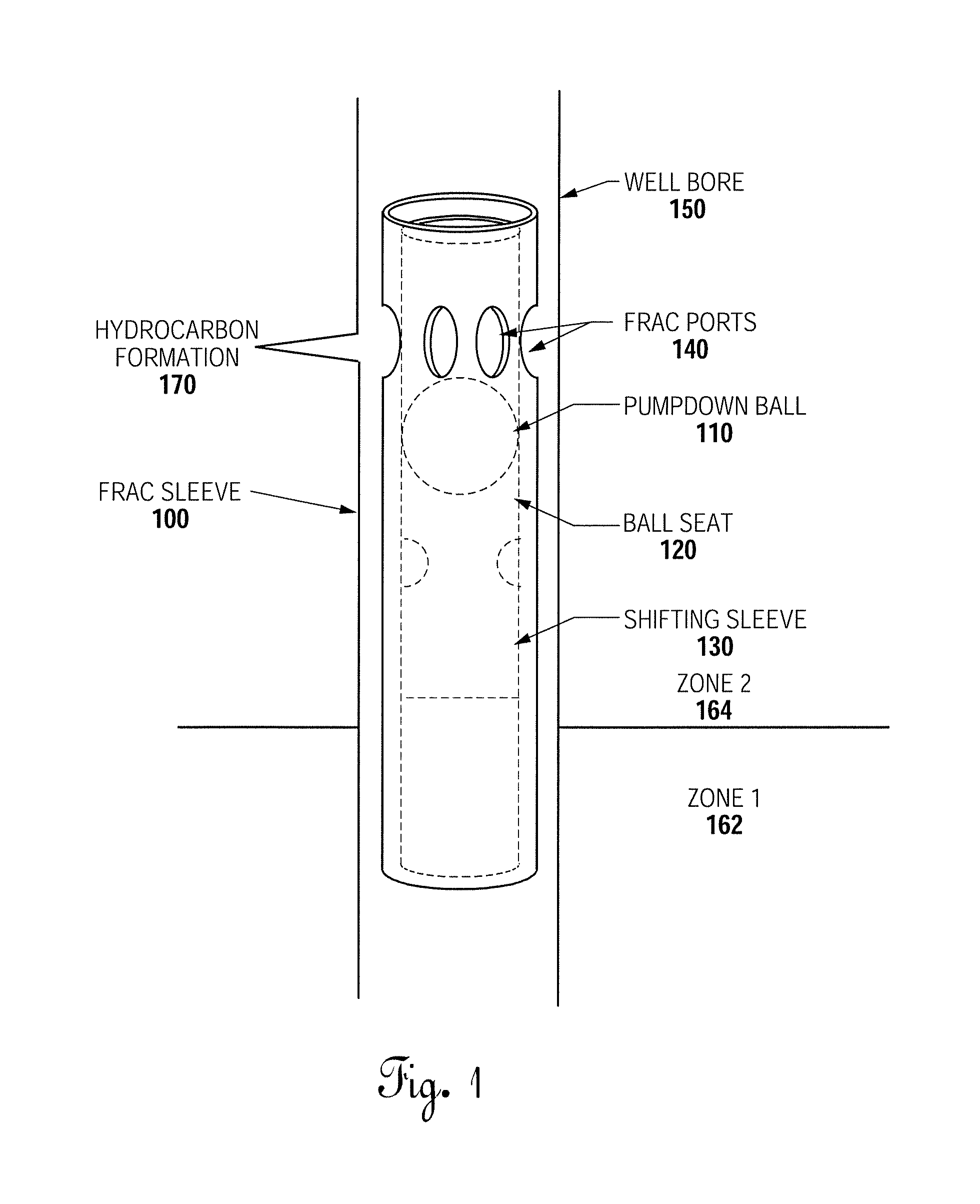
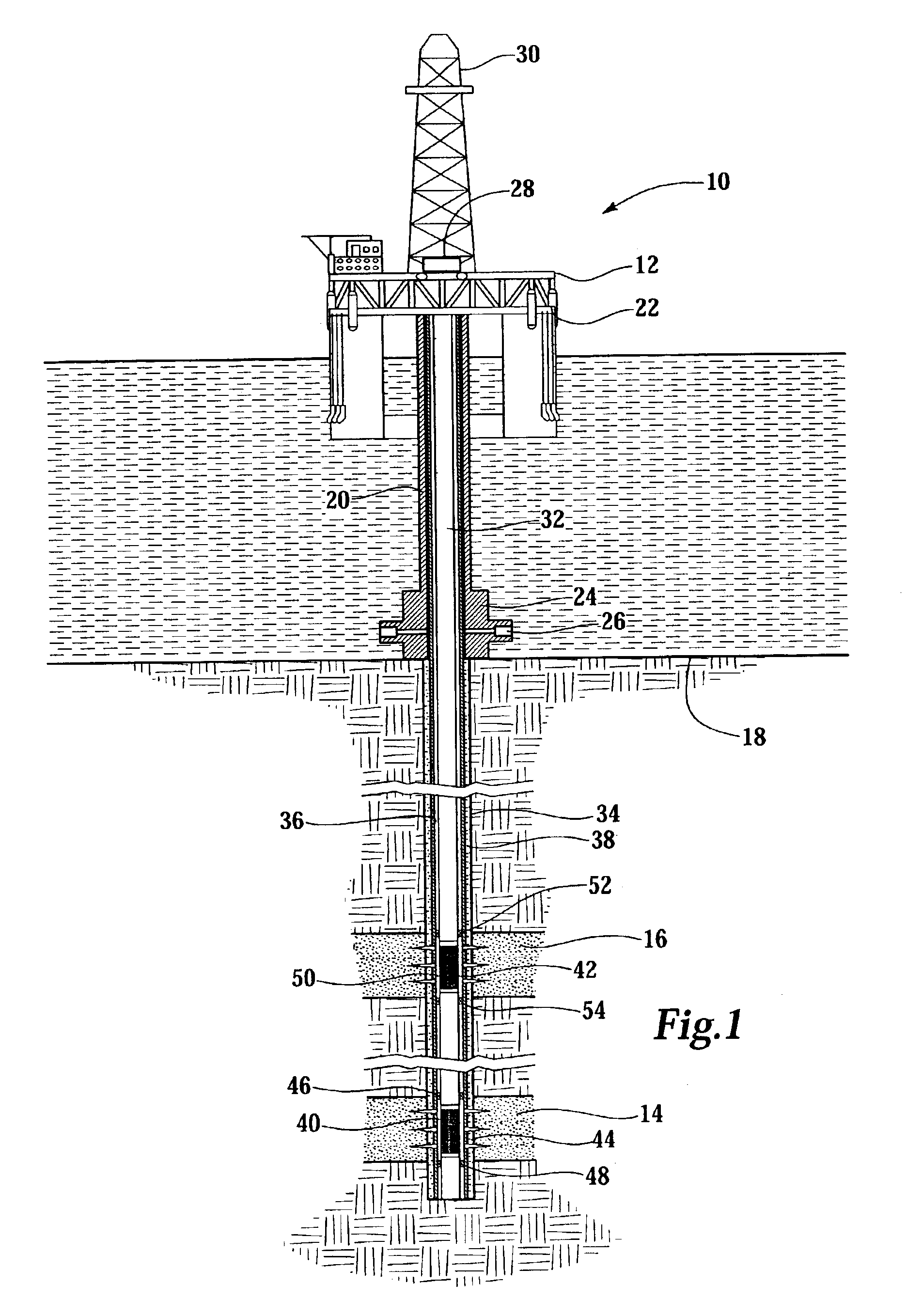
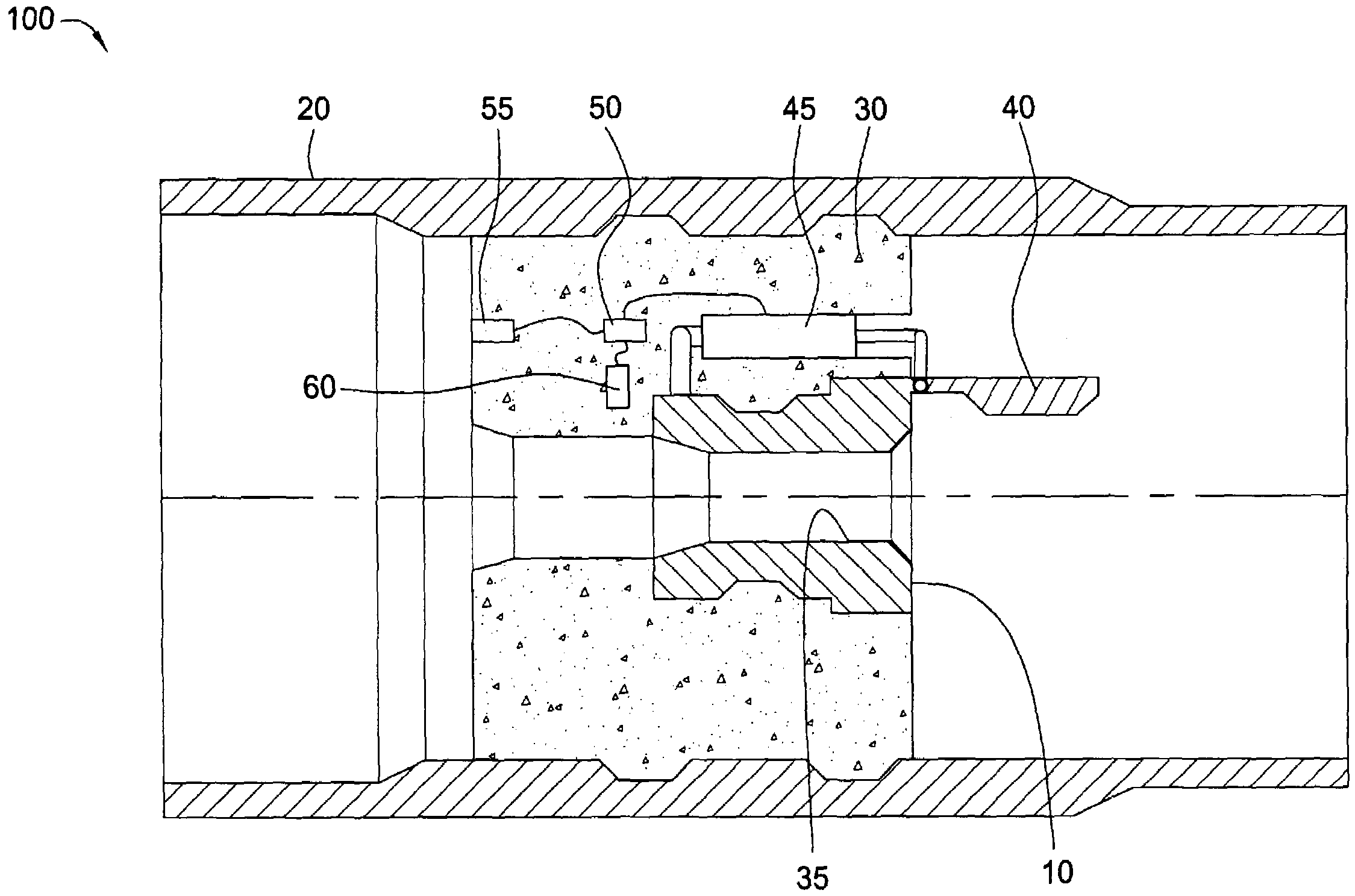
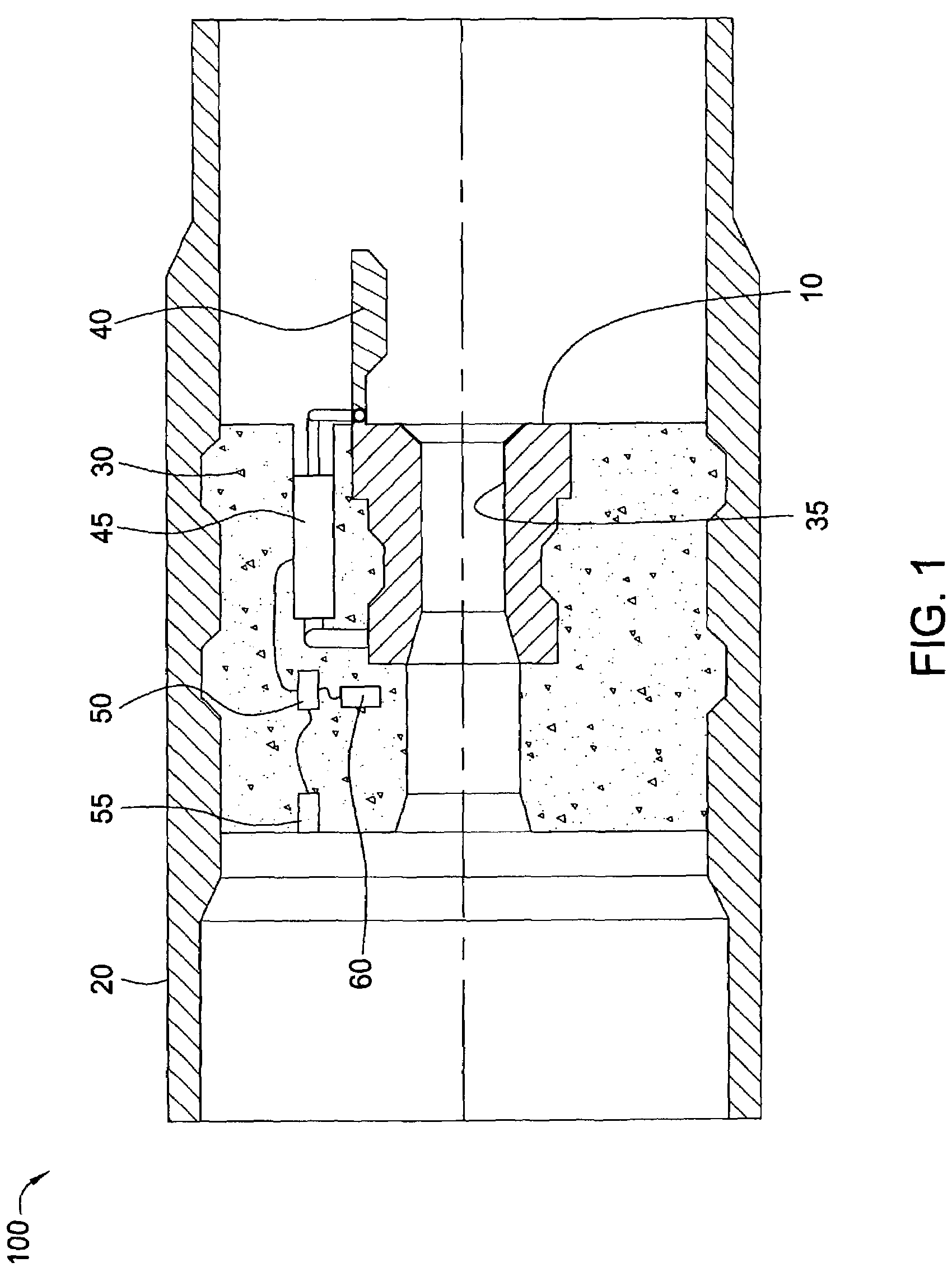
System for Completing Multiple Well Intervals
A system and method for completing a well with multiple zones of production is provided, including a casing having a plurality of valves integrated therein for isolating each well zone, establishing communication between each underlying formation and the interior of the casing, and delivering a treatment fluid to each of the multiple well zones. Furthermore, the present invention further discloses mechanisms for actuating one or more of the valves including, but not limited to, a dart, a drop ball, a running tool, and control line actuating system.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Biodegradable downhole tools
A disposable downhole tool or a component thereof comprises an effective amount of biodegradable material such that the tool or the component thereof desirably decomposes when exposed to a wellbore environment. In an embodiment, the biodegradable material comprises a degradable polymer. The biodegradable material may further comprise a hydrated organic or inorganic solid compound. The biodegradable material may also be selected to achieve a desired decomposition rate when the tool is exposed to the wellbore environment. In an embodiment, the disposable downhole tool further comprises an enclosure for storing a chemical solution that catalyzes decomposition. The tool may also comprise an activation mechanism for releasing the chemical solution from the enclosure. In various embodiments, the disposable downhole tool is a frac plug, a bridge plug, or a packer.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
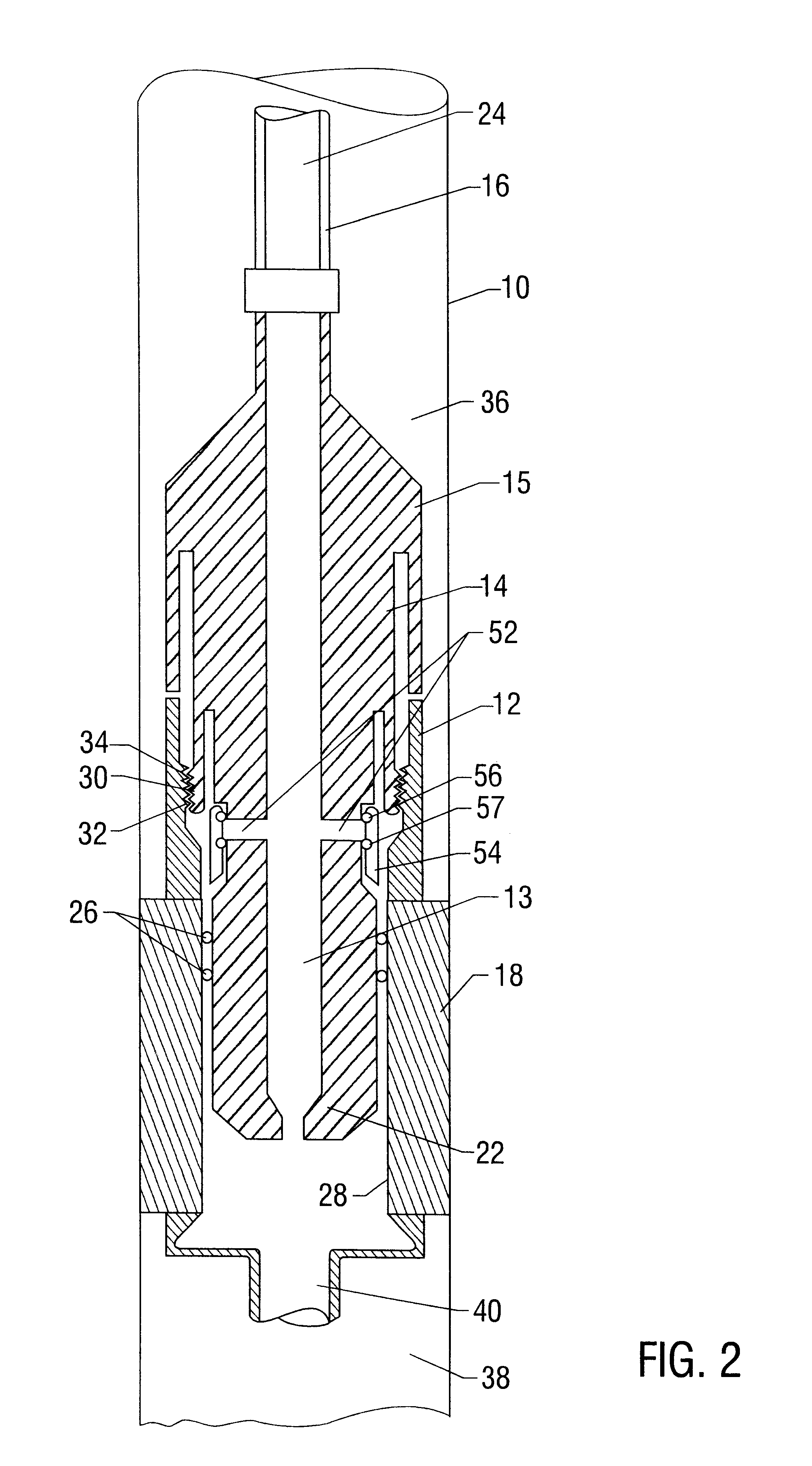
System for completing multiple well intervals
A system and method for completing a well with multiple zones of production is provided, including a casing having a plurality of valves integrated therein for isolating each well zone, establishing communication between each underlying formation and the interior of the casing, and delivering a treatment fluid to each of the multiple well zones. Furthermore, the present invention further discloses mechanisms for actuating one or more of the valves including, but not limited to, a dart, a drop ball, a running tool, and control line actuating system.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Biodegradable downhole tools
A disposable downhole tool or a component thereof comprises an effective amount of biodegradable material such that the tool or the component thereof desirably decomposes when exposed to a wellbore environment. In an embodiment, the biodegradable material comprises a degradable polymer. The biodegradable material may further comprise a hydrated organic or inorganic solid compound. The biodegradable material may also be selected to achieve a desired decomposition rate when the tool is exposed to the wellbore environment. In an embodiment, the disposable downhole tool further comprises an enclosure for storing a chemical solution that catalyzes decomposition. The tool may also comprise an activation mechanism for releasing the chemical solution from the enclosure. In various embodiments, the disposable downhole tool is a frac plug, a bridge plug, or a packer.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
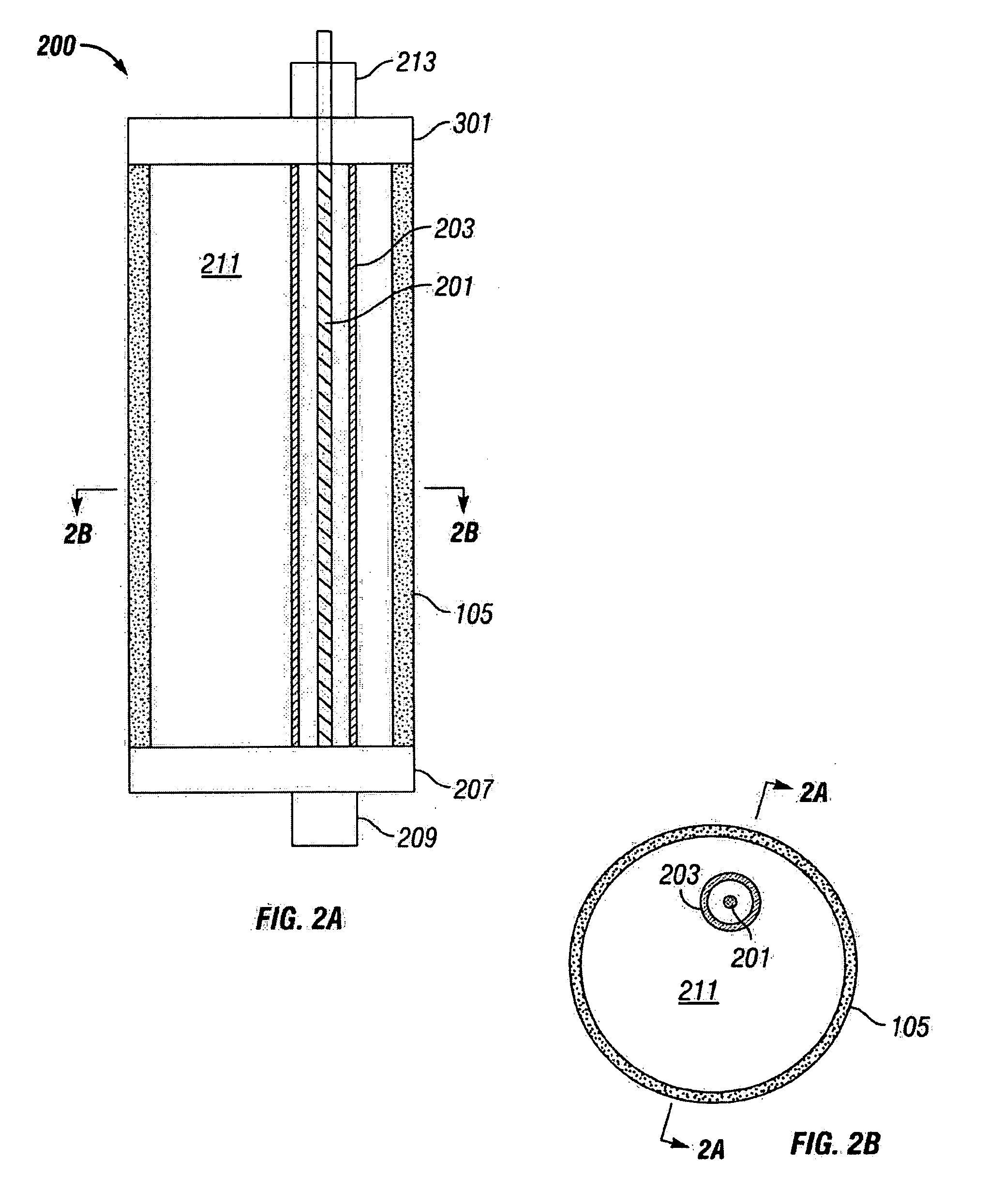
One-time use composite tool formed of fibers and a biodegradable resin
ActiveUS7093664B2Eliminates and at least minimizes drawbackFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsFiberChemical Linkage
The present invention is directed to disposable composite downhole tool formed of a resin-coated fiber. The fiber is formed of a degradable polymer, such as a poly(lactide) or polyanhydride. The resin is formed of the same degradable polymer as the fiber. It chemically bonds to the fiber, thereby making a strong rigid structure once cured. The fiber may be formed into a fabric before being coated with the resin. Alternatively, the fiber is formed of a non-biodegradable material.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
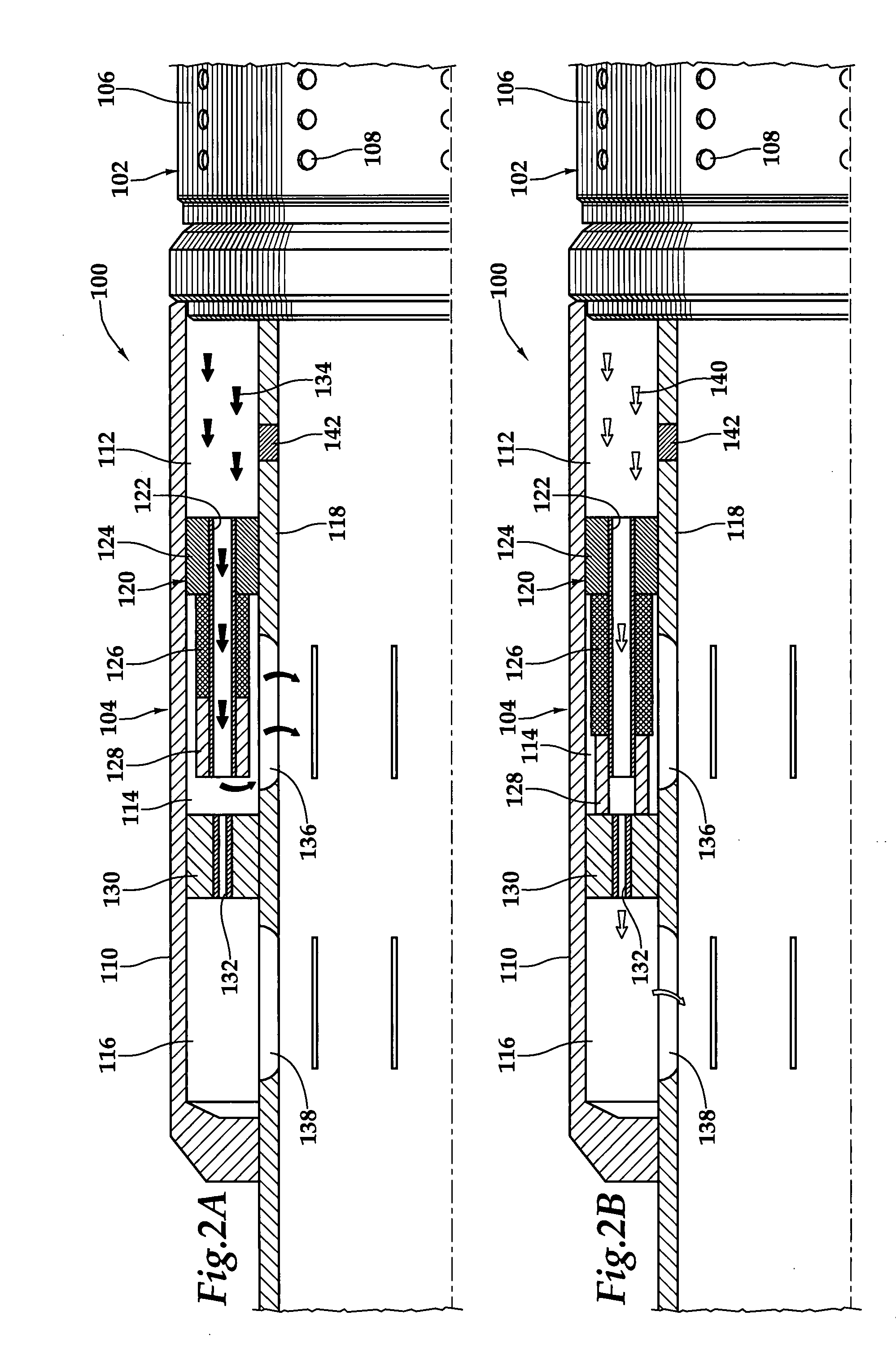
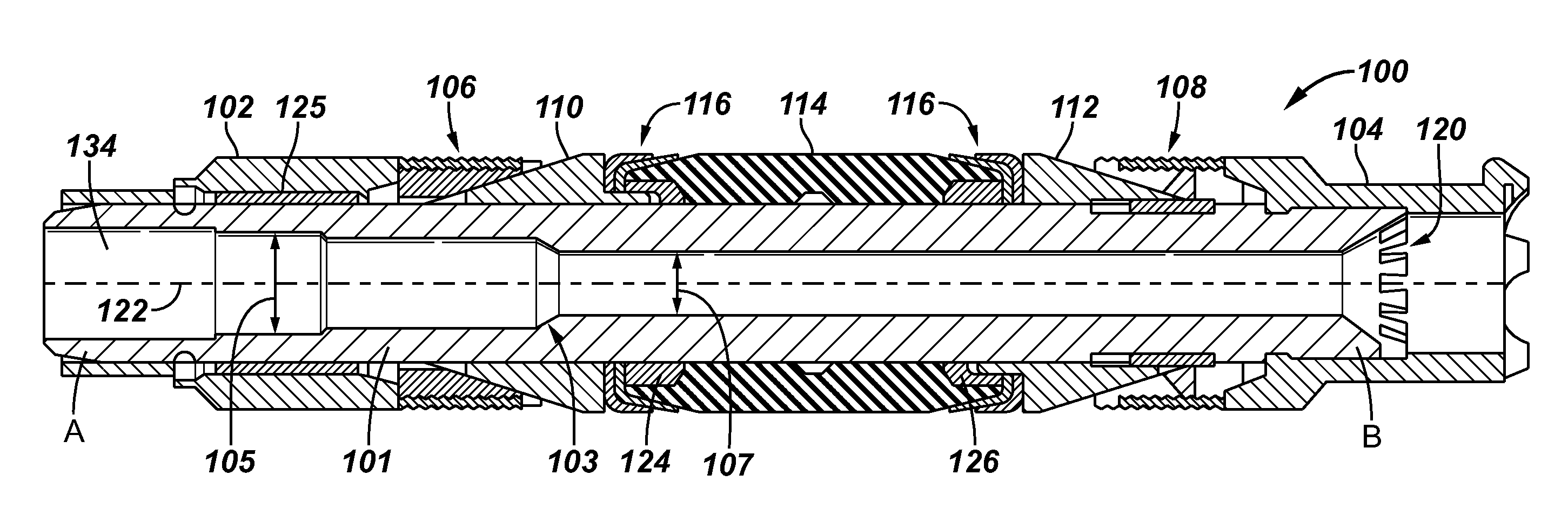
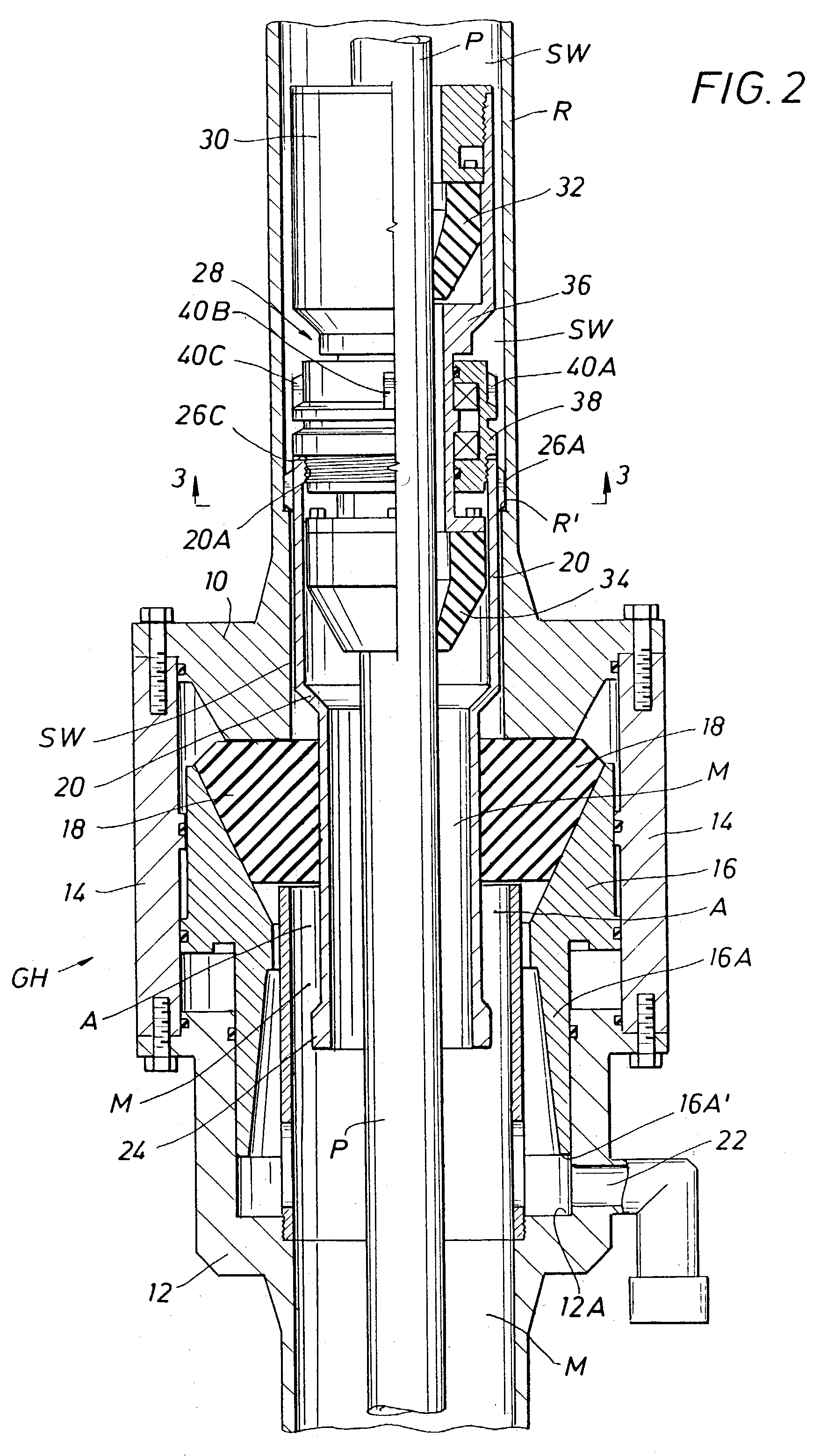
Apparatus for autonomously controlling the inflow of production fluids from a subterranean well
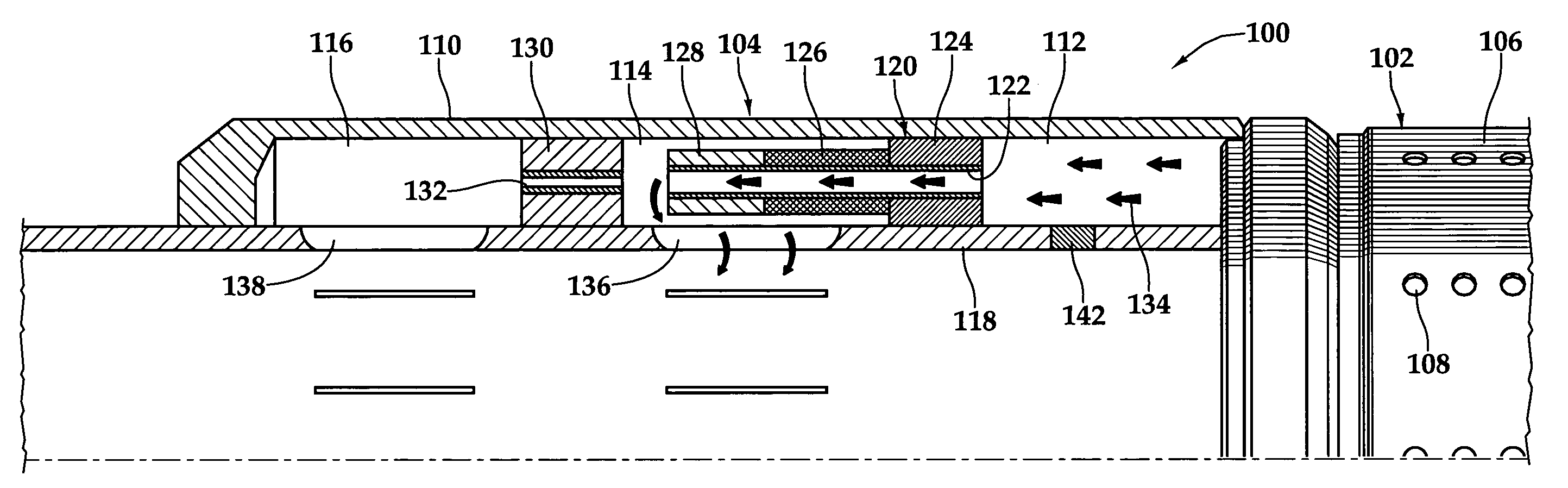
InactiveUS20080283238A1Reduce trafficReduce the cross-sectional areaFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringActuator
A flow control apparatus (100) for controlling the inflow of production fluids (134, 140) from a subterranean well includes a tubular member (118) having at least one opening (138) that allows fluid flow between an exterior of the tubular member (118) and an interior flow path of the tubular member (118) and a flow restricting device (120) operably positioned in a fluid flow path between a fluid source and the at least one opening (138). The flow restricting device (120) includes a valve (128, 130) and an actuator (126). The actuator (126) includes a material that swells in response to contact with an undesired fluid (140), such as water or gas. The flow restricting device (120) is operable to autonomously reduce the fluid flow through the flow control apparatus (100) in response to contact between the material and the undesired fluid (140).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Oilfield Elements Having Controlled Solubility and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20070107908A1Ease of the element traversingFluid removalDrilling compositionPolyamideSubject matter
Oilfield elements are described, one embodiment comprising a combination of a normally insoluble metal with an element selected from a second metal, a semi-metallic material, and non-metallic materials; and one or more solubility-modified high strength and / or high-toughness polymeric materials selected from polyamides, polyethers, and liquid crystal polymers. Methods of using the oilfield elements in oilfield operations are also described. This abstract allows a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure. It will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
One-time use composite tool formed of fibers and a biodegradable resin
ActiveUS20050205265A1Eliminates and at least minimizes drawbackFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsLactideFiber Chemistry
The present invention is directed to disposable composite downhole tool formed of a resin-coated fiber. The fiber is formed of a degradable polymer, such as a poly(lactide) or polyanhydride. The resin is formed of the same degradable polymer as the fiber. It chemically bonds to the fiber, thereby making a strong rigid structure once cured. The fiber may be formed into a fabric before being coated with the resin. Alternatively, the fiber is formed of a non-biodegradable material.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
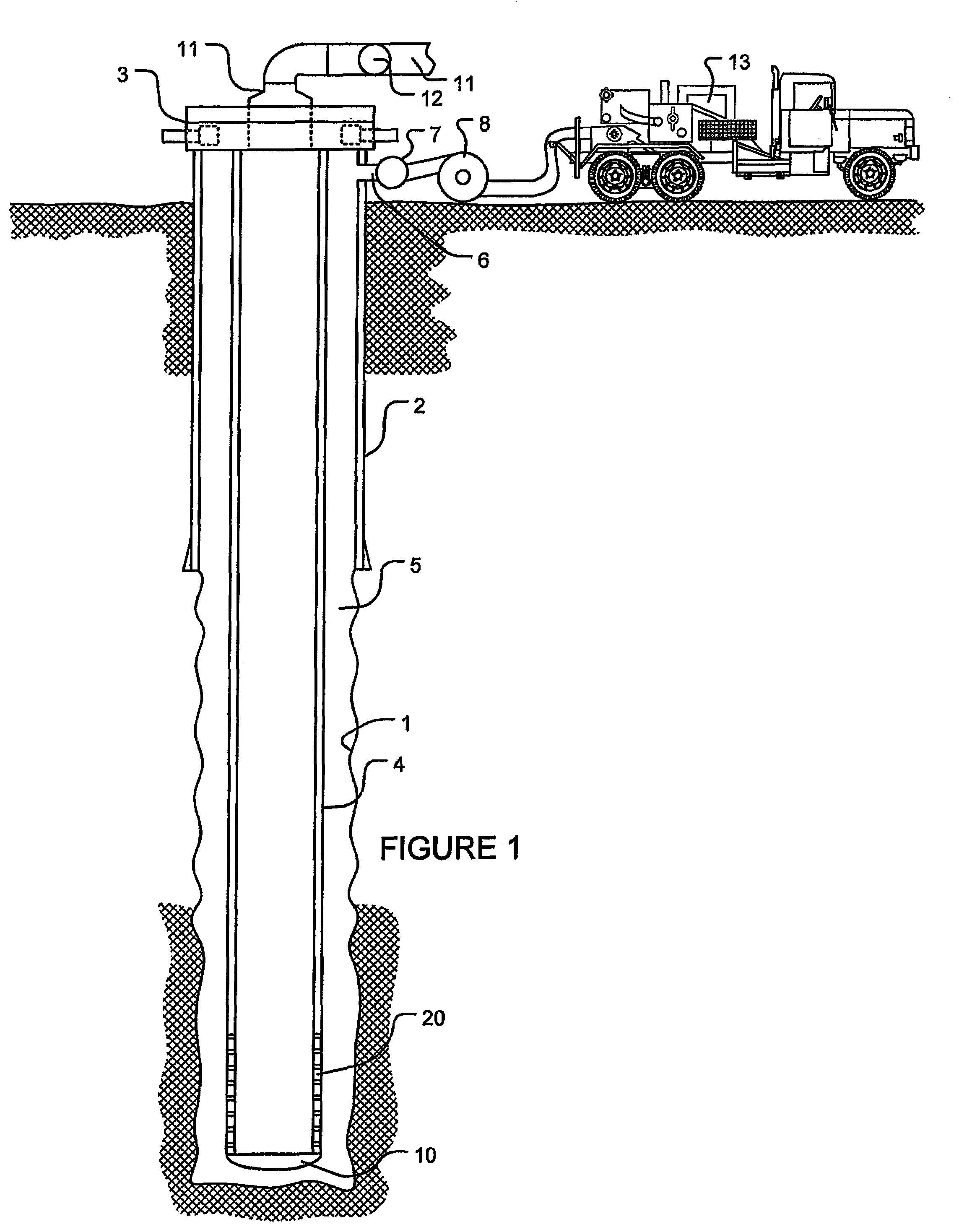
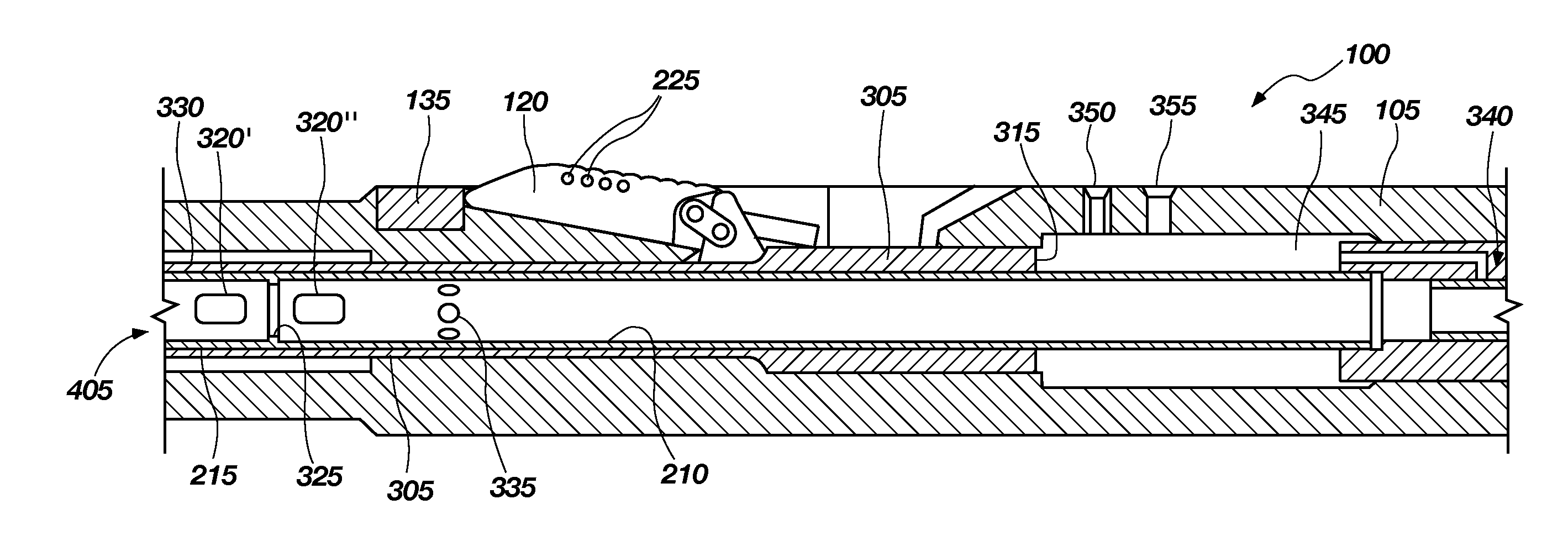
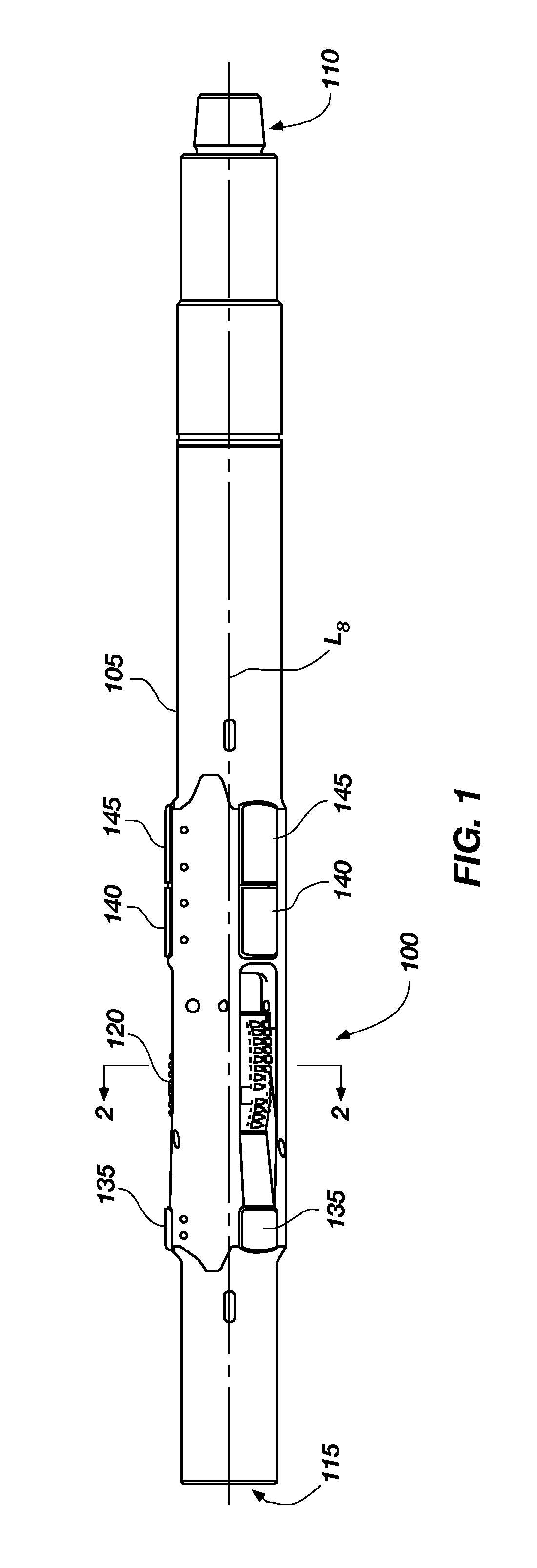
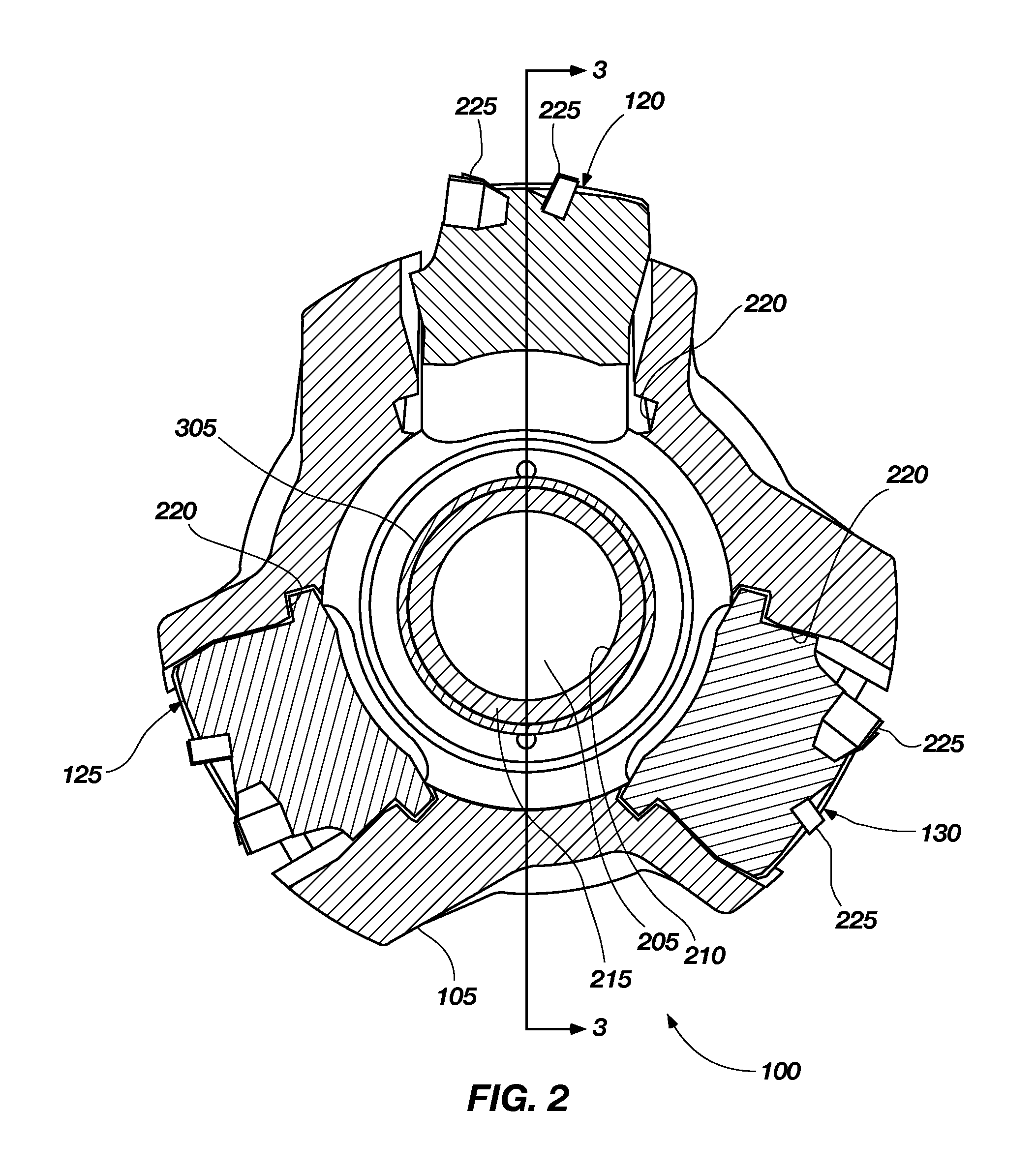
Method and apparatus for wellbore fluid treatment
A tubing string assembly is disclosed for fluid treatment of a wellbore. The tubing string can be used for staged wellbore fluid treatment where a selected segment of the wellbore is treated, while other segments are sealed off. The tubing string can also be used where a ported tubing string is required to be run in in a pressure tight condition and later is needed to be in an open-port condition.
Owner:PACKERS PLUS ENERGY SERVICES INC
Isolation tool release mechanism
A release mechanism for use with setting wellbore isolation tools, such as packers or bridge plugs. The release mechanism typically includes a release piston which selectively isolates equalization ports extending from the interior to the exterior of a setting tool body. The release piston may be activated to allow equalization of pressure across the sealing elements of a set isolation tool, typically by applying pressure to the annular space above the isolation tool. The release mechanism may be used to allow a tool body (such as a setting or retrieving tool) to be removed from a set isolation tool under conditions in which high pressure differential exists across the isolation tool.
Owner:BJ SERVICES CO
Casing shoes and methods of reverse-circulation cementing of casing
A method having the following steps: running a circulation valve comprising a reactive material into the well bore on the casing; reverse-circulating an activator material in the well bore until the activator material contacts the reactive material of the circulation valve; reconfiguring the circulation valve by contact of the activator material with the reactive material; and reverse-circulating a cement composition in the well bore until the reconfigured circulation valve decreases flow of the cement composition. A circulation valve for cementing casing in a well bore, the valve having: a valve housing connected to the casing and comprising a reactive material; a plurality of holes in the housing, wherein the plurality of holes allow fluid communication between an inner diameter of the housing and an exterior of the housing, wherein the reactive material is expandable to close the plurality of holes.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
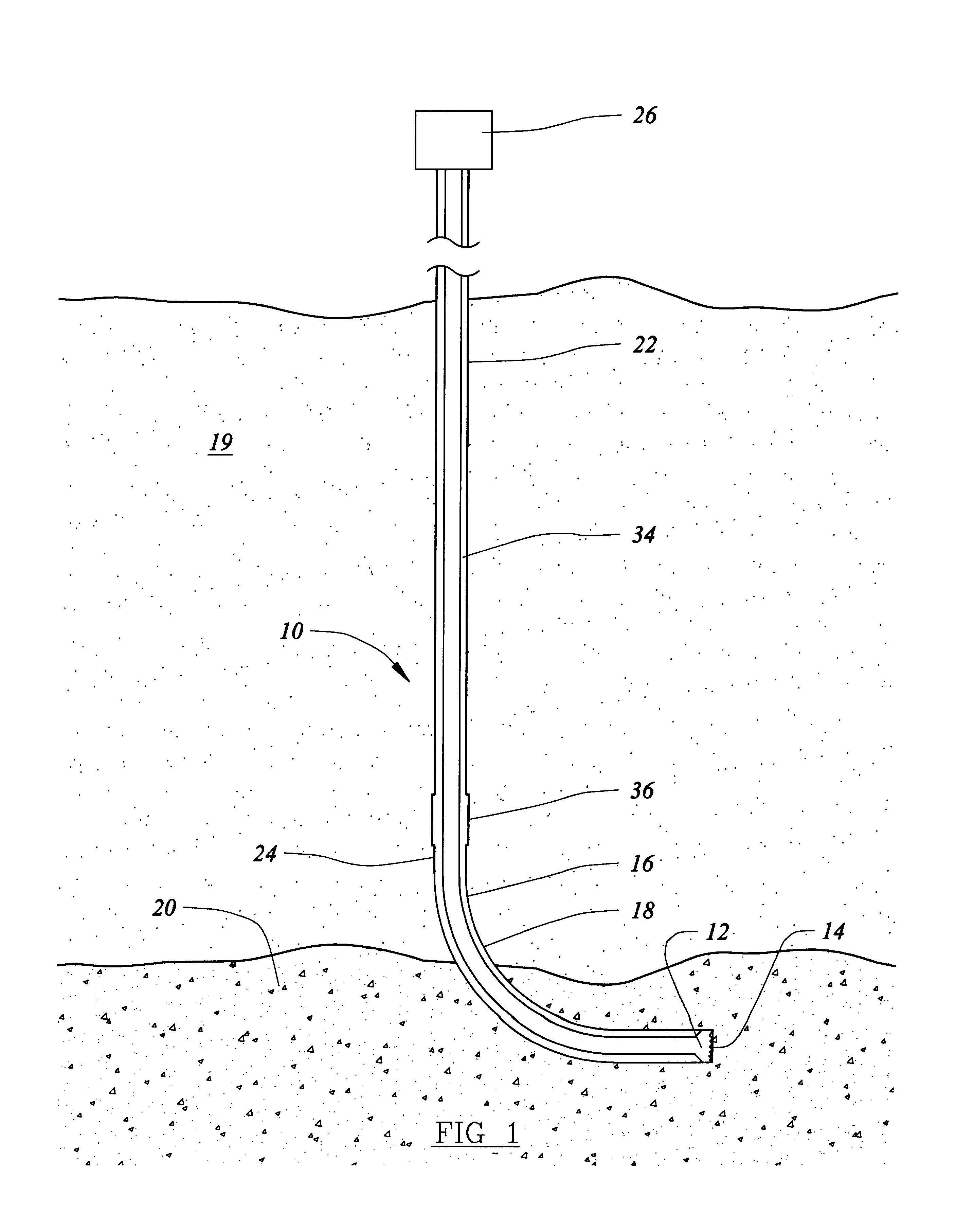
Permanent downhole, wireless, two-way telemetry backbone using redundant repeaters
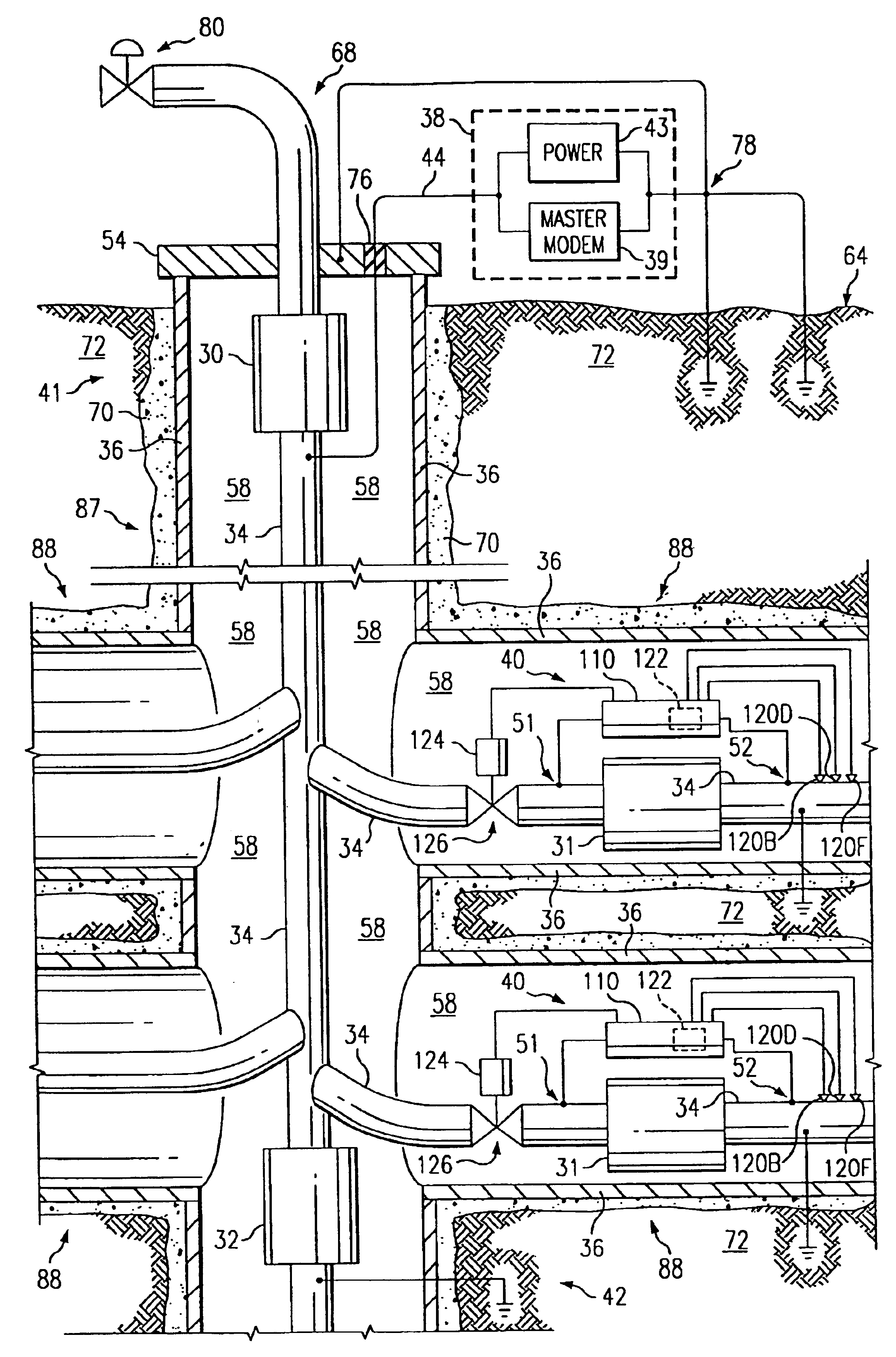
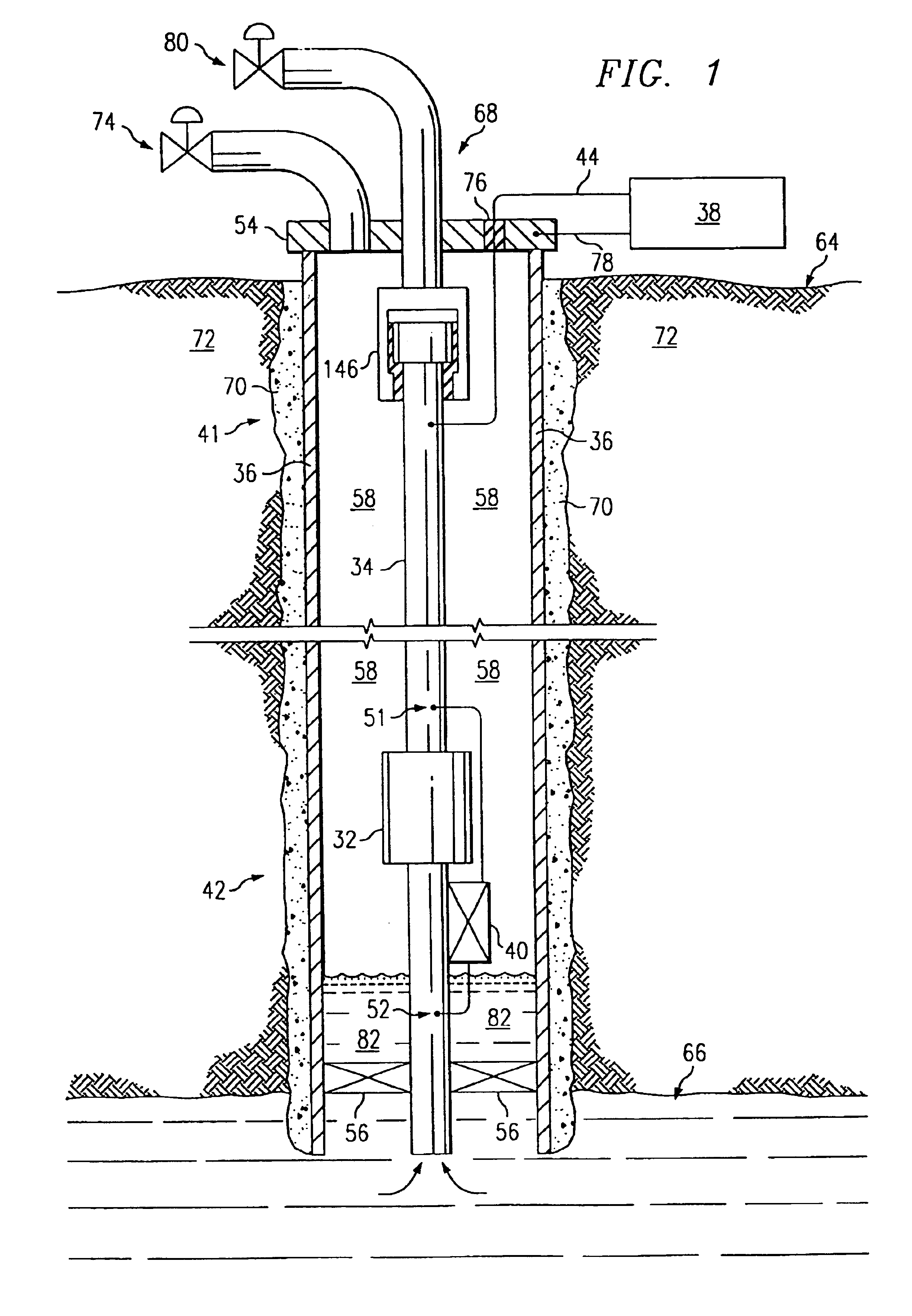
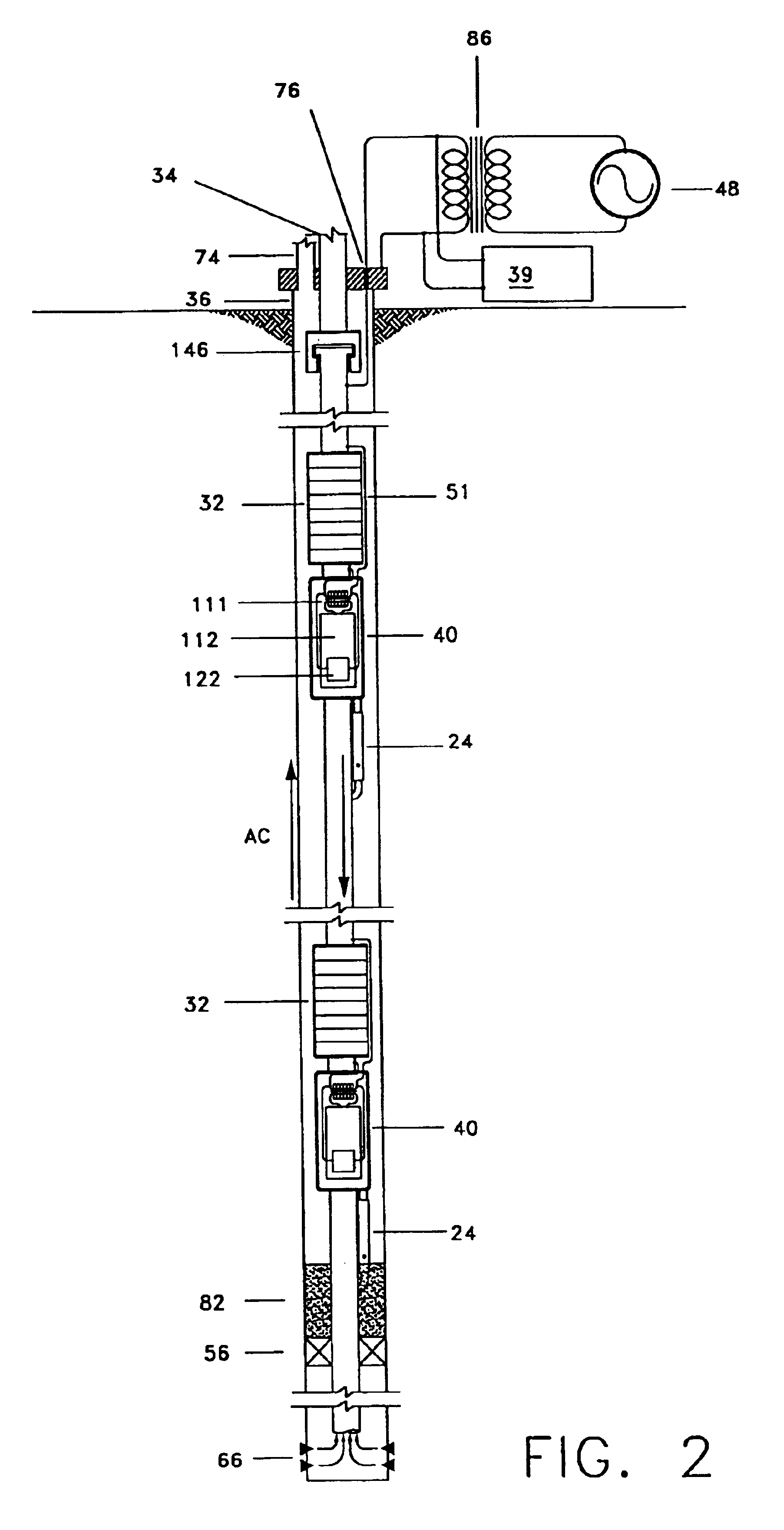
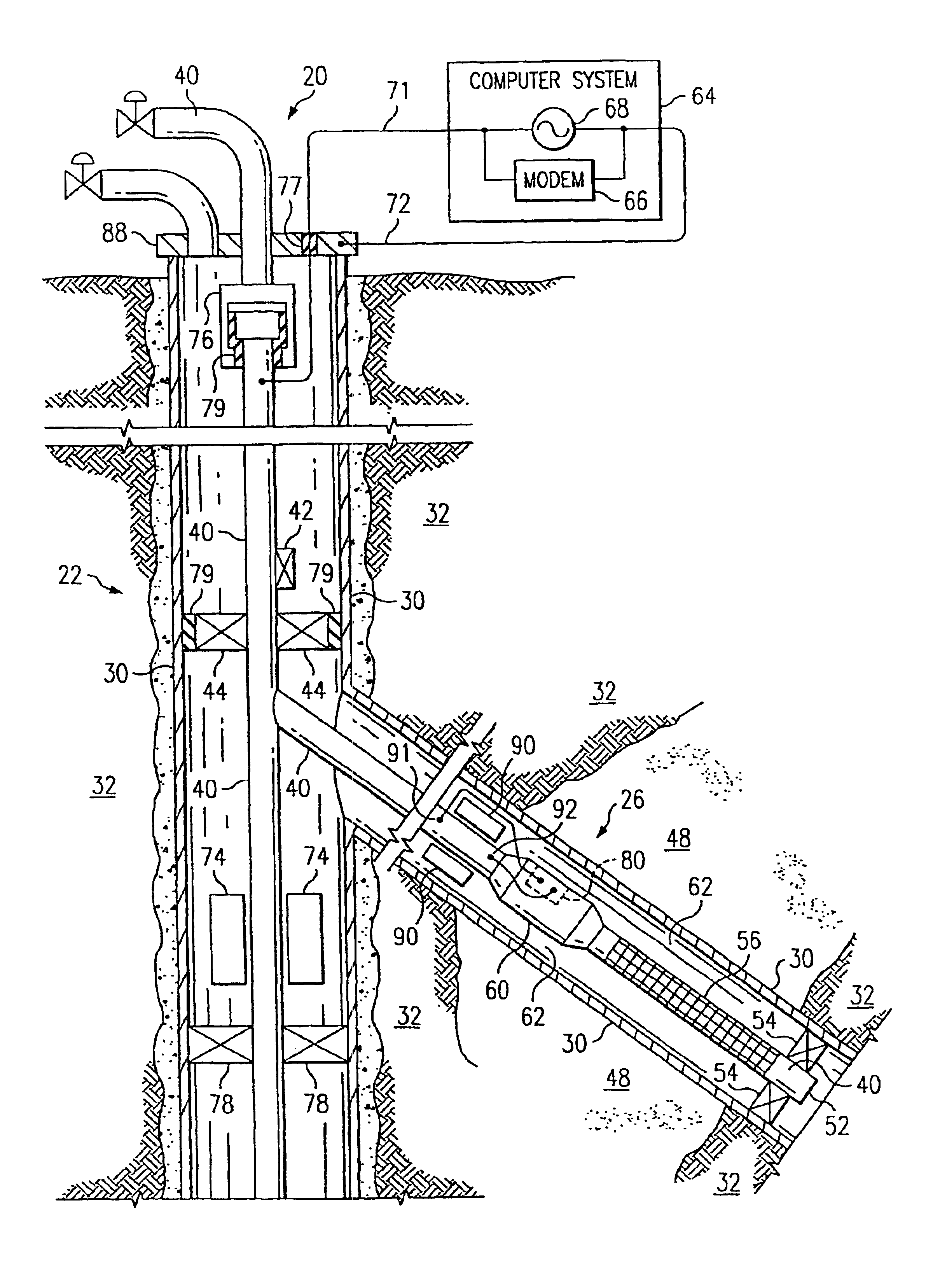
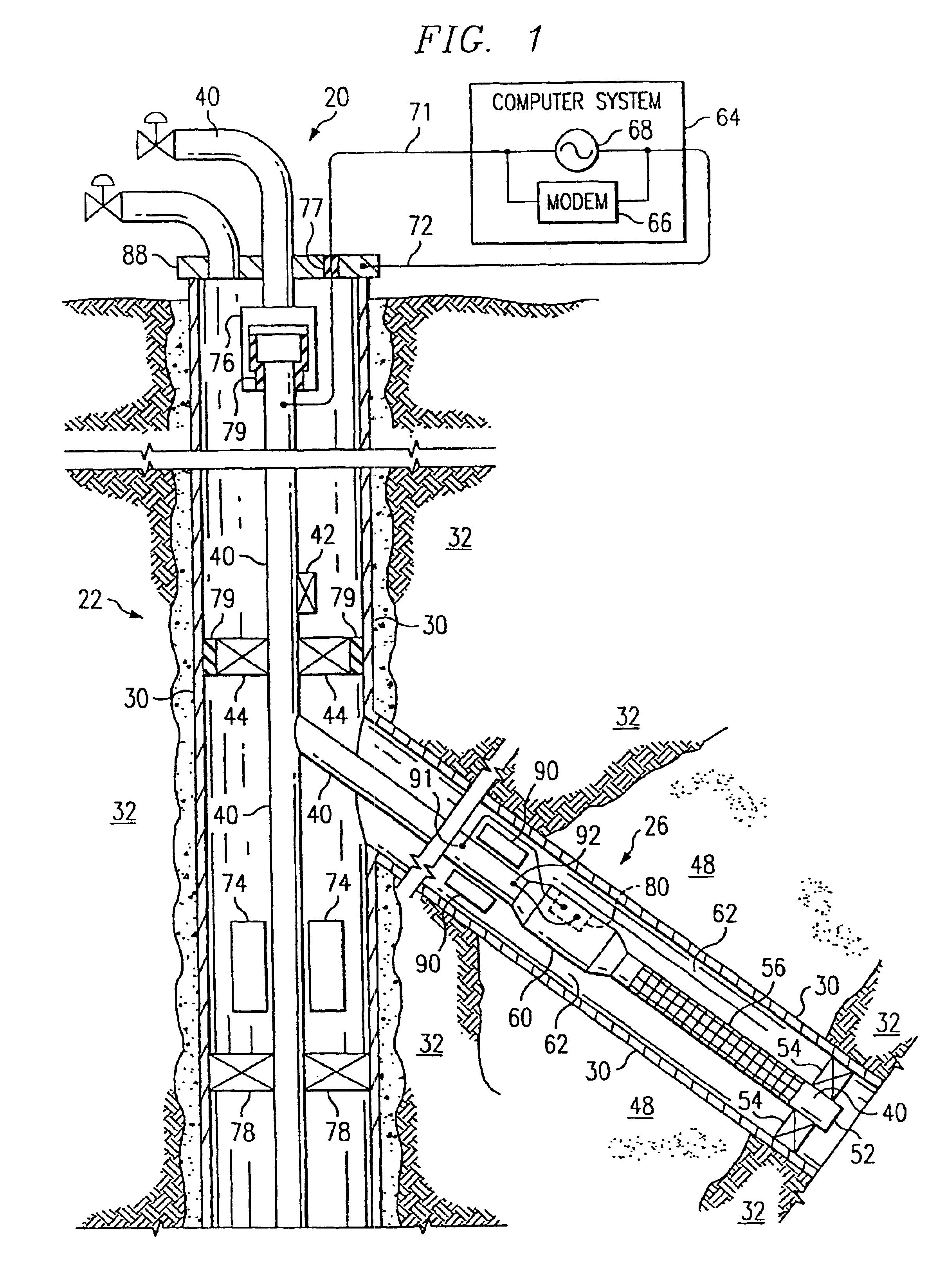
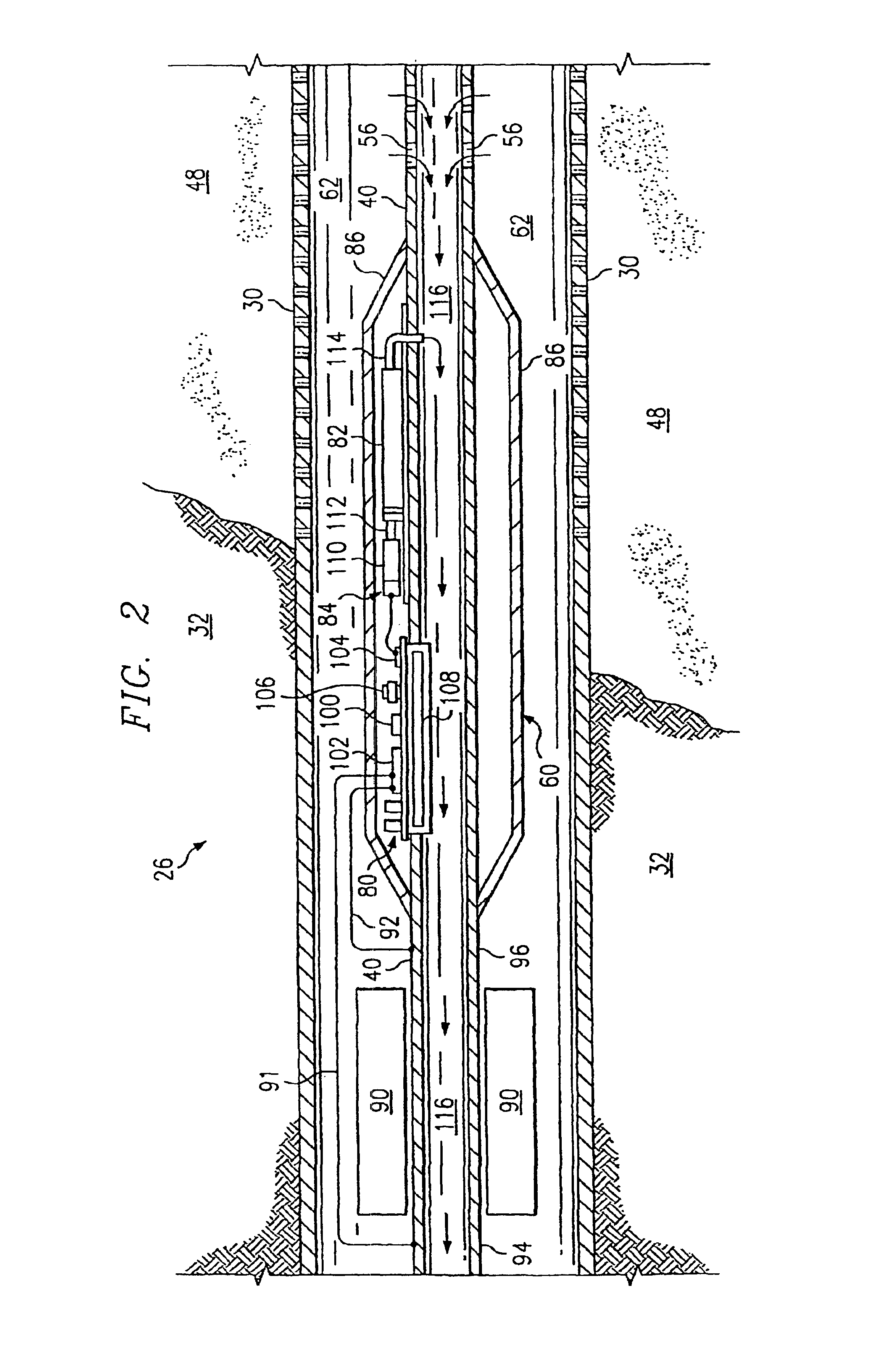
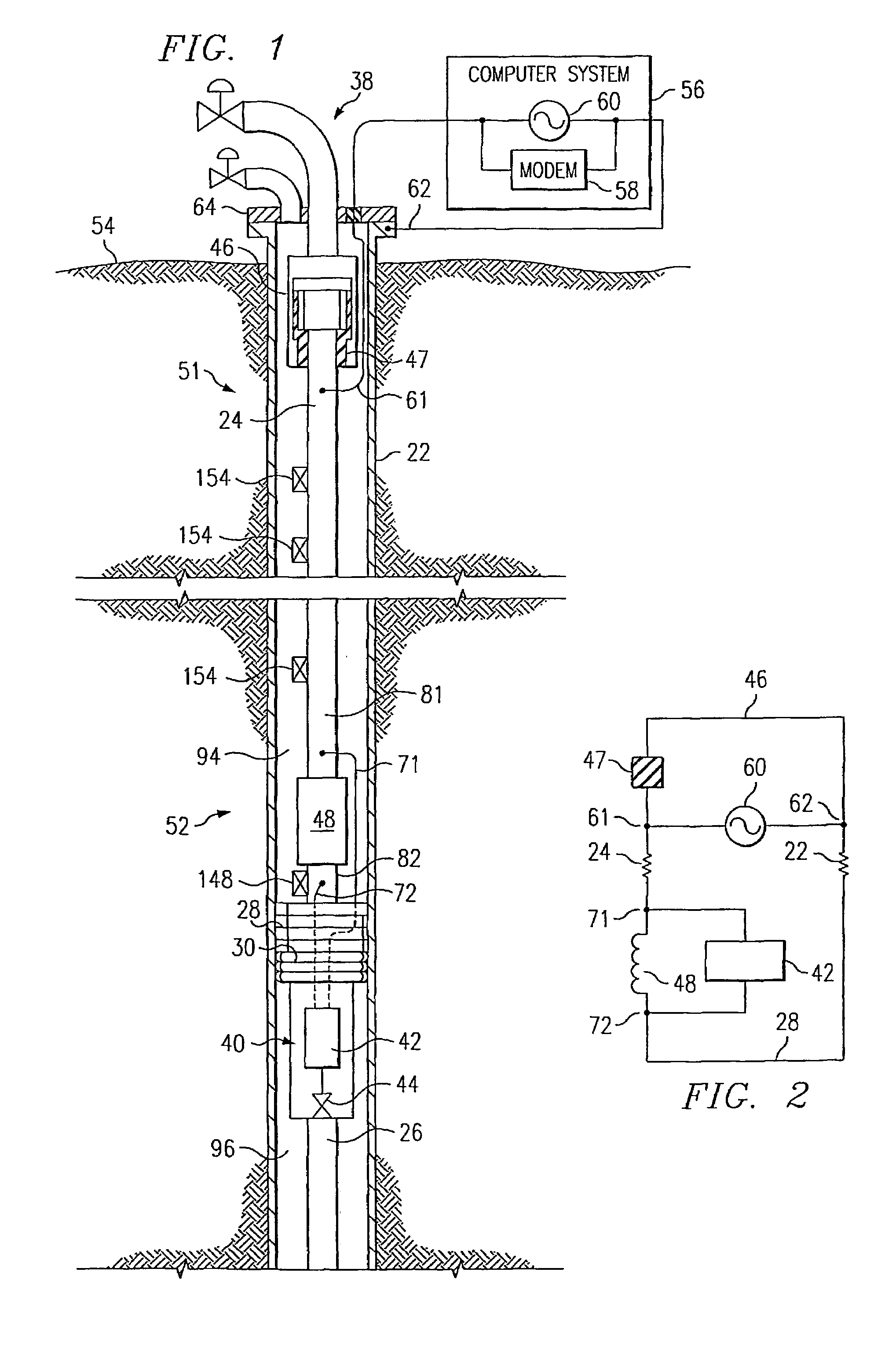
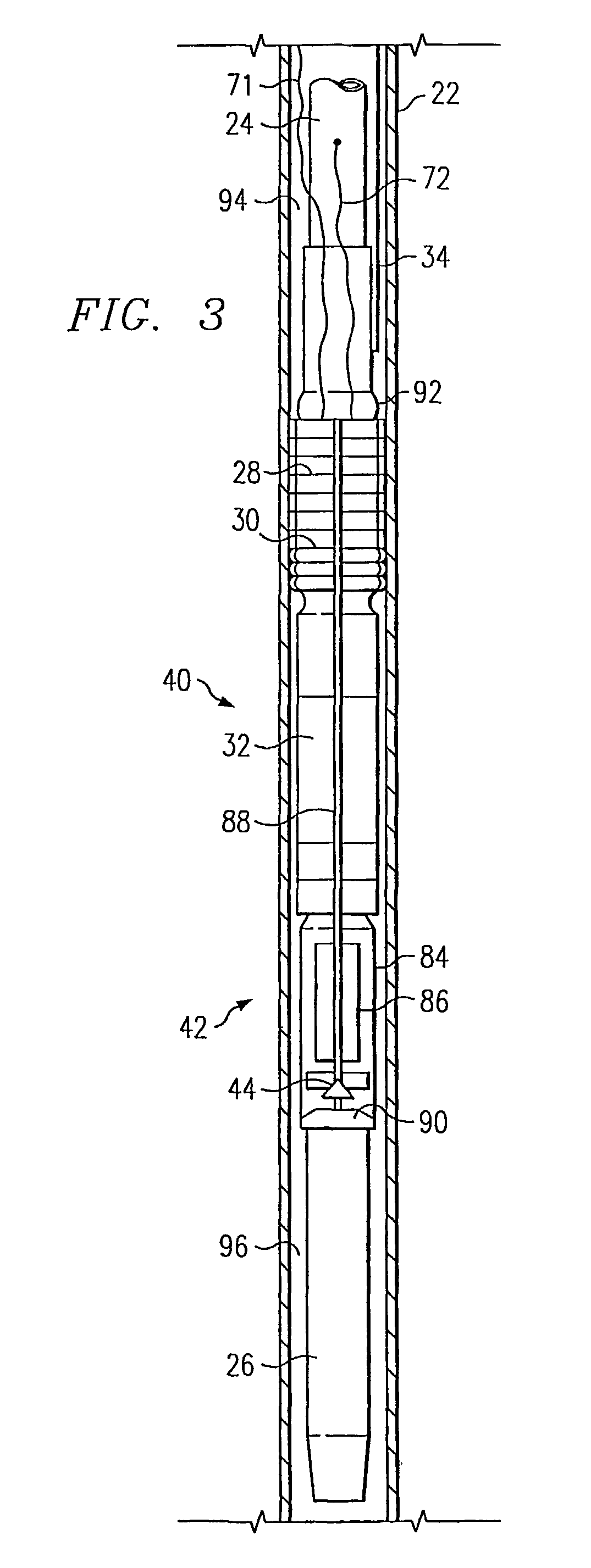
A system and method of communicating among devices via a piping structure using at least one induction choke about the piping structure to route a time-varying current carrying communication signals between the devices. A communications system comprises a piping structure, a first communication device, a second communication device, and an induction choke. The piping structure comprises a first location, a second location, and an electrically conductive portion extending between the first and second locations. The first and second locations are distally spaced along the piping structure. The first and second communication devices are each electrically connected to the electrically conductive portion of the piping structure along the first location and second location, respectively, and each is adapted to send and receive communication signals via time-varying current. The induction choke is located about an electrically choked portion of the electrically conductive portion of the piping structure, such that the induction choke is adapted to route time-varying current within the piping structure between the electrical connection location for the first communication device and the electrical connection location for the second communication device, and such that the first communication device can communicate with the second communication device via the piping structure. A preferred application of the present invention is a well for producing petroleum products (e.g., oil, natural gas), comprising a communication system as described above.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
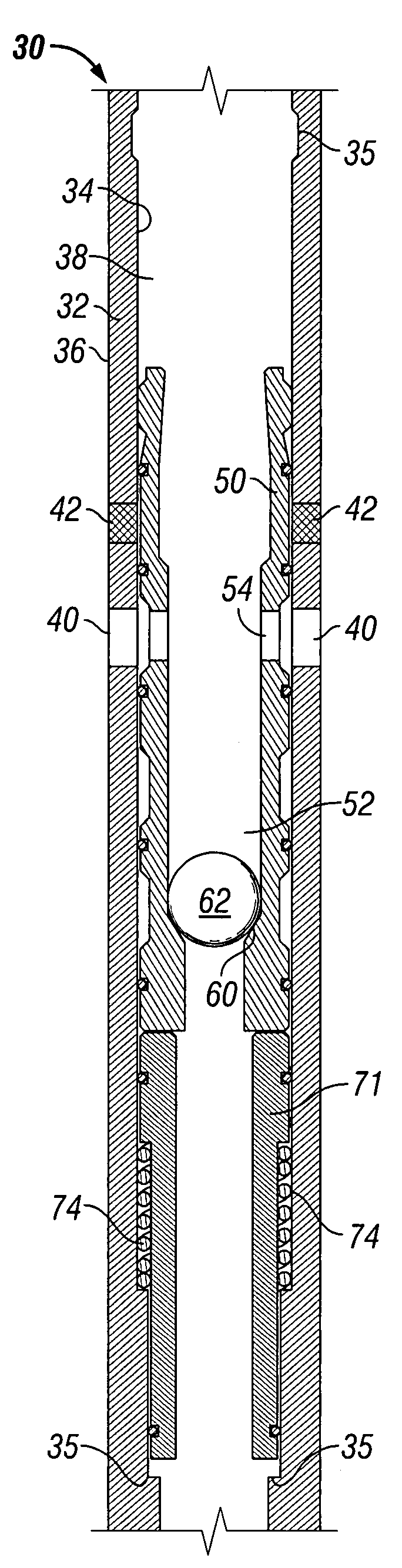
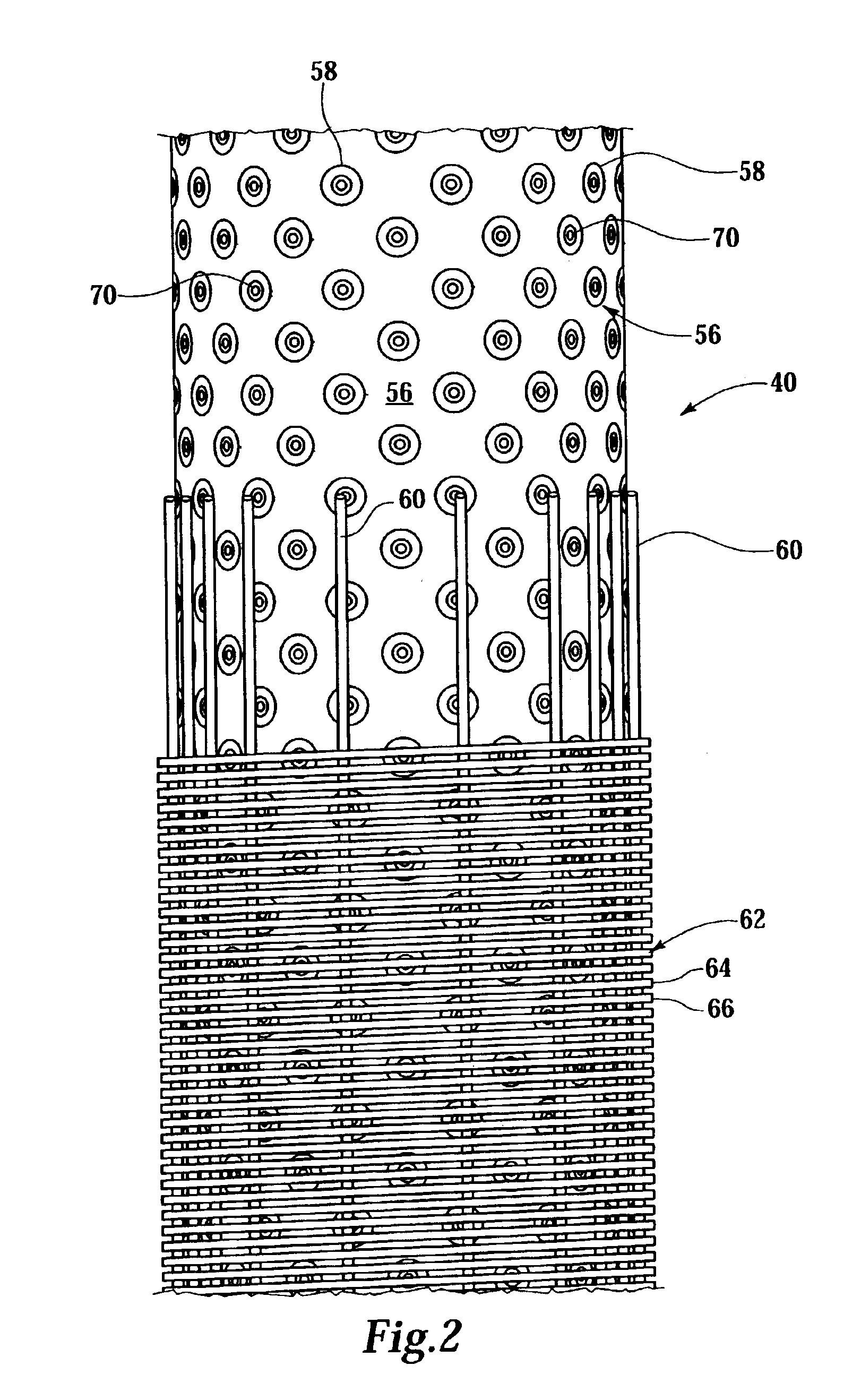
Fluid flow control device and method for use of same
InactiveUS7055598B2Not difficult and expensive to manufactureIncrease pressureSurveyFluid removalStream flowEngineering
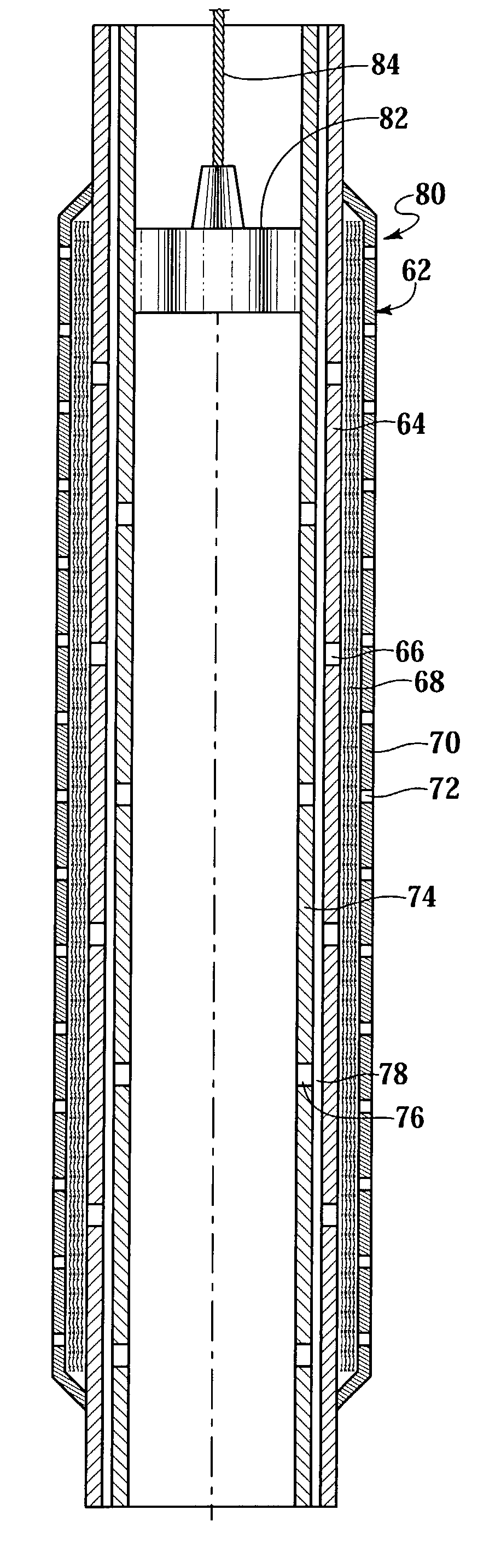
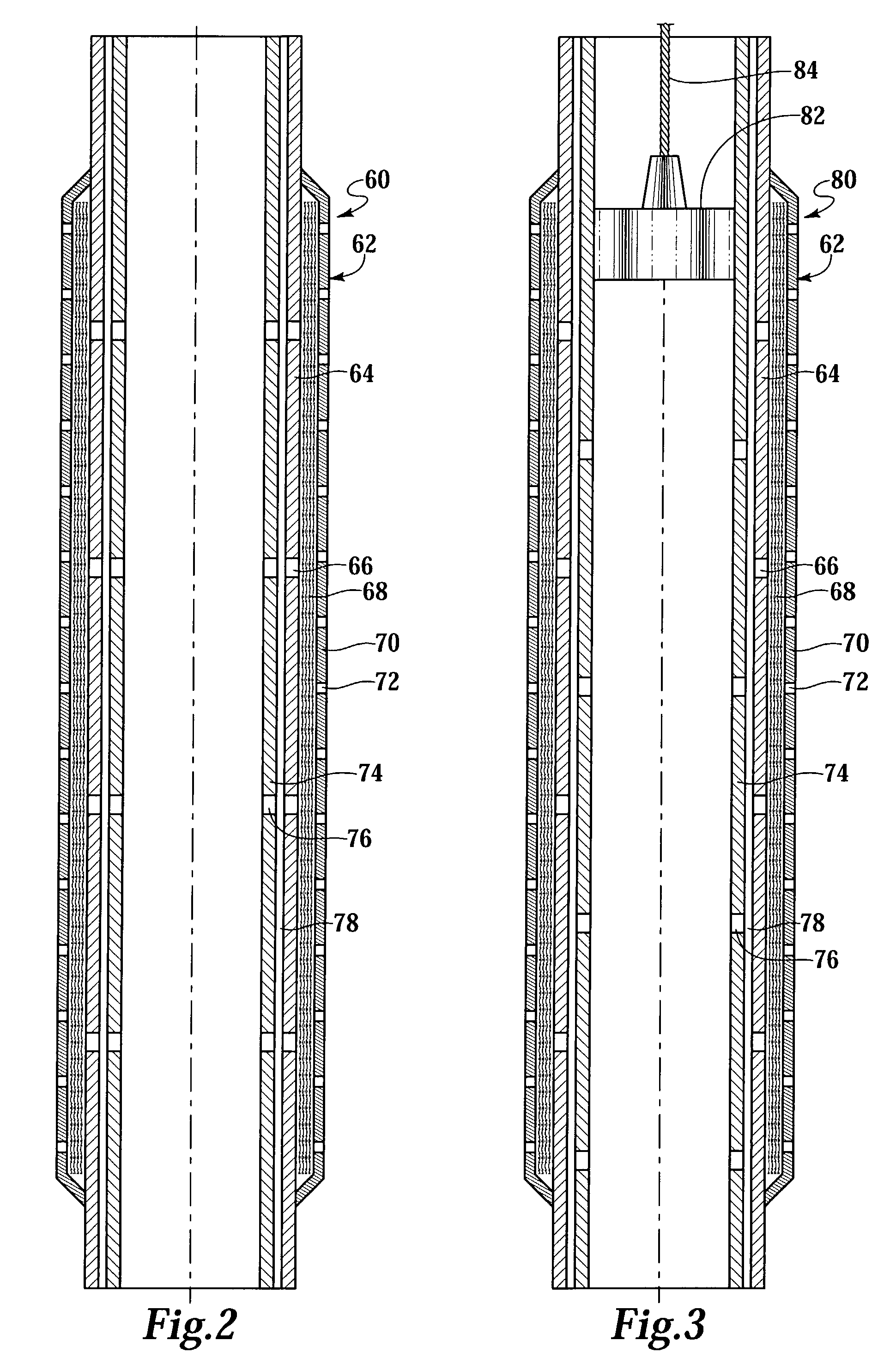
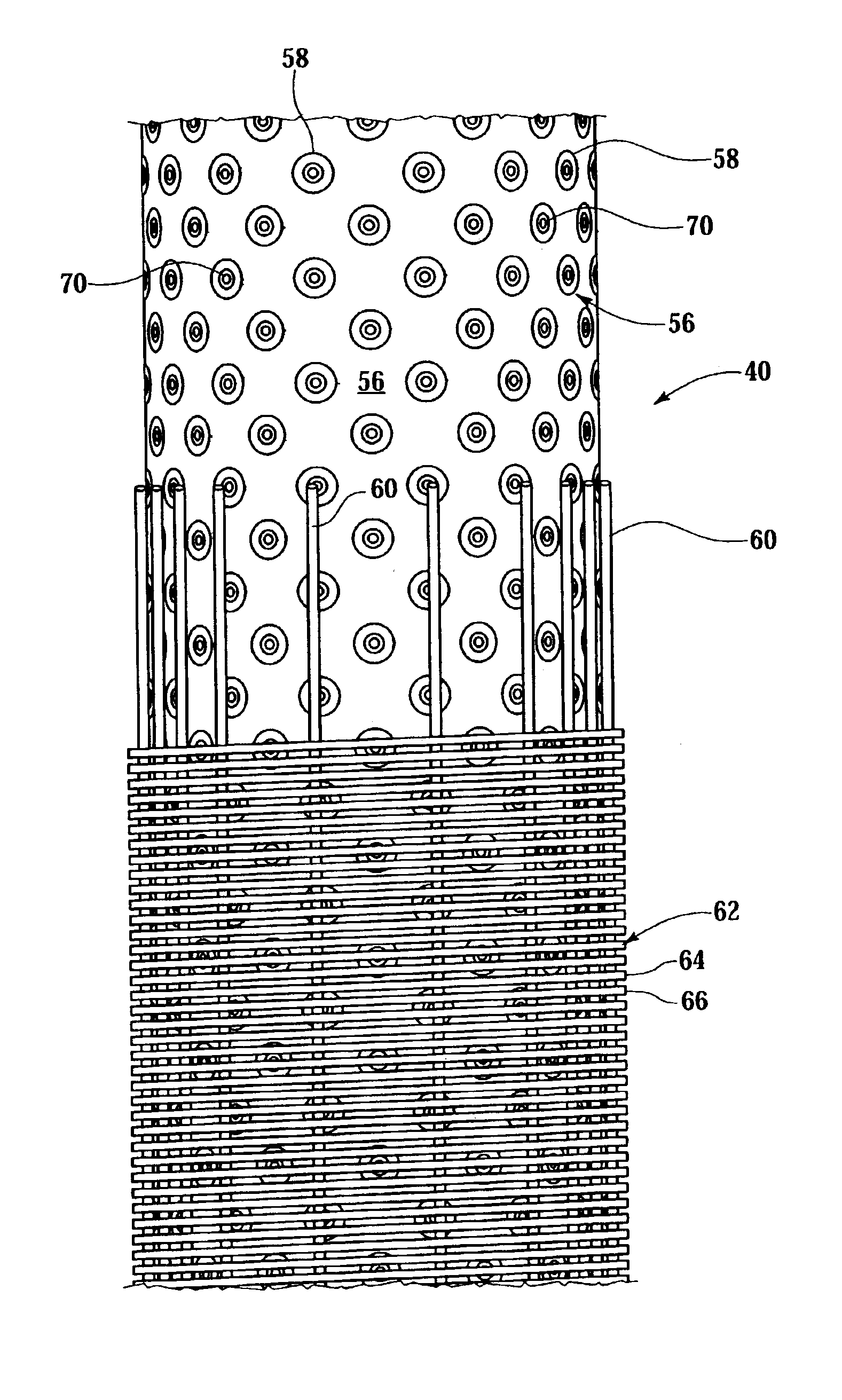
A fluid flow control device (60) for use in a wellbore to control the inflow of production fluids comprises a sand control screen (62) having a base pipe (64) with a first set of openings (66) that allows the production fluids to flow therethrough and a sleeve (74) coaxially disposed adjacent to the base pipe (64). The sleeve (74) has a second set of openings (76) that allows the production fluids to flow therethrough. The sleeve (74) is selectively positionable relative to the base pipe (64) such that a pressure drop in the production fluids is selectively controllable by adjusting an alignment of the first set of openings (66) relative to the second set of openings (76).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
System and methods using fiber optics in coiled tubing
Apparatus having a fiber optic tether disposed in coiled tubing for communicating information between downhole tools and sensors and surface equipment and methods of operating such equipment. Wellbore operations performed using the fiber optic enabled coiled tubing apparatus includes transmitting control signals from the surface equipment to the downhole equipment over the fiber optic tether, transmitting information gathered from at least one downhole sensor to the surface equipment over the fiber optic tether, or collecting information by measuring an optical property observed on the fiber optic tether. The downhole tools or sensors connected to the fiber optic tether may either include devices that manipulate or respond to optical signal directly or tools or sensors that operate according to conventional principles.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Underbalanced drill string deployment valve method and apparatus
Apparatus and methods for a deployment valve used with an underbalanced drilling system to enhance the advantages of underbalanced drilling. The underbalanced drilling system may typically comprise elements such as a rotating blow out preventer and drilling recovery system. The deployment valve is positioned in a tubular string, such as casing, at a well bore depth at or preferably substantially below the string light point of the drilling string. When the drilling string is above the string light point then the upwardly acting forces on the drilling string become greater than downwardly acting forces such that the drilling string begins to accelerate upwardly. The deployment valve has a bore sufficiently large to allow passage of the drill bit therethrough in the open position. The deployment valve may be closed when the drill string is pulled within the casing as may be necessary to service the drill string after drilling into a reservoir having a reservoir pressure. To allow the drill string to be removed from the casing, the pressure produced by the formation can be bled off and the drill string removed for servicing. The drill string can then be reinserted, the pressure in the casing above the deployment valve applied to preferably equalize pressure above and below the valve and the drill string run into the hole for further drilling.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Interventionless multi-position frac tool
ActiveUS20090056934A1Reduce flow pressureConstructionsFluid removalEngineeringMechanical engineering
Fracturing tools for use in oil and gas wells are disclosed. The fracturing tools have a run-in position and two operational positions. A sleeve disposed in the bore of the fracturing tool comprises a sleeve port alignable with a first port in the housing of the frac tool, i.e., the first operational position, during fracturing operations. A second port having a restriction member is disposed in the housing and is closed by the sleeve during fracturing operations. After fracturing operations are completed, a return member in the frac tool moves the sleeve from the first operational position to a second operational position for production operations. In this second operational position, the first port is closed and the sleeve port is aligned with the second port. Movement of the sleeve from the first operational position to the second operational position is performed without the need for an additional well intervention step.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Configurable bridge plugs and methods for using same
An insert for a downhole plug for use in a wellbore is provided, comprising a body having a bore at least partially formed therethrough, wherein one or more threads are disposed on an outer surface of the body for engaging the plug; and at least one interface is disposed on an end of the body for connecting to a tool to screw the insert into at least a portion of the plug.
Owner:NINE DOWNHOLE TECHNOLOLGIES LLC
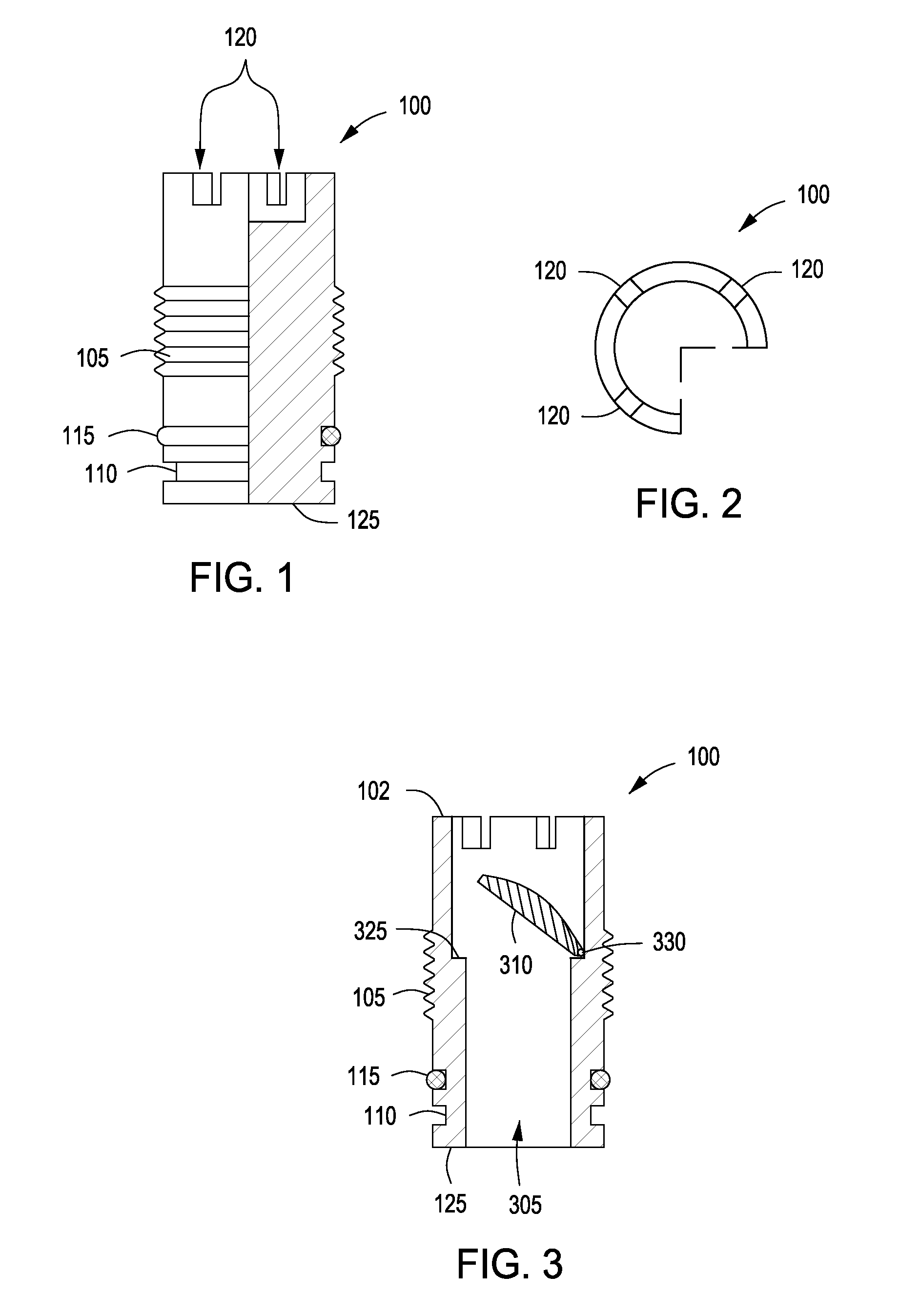
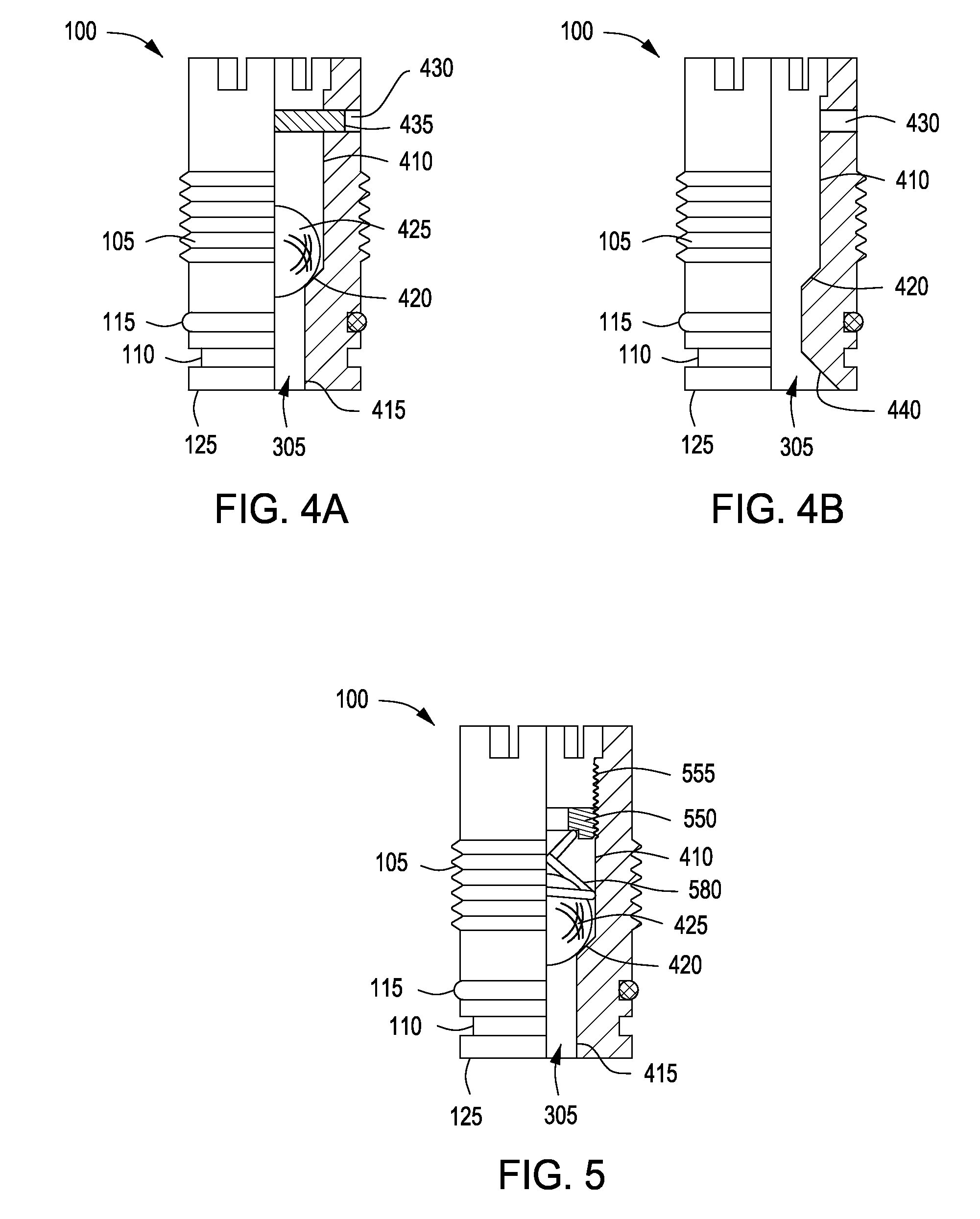
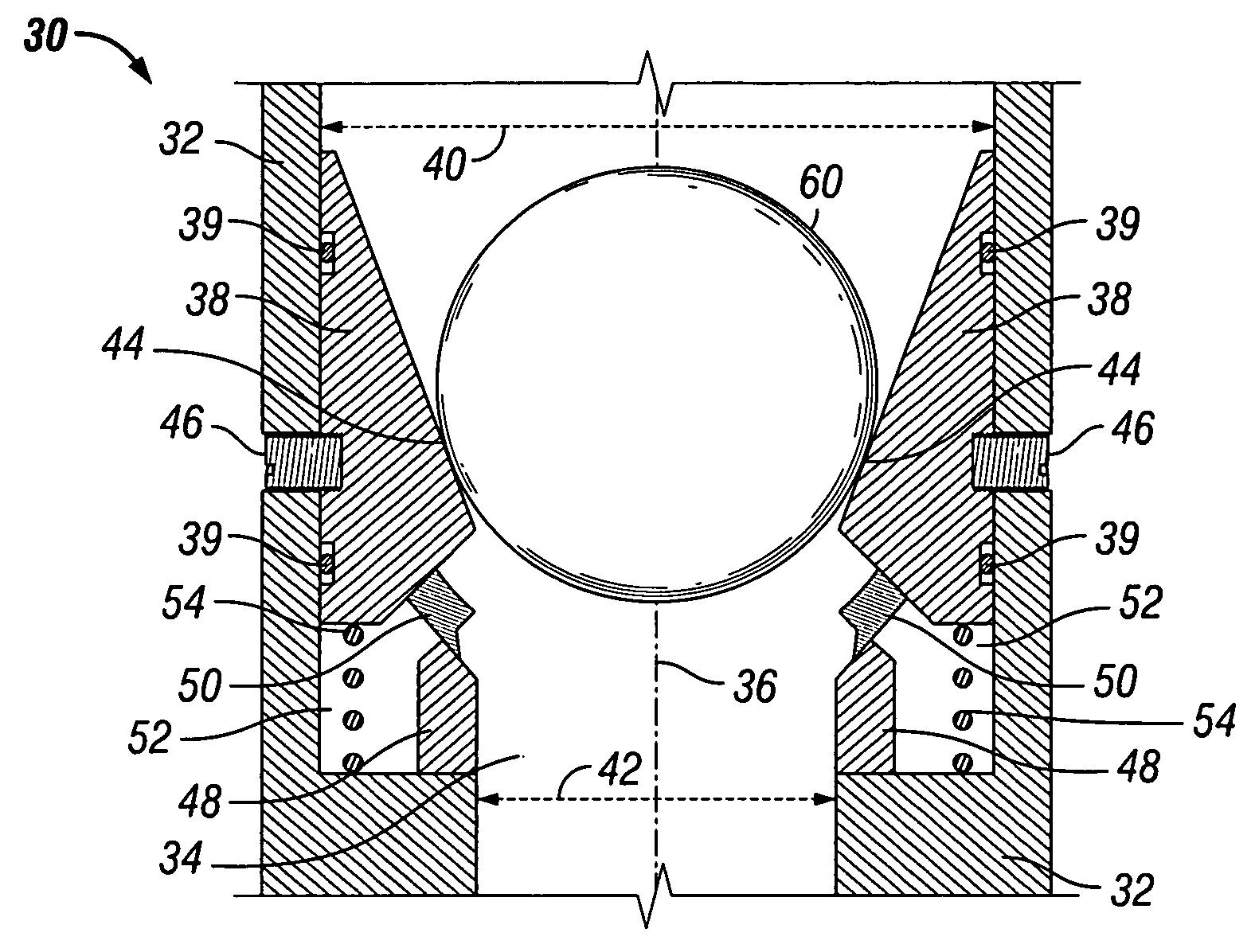
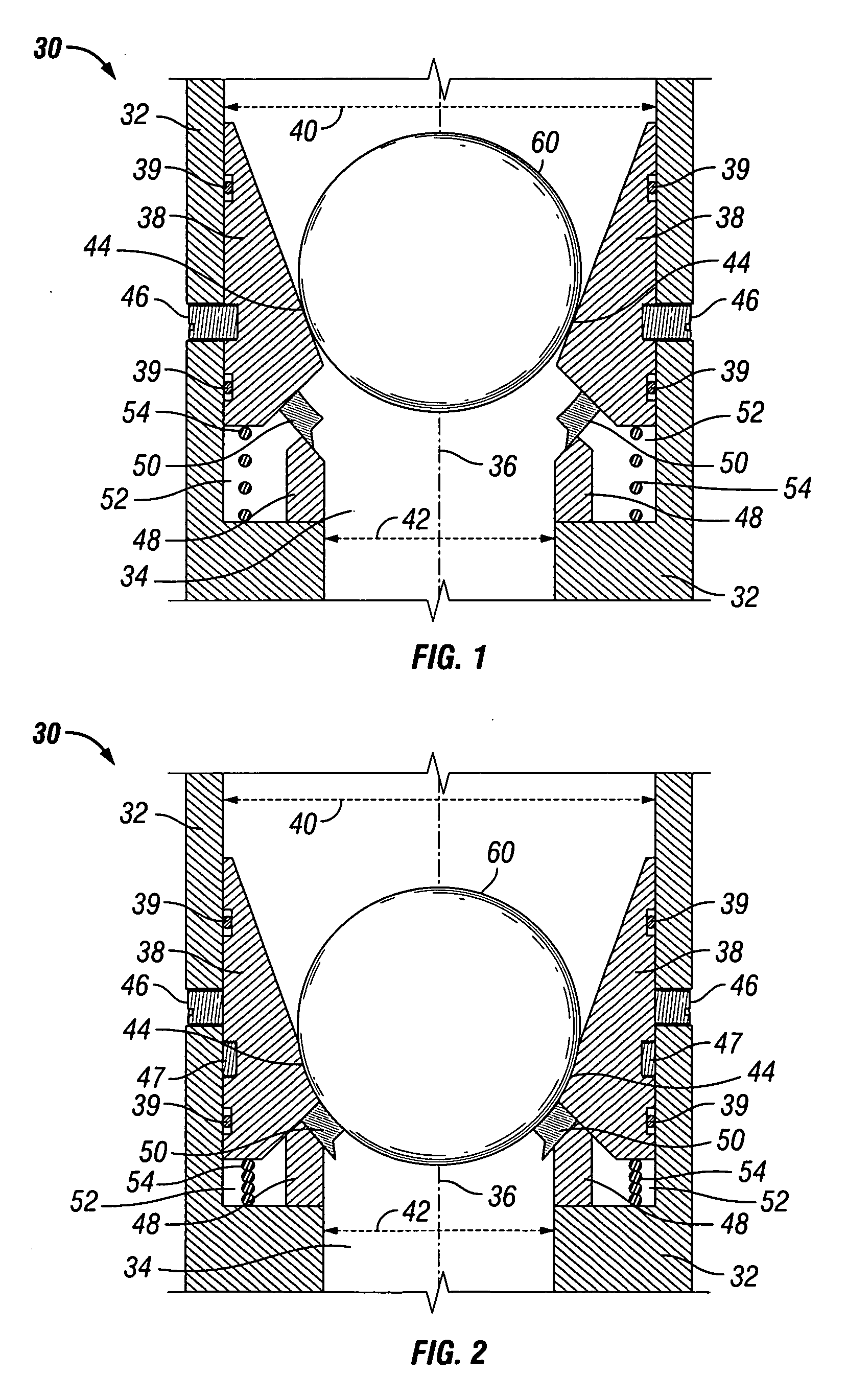
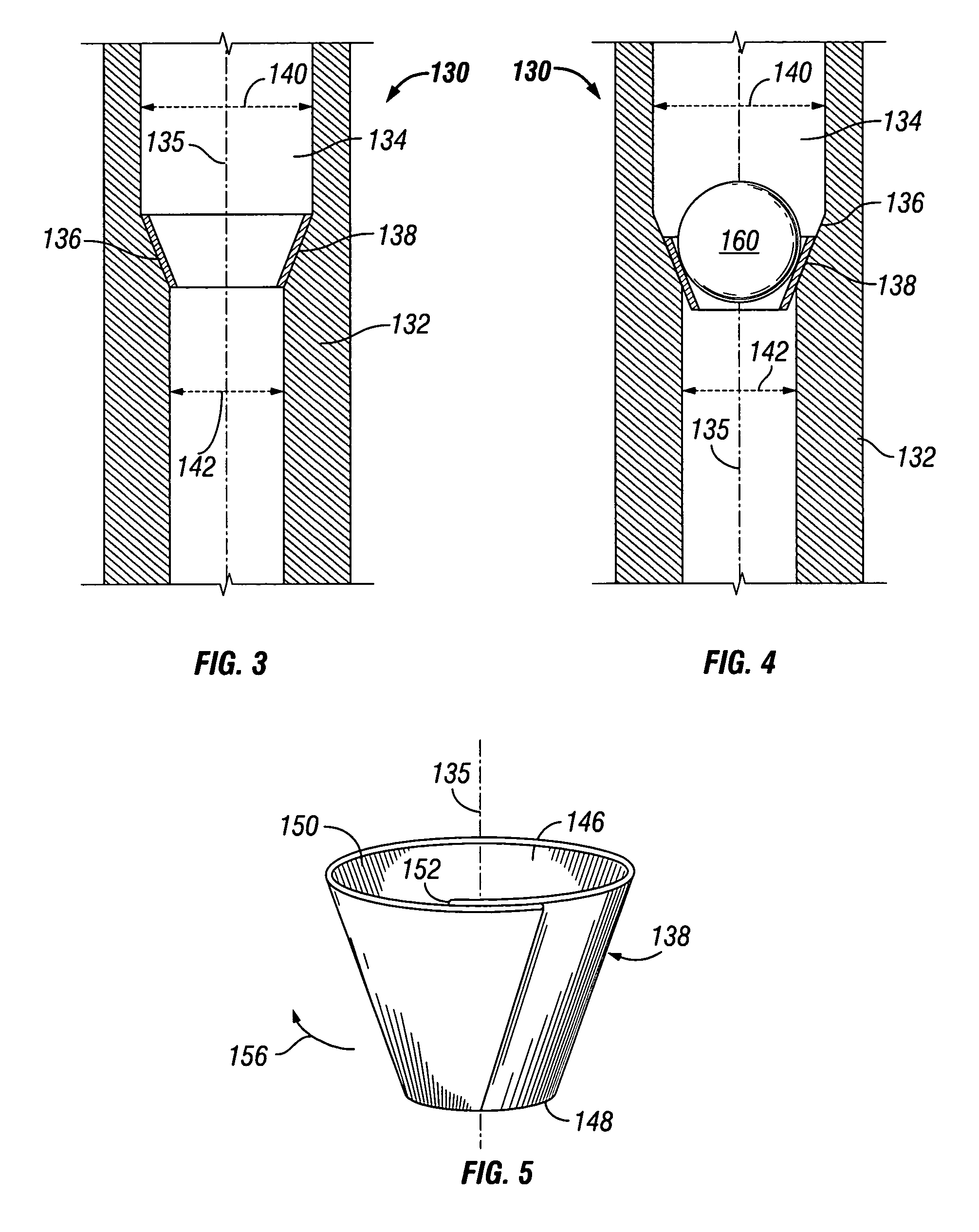
Ball seat having segmented arcuate ball support member
ActiveUS20090159289A1Increase pressureReduce the possibilityFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
High pressure and high temperature ball seat
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Downhole tools having non-toxic degradable elements and methods of using the same
Downhole tools for use in oil and gas production which degrade into non-toxic materials, a method of making them and methods of using them. A frac ball and a bridge plug comprised of polyglycolic acid which can be used in fracking a well and then left in the well bore to predictably, quickly, and safely disintegrate into environmentally friendly products without needing to be milled out or retrieved.
Owner:NINE DOWNHOLE TECHNOLOLGIES LLC
Well treatment apparatus and method
InactiveUS20040040707A1Improve reliabilityImprove securitySurveyDrilling rodsElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
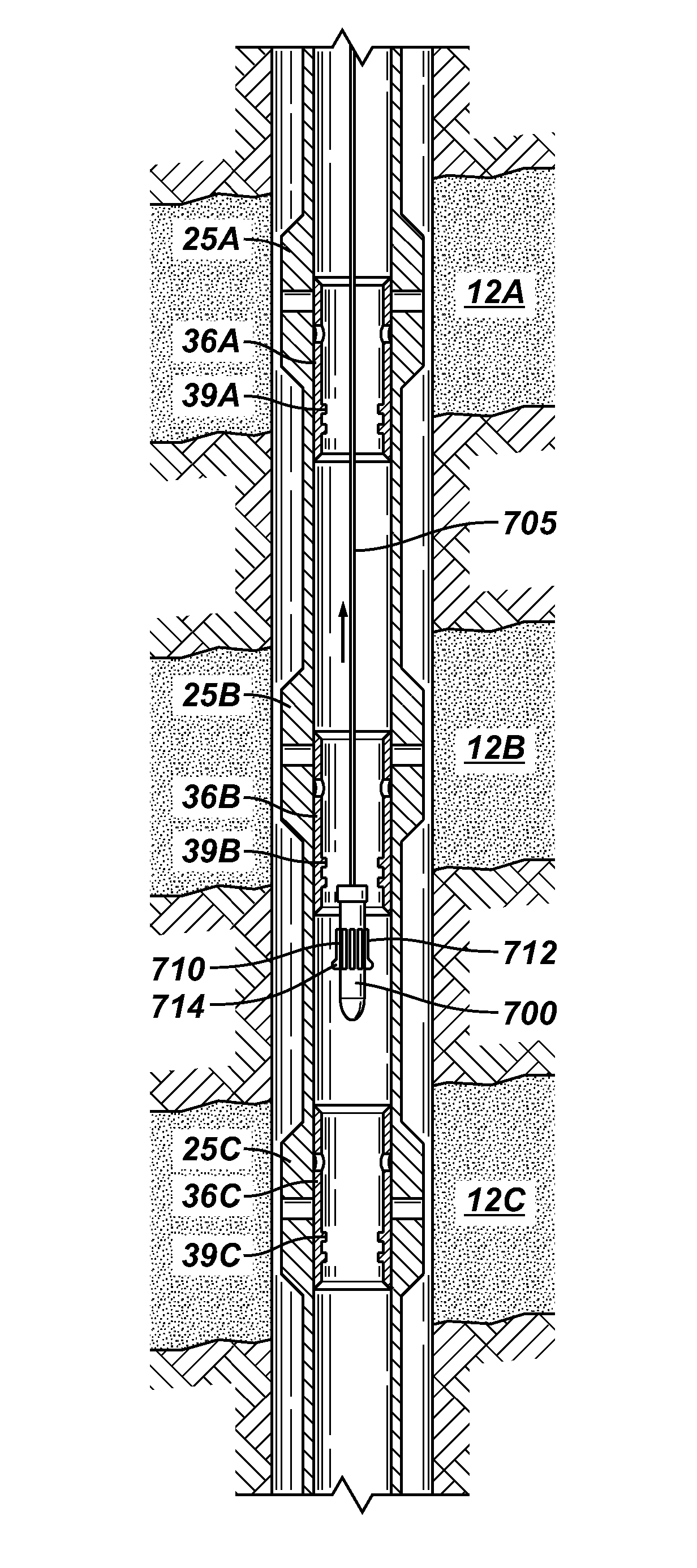
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for sequentially treating multiple zones in underground formation in a single trip of the well treatment work string. In the one embodiment, the work string includes composite tubing having electrical conductors embedded within the walls, the conductors enabling power transmission and two way communication between the surface and the sensor or detectors downhole so that real time data can be sensed and communicated. Isolation packers are actuated via electrical signals from the surface communicated to the bottom hole assembly via the conductors. A detector located in the bottom hole assembly may be provided to detect perforations or other anomalies in the casing, such as joints, enabling the surface controller to position packers properly in blank segments of casing so that well intervals can be properly isolated and the adjacent formation effectively treated.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
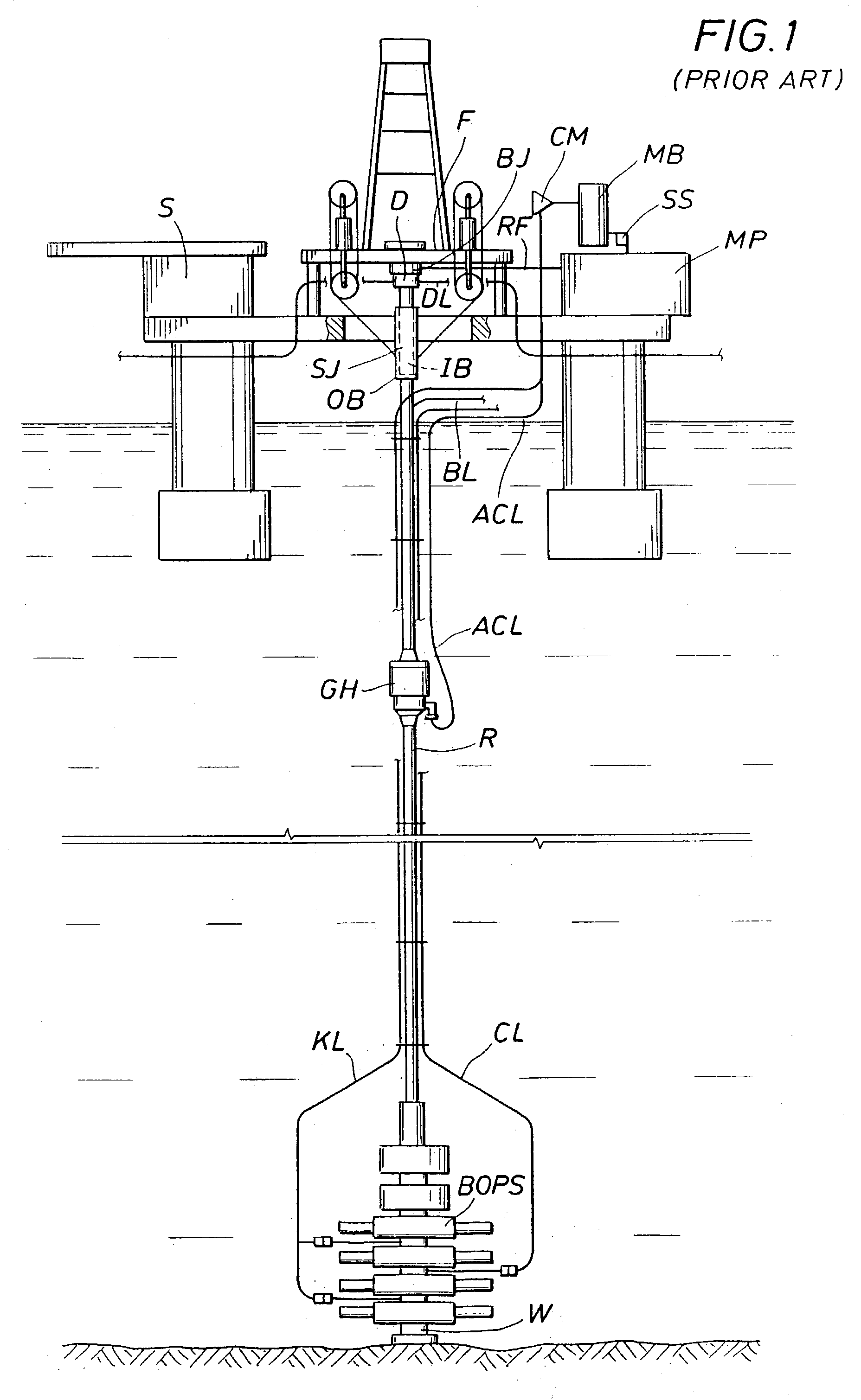
Method and system for return of drilling fluid from a sealed marine riser to a floating drilling rig while drilling
A floating rig or structure for drilling in the floor of an ocean using a rotatable tubular includes a seal housing having a rotatable seal connected above a marine riser fixed to the floor of the ocean. The seal rotating with the rotating tubular allows the riser and seal housing to maintain a predetermined pressure in the system that is desirable in underbalanced drilling, gas-liquid mud systems and pressurized mud handling systems. A flexible conduit or hose is used to compensate for the relative movement of the seal housing and the floating structure since the floating structure moves independent of the seal housing. A method for use of the system is also disclosed.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Controlled downhole chemical injection
InactiveUS6981553B2Improve efficiencyImprove flow characteristicsNear-field transmissionSurveyElectrical conductorPetroleum
A petroleum well having a well casing, a production tubing, a source of time-varying current, a downhole chemical injection device, and a downhole induction choke. The casing extends within a wellbore of the well. The tubing extends within the casing. The current source is located at the surface. The current source is electrically connected to, and adapted to output a time-varying current into, the tubing and / or the casing, which act as electrical conductors for providing downhole power and / or communications. The injection device having a communications and control module, a chemical container, and an electrically controllable chemical injector. The communications and control module is electrically connected to the tubing and / or the casing. The chemical injector is electrically connected to the communications and control module, and is in fluid communication with the chemical container. The downhole induction choke is located about a portion of the tubing and / or the casing. The chemical injector is electrically connected to the communications and control module, and is in fluid communication with the chemical container. The downhole induction choke is located about a portion of the tubing and / or the casing. The induction choke is adapted to route part of the electrical current through the communications and control module by creating a voltage potential between one side of the induction choke and another side of the induction choke. The communications and control module is electrically connected across the voltage potential. Also, a method is provided for controllably injecting a chemical into the well downhole, which may be used to: improve lift efficiency with a foaming agent, prevent deposition of solids with a paraffin solvent, improve a flow characteristic of the flow stream with a surfactant, prevent corrosion with a corrosion inhibitor, and / or prevent scaling with scale preventers.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
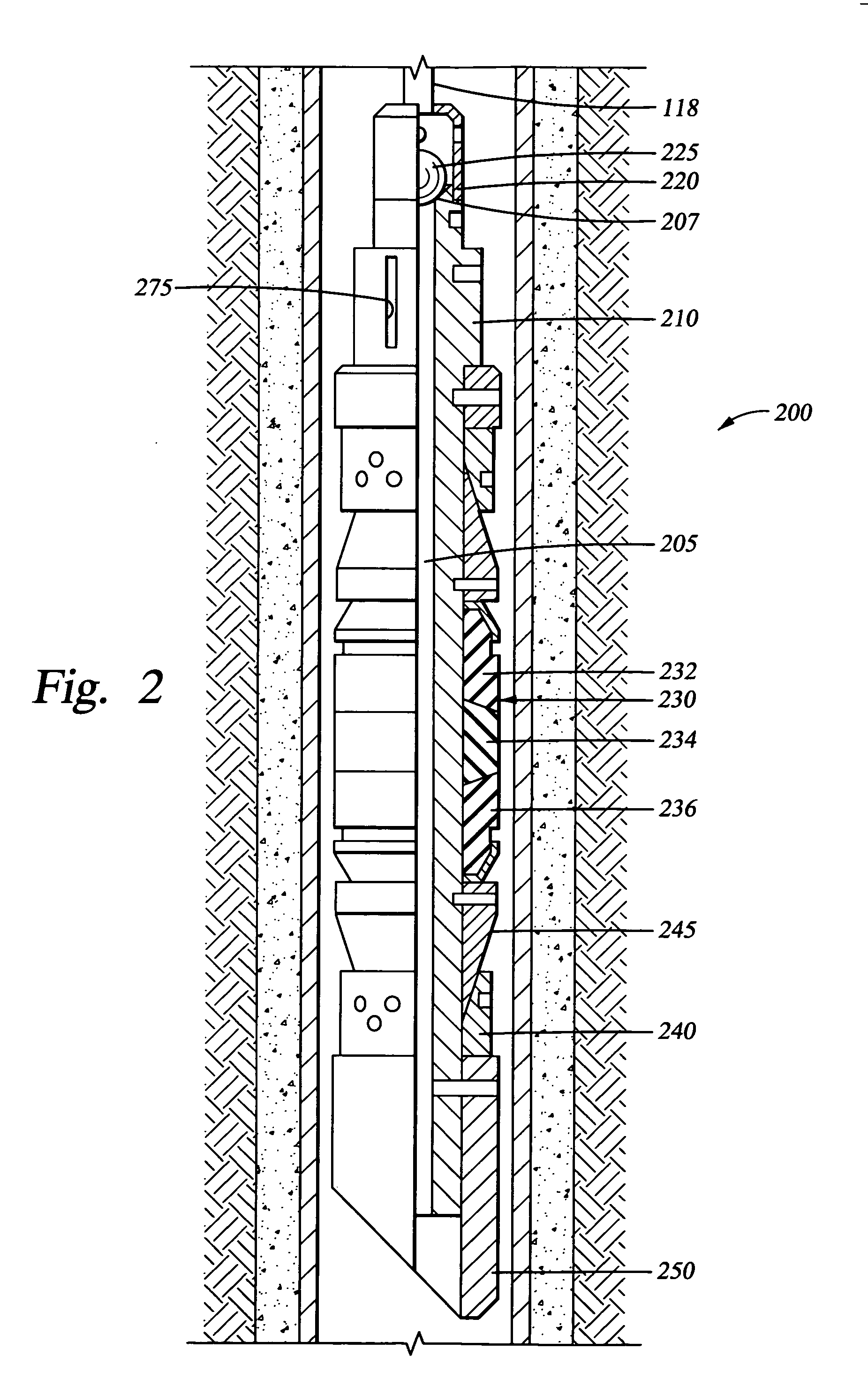
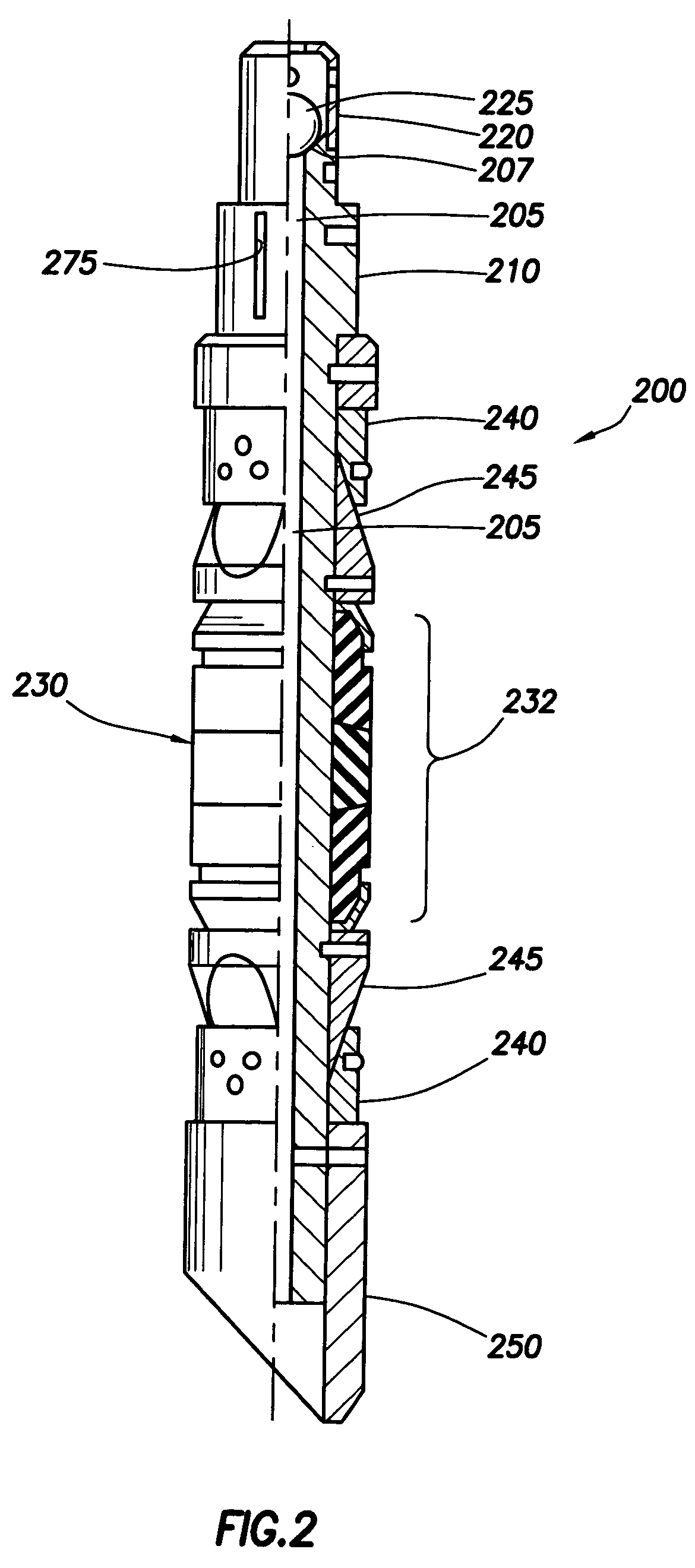
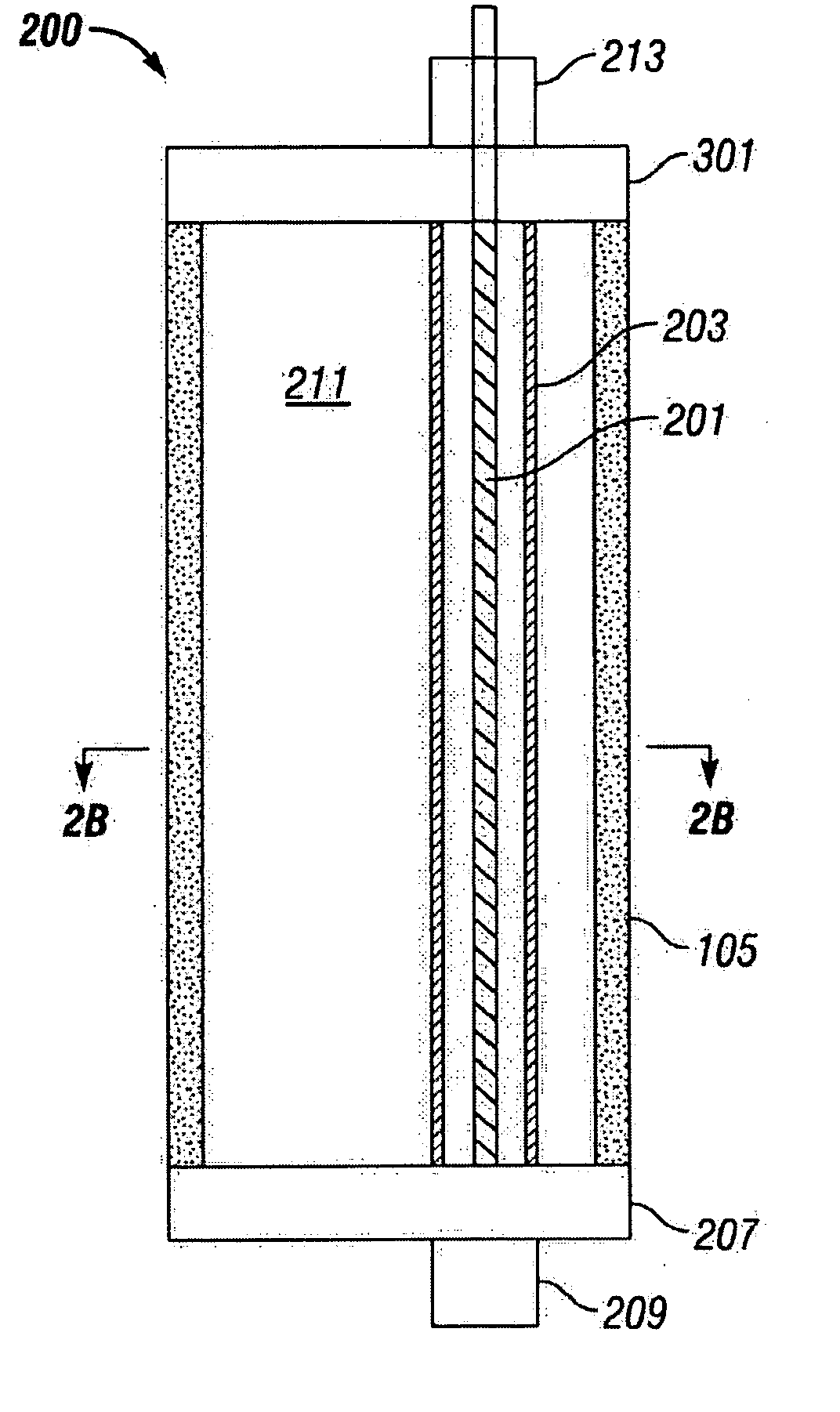
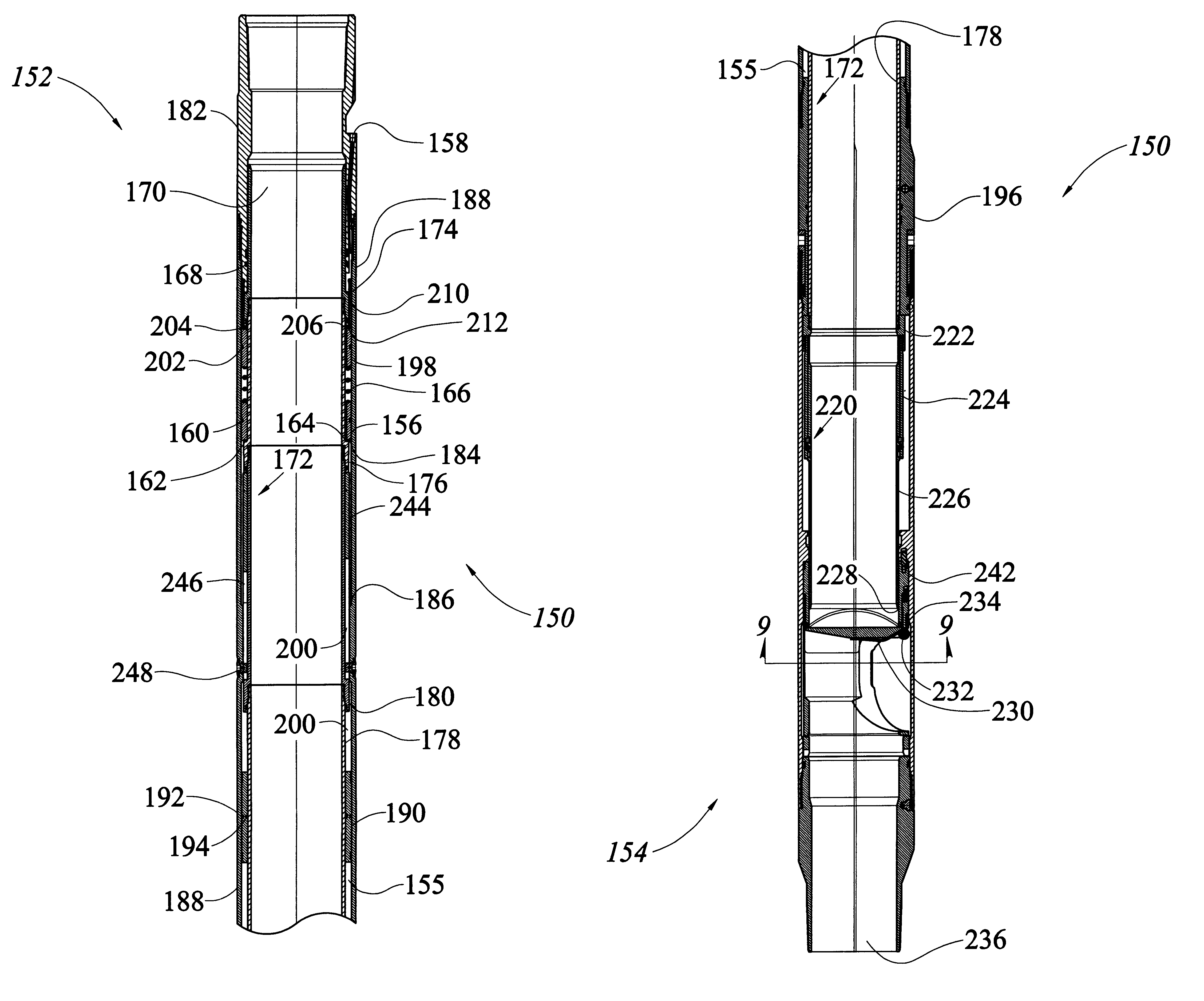
Sand control screen assembly and treatment method using the same
A sand control screen assembly (200) positionable within a production interval of a wellbore that traverses a subterranean hydrocarbon bearing formation comprises a base pipe (202) having openings (204) in a sidewall section thereof that allow fluid flow therethrough. A filter medium (210) is positioned about the exterior of at least a portion of the base pipe (202). The filter medium (210) selectively allows fluid flow therethrough but prevents the flow of particulate of a predetermined size therethrough. A seal member (218, 220, 222) is operably associated with the base pipe (202). The seal member (218, 220, 222) has a one-way valve configuration and a valve open configuration such that the seal member (218, 220, 222) controls fluid flow through the openings (204) of the base pipe (202).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Internal riser rotating control head
A holding member provides for releasably positioning a rotating control head assembly in a subsea housing. The holding member engages an internal formation in the subsea housing to resist movement of the rotating control head assembly relative to the subsea housing. The rotating control head assembly is sealed with the subsea housing when the holding member engages the internal formation. An extendible portion of the holding member assembly extrudes an elastomer between an upper portion and a lower portion of the internal housing to seal the rotating control head assembly with the subsea housing. Pressure relief mechanisms release excess pressure in the subsea housing and a pressure compensation mechanism pressurize bearings in the bearing assembly at a predetermined pressure.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Remotely controlled apparatus for downhole applications and methods of operation
An apparatus for use downhole is disclosed that, in one configuration includes a downhole tool configured to operate in an active position and an inactive position and an actuation device, which may include a control unit. The apparatus includes a telemetry unit that sends a first pattern recognition signal to the control unit to move the tool into the active position and a second pattern recognition signal to move the tool into the inactive position. The apparatus may be used for drilling a subterranean formation and include a tubular body and one or more extendable features, each positionally coupled to a track of the tubular body, and a drilling fluid flow path extending through a bore of the tubular body for conducting drilling fluid therethrough. A push sleeve is disposed within the tubular body and coupled to the one or more features. A valve assembly is disposed within the tubular body and configured to control the flow of the drilling fluid into an annular chamber in communication with the push sleeve; the valve assembly comprising a mechanically operated valve and / or an electronically operated valve. Other embodiments, including methods of operation, are provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC
Methods and apparatus for actuating a downhole tool
The present invention relates to apparatus and methods for remotely actuating a downhole tool. In one aspect, the present invention provides an apparatus for activating a downhole tool in a wellbore, the downhole tool having an actuated and unactuated positions. The apparatus includes an actuator for operating the downhole tool between the actuated and unactuated positions; a controller for activating the actuator; and a sensor for detecting a condition in the wellbore, wherein the detected condition is transmitted to the controller, thereby causing the actuator to operate the downhole tool. In one embodiment, conditions in the wellbore are generated at the surface, which is later detected downhole. These conditions include changes in pressure, temperature, vibration, or flow rate. In another embodiment, a fiber optic signal may be transmitted downhole to the sensor. In another embodiment still, a radio frequency tag is dropped into the wellbore for detection by the sensor.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Use of downhole high pressure gas in a gas-lift well and associated methods
InactiveUS7147059B2Simplified installation procedureLow costNear-field transmissionSurveyElectrical conductorPetroleum product
A gas-lift petroleum well and method for producing petroleum products using downhole pressurized gas to provide lift. The gas-lift well having a well casing, a production tubing, a packer, and a gas-lift valve. The well casing extends within a wellbore of the well, and the wellbore extends through oil and gas zones. The production tubing extends within the casing. The tubing having an opening formed therein, which is in fluid communication with an oil zone. The packer is located downhole in the casing and coupled to the tubing. The packer can have an electrically controllable packer valve, which is adapted to control a flow of downhole pressurized gas from one side of the packer to another. The downhole pressurized gas is provided by a gas zone that the wellbore passes through. The downhole gas-lift valve is coupled to the tubing and is adapted to control a flow of downhole pressurized gas into oil in the tubing for lifting the oil. The gas-lift valve can be an electrically controllable valve. The tubing and casing are used as electrical conductors for supplying power and / or communications downhole. The current in the tubing is routed using a ferromagnetic induction choke to create a voltage potential, which provides electrical power to downhole electrical devices. Also, there may be a bypass passageway to route downhole gas to gas-lift valves. There may also be downhole sensors to measure physical quantities (e.g., pressure). Such measurements can be used for feedback control of downhole electrically controllable valves.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Sliding sleeve sub and method and apparatus for wellbore fluid treatment
A tubing string assembly is disclosed for fluid treatment of a wellbore The tubing string can be used for staged wellbore fluid treatment where a selected segment of the wellbore is treated, while other segments are sealed off The tubing string can also be used where a ported tubing string is required to be run-m in a pressure tight condition and later is needed to be in an open-port condition A sliding sleeve in a tubular has a driver selected to be acted upon by an inner bore conveyed actuating device, the driver drives the generation of a ball stop on the sleeve.
Owner:PACKERS PLUS ENERGY SERVICES INC
Multi-Position Valve for Fracturing and Sand Control and Associated Completion Methods
A completion tubular is placed in position adjacent the zone or zones to be fractured and produced. It features preferably sliding sleeve valves that can assume at least two configurations: wide open and open with a screen material juxtaposed in the flow passage. In a preferred embodiment the valve assembly has three positions, adding a fully closed position to the other two mentioned. After run in, the valves can be put in the wide open position in any order desired to fracture. After fracturing, the valves can be closed or selectively be put in filtration position for production from the fractured zones in any desired order. Various ways are described to actuate the valves. The tubular can have telescoping pistons through which the fracturing can take place if the application calls for a cemented tubular. Alternatively, the tubular can be in open hole and simply have openings for passage of fracture fluid and external isolators to allow fracturing in any desired order.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com