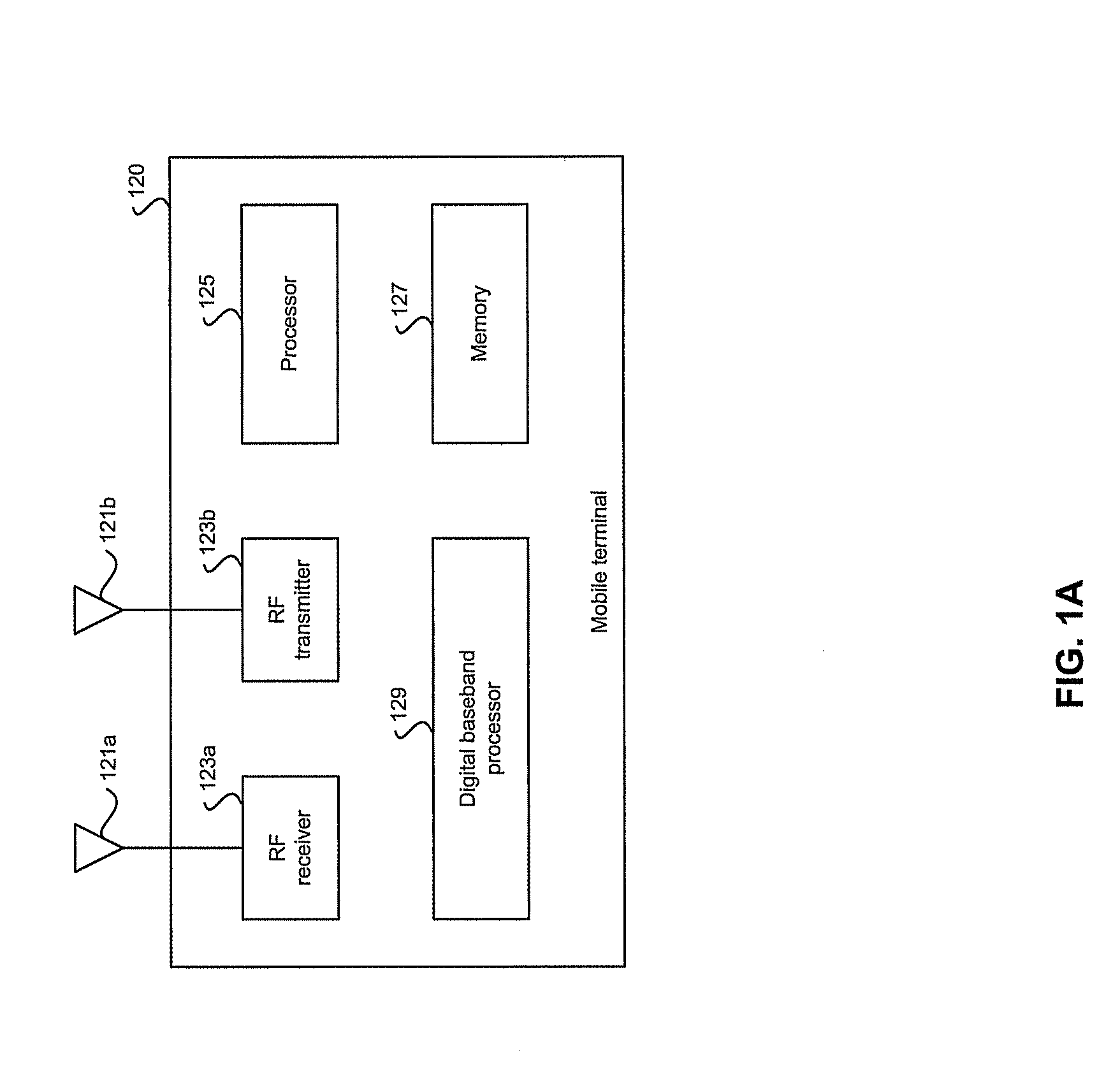
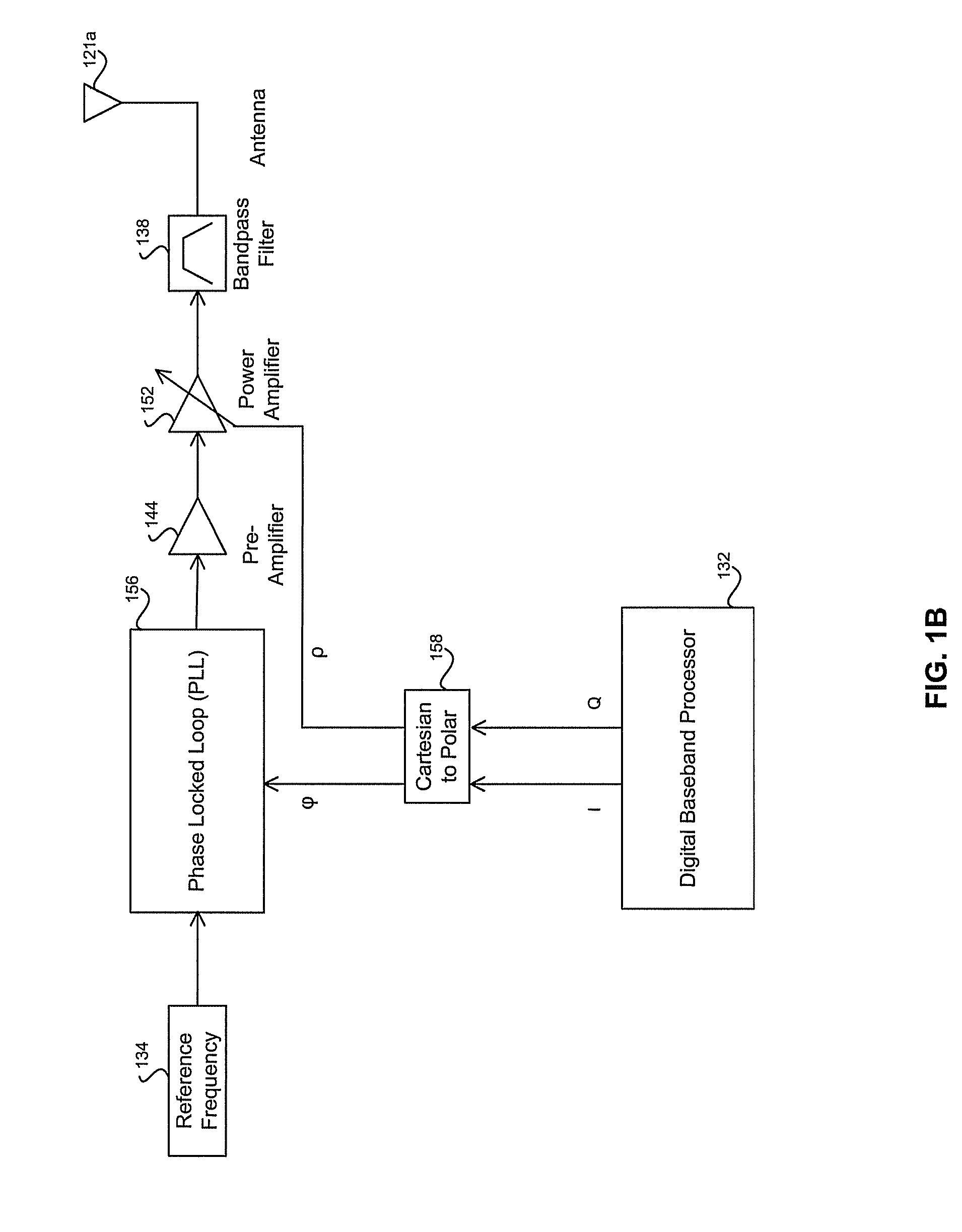
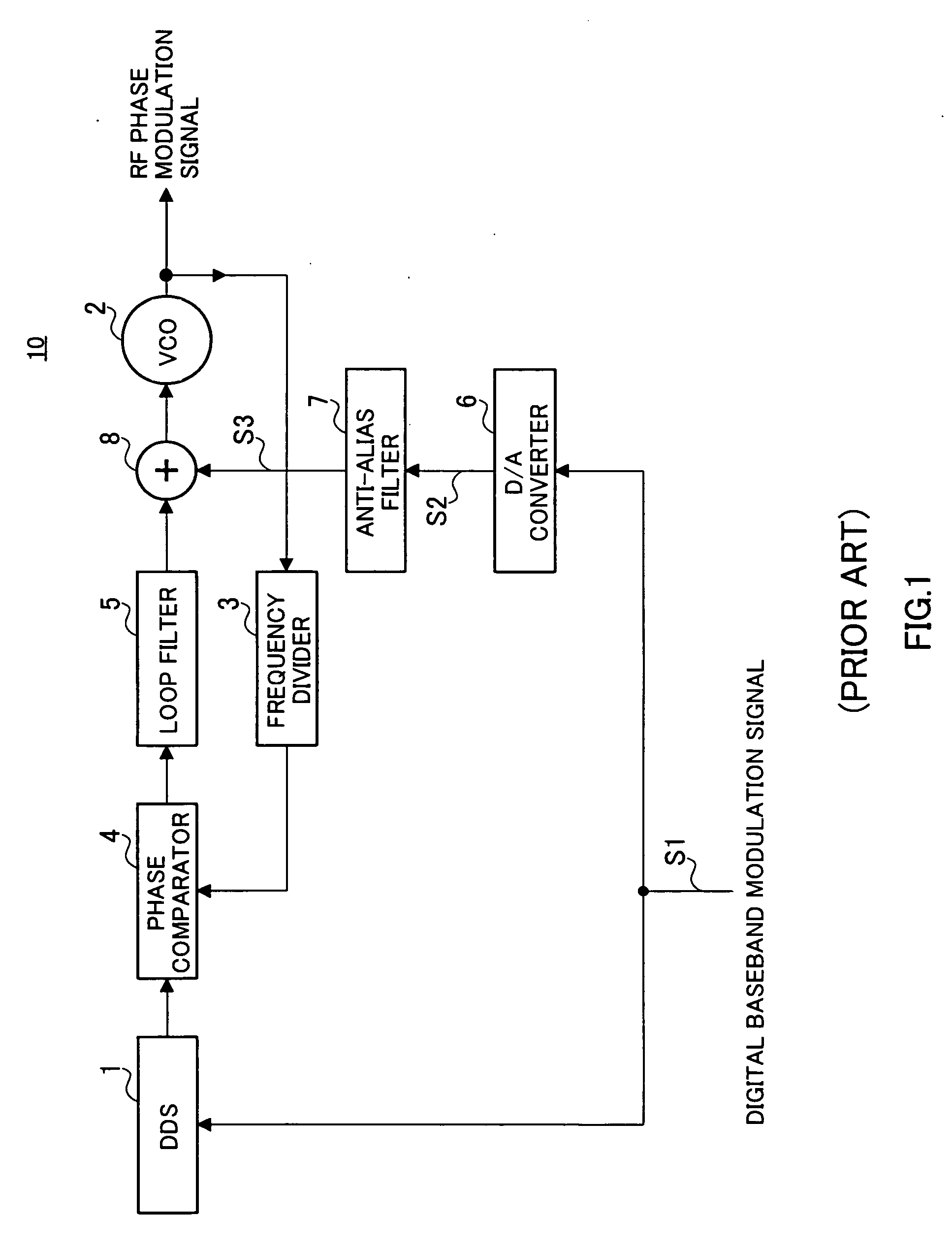
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
258 results about "Polar modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
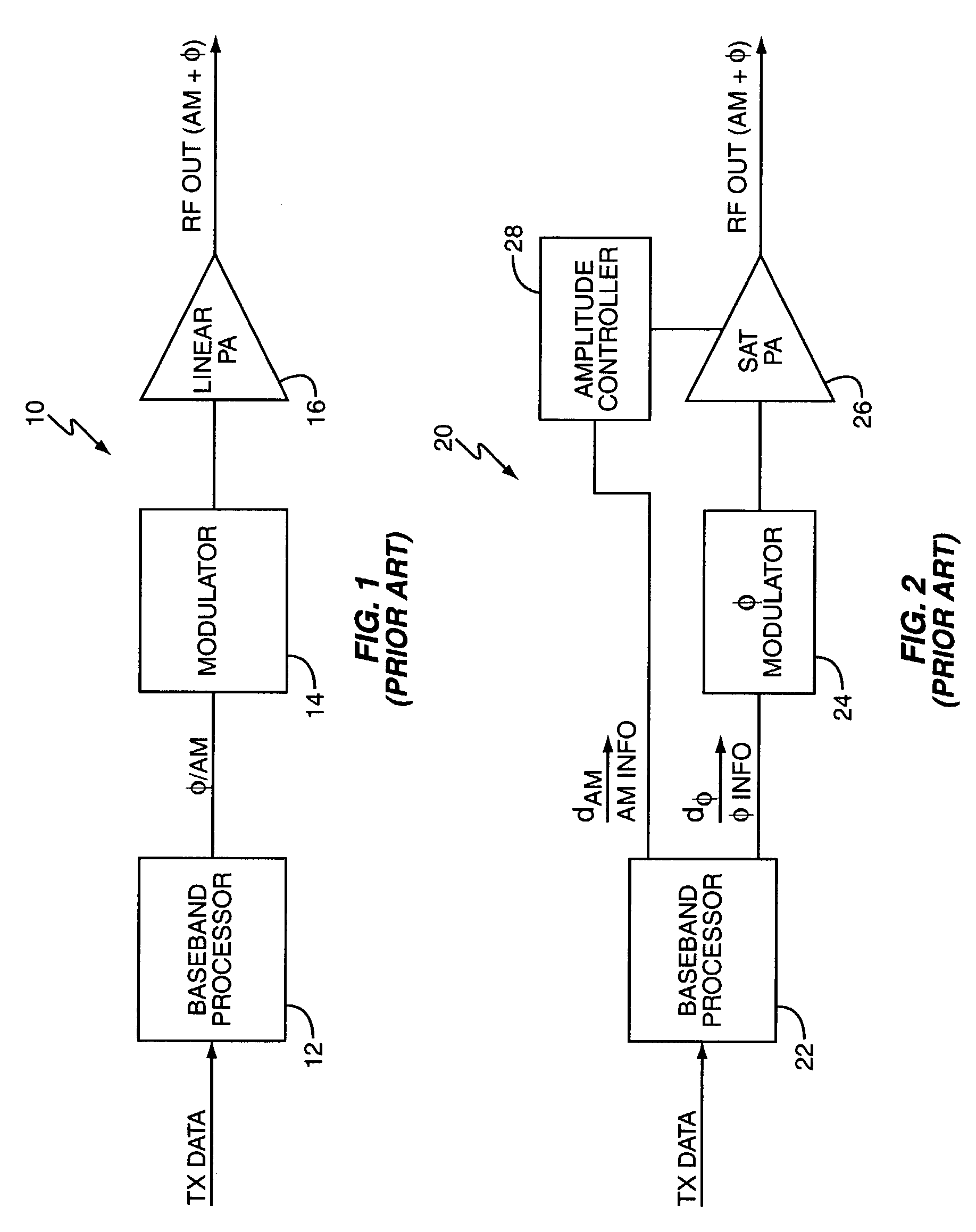
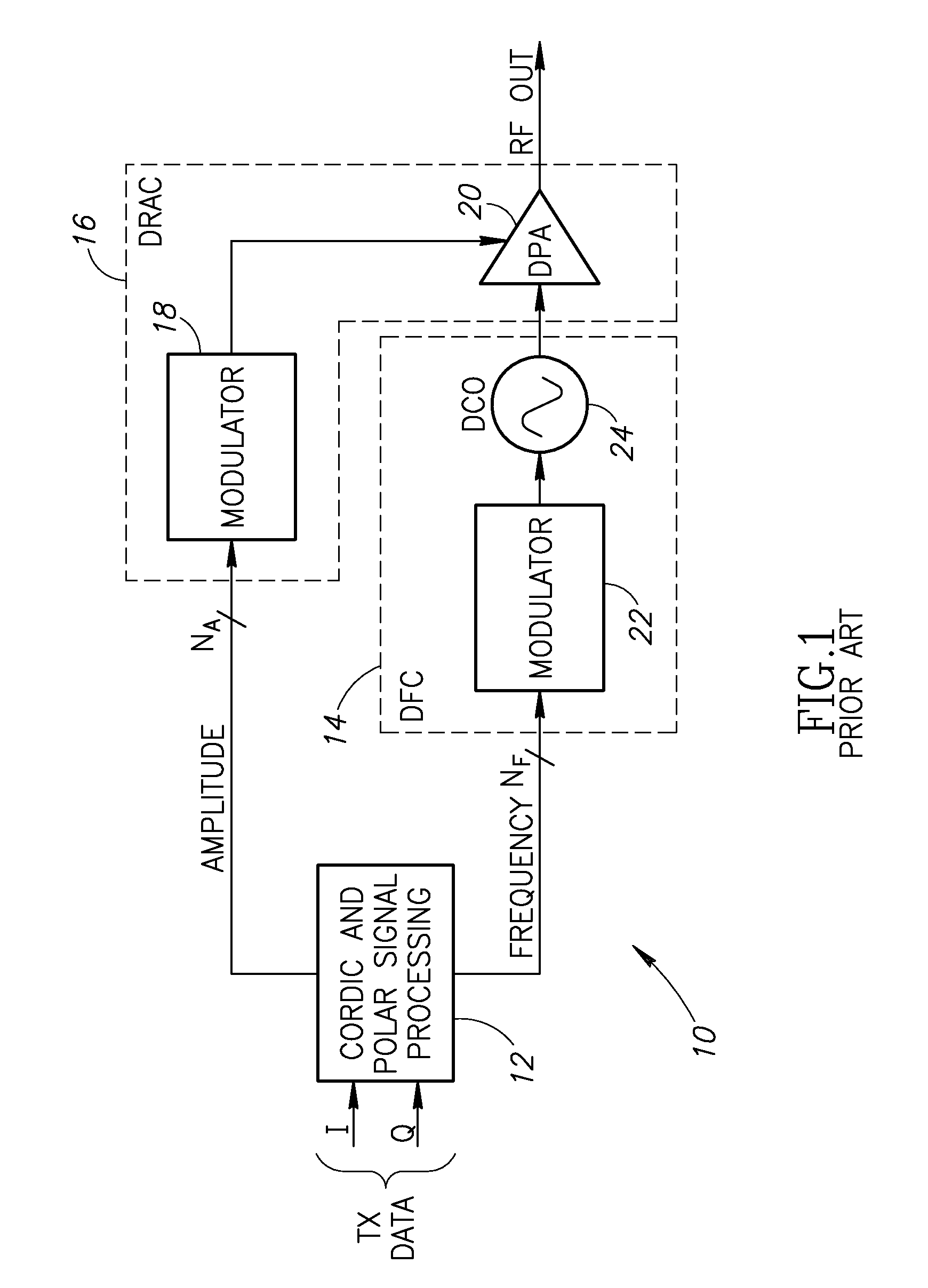
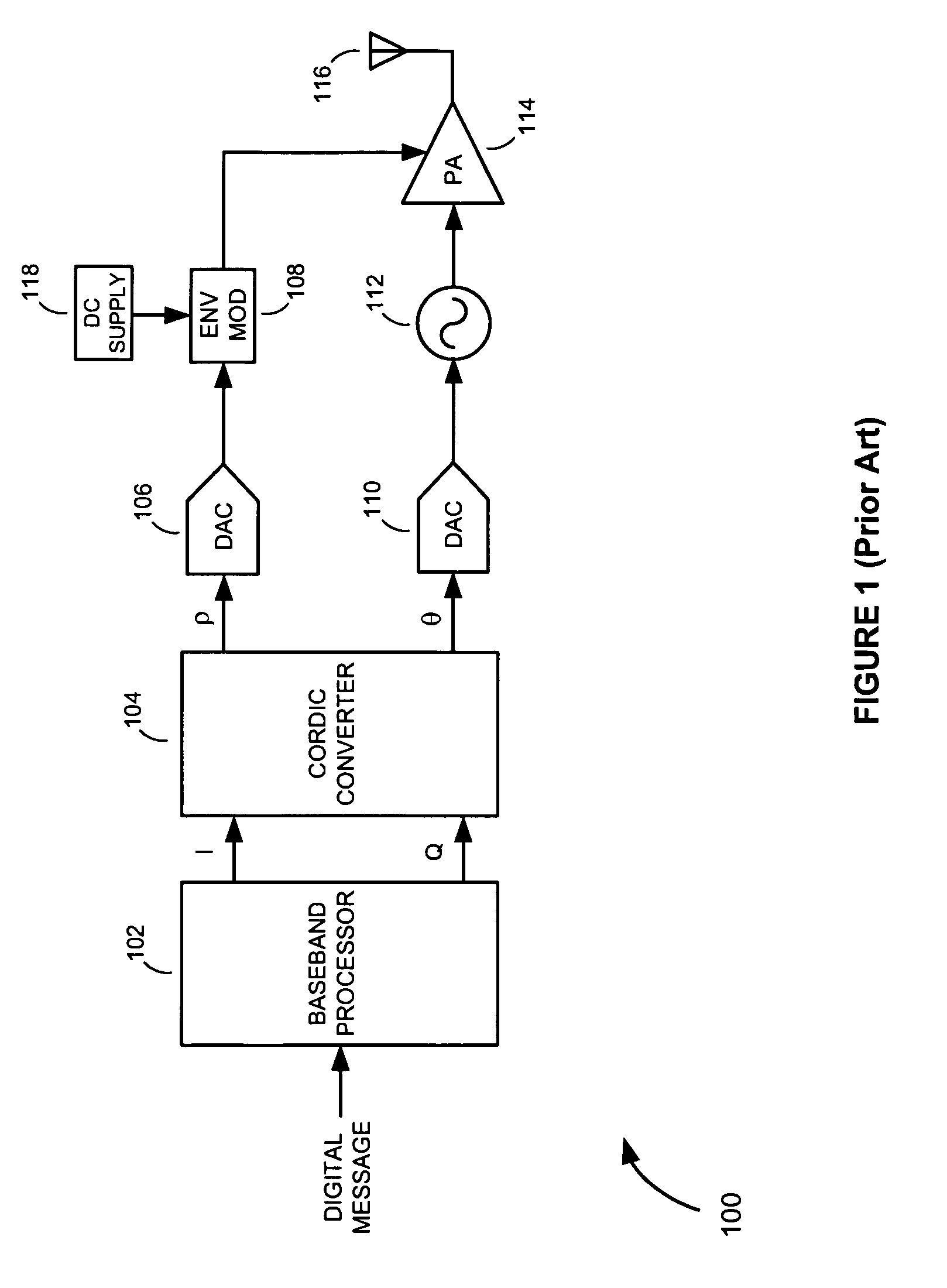
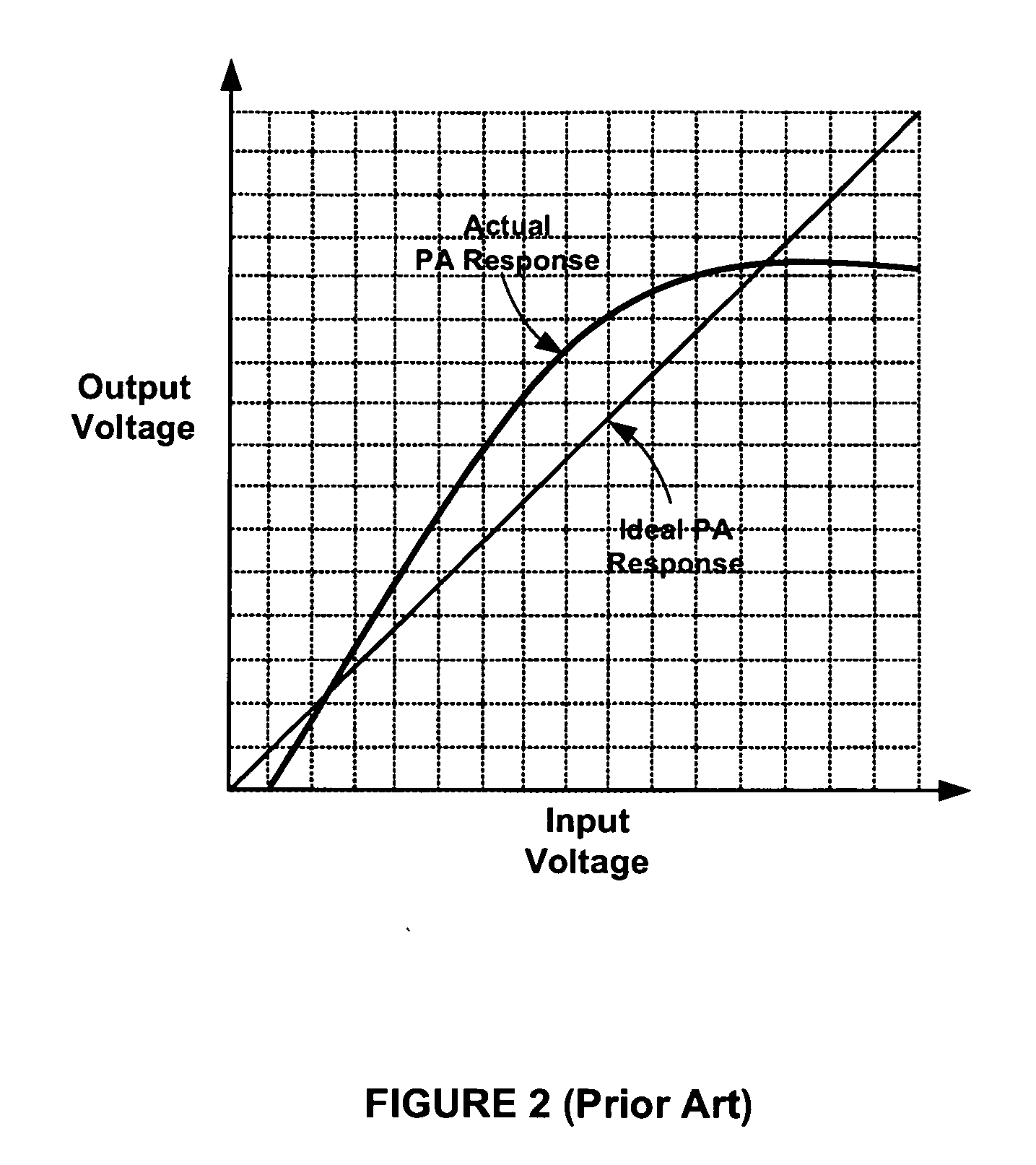
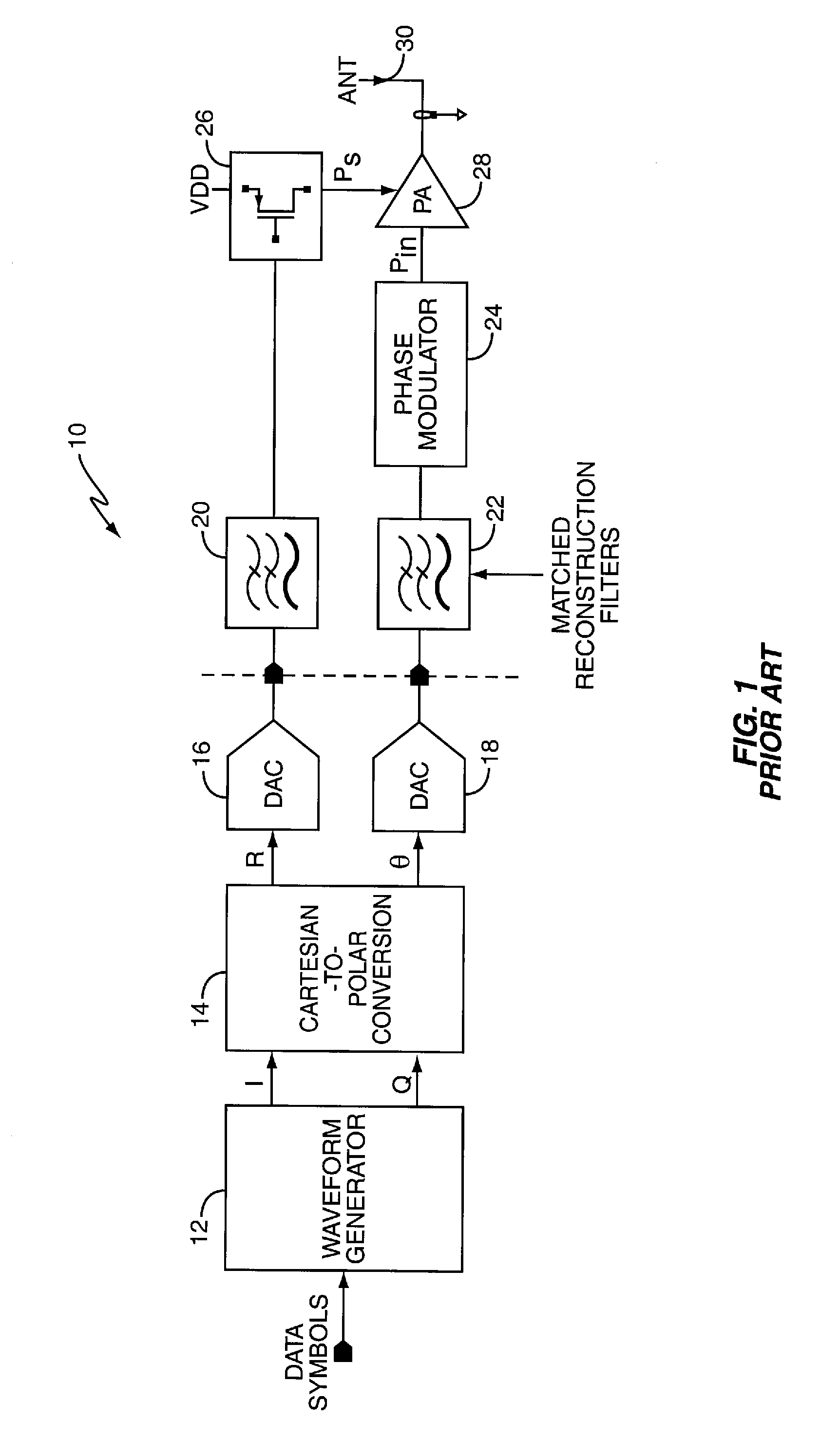
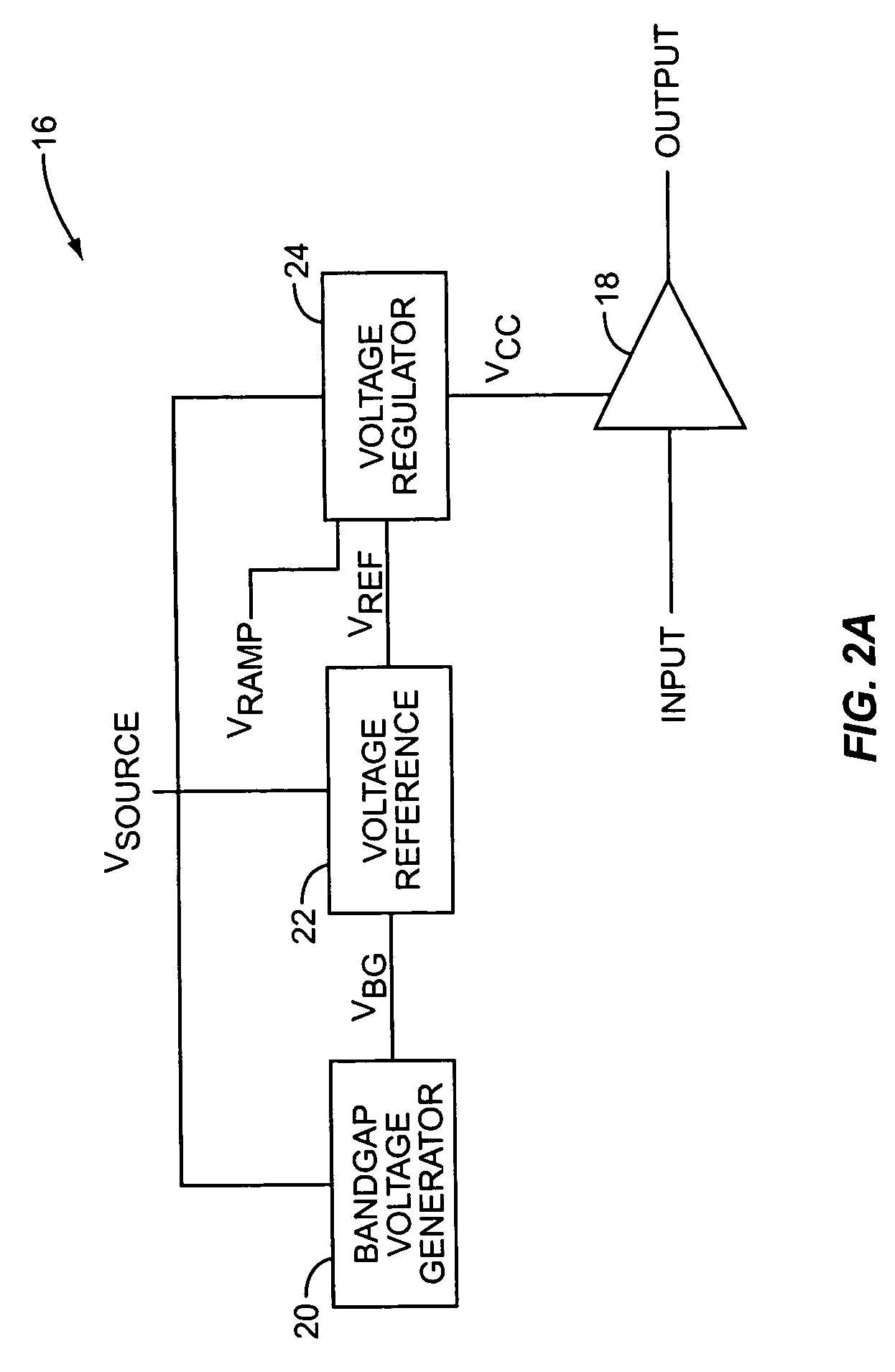
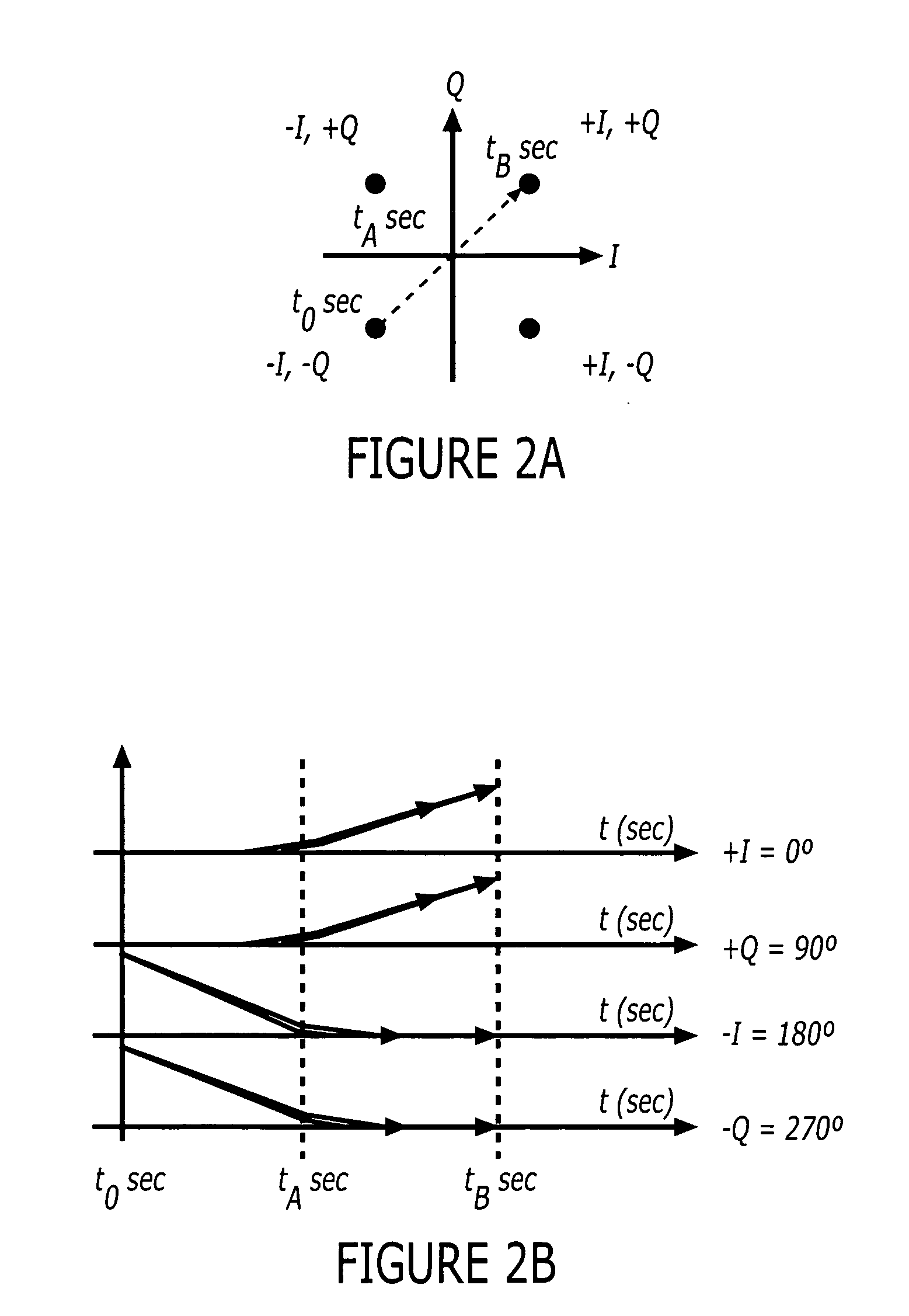
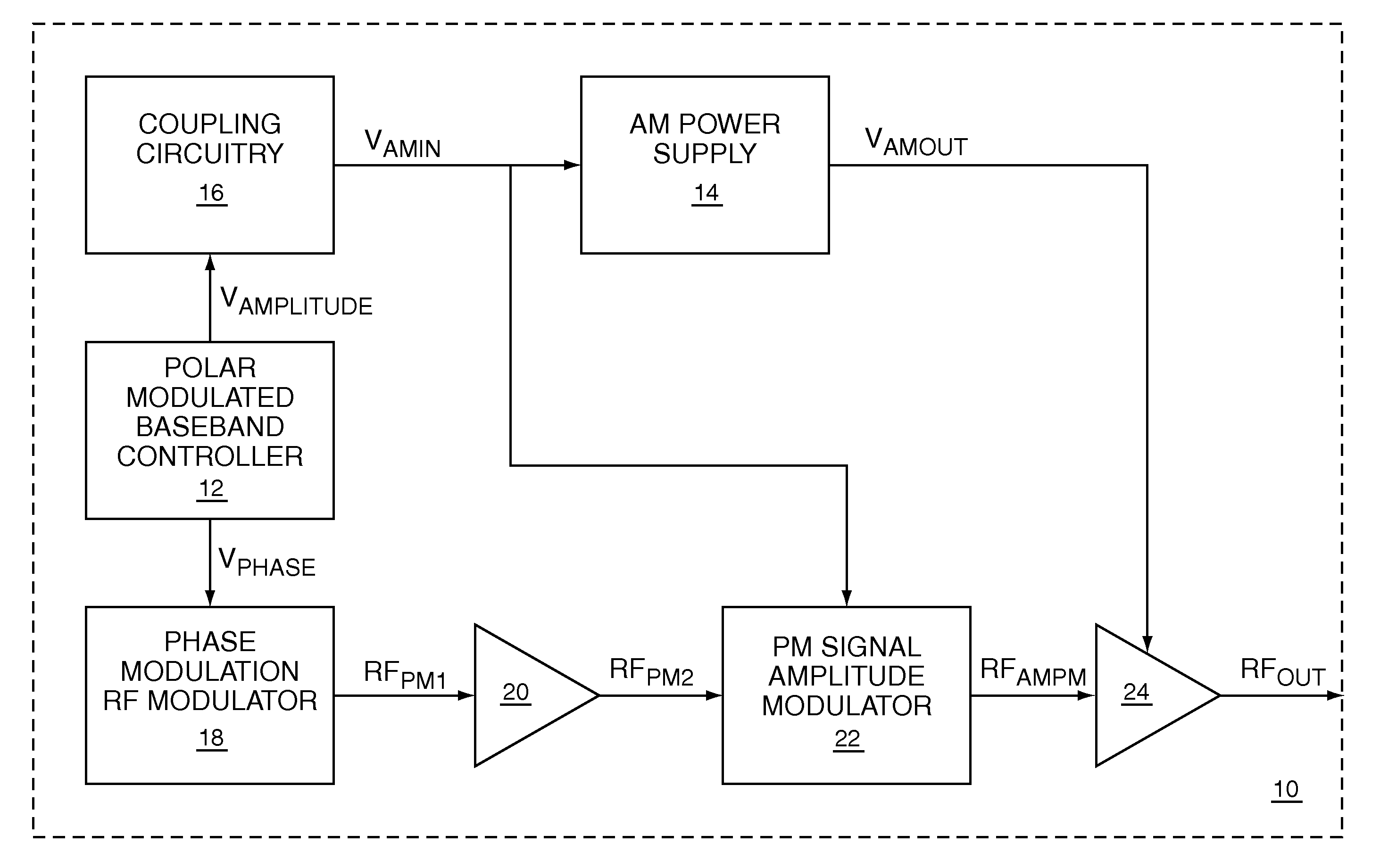
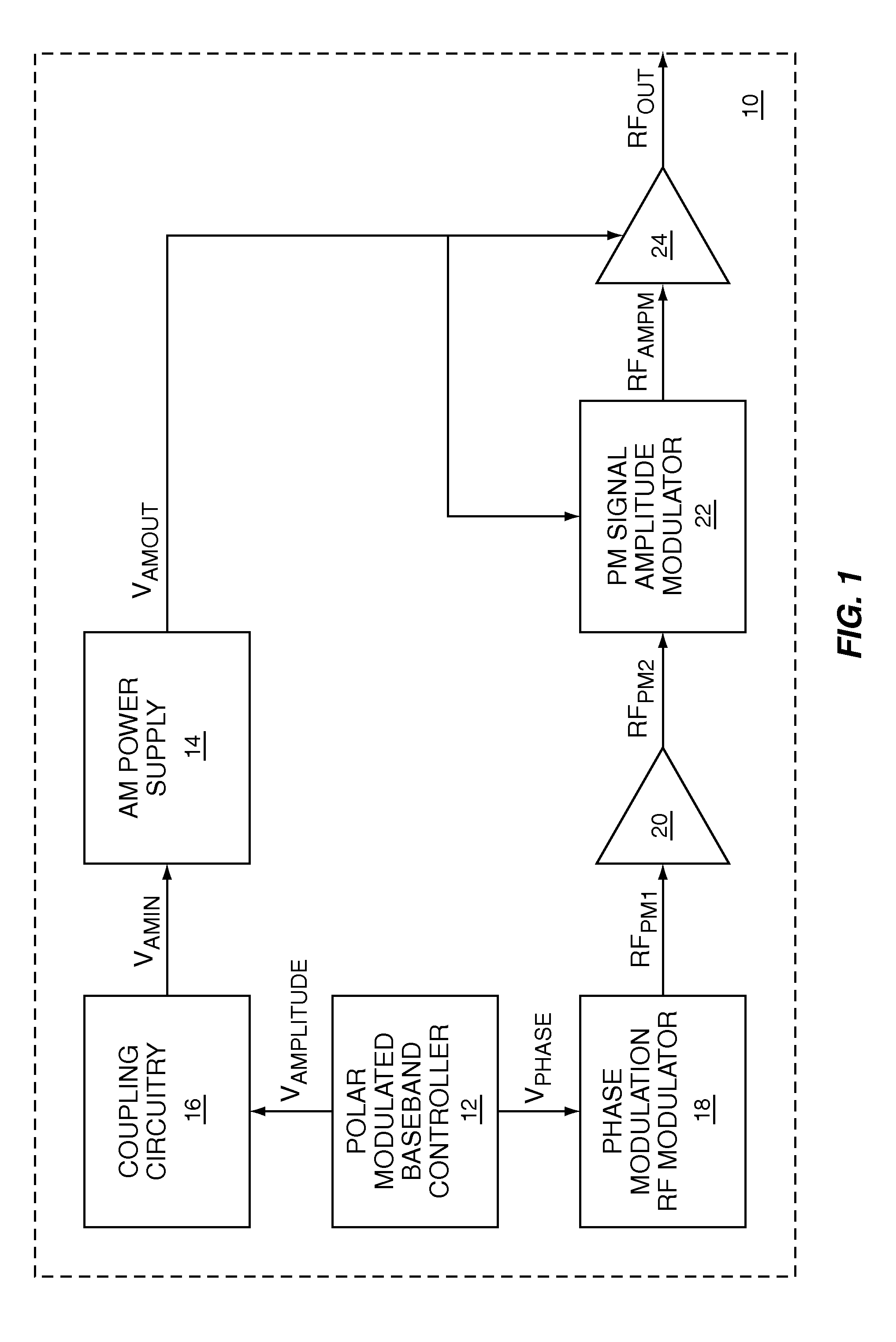
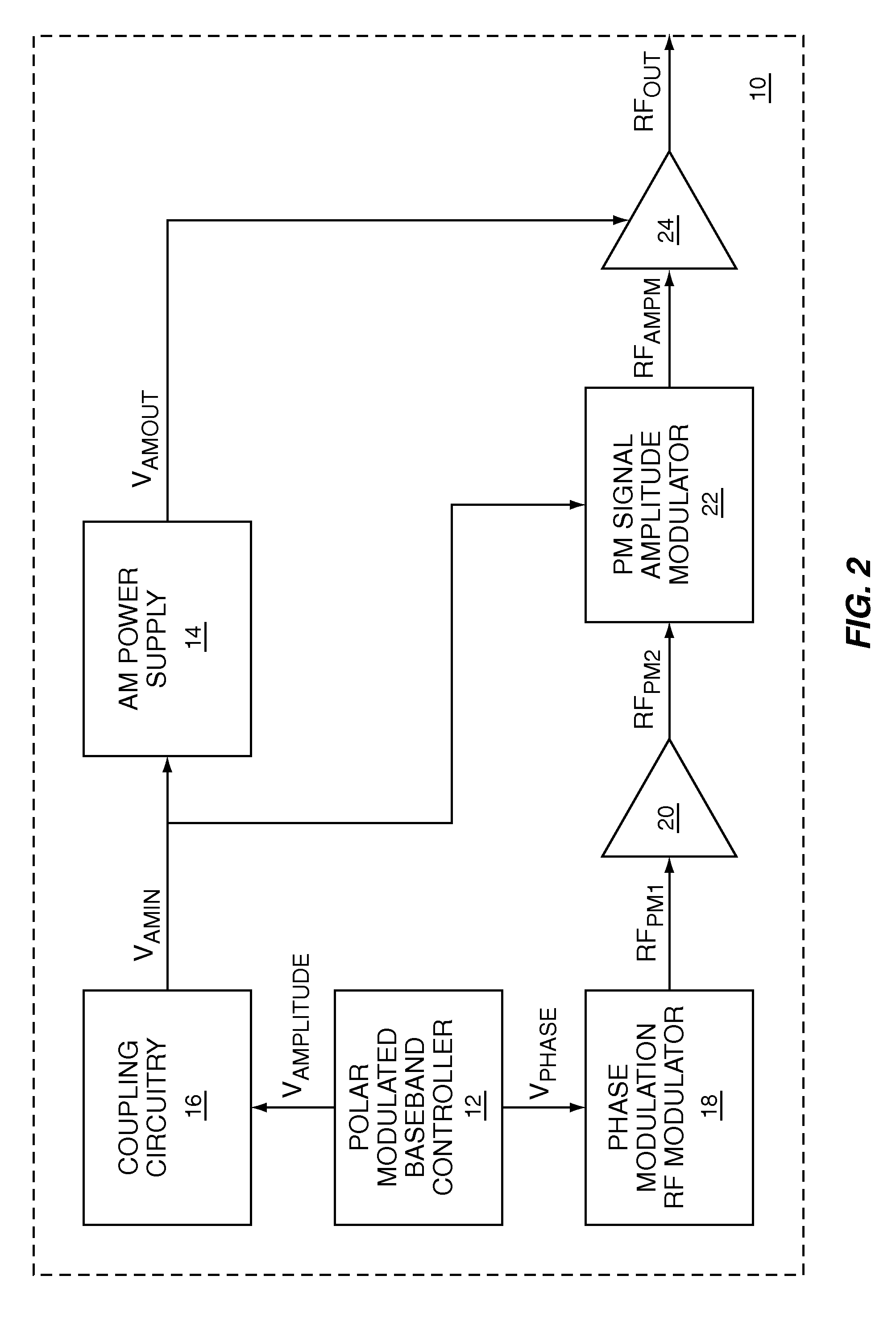
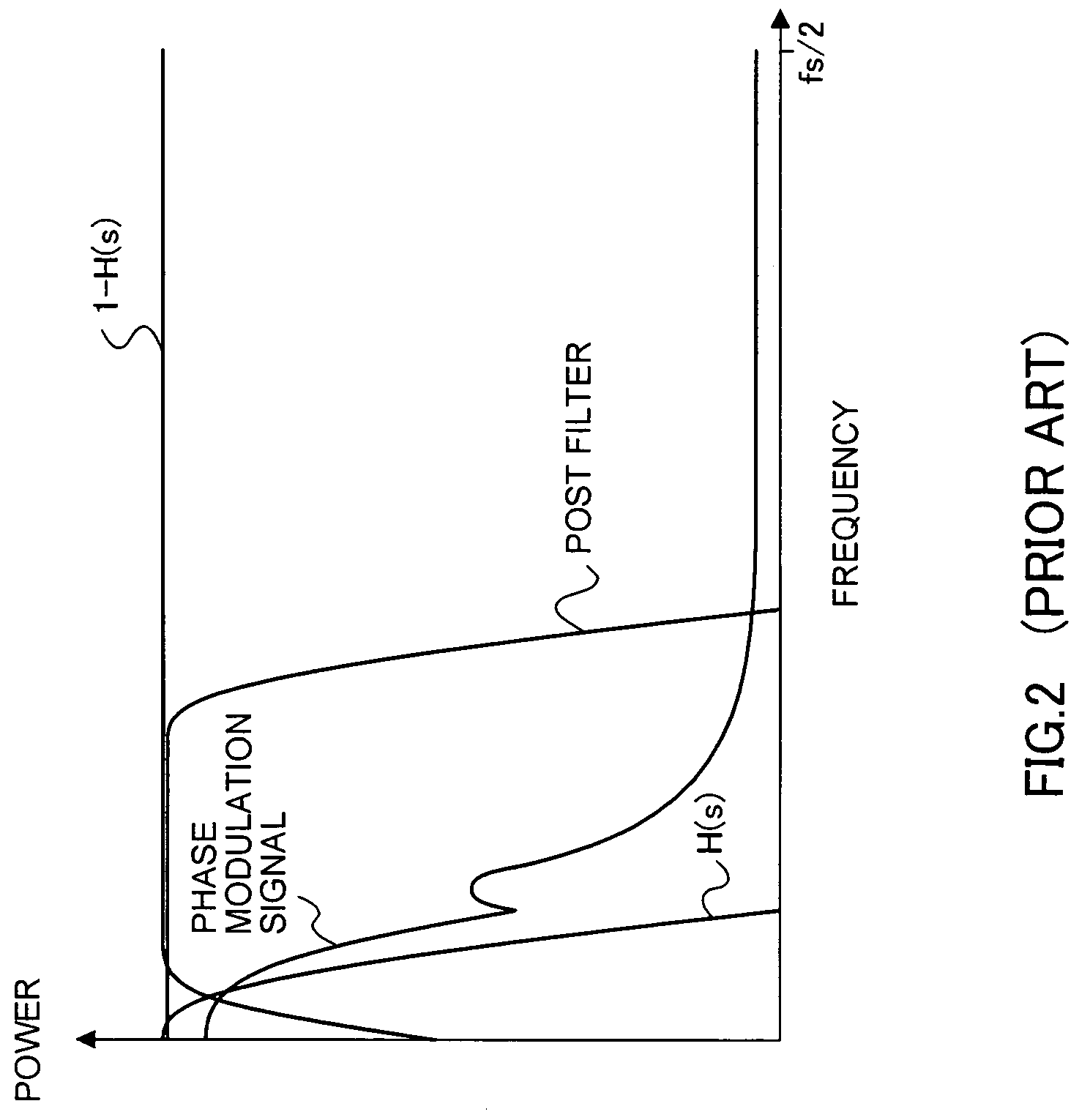
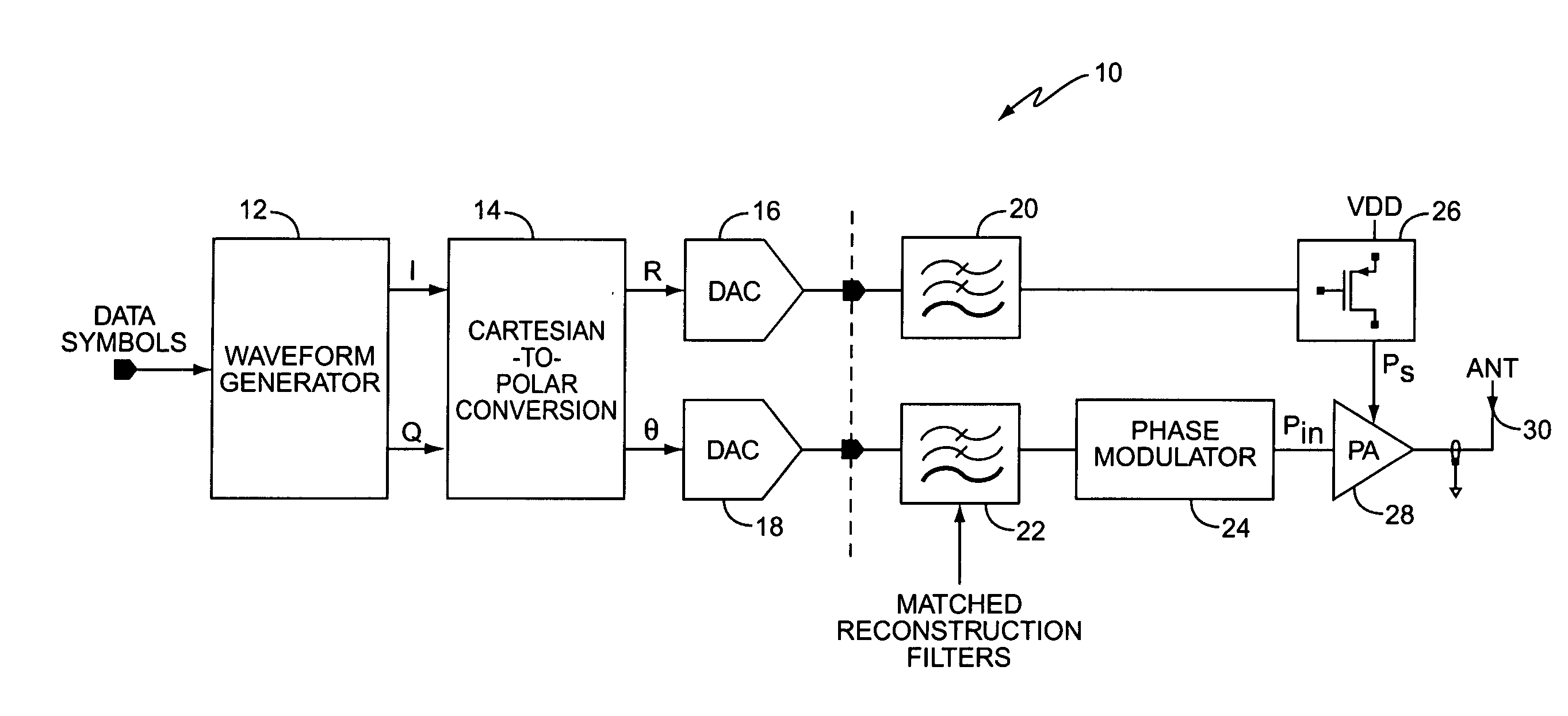
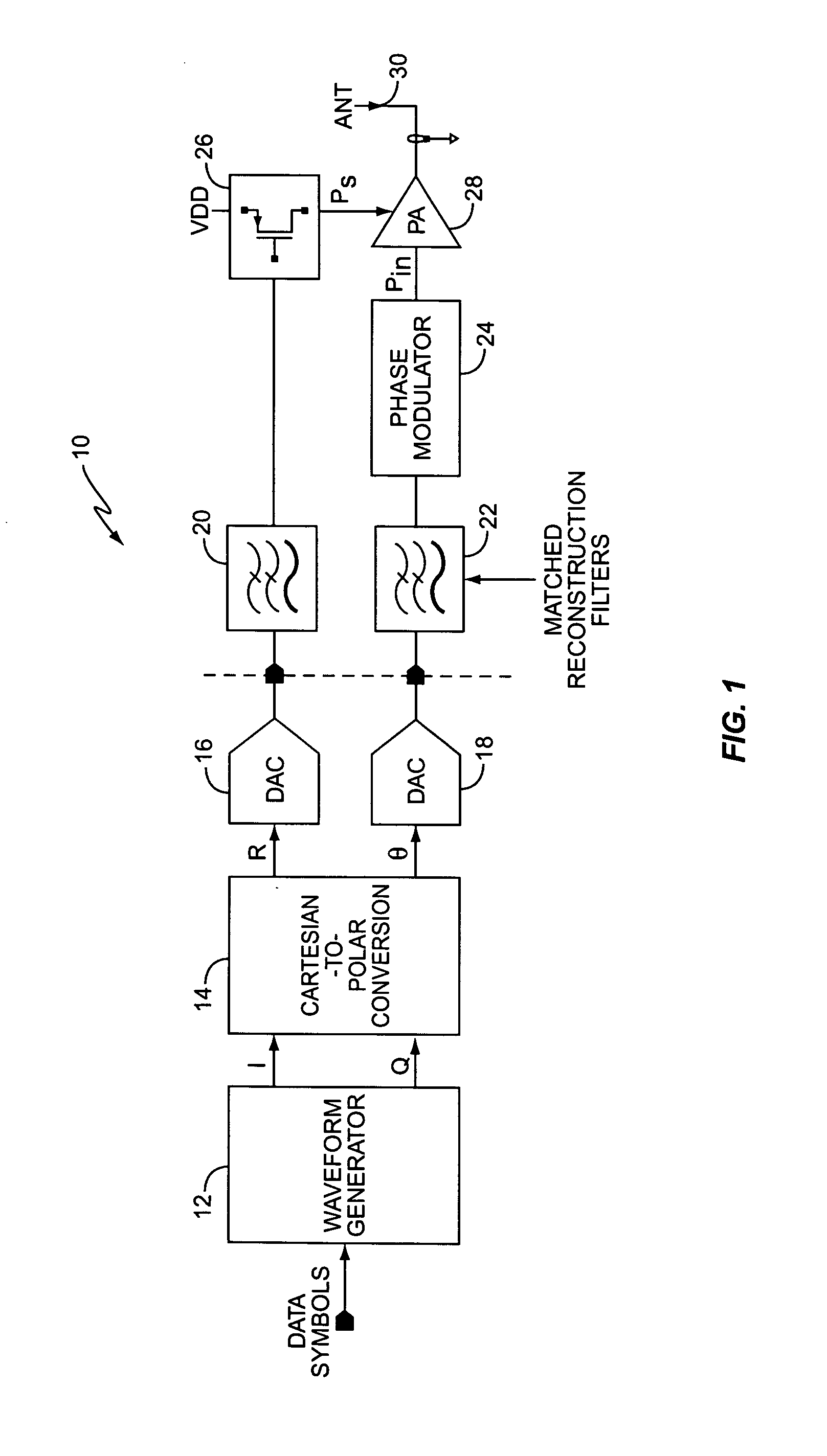
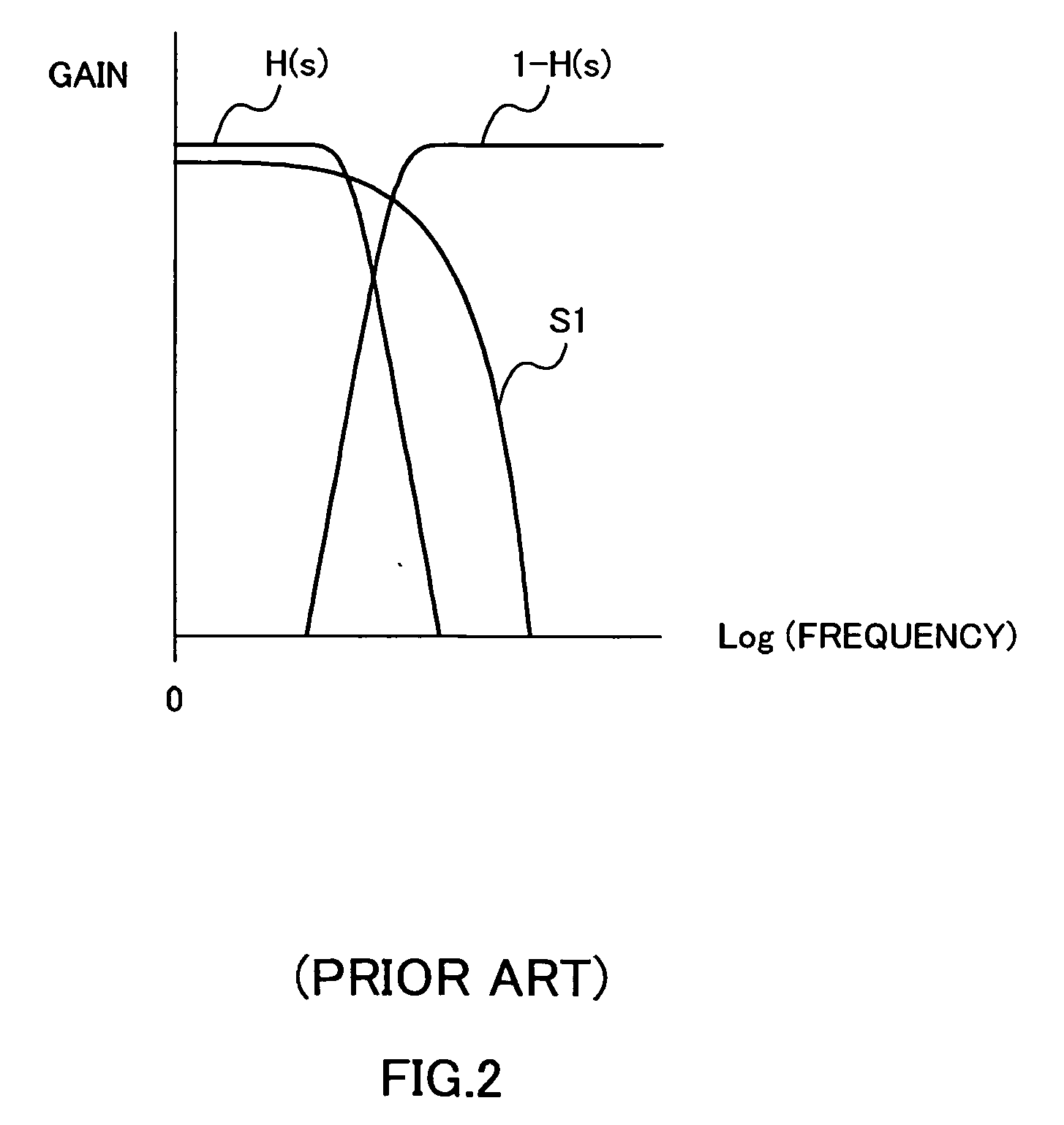
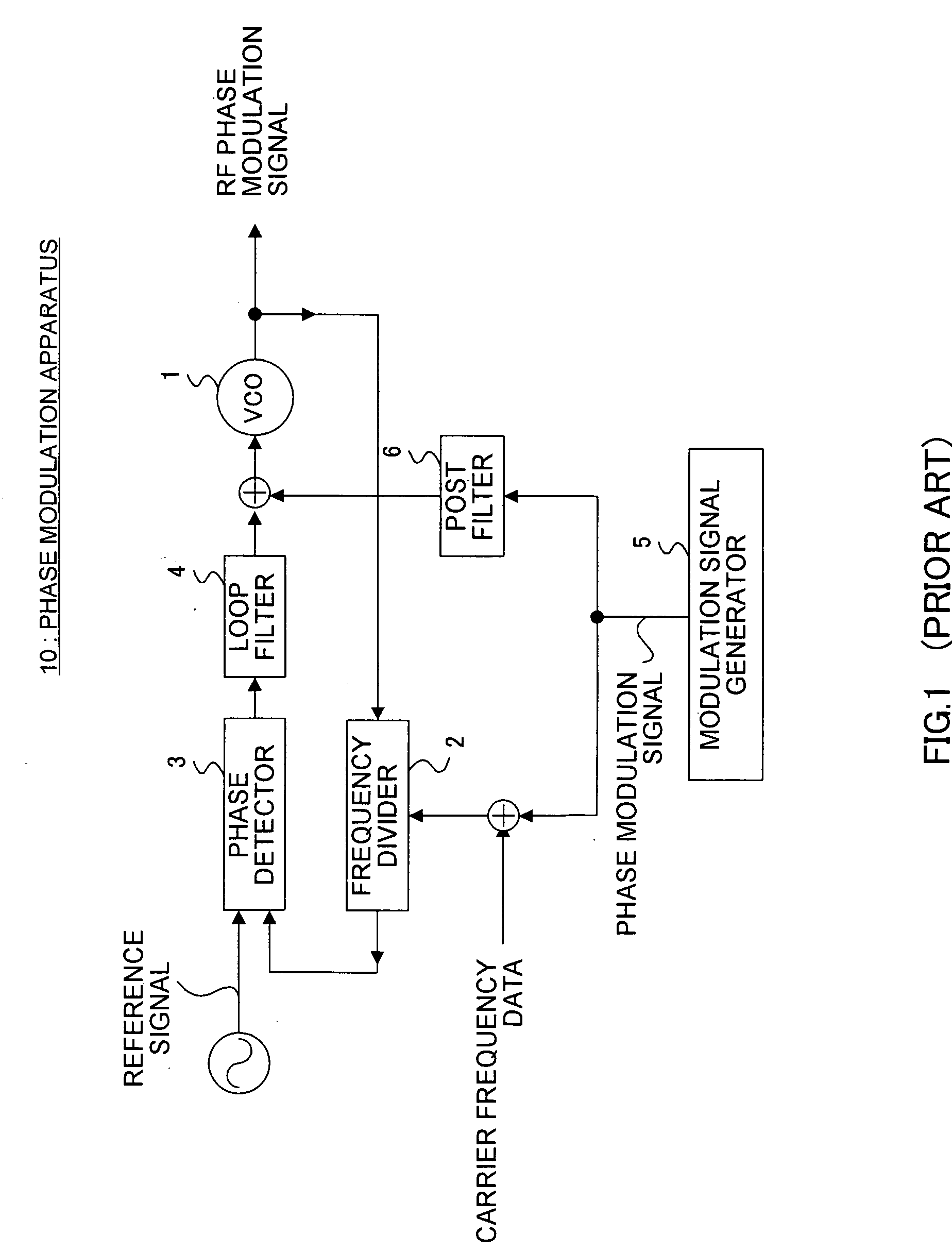
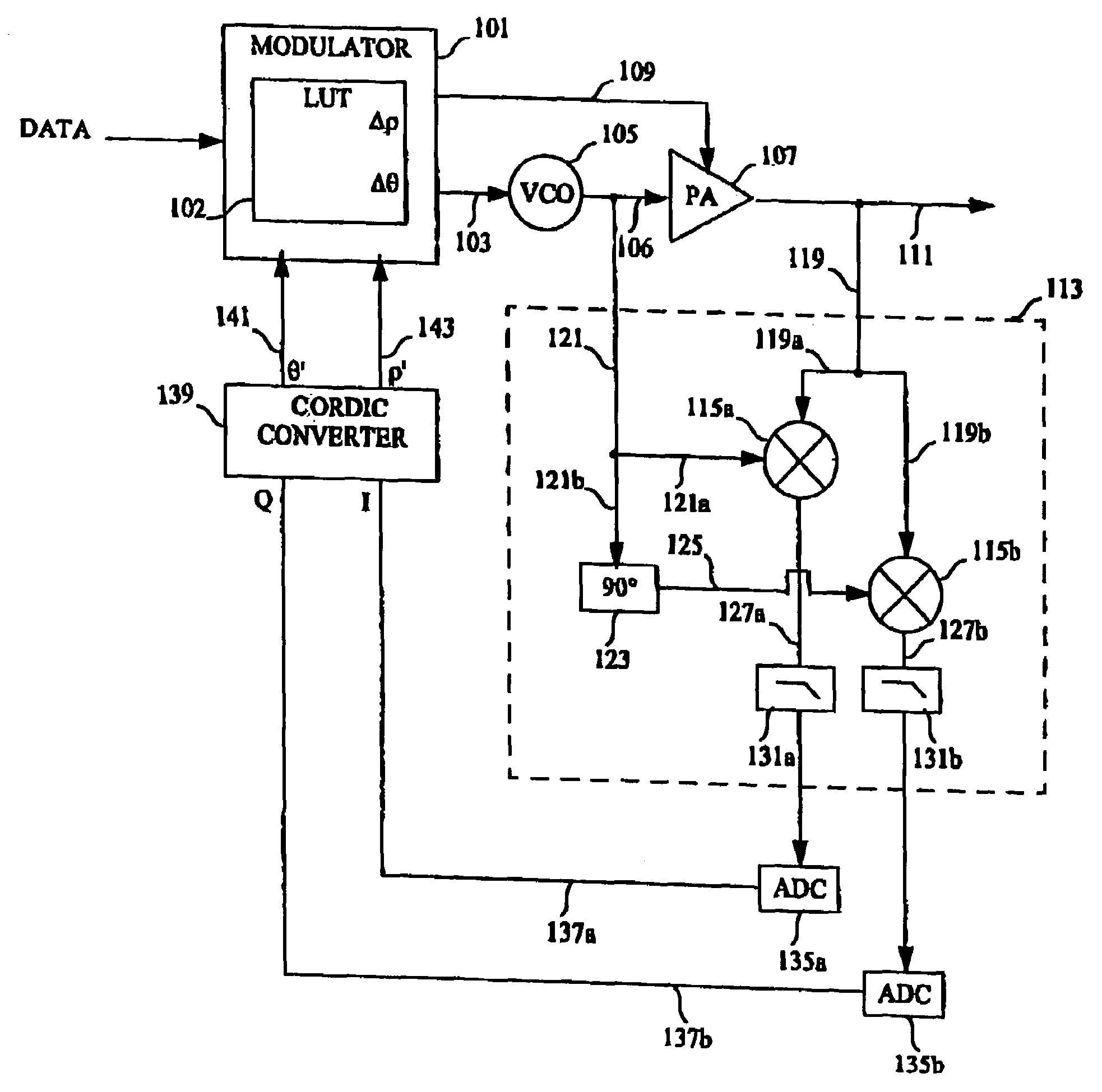
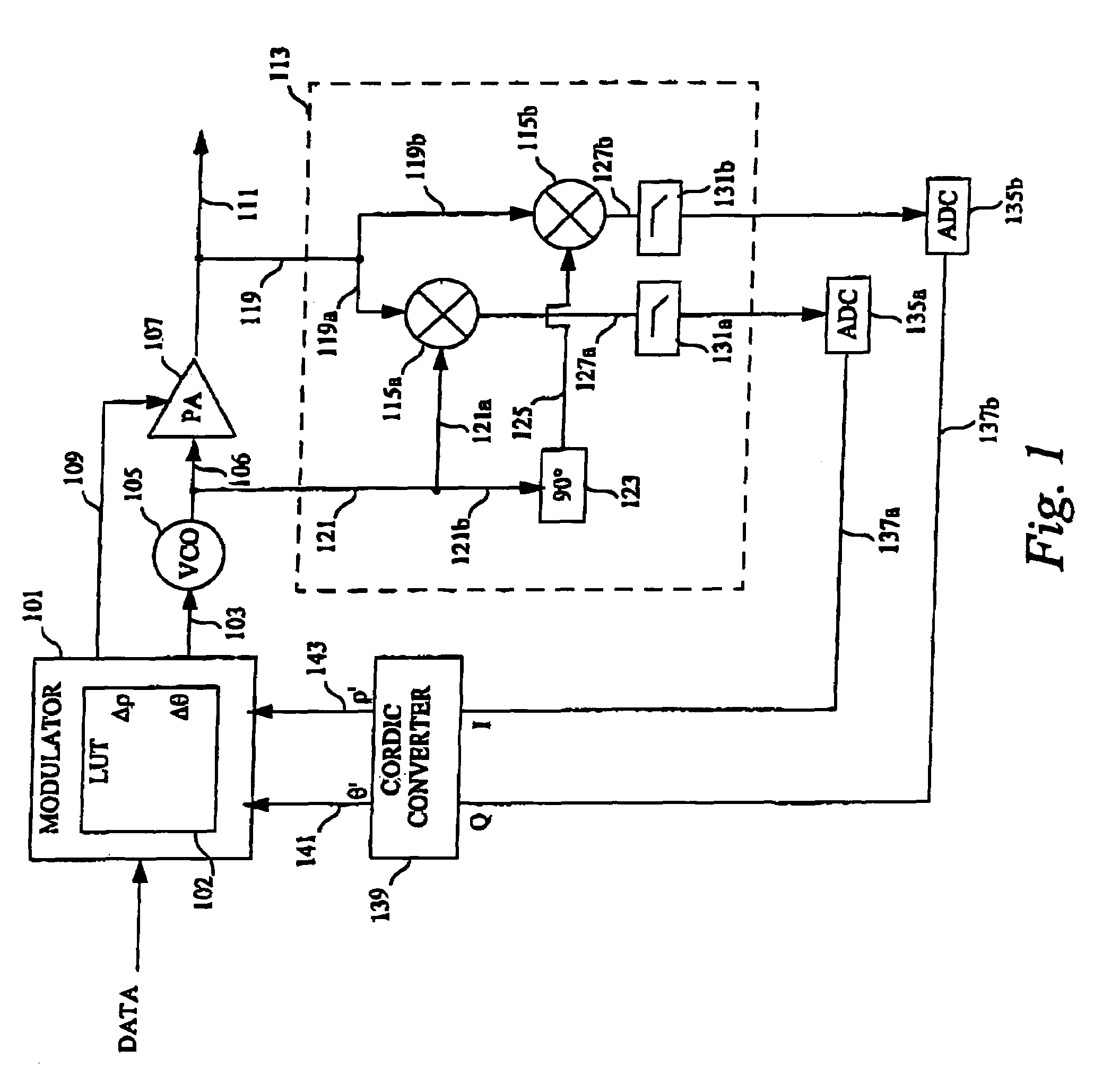
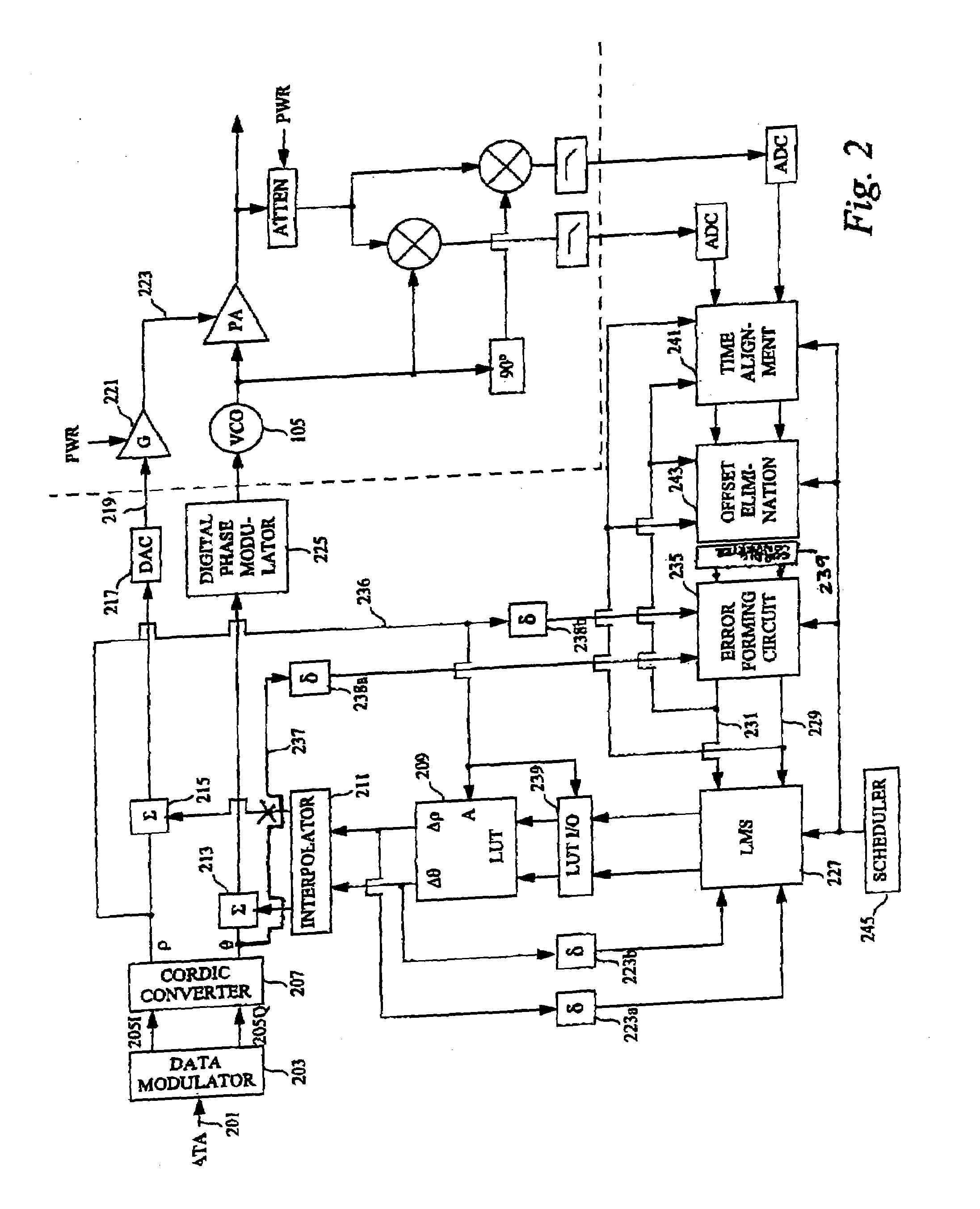
Polar modulation is analogous to quadrature modulation in the same way that polar coordinates are analogous to Cartesian coordinates. Quadrature modulation makes use of Cartesian coordinates, x and y. When considering quadrature modulation, the x axis is called the I (in-phase) axis, and the y axis is called the Q (quadrature) axis. Polar modulation makes use of polar coordinates, r (amplitude) and Θ (phase).
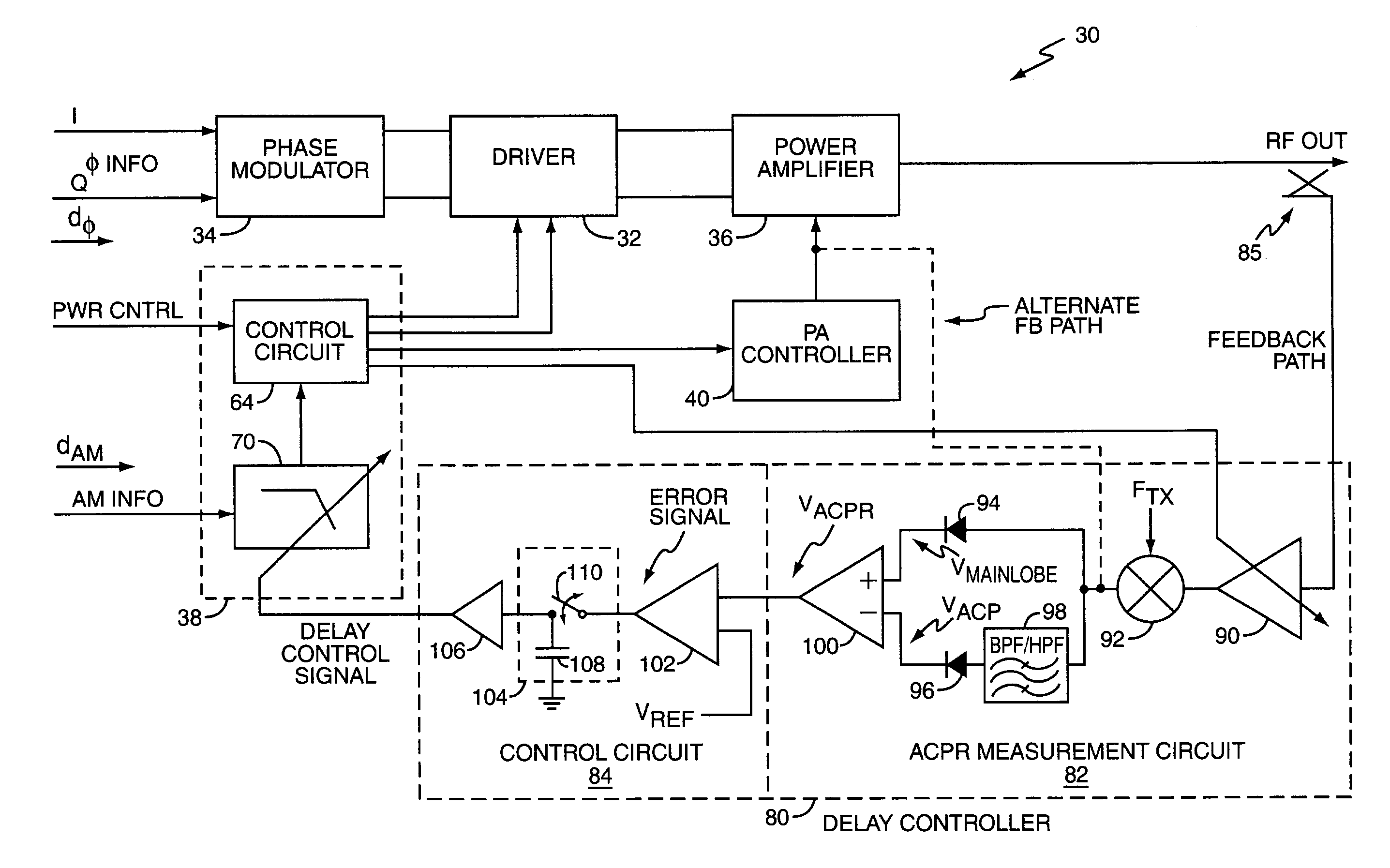
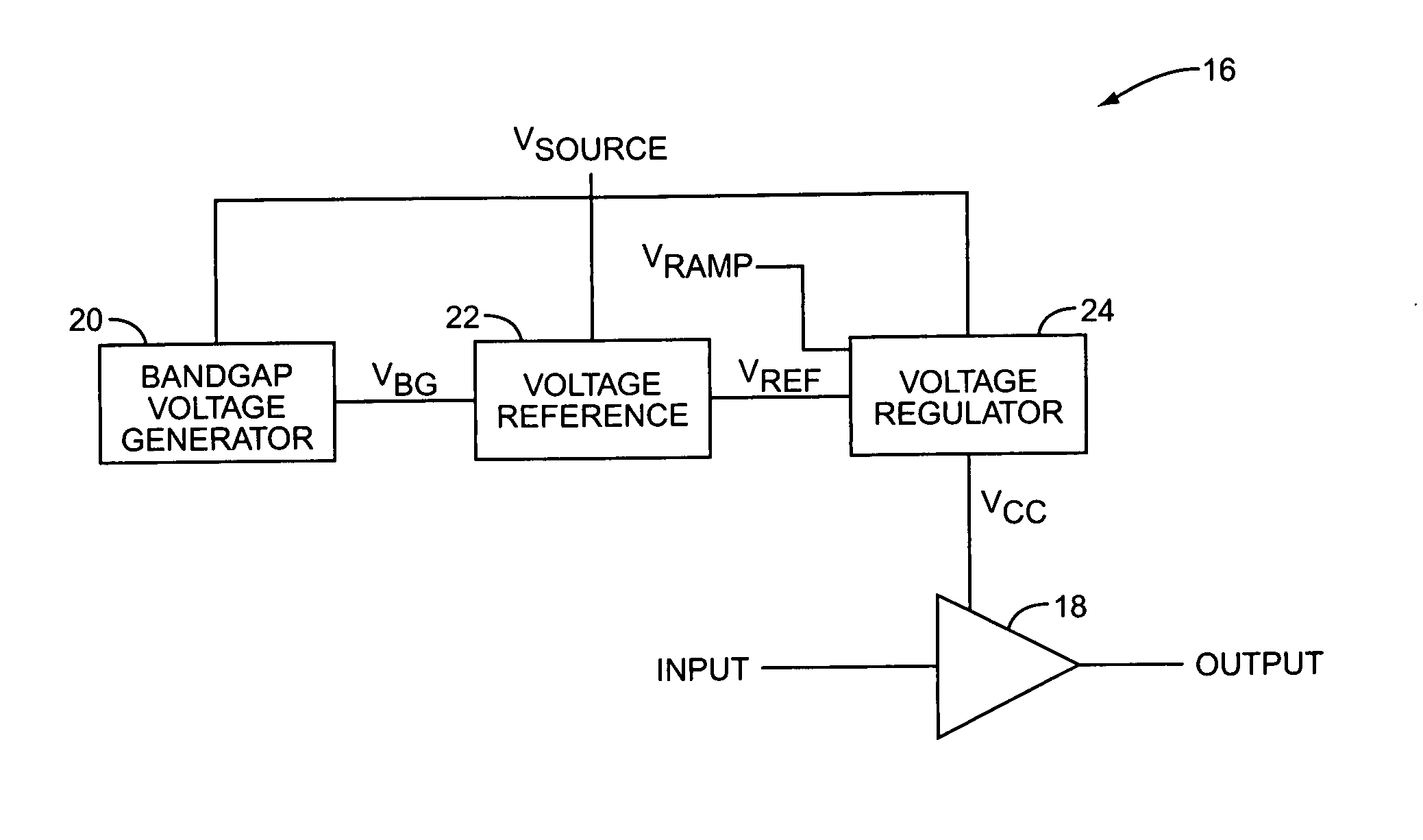
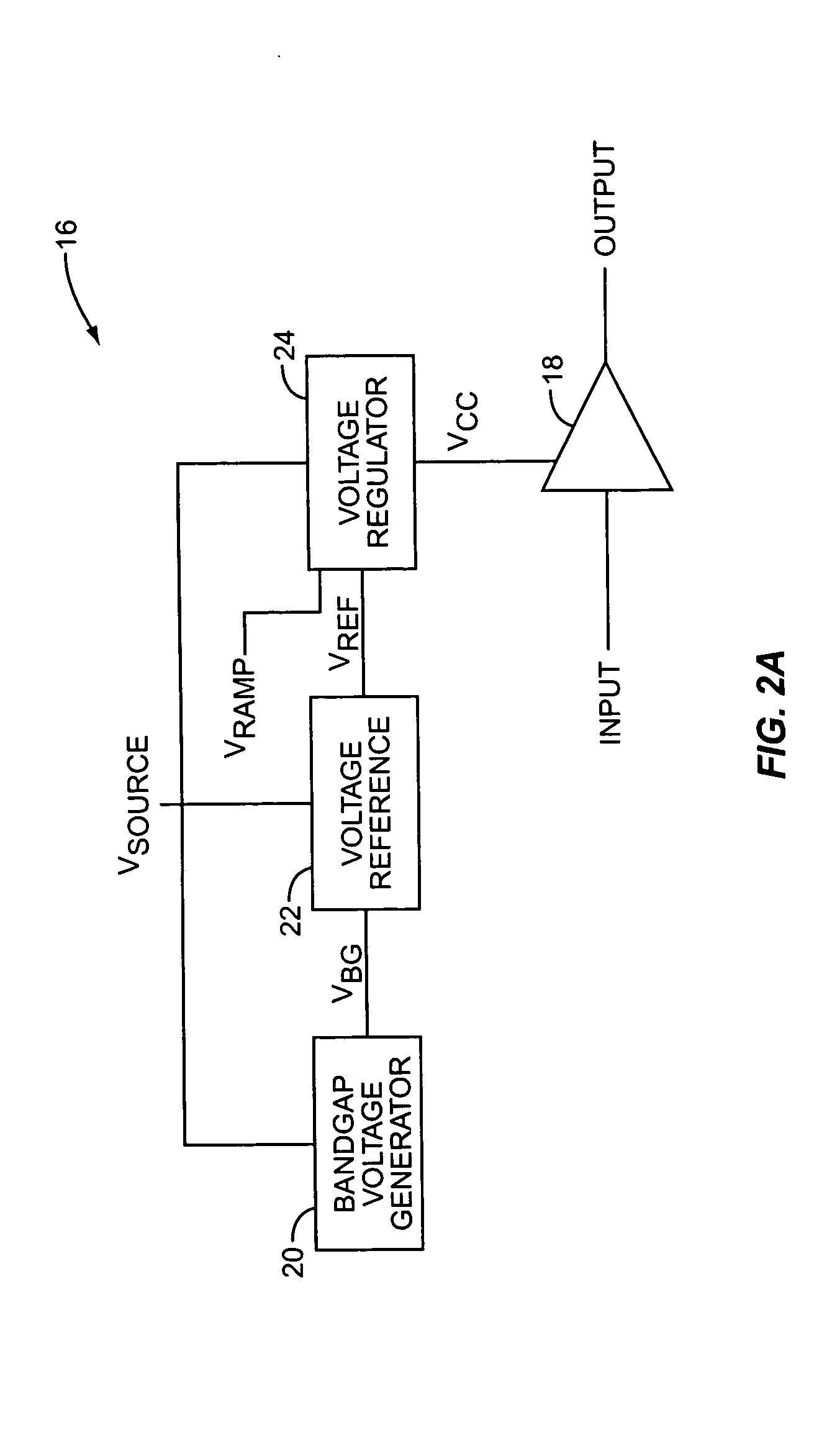
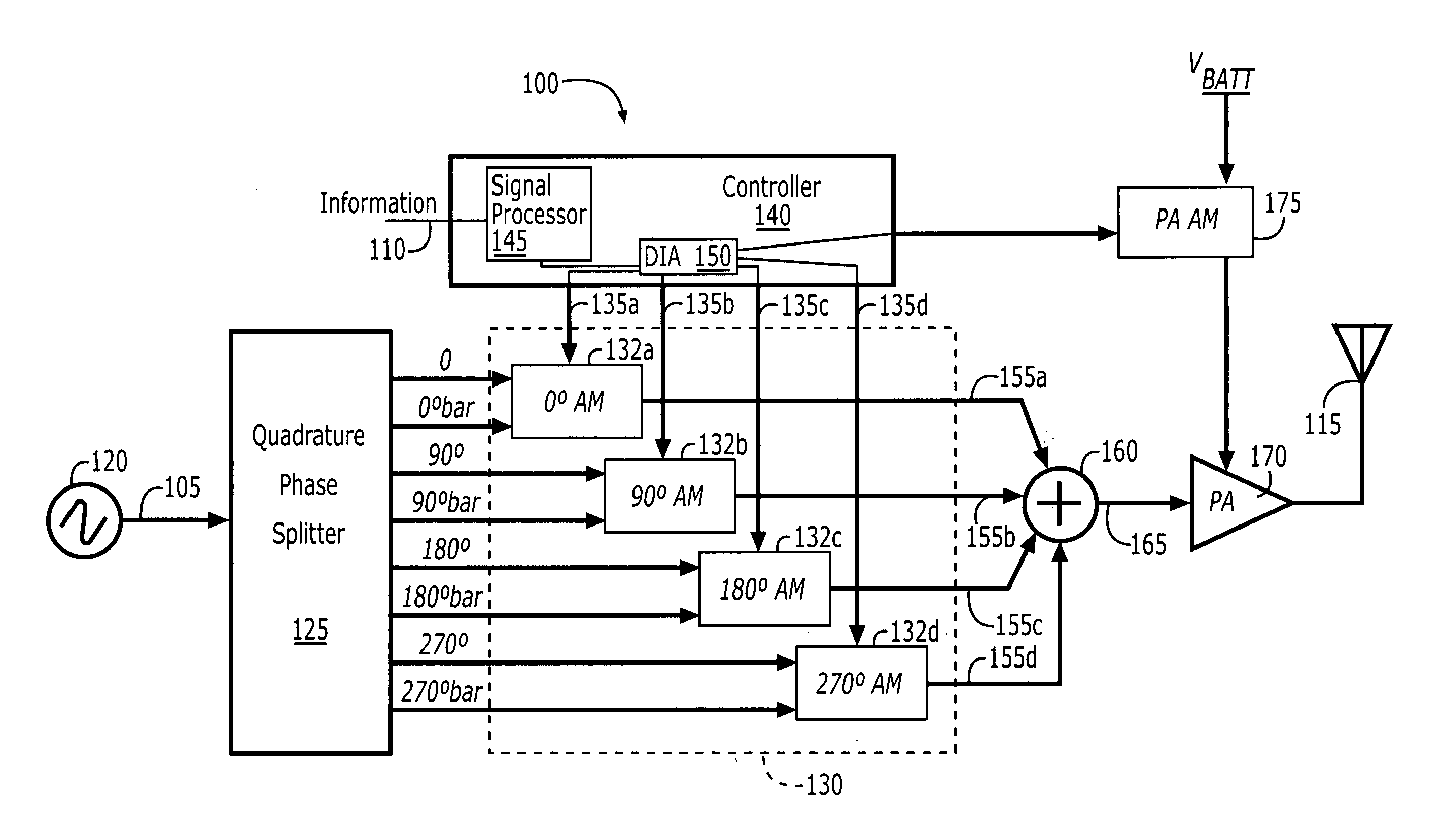
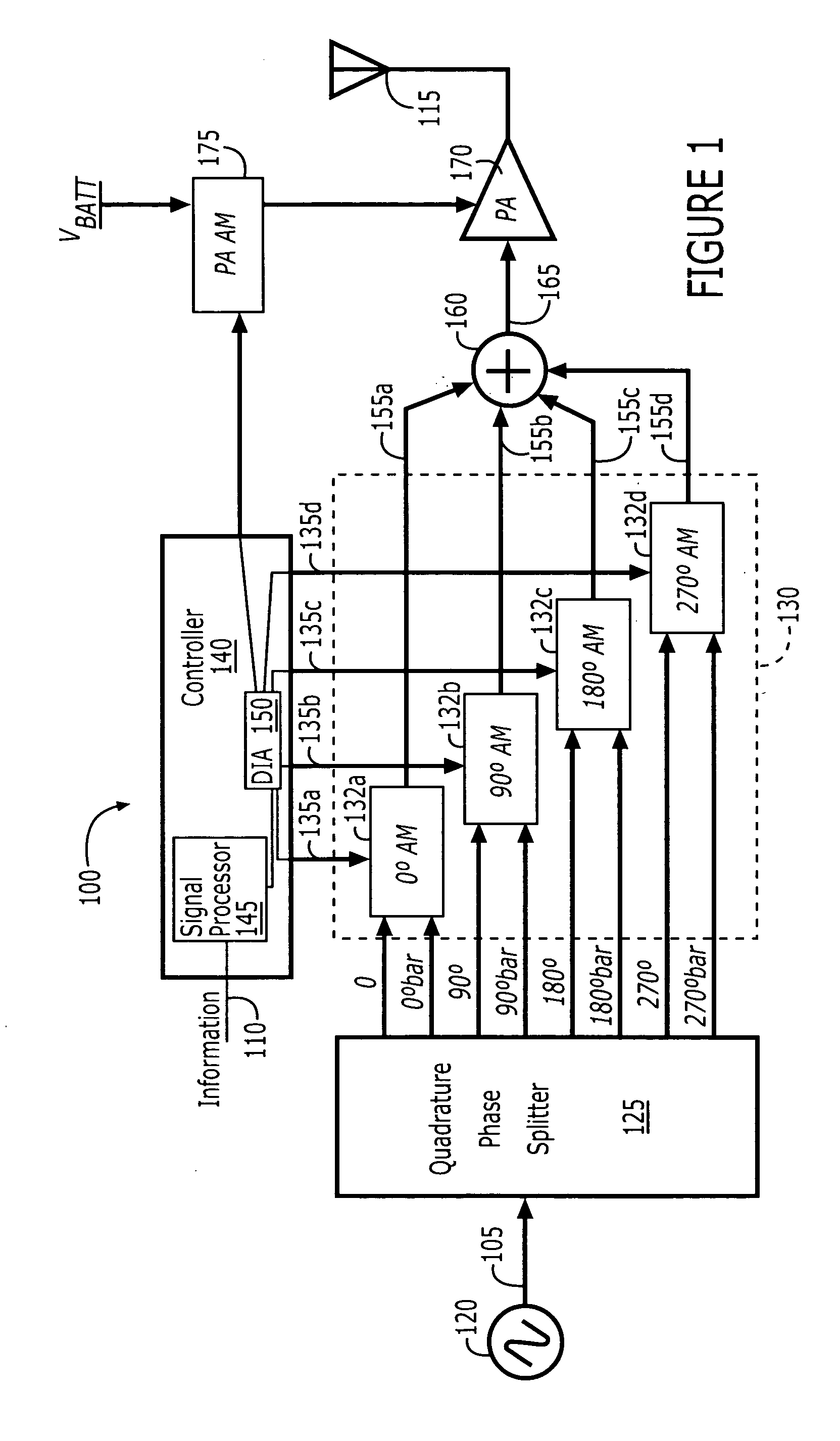
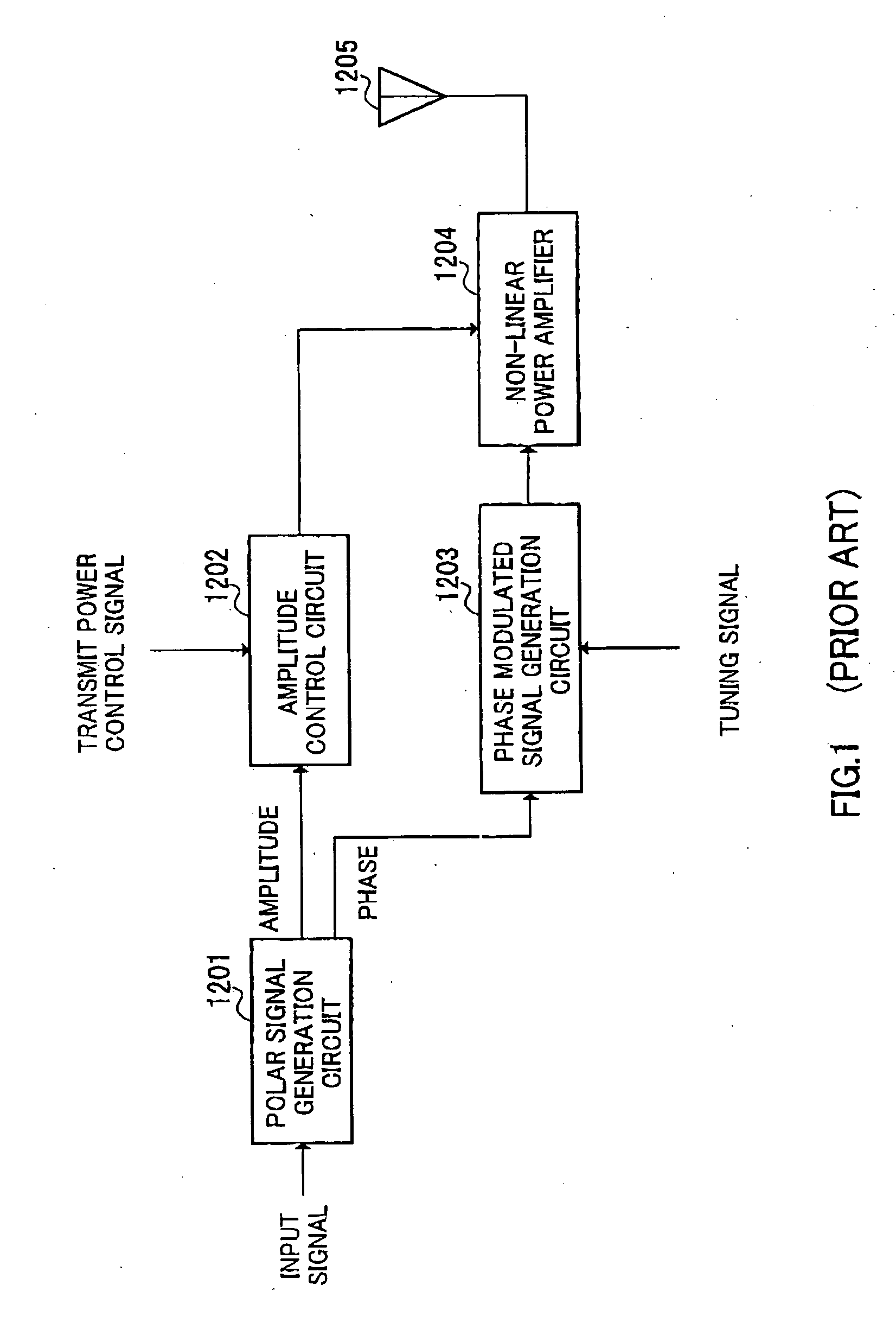
Polar modulation transmitter
ActiveUS7072626B2Improve performanceReduce ratio of average powerResonant long antennasPower amplifiersTransceiverAudio power amplifier
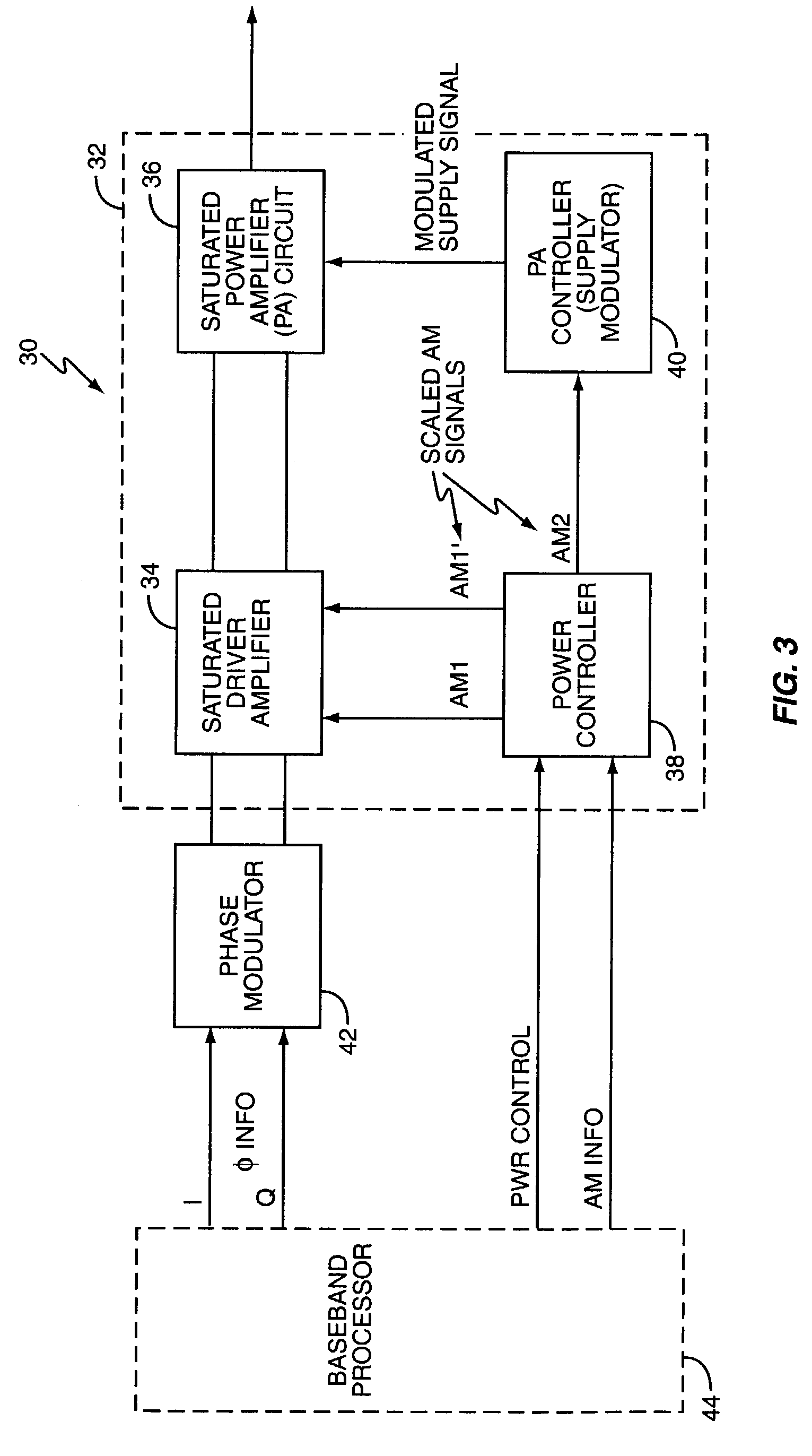
A polar modulation transmitter circuit provides reduced ACPR in its output signal by controlling the relative delay between its envelope and phase modulation operations based on direct or indirect feedback measurement the output signal's ACPR. Such measurement and associated control may be based on a delay controller that includes an ACPR measurement circuit and a delay control circuit. Additionally, or alternatively, the polar modulation transmitter circuit provides a greatly extended transmit power control range by using a staged amplifier circuit that includes a driver amplifier circuit operating in combination with a power amplifier circuit to impart desired envelope modulation. In an exemplary embodiment, the driver amplifier circuit is implemented as differential transistor pairs responsive to tail current modulation. As such, the driver amplifier circuit is suited in particular for economical and space saving integration within a transmitter or transceiver integrated circuit (IC).
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
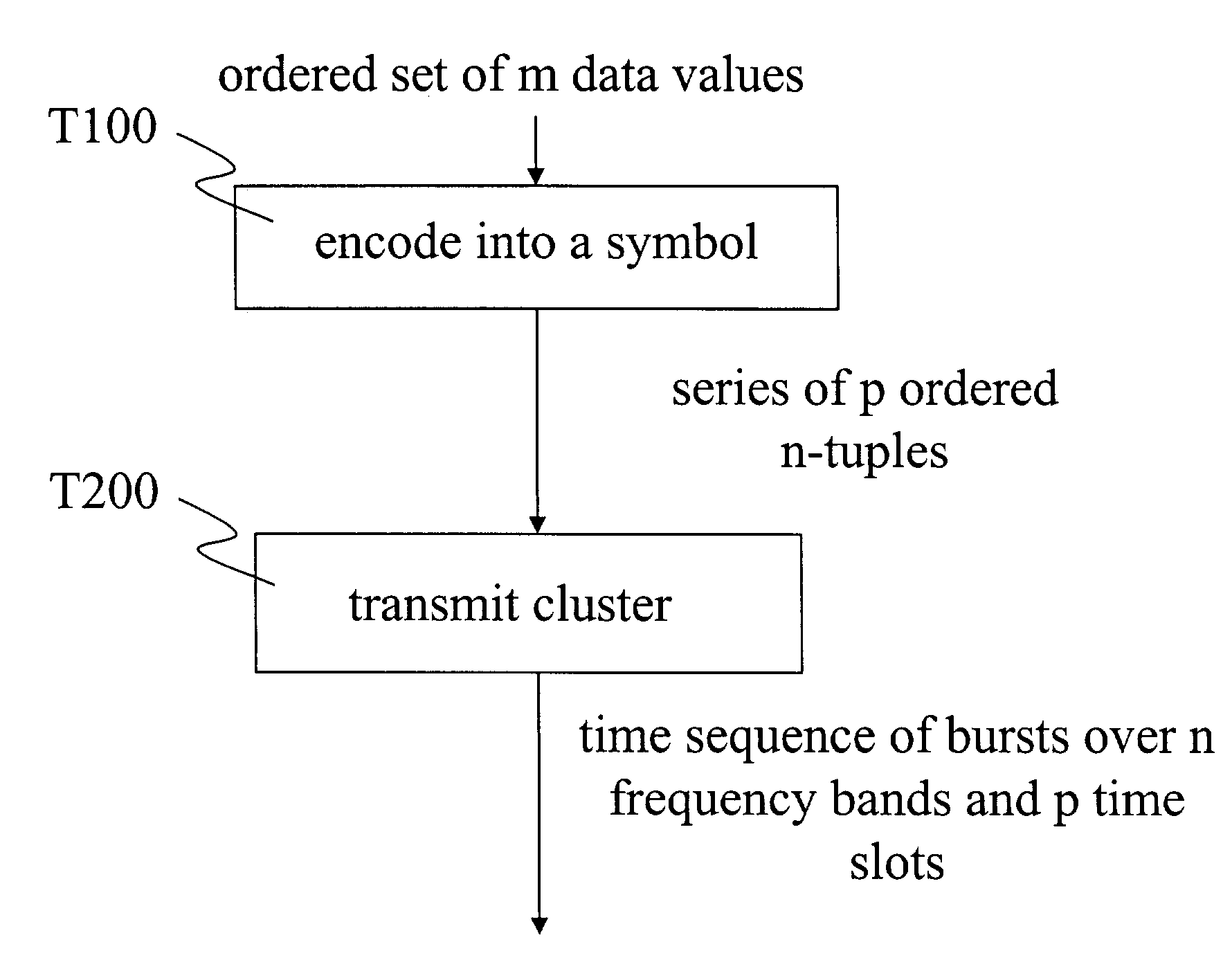
Method and apparatus for data transfer using a time division multiple frequency scheme supplemented with polarity modulation
A method of data transmission according to one embodiment of the invention includes encoding a set of data values to produce a corresponding series of ordered n-tuples. The method also includes transmitting, according to the series of ordered n-tuples, a plurality of bursts over a plurality n of frequency bands. Specifically, for each of the plurality of bursts, a frequency band occupied by the burst is indicated by the order within its n-tuple of an element corresponding to the burst. A bandwidth of at least one of the plurality of bursts is at least two percent of the center frequency of the burst. Information is encoded into a polarity of at least one of the plurality of bursts.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Wireless transmission apparatus, polar modulation transmission apparatus, and wireless communication apparatus
InactiveUS20060293005A1Improve power efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTResonant long antennasSignal processing circuitsHigh frequency power
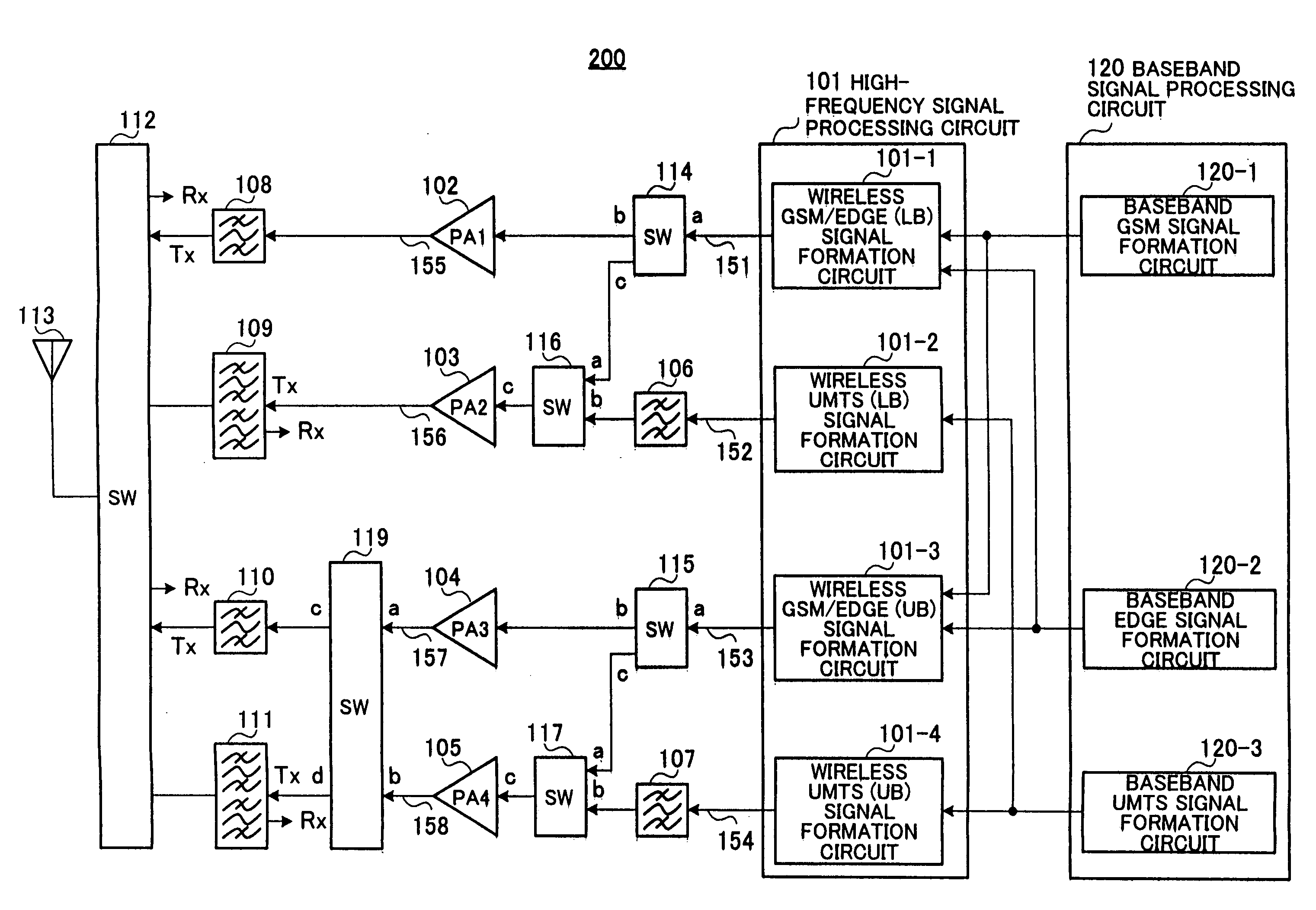
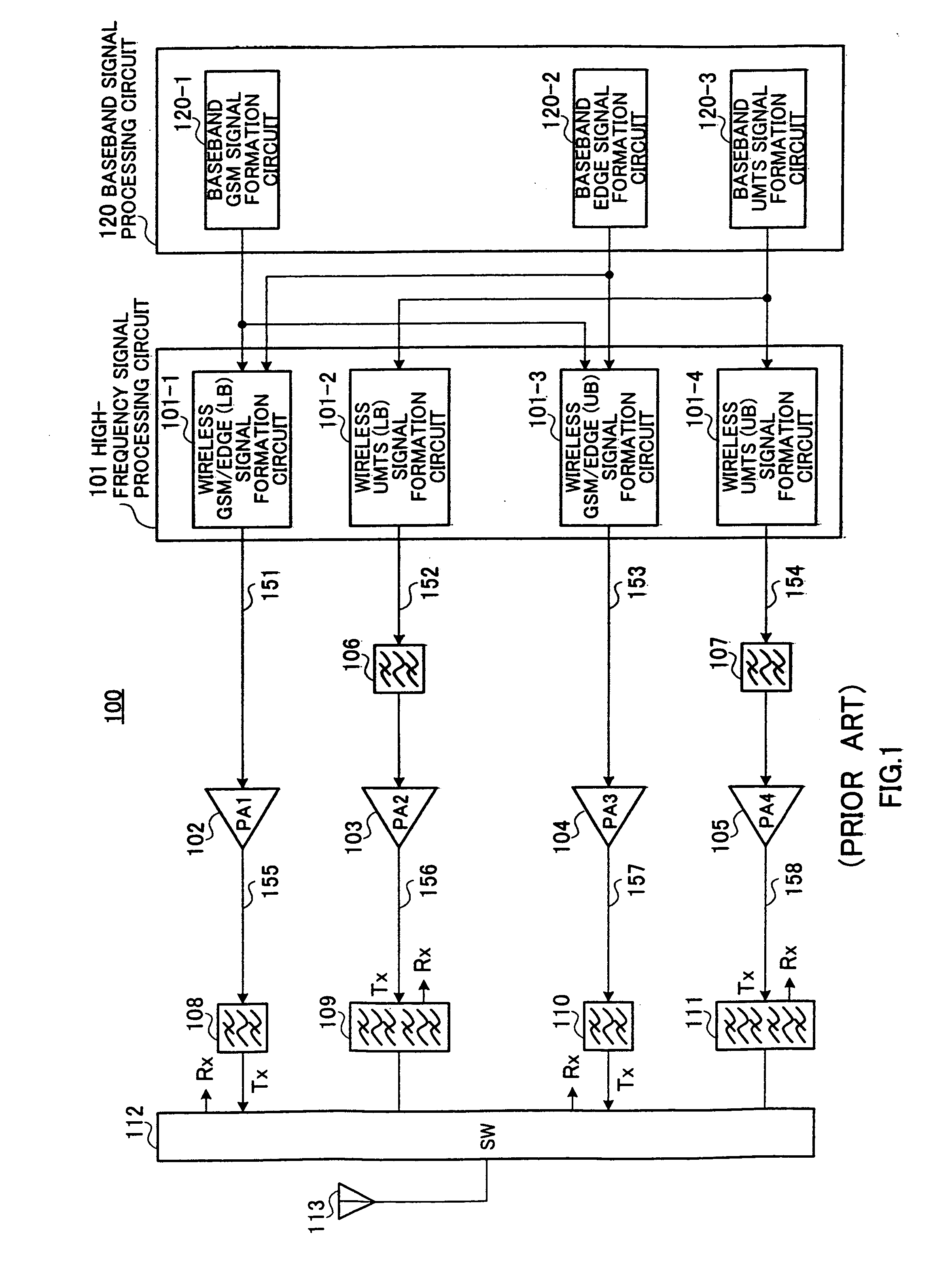
A wireless transmission apparatus of multi-mode operation with superior power efficiency is provided. Switches (115 and 117) are switched over in such a manner that a modulation signal outputted from a wireless GSM / EDGE (UB) signal formation circuit (101-3) of a high-frequency signal processing circuit (101) is outputted to a high-frequency power amplifier (104) at the time of output of a GSM modulation signal, and is outputted to a high-frequency amplifier (105) at the time of output of an EDGE modulation signal. As a result, the EDGE modulation signal is power amplified using a high-frequency power amplifier (105) for an UMTS modulation signal use that is compatible with regards to the EDGE modulation signal and the maximum output power and presence or absence of envelope fluctuation. It is therefore possible to amplify the EDGE modulation scheme wireless signal with high efficiency.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Polar modulation transmission apparatus and polar modulation transmission method
ActiveUS20090258611A1Compensate characteristic degradation reliablySimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasEngineeringPolar modulation
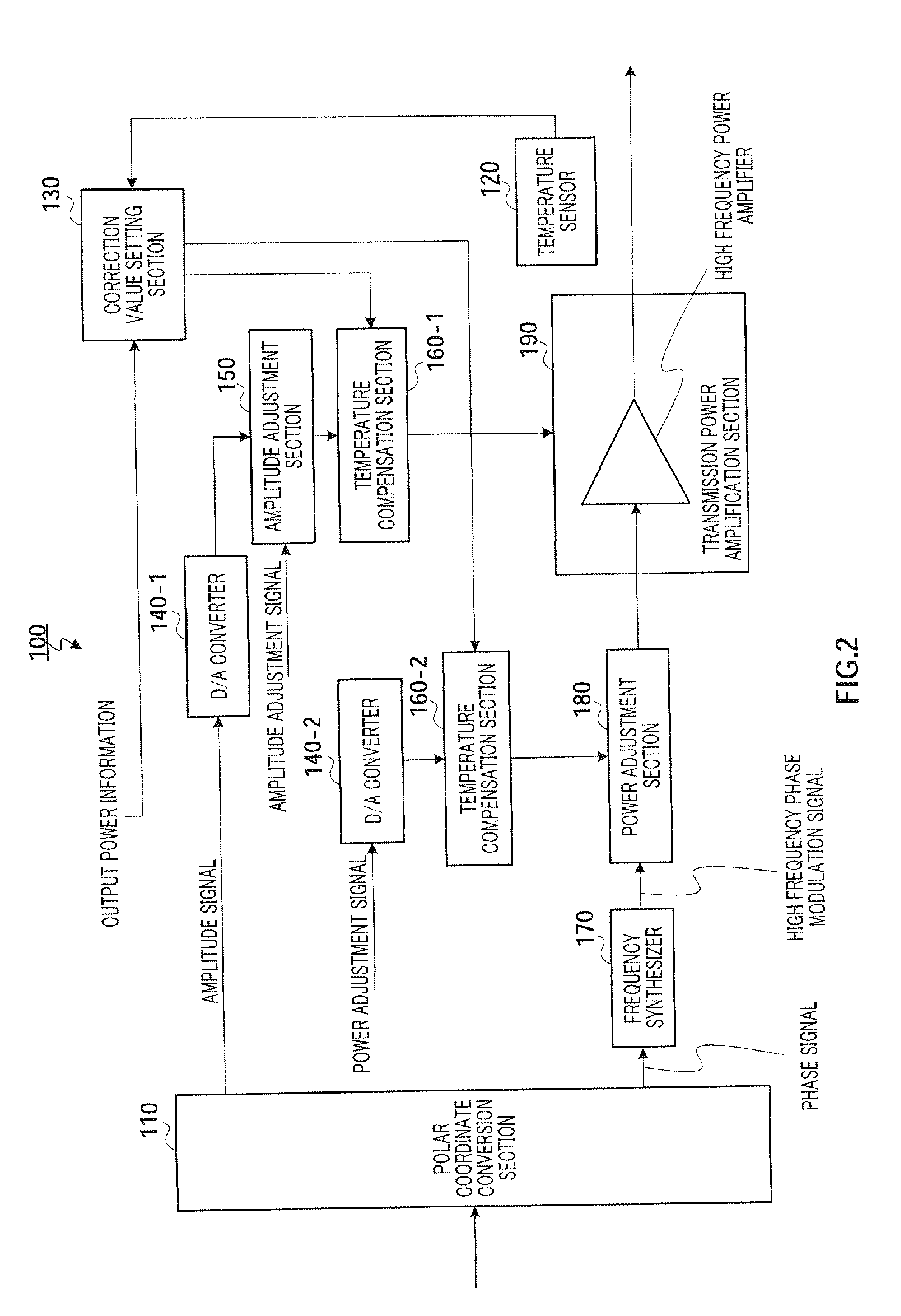
The polar modulation apparatus of the present invention can control the output power of a transmission signal over a wide range and compensate characteristic degradation reliably upon temperature change. Polar modulation transmission apparatus 100 is provided with: temperature sensor 120; temperature compensation section 1601 that corrects an amplitude signal and performs temperature compensation for transmission power amplification section 190; temperature compensation section 160-2 that corrects a power amplification signal and performs temperature compensation for power adjustment section 180; and correction value setting section 130 that sets correction values for temperature compensation section 160-1 and temperature compensation section 160-2, and, while only the amplitude signal is corrected according to a measurement result in temperature sensor 120 in the first mode, the amplitude signal and the power adjustment signal are corrected according to a measurement result in the second mode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Temperature compensated power amplifier power control
ActiveUS20050088237A1Accurate and repeatableNo fluctuationGain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierPolar modulation
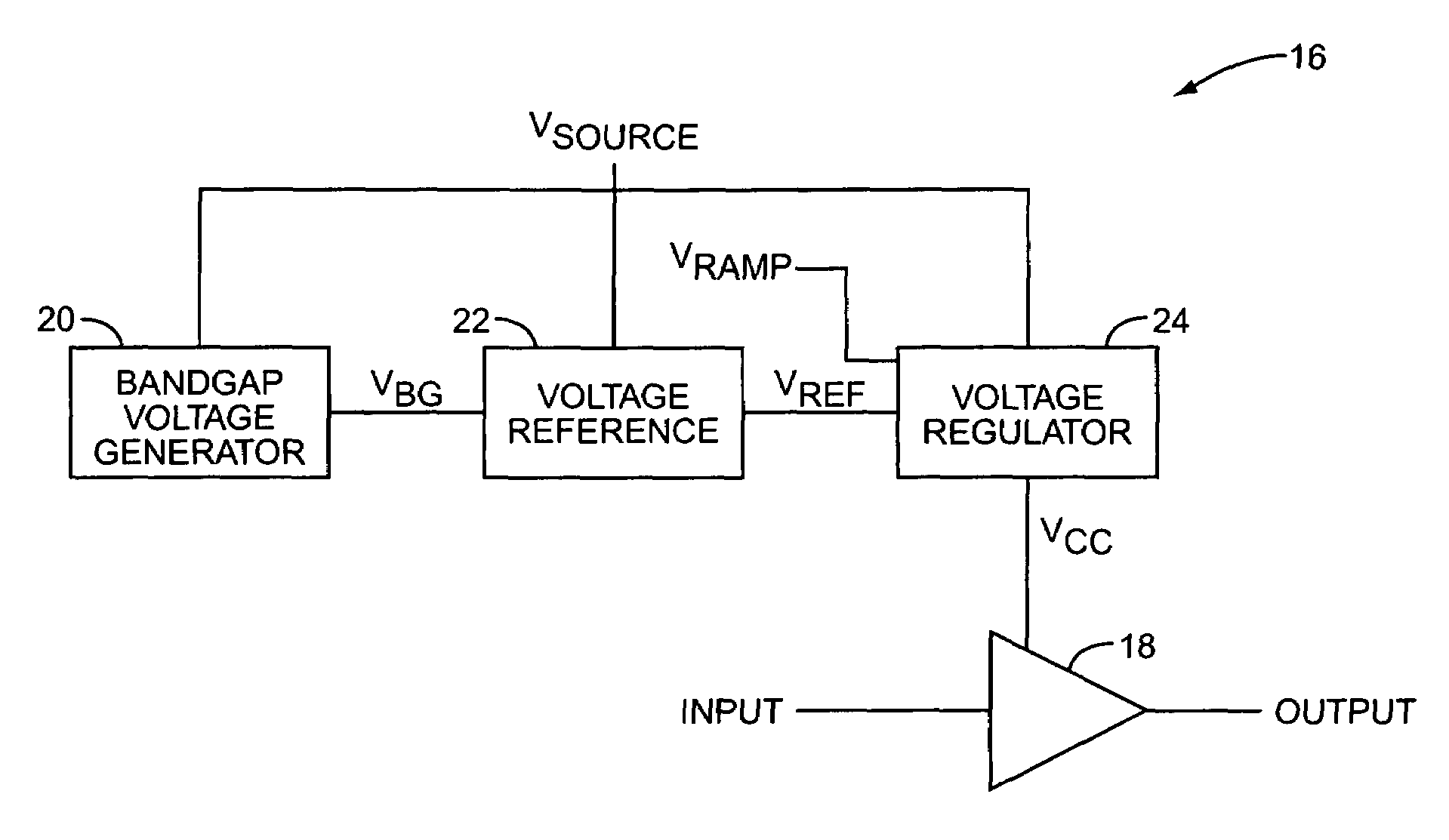
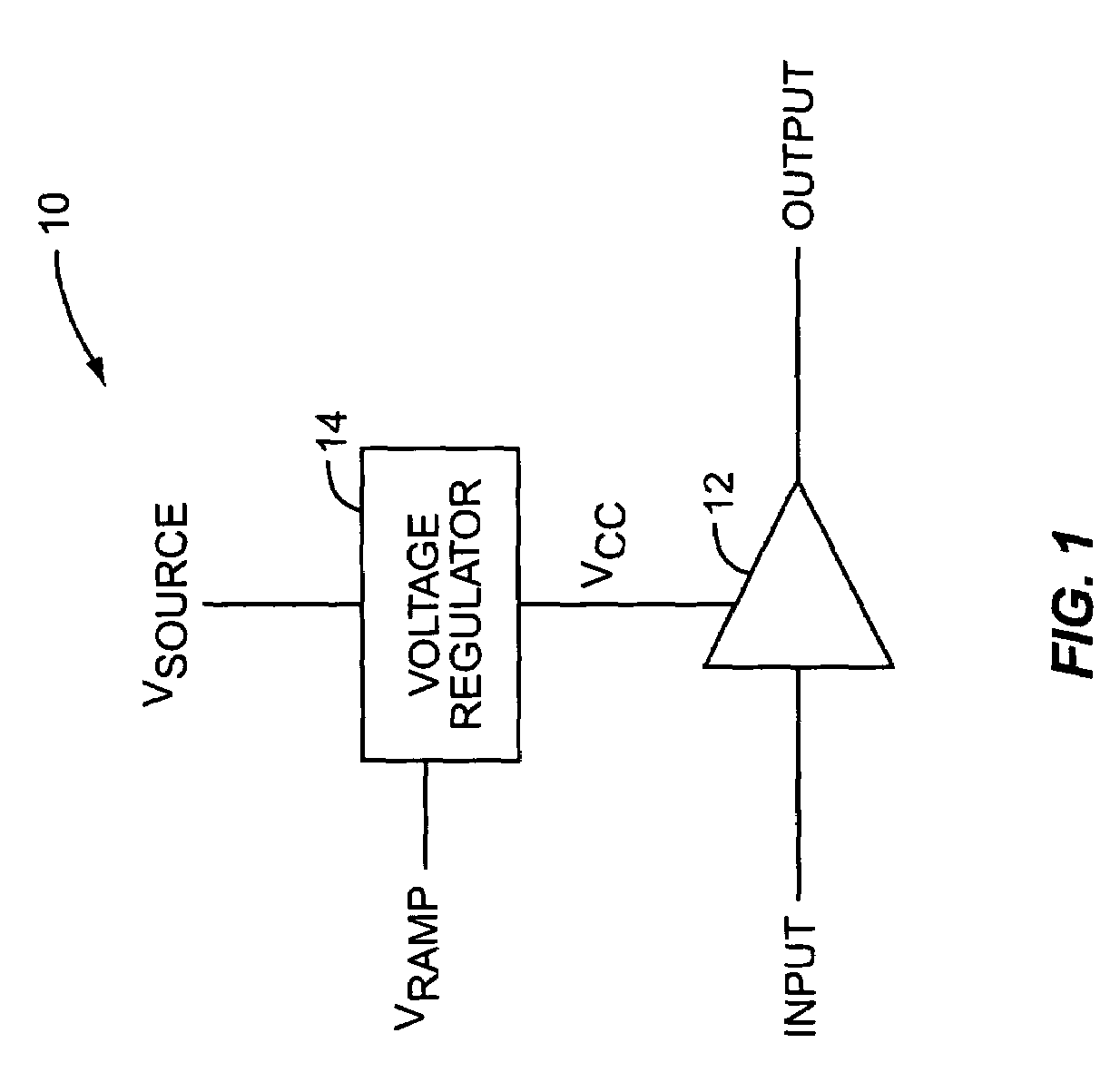
The present invention provides temperature compensation for a power amplifier by varying a supply voltage applied to the power amplifier. The supply voltage is varied based on operating temperature in light of the temperature characteristics of the power amplifier. Thus, the variation in the supply voltage offsets variations in the characteristics of the power amplifier due to changes in temperature. Whether the power amplifier is used to control the output power of a transmitter or as part of a polar modulation system, temperature compensation of the power amplifier allows the power amplifier to provide an accurate and repeatable output signal having essentially no fluctuations due to changes in temperature.
Owner:QORVO US INC
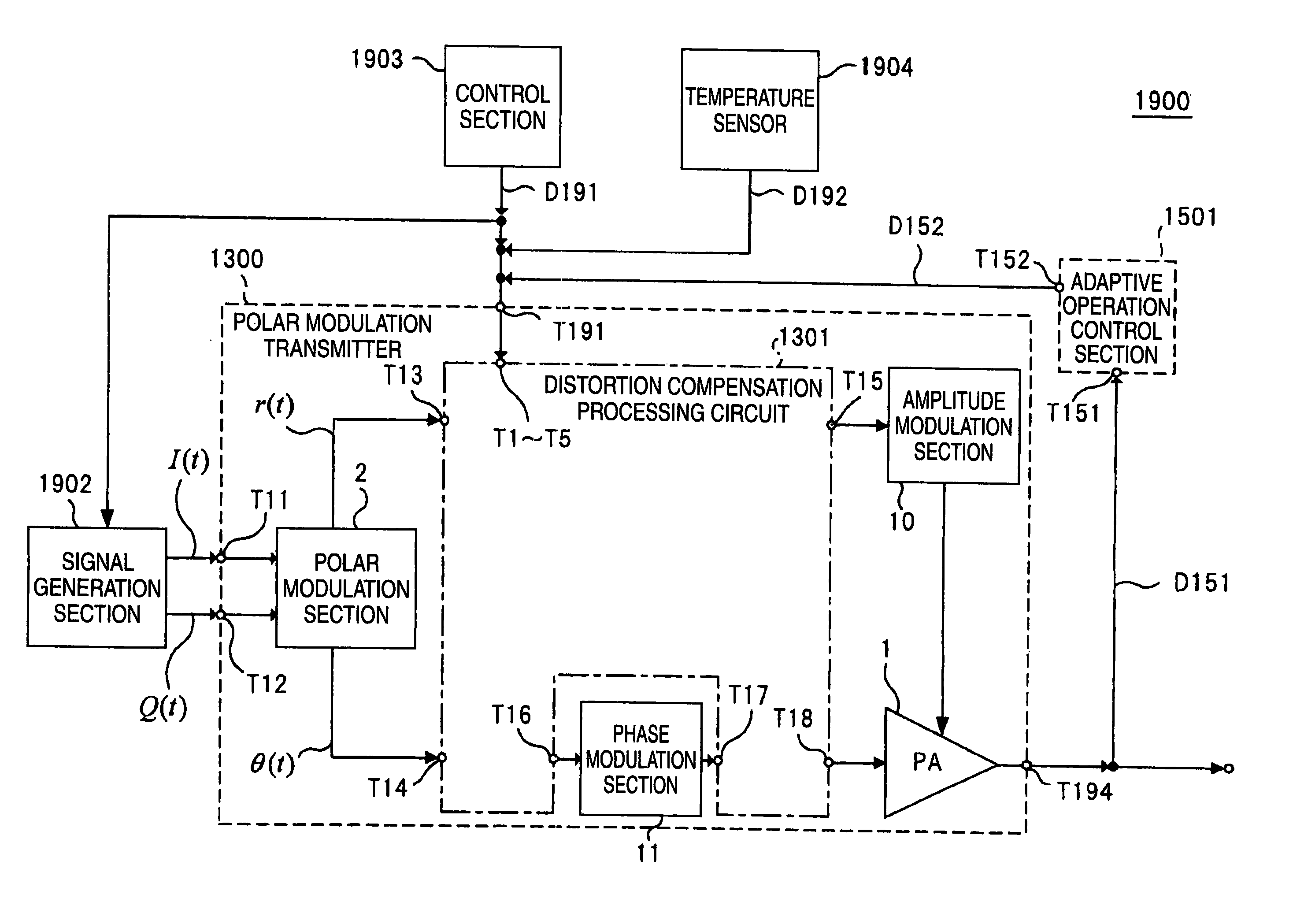
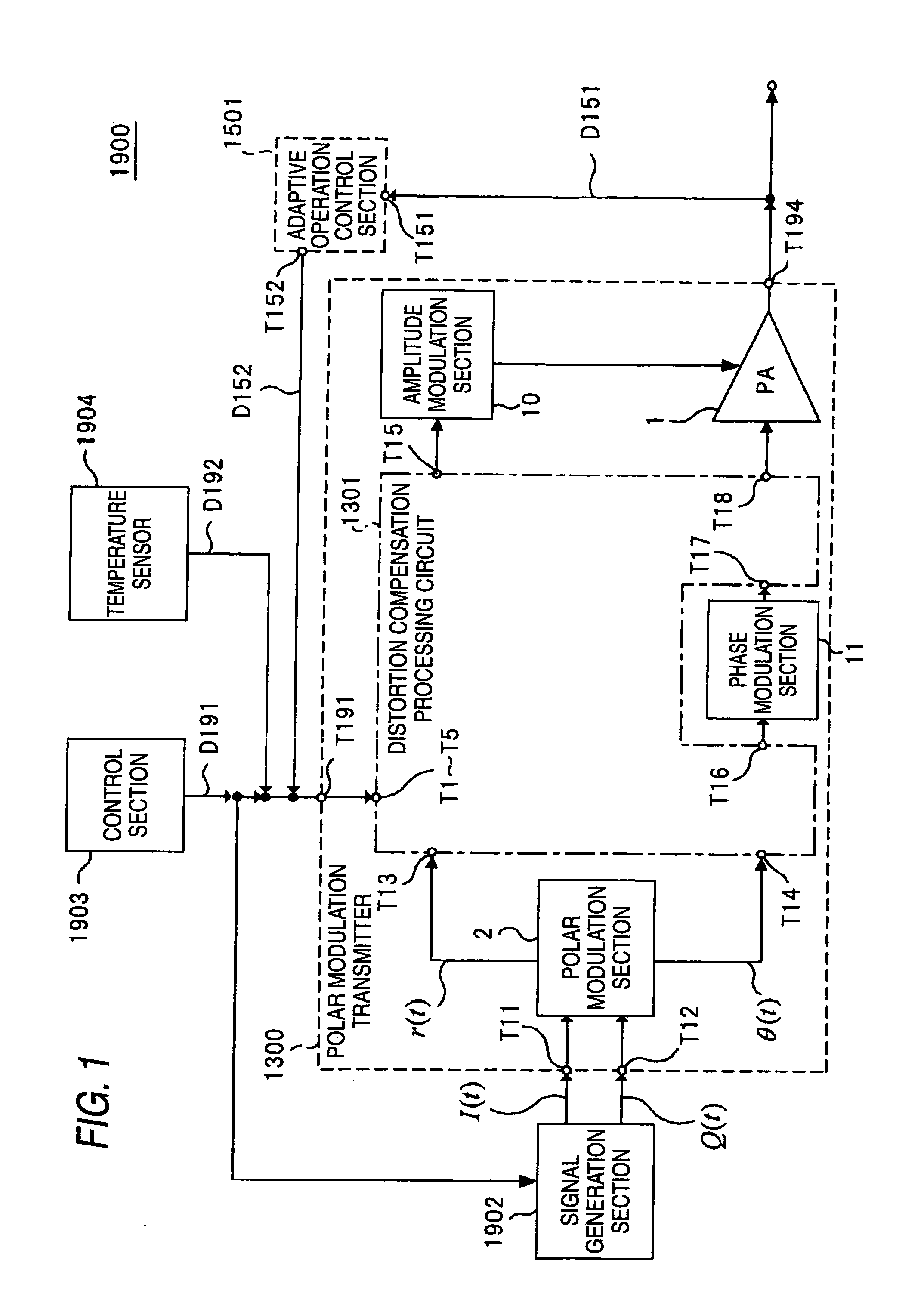
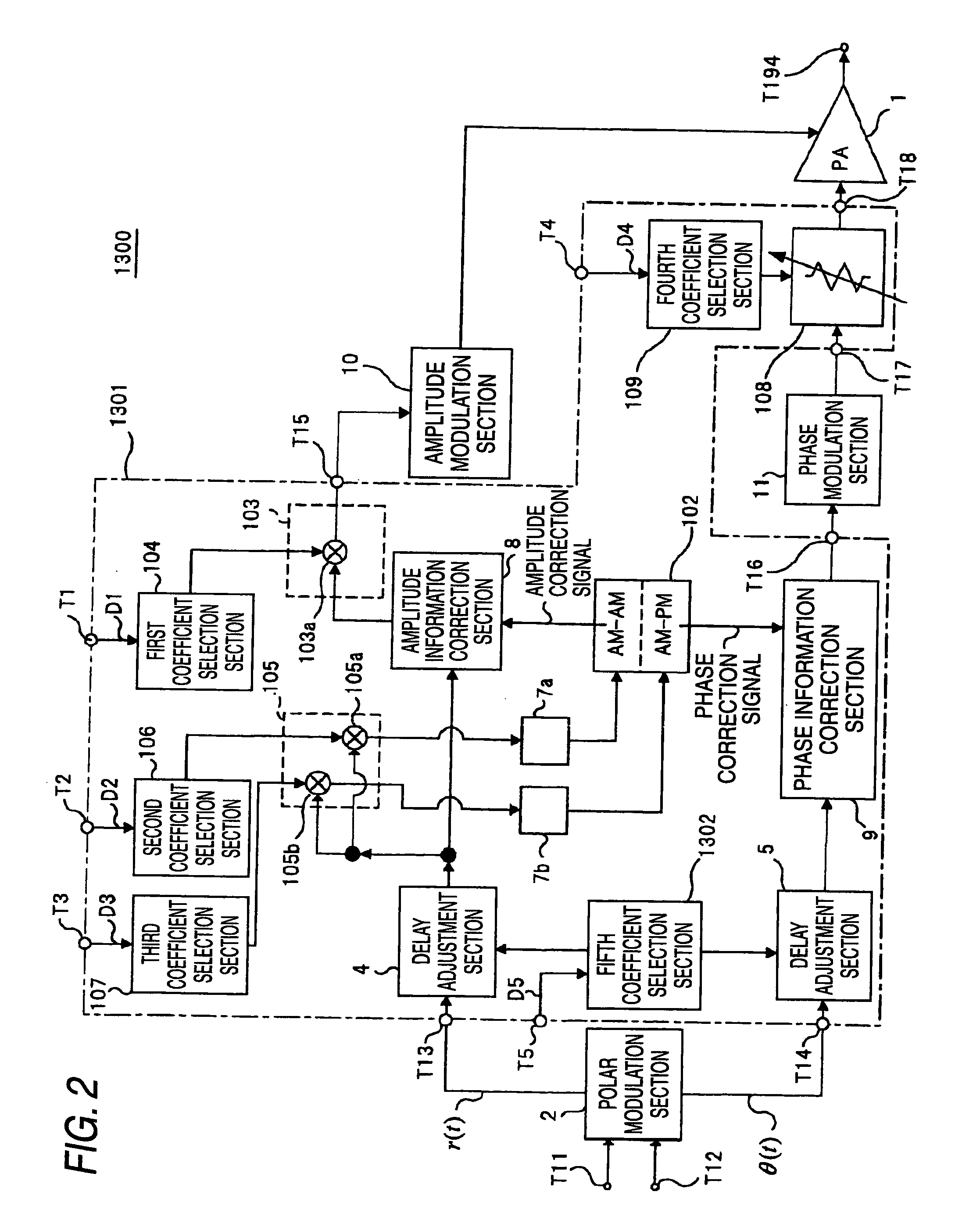
Polar modulation transmitter, adaptive distortion compensation processing system, polar modulation transmission method, and adaptive distortion compensation processing method
ActiveUS20100222015A1Low distortion characteristicCircuit scale increaseResonant long antennasAmplifier with control circuitsFrequency spectrumAudio power amplifier
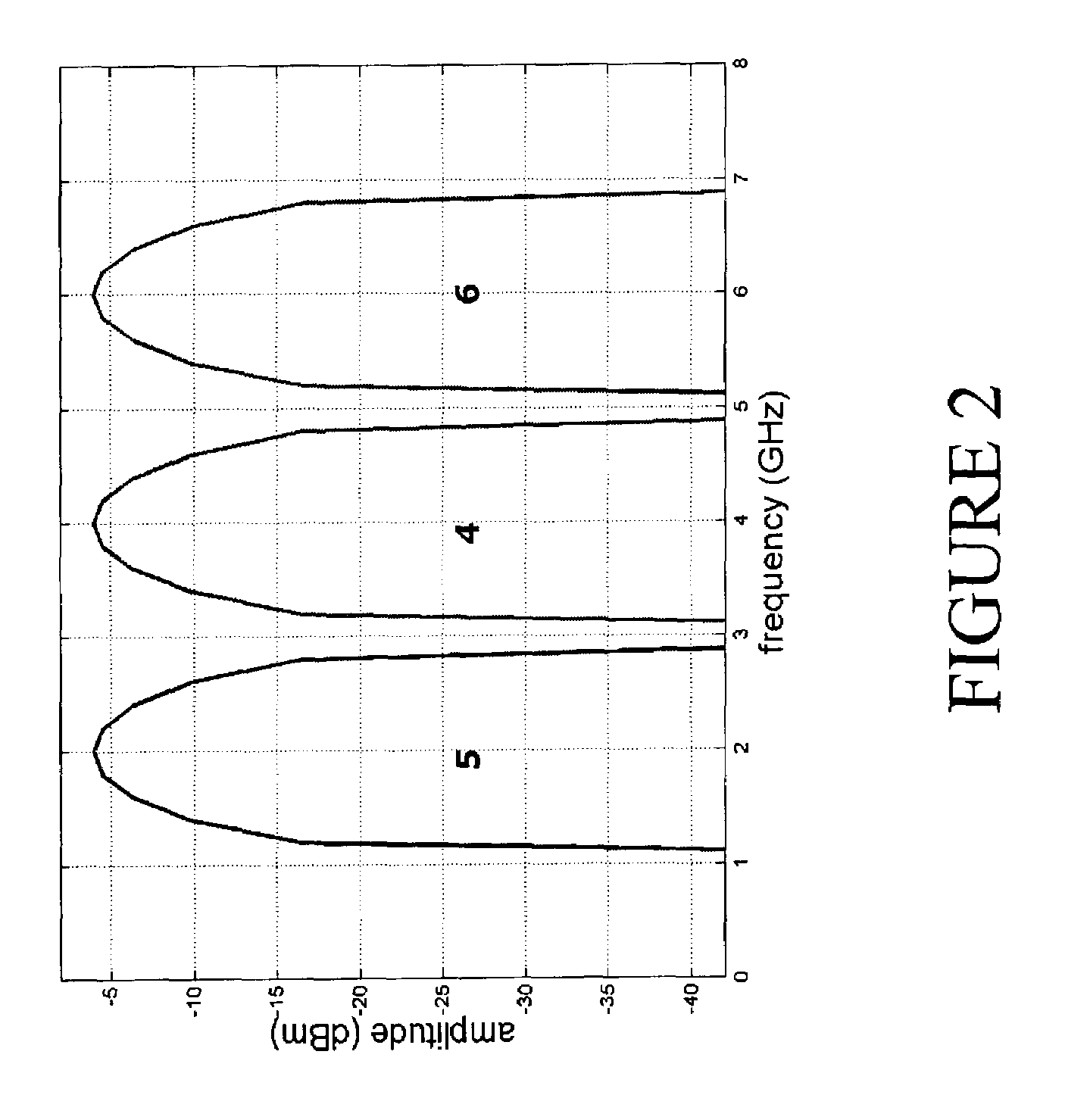
An object of the invention is to provide a polar modulation transmitter that can perform adaptive distortion compensation processing without the need for a synchronization adjustment circuit for synchronizing an input baseband signal and an output signal of a power amplifier. An adaptive operation control section 1501 measures the unbalance amount of an output spectrum of a power amplifier 1 and a coefficient adjustment determination section of the adaptive operation control section 1501 performs iteration control so that if the unbalance amount is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value, coefficient information output to a distortion compensation processing circuit 1301 is adjusted and an adjustment is made to distortion compensation processing in the distortion compensation processing circuit 1301 and if the unbalance amount is less than the predetermined threshold value, the coefficient information is maintained, whereby the characteristic change of the power amplifier 1 at the environmental temperature change time can be adaptively compensated for without using a synchronization adjustment circuit for synchronizing an input baseband signal and an output signal from the power amplifier 1.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Pseudo-polar modulation for radio transmitters
ActiveUS20050046507A1Reduce the amplitudeSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationSecret communicationRadiotransmitterEngineering
Methods of modulating a radio transmitter. An amplitude modulation signal is generated based on in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components of an information signal, and so that it has a reduced predetermined characteristic compared to the magnitude of the I and Q components of the information signal. A complex signal is formed that has substantially the same phase angle variation as the I and Q components of the information signal so that the product of the complex signal and the amplitude modulation signal is substantially equal to the information signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Bandwidth reduction mechanism for polar modulation
ActiveUS20090258612A1Reducing polar modulation bandwidthDegradation of modulation bandwidthSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulated-carrier systemsFrequency spectrumPhase bandwidth
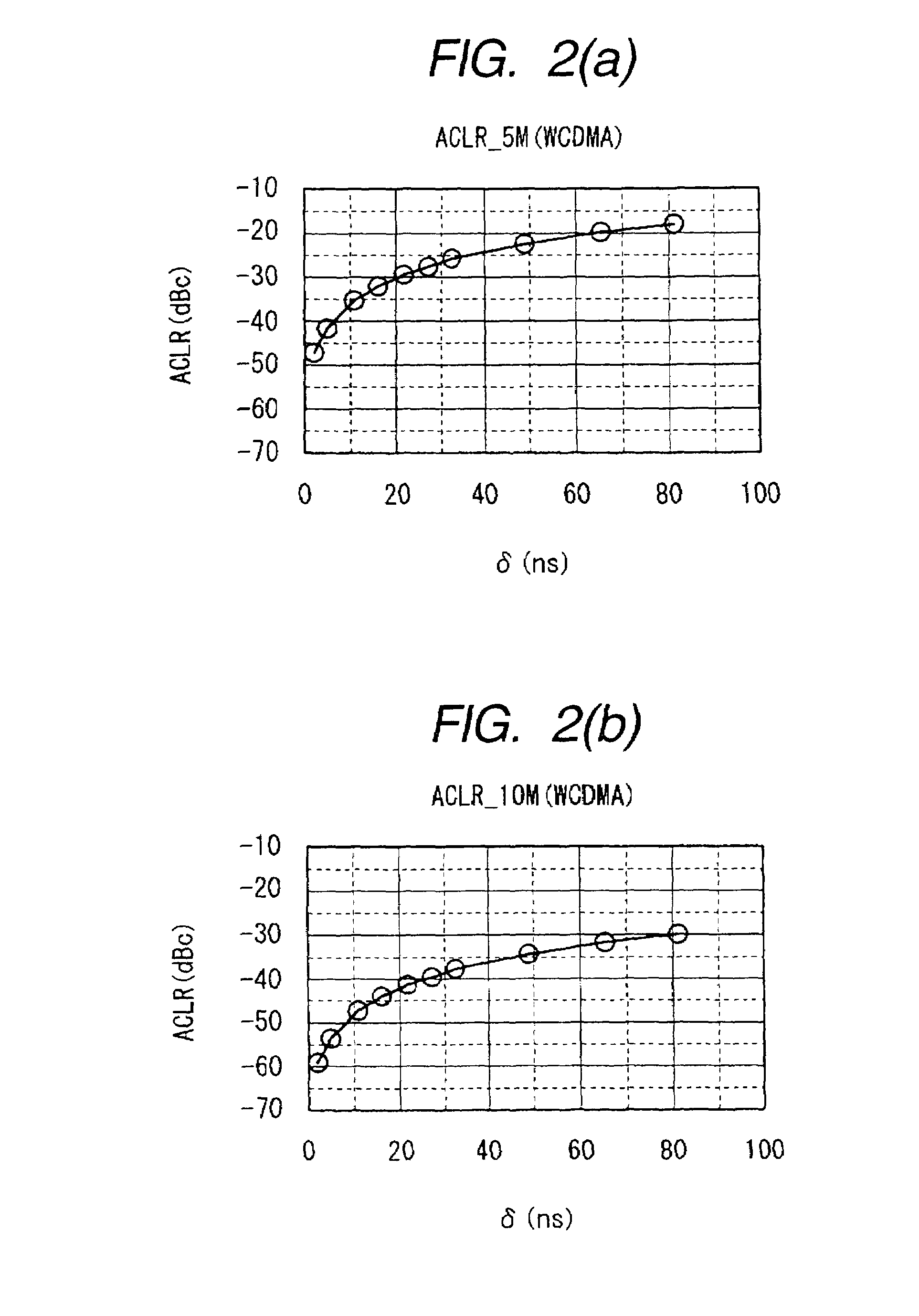
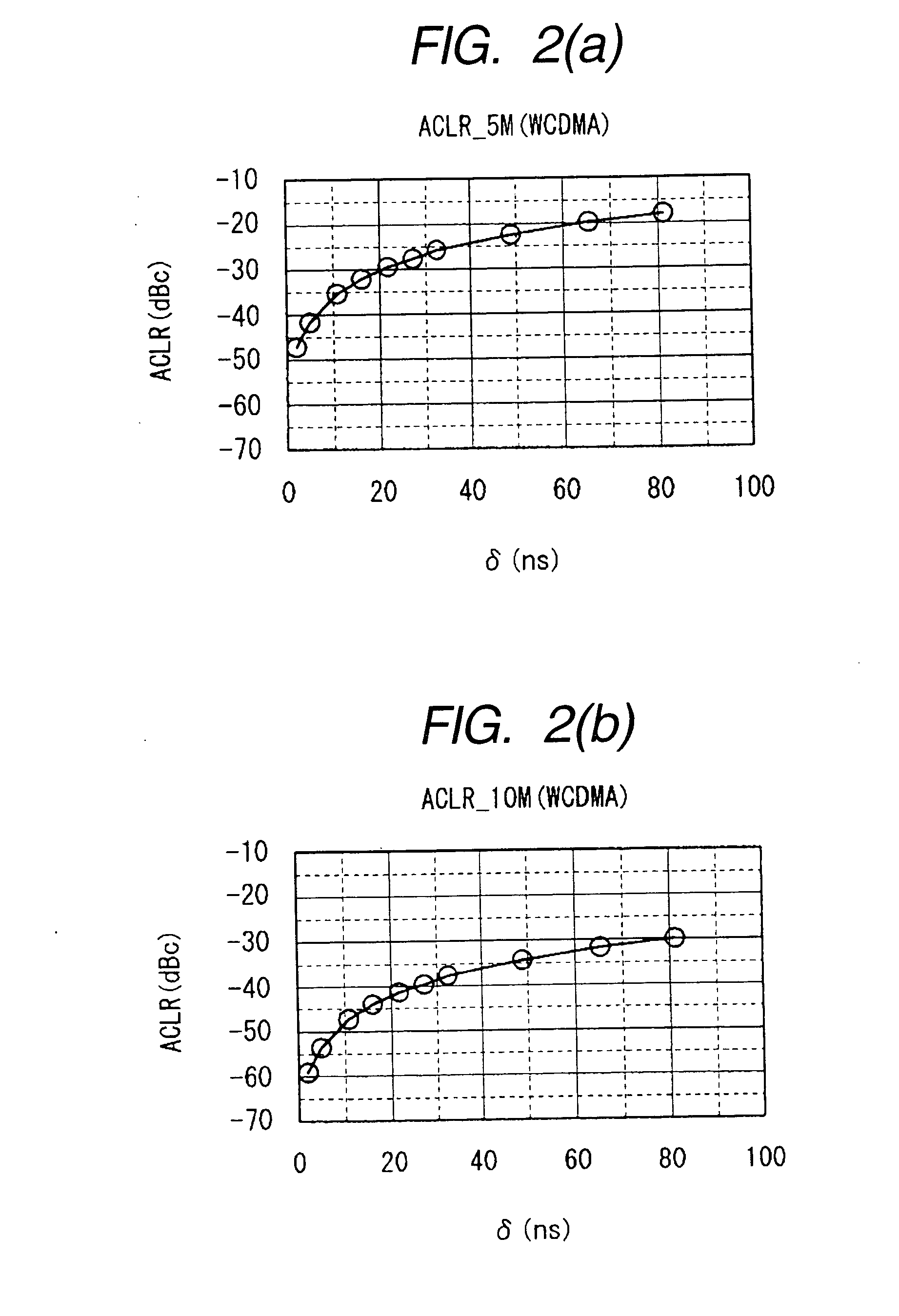
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of reducing phase and amplitude modulation bandwidth in polar transmitters. The bandwidth reduction mechanism of the present invention effectively reduces the phase modulation bandwidth of the polar modulation performed in the transmitter by modifying the zero-crossing trajectories in the IQ domain. This significantly reduces the phase modulation bandwidth while still meeting the output spectrum and error vector magnitude (EVM) requirements of the particular modern wideband wireless standard, such as 3G WCDMA, etc. The mechanism detects a zero crossing or a near zero crossing within a predetermined threshold of the origin and an offset vector is generated that when added to the input TX IQ data, shifts the trajectory to avoid the origin thus reducing the resultant polar modulation amplitude and phase bandwidth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
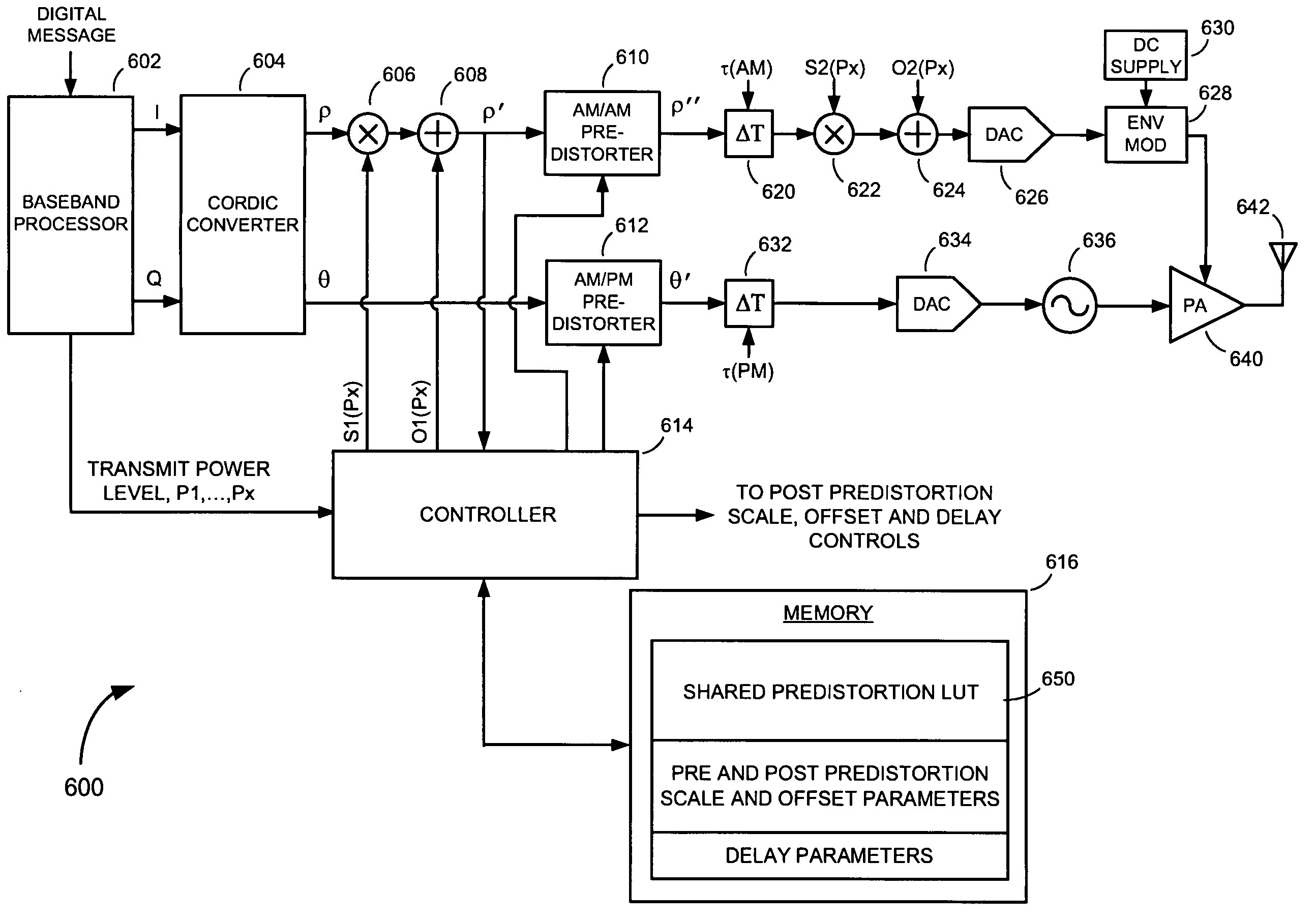
Predistortion methods and apparatus for polar modulation transmitters
ActiveUS20090252255A1Less memoryModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationAudio power amplifierPolar modulation
Methods and apparatus for predistorting signals in a polar modulation transmitter. An exemplary method includes predistorting an envelope component signal in an amplitude path of a polar modulation transmitter according to a set of AM / AM predistortion coefficients, and predistorting a phase component signal in a phase path of the polar modulation transmitter according to a set of AM / PM predistortion coefficients. The AM / AM and AM / PM predistortion coefficients are stored in a memory in the form of a look up table (LUT). The envelope component signal is scaled and / or offset, before predistortion is applied, by an amount dependent upon which average power level of a plurality of average power levels the power amplifier of the polar modulation transmitter is configured to operate. Scaling and / or offsetting the envelope component signal prior to applying predistortion affords the ability to share the AM / AM and AM / PM predistortion coefficients of the predistortion LUT over the plurality of average power levels.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
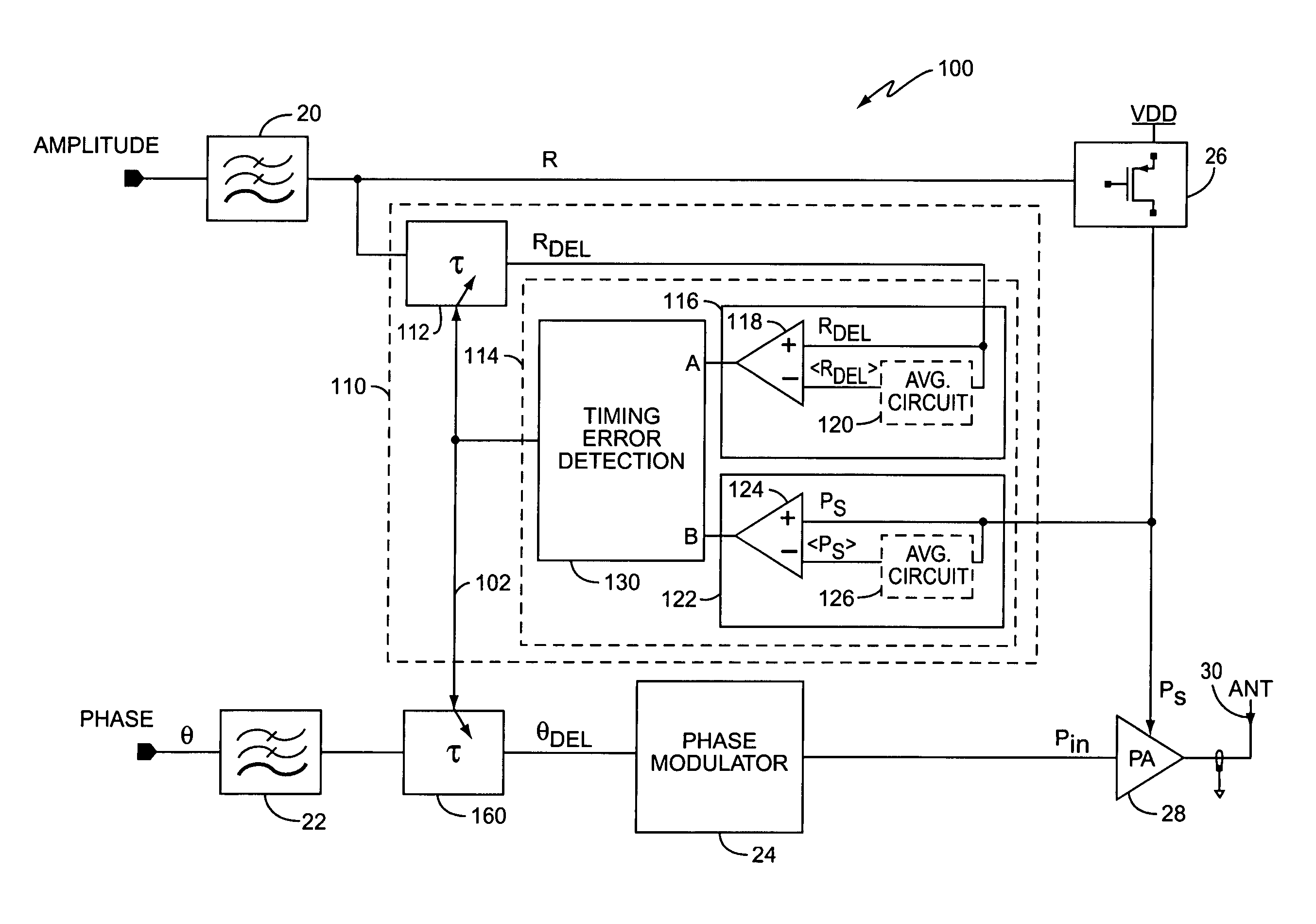
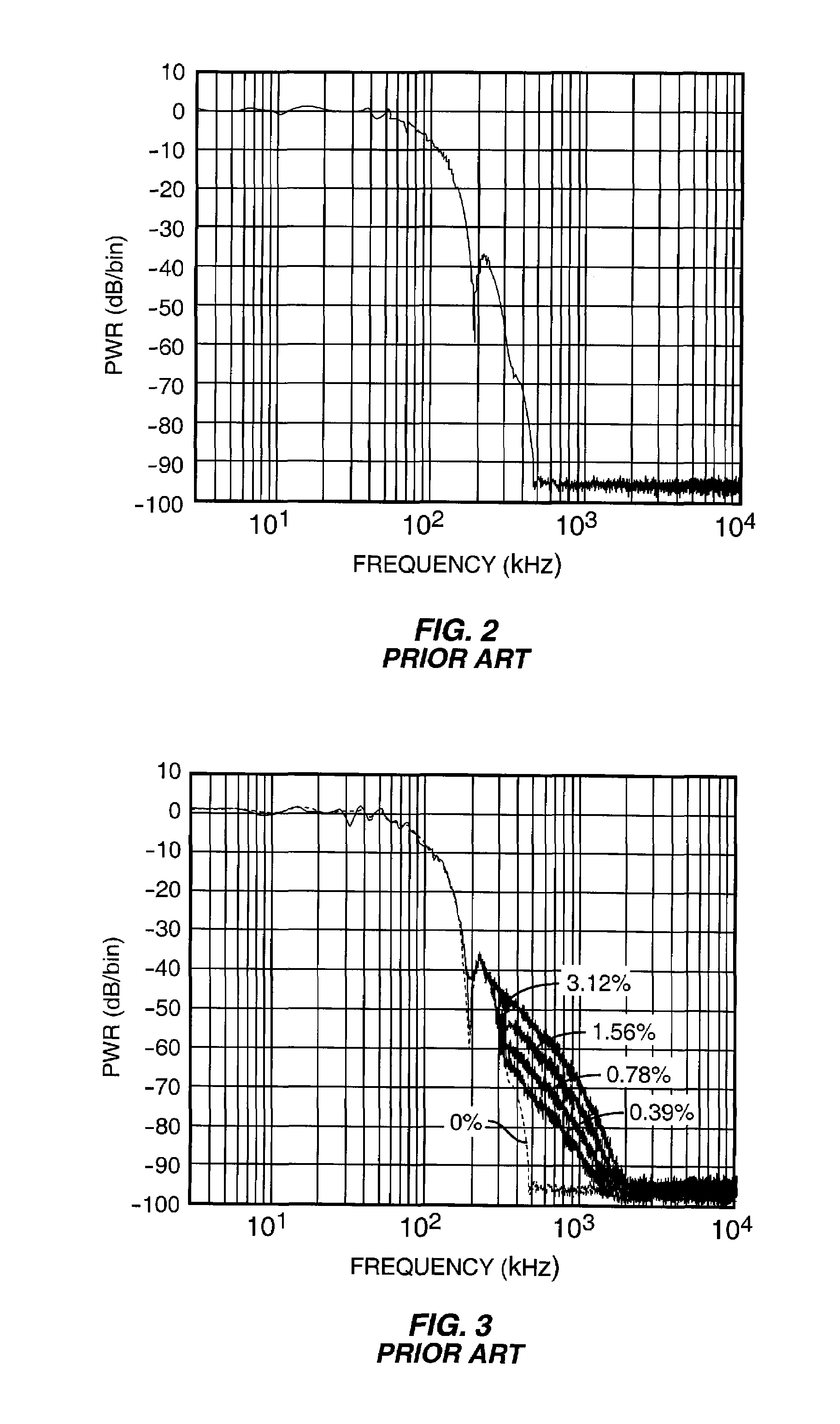
Delay calibration in polar modulation transmitters
ActiveUS7359680B2Modulated-carrier systemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierEngineering
A method and apparatus for dynamically compensating for delay mismatch between a supply signal and an input signal of a power amplifier in polar modulation transmitters. One exemplary polar modulation transmitter according to the present invention comprises a power amplifier, a phase modulator, a regulator, a delay tracking circuit, and a delay circuit. The phase modulator derives the amplifier input signal responsive to one or more phase signals, while the regulator derives the amplifier supply signal responsive to an amplitude signal. Based on the amplitude signal and the amplifier supply signal, the delay tracking circuit tracks an observed amplitude path delay. The delay circuit adjusts a path delay associated with the phase signal, responsive to the observed amplitude path delay, to compensate for the delay mismatch.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Transmitter apparatus and method using polar modulation with signal timing adjustment
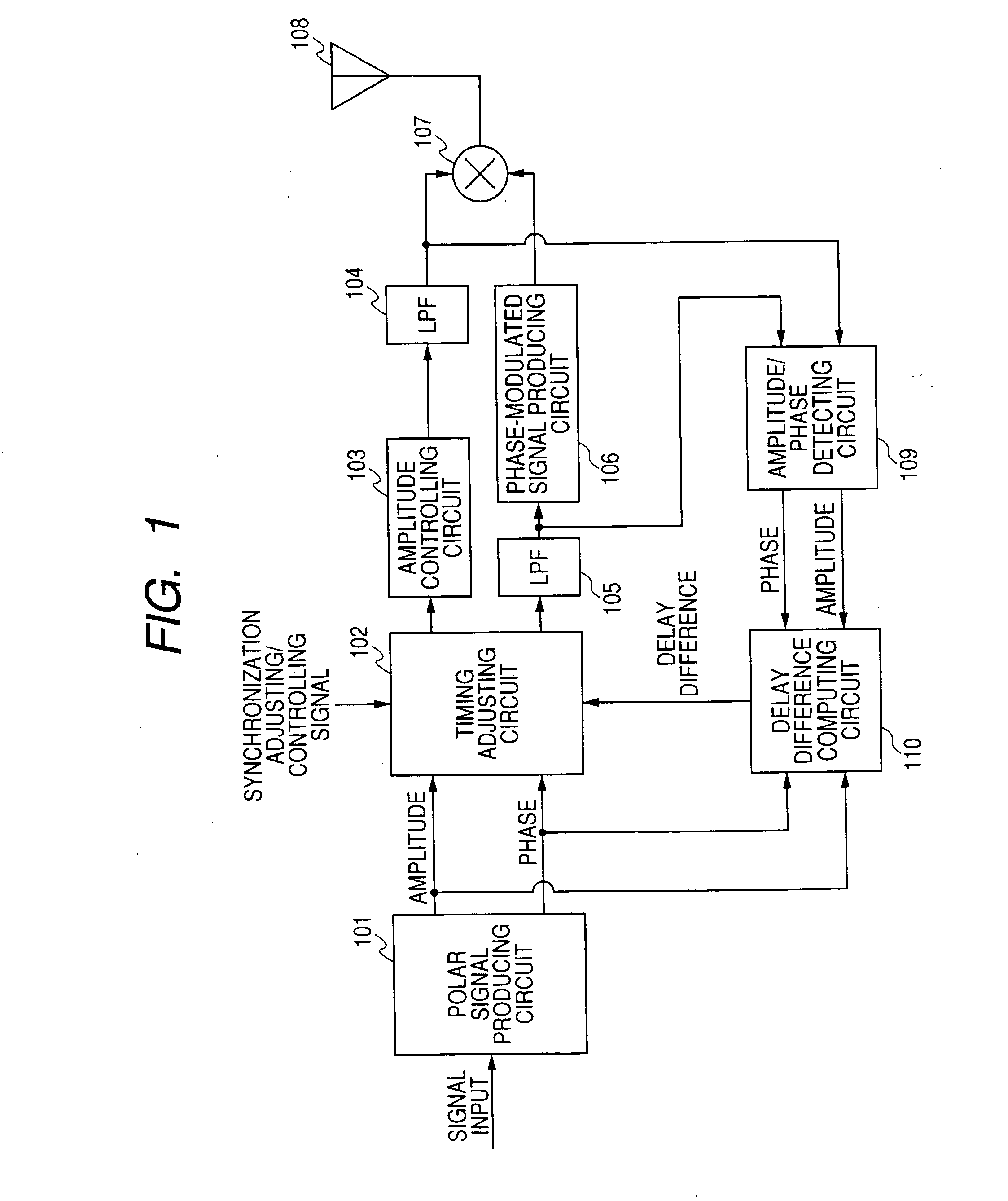
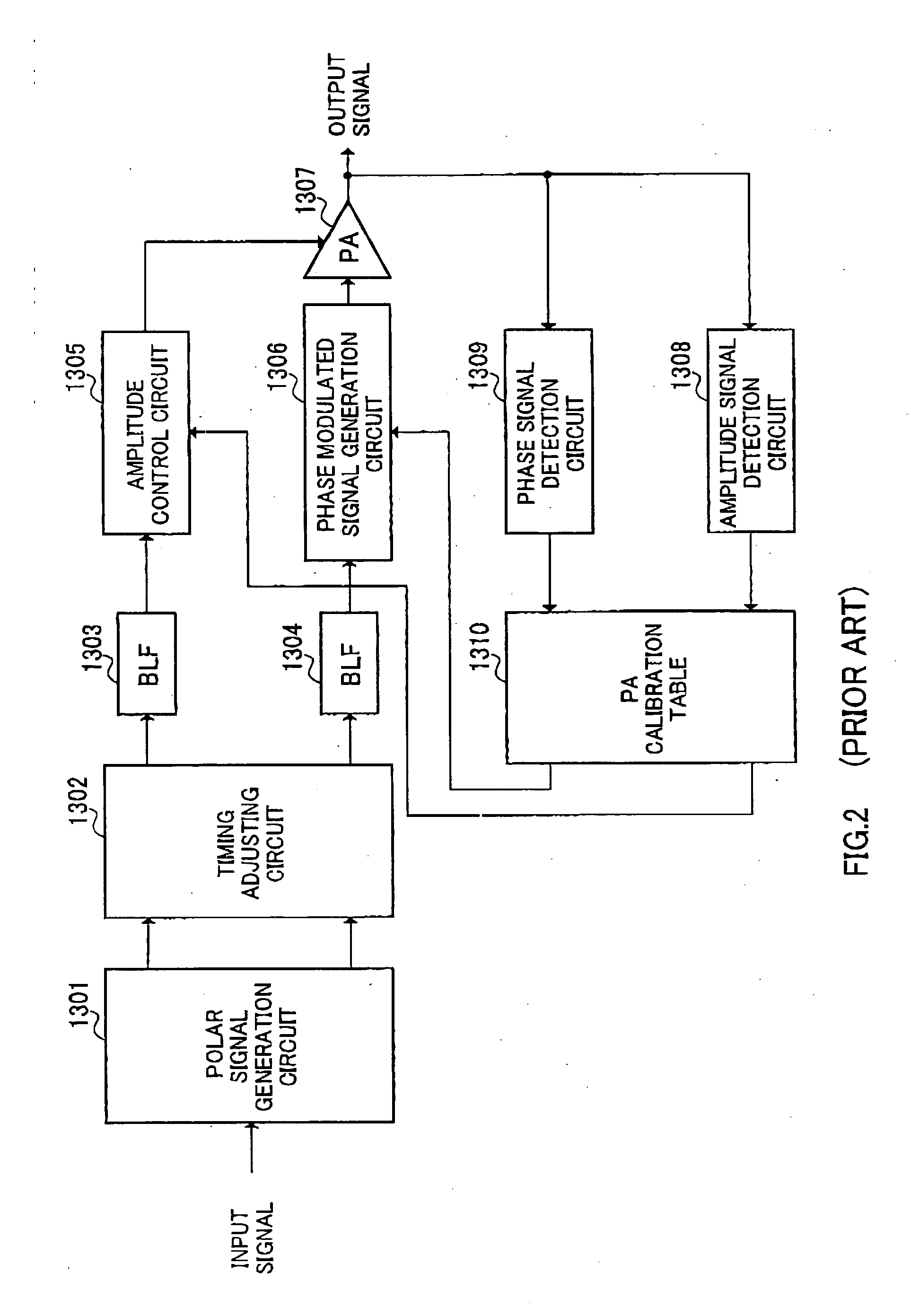
InactiveUS7379715B2Eliminate having large delayImprove accuracyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasSignal onDelayed time
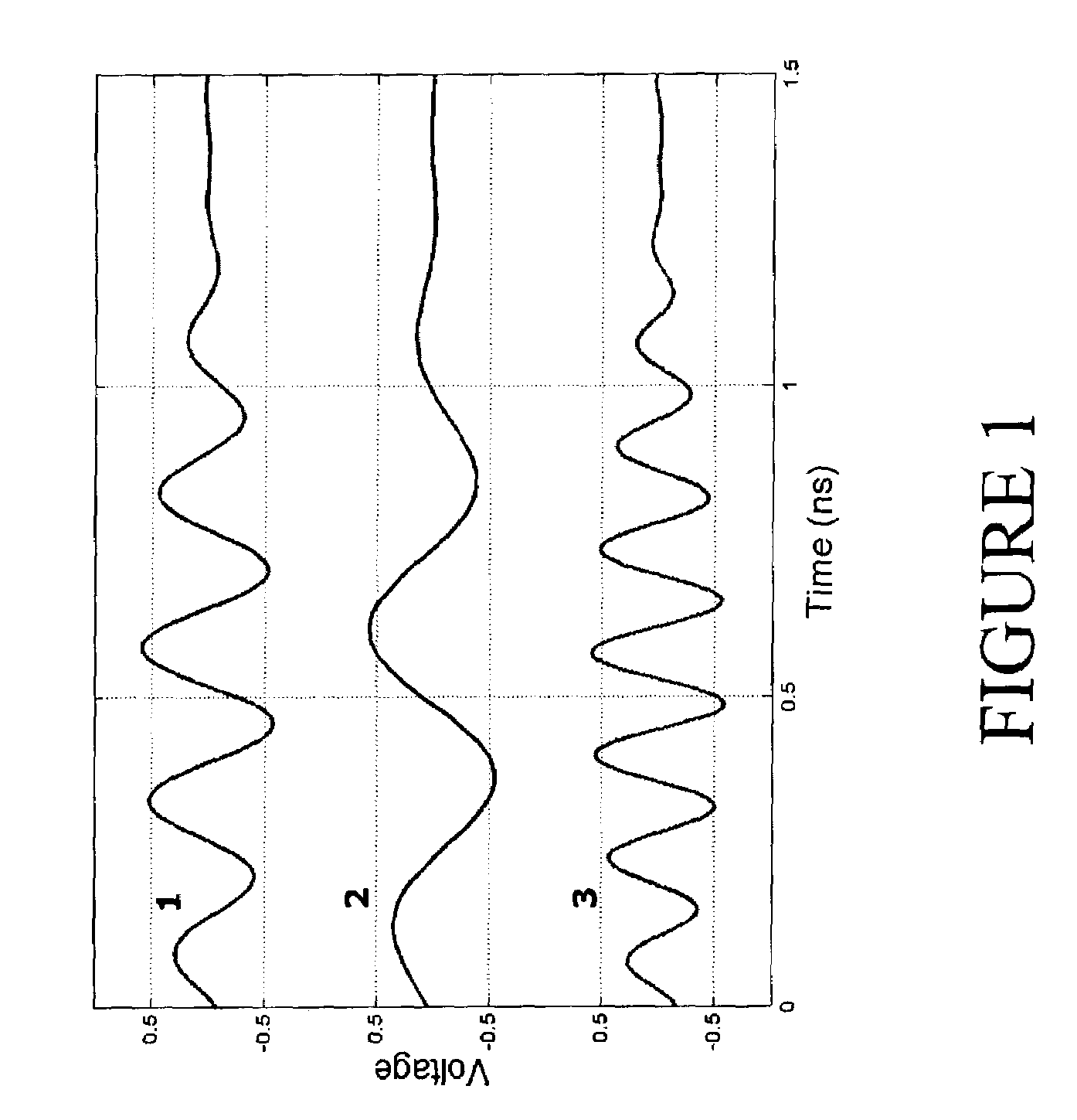
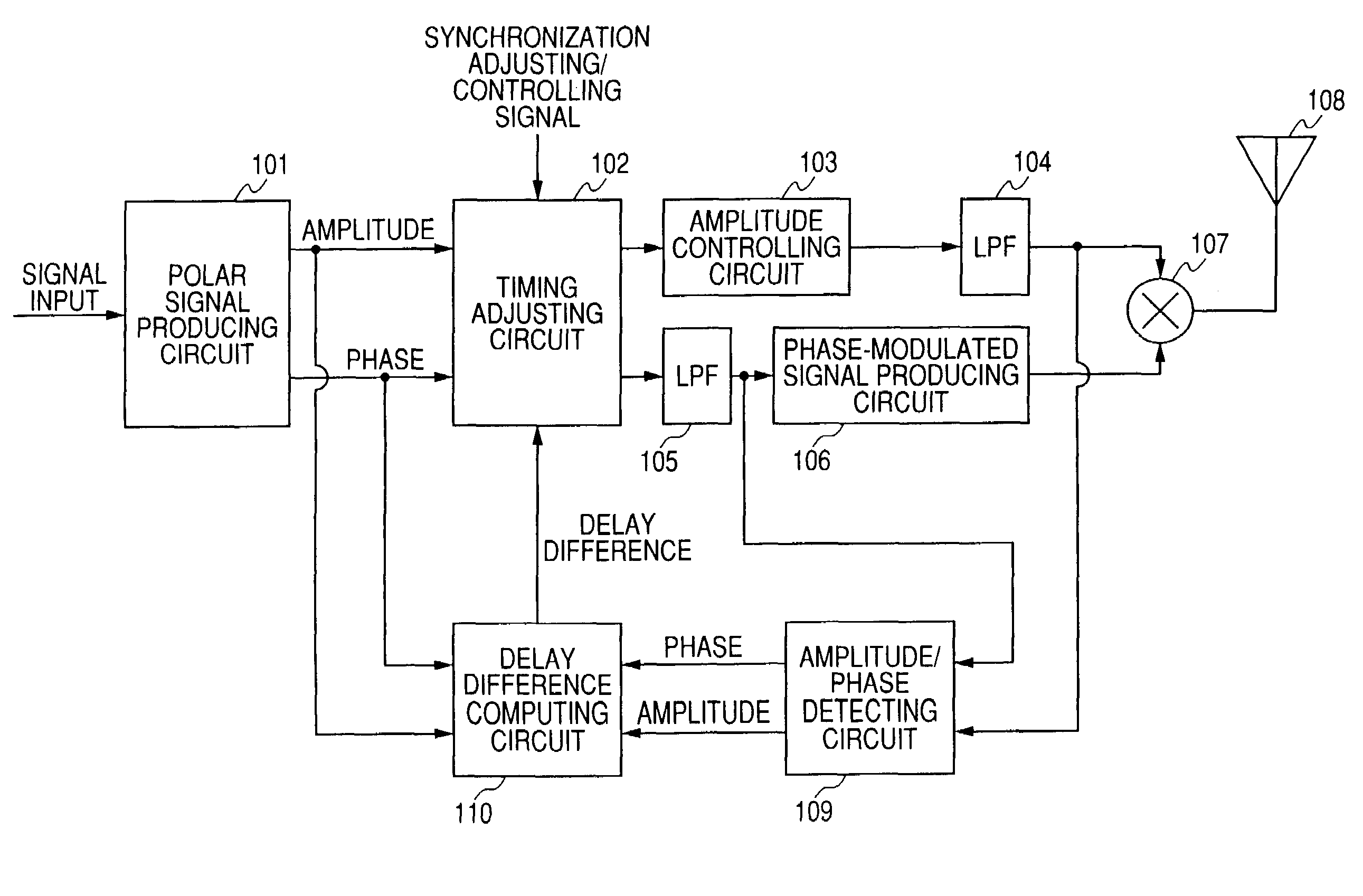
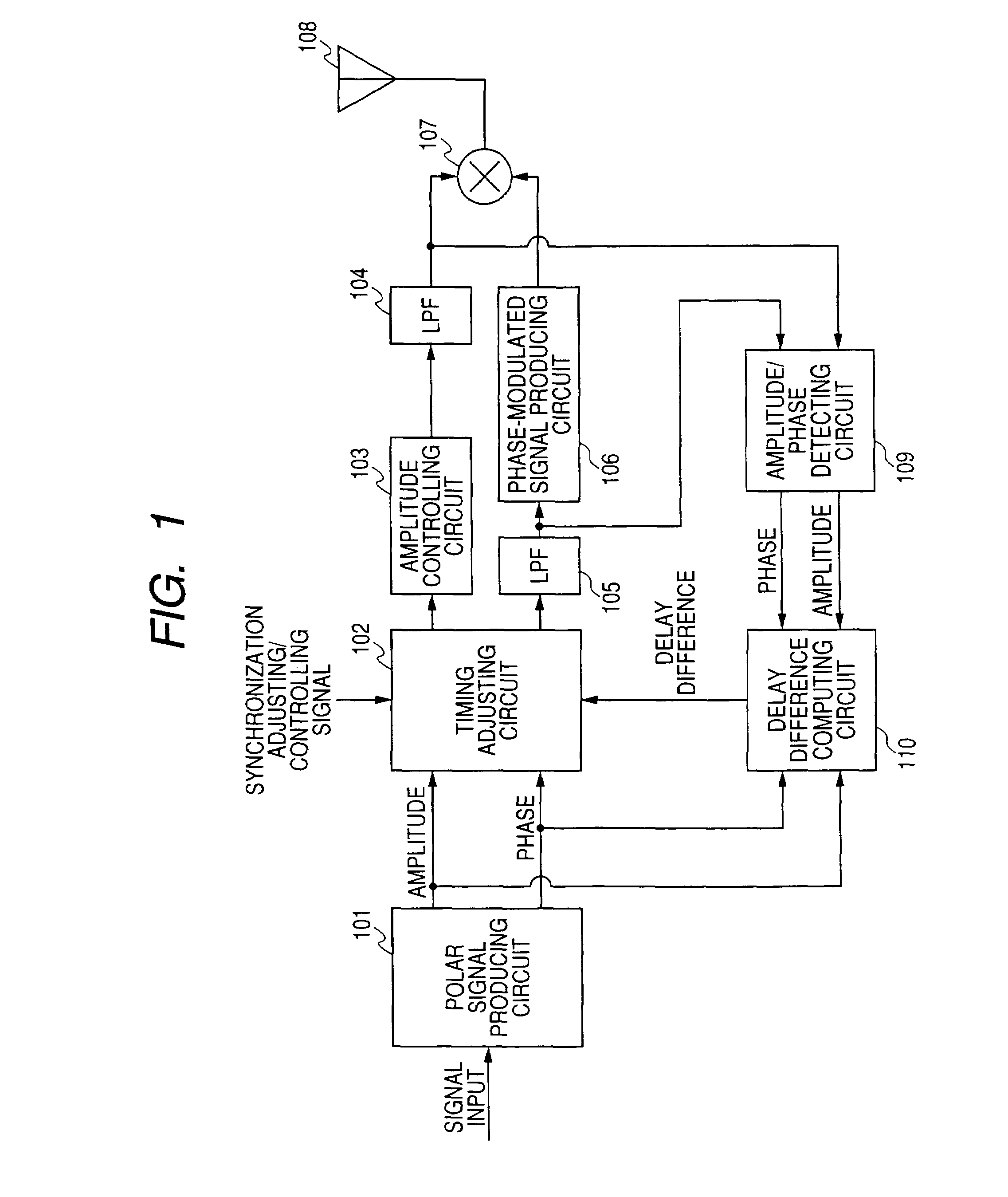
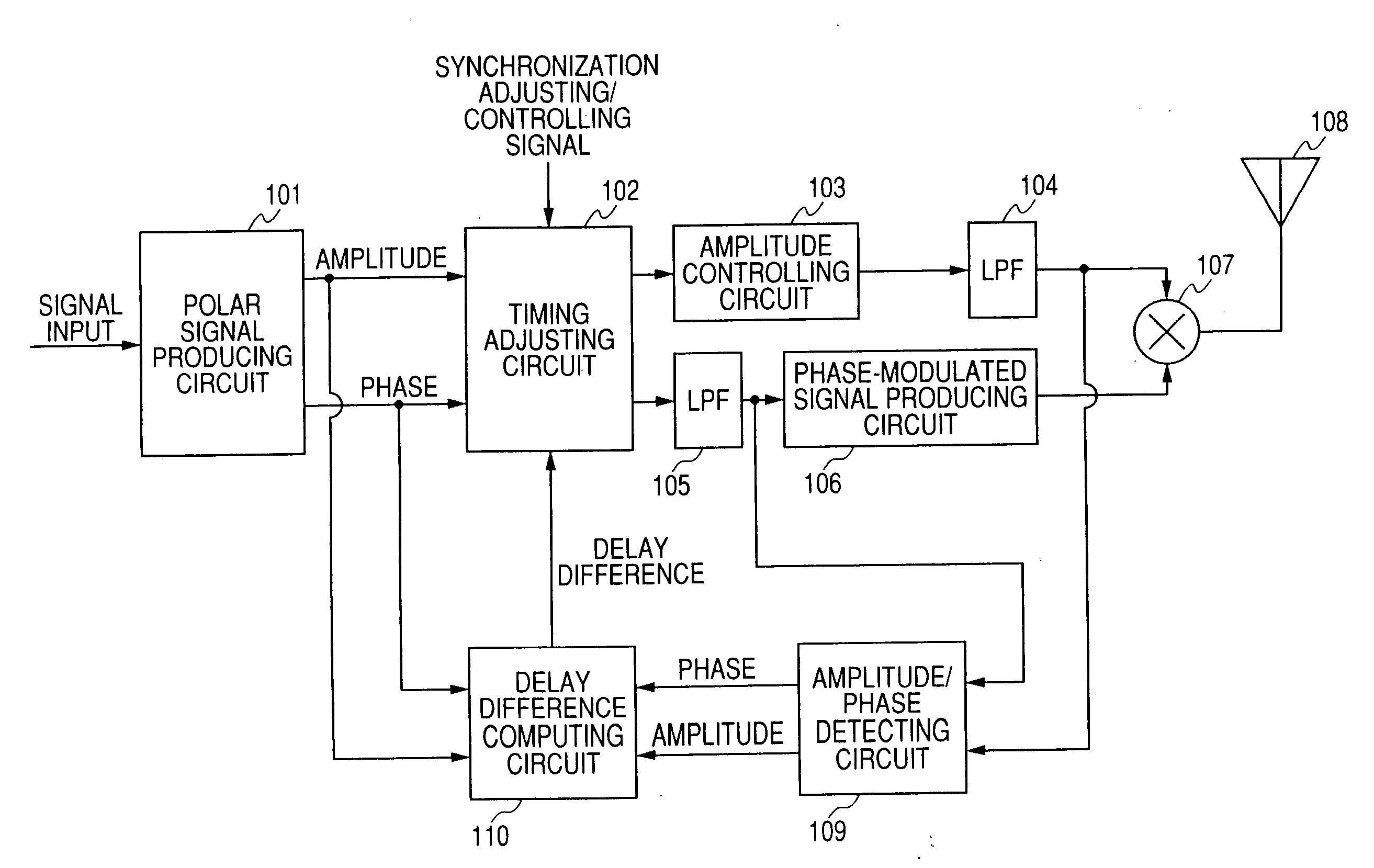
A transmitting apparatus includes a polar signal producing circuit which produces signals corresponding to the amplitude and the phase of a transmitting modulated wave from an input signal and multiplies the amplitude signal by the phase signal by a multiplying circuit to amplitude modulate a phase-modulated wave to produce a transmitting modulated wave and radiates this transmitting modulated wave as radio wave from an antenna. An amplitude / phase detecting circuit detects an amplitude signal and a phase signal from the input of the multiplying circuit and the input of a phase-modulated signal producing circuit. A delay difference computing circuit computes a correlation function between the amplitude signal produced by the polar signal producing circuit and the amplitude signal detected by the amplitude / phase detecting circuit and a correlation function between the phase signal produced by the polar signal producing means and the phase signal detected by the amplitude / phase detecting means, and computes a delay difference between the amplitude signal and the phase signal from maximum values of the respective correlation functions. Then, a timing adjusting circuit adjusts the delay time between the amplitude signal and the phase signal on the base of the computed delay difference.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Transmitter apparatus
InactiveUS20060246856A1Synchronous regulationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasSignal onDelayed time
The object of the present invention is to automatically adjust the synchronization of an amplitude signal and a phase signal in a transmitting apparatus such as polar modulation transmitting apparatus. A polar signal producing circuit (101) produces signals corresponding to the amplitude and the phase of a transmitting modulated wave from an input signal and multiplies the amplitude signal by the phase signal by a multiplying circuit (107) to amplitude modulate a phase-modulated wave to produce a transmitting modulated wave and radiates this transmitting modulated wave as radio wave from an antenna (108). An amplitude / phase detecting circuit (109) detects an amplitude signal and a phase signal from the input of the multiplying circuit (107) and the input of a phase-modulated signal producing circuit (106). A delay difference computing circuit (110) computes a correlation function between the amplitude signal produced by the polar signal producing circuit and the amplitude signal detected by the amplitude / phase detecting circuit and a correlation function between the phase signal produced by the polar signal producing means and the phase signal detected by the amplitude / phase detecting means, and computes a delay difference between the amplitude signal and the phase signal from maximum values of the respective correlation functions. Then, a timing adjusting circuit (102) adjusts the delay time between the amplitude signal and the phase signal on the base of the computed delay difference.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Temperature compensated power amplifier power control
InactiveUS6998919B2Accurate and repeatableNo fluctuationGain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:QORVO US INC
Pseudo-polar modulation for radio transmitters
ActiveUS7126999B2Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationSecret communicationEngineeringPolar modulation
Methods of modulating a radio transmitter. An amplitude modulation signal is generated based on in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components of an information signal, and so that it has a reduced predetermined characteristic compared to the magnitude of the I and Q components of the information signal. A complex signal is formed that has substantially the same phase angle variation as the I and Q components of the information signal so that the product of the complex signal and the amplitude modulation signal is substantially equal to the information signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
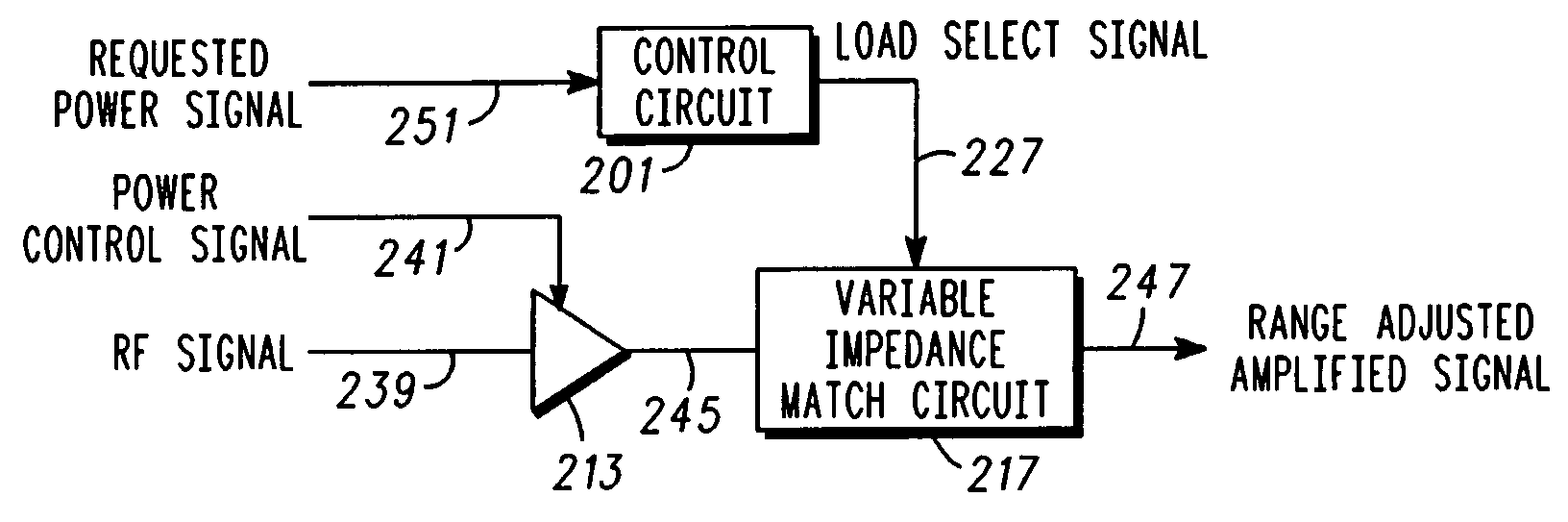
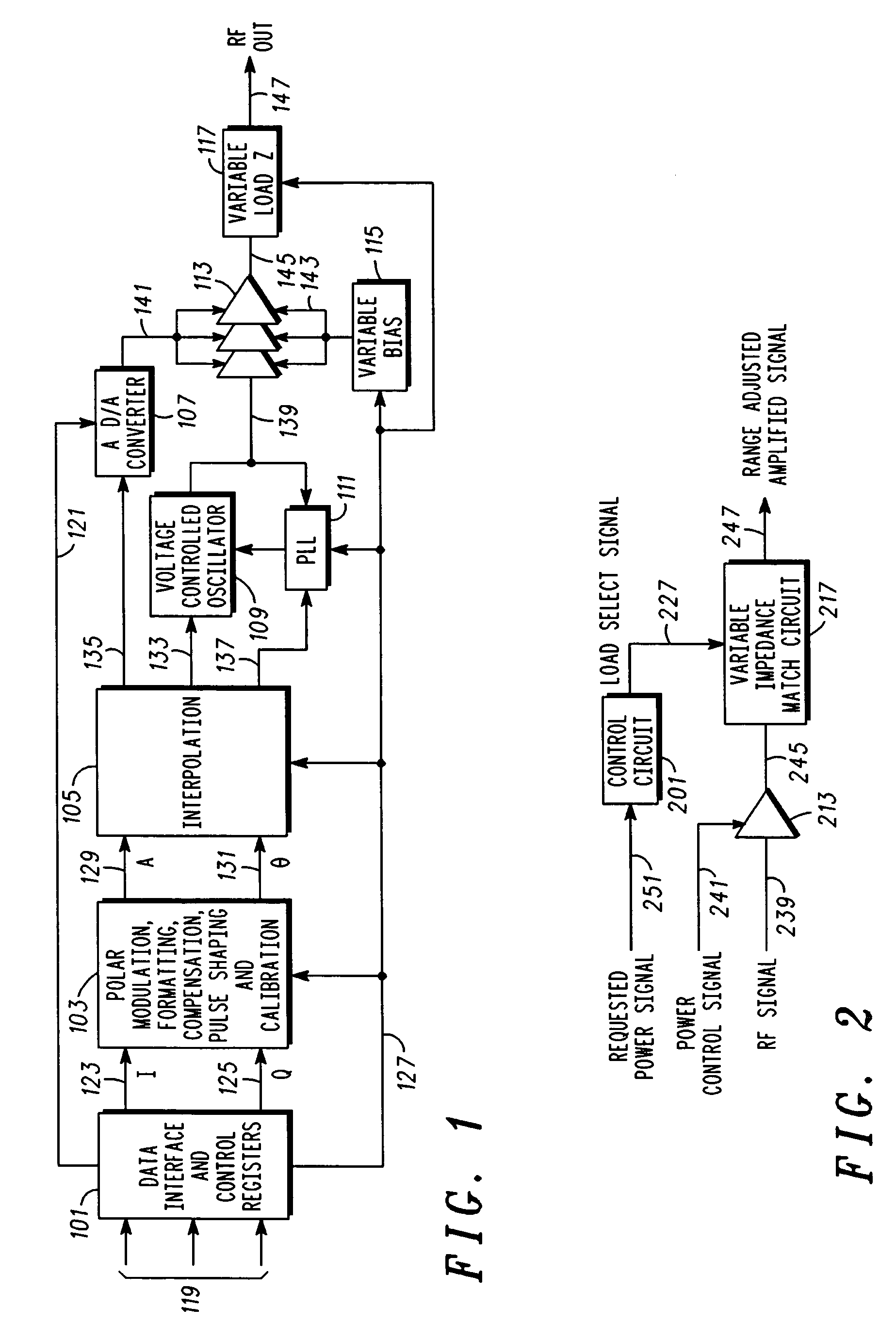
Multi-state load switched power amplifier for polar modulation transmitter
ActiveUS7183844B2Improve appreciationInvention is limitedAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
A polar modulation power amplifier circuit includes a control circuit (101) to determine and provide a load selection signal (127), wherein the load selection signal (127) is determined responsive to a requested power signal (119). A power amplifier (113) is responsive to a power control signal (141), for amplifying an RF signal (139) to produce an amplified signal (145), having an output power level. A variable impedance matching circuit (117) is responsive to the load selection signal (127), to adjust a relationship between the control level and the output power level, to produce a range-adjusted amplified signal (147).
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Polar modulation using amplitude modulated quadrature signals
ActiveUS20050134396A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAngle to amplitude modulation conversionPhase splitterControl signal
Polar modulators include a phase splitter, a controller, variable current sources, transistor circuits, and a combiner. The phase splitter splits a RF carrier signal into quadrature component signals that are 90 degrees out of phase with each other. The controller generates modulation control signals based on information that is to be transmitted. The variable current sources each generate a variable amplitude current signal based on a different one of the modulation control signals. Each of the transistor circuits amplify a different one of the quadrature component signals with a variable amplification based on the variable amplitude current signal from a different one of the variable current sources to generate an amplitude adjusted quadrature component signal. The combiner combines the amplitude adjusted quadrature component signals from each of the transistor circuits to generate a phase-modulated RF carrier output signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
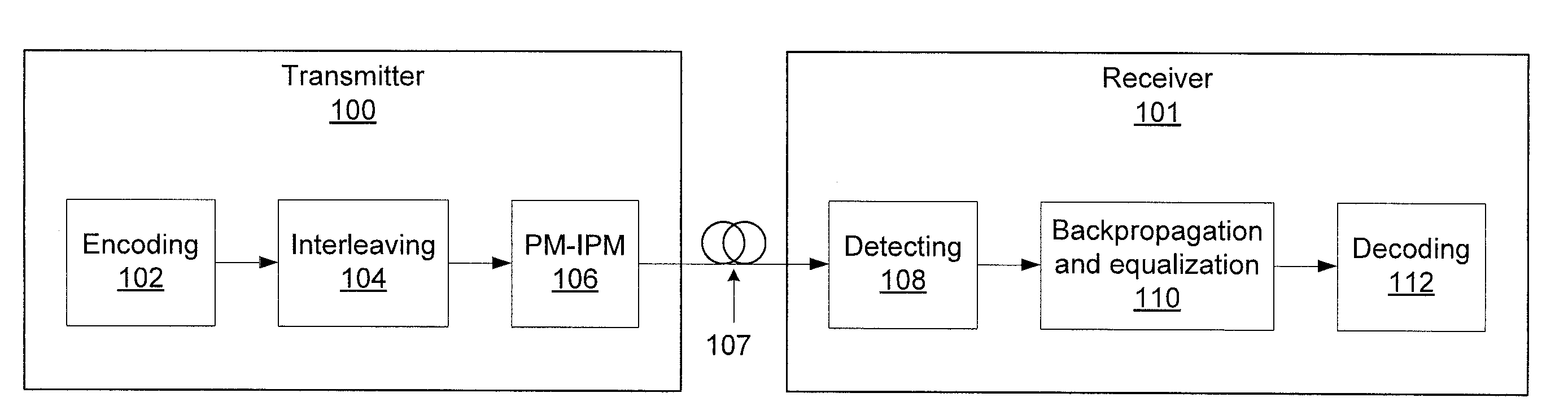
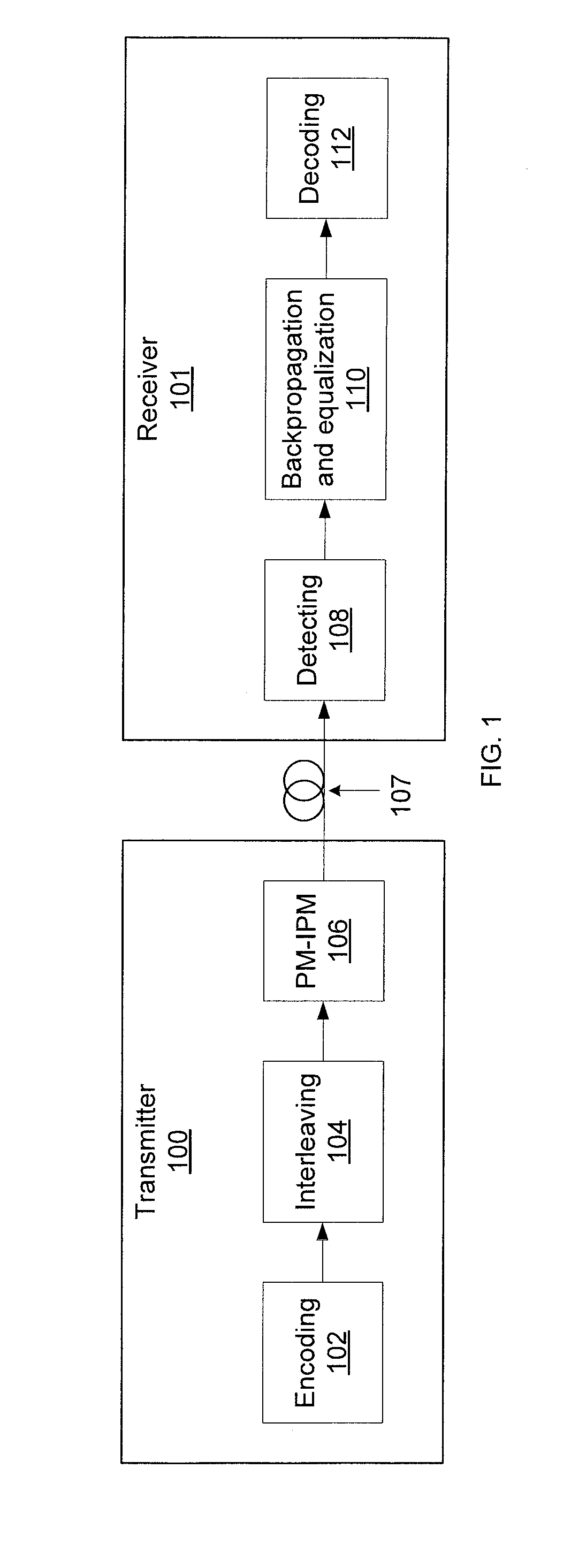
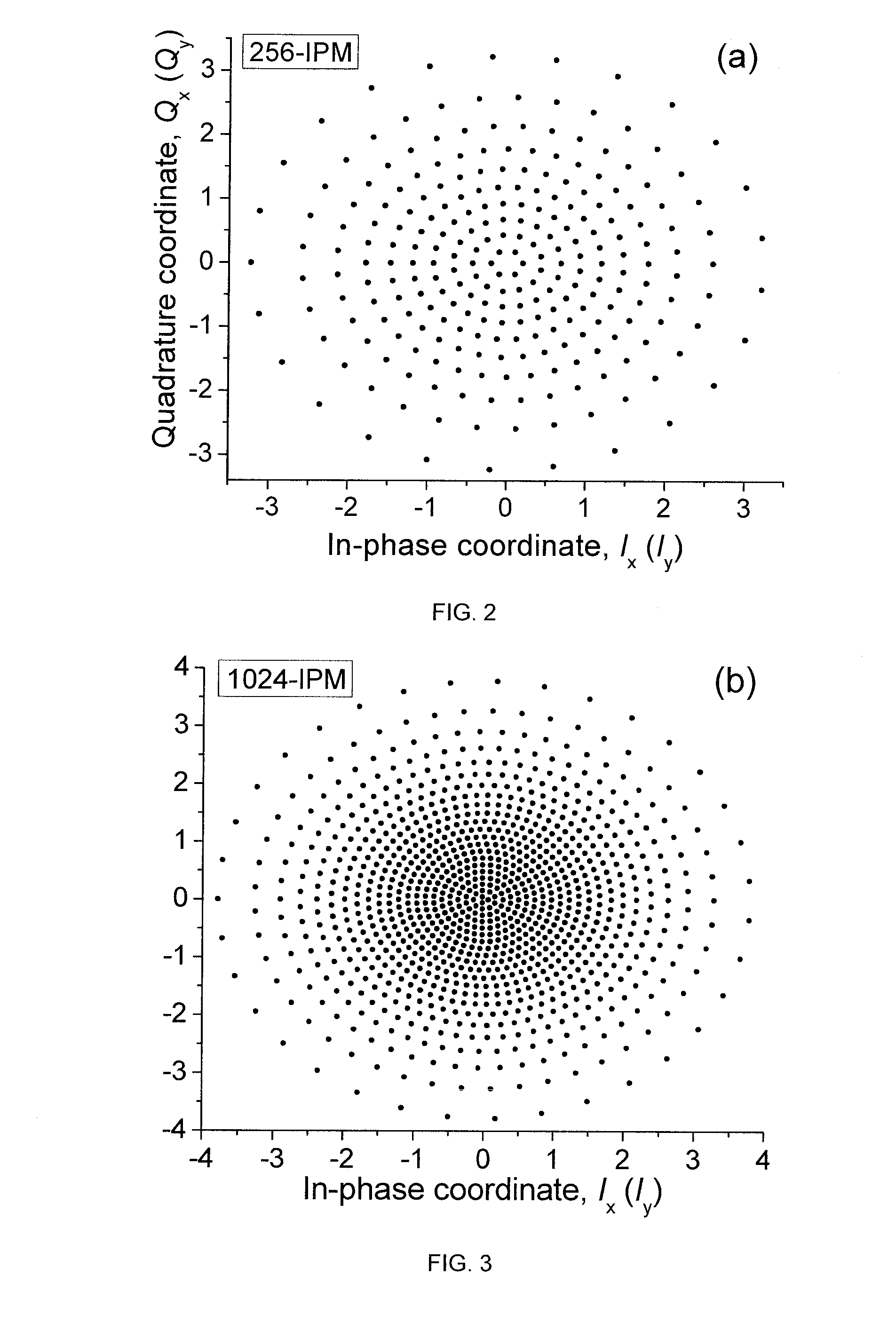
Coded polarization-multiplexed iterative polar modulation
ActiveUS20110085624A1Reducing channel memoryRemoving channel impairmentPolarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingData streamPolarization multiplexed
Systems and methods for optical communication that use a transmitter / receiver. The systems and methods include receiving a modulated, encoded input stream. Channel memory is reduced using coarse digital backpropagation and other channel impairments are removed using turbo equalization. Symbols are detected in the input stream that conform to a non-uniform, polar constellation having a Gaussian source distribution to produce a stream of encoded data. The stream of encoded data is decoded with one or more low density parity check (LDPC) decoders.
Owner:NEC CORP
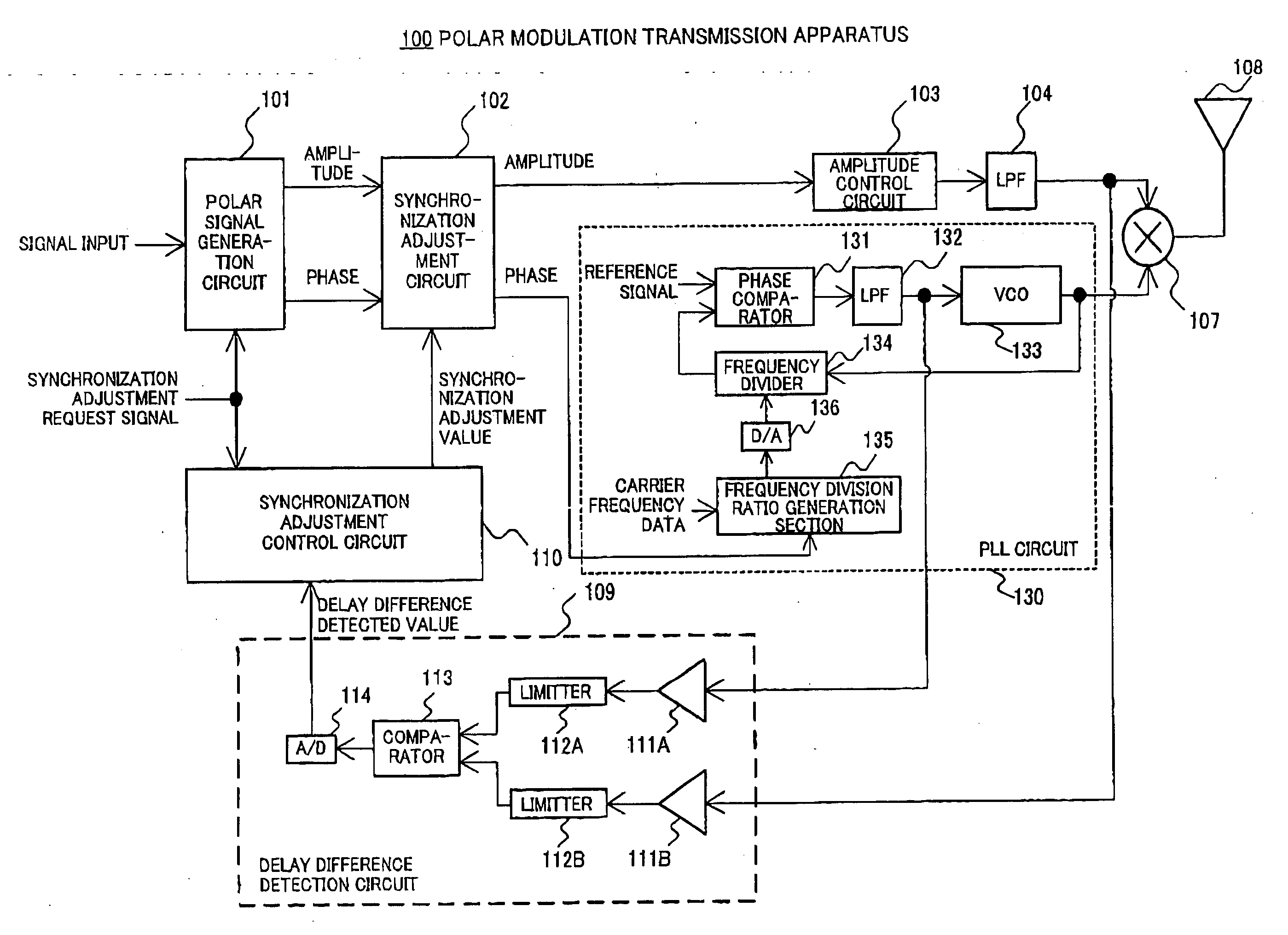
Polar modulation transmission apparatus and radio communication apparatus
InactiveUS20050245208A1Configuration accurately and automaticallySimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasLow-pass filterEngineering
A polar modulation transmission apparatus is provided which can adjust synchronization between an amplitude signal and phase signal in a simple configuration accurately and automatically. A polar signal generation circuit 101 sends an amplitude signal and phase signal for synchronization adjustment to transmission lines of these signals, incorporates the amplitude signal and phase signal for synchronization adjustment output from low pass filters 104, 132 which are final stage circuits that process the respective signals in their baseband signal states into a delay difference detection circuit 109, a synchronization adjustment control circuit 110 obtains a synchronization adjustment value at which the delay difference between the signals is eliminated based on the delay difference detection result and a synchronization adjustment circuit 102 gives delays corresponding to the synchronization adjustment value to the respective signals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Large signal polar modulated power amplifier
ActiveUS7593698B1Extends effective amplitude rangeReduce the amplitudeModulation with suppressed carrierAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierPolar modulation
Polar modulation input signals to a polar modulated power amplifier include a phase modulated (PM) input signal, which feeds a power amplifier input, and an amplitude modulated (AM) input signal, which provides an envelope supply voltage for the power amplifier. The present invention is a large signal polar modulated power amplifier that extends the effective amplitude range of AM input signals that can be handled by the power amplifier by amplitude modulating the PM input signal using the AM input signal. Amplitude modulating the PM input signal effectively lowers the amplitude of the PM input signal when the amplitude of the AM input signal is lowered, which maintains adequate headroom between the power amplifier's signal input and envelope supply voltage input in the presence of large amplitude AM input signals. As a result, the power amplifier can amplify larger amplitude AM input signals than traditional power amplifier designs.
Owner:QORVO US INC
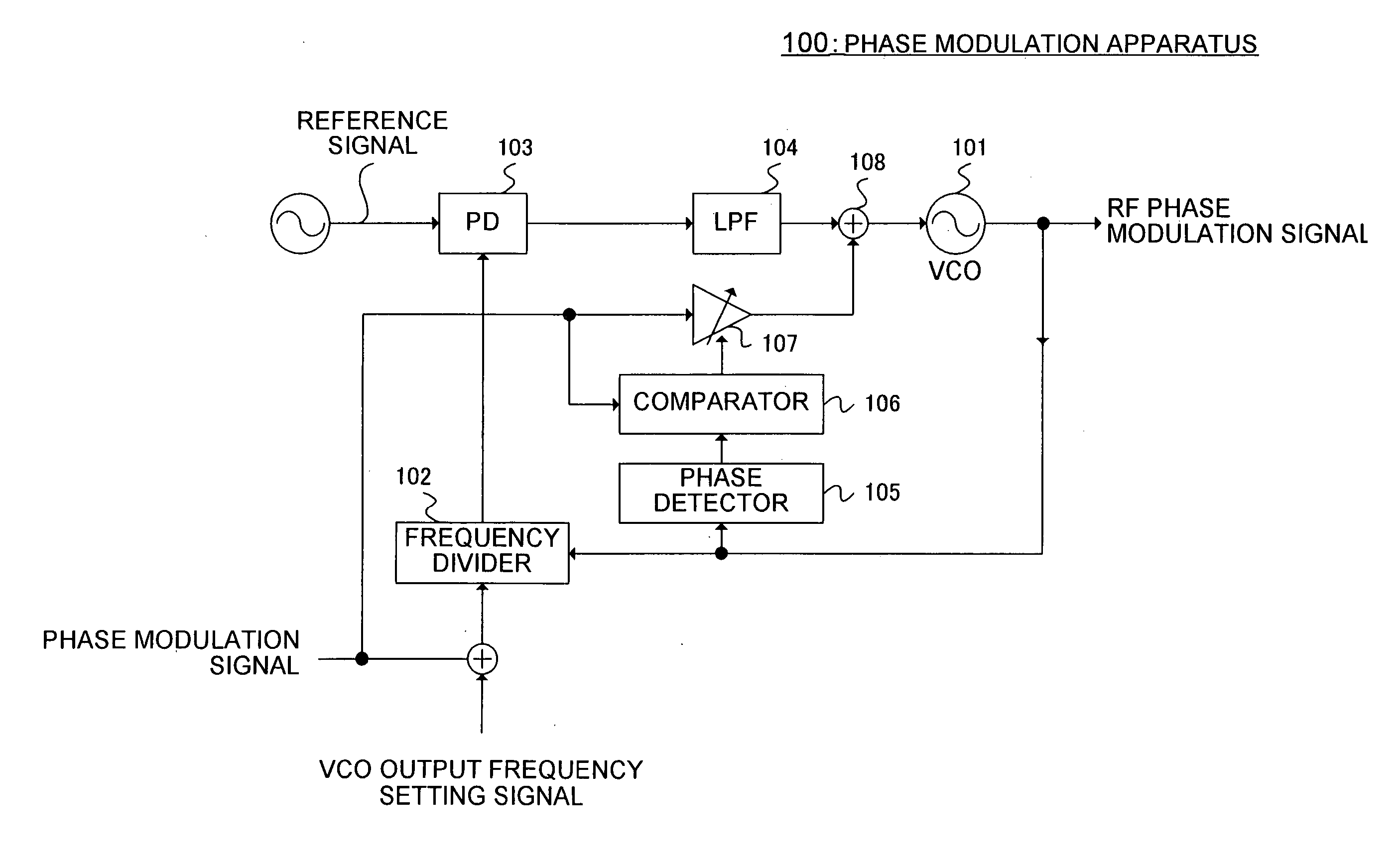
Phase modulation apparatus, polar modulation transmission apparatus, wireless transmission apparatus and wireless communication apparatus
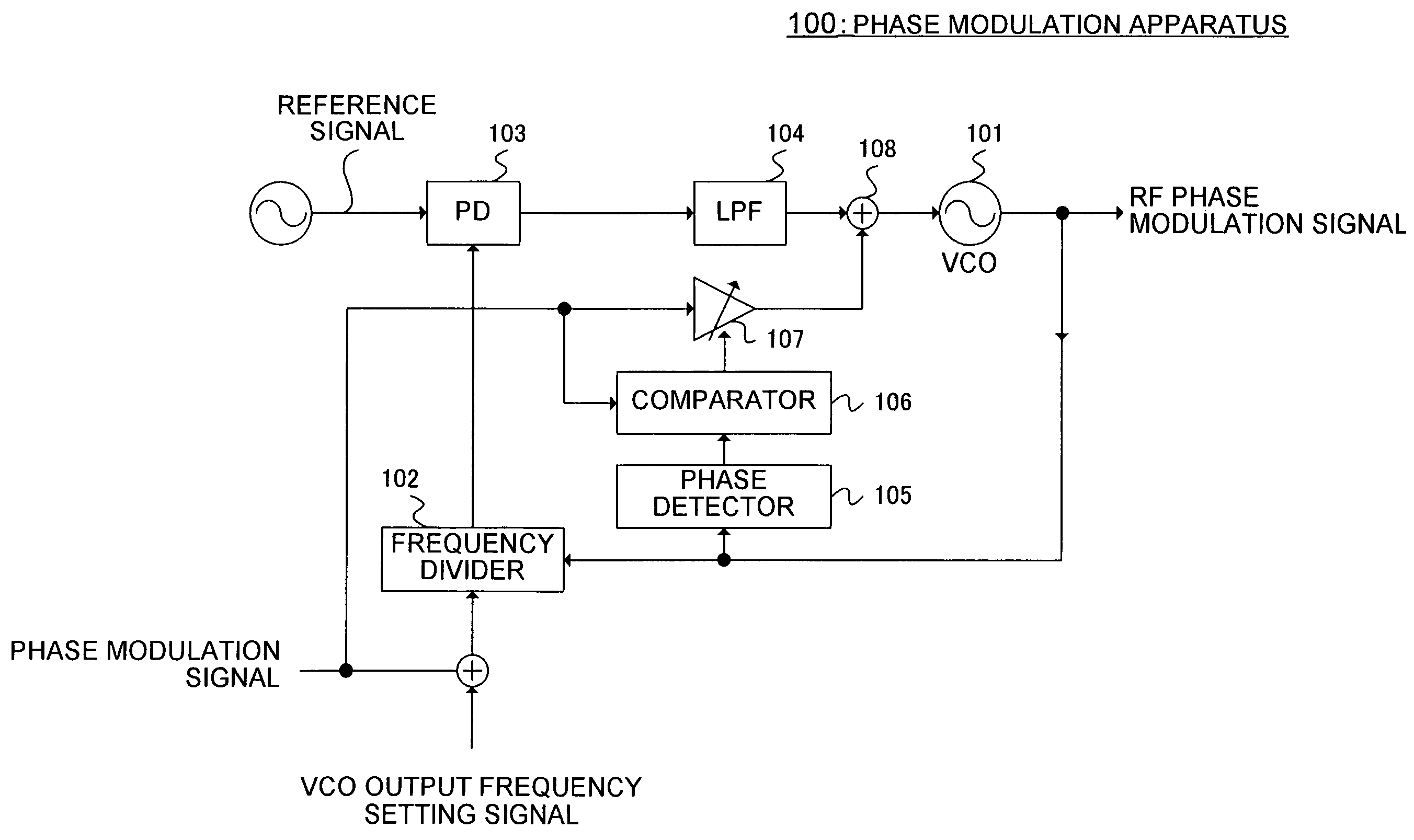
InactiveUS7215215B2Excellent RF phase modulation signalQuality improvementPulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsPhase detectorWireless transmission
A phase modulation apparatus is provided whereby excellent RF phase modulation signals can be obtained even when the modulation sensitivity of a voltage controlled oscillator varies. Phase modulation apparatus 100 has: phase detector 105 that performs phase detection with respect to an RF phase modulation signal outputted from VCO 101; comparator 106 that compares the phase of the detected signal with the phase of a baseband phase modulation signal and outputs the difference between the signals; variable gain amplifier 107 that controls the gain of the baseband phase modulation signal based on the output of comparator 106 and supplies the gain-controlled baseband phase modulation signal to VCO 101. By this means, the signal level of the baseband phase modulation signal that is supplied to VCO 101 can be controlled in accordance with the modulation sensitivity of VCO 101, so that phase modulation apparatus 100 can be realized whereby excellent RF phase modulation signals even when the modulation sensitivity of VCO 101 varies.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Polar modulation circuit, integrated circuit and radio apparatus
InactiveUS20090023402A1Improve scaleCompensation DistortionTransmissionAmplifier detailsEngineeringIntegrated circuit
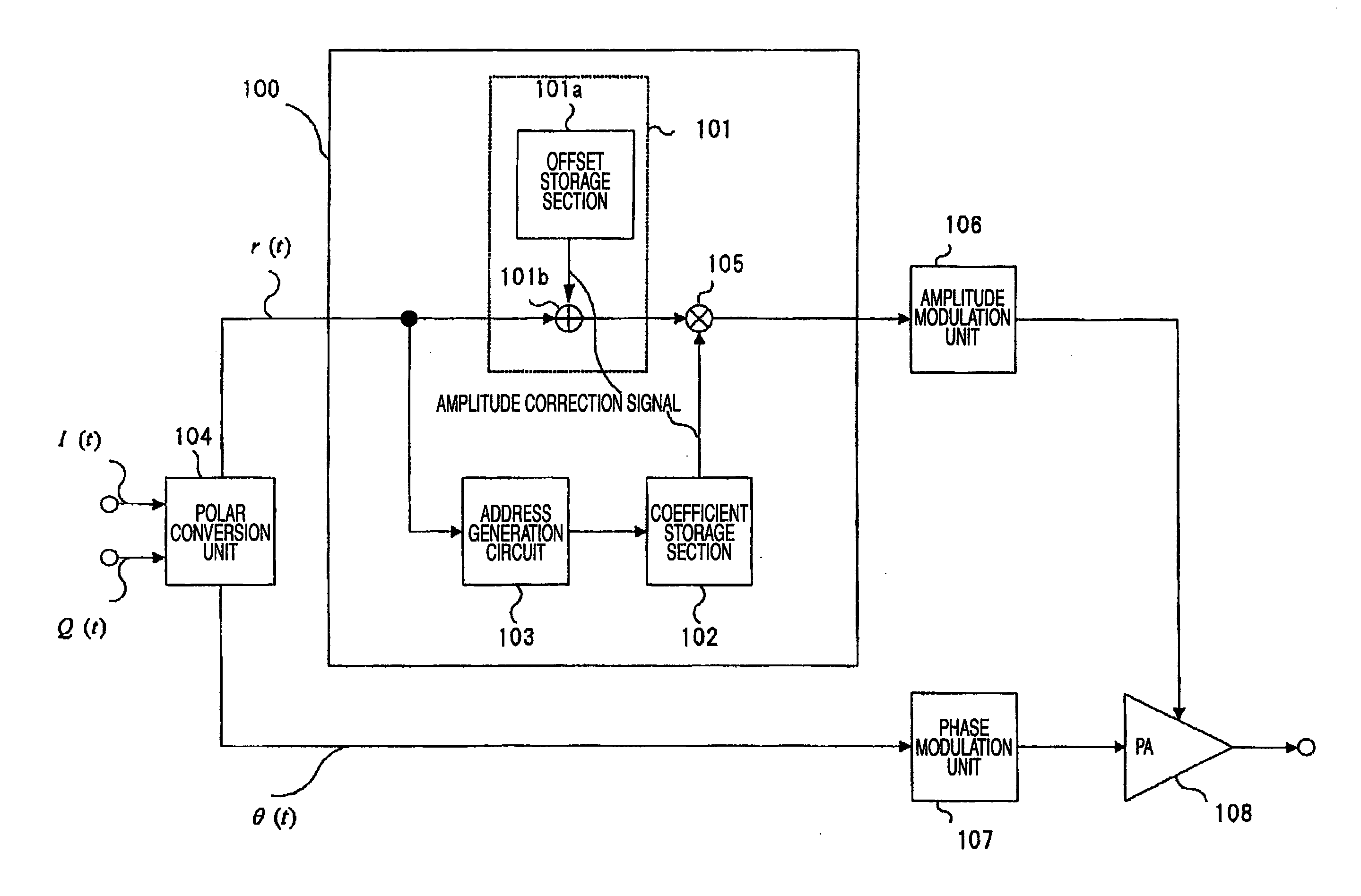
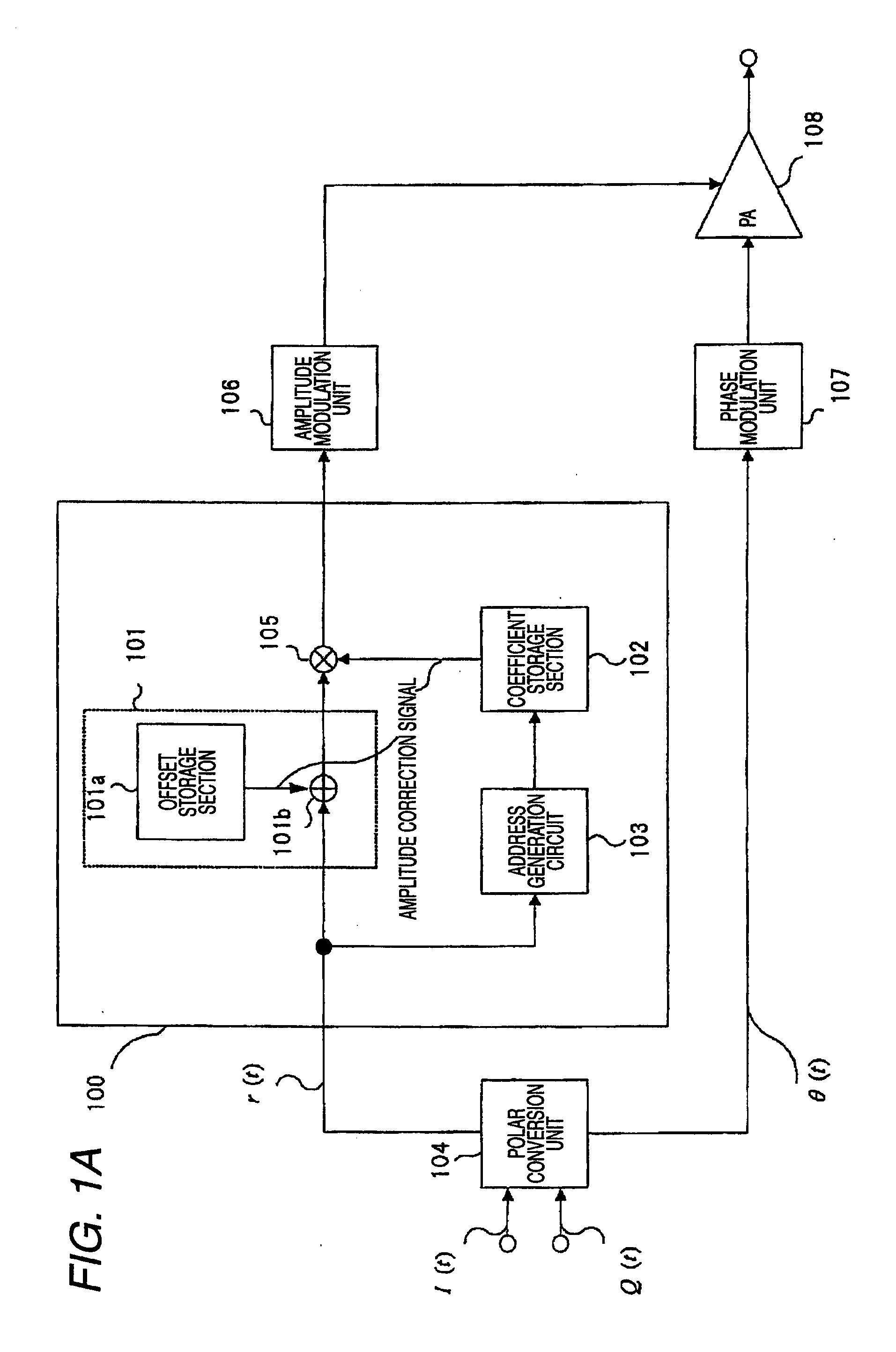
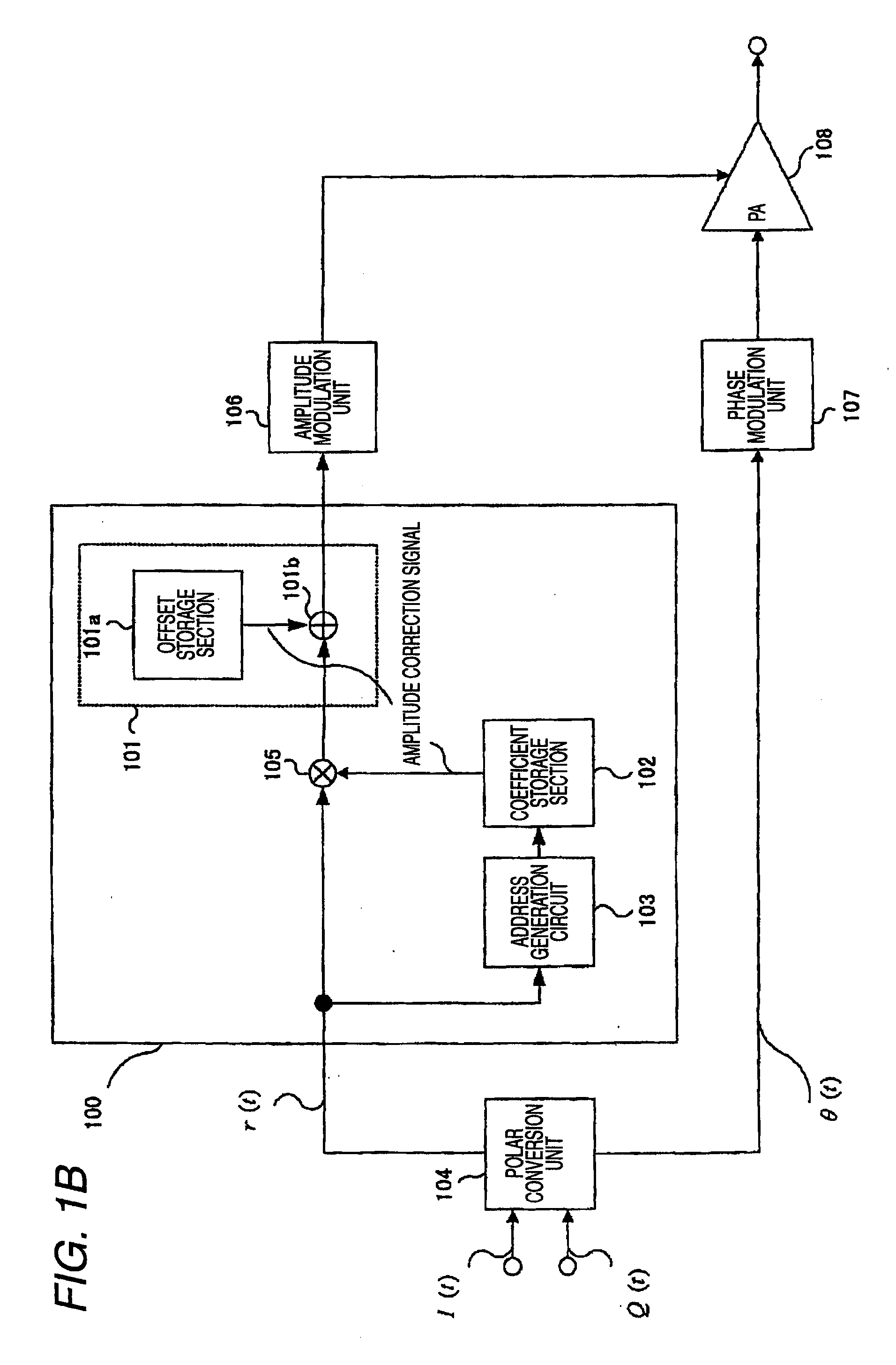
An object of the invention is to provide a polar modulation circuit capable of reducing the capacity of data stored in memory and suppressing an increase in the circuit scale related to distortion compensation while assuring the compensation accuracy. The polar modulation circuit according to the invention stores output signal characteristic relative to the control voltage at the steady state after input of the control voltage for a predetermined input amplitude of an input high frequency signal as the basis of distortion compensation of an amplifier separately into an offset storage section 101a which stores data used to add a predetermined DC offset voltage and a coefficient storage section 102 which stores data used for multiplication by a predetermined constant, thus reducing the circuit scale related to distortion compensation while assuring the compensation accuracy.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Delay calibration in polar modulation transmitters
ActiveUS20060057976A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierPolar modulation
A method and apparatus for dynamically compensating for delay mismatch between a supply signal and an input signal of a power amplifier in polar modulation transmitters. One exemplary polar modulation transmitter according to the present invention comprises a power amplifier, a phase modulator, a regulator, a delay tracking circuit, and a delay circuit. The phase modulator derives the amplifier input signal responsive to one or more phase signals, while the regulator derives the amplifier supply signal responsive to an amplitude signal. Based on the amplitude signal and the amplifier supply signal, the delay tracking circuit tracks an observed amplitude path delay. The delay circuit adjusts a path delay associated with the phase signal, responsive to the observed amplitude path delay, to compensate for the delay mismatch.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Polar modulator and method for modulation of a signal
InactiveUS20060160499A1Reduce power supply voltageFunction increaseResonant long antennasModulated-carrier systemsCarrier signalEngineering
A modulated carrier signal is produced from a phase modulation signal in a phase locked loop in a polar modulator. This carrier signal is converted via a limiting amplifier to a square-wave signal, which is supplied to an amplifier. At the same time, an amplitude modulation signal at one input is connected to a control input of a controllable current source. The controllable current source is designed to emit a supply current at a current output as a function of the amplitude modulation signal at the control input. The current output of the controllable current source is connected to a supply input of the amplifier. The supply current for the amplifier is thus modulated on the basis of the amplitude information to be transmitted. The processing of the amplitude information within the current domain makes it possible to produce the polar modulator according to the invention as an integrated circuit, using CMOS technology.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
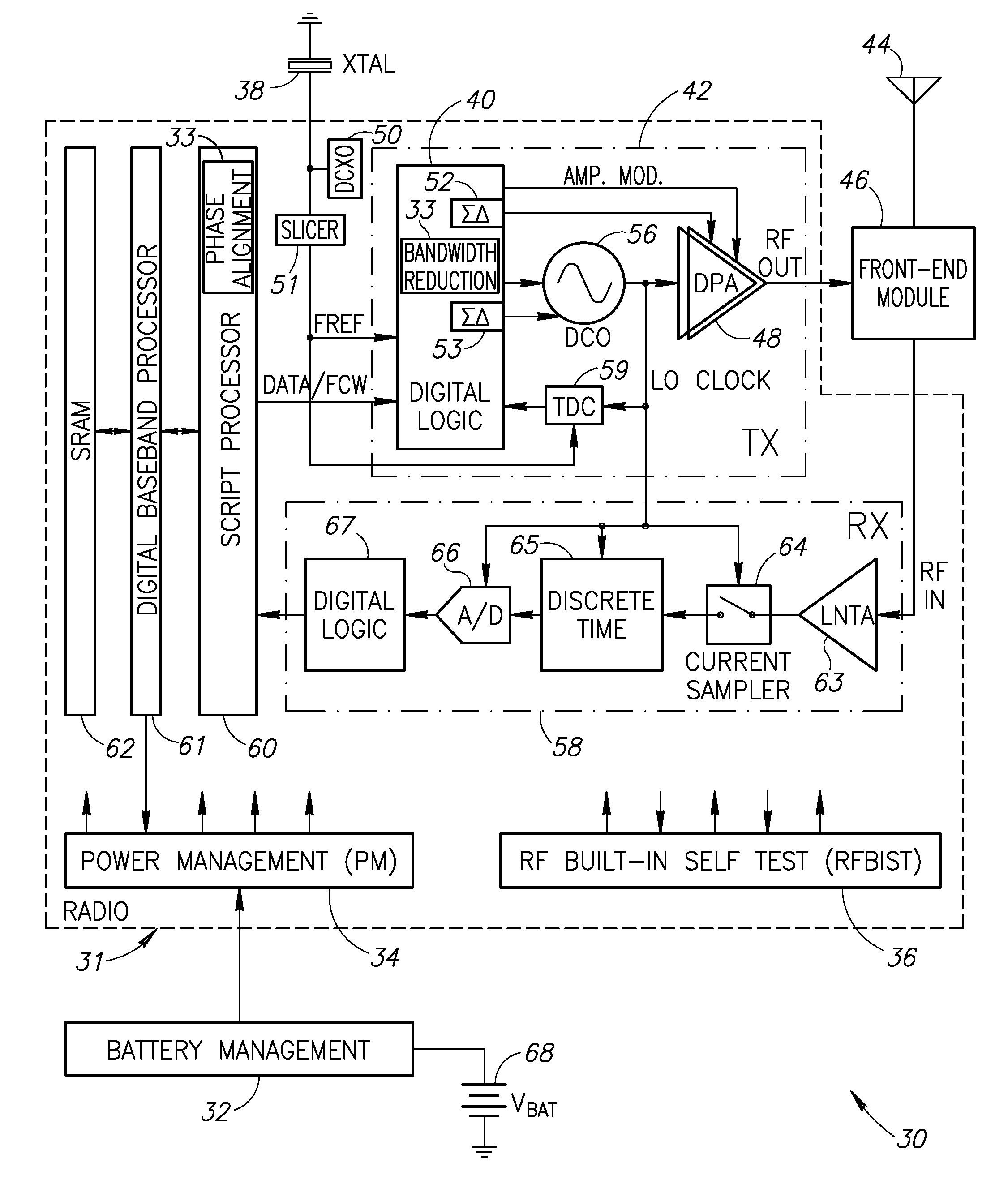
Method and System for Digital Tracking in Direct and Polar Modulation
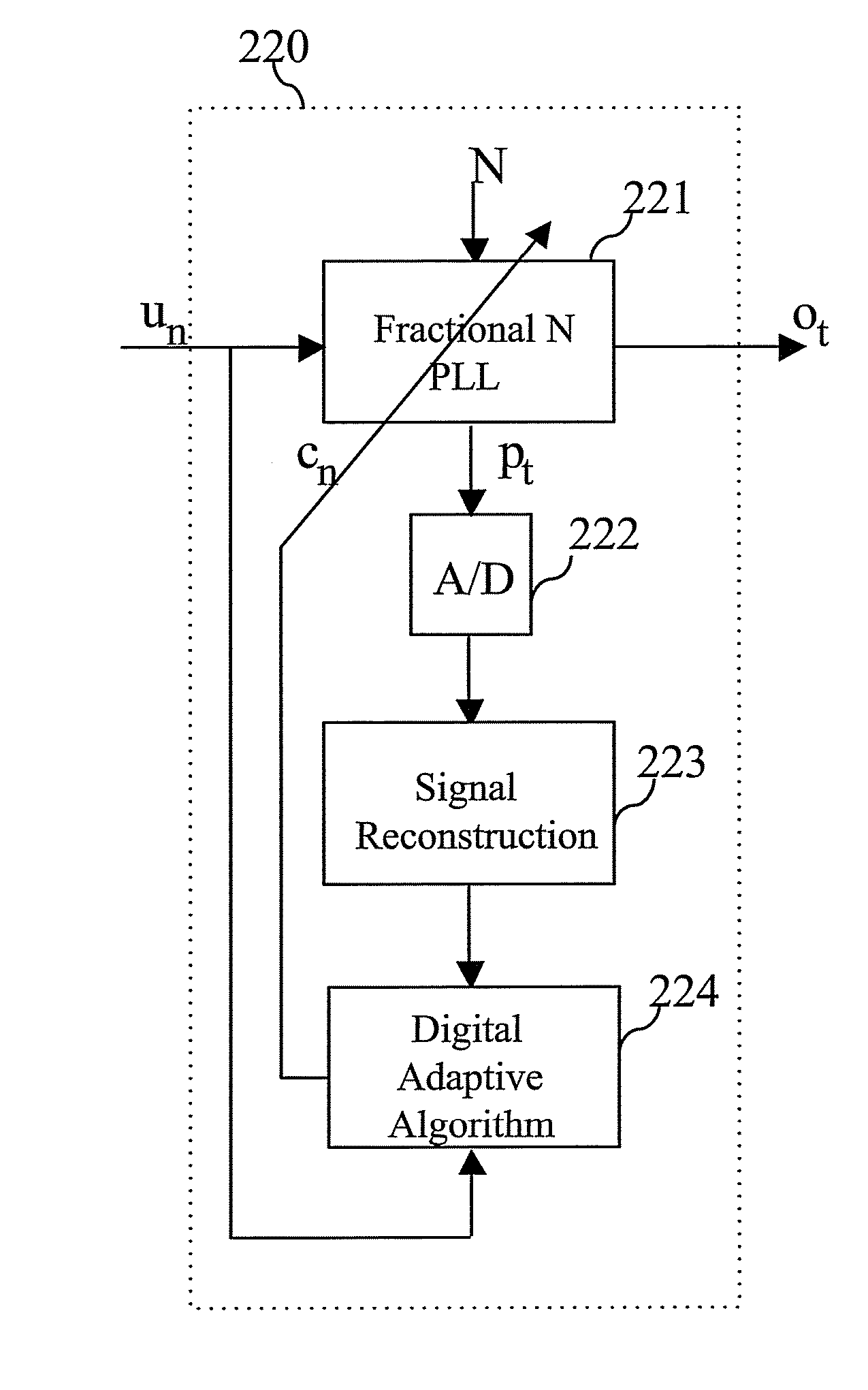
InactiveUS20080095269A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAngle modulationSelf adaptiveDigital control
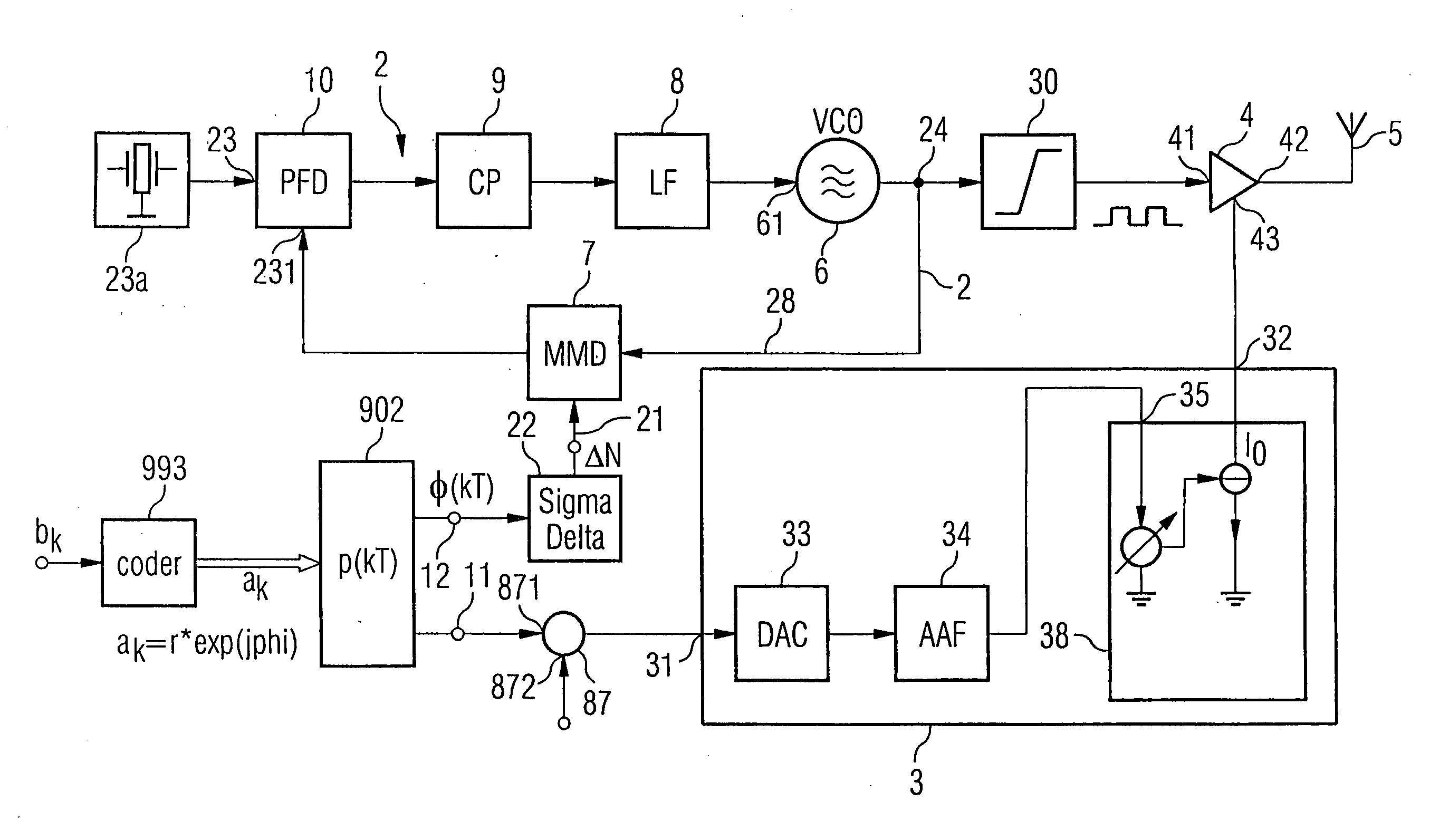
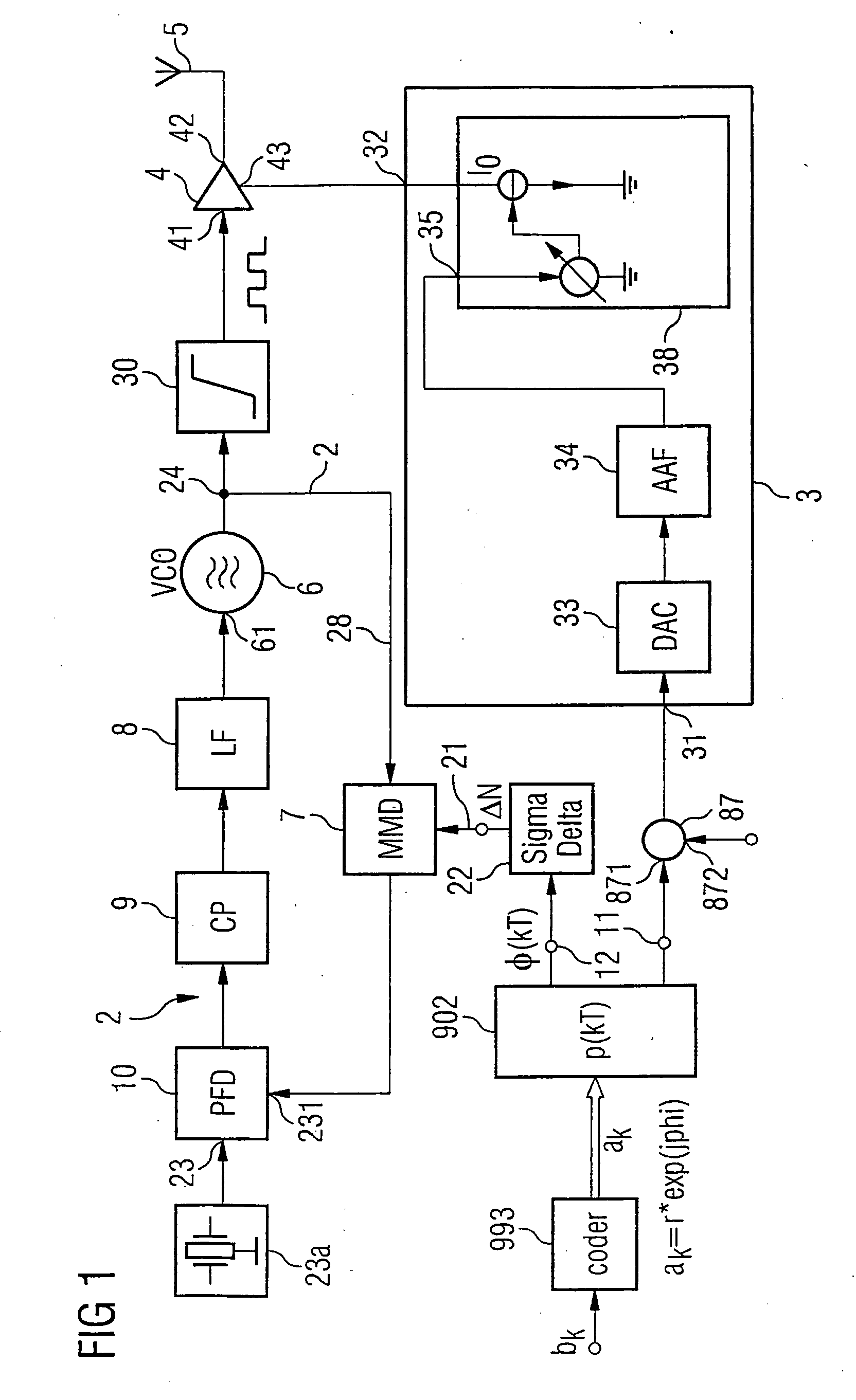
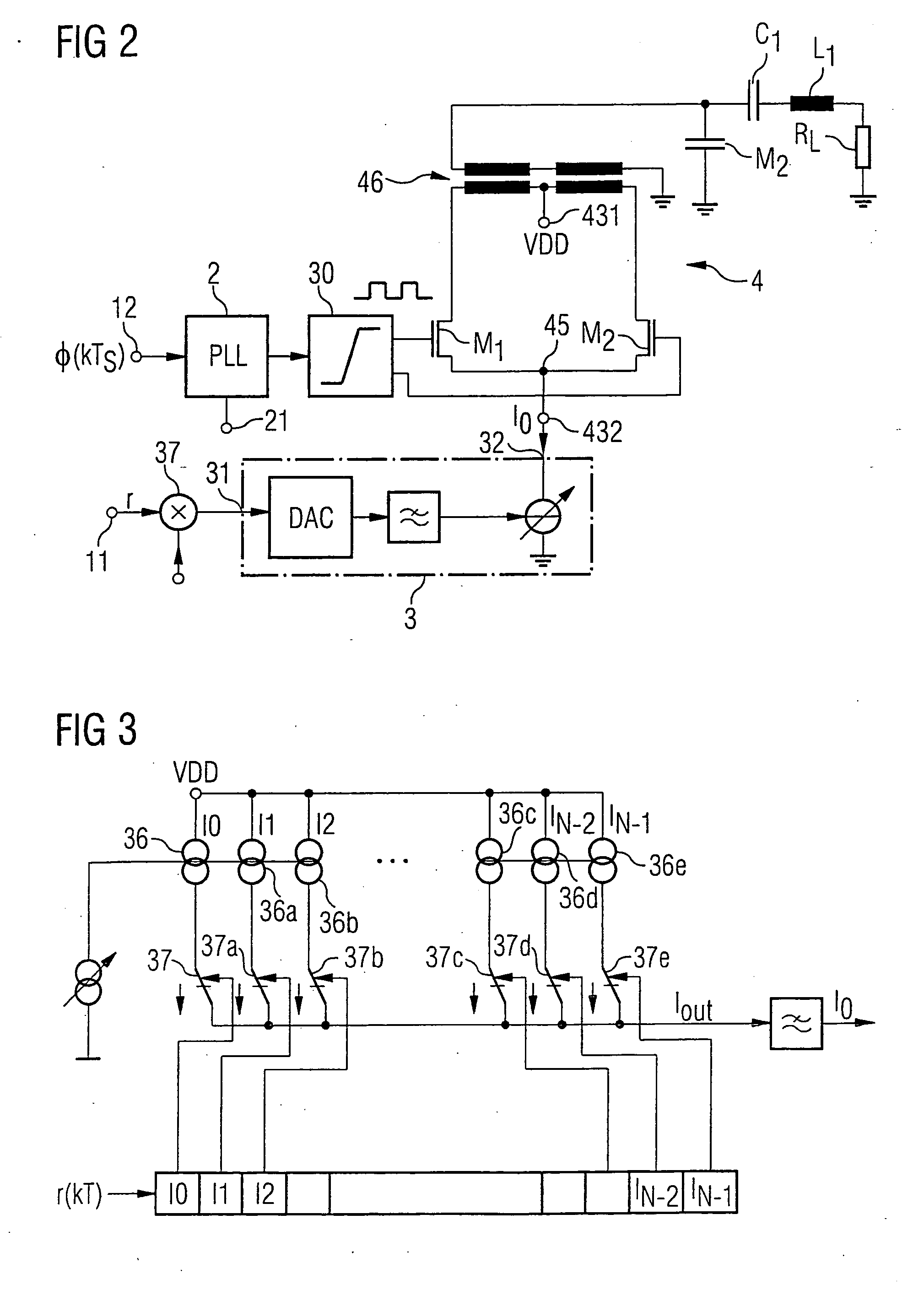
Aspects of a method and system for digital tracking in direct and polar modulation are presented. Aspects of the system may include at least one circuit within a phase locked loop (PLL) circuit that enables adaptive and digital control of an analog fractional N (Frac N) PLL during direct modulation of a signal or polar modulation of the signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Two-point modulation type phase modulation apparatus, polar modulation transmission apparatus, wireless transmission apparatus and wireless communication apparatus
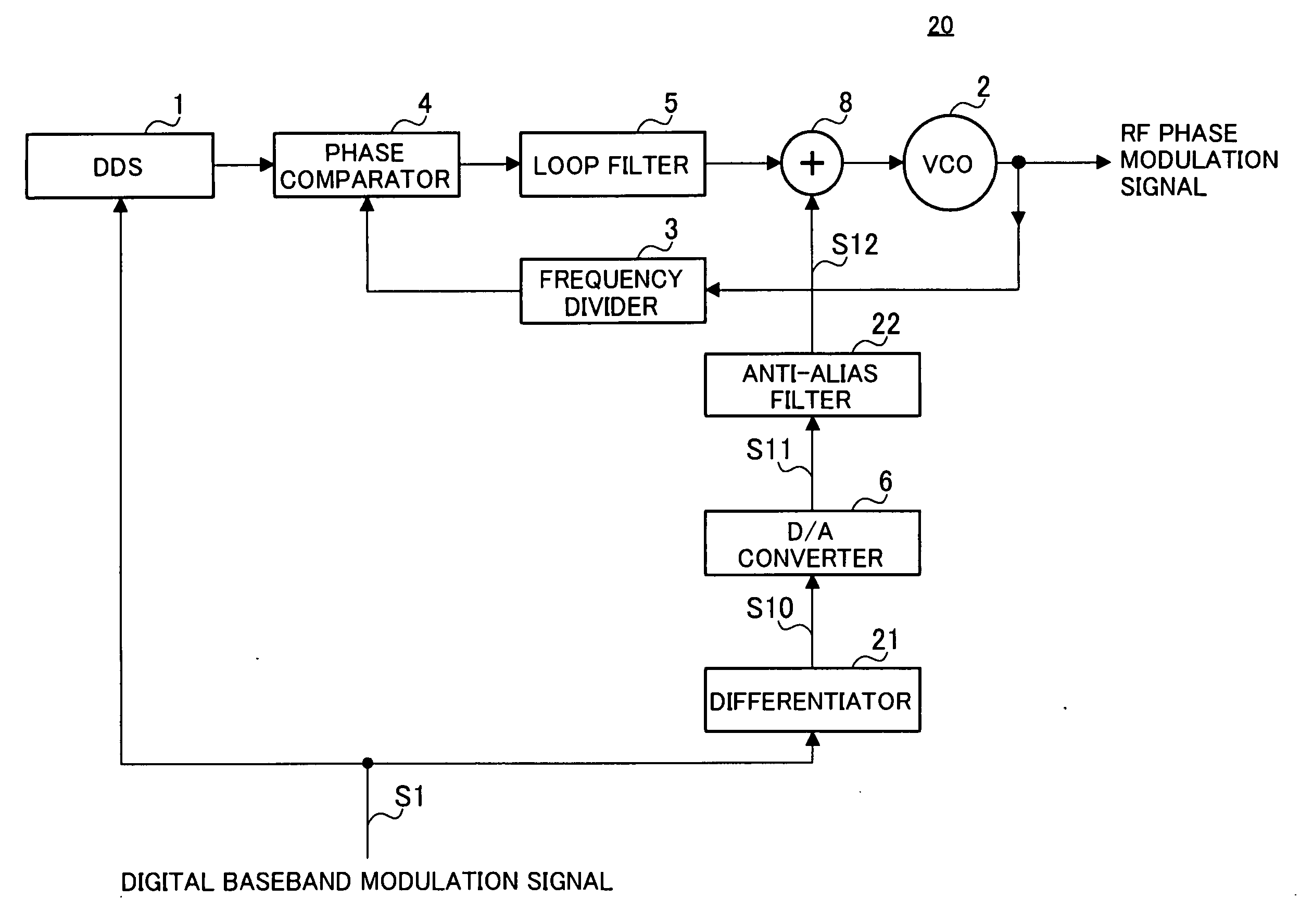
ActiveUS20070013447A1Superior modulation precisionLow costPulse automatic controlAngle modulationDifferentiatorEngineering
There provides a two-point modulation phase modulation apparatus capable of obtaining an RF phase modulation signal of superior modulation precision with low power consumption and a simple configuration even in the event of inputting a wide band baseband modulation signal. A differentiator (21) of the opposite characteristics to the attenuation characteristics of anti-alias filter (22) is provided at the front stage of a D / A converter (6). As a result, it is possible to sufficiently suppress an alias signal without raising the sampling frequency of the D / A converter (6) (i.e. low power consumption) using an anti-alias filter (22) of a simple configuration (i.e. low cost) with a low order for a narrower bandwidth than a PLL modulation frequency bandwidth, and it is possible to obtain an RF phase modulation signal where the entire frequency band of input digital baseband modulation signal (S1) is reflected in a superior manner.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Phase moulation apparatus, polar modulation transmission apparatus, wireless transmission apparatus and wireless communication apparatus
InactiveUS20050285688A1Excellent RF phase modulation signalQuality improvementPulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsPhase detectorWireless transmission
A phase modulation apparatus is provided whereby excellent RF phase modulation signals can be obtained even when the modulation sensitivity of a voltage controlled oscillator varies. Phase modulation apparatus 100 has: phase detector 105 that performs phase detection with respect to an RF phase modulation signal outputted from VCO 101; comparator 106 that compares the phase of the detected signal with the phase of a baseband phase modulation signal and outputs the difference between the signals; variable gain amplifier 107 that controls the gain of the baseband phase modulation signal based on the output of comparator 106 and supplies the gain-controlled baseband phase modulation signal to VCO 101. By this means, the signal level of the baseband phase modulation signal that is supplied to VCO 101 can be controlled in accordance with the modulation sensitivity of VCO 101, so that phase modulation apparatus 100 can be realized whereby excellent RF phase modulation signals even when the modulation sensitivity of VCO 101 varies.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Hybrid polar modulator differential phase Cartesian feedback correction circuit for power amplifier linearization
ActiveUS7409004B2Accurate estimateAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionMemory effect compensationAmplitude distortionAudio power amplifier
The present invention, generally speaking, provides a method of obtaining very accurate estimates of the phase and amplitude distortions introduced by radio frequency or microwave power amplifiers even where polar modulation is used.
Owner:APPLE INC
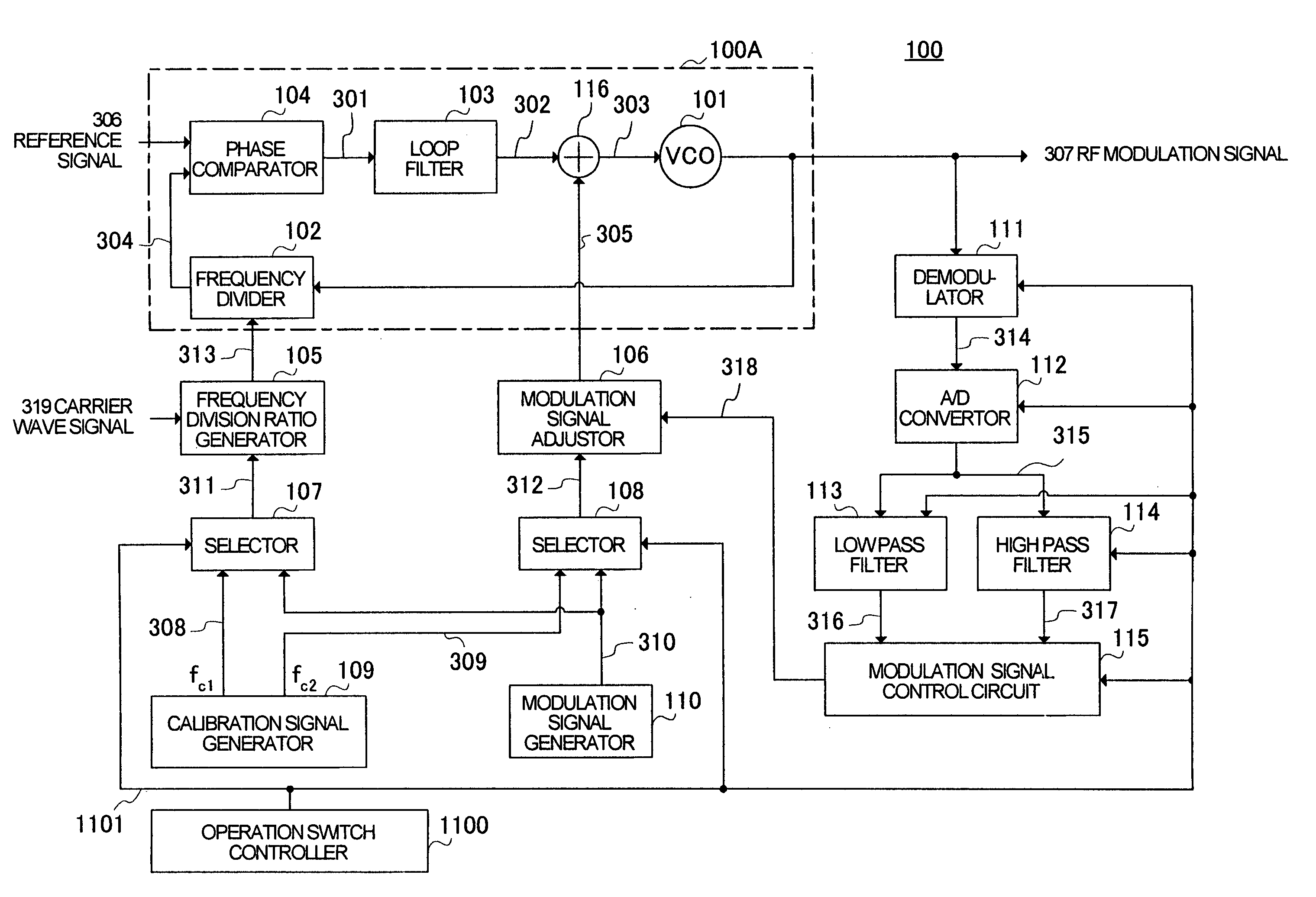
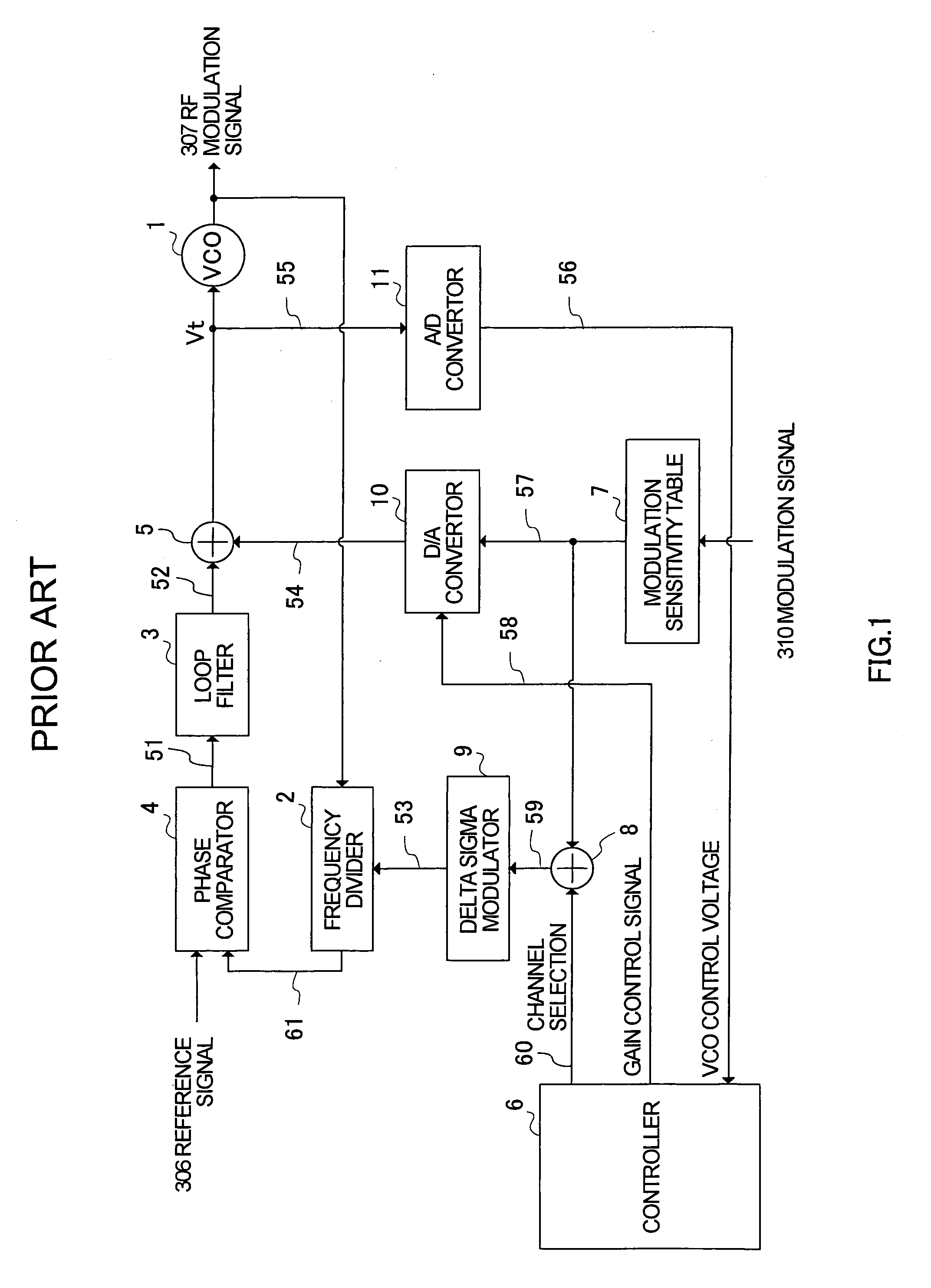
PLL modulation circuit and polar modulation apparatus
InactiveUS7157985B2High modulation accuracySimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPulse automatic controlControl signalEngineering
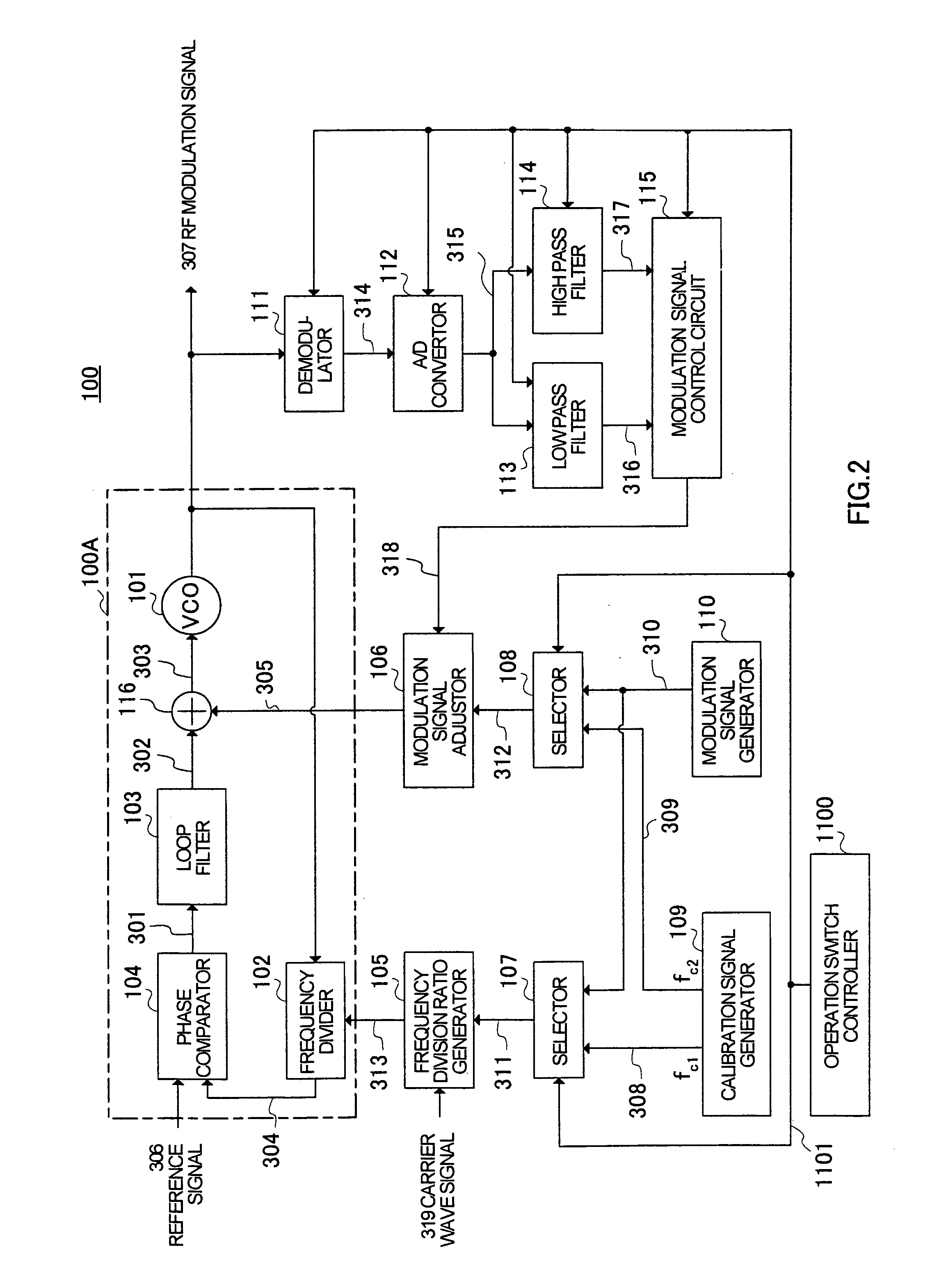
First and second calibration signals (308, 309) are sent to a frequency divider (102) and an adder (116) of a PLL section (100A), demodulated in a demodulator (111), filtered through a low pass filter (113) and a high pass filter (114) and thereafter sent to a modulation signal control circuit (115). The modulation signal control circuit (115) generates control information (318) in comparison with the phase and amplitude of the first and second calibration signals (308 and 309) and sends the control information (318) to a modulation control signal generator (106). Modulation control signal generator (106) holds the control information (318) and controls the values of the first modulation signal and second modulation signal sent to the frequency divider (102) and adder (116) on the based on the control information (318) held in modulation operation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for linear envelope eliminating and recovering transmitters
InactiveCN101090380AHigh bandwidthEnergy efficient ICTSynchronous/start-stop systemsMemory effectAudio power amplifier
The invention provides systems, methods and apparatuses for linear envelope elimination and restoration transmitters, based on the polar modulation operation combined with the orthogon recursive predistortion. The polar modulation technique dynamicly regulates bias level to increase battery life. Moreover, the analogy orthogon recursive predistortion corrects amplitude and phase errors in a radiofrequency (RF) power amplifier (PA) effectively, enhances PA output capability. Even-order distortion components are used for predistortion of input signals by means of multiplication, improve effective correcting bandwidth. Moreover, the predistortion proposal of a temporary feedback envelope distortion signal allows to correct any distortion of correcting loop bandwidth including envelope memory effect.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
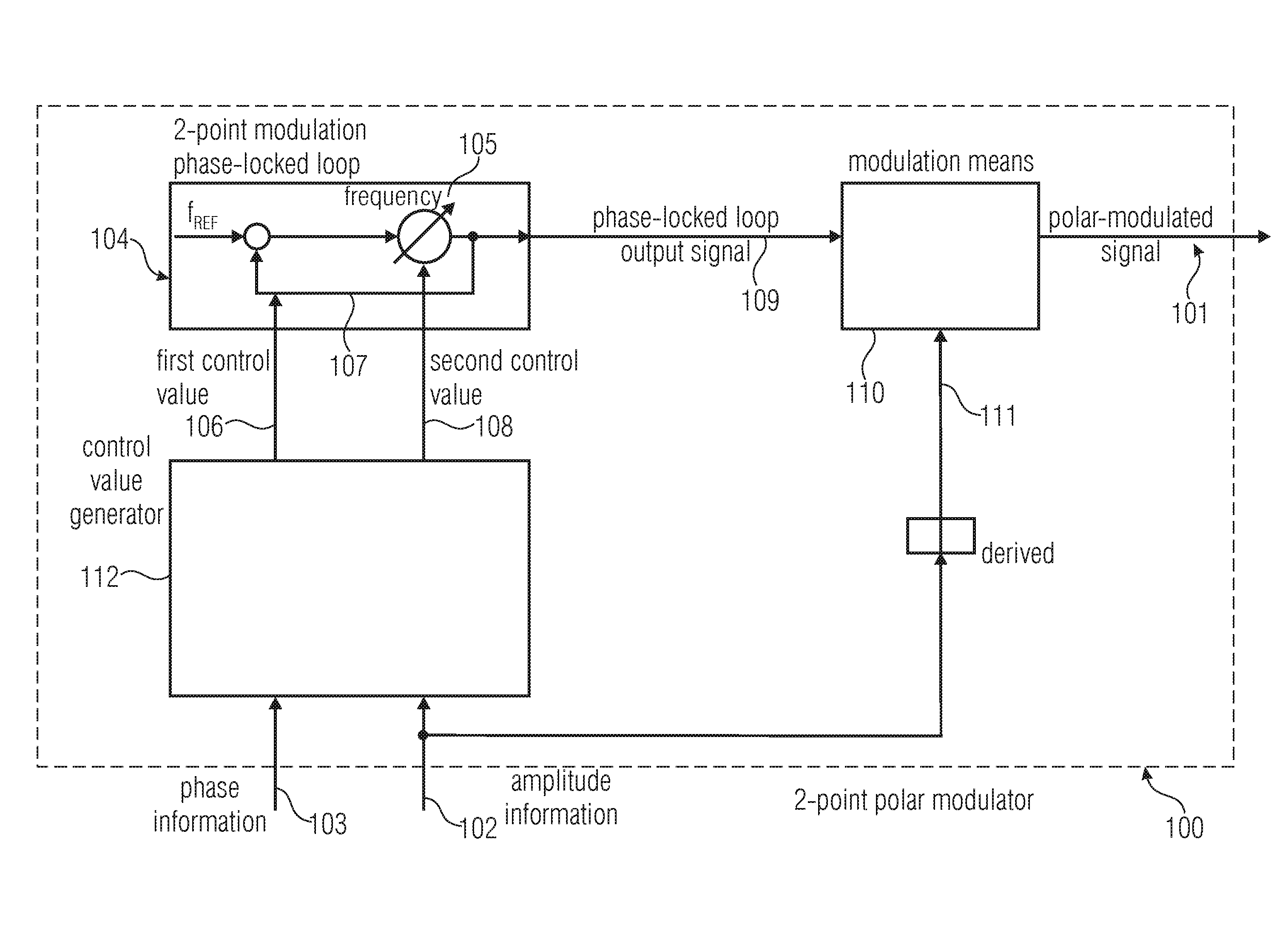
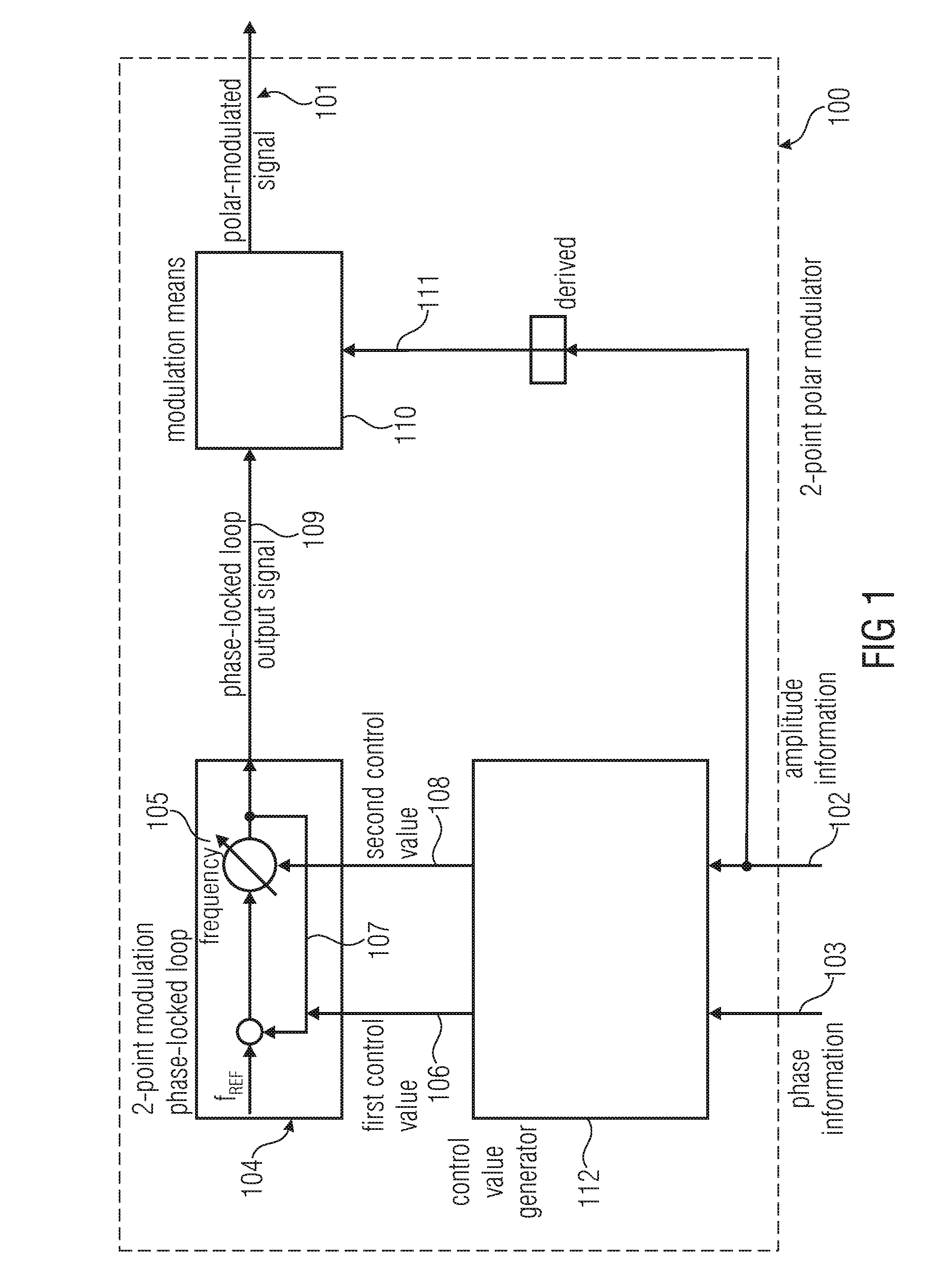
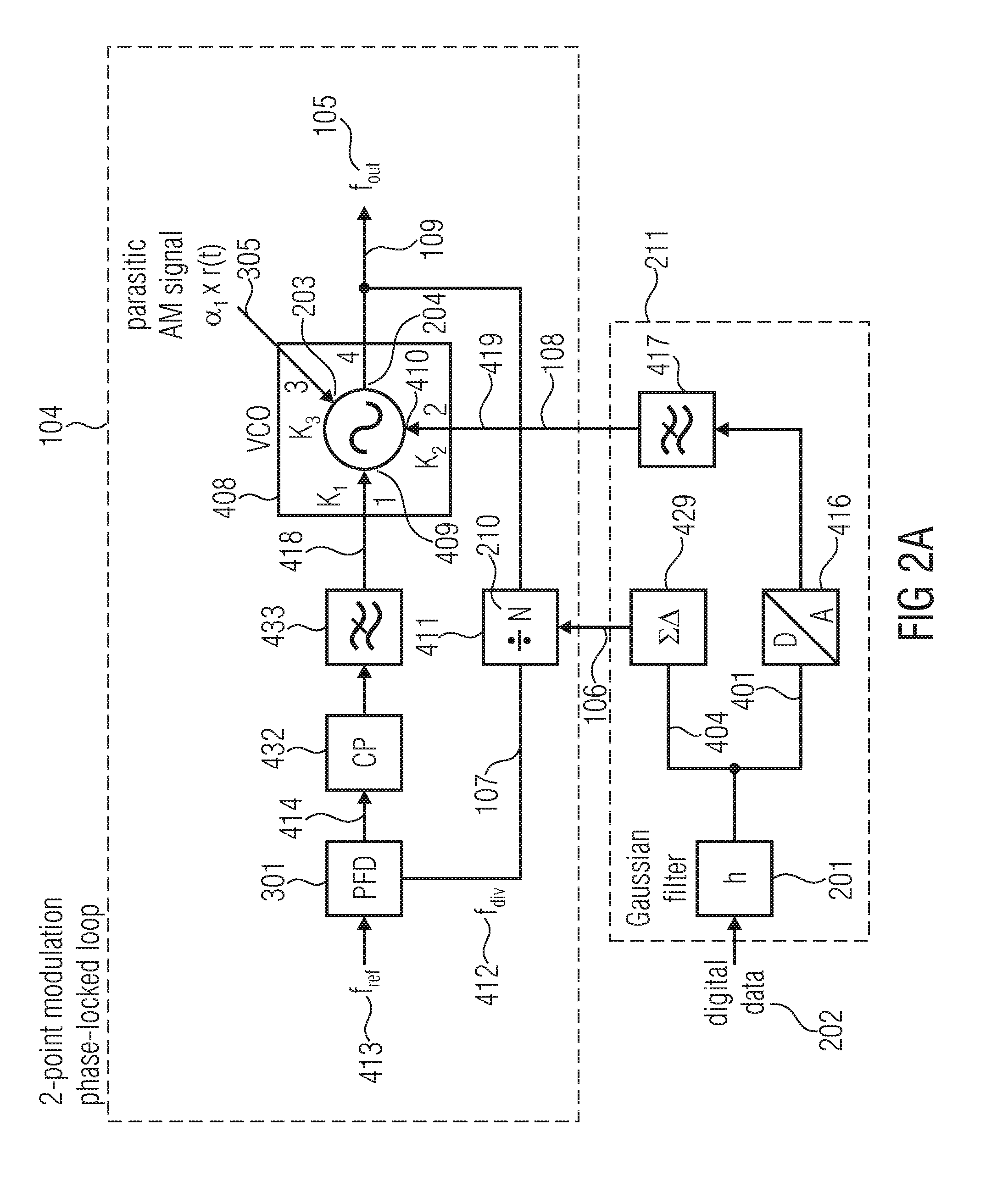
Two-Point Polar Modulator and Method for Generating a Polar-Modulated Signal Based on Amplitude Information and Phase Information
A two-point polar modulator for generating a polar-modulated signal based on an amplitude information and a phase information includes a two-point modulation phase-locked loop which is implemented to enable a frequency setting depending on a first control value via a feedback path of the two-point modulation phase-locked loop and to enable a frequency setting depending on a second control value, directly, bypassing the feedback path, wherein the two-point modulation phase-locked loop is implemented to provide a phase-locked loop output signal depending on the two control values. The two-point polar modulator further includes a modulator which is implemented to combine an amplitude signal derived from the amplitude information with the phase-locked loop output signal, to generate the polar-modulated signal and a control value generator which is implemented to generate the first control value depending on the phase information and independent of the amplitude information and which is implemented to generate the second control value depending on the amplitude information.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com