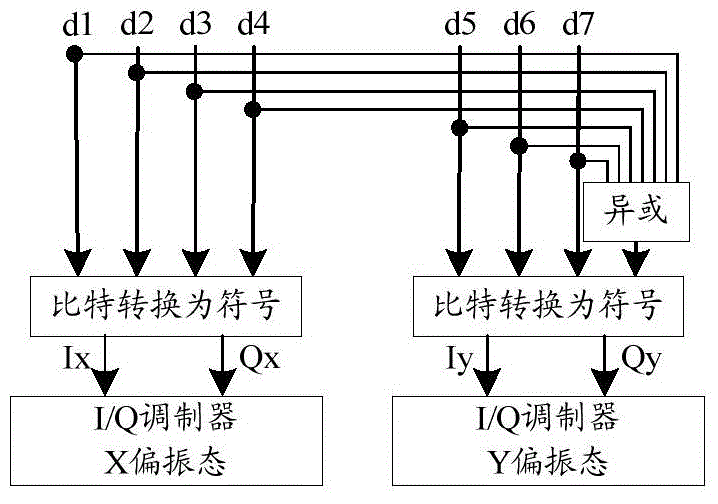
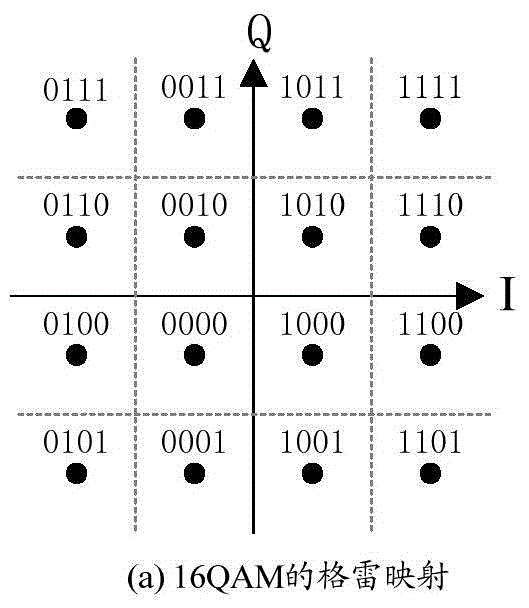
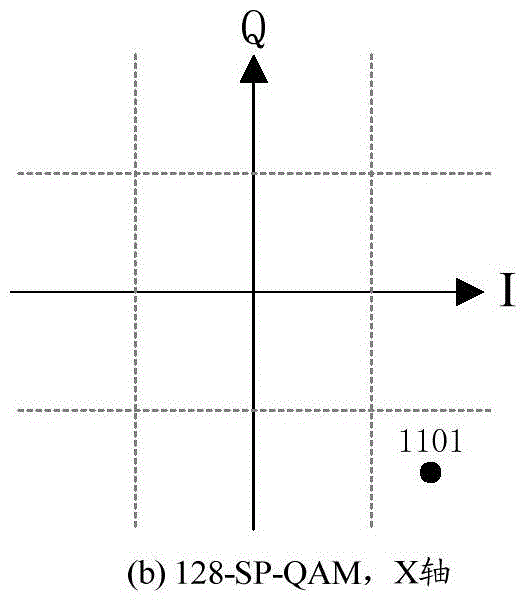
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54results about "Coherence multiplexing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
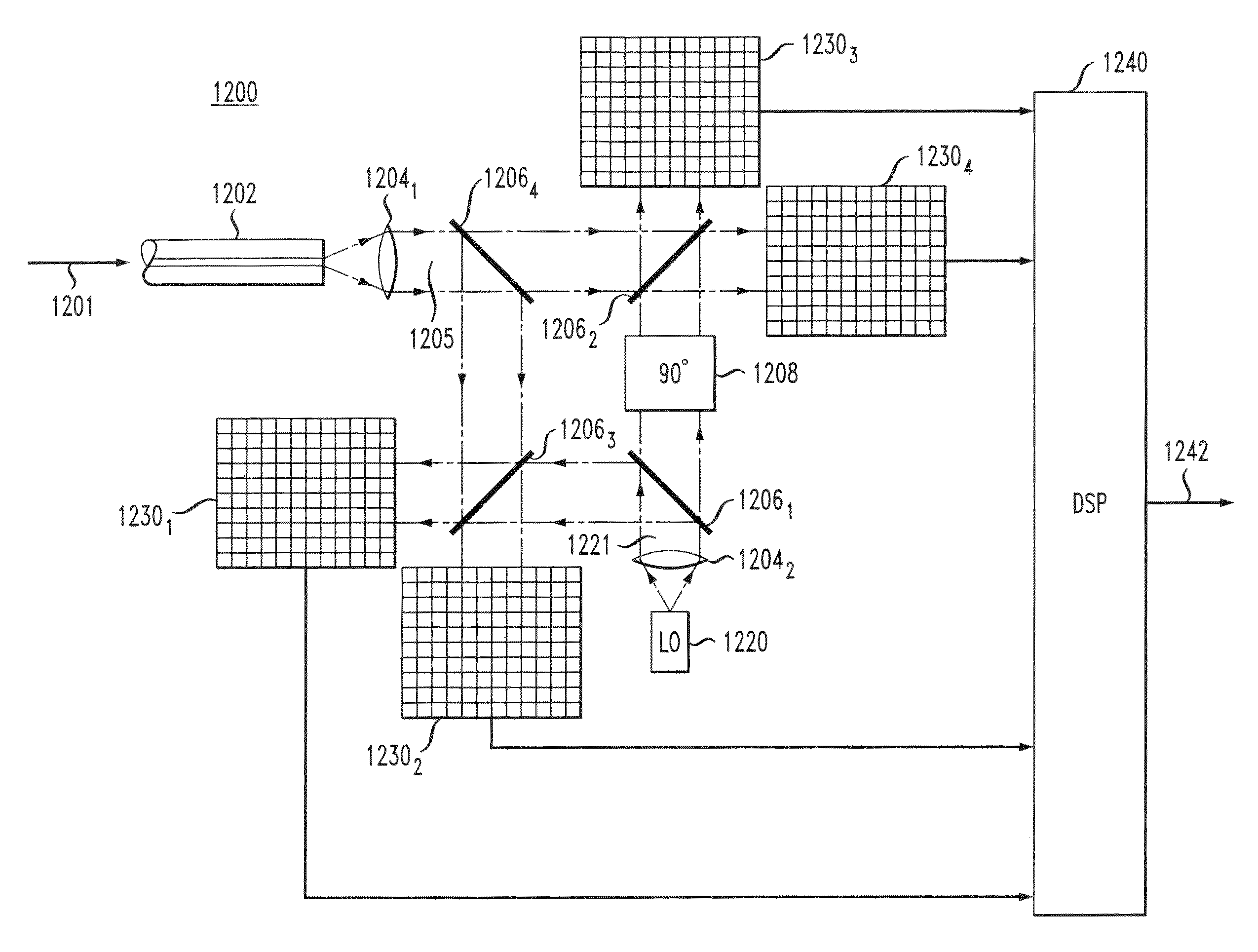
Passive optical network with asymmetric modulation scheme
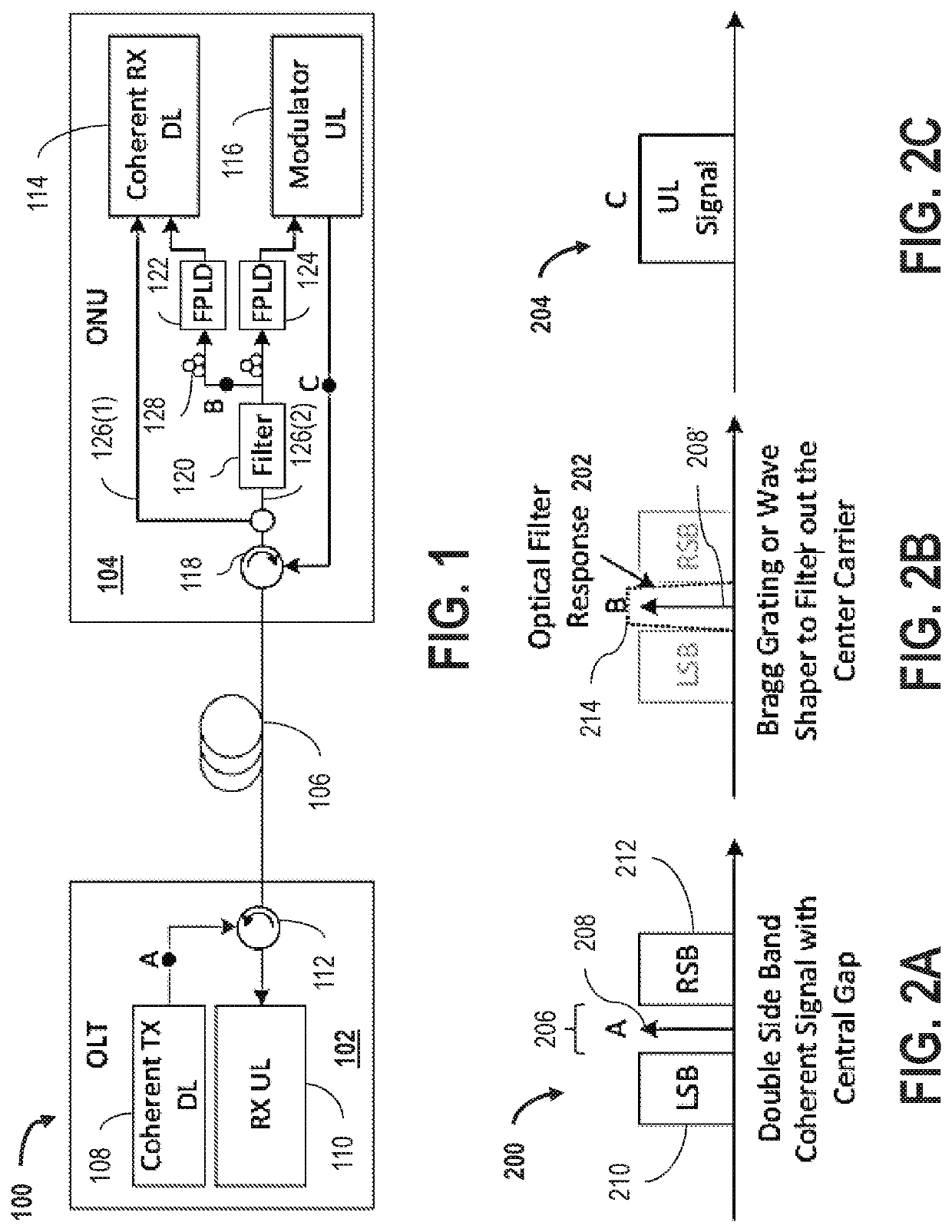
A passive optical network couples a WDM optical line terminal (“OLT”) to WDM optical network units (“ONUs”). The WDM OLT includes an optical transmitter array with coherent transmitters to generate downstream WDM signals encoded using phase modulation, an optical receiver array with direct detection photo-detectors to receive upstream WDM signals encoded with amplitude modulation, and an optical diplexer optically coupled to the optical transmitter array and the optical receiver array. The WDM ONU includes a tunable optical transmitter having a first tunable laser source coupled to generate a selectable upstream carrier wavelength and direct amplitude modulation circuitry coupled to amplitude modulate the first tunable laser source and a tunable optical receiver having coherent detection circuitry to demodulate phase information from the downstream WDM signals and a second tunable laser source operated as a local oscillator and coupled to tune to a selectable downstream carrier wavelength.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
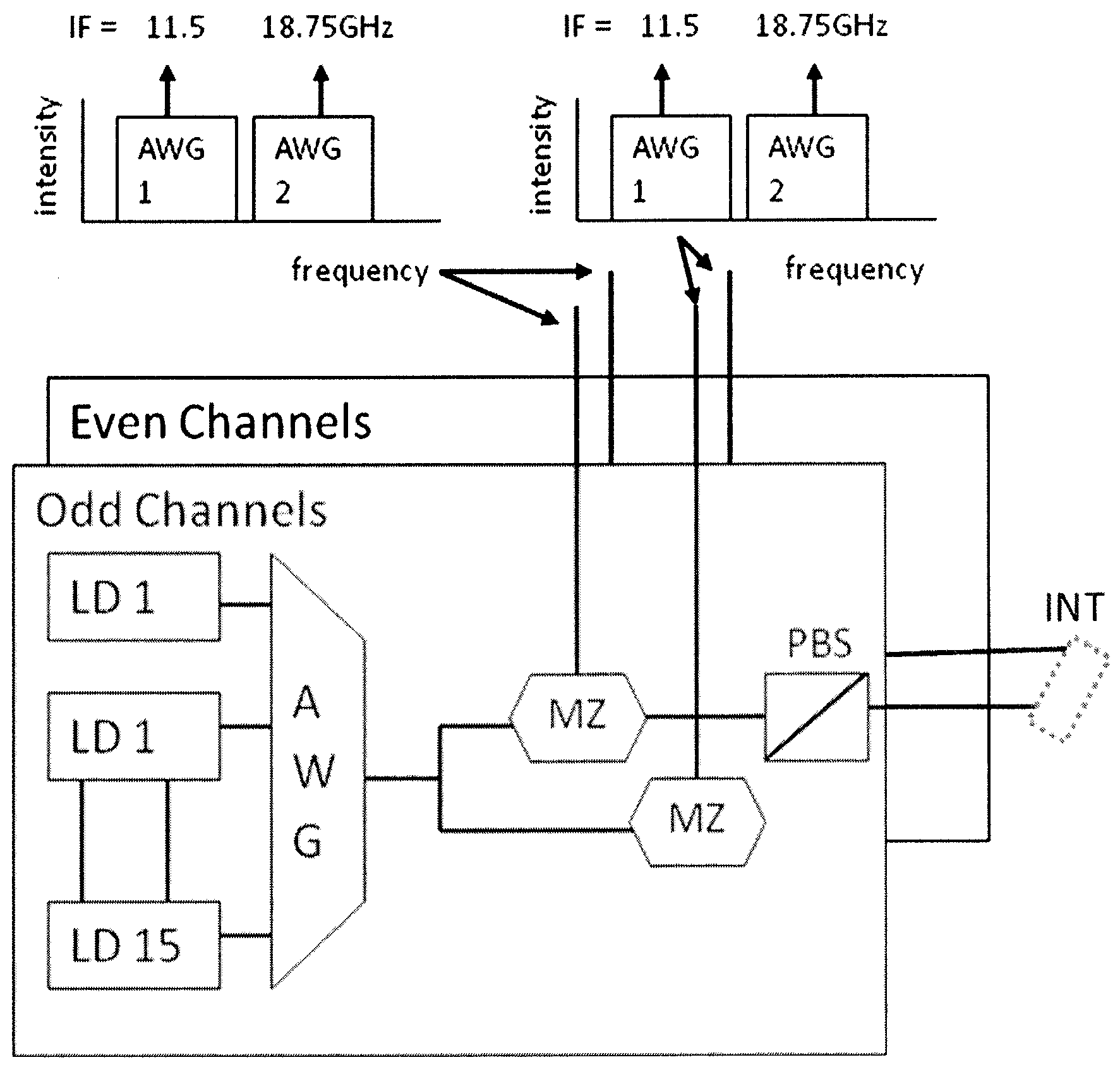
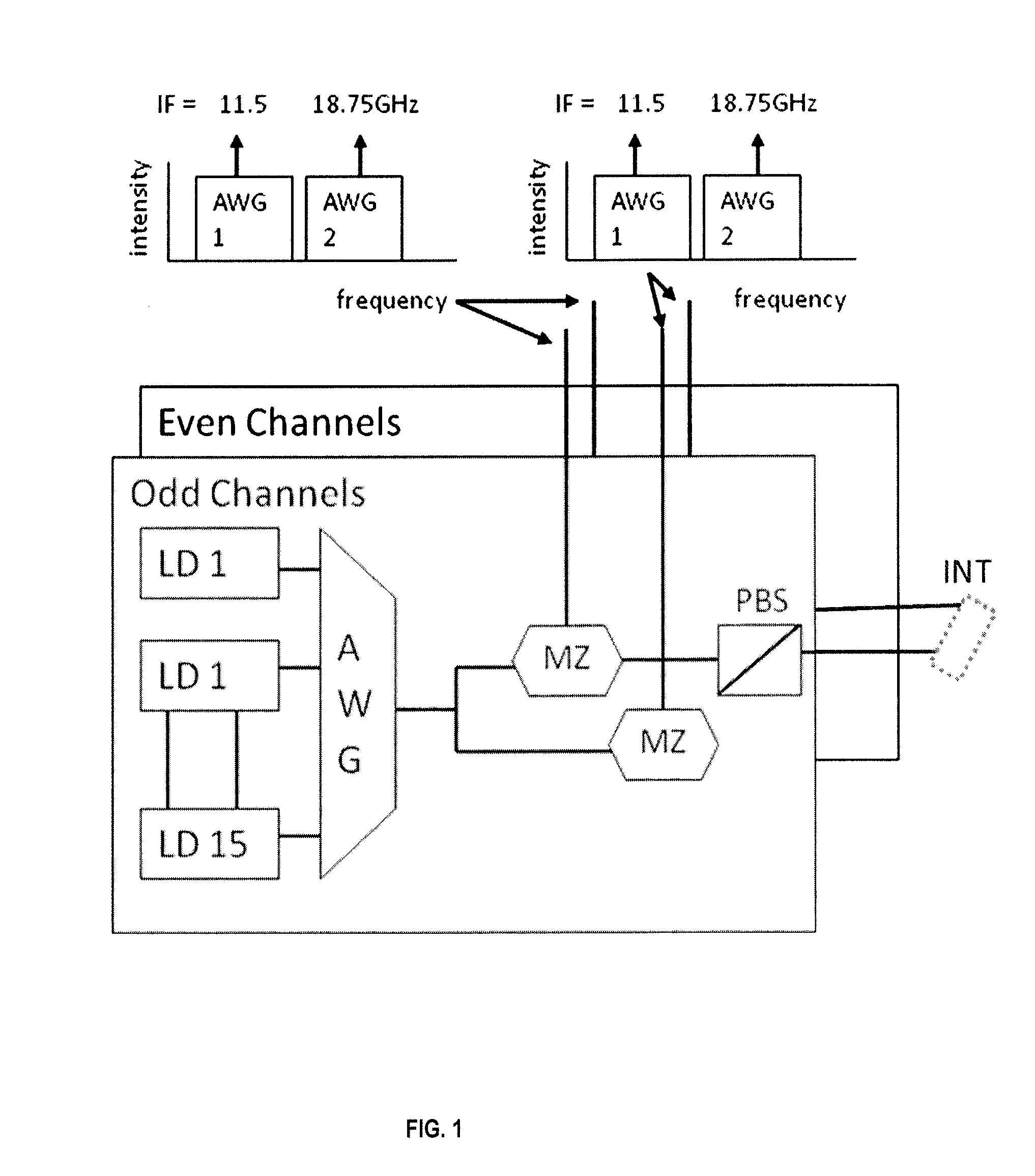
WDM telecommunications link with coherent detection and optical frequency comb sources
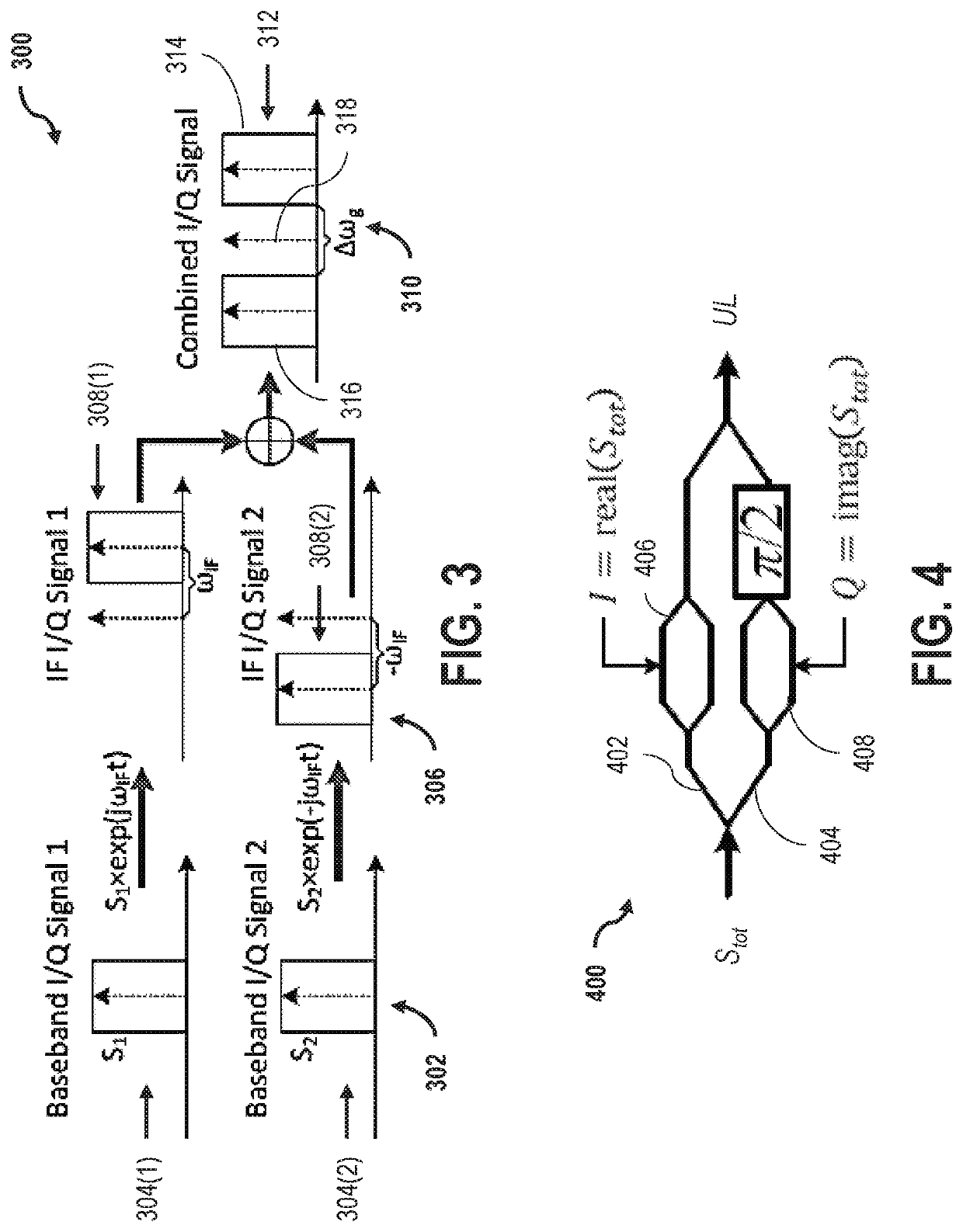
ActiveUS20140064734A1Increase the number ofReduce complexityWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingTelecommunications linkIntermediate frequency
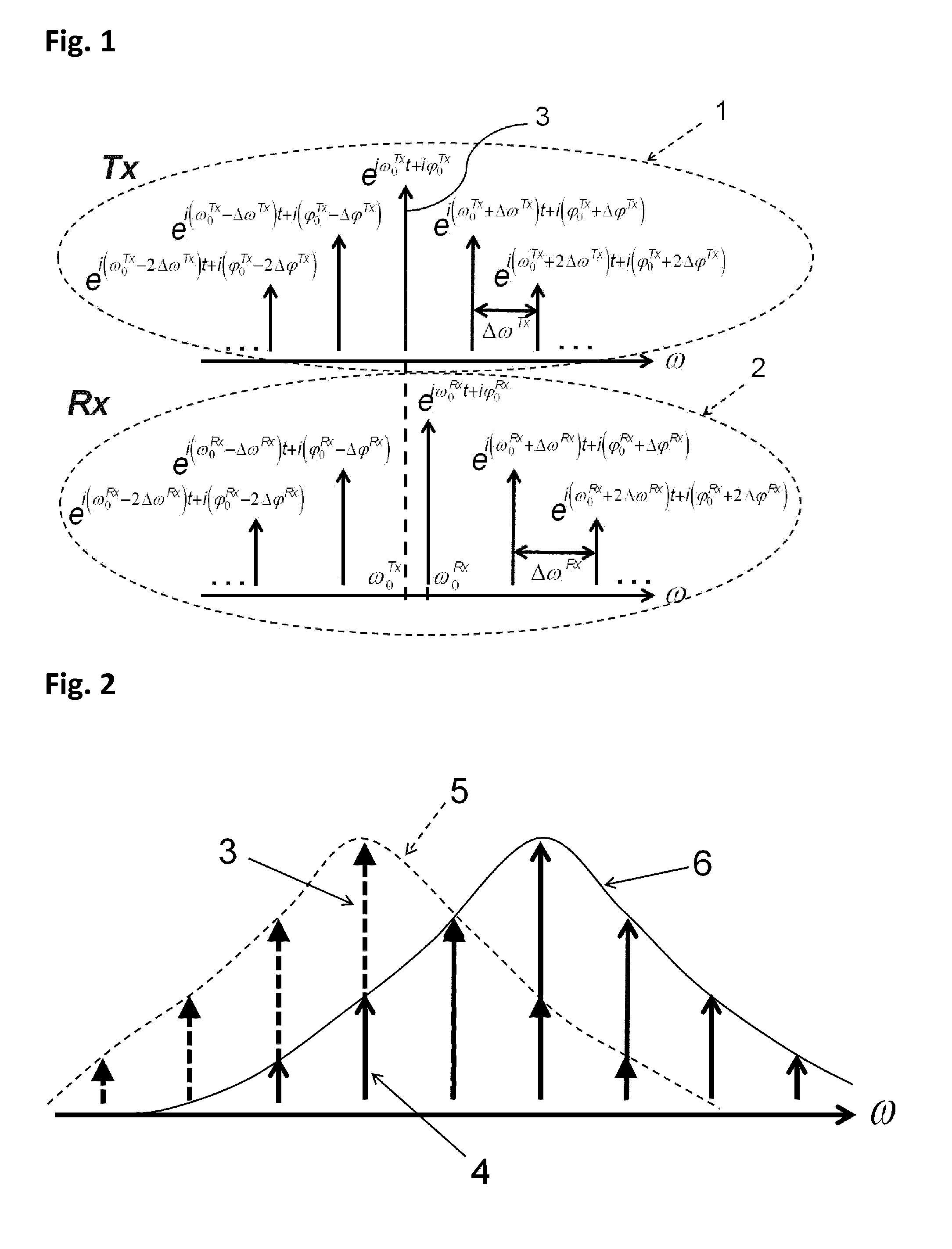
An optical data link has a transmitter and a receiver with coherent detection at the receiver and more than one optical carrier frequency. The optical carrier frequencies are generated by a frequency comb source in both the transmitter and the receiver. The frequency comb sources generate frequency combs that have frequency components and a free spectral range. The optical carrier frequencies transport more than one optical channel. Either at least one frequency component or the free spectral range of the optical comb generated at the receiver is locked to the comb generated at the transmitter by an optical phase locked loop, or an electrical phase locked loop or a feed-forward carrier recovery generates an intermediate frequency carrier reference that is routed to more than one channel to demodulate the data.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIV
Adaptive crossing frequency domain equalization (FDE) in digital polmux coherent systems
ActiveUS20100142952A1Efficient use ofSimple multiplicationPolarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingPolarization multiplexedSelf adaptive
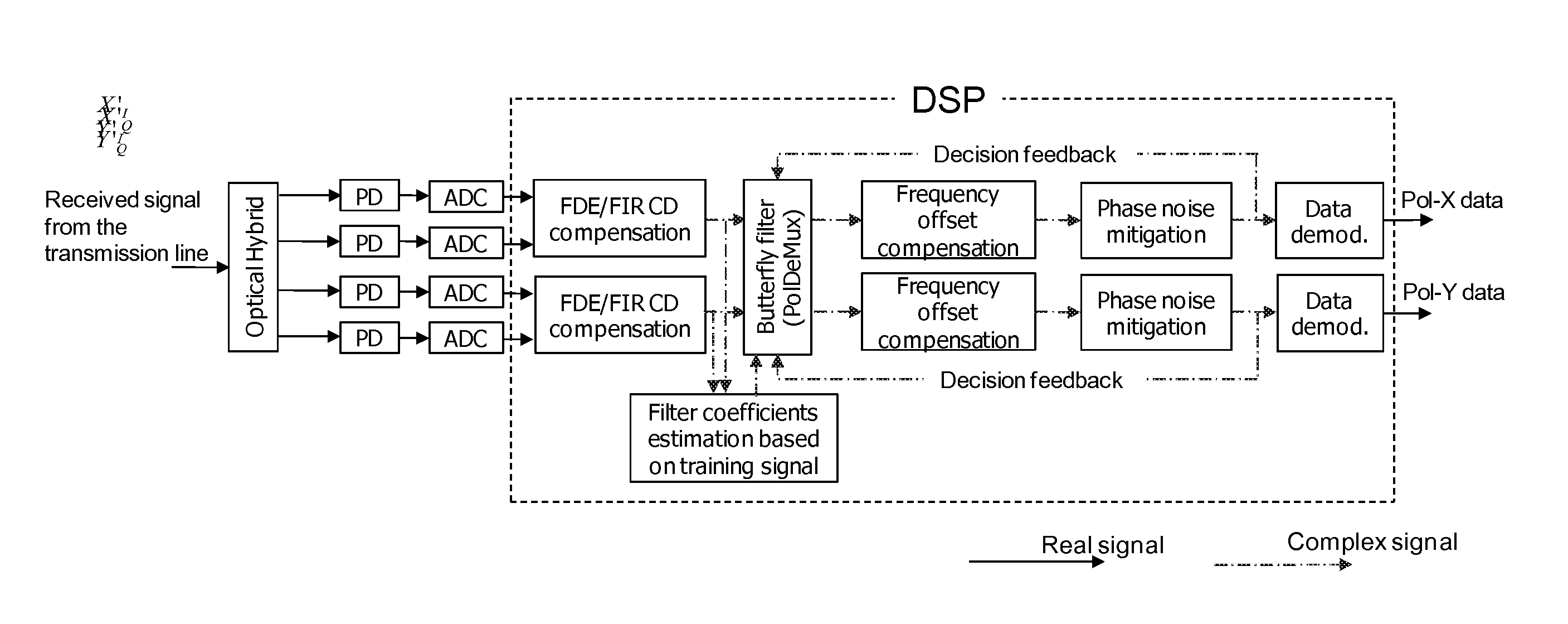
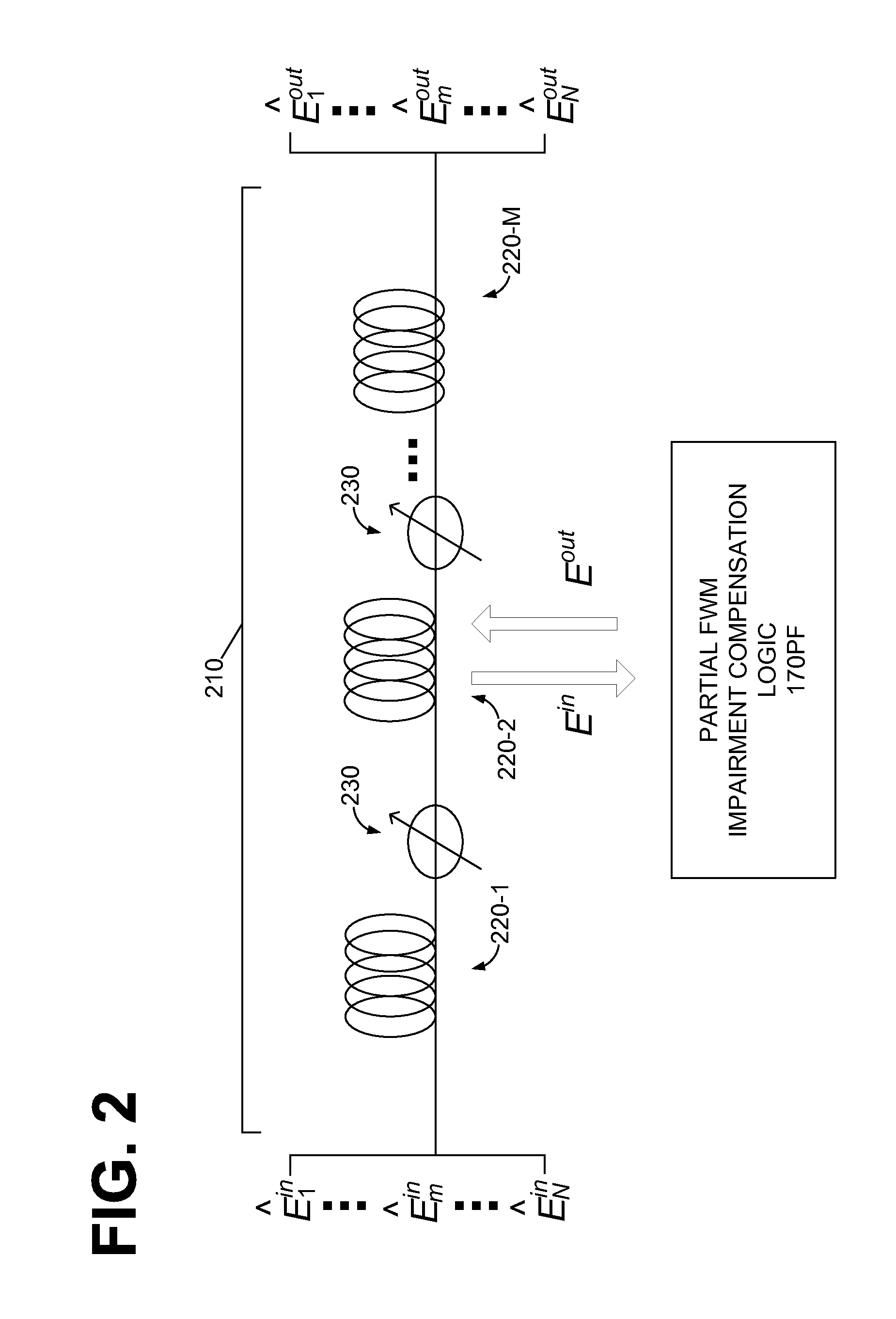
A method for the polarization independent frequency domain equalization (FDE) on polarization multiplexing (POLMUX) coherent systems employing an adaptive crossing FDE which advantageously produces CD compensation, PMD compensation and PolDeMux within one functional block of a digital signal processor (DSP).
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical transmitter, optical transmitter and receiver system, optical transmitting method and optical transmitting and receiving method
ActiveUS20110097085A1Polarisation multiplex systemsTime-division optical multiplex systemsMultiplexerEngineering
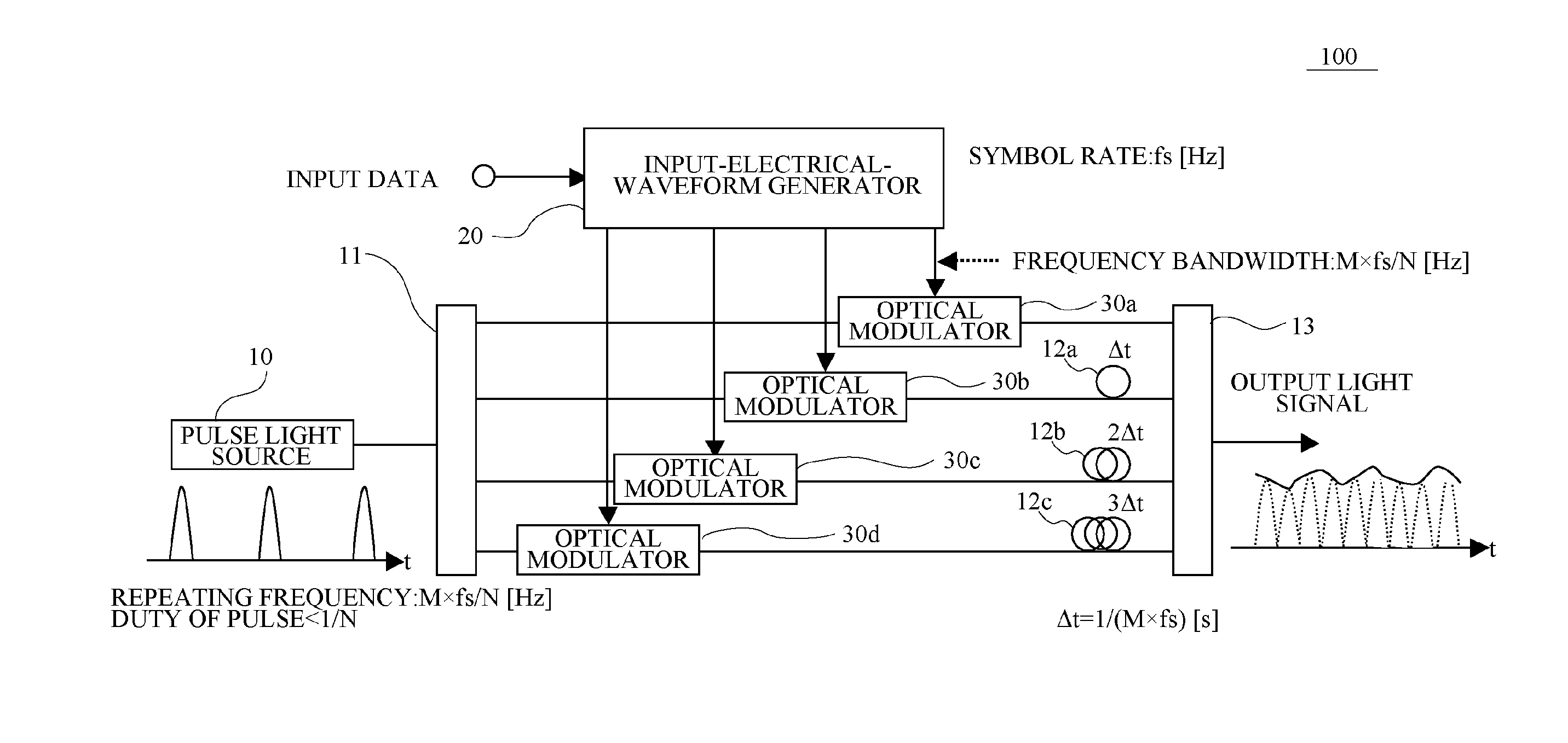
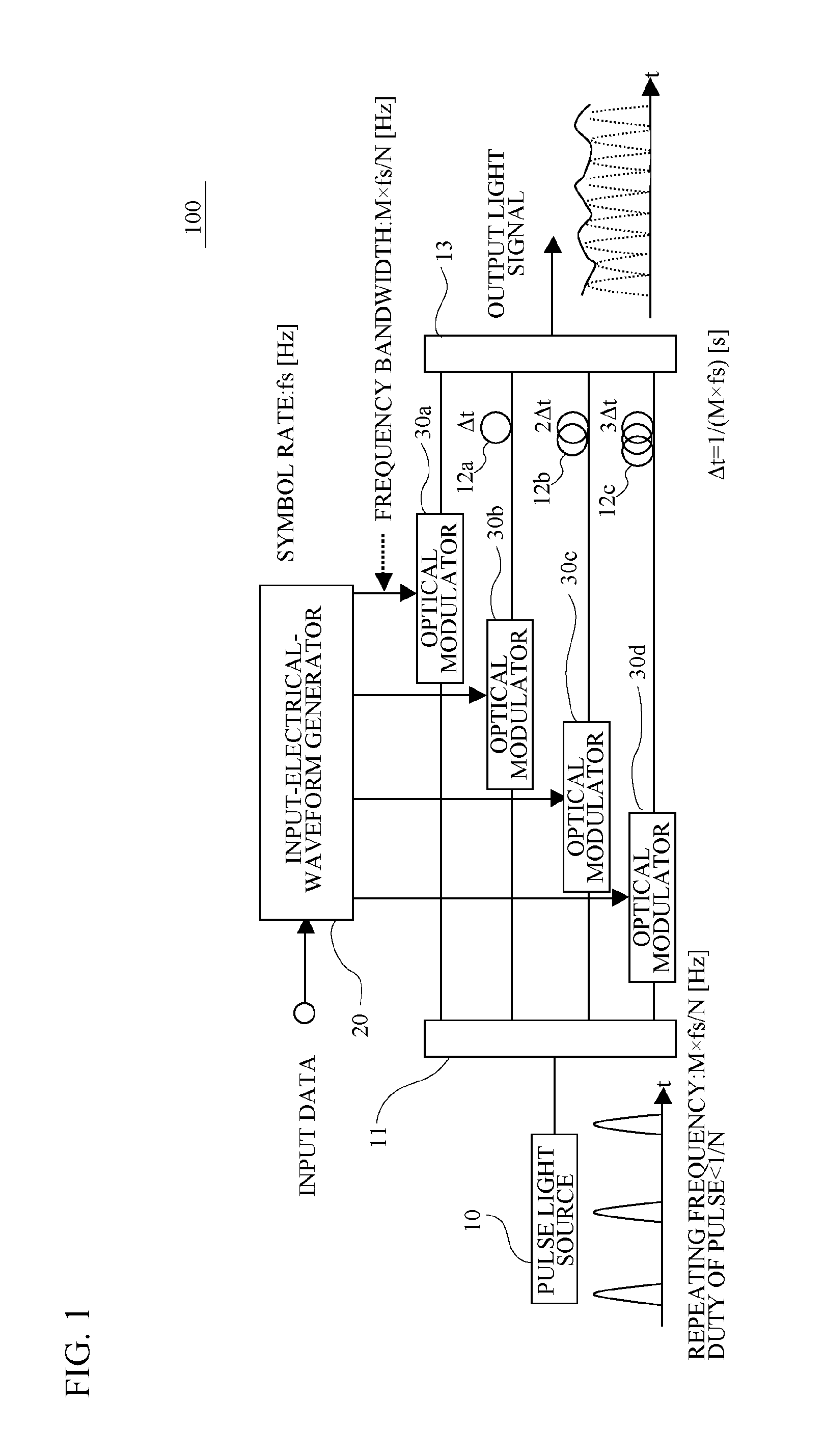
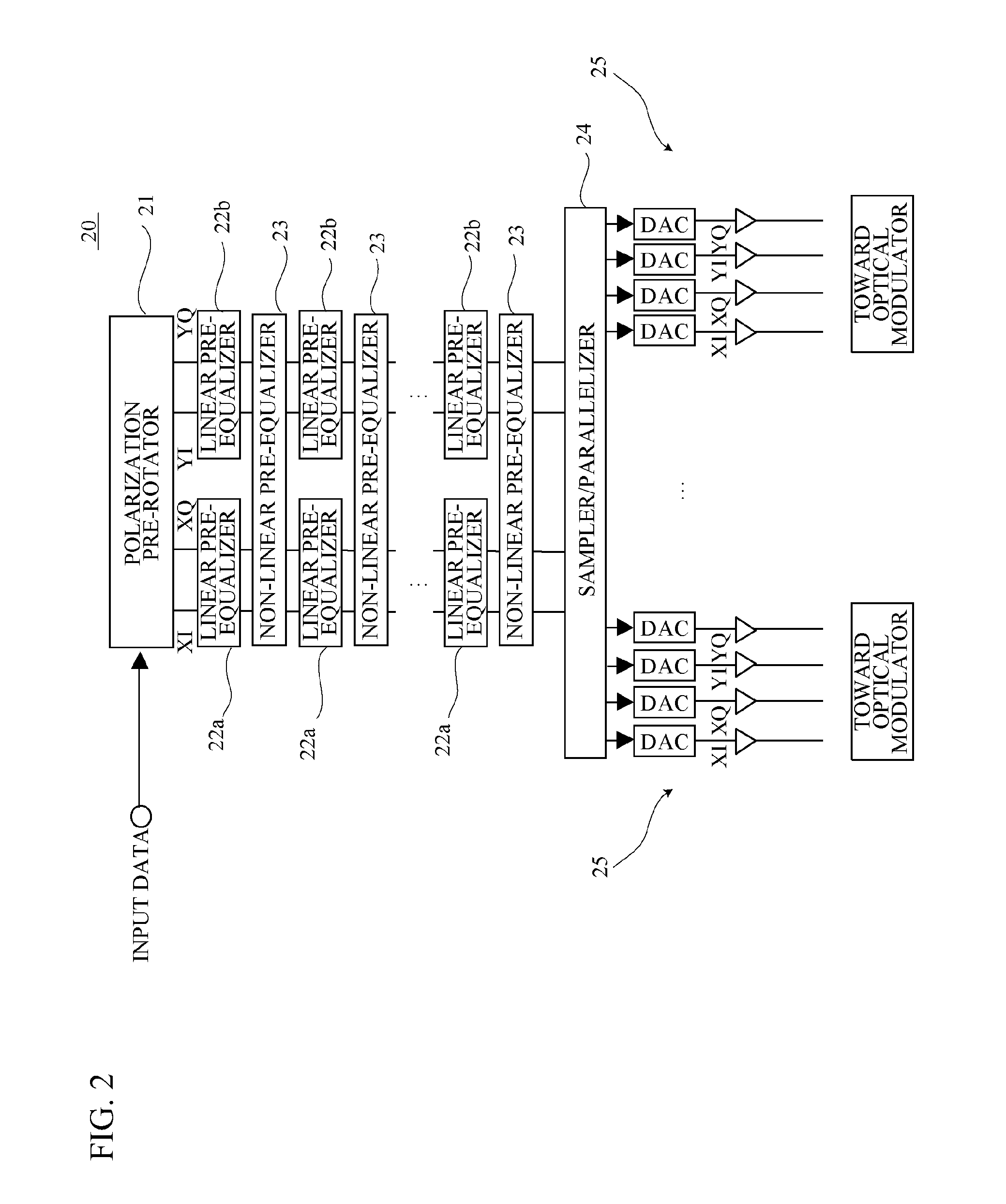
An optical transmitter includes: a pre-compensator calculating an electrical field of an optical signal subjected to an electronic pre-compensation with respect to an input digital signal; a parallelizer parallelizing the electrical field of the optical signal calculated by the pre-compensator; a plurality of optical modulators modulating an optical signal based on each of parallelized electrical fields of optical signals; and a time-division multiplexer time-division-multiplexing an optical signal output from the plurality of the optical modulators.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
System, method and apparatus for coherent optical OFDM
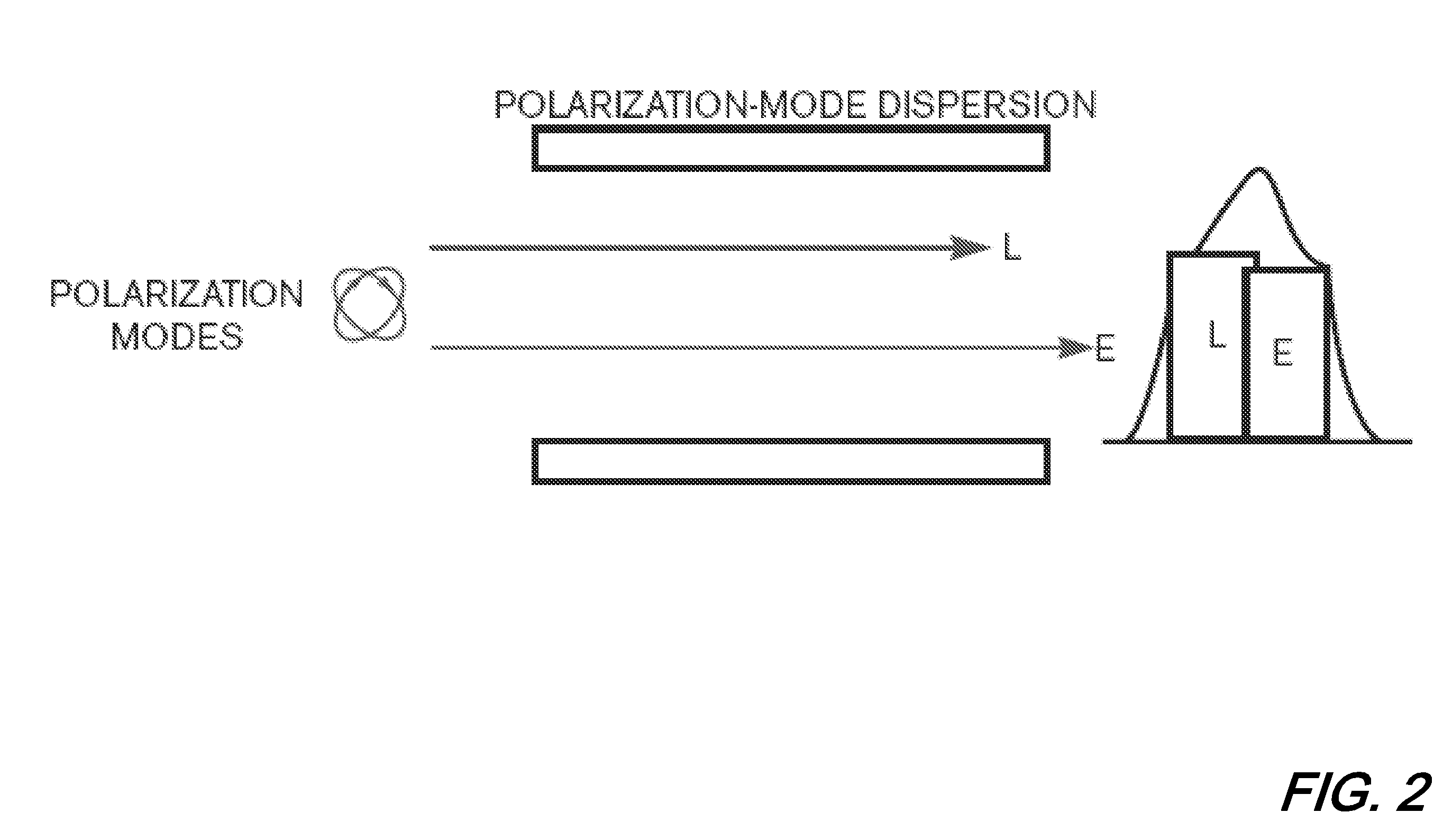
ActiveUS8218979B2Facilitate frequency estimationEase the frequency stabilization taskModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringPolarization mode dispersion
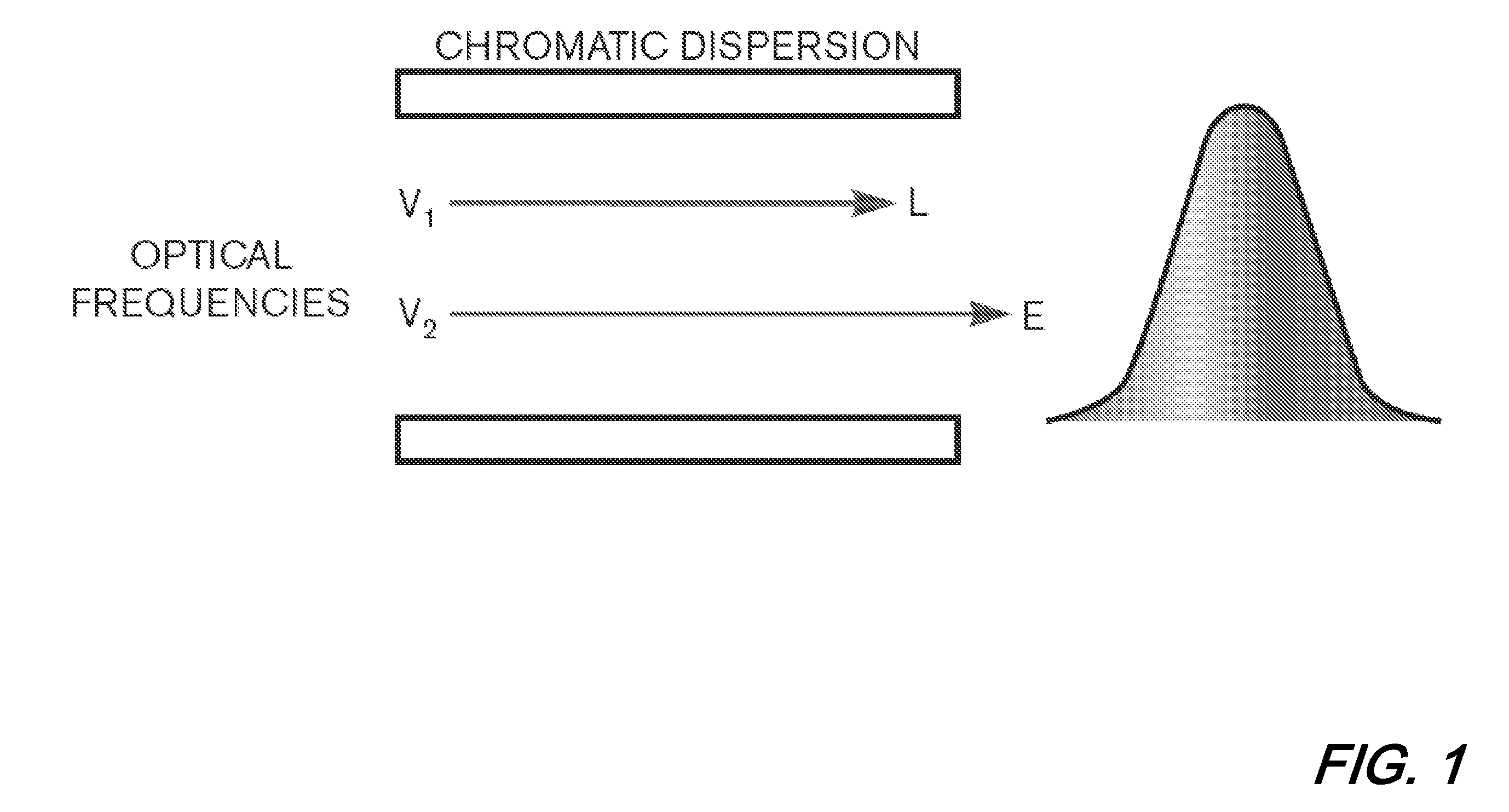
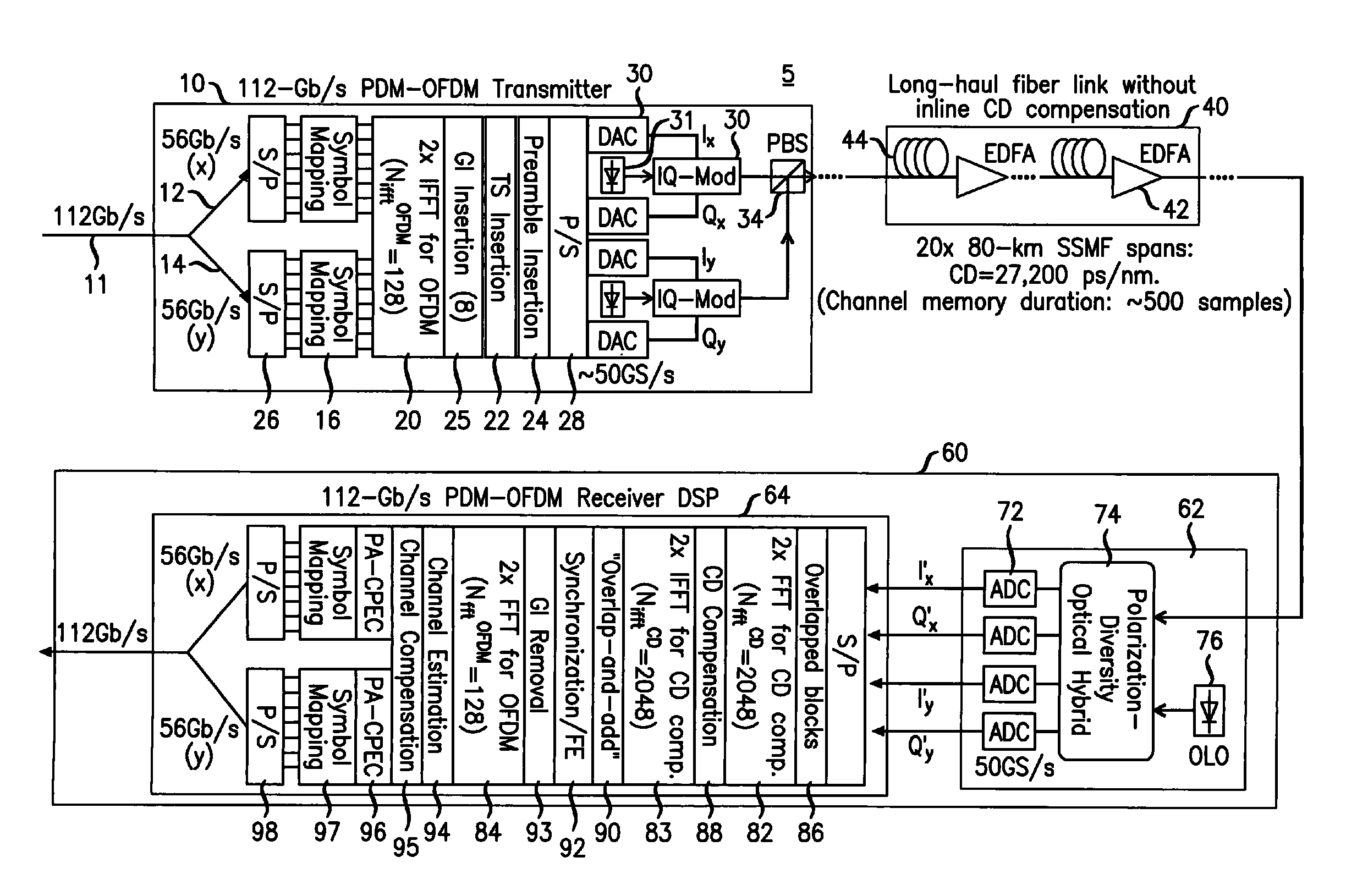
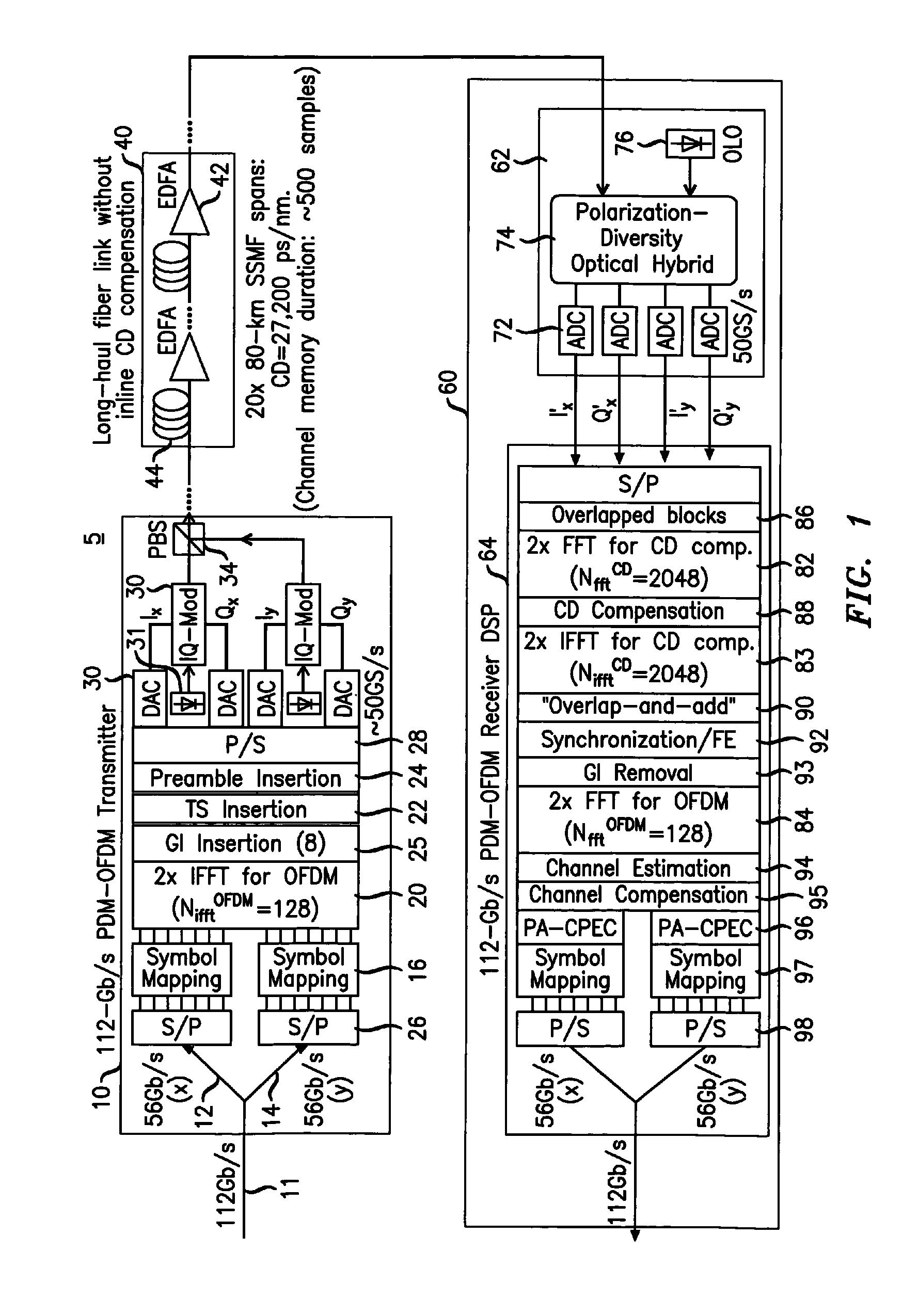
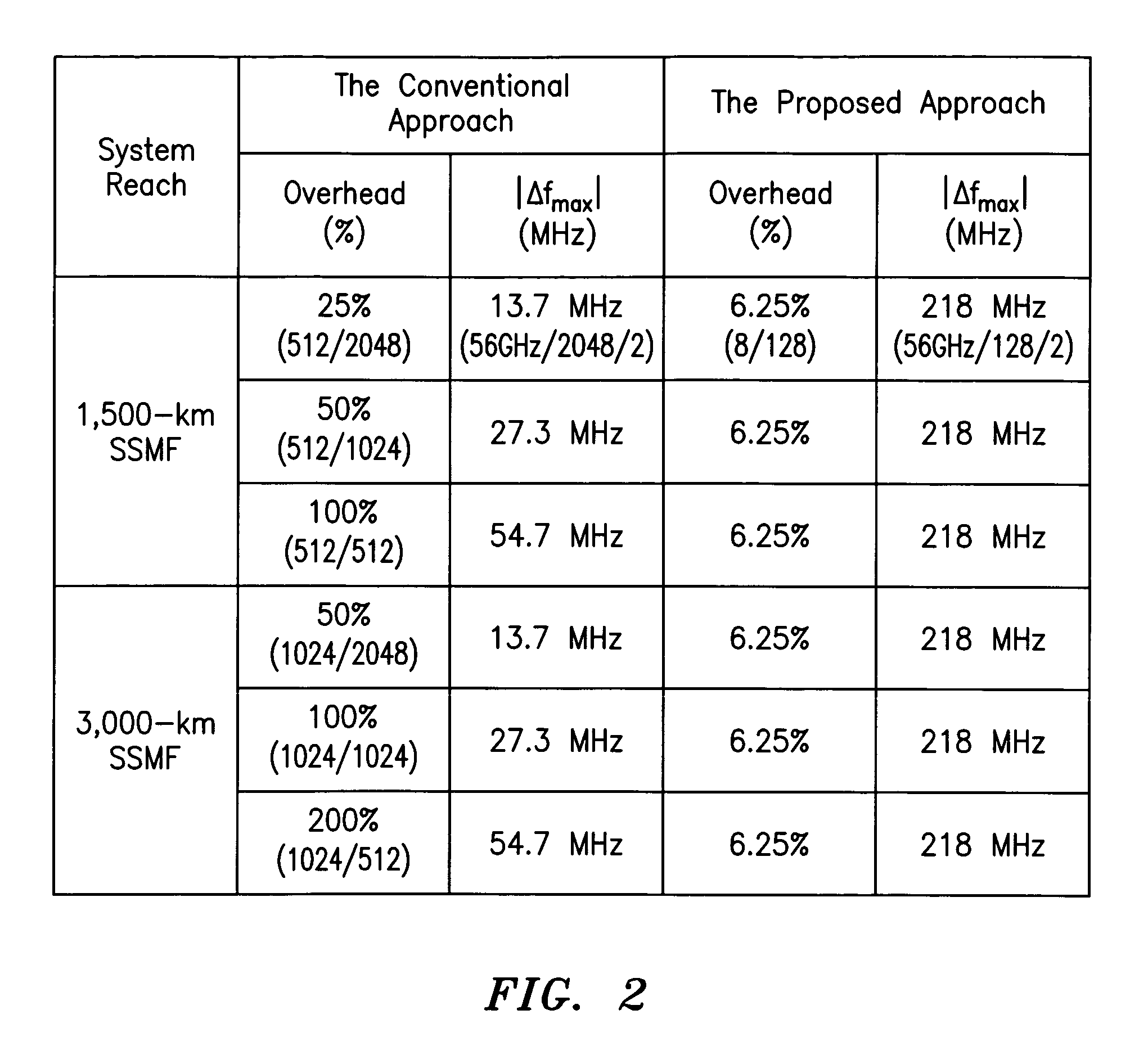
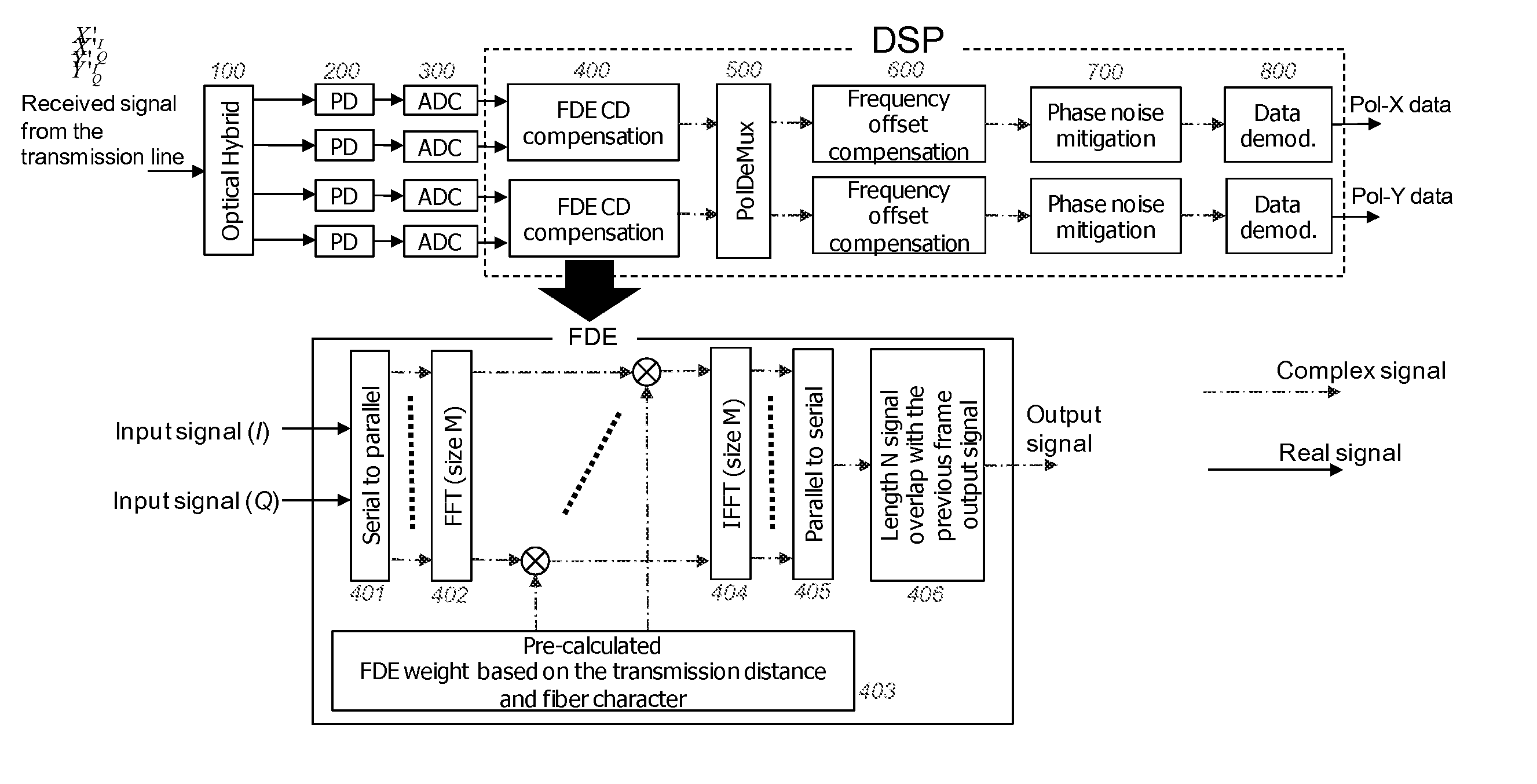
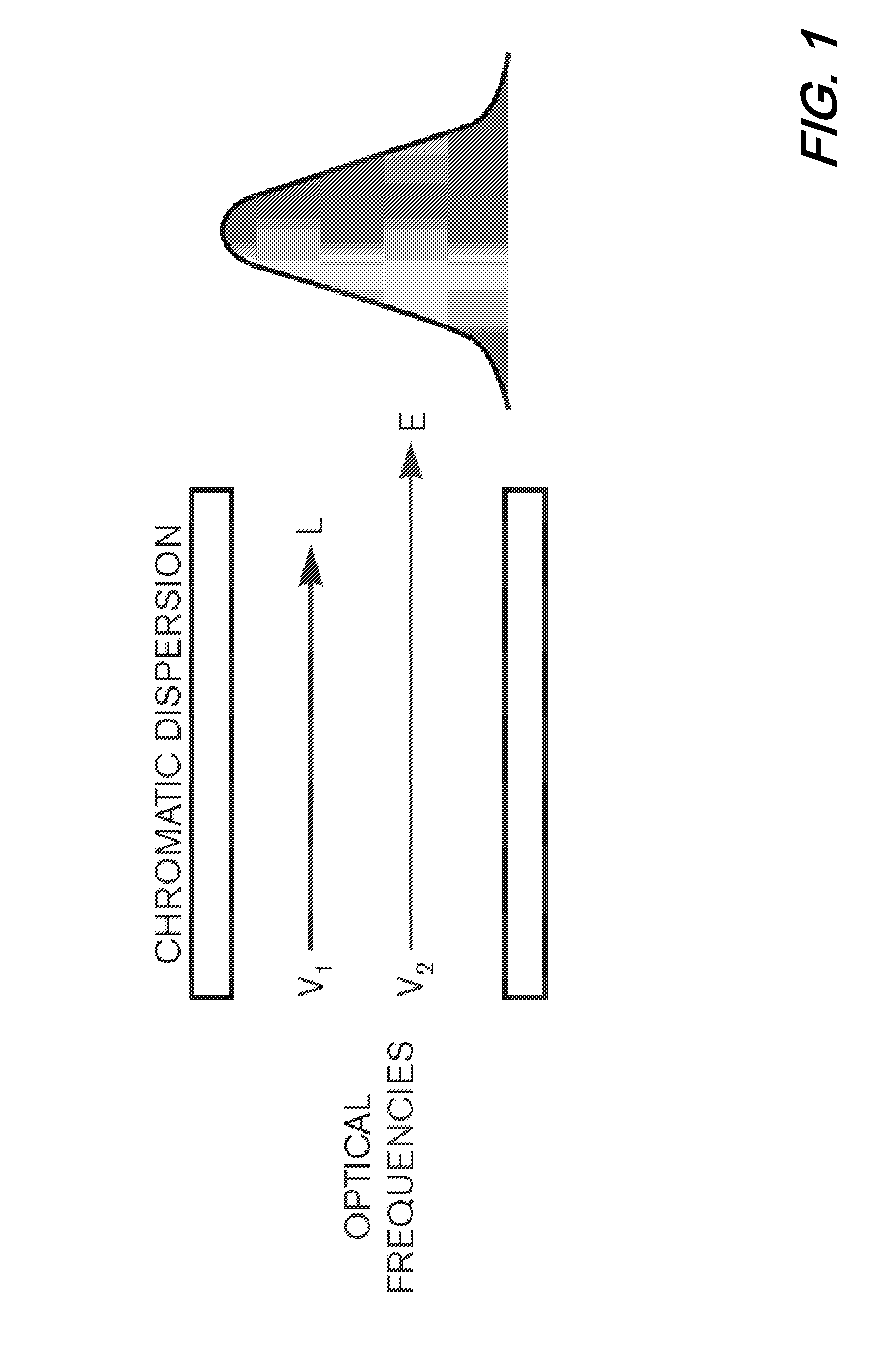
Digital compensation of chromatic dispersion (CD) effect experienced by optical orthogonal frequency-division multiplexed (OFDM) signal in fiber transmission is provided in the frequency domain using a Fast Fourier Transform / Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (FFT / IFFT) pair with equal length of digital samples prior to OFDM receiver signal processing, wherein the equal length is larger than the length of a FFT used for OFDM subcarrier demultiplexing of the received signal. The OFDM signal processing is independent of fiber CD, so small guard-interval (GI) can still be used to achieve high spectral efficiency even under the experience of large CD. The GI need only to be large enough to accommodate other effects such as polarization-mode dispersion. The length of an IFFT used for OFDM subcarrier multiplexing, as well as the FFT for OFDM demultiplexing can be sufficiently small so subcarrier spacing is sufficiently large to tolerate typical frequency offsets between the transmitter laser and the optical local oscillator.
Owner:RPX CORP
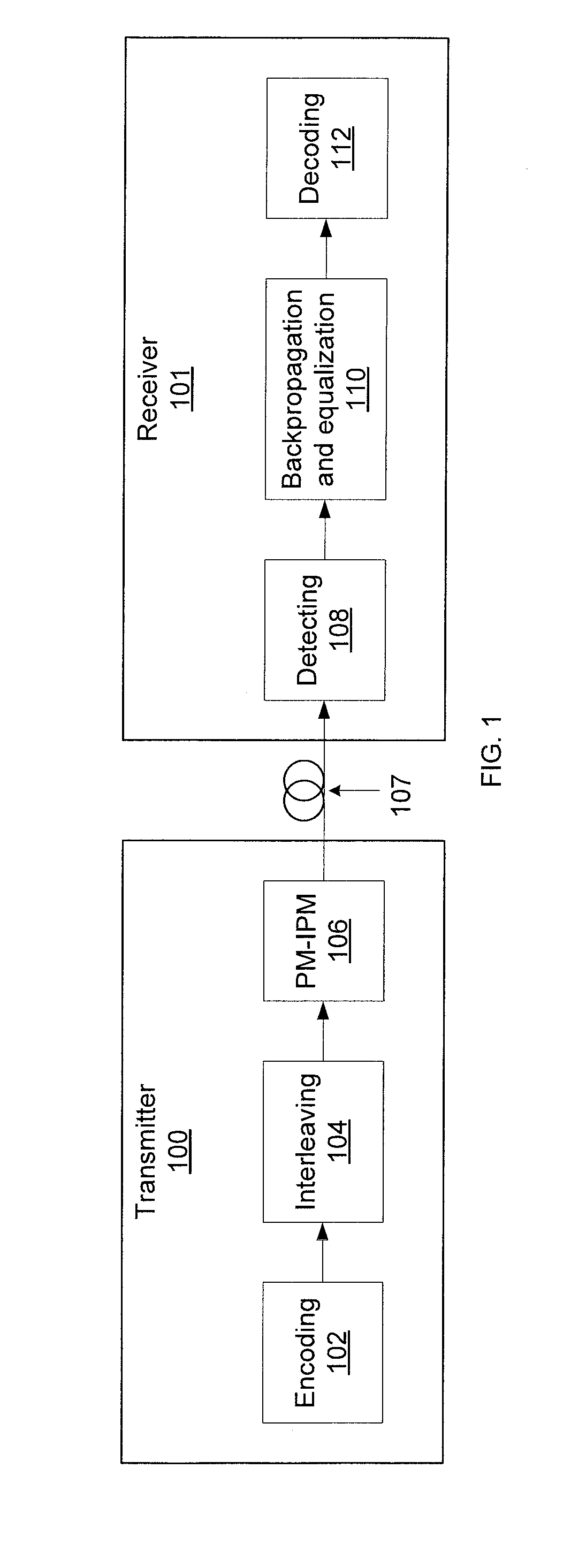
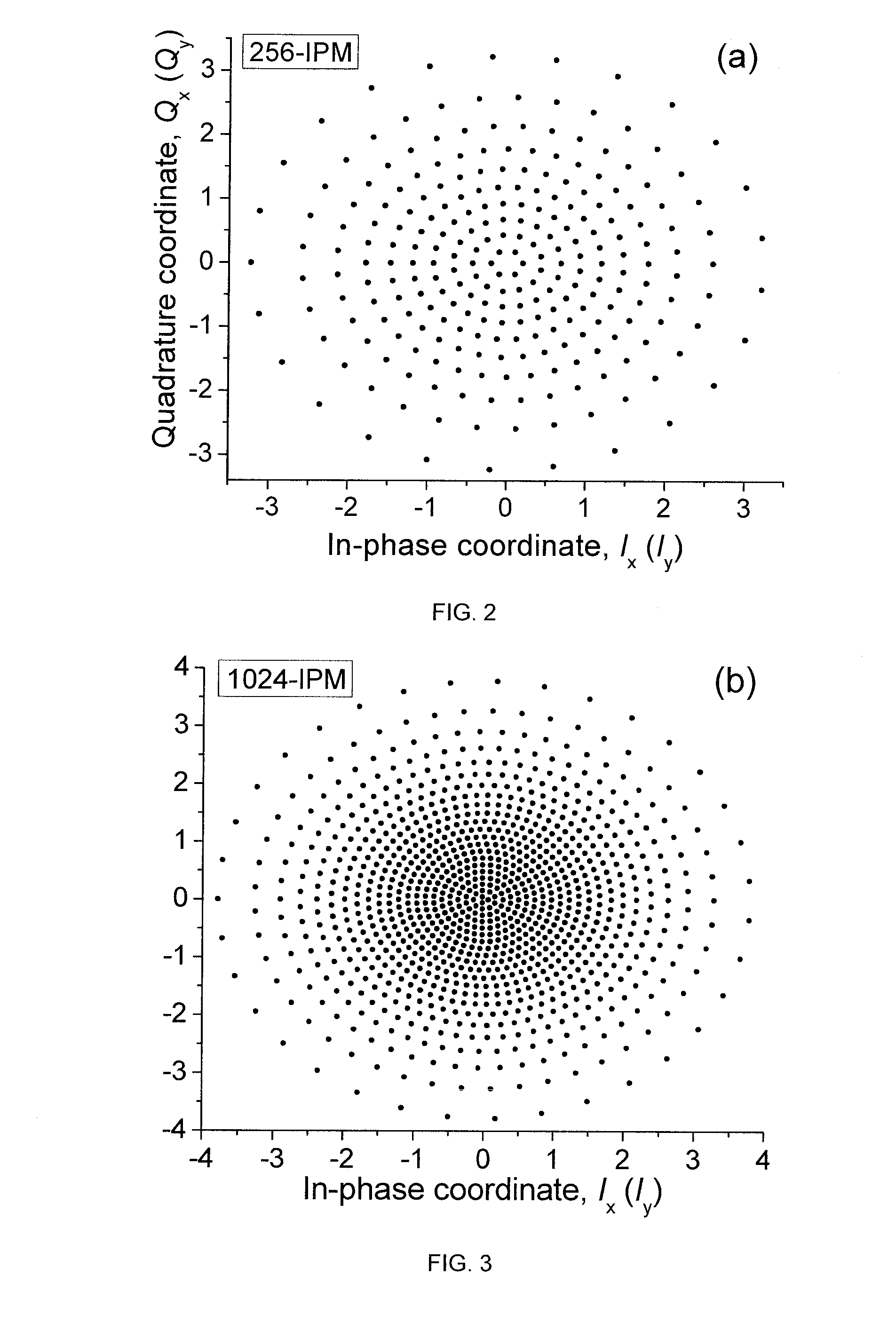
Coded polarization-multiplexed iterative polar modulation
ActiveUS20110085624A1Reducing channel memoryRemoving channel impairmentPolarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingData streamPolarization multiplexed
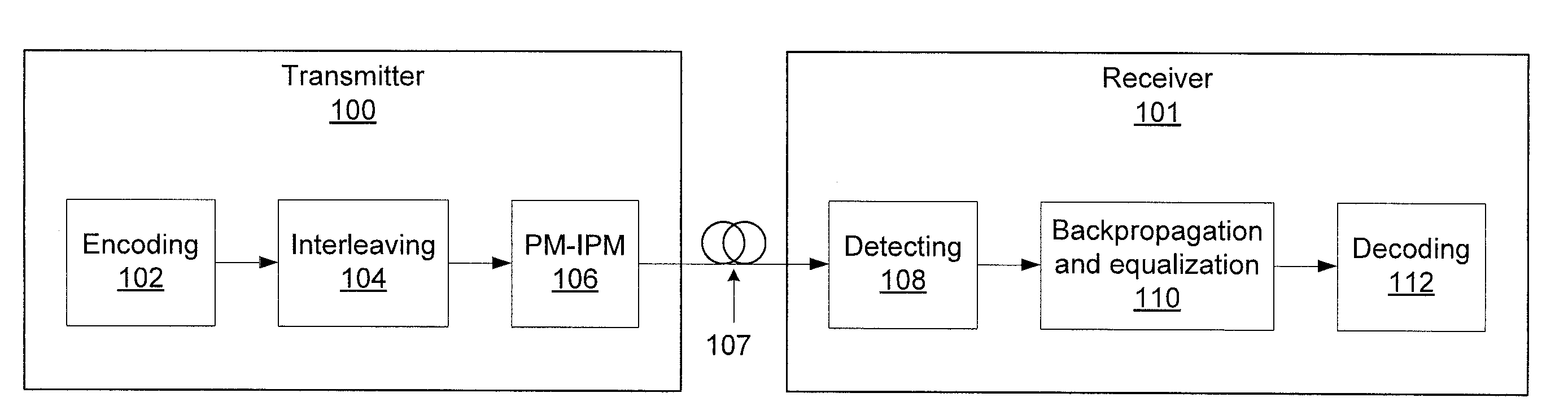
Systems and methods for optical communication that use a transmitter / receiver. The systems and methods include receiving a modulated, encoded input stream. Channel memory is reduced using coarse digital backpropagation and other channel impairments are removed using turbo equalization. Symbols are detected in the input stream that conform to a non-uniform, polar constellation having a Gaussian source distribution to produce a stream of encoded data. The stream of encoded data is decoded with one or more low density parity check (LDPC) decoders.
Owner:NEC CORP
Compensation of Optical Transmission Impairments Using Digital Backward Propagation
ActiveUS20100239262A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingFiber chromatic dispersionTransmission channel
Systems and method of compensating for transmission impairment are disclosed. One such method comprises receiving a wavelength-division multiplexed optical signal. The received optical signal has been distorted in the physical domain by an optical transmission channel. The method further comprises propagating the distorted optical signal backward in the electronic domain in a corresponding virtual optical transmission channel. The backward propagation fully compensates for fiber dispersion, self-phase modulation, and cross-phase modulation (XPM) and partially compensates for four-wave mixing (FWM).
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Polarization independent frequency domain equalization (FDE) for chromatic dispersion (CD) compensation in polmux coherent systems
ActiveUS20100196009A1Polarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingTime domainPolarization multiplexed
Owner:NEC CORP
Receiver for optical transverse-mode-multiplexed signals
ActiveUS8355638B2Polarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsTransverse modeOptical detector
A representative optical receiver of the invention receives an optical transverse-mode-multiplexed (TMM) signal through a multimode fiber that supports a plurality of transverse modes. The optical receiver has a plurality of optical detectors operatively coupled to a digital signal processor configured to process the TMM signal to determine its modal composition. Based on the determined modal composition, the optical receiver demodulates each of the independently modulated components of the TMM signal to recover the data encoded onto the TMM signal at the remote transmitter.
Owner:RPX CORP
Dual Fiber Stretchers for Dispersion Compensation
InactiveUS20100238452A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansPath lengthEngineering
An optical system having at least two waveguides that are deformable to provide adjustments to dispersion and path length.
Owner:SOUTHERN PHOTONICS
WDM telecommunications link with coherent detection and optical frequency comb sources
ActiveUS9088371B2Increase the number ofReduce complexityWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingTelecommunications linkIntermediate frequency
An optical data link has a transmitter and a receiver with coherent detection at the receiver and more than one optical carrier frequency. The optical carrier frequencies are generated by a frequency comb source in both the transmitter and the receiver. The frequency comb sources generate frequency combs that have frequency components and a free spectral range. The optical carrier frequencies transport more than one optical channel. Either at least one frequency component or the free spectral range of the optical comb generated at the receiver is locked to the comb generated at the transmitter by an optical phase locked loop, or an electrical phase locked loop or a feed-forward carrier recovery generates an intermediate frequency carrier reference that is routed to more than one channel to demodulate the data.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIV
100 Gbit/s OFDM Optical Signal Generation
ActiveUS20090214210A1Polarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingPolarization multiplexedSideband
A method includes modulating lightwaves to provide first and second OFDM signal sidebands at a first polarization direction and first and second OFDM signal sidebands at a second polarization direction, and combining sidebands that are oppositely positioned and joined from the first and second OFDM signal sidebands at each polarization direction to provide a polarization multiplexing OFDM signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and device for realizing direct detection and coherent detection
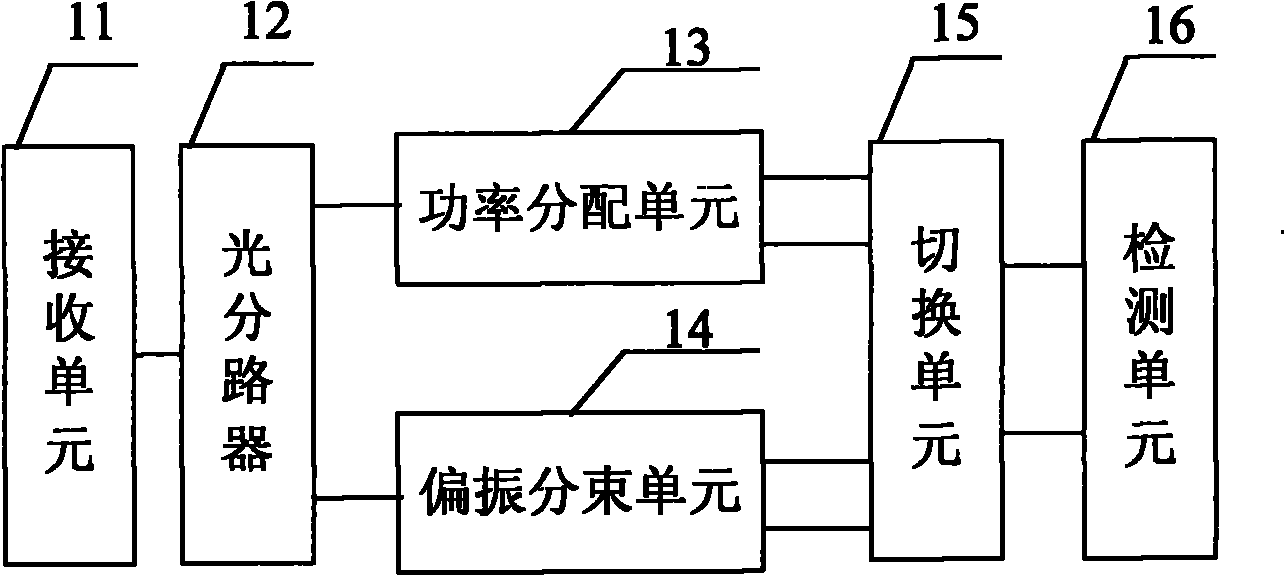
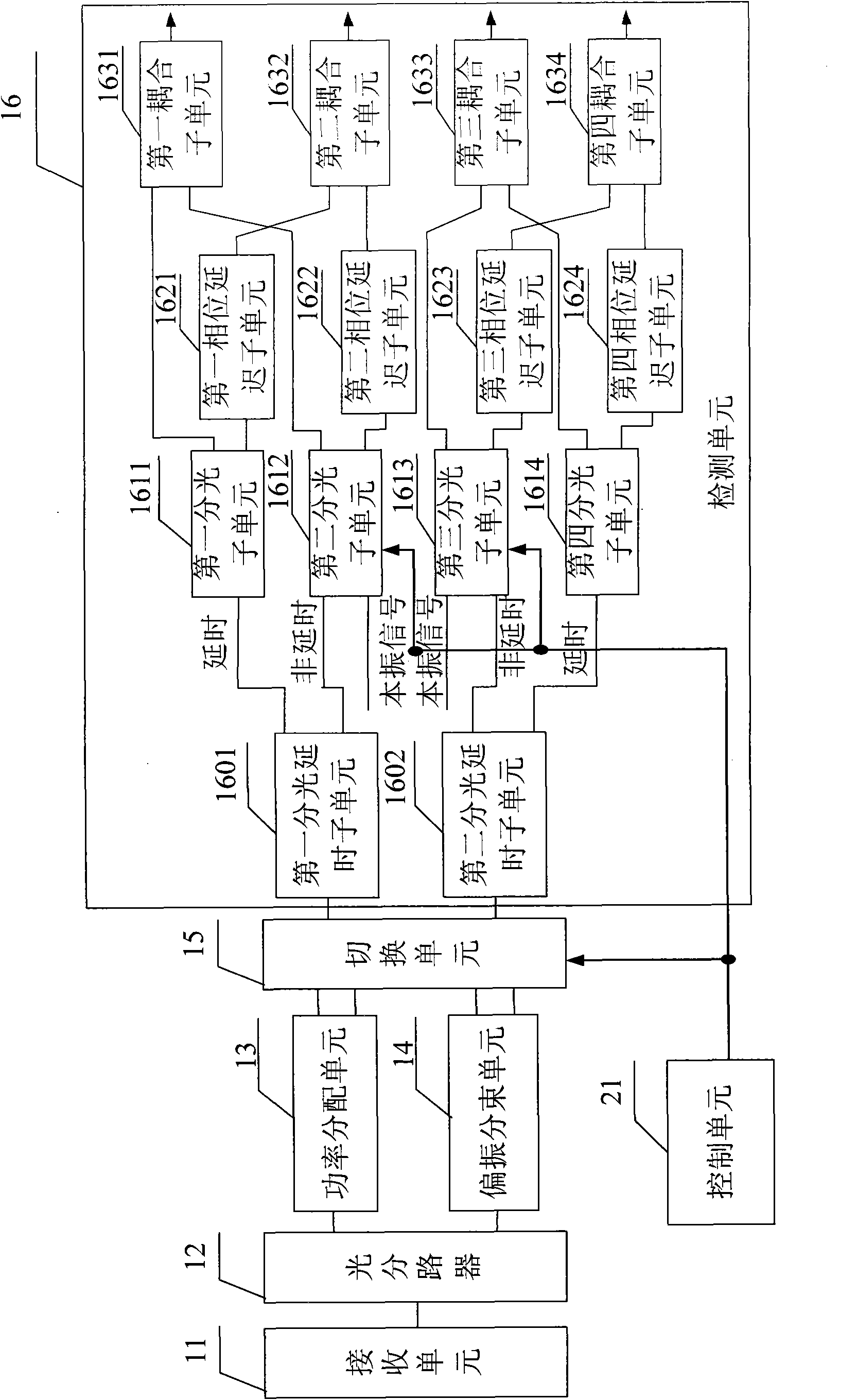
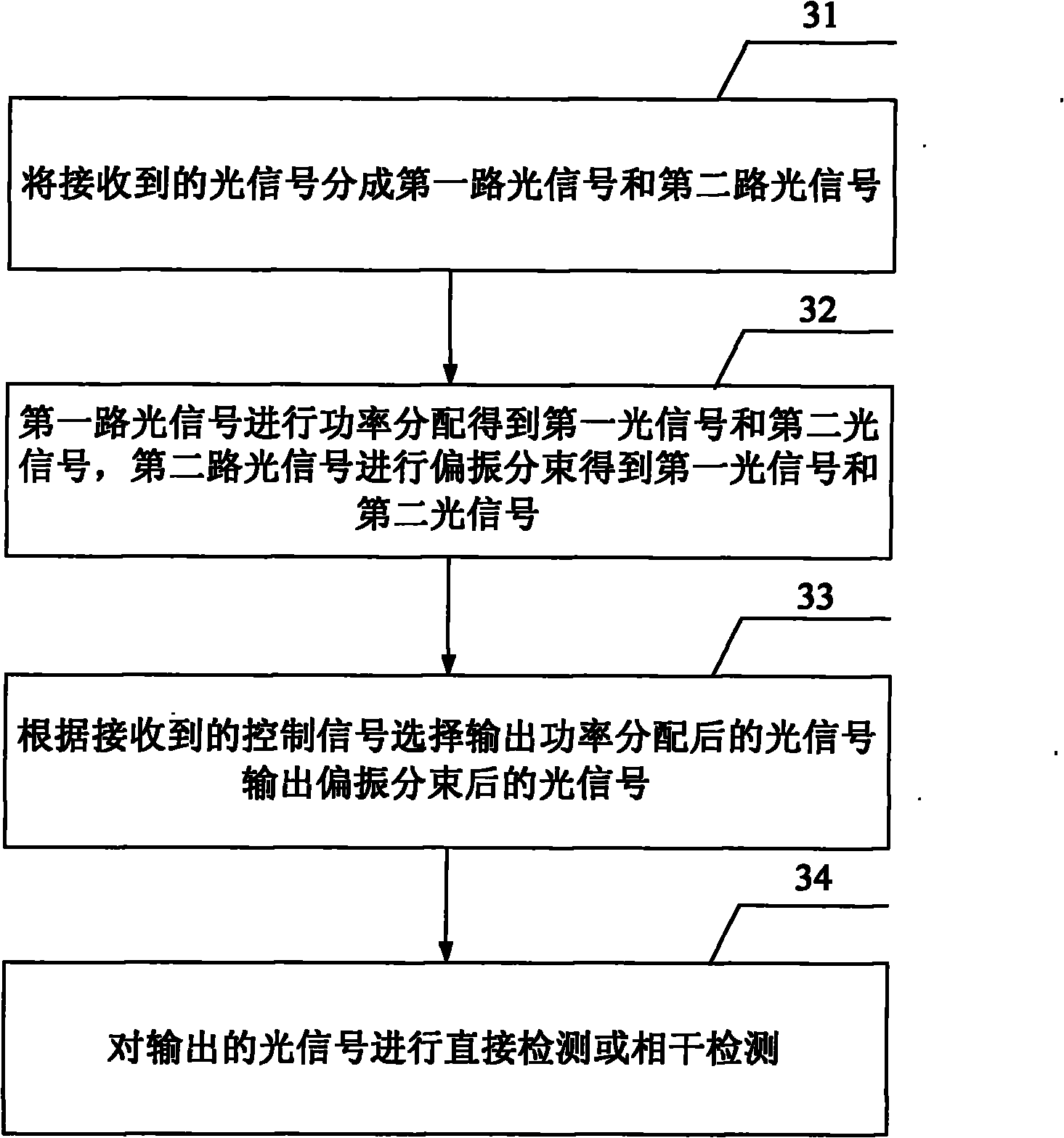
InactiveCN102142902AFlexible detectionPolarisation multiplex systemsModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexingControl signal
The invention provides a method and device for realizing direct detection and coherent detection. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, dividing received optical signals into a first path of optical signals and a second path of optical signals, carrying out power allocation on the first path of optical signals to obtain a first optical signal and a second optical signal, and carrying out polarization splitting on the second path of optical signals to obtain a first optical signal and a second optical signal; secondly, selecting an optical signal subjected to output power allocation or an optical signal subjected to output polarization splitting according to a received control signal; and finally, carrying out direct detection or coherent detection on the output optical signal. Power allocation or polarization splitting is carried out on the optical signal according to the control signal, and direct detection or coherent detection can be flexibly carried out to ensure that a single-polarization or polarization multiplexing system can adapt to different rates of an intermediate node.
Owner:江苏科利新材料有限公司
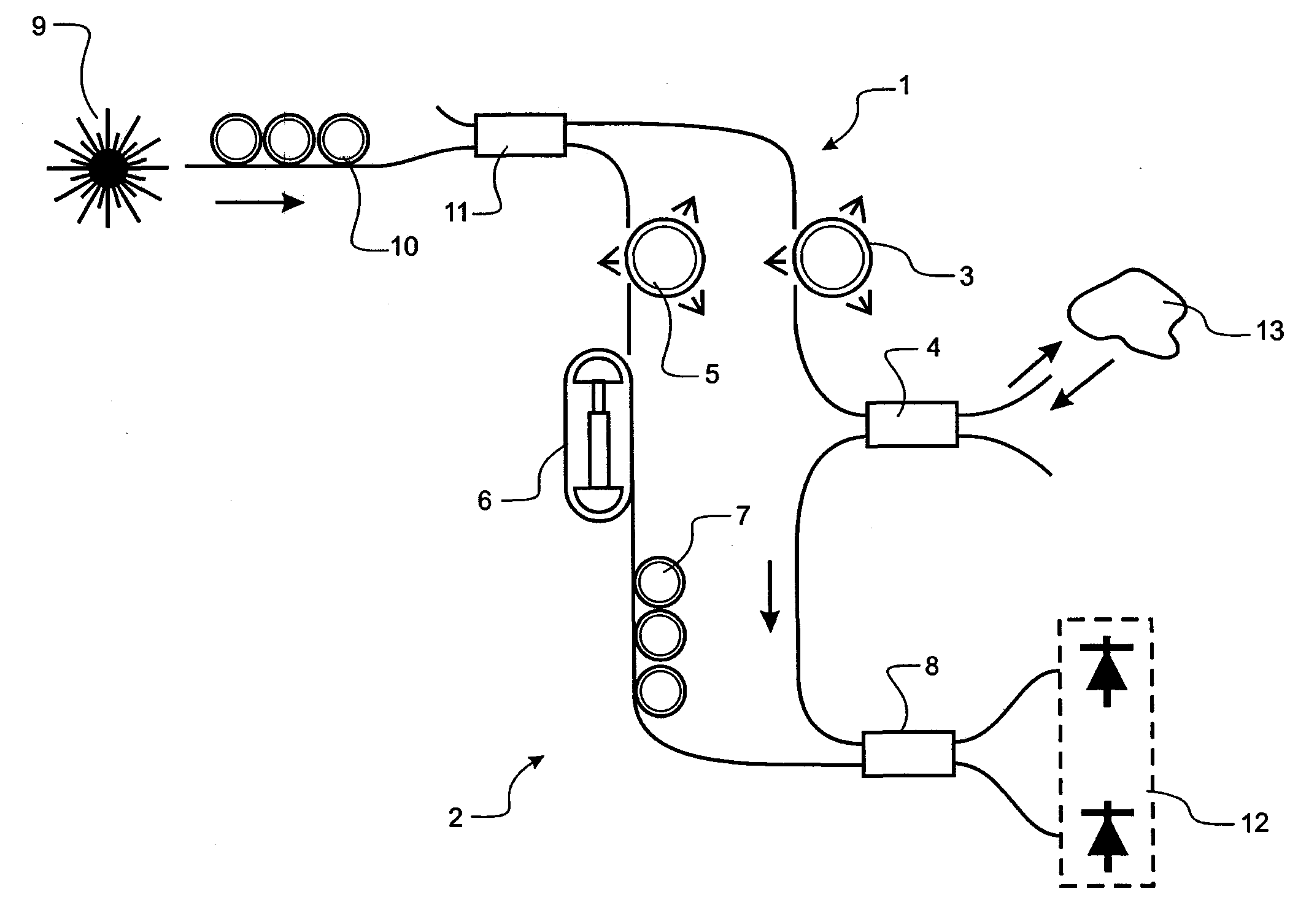
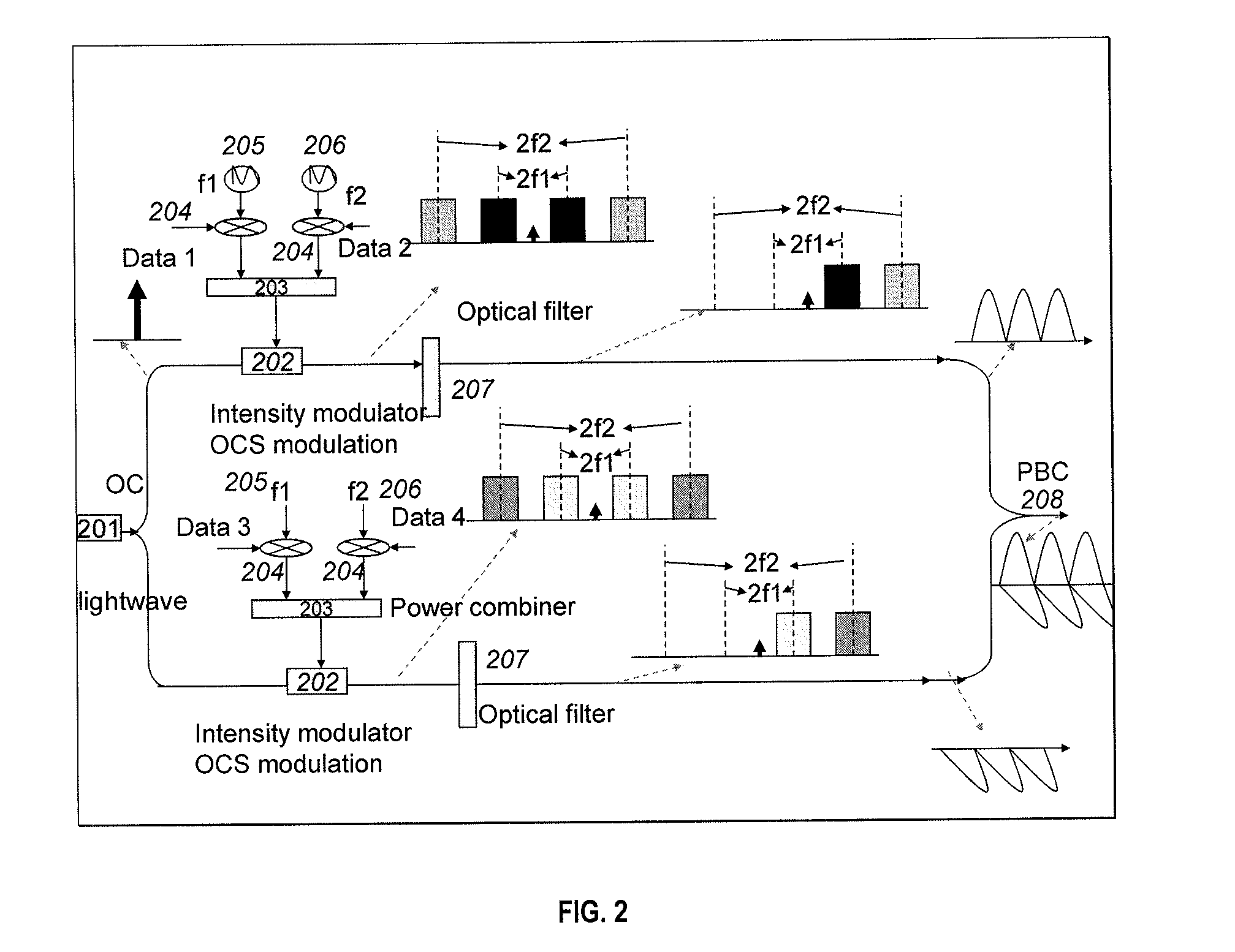
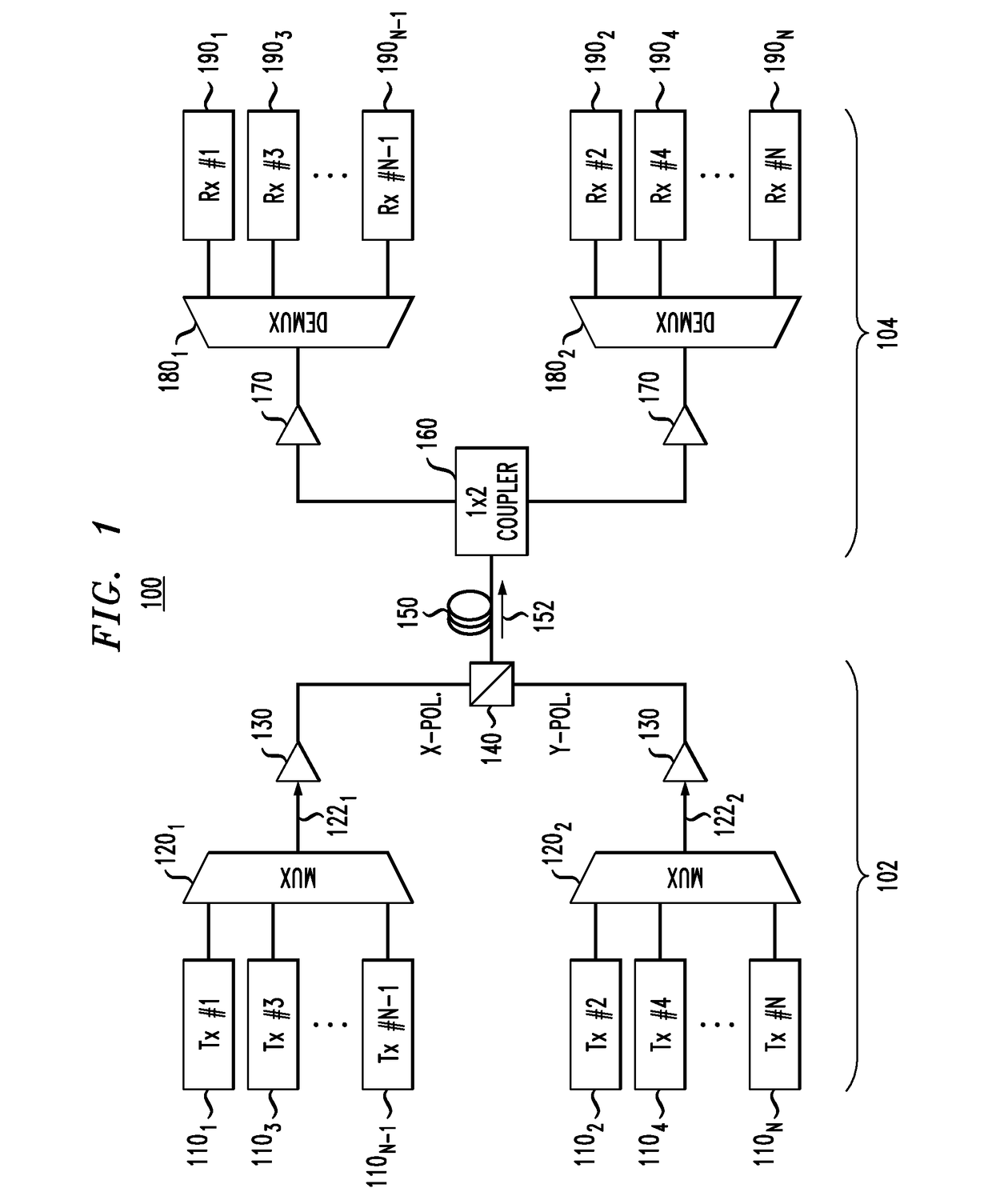
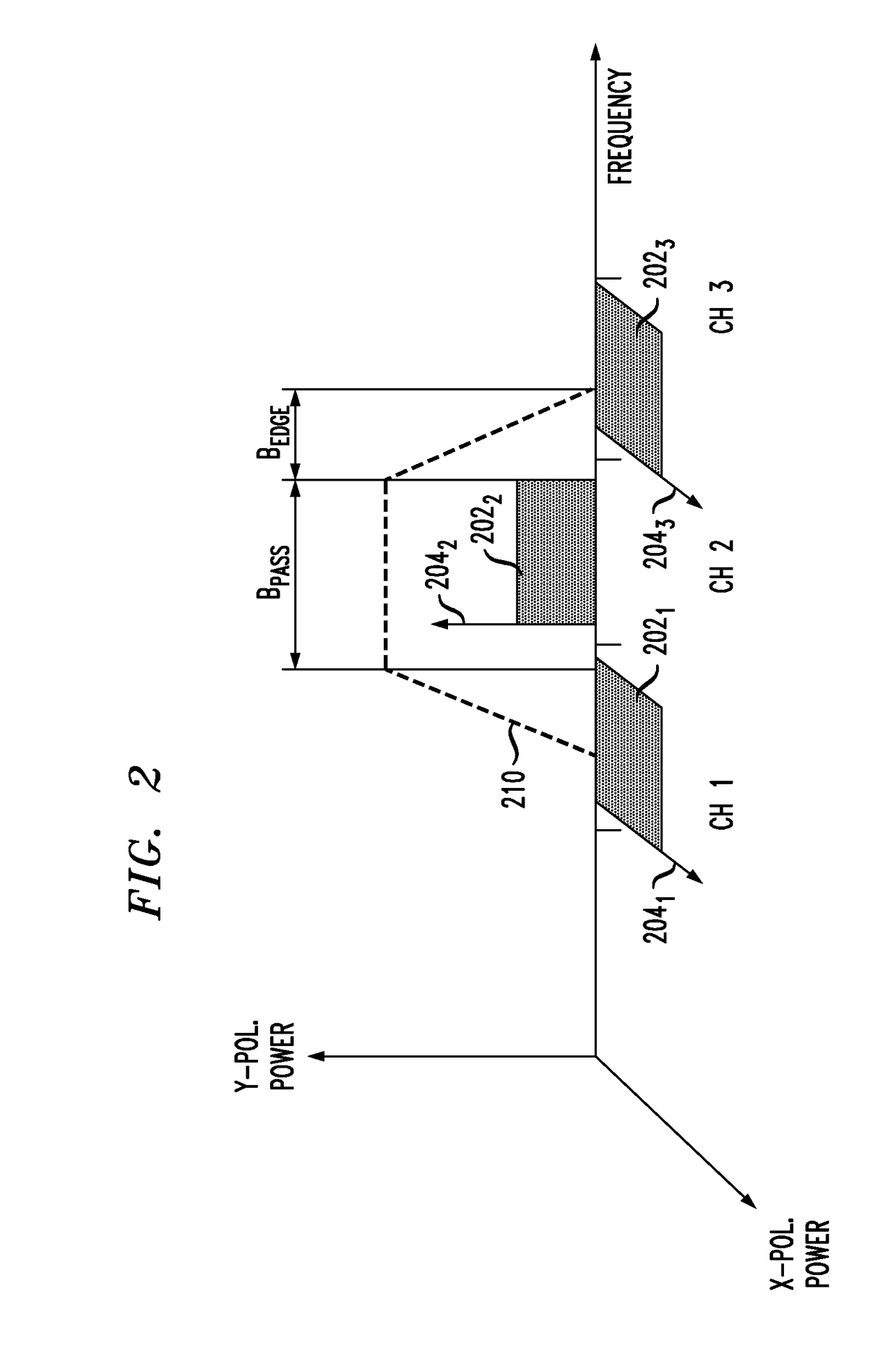
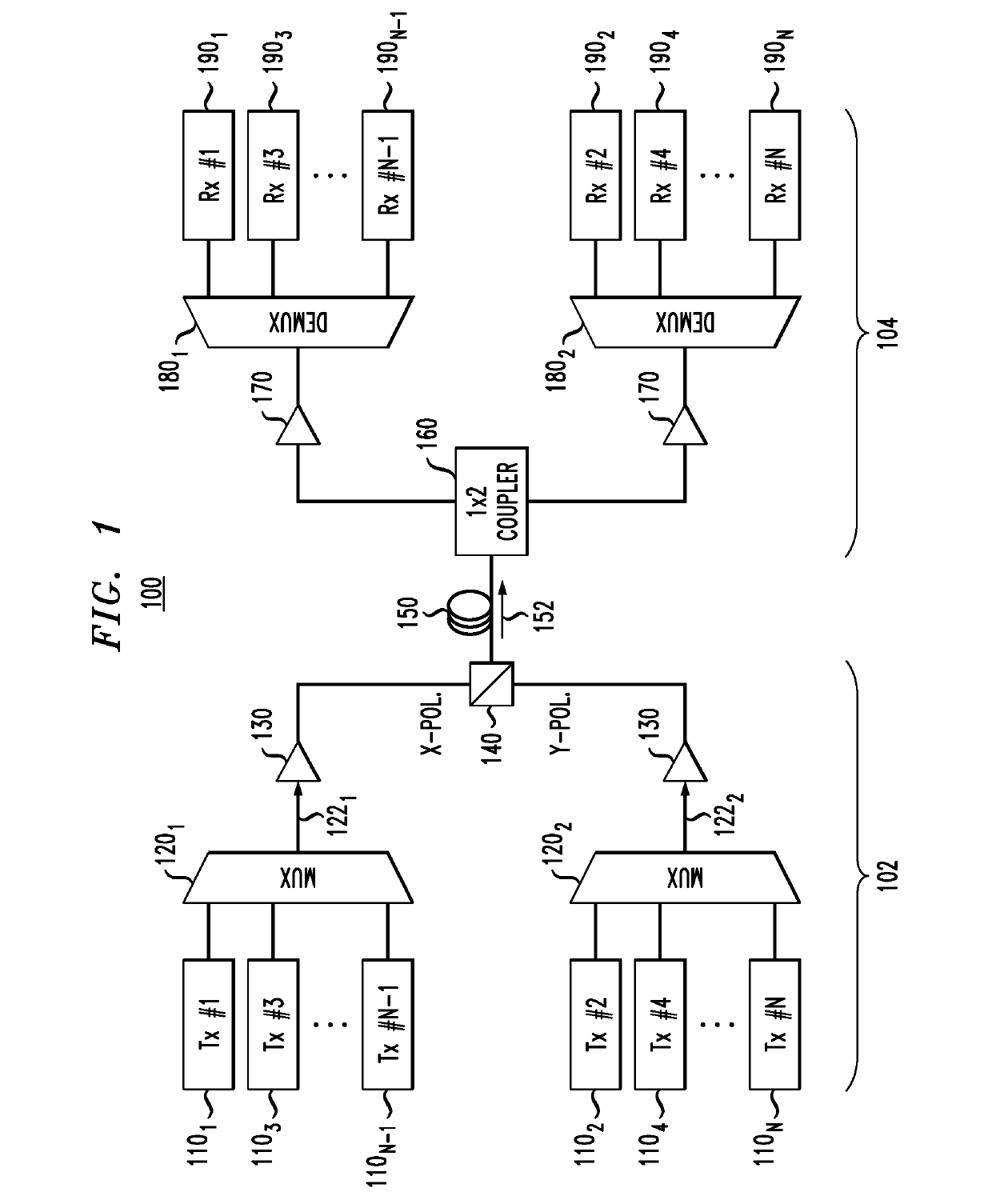
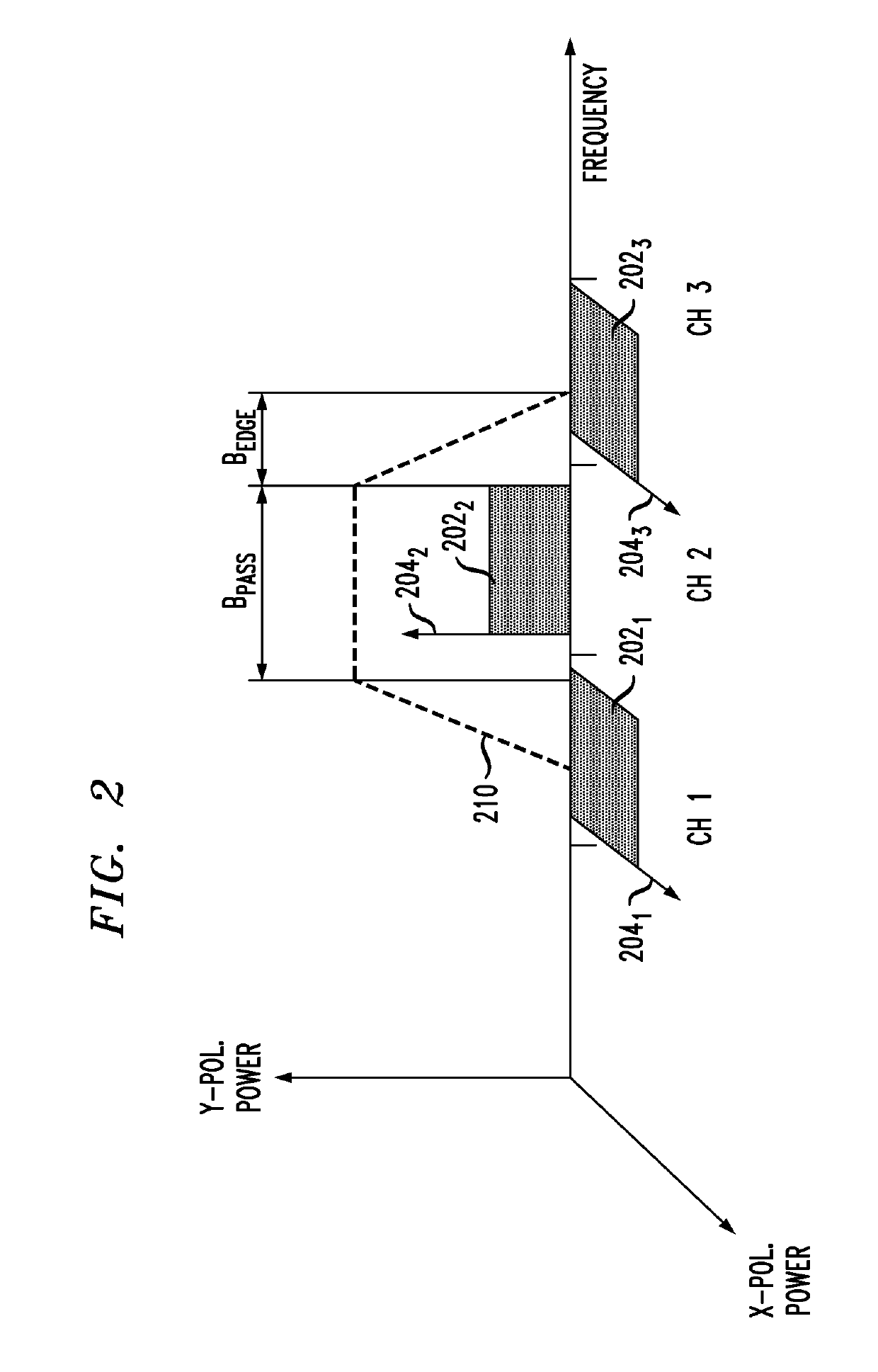
Multichannel optical communication system and method utilizing wavelength and coherence division multiplexing
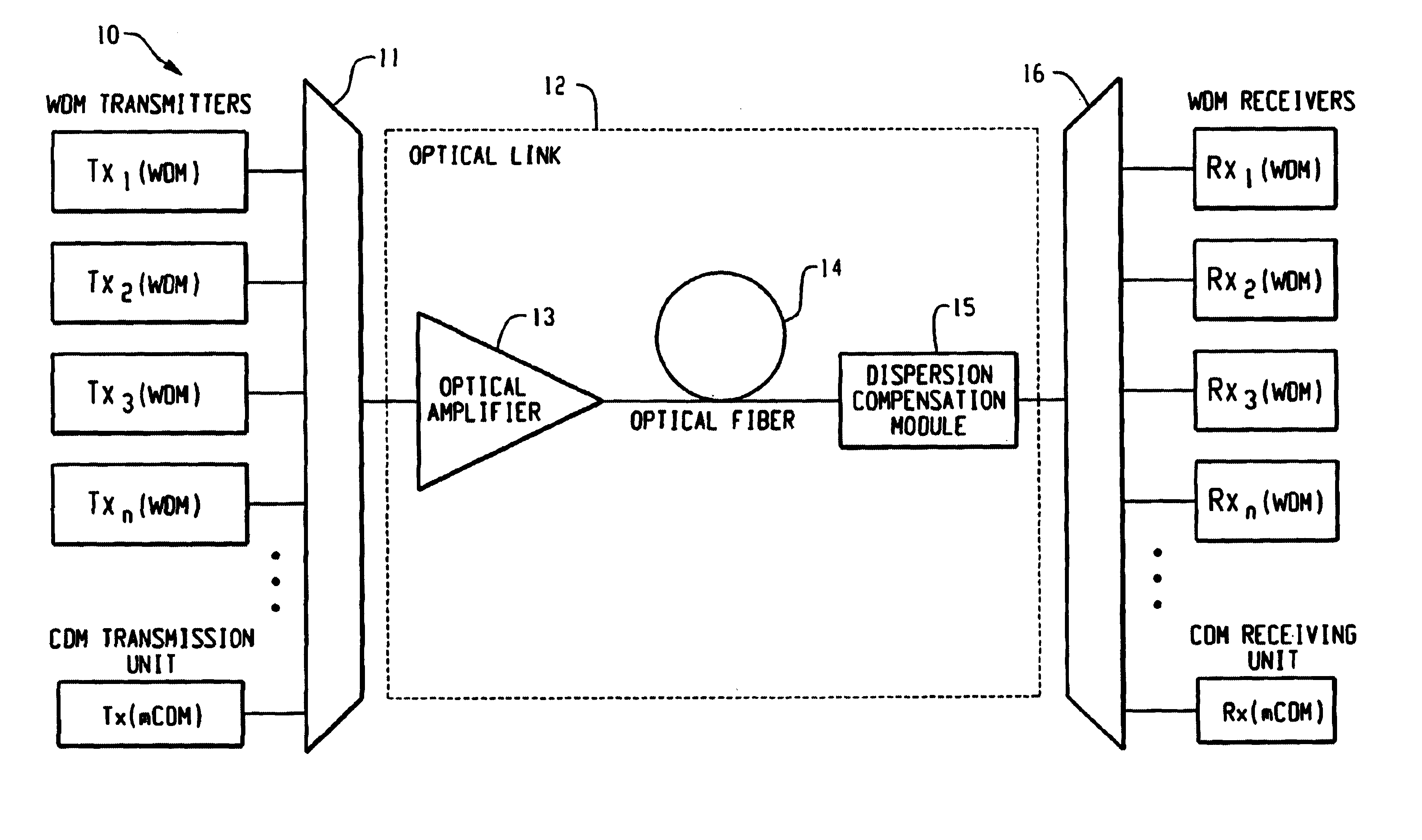
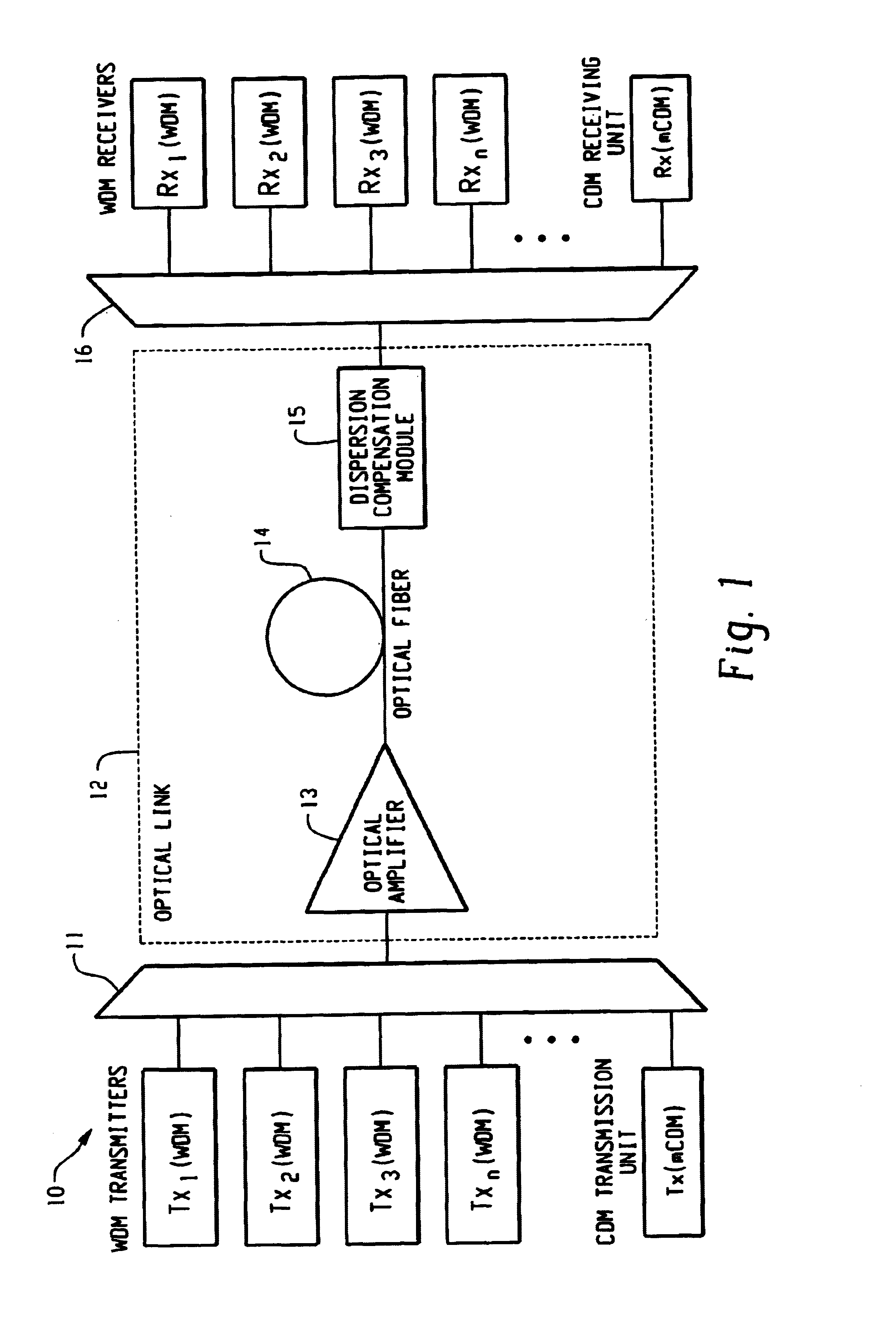
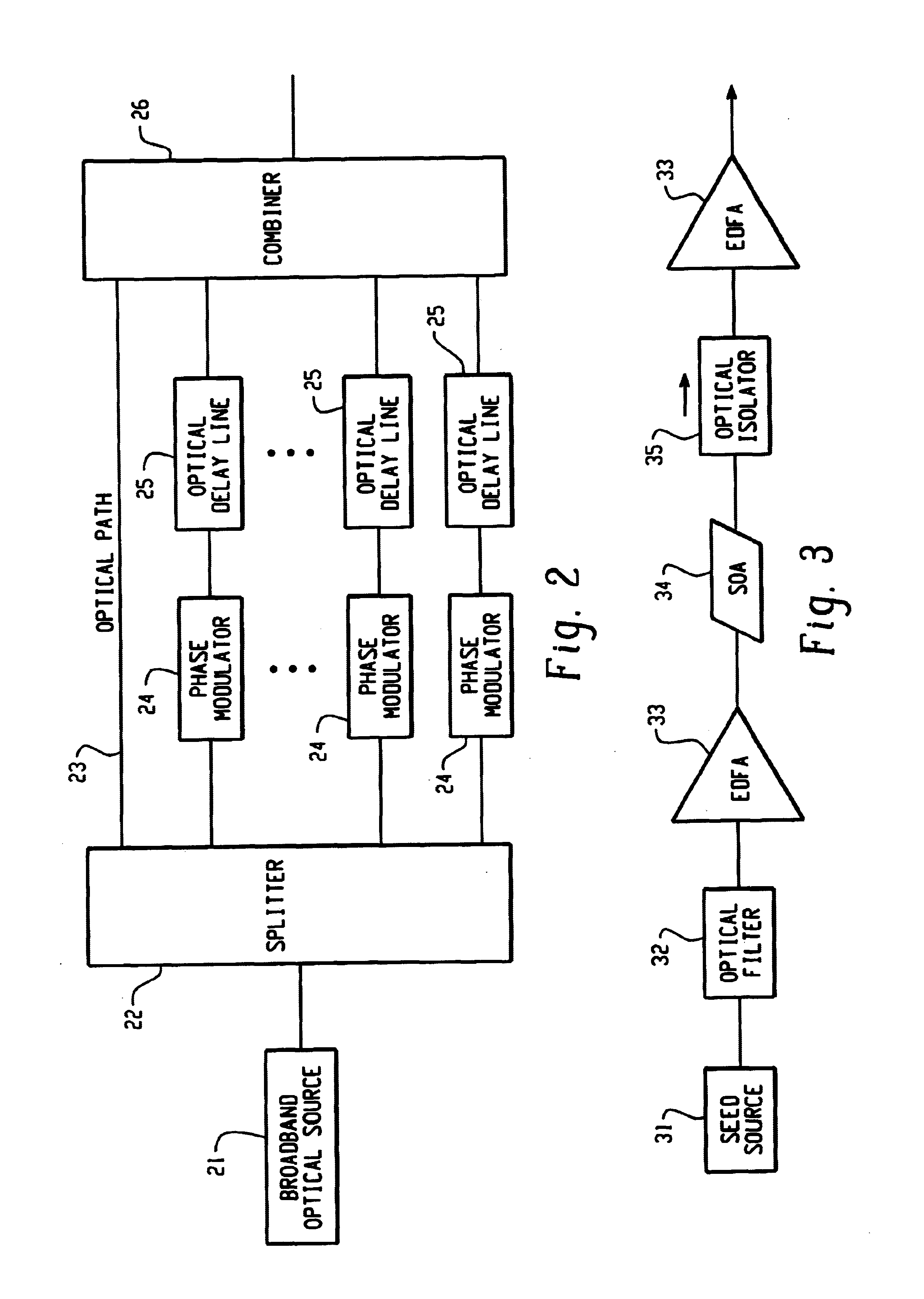
InactiveUS7061657B1Raise countVary numberTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
Method and system thereof for transmission of several coherence division multiplexed (CDM) optical signals via one wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) transmission channel of a multichannel WDM telecommunication system to extend the network capacity to a theoretical limit. A broadband optical source generates light within the spectral range of at least one WDM transmission channel. Several CDM channels share this spectral range to transmit and detect phase modulated optical signals through optical fiber links.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
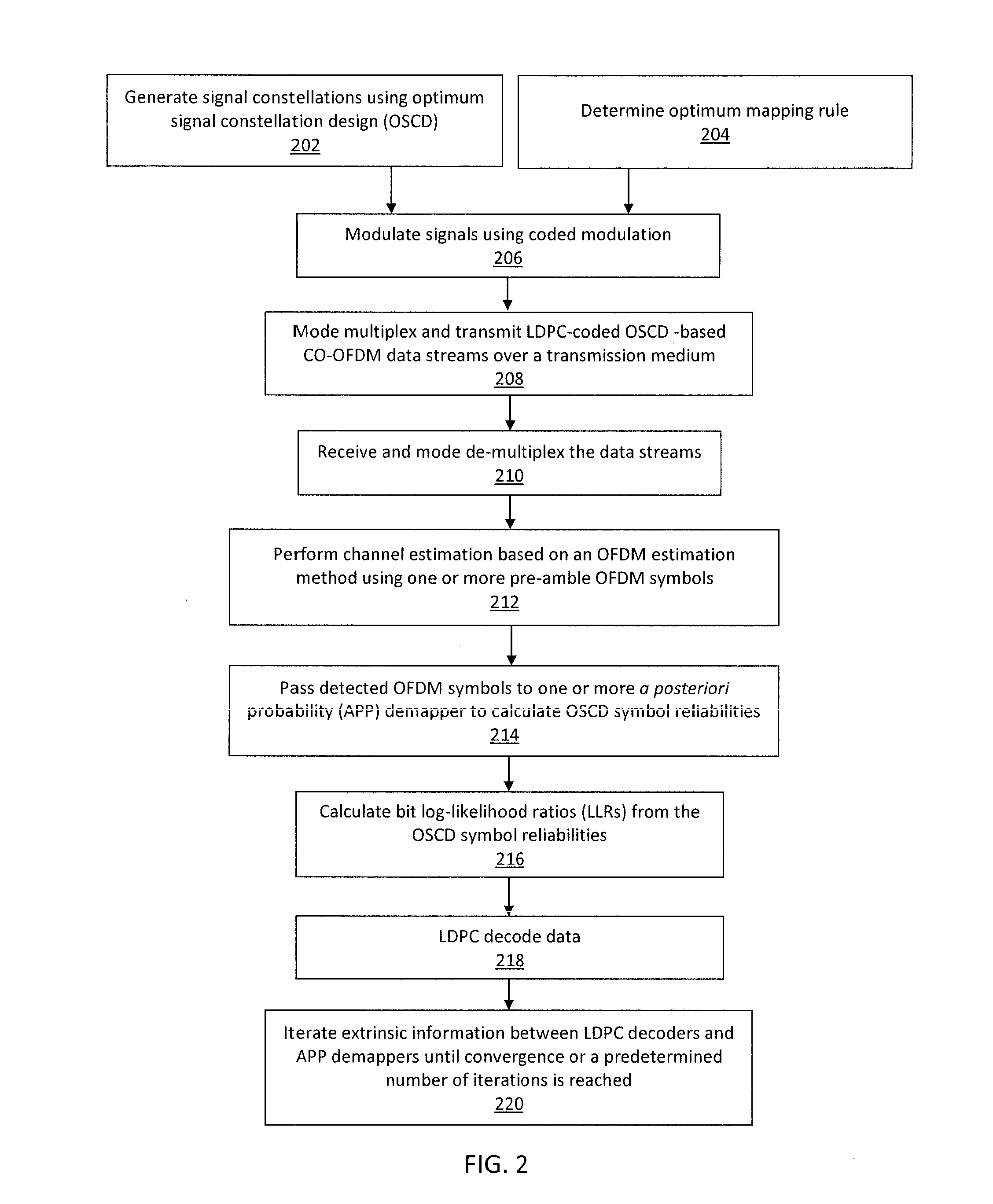
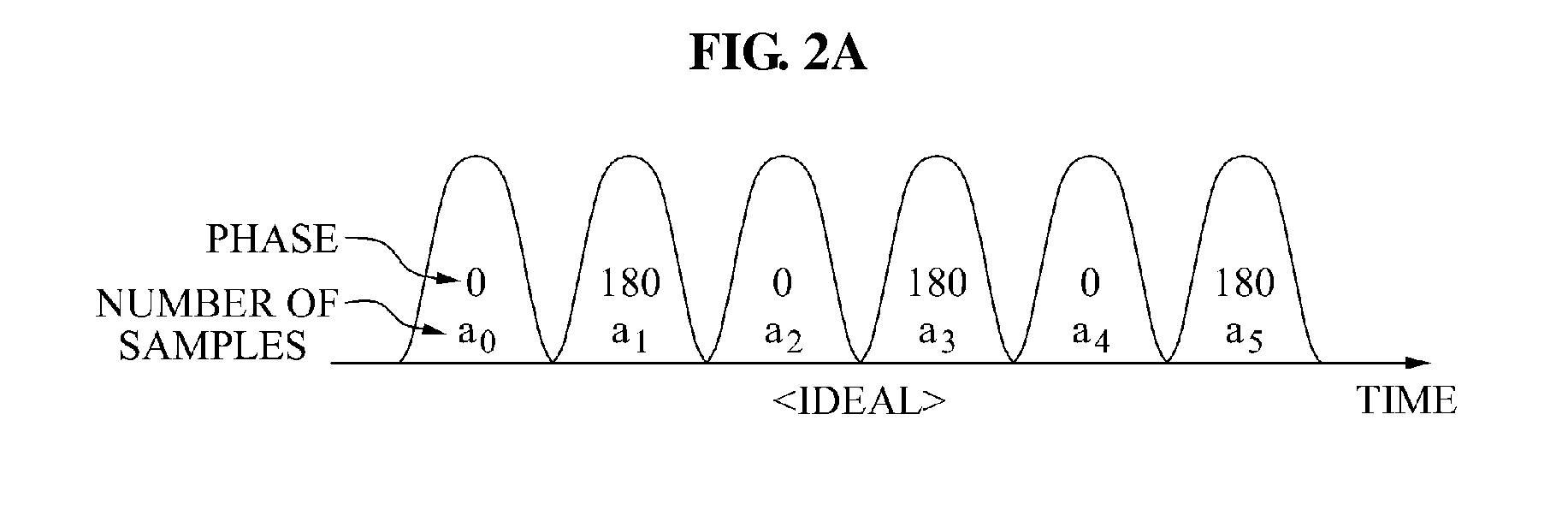
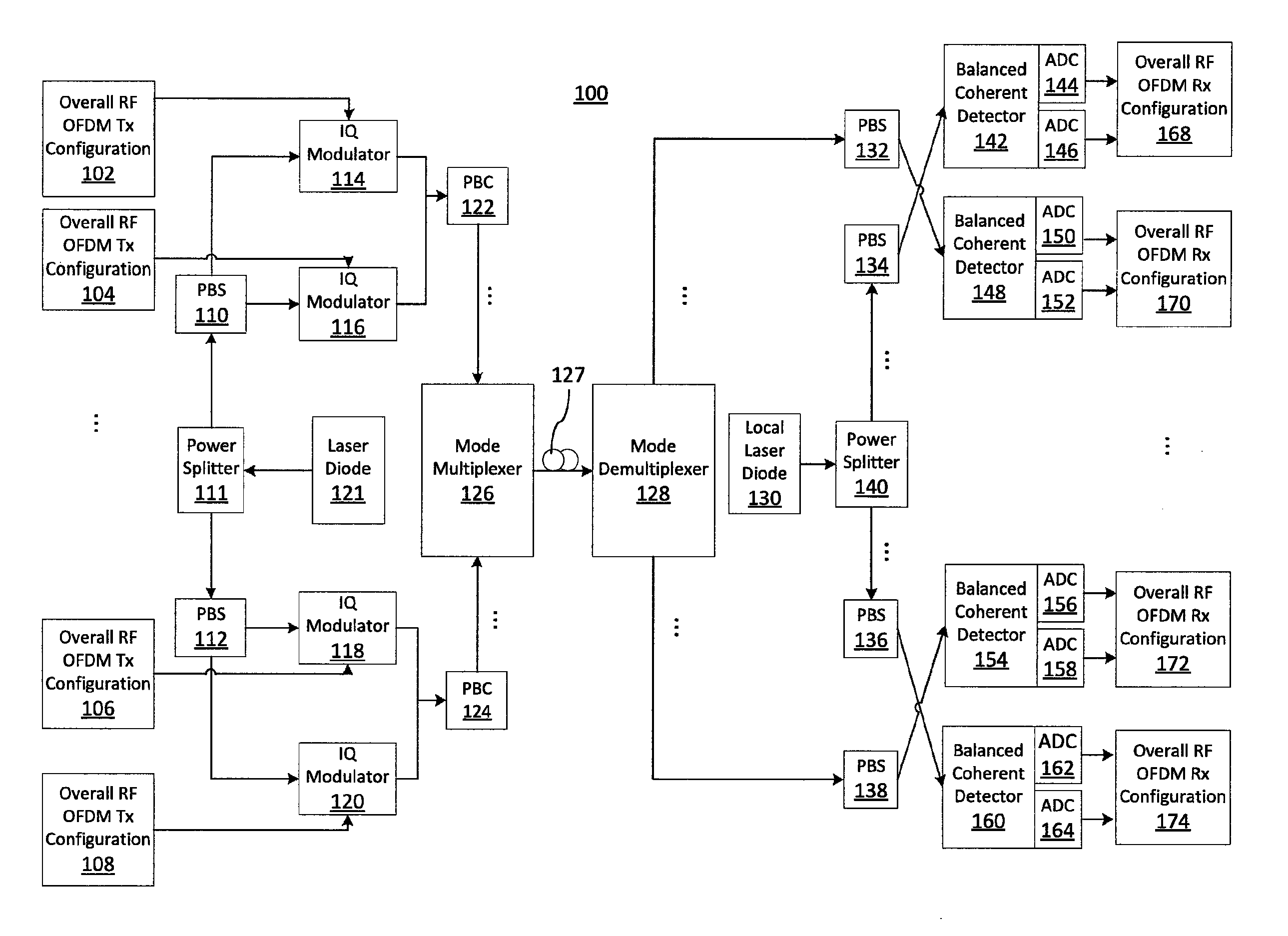
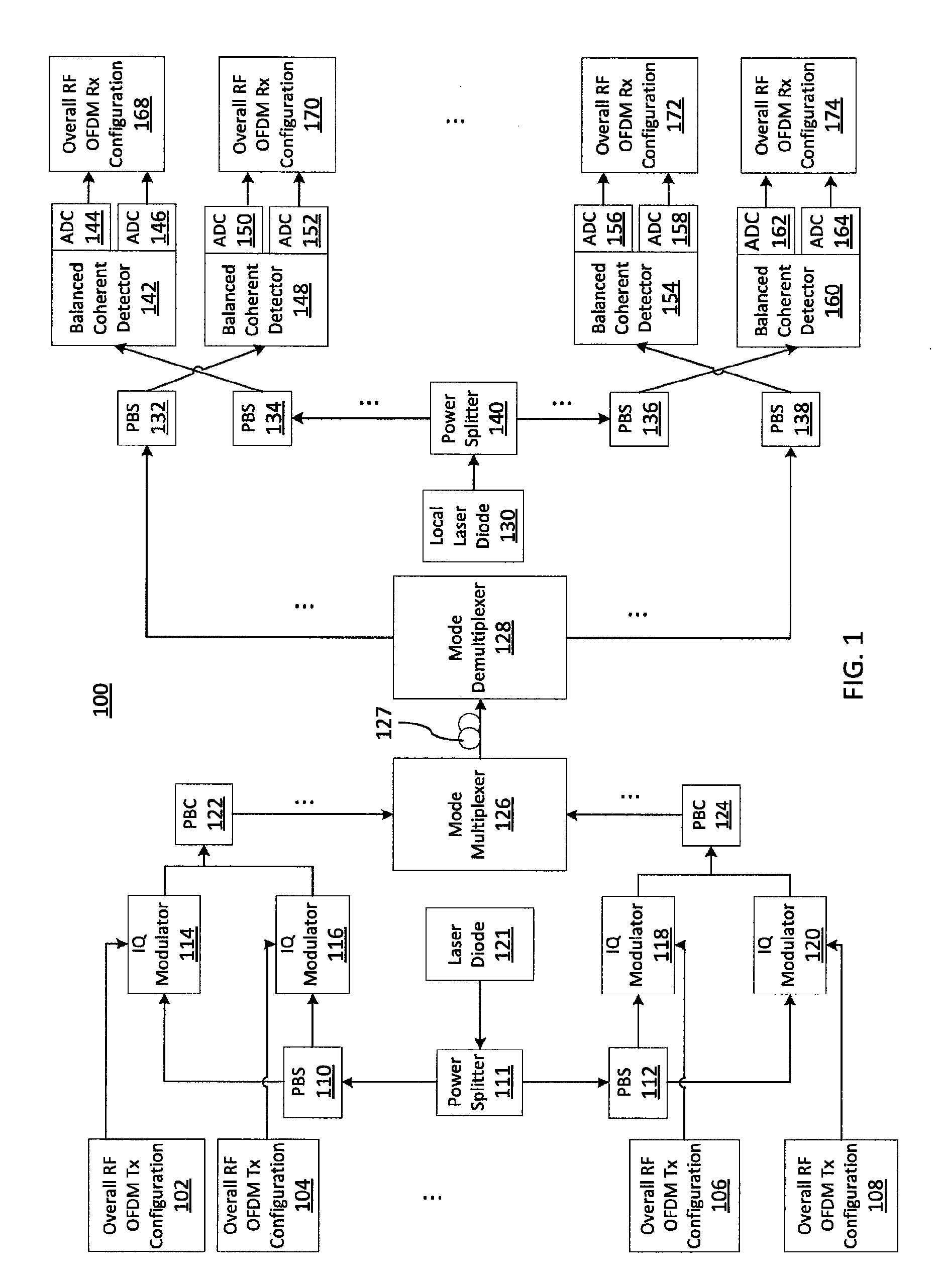
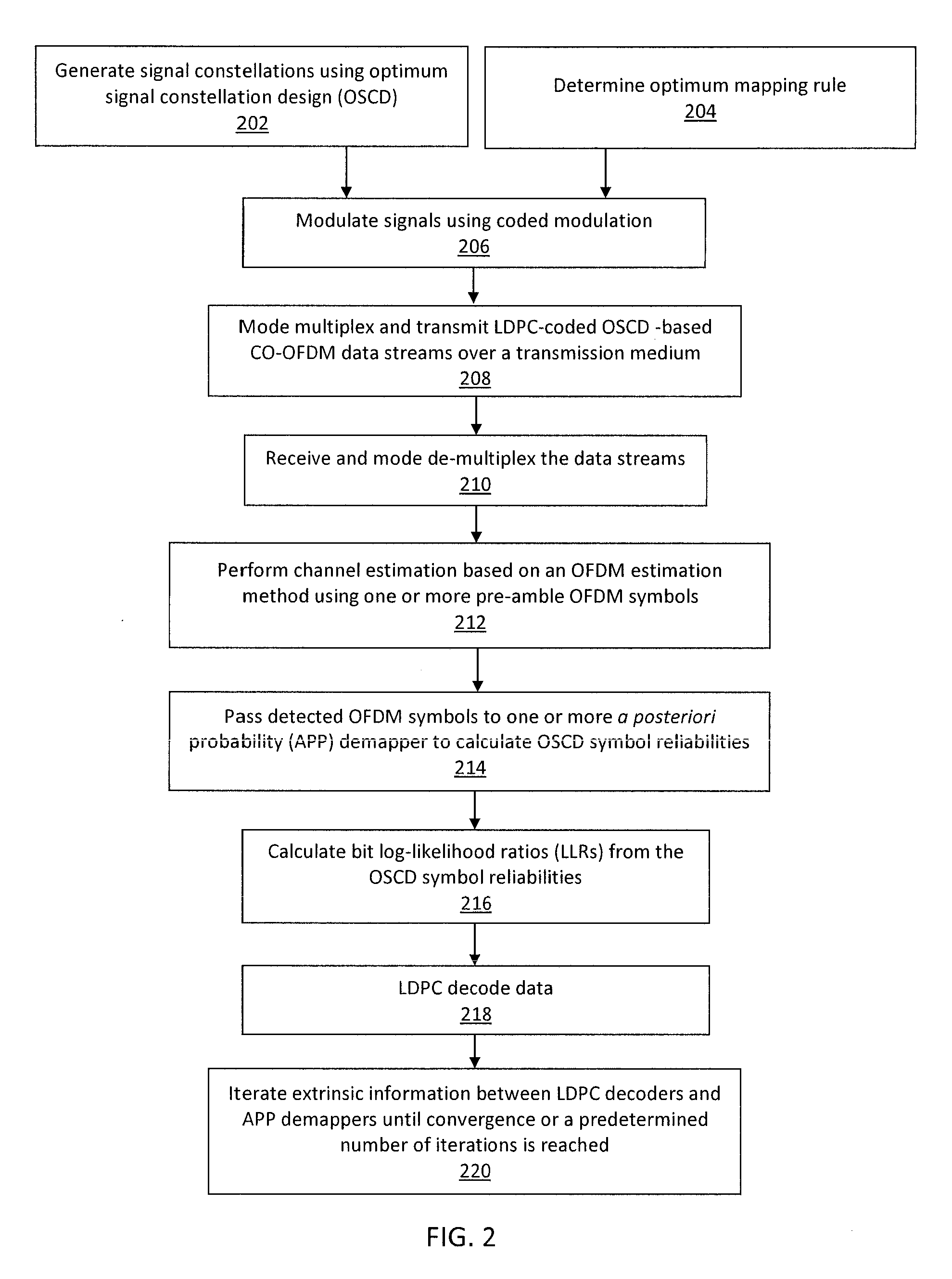
Optimum signal constellation design and mapping for few-mode fiber based ldpc-coded co-ofdm
ActiveUS20150229437A1Error correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsFew mode fiberData stream
A system / method for data transport, including encoding one or more streams of input data using one or more Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) encoders; employing one or more signal constellations obtained using an optimum signal constellation design (OSCD); determining an optimum mapping rule by comparing cost functions of each of a plurality of mapping rules; combining one or more LDPC-coded OSCD signal constellation data streams with coherent optical-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CO-OFDM) coded modulation to achieve channel capacity; and mode-multiplexing and transmitting one or more independent LDPC-coded optimum signal constellation design (OSCD) data streams over a transmission medium.
Owner:NEC CORP
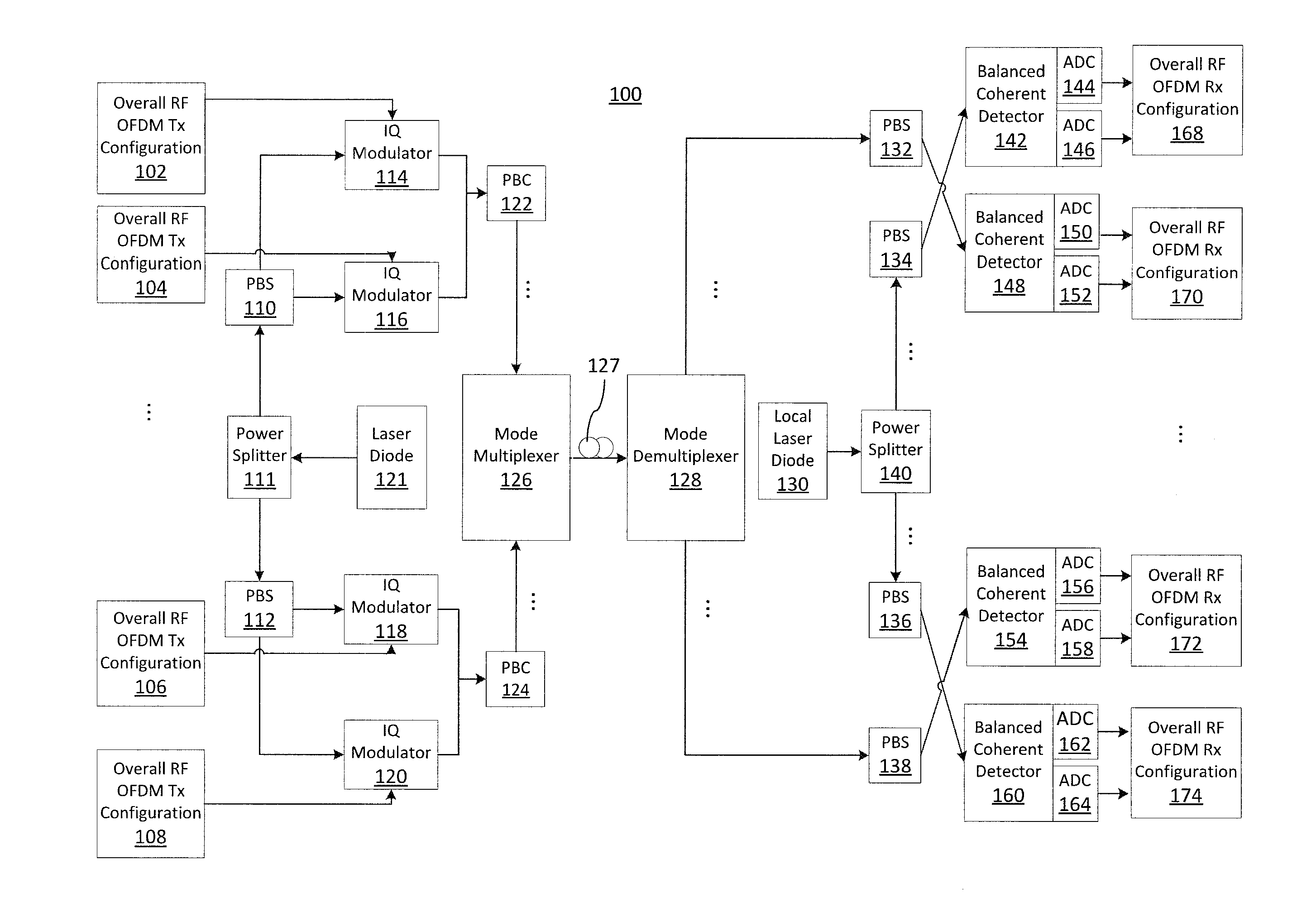
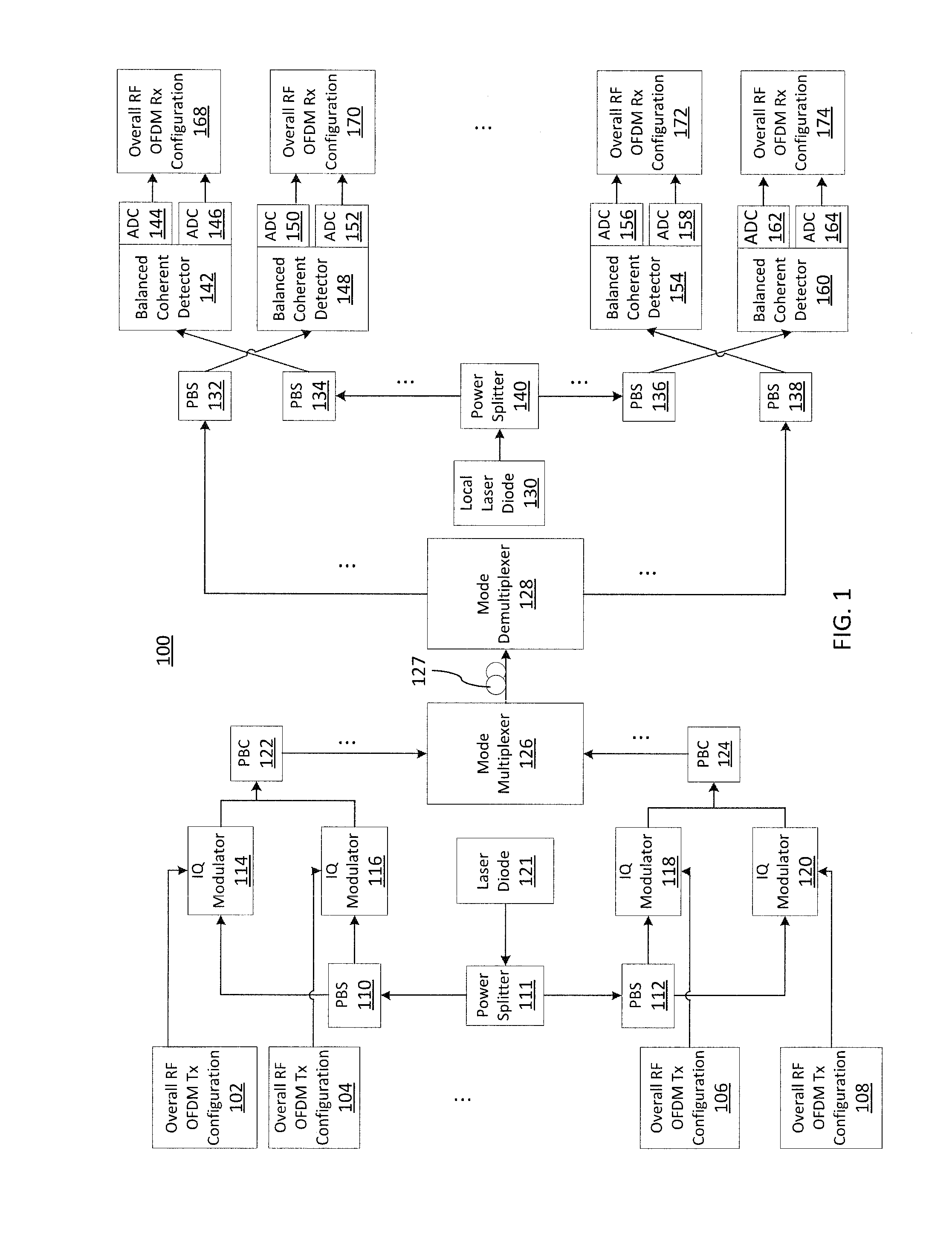
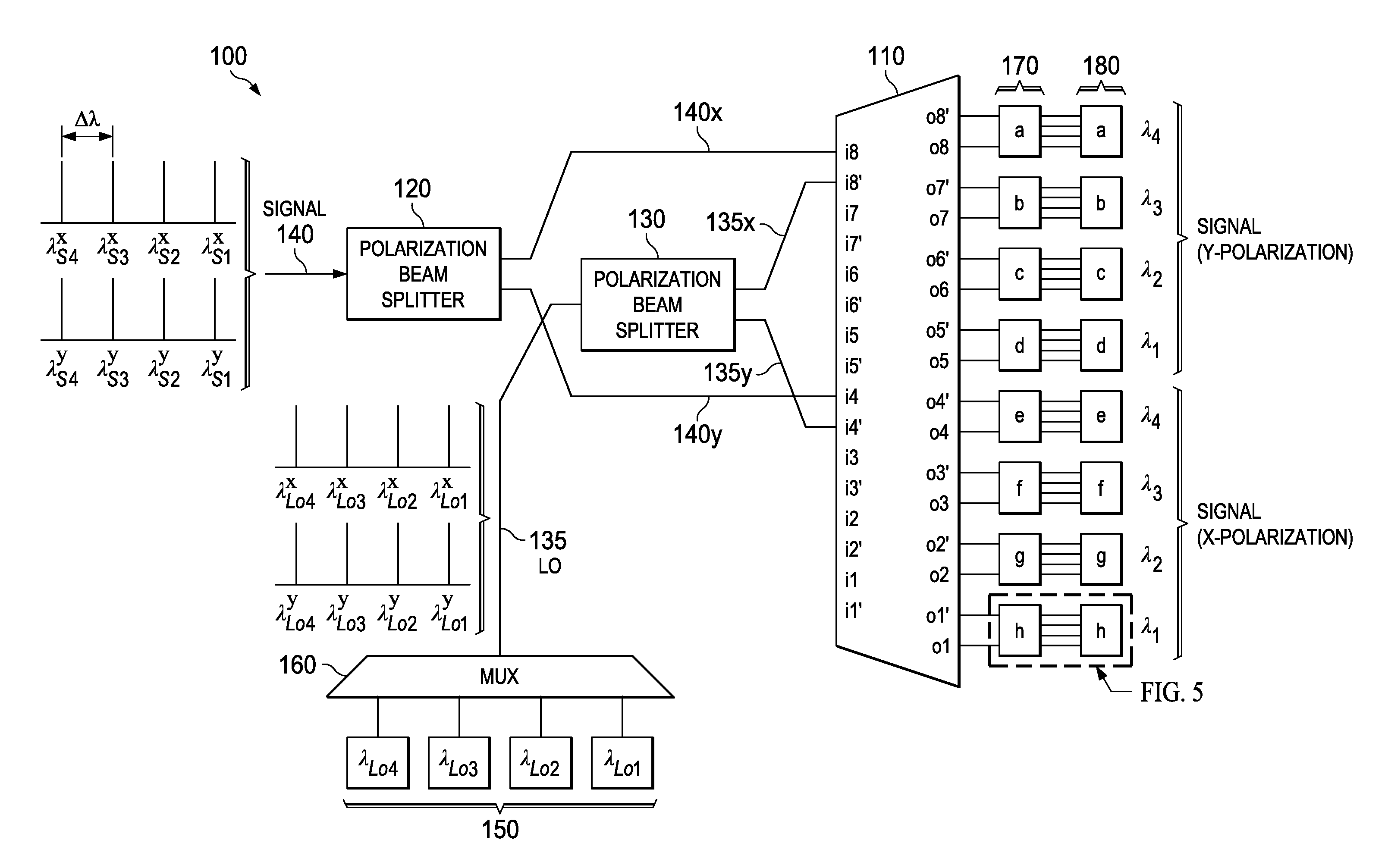
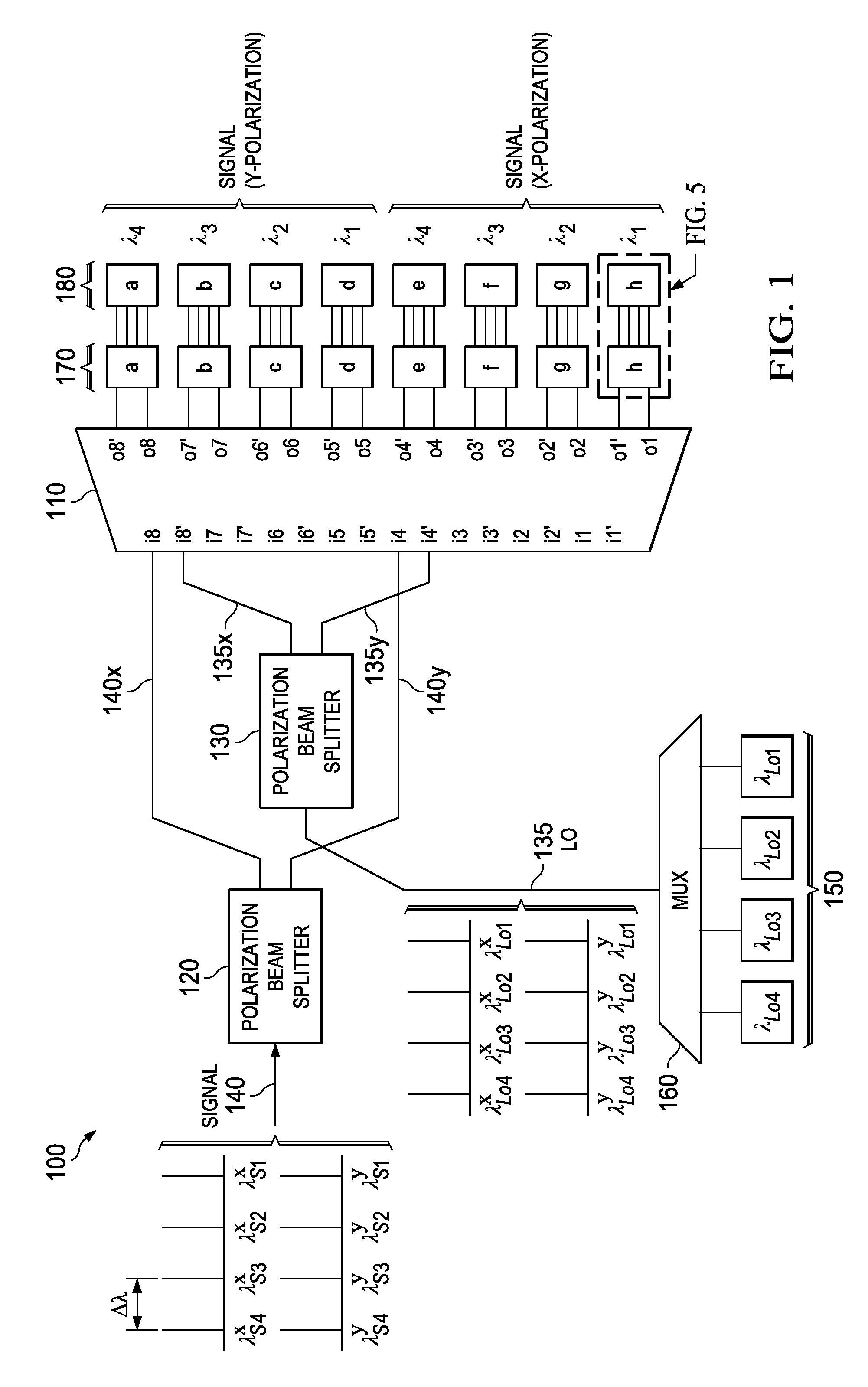
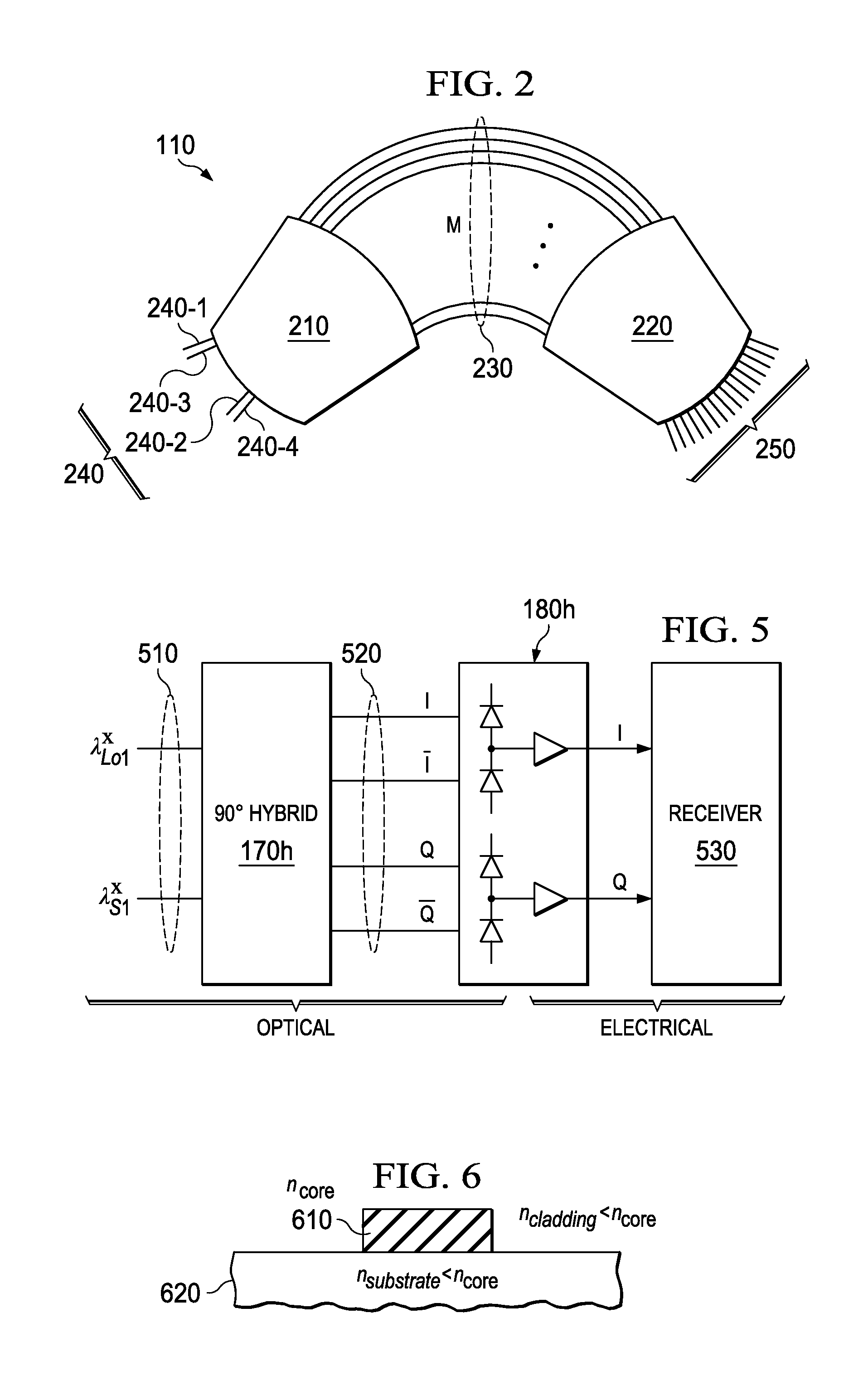
Dual-polarization multi-wavelength coherent receiver frontend
InactiveUS20130177027A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringMulti wavelength
An apparatus includes an AWG demultiplexer having first and second adjacent input ports. The first input port is configured to receive a first WDM data-bearing signal, the second input port is configured to receive a first WDM LO signal. The first and second input ports are located such that individual channels of said WDM data-bearing signal route to a first set of output ports, and individual channels of said WDM LO signal route to a second set of output ports interleaved with the first set.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
100 Gbit/s OFDM optical signal generation
ActiveUS8135287B2Polarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingPolarization multiplexedEngineering
A method includes modulating lightwaves to provide first and second OFDM signal sidebands at a first polarization direction and first and second OFDM signal sidebands at a second polarization direction, and combining sidebands that are oppositely positioned and joined from the first and second OFDM signal sidebands at each polarization direction to provide a polarization multiplexing OFDM signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical transport system employing direct-detection self-coherent receivers and compatible transmitters
ActiveUS20180294913A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransport systemCarrier signal
An optical WDM system configured to use direct detection of communication signals that is compatible with electronic CD compensation on a per-channel basis. In an example embodiment, to enable full (e.g., amplitude and phase) electric-field reconstruction at the receiver, the optical WDM system uses a carrier-frequency plan according to which the carrier-frequency comb used at one end of the WDM link and the carrier-frequency comb used at the other end of the WDM link are offset with respect to one another by one half of the bandwidth of an individual WDM component transmitted therethrough. This frequency offset places each local carrier frequency at a roll-off edge of the corresponding incoming data-modulated signal. As a result, the corresponding combined optical signal beneficially lends itself to direct detection that can be followed by full electric-field reconstruction using a known self-coherent Kramers-Kronig method and then by conventional electronic CD compensation.
Owner:NOKIA OF AMERICA CORP
Optical transport system employing direct-detection self-coherent receivers and compatible transmitters
InactiveUS10404400B2Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransport systemCarrier signal
An optical WDM system configured to use direct detection of communication signals that is compatible with electronic CD compensation on a per-channel basis. In an example embodiment, to enable full (e.g., amplitude and phase) electric-field reconstruction at the receiver, the optical WDM system uses a carrier-frequency plan according to which the carrier-frequency comb used at one end of the WDM link and the carrier-frequency comb used at the other end of the WDM link are offset with respect to one another by one half of the bandwidth of an individual WDM component transmitted therethrough. This frequency offset places each local carrier frequency at a roll-off edge of the corresponding incoming data-modulated signal. As a result, the corresponding combined optical signal beneficially lends itself to direct detection that can be followed by full electric-field reconstruction using a known self-coherent Kramers-Kronig method and then by conventional electronic CD compensation.
Owner:NOKIA OF AMERICA CORP
Digital phase conjugation for fiber-optic links
InactiveUS8594515B2Good effectImprove toleranceModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical phase conjugationNon-linear effects
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
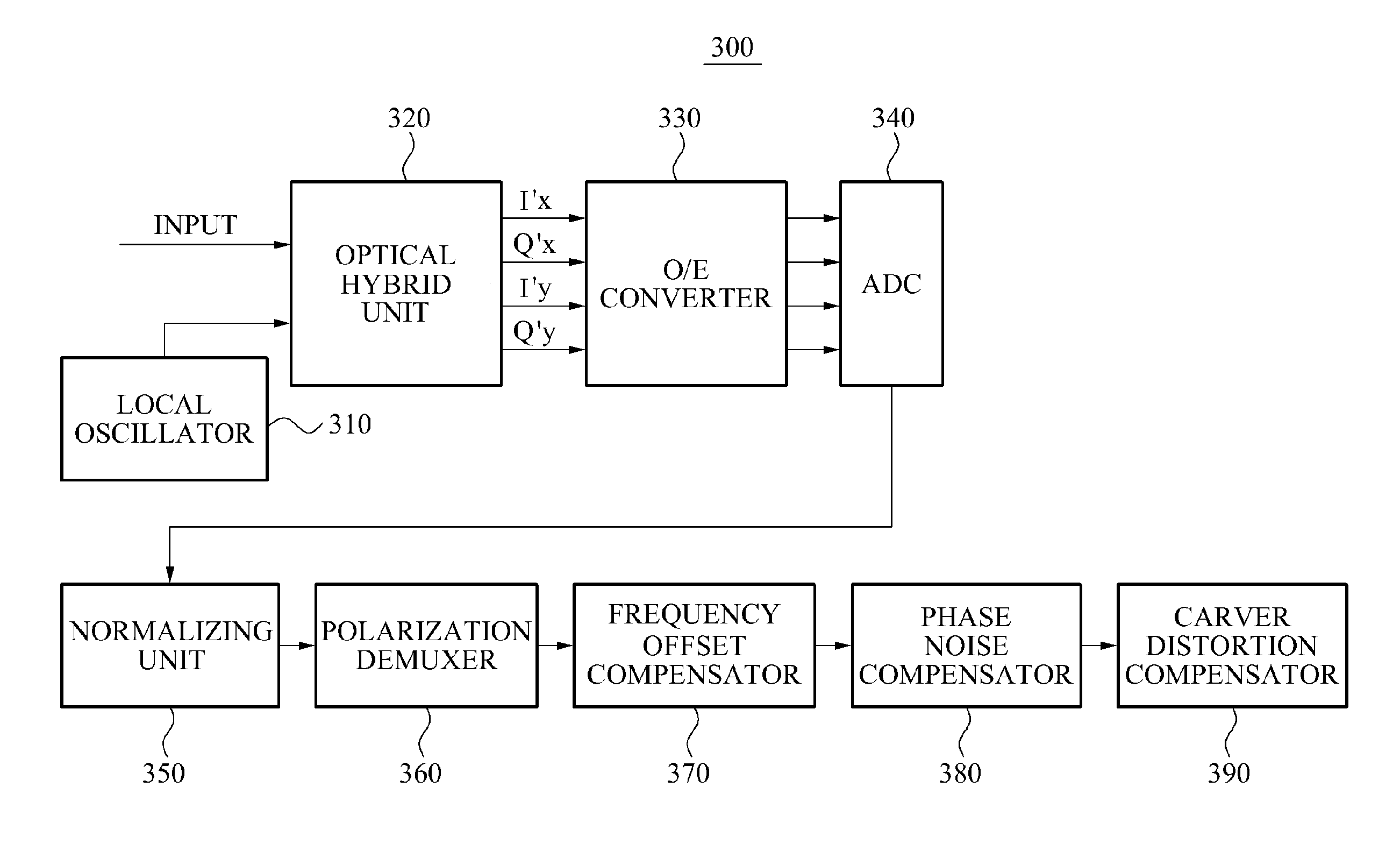
Coherent optical receiving apparatus and optical signal processing method
Provided is a coherent optical receiving apparatus and an optical signal processing method. The coherent optical receiving apparatus may include an optical hybrid unit to generate an optical signal by combining a first optical signal inputted from an optical transmitting apparatus and a second optical signal inputted from a local oscillator, a polarization demuxer to demultiplex the optical signal outputted from the optical hybridizing unit, a frequency offset compensator to estimate a frequency offset of at least one of even-numbered samples and odd-numbered samples, and to compensate for a frequency offset of the even-numbered samples and a frequency offset of the odd-numbered samples using the at least one estimated frequency offset, and a carver distortion compensator to compensate for phase distortions of the samples for which the compensation for the frequency offset is performed, the phase distortions being generated by the optical transmitting apparatus.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
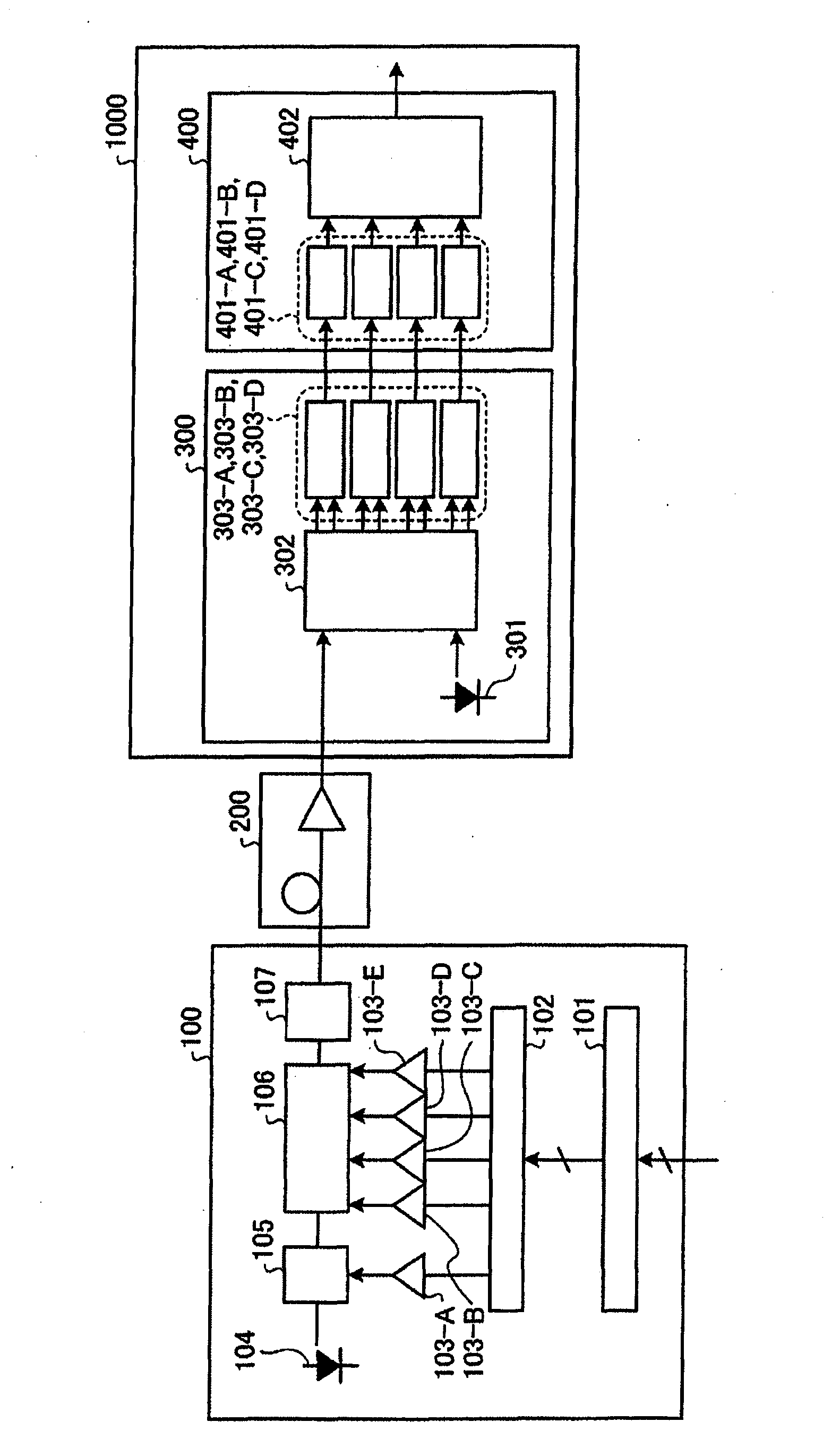
Optical transport system, optical transmitter device and optical receiver device
InactiveCN103141037AReduce nonlinear interferenceImprove delivery qualityPolarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingTransport systemLocal oscillator
In an optical transport system as laid out in the present invention: at an optical transmitter unit (100), an optical signal is generated such that each polarization component is present so as to be interleaved upon a time axis, wherein the time during which the polarization components are simultaneously present is approximately zero, and the symbol repeating period of the optical signal of each polarization component becomes Ts; at an optical receiver unit (300), after a local oscillator light and the received optical signal are caused to interfere with each other, the optical signal after interference is converted to an electrical signal; and at a received electrical signal processing unit (400), analog / digital conversion of the electrical signal, removal of a delay difference of Ts / 2 between each polarization signal component, and adaptive equalization of distortion of other than the delay differences are performed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Coherent optical receiving apparatus and optical signal processing method
InactiveUS20120070149A1Accurate estimateImprove performancePolarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingPhase distortionLocal oscillator
Provided is a coherent optical receiving apparatus and an optical signal processing method. The coherent optical receiving apparatus may include an optical hybrid unit to generate an optical signal by combining a first optical signal inputted from an optical transmitting apparatus and a second optical signal inputted from a local oscillator, a polarization demuxer to demultiplex the optical signal outputted from the optical hybridizing unit, a frequency offset compensator to estimate a frequency offset of at least one of even-numbered samples and odd-numbered samples, and to compensate for a frequency offset of the even-numbered samples and a frequency offset of the odd-numbered samples using the at least one estimated frequency offset, and a carver distortion compensator to compensate for phase distortions of the samples for which the compensation for the frequency offset is performed, the phase distortions being generated by the optical transmitting apparatus.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optimum signal constellation design and mapping for few-mode fiber based LDPC-coded CO-OFDM
ActiveUS9203555B2Error correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsFew mode fiberData stream
Owner:NEC CORP
Orthogonal intersection amplitude modulation signal phase ambiguity processing method and apparatus
ActiveCN106301589AReduce error rateReduce overheadPolarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingAmbiguitySymbol of a differential operator
The invention provides an orthogonal intersection amplitude modulation signal phase ambiguity processing method and apparatus. The phase ambiguity processing method comprises steps of judging symbols in the X polarization state and the Y polarization state of a reception signal, and carrying out mapping to obtain first bit information, wherein the reception signal comprises multiple first signals; carrying out verification analysis of the first bit information to generate a first verification result; judging the first verification result to obtain a judgment result that whether phase ambiguity occurs to the reception signal or not; when the judgment result shows that phase ambiguity occurs to the reception signal, obtaining at least one first signal in the reception signal; subjecting the first signal to phase rotation to obtain a second signal; carrying out verification analysis of the second signal, storing the second signal if the verification result is normal, and enabling the second signal to be used for decoding instead of the first signal. In the verification of the QAM signal, the QAM signal is corrected when phase ambiguity exists, so that the error rate of QAM signal differential decoding is lowered, the system expense is reduced, and the system performance is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Optical transmitter, optical communication system, and optical communication method
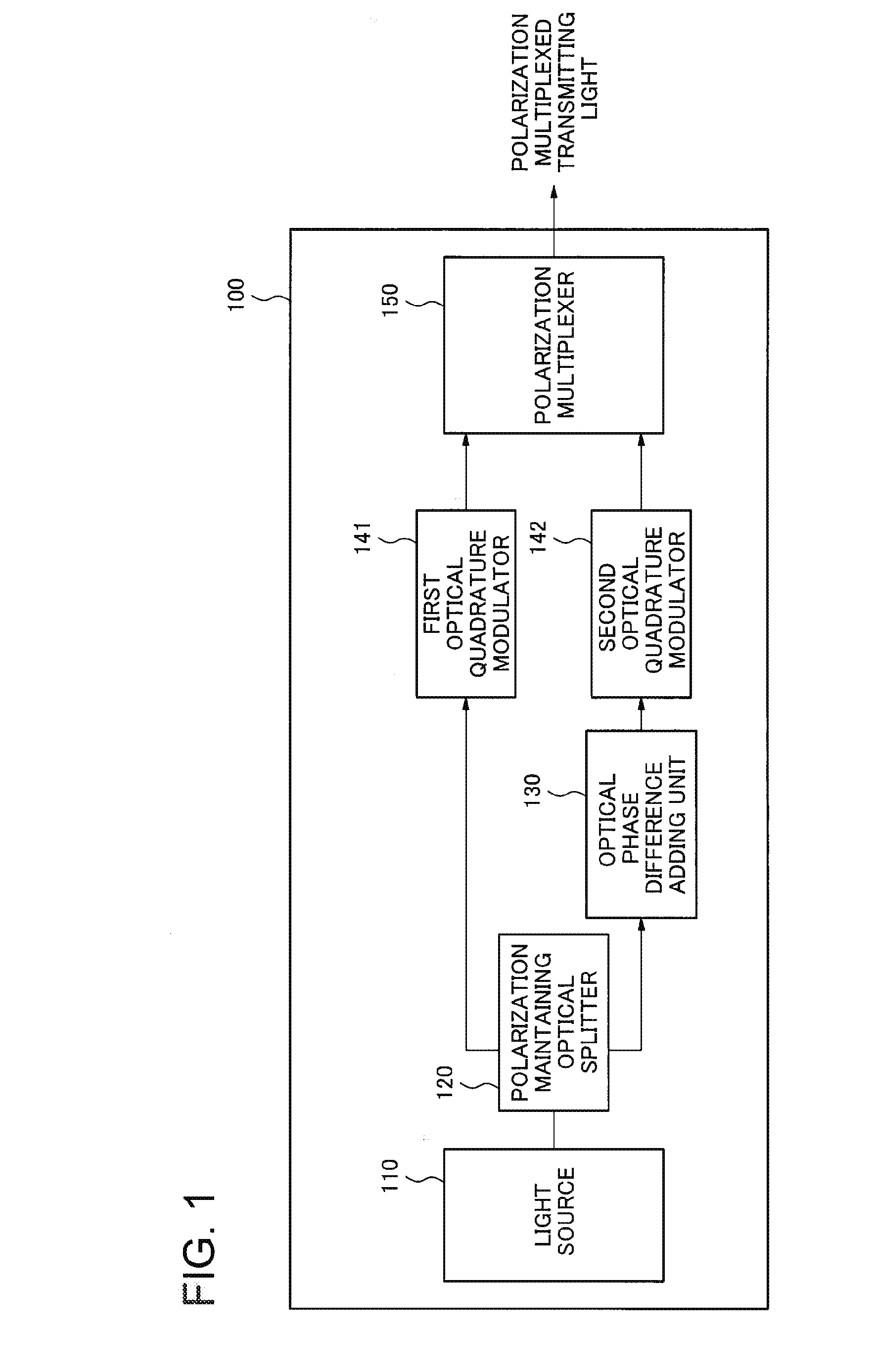
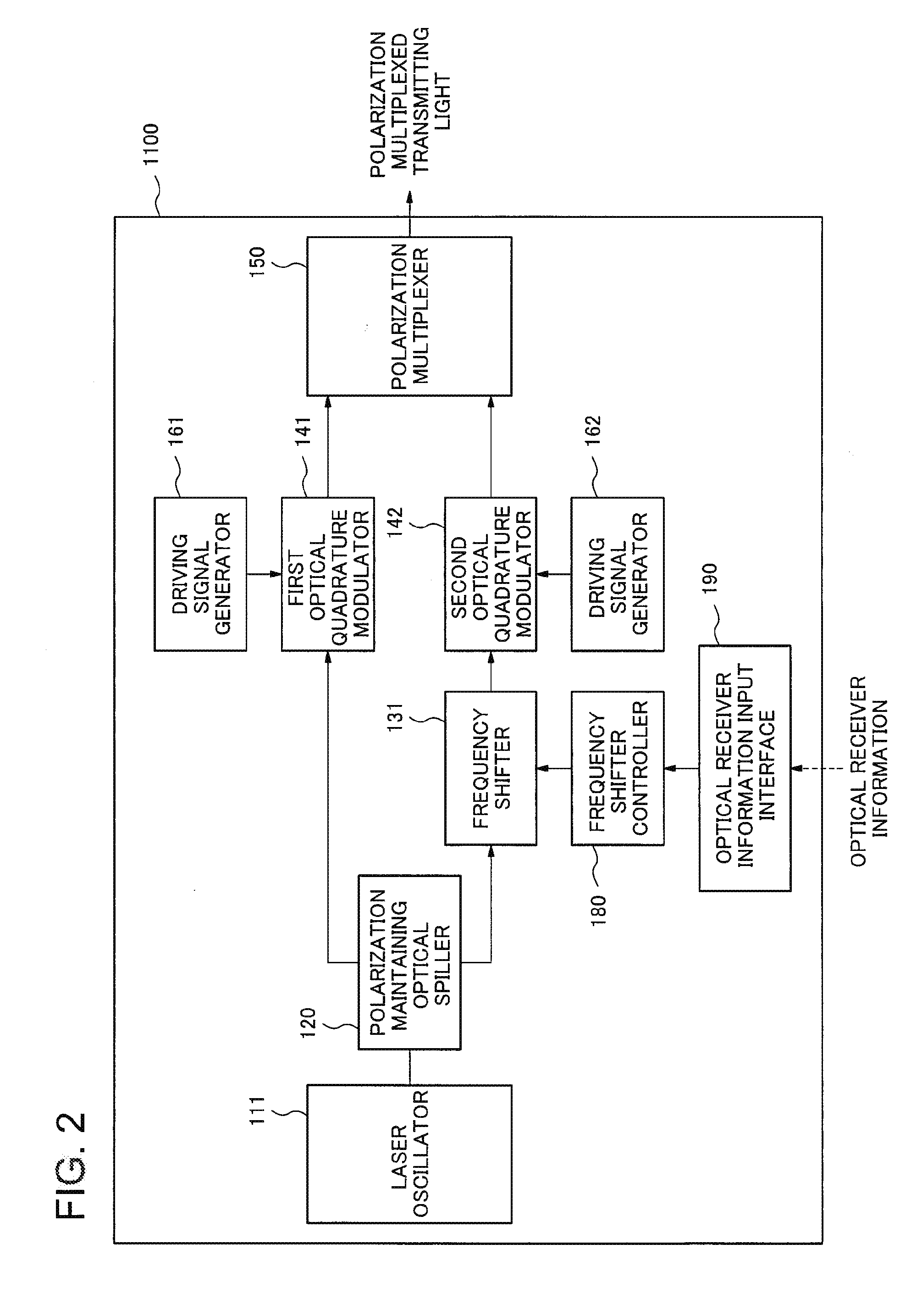
ActiveUS20150030330A1Polarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingContinuous lightPhase difference
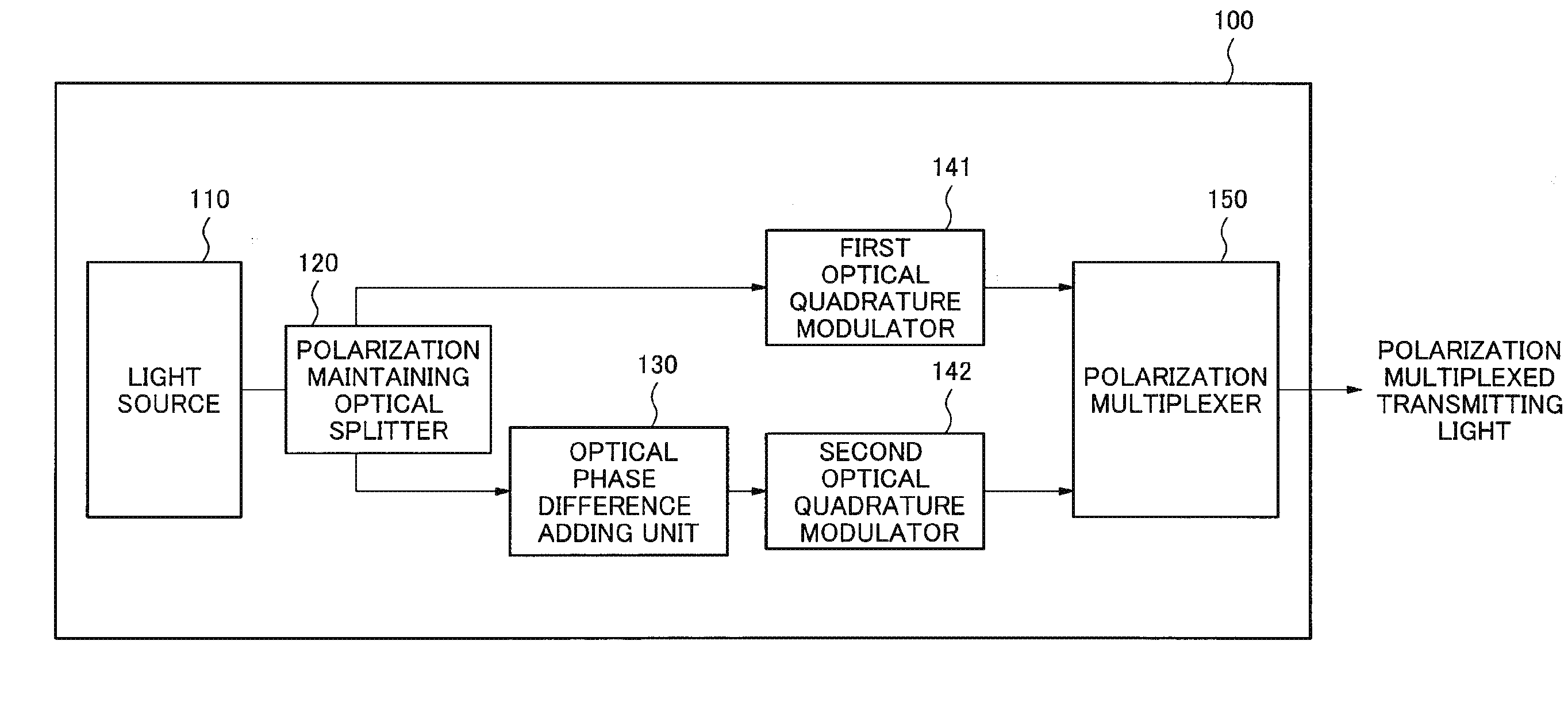
It becomes difficult to regenerate transmitting signals depending on modulation systems for the optical phase modulation in a polarization multiplexed optical communication system employing the optical digital coherent communication system, therefore, an optical transmitter according to an exemplary aspect of the invention includes first optical quadrature modulation means for performing a phase modulation on a first continuous light beam and outputting a first transmitting light beam; second optical quadrature modulation means for performing a phase modulation on a second continuous light beam belonging in the same frequency band as that of the first continuous light beam and outputting a second transmitting light beam; optical phase difference adding means for adding an optical phase difference varying temporally between the first transmitting light beam and the second transmitting light beam; and polarization multiplexing means for polarization-multiplexing the first transmitting light beam and the second transmitting light beam in the state where their polarizations are made to be orthogonal to each other and outputting a polarization multiplexed transmitting light beam.
Owner:NEC CORP
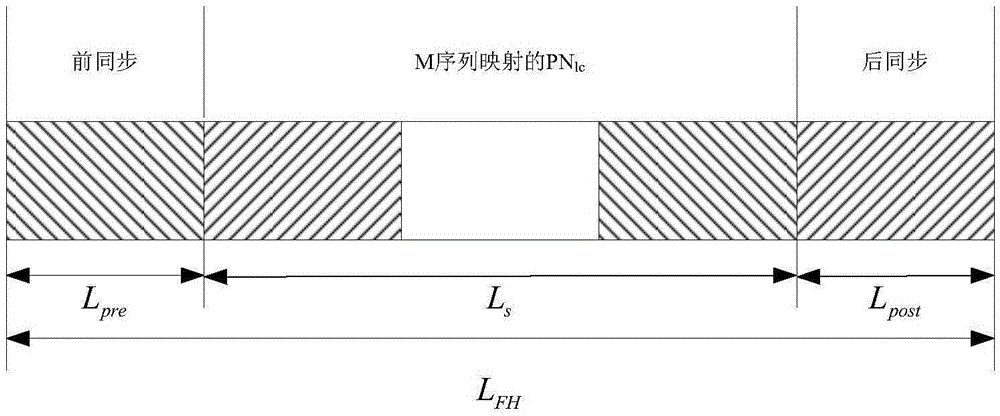
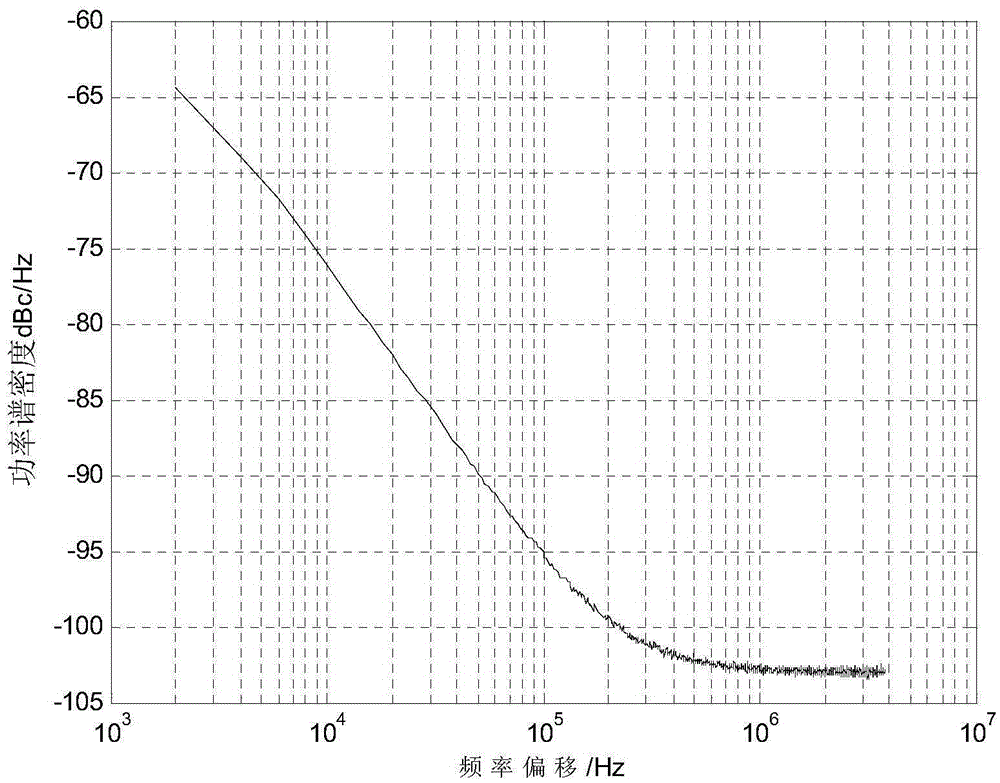
Combined suppression method of ISI and phase noise in TDS-OFDM communication system
InactiveCN105610539AReduce distractionsCoherence multiplexingMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainPhase noise
The invention discloses a combined suppression method of ISI and phase noise in a TDS-OFDM communication system. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out synchronization processing to received signals; extracting a PN sequence; carrying out channel estimation processing; carrying out phase noise primary estimation and suppression processing to the synchronized receivedsignals, thus obtaining first denoised frequency domain signals, first output signals and first denoised time domain signals; obtaining a current time domain sign based on the current first output signals; repeatedly executing ISI elimination processing to the first denoised time domain signals based on the trailing of the PN part and the current time domain sign until reaching a preset end condition; carrying out hard decision and IDFT conversion to the current first output signals; reconstructing time domain transmitting signals; obtaining a second phase noise estimation value based on the time domain transmitting signals; carrying out phase noise elimination processing and ISI elimination processing to the data part of the received signals; and outputting the final result. In application of the method disclosed by the invention, the phase noise interference existing in the present ISI compensation method can be effectively reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Systems and methods for full duplex coherent optics
ActiveUS20200044765A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingTransceiverEngineering
A full duplex communication network includes an optical transmitter end having a first coherent optics transceiver, an optical receiver end having a second coherent optics transceiver, and an optical transport medium operably coupling the first coherent optics transceiver to the second coherent optics transceiver. The first coherent optics transceiver is configured to simultaneously transmit a downstream optical signal and receive an upstream optical signal. The second coherent optics transceiver is configured to simultaneously receive the downstream optical signal from the first coherent optics transceiver and transmit the upstream optical signal first coherent optics transceiver. At least one of the downstream optical signal and the upstream optical signal includes at least one coherent optical carrier and at least one non-coherent optical carrier.
Owner:CABLE TELEVISION LAB
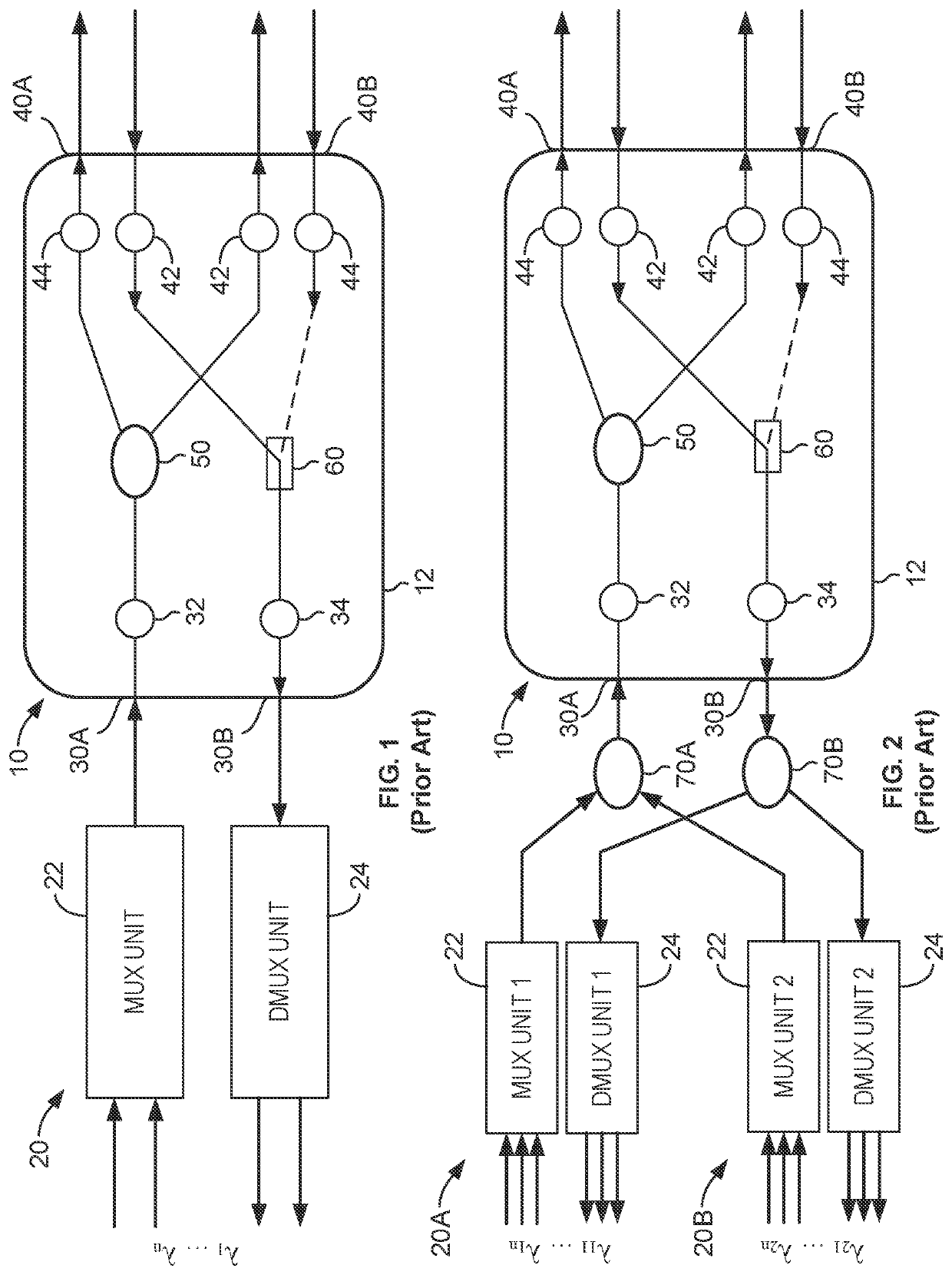
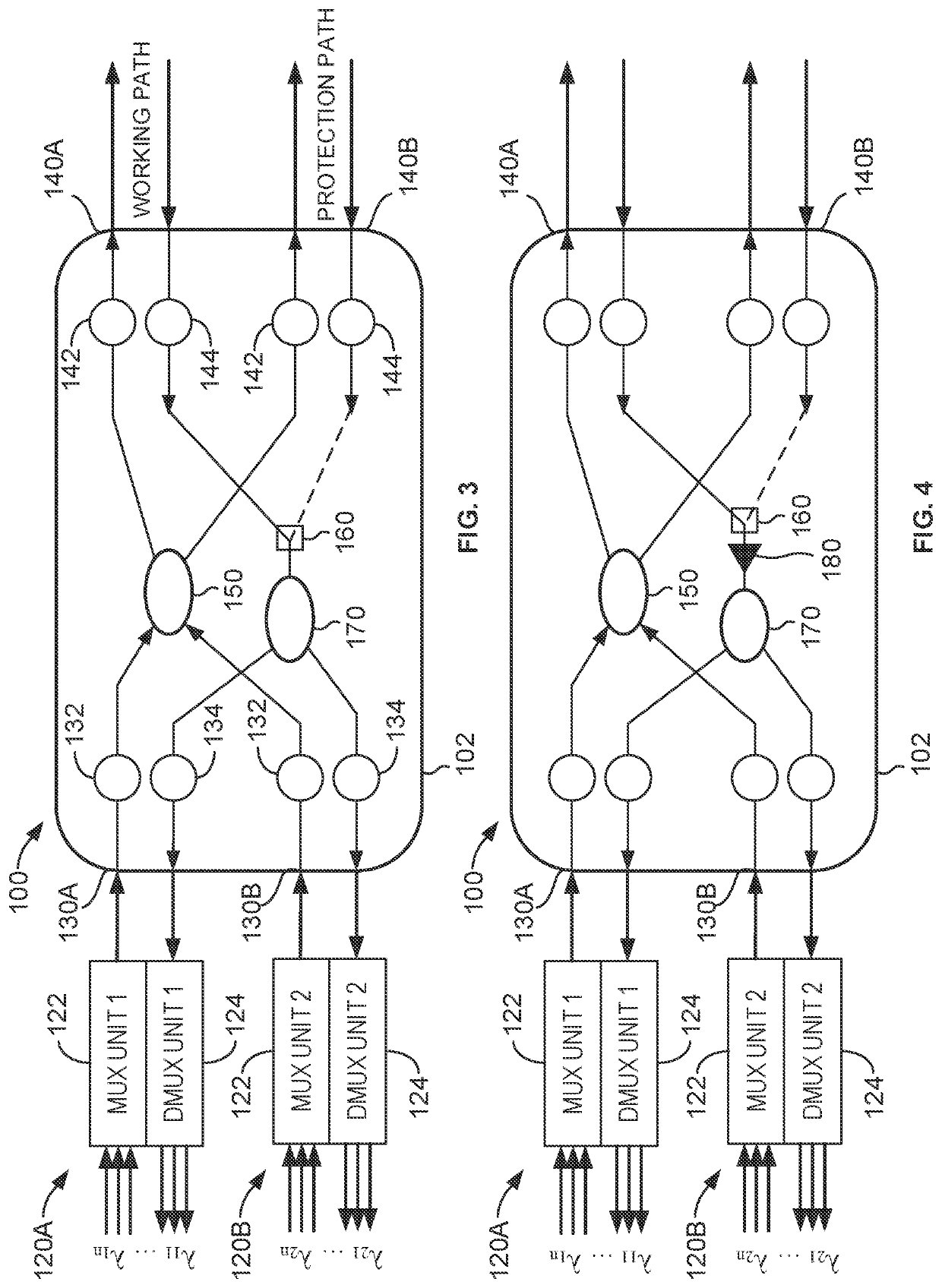
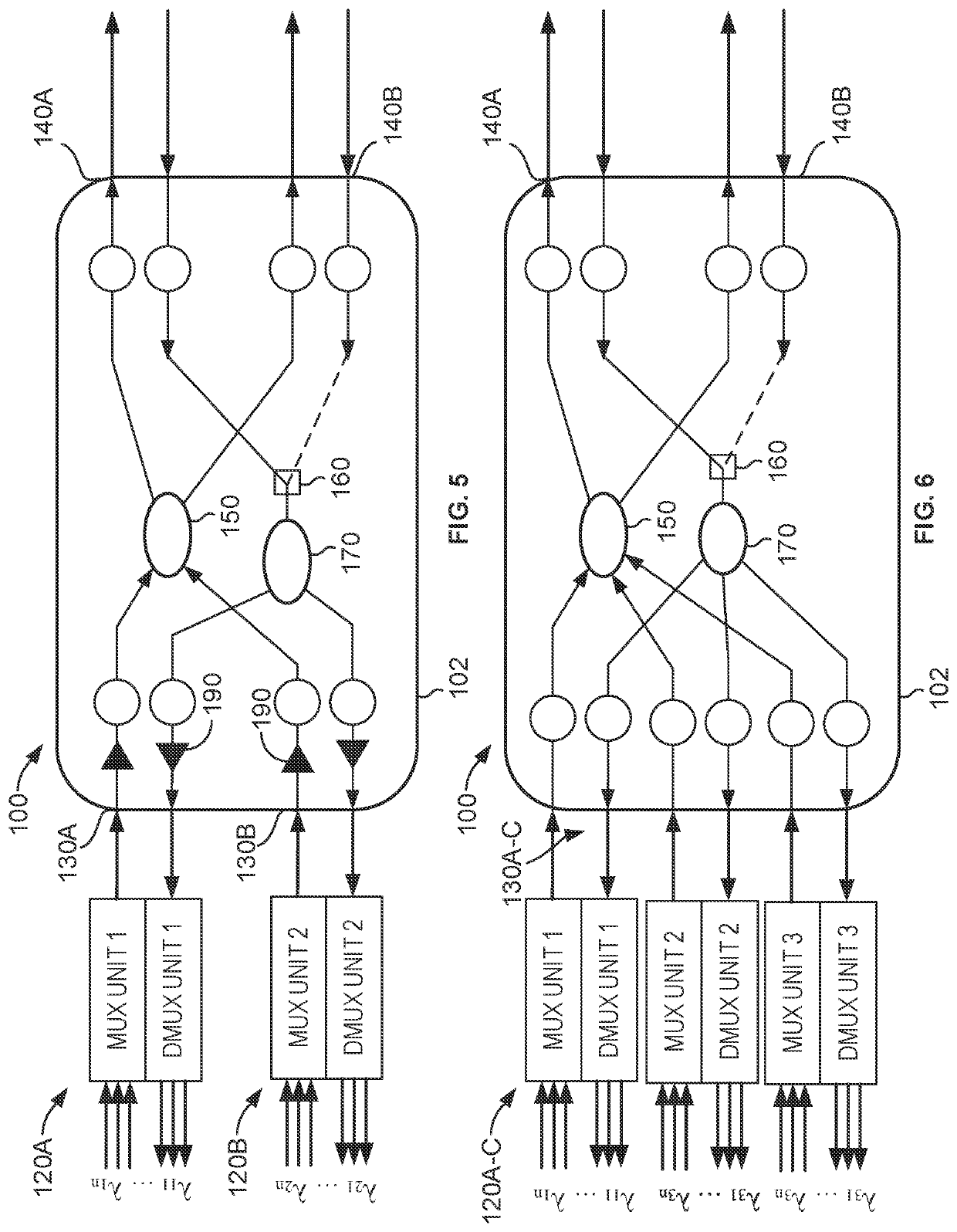
Apparatus and method for coherent optical multiplexing 1+1 protection
ActiveUS11374673B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingMultiplexingMultiplexer
Coherent optical multiplexing 1+1 protection disclosed herein uses multiplexers, each having multiplexing and demultiplexing sub-units. Relay ports of a node are connected with the multiplexers, and each relay port is configured to input and output optical signals with the corresponding multiplexer. Two transmission ports of the node are connected with disjoint paths and are configured to input and output optical signals therewith. The node includes: a first optical splitter having input ports connected with the relay ports and two output ports connected with the two transmission ports; an optical switch connected with the transmission ports respectively via two input interfaces; a second optical splitter, which is a 1×N optical splitter, having one input port connected with an output interface of the optical switch and having output ports connected with the relay ports. The solution is reliable in implementation, has low insertion loss, and has good transmission performance.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Systems and methods for dual-band modulation and injection-locking for coherent PON
ActiveUS20190393974A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingInjection lockedDual frequency
An optical communication network includes a downstream optical transceiver. The downstream optical transceiver includes at least one coherent optical transmitter configured to transmit a downstream coherent dual-band optical signal having a left-side band portion, a right-side band portion, and a central optical carrier disposed within a guard band between the left-side band portion and the right-side band portion. The network further includes an optical transport medium configured to carry the downstream coherent dual-band optical signal from the downstream optical transceiver. The network further includes at least one modem device operably coupled to the optical transport medium and configured to receive the downstream coherent dual-band optical signal from the optical transport medium. The at least one modem device includes a downstream coherent optical receiver, and a first slave laser injection locked to a frequency of the central optical carrier.
Owner:CABLE TELEVISION LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com