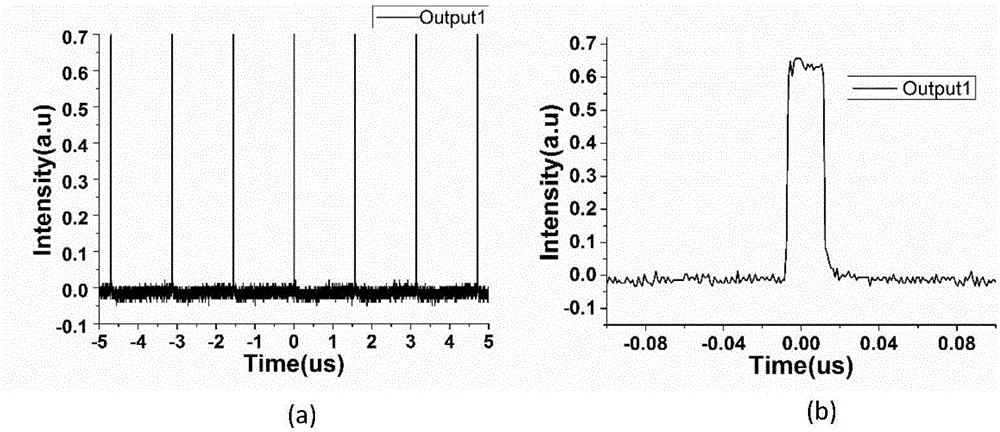
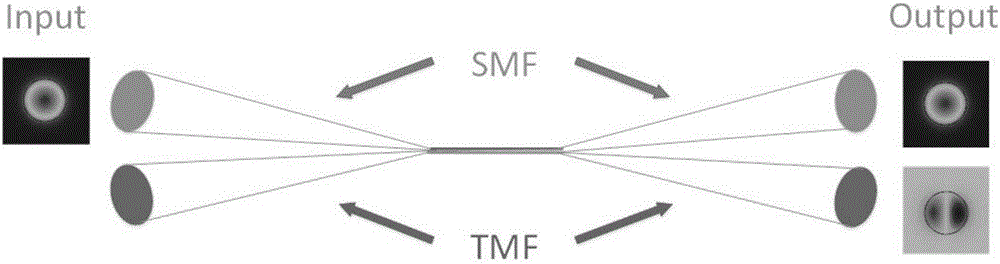
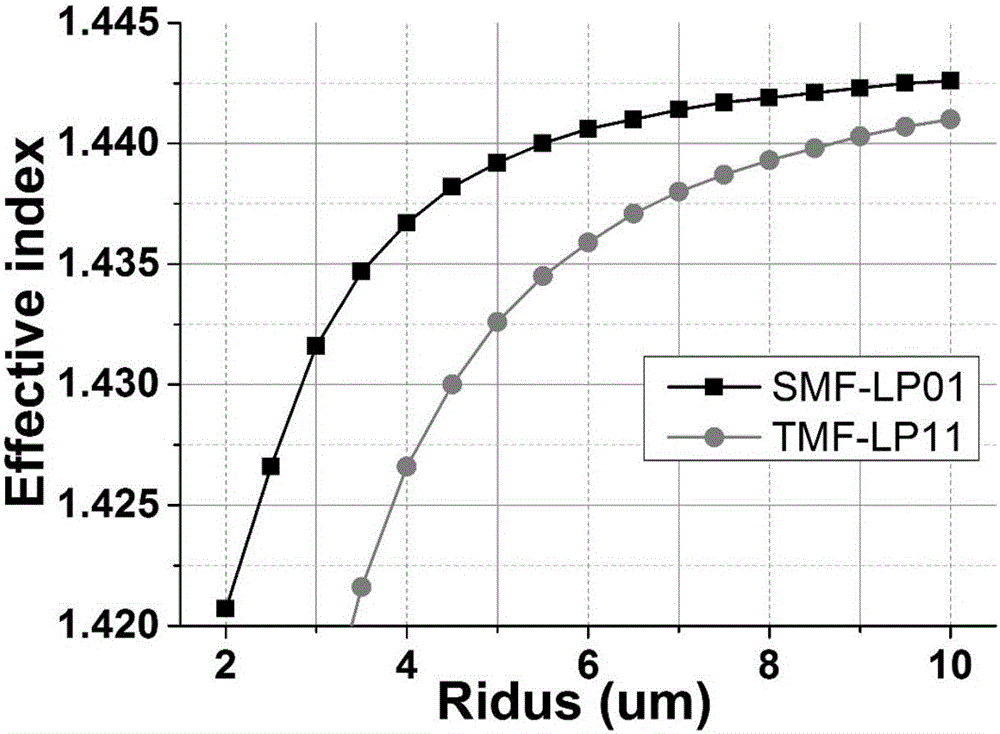
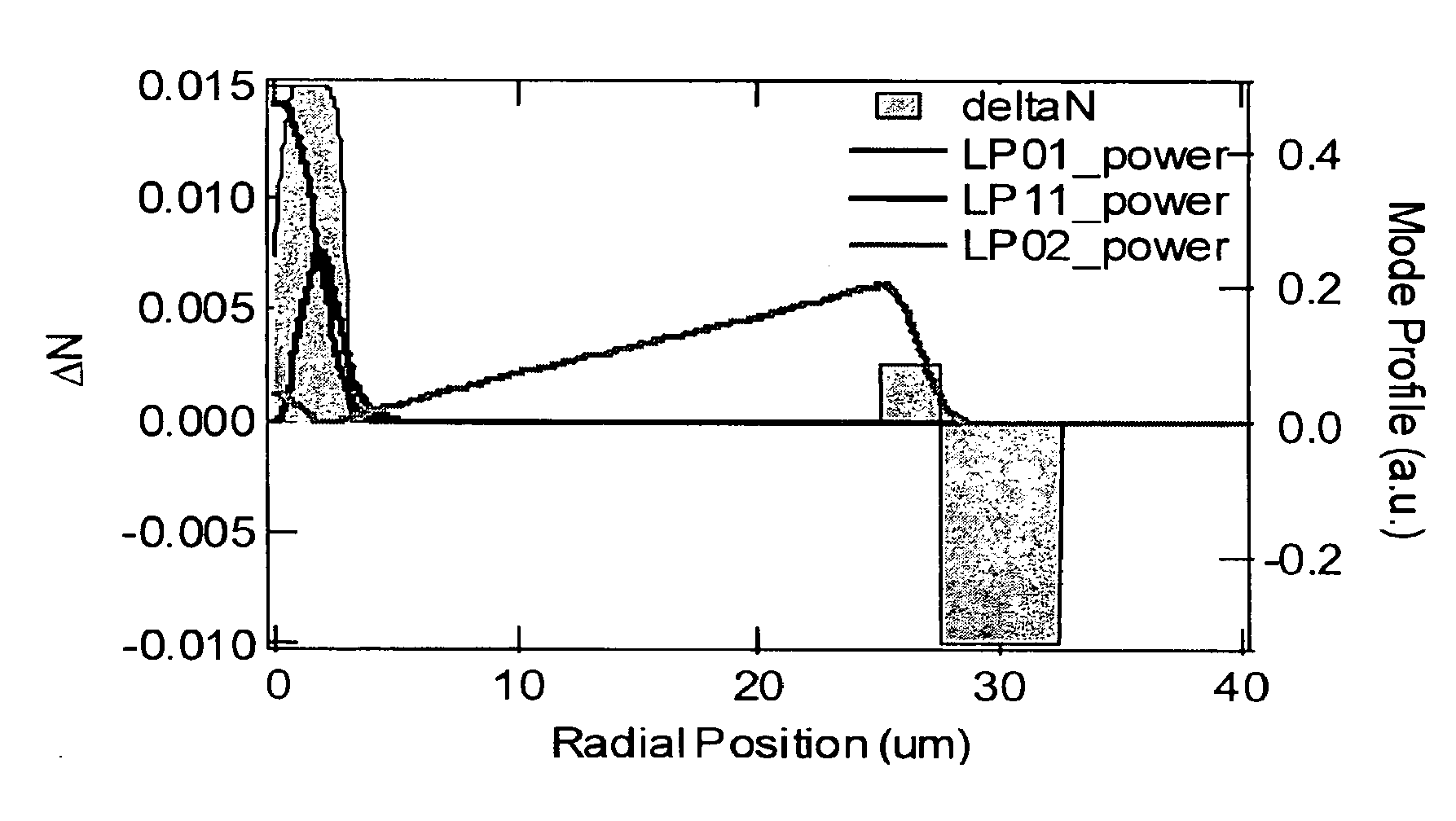
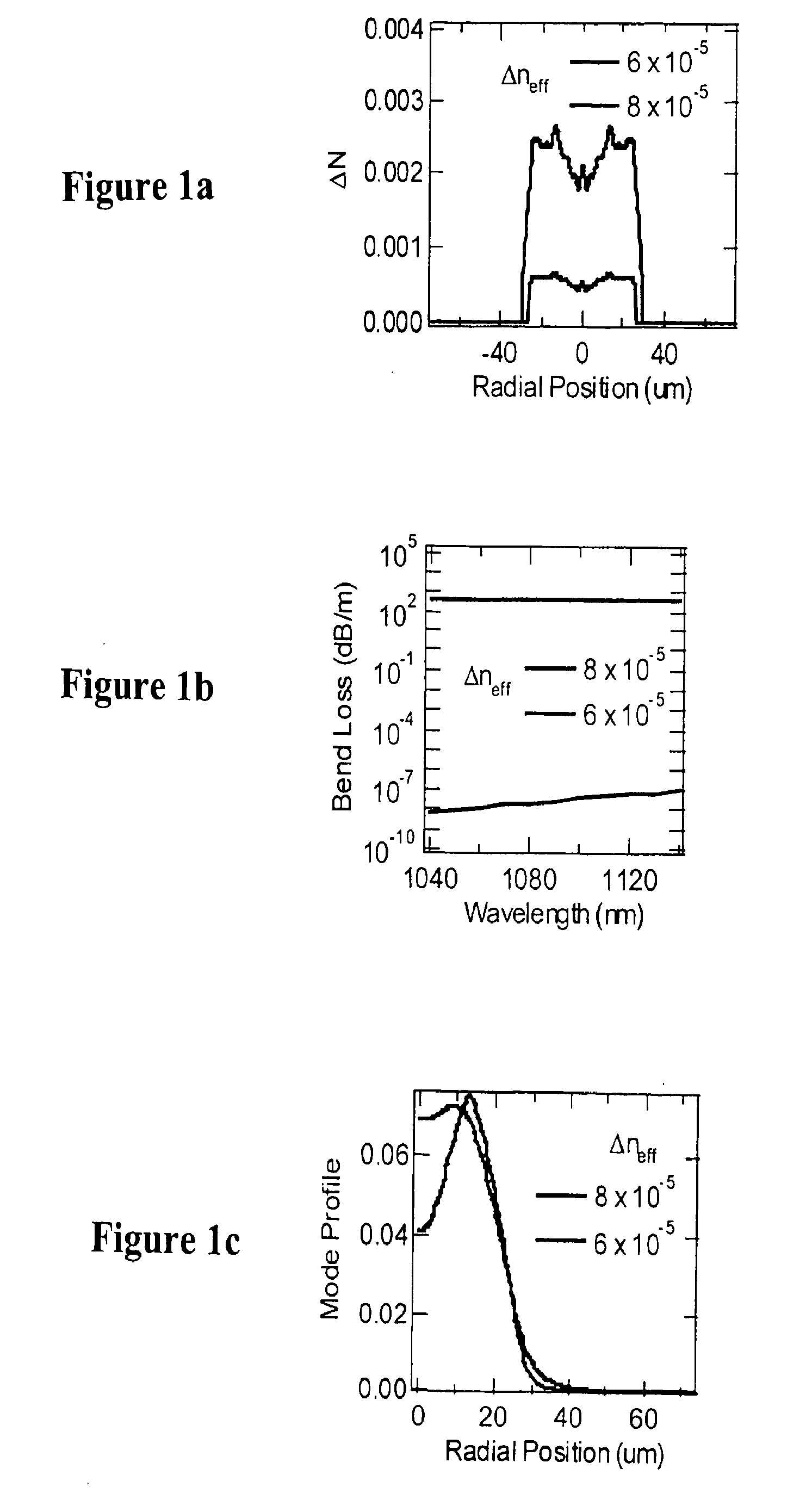
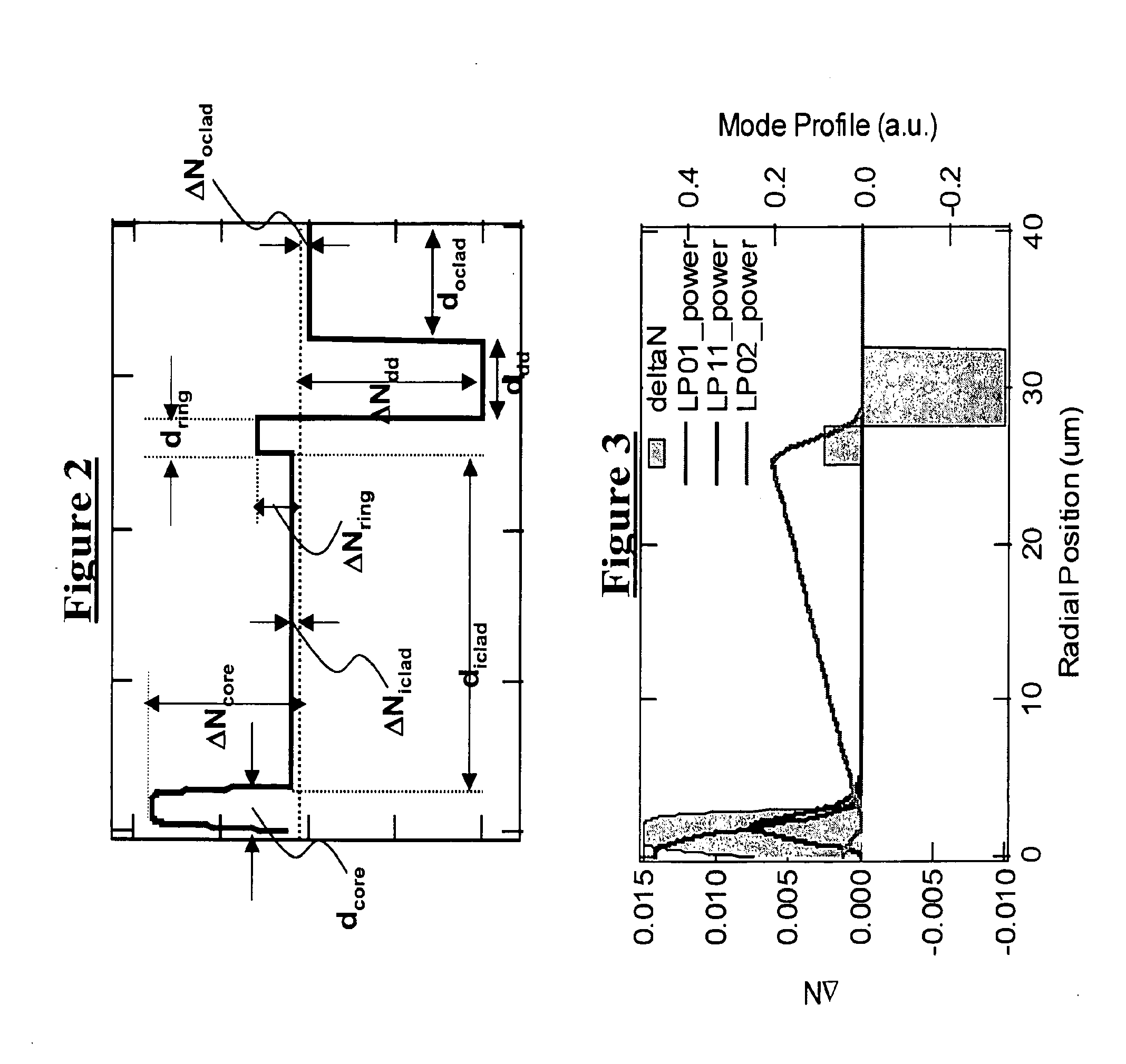
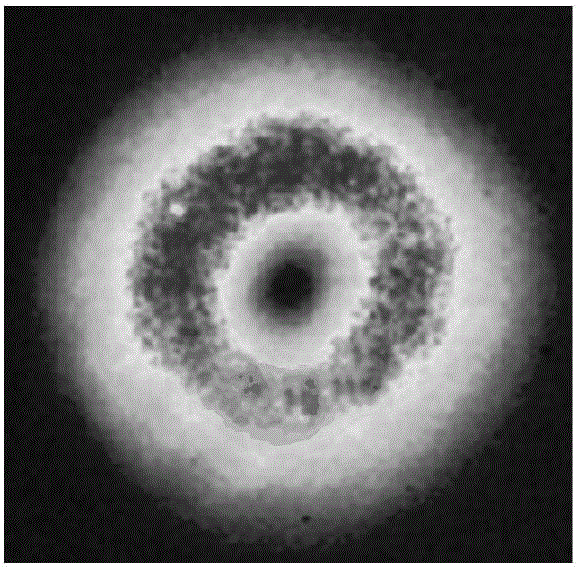
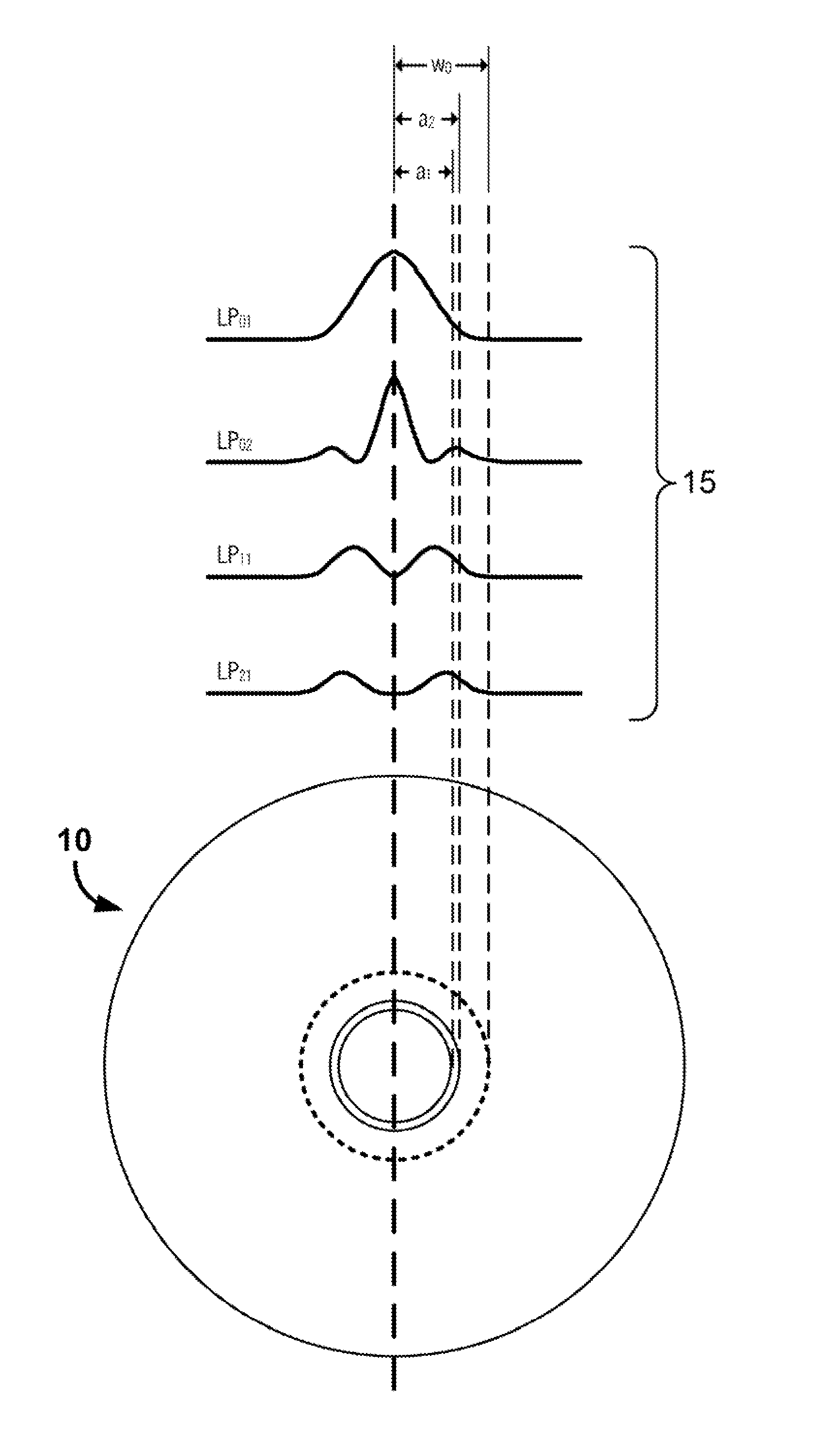
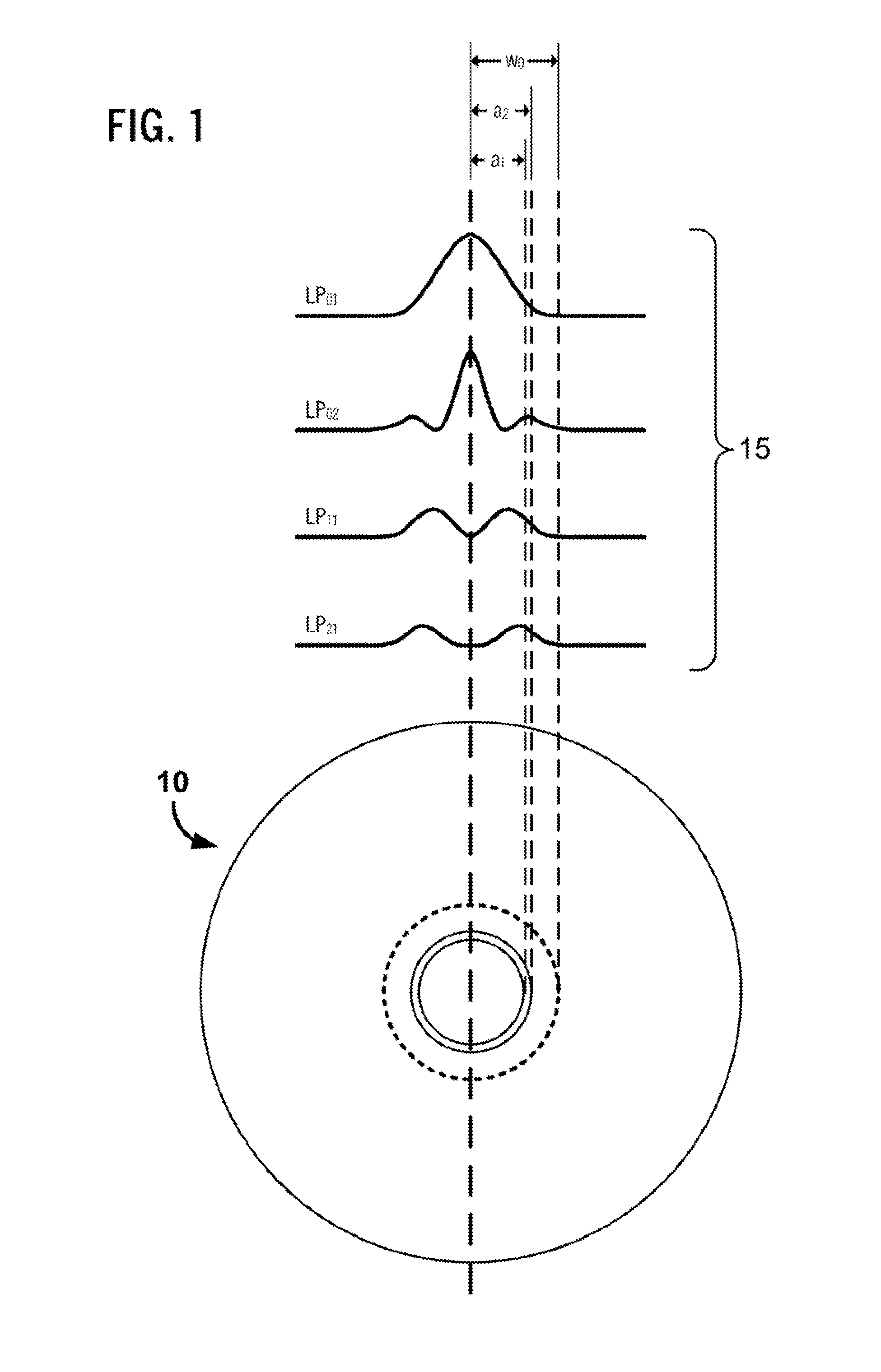
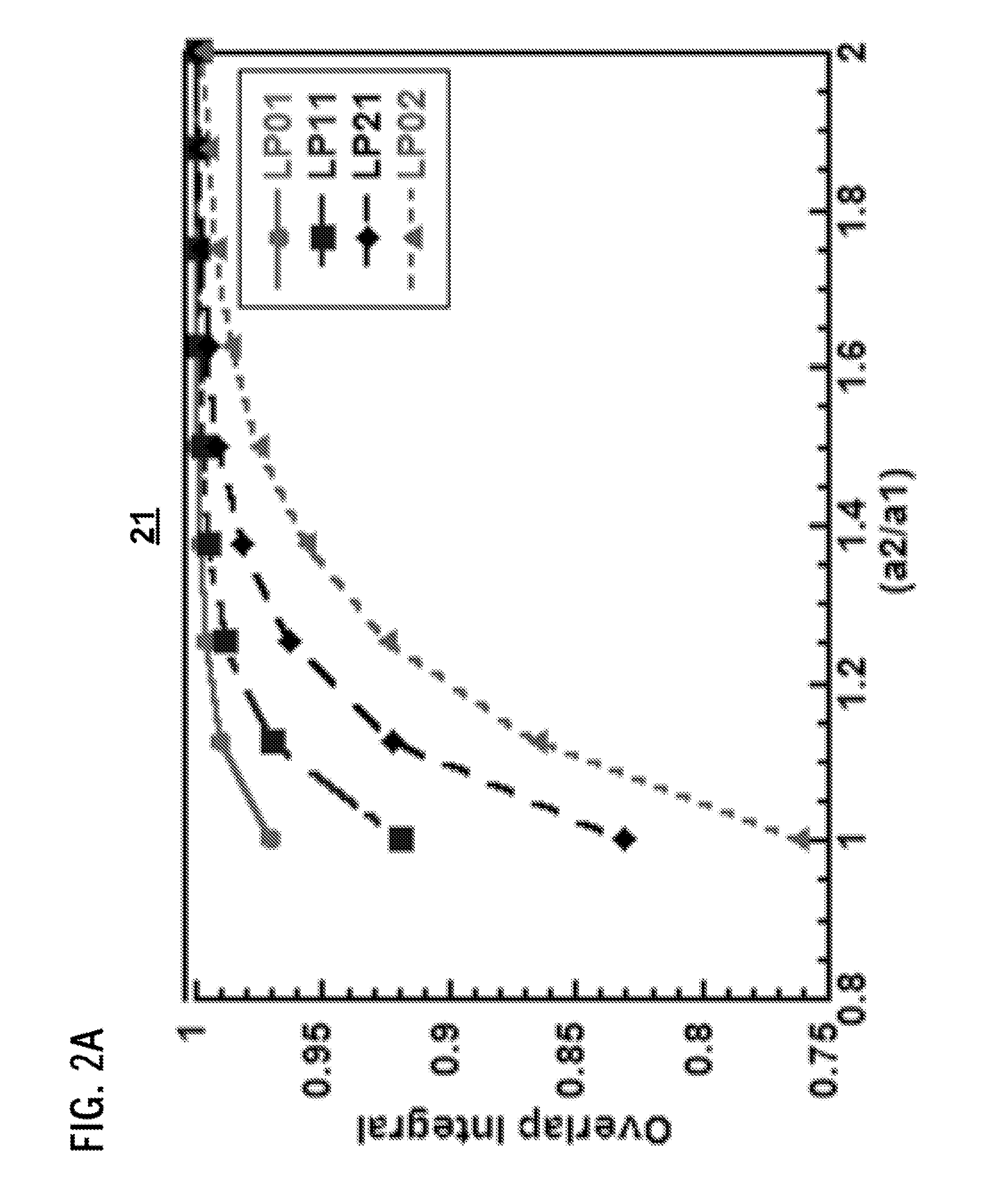
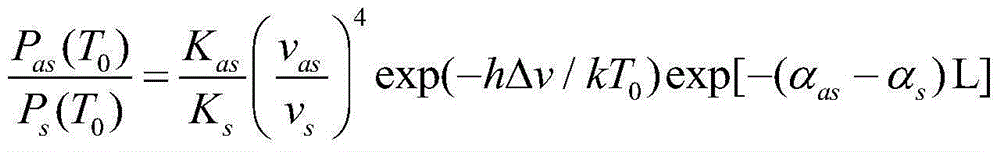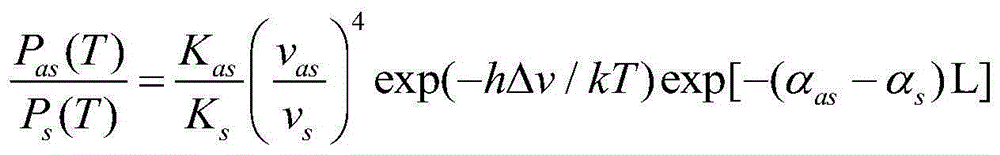Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
304 results about "Few mode fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
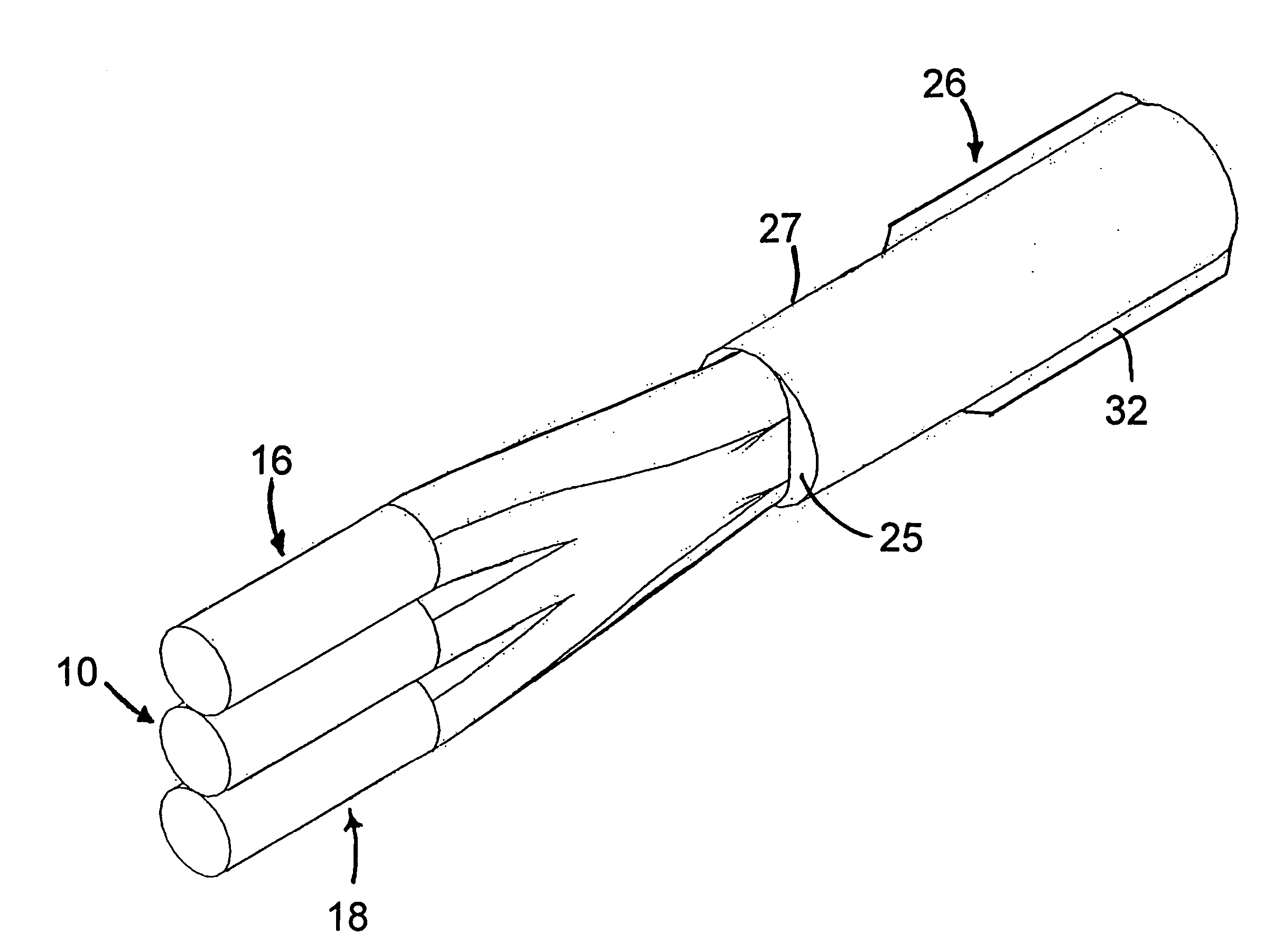
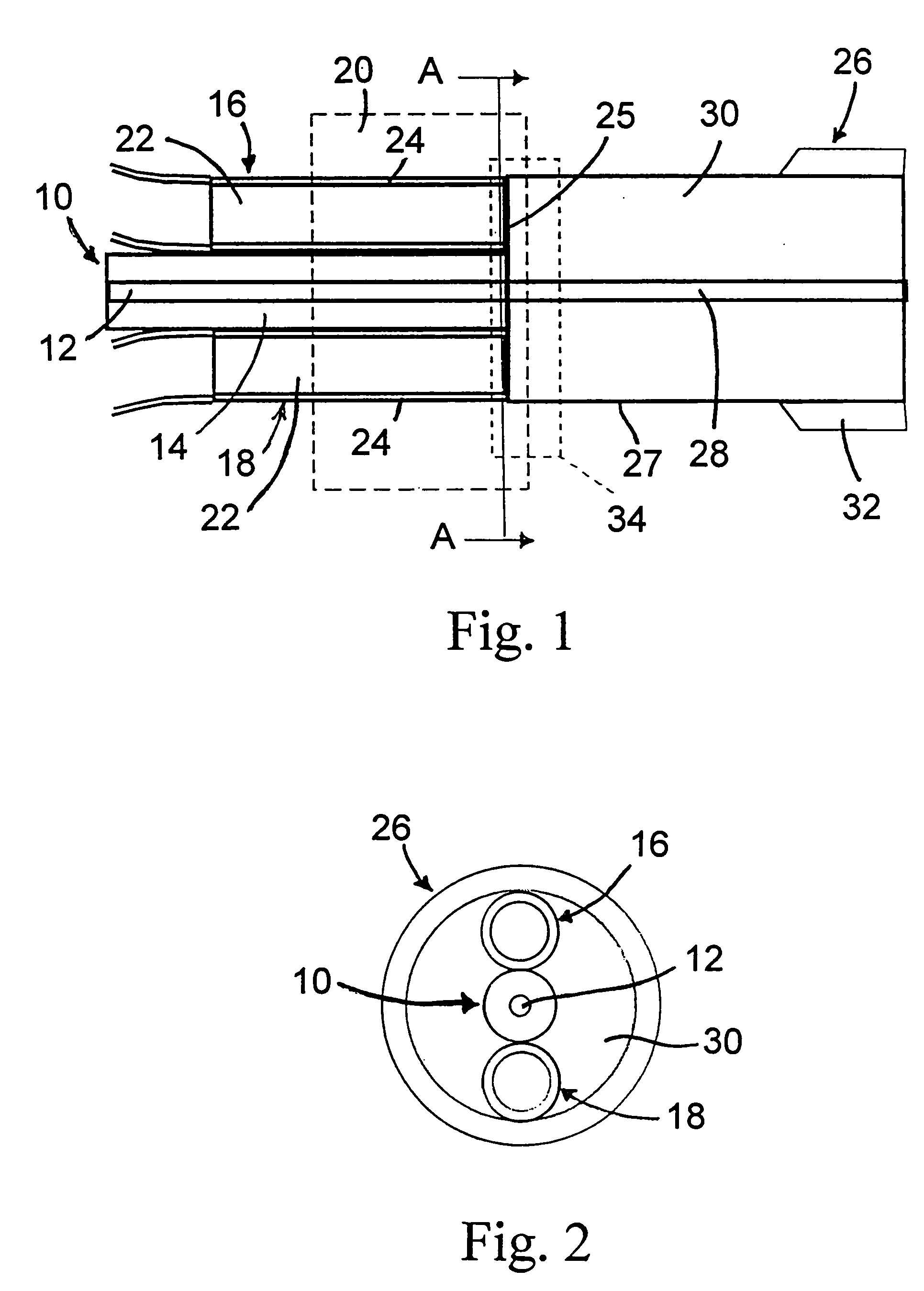
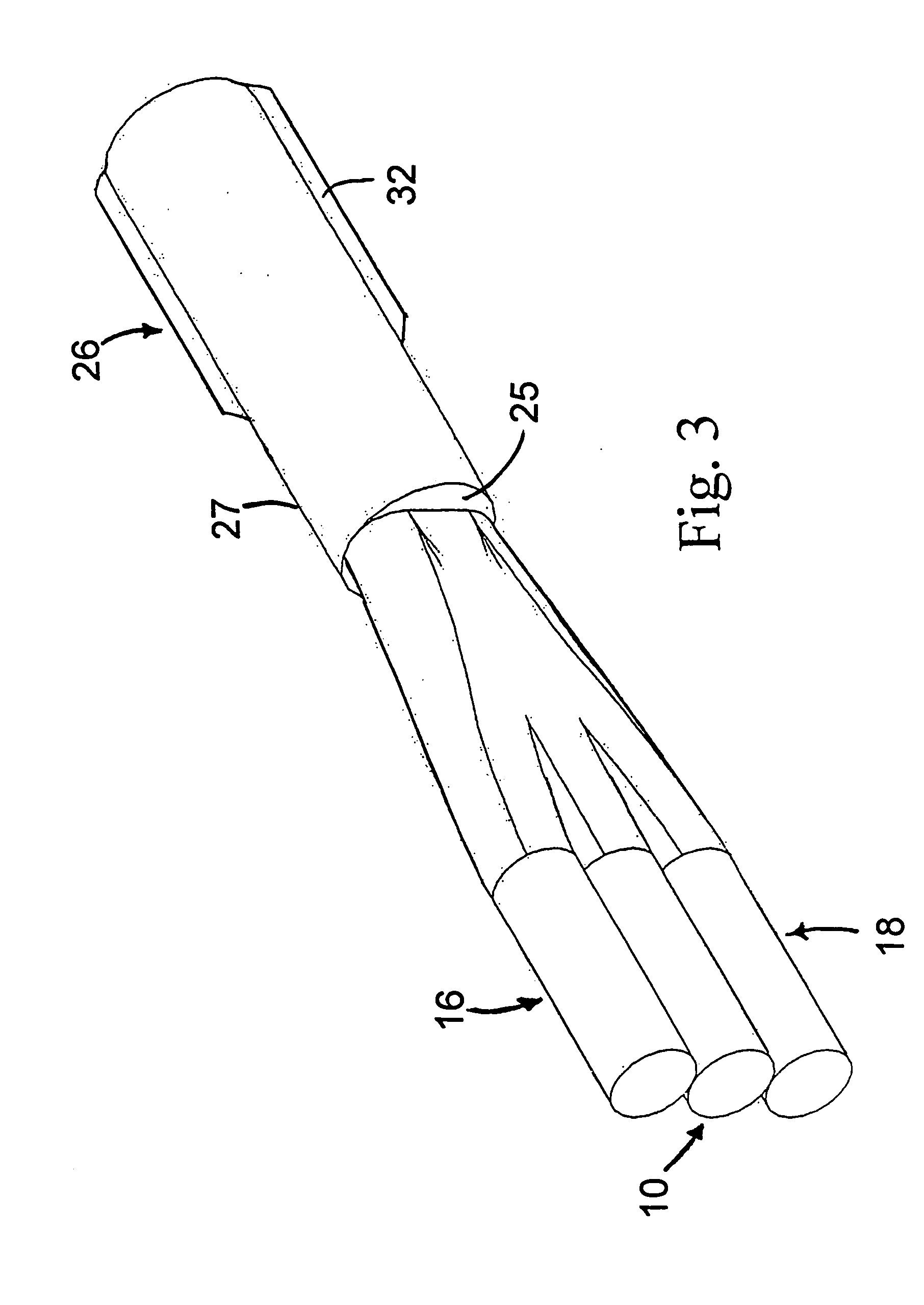
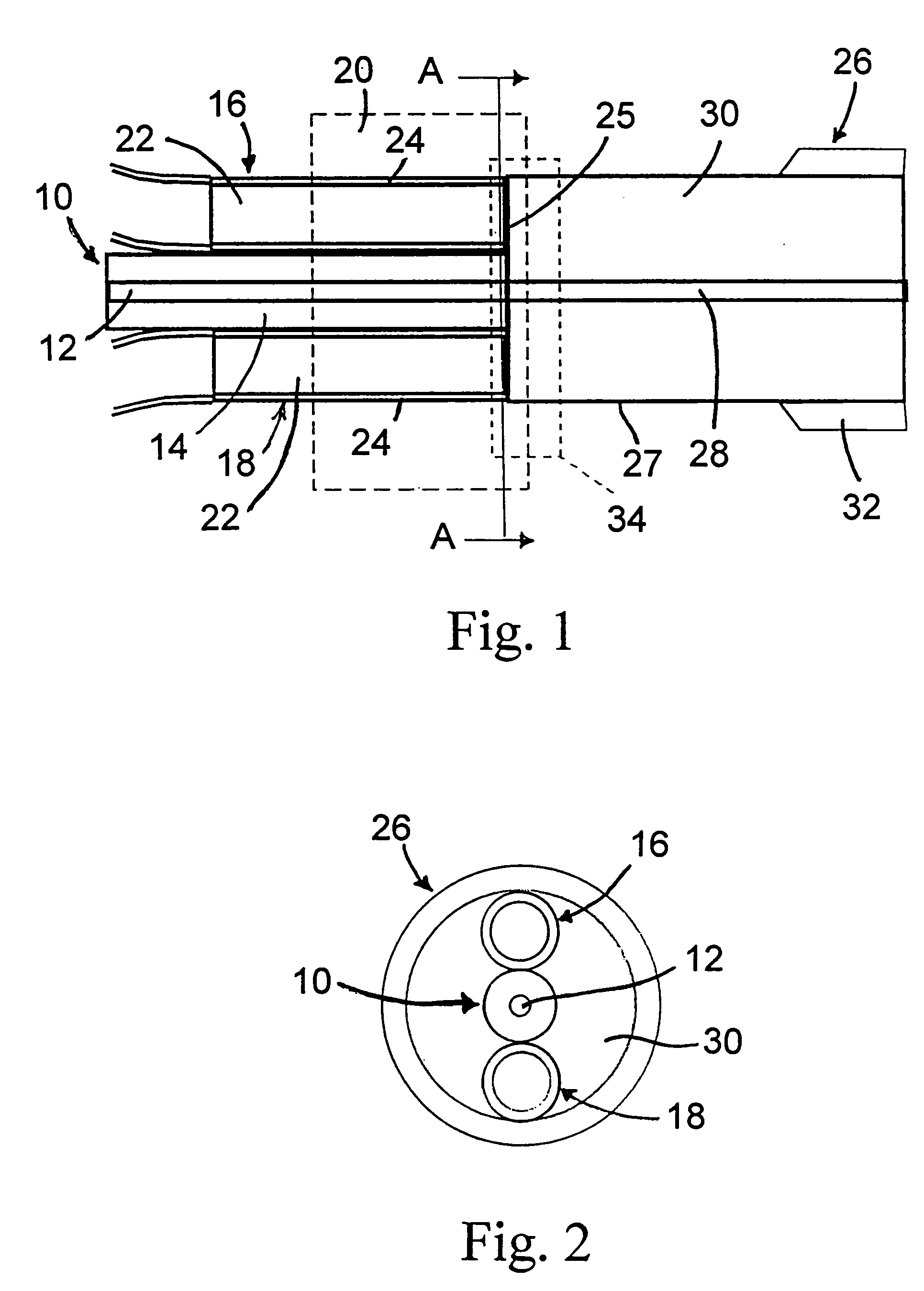
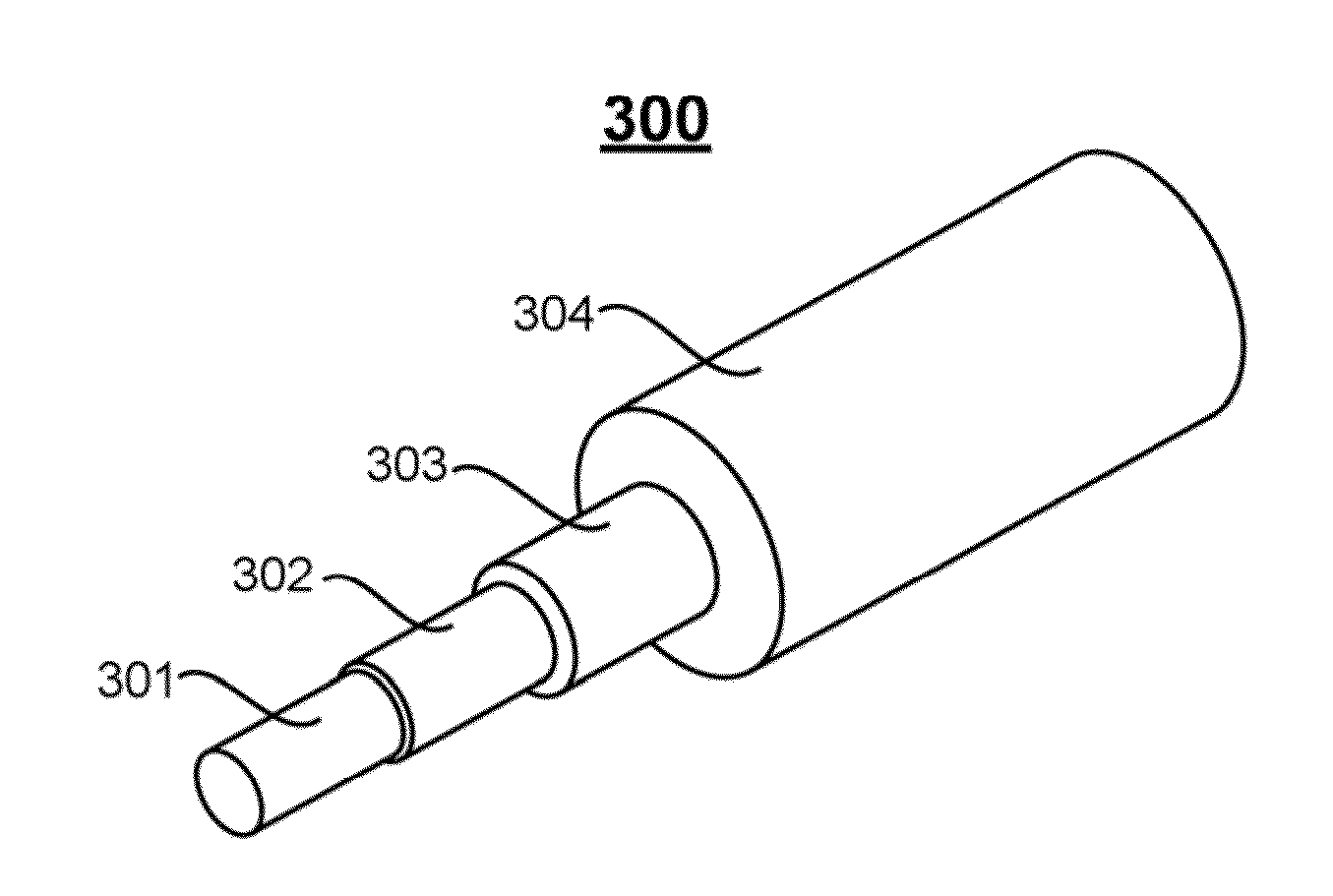
Optical coupler comprising multimode fibers and method of making the same
ActiveUS20050094952A1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesFew mode fiberDouble-clad fiber
An optical coupler is provided. It has a bundle of multimode fibers with a few-mode fiber in its centre. Such bundle is fused at one end which is the output end for the signal that is transmitted by the few-mode fiber. To make the coupler, this output end of the bundle is aligned and spliced with a large area core double clad fiber while preserving the modal content of the feed-through. A method for making such optical coupler is also provided. It includes the steps of bundling a central few-mode fiber with a plurality of multimode fibers and then fusing one end of such bundle and aligning it and splicing with a large core double clad fiber, while preserving fundamental mode transmission from one to the other.
Owner:ITF TECH +1
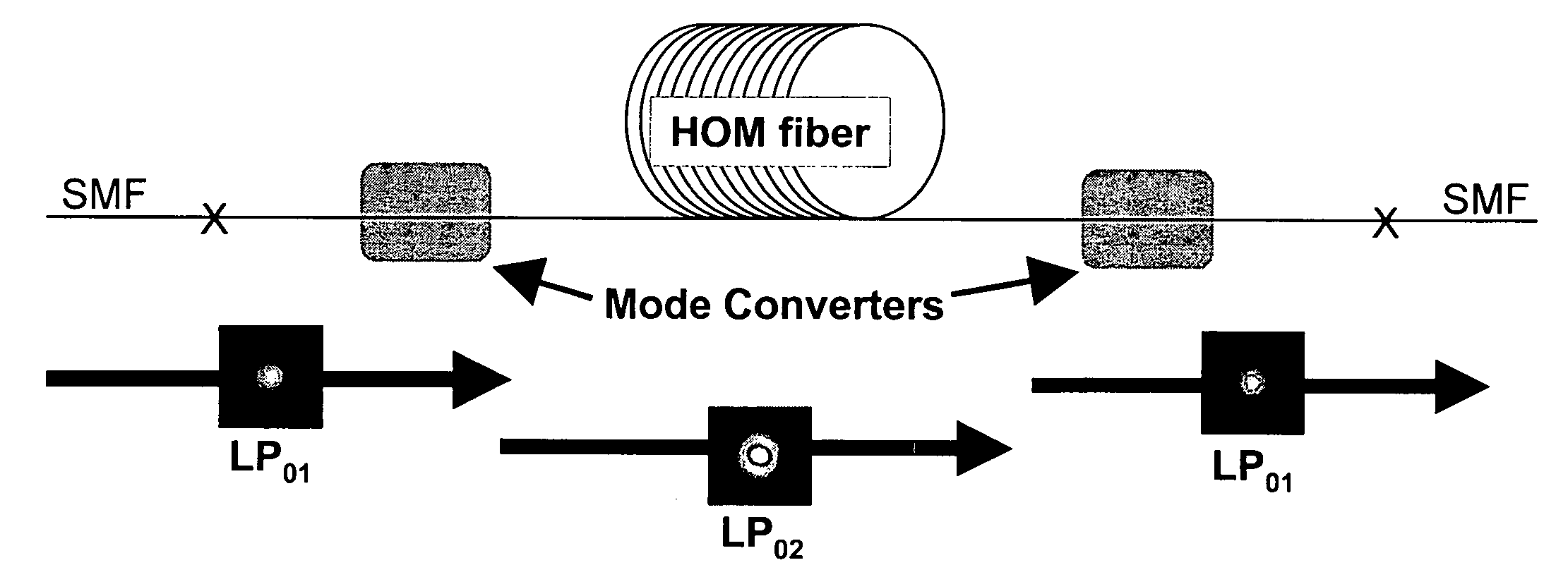
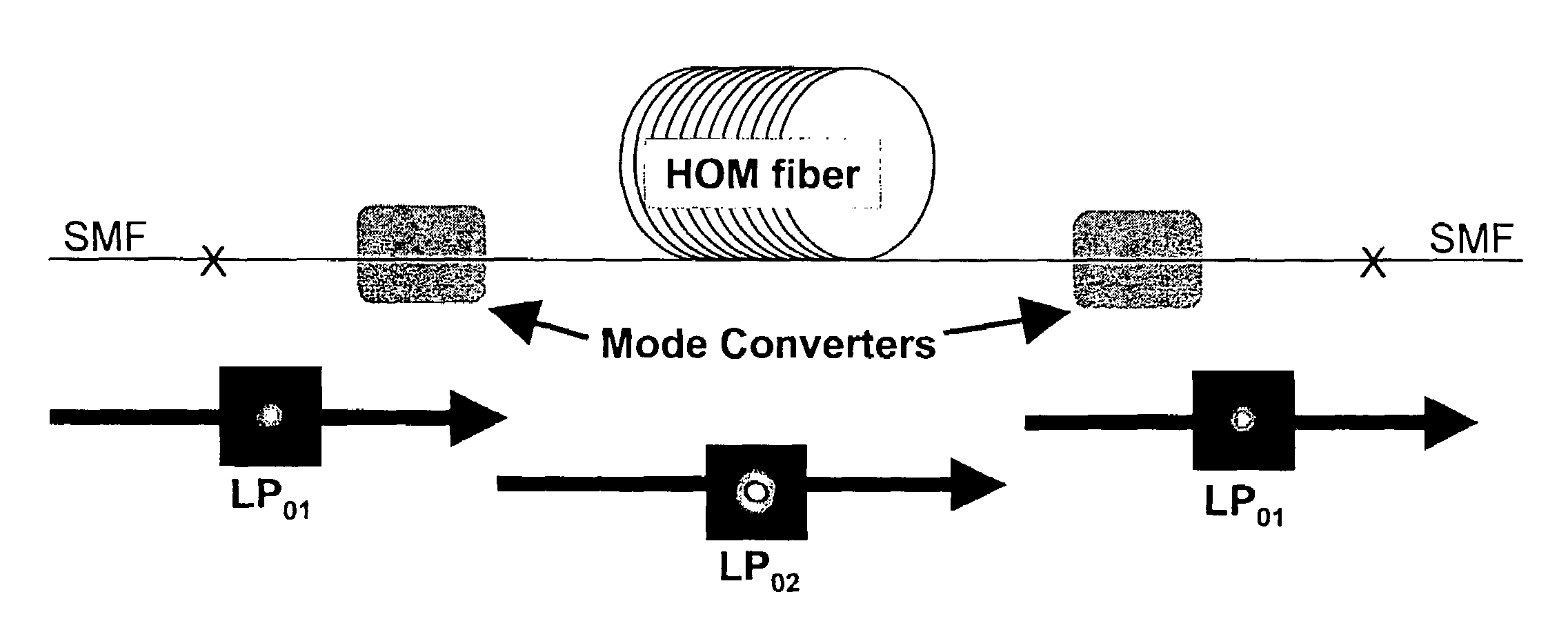
Large mode area fibers using higher order modes
ActiveUS20060103919A1Increase the areaImprove loss performanceLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFew mode fiberEngineering
The specification describes an optical fiber device wherein a LOM is converted to an HOM prior to entering the gain section. The gain section is a few mode fiber that supports the HOM. The output from the gain section, i.e. the HOM, may be utilized as is, or converted back to the LOM. With suitable design of the few mode fiber in the gain section of the device, the effective area, Aeff, may be greater than 1600 μm2. The large mode separation in the gain section reduces mode coupling, allowing greater design freedom and reducing the bend sensitivity of the optical fiber.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Optical fiber systems for delivering short high power pulses
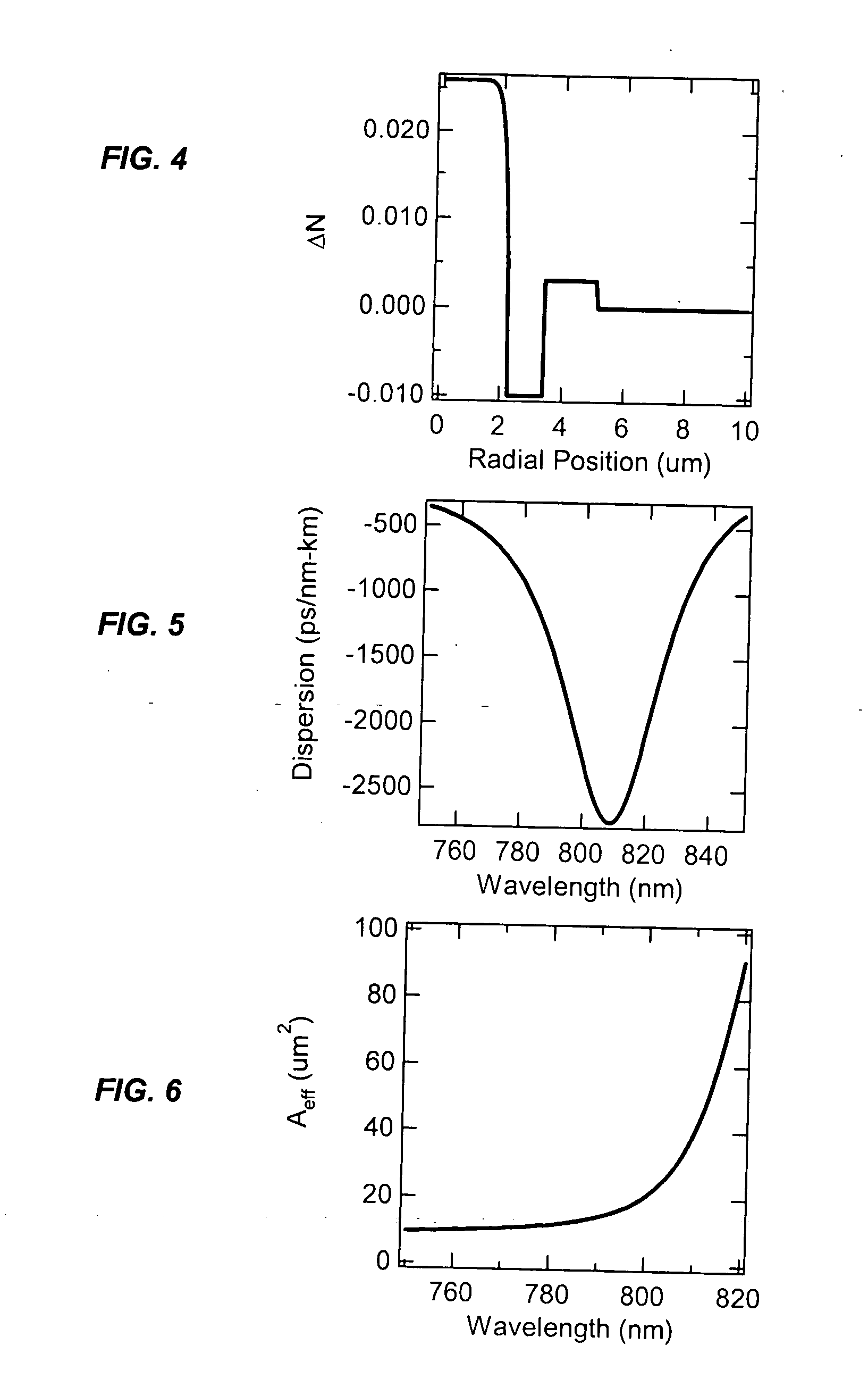
InactiveUS20060233554A1Minimal distortionMinimum non-linear impairmentDistortion/dispersion eliminationOptical light guidesNonlinear distortionFew mode fiber
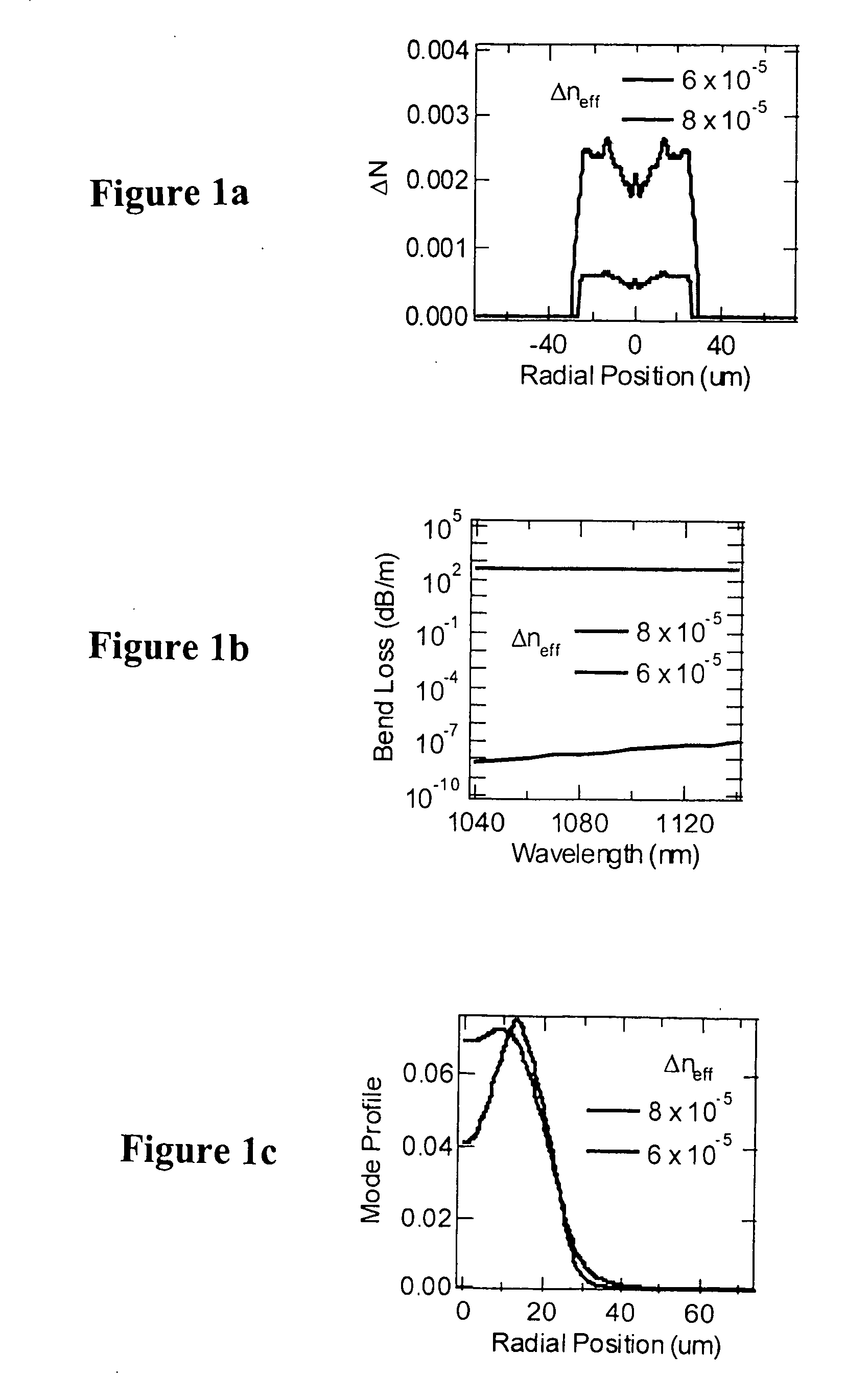
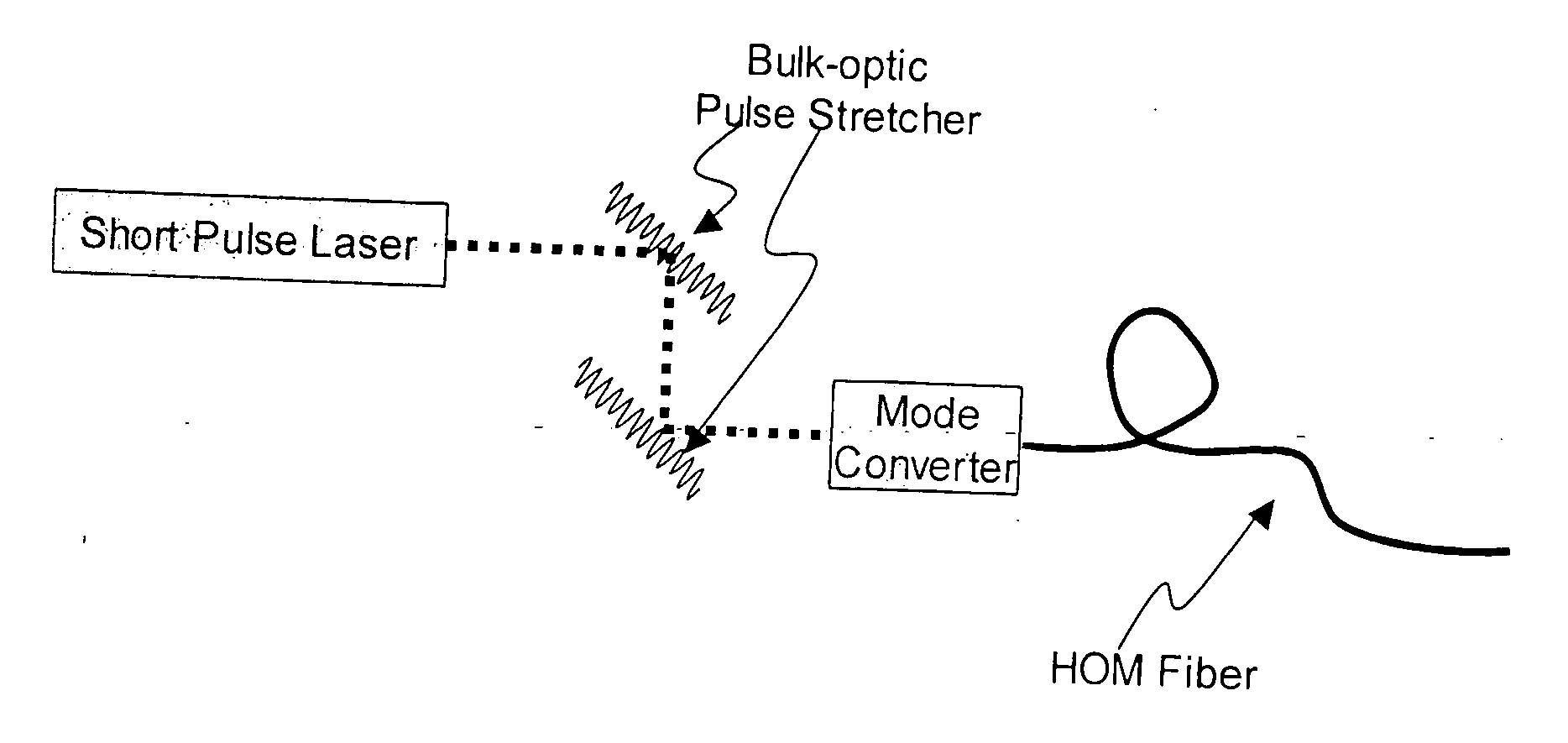
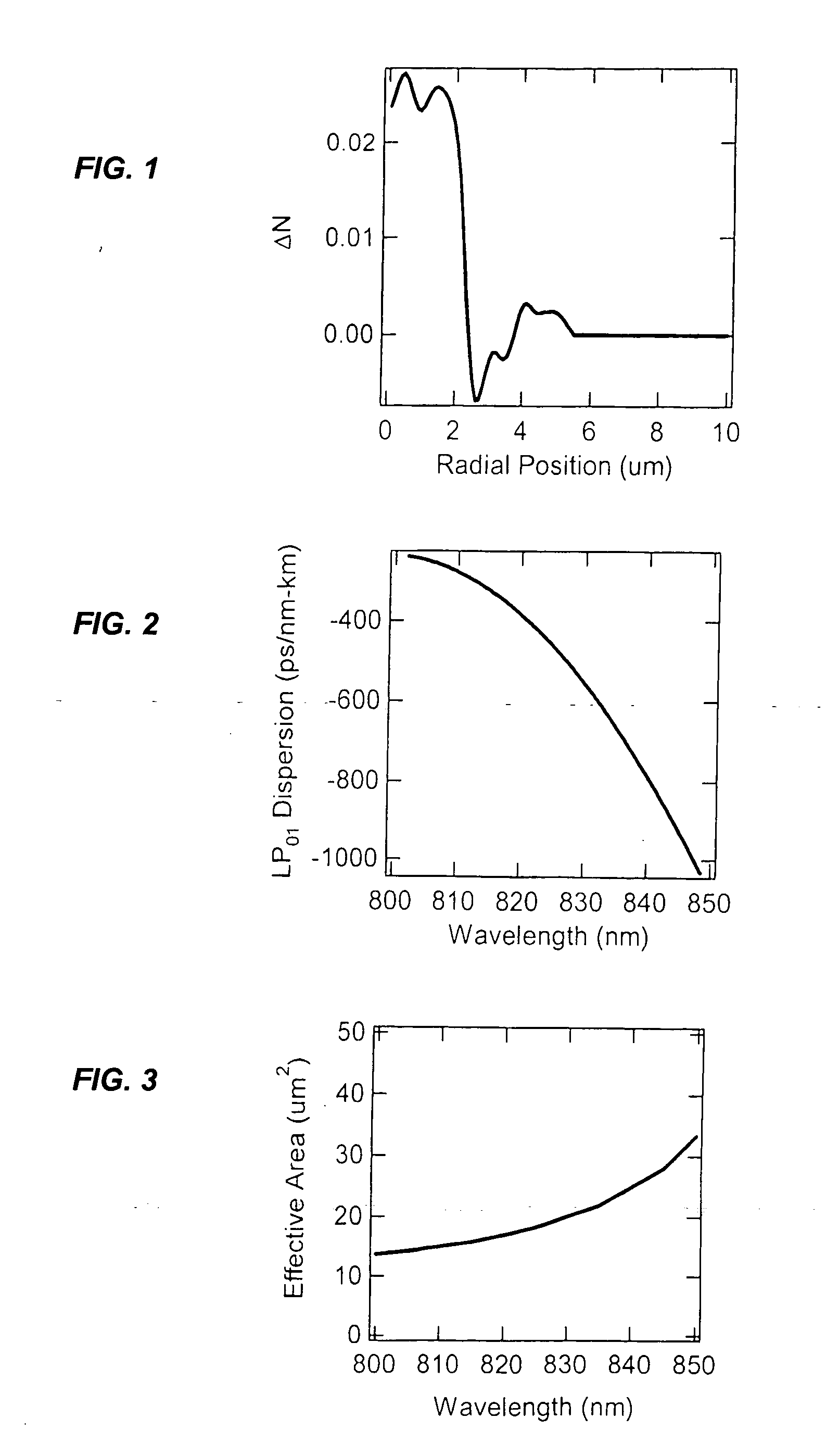
Described is an optical fiber system for delivering ultrashort pulses with minimal distortions due to nonlinearity. The system is based on delivering the optical pulses in a higher order mode (HOM) of a few-moded fiber. The fiber is designed so that the dispersion for the HOM is very large. This results in a dispersion length LD for the delivery fiber that is exceptionally small, preferably less than the non-linear length LNL. Under these conditions the system may be designed so the optical pulses experience minimum non-linear impairment, and short pulse / high peak power levels are reproduced at the output of the delivery fiber.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing
ActiveCN103095373AImprove spectrum utilizationImprove nonlinear toleranceFibre transmissionElectromagnetic receiversFrequency spectrumLine width
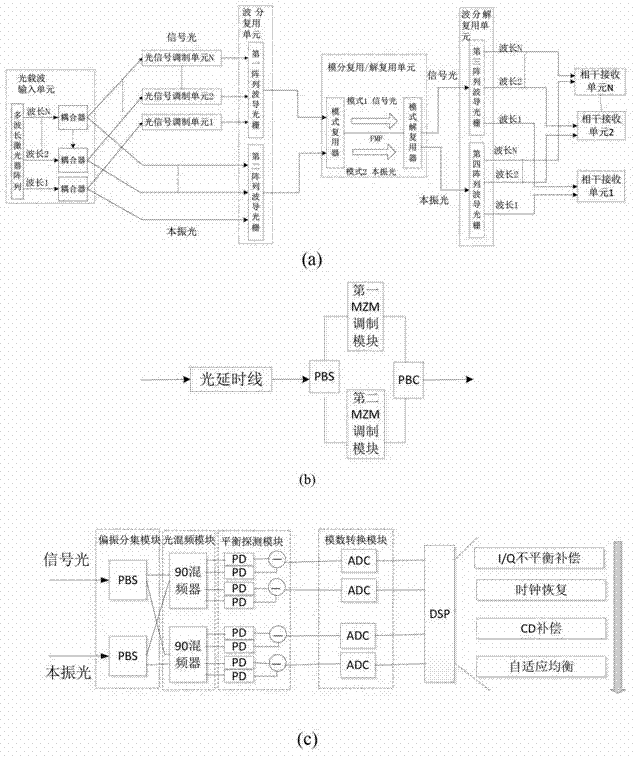
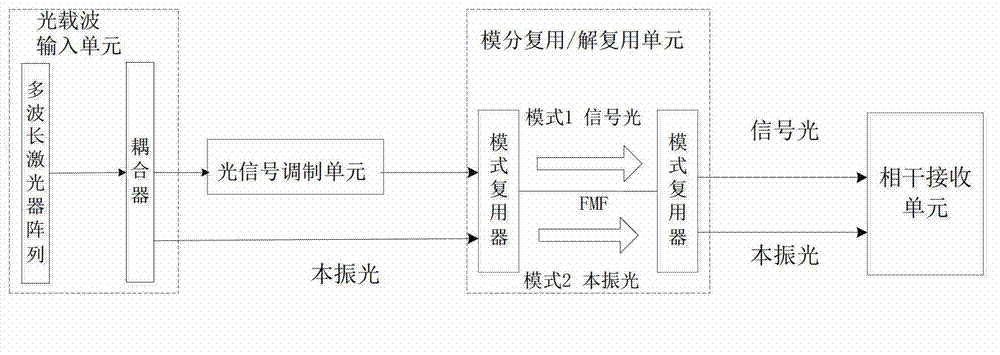
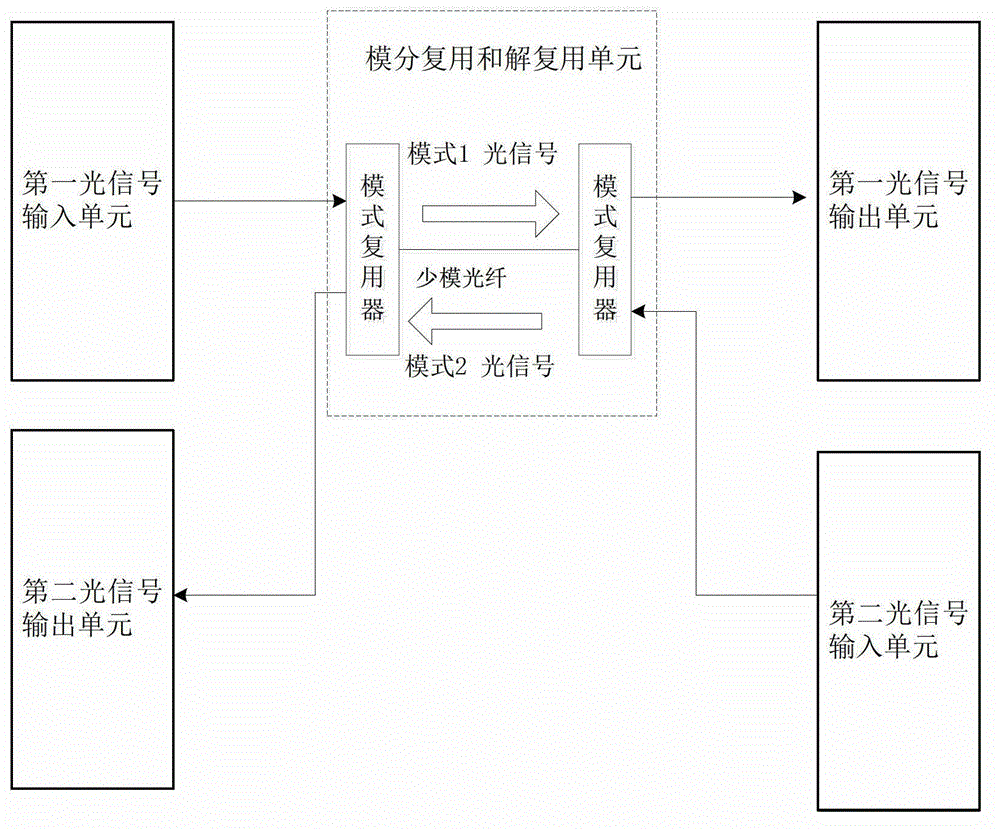
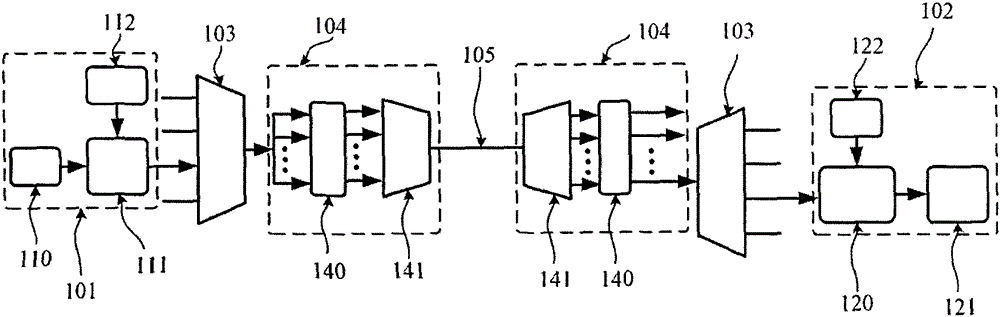
The invention discloses a self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing. The self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing comprises an optical carrier input unit, optical signal modulation units, a wavelength division multiplexing unit, a mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing unit, a wavelength division multiplexing unit and coherent reception units. The mode division multiplexing and reconciliation multiplexing unit comprises a mode multiplexer and mode demultiplexer, and the mode multiplexer and the mode demultiplexer are connected through few-mode optical fibers. The optical carrier input unit is connected with each optical signal modulation unit, the wavelength division multiplexing unit and the mode multiplexer through single-mode optical fibers. The mode multiplexer is connected with the mode demultiplexer through few-mode optical fibers. The mode demultiplexer is connected with the wavelength division multiplexing unit and each coherent reception unit through single-mode optical fibers. The optical carrier input unit is further connected with the wavelength division multiplexing unit. The self-correlation optical fiber communication system based on mode division multiplexing eliminates an expensive narrow line width adjustable local oscillator light source which is arranged at a reception end, enables a laser to be conveniently managed and maintained, is free from using frequency offset estimation in a digital signal processor (DSP) and phase retrieval algorithm, reduces complexity of the DSP and has the advantages of being high in spectrum effectiveness and big in nonlinearity tolerance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Large mode area fibers using higher order modes
ActiveUS7171074B2Increase the areaImprove loss performanceLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFew mode fiberEngineering
The specification describes an optical fiber device wherein a LOM is converted to an HOM prior to entering the gain section. The gain section is a few mode fiber that supports the HOM. The output from the gain section, i.e. the HOM, may be utilized as is, or converted back to the LOM. With suitable design of the few mode fiber in the gain section of the device, the effective area, Aeff, may be greater than 1600 μm2. The large mode separation in the gain section reduces mode coupling, allowing greater design freedom and reducing the bend sensitivity of the optical fiber.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Method And Apparatus For Space-Division Multiplexing Systems
ActiveUS20130236175A1Reducing performance variationImprove system performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFew mode fiberSignal on
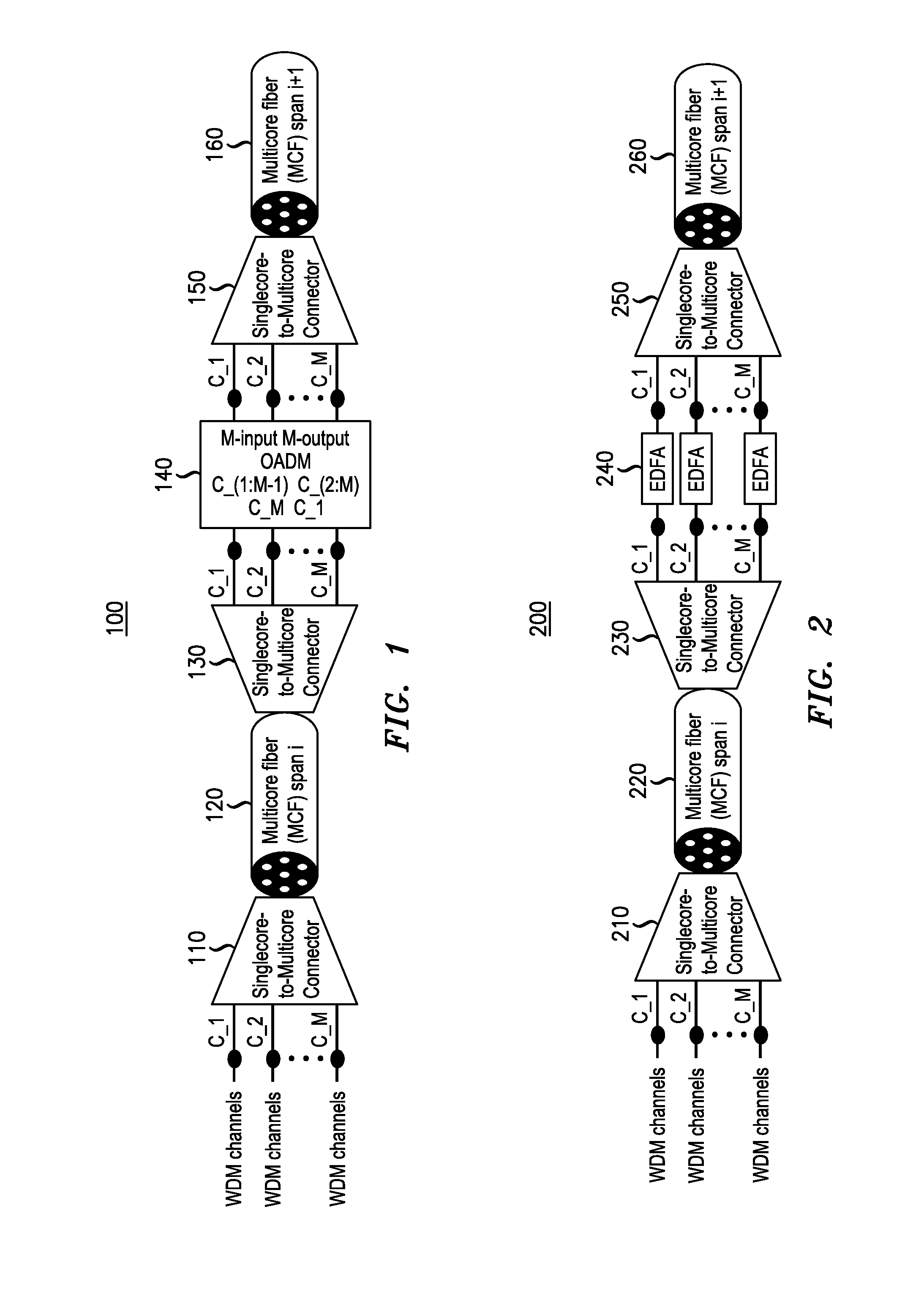
A space division multiplexed (SDM) transmission system that includes at least two segments of transmission media in which a spatial assignment of the two segments is different is provided. For example, the SDM transmission may include a first segment of transmission media having a first spatial assignment and a second segment of transmission media having a second spatial assignment, wherein the first spatial assignment differs from the second spatial assignment. An example method obtains an optical signal on a first segment of transmission media having a first spatial assignment and forwards the optical signal on a second segment of transmission media with a different spatial assignment. The transmission media may be a multi-core fiber (MCF), a multi-mode fiber (MMF), a few-mode fiber (FMF), or a ribbon cable comprising nominally uncoupled single-mode fiber (SMF).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on mode division multiplexing
ActiveCN103152099AOvercome backscatterImprove spectrum utilizationDistortion/dispersion eliminationPolarization diversityPolarization multiplexed
The invention discloses a single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on mode division multiplexing. The single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on the division multiplexing mainly comprises two optical signal input units, two optical signal output units and a mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing unit, wherein the mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing unit comprises two mode-type multiplexers which are connected through few-mode fiber. Polarization multiplexing optical signals are generated by the signal input units, the polarization multiplexing optical signals are enabled to be coupled into a mode field of the few-mode fiber by the mode-type multiplexer to finish the mode division multiplexing, the polarization multiplexing optical signals carried by the mode field are sent to the other mode-type multiplexer through the few-mode fiber, the received polarization multiplexing optical signals are enabled to be coupled into single-mode fiber by the other mode-type multiplexer and sent to the optical signal output units through the single-mode fiber, polarization diversity, mixing and balance detection are carried out on the received optical signals by the signal output units, then the received optical signals are changed into electric signals and then changed into digital signals. According to the single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on the mode division multiplexing, the few-mode fiber is used for overcoming Rayleigh backward scattering effect, single-fiber bidirectional transmission is achieved, and use efficiency of optical fiber and wavelength resources is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
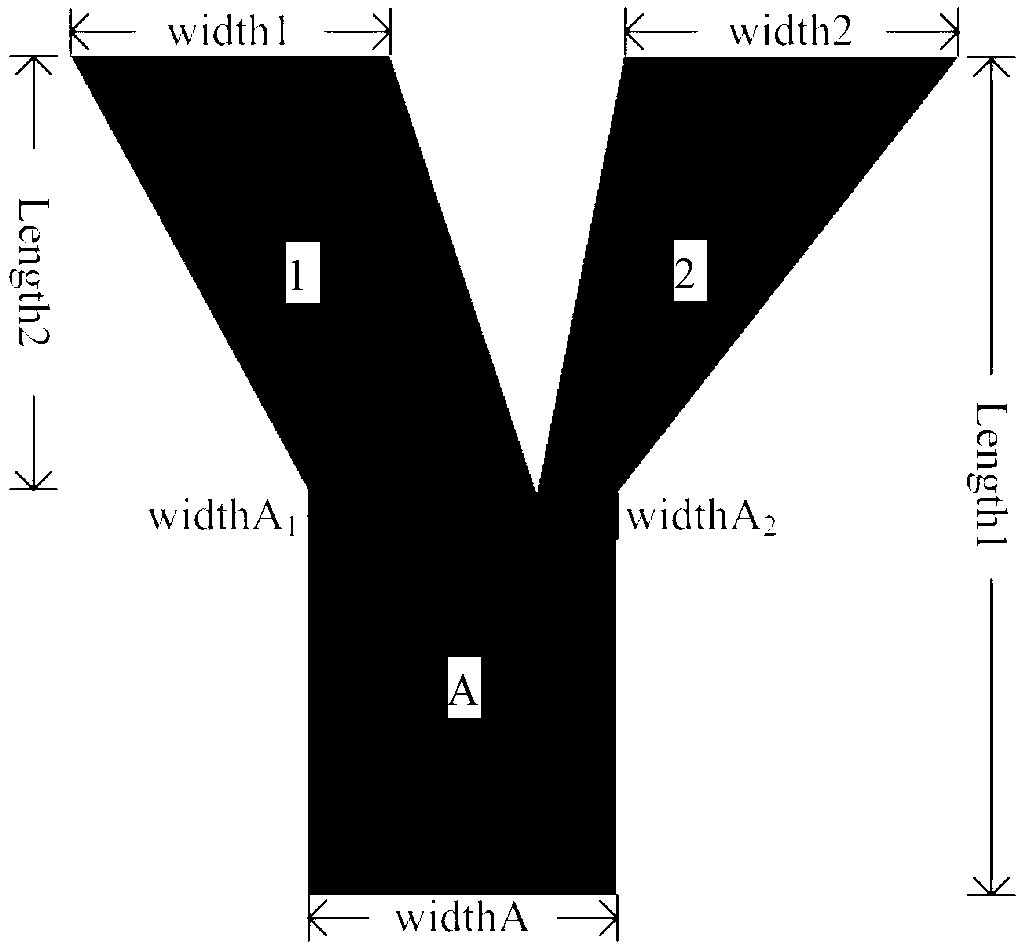
Asymmetric planar optical waveguide mode multiplexing/demultiplexing device based on few-mode fibers
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication, relates to an asymmetric planar optical waveguide mode multiplexing / demultiplexing device based on few-mode fibers, in particular to a planar optical waveguide mode multiplexing / demultiplexing device which is used for mode diversity multiplexing communication and facilitates interconnection. The device is of a Y-shaped structure and composed of a waveguide main arm and a plurality of waveguide branch arms, wherein the number of the waveguide branch arms is same as the number of transmission modes of the few-mode fibers; the waveguide main arm and the waveguide branch arms are respectively composed of a core layer and a cladding, and the refraction index of the core layers of each of the waveguide main arm and the waveguide branch arms and the refraction index of the cladding of each of the waveguide main arm and the waveguide branch arms are same as the refraction index of a fiber core of each few-mode fiber and the refraction index of a cladding of each few-mode fiber respectively. The asymmetric planar optical waveguide mode multiplexing / demultiplexing device is simple in structure, low in loss, easy to integrate, stable in performance, wide in broadband, simple and efficient.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Optical coupler comprising multimode fibers and method of making the same
ActiveUS7046875B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesFew mode fiberDouble-clad fiber
An optical coupler is provided. It has a bundle of multimode fibers with a few-mode fiber in its centre. Such bundle is fused at one end which is the output end for the signal that is transmitted by the few-mode fiber. To make the coupler, this output end of the bundle is aligned and spliced with a large area core double clad fiber while preserving the modal content of the feed-through. A method for making such optical coupler is also provided. It includes the steps of bundling a central few-mode fiber with a plurality of multimode fibers and then fusing one end of such bundle and aligning it and splicing with a large core double clad fiber, while preserving fundamental mode transmission from one to the other.
Owner:ITF TECH +1
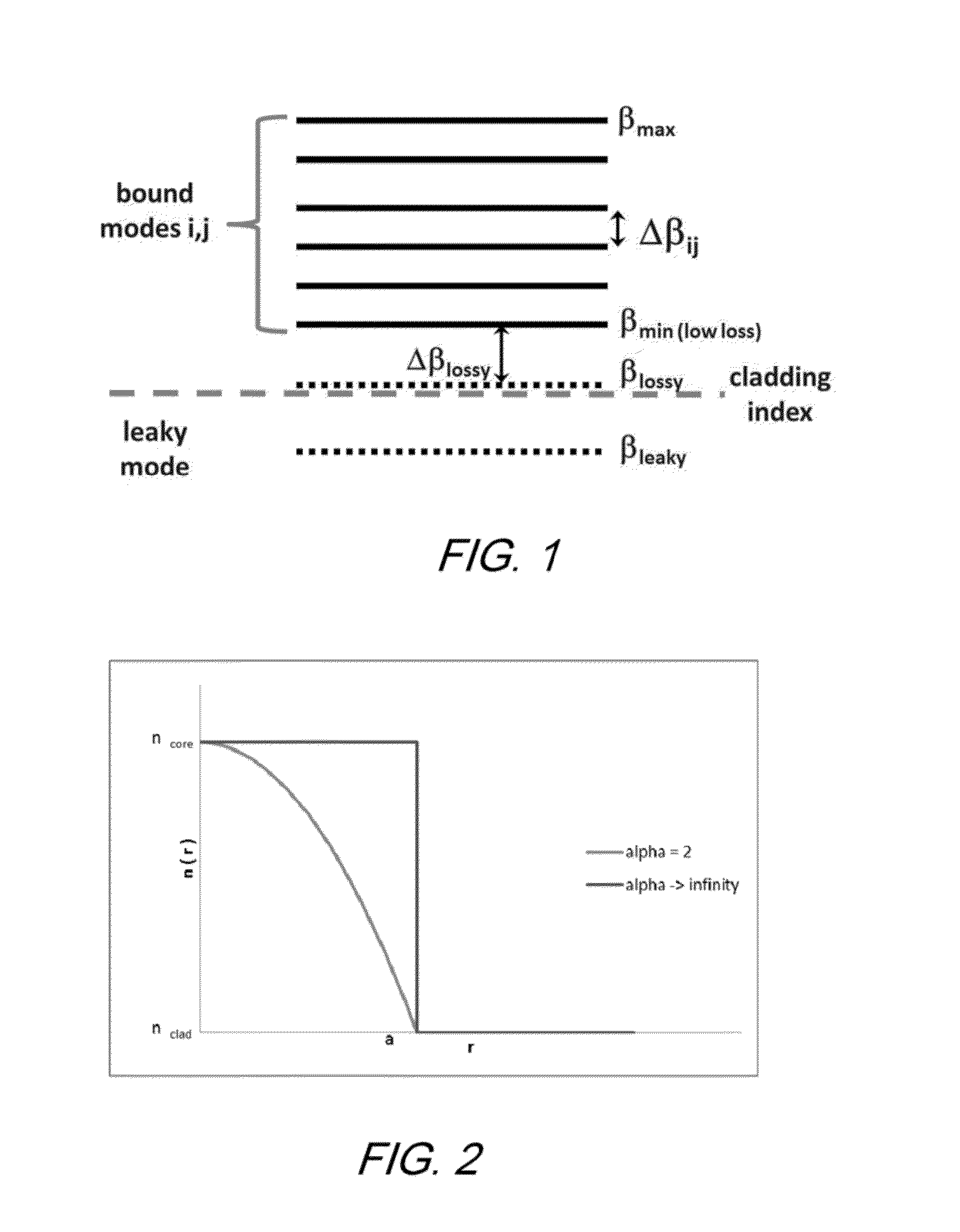
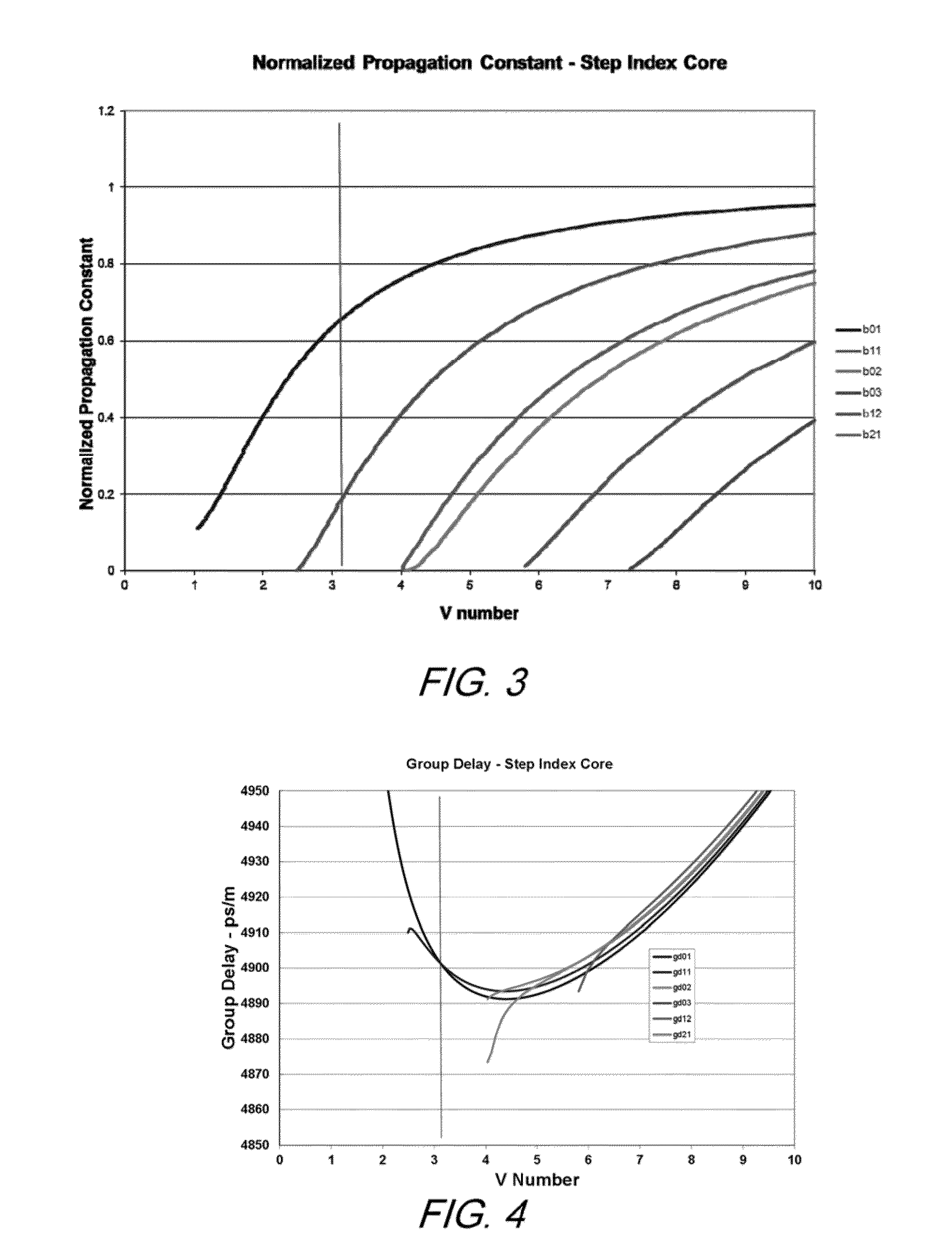
Step-Index Few-Mode Fiber Designs For Spatial Multiplexing
ActiveUS20140093205A1Avoid couplingLower levelCoupling light guidesMulticore optical fibreFew mode fiberCoupling
A few-mode optical fiber comprises a core surrounded by a cladding, having a step index profile that is structured to support propagation of a plurality of desired signal-carrying modes, while suppressing undesired modes. The core and cladding are configured such that the undesired modes have respective effective indices that are close to, or less than, the cladding index such that the undesired modes are leaky modes. The index spacing between the desired mode having the lowest effective index and the leaky mode with the highest effective index is sufficiently large so as to substantially prevent coupling therebetween.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
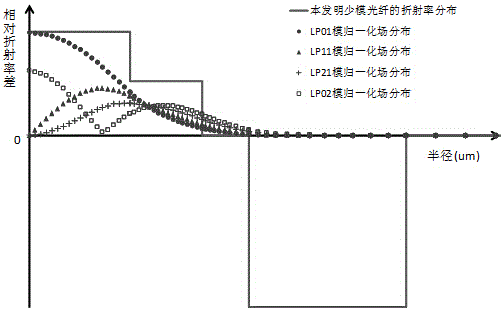
Few mode optical fibers for mode division multiplexing
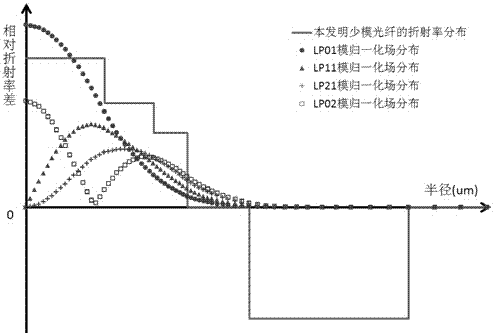
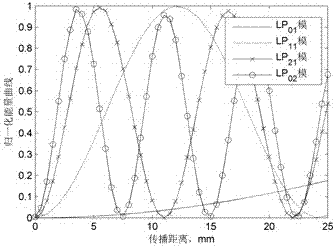
ActiveCN104067152AOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFew mode fiberRelative refractive index
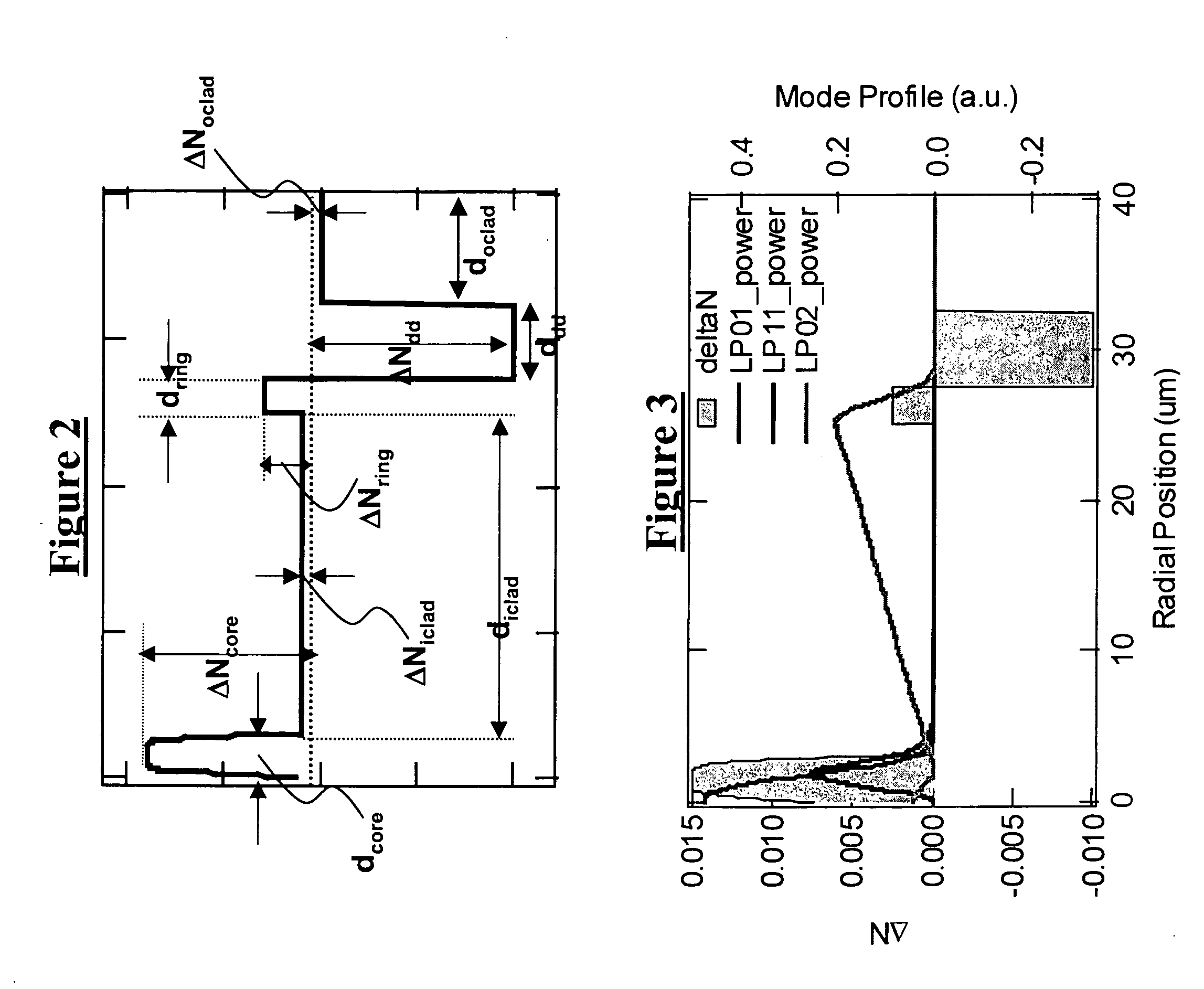
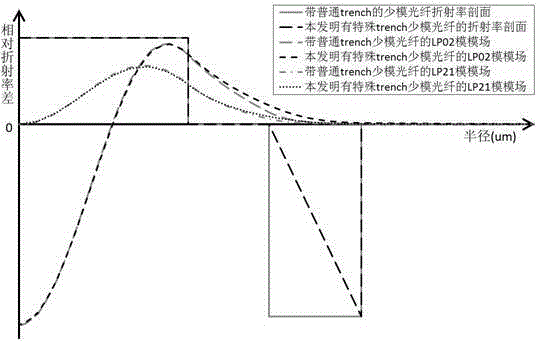
A few mode optical fiber suitable for use in a mode division multiplexing (MDM) optical transmission system is disclosed. The optical fiber has a graded-index core with a radius R1 in the range from 8 [mu]m to 14 [mu]m, an alpha value greater than or equal to about 2.3 and less than about 2.7 at a wavelength of 1550 nm, and a maximum relative refractive index Delta1MAX from about 0.3% to about 0.6% relative to the cladding. The optical fiber also has an effective area greater than about 90 [mu]m2 and less than about 160 [mu]m2. The core and cladding support only the LP01 and LP11 modes at wavelengths greater than 1500 nm. The cladding has a maximum relative refractive index Delta4MAX such that Delta1MAX>Delta4MAX, and the differential group delay between the LP01 and LP11 modes is less than about 0.5 ns / km at a wavelength of 1550 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Multiple LP-mode fiber designs for mode-division multiplexing
ActiveUS20150168643A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFew mode fiberCoupling
A few-mode fiber is described, having a graded-index core and a surrounding cladding comprising a ledge between the core and the trench, a down-doped trench abutting the ledge, and an undoped cladding region abutting the trench. The fiber's refractive index profile is configured to support 9 or more LP modes for transmission of a spatially-multiplexed optical signal. Undesired modes have respective effective indices that are close to, or less than, the cladding index so as to result in leakage of the undesired modes into the outer cladding. The index spacing between the desired mode having the lowest effective index and the leaky mode with the highest effective index is sufficiently large so as to substantially prevent coupling therebetween.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Low-attenuation few-mode fiber
ActiveCN104698534ALow DGD valueLow refractive indexOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingUltrasound attenuationFew mode fiber
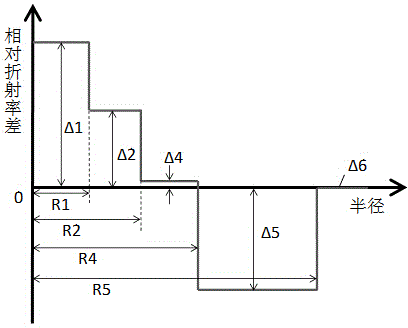
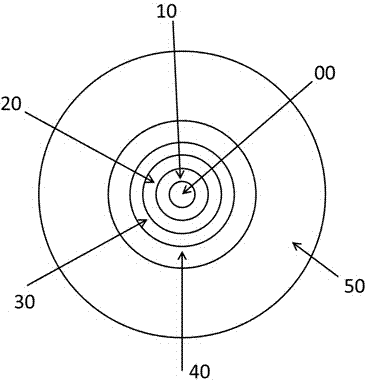
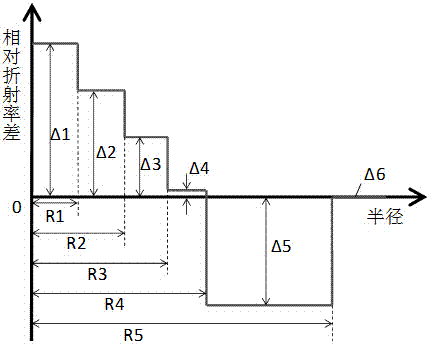
The invention relates to a low-attenuation few-mode fiber. The low-attenuation few-mode fiber is that two core layers are provided; three wrapping layers ware arranged at the outsides of the core layers from inside to outside; the relative refractive rate difference delta 1 of the first core layer is 0.30 to 0.42%, and the radius R1 is 5.4 to 8 microns; the relative refractive rate difference delta 2 of the second core layer is 0.20 to 0.25%, and the radius R2 is 10 to 13 microns; the first wrapping layer is an inner wrapping layer which is closely arranged around the core layers, the relative refractive rate difference delta 4 is -0.02 to 0.02%, and the radius R4 is 13.6 to 17 microns; the second wrapping layer is a sunken wrapping layer which is arranged closely around the inner wrapping layers, the relative refractive rate difference delta 5 is -0.8 to 0.4%, and the radius R5 is 17.5 to 30 microns; the third wrapping layer is an outer wrapping layer which is arranged closely around the sunken wrapping layer and is a pure quartz glass layer. The low-attenuation few-mode fiber supports four stable transmission modes under 1550nm, is relatively small in DGD, simple in process, convenient to manufacture, relatively low in attenuation and relatively high in bending resistance.
Owner:SHANTOU HIGH TECH ZONE AOXING OPTICAL COMM EQUIP
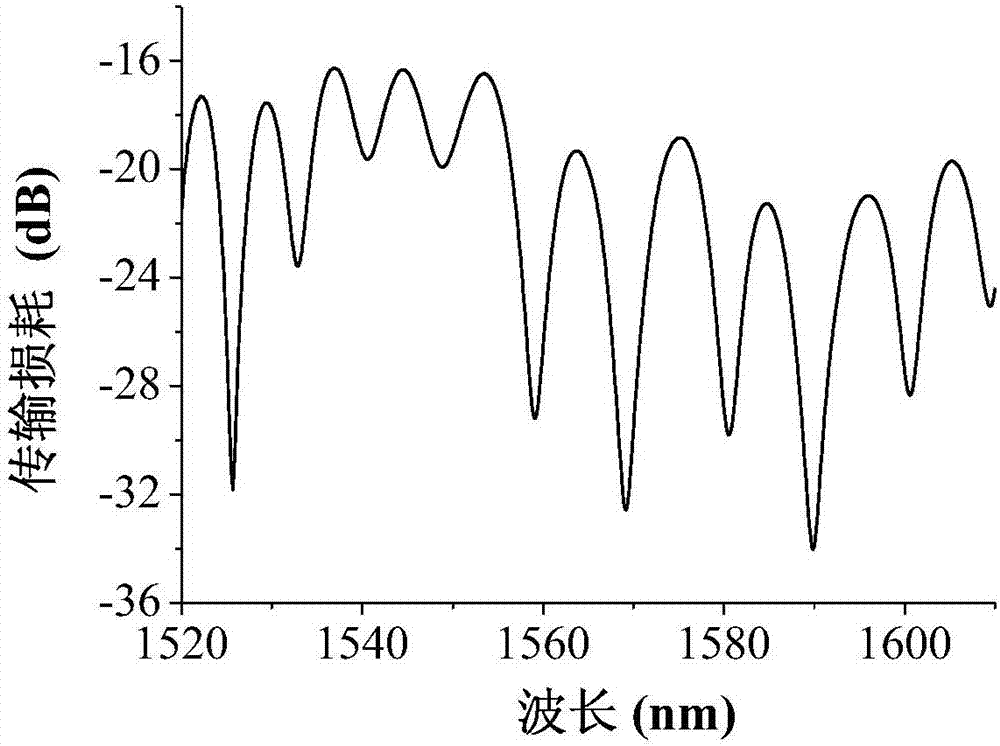
Few-mode fiber mode coupling measurement device based on two-photon lantern and few-mode fiber circulator
ActiveCN106895959AEasy to implementEasy to operateTesting fibre optics/optical waveguide devicesRayleigh scatteringMeasurement device
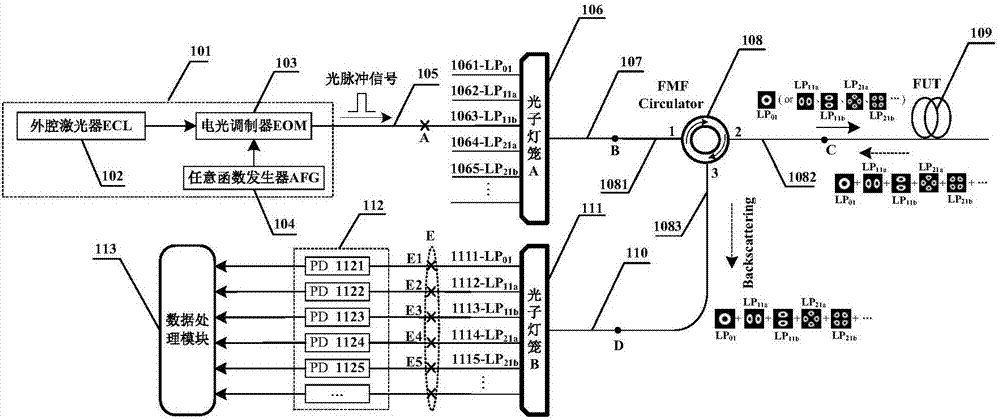
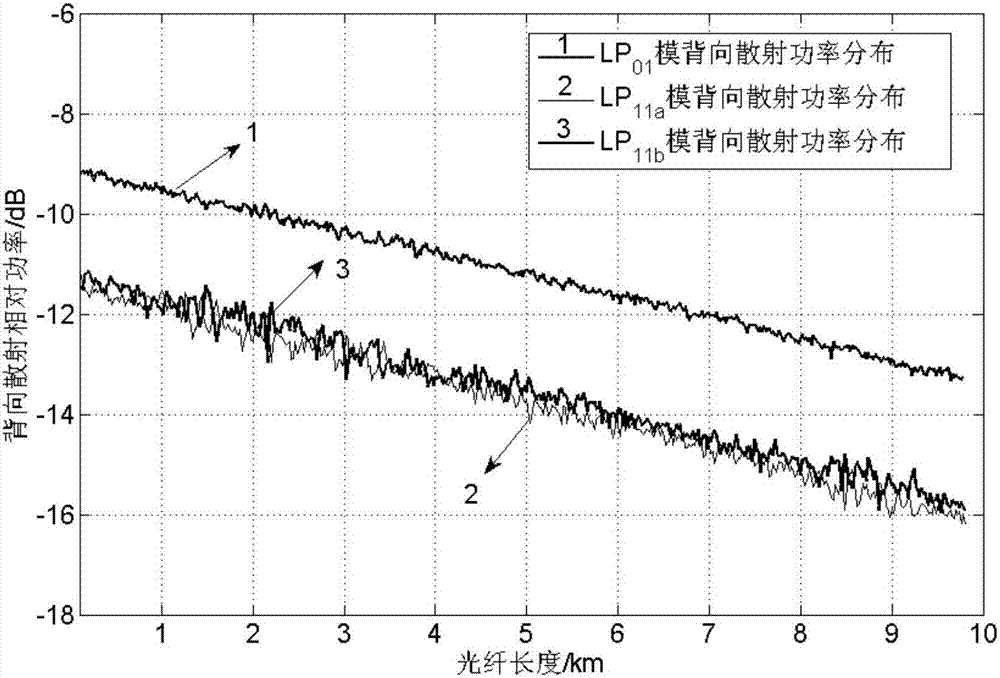
The invention provides a few-mode fiber mode coupling measurement device based on a two-photon lantern and a few-mode fiber circulator and belongs to the technical field of fiber characteristic measurement. The few-mode fiber mode coupling measurement device is composed of a light source, a photon lantern A, a few-mode fiber circulator, a measured fiber, a photon lantern B, a photoelectric detection module and a signal processing module. An optical pulse signal generated by the light source is subjected to spatial mode conversion through the photon lantern A to output a designated single stimulus mode, combined with the single-way transmission characteristics of the few-mode fiber circulator, the stimulus mode enters the measured fiber through the few-mode fiber circulator, a backward Rayleigh scattered light generated by coupling the stimulus mode in the measured fiber and the stimulus mode to the non-stimulus mode enters the photon lantern B through the few-mode fiber circulator for spatial model demultiplexing and being output from a corresponding mode port, and the output backward scattered light of each path is subjected to photoelectric detection and data processing, so that the measurement of the few-mode fiber mode coupling coefficient is achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Few-mode fiber with relatively low different group delay (DGD)
ActiveCN105204110ALow DGD valueBig MFDOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFew mode fiberMicrometer
The invention relates to a few-mode fiber with relatively low different group delay (DGD). The few-mode fiber comprises a core layer and claddings, and is characterized in that the relative refractive index difference delta 1 of the core layer is 0.24% to 0.36%; the radius R1 of the core layer is 9-12 micrometers; the claddings coating the core layer comprise an inner cladding, a sunken cladding and an outer cladding from inside to outside; the relative refractive index difference delta 2 of the inner cladding is -0.02% to 0.02%; the radius R2 of the inner cladding is 13.6-18 micrometers; the sunken cladding is divided into a first sunken cladding and a second sunken cladding; the radius R3 of the first sunken cladding is 16-30 micrometers; the difference between R3 and R2 is larger than or equal to 2 micrometers; the relative refractive index difference of the first sunken cladding is alpha-type refractive index distribution gradually reduced from delta 2 at R2 to delta 3 at R3; delta 3 is -0.8% to -0.4%; the relative refractive index difference of the second sunken cladding is delta 3; the radius R4 is 18.6-30 micrometers; R4 is larger than or equal to R3; the quotient of the difference between R3 and R2 divided by the difference between R4 and R2 is larger than or equal to 0.5 and smaller than or equal to 1; the outer cladding is a pure quartz glass layer. The few-mode fiber has lower DGD and relatively high MFD, and keeps relatively good anti-bending performance.
Owner:SICHUAN LEFEI OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Low-attenuation and few-mode fiber
ActiveCN104714273ALow DGD valueLow refractive indexOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingUltrasound attenuationFew mode fiber
The invention relates to a low-attenuation and few-mode fiber. A core layer has three layers and comprises three claddings from inside to outside; the relative refractive index difference delta 1 of a first core layer is 0.34%-0.45%, R1 ranges from 4.5 mu m to 7.5 mu m, the relative refractive index difference delta 2 of a second core layer is 0.20%-0.29%, R2ranges from8 mu m to 10 mu m, the relative refractive index difference delta 3 of a third core layer is 0.15%-0.24%, R3 ranges from 10 mu m to 13 mu m, the relative refractive index difference delta 4 of a first cladding is minus 0.02%-0.02%, R4 ranges from14 mu m to 18 mu m, the second cladding is a concave cladding, the relative refractive index difference delta 5 of the second cladding is minus 0.8%-minus 0.4%, R5 ranges from19 mu m to 31 mu m, and a third cladding is a pure quartz glass layer. According to the low-attenuation and few-mode fiber, four stable transmission modes are supported within 1550 nm, small DGD is provided, the process is simple, and the manufacturing is easy; at the same time, the low-attenuation and few-mode fiber has low attenuation and better bending resistance.
Owner:SHANTOU HIGH TECH ZONE AOXING OPTICAL COMM EQUIP
Optical communication system based on hybrid mode multiplexing
InactiveCN106411452AImprove transmission capacityImprove transmission performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsData informationEngineering
The invention relates to an optical communication system based on hybrid mode multiplexing, specifically an optical communication method and device based on hybrid mode multiplexing. The method comprises the steps that optical signal modulation units generate single-wavelength fundamental mode modulation output optical signals under modulation of a baseband data signal; hybrid mode multiplexing optical signals are formed; the hybrid mode multiplexing optical signals are transmitted in a transmission medium, and hybrid mode multiplexing output optical signals are generated; single-wavelength channel or wavelength division multiplexing multichannel fundamental mode output optical signals are formed according to the hybrid mode multiplexing output optical signals; multi-way single-wavelength channel fundamental mode output optical signals are formed according to the wavelength division multiplexing multichannel fundamental mode output optical signals; each single-wavelength channel fundamental mode output optical signal passes an optical signal modulation unit, thereby outputting transmitted data information. According to the method and the device, mode resources of a free space or communication transmission few-mode optical fibers are utilized fully, mode utilization rates can be improved to the greatest extent, and the transmission capability and transmission performance of an optical communication system are increased.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Mode selection coupler based 8-shaped cavity mode locking column vector fiber laser
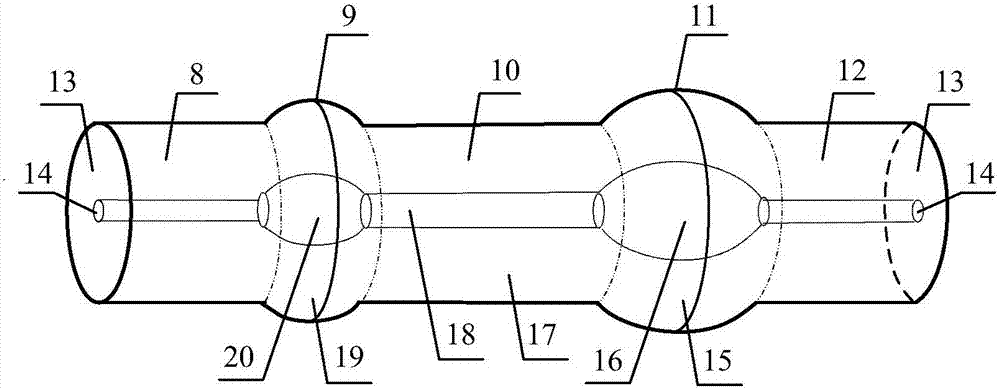
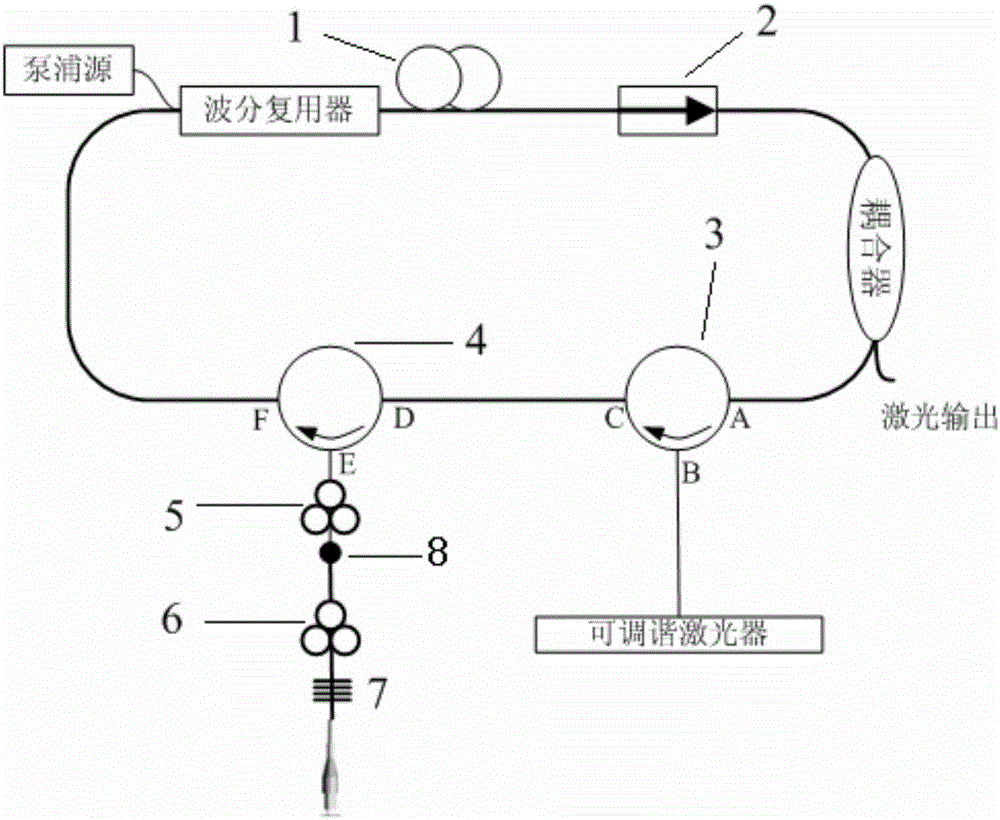
PendingCN106848823ALow insertion lossIncreased Polarization PurityActive medium shape and constructionEngineeringGain
The invention discloses a mode selection coupler based 8-shaped cavity mode locking column vector fiber laser including a pump source, a wavelength division multiplexer, a gain fiber, a single-mode fiber, a first polarization controller, a second polarization controller, a 3dB coupler, an isolator, a coupler and a mode selection coupler. The output terminal of the pump source is connected with a short wavelength input terminal of the wavelength division multiplexer. The output terminal of the wavelength division multiplexer is connected with a 1 port input terminal of the 3dB coupler through the gain fiber, the single-mode fiber and the first polarization controller successively. A 2 port input terminal of the 3dB coupler is connected with a long wavelength port of the wavelength division multiplexer. A 4 port is connected with a 3 port of the 3dB coupler through the isolator, the coupler and the mode selection coupler successively. Therefore, an 8-shaped resonance cavity is formed. The second polarization controller is connected with a less-mode fiber output terminal of the mode selection coupler. The invention has advantages of being narrow in fiber laser output pulses, high in column vector laser polarization purity, small in loss and low in cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multidimensional coded-modulation for high-speed optical transport over few-mode fibers
Systems and methods for data transport are provided which encode streams of data using low density parity check (LDPC) encoders and map data streams to symbols, by assigning bits of symbols to a signal constellation and associating bits with constellation points. Constellation points are generated using a D-dimensional optimum signal constellation design (OSCD) method. The OSCD determines an optimum source distribution for an optical channel, generates D-dimensional training sequences from the optimum source distribution, determines new signal constellation points as the center of mass for each D-dimensional cluster of points, and repeats these steps until convergence or until a predetermined number of iterations is reached. Coordinates obtained by the D-dimensional OSCD method are stored in a look-up-table (LUT), points are selected from the LUT using encoded data streams, coordinates are input into a D-dimensional modulator after digital-to-analog conversion (DAC), and a modulated signal is transmitted over an optical medium.
Owner:NEC CORP
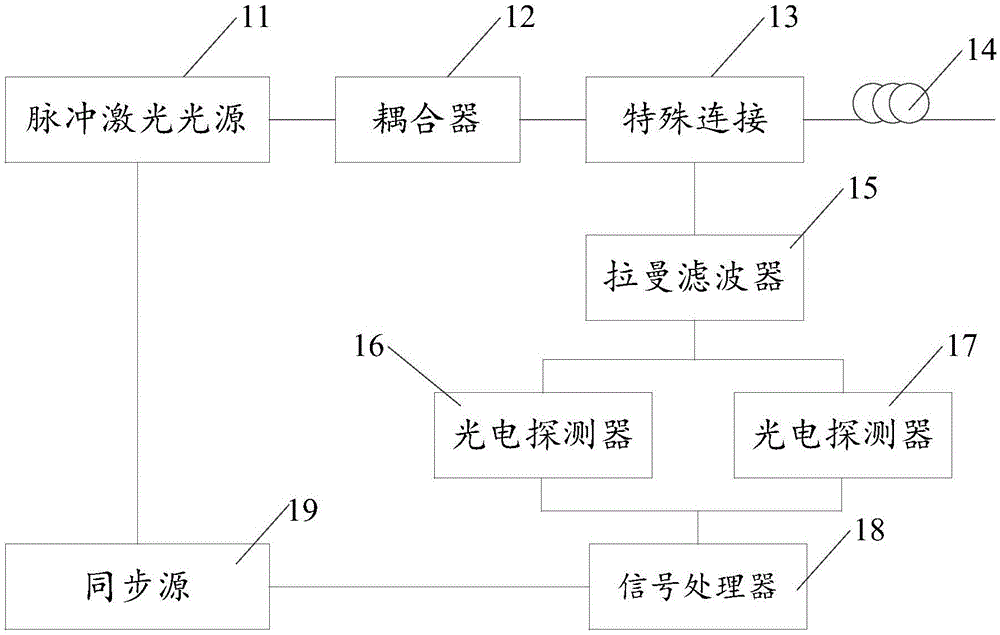
Few-mode fiber based Raman distributed temperature measurement system and temperature measurement method
ActiveCN105043586AImprove detection distanceImprove spatial resolutionThermometers using physical/chemical changesLaser lightTransmission loss
The invention discloses a few-mode fiber based Raman distributed temperature measurement system and a temperature measurement method. The temperature measurement system comprises a pulse laser light source, a coupler, special connector, a few-mode fiber, a Raman filter, two photoelectric detectors and a signal processor, and is characterized in that pulse laser outputted by the coupler gets into the few-mode fiber through the special connector, and back-scattering light is generated in the transmission process of the pulse laser in the few-mode fiber; the back-scattering light is inputted into the Raman filter through a back output port of the coupler, and the Raman filter carries out filtering on Raman Stokes light and Raman anti-Stokes light respectively; the two photoelectric detector respectively receive scattered light outputted from the two ports and carry out photoelectric conversion; and the signal processor carries out processing on outputted electric signals so as to acquire temperature information. According to the invention, the few-mode fiber is low in transmission loss, and the intermodal dispersion is far less than that of a multi-mode fiber, thereby not only increasing the detecting distance of the temperature measurement system, but also improving the spatial resolution of the temperature measurement system.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
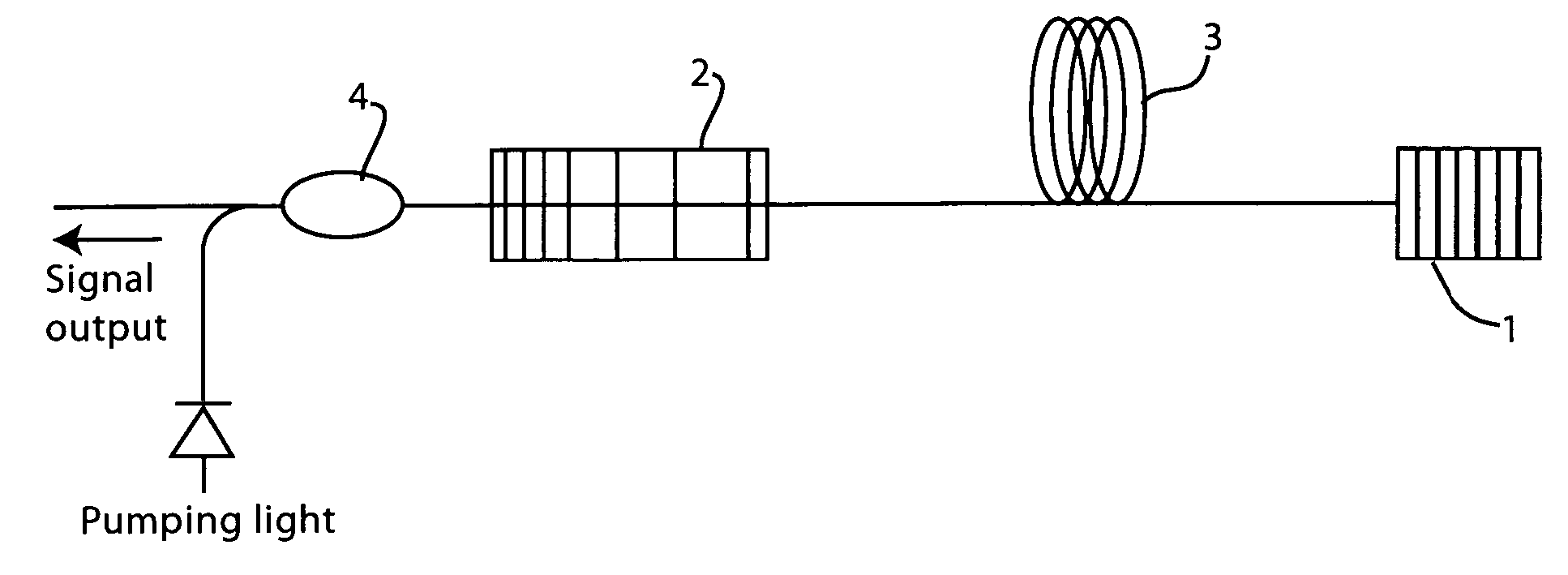
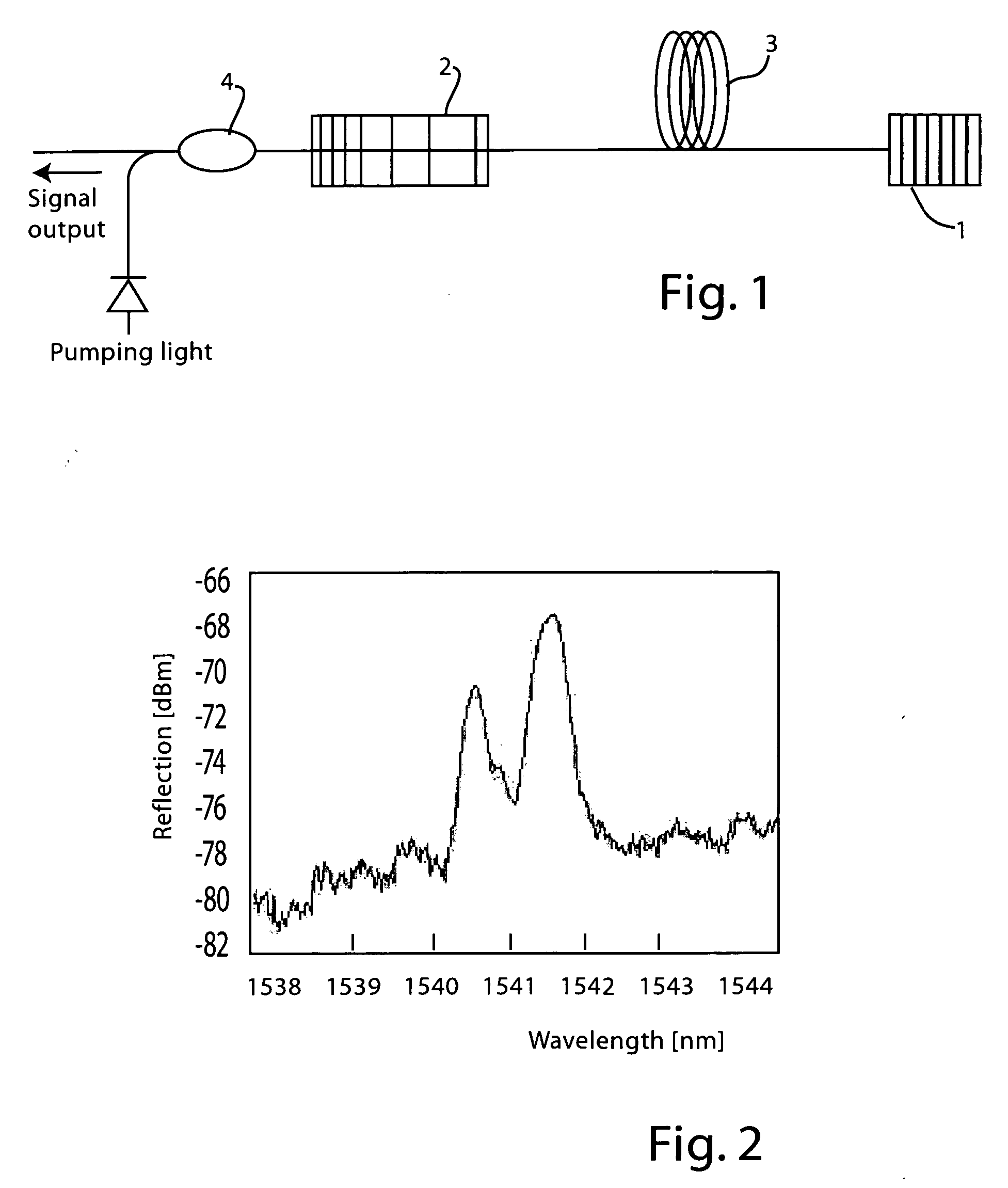
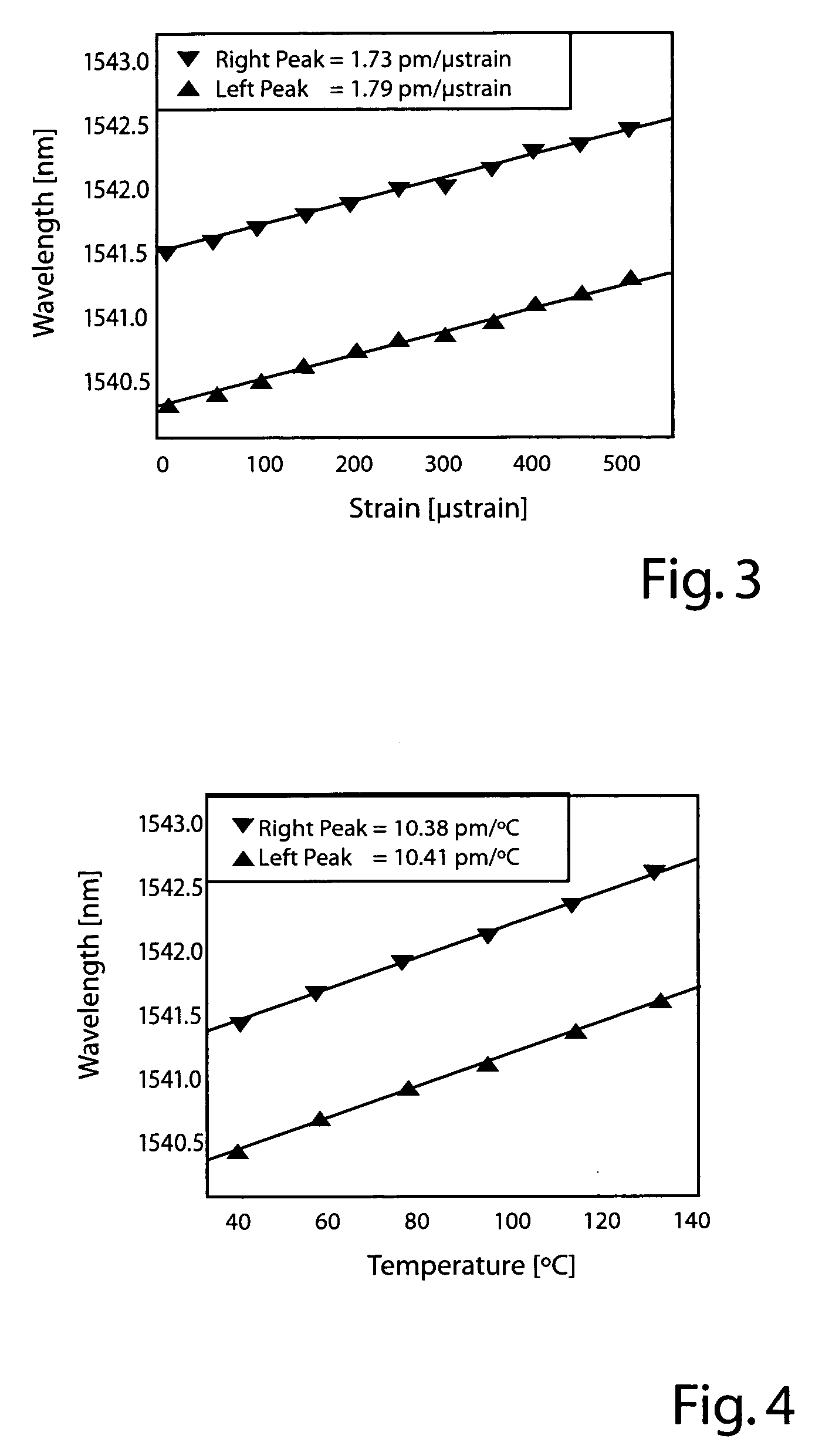
Raman or erbium-doped fiber laser using few-mode fiber grating, and long-distance remote sensor for simultaneously measuring temperature and strain by separating temperature and strain components using the same
Disclosed are a Raman or erbium-doped fiber laser using a few-mode fiber grating, and a long-distance remote sensor using the same that can simultaneously measure temperature and strain by separating temperature and strain components using Raman amplification or erbium amplification. When a multi-wavelength Raman or erbium-doped laser is configured by means of a short-period fiber grating serving as a few-mode fiber grating at one side of a resonator and a chirped fiber Bragg grating or tunable chirped fiber Bragg grating at the other side of the resonator, multi-wavelength laser signals are generated in different modes. Because wavelength shift and reflectivity vary with a change in temperature and strain, temperature and strain components can be simultaneously measured. Because an optical fiber of several tens of kilometers is used, it can be utilized as a sensing probe of the long-distance remote sensor.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Large Mode Area Fibers Using Higher Order Modes
ActiveUS20060269200A1Increase the areaImprove loss performanceLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFew mode fiberEngineering
The specification describes an optical fiber device wherein a LOM is converted to an HOM prior to entering the gain section. The gain section is a few mode fiber that supports the HOM. The output from the gain section, i.e. the HOM, may be utilized as is, or converted back to the LOM. With suitable design of the few mode fiber in the gain section of the device, the effective area, Aeff, may be greater than 1600 μm2. The large mode separation in the gain section reduces mode coupling, allowing greater design freedom and reducing the bend sensitivity of the optical fiber.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
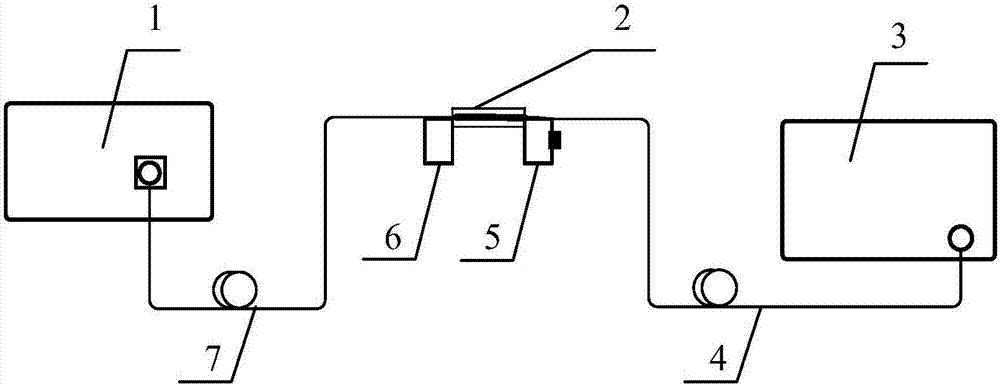
Optical fiber mode add-drop multiplexer
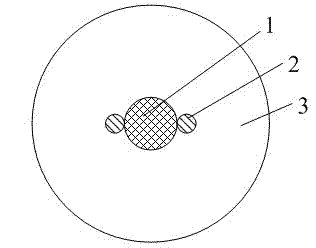
InactiveCN103698842AImprove coupling efficiencyIncrease the effect of selective couplingCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesFew mode fiberMultiplexer
The invention discloses an optical fiber mode add-drop multiplexer. The add-drop multiplexer is a multi-core optical fiber; optical fiber cores comprise two main body optical fiber cores and a plurality of auxiliary optical fiber cores, wherein the connecting line of the centers of all the optical fiber cores is a straight line; the auxiliary optical fiber cores are positioned between the two main body optical fiber cores; the center distances of two adjacent auxiliary optical fiber cores are the same; the auxiliary optical fiber cores are single-mode optical fibers. A plurality of multiplexing modes to be separated are input from one main body optical fiber core, one mode is output from the other main body optical fiber core, and the other modes are still output from the original main body optical fiber core. According to the optical fiber mode add-drop multiplexer, the coupling length differences among different modes are increased by introducing the auxiliary optical fiber cores and coupling specific modes of the main body optical fiber cores, effective separation of the modes is realized, interference among the modes is inhibited effectively, and the functions of selectively extracting or inserting the specified modes of a plurality of modes transmitted in a few-mode optical fiber are realized.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
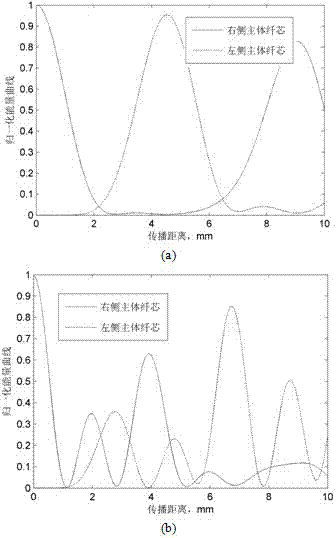
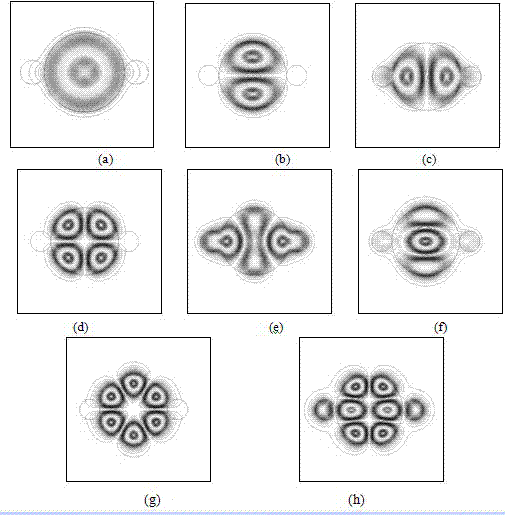
Low-degeneracy few-mode fiber
ActiveCN103698843AGood circular symmetryIncrease the effective refractive index differenceLaser detailsMulticore optical fibreFew mode fiberMechanical engineering
The invention provides a low-degeneracy few-mode fiber, which comprises a fiber core and a cladding. The fiber core consists of a main fiber core and 2N auxiliary fiber cores; the main fiber core is located in the center of the fiber; the 2N auxiliary fiber cores are symmetrically arranged at both sides of the main fiber core; the center of the main fiber core and the centers of the 2N auxiliary fiber cores are located on the same straight line; the main fiber core and the auxiliary fiber cores are the same in refractive index; the boundary of the main fiber core is tangential to the boundary of the adjacent auxiliary fiber cores; the boundaries of the two adjacent auxiliary fiber cores are tangential; the diameter of each auxiliary fiber core is smaller than that of the main fiber core, and the diameters the auxiliary fiber cores are decreased progressively from inside to outside. According to the low-degeneracy few-mode fiber provided by the invention, by introducing the auxiliary fiber cores, the circular symmetry of the refractive index distribution of the fiber is broken to form refractive index distribution with double symmetry. Through the refractive index distribution with the double symmetry, a high-order mode with fourfold degeneracy drops to a twofold-degeneracy mode, and therefore, the effective refractive index difference of the main fiber core and the auxiliary fiber cores is increased, and the mode field distribution form of the high-order mode is fixed.
Owner:JIANGYIN ZHICHANGHUI INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OPERATION CO LTD
Device and method for generating hollow beam with adjustable polarization state
InactiveCN102289075AQuality improvementLess distracting factorsOptical elementsFew mode fiberLight beam
A device and method for generating a hollow beam with an adjustable polarization state. The device includes a laser light source. Along the laser output direction of the laser source, a polarizer, a quarter-wave plate, a microscope objective lens, an optical fiber, and a collimator are sequentially arranged. lens and multidimensional adjustment mount, the microscopic objective lens is fixed on the fixture of the multidimensional adjustment mount, the input end of the optical fiber is fixed on the fiber support of the multidimensional adjustment mount, and the end face of the input end is located at the On the rear focal point of the above-mentioned microscopic objective lens, the end face of the output end of the optical fiber is located at the front focal point of the collimator lens, the optical fiber is a few-mode optical fiber, and the multi-dimensional adjustment frame also has a first knob, The second knob and the third knob respectively adjust the horizontal and pitch angles of the microscope objective lens through the fixture, so as to realize the off-axis incidence of the focused light beam on the optical fiber. The invention has the advantages of simple device structure and easy operation, and can realize high-quality hollow beam output with adjustable polarization state.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
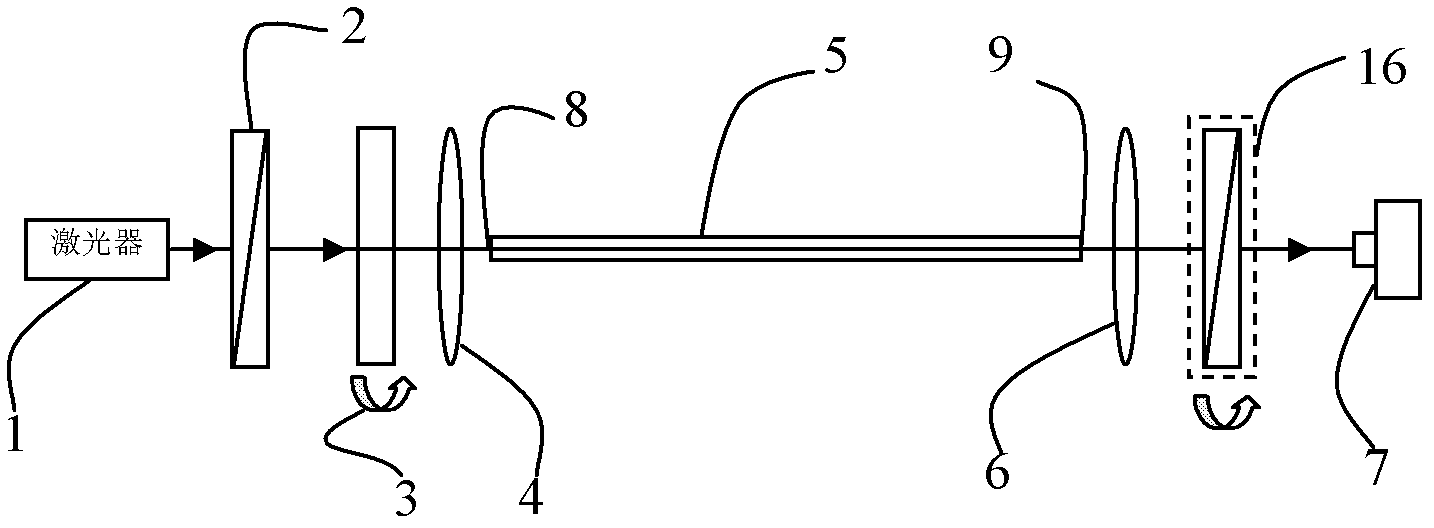
Asymmetric coarse taper structure few-mode fiber strain sensor
InactiveCN107121083ACompact structureEasy to makeUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyFew mode fiberSpectrograph
The invention discloses an asymmetric coarse taper structure few-mode fiber strain sensor. The asymmetric coarse taper structure few-mode fiber strain sensor comprises a broadband light source, a sensing unit and a spectrograph, wherein the sensing unit comprises an incidence single-mode optical fiber, a few-mode optical fiber and an outgoing single-mode optical fiber, one end of the incidence single-mode optical fiber is connected with a light source by virtue of a lead-in single-mode optical fiber, the other end of the incidence single-mode optical fiber is connected with one end lumber spine of the few-mode optical fiber in an amplification and fusing manner, the other end of the few-mode optical fiber is connected with a lumber spine of the outgoing single-mode optical fiber in an amplification and fusing manner, and the other end of the outgoing single-mode optical fiber is connected with a spectrograph. The asymmetric coarse taper structure few-mode fiber strain sensor is compact in structure, simple in preparation, capable of measuring transverse tensile and longitudinal curvature, accurate in measurement result, high in sensitivity and wide in application potential in various strain measurement fields.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
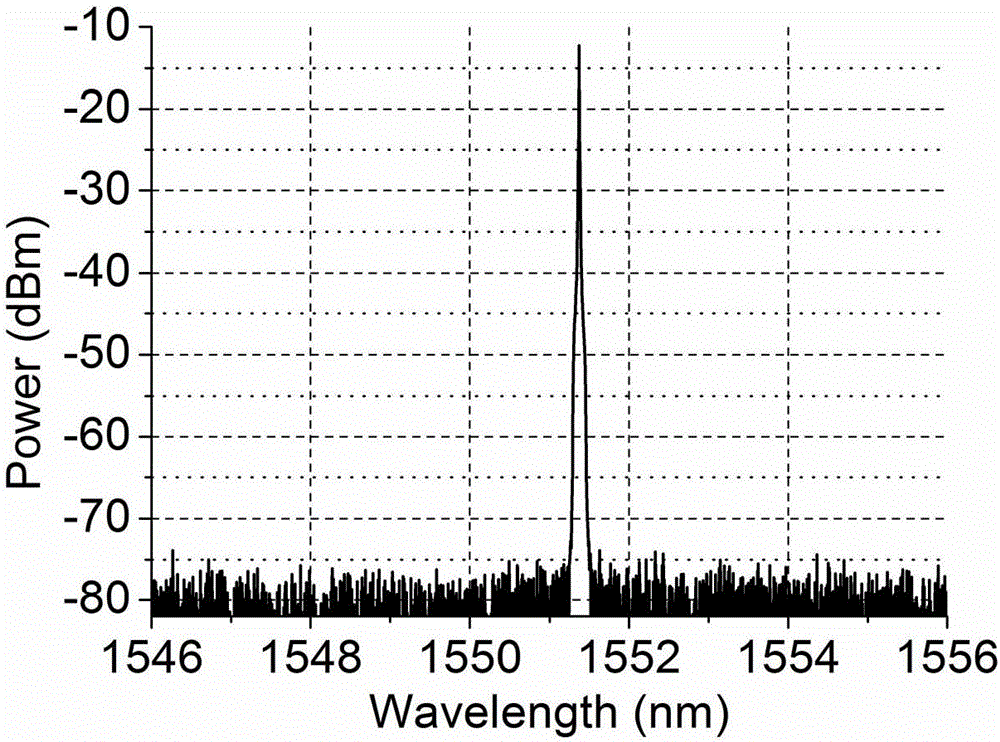
Active ring resonator-based single longitudinal mode low noise narrow band column vector fiber laser
InactiveCN106253039AIncreased Polarization PurityStable output powerActive medium shape and constructionLow noiseGrating
The invention discloses an active ring resonator-based single longitudinal mode low noise narrow band column vector fiber laser. The single longitudinal mode low noise narrow band column vector fiber laser comprises a pumping source, a wavelength division multiplexer, a gain fiber, an isolator, a coupler, a seed source, a first optical circulator, a second optical circulator, a single-mode fiber, a few-mode fiber engraved with a grating, a first polarization controller and a second polarization controller which are connected with one another in a closed end-to-end manner through a fiber coupling way to form a ring optical fiber resonator. The components of the single longitudinal mode low noise narrow band column vector fiber laser adopts an all-fiber coupling mode; the structure is compact, the polarization purity of output column vector laser is high, the coherence is well, a single longitudinal mode working manner is realized, and the spectrum stability is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Gain-Equalized Few-Mode Fiber Amplifier
A few-mode rare-earth-doped amplifier fiber has equalized gain for the supported signal transmission modes. The fiber has a raised-index core surrounded by a lower-index cladding region. The core has a radius a1 and an index difference Δn1 relative to the surrounding cladding region and is configured to support, at a selected signal wavelength, a set of lower-order fiber modes having an optical field with a diameter greater than 2·a1. The fiber further includes an active region, doped with a rare-earth dopant, comprising an inner portion that is coextensive with the core and an outer portion that surrounds the inner portion and extends into the cladding. The active region has an outer radius a2 greater than a1 that encompasses the optical field of the set of lower-order fiber modes at the selected signal wavelength.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Few-mode time-domain reflectometer
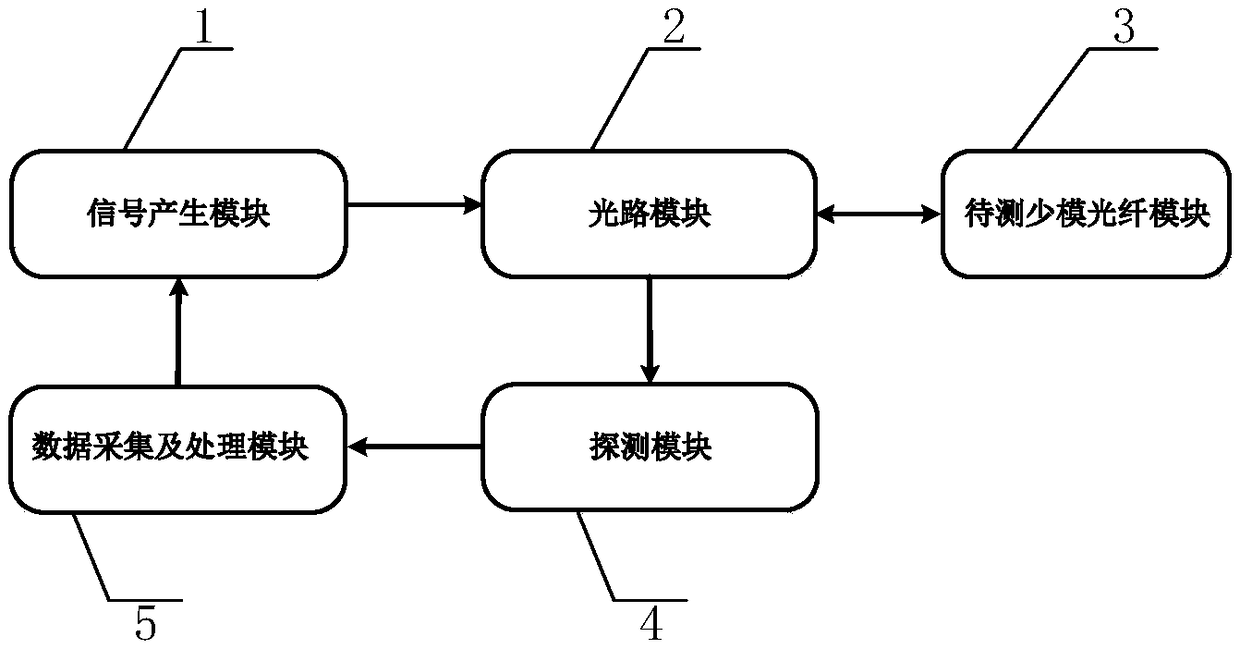
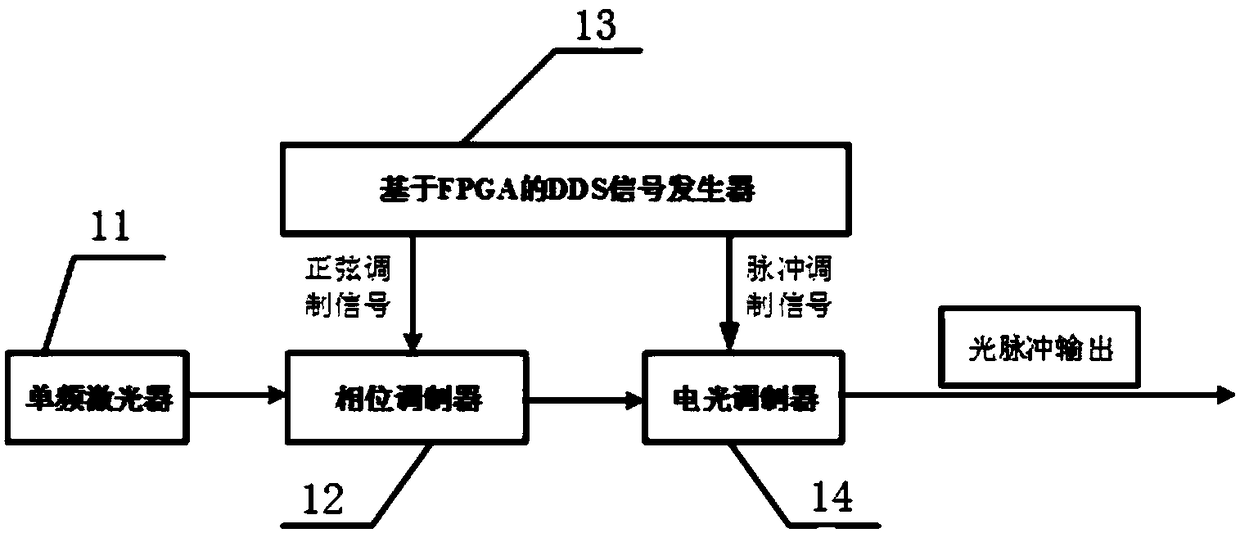
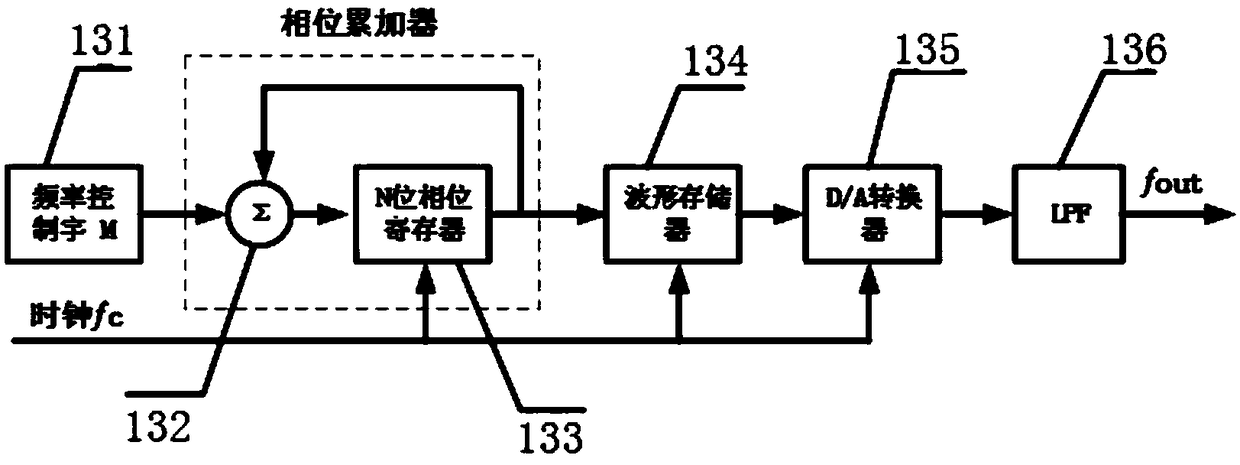
InactiveCN109120337ARegulatory intelligenceTroubleshooting multimodal survey measurementsElectromagnetic transmittersRayleigh scatteringTime-domain reflectometer
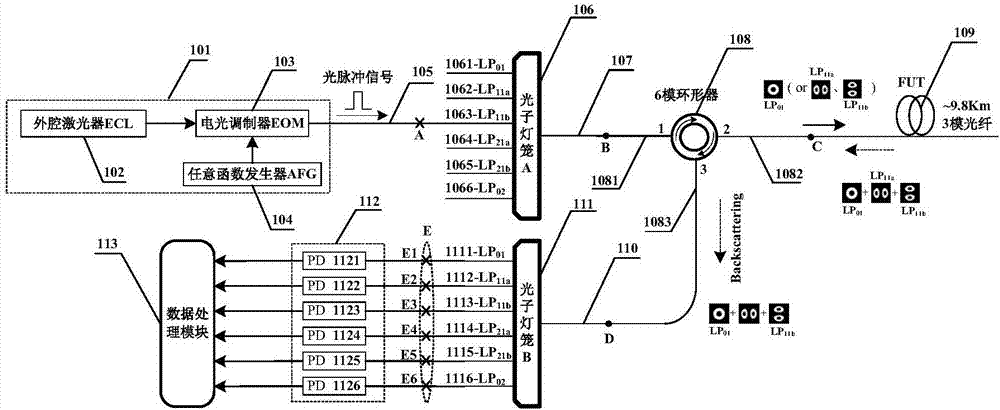
The invention discloses a few-mode time-domain reflectometer, and belongs to the technical field of fiber characteristic measurement. The reflectometer is composed of a signal generation module, an optical path module, a few-mode fiber module to be tested, a detection module and a data collection and processing module; the signal generation module generates a multi-frequency light pulse signal, the multi-frequency light pulse signal is input to the optical path module, a spatial mode is converted in the optical path module, the light signal after conversion is input to the few-mode fiber module to be tested, backward rayleigh scattered light of the few-mode fiber module to be tested is returned to the optical path module for mode separation, the mode separated light signal is input to thedetection module for photoelectric conversion, and the converted signals is input to the data collection and processing module to realize signal collection, processing and display. The reflectometer fills the blank in an online monitor applied to few-mode fibers, and intelligent network monitoring, damage measurement and fault location of the few-mode fibers are realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
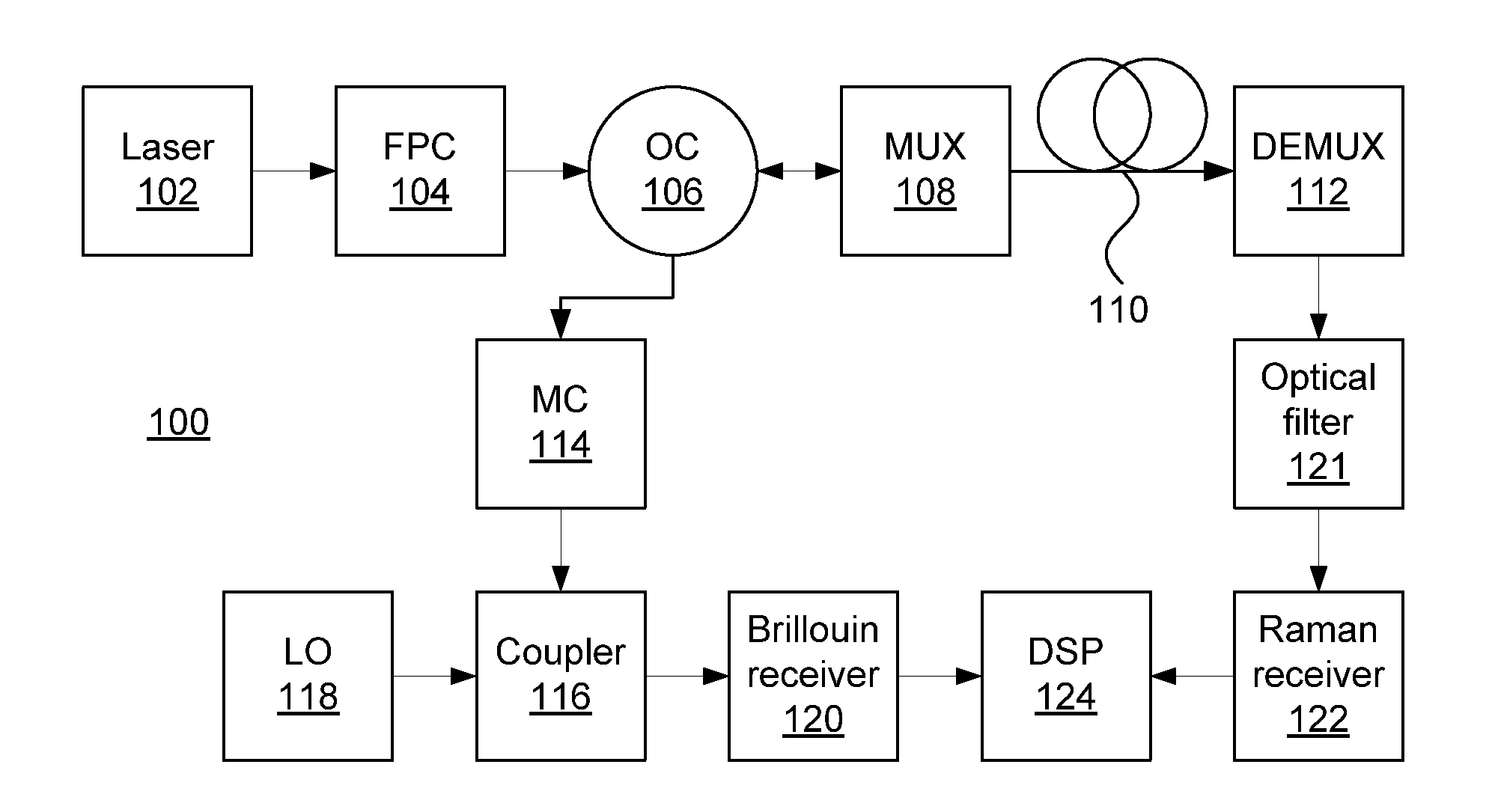
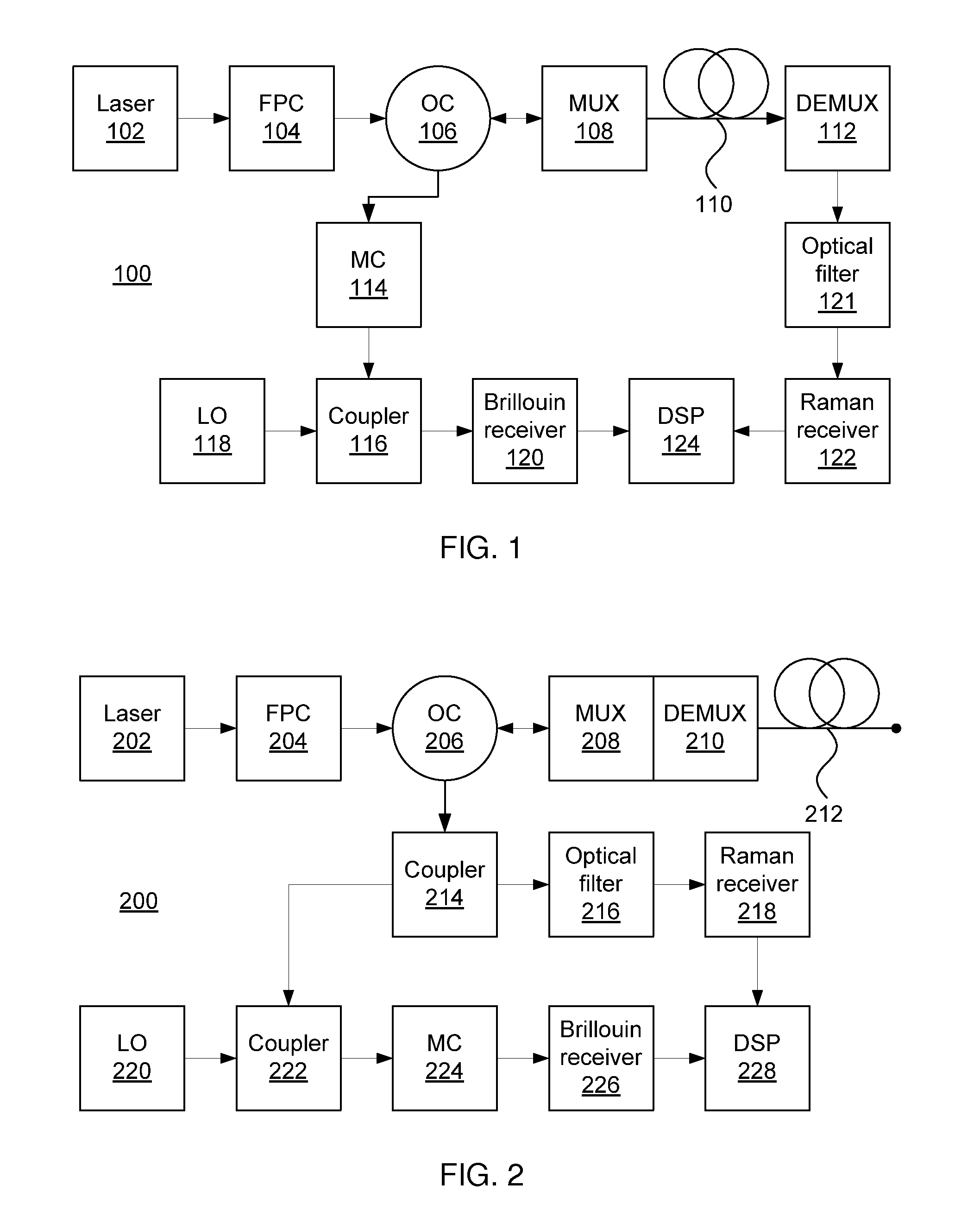
Hybrid raman and brillouin scattering in few-mode fibers
ActiveUS20160109222A1Force measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansFew mode fiberLight beam
Methods and systems of sensing conditions in a fiber includes launching a light beam into a fiber. A first branch of scattered light is set to a mode other than a fundamental mode. A second branch of scattered light is optically filtered to remove unscattered input light. Brillouin scattered light is coherently detected on the first branch to produce a combined temperature / strain profile of the fiber. Raman scattered light on the second branch is directly detected to produce a temperature profile of the fiber. A strain profile of the fiber is determined, using a processor, based on the combined temperature / strain profile and the temperature profile.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com