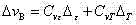Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1117 results about "Erbium doping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is a device that amplifies an optical fiber signal. It is used in the telecommunications field and in various types of research fields. An EDFA is "doped" with a material called erbium.
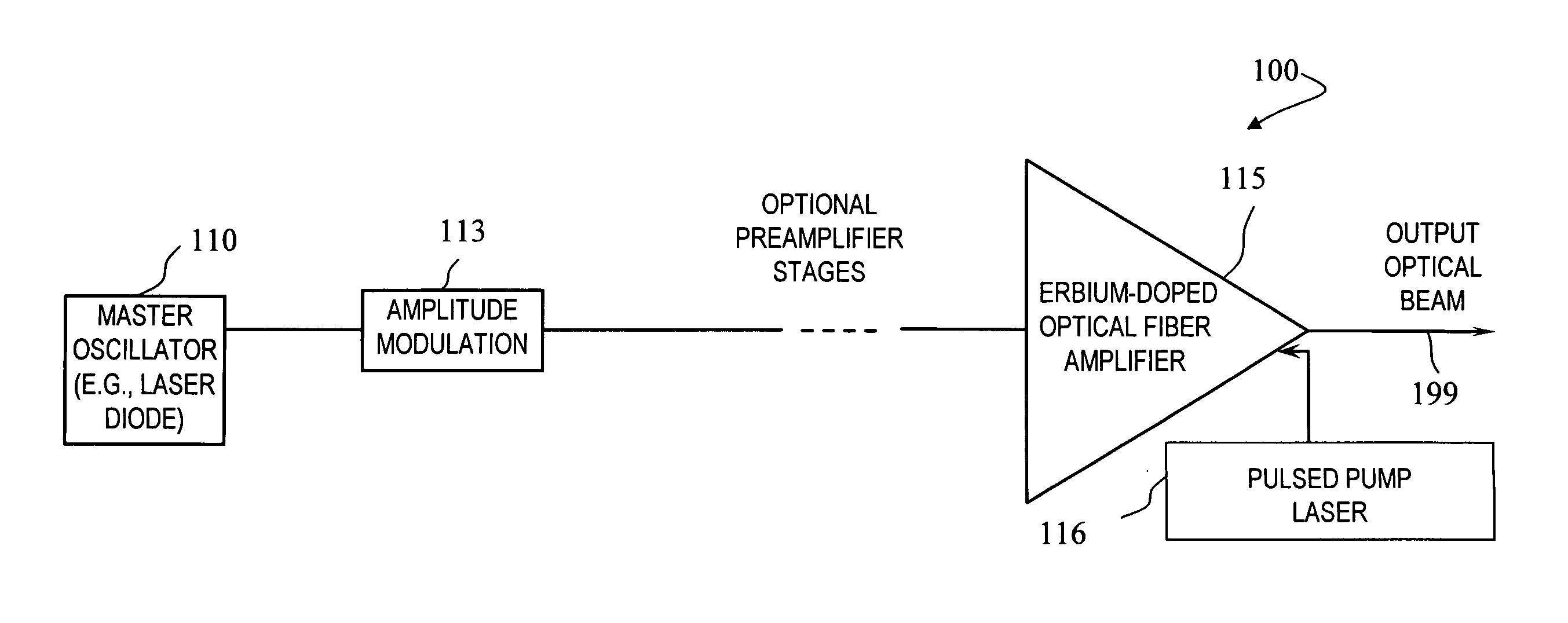
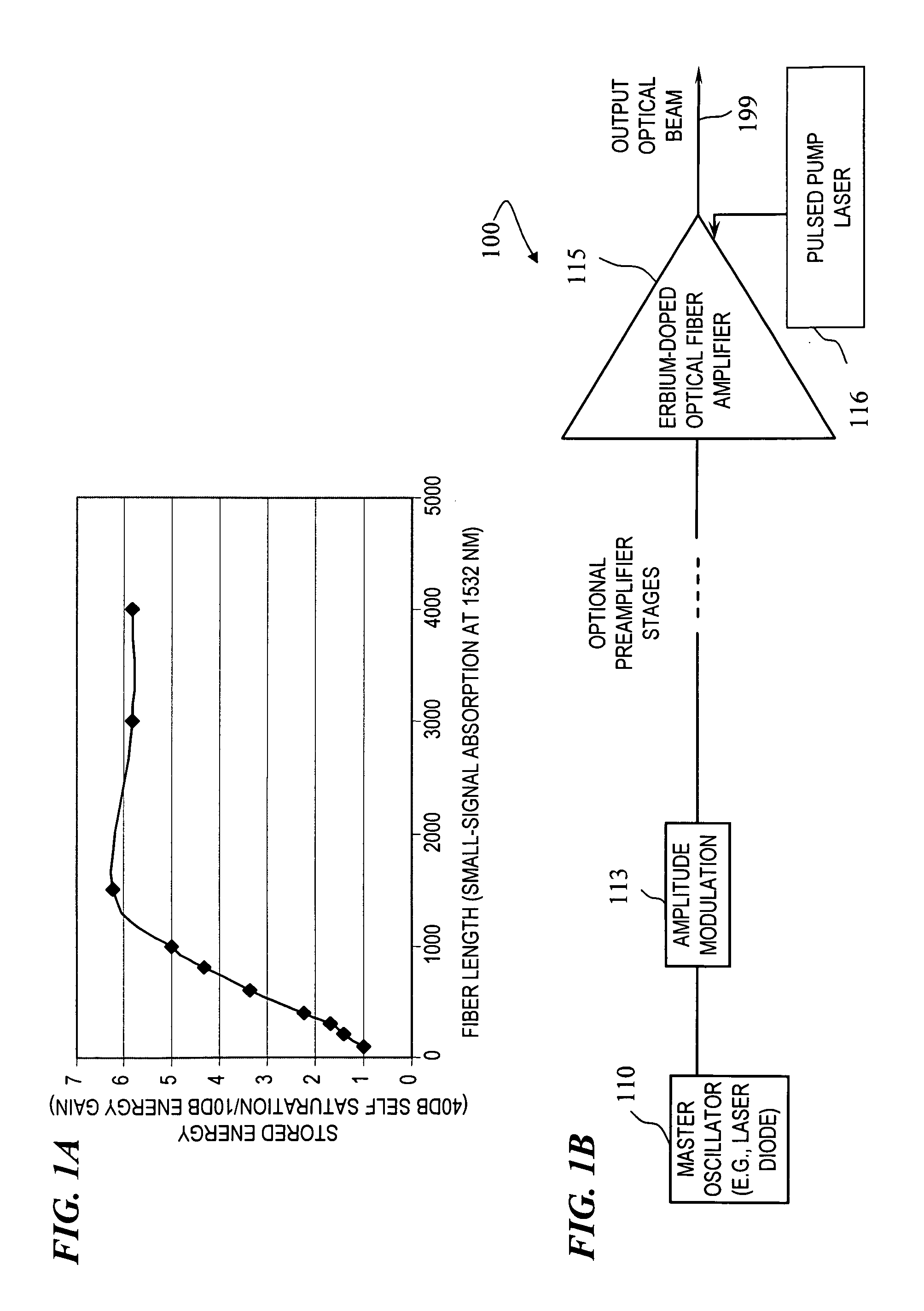
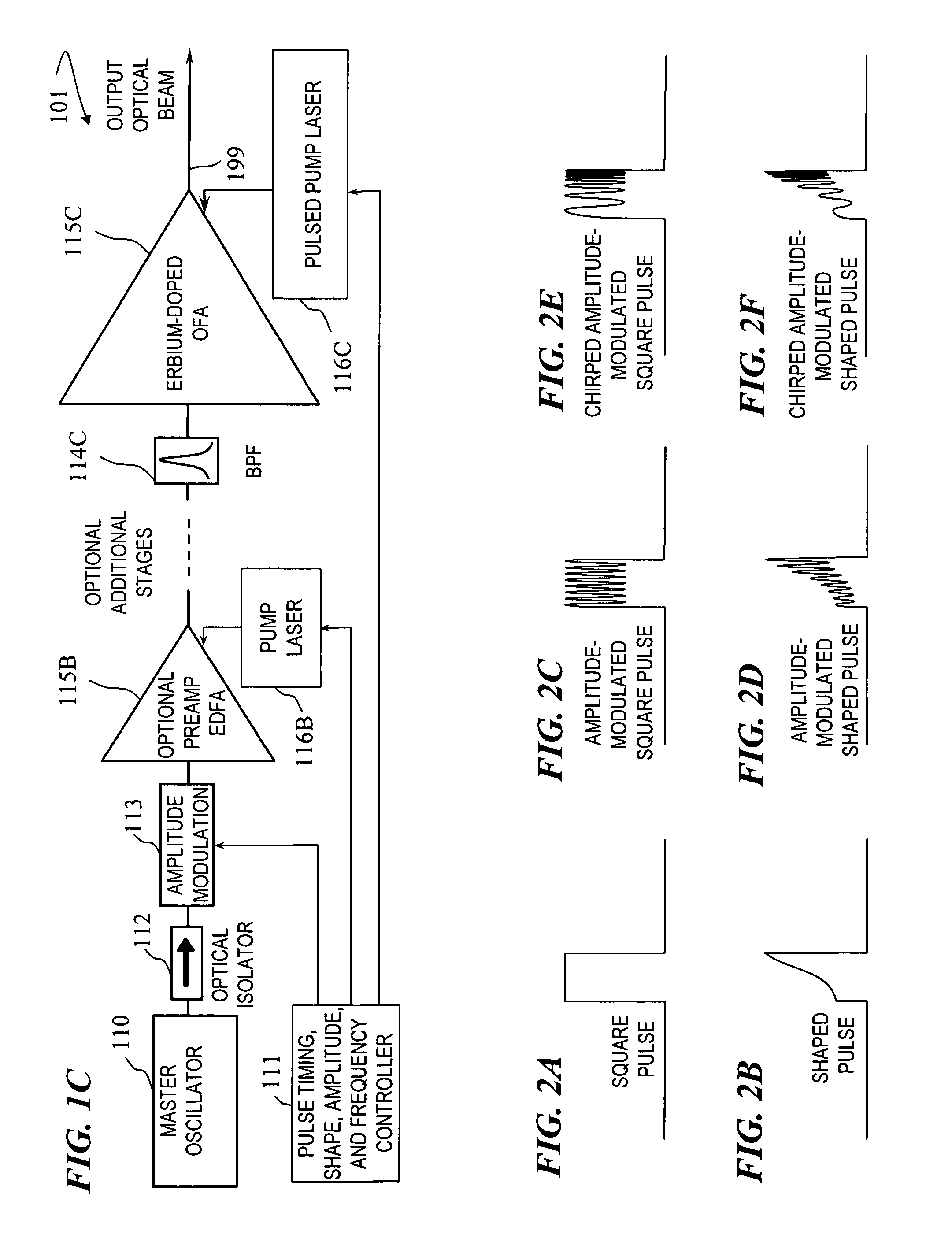
High-energy eye-safe pulsed fiber amplifiers and sources operating in erbium's L-band
InactiveUS7872794B1Enhance efficiency and energy storageHigh energyLaser detailsFibre transmissionFiberHigh energy
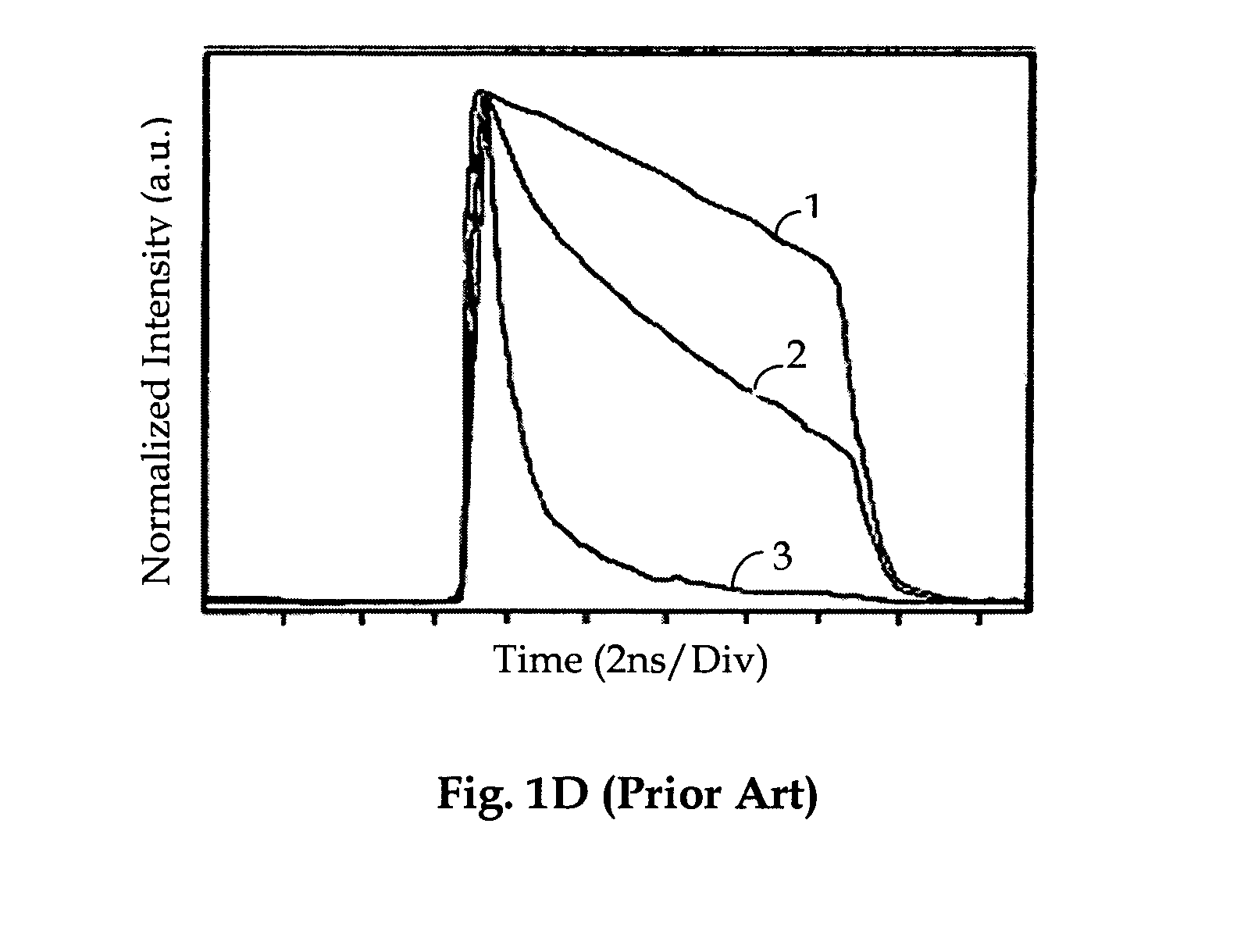
An apparatus and that provide an optical-fiber amplifier having at least one erbium-doped fiber section and an optical pump coupled to the erbium-doped fiber section, wherein the apparatus is operable to amplify signal pulses to high energy in the erbium-doped fiber section, the pulses having a wavelength in the range of about 1565 nm to about 1630 nm. In some embodiments, the amplifying fiber is ytterbium free.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
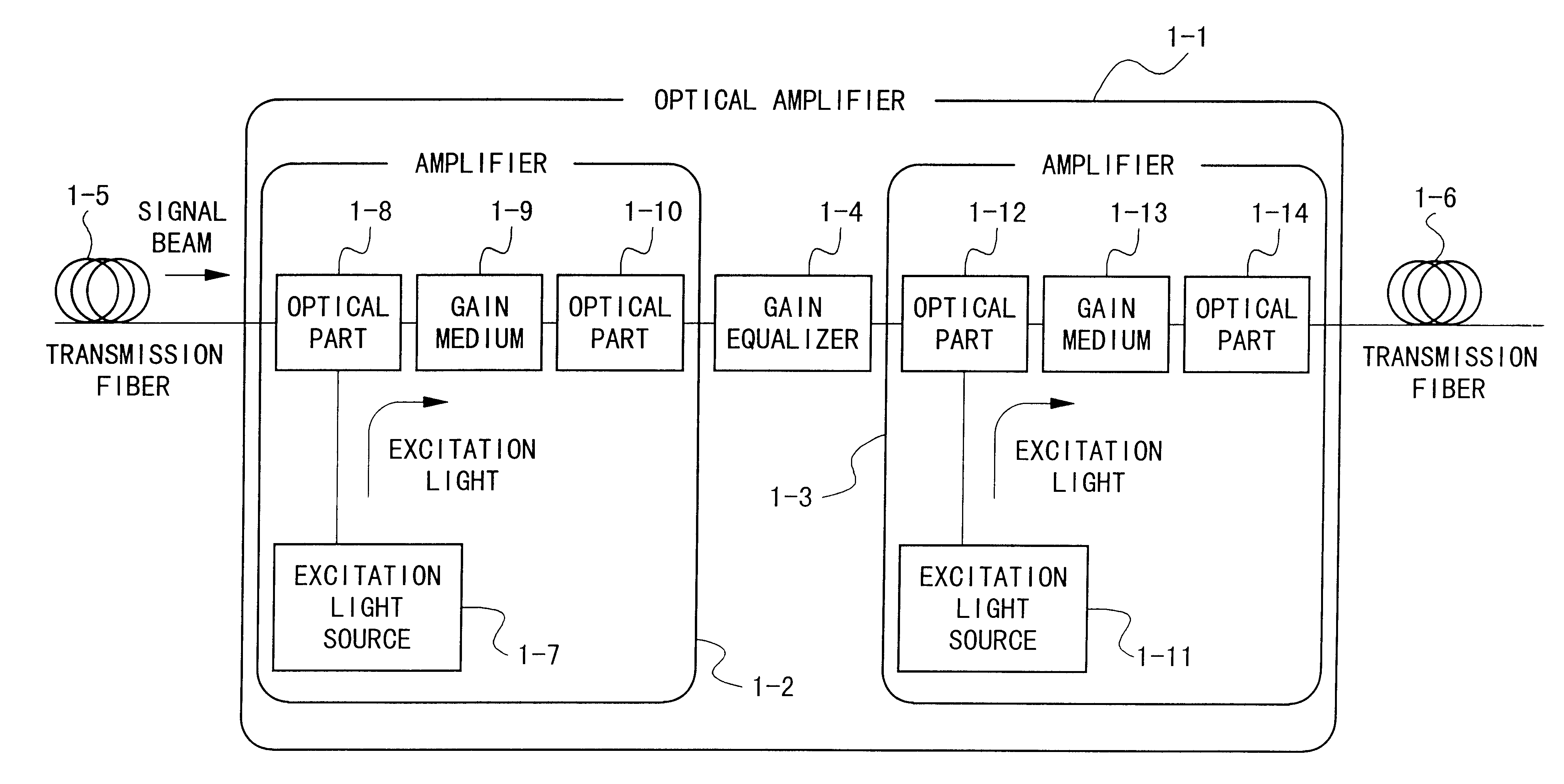
Optical amplifier and transmission system using the same
InactiveUS6172803B1Laser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesFiberErbium doping
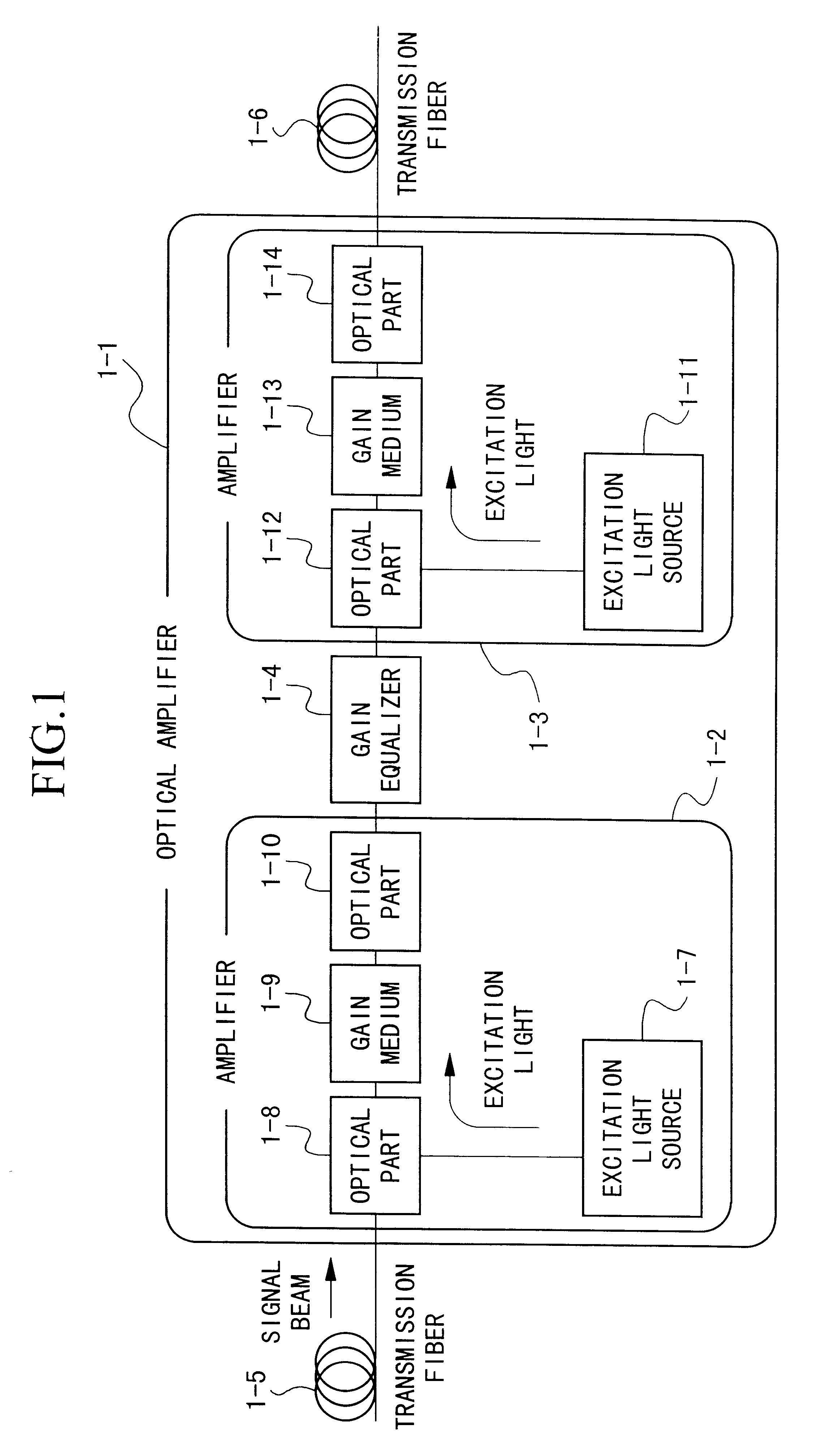
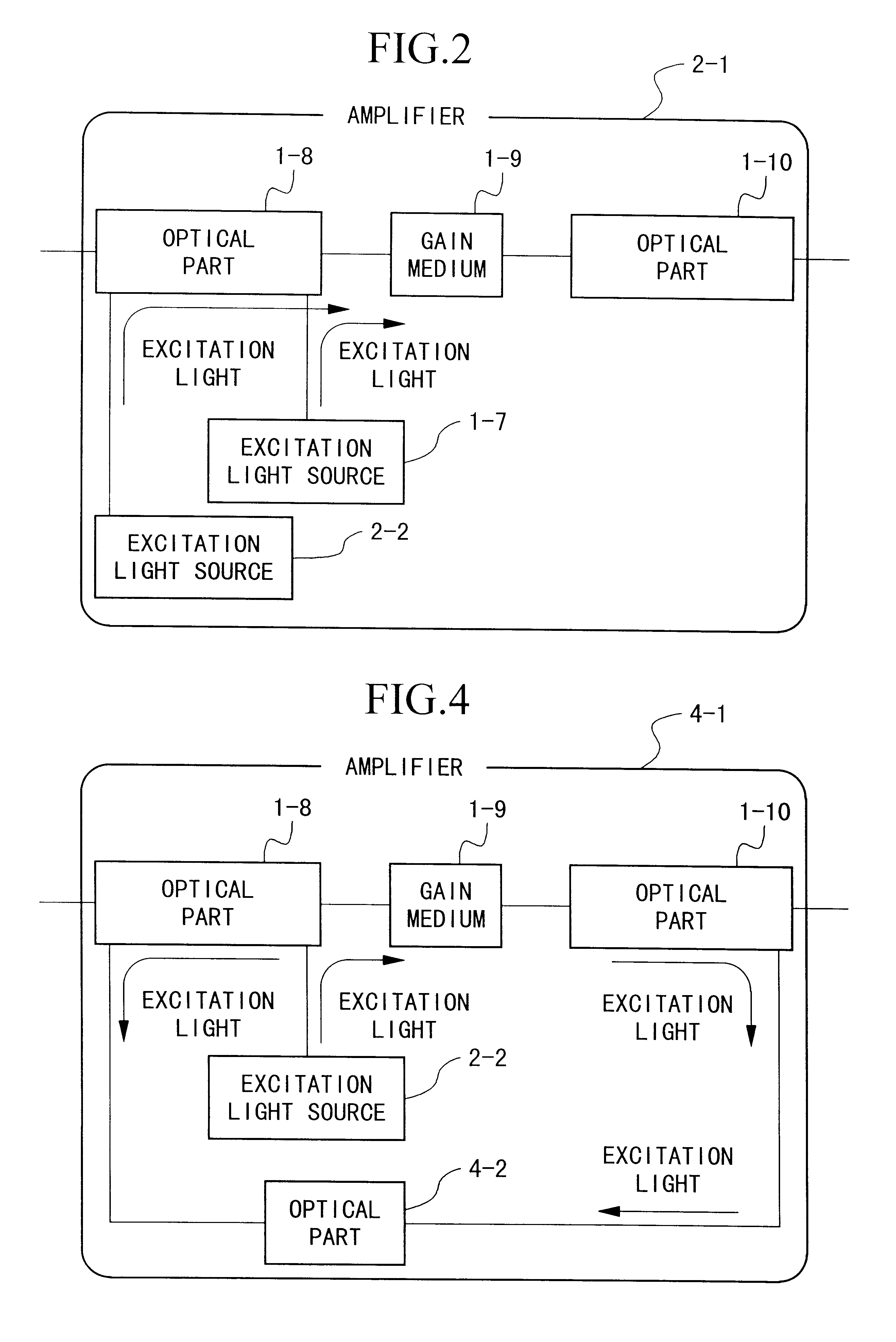
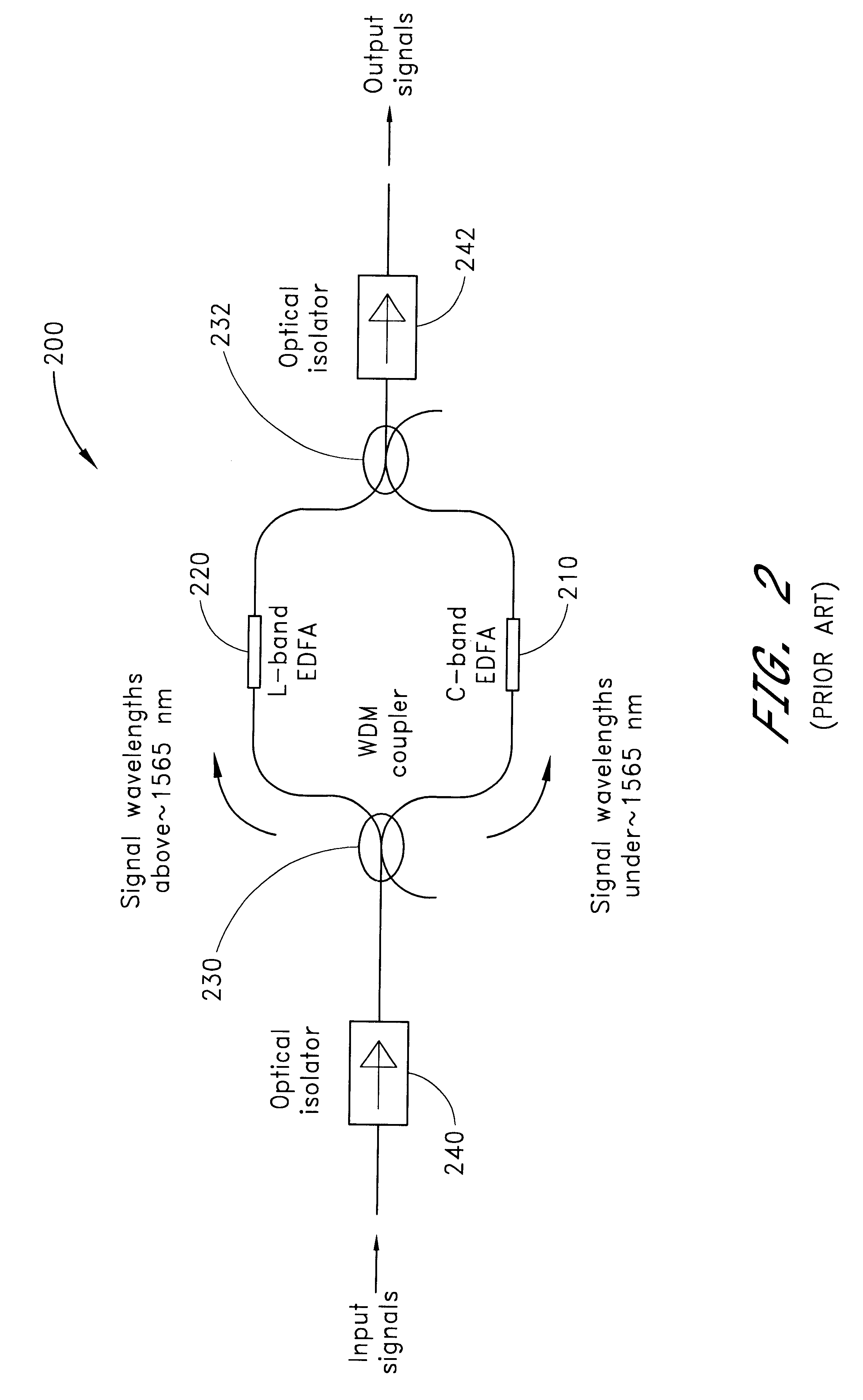
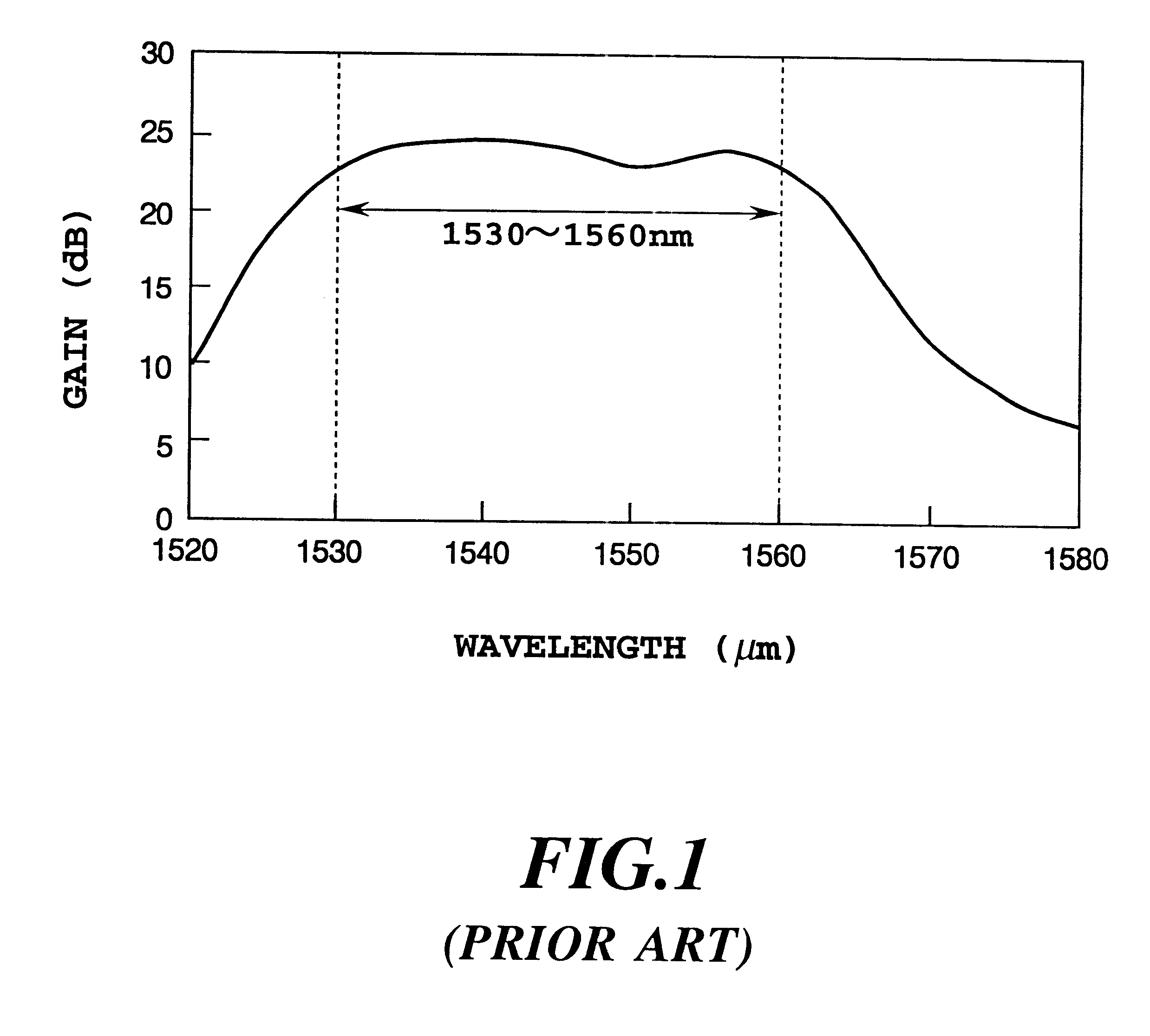
An optical amplifier having a two-stage construction using an erbium doped fiber (EDF) as a gain medium. The erbium dopant concentration is 1000 ppm, and the unsaturated absorption coefficient of the signal beam at 1550 nm is 1 dB / m. The length of the EDF 14-8 is 10 m, and the length of the EDF 14-12 is 70 m. The excitation light sources 14-6 and 14-10 are semiconductor lasers of 1.53 mum, and the excitation light power is 100 mW. Multiplexers 14-7 and 14-11 are inductive multi-layer film filters, and the gain equalizer 14-4 is a Fourier filter. The peak loss of the Fourier filter is 17 dB. The gain of the EDF 14-8 is 25 dB, and the gain of the EDF 14-12 is 15 dB. Two optical isolators are installed on a pre-stage amplifier, and one on a post-stage amplifier in order to prevent laser oscillation.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method of amplifying optical signals using doped materials with extremely broad bandwidths
InactiveUS6490081B1Eliminate chemical pollutionIncreased formationActive medium materialFibre transmissionErbium dopingRare earth
In a method of amplifying optical input signals over a wide bandwidth, the optical input signals are applied to an optical waveguide made from a rare-earth-doped amorphous material (e.g., erbium-doped yttrium aluminum oxide material). The optical input signals include optical signals having wavelengths over a range of at least 80 nanometers, and, preferably, over a range of at least 160 nanometers. Pump light is applied to the optical waveguide to cause the waveguide to provide optical gain to the optical input signals. The optical gain causes the optical signals to be amplified within the waveguide to provide amplified optical signals over the extended 80-160-nanometer range, including, in particular, optical signals having wavelengths at one end of the range and optical signals having wavelengths at a second end or the range.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Optical frequency division multiplexing phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer
InactiveCN102645268AHigh sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansLine widthLow-pass filter
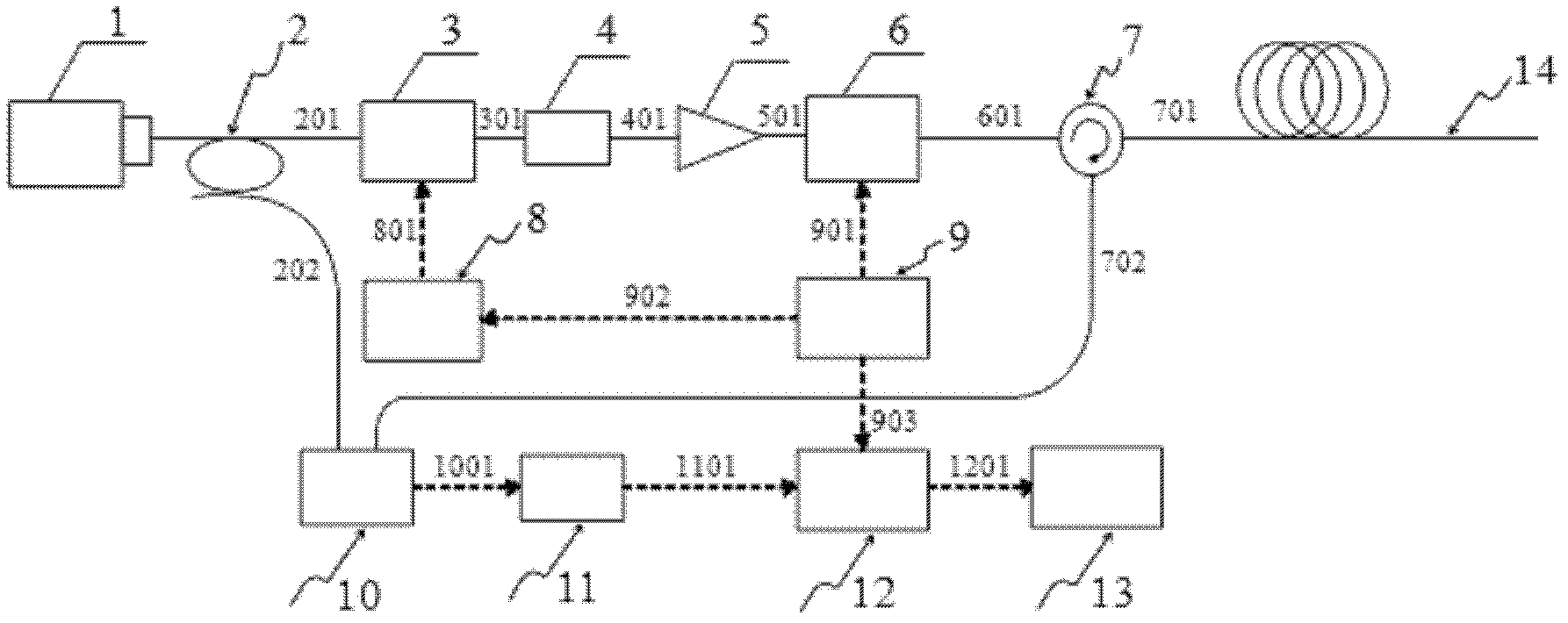
The invention discloses an optical frequency division multiplexing phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer which comprises a narrow line width laser, an optical fiber coupler, a phase modulator, a scrambler, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, an acoustic optical modulator, an optical fiber circulator, a signal generator module, a trigger source, a double balance detector, a low pass filter, a data acquisition card, a computer and a long-distance sensing optical fiber. According to the optical frequency division multiplexing phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer, the fundamental contradictions between the measuring distance and sampling rate in a distributed sensing system can be solved, and remoter or higher-frequency vibration is detected; and moreover, due to amplitude and phase information, the characteristics of a vibration source are judged at the first time, and the early warning can be provided immediately.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
No-time-delay flat-frequency-spectrum broadband photon integrated chaos semiconductor laser
ActiveCN104158085ASpectrum flatFlat outputLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionFrequency spectrumTime delays
The invention relates to a semiconductor laser, in particular to a no-time-delay flat-frequency-spectrum broadband photon integrated chaos semiconductor laser which solves the problems that chaos lasers generated by an existing semiconductor laser have the time delay characteristic, the signal band width is small, and the frequency spectrum is not flat. The no-time-delay flat-frequency-spectrum broadband photon integrated chaos semiconductor laser comprises a chip substrate, an optical waveguide, an erbium-doped passive optical waveguide, a left distributed feedback semiconductor laser chip, a no-isolation two-way amplified semiconductor light amplification chip, a right distributed feedback semiconductor laser chip and a high-speed photoelectric detection chip. The no-time-delay flat-frequency-spectrum broadband photon integrated chaos semiconductor laser is suitable for the fields of synchronization of chaos, secrecy light communication, high-speed random number secret key generation, laser radar, optical fiber network fault detection, ultra broadband technology, distributed optical fiber sensing and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method of amplifying optical signals using erbium-doped materials with extremely broad bandwidths
InactiveUS6469825B1Eliminate chemical pollutionIncreased formationActive medium materialFibre transmissionRare earthErbium doping
In a method of amplifying optical input signals over a wide bandwidth, the optical input signals are applied to an optical waveguide made from a rare-earth-doped amorphous yttrium aluminum oxide material (e.g., erbium-doped yttrium aluminum oxide material). The optical input signals include optical signals having wavelengths shorter than 1,520 nanometers and optical signals having wavelengths longer than 1,610 nanometers. Preferably, the wavelengths range from as short as approximately 1,480 nanometers to as long as approximately 1,650 nanometers. Pump light is applied to the optical waveguide to cause the waveguide to provide optical gain to the optical input signals. The optical gain causes the optical signals to be amplified within the waveguide to provide amplified optical signals over the extended range from approximately 1,480 nanometers to approximately 1,650 nanometers, including, in particular, optical signals having wavelengths shorter than 1,520 nanometers and optical signals having wavelengths longer than 1,610 nanometers. Alternatively, the wavelengths of the optical input signals may be in the range from approximately 1,480 nanometers to approximately 1,565 nanometers. As a further alternative, the wavelengths of the optical input signals may be in the range from approximately 1,565 nanometers to approximately 1,650 nanometers.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
System and method for a passively Q-switched, resonantly pumped, erbium-doped crystalline laser
The laser includes a resonant cavity formed between a first mirror and a second mirror. An unsensitized Erbium-doped crystal gain medium for producing laser gain is disposed within the resonant cavity. A saturable absorber is disposed within the resonant cavity. A pump source is positioned to energize the gain medium. The saturable absorber, the laser gain, the resonator length, and the second mirror being selected so that output pulses having a duration of less than 75 nanoseconds are generated by the laser.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
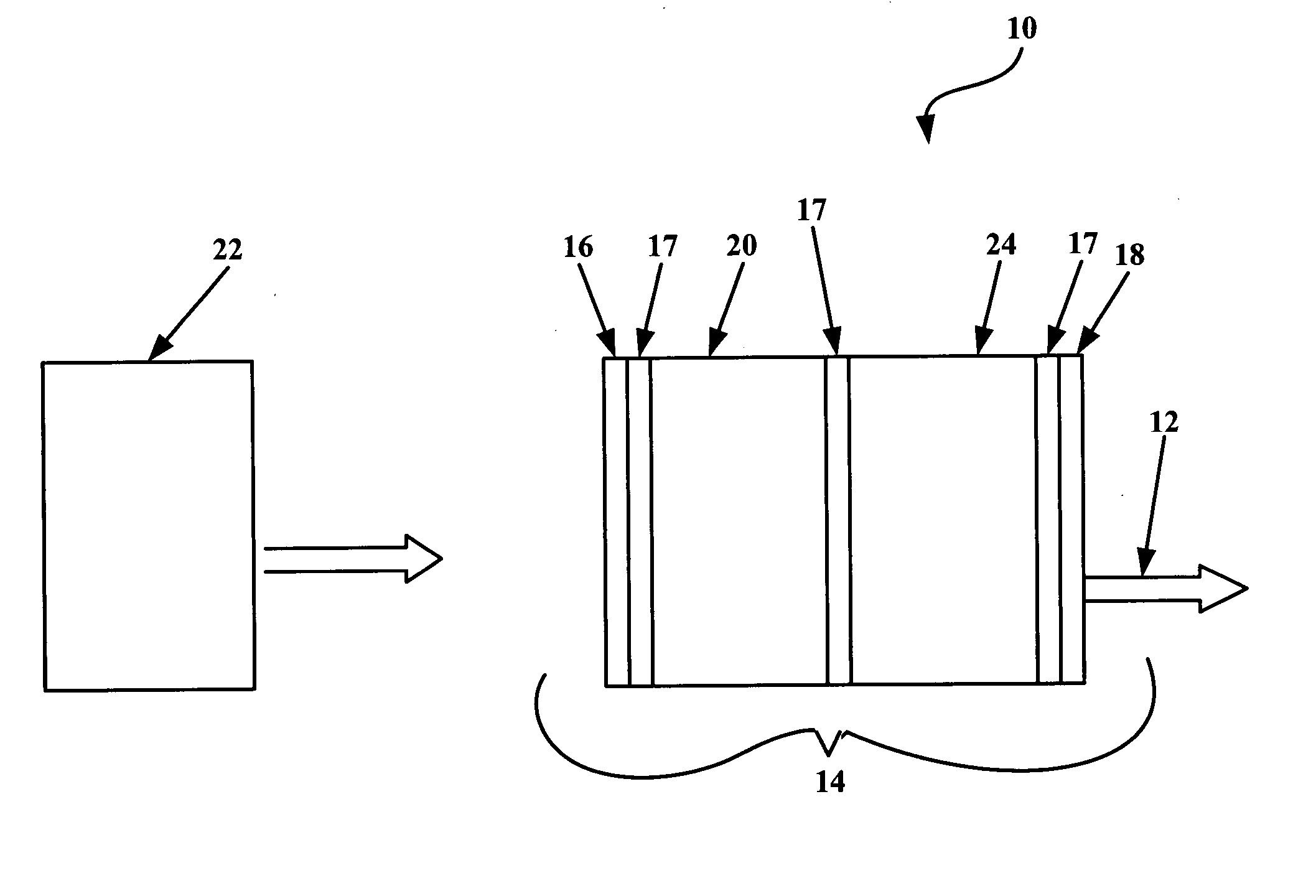
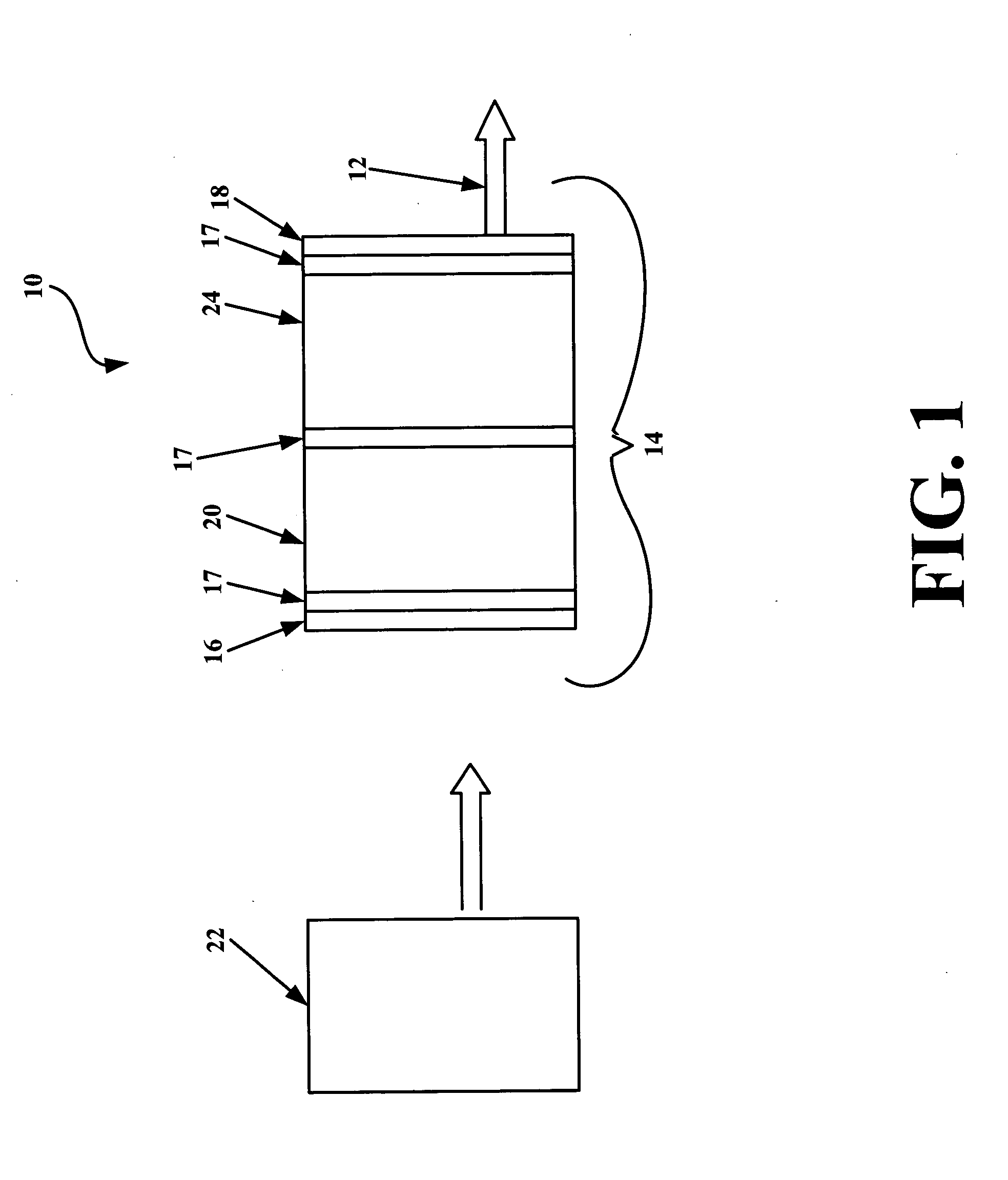
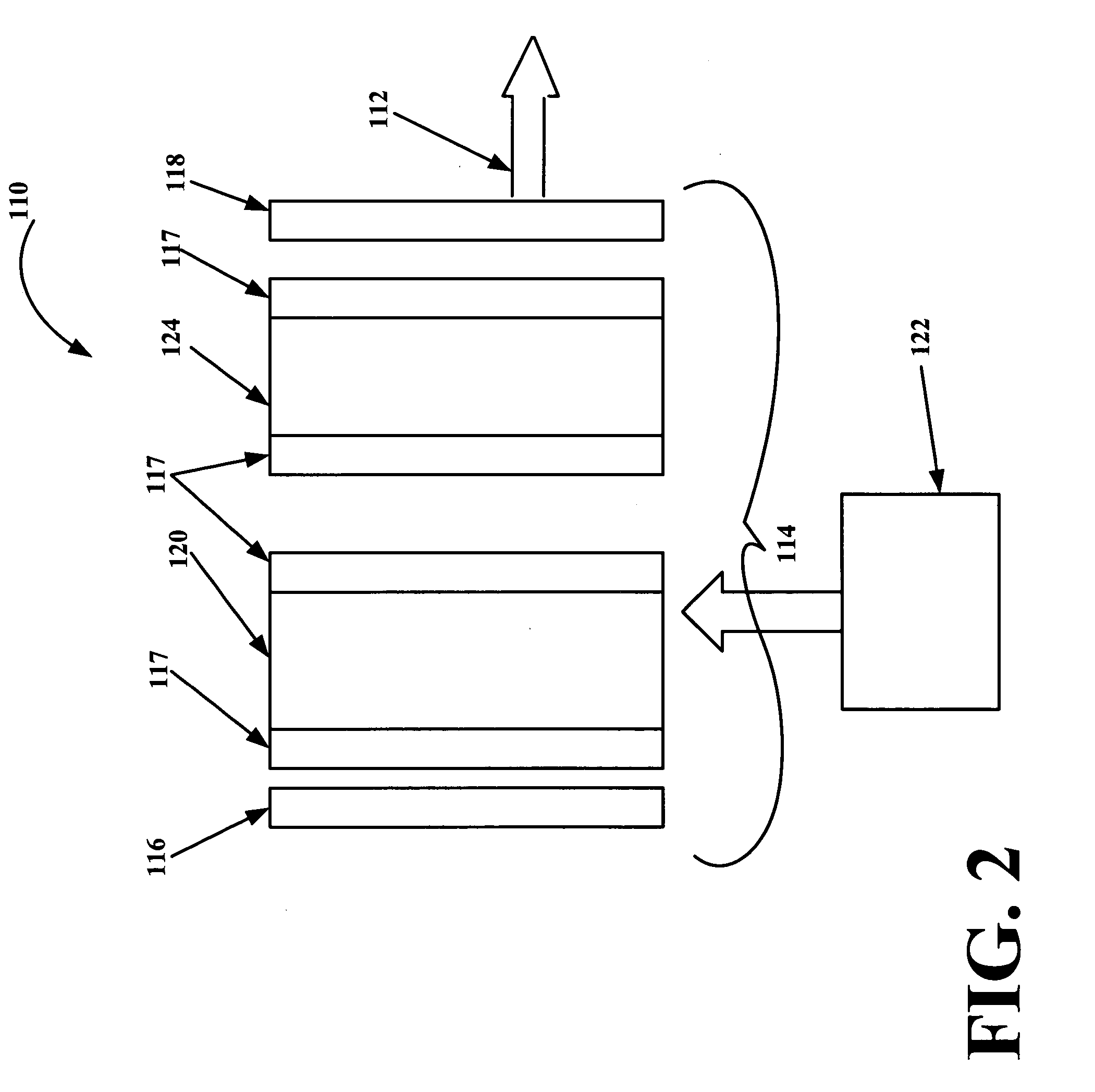
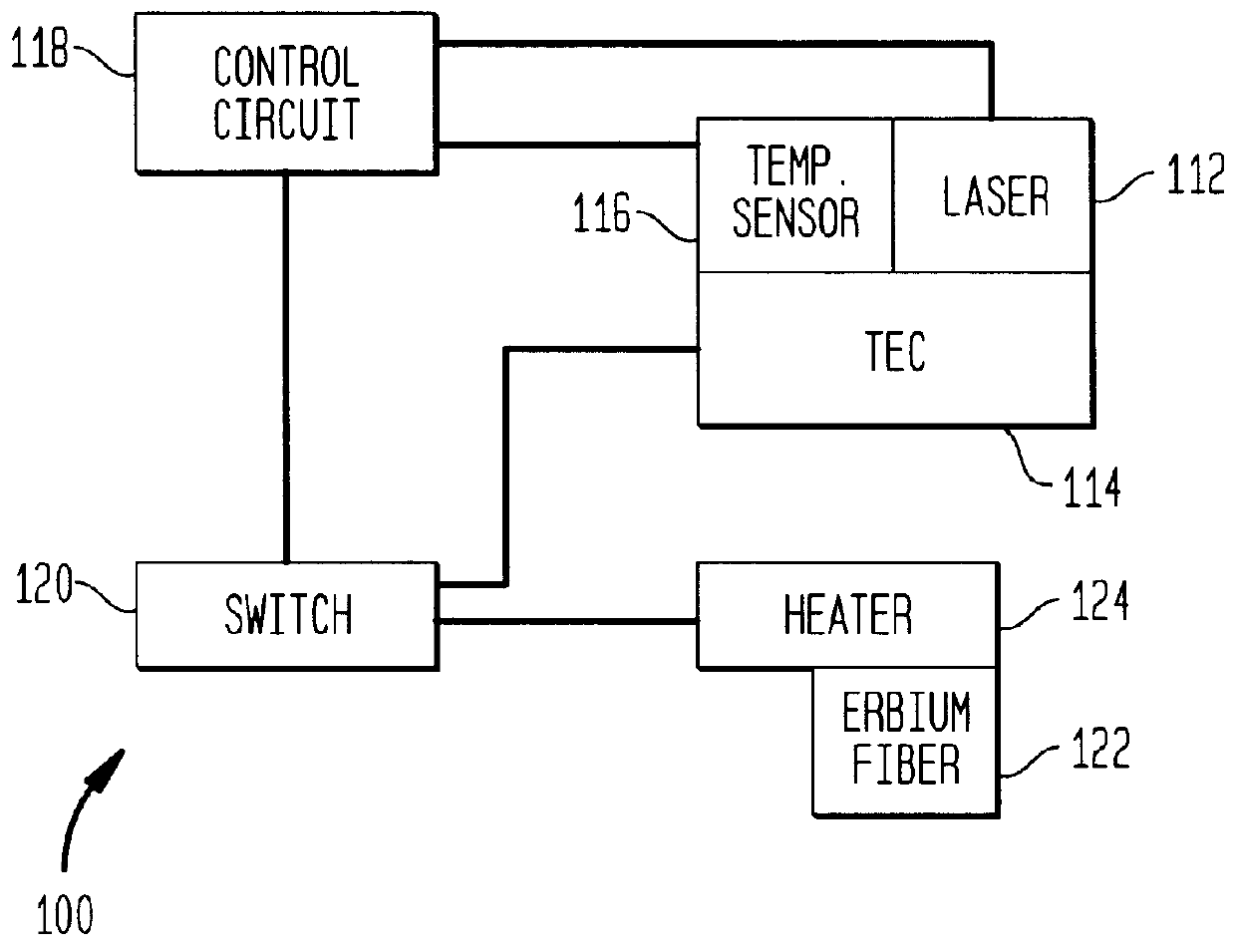
Retrofit heater for erbium fiber in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA)
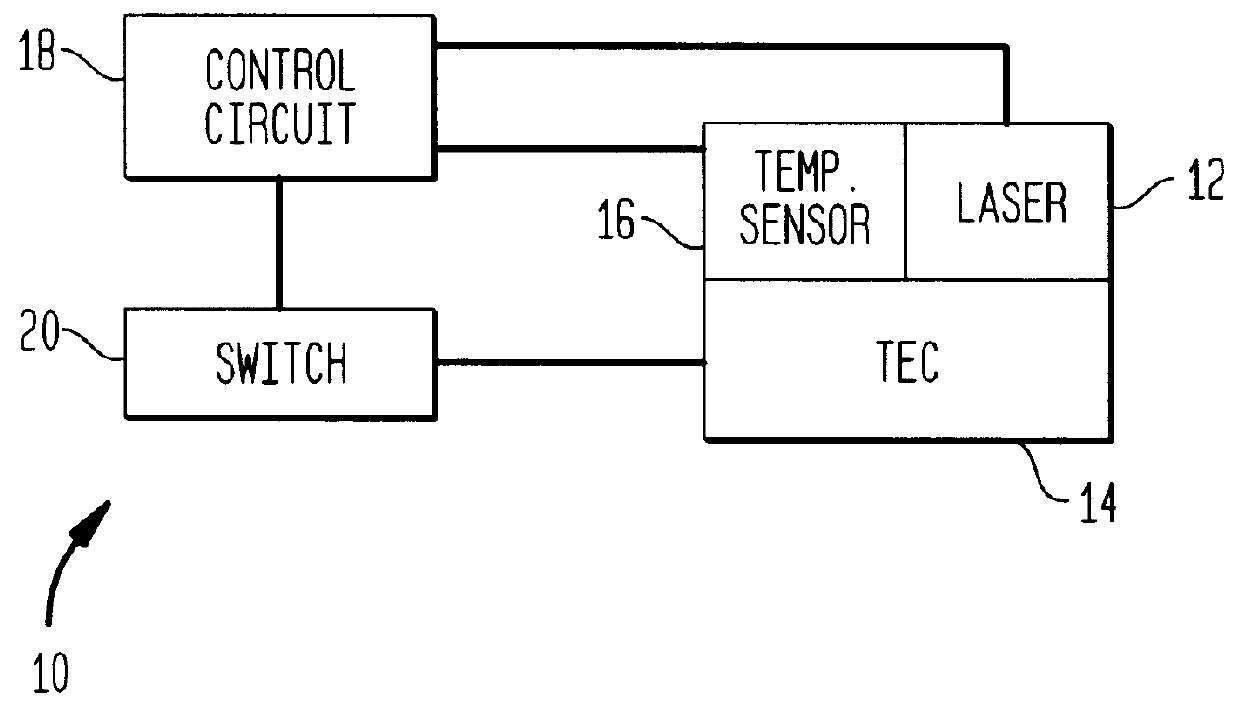
A heater system for heating an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) of a fiber optic communication system operable in an environment. The heater system includes a pump laser for providing optical power to an erbium fiber in the EDFA. The pump laser is cooled by a thermoelectric cooler (TEC) when a predetermined maximum temperature is reached to maintain the temperature of the laser below the maximum temperature value. The temperature of the laser is sensed by a temperature sensor and is conveyed to a control circuit for generating a control signal. A heater unit is thermally connected to the erbium fiber and is controlled by the control signal in the event that the sensed temperature falls below a predetermined minimum value to maintain the temperature of the fiber above the minimum temperature value. A switch is connected between the control circuit, the TEC and the heater to automatically direct current to either the heater or the TEC depending on the sensed temperature.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
Distributed ultrahigh-speed disturbance quantitative detection method and device
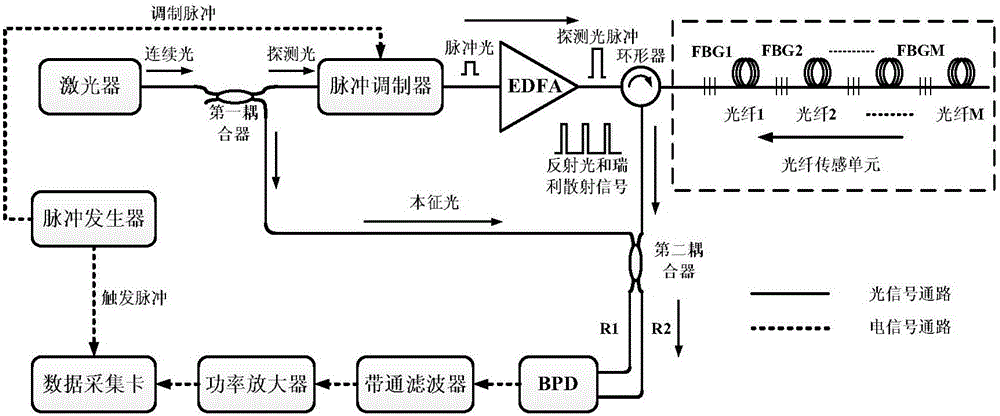
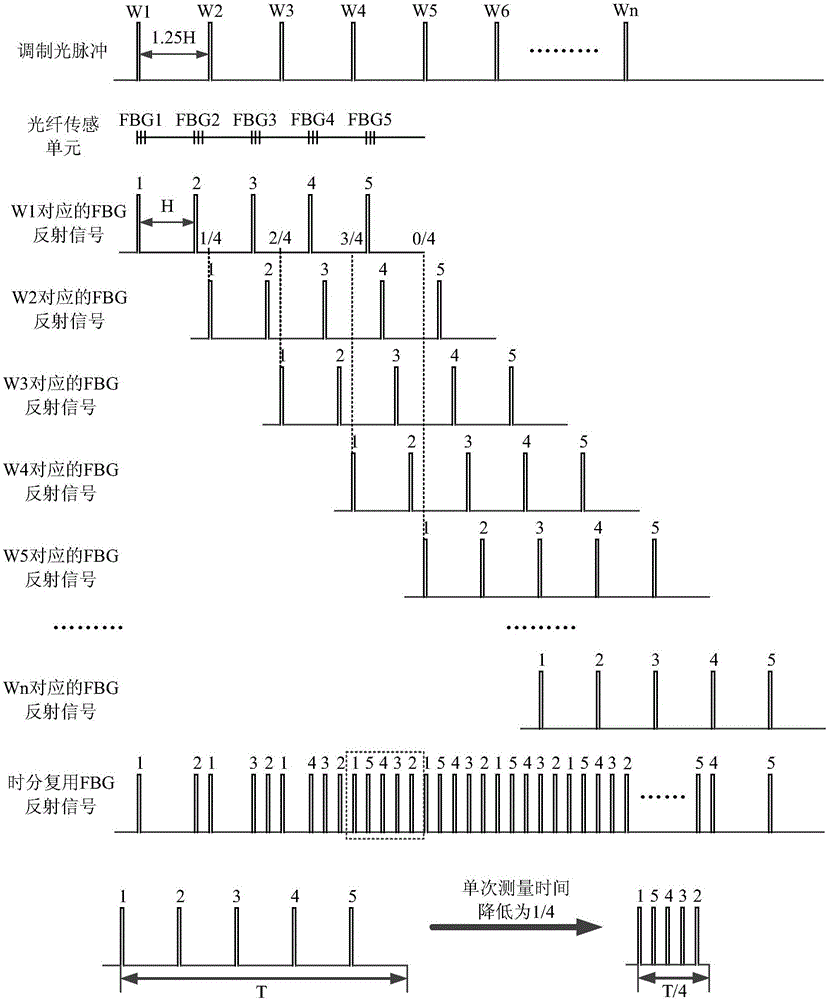
ActiveCN106248119AHigh repetition rateUltra-high-speed disturbance detectionConverting sensor output opticallyGratingBand-pass filter
The invention discloses a distributed ultrahigh-speed disturbance quantitative detection method. Ultrahigh-speed disturbance detection can be realized through a time division multiplexing method; and phase demodulation is carried out through phase demodulation methods such as Hilbert transformation and orthogonal transformation so as to be able to realize real-time detection on the disturbance position, frequency and amplitude. The invention further discloses a distributed ultrahigh-speed disturbance quantitative detection device, which comprises a pulse generator, a laser, a first coupler, a pulse modulator, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, a circulator, an optical fiber sensing unit, a second coupler, a balance detector, a band-pass filter, a power amplifier and a data acquisition card. According to the invention, the repetition frequency of detecting light pulses is improved through a time division multiplexing technology, so that a reflecting grating based phi-OTDR system is enabled to realize ultrahigh-speed disturbance detection; and real-time detection for the disturbance position, frequency and amplitude is realized through the phase demodulation method by using a coherent detection structure and combining a phase unwrapping algorithm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Distributed optical fiber sensing system based on phase generated carrier technology
ActiveCN103759750ARealize dynamic measurementEliminate phase destructive fading problemsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFiberGrating
A distributed optical fiber sensing system based on the phase generated carrier technology comprises a narrow-linewidth laser device, a modulator, an optoisolator, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, an optical circulator, a fiber grating, a sensing fiber, a Michelson interferometer, a carrier circuit, a photoelectric detector, a data acquisition card, a signal processor and a pulse generator. The input end of the modulator is connected with the output end of the narrow-linewidth laser device. The input end of the optoisolator is connected with the output end of the modulator. The input end of the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier is connected with the output end of the optoisolator. A port a of the optical circulator is connected with the output end of the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier. The fiber grating is connected with a port b of the optical circulator. The output end of the carrier circuit is connected with an electrical interface of the Michelson interferometer. The input end of the photoelectric detector is connected with the output end of the Michelson interferometer. One input end of the data acquisition card is connected with the output end of the photoelectric detector, and the other input end of the data acquisition card is connected with the output end of the carrier circuit. The input end of the signal processor is connected with the output end of the data acquisition card. The input end of the pulse generator is connected with the trigger input end of the data acquisition card, and the output end of the pulse generator is connected with an electrical interface of the modulator.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for a passively Q-switched, resonantly pumped, erbium-doped crystalline laser
The laser includes a resonant cavity formed between a first mirror and a second mirror. An unsensitized Erbium-doped crystal gain medium for producing laser gain is disposed within the resonant cavity. A saturable absorber is disposed within the resonant cavity. A pump source is positioned to energize the gain medium. The saturable absorber, the laser gain, the resonator length, and the second mirror being selected so that output pulses having a duration of less than 75 nanoseconds are generated by the laser.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
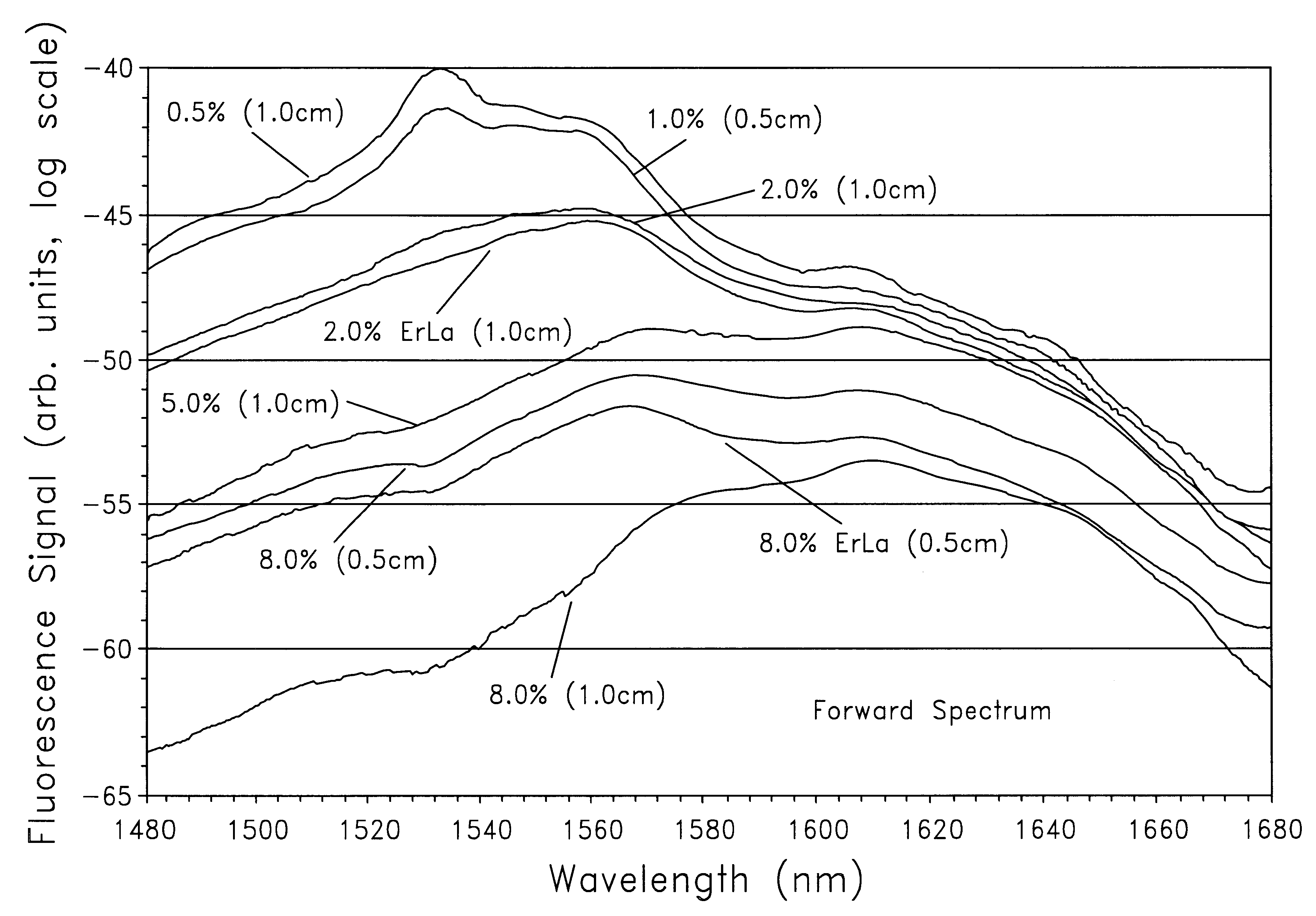
Erbium and ytterbium co-doped phosphate glass optical fiber amplifiers using short active fiber length
InactiveUS6611372B1High gain per unit lengthHigh gain amplificationLaser arrangementsActive medium materialErbium dopingPhosphate glass
An optical fiber amplifier utilizing a phosphate glass optical fiber highly doped with rare-earth ions such as erbium to exhibit high gain per unit length, enabling the use of short fiber strands to achieve the needed gain in practical fiber optical communication networks. The high-gain phosphate optical glass fiber amplifiers are integrated onto substrates to form an integrated optics amplifier module. An optical pump such as a semiconductor laser of suitable wavelength is used to promote gain inversion of erbium ions and ultimately provide power amplification of a given input signal. Gain inversion is enhanced in the erbium doped phosphate glass fiber by co-doping with ytterbium. A phosphate fiber amplifier or an integrated optics amplifier module utilizing this power amplification can be combined with other components such as splitters, combiners, modulators, or arrayed waveguide gratings to form lossless or amplified components that do not suffer from insertion loss when added to an optical network. The fiber amplifier can be a single fiber or an array of fibers. Further, the phosphate glass fibers can be designed with a temperature coefficient of refractive index close to zero enabling proper mode performance as ambient temperatures or induced heating changes the temperature of the phosphate glass fiber. Large core 50-100 .mu.m fibers can be used for fiber amplifiers. The phosphate glass composition includes erbium concentrations of at least 1.5 weight percentage, preferably further including ytterbium at 1.5 weight percentage, or greater.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
High power pulse shaping fiber laser for high data rate free space telecommunication systems
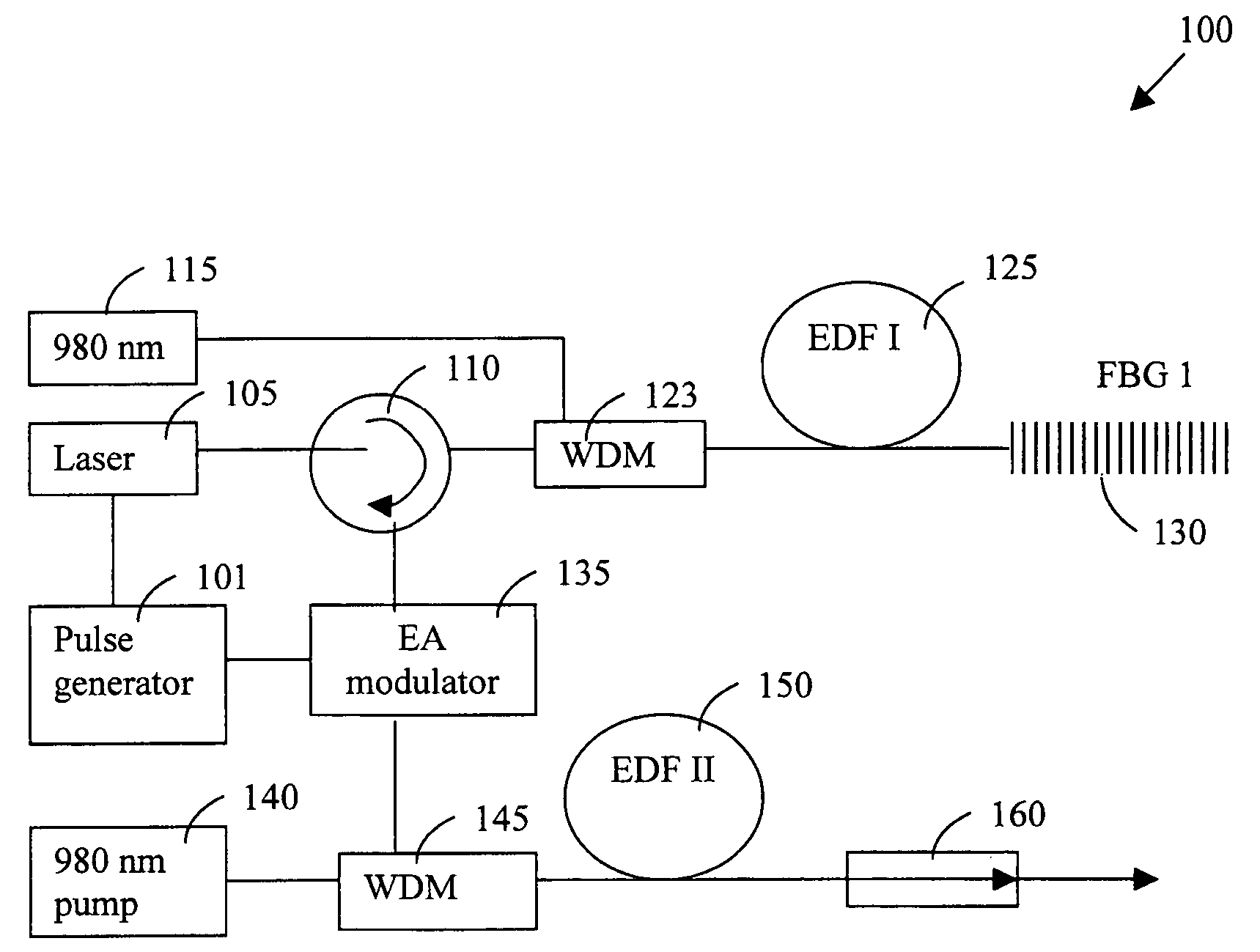
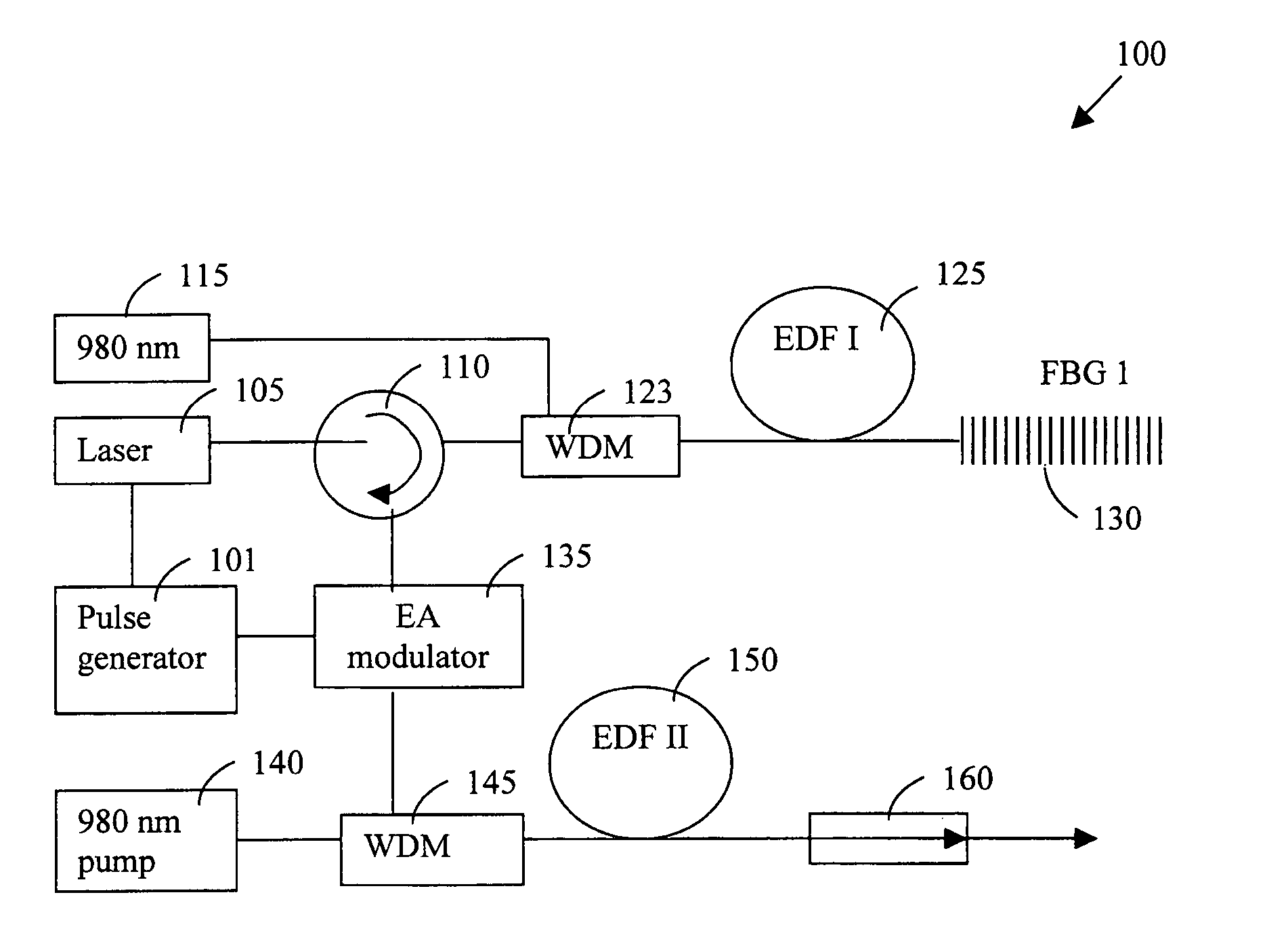
An amplified laser source for amplifying a laser projection that includes a diode laser source modulated by a pulse generator applying an alternate high and low voltages higher and lower than a threshold voltage for projecting a modulated optical signal. The laser source further includes a first erbium-doped fiber (EDF) for amplifying the modulated optical signal. The laser source further includes a set of Bragg gratings for receiving the modulated optical signal from the first EDF for reflecting a grating-specific pulse-distortion-reduced optical signal. The laser source further includes an electro-absorption (EA) modulator synchronized with the pulse generator for increasing an extinction ratio of the optical signals. The laser source further includes a second erbium doped fiber (EDF) for receiving and amplifying the optical signal from the EA modulator wherein the second erbium doped fiber (EDF) having a length of several meters and a diameter greater than or equal to thirty-five micrometers.
Owner:LIU JIAN
High power pulse shaping fiber laser for high data rate free space telecommunication systems
An amplified laser source for amplifying a laser projection that includes a diode laser source modulated by a pulse generator applying an alternate high and low voltages higher and lower than a threshold voltage for projecting a modulated optical signal. The laser source further includes a first erbium-doped fiber (EDF) for amplifying the modulated optical signal. The laser source further includes a set of Bragg gratings for receiving the modulated optical signal from the first EDF for reflecting a grating-specific pulse-distortion-reduced optical signal. The laser source further includes an electro-absorption (EA) modulator synchronized with the pulse generator for increasing an extinction ratio of the optical signals. The laser source further includes a second erbium doped fiber (EDF) for receiving and amplifying the optical signal from the EA modulator wherein the second erbium doped fiber (EDF) having a length of several meters and a diameter greater than or equal to thirty-five micrometers.
Owner:LIU JIAN
Microwave signal optical fiber stationary phase transmission system based on microwave phase shifter
ActiveCN104065416AAchieving phase-stable transmissionHigh bandwidthRadio-over-fibreMicrowave phase shifterLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a microwave signal optical fiber stationary phase transmission system based on a microwave phase shifter. The system comprises a central station, a far end and a single-mode optical fiber. The central station is connected with the far end through the single-mode optical fiber. The central station is composed of a semiconductor laser device, a dual-drive Mach-Zehnder modulator, a microwave signal source, a first power divider, a first optical filter, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, an optical coupler, a first array waveguide grating, a first photoelectric detector, a frequency eliminator, a second power divider, an optical source, a strength modulator, a second optical filter, an optical circulator, a second photoelectric detector, a first electric mixer, a band-pass filter, a second electric mixer, a low-pass filter and a linear voltage amplification circuit. The far end is composed of a second array waveguide grating, a third photoelectric detector and a Faraday polariscope. According to the invention, the advantage of low building and maintenance cost can be realized; and the phase jitter of microwave signals can be extracted and fed back on a real-time basis.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
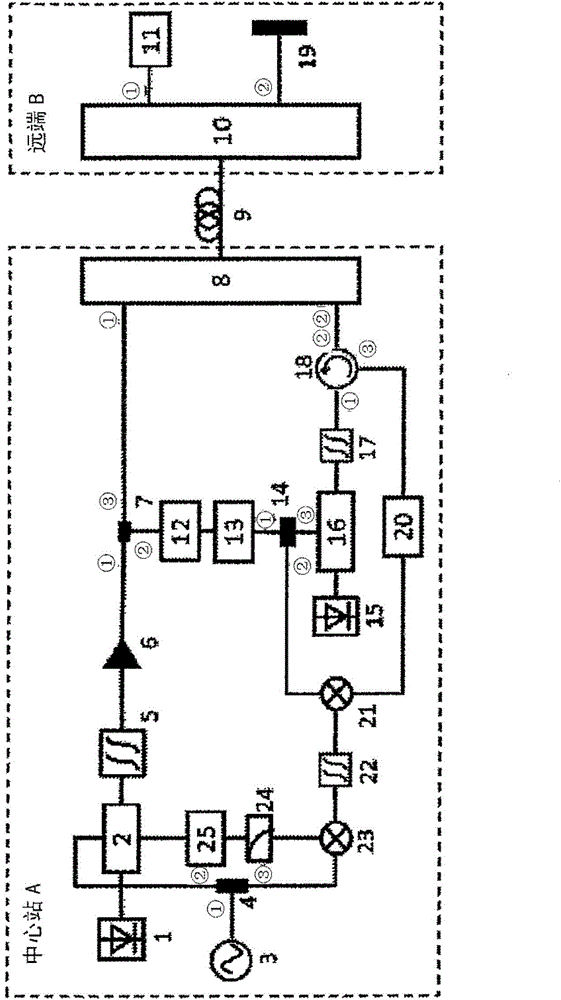
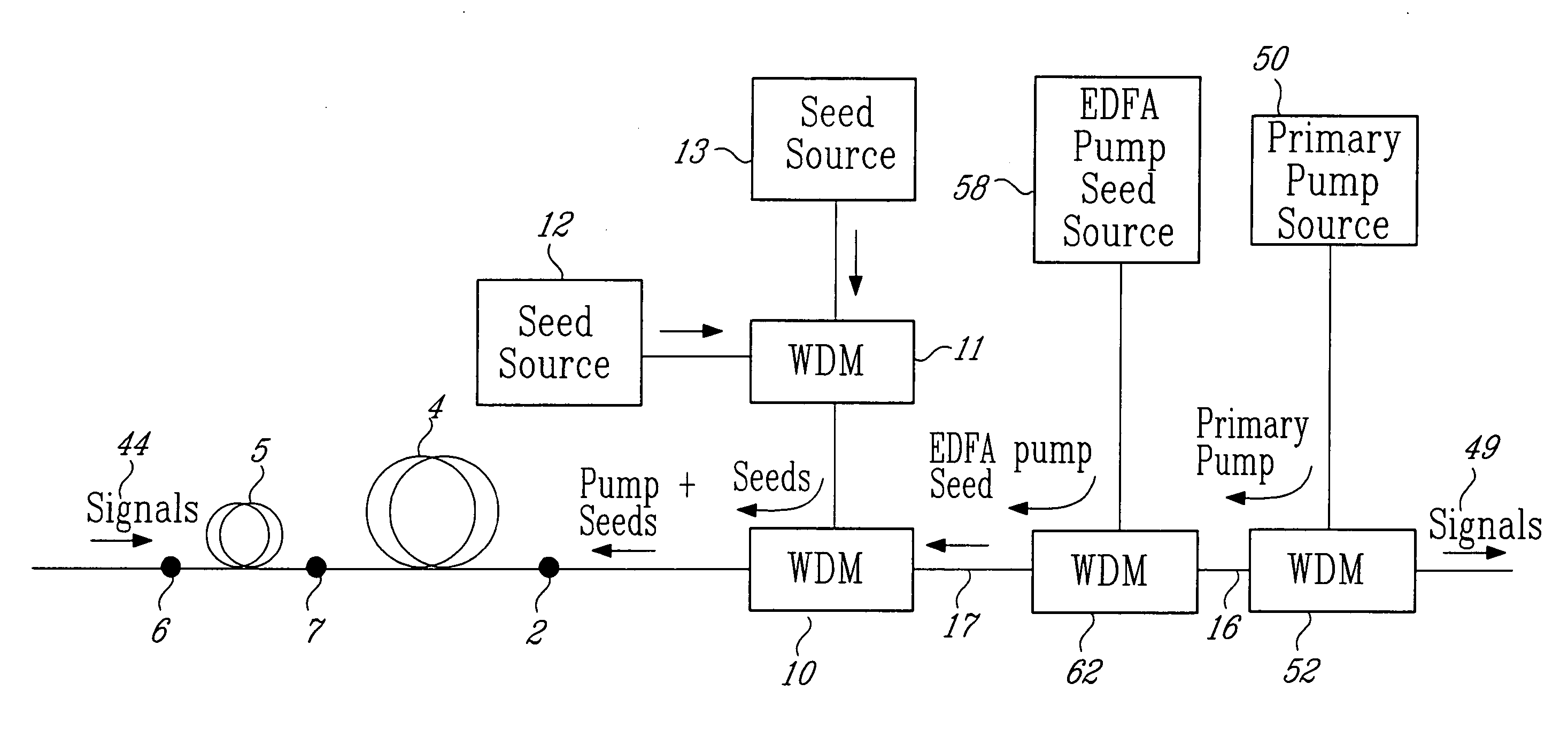
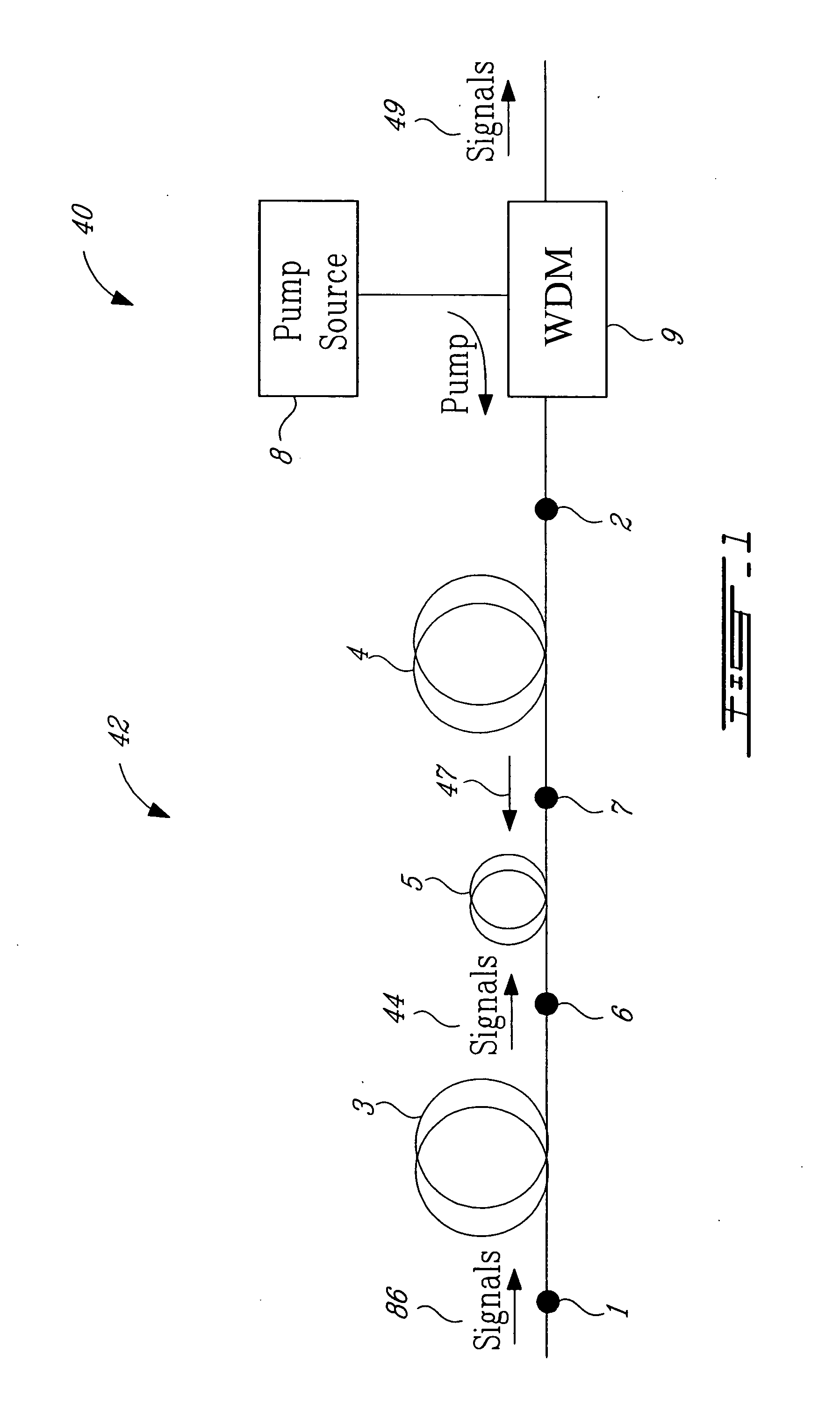
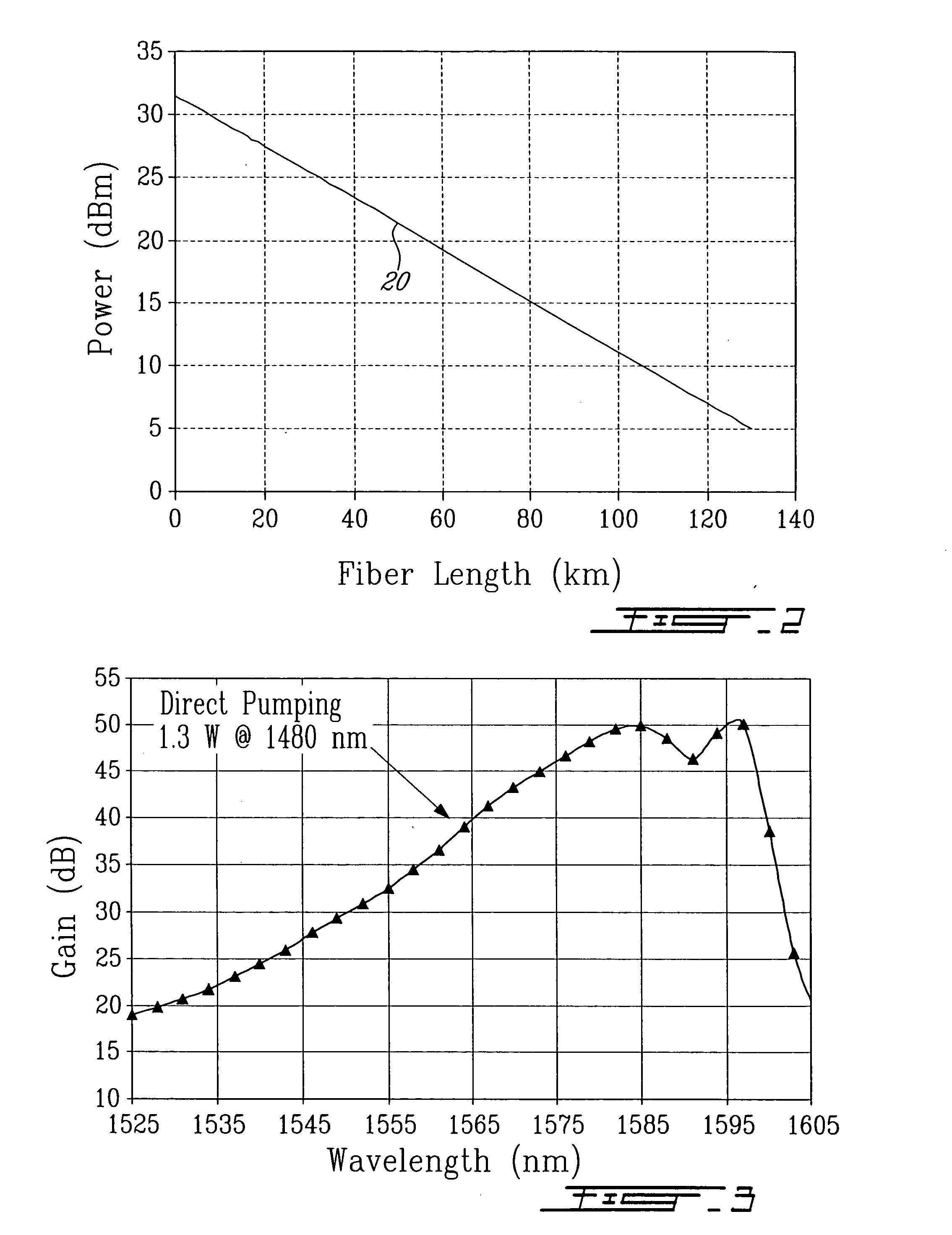
Cascaded pump delivery for remotely pumped erbium-doped fiber amplifiers
ActiveUS20060209394A1Increase volumeWeaken energyLaser detailsFibre transmissionErbium dopingEngineering
A method for pumping remote optically-pumped fiber amplifiers (ROPAs) in fiber-optic telecommunication systems is disclosed which uses cascaded Raman amplification to increase the maximum amount of pump power that can be delivered to the ROPA. According to the prior art, high power at the ROPA pump wavelength, λp, is launched directly into the fiber and the maximum launch power is limited by the onset of pump depletion by Raman noise and oscillations due to the high Raman gain at ˜(λp+100) nm. In preferred embodiments of the present invention, a ‘primary’ pump source of wavelength shorter than λp is launched into the delivery fiber along with two or more significantly lower-power ‘seed’ sources, among which is included one at λp. The wavelength and power of the seed source(s) are chosen such that, when combined with the high-power primary source, a series, n, where n≧2, of Raman conversions within the fiber ultimately leads to the development of high power at λp. In another embodiment, one or more of the seed sources at wavelengths shorter than λp are replaced by reflecting means to return, into the fiber, backward-travelling amplified spontaneous Raman scattered light resulting from high power in the fiber at a wavelength one Raman shift below the particular seed wavelength. In either case, the high power at λp is developed over a distributed length of the fiber, reaching its maximum some distance into the fiber and exceeding the maximum power possible at that point with the prior art.
Owner:MPB COMM
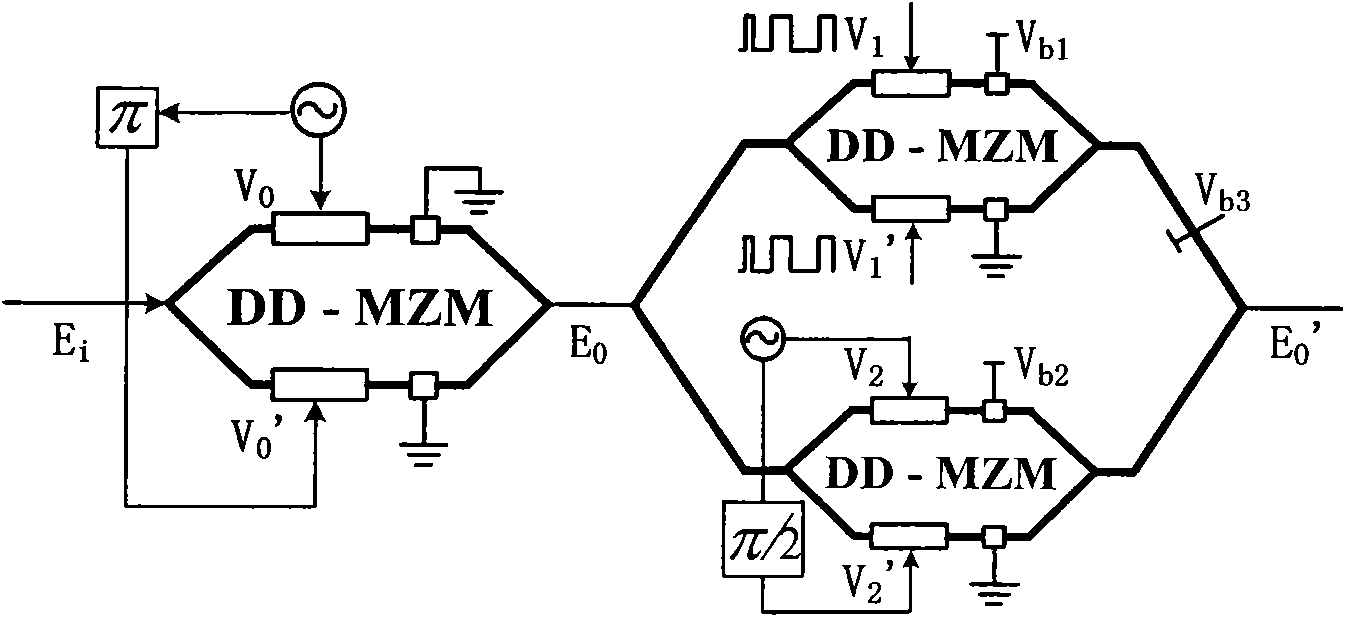
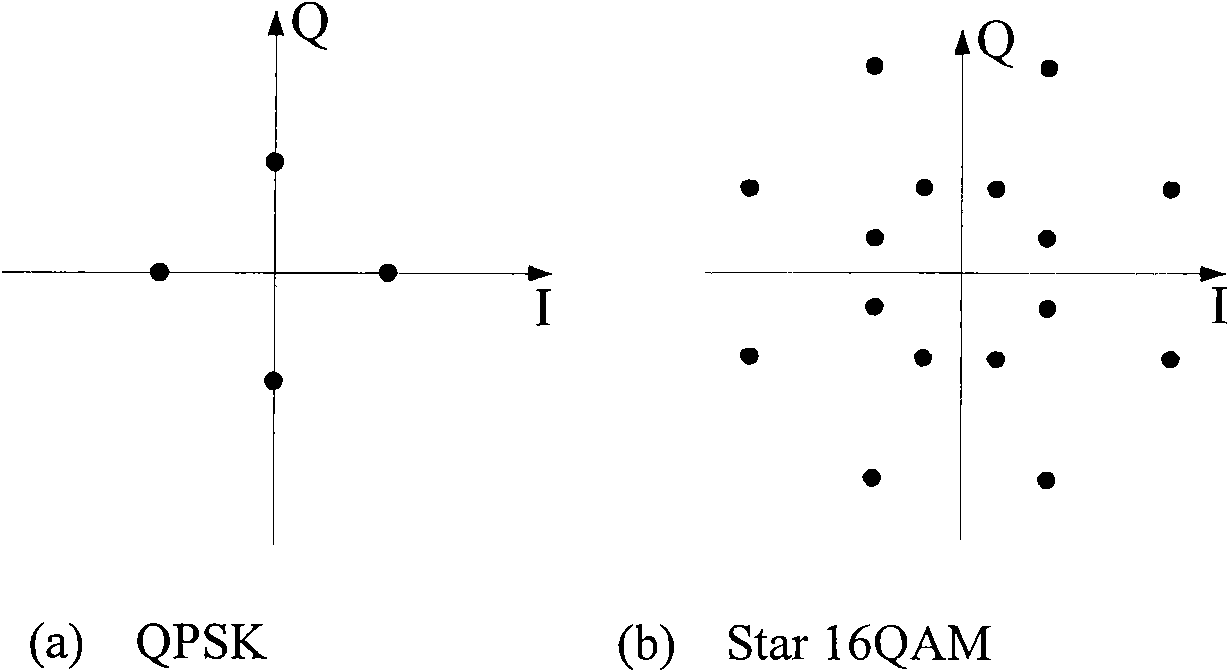
Serial-parallel connection modulation optical frequency multiplication millimeter-wave RoF (Radio Over Fiber) system and QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) /16QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) modulation method thereof
InactiveCN101964683AAvoid separate transfersAvoid interferencePhase-modulated carrier systemsRadio-over-fibreBandpass filteringFiber
The invention relates to a serial-parallel connection modulation optical frequency multiplication millimeter-wave RoF (Radio Over Fiber) system and a QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) / 16QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) modulation method thereof. The system comprises a central station, a base station and fiber connection thereof, wherein the central station comprises a single longitudinal mode laser, a double-electrode Mach-Zehnder optical modulator, an IQ optical modulator, two microwave signal sources, a pi phase shifter, a pi / 2 phase shifter and an erbium doped fiber amplifier; and the base station comprises an optical detector, a front low-noise amplifier, two millimeter-wave bandpass filters, two millimeter-wave amplifiers, a millimeter-wave duplexer and a millimeter-wave antenna. In the method, the cascading of the double-electrode Mach-Zehnder optical modulator and the IQ optical modulator is adopted, and a balanced optical waveguide structure formed by integrating the two optical modulators avoids the influence of optical source phase interference noise caused by support arm optical delay inequality on modulation signals.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
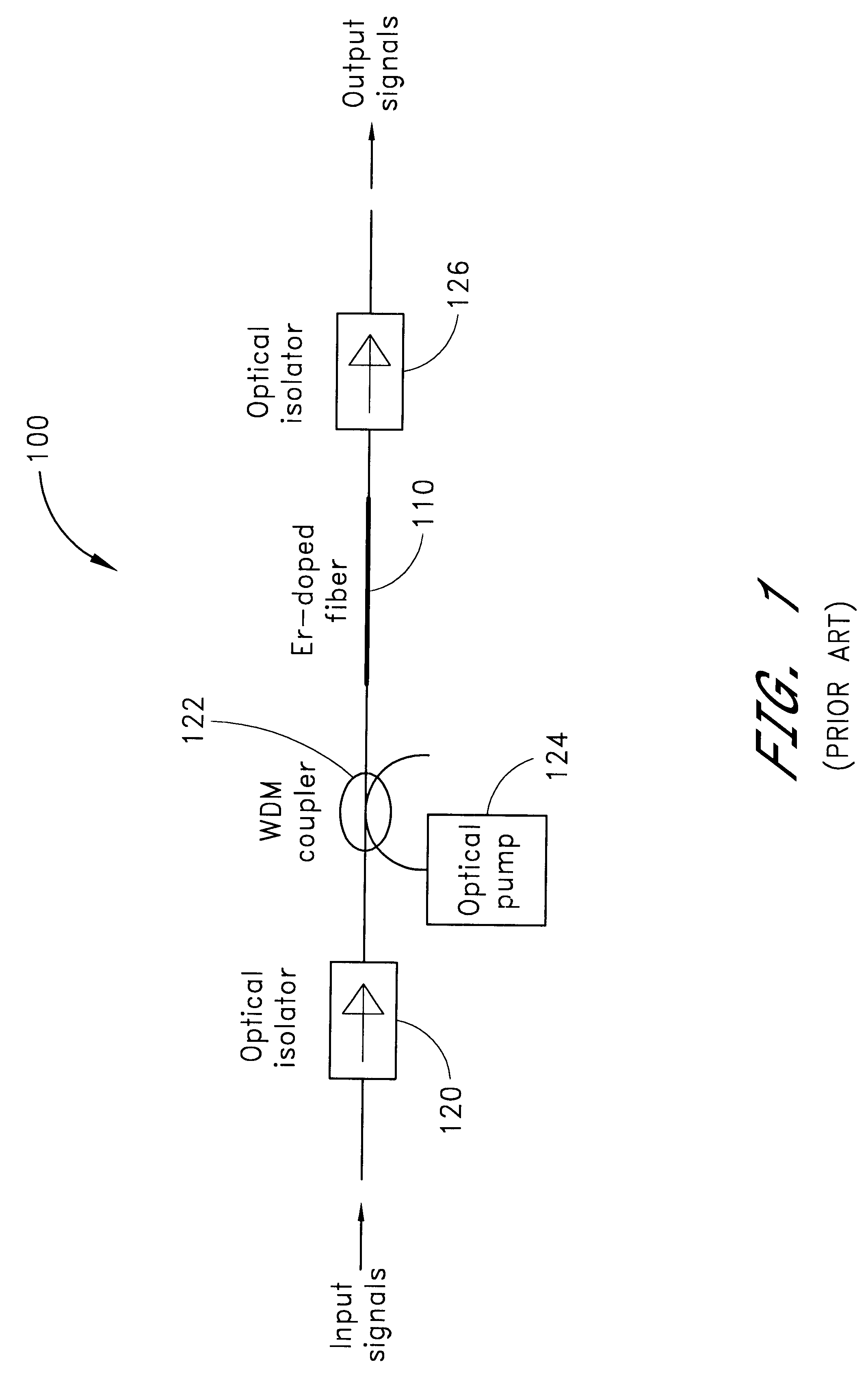
Optical fiber amplifier and optical amplification method
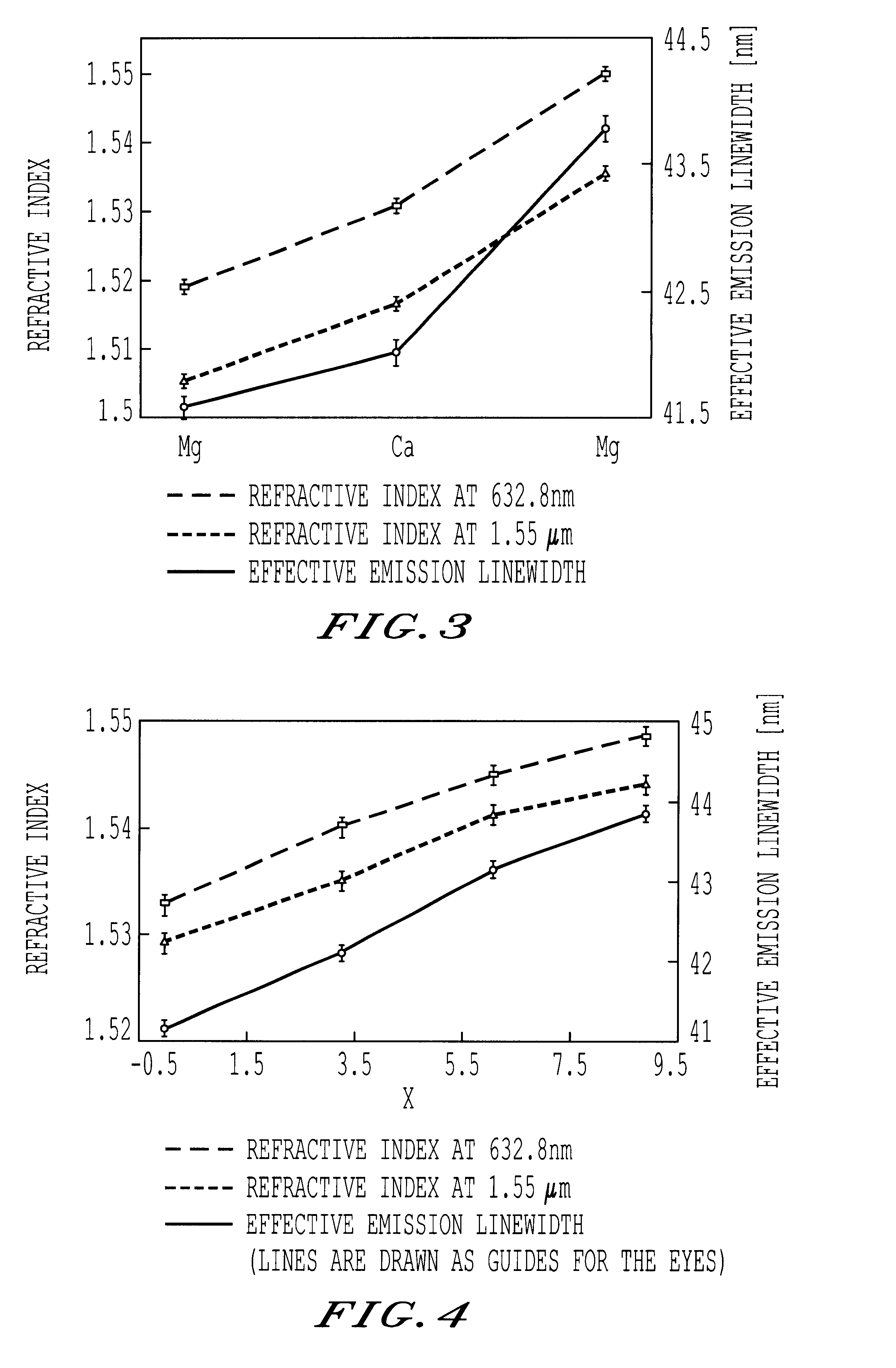
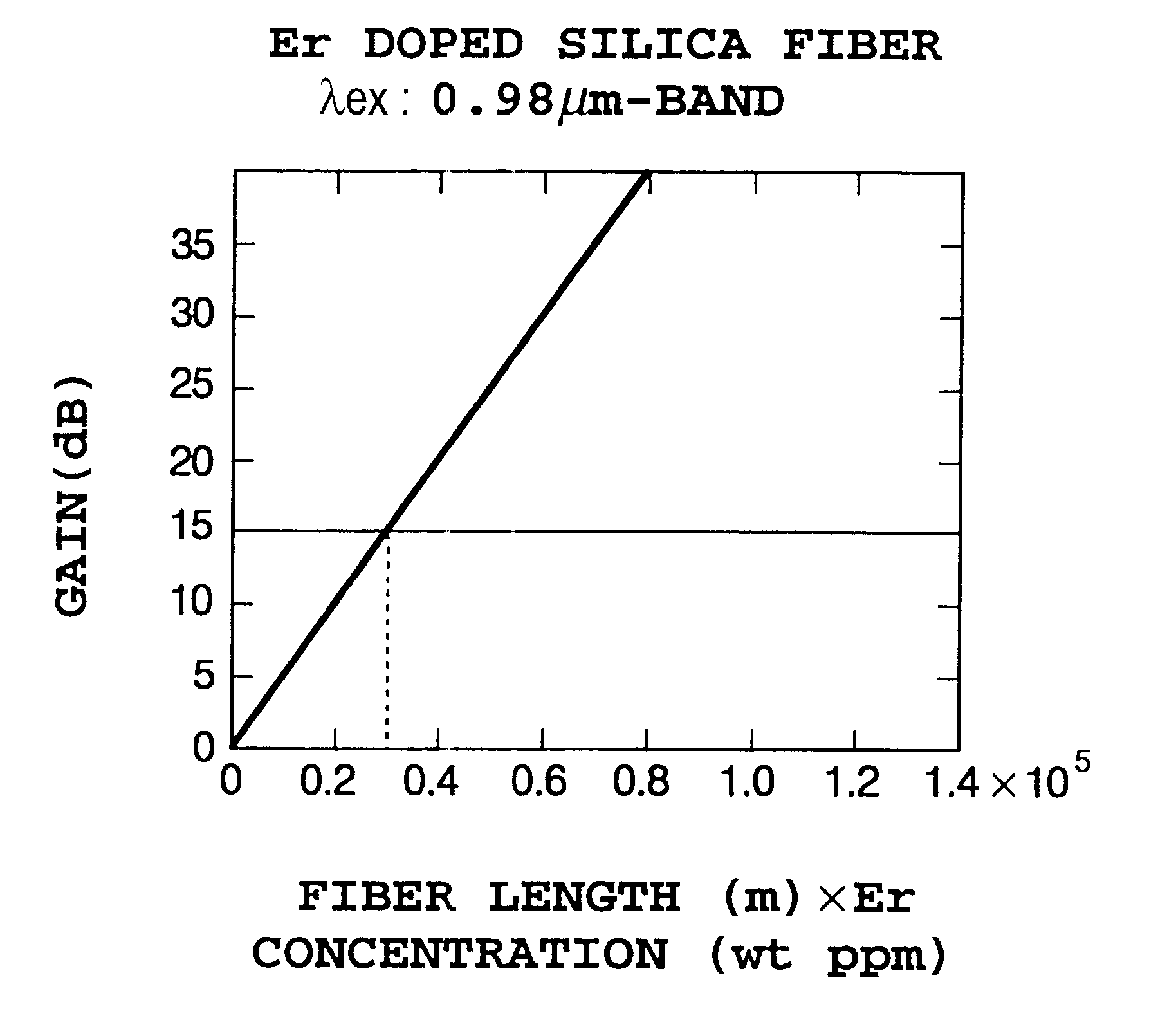
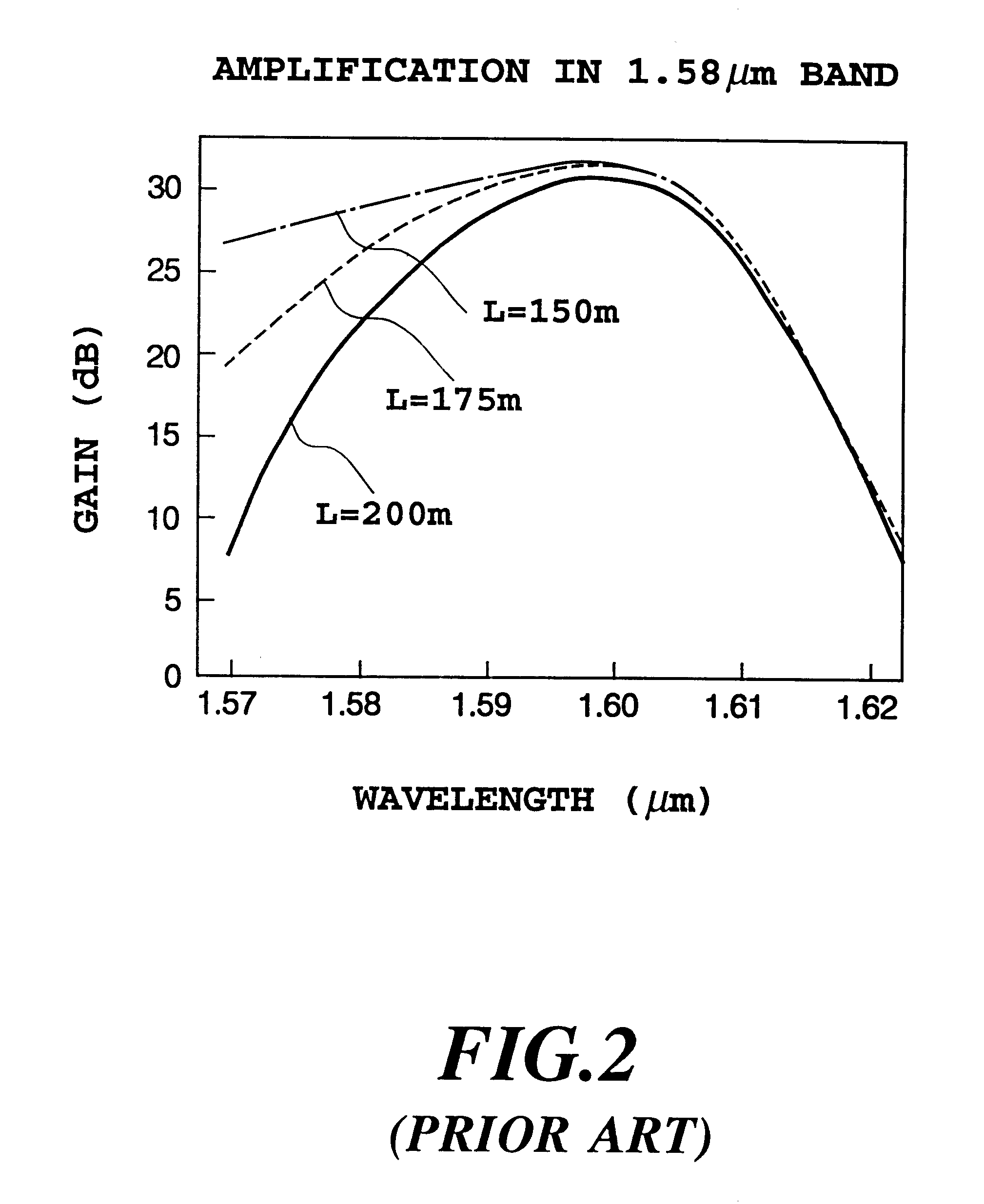
An optical amplifier includes an erbium doped fiber of which at least one of a core part and a clad part is doped with erbium, excitation light sources or exciting the optical fiber, optical means for inputting excitation light from the excitation light source and signal light to the Er-doped fiber, and an optical isolator. The erbium doped fiber is a 1.58 mum band optical fiber having an equivalent fiber length as a product of a fiber length (m) and an erbium doping concentration (ppm by weight), which length provides a signal gain obtained at a wavelength of the excitation light source used for excitation of the erbium doped fiber of more than a predetermined practical reference value.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
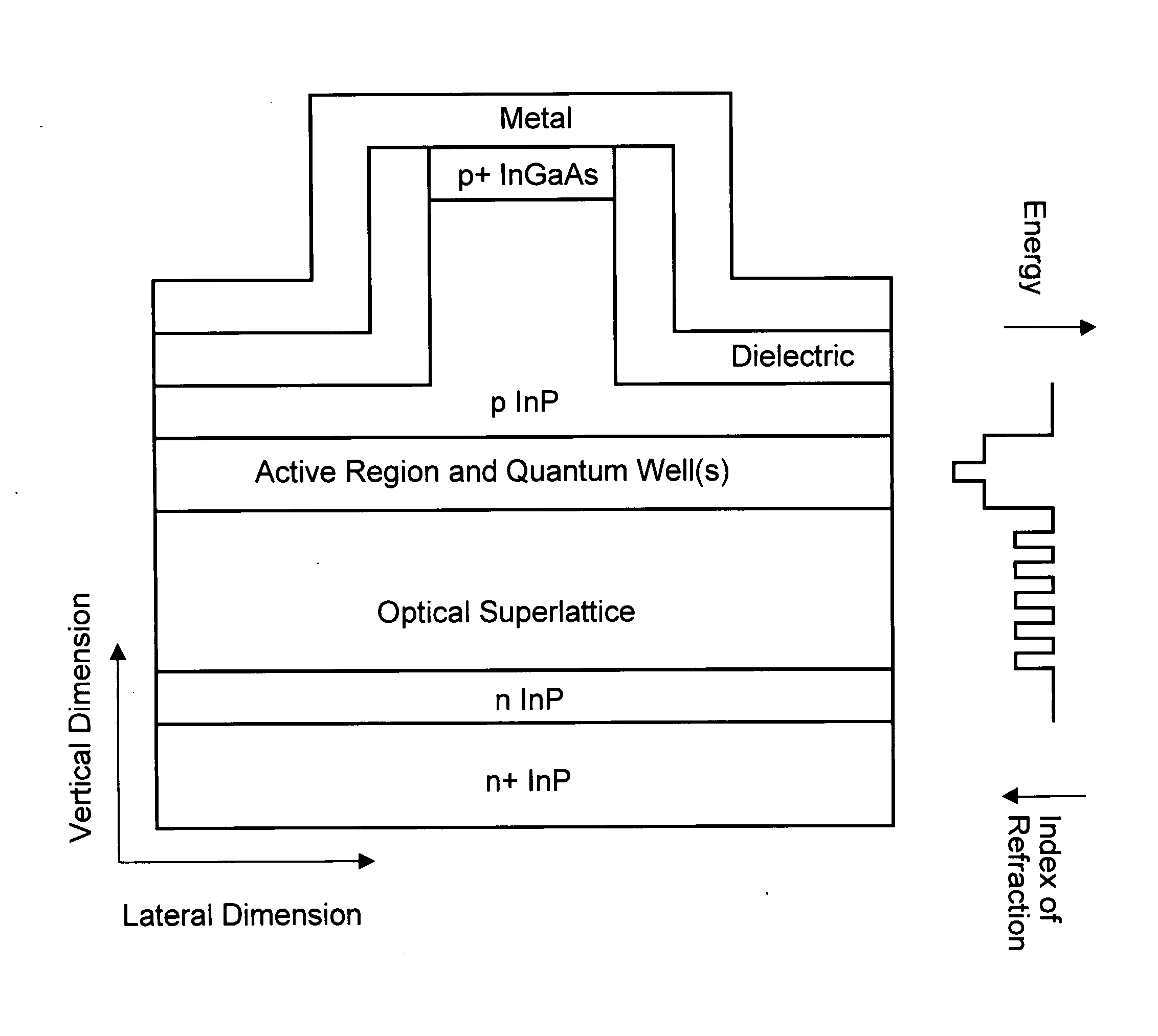
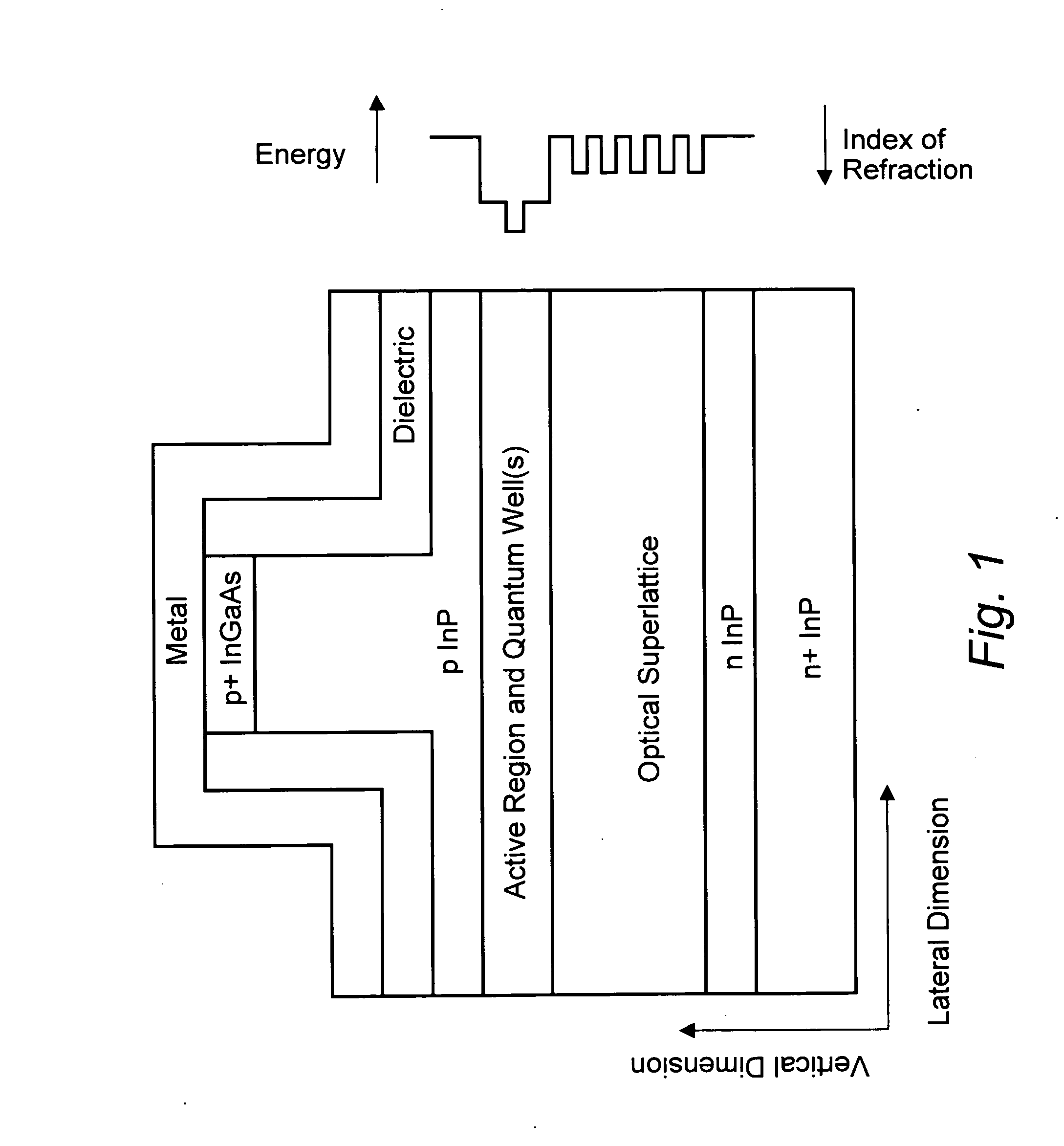
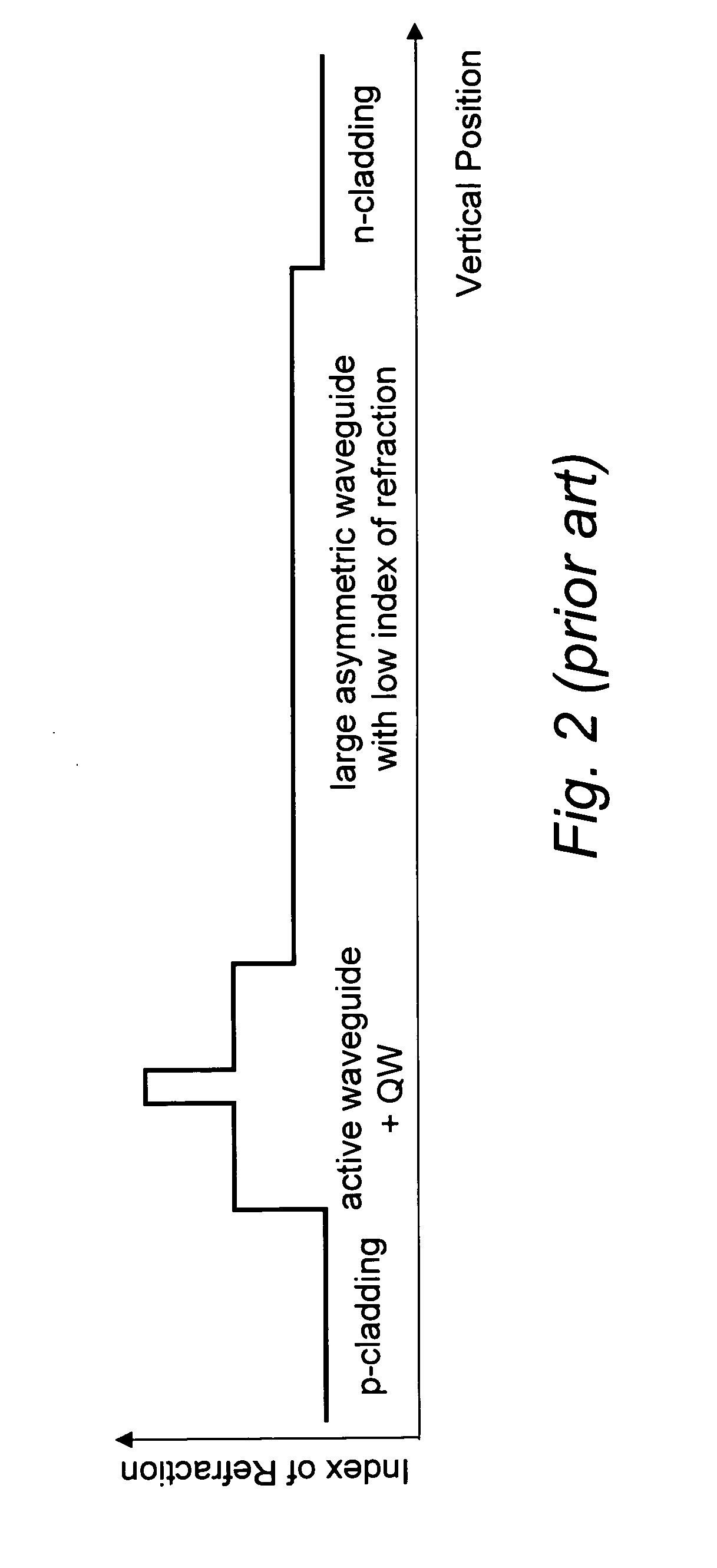
High power semiconductor laser with a large optical superlattice waveguide
ActiveUS20040208213A1Low indexLow vertical farfieldOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsFiberRaman amplifiers
The invention relates to high power semiconductor diode lasers of the type commonly used in opto-electronics, mostly as so-called pump lasers for fiber amplifiers in the field of optical communication, e.g. for an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) or a Raman amplifier. Such a laser, having a single cavity and working in single transverse mode, is improved by placing a multilayer large optical superlattice structure (LOSL) into at least one of the provided cladding layers. This LOSL provides for a significantly improved shape of the exit beam allowing an efficient high power coupling into the fiber of an opto-electronic network.
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD +1
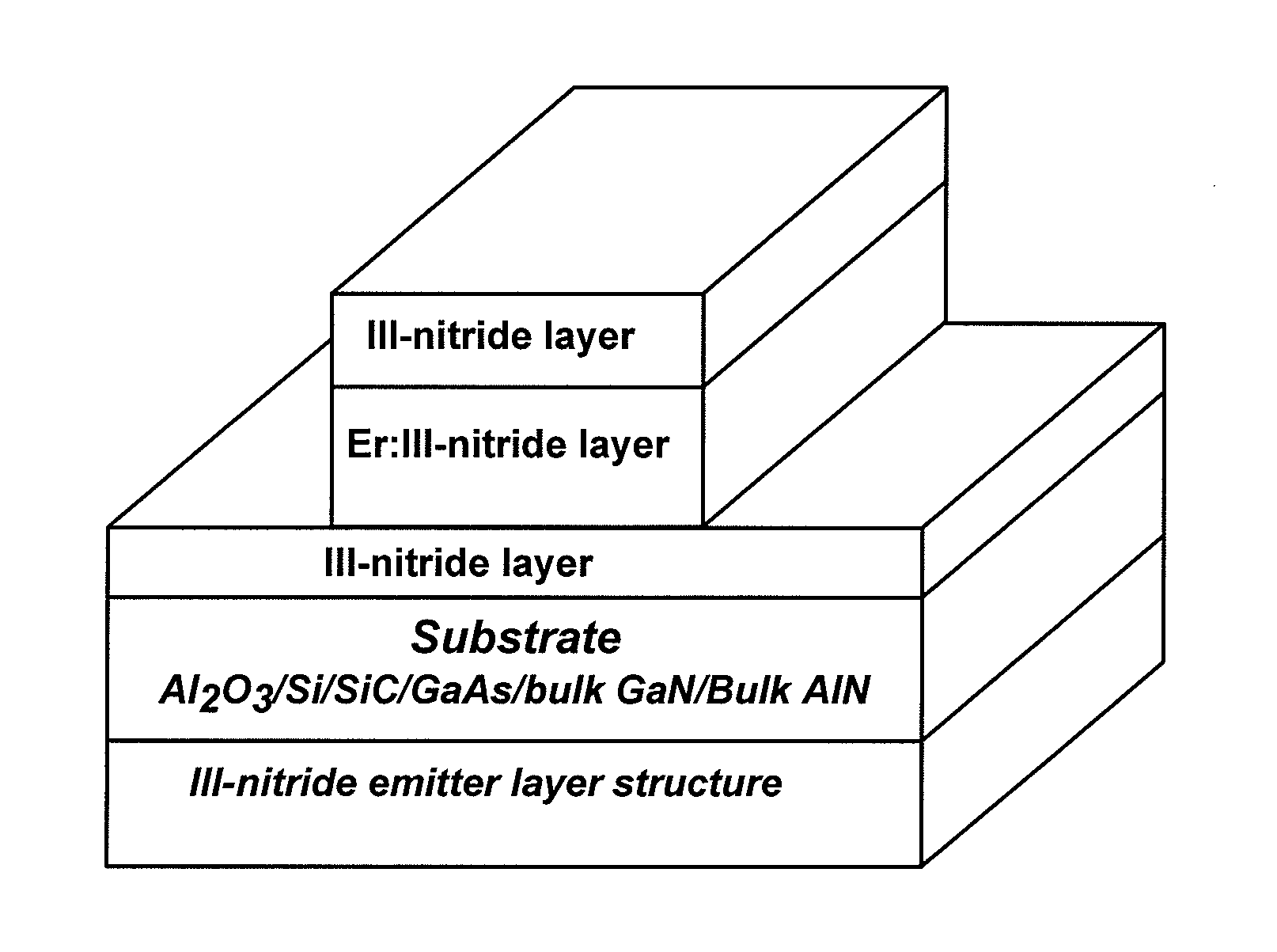
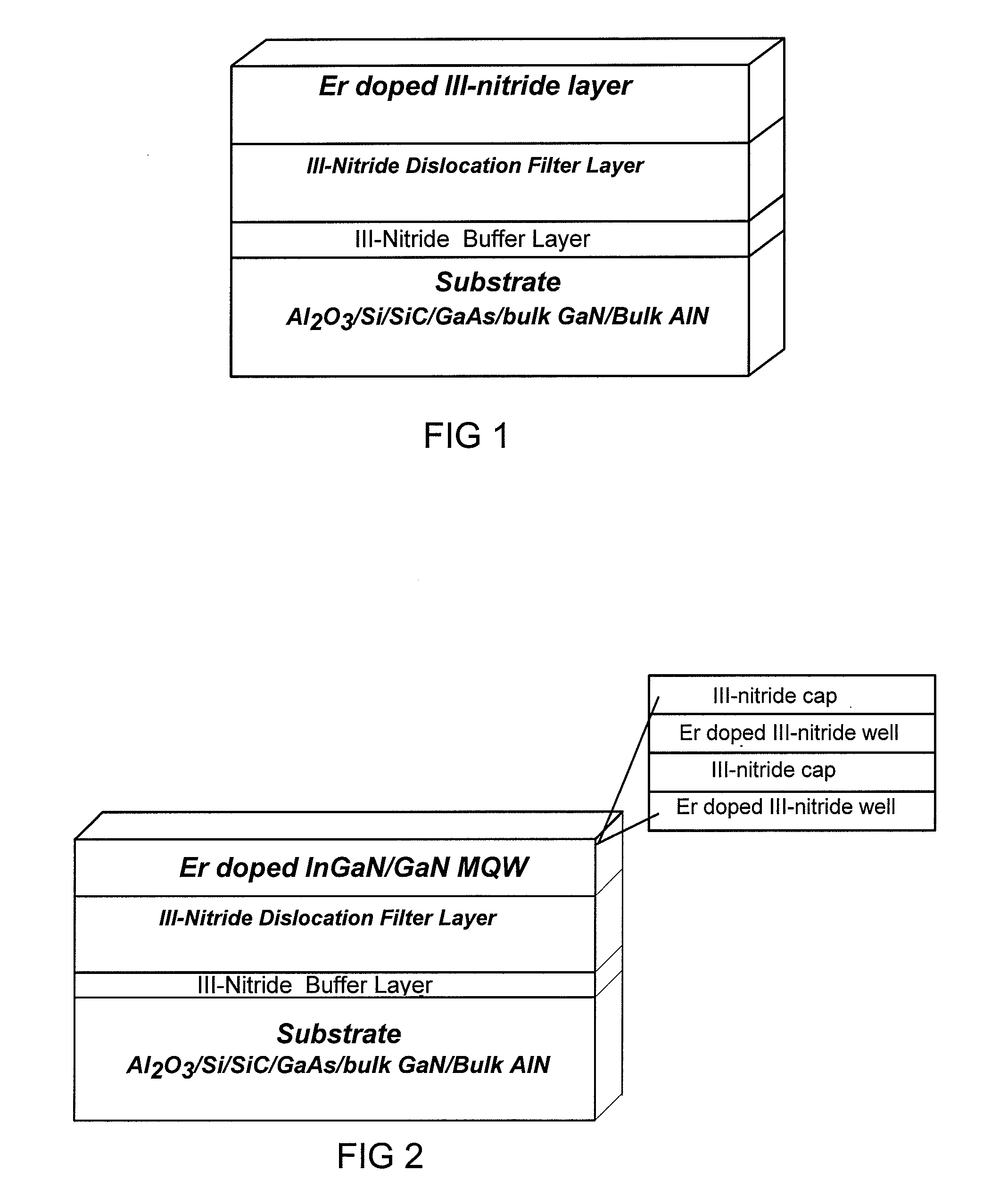
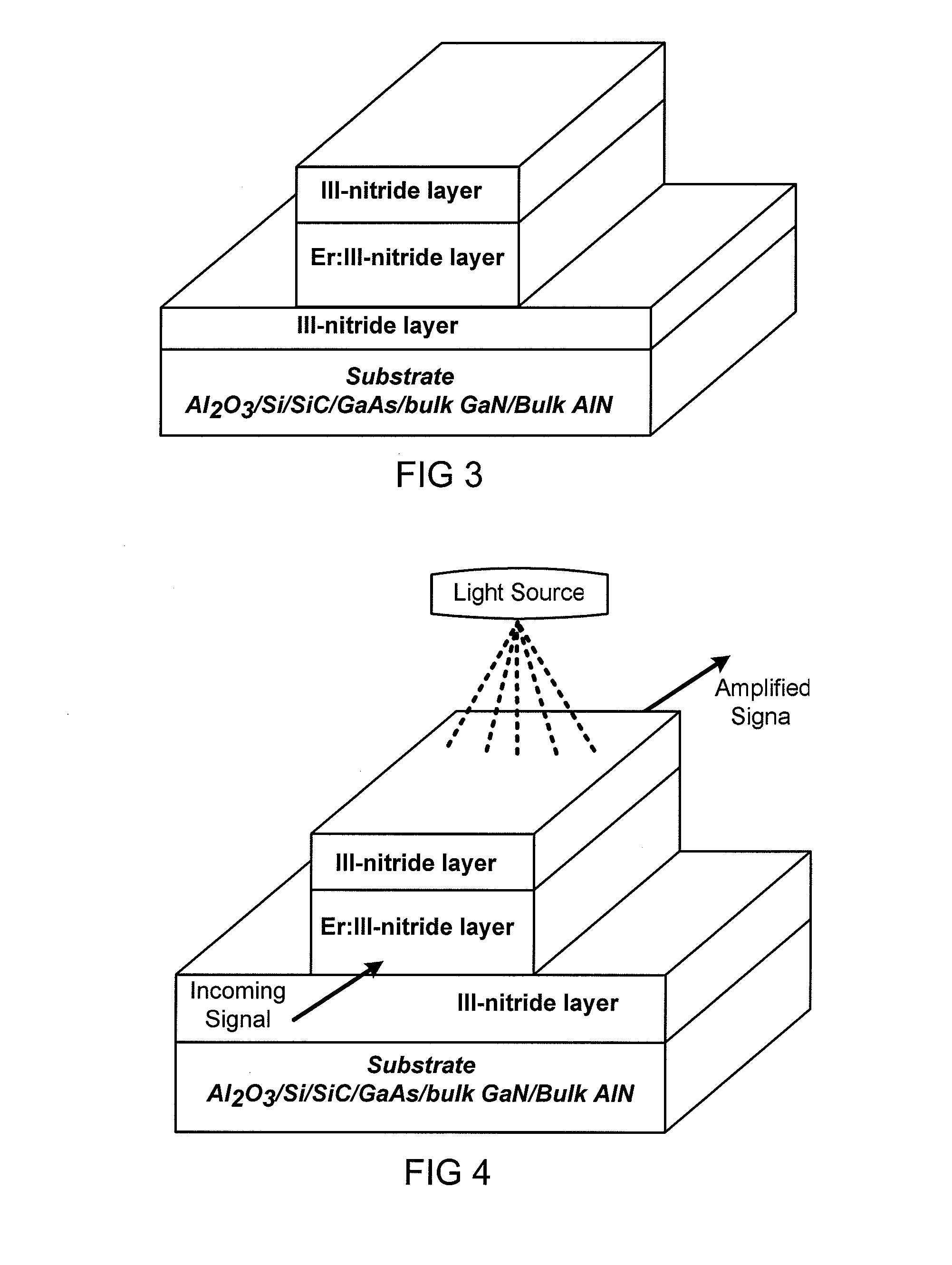
ER Doped III-Nitride Materials And Devices Synthesized by MOCVD
This disclosure relates to the synthesis of Er doped GaN epilayers by in-situ doping by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). In an embodiment, both above and below bandgap excitation results in a sharp PL emission peak at 1.54 μm. Contrary with other growth methods, MOCVD grown Er-doped GaN epilayers exhibit virtually no visible emission lines, an present a small thermal quenching effect. The Er incorporation has very little effect on the electrical conductivity of the GaN epilayers and Er doped layers retain similar electrical properties as those of undoped GaN.
Owner:JIANG HONGXING +3
Distributed Raman amplification-based Brillouin optical time domain analysis system
InactiveCN101762290AImprove distribution uniformityGuaranteed temperature/strain resolutionNon-linear opticsConverting sensor output opticallyTime domainErbium doped fiber amplifier
The invention discloses a bidirectional distributed Raman amplification-based Brillouin optical time domain analysis system. The system comprises a laser 1, a coupler 3, a first electro-optical modulator 6, a second electro-optical modulator 17, a polarization scrambler 8, a first erbium-doped fiber amplifier 9, a second erbium-doped fiber amplifier 18, an optical circulator 12, a tunable filter 11, a detector 10, a data acquisition processing system 7 and a Raman amplification system. In the system, the bidirectional distributed Raman amplification technology is applied in the Brillouin optical time domain analysis system to improve the distribution evenness of Brillouin detection signal gain on a whole section of a sensing fiber, so that the temperature / strain resolution of the whole section of the sensing fiber can be ensured, and long distance distribution sensing in true sense can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Contact type temperature non-inductive three-dimensional detection sensor based on fiber Bragg grating (FBG)
InactiveCN102589439ACapable of 3D detectionRealize three-dimensional space position signal detectionUsing optical meansFiberGrating
The invention discloses a contact type temperature non-inductive three-dimensional detection sensor based on a fiber Bragg grating (FBG) and belongs to the technical field of precision instrument manufacturing and precision test measurement. The sensor comprises a broadband light source system which consists of a pump laser, a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) coupler, an erbium-doped fiber and a beam splitter, a temperature compensation system which consists of an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA), a first circulator, a guide pipe, a reference FBG and a fiber barrier, a probe, and a signal receiving system which consists of an optical spectrum analyzer, a fiber coupler and an index-matching fluid, wherein the reference FBG of the temperature compensation system is arranged in a spatial distance of 30 cm of the probe. By the sensor, three-dimensional sensing is realized, and the environmental adaptability of the sensor is greatly improved. The sensor has the characteristics of simple structure and high real-time performance and is easy to practically use. The sensor has the advantage of quick and ultra-precise measurement and calibration of small cavity size.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Device and method for generating microwave signals by using multi-wavelength Brillouin laser
InactiveCN101807773APower spectrum distribution is flatSuppression of four-wave mixing effectsLaser using scattering effectsGratingPhotodetector
The invention relates to a device and a method for generating microwave signals by using a multi-wavelength Brillouin laser. An existing device obtains a high frequency difficultly. The device of the invention comprises an adjustable narrow-band light source, two isolators, three couplers, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, two optical fiber circulators, a Sagnac loop mirror, an optical fiber Bragg grating and a photodetector. The adjustable narrow-band light source is in optical connection with the isolators; the isolators are in optical connection with the couplers; outputs of the couplers are in optical connection with another coupler respectively; one of optical paths is provided with the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, the two optical fiber circulators and the Sagnac loop mirror. The method for generating the microwave signals by using the device comprises the following steps that: pump spectrum light emitted by the adjustable narrow-band light source is split into two paths of pump spectrum light after passing through the isolators and the couplers, one path of the pump spectrum light performs beat frequency with the other path of the pump spectrum light after outputting single-channel high-order Stocks light so as to obtain high-frequency microwave signals. The device and the method change the wavelength of the pump spectrum light to make a multi-wavelength pass band continuously adjustable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Silicon nanocrystal/erbium doped waveguide (SNEW) laser
InactiveUS20060039433A1High refractive indexLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersEnergy transferErbium doping
A rare earth-doped solid-state integrated laser which includes an optical waveguide, and a laser cavity including at least one subwavelength mirror. The subwavelength mirror is disposed in or on the optical waveguide. The optical waveguide portion within the laser cavity includes active media comprising both a rare earth and semiconducting atoms or compounds. A structure for pumping the semiconducting semiconducting atoms or compounds is provided, such as electrodes sandwiching the active media wherein the semiconducting atoms or compounds transfer energy obtained from the pumping to the rare earth, thus permitting the laser to laze.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
High bandwidth tunable double-passband microwave photon filter
InactiveCN103986529AThe center frequency of the passband can be adjusted arbitrarilyChange bandwidthTransmission control/equalisingPhotonic quantum communicationErbium dopingMicrowave photonic
The invention discloses a high bandwidth tunable double-passband microwave photon filter, belongs to the field of microwave photonics, and relates to the high bandwidth tunable double-passband microwave photon filter based on high non-linear optical fiber excited brillouin scattering effects and multiple pumping signals. The filter consists of a first laser, a first phase modulator, an opto-isolator, a vector network analyzer, a high non-linear optical fiber, a second laser, a strength modulator, a microwave signal source, a second phase regulator, a pulse code generator, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, an optical circulator and a photoelectric detector. The filter is based on phase modulation and excited brillouin scattering effects caused by two pumping signals, and thus double-passband output of the microwave photon filter is achieved. By changing the frequency of the two pumping signals, the frequency of two passband centers can be randomly modulated within a certain frequency range. Through binary phase shift keying modulation on the pumping signals, the bandwidth of the pumping signals can be changed, and thus adjustment on the output bandwidth of the filter is achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Sensing signal detecting device and method based on fiber Brillouin ring laser
InactiveCN102538985AFacilitate coherent detectionImprove signal-to-noise ratioOptical measurementsLaser detailsLine widthErbium doping
The invention discloses a sensing signal detecting device and a sensing signal detecting method based on a fiber Brillouin ring laser. The device comprises a narrow linewidth DFB (distributed feedback) laser, three optical fiber couplers, a pulse modulator, two erbium-doped fiber amplifiers, two optical fiber circulators, two single-mode fibers, an optical isolator, a polarization controller and a photoelectric detector, wherein the fiber Brillouin ring laser is composed of the second optical fiber circulator, the second single mode fiber, the optical isolator, the second optical fiber coupler and the polarization controller. Light emitted from the laser is divided into two beams of light via the optical fiber couplers, wherein the probe light is modulated into pulsed light which enters into sensing optical fiber after passing through the erbium-doped fiber amplifiers to ensure that back spontaneous Brillouin scattered signals are generated; the reference light passes through the center frequency of the fiber Brillouin ring laser to ensure that a Brillouin frequency shift is generated; and the coherent detection is carried out on the two Brillouin scattered signals which are scattered back to ensure that the advantages of rapid high-accuracy detection and simple structure are realized by utilizing low-cost devices.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Microwave photon mixing method and system based on local oscillator frequency doubling
ActiveCN108667517AReduce frequency requirementsReduce spurious signalsElectromagnetic transmittersLocal oscillator signalBand-pass filter
The invention discloses a microwave photon mixing method and system based on local oscillator frequency doubling, and belongs to the fields of optical communication and microwave photonics. The microwave photon mixing system based on local oscillator frequency doubling is formed by utilizing a double-polarization double-parallel mach-zehnder modulator through combination with devices such as a laser, a front polarization controller, a microwave 90-degree coupler, a rear polarization controller, an optical fiber polarizer, an adjustable optical band-pass filter, an erbium-doped fiber amplifier,a photoelectric detector and the like. The system adopts second-order local oscillator sideband and first-order radio frequency sideband beat frequencies, and mixing processing based on local oscillator frequency doubling can be realized; on one hand, the frequency requirement of a mixing system on a local oscillator signal is reduced, and on the other hand, due to the fact that a single-sidebandmodulation mode is adopted, stray signals can be effectively reduced. In addition, the mixing method can realize switching of up conversion and down conversion by changing a direct current bias voltage, and can be used for time-sharing transmitting and receiving of radio frequency.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
High non-linear optical fiber excited Brillouin scattering effect and amplitude ratio based microwave frequency measurement method and device
ActiveCN107144731AEasy to chooseImprove scalabilityFrequency measurement arrangementErbium dopingMicrowave photonic
The invention provides a high non-linear optical fiber excited Brillouin scattering effect and amplitude ratio based microwave frequency measurement method and device and belongs to the technical field of microwave photonics. The device provided by the invention is composed of a tunable laser, a coupler, a phase modulator, a strength modulator, a vector network analyzer, an opto-isolator, a high non-linear optical fiber, a circulator, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, a microwave signal source, a DC voltage stabilizing power source and a photoelectric detector. The frequency range of to-be-detected microwave signals can be enlarged through increasing bandwidths of the strength modulator and the phase modulator and enlarging the scanning range of the vector network analyzer and measurement precision can be improved through reducing noise in optical links and increasing the magnitude of energy transfer of excited Brillouin scattering effect. According to the invention, an amplitude ratio function curve is constructed based on the high non-linear optical fiber excited Brillouin scattering effect and a frequency value of to-be-detected microwave signals is obtained through the amplitude ratio function curve. Therefore, the measurement precision is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Methods and apparatus for upgrading passive optical networks
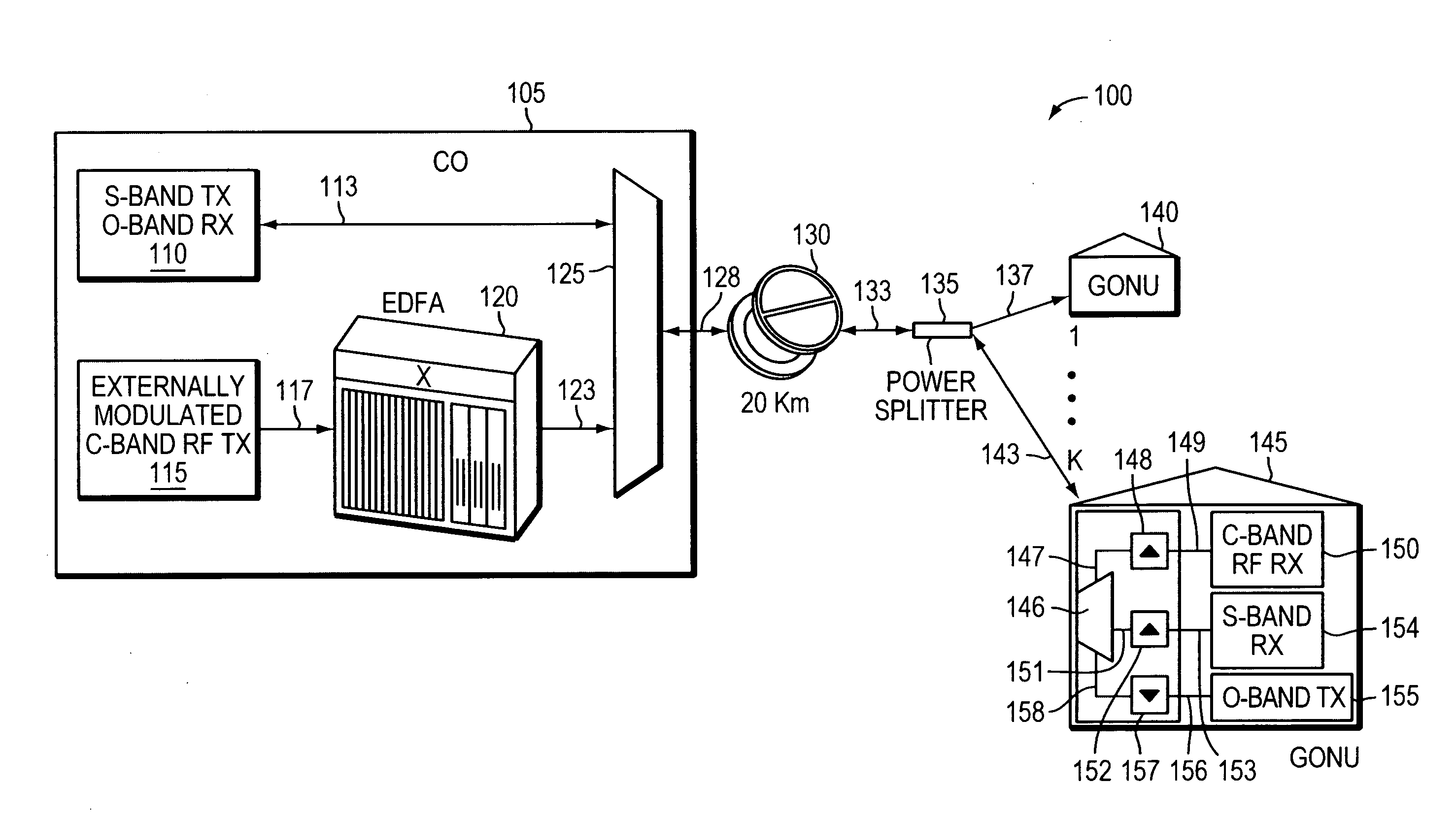
InactiveUS20090010648A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionErbium doped fiber amplifierMultiplexer
An optical network system can be used to update legacy passive optical networks by adding an optical transmitter, blocking filter, and / or pluggable or unpluggable optics. In one embodiment, an optical network system, including several optical transmitters and receivers, multiplexers, demultiplexers, erbium-doped fiber amplifier, and blocking filter, may be employed. The additional transmitter increases available bandwidth, while the blocking filter allows existing customers' service(s) to not be impacted. Another embodiment uses pluggable or unpluggable optics, instead of the aforementioned blocking filter, to receive and modulate optical signals to transmit services to end users. In one embodiment, an optical network system can be employed that allows for simultaneous upgrading of the system and providing of legacy services, while allowing for the of removal existing optical network components over time.
Owner:TELLABS BEDFORD
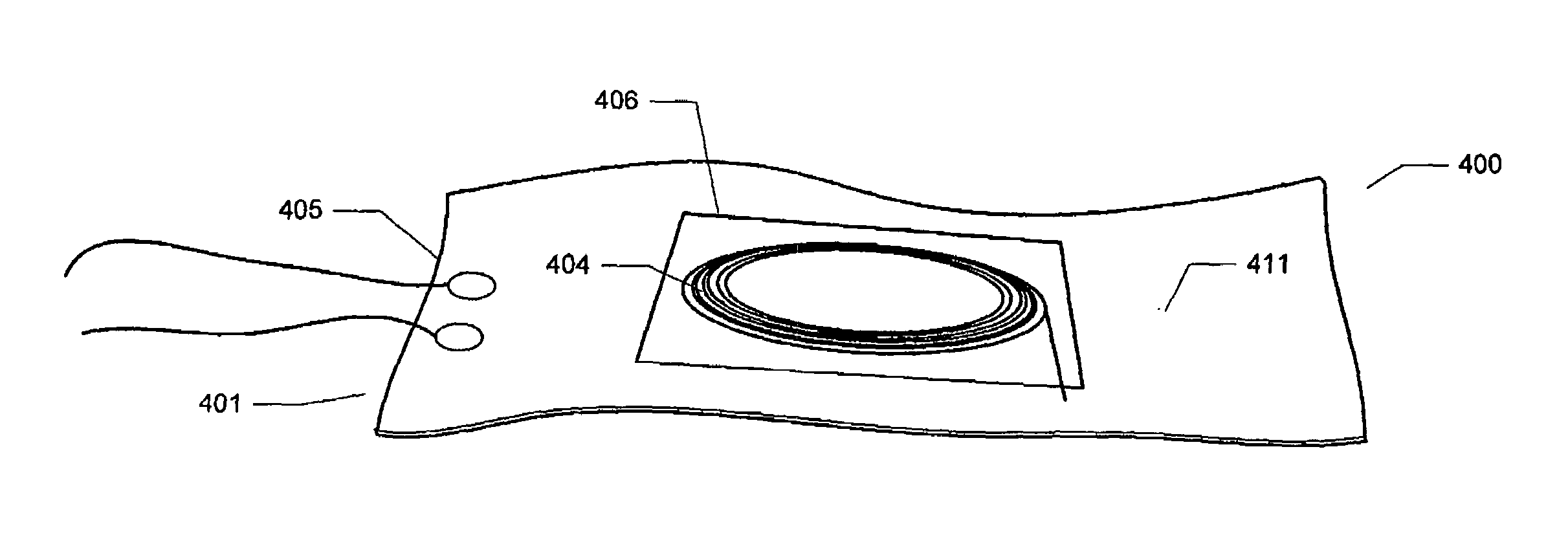
Temperature-controlled flexible optical circuit for use in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier and method for fabricating the flexible optical circuit
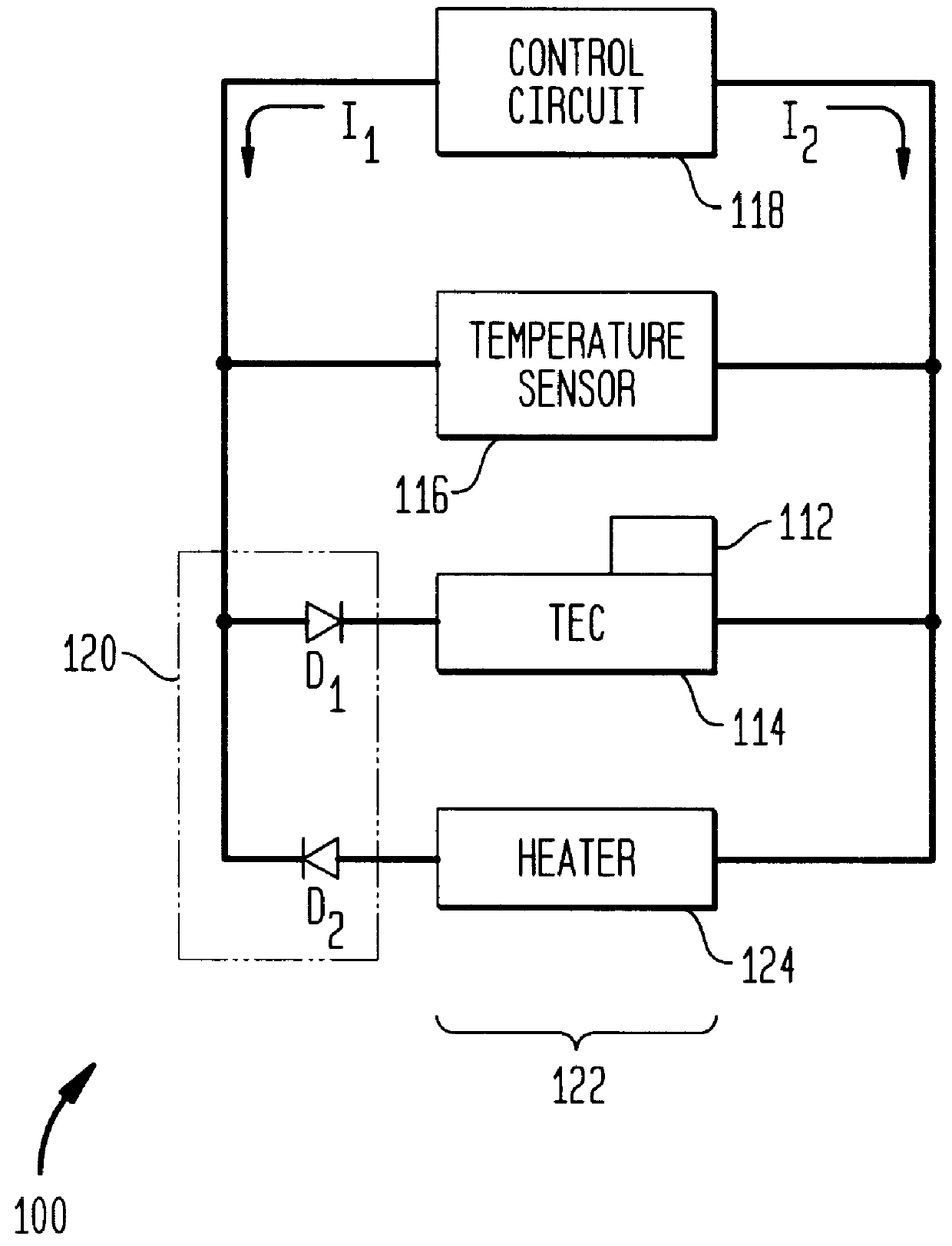
InactiveUS7233712B2Coupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresTemperature controlErbium doped fiber amplifier
A temperature-controlled flexible optical circuit includes a length of pre-fabricated optical fiber secured to a partially flexible heater circuit for heating and maintaining the optical fiber at a substantially constant temperature. Heater circuit may also comprise temperature sensors.
Owner:SANMINA-SCI CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com