Microwave signal optical fiber stationary phase transmission system based on microwave phase shifter
A microwave phase shifter and microwave signal technology, applied in the field of microwave photonics, can solve the problems of bandwidth limitation of transmission signals, large phase jitter of transmission signals, and difficulty in real-time compensation of phase jitter, etc. The effect of low maintenance costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
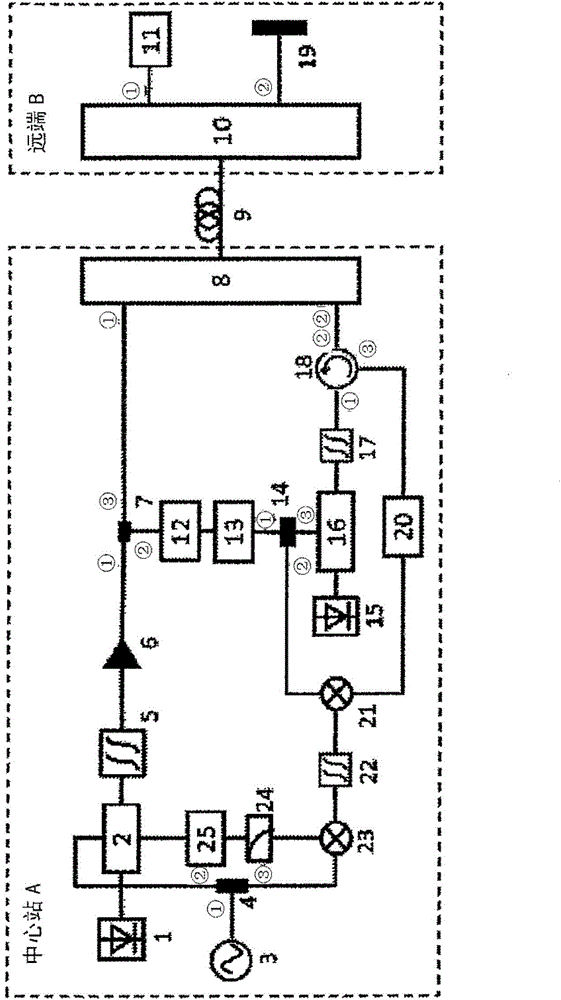
[0036] see figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a microwave signal optical fiber phase-stable transmission system based on a microwave phase shifter, including: a central station A, a remote B and a single-mode optical fiber 9, and the central station A passes through the single-mode optical fiber 9 Connect with remote B, where:
[0037] Described central station A comprises:
[0038] A semiconductor laser 1, which is used to provide continuous optical carrier;
[0039] A dual-drive Mach-Zehnder modulator 2, the optical input of which is connected to the output of the semiconductor laser 1;
[0040] A microwave signal source 3, the microwave signal source 3 is a vector network analyzer or a microwave signal source, used to generate a local oscillator microwave signal, which is a signal that needs to be transmitted;
[0041] A first power divider 4, its input port 1 is connected with the output end of the microwave signal source 3, and its output port 2 is conne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com