Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1055 results about "Frequency-division multiplexing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
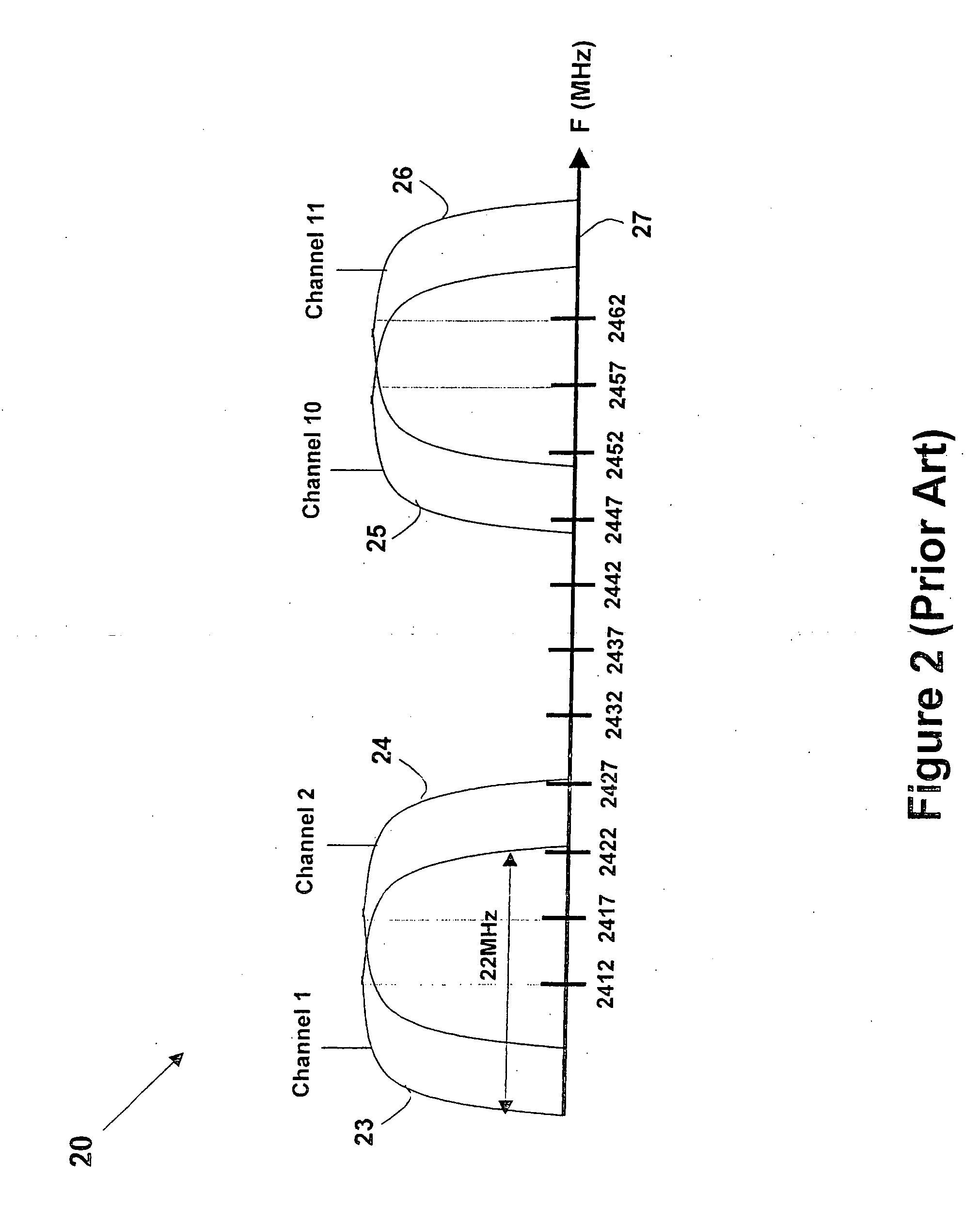
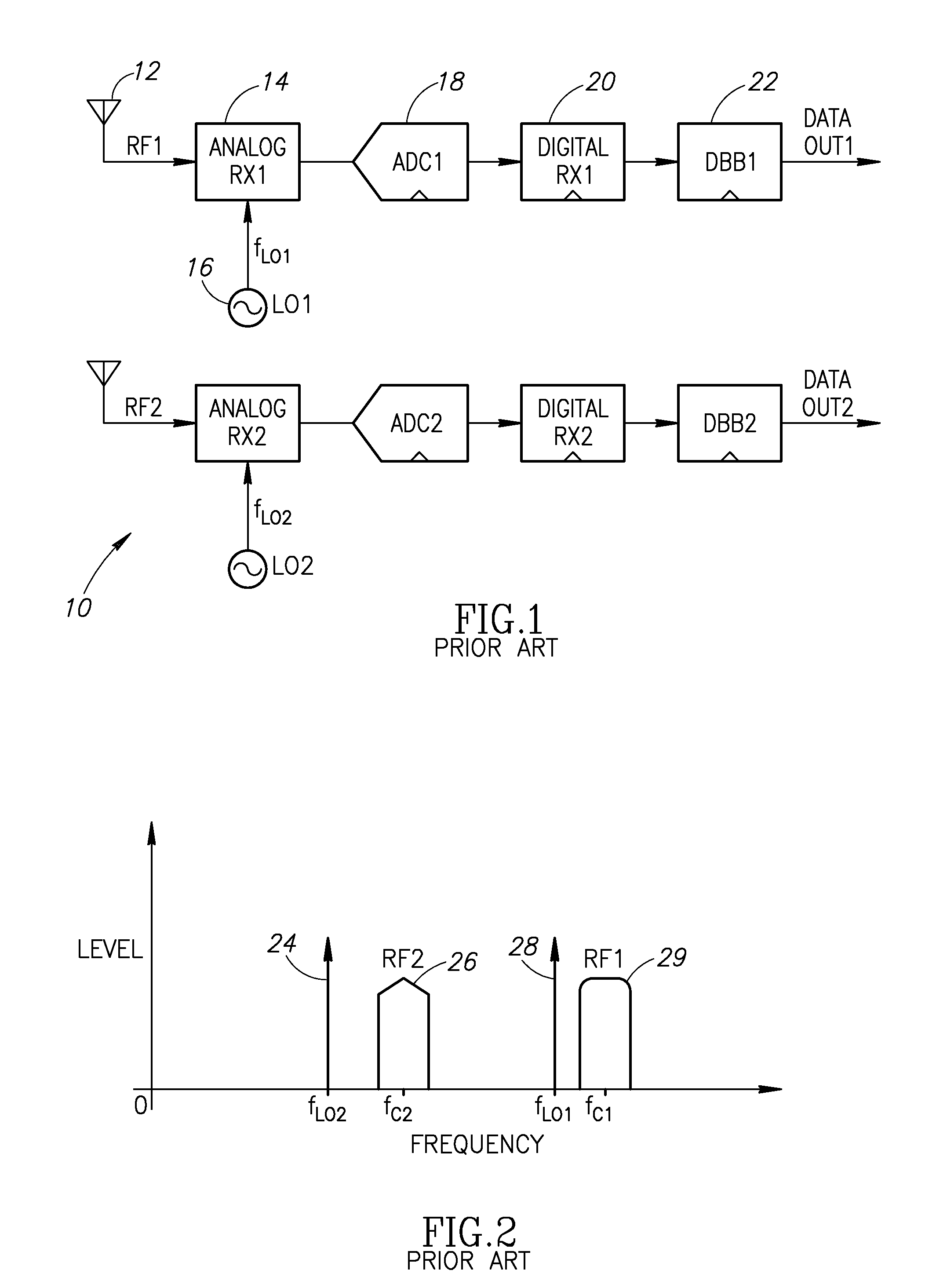
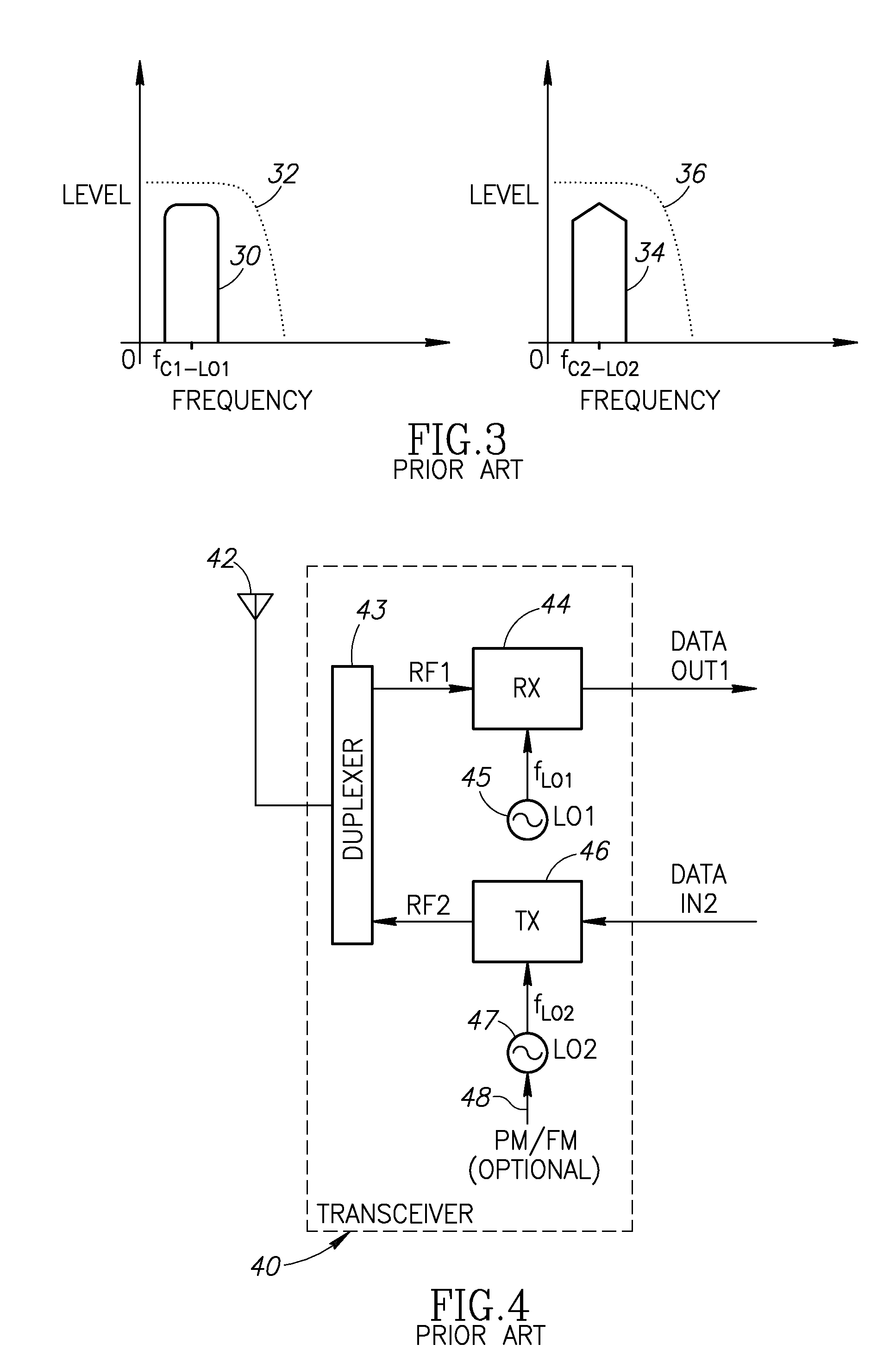
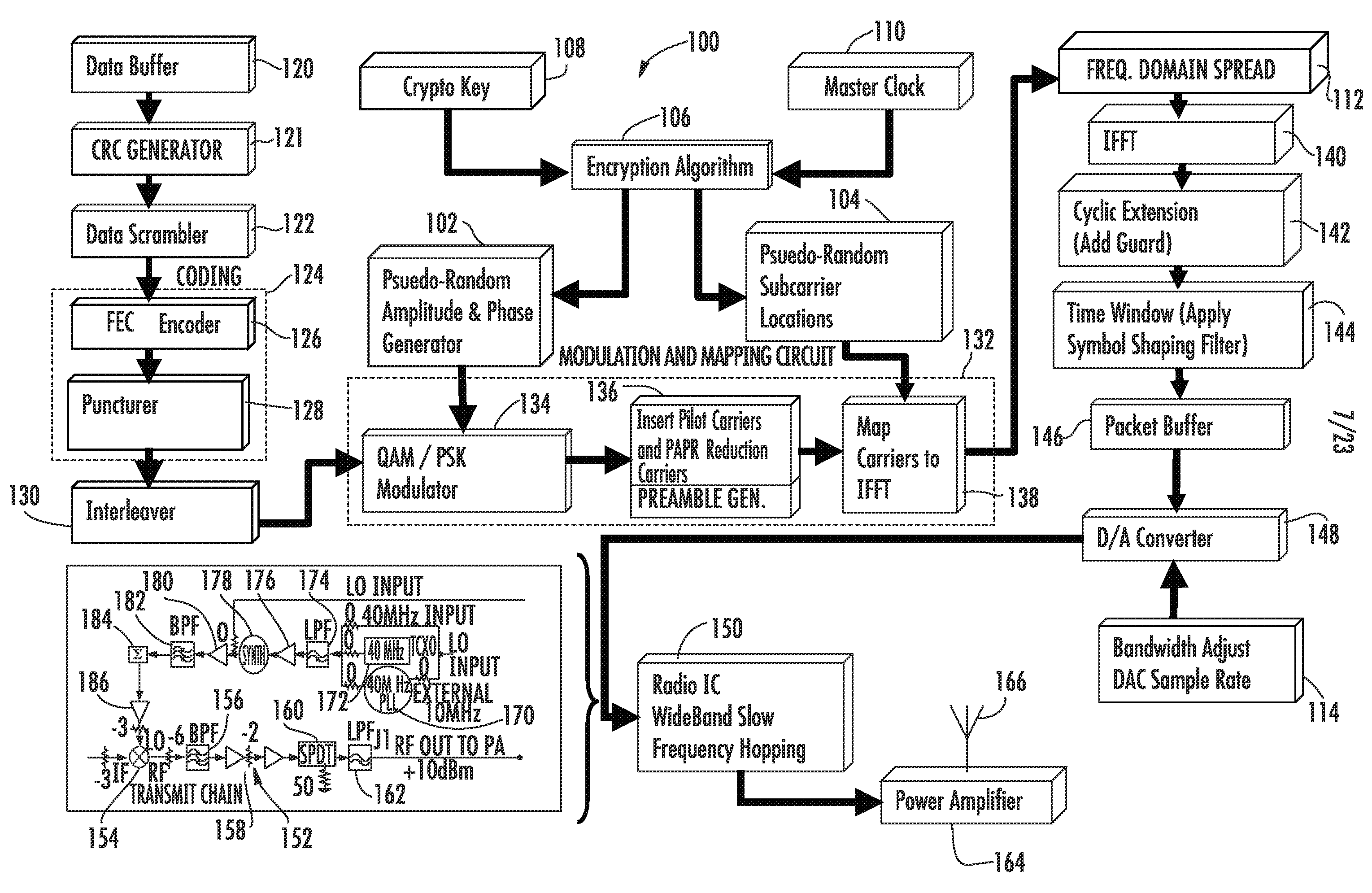
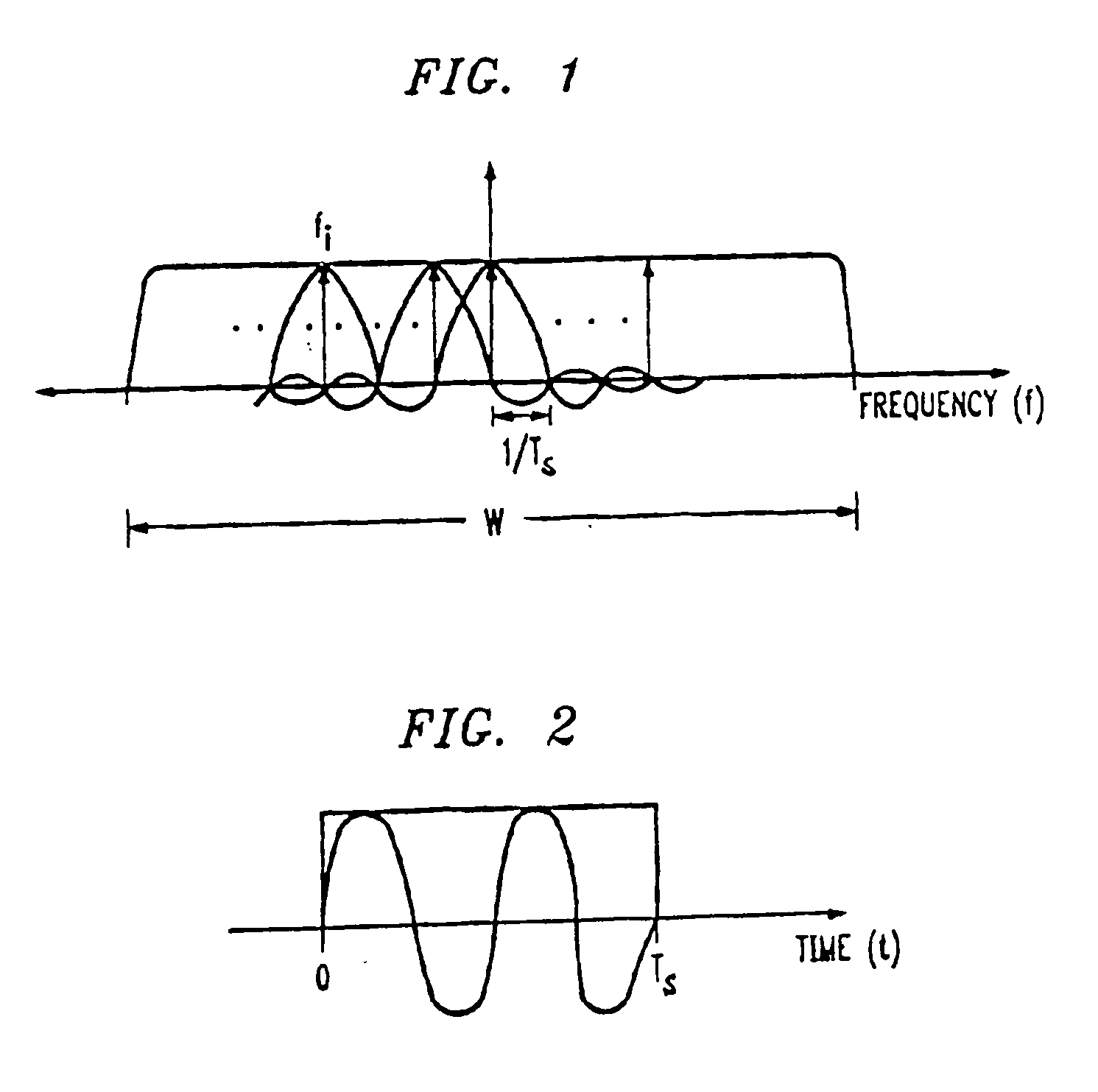
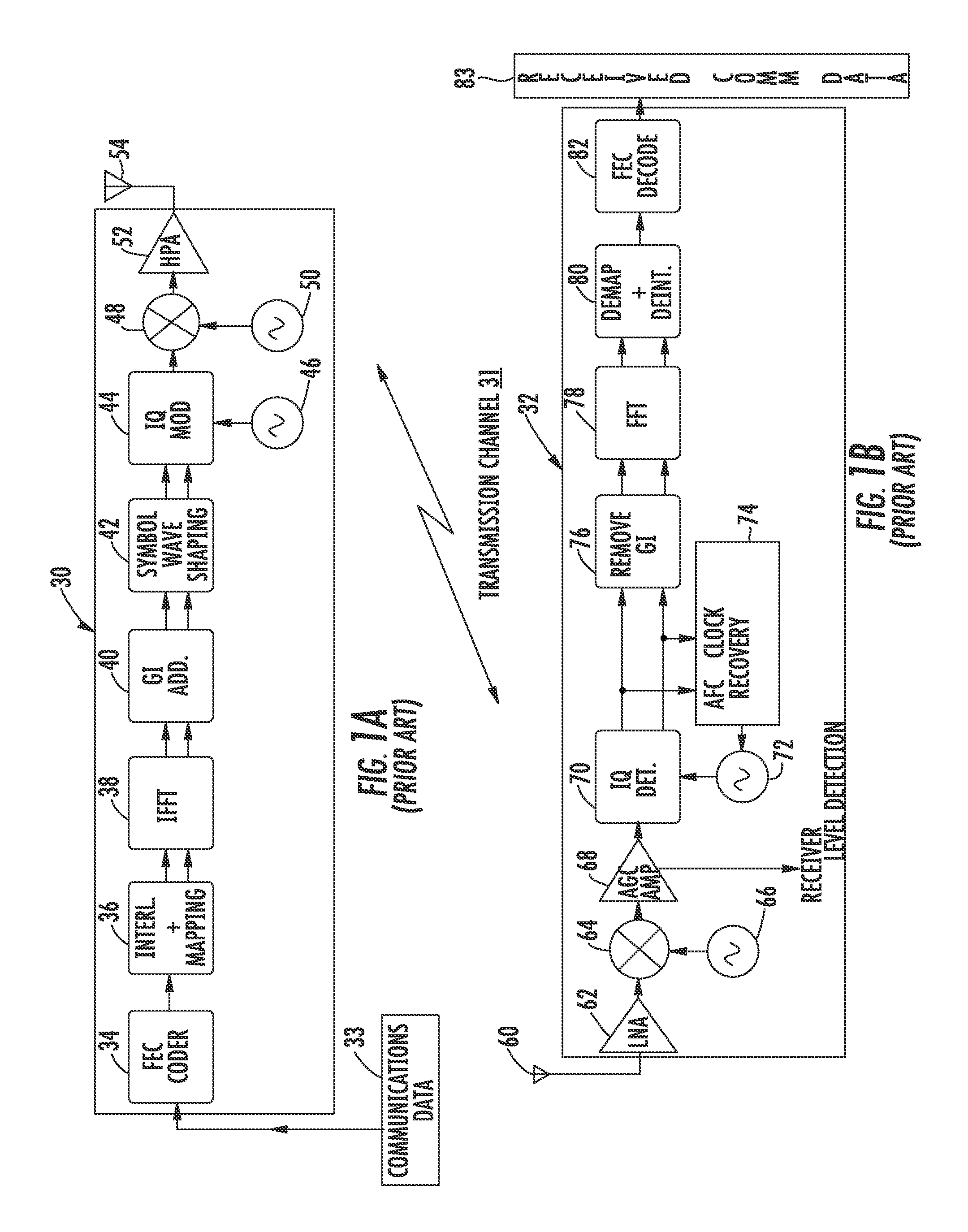
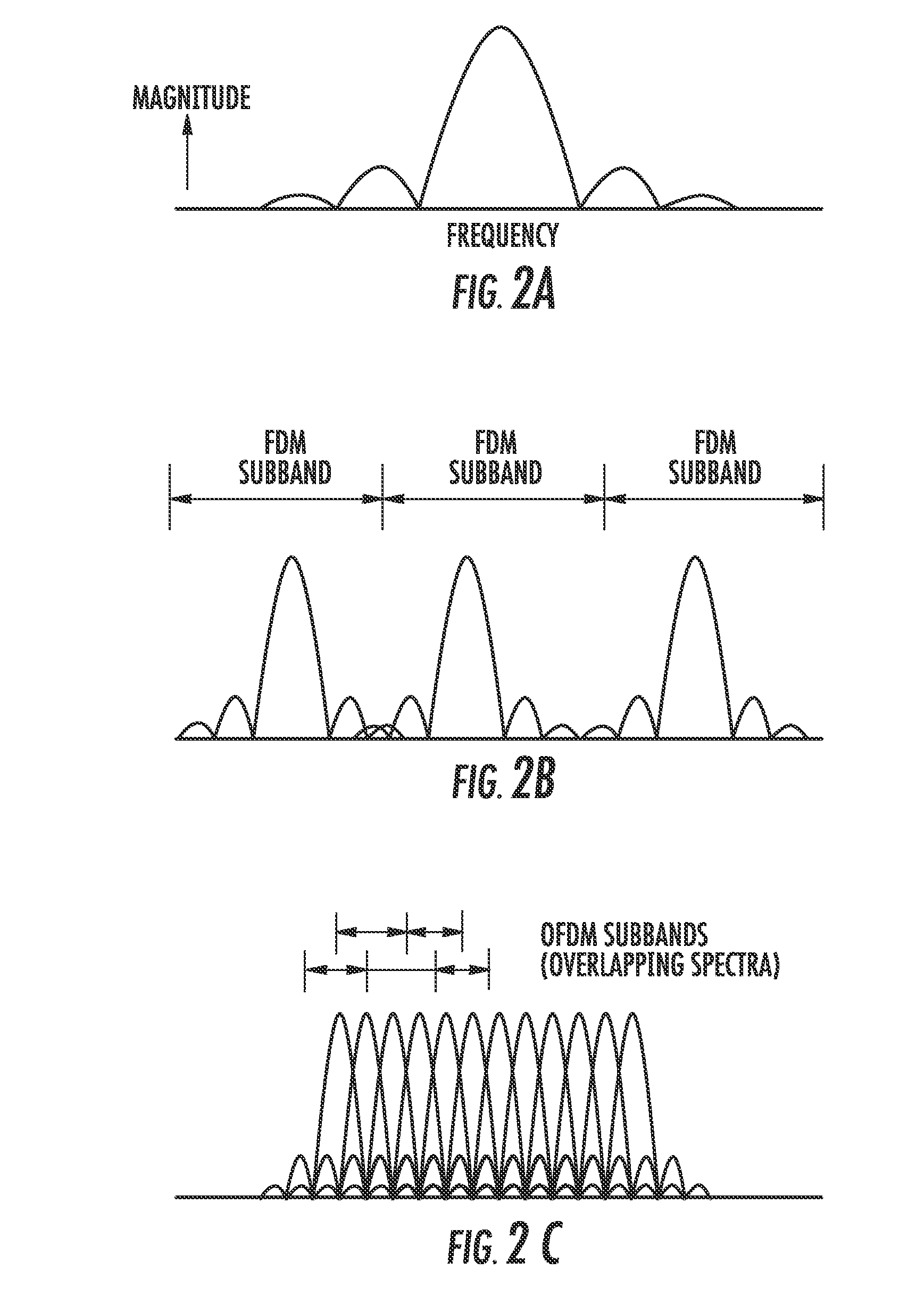
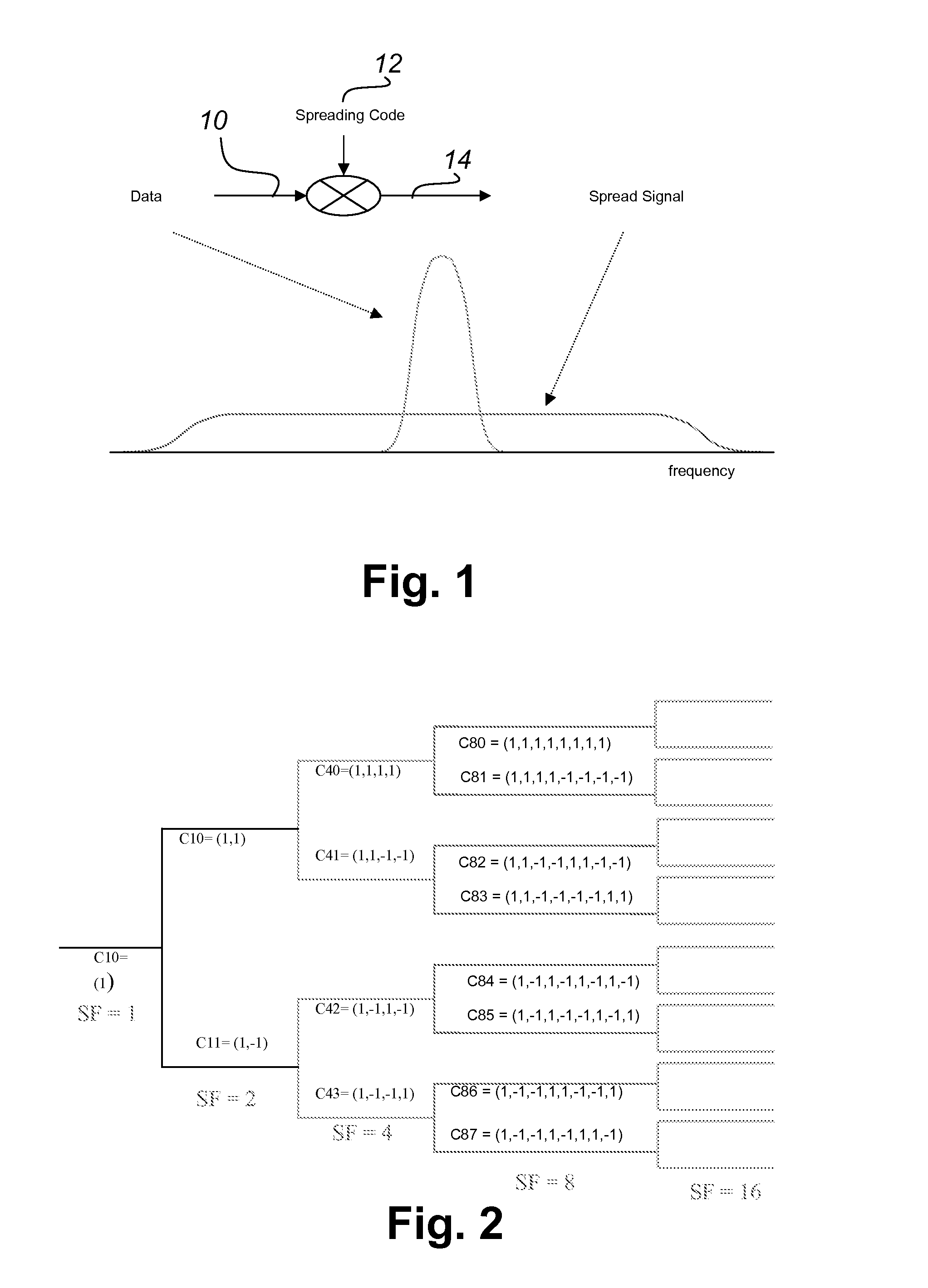
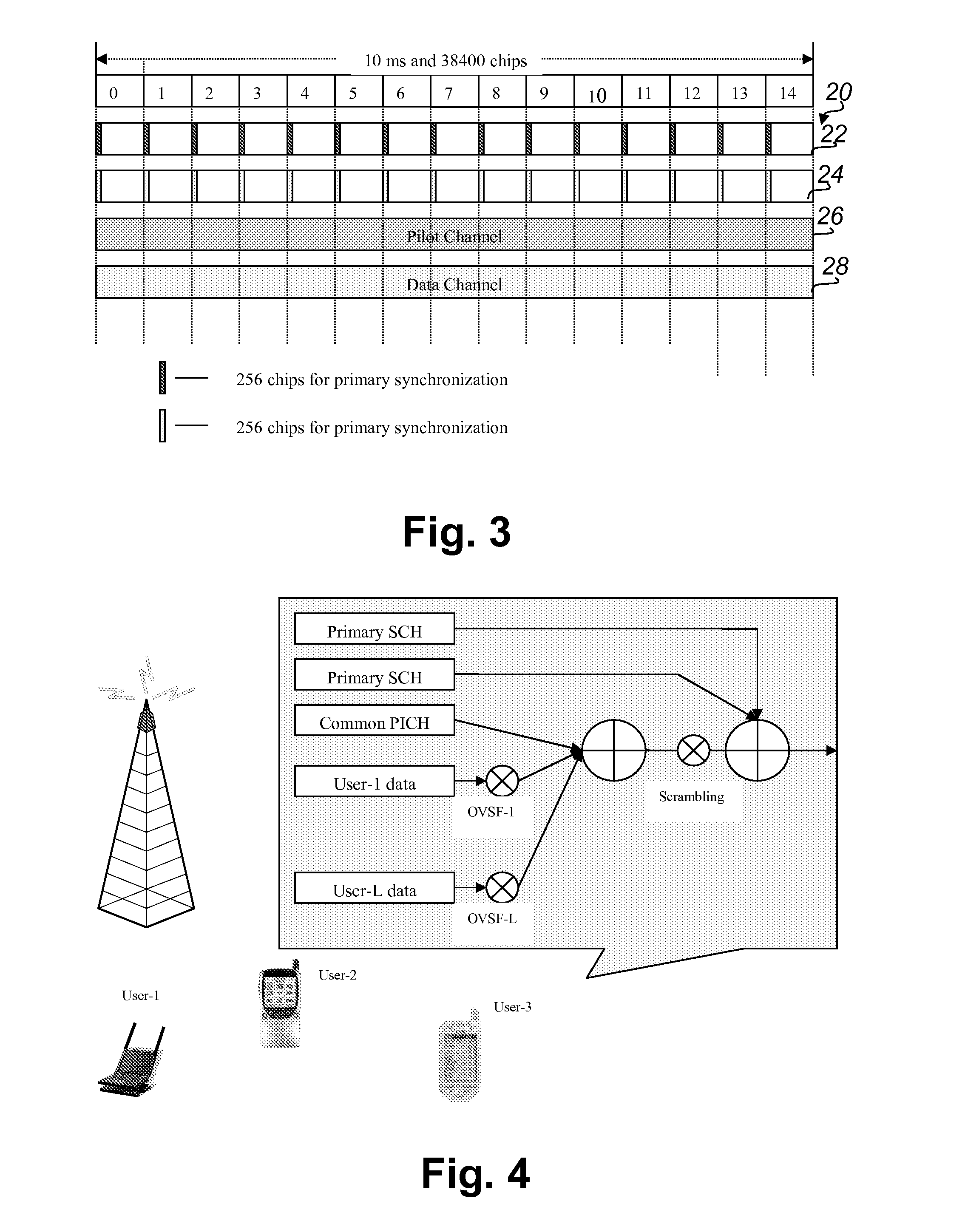
In telecommunications, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is a technique by which the total bandwidth available in a communication medium is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands, each of which is used to carry a separate signal. This allows a single transmission medium such as a cable or optical fiber to be shared by multiple independent signals. Another use is to carry separate serial bits or segments of a higher rate signal in parallel.
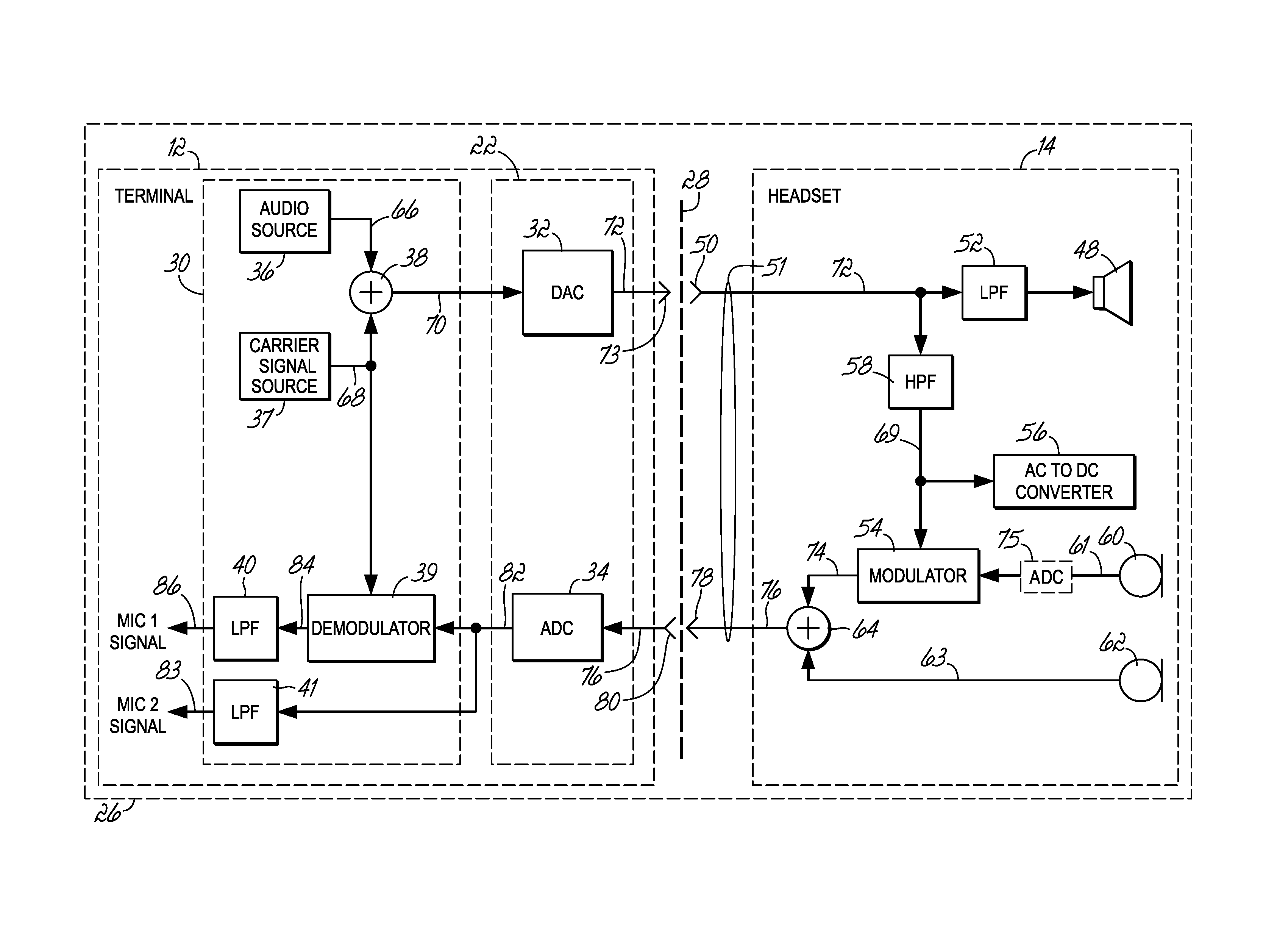
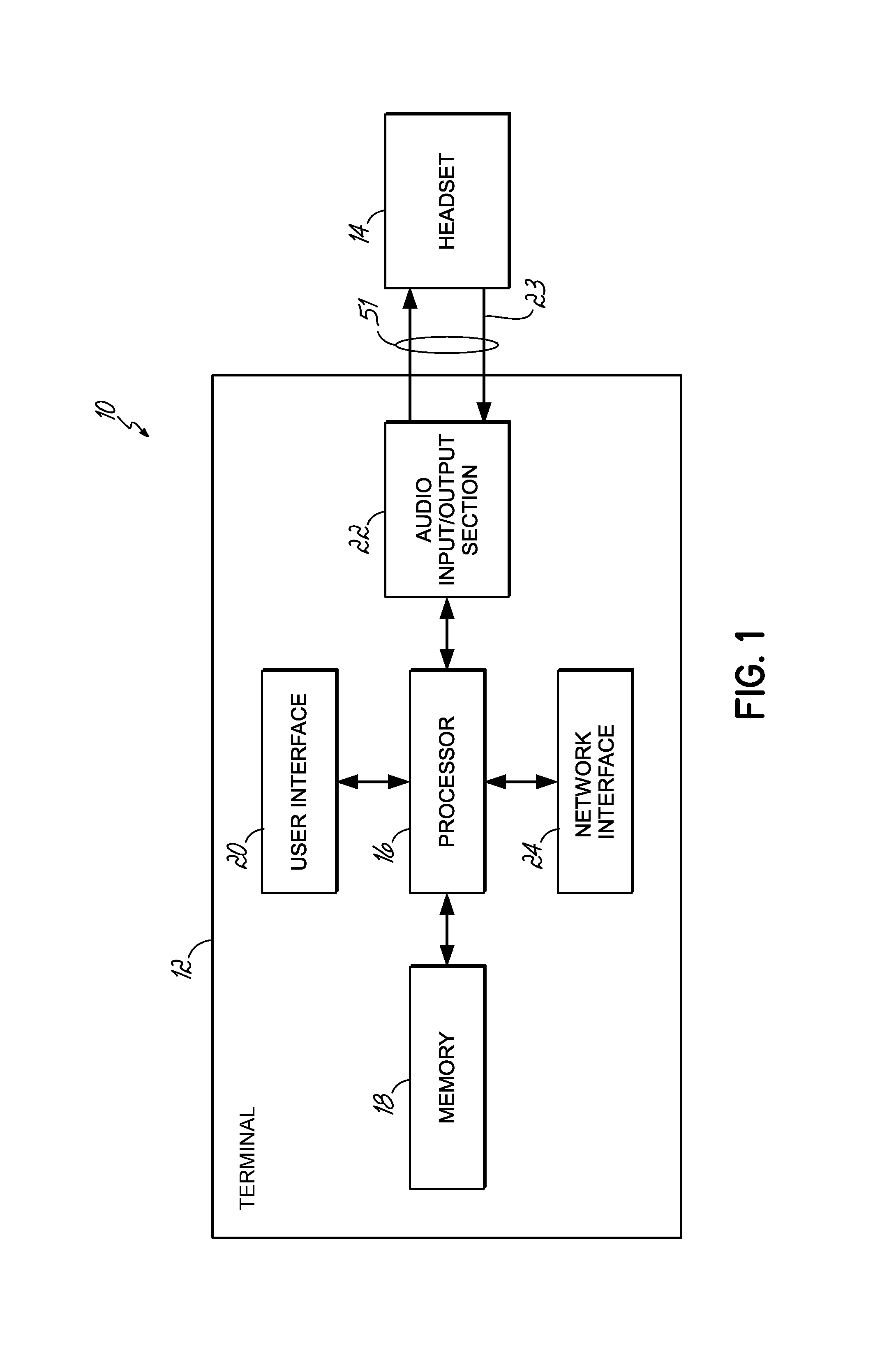
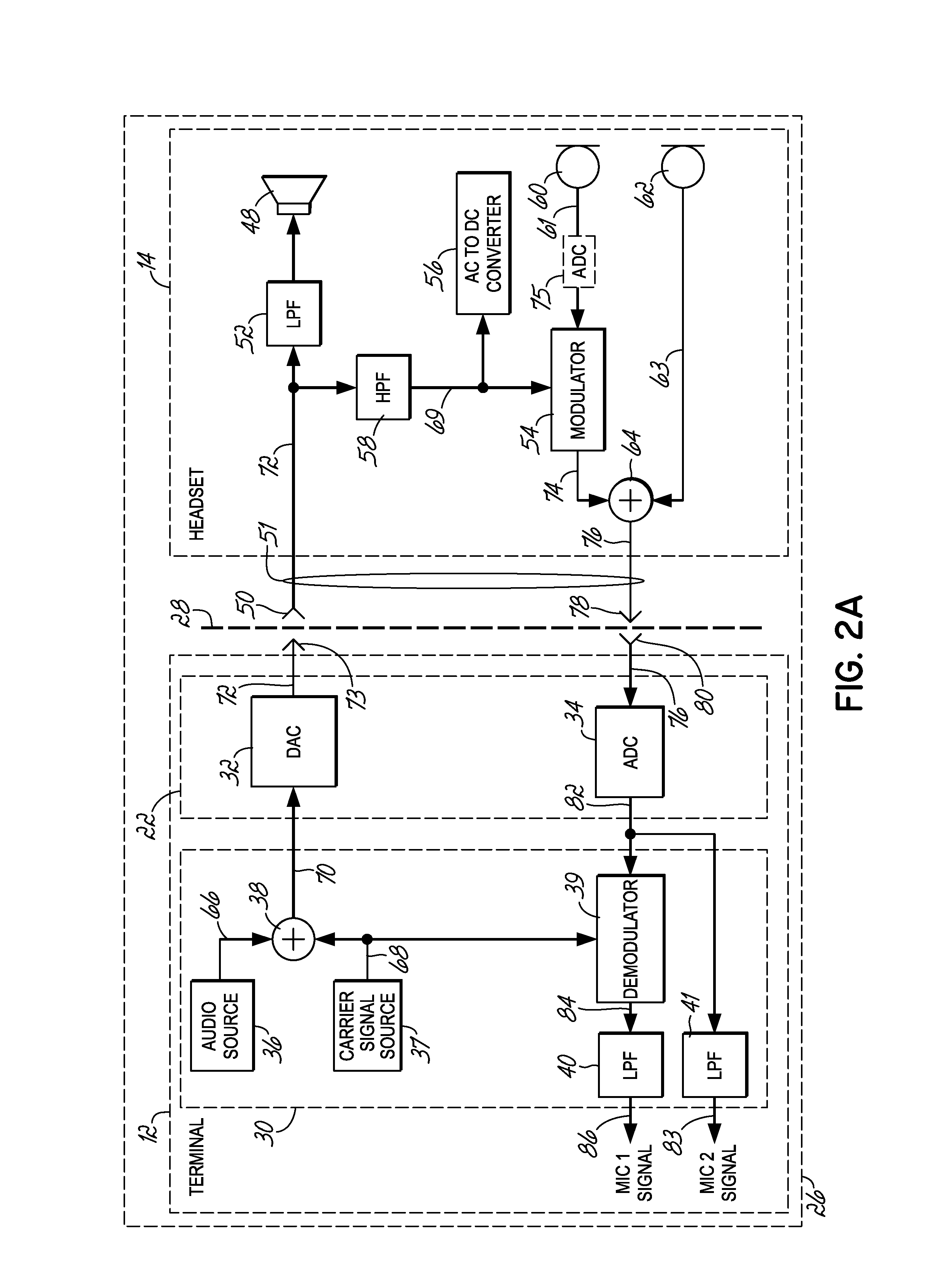
Headset signal multiplexing system and method
Owner:VOCOLLECT
System and method for carrying a wireless based signal over wiring
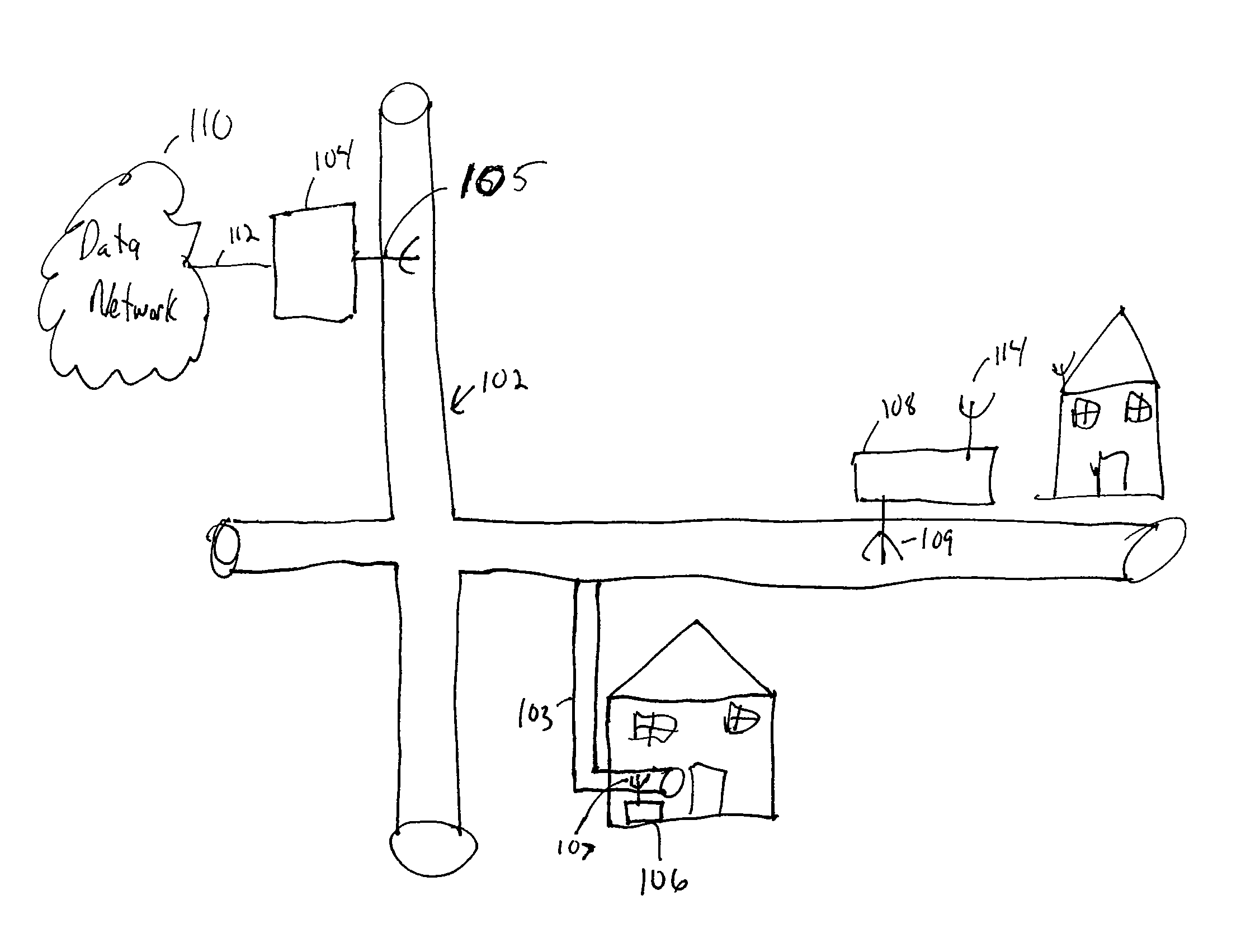
InactiveUS20050249245A1Power distribution line transmissionFrequency-division multiplexData connectionModem device
A device, network and method wherein a standard wireless modem is coupled to wiring for carrying a wireless baseband signal that may be OFDM based, and may be directly generated by the wireless IF modem, or extracted from the modem RF signal. The wiring may be a building utility wiring, such as telephone, AC power or CATV wiring. The baseband signal is carried simultaneously with the utility service signal over the utility wiring using Frequency Division Multiplexing. The device may be enclosed with a data unit, a standalone dedicated enclosure, within an outlet or as a plug-in outlet adapter. Data units may couple the device by a wiring port such as standard data connector, or via wireless connection. The device may be locally powered or via a power signal carried over the wiring. This abstract is not intended to limit or construe the scope of the claims.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM WIRELESS
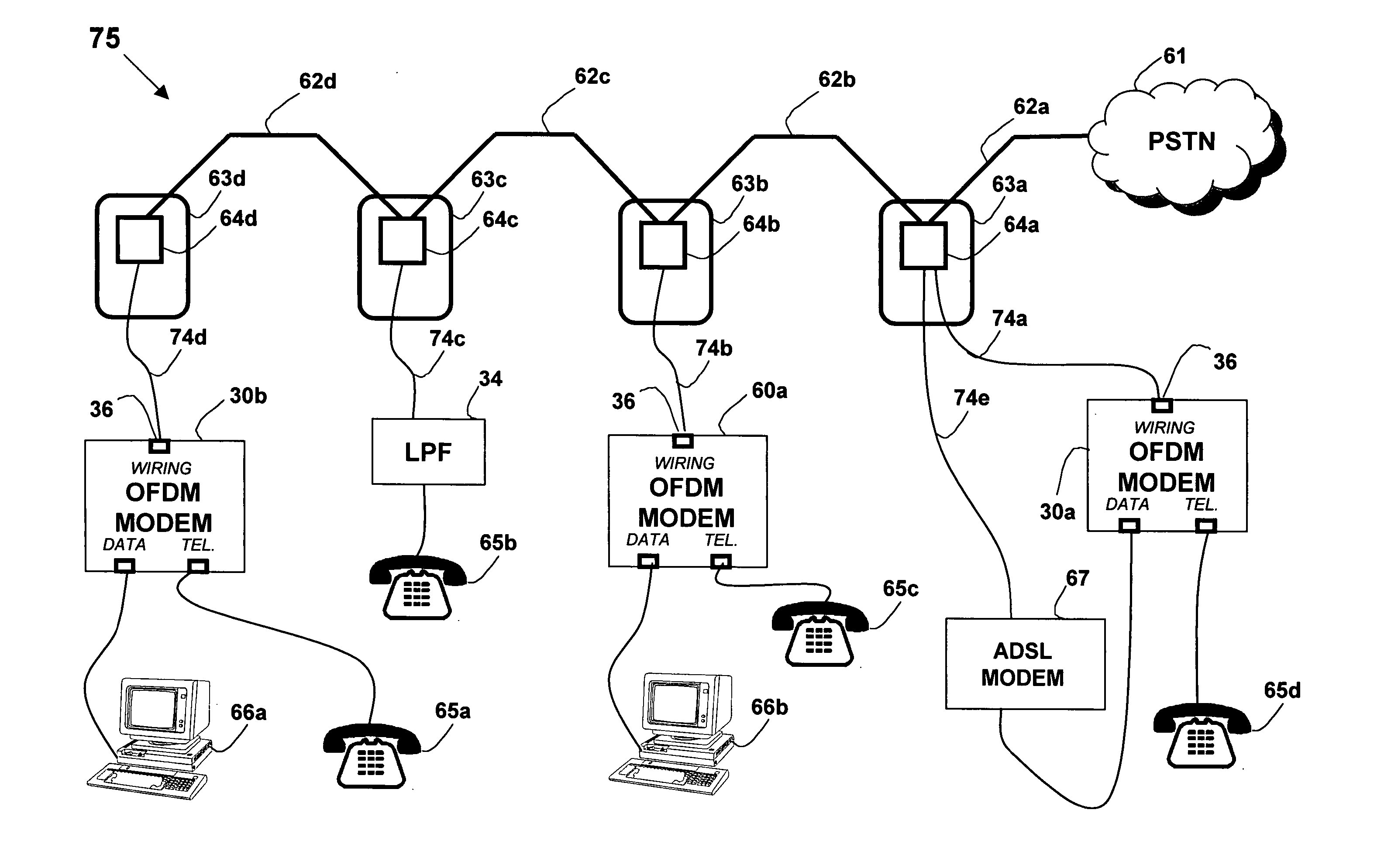
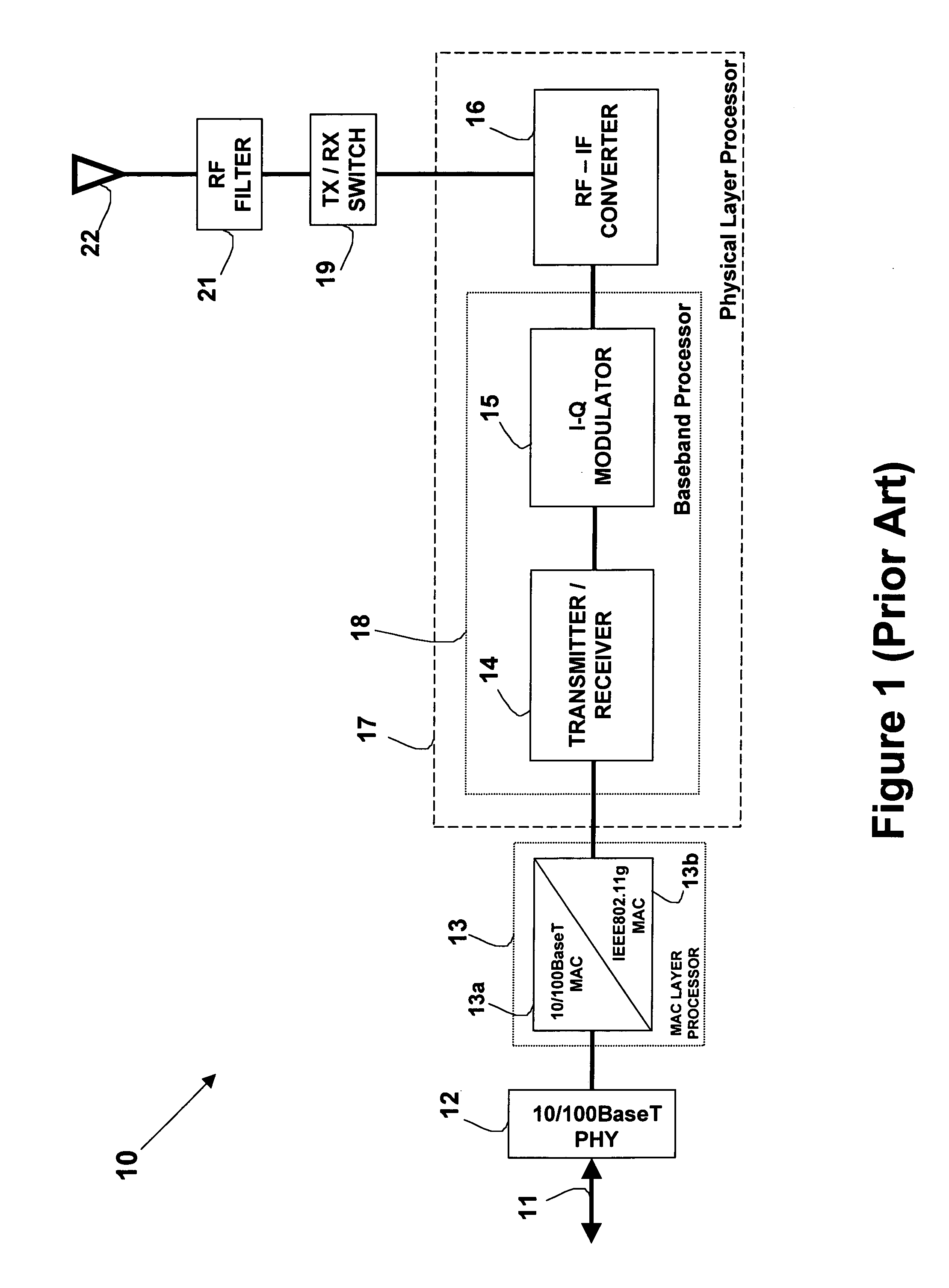
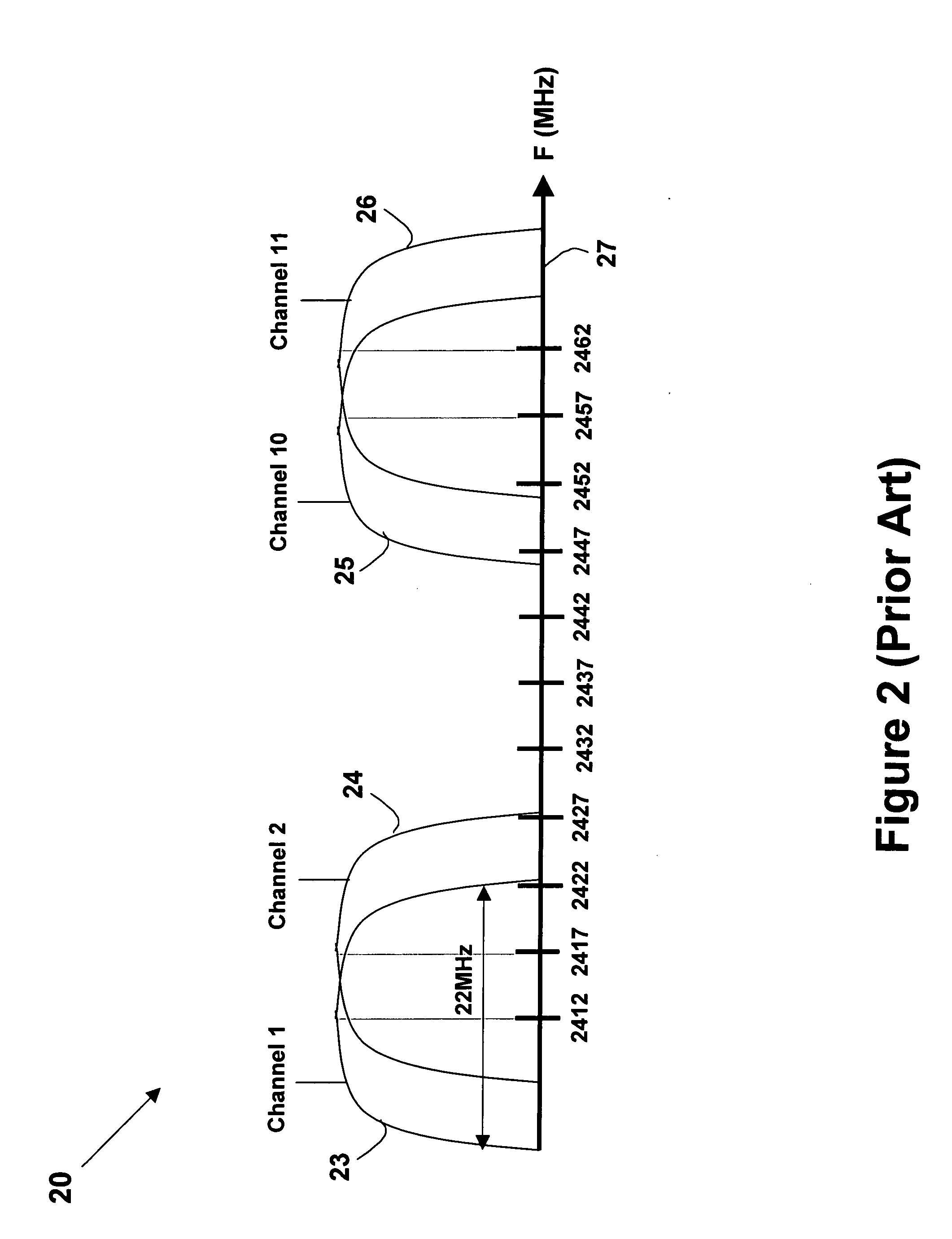
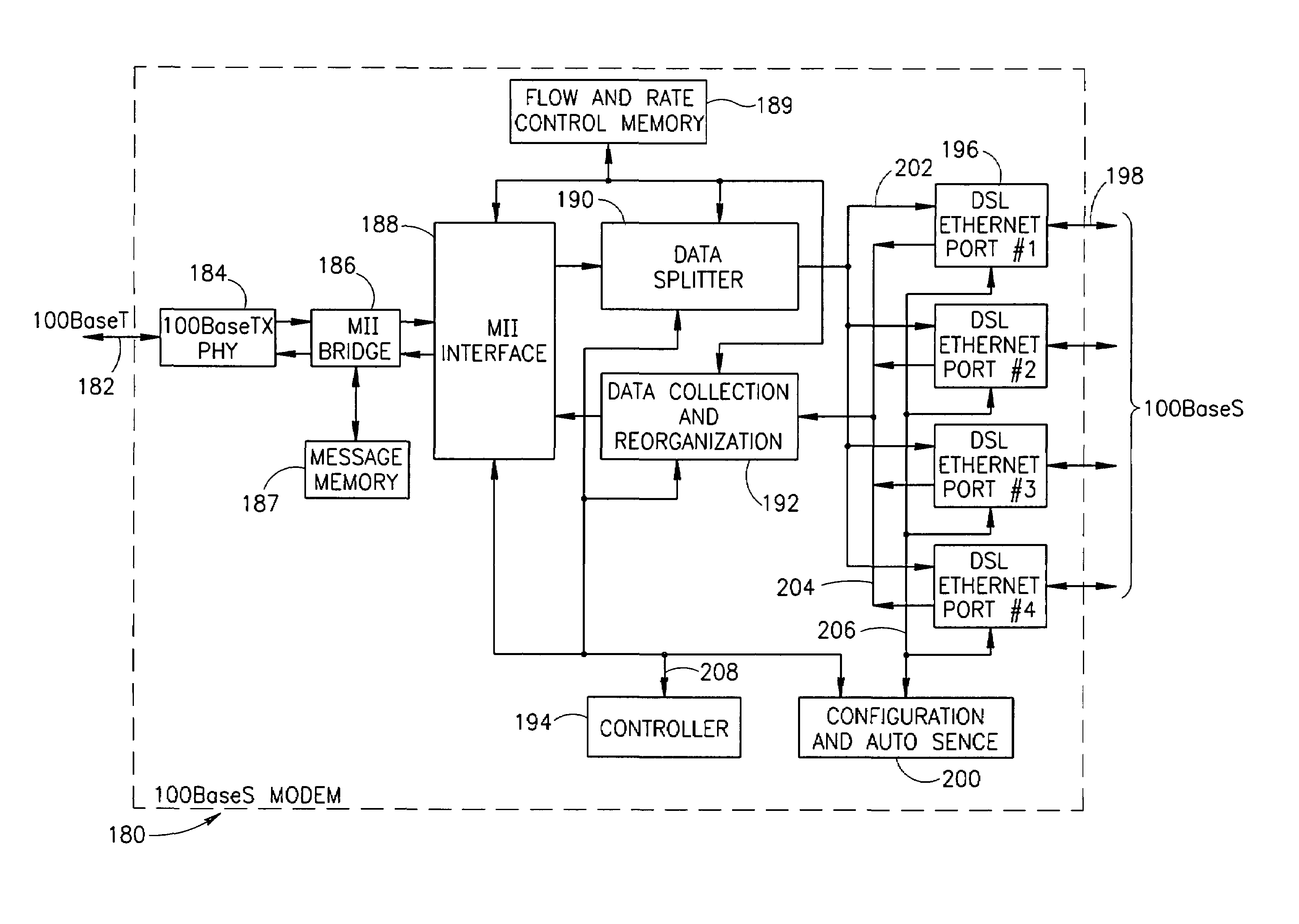
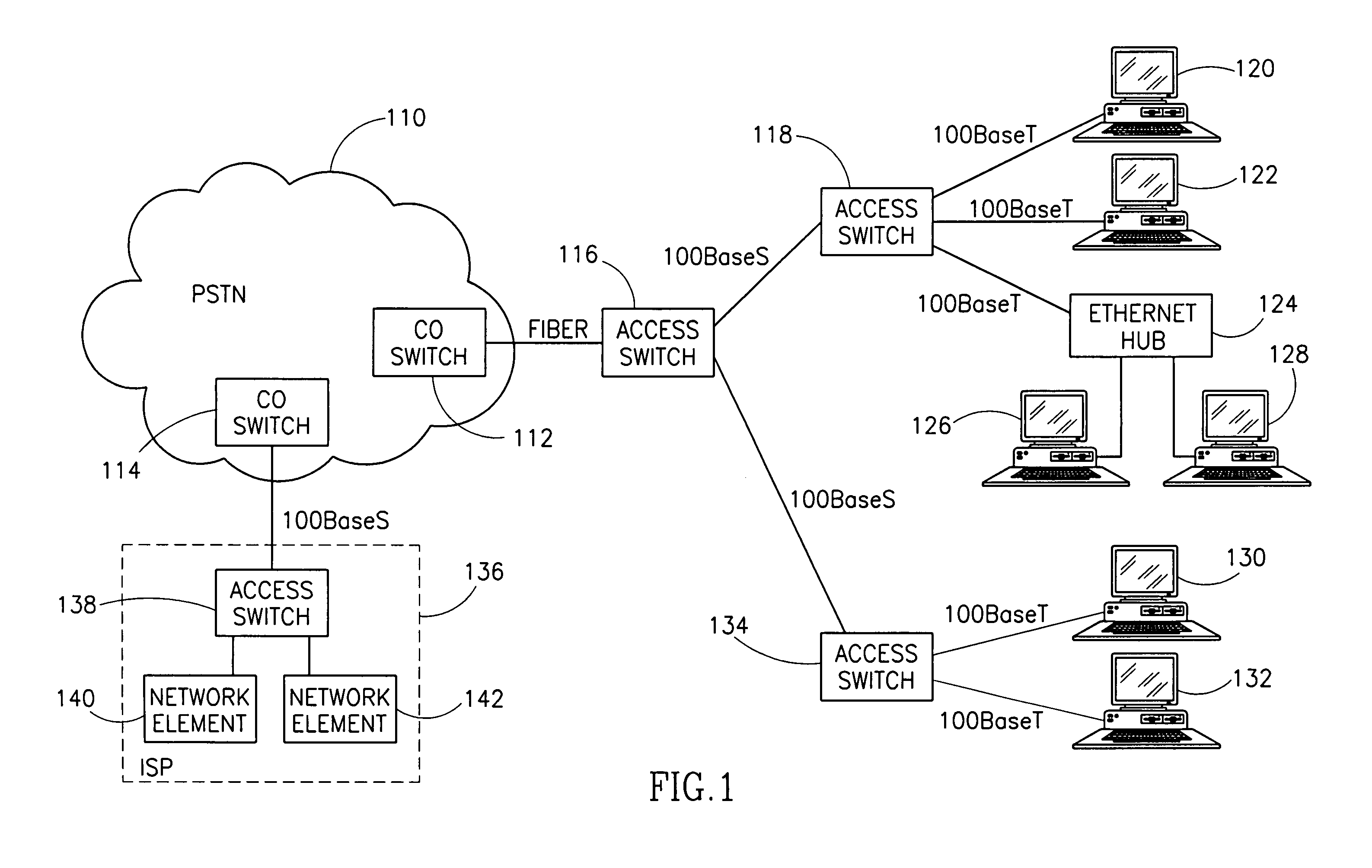
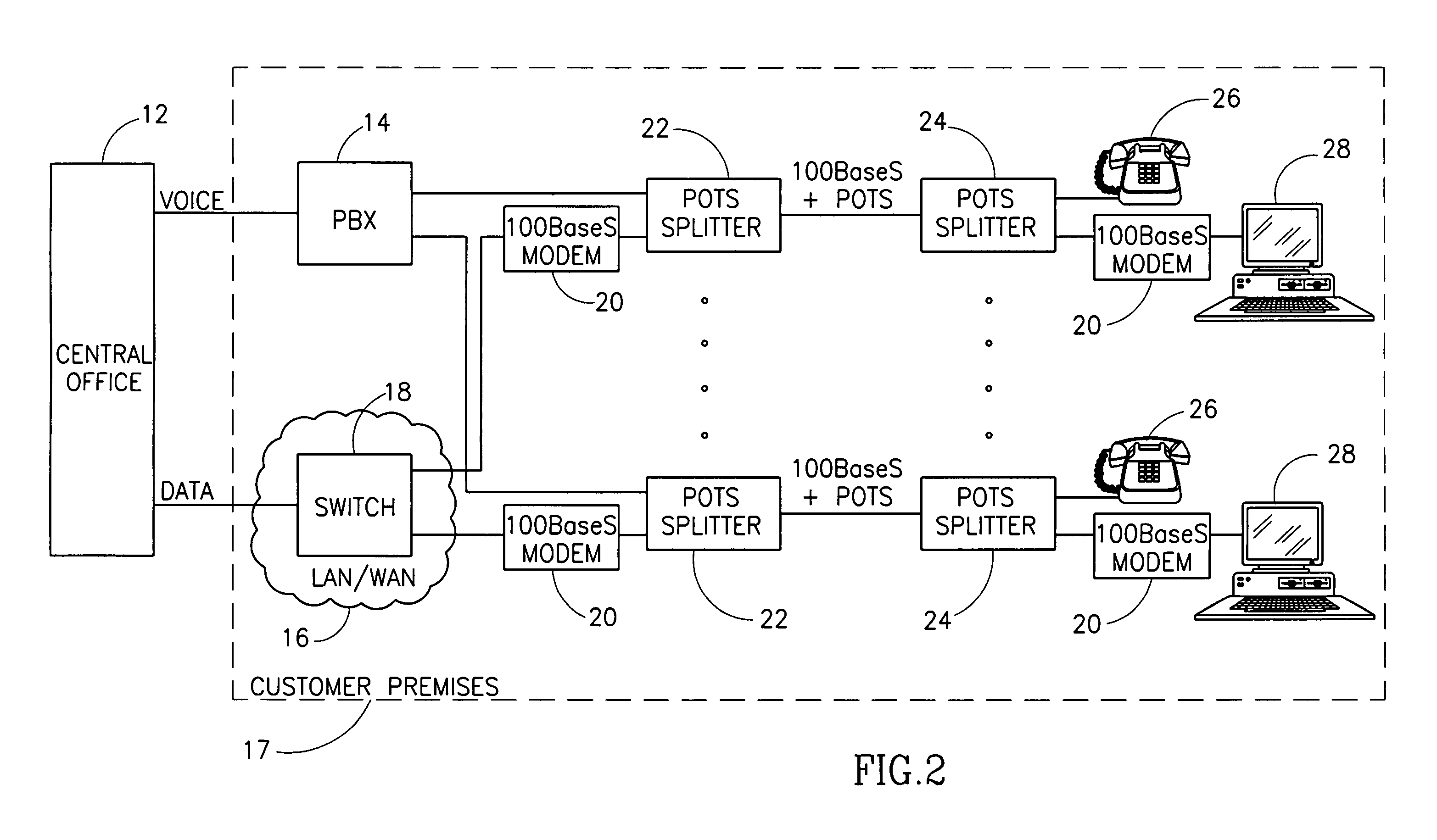
High data rate ethernet transport facility over digital subscriber lines
InactiveUS7054376B1Simple and cost-effectiveIncrease transfer speedMultiple-port networksError preventionTransport systemModem device
A facility transport system for transporting high speed Ethernet data over digital subscriber lines. The system, referred to as 100BaseS, is capable of transmitting 100 Mbps Ethernet over existing copper infrastructure up to distances of approximately 400 meters. The system achieves bit rates from 25 to 100 Mbps in increments of 25 Mbps with each 25 Mbps increment utilizing a separate copper wire pair. Each pair used provides a bidirectional 25 Mbps link with four copper wire pair connections providing 4×25 Mbps downstream channels and 4×25 Mbps upstream channels. The system utilizes framing circuitry to adapt the 100BaseT input data signal to up to four separate output signals. A DSL Ethernet Port card couples the modem to each twisted pair used. Each DSL Ethernet Port card comprises modem transmitter and receiver circuitry for sending and receiving 100BaseS signals onto twisted pair wires. The system utilizes QAM in combination with frequency division multiplexing (FDM) to separate downstream channels from upstream channels and to separate both the downstream and the upstream channels from POTS and ISDN signals.
Owner:LANTIQ BET GMBH & CO KG
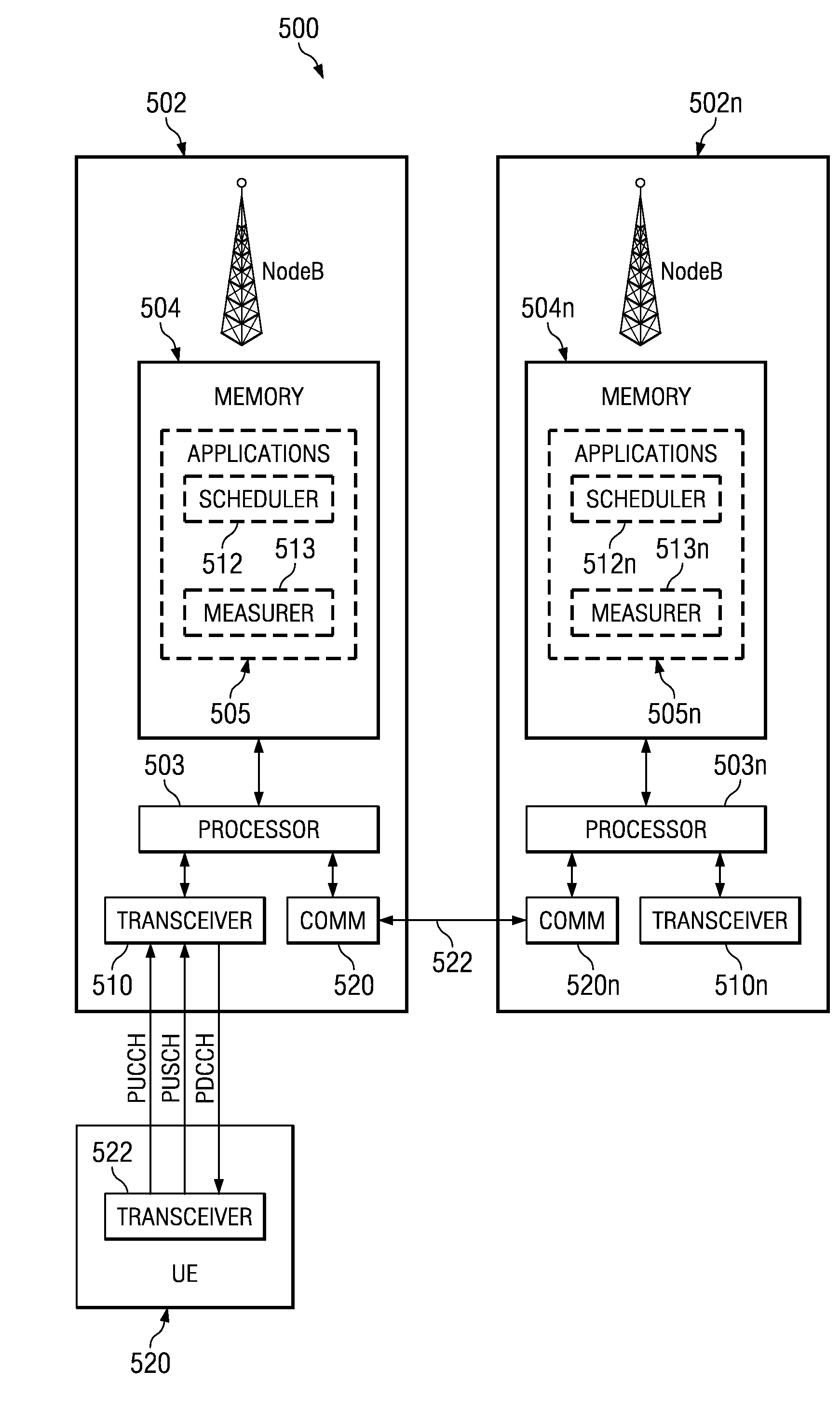
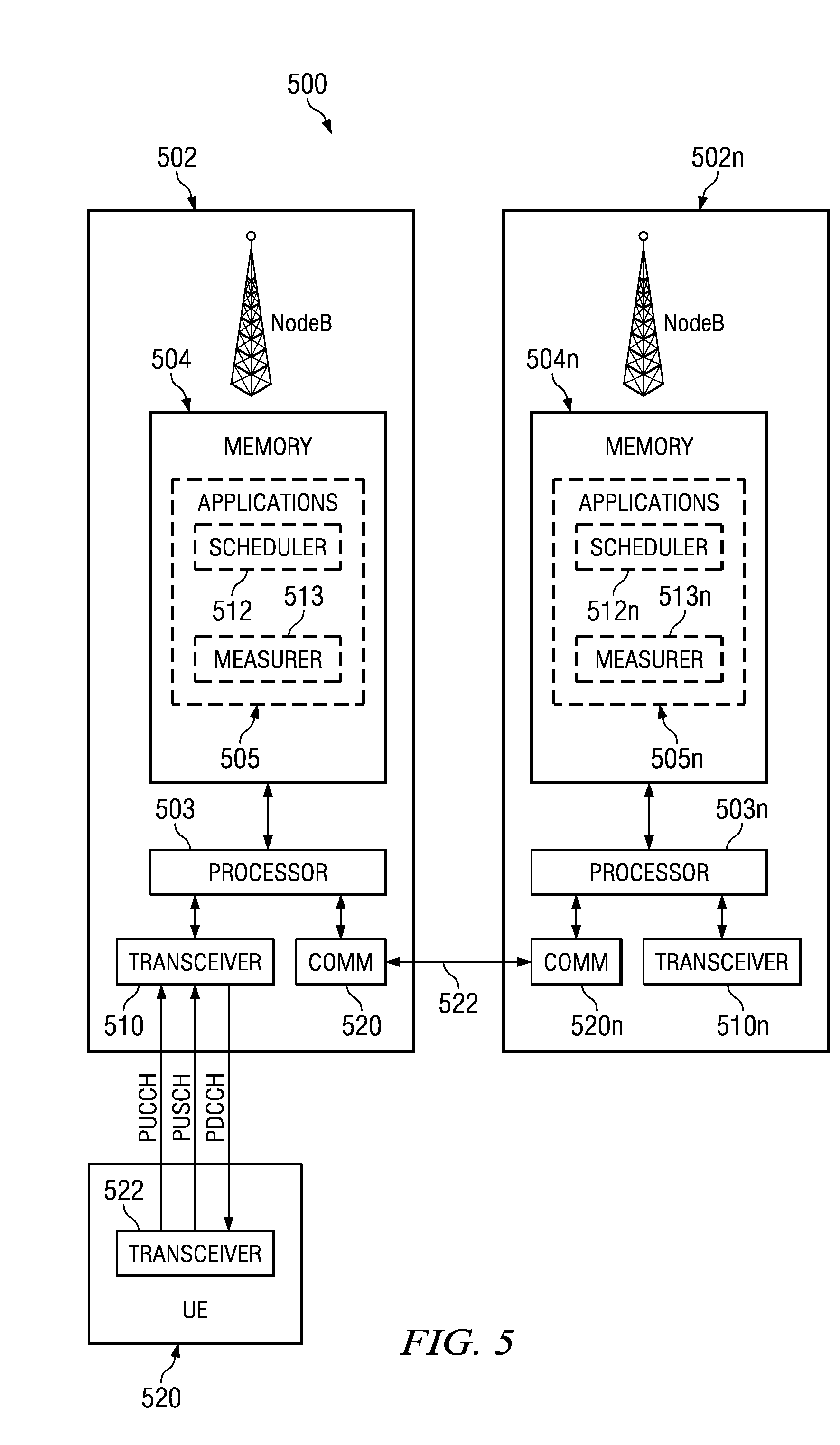
Network-Based Inter-Cell Power Control For Multi-Channel Wireless Networks
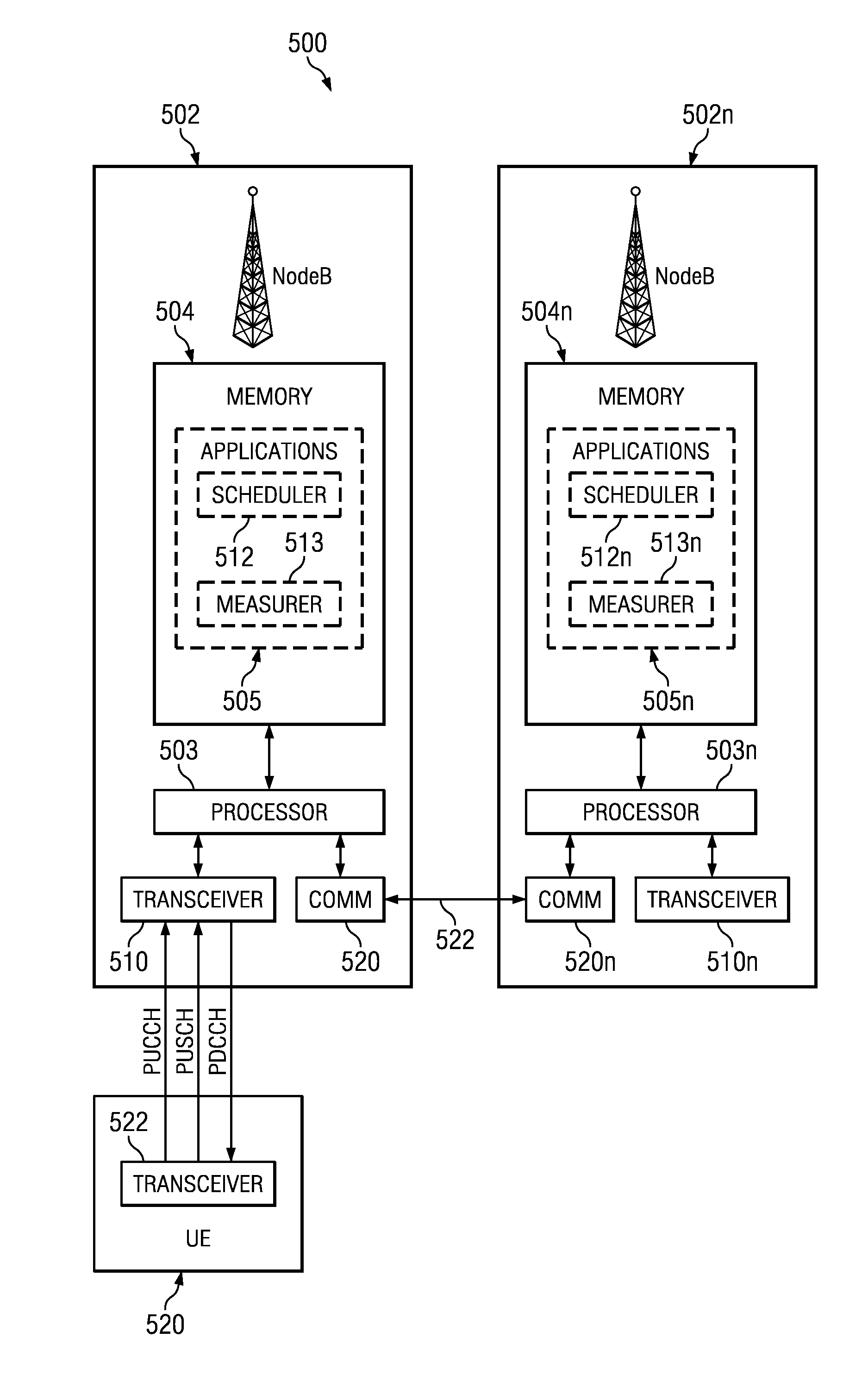
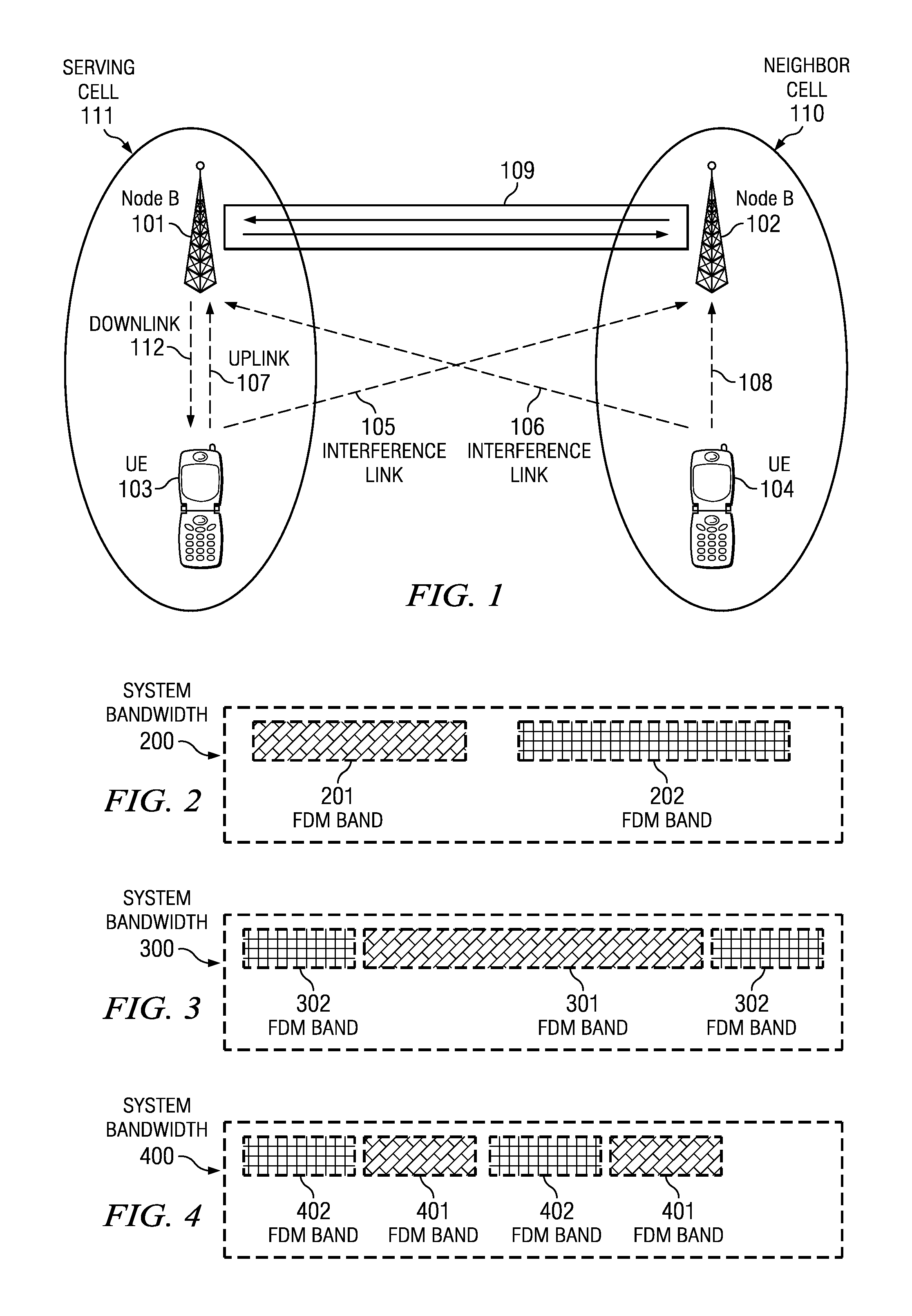
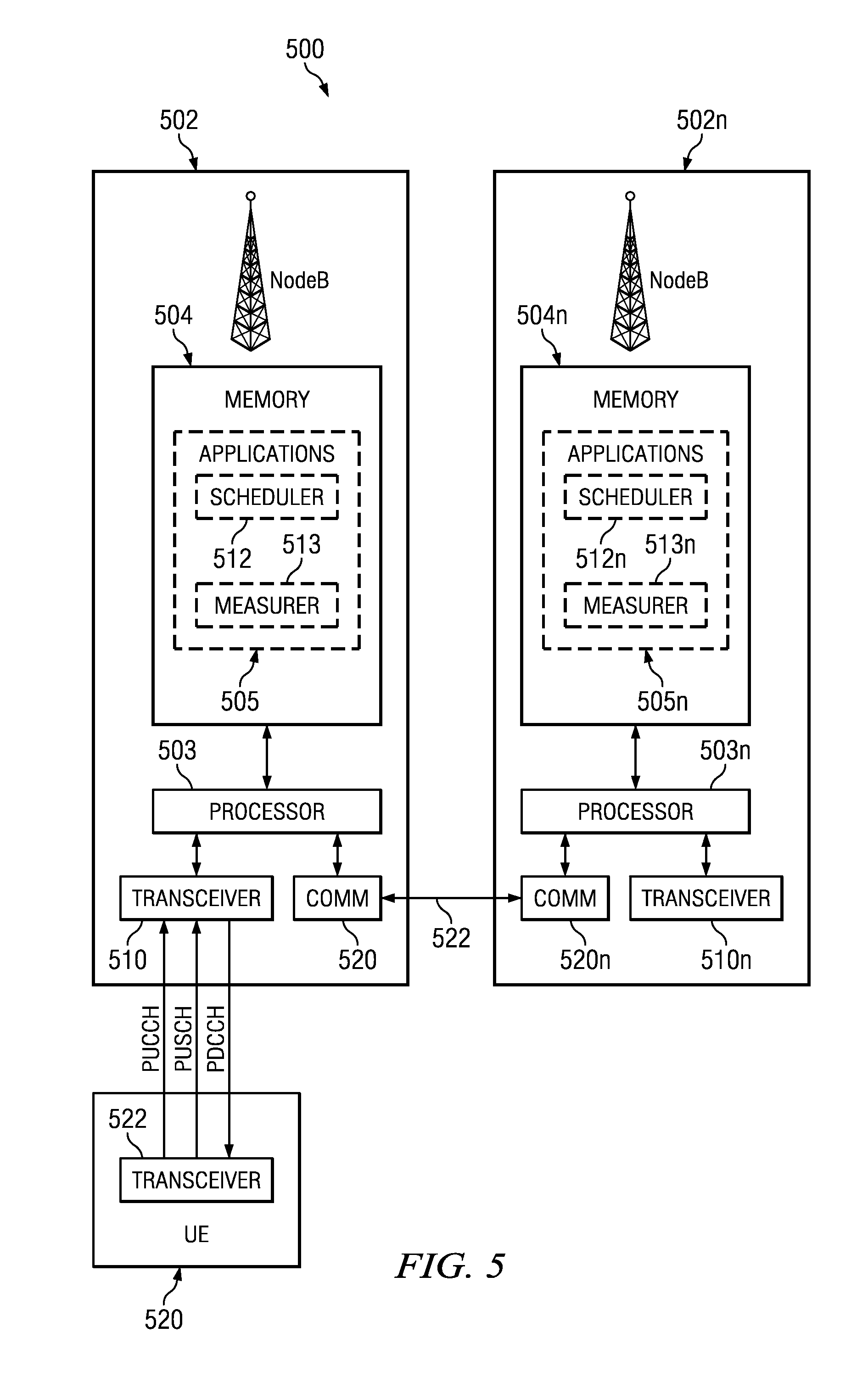
ActiveUS20080247375A1Frequency-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplexingUser equipment
A method is described for operating a cellular network, where the cellular network uses a plurality of frequency division multiplexing (FDM) bands for wireless communication from user equipment (UE) to a base station (NodeB). At least one band-specific cell parameter is computed for at least one the plurality of FDM bands by a serving NodeB. The band-specific cell parameters are transmitted from the NodeB serving a first cell to a NodeB serving a second cell. The band-specific cell parameters may be computed in response to scheduling information and / or channel specific measurements made by the NodeB. A UE receives a first Power Configuration, a Second Power Configuration, and a Scheduling Message indicative of an FDM band from the set comprising at least from First FDM band and Second FDM band. UE transmits with the First Power Configuration if the Scheduling Message was indicative of First FDM band, and with the Second Power Configuration otherwise.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for providing broadband access to a data network via gas pipes
ActiveUS8159933B2Efficiently providedSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsDigital dataFrequency-division multiplexing
Owner:AT&T CORP
Random Access Channel Hopping for Frequency Division Multiplexing Access Systems
ActiveUS20080267126A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsCode division multiplexTelecommunicationsFrequency-division multiplexing
A method of coordinating resources for repetition of random access bursts performed by a mobile terminal, the method comprising: determining groups of access slots based on parameters from a network, wherein each access slot is defined by any combination of frequency, time and code, and the access slots are organized according to a frequency pattern; transmitting an access burst on an access slot from a chosen group of access slots; and re-transmitting the access burst on the next access slot from the chosen group of access slots.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
System and Method for Carrying a Wireless Based Signal Over Wiring
InactiveUS20080280569A1Coupling device connectionsElectric signal transmission systemsModem deviceFrequency-division multiplexing
A device, network and method wherein a standard wireless modem is coupled to wiring for carrying a wireless baseband signal that may be OFDM based, and may be directly generated by the wireless IF modem, or extracted from the modem RF signal. The wiring may be a building utility wiring, such as telephone, AC power or CATV wiring. The baseband signal is carried simultaneously with the utility service signal over the utility wiring using Frequency Division Multiplexing. The device may be enclosed with a data unit, a standalone dedicated enclosure, within an outlet or as a plug-in outlet adapter. Data units may couple the device by a wiring port such as standard data connector, or via wireless connection. The device may be locally powered or via a power signal carried over the wiring. This abstract is not intended to limit or construe the scope of the claims.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM WIRELESS
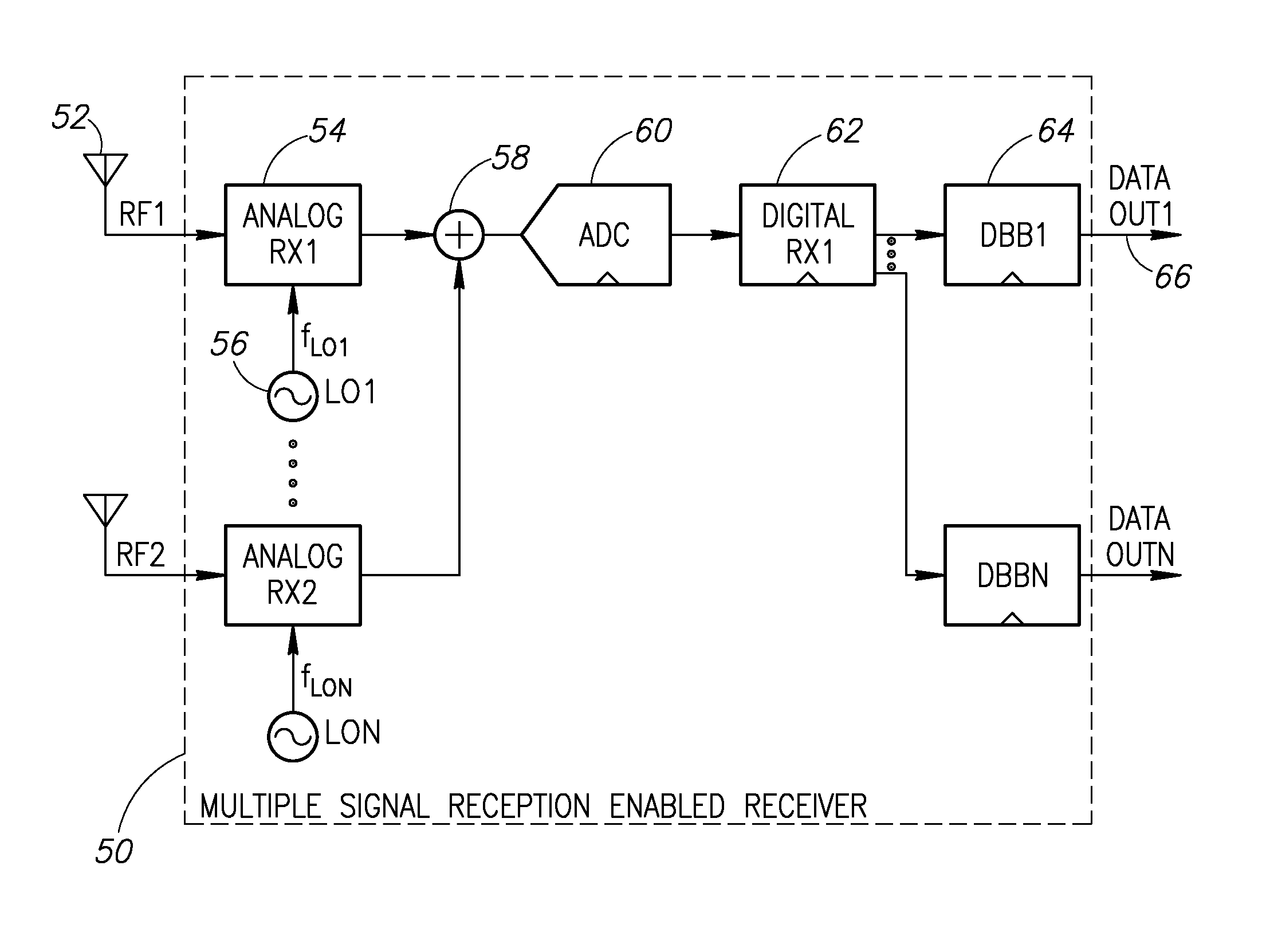
Simultaneous multiple signal reception and transmission using frequency multiplexing and shared processing
ActiveUS20100091688A1Reduce total powerReduce spacingModulation transferenceModulated-carrier systemsDigital signal processingMultiplexing
A novel mechanism for simultaneous multiple signal reception and transmission using frequency multiplexing and shared processing. Multiple RF signals, which may be of various wireless standards, are received using one or more shared processing blocks thereby significantly reducing chip space and power requirements. Shared components include local oscillators, analog to digital converters, digital RX processing and digital baseband processing. In operation, multiple RX front end circuits, one for each desired wireless signal, generate a plurality of IF signals that are frequency multiplexed and combined to create a single combined IF signal. The combined IF signal is processed by a shared processing block. Digital baseband processing is performed on each receive signal to generate respective data outputs. Further, simultaneous full-duplex transmission and reception is performed using a single local oscillator. The phase / frequency modulation of the frequency synthesizer used in the TX is removed from the local oscillator signal for use in the receiver.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Single sideband and quadrature multiplexed continuous phase modulation
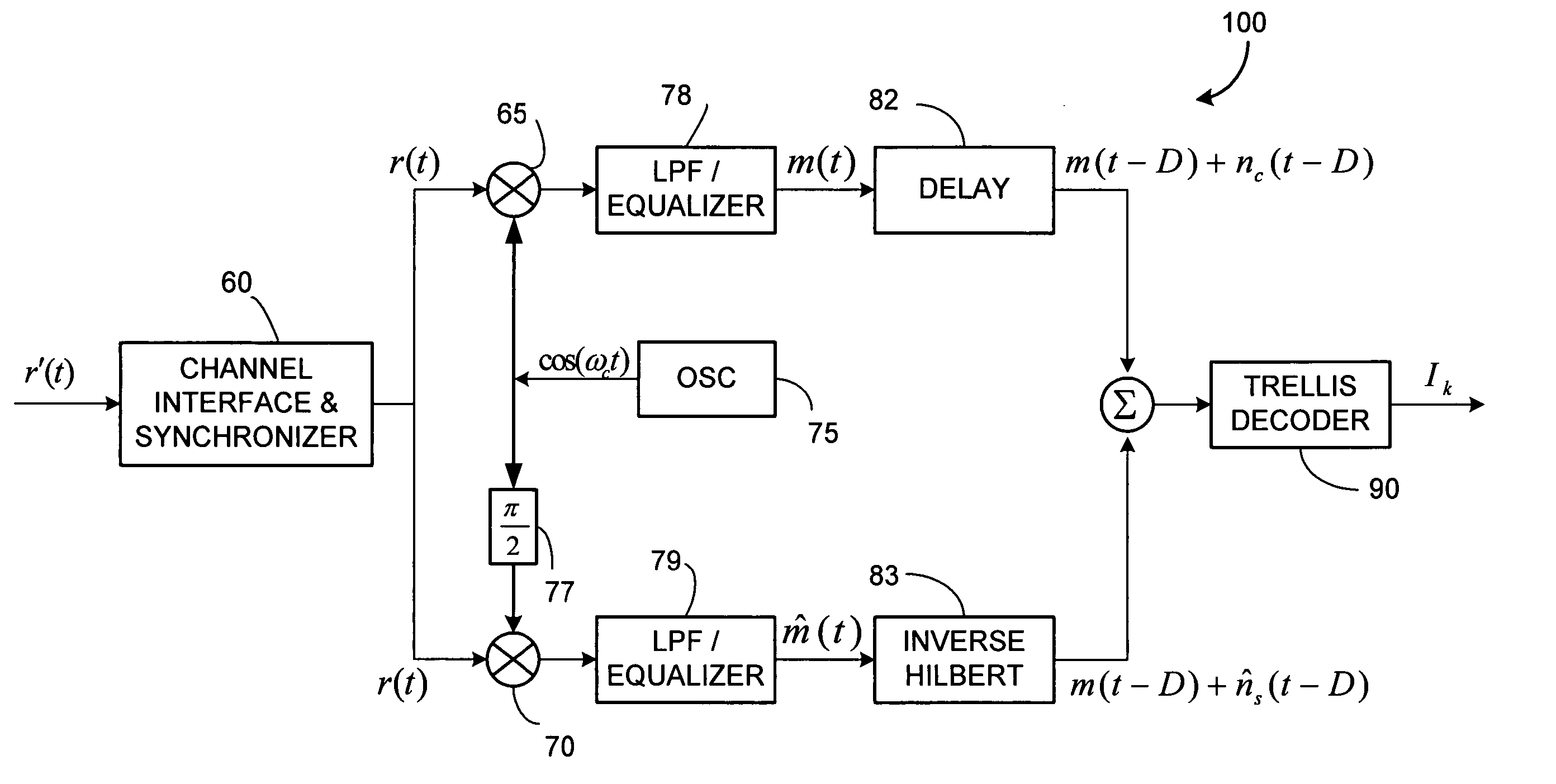
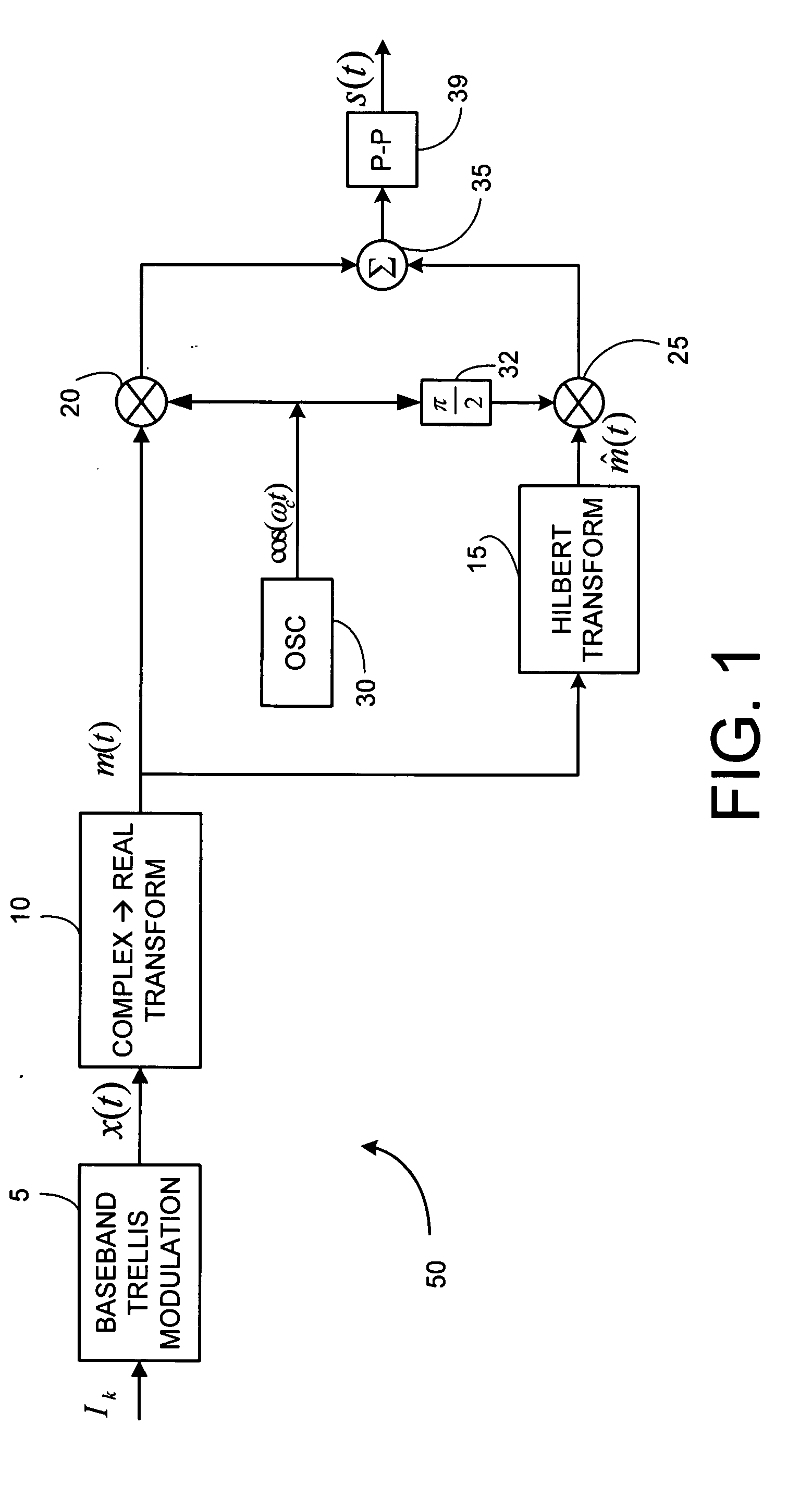
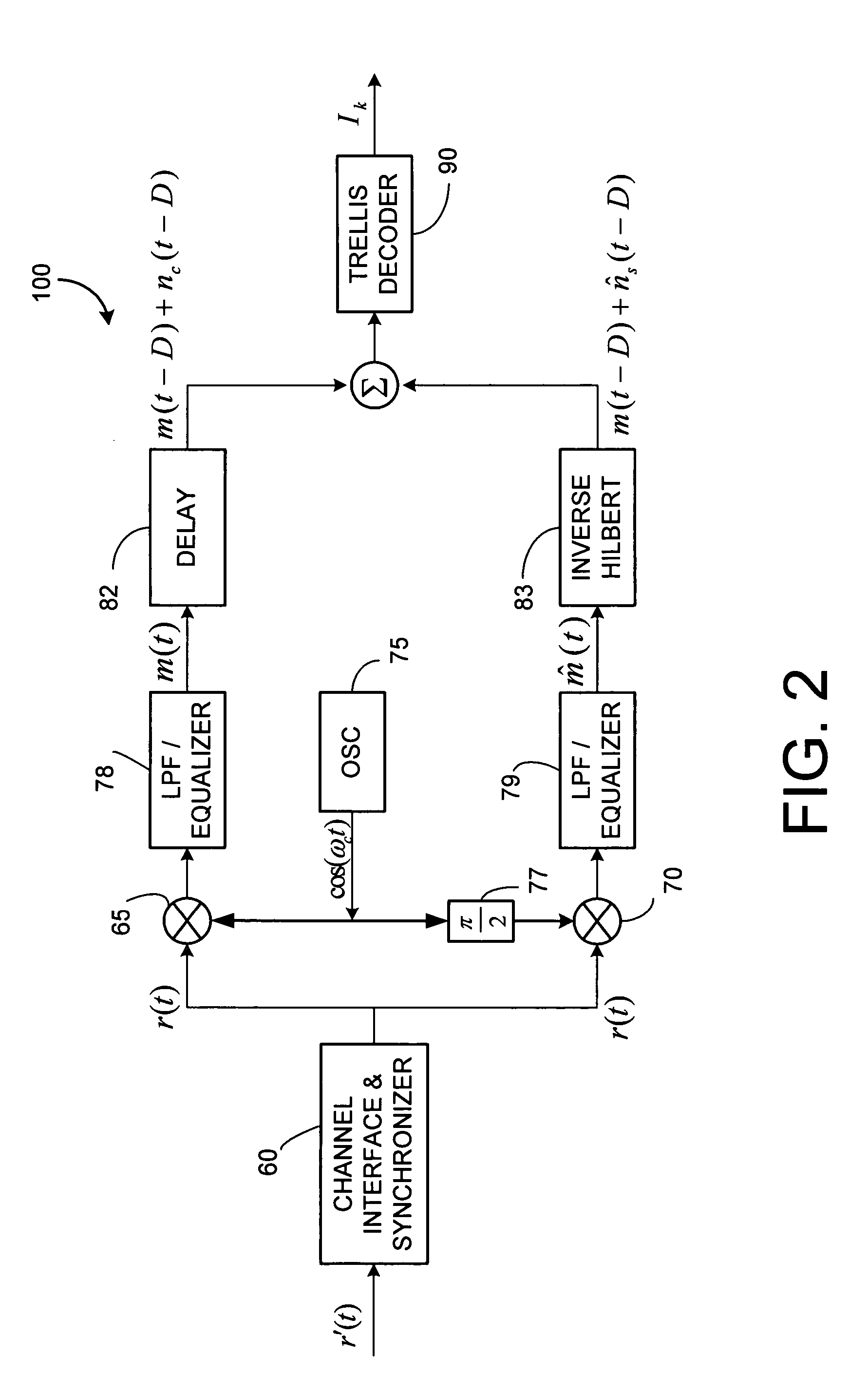
InactiveUS20070092018A1Error preventionSecret communicationCommunications systemFrequency-division multiplexing
A class of bandwidth reduction techniques are used develop a broad class of modulation types collectively called SSB-FM. These signals can be used to construct communication systems that provide bandwidth-normalized performance gains of 10 dB or more when compared to popular prior art modulation methods. An aspect of the invention involves mapping trellis paths in a complex signal space onto corresponding real-valued trellis signals with desirable spectral properties. The invention can be used map continuous phase modulated (CPM) signals onto simpler amplitude-modulated trellis signals having double the channel capacity of prior art CPM signals. Multi-amplitude signaling and frequency division multiplexing may also be incorporated to further accommodate more information per symbol.
Owner:TRELLIS PHASE COMM LP
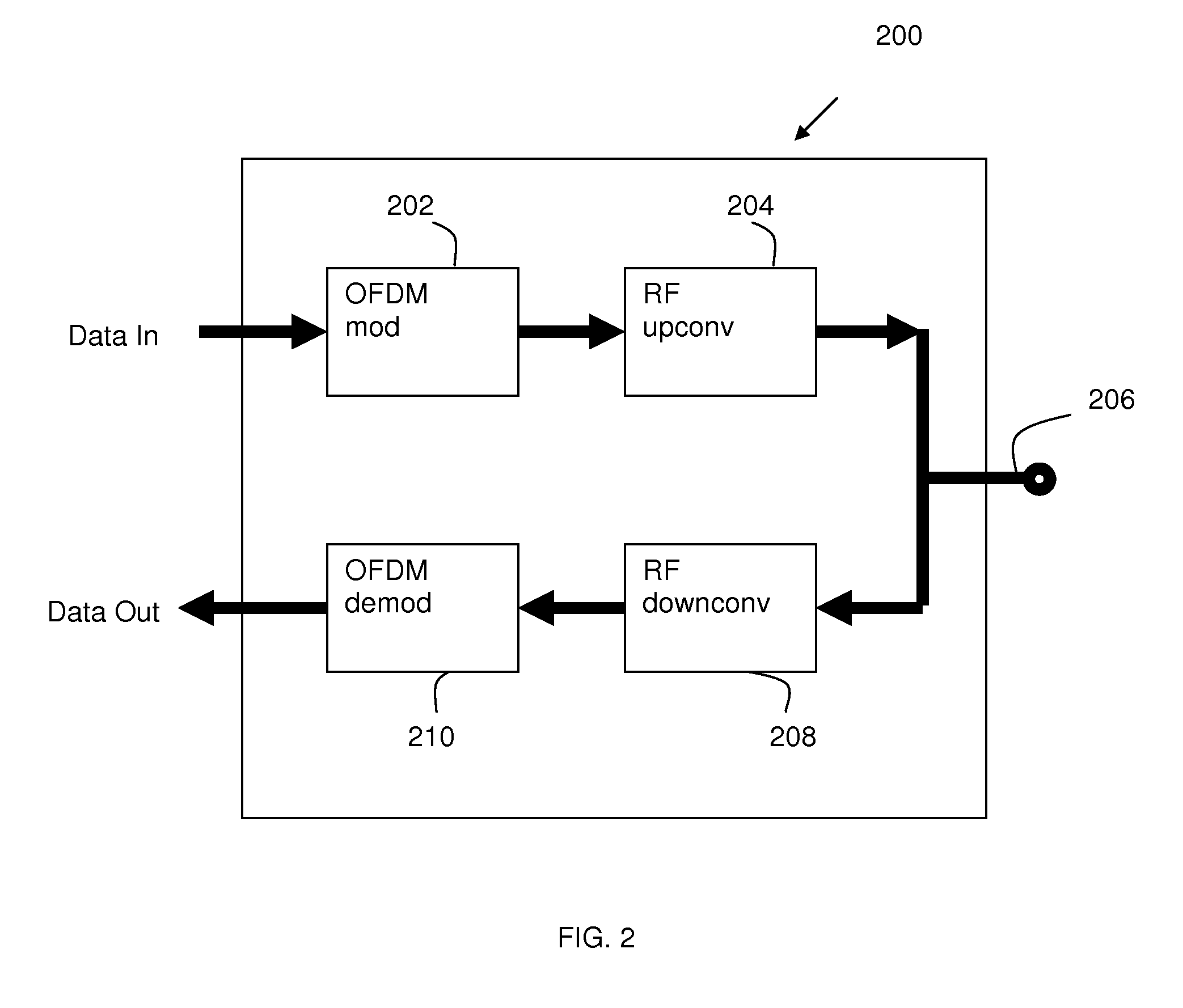
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communications device and method that incorporates low papr preamble with circuit for measuring frequency response of the communications channel
ActiveUS20100080312A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationFrequency spectrumFrequency-division multiplexing
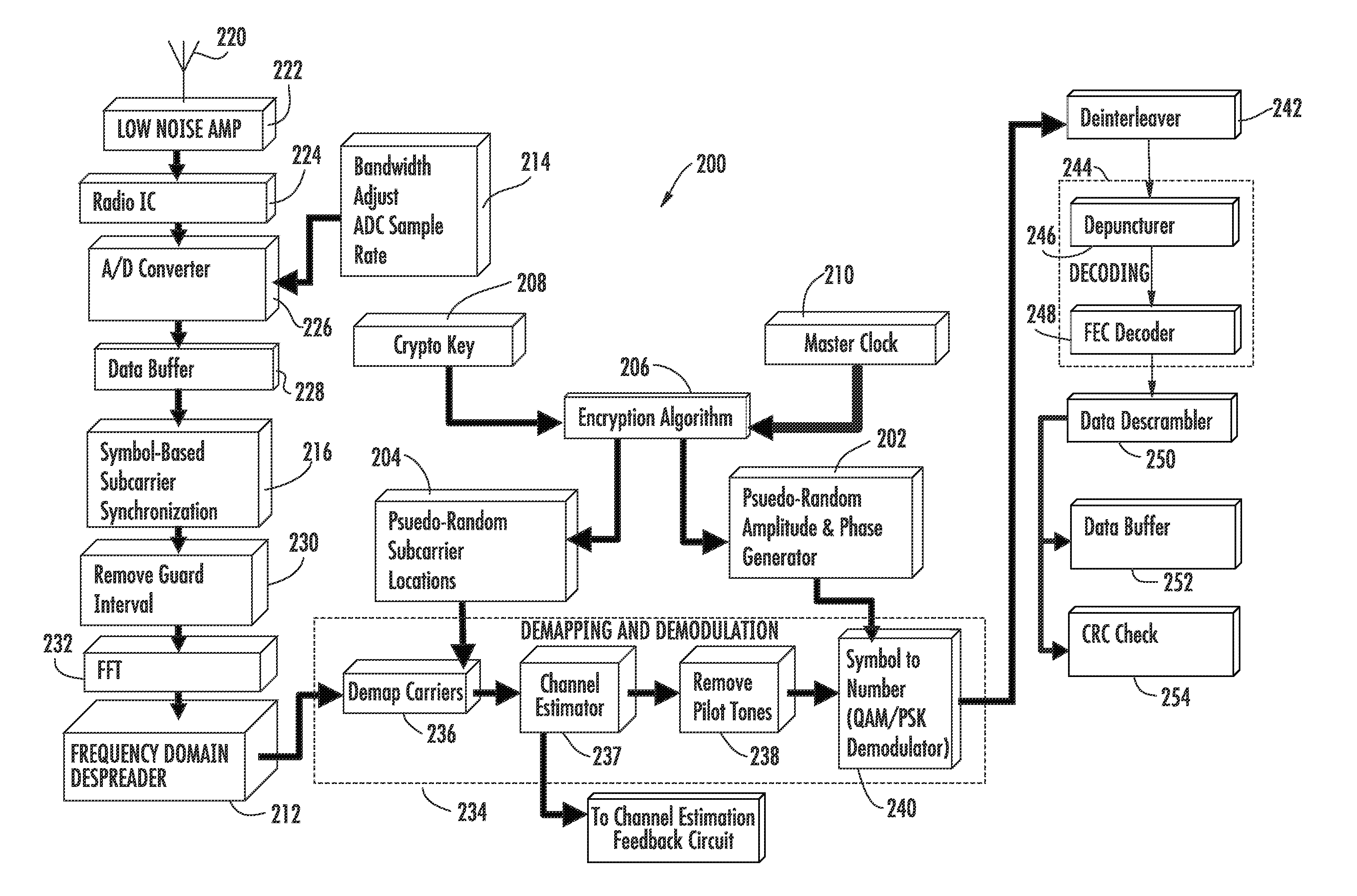
A communications device includes a demapping and demodulation circuit and processes an OFDM communications signal that includes modulated subcarriers carrying communications data forming a data payload and modulated subcarriers carrying a training sequence forming a preamble. Those OFDM subcarriers carrying the training sequence have a sample for each subcarrier at a frequency bin using evenly spaced, equal amplitude subcarriers that have a set phase of each sinusoid to a specific angle with quadratic phase to form a low peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) preamble with about a PAPR value of 2.6 decibels (dB). A channel estimate circuit is operative for measuring fluctuations within a flat-top spectrum of the received OFDM communications signal corresponding to the preamble to reflect the frequency response of the communications channel.
Owner:SMARTSKY NETWORKS
Synchronization in a multiple-input/multiple-output (MIMO) orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system for wireless applications
ActiveUS7009931B2Spatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplexSampling clock offsetFrequency-division multiplexing
Methods and apparatus are described for time synchronizing a receiver to orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) signals in a multiple-input / multiple-output (MIMO) system, the signals being transmitted from multiple transmitters and received at multiple receivers. The method includes determining the frequency offset and the sampling clock offset of the received signals.
Owner:APPLE INC
Oversampling pulse oximeter
InactiveUS7062307B2Increased complexityIncrease expensesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDigital signal processingPulse oximeters
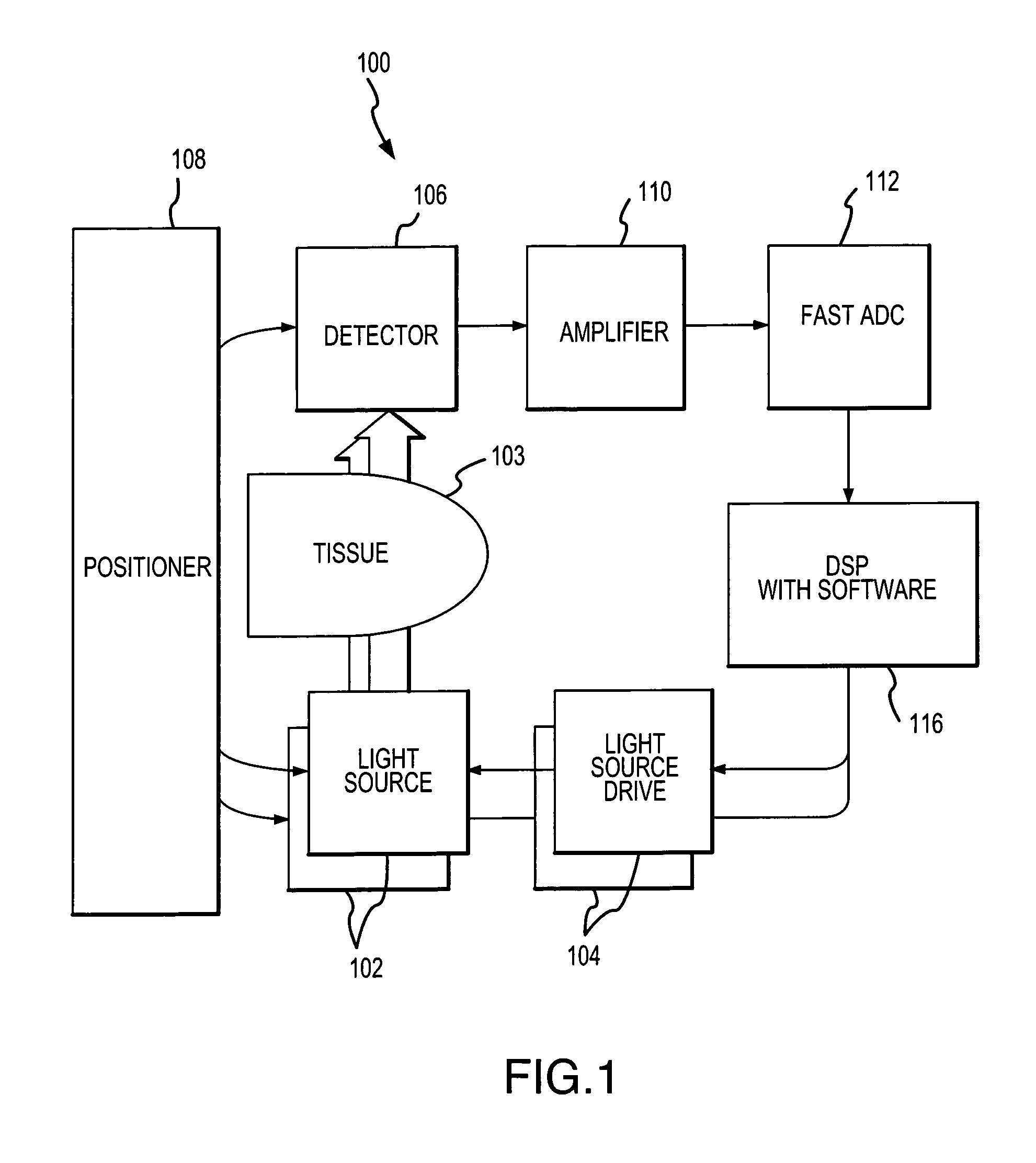
An oversampling pulse oximeter includes an analog to digital converter with a sampling rate sufficient to take multiple samples per source cycle. In one embodiment, a pulse oximeter (100) includes two or more light sources (102) driven by light source drives (104) in response to drive signals from a digital signal processing unit (116). The source drives (104) may drive the sources (102) to produce a frequency division multiplex signal. The optical signals transmitted by the light sources (102) are transmitted through a patient's appendage (103) and impinge on a detector (106). The detector (106) provides an analog current signal representative of the received optical signals. An amplifier circuit (110) converts the analog current signal to an analog voltage signal in addition to performing a number of other functions. The amplifier circuit (110) outputs an analog voltage signal which is representative of the optical signals from the sources (102). This analog voltage signal is received by a fast A / D converter (112) which samples the analog voltage signal to generate a digital voltage signal which can be processed by the digital signal processing unit (116). The fast A / D converter (112) operates at a rate sufficient to take multiple samples per source cycle and may have a sampling frequency, for example, of over 41 kHz. The digital signal processing unit (116) implements software for averaging the samples over a source cycle for improved measurement consistency, improved signal to noise ratio and reduced A / D converter word length.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
Method and apparatus for transmitting reference signal in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20120020323A1Demodulation efficiencyCode division multiplexPilot signal allocationCommunications systemFrequency-division multiplexing
A method and apparatus of transmitting a reference signal in a wireless communication system is provided. Demodulation Reference Signals (DMRSs) for a plurality of respective antennas is generated. The DMRSs are mapped to a resource region, and transmitted through the respective corresponding antennas. The DMRSs are multiplexed using at least one of frequency division multiplexing (FDM), code division multiplexing (CDM), and time division multiplexing (TDM) methods and mapped in the resource region. Also, a position of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbol to which the DMRSs are mapped in the resource region is an OFDM symbol to which a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) and a legacy cell-specific reference signal (CRS) are not mapped.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
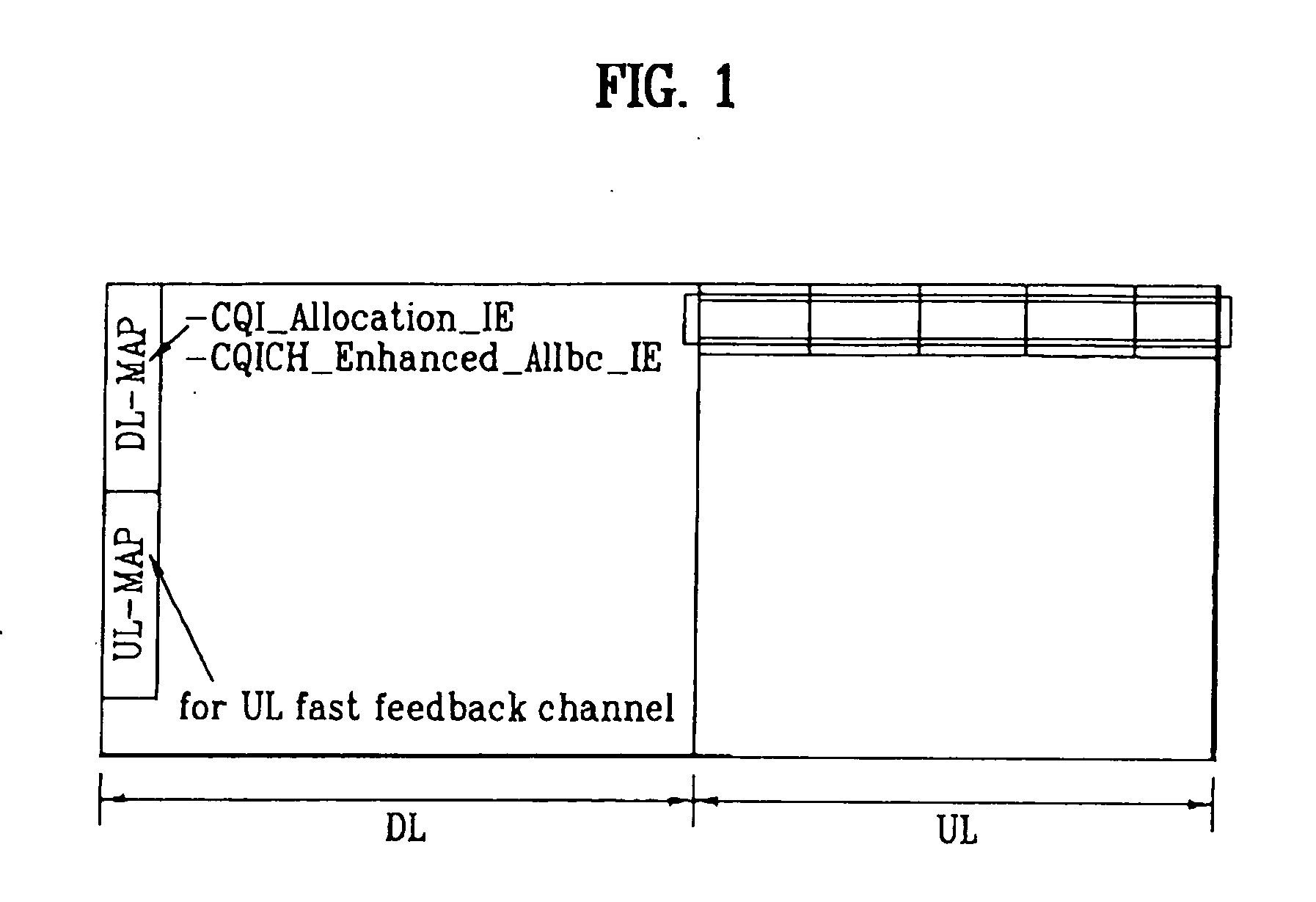
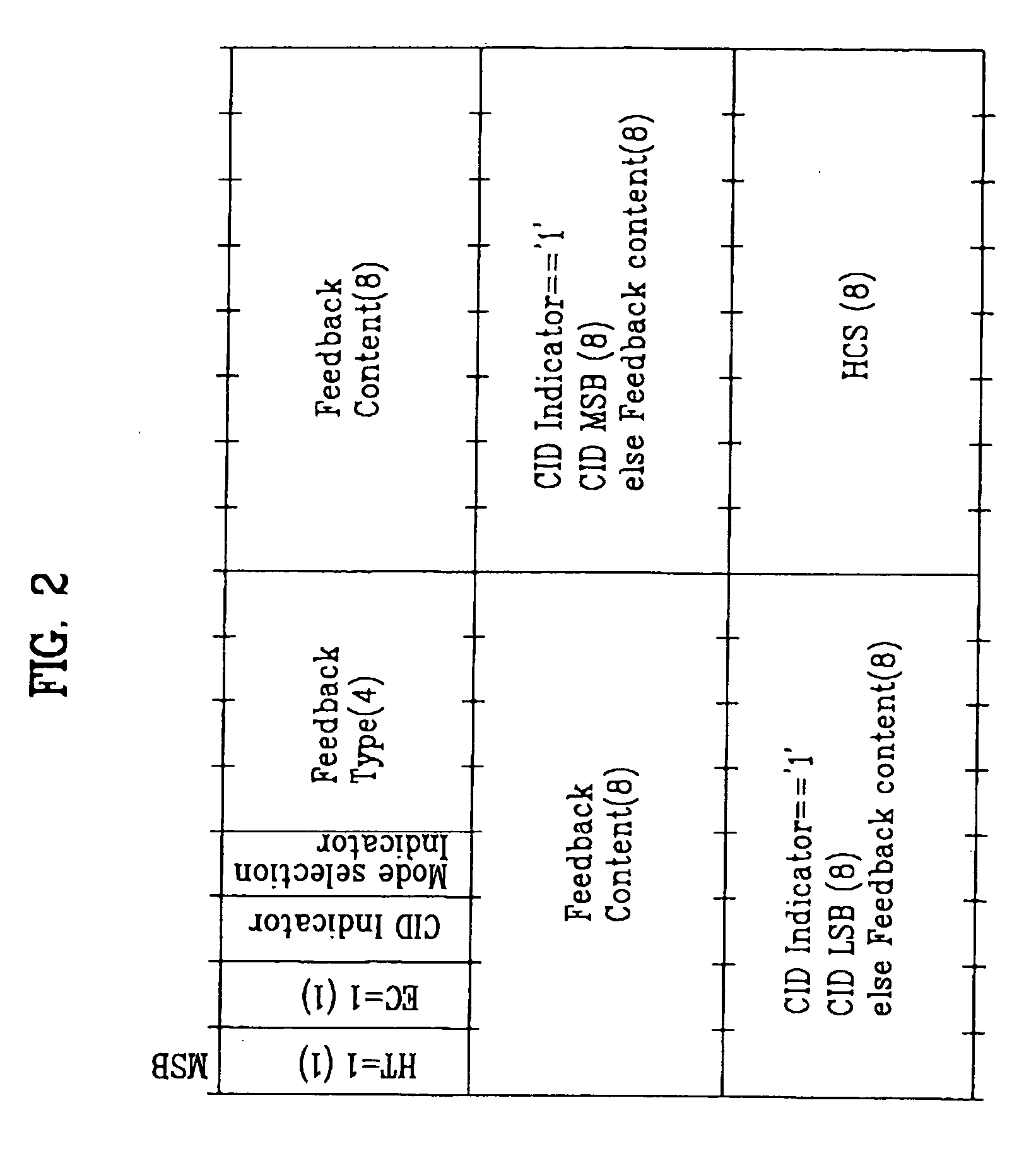
Method of transmitting feedback information in an orthogononal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)/ OFDM access (OFDMA) mobile communication system
InactiveUS20060111129A1Eliminate the problemMultiplex communicationSignal allocationCommunications systemFrequency-division multiplexing
A method of transmitting feedback information in a wireless communication system is disclosed. More specifically, the method comprises a mobile station (MS) which determines whether to transmit feedback information to a base station (BS) without solicitation from the BS. After determining to do so, the MS transmits a request message to request the BS to allocate an uplink resource for transmitting at least one unsolicited header and thereafter receives the uplink resource allocation from the BS. Lastly, the MS transmits the at least one unsolicited header via the allocated uplink resource.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
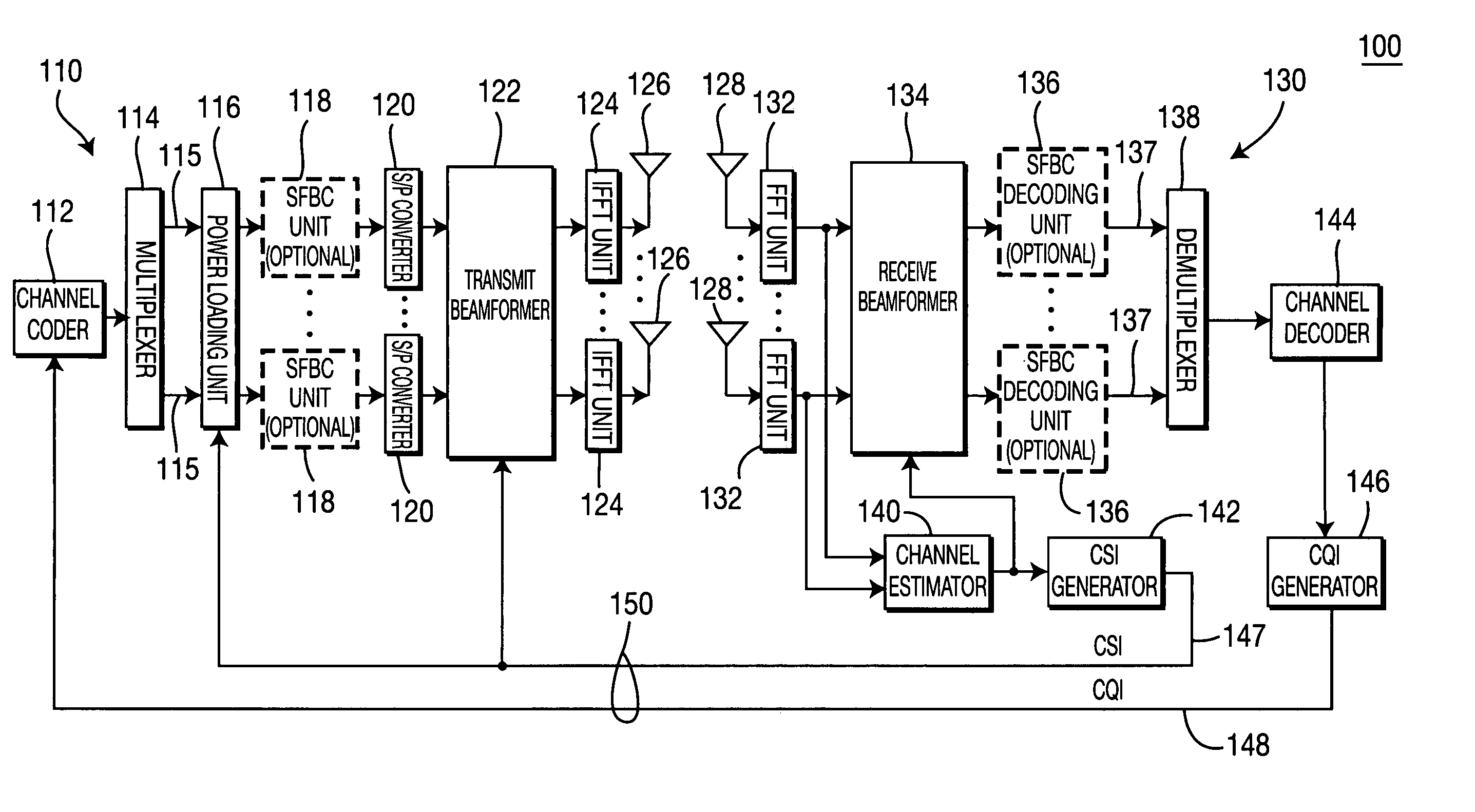
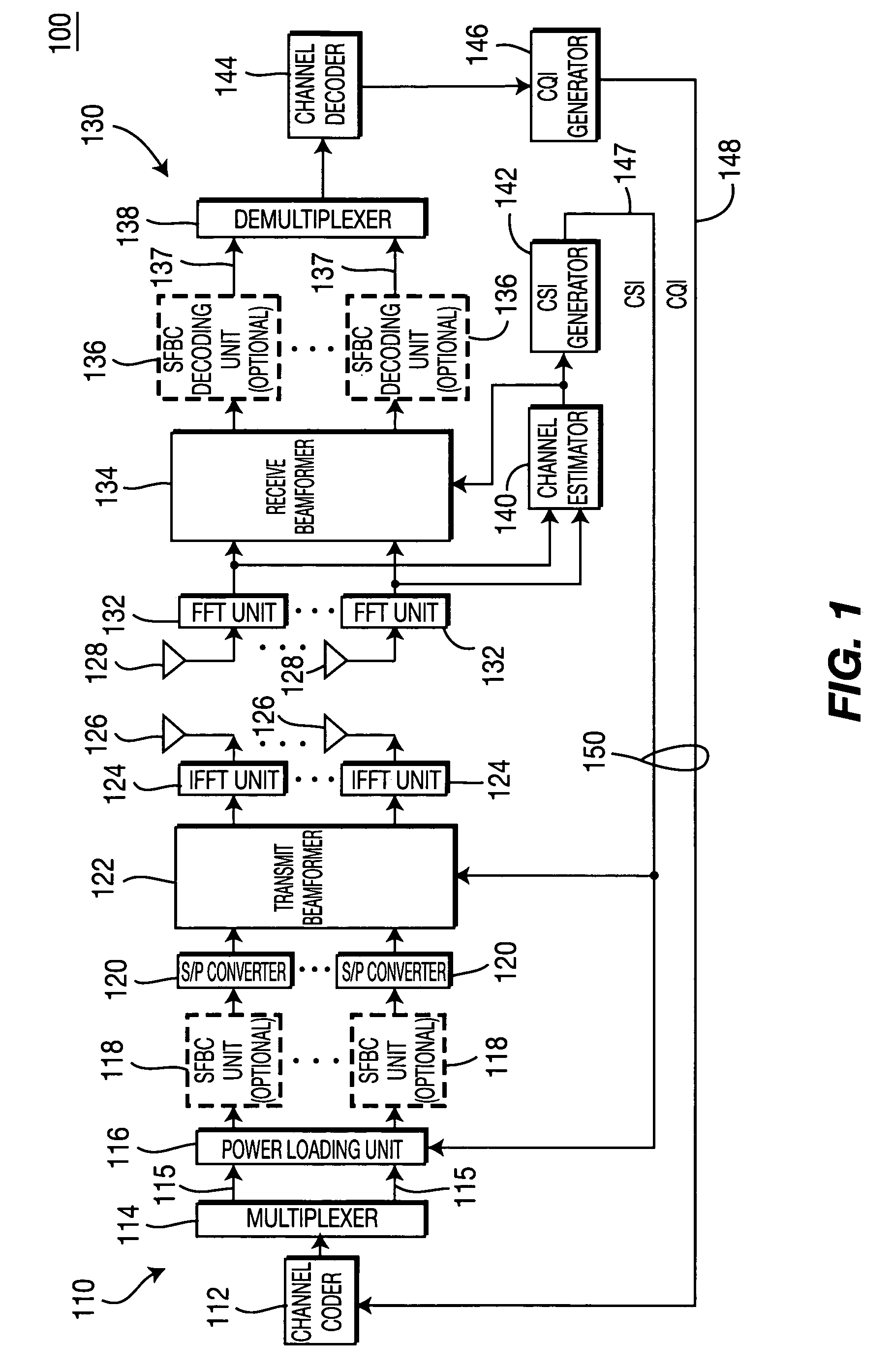
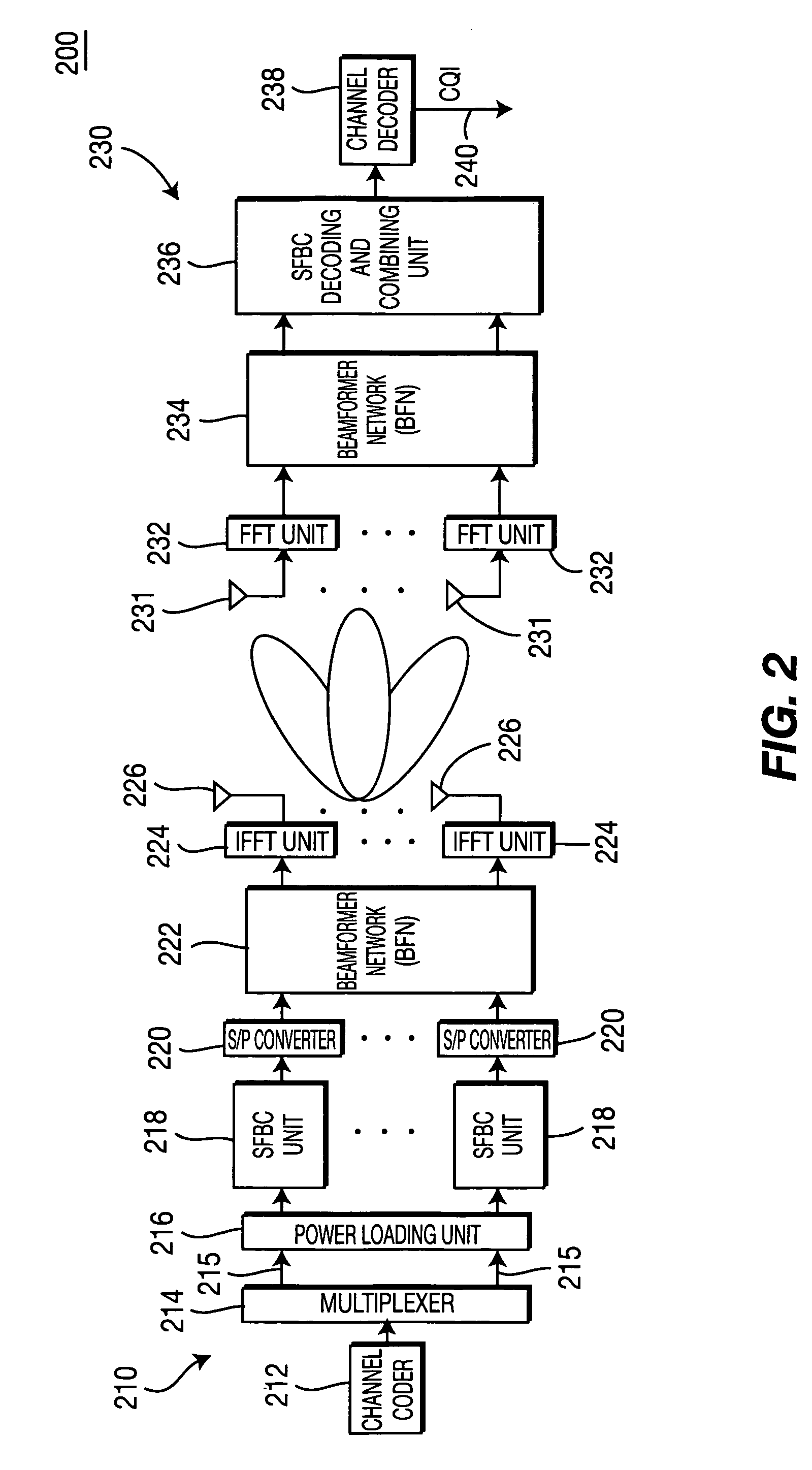
Method and apparatus for combining space-frequency block coding, spatial multiplexing and beamforming in a MIMO-OFDM system
ActiveUS20060133530A1Modulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionData streamFrequency-division multiplexing
A method and apparatus for combining space-frequency block coding (SFBC), spatial multiplexing (SM) and beamforming in a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system. The system includes a transmitter with a plurality of transmit antennas and a receiver with a plurality of receive antennas. The transmitter generates at least one data stream and a plurality of spatial streams. The number of generated spatial streams is based on the number of the transmit antennas and the number of the receive antennas. The transmitter determines a transmission scheme in accordance with at least one of SFBC, SM and beam forming. The transmitter transmits data in the data stream to the receiver based on the selected transmission scheme.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
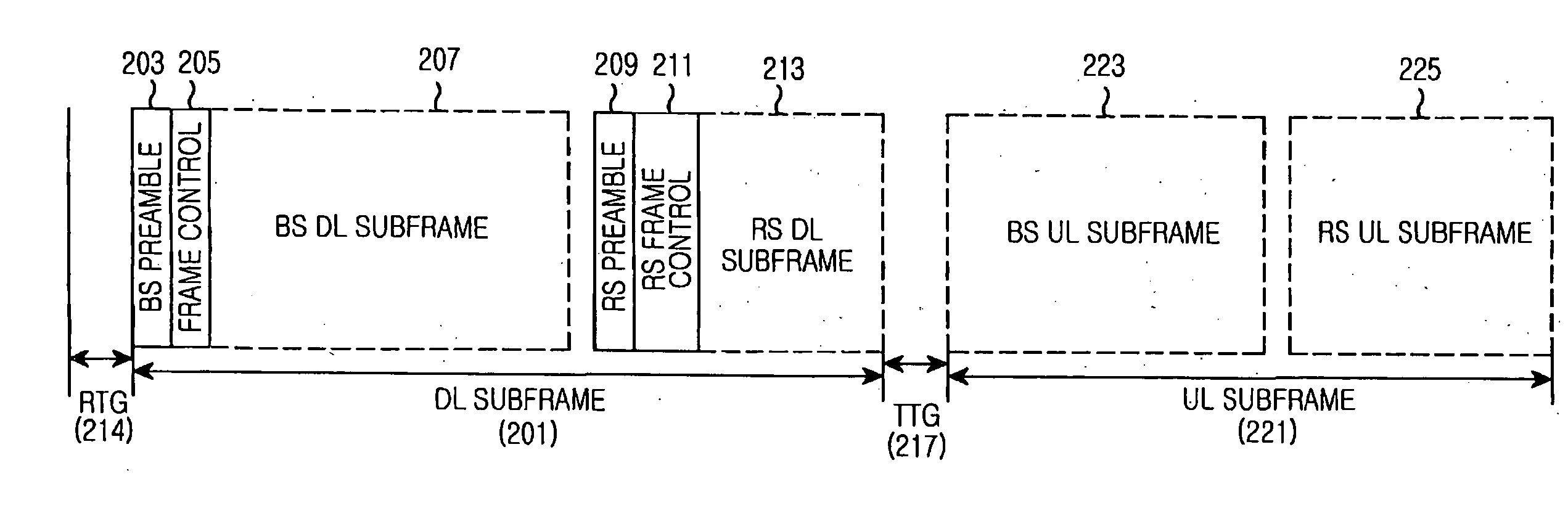
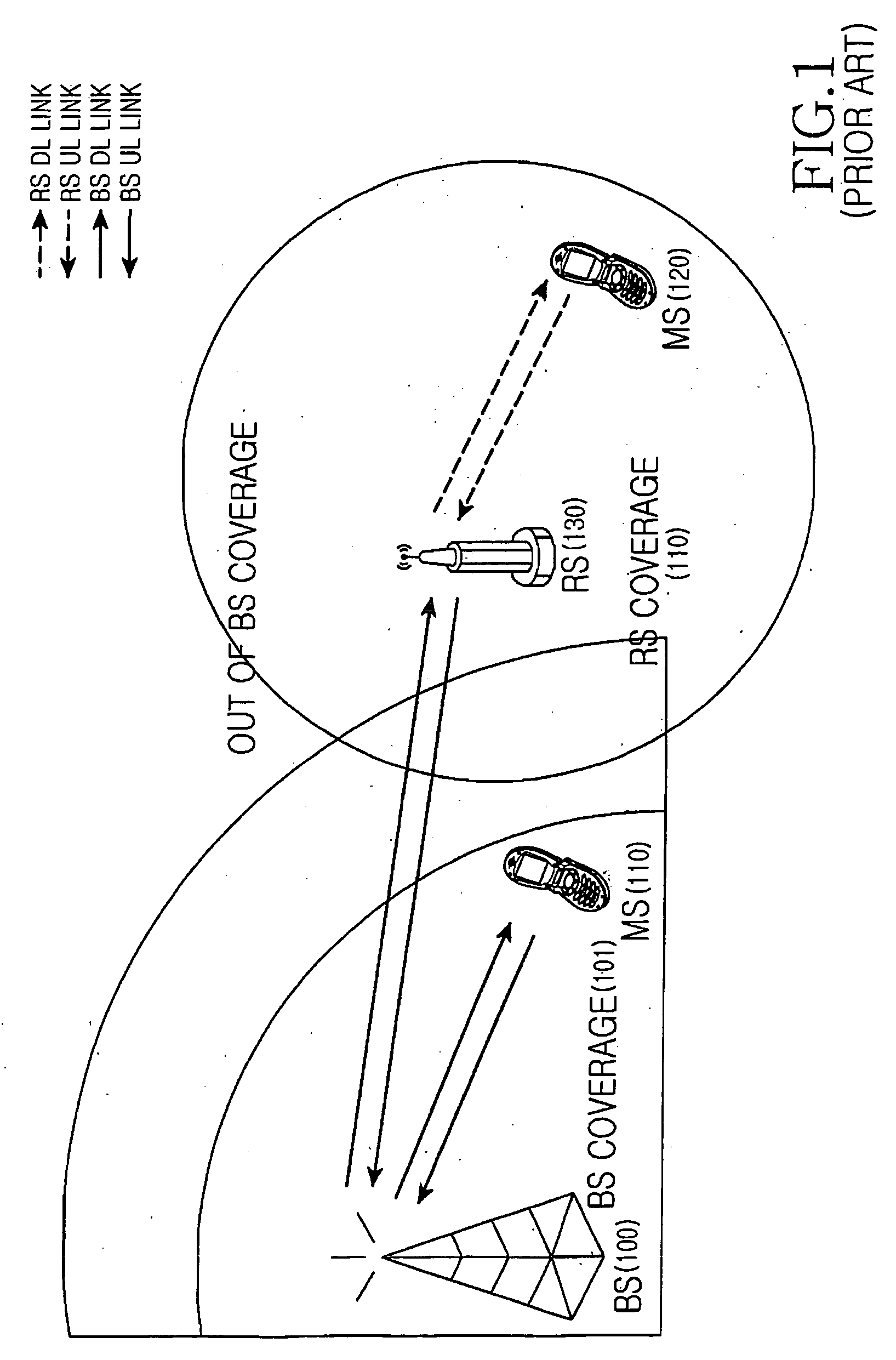
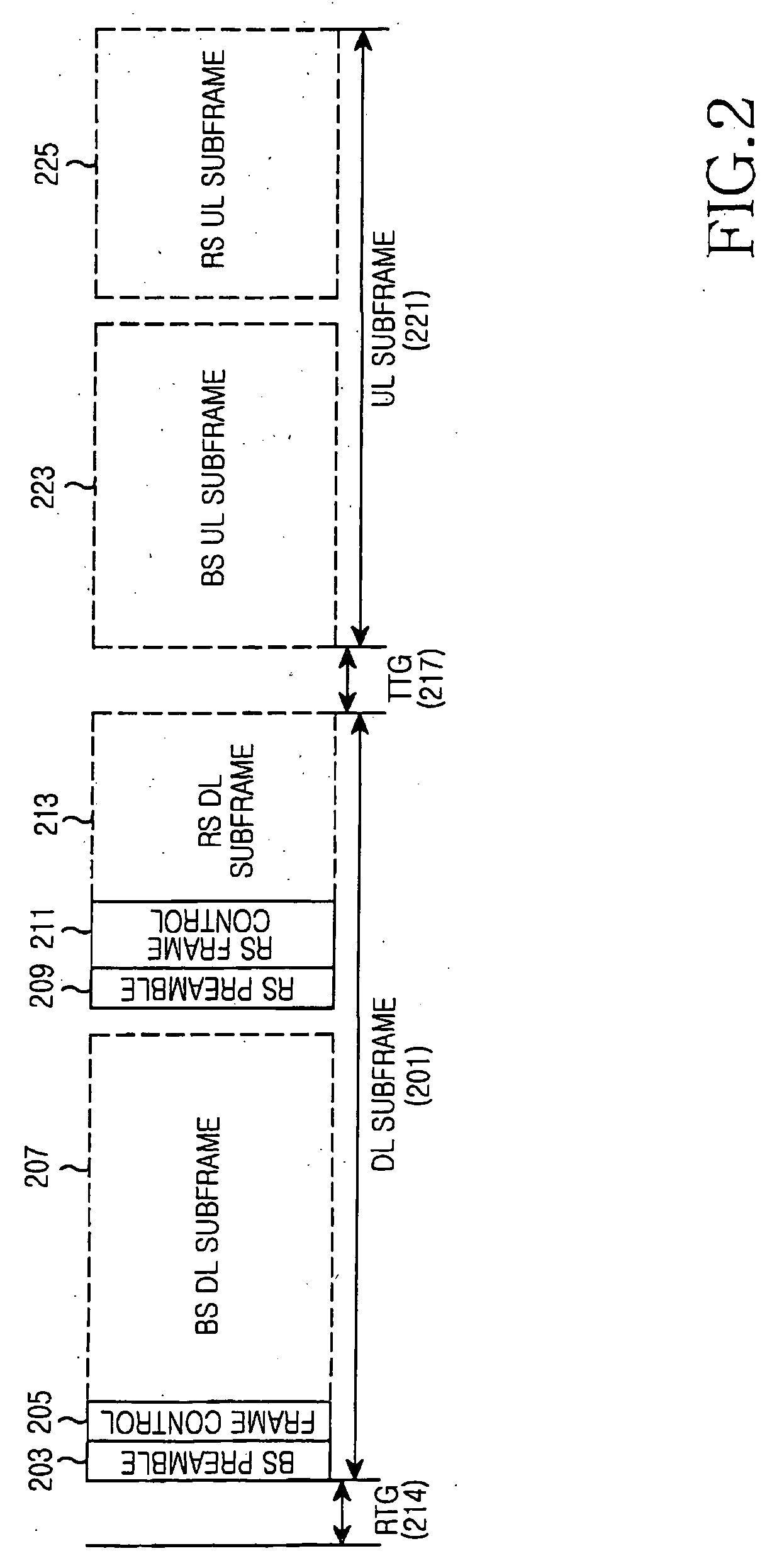
Apparatus and method for supporting multi-link in multi-hop relay cellular network
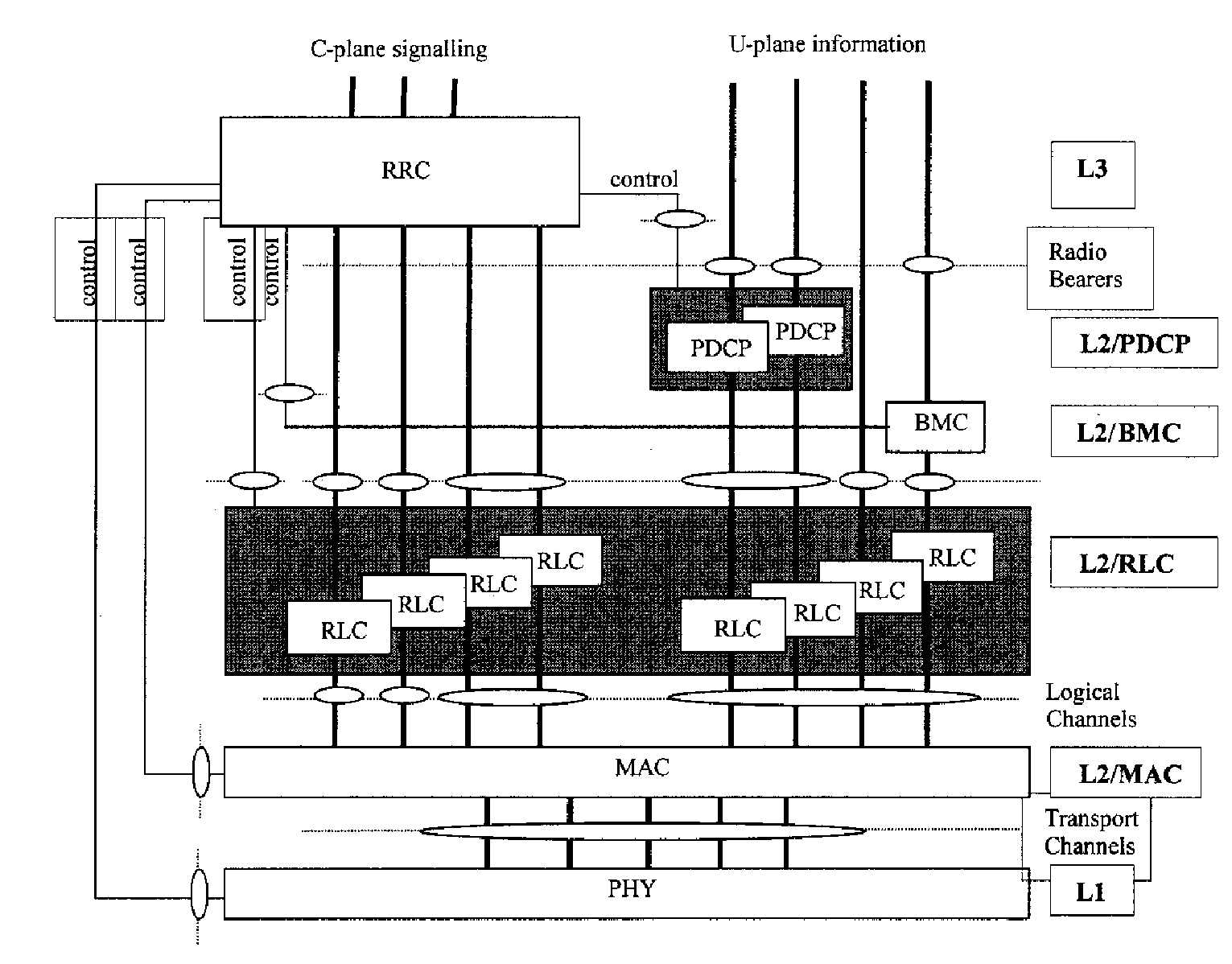
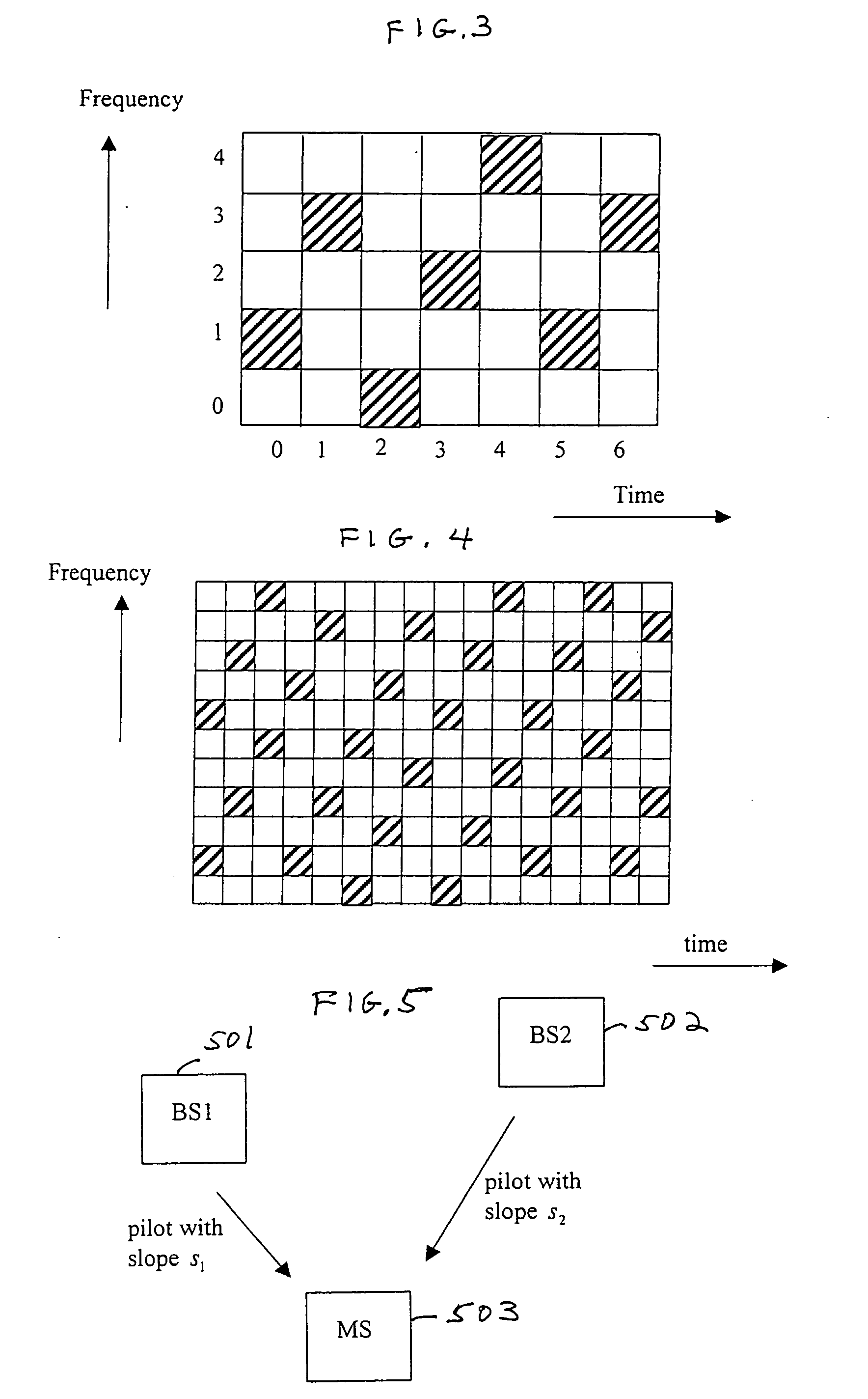
A framing method of fixing a training signal and a control channel for multi-link (direct link and relay link) synchronization in a multi-hop relay cellular network, and a transmitting / receiving apparatus for supporting the framing method. A base station (BS) transmits BS downlink (DL) subframe sequentially including a preamble, control information, and a DL burst to a relay station (RS) or a first mobile station (MS) connected to the BS by direct link. The RS transmits an RS DL subframe sequentially including a DL burst, a postamble, and control information to a second MS connected to the BS by relay link. Therefore, difficulties of initial synchronization, handoff, and cell search can be removed from MSs. Furthermore, multi-link bursts can be located between the preamble and the postamble by Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) or Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
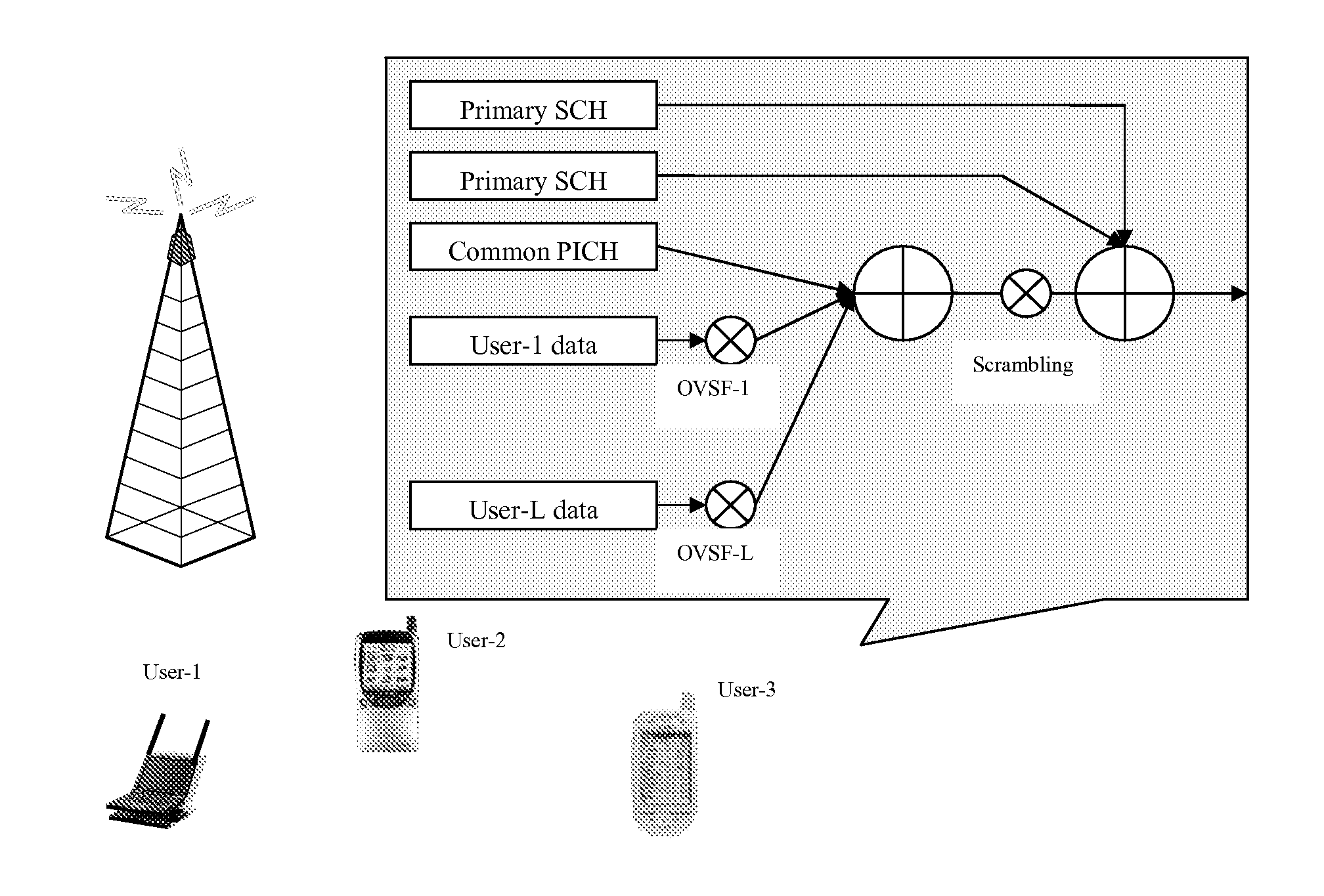
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access Based Optical Ring Network
ActiveUS20090092389A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission path divisionData streamCarrier signal
A fiber optic network transmits data between a hub node and a plurality of local nodes connected by at least one unidirectional fiber ring. Downstream data streams are carried on wavelength-division-multiplexed optical carriers from the hub node to the local nodes. An optical carrier corresponding to a specific wavelength carries downstream data streams to a specific local node. Downstream data streams are multiplexed onto an optical carrier via orthogonal frequency division multiplexing. A parallel signal detector in each local node detects all downstream optical carriers. A signal processing module demultiplexes the data stream from the optical carrier having the specific wavelength corresponding to the local node. An upstream data stream is multiplexed via orthogonal frequency division multiplexing onto an upstream optical carrier having the same specific wavelength and transmitted from the local node to the hub node. Upstream data awaiting transmission is allocated to specific subcarriers and time slots.
Owner:NEC CORP
Random Access Dimensioning Methods And Procedues For Frequency Division Multiplexing Access Systems
ActiveUS20080279257A1Maximize probabilityMinimizing false detectionCriteria allocationInter user/terminal allocationSignal qualityFrequency-division multiplexing
A method of determining random access resources performed by a mobile terminal, the method comprising: receiving information on available random access resources from a network; deciding how to derive the random access resources to be allowed based on default values or information received from the network; measuring received signal quality of at least one of a cell to be accessed and a neighboring cell; and deriving the allowed random access resources based on the deciding and the measuring.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for configuring control channel for nr in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20190356524A1Efficiently definedTransmission path divisionAssess restrictionBroadcast channelsCommunications system
A method and apparatus for determining a control resource set for system information in a wireless communication system is provided. A user equipment (UE) receives a configuration of control resource set (CORESET) for remaining system information (RMSI) via a synchronization signal (SS) block from a network, and determines the control resource set for the RMSI according to the configuration. The SS block may include a physical broadcast channel (PBCH). A time and frequency location of a common search space (CSS) for the RMSI may be aligned with the SS block by at least one of time division multiplexing (TDM) or frequency division multiplexing (FDM).
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Frequency division multiplexing system with selectable rate
InactiveUS6992972B2Increase delayIncrease rangeLine-faulsts/interference reductionMulti-frequency code systemsFourier transform on finite groupsCarrier signal
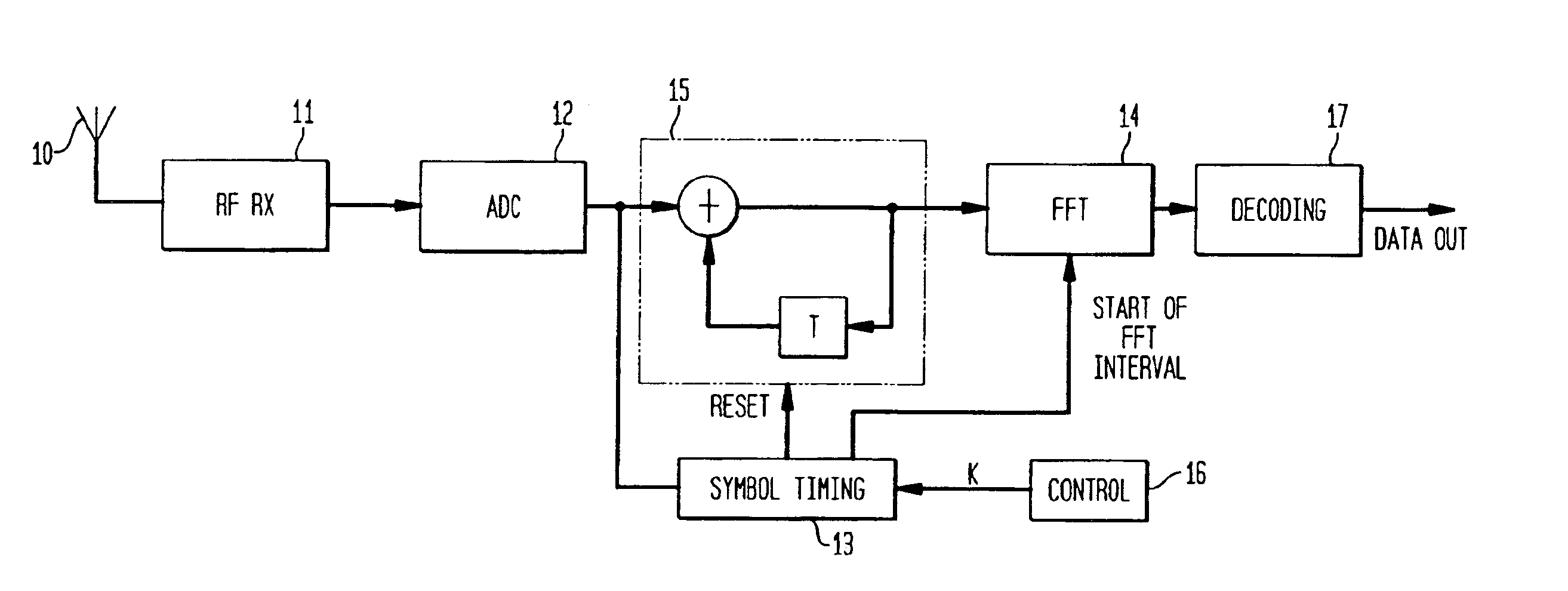
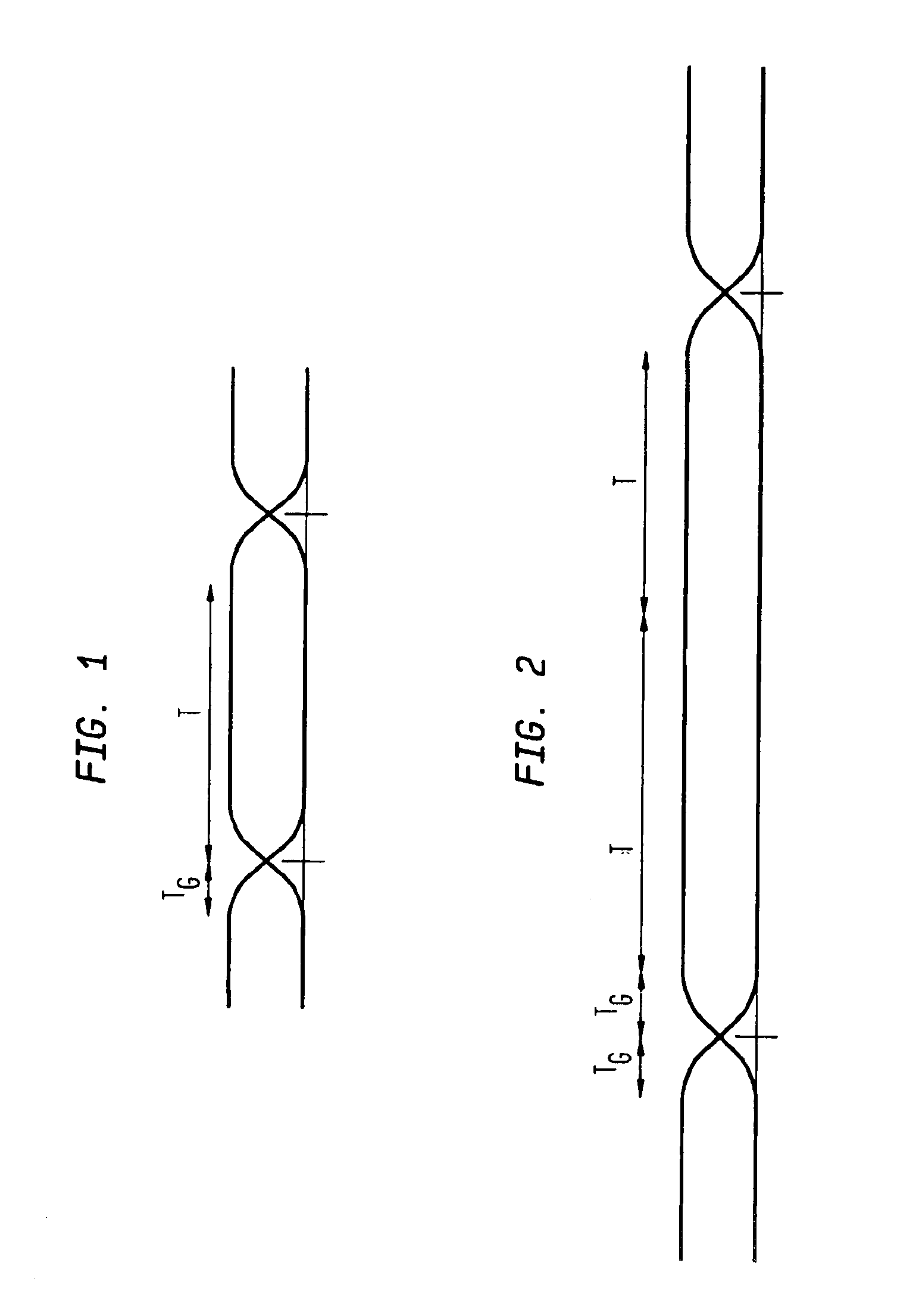
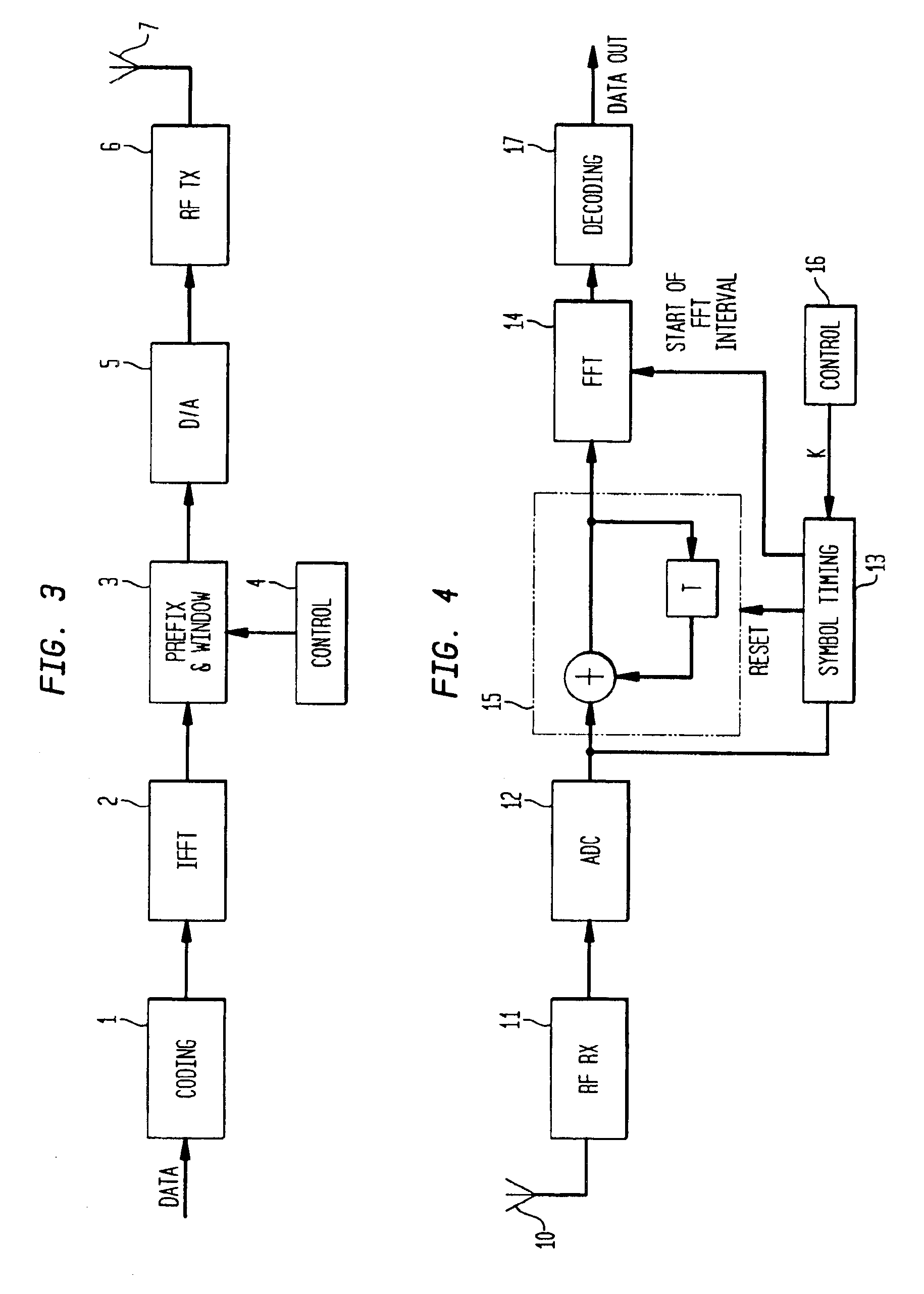
An OFDM system uses a normal mode which has a symbol length T, a guard time TG and a set of N sub-carriers, which are orthogonal over the time T, and one or more fallback modes which have symbol lengths KT and guard times KTG where K is an integer greater than unity. The same set of N sub-carriers is used for the fallback modes as for the normal mode. Since the same set of sub-carriers is used, the overall bandwidth is substantially constant, so alias filtering does not need to be adaptive. The Fourier transform operations are the same as for the normal mode. Thus fallback modes are provided with little hardware cost. In the fallback modes the increased guard time provides better delay spread tolerance and the increased symbol length provides improved signal to noise performance, and thus increased range, at the cost of reduced data rate.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Base station identification in orthongonal frequency division multiplexing based spread spectrum multiple access systems
InactiveUS20050238083A1Inherent latencyRadio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency-division multiplexingFrequency-shift keying
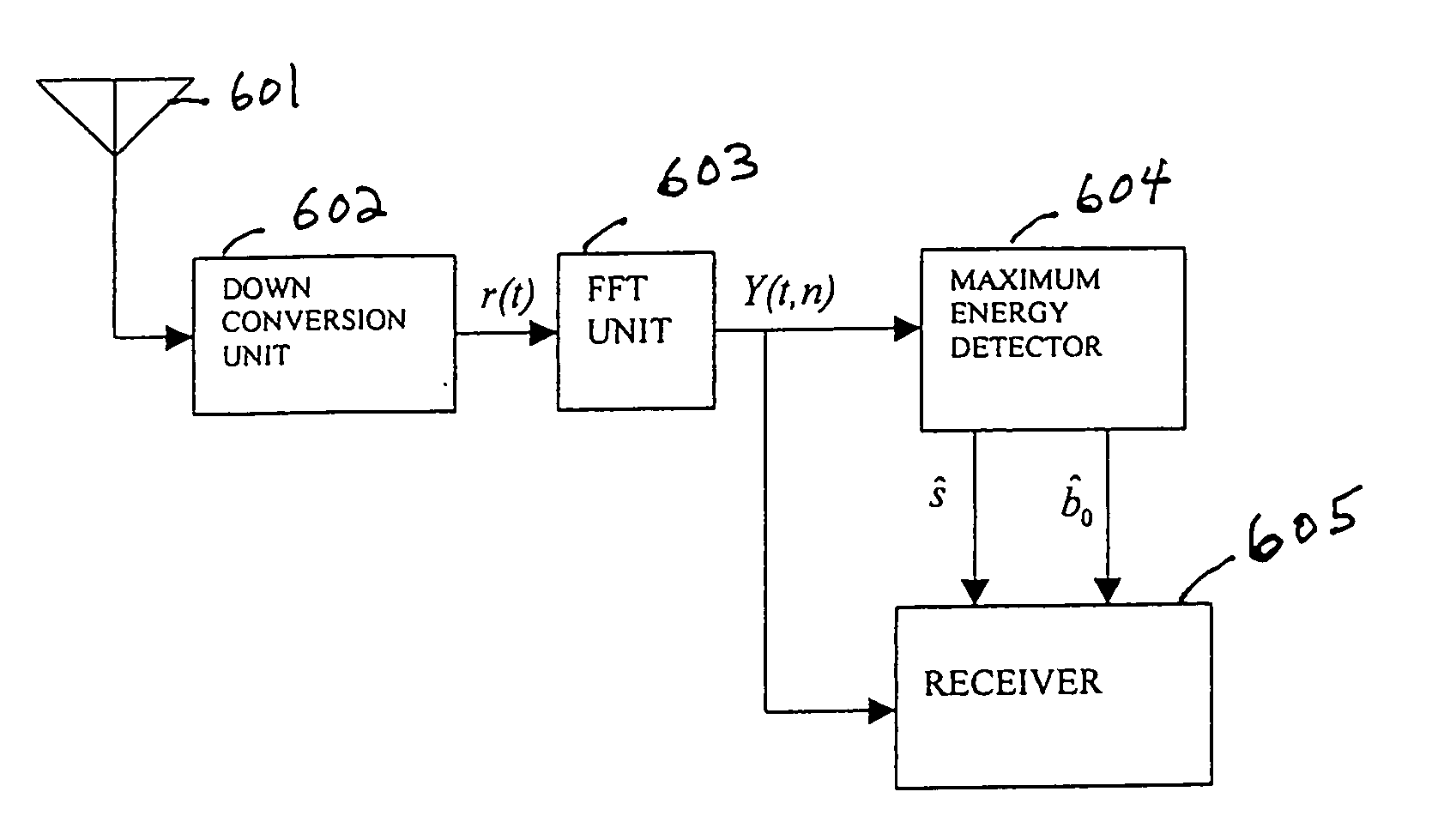
A base station having the strongest downlink signal is identified by utilizing a unique slope of a pilot tone hopping sequence being transmitted by a base station. Specifically, base station identification is realized by determining the slope of the strongest received pilot signal, i.e., the received pilot signal having the maximum energy. In an embodiment of the invention, the pilot tone hopping sequence is based on a Latin Squares sequence. With a Latin Squares based pilot tone hopping sequence, all a mobile user unit needs is to locate the frequency of the pilot tones at one time because the pilot tone locations at subsequent times can be determined from the slope of the Latin Squares pilot tone hopping sequence. The slope and initial frequency shift of the pilot tone hopping sequence with the strongest received power is determined by employing a unique maximum energy detector. In one embodiment, the slope and initial frequency shift of the pilot signal having the strongest received power is determined by finding the slope and initial frequency shift of a predicted set of pilot tone locations having the maximum received energy. In another embodiment, the frequency shift of the pilot signal with the strongest, i.e., maximum, received power is estimated at each of times “t”. These frequency shifts are employed in accordance with a prescribed relationship to determine the unknown slope and the initial frequency shift of the pilot signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and circuit arrangement for improving carrier separation for the transmission of OFDM signals
InactiveUS6088327AEasy to receiveEasy to separateMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 02209 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 17, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 17, 1997 PCT Filed May 23, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 41458 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 19, 1996In the case of the OFDM method, a large number of modulated carriers are transmitted using frequency division multiplexing, a spectrum having a virtually rectangular shape being produced as a result of the large number of carriers. In order to separate the carriers from one another again in the receiver, a Fast-Fourier-Transformation is carried out, it then being possible to separate each carrier cleanly from the others provided the carriers are exactly orthogonal with respect to one another. The carrier orthogonality can, however, be disturbed by various causes. Furthermore, the wanted signal must be separated from the undesired adjacent channel signals by analog or digital filtering in the receiver. In order to improve carrier and channel separation, the selectivity of the FFT filtering can be increased by enlarging the number of FFT components. However, this normally leads to an undesirably sharp increase in the computation complexity. The refinement according to the invention of the time window which is used for the FFT and the oversampling before the FFT make it possible, however, to dispense with calculation of some of the coefficients.
Owner:DEUTSCHE THOMSON-BRANDT GMBH
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communications device and method that incorporates low papr preamble and receiver channel estimate circuit
ActiveUS20100080311A1Secret communicationChannel estimationGuard intervalFrequency-division multiplexing
A communications device includes a demapping and demodulation circuit that demaps and demodulates an OFDM communications signal as modulated subcarriers carrying communications data and modulated subcarriers carrying a training sequence forming a preamble that includes a long sync sequence for channel and frequency offset estimation having a extended guard interval (GI). The OFDM subcarriers carrying the training sequence have a quadratic modulation to produce a low peak-to-average power (PAPR) preamble with PAPR of approximately 2.6 decibels (dB). A channel estimate circuit is positioned to receive signals after processing within a FFT circuit and subcarrier demapper circuit and estimates the channel characteristics of the communications channel based on splitting the extended guard interval from the long sync sequence and processing into values that represent the low PAPR preamble as plus or minus one (±1) values in a real or imaginary component as adds and subtracts.
Owner:SMARTSKY NETWORKS
Opening gas multi-element monitoring instrument and monitoring method
InactiveCN101021474AReal-time online monitoringOvercome speedColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberFiber coupler
The invention discloses a multi-wavelength high-sensitivity online monitor of multi-component NH3 and H2O based on semiconductor laser absorption spectroscopy. It contains host chassis and open long-path system. Equip power receptacle, switch, fiber connector and data transmission interface. It is characterized in that: there are near-infrared semiconductor laser, semiconductor laser controller, phase-locked amplifier, signal generator, data collecting and controlling module and infrared detector in host chassis which is connected with field optical system by fiber. Open optical system contains send-receive optical telescope and multielement reflector array. Optical telescope has input and output fiber couplers. The device realizes simultaneous testing of gas multi-component by using multi-wavelength and frequency division multi-signal detecting technique.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Network-based inter-cell power control for multi-channel wireless networks
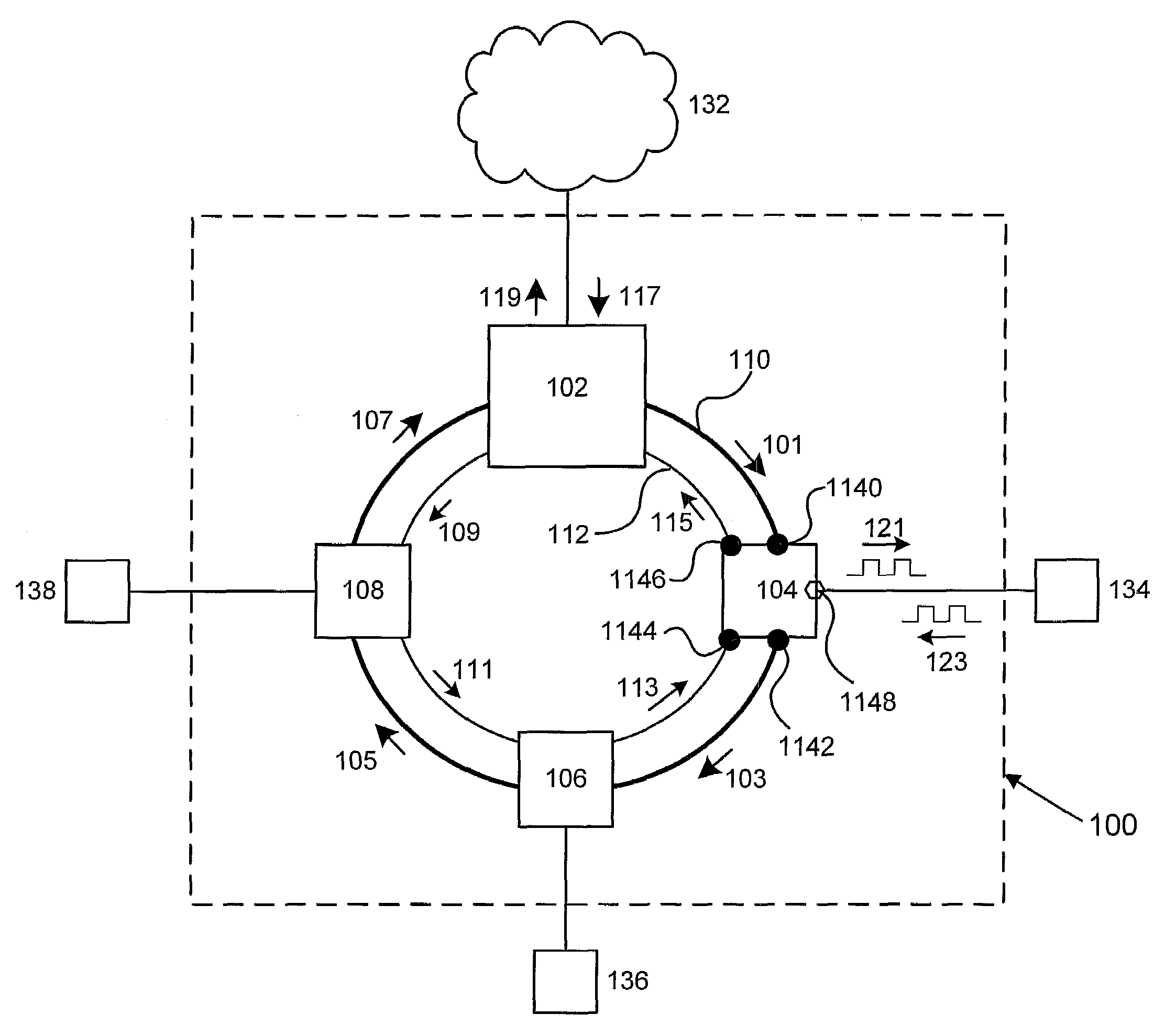
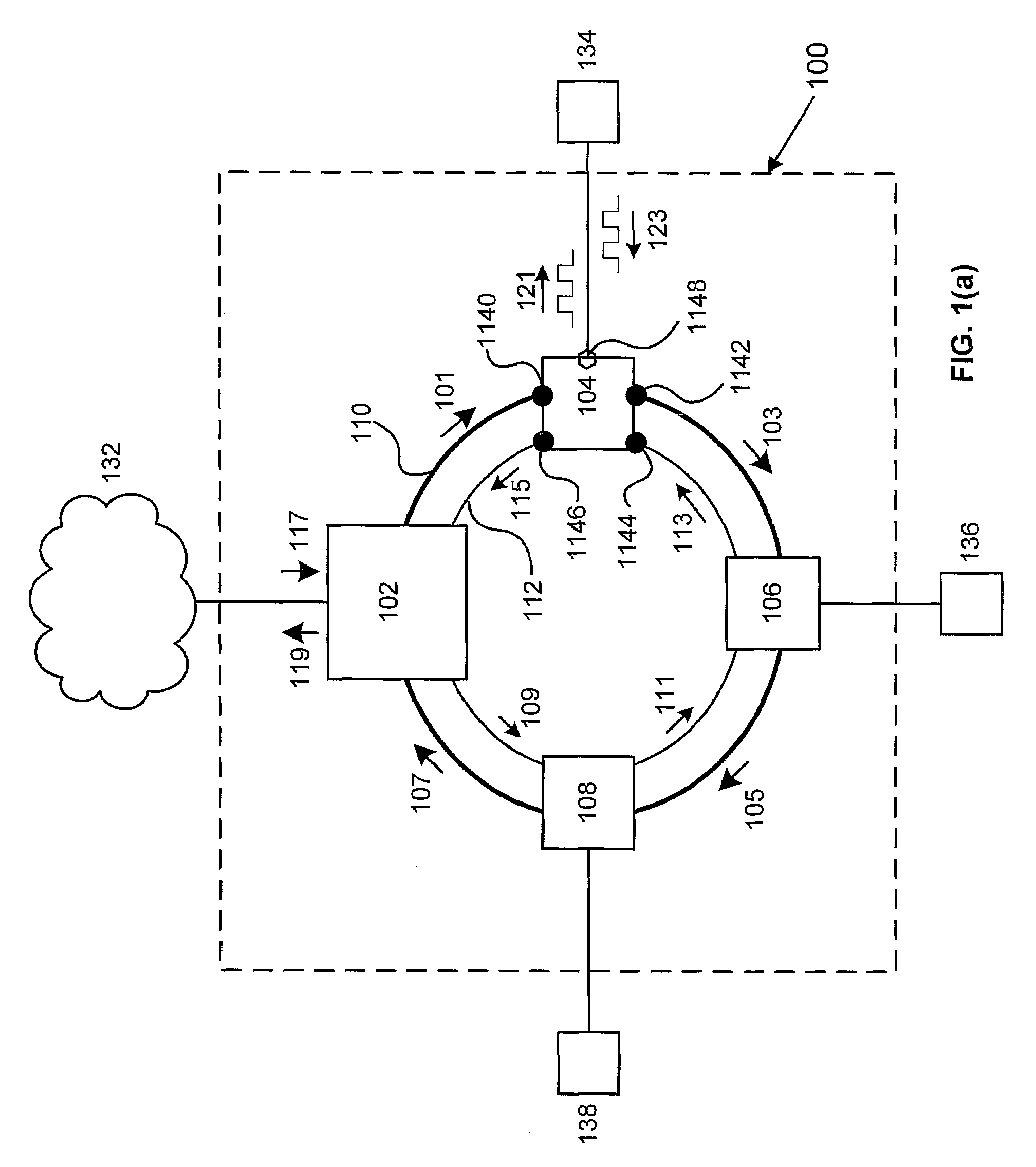
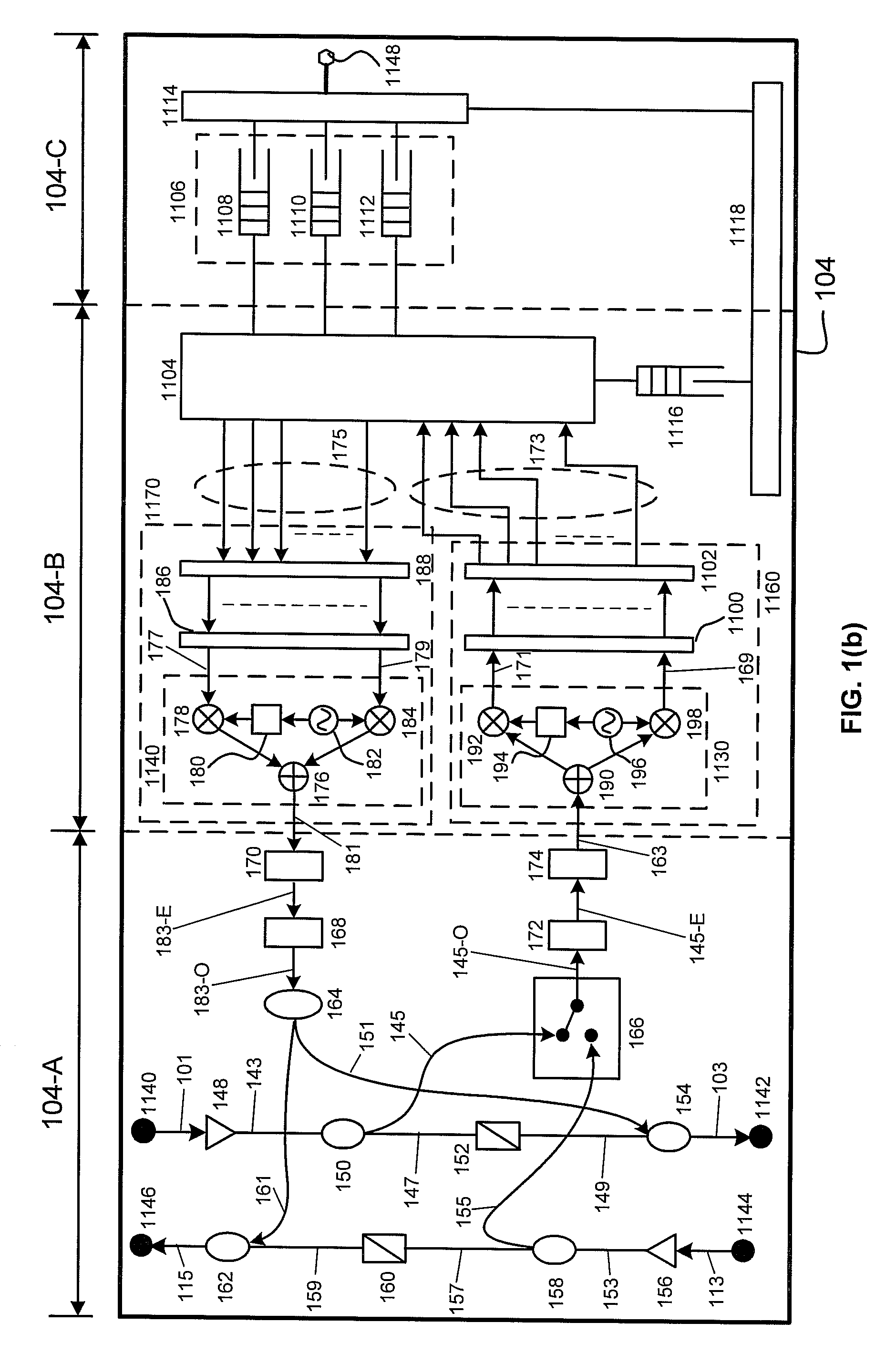
ActiveUS8072918B2Frequency-division multiplexRadio transmissionFrequency-division multiplexingCell parameter
Owner:APPLE INC
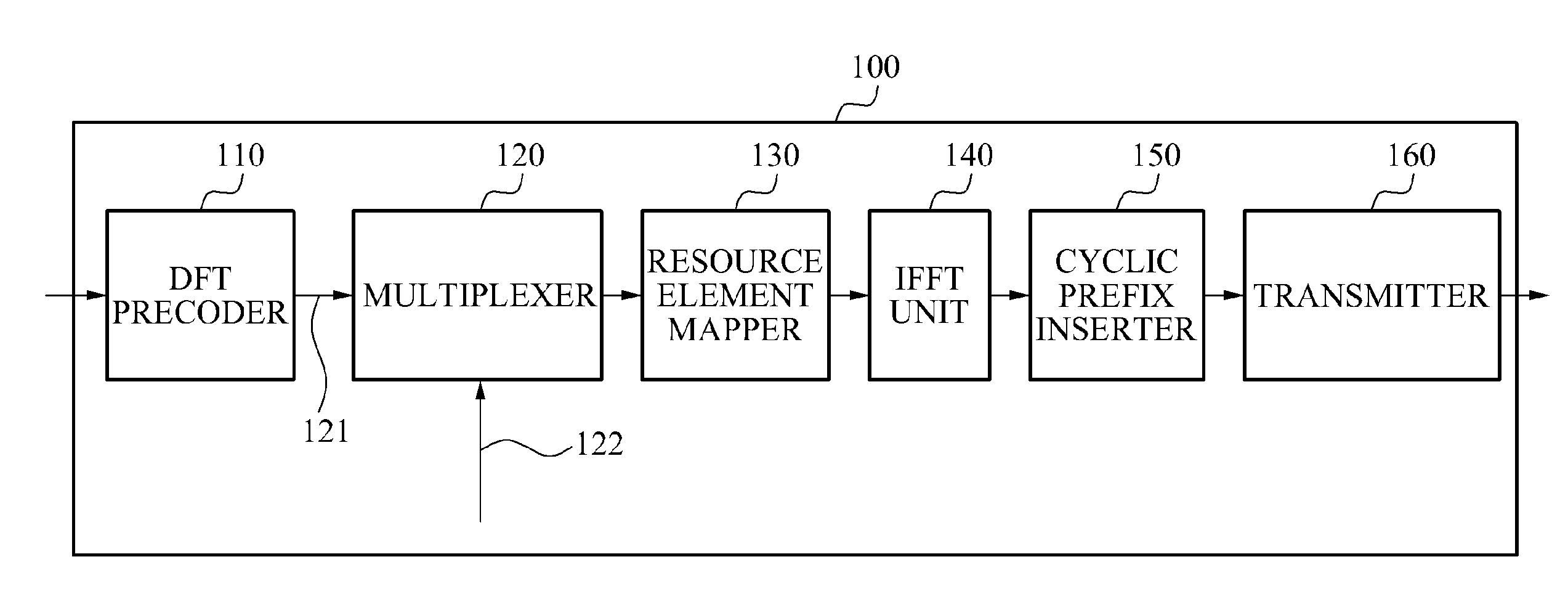
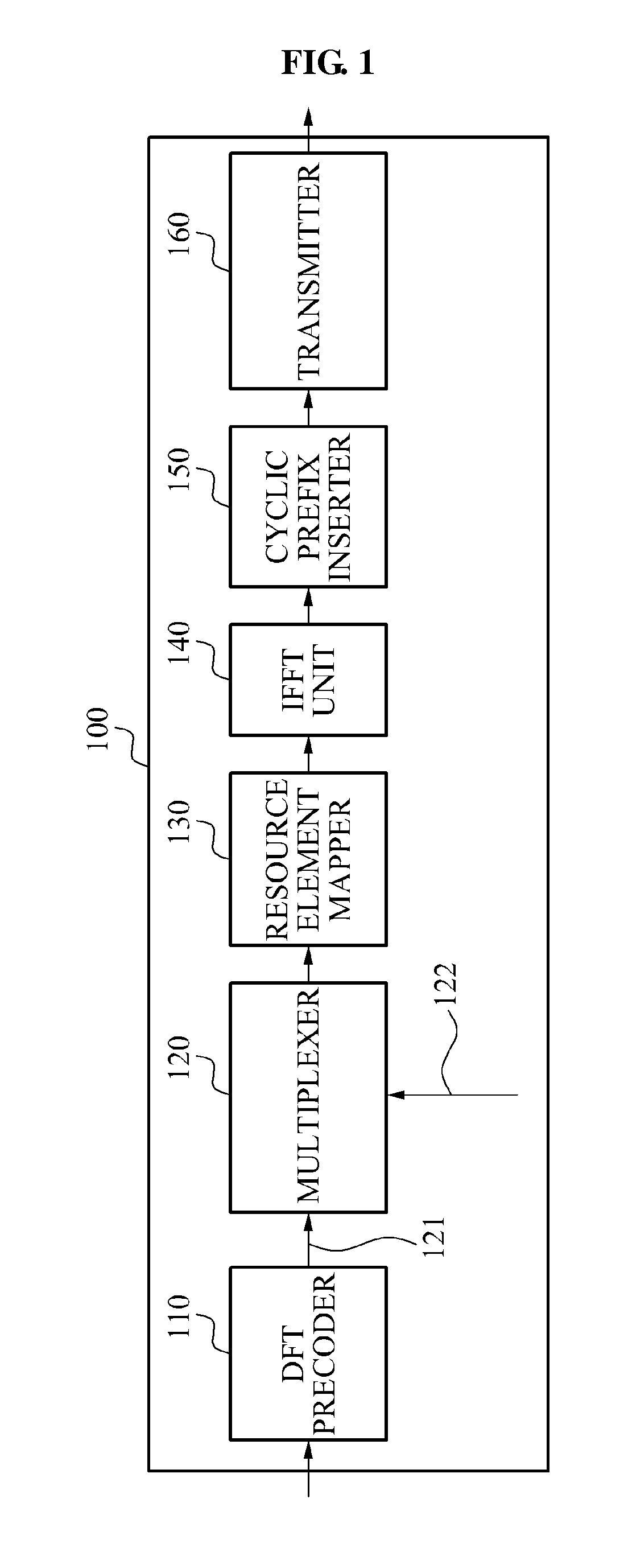
Reference symbol structure for dft spread OFDM system
ActiveUS20120087393A1Increase overheadMinimized increaseModulated-carrier systemsPilot signal allocationFrequency-division multiplexingData transmission
Provided is a data transmission apparatus to transmit a reference orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbol generated by frequency division multiplexing a reference symbol and a data symbol, and a data reception apparatus to estimate a channel using the reference OFDM symbol. Since the reference symbol and the data symbol are frequency division multiplexed, a Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR) may not increase greatly, and the transmission apparatus may transmit the reference OFDM symbol to the data reception apparatus more frequently. Accordingly, the data reception apparatus may estimate a channel accurately.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Network oriented spectrum sharing system
ActiveUS20080112361A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumTransceiver
There is provided a system and method for sharing a wireless spectrum compromising a first transceiver for establishing the communication channels within the allocated bandwidth using a first protocol, a broker for determining the unused bandwidth within the allocated bandwidth, and a second transceiver for establishing the further communication channels within the unused allocated bandwidth using a second protocol. The first protocol is UMTS and the second protocol is WiMax. The broker may monitor UMTS traffic and allocate bandwidth to WiMax traffic whenever resources are idle or traffic are low or allocate bandwidth in dependence upon time division multiplexing, or frequency division multiplexing or may overlap a WiMax signal with a UMTS signal.
Owner:WU SHIQUAN
System information sending and receiving method, base station and user equipment
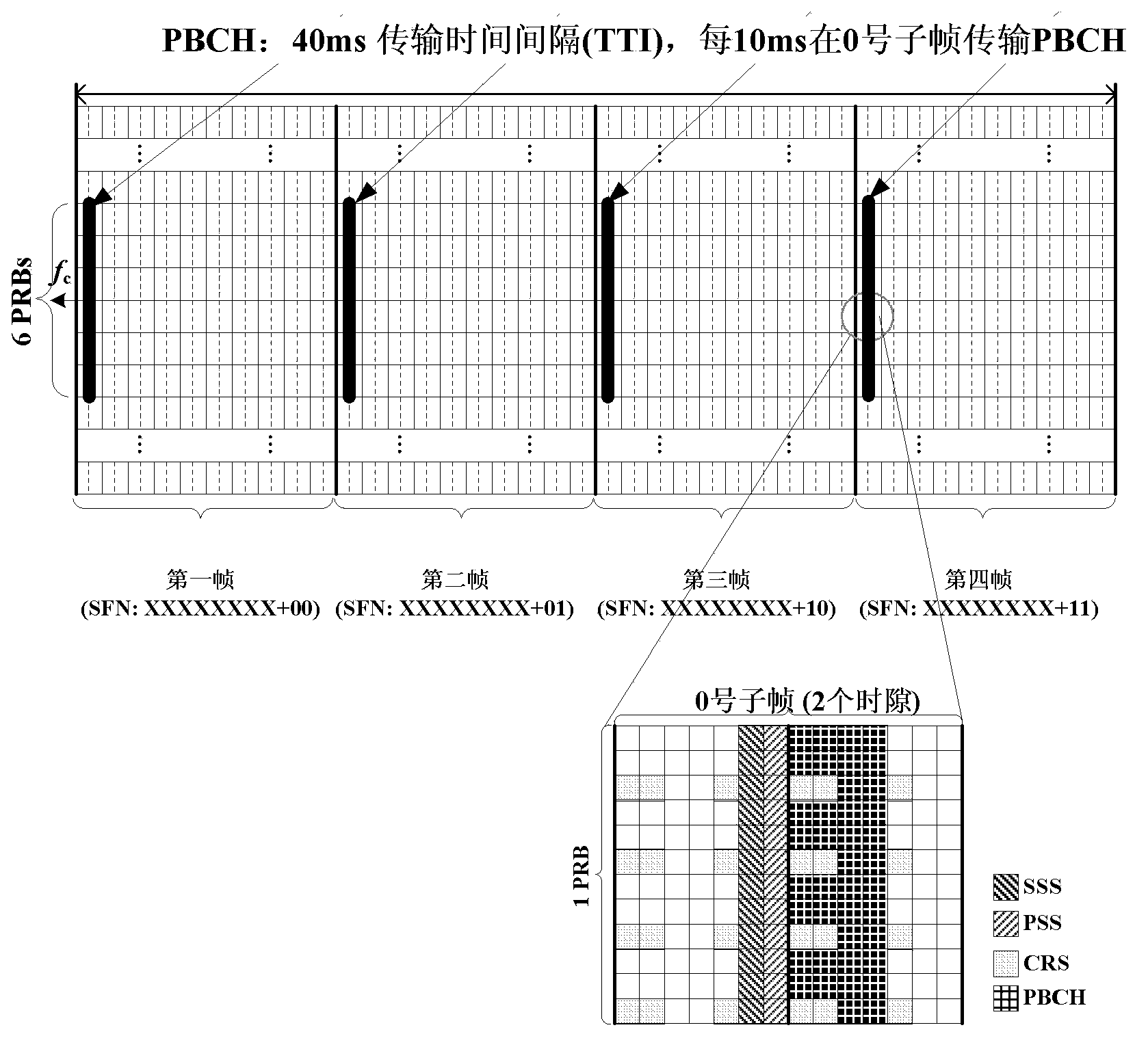
InactiveCN103906139AReduce time/frequency resource conflictsImprove energy efficiencyFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementBroadcast channelsFrequency spectrum
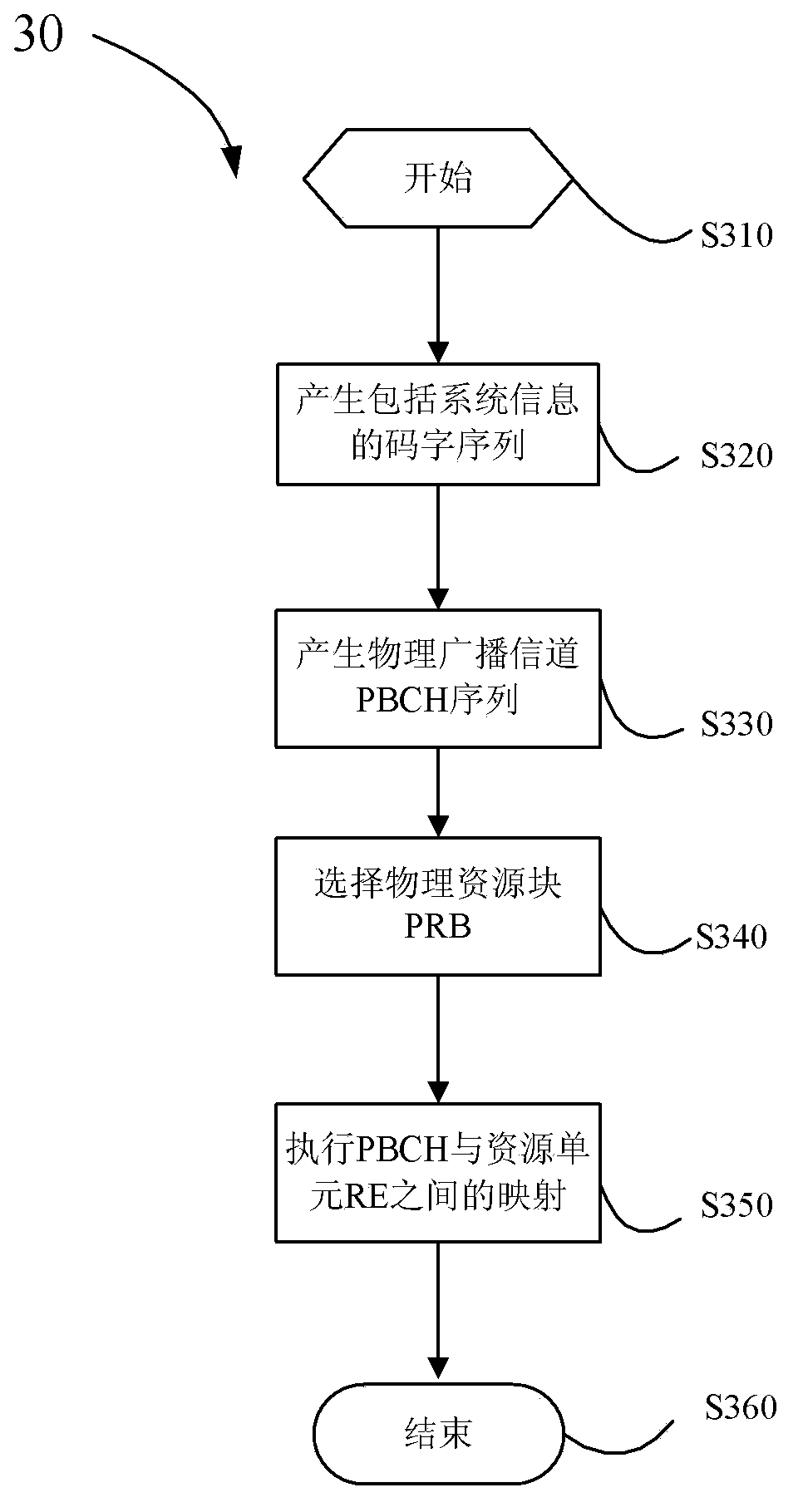
The present invention provides a method executed by a base station. The method comprises: (S320) generating a code word sequence comprising system information of the base station; (S330) modulating the code word sequence, and generating a physical broadcast channel (PBCH) sequence; (S340) selecting a physical resource block (PRB) for each PBCH in the PBCH sequence; and (S350) executing the mapping between the PBCH and a resource element (RE) in the selected PRB. The PRB has a distributed PRB frequency division multiplexing format or an integrated PRB frequency division multiplexing format. The present invention further provides a method executed by a user equipment and a corresponding base station and a user equipment. By using the present invention, the energy utilization rate can be enhanced and the frequency spectrum efficiency in an LTE-Advanced system can be improved, and time / frequency resource conflicts between cells can be reduced.
Owner:SHARP KK
Multi-antenna communication method for time division duplexing mode frequency division multiplexing system
ActiveCN101394213AReduce uplink and downlink interferenceSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCarrier signalFrequency-division multiplexing
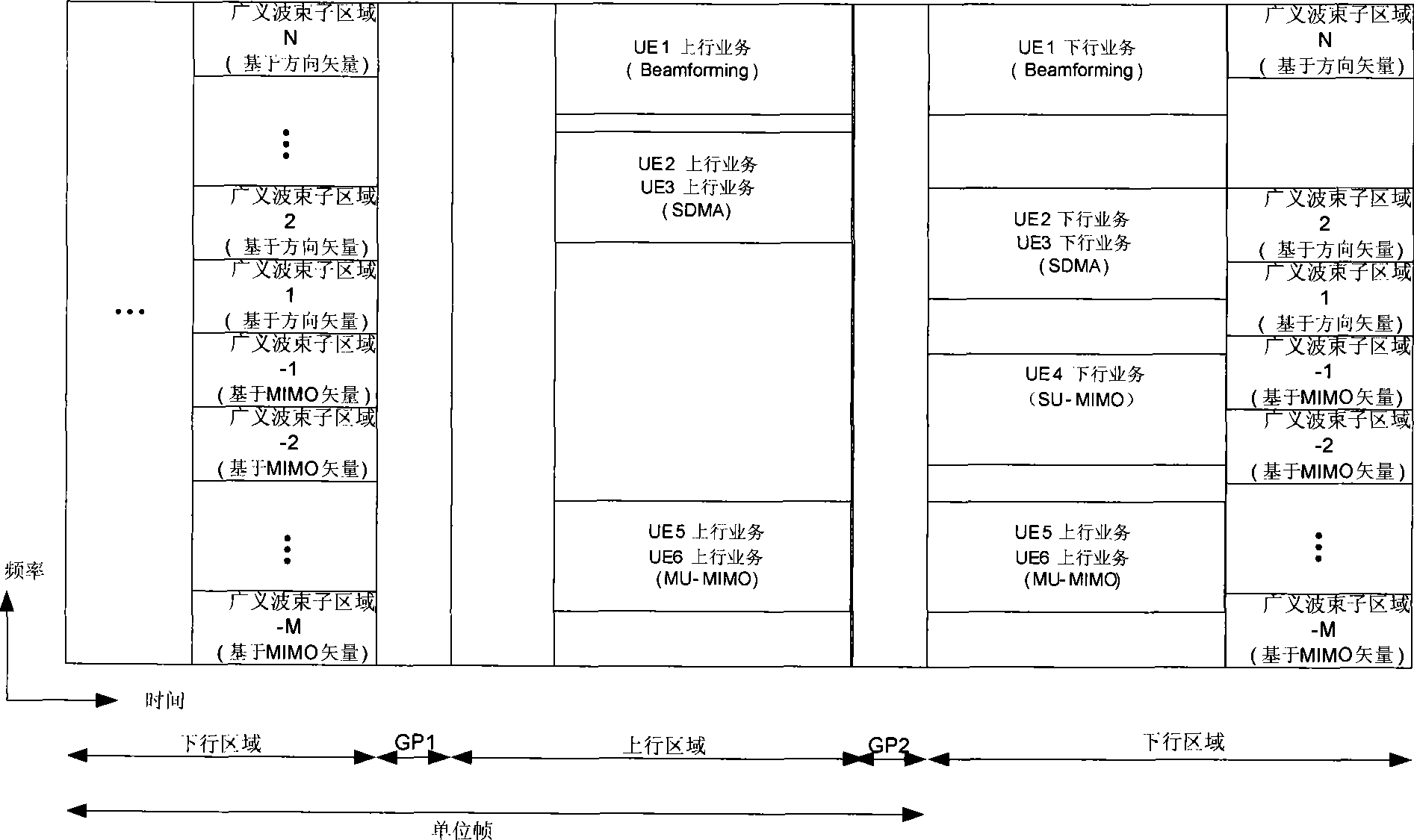
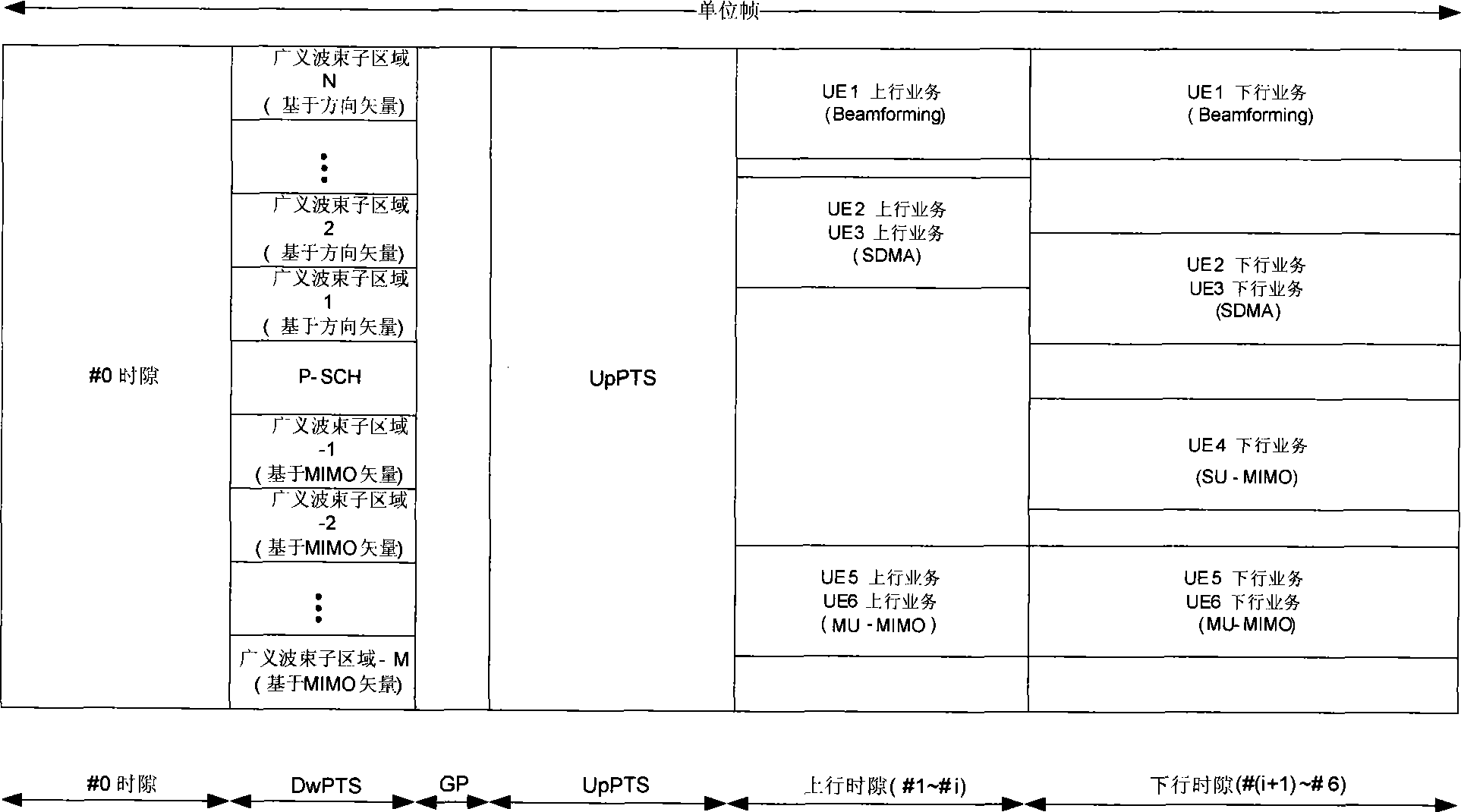
A multi-antenna communication method of a frequency division multiplexing system of a time division duplex is characterized in that a generalized beam area is arranged in a downstream area of a unit frame; the generalized beam area is divided to M plus N generalized beam subsections in a frequency domain, and a pilot channel which is composed of a subcarrier or a plurality of subcarriers is arranged in each generalized beam subsection; a pilot channel to which a pre-coding vector UI conducts the pre-coding is sent by a base station in the I generalized beam subsection; wherein, M of the pre-coding vector UI are different MIMO pre-coding vectors which are used in a large-angle expand channel and based on the latent beam forming, N of the pre-coding vector UI are pre-coding vectors which are used in a small-angle expand channel and based on the beam forming direction, and pre-coding vector index is I is equal to 1, 2,..., M+N; and the frequency division multiplexing system is a single carrier or multi-carrier transmission system which is based on a frequency division multiplexing technology.
Owner:莒县城阳水泥有限公司
MIMO based network coding network
ActiveUS20090067533A1Simpler resource allocationSite diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemMimo transmission
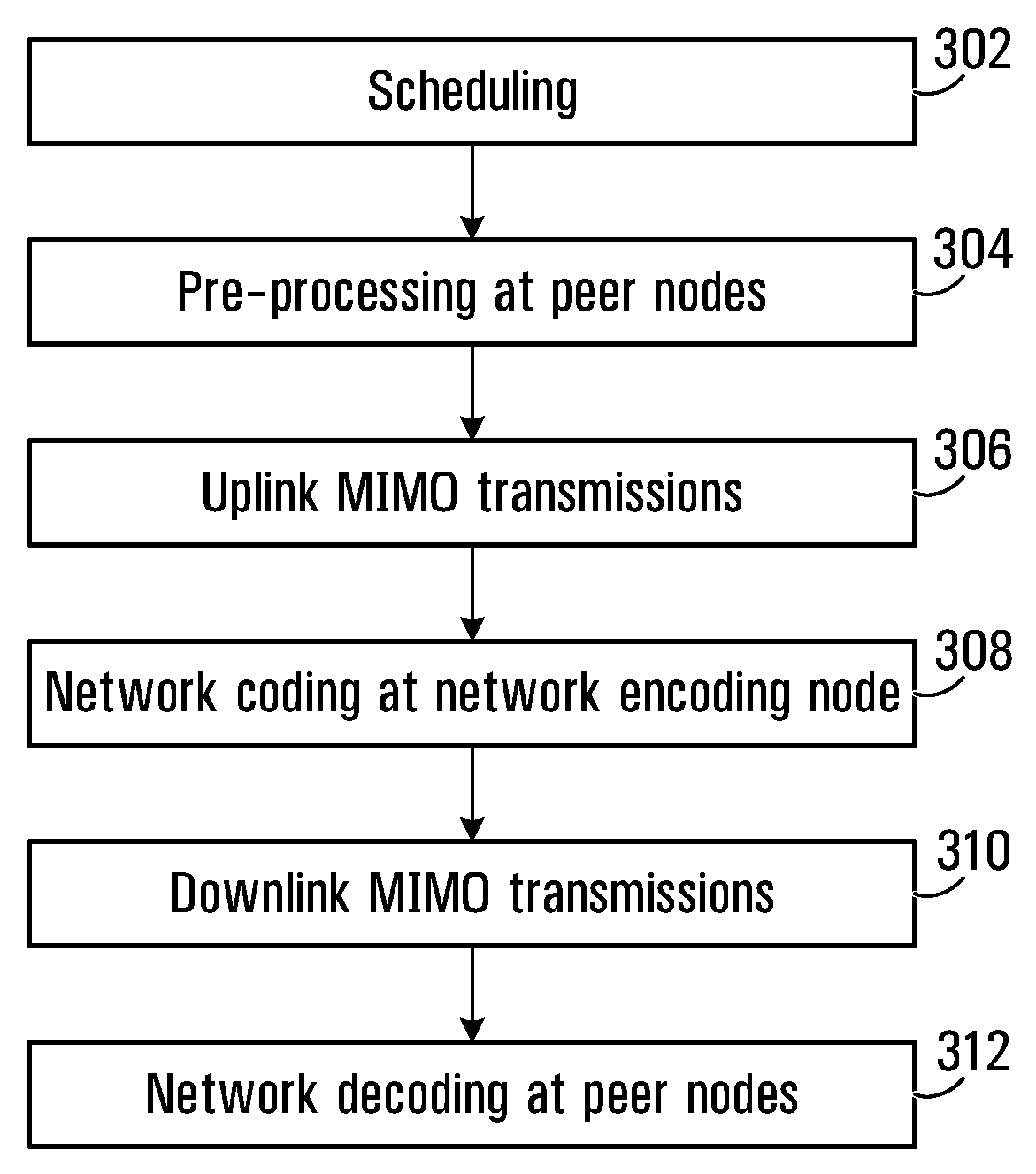
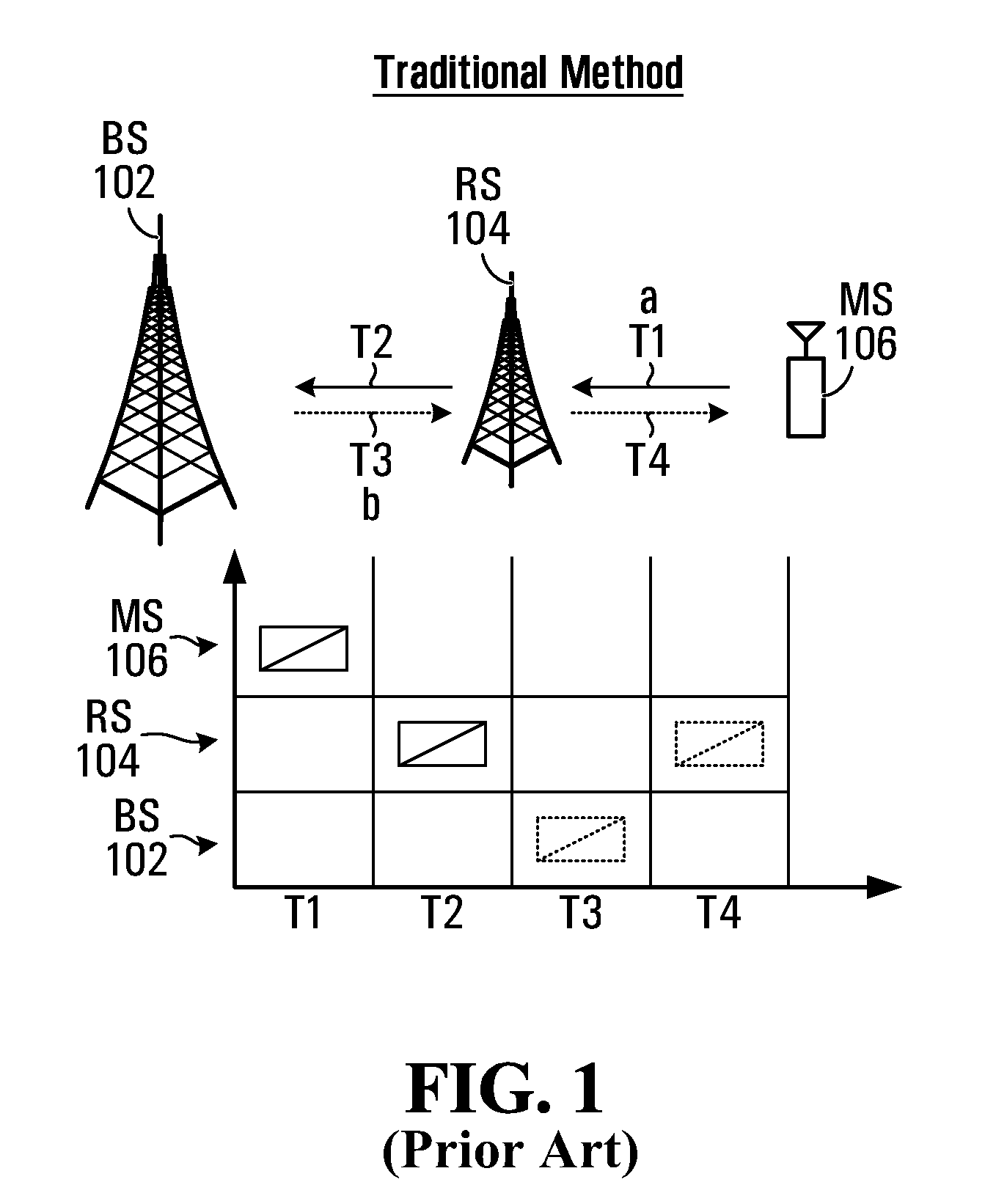
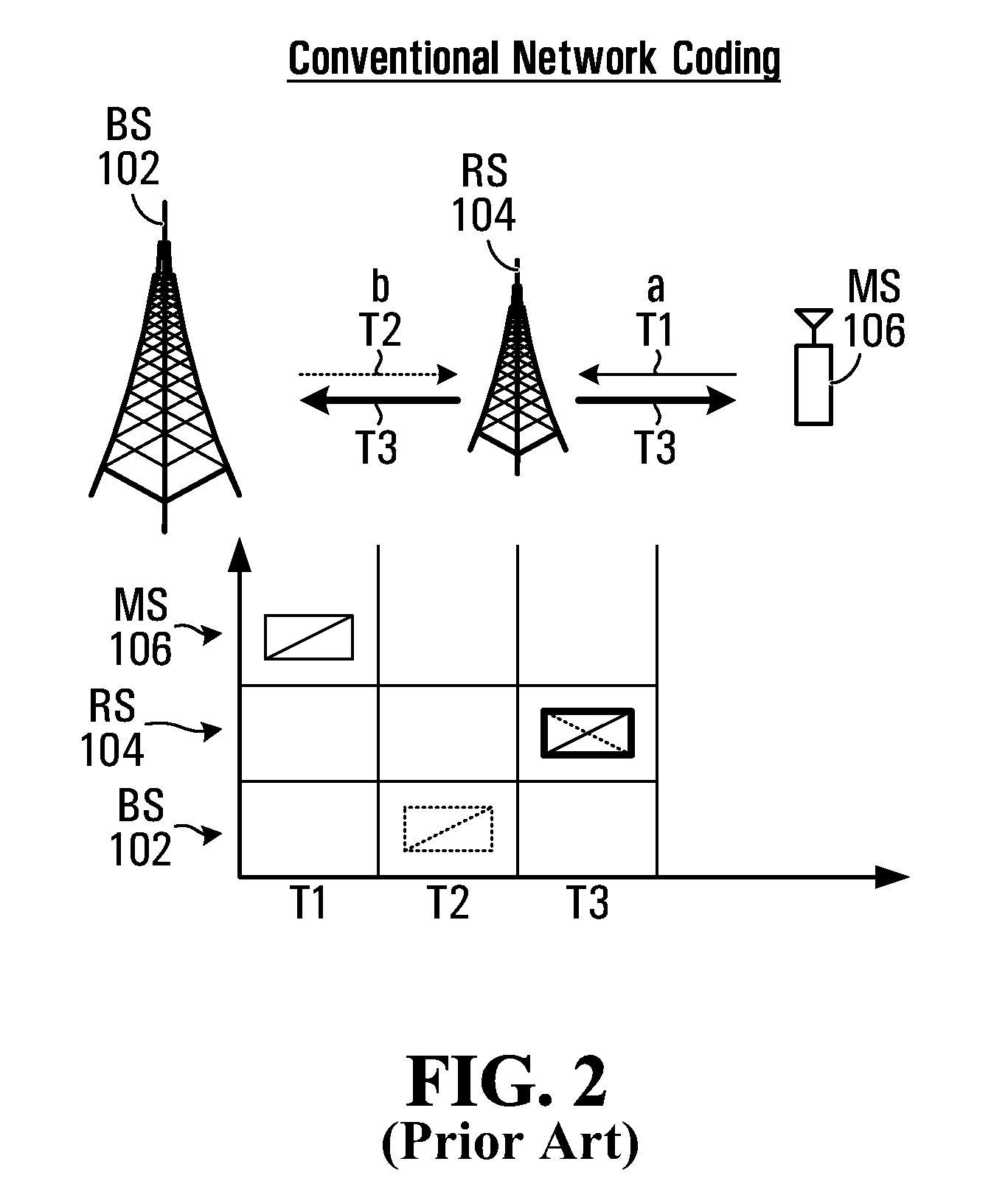
A wireless communication system includes an intermediate node, a first node and a second node. There is described a method for implementing MIMO based network coding, comprising the first node transmitting first data to the intermediate node, and the second node transmitting second data to the intermediate node. Both the first node and the second node may use spatial multiplexing or time division multiplexing or frequency division multiplexing on a common / different resource. The intermediate node receives the transmissions from the first node and second node, and performs network coding on the first data and second data using a predefined network coding scheme to produce network coded information. The intermediate node transmits the network coded information to the first node and second node using multi-user MIMO; and; each first or second node receives the MIMO transmissions from the intermediate node and applies network decoding procedures to recover the first data and second data. Network coding schemes include Decode and Forward (DF), Map and Forward (MF) and Amplify and Forward (AF). The first node and second node may be members of groups of nodes all within the same coverage area. A method for scheduling MIMO-based network coded transmissions is also described. Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (HARQ) transmission may also be network encoded.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com