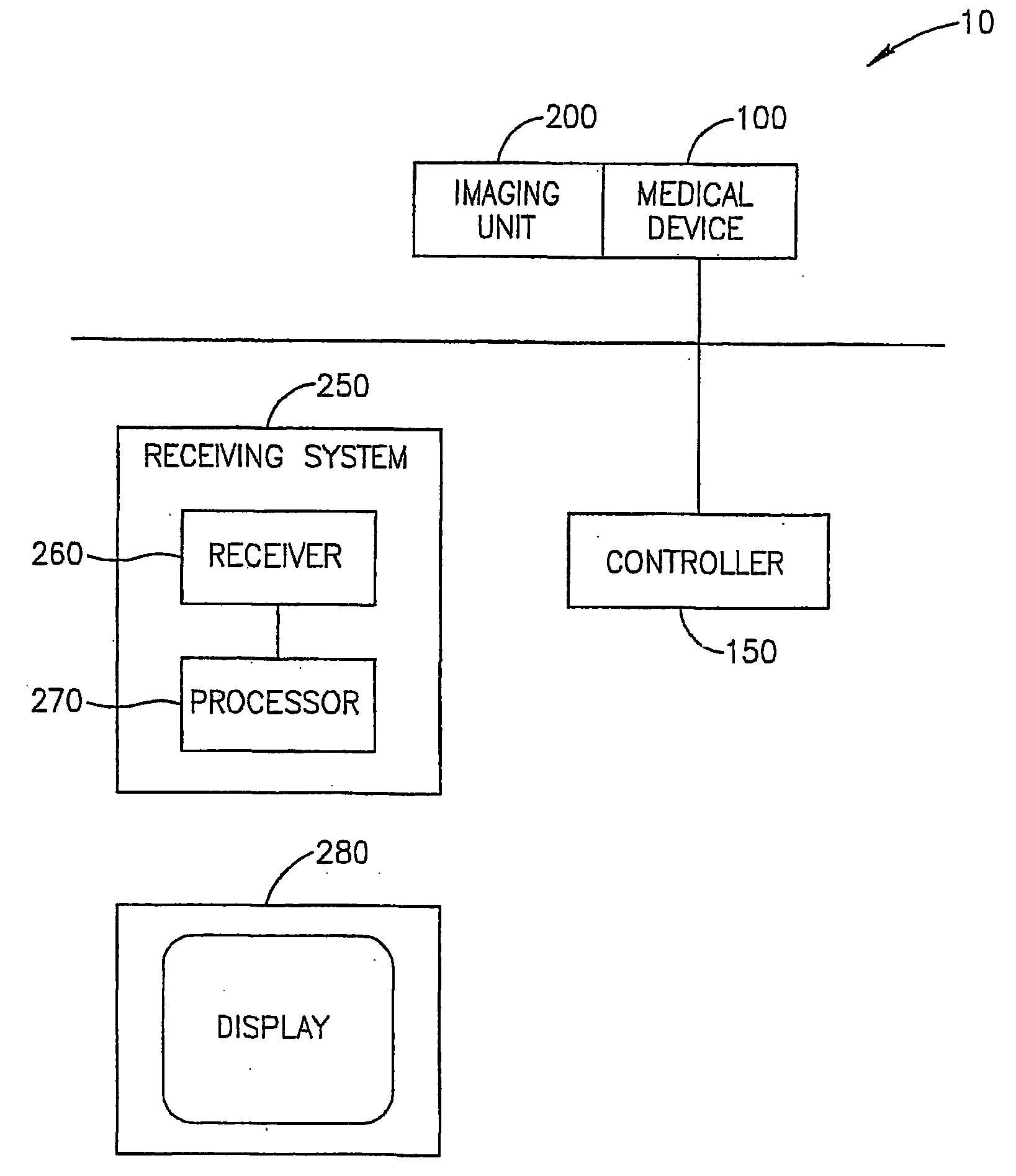
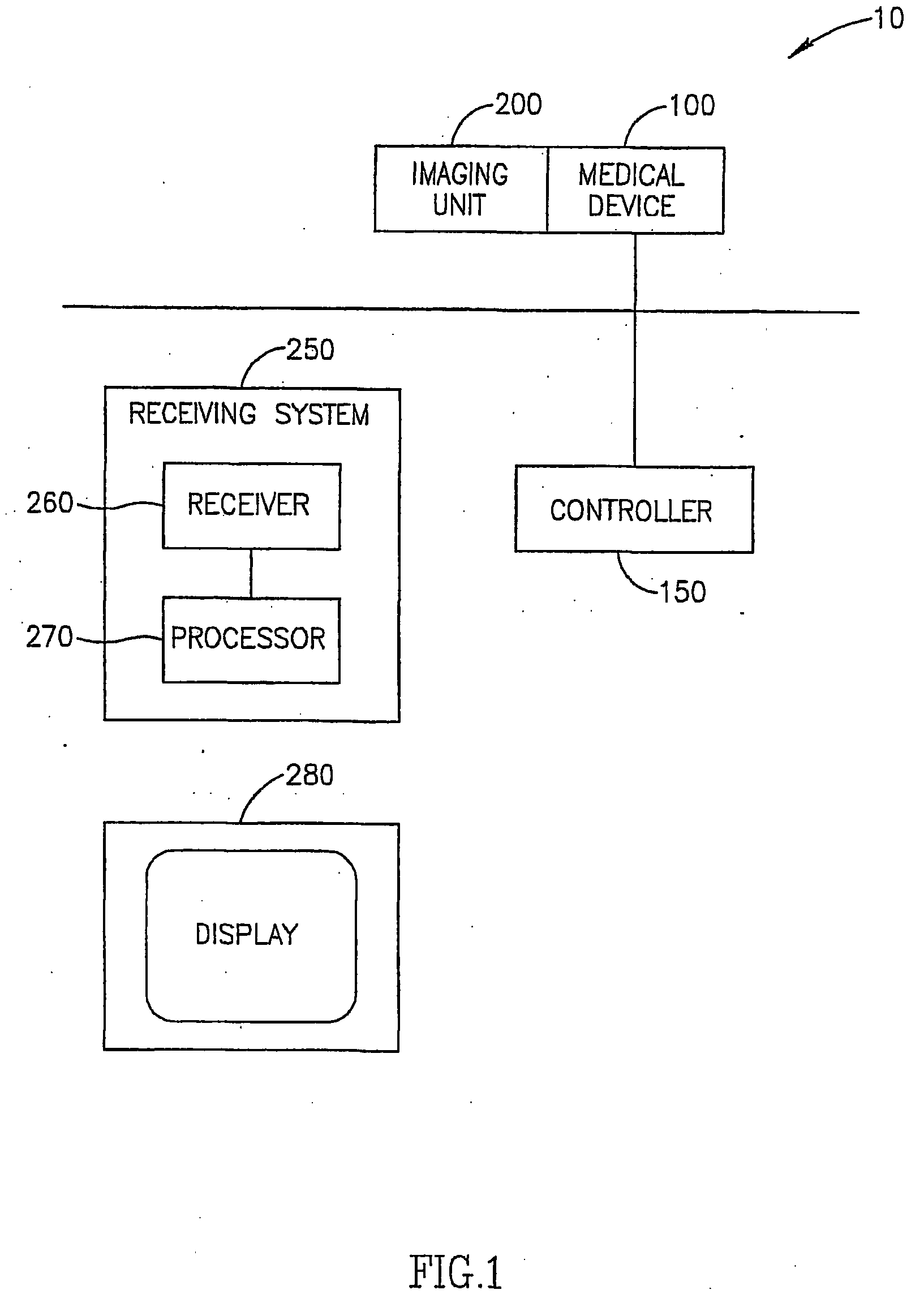
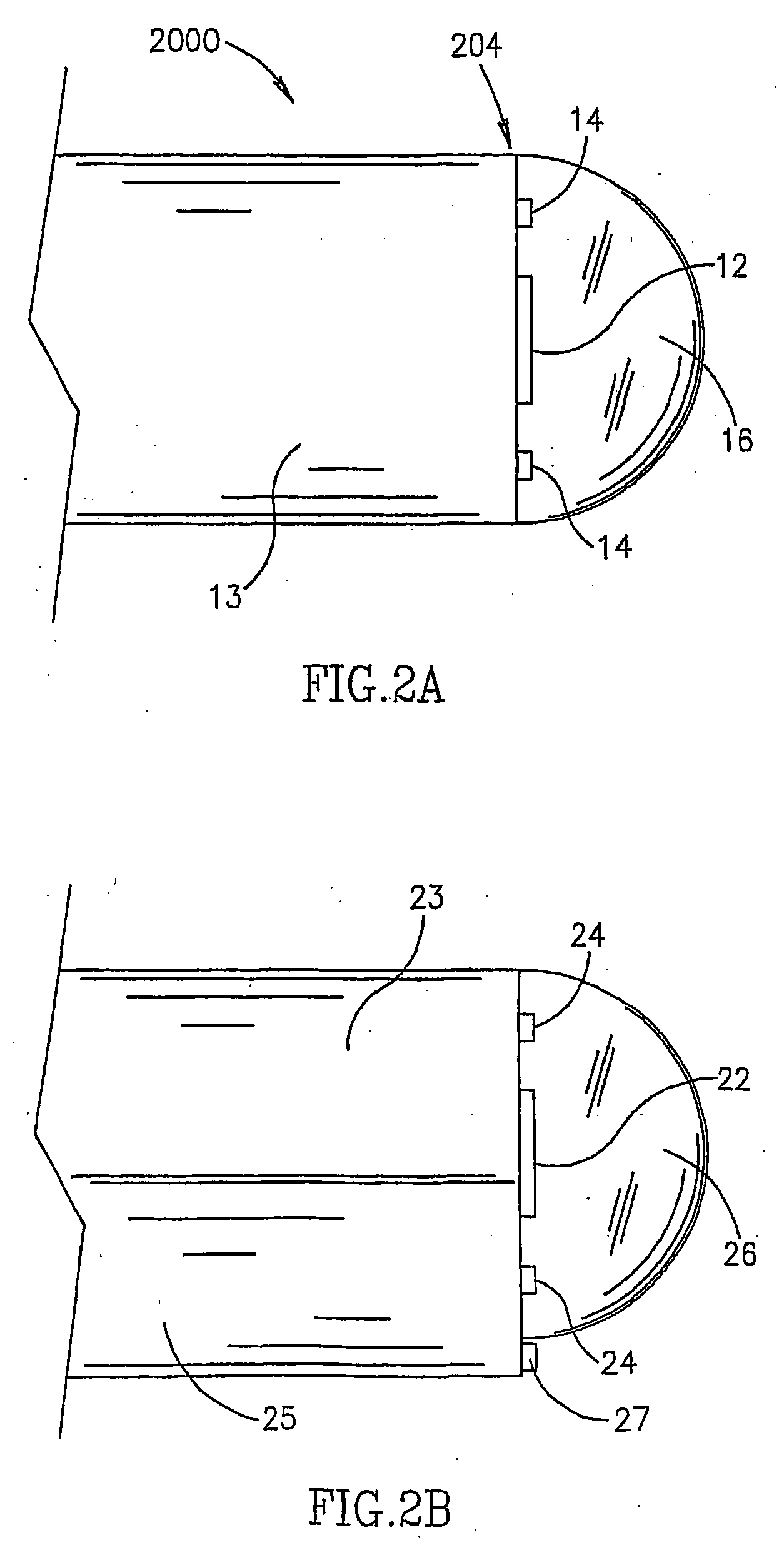
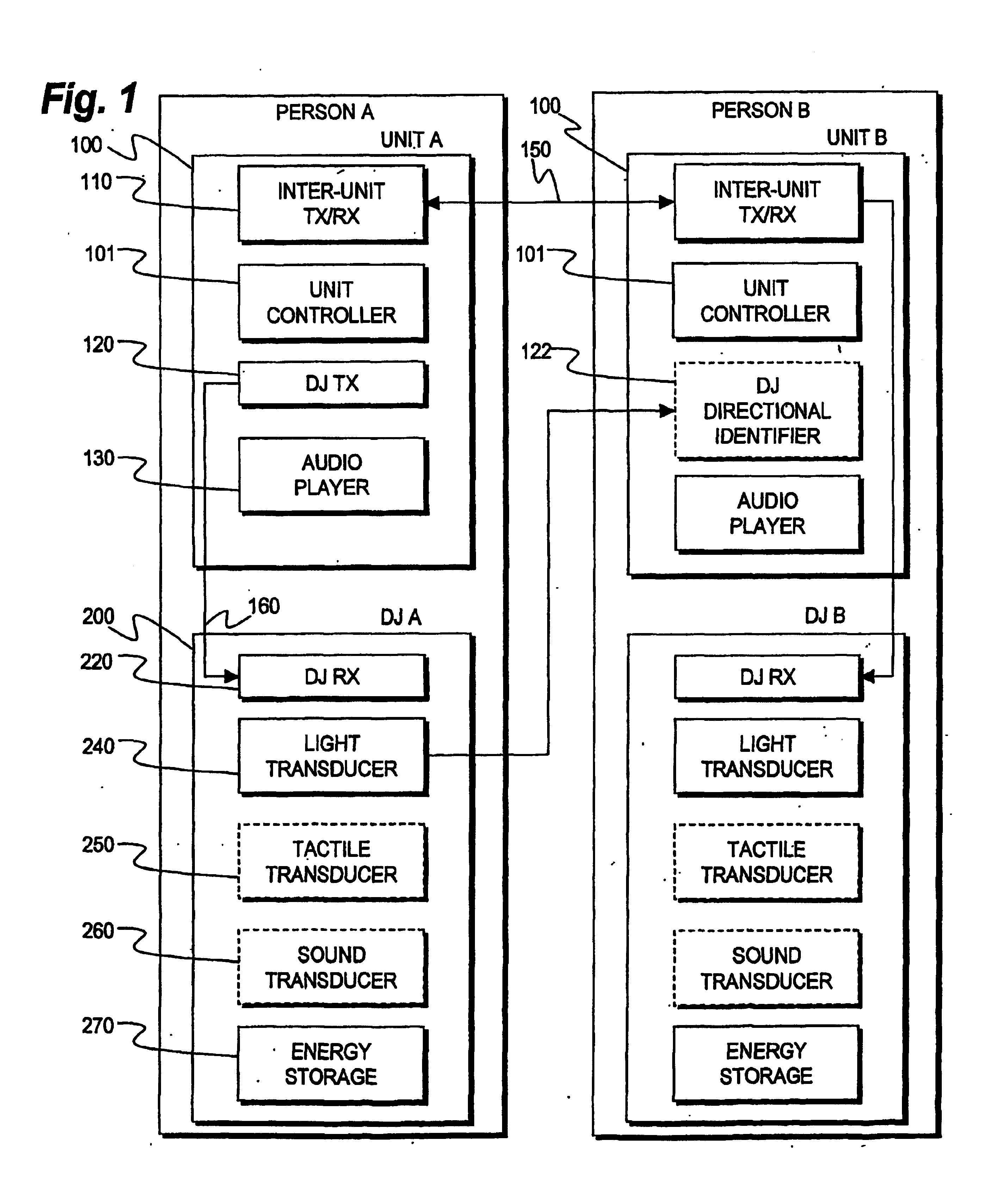
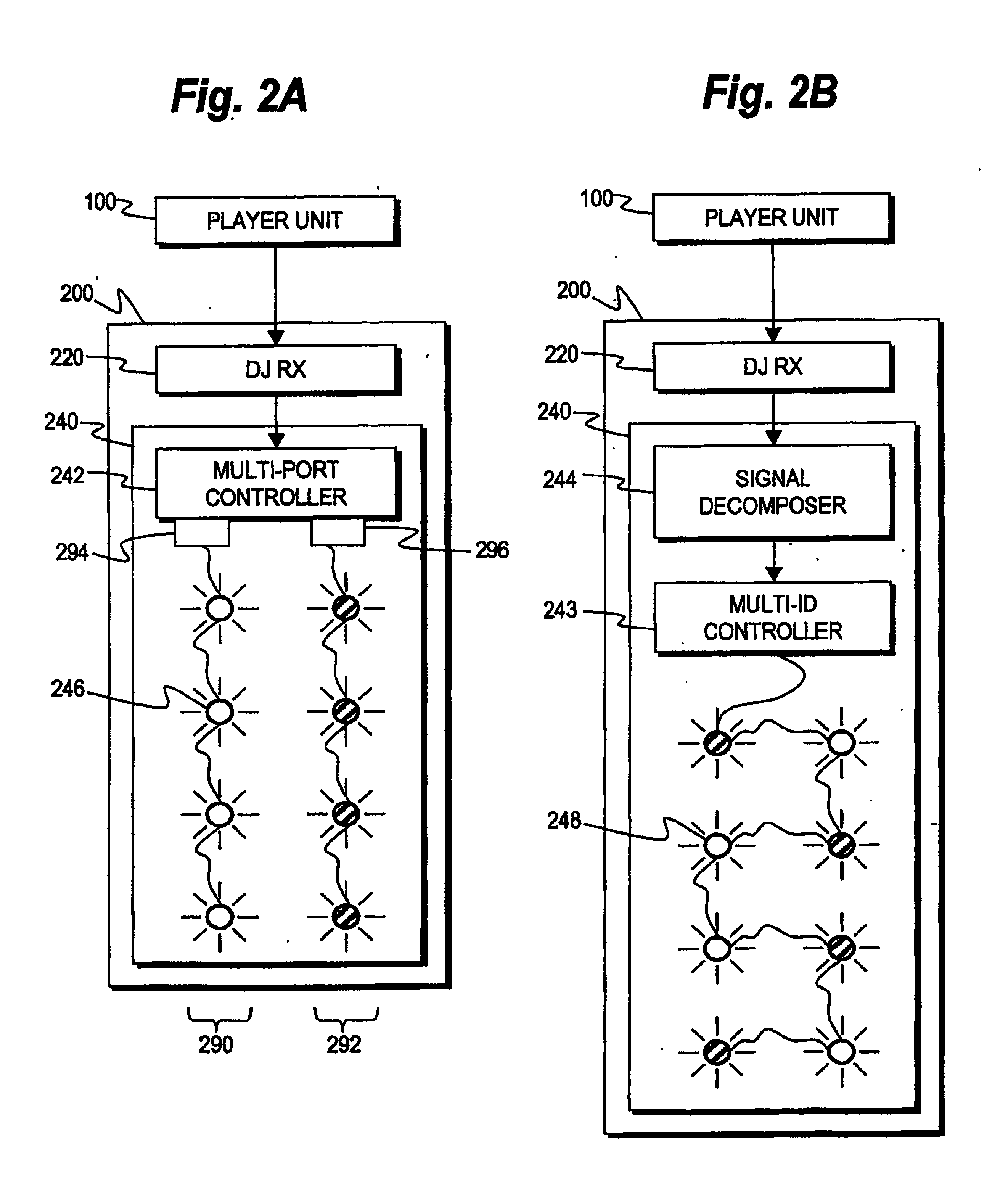
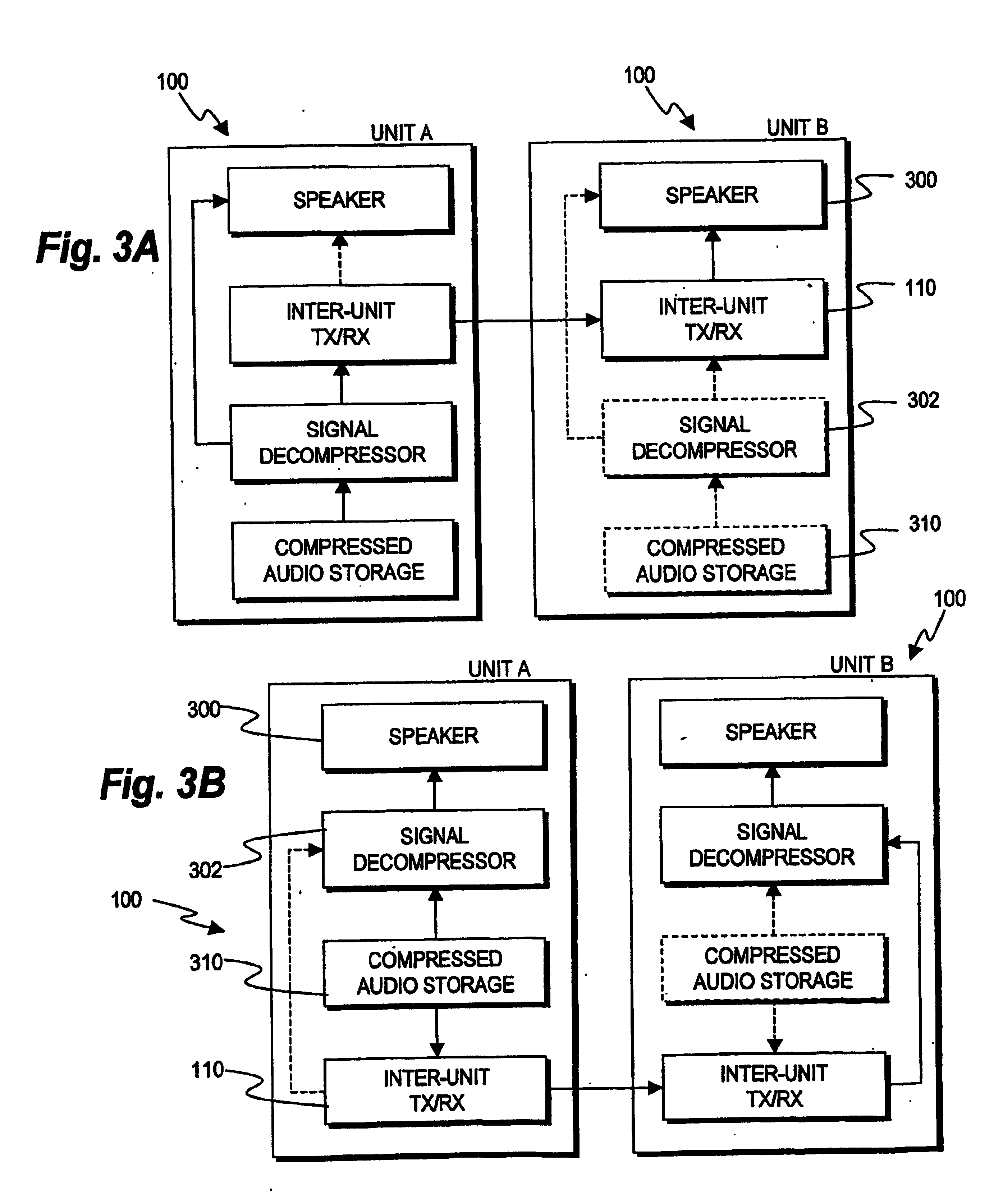
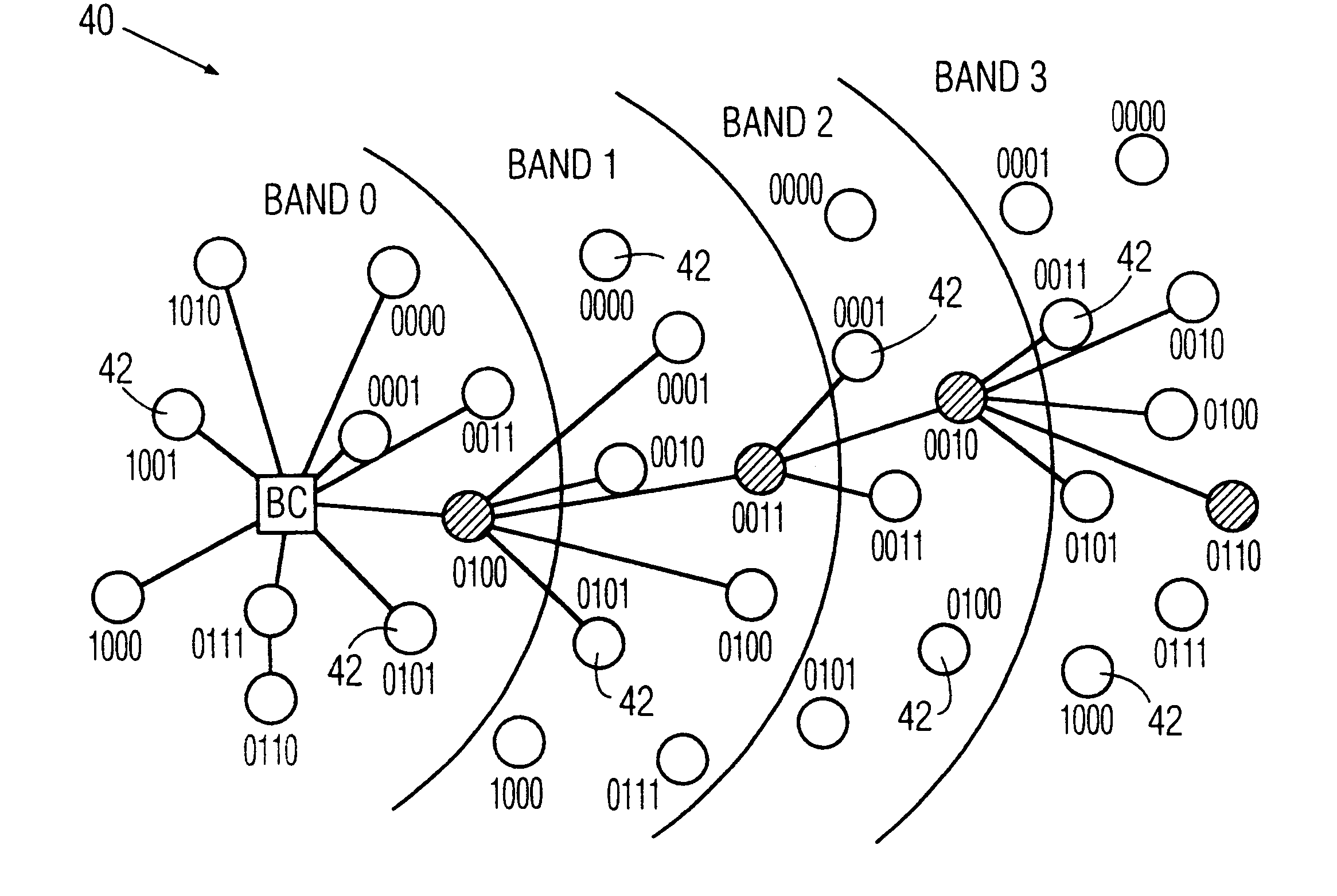
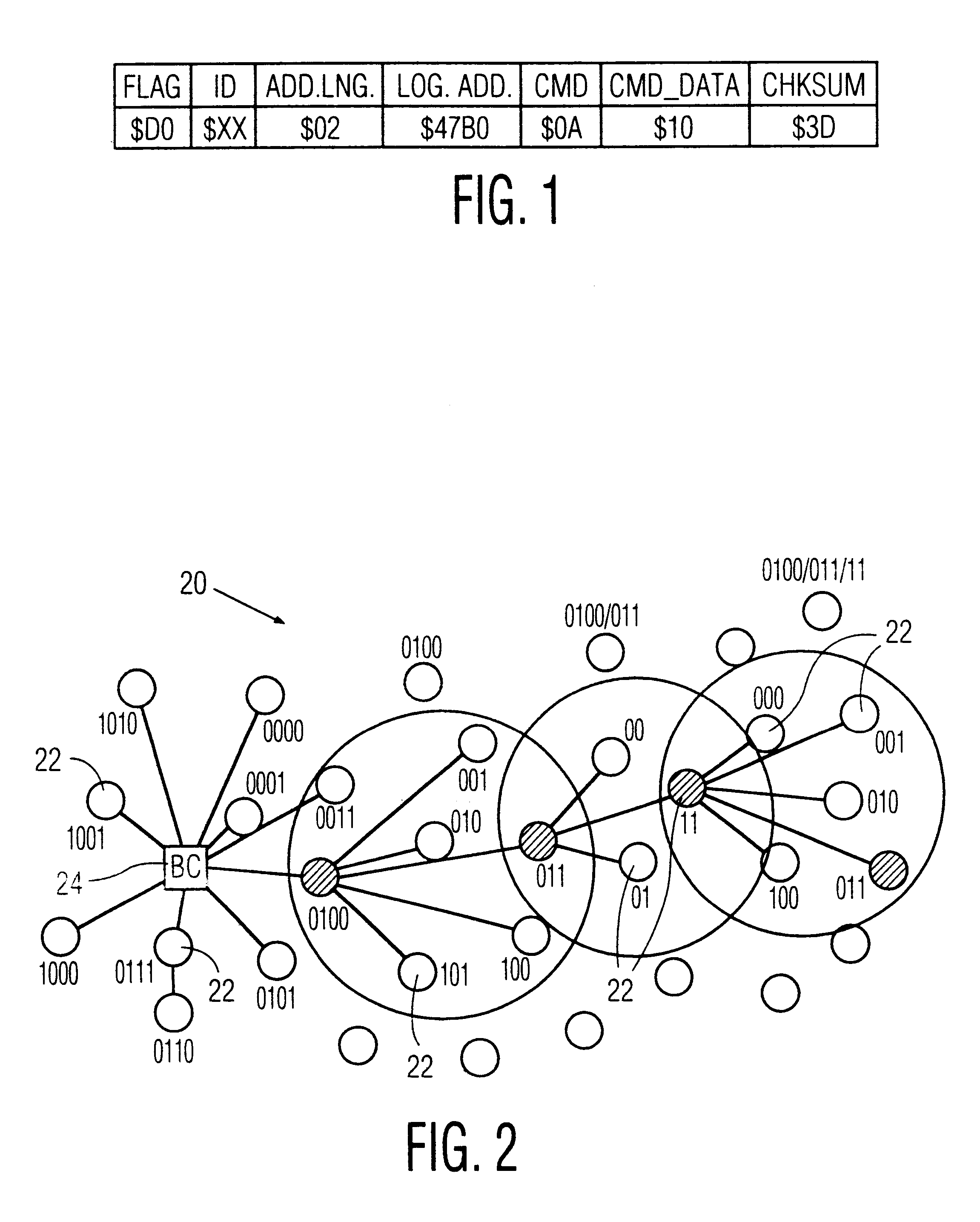
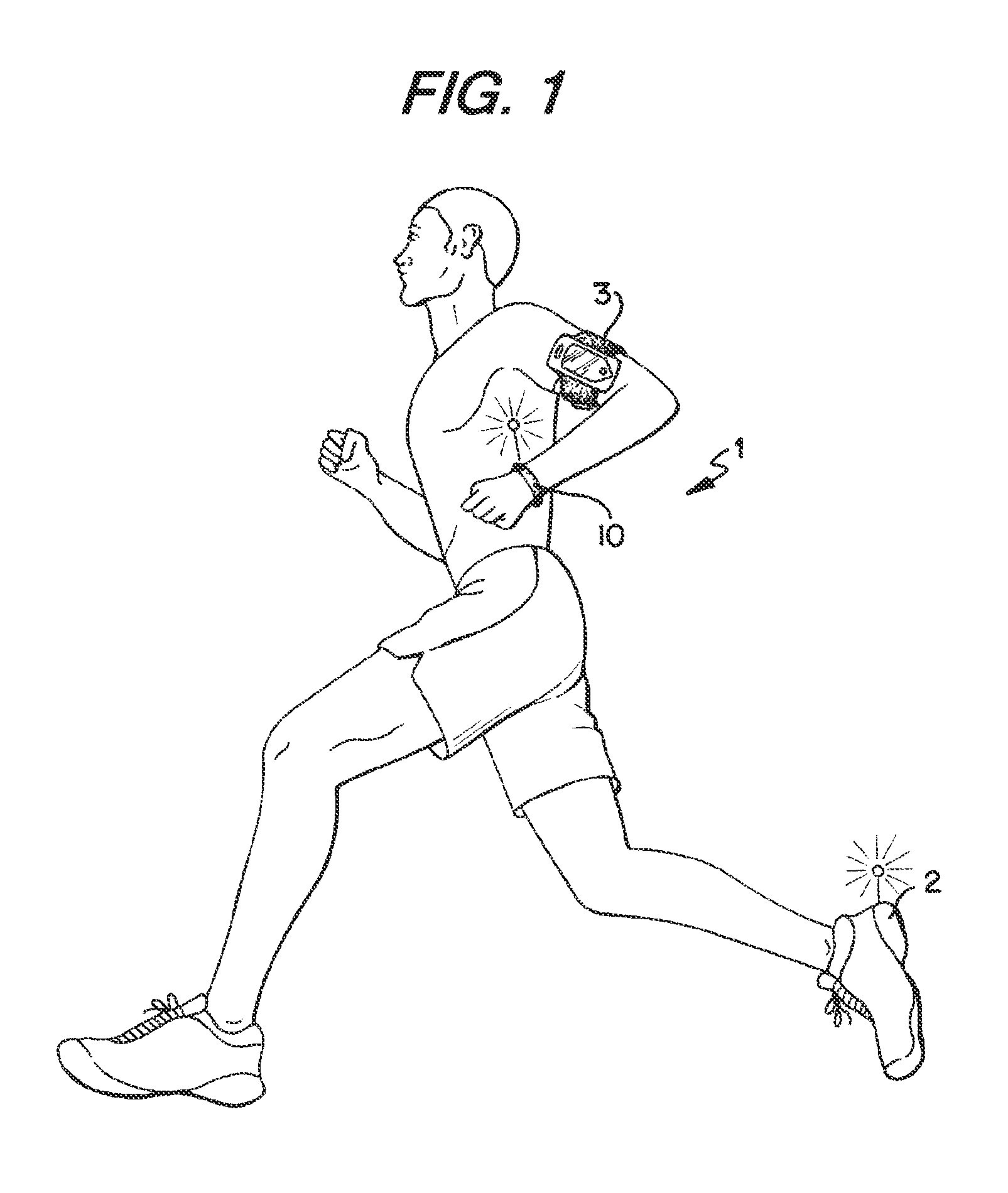Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
20133results about "Radio transmission for post communication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
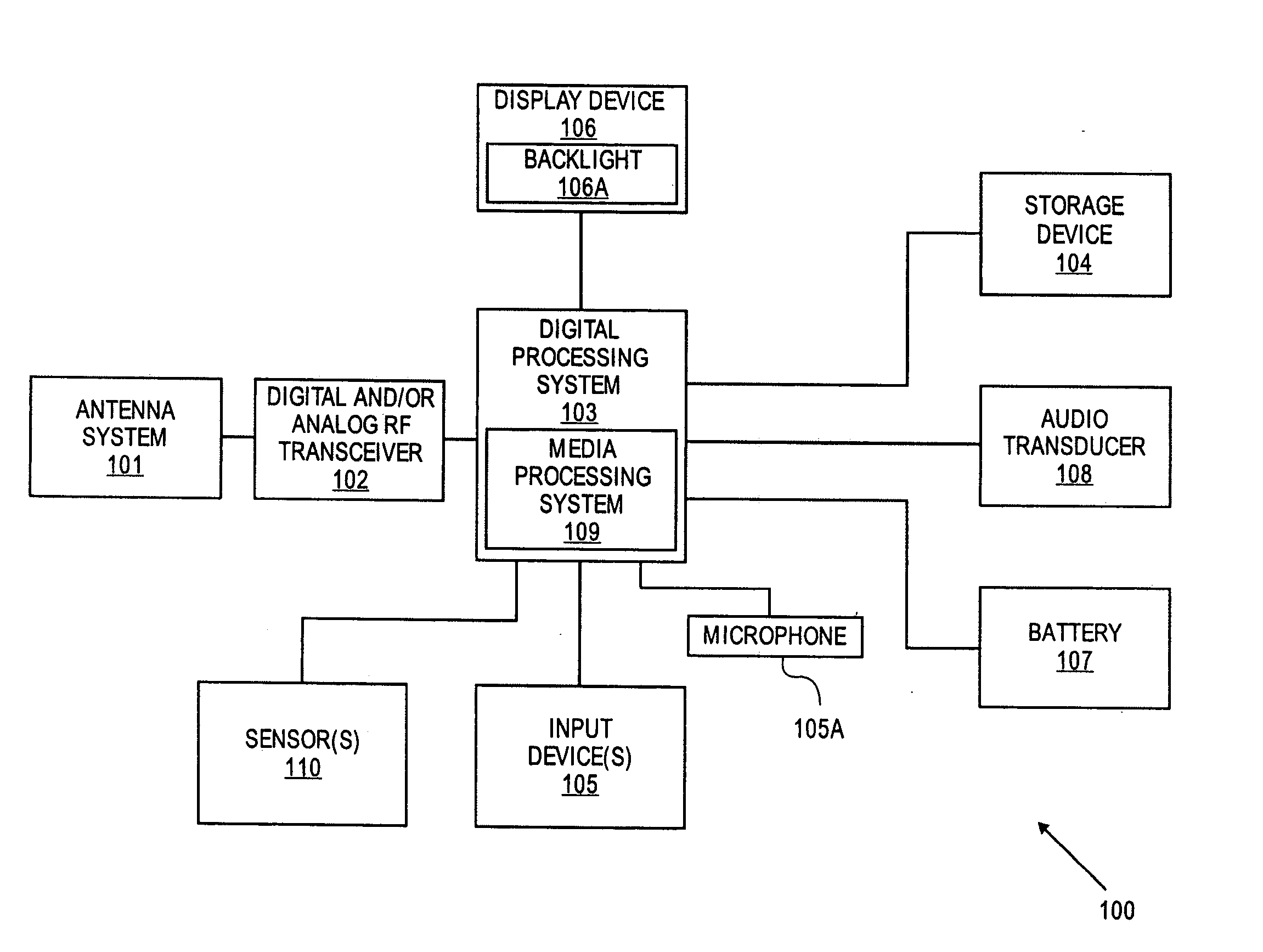
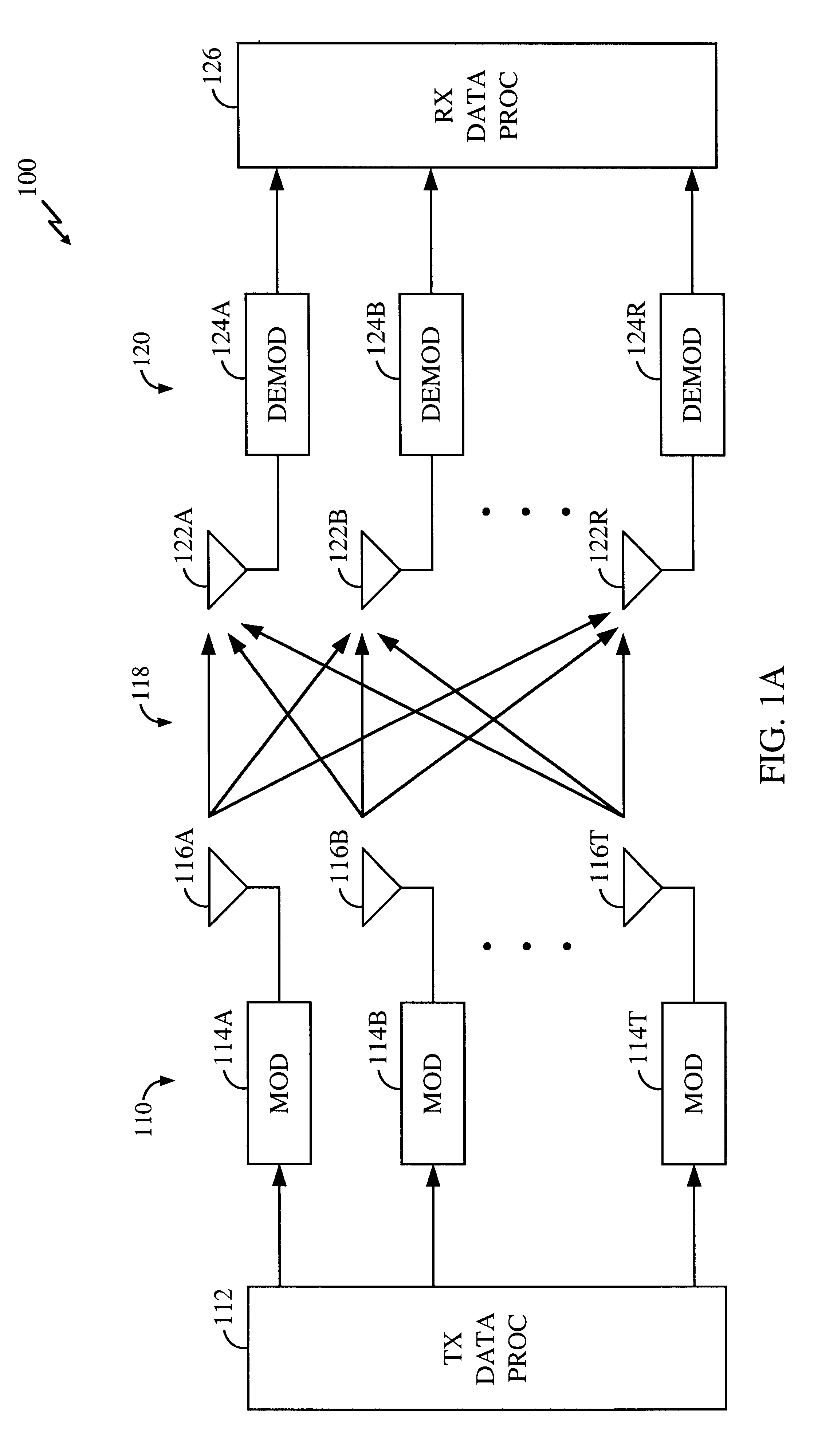
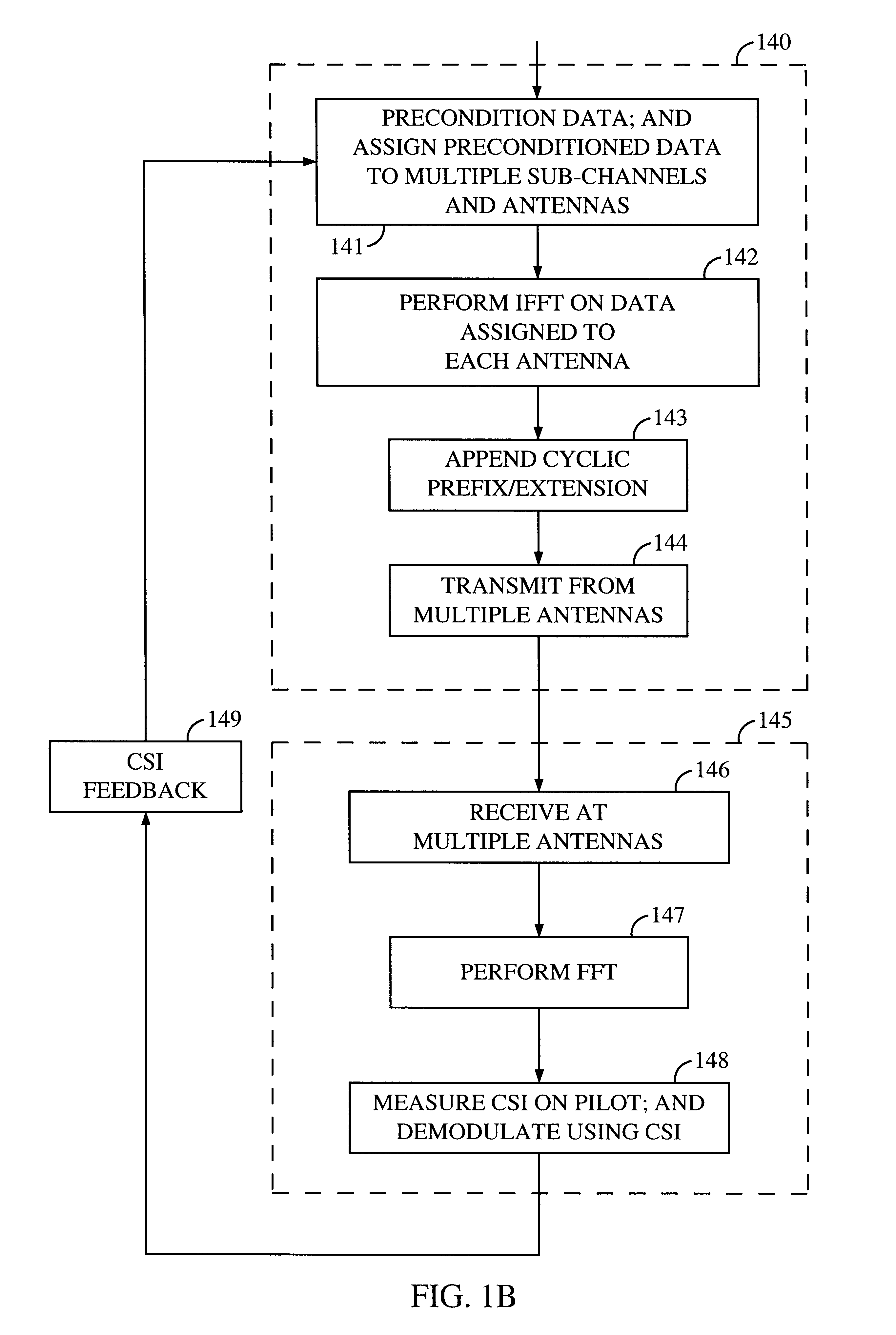
Method and apparatus for measuring reporting channel state information in a high efficiency, high performance communications system
InactiveUS6473467B1Efficient sharingInterference minimizationSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityChannel state informationCommunications system
Channel state information (CSI) can be used by a communications system to precondition transmissions between transmitter units and receiver units. In one aspect of the invention, disjoint sub-channel sets are assigned to transmit antennas located at a transmitter unit. Pilot symbols are generated and transmitted on a subset of the disjoint sub-channels. Upon receipt of the transmitted pilot symbols, the receiver units determine the CSI for the disjoint sub-channels that carried pilot symbols. These CSI values are reported to the transmitter unit, which will use these CSI values to generate CSI estimates for the disjoint sub-channels that did not carry pilot symbols. The amount of information necessary to report CSI on the reverse link can be further minimized through compression techniques and resource allocation techniques.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
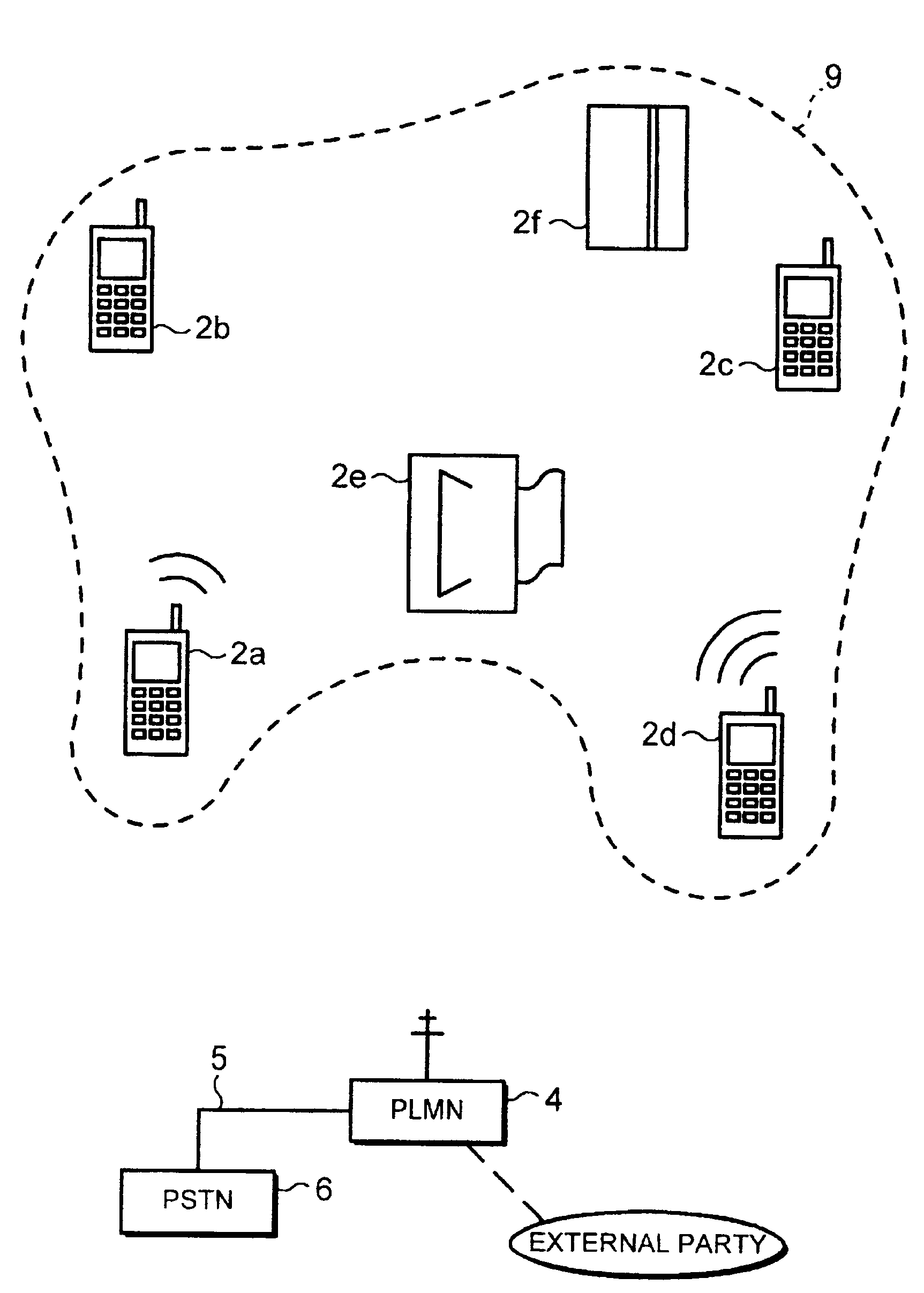
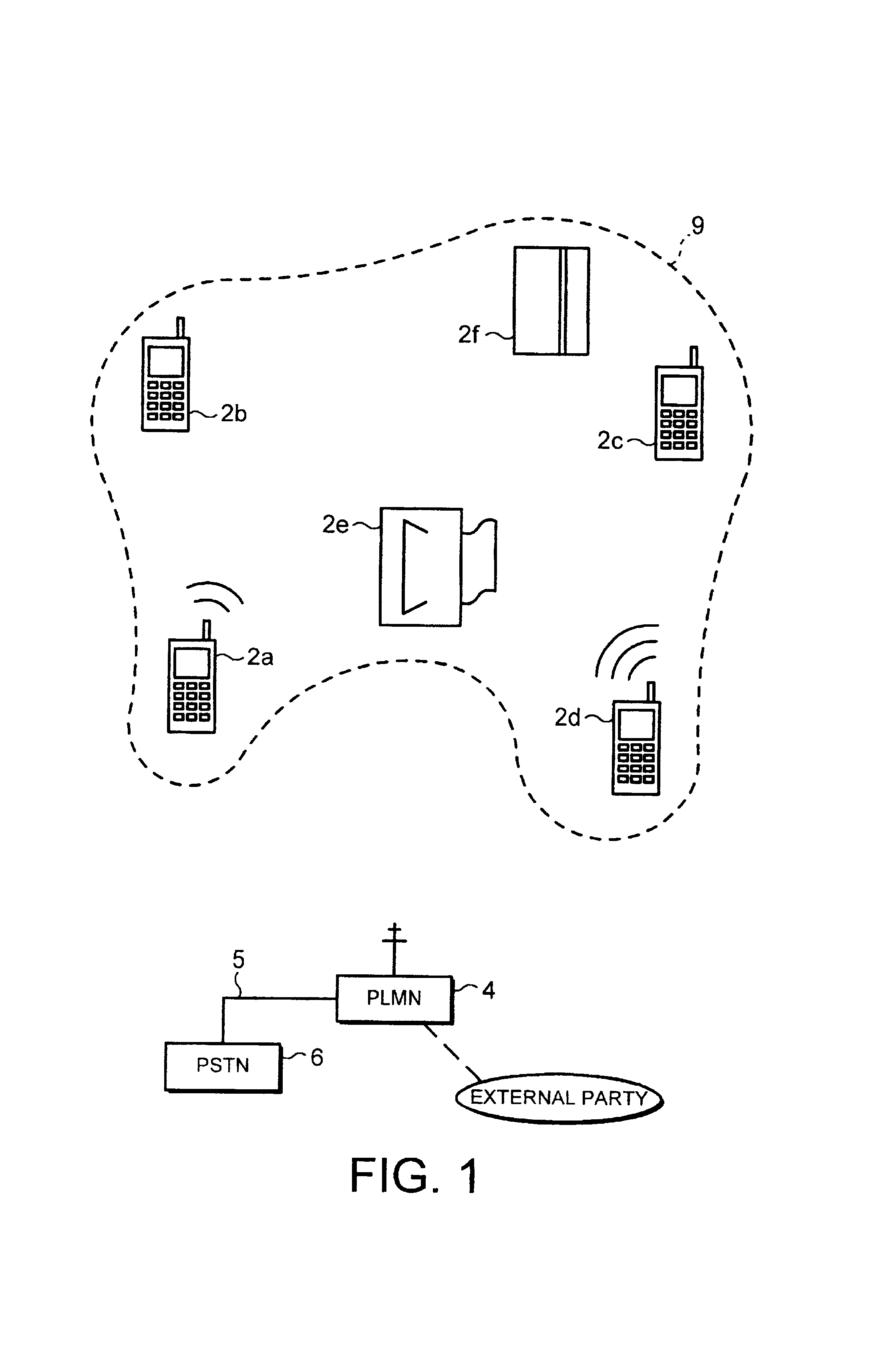
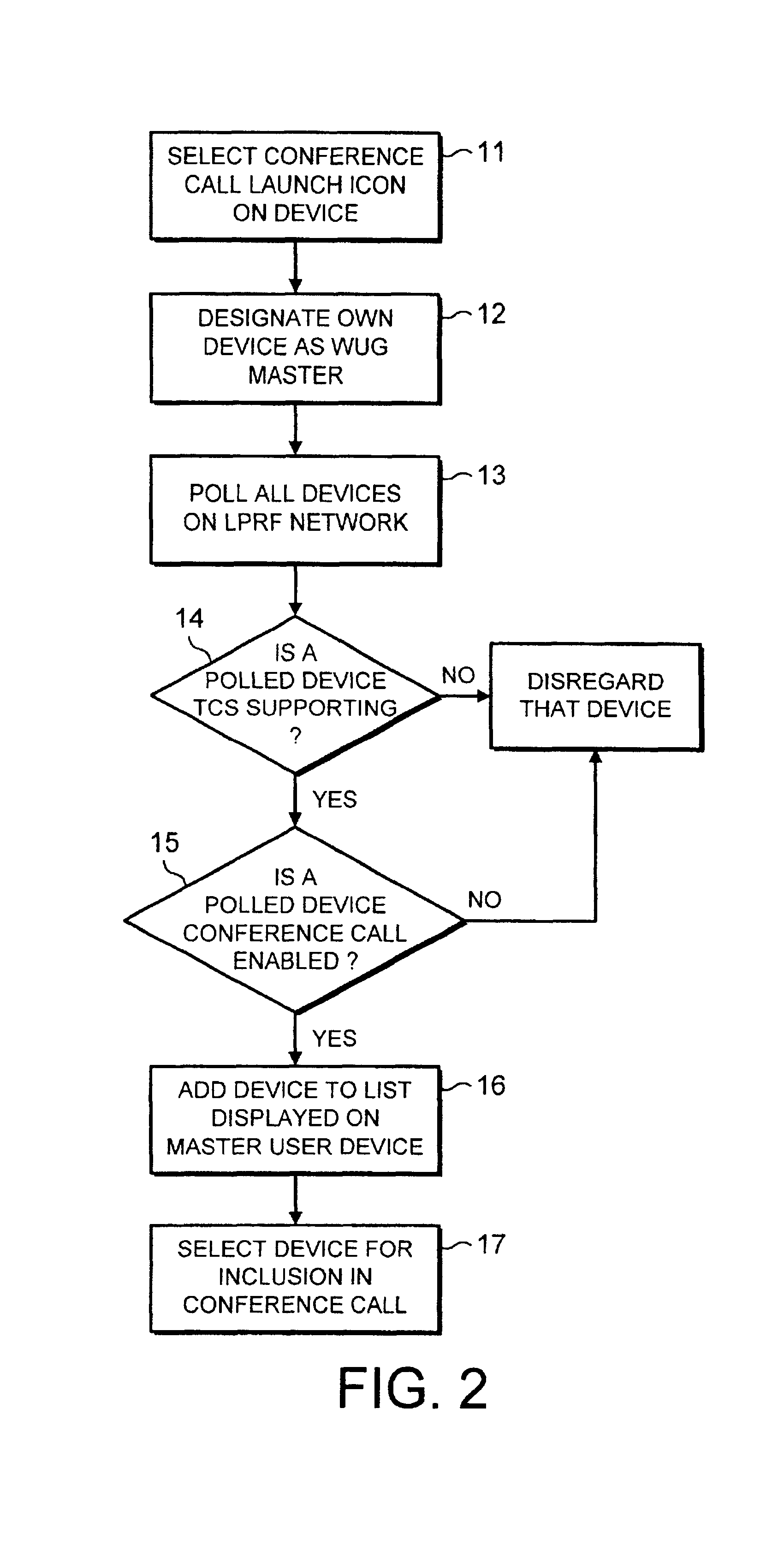
Conference call method and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7236773B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationConference callRadio frequency
A conference call facility is described in which one (2a) of a group of communication devices (2a,2b,2c,2d) connected to a low power radio frequency network (9) is able to set up a call to a party external of the network (9) and then selectively add further devices (2a,2b,2c) to the call under the control of the user of the one device (2a). The users of the other devices (2b,2c) are able to enable or disable the selection of their device in a conference call. One or more of the communication devices may be a mobile radio telephone equipped with the necessary network interface (1).
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
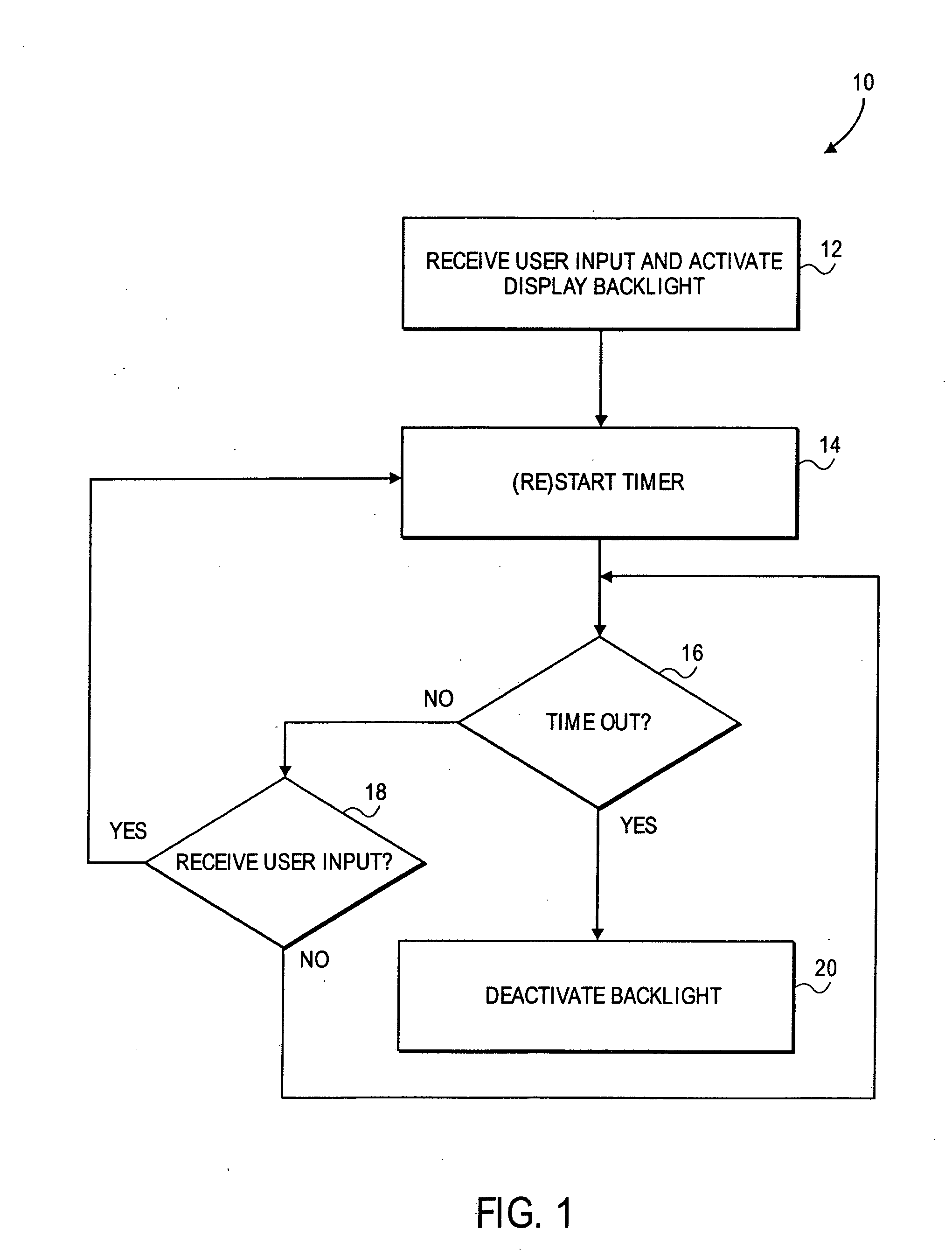
Automated response to and sensing of user activity in portable devices
ActiveUS7633076B2Input/output for user-computer interactionGain controlComputer scienceEquipment state
Owner:APPLE INC
Device and system for in-vivo procedures
A system for performing in vivo procedures is provided. The system may include a tool for performing an in vivo procedure. The tool may have an in vivo sensor for obtaining in vivo information; a functional element for performing an interventional or diagnostic in-vivo procedure; a processor in communication with the tool for receiving and optionally processing the in vivo information obtained by the tool and a monitor in communication with the processor for displaying the optionally processed in vivo information. The communication between the elements of the system may be wireless, or, optionally, wired.
Owner:GILREATH MARK G +1
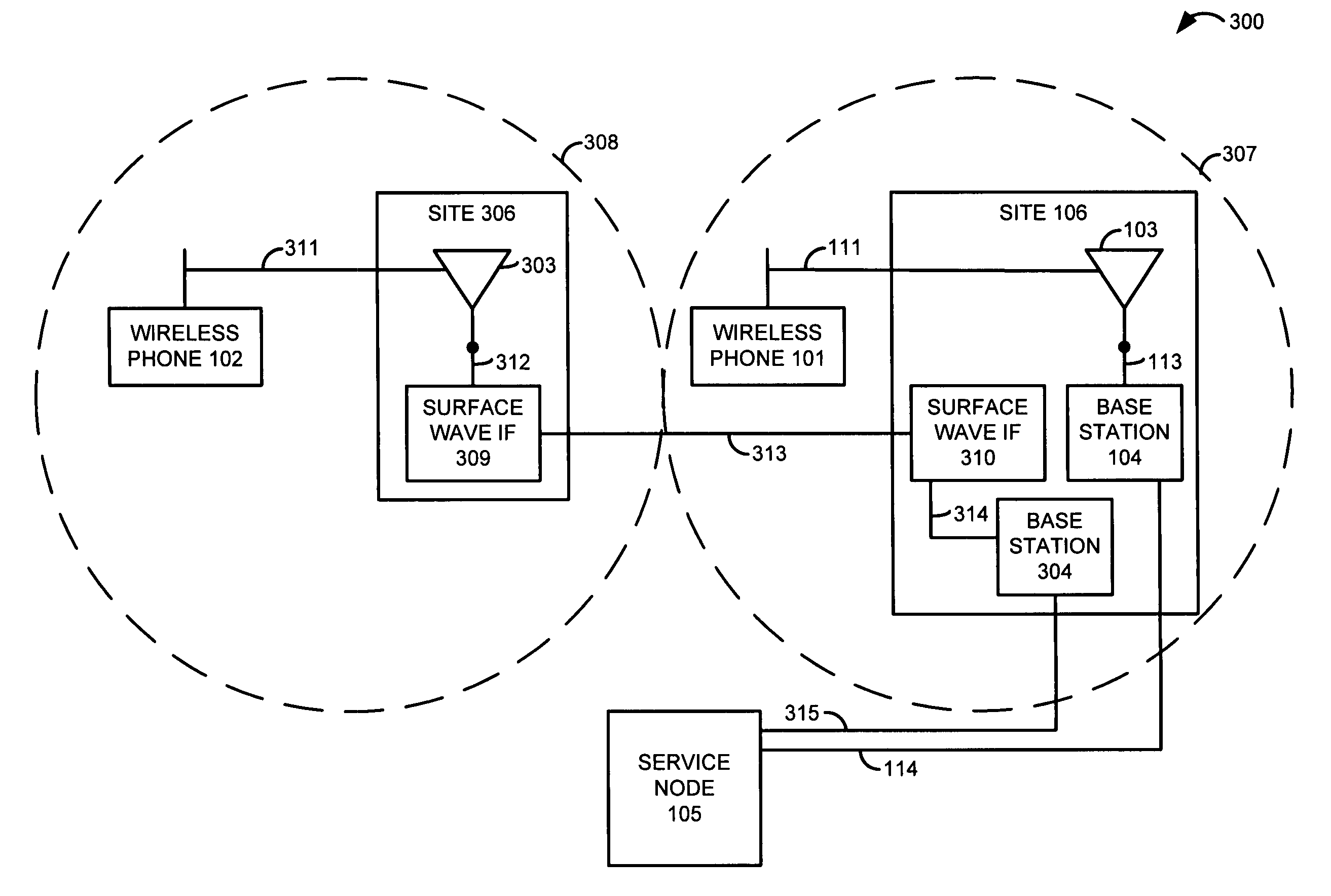
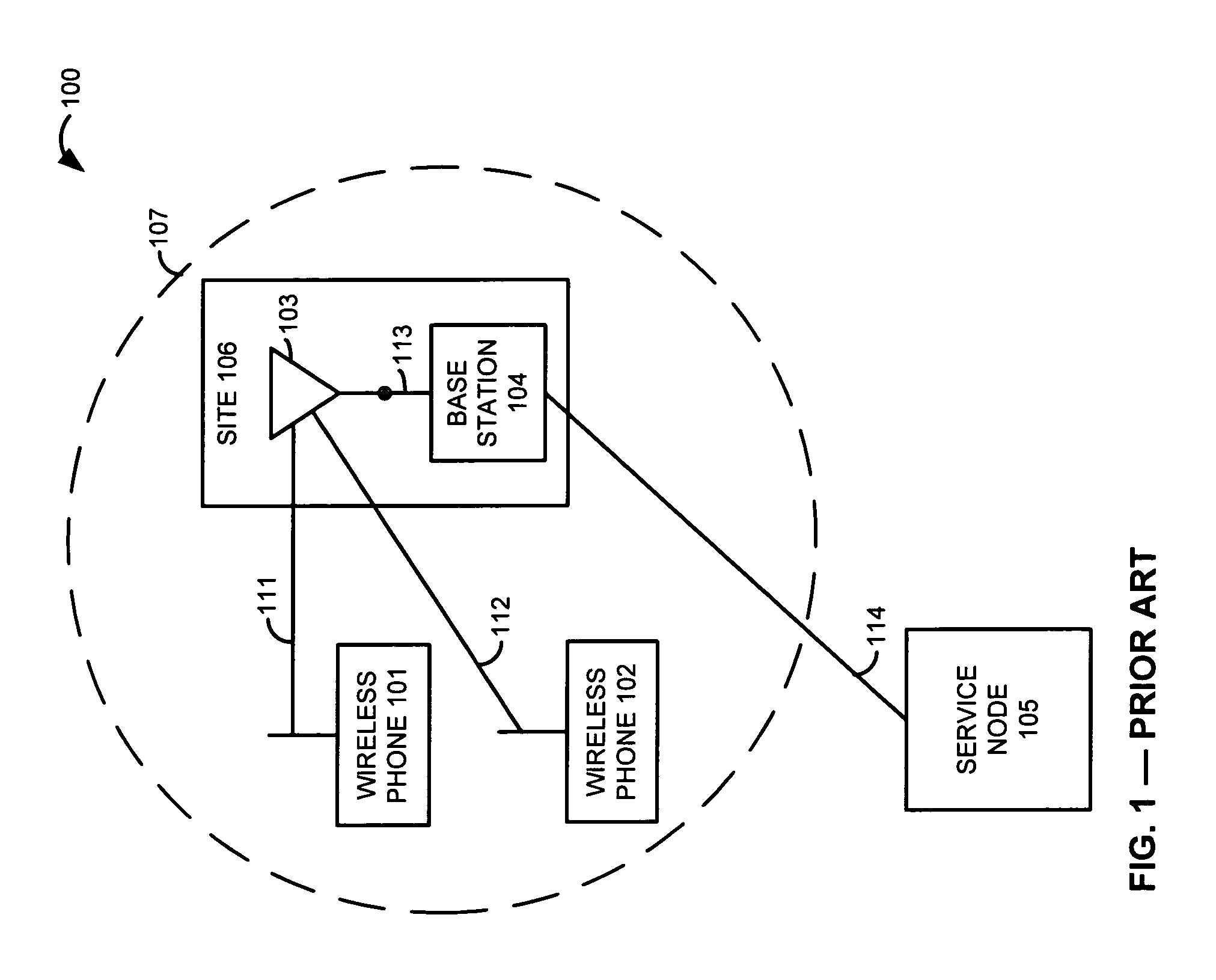
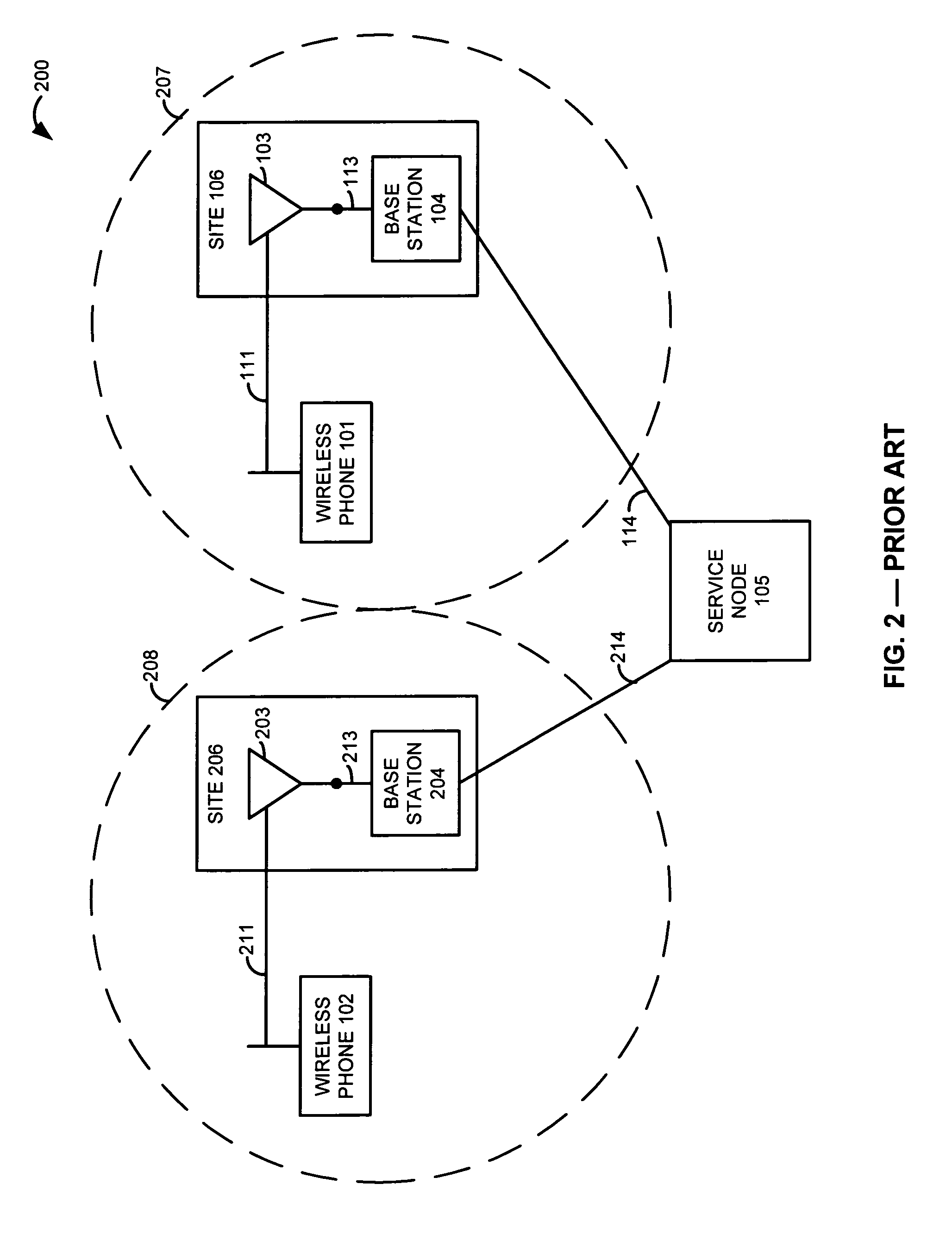
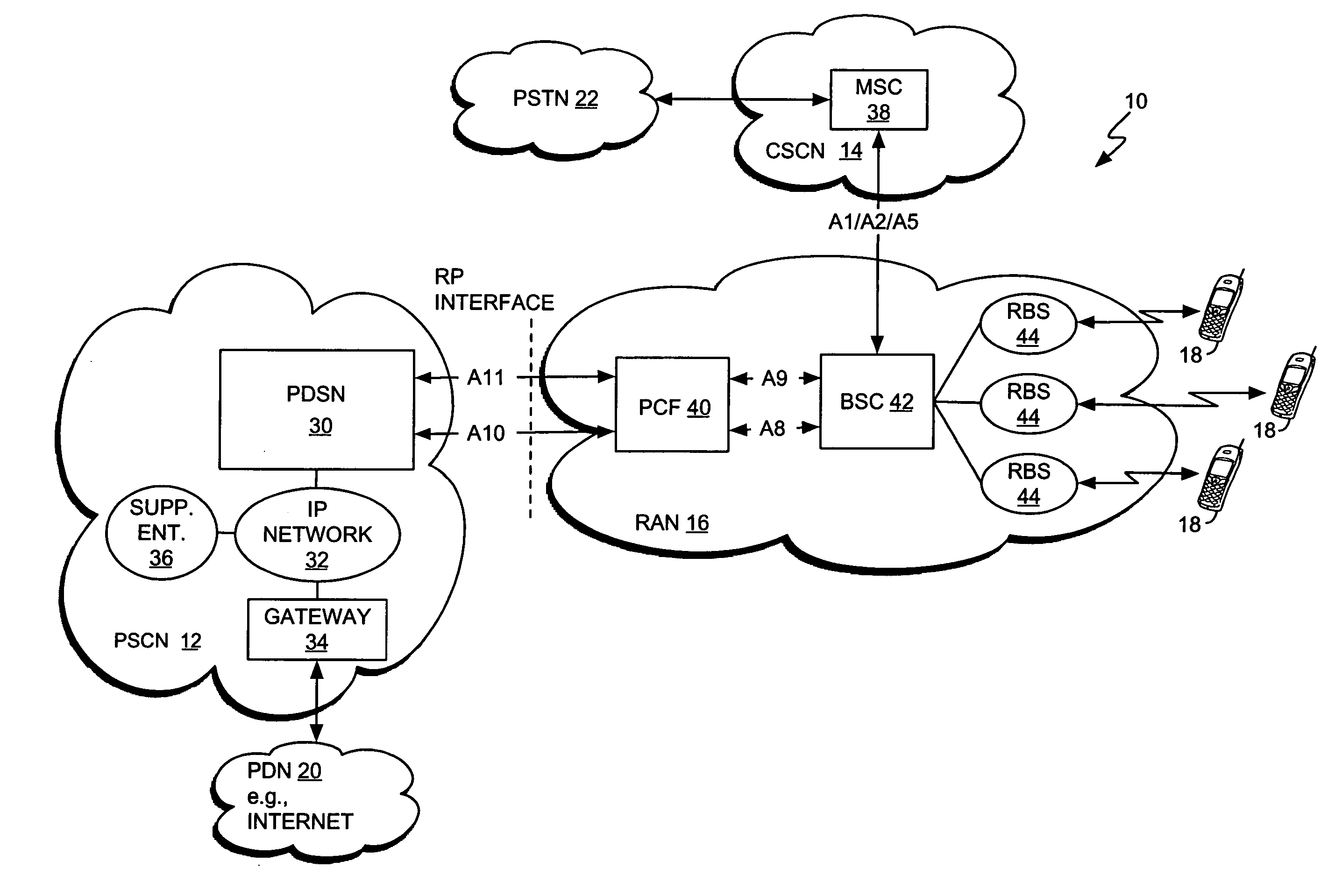
Surface wave communications between a remote antenna and a base station that is co-located with another base station
ActiveUS7590404B1Interconnection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementSurface waveBase station
At a first site, a first antenna exchanges first communications with wireless devices, and exchanges the first communications with a first base station. The first base station exchanges the first communications with a service node. At a second site, a second antenna exchanges second communications with other wireless devices, and exchanges the second communications with a first surface wave interface. The first surface wave interface exchanges the second communications with a second surface wave interface at the first site. The second surface wave interface exchanges the second communications with a second base station at the first site. The second base station exchanges the second communications with the service node. The service node processes the first and second communications to provide a communication service to the wireless devices.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
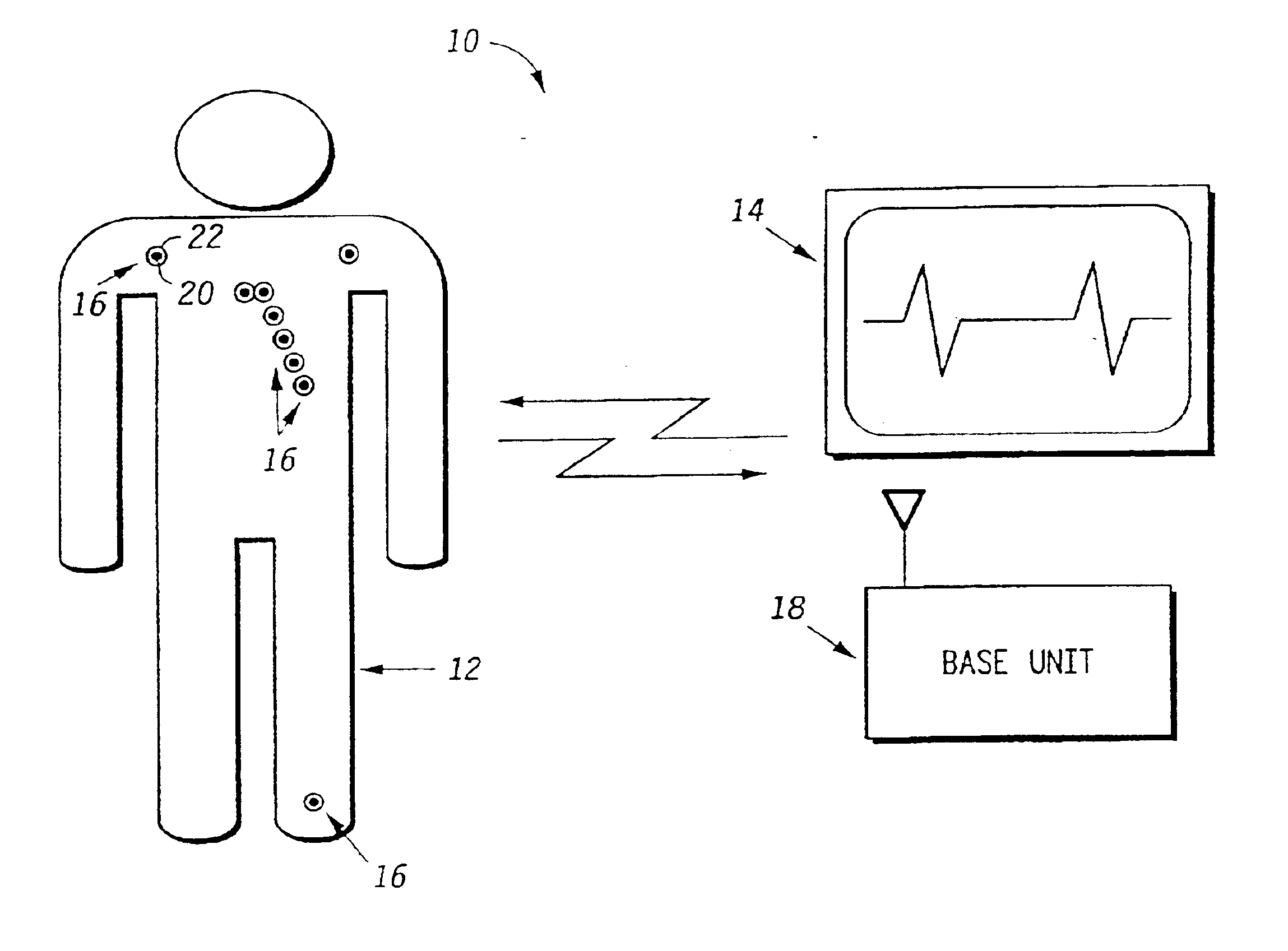
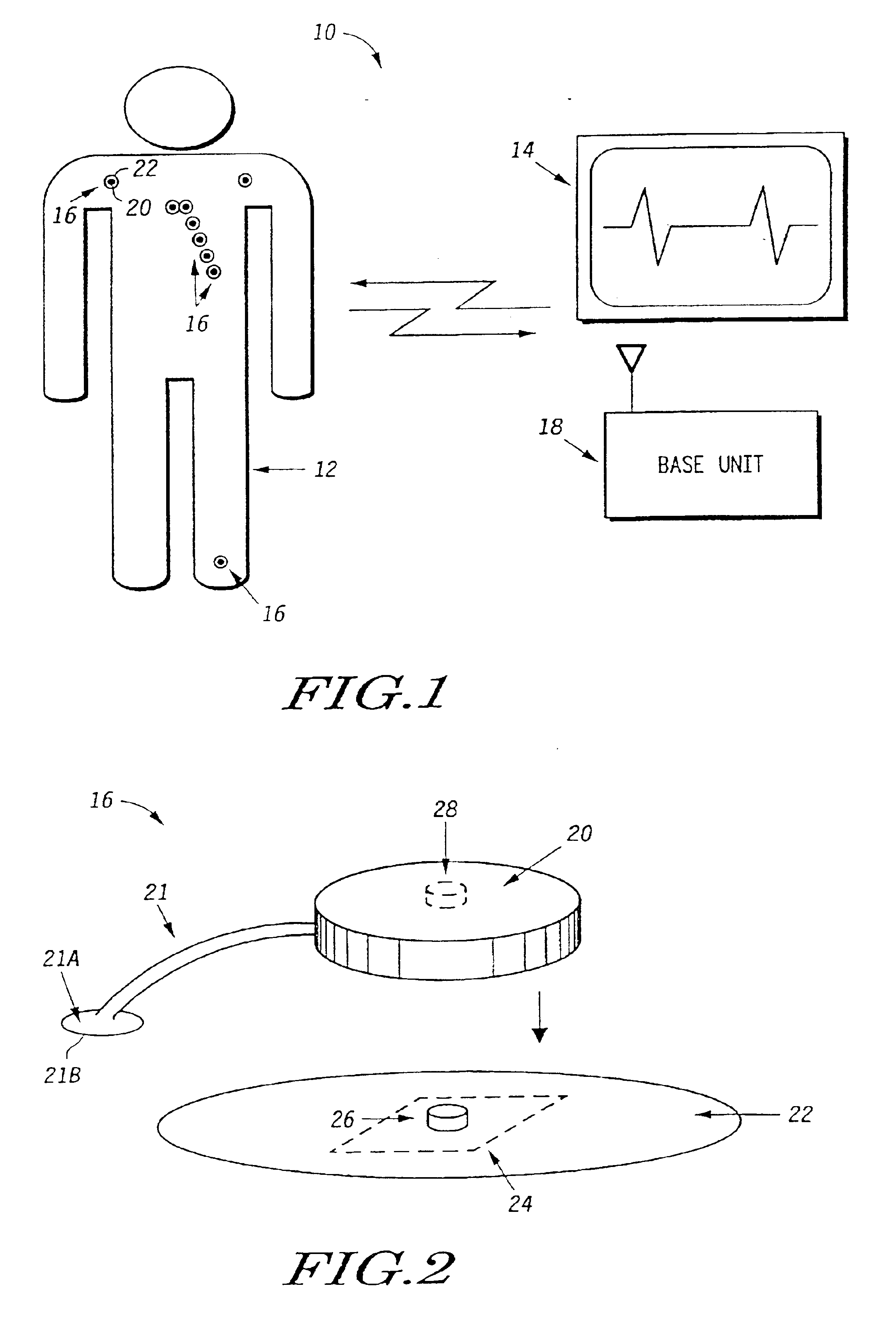
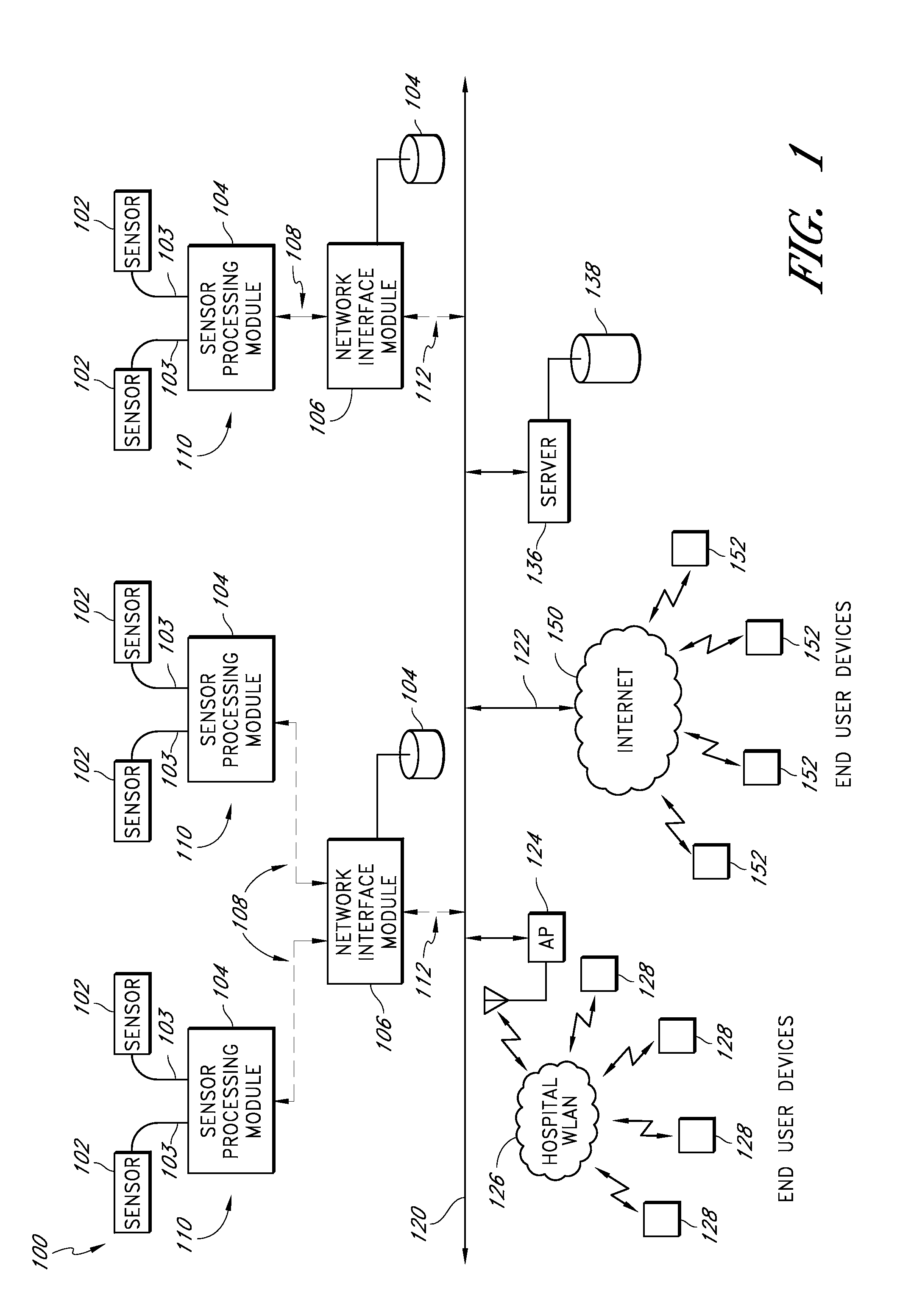
Wireless system protocol for telemetry monitoring
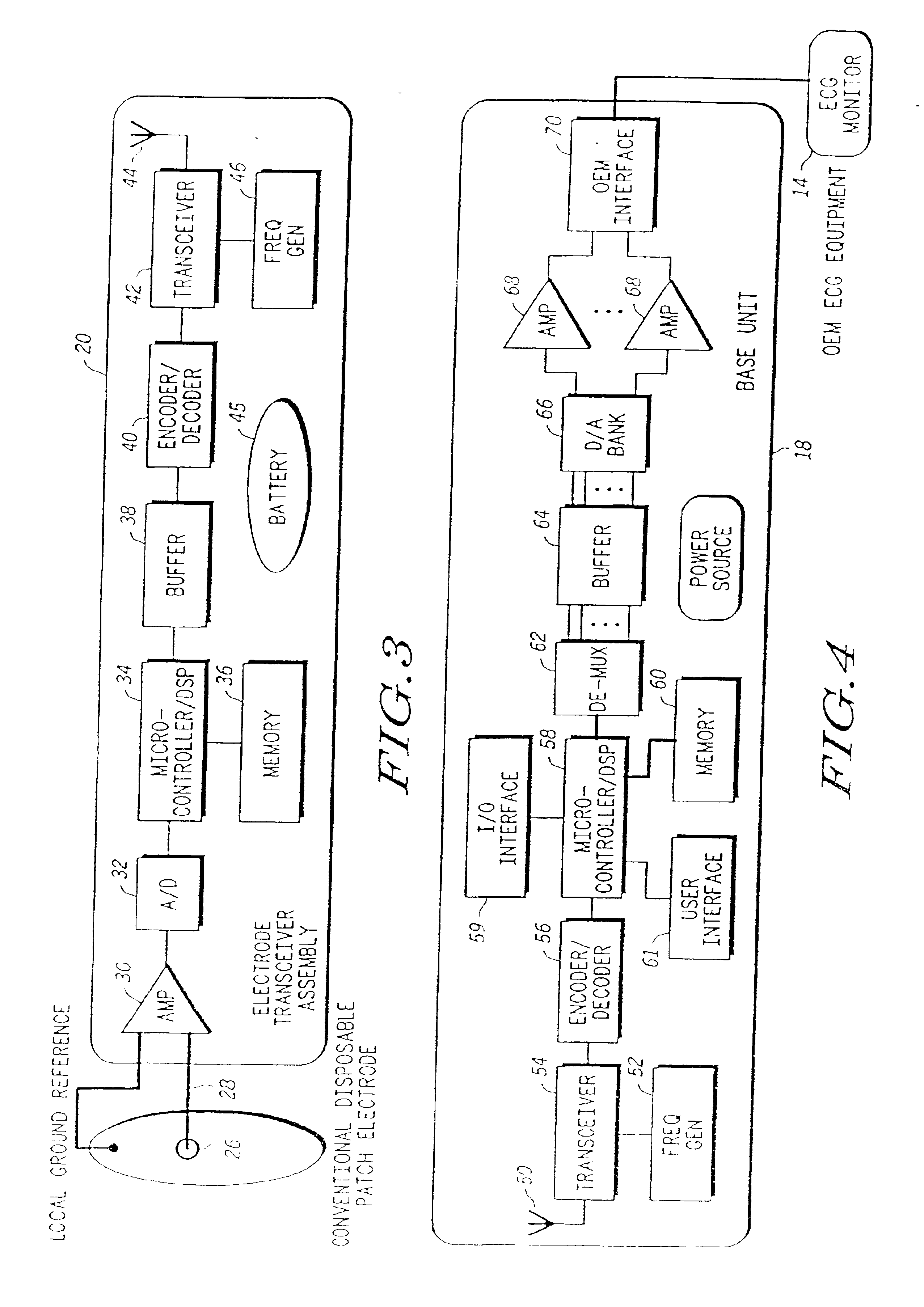
InactiveUS6897788B2Consider flexibilityElectroencephalographyElectric signal transmission systemsWireless transceiverTransceiver
A wireless, programmable system for medical monitoring includes a base unit and a plurality of individual wireless, remotely programmable biosensor transceivers. The base unit manages the transceivers by issuing registration, configuration, data acquisition, and transmission commands using wireless techniques. Physiologic data from the wireless transceivers is demultiplexed and supplied via a standard interface to a conventional monitor for display. Initialization, configuration, registration, and management routines for the wireless transceivers and the base unit are also described.
Owner:LIFESYNC
Radio communication system
InactiveUS7043271B1Reduce in quantityReduces constitutionTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityCarrier signalEngineering
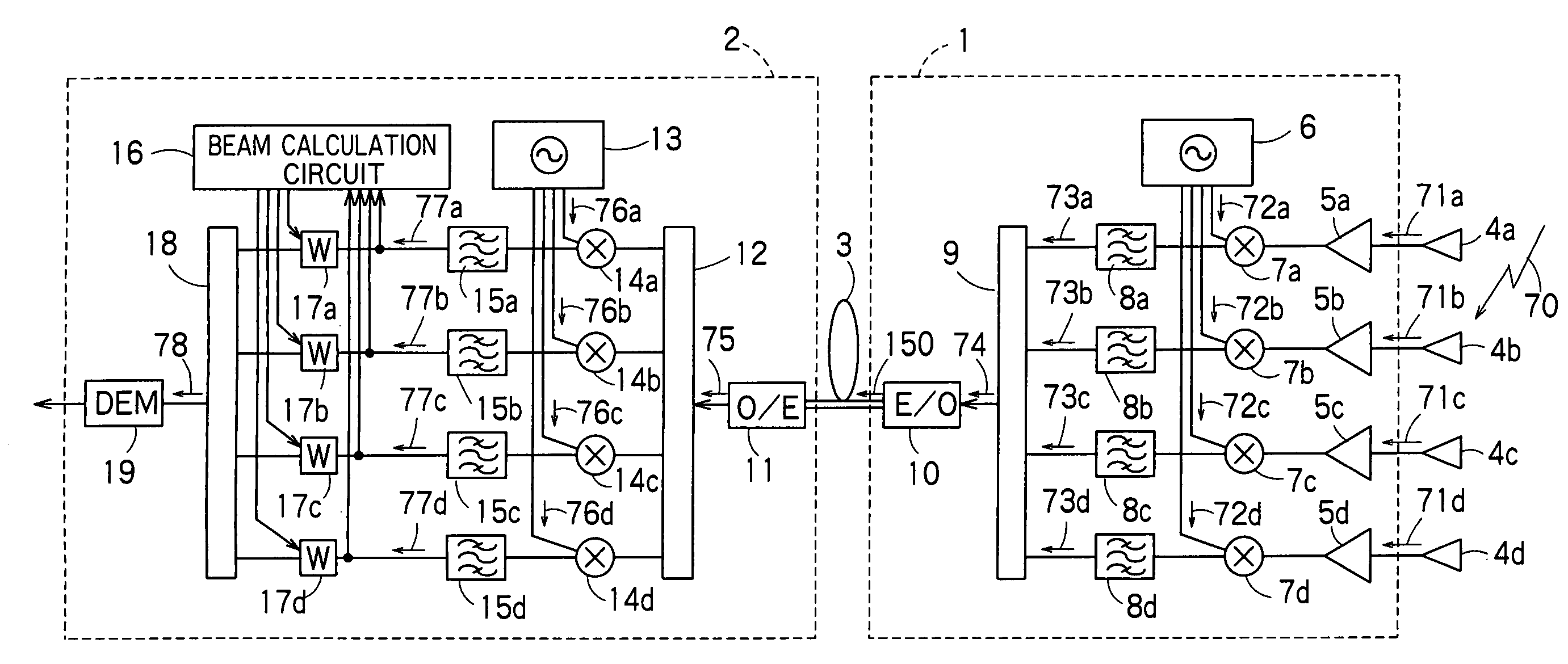
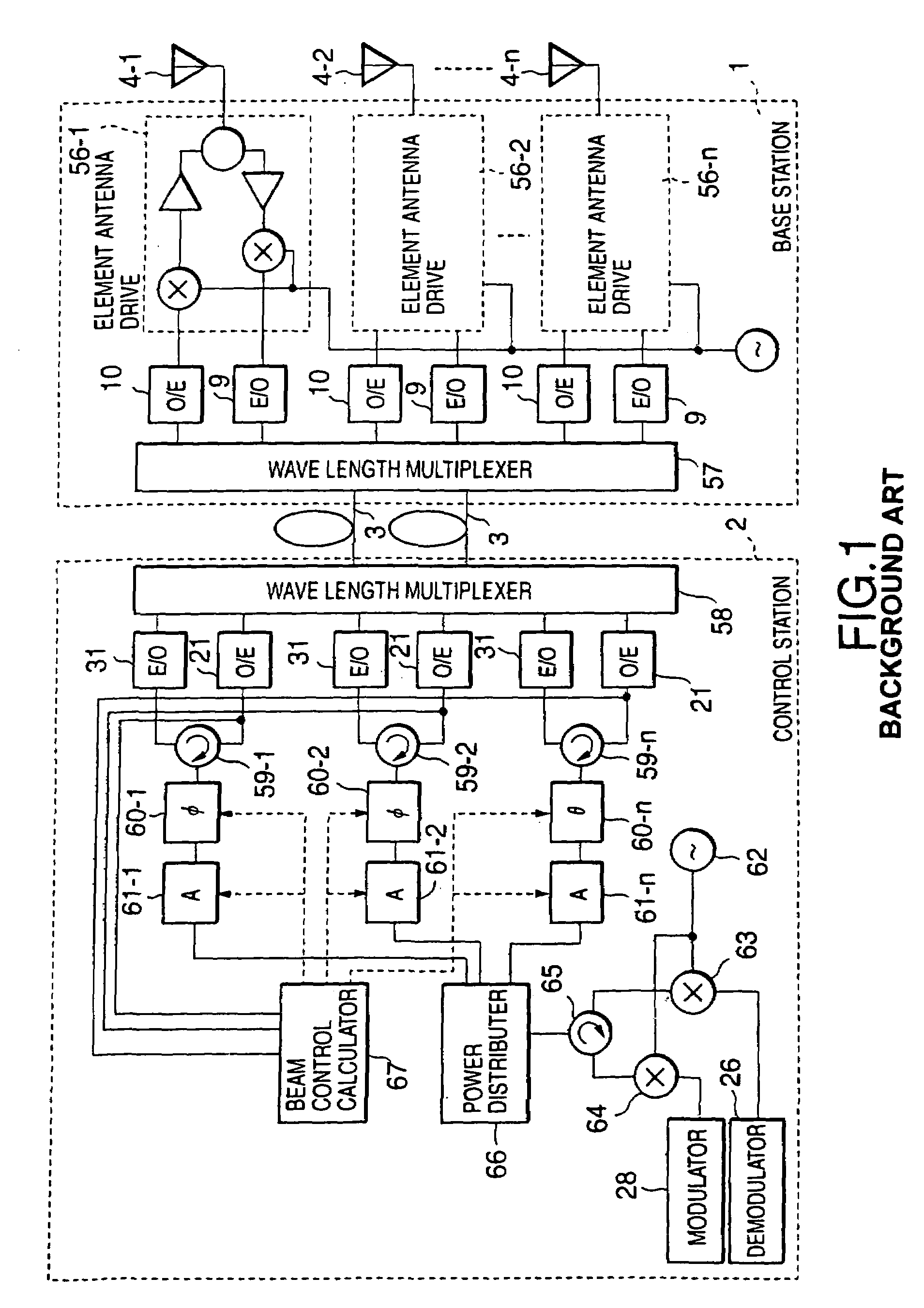
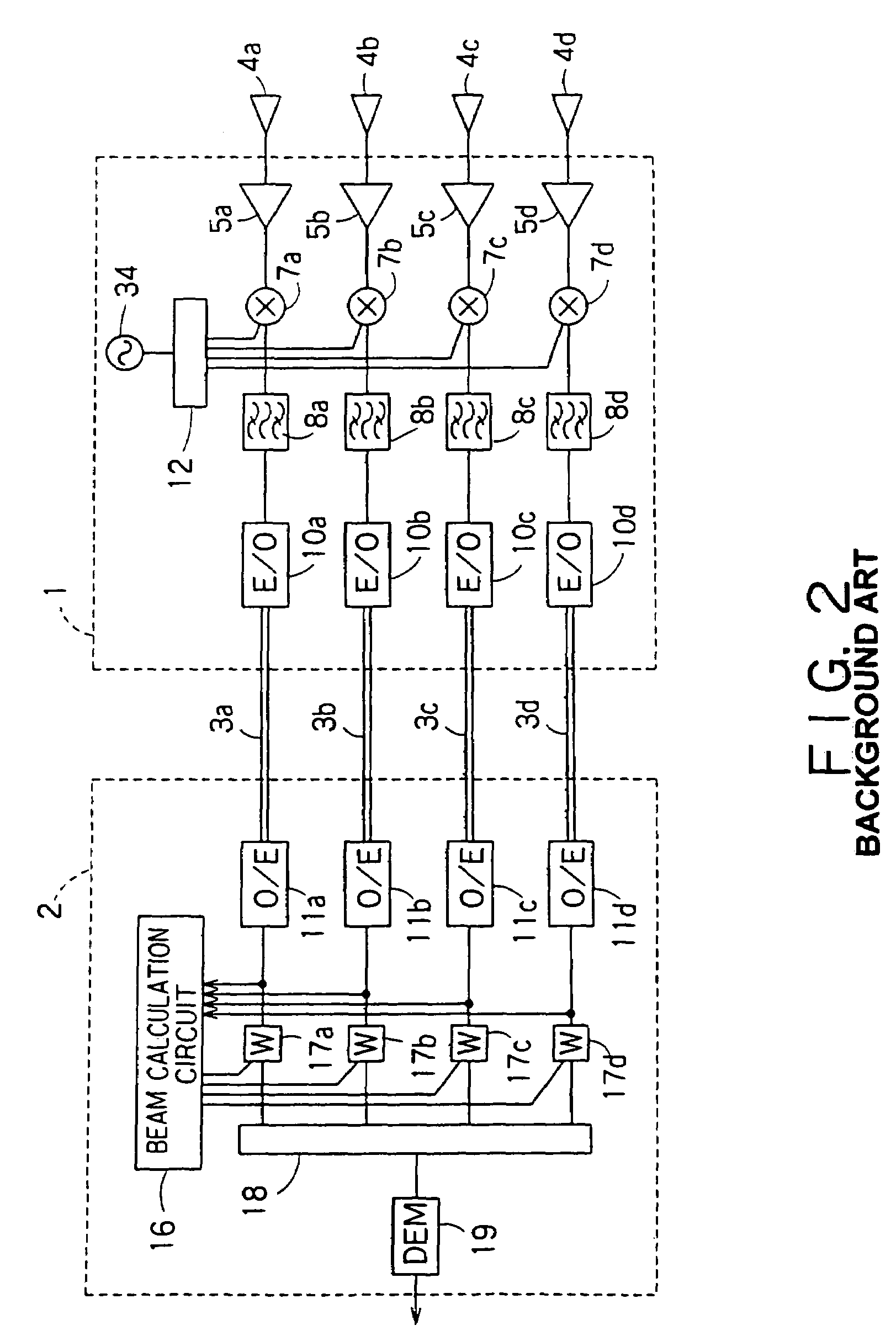
There is disclosed a radio communication system in which a constitution of a base station and further a control station can be simplified. A radio communication system according to the present invention converts a received signal received by a plurality of antenna elements in a base station to a signal of different frequency band, and then conflates the converted signal in order to generate sub-carrier wave multiplex signal. The signal is converted to an optical signal, and then the optical signal is transmitted to a control station via an optical fiber. Or the control station performs weighting to phase of the transmitted signal transmitted from a plurality of antennas of a base station, and then performs frequency conversion to different frequency band, and then conflates the converted signal in order to generate the sub-carrier wave multiplex signal. The signal is converted to an optical signal, and then an optical signal is transmitted to the base station side via the optical fiber. The control station and the base station divides the received sub-carrier wave multiplex signal by each frequency band, and then the frequency of the divided signals are converted to the same frequency band in order to generate the transmitted / received signal of each antenna element. By such a constitution, it is possible to reduce constituent of the optical transmission components to the minimum and to simplify the constitution of the base station. Furthermore, it is possible to maintain the relative phase difference and the relative intensity of the transmitted / received signal of each antenna element. Because of this, it is possible to estimate an arrival direction of the received signal and to control radiation beam pattern of the transmitted signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
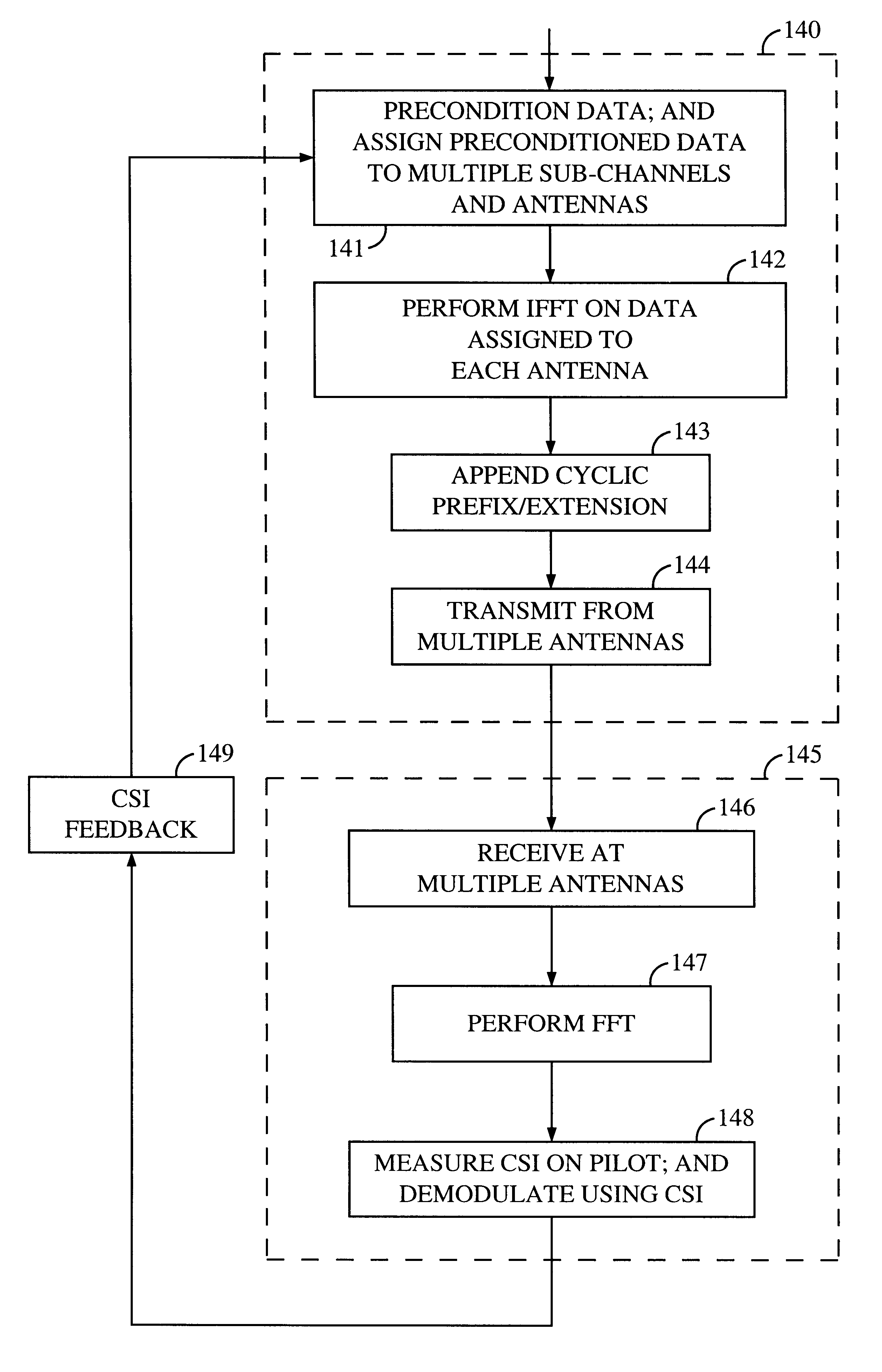
High efficiency high performance communications system employing multi-carrier modulation
InactiveUS20020154705A1Increase diversityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityData streamHigh performance communication
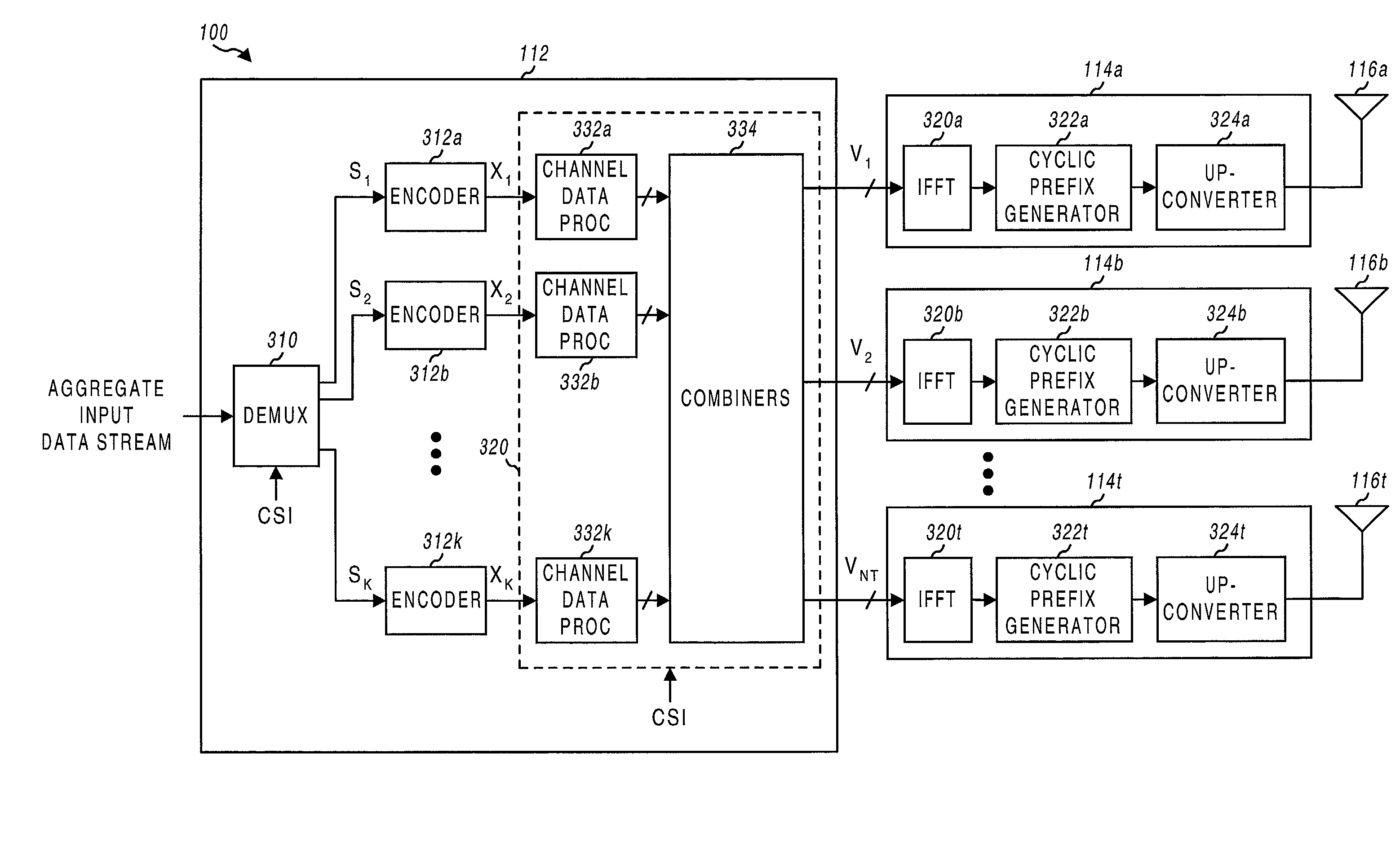
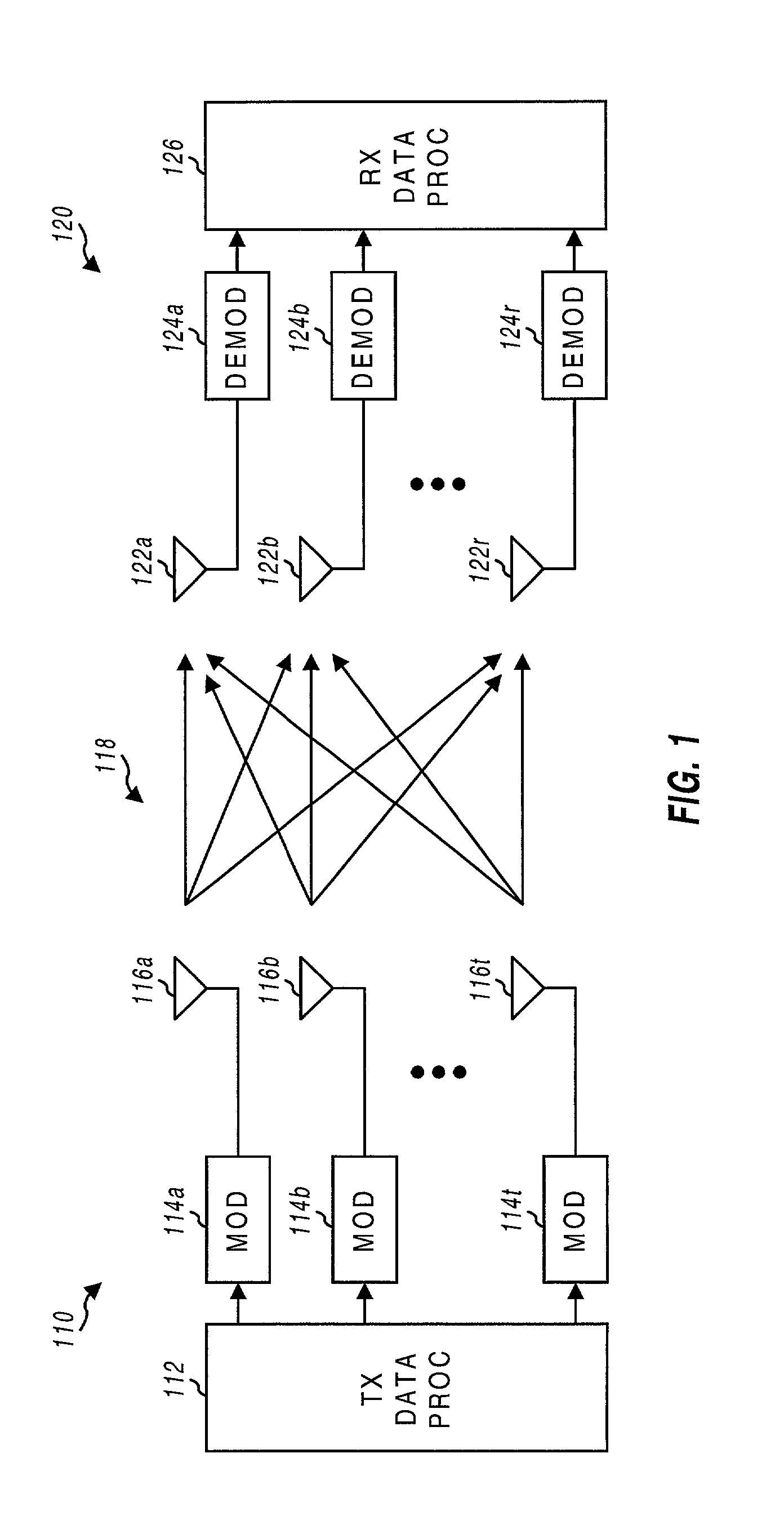
Transmitter and receiver units for use in a communications system and configurable to provide antenna, frequency, or temporal diversity, or a combination thereof, for transmitted signals. The transmitter unit includes a system data processor, one or more modulators, and one or more antennas. The system data processor receives and partitions an input data stream into a number of channel data streams and further processes the channel data streams to generate one or more modulation symbol vector streams. Each modulation symbol vector stream includes a sequence of modulation symbol vectors representative of data in one or more channel data streams. Each modulator receives and modulates a respective modulation symbol vector stream to provide an RF modulated signal, and each antenna receives and transmits a respective RF modulated signal. Each modulator may include an inverse (fast) Fourier transform (IFFT) and a cyclic prefix generator. The IFFT generates time-domain representations of the modulation symbol vectors, and the cyclic prefix generator repeats a portion of the time-domain representation of each modulation symbol vector. The channel data streams are modulated using multi-carrier modulation, e.g., OFDM modulation. Time division multiplexing (TDM) may also be used to increase flexibility.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
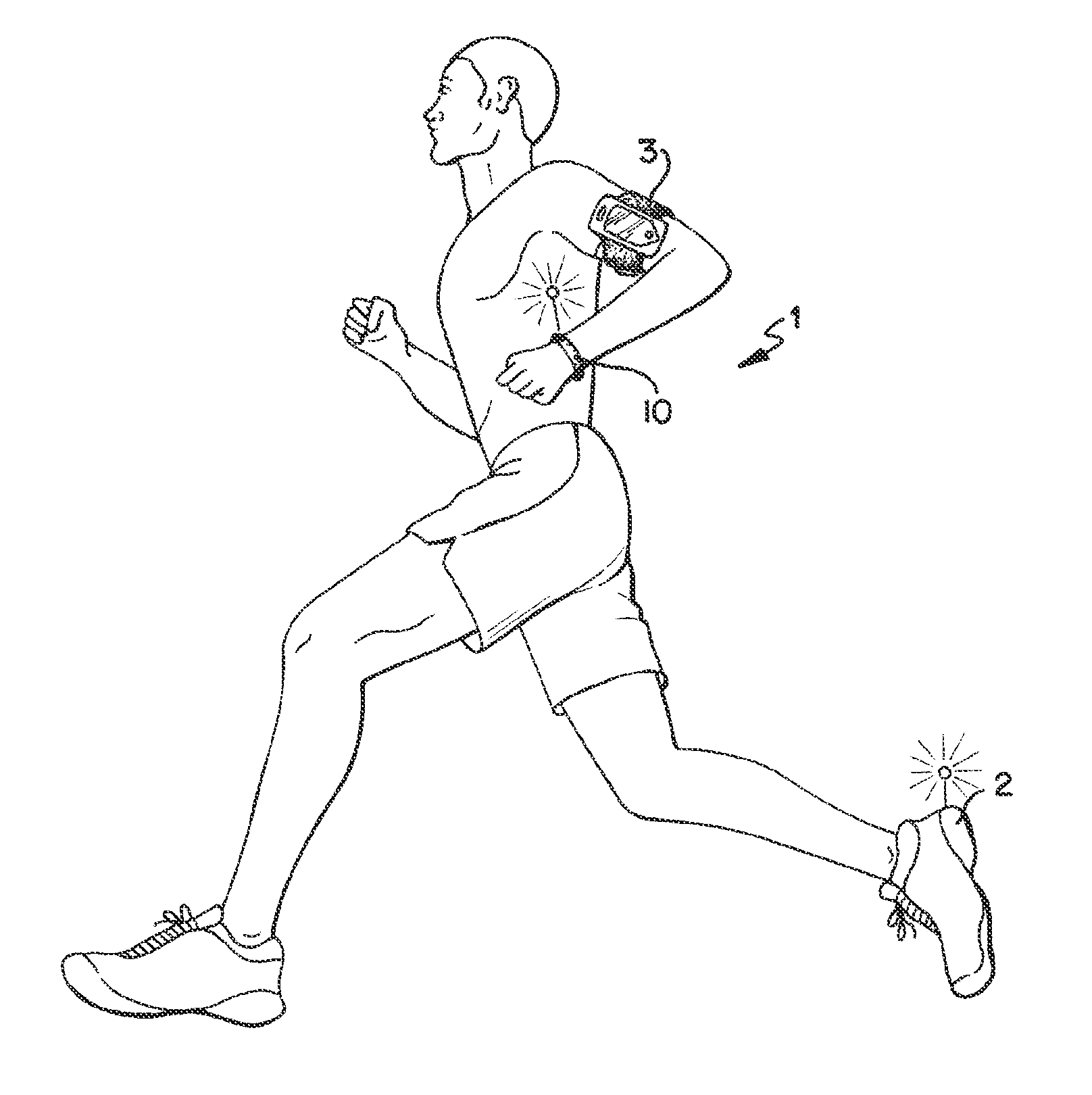
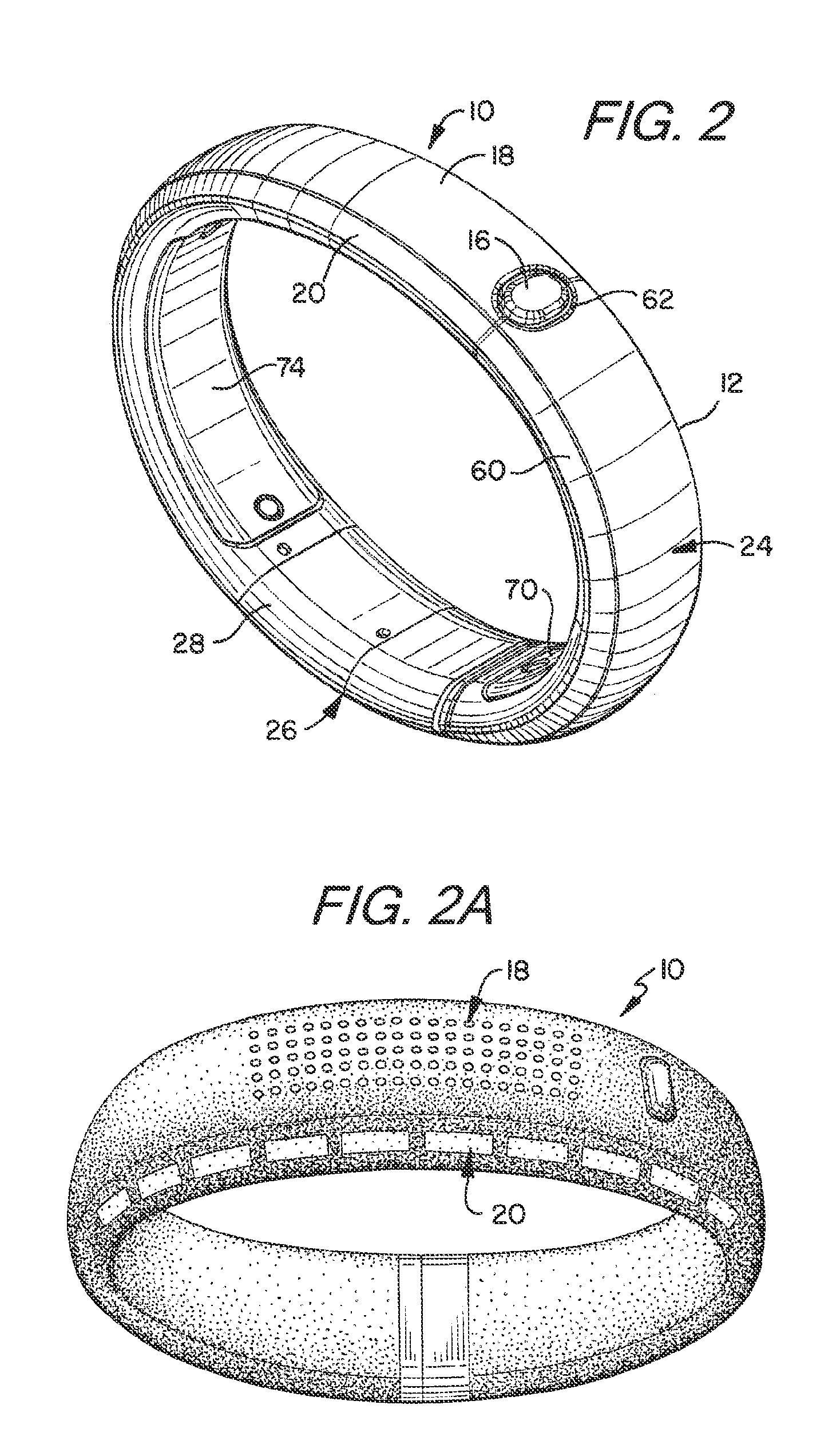
Wearable Device Assembly Having Athletic Functionality
ActiveUS20130106684A1Physical therapies and activitiesElectronic time-piece structural detailsDisplay deviceFunction motor
A wearable device assembly has a housing supporting a controller, display and indicator system thereon. The controller has at least one sensor wherein activity of a user wearing the device is detected. The controller selectively illuminates the indicator system to indicate a level of activity of the user.
Owner:NIKE INC
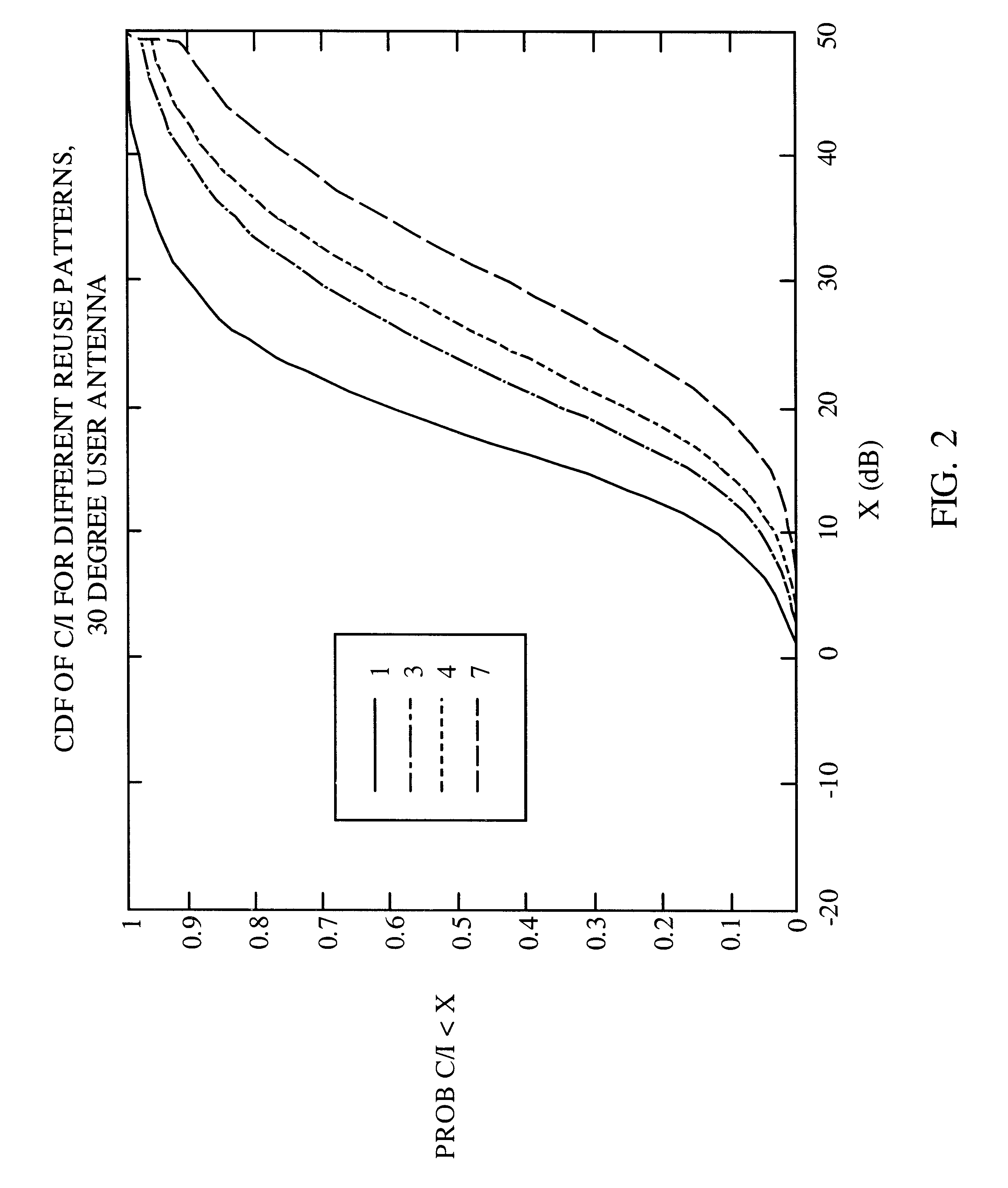
Method and apparatus for controlling transmissions of a communications systems
InactiveUS6493331B1Reduce the amount of noiseLower Level RequirementsEnergy efficient ICTPower managementControl communicationsSystem requirements
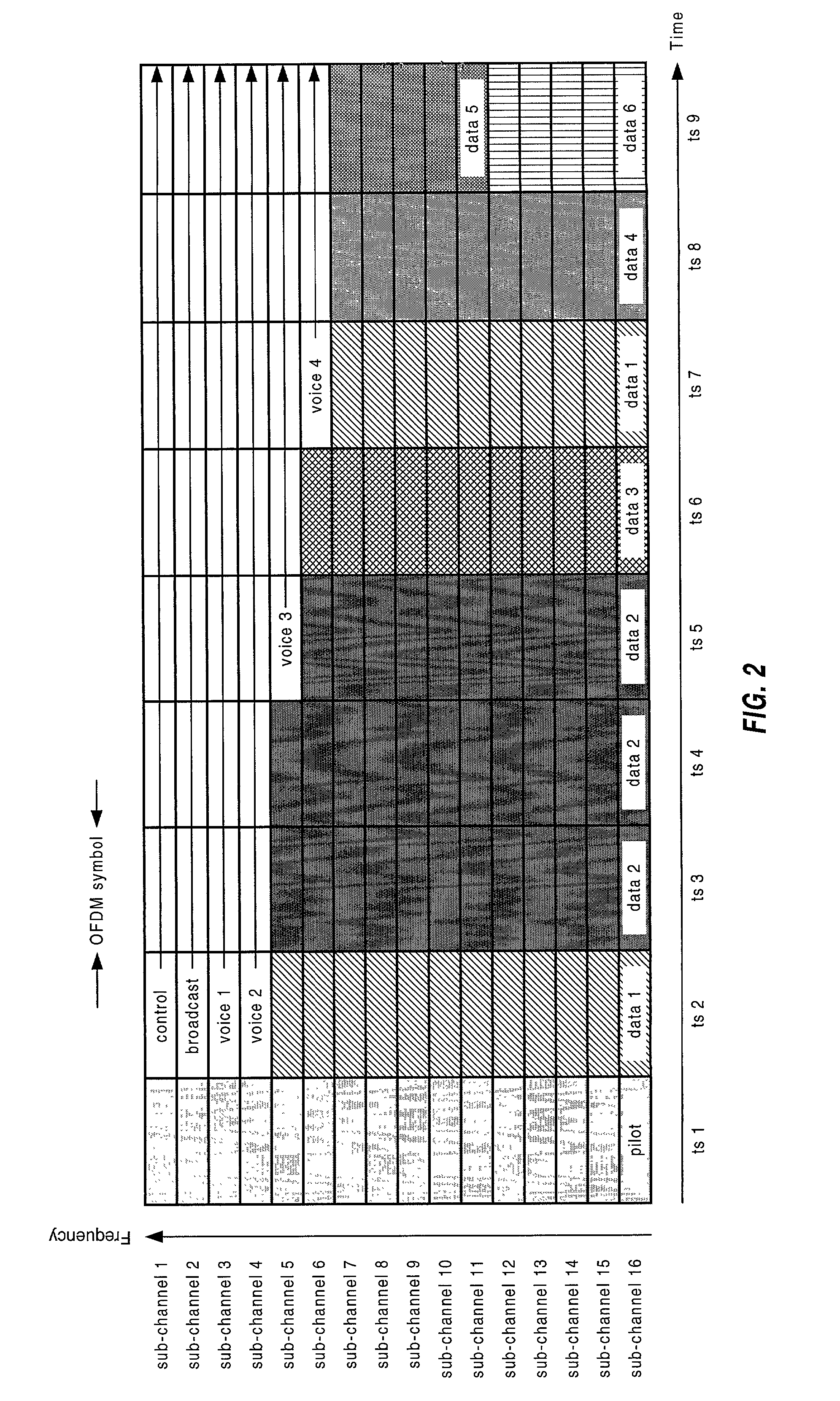
In some aspects, each cell in the communications system can be designed to operate in accordance with a set of back-off factors that identify the reductions in peak transmit power levels for the channels associated with the back-off factors. The back-off factors are defined to provide the required power to a large percentage of the users while reducing the amount of interference. In some other aspects, the cells operate using an adaptive reuse scheme that allows the cells to efficiently allocate and reallocate the system resources to reflect changes in the system. A reuse scheme is initially defined and resources are allocated to the cells. During operation, changes in the operating conditions of the system are detected and the reuse scheme is redefined as necessary based on the detected changes. For example, the loading conditions of the cells can be detected, and the resources can be reallocated and / or the reuse scheme can be redefined. In yet other aspects, techniques are provided to efficiency schedule data transmissions and to assign channels to users. Data transmissions can be scheduled based on user priorities, some fairness criteria, system requirements, and other factors. Users are assigned to available channels based on a number of channel assignment schemes. Channel metrics are also provided, which can be used to prioritize users and for channel assignments.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
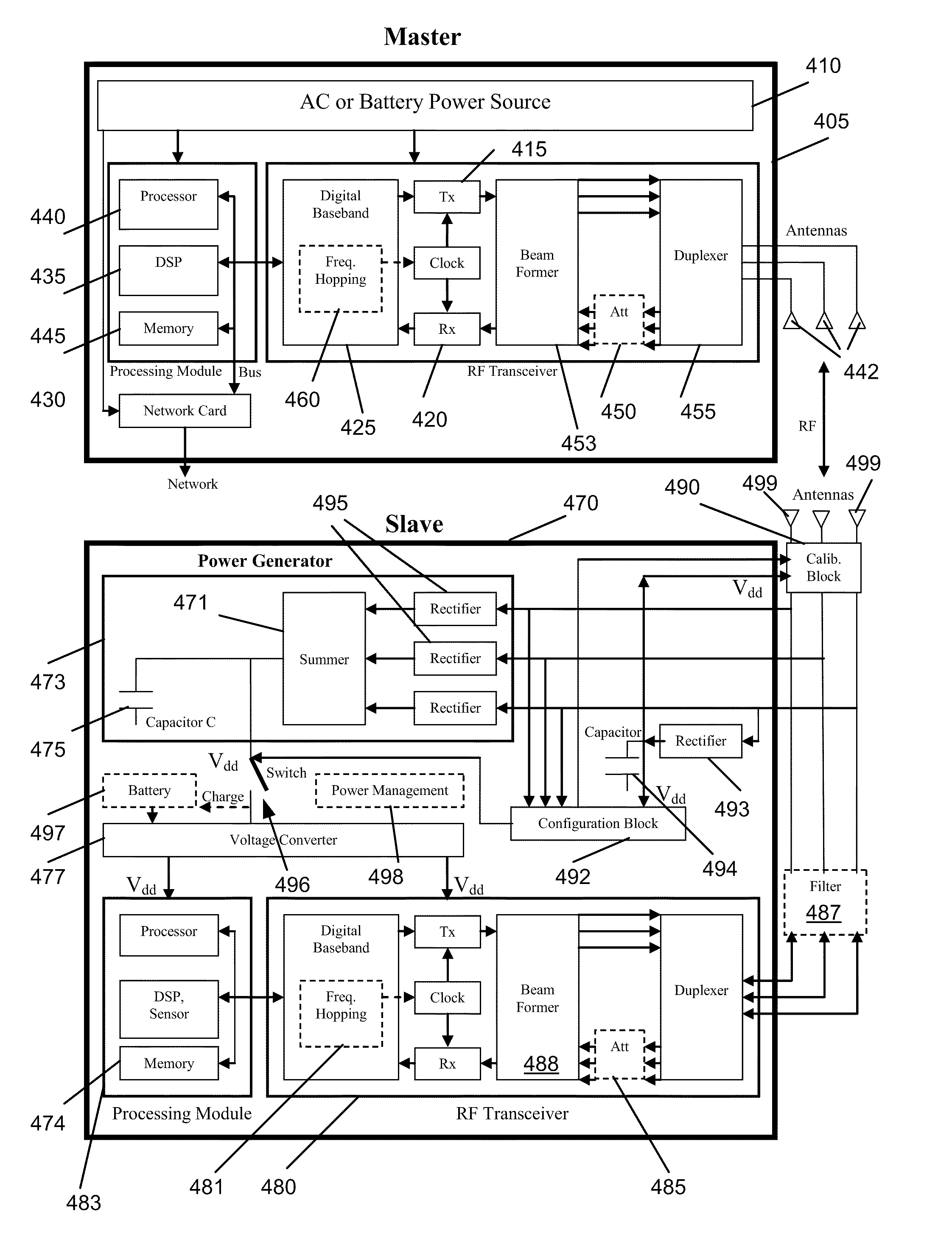
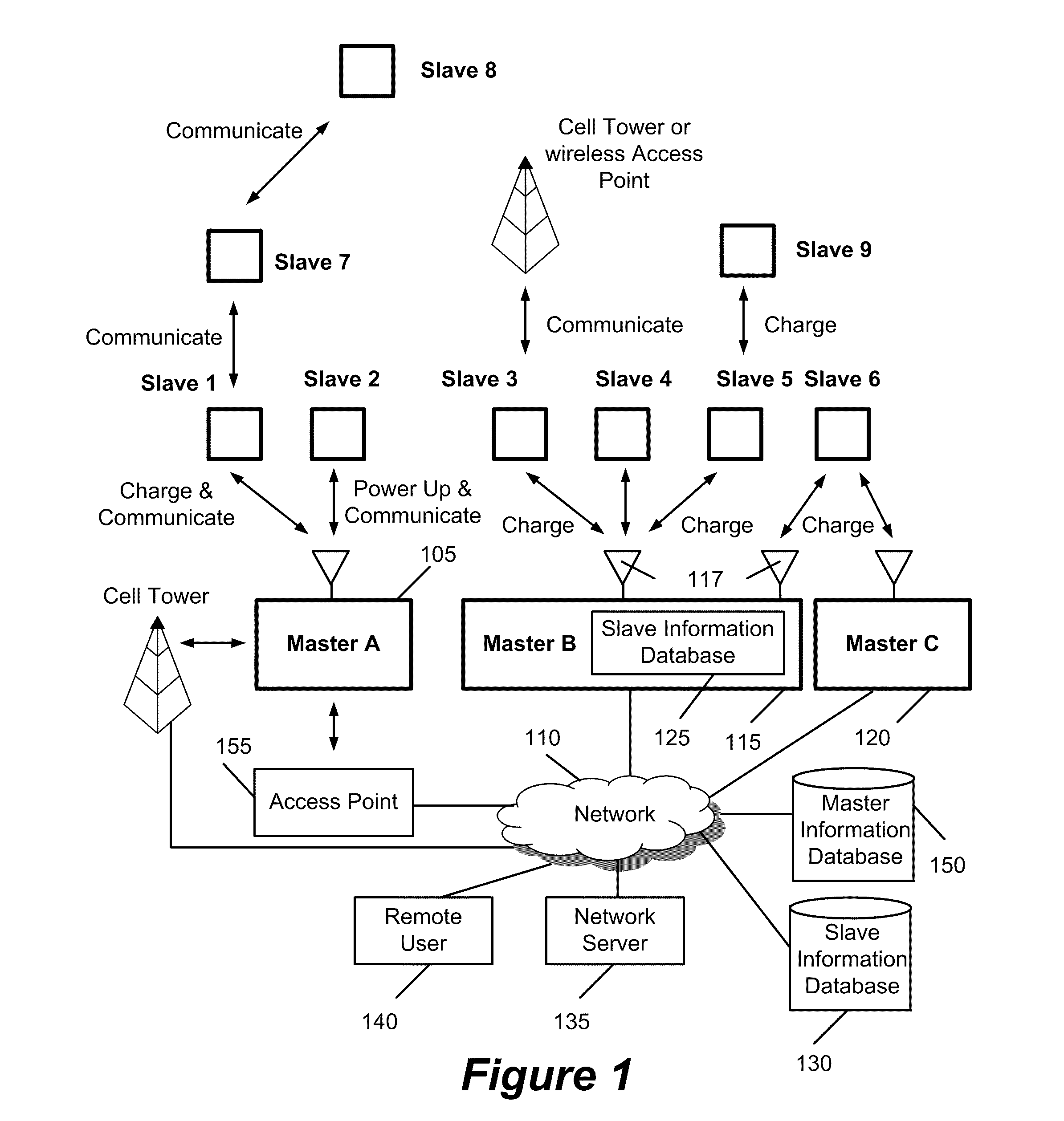
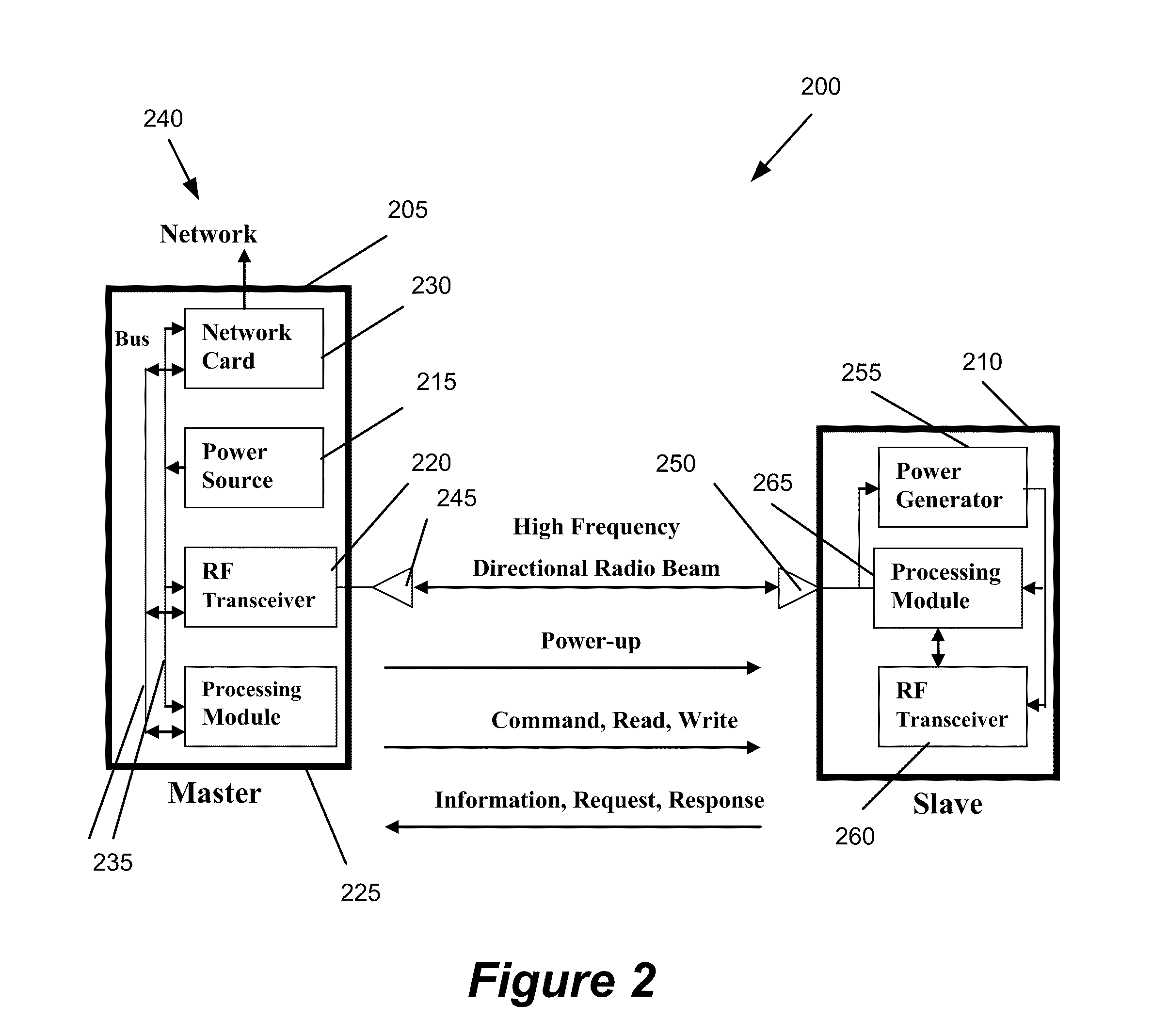
Method and apparatus for wirelessly transferring power and communicating with one or more slave devices
InactiveUS20110156640A1Improve communication efficiencyImprove power efficiencyCircuit authenticationElectromagnetic wave systemWireless transmissionDirectional antenna
Some embodiments provide a system for charging devices. The system includes a master device and a slave device. Some embodiments provide a method for charging devices in a system that includes a slave device and a master device. The slave device includes (1) an antenna to receive a radio frequency (RF) beam and (2) a power generation module connected to the antenna that converts RF energy received by the slave antenna to power. The master device includes (1) a directional antenna to direct RF power to the antenna of the slave device and (2) a module that provides power to the directional antenna of the master device.
Owner:CREEKVIEW IP LLC
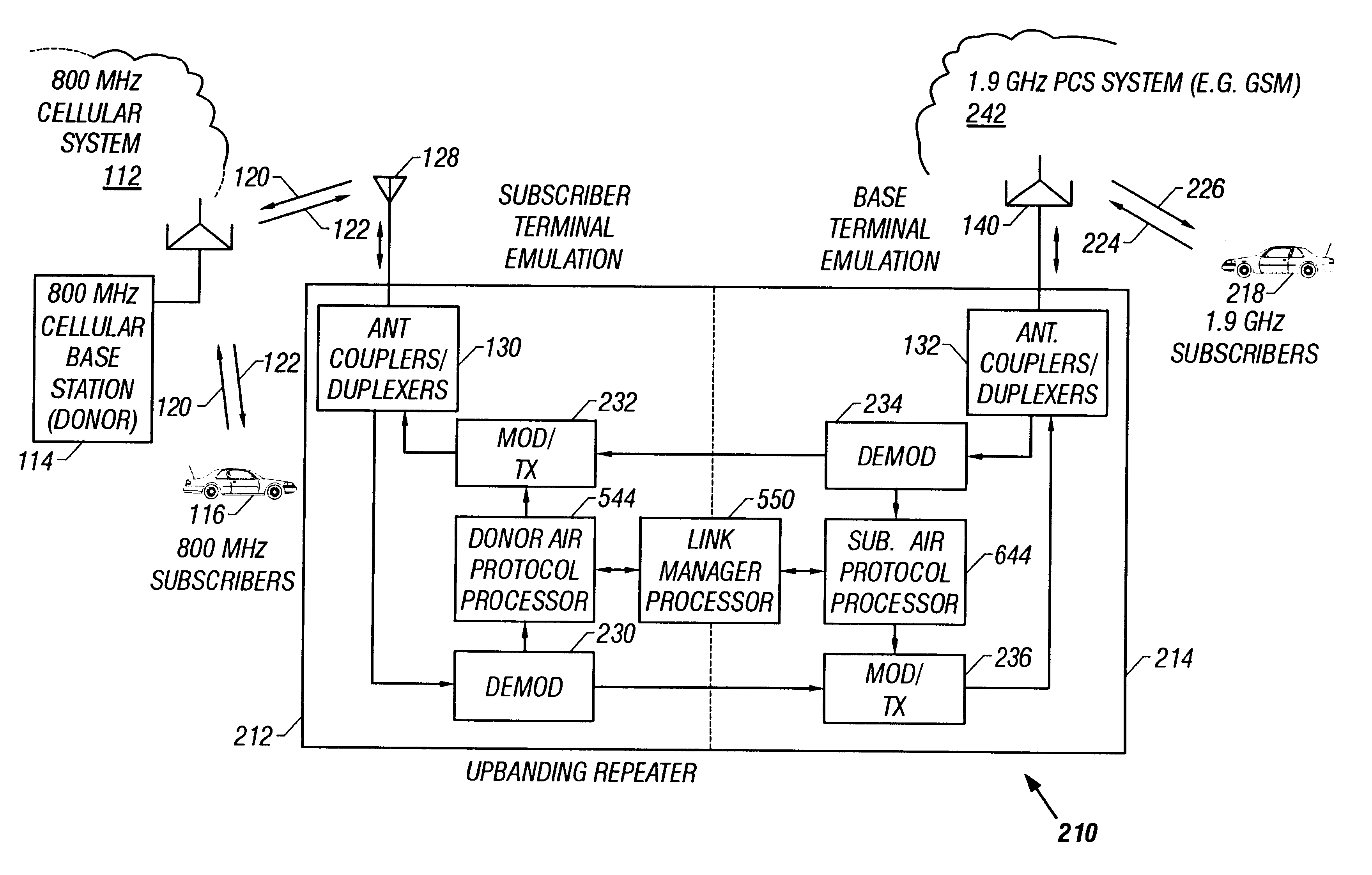
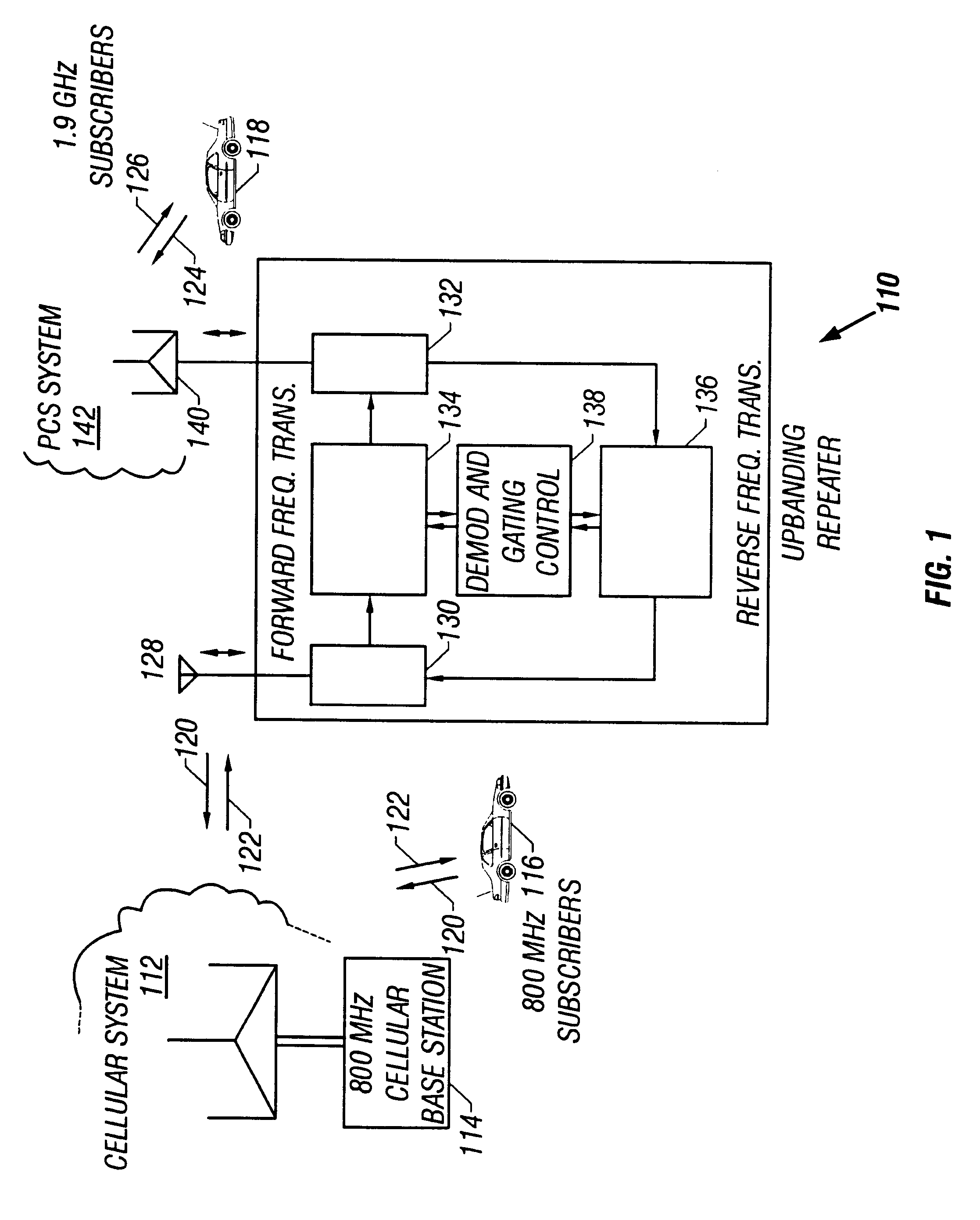
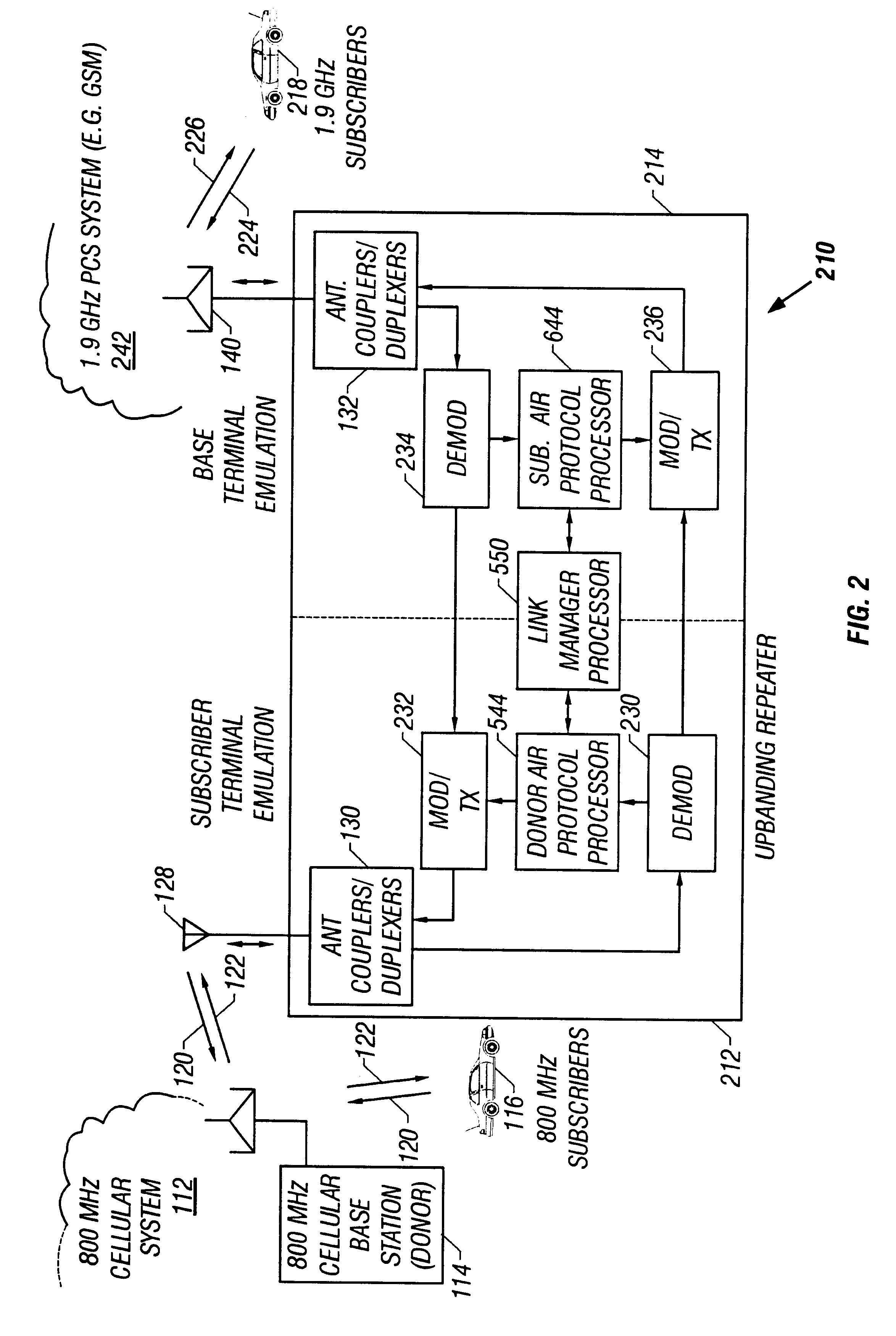
Band-changing repeater with protocol or format conversion
InactiveUS6404775B1Facilitate communicationInterference minimizationFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemOperating frequency
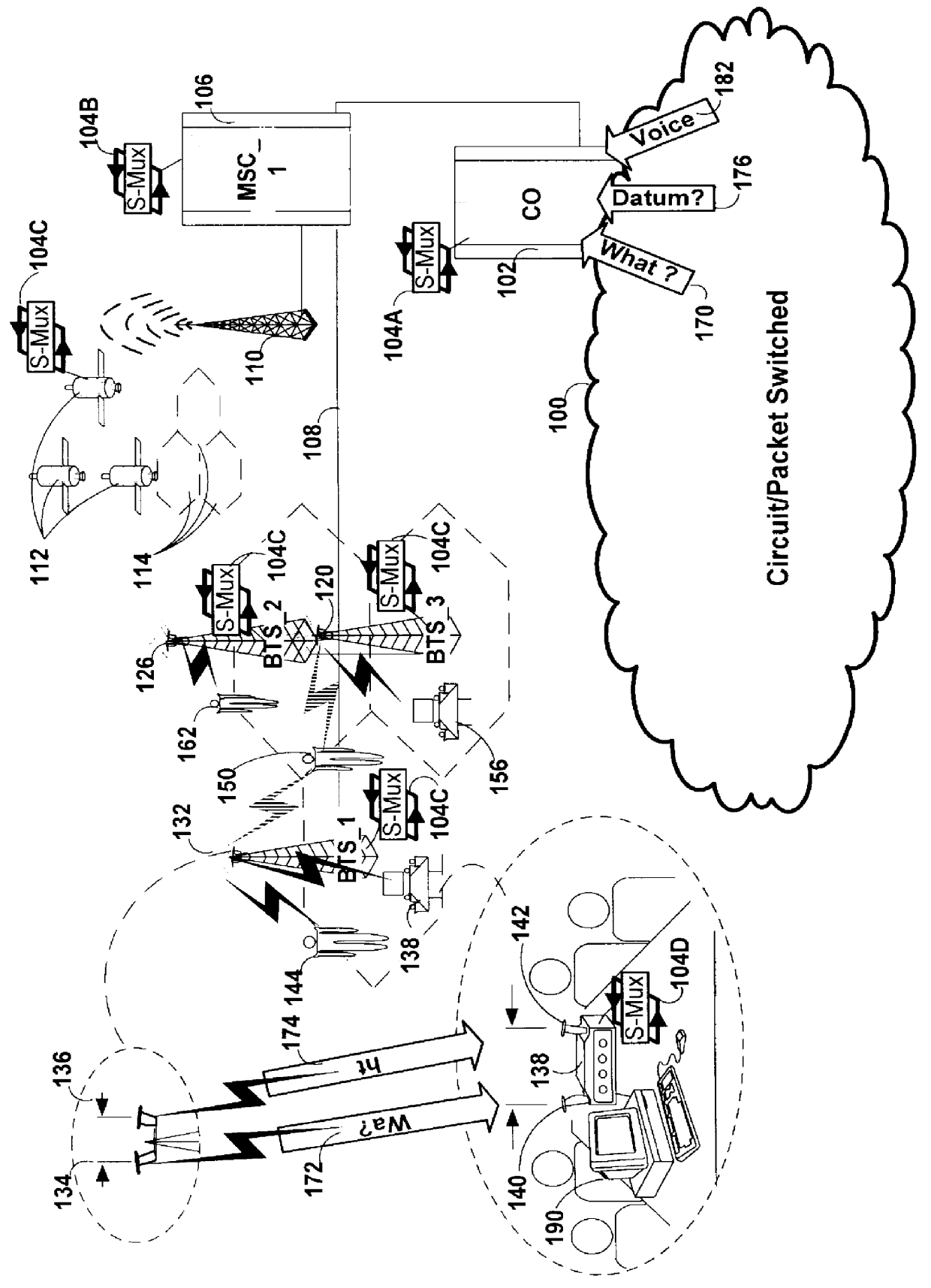
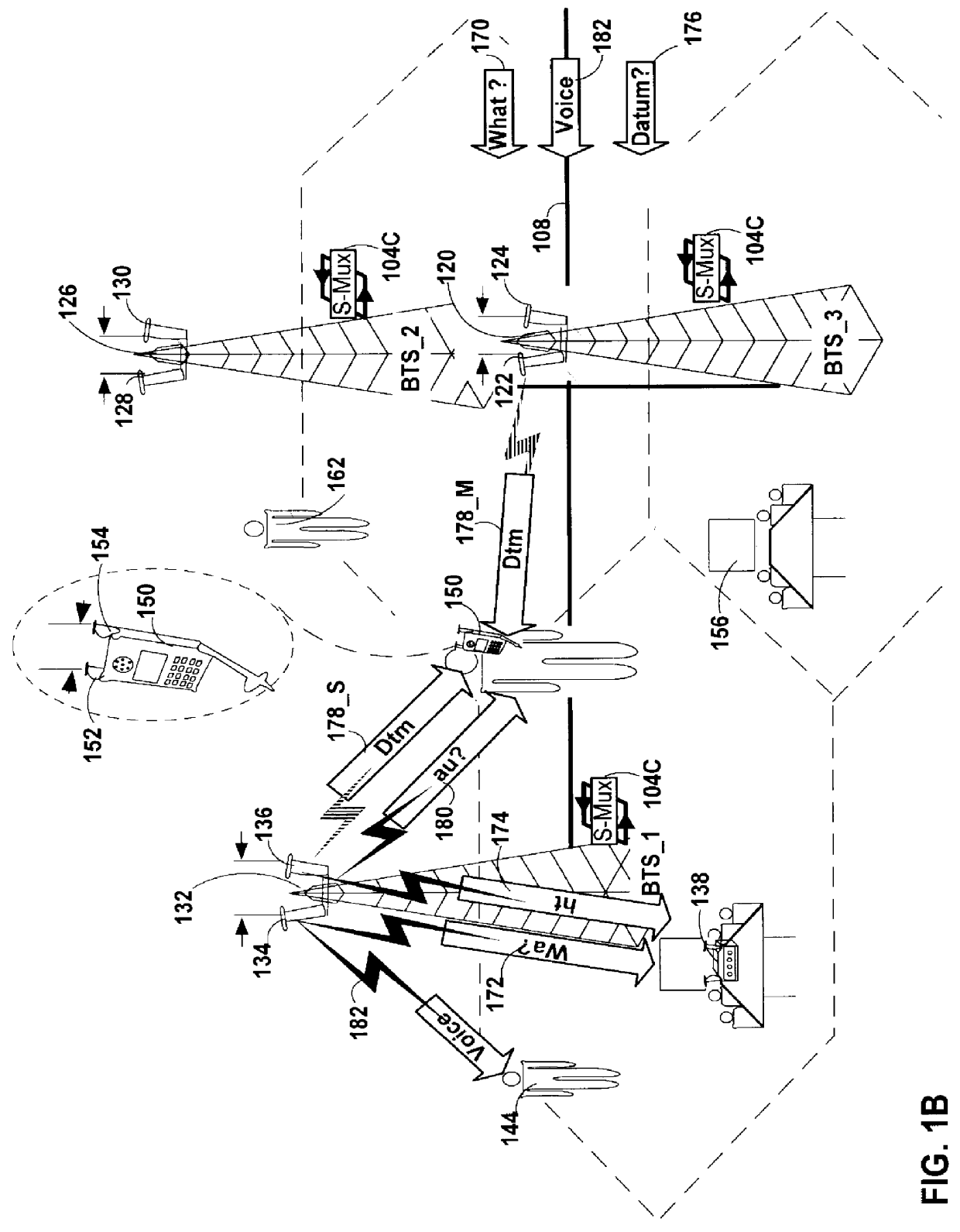
A repeater allows terminals of a first communications system, employing a first air protocol or radio interface, to communicate with terminals of a second communications system, employing a second air protocol or radio interface different from the first. Where the first and second air protocols differ only in operating frequency, but are otherwise compatible, the repeater may linearly translate signals from the first operating frequency to the second operating frequency, and vice versa, without demodulating and remodulating the signals. Where the air protocols differ in other ways, the repeater receives and demodulates signals from the first system, converts the signals to a common format, and remodulates and retransmits the signals according to the second air protocol (and vice versa), in the same frequency bands or in different frequency bands. The repeater translates control and signalling information transmitted in compliance with one air protocol to a format which complies with the other air protocol and has the same or equivalent effect. For each of the two communications system, the repeater emulates the functions of a terminal in that communications system, so that corresponding terminals in that system may communicate transparently with the repeater. The repeater provides a connection between the two emulated terminals, thereby allowing a terminal of the first system to use the repeater to communicate with an otherwise incompatible terminal of the second system.
Owner:ALLEN TELECOM LLC
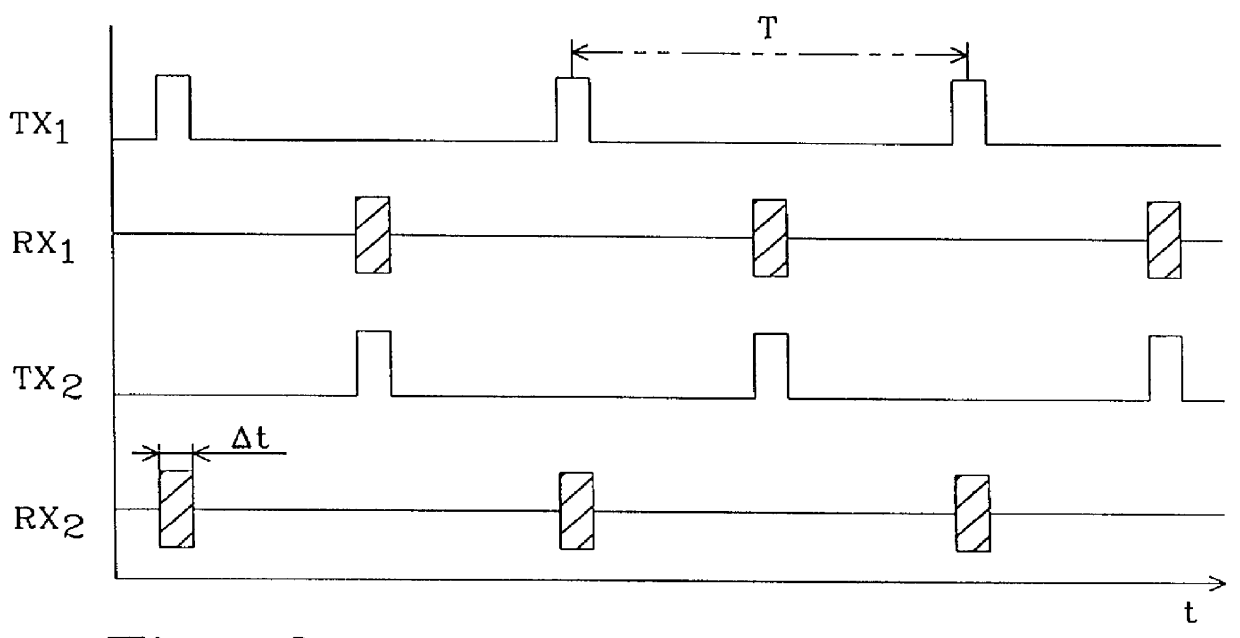
Method and arrangement for radio communication
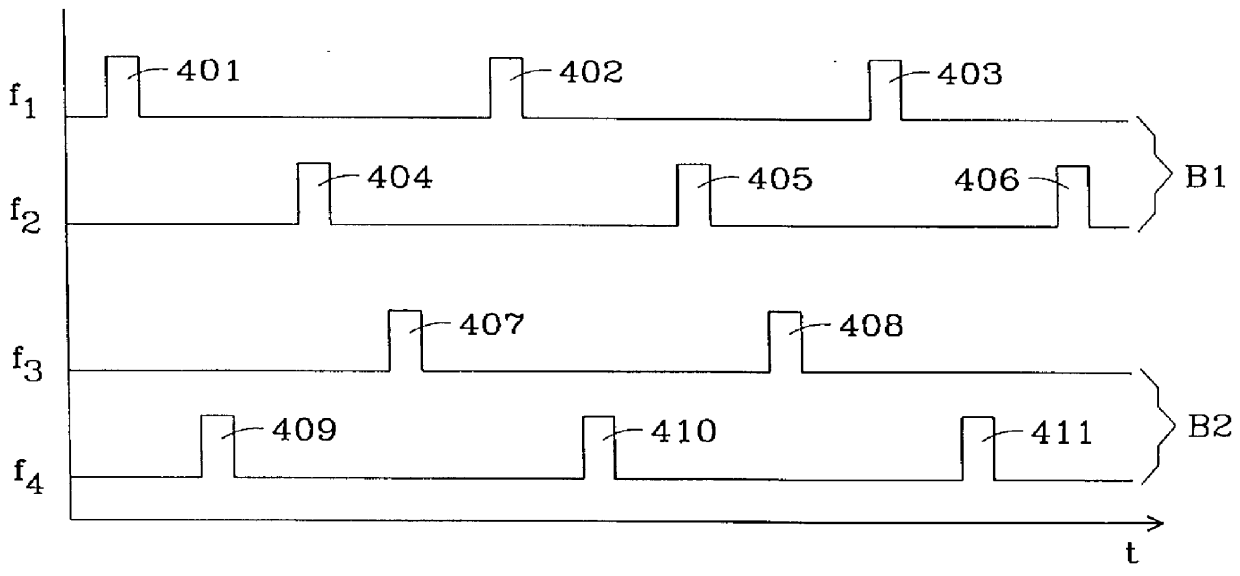
InactiveUS6028853ATime-division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationTime windowsAir interface
The present invention relates to a method and arrangement in an ad-hoc network for synchronizing a multiple of radio transceiver arrangements with different characteristics that make use of a common air interface. Each transceiver arrangement comprises at least two transceivers which mutually communicate via a radio transmission link. All transceivers synchronize to a common synchronization signal comprising two staggered beacon pulse series signals (TX1, TX2) which have the same repetition rate. The transceivers synchronize their internal timers which control the signal transmission from the transceivers, to the strongest one of the two beacon pulse series signals (TX1, TX2) by listening during one of the corresponding sets of time windows (RX1, RX2). Between the reception of two beacon pulses, each transceiver transmits beacon pulses itself, thus contributing to the generation of the other beacon pulse series signal, on which other transceivers can lock.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
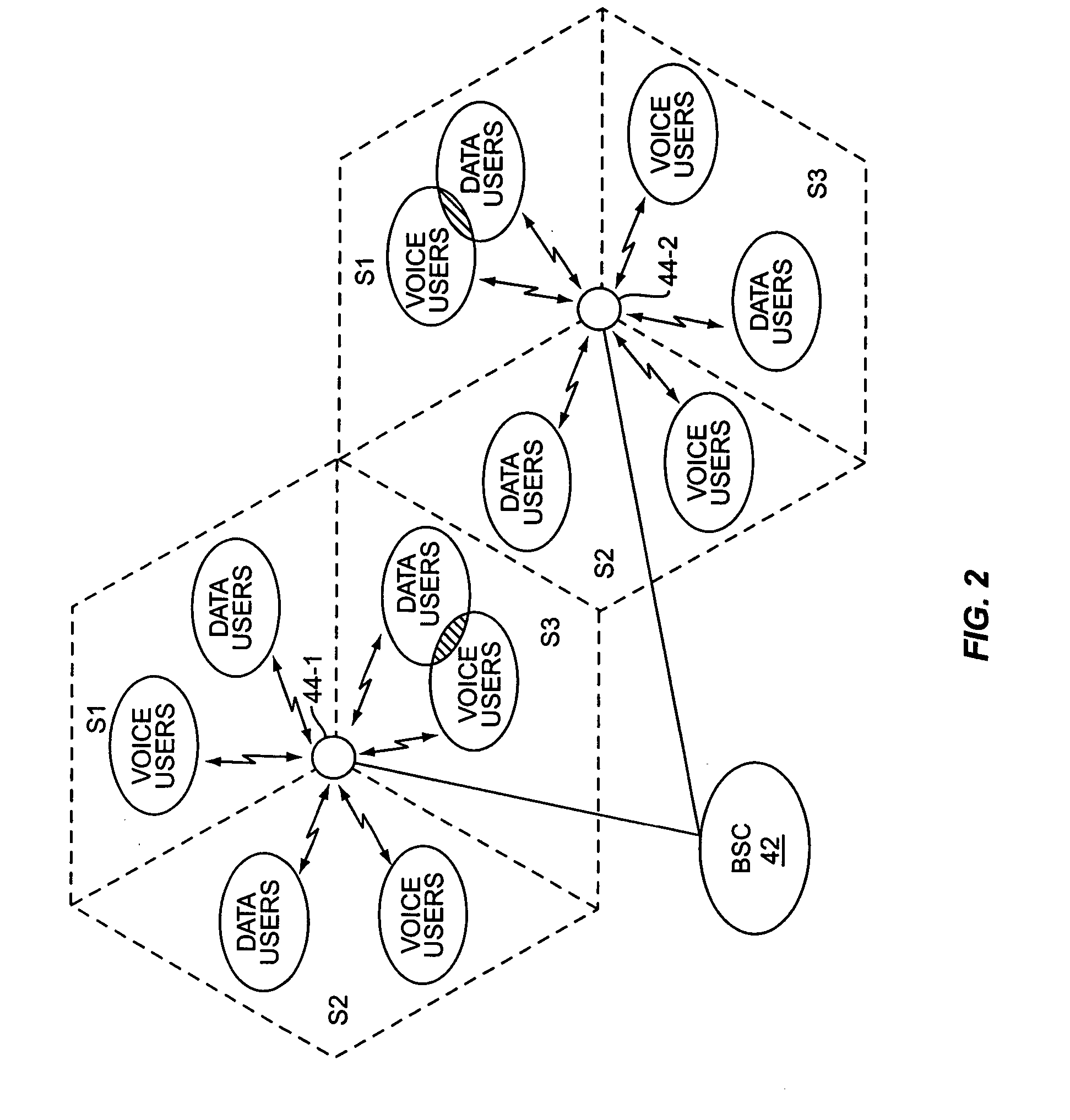
Spatial multiplexing in a cellular network
InactiveUS6067290ASpatial transmit diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementData streamControl signal
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for implementing spatial multiplexing in conjunction with the one or more multiple access protocols during the broadcast of information in a wireless network. A wireless cellular network for transmitting subscriber datastream(s) to corresponding ones among a plurality of subscriber units located within the cellular network is disclosed. The wireless cellular network includes base stations and a logic. The base stations each include spatially separate transmitters for transmitting, in response to control signals, selected substreams of each subscriber datastream on an assigned channel of a multiple access protocol. The logic communicates with each of the base stations. The logic assigns an available channel on which to transmit each subscriber datastream. The logic routes at least a substream of each datastream to at least a selected one of the base stations. The logic also generates control signals to configure the at least a selected one of the base stations to transmit the selected substreams to a corresponding one among the plurality of subscriber units on the assigned channel. A subscriber unit for use in a cellular system is also disclosed. The subscriber unit includes: spatially separate receivers, a spatial processor, and a combiner. The spatially separate receivers receive the assigned channel composite signals resulting from the spatially separate transmission of the subscriber downlink datastream(s). The spatial processor is configurable in response to a control signal transmitted by the base station to separate the composite signals into estimated substreams based on information obtained during the transmission of known data patterns from at least one of the base stations. The spatial processor signals the base stations when a change of a spatial transmission configuration is required. The combiner combines the estimated substreams into a corresponding subscriber datastream.
Owner:INTEL CORP
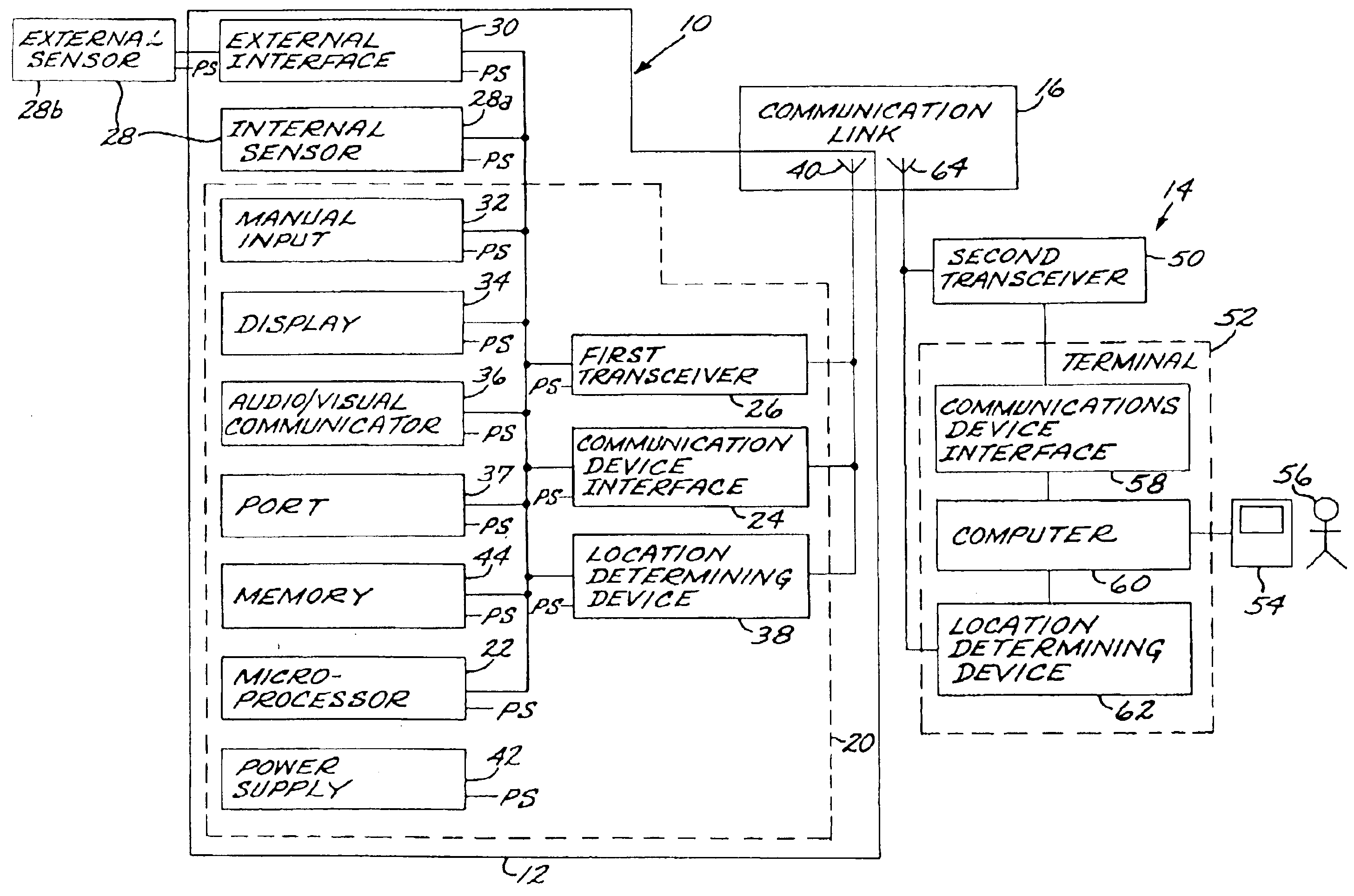
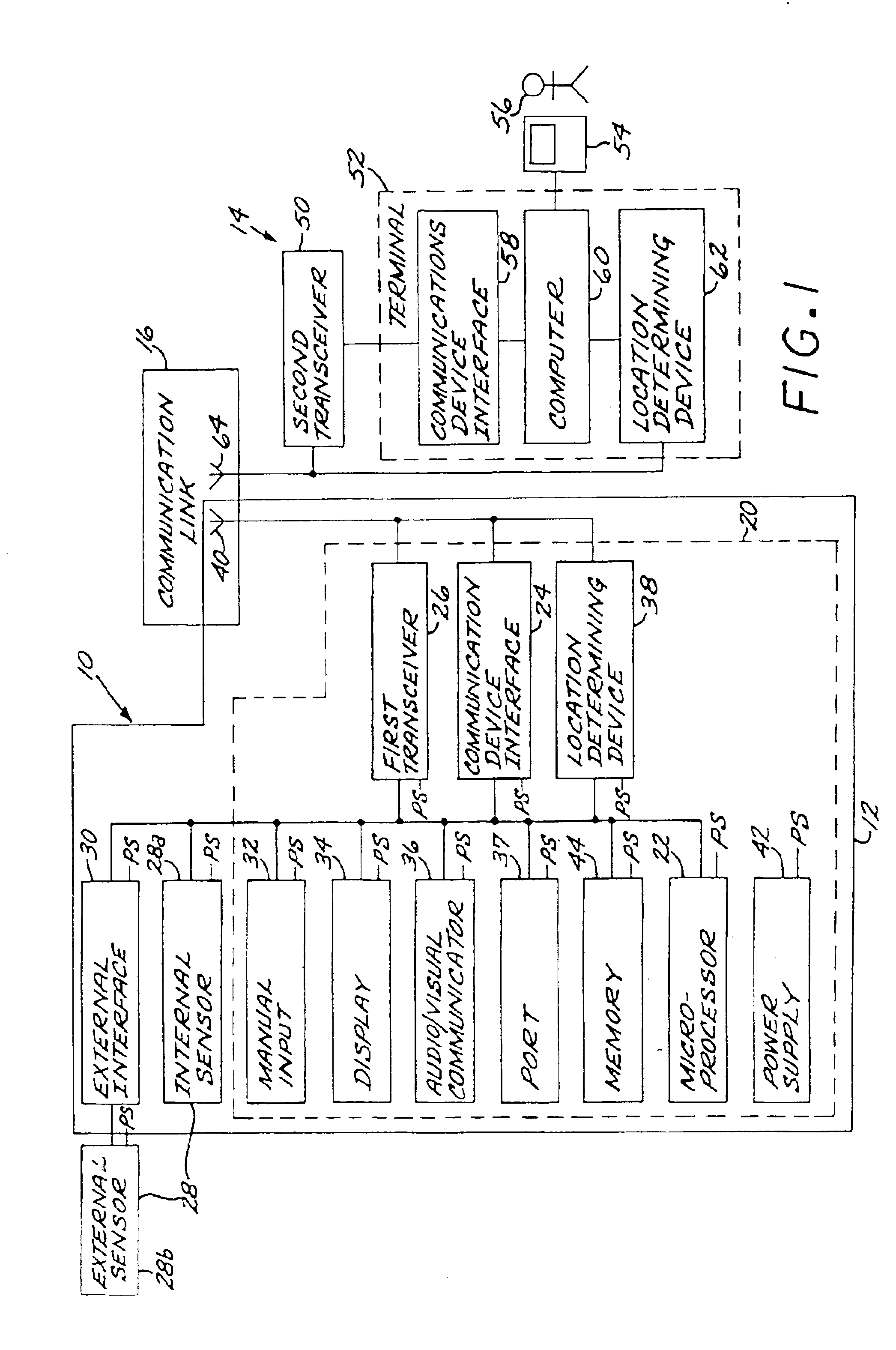
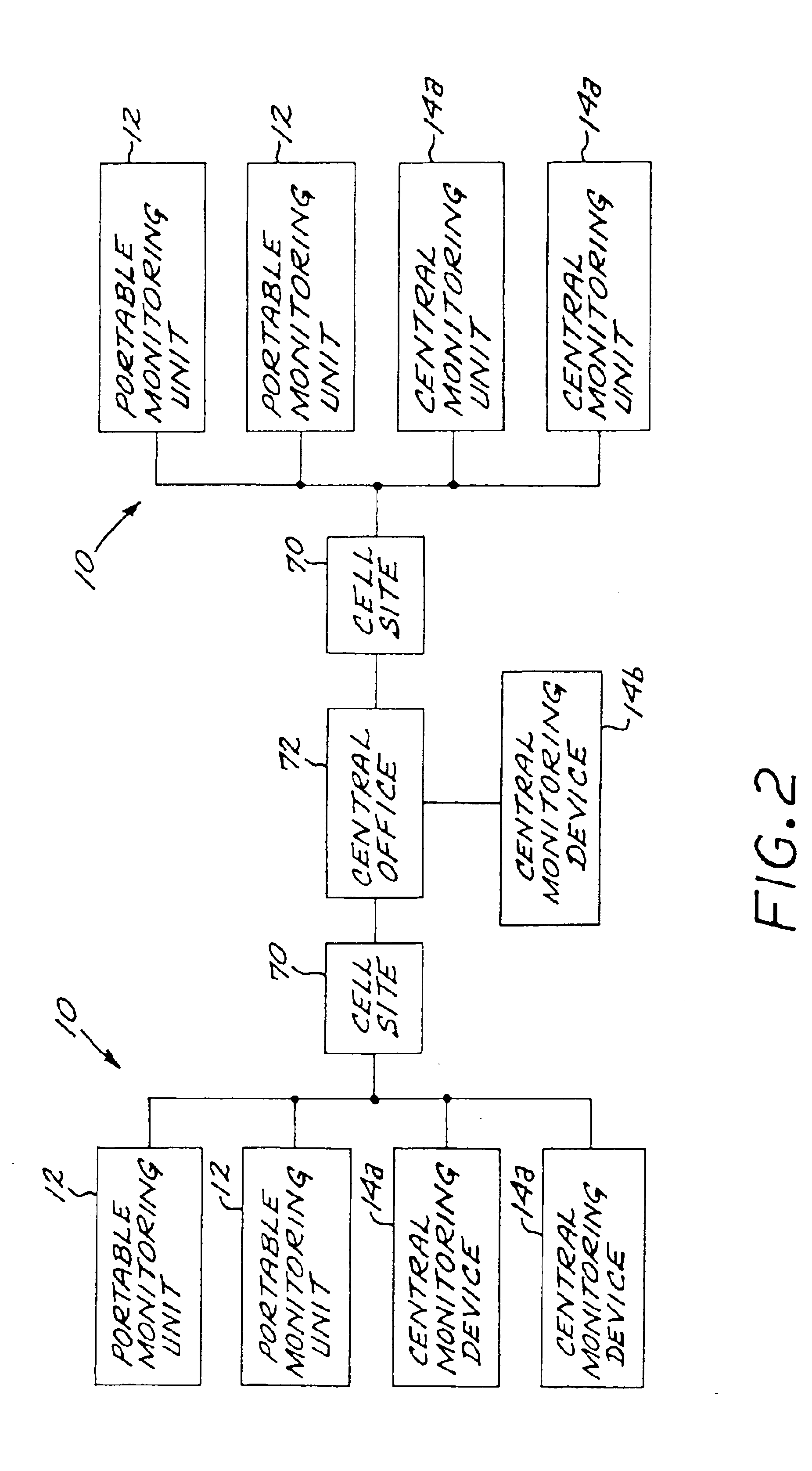
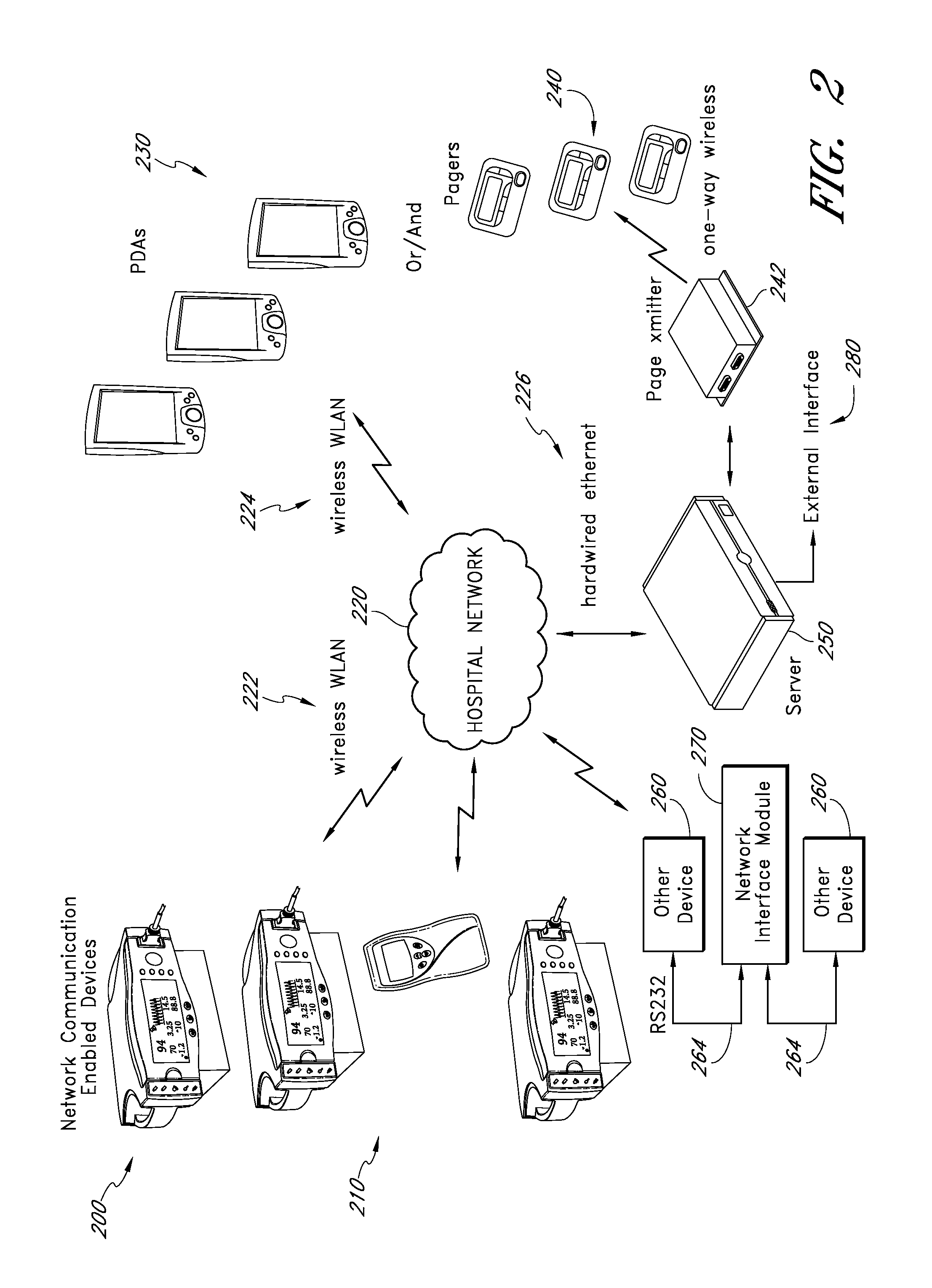
Reprogrammable remote sensor monitoring system
An automated, real-time, reprogrammable monitoring and control system for portable, remote sensors and subjects includes one or more portable monitoring units, each of the portable monitoring units having a sensor, a location-determining device, and a sensor interface unit. Each sensor interface unit is separately configured to monitor its sensor and to transmit that sensor's data, via a digital wireless communications network, to a central monitoring device. The portable unit is carried or worn by a person or animal, or affixed to an inanimate subject.
Owner:BRAEMAR MFG
Health care sanitation monitoring system
ActiveUS9323894B2Local control/monitoringRadio transmission for post communicationMonitoring systemMedical emergency
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
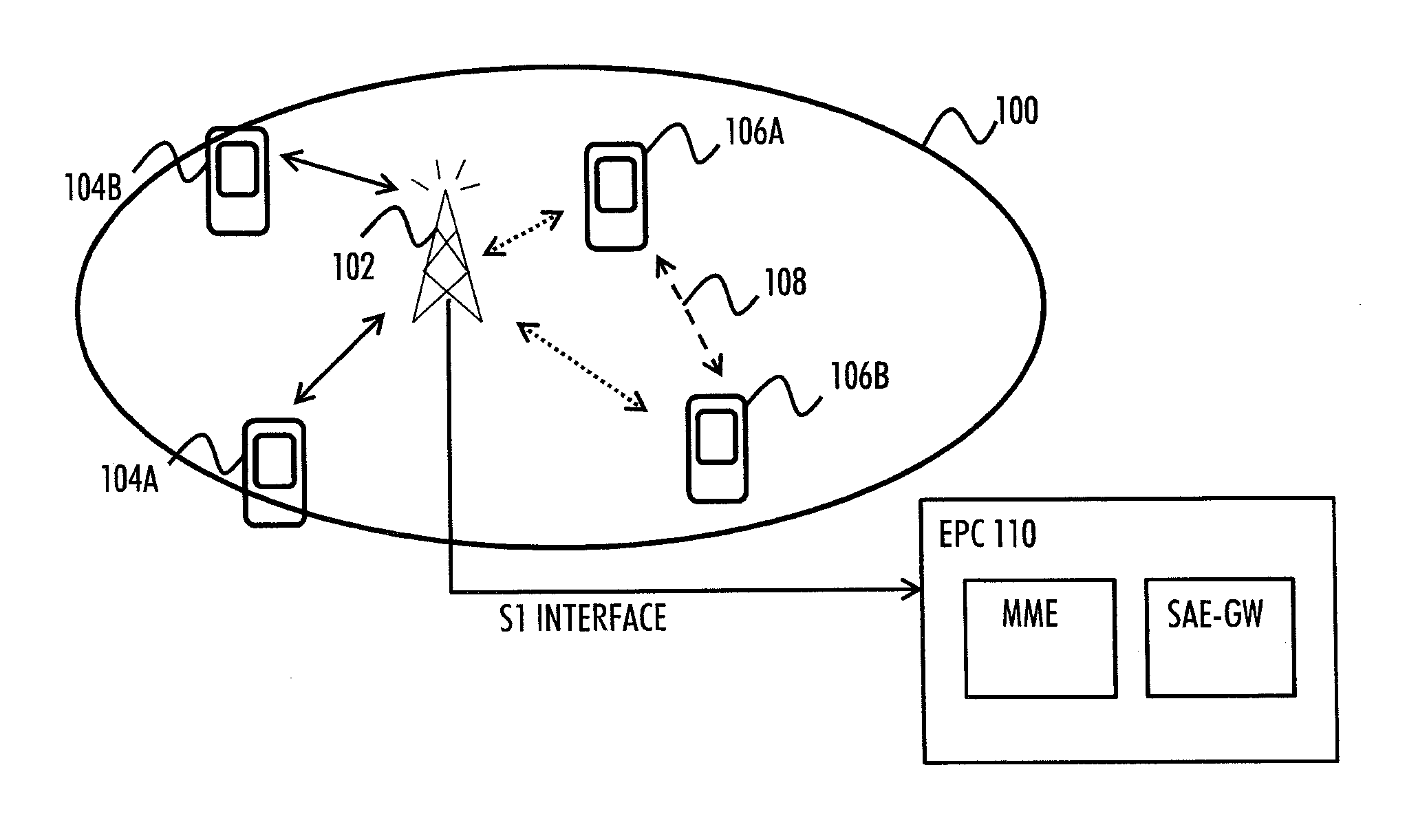
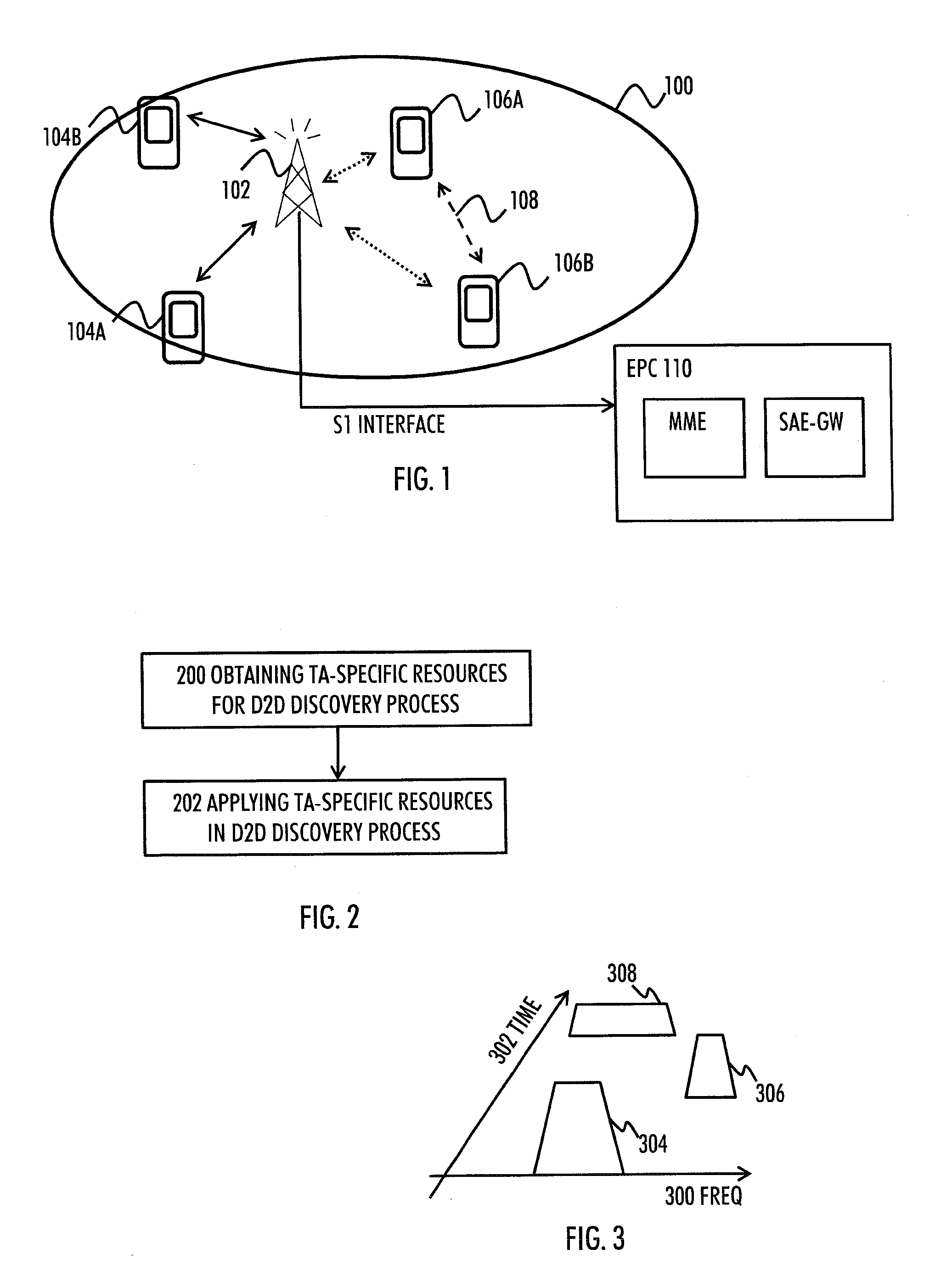
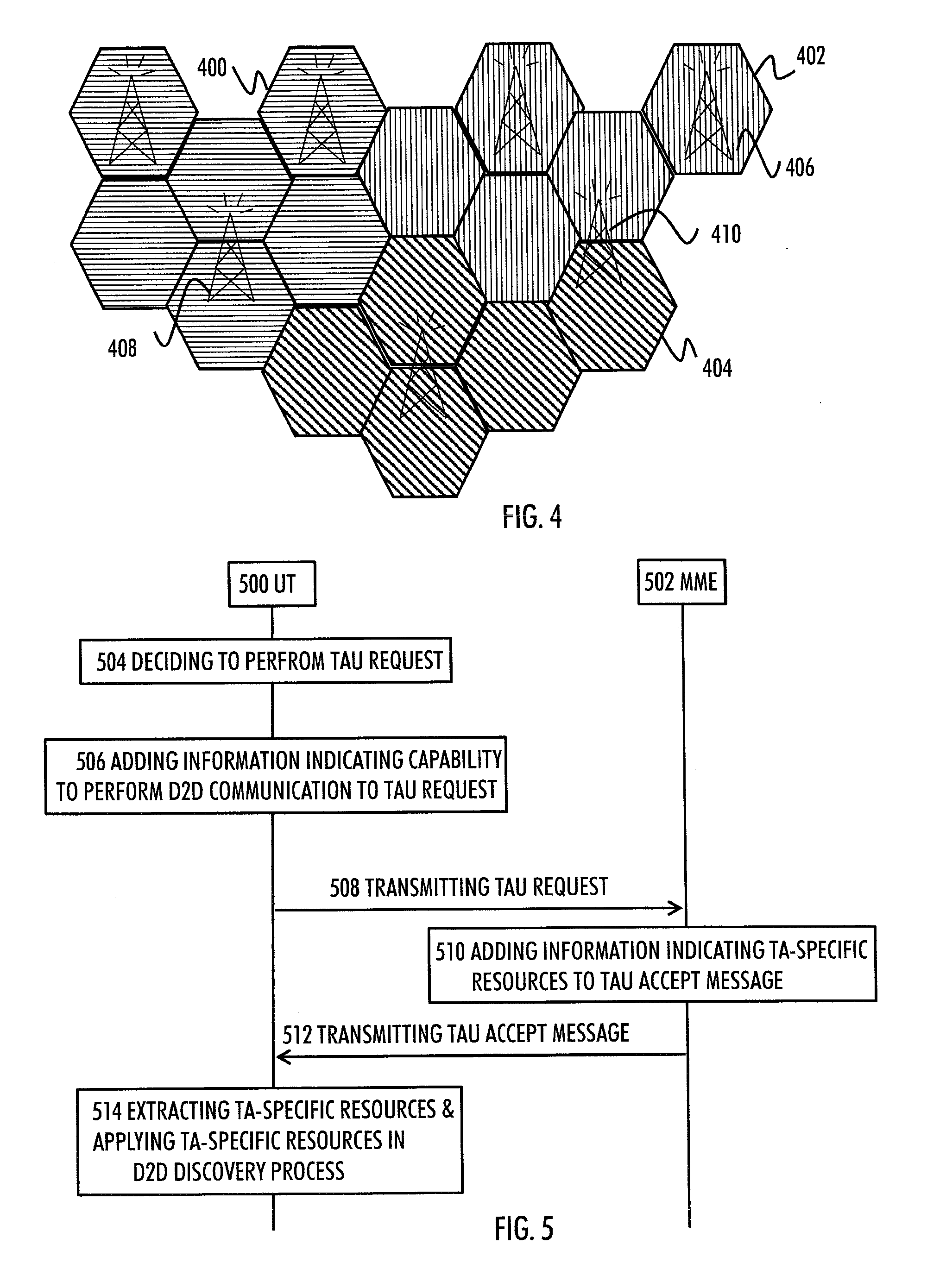
D2D Discovery Process
InactiveUS20130109301A1Improve D2D discovery processNetwork topologiesConnection managementAir interfaceDirect device
There is provided a method including obtaining, by a user terminal capable to perform direct device-to-device, D2D, communication with another user terminal, information indicating tracking area-specific resources for a D2D discovery process; and applying the obtained tracking area-specific resources in performing the D2D discovery process within the tracking area, wherein the D2D discovery process is for discovering D2D communication capable devices in the tracking area over an air interface of a cellular network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
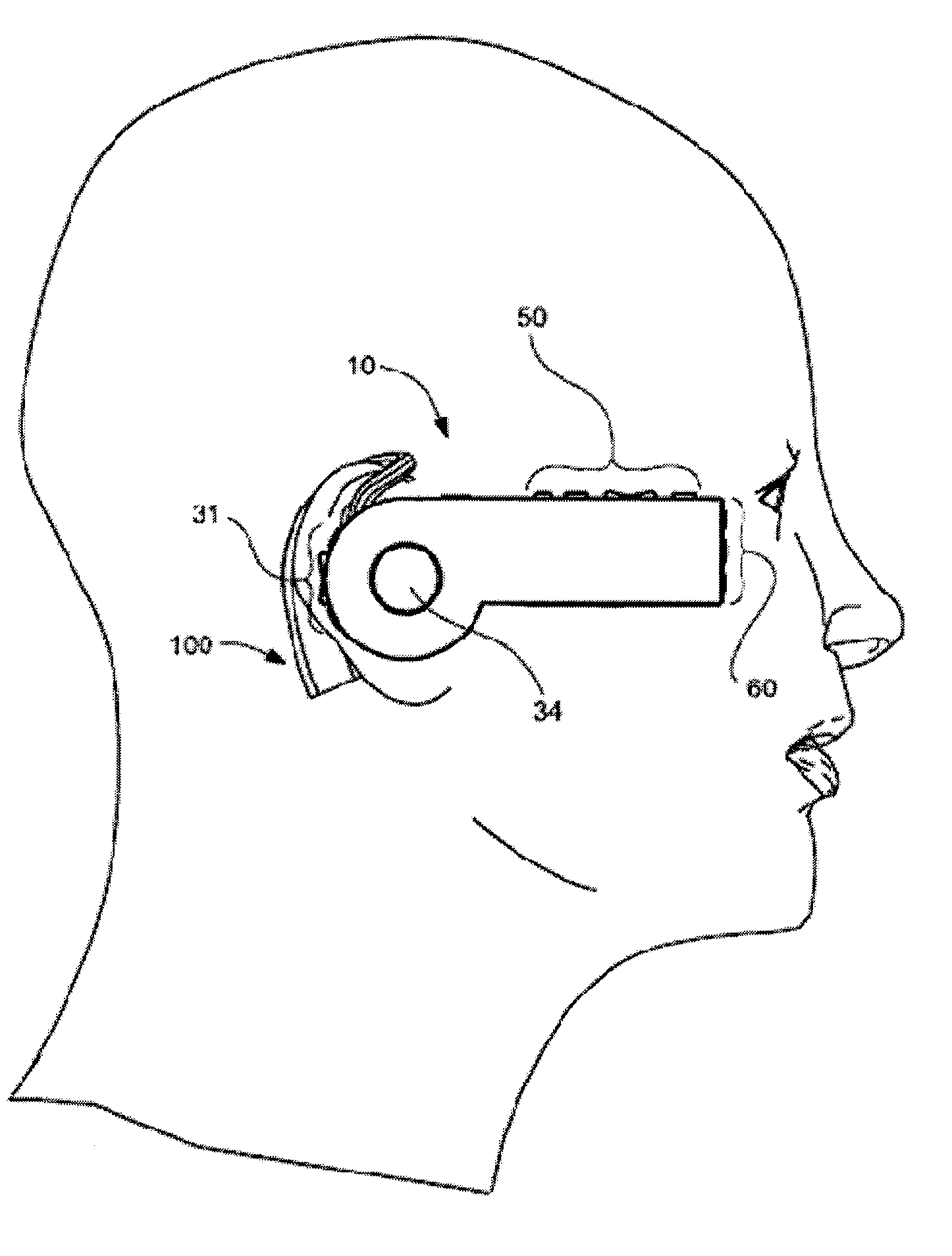
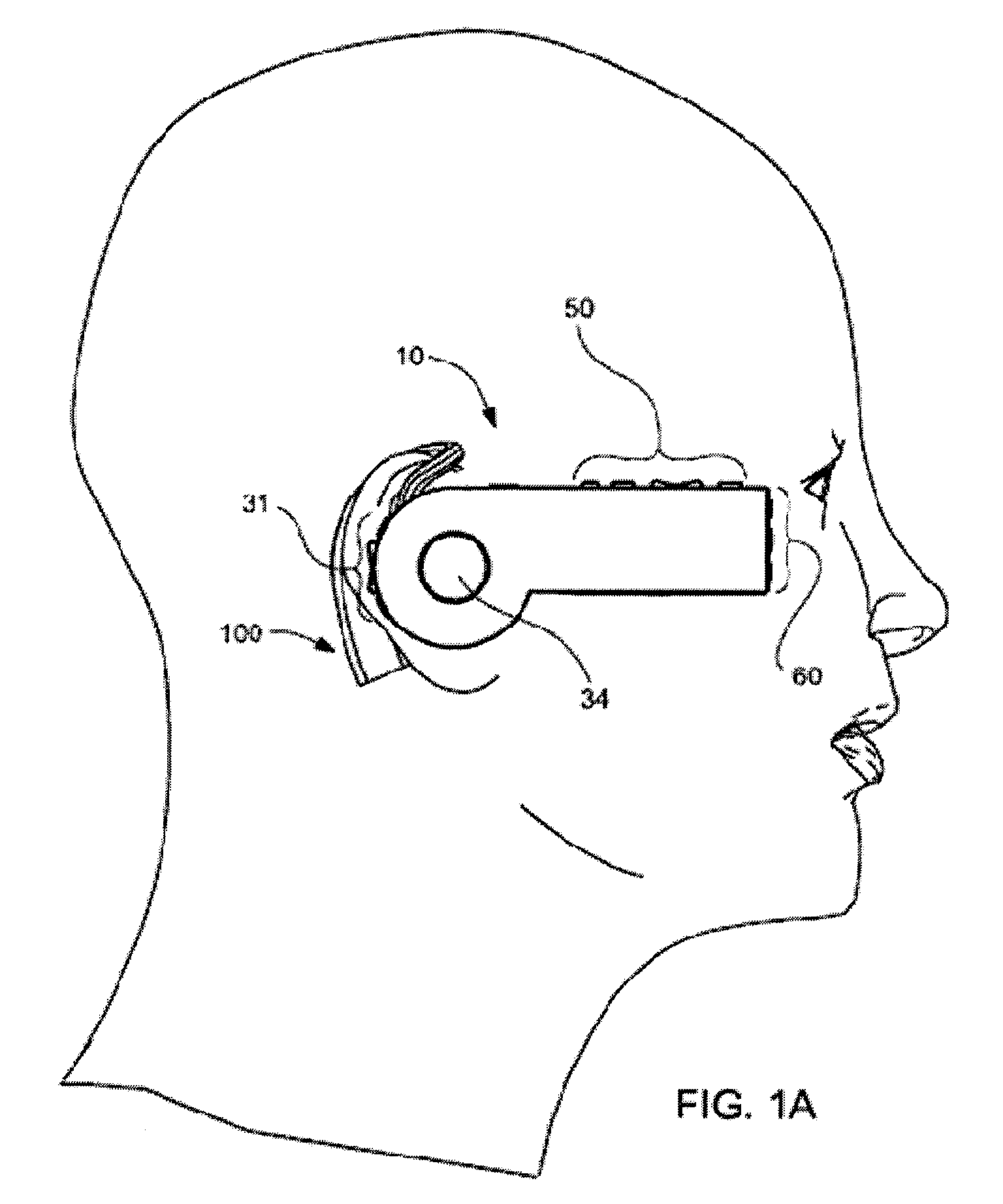
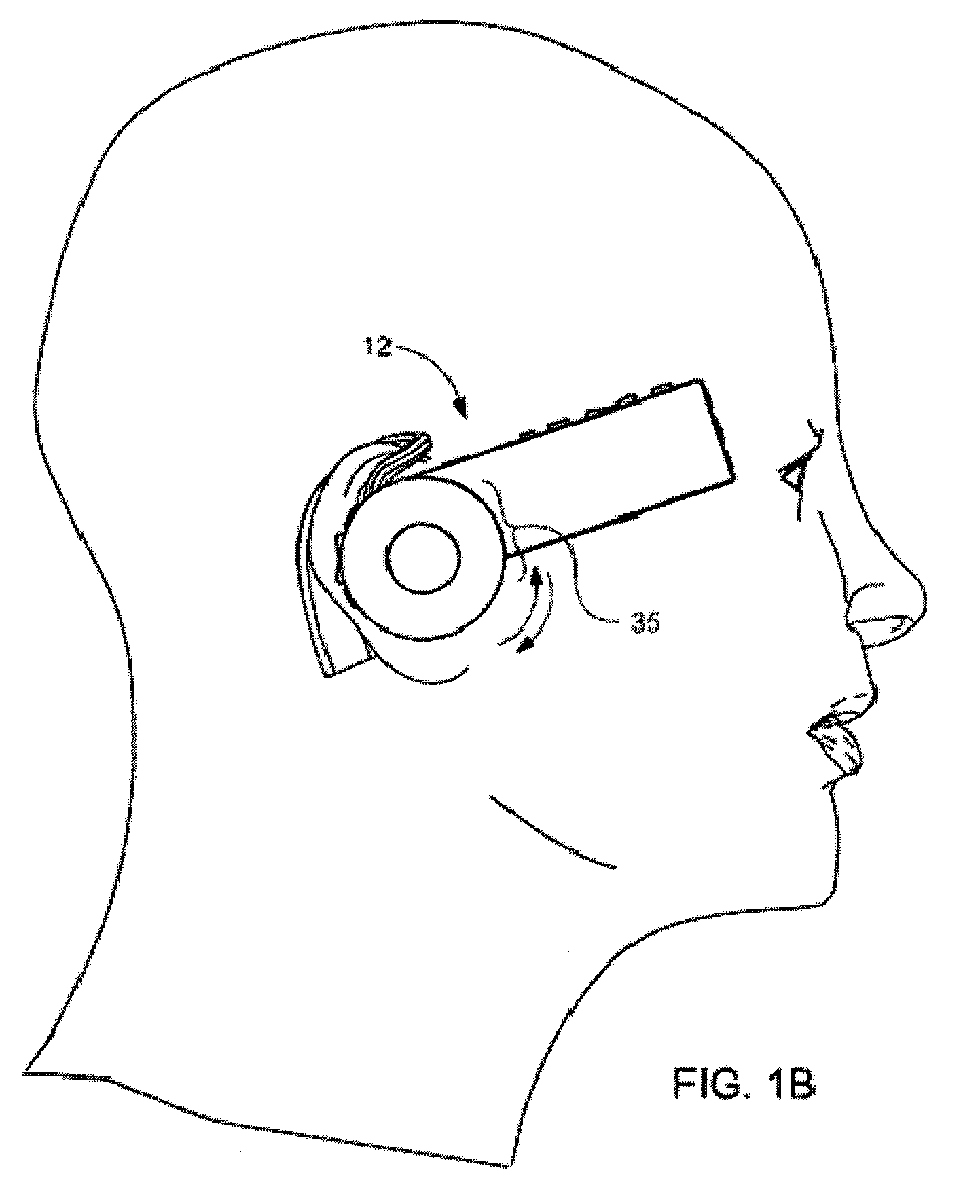
Headset-Based Telecommunications Platform
ActiveUS20100245585A1Extend battery lifeTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersData streamPeer-to-peer
A hands-free wireless wearable GPS enabled video camera and audio-video communications headset, mobile phone and personal media player, capable of real-time two-way and multi-feed wireless voice, data and audio-video streaming, telecommunications, and teleconferencing, coordinated applications, and shared functionality between one or more wirelessly networked headsets or other paired or networked wired or wireless devices and optimized device and data management over multiple wired and wireless network connections. The headset can operate in concert with one or more wired or wireless devices as a paired accessory, as an autonomous hands-free wide area, metro or local area and personal area wireless audio-video communications and multimedia device and / or as a wearable docking station, hot spot and wireless router supporting direct connect multi-device ad-hoc virtual private networking (VPN). The headset has built-in intelligence to choose amongst available network protocols while supporting a variety of onboard, and remote operational controls including a retractable monocular viewfinder display for real time hands-free viewing of captured or received video feed and a duplex data-streaming platform supporting multi-channel communications and optimized data management within the device, within a managed or autonomous federation of devices or other peer-to-peer network configuration.
Owner:EYECAM INC
Localized audio networks and associated digital accessories
InactiveUS20050160270A1Reduce the amount requiredElectrophonic musical instrumentsUser identity/authority verificationTransducerHeadphones
Owner:TUNNEL IP LLC
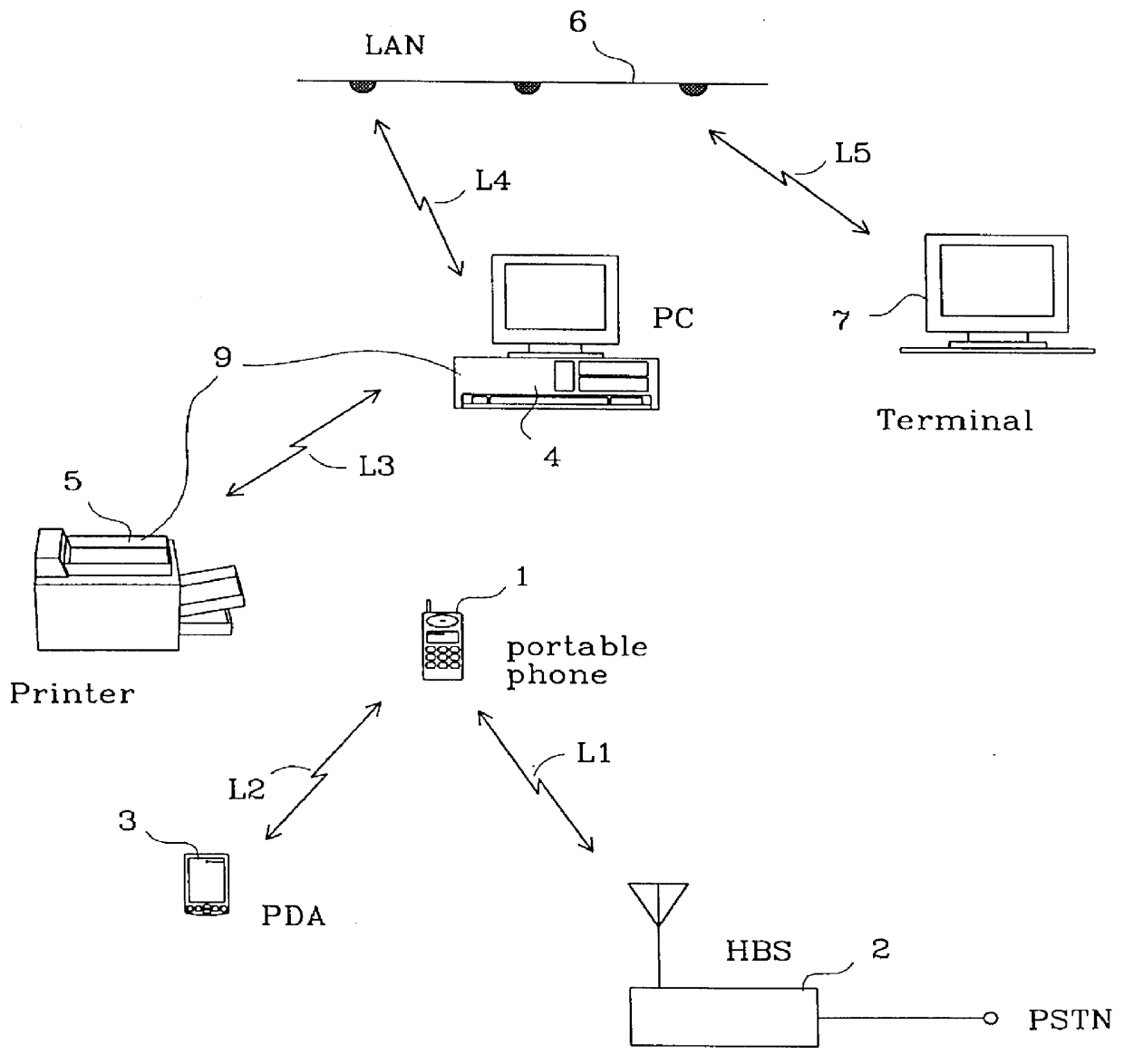
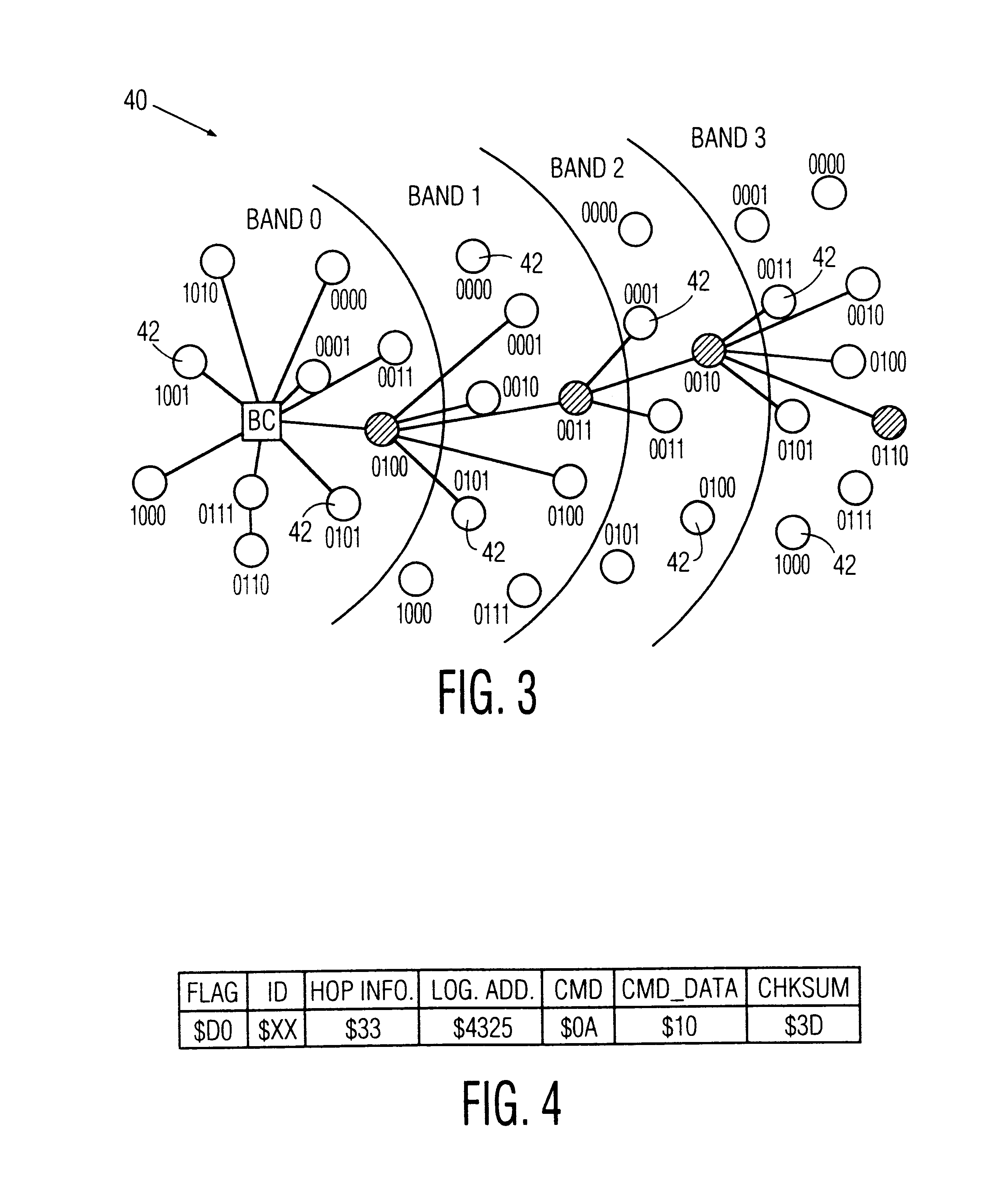
Method for configuring and routing data within a wireless multihop network and a wireless network for implementing the same
InactiveUS6842430B1Active radio relay systemsData switching by path configurationDistributed computingWireless network
A method for configuring a wireless network comprised of a control node and a multiplicity of individual nodes includes the steps of logically organizing the network into a plurality of bands Bi, wherein each of the bands Bi includes a plurality of the individual nodes and is located a number i of hops away from the control node, where i=0 through N, and N≧1, and then assigning a logical address to each of the individual nodes, and storing the assigned logical addresses in the respective individual nodes. The assigned logical address for each individual node includes a first address portion which indicates the band Bi in which that individual node is located, and a second address portion that identifies that node relative to all other individual nodes located in the same band. The network is preferably a packet-hopping wireless network in which data is communicated by transferring data packets from node-to-node over a common RF channel. Each of the individual nodes is preferably programmed to perform the step of comparing its own logical address to a routing logical address contained in each packet which it receives, and to either discard, re-transmit, or process the packet based upon the results of the comparison. The routing logical address contained in a received packet contains the full routing information required to route the packet from a sending node to a destination node along a communication path prescribed by the routing logical address. The control node is programmed to control the routing of packets by inserting the routing logical address into each packet which it transmit, detecting any unsuccessfully transmitted packets, detecting a faulty node in the communication path prescribed by the routing logical address in response to detecting an unsuccessfully transmitted packet, and changing the routing logical address of the unsuccessfully transmitted packet to a new routing logical address which prescribes a new communication path which does not include the detected faulty node. Also disclosed are a wireless network and a network node which are designed to implement the foregoing network configuration and / or routing methods.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
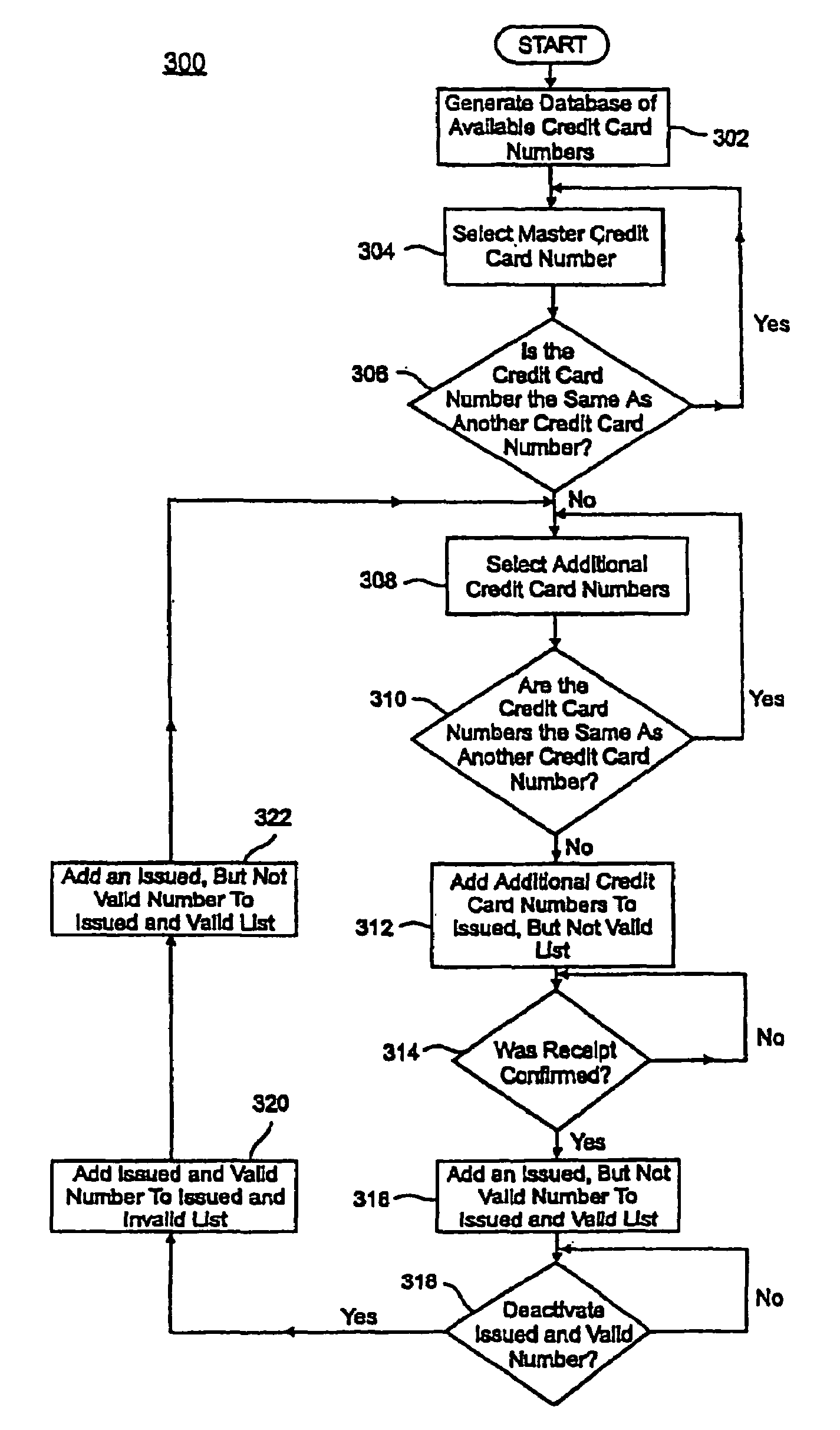
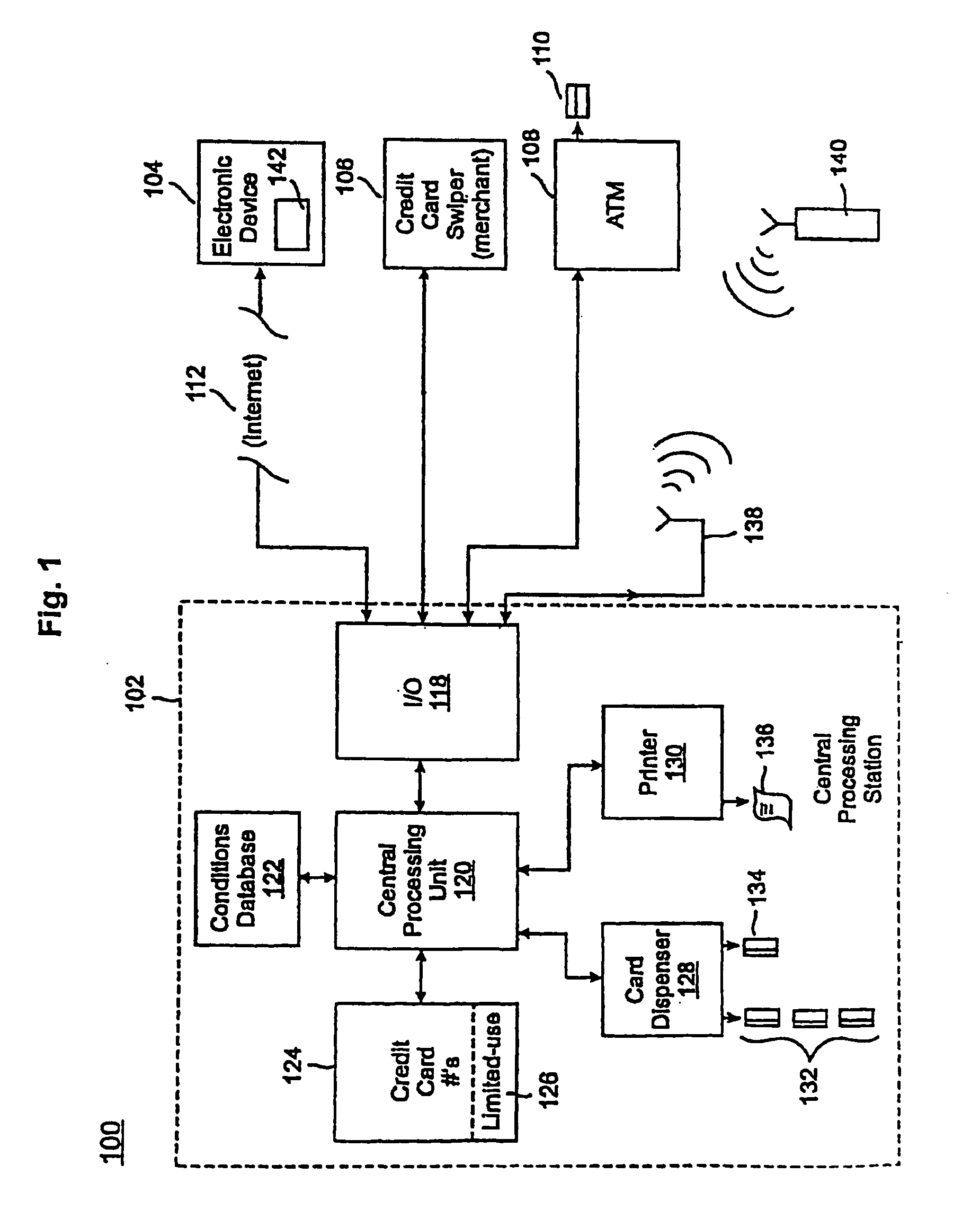
Credit cards system and method having additional features
InactiveUS20090037333A1Complete banking machinesCredit registering devices actuationCredit cardComputer hardware
A credit card system is provided which has the added feature of providing additional limited use credit card numbers and / or cards. These numbers and / or cards can be used for a single or limited use transaction, thereby reducing the potential for fraudulent reuse of these numbers and / or cards. The credit card system finds application to “card remote” transactions such as by phone or Internet. Additionally, when a single use or limited use credit card is used for “card present” transactions, so called “skimming” fraud is eliminated. Various other features enhance the credit card system, which will allow secure trade without the use of elaborate encryption techniques. Methods for limiting, distributing and using a limited use card number, controlling the validity of a limited use credit card number, conducting a limited use credit card number transaction and providing remote access devices for accessing a limited use credit card number are also provided.
Owner:ORBIS PATENTS
System and method of accessing and recording messages at coordinate way points
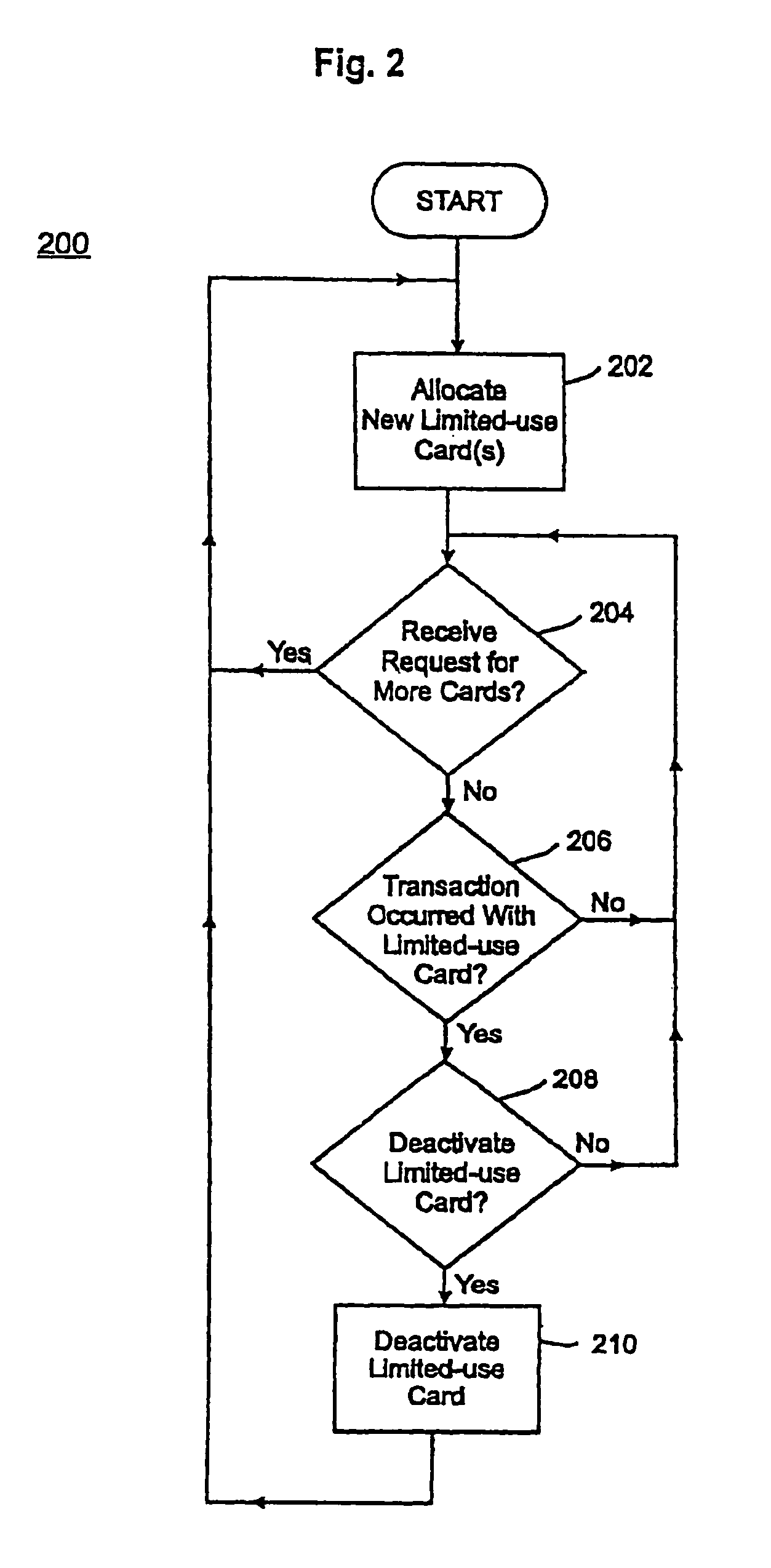
InactiveUS6377793B1Speed up complianceLow costInstruments for road network navigationSpecial service for subscribersMobile radioTechnician
The present invention is essentially a method and system for leaving and retrieving messages at specific coordinate way points within a commercial mobile radio service (CMRS) provider network. Users carry or transport interface devices for communicating over the network and are able to record and view messages at specific coordinate locations while traveling in the network. The location of the device is calculated by the device or by the network while the device is powered on and in within the physical boundaries of the network, or through a combination of both. Messages can be made available to network subscribers when their interface devices come within an area centered about a physical coordinate location. Personalized messages can also be left by subscribers at any coordinate point within the boundaries of the network. The invention can also be used to facilitate access of information about an asset when a technician comes within a physical proximity threshold relative to said asset.
Owner:EMPIRE IP LLC +1
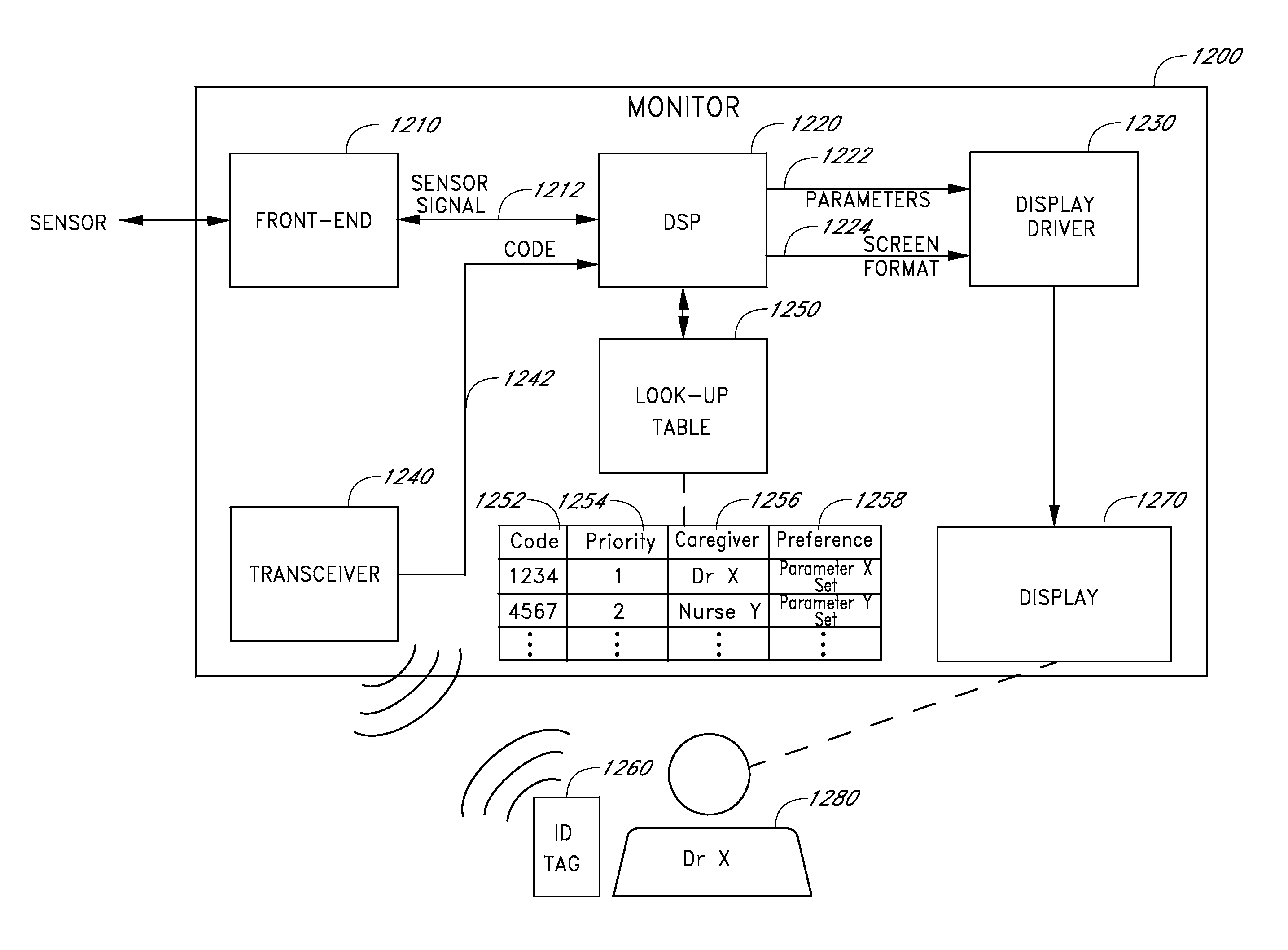
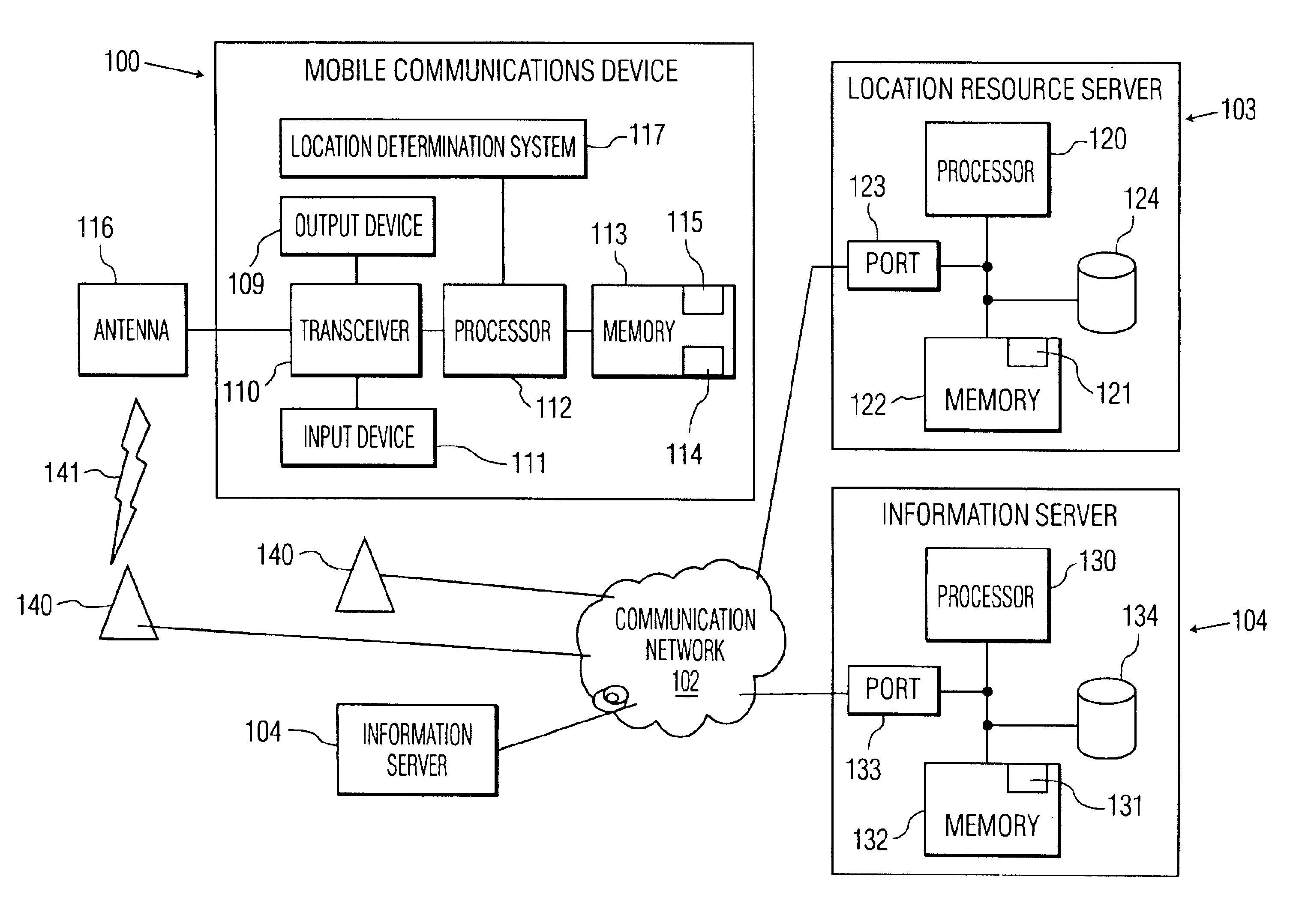
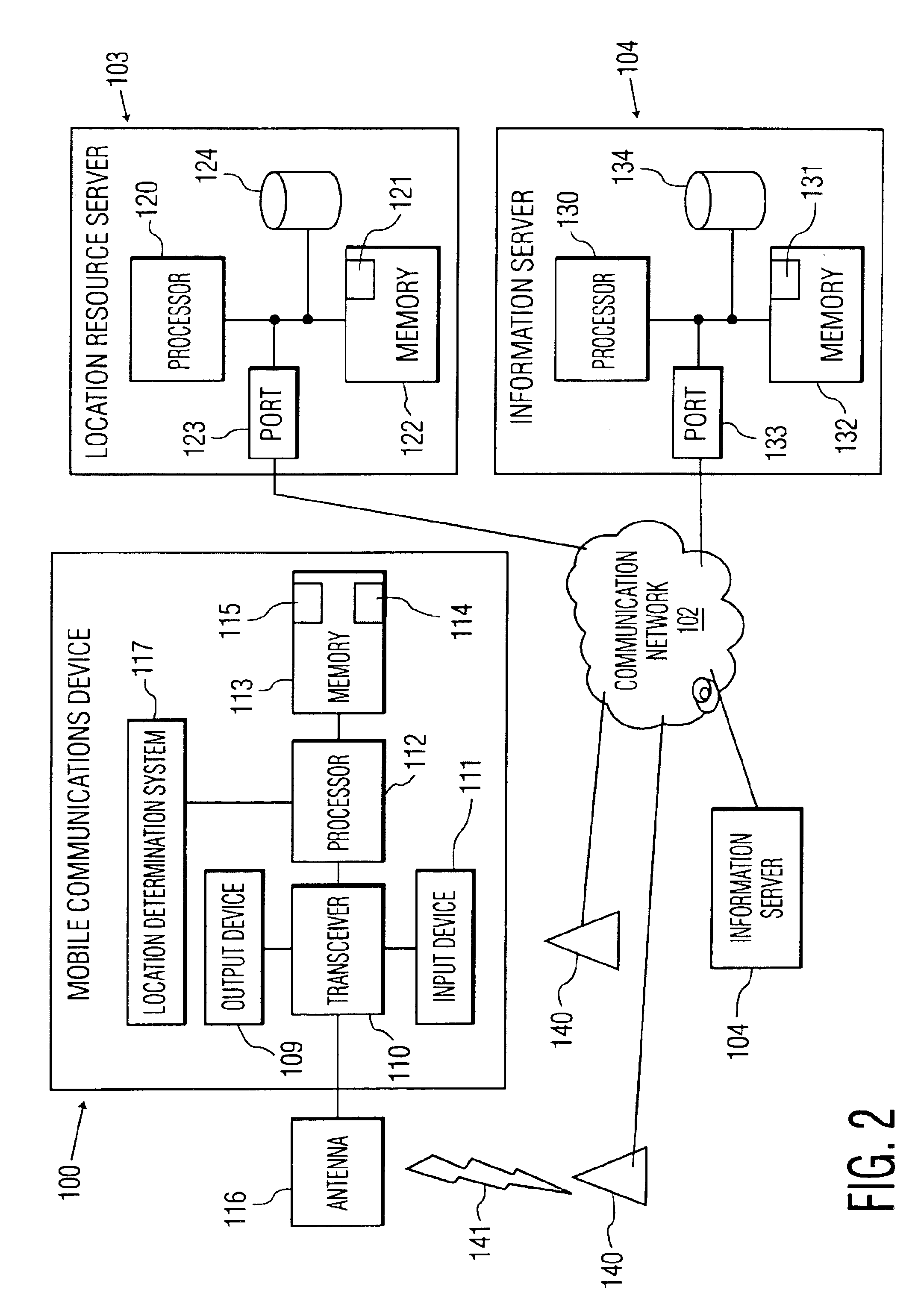
Body-Associated Receiver and Method
Receivers, which may be external or implantable, are provided. Aspects of receivers of the invention include the presence of one or more of: a high power-low power module; an intermediary module; a power supply module configured to activate and deactivate one or more power supplies to a high power processing block; a serial peripheral interface bus connecting master and slave blocks; and a multi-purpose connector. Receivers of the invention may be configured to receive a conductively transmitted signal. Also provided are systems that include the receivers, as well as methods of using the same. Additionally systems and methods are disclosed for using a receiver for coordinating with dosage delivery systems.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
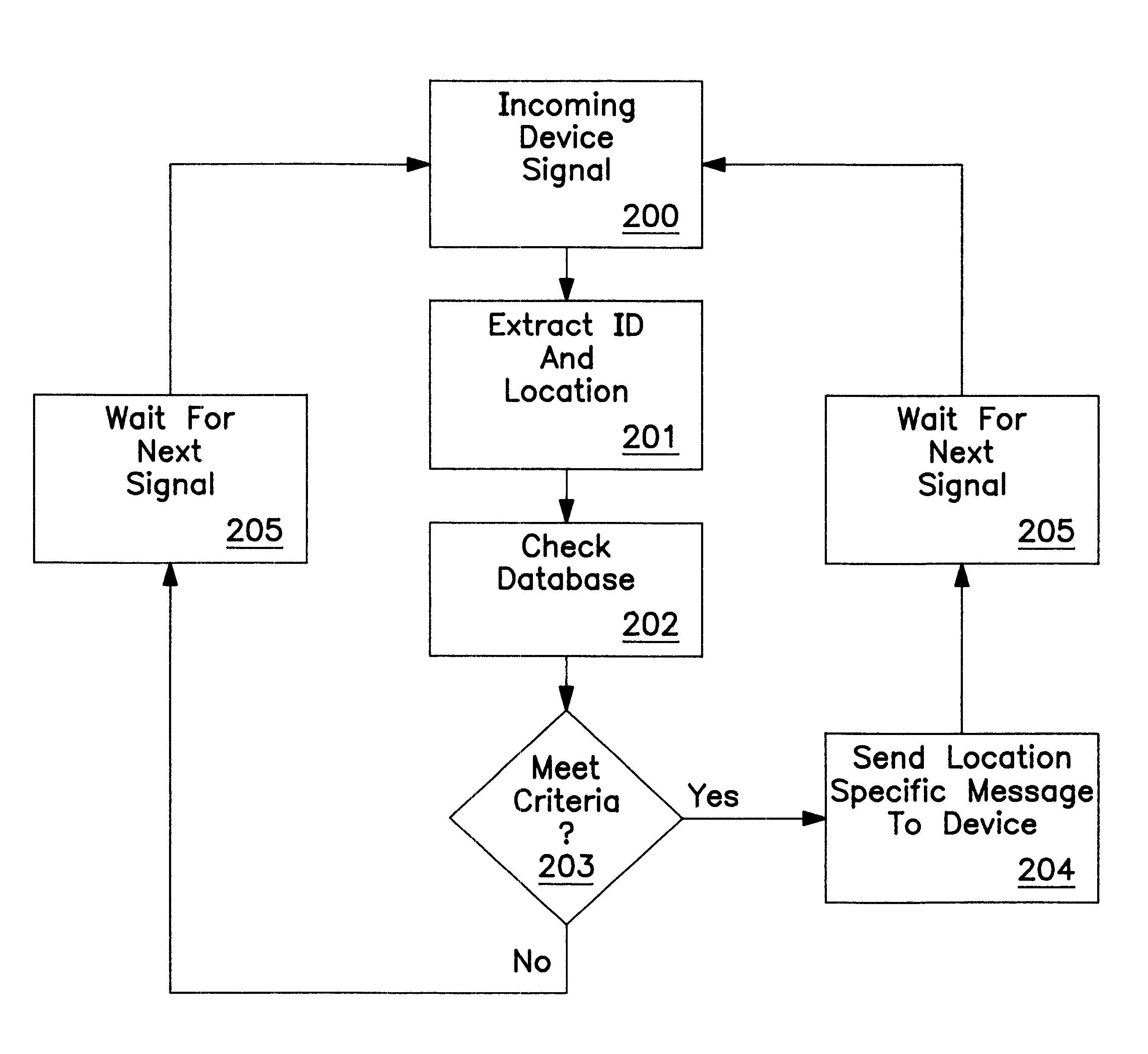
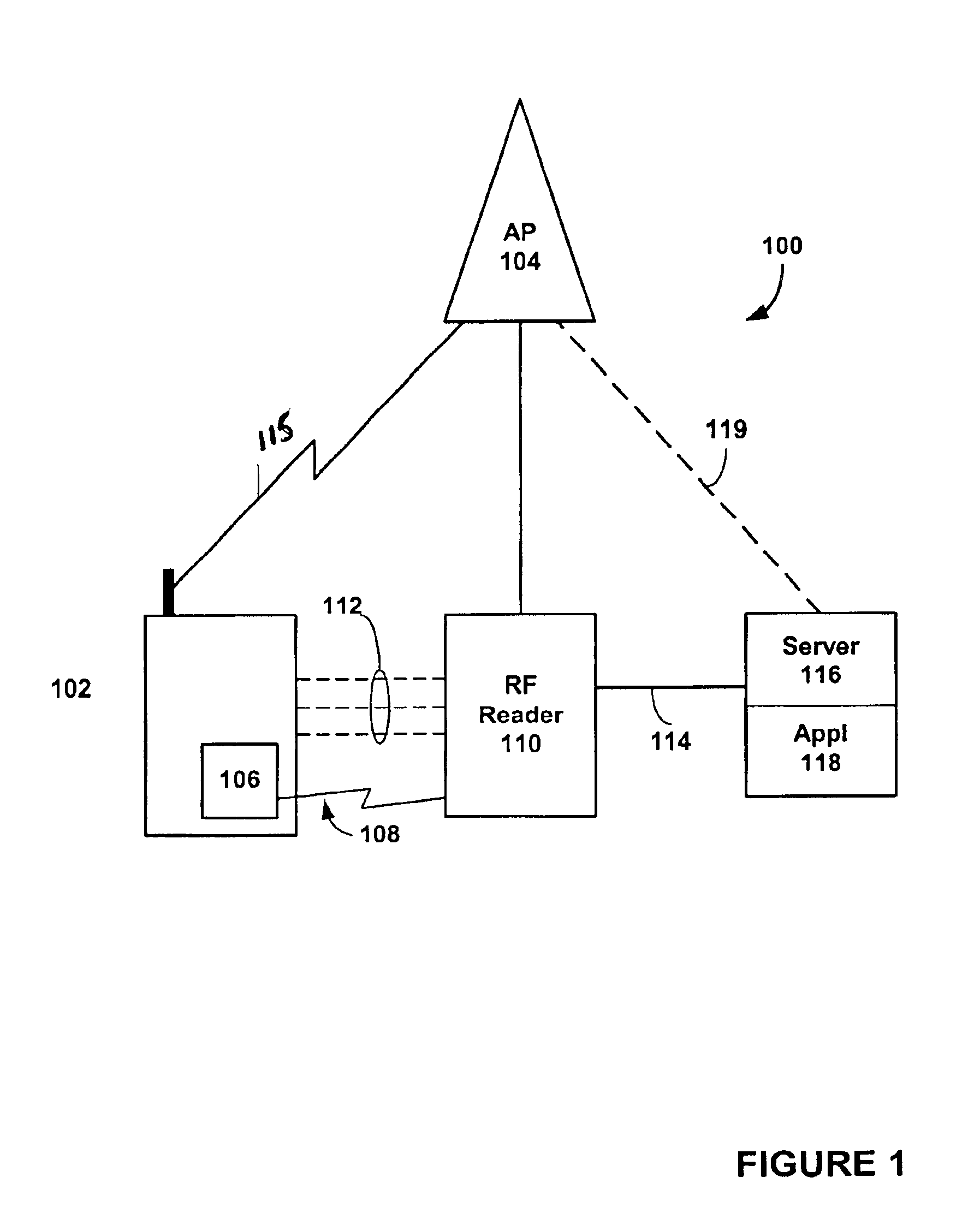
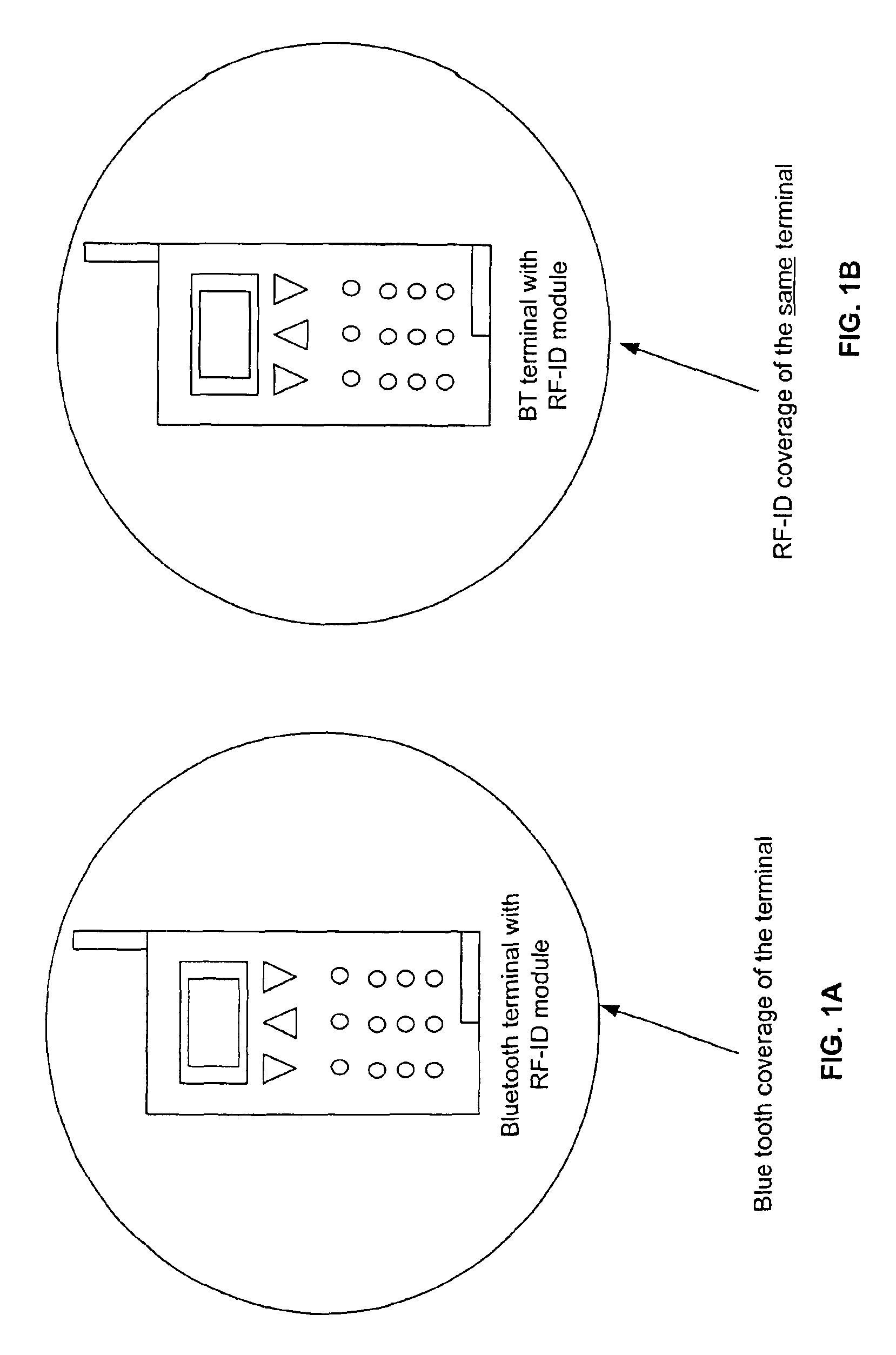
Radio frequency identification (RF-ID) based discovery for short range radio communication
InactiveUS6892052B2Shorten sessionShorten the timeCordless telephonesConnection managementRf fieldConnectionless communication
A RF-ID based wireless terminal has shortened session set-up and user identification time for conducting transactions with interactive service applications. The wireless terminal includes a terminal identification number and a user identification as a RF-ID tag. A RF-ID reader transmits a RF field for detecting the RF-ID tag in the terminal and provides an output signal when the terminal is within the reader field. The output signal establishes a connectionless communication to an access point or other terminal which initiates a wireless paging operation, in lieu of conducting a terminal discovery process, based upon the content of the RF-ID tag. The terminal initiates a wireless session between the terminal and the access point or terminal for conducting transactions with a service application linked to the access point or terminal.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
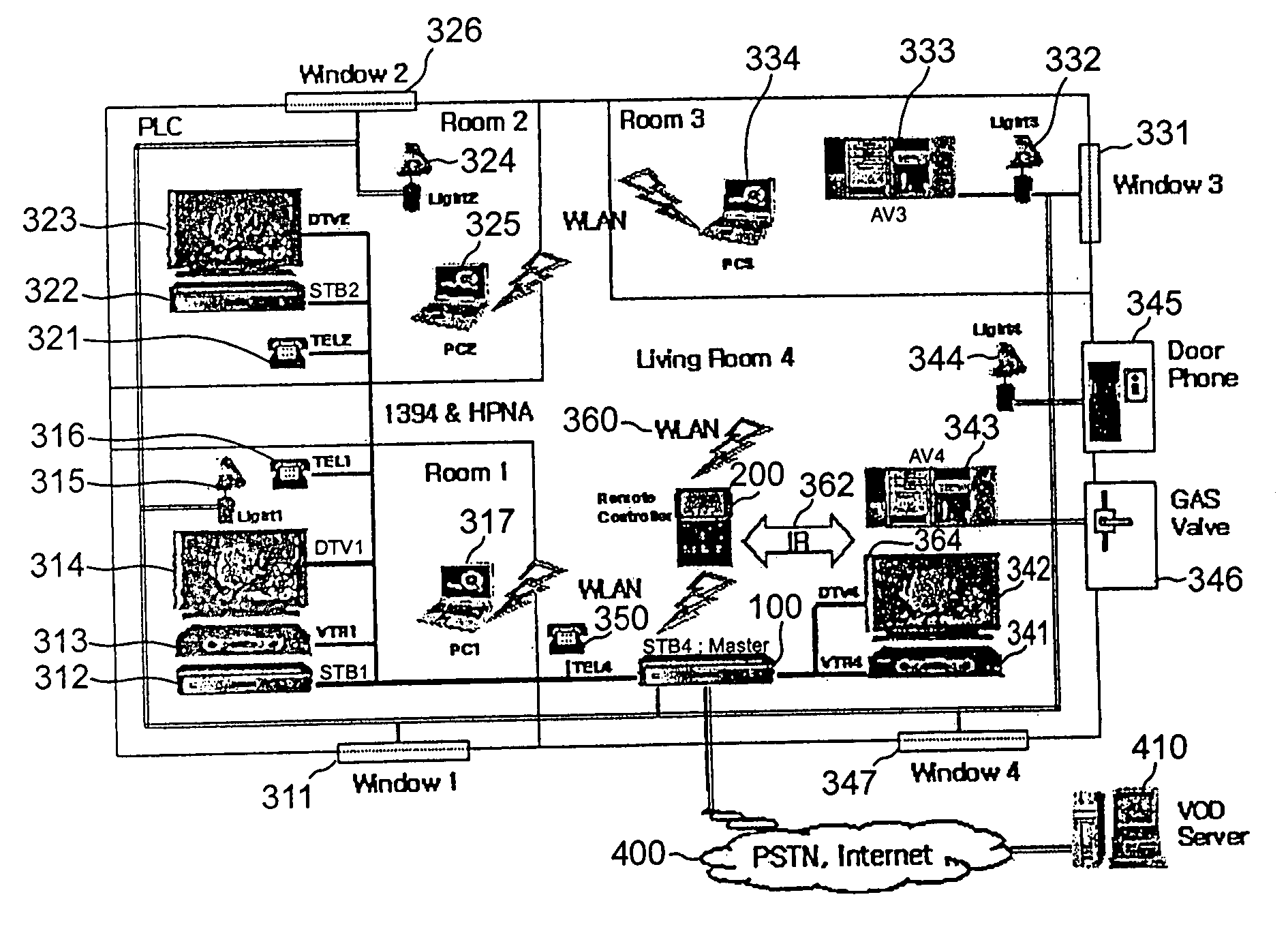
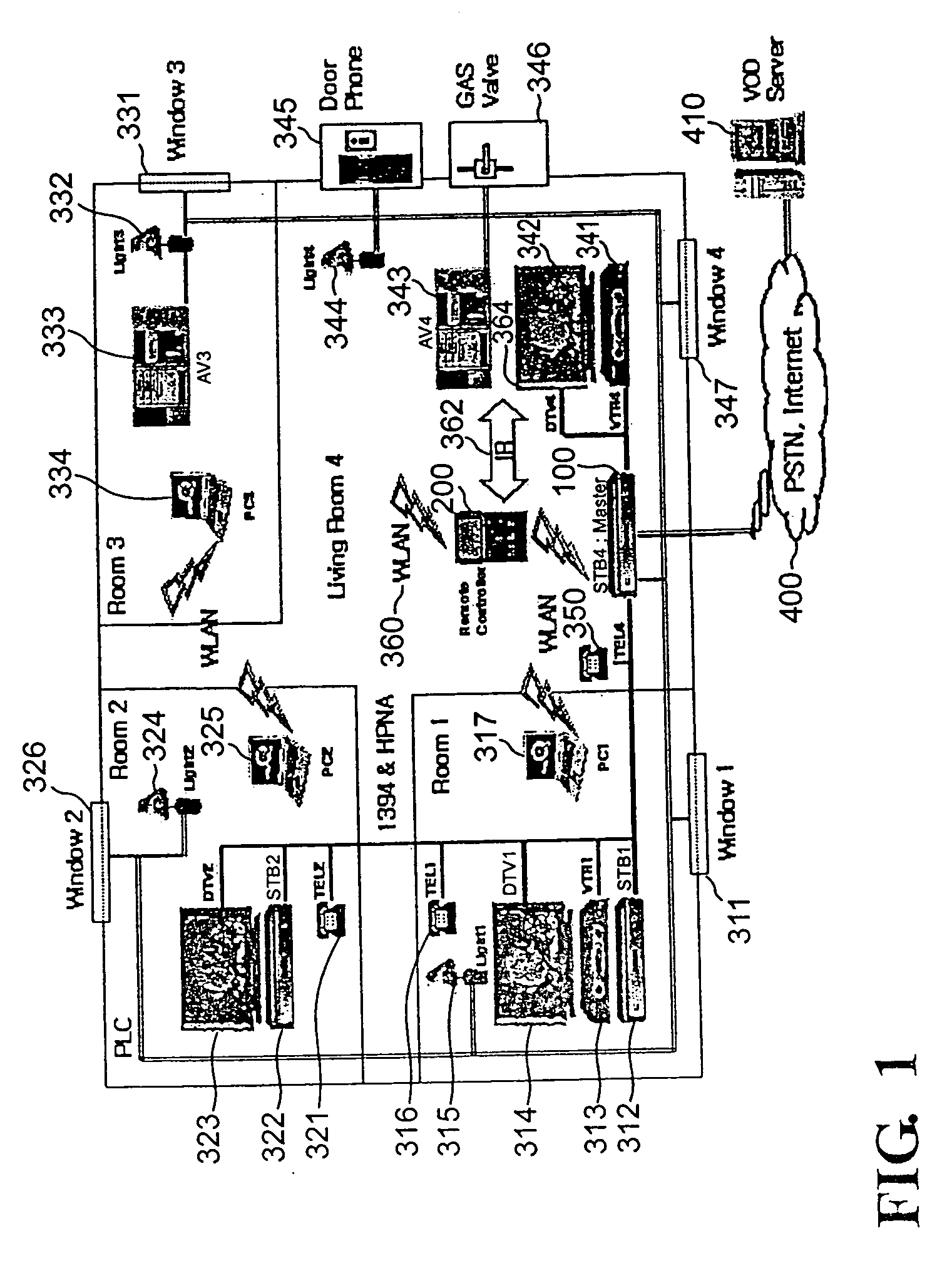
Remote controller and set-top-box therefor
InactiveUS20040148632A1Confident in accuracyConfident in dependabilityTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsControl signalEngineering
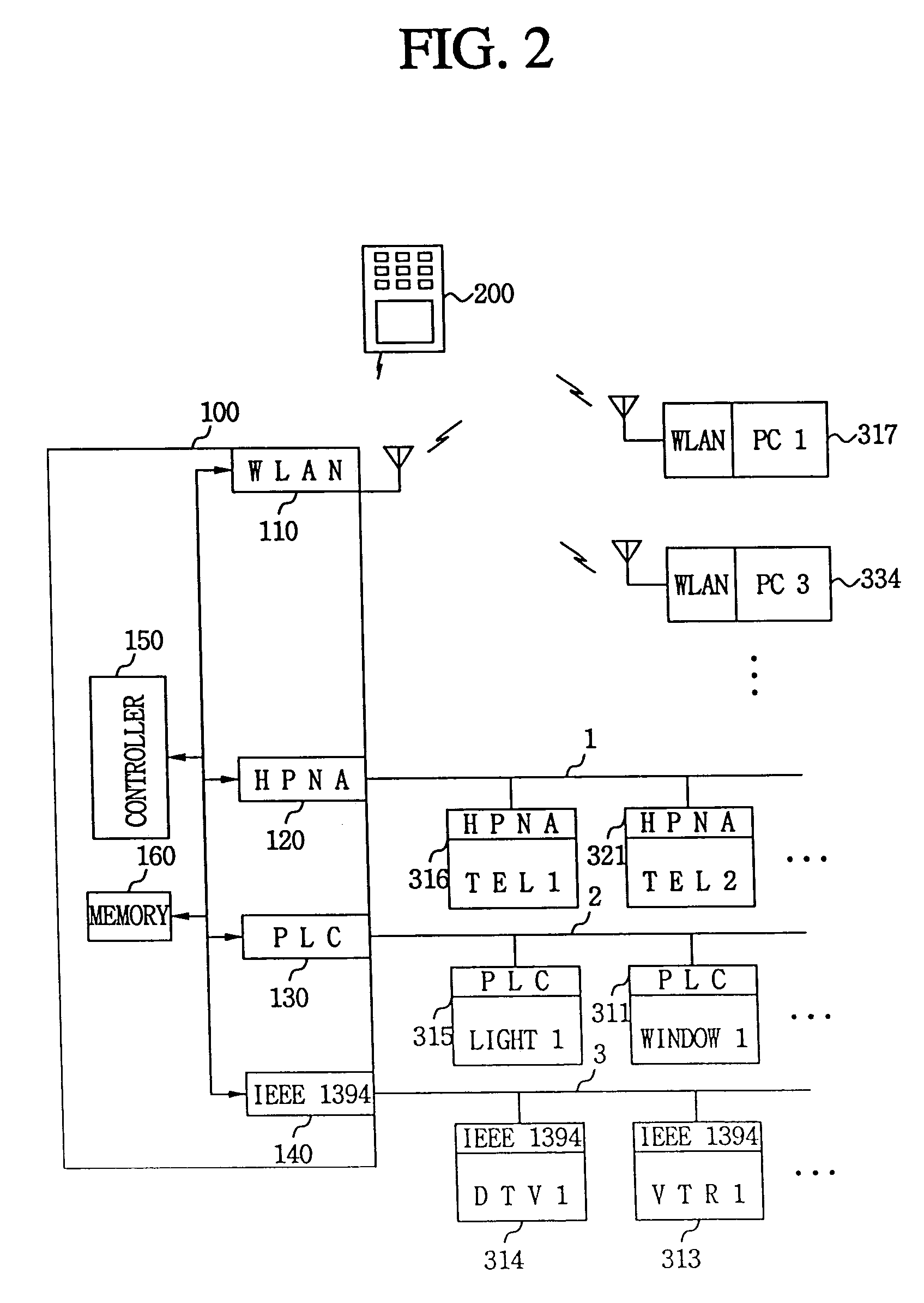
An integrated remote controller and a main set-top-box therefor, wherein the integrated remote controller performs communication with the main set-top-box of home network system through WLAN and provides appliance control signals to a corresponding appliances connected to the main set-top-box through wires or wirelessly. Every home networked household appliance can be controlled by one integrated remote controller through intuitive and easy user interface, irrespective of where a user is, whereby the user can easily control any appliance, check a control result in response to a control request right away, and check or control the status of appliances through a regular monitoring function. As a result, user mobility, convenience, and functionality can be maximized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dynamic voice over data prioritization for wireless communication networks
InactiveUS20050107091A1Reduce overheadIncrease network resource availableError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData rateRate reduction
In a wireless communication network providing voice and data services, one or more entities in the network, such as a base station controller and / or radio base station, can be configured to reduce data services overhead responsive to detecting a congestion condition, thereby increasing the availability of one or more network resources for voice services. In one or more exemplary embodiments, one or more current data services users are targeted for modification of their ongoing data services to effect the reduction in data services overhead. Modifications can include, but are not limited to, any one or more of the following: forward or reverse link data rate reductions, and shifting of forward or reverse link traffic from dedicated user channels to shared user channels. Targeting of users for service modification can be based on reported channel quality information. For example, users reporting poor radio conditions can be targeted first for service modifications.
Owner:IDTP HLDG
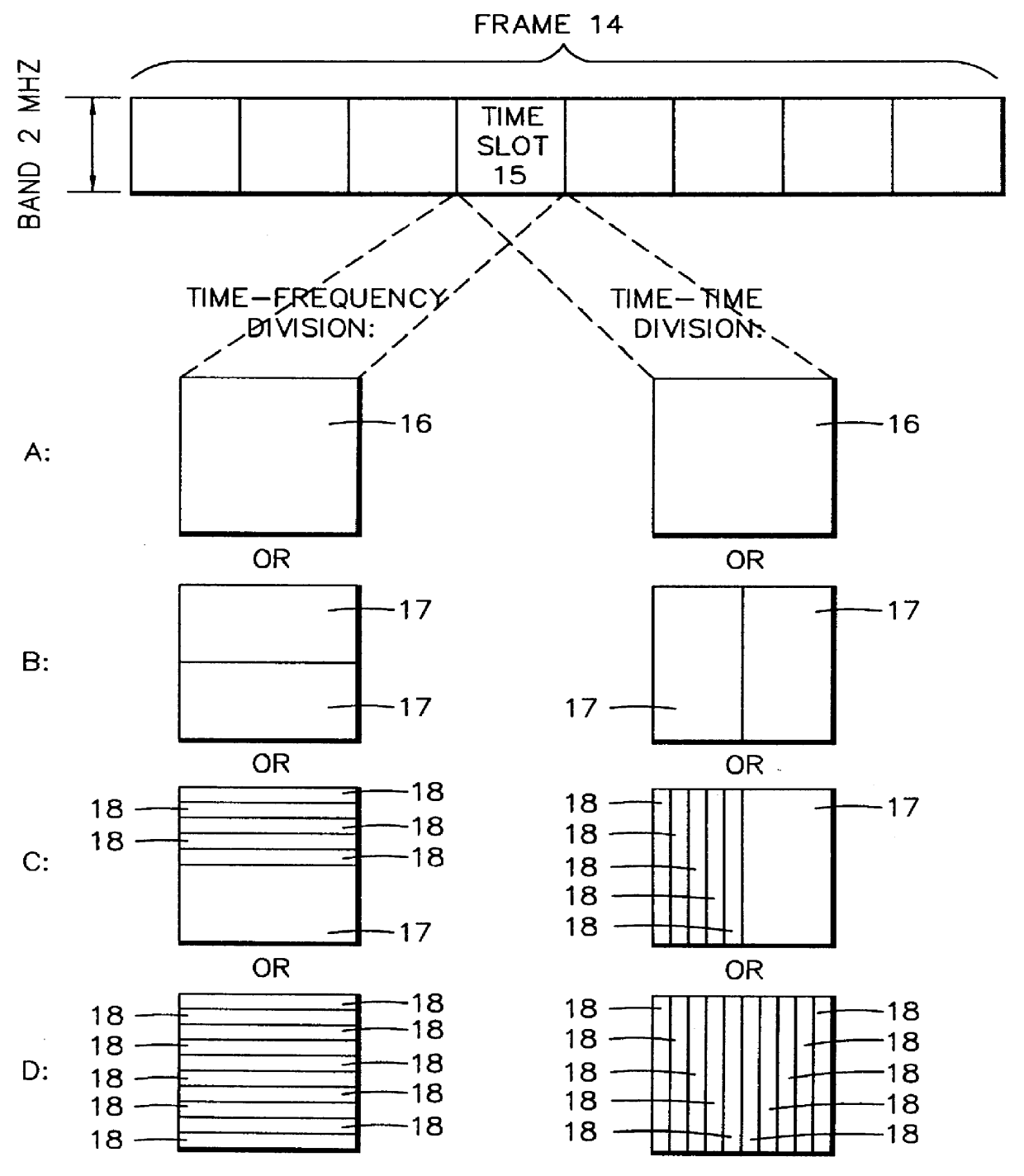
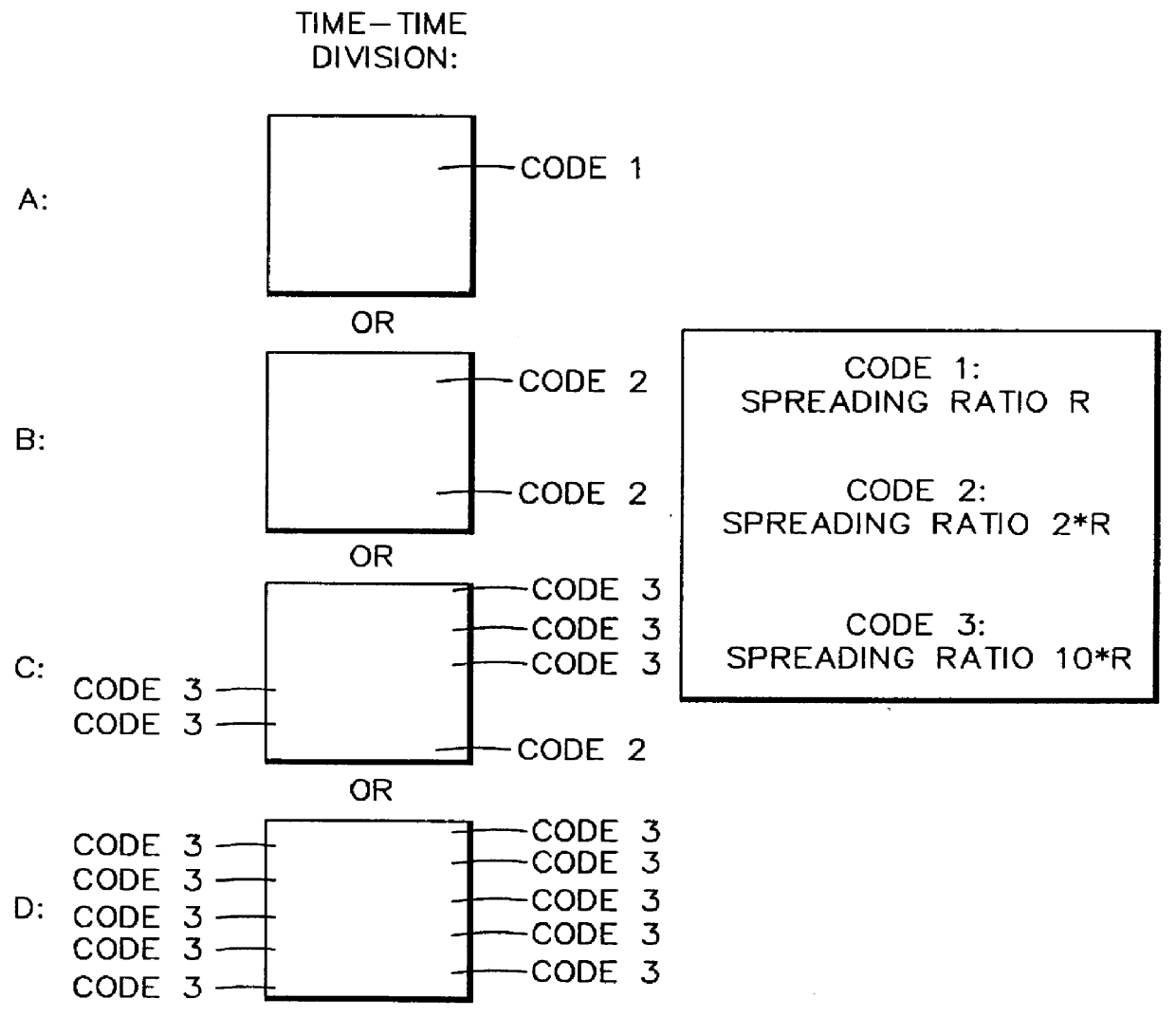
Method for radio resource control
In order to control the use of physical radio resources, the physical radio resources are divided into chronologically consecutive frames (14), so that a frame contains slots (16, 17, 18) of various sizes, which slots represent a given share of the physical radio resources contained in the frame and can be individually allocated to different radio connections. The first dimension of a frame is time and the second dimension can be time, frequency or code. In the direction of the second dimension the slots represent various sizes, and a given first integral number of slots of the first size can be modularly replaced by another integral number of slots of another size. A certain number of consecutive frames form a superframe (19), in which case frames with corresponding locations in consecutive superframes are equal in slot division and allocations, if the data transmission demands do not change. Changes in the state of occupancy of the slots are possible at each superframe. In order to form an uplink connection, the mobile station sends a capacity request, where it indicates the type of requested connection and the demand of resources. In order to form a downlink connection, the base station subsystem sends a paging call, where it indicates the location in the superframe of the slots allocated to the connection. In order to indicate the state of occupancy, the base station subsystem maintains a superframe-size parametrized reservation table.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Health care sanitation monitoring system
ActiveUS20130045685A1Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageMonitoring systemMedical emergency
A medical sanitation device may include a detector for detecting the physical presence of a clinician token within a detection area in the vicinity of the medical sanitation device. The clinician token may be indicative of the identity of a clinician. The medical sanitation device also includes a sanitation module configured to be used by the clinician to perform a sanitation task. Detection of a clinician in proximity to the medical sanitation device may be used to at least partially control access to, or operation of, a medical patient monitoring device.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
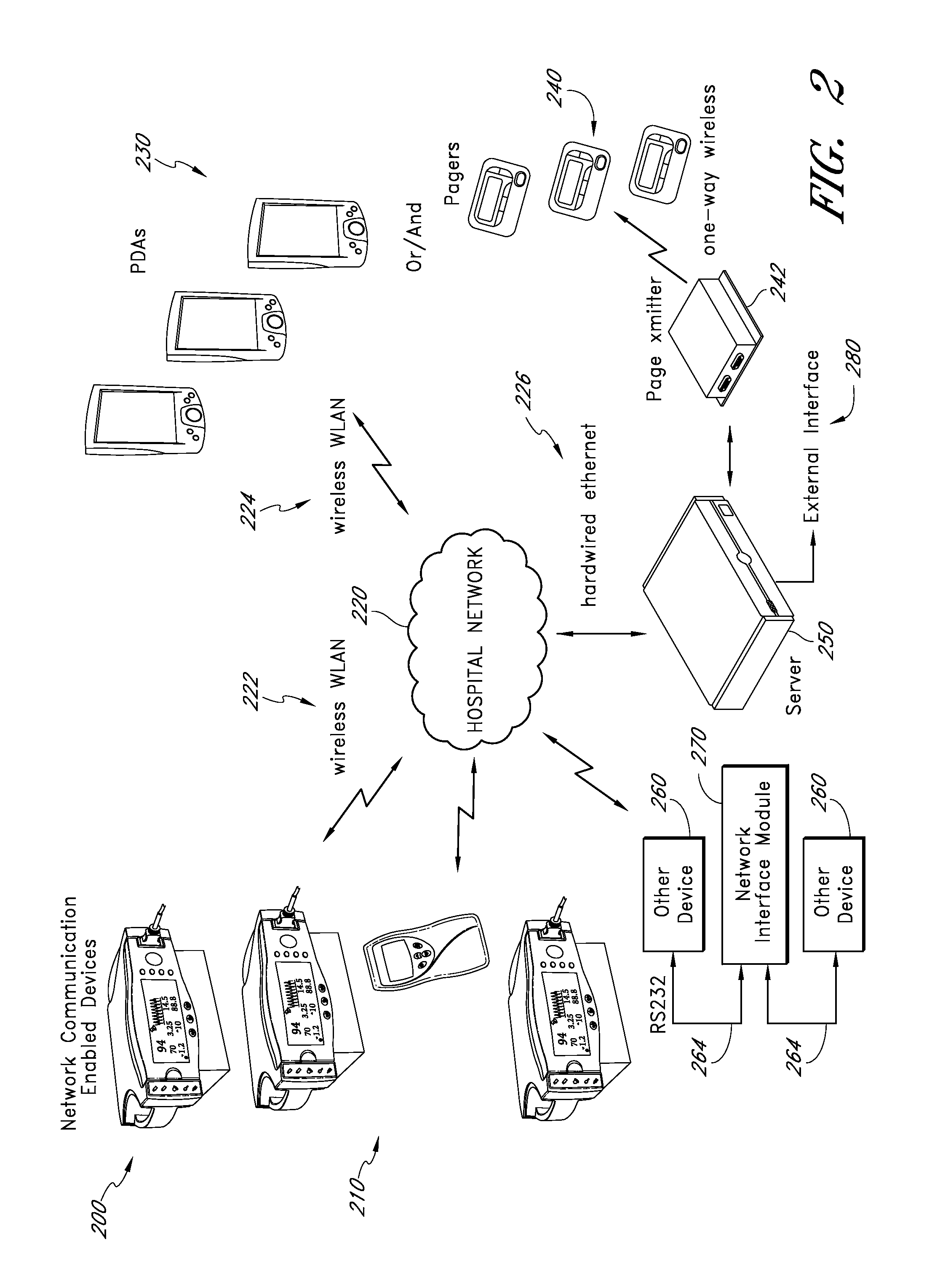
Distributed location based service system
InactiveUS6879838B2Improve abilitiesAccurately determineRoad vehicles traffic controlSpecial service for subscribersGeolocationGlobal Positioning System
A system, apparatus, and method for providing a distributed location based service system to a mobile user. Information related to a particular geographic location may be electronically transferred to a mobile electronic device, without a request from the user, and interpreted locally on the device in the form of a virtual map of location based resources. The mobile device is capable of determining its location using a GPS (Global Positioning System) or a process of measurement and prediction based on calculation. The mobile device can then use the location information and compare it to available location based resources within the device.
Owner:MOBILE ENHANCEMENT SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com