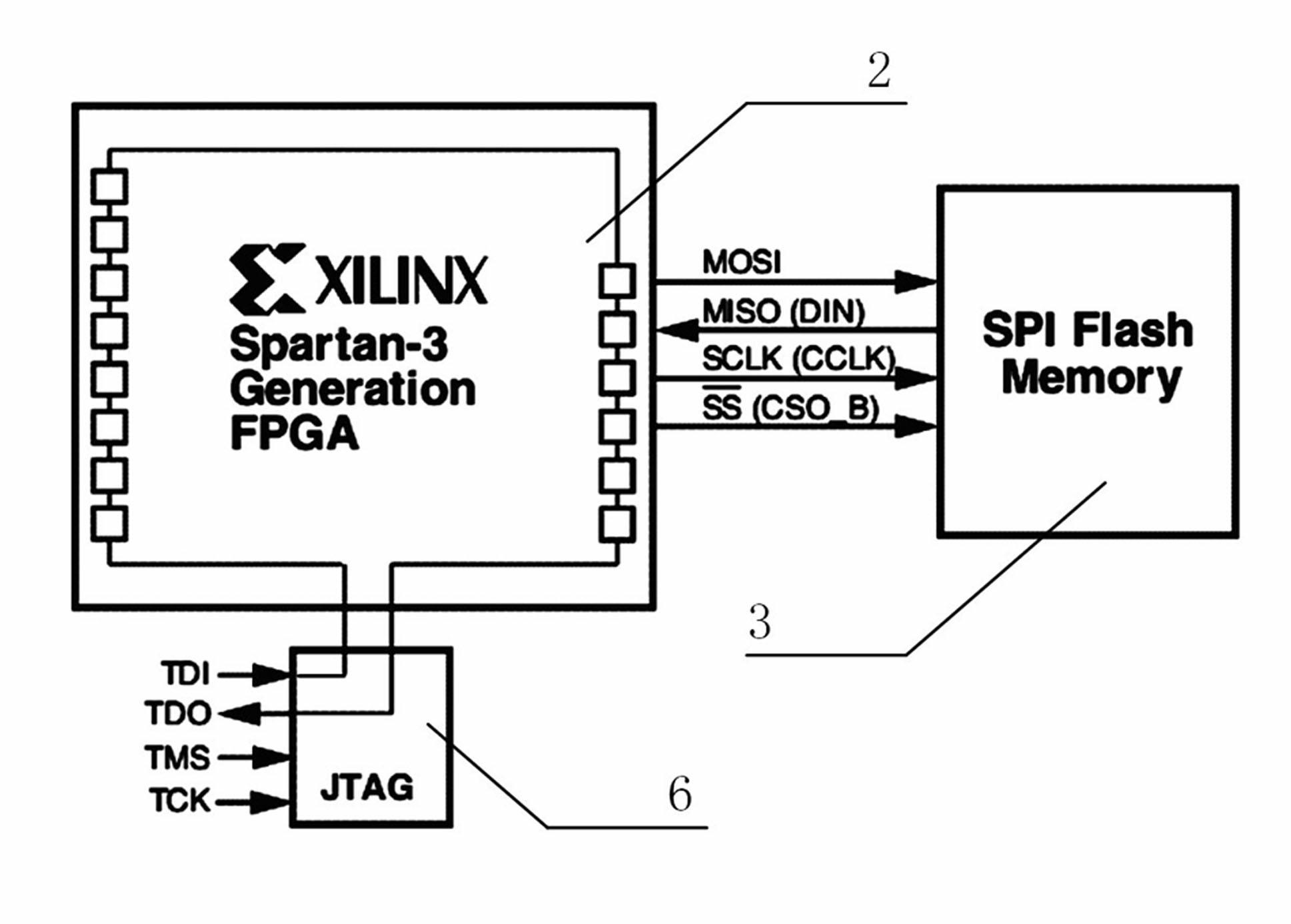
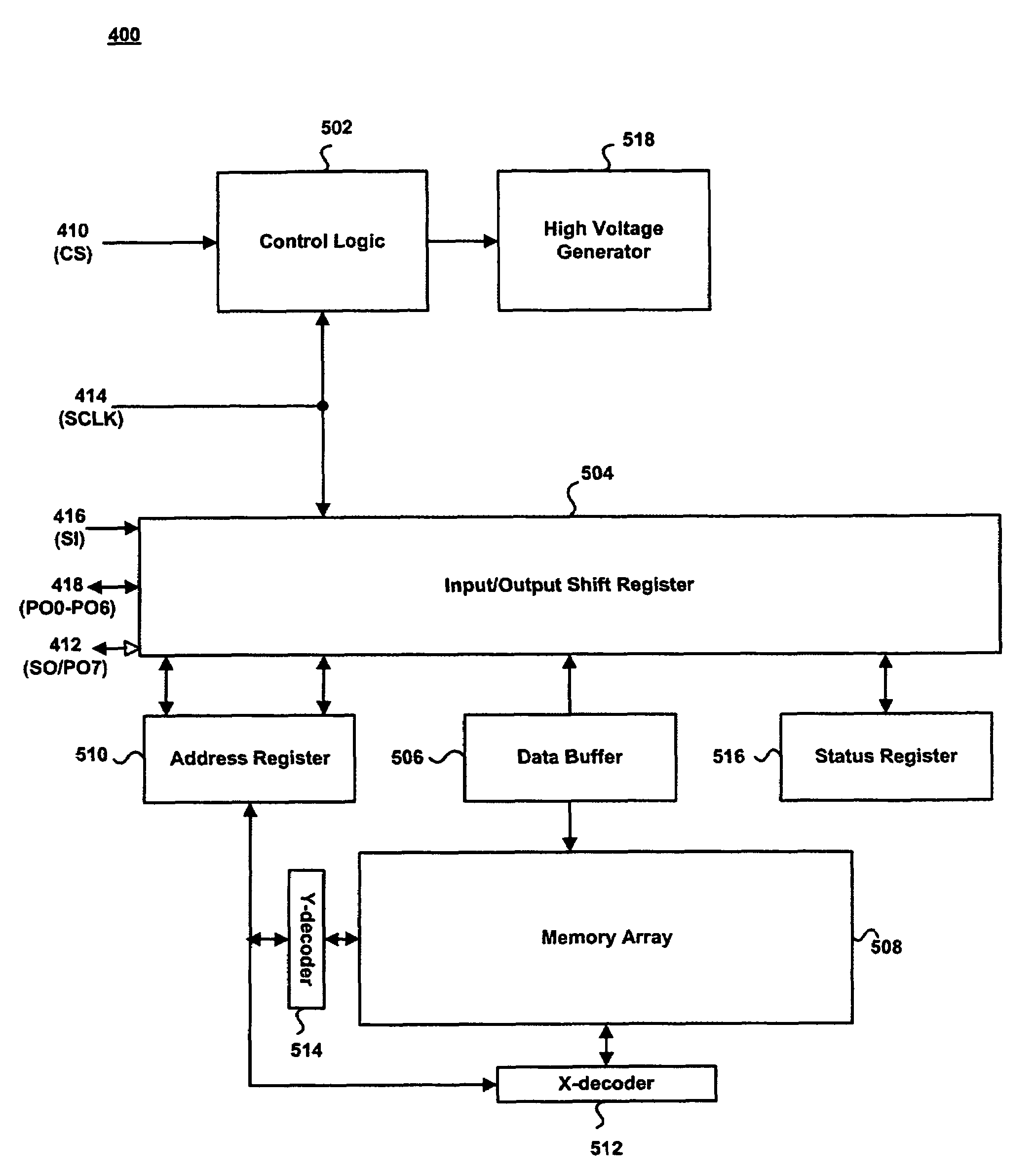
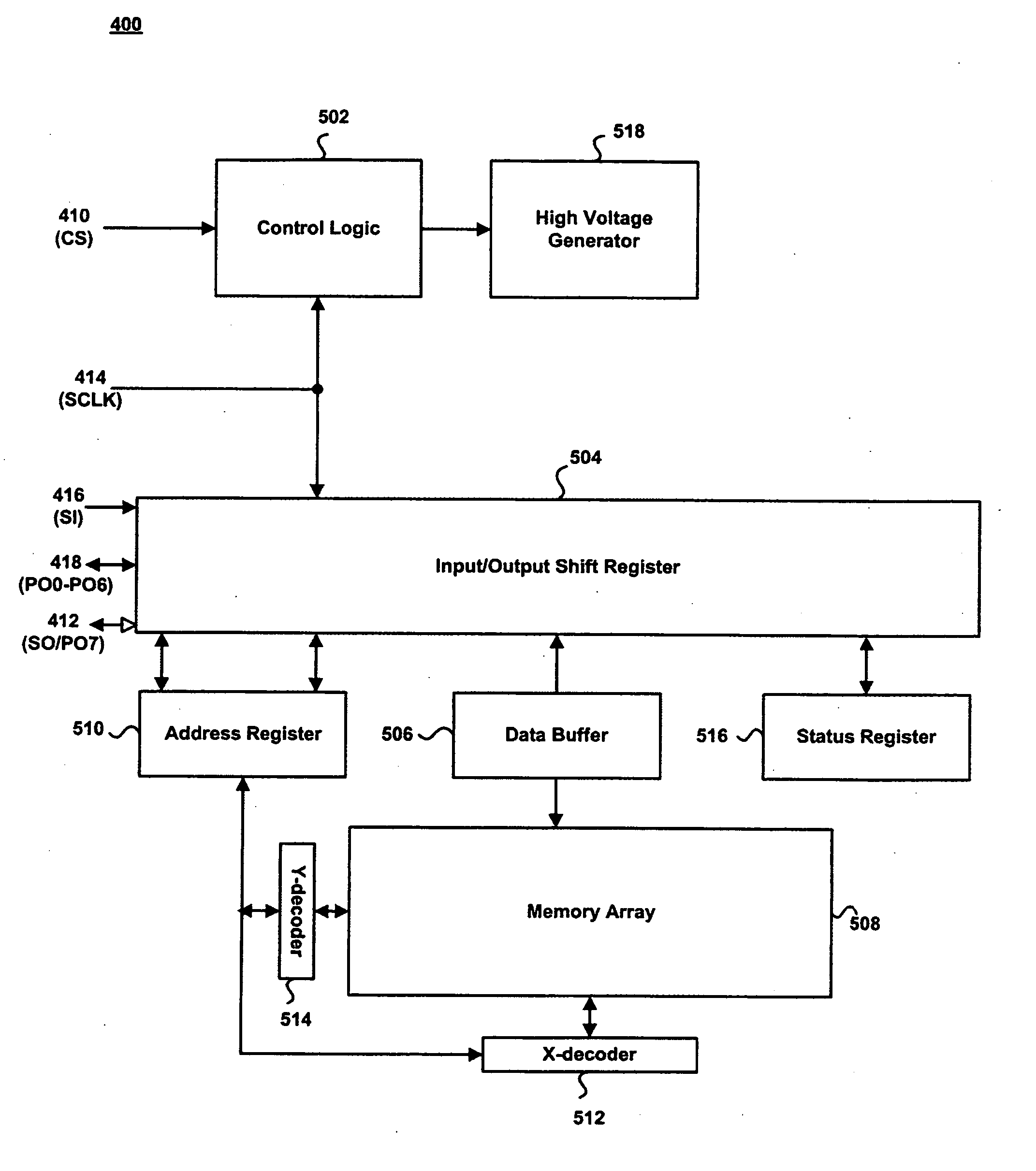
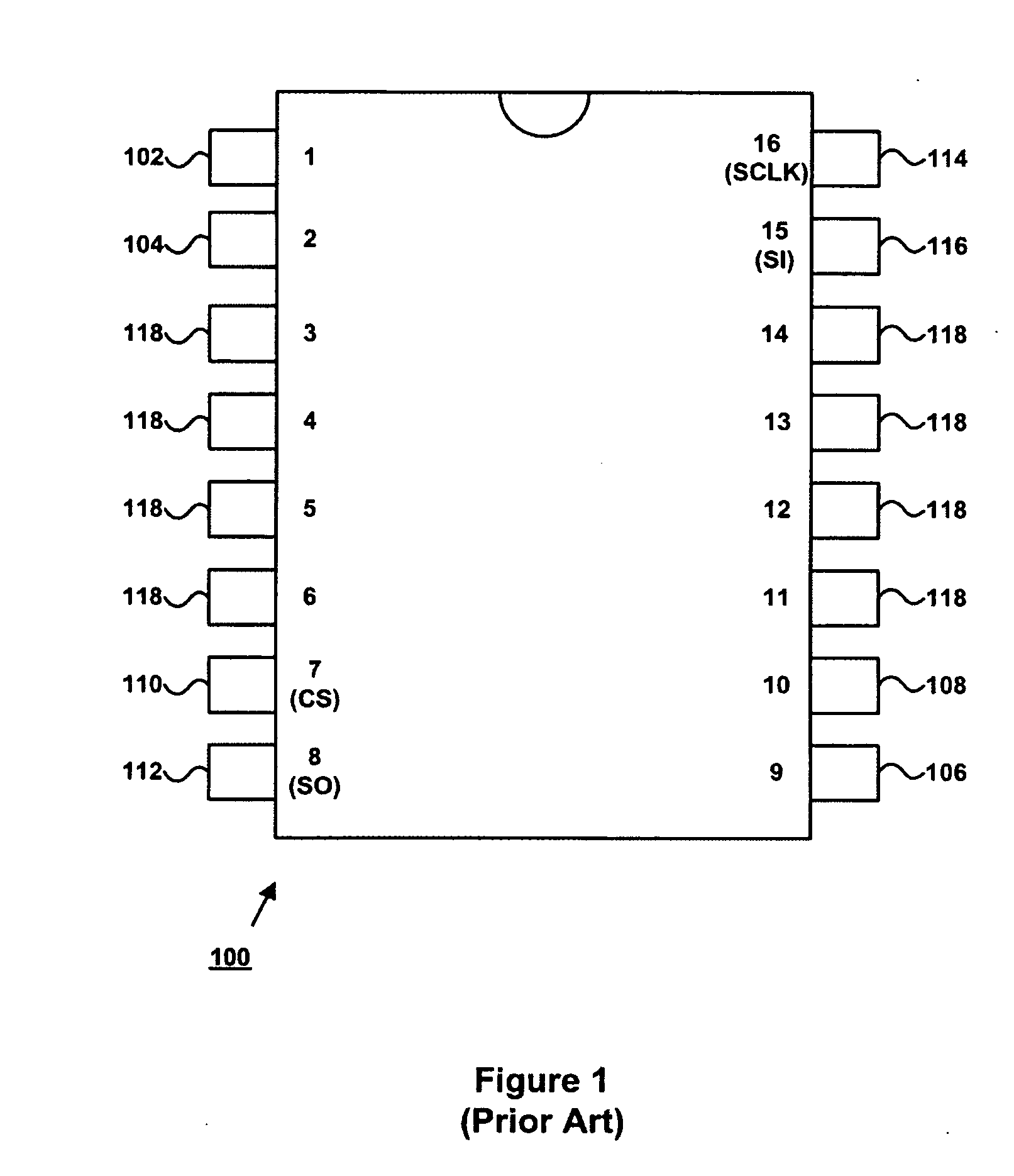
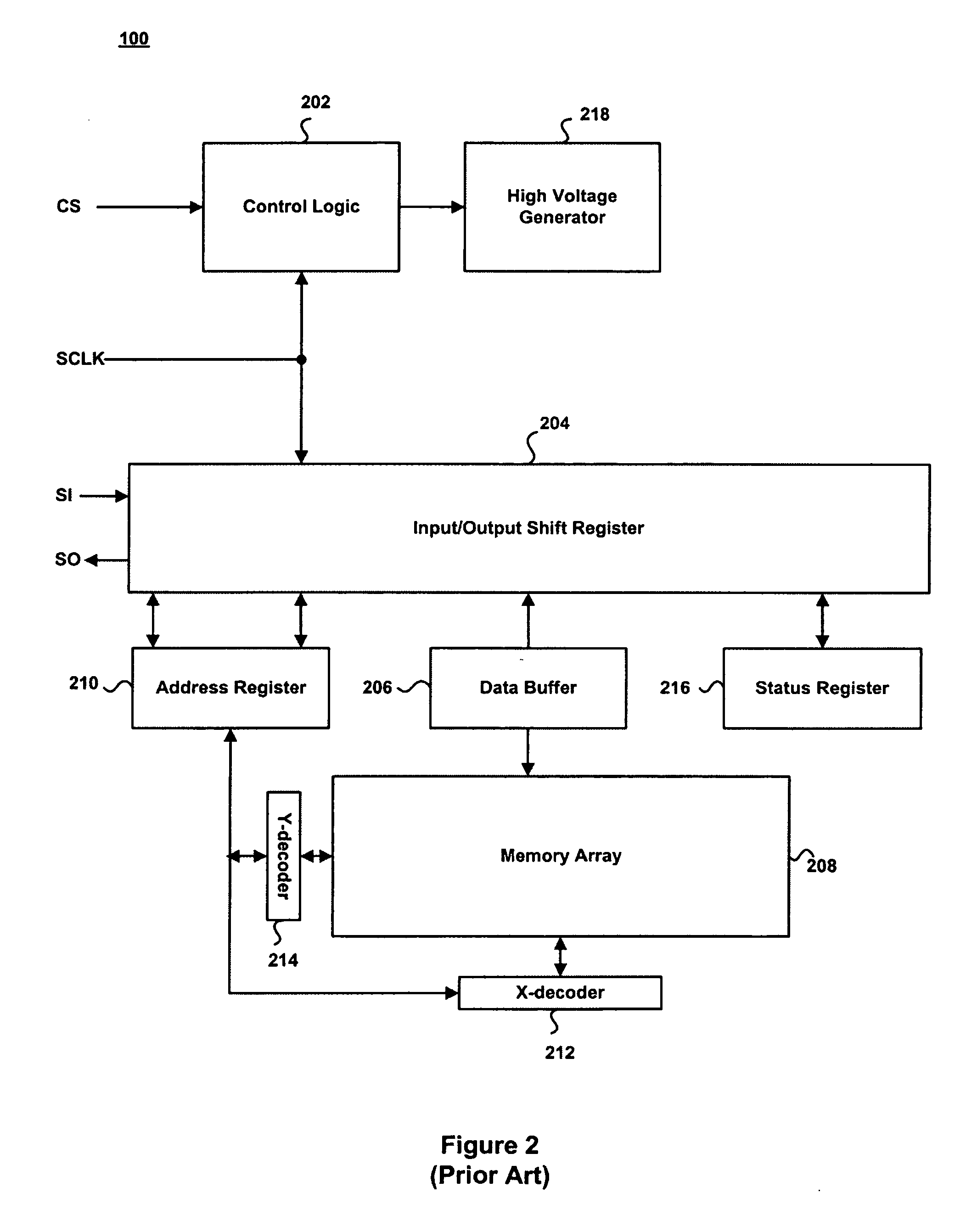
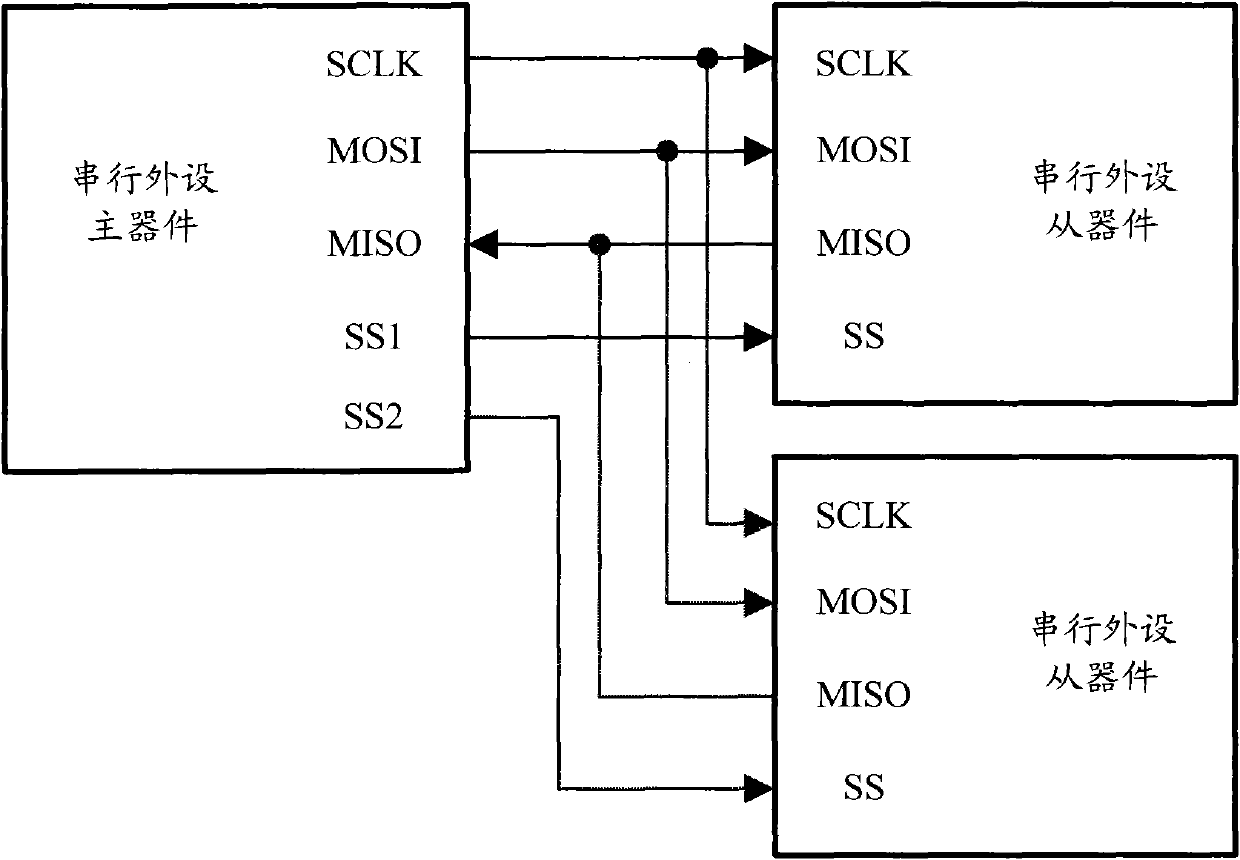
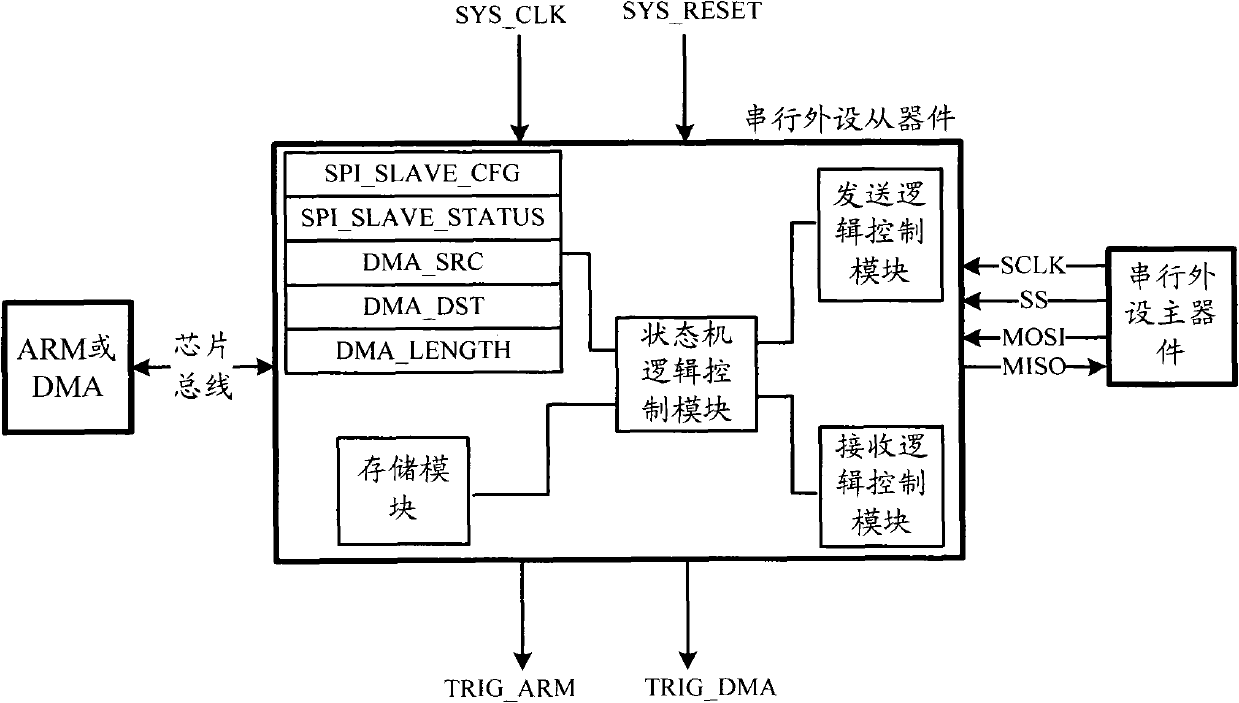
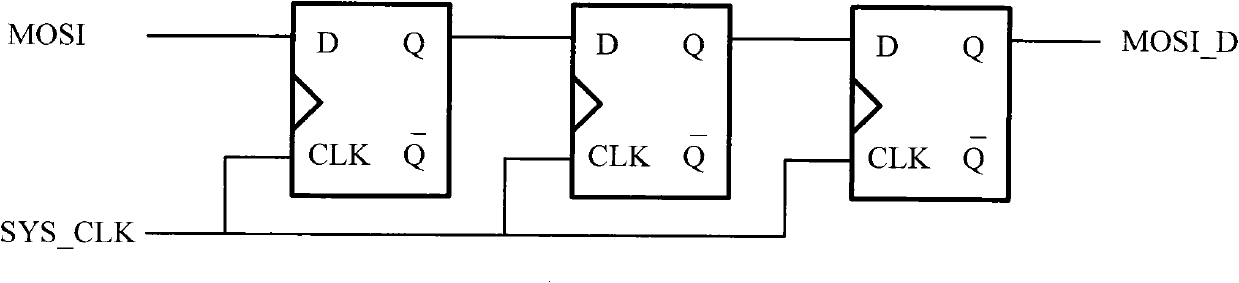
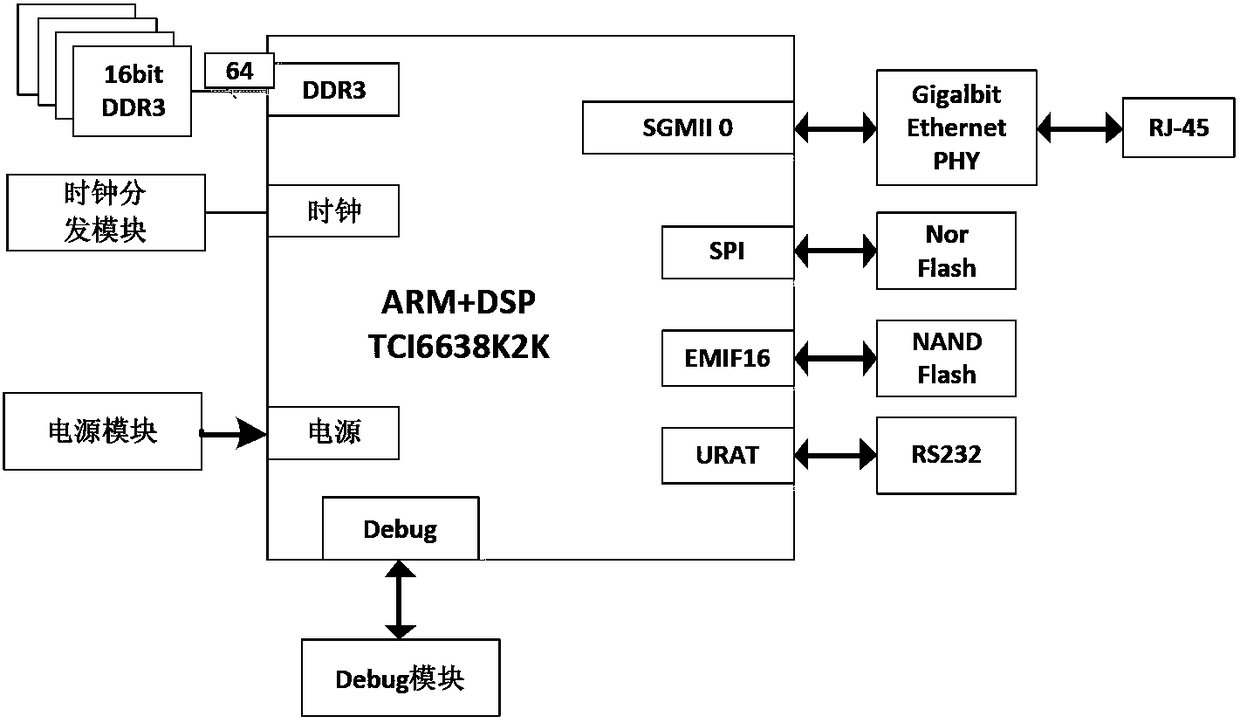
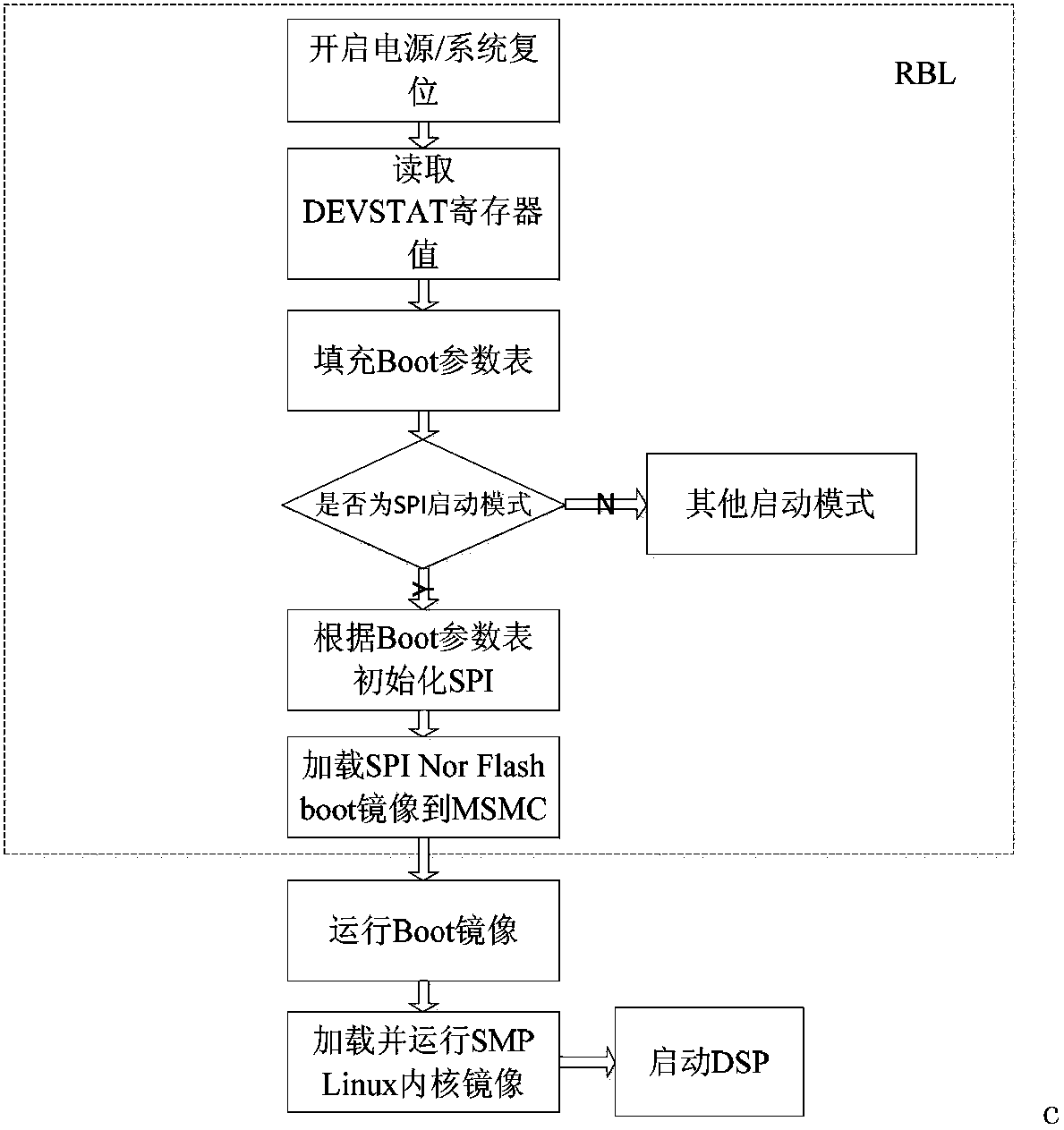
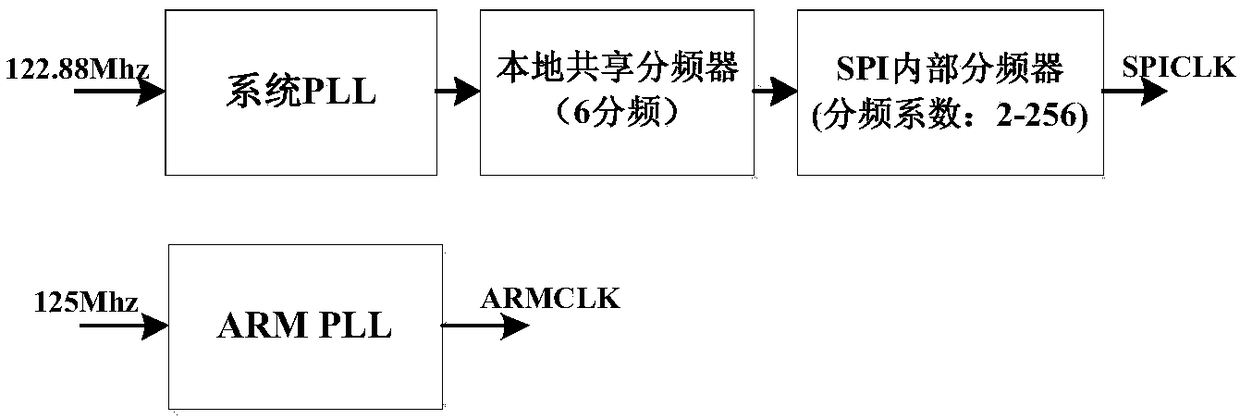
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1146 results about "Serial Peripheral Interface Bus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
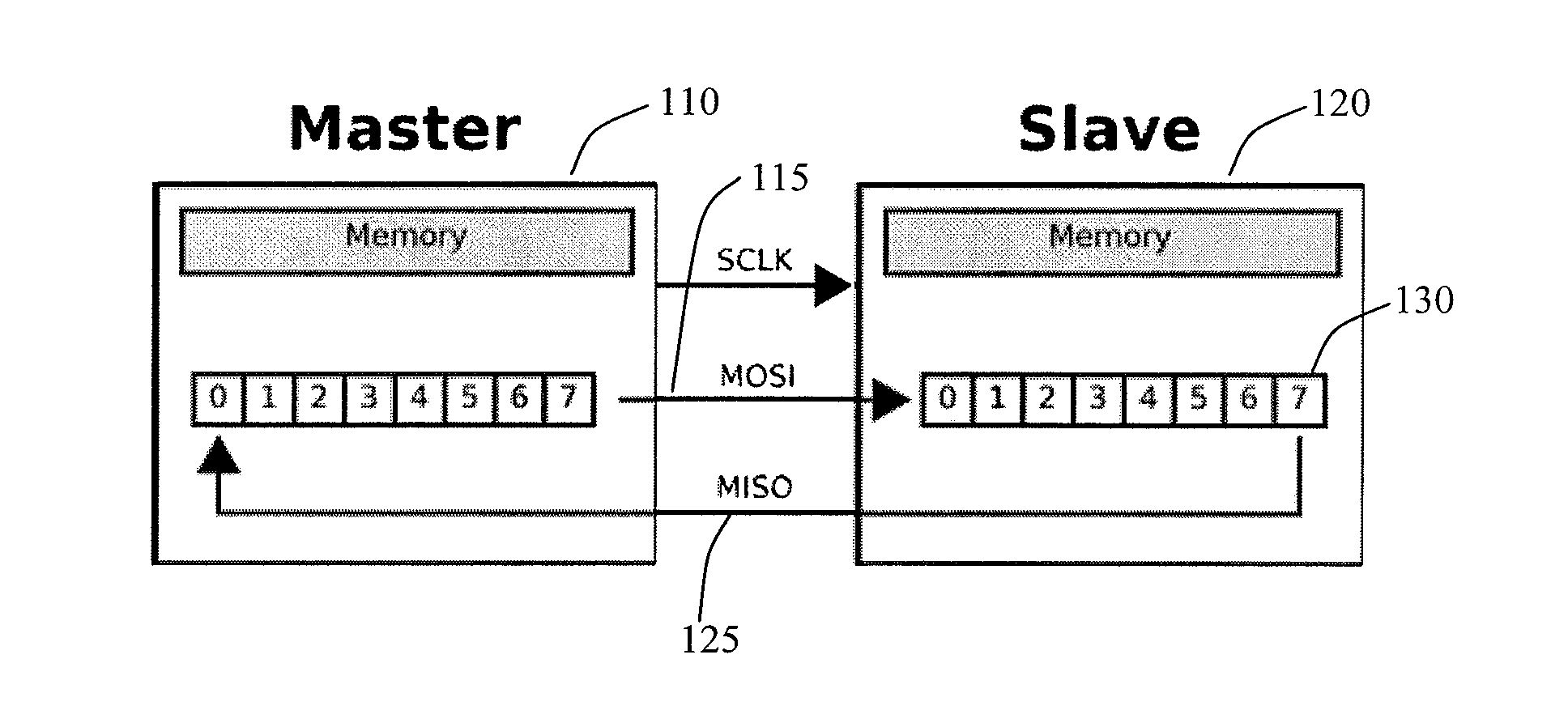
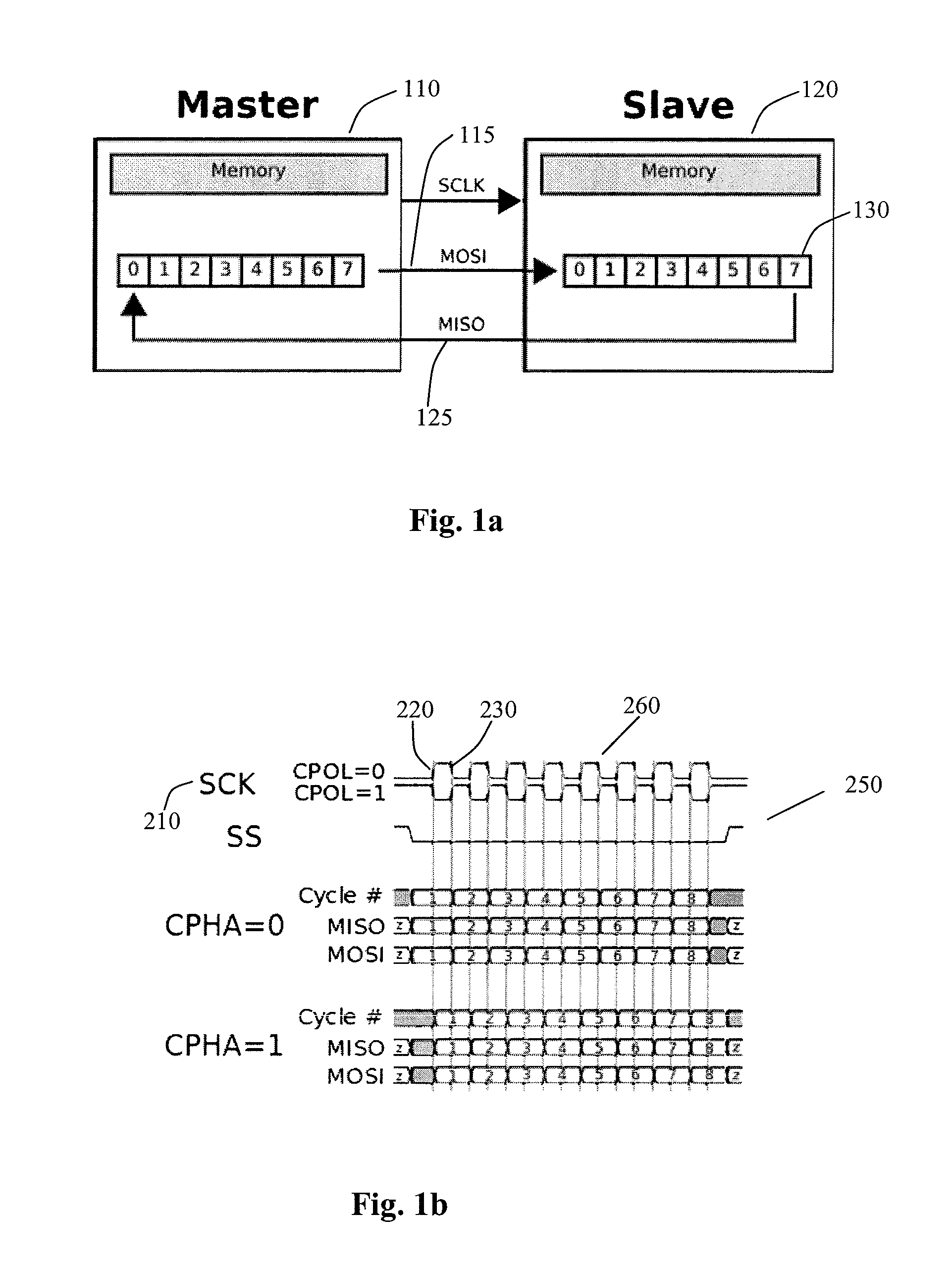
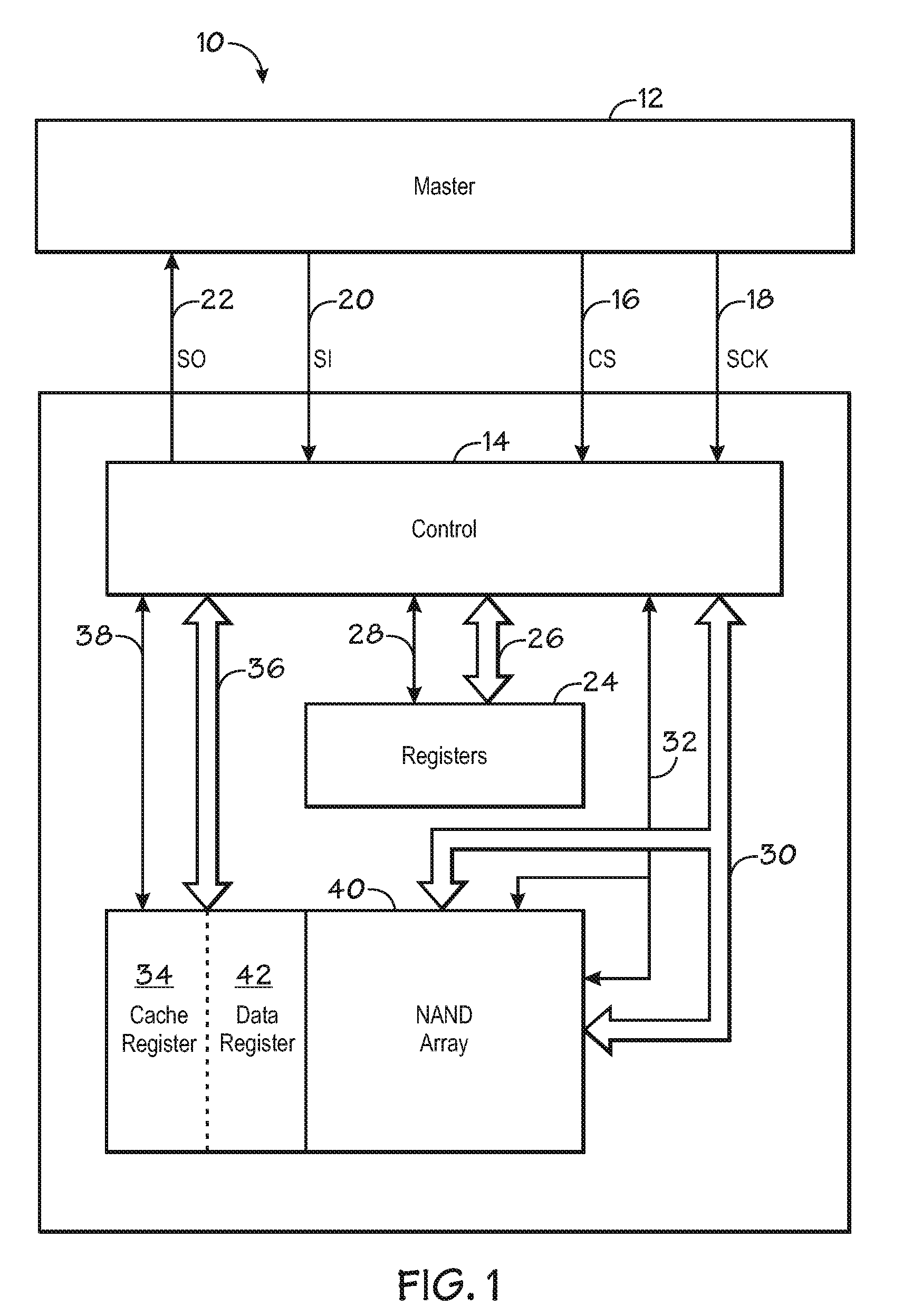
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short-distance communication, primarily in embedded systems. The interface was developed by Motorola in the mid-1980s and has become a de facto standard. Typical applications include Secure Digital cards and liquid crystal displays.
Method and system to reduce system boot loader download time for spi based flash memories
InactiveUS20140115229A1High frequencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageLoad timePeripheral
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
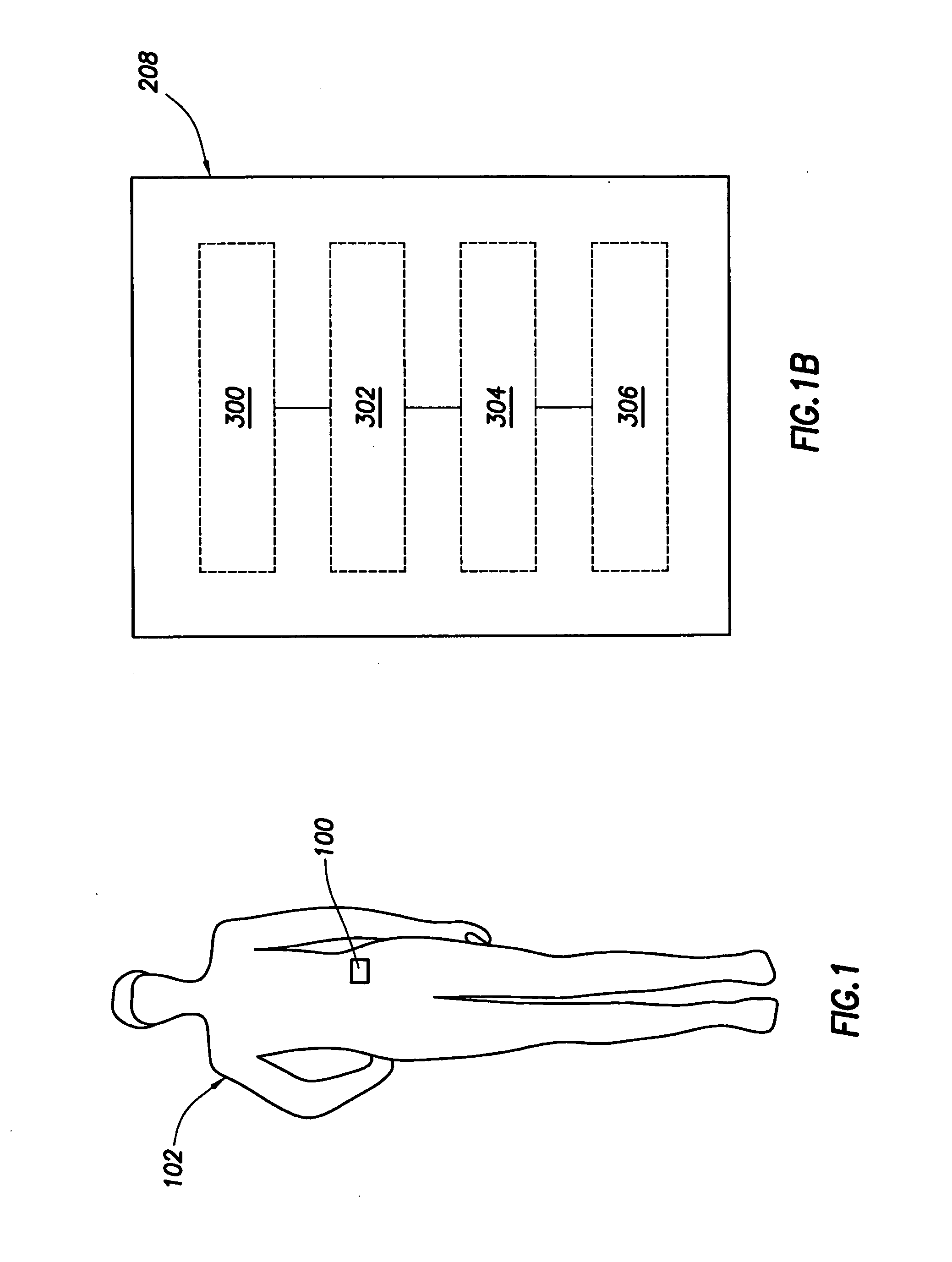
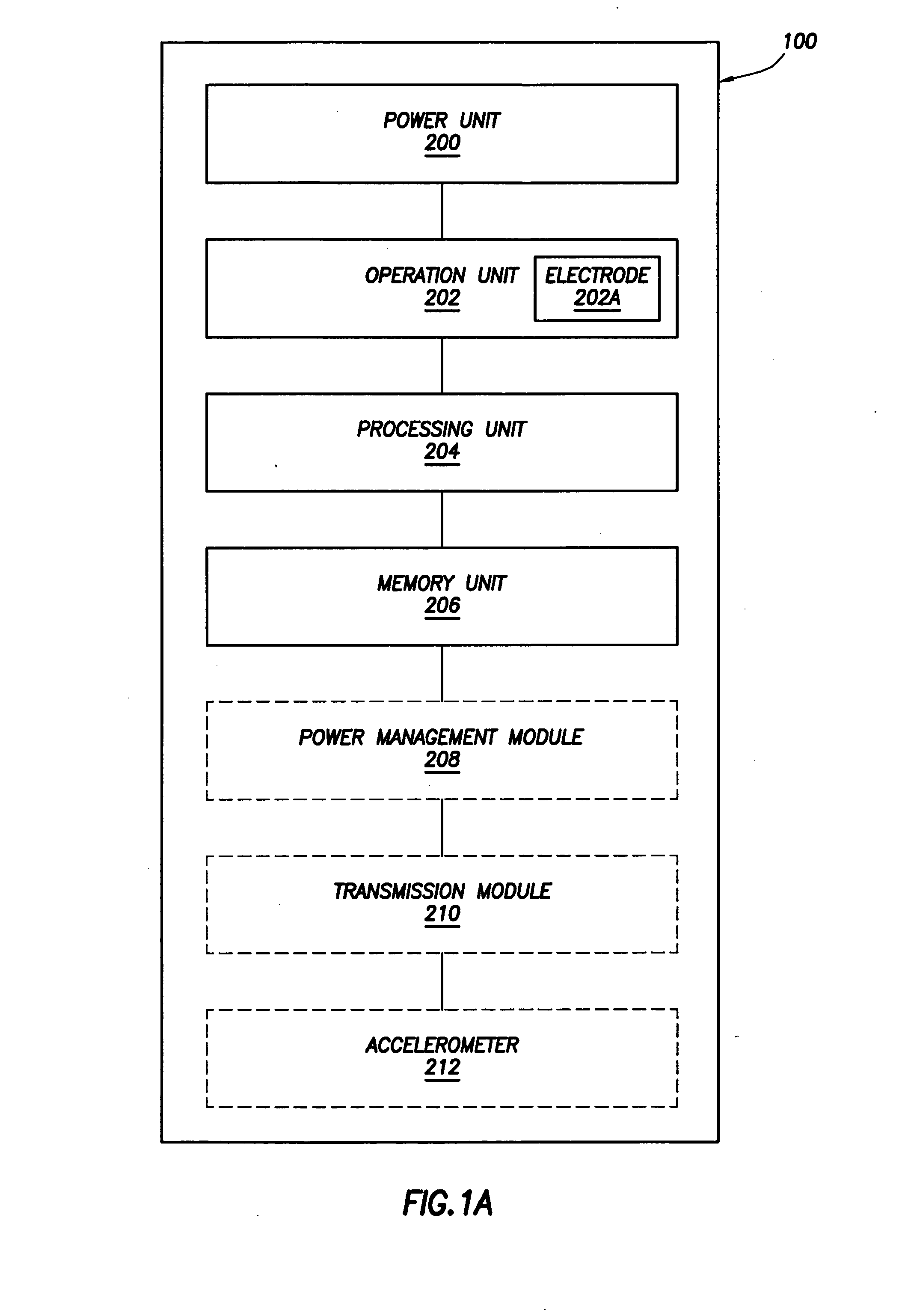
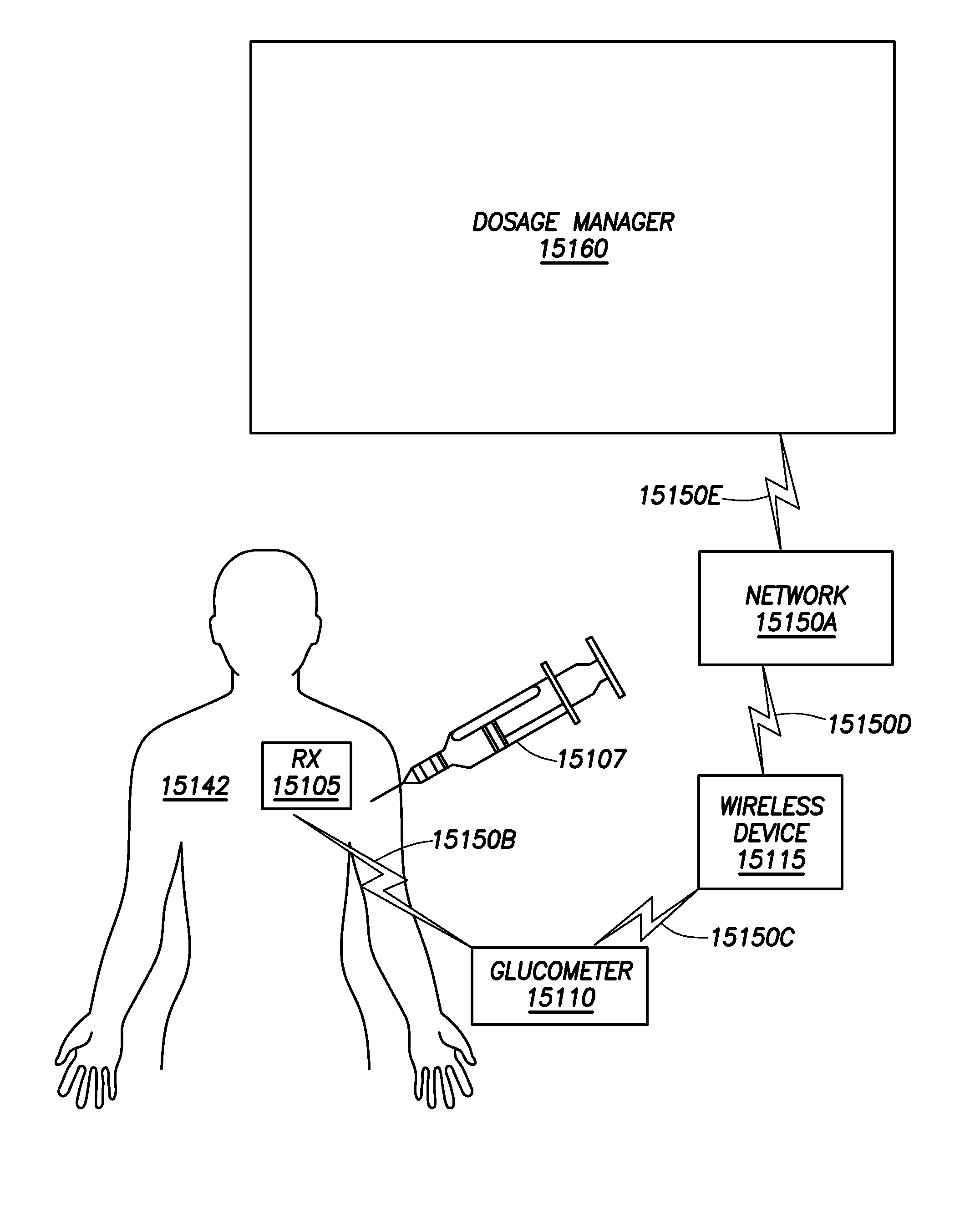
Body-Associated Receiver and Method
Receivers, which may be external or implantable, are provided. Aspects of receivers of the invention include the presence of one or more of: a high power-low power module; an intermediary module; a power supply module configured to activate and deactivate one or more power supplies to a high power processing block; a serial peripheral interface bus connecting master and slave blocks; and a multi-purpose connector. Receivers of the invention may be configured to receive a conductively transmitted signal. Also provided are systems that include the receivers, as well as methods of using the same. Additionally systems and methods are disclosed for using a receiver for coordinating with dosage delivery systems.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
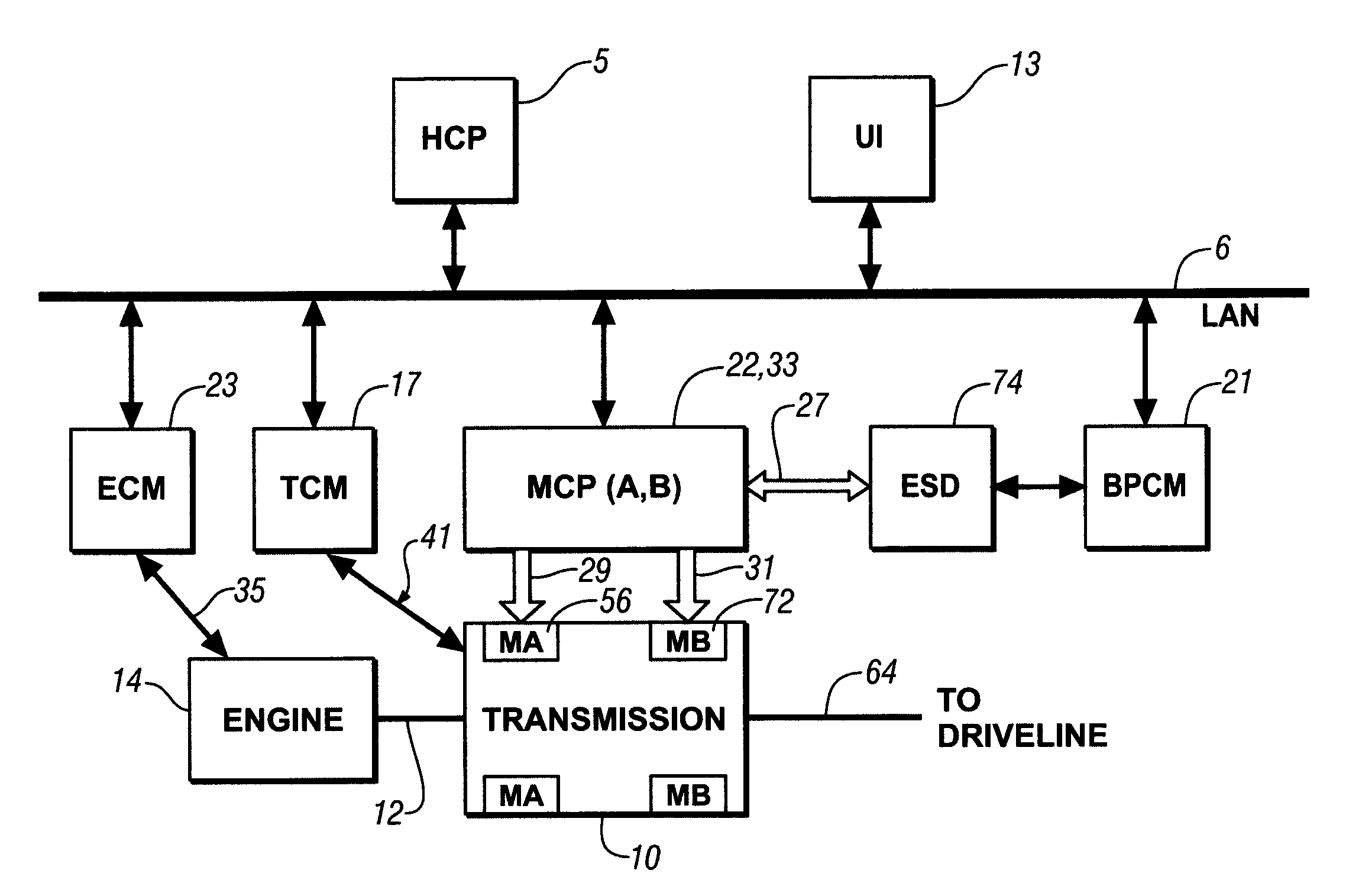
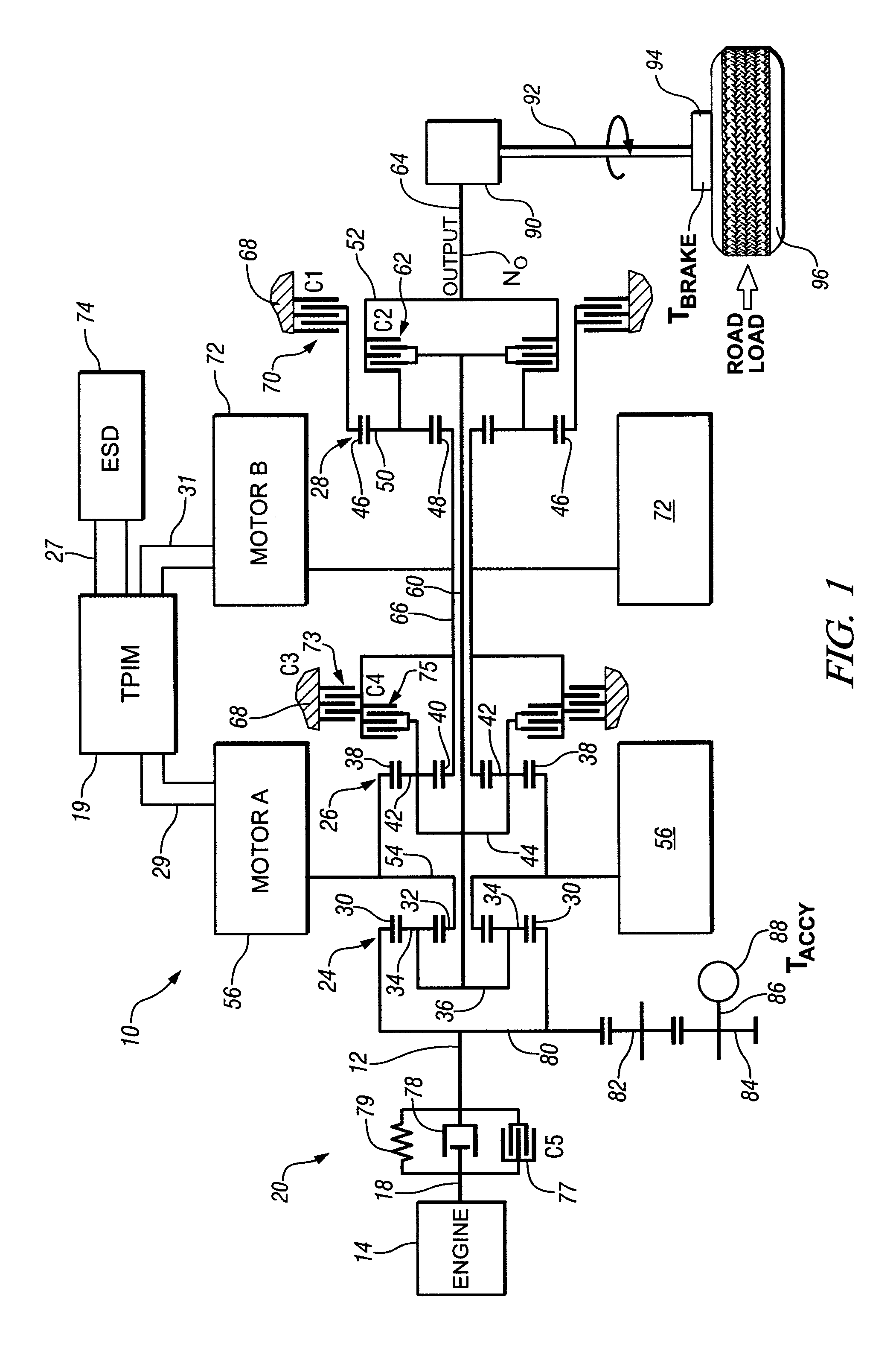
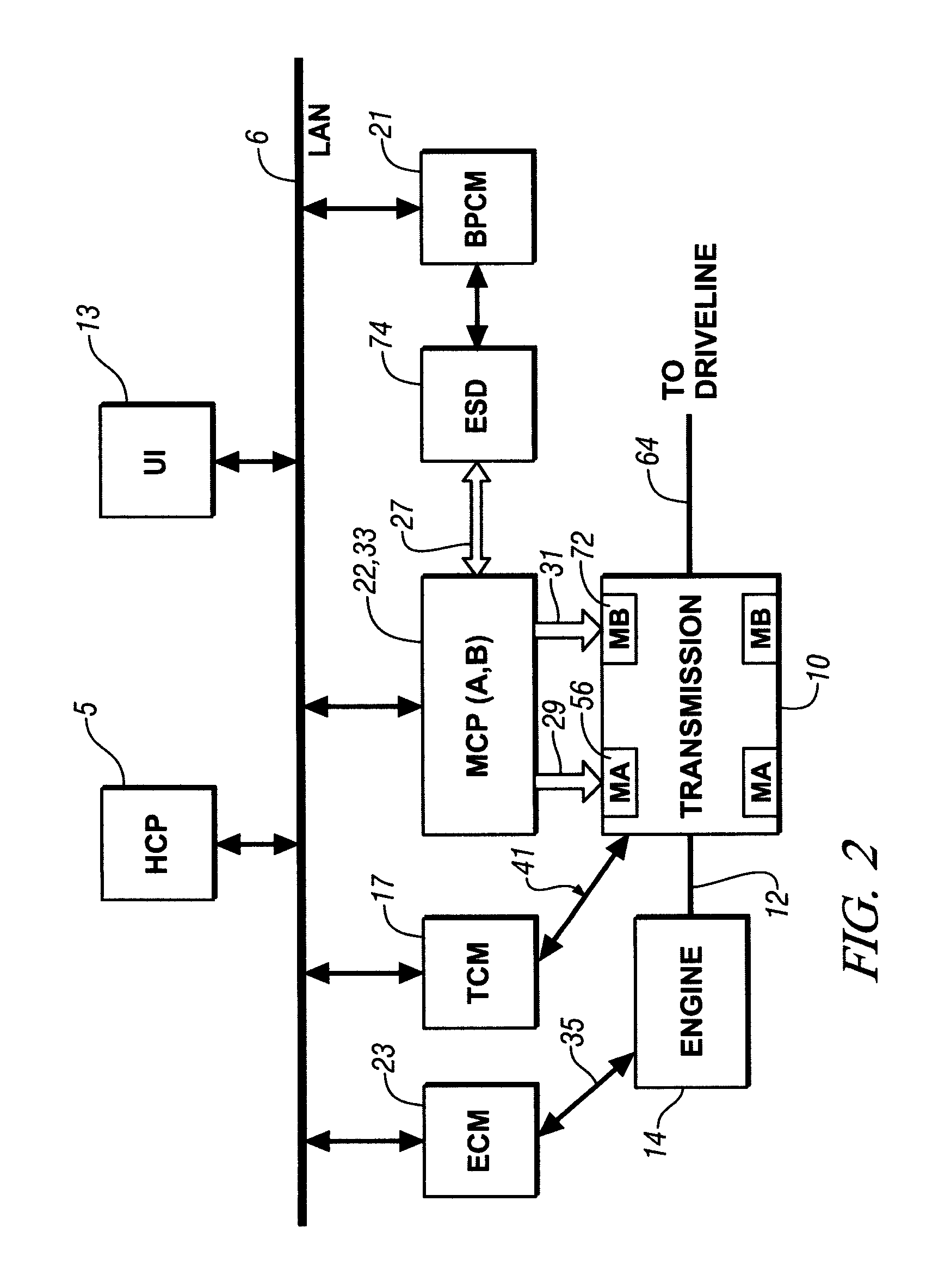
Control system architecture for a hybrid powertrain
InactiveUS20080064559A1Hybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingDrivetrainInternal combustion engine
A control apparatus for a powertrain system comprising an engine and two electrical machines operably coupled to a two-mode compound-split electro-mechanical transmission is provided. It includes a system controller and two motor control processors. The system controller communicates with the motor control processors via two high speed communications buses and directly-linked serial peripheral interface buses. The motor control processors control flow of electrical power between the electrical machines and an electrical energy storage device. A second control device is operable to control the engine, preferably to control torque output. The internal combustion engine preferably has a crank position sensor which is signally connected to a dedicated input to the second control device and to a dedicated input to the system controller of the first control device.
Owner:ELECTRONICS DATA SYST CORP +1
Body-associated receiver and method
Receivers, which may be external or implantable, are provided. Aspects of receivers of the invention include the presence of one or more of: a high power-low power module; an intermediary module; a power supply module configured to activate and deactivate one or more power supplies to a high power processing block; a serial peripheral interface bus connecting master and slave blocks; and a multi-purpose connector. Receivers of the invention may be configured to receive a conductively transmitted signal. Also provided are systems that include the receivers, as well as methods of using the same. Additionally systems and methods are disclosed for using a receiver for coordinating with dosage delivery systems.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
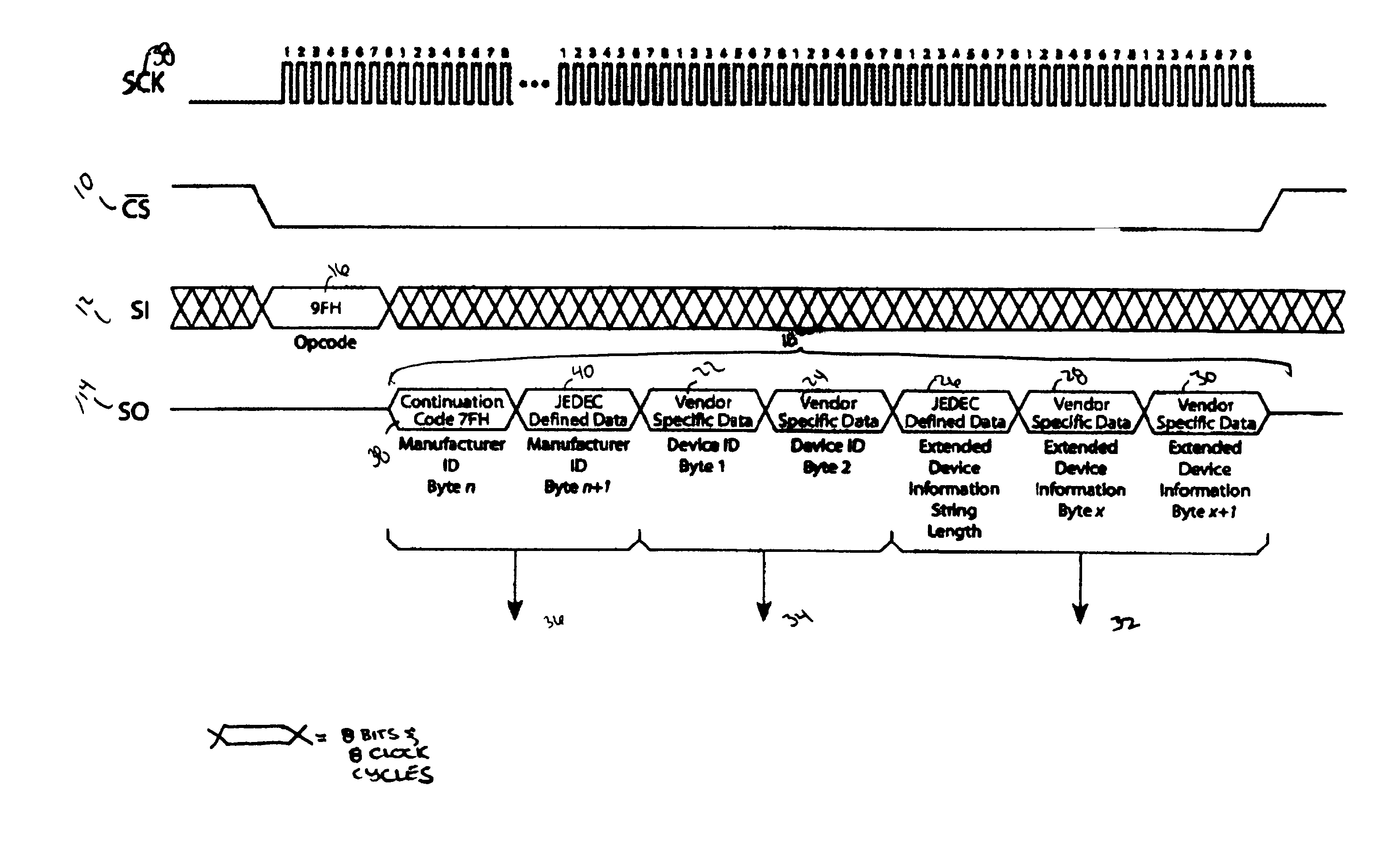
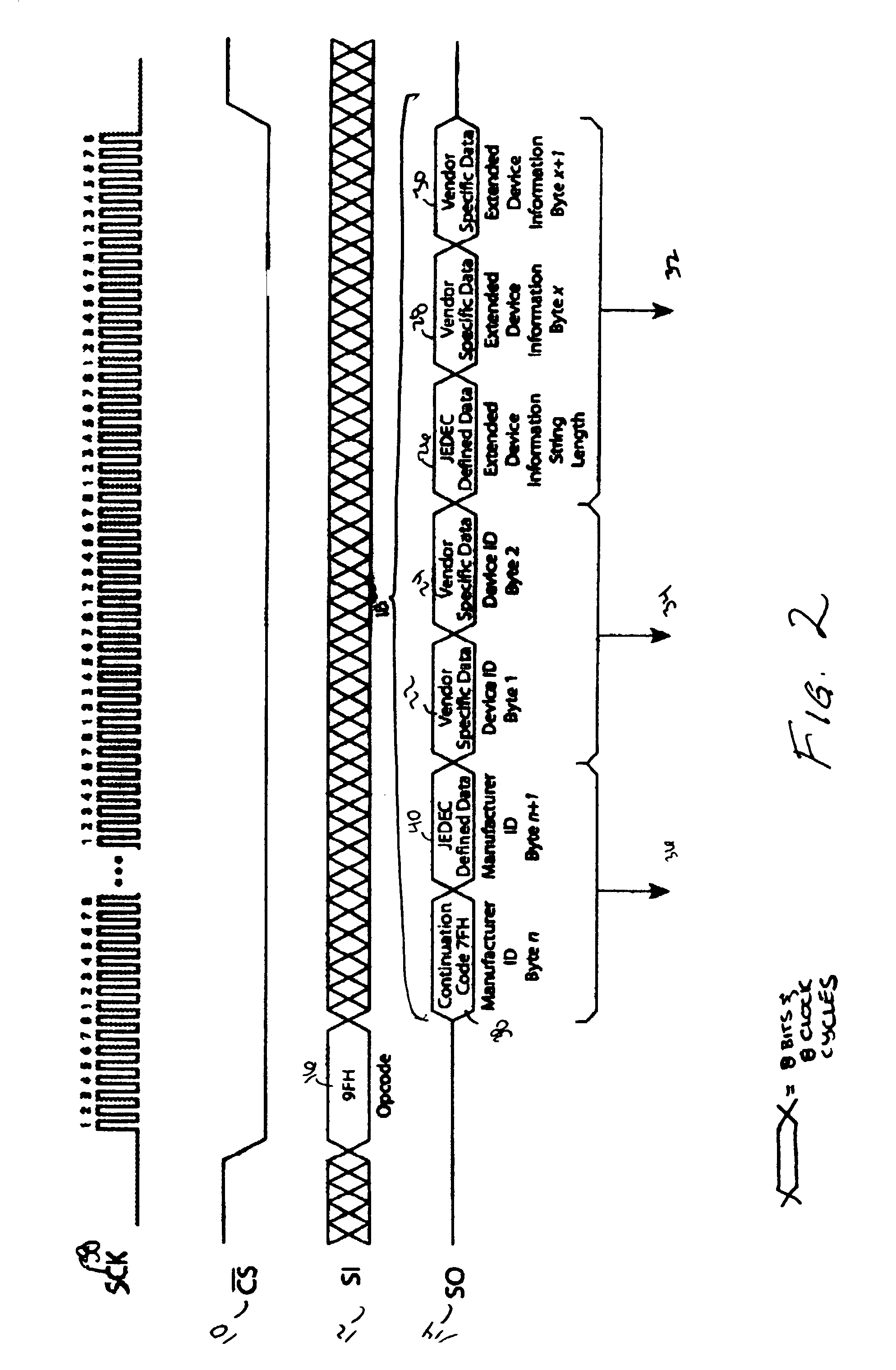
Method for identification of SPI compatible serial memory devices
ActiveUS7032039B2Unnecessary data is preventedAvoid dataRead-only memoriesDigital storageContinuationByte
A method for identifying Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible serial interface memory devices. A microprocessor sends a single command requesting identification information to an SPI device installed on the SPI bus. A byte string, including the JEDEC manufacturer ID, device ID, and any extended device information, is sent back to the microprocessor. The byte string may include one or more continuation codes when the manufacturer ID exceeds 1 byte. The byte string also includes one byte indicating how many bytes of extended device information should be read by the microprocessor. The identification process, issuing the command and receiving the reply, is completed in one operation.
Owner:ARTEMIS ACQUISITION
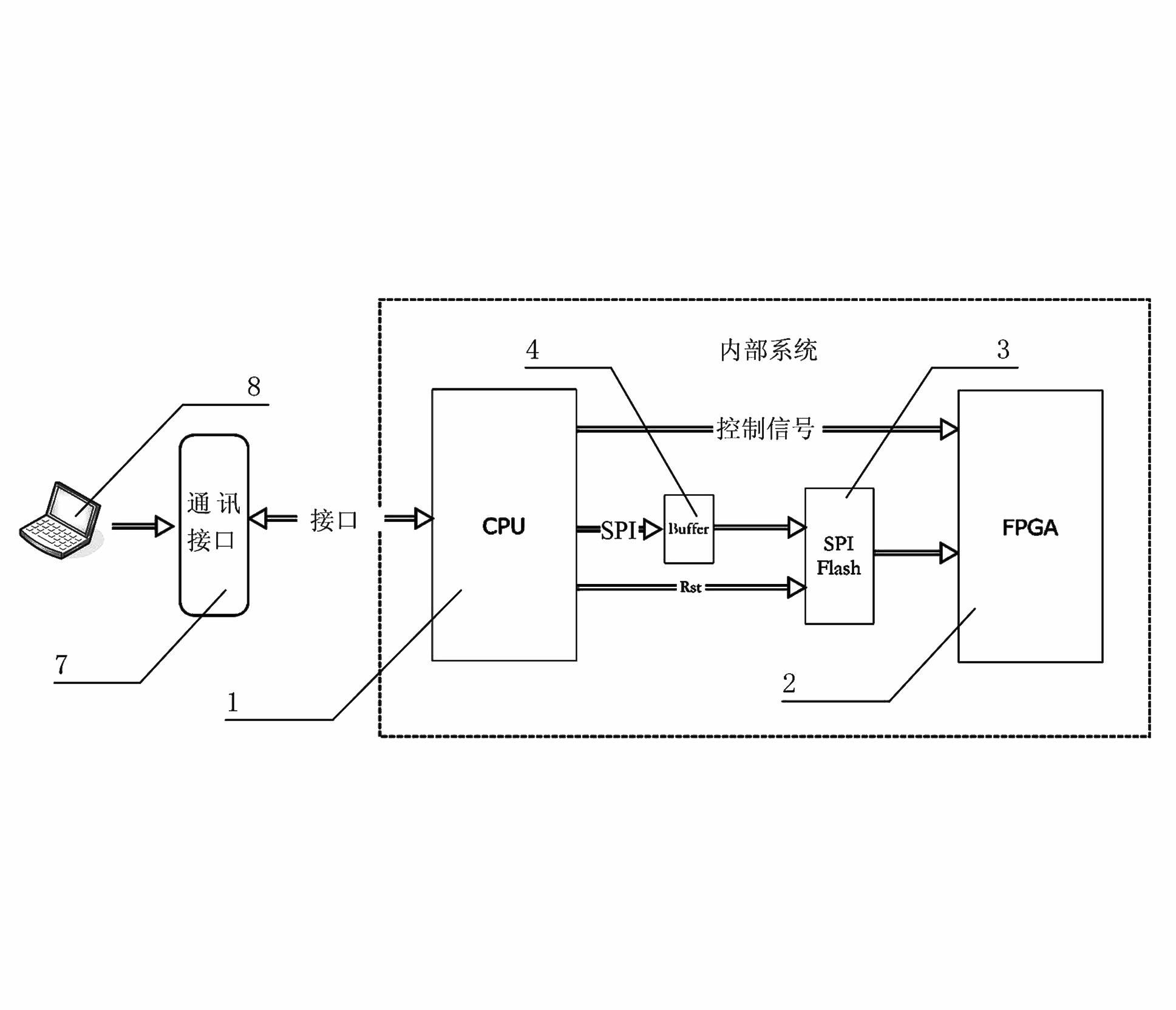
System for updating FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) configuration program from a long distance based on control of processor and method therefor
ActiveCN102609286AAvoid disassemblyReal-time online updateProgram loading/initiatingCommunication interfaceField-programmable gate array
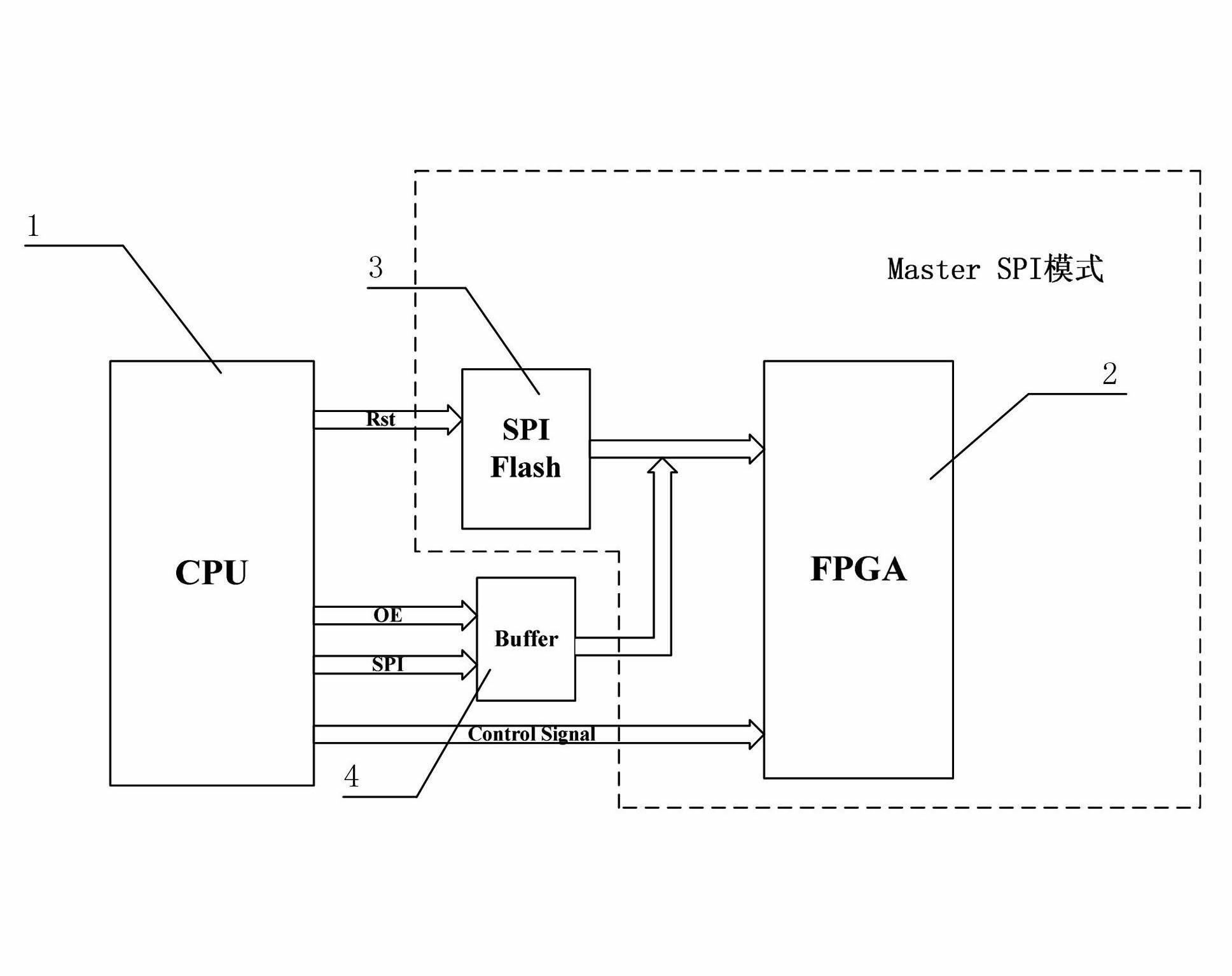
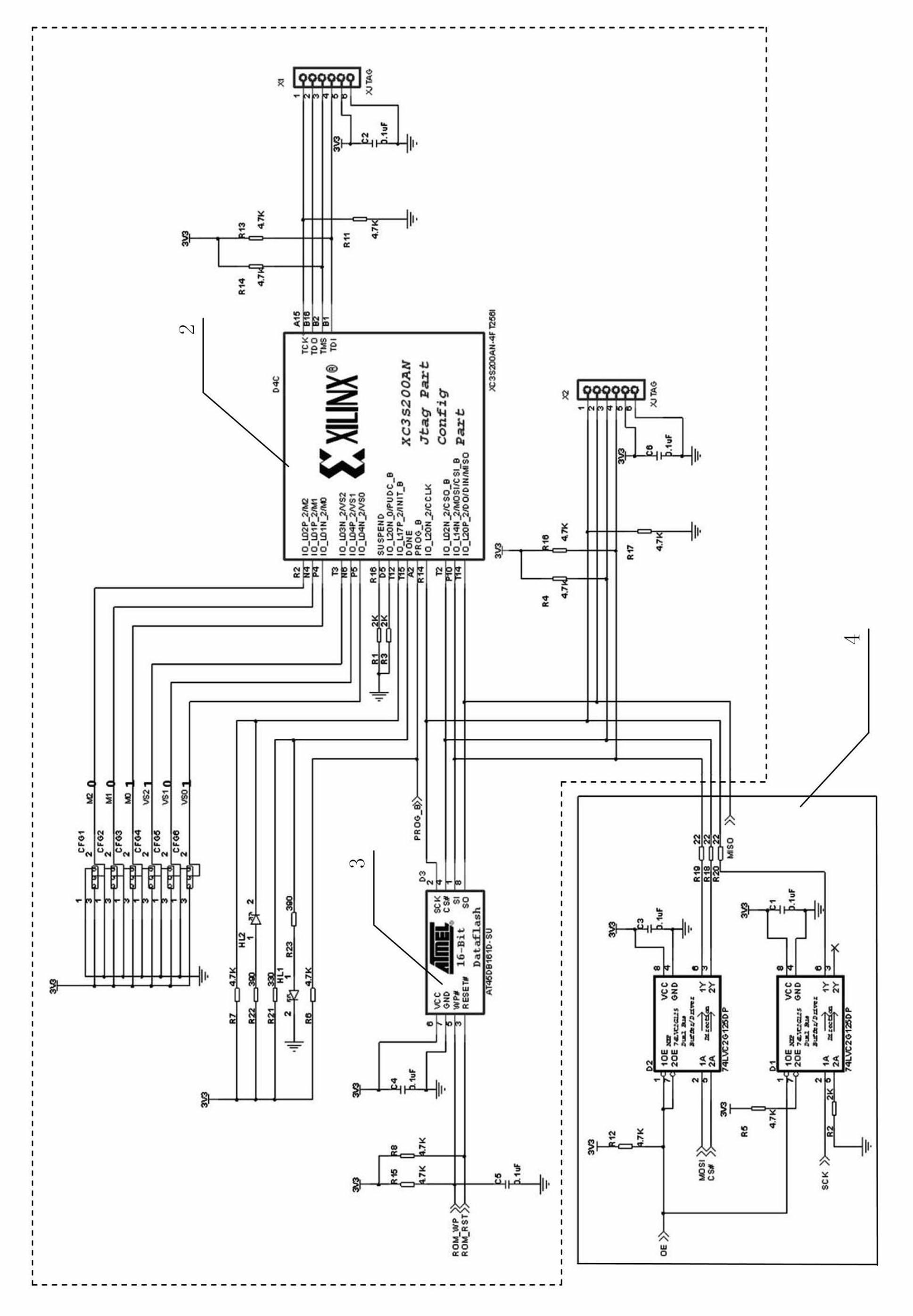
The invention discloses a system for updating an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) configuration program from a long distance based on the control of a processor and a method for updating the FPGA configuration program from a long distance based on the control of the processor. The system comprises a processor module, an FPGA module, an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) memory module and a buffer module, wherein the processor module is connected with the SPI memory module and is connected with a communication interface, the SPI memory module is connected with the FPGA module, and the processor module is connected with the SPI memory module by the buffer module. When the configuration program of an FPGA requires to be updated, an upper computer or a terminal downloads the FPGA configuration program into the SPI memory module through the communication interface and the processor module, and the FPGA module can automatically load the configuration program memorized in the SPI memory module in a MasterSPI mode. According to the system and the method, the FPGA configuration program is updated from a long distance, the function of updating the configuration program on line under the non-outage situation is realized, and therefore, the system and the method are particularly suitable for on-site application.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
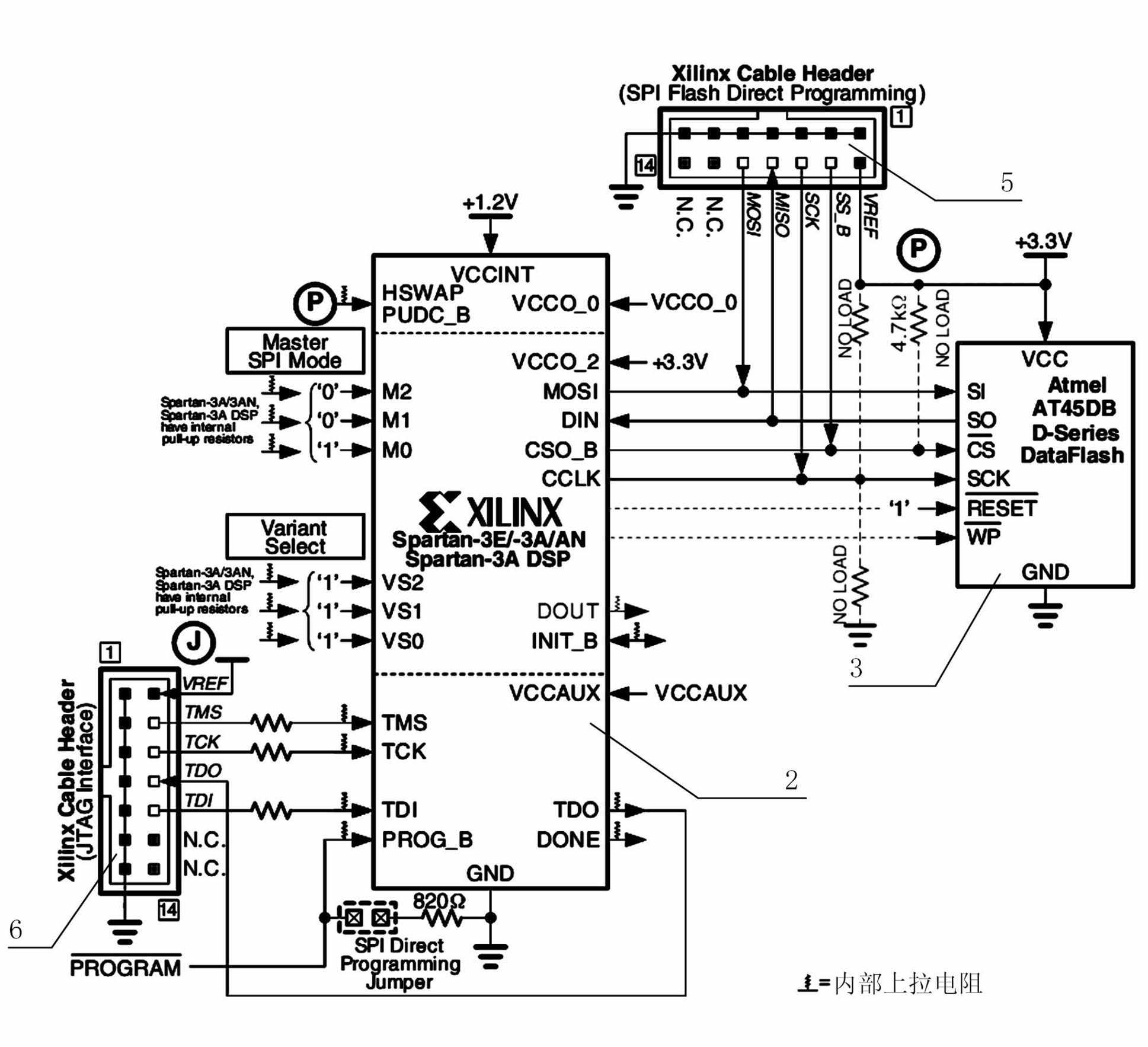
Flexible scheme for configuring programmable semiconductor devices using or loading programs from SPI-based serial flash memories that support multiple SPI flash vendors and device families
ActiveUS7281082B1Reduce configuration costsEasy to processRead-only memoriesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsMemory typeControl signal
A method and structure for configuring a programmable logic device (PLD) from a serial peripheral interface (SPI) based serial memory. The type of the SPI memory is initially identified by the PLD. The PLD then selects the appropriate read command in response to the SPI memory type. The PLD then issues the read command to the SPI memory. In response, the SPI memory continuously provides a set of configuration data to the PLD. The PLD is configured in response to the configuration data. The PLD can identify the SPI memory type in response to control signals on pins of the PLD. Alternately, the PLD can identify the SPI memory type by performing a search. The search can include issuing a plurality of known read commands to the SPI memory, and then determining which read command causes the SPI memory to respond.
Owner:XILINX INC
Interface Protocol and API for a Wireless Transceiver
ActiveUS20090137318A1Well formedApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesWireless transceiverTransceiver
A wireless protocol may be implemented in a smart transceiver device that contains the physical (PHY) and media access control (MAC) layers of the wireless protocol stack. In various embodiments, a serial peripheral interface (SPI) based design may be used. Disclosed is an embodiment of a protocol which may be used to provide control and data transfer to and from the smart transceiver. In particular, an exemplary format of the protocol, the commands, and responses is disclosed. In a further embodiment, an application programming interface (API) is disclosed. The API may provide hardware independent services that can be used to establish, maintain, and transport data to and from the system and the smart transceiver device. In particular, an exemplary and non-limiting set of services, function calls, configuration methods, events, and parameters is disclosed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
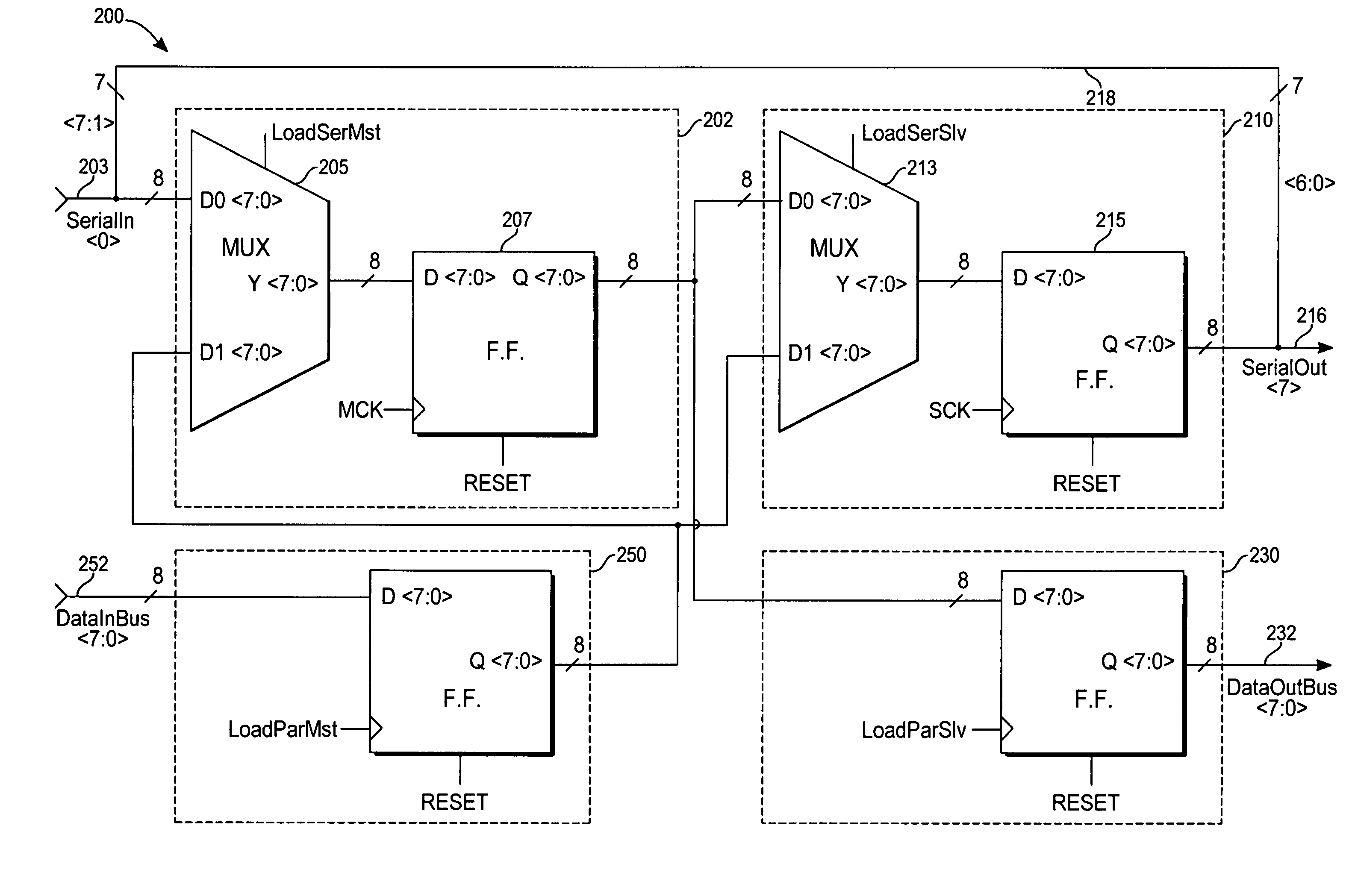
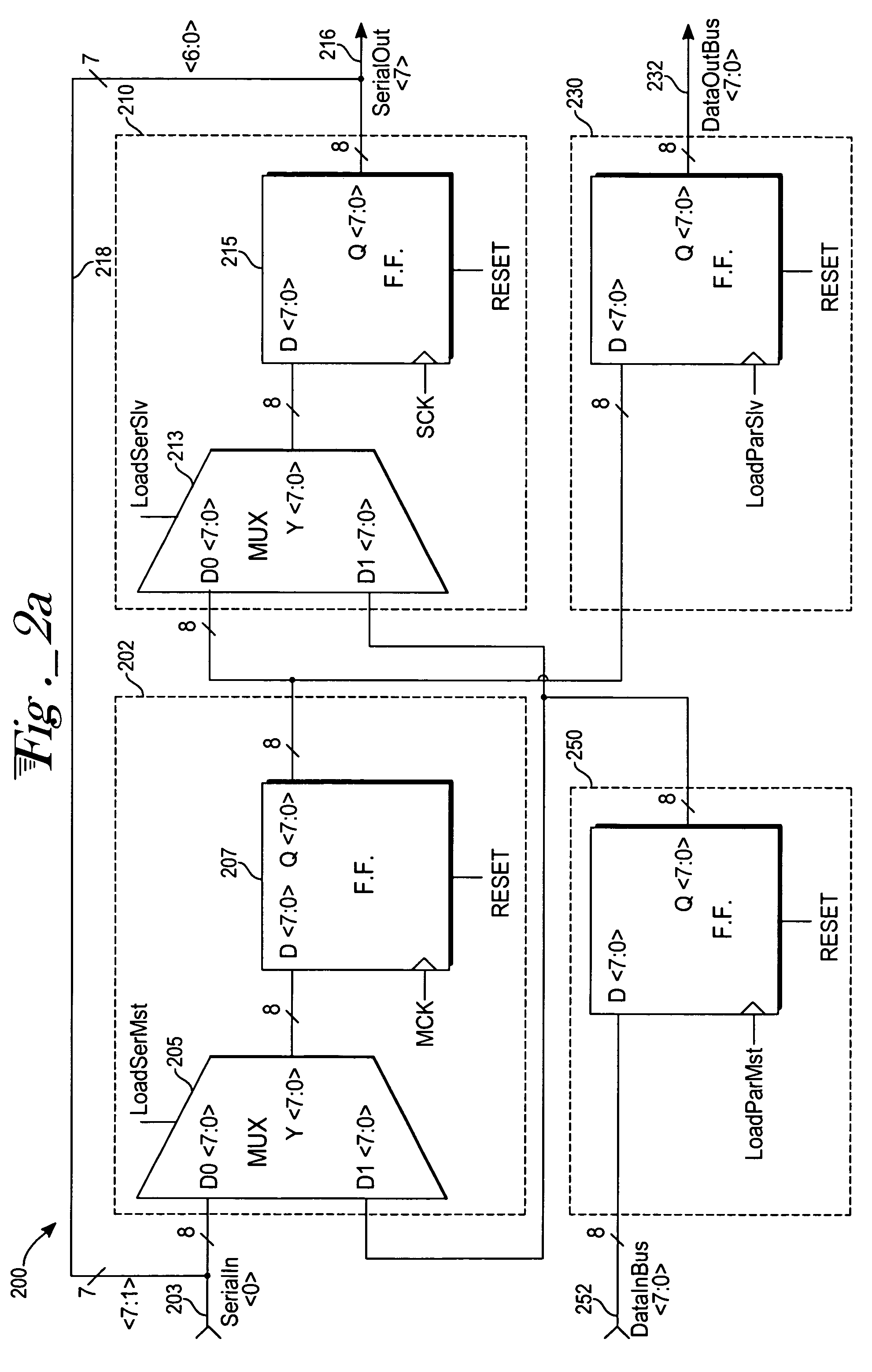
Addressable Serial Peripheral Interface
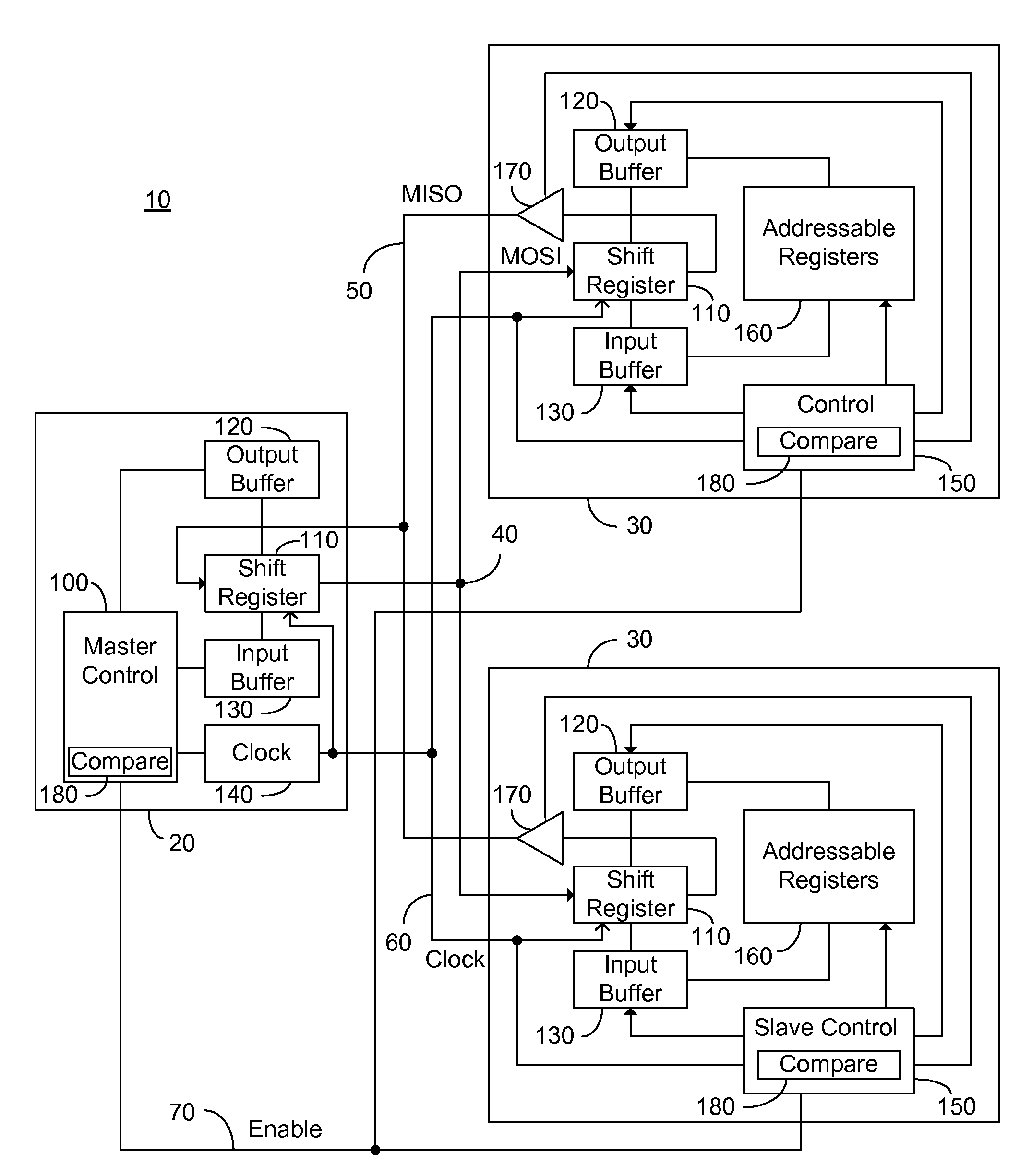
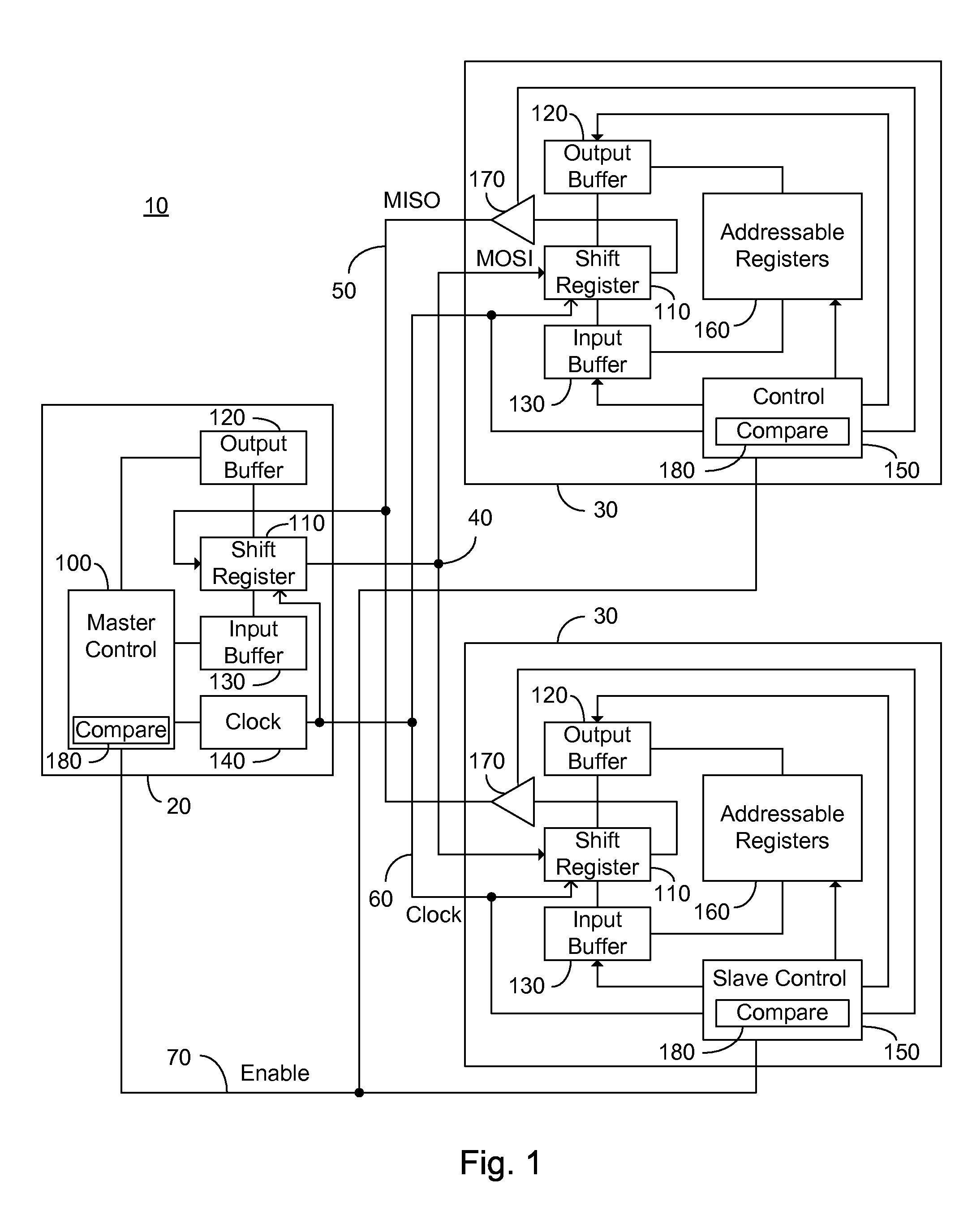
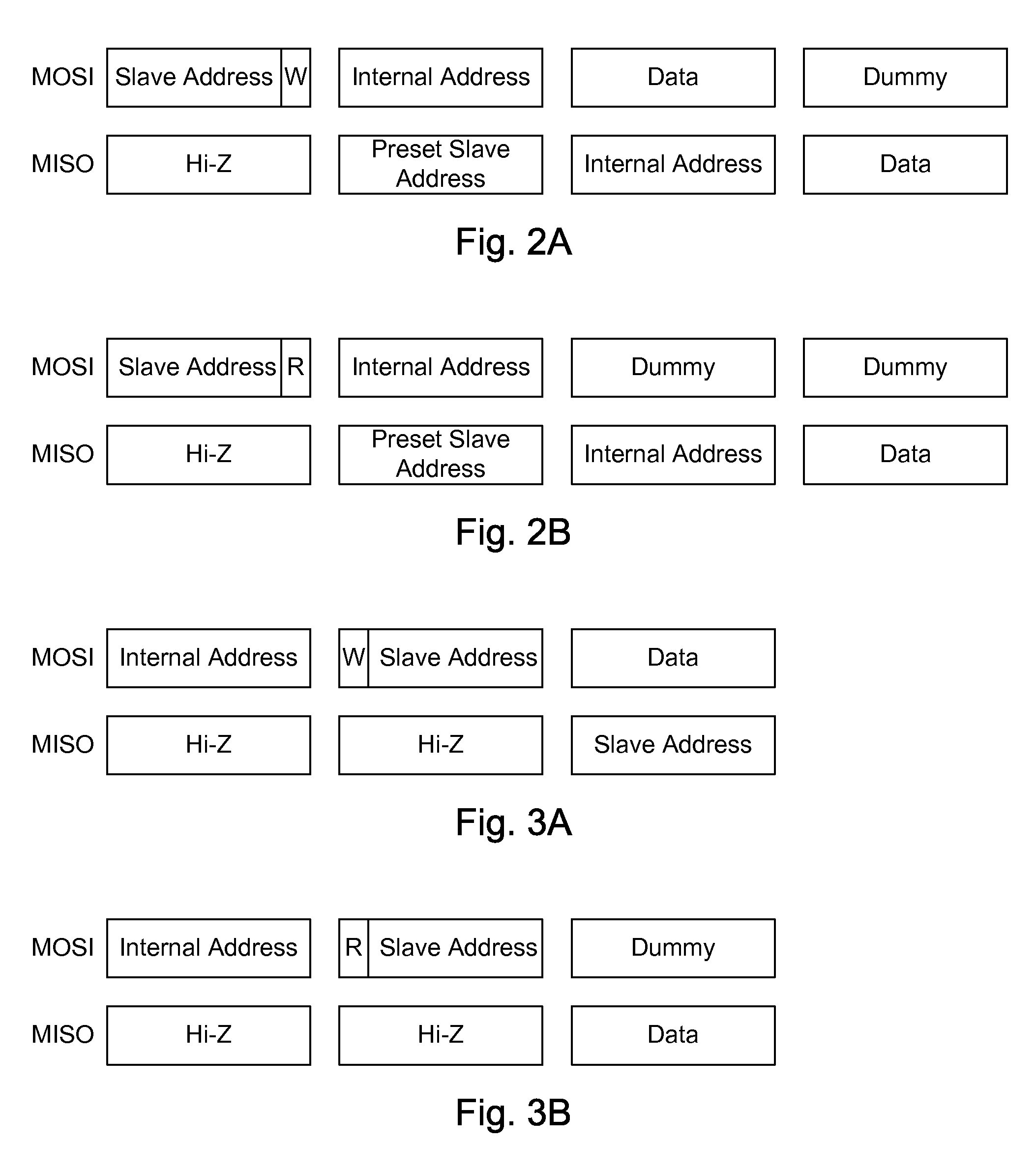
ActiveUS20080183928A1Lower latencyCircuit arrangementsCode conversionShift registerSerial Peripheral Interface Bus
An addressable SPI bus and an associated communication protocol. The addressable SPI bus comprises a plurality of slaves each exhibiting a particular address and a shift register whose output is connected to a common MISO bus by a buffer exhibiting a three state output, also known as a tri-state output. The master asserts a single SS line, which is connected in parallel to each of the plurality of slaves, indicating the beginning of a frame, and transmits via the MOSI bus the address of a particular slave of the plurality of slaves, denoted interchangeably the target or destination slave. Responsive to the received address, the target slave enables the three state output associated therewith thus transmitting the output of the target slave shift register to the master via the MISO bus.
Owner:MICROSEMI
Device for updating FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) from a long distance by CPU (Central Processing Unit) and method therefor
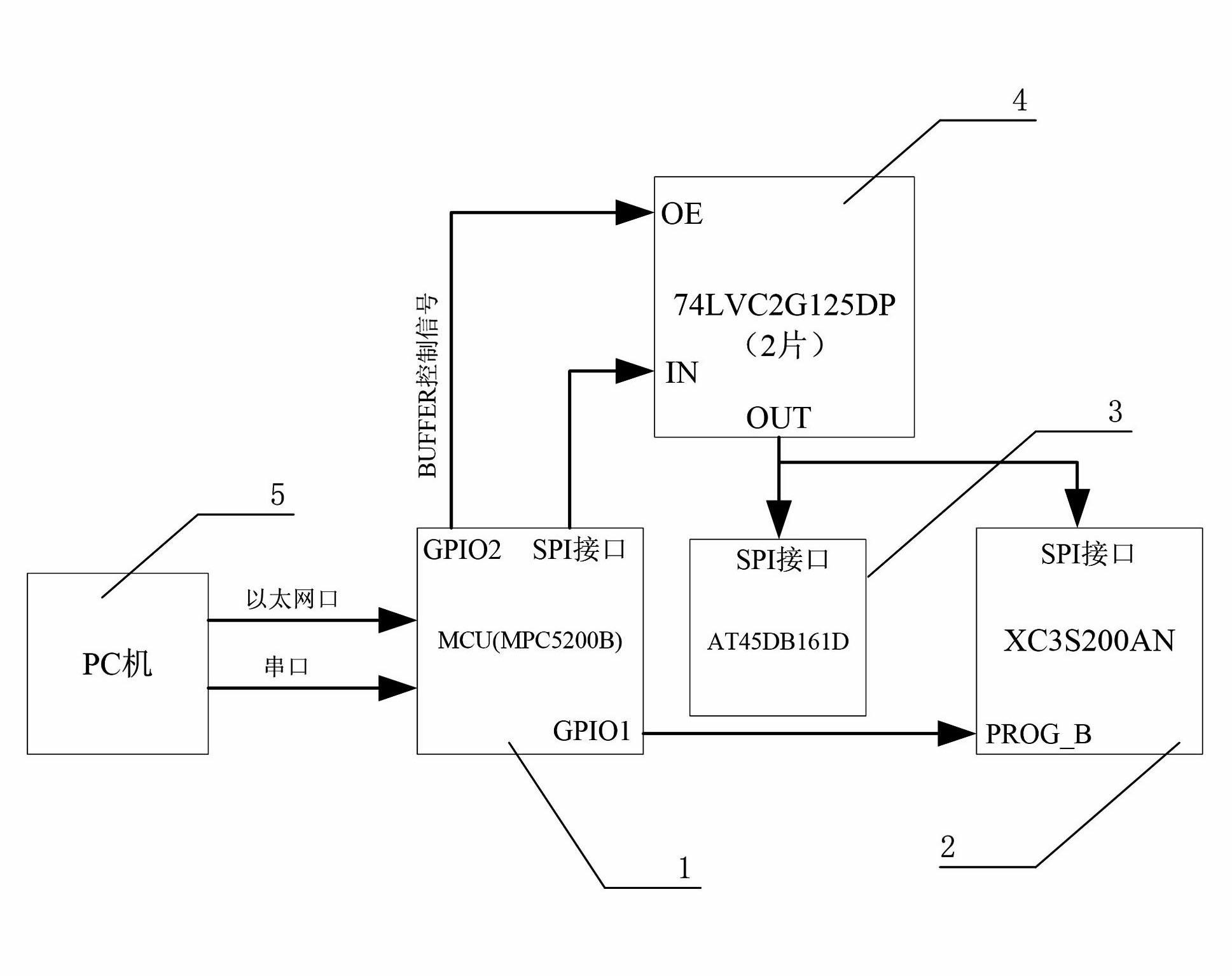
ActiveCN102609287ALow costEasy to operateProgram loading/initiatingOperabilityReal-time operating system
The invention discloses a device for updating an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) from a long distance by a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and a method for updating the FPGA from a long distance by the CPU. The device comprises a controller module, an FPGA module, a configuration module and a buffer module, wherein the controller module is connected with an upper computer in a wired / wireless way, a second GPIO (General Purpose Input / Output) interface of the controller module is connected with an enable pin of the buffer controller, an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) of the controller module is connected with a data input end of the buffer module, a first GPIO interface of the controller module is connected with a configuration signal of the FPGA module, a data output end of the buffer module is connected with SPIs of the FPGA module and the configuration module respectively, a FPGA configuration file is updated from a long distance based on MPC5200B and a real-time operation system VxWorks. According to the device and the method, the cost is saved, the operability of the system is improved, the design difficulty is reduced, the on-line updating of the FPGA is easily realized, and the configuration efficiency and the configuration flexibility of the FPGA are improved.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
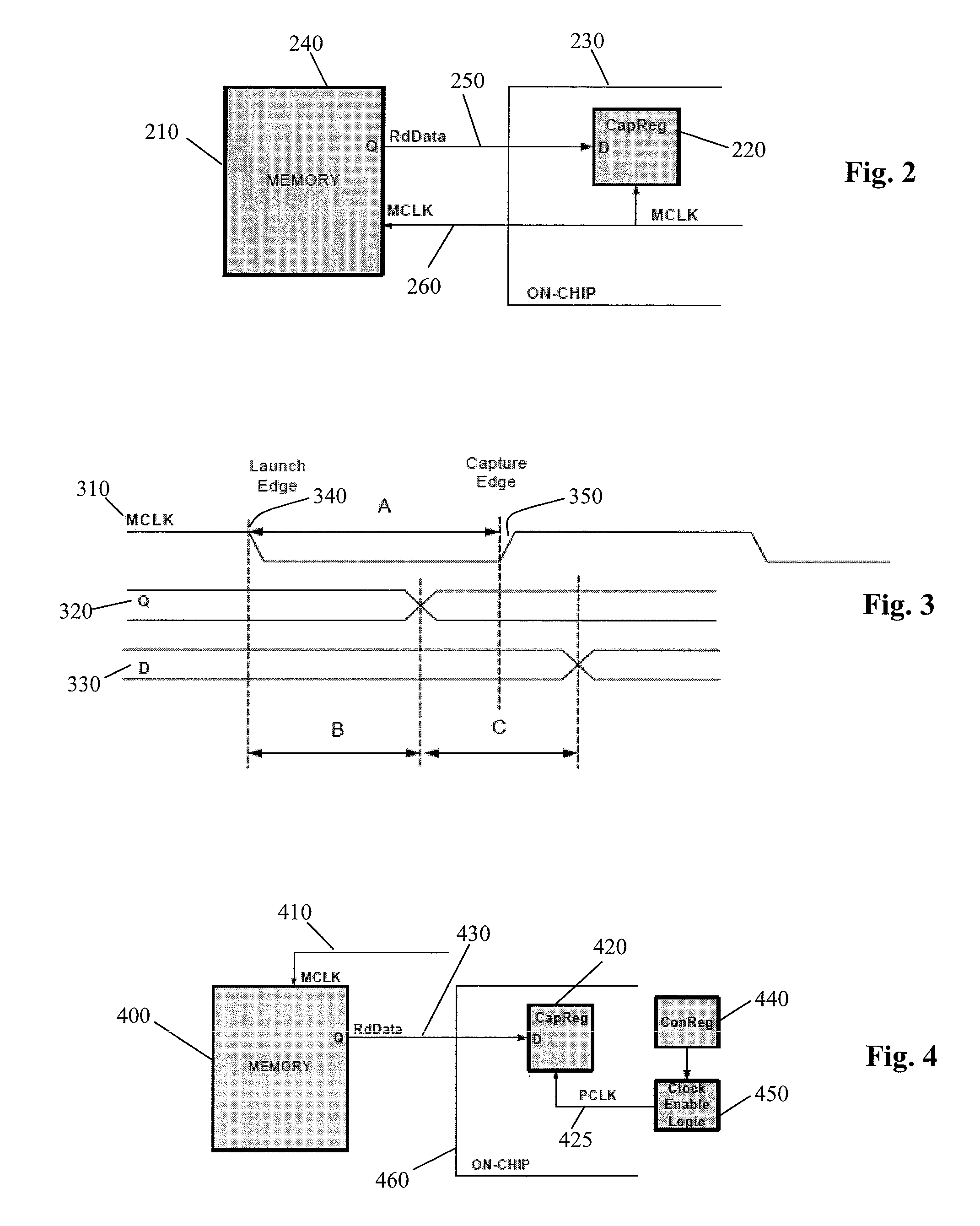
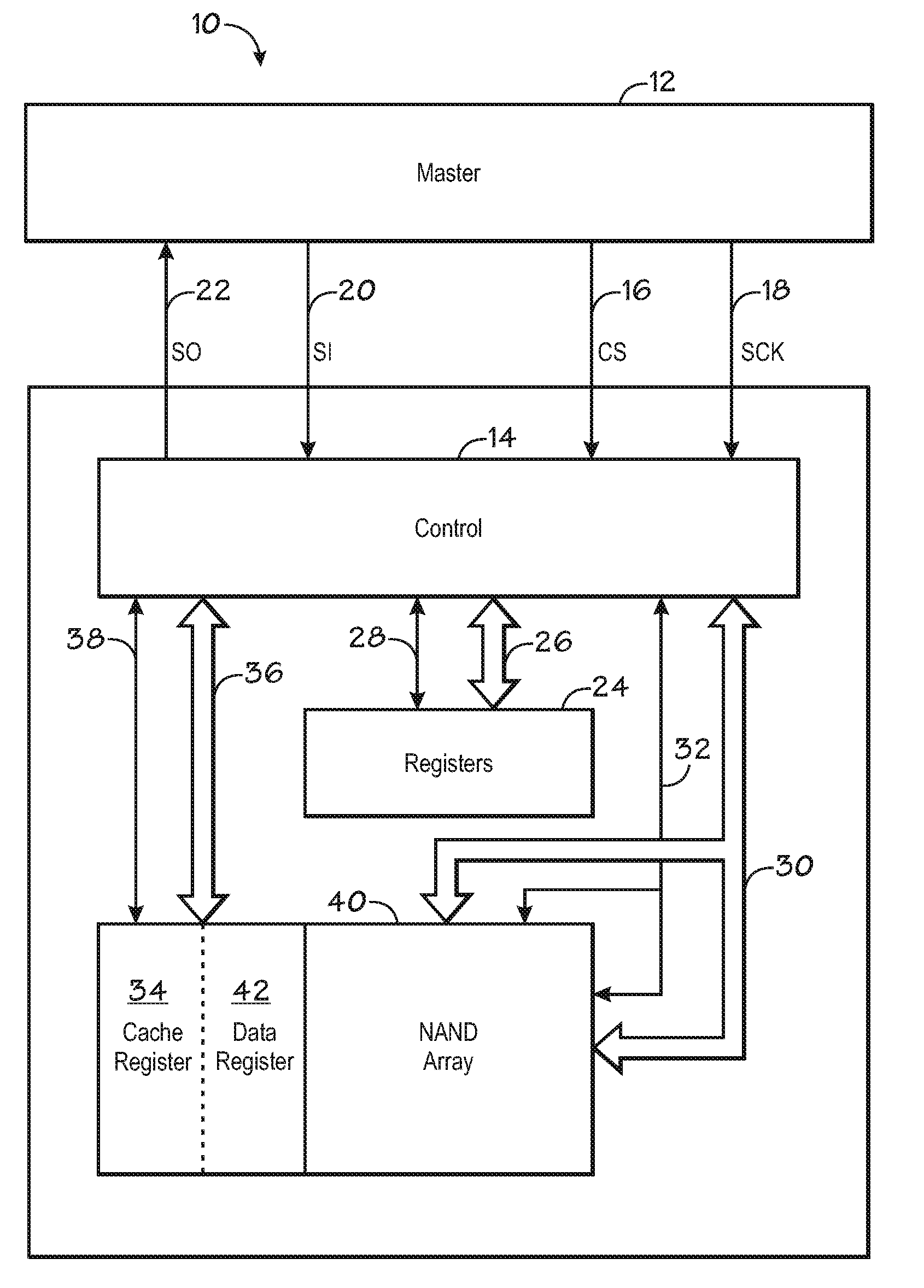
Memory architecture with serial peripheral interface
ActiveUS20070115743A1High densityQuick eraseRead-only memoriesDigital storageTerm memoryMemory architecture
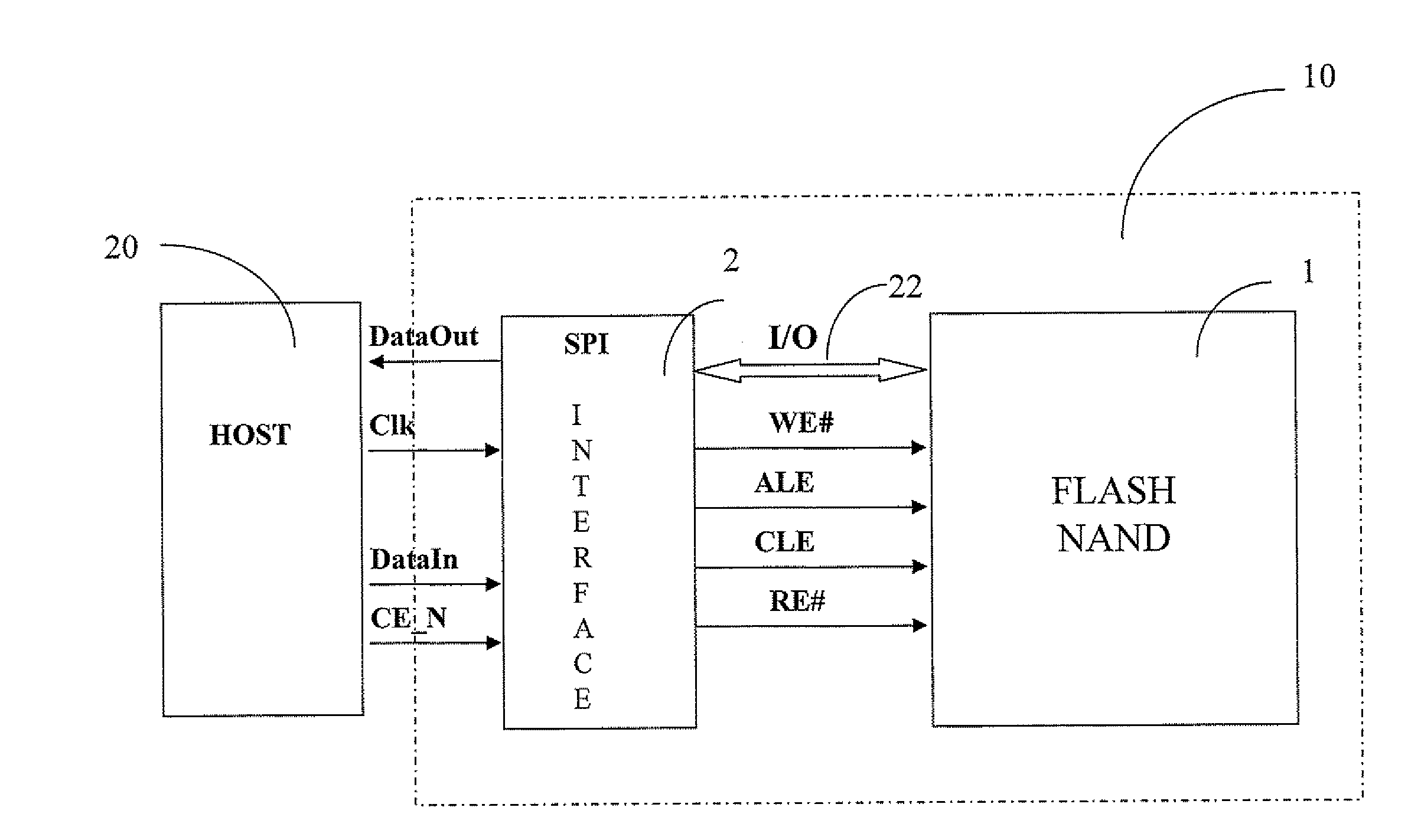
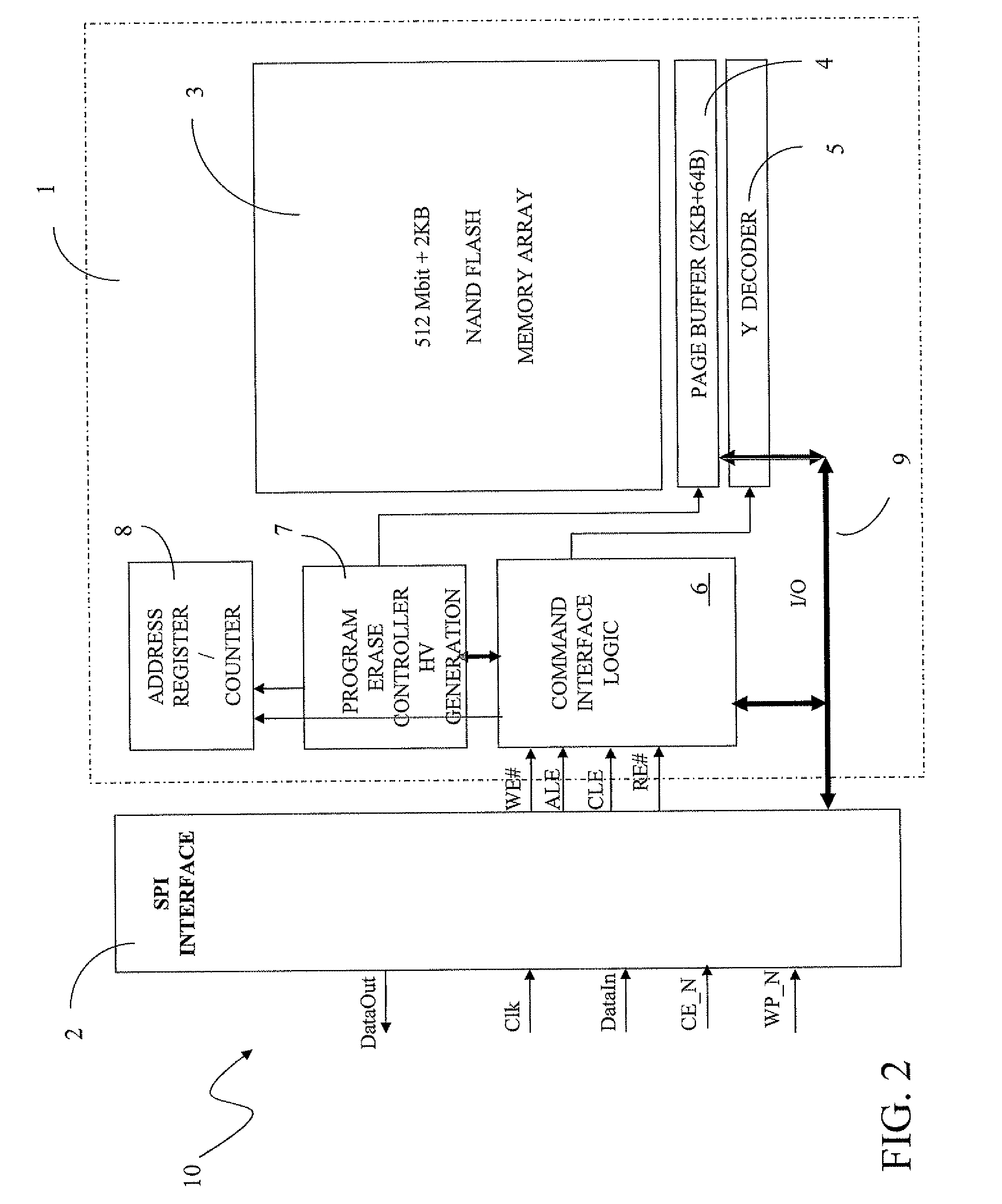
A memory architecture includes a memory including a Command Set, and a serial peripheral interface (SPI) for connecting the memory to a generic host device. The SPI includes a data in line for supplying output data from the host device to inputs of the memory; a data out line for supplying output data from the memory to input of the host device; a clock line driven by the host device; and an enable line that allows the memory to be turned on and off by the host device. The memory is a NAND Flash Memory. The SPI includes an I / O registers block, including an SPI label register and a data register for driving separately data, commands and addresses directed to the memory from the corresponding SPI label registers.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
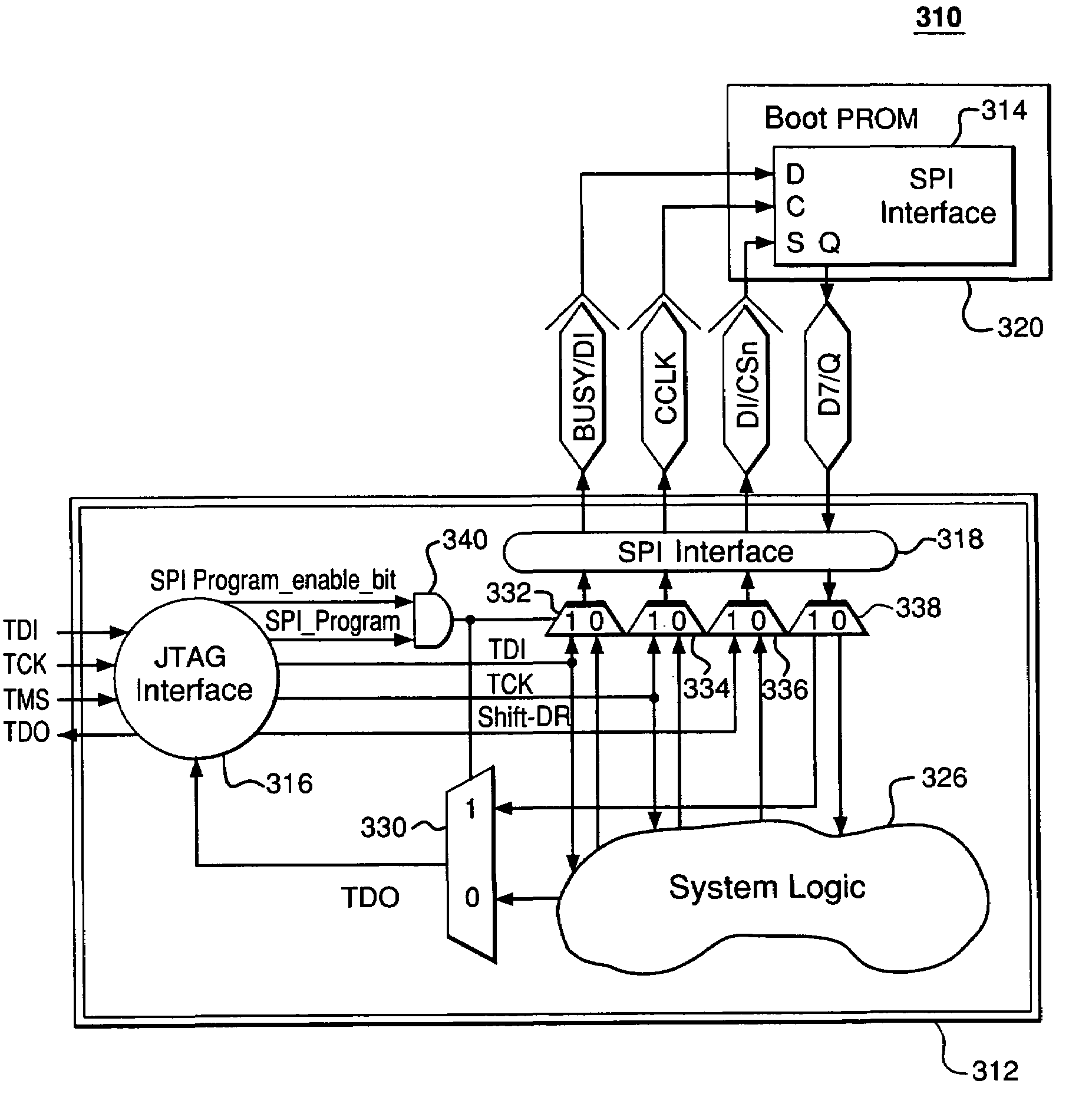
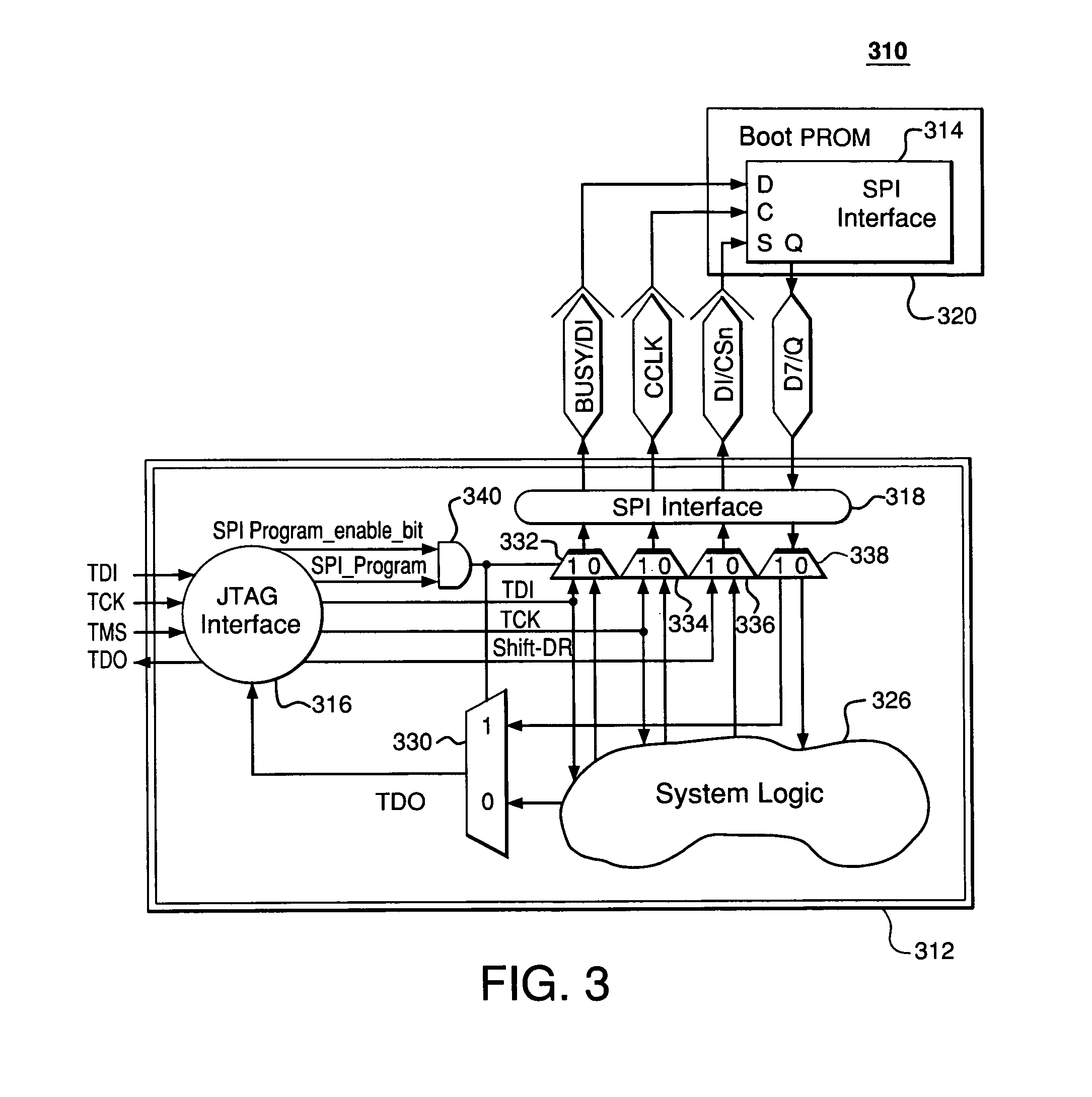
In-system programming of non-JTAG device using SPI and JTAG interfaces of FPGA device
ActiveUS7265578B1Electronic circuit testingLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsIn-system programmingJoint Test Action Group
A first programmable device comprises non-dedicated, programmable resources including programmable logic; dedicated circuitry; a Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) interface adapted to selectively interchange signals with the programmable logic via the dedicated circuitry; and a Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) interface adapted to (1) selectively interchange signals with the programmable logic via the dedicated circuitry and (2) selectively interchange signals with the JTAG interface via the dedicated circuitry. The JTAG interface is adapted to be connected to a first external device. The SPI interface is adapted to be connected to a second external device. The first programmable device is adapted to transfer signals from the first external device to the second external device via the JTAG interface, the dedicated circuitry, and the SPI interface without relying on any of the programmable resources.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
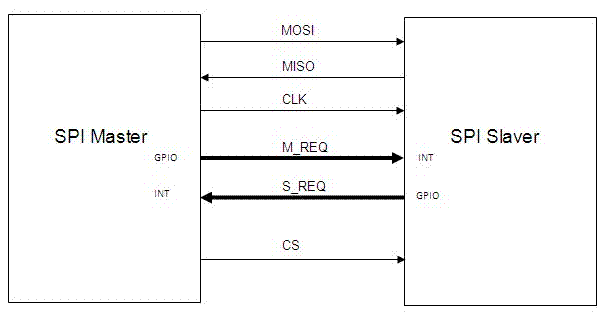
Serial communication system between devices and method
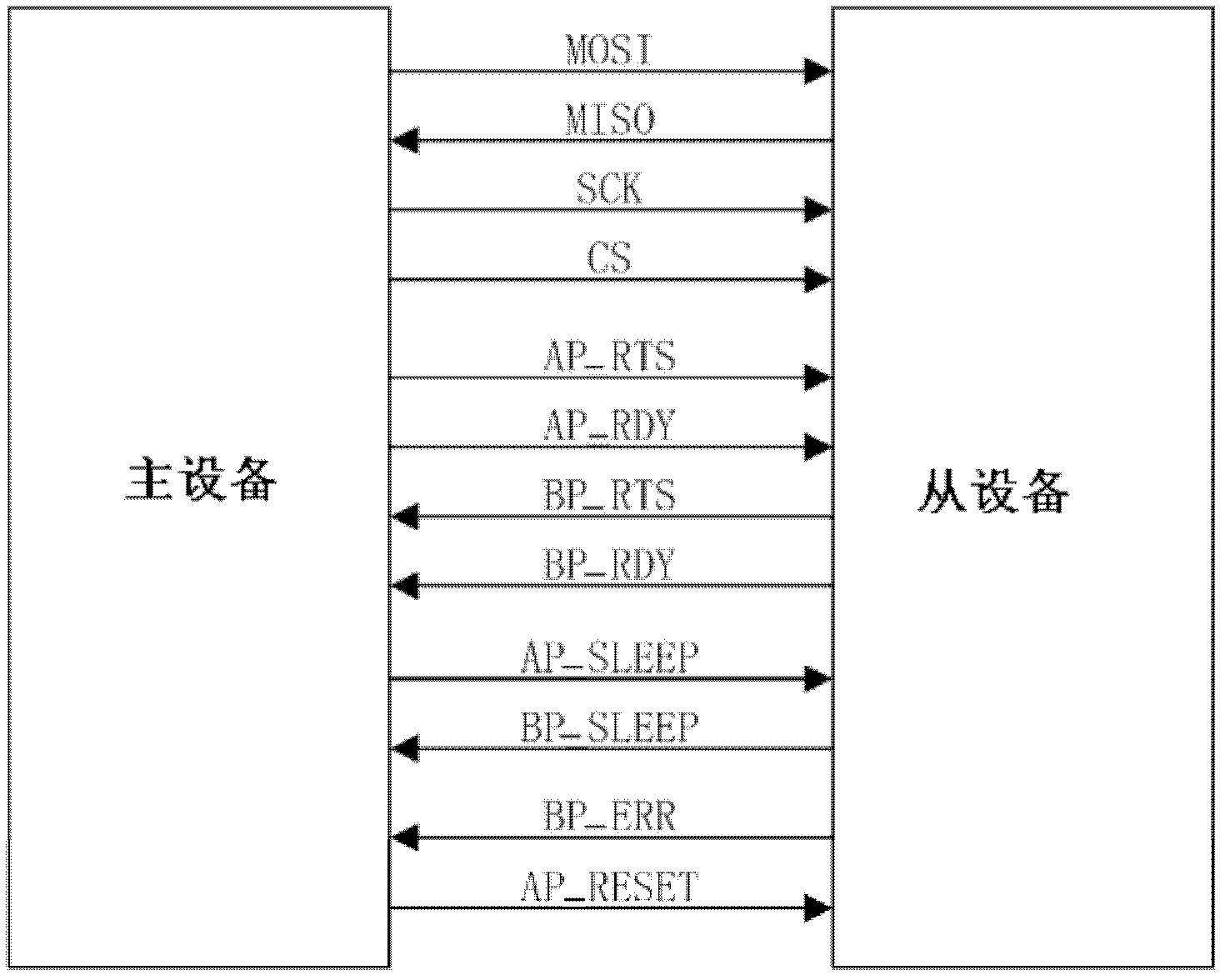
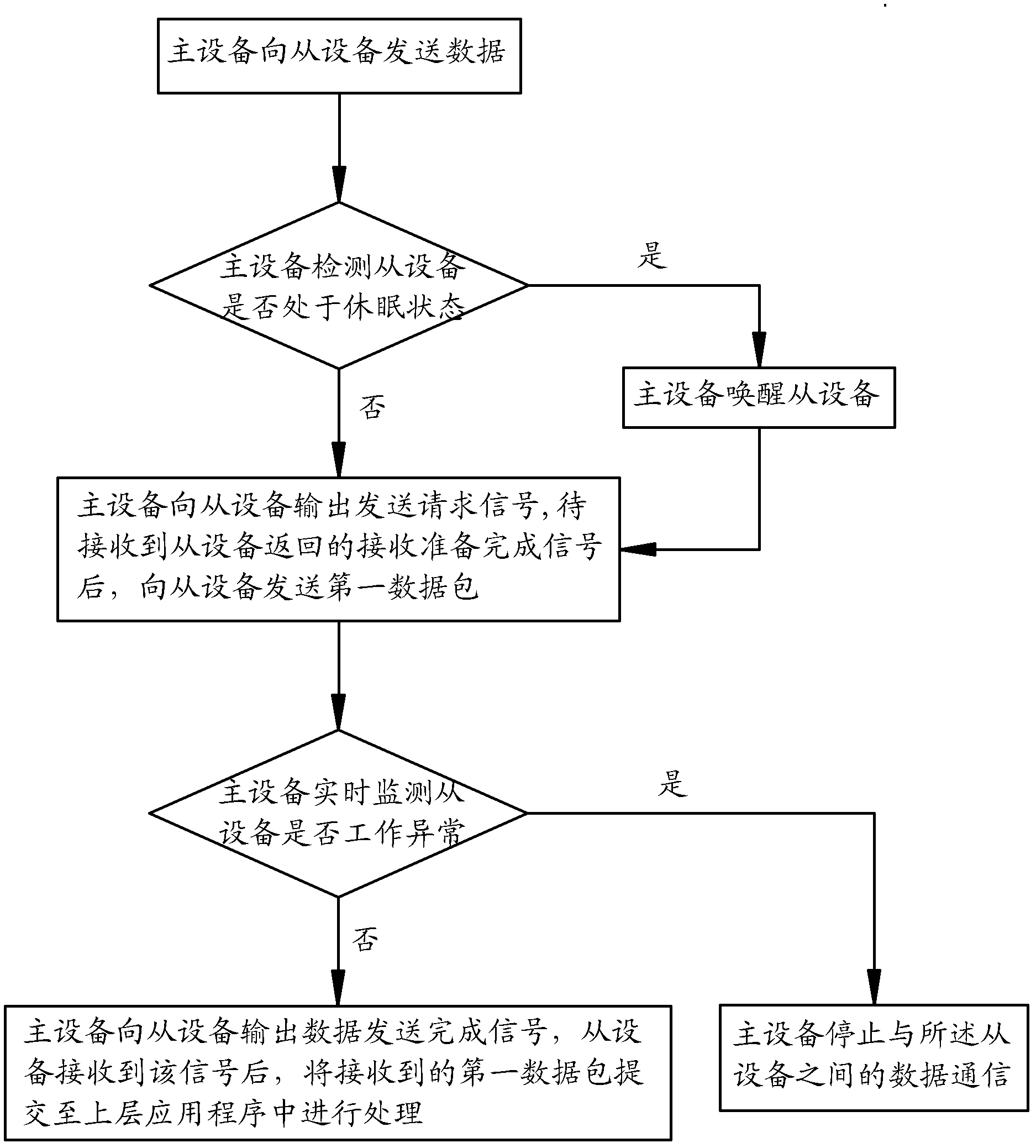
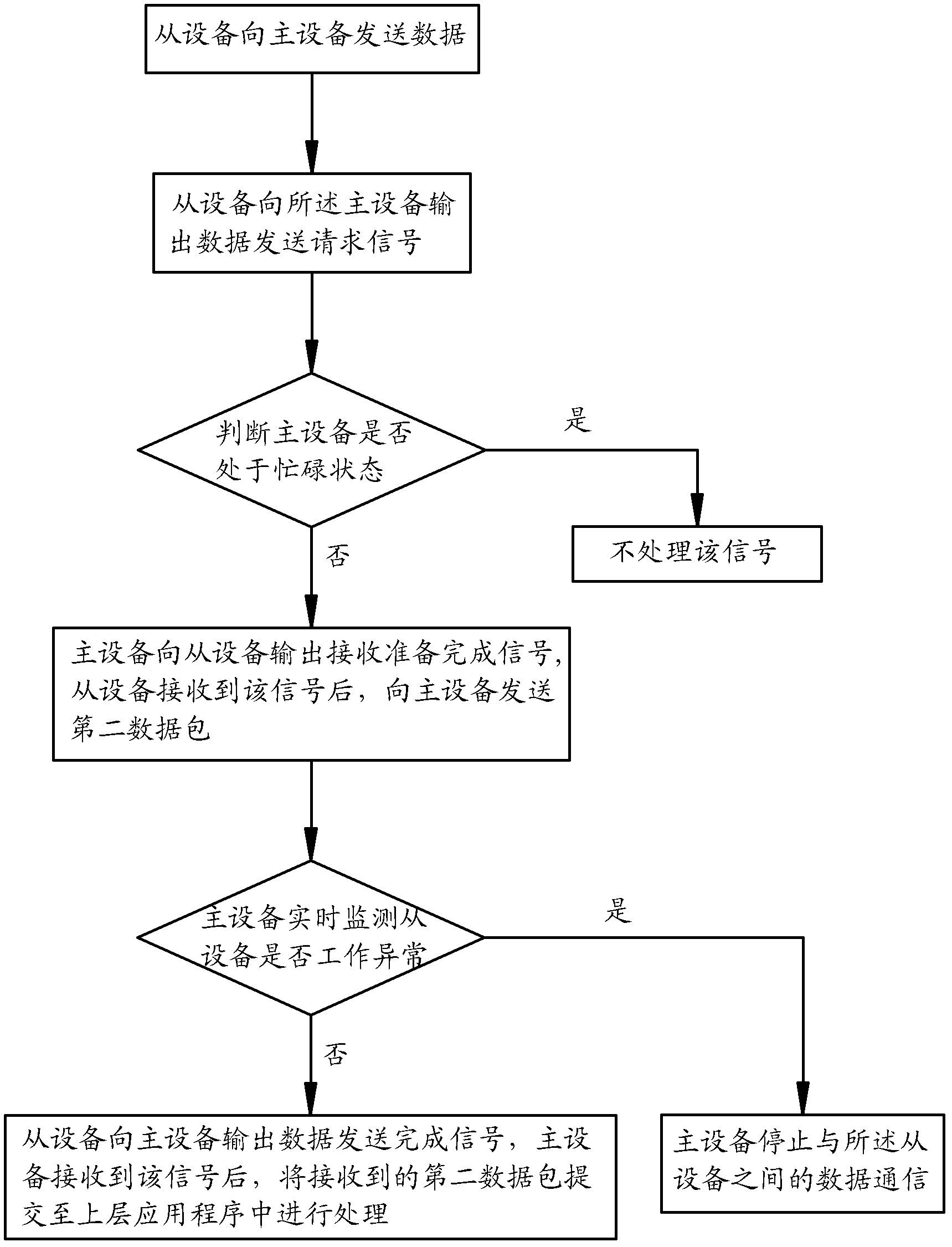
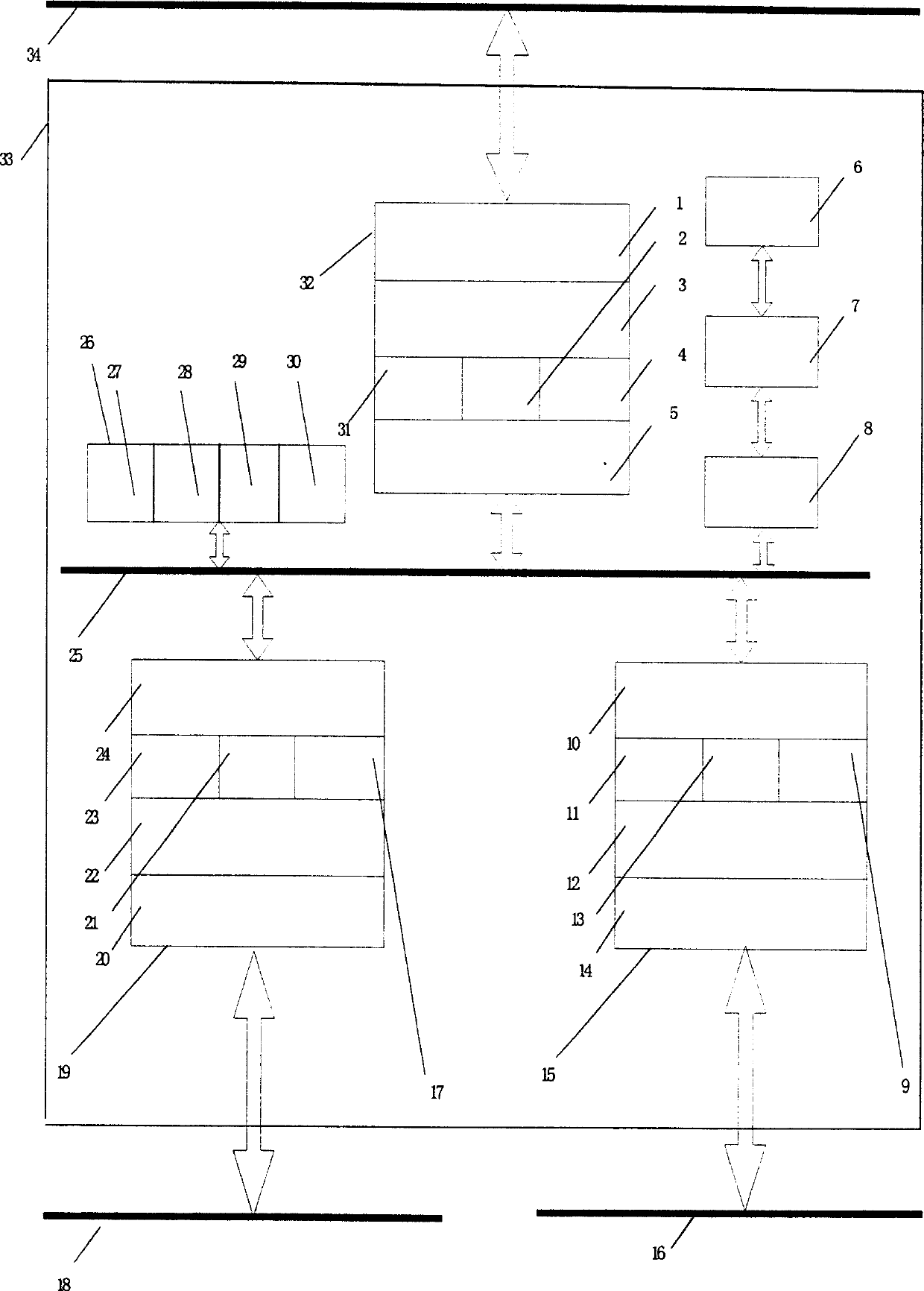
InactiveCN102354305AFast transmissionLow costPower supply for data processingEnergy efficient computingSleep stateSerial Peripheral Interface Bus
The invention discloses a serial communication system between devices and a method. The serial communication system between the devices comprises a master device, at least one slave device and an SPI (serial peripheral interface) bus for communication between the master device and the slave device. The SPI bus comprises a master-out slave-in signal line MOSI, a master-in slave-out signal line MISO, a clock signal line SCK, a chip selection signal line CS, a master transmission request and transmission completion signal line AP_RTS, a master reception preparation and completion signal line AP_RDY, a slave transmission request and transmission completion signal line BP_RTS, a slave reception preparation and completion signal line BP_RDY, a signal line AP_SLEEP for a master to awaken up a slave or control the slave to sleep, a slave sleeping state signal line BP_SLEEP and a slave abnormality state signal line BP_ERR. By adopting the system and the method, the transmission speed is high, and the cost of implementation is low. In addition, the system also has the functions of awakening up the sleep state and processing abnormalities, the failure in data communication in the sleep state of the slave device can be controlled promptly, the power consumption can be reduced, and the real-time monitoring of abnormal working states of the slave device can be achieved.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Multi protocol conversion method and device between MODBUS/TCP industry Ethernet and field bus device network as well as field bus of PRofibus DP
InactiveCN1697448ARealize the interface functionRealize the master node functionNetwork connectionsBus networksInformation layerHigh rate
Software in MPU builds united message model to realize protocol conversion in application layer among MODBUS / TCP industrial Ethernet, DeviceNet field bus and Profibus DP field bus. Corresponding interface module and communication adapter modules at main nodes realize their relevant protocols. Through an internal bus, protocol conversion device built from a MPU is connected to industrial Ethernet interface module, DeviceNet communication adapter module at main node, Profibus DP communication adapter module at main node and a SRAM. Through a serial peripheral interface, MPU is connected to an electrically erasable memory. The invention solves converting protocols based on different standards. One communication frame is compatible to multiple industrial communication networks so as to meet requirements of network real-time at low-layered devices as well as high rate and large capacity of network on information layer.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
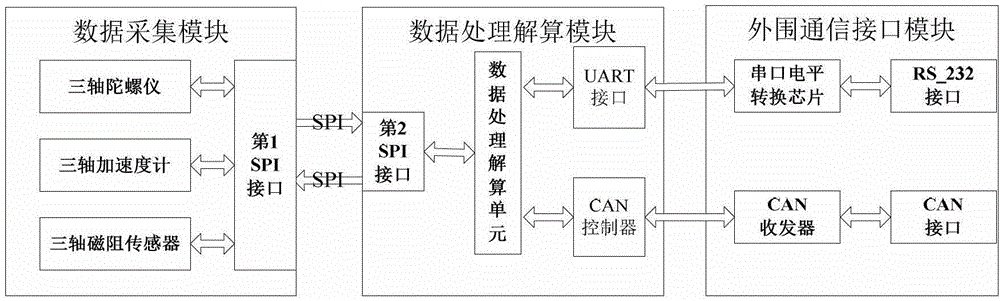
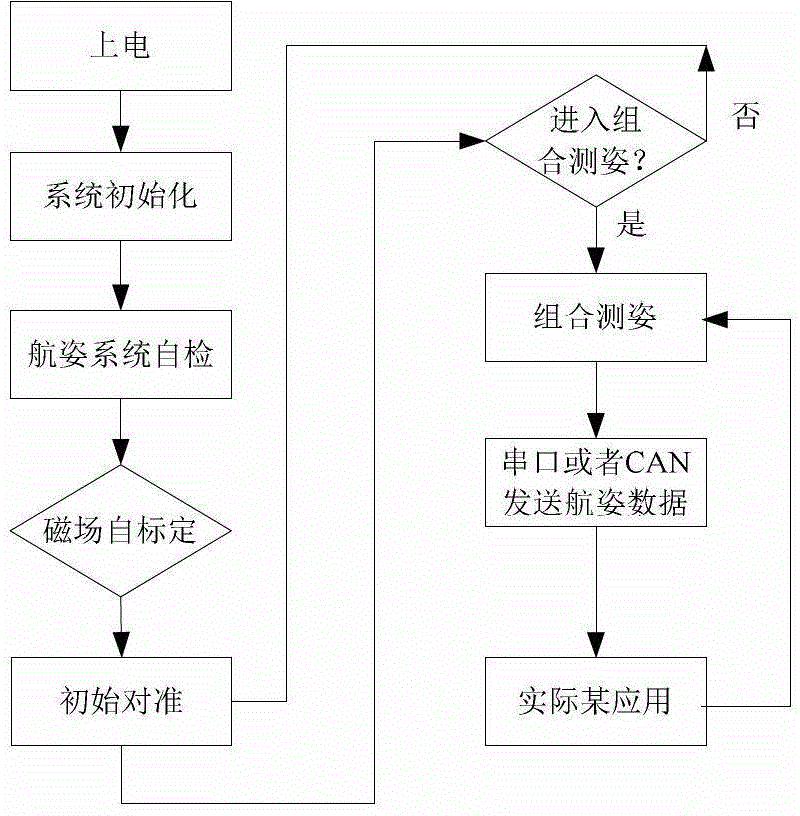
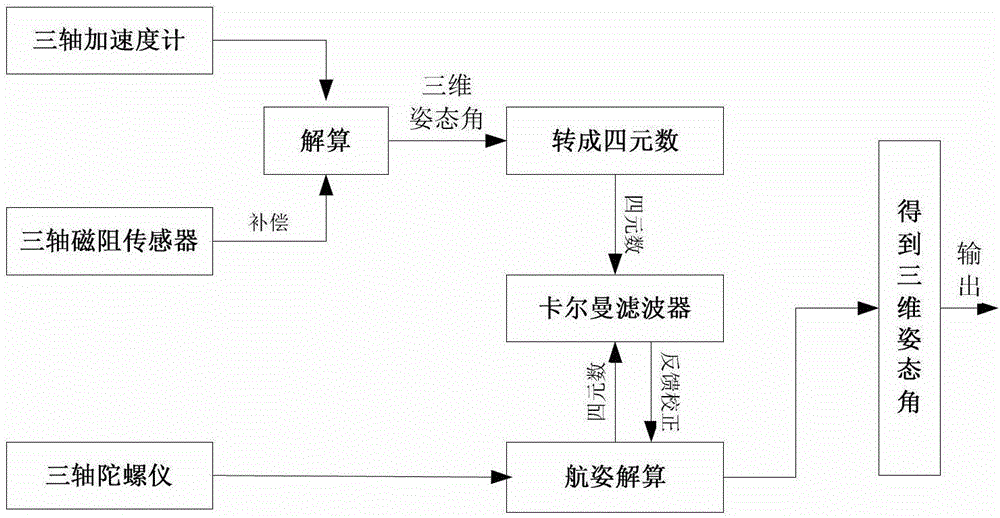
Micro-strapdown altitude heading reference system and working method thereof
InactiveCN102980577ALow costHighly integratedNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMicrocontrollerArea network
The invention relates to a micro-strapdown altitude heading reference system and a working method of the micro-strapdown altitude heading reference system. The system comprises a data acquisition module, a data processing resolving module and a peripheral communication interface module, wherein the data acquisition module integrates a three-axis gyroscope, a three-axis accelerometer, a three-axis magnetic resistance sensor and an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) into an integrated micro-electronic mechanical system sensor; the data processing resolving module adopts a 32-bit ARM (Advanced RISC Machine) microcontroller; and the peripheral communication interface module consists of a serial port level switching chip, an RS-232 interface, a CAN (Controller Area Network) transceiver and a CAN interface. The working method of the system comprises the working steps as follows: the system is electrified and initialized; the system is self-tested; a magnetic field is self-calibrated; initial alignment is conducted; measured attitudes are combined: resolving the information of attitude headings according to initial three-dimensional altitude and altitude resolving algorithm of the strapdown altitude heading reference system, and resolving the three-dimensional magnetic altitude angle according to the compensated magnetic field information and acceleration information, conducting the information merging algorithm and finally obtaining the stable altitude heading reference information; and the altitude heading reference information is sent to application equipment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
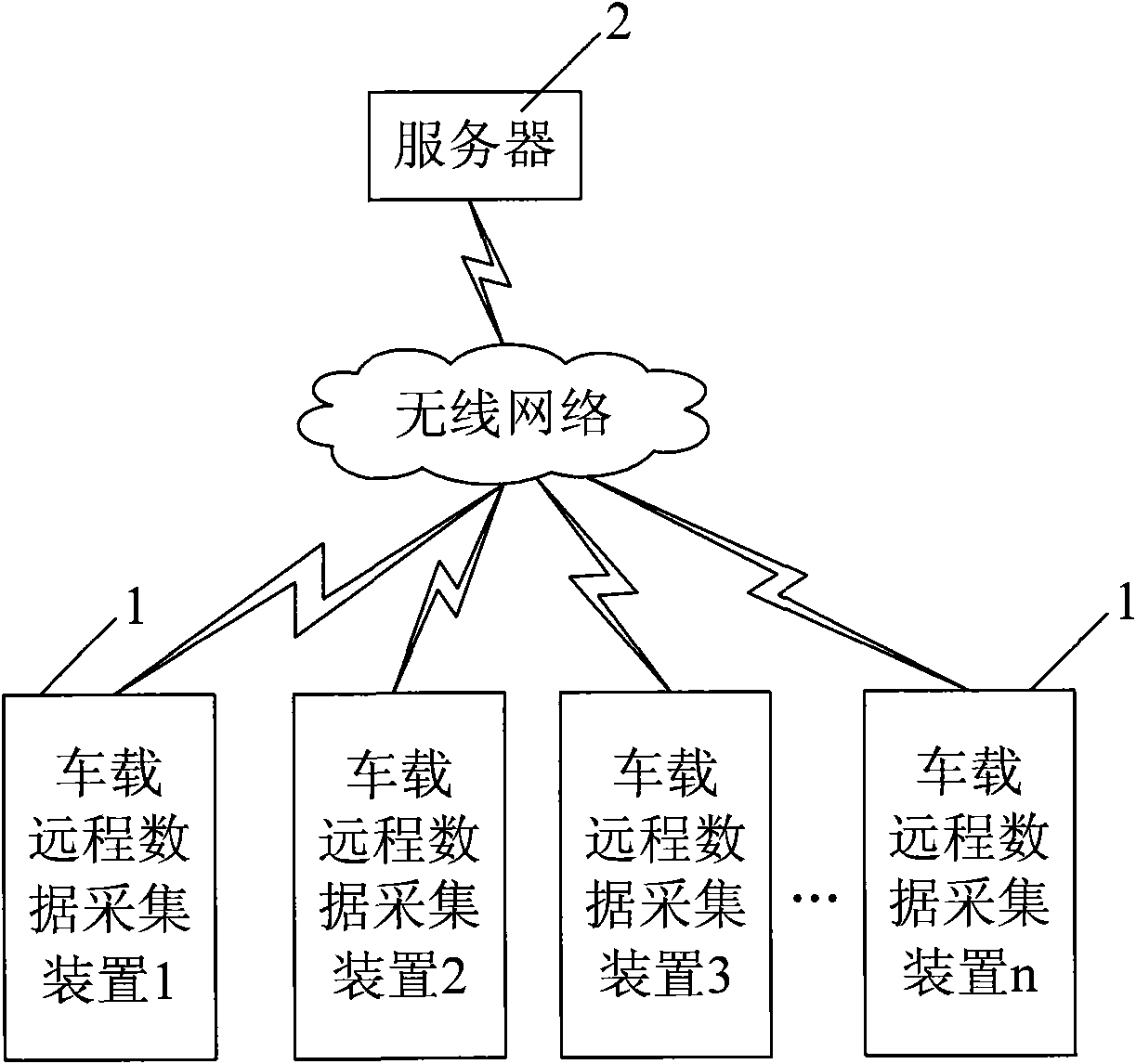
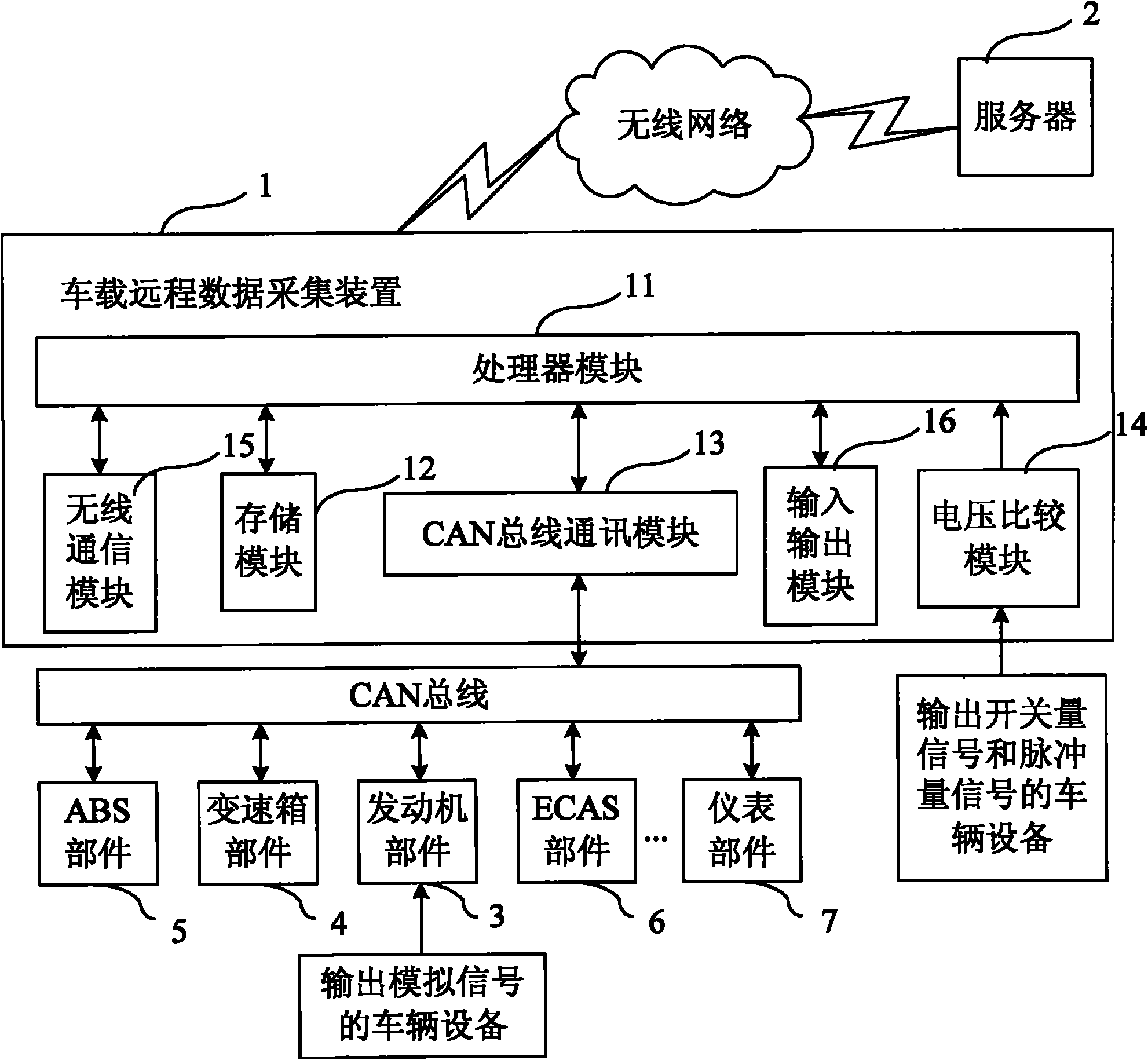
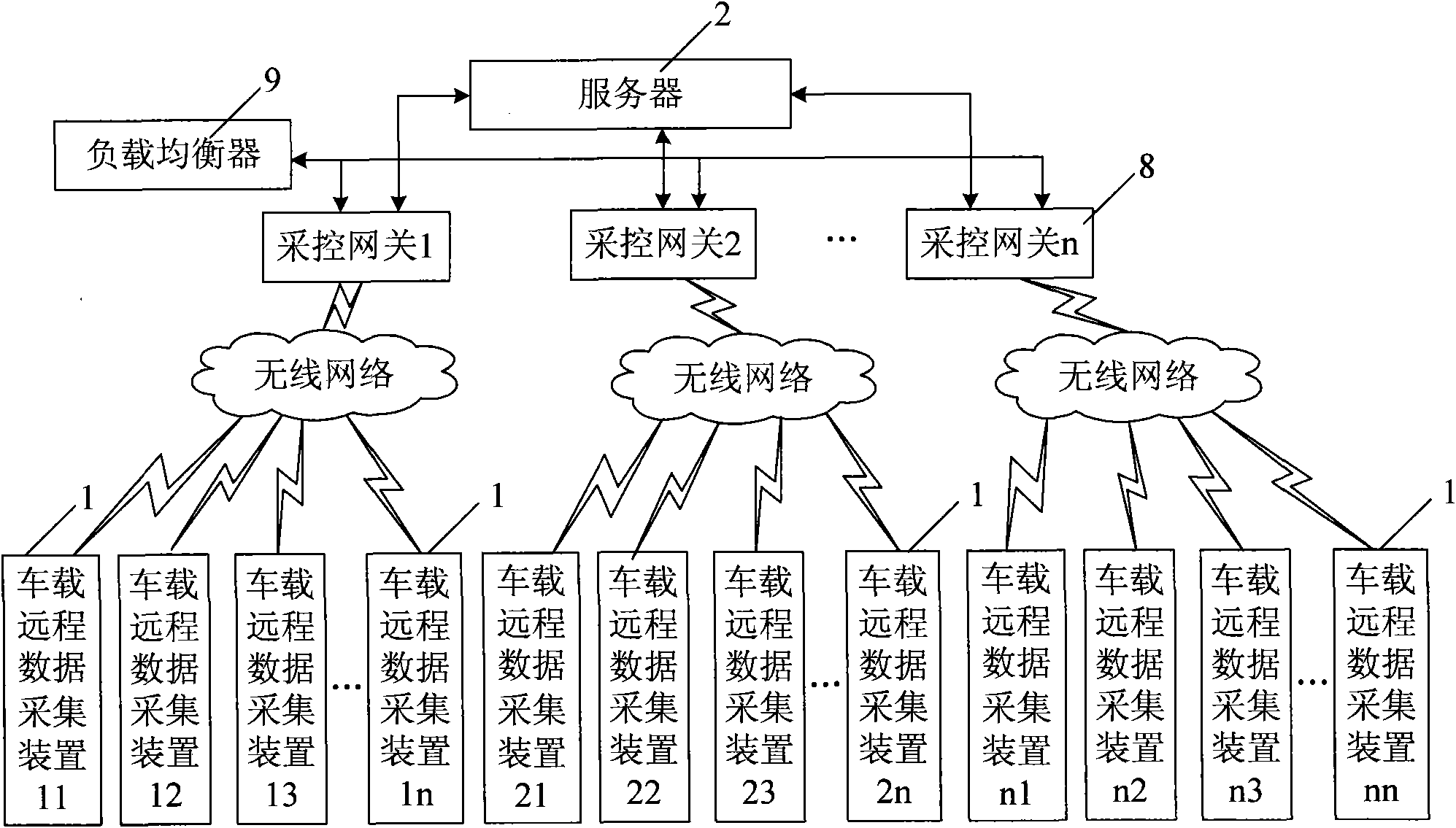
Vehicle remote data acquisition system based on CAN (Controller Area Network) bus
InactiveCN101853021AEasy to collectComprehensive dataTransmissionTotal factory controlArea networkData acquisition
The invention discloses a vehicle remote data acquisition system based on a CAN (Controller Area Network) bus, comprising a remote server and at least one vehicle-mounted remote data acquisition device, wherein each vehicle-mounted remote data acquisition device comprises a processor module, a CAN bus communication module, a voltage comparison module and a radio communication module; input signals of the voltage comparison modules are switching value signals and pulse value signals which are output by vehicle equipment; analog value signals output by the vehicle equipment are processed by an engine ECU (Electronic Control Unit), then transmitted to the CAN bus and received by the CAN bus communication modules; the CAN bus communication module are also used for receiving equipment signals hung on the CAN bus, and the output ends of the CAN bus communication modules are connected with the processor modules through an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) bus; and the radio communication modules are used for carrying out radio communication with the server. The system can acquire various information of the vehicle equipment on a plurality of vehicles, data is transmitted to the server for storing through radio communication, and reliable references are provided for the maintenance and the management of the vehicles according to acquired data.
Owner:HIGER
Serial peripheral interface memory device with an accelerated parallel mode
A serial peripheral flash memory device uses a plurality of dummy input / output terminals to enable the selection of a parallel mode for devices that have a slower serial clock speed. In parallel mode, data is transmitted over the plurality of dummy input / output terminals to allow a plurality of bits to be transmitted at the same time improving the data transmission rate at the slower serial clock speed.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Serial peripheral interface memory device with an accelerated parallel mode
ActiveUS20060268642A1Read-only memoriesDigital storageData transmissionSerial Peripheral Interface Bus
A serial peripheral flash memory device uses a plurality of dummy input / output terminals to enable the selection of a parallel mode for devices that have a slower serial clock speed. In parallel mode, data is transmitted over the plurality of dummy input / output terminals to allow a plurality of bits to be transmitted at the same time improving the data transmission rate at the slower serial clock speed.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Serial peripheral slave device interface structure in integrated circuit chip and data reading and writing method
ActiveCN102023956AEasy to operateSimple structureElectric digital data processingWork performanceComputer module
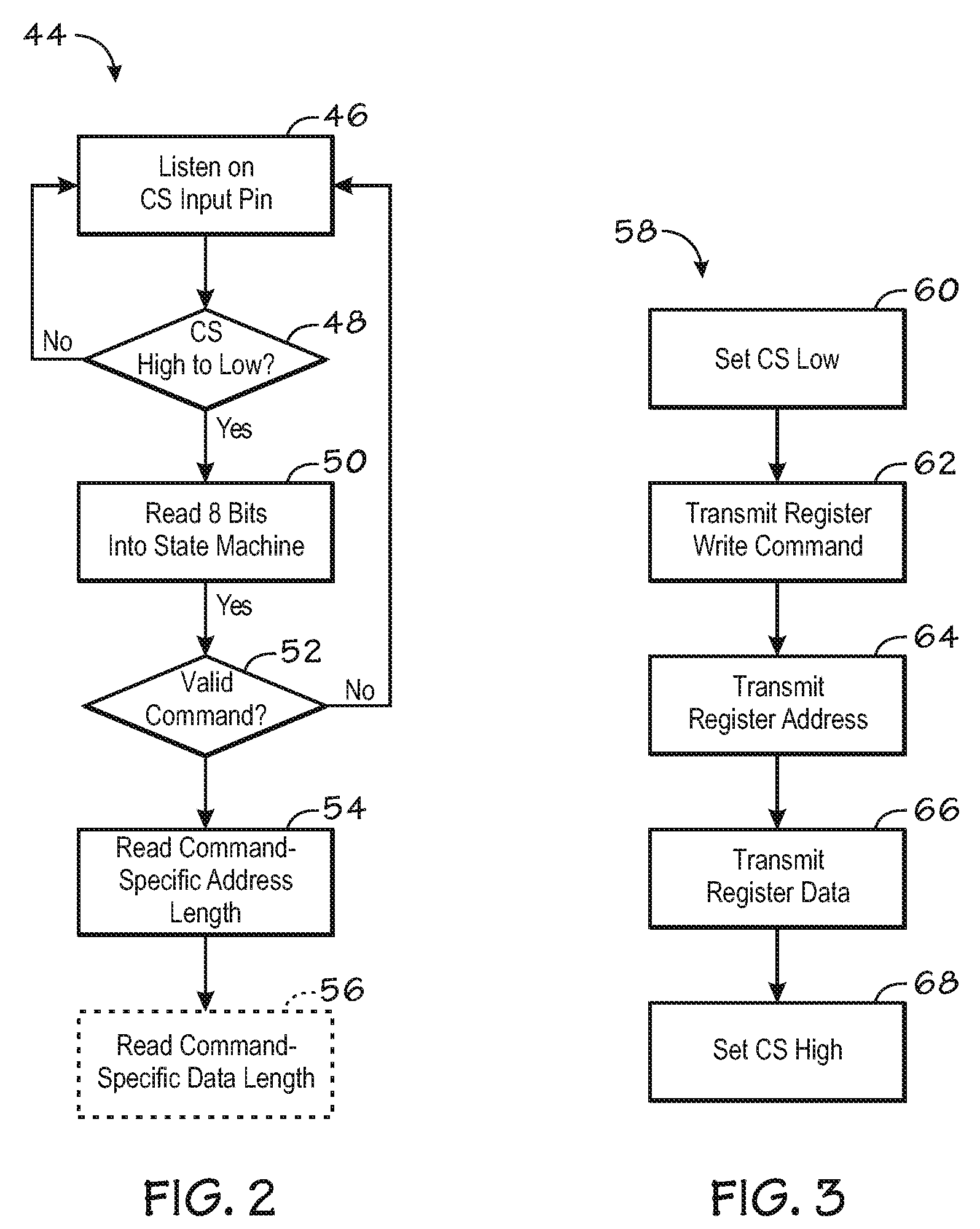
The invention relates to a serial peripheral slave device interface structure in an integrated circuit chip. The serial peripheral slave device interface structure comprises a register module, a storage module and a state machine logic control module. The serial peripheral slave device interface structure is connected with a central processor of the chip through an internal bus of the chip and is also connected with an external serial peripheral master device through a data transmission wire. The invention also relates to a method for rapidly reading and writing serial peripheral interface data in the integrated circuit chip through the interface structure. The method comprises steps of reading the data through the serial peripheral master device and writing the data through the serial peripheral master device. Through the serial peripheral slave device interface structure in the integrated circuit chip and the data reading and writing method, the data transmission rate is ensured to be much higher than that of an ordinary serial peripheral interface (SPI); the structure is simple; the operation mode is convenient and quick; the development cost is low; the working performance is stable and reliable; the application range is relatively wide; the high speed data transmission interface solution of an integrated circuit is widened; and the structure and the method have wide application prospect.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Operating system startup booting method capable of aiming at system on chip
The invention provides an operating system startup booting method capable of aiming at a system on chip. The method comprises the following steps that: 1) after the system on chip is electrified, starting an onboard RBL (ROM (Read Only Memory) bootloader), reading a first-level bootloader into memory from Nor Flash, wherein the first-level bootloader only comprises a PLL (Phase Locked Loop) configuration unit, a first board level hardware initialization unit used for supporting PLL configuration, and a second-level bootloader loading unit; 2) operating the first-level bootloader in the memory,executing the code of the first board level hardware initialization unit by a processor to finish the initialization of the board level hardware used for supporting the PLL configuration, executing the code of the PLL configuration unit to maximize the clock frequency of an ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) core and the clock frequency of an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) bus, and executing the code of the second-level bootloader loading unit to load a second-level bootloader to the memory from the Nor Flash; and 3) executing the code of the second-level bootloader to finish Linux startup booting. By use of the method, the startup booting time of the operating system of the SoC can be shortened.
Owner:北京中科晶上科技股份有限公司
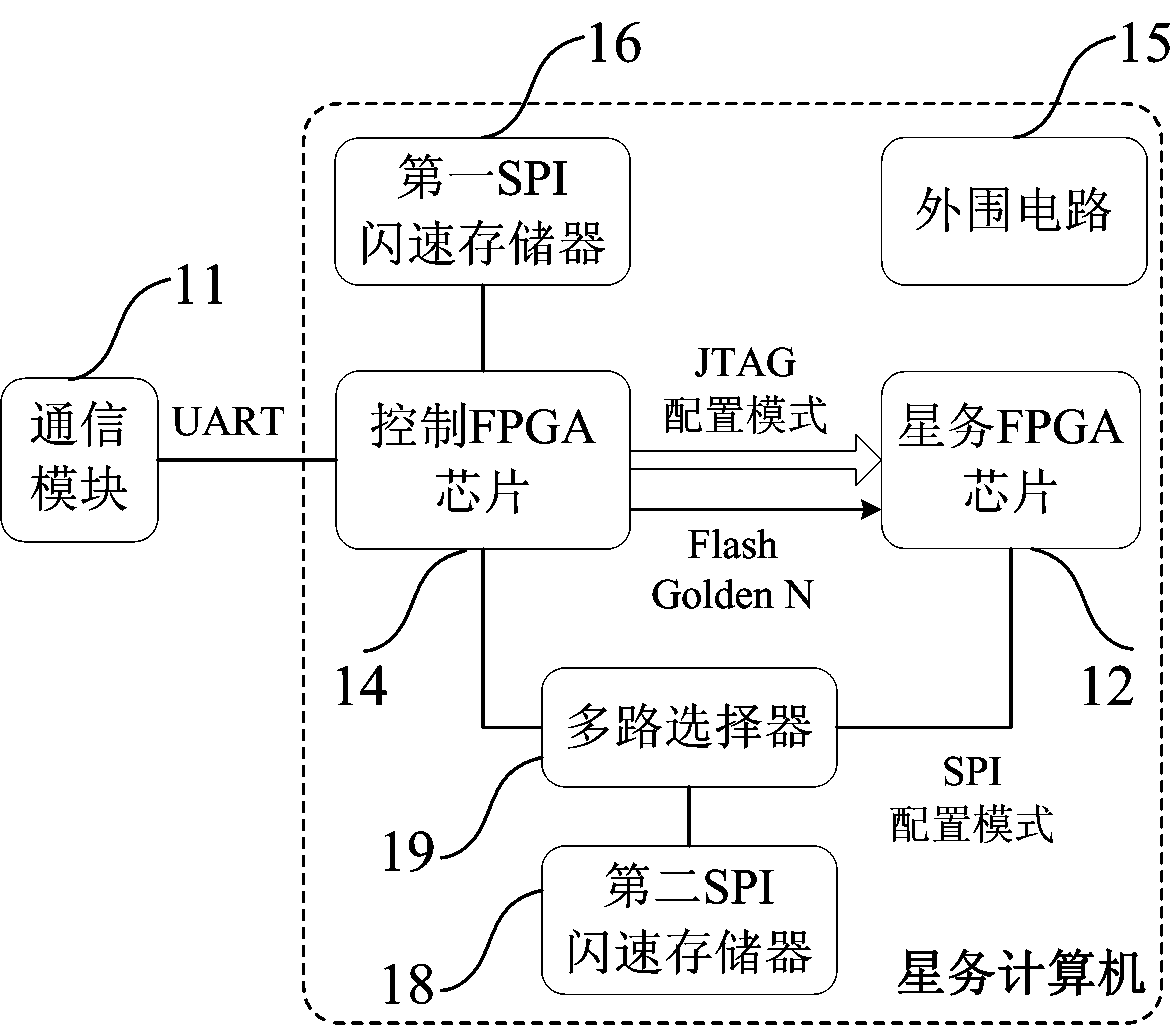
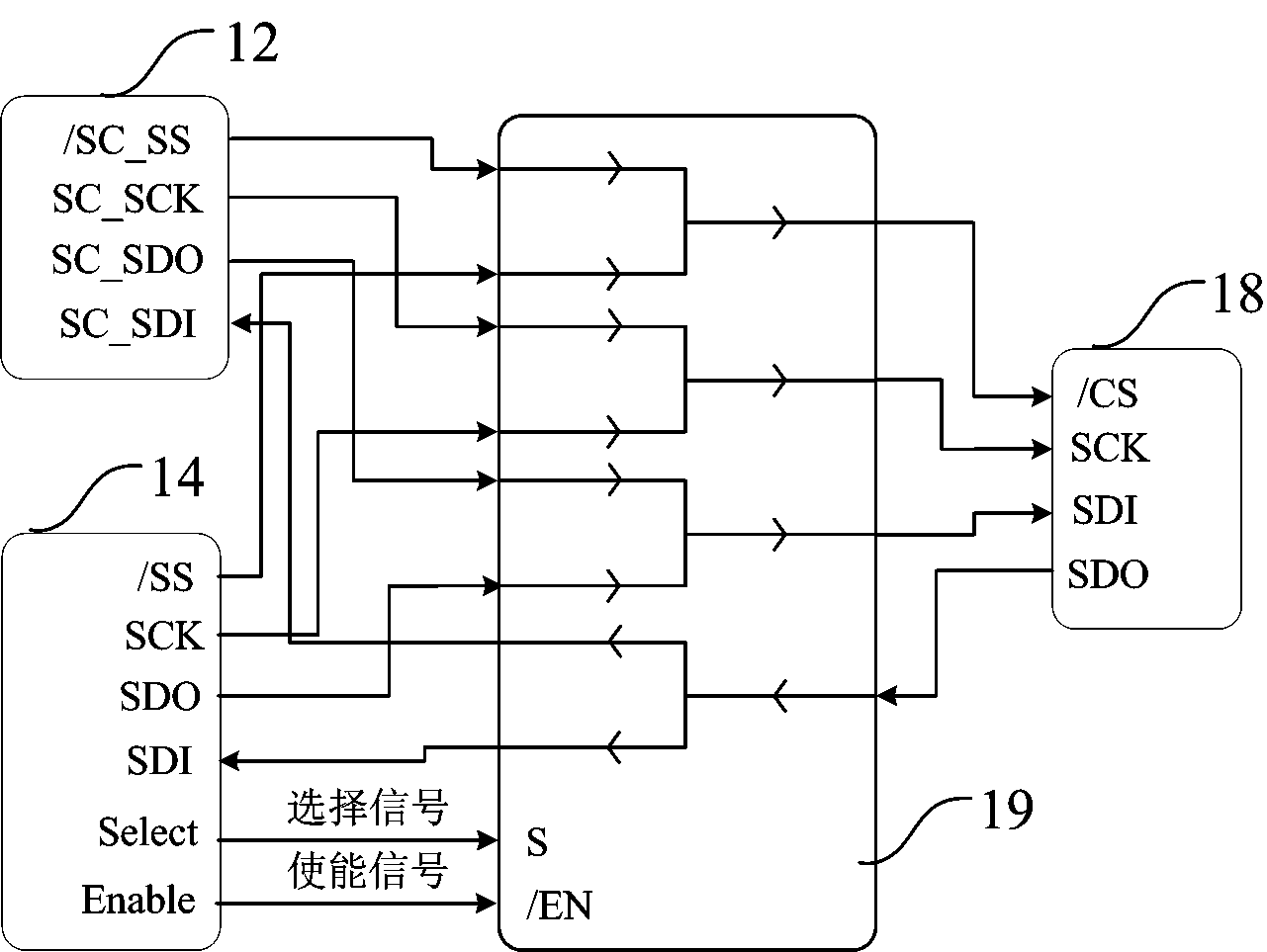
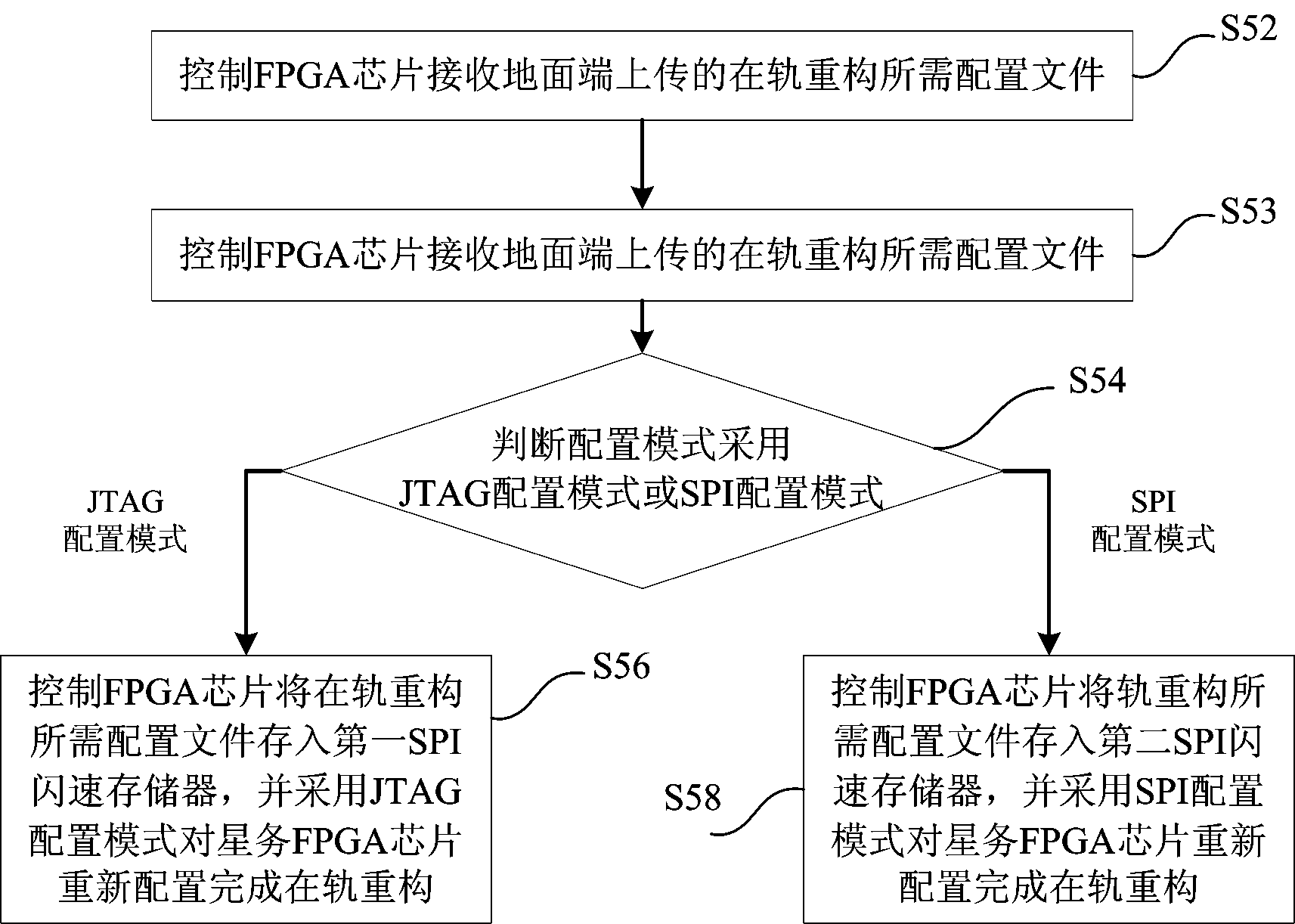
FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)-based on-orbit reconfiguration system and method for satellite on-board computer
InactiveCN104239090AFlexible allocationControl allocationProgram loading/initiatingOn boardJoint Test Action Group
The invention discloses an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)-based on-orbit reconfiguration system for a satellite on-board computer. The FPGA-based on-orbit reconfiguration system comprises an on-board FPGA chip, a control FPGA chip and an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) flash memory unit, wherein the on-board FPGA chip is internally integrated with CPU cores; the control FPGA chip is used for receiving configuration files, which are uploaded by a communication module of a satellite, for on-orbit reconfiguration, unloading the configuration files in the SPI flash memory unit, and controlling the on-orbit reconfiguration of the on-board FPGA chip; the SPI flash memory unit is used for storing the configuration files required for on-orbit reconfiguration; in the process of realizing on-orbit reconfiguration by means of running a JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) configuration mode, the control FPGA chip reads the configuration files required for the JTAG configuration mode from the SPI flash memory unit, and sends the configuration data to the on-board FPGA chip; in the process of realizing on-orbit reconfiguration by means of running an SPI configuration mode, the control FPGA chip informs the on-board FPGA chip of starting the SPI configuration mode, and the on-board FPGA chip reads the configuration files required for the SPI configuration mode from the SPI flash memory unit.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
System and method for setting access and modification for synchronous serial interface NAND
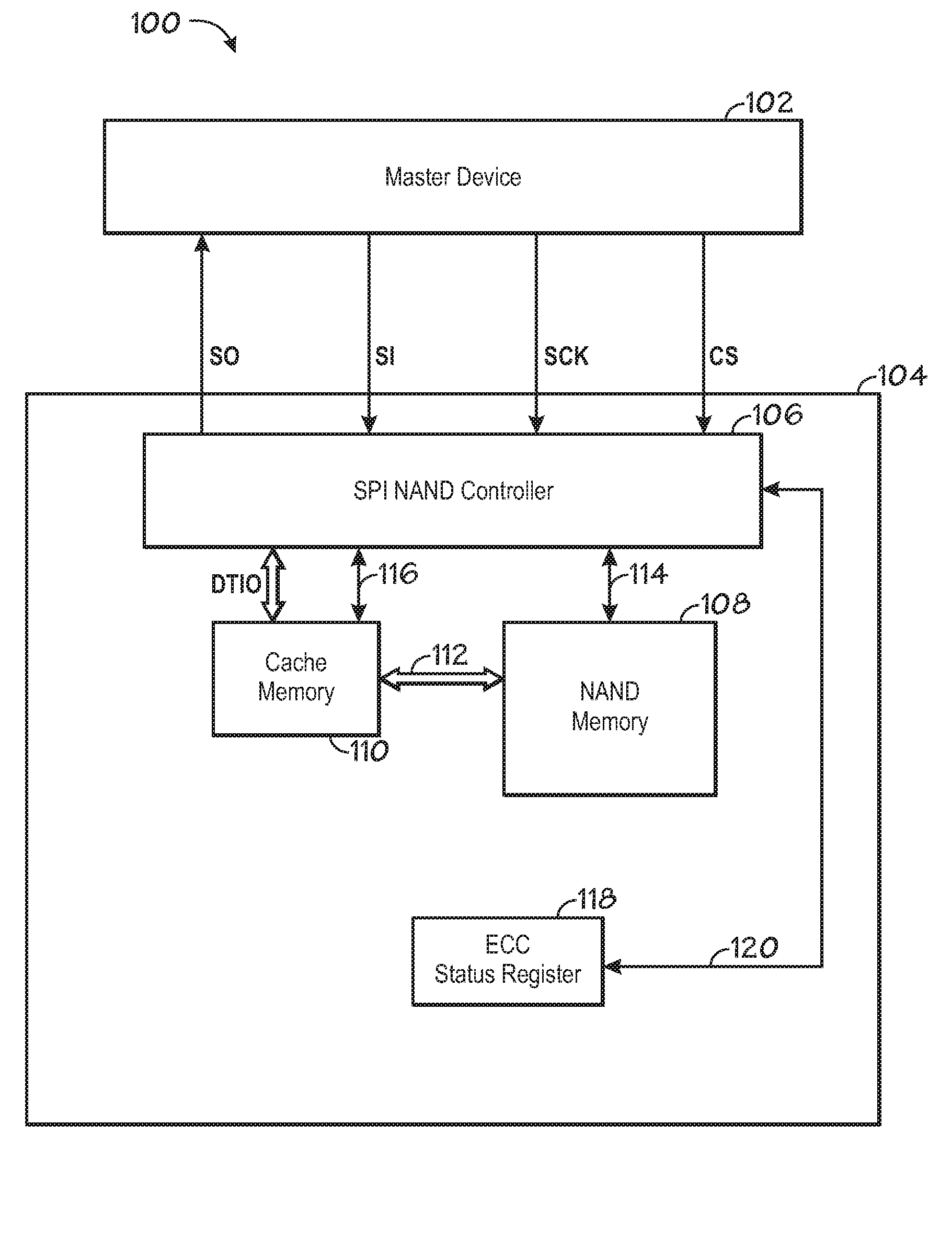
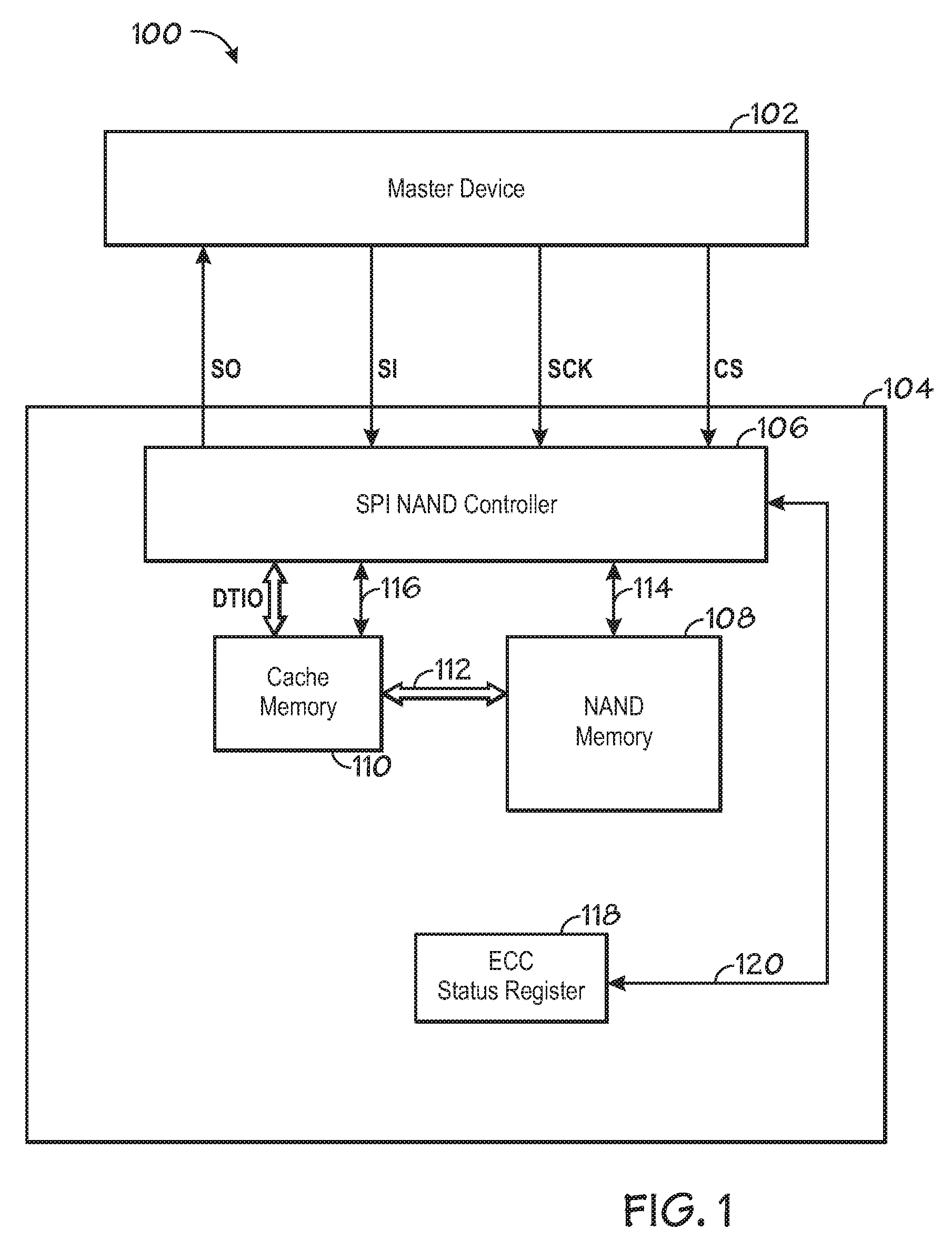
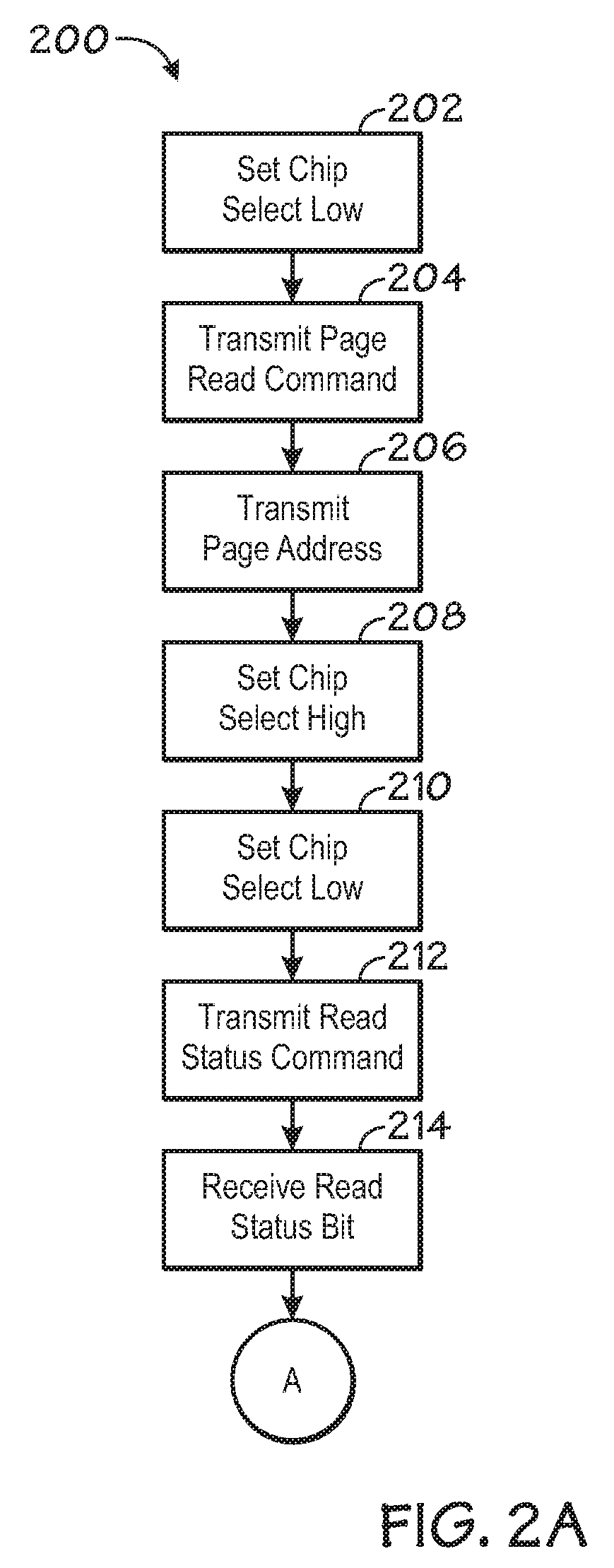
ActiveUS20090103362A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesProcessor registerMemory circuits
The invention includes a system and method of modifying a setting of a NAND flash memory device using serial peripheral interface (SPI) communication from a master to the NAND flash memory device. One embodiment generally includes sending an enable signal to a first memory circuit input, sending a clock signal to a second memory circuit input, sending a command signal synchronized to the clock signal to a third memory circuit input, sending a memory register address signal synchronized to the clock signal to the third memory circuit input, and sending a setting signal synchronized to the clock signal to the third memory circuit input.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
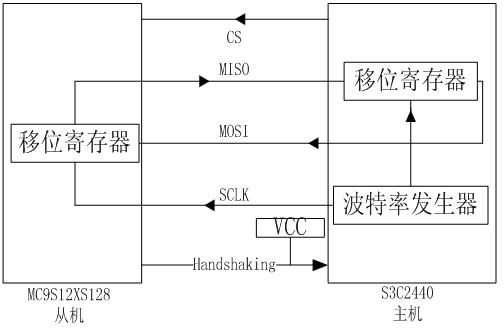
Dual-processor communication method based on SPI (serial peripheral interface) bus
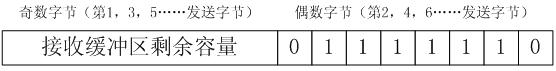
InactiveCN102508812AMeet the requirements of high-speed communicationImprove scalabilityDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingComputer architectureMulti processor
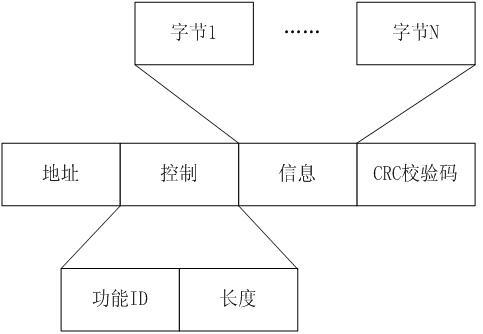
The invention relates to a dual-processor communication method based on an SPI (serial peripheral interface) bus, which is used for high-speed two-way communication between double processors by the aid of the SPI bus. The method includes: adding a handshaking wire based on a four-wire system of a physical layer of the SPI bus to form a five-wire SPI bus capable of being used for two-way communication; completing mechanism synchronization of the five-wire SPI bus on a data link layer by using the '0-bit interpolation method' and combining CS (chip select) signals, handshaking signals and feedback information; controlling flow of the five-wire SPI bus by using 'receiving buffer zone residual capacity' in the feedback information; and using CRC (cyclic redundancy check) and confirm character'0x7F' in the feedback information to complete error processing of the five-wire SPI bus. The method has the advantages of simplicity in expansion, convenience in application and compatibility to other buses, and meanwhile, extremely high communication rate can be obtained to meet requirements of high-speed communication between the double processors, and the method is widely applicable to designof multi-processor systems.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Rotating transformer position measuring system and method
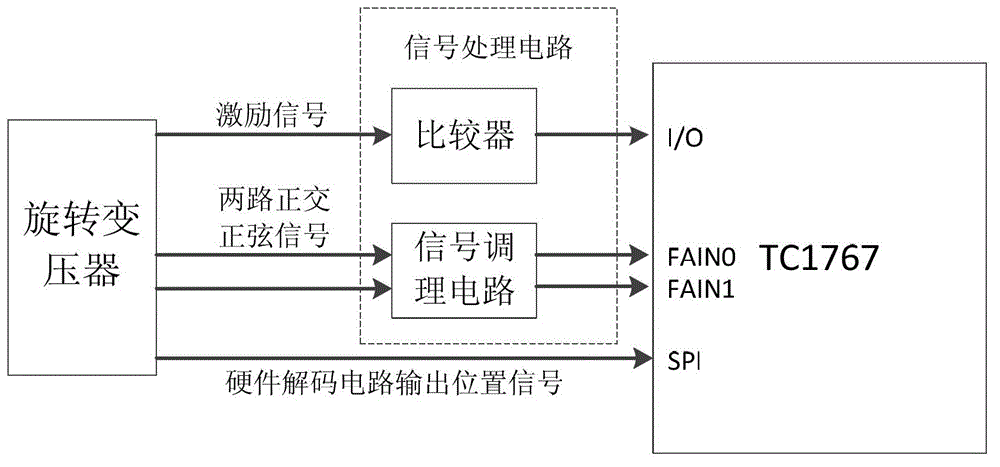
ActiveCN102721362AImplement redundant functionsImprove reliabilityUsing electrical meansMicrocontrollerCommunication interface
The invention discloses a rotating transformer position measuring system. The system comprises a signal processing circuit, a hardware decoding circuit and a singlechip, wherein the signal processing circuit is electrically connected with a rotating transformer and the singlechip, and is used for receiving and processing an excitation signal of the rotating transformer and two channels of orthogonal sinusoidal signals and outputting the signals to an input / output (I / O) port of the singlechip and two input channels of a quick analog / digital (A / D) sampling module; and the hardware decoding circuit is electrically connected with the rotating transformer and the singlechip, and is used for decoding rotating transformer position information and generating and outputting a position signal to a serial peripheral interface (SPI) communication interface of the singlechip. The quick A / D sampling function of the singlechip is used, the two channels of orthogonal sinusoidal signals of a secondary coil of the rotating transformer are acquired by the singlechip, the rest part of signal processing is finished in the singlechip through programming, and the redundancy function of the system can be realized by only a few peripheral circuits, so that the reliability of the system is greatly improved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Data transmission system and a programmable spi controller
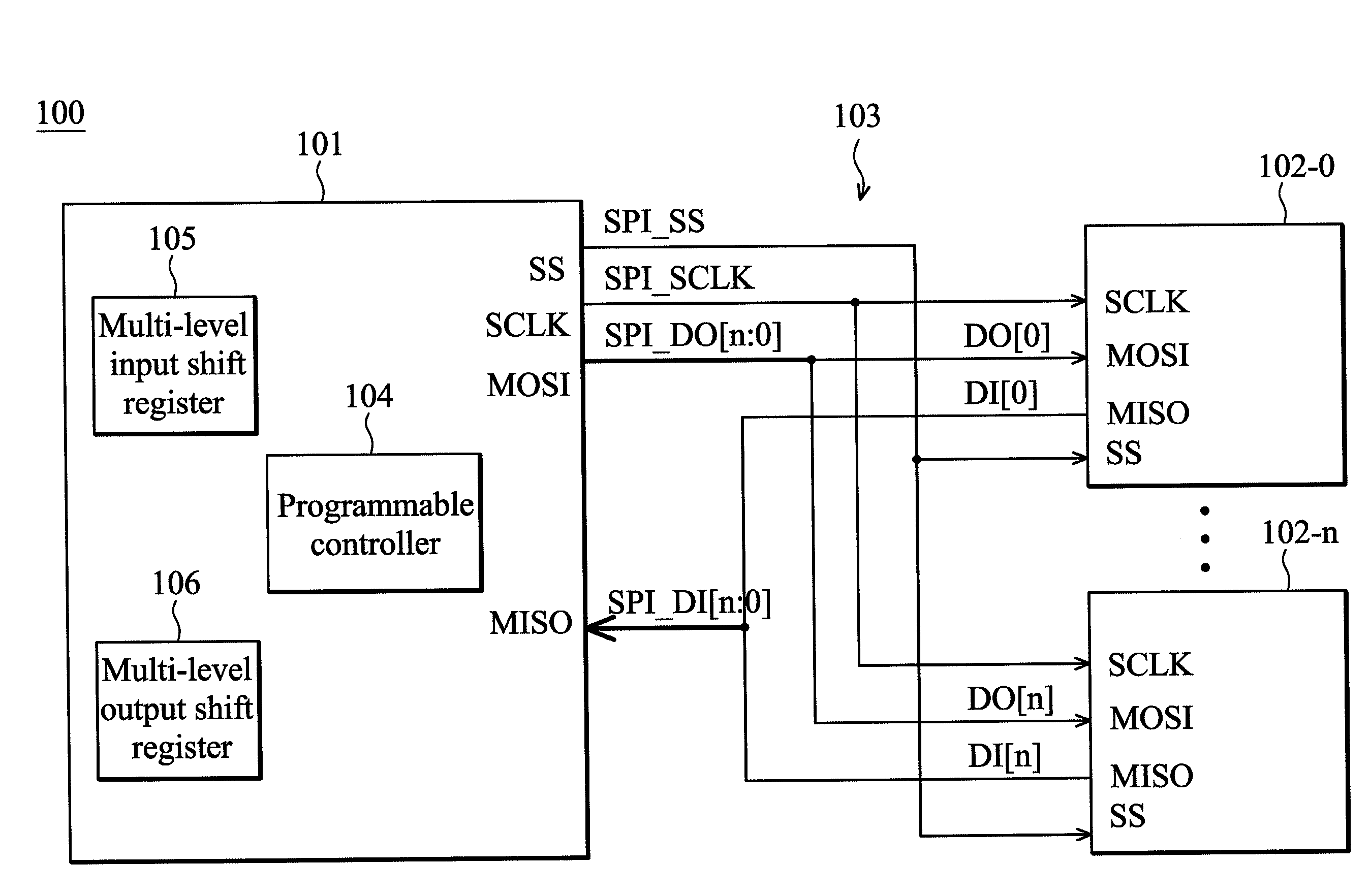
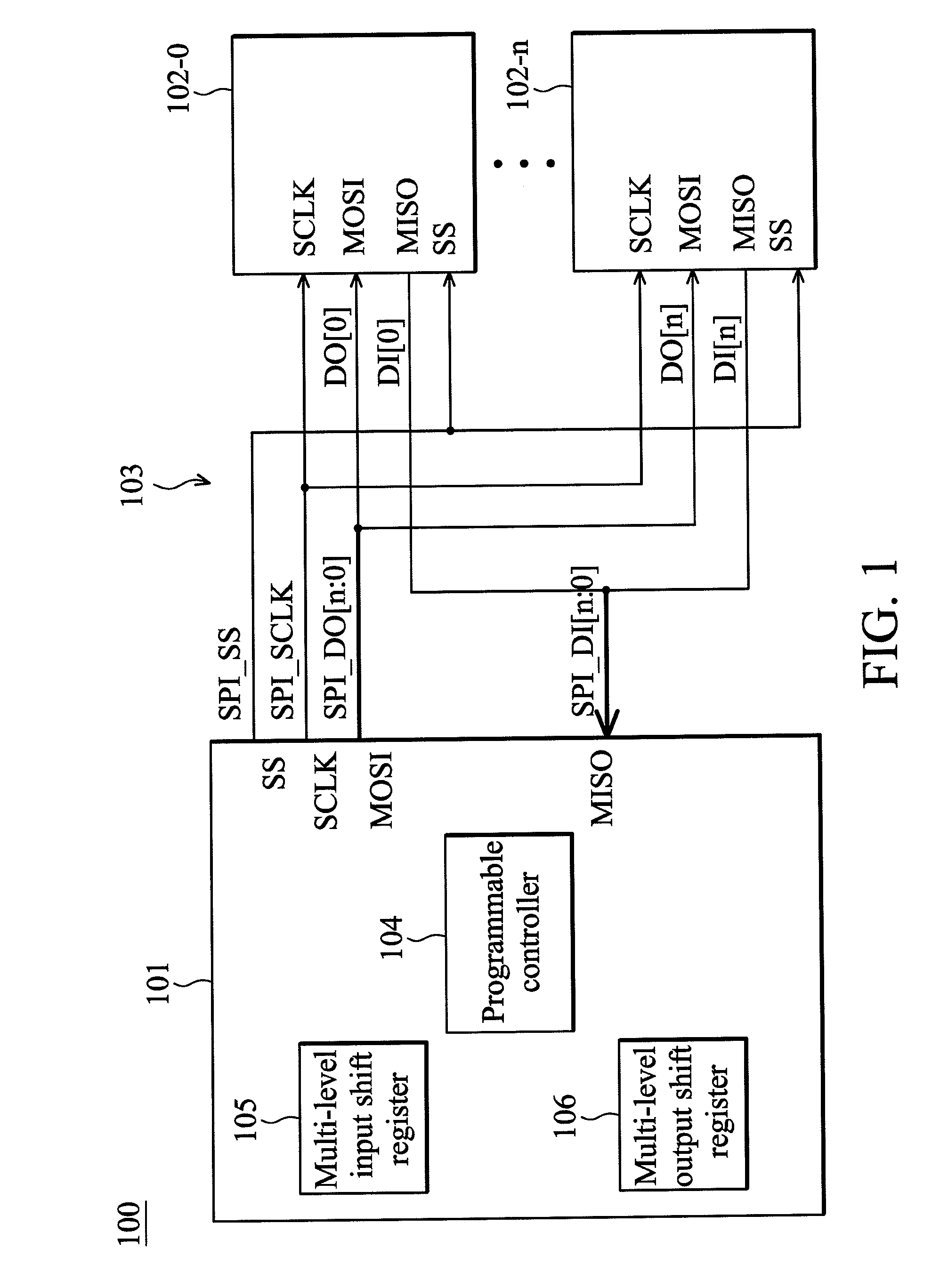
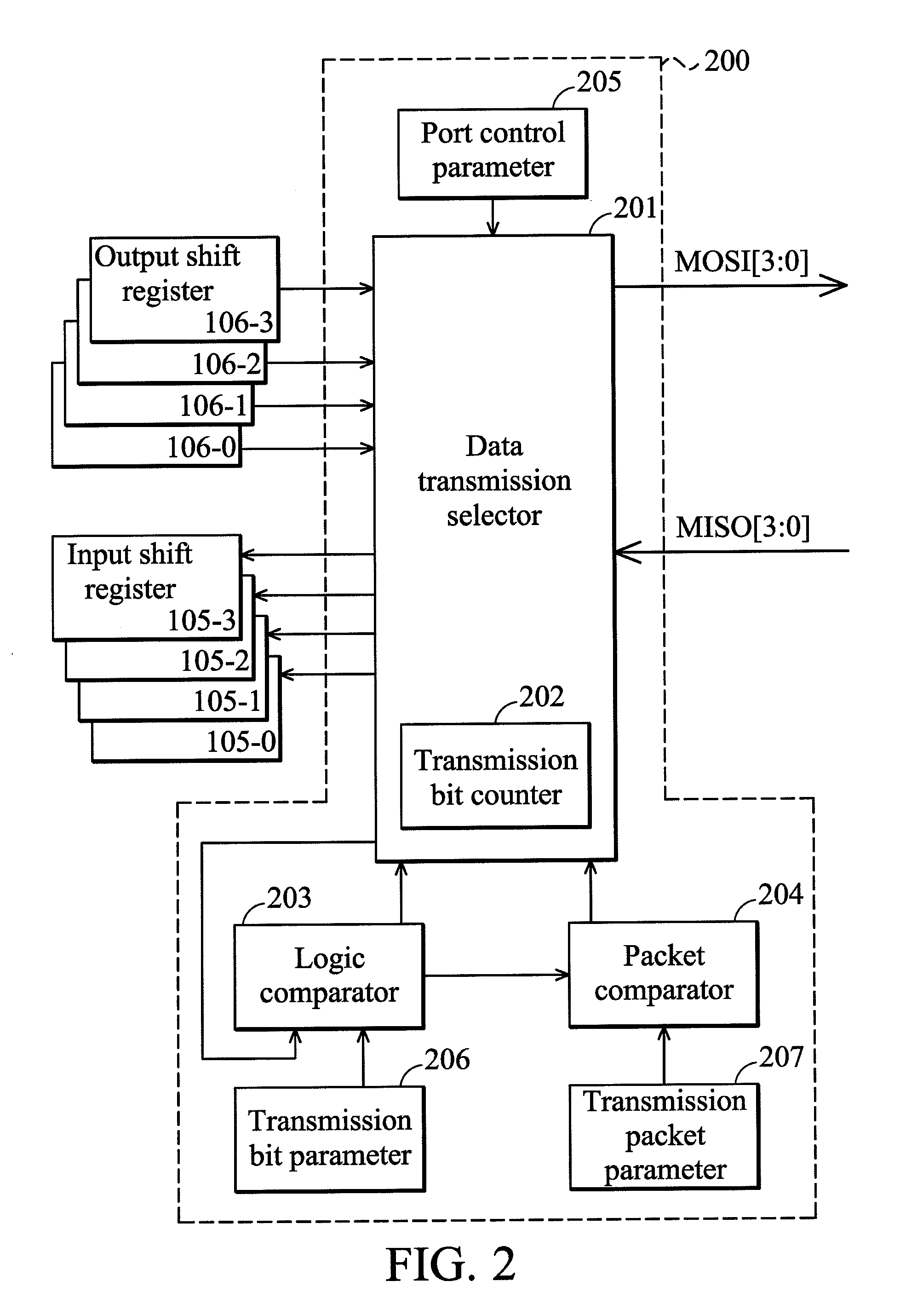
ActiveUS20110225339A1Input/output processes for data processingProgrammable logic controllerTransfer mode
A data transmission system is provided. The data transmission system includes a serial peripheral interface (SPI) and a programmable controller. The SPI is coupled between a first device and at least one second device. The programmable controller controls the SPI to switch between a single port data transmission mode and a multi-port data transmission mode. When there are more than one second device coupled to the SPI, the SPI is switched to the multi-port data transmission mode so as to perform multi-port data transmission between the first device and the second devices. At this time, the first device concurrently transmits data to each of the second devices via a first transmission bus terminal, and concurrently receives data from each of the second devices via a second transmission bus terminal.
Owner:NUVOTON
Full-duplex communication device based on SPI and method thereof
ActiveCN102819512AIntegrity guaranteedGuaranteed accuracyElectric digital data processingSource Data VerificationCommunication device
The invention relates to a full-duplex communication device based on an SPI (serial peripheral interface) and a method thereof. The device comprises a main component, a slave component, a data line used for the mutual communication between the main component and the slave component, a synchronous clock signal line, a slave component selecting signal line and a signal line which is used for requesting the slave component to receive data by the main component and requesting the main component to receive data by the slave component, and the lines are arranged between the main component and the slave component. The communication method comprises the steps that data are sent simultaneously by the main component and the slave component to each other, data are sent from the main component to the slave component, data are sent from the slave component to the main component, and data frames are used for the communication between the main component and the slave component. According to the full-duplex communication device based on the SPI and the method thereof, a full-duplex communication mode is realized, under the condition that the communication rate is invariable, communication efficiency is improved, system response time is improved, and communication data throughput is increased by one time in an ideal condition; and the integrality and the accuracy of respective data frame when data are sent by both of the SPI communication sides at the same time are guaranteed through data verification and the like.
Owner:HUIZHOU DESAY SV AUTOMOTIVE
SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) controller and communication method for SPI controller
ActiveCN104809094AMeet Timing RequirementsFast communicationElectric digital data processingLow speedData transmission
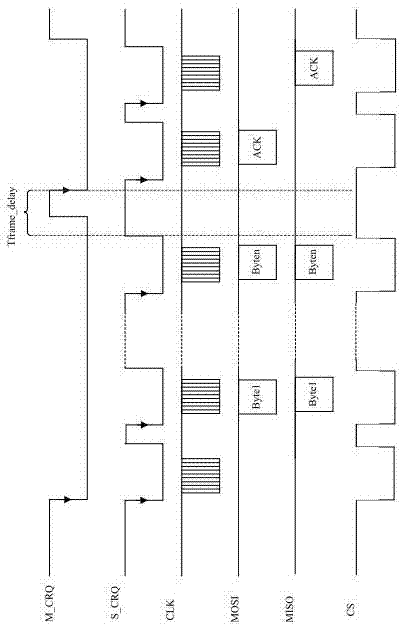
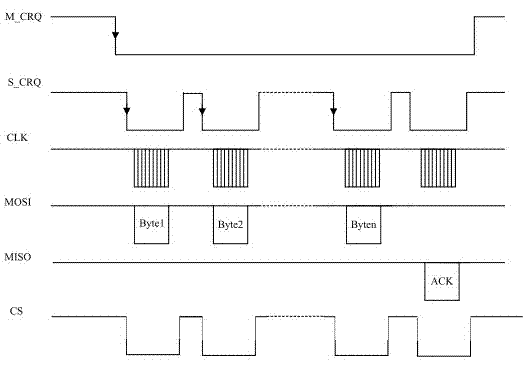
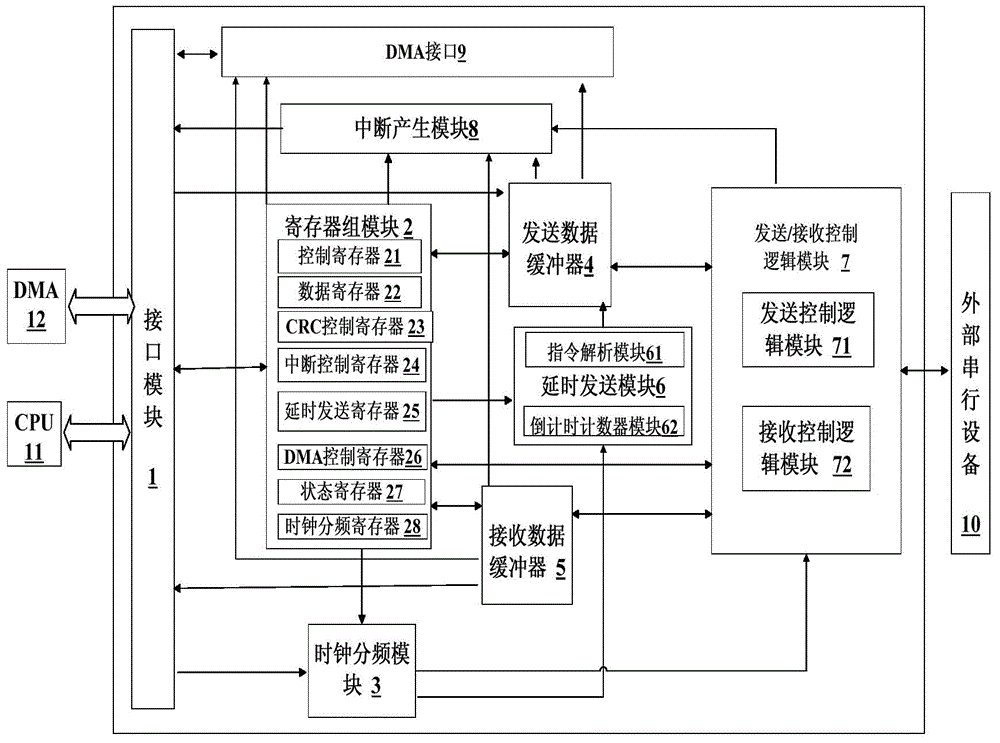
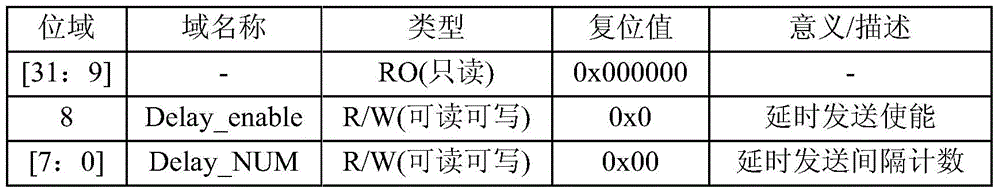
The invention discloses an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) controller. The controller comprises an interface module (1), a register set module (2), a clock division module (3), a data transmission buffer (4), a data reception buffer (5), a delay transmission module (6), a transmission / reception control logic module (7) and an interruption generation module (8). In addition, the invention discloses a communication method by utilization of the SPI controller. The SPI controller and the communication method by utilization of the SPI controller have the advantages that a delay transmission control function can be realized, the high-speed performance of interface operation is guaranteed, and the requirements of a low-speed interface device on operation time sequence are also met.
Owner:NO 47 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
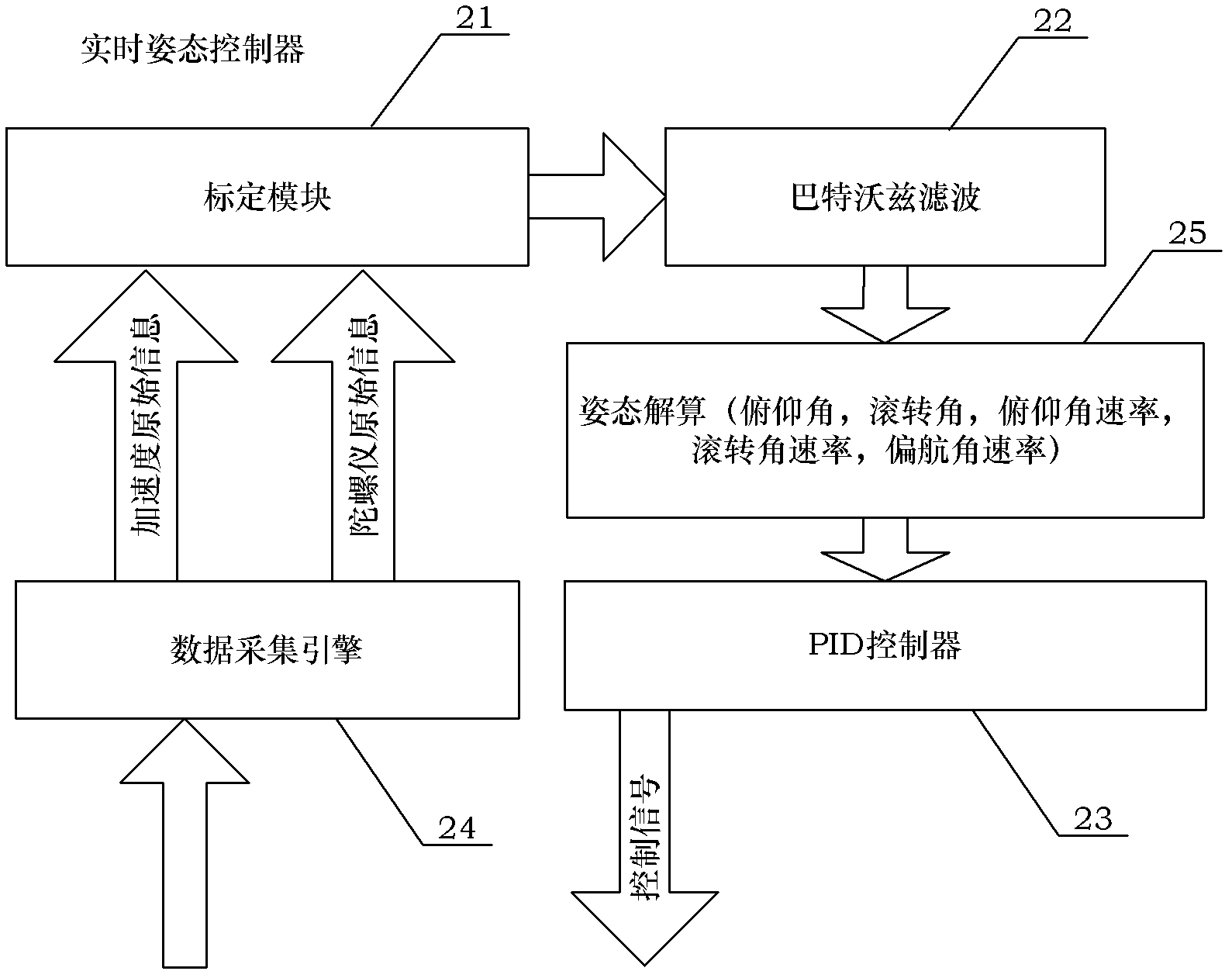
Ground control system applicable to rotor-wing unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN102426458AAvoid unreliabilityLow costAttitude controlHuman–machine interfaceAttitude control
The invention discloses a ground control system applicable to a rotor-wing unmanned aerial vehicle. The ground control system comprises a personal computer (PC) (4), a real-time attitude controller (2), a serial peripheral interface (SPI) communication acquirer (3) and a driver (1), wherein the driver (1) receives a movement instruction Din which is output by the real-time attitude controller (2), and according to the movement instruction Din, the driver (1) outputs a motor control signal D2 to drive a motor (12) to move, outputs an A-th path of steering engine signal DA to drive an A steering engine (13) to move, outputs a B-th path of steering engine signal DB to drive a B steering engine (14) to move, outputs a C-th path of steering engine signal DC to drive a C steering engine (15) tomove and outputs a D-th path of steering engine signal DD to drive a D steering engine (16) to move; the SPI communication acquirer (3) acquires parameter information D1 which is measured by an inertia measurement unit (11) on the rotor-wing unmanned aerial vehicle and outputs linear acceleration signals alpha and angular speed signals omega of three degrees of freedom of the rotor-wing unmanned aerial vehicle to the real-time attitude controller (2); and the PC (4) communicates with the real-time attitude controller (2) through a transmission control protocol (TCP) / internet protocol (IP) and provides a friendly human-computer interface for an operator.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and method for data read of a synchronous serial interface NAND
A method and system is disclosed for operating a NAND memory device. The NAND memory device is operated by transmitting serial peripheral interface signals from a host to a NAND memory device, whereby the signals are communicated to a NAND memory in the NAND memory device without modifying the signals into a standard NAND memory format. Similarly, a method and system is disclosed for receiving signals from the NAND memory device without modifying the signals from a standard NAND format into a serial format. The system also incorporates error detection and correction techniques to detect and correct errors in data stored in the NAND memory device.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Serial peripheral interface (SPI) apparatus with write buffer for improving data throughput
ActiveUS7082481B2Function increaseAvoid stretchingInput/output processes for data processingData conversionSerial transferData set
A serial peripheral interface apparatus has a second parallel write buffer to load in a subsequent data byte while a current data byte is being transferred serially through the apparatus instead of waiting for the previous data byte to complete the serial transfer and other commands to avoid write collision. The subsequent data byte is transferred into the second parallel write buffer only after the software driven CPU examines the status of a load enable and the status of a write buffer provided by a finite state machine controller. The software driven CPU orders the subsequent data byte to be transferred into the second parallel write buffer when the load enable is favorable and the second parallel write buffer is available. The load enable becomes favorable when a bit counter counts the first half of the transfer of the previous data set. Thus, the second parallel write buffer avoids the stretching the master clock and improves data throughput of the system.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com