Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
879 results about "Superframe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
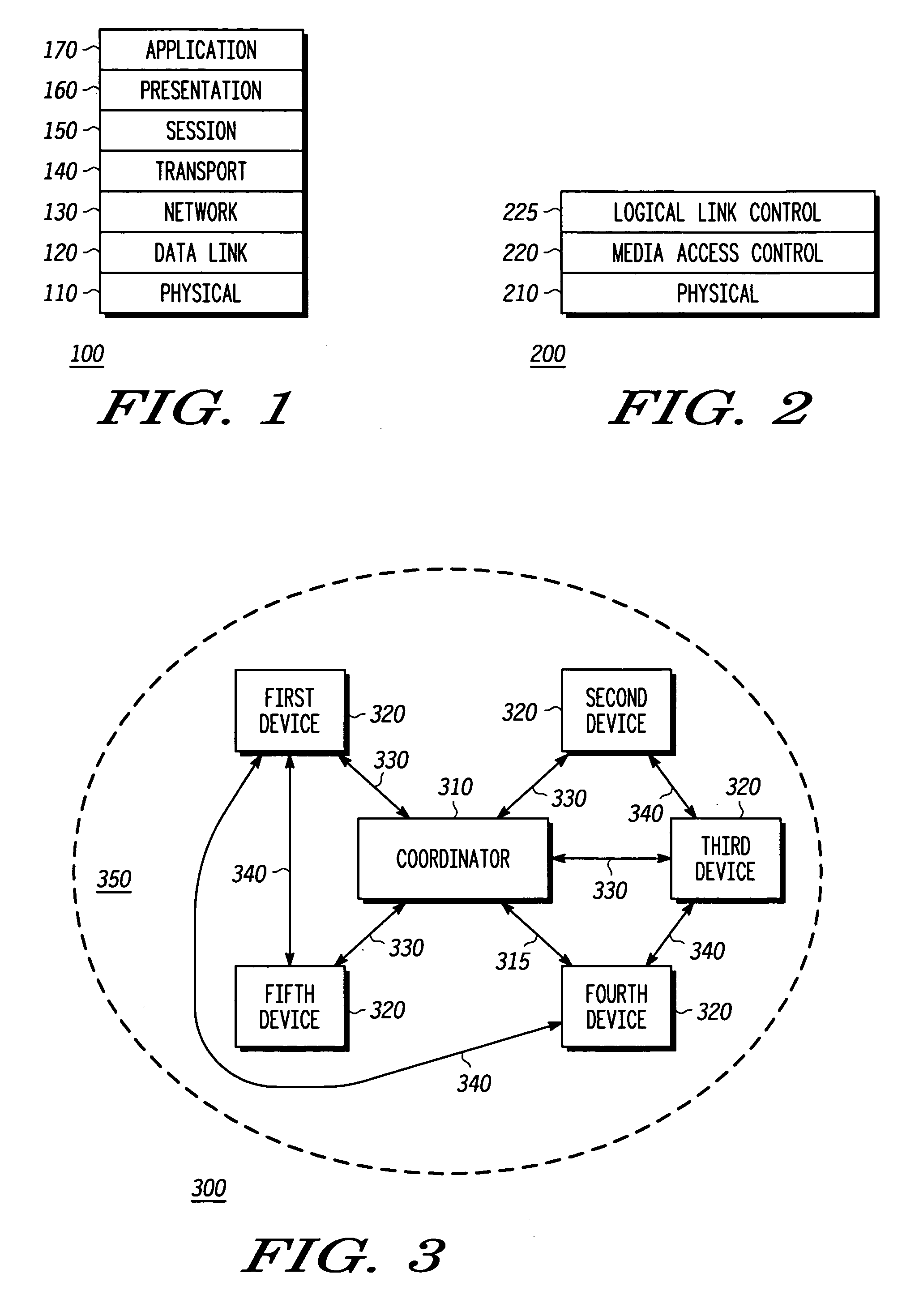
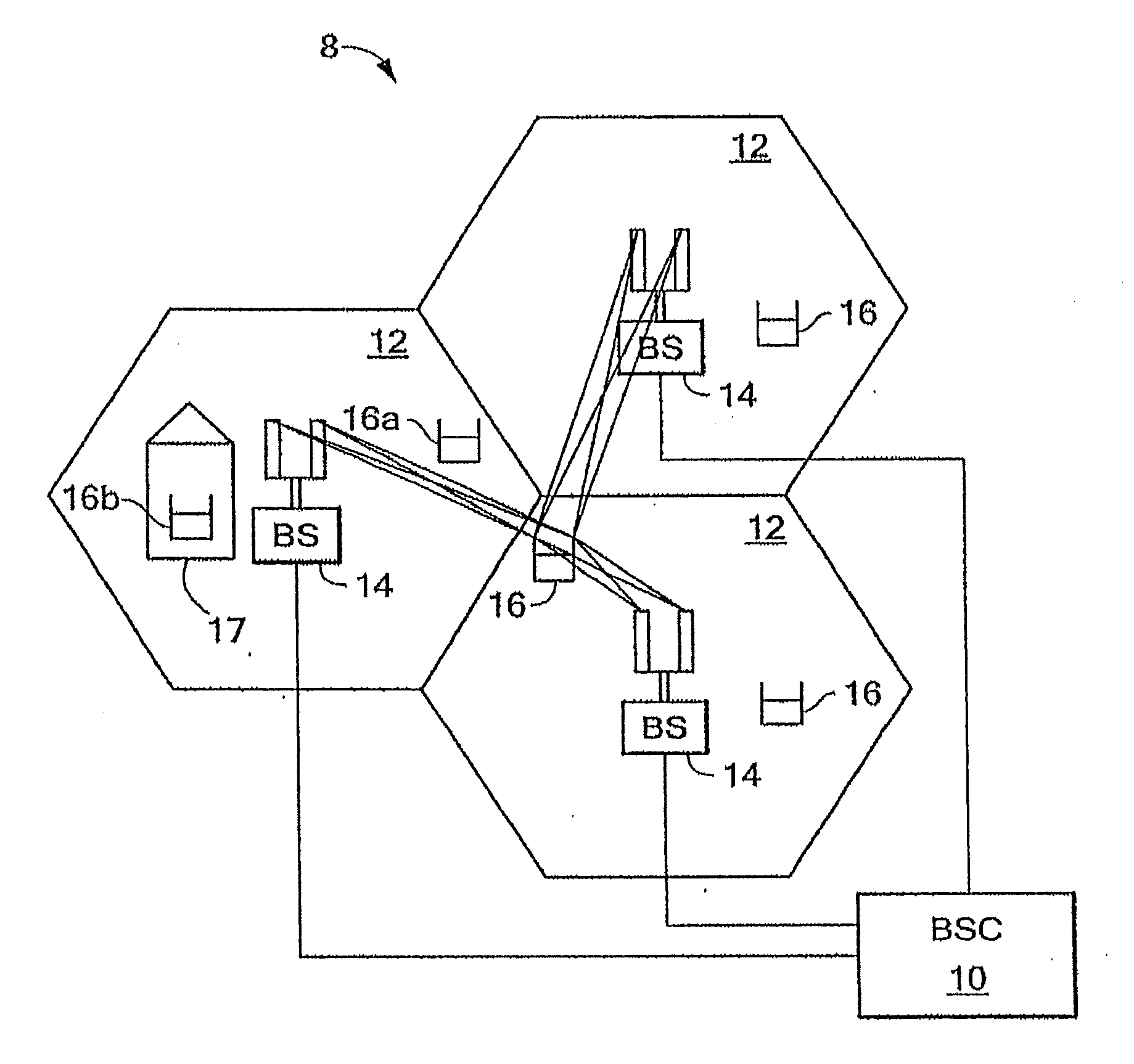
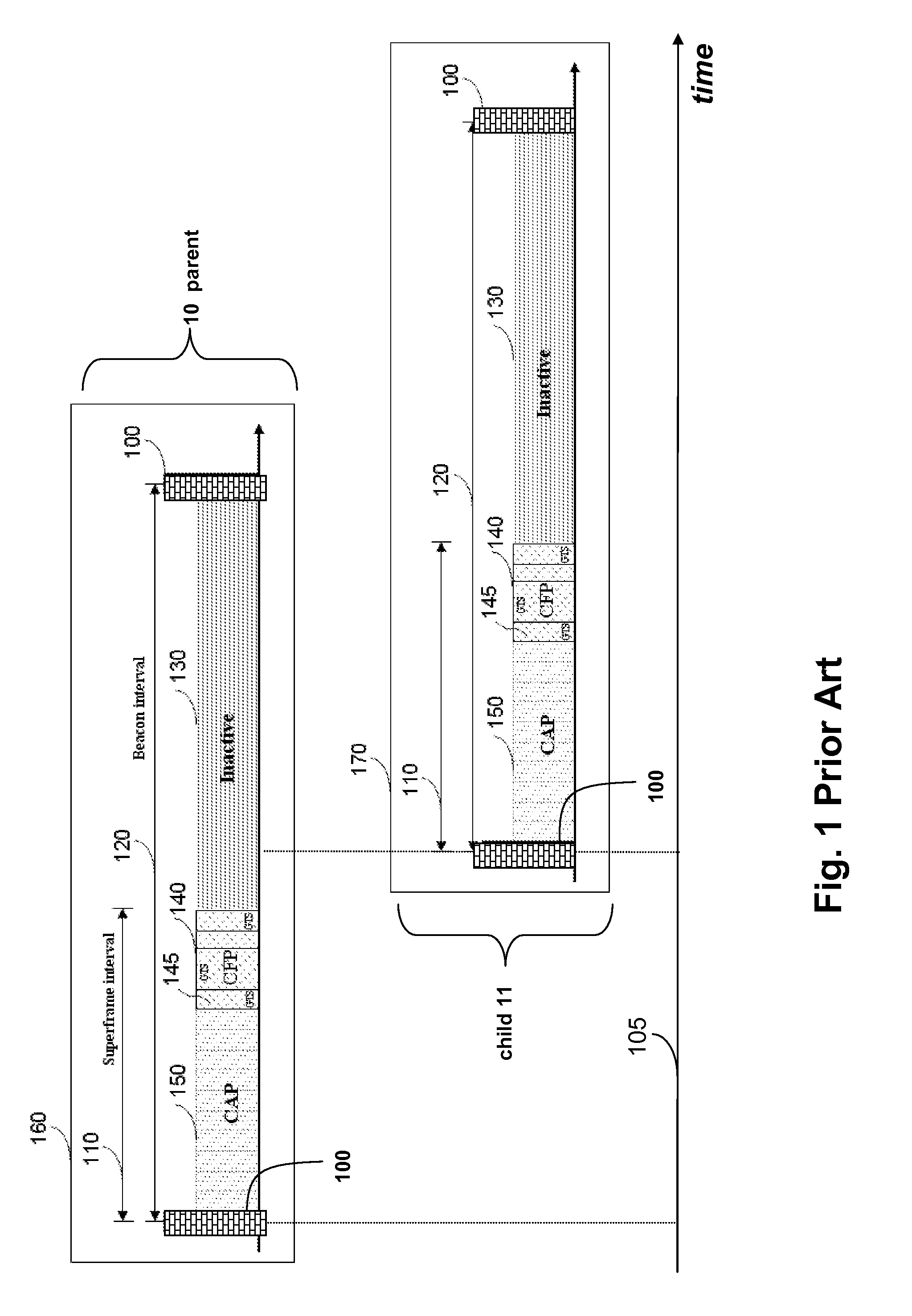
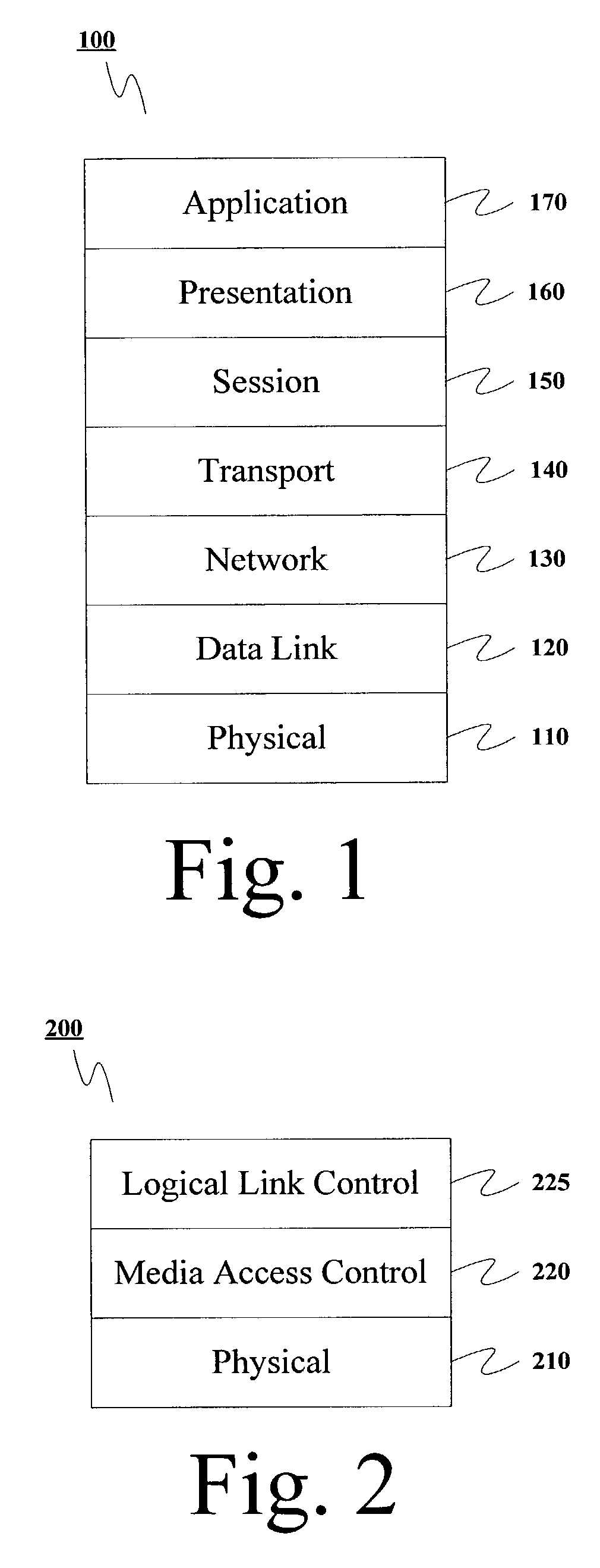
In telecommunications, superframe (SF) is a T1 framing standard. In the 1970s it replaced the original T1/D1 framing scheme of the 1960s in which the framing bit simply alternated between 0 and 1. Superframe is sometimes called D4 Framing to avoid confusion with single-frequency signaling. It was first supported by the D2 channel bank, but it was first widely deployed with the D4 channel bank.
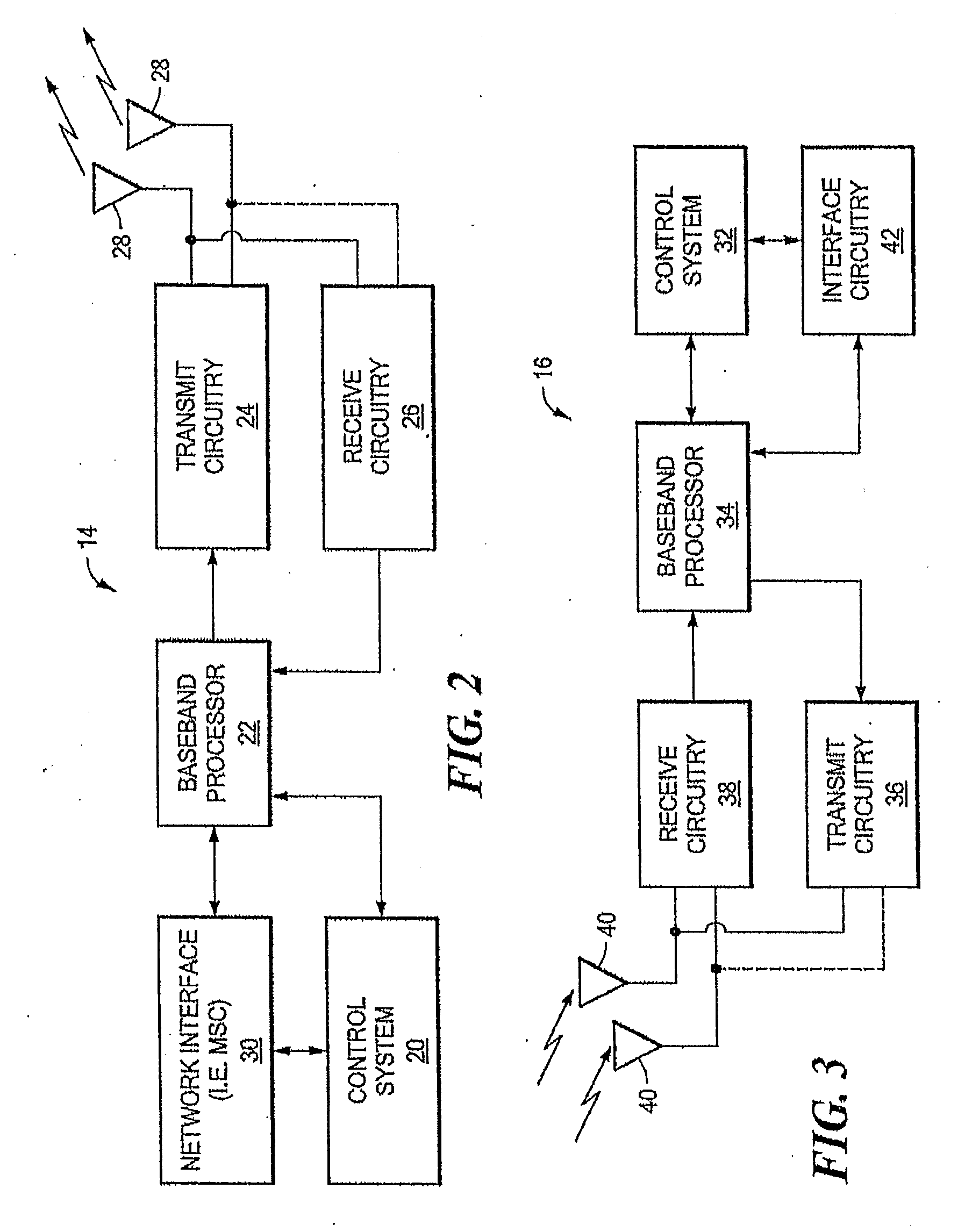
Method for radio resource control
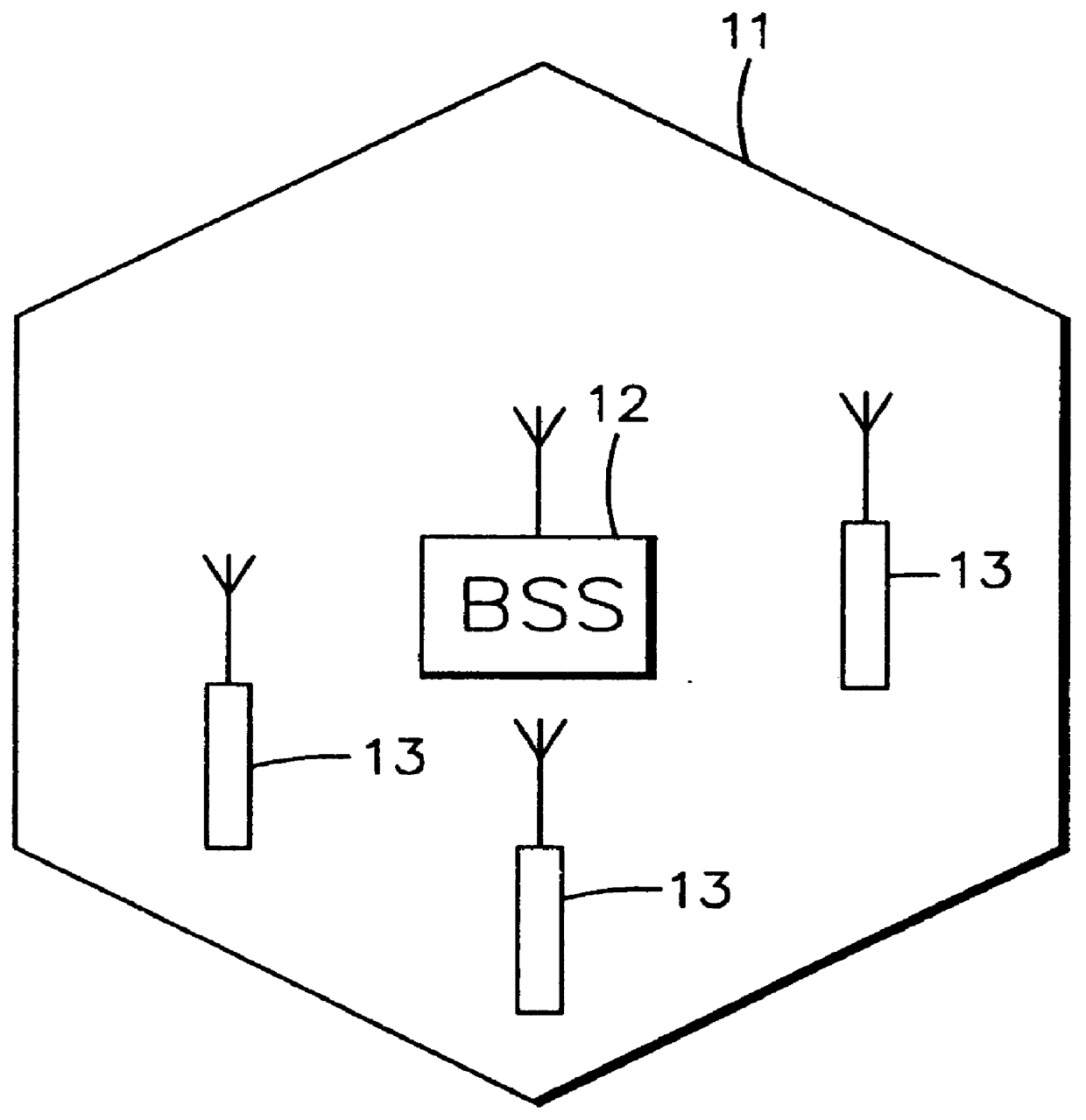
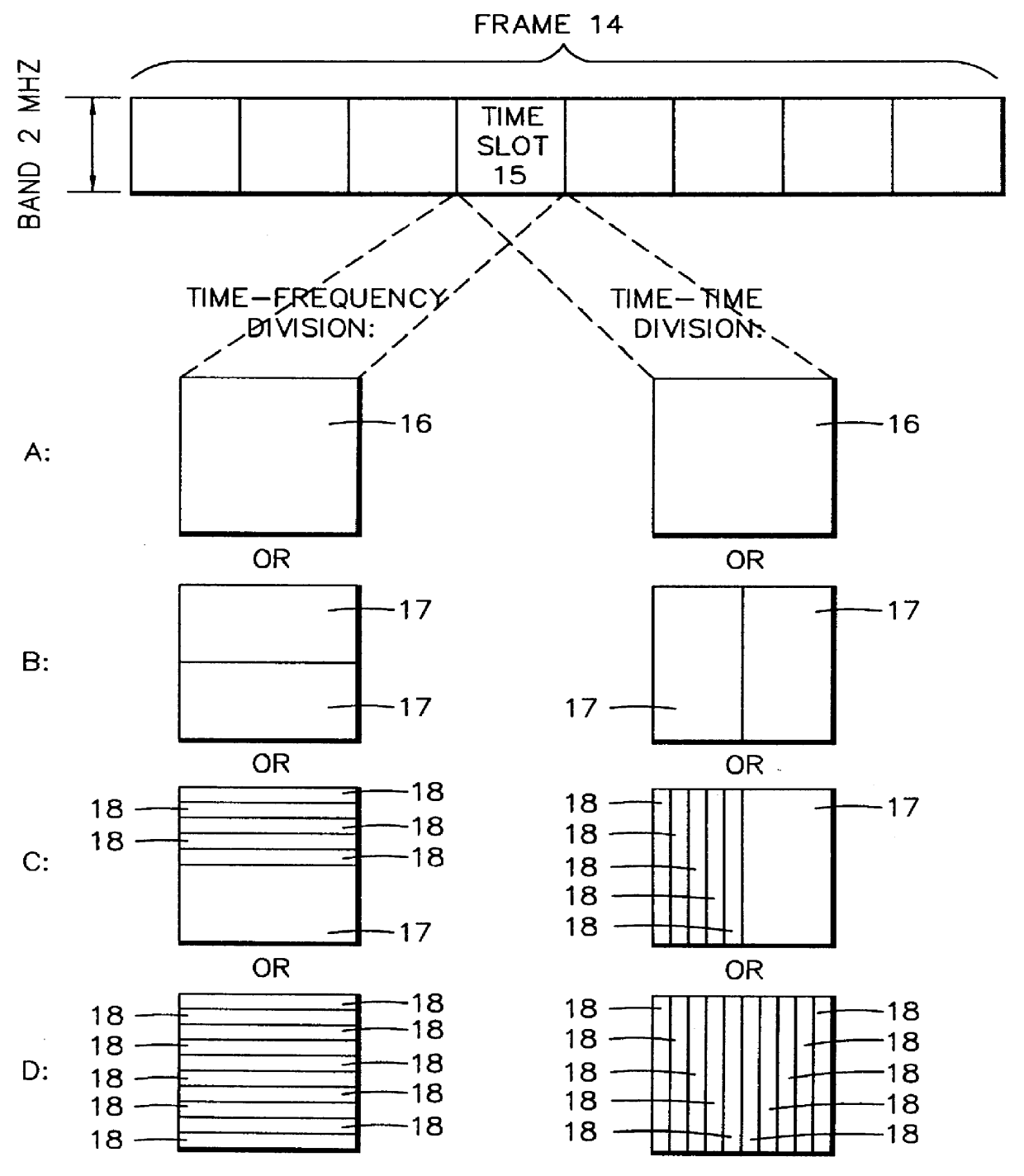
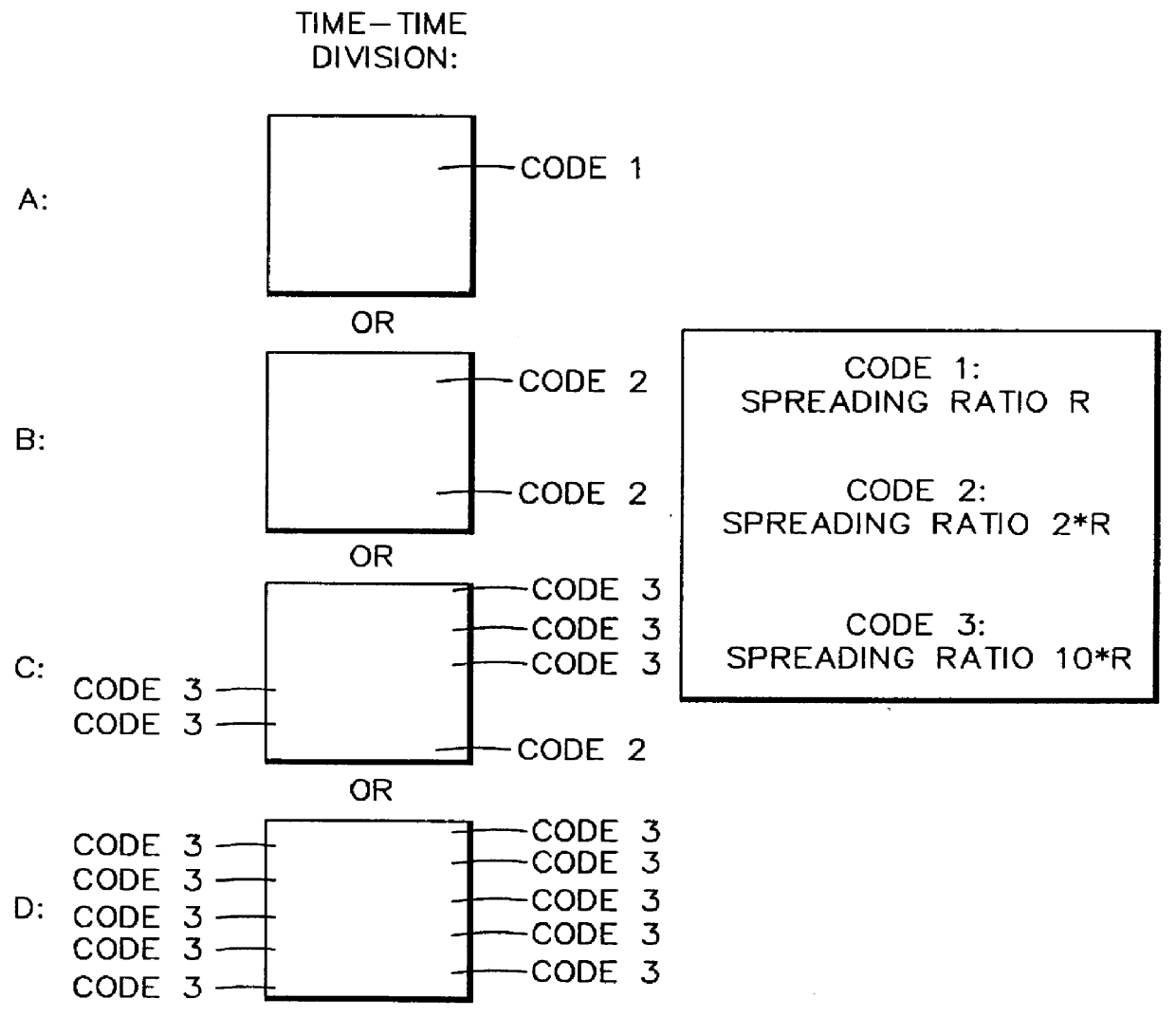
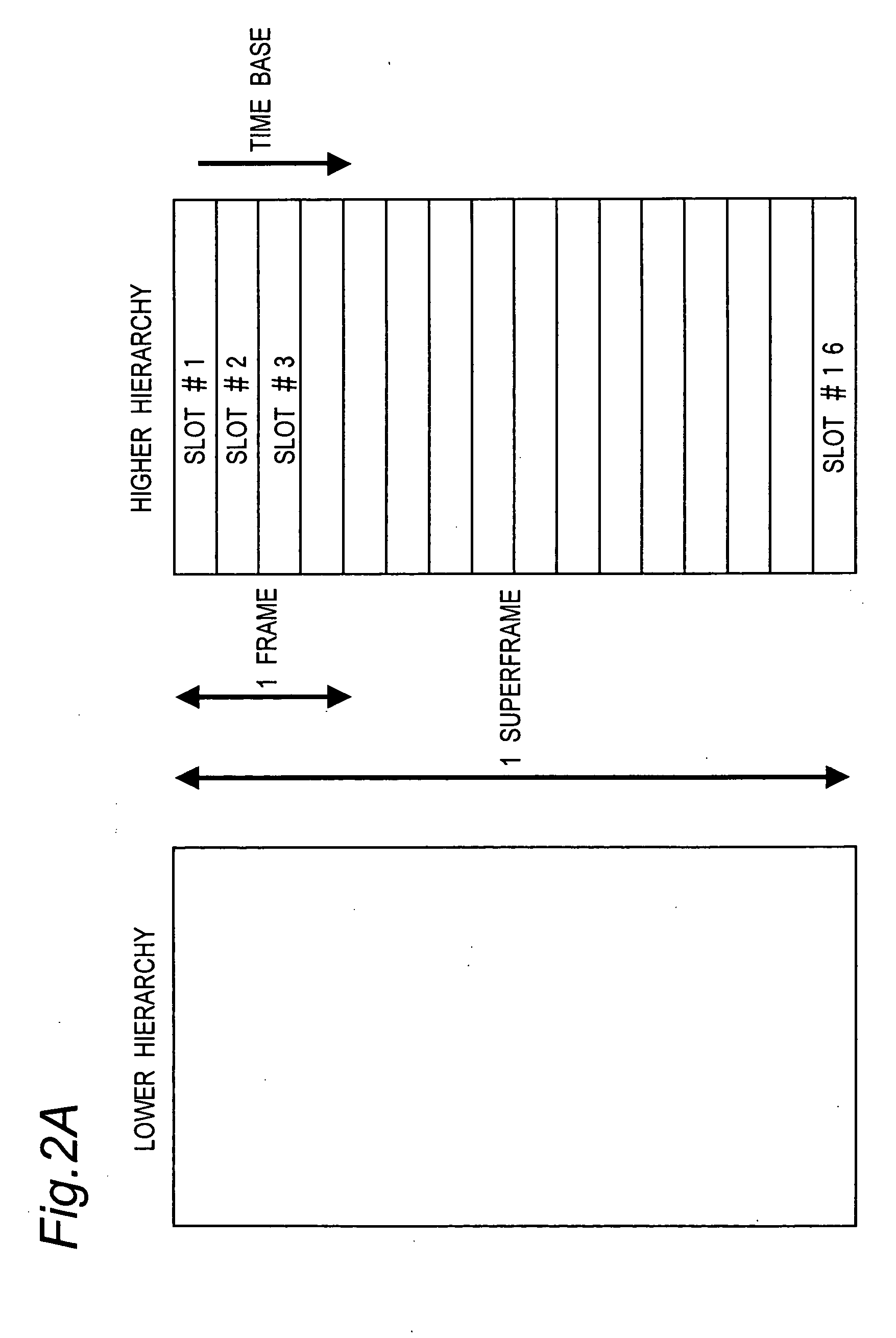
In order to control the use of physical radio resources, the physical radio resources are divided into chronologically consecutive frames (14), so that a frame contains slots (16, 17, 18) of various sizes, which slots represent a given share of the physical radio resources contained in the frame and can be individually allocated to different radio connections. The first dimension of a frame is time and the second dimension can be time, frequency or code. In the direction of the second dimension the slots represent various sizes, and a given first integral number of slots of the first size can be modularly replaced by another integral number of slots of another size. A certain number of consecutive frames form a superframe (19), in which case frames with corresponding locations in consecutive superframes are equal in slot division and allocations, if the data transmission demands do not change. Changes in the state of occupancy of the slots are possible at each superframe. In order to form an uplink connection, the mobile station sends a capacity request, where it indicates the type of requested connection and the demand of resources. In order to form a downlink connection, the base station subsystem sends a paging call, where it indicates the location in the superframe of the slots allocated to the connection. In order to indicate the state of occupancy, the base station subsystem maintains a superframe-size parametrized reservation table.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Radio communication system, radio communication apparatus and radio communication method for UWB impulse communication
ActiveUS20090067389A1Minimize power consumptionDecentralize trafficEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexTime informationUltra-wideband
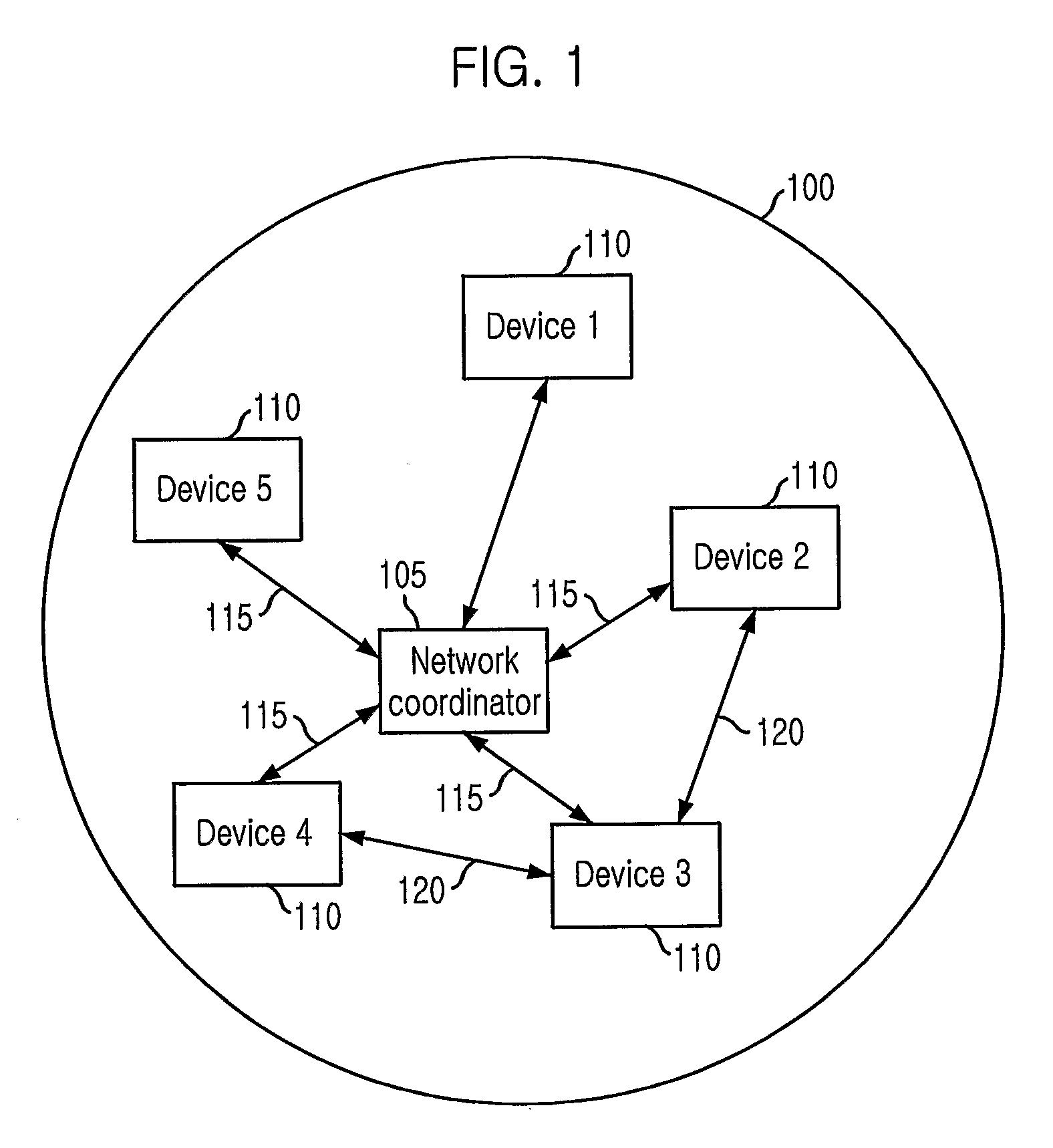
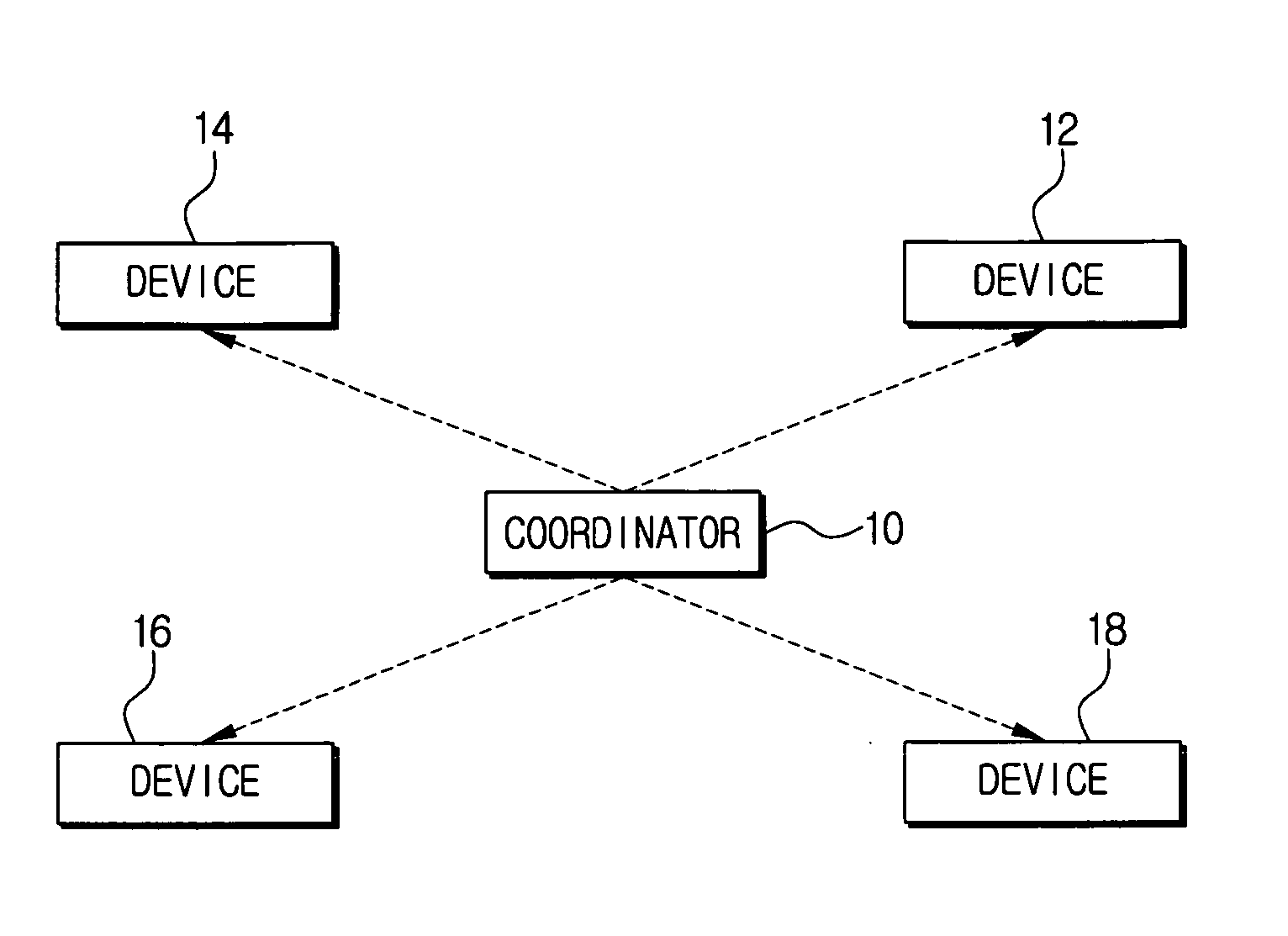
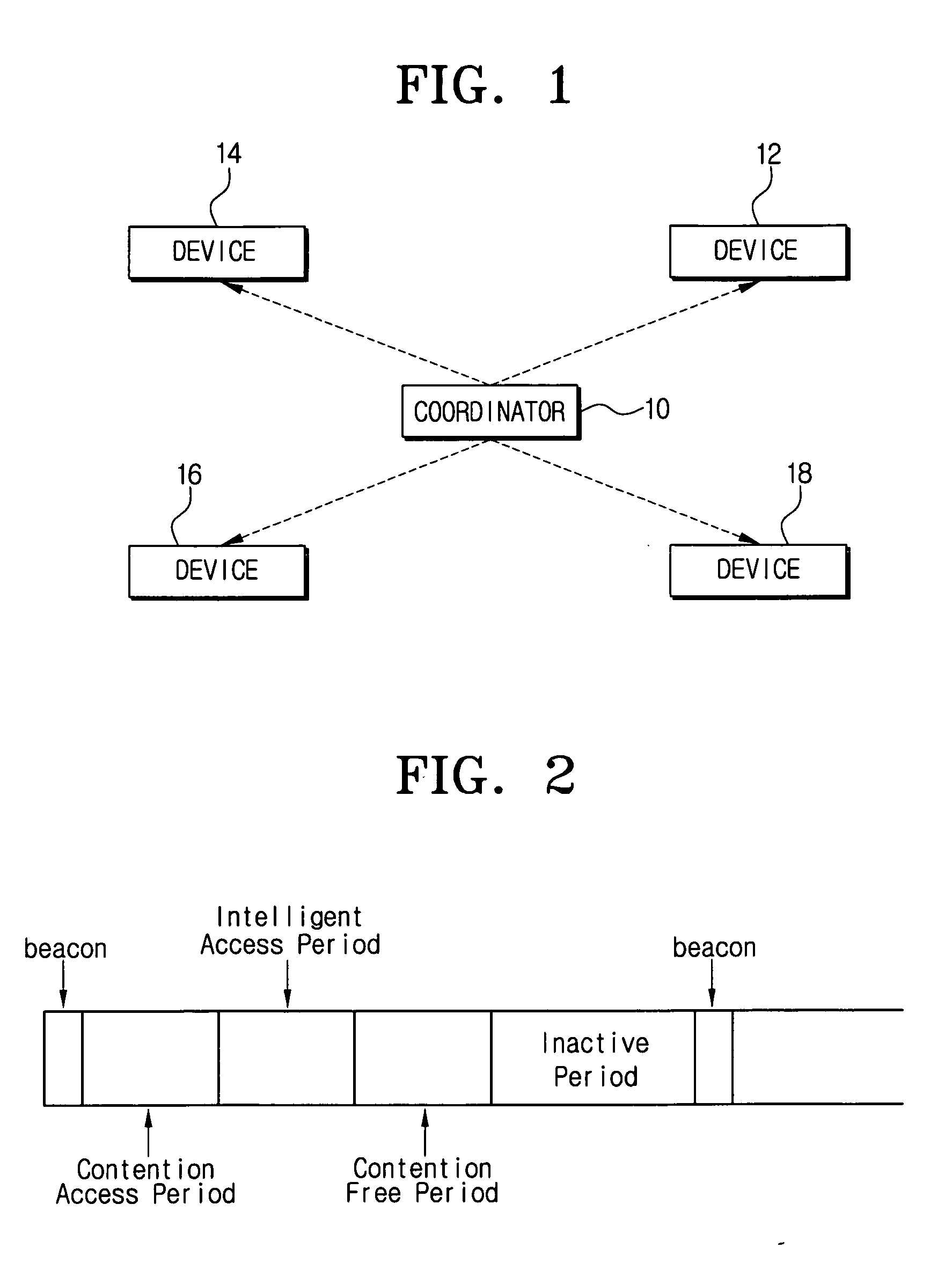
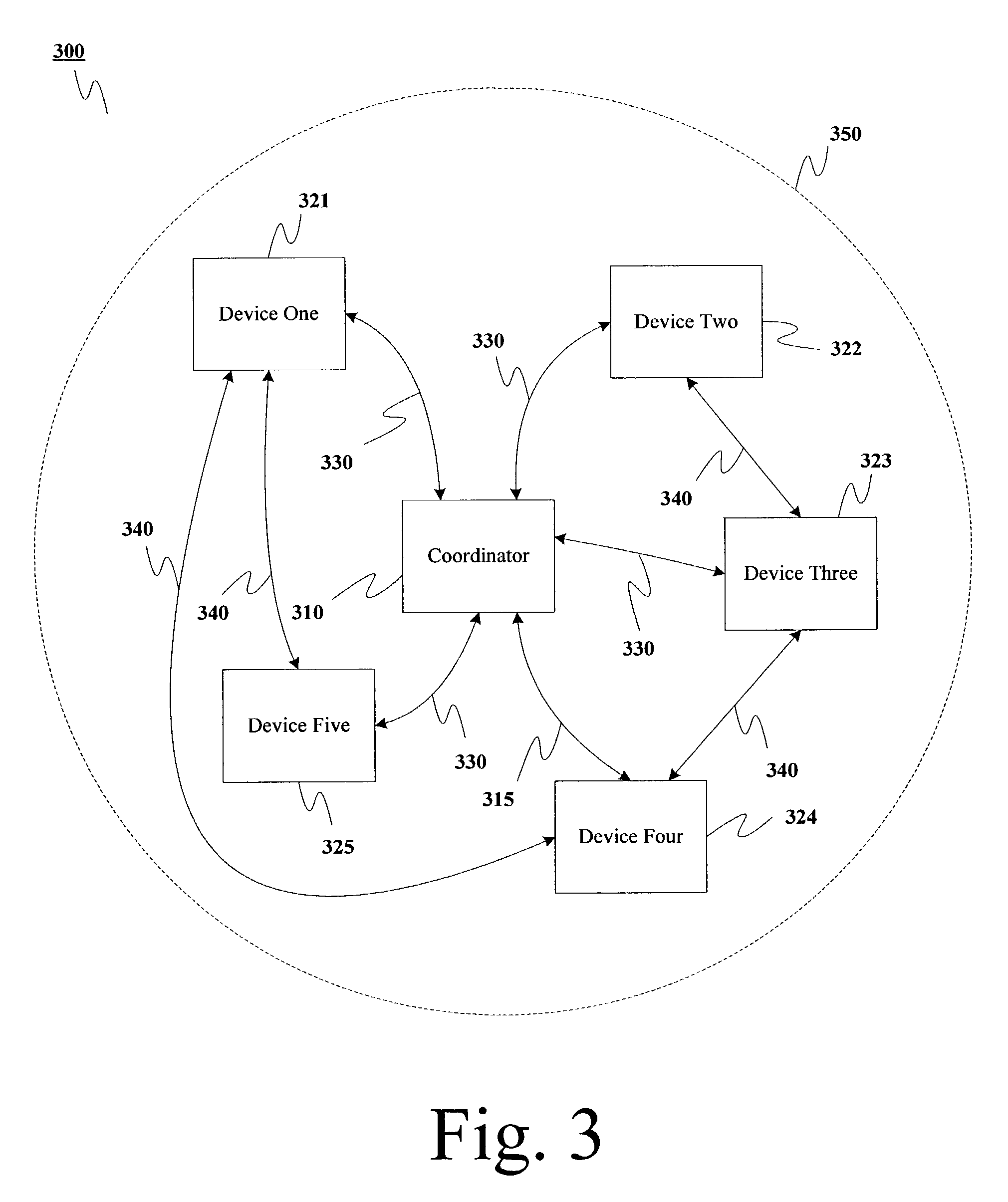
Provided is a radio communication system for ultra wideband (UWB) impulse communications and a radio communication apparatus and method thereof. The present patent provides a radio communication system that can minimize power consumption by eliminating a need for carrier detection and sharing transmission / reception time information in UWB impulse communications. The system includes a network coordinator; and one or more devices communicating on a superframe basis in subordination to the network coordinator. The devices perform data transmission / reception in predetermined time slots and then they are inactivated to thereby reduce power consumption.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Infrared and near-infrared camera hyperframing
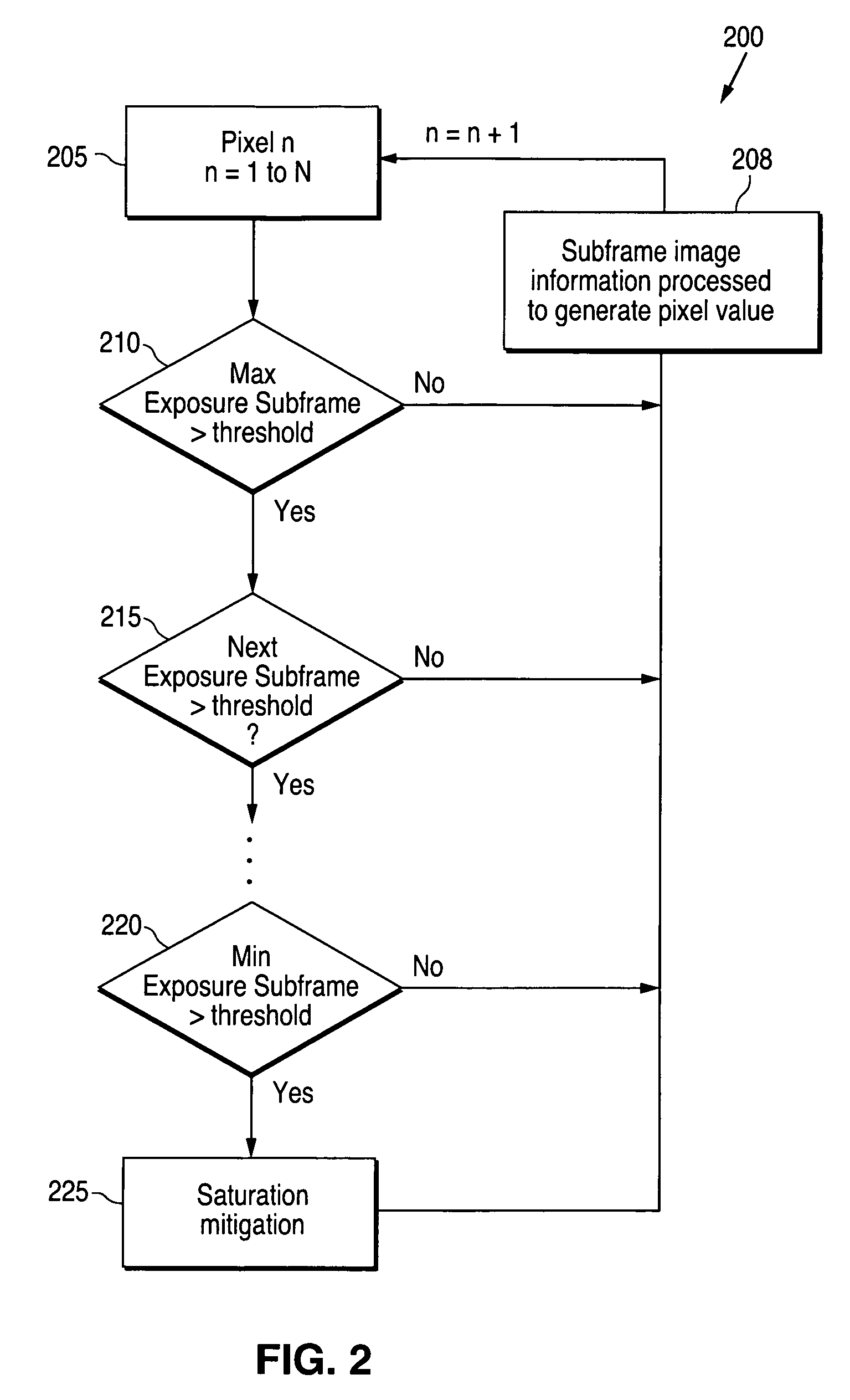
ActiveUS7606484B1Improved dynamic range detectionTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryDetector arraySuperframe
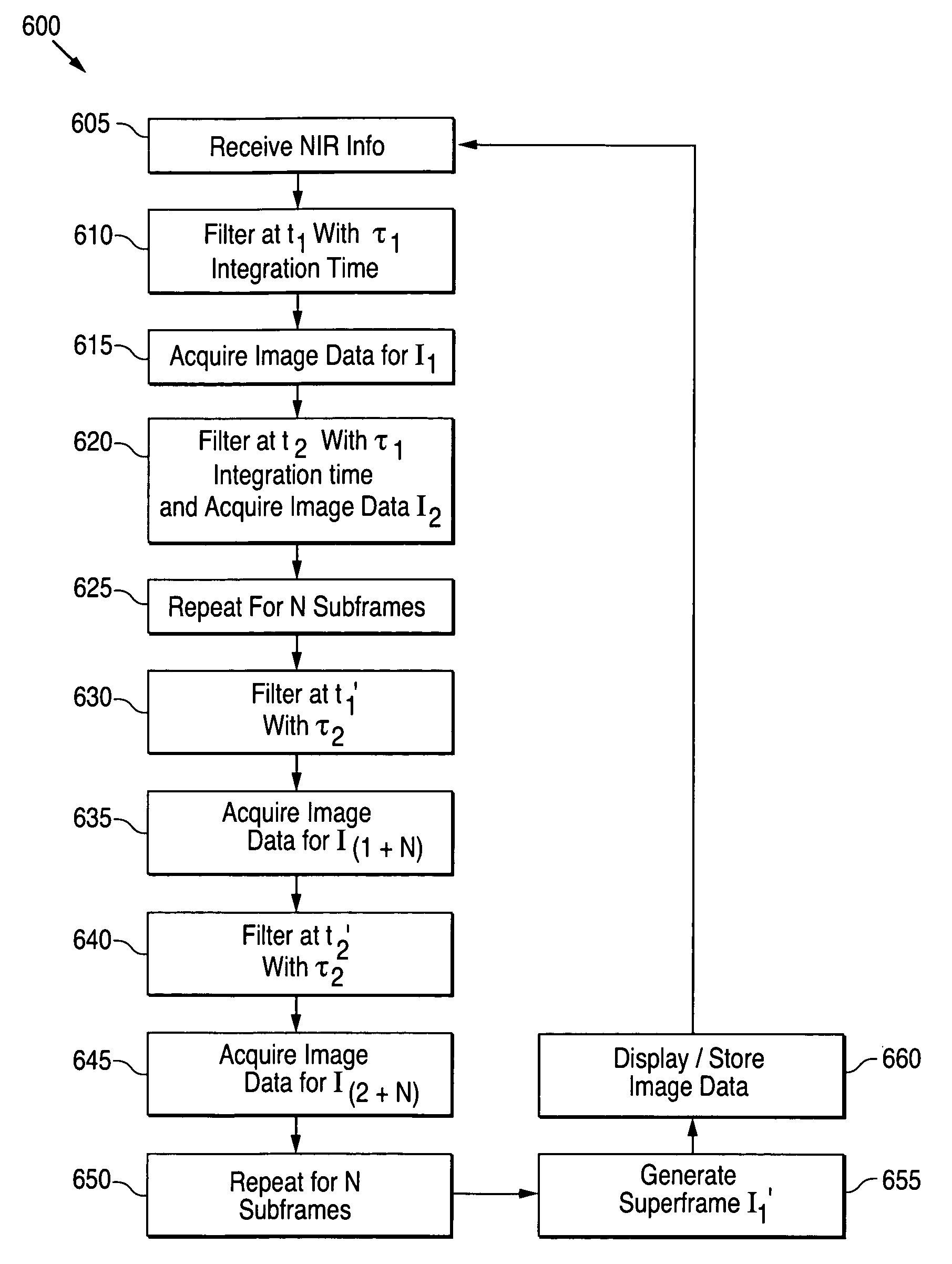
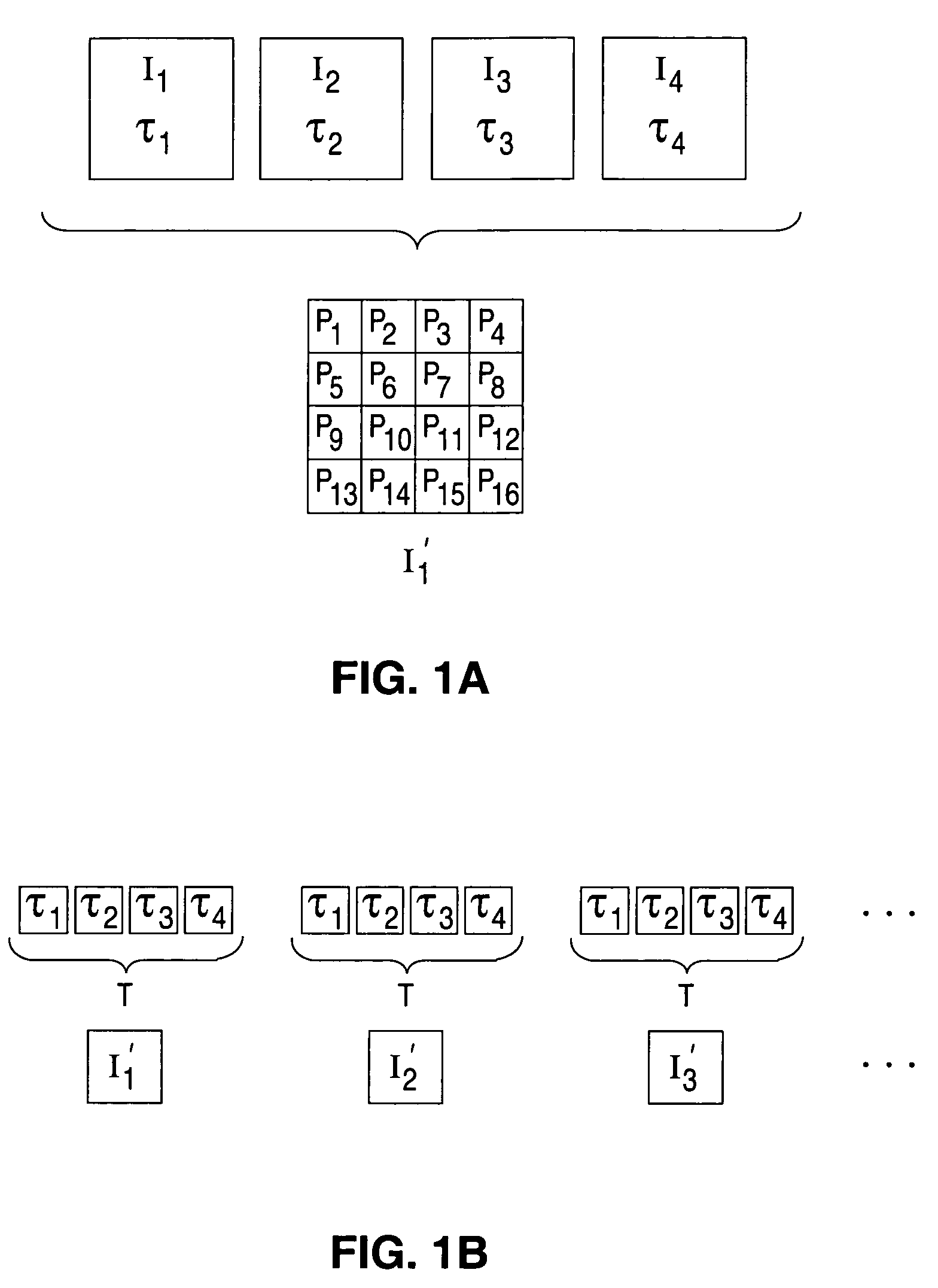
Systems and techniques for improving the dynamic range of infrared detection systems. For example, a mechanical superframing technique may comprise positioning a first filter in the optical path of an infrared camera at a first time, receiving infrared light from an object through the first filter at a detector array, acquiring first subframe image data for the object, positioning a second filter in the optical path of the infrared camera at a later time, receiving infrared light from the object through the second filter, acquiring second subframe image data for the object, and generating first superframe data based on at least some of the first subframe image data and at least some of the second subframe image data.
Owner:FLIR SYST INC
Operation method in heterogeneous networks and gateway and wireless communication device using the same
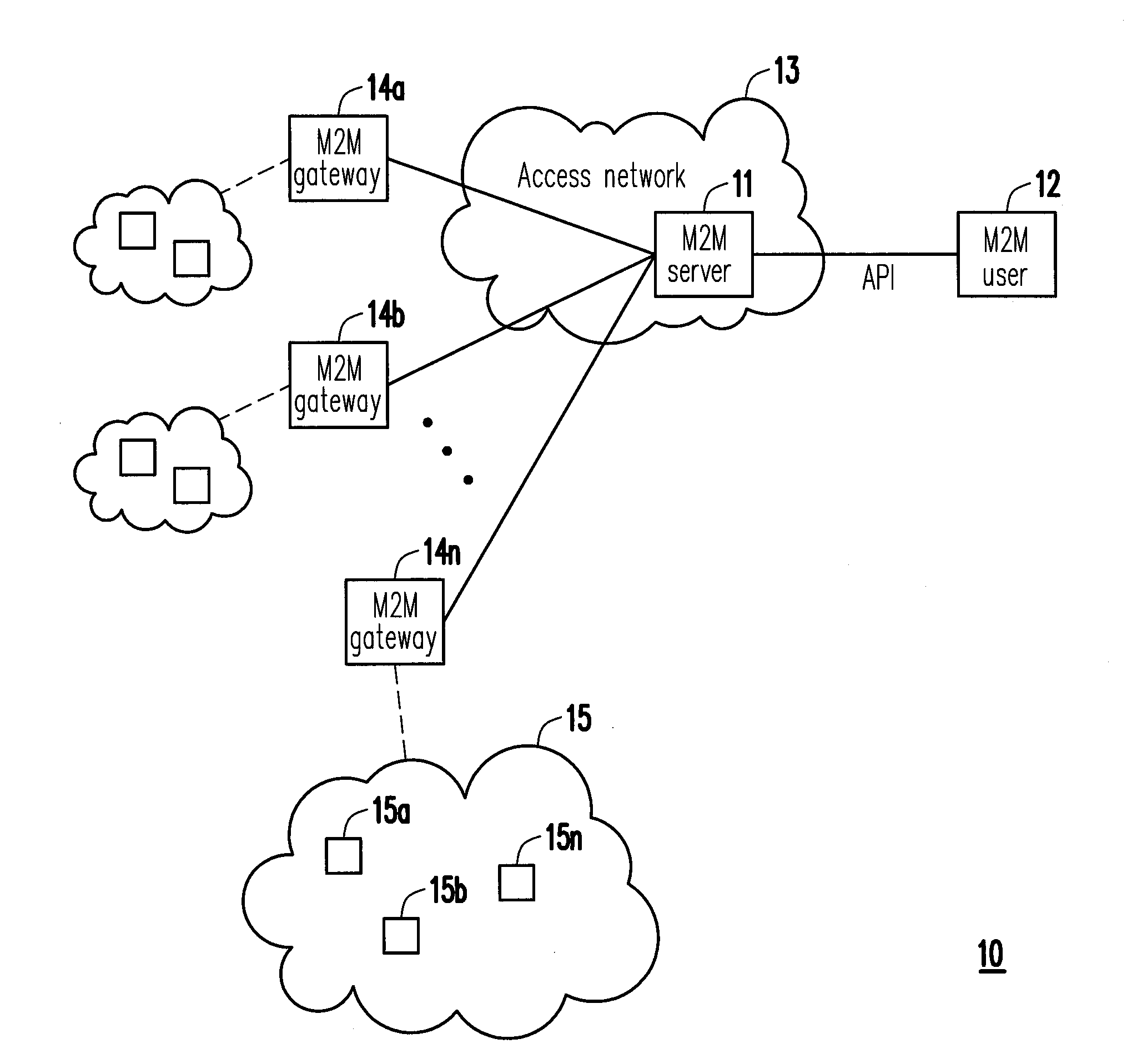
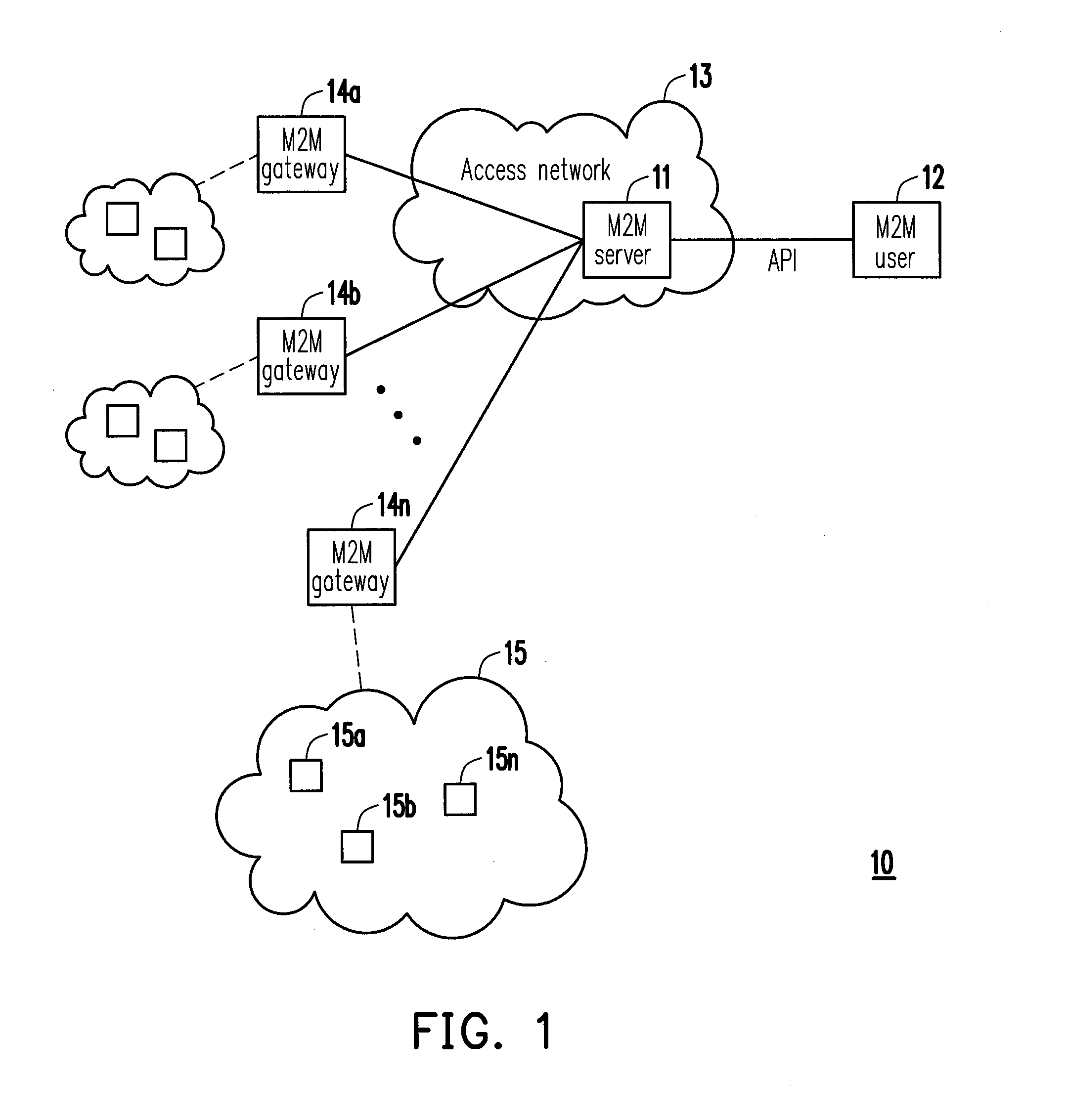
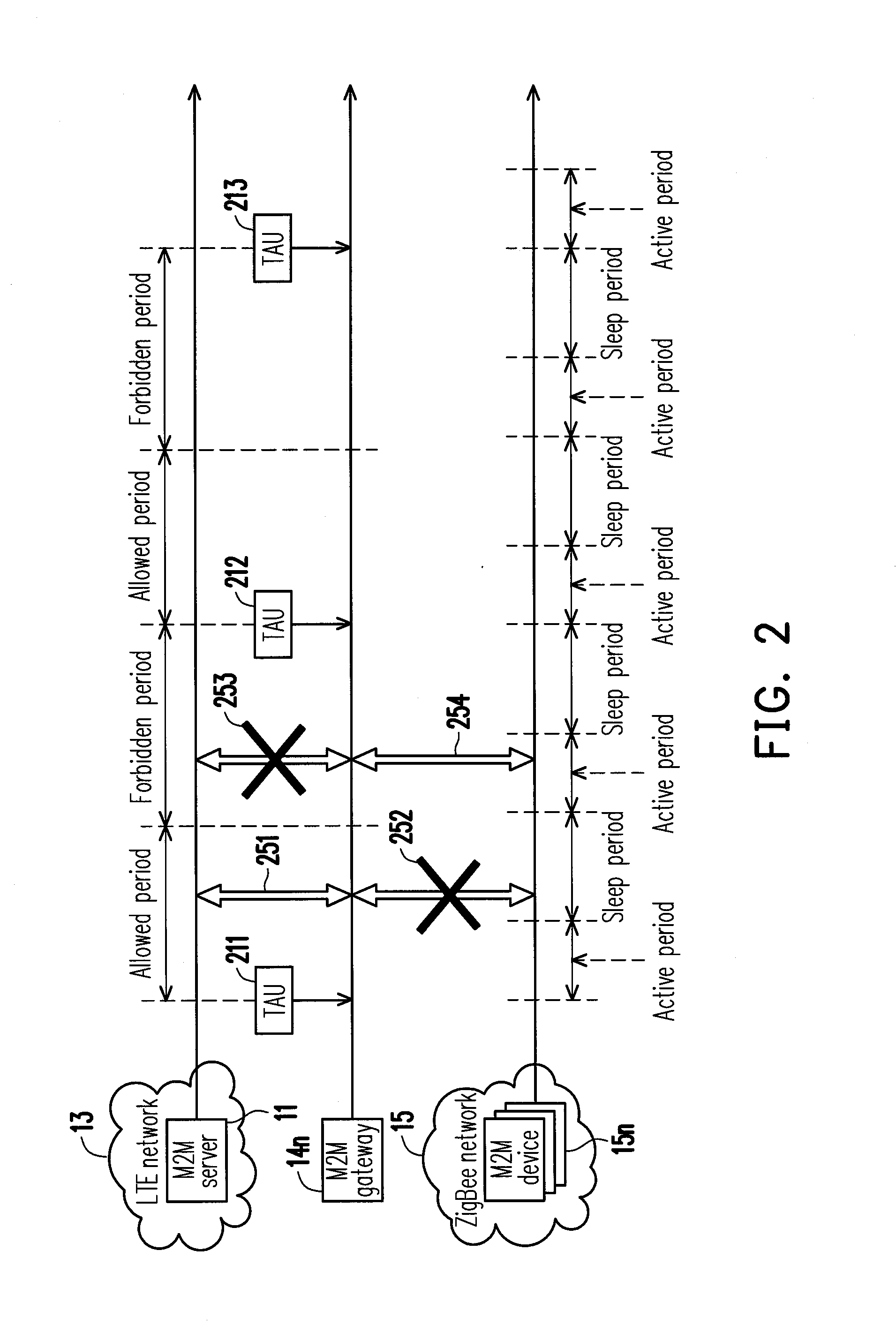
An operation method in heterogeneous networks, and a gateway and a wireless communication device using the same are disclosed. The operation method in heterogeneous networks includes followings. When a gateway, connecting a first communication network and a second communication network, operates in a beacon mode, the gateway determines whether the first communication network is in an allowed period or a forbidden period, and generates a determination result. Then, the gateway adaptively adjusts a ratio of a superframe duration to a beacon interval of a periodic beacon of the second communication network according to the determination result. In addition, the gateway is connected to a M2M communication server via the first communication network, and the gateway is connected to at least one M2M communication device via the second communication network.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Wireless media access method
The present invention is a wireless media access method on a wireless network synchronized by a synchronizing signal broadcasted from a coordinator. In the method, priority is assigned to a plurality of devices interconnected over the wireless network for securing wireless resources in accordance with application characteristics of a packet to be transmitted, and if the devices request communication, dividing at least one slot within a superframe into a plurality of minislots. Minislots are then allocated to the devices, respectively, according to the priority, and information about the allocated minislots is inserted into the synchronizing signal. The information is then broadcast, thereby allowing each of the devices with the allocated minislots to exclusively use the allocated minislot for data communication.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ofdm signal transmission method, transmission apparatus, and reception apparatus
ActiveUS20070064588A1Maintain compatibilityReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDVB-TEnergy dispersion
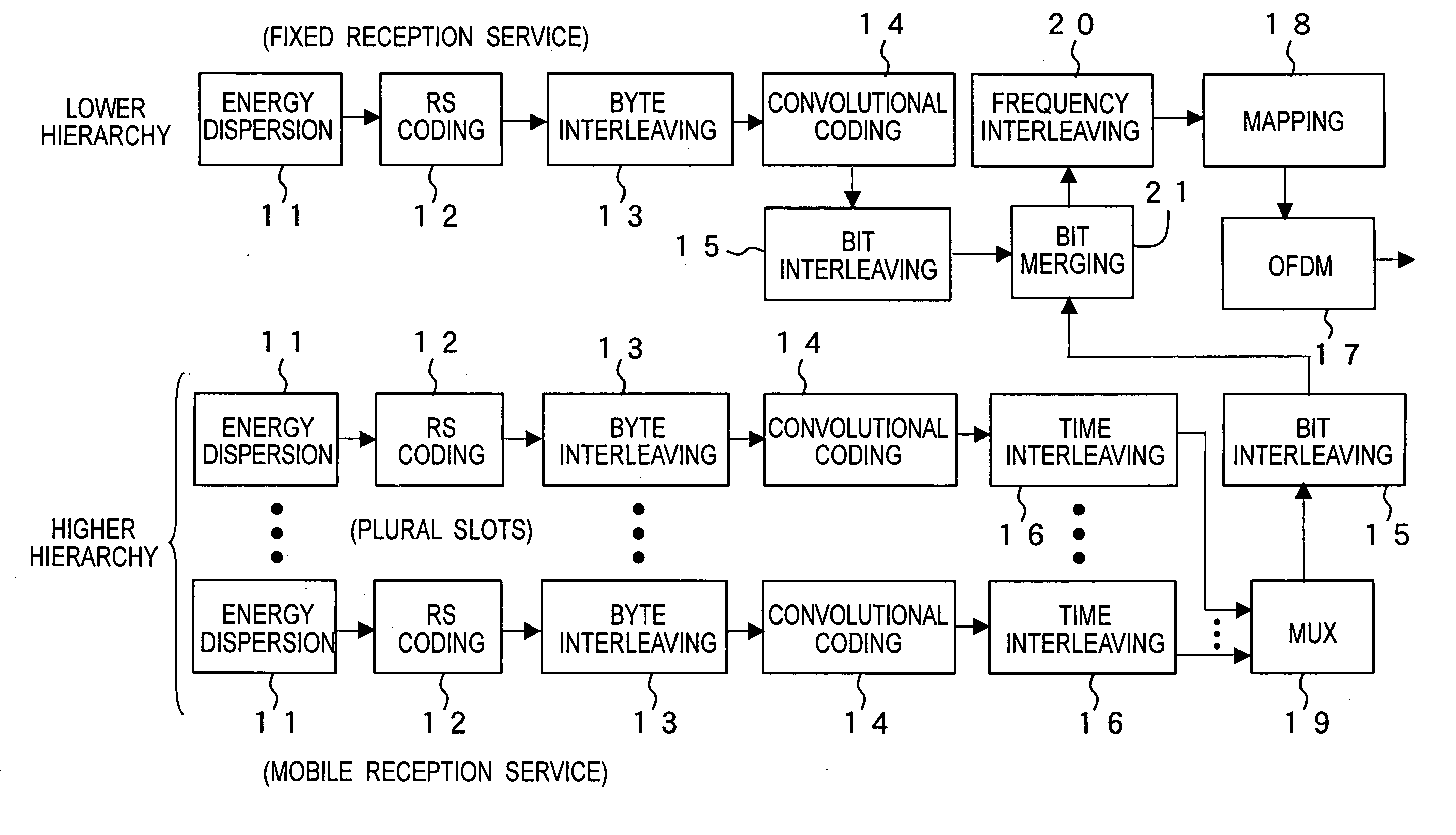
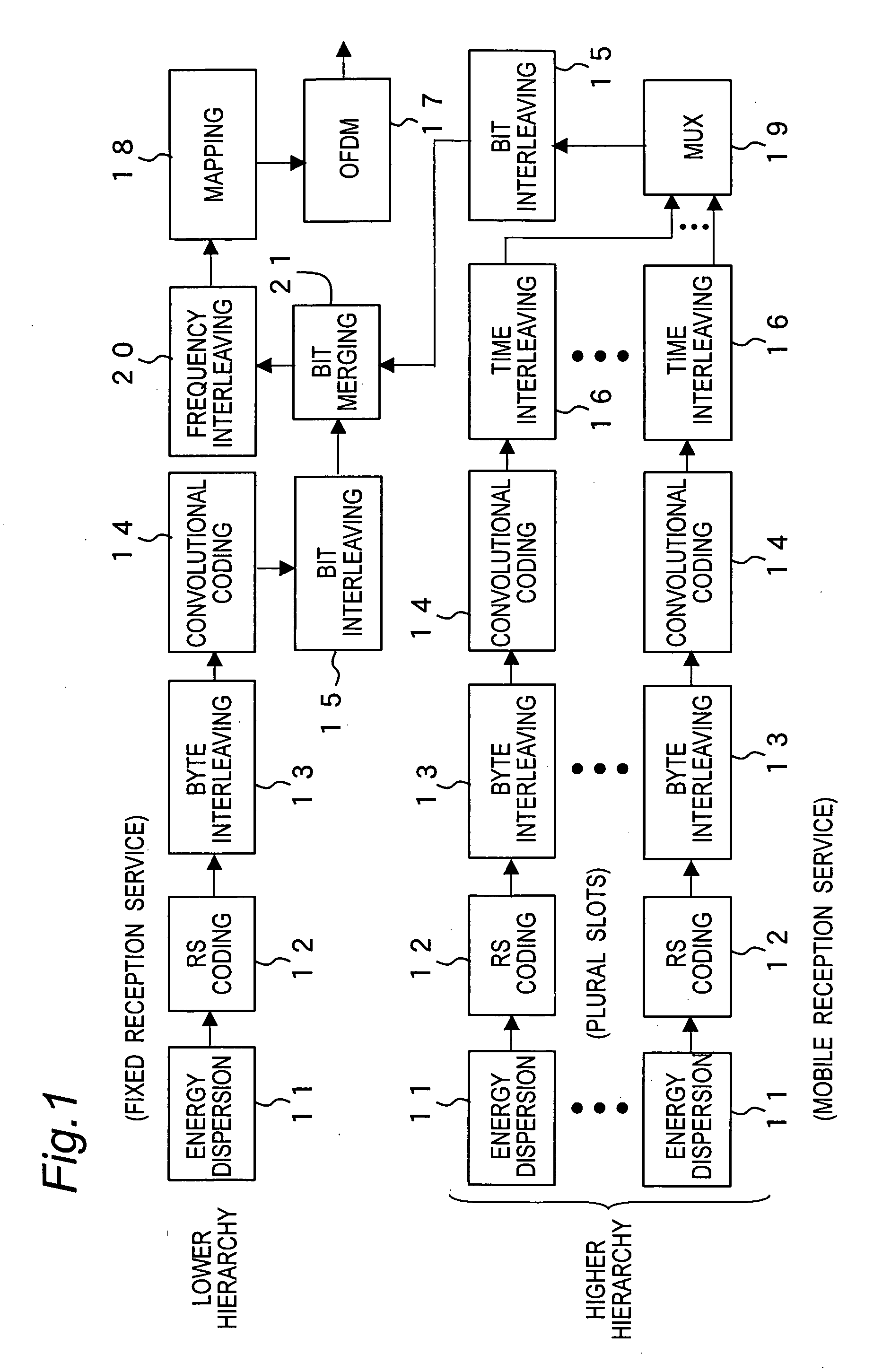
A transmission method of a digital broadcast which is compatible with the DVB-T terrestrial digital broadcast system in Europe and saves a battery in a mobile terminal is provided. Superframes in DVB-T are divided into units each including plural symbols so that an integer number of TS packets can be carried in each slot. At least one slot is used to transmit one service. Energy dispersion, Reed-Solomon coding, byte interleaving, convolutional coding, and time interleaving are applied to each service. When services for mobile terminal reception and services for fixed terminals are transmitted as the provided services, null packets may be transmitted before and after the slot carrying the mobile receiver service so that the fixed reception service and the mobile reception services are not mixed. If the fixed terminal handles TS packets of the mobile reception service as error packets, it could have no problem in reception.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
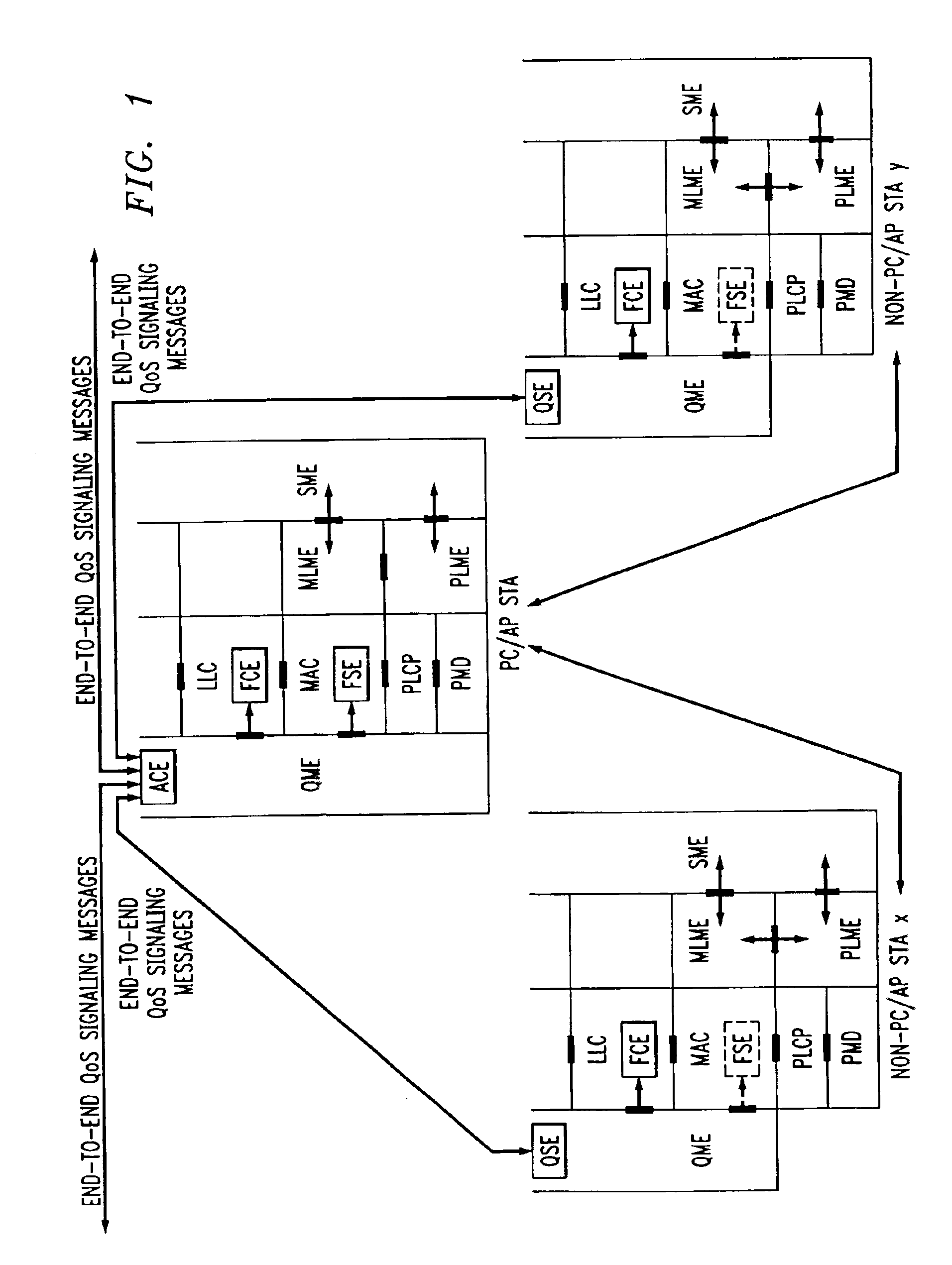
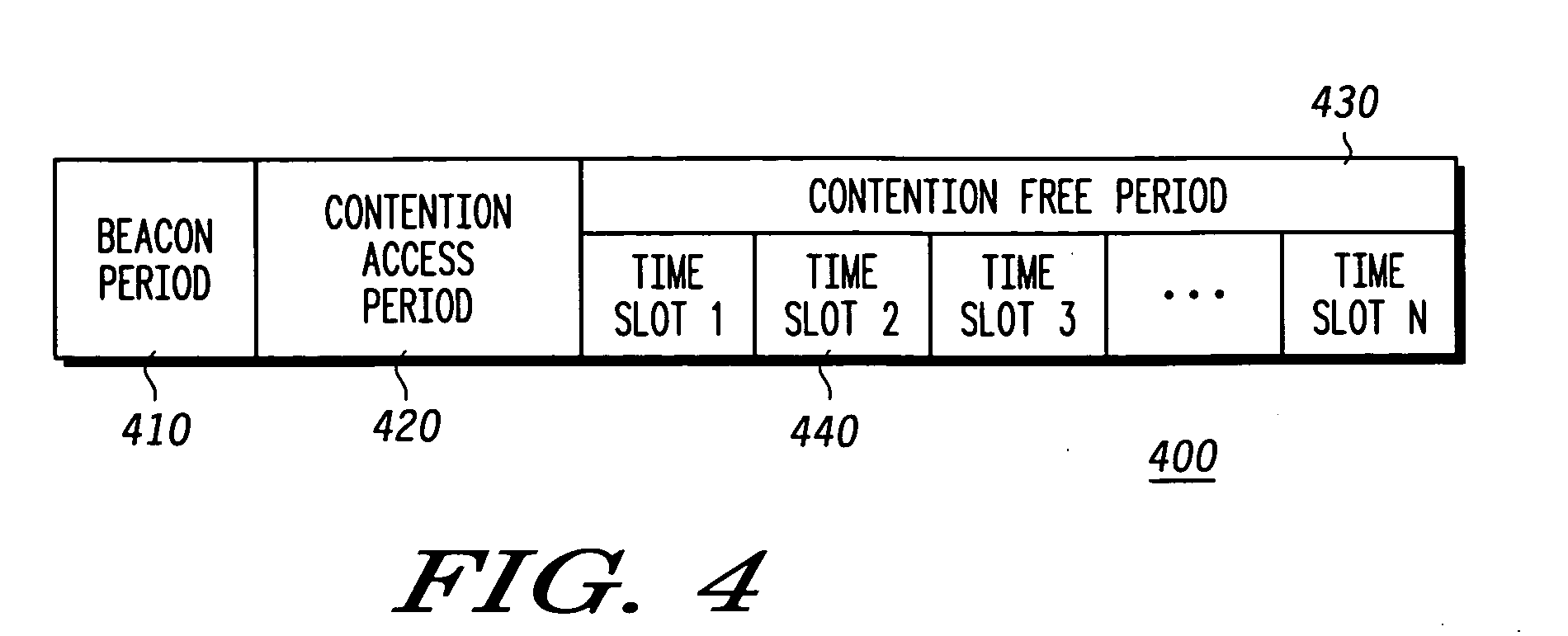
Centralized contention and reservation request for QoS-driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS7031287B1Maximizes channel throughputNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceBasic service
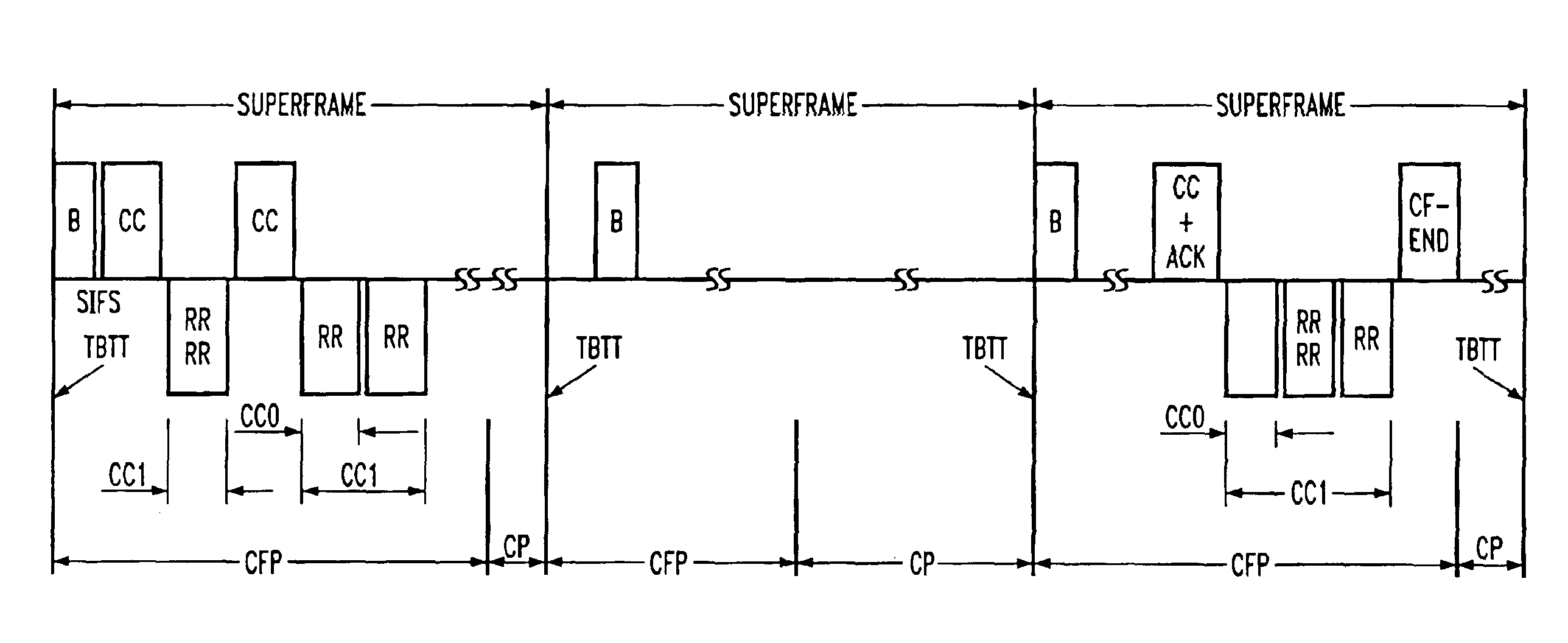
A method and a system is disclosed for providing quality of service (QoS)-driven channel access within a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN). A contention control (CC) frame is sent from a point coordinator (PC) of the BSS during a contention-free period (CFP) of a superframe that includes the contention-free period (CFP) and a contention period (CP). The CC frame contains information relating to at least one of a priority limit for a next centralized contention interval (CCI), a length of the next CCI, a permission probability associated with the next CCI and information relating to a reservation request (RR) frame successfully received by the PC in a previous CCI. A non-colliding RR frame is then received at the PC in the CCI following the CC frame. The received RR frame is sent from a non-PC station in the BSS when at least one centralized contention opportunity (CCO) is available during the CCI after the CC frame. The RR frame indicates that the non-PC station sending the RR frame has at least one buffered data frame for transmission.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
System and method for wireless communication systems
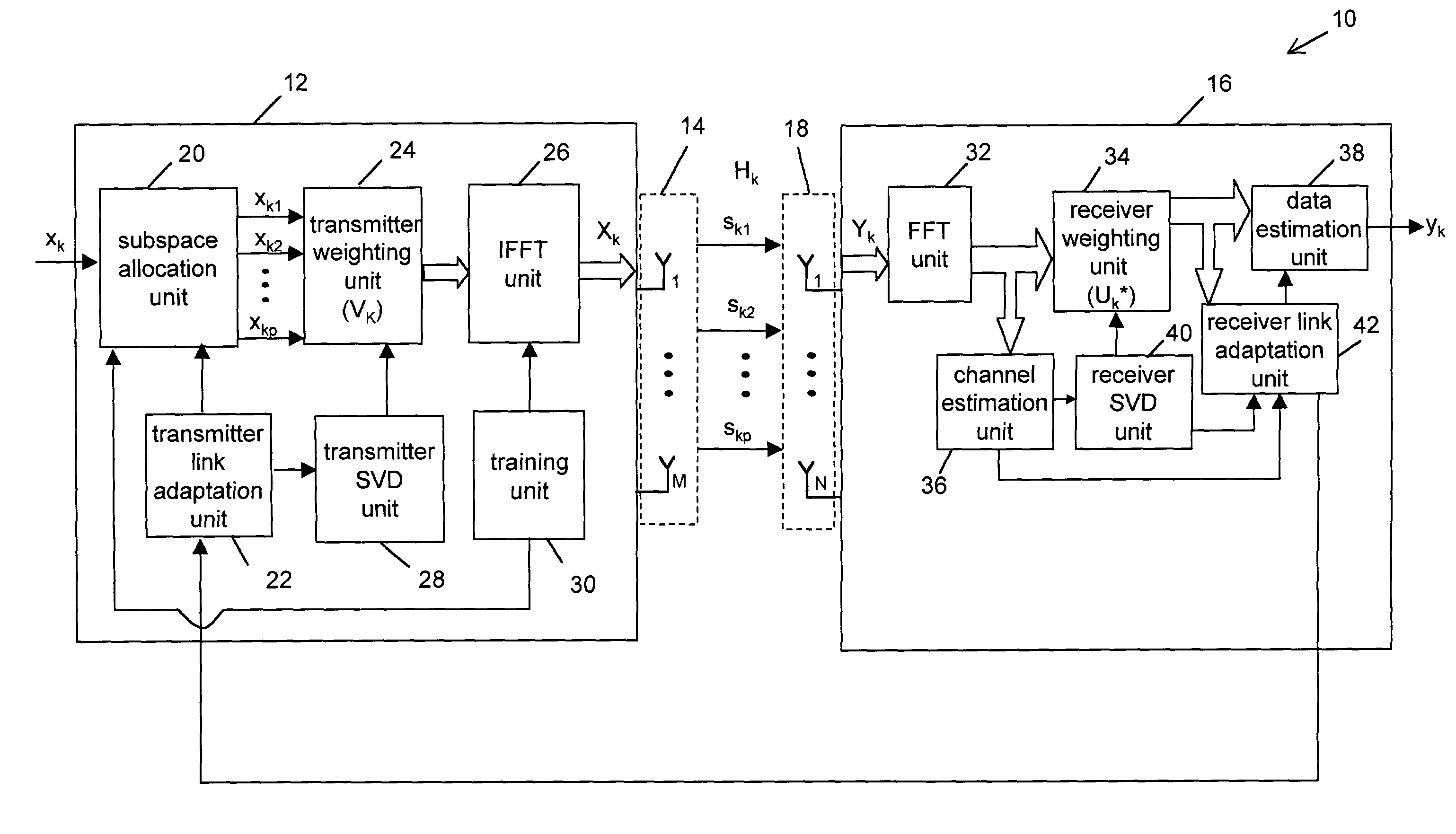
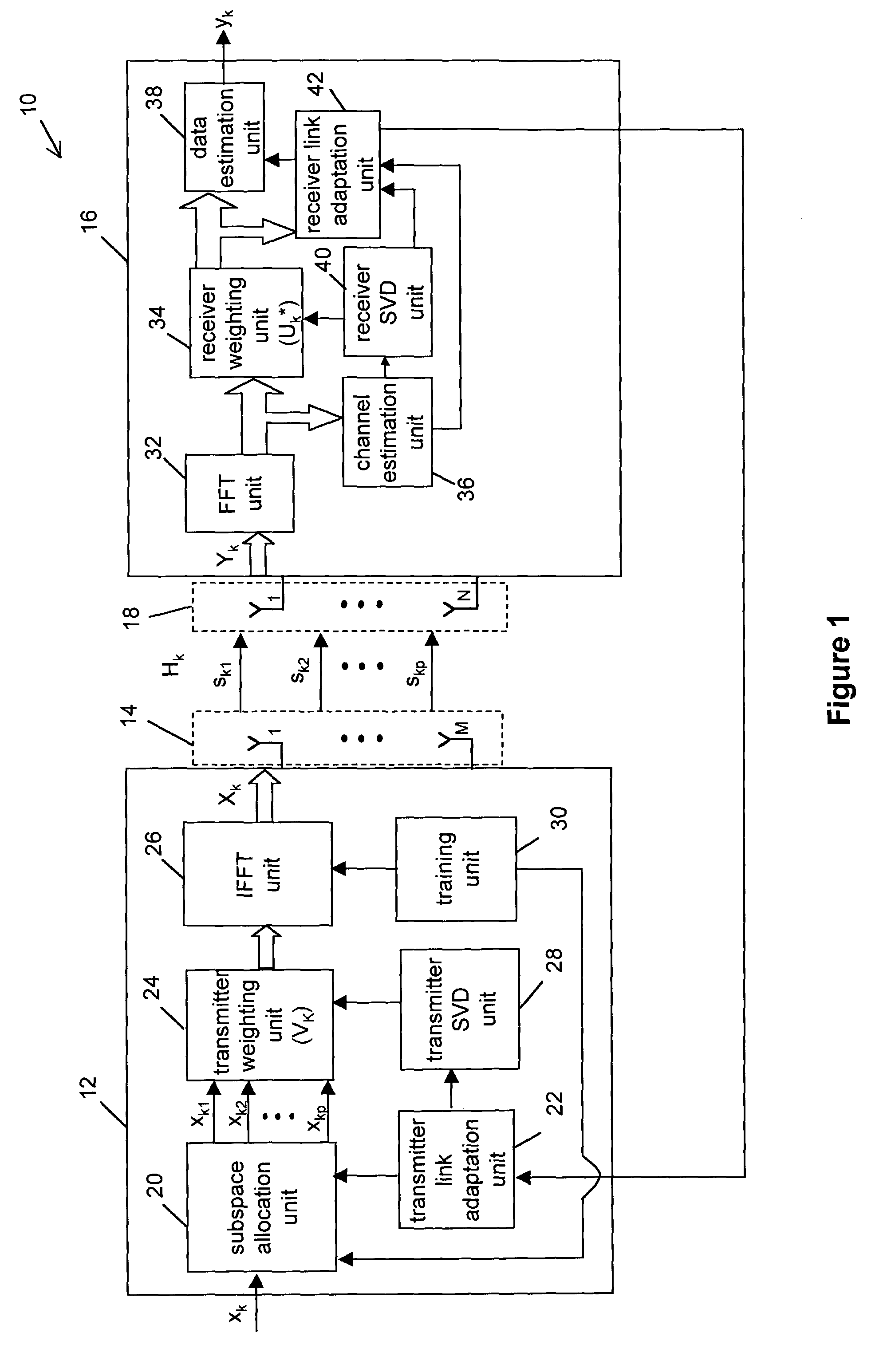
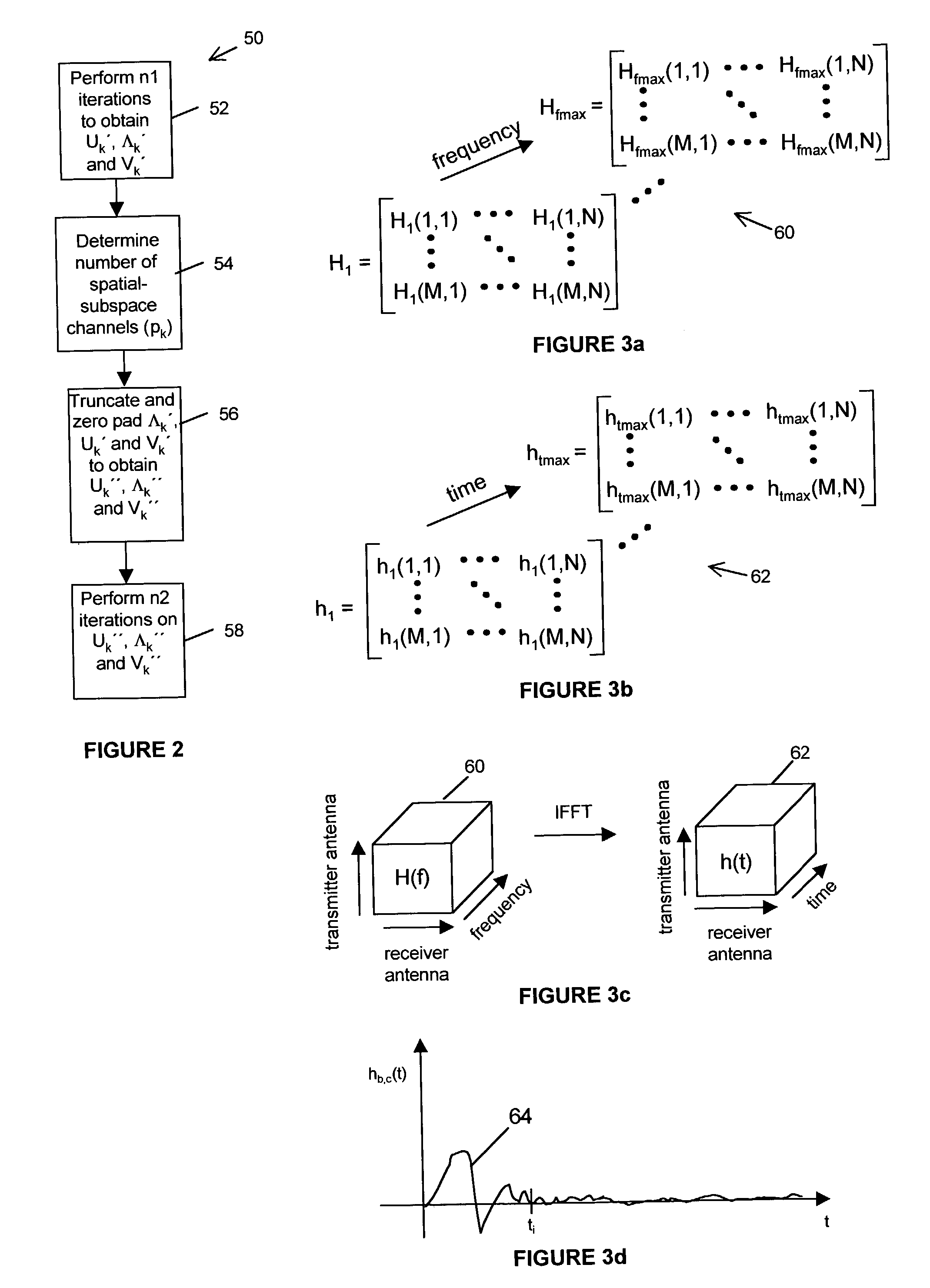
ActiveUS7327795B2Spatial transmit diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionSingular value decompositionCommunications system
A system and method for transmitting a plurality of input data symbol sub-streams over a plurality of spatial-subspace channels of a sub-carrier between a transmitter and the receiver. The plurality of input data symbol sub-streams are partitioned in a plurality of super-frames of data and weighted by a weight matrix derived from the singular value decomposition of a channel matrix corresponding to the sub-carrier by applying a partial SVD algorithm. The transmitter further inserts subspace training symbols into the plurality of input data symbol sub-streams and the receiver periodically processes the sub-space training symbols during each super-frame of the plurality of super-frames for estimating output data related to the input data symbol stream.
Owner:VECIMA NETWORKS
Wireless LANs and neighborhood capture
ActiveUS7280517B2Eliminates unfairnessReduce decreaseSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTimestampAccess method
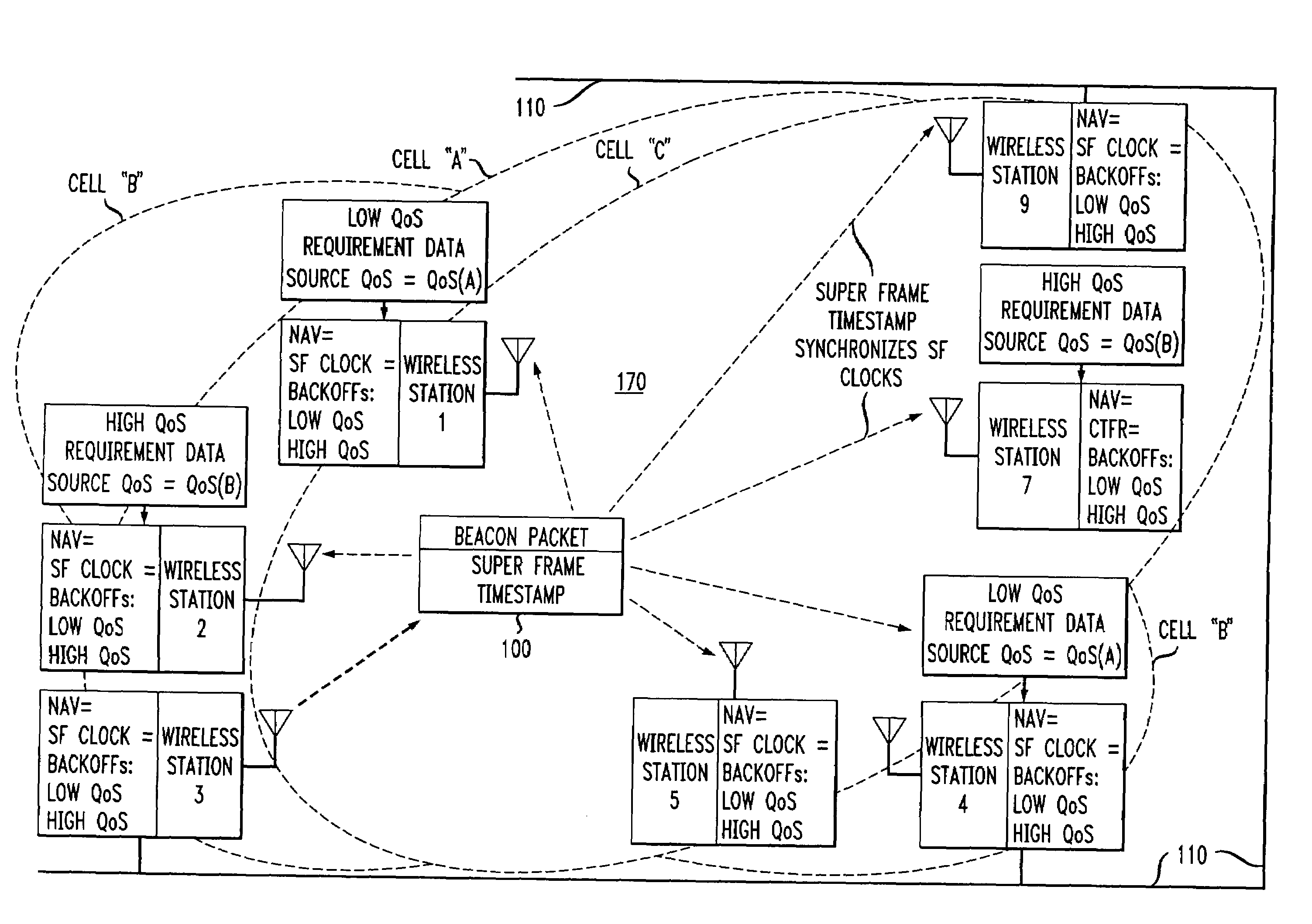
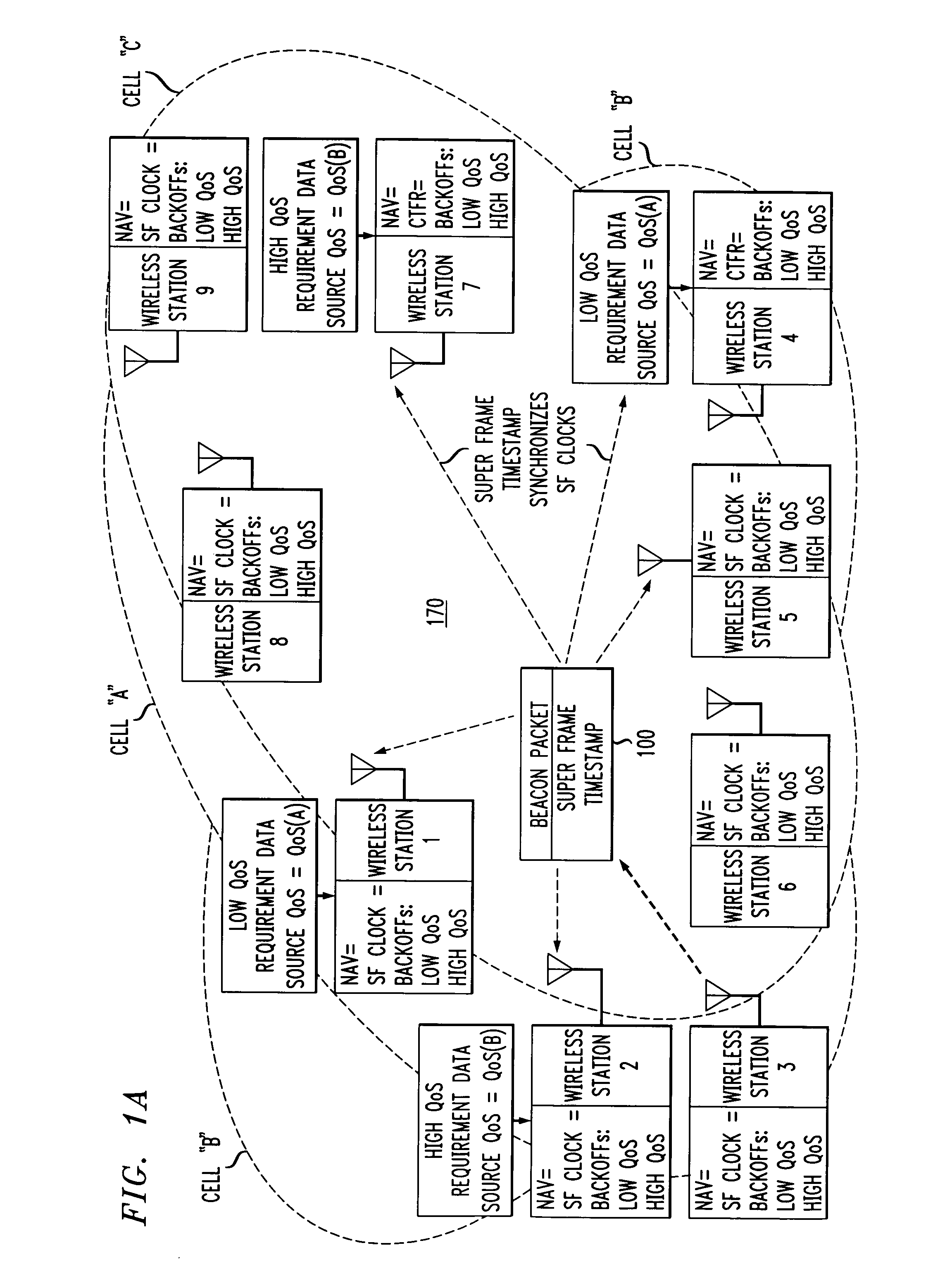
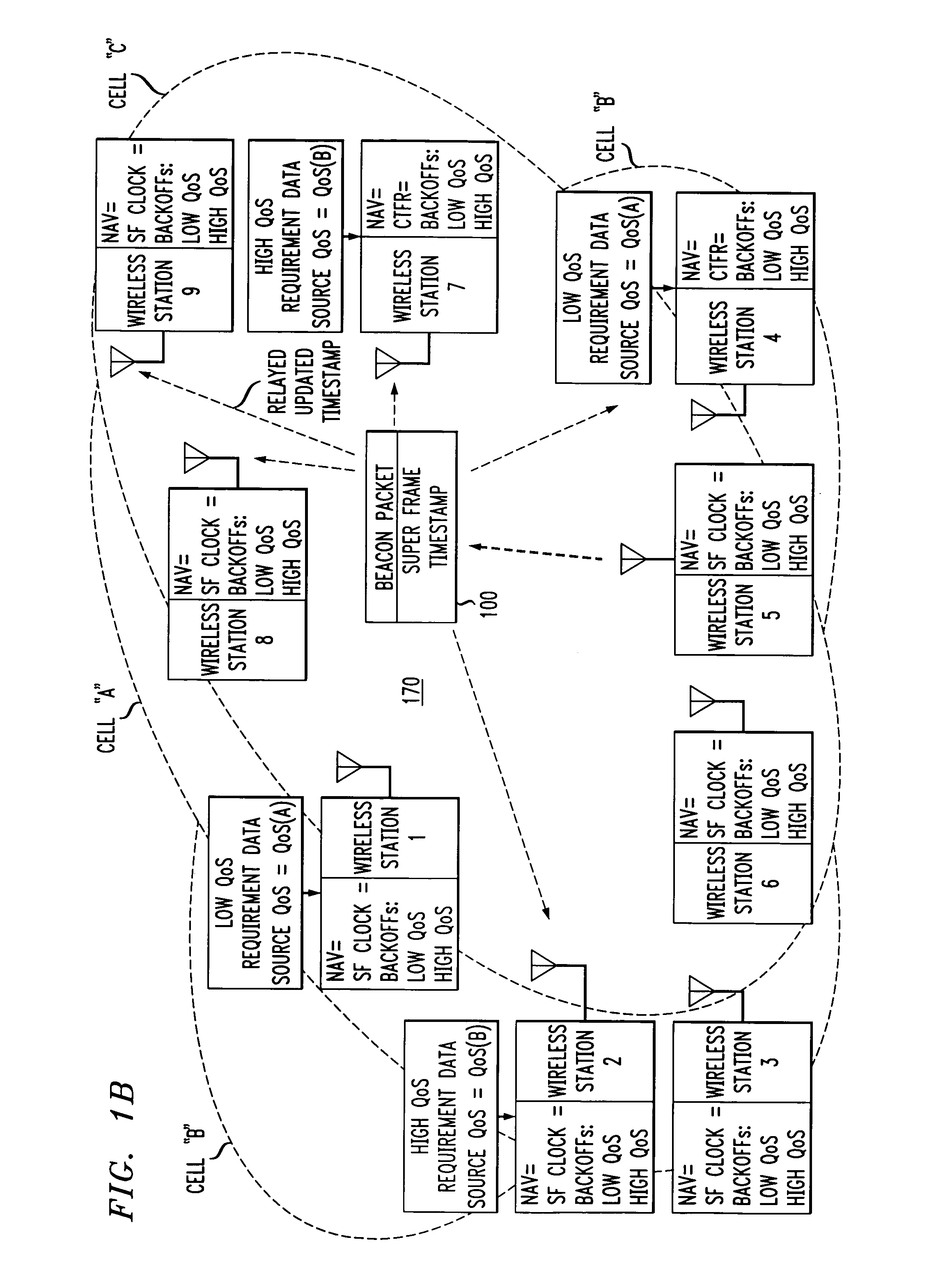
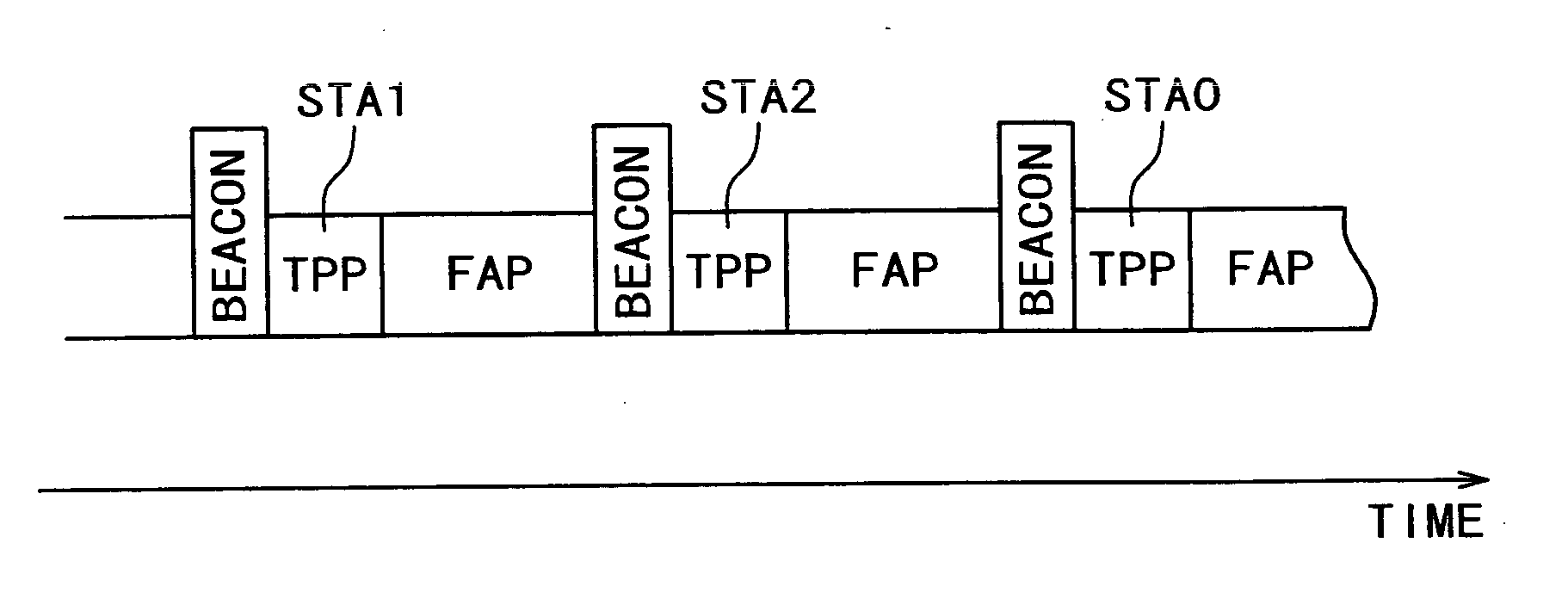
Overlapped wireless LAN cells in a medium have an equal chance at establishing a session on the medium. A first member station in the first cell transmits a timing packet containing a timestamp value, which is received at a second member station in the second cell. This synchronizes member stations in the first and second cells to interrupt transmissions at a global channel release instant corresponding to the timestamp value. The member stations in the first and second cells then have the opportunity to contend for access to the medium following the global channel release instant, using a slotted CSMA / CA access method. Each of the member stations in the first and second cells has a superframe clock that is synchronized based on the timestamp value, thereby establishing a periodic global channel release instant during each of a plurality of periodic superframes. The member stations can then periodically interrupt transmissions at the periodic global channel release instant to contend for the medium. The periodic global channel release instant occurs at intervals that are sufficiently close to meet delay and jitter restrictions for time-critical voice and video applications.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method, and computer program
InactiveUS20050025092A1Wide bandwidthNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsComputer science
The present invention is to provide each communication station with a transmission prioritised period without any useless latency in an ad-hoc communication environment including no control station. For this end, each communication station periodically transmits the beacon signal and acquires the transmission prioritised period immediately after transmission of the beacon. If the number of communication stations in the network is small, a communication station transmit a supplementary beacon within the super frame period, thereby effectively shortening the beacon interval and reducing latency at the start of transmission. At the time when a new communication station enters the network, the supplementary beacon is released in order to accommodate such new communication station.
Owner:SONY CORP
Enhanced channel access mechanisms for QoS-driven wireless lans
InactiveUS7068633B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionQuality of serviceWireless lan
A method and a system is disclosed for providing quality of service (QoS)-driven channel access within a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless network. A contention control (CC) frame is sent from a point coordinator (PC) station of the BSS. The CC frame contains information relating to a number of available centralized contention opportunities (CCOs) for receiving a reservation request (RR) in a centralized contention interval (CCI) following the CC frame. The CC frame also contains information relating to the identification of stations from which an RR was successfully received by the PC station in a preceding CCI. The CC frame is sent by the PC station during a contention-free period (CFP) of a superframe. The superframe includes a contention-free period (CFP) and a contention period (CP). The CC frame is received at a non-PC station in the BSS. An RR is then sent in a selected one of the available CCOs in the CCI in response to the received CC frame. The RR is sent from the non-PC station when the non-PC station has a burst of data frames to send, and the RR indicating an amount of bandwidth requested by the non-PC station sending the RR for transmitting the burst. The RR frame is received at the PC-station in one of the CCOs of the CCI. A multipoll frame is then sent from the PC station containing information relating to at least two transmission opportunities (TOs) assigned to at least one non-PC station in the BSS for data transmission. The information contained in the multipoll frame can include information relating to a length of each TO.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Common signalling mode for use with multiple wireless formats
A method is provided for operating a wireless local device. In this method a local device receives a beacon for a current superframe in a common signal format. The beacon includes time slot assignment information. The local device then determines a device format for the transmission of data to a remote device based on format determination information. The device format can be one of a common signal format, and one or more wireless formats. The local device then determines one or more remote device time slots in the superframe assigned for transmission of the data to the remote device based on the time slot assignment information. Finally, the local device transmits the data in the one or more remote device time slots to the remote device using the device format.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Method and system for wireless communication in multiple operating environments
InactiveUS20080039133A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsOperation mode
A wireless communication method and system are provided. A first wireless communication numerology, e.g., OFDM operating parameters, corresponding to a first operational mode is established. A second wireless communication numerology corresponding to a second operational mode is also established. The first wireless communication numerology is different than the second wireless communication numerology. One of the first operational mode and the second operational mode is selected. One of the first wireless communication numerology and the second wireless communication numerology corresponding the selected operational mode is used in which communication in the first operational mode and the second operational mode use substantially similar synchronization channels. The present invention also uses the same superframe structure for the first and second operational modes for Ultra-Mobile Broadband (“UMB”) networks and the same frame structure for the first and second operational modes for Long Term Evolution (“LTE”) networks.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Superframe error coding in digital audio broadcasting systems
InactiveUS20050262419A1Increase the number ofSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelComputer hardwareData field
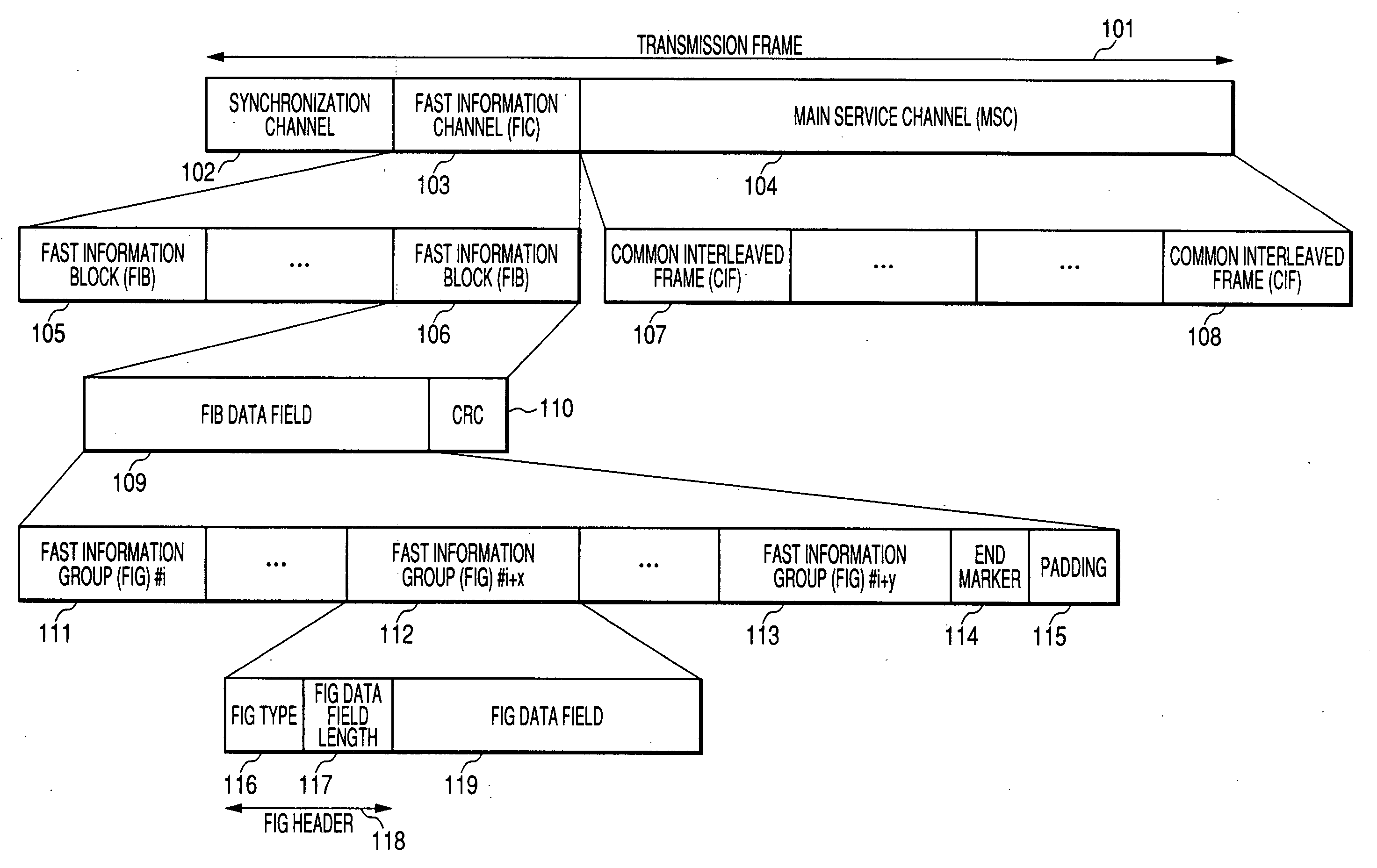
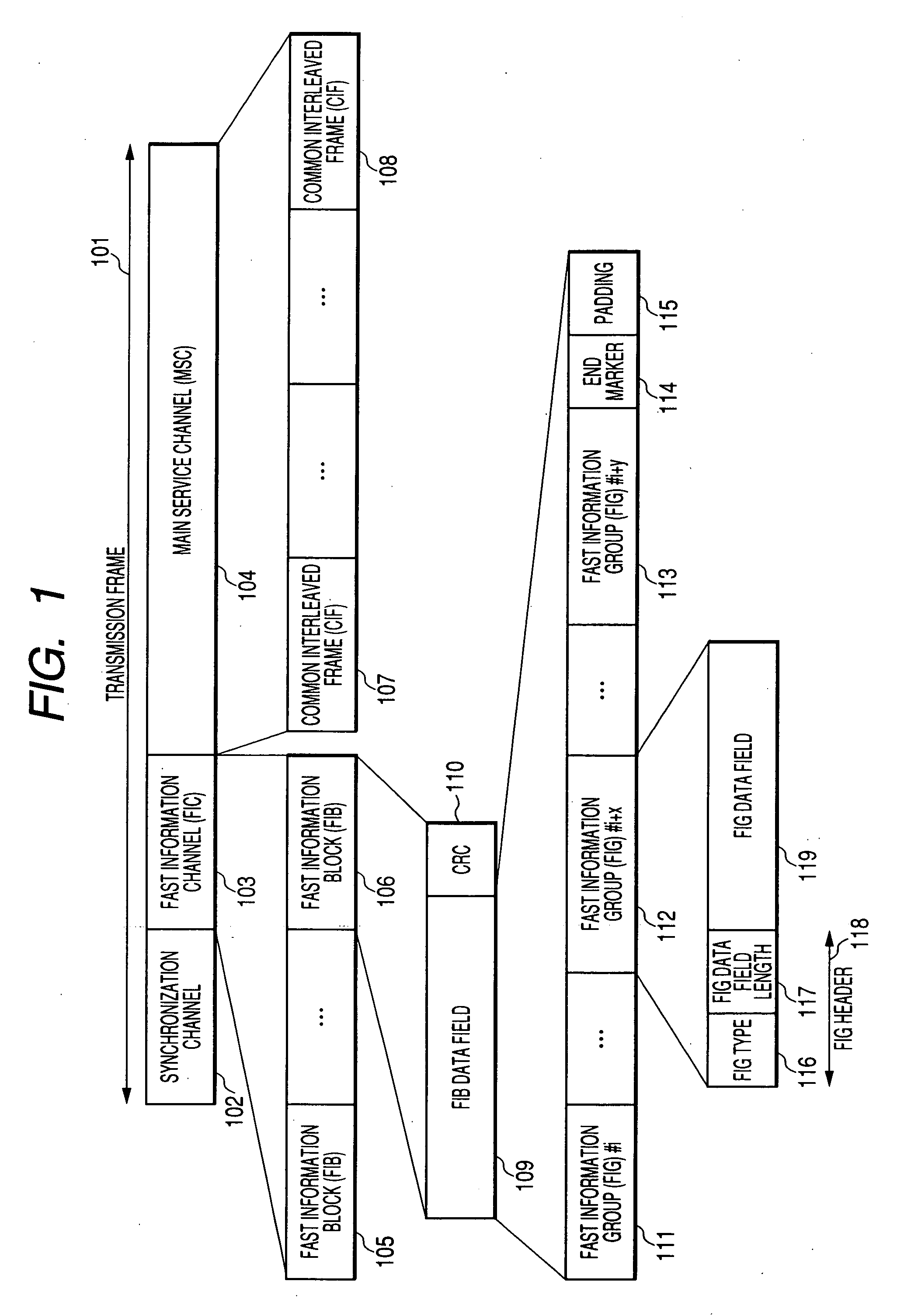
The present invention relates to a subchannel structure within a main service channel for transmitting data of at least one application in a digital audio broadcasting system, such as DAB or DRM. Further methods for transmitting and receiving application data using the subchannel structure, as well as a corresponding broadcasting station and receiving terminal are provided. To increase the number of data packets of which undamaged data can be derived under identical reception conditions in a backward-compatible way the present invention provides a subchannel structure comprising a predetermined number of data packets and a predetermined number of error control packets, wherein each of the error control packets comprises an error control code field the data of which is generated based on at least a part of the packet data field and / or at least a part of the packet header of the data packets and a CRC field preceding the error control code field for protecting same.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
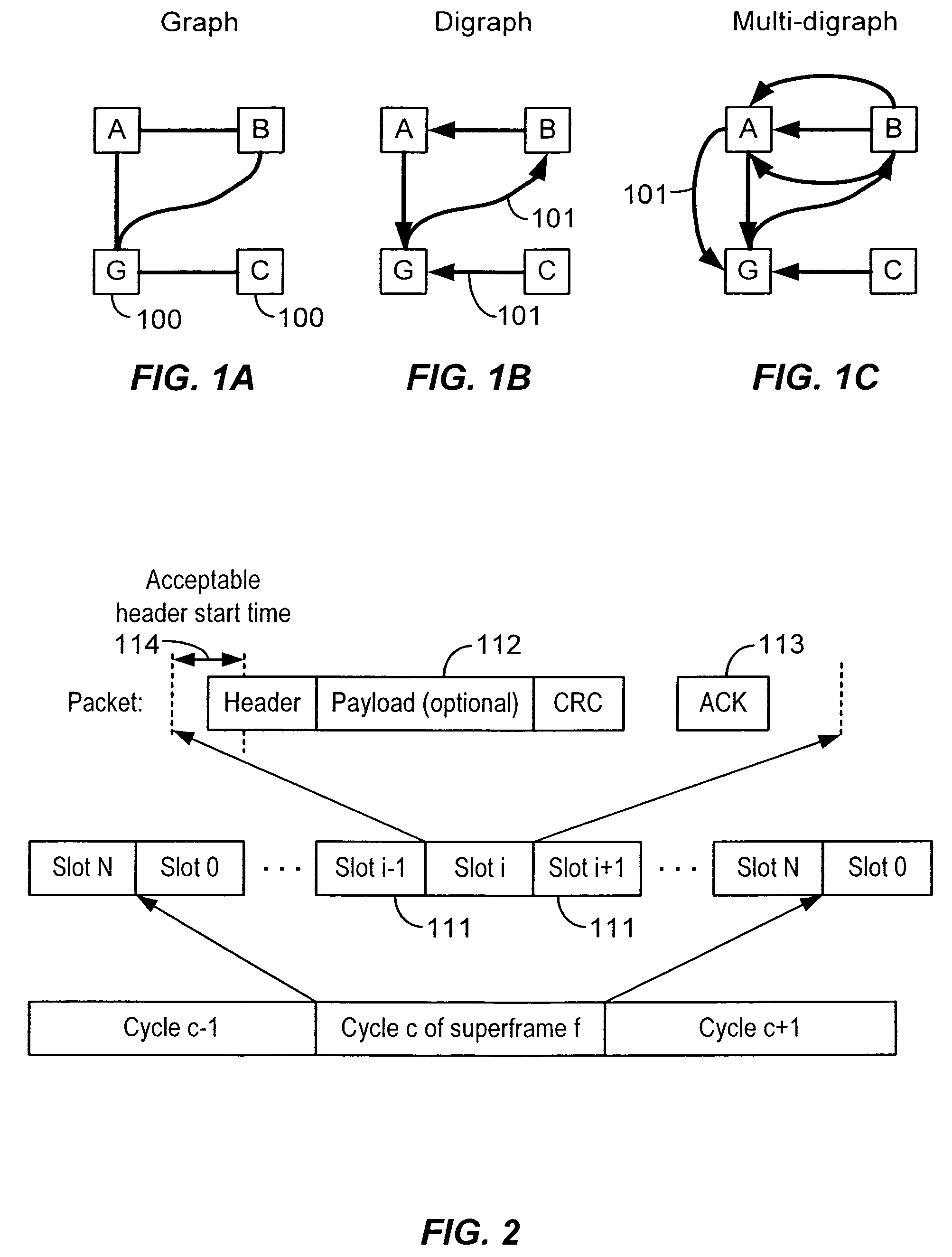
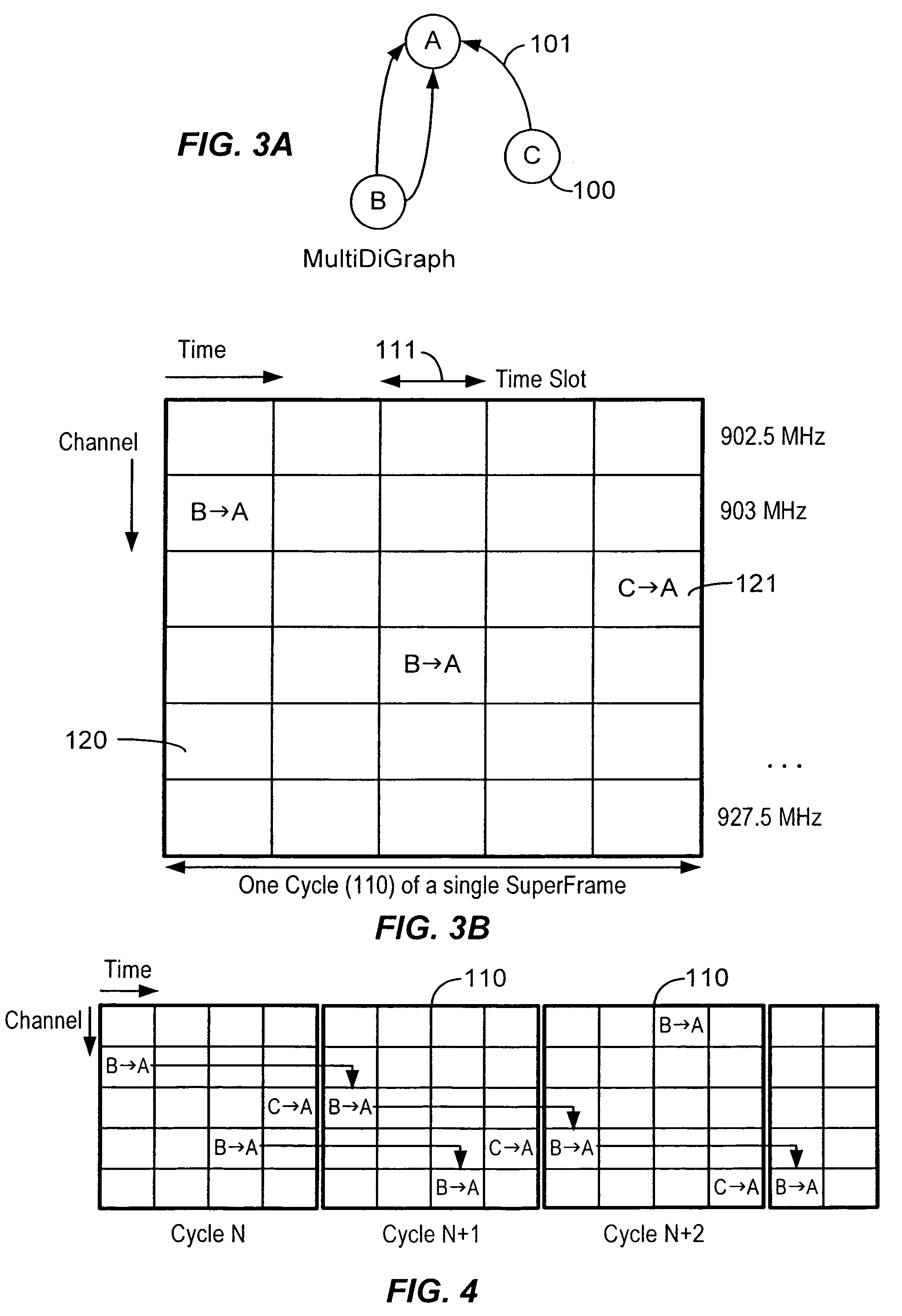
Increasing Reliability and Reducing Latency in a Wireless Network
ActiveUS20080279204A1Efficient inactivationSave powerSynchronisation arrangementMeasurement devicesGraphicsSignal quality
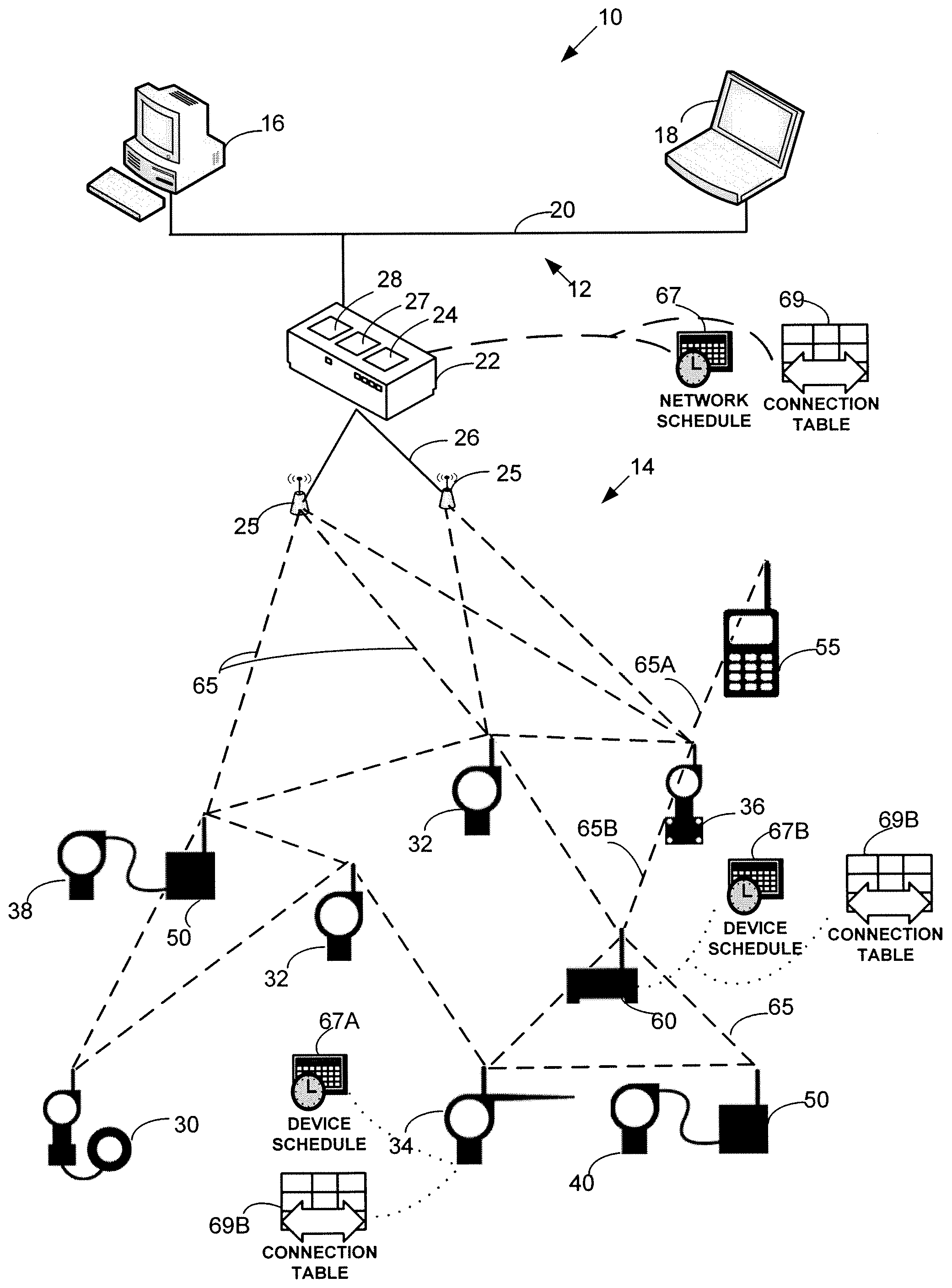
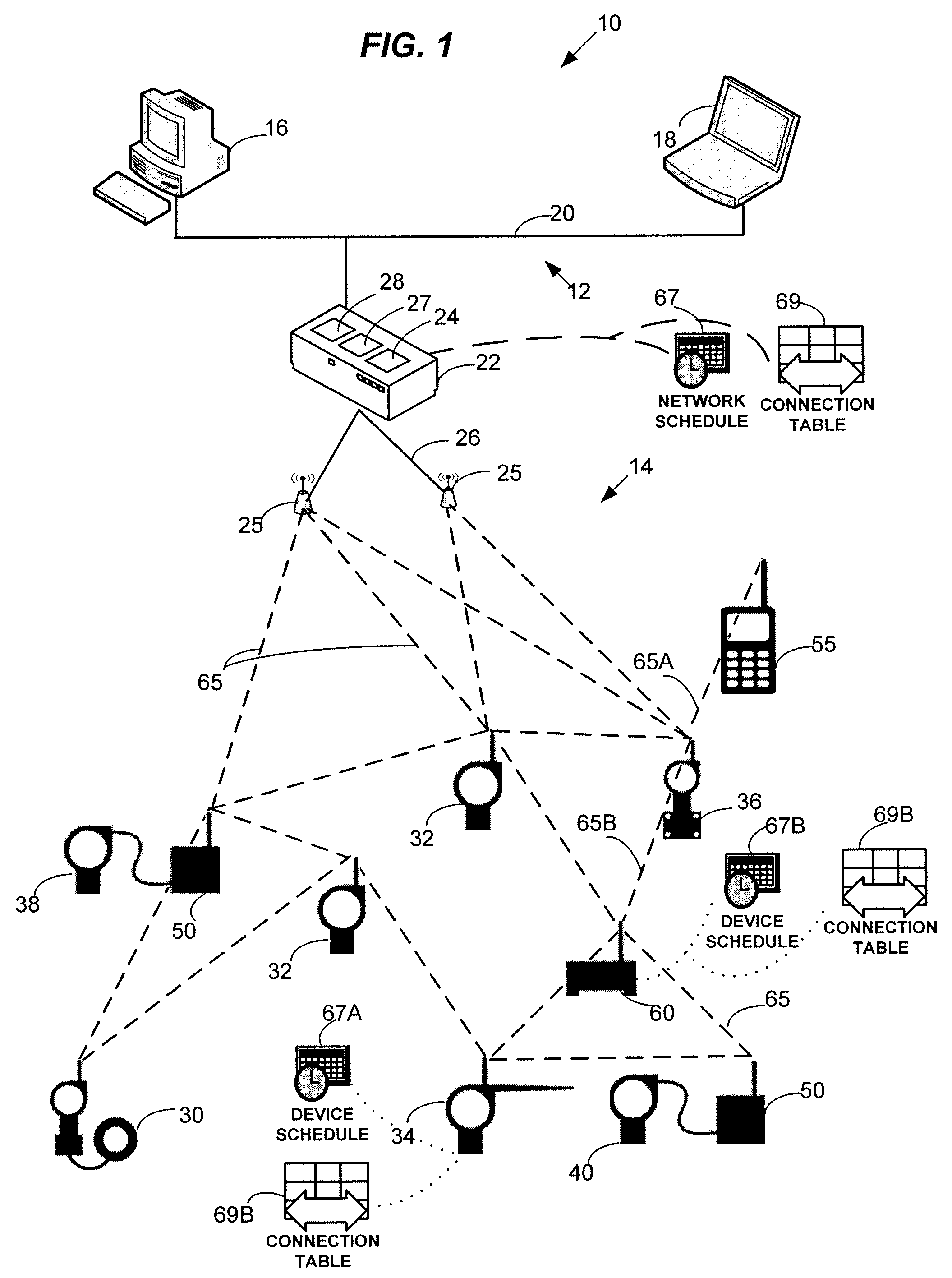
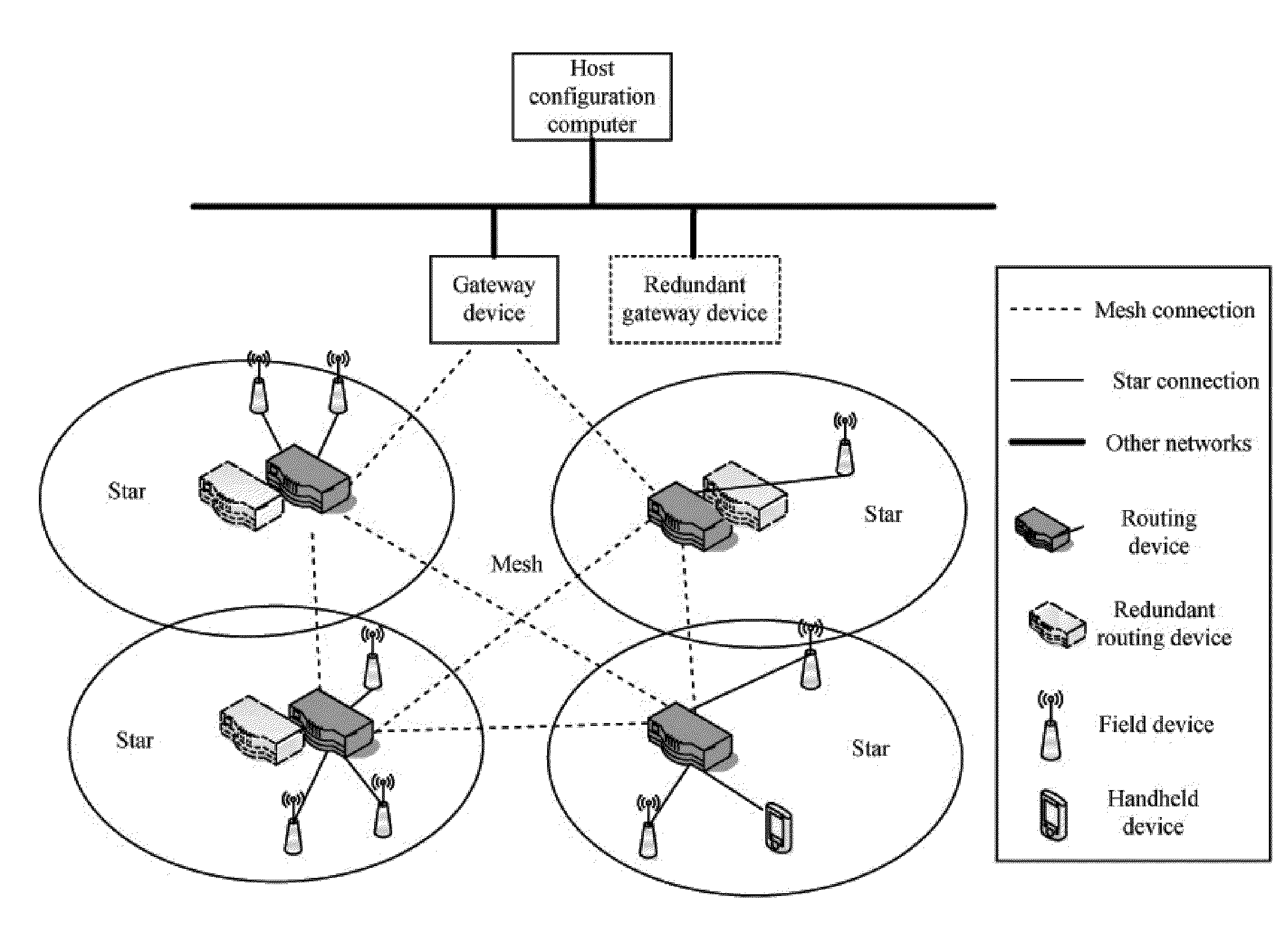
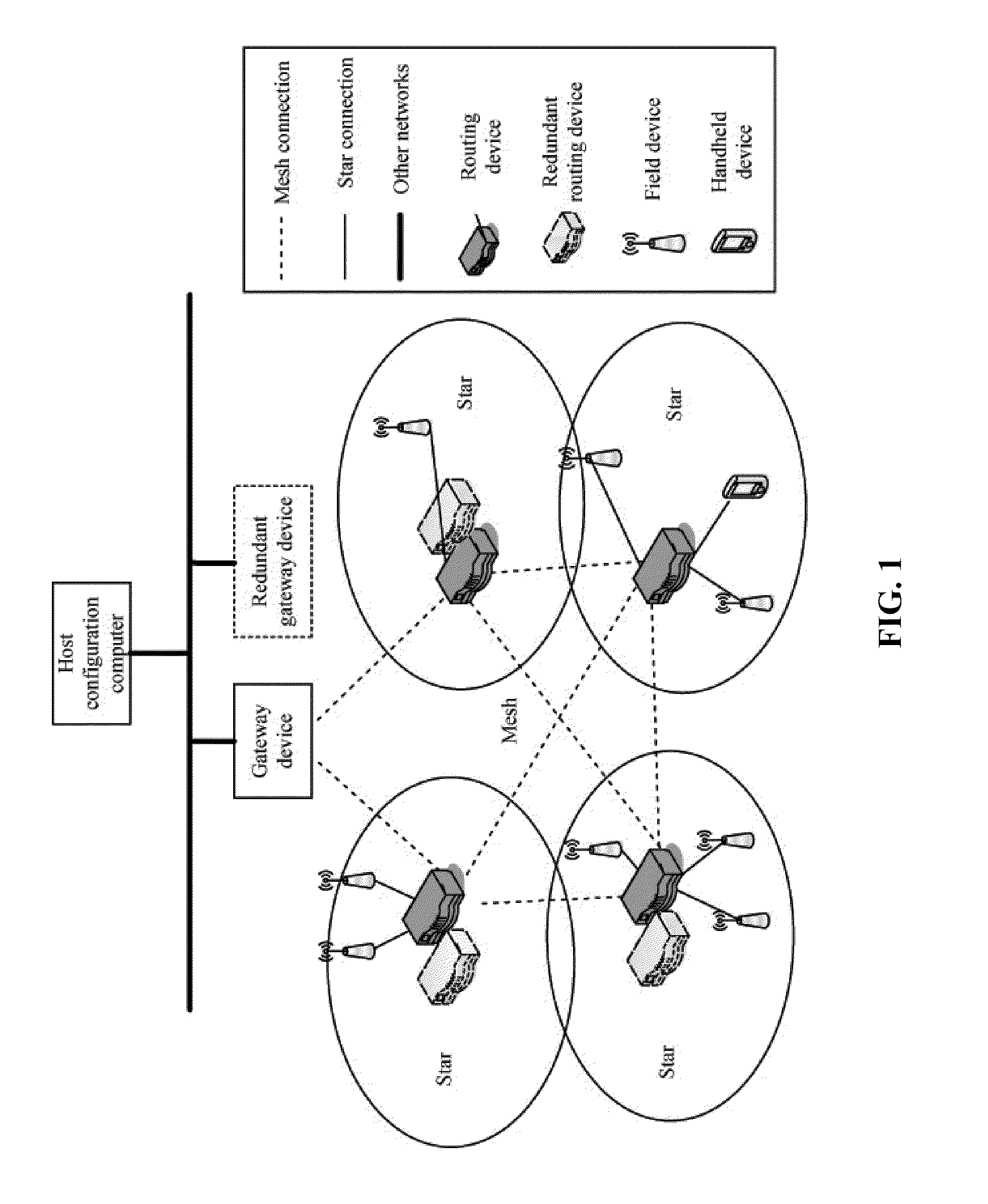
A mesh communication network for use in, for example, process control plants includes a plurality of network devices transmitting and receiving data according to a network schedule defined as a set of concurrent overlapping superframes, and along a set of graphs defining communication paths between pairs of network devices. A network manager residing in or outside the communication network develops a routing scheme for the network by analyzing the topology of the network and defining a set of graphs for use in routing or transmitting data between various nodes of the network, each graph including one or more communication paths between pairs of network devices. Concurrently or consequently, the network manager defines the network schedule in view of at least transmission requirements, power availability, and signal quality at each network device. If desired, the network manager may begin to define the network schedule upon completing the definition of the graphs of the communication network, so that the network manager may define the network schedule in view both the defined graphs and the transmission, power, etc. parameters associated with each network device.
Owner:FIELDCOMM GRP INC
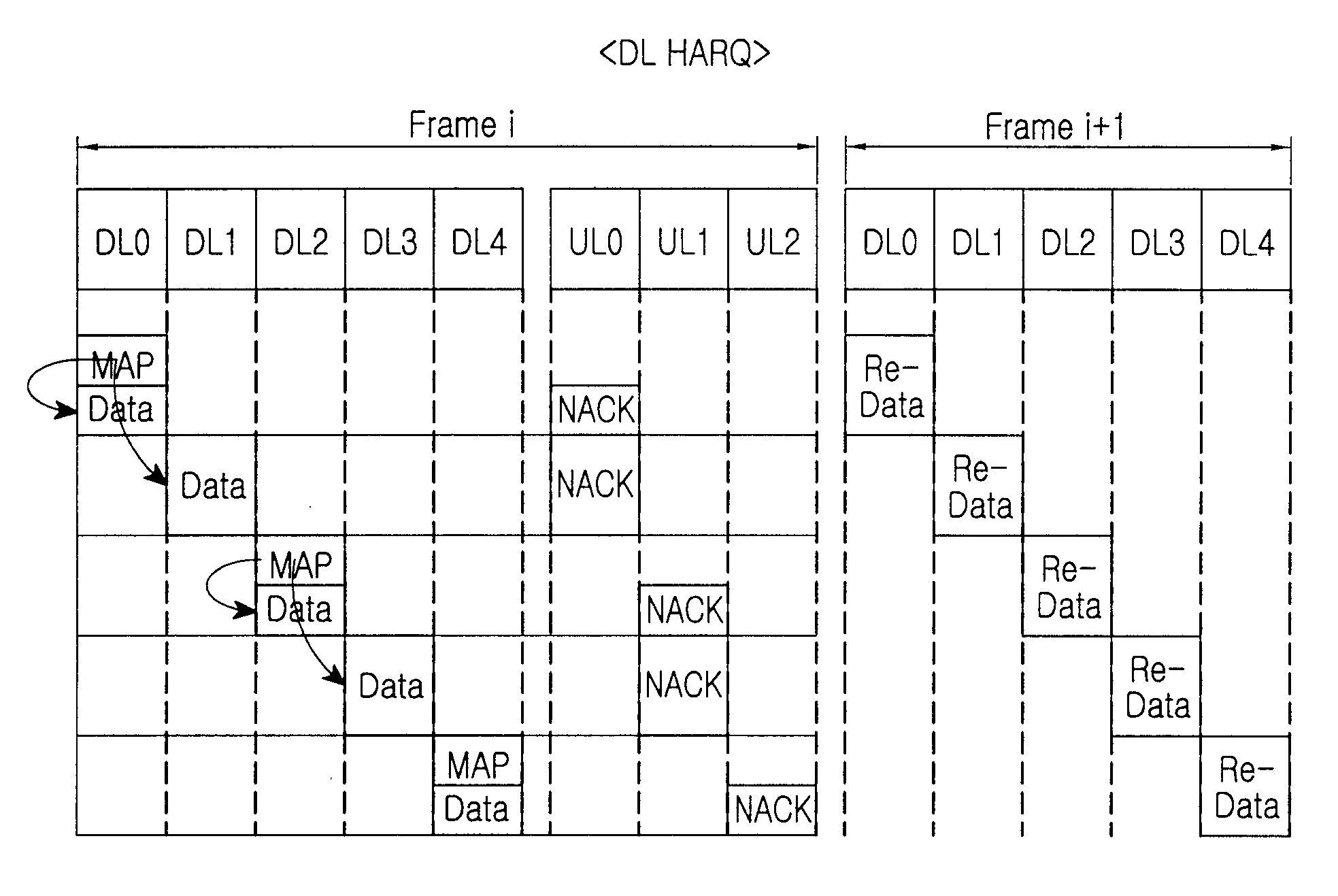
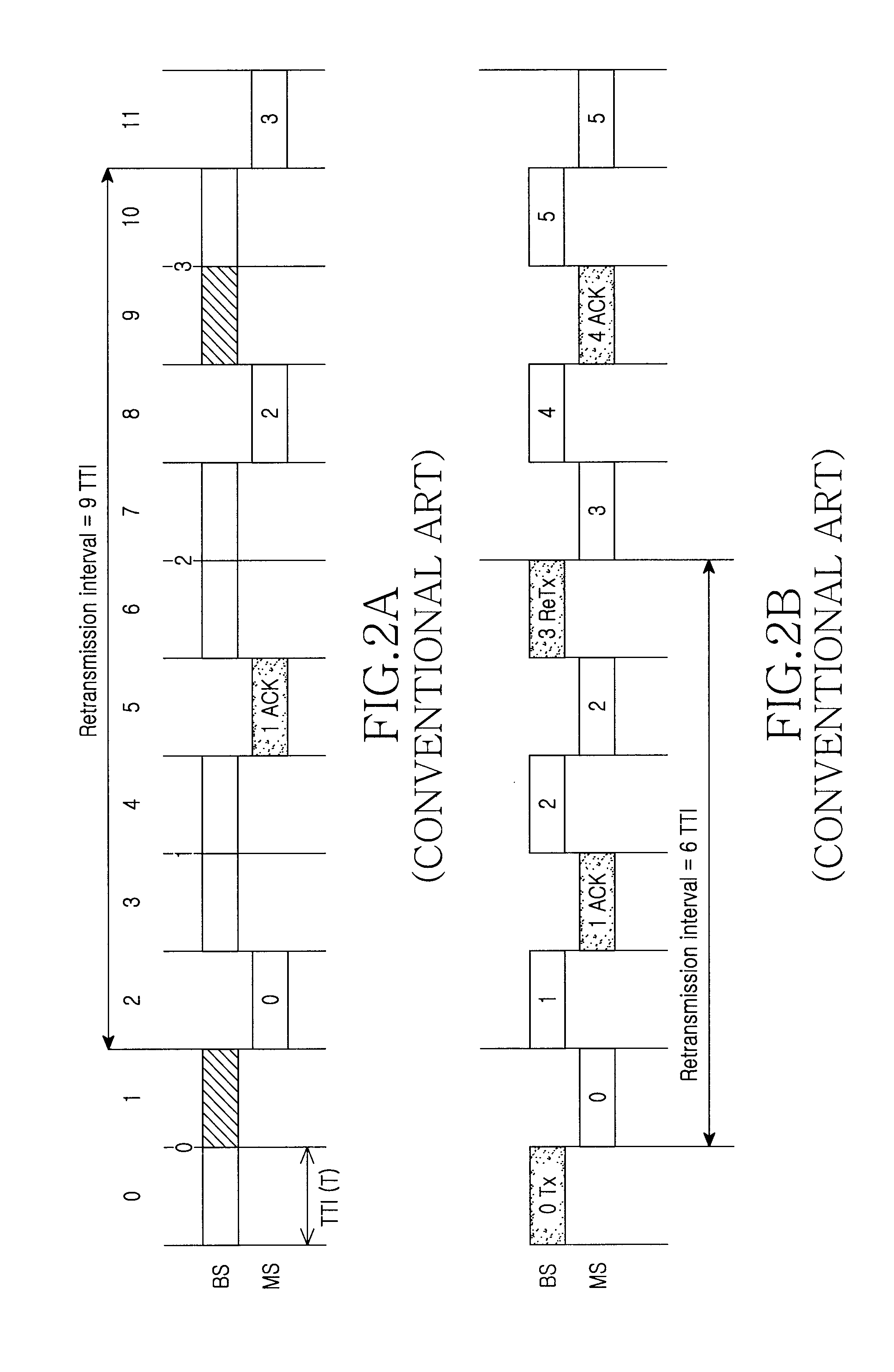
Method for signal transmission/reception based on HARQ scheme in wireless mobile communication system
ActiveUS20090181689A1Smoothly determiningSmoothly maximizingError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementSuperframeTransmitter
A method of signal transmission / reception by a transmitter in a wireless mobile communication system is provided. The method includes determining a signal transmission / reception corresponding relation between a downlink and an uplink of the wireless mobile communication system using a super-frame, the super-frame including at least one frame, said at least one frame including at least one downlink sub-frame and at least one uplink sub-frame, the signal transmission / reception corresponding relation enabling each sub-frame within a link including fewer sub-frames to correspond to at least one sub-frame within a link including more sub-frames when the downlink and the uplink of the wireless mobile communication system include different numbers of sub-frames, wherein the signal transmission / reception corresponding relation is also determined when the downlink and the uplink of the wireless mobile communication system include a same number of sub-frames, and transmitting and receiving signals to and from a receiver through at least one downlink sub-frame and at least one uplink sub-frame according to the determined signal transmission / reception corresponding relation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and System for Wireless Communication in Multiple Operating Environments
InactiveUS20130028150A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsStructure of Management Information
A wireless communication method and system are provided. A first wireless communication numerology, e.g., OFDM operating parameters, corresponding to a first operational mode is established. A second wireless communication numerology corresponding to a second operational mode is also established. The first wireless communication numerology is different than the second wireless communication numerology. One of the first operational mode and the second operational mode is selected. One of the first wireless communication numerology and the second wireless communication numerology corresponding to the selected operational mode is used in which communication in the first operational mode and the second operational mode use substantially similar synchronization channels. The present invention also uses the same superframe structure for the first and second operational modes for Ultra-Mobile Broadband (“UMB”) networks and the same frame structure for the first and second operational modes for Long Term Evolution (“LTE”) networks.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
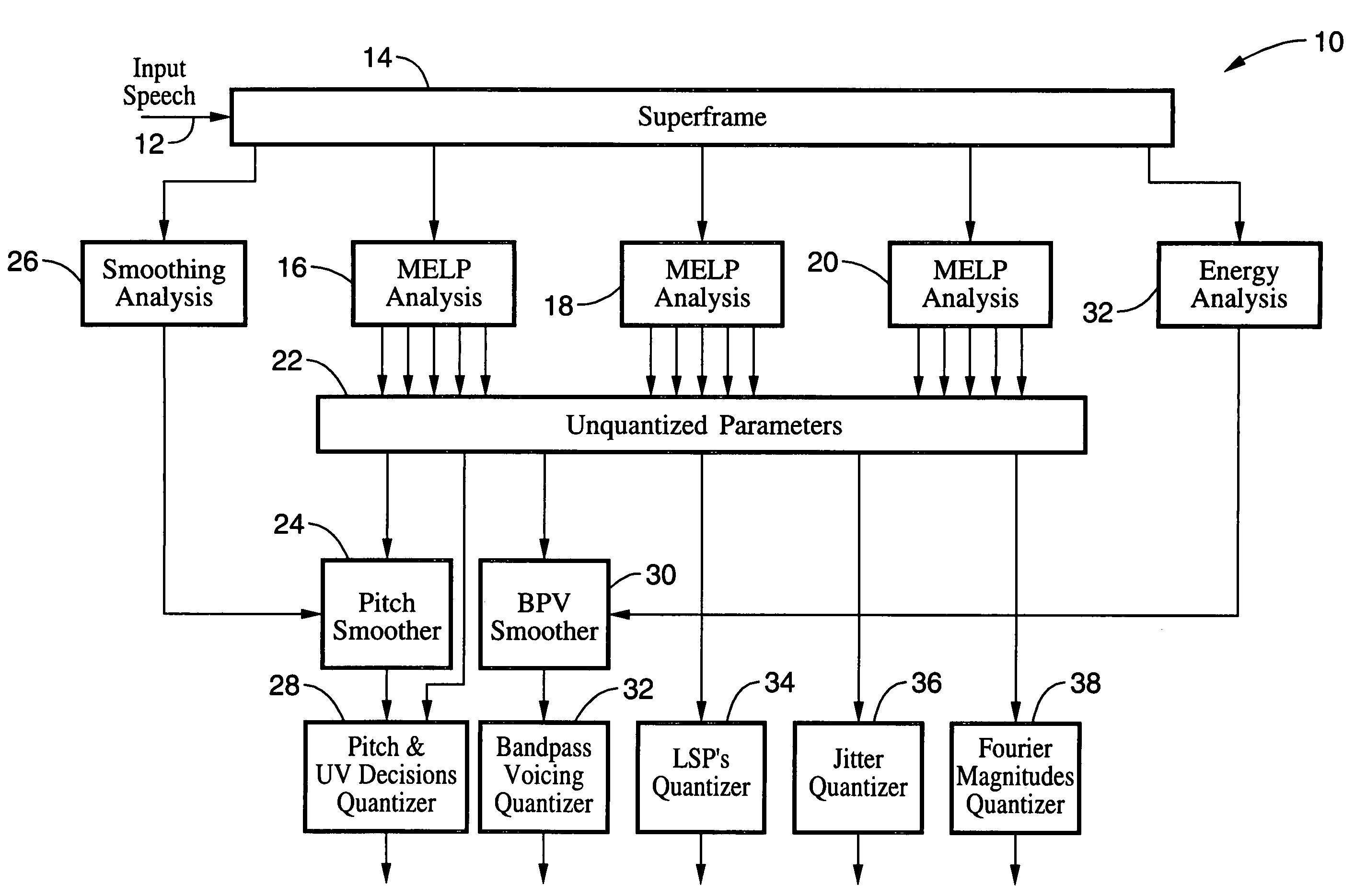
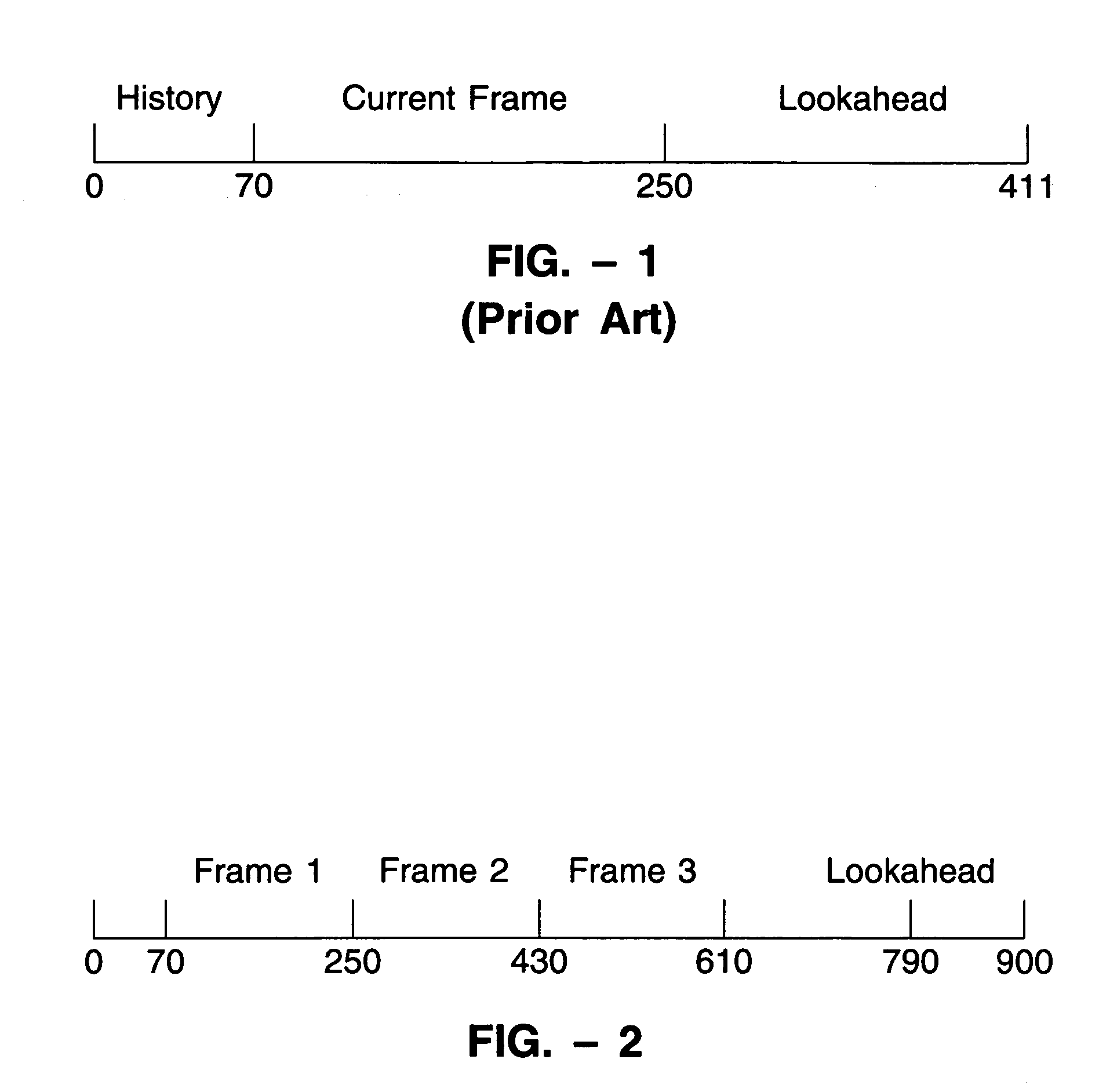
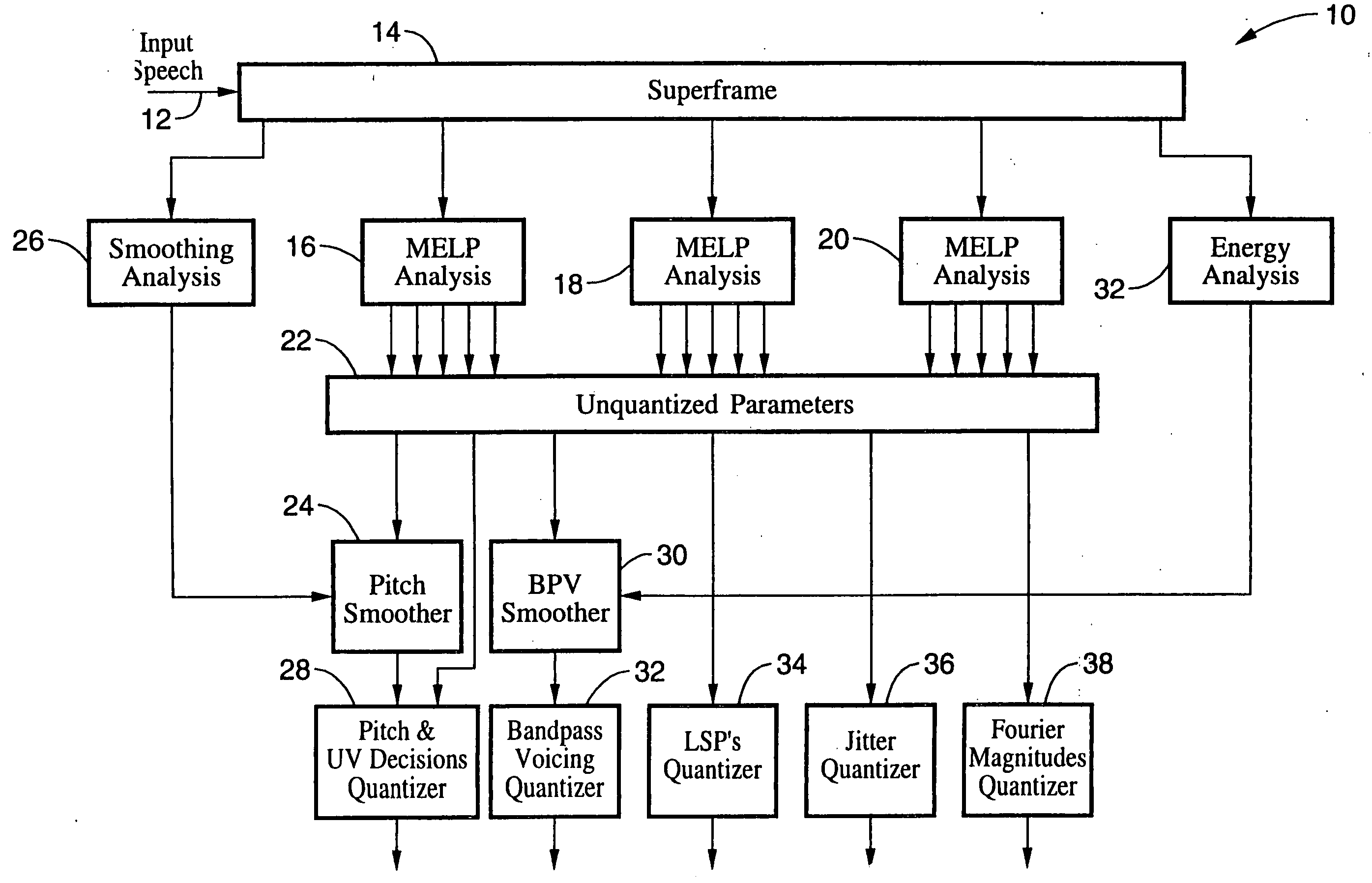
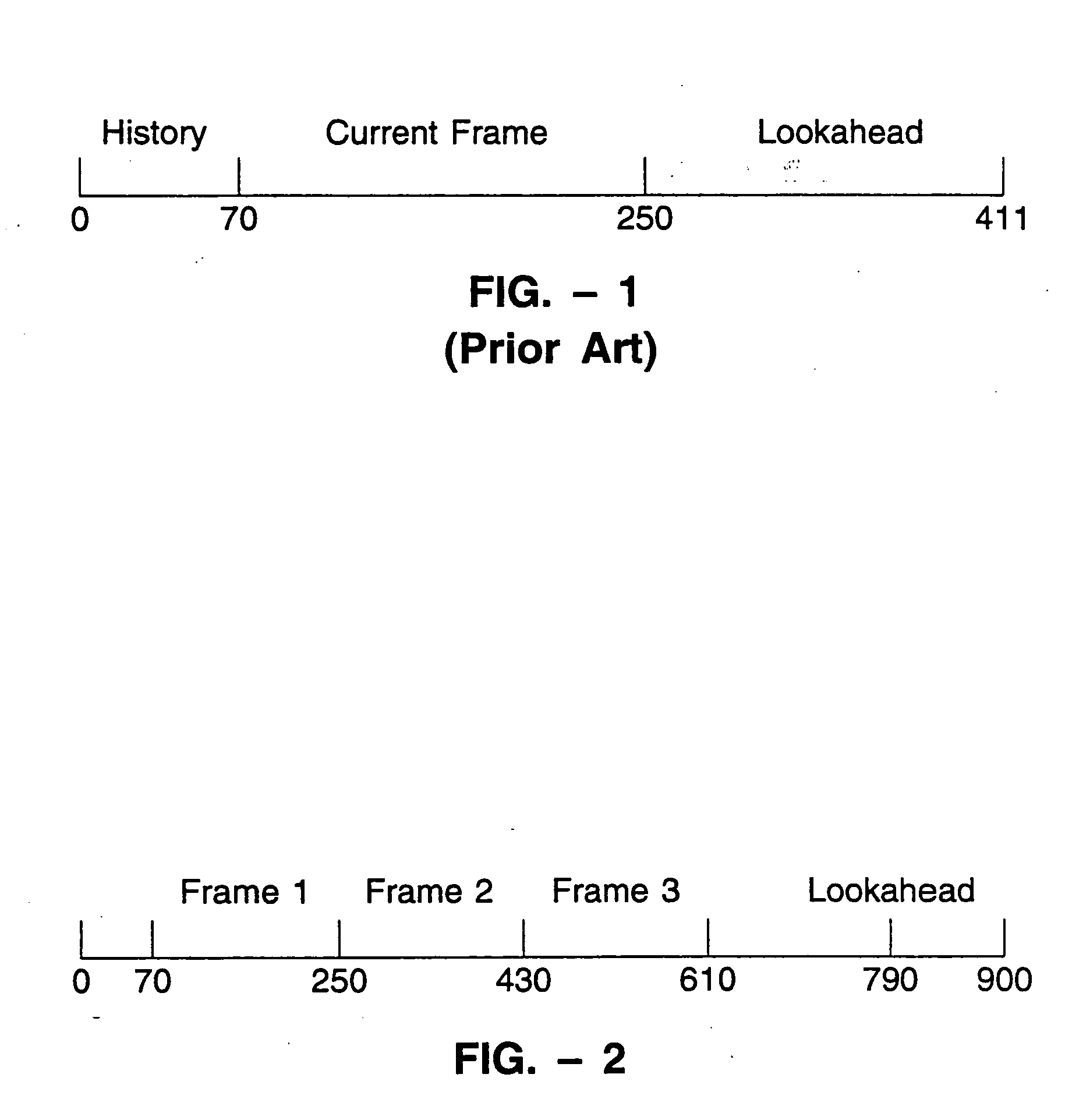
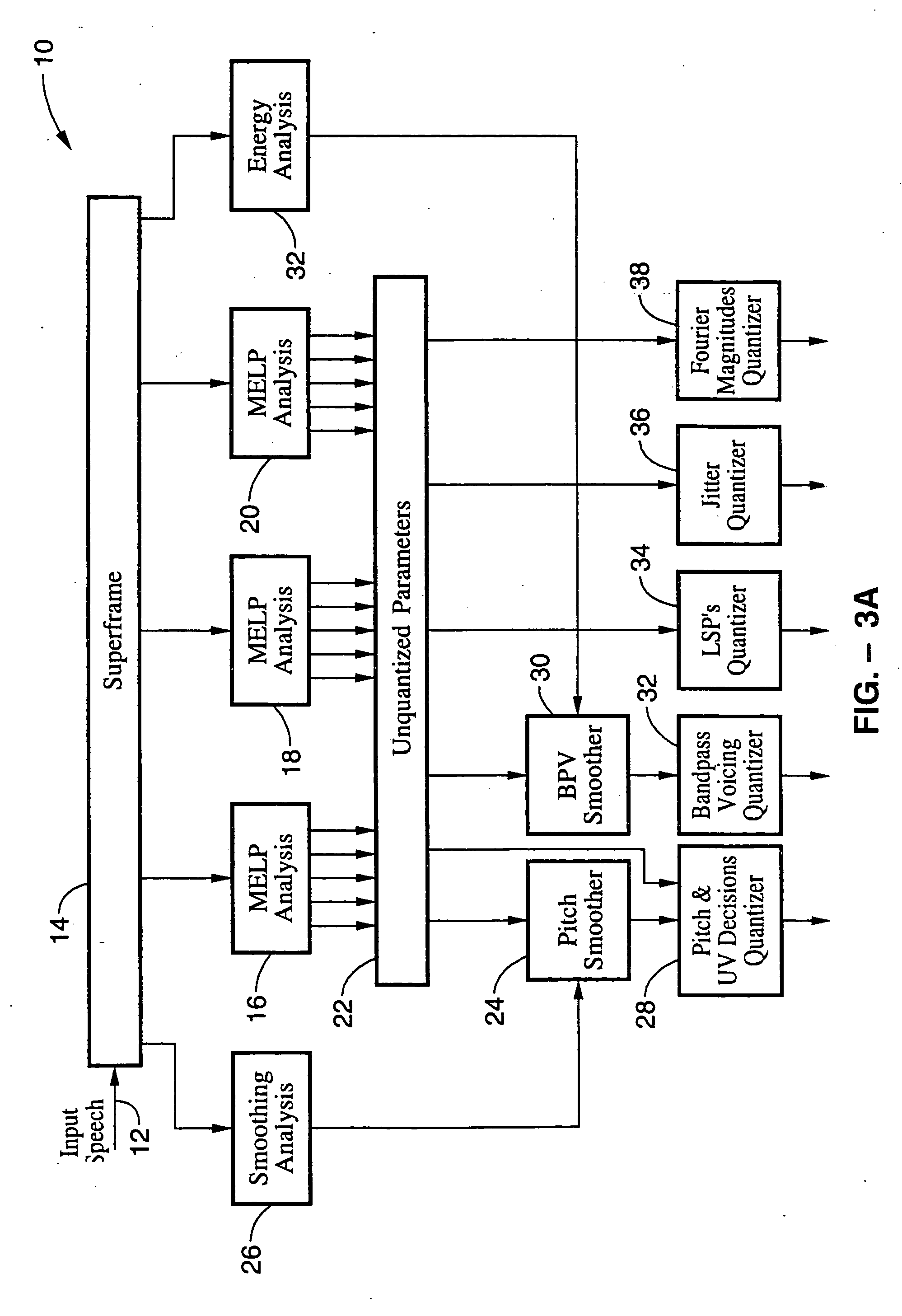
LPC-harmonic vocoder with superframe structure
An enhanced low-bit rate parametric voice coder that groups a number of frames from an underlying frame-based vocoder, such as MELP, into a superframe structure. Parameters are extracted from the group of underlying frames and quantized into the superframe which allows the bit rate of the underlying coding to be reduced without increasing the distortion. The speech data coded in the superframe structure can then be directly synthesized to speech or may be transcoded to a format so that an underlying frame-based vocoder performs the synthesis. The superframe structure includes additional error detection and correction data to reduce the distortion caused by the communication of bit errors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Access point for providing WLAN virtualization, WLAN virtualization system and method of providing access to wireless communication network
ActiveUS20110013608A1Guaranteed independenceImprove throughputNetwork topologiesLoop networksVirtualizationService provision
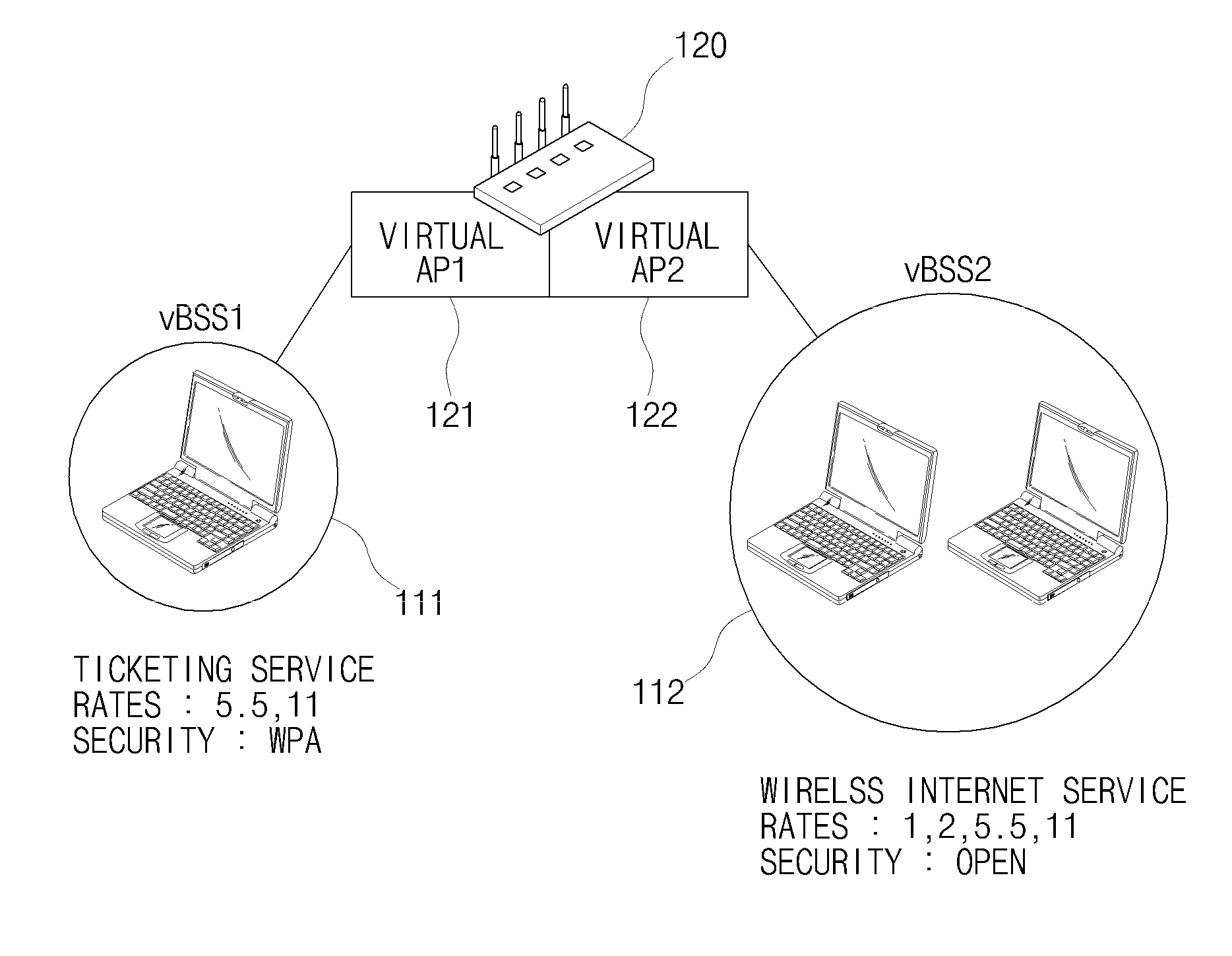
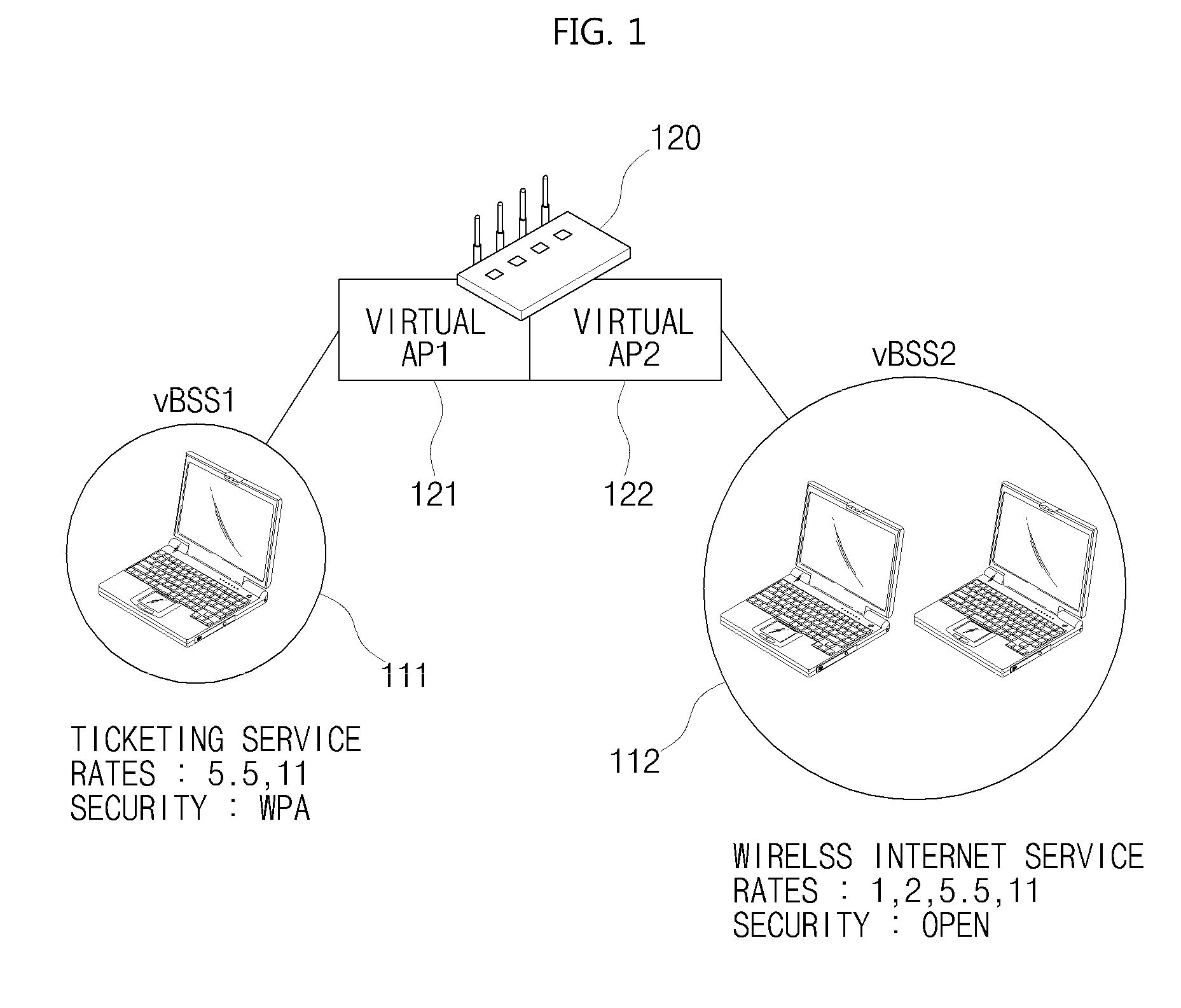
The present invention relates to a WLAN virtualization system which is capable of efficiently separating a Basic Service Set (BSS) into a plurality of virtual BSSs in a Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) manner. The WLAN virtualization system includes an Access Point (AP) for providing a plurality of vBSSs, and a plurality of stations corresponding to the vBSSs provided by the AP. Each of the vBSSs is operated on a superframe basis, the superframe being scheduled by a beacon frame transmitted from the AP. The superframe includes the beacon frame, one contention-free period, and one contention period. The CPs of the vBSSs include intervals which do not overlap each other. The vBSSs can be classified into any groups designated by a service provider based on certain criteria such as physical layer, QoS, security level, or network access authority, and times can be allocated to superframes at different rates or frequencies.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Digital broadcast receiver capacity signalling metadata
ActiveUS20090203326A1Broadcast with distributionSpecific information broadcast systemsTelecommunicationsPhysical layer
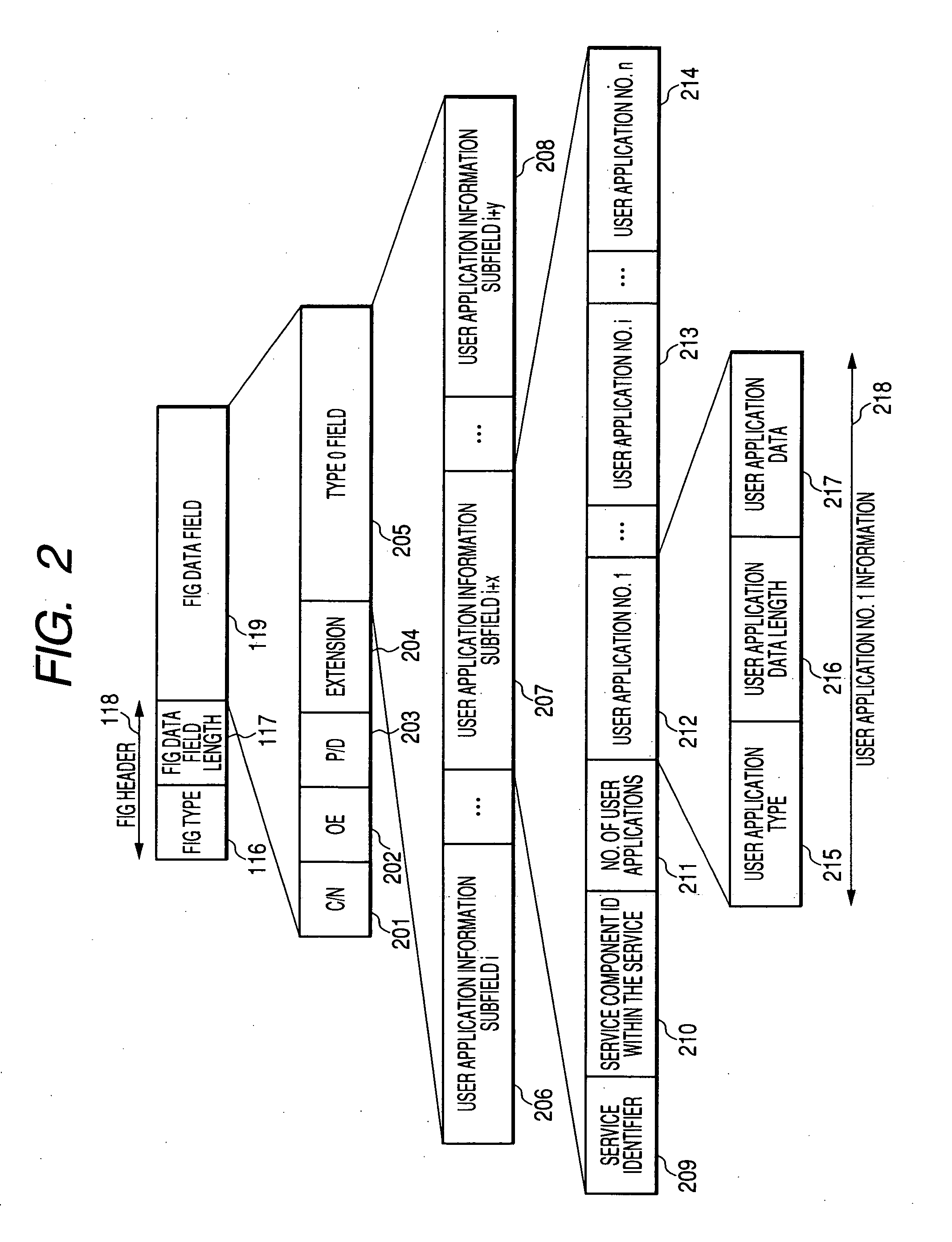
Embodiments are directed to transmitting receiver-capacity-signalling data that specifies a plurality of receiver capacities to be used for receiving a service. The signalled receiver capacities may include: a type of time interleaver being used and a minimum burst interval between two consequent bursts. The signaled receiver capacities may also specify: how often a physical layer pipe appears in frames, and / or a number of a frame in which a physical layer pipe appears for a first time during a super frame. Embodiments are directed to receiving the receiver-capacity-signalling data and if, based on the received receiver-capacity-signalling data, receiver capacity is sufficient for one or more selected services, performing service discovery and decoding the one or more services. Otherwise, decoding the one or more services may not be performed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hybrid Multiple Access Method and System in Wireless Networks with extended Content Free Access Period
ActiveUS20090238160A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementFree accessWireless mesh network
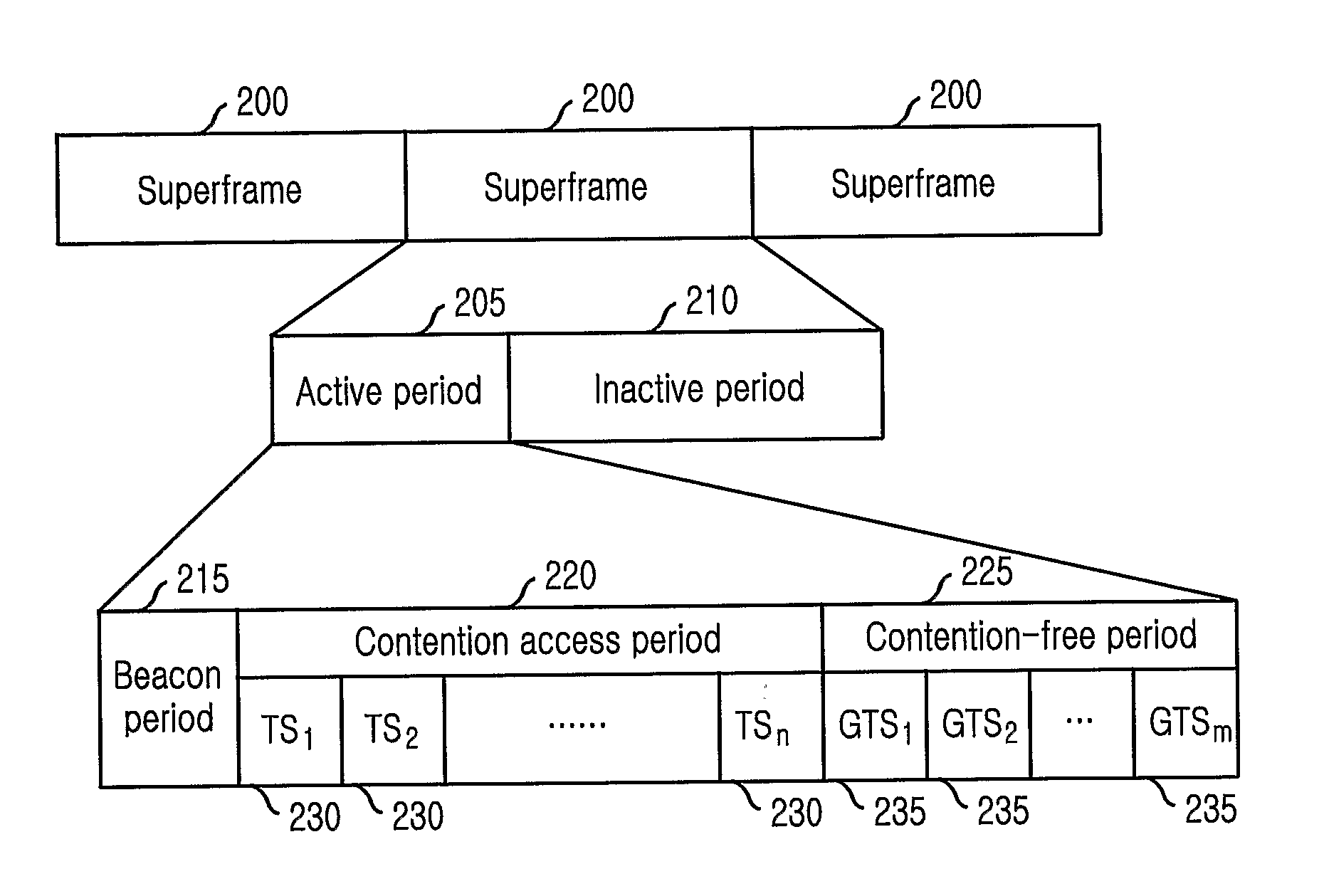
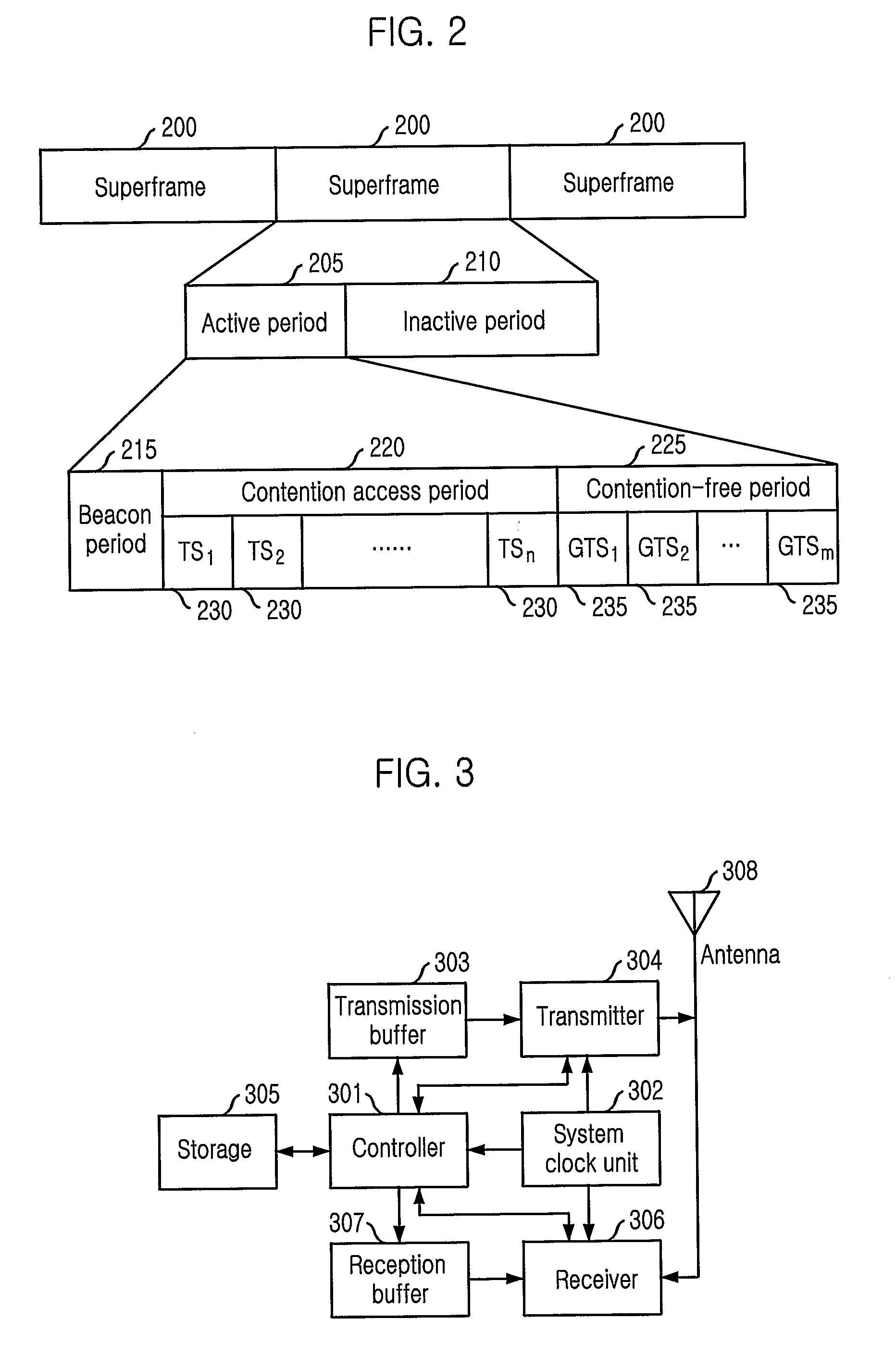
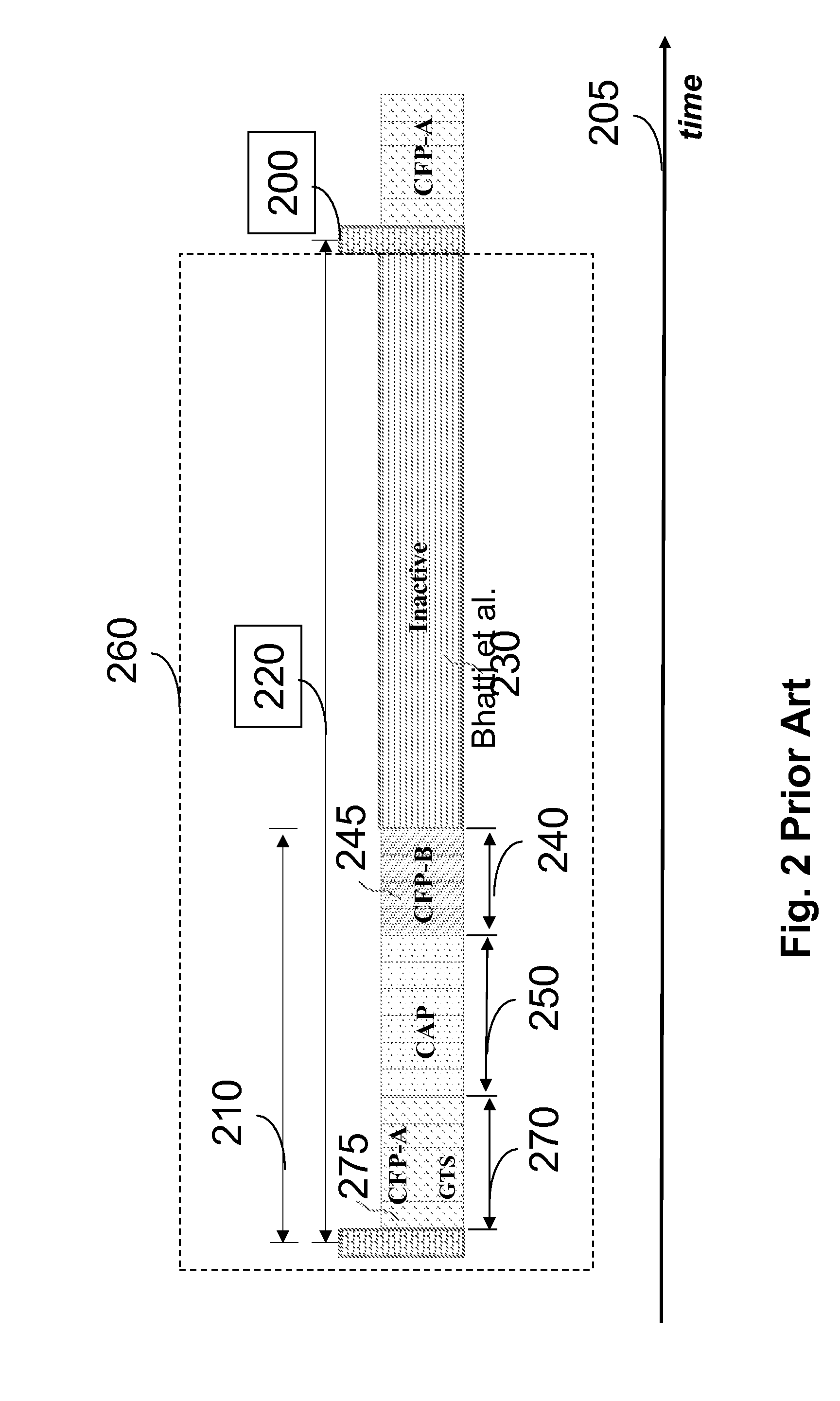
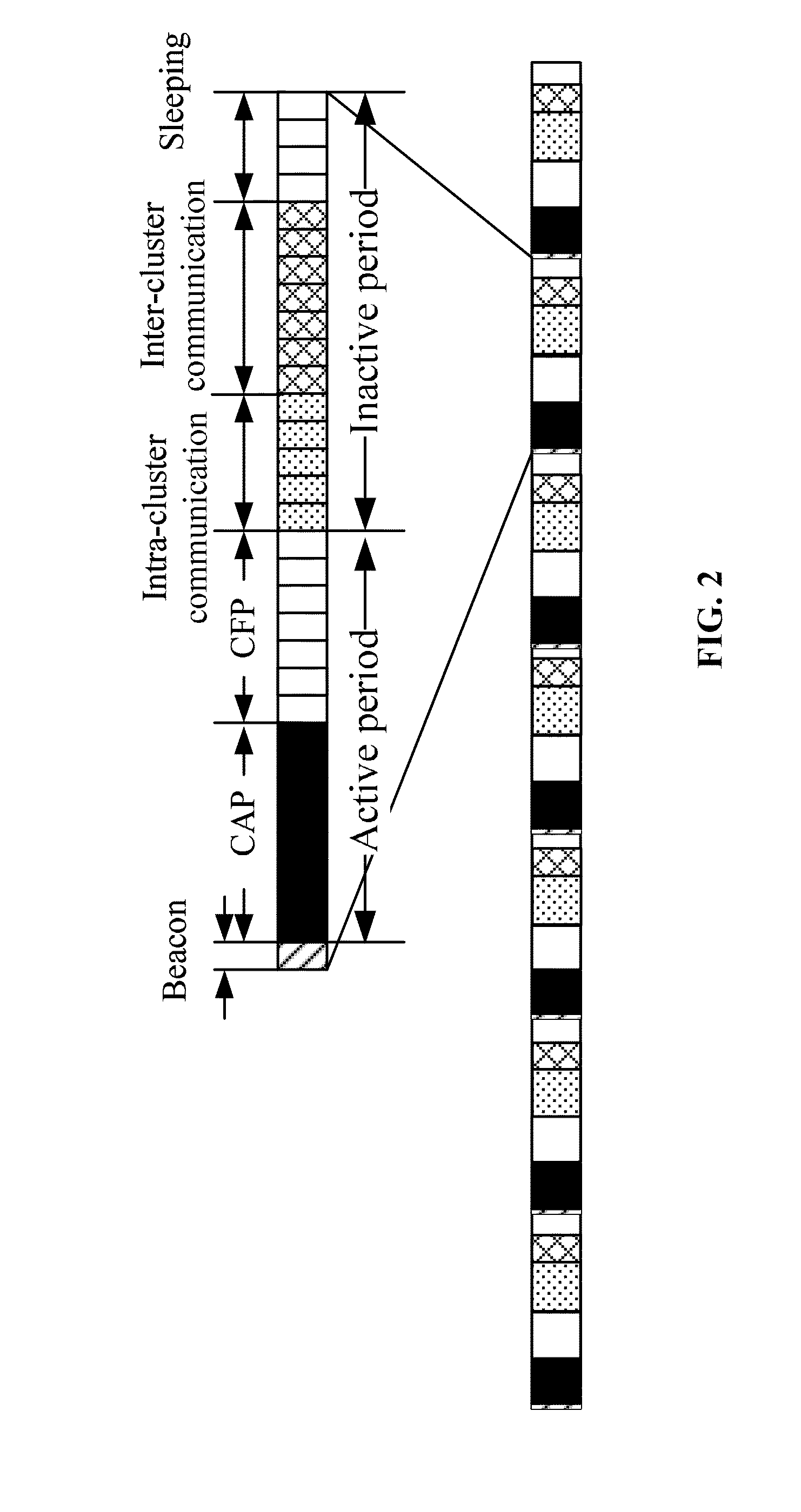
A method for communicating in a network including a coordinator node and a set of leaf nodes transmits periodically, from the coordinator node to the set of leaf nodes, a beacon defining a superframe, wherein the supper frame includes an active period and an inactive period, and wherein the active period includes a first contention access period (CAP-1), a first contention free period (CFP-1), a first group acknowledgement (GACK-1), a second CFP-2, a second GACK-2, and a second CAP-2, and wherein each CFP includes a guaranteed time slot (GTS) assigned to each leaf node. Then, each leaf node transmits to the coordinator node only during the GTS assigned to the leaf node during each CFP.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Communication method for mesh and star topology structure wireless sensor network
ActiveUS20110310770A1Power managementNetwork topologiesStructure of Management InformationBeacon frame
A method of achieving wireless sensor network (WSN) communication in a mesh and star topology network (MSTN), including: a) connecting a plurality of nodes in a WSN to form a mesh and star hybrid topology structure; b) based on the topology structure, defining a superframe structure based on IEEE 802.15.4-2006; c) based on the topology structure and superframe structure, defining methods for long period data processing, connectivity assessment, medium access control, channel measurement, frequency hopping, beacon frame formation, and two-stage resource allocation; d) based on the topology structure, superframe structure, and methods, defining a method for network establishment; and e) based on the network establishment method, defining a method for MSTN communications. The method features real-time communication, high reliability, and low energy consumption.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
LPC-harmonic vocoder with superframe structure
InactiveUS20050075869A1Efficiently quantizedSimplified descriptionSpeech analysisFrame basedHarmonic
An enhanced_low-bit rate parametric voice coder that groups a number of frames from an underlying frame-based vocoder, such as MELP, into a superframe structure. Parameters are extracted from the group of underlying frames and quantized into the superframe which allows the bit rate of the underlying coding to be reduced without increasing the distortion. The speech data coded in the superframe structure can then be directly synthesized to speech or may be transcoded to a format so that an underlying frame-based vocoder performs the synthesis. The superframe structure includes additional error detection and correction data to reduce the distortion caused by the communication of bit errors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of operating a media access controller
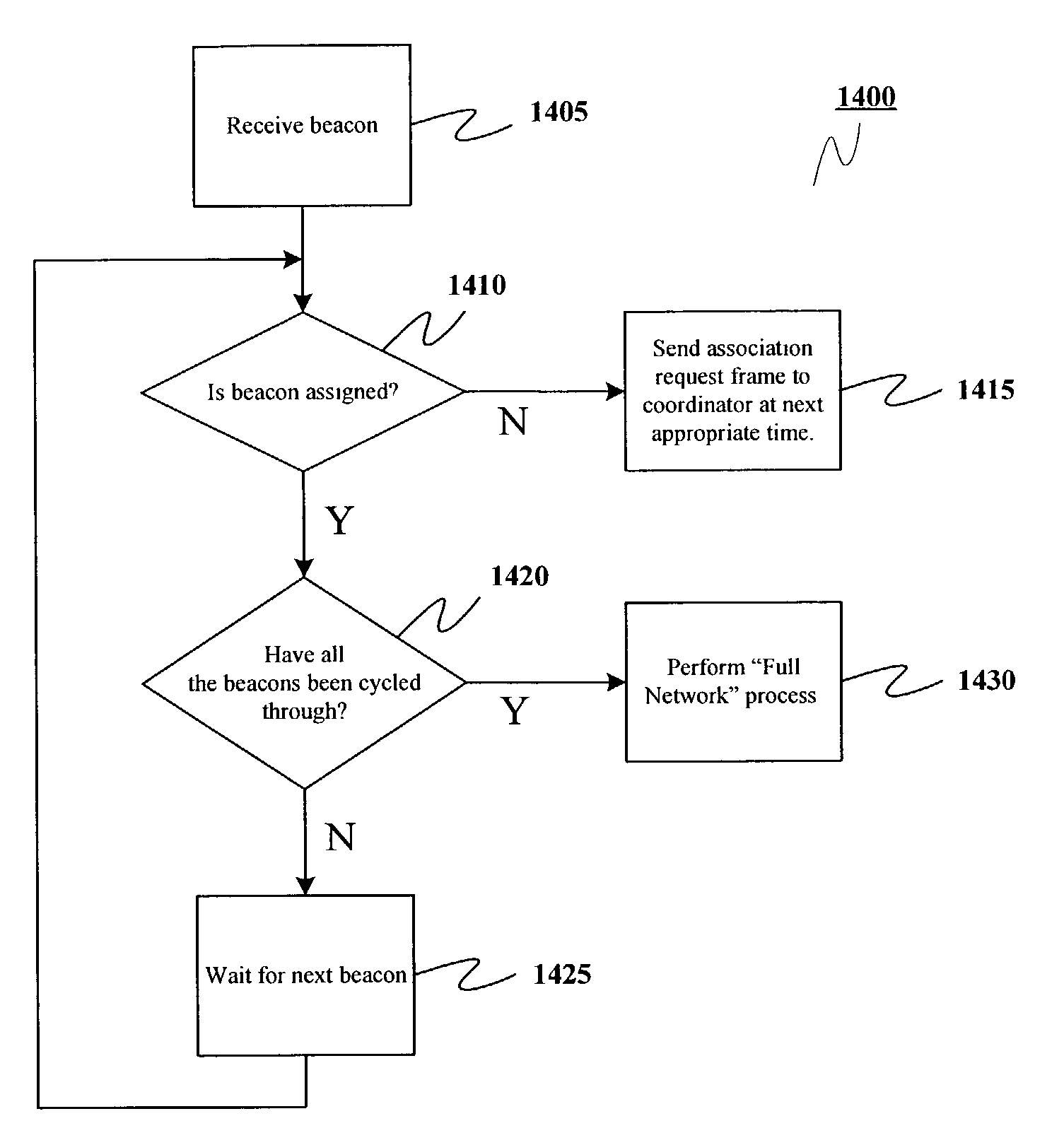
InactiveUS7280518B2Avoid collisionNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexMedia access controllerSuperframe
A method is provided for a remote device to monitor and communicate with a wireless network using cyclic beacons. The remote device receives a beacon, which beacon includes beacon information that defines a superframe. From the beacon information, the remote device determines whether the received beacon and the associated superframe are assigned to a network device or are unassigned. By receiving as many beacons as there are allowable devices in the network, the remote device can determine if the network is full. If the remote device runs through all of the beacons and all indicate that their associated superframes are assigned, then the remote device determines that the network is full and performs a network-full function. If the remote device receives a beacon that indicates that its associated superframe is unassigned, it determines that the network is not full and performs an association request during the unassigned superframe.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Synchronization of media access control (MAC) superframes
ActiveUS20070072636A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexClock rateMedia access control
A device and method for of synchronizing a MAC superframe of a wireless device is disclosed. The wireless device can be located within a chain of a plurality of other wireless devices. The method includes receiving beacons from at least one other device during a superframe of the wireless device, determining a superframe offset for each of the other wireless devices based on timing of the received beacons, determining a corrective delay based on the superframe offsets, inserting the corrective delay within a current superframe of the wireless device, and inserting a predictive delay within the current superframe, the predictive delay being determined by an estimate of a difference between a frequency a clock of the wireless device and a frequency of a slowest clock of the other wireless devices within the chain.
Owner:NOVANTA INC
Time division multiplexed transmission of OFDM symbols
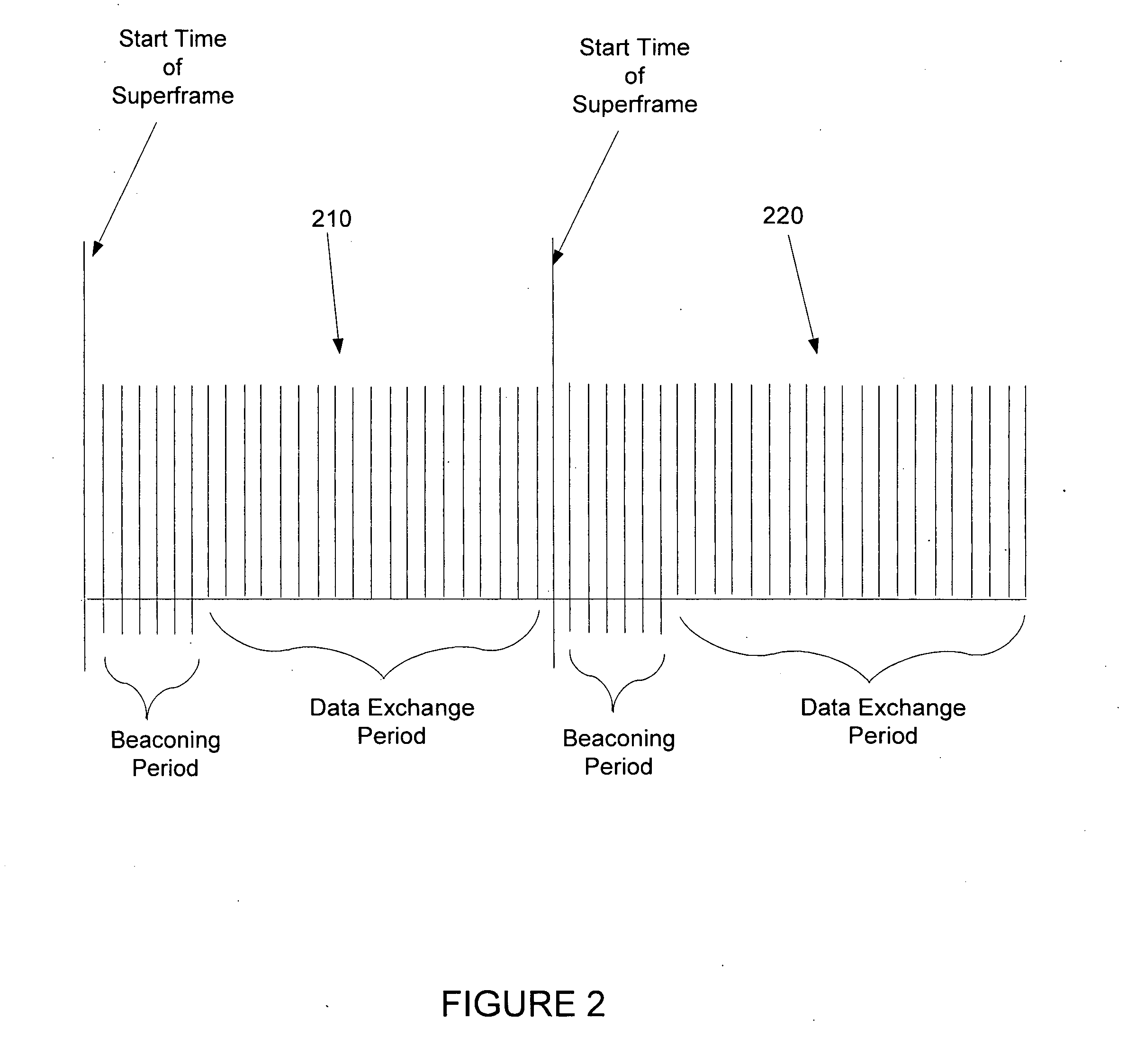
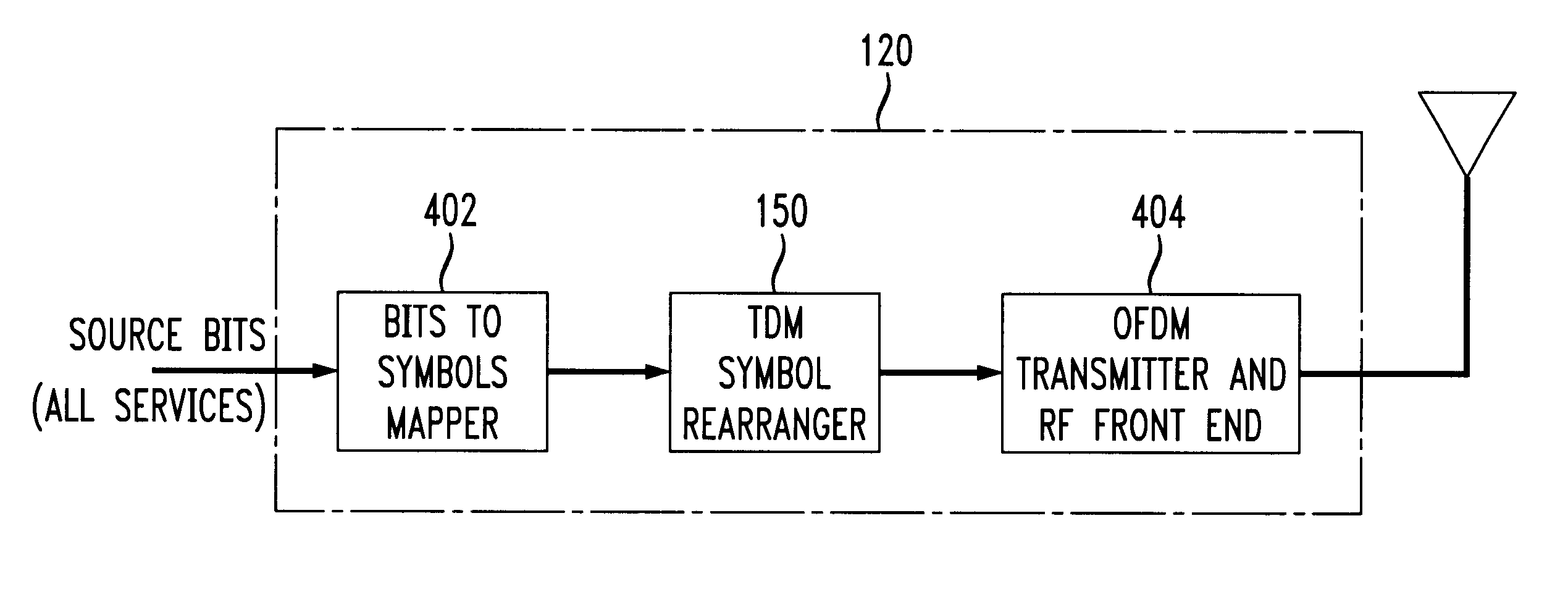
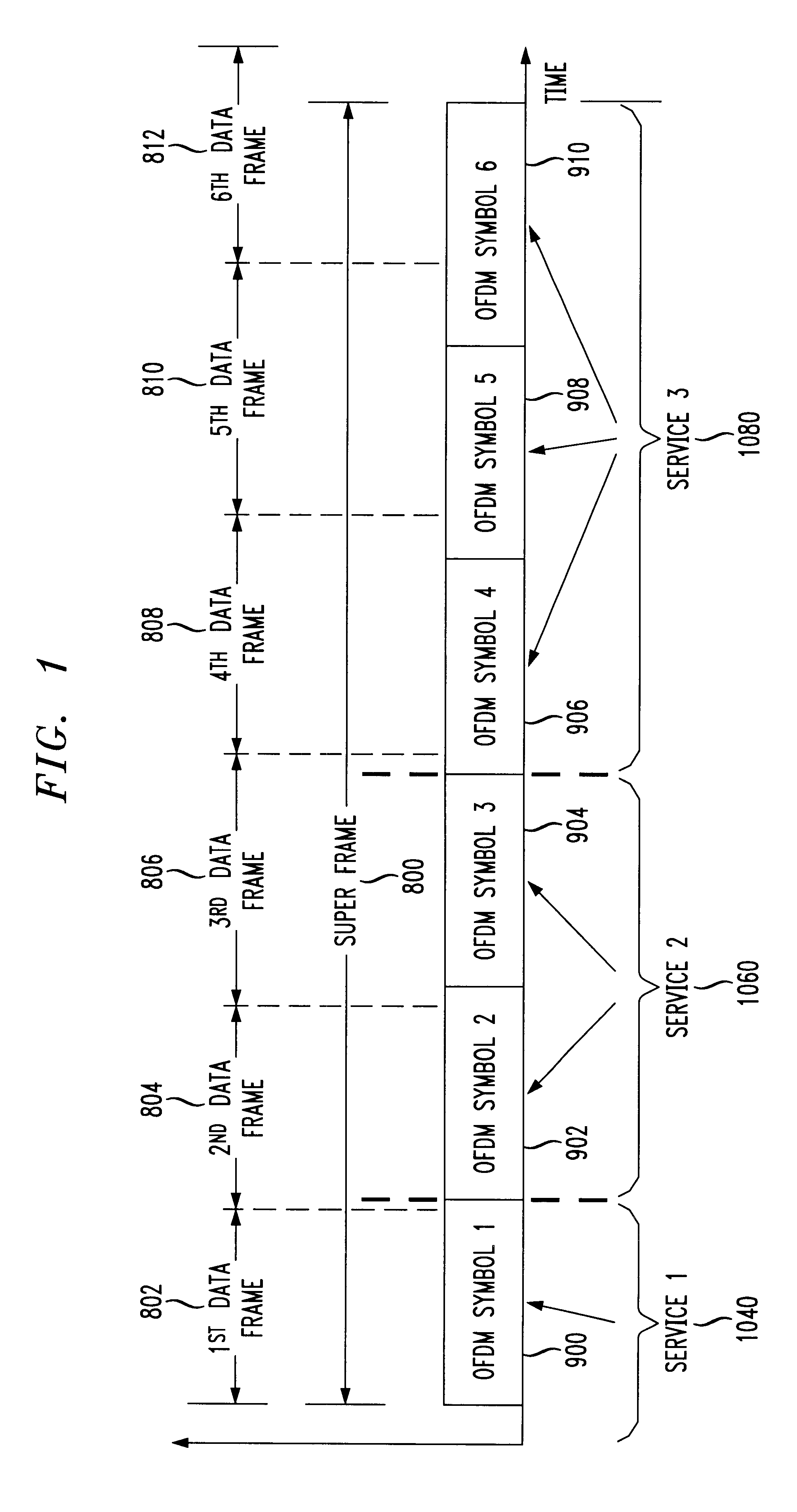
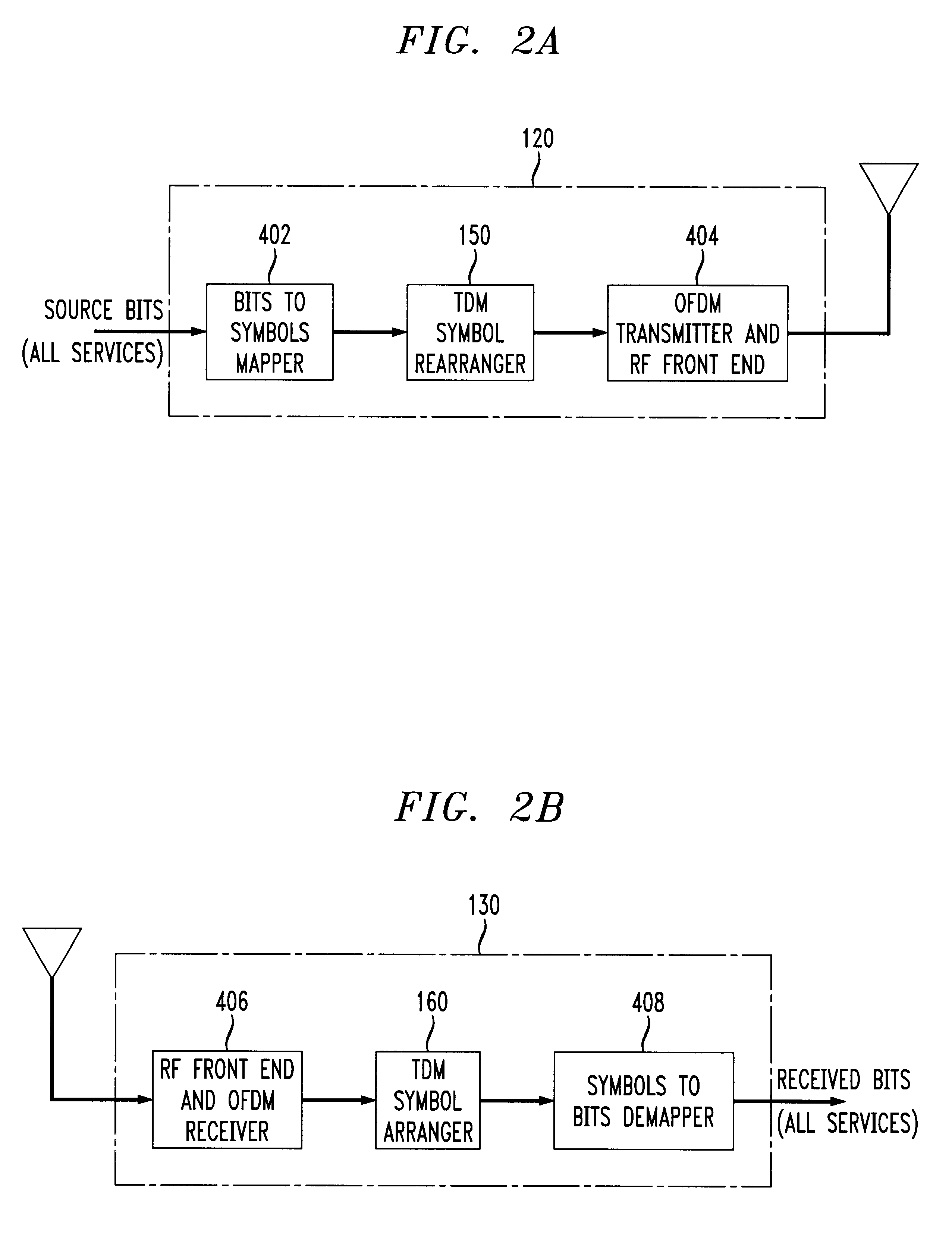
An orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) technique which is time division multiplexed to reduce the overall effect on individual services from conditions such as selective fading. In accordance with the principles of the present invention, all available subcarriers in a channel are assigned to fewer than all of the requesting services, e.g., to just one particular service for a period of time. The period of time is preferably independent of the length of a conventional data frame. Thereafter, a second service is assigned access to the use of all available subcarriers for a period of time corresponding to its required bandwidth, and so on until all requesting services are allotted a portion of time for access to all available subcarriers. Any one service may utilize any number of the available subcarriers in a particular superframe containing one cycle of transmissions for all services.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Apparatus and method for allocating channel time to applications in wireless PAN
InactiveUS20050013267A1Effective distributionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProtocol ApplicationSuperframe
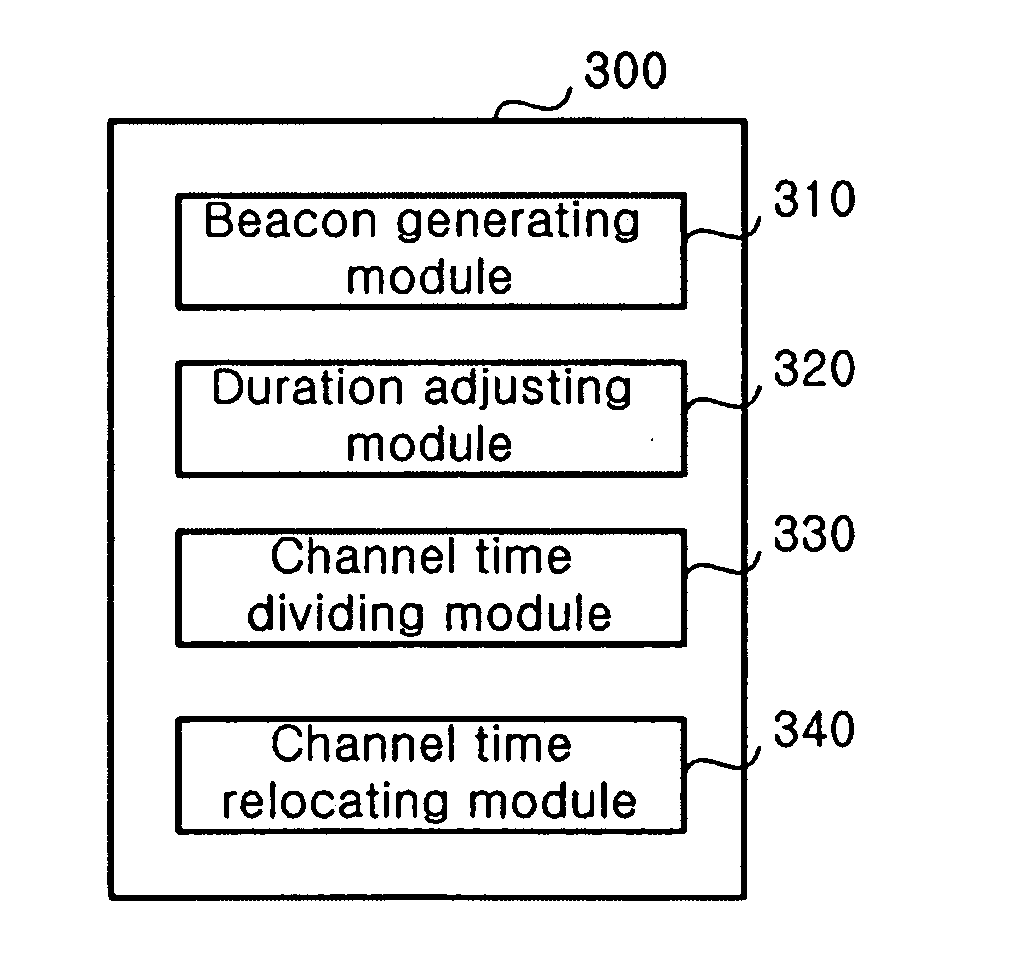
An apparatus and method for allocating channel time for each application in a single superframe when applications such as wireless USB and IEEE 802.2, which are implemented in a MAC layer, coexist on a wireless PAN. The apparatus includes a beacon generating module for generating a superframe; a duration adjusting module for adjusting a duration of the superframe to be a multiple of a frame of an upper application layer of a device; a channel time dividing module for comparing an allowable size of maximum CTA in the frame of the upper application layer of the device with a size of isochronous CTA of another device and dividing the CTA, if necessary; and a channel time relocating module for comparing a super-rate of CTA previously located in the superframe with a super-rate of CTA to be newly added and relocating the newly added CTA.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low-power autonomous node for mesh communication network
ActiveUS7529217B2Easy to useMinimal expenditure of powerPower managementEnergy efficient ICTPacket communicationFrequency spectrum
In a packet communication network, a method and apparatus for packet switched transport is provided among intelligent nodes wherein the duty cycling of the intelligent nodes is minimized in order to maximize power life using a synchronization algorithm that assures all nodes are able to propagate information through the network without undue use of transmission and reception power. Frequency hopping time-division multiple access supports packet communication between intelligent nodes via assigned directed links, each link being assigned to a time-channel offset (cell) in a superframe, so that a link carrying a packet string between any two intelligent nodes is active only during its assigned time slot. The result is efficient use of spectrum and minimal expenditure of power.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
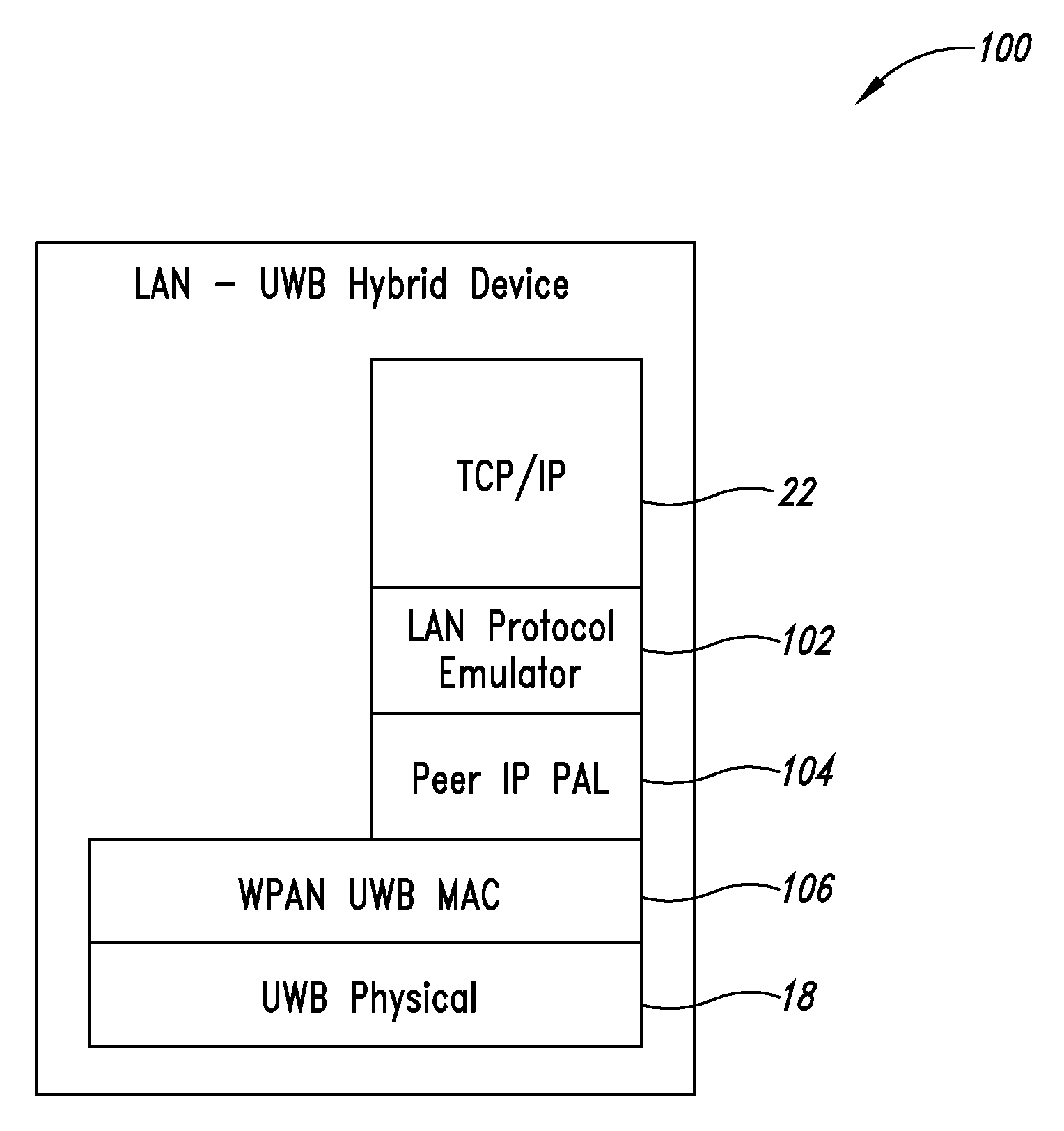
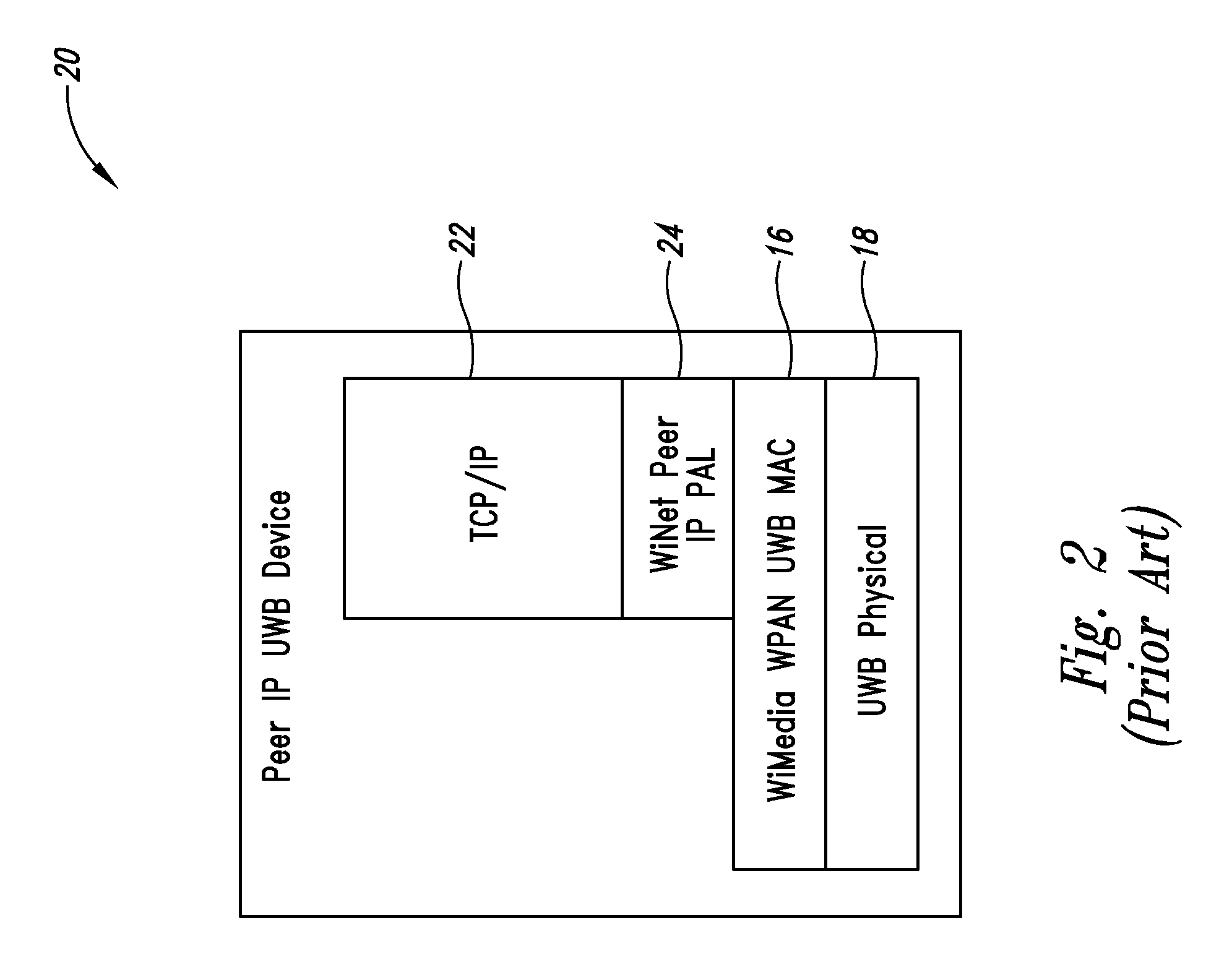
LAN by ultra-wideband system and method
An ultra-wideband (UWB) system and method provide a local area network (LAN) and / or LAN access. LAN access versions of the UWB system includes an emulator layer and bridge that allow data to be transmitted between a LAN-UWB hybrid device and a LAN network switch, such as an IEEE 802 network switch, through in part a UWB node of a UWB WPAN that can receive UWB super-frames from the LAN-UWB hybrid device. In some implementations the LAN-UWB hybrid device uses WiFi protocol layers above the emulator layer and a WiNet Peer IP PAL layer below the emulator layer.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC +1
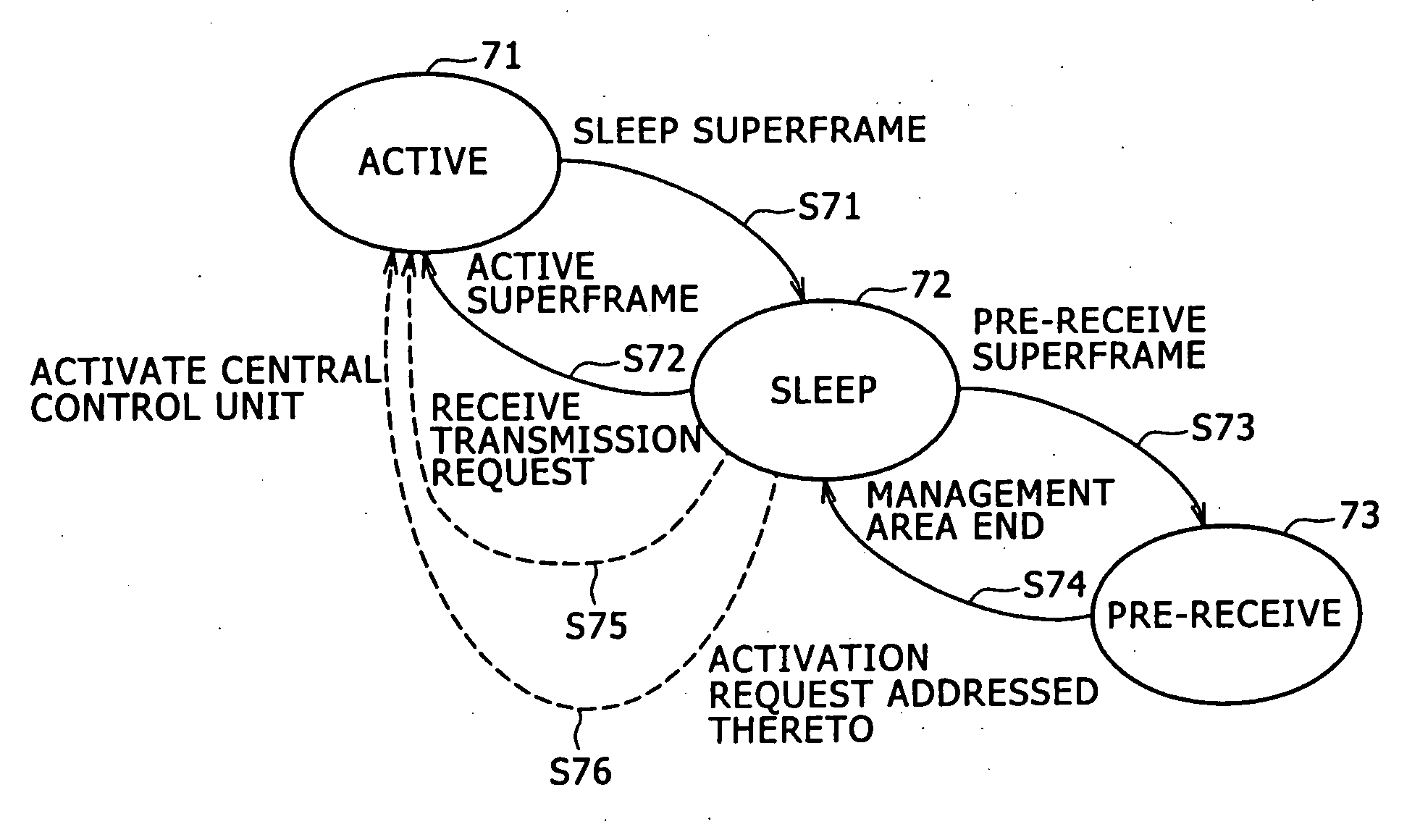
Wireless communication system and wireless communication apparatus
ActiveUS20070053315A1Efficient networkingEasy to operatePower managementAssess restrictionCommunications systemSleep state
A wireless communication system includes plural wireless communication apparatuses which form an ad-hoc network. In the system, an operating state of each superframe of each wireless communication apparatus is determined from three operating states: an active state in which beacon signal transmission / reception and data transmission / reception are performed as necessary; a sleep state in which beacon signal transmission / reception and data transmission / reception are not performed; and a pre-receive state in which a beacon signal is received and afterward beacon signal transmission and data transmission are not performed.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com