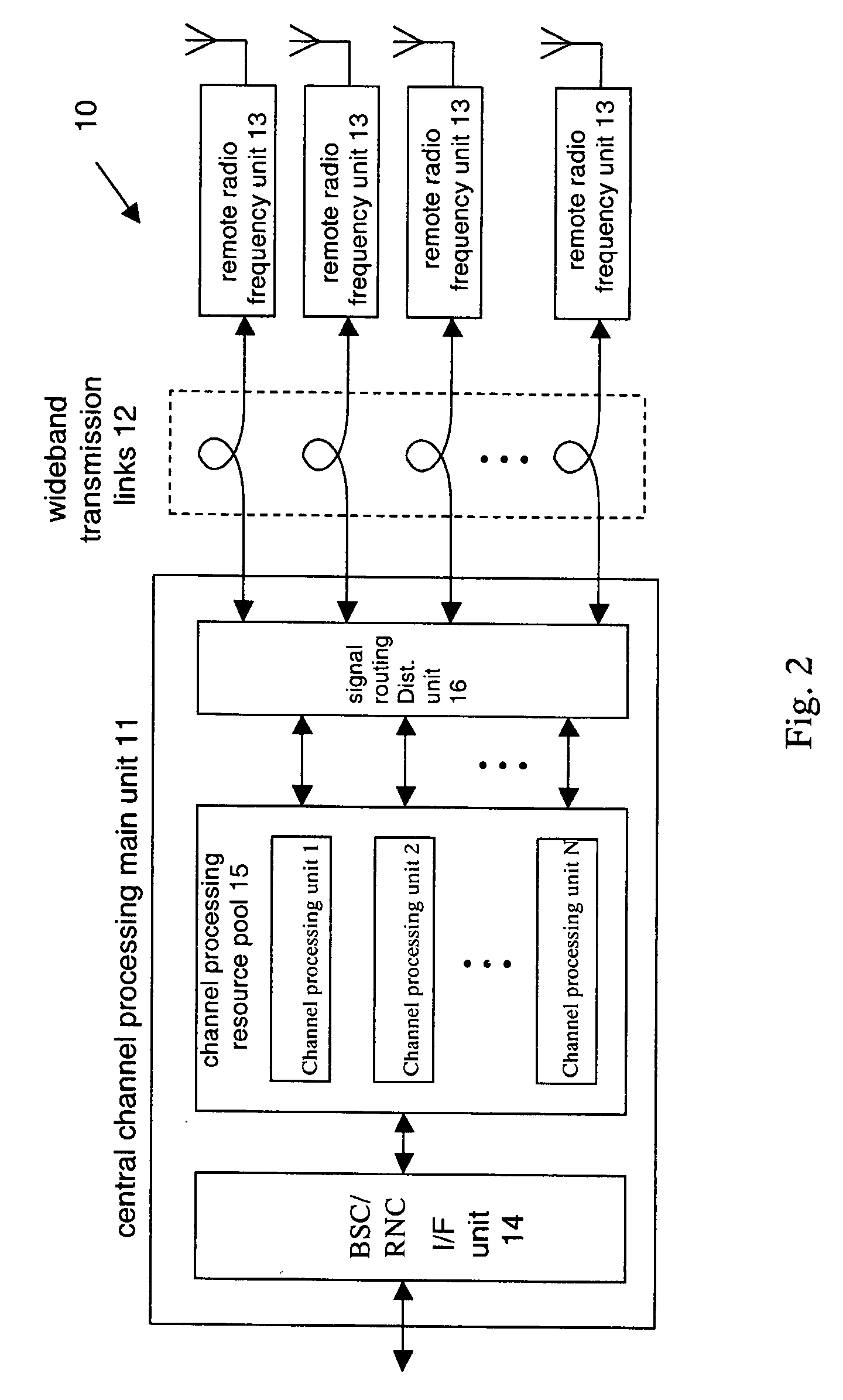
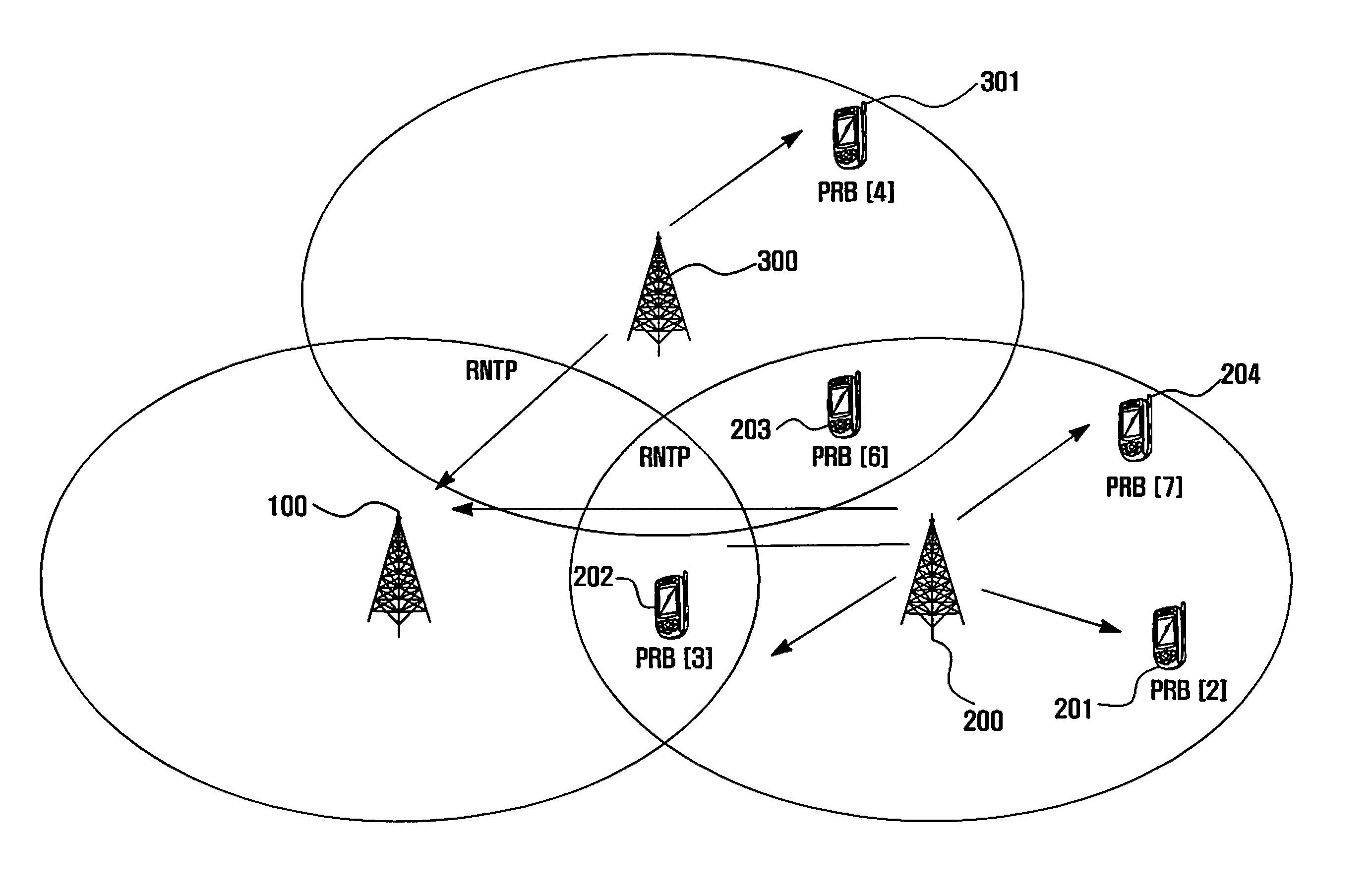
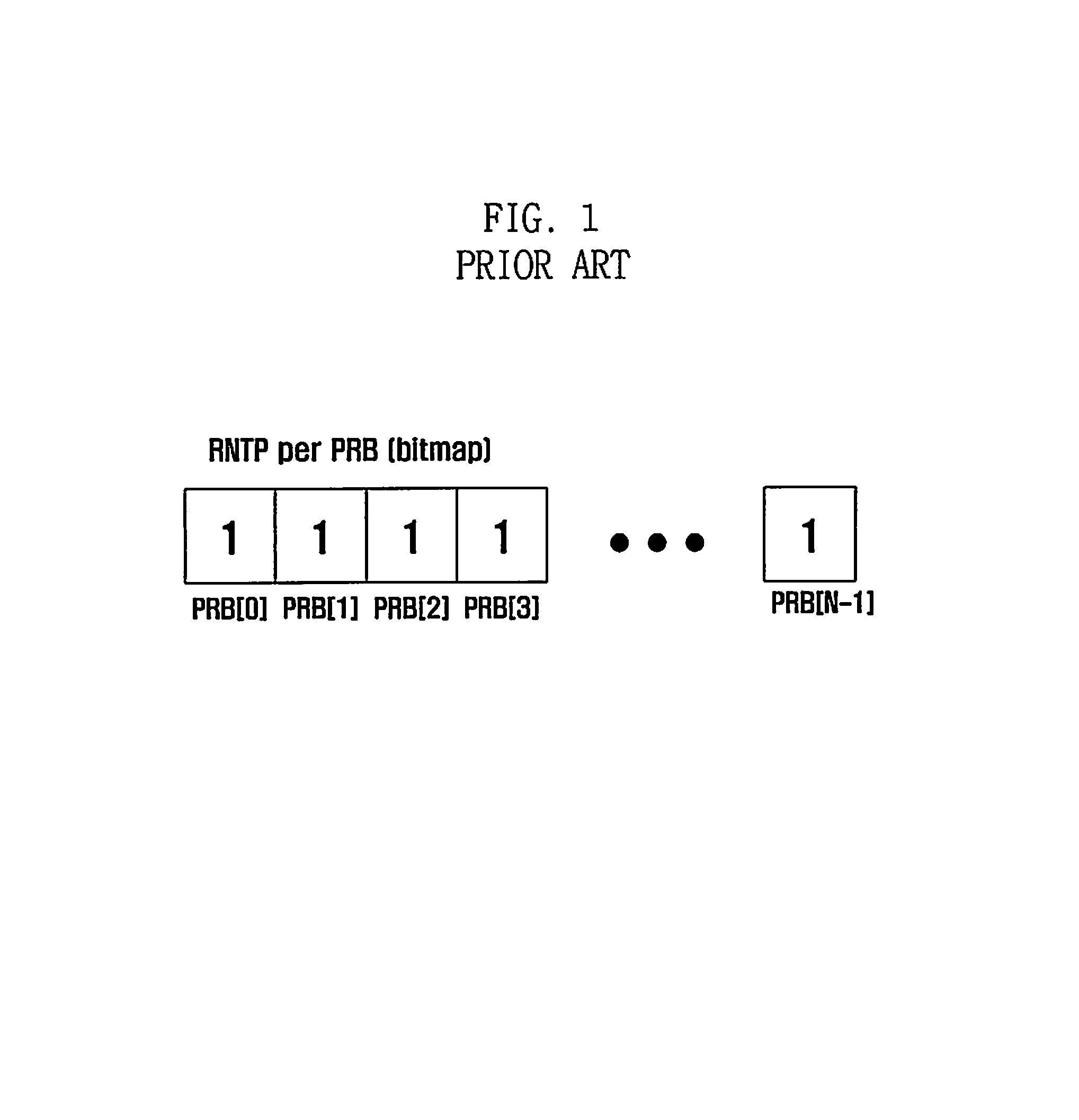
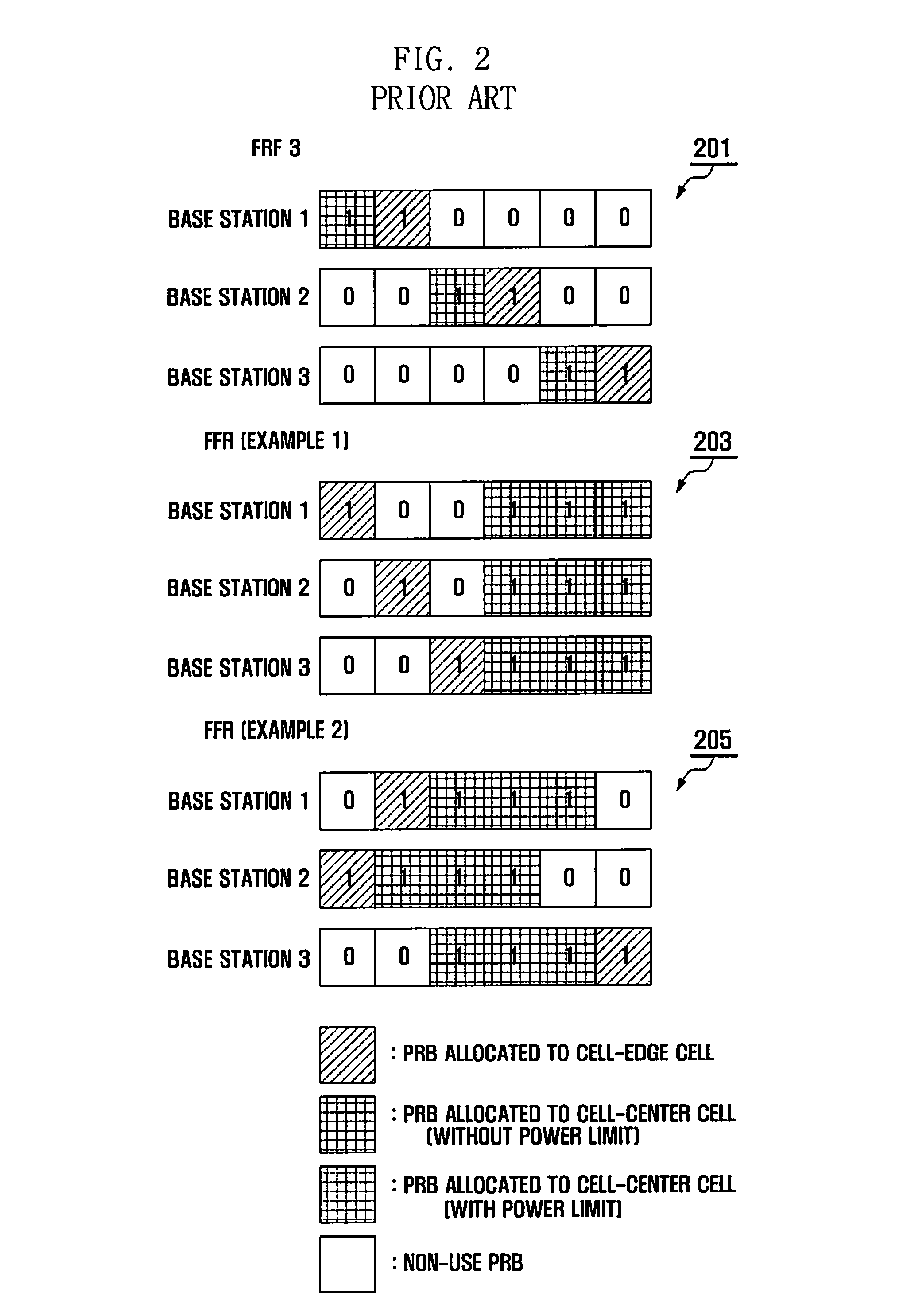
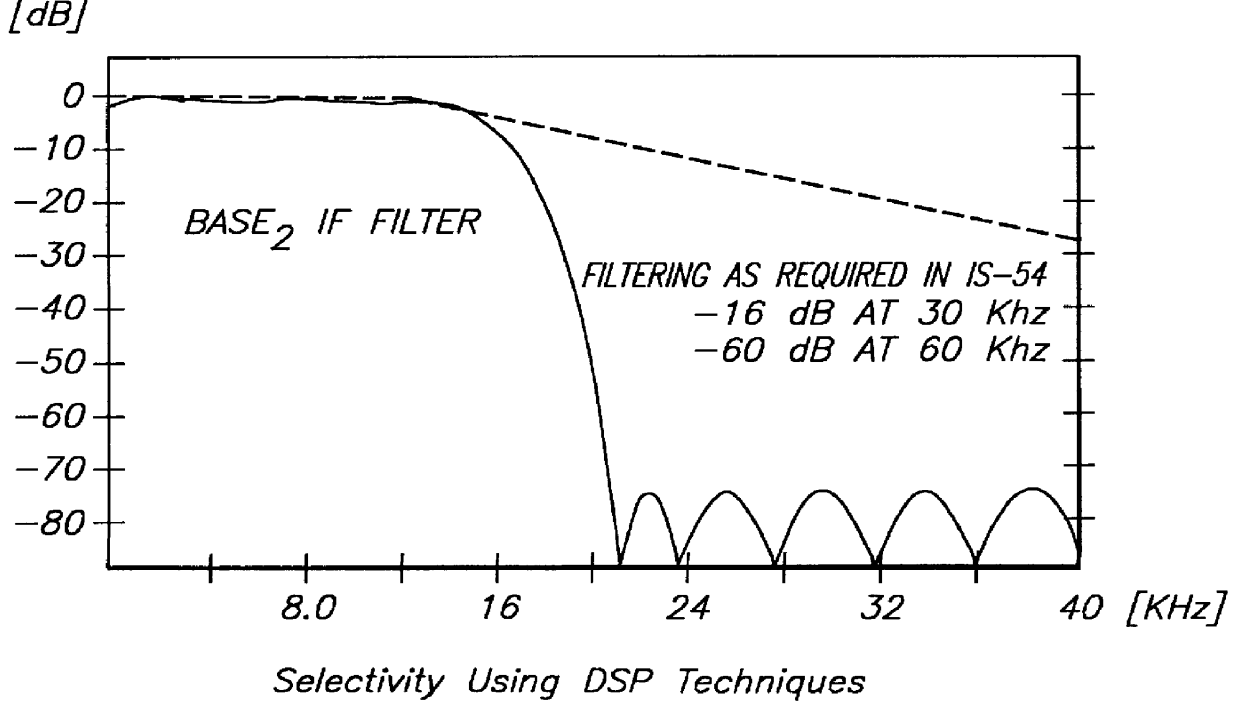
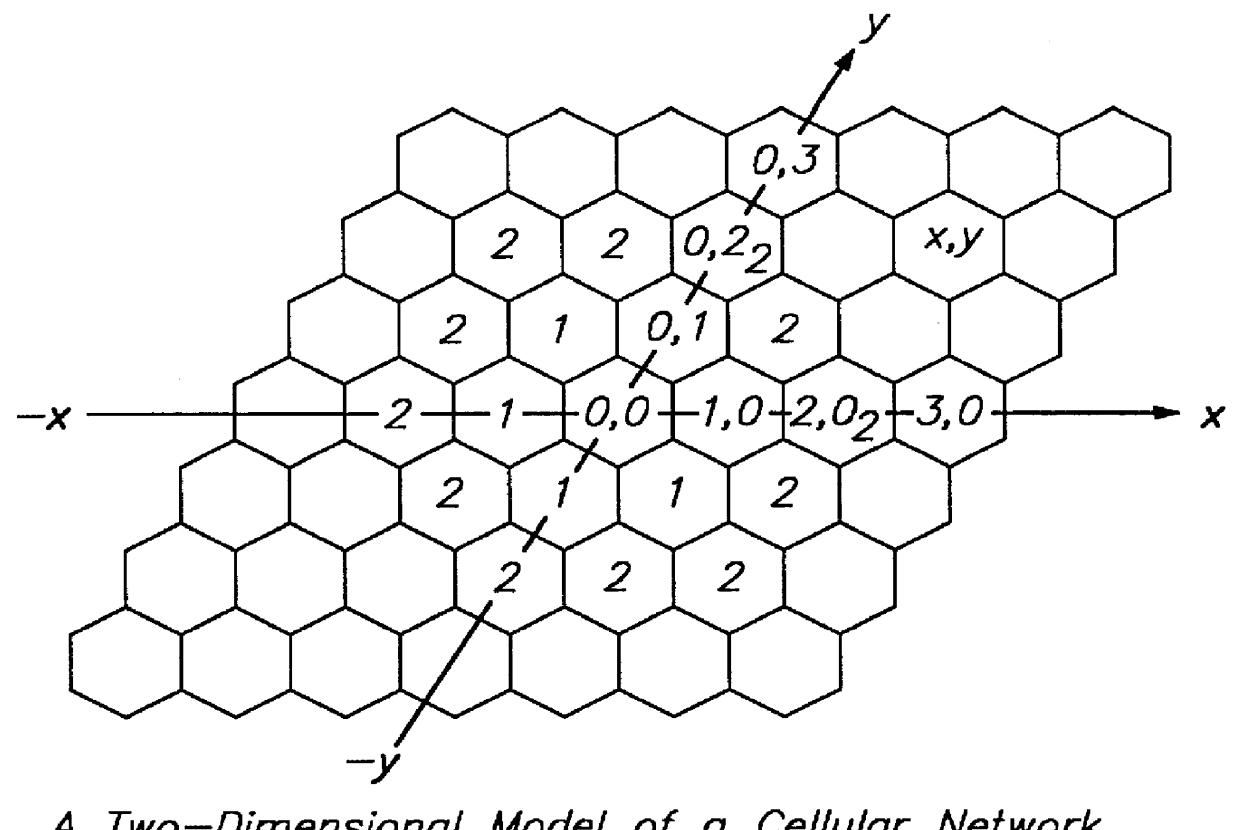
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
565 results about "Base station subsystem" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
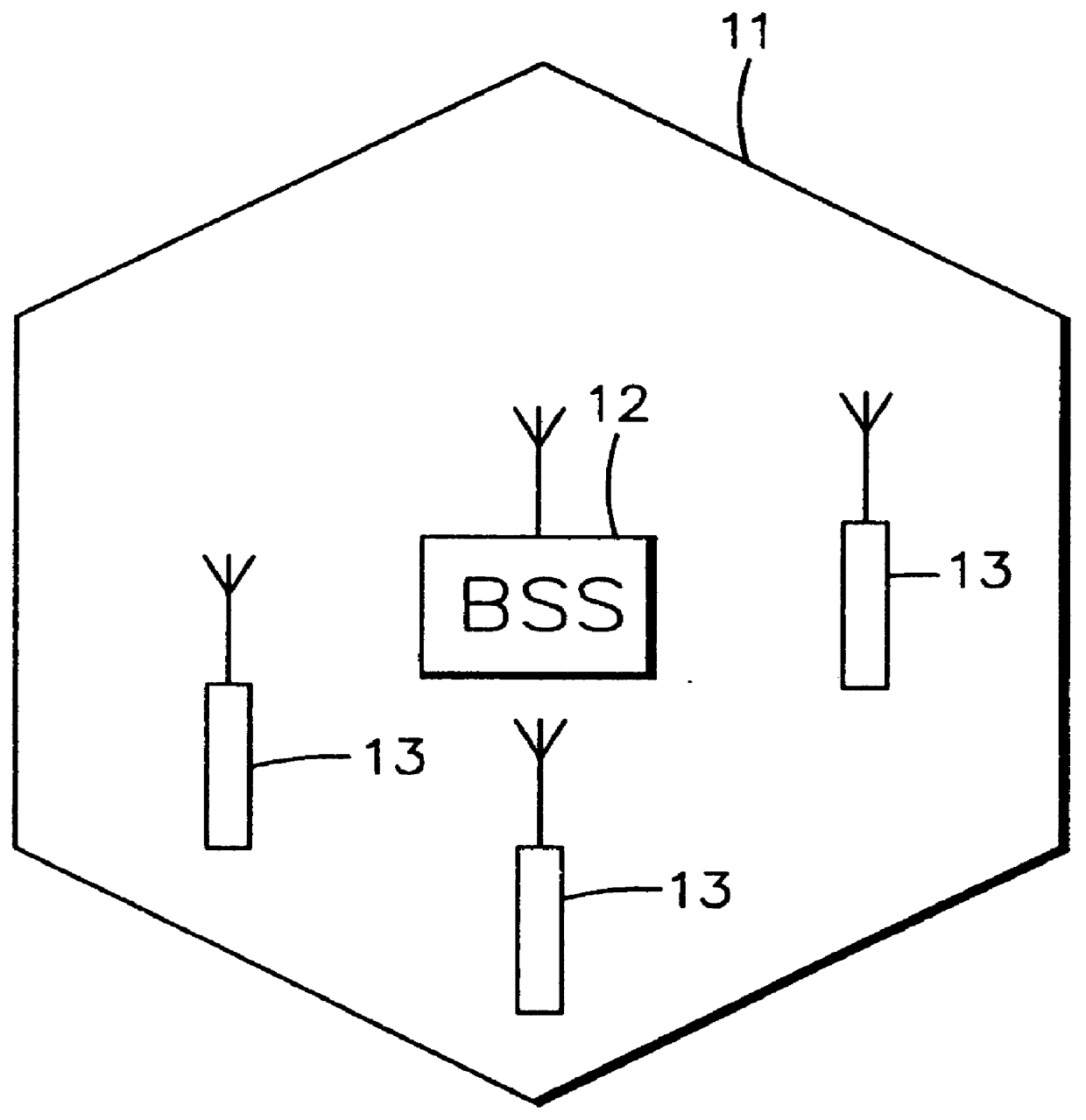
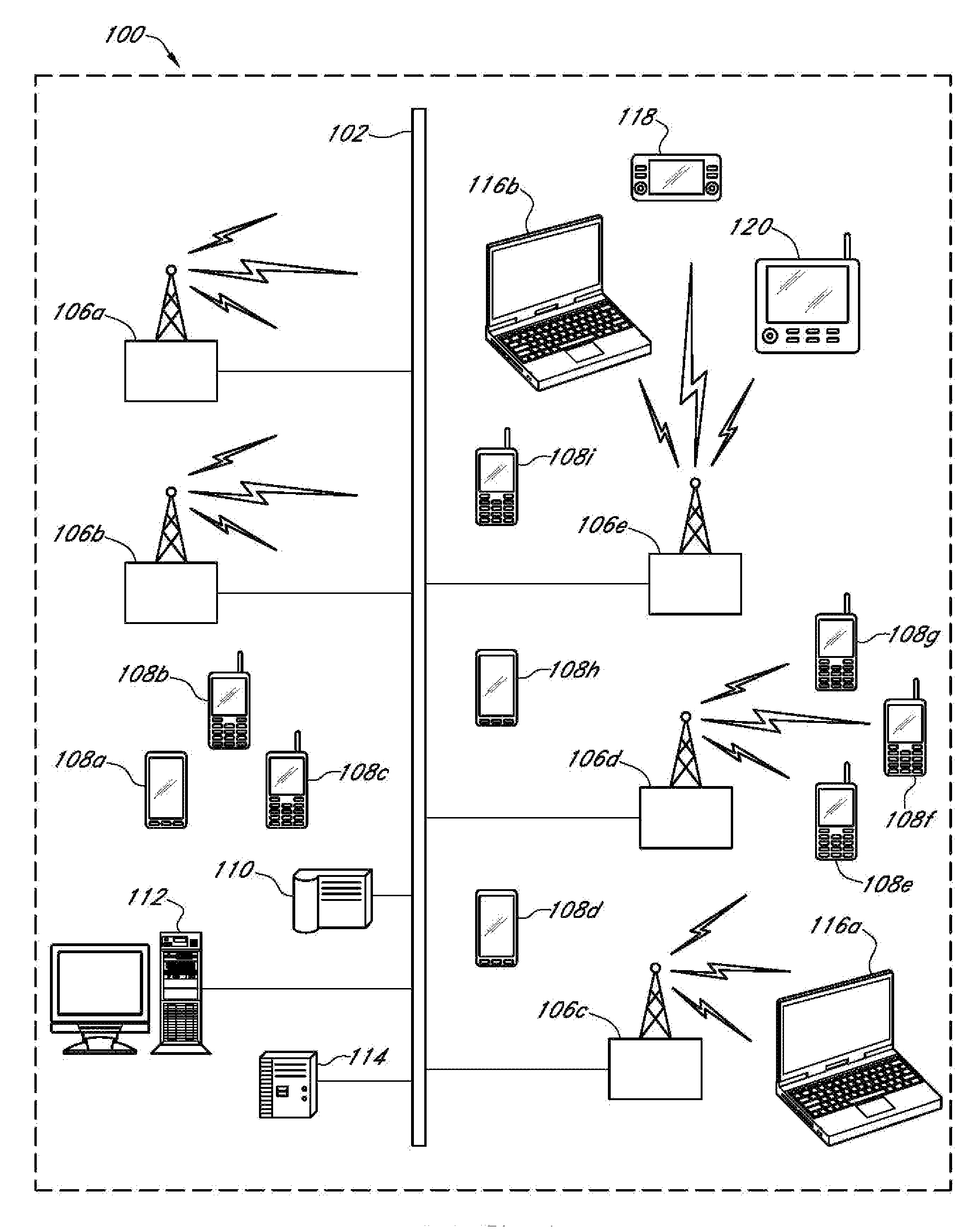
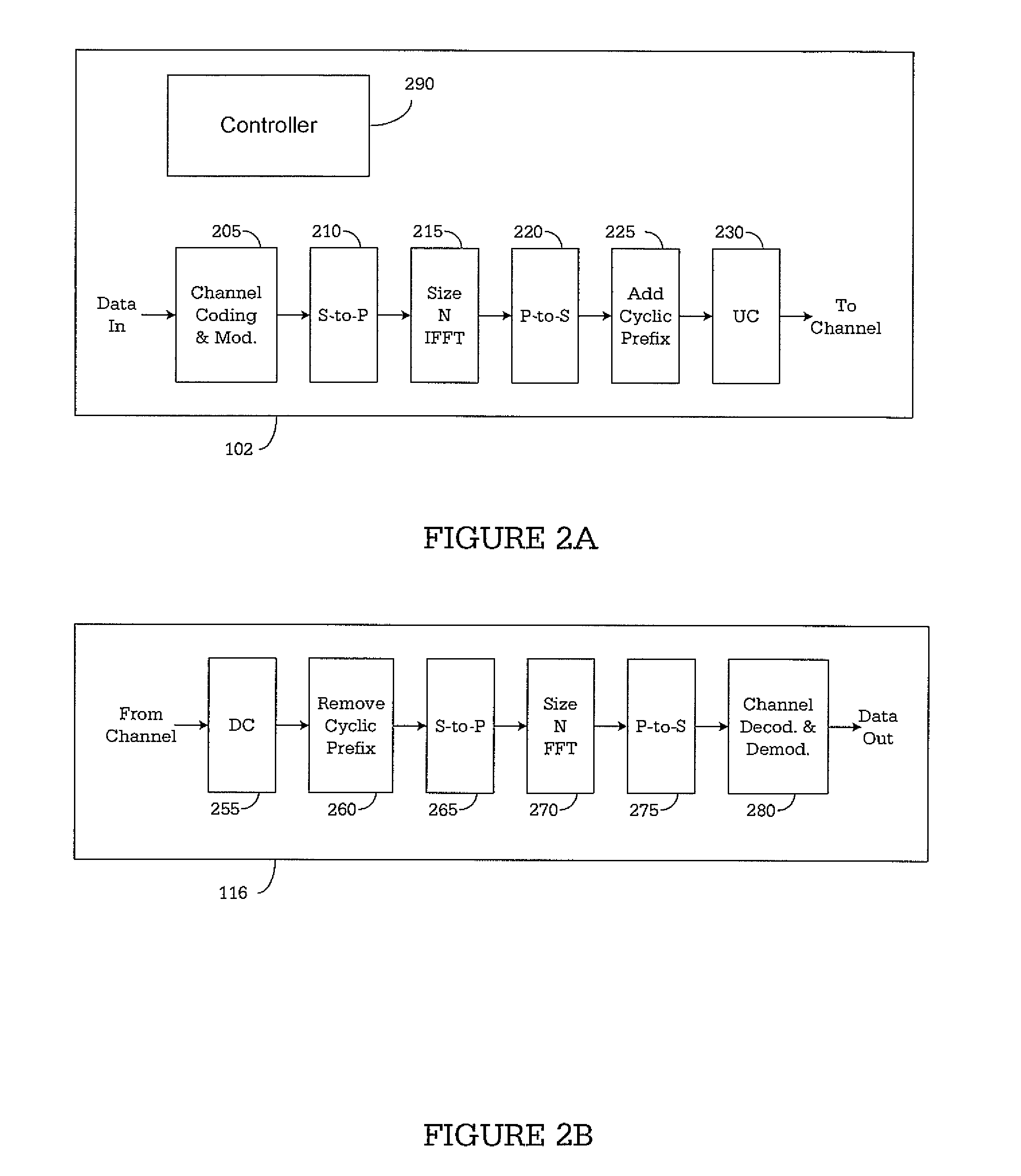
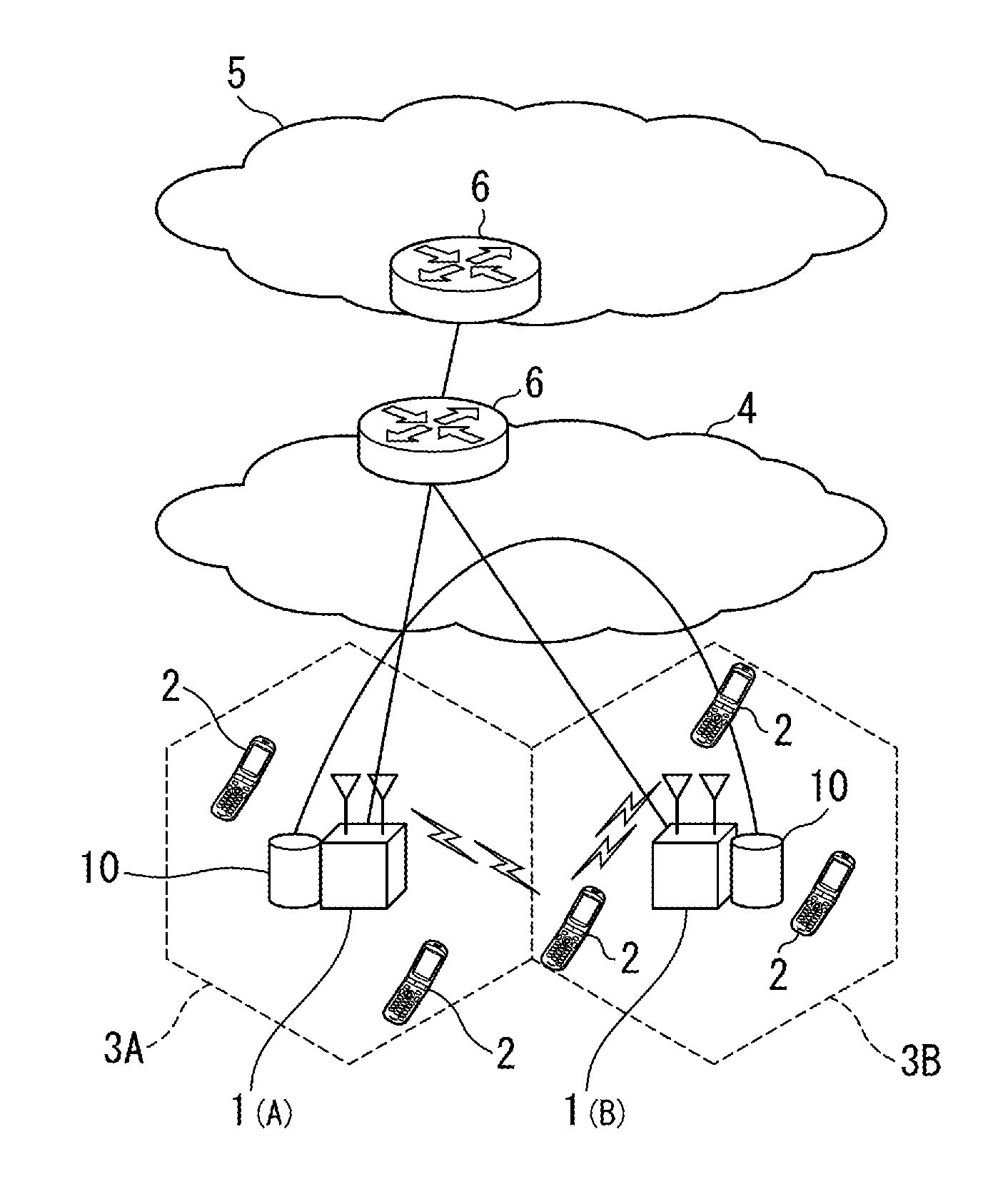
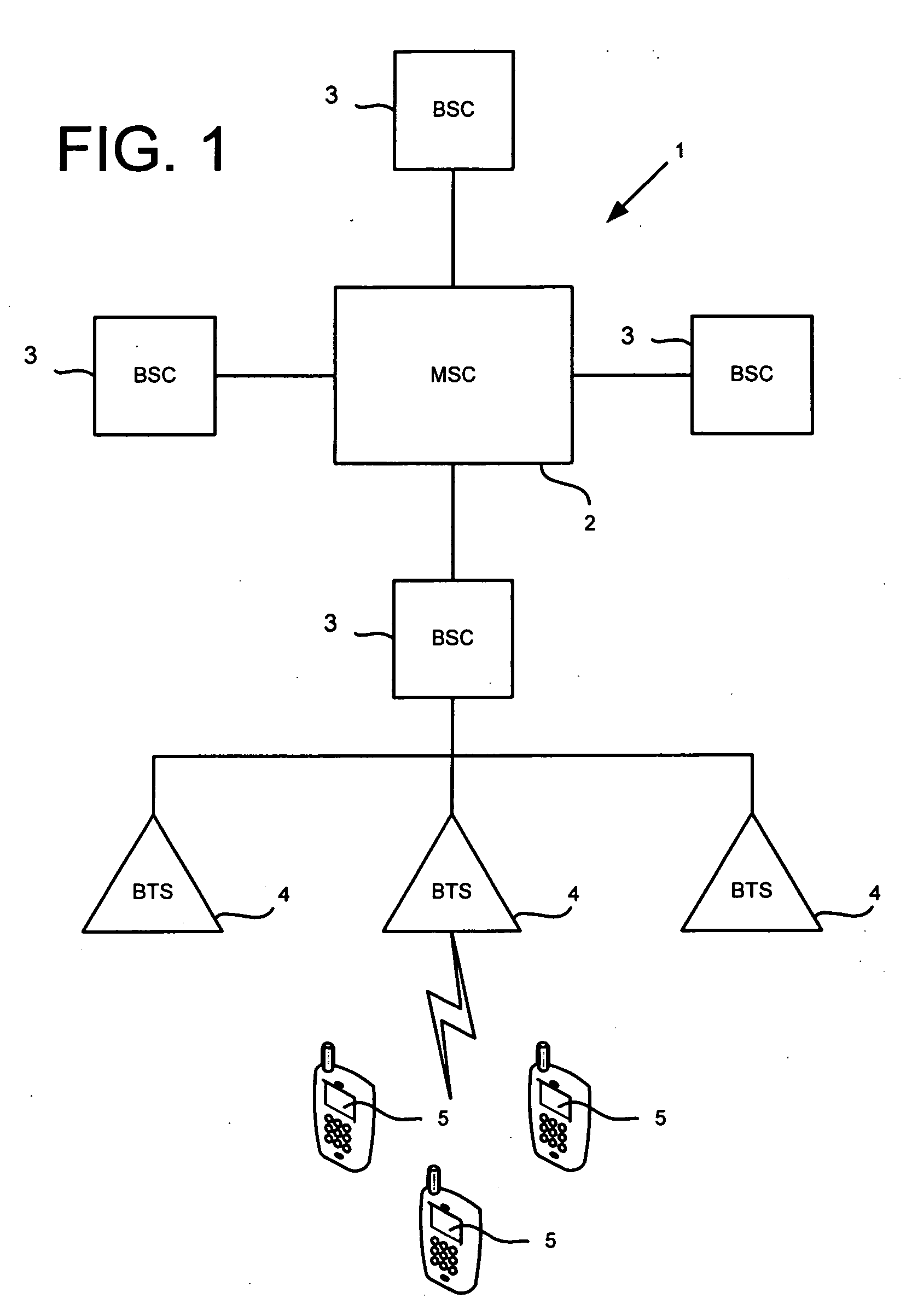
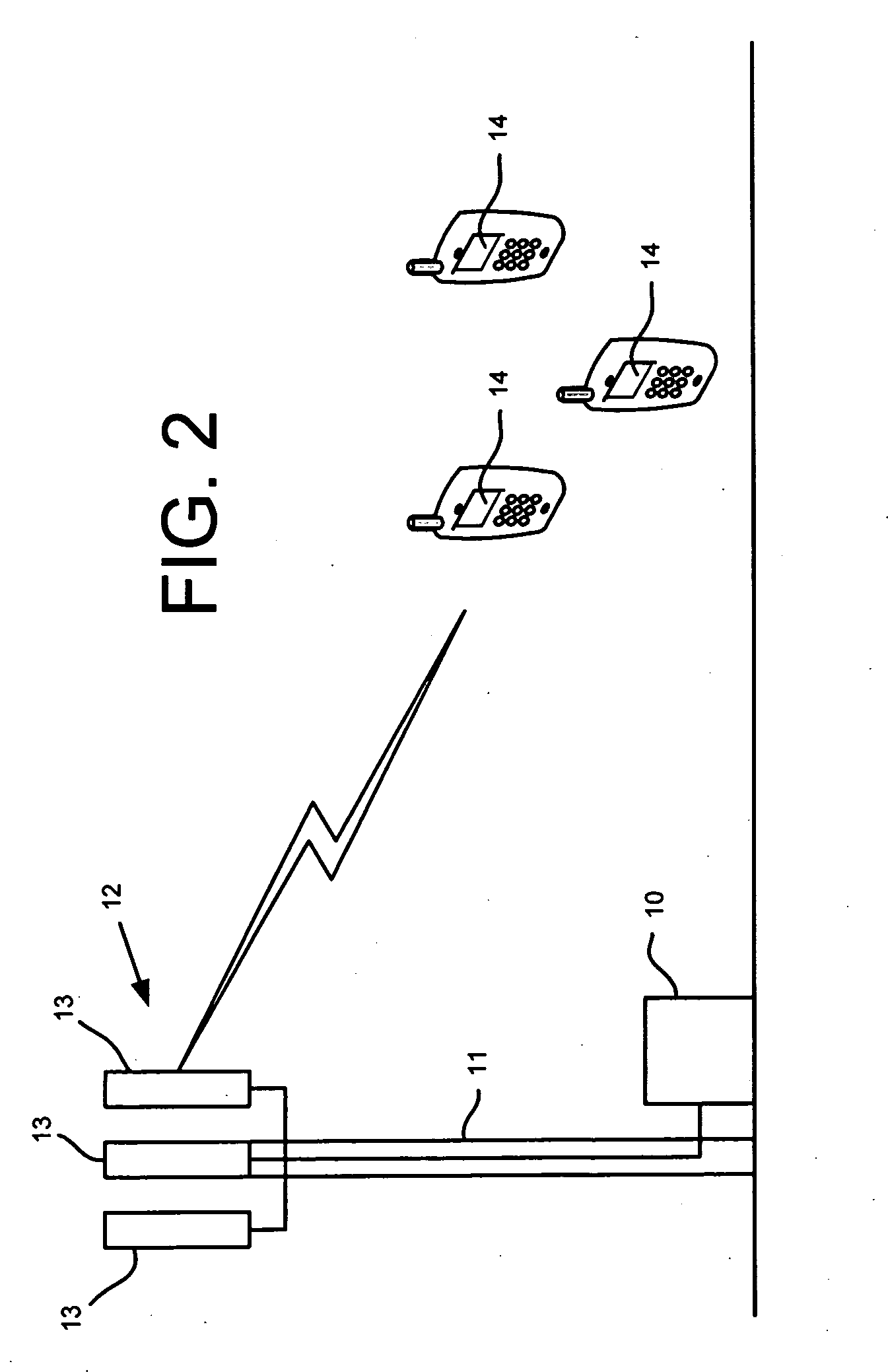
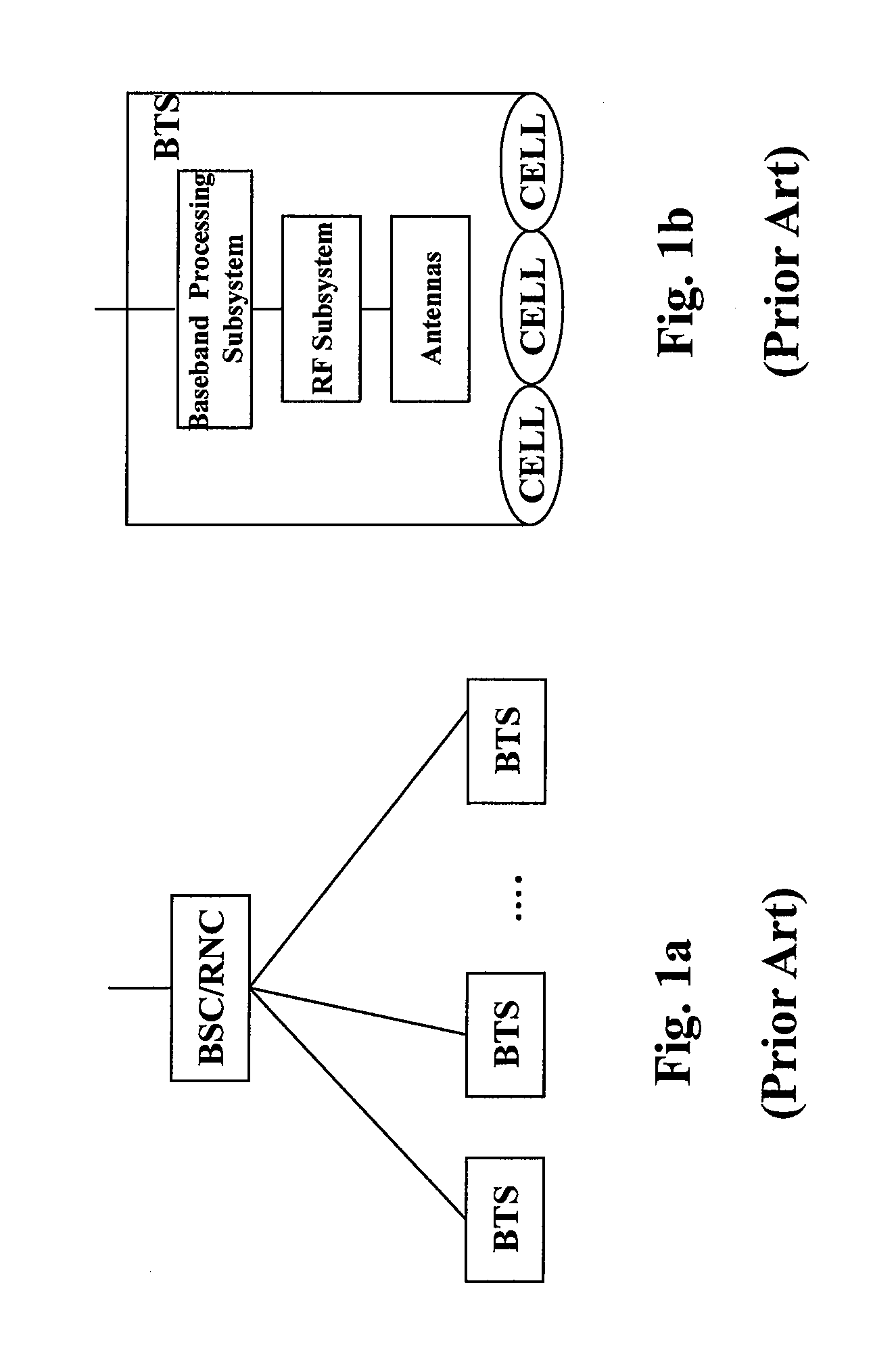
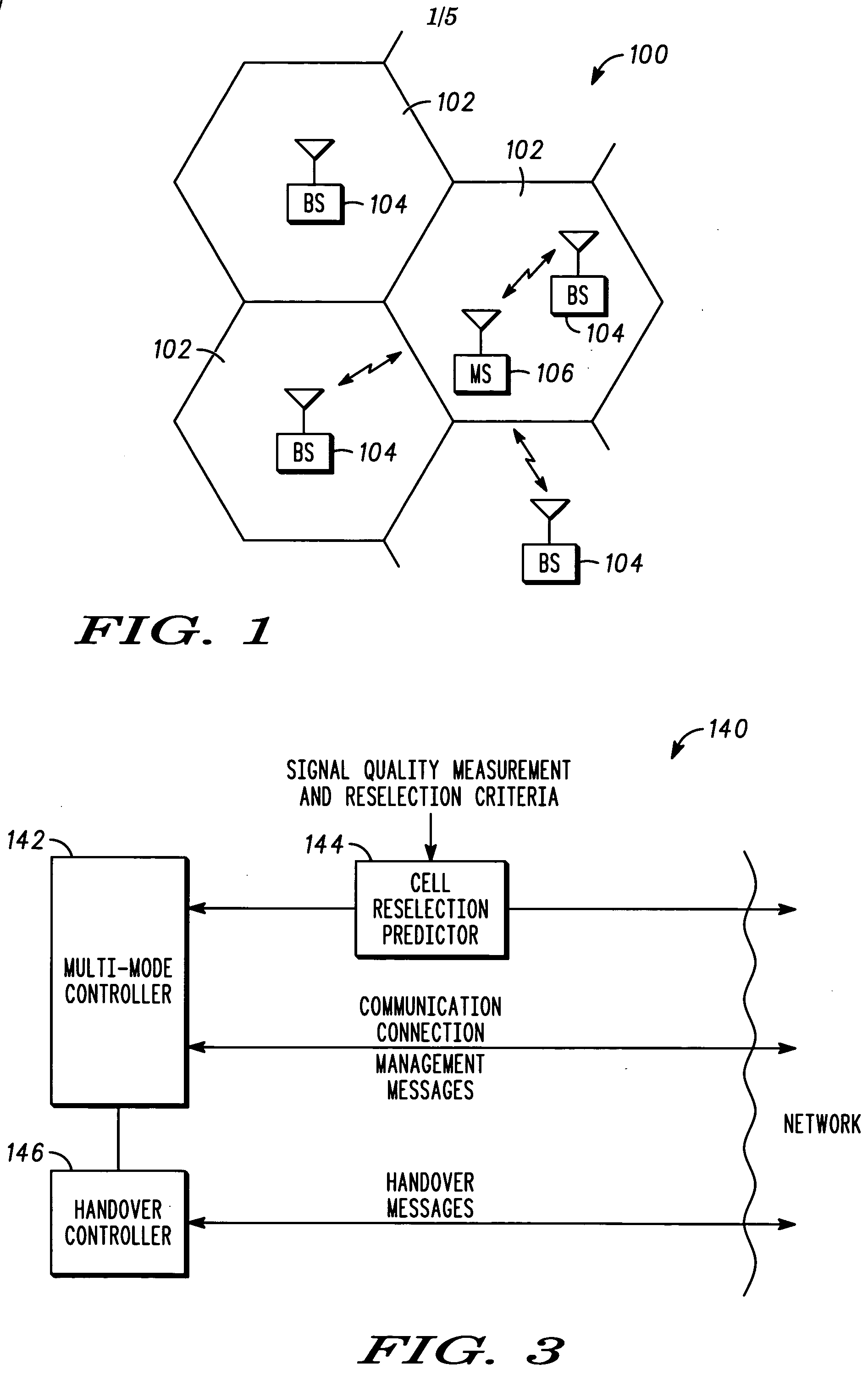
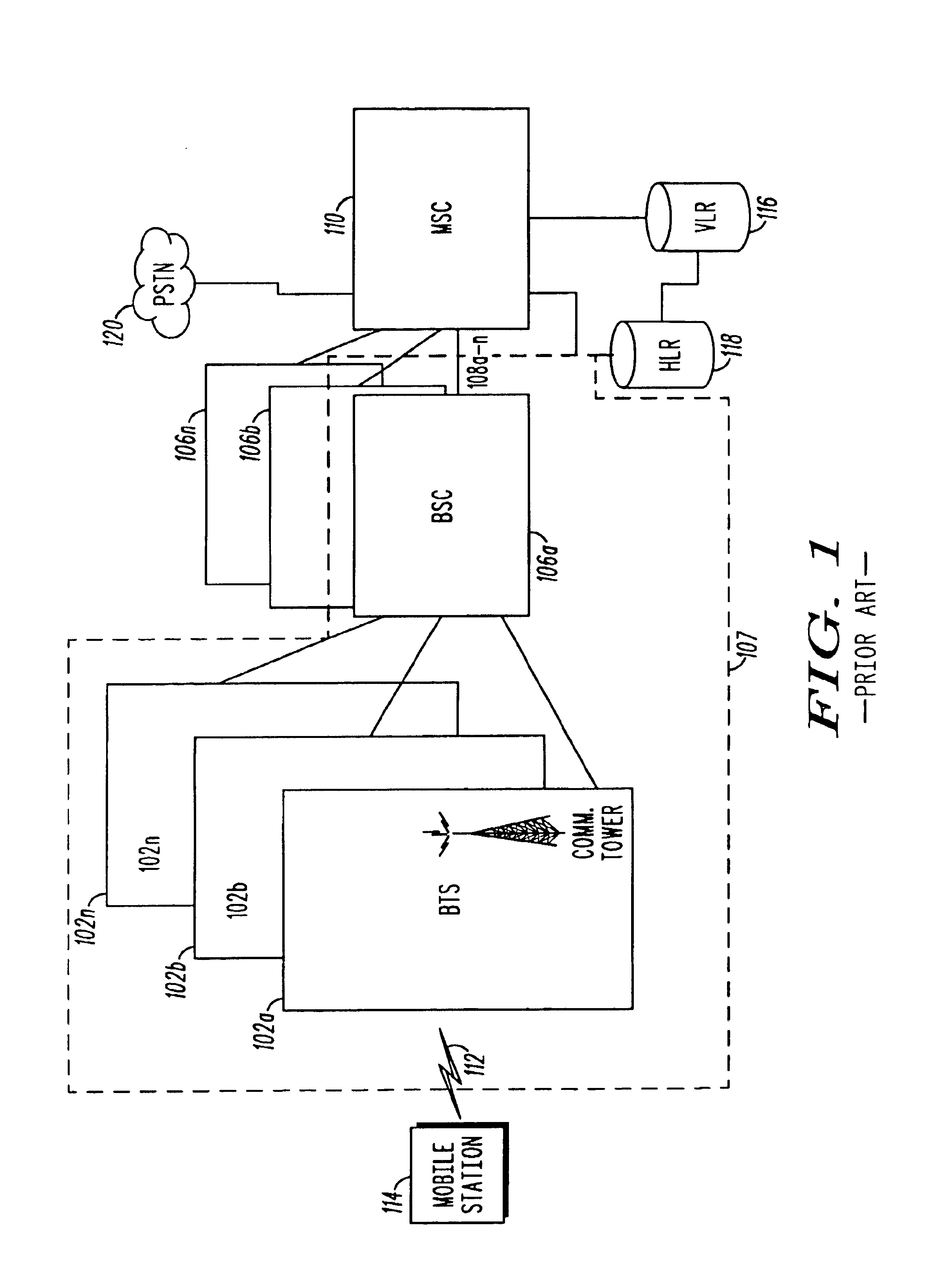
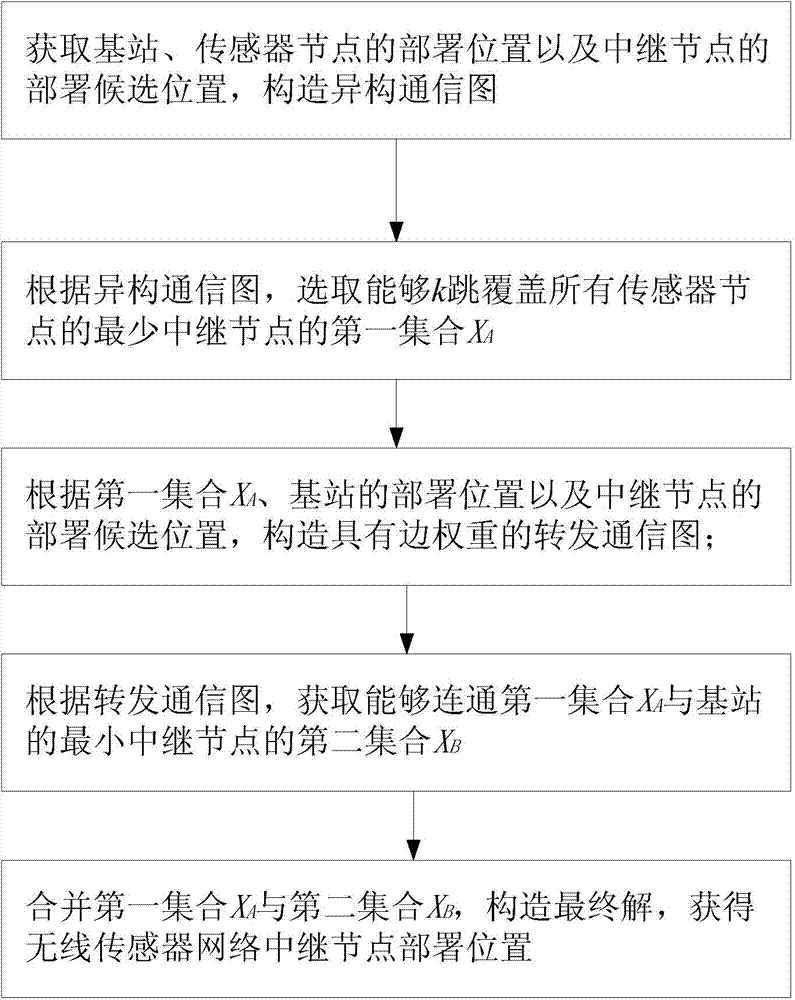
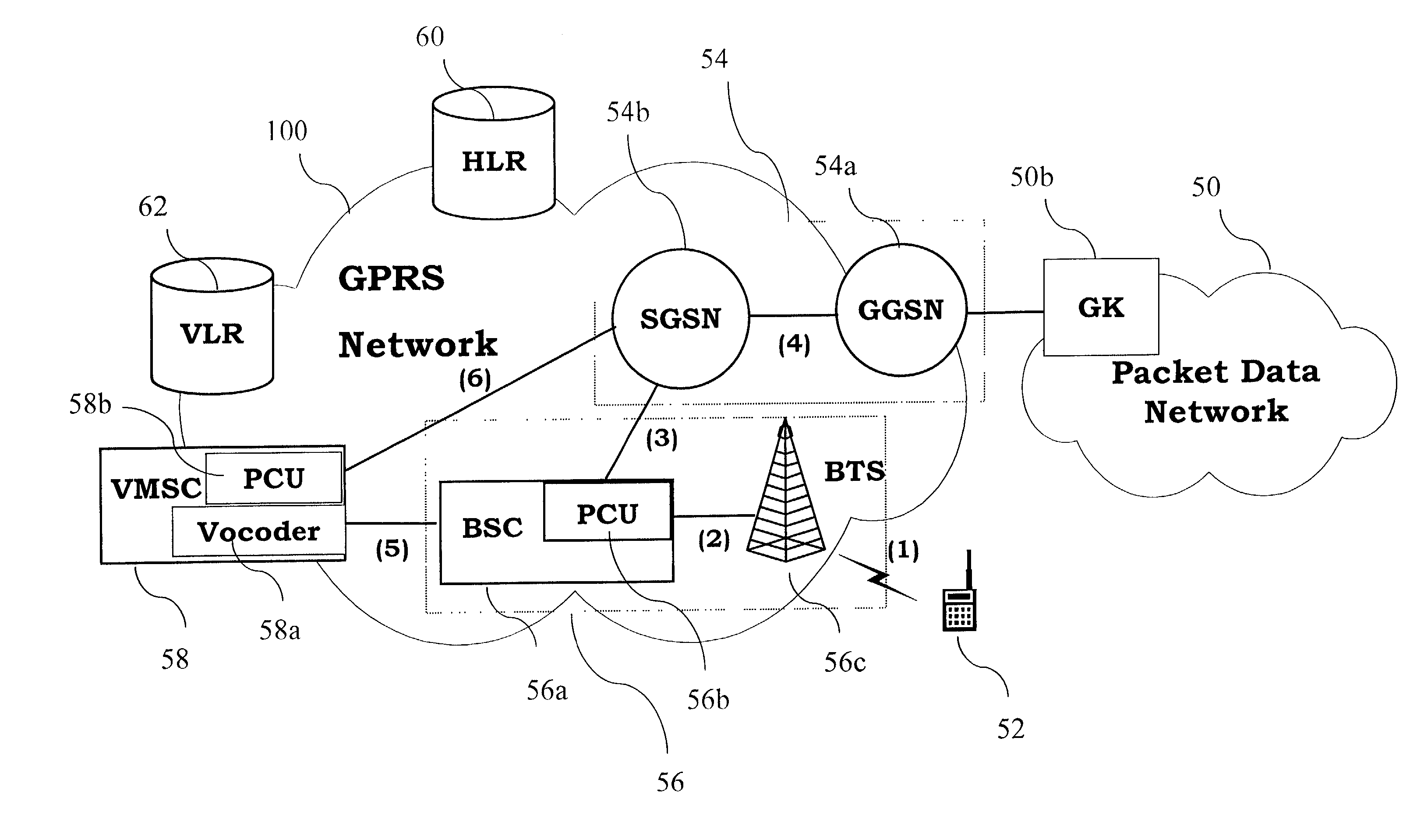
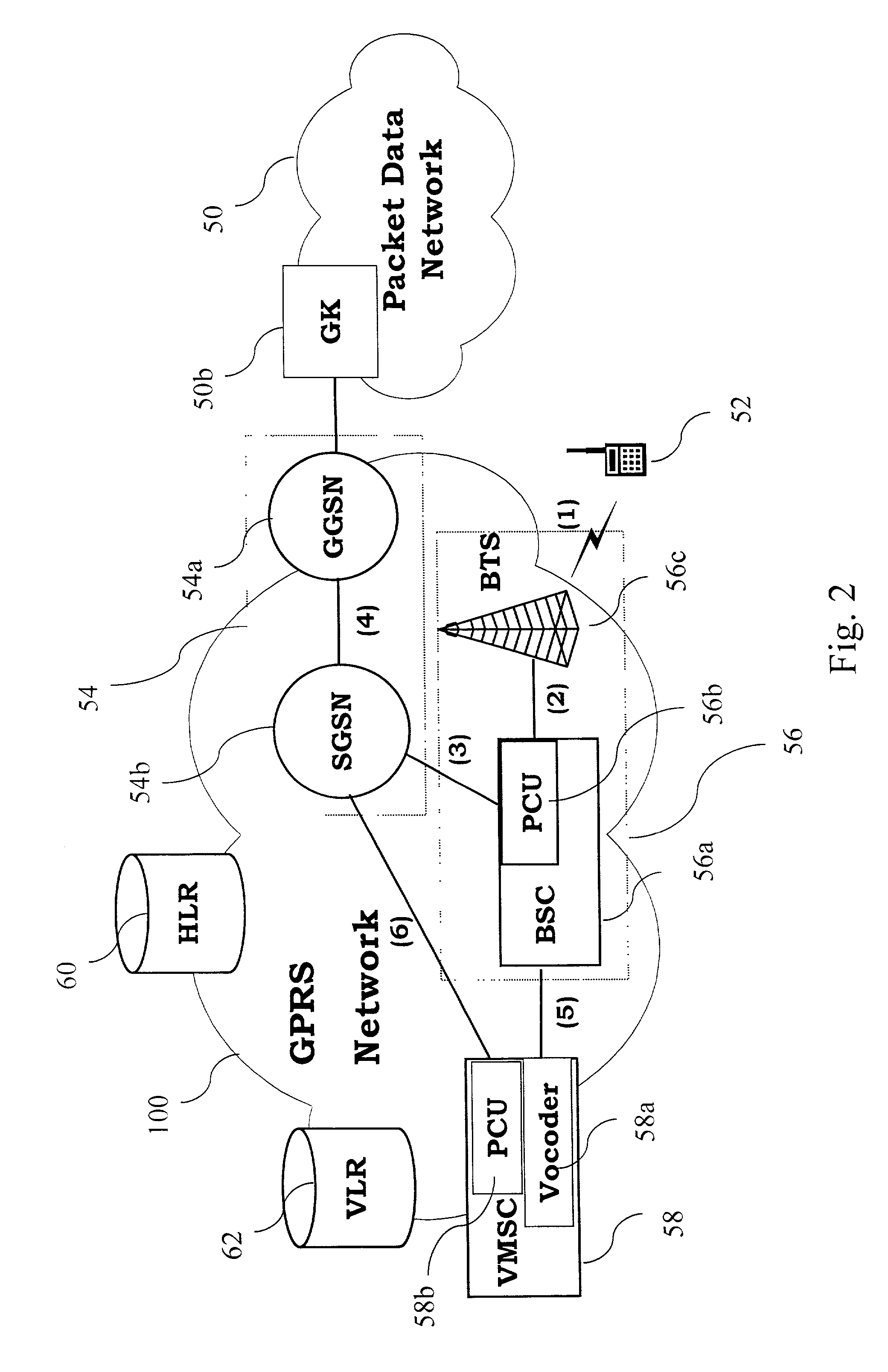
The base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, transmission and reception over the air interface and many other tasks related to the radio network.
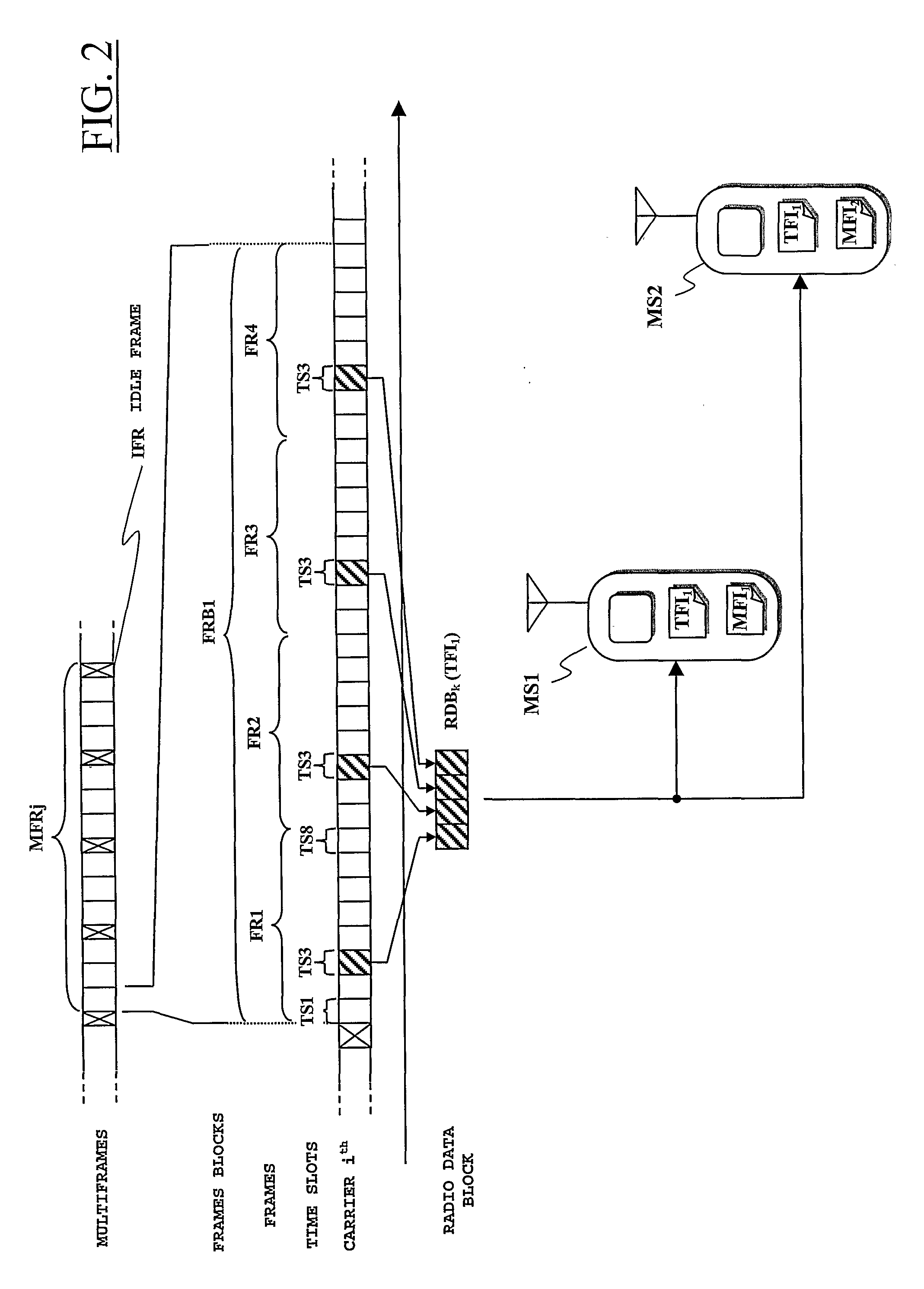
Method for radio resource control
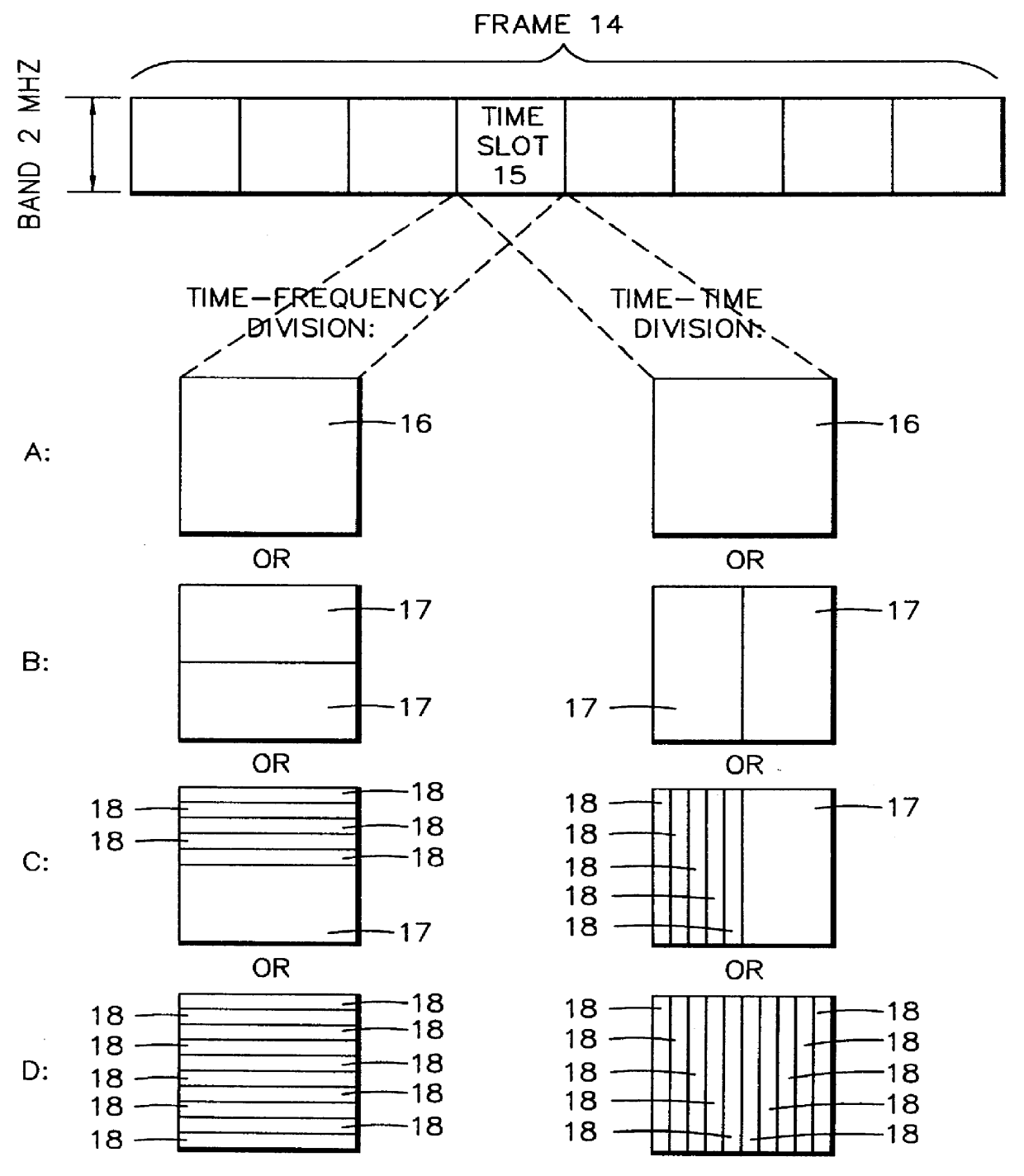
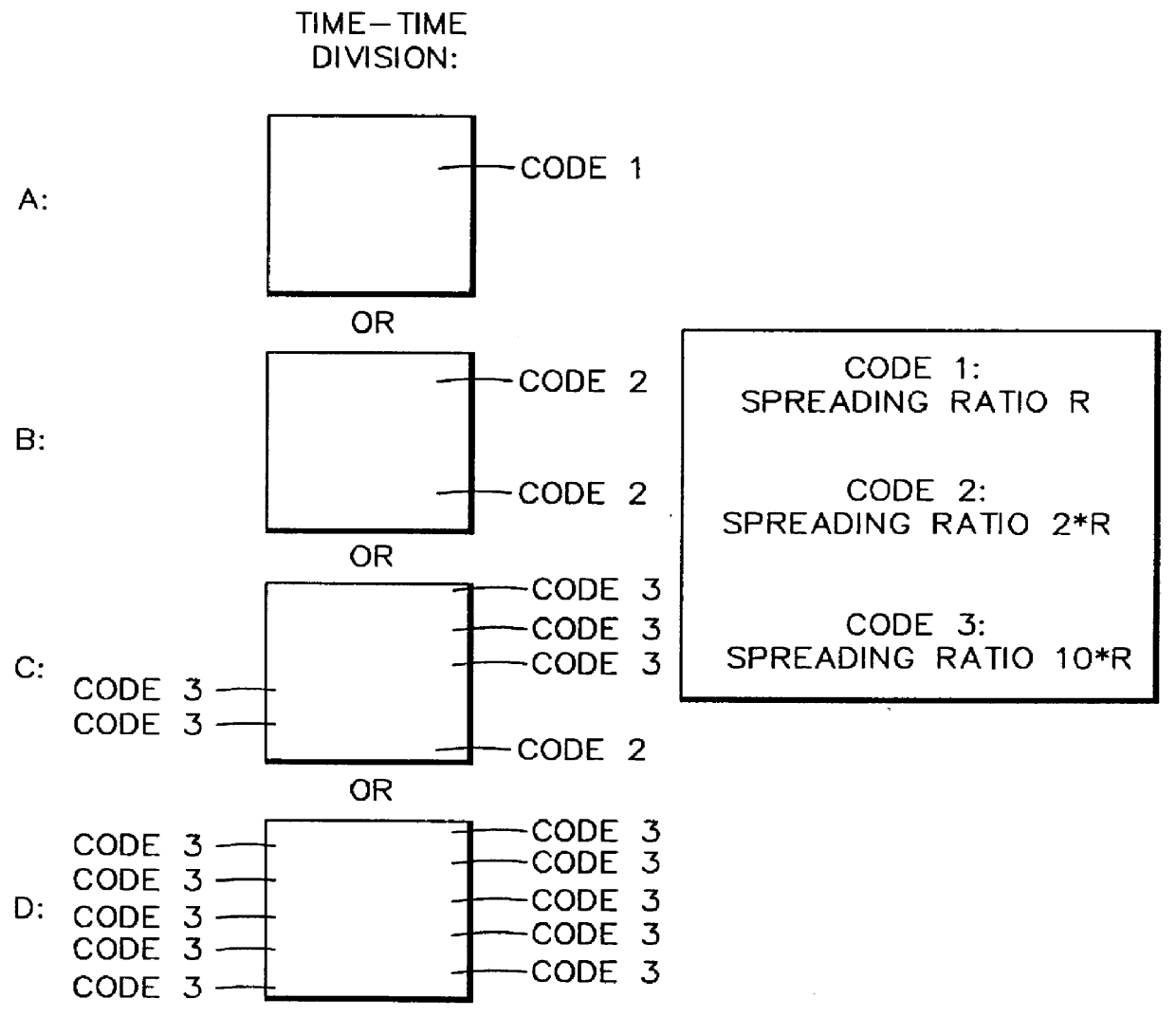
In order to control the use of physical radio resources, the physical radio resources are divided into chronologically consecutive frames (14), so that a frame contains slots (16, 17, 18) of various sizes, which slots represent a given share of the physical radio resources contained in the frame and can be individually allocated to different radio connections. The first dimension of a frame is time and the second dimension can be time, frequency or code. In the direction of the second dimension the slots represent various sizes, and a given first integral number of slots of the first size can be modularly replaced by another integral number of slots of another size. A certain number of consecutive frames form a superframe (19), in which case frames with corresponding locations in consecutive superframes are equal in slot division and allocations, if the data transmission demands do not change. Changes in the state of occupancy of the slots are possible at each superframe. In order to form an uplink connection, the mobile station sends a capacity request, where it indicates the type of requested connection and the demand of resources. In order to form a downlink connection, the base station subsystem sends a paging call, where it indicates the location in the superframe of the slots allocated to the connection. In order to indicate the state of occupancy, the base station subsystem maintains a superframe-size parametrized reservation table.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Centralized base station system based on advanced telecommunication computer architecture platform
InactiveUS20090149221A1Type of reductionSaving slotSubstation equipmentTransmissionNetwork switchControl switch
A centralized base station system based on ATCA, comprising a main base station subsystem and one or more remote radio frequency subsystems, the main base station subsystem comprising: one or more shelves based on ATCA platform, each shelf comprising at least one control switch module of ATCA board form; one or more base station controller interface module; a signaling module; one or more baseband processing modules; one or more remote radio frequency interface modules; a first switch network comprising first switch network shelf back board BASE interface link, a control switch module and a first network switch unit; a second switch network comprising a shelf back board FABRIC interface link, a control switch module and a second network switch unit; a clock synchronization network comprising a shelf back board clock synchronization bus, a control switch module and a clock unit; and a signal transmission network, wherein the second network switch unit and the clock unit are further connected to the first network switch unit, one of the control switch modules of all the shelves is the main control module.
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD
CPRI-based multiprotocol signal transmission method and apparatus in distributed base station system
InactiveUS20070091896A1EffectiveNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesSTM-1Interface protocol
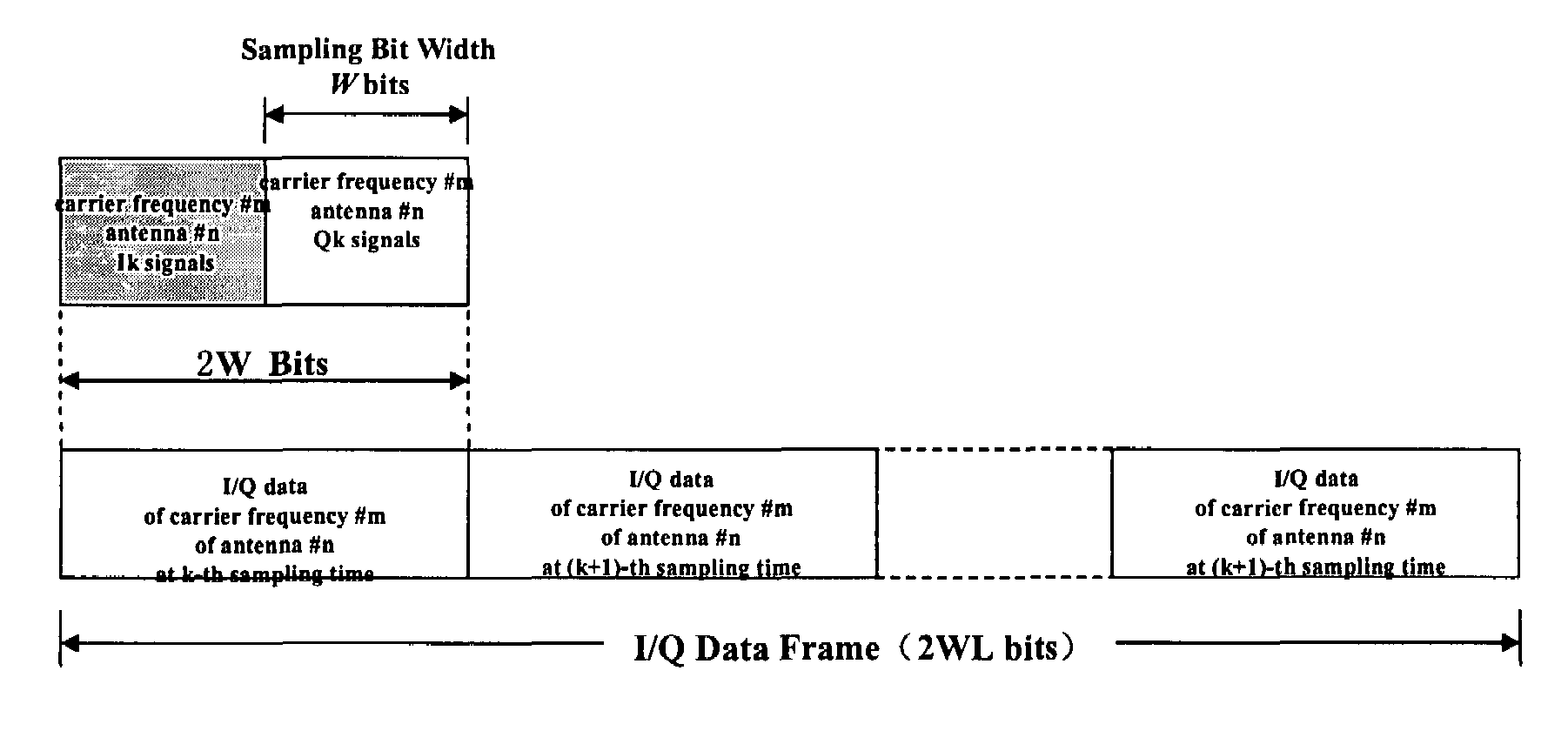
The present invention provides a method for realizing transmission of multiprotocol client signals in a distributed base station subsystem, comprising: encapsulating client signals by a GFP-T frame; and mapping said GFP-T frame into a lower-layer transmission link to realize the transmission of client signals. Said lower-layer transmission link is a common public radio interface CPRI link. Said client signals are one of the following: baseband I / Q signals of WCDMA supported by CPRI protocol, baseband I / Q signals of radio interface protocols other than WCDMA, structured signals of E1 / T1, STM-1 and other constant-rate links, structured variable-rate link signals such as Ethernet MAC frame signals, PPP / HDLC frame signals, etc. This method is also applicable to other types of synchronous transmission links between a remote radio unit and a primary baseband processing unit, e.g., the links as specified by OBSAI (Open Base Station Architecture Initiative).
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD
Inter-cell interference coordination method and apparatus for wireless communication system
ActiveUS8412256B2Good reliefPower managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemResource block
An inter-cell interference coordination method and apparatus is provided for mitigating inter-cell interference in a wireless communication system by using interference coordination information exchanged among neighbor base stations. The method includes receiving, at a serving base station, power control messages transmitted by neighbor base stations, receiving incoming interference coordination messages transmitted by neighbor base stations, each message including interference indicators of resource blocks, allocating the resource blocks with transmission power per resource block to user equipments served by the base station based on the power control and interference coordination messages, generating outgoing interference coordination messages for the respective neighbor base stations based on the resource block allocation result, and transmitting the interference coordination messages to the neighbor base stations, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wireless communication system with dynamic channel allocation
InactiveUS6023622AFacilitate communicationReduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDynamic channelTransceiver
A plurality of base stations communicate with a plurality of mobile units. Each base station includes a base station transceiver that receives inbound information from the mobile units and transmits outbound information to the mobile units. A mobile switching center (MSC) is coupled to the base stations and communicates the inbound information and outbound information with the base stations. The base stations each include signal detectors that detect signal strength of the inbound information, co-channel information and adjacent channel information. The MSC maintains a table of signal strength per communication channel and allocates communication channels to the base stations based on the signal strength information. The inventive dynamic channel allocation includes several channel allocation algorithms that can be active at the same time. Only one of the algorithms is active at a time. The choice of the algorithm is based on current interference conditions and traffic load. The invention is implemented in the MSC and base stations of a digital cellular network using wideband technology for its air interface. While the decision-making mechanism and the channel allocation algorithms are implemented in the MSC, the protocol between the MSC and base stations is extended to support the proposed concept for dynamic channel allocation. Advantages of the invention includes improved communication and reduced interference.
Owner:WJ COMM
Method of reducing delay
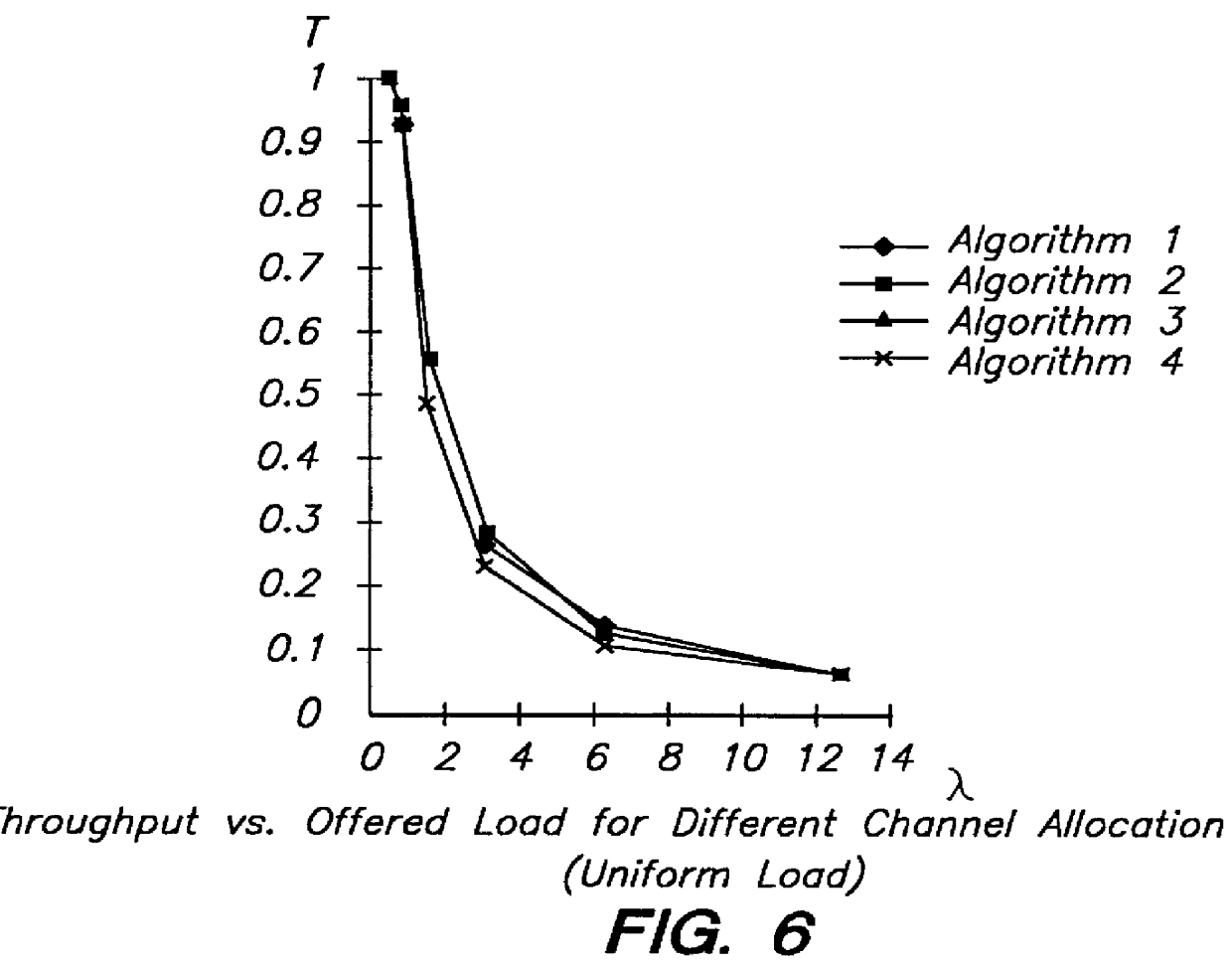
ActiveUS20070123284A1Reduce setup delayService delayNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesPush-to-talkDelay sensitive
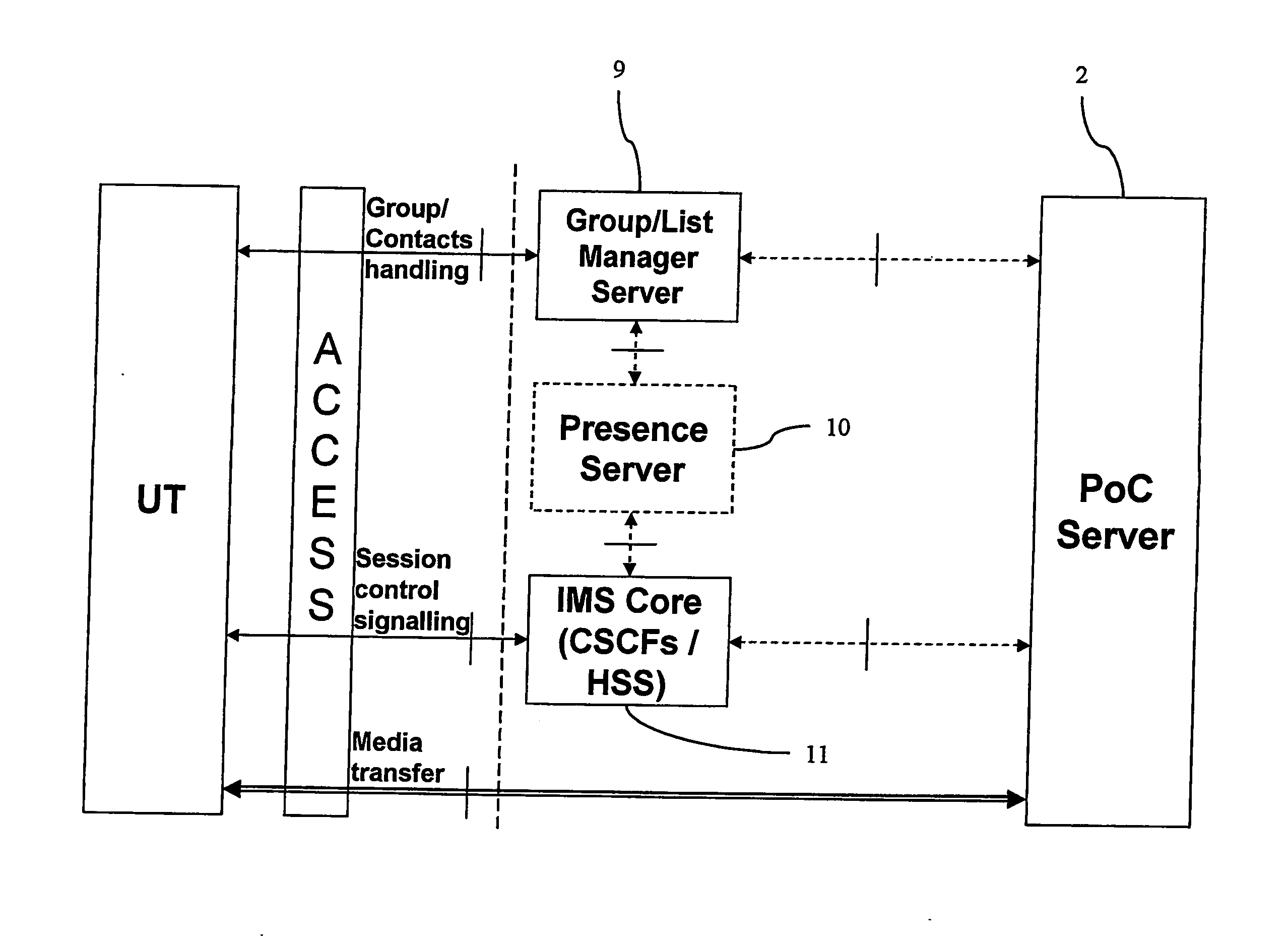
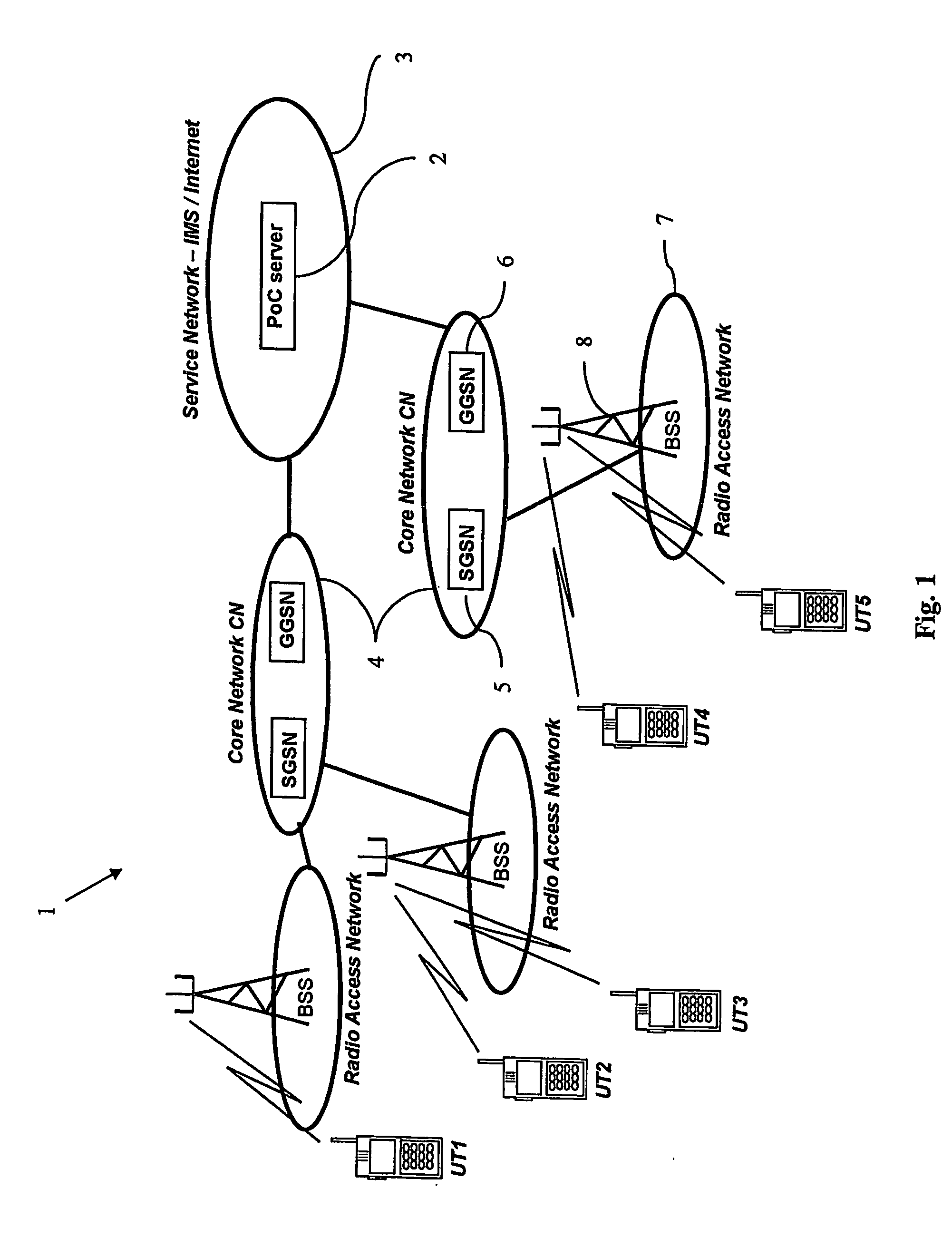
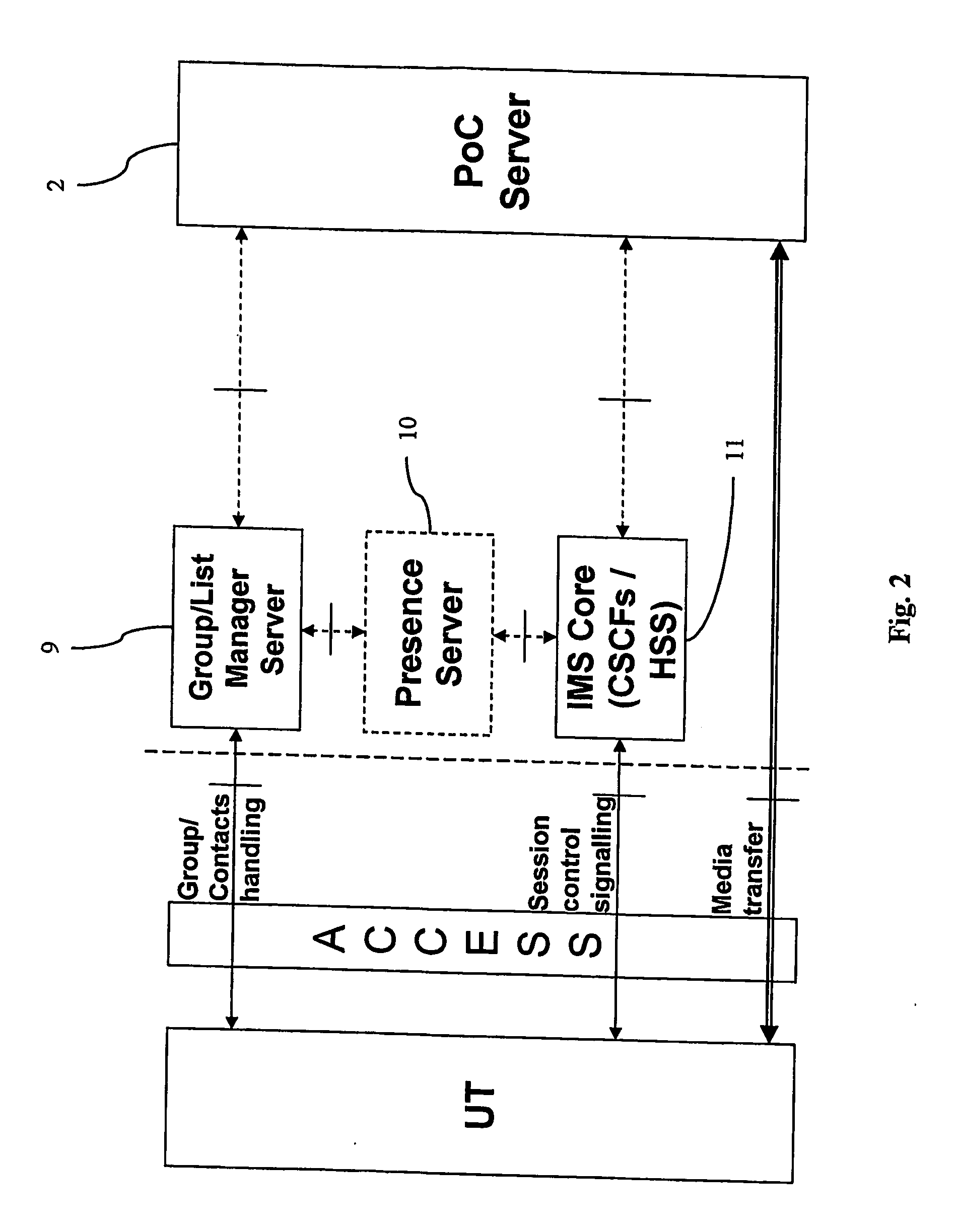
The present invention relates to a method of reducing setup delay for an uplink message from a user terminal (UT) in a delay sensitive service in a radio telecommunications system, such as a push to talk service (PoC), by predicting that delay sensitive data is about to be transmitted, sending, as a response to the prediction, a connection setup signal from the terminal to a basestation subsystem (BSS) in order to set up an early uplink radio connection, and transmitting the delay sensitive data via the early uplink connection. There is also provided a user terminal (UT) and a radio telecommunications system.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Systems and methods for mitigating intercell interference by coordinated scheduling amongst neighboring cells
ActiveUS20110235598A1Facilitate centralized power schedulingReduce distractionsPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementUser equipmentComputing systems
A networked computing system capable of mitigating interference amongst neighboring base stations. The networked computing system includes multiple base stations, user equipment, a network resource controller, and a data communications network facilitating data communications amongst all network devices. A serving base station is configured to acquire interference metrics from its local user equipment and then generate an aggregate representation from the acquired interference metrics. The network resource controller is configured to acquire the aggregate representation, determine an interference reduction associated with a neighbor base station for each of the user equipment serviced by the serving base station, determine a power schedule for the first base station based on the aggregate representation and the determined interference reduction, and then modify a power schedule for the neighbor base station based on the determined interference reduction.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Methods and apparatus to support base station detection and selection in multi-tier wireless networks
A subscriber station can efficiently determine an accessible base station by scanning a subset of base stations based on an optimized list received from a serving base station. The subscriber station includes a white list that contains information regarding a number of closed subscriber group (CSG) base stations to which the subscriber station is subscribed. The subscriber station can transmit a request message that includes one or more of: indication of whether the detected identifier of the femto base station is in the whitelist or not; and its location information. In response, the base station can send a message that includes the nearby femtocells and whether the femtocell is accessible or inaccessible to the subscriber station. The femto base station can be designed to be in transmission off mode when none of its subscribers is in its coverage. The serving base station can select a set of the accessible femtocells to the subscriber station, and request the selected femtocells to monitor an uplink signaling of the subscriber station so that the femtocell can be awaken when the femtocell is in transmission off mode or be aware that the subscriber station is in proximity, if the uplink signaling is detected.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
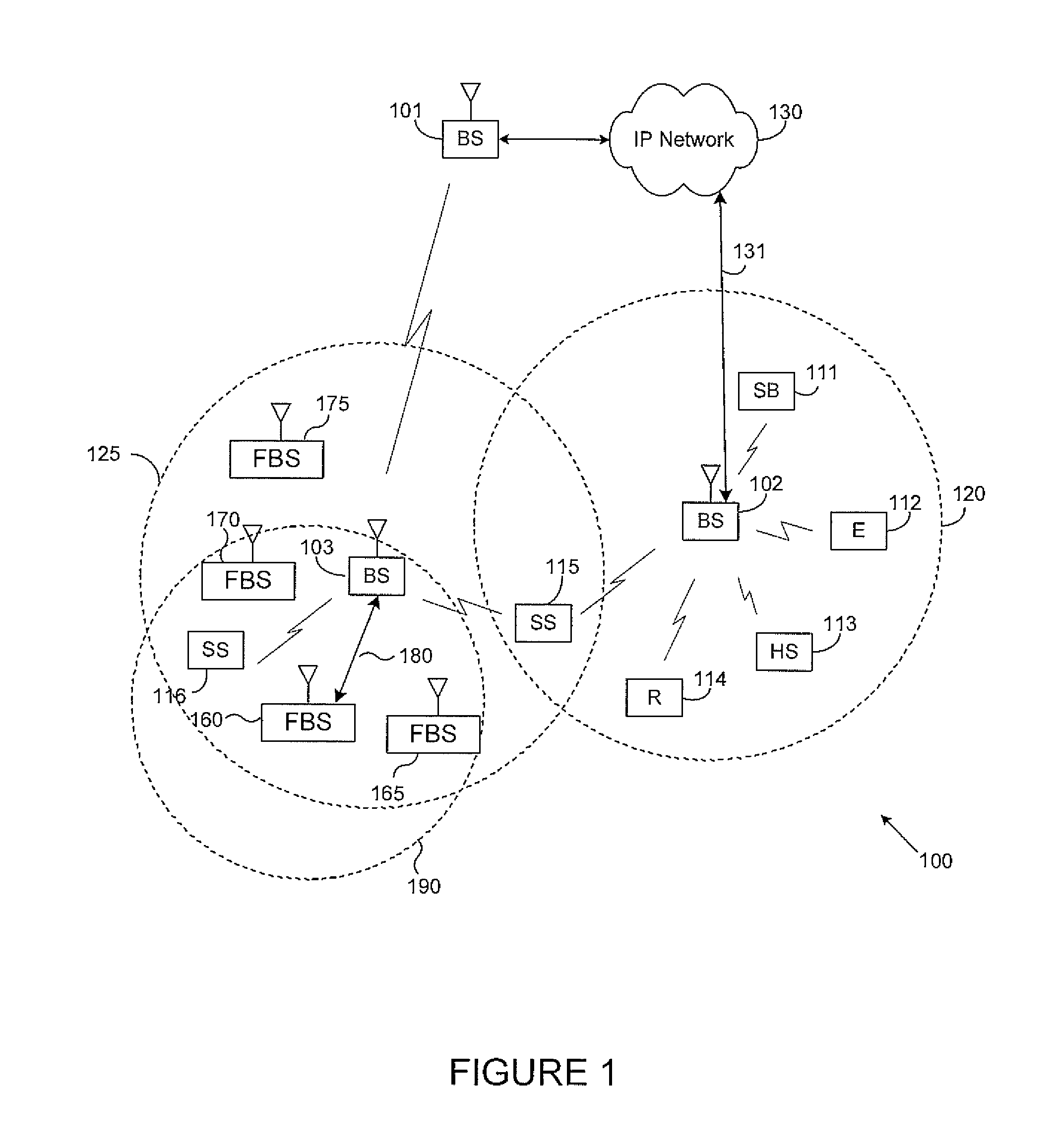
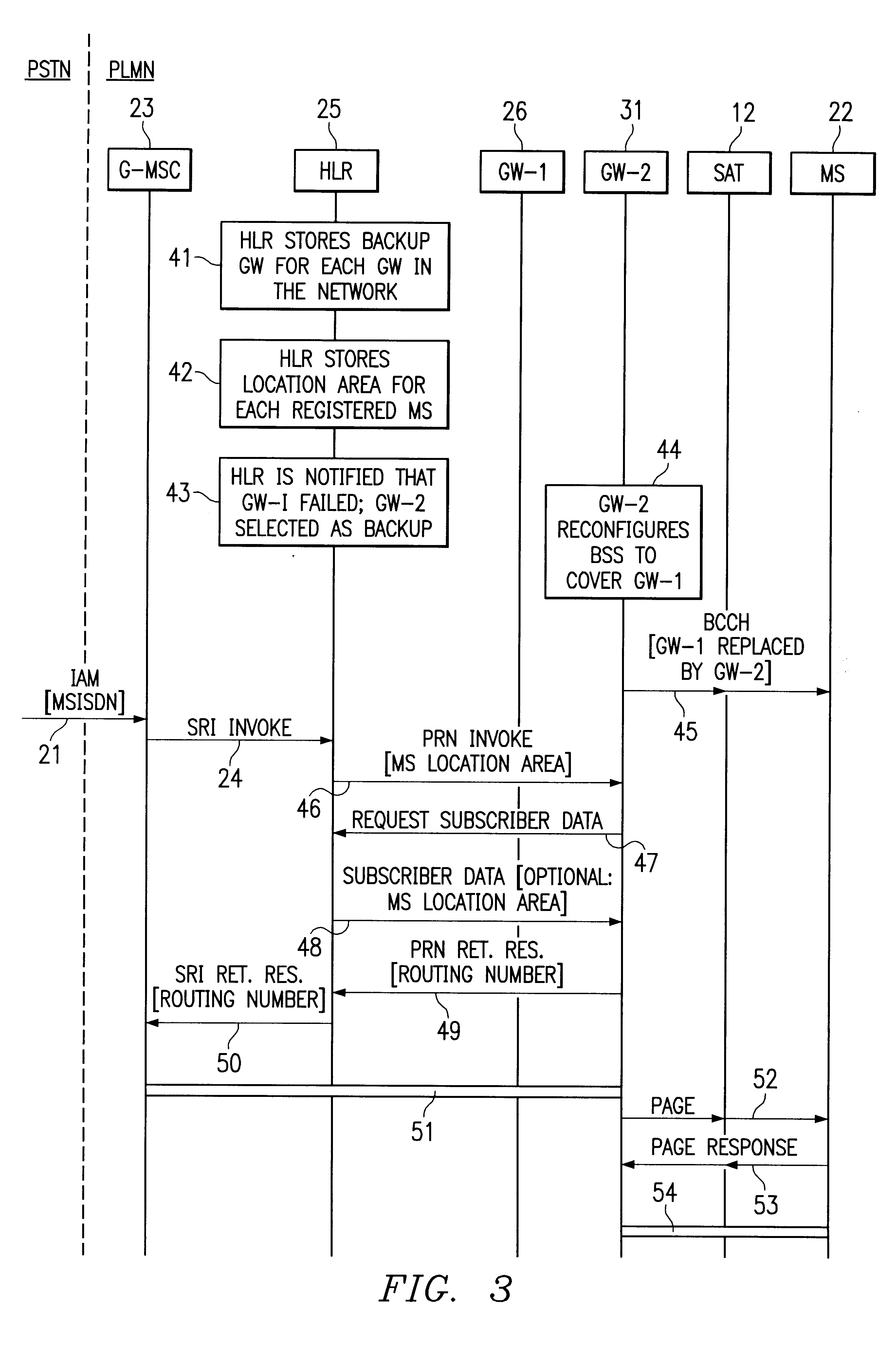
System and method of reallocating satellite gateways in a radio telecommunications network
InactiveUS6219546B1Special service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunications networkProcessor register
A method of handling an incoming call to a mobile station (MS) in a radio telecommunications network having a gateway mobile switching center (G-MSC) and a home location register (HLR), and the MS communicates with the network via a satellite link comprising a satellite and a satellite gateway. The method includes storing in the HLR, a plurality of primary gateways and an associated backup gateway for each primary gateway in the network. If the primary gateway serving the MS fails while the satellite is still operational, the incoming call is routed from the G-MSC to the backup gateway. The backup gateway's base station subsystem (BSS) is reconfigured to cover the service area of the primary gateway, and the MS is notified that the backup gateway has replaced the primary gateway as the MS's serving gateway. Subscriber data for the called MS is provided to the backup gateway by the HLR. If the satellite fails, the HLR instructs the G-MSC to route the call directly to voice mail when the HLR receives a request for routing information from the G-MSC.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Cellular mobile communication system, base station control device, and interstation-cooperated communication control method
InactiveUS20110255526A1Increase the areaPower managementSite diversityBase station subsystemCommunication control
A cellular mobile communication system, in which a plurality of base stations communicate with mobile stations, provides a retrieval unit, in which each base station retrieves the information regarding the radio communication status of each base station communicating with the predetermined mobile station, a decision unit, which makes a decision as to whether or not to permit interstation-cooperated communication with each base station based on the information, and a determination unit which determines the communication method adopted in the mobile station based on the decision result.
Owner:KDDI CORP +1
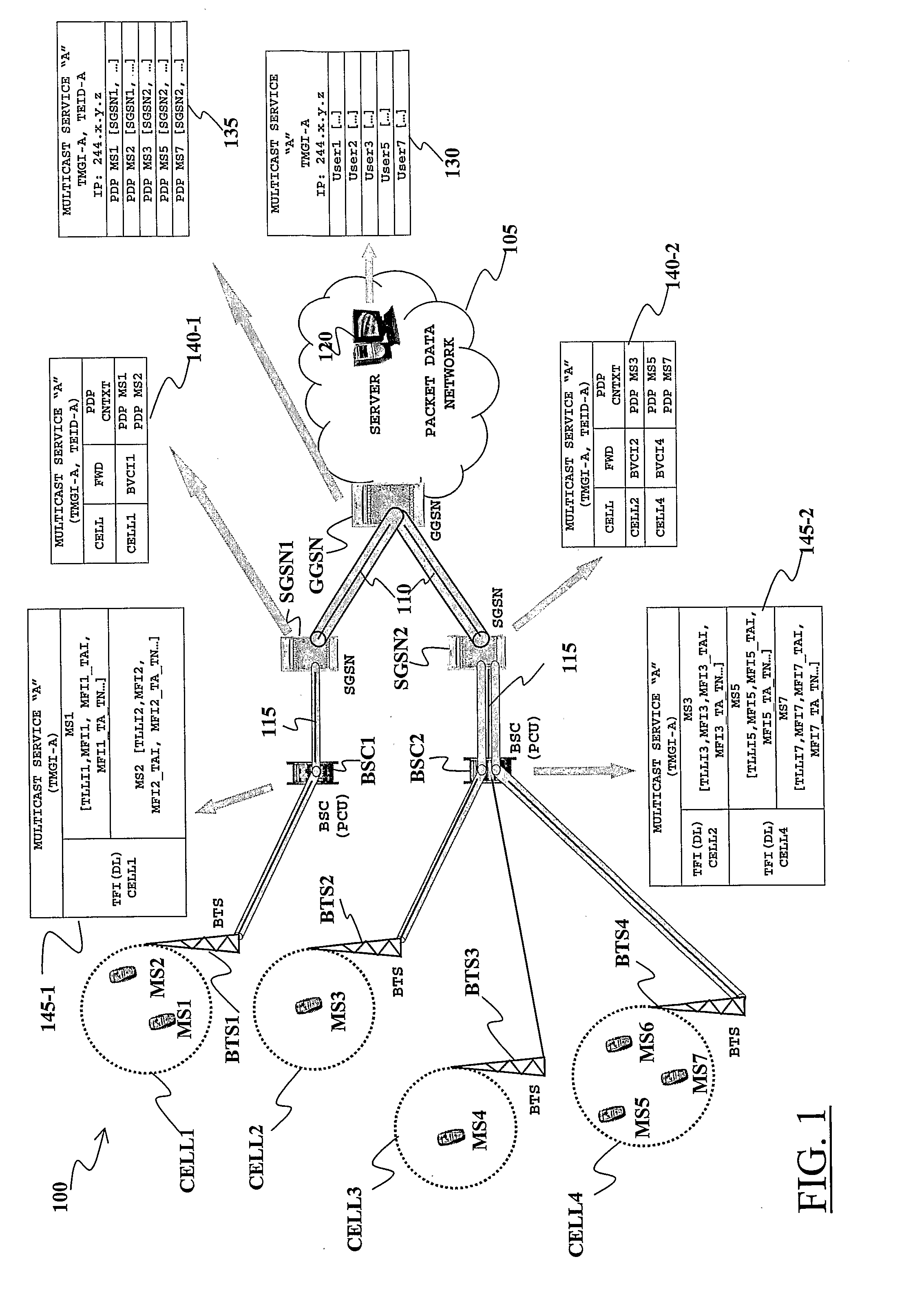
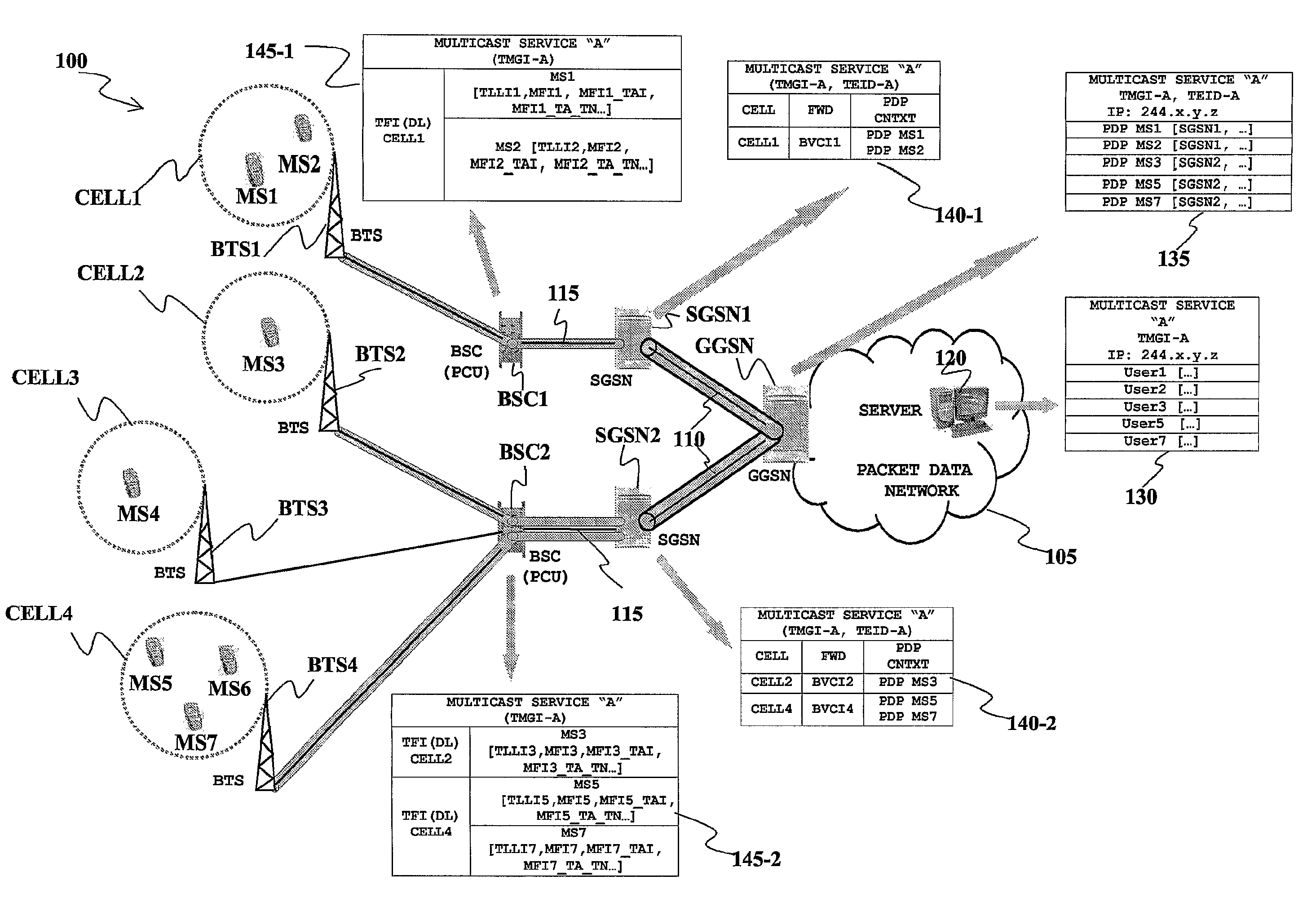
Method and system for efficient distribution of multicast services in a mobile network
InactiveUS20070178916A1Reduce transmission delaySpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelCoding decodingMobile Web
An acknowledged MBMS service in which a procedure for providing retransmissions of incorrectly received data blocks is performed, together with an outer coding of the data blocks to be transmitted to the MBMS MSs. A sequence of data blocks carrying information related to the MBMS service is encoded at a BSS (Base Station Sub-system) of the mobile network by an outer coding unit. After the outer coding, the resulting data block sequence is sent to the MBMS MSs. If a data block of the outer coded sequence is badly received by a number of MBMS MSs, corresponding negative acknowledgements (nacks) are sent by such MSs to the BSS. The MSs also notify the BSS, with a positive acknowledgement, if they succeed in outer code decoding the sequence of the MBMS carrying information data blocks, in spite of possible badly received data blocks. The BSS manages retransmissions of the nacked data blocks taking into account the positive acknowledgements related to the outer code decoding by disabling retransmission of nacked data blocks of a positively acknowledged sequence.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Cellular base station subsystem
A method of operating a cellular base station subsystem such as a smart bias tee. The method comprising: modulating a first control data signal to generate a first modulated carrier signal; multiplexing said first modulated carrier signal with a first RF antenna signal onto a feed line; demultiplexing a second RF antenna signal and a second modulated carrier signal from said feed line; demodulating the second modulated carrier signal to generate a second control data signal; analyzing at least one of said signals to generate diagnostic data; and outputting said diagnostic data. The subsystem also has an addressable memory adapted to provide data on request from said subsystem.
Owner:ANDREW LLC
Methods of Enabling Base Station Functionality in a User Equipment
ActiveUS20160029430A1Enhancing normal consumer-grade power characteristicBoost battery powerNetwork topologiesConnection managementUser equipmentSoftware
In this invention, we disclose methods for enabling ad hoc cellular base station functionality within a user equipment when the connection quality between a base station and the user equipment is limited or nonexistent. These methods include measuring a connection quality between a user equipment and its serving base station. If the connection quality is below a threshold, the user equipment can enable its internal ad hoc cellular base station functionality. This is done by running a software within the user equipment that (a) checks the connection quality periodically, and (b) enables ad hoc cellular base station functionality of the connection threshold dips below a certain value. In one embodiment, that threshold could be the same threshold value that a user equipment would use if it were making a decision to handoff to another base station based on poor connection quality.
Owner:PARALLEL WIRELESS
CPRI-based multiprotocol signal transmission method and apparatus in distributed base station system
InactiveUS7656897B2Network traffic/resource managementInformation formatCommon Public Radio InterfaceEthernet
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD
Communication controller and method for maintaining a communication connection during a cell reselection
ActiveUS20050049000A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCircuit Switched DataOperation mode
The present invention provides a communication controller and a method for maintaining a communication connection during a cell reselection. The communication connection is maintained by changing between a first operating mode, such as a packet data mode, which does not support the maintenance of a communication connection throughout a cell reselection, and a second operating mode, such as a circuit switched mode, which does support maintenance of a communication connection during a handover. Use of a virtual mobile switching center in the base station subsystem facilitates the conversion and routing of circuit switched data, transmitted between the mobile subscriber and the base transceiver station, to the packet data network while in a circuit switched mode.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
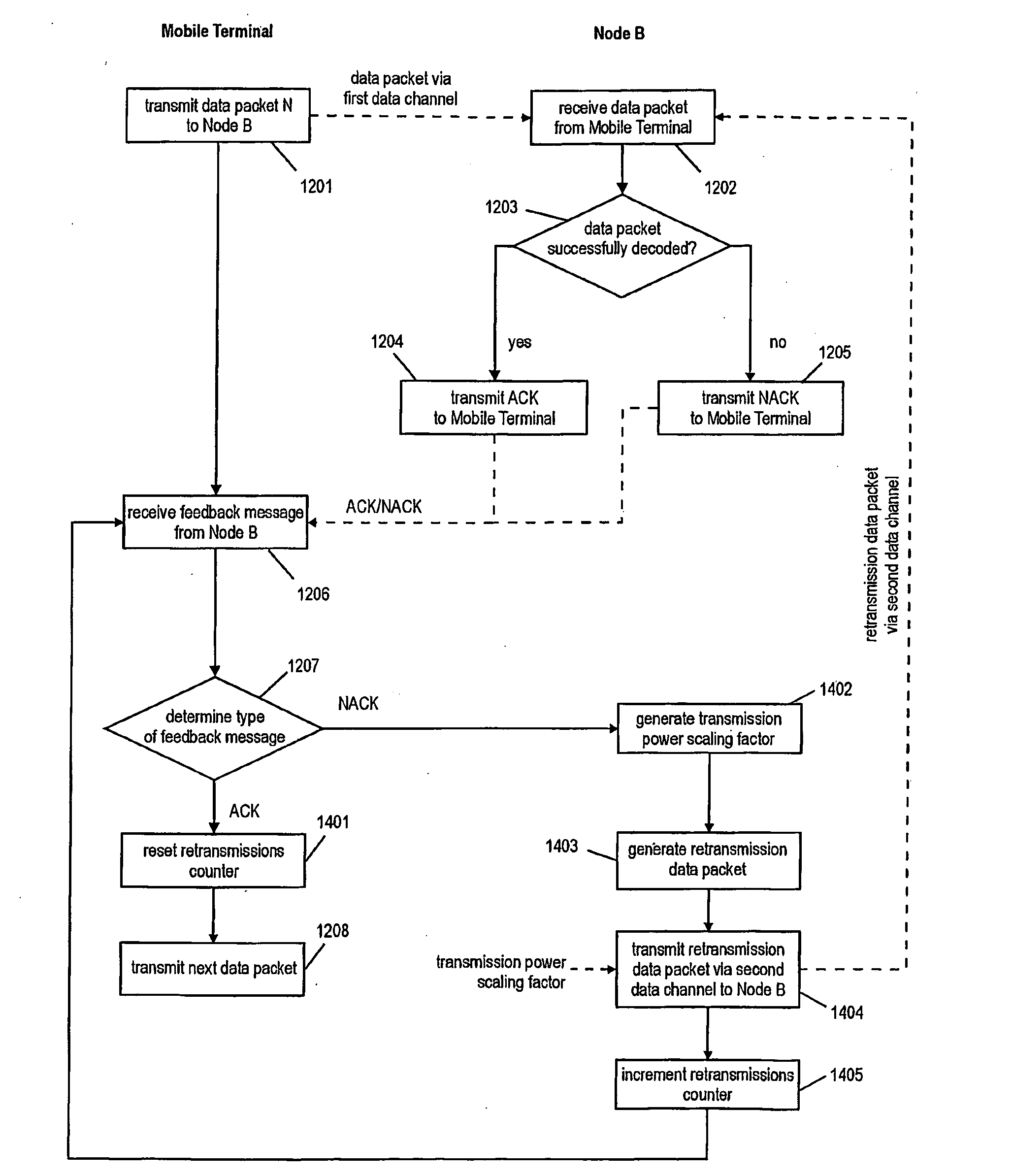
Interference Limitation for Uplink Retransmissions
InactiveUS20080276148A1Reduce transmit powerError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementCommunications systemComputer terminal
The present invention relates to a method for transmitting data packets from a mobile terminal to a base station using a hybrid automatic repeat request protocol and soft combining of received data. Further, the present invention provides a base station and a mo-bile terminal both configured to perform the respective method steps. Moreover, a communication system is provided which comprises at least one base station and at least one mobile terminal. In order to decrease the interference caused by retransmissions, the present invention suggests the use of separated channels for initial transmissions and their retransmissions. In order to decrease the interference caused by retransmissions, the present invention suggests the use of separated channels for initial transmissions and their retransmissions.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and system for providing location information for emergency services
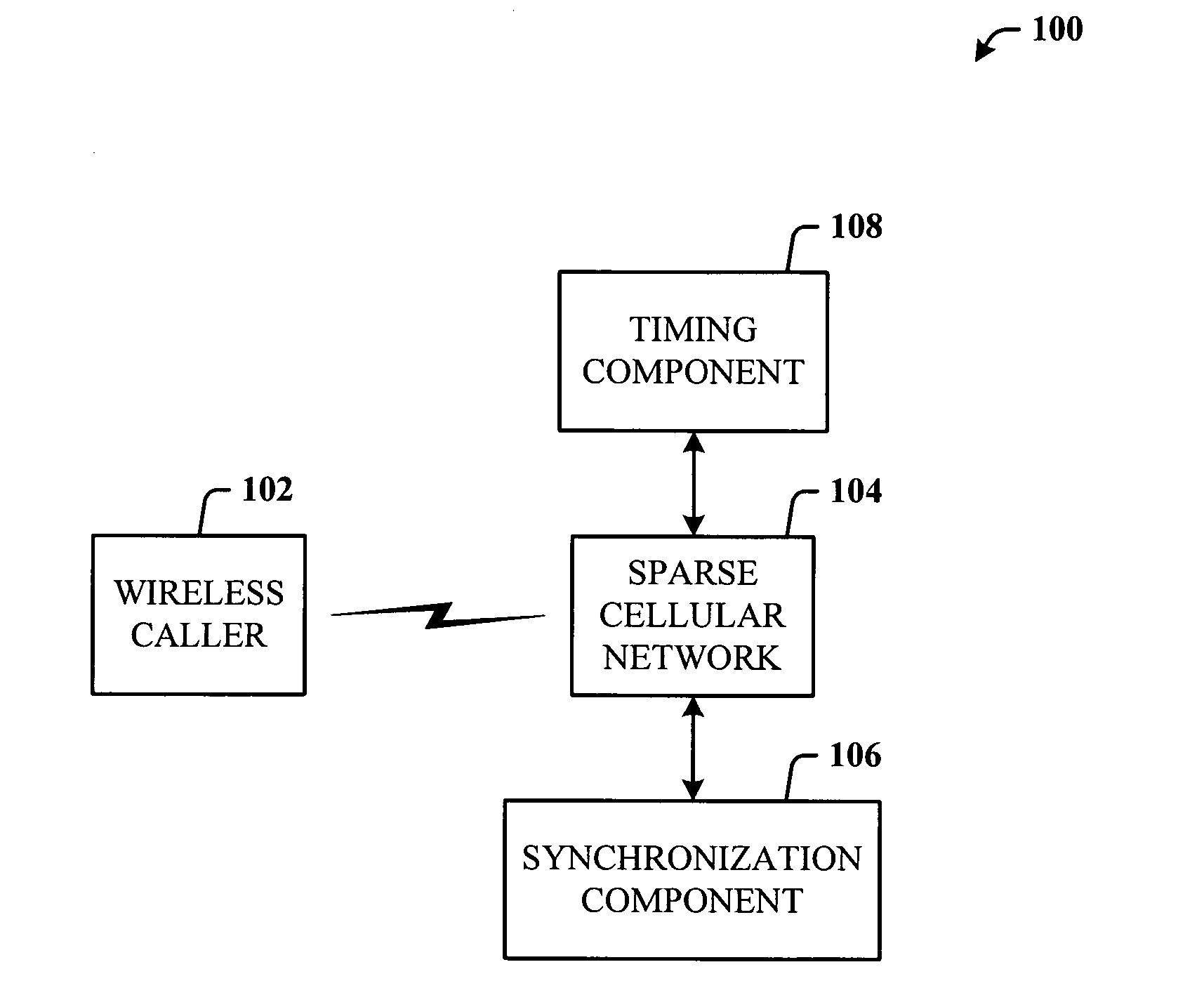
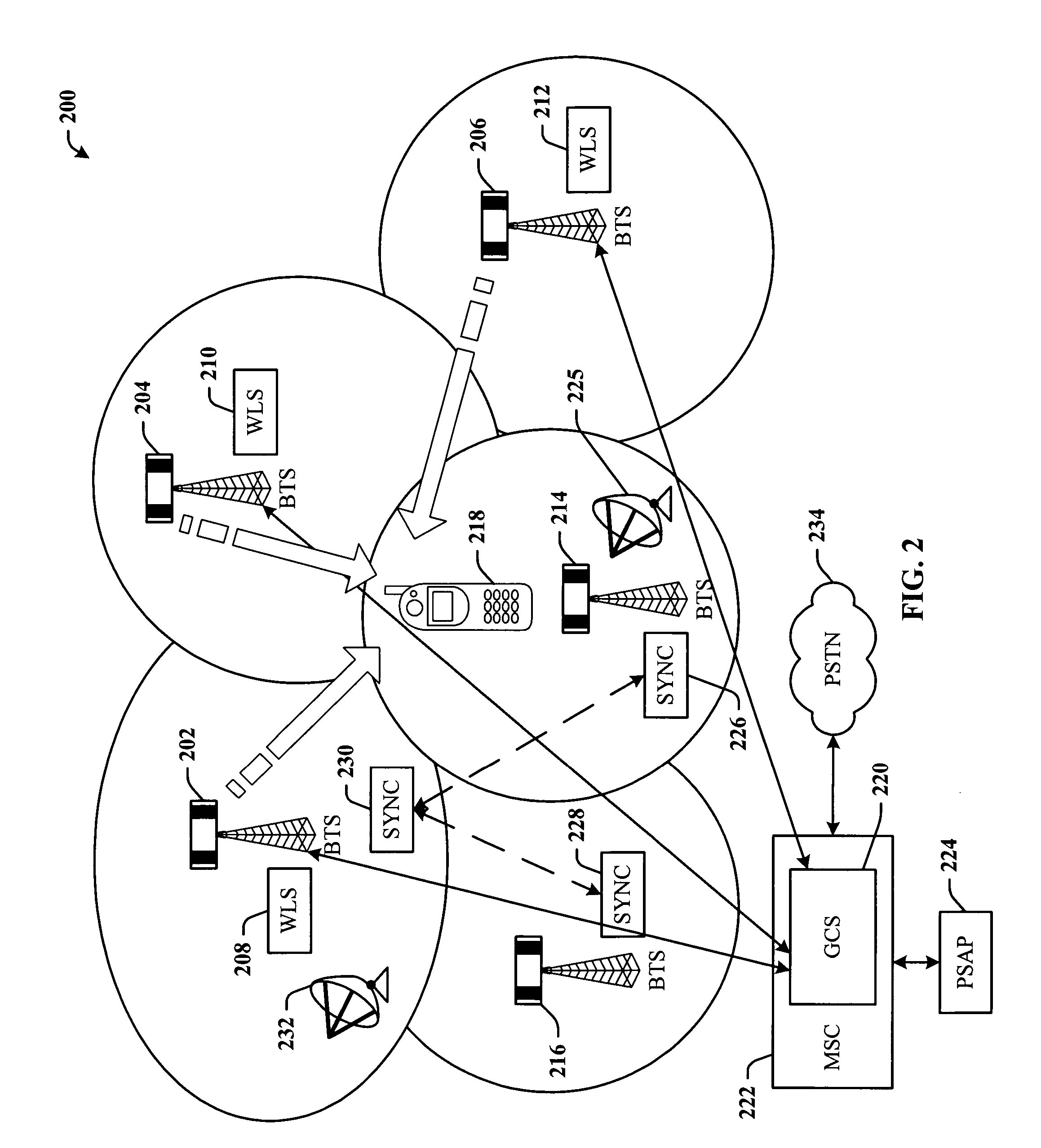
Emergency Services architecture for determining the location of a wireless caller. The architecture leverages a synchronization feature of GSM networks of the Base Station Subsystem (BSS) to enable employment of sparse networks by removing WLS (Wireless Location Sensor) equipment from selected cell sites. Thus, the location of a wireless caller within a sparse site can be determined. Sparse network location services can be provided further utilizing Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) technology, and other network-based location technologies such as Enhanced Observed Time Difference (EOTD) and Angle of Arrival (AOA). Hybrid network-based / handset-based location technologies may also be used with the disclosed invention.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Indoor and outdoor positioning system and method integrating GPS and inertial navigation based on UWB (Ultra Wideband)
ActiveCN109283565AEasy to carry and usePrevent deviationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingUltra-widebandData acquisition
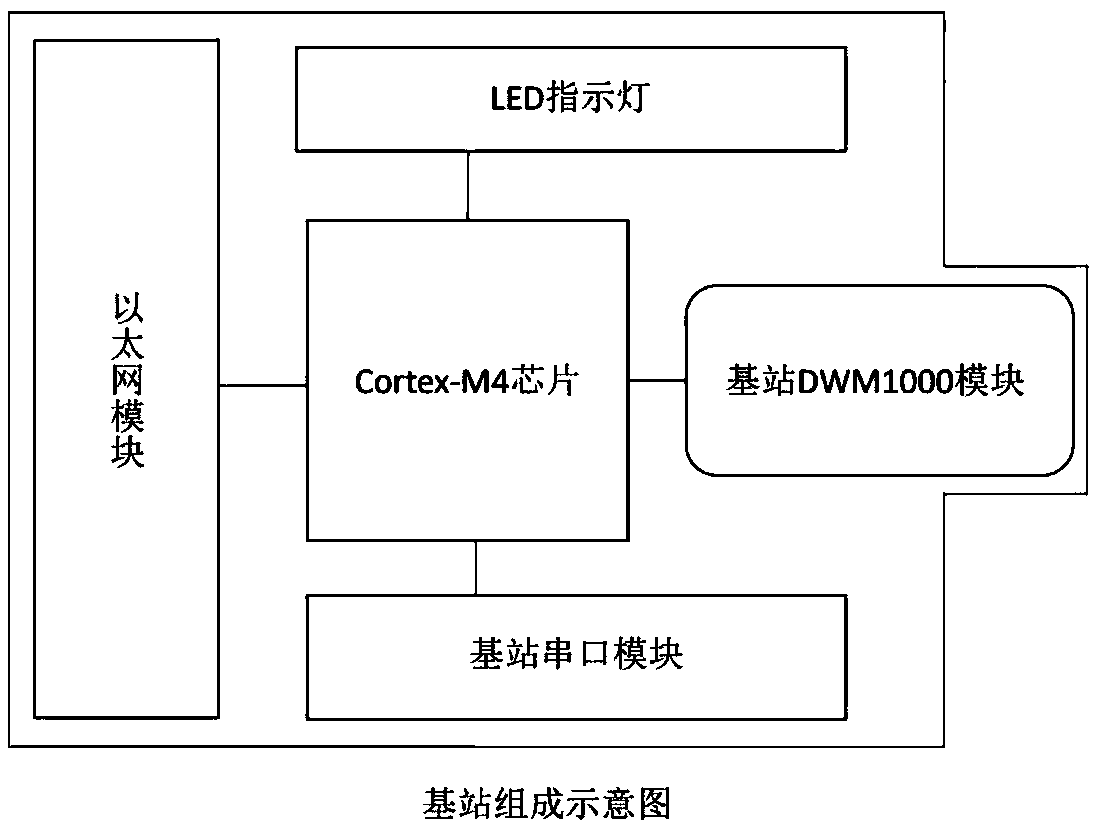
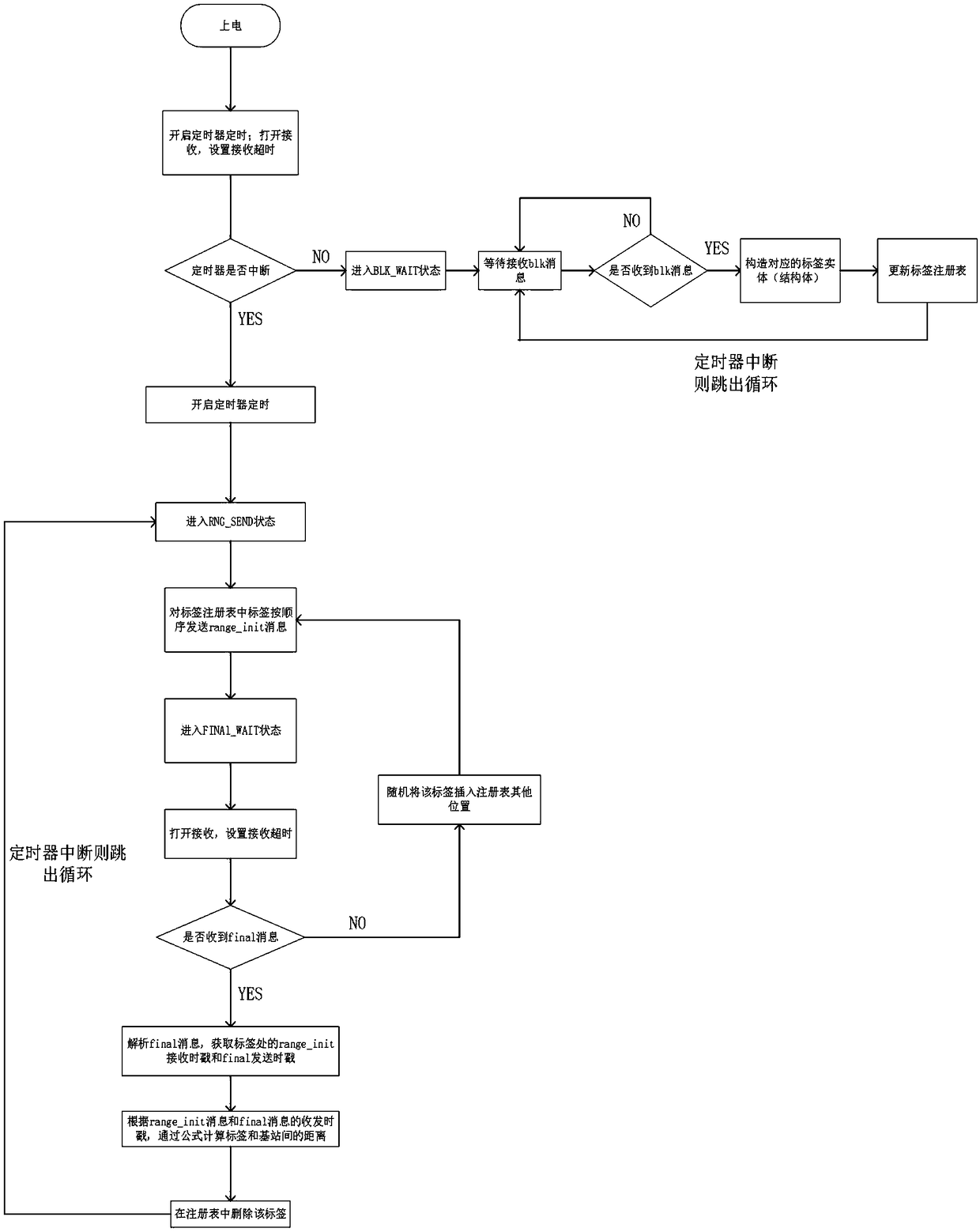
The invention discloses an indoor and outdoor positioning system and method integrating the GPS and inertial navigation based on the UWB (Ultra Wideband). The indoor and outdoor positioning system iscomposed of a label subsystem, a base station subsystem and a data processing subsystem. Disclosed by the invention is an indoor and outdoor positioning system and method integrating the GPS and inertial navigation based on the UWB, and dynamic accurate positioning and complete data acquisition of a target user in different indoor and outdoor environments are realized by using the UWB technology and inertial navigation. The indoor and outdoor positioning system and method are mainly applied to the Internet of things industry, the tourism industry, business places, airports, fire protection, public security, military, parking lots, hospitals, robots, unmanned aerial vehicles, tunnel mines and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ZHENJIANG POWER SUPPLY CO +1
System and method of servicing mobile communications with a proxy switch
The present invention provides a proxy switch, communication methods, and communication logic for use in a mobile network. A proxy switch is deployed between a base station subsystem and a mobile station center. The proxy switch receives signaling messages and either retransmits them, blocks them, converts them, or siphons them to an alternative network. Besides providing an ability to offload mobile traffic it provides a platform for new communication services.
Owner:WINPHORIA NETWORKS
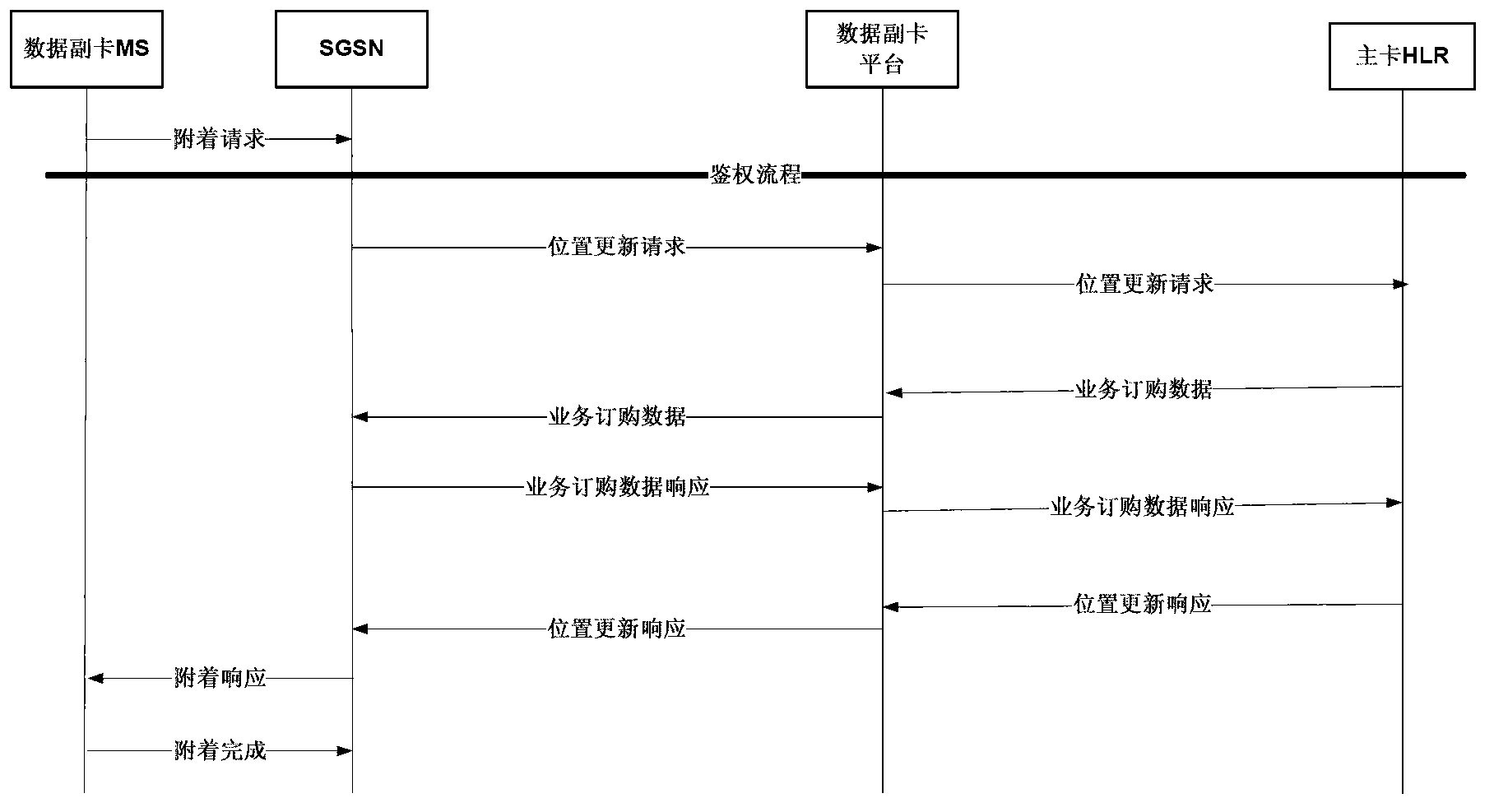
Method and system for implementing flow sharing of multiple mobile terminal cards
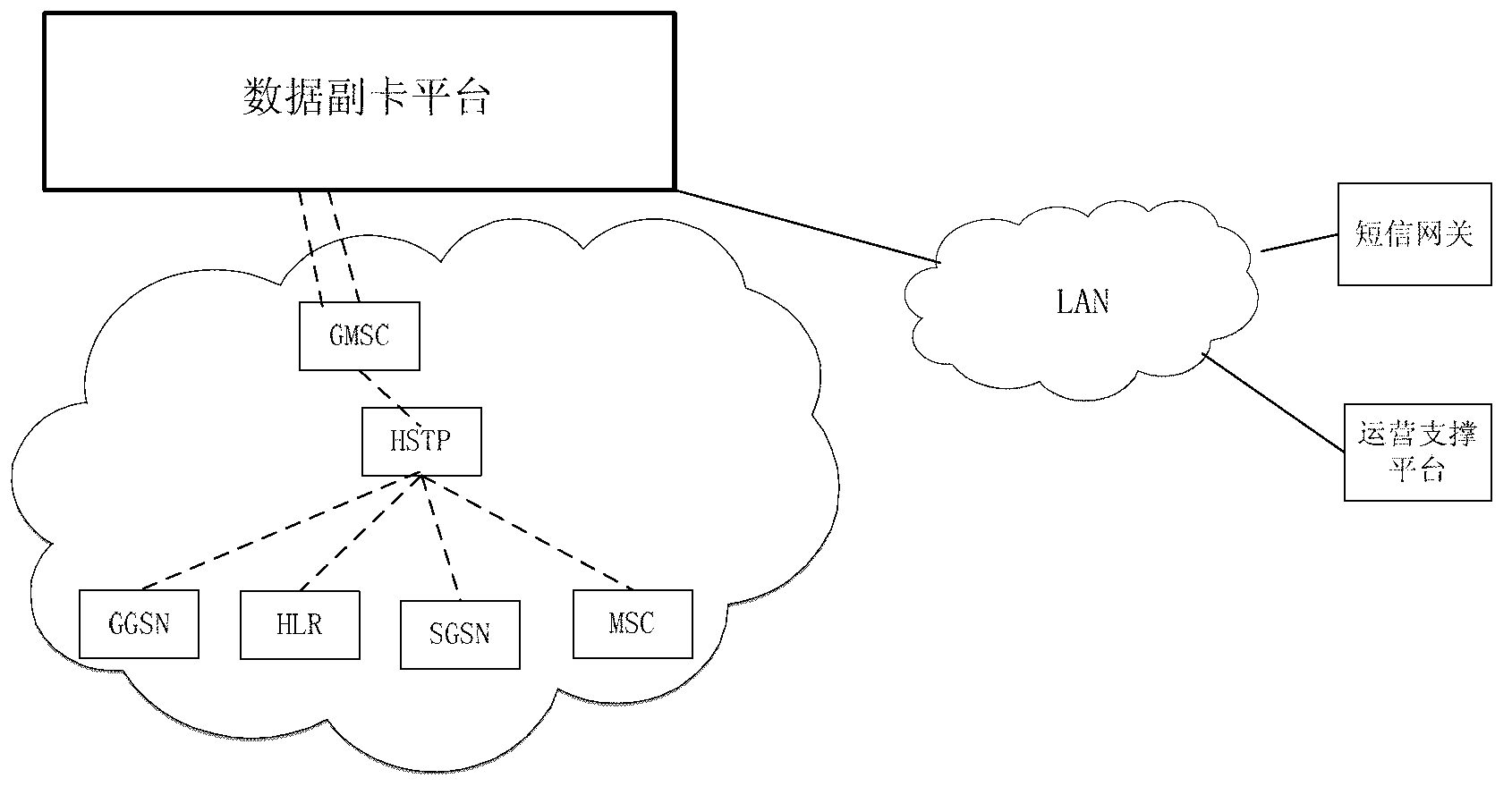
InactiveCN102843668AMeet the conditions for trial commercial useCompliance with specificationsConnection managementNetwork planningGeneral Packet Radio ServiceIntegrated Services Digital Network
The invention provides a method and a system for implementing the flow sharing of multiple mobile terminal cards. The method concretely comprises the following steps: an additional data card platform is established; E. 214 route data are configured for an HSTP (high signaling transfer point), and a special IMSI (international mobile subscriber identity) number segment route for an additional data card is directed to the additional data card platform; the additional data card platform participates in the PS (packet switched) domain attachment process of the additional data card, so that the additional card generates Internet call tickets taking a main card MSISDN (mobile subscriber ISDN (integrated services digital network) number) and an additional card IMSI as identifiers in an SGSN (serving GPRS support node) and a GGSN (gateway GPRS (general packet radio service) support node); and after acquiring a billing center, the call tickets are combined through taking MSISDN as an identifier, so that the Internet call ticket of the additional card is merged into an account of the main card. According to the invention, through providing the additional data card platform, the flow sharing of multiple mobile terminal cards is implemented through the signaling exchange between the additional data card platform and a core network, no improvement on the core network, a BSS (base station subsystem) and a CRM system is required, the service processes of the existing BSS, SGSN (service GPRS supporting node) and CRM and the like are not affected, and no influence is caused on an operator network, thereby realizing the inter-flow sharing of 3G main number packages.
Owner:BEIJING DASCOM TECH
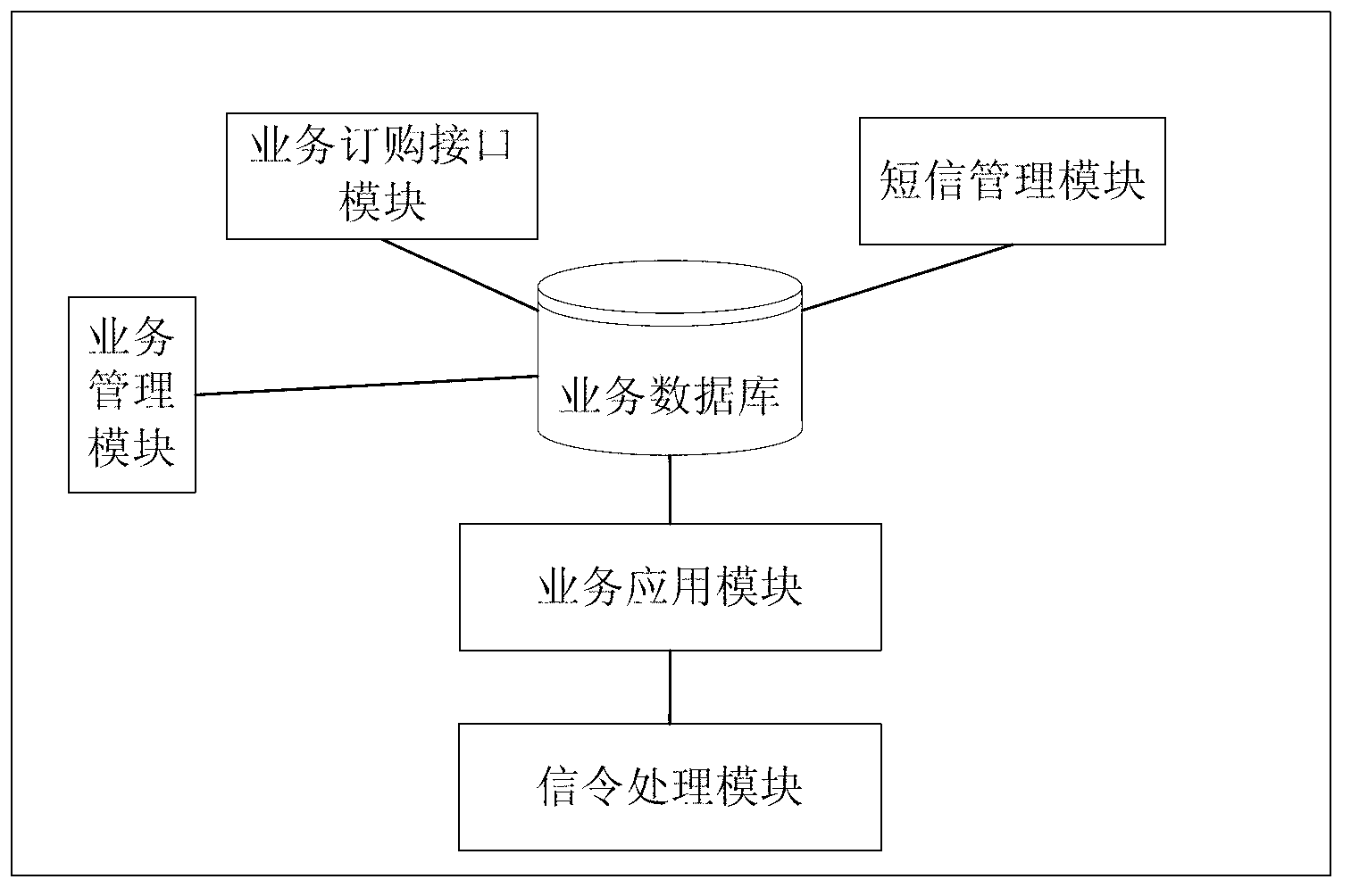
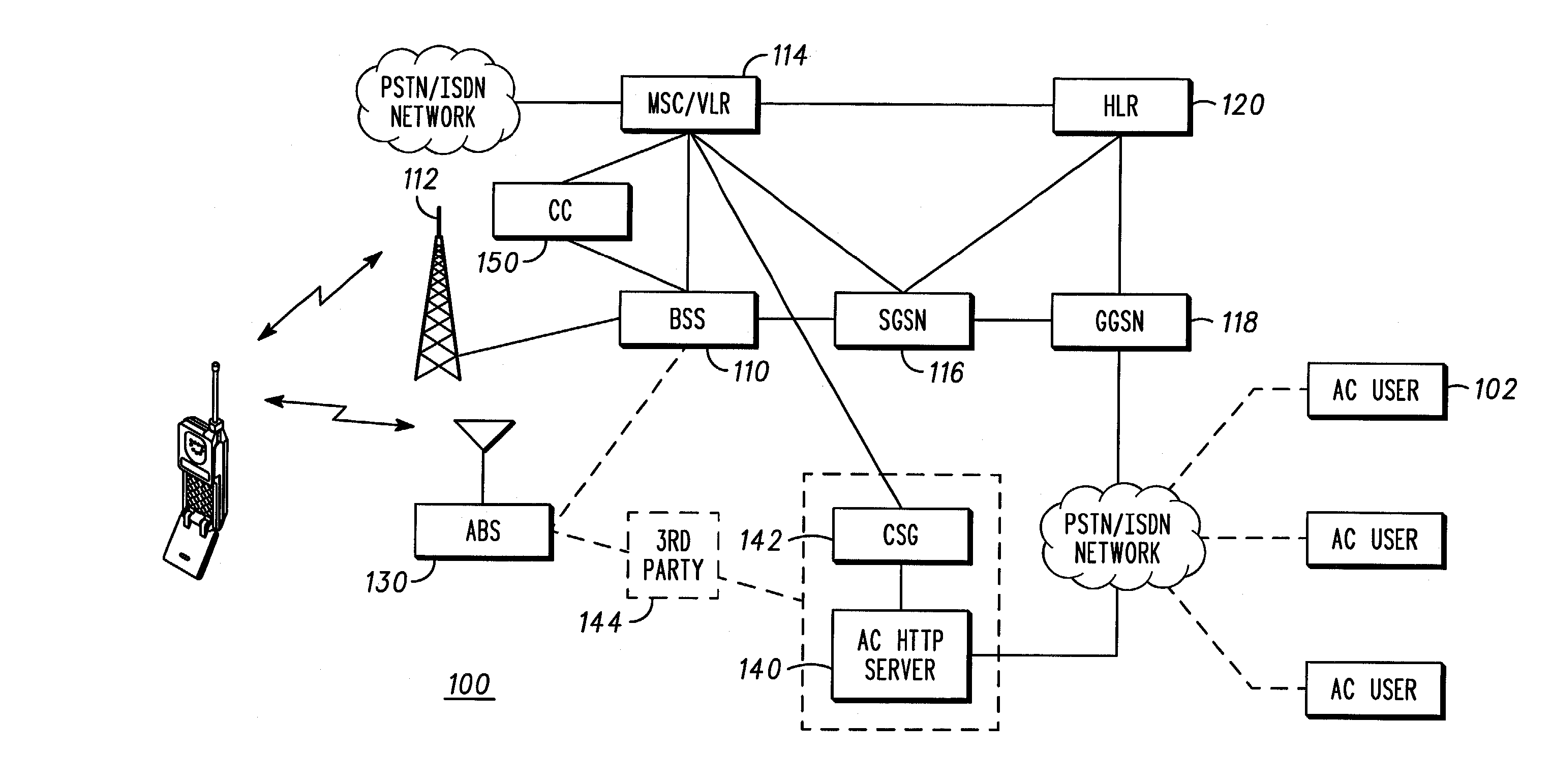
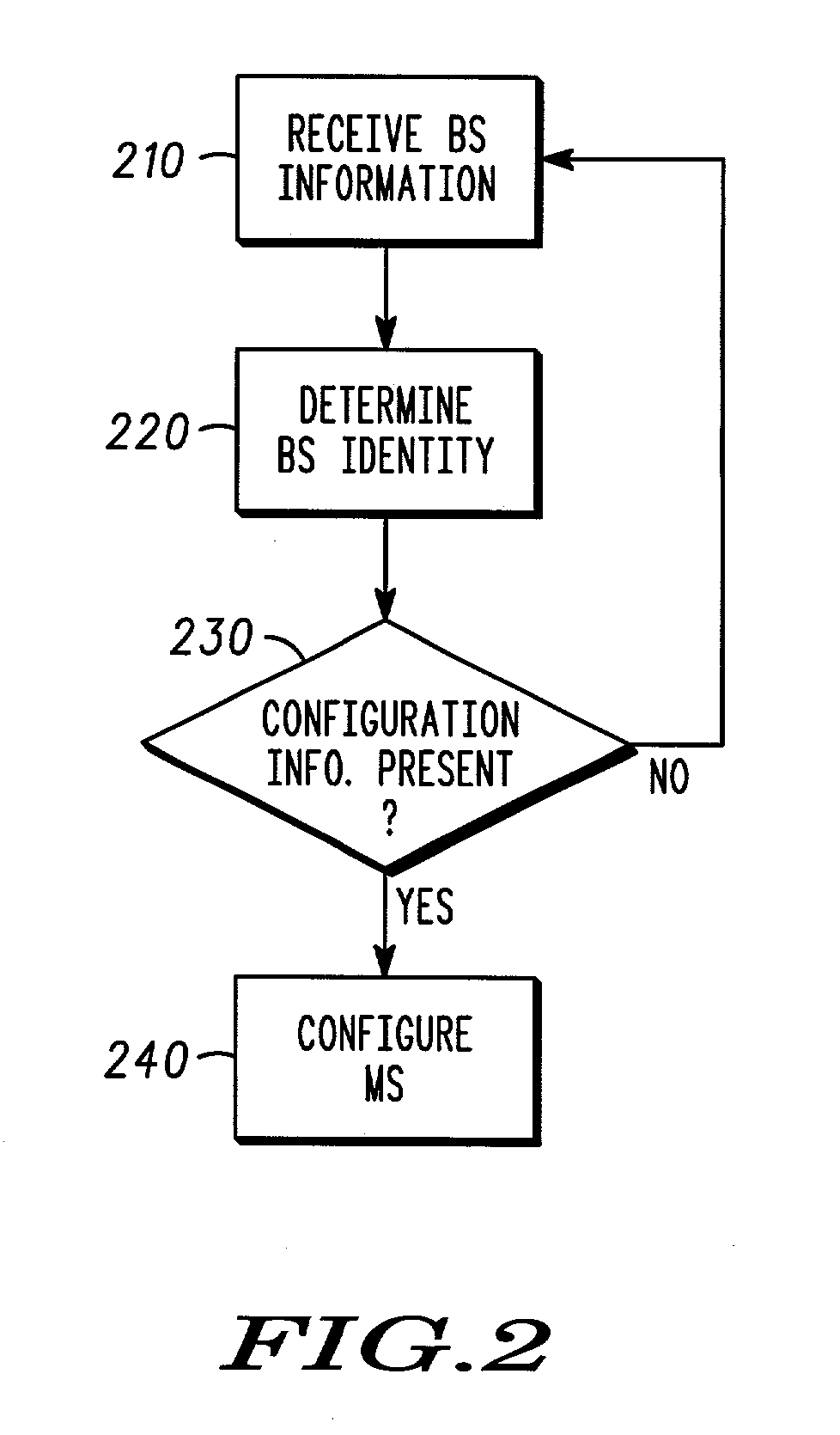
Dynamic mobile station configuration in wireless communications systems and methods therefor
ActiveUS20030224772A1Assess restrictionConnection managementCommunications systemCommunication device
A cellular communications network including a base station subsystem (110) including a base station controller communicably coupled to a plurality of base stations (112), a user accessible mobile wireless communications device configuration control server (140) coupled to the base station subsystem (110), an network broadcast transmitting assisting base station (130), which may be coupled to the user accessible mobile wireless communications device configuration control server or to the base station subsystem. A mobile station is configured with configuration information associated with the assisting base station when the mobile station monitors the assisting base station.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Base Station System
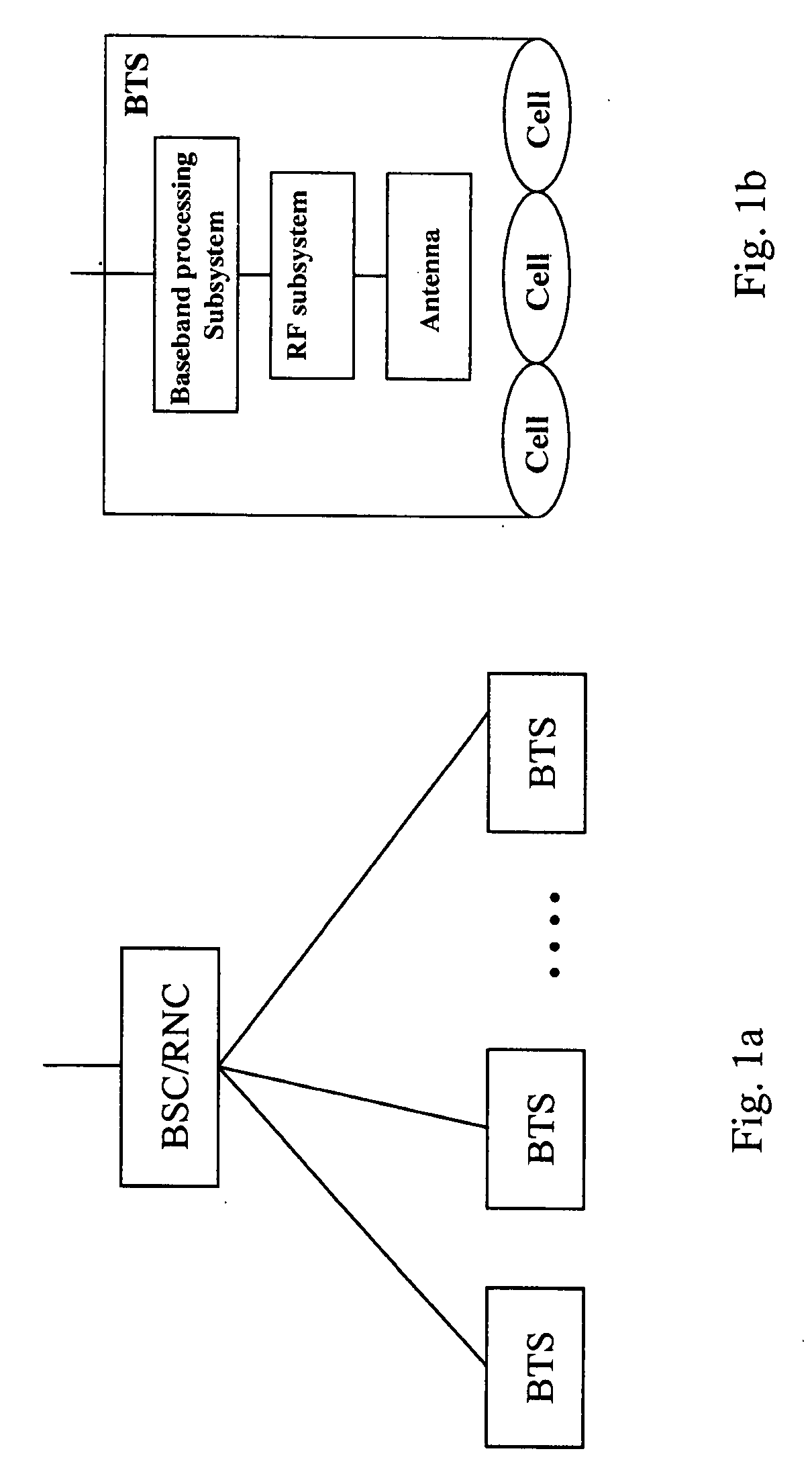
ActiveUS20080317464A1Increase coverageReduce network operating costsSubstation equipmentOptical multiplexTransceiverSmart antenna
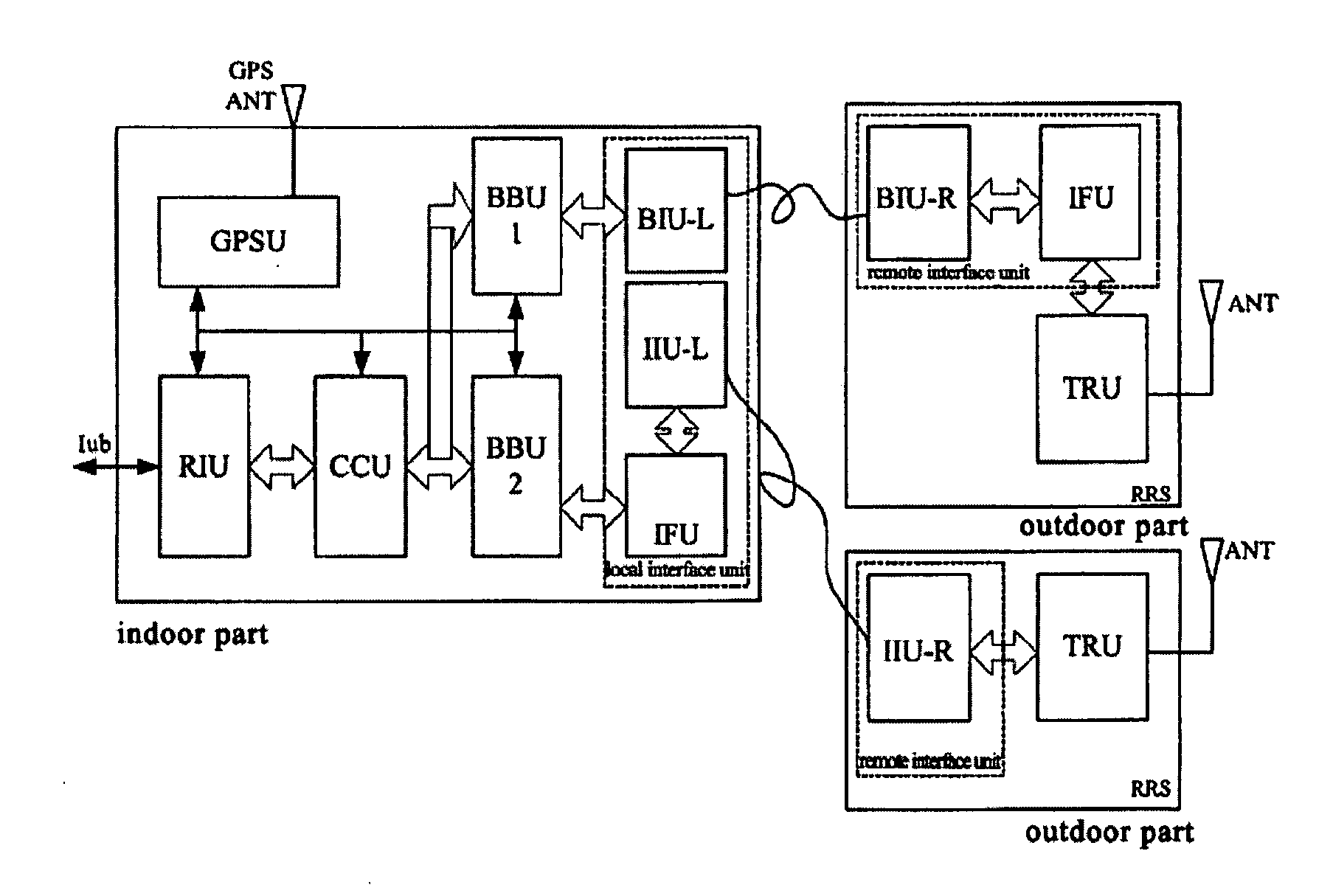
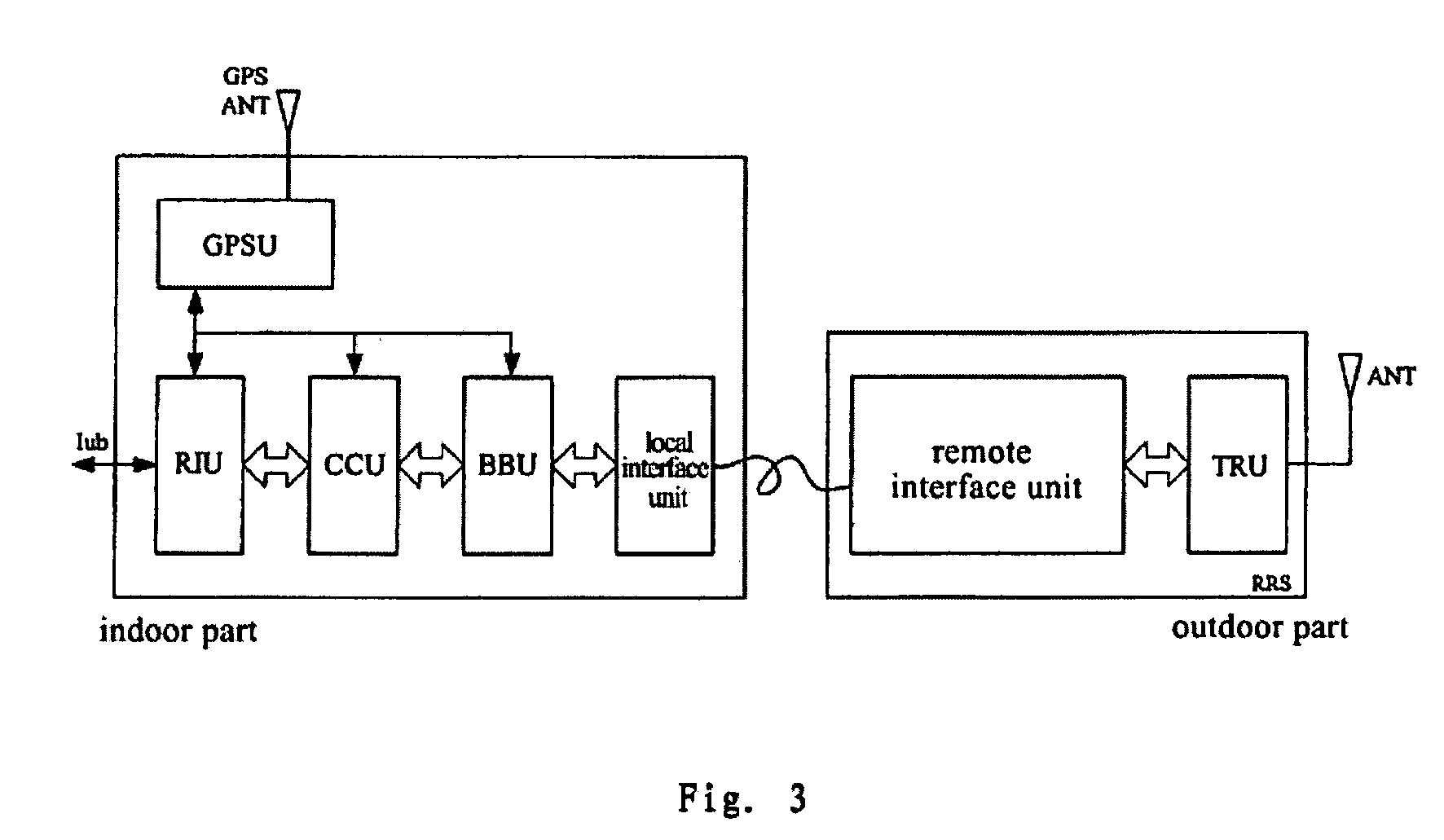
The present invention discloses a base station system, including an indoor part and a remote RF subsystem (RRS). The indoor part includes a RIU, a CCU, a BBU, a GPSU and a local interface unit. The RRS includes a remote interface unit, a RF transceiver unit (TRU) and an antenna. The local interface unit and the remote interface unit are for signal intercommunicating between the indoor part of the base station and the RSS. The TRU is a RF transceiver module of the conventional RFU, for amplifying an analog RF signal from the remote interface unit and transmitting the signal to the antenna. By flexibly selecting between an optical cable and an If cable, the interface unit of the present invention provides a digital baseband remote manner and an IF remote manner. According to the structure of the base station of the present invention, the number of the base station sites and the network operating cost decreases; on the other side, since one base station may cover a cell by smart antenna with only one optical cable or IF cable, the difficulty in mounting is reduced.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
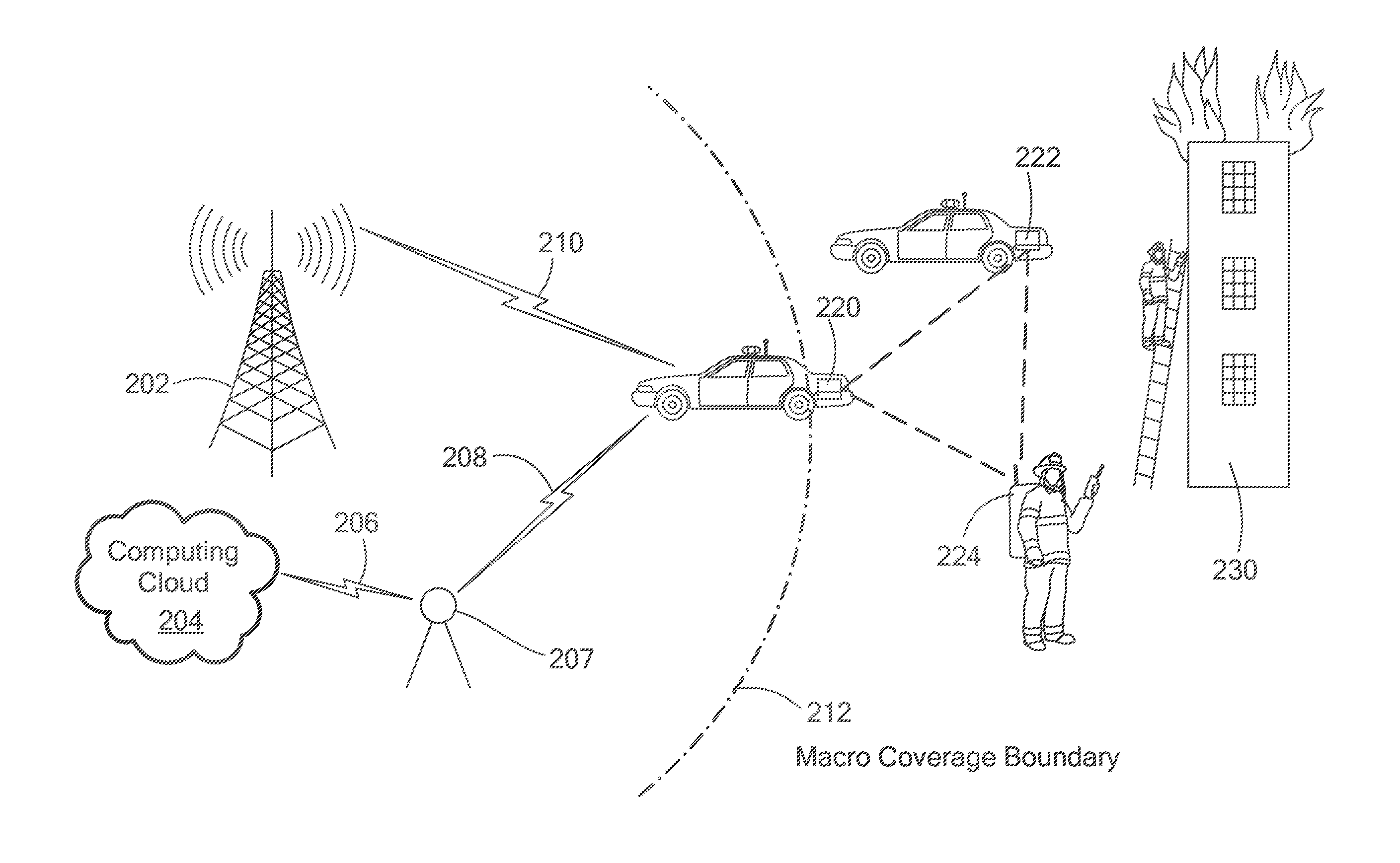
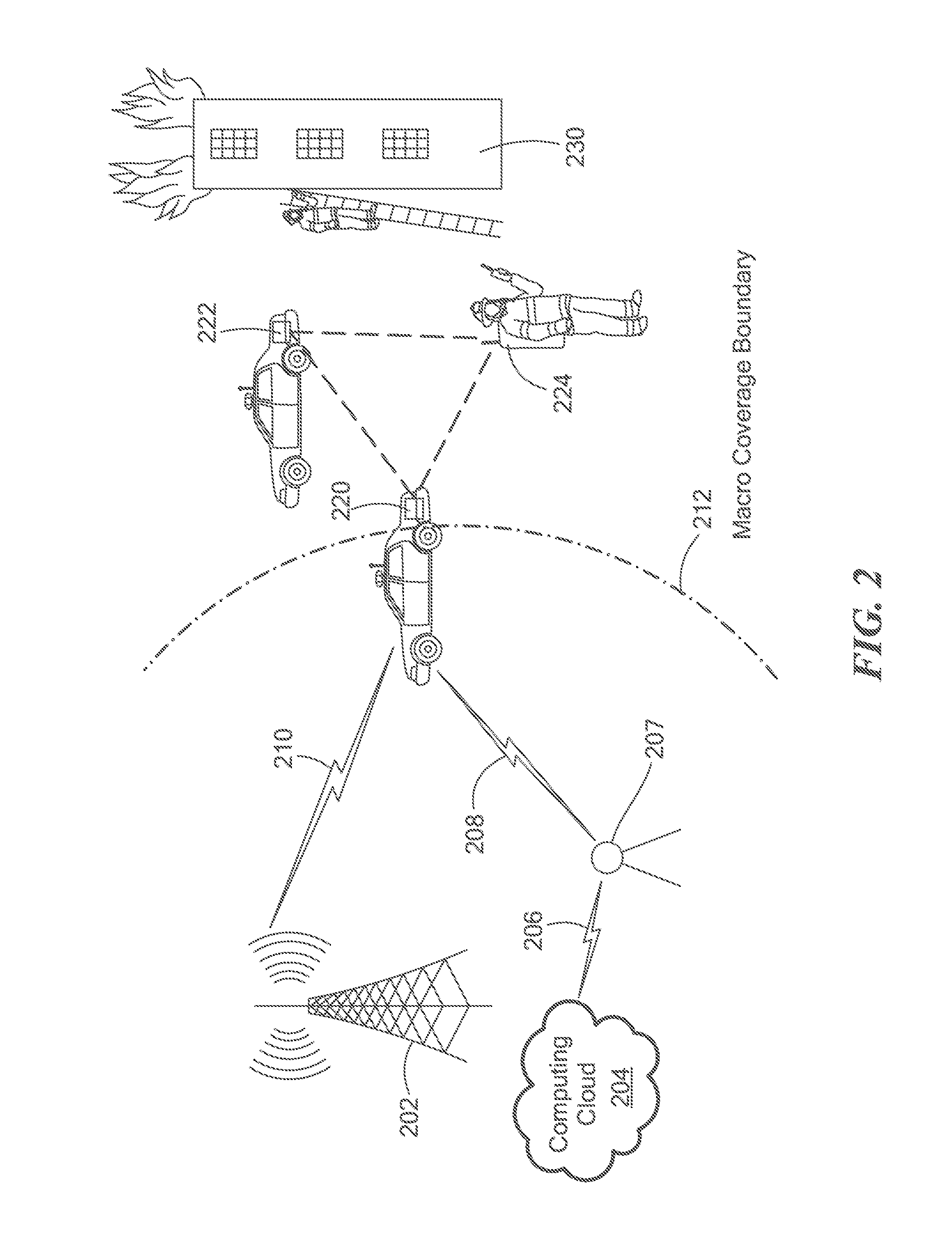
Firefighter locator
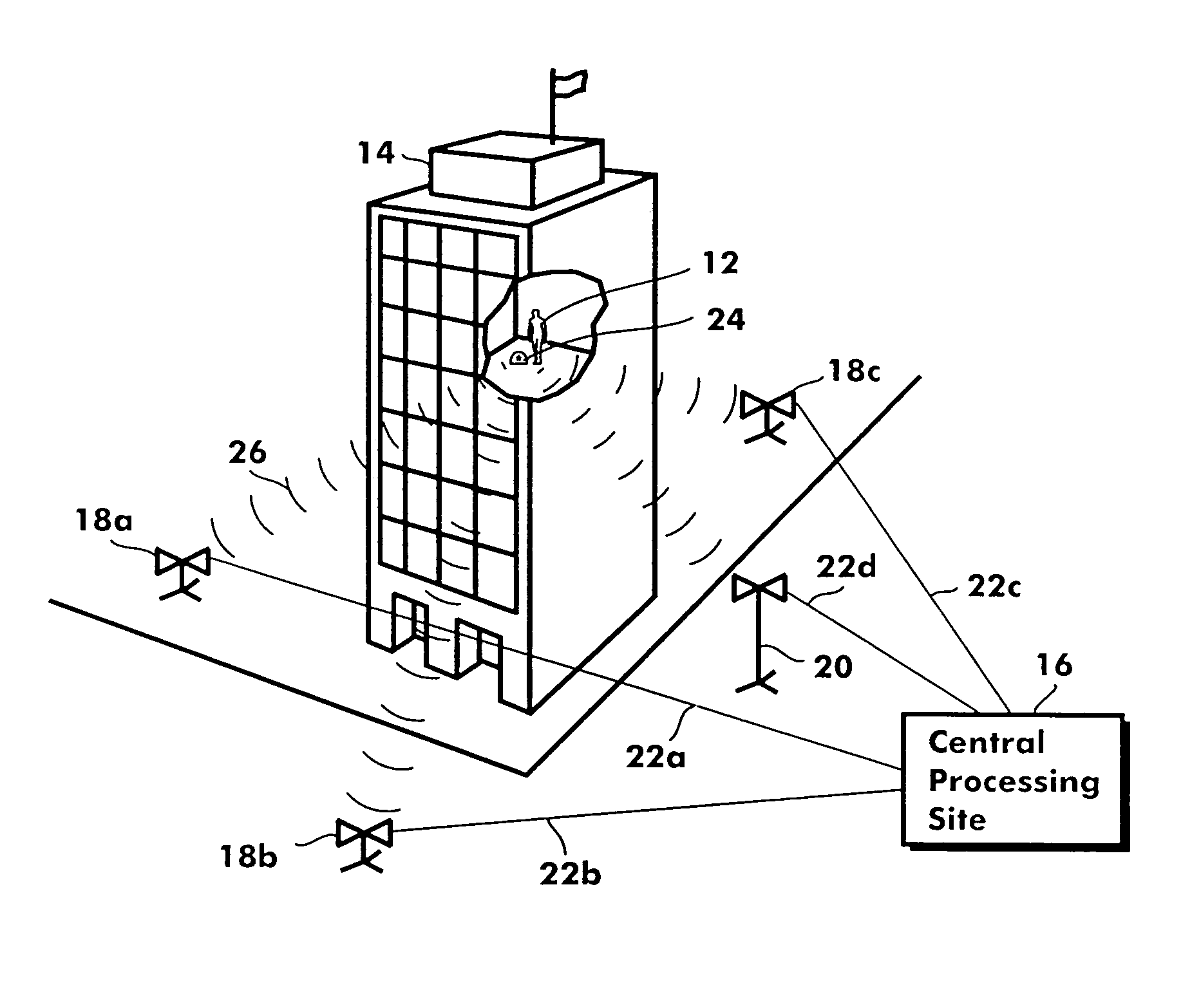
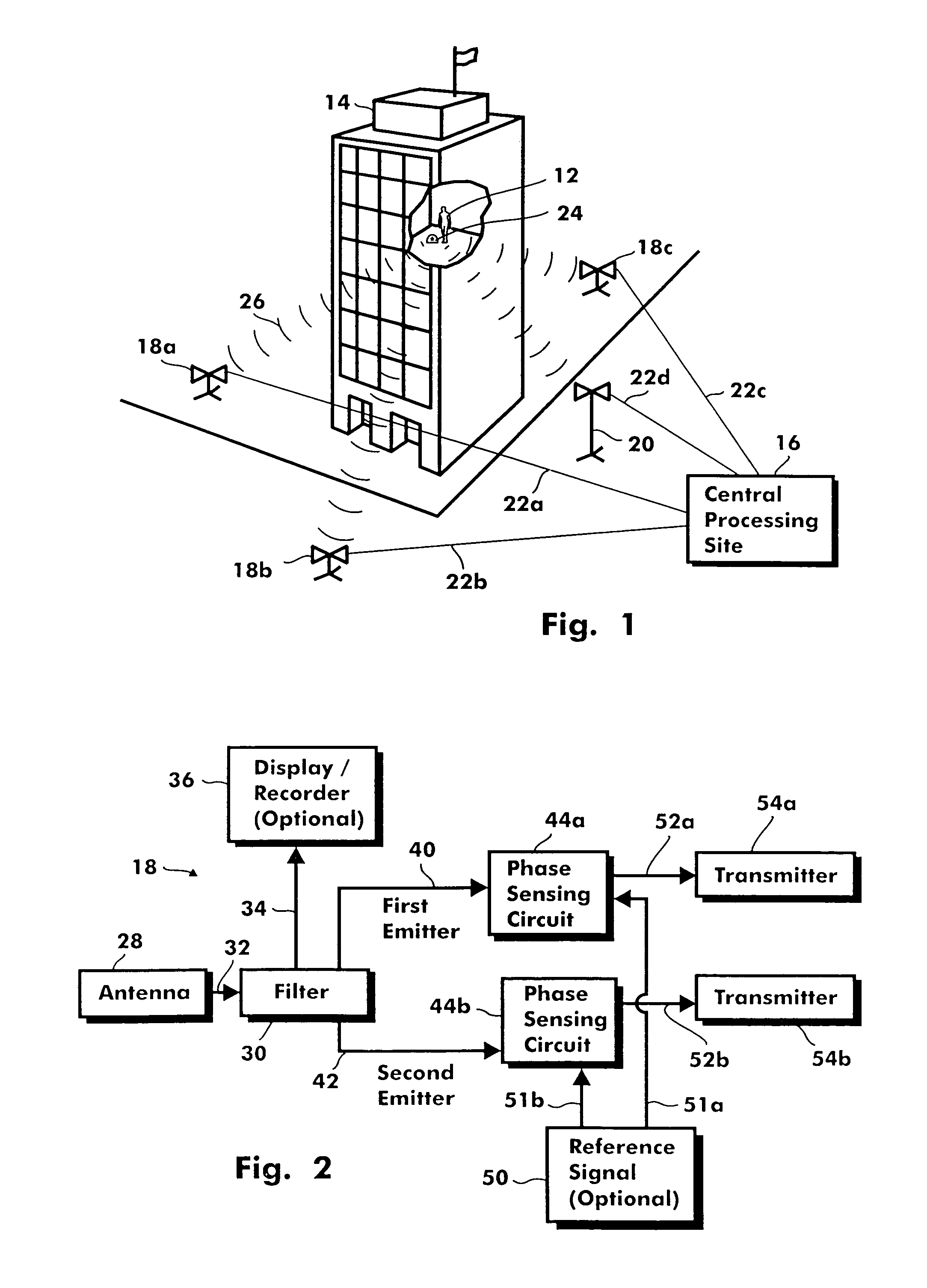
InactiveUS6965344B1Reduce and eliminate ambiguityReduce ambiguityBreathing protectionDirection finders using radio wavesRelative phaseOmni directional
A wireless system and method for locating the position of a movable signal emitter located inside or adjacent to a structure includes establishing at least three base station sites at known locations around the structure. The signal emitter then transmits an omni-directional, low frequency, RF signal that is received at the base station sites. Phase information is measured at each base station site and communicated to a central processing site. At the central processing site, relative phase delays are used to geometrically calculate the position of the signal emitter.
Owner:INFORMATION SYST LAB
Communication controller and method for maintaining a communication connection during a cell reselection
InactiveUS6975881B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCircuit Switched DataOperation mode
The present invention provides a communication controller and a method for maintaining a communication connection during a cell reselection. The communication connection is maintained by changing between a first operating mode, such as a packet data mode, which does not support the maintenance of a communication connection throughout a cell reselection, and a second operating mode, such as a circuit switched mode, which does support maintenance of a communication connection during a handover. Use of a virtual mobile switching center in the base station subsystem facilitates the conversion and routing of circuit switched data, transmitted between the mobile subscriber and the base transceiver station, to the packet data network while in a circuit switched mode.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
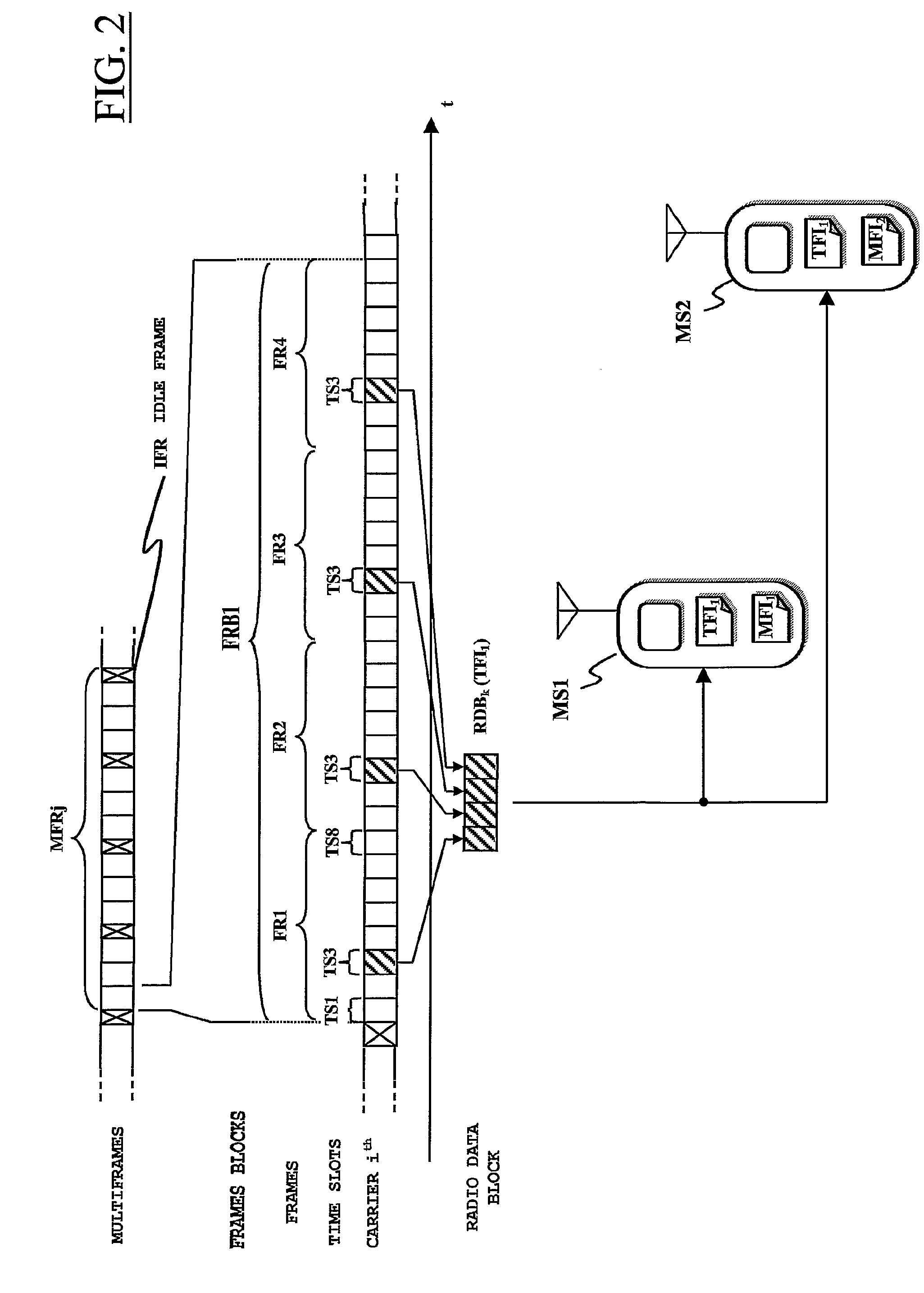
Method and system for distributing multimedia contents through a wireless communications network, particularly a mobile telephony network
ActiveUS8238895B2Efficient implementationSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementMobile telephonyBase station subsystem
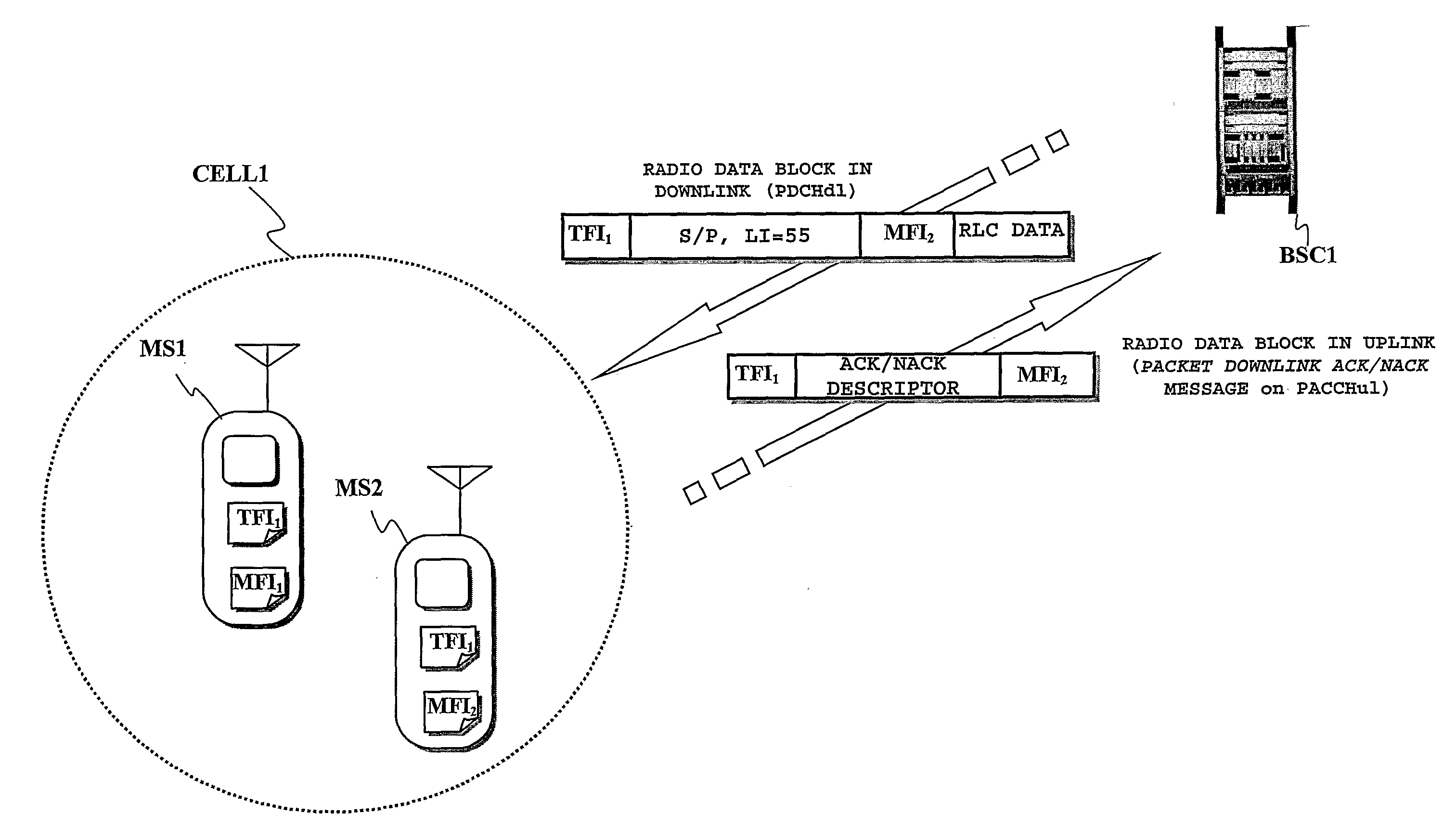
In a wireless communications network having a base station subsystem controlling at least one network cell, and in which the base station subsystem communicates with mobile stations in the cell through radio blocks, a method of distributing information contents received in data packets at the base station subsystem to the mobile stations, includes obtaining, starting from the data packets, radio blocks to be transmitted through the network cell, labeling the radio blocks with a first radio link identifier, identifying a logic connection between a mobile station and the base station subsystem, communicating the first radio link identifier to a first mobile station in the network cell, and in case at least one second mobile station in the network cell, asks to receive the information contents, communicating thereto the first radio link identifier. The method further includes having the first mobile station and the at least one second mobile station assigned respective second radio link identifiers to be included in the radio blocks.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
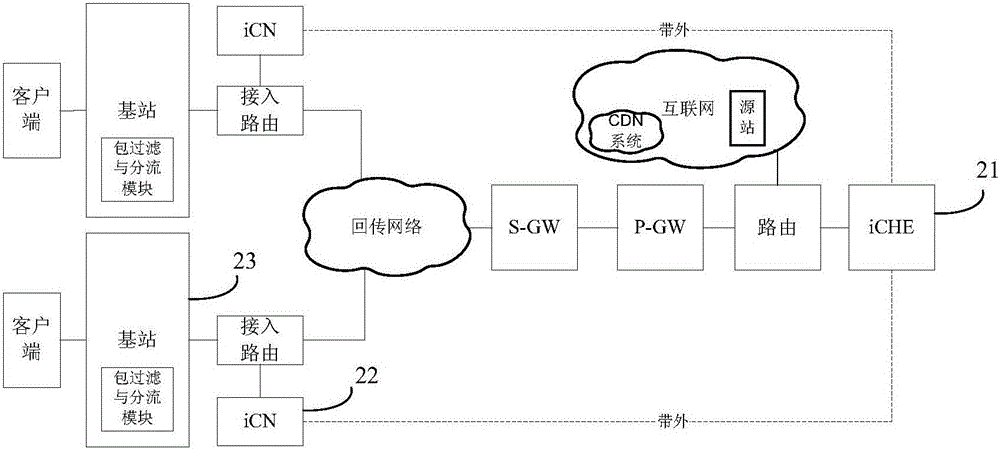
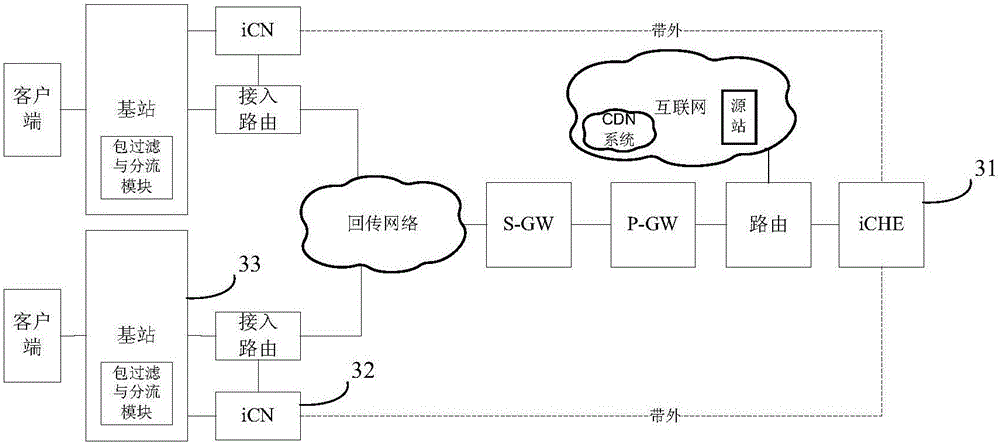
Mobile network based edge service communication method and system
InactiveCN105791392AFlexible deploymentImprove experienceData switching networksData transmission timeMobile Web
The invention discloses a mobile network based edge service communication method and system. The mobile network based edge service communication method comprises the steps of, by a control node, analyzing a first request sent by a base station and searching a first storage node in a first preset storage node set based on the first request; if the first storage node is searched, sending a first response which includes the address of the first storage node to the base station; sending a second request which includes the first request to the first storage node based on the address of the first storage node by the base station; and sending a second response to the base station based on the second request by the first storage node. The position of a storage node where request content is stored can be obtained by pre-storing the storage node set in a control node, so that the specific deployment position of each storage node is unnecessary to consider, and each storage node can be deployed flexibly; meanwhile, as the request content is sent to the base station directly by each storage node, the data transmission time is reduced greatly, and the use experience is enhanced.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CAS
Wireless sensor network relay node deployment method
ActiveCN103716803AGuaranteed connectivityScalableNetwork topologiesNetwork planningWireless sensor networkingNode deployment
The invention discloses a wireless sensor network relay node deployment method. The method comprises the following steps of 1) obtaining deployment positions of base stations and sensor nodes as well as deployment candidate positions of relay nodes and constructing a heterogeneous communication diagram; 2) selecting a first set XA of the least relay nodes which can perform k-coverage of all the sensor nodes based on the heterogeneous communication diagram; 3) constructing a forwarding communication graph with edge weight based on the first set XA, the deployment positions of the base stations, and the deployment candidate positions of the relay nodes; 4) obtaining a second set XB of the least relay nodes which can connect the first set XA and the base stations based on the forwarding communication graph; and 5) combining the first set XA and the second set XB and constructing a final solution. The wireless sensor network relay node deployment method is capable of ensuring the network connectivity, guaranteeing that each sensor node has at least one path to connect with the corresponding base station, and also ensuring that the fewest possible relay nodes are deployed on the premise of ensuring the network connectivity.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
System and method for providing voice communications for radio network
InactiveUS7061894B2Eliminate the problemUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsPacket communicationRadio networks
A system for providing voice communications between an end terminal in a packet data network and a wireless communication device includes a packet communication supporting subsystem, a base station subsystem, and a Voice-over-Internet-Protocol Mobile Switching Center (“VMSC”). The packet communication supporting subsystem communicates with the packet data network and also operates to locate the wireless communication device. The base station subsystem communicates with the wireless communication device, and also communicates the packet data network through the packet communication supporting subsystem in the form of data packets. The VMSC communicates with the packet communication supporting subsystem through a packet-switched network and communicating with the base station subsystem through a circuit-switched network. In addition, registration, call-making, call-releasing, and call-receiving methods are provided for a wireless communication device to provide voice communications between the wireless communication device and an end terminal in a packet data network.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
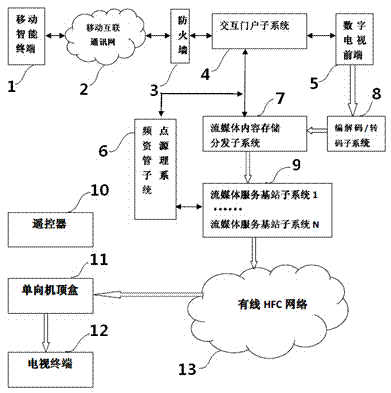
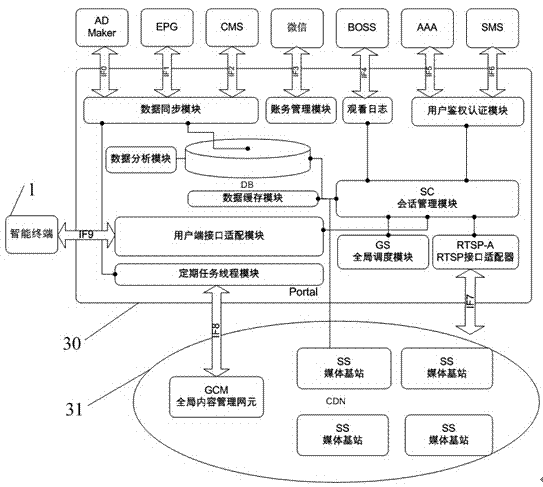
System and method of implementing video on demand and review of unidirectional set-top box through mobile intelligent terminal
InactiveCN104202620AOriginalityReasonable useSelective content distributionMobile communication networkDemand response
The invention relates to a system of implementing video on demand and review of a unidirectional set-top box through a mobile intelligent terminal. In the system, both-way communication between the mobile intelligent terminal and an interactive portal sub-system is carried out through mobile Internet, a mobile communication network and a firewall, both-way communication between the interactive portal sub-system and a streaming media content storage and distribution sub-system is carried out, the streaming media content storage and distribution sub-system pushes flow to a streaming media base station sub-system, after a plug flow signal is changed into a radio frequency signal by the streaming media base station sub-system, the plug flow signal is transmitted to a coaxial cable network of a cable television, the unidirectional set-top box and a television terminal, an available channel number is transmitted to an intelligent terminal interface by a frequency point resource management sub-system, when the television terminal is switched to the available channel number, all kinds of reception operations can be implemented through the intelligent terminal. According to the system, limited frequency points and broadband resources are reasonably utilized, the unique interactive portal sub-system is capable of skilfully making the mobile intelligent terminal and a digital television form an organic whole, so that video on demand and review can be implemented under the condition of the unidirectional set-top box, and sub-millisecond demand response is achieved.
Owner:NANJING CHAOJU COMM TECH
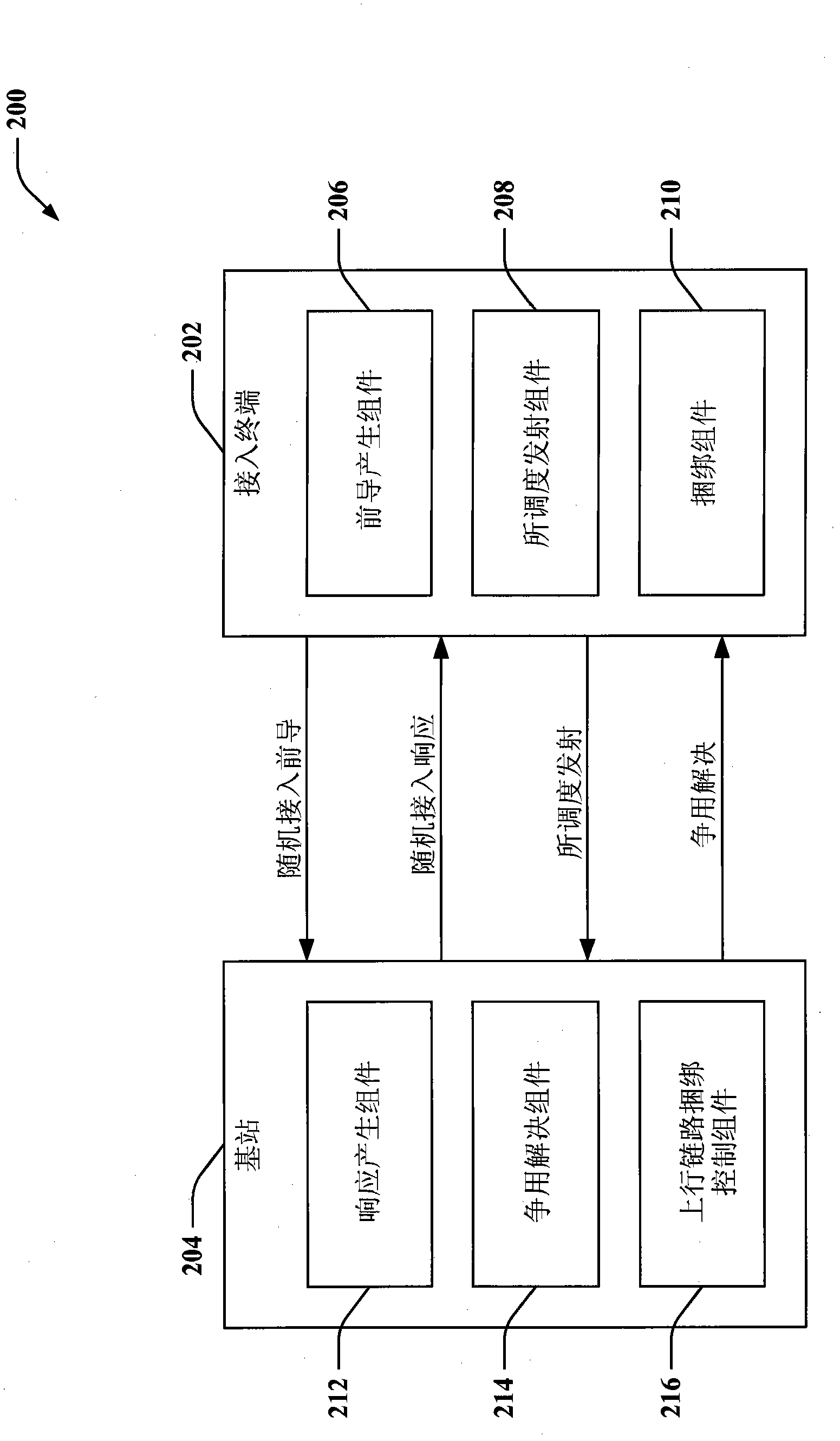
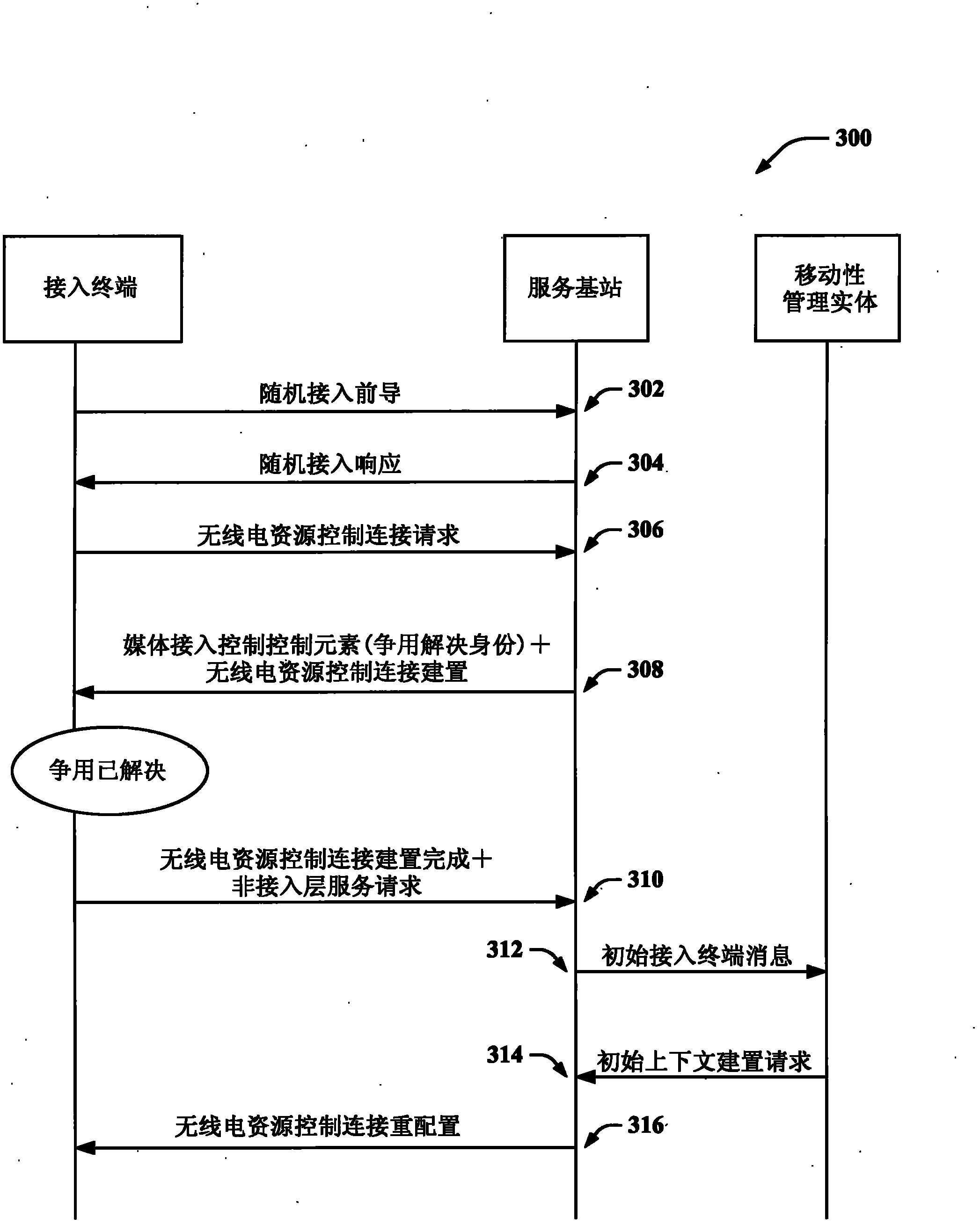
TTI bundling in a random access procedure
ActiveCN102124774AError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementComputer terminalTransmission Time Interval
Systems and methodologies are described that facilitate effectuating a random access procedure in a wireless communication environment. A random access preamble can be sent from an access terminal to a base station, and a random access response can be sent from the base station to the access terminal in response. The random access response can allocate resources to be utilized by the access terminal for a scheduled transmission (e.g., message 3,...). Further, a plurality of Transmission Time Intervals (TTIs) can be bundled for the scheduled transmission. Moreover, a payload of the scheduled transmission can be transmitted to the base station from the access terminal within a common Transport Block (TB) using the bundled plurality of TTIs. According to an example, employment of TTI bundling can be controlled on a per network basis, per base station basis, or per access terminal basis.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com