Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
285 results about "Delay sensitive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
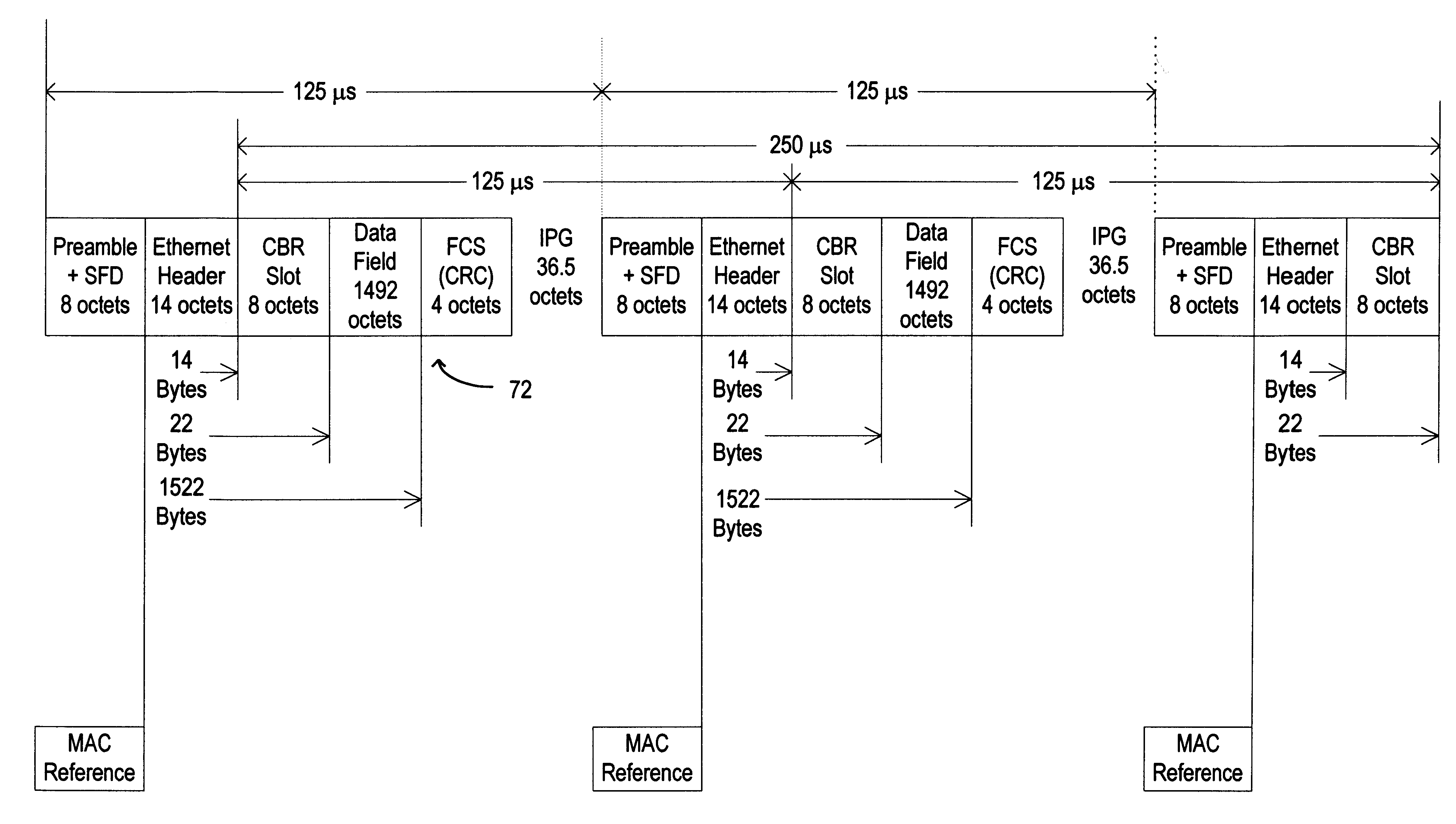
Local area network for the transmission and control of audio, video, and computer data
InactiveUS6215789B1Ensuring quality of serviceData switching by path configurationHybrid transportEthernetSpeech sound
An Ethernet Local Area Network uses a star topology connecting user stations to a Communications Switching Module (CSM) with 10Base-T or 100 Base-TX UTP cable. Each user station typically has a digital telephone and a data communication device, such as a PC communicating with the CSM through a common UTE adapter. Delay-sensitive digital voice signals and non-delay sensitive user data are transported in master Ethernet packets of fixed length transmitted at a fixed rate. Segmentation and re-assembly of data is performed in the UTE adapters and in the CSM.
Owner:NETWORK 1 TECH
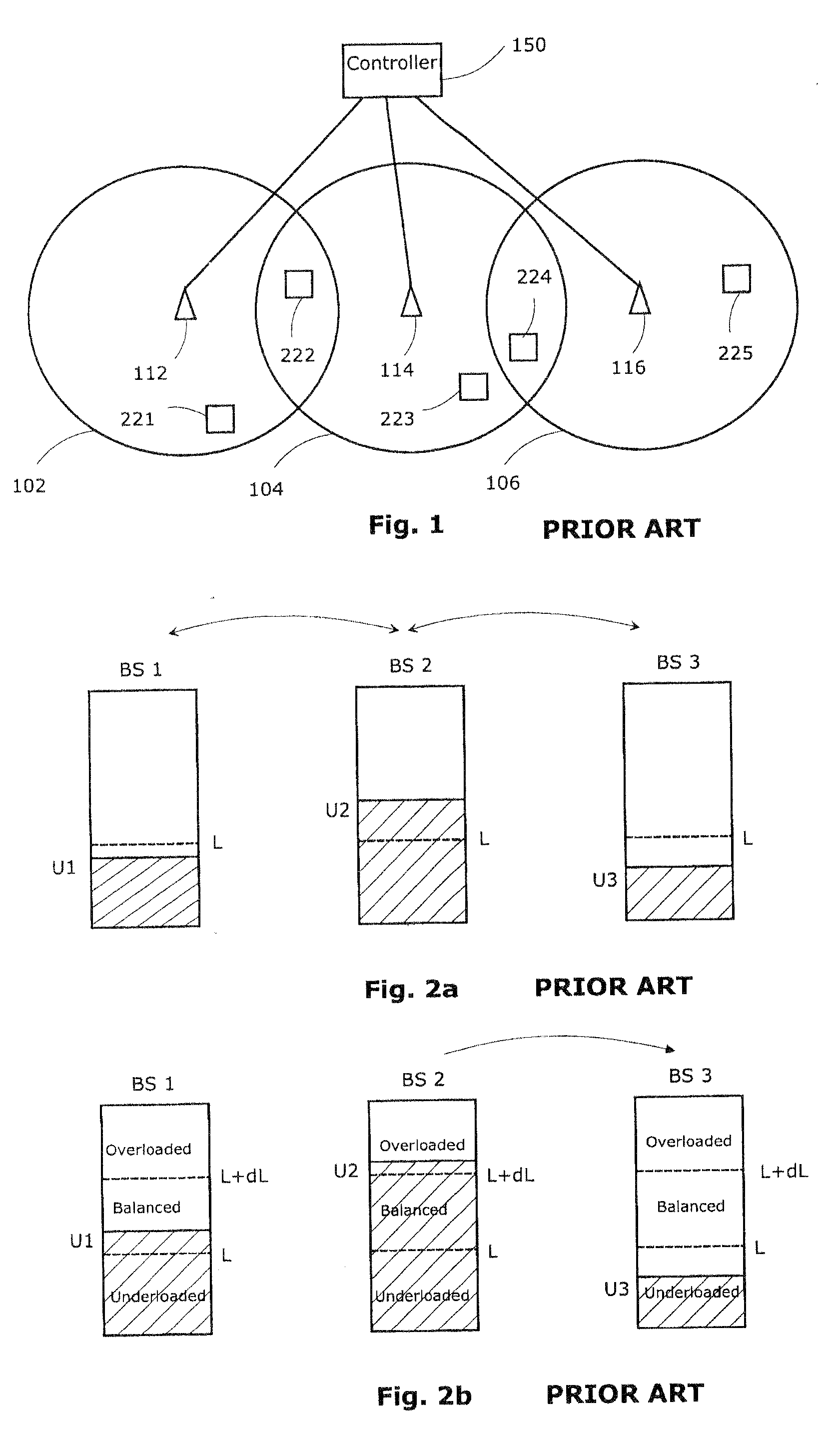
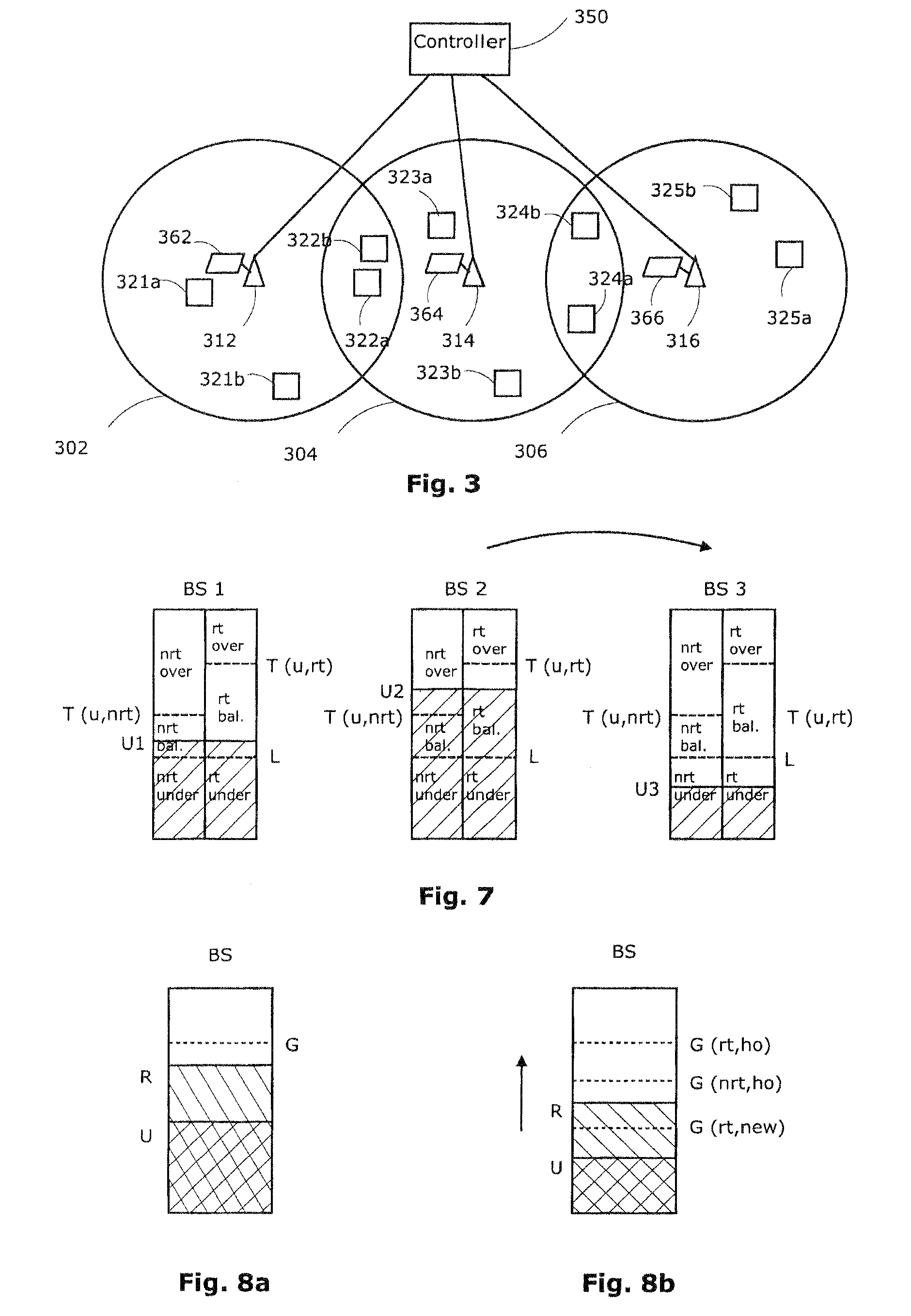
Load balancing in mobile environment
InactiveUS20090163223A1Unbalanced loadImprove QoSRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationResource utilizationHandover
In next generation wireless networks such as a Mobile WiMAX traffic prioritization is used to provide differentiated quality of service (QoS). Unnecessary ping-pong handovers that result from premature reaction to fluctuating radio resources pose a great threat to the QoS of delay sensitive connections such as VoIP which are sensitive to scanning and require heavy handover mechanisms. Traffic-class-specific variables are defined to tolerate unbalance in the radio system in order to avoid making the system slow to react to traffic variations and decreasing system wide resource utilization. By setting thresholds to trigger load balancing gradually in fluctuating environment the delay sensitive connections avoid unnecessary handovers and the delay tolerant connections have a chance to react to the load increase and get higher bandwidth from a less congested BS. A framework for the resolution of static user terminals in the overlapping area within adjacent cells will be described.
Owner:ELEKTROBIT WIRELESS COMM LTD
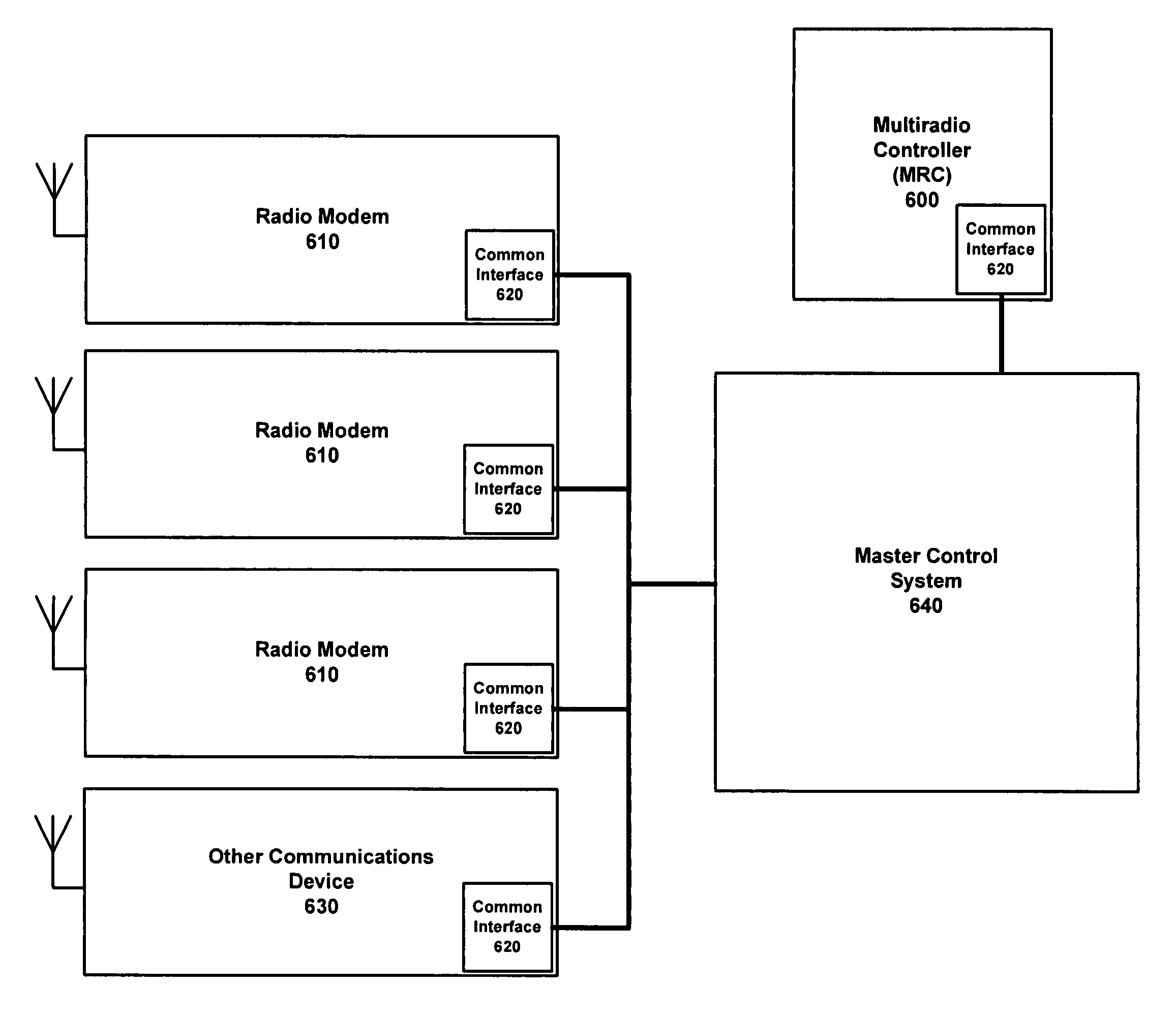
Distributed multiradio controller
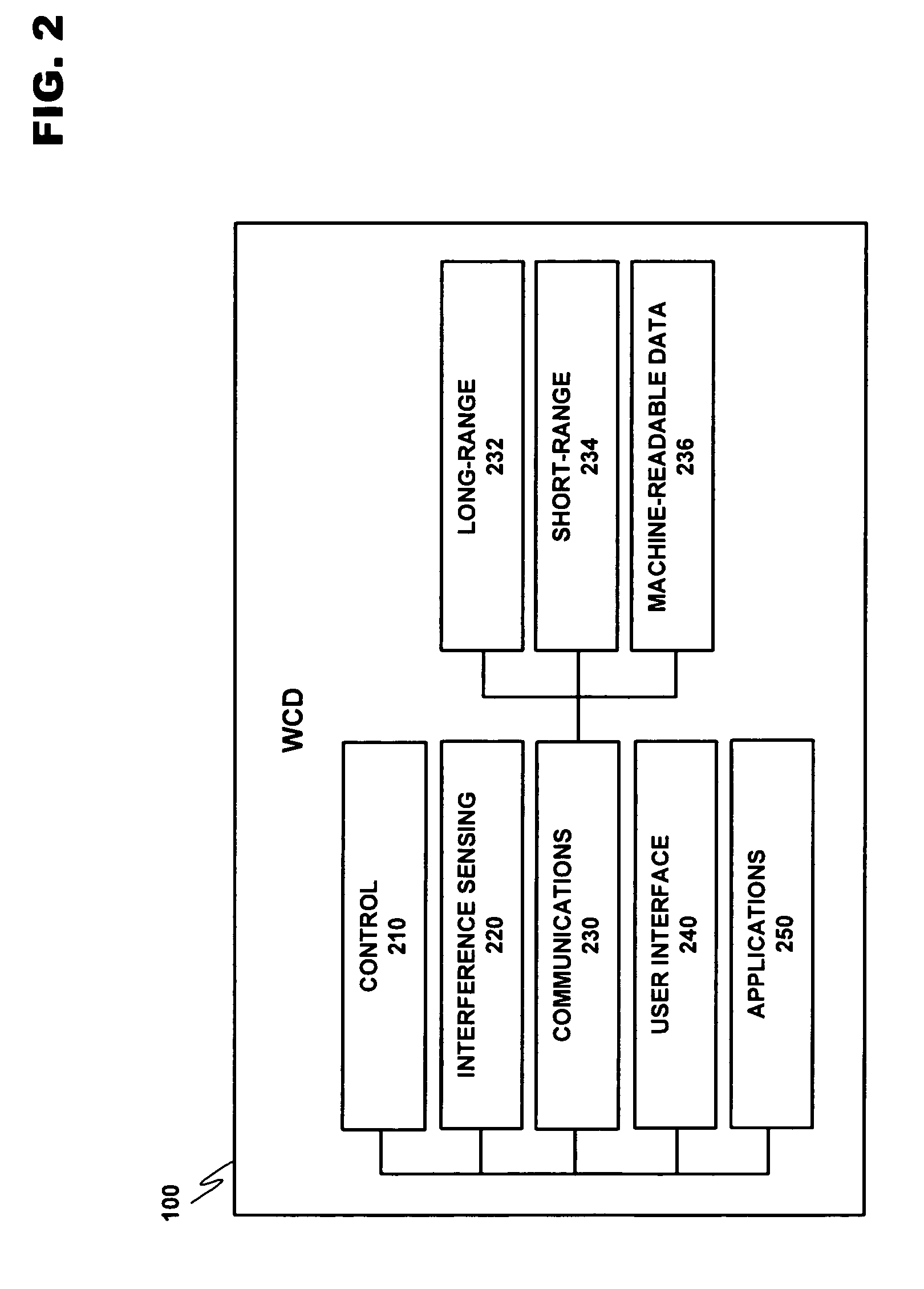
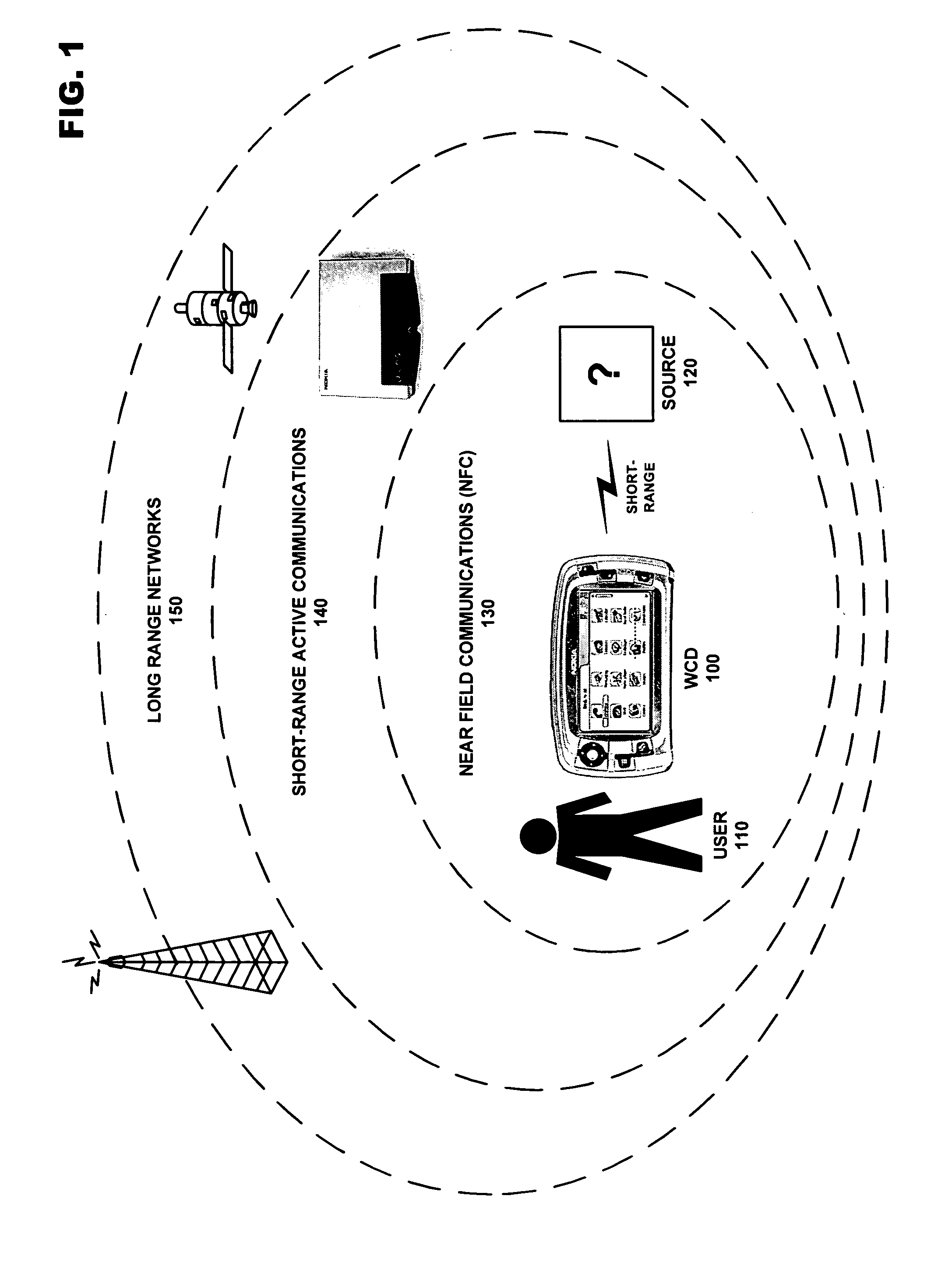
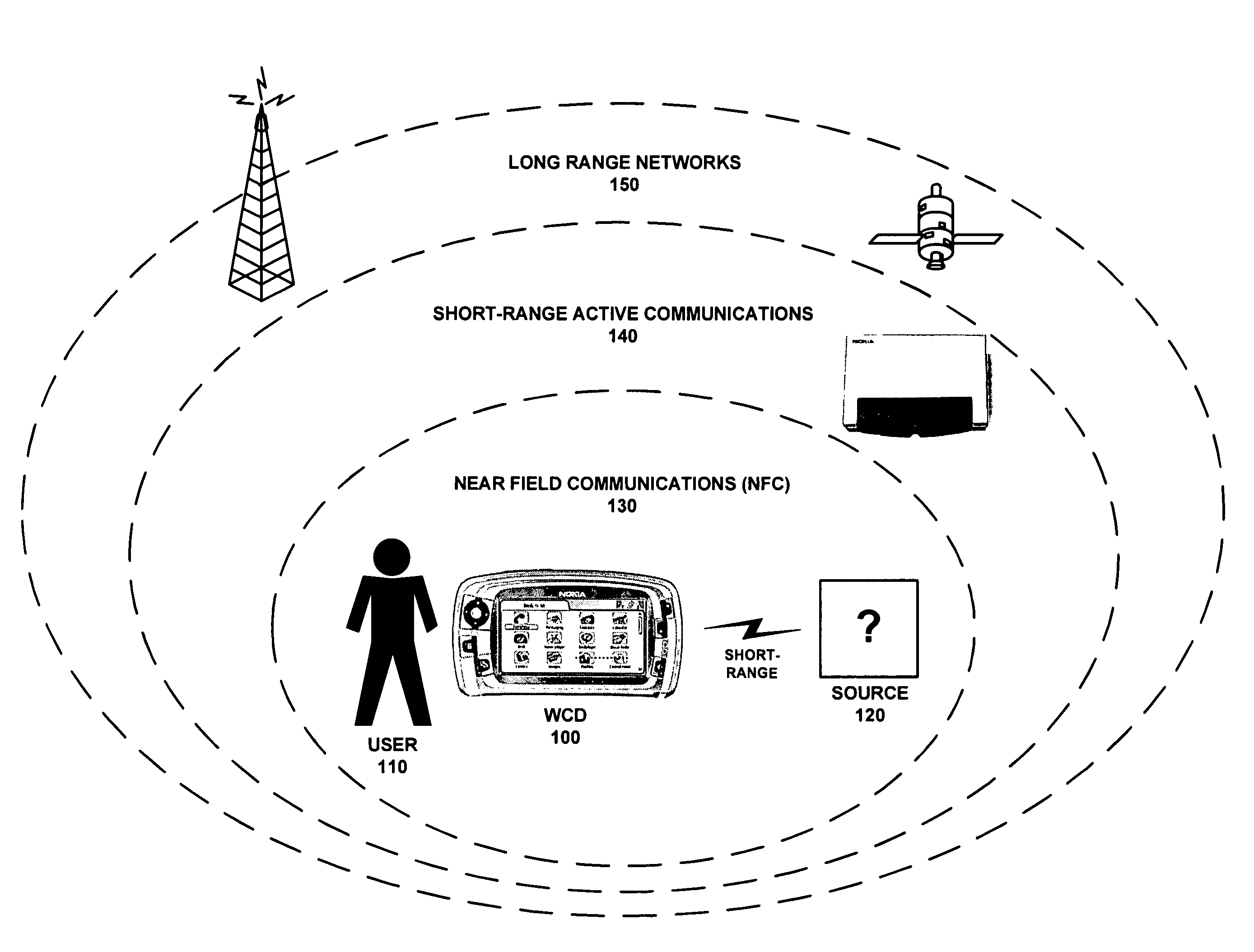
A system for managing the simultaneous operation of a plurality of radio modems in a single wireless communication device (WCD). The multiradio control may be integrated into a WCD as a subsystem responsible for scheduling wireless communications by temporarily enabling or disabling a plurality of radio modems. The multiradio control system may include a plurality of distributed control components, some or all of which are coupled to a dedicated radio interface. The radio interface is dedicated to quickly conveying delay sensitive information to and from the distributed control components. This information may be requested by any or all of the distributed control components, or provided by any or all of the radio modems if a change occurs during operation.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
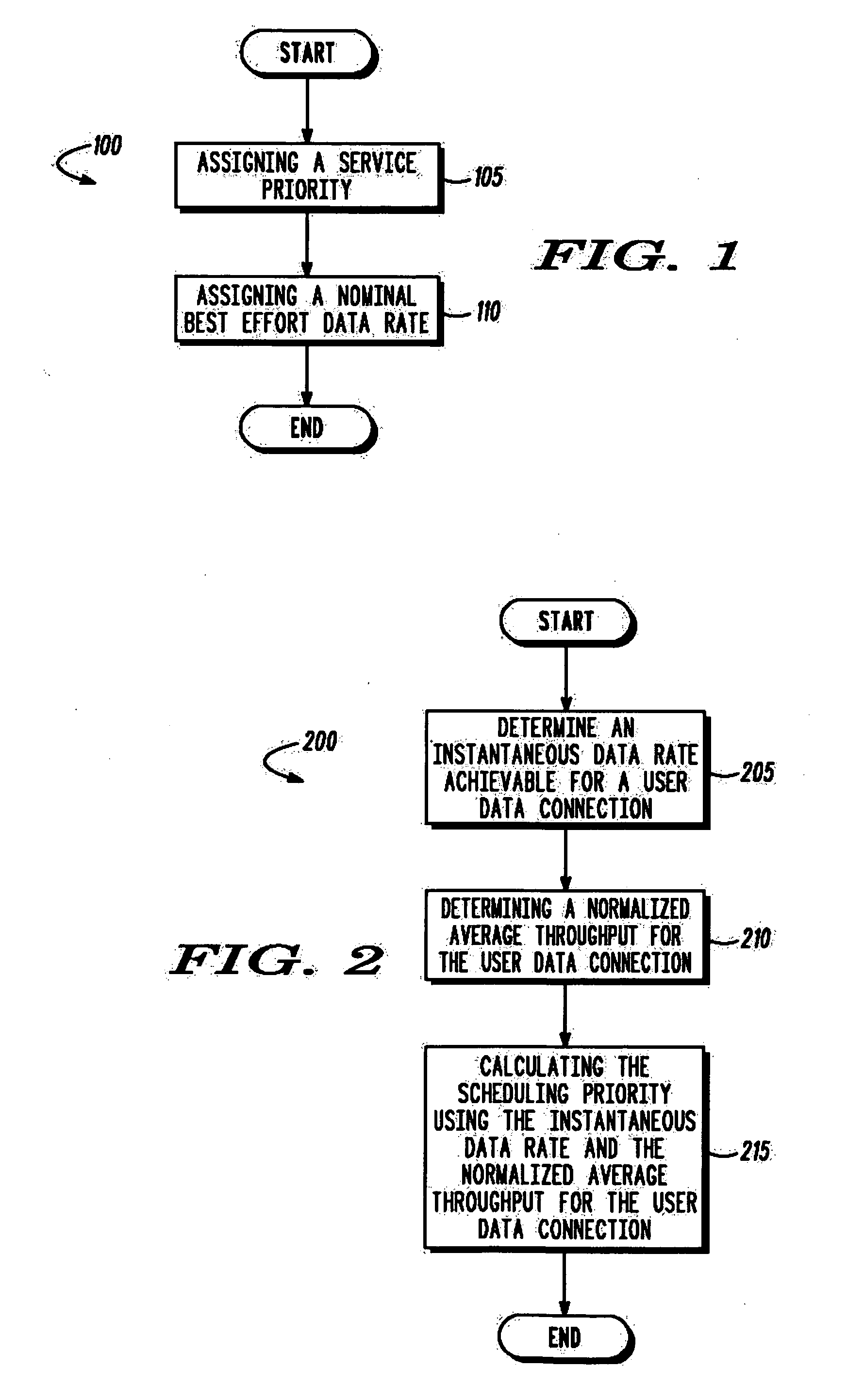
Method to determine a scheduling priority value for a user data connection based on a quality of service requirement
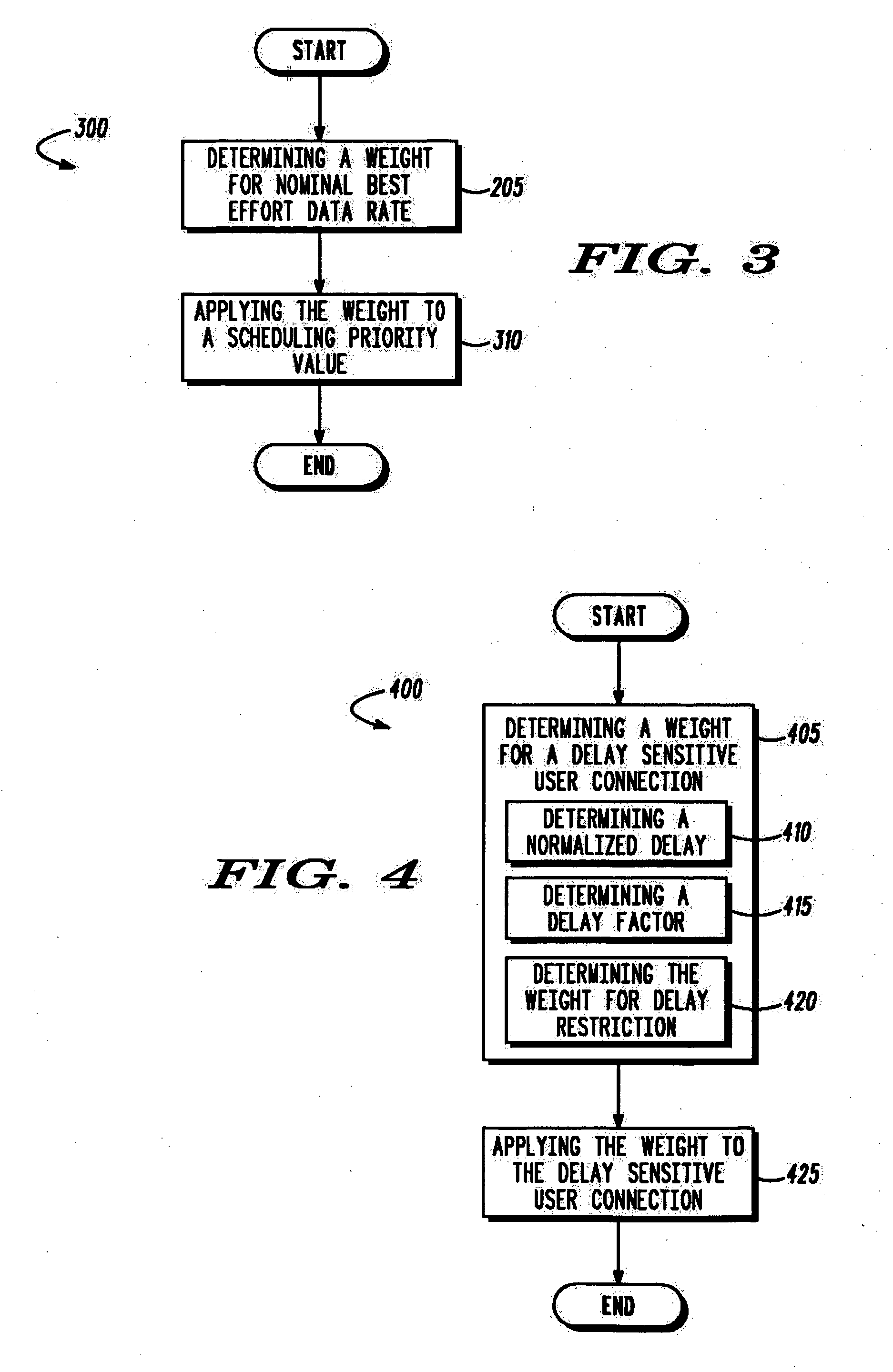
A method to provide a nominal best effort data rate based on a Quality of Service (QoS) requirement of a user data connection, the method comprising assigning (105) a service priority based on the QoS requirement, and assigning (110) the nominal best effort data rate for the service priority using a predetermined function. Further, it comprises of a method to determine a scheduling priority value for a user data connection by providing a relative fairness. Furthermore, the method comprises a method to satisfy a delay requirement for a delay sensitive data connection through a scheduling.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
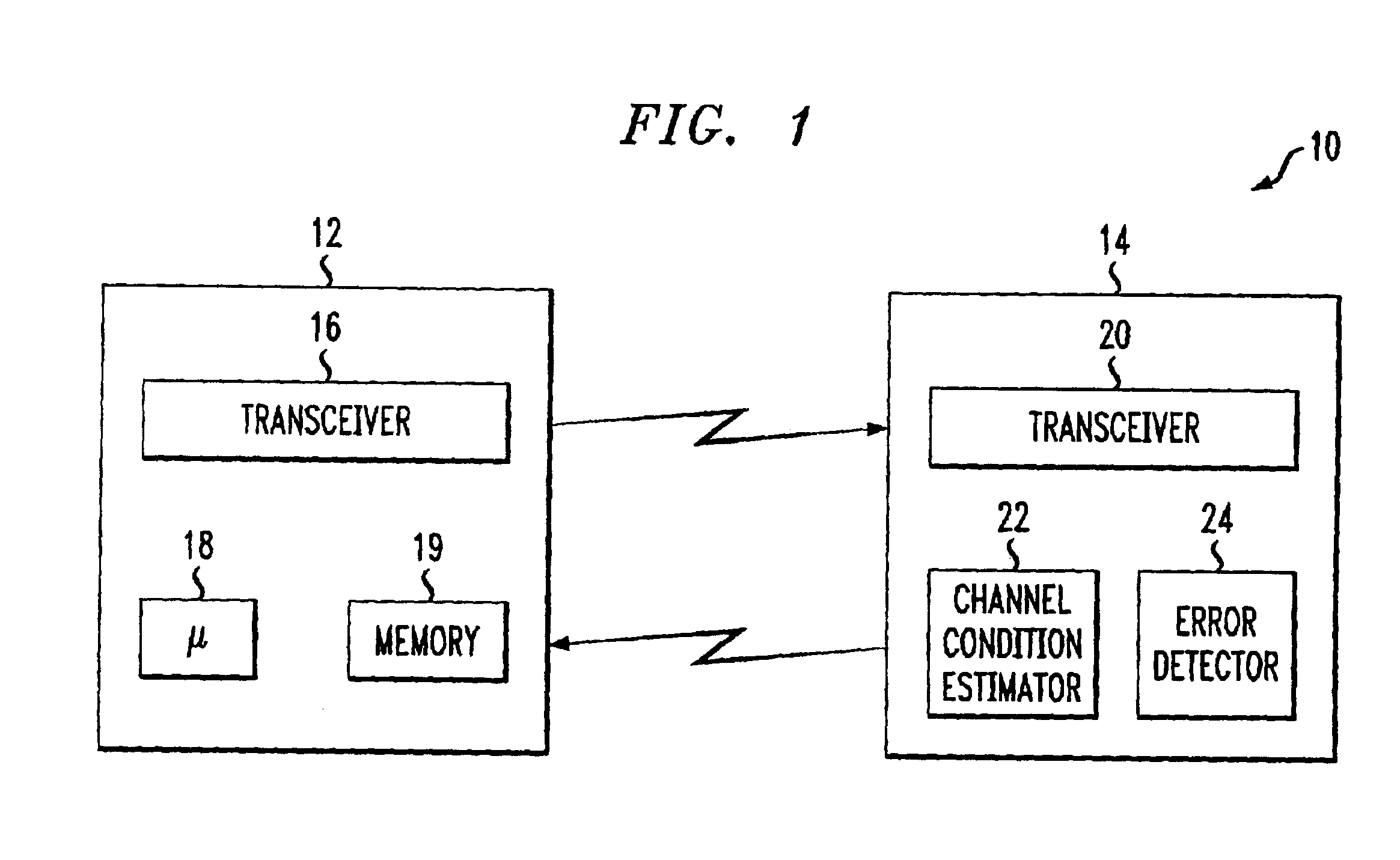
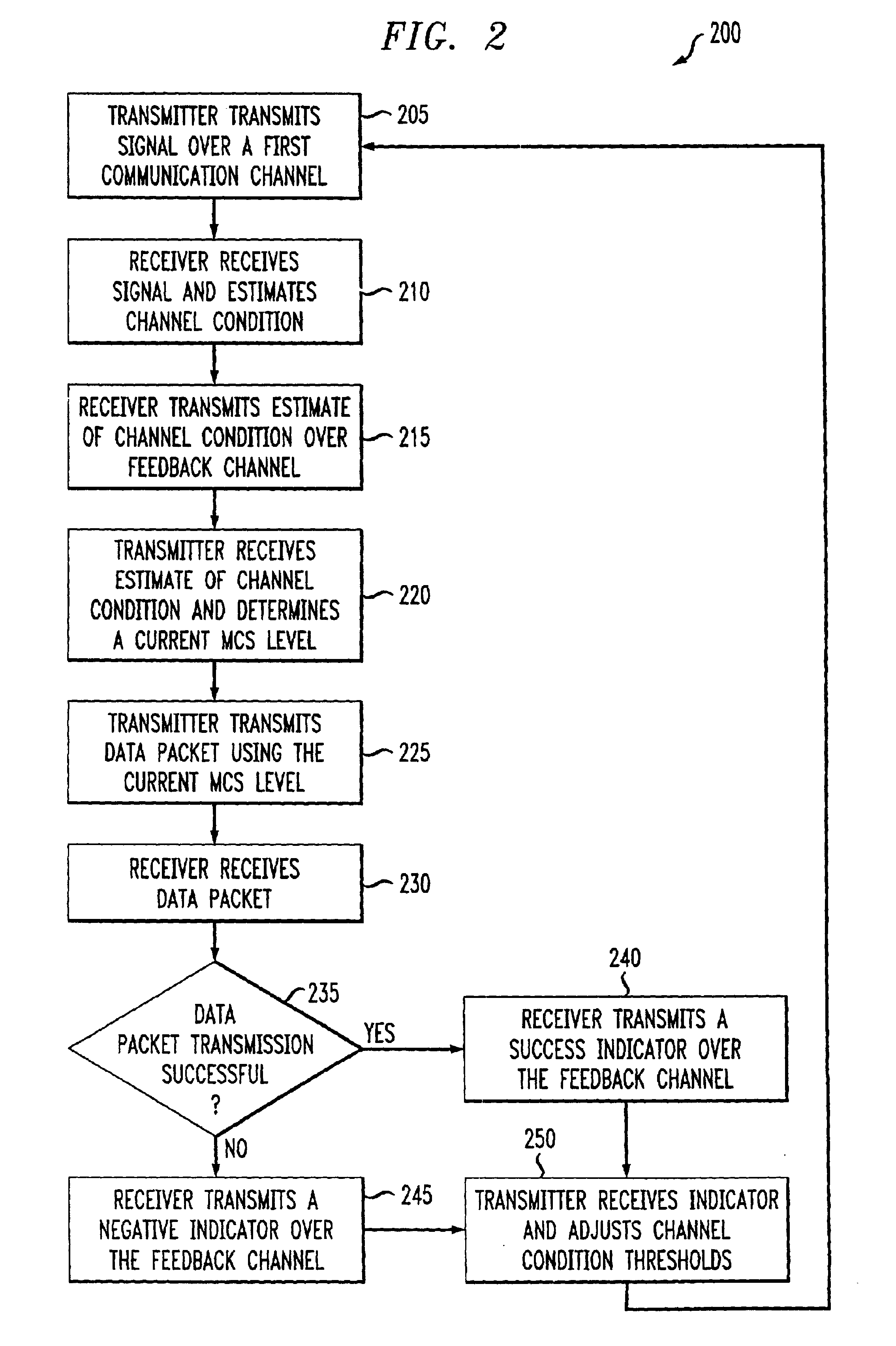
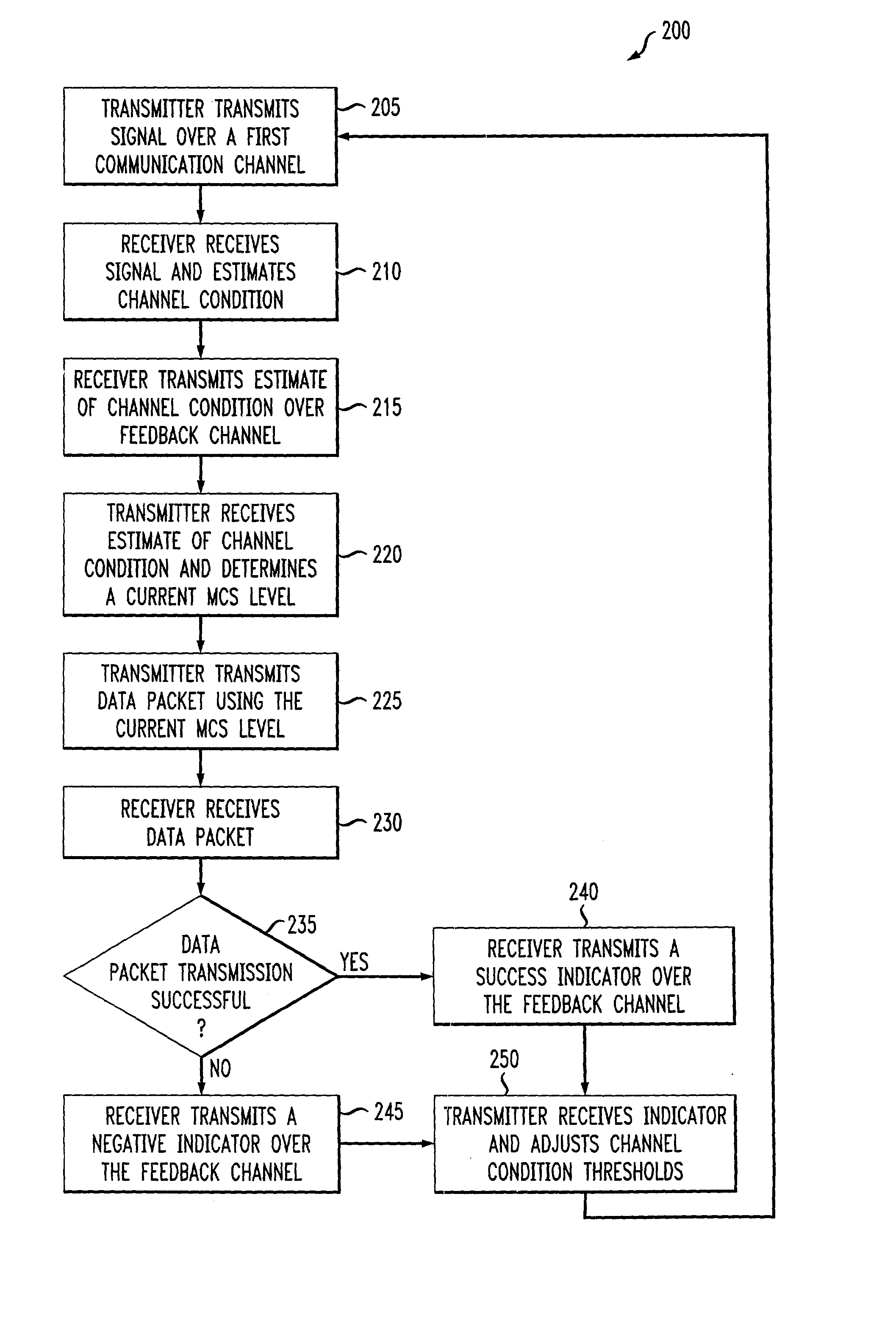
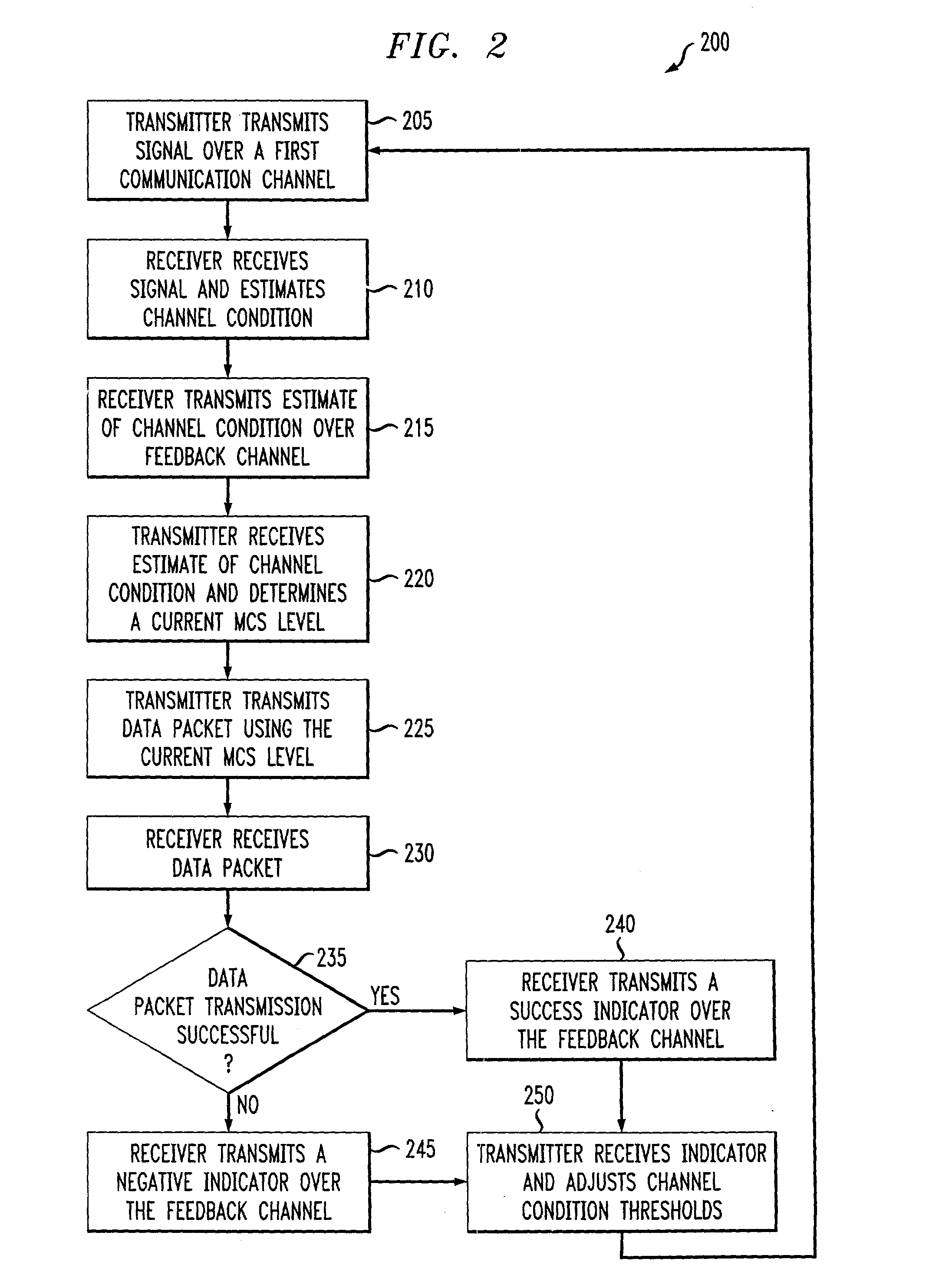
Delay sensitive adaptive quality control loop for rate adaptation
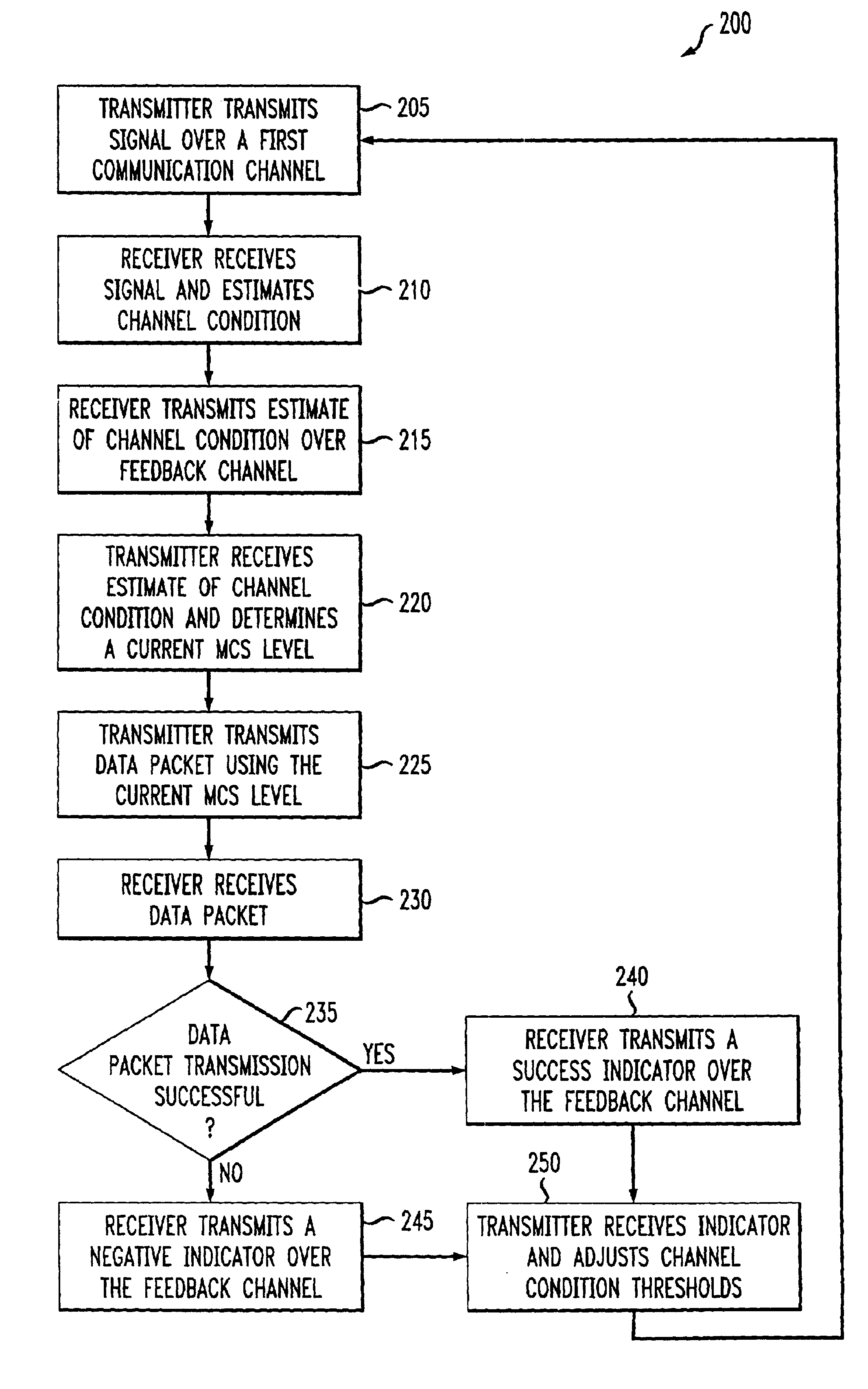
InactiveUS6915477B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelMultiple-port networksCommunications systemRate adaptation
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation that selectively adjusts channel condition thresholds based on delay sensitivity of data packets being transmitted. For wireless communication systems incorporating an error correction scheme using re-transmissions, the quality control loop adaptively adjusts channel condition thresholds more frequently for delay sensitive data packets, such as video, and less frequently for delay insensitive data packets, such as text messaging. Channel condition thresholds may be adjusted using fixed or variable steps based on error detection results.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method of reducing delay
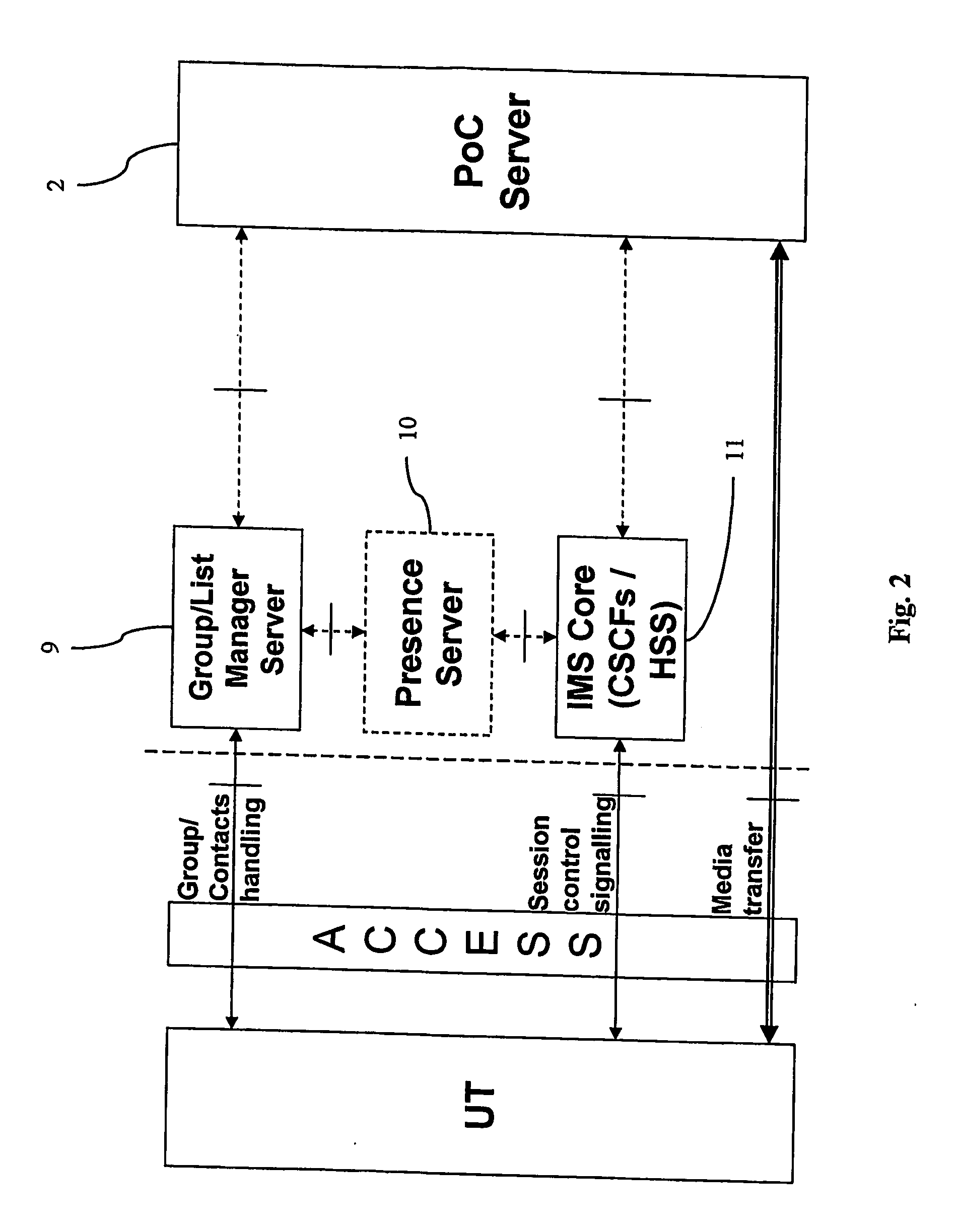
ActiveUS20070123284A1Reduce setup delayService delayNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesPush-to-talkDelay sensitive
The present invention relates to a method of reducing setup delay for an uplink message from a user terminal (UT) in a delay sensitive service in a radio telecommunications system, such as a push to talk service (PoC), by predicting that delay sensitive data is about to be transmitted, sending, as a response to the prediction, a connection setup signal from the terminal to a basestation subsystem (BSS) in order to set up an early uplink radio connection, and transmitting the delay sensitive data via the early uplink connection. There is also provided a user terminal (UT) and a radio telecommunications system.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multi-hop wireless backhaul network and method
ActiveUS7646752B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHigh densityCommunications system
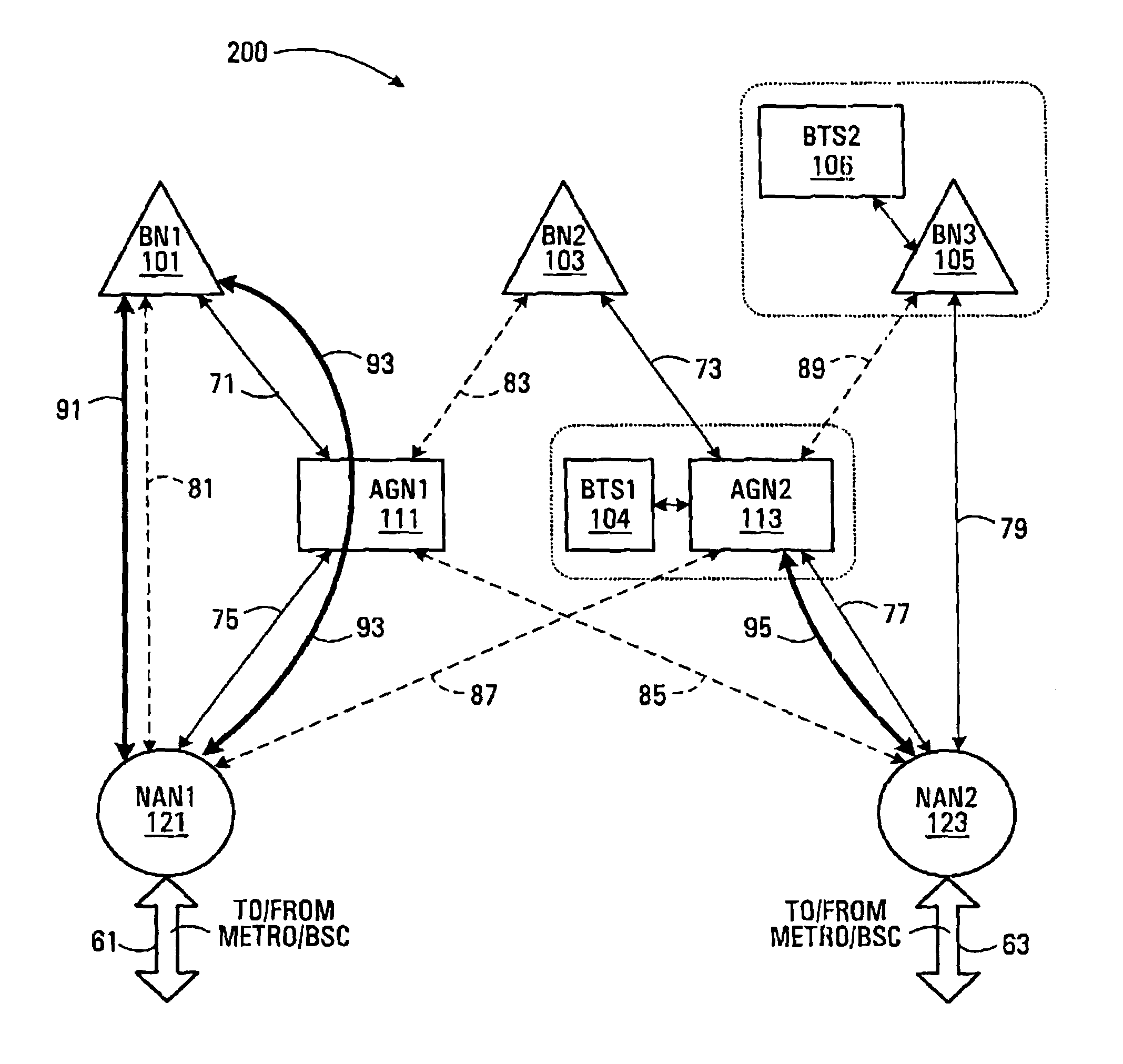
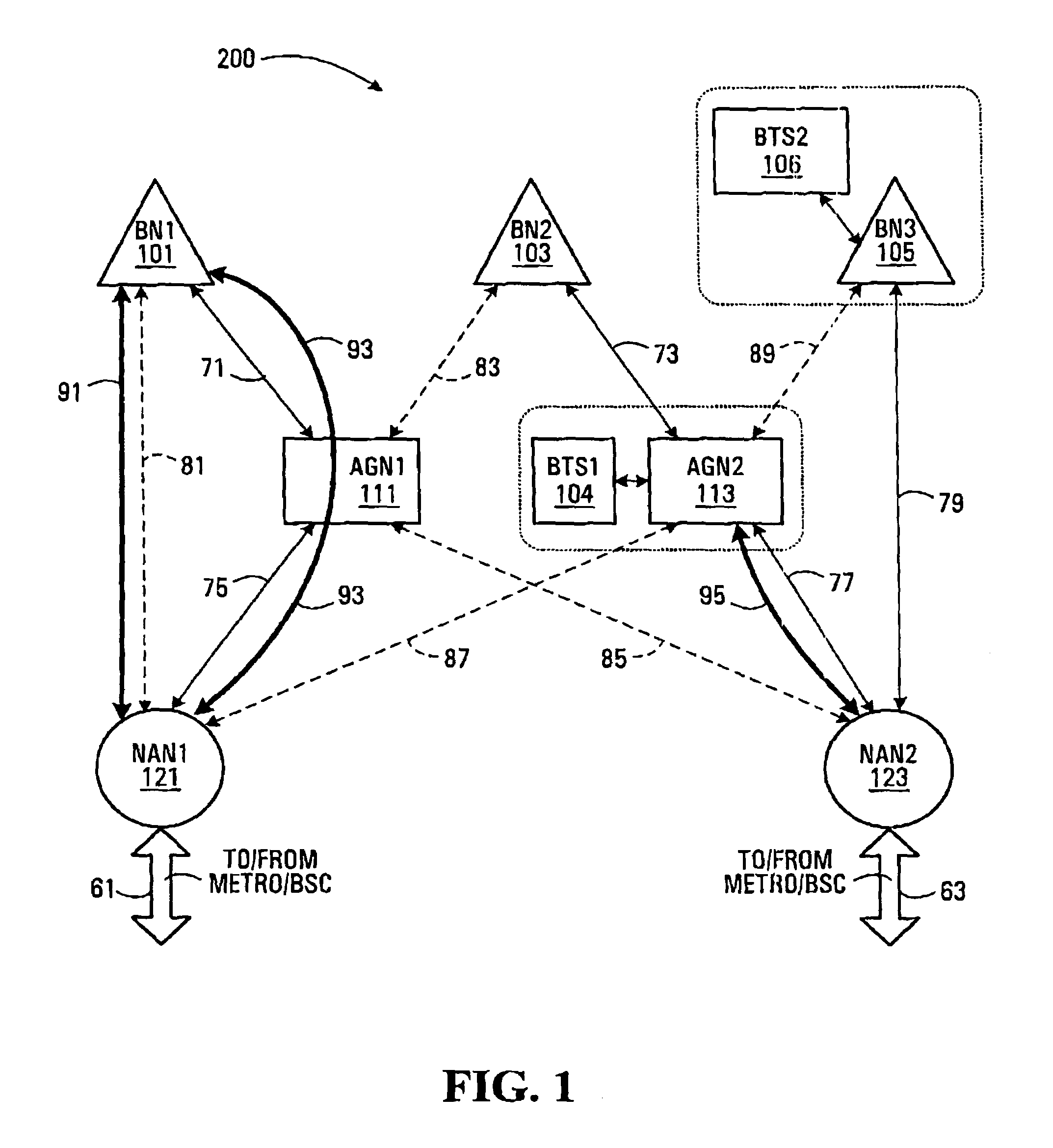
Some embodiments of the invention provide an implementation for a multi-hop wireless backhaul network. These embodiments can advantageously be deployed in dense urban areas and / or co-located with wireless access nodes, such as base-stations of a cellular wireless communication system. Preferably wireless links between constituent network nodes are set-up hierarchically. A basic result of this is that peer-to-peer (child-to-child) communication is generally prohibited and circuits are forced to conform to a topology. The multi-hop wireless backhaul network may be used to carry delay sensitive, high-density last mile circuit traffic over Non-Line-Of-Sight (NLOS) broadband radio links. Moreover, some embodiments of the invention provide a method of path-healing for re-routing of circuit traffic from circuits that have experienced catastrophic failures.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus for dynamically securing voice and other delay-sensitive network traffic
InactiveUS20080229095A1Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityPrivate network
A method comprises receiving a request for secure network traffic from a device having a private network address at a source node, obtaining the private network address of a requested destination device at a destination node from a route server based on signaling information associated with the request, obtaining the public network address of the destination node associated with the private network address, creating in response to the request a virtual circuit between the source node and the destination node based on the public network address of the destination node, and encrypting network traffic for transporting at least from the source node to the destination node through the virtual circuit. The process is dynamic in that the virtual circuit is created in response to the request. Hence, the process operates as if a fully meshed network exists but requires less provisioning and maintenance than a fully meshed network architecture. Furthermore, the process is readily scalable as if a hub and spoke network exists but is more suitable for delay-sensitive traffic, such as voice and video, than a hub and spoke network architecture.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Delay sensitive adapative quality control loop for rate adaptation
InactiveUS20030126536A1Multiple-port networksError prevention/detection by using return channelRate adaptationCommunications system
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation that selectively adjusts channel condition thresholds based on delay sensitivity of data packets being transmitted. For wireless communication systems incorporating an error correction scheme using retransmissions, the quality control loop adaptively adjusts channel condition thresholds more frequently for delay sensitive data packets, such as video, and less frequently for delay insensitive data packets, such as text messaging. Channel condition thresholds may be adjusted using fixed or variable steps based on error detection results.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Bit error resilience for an internet protocol stack
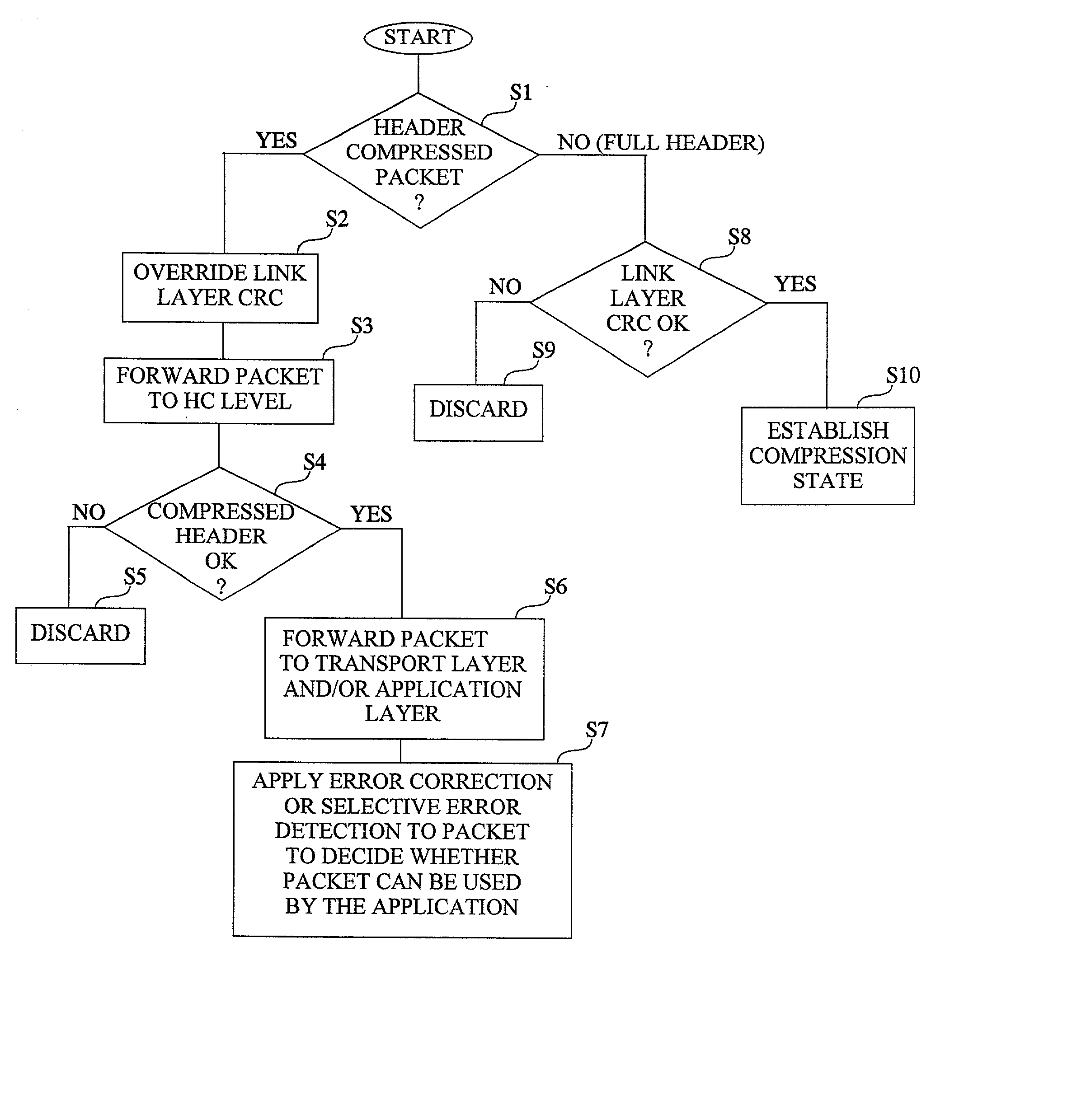
ActiveUS20020071432A1Accurate protectionWithout seriously degrading application qualityError preventionTransmission systemsInternet protocol suitePacket loss
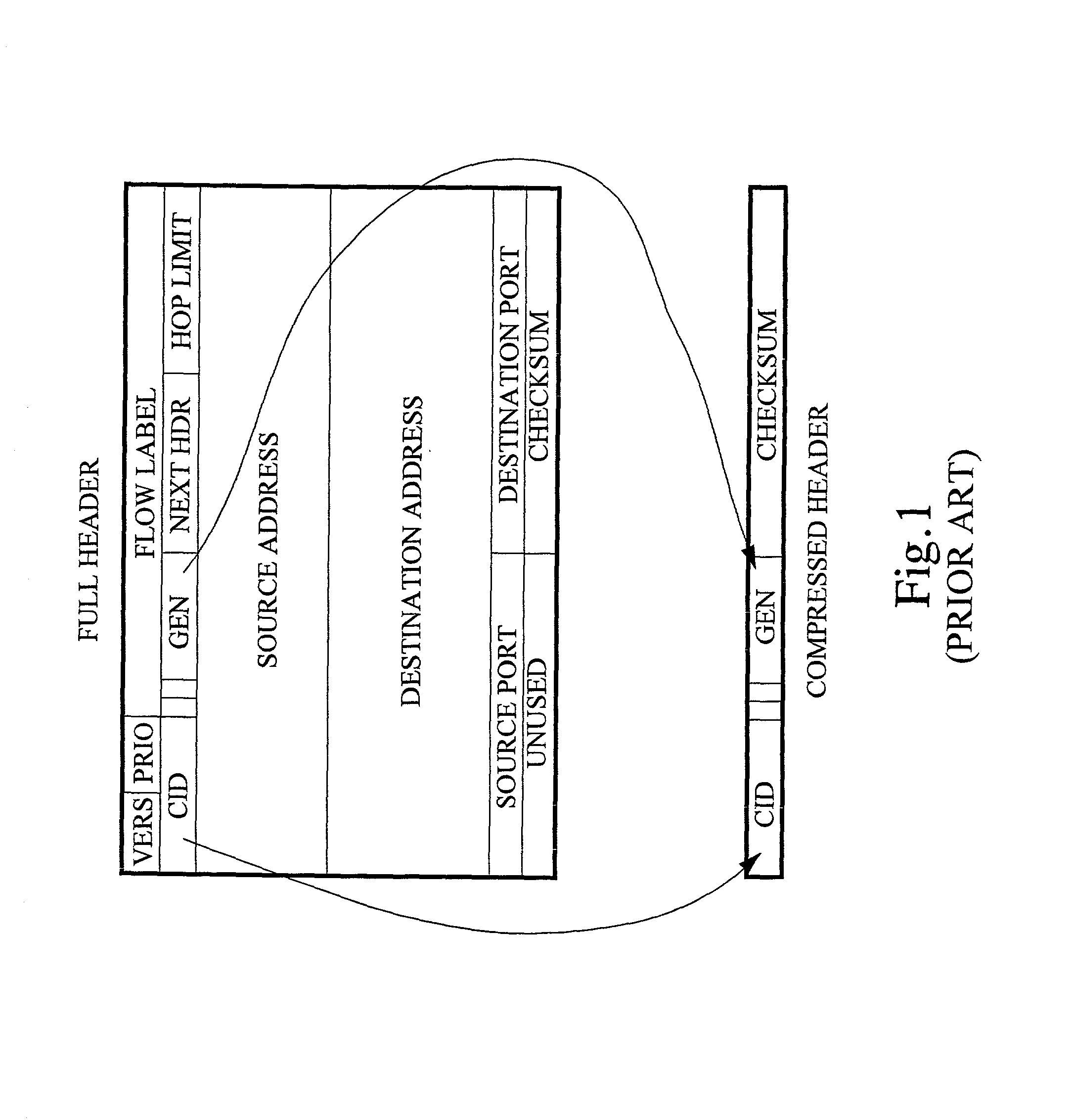
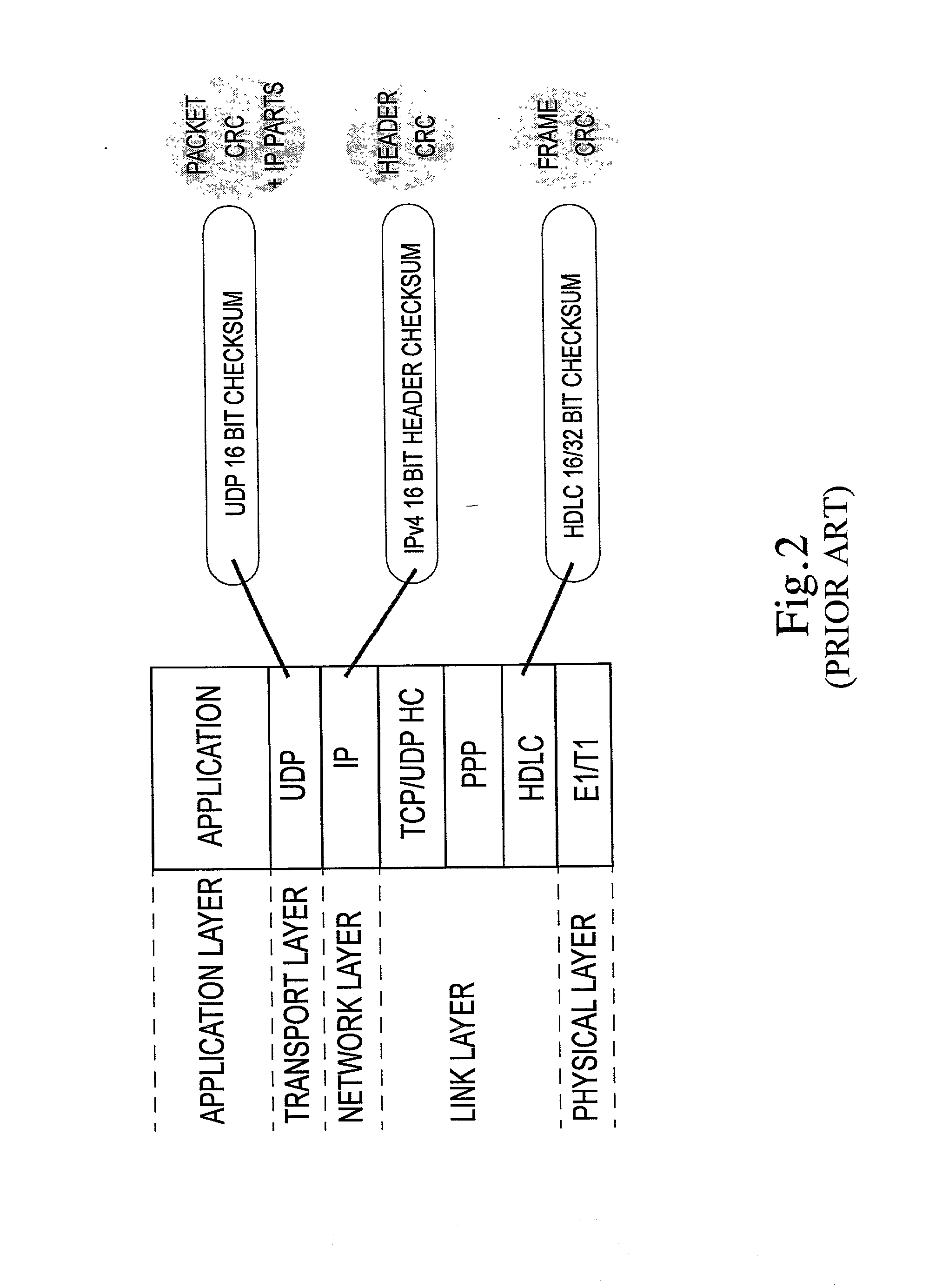
The invention concerns the bit error resilience of an IP protocol stack based on a secure link layer, in which packet flows are header compressed according to a suitable header compression standard. According to the invention, by analyzing each packet at the link layer it can be determined whether the packet is a full header packet, in which case the link layer checksum evaluation is used as normal for discarding faulty full header packets, or a header compressed packet in which case the link layer checksum evaluation is ignored and the packet is propagated upwards in the protocol stack. This solution not only opens up for more intelligent higher-level handling of faulty header compressed packets, but also solves the problem of properly protecting full header packets at the link layer. In order to compensate for ignoring the link layer checksum evaluation for header compressed packets, header protection is introduced at the header compression level of the link layer by using one or more local checksums. The invention is particularly applicable to delay-sensitive real-time data such as compressed voice or video.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
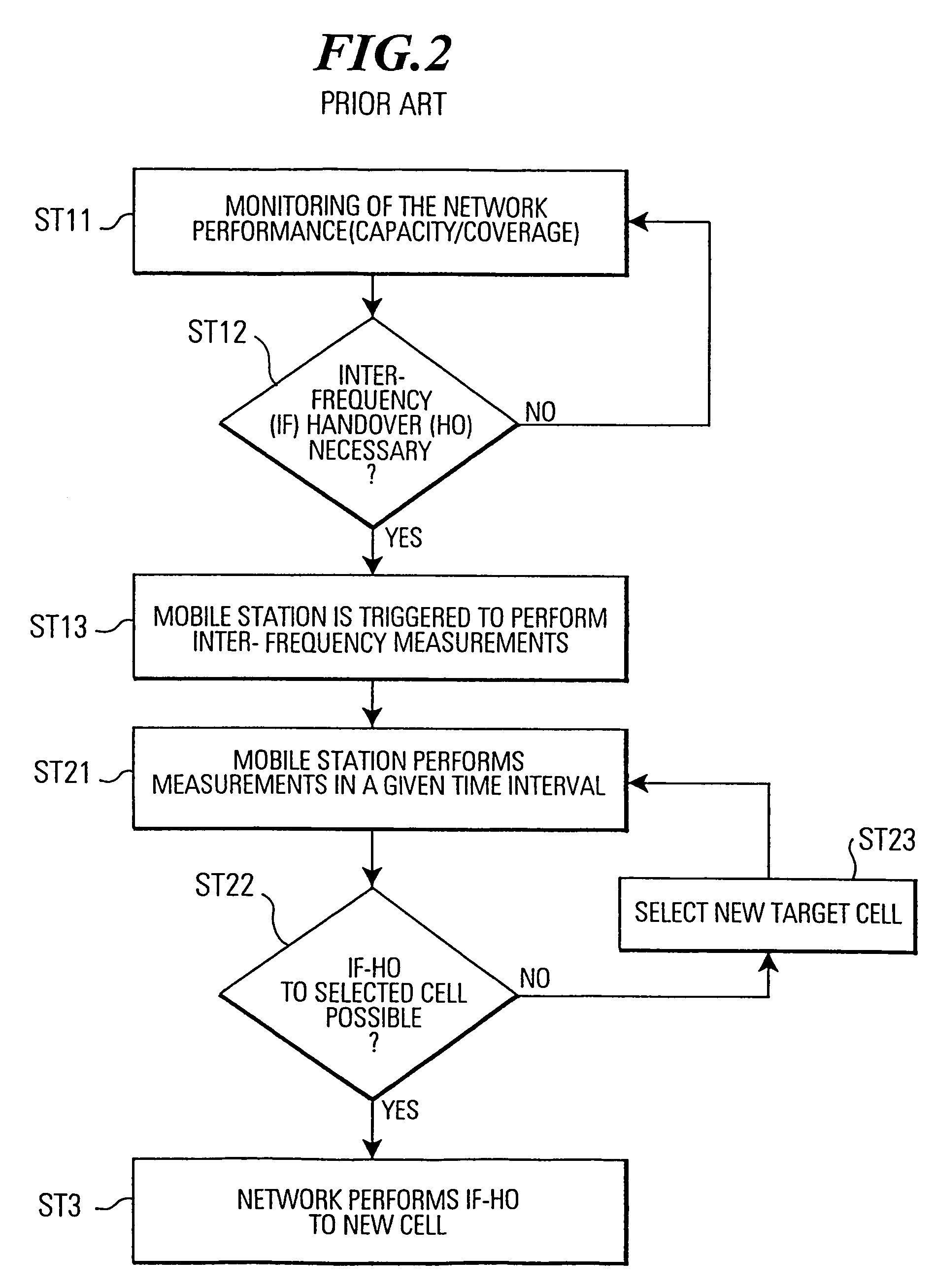
Subscriber station, network control means and method for carrying out inter-frequency measurements in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS7016320B1Maintain qualityEasy to measurePower managementTransmission control/equalisingIdle timeFrequency measurements
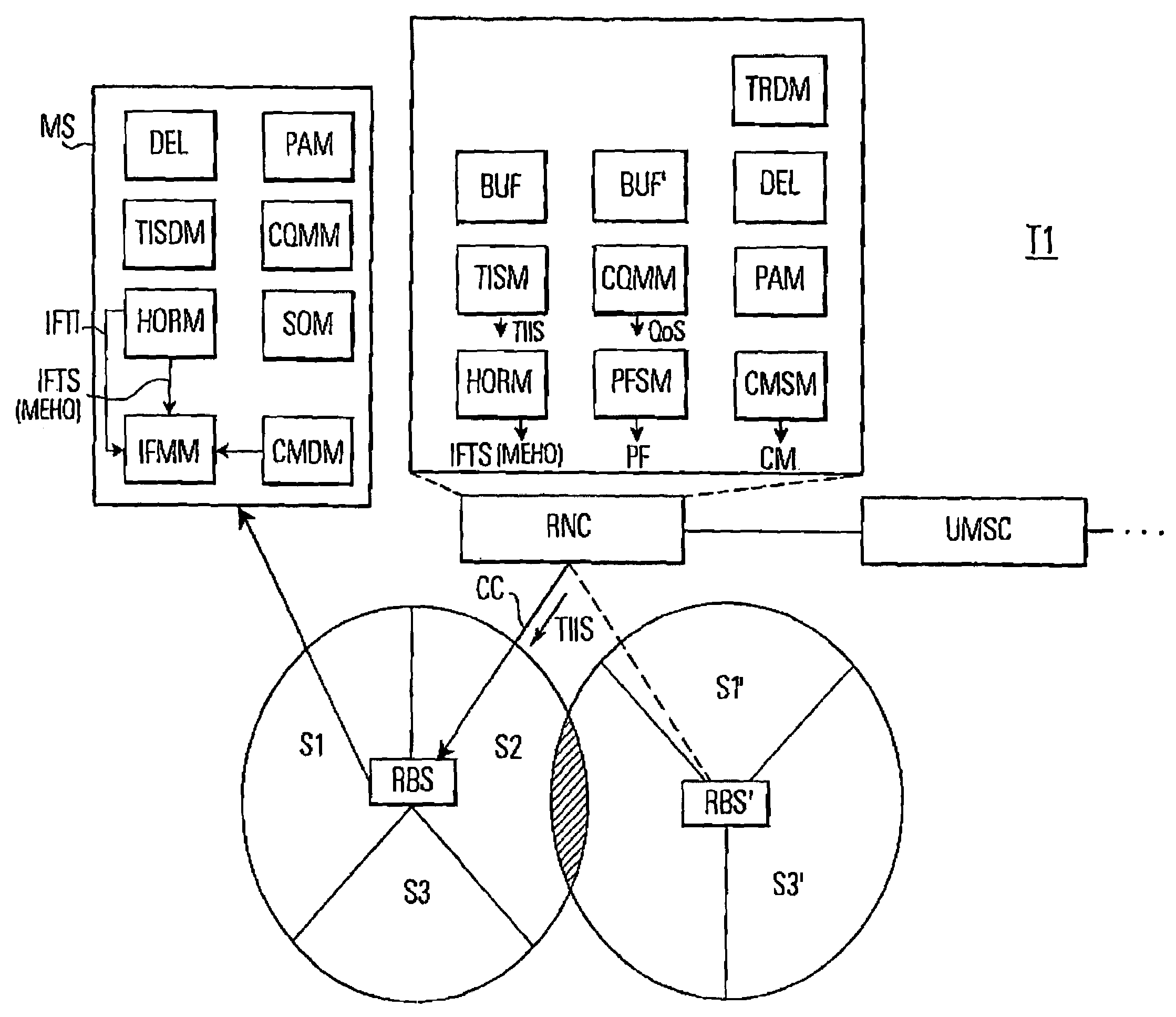
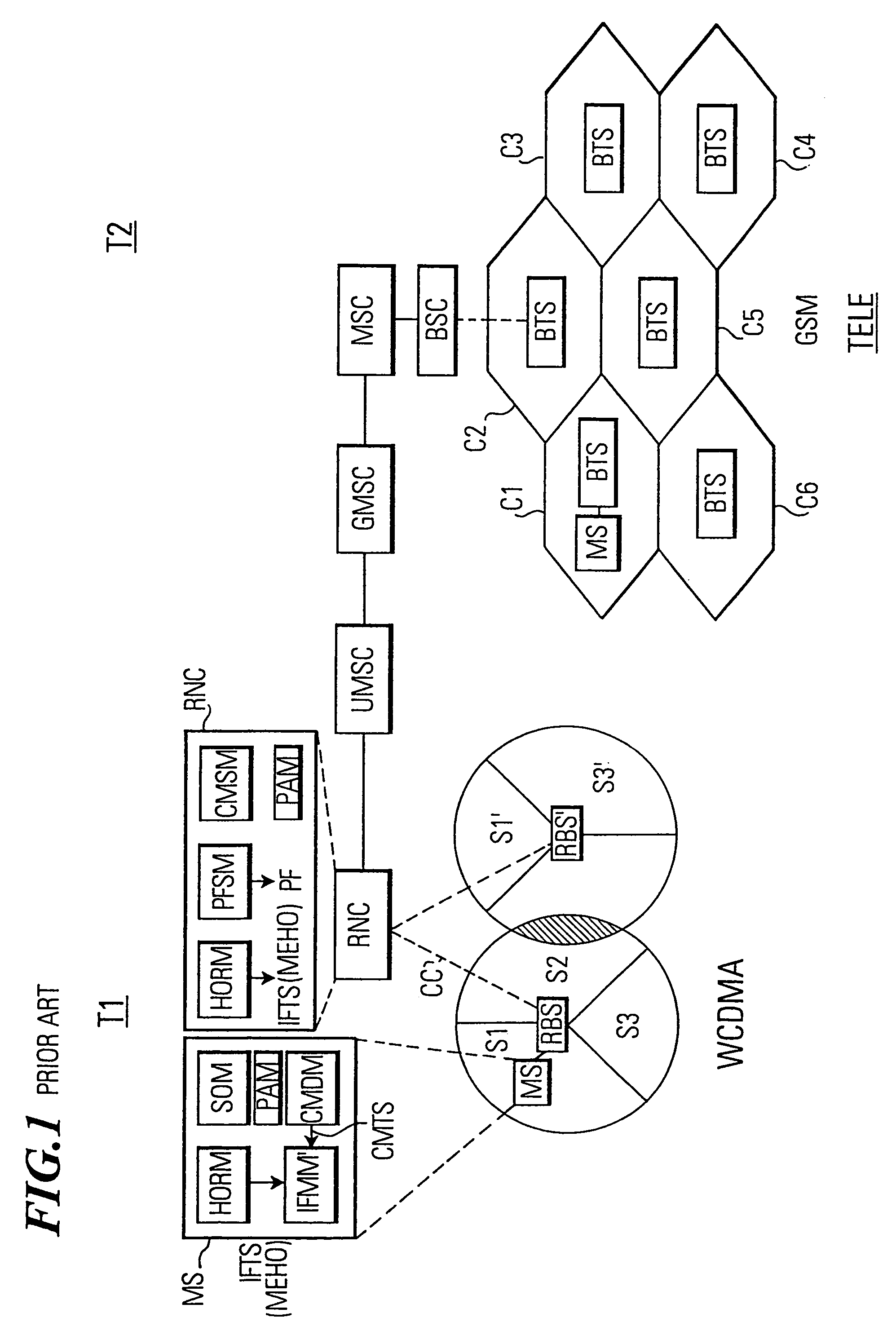
In a mobile communication system (T1) a time interval selection means (TISM) in a network control means (RNC) determines a time interval and sends an indication about this time interval to a subscriber station (MS) in a time interval indication signal. A time interval signal determining means (TISDM) in the subscriber station (MS) detects the time interval and an IF measurement means (IFMM) carries out inter-frequency / inter-system measurements in the detected time interval specified by the network control means (RNC). In this time interval the temporary reduction of the quality of service QoS on the communication connection (CC) is planed by the network control means (RNC). However, independent as to whether a delay-sensitive or loss-sensitive data transmission is carried out, the network control means (RNC) can make provisions in order to compensate the temporary reduction of the quality of service. Such procedure is superior to performing IF measurements in an idle time interval of a compressed time slot in which a temporary degradation of the quality of service must always be accepted due to a compressed mode of operation.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Scheduling method for wireless packet data channel
InactiveUS20060153216A1Increase urgencyIncrease effective capacityNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationPhysical layer packetMobile station
A scheduler at a base station may schedule packet data traffic based on a ranking metric that varies directly with the mobile station's scheduling downlink transmission rate and a delay factor indicative of the staleness of the corresponding queued data. The ranking metric may advantageously vary in a direct non-linear fashion with the delay factor to allow for delay sensitive data, such as VoIP data, to be scheduled with increased urgency when quality of service is about to be compromised. The scheduler may attempt to pack a multi-user downlink physical layer packet by selecting a tentative rate and determining if an aggregate amount of data in the packet may be increased by transmitting the packet at a lower rate. If so, additional queued data is added to the packet and the transmission rate for the packet is lowered. Such an approach allows for greater link efficiency to be achieved.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
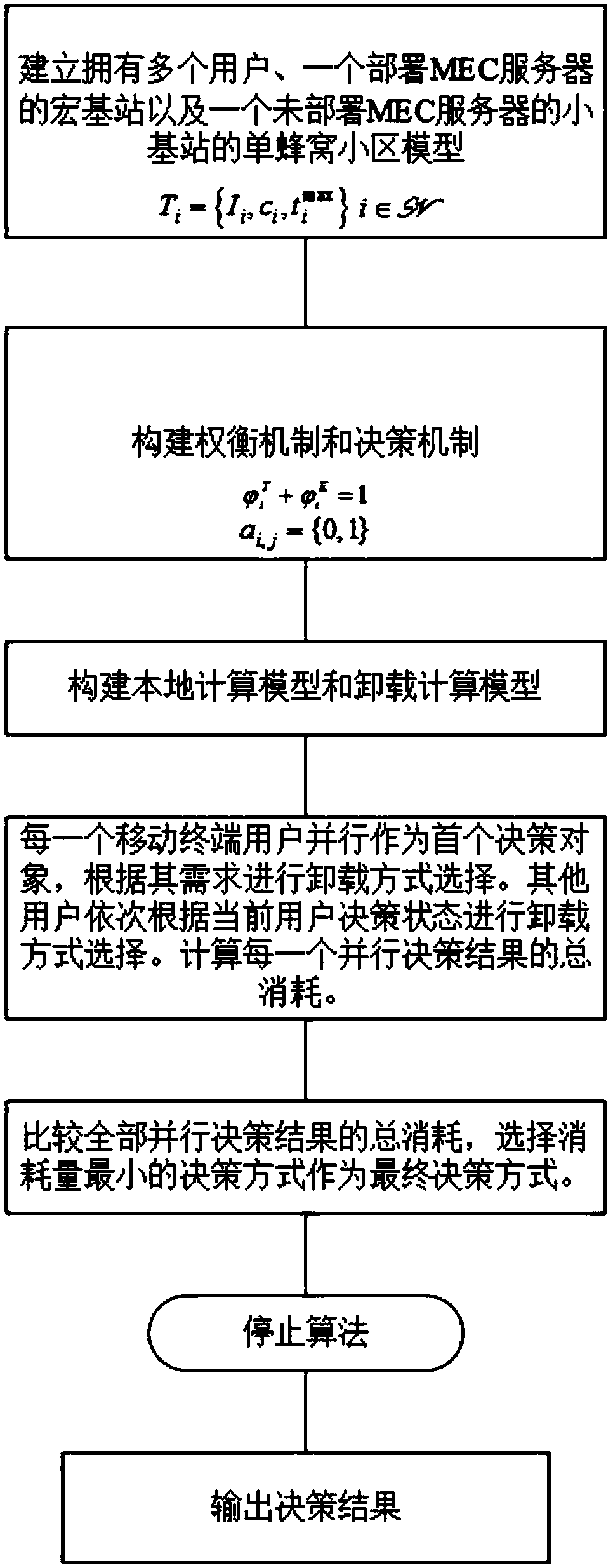
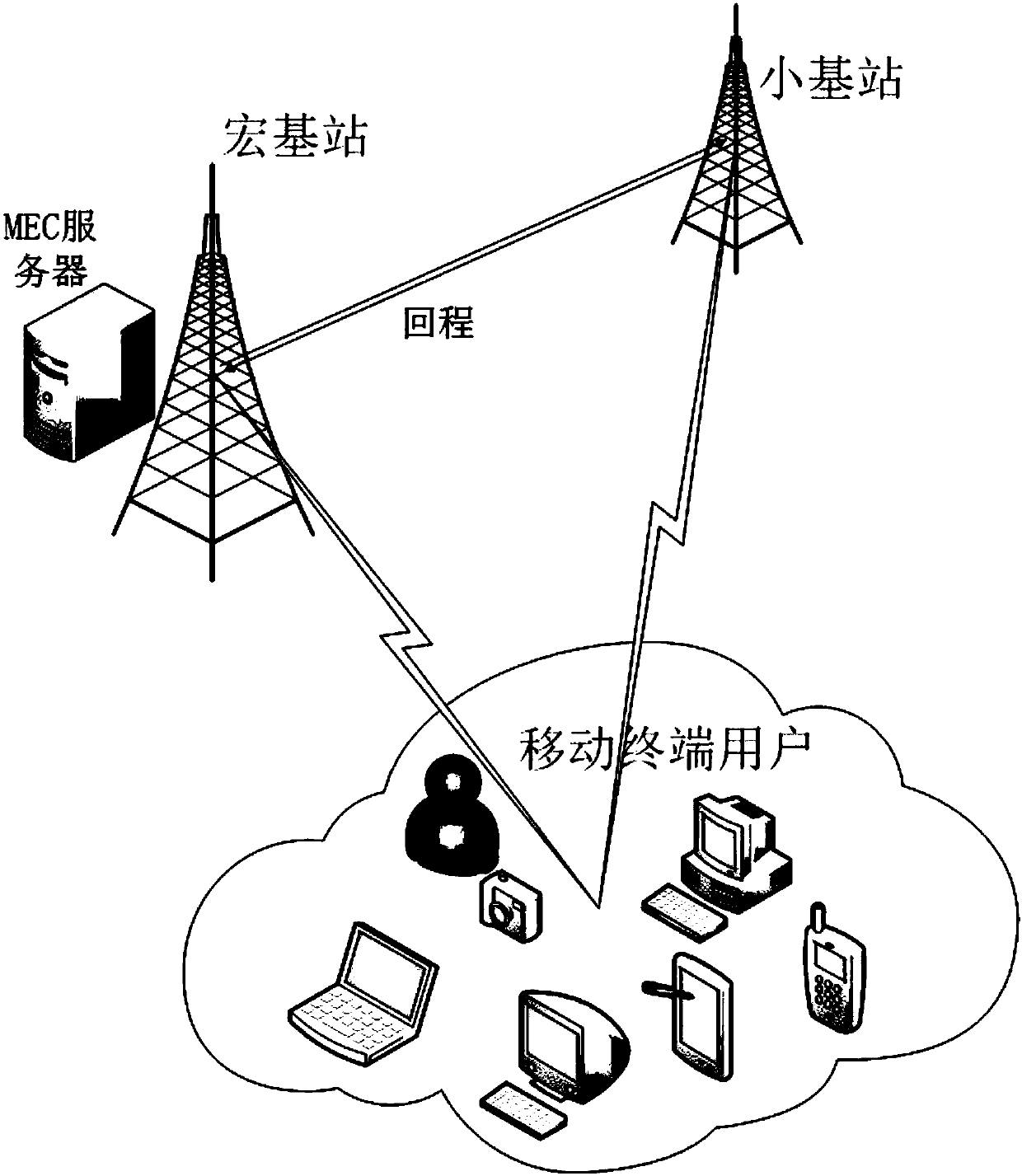
Delay and energy consumption-based efficient offloading method for computing task of mobile edge computing system
The invention discloses a delay and energy consumption-based efficient offloading method for a computing task of a mobile edge computing system. The method comprises the steps of building a macro basestation with multiple users and one deployment mobile edge computing (MEC) server and a single-cell cell model of a small base station without an MEC server; then building a mathematical model basedon a wireless communication theory; and finally, designing a delay and energy consumption-based efficient offloading solution for a computing task of the MEC system through a parallel greedy algorithm, and analyzing and providing the performance of the solution. Compared with existing efficient energy consumption offloading solution, the method well weights the delay sensitive demand and energy consumption demand of a terminal user, and lowers delay and total energy consumption of the system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
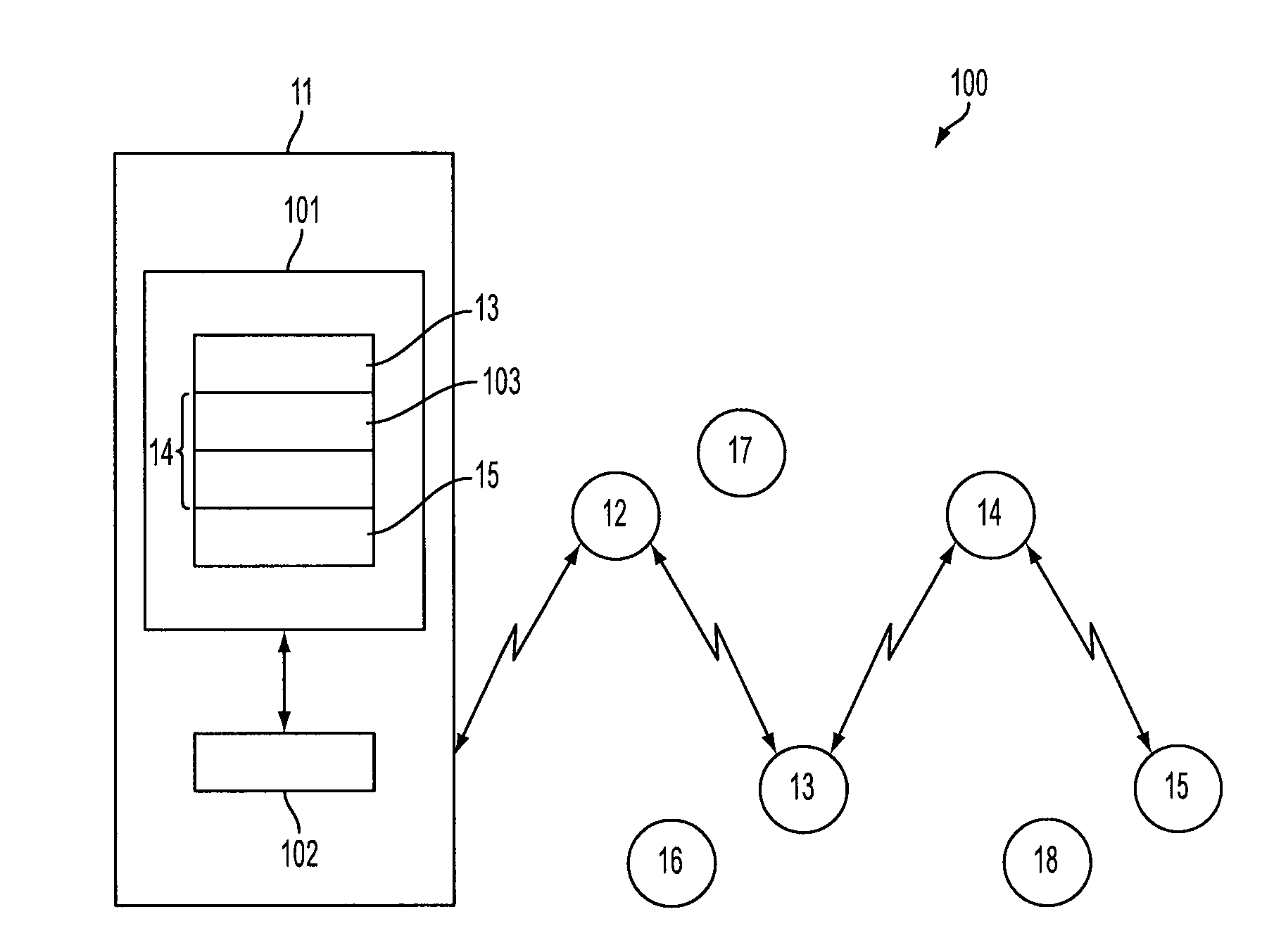
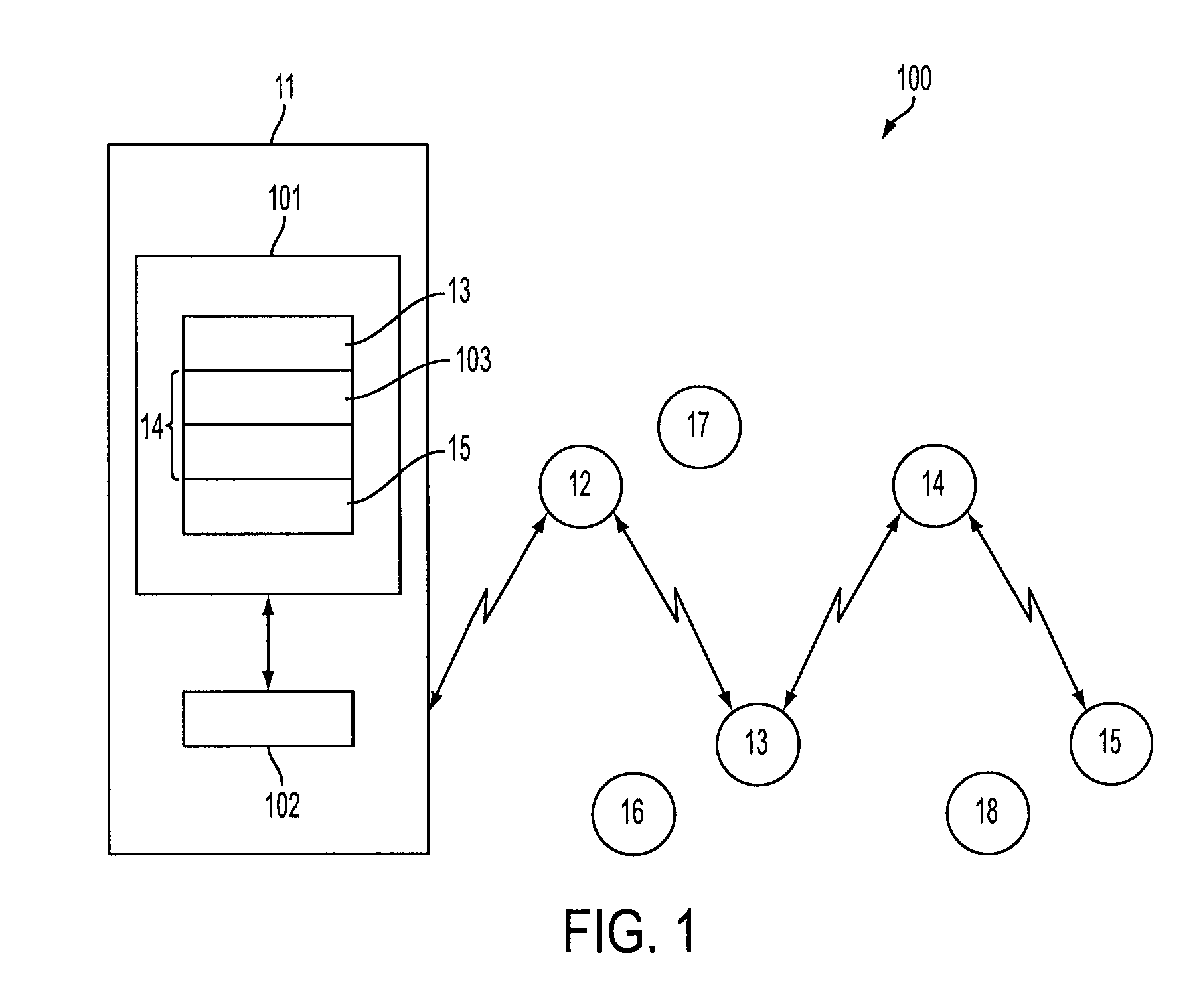
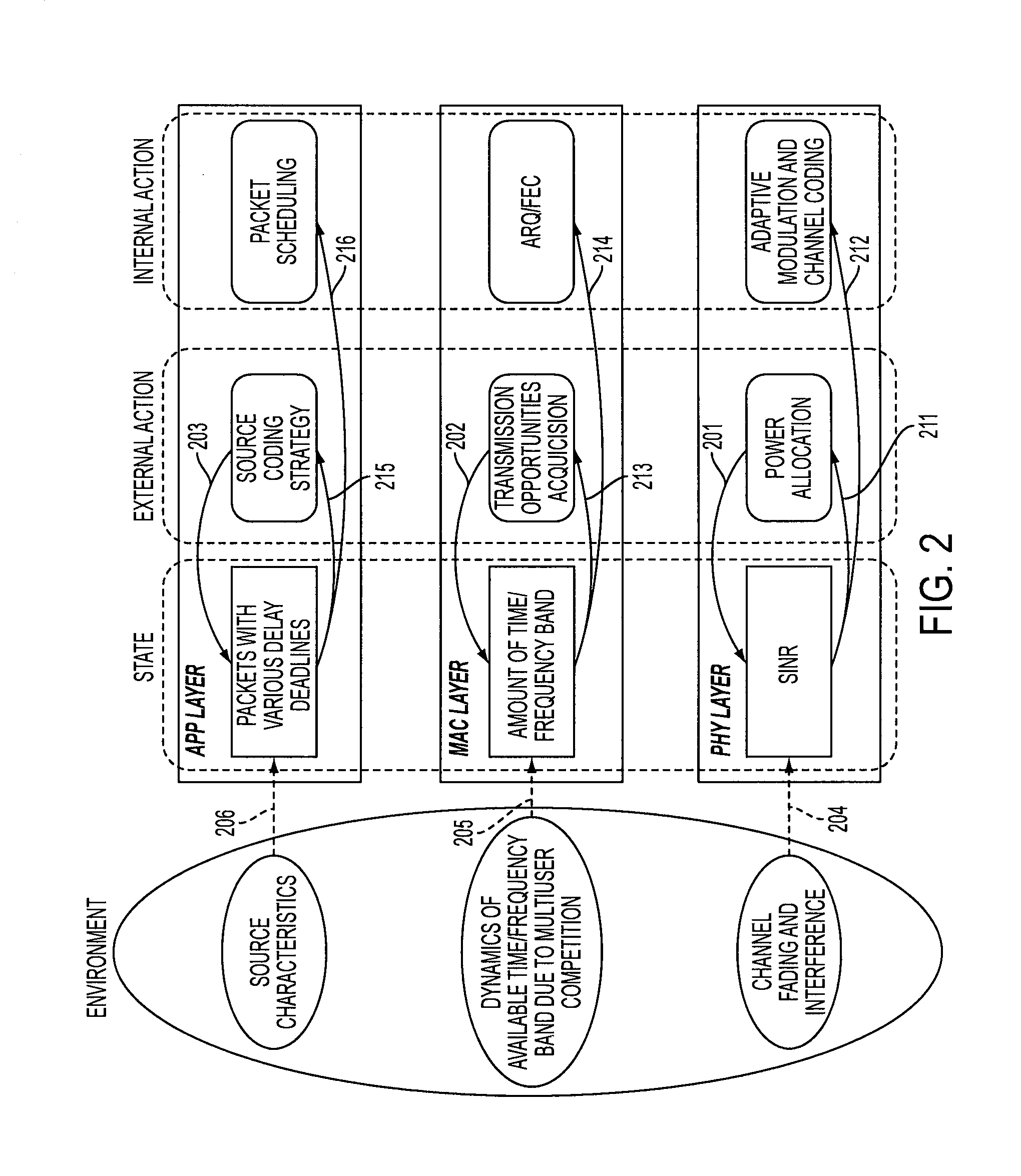
Adaptive network system with online learning and autonomous cross-layer optimization for delay-sensitive applications
InactiveUS20110019693A1Sub-optimal performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexReliable transmissionNetworked system
A network system providing highly reliable transmission quality for delay-sensitive applications with online learning and cross-layer optimization is disclosed. Each protocol layer is deployed to select its own optimization strategies, and cooperates with other layers to maximize the overall utility. This framework adheres to defined layered network architecture, allows layers to determine their own protocol parameters, and exchange only limited information with other layers. The network system considers heterogeneous and dynamically changing characteristics of delay-sensitive applications and the underlying time-varying network conditions, to perform cross-layer optimization. Data units (DUs), both independently decodable DUs and interdependent DUs, are considered. The optimization considers how the cross-layer strategies selected for one DU will impact its neighboring DUs and the DUs that depend on it. While attributes of future DU and network conditions may be unknown in real-time applications, the impact of current cross-layer actions on future DUs can be characterized by a state-value function in the Markov decision process (MDP) framework. Based on the dynamic programming solution to the MDP, the network system utilizes a low-complexity cross-layer optimization algorithm using online learning for each DU transmission.
Owner:SANYO NORTH AMERICA CORP +1
Dynamic automatic retransmission request in wireless access networks
InactiveUS7032153B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSignalling characterisationAccess networkWireless mesh network
A method and system for providing dynamic ARQ, on a per packet basis, in a wireless telecommunications access network. By taking into consideration both per packet QoS based on, for example, packet delay bound, and potential delays caused by retransmission, a dynamic NAK-based ARQ scheme is presented that dynamically adapts the retransmission parameters to the per packet QoS to provide improved radio link quality, particularly for non-delay sensitive services and applications. The ARQ parameters that are dynamically adjusted can include the number of retransmission rounds, and the number of retransmissions in each round.
Owner:APPLE INC
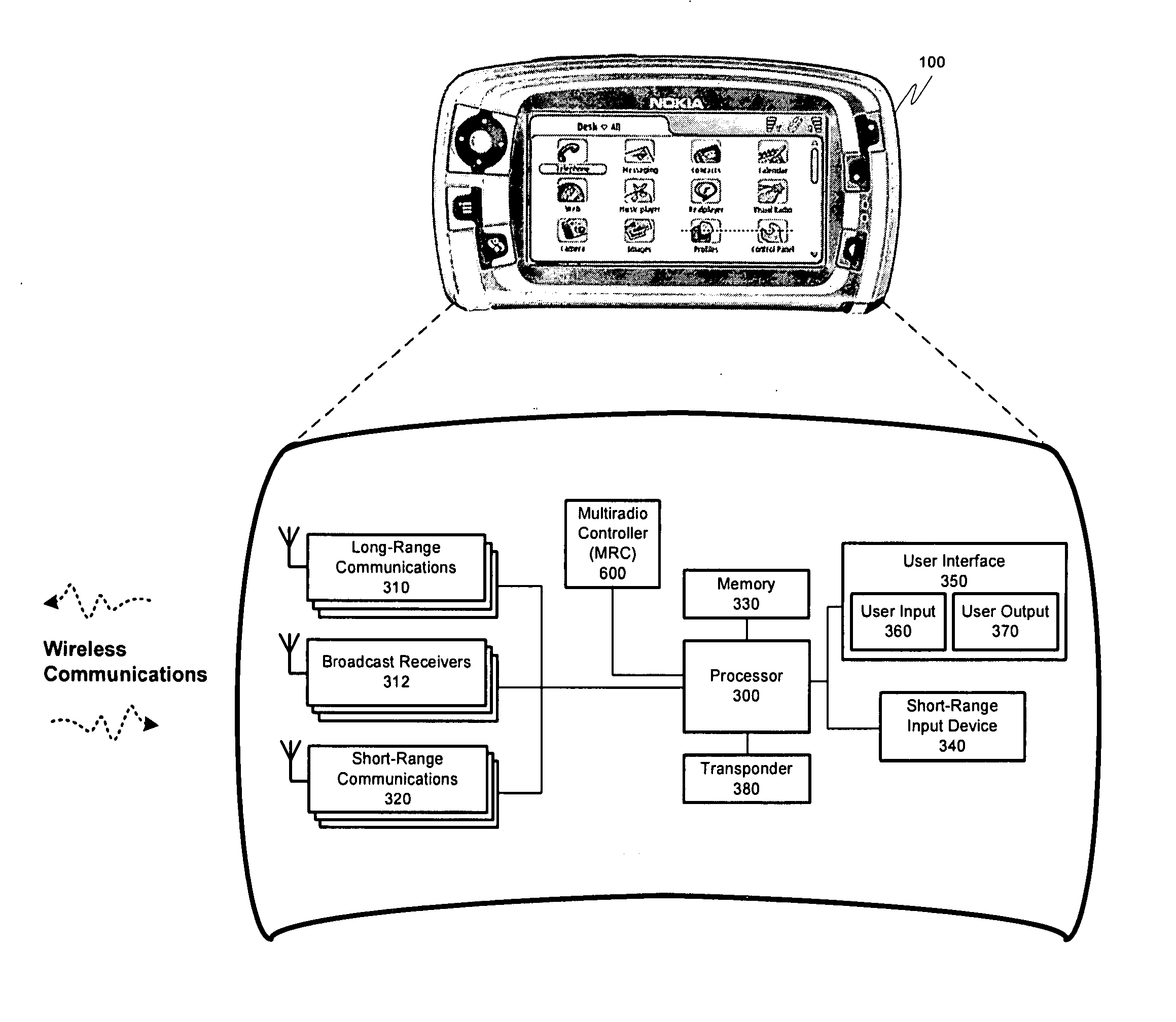
Multiradio control interface
ActiveUS20070263709A1Fast transferImmune from any communication overheadSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionControl systemRadio modem
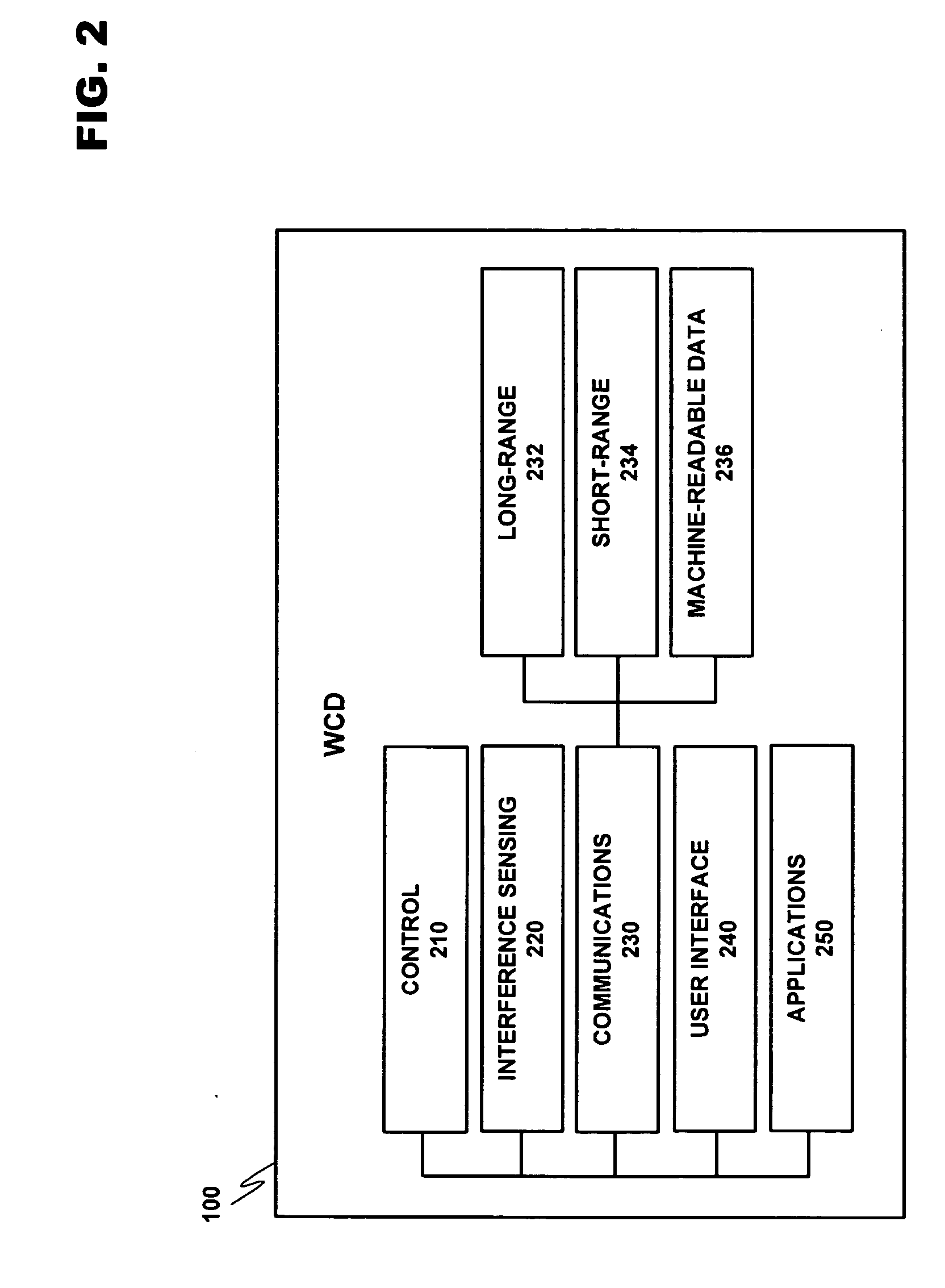
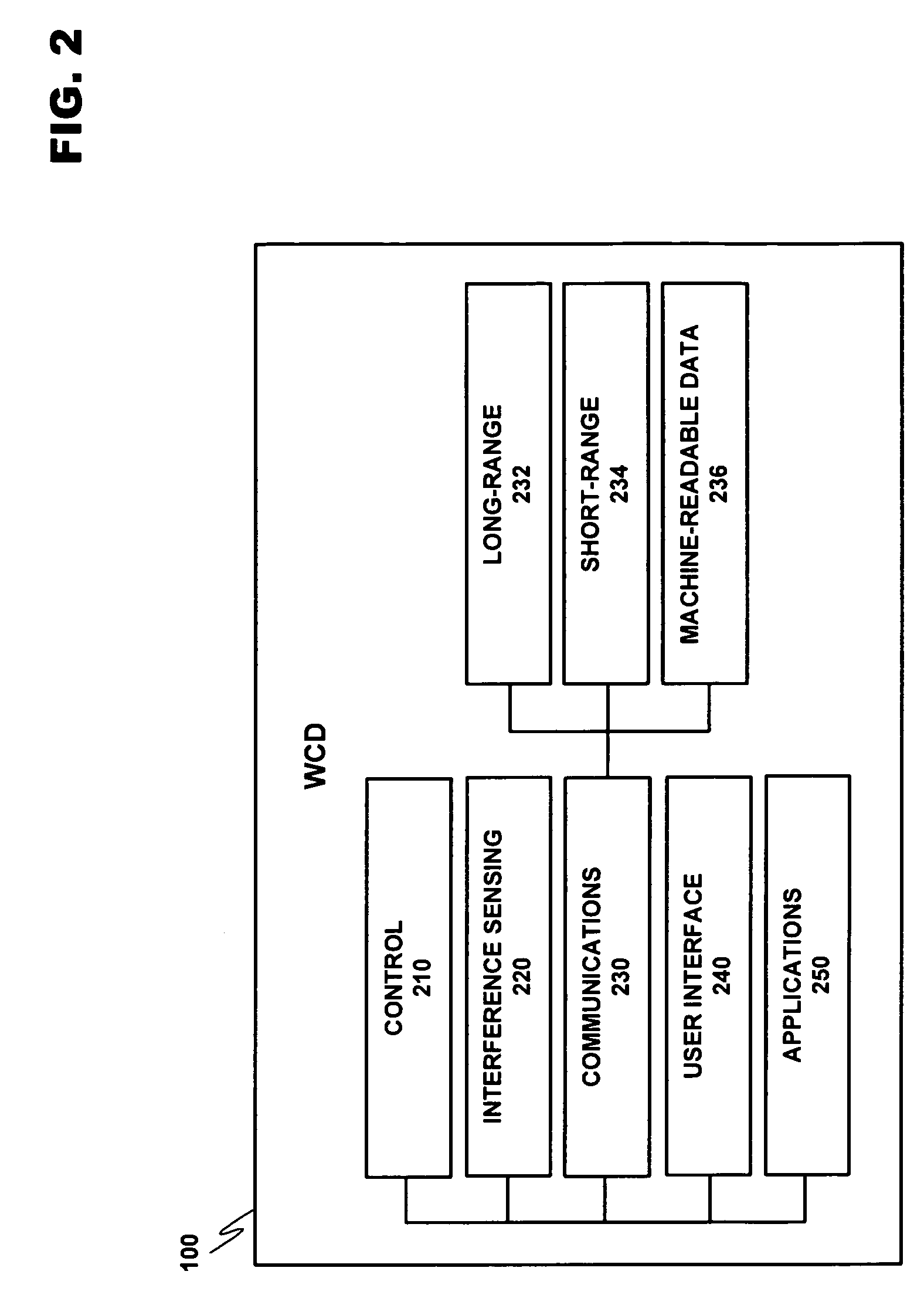
A system for managing the simultaneous operation of a plurality of radio modems in a single wireless communication device (WCD). The multiradio control may be integrated into the WCD as a subsystem responsible for scheduling wireless communications by temporarily enabling or disabling the plurality of radio modems within the device. The multiradio control system may comprise a multiradio controller (MRC) and a plurality dedicated radio interfaces. The radio interfaces are dedicated to quickly conveying delay sensitive information to and from the radio modems. This information may be requested by the MRC, or provided by one or more of the plurality of radio modems, if a change occurs during operation.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Radio transmission scheduling according to multiradio control in a radio modem
ActiveUS20070281743A1Fast transferImmune from any communication overheadTime-division multiplexSubstation equipmentModem deviceControl system
A system for managing the simultaneous operation of a plurality of radio modems in a single wireless communication device (WCD). The multiradio control may be integrated into the WCD as a subsystem responsible for scheduling wireless communications by temporarily enabling or disabling the plurality of radio modems within the device. The multiradio control system may comprise a multiradio controller (MRC) and a plurality dedicated radio interfaces. The radio interfaces are dedicated to quickly conveying delay sensitive information to and from the radio modems. The modems may further include control features that take information from the MRC as an input in determining the priority of messages to be sent out to a receiving device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Scheduling a mix of best effort (BE) and delay QOS flows
ActiveUS20090116439A1Well formedNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless commuication servicesDelay sensitiveReal-time computing
Systems and methodologies are described that facilitate dynamically adjusting scheduling priorities in relation to a combination of delay sensitive flows with delay requirements and best effort flows. The systems and methodologies provide optimal and efficient techniques to enable real time adjustment and assignment of bandwidth for a combination of best effort flows and delay sensitive flows. In particular, the bandwidth allocation is adjusted for each data packet such that delay requirements are met and the remaining bandwidth can be assigned to best effort flows.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Multi-hop wireless backhaul network and method
InactiveUS20100067476A1Data switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemHigh density
Some embodiments of the invention provide an implementation for a multi-hop wireless backhaul network. These embodiments can advantageously be deployed in dense urban areas and / or co-located with wireless access nodes, such as base-stations of a cellular wireless communication system. Preferably wireless links between constituent network nodes are set-up hierarchically. A basic result of this is that peer-to-peer (child-to-child) communication is generally prohibited and circuits are forced to conform to a topology. The multi-hop wireless backhaul network may be used to carry delay sensitive, high-density last mile circuit traffic over Non-Line-Of-Sight (NLOS) broadband radio links. Moreover, some embodiments of the invention provide a method of path-healing for re-routing of circuit traffic from circuits that have experienced catastrophic failures.
Owner:RES IN MOTION LTD
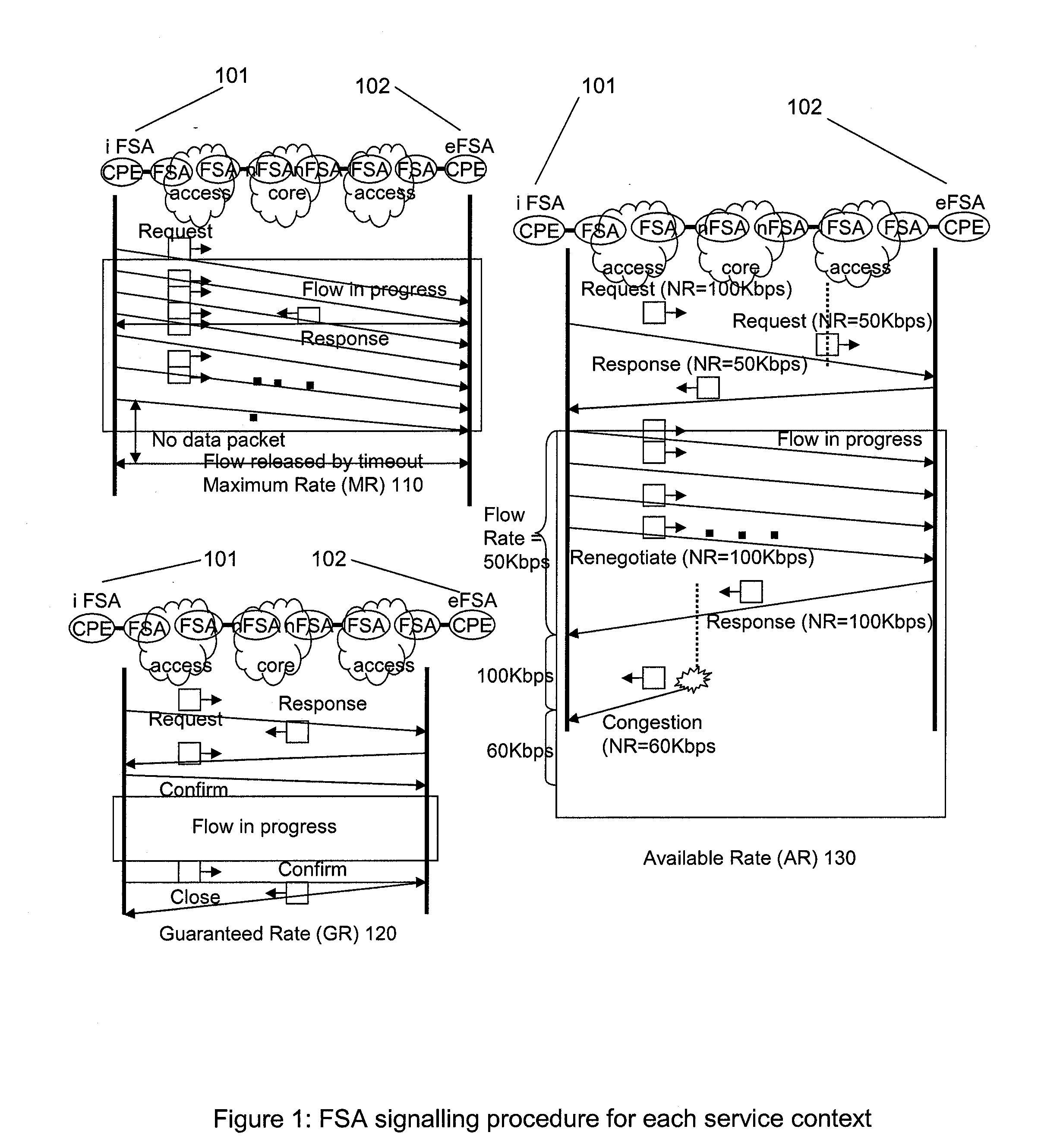
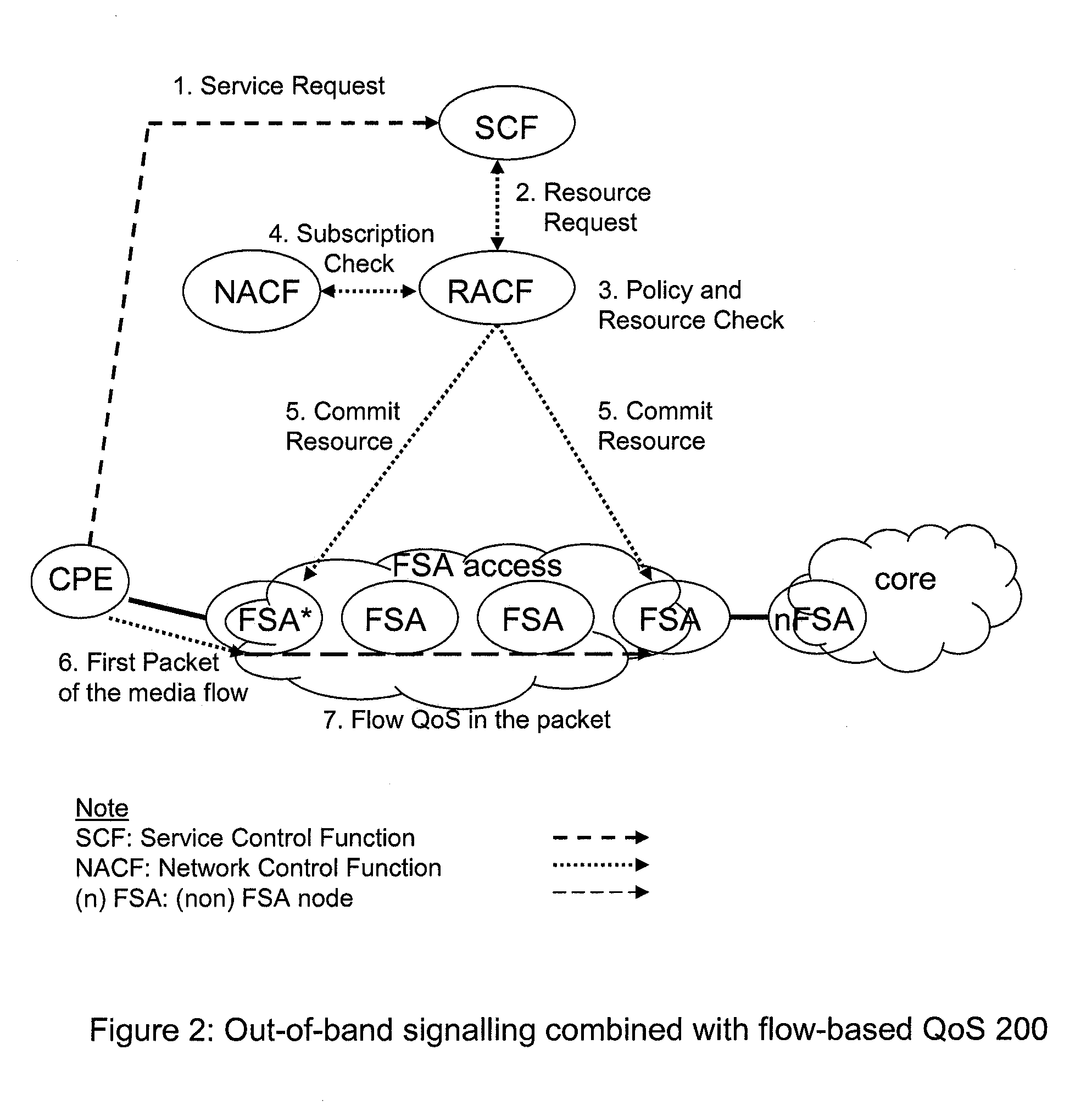
Flow State Aware QoS Management Without User Signalling
InactiveUS20100135158A1Improve service qualityFacilitate communicationEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTraffic capacityQos management
Conventional packet network nodes react to congestion in the packet network by dropping packets in a manner which is perceived by users to be indiscriminate. In embodiments of the present invention, indiscriminate packet discards are prevented by causing packets to be discarded according to bandwidth allocations that intelligently track flow sending rates. Flows are allocated bandwidth based on policy information. Where such policy information indicates that the flow should be treated as delay-sensitive, the present invention includes means to allocate an initial minimum rate that will be guaranteed and such flows will also have the use of an additional capacity that varies depending on the number of such flows that currently share an available pool of capacity. This provides a congestion alleviation method which is less annoying to users since communications that have been in existence for longer are less susceptible to component packets being deleted.
Owner:RAZOOM
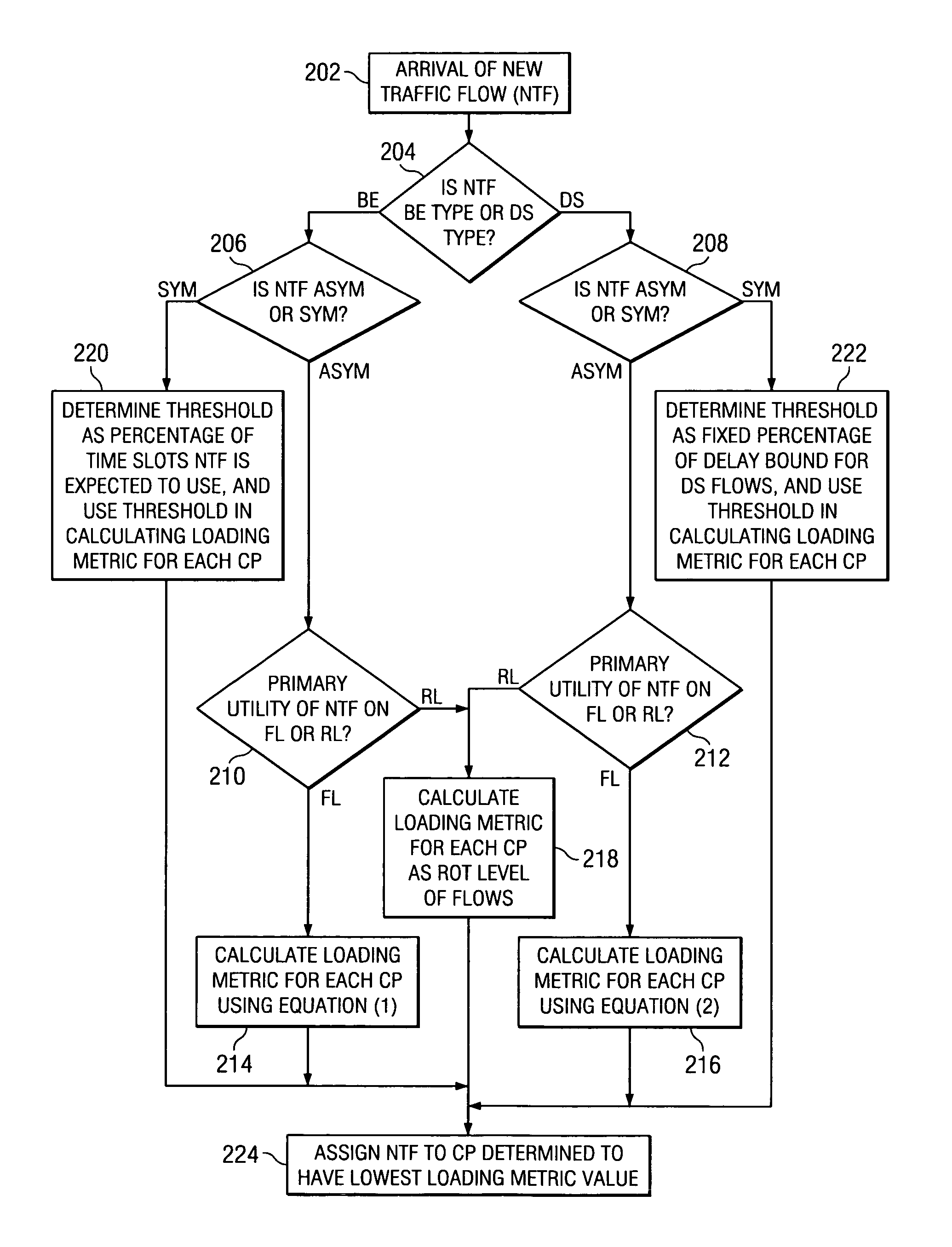
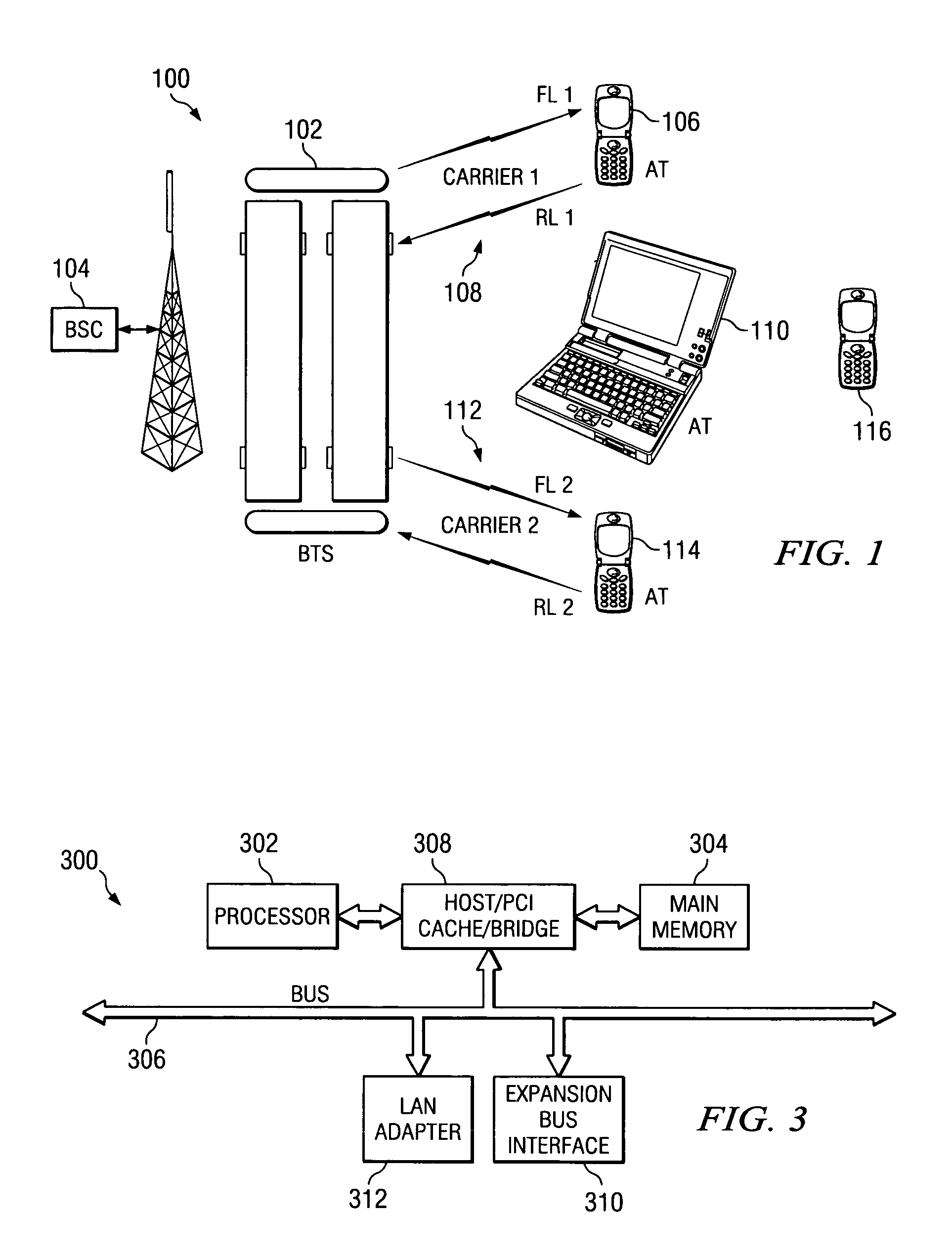
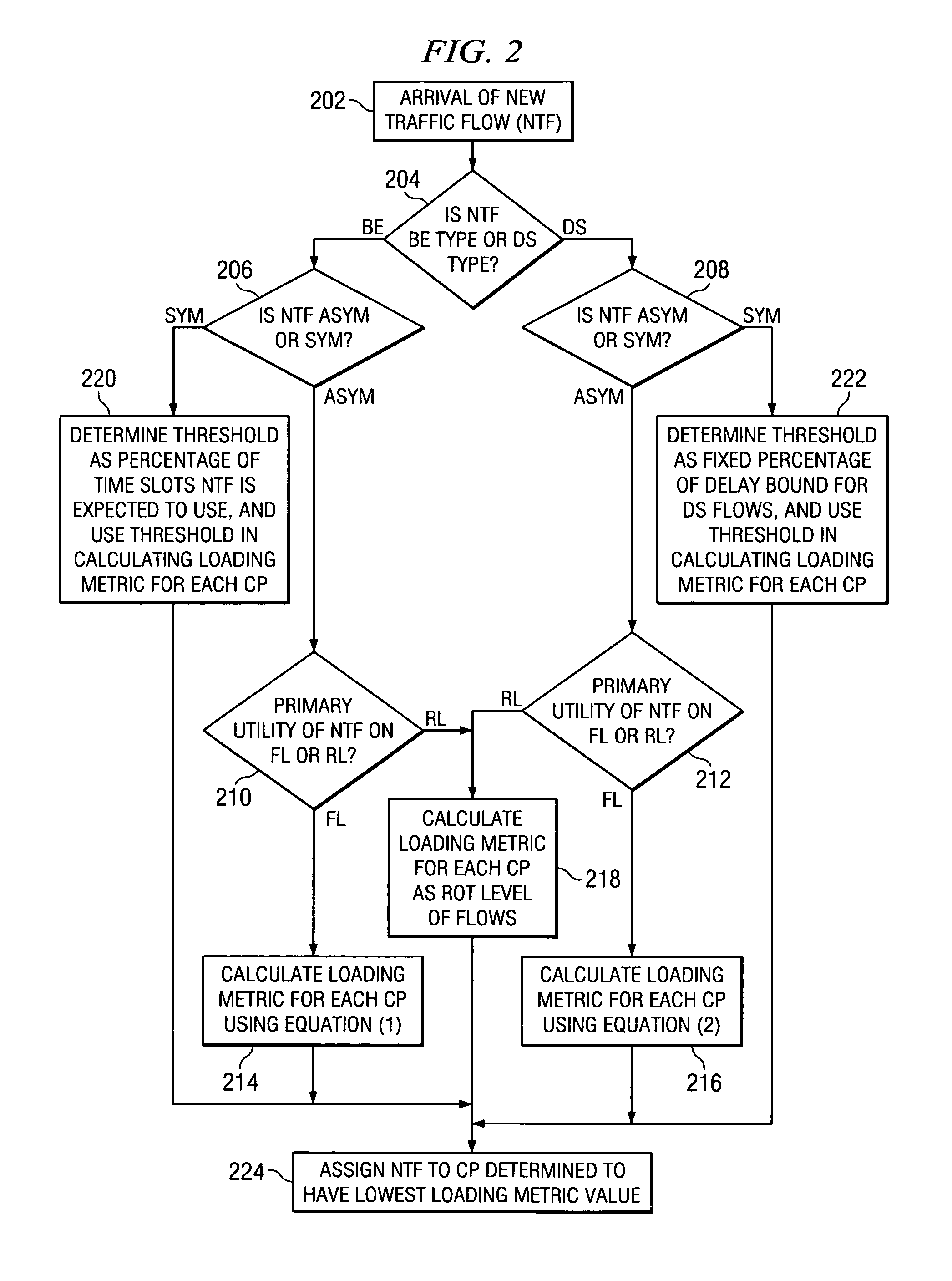
Method of multi-carrier traffic allocation for wireless communication system
ActiveUS7496367B1Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationCommunications systemStation
A dynamic distribution of traffic load across multiple carriers in a wireless communication system. The wireless communication system includes a Base Transmittal Station (BTS) and one or more Access Terminals (ATs). An arriving traffic flow is placed on the carrier pair preferably having the most excess capacity. It is determined whether the new traffic flow is symmetric or asymmetric, and whether it is a best effort (BE) or a delay sensitive (DS) flow type. A procedure is then selected and used to calculate a loading metric for each carrier pair, the new traffic flow being assigned to the carrier pair having the lowest metric.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
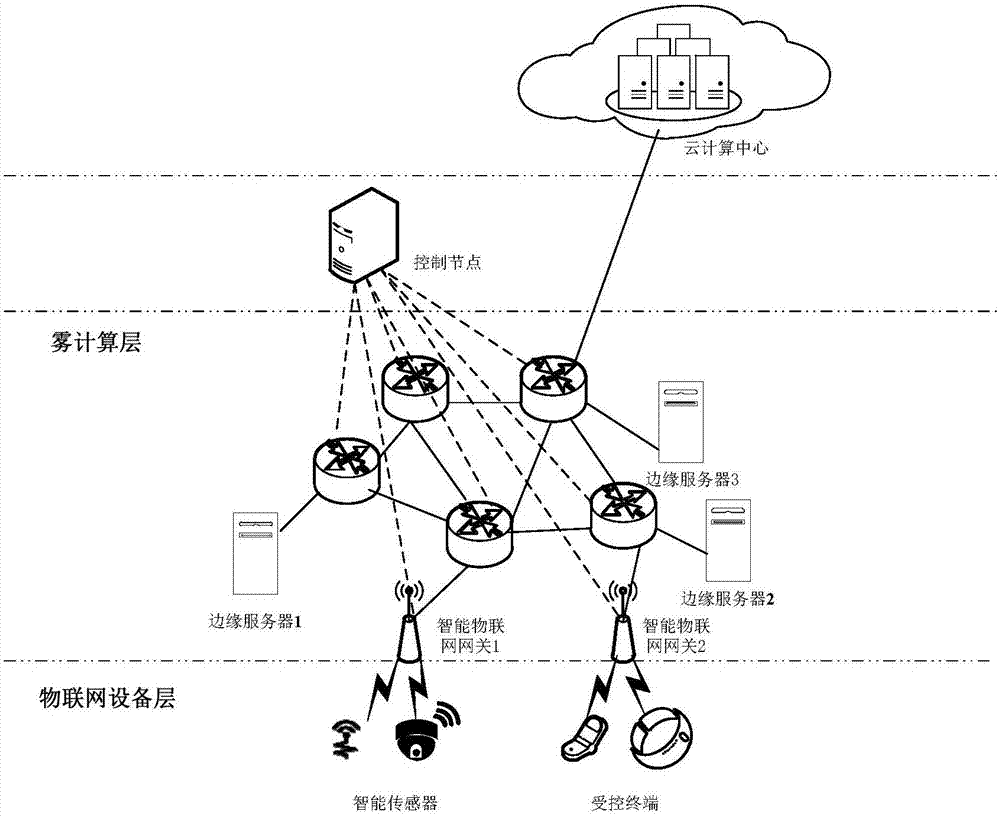
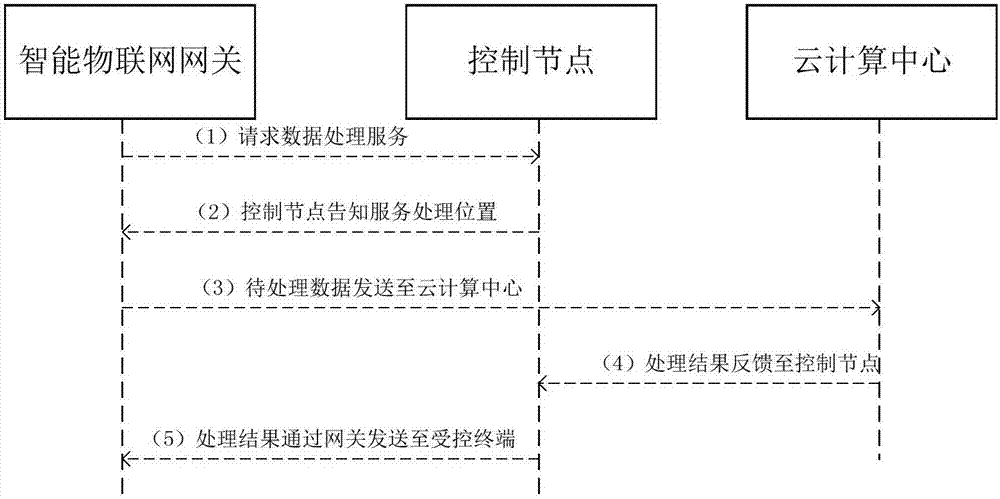
Architecture based on fog computing in SDN (Software Defined Network) and processing method thereof
The invention relates to an architecture based on fog computing in an SDN (Software Defined Network). The architecture comprises an Internet of Things equipment layer, a fog computing layer, a control node and a cloud computing center. A processing method of the architecture based on the fog computing in the SDN comprises the following steps: step (1), sending a request to the control node by an intelligent sensor via an intelligent Internet of Things gateway; step (2), if not being a delay-sensitive service, turning to step (3), otherwise turning to step (4); step (3), transmitting data to the cloud computing center by the control node, and feeding a result back to a controlled terminal by the cloud computing center; step (4), if a data processing service request is less than a threshold, turning to step (5), otherwise turning to step (6); step (5), searching a server occupancy table and processing the server occupancy table by selected edge servers and feeding the result back to the controlled terminal; and step (6), inquiring the server occupancy table, selecting the edge servers whose CPU utilization rate and memory usage are greater than the threshold by the control node, performing data processing by the plurality of selected edge servers, and returning a processing result to the controlled terminal.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
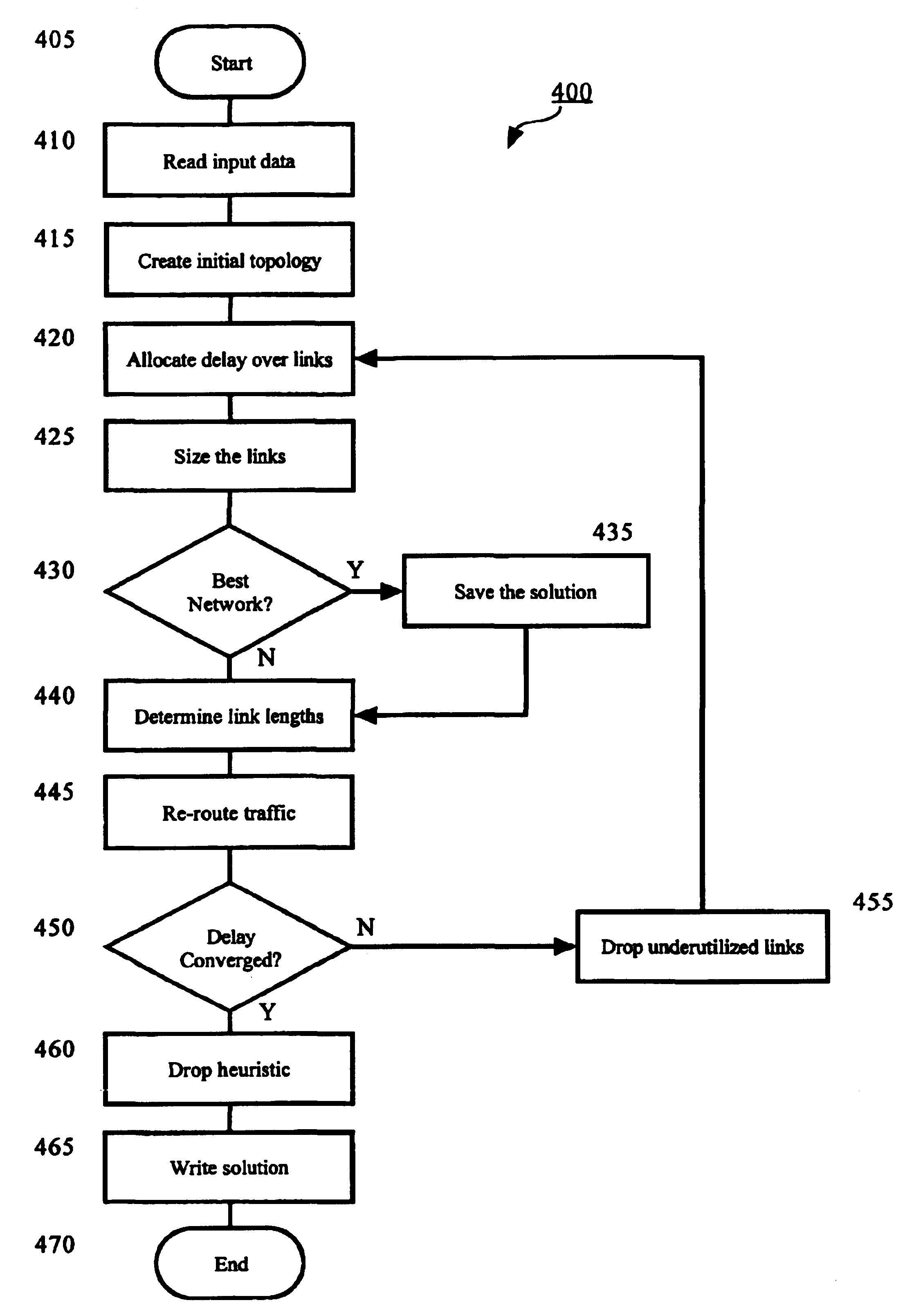
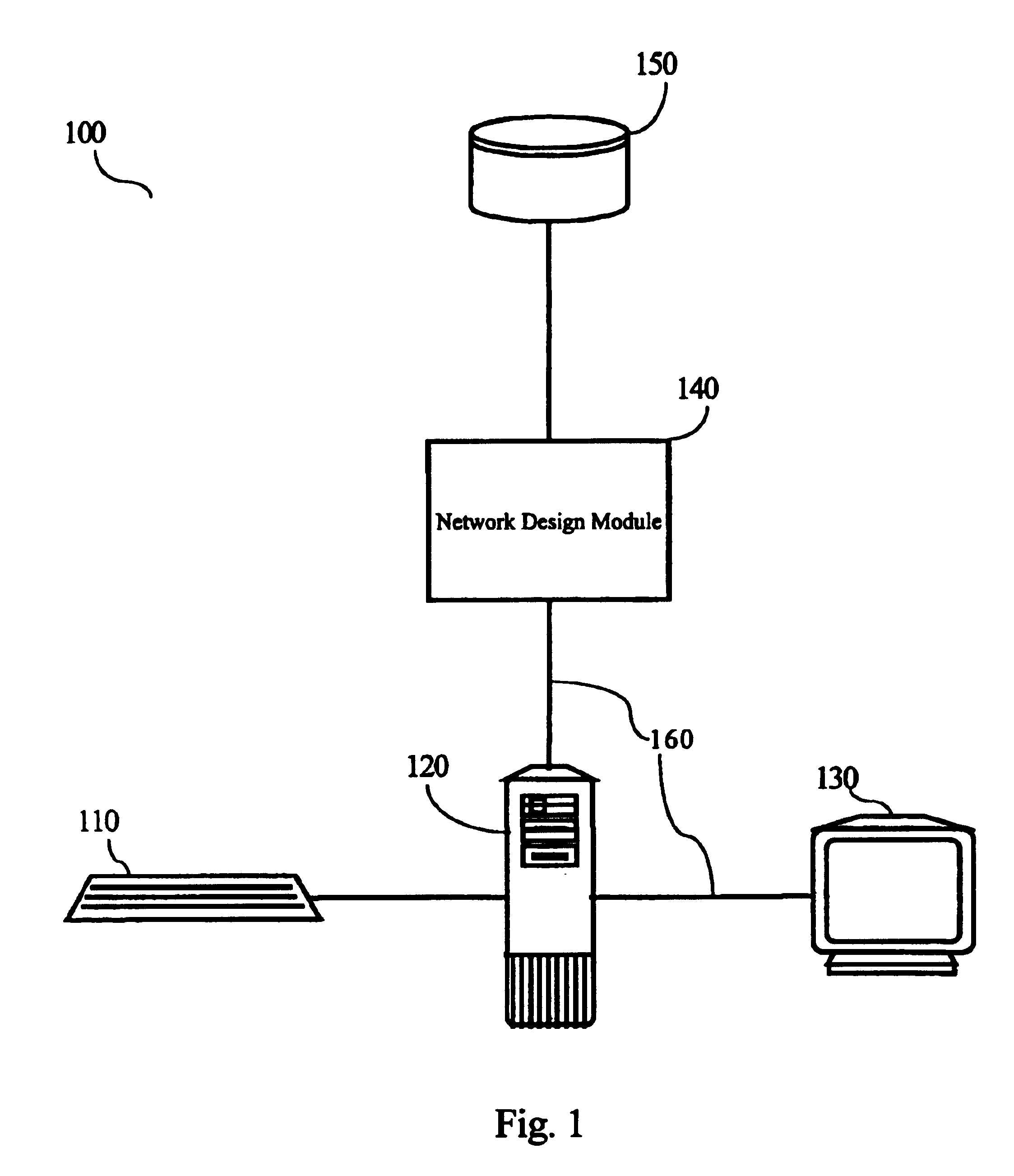
Apparatus and method for designing a network
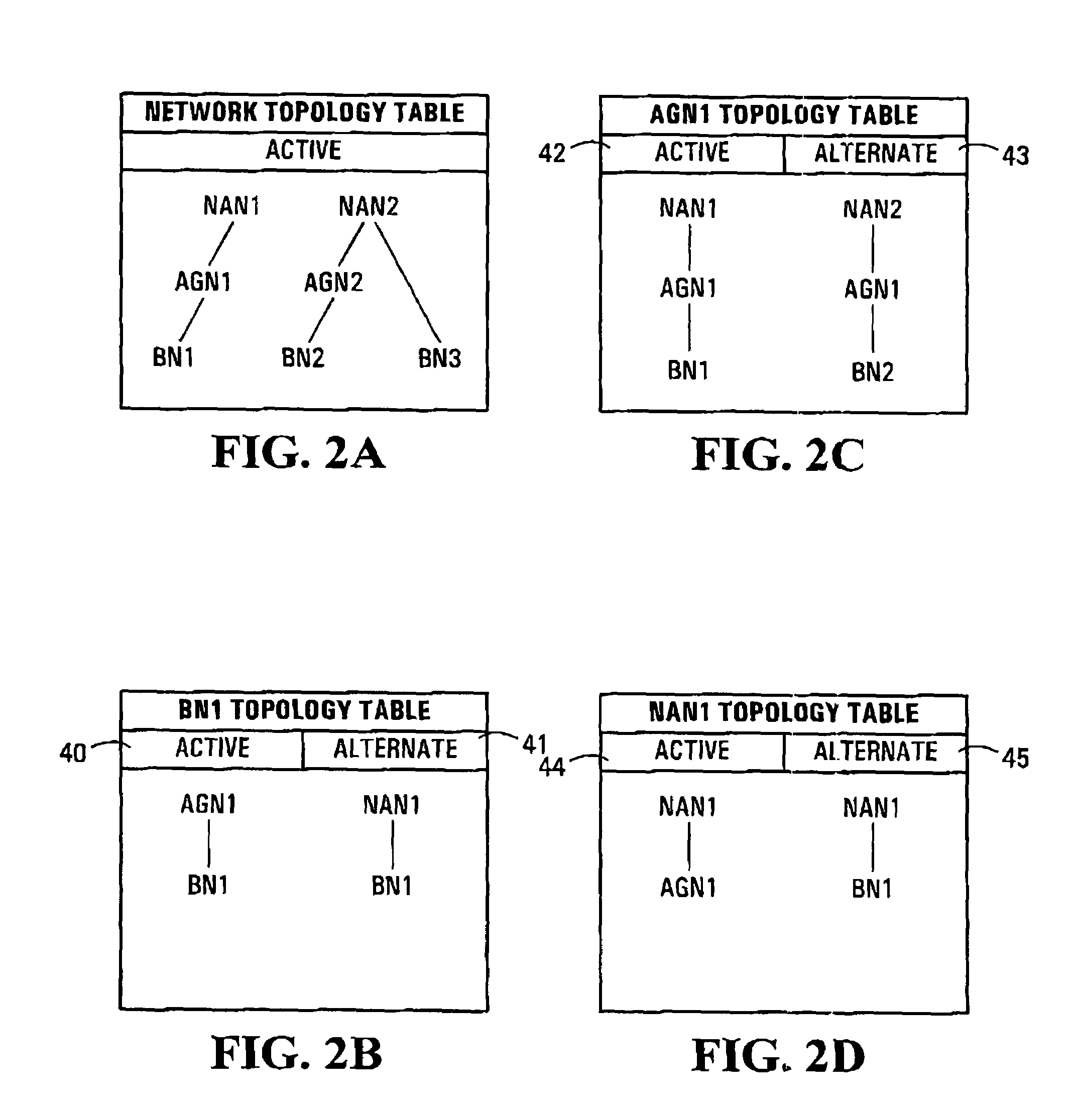
InactiveUS6934259B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityMaximum latency
An apparatus and method for designing a network are disclosed. The network is designed wherein nodes originate and terminate traffic to keep delay related to node-to-node delay-sensitive communication below a specified threshold. The method obtains an initial network topology including links and traffic routing based on a volume of traffic, allocates a maximum delay to each link in the network topology in proportion to the square root of an imputed cost for each link, sizes a bandwidth required for each link based on a current traffic routing and at least one of a maximum delay allocated to the link, determines link lengths and reroutes traffic according to shortest paths with respect to the determined link lengths.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
System and method for prioritizing individual streams within a multimedia flow
ActiveUS20060268701A1Reducing level of jitterQuality improvementError preventionTransmission systemsDelay sensitiveReal-time computing
The present invention provides a system and method for prioritizing delay-sensitive packets relative to each other for transmission from a router in a network, based on a delay variation estimated for each delay-sensitive packet by a quality of service monitor. In accordance with the present invention, late delay-sensitive packets are assigned a higher priority than, and are transmitted before, other delay-sensitive packets, thereby reducing the level of jitter and improving the quality of the packet streams that comprise late delay-sensitive packets.
Owner:TELCHEMY
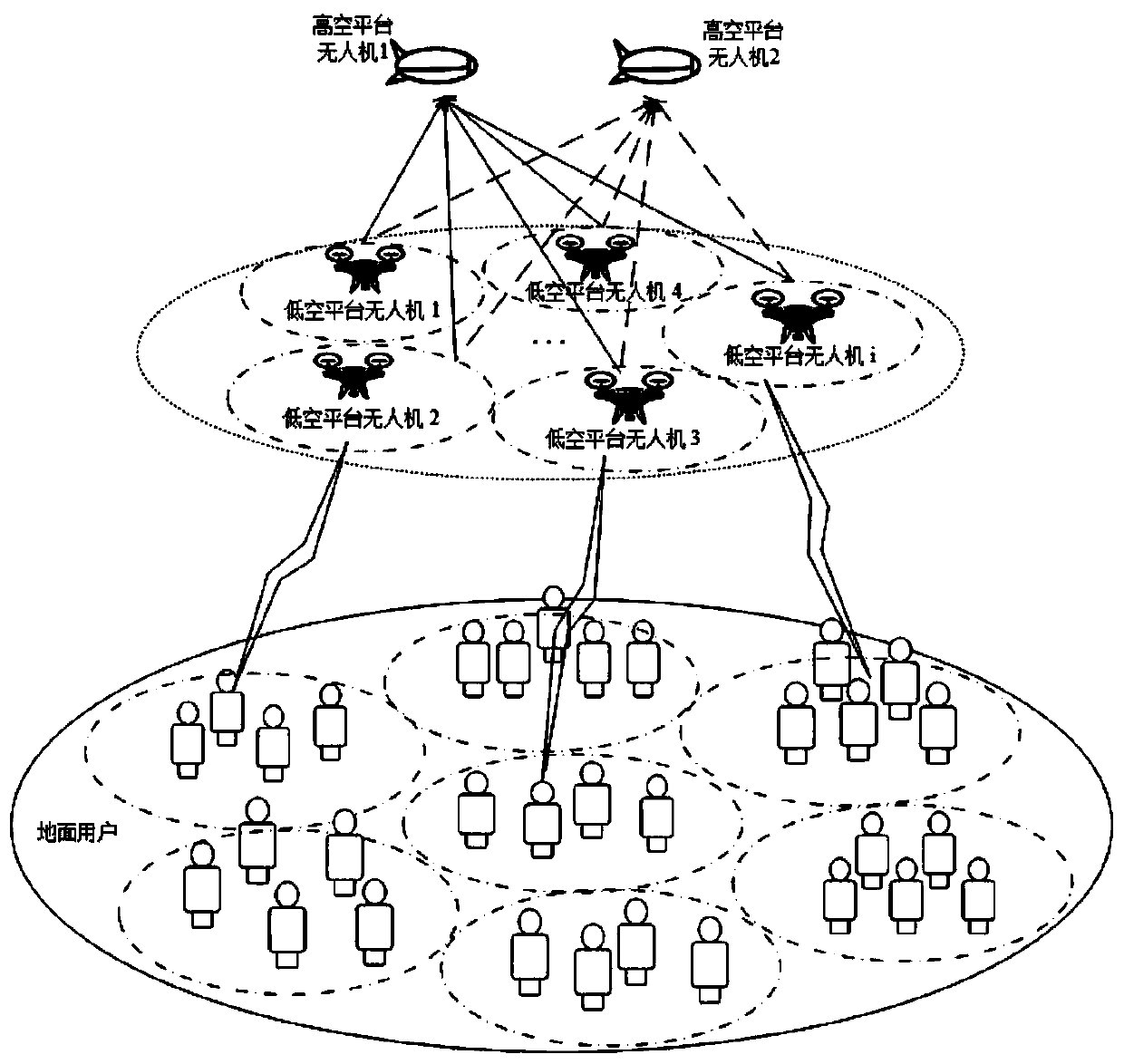
Unloading task allocation method of mobile edge computing system based on double-layer unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN110336861ARealize unloadingReduce complexityData switching networksOptimization problemDelay sensitive
The invention discloses an unloading task allocation method of a mobile edge computing system based on a double-layer unmanned aerial vehicle. The mobile edge computing system comprises two high-altitude platform unmanned aerial vehicles provided with mobile edge computing servers and a plurality of low-altitude platform unmanned aerial vehicles, and the two high-altitude platform unmanned aerialvehicles are used for executing computing tasks unloaded by the low-altitude platform unmanned aerial vehicles; the unloading task allocation method comprises the following steps: modeling calculationtask unloading allocation problems of the low-altitude platform unmanned aerial vehicle and the high-altitude platform unmanned aerial vehicle through a game, and establishing a utility function of the upper-layer high-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle and a cost function of the lower-layer low-altitude platform unmanned aerial vehicle based on the price; and solving an equilibrium planning problem with equilibrium constraints obtained after modeling: on the basis of a strategy of fixing an upper-layer leader, firstly solving an equilibrium solution of an optimization problem of a plurality ofusers at a lower layer of the game, and then solving an equilibrium solution of a plurality of unmanned aerial vehicle base stations at an upper layer. The problems existing when an existing unmannedaerial vehicle executes calculation-intensive and delay-sensitive tasks are solved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
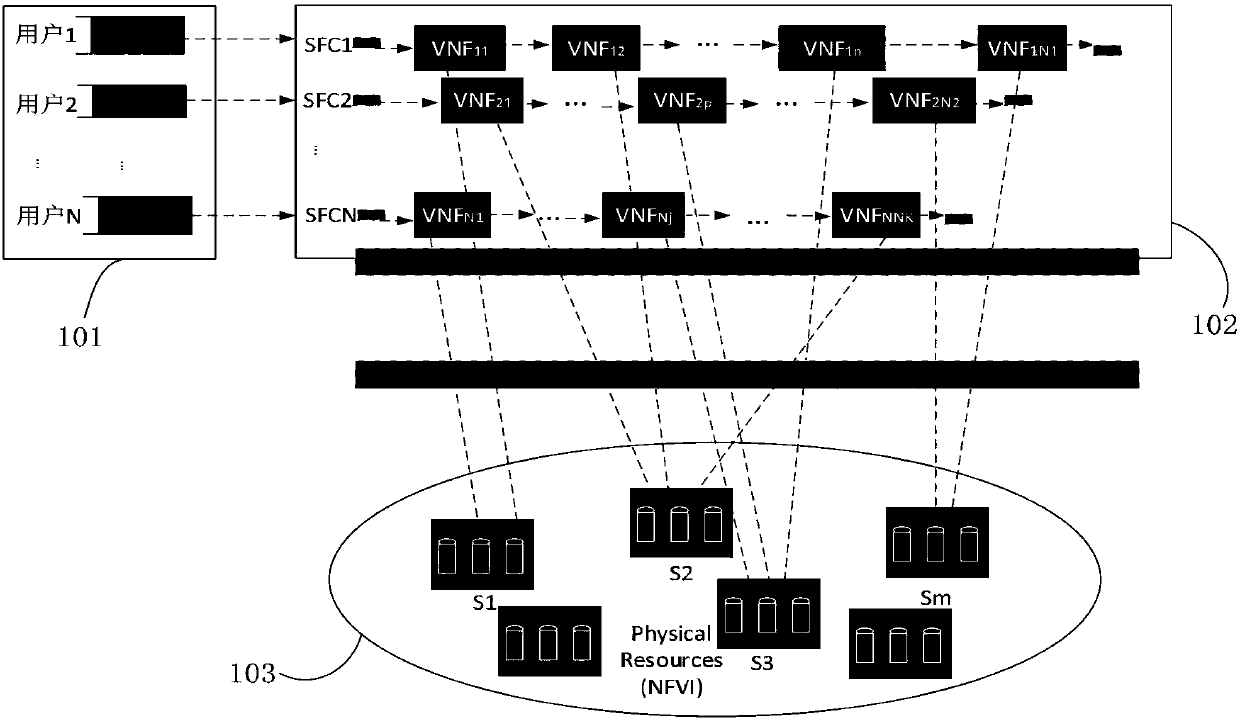
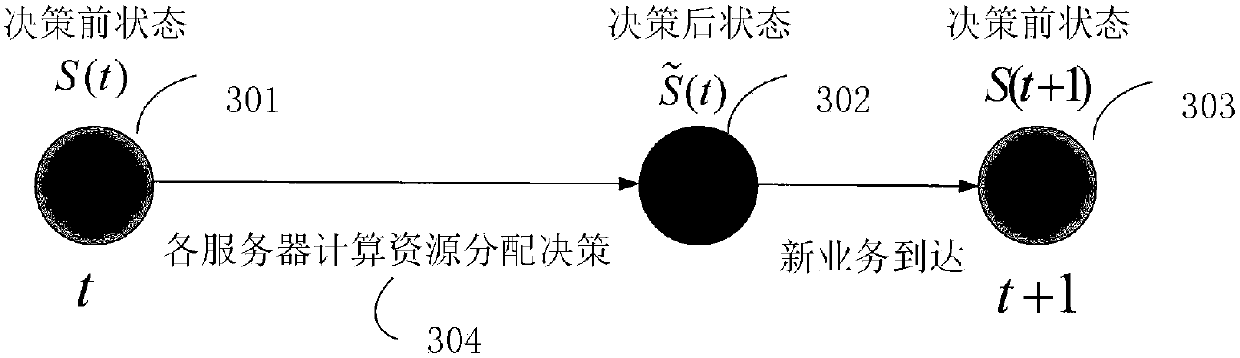
Network slice dynamic resource distributing method based on MDP
The invention relates to a network slice dynamic resource distributing method based on a Markov decision process (MDP), and belongs to the field of the mobile communication. The method comprises the following steps: guaranteeing serious delay requirements of all delay sensitive operations in each network slice to realize dynamic resource distribution performed by the taking the compromise betweenthe maximum network throughput capacity and the minimum energy consumption as a target; and distributing appropriate computational resource amount for a virtual network function (VNF) on a service function chain (SFC) of each user in the slice and dynamically adjusting the amount of the started server for providing the computational resource according to cache queue state information of the user in each network slice and real-time price state information of the electric power consumed by the server on each discrete time slot. Through the network slice dynamic resource distribution method basedon the MDP provided by the invention, the delay constraint of the user operation can be satisfied while the compromise between the maximum network throughput capacity and the minimum energy consumption is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Apparatus and method for adaptive, multimode decoding
ActiveUS7003712B2Improve received signal qualityImprove errorOther decoding techniquesOther error detection/correction/protectionCommunications systemSignal quality
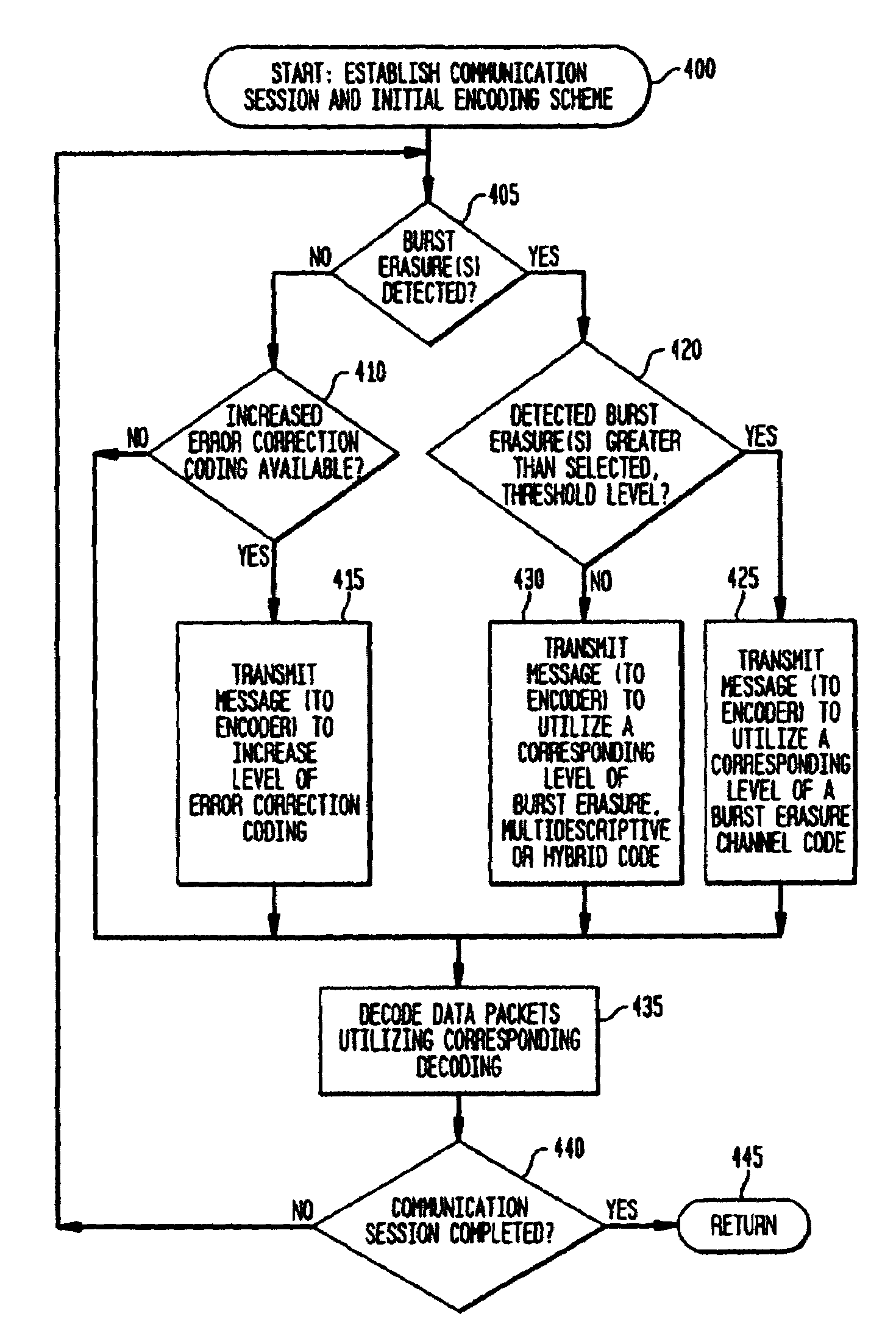
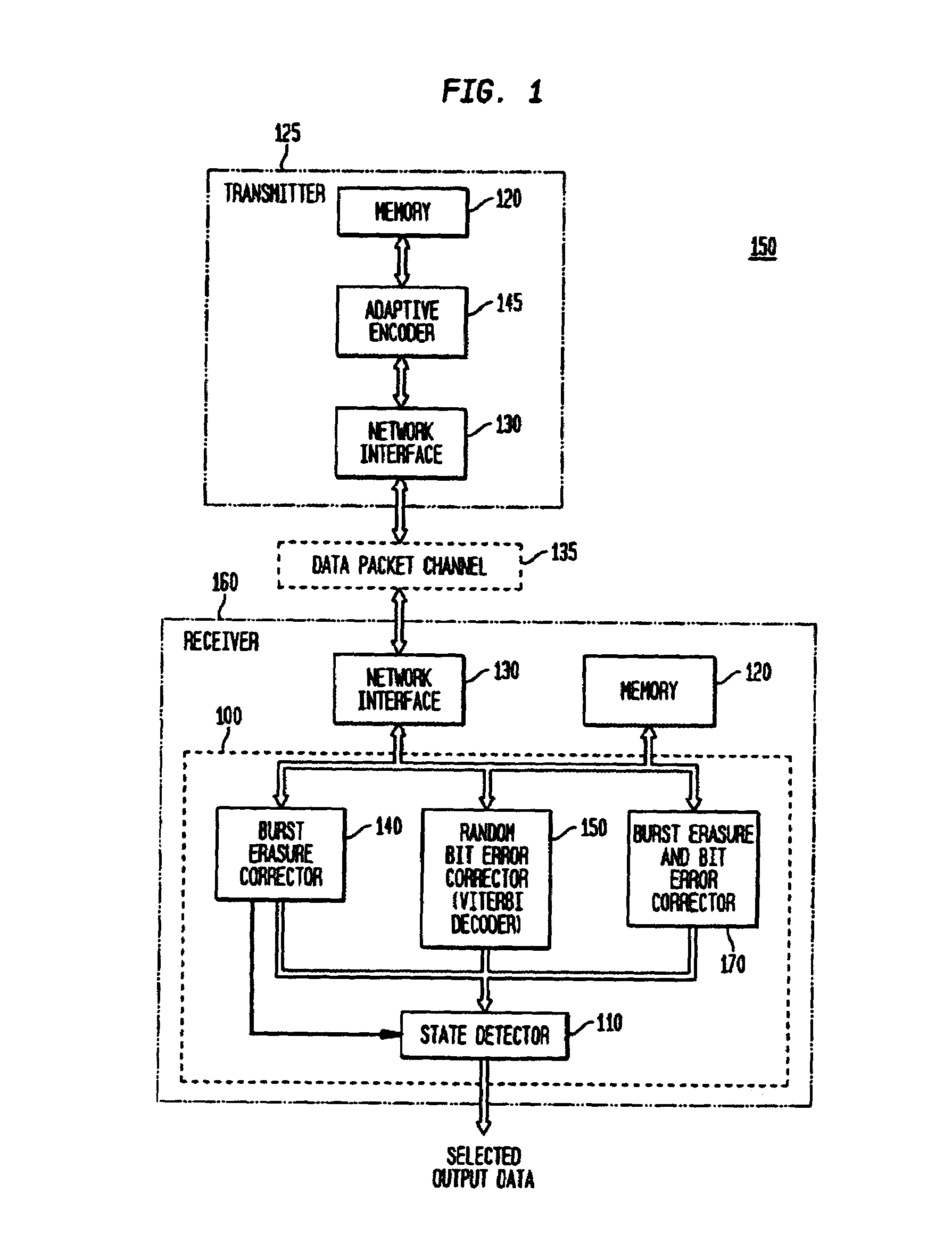
The present invention provides for adaptive and multimode decoding, in a data packet-based communication system, to provide improved received signal quality in the presence of burst erasures or random bit errors, with particular suitability for real-time, delay sensitive applications, such as voice over Internet Protocol. In the presence of burst erasures, the adaptive multimode decoder of the present invention provides burst erasure correction decoding, preferably utilizes a maximally short (MS) burst erasure correcting code, which has a comparatively short decoding delay. Depending upon the level of such burst erasures, different rate MS codes may be utilized, or other codes may be utilized, such as hybrid or multidescriptive codes. When no burst erasures are detected, the adaptive multimode decoder of the present invention provides random bit error correction decoding, in lieu of or in addition to corresponding burst erasure correction coding.
Owner:AGERE SYST GUARDIAN
Channel quality indication adjusting method and base station node
ActiveCN101018387AImprove performanceImprove throughputEnergy efficient ICTError preventionComputer scienceType selection
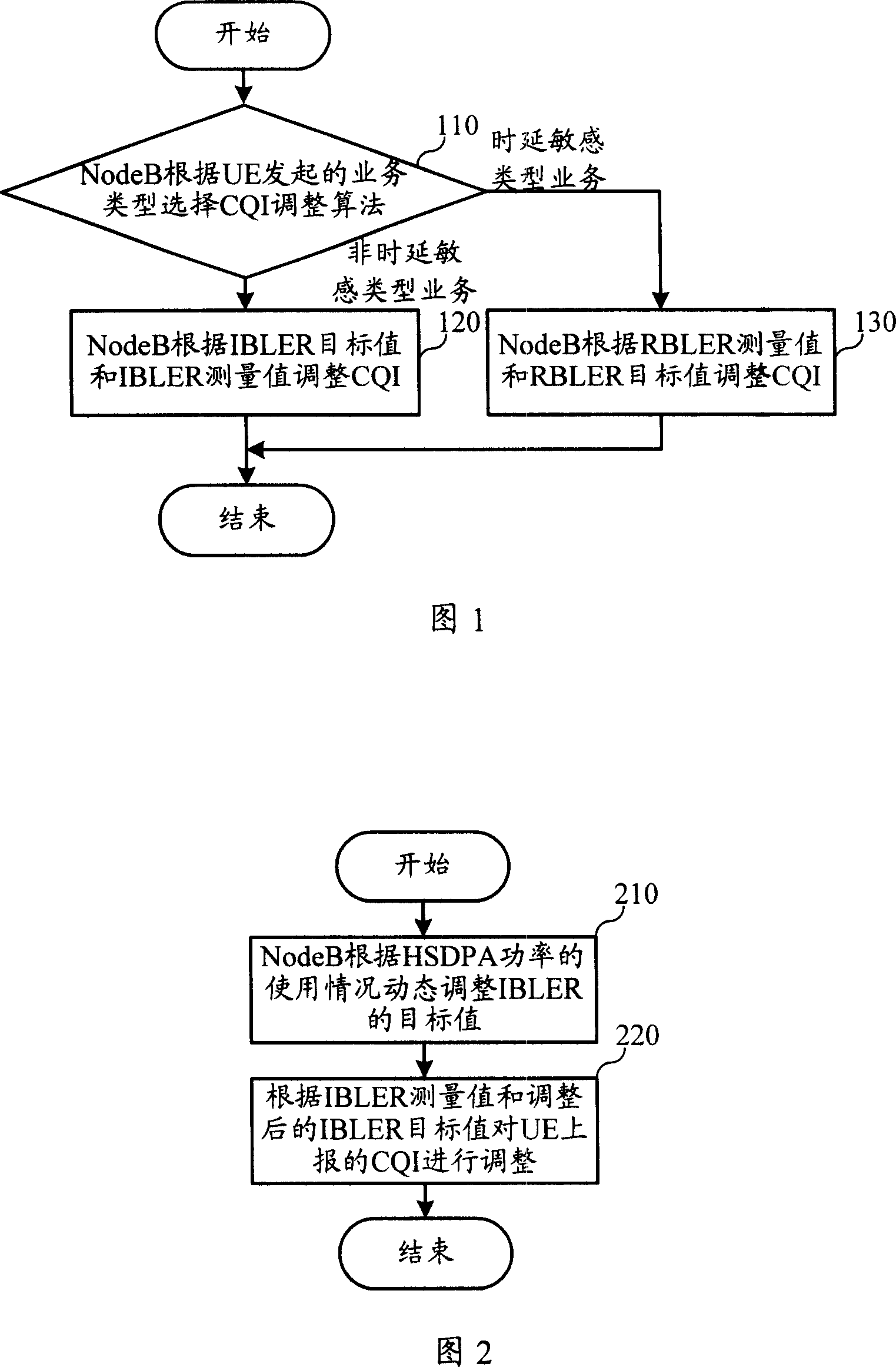
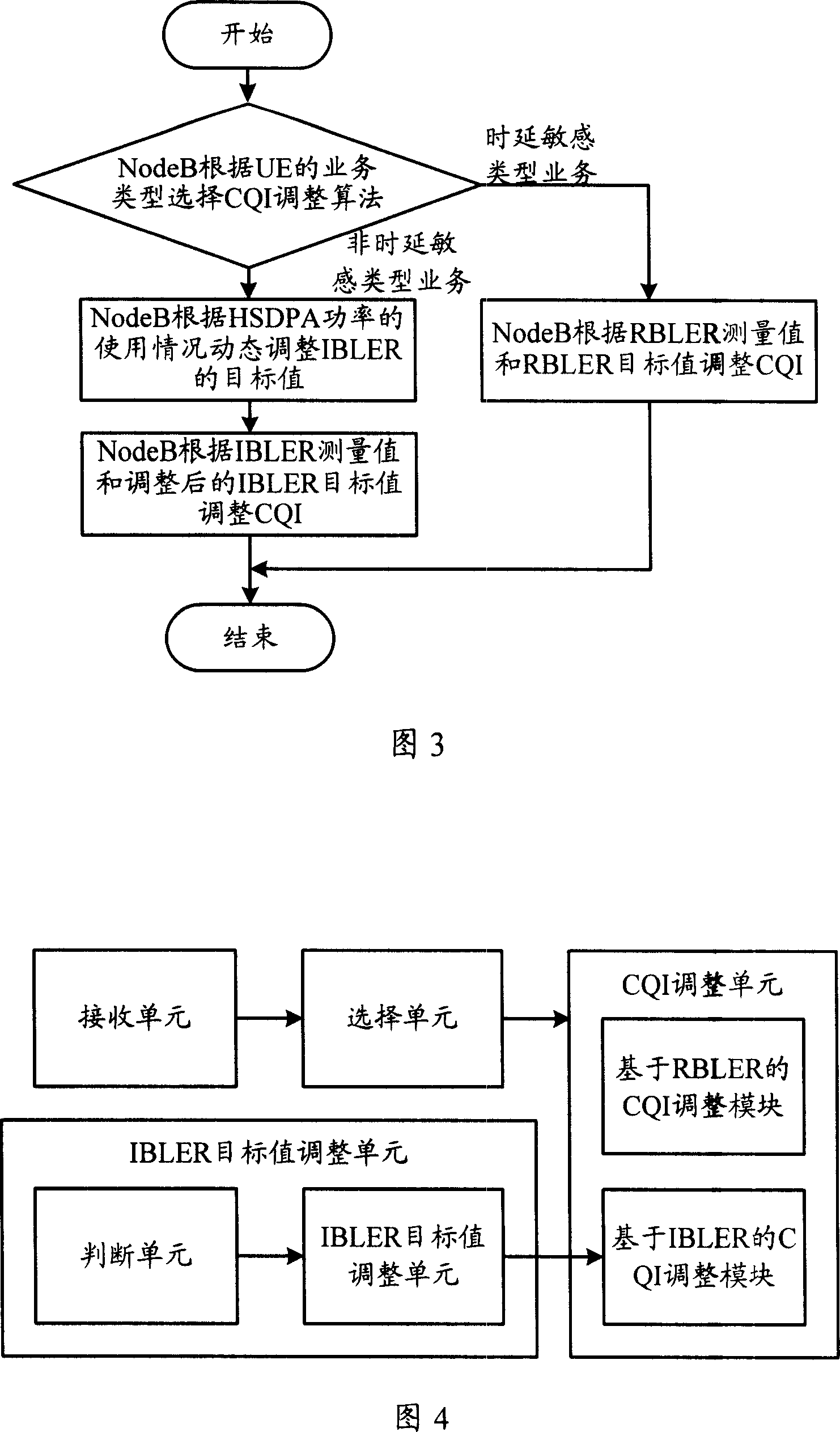
The disclosed adjustment method on channel quality indication for HSDPA system comprises: according to business type, selecting relative CQI adjustment algorithm to adjust reported CQI; to non-delay sensitive business, selecting CQI algorithm based on IBLER, while selecting CQI algorithm based on RBLER for delay sensitive business. This invention can adjust IBLER target value according to load condition.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Software-defined network (SDN)-based data center service quality assurance method
ActiveCN106059821AReduce latencyHigh and stable available bandwidthData switching networksData centerStructure of Management Information
The present invention requests to protect a software-defined network (SDN)-based data center service quality assurance method that is a method applicable to a transmission network of a separation delay sensitive application and a bandwidth sensitive application in a data center. According to the method, a core layer switch and a convergence layer switch or only the core layer switch (this is determined according to a network topological structure) are or is divided into two parts, and the two parts respectively process the delay sensitive application or the bandwidth sensitive application, so that the isolated traffic transmission of the two types of application is realized. Compared with the prior art, on the one hand, different types of application acquire better service quality and do not interfere with each other; and on the other hand, a network resource use ratio is improved due to adoption of a flexible multi-path forwarding policy. In addition, due to use of SDN advantages, a custom-defined platform that is applicable to the data center and ensures the service quality policy is provided for the user, so that an efficient data center is made conveniently, the network is managed and controlled more easily, and both the network construction cost and later running maintenance cost are reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
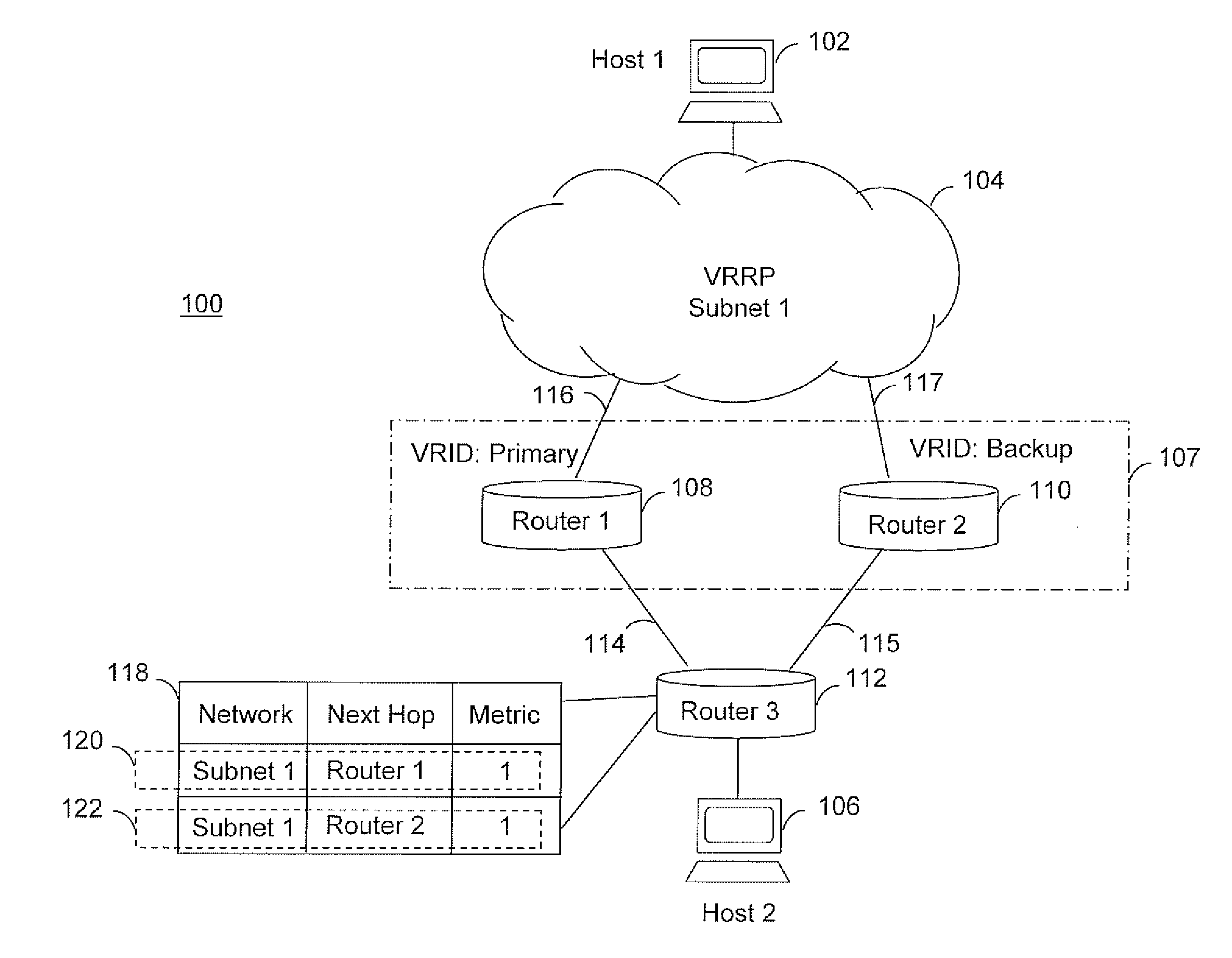
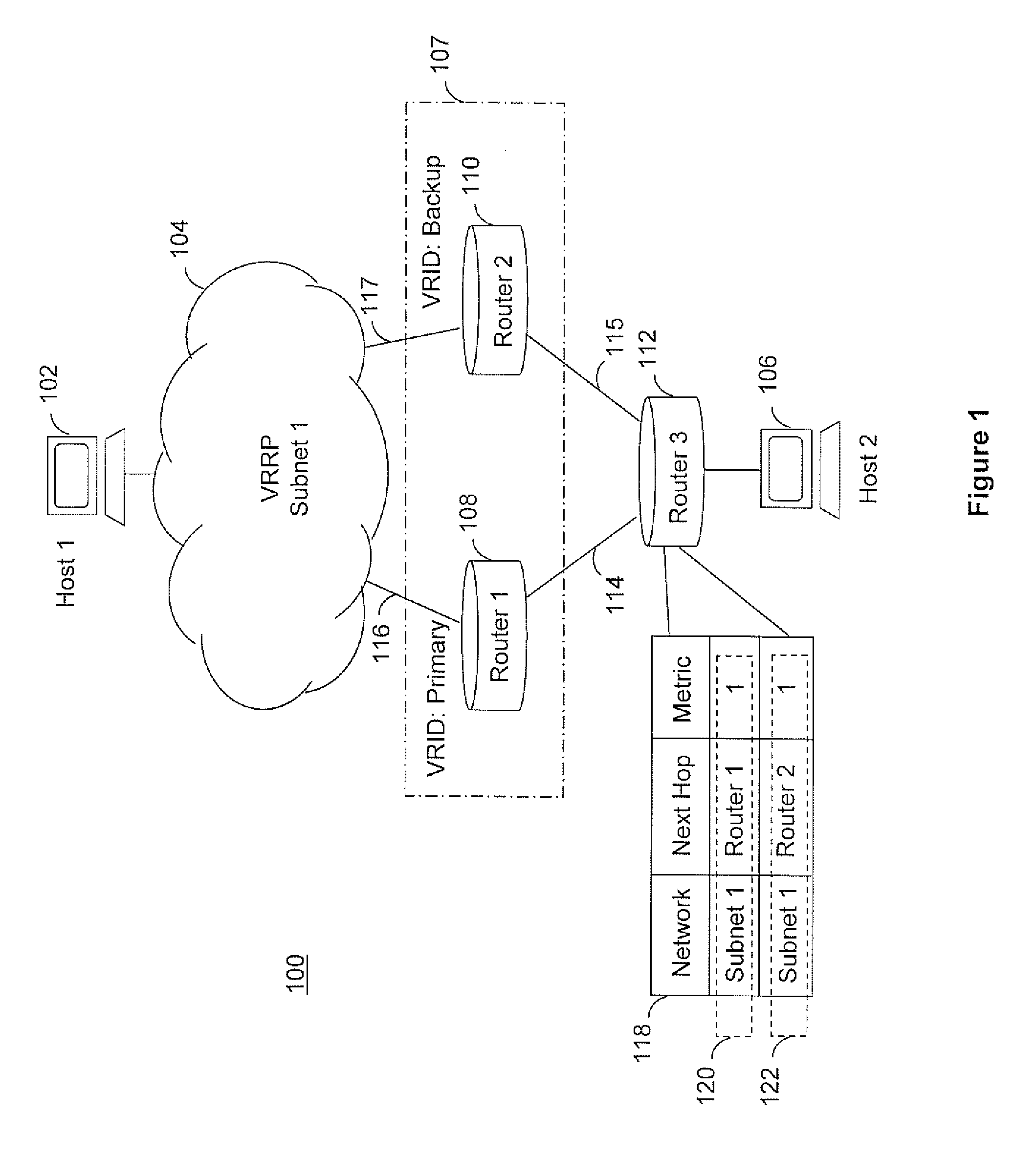
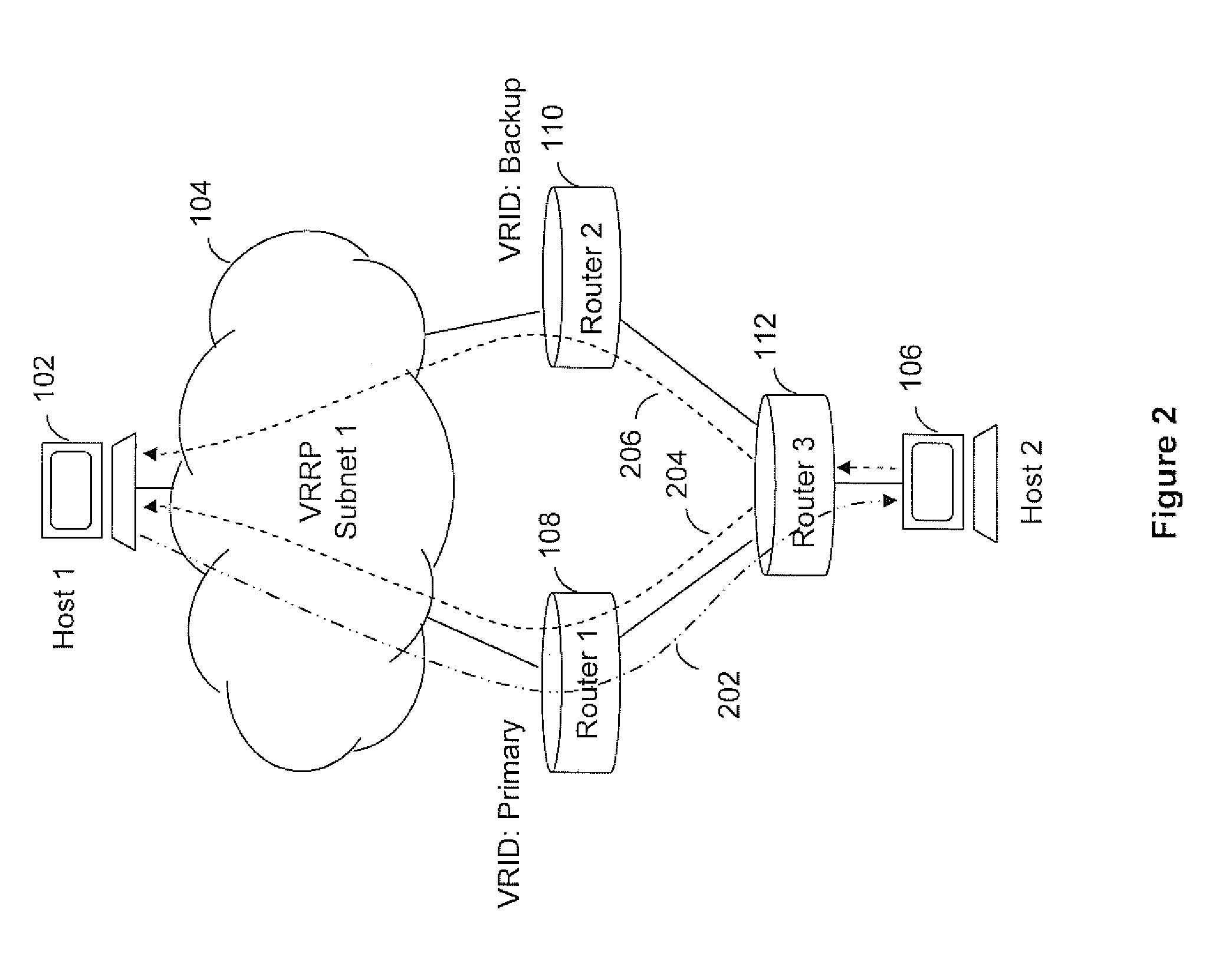
Dynamic route cost adjustment of vrrp enabled subnets for routing protocols
ActiveUS20110292933A1Data switching by path configurationService-level agreementVirtual Router Redundancy Protocol
The invention is directed to routing data packets in networks having routers configured as a virtual router using virtual router redundancy protocol (VRRP). Embodiments of the invention adjust route metrics to aid in providing predictable selection of routes into VRRP subnets. Advantageously, providing predictable selection of routes into VRRP subnets enhances a network operator's ability to meet service level agreements for critical or delay sensitive applications.
Owner:RPX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com