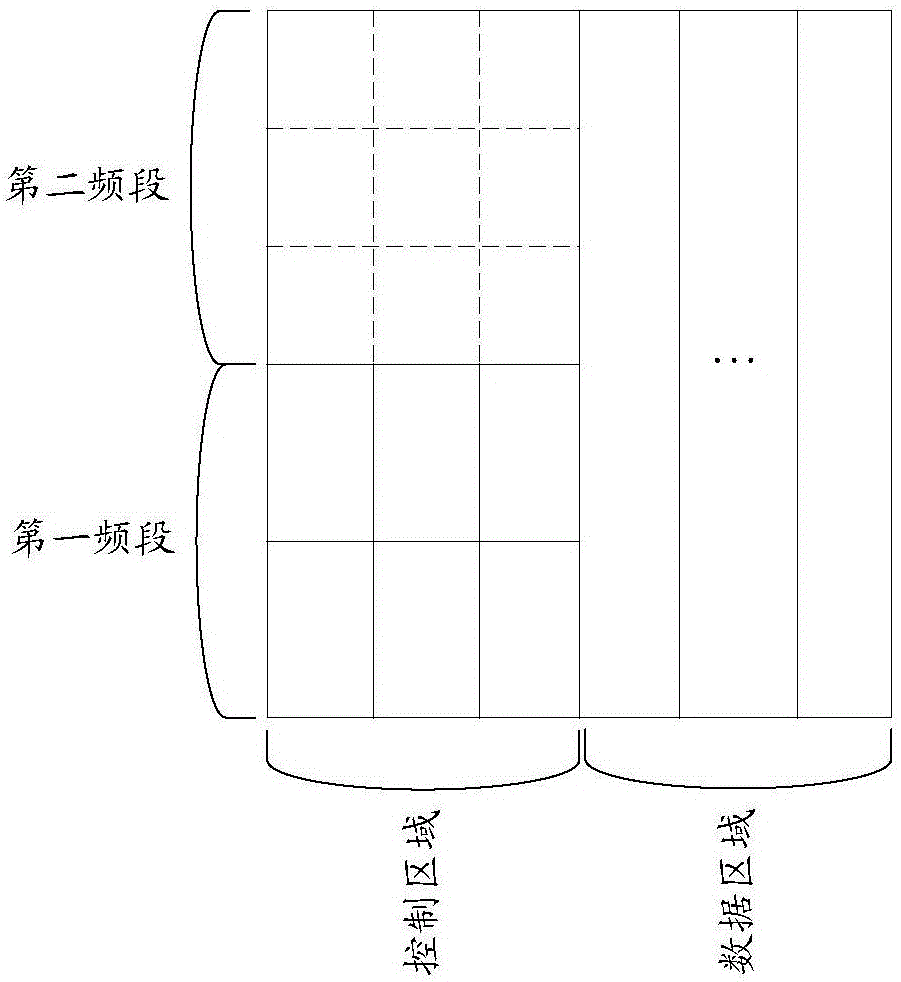
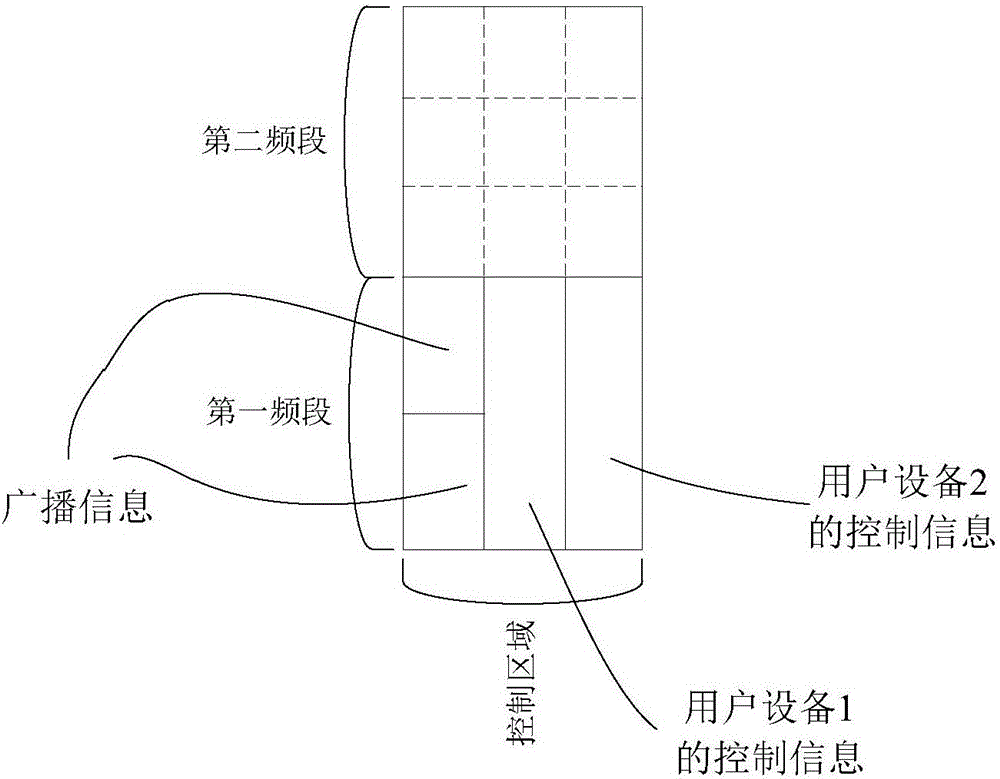
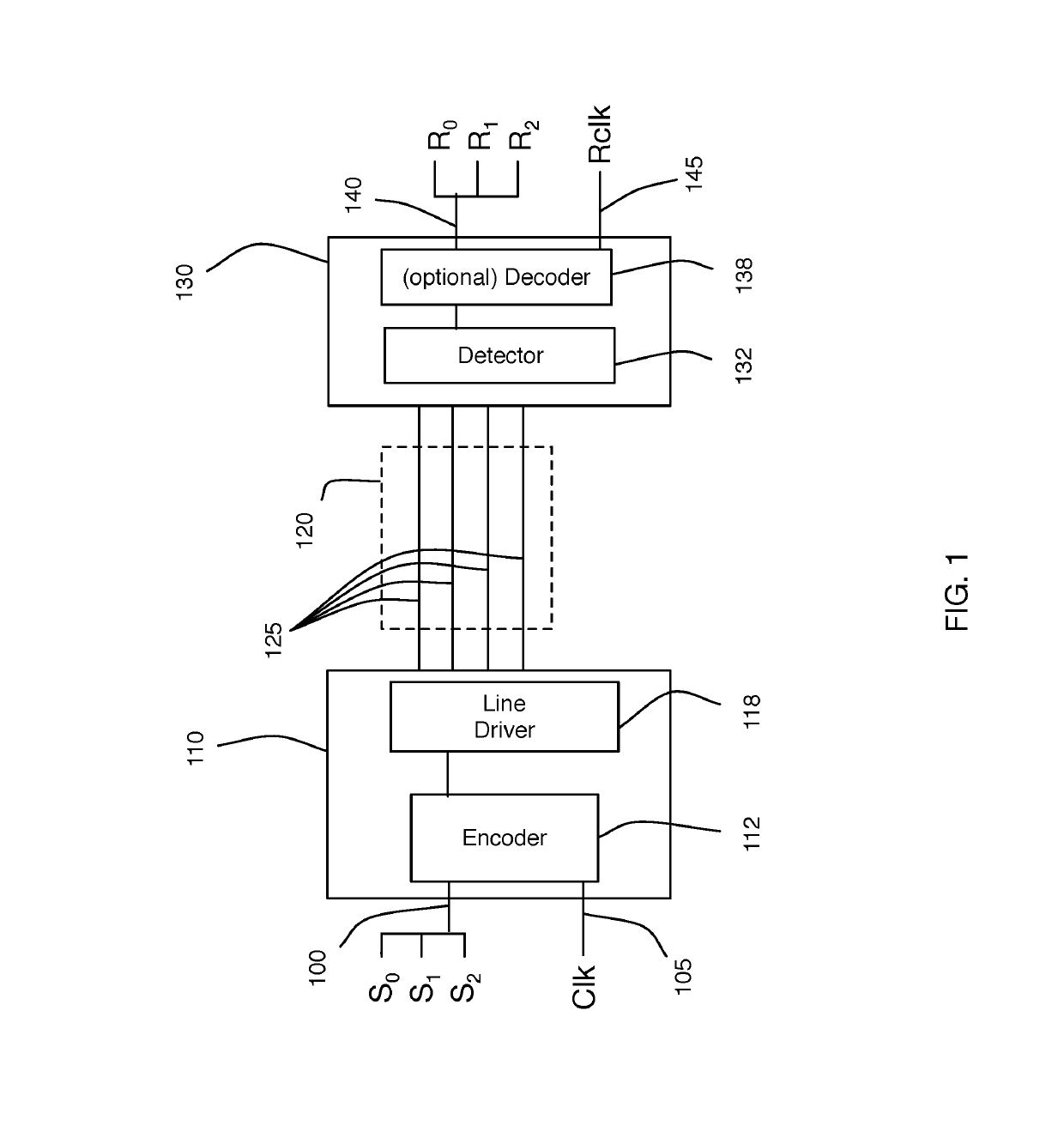
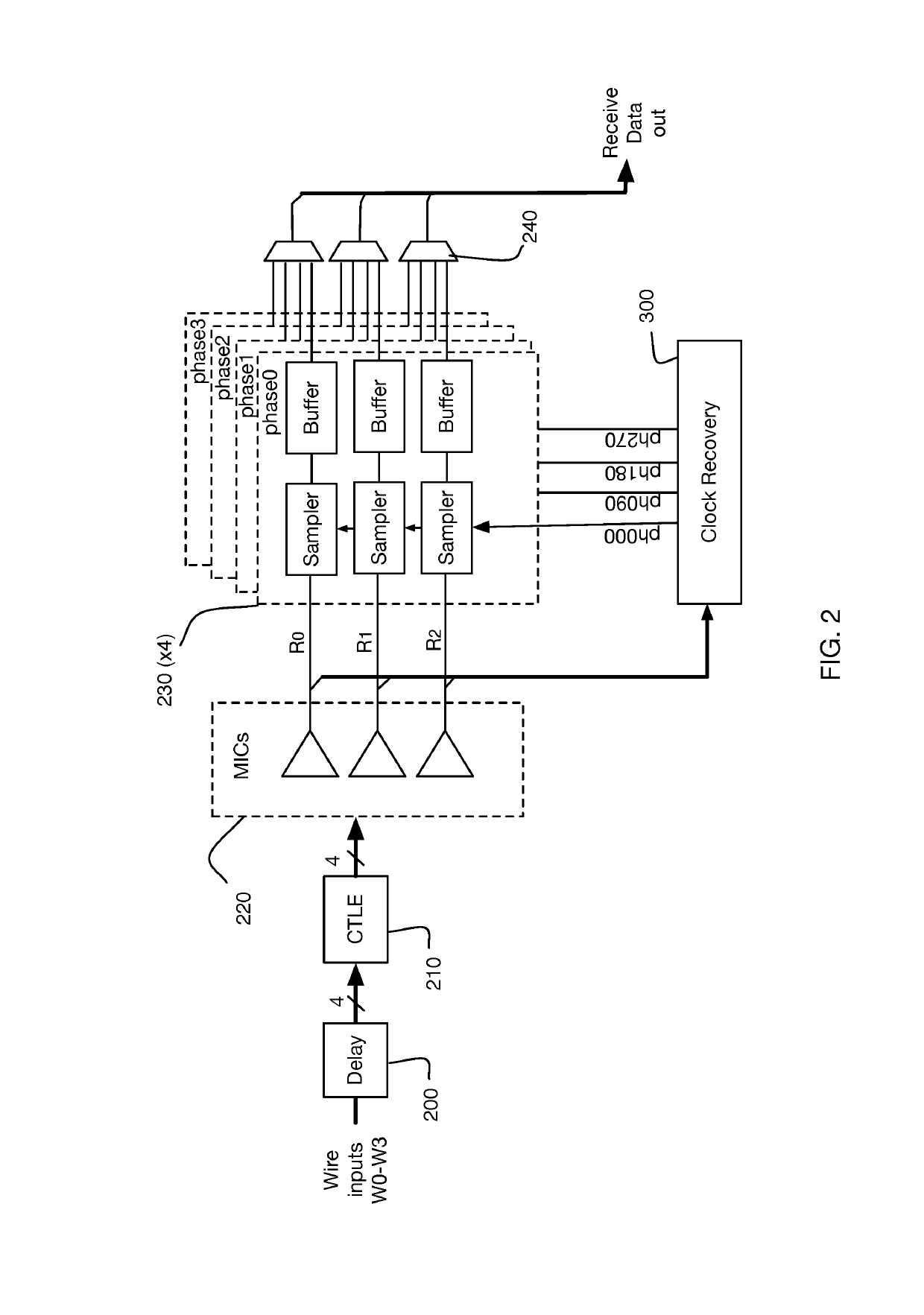
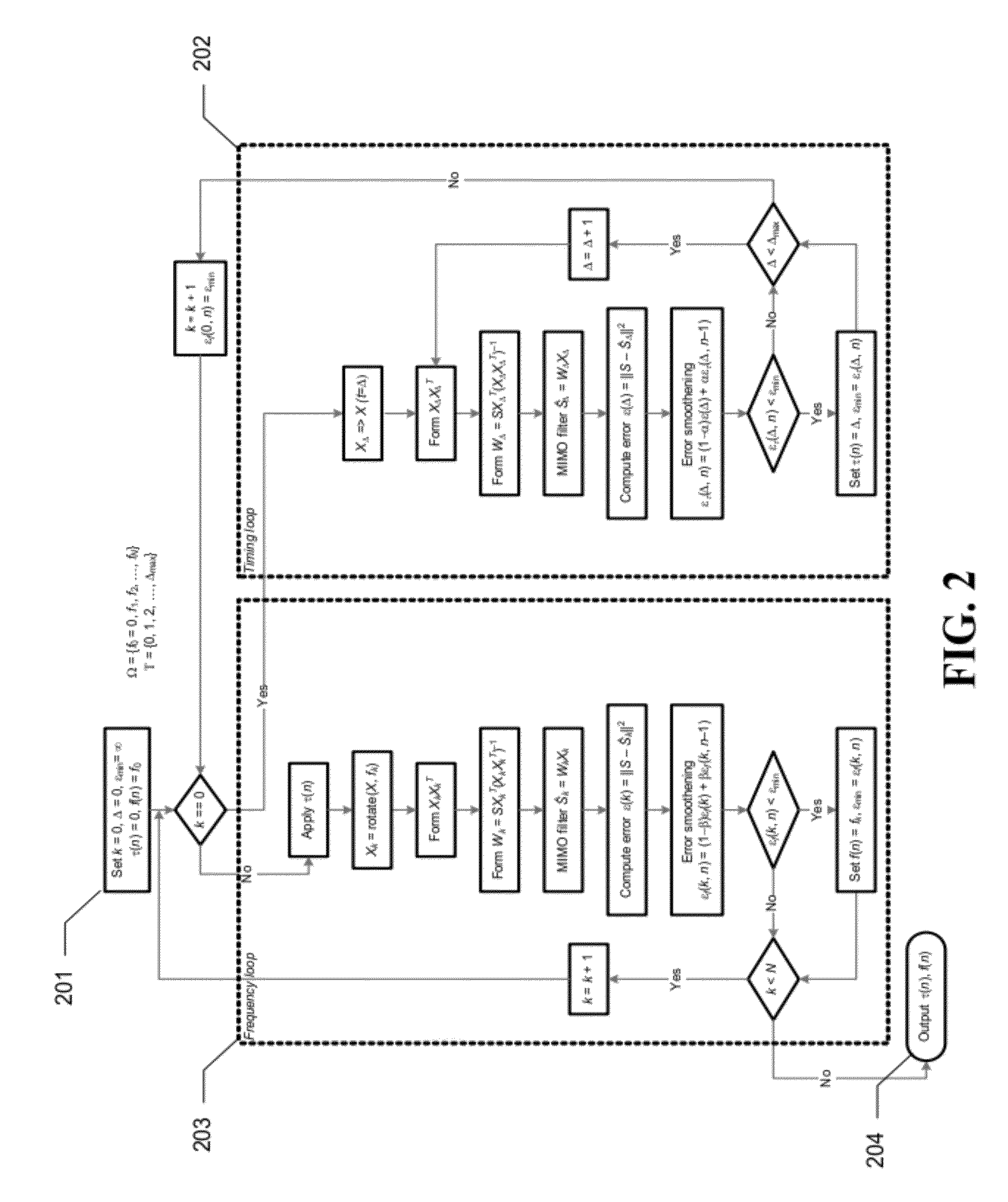
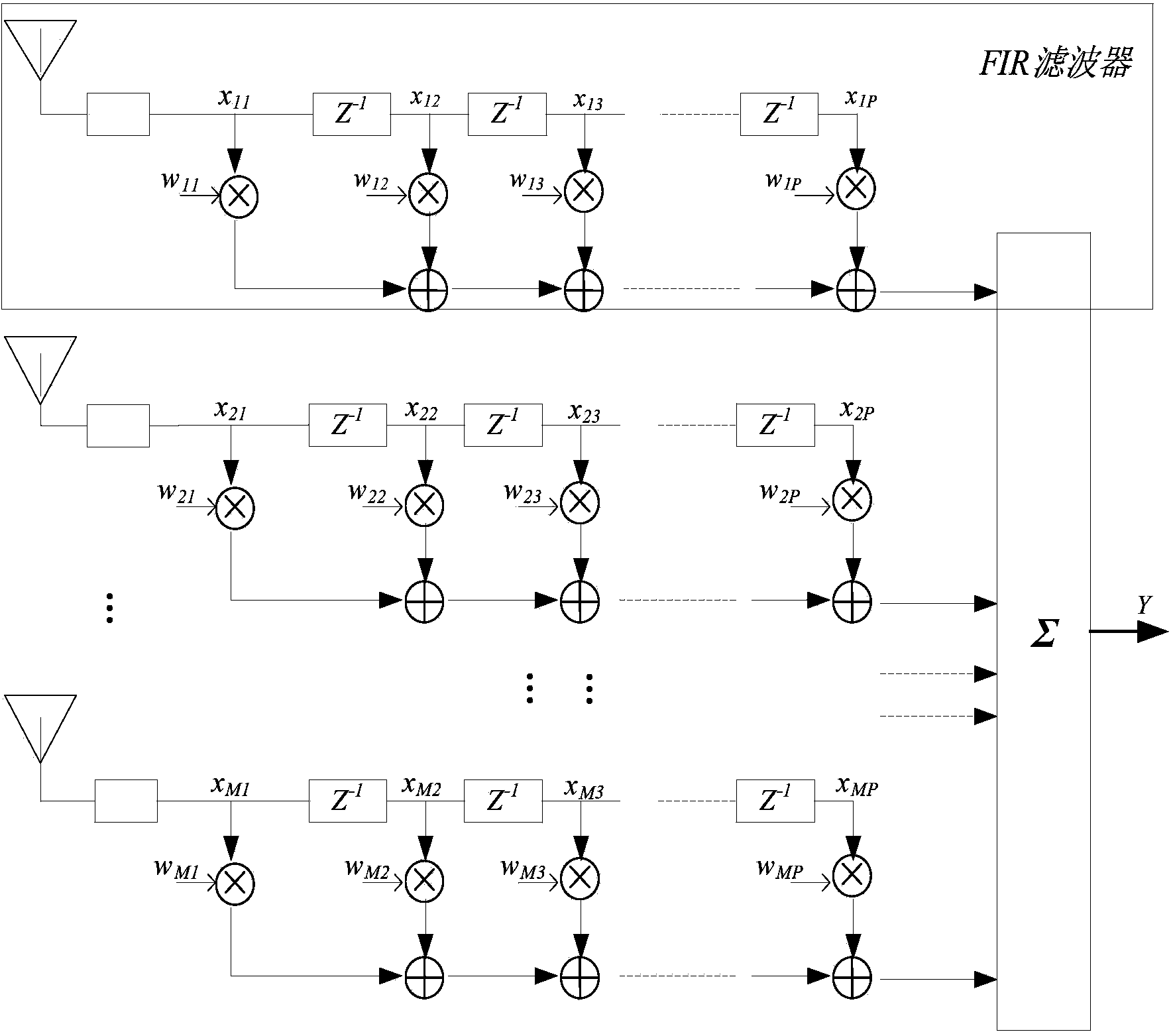Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78results about How to "Improve received signal quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
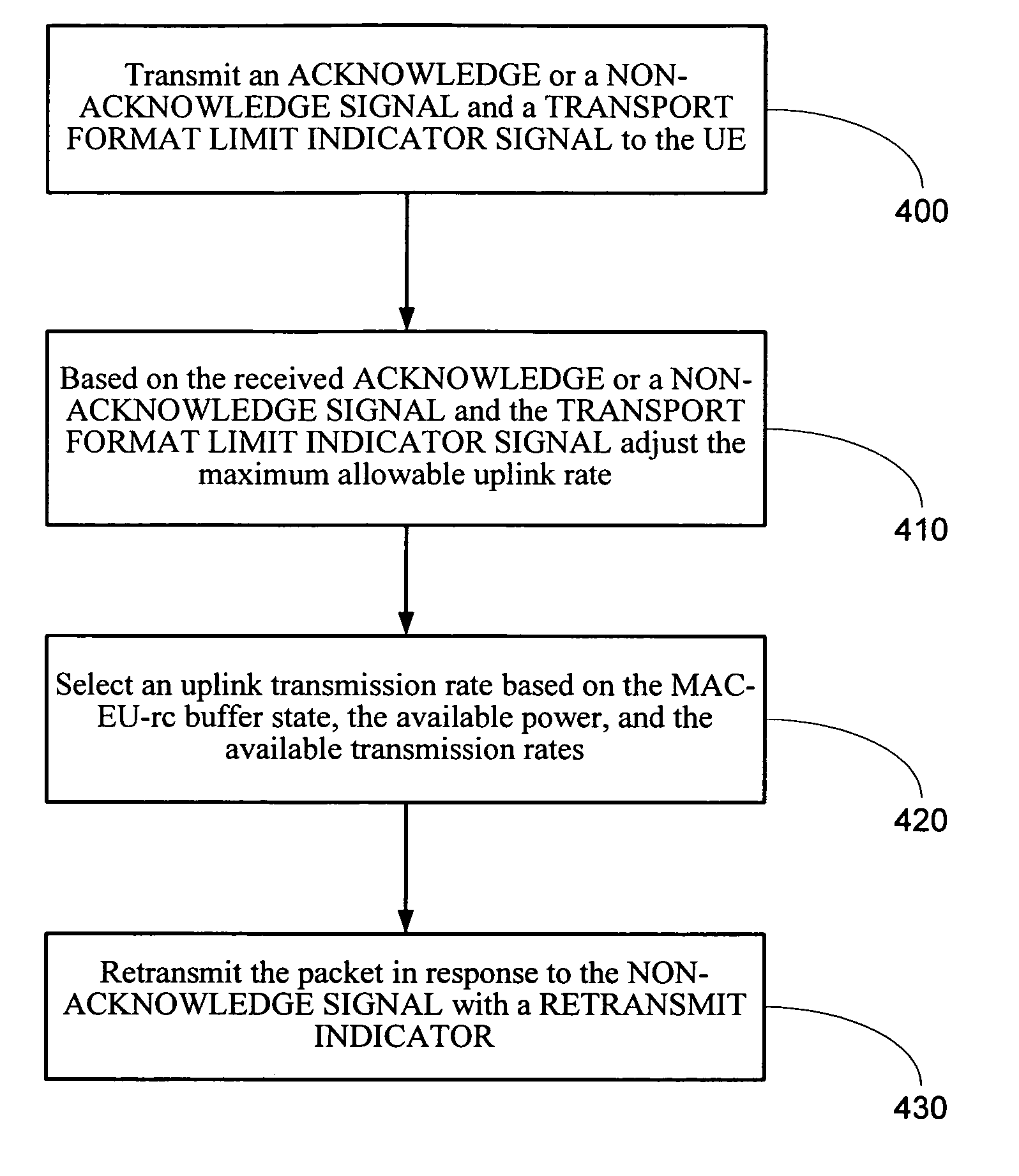
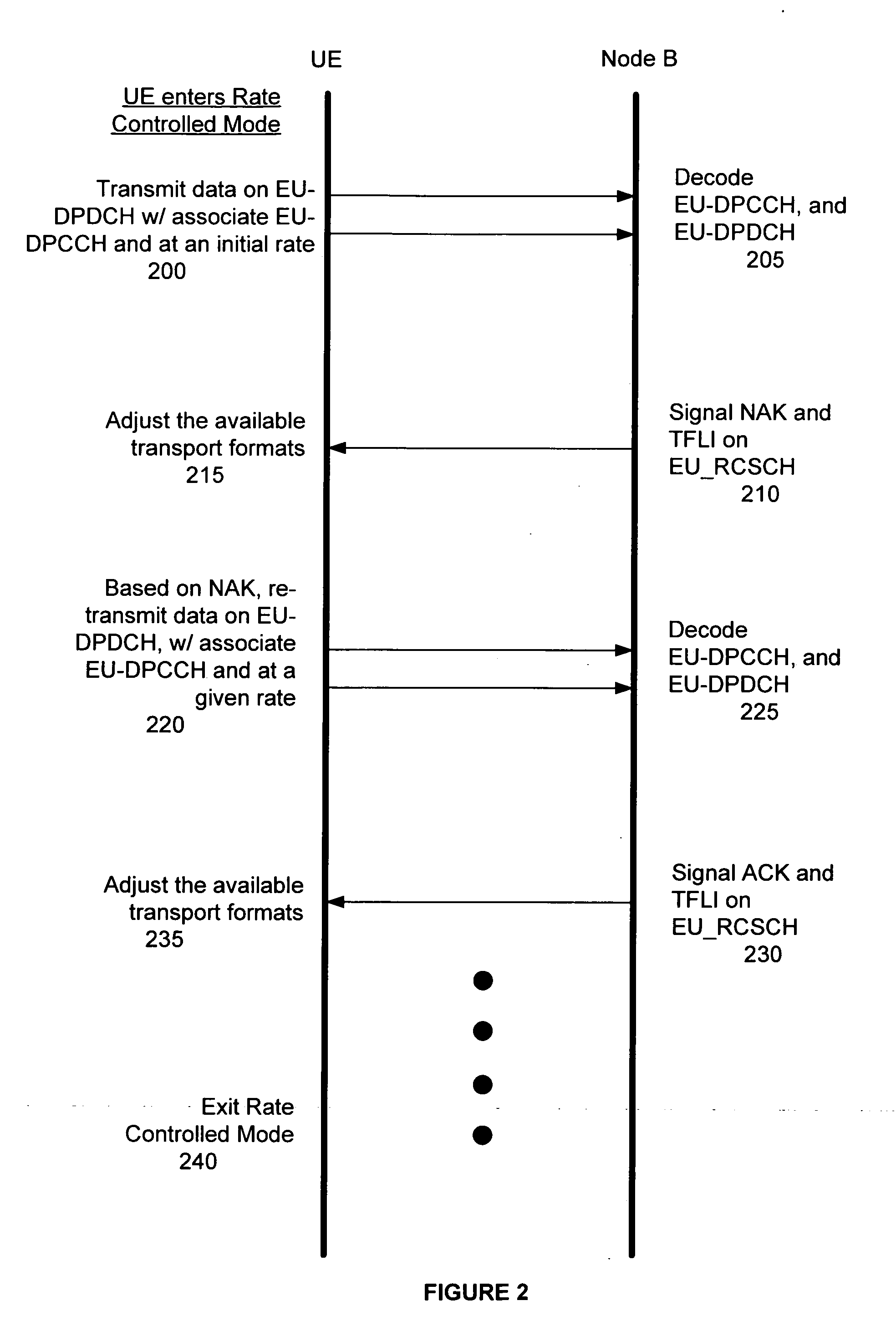
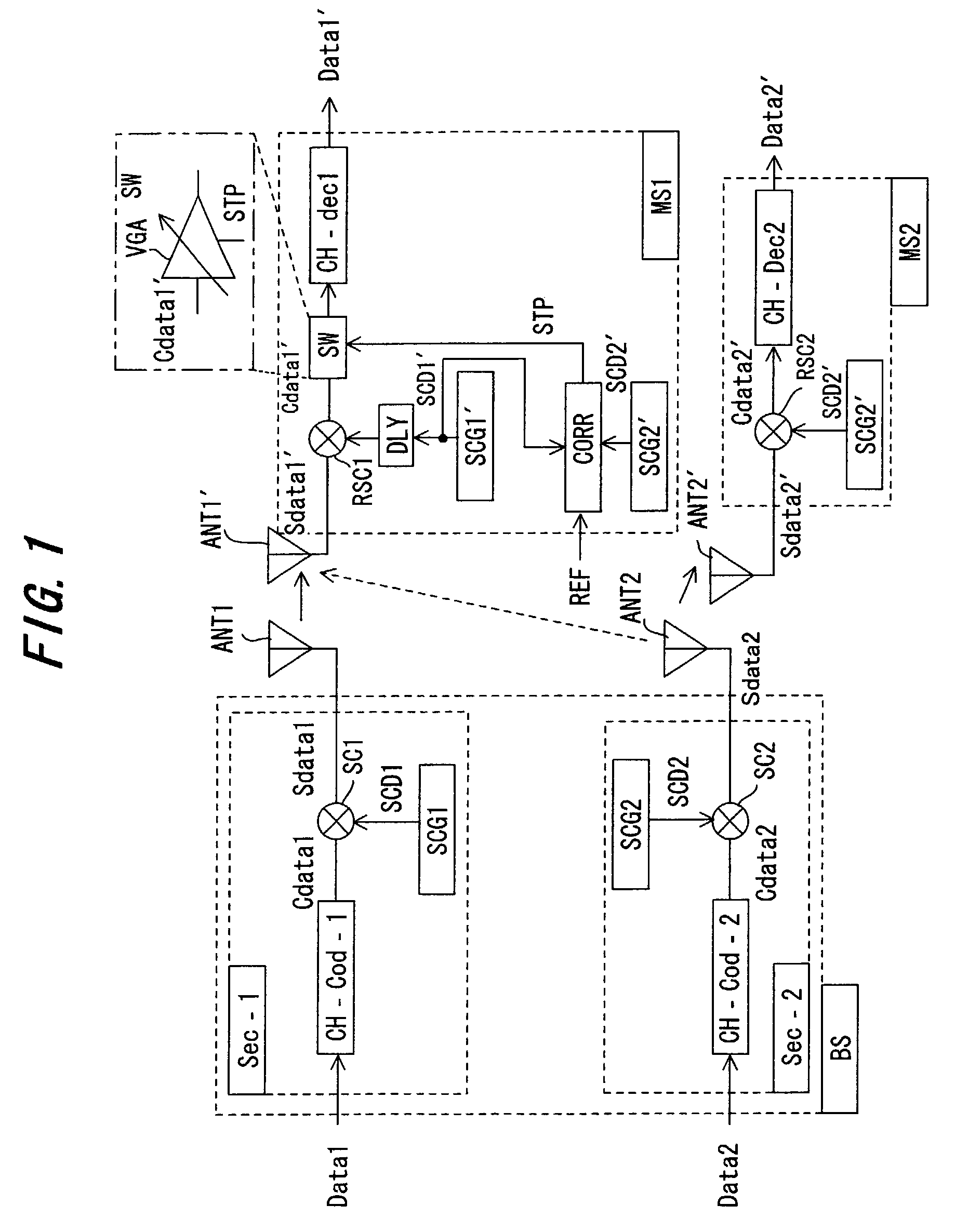
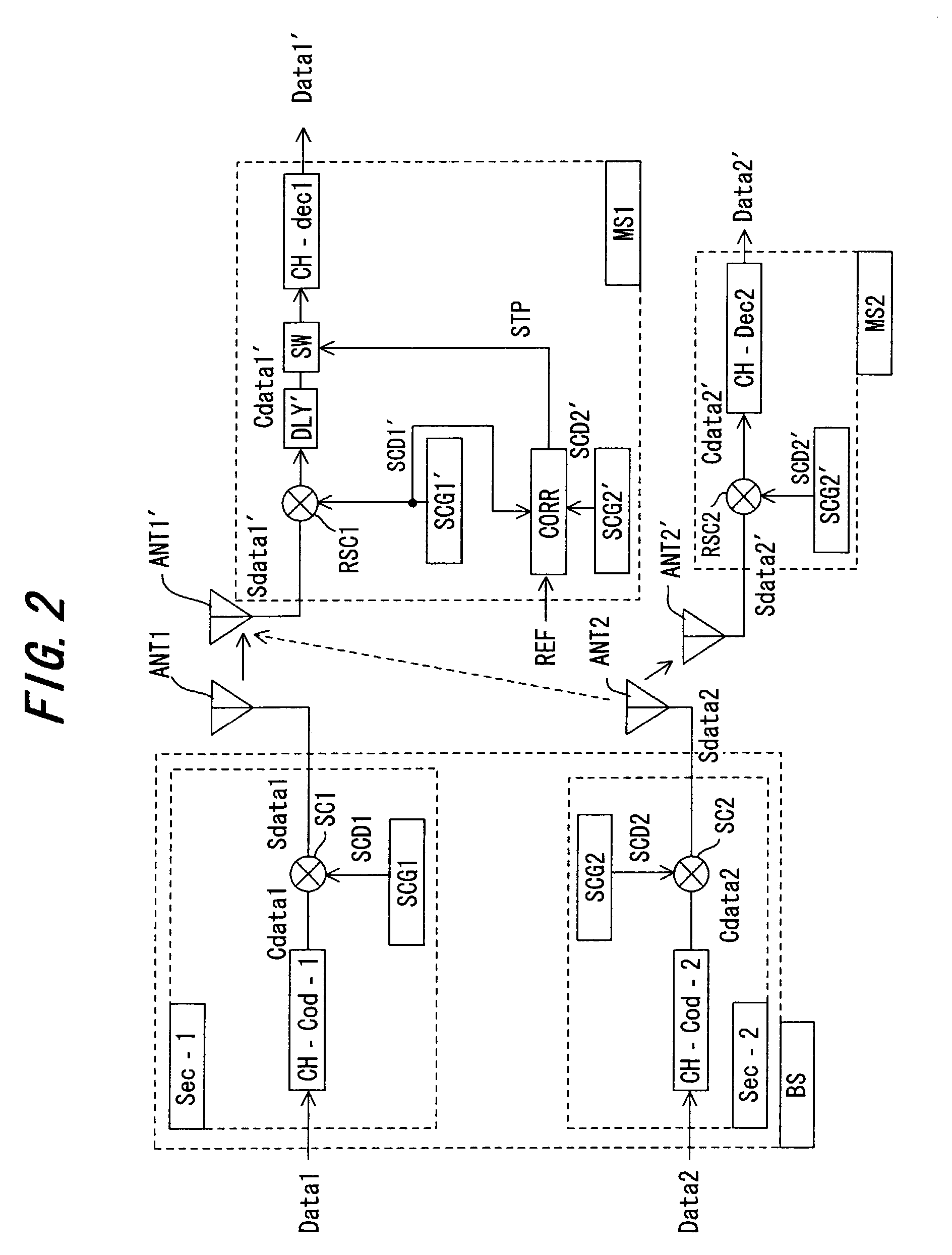
Method and system for rate-controlled mode wireless communications
InactiveUS20050237932A1Flexibly and efficiently adjustingError rateError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemData transmission
A method and system is described that flexibly and efficiently adjusts uplink data transmission rates in a wireless communication system. In particular, a transport format limit indicator (TFLI) indicating the allowed changes to available transport formats, including, for example, the maximum allowed uplink data transmission rate, is sent by a network node to a user equipment, without a prior request from the user equipment for such information. The user equipment may then adjust its uplink rate based on the TFLI when desired without having to make a request for rate information from the network node.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
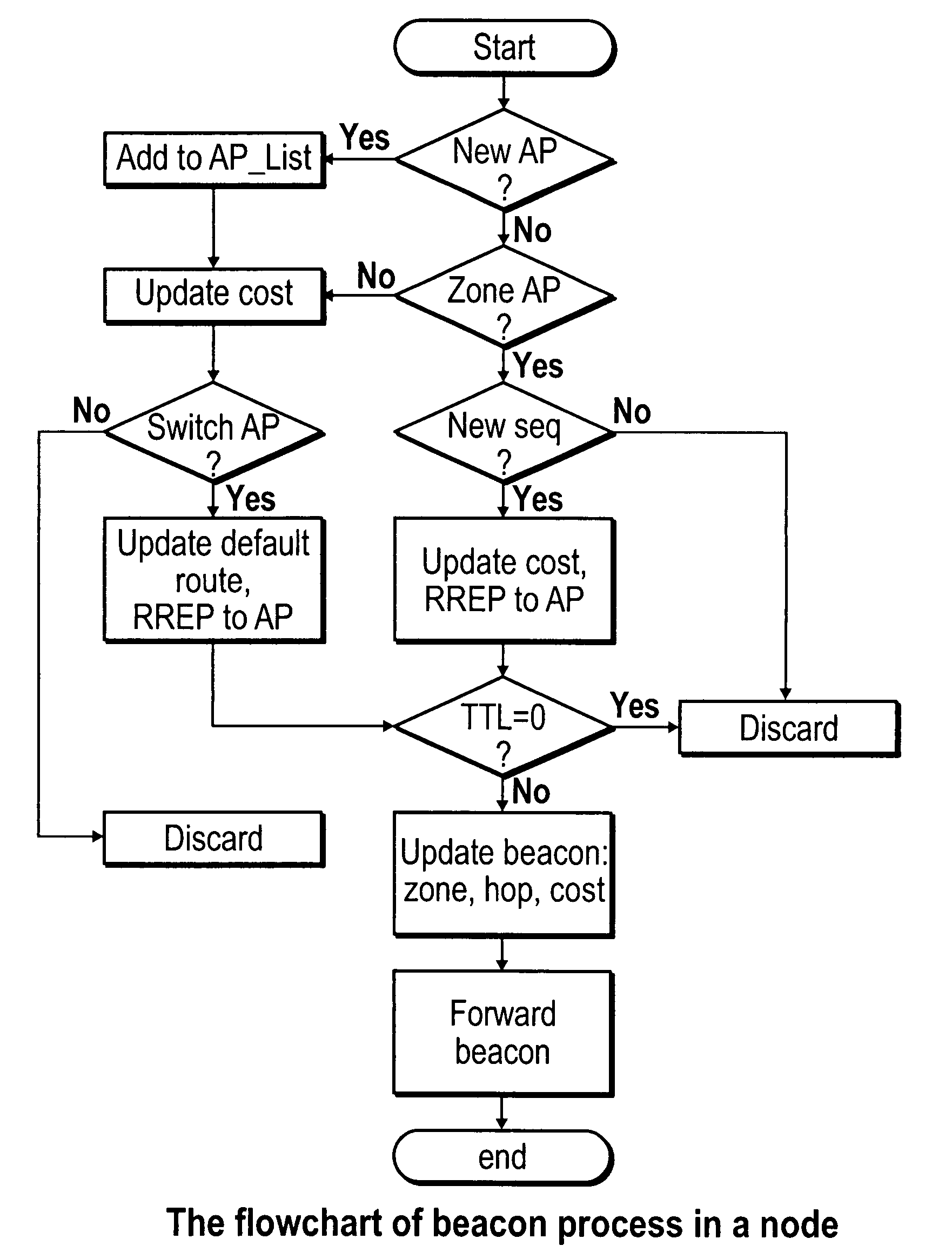
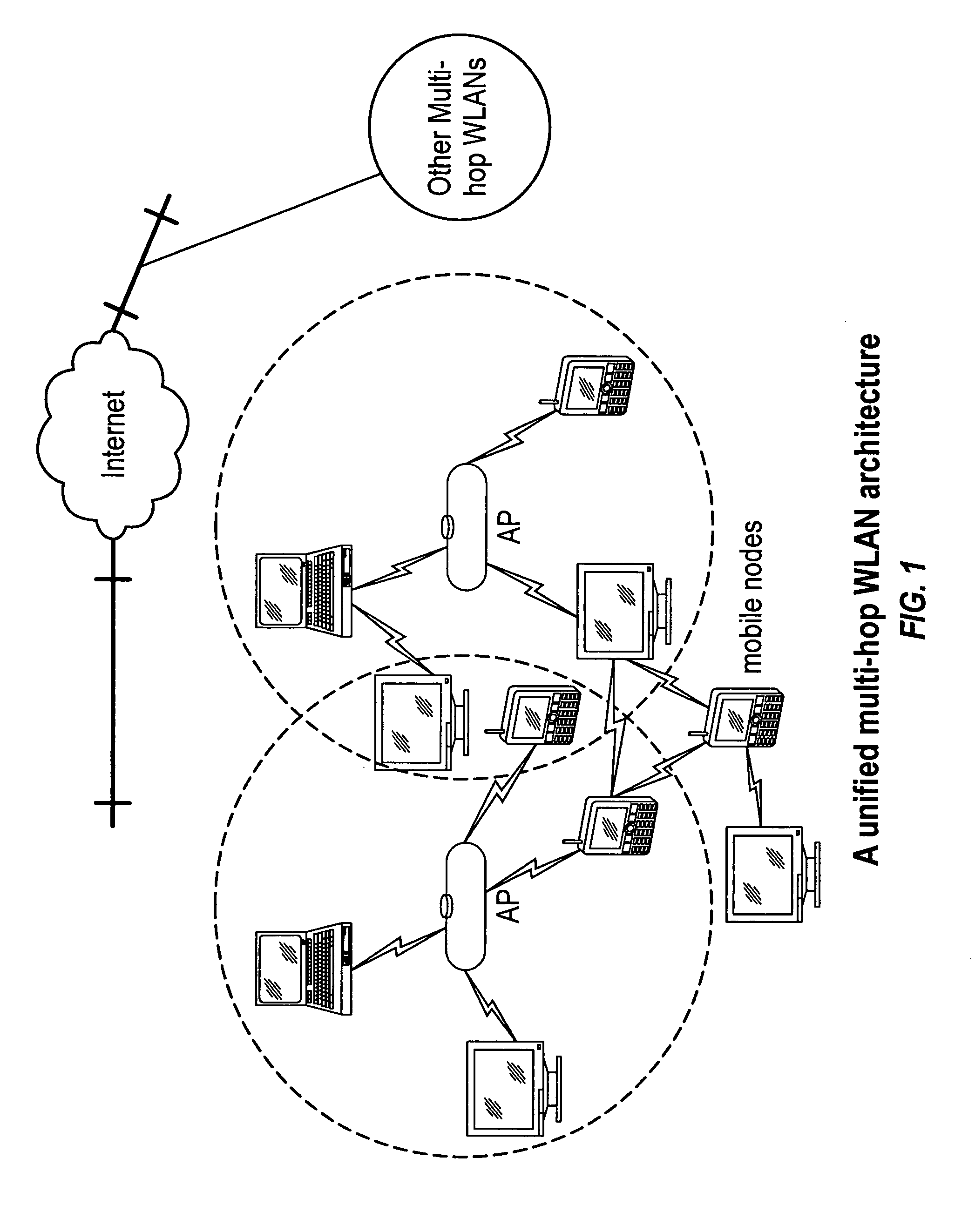
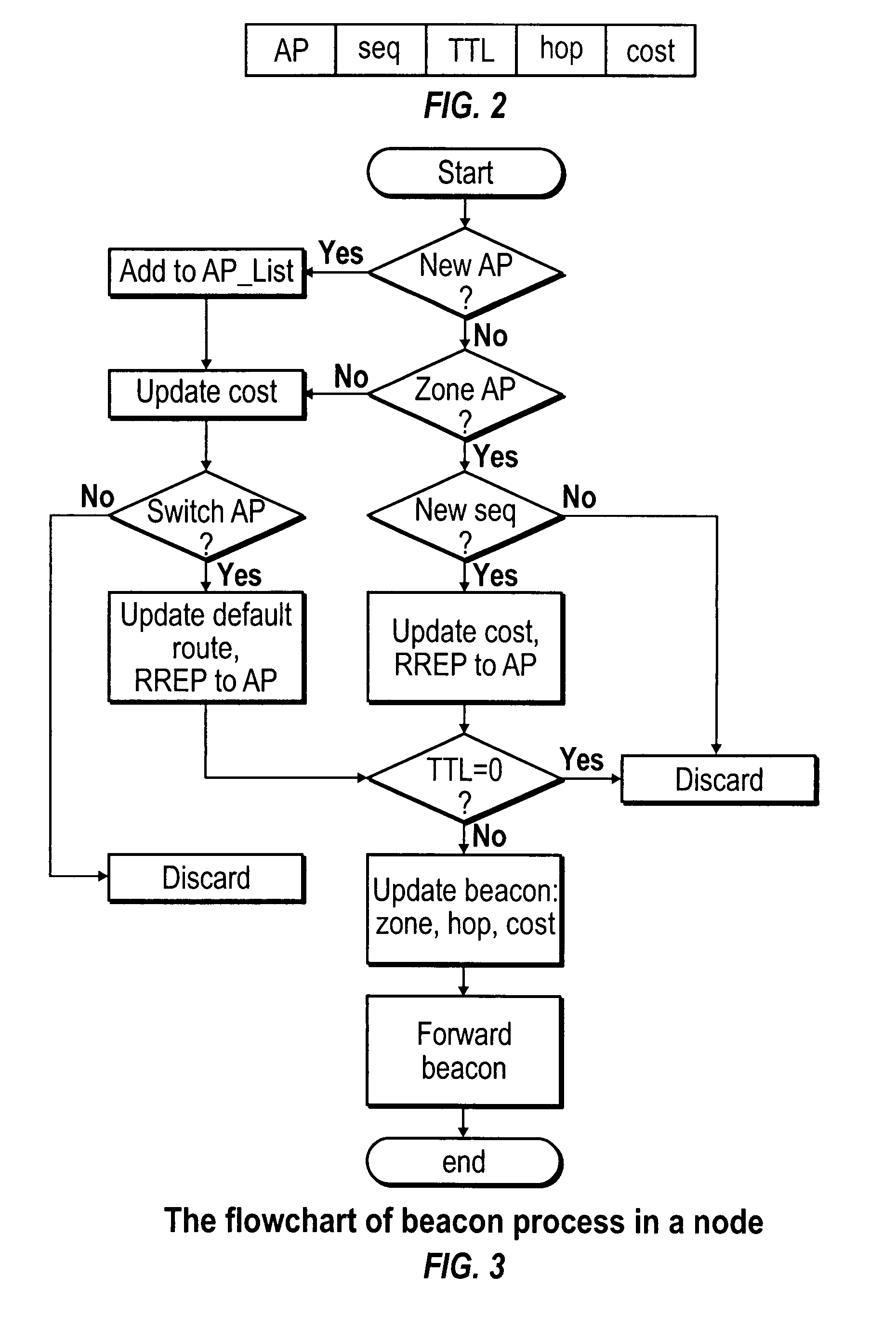
Wireless infrastructure and ad hoc network integration
ActiveUS7808960B1Lower deployment costsExtend wireless coverageNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionNetwork integrationComputer science
A system and method for integrating infrastructure and ad hoc wireless networks. In one example embodiment, a plurality of nodes and access points exchange beacons and route replies which are forwarded by intervening nodes. Nodes determine whether to switch access points based on cost values contained in the received beacons. Intervening nodes store routes with weights to the source node, such that the access points maintain weights to every node in their zones.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
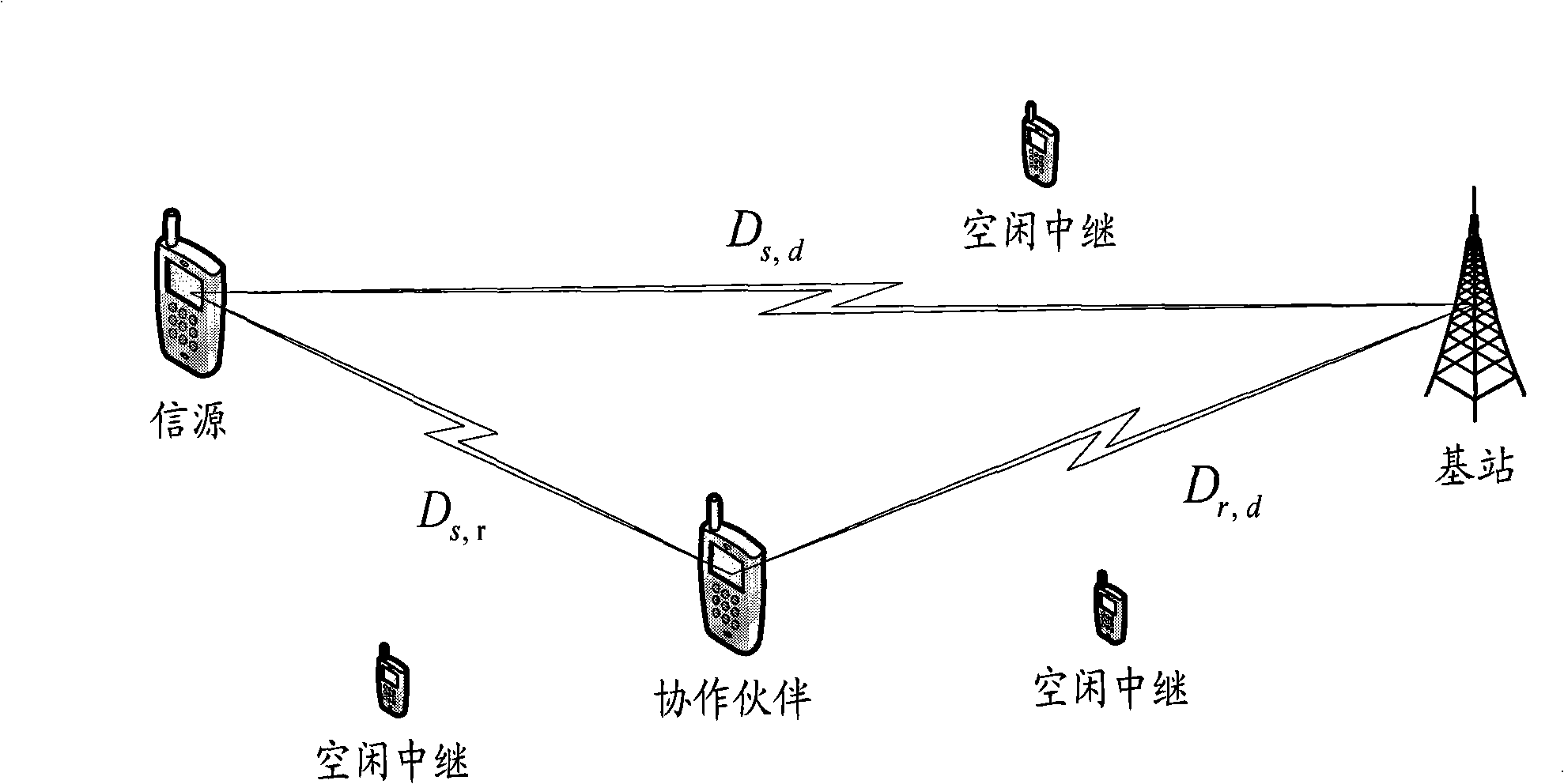
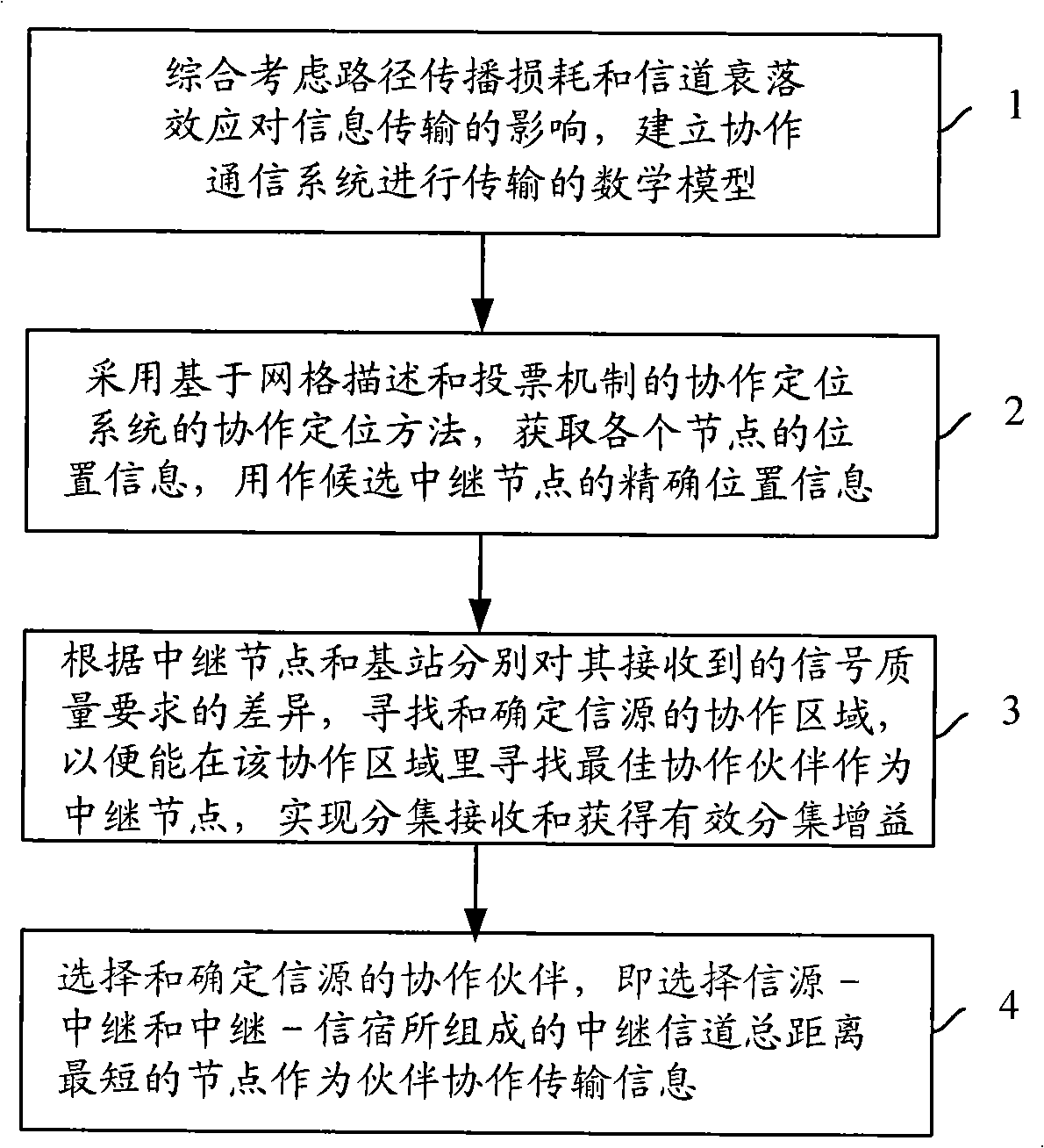
Method for implementing partner selection and collaboration transmission combining position information
InactiveCN101355409AExpand coverageImprove received signal qualitySpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringRelay channelInformation transfer
The invention provides a method for realizing partner selection and cooperative transmission combining with position information. The method is to obtain the position information of each node by directly using a cooperative positioning technology of a cooperative communication system and provide a partner selection strategy according to the large-scale fading condition of information transmission: an information source firstly calculates a distance between the information source and each candidate trunk node; the information source adds the distance between the information source and each trunk node and the distance between each trunk node and a base station by combining the obtained position information of each candidate trunk node and the distance information between the candidate trunk node and the base station; the information source selects a trunk node with the minimum total distance value of a trunk information channel as a cooperative partner of the information source to help the information source transmit information, after the total distance value of the trunk information channel of each trunk node is known, thereby realizing gain of space diversity reception, reducing path loss, and achieving the aims of reducing the bit error probability during transmitting, improving the signal quality and expanding the network coverage.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
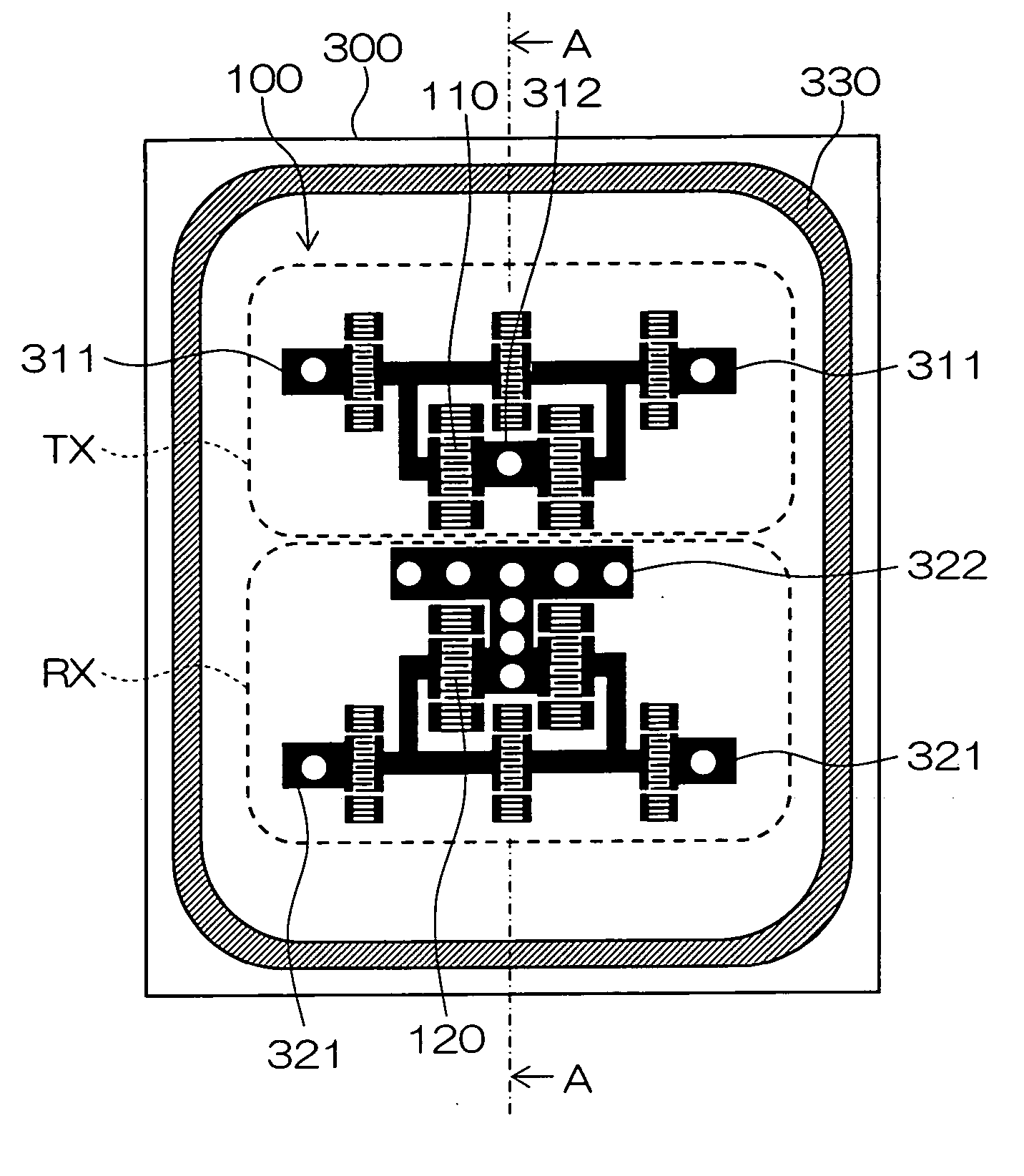
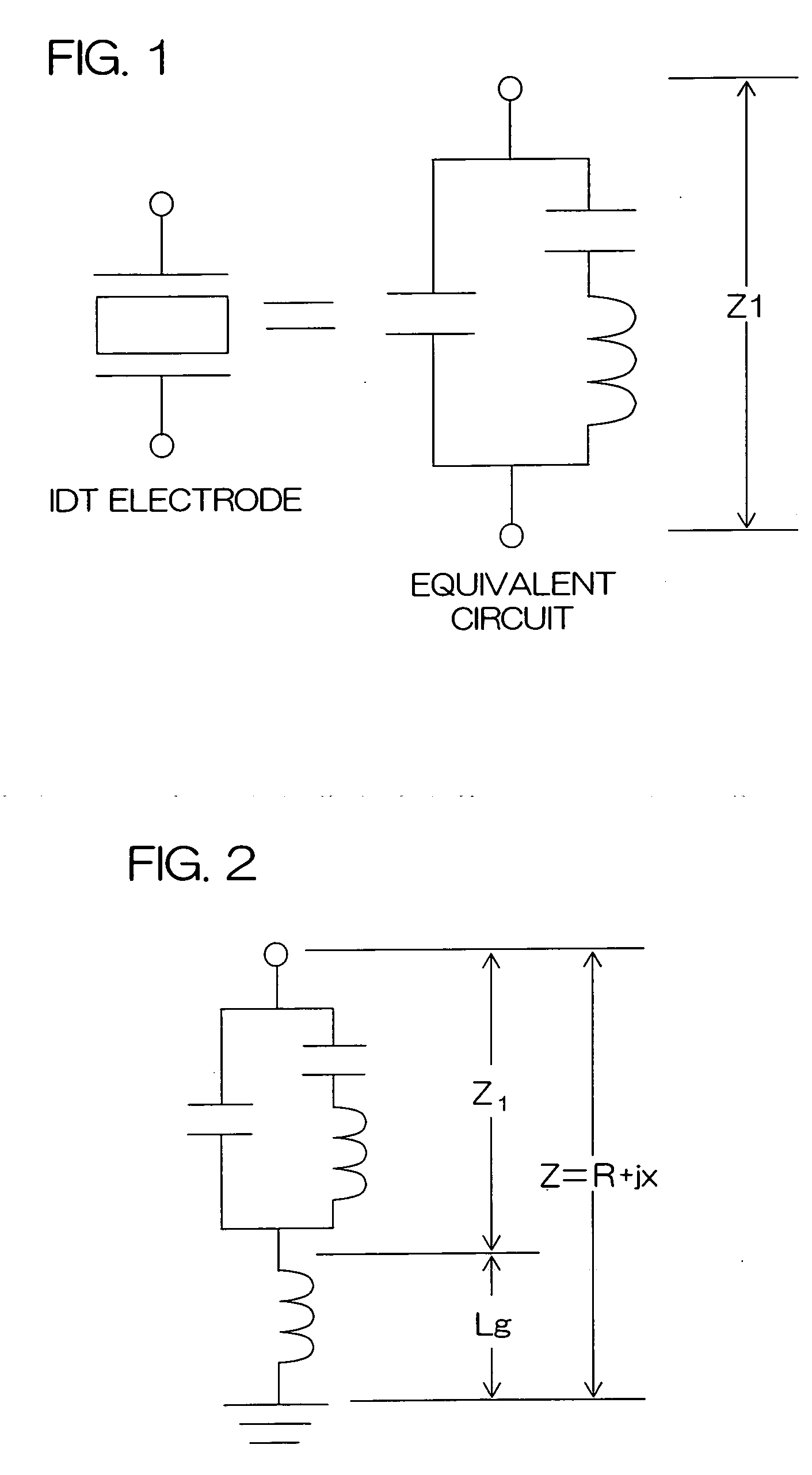
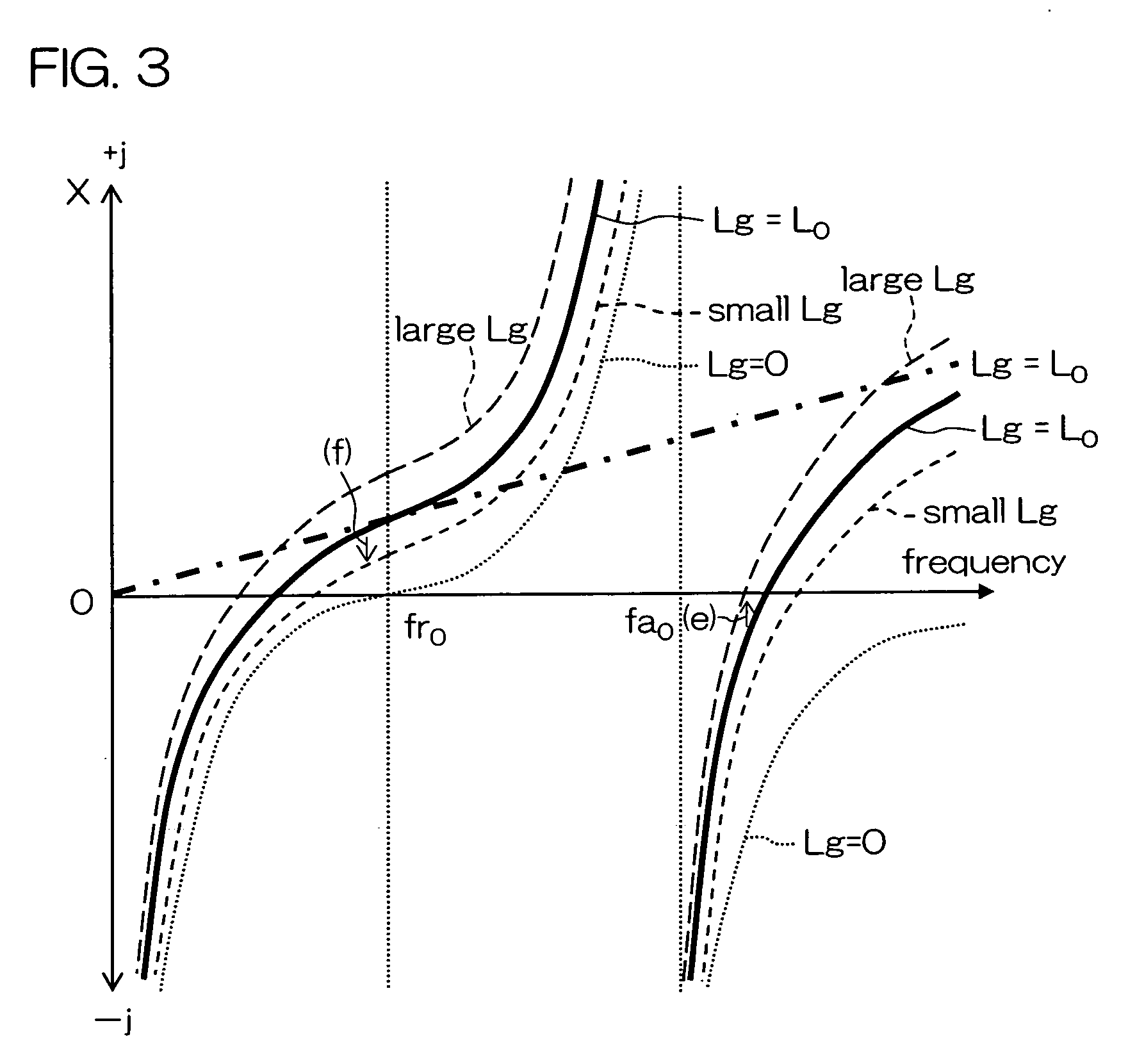
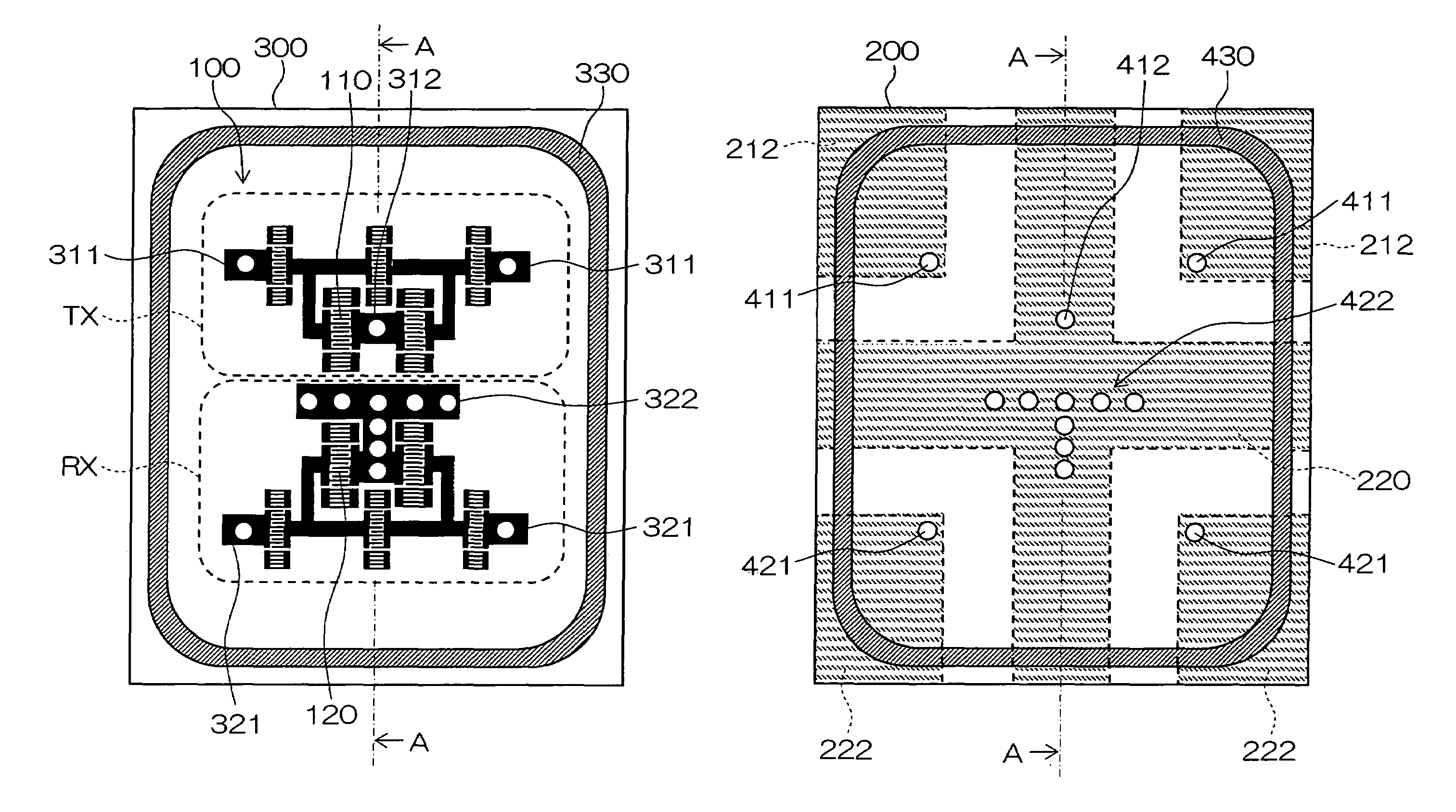
Surface acoustic wave device and communication apparatus
ActiveUS20050264375A1Small sizeSuperior communication qualityImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesSurface acoustic wave sensorEngineering
In a surface acoustic wave device according to the present invention, a transmitting filter element TX and a receiving filter element RX are formed on one main surface of a piezoelectric substrate 300, and are mounted by face down on an upper surface of a circuit board 200. A ground electrode 322 in the receiving filter element RX is connected to three linear via conductors 221′ formed on the circuit board 200, and a ground electrode 312 in the transmitting filter element TX is connected to a crank-shaped via conductor 211′ formed on the circuit board 200.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
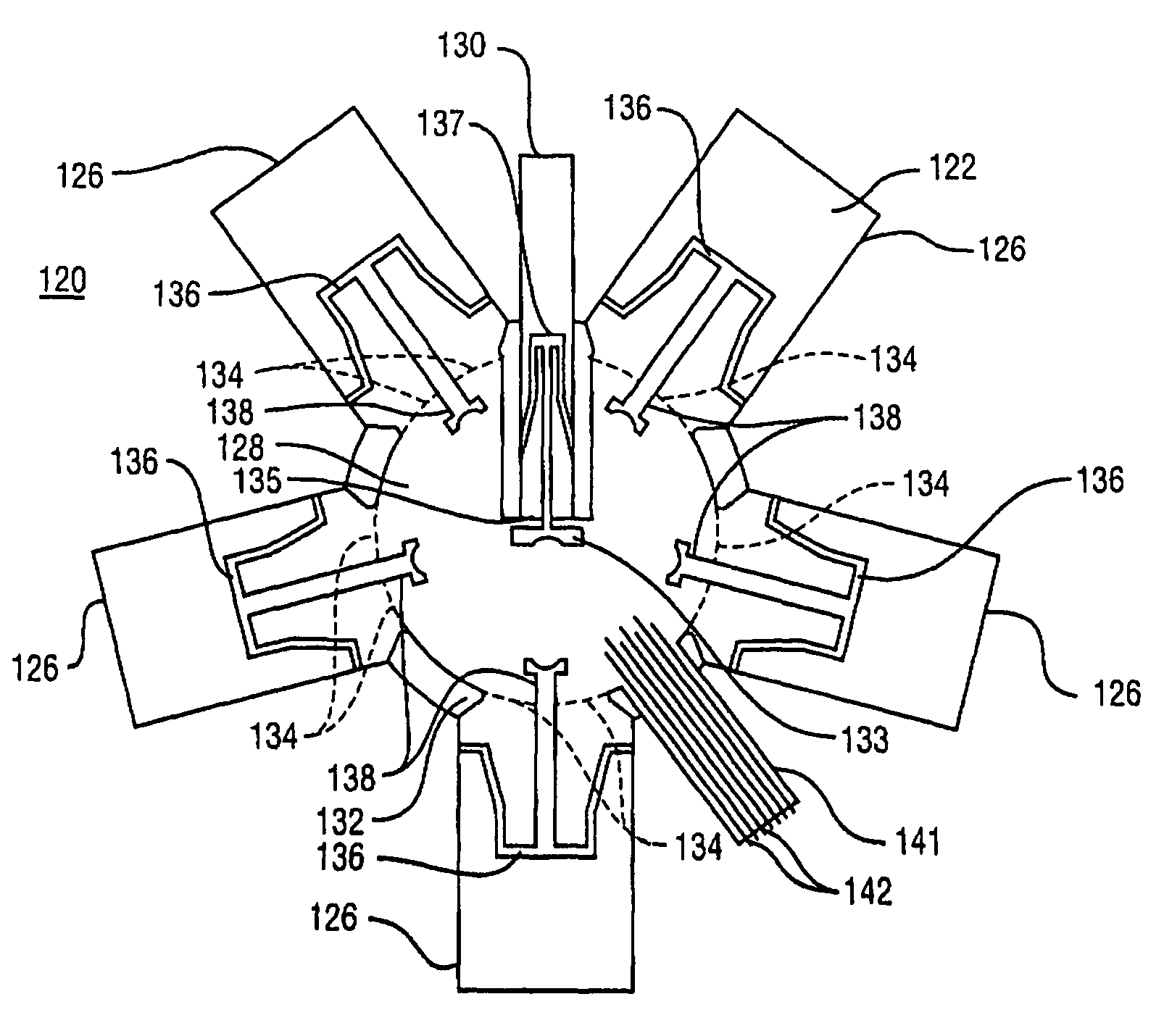
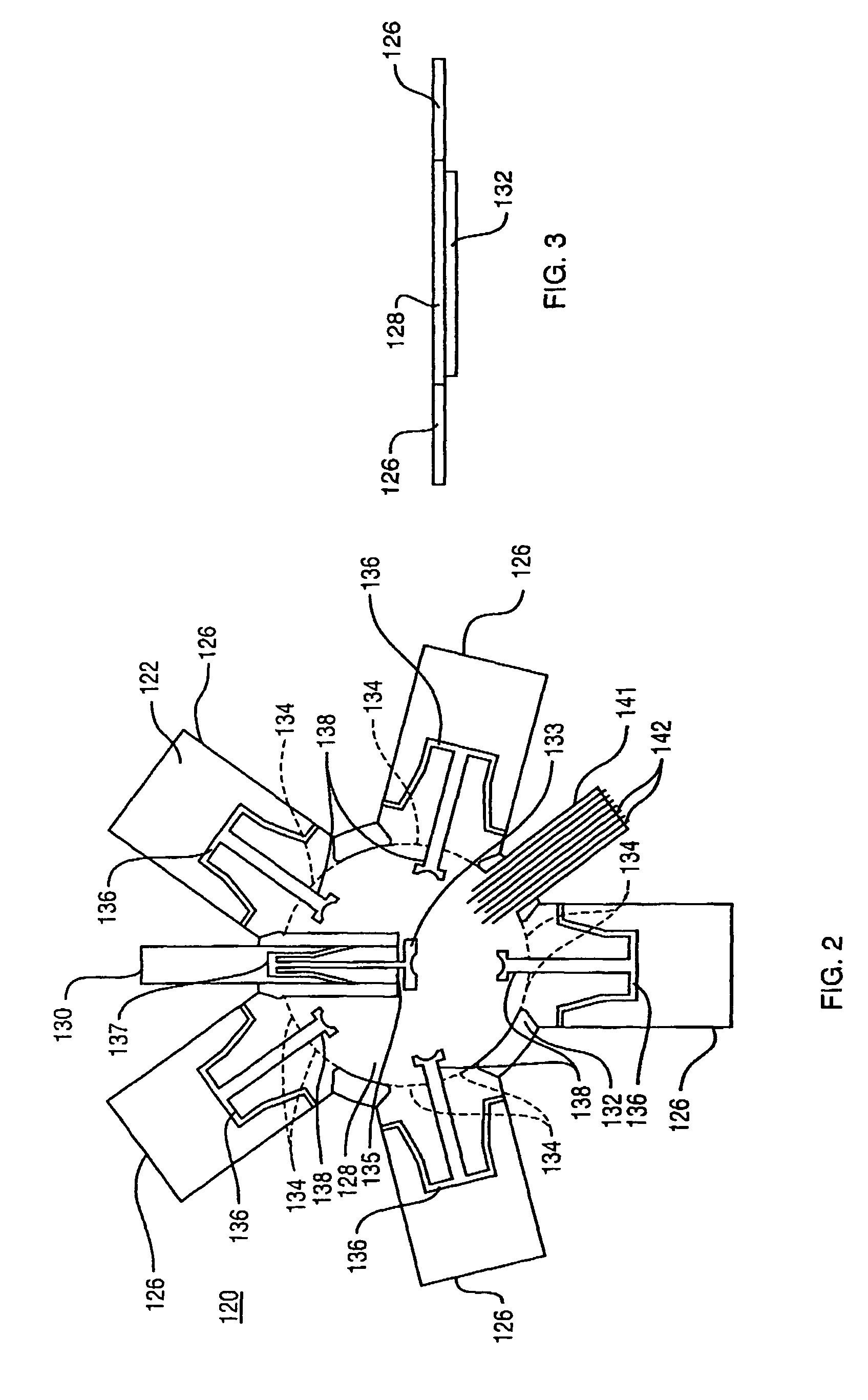
Folding directional antenna
InactiveUS20050062649A1Improve received signal qualityIncrease power levelSimultaneous aerial operationsPivotable antennasDirectional antennaBeam pattern
An antenna array formed on a deformable dielectric material or substrate includes a center element and plurality of radial elements extending from a center hub. In the operative mode, the radial elements are folded upwardly into an approximately vertical position, with the center element at the center of the hub and the radial elements circumferentially surrounding the center element. In one embodiment the center element serves an active element of the antenna array and the radial elements are controllable in a directive or reflective state to effect a directive beam pattern from the antenna array. When not in use, the antenna elements are deformed into a plane and can therefore be integrated into a housing for compact storage. In a phased array embodiment, the center element is absent and the plurality of radial elements, are controllable to steer the antenna beam.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
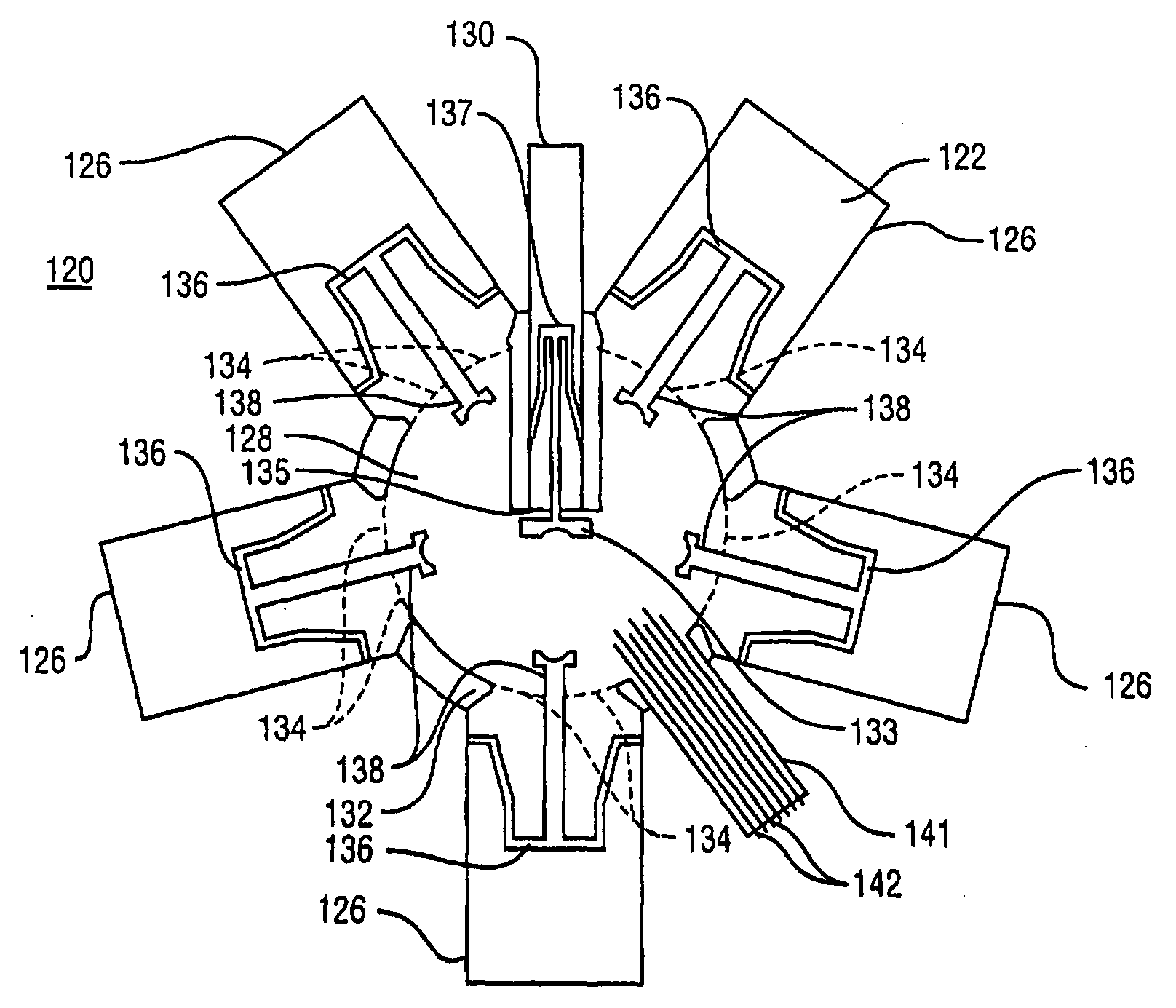
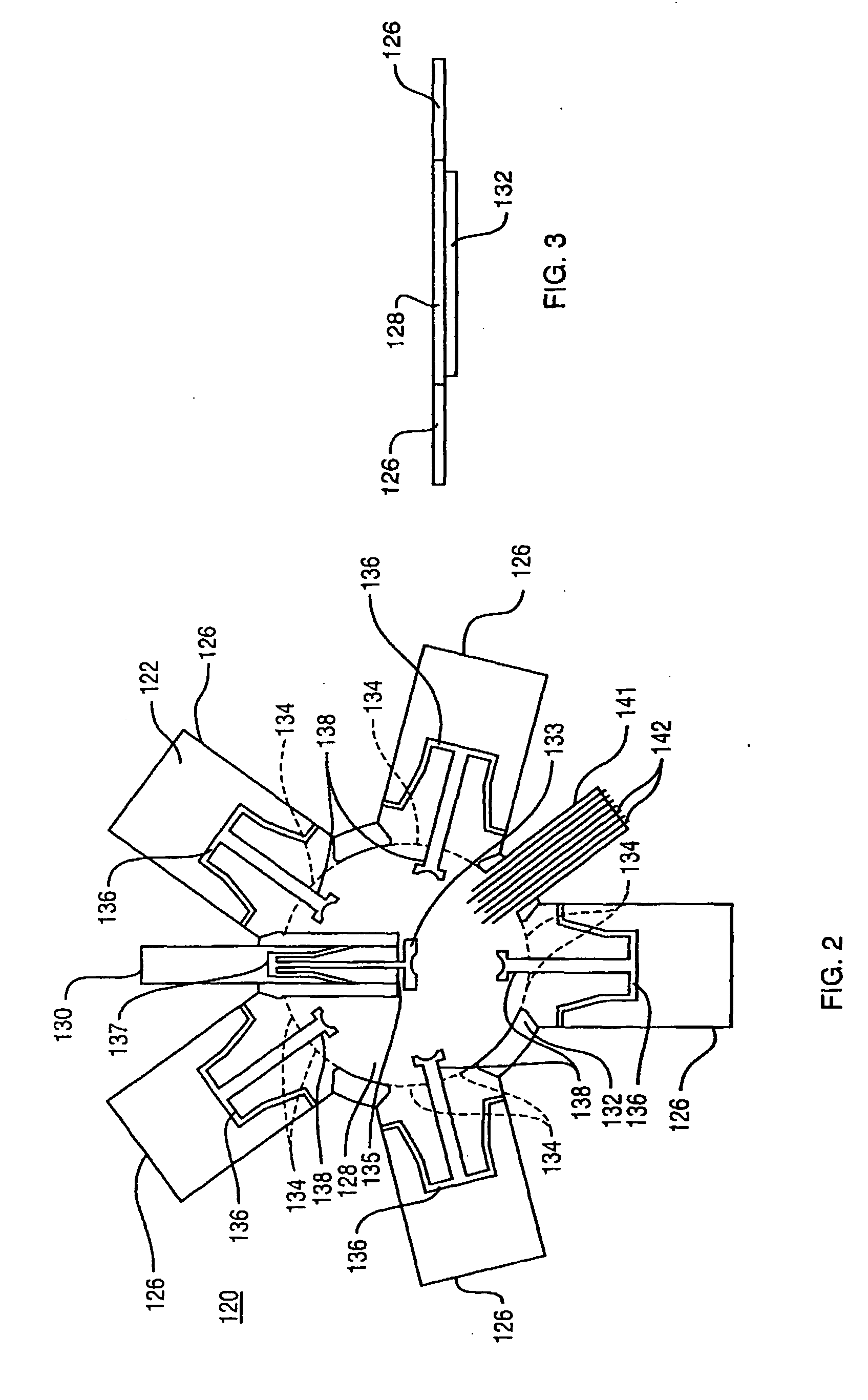
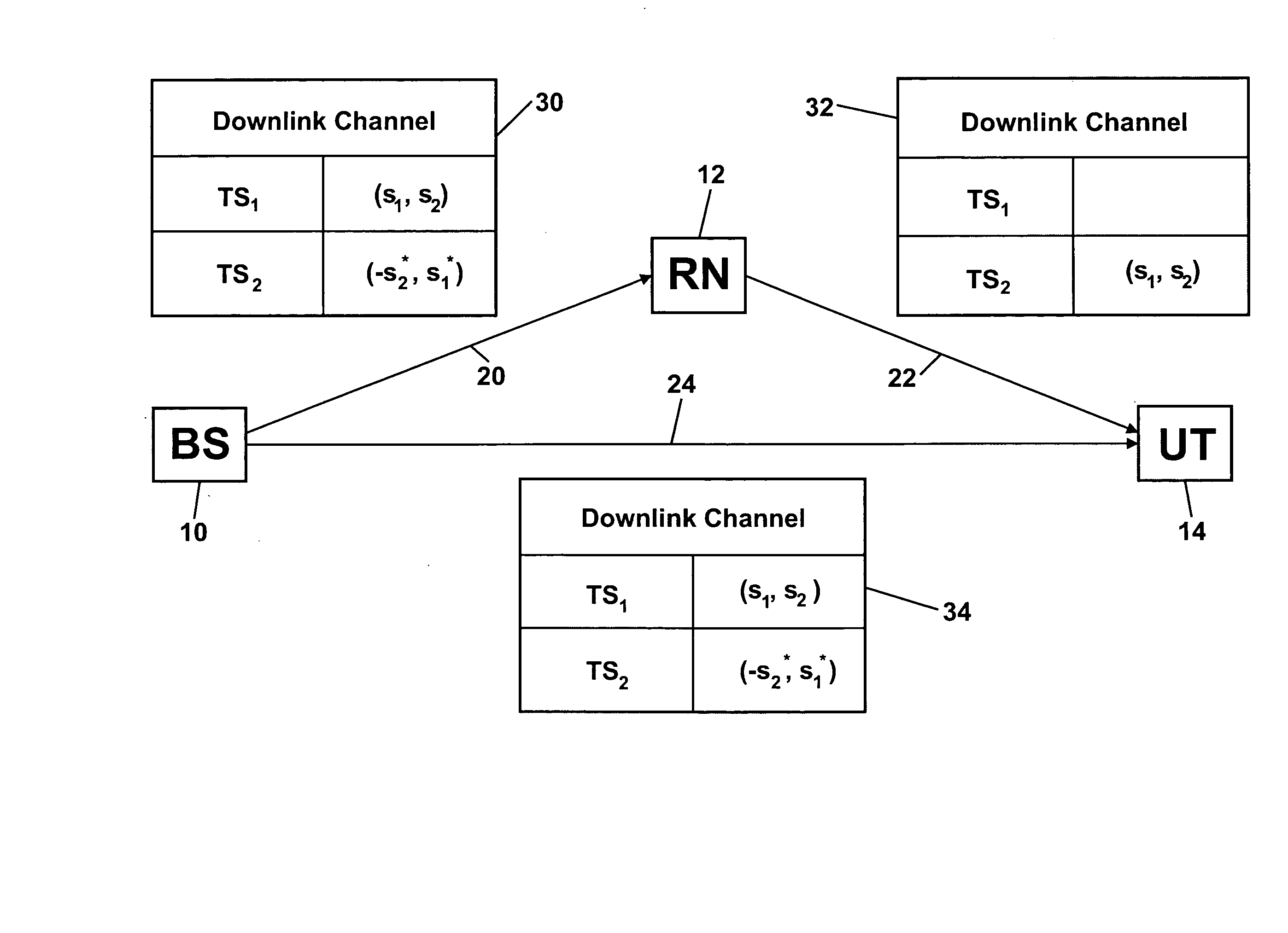
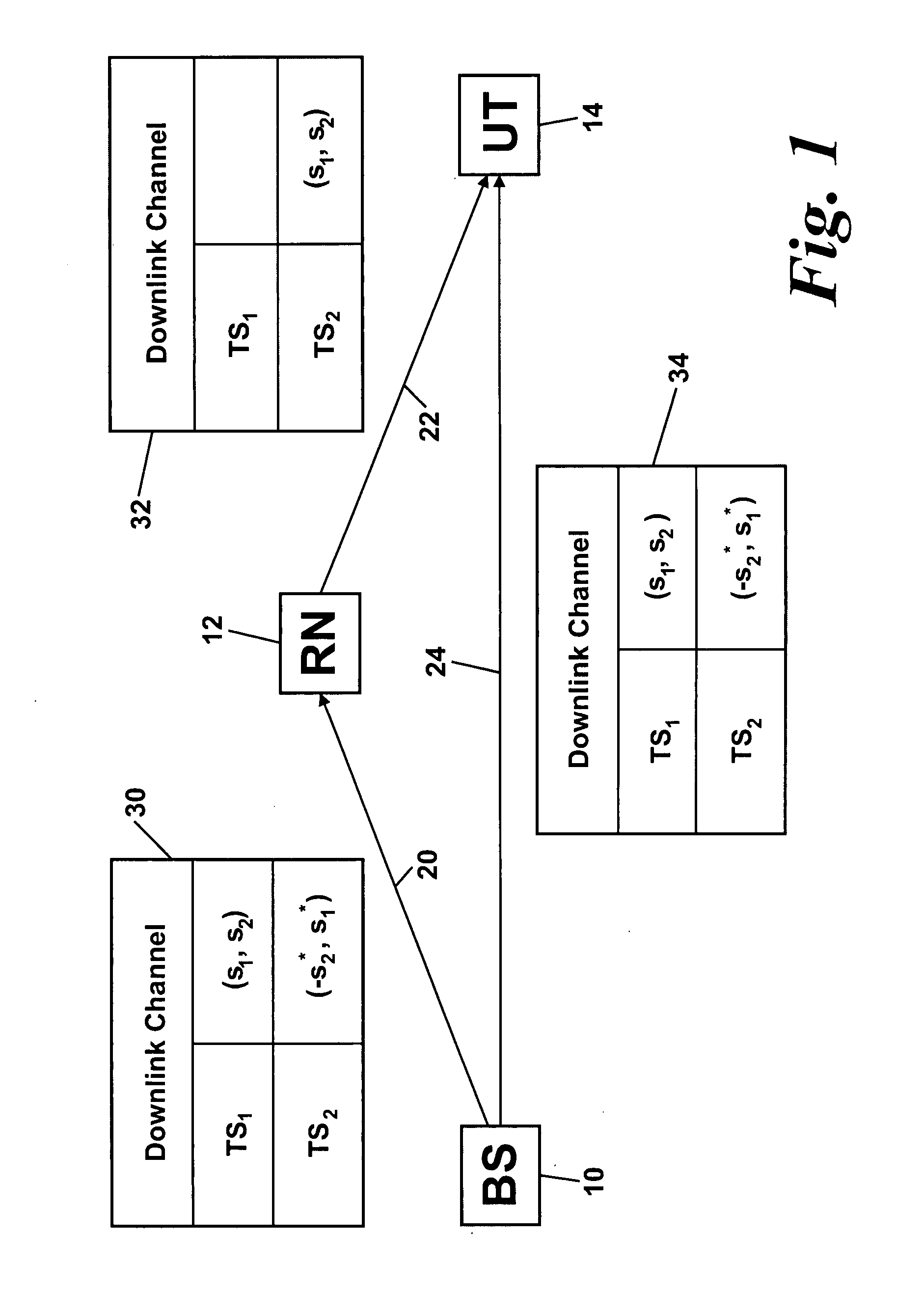
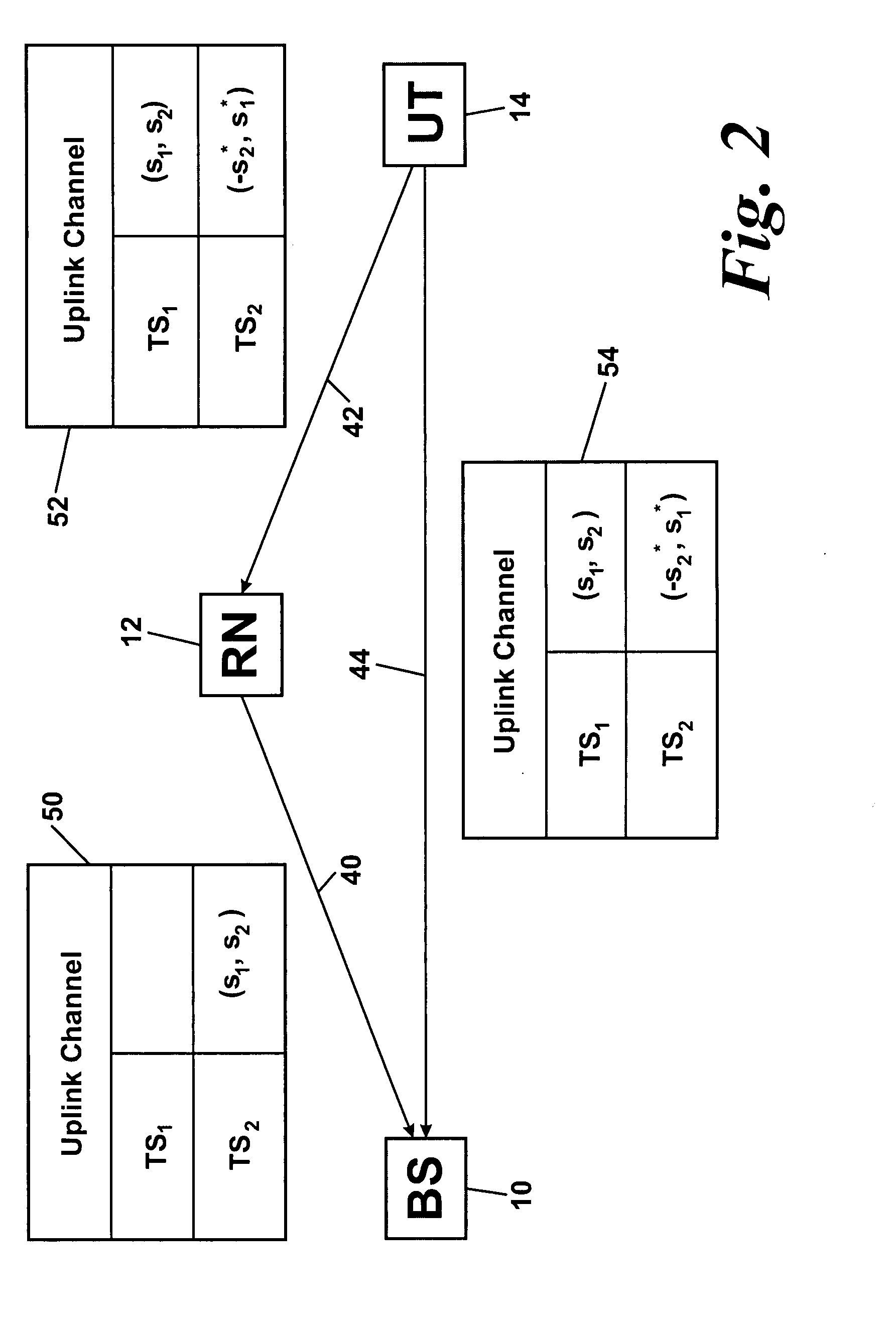
Space Time Block Code Communications with Co-Operative Relays
InactiveUS20080025248A1Quality improvementImprove received signal qualityFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemTime space
Methods, systems and apparatuses are provided for transmitting and receiving space-time block coded data in a wireless communications system with co-operative relays. A source node transmits RF signals representing first and second sets of data symbols in respective first and second channels (in time frequency code or any combination) of a wireless communications system, the first and second sets of data symbols being for transmission from separate antennas respectively according to a space-time block code. A relay node receives the RF signals representing the first set of data symbols in the first channel and transmits RF signals representing the first set of data symbols in the second channel. A destination node received the RF signals representing the second set of data symbols from the source node and the RF signals representing the first set of data symbols from the relay node. This enables decoding of the received RF signals representing the first and second sets of data symbols according to the space-time block code.
Owner:APPLE INC
Surface acoustic wave device and communication apparatus
ActiveUS7298231B2Small sizeImprove reliabilityImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesElectrical conductorSurface acoustic wave sensor
In a surface acoustic wave device according to the present invention, a transmitting filter element TX and a receiving filter element RX are formed on one main surface of a piezoelectric substrate 300, and are mounted by face down on an upper surface of a circuit board 200. A ground electrode 322 in the receiving filter element RX is connected to three linear via conductors 221′ formed on the circuit board 200, and a ground electrode 312 in the transmitting filter element TX is connected to a crank-shaped via conductor 211′ formed on the circuit board 200.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
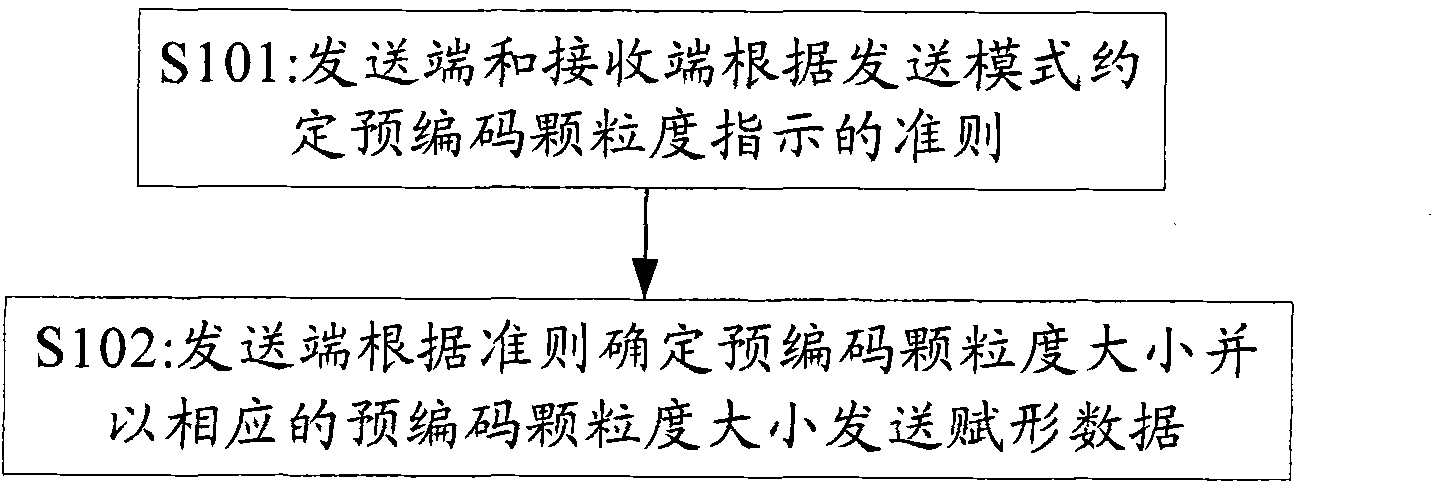
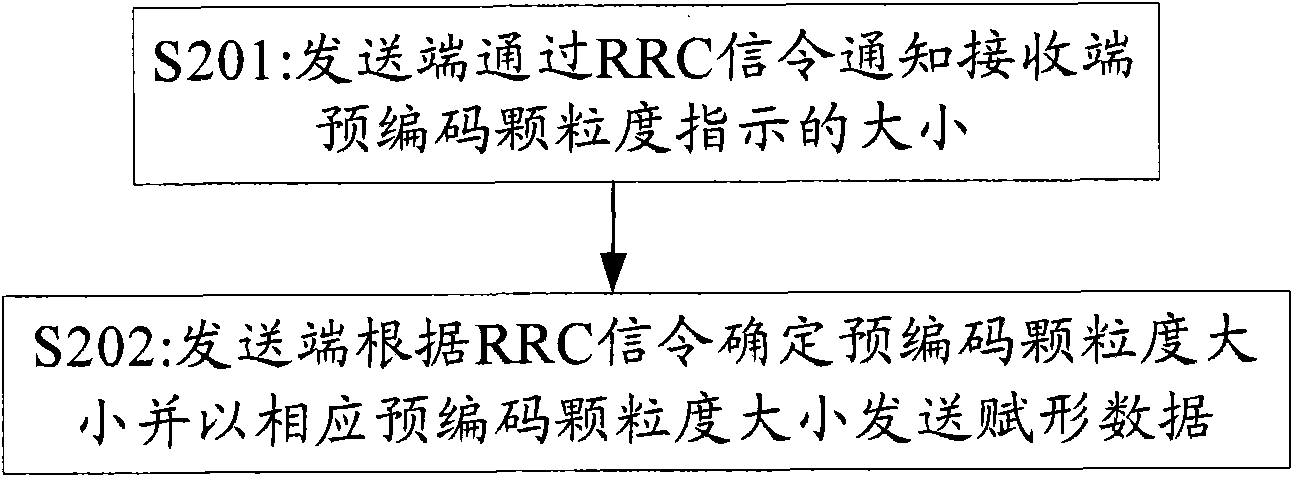
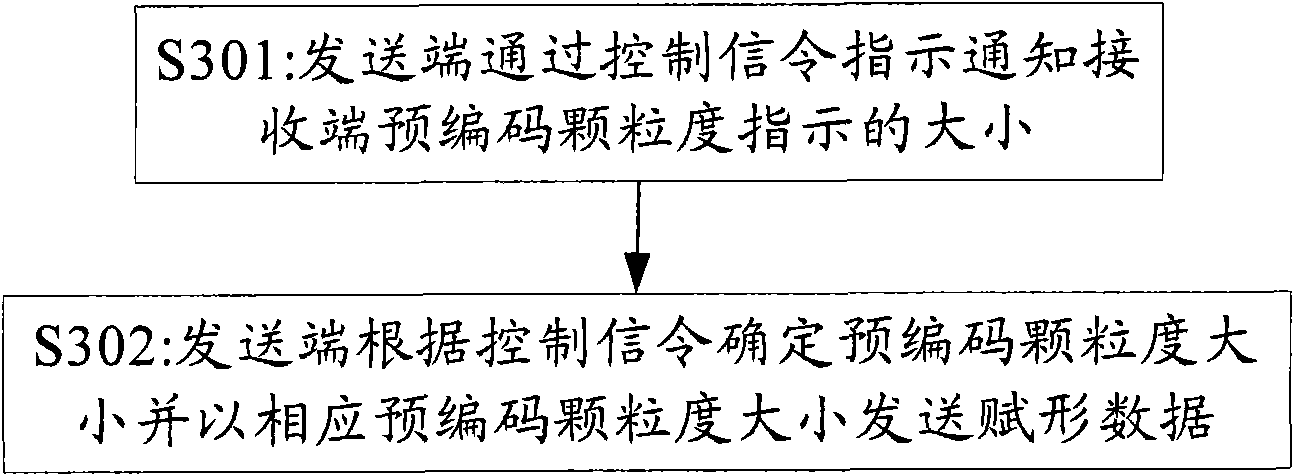
Method and device for information indication
ActiveCN101931442AFix instructionsImprove received signal qualitySpatial transmit diversityFrequency spectrumSystem capacity
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for precoding granularity indication, comprising the following steps: a transmitting end and a receiving end appoint a standard of precoding granularity indication according to a transmission mode; and the transmitting end determines the size of precoding granularity according to the standard and transmits precoding data on basis of the size of precoding granularity. The embodiment of the invention also provides a transmitting device capable of realizing the precoding granularity indication. The technical scheme of the invention provided by the invention solves the problem of precoding granularity indication in an MIMO system through coordinately appointing the size of the precoding granularity by the transmitting end and the receiving end, thereby improving the quality of signals received by users, reducing cell interference and effectively improving system capacity and edge user spectrum efficiency.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
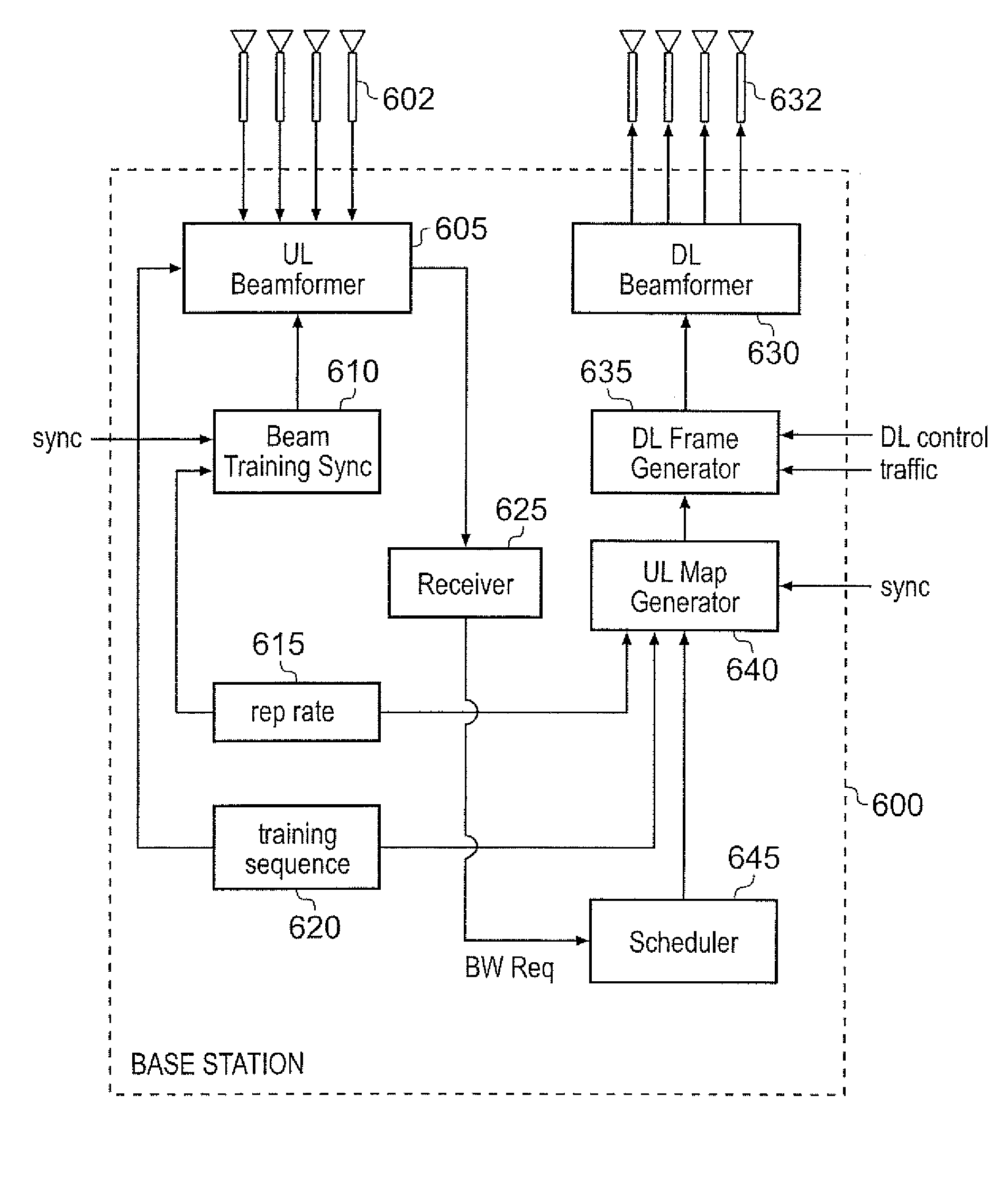
Point to multipoint device for communication with a plurality of telecommunications units
ActiveUS7627348B2Improve received signal qualityReduce CCISpatial transmit diversityTime-division multiplexControl dataControl logic
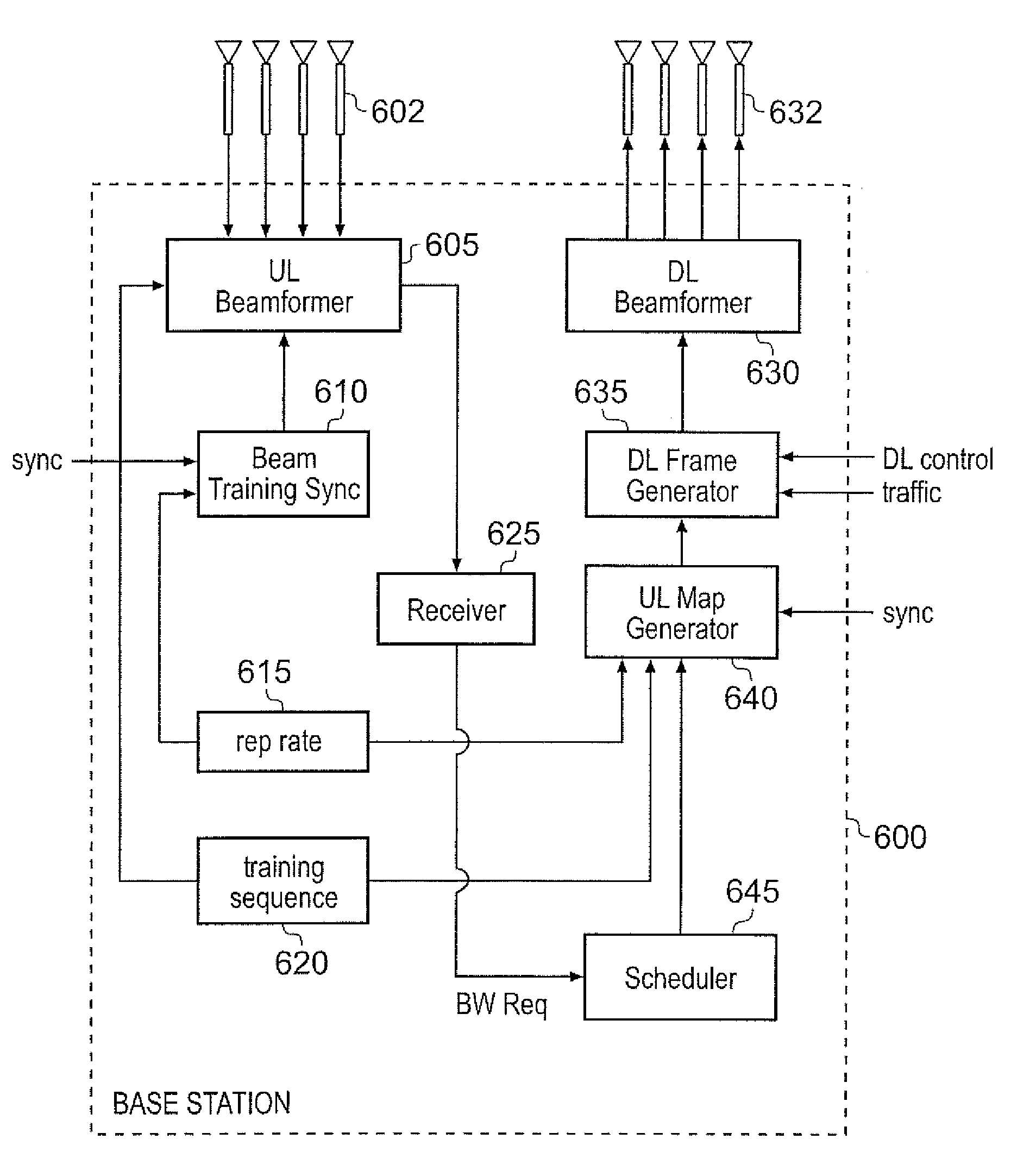
A point to multipoint device for use in a wireless network operates a sequence of variable duration communication channels, allocatable to telecommunications units. A training sequence indication and a repetition rate indication are stored indicating a training sequence and repetition rate for the training sequence in the sequence of communication channels associated with the point to multipoint device. An interface receives a synchronization signal issued to all point to multipoint devices in the wireless network, and uses it to determine a time for a first occurrence of the training sequence to occur. Communication channel control logic causes control data to be transmitted to the telecommunications units identifying the sequence of channels, the training sequence indication and the repetition rate. Beamforming logic determines beamforming weights used to produce a reception beam at an antenna array.
Owner:AIRSPAN IP HOLDCO LLC
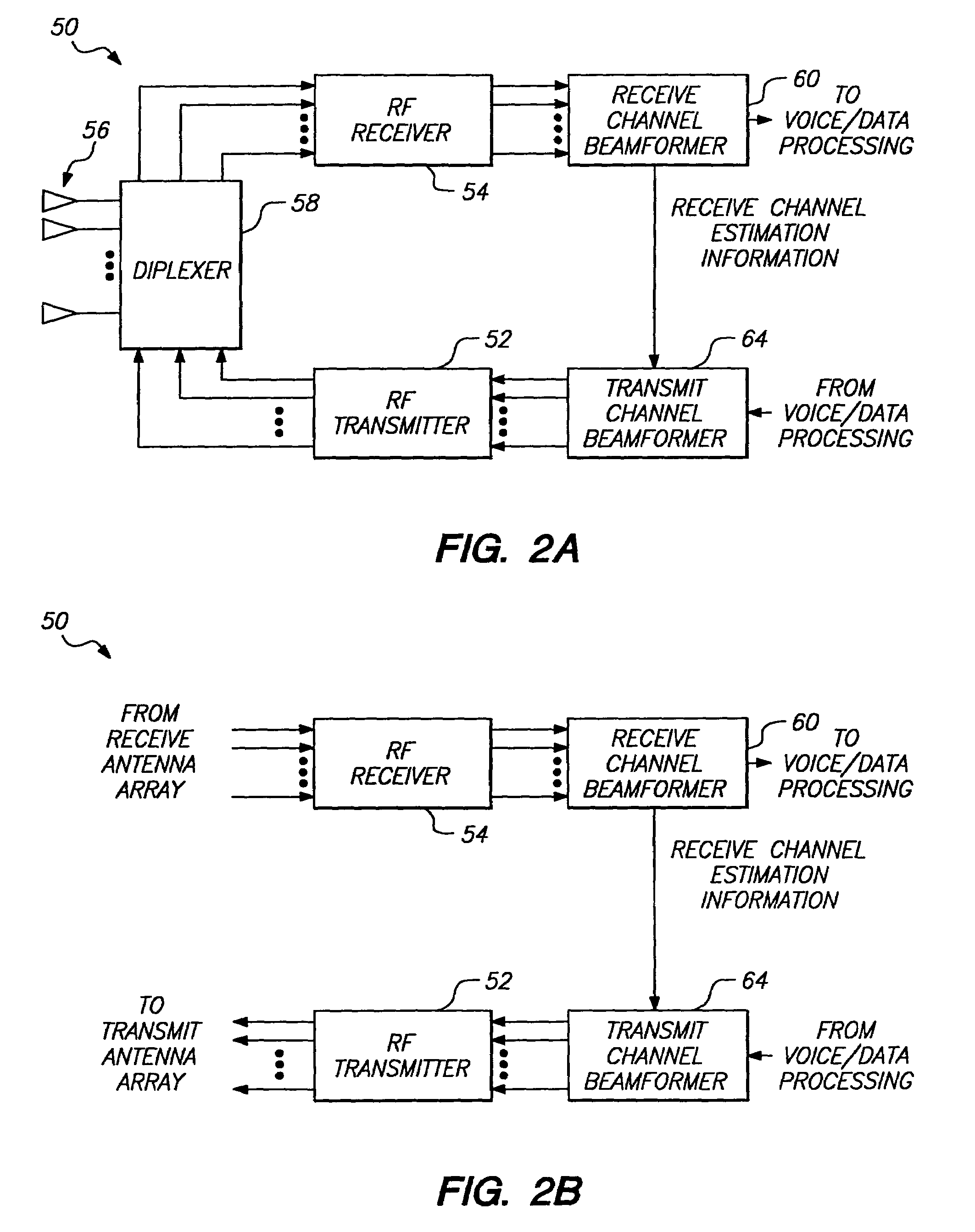
Method and apparatus for adaptive transmission beam forming in a wireless communication system
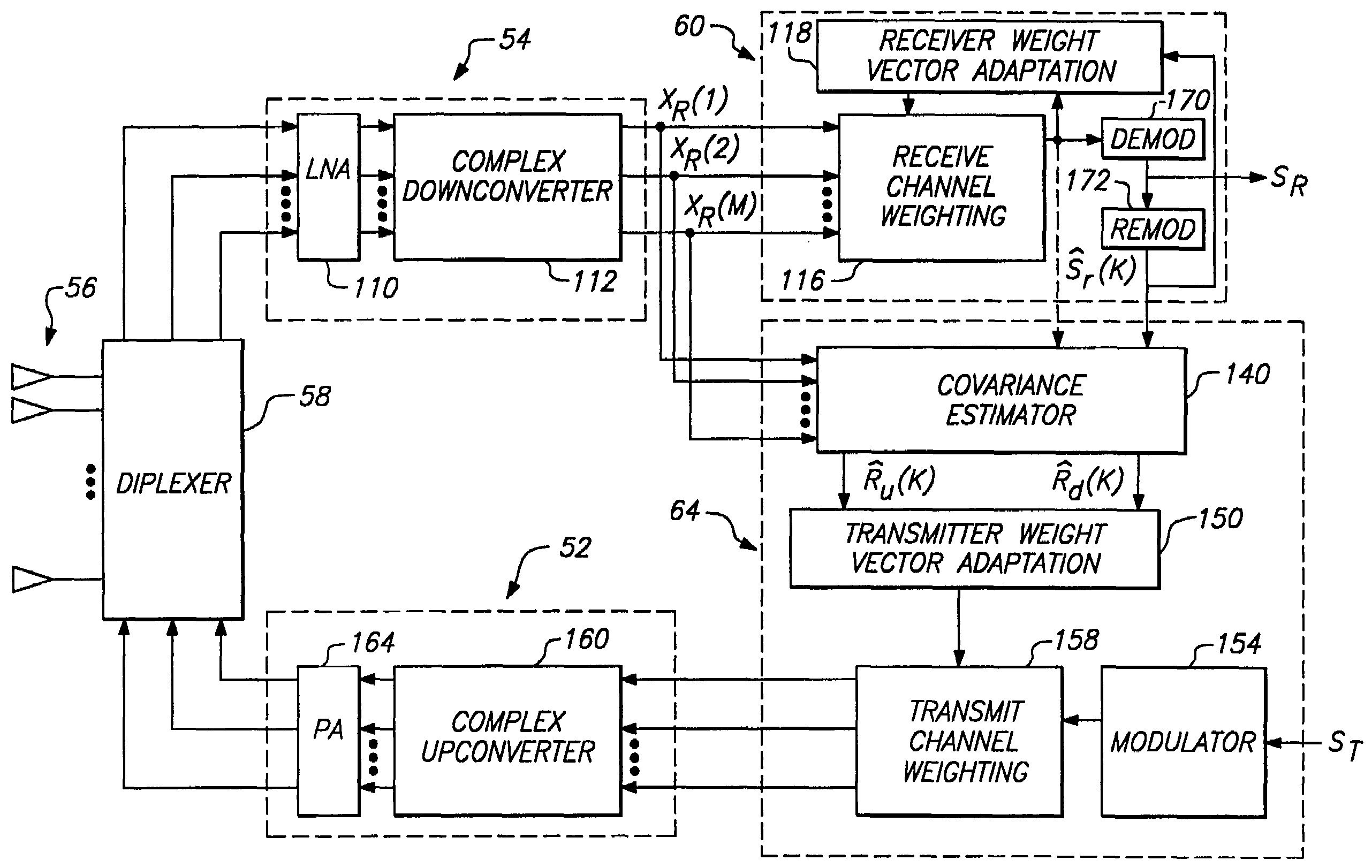
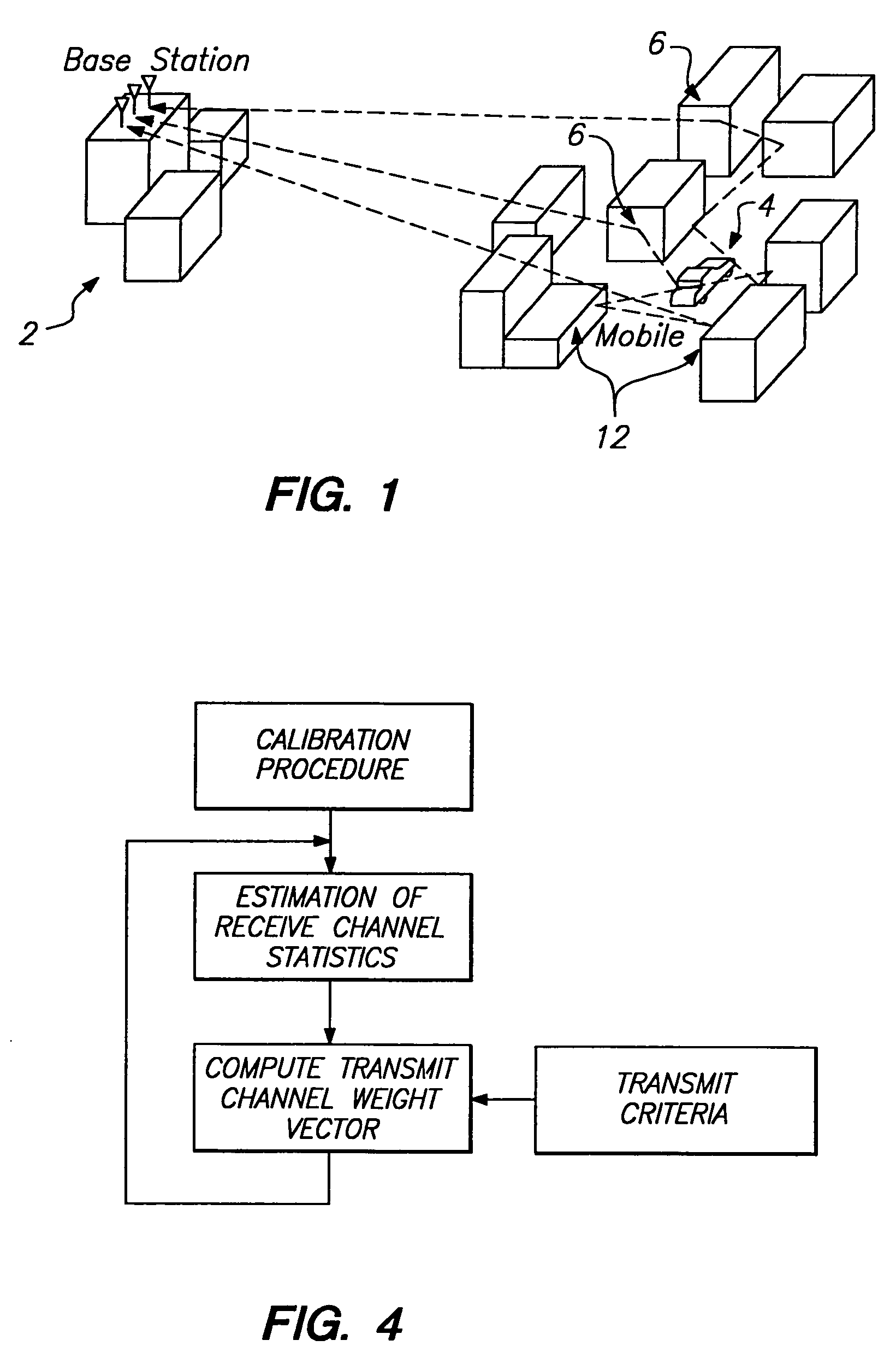
InactiveUS7286855B2Improve received signal qualityImprove signal qualityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentCovarianceEngineering
A method for forming an adaptive phased array transmission beam pattern at a base station without any knowledge of array geometry or mobile feedback is described. The approach is immune to the problems which plague methods which attempt to identify received angles of arrival from the mobile and map this information to an optimum transmit beam pattern. In addition, this approach does not suffer the capacity penalty and mobile handset complexity increase associated with mobile feedback. Estimates of the receive vector propagation channels are used to estimate transmit vector channel covariance matrices which form objectives and constraints in quadratic optimization problems leading to optimum beam former solutions for the single user case, and multiple user case. The new invention in capable of substantial frequency re-use capacity improvement in a multiple user cellular network.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
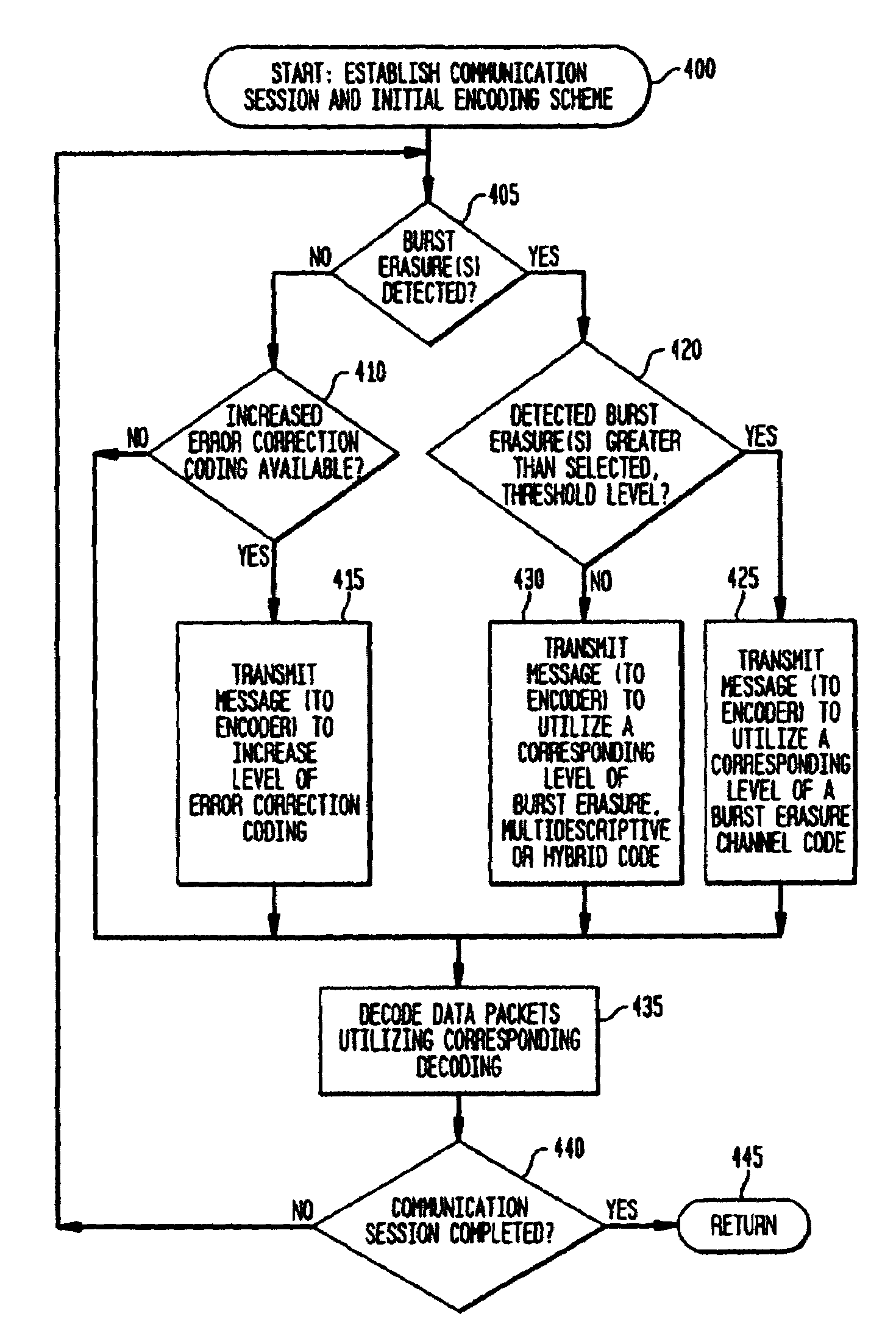
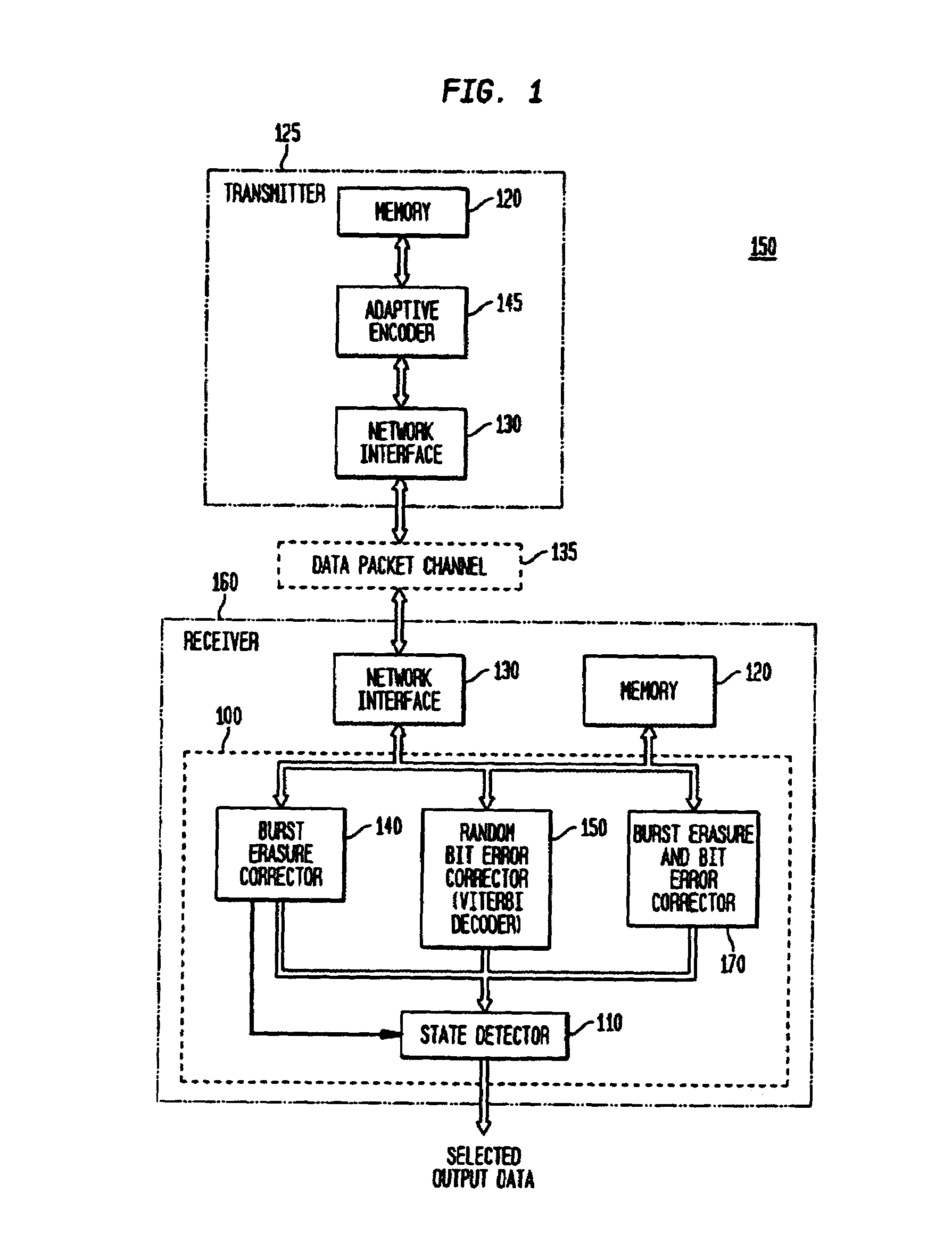
Apparatus and method for adaptive, multimode decoding
ActiveUS7003712B2Improve received signal qualityImprove errorOther decoding techniquesOther error detection/correction/protectionCommunications systemSignal quality
The present invention provides for adaptive and multimode decoding, in a data packet-based communication system, to provide improved received signal quality in the presence of burst erasures or random bit errors, with particular suitability for real-time, delay sensitive applications, such as voice over Internet Protocol. In the presence of burst erasures, the adaptive multimode decoder of the present invention provides burst erasure correction decoding, preferably utilizes a maximally short (MS) burst erasure correcting code, which has a comparatively short decoding delay. Depending upon the level of such burst erasures, different rate MS codes may be utilized, or other codes may be utilized, such as hybrid or multidescriptive codes. When no burst erasures are detected, the adaptive multimode decoder of the present invention provides random bit error correction decoding, in lieu of or in addition to corresponding burst erasure correction coding.
Owner:AGERE SYST GUARDIAN
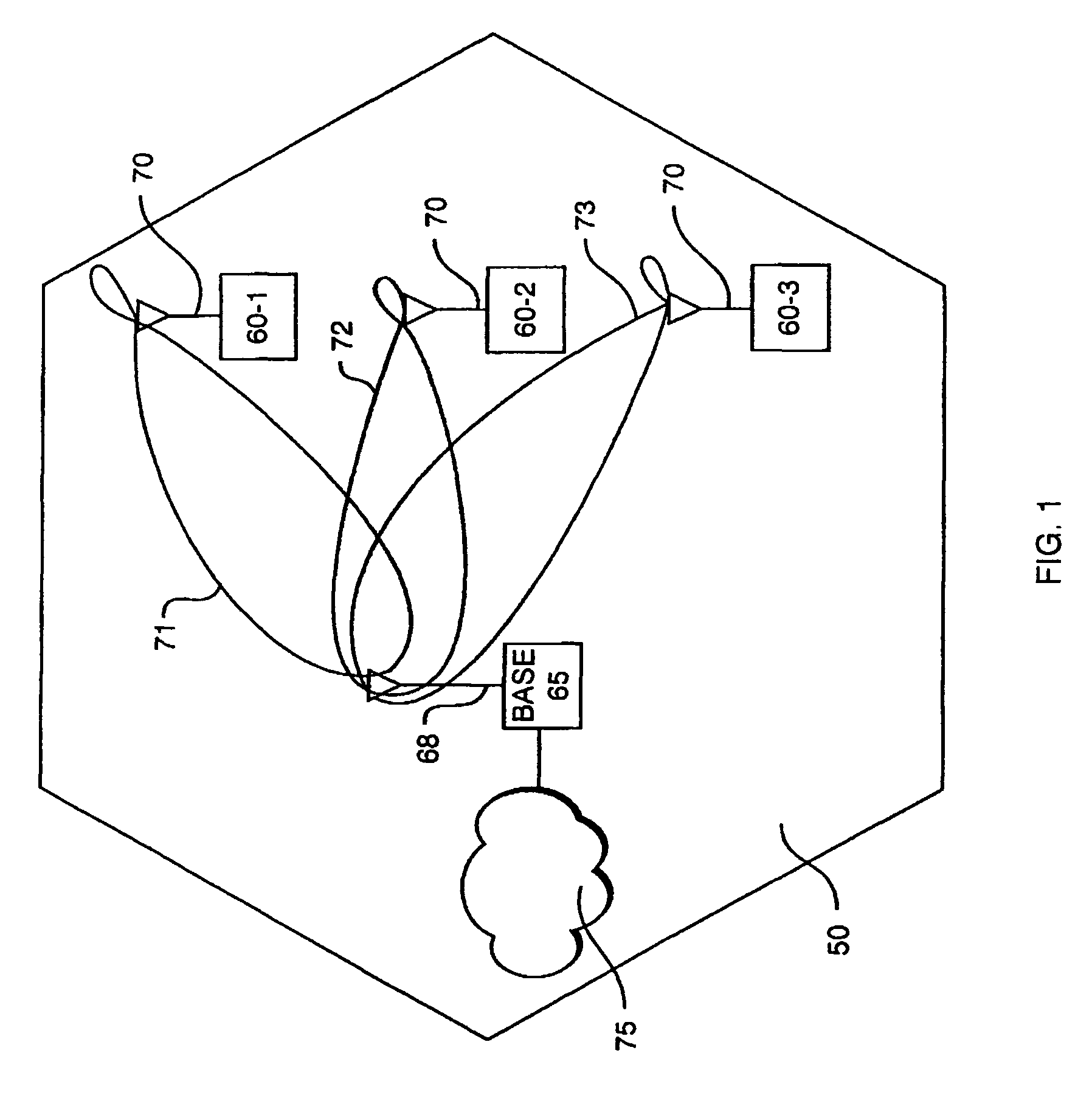
Multi-domain wireless broadcast multicast network system and method based on coordination technique
ActiveCN101420769AImprove signal reception qualityImprove received signal qualityNetwork topologiesBroadcast service distributionSingle-frequency networkBroadcast multicast
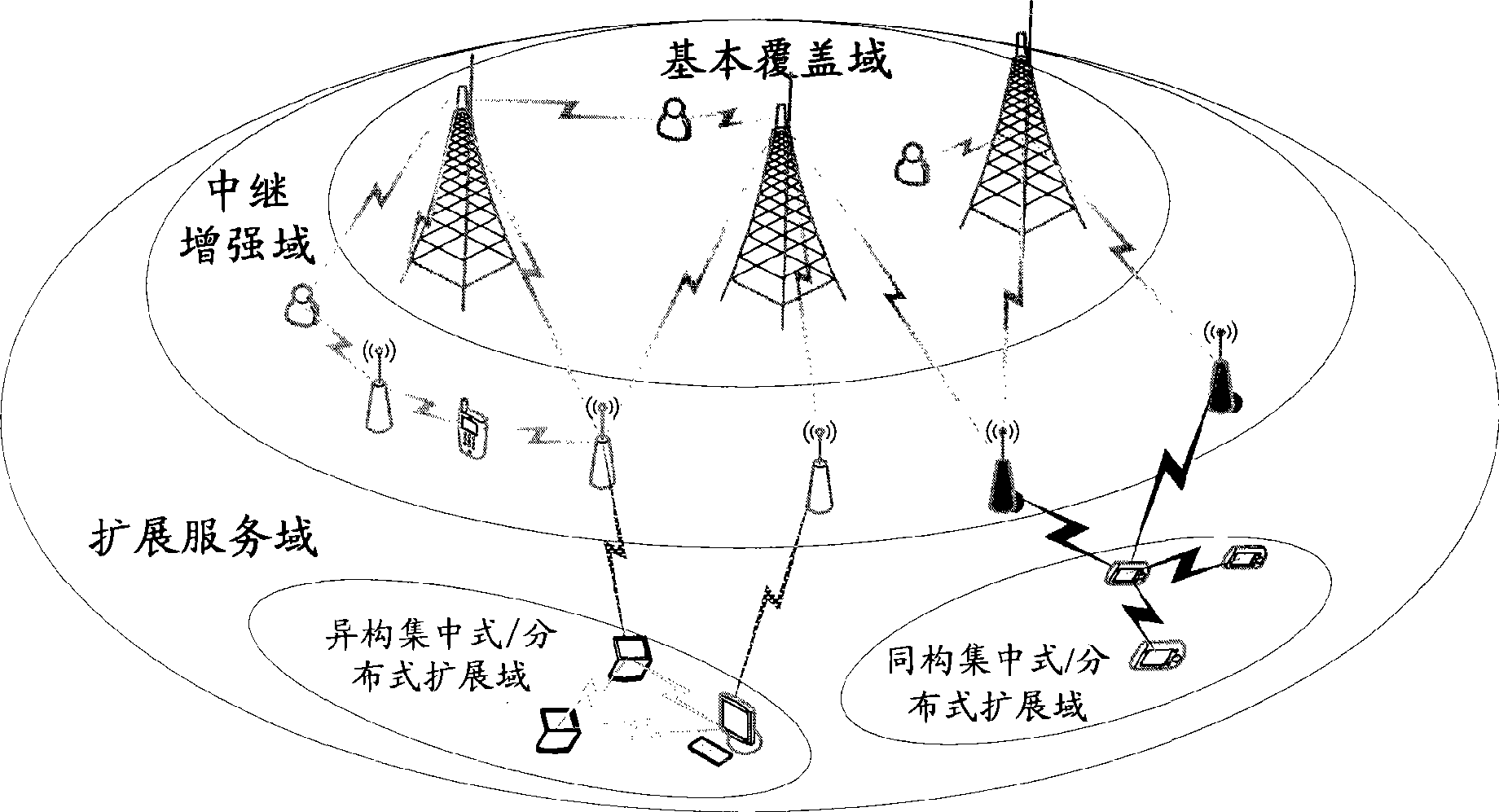
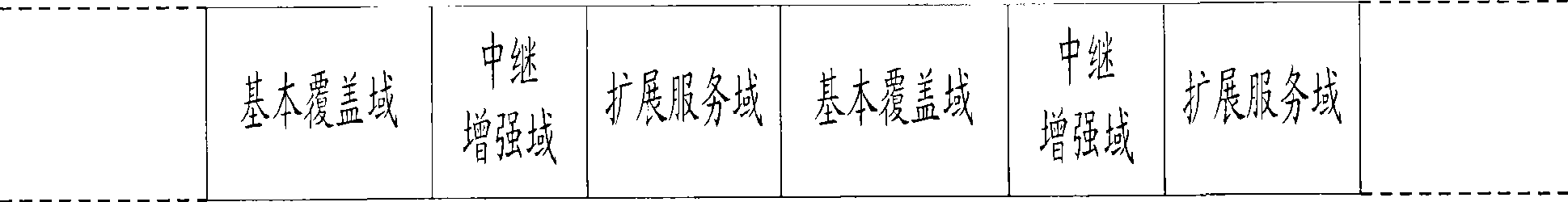
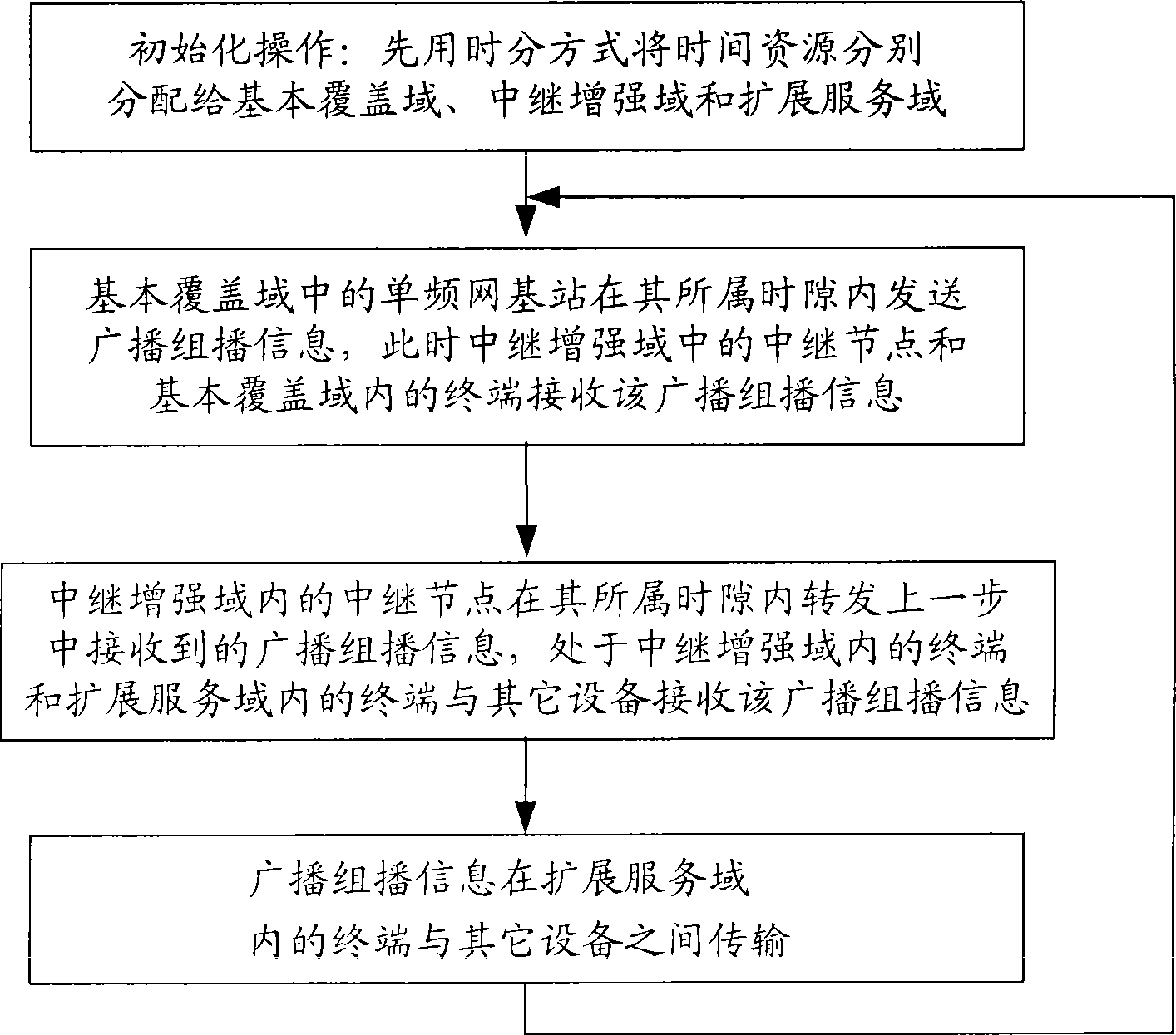
A multi-domain radio broadcast multicast network system based on a cooperative communication technology and a method thereof. The system comprises a basic overlay domain, a relay enhancement domain and an expanded service domain. The basic overlay domain composed of a radio broadcast multicast single frequency network is taken as a core, the overlay range of the radio broadcast multicast single frequency network is expanded by the relay enhancement domain so as to realize seamless overlay of the radio broadcast multicast single frequency network and a homogeneous radio broadcast multicast network and accomplish a fusion of the radio broadcast multicast single frequency network and an heterogeneous radio broadcast multicast network. The system acquires a diversity-multiplexing gain of radio transmission by the cooperative communication technology, thus solving a bottle-neck problem of radio broadcast data service transmission among different domains. The method and the system can expand the overlay range of the radio broadcast multicast network, enhance system capacity and service quality, realize convenient networking, and satisfy high-quality and high-speed transmission demand of the next generation of the radio broadcast multicast.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM TECH (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD
Control information sending method, base station, user equipment and control information sending system
InactiveCN106851846AImprove reception success rateImprove received signal qualityWireless communicationControl channelSignal quality
The embodiment of the invention discloses a control information sending method, a base station, user equipment and a control information sending system. The method comprises the steps of determining control information of at least one piece of user equipment in N pieces of user equipment scheduled by a current sub-frame, wherein N is a positive integer; determining a first time frequency position and a second time frequency position occupied by the control information; and sending the control information of the first time frequency position to the at least one piece of user equipment by using a first type of beams, and sending the control information of the second time frequency position to the at least one piece of user equipment by using a second type of beams. With the application of the method provided by the invention, a successful receiving rate of a control channel can be improved, received signal quality of the control channel can be enhanced, and an error rate of the control channel can be reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN GIONEE COMM EQUIP
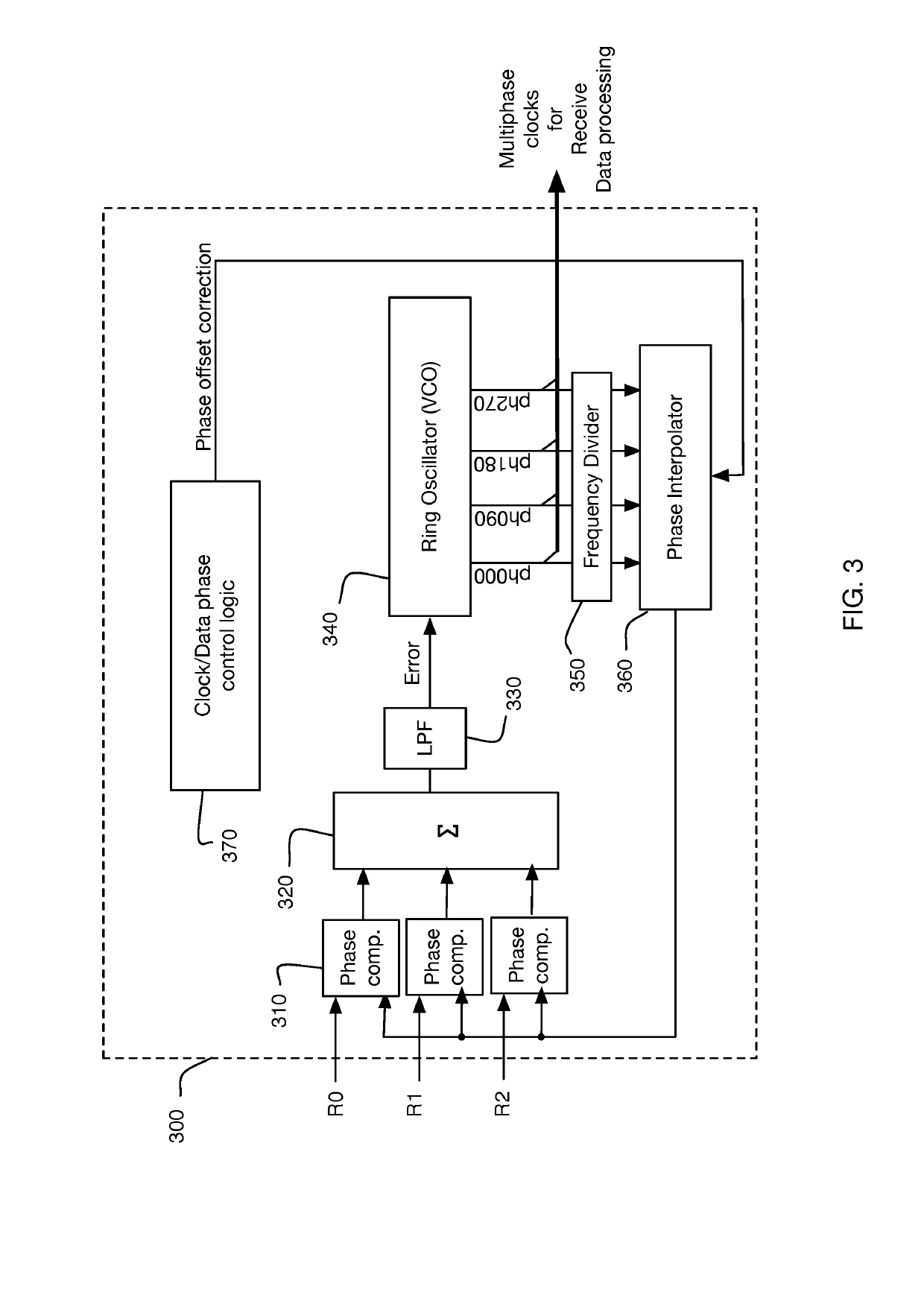
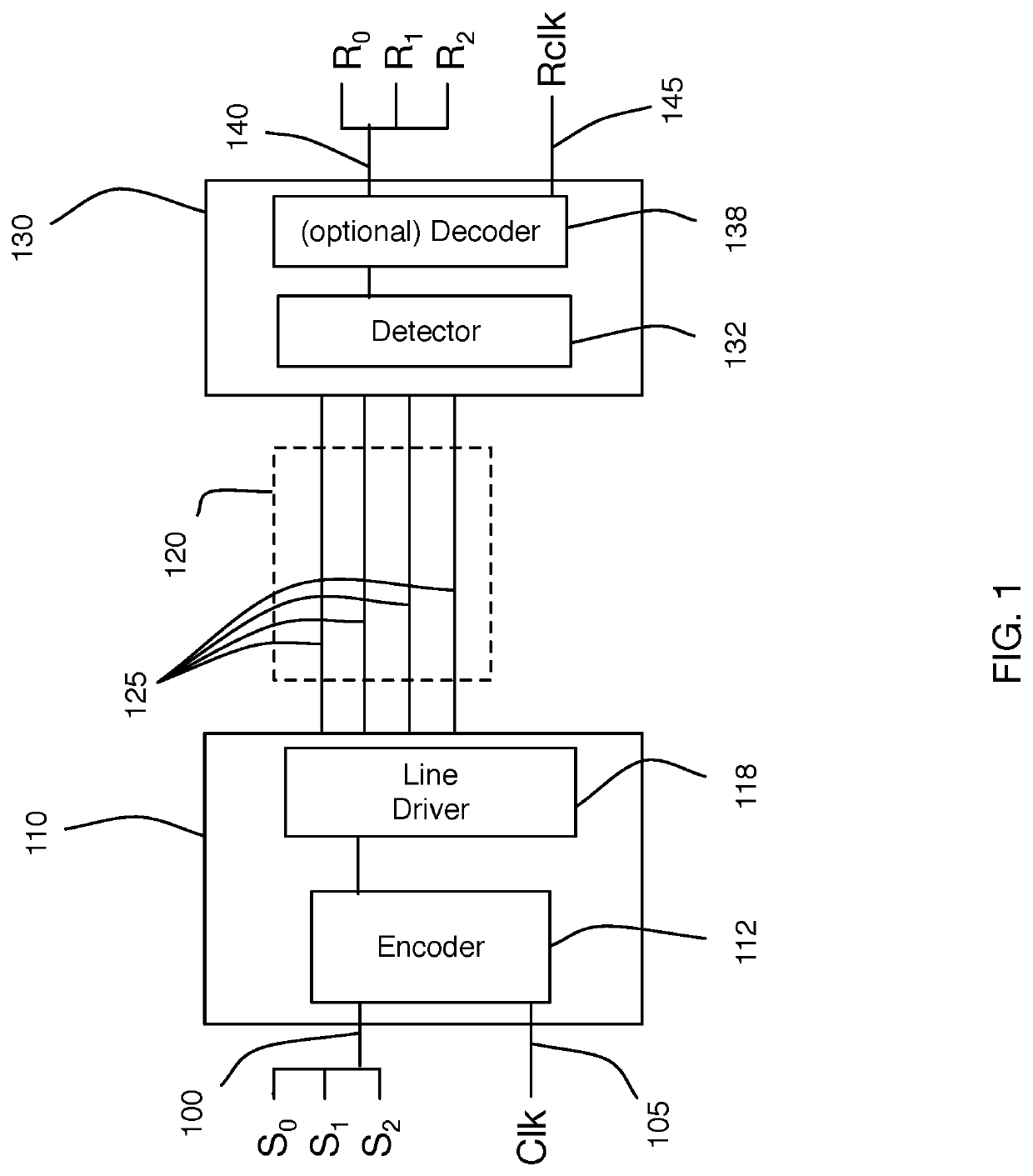
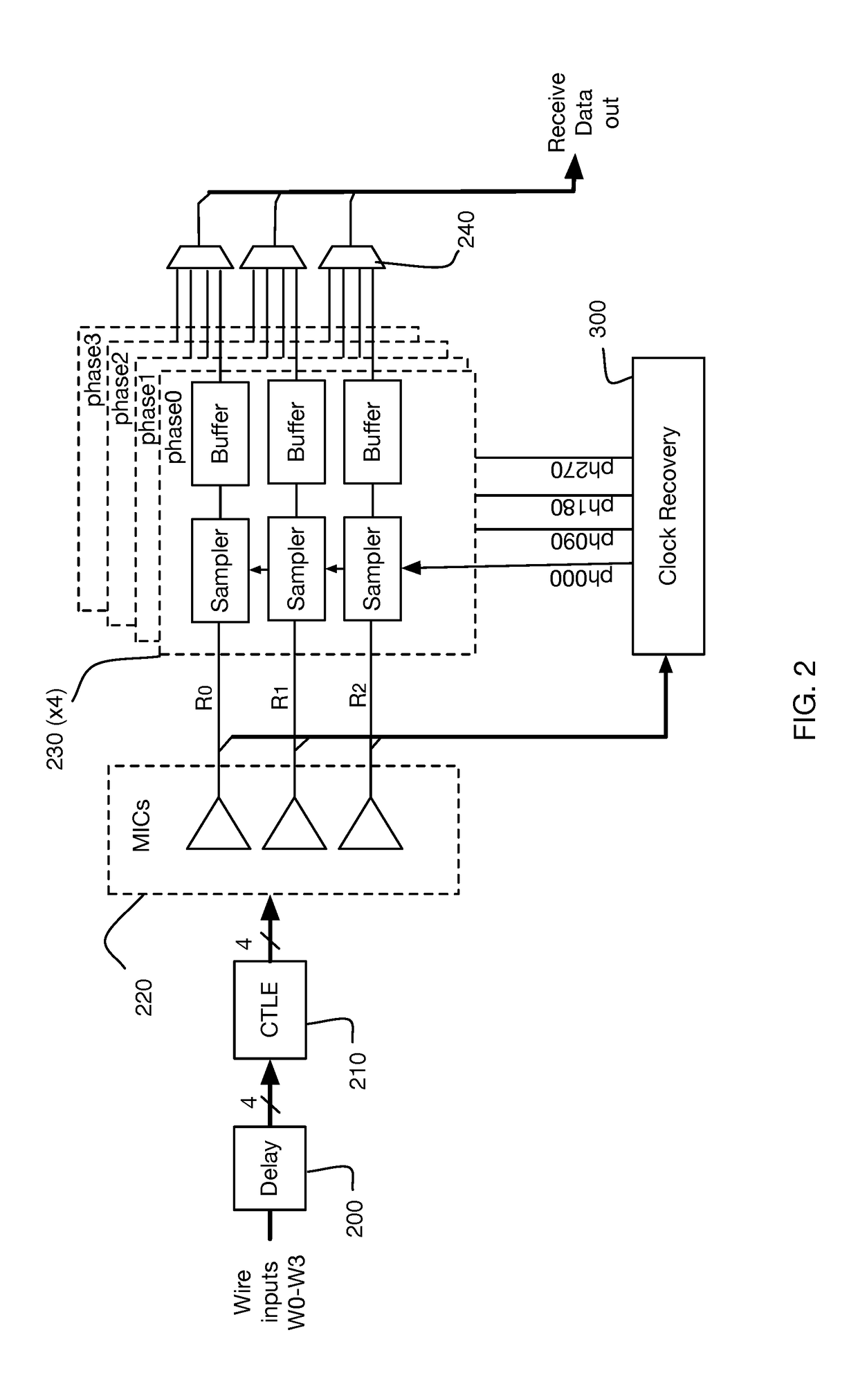
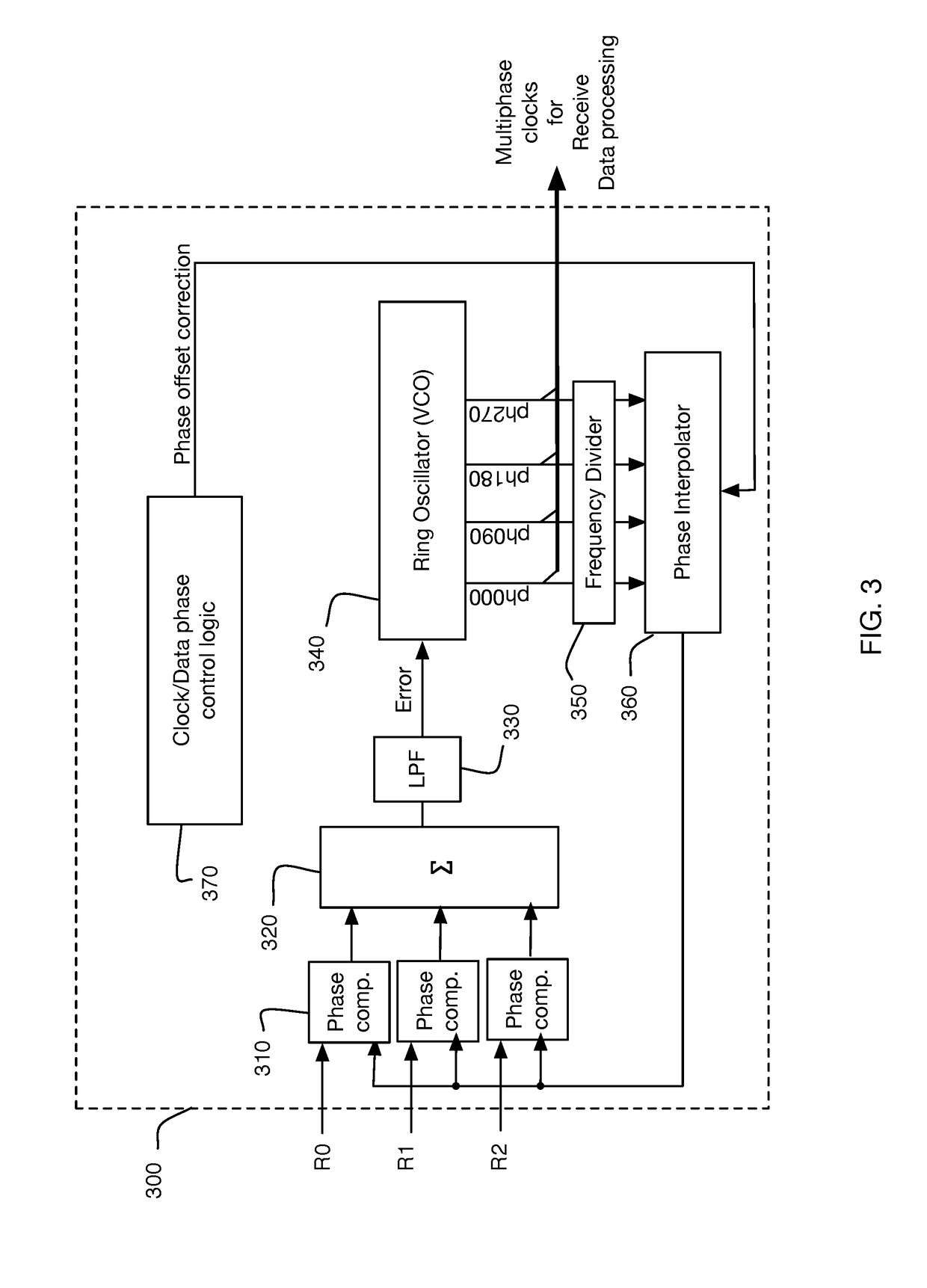
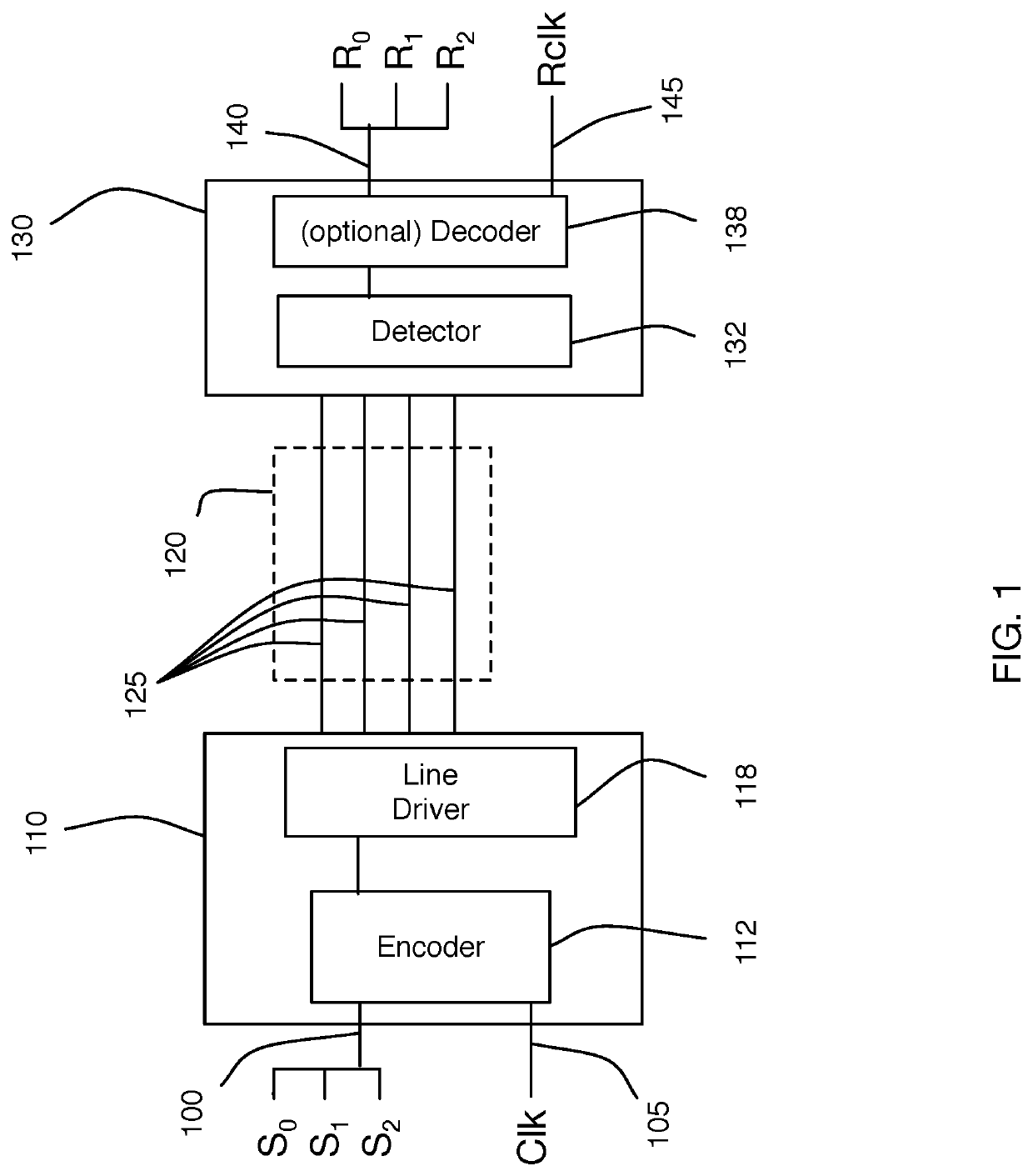
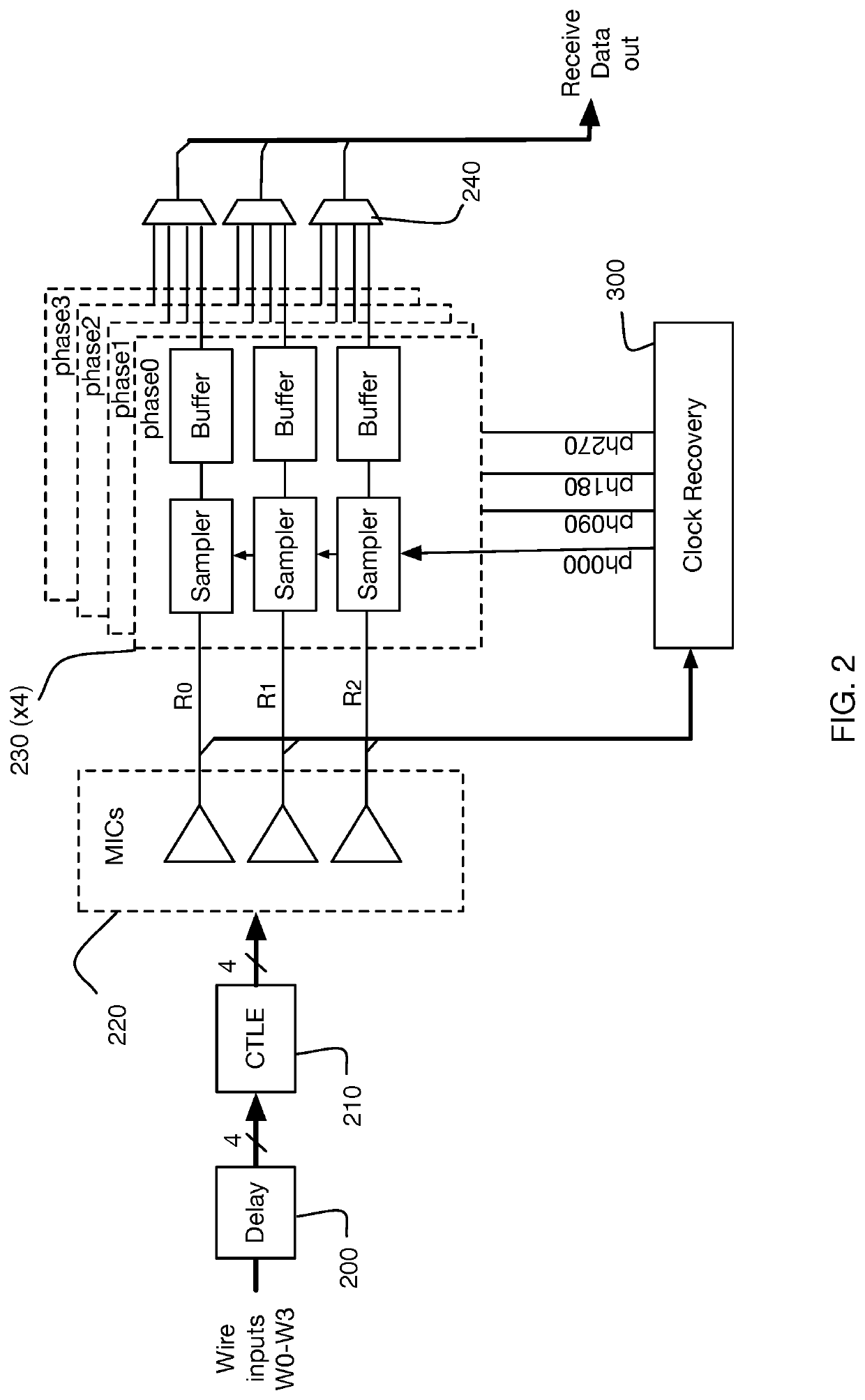
Method and system for calibrating multi-wire skew
ActiveUS10243614B1Reliable detectionAccurate interpretationExclusive-OR circuitsChannel dividing arrangementsMulti inputEngineering
Methods and systems are described for receiving, over a plurality of consecutive signaling intervals, a plurality of codewords, each codeword received as a plurality of symbols via wires of a multi-wire bus, the plurality of symbols received at a plurality of multi-input comparators (MICs), wherein each symbol is received by at least two MICs, generating, for each codeword, a corresponding linear combination of the received symbols, generating a plurality of composite skew measurement signals over the plurality of consecutive signaling intervals, each composite skew measurement signal based on samples of one or more linear combinations, and updating wire-specific skew values of the wires of the multi-wire bus, wherein one or more wire-specific skew values are updated according to composite skew measurement signals associated with linear combinations formed by at least two different MICs.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
Point to multipoint device for communication with a plurality of telecommunications units
ActiveUS20070135172A1Improve received signal qualityReduce CCISpatial transmit diversityTime-division multiplexIsochronous signalCo-channel interference
A point to multipoint device for use in a wireless network to provide wireless communication with a plurality of telecommunications units is described. For communication from the telecommunications units to the point to multipoint device, the point to multipoint device is operable to define a sequence of variable duration communication channels, each communication channel being allocatable to one of the telecommunications units. The point to multipoint device has training sequence storage for storing a training sequence indication indicating a training sequence associated with the point to multipoint device. Repetition rate storage is also provided for storing a repetition rate at which the training sequence is to be repeated in the sequence of communication channels, the repetition rate being the same for all point to multipoint devices in the wireless network. An interface receives a synchronisation signal issued to all point to multipoint devices in the wireless network, with the synchronisation signal being used to determine a time at which a first occurrence of the training sequence is to occur within the sequence of communication channels. Communication channel control logic defines the sequence of variable duration communication channels and causes control data to be transmitted to the telecommunications units identifying the sequence of channels, the training sequence indication and the repetition rate. An antenna array provides a reception beam for receiving the communication from the telecommunications units, and beamforming logic is used to determine beamforming weights used to produce the reception beam. The beamforming logic repeats the determination of beamforming weights at the repetition rate coincident with the appearance of the training sequence in the sequence of communication channels. This provides a particularly effective technique for reducing co-channel interference within the wireless network.
Owner:AIRSPAN IP HOLDCO LLC
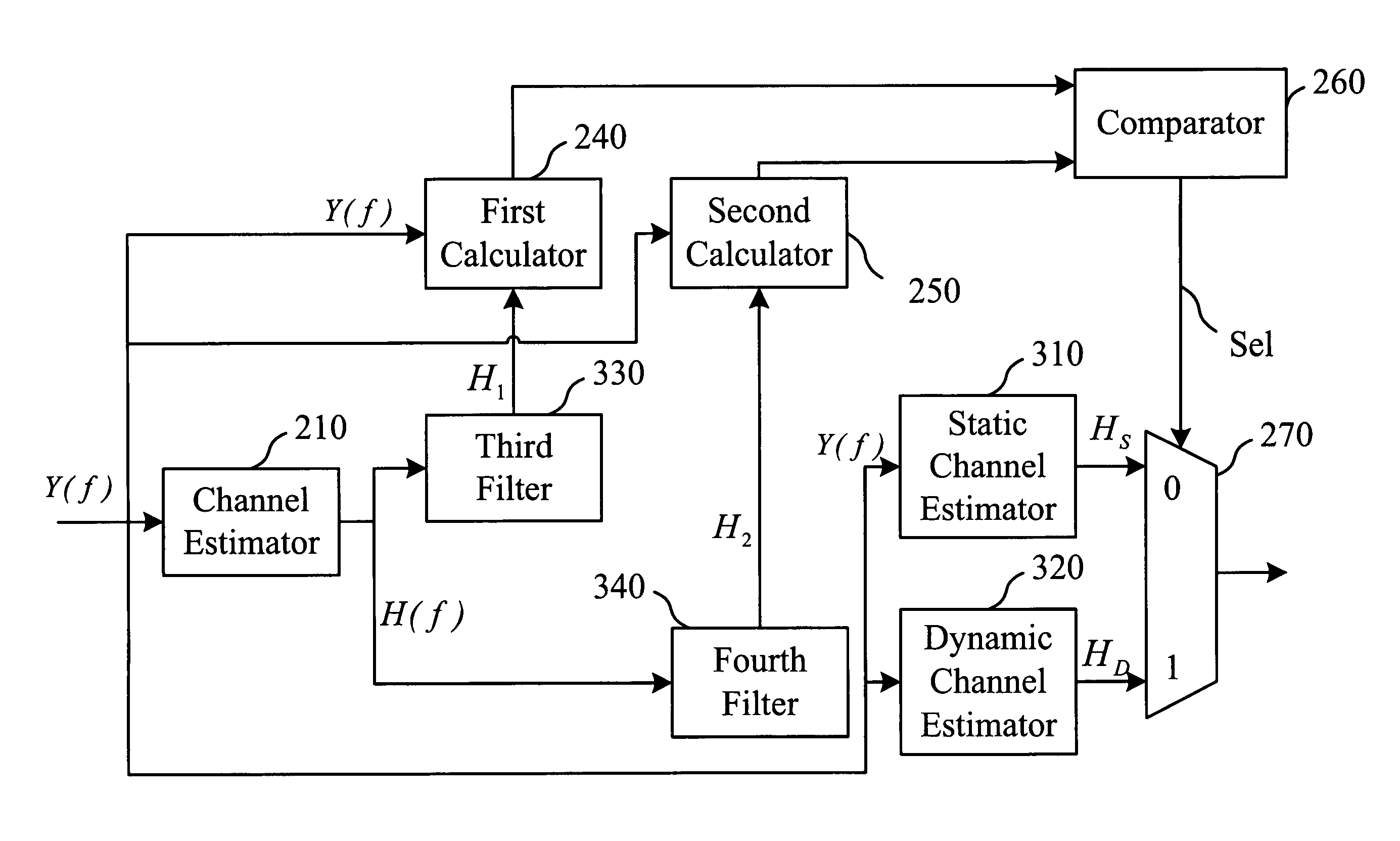
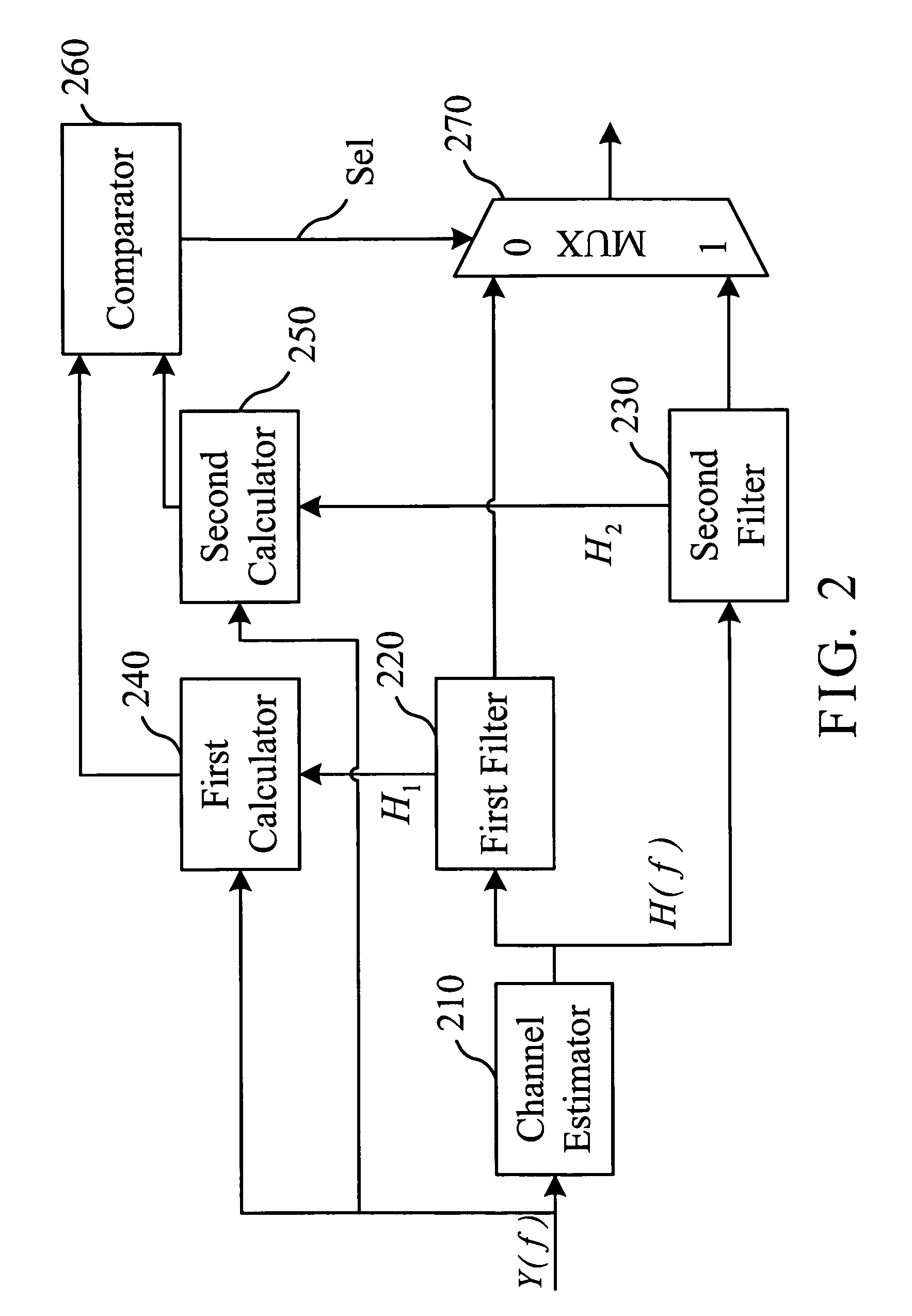
Real-time channel estimation system
InactiveUS7995691B2Improve received signal qualityEffective estimateAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsChannel estimationWireless transmissionMultiplexer
A real-time channel estimation system, which receives a wireless transmission signal through a wireless channel and estimates channel parameters of the wireless channel in real-time. The system includes a channel estimator to receive the wireless transmission signal and output the channel parameters; first and second filters to filter the channel parameters for producing a first and a second sets of filtered channel parameters; first and second calculators to compute according to the first and the second sets of filtered channel parameters and the wireless transmission signal for producing a first and a second probabilities; a comparator to compare the first and the second probabilities for producing an indicative signal; and a multiplexer to receive the indicative signal for accordingly selecting the first or second set of filtered channel parameters as an output.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
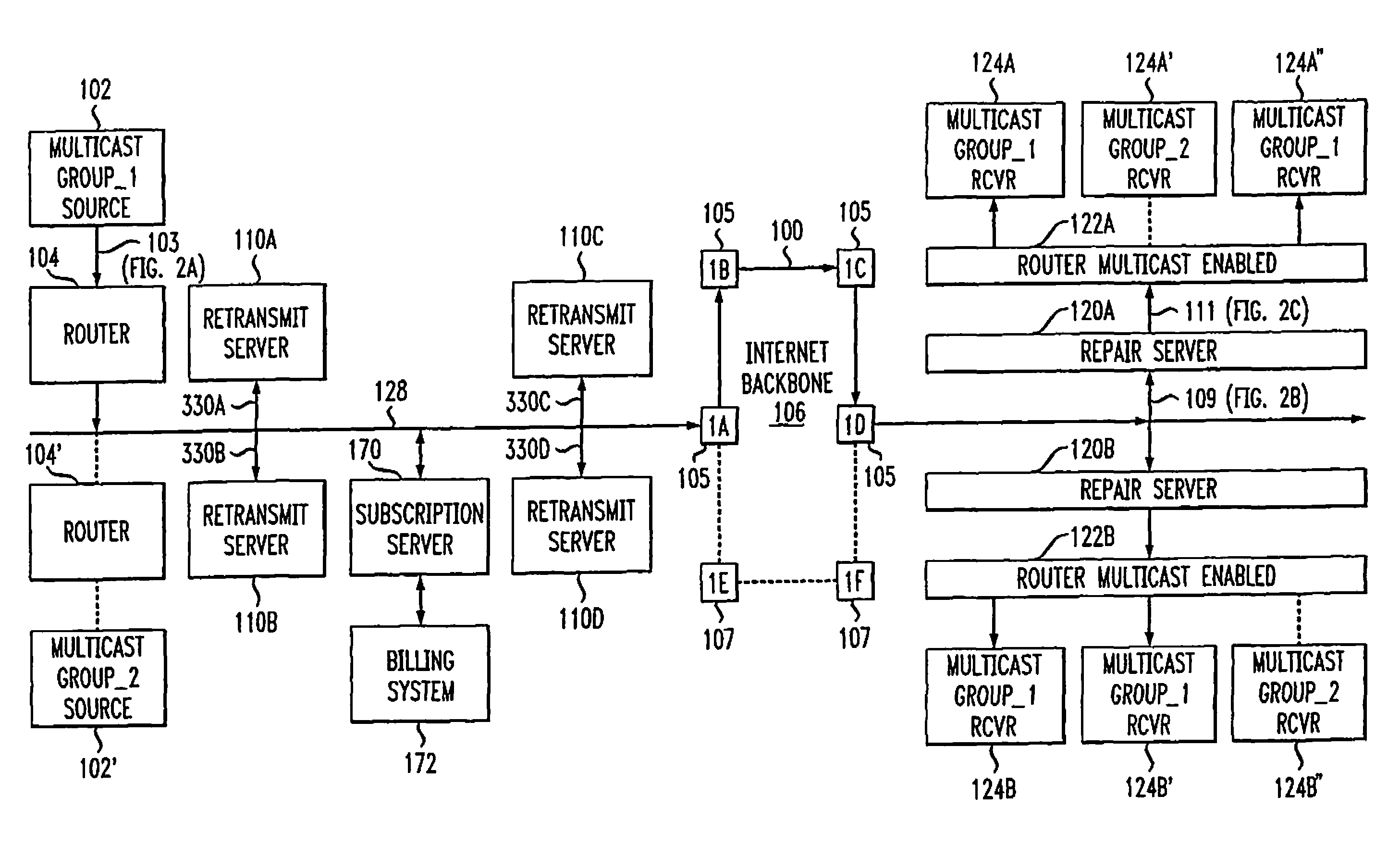
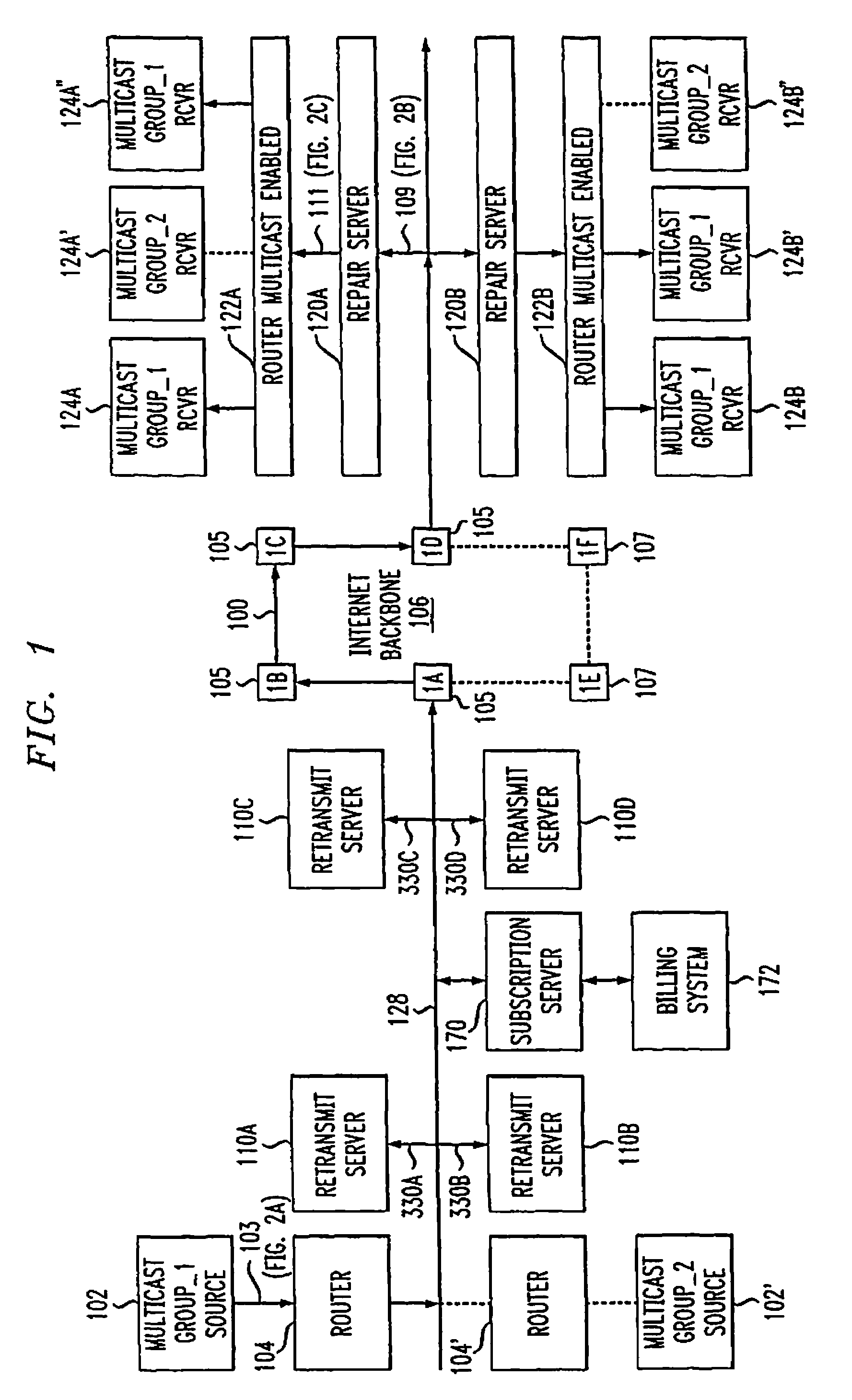
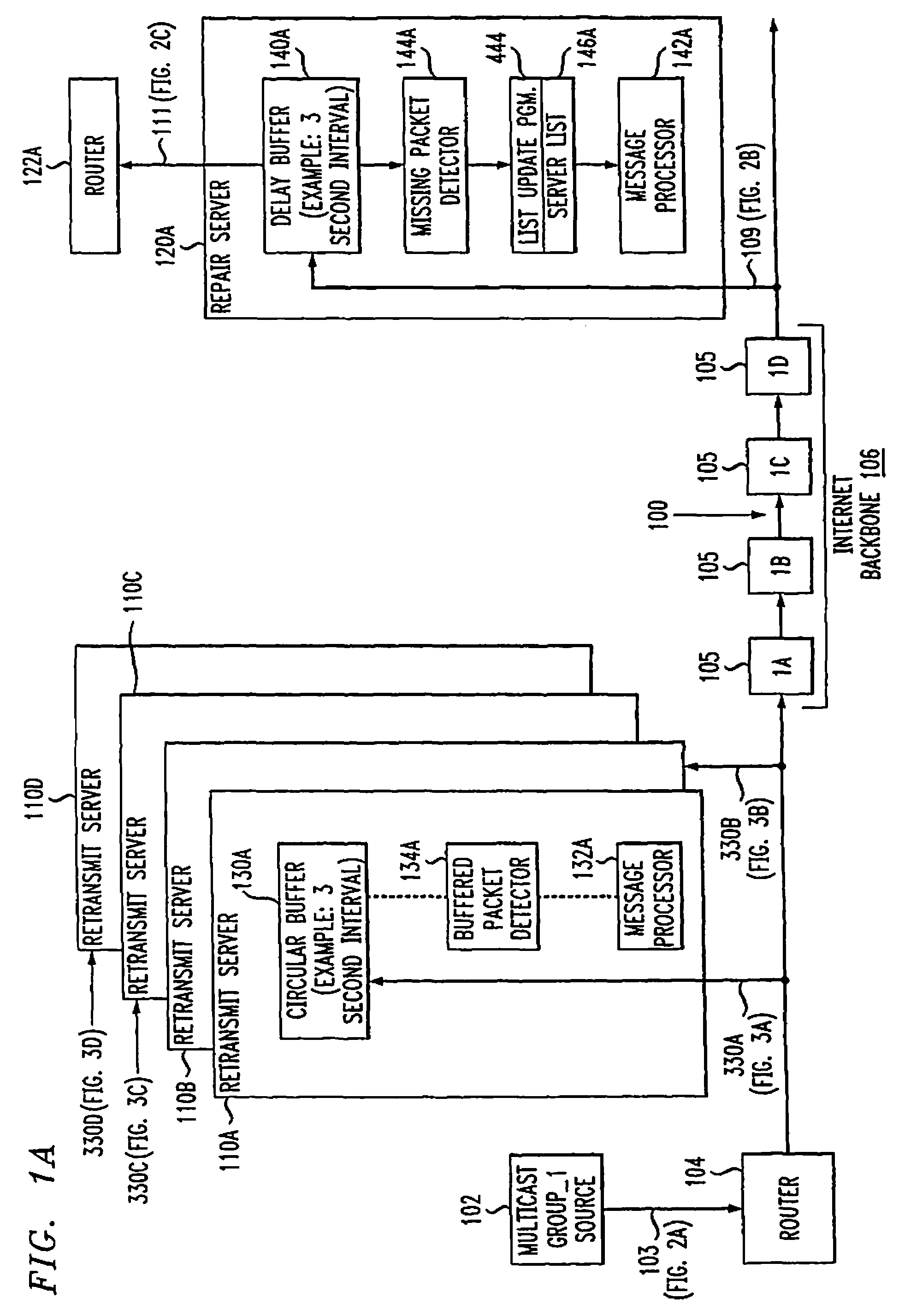
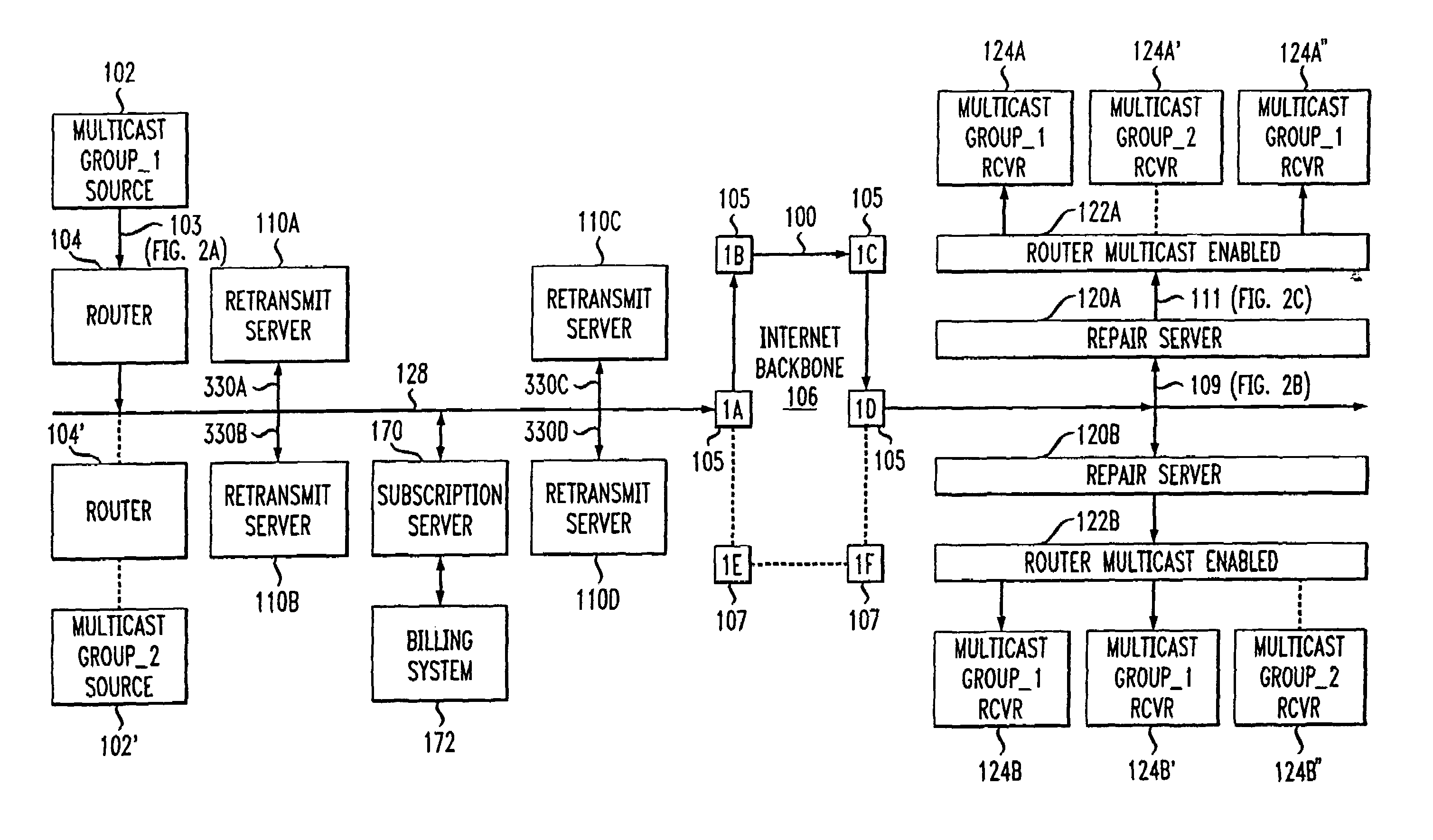
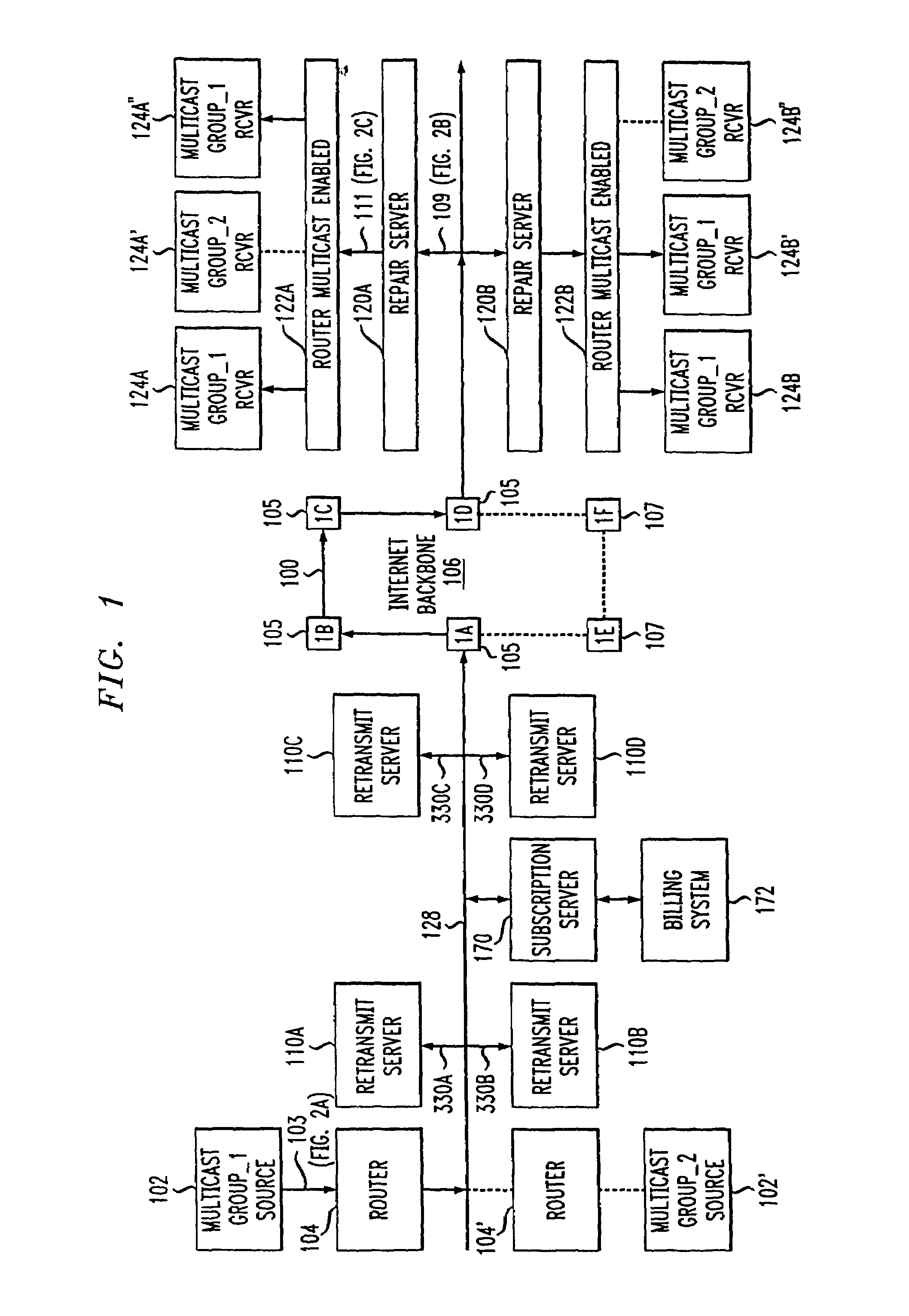
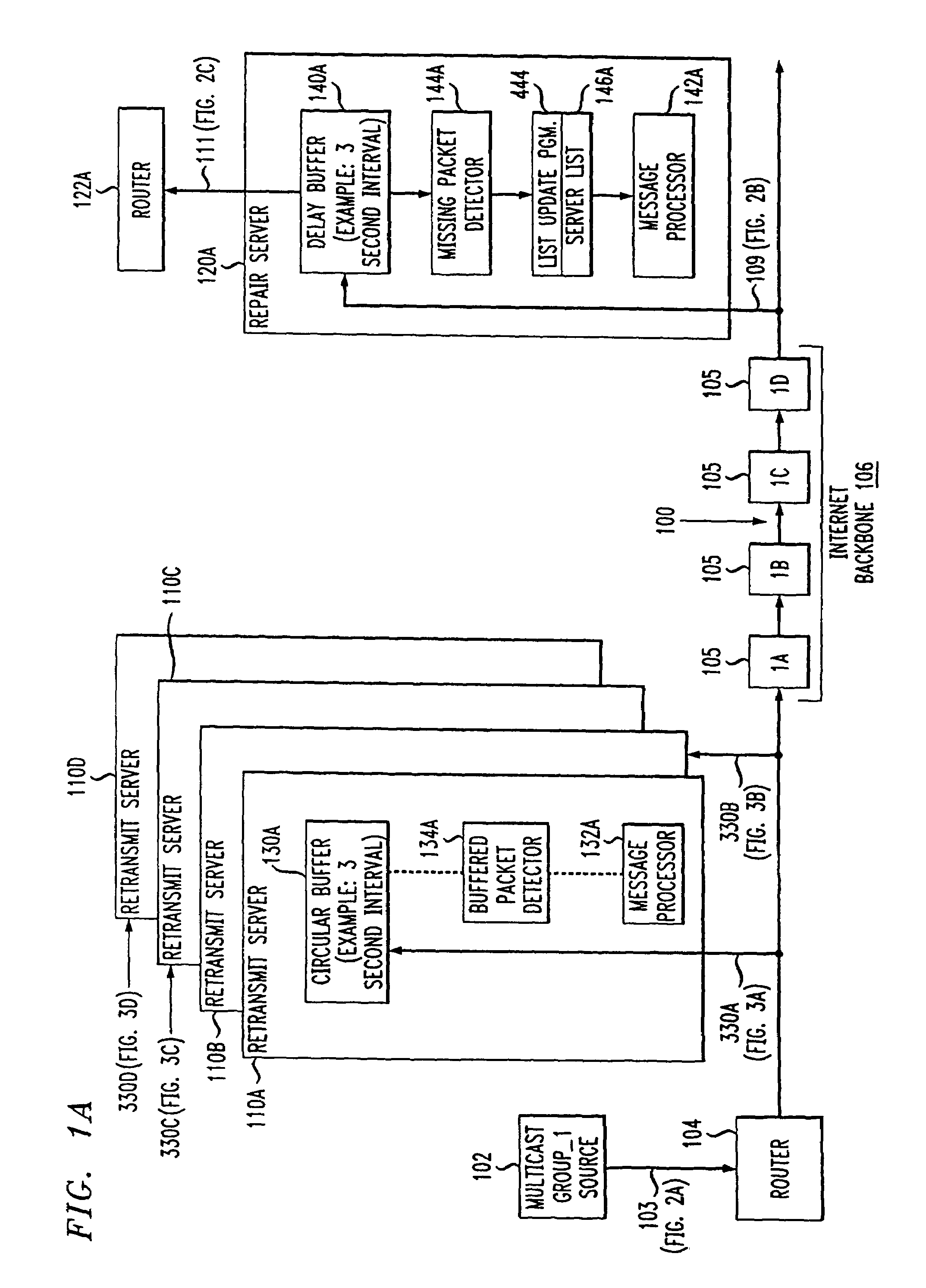
Network-based service for the repair of IP multicast sessions
InactiveUS7620847B1Improve received signal qualityQuality improvementSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork packetIP multicast
A system and method are disclosed for the repair of IP multicast sessions. A repair server polls multiple transmit servers to accumulate as many of the packets missing from the multicast session as possible. A network includes a source of multicast packets in a multicast session and a plurality of multicast recipients in that session. A repair server in the network provides the packets it receives to the recipients. The repair server includes a missing packet detector. There is a plurality of retransmit servers in the network buffering portions of the packets they respectively receive during the session. The repair server maintains an ordered list of the retransmit servers that are most likely to have buffered copies of packets missing from the session. When the repair server detects that there are packets missing from the session it has received, it uses the ordered list to sequentially request the missing packets from respective ones of the plurality of retransmit servers.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
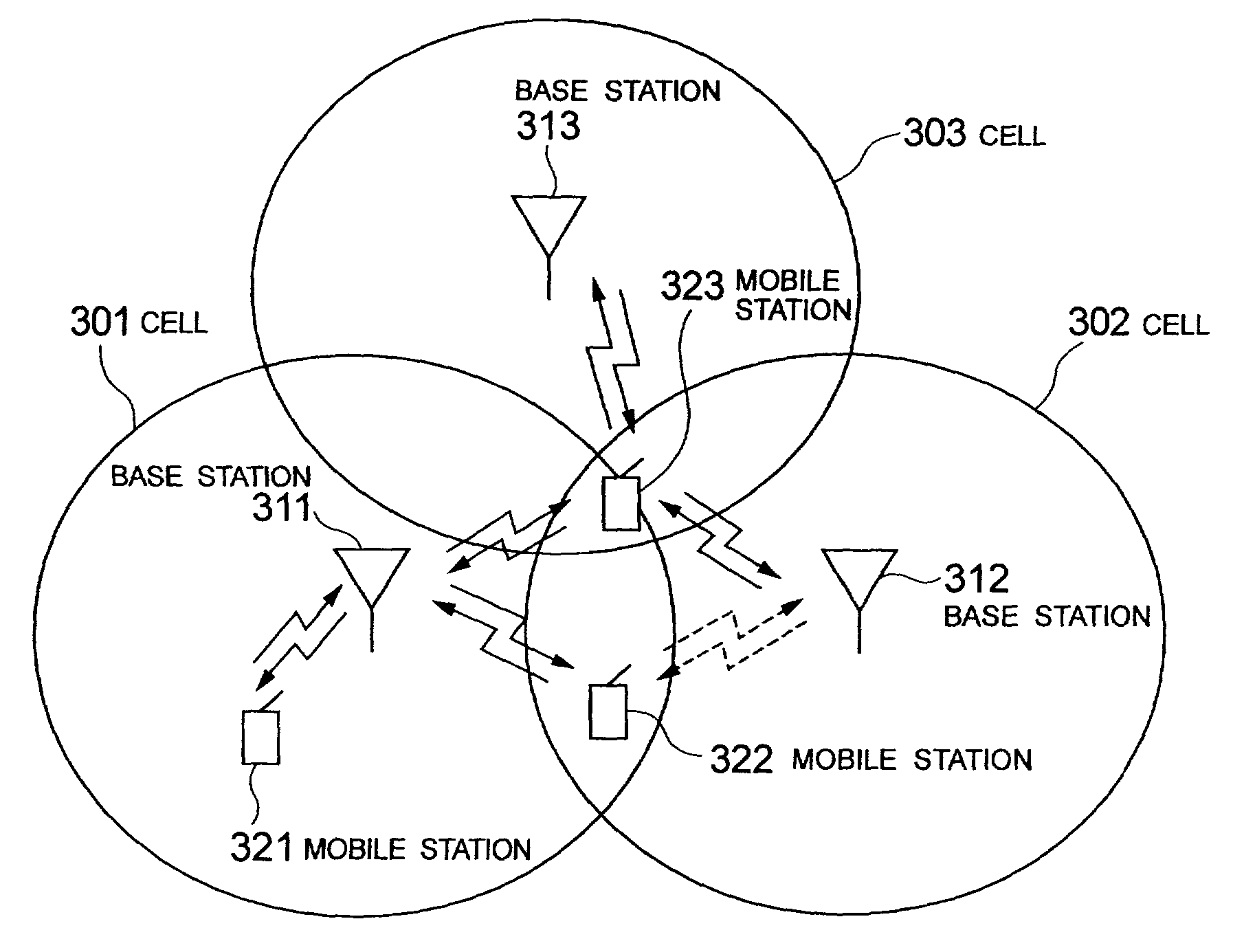
Mobile communication control method and system and mobile station thereof
InactiveUS7031712B2Increase capacityImprove received signal qualityPower managementSite diversitySignal qualityTransmitted power
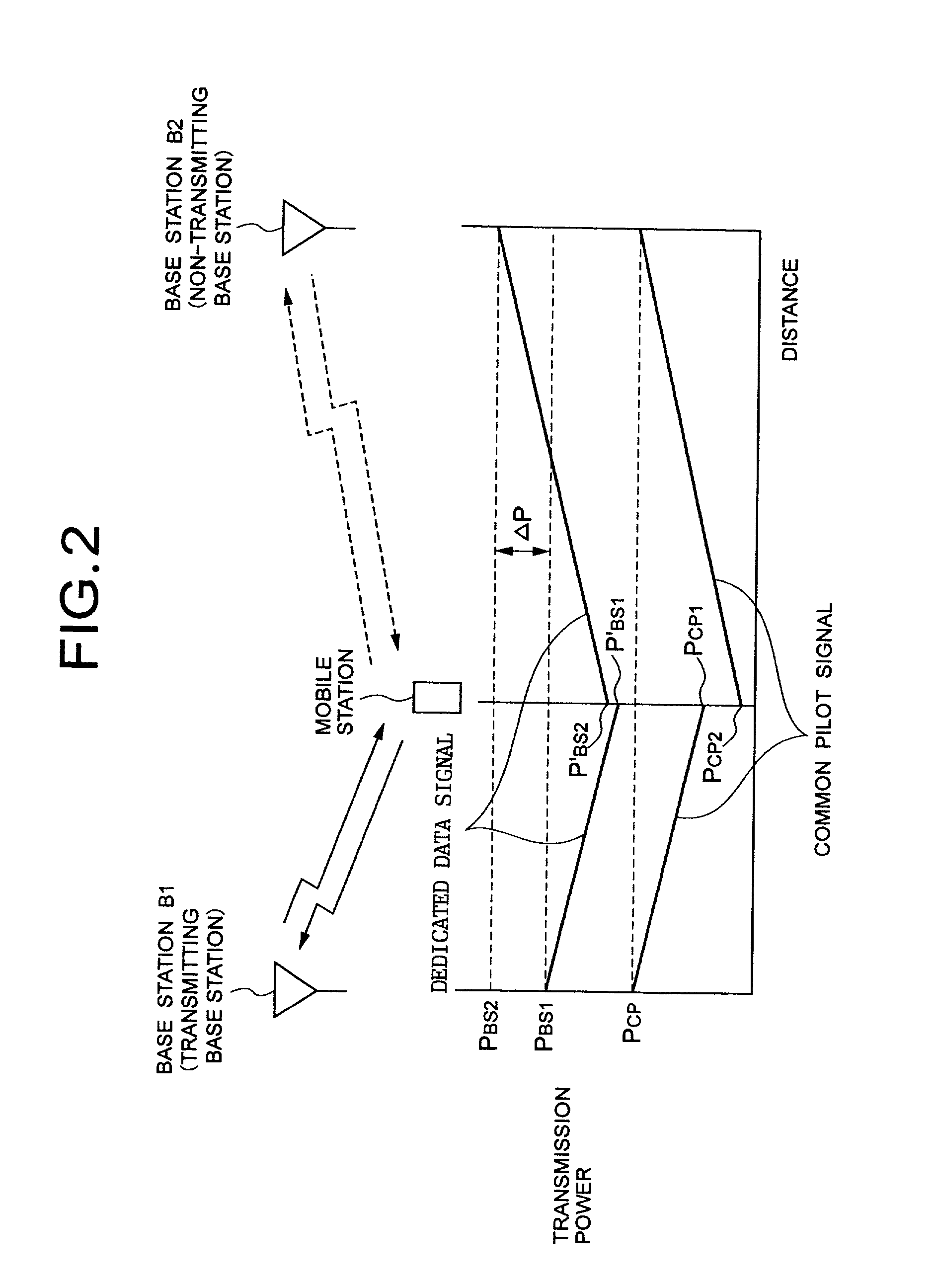
In case of making site selection diversity transmit power control, all handover base stations are enabled for transmission depending on a state of the transmission power value of a dedicated data signal from the base stations, thereby preventing a trafic capacity from decreasing due to an increase in the transmission power of a dedicated control signal at a non-transmitting base station, or a received signal quality from degrading at a mobile station because the transmission power value of the transmitting base station reaches a maximum transmission power of base station. A mobile station measures a common pilot signal and a dedicated control signal transmitted from each handover base station by means of a receiving monitor, estimates the transmission power value of the dedicated control signal at each handover base station from a difference thereof, and estimates a difference in the transmission power value of the dedicated control signal between the handover base stations. In the case where this difference is greater than or equal to a predetermined threshold value, a transmitting base station designating section designates all of the handover base stations to be enabled for transmission.
Owner:NEC CORP
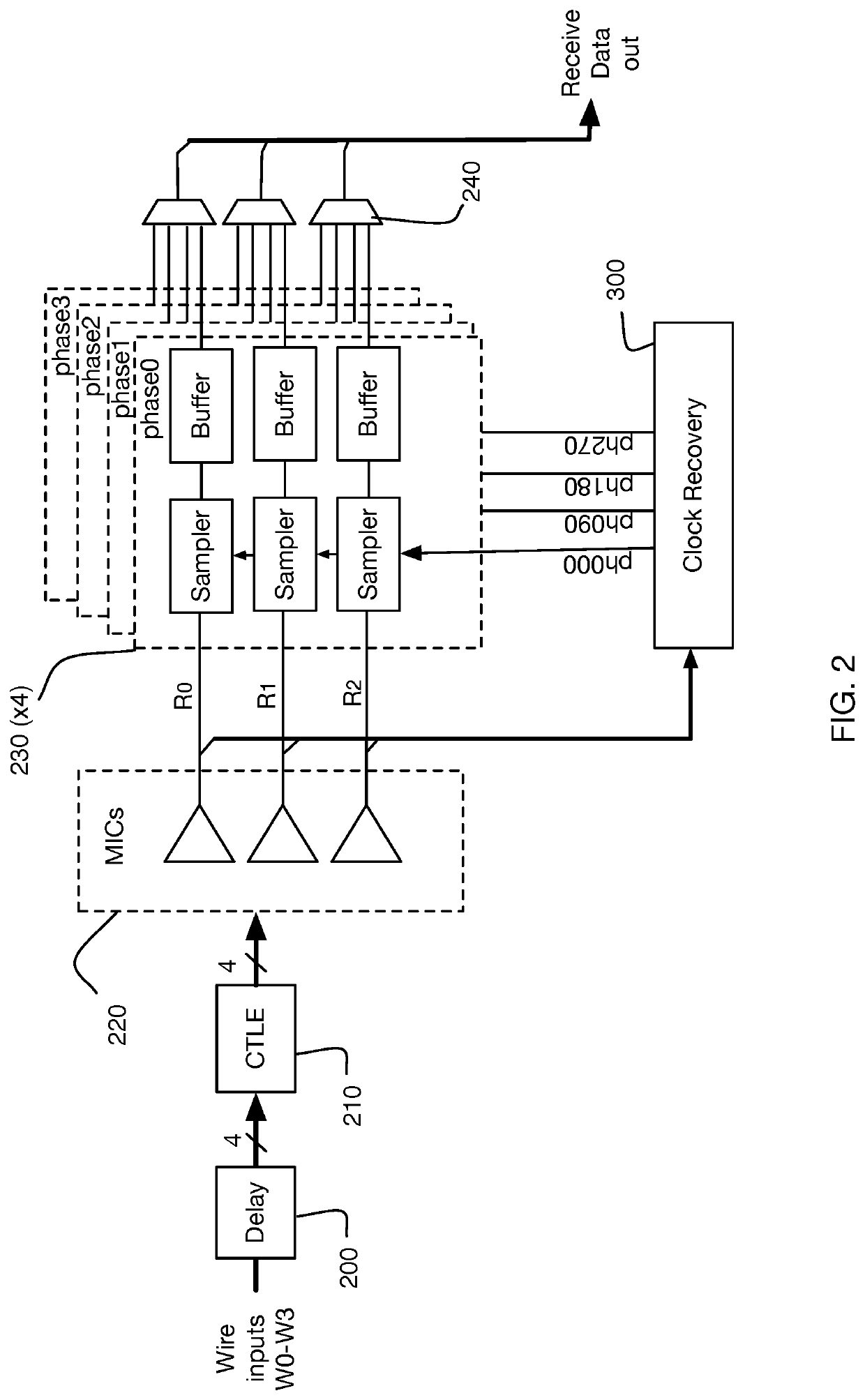
Method for measuring and correcting multi-wire skew
ActiveUS20200313841A1Reliable detectionAccurate interpretationChannel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation error correctionData signalSkew
Generating, during a first and second signaling interval, an aggregated data signal by forming a linear combination of wire signals received in parallel from wires of a multi-wire bus, wherein at least some of the wire signals undergo a signal level transition during the first and second signaling interval; measuring a signal skew characteristic of the aggregated data signal; and, generating wire-specific skew offset metrics, each wire-specific skew offset metric based on the signal skew characteristic.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
Network-based service for the repair of IP multicast sessions
InactiveUS7590889B1Improve reliabilityEnhanced reliability streamSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork packetIP multicast
A system and method are disclosed for the repair of IP multicast sessions. A repair server polls multiple transmit servers to accumulate as many of the packets missing from the multicast session as possible. A network includes a source of multicast packets in a multicast session and a plurality of multicast recipients in that session. A repair server in the network provides the packets it receives to the recipients. The repair server includes a missing packet detector. There is a plurality of retransmit servers in the network buffering portions of the packets they respectively receive during the session. The repair server maintains an ordered list of the retransmit servers that are most likely to have buffered copies of packets missing from the session. When the repair server detects that there are packets missing from the session it has received, it uses the ordered list to sequentially request the missing packets from respective ones of the plurality of retransmit servers.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
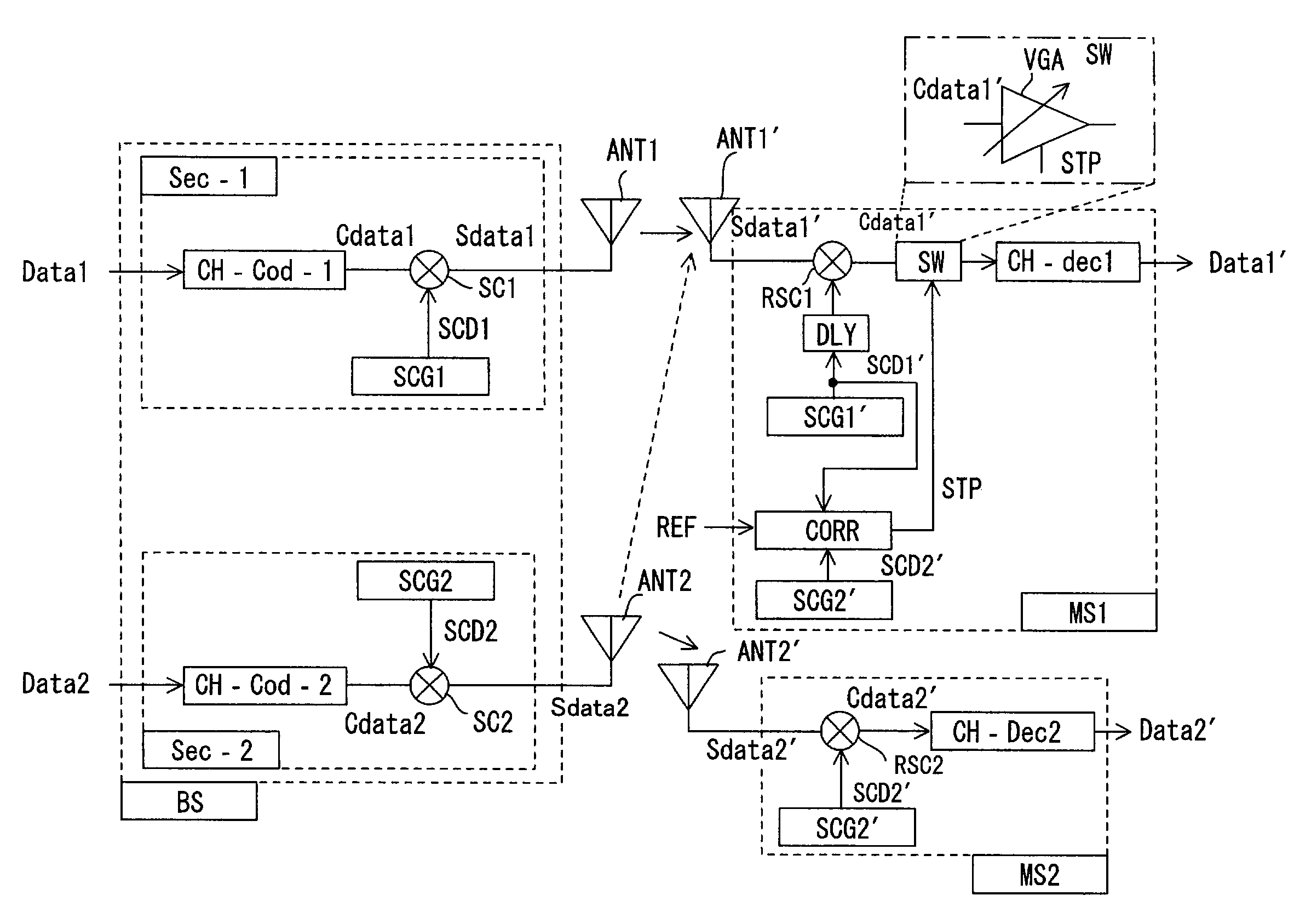
Code division multiple access signal receiving apparatus
InactiveUS7020183B2Improve received signal qualityIncrease in interference noiseSpatial transmit diversityCode conversionDiscriminatorTime division multiple access
In a code division multiple access signal receiving apparatus for demodulating transmit data by subjecting a receive signal to despread processing using a code sequence identical with a spreading-code sequence on a transmitting side, a cross-correlation detector calculates a cross-correlation value, on a per-symbol basis, between a spreading-code sequence for spread-spectrum modulating local-station-addressed transmit data and a spreading-code sequence for spread-spectrum modulating other-station-addressed transmit data; a discriminator discriminates whether the calculated cross-correlation value has exceeded a threshold value; and a switch halts input, to a decoder, of a portion of the receive signal that corresponds to the full interval or partial interval of a symbol where the cross-correlation value exceeds the threshold value.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Folding directional antenna
InactiveUS7046202B2Improve received signal qualityIncrease power levelSimultaneous aerial operationsPivotable antennasDirectional antennaDielectric substrate
An antenna array includes a dielectric substrate comprising an integral center hub including a pivotal center section therein, and a pivotal wings extending radially from the integral center hub. An active antenna element is on the pivotal center section of the integral center hub, and passive antenna elements are on the pivotal wings. The active antenna element and the passive antenna elements are pivotal between a stored position and an operational position. The active antenna element and the passive antenna elements are substantially planar when in the stored position, and are substantially perpendicular to the integral center hub when in the operational position.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
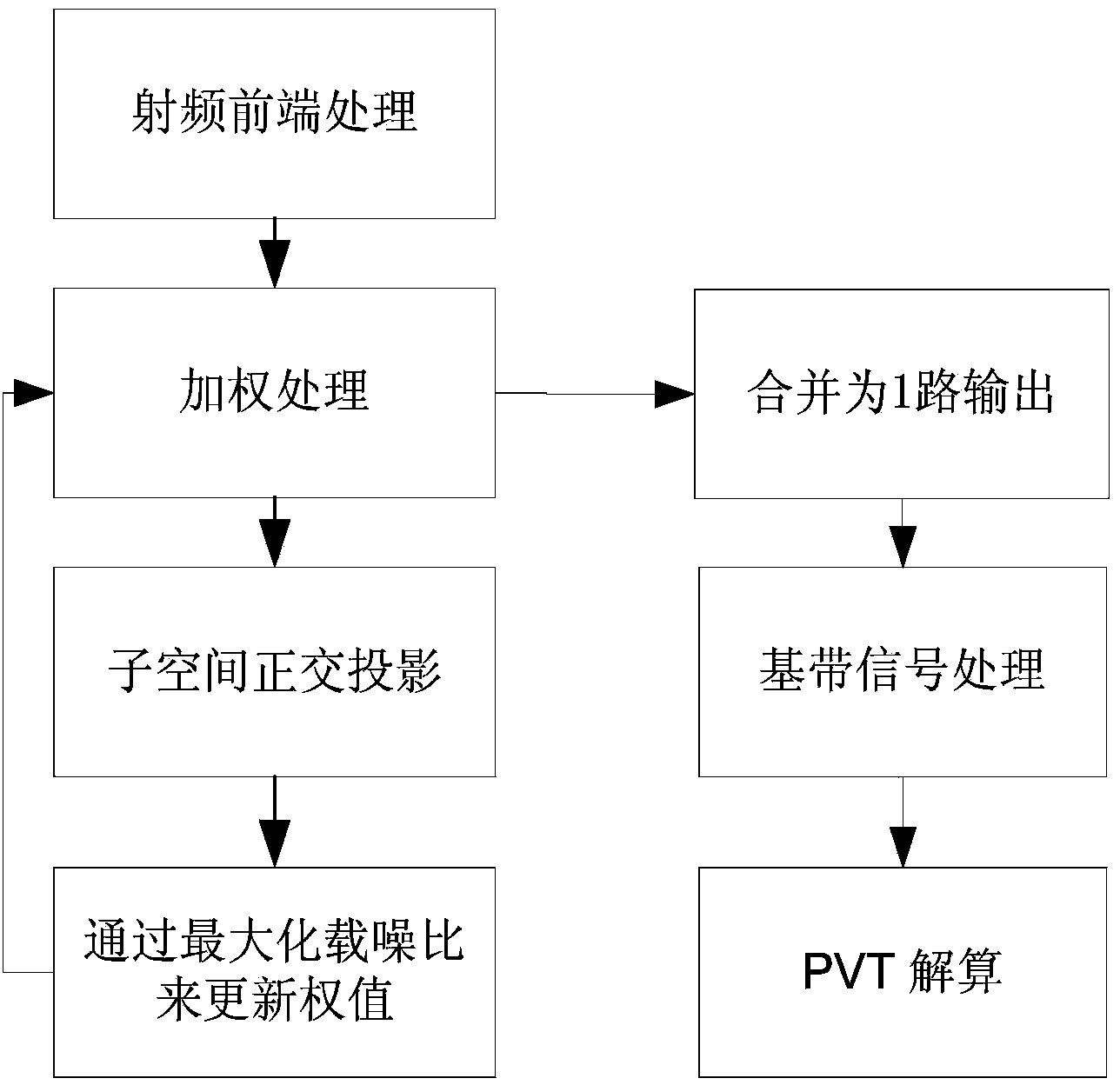
Space-time adaptive anti-interference method for satellite navigation receiver
InactiveCN104345321AEffective filteringImprove received signal qualitySatellite radio beaconingFeature vectorDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of space-time adaptive processing and particularly relates to a space-time adaptive anti-interference method for a satellite navigation receiver. The space-time adaptive anti-interference method comprises the following specific steps of performing eigenvalue decomposition on a covariance matrix Rxx of a signal received by an antenna array of the satellite navigation receiver at n time; combining feature vectors corresponding to minimum M-L eigenvalues of the Rxx into a signal subspace PG, and obtaining a projection ysub of a signal X(n) received by the antenna array of the satellite navigation receiver at the n time, in the signal subspace PG; obtaining an expression of the carrier-to-noise ratio (C / N0) of the signal after an output signal subjected to the space-time adaptive processing at the n time is correlated, and establishing an optimization model about a weight vector by taking the carrier-to-noise ratio (C / N0) of the signal after maximization correlation as an object; solving the optimization model about the weight vector to obtain an optimal weight vector w0; performing weighting processing on the projection ysub of the signal X(n) received by the antenna array of the satellite navigation receiver at the n time, in the signal subspace PG to obtain an output signal Y(n) subjected to the space-time adaptive processing at the n time.
Owner:西安烽火电子科技有限责任公司
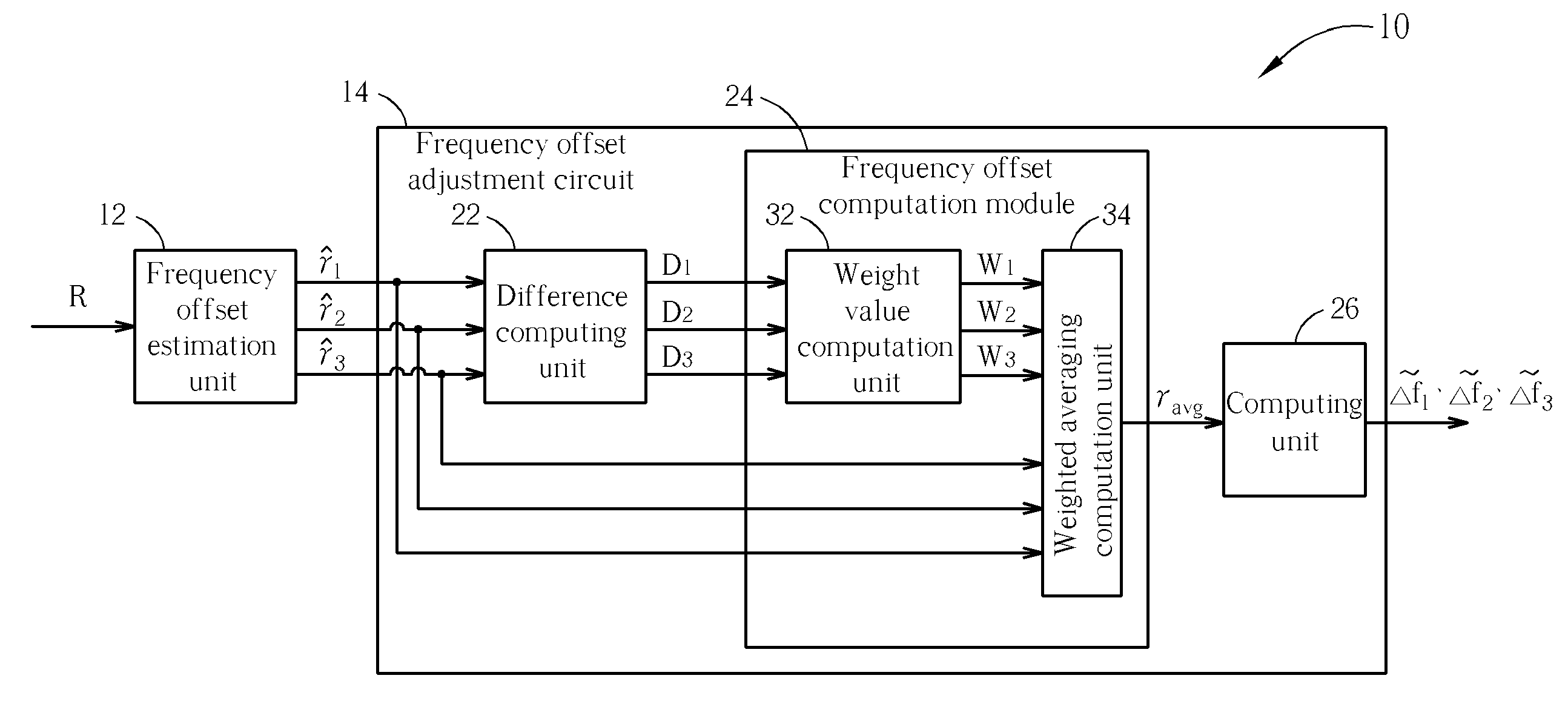
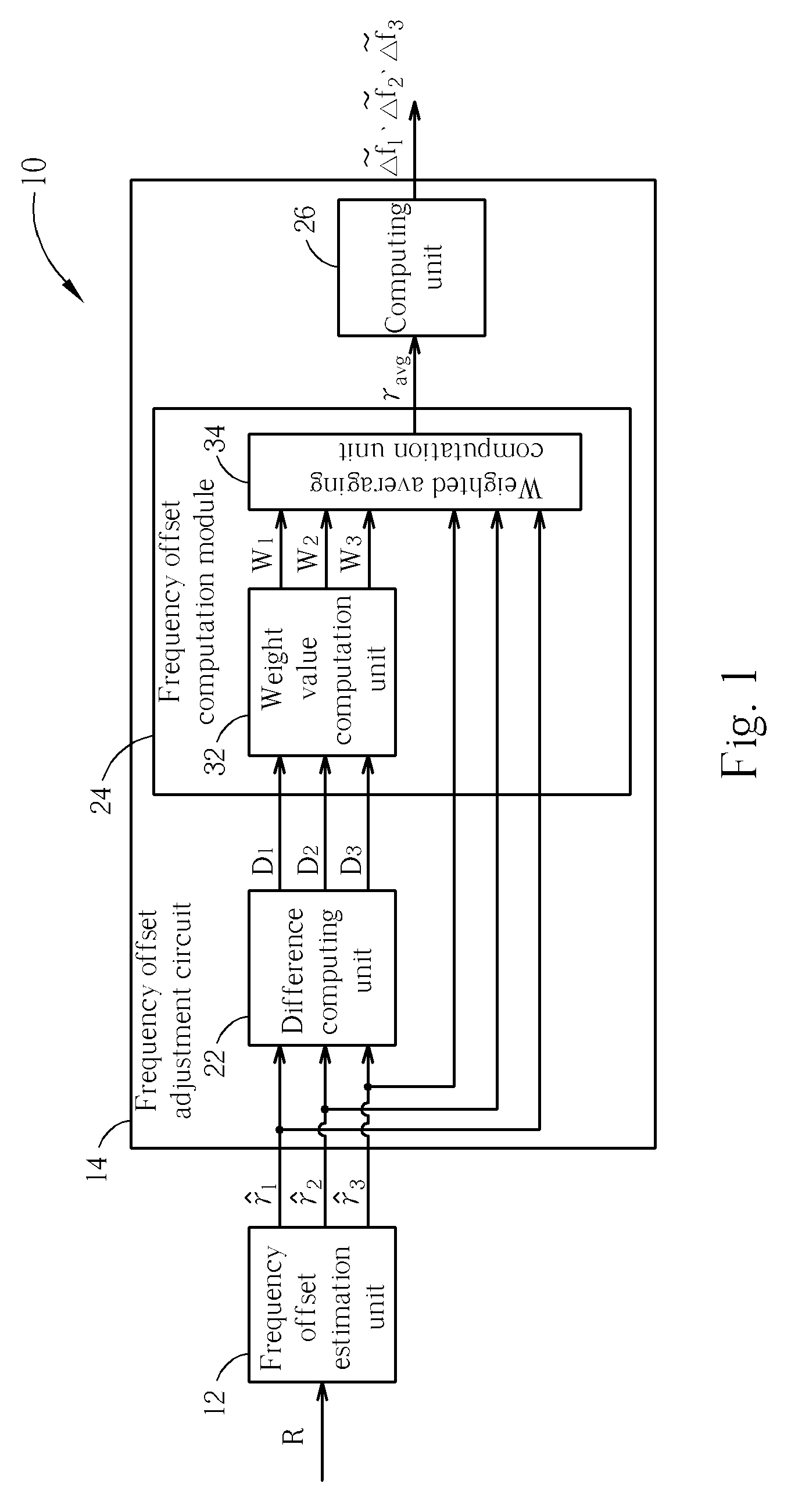
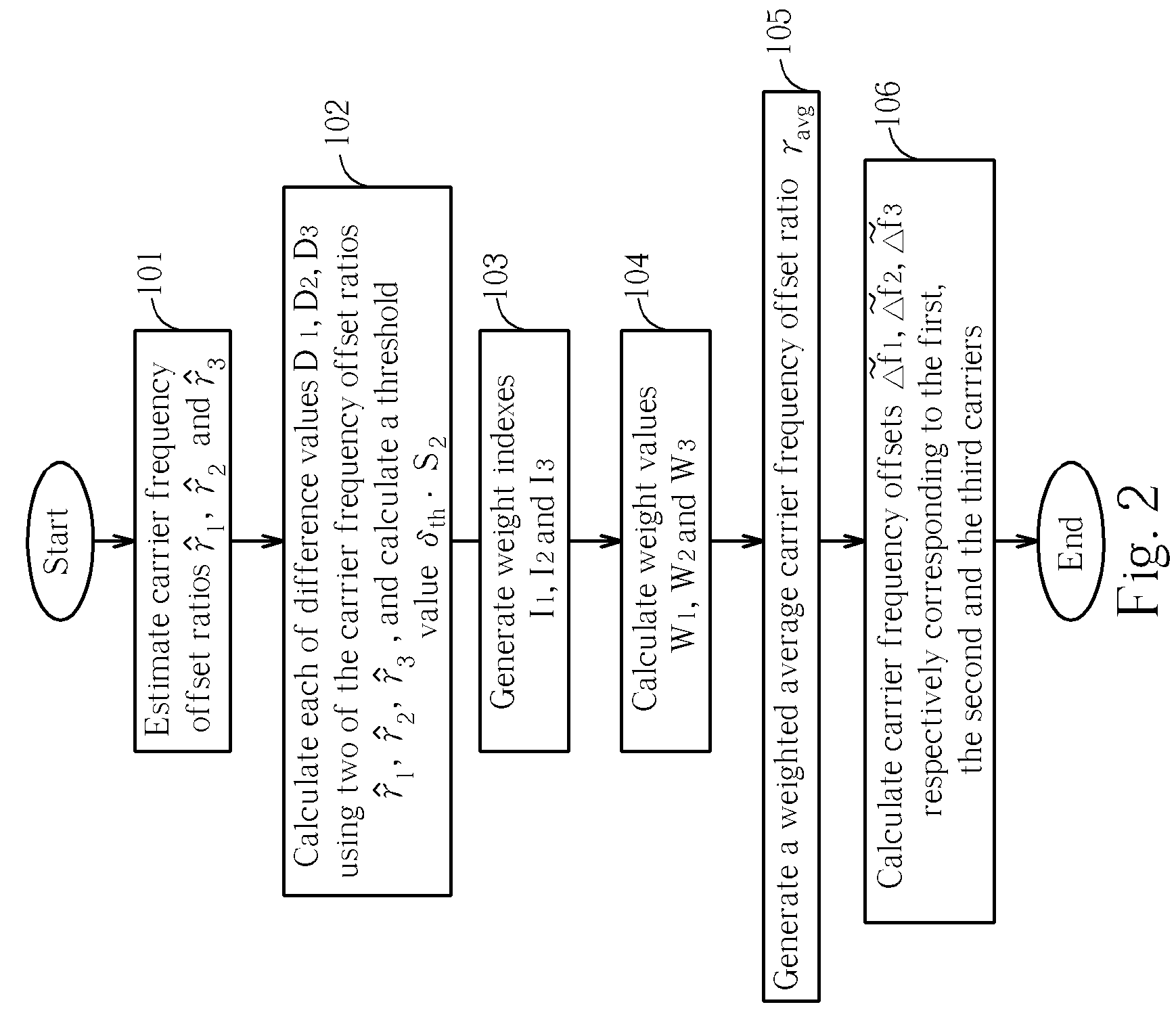
Band averaging circuit and related method for carrier frequency offset estimation in a multi-band multi-carrier communication system
ActiveUS20060067430A1Reduce distractionsImprove received signal qualityModulated-carrier systemsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationMulti bandCommunications system
A band averaging circuit and a related method for estimating a carrier frequency offset are applied in a multi-band multi-carrier communication system. A packet of the multi-band multi-carrier communication system is transmitted via a plurality of carriers. The band averaging circuit includes a frequency offset estimation unit for generating a plurality of carrier frequency offset ratios corresponding to the carriers according to a received packet; and a frequency offset adjustment circuit coupled to the frequency offset estimation unit for calculating a weighted average carrier frequency offset ratio according to carrier frequency offset ratios and comparison results of the carrier frequency offset ratios, and also for calculating a carrier frequency offset of each carrier according to the weighted average carrier frequency offset ratio and a center frequency of the carrier.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Interference cancellation under non-stationary conditions
InactiveUS8675796B2Improve received signal qualitySynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsStationary conditionsFrequency offset
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Iterative adaptive channel denoising method and iterative adaptive channel denoising device
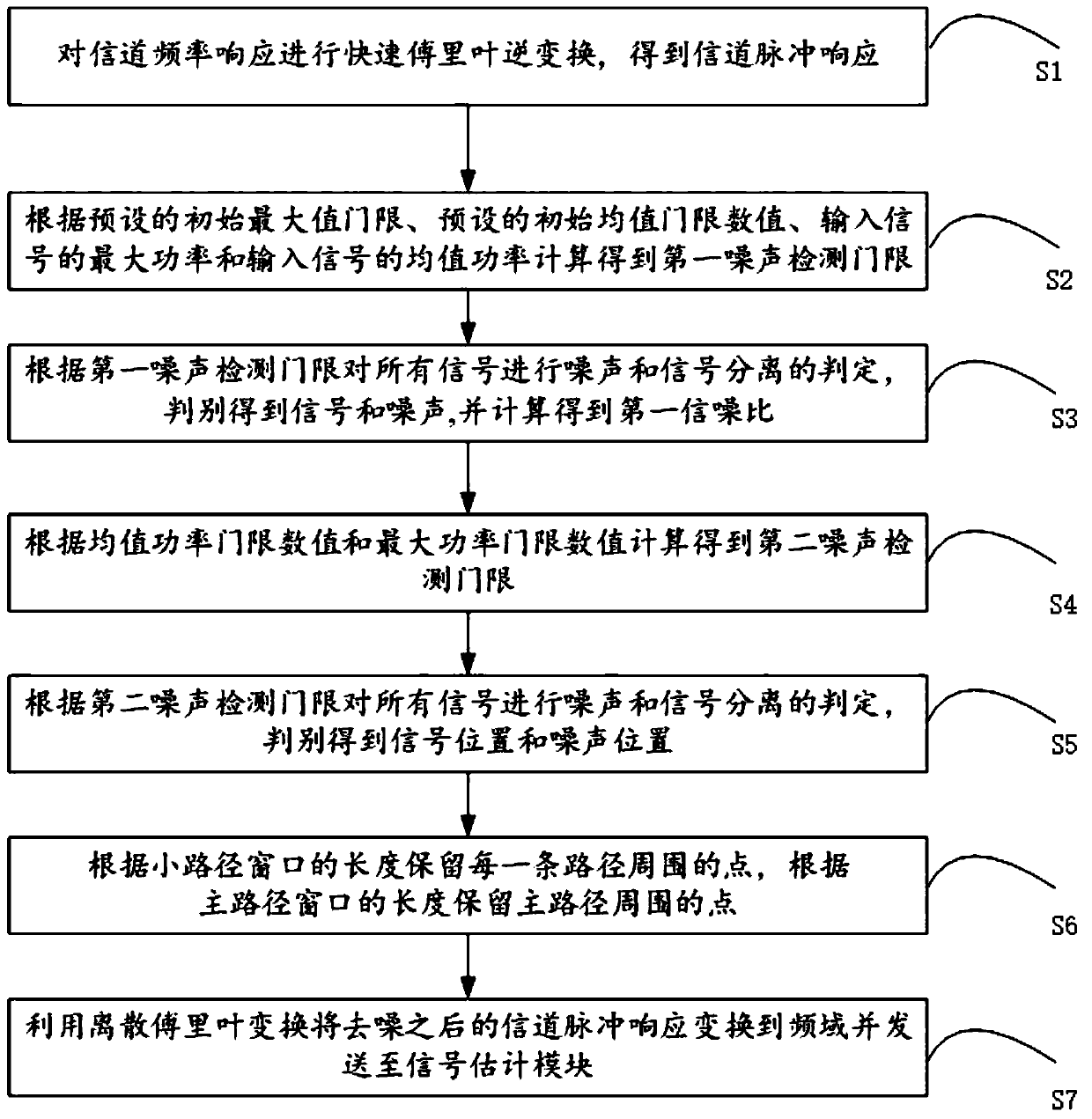
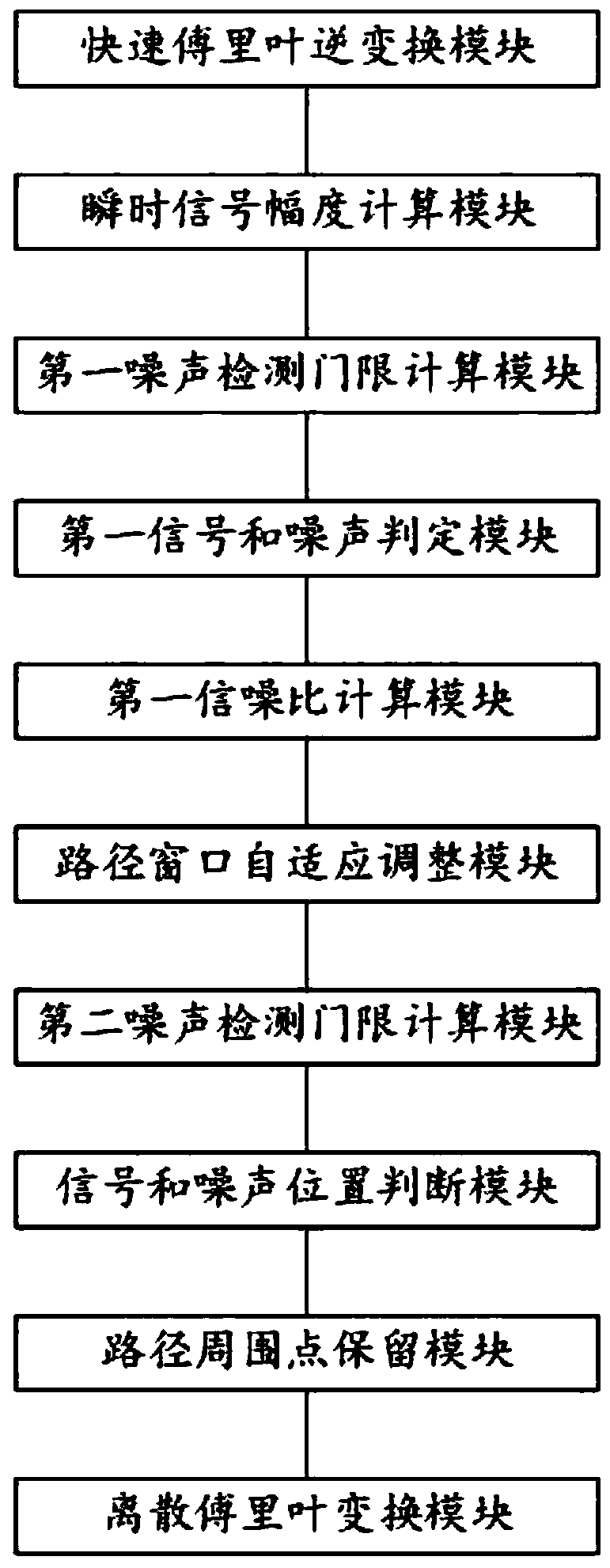
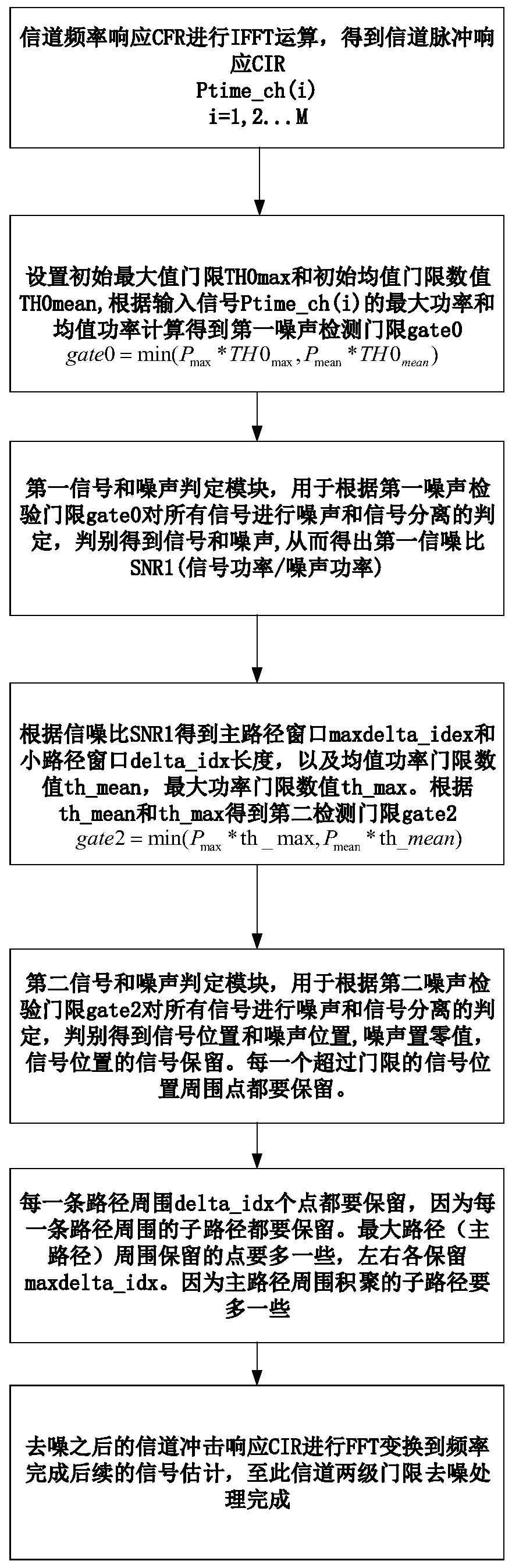
ActiveCN110445733AEfficient removalImprove signal qualityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksPattern recognitionSignal quality
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, in particular to an iterative adaptive channel denoising method and an iterative adaptive channel denoising device. The method comprises the following steps: S1, performing inverse fast Fourier transform on channel frequency response to obtain channel impulse response; S2, calculating to obtain a first noise detection threshold; S3, calculating to obtain a first signal-to-noise ratio; S4, calculating to obtain a second noise detection threshold; S5, performing noise and signal separation judgment on all the signals according to a second noise detection threshold; S6, reserving points around each path according to the length of the small path window, and reserving points around the main path according to the length of the main path window; and S7, transforming the denoised channel impulse response to a frequency domain by using discrete Fourier transform and sending the denoised channel impulse response to a signalestimation module. According to the invention, denoising processing is carried out on the channel by using different denoising thresholds according to different signal-to-noise ratios. Therefore, thenoise can be effectively removed and the quality of the received signal is greatly improved.
Owner:西安宇飞电子技术有限公司
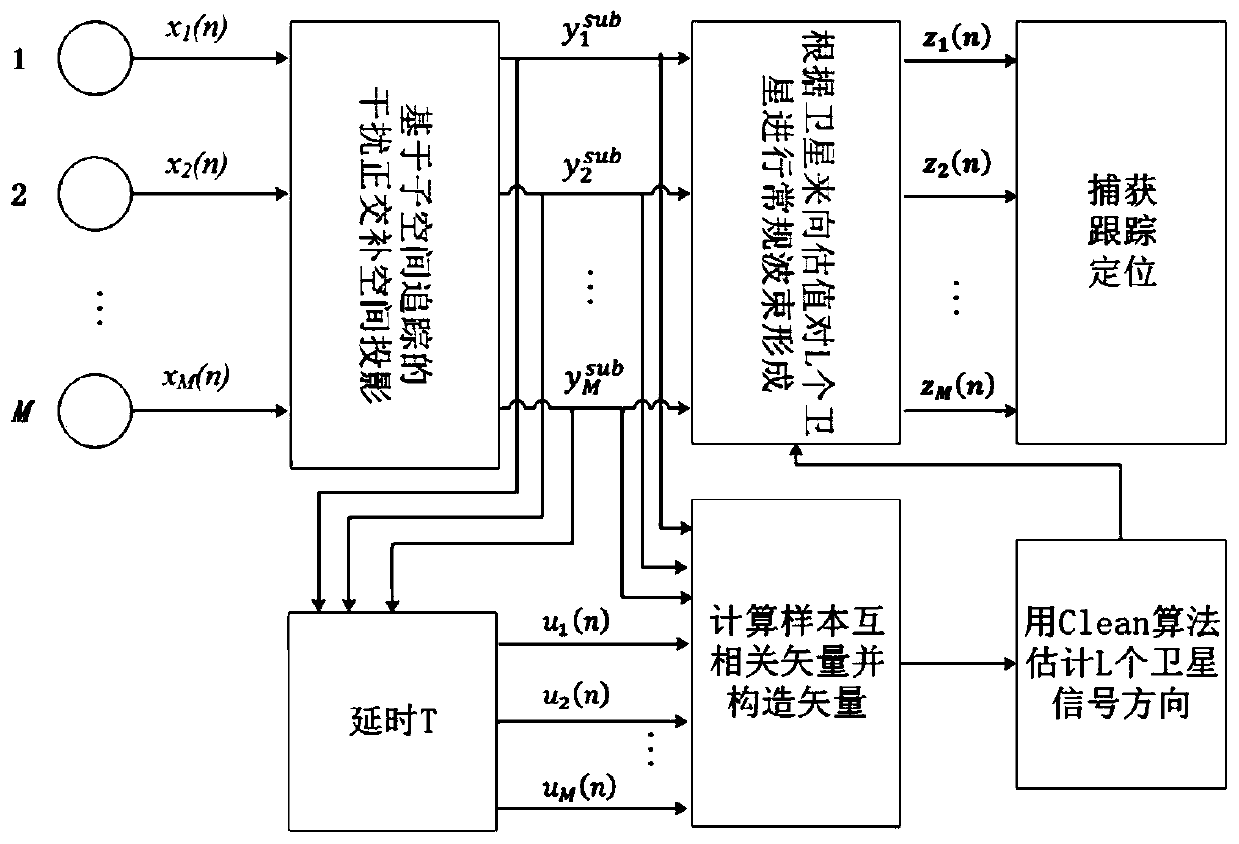
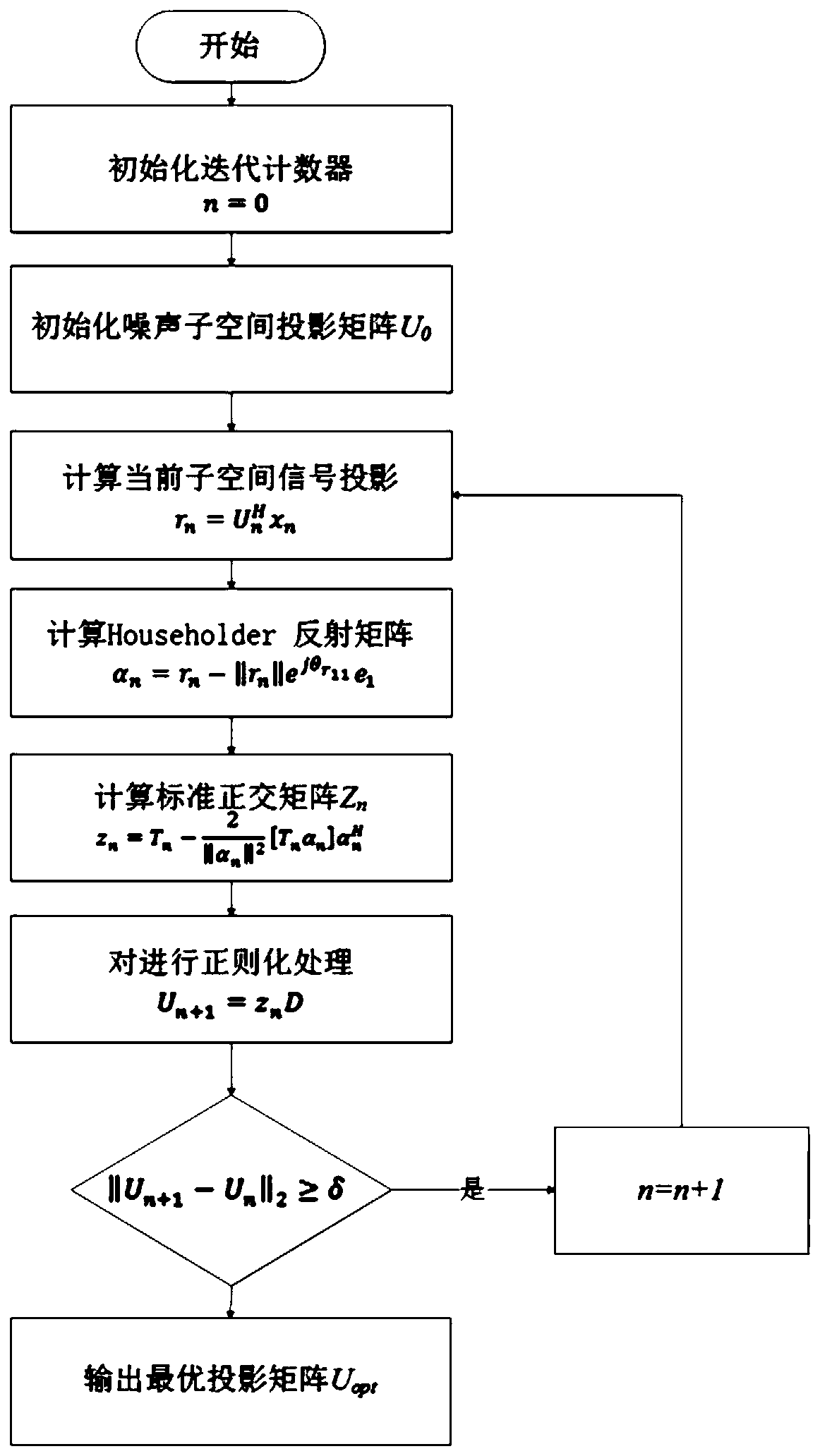
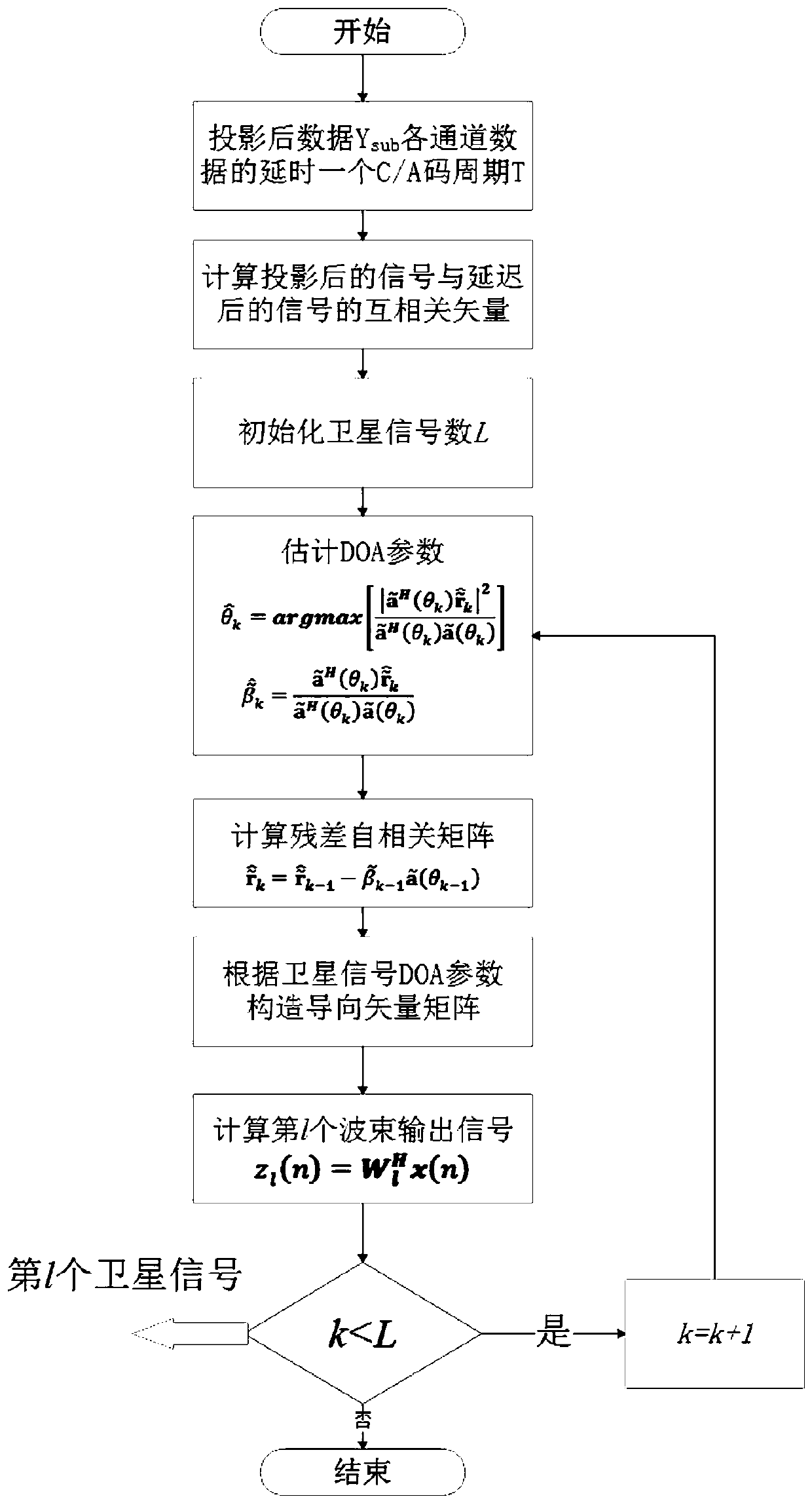
GNSS receiver multi-beam pointing anti-interference method based on subspace tracking
ActiveCN110361760AImprove SINRSuppression strong interference signalSatellite radio beaconingAdaptive algorithmMeteorology
The invention discloses a GNSS receiver multi-beam pointing anti-interference method based on subspace tracking. The noise subspace tracking technique is applied to eliminate the high interference signal, and then the correlation between the multi-channel periodically delayed signal and the satellite navigation signal is applied and the DOA estimation method based on the Clean idea is applied to estimate the steering vector of each satellite navigation signal. Finally, the steering vector is utilized to construct the beamforming weight vector matrix for each satellite to enhance the directionof satellite signal. Thee transmitted navigation symbol and the satellite orientation do not need to be known and the method is a blind adaptive algorithm which can effectively improve the signal-to-interference-noise ratio of the navigation signal while suppressing the complex interference signal and can improve the receiving ability of the system to the satellite navigation signal under the complex environment to a certain extent.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
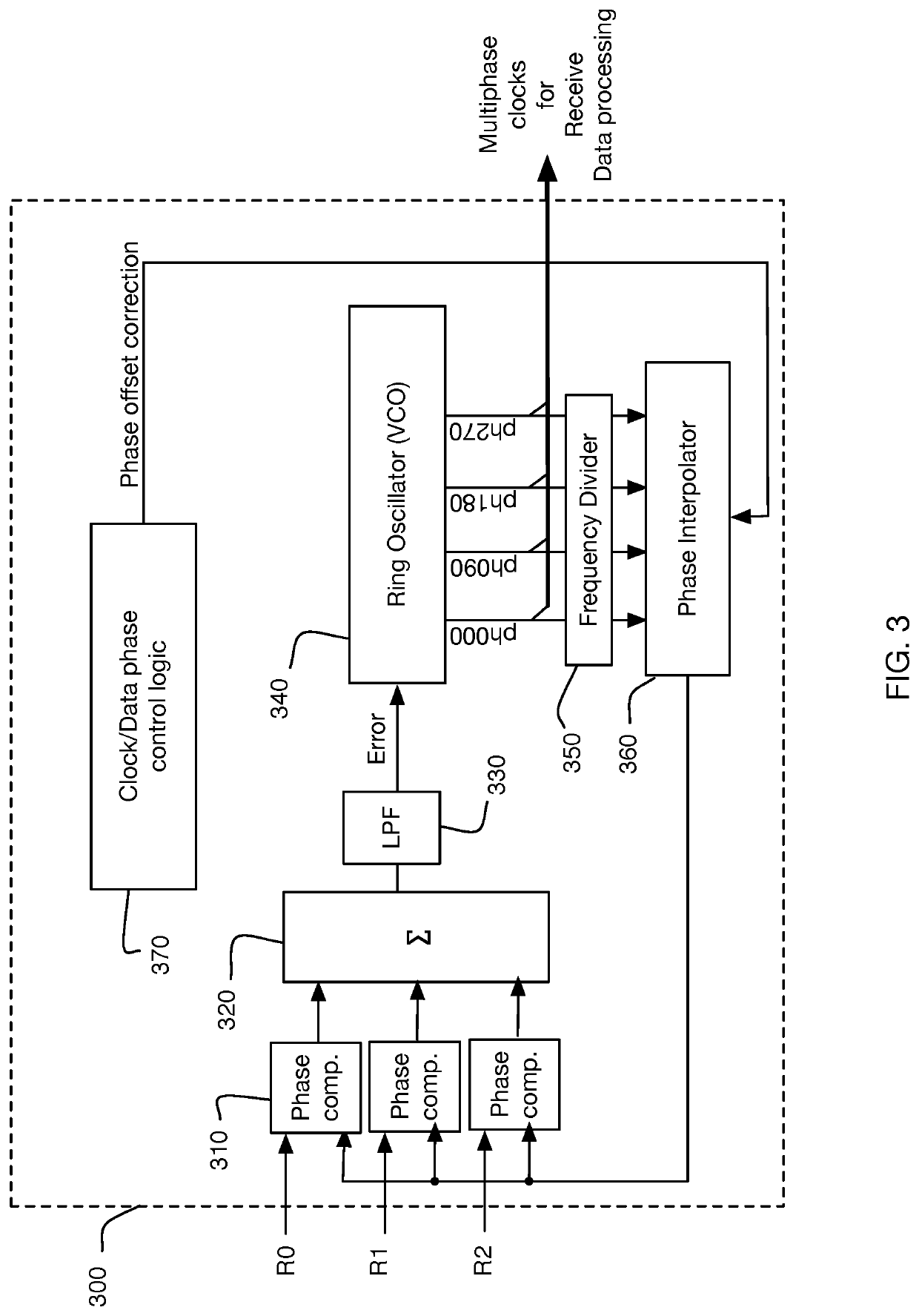
Method for Measuring and Correcting Multi-Wire Skew
ActiveUS20190013927A1Increase aggregate bandwidthReliable detectionChannel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation error correctionVIT signalsData signal
Generating, during a first and second signaling interval, an aggregated data signal by forming a linear combination of wire signals received in parallel from wires of a multi-wire bus, wherein at least some of the wire signals undergo a signal level transition during the first and second signaling interval; measuring a signal skew characteristic of the aggregated data signal; and, generating wire-specific skew offset metrics, each wire-specific skew offset metric based on the signal skew characteristic.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
Method for measuring and correcting multi-wire skew
ActiveUS10686583B2Reliable detectionAccurate interpretationChannel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation error correctionData signalSkew
Generating, during a first and second signaling interval, an aggregated data signal by forming a linear combination of wire signals received in parallel from wires of a multi-wire bus, wherein at least some of the wire signals undergo a signal level transition during the first and second signaling interval; measuring a signal skew characteristic of the aggregated data signal; and, generating wire-specific skew offset metrics, each wire-specific skew offset metric based on the signal skew characteristic.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
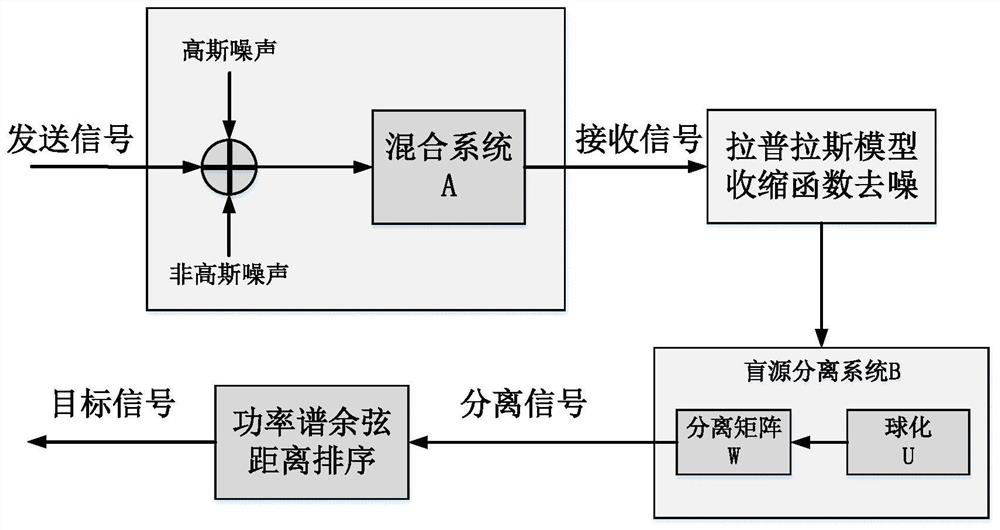
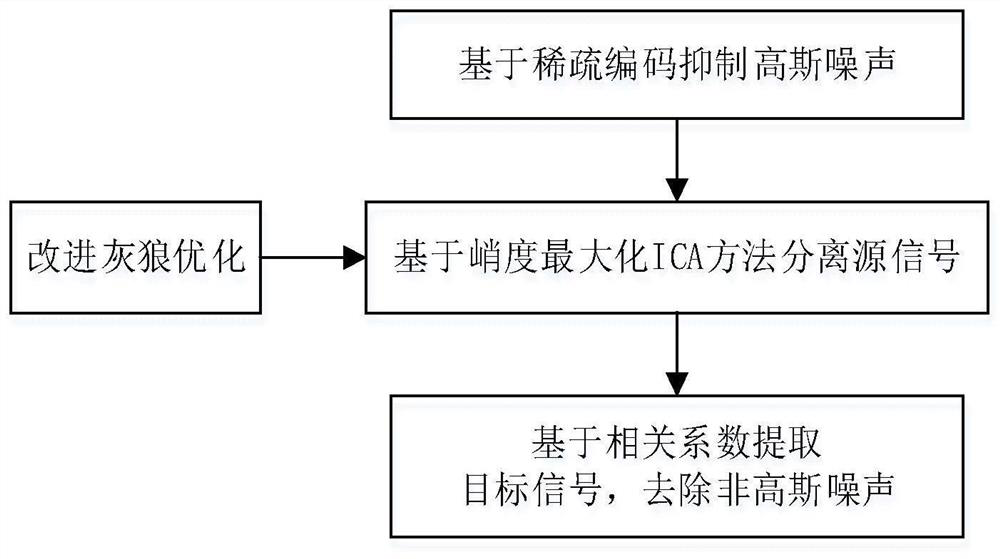
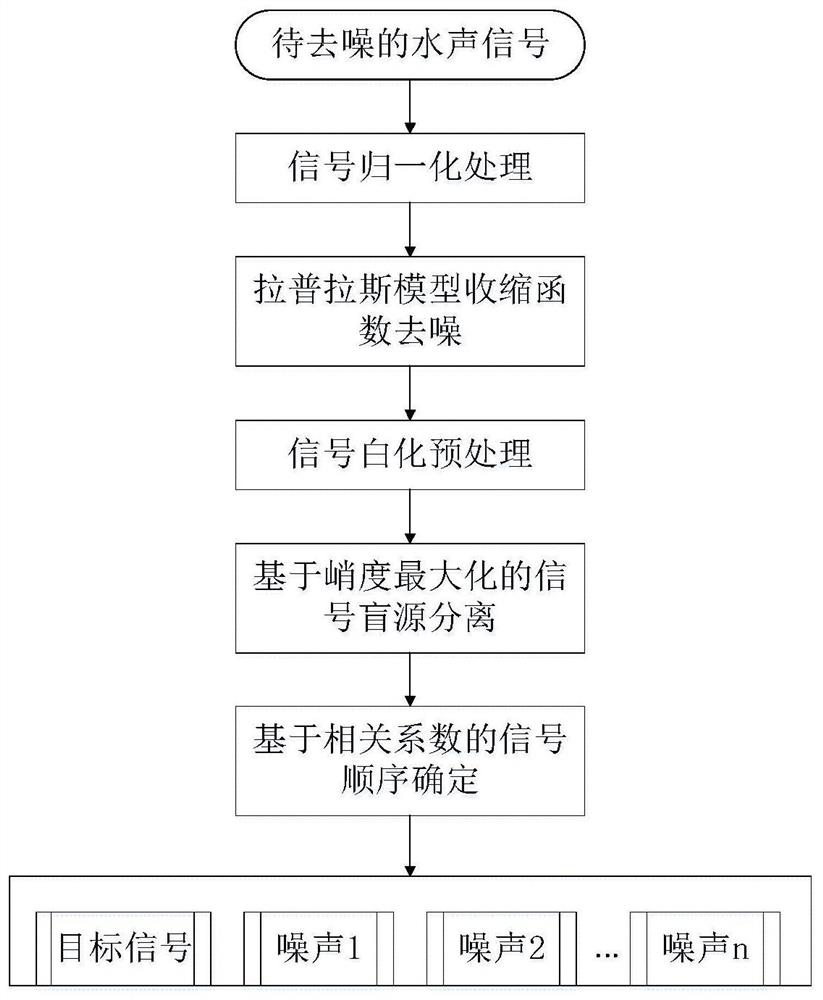
Underwater acoustic signal Gaussian/non-Gaussian noise suppression method based on blind source separation
ActiveCN112133321AImprove received signal qualityEfficient removalSpeech analysisArtificial lifeTarget signalNoise
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic signal Gaussian / non-Gaussian noise suppression method based on blind source separation. The method is used for underwater acoustic communication signal denoising. Firstly, Gaussian noise is removed in advance by adopting a sparse coding theory based on underwater acoustic signal sparse characteristics, including constructing a sparse penalty functionbased on a Laplace distribution model and solving a sparse component under the condition of maximum likelihood estimation; and then based on the non-Gaussian characteristic of the underwater acousticsignal, the non-Gaussian random noise is regarded as a source signal, and based on an improved grey wolf optimization algorithm, solving the blind source separation problem of the underwater acousticsignal; and finally, a target signal is extracted based on the correlation coefficient matrix between the separated signal and the received signal, and non-Gaussian noise is removed. According to themethod, Gaussian and non-Gaussian noise in a complex underwater acoustic environment can be effectively suppressed, and the underwater acoustic signal receiving quality is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com