Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "Stationary conditions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
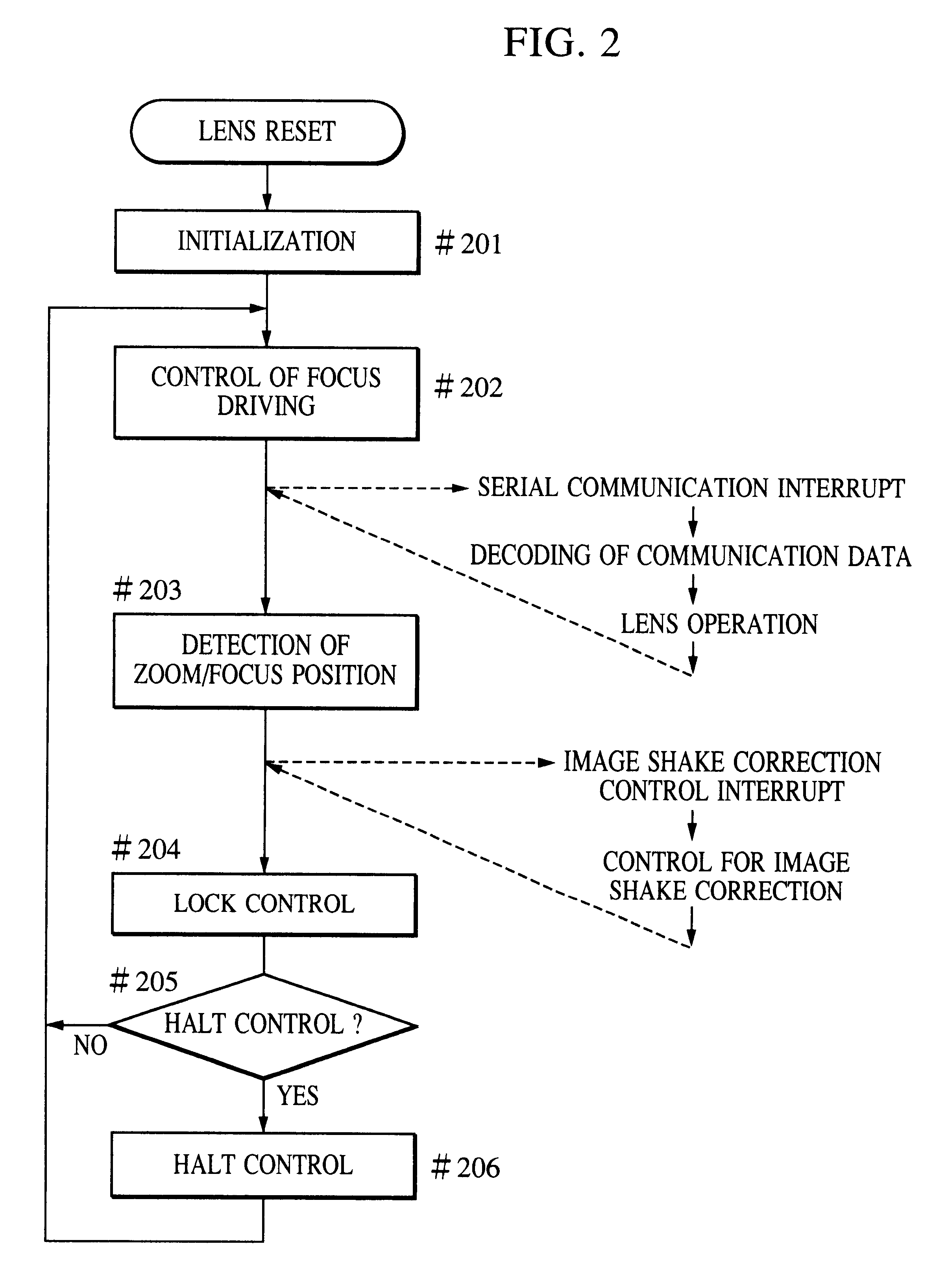
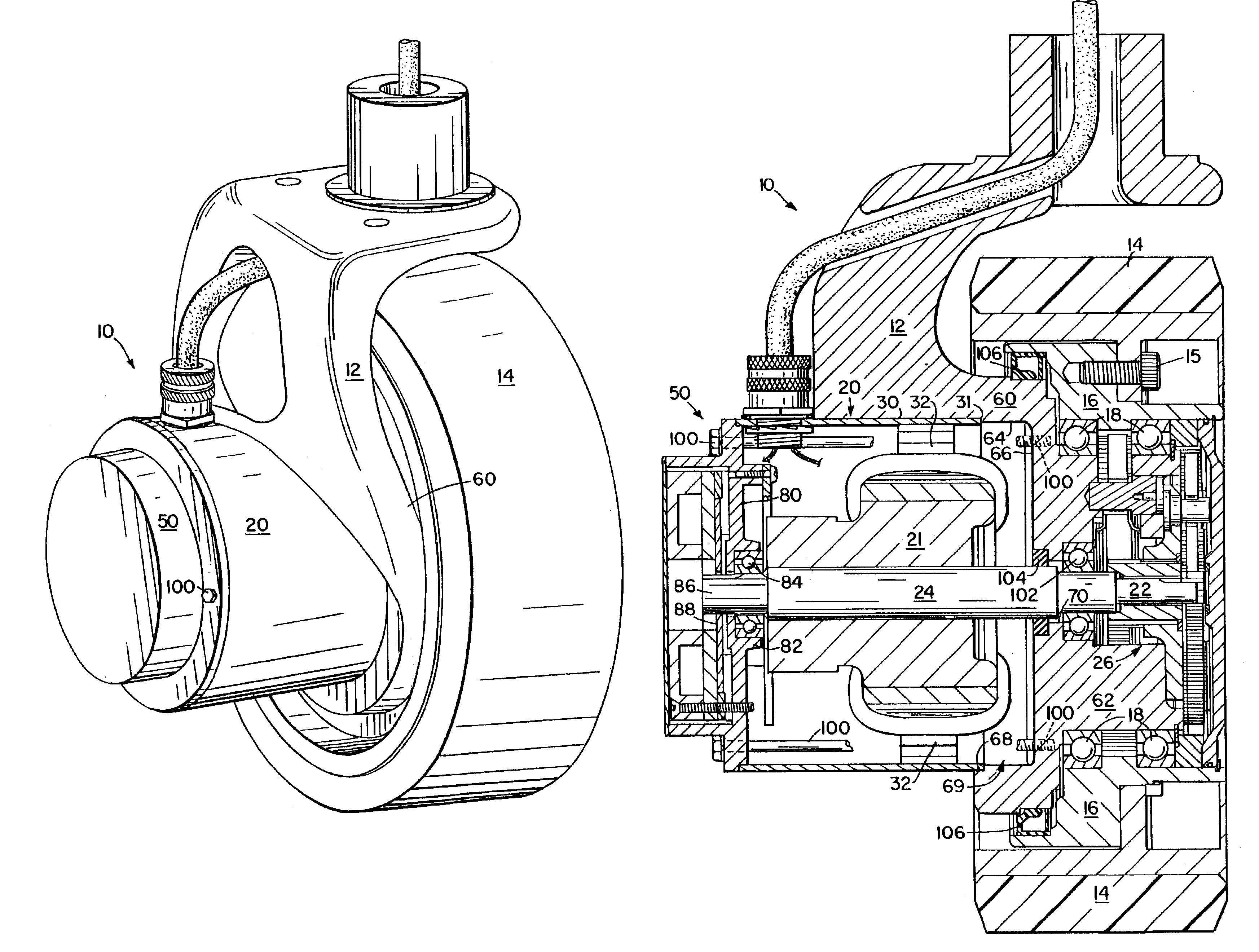
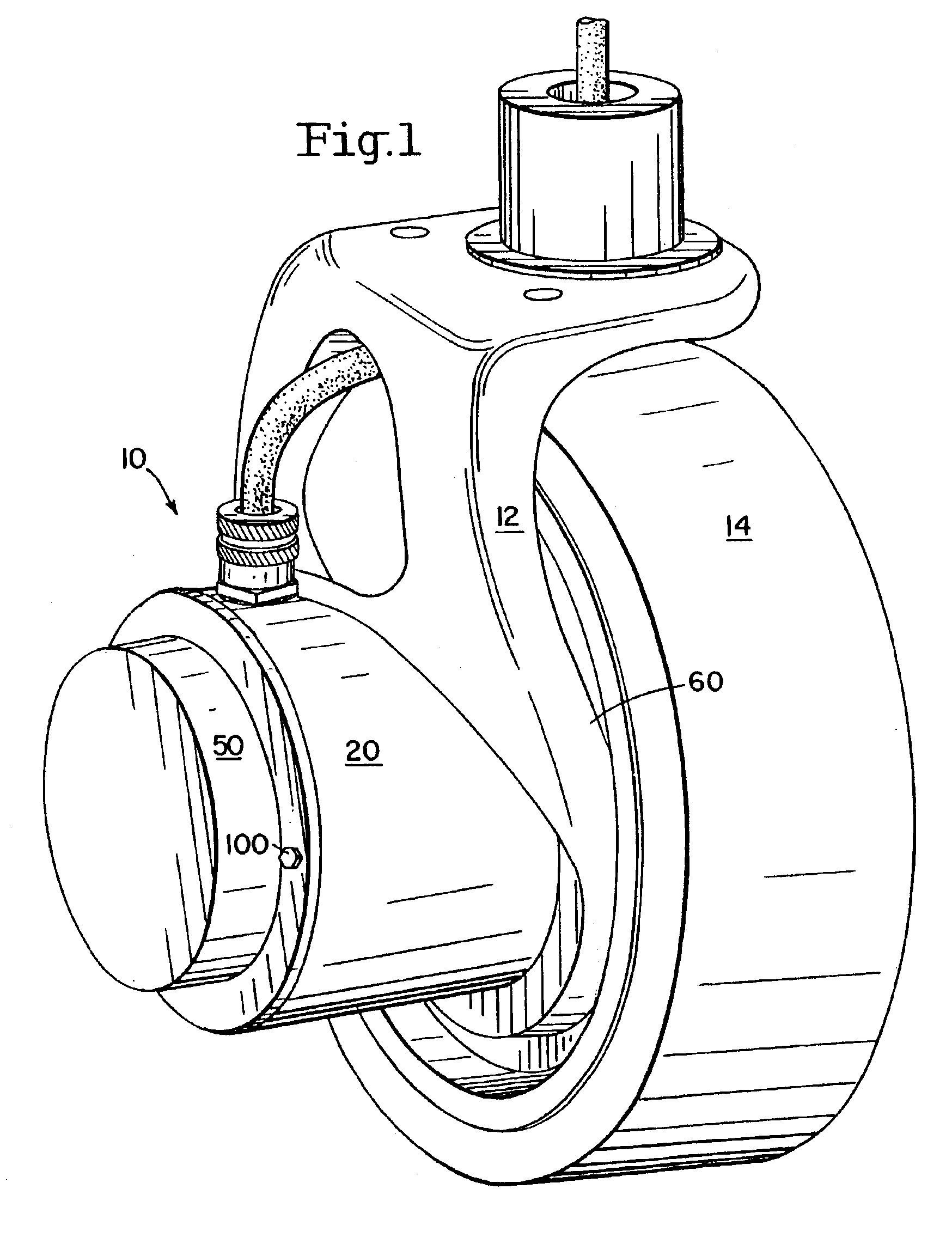
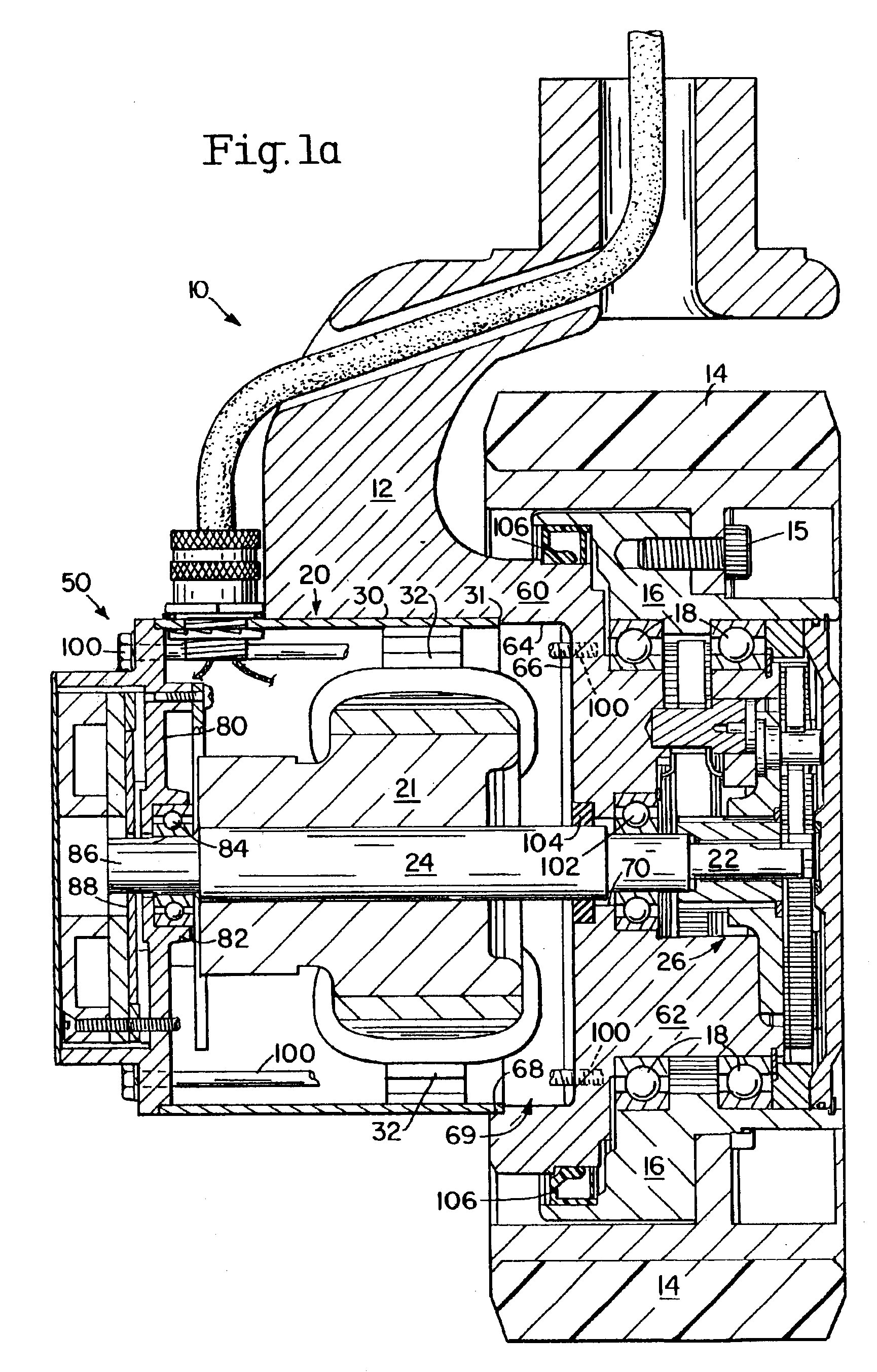
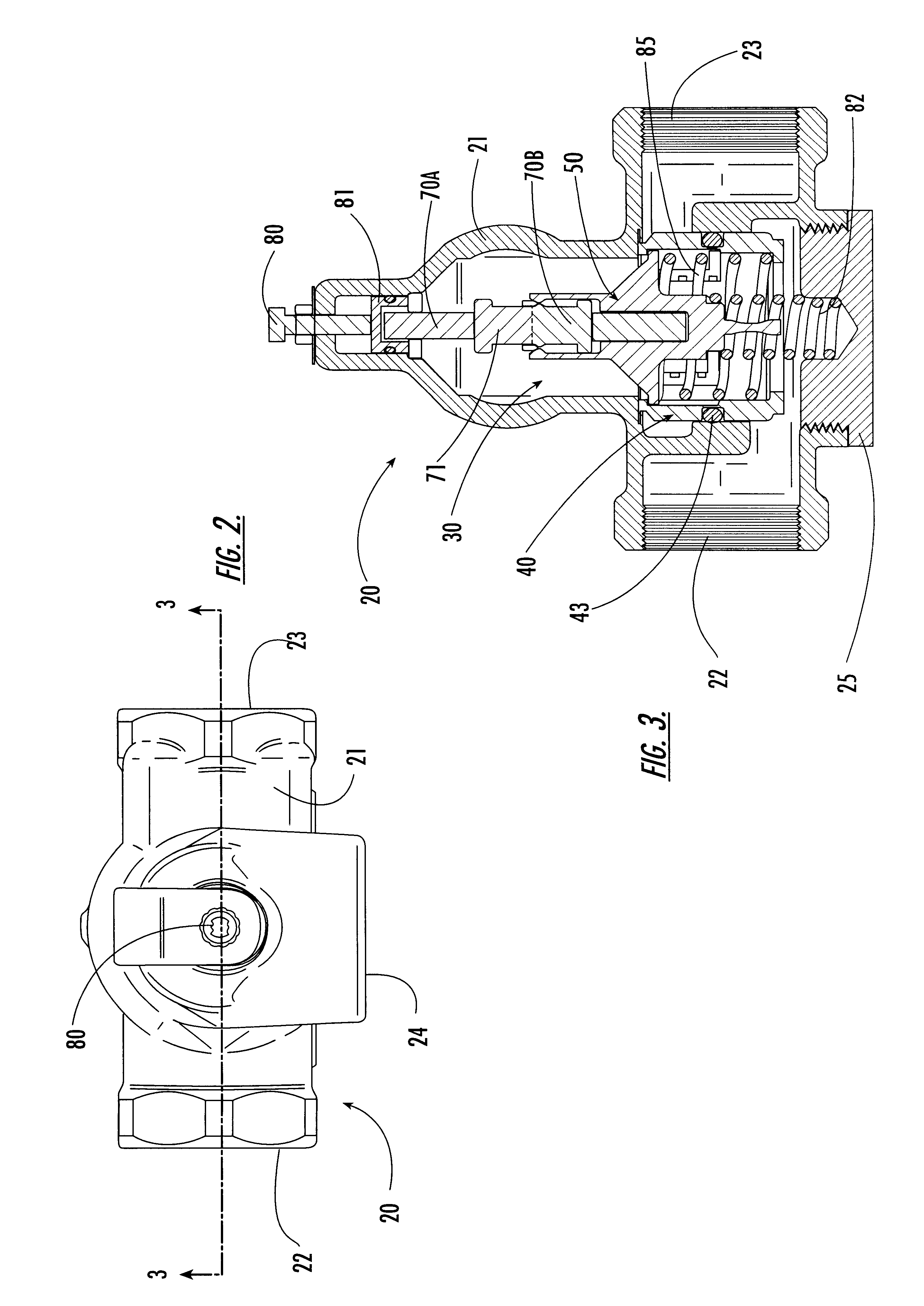
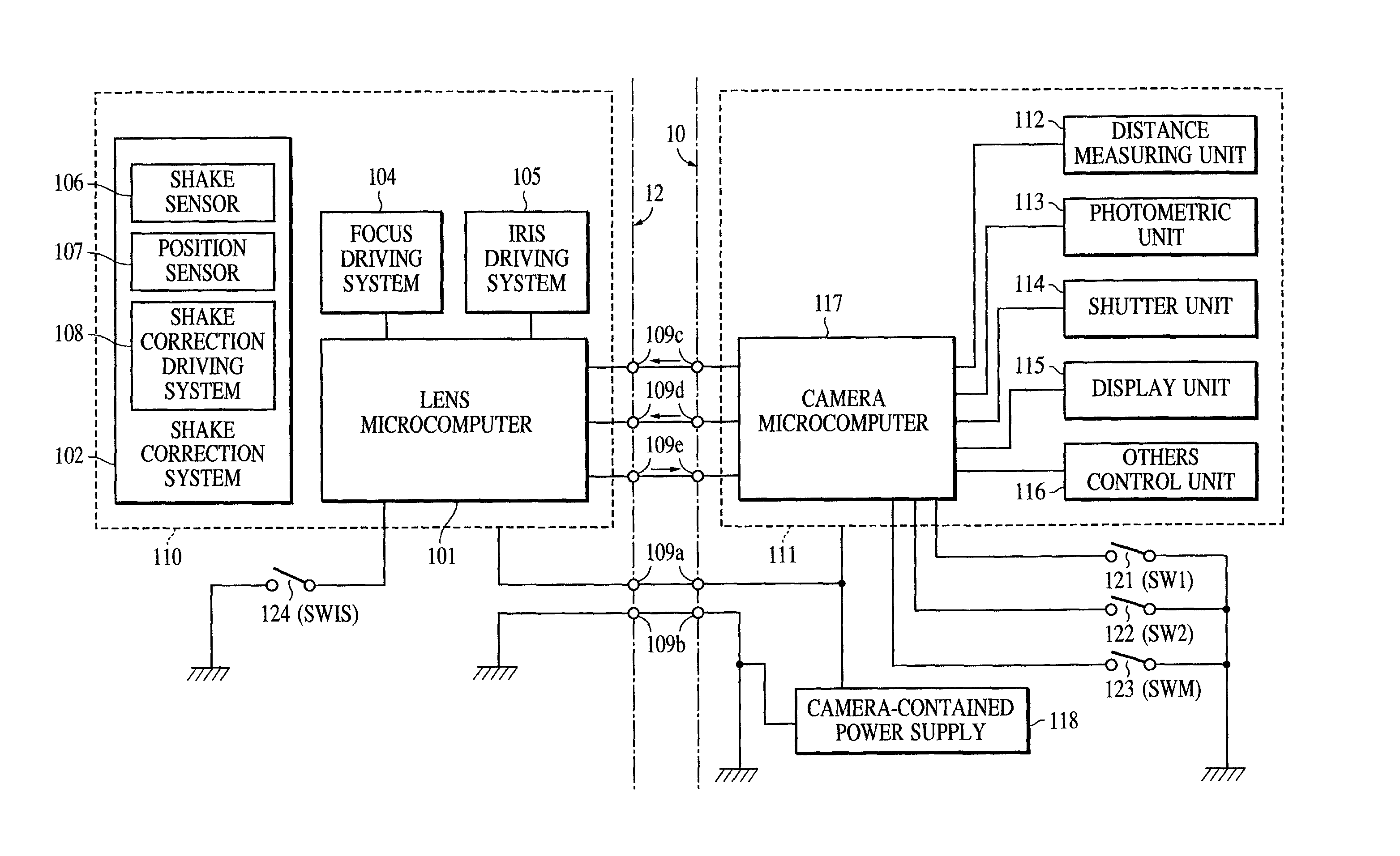
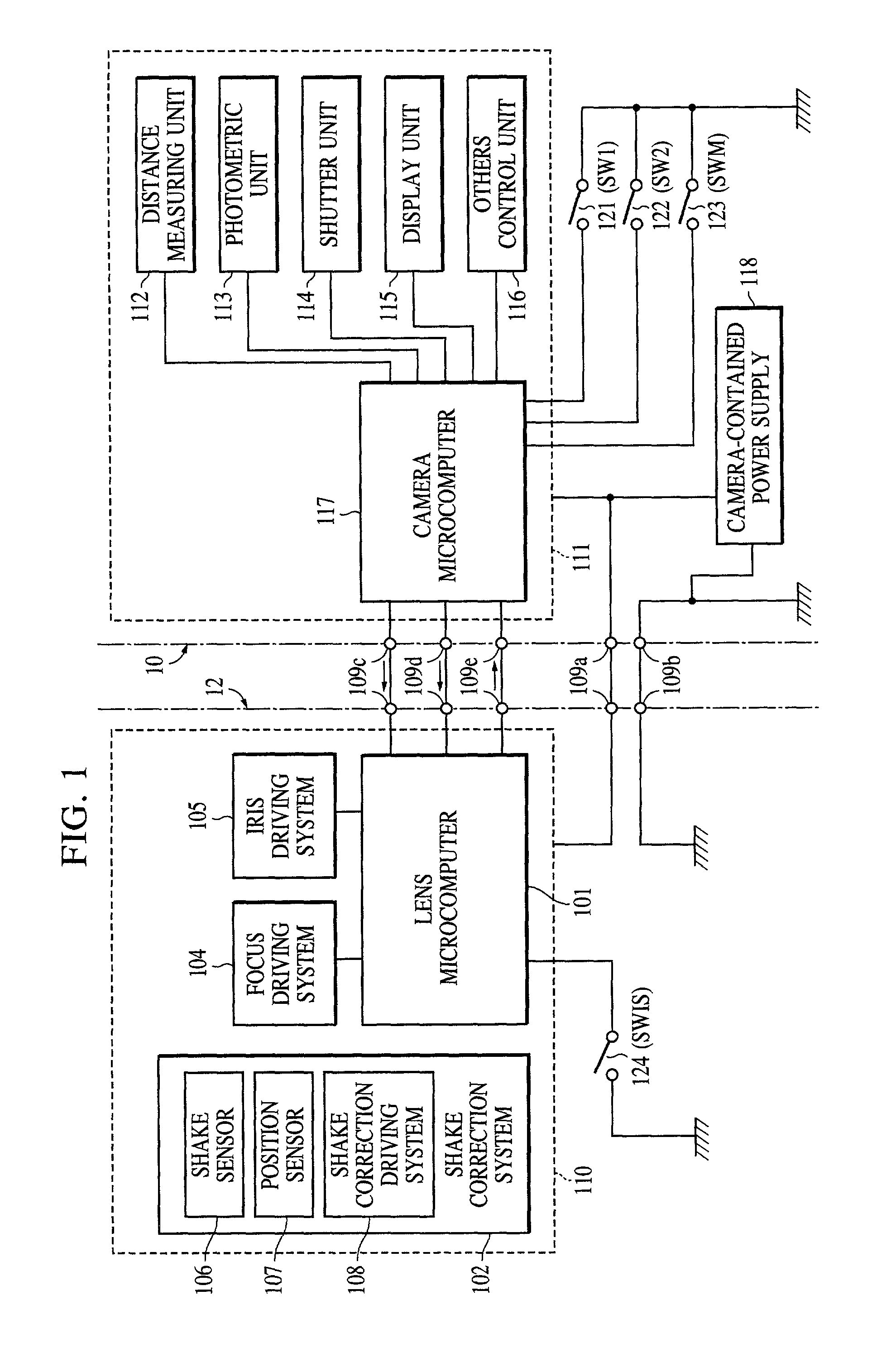
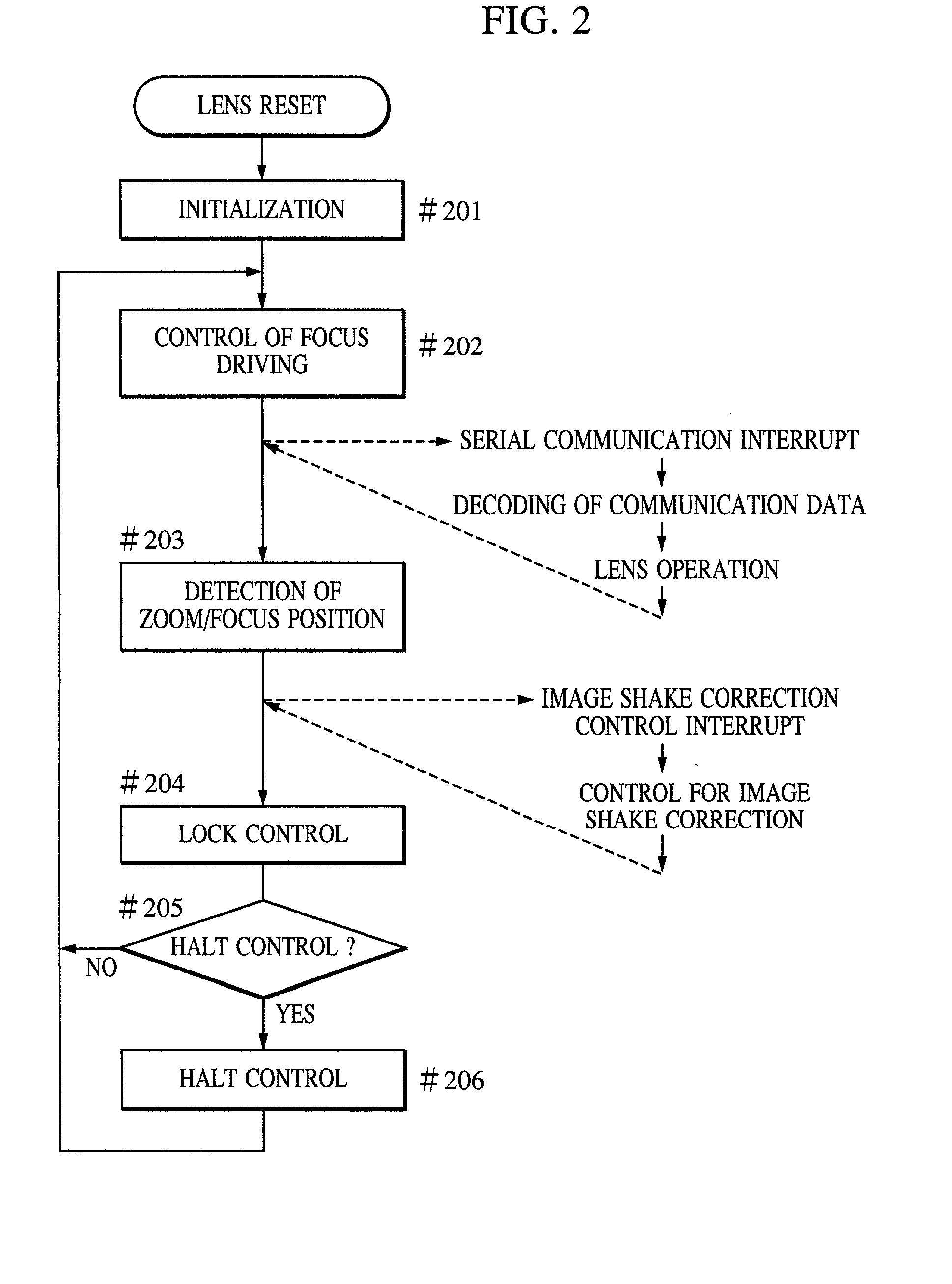
Image shake correcting device
An image shake correcting device is provided for use with an apparatus (e.g., a camera) in which image shake is to be corrected. The device comprises an image shake correcting unit for correcting image shake in accordance with an output of a shake detecting unit for detecting a shake condition; a support condition determining unit for determining whether the apparatus, in which image shake is to be corrected, is supported in a predetermined stationary condition; a shutter speed information determining unit for determining a shutter speed at photo-shooting; and a varying unit for varying a response manner of the image shake correcting means to the output of the shake detecting means in accordance with a combination of the determination made by the support condition determining means and the determination made by the shutter speed information determining means. The image shake correcting device is operated in an optimum mode fit for situations in use, such as whether the apparatus (camera) is held by the hands or fixedly supported on a tripod or the like.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for printing images
InactiveUS20100186610A1Accurate and clear applicationPermit some movementPrinting mechanismsTypewritersStationary conditionsRelative motion
A tray for holding at least one object while an image is printed on a predetermined exposed portion of the object, including at least one object retainer carried by the tray and for positioning the object in a stationary condition in relation to the tray during printing, a panel carried by the tray and having at least one opening positioned in relation to the object retainer such that the exposed portion of the object is exposed to ink projected onto the object from an ink-projecting apparatus positioned in spaced-apart relation to the object, and an indexer carried by the tray for permitting relative movement between the tray and the ink-projecting apparatus as the image is printed on the exposed portion of the object.
Owner:SAIN TODD
Wheel assembly including a DC motor mounted within the HUB and drive connected to the wheel
InactiveUS7100722B2Easy to controlIncrease speedDC motor speed/torque controlElectric propulsion mountingStationary conditionsDrive motor
A modular, self-driven vehicle wheel assembly including a drive motor carried by the wheel assembly. The assembly includes a hub, a wheel rotatably mounted on the hub, and a planetary speed-reducing unit mounted on the hub and drivingly connected with the wheel. The drive motor is a shunt wound DC motor that is coaxially mounted adjacent to the wheel and within a chamber formed in the hub. The motor is drivingly connected with the planetary speed-reducing unit to transmit motor torque to rotate the wheel in either a forward direction or a reverse direction. A brake assembly is carried adjacent to the motor for selectively applying a braking force to brake the motor armature when the wheel is to remain in a stationary condition.
Owner:PEERLESS WINSMITH
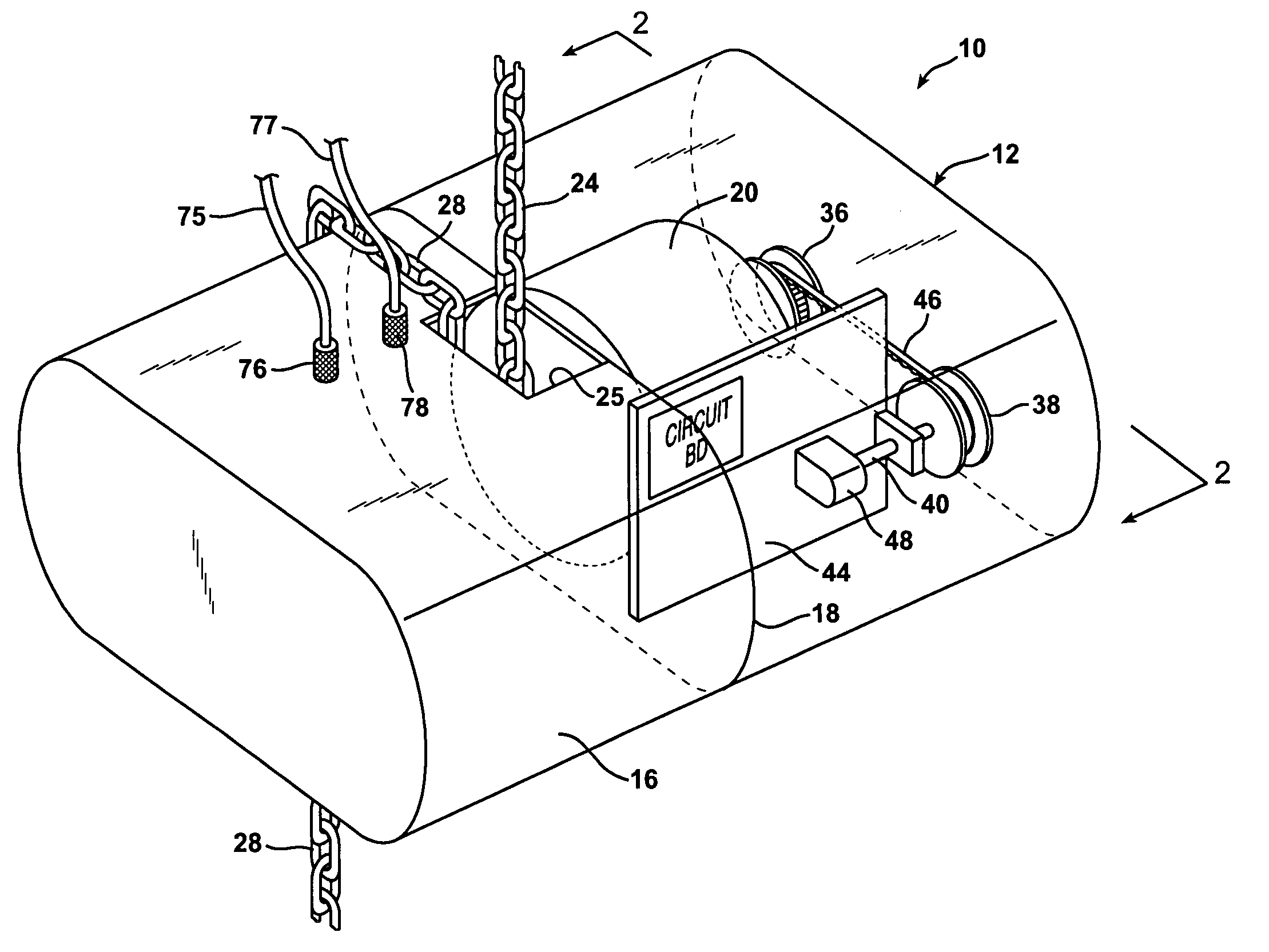
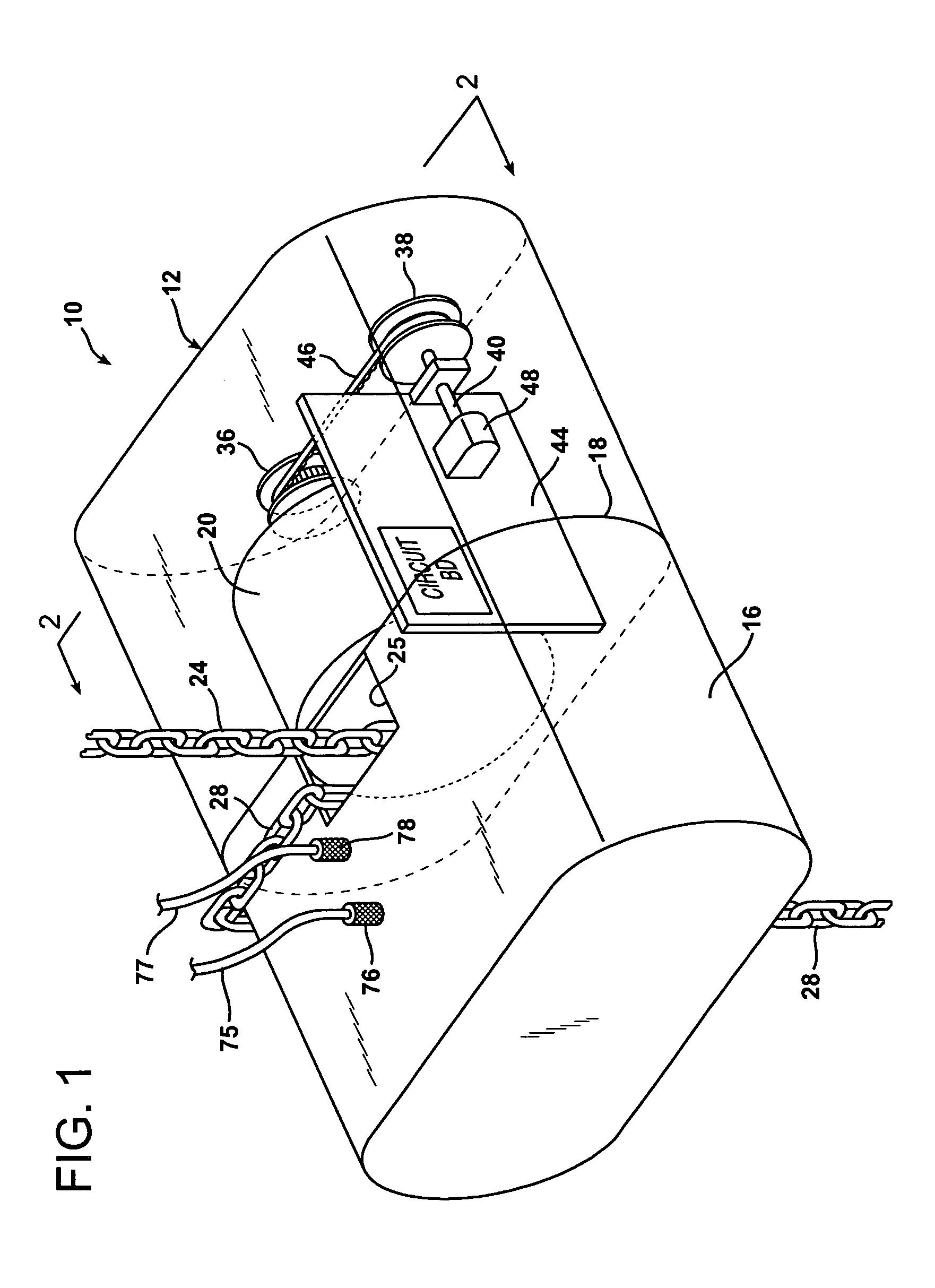
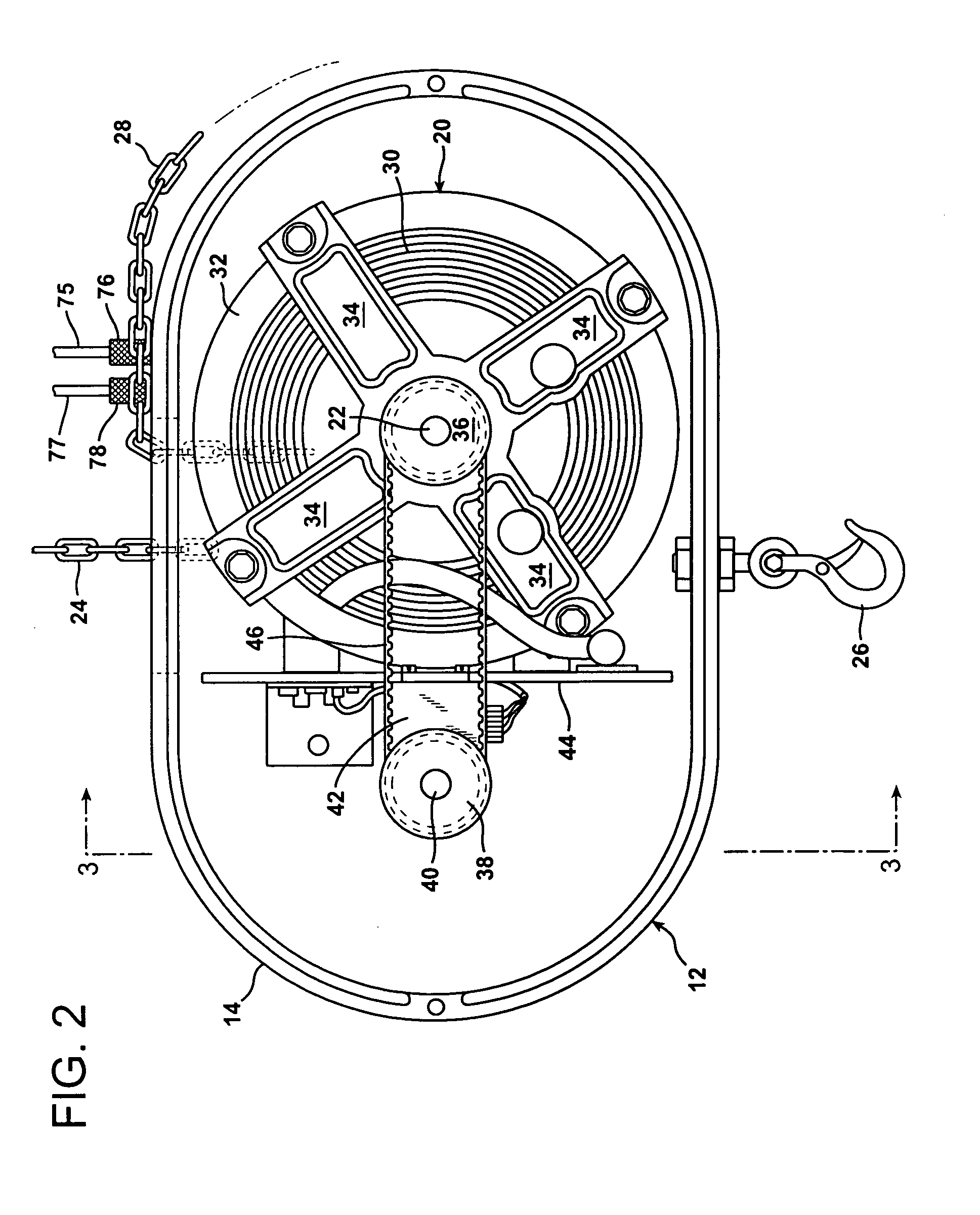
Chain motor drive control system
InactiveUS7080825B1Precise applicationProtection from damagePortable liftingWinding mechanismsStationary conditionsMotor drive
An improved chain motor drive controller is provided for a chain hoist. The system employs a position encoder including a position sensor located within the casing of the chain hoist to producing encoded electrical position signals. A motor pulley is mounted on the chain motor rotary drive shaft and is coupled by a cogged belt to rotate an encoder pulley that is mounted on the same shaft as the position sensor. A mechanical coupling is thereby provided entirely within the casing of the chain hoist to transmit rotary motion from the rotary drive shaft directly to the position sensor. Also, tracking circuitry, likewise located entirely within the chain hoist casing, receives electrically encoded destination signals and compares these to signals from the position sensor. The tracking circuitry accelerates rotation of the chain motor drive shaft starting from a stationary condition and decelerates rotation of the chain motor drive shaft as the differences between the encoded position signals and the encoded destination signals approach zero.
Owner:GEORGE HYRA S MRS +1
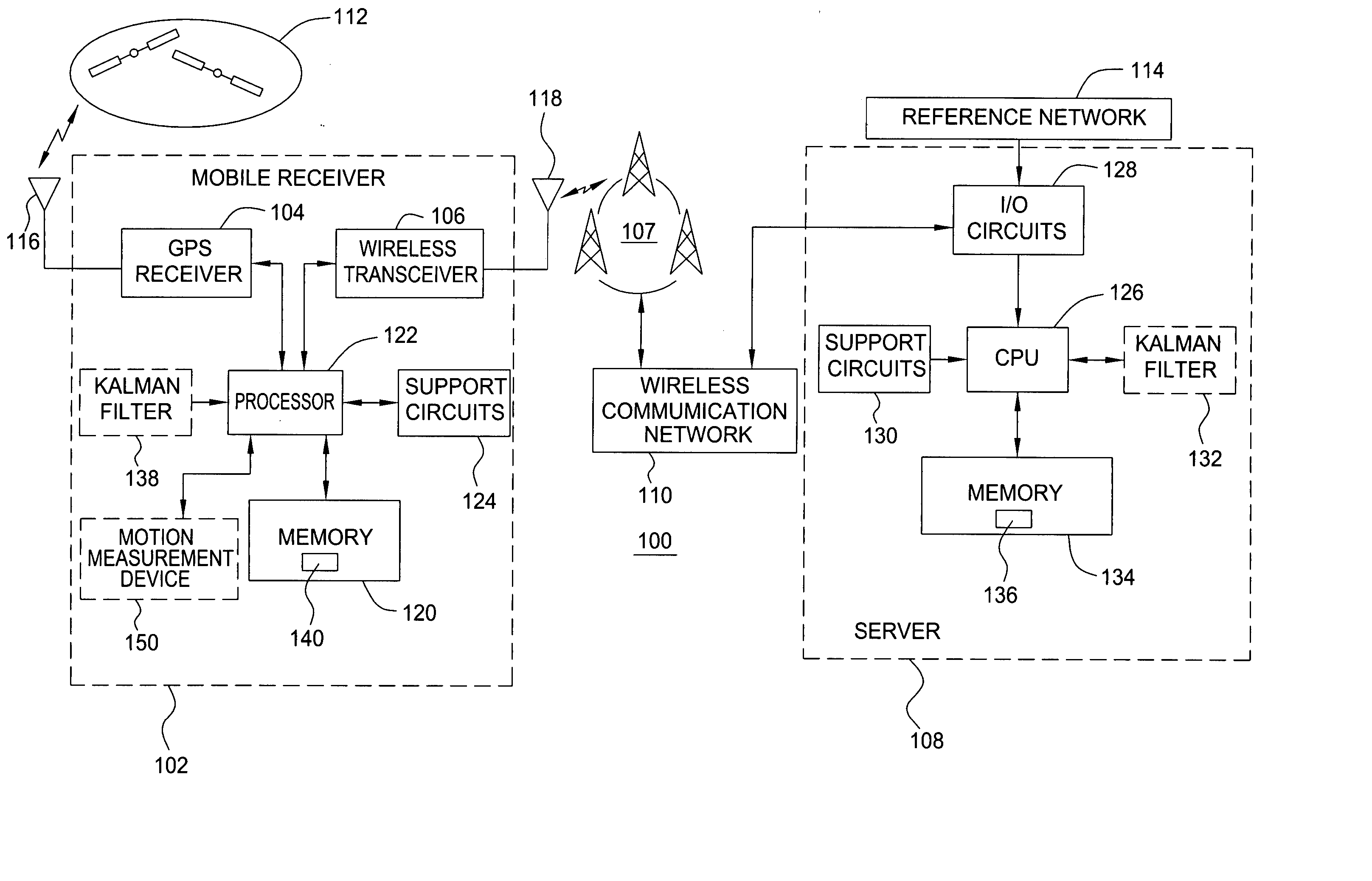
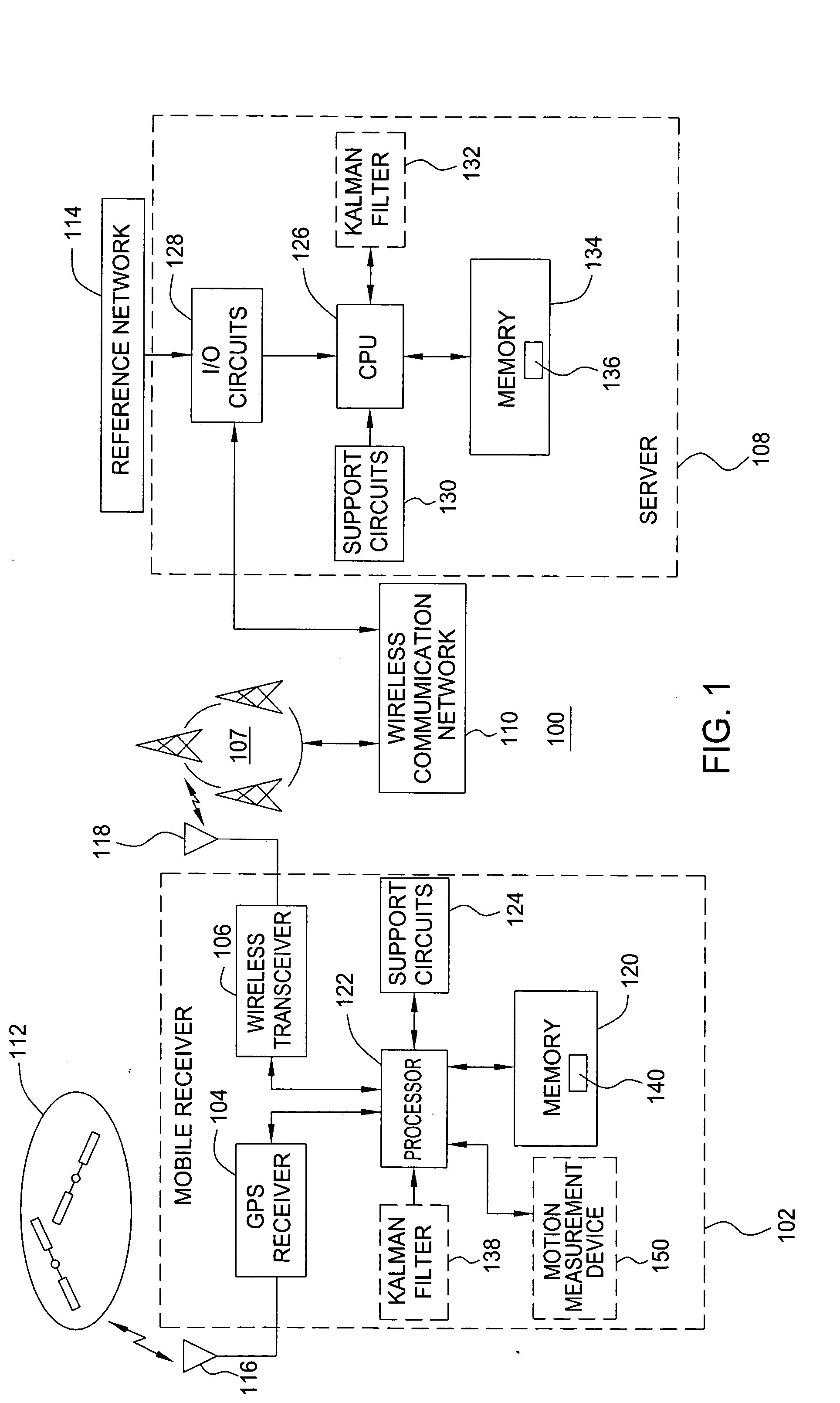
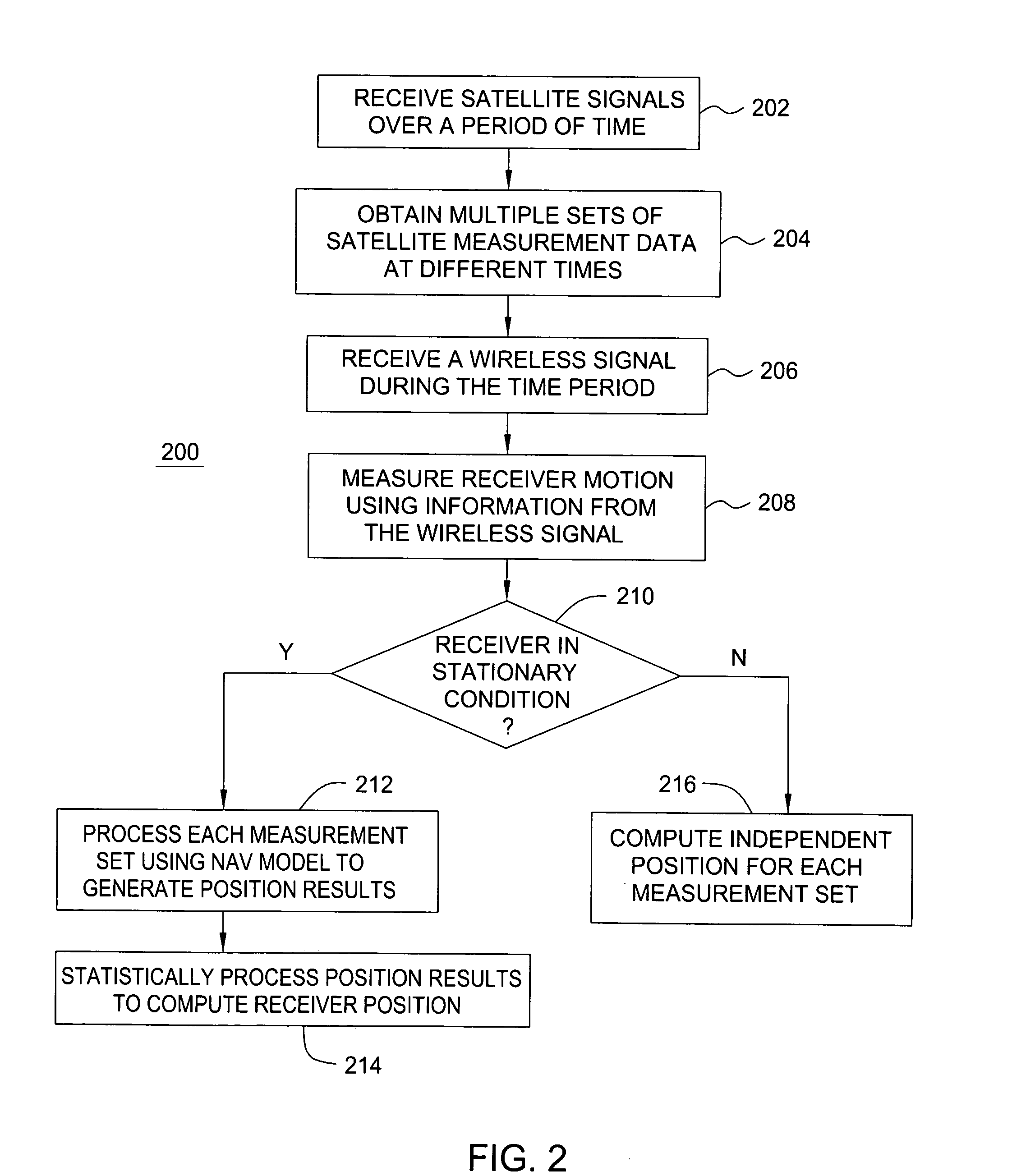
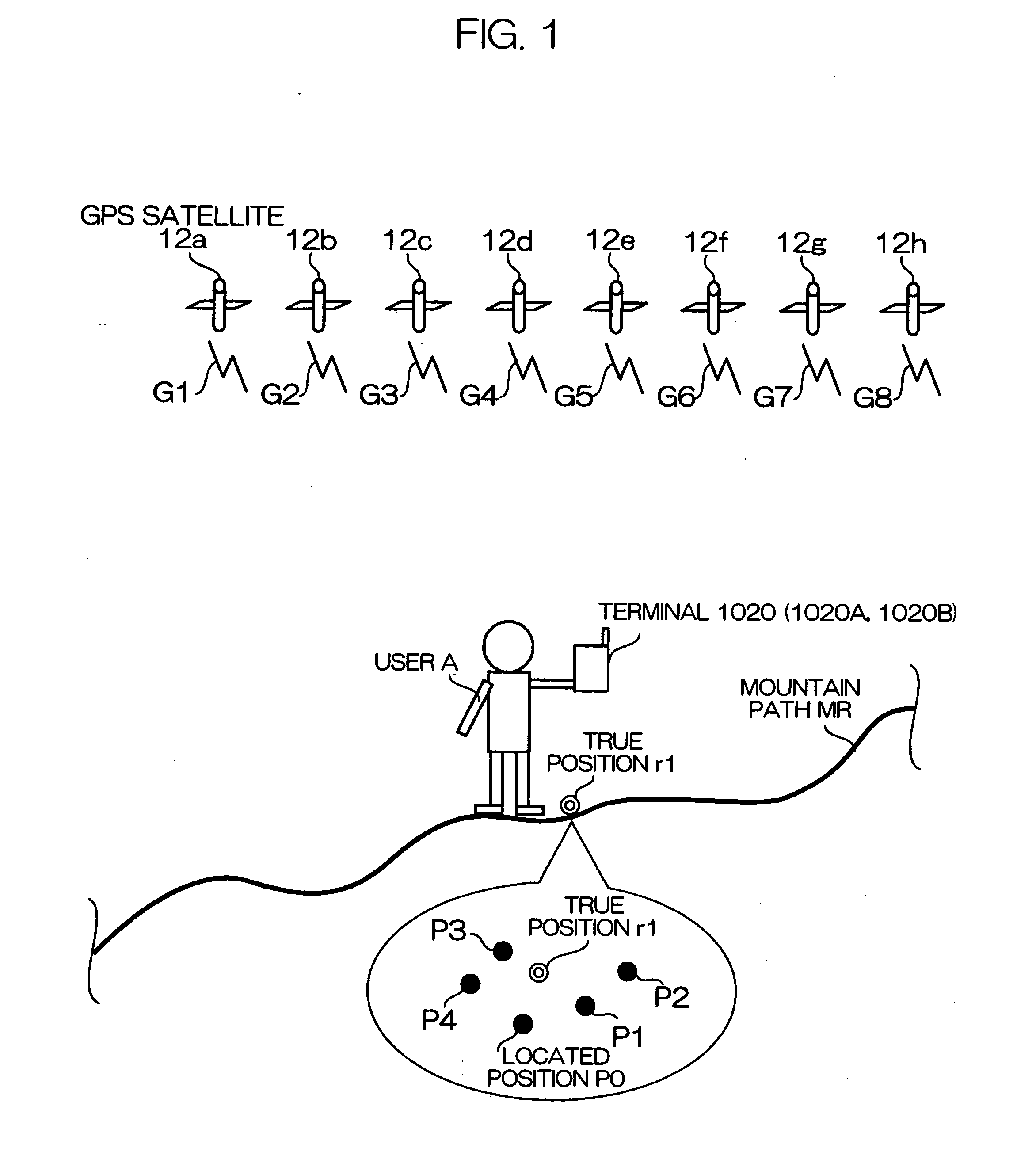
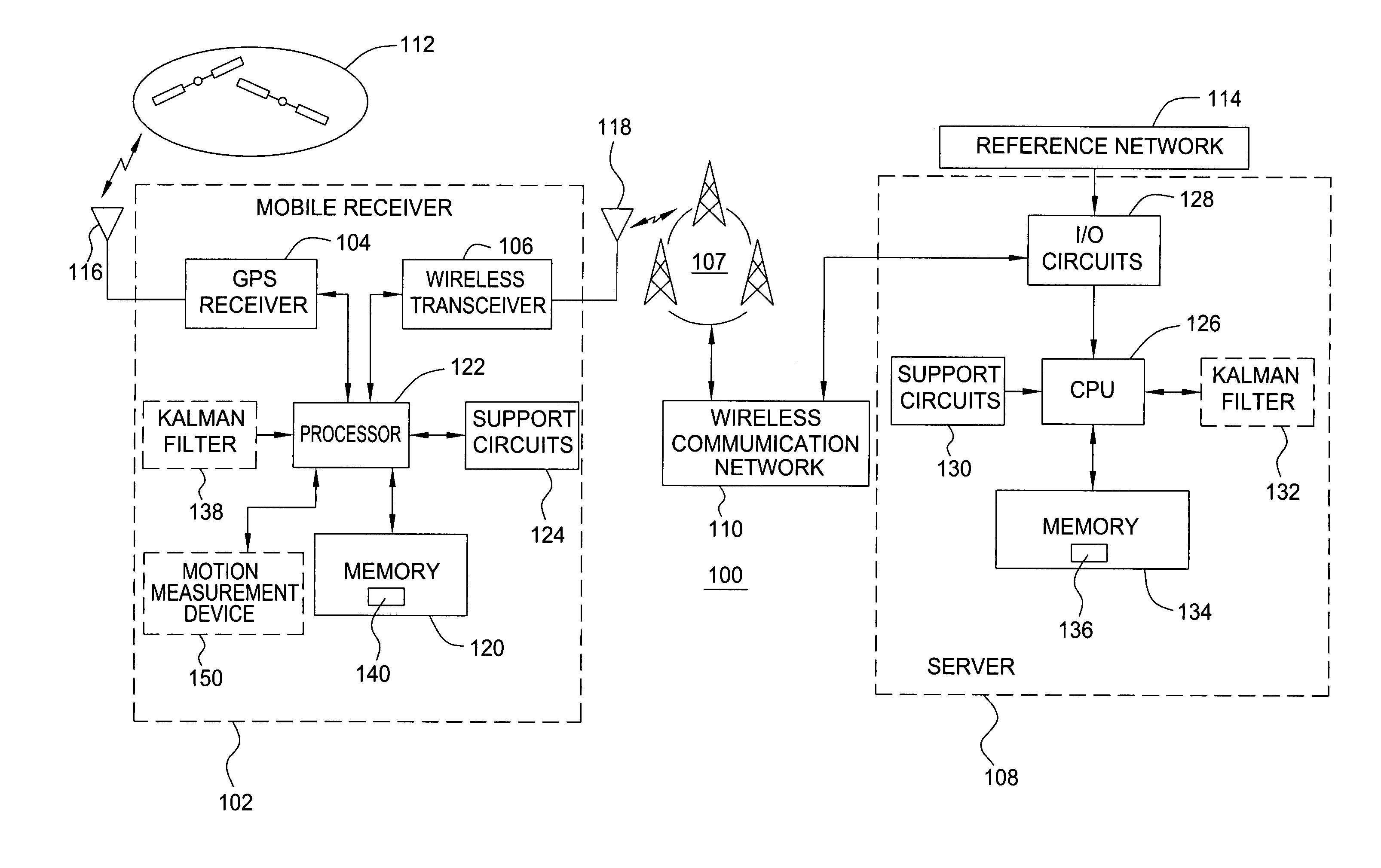
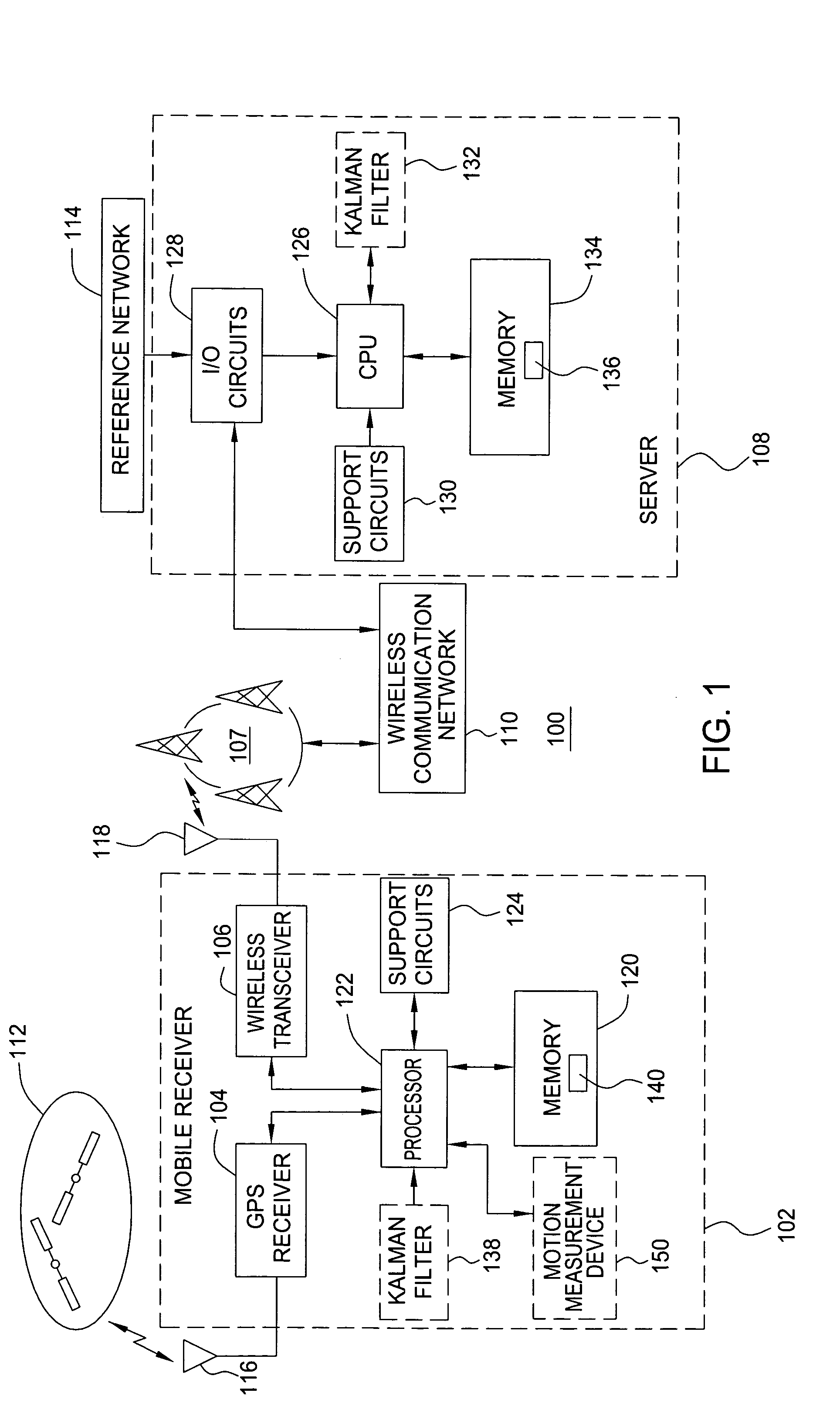
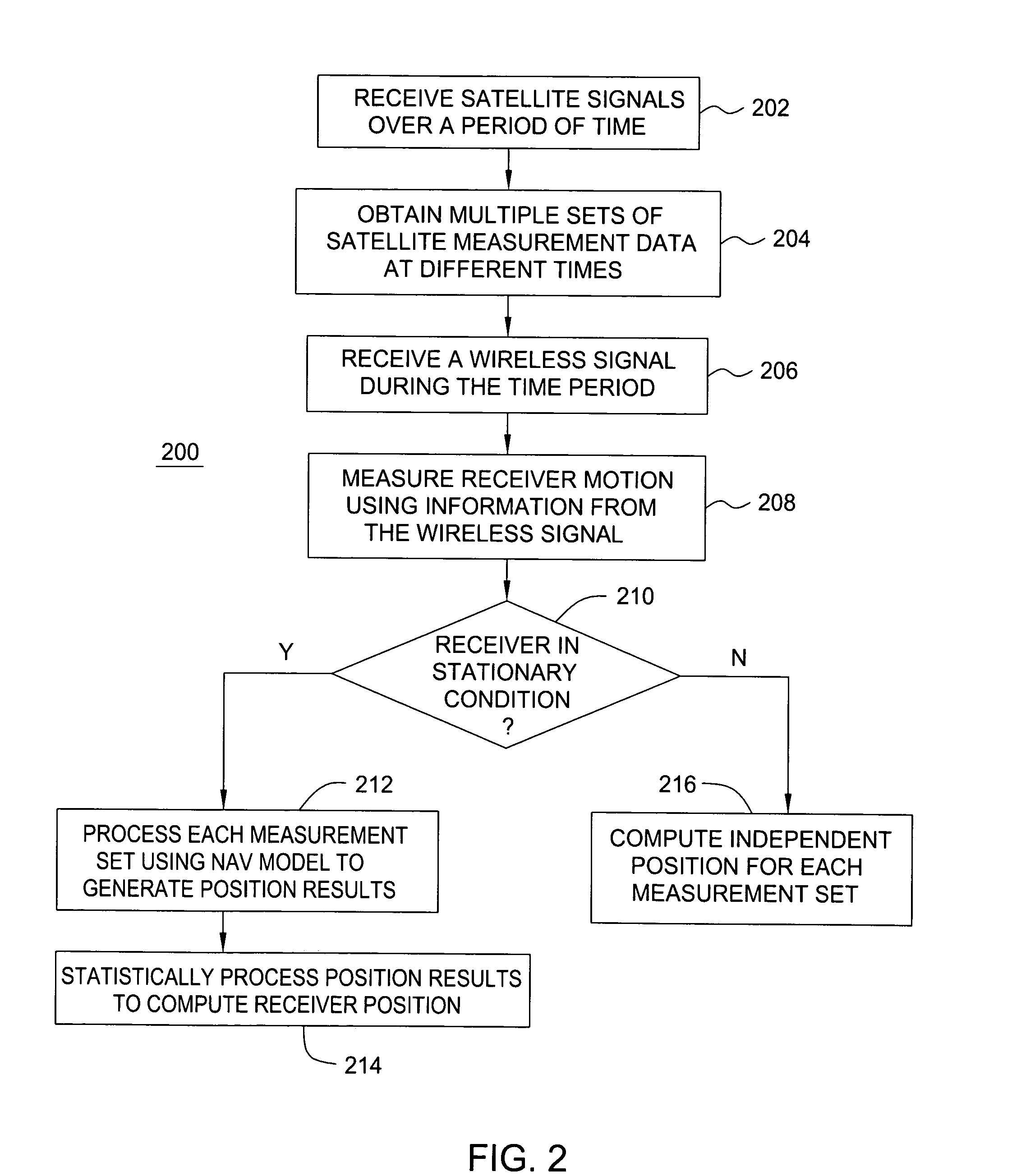
Method and apparatus for locating position of a mobile receiver
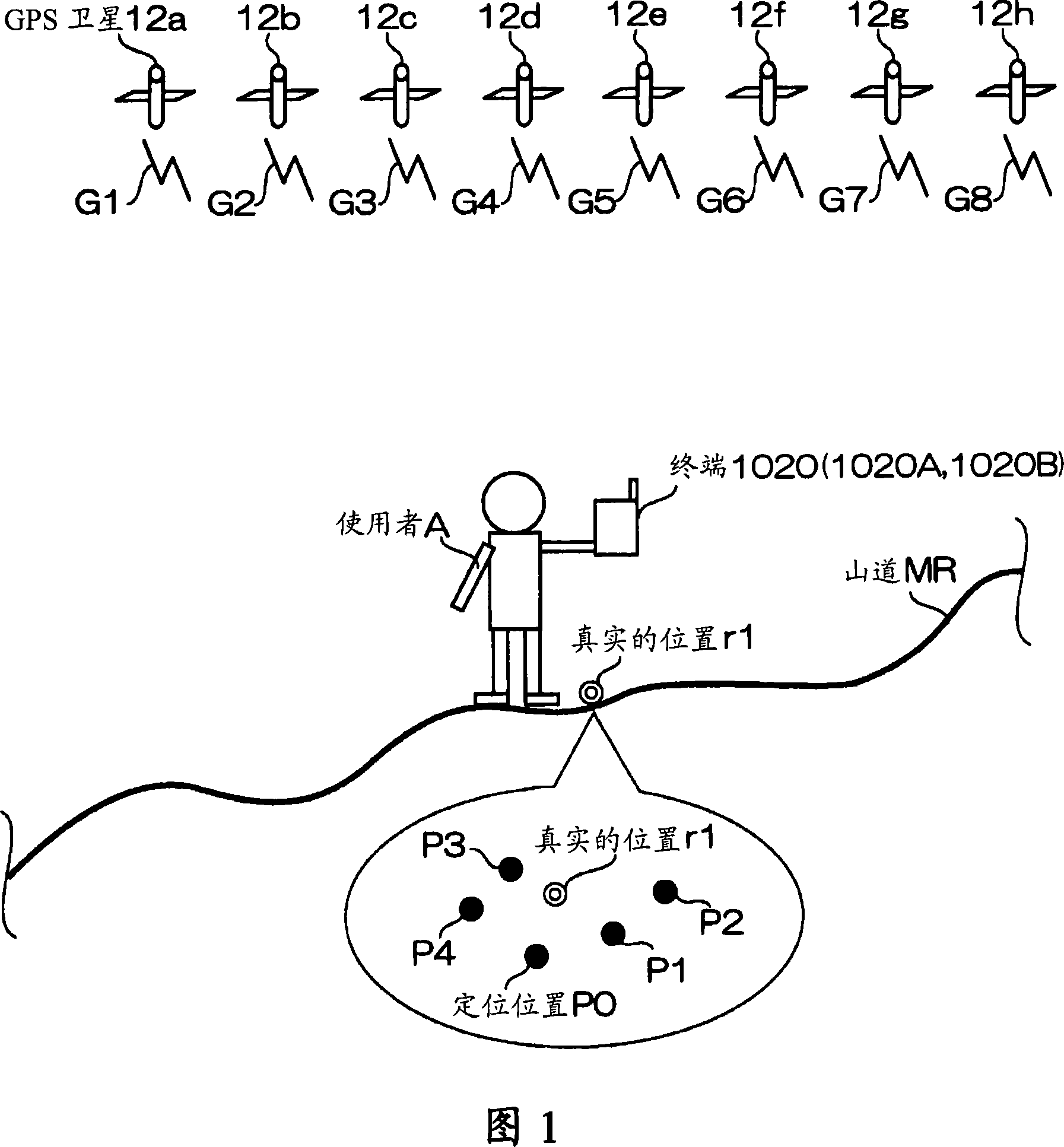
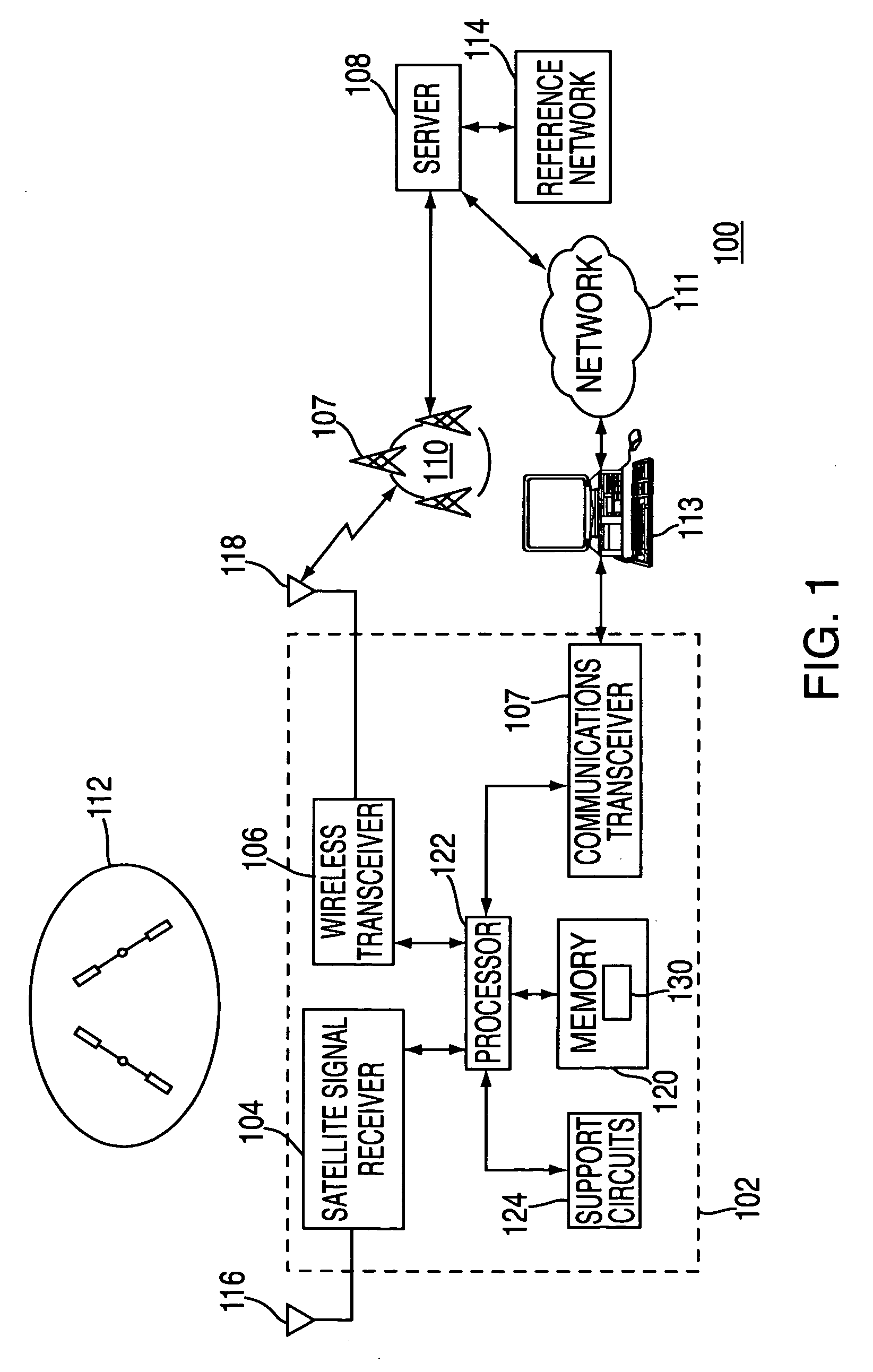
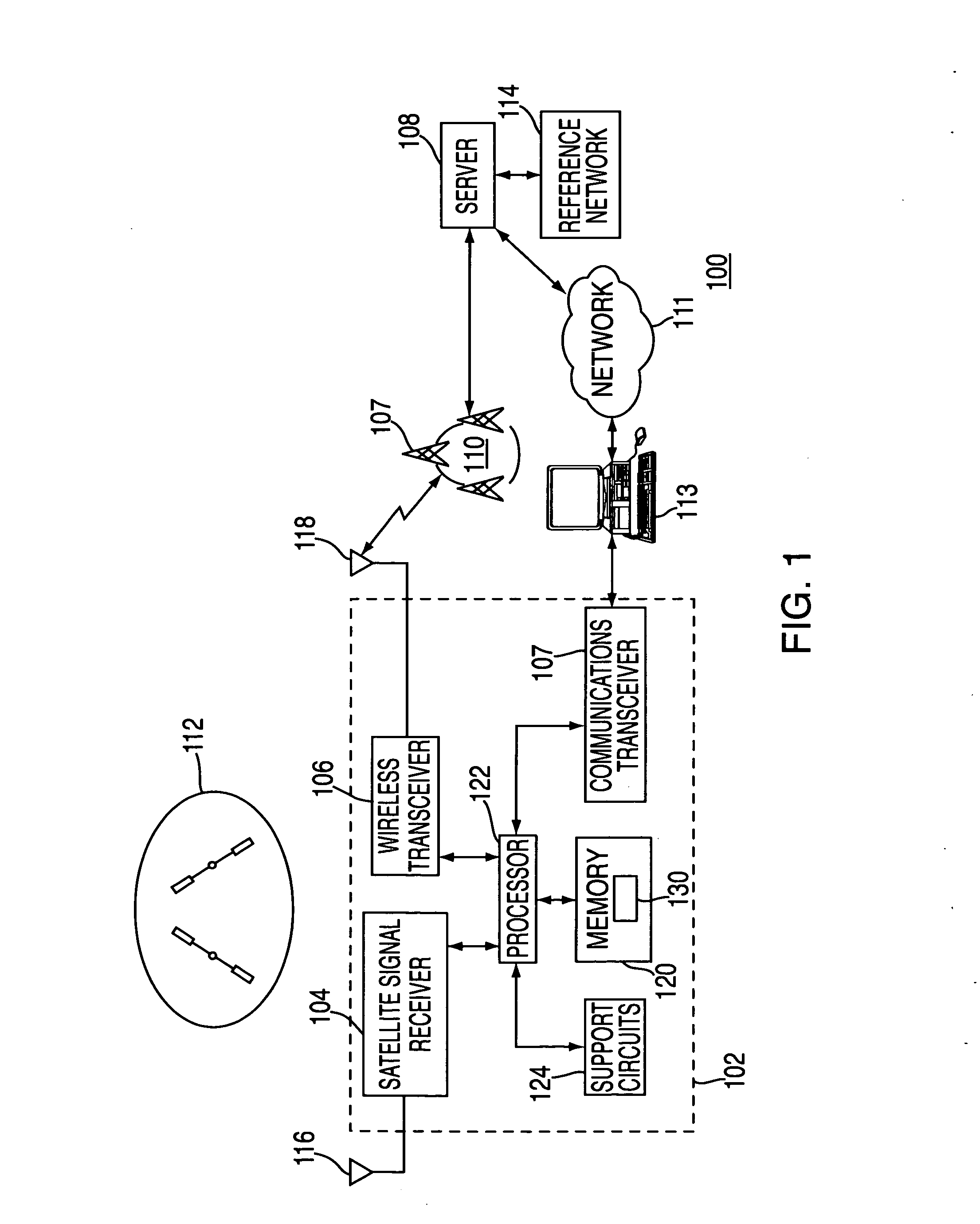
A method and apparatus for locating position of a mobile receiver is described. In one example, sets of satellite measurements are determined with respect to a plurality of satellites over a period of time. A determination is made as to whether the mobile receiver is in a stationary condition over the period of time. A position of the mobile receiver is then computed using the sets of satellite measurements in response to detection of the stationary condition.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
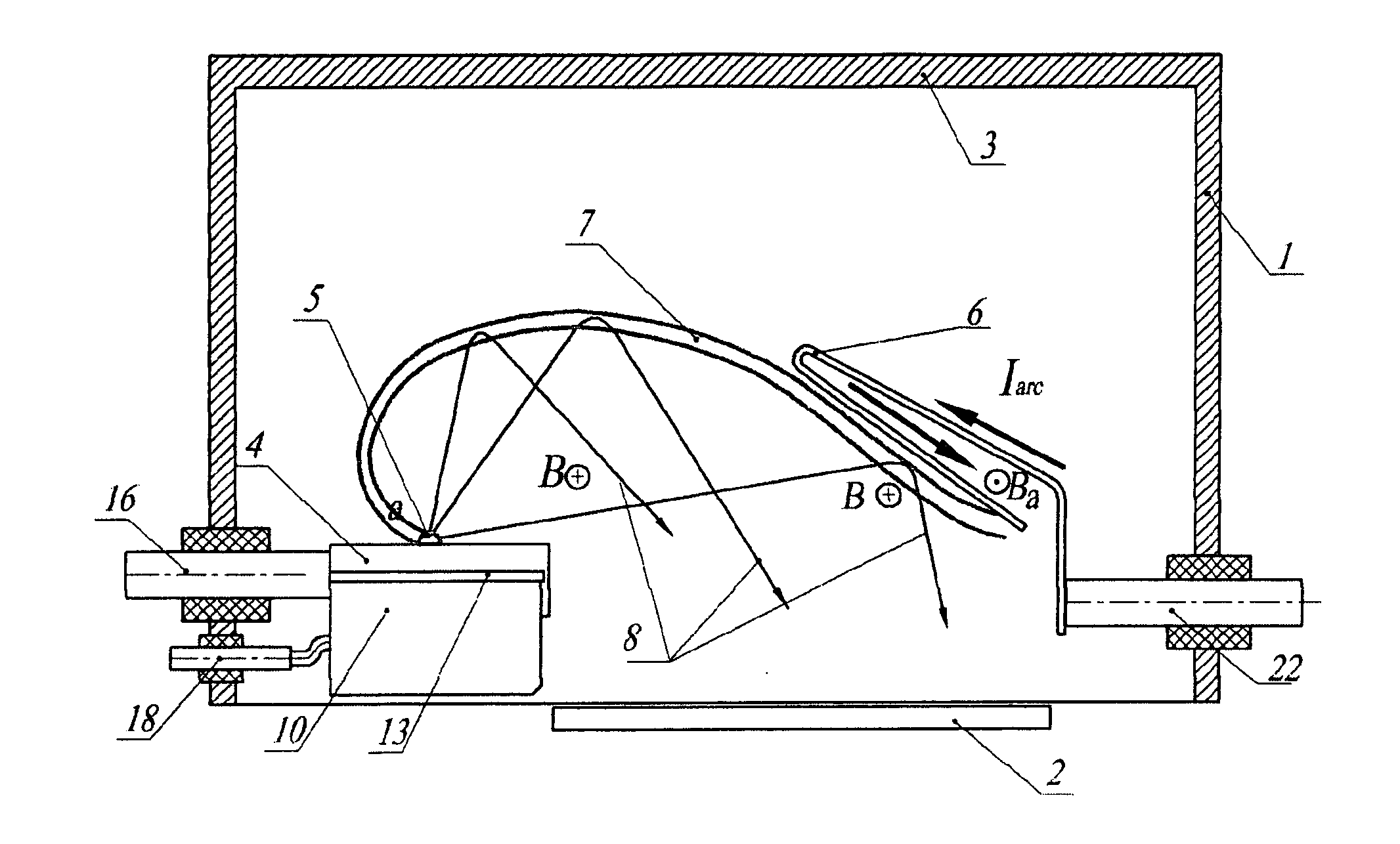
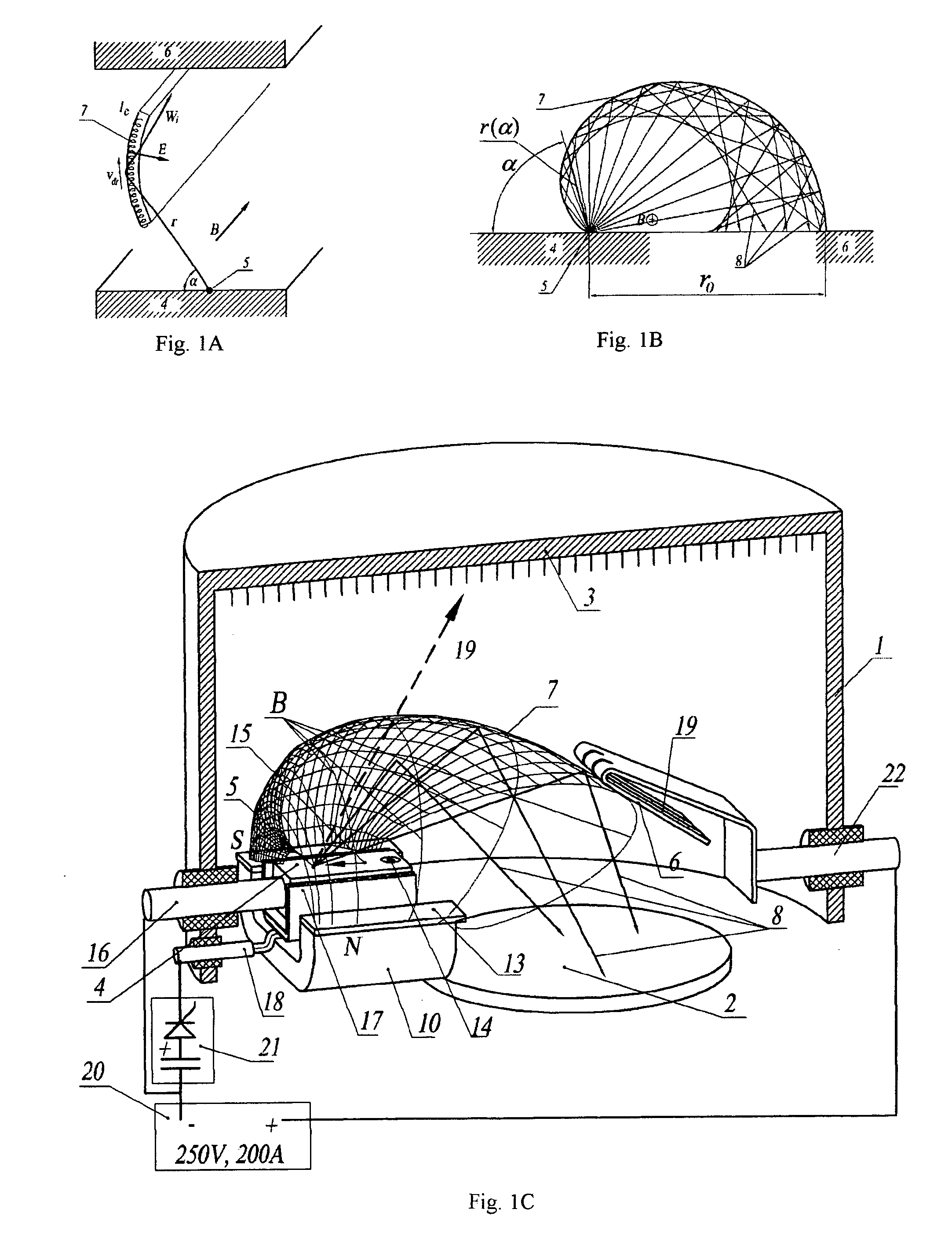
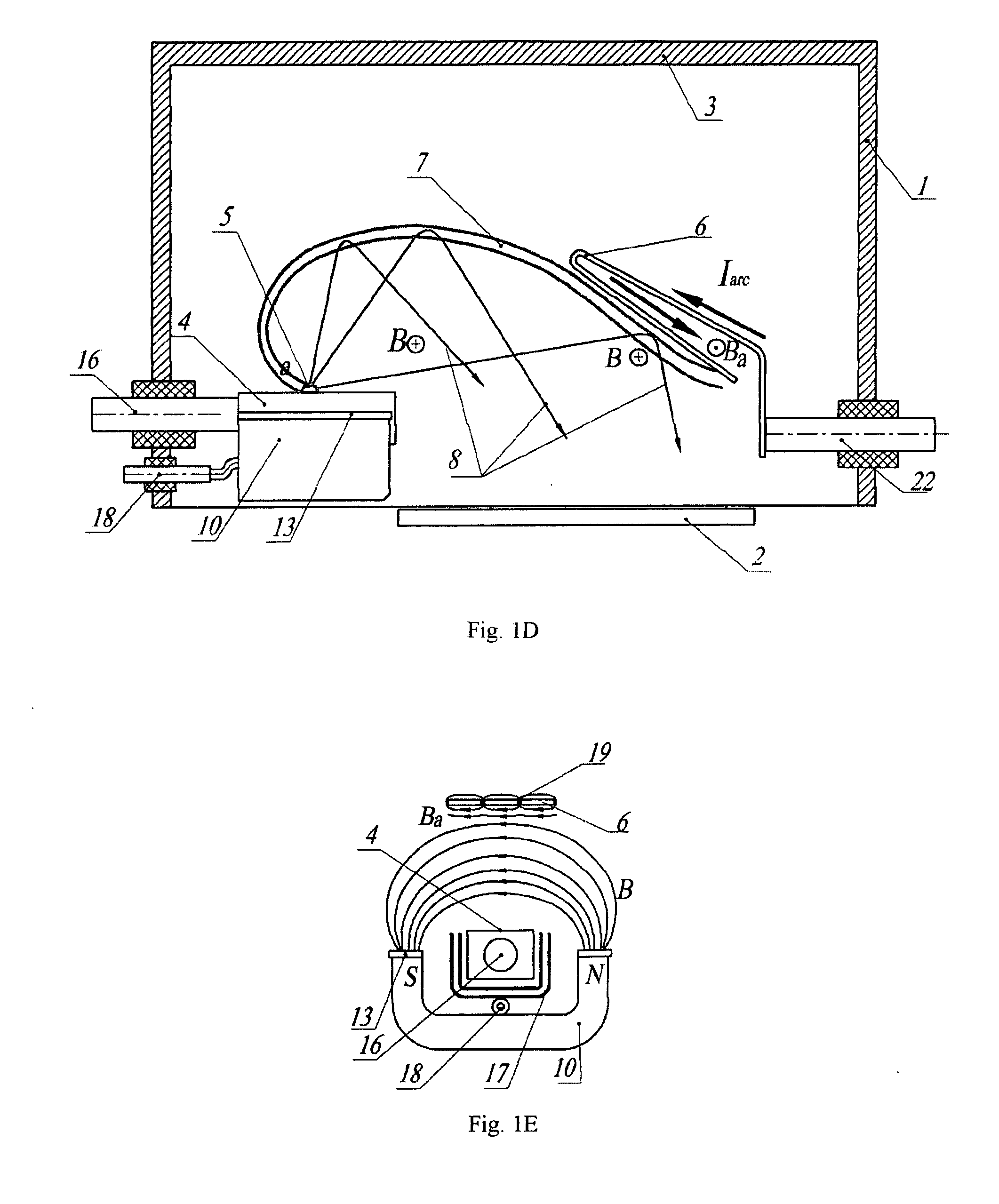
Cathode-arc source of metal/carbon plasma with filtration
InactiveUS20070034501A1Improve transportation efficiencyIncrease the number ofCellsElectric discharge tubesStationary conditionsCurrent sheet
The a cathode-arc source of metal plasma with filtration, used, in particular, for deposition of DLC, utilizes the effect of fast ions reflection from the Hall stratum in a transversal arched magnetic field to filtrate vacuum arc plasma arc from contaminating macroparticles and vapor. Various embodiments for producing maximal plasma flux at the source outlet, in particular, a pulse source with more the one cathode units for deposition of coating inside pipes / cavities, for deposition of coating in a stationary / quasi-stationary condition are offered. The cathode is made of a consumable material and is exposed to poles of magnets on both ends of cathode for creating a transversal magnetic field of an arched configuration in a discharge gap between the cathode and the anode. The anode geometry adequate to the mechanism of the arc current passage through a transversal magnetic field is offered. To avoid longitudinal and transverse short circuits of the current layer, an installation of non-conducting surfaces at ends or sectioned shields under a floating potential at the cathode sides is provided. The method of creating the Hall stratum in said transversal magnetic field of arched configuration is offered.
Owner:BENDER EFIM
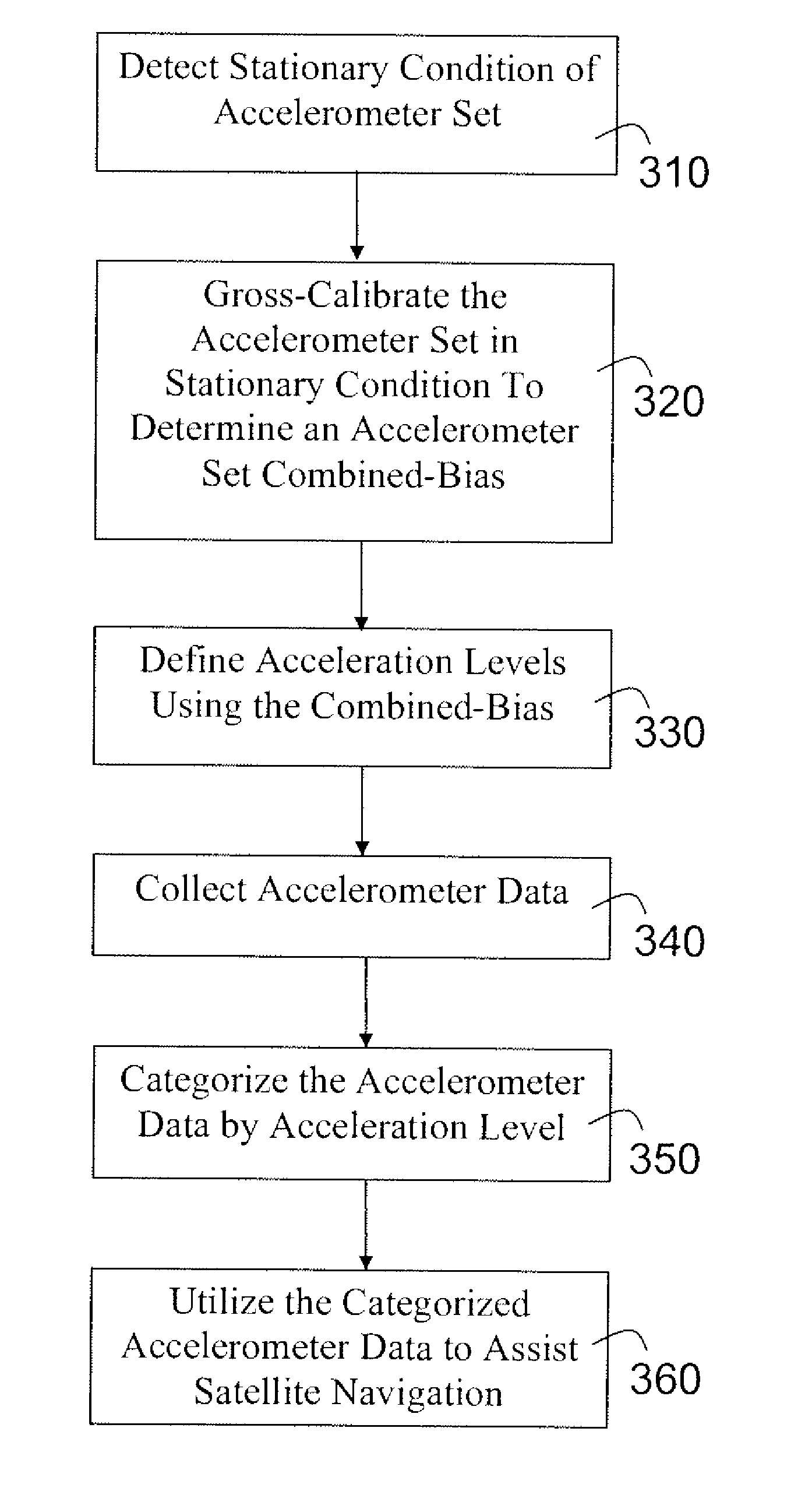
Use of accelerometer only data to improve GNSS performance
InactiveUS20110184645A1Low costAssist with image stabilizationInstruments for road network navigationTesting/calibration apparatusAccelerometer dataStationary conditions
The present invention provides apparatus and methods for improving satellite navigation by assessing the dynamic state of a platform for a satellite navigation receiver and using this data to improve navigation models and satellite tracking algorithms. The dynamic state of the receiver platform may be assessed using only accelerometer data, and does not require inertial navigation system integration. The accelerometers may not need to be very accurate and may not need to be aligned and / or accurately calibrated. A method of accelerometer assisted satellite navigation may comprise: detecting a stationary condition of an accelerometer set; gross-calibrating the accelerometer set when in the stationary condition, wherein gross-calibrating includes determining a combined-bias of the accelerometer set; defining at least two acceleration levels using the combined-bias; collecting accelerometer data; categorizing the accelerometer data into one of the acceleration levels; and utilizing the categorized accelerometer data to enhance satellite navigation.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
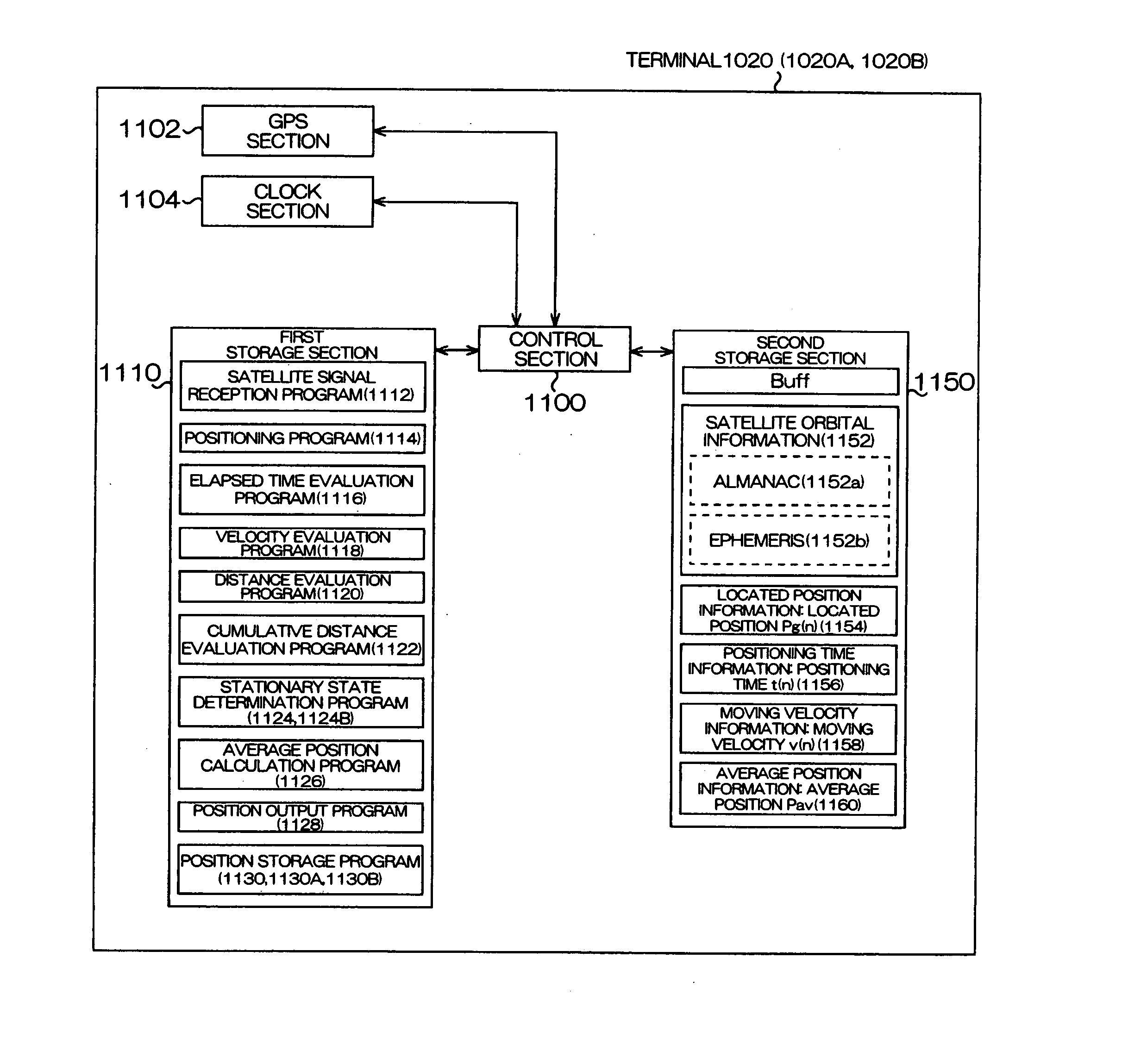
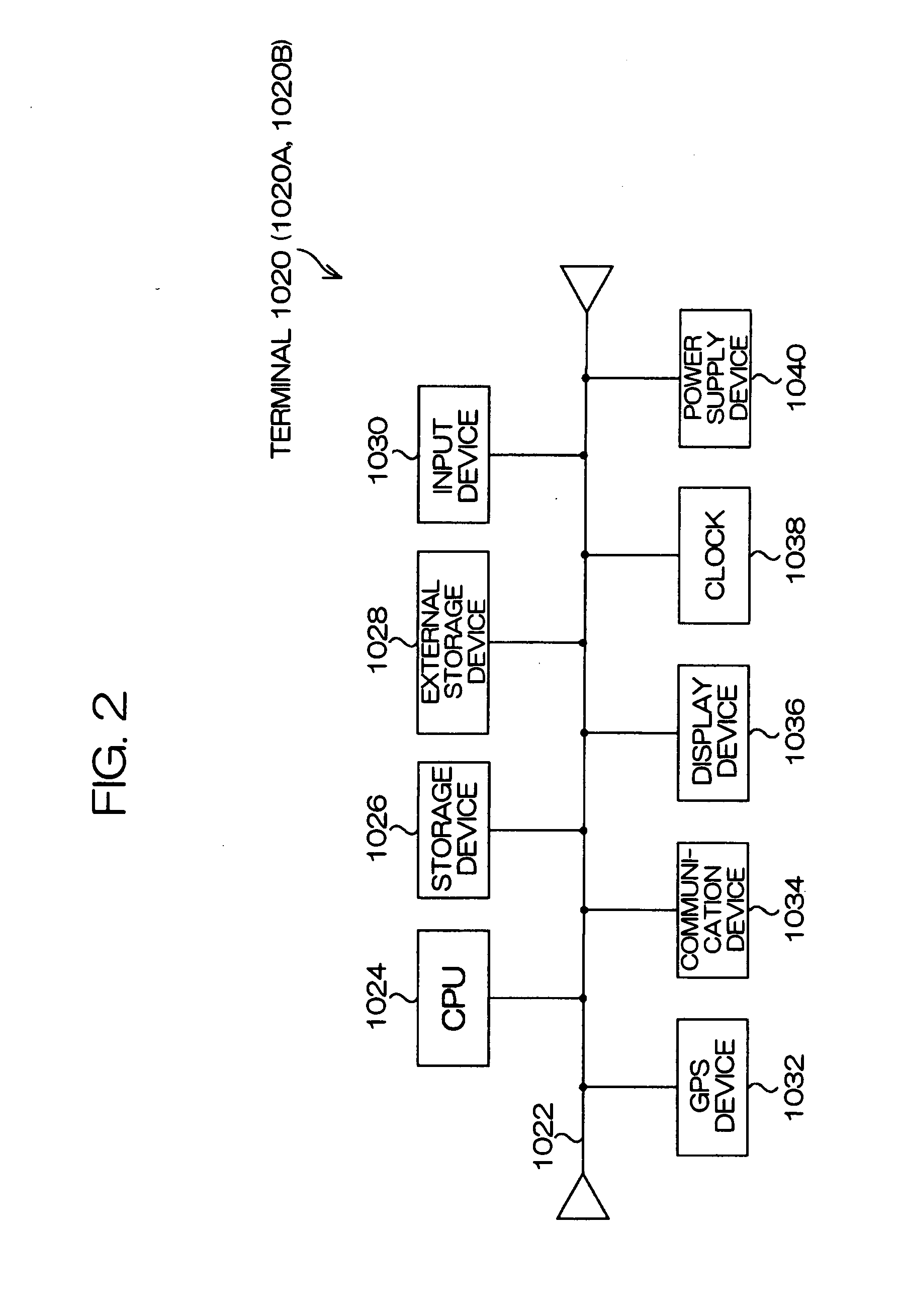
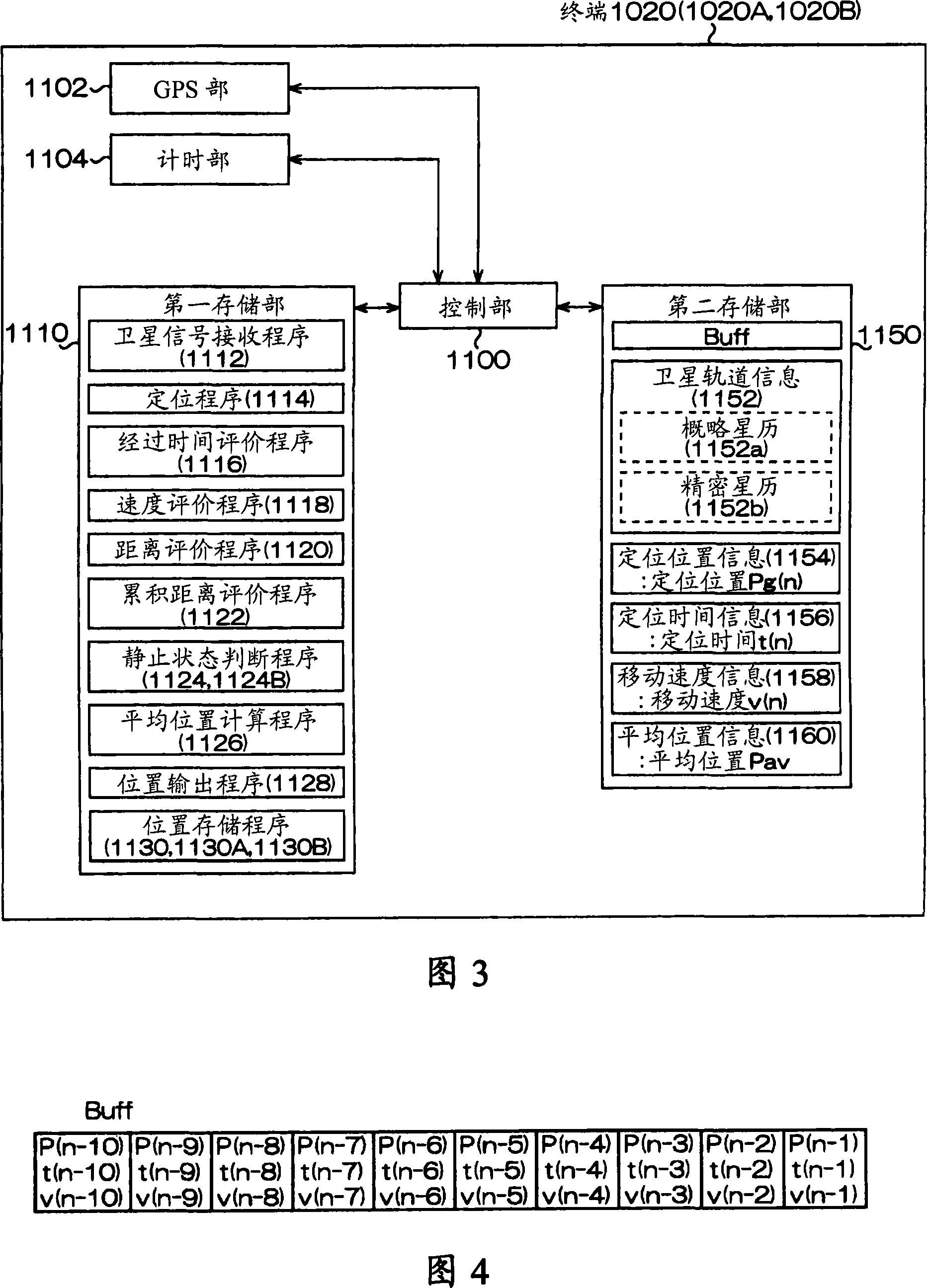
Positioning device, method of controlling positioning device, and recording medium
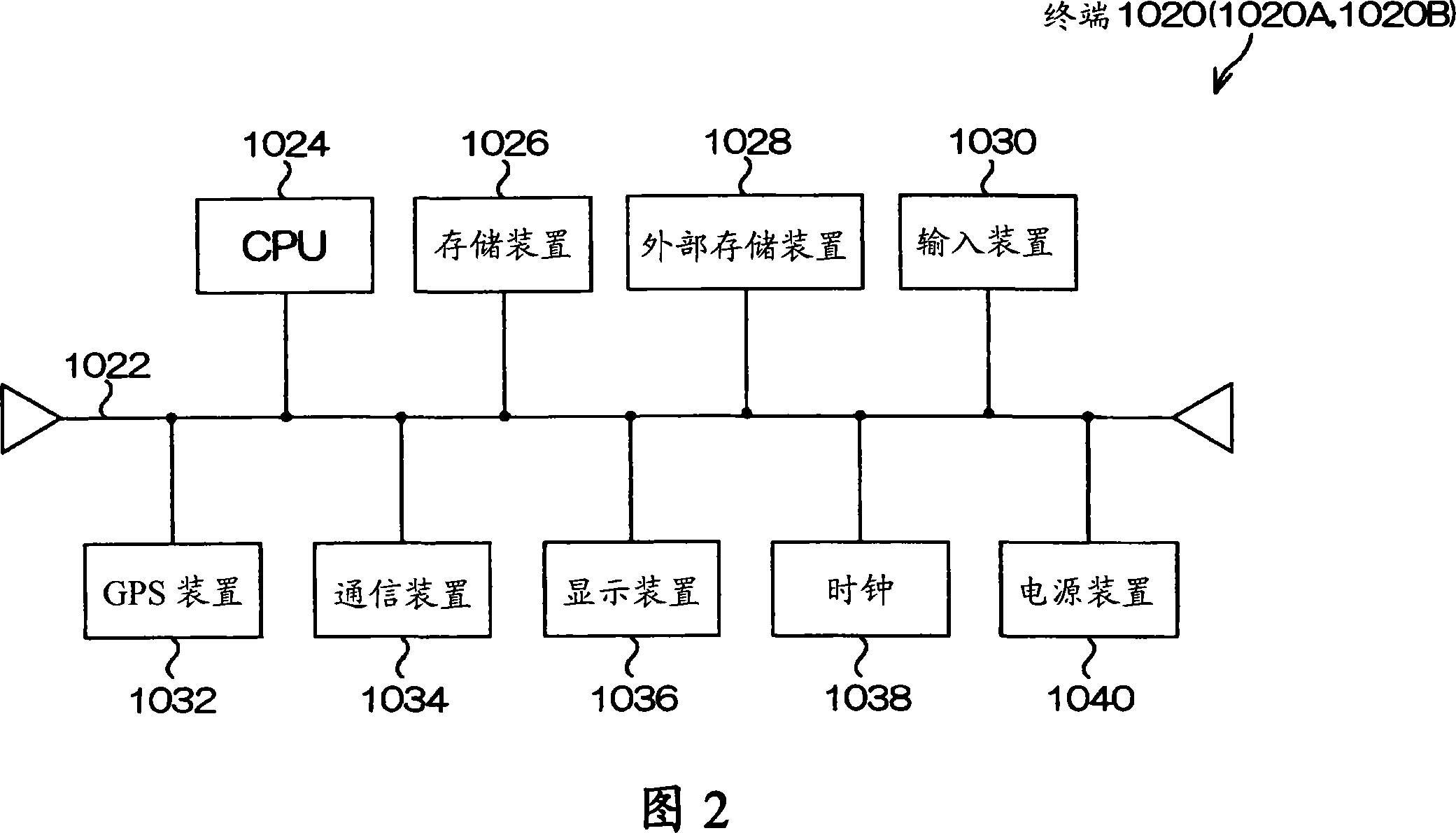
A positioning device, which locates a position based on satellite signals which are signals from positioning satellites, includes a position holding section which holds a reference position P, a stationary condition determination section which determines whether or not the reference position P satisfies stationary conditions B, an average position calculation section which averages the reference position P satisfying the stationary conditions B and a present located position Pg calculated by positioning to calculate an average position Pav, a position output section which outputs the average position Pav, and a position storage section which stores the average position Pav in the position holding section as the reference position P.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Input device
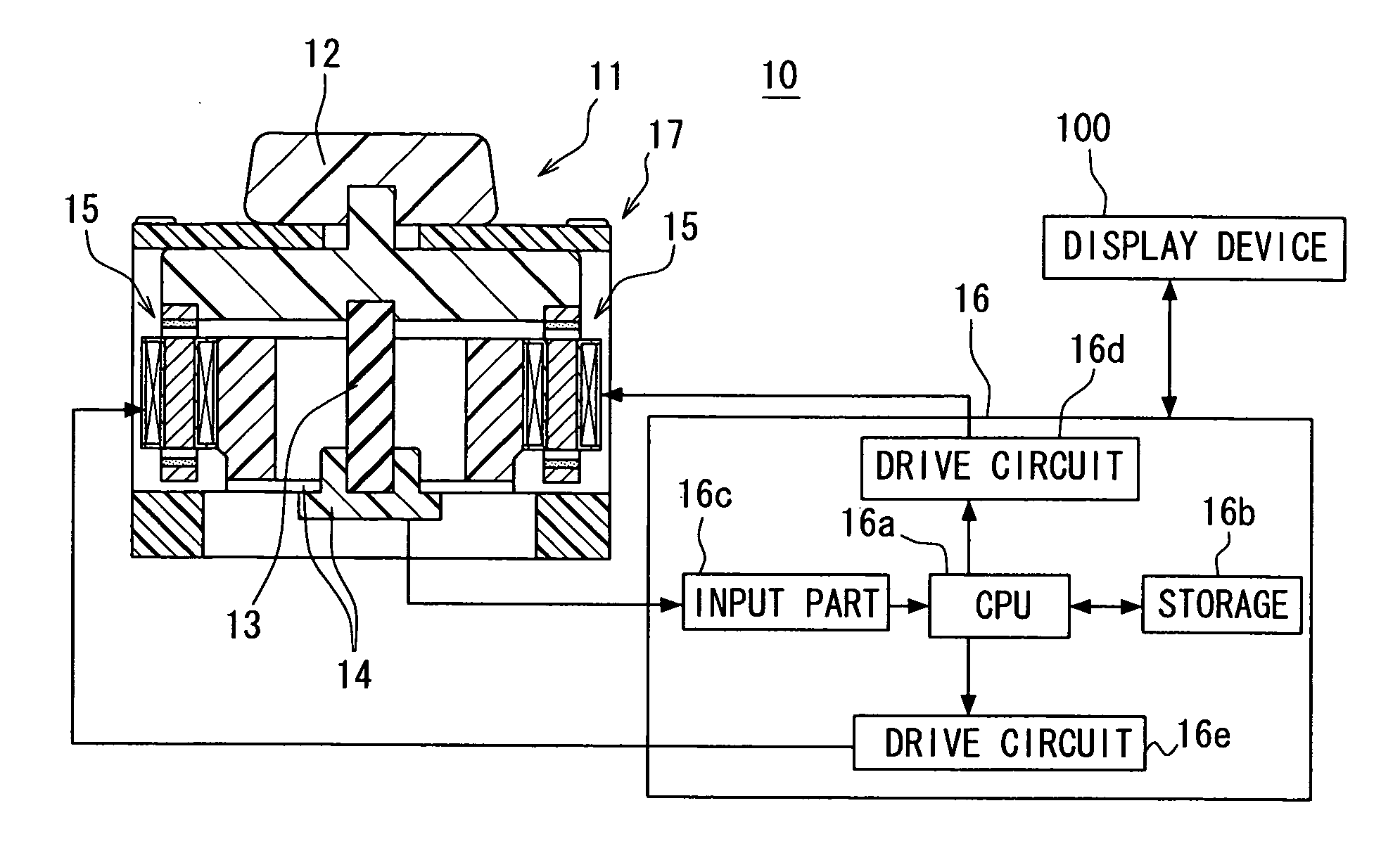
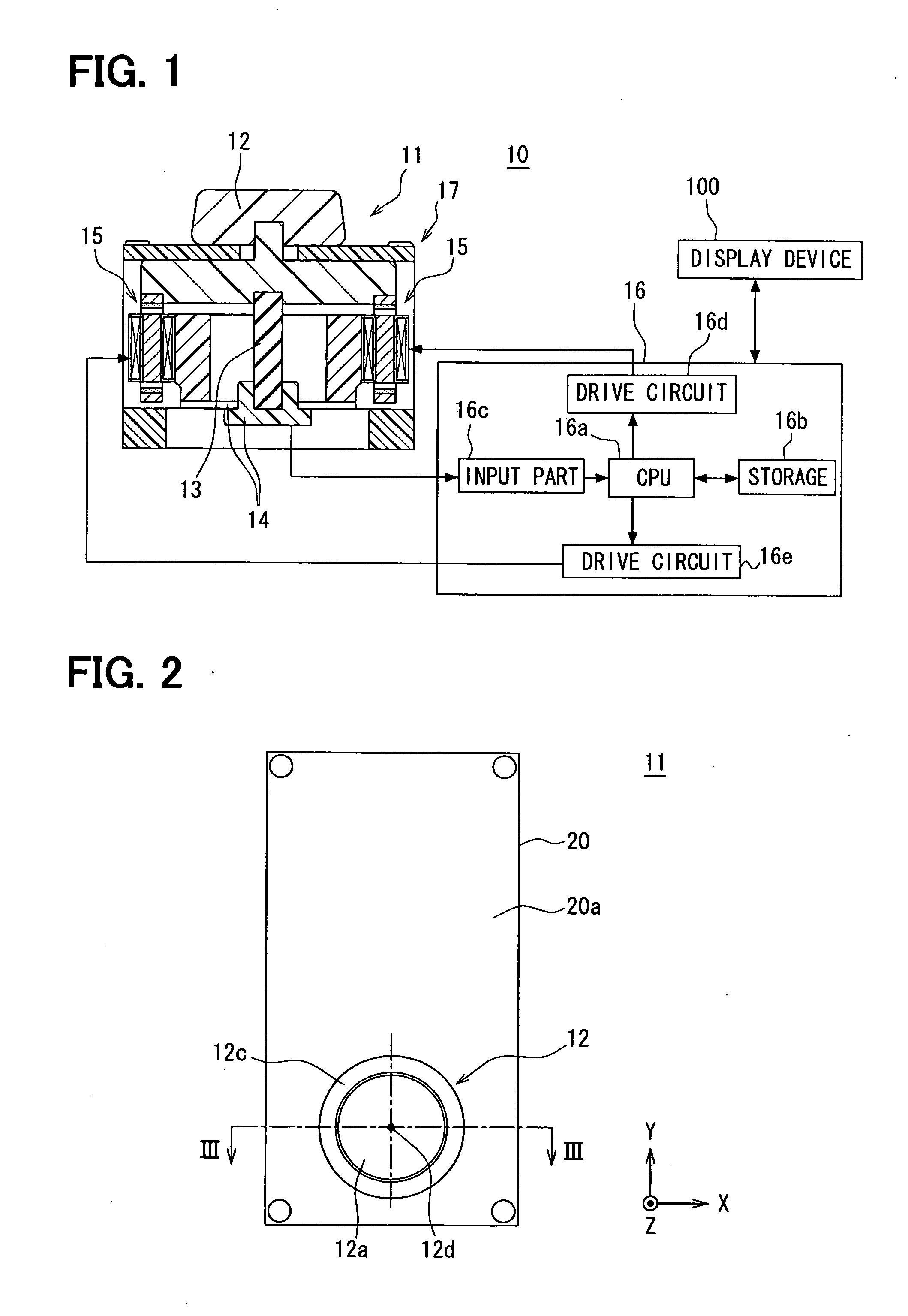
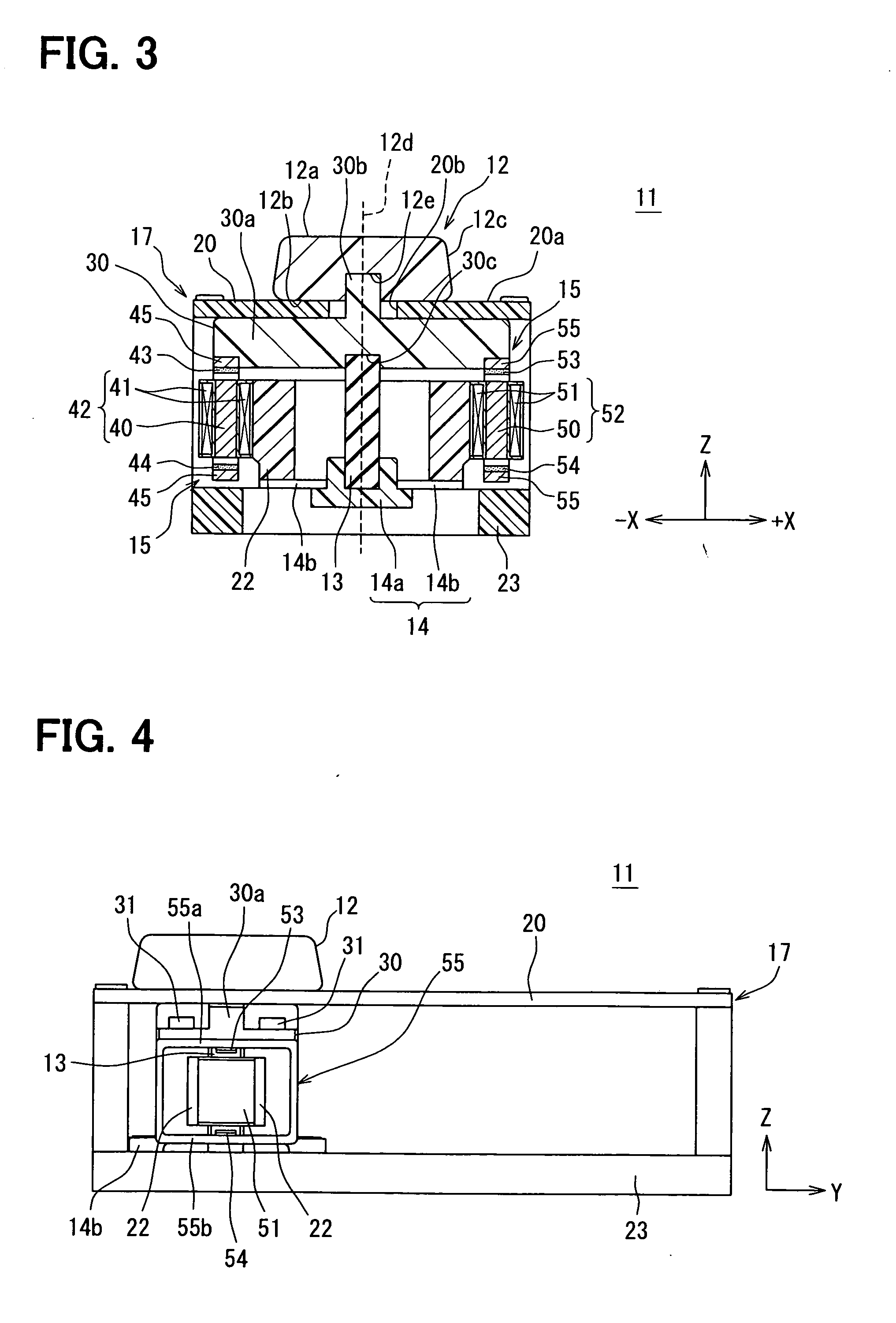
InactiveUS20110140818A1Easy to operateEasy to confirmManual control with multiple controlled membersLimiting/preventing/returning movement of partsStationary conditionsActuator
An input device includes an operating member, a restoring force generating part for automatically returning the operating member to a stationary position, a detector for detecting an operation state of the operating member, an actuator for applying an external force to the operating member and a controller for controlling the actuator. The operating member is displaceable in directions along a XY plane including an X axis and a Y axis and rotatable about a Z axis. The actuator includes a first magnet, a second magnet and an electromagnet having a core and a coil. One of the electromagnet and the first and second magnets is integrated with the operating member. At least in a stationary condition, the first magnet and the second magnet are located on opposite sides of an axis of rotation of the operating member, and are opposed to end surfaces of the core across predetermined clearances, respectively.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
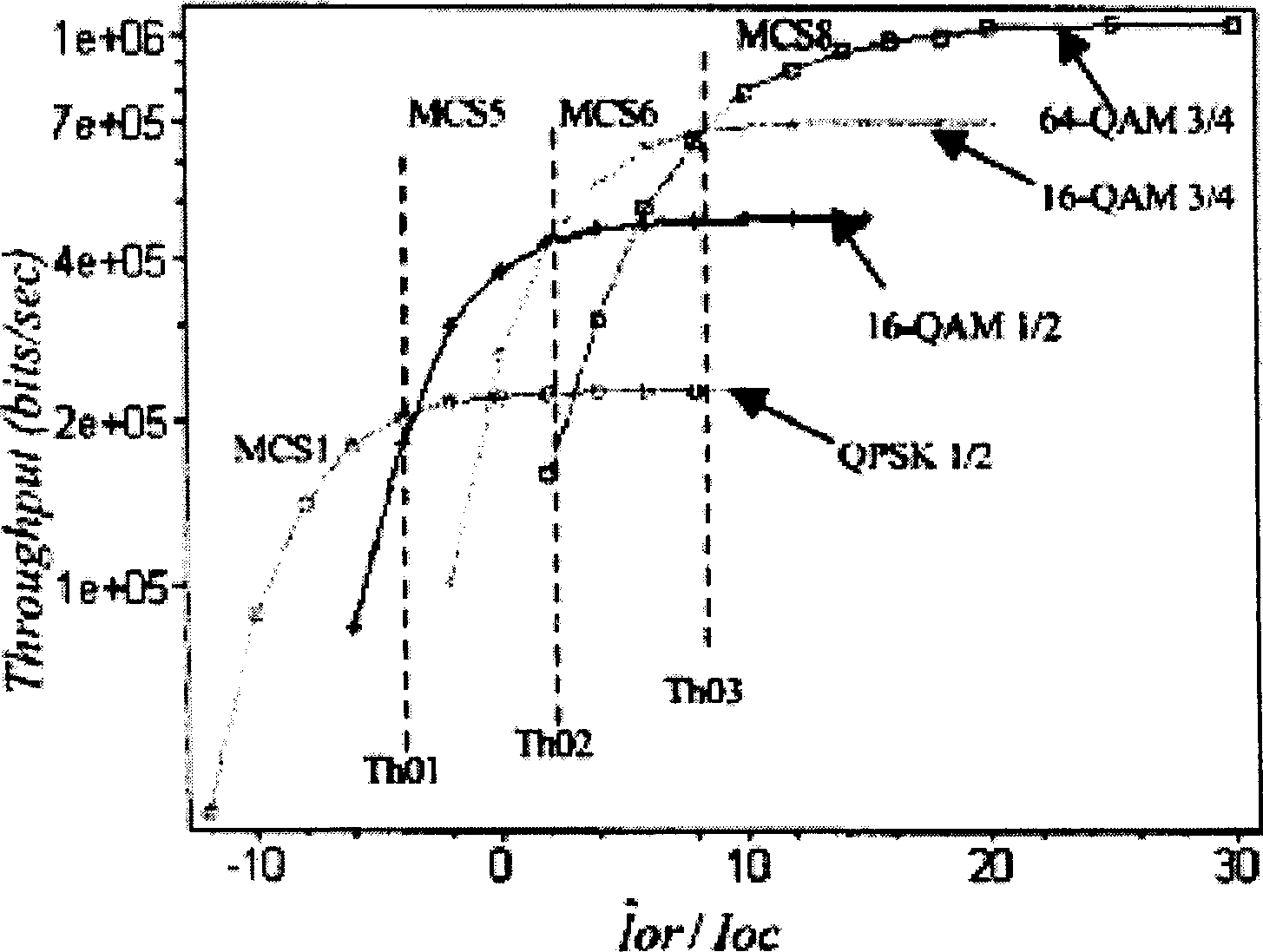
Self-adaptive code modulating method
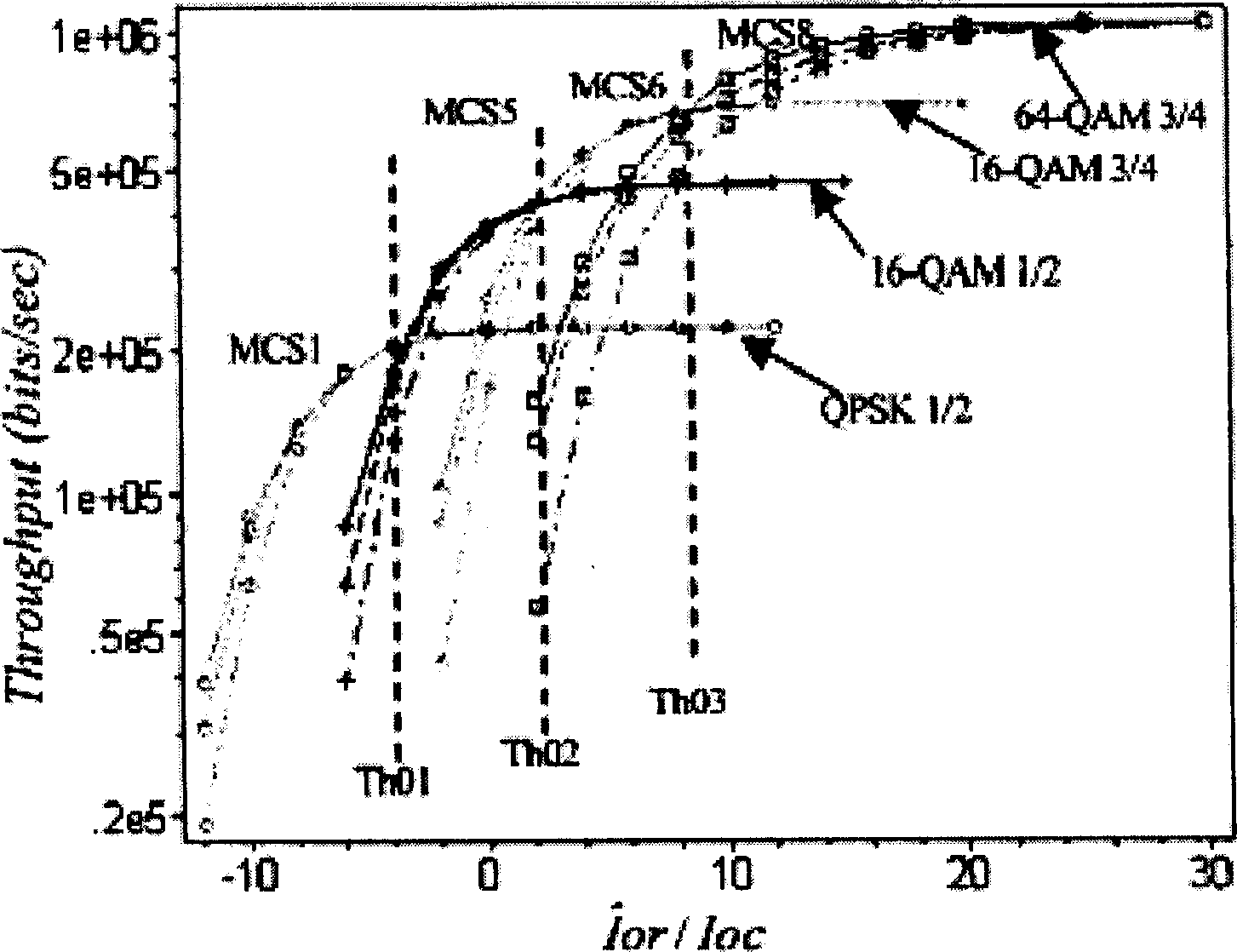
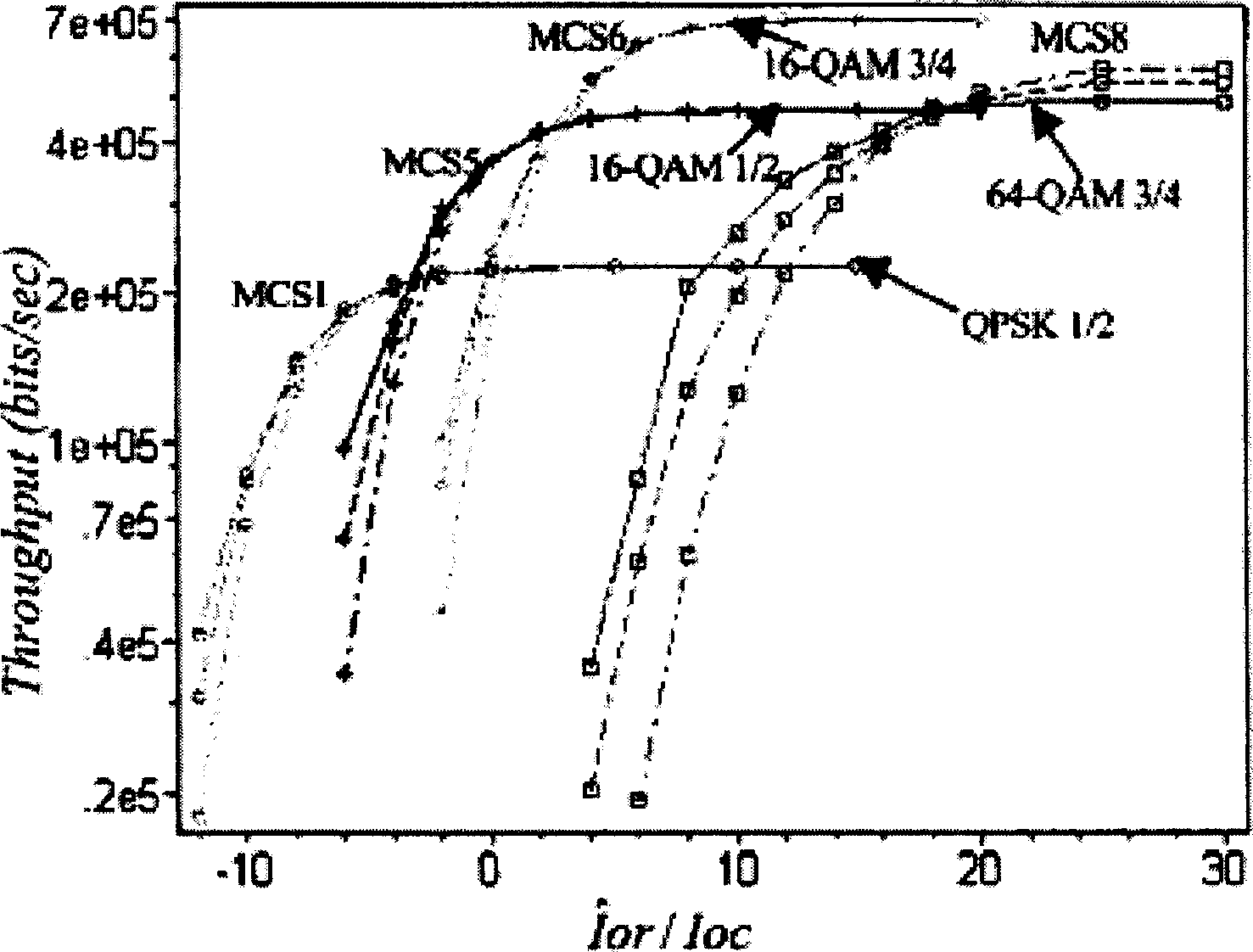
The modulation method for self-adaptive code comprises: determining initial MCS threshold by simulation tested SINR and MCS throughput on single-path quasi-stationary condition; detecting continuously the real-time SINR value; when SINR within prescribed range, detecting the CRC check result, if right, then defining new threshold of MCS equals to the old minus D; or else, defining new threshold of MCS equals to the old plus U; returning to detect real-time SINR value. This invention reduces the sensitivity to SINR as well as to FER variation, and obtains immunity function to common error frame and throughput gain.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Positioning device, method of controlling positioning device
InactiveCN101082665AReliableHigh precisionPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsStationary conditionsSatellite
A positioning device, which locates a position based on satellite signals which are signals from positioning satellites, includes a position holding section which holds a reference position P, a stationary condition determination section which determines whether or not the reference position P satisfies stationary conditions B, an average position calculation section which averages the reference position P satisfying the stationary conditions B and a present located position Pg calculated by positioning to calculate an average position Pav, a position output section which outputs the average position Pav, and a position storage section which stores the average position Pav in the position holding section as the reference position P.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Battery Conservation in Stationary Conditions for a Wireless Device
ActiveUS20140065974A1Improve battery lifeConsiderable energy savingPower managementTransmission monitoringTelecommunicationsSignal quality
Conserving battery by a wireless user equipment (UE) device in substantially stationary conditions. A first wireless link may be established with a first cell. It may be determined that the UE device is substantially stationary. One or more signal strength and / or signal quality metrics associated with the first wireless link may be measured. The one or more signal strength and / or signal quality metrics may be below a first threshold. The UE may ordinarily be configured to perform a search for neighboring cells if the one or more signal strength and / or signal quality metrics are below the first threshold. The UE may not actually perform a search for neighboring cells, based on determining that the UE is substantially stationary.
Owner:APPLE INC
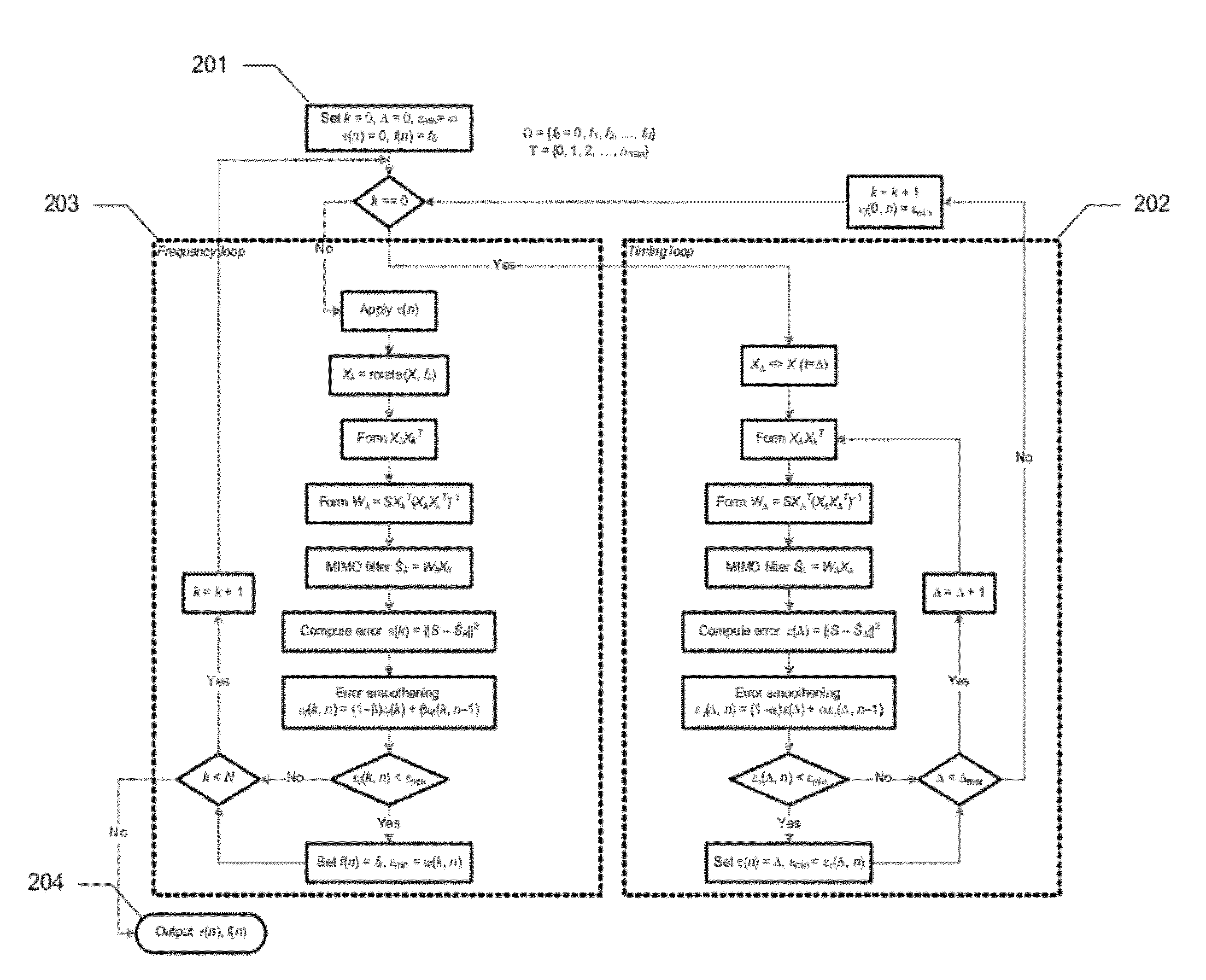
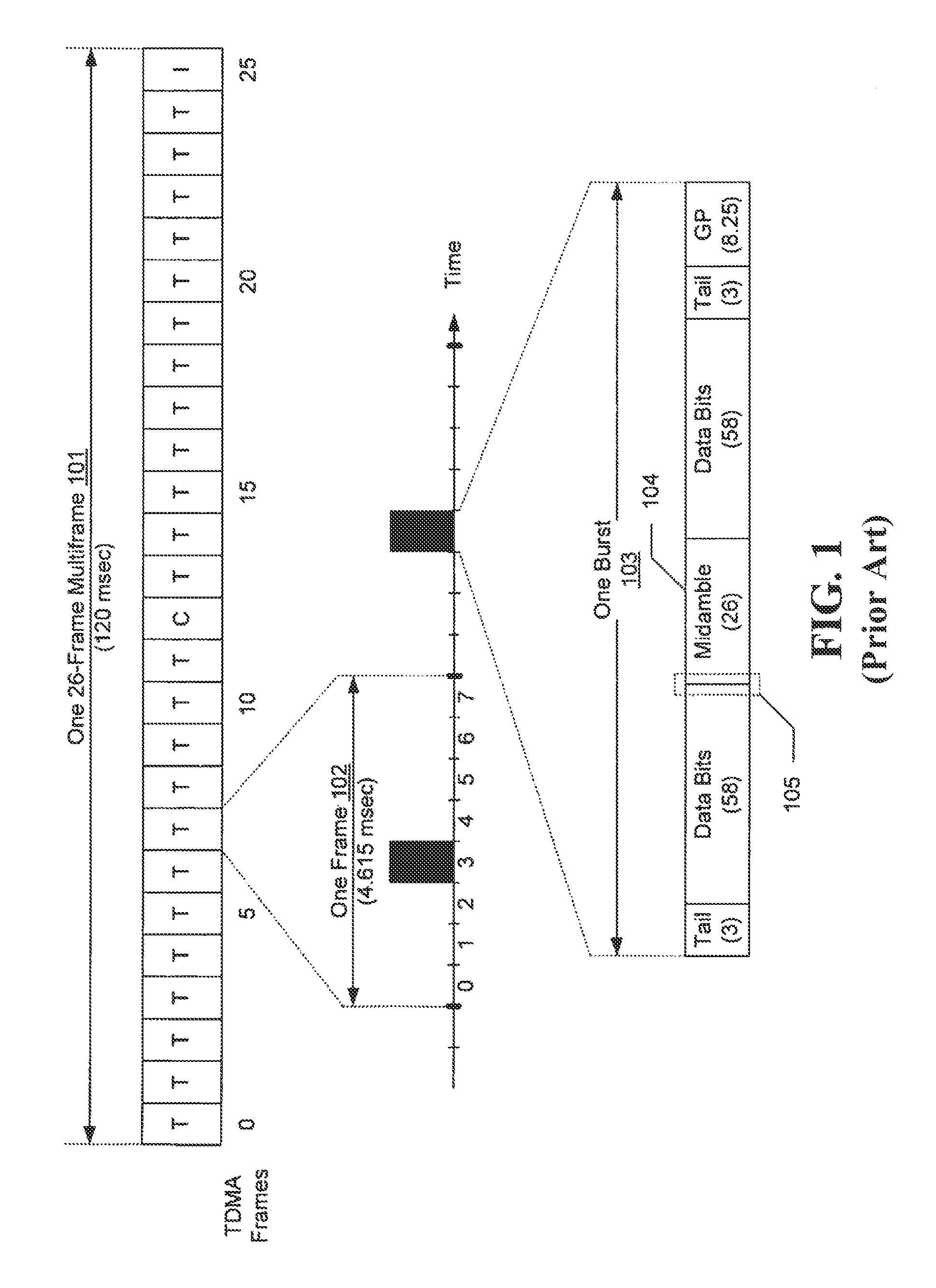
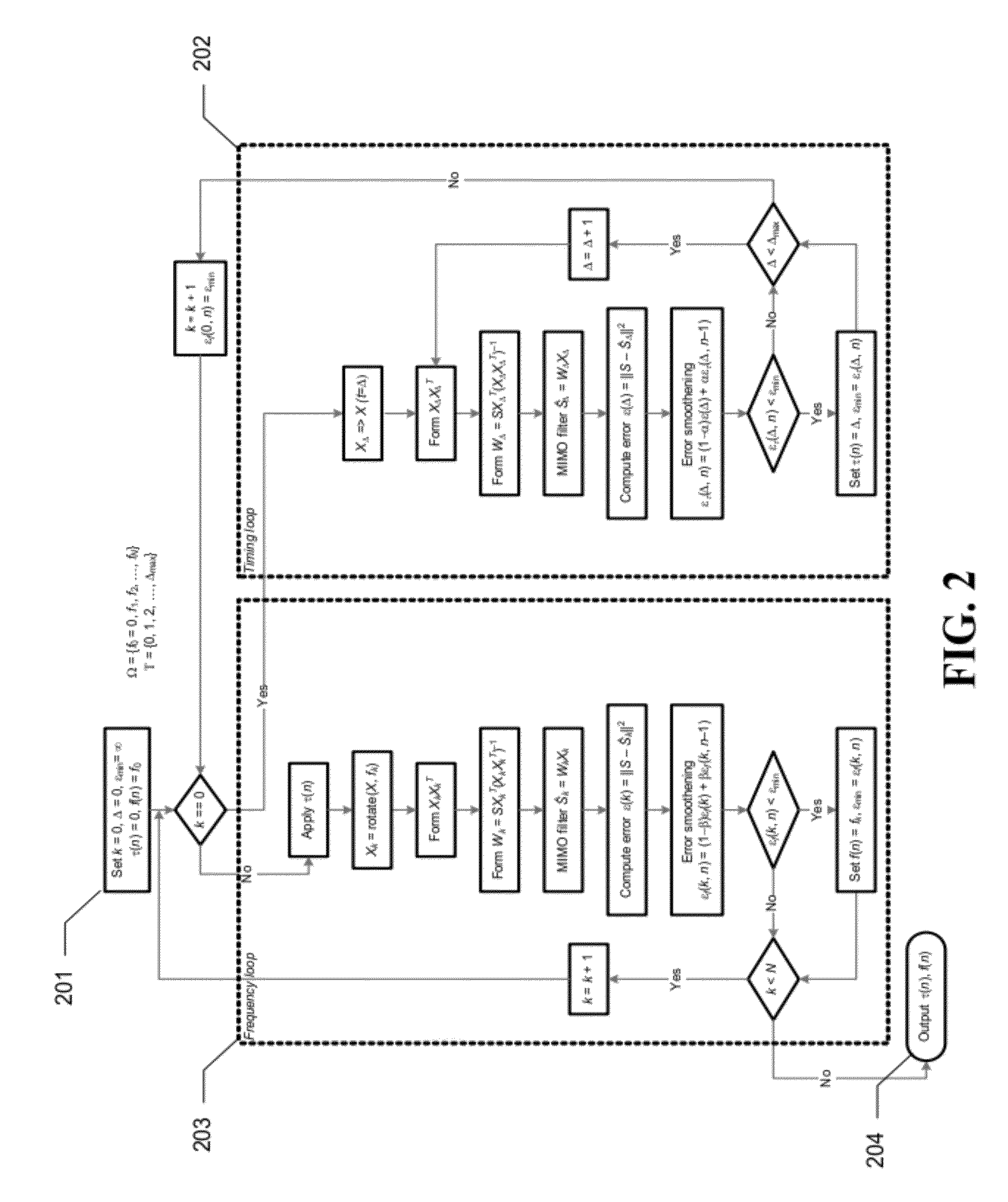
Interference cancellation under non-stationary conditions
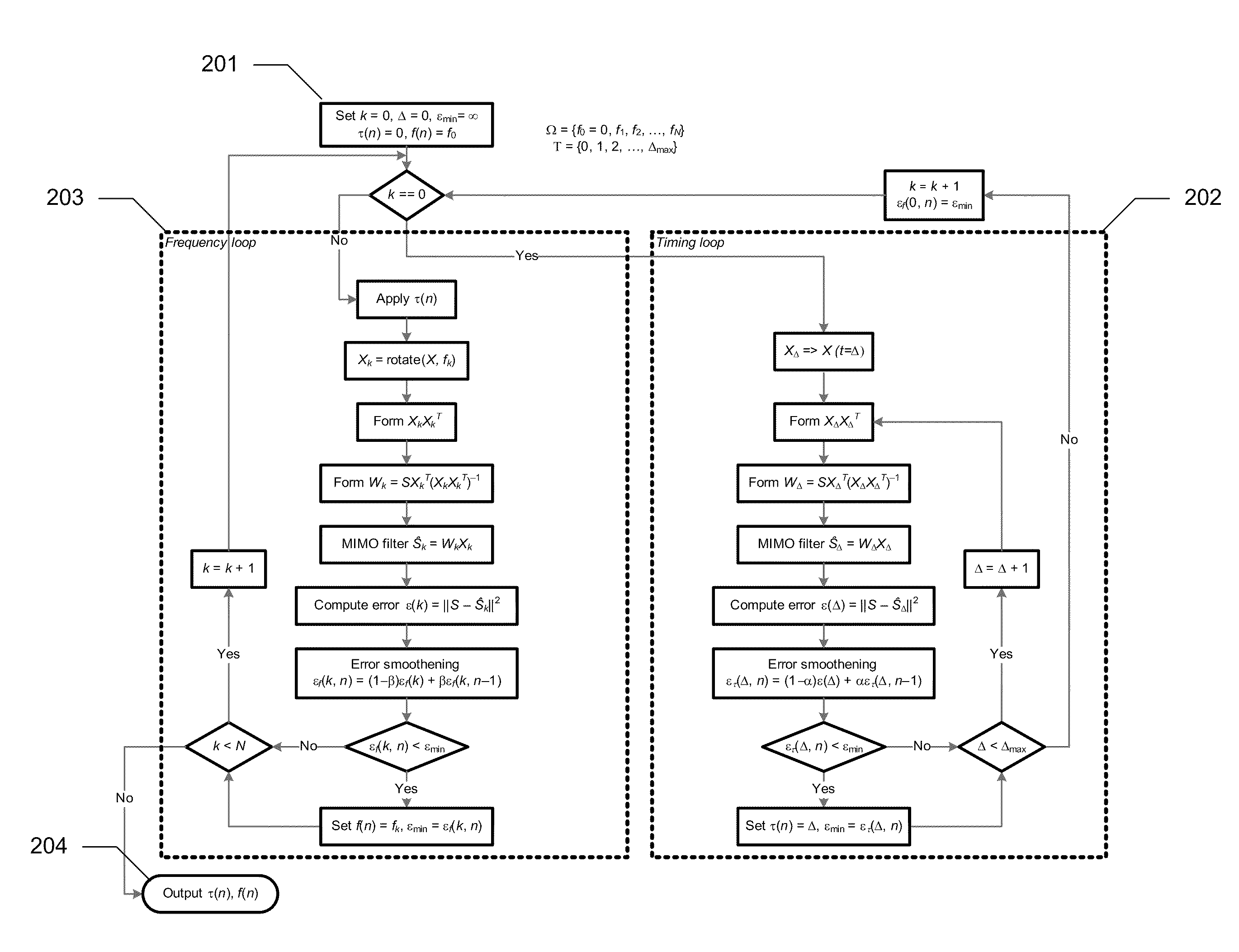
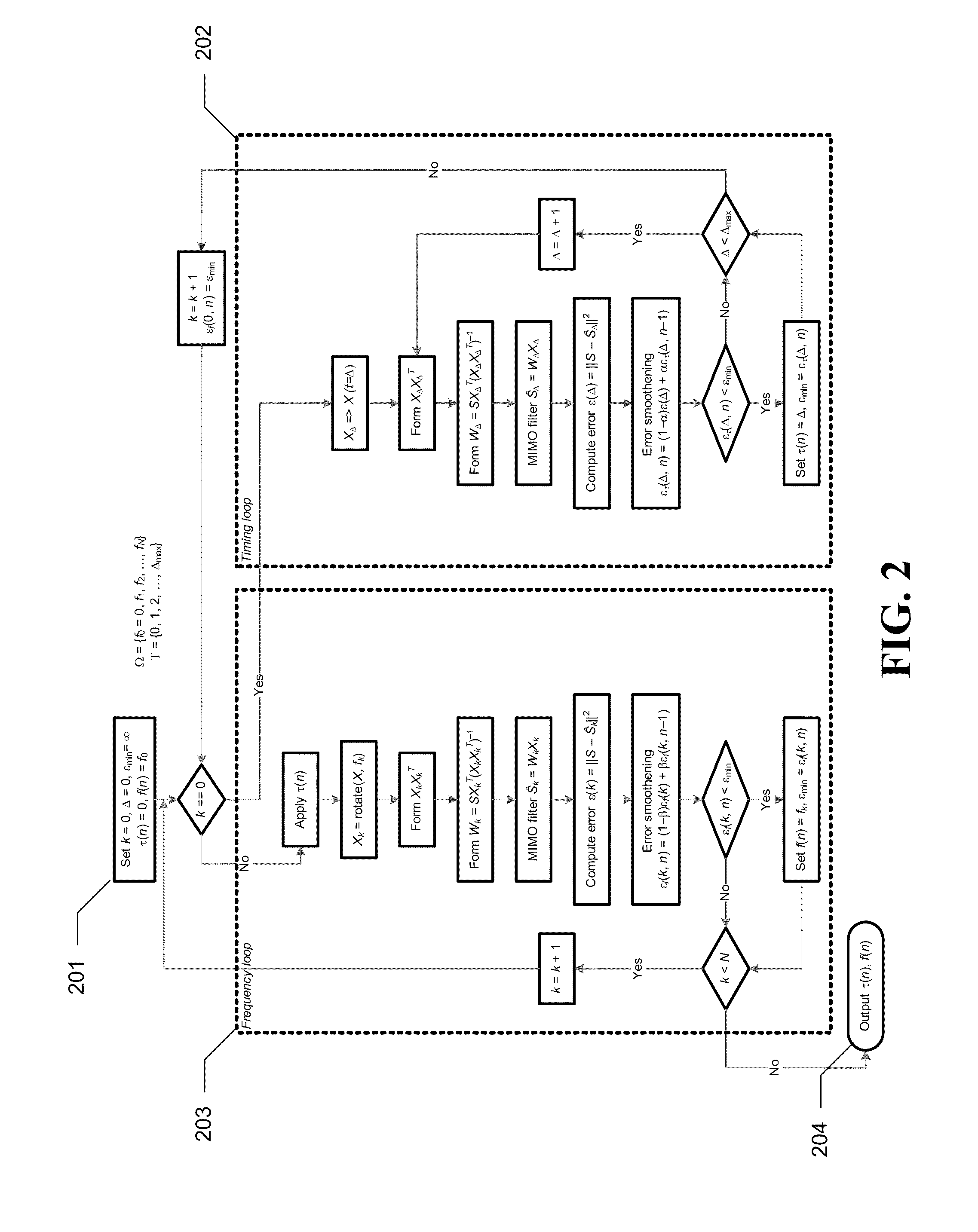
InactiveUS20110305303A1Improve received signal qualityEstimate degradedSynchronisation arrangementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsStationary conditionsComputer science
A method for timing and frequency synchronization in a wireless system is provided. The method comprises the steps of receiving a burst of symbols, selecting a subset of the burst of symbols, iteratively adjusting the subset of the burst of symbols by a plurality of timing offsets and calculating, for each timing offset, a first performance metric corresponding to the adjusted subset. The method further comprises the steps of determining one of the plurality of timing offsets to be a preferred timing offset based upon the first performance metric thereof, iteratively rotating the subset of the burst of symbols by a plurality of frequency offsets and calculating, for each frequency offset, a second performance metric corresponding to the rotated subset, and determining one of the plurality of frequency offsets to be a preferred frequency offset based upon the second performance metric thereof.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Hydrodynamic bore seal
Owner:EXPONENTIAL TECHNOLOGY
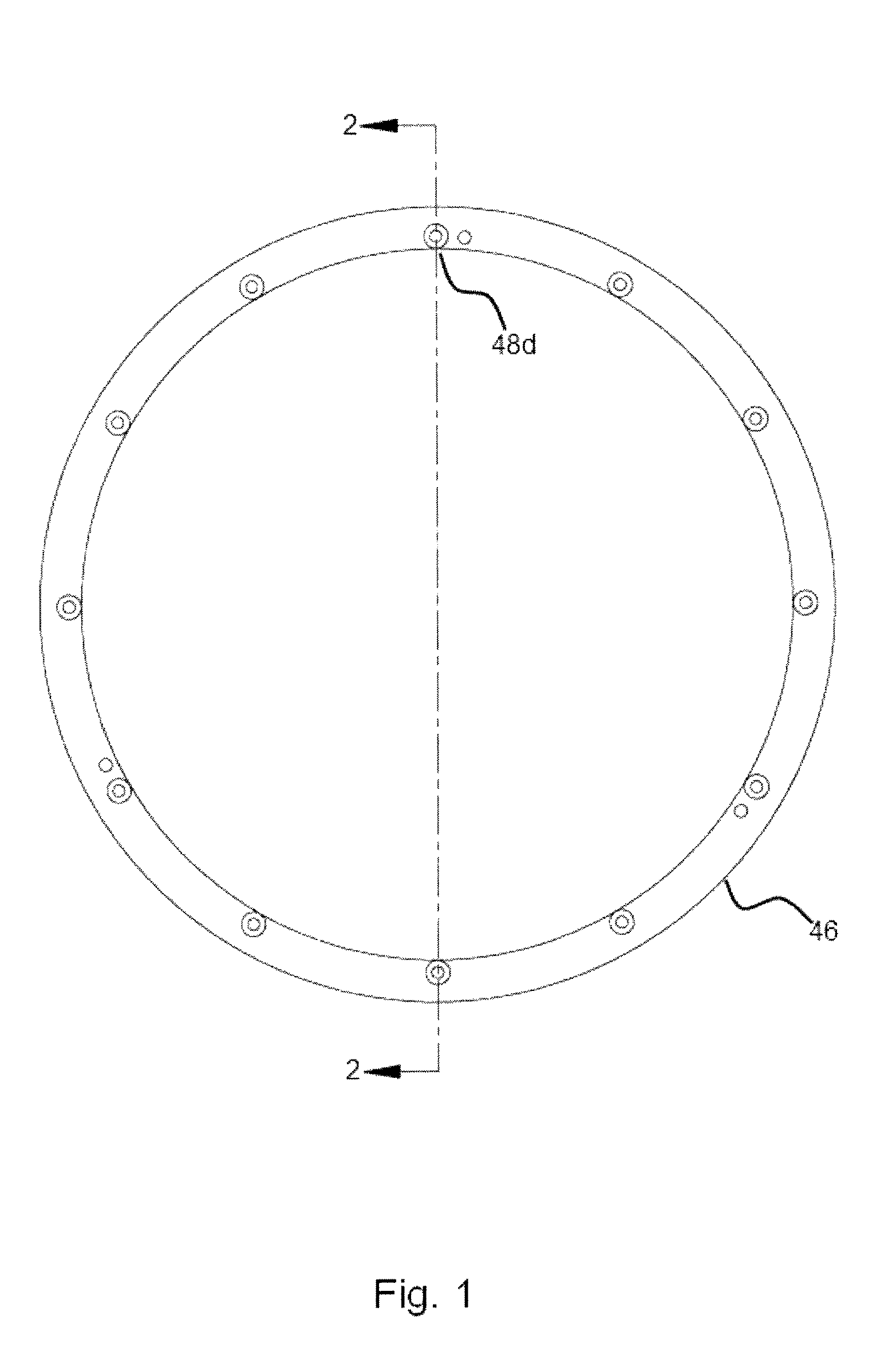
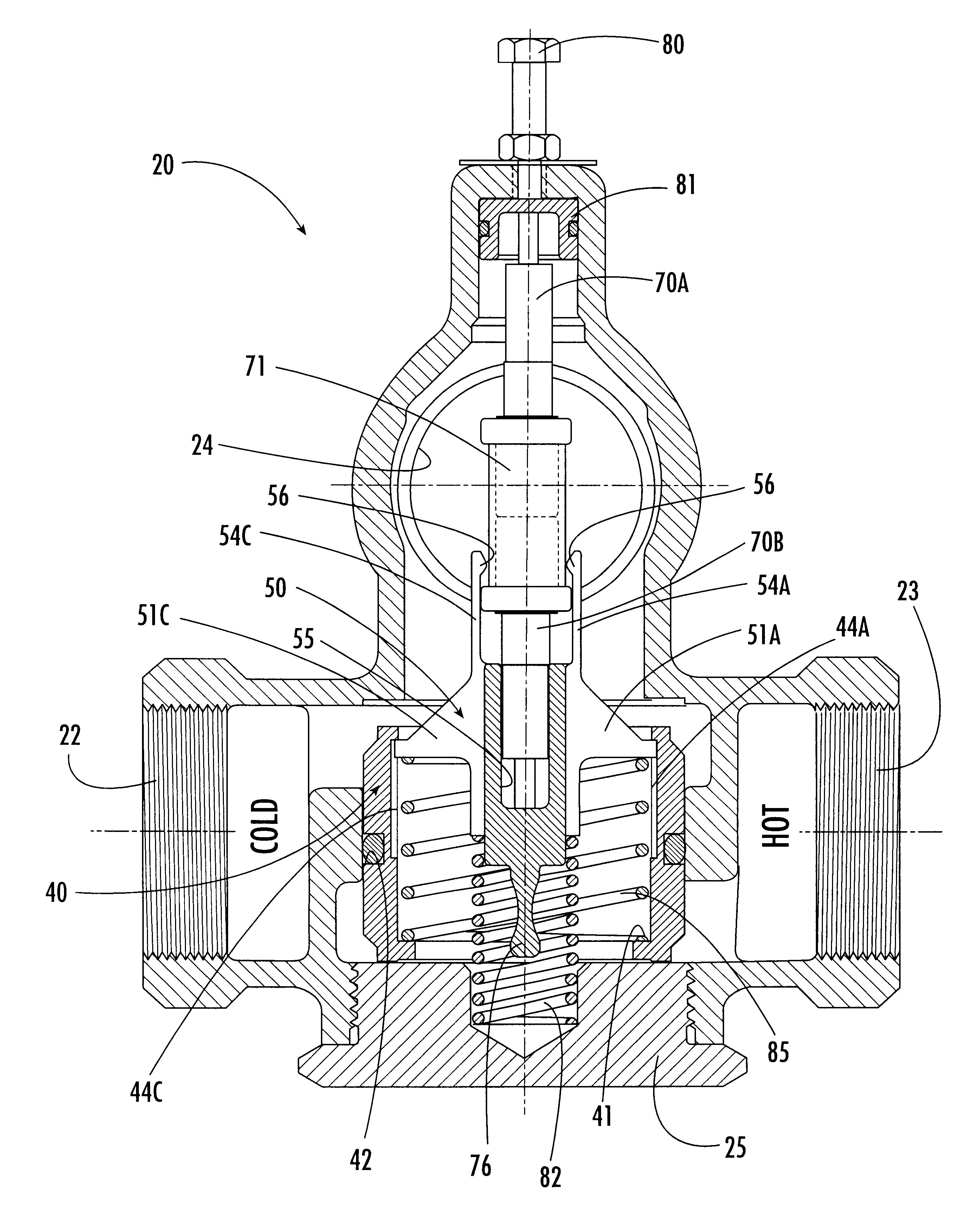
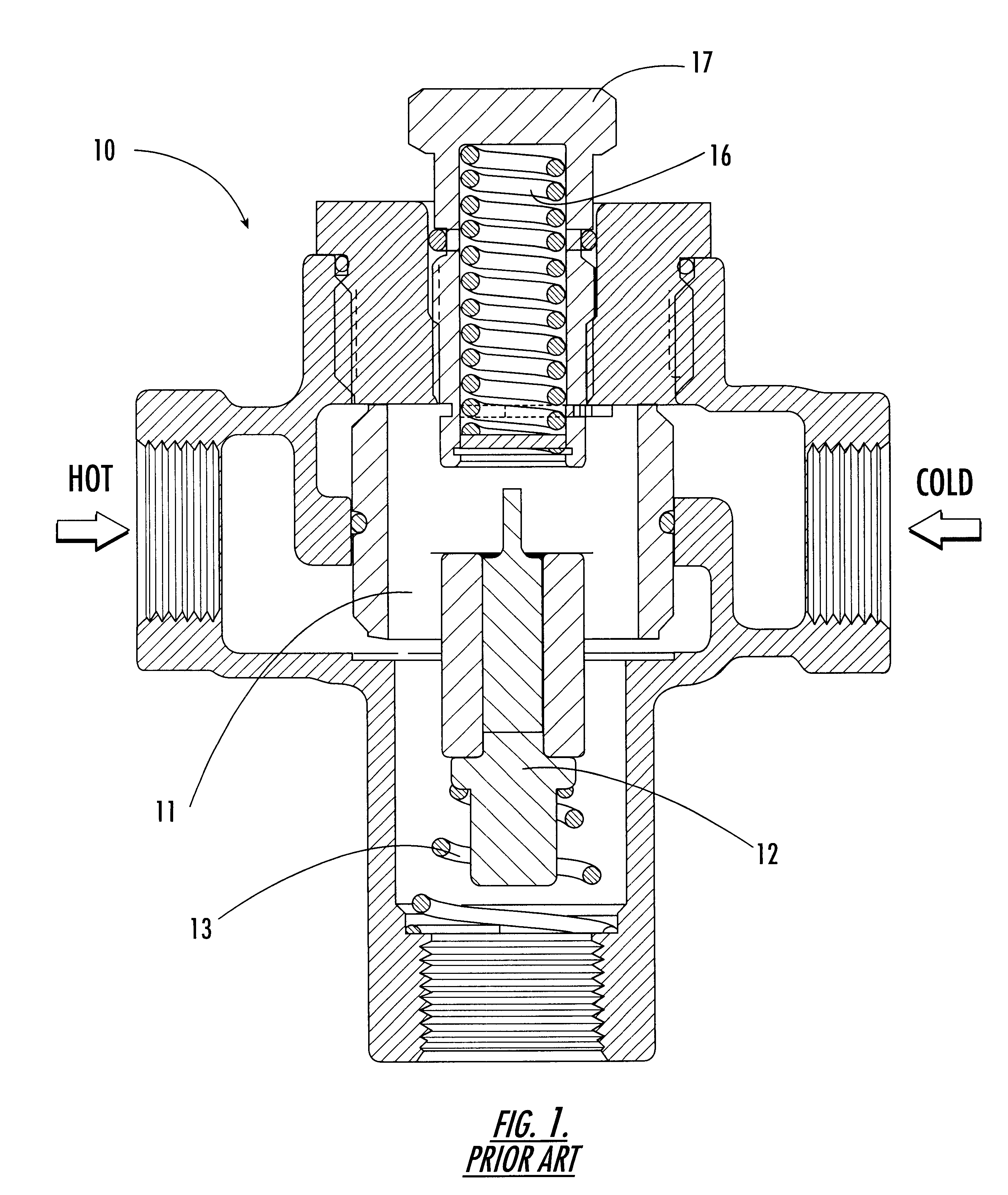
Temperature-responsive mixing valve
InactiveUS6328219B1Easy to disassembleExpand the effective rangeTemperature control without auxillary powerThin material handlingTemperature responseThermal energy
A temperature-actuated mixing valve for controlling outlet temperature in a fluid flow system including a valve housing having first and second fluid supply inlets for introducing first and second respective supply fluids and a fluid outlet for dispensing a fluid at a predetermined outflow temperature. The mixing valve includes a shuttle assembly positioned in the housing. The shuttle assembly includes a valve member mounted for movement within the housing responsive to the temperature of the supply fluids to vary the mixture ratio of the first and second supply fluids as required to dispense fluid at the predetermined outflow temperature. A shuttle member is positioned within the valve member and is moveable as a unit therewith within a predetermined range of motion responsive to supply fluid temperature variation. A thermal actuator is provided of the type which converts thermal energy into mechanical movement by movement of a piston. A first end of the thermal element engages the movable shuttle member and an opposing second end engages a stationary portion of the housing whereby movement of the piston of the thermal actuator produces corresponding movement of the valve member. An overtravel spring is captured in a tensioned condition between the valve member and the shuttle member for maintaining the shuttle member and the valve member in a stationary condition relative to each other within the predetermined range of motion of the valve member and for permitting movement of the shuttle member relative to the valve member sufficient to accommodate movement of the piston of the thermal actuator when the valve member has reached its limit of travel without accommodating the full extent of movement of the piston of the thermal actuator.
Owner:HILCO CAPITAL
Preparation method of flaky nano-cerium oxide
InactiveCN103991891ANo pollution in the processEasy to prepareNanotechnologyRare earth metal compoundsStationary conditionsCerium
The invention relates to a preparation method of flaky nano-cerium oxide, comprising the following steps: preparing an aqueous solution of water-soluble cerium salt and an aqueous solution of a precipitant carbonate; adding the aqueous solution of carbonate into the aqueous solution of cerium salt within the temperature range of 0-50 DEG C under the condition of stirring; continuously stirring to react for 0.2-2 h so as to obtain a precipitate solution; aging the precipitate solution for 0-48 h under stationary condition and at the temperature of 0-50 DEG C; collecting a precipitate from the precipitate solution; and washing, drying and roasting to obtain flaky nano-cerium oxide. Hydrothermal / alcohol-thermal processes are not required. Flaky nano-cerium oxide is synthesized at one step of solution precipitation reaction at low temperature. Problems of many required raw materials, complex process, harsh production conditions and the like by a hydrothermal / alcohol-thermal method, sol-gel method, micro-emulsion method or traditional liquid phase method are avoided. Technological conditions are mild and easy to control, and the preparation method is environmentally friendly and pollution-free.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
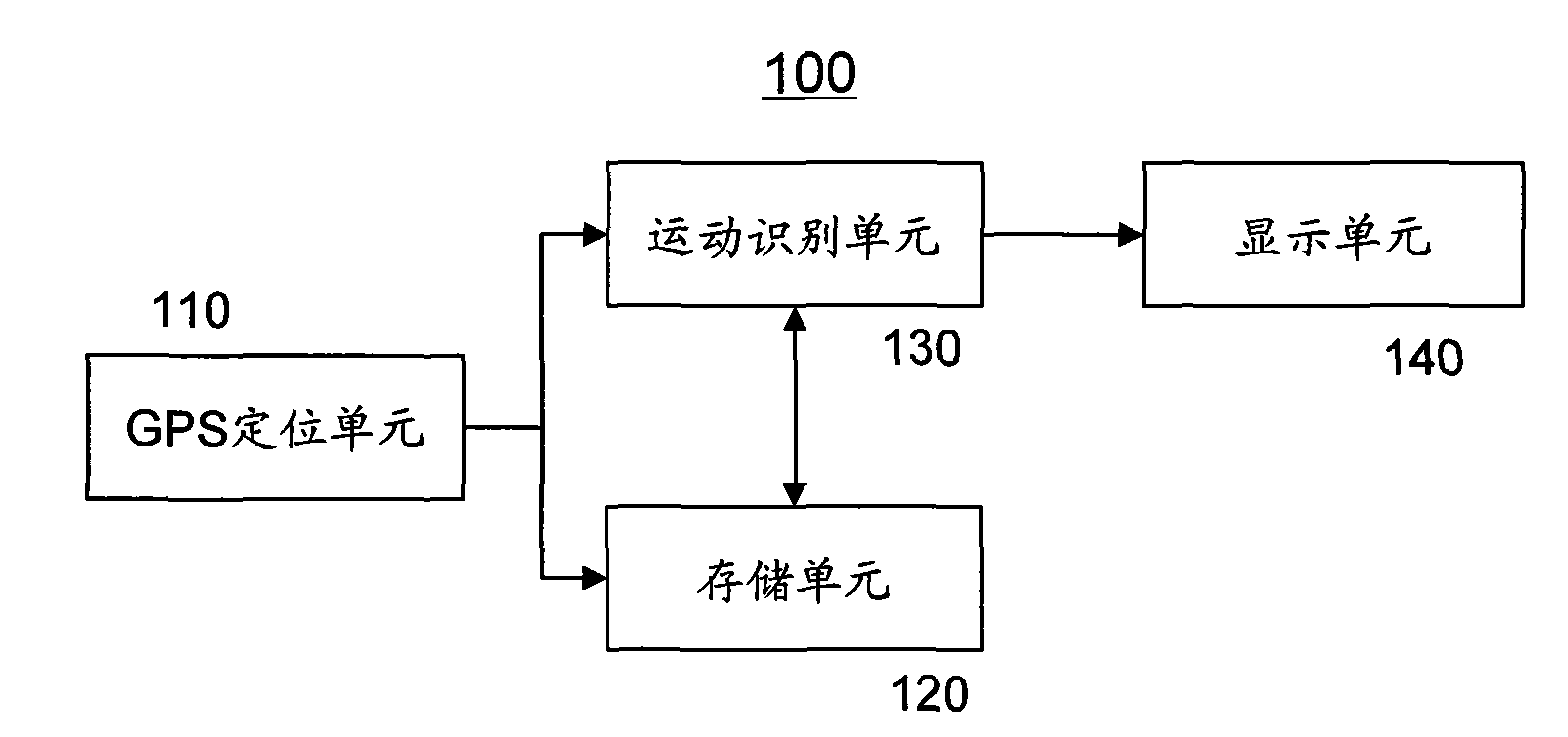
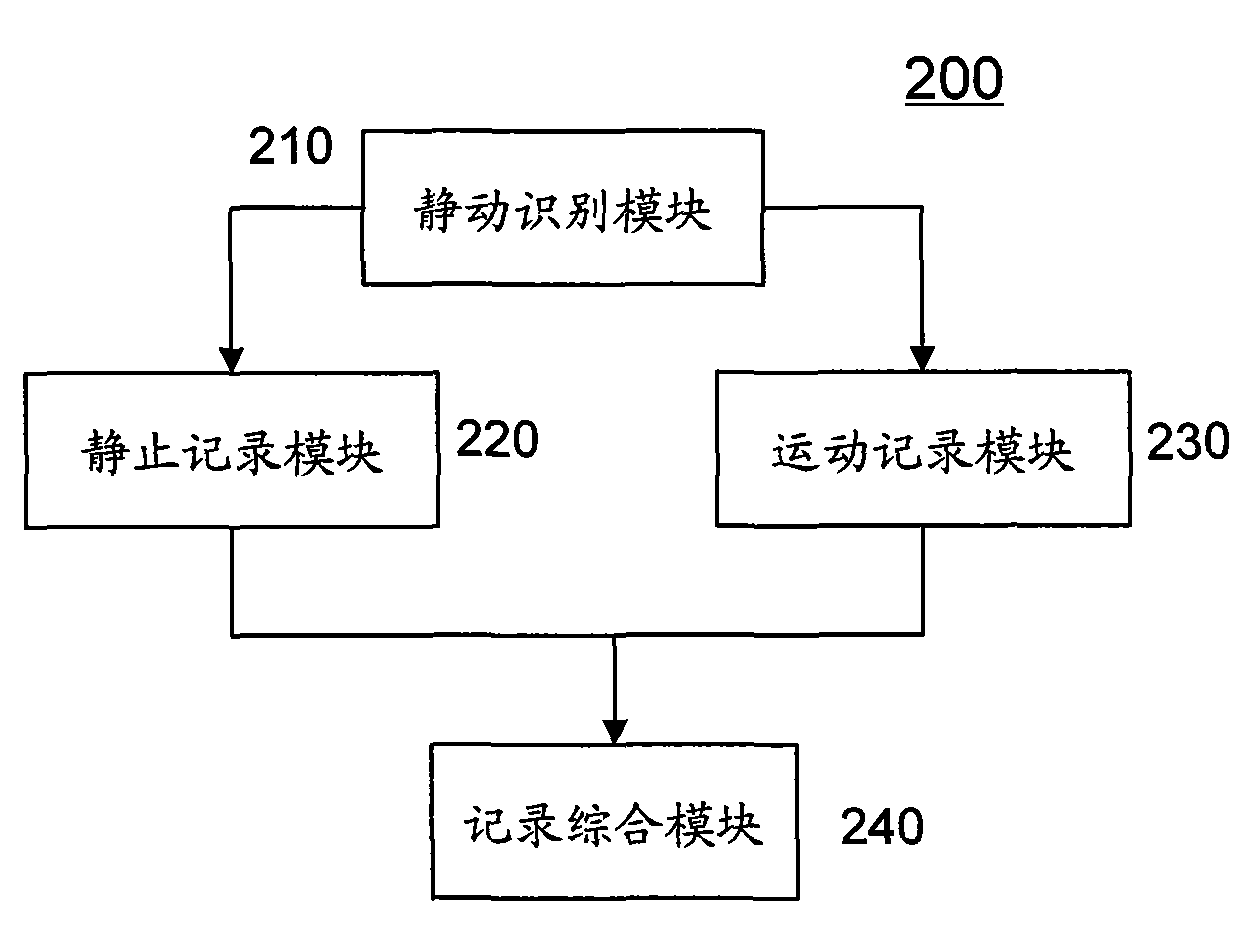
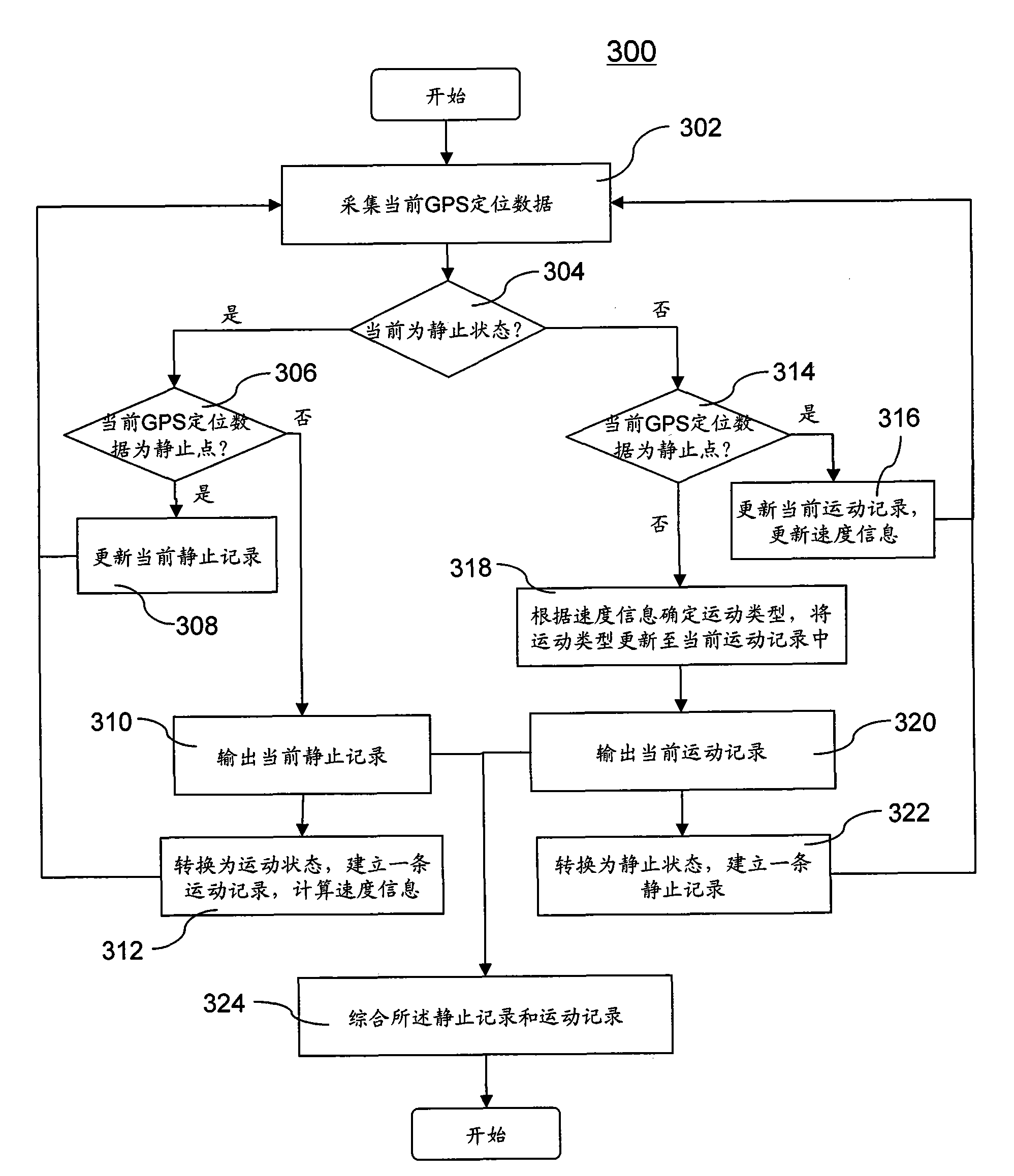
Movement recorder based on GPS positioning and method thereof
InactiveCN101614560AReasonable arrangementUnderstand comprehensivelyPosition fixationRecording measured valuesTime informationStationary conditions
The invention discloses a movement recording method based on GPS positioning, which comprises the following steps: acquiring GPS positioning data every preset interval, wherein the GPS positioning data comprises position coordinates and time; and performing movement identification on the GPS positioning data in a period of time to obtain a movement record and a stationary record of the period of time, wherein the movement record at least comprises movement distance information; and the stationary record at least comprises stationary time information. Therefore, the movement record and the stationary record in the period of time can be obtained by movement identification on the GPS positioning data in a day, a week, a month or a year, and a user views the records to comprehensively understand and master the own movement condition and stationary condition in the period of time.
Owner:WUXI ARIXIN ELECRONICS
Method and apparatus for locating position of a mobile receiver
ActiveUS7158882B2Instruments for road network navigationPosition fixationStationary conditionsSatellite
A method and apparatus for locating position of a mobile receiver is described. In one example, sets of satellite measurements are determined with respect to a plurality of satellites over a period of time. A determination is made as to whether the mobile receiver is in a stationary condition over the period of time. A position of the mobile receiver is then computed using the sets of satellite measurements in response to detection of the stationary condition.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
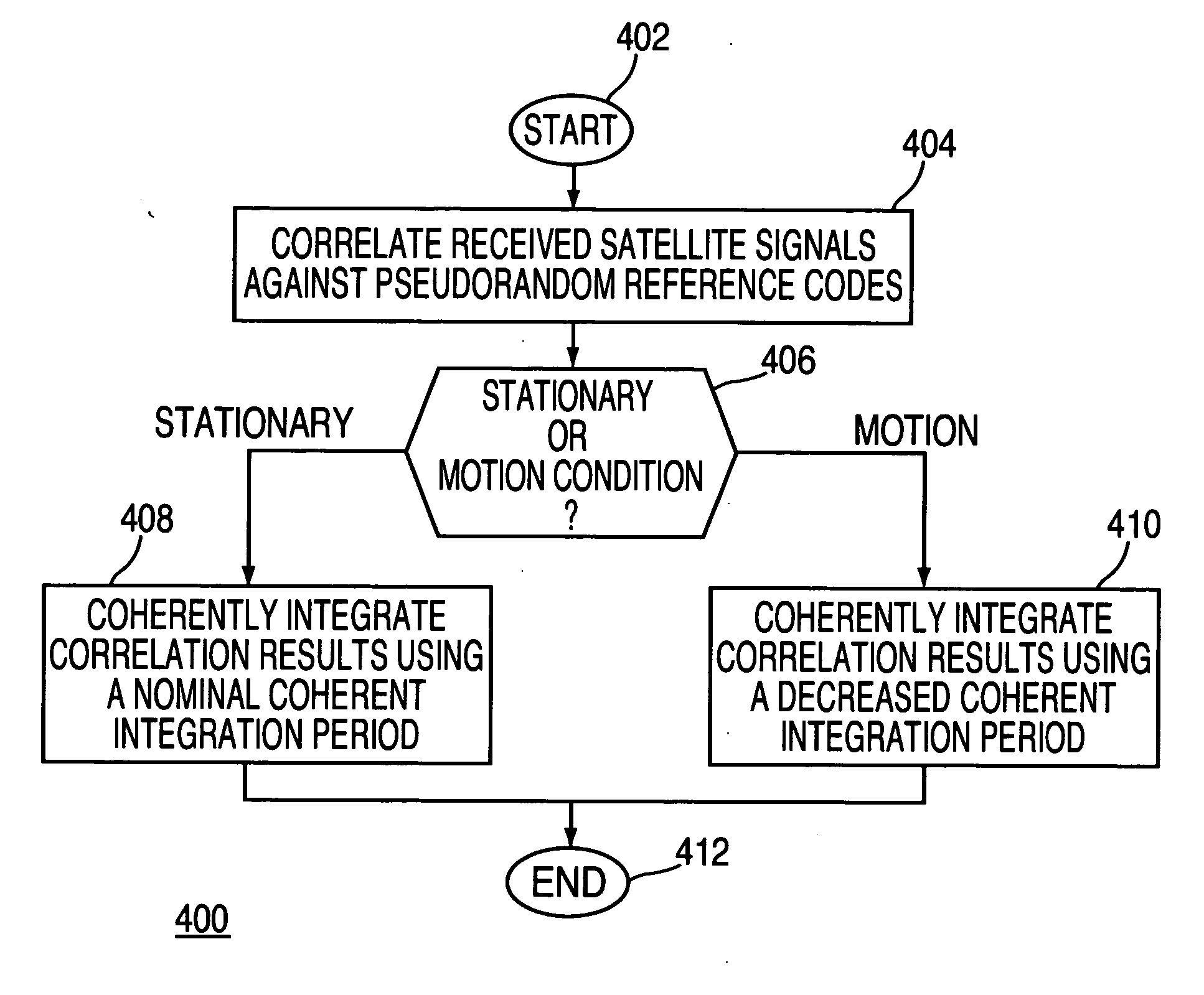
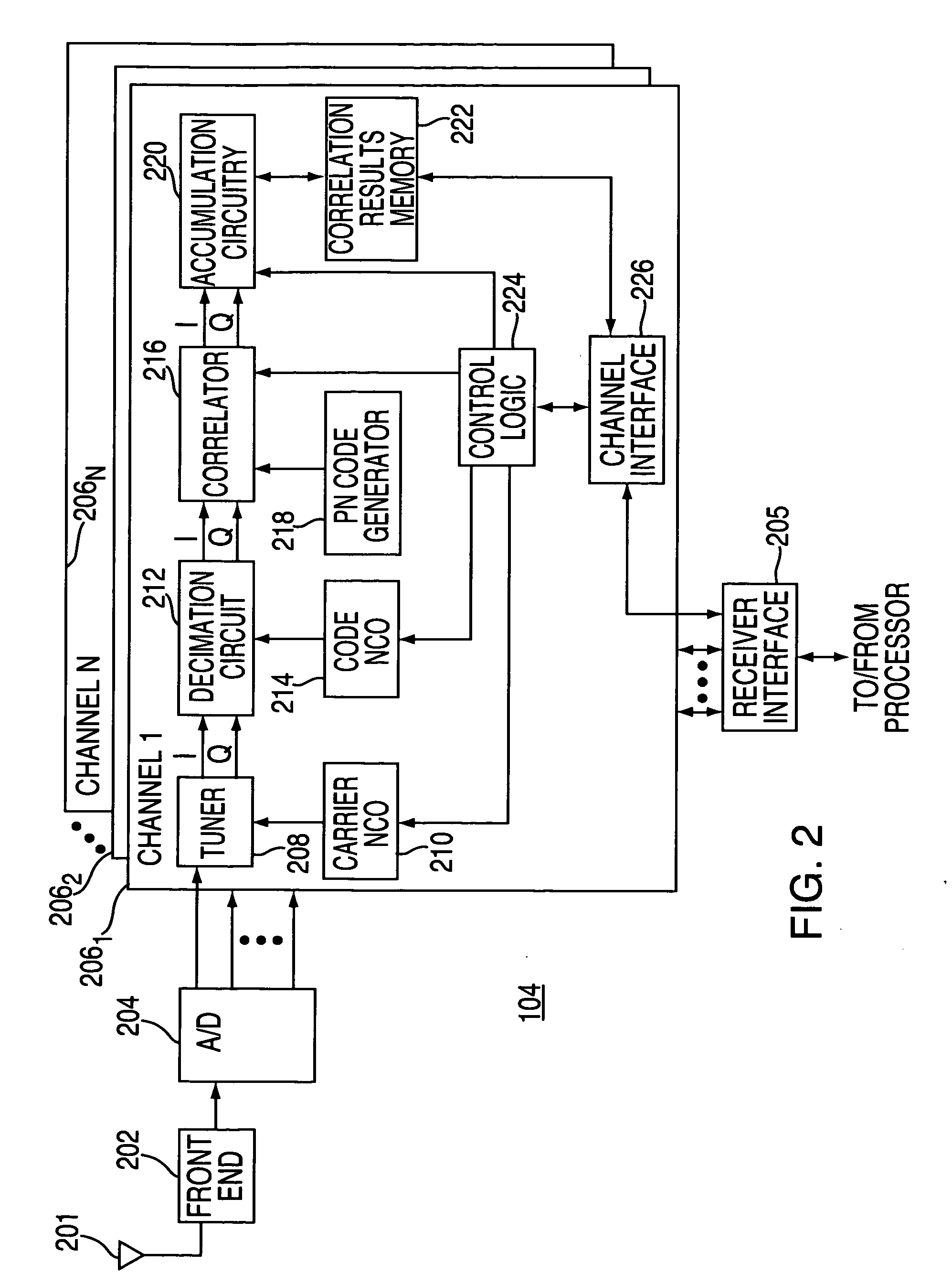
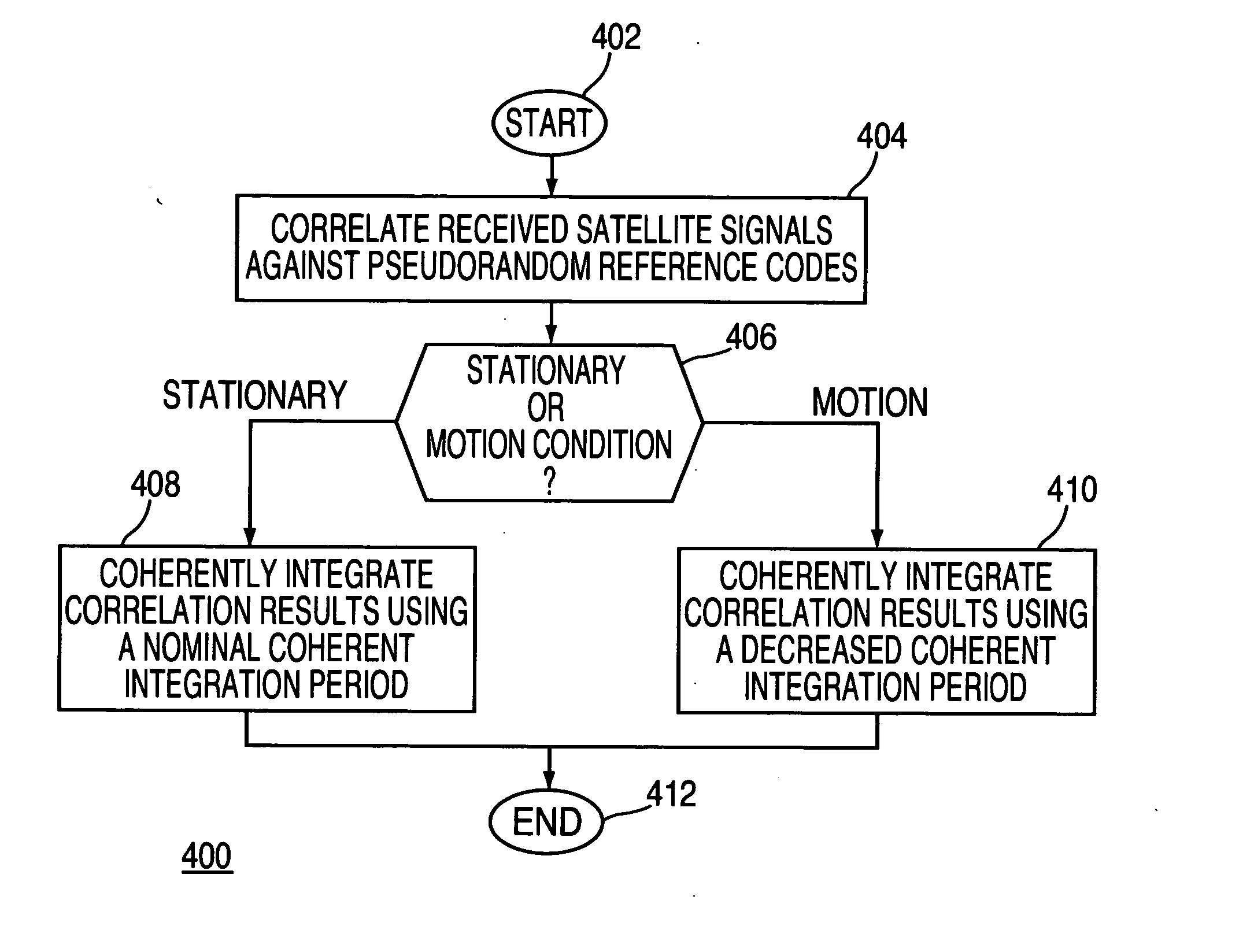
Method and apparatus for processing satellite signals at a satellite positioning system receiver
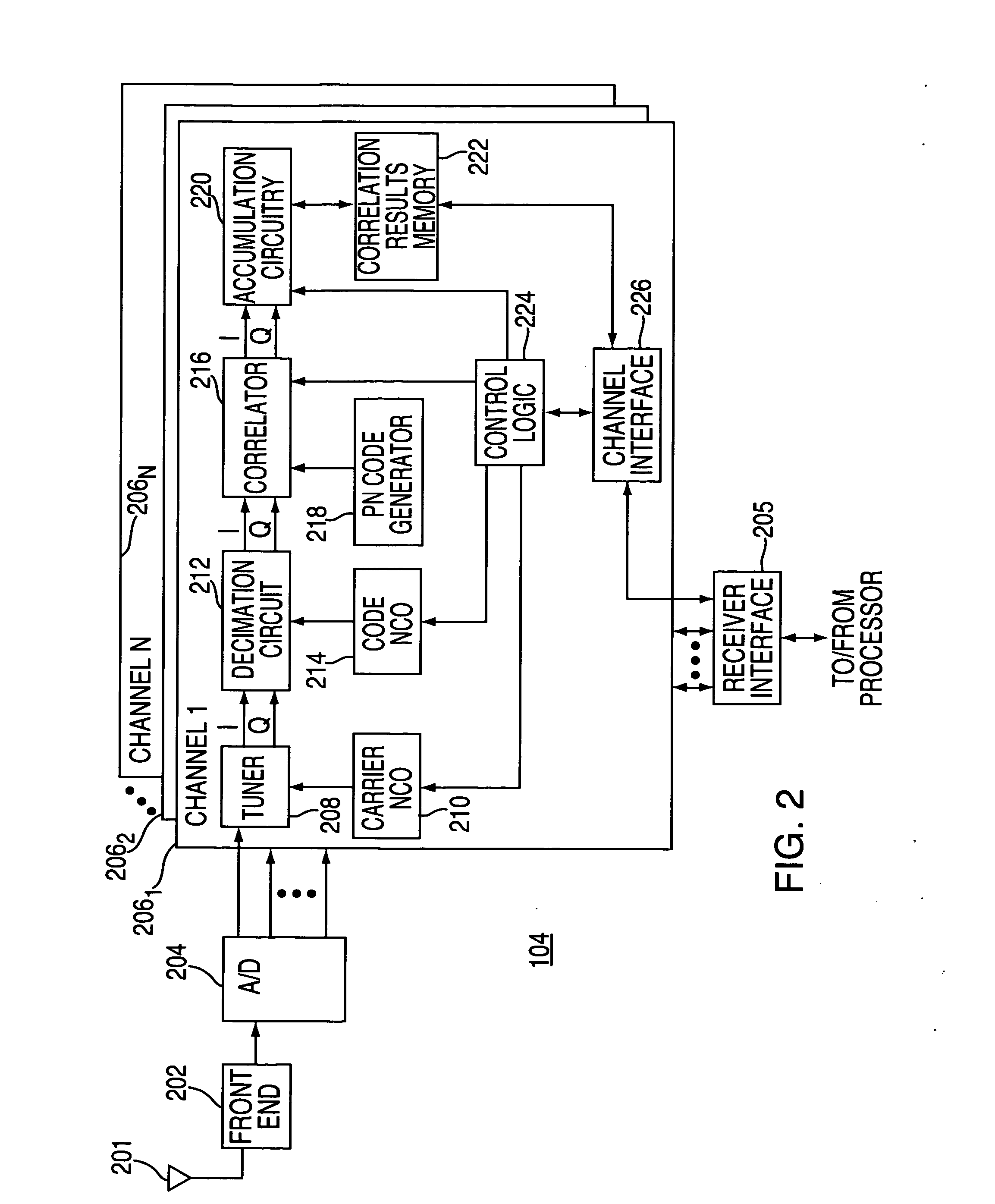
Method and apparatus for processing satellite signals in an SPS receiver is described. In one example, the satellite signals are correlated against pseudorandom reference codes to produce correlation results. A determination is made whether the SPS receiver is in a motion condition or a stationary condition. The correlation results are coherently integrated in accordance with a coherent integration period. The coherent integration period is a value that depends upon the motion condition of the SPS receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for processing satellite signals at a satellite positioning system receiver
Method and apparatus for processing satellite signals in an SPS receiver is described. In one example, the satellite signals are correlated against pseudorandom reference codes to produce correlation results. A determination is made whether the SPS receiver is in a motion condition or a stationary condition. The correlation results are coherently integrated in accordance with a coherent integration period. The coherent integration period is a value that depends upon the motion condition of the SPS receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20070069445A1Easy to assembleElectrographic process apparatusArticle feedersStationary conditionsImage formation
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
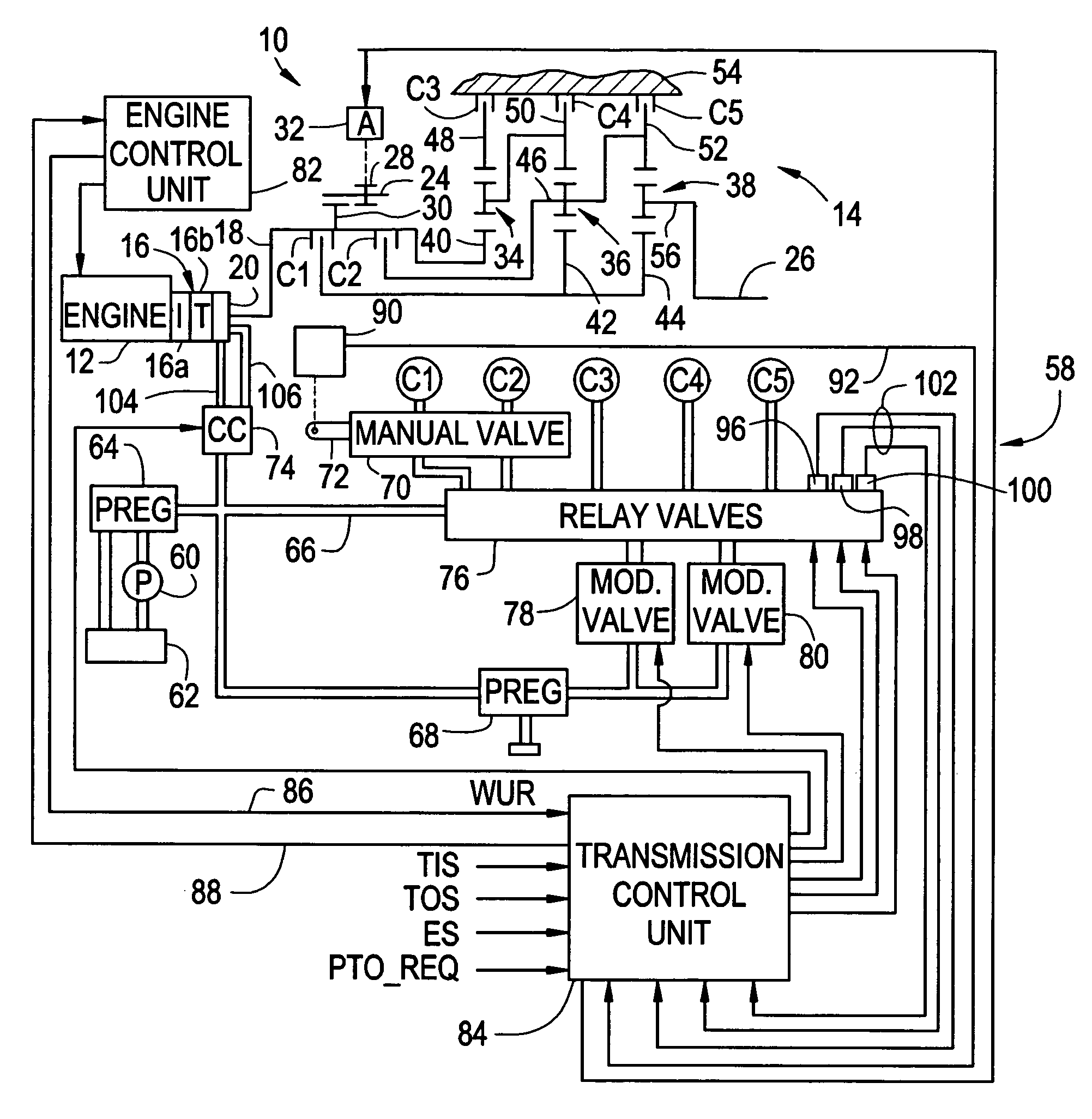
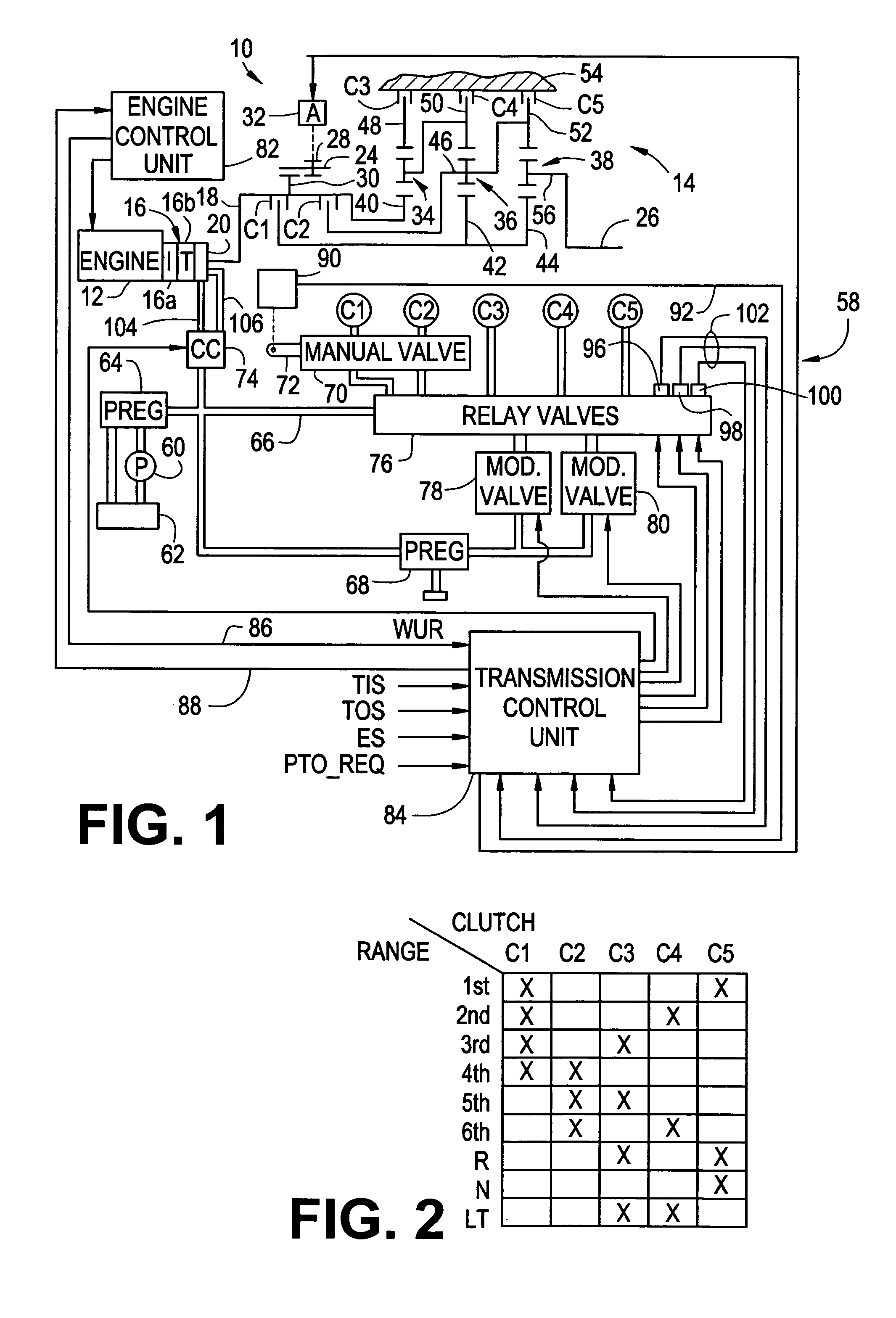
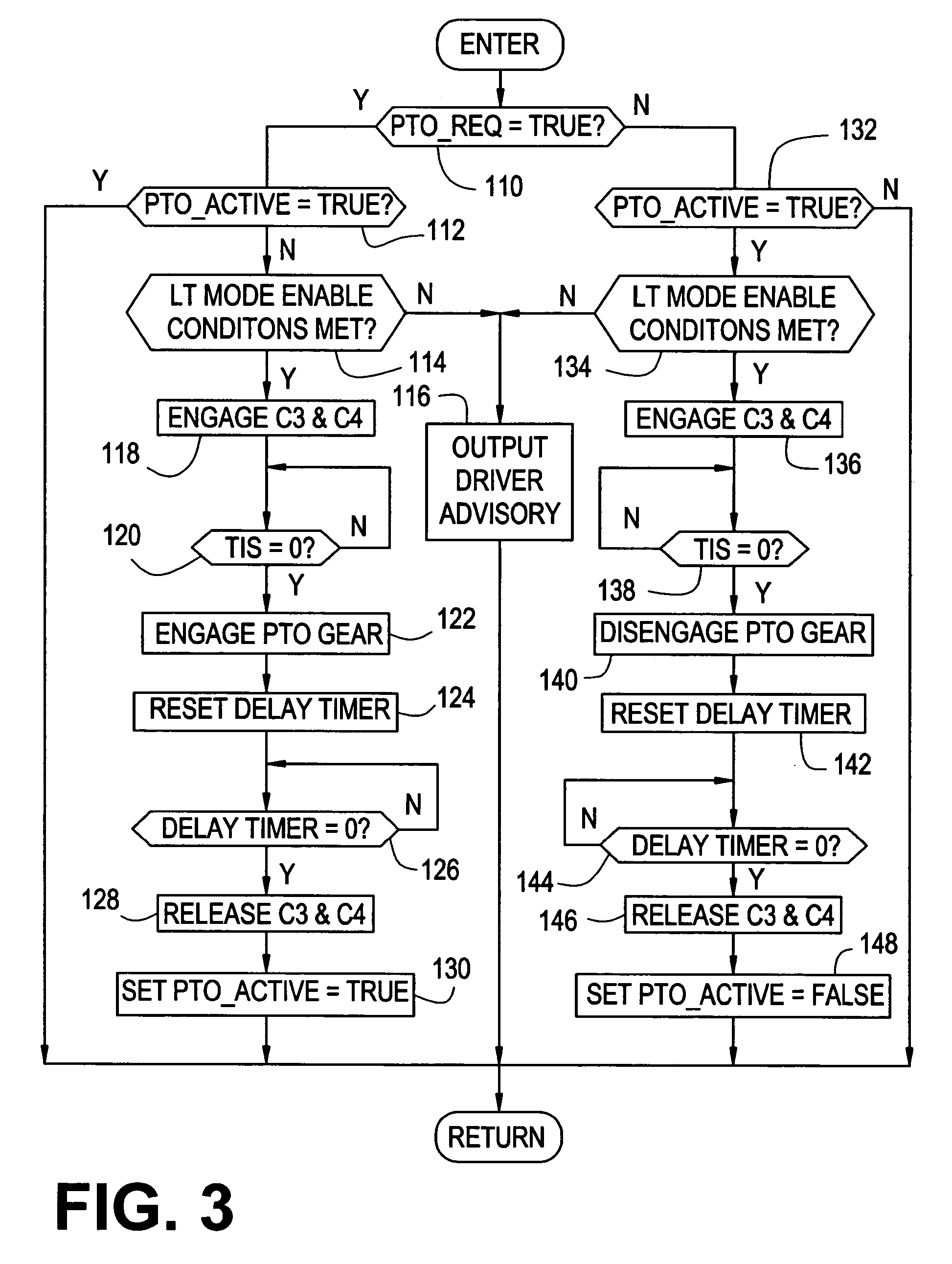
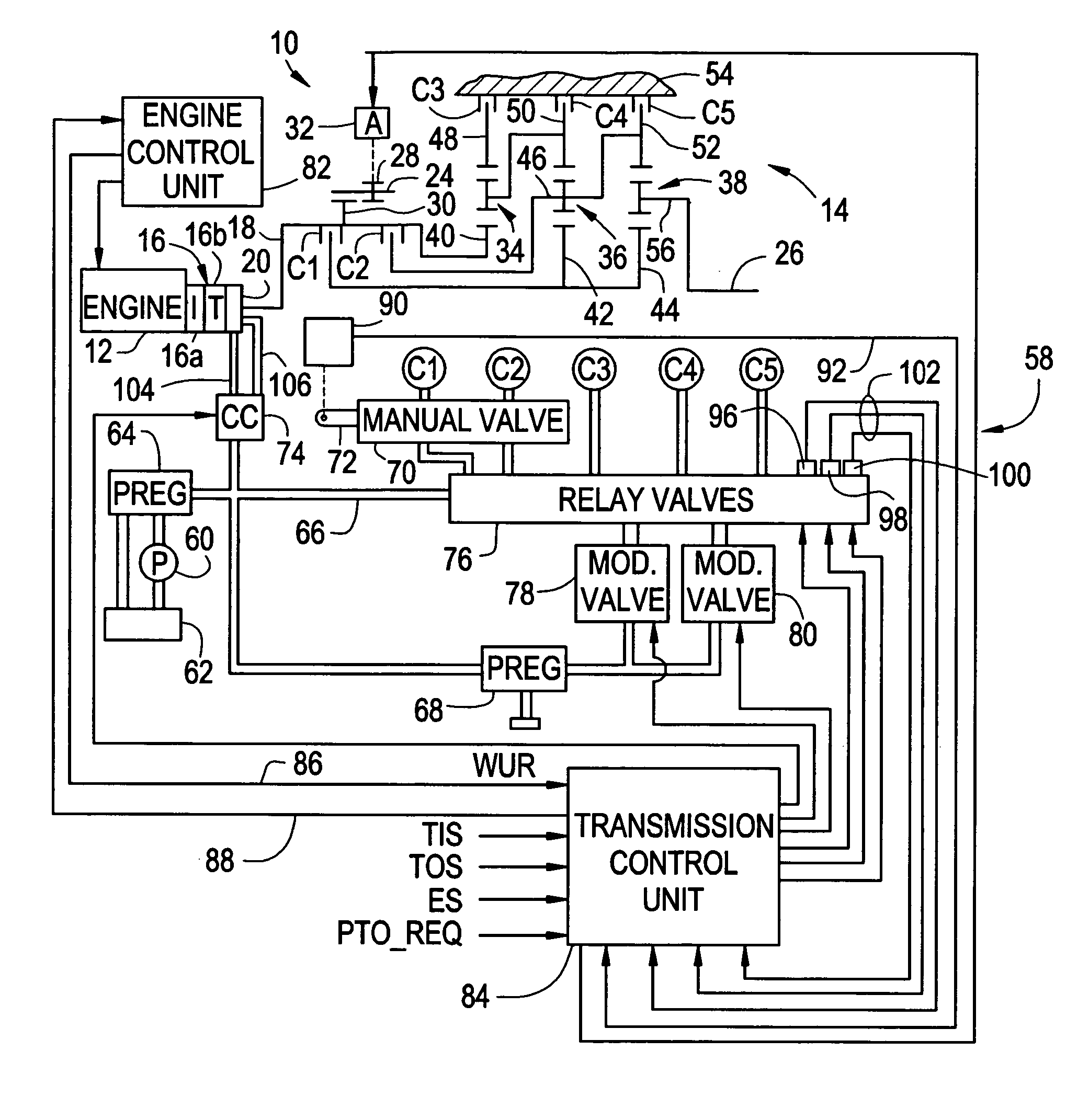
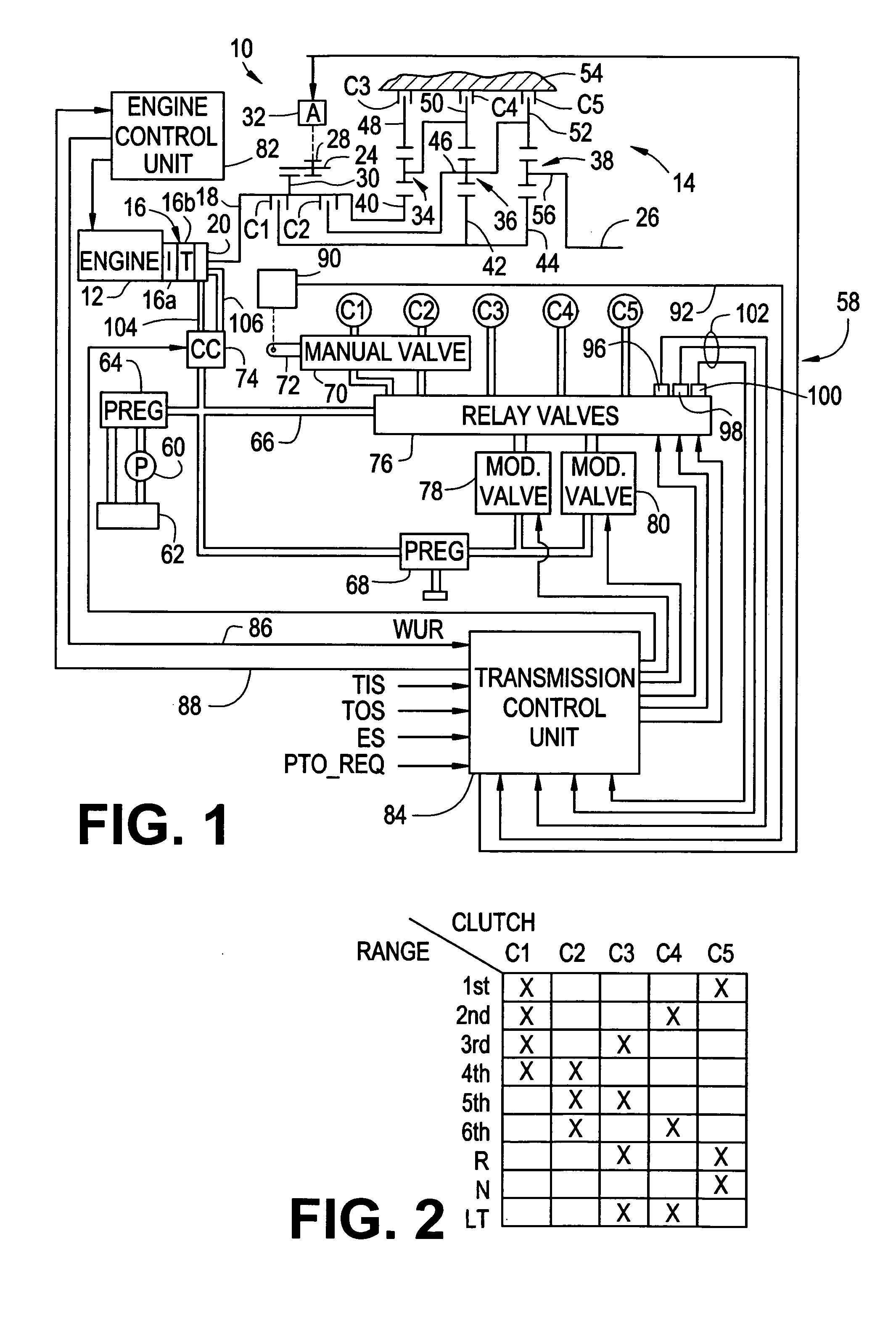
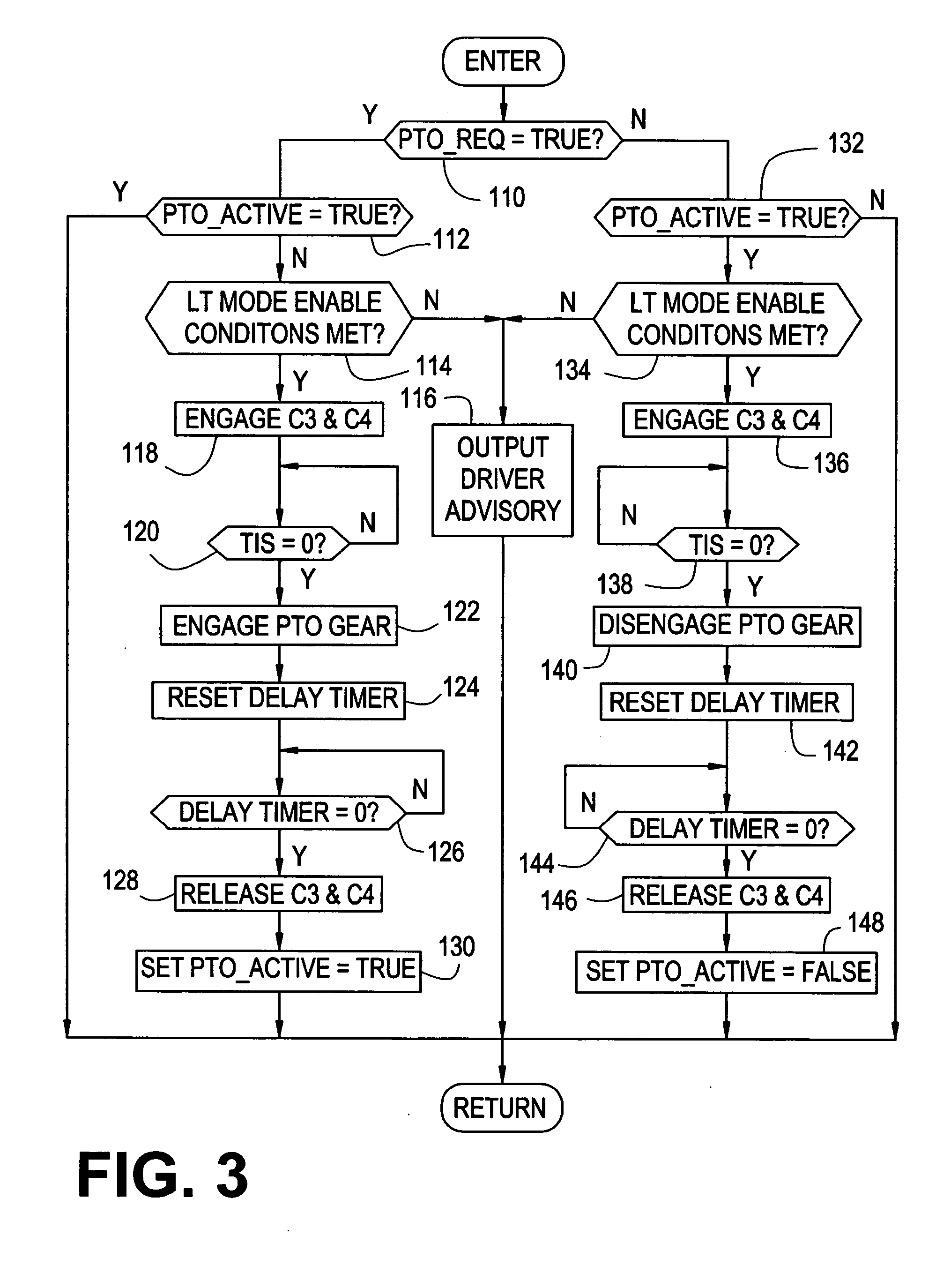
Method and apparatus for synchronized PTO control in a motor vehicle powertrain
One or more friction devices of a transmission coupled to an engine through a fluid coupling are used during engine neutral idle operation to control the state of the fluid coupling for synchronous engagement and disengagement of a PTO input gear with a transmission-driven gear. The fluid coupling includes an input member connected to the engine and an output member connected to the input shaft of the transmission, and the transmission friction devices temporarily ground the output member without mechanically coupling the transmission input and output shafts under specified enable conditions. This maintains the transmission input shaft in a stationary condition while an actuator engages or disengages the PTO input gear with the transmission-driven gear. Following engagement or disengagement of the PTO input gear, the friction devices are released to resume normal operation of the fluid coupling.
Owner:ALLISON TRANSMISSION INC
Image shake correcting device
An image shake correcting device is provided for use with an apparatus (e.g., a camera) in which image shake is to be corrected. The device comprises an image shake correcting unit for correcting image shake in accordance with an output of a shake detecting unit for detecting a shake condition; a support condition determining unit for determining whether the apparatus, in which image shake is to be corrected, is supported in a predetermined stationary condition; a shutter speed information determining unit for determining a shutter speed at photo-shooting; and a varying unit for varying a response manner of the image shake correcting means to the output of the shake detecting means in accordance with a combination of the determination made by the support condition determining means and the determination made by the shutter speed information determining means. The image shake correcting device is operated in an optimum mode fit for situations in use, such as whether the apparatus (camera) is held by the hands or fixedly supported on a tripod or the like.
Owner:CANON KK
Machine status interlock for reversing fan control
InactiveUS7459870B2DC motor speed/torque controlLighting and heating apparatusAir cycleStationary conditions
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
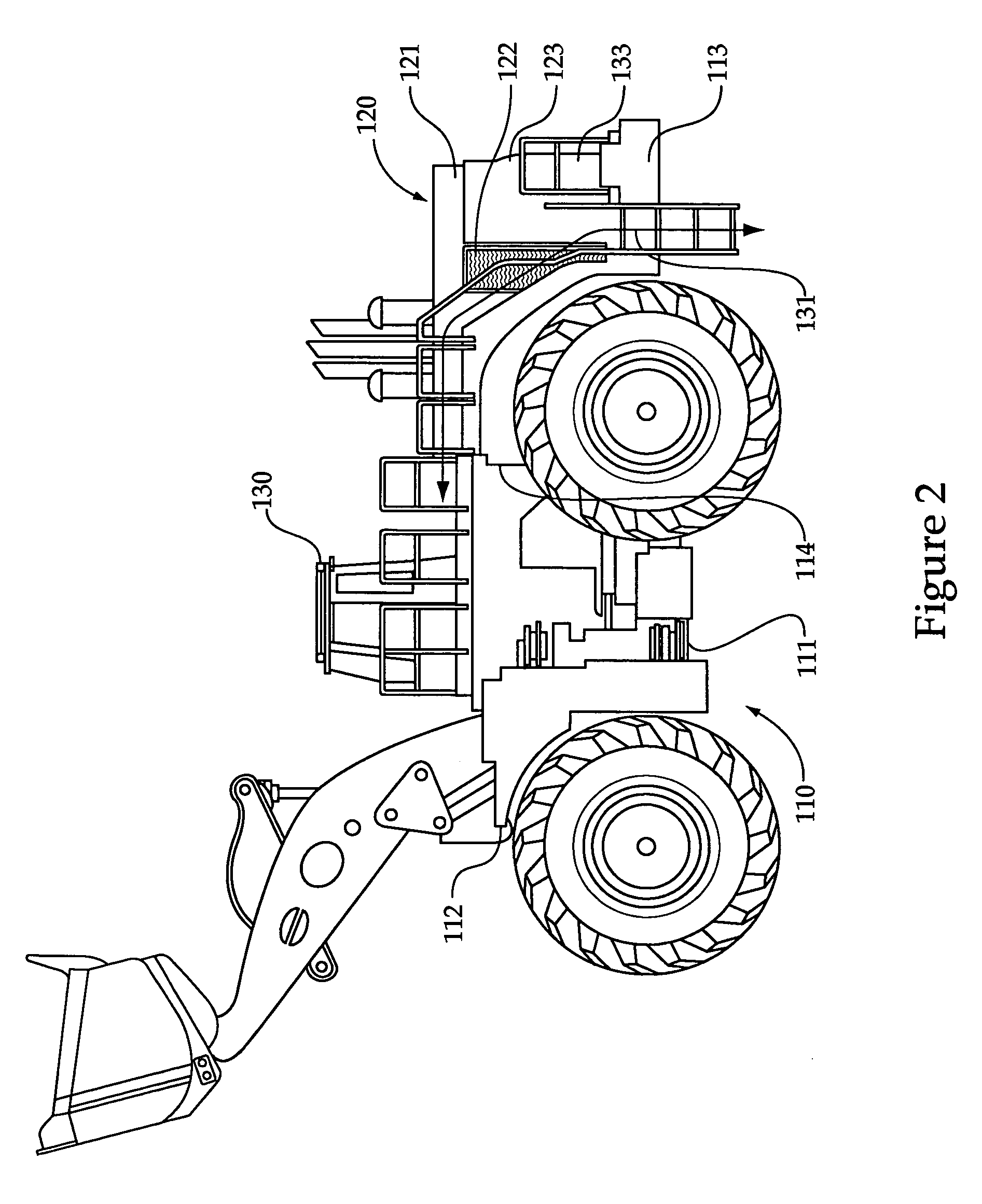
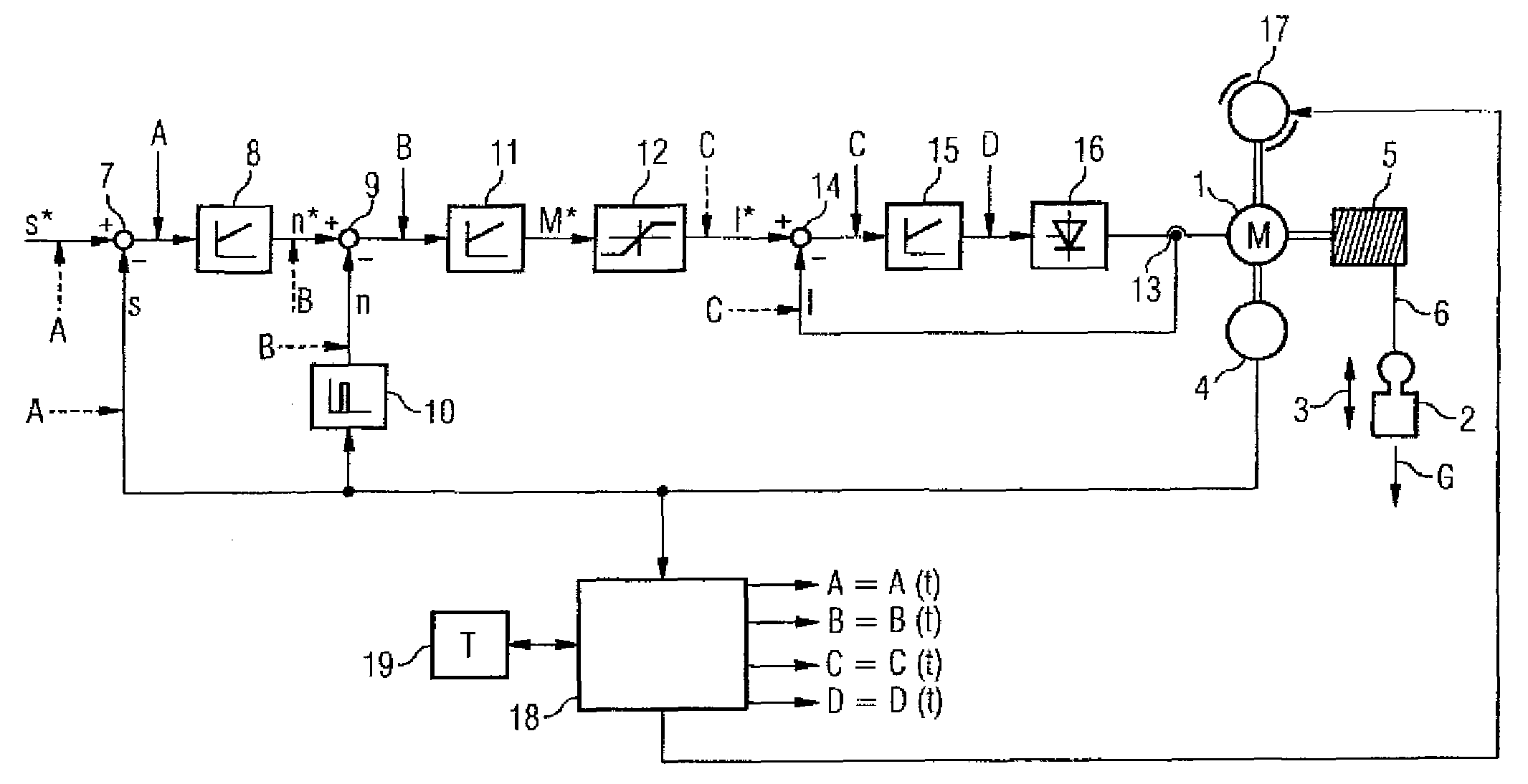
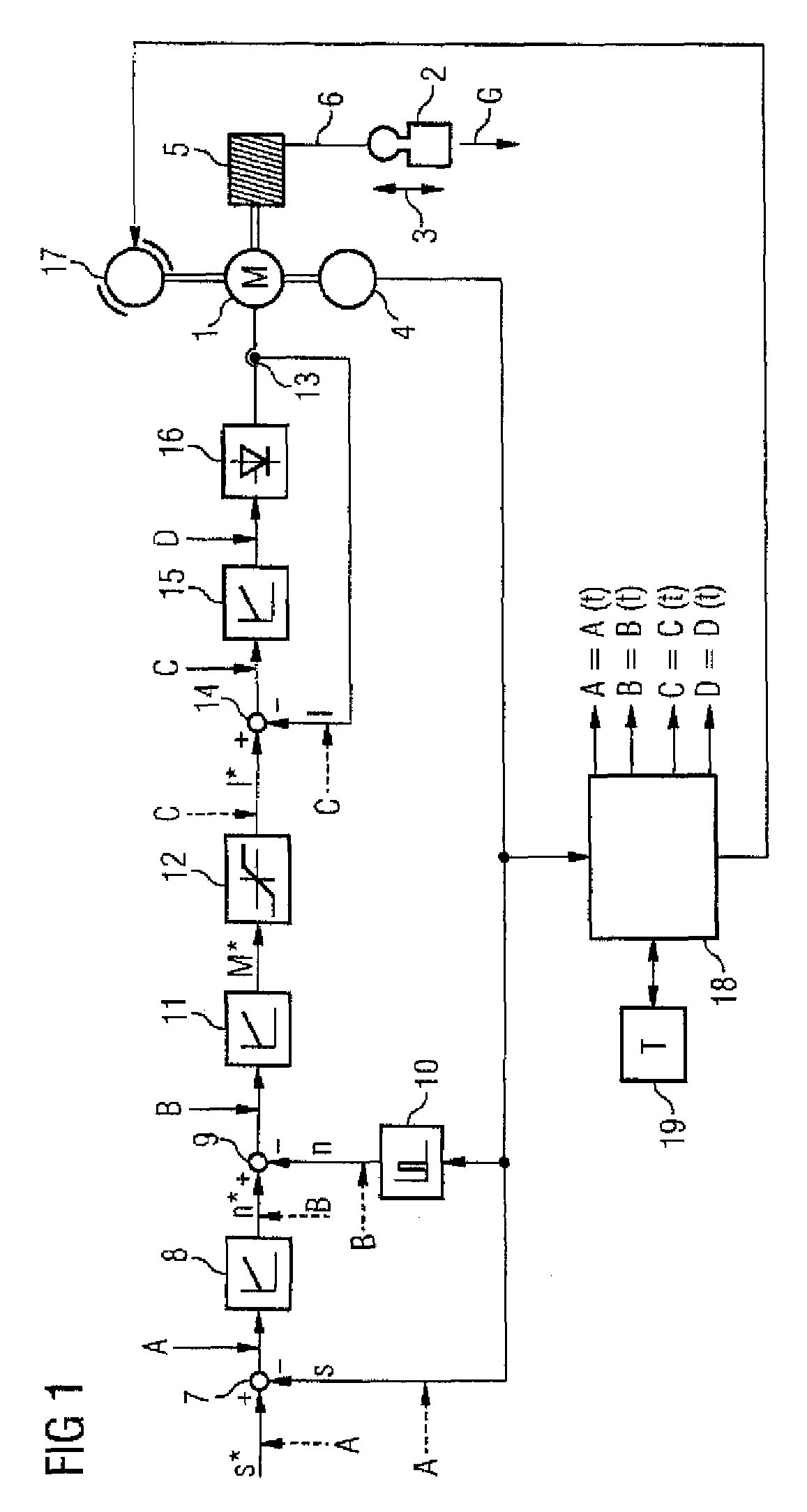
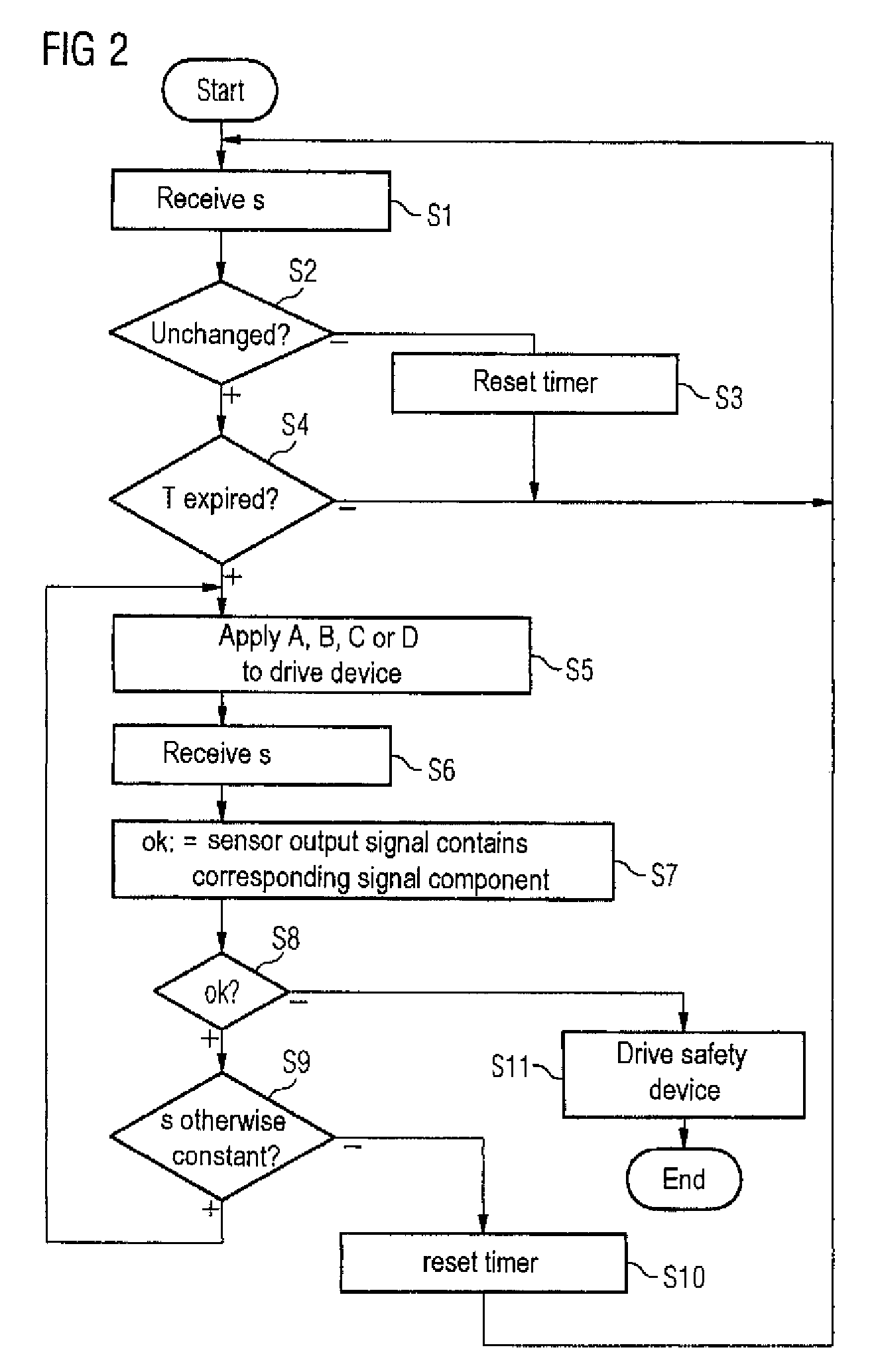
Method for monitoring a drive device for a standstill condition, monitoring system therefore, and drive system therefore
ActiveUS7482771B2Reliable detectionDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical testingPhase shiftedStationary conditions
In a method for monitoring a stationary condition of a drive device, a monitoring device provides the drive device with a temporally varying monitoring signal which, when a sensor device connected to the drive device functions properly, modulates a sensor output signal of the sensor device in accordance with the monitoring input signal. The monitoring device receives the sensor signal and monitors it for the presence of a corresponding signal component. In the absence of such a signal component, the monitoring device controls a safety device which converts the drive device into a safe state. When the drive device is controlled by means of at least two phase-shifted current regulators, it is possible for the monitoring device to monitor an output signal of at least one of the current regulators for constancy and to control the safety device when the output signal of the at least one current regulator changes.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Automatic transmission system and method for controlling thereby
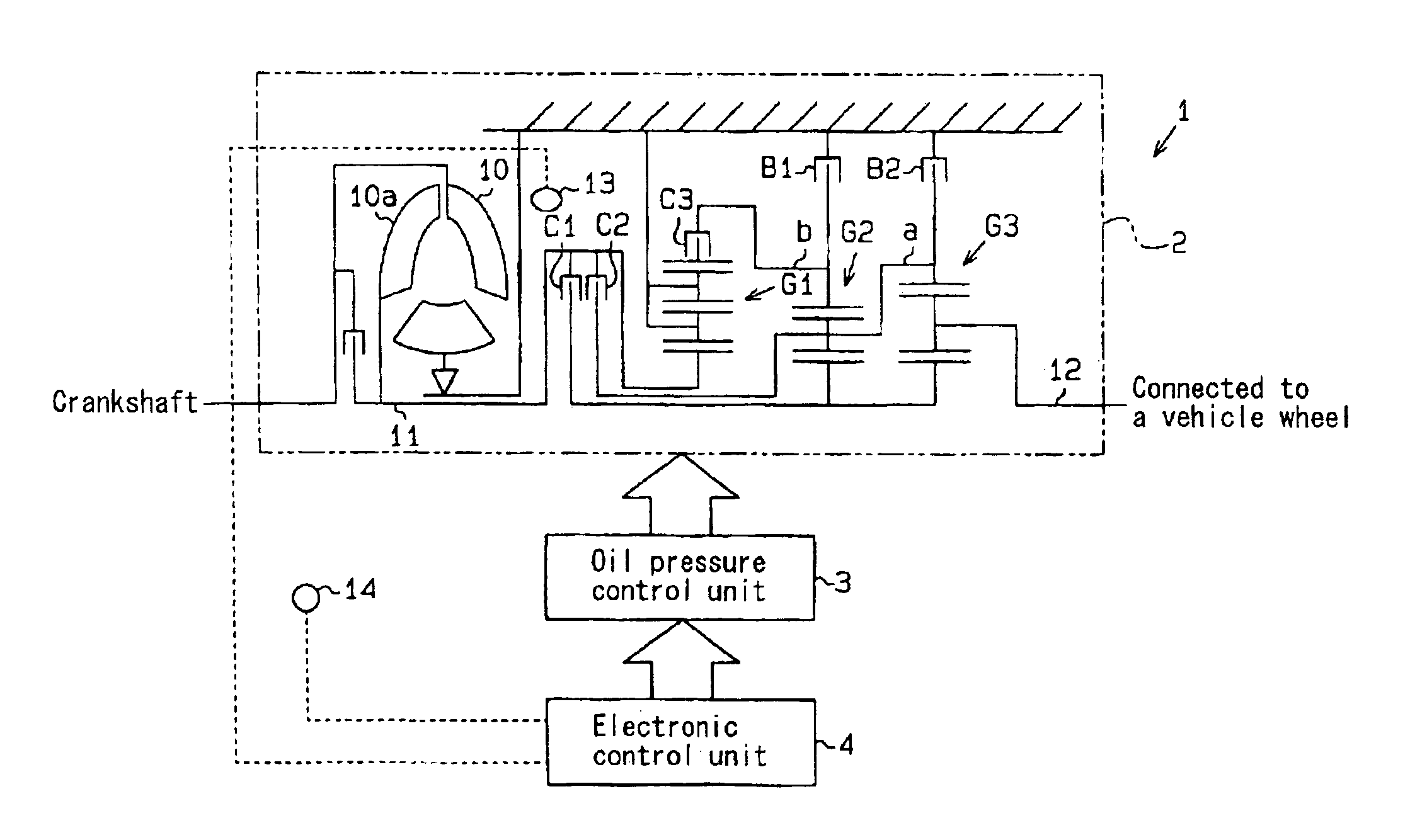
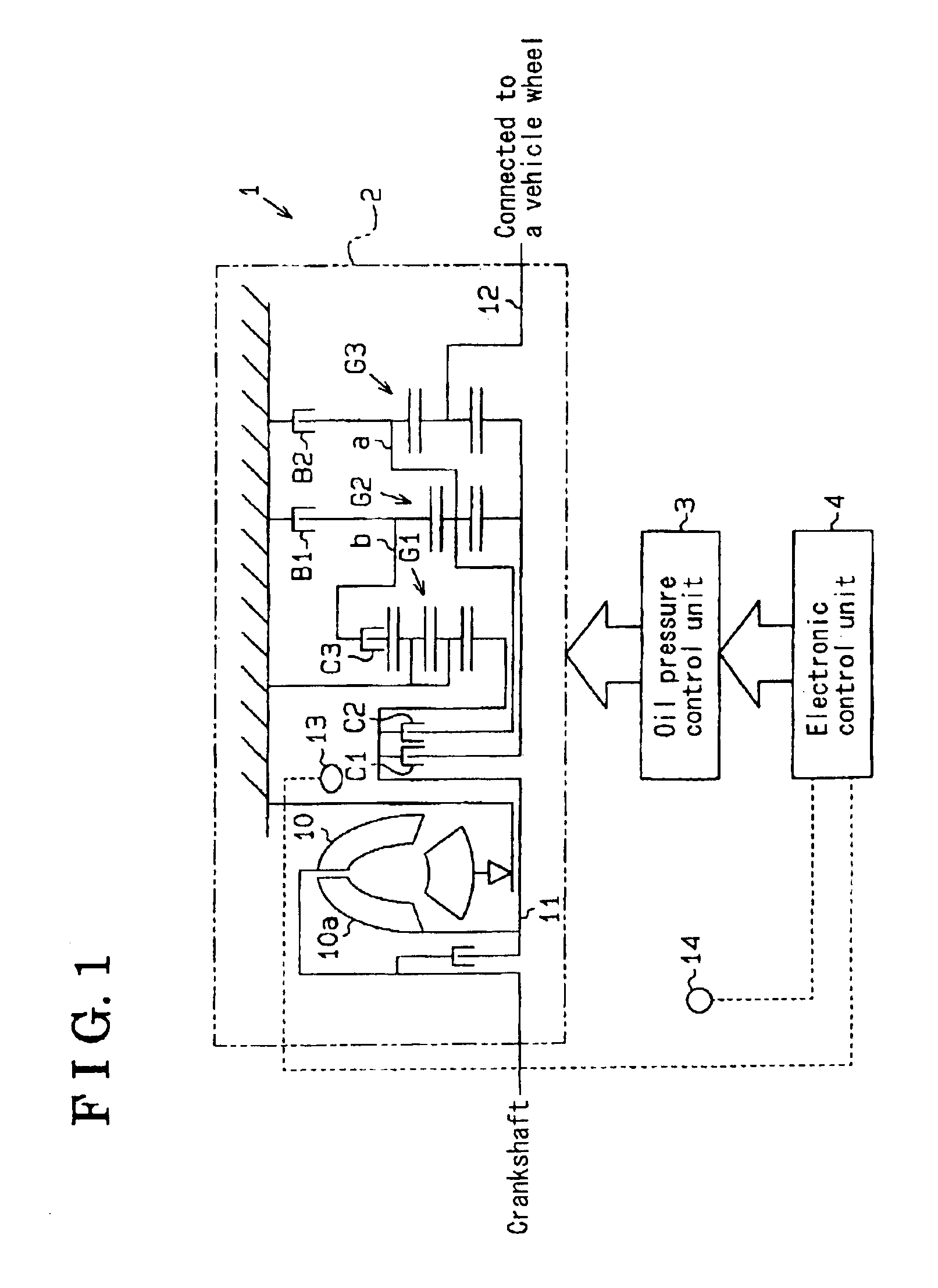
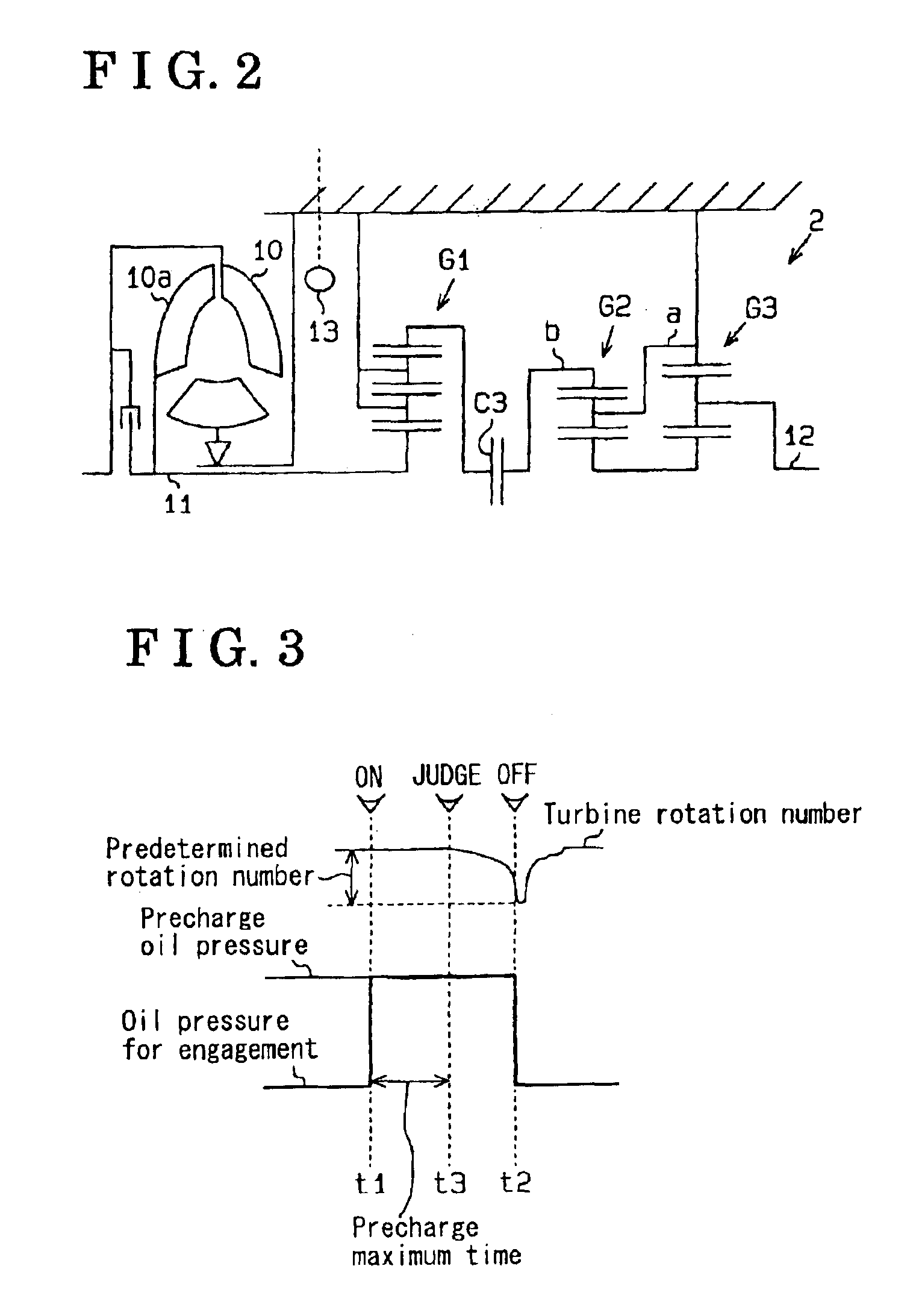
InactiveUS6872166B2Gearing controlEngine controllersStationary conditionsAutomatic transmission system
An automatic transmission system for a vehicle includes a rotational speed detector for detecting a variation of a rotation number of driving torque transmitting member when a friction engagement element, which has been disengaged based upon oil pressure controlled by a control unit, a side of which has been transmitted with the rotation of the driving torque transmitting member, and the other side of which is locked not to be rotated during the vehicle at a stationary condition, is controlled to be engaged, wherein an oil pressure characteristic value of the friction engagement element is learned by the control unit based upon the variation of the rotation number of the driving torque transmitting member when the friction engagement element is initially engaged.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Interference cancellation under non-stationary conditions
InactiveUS8675796B2Improve received signal qualitySynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsStationary conditionsFrequency offset
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for synchronized PTO control in a motor vehicle powertrain
One or more friction devices of a transmission coupled to an engine through a fluid coupling are used during engine neutral idle operation to control the state of the fluid coupling for synchronous engagement and disengagement of a PTO input gear with a transmission-driven gear. The fluid coupling includes an input member connected to the engine and an output member connected to the input shaft of the transmission, and the transmission friction devices temporarily ground the output member without mechanically coupling the transmission input and output shafts under specified enable conditions. This maintains the transmission input shaft in a stationary condition while an actuator engages or disengages the PTO input gear with the transmission-driven gear. Following engagement or disengagement of the PTO input gear, the friction devices are released to resume normal operation of the fluid coupling.
Owner:ALLISON TRANSMISSION INC
Cooling assembly for chilling or freezing liquid ingredients
ActiveUS20140318172A1Improve impact resistanceLow thermal conductivityDomestic cooling apparatusClosuresStationary conditionsAdditive ingredient
Cooling assemblies having a sealable cooling chamber formed as the interior volume of a curved or spherical outer container and a sealable inner canister are disclosed. The outer container may be provided as a multi-layer container having an external elastomeric shell. The external elastomeric shell may have an inner framework including a plurality of longitudinal ribs and a reinforcing wall. A movable flap adjustable between a projecting condition in which the flap extends from the exterior surface of the outer container and a closed position in which the flap doesn't project may be provided for supporting the cooling assembly in a stationary condition and the flap may be used as a handle for opening a lid.
Owner:INDAL REVOLUTION
Method of separating two dispersed-phase immiscible liquids
InactiveUS20120125868A1Water/sewage treatmentSedimentation separationStationary conditionsPhysical separation
Method of separating two dispersed-phase immiscible liquids. The two liquids are fed into a gravity separator where both liquids are separated by decantation. A first phase consisting of a first liquid is obtained at the bottom of the separator, a second phase consisting of the second liquid is obtained at the tap of the separator, a third phase containing the two dispersed-phase immiscible liquids and a fourth phase containing the two immiscible liquids in a dense bed are obtained. Physico-chemical properties of the liquids and of the dispersed phase are measured, and a physical separation model is defined. This model is defined considering that the separator works under stationary conditions, using a matter conservation balance for the first fluid within the dense bed, while taking account of a first phenomenon of coalescence between water drops within the third phase, and of a second phenomenon of coalescence between water drops of the fourth phase and the first phase. This model is then used to optimize implementation of the separation. Application to the separation of petroleum effluents for example.
Owner:FALAPPI STEFANO +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com