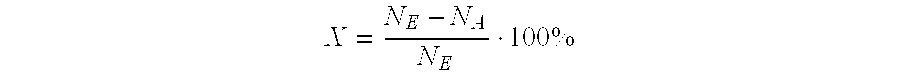Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36results about How to "Considerable energy saving" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for preparing a catalyst
InactiveUS6342465B1Uniform penetrationConsiderable energy savingOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPowder mixtureActive component
A process for preparing a catalyst which has a catalytically active coating of high surface area finely divided materials and catalytically active components on an inert carrier structure. A powder mixture of the finely divided materials used is impregnated with a solution of precursor compounds of the catalytically active components. By suitable combination of the finely divided materials and the precursor compounds and appropriate management of the impregnation process, a highly dispersed deposition and adsorption of the catalytically active components is ensured on the finely divided materials. Then ai aqueous coating dispersion is produced using the impregnated powder mixture and the carrier structure is coated therewith. The coating is then dried and calcined.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Apparatus and method for purifying water with an immersed galvanic cell
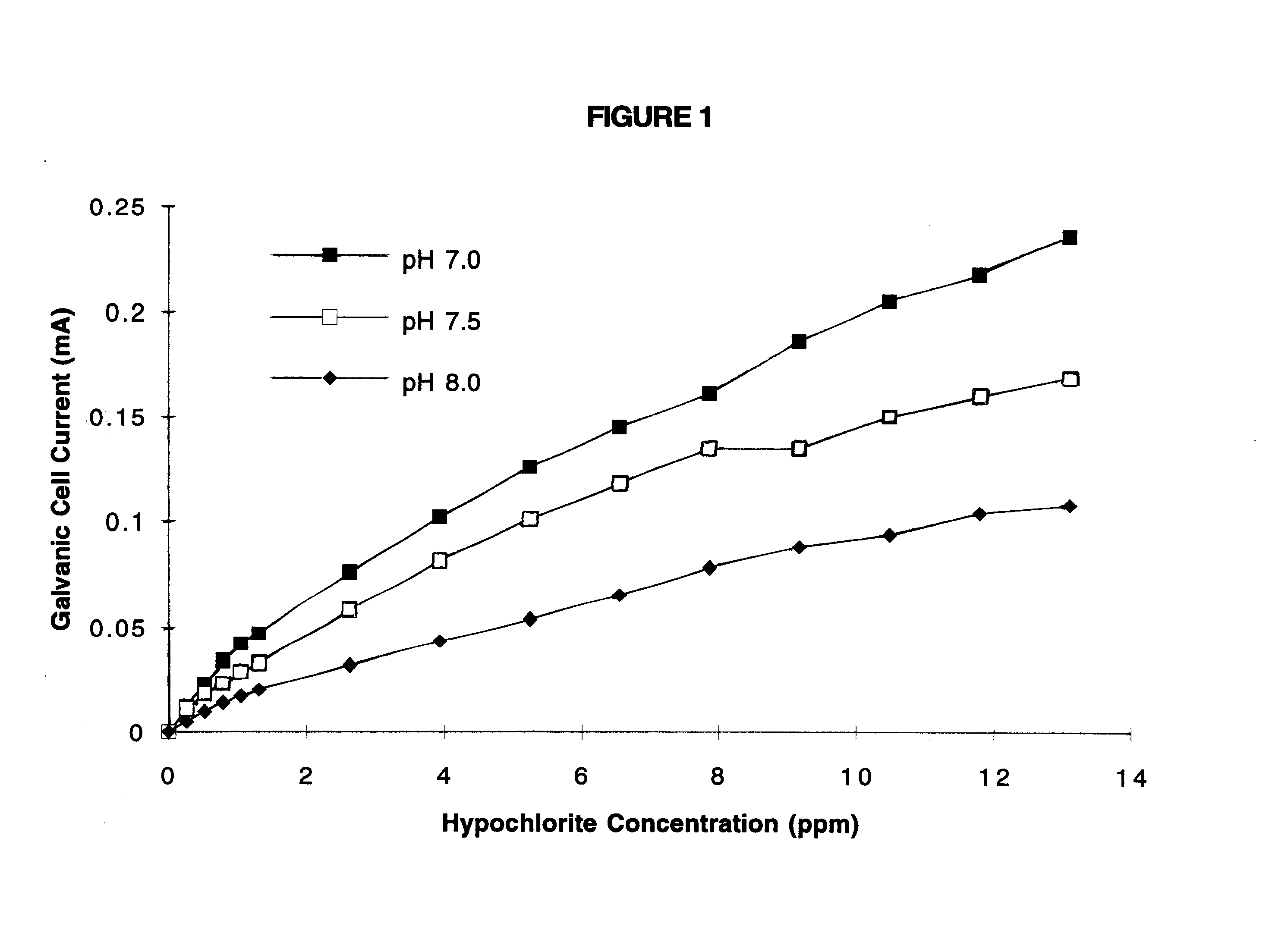
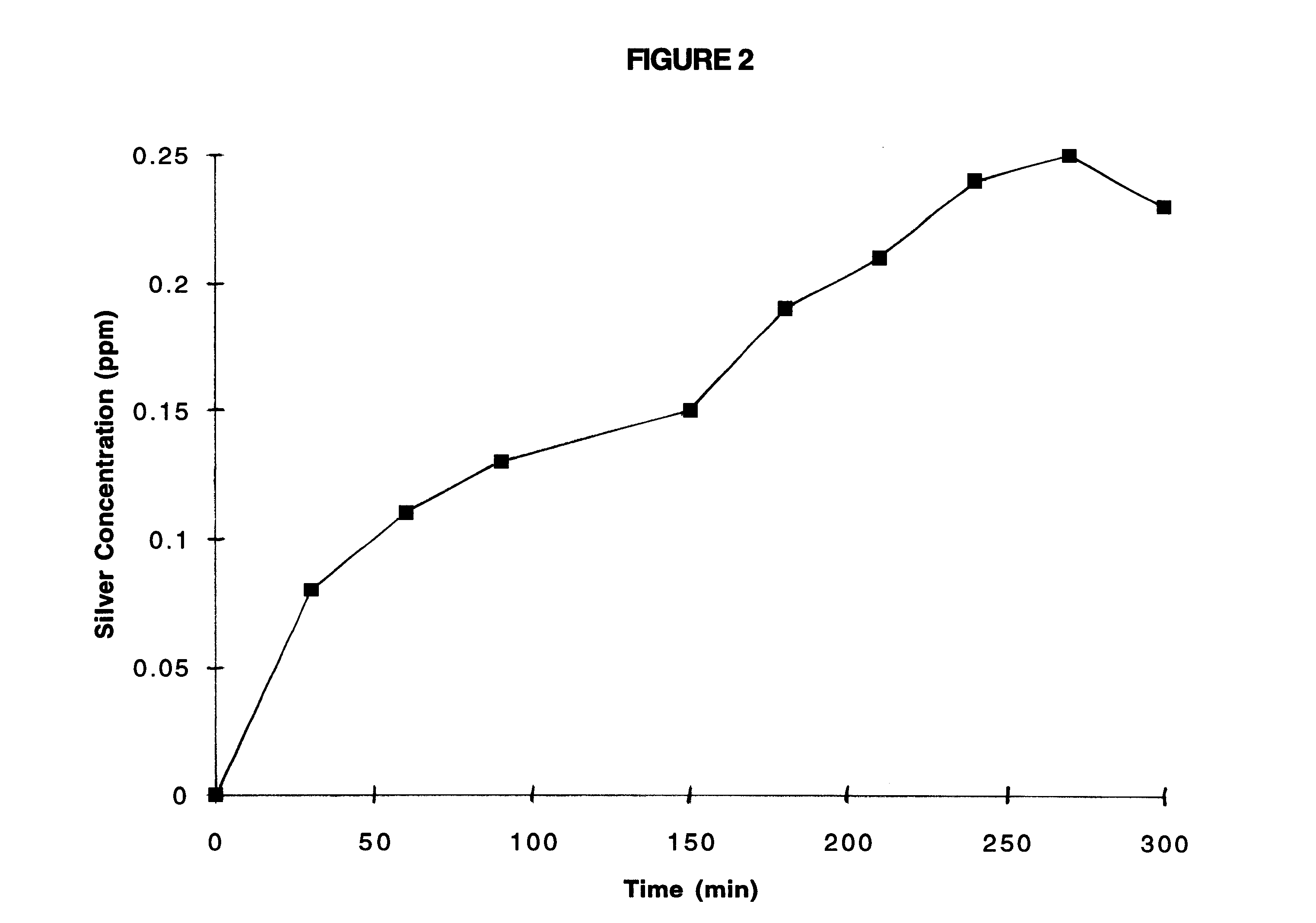
InactiveUS6287450B1Considerable energy savingReduce total usageCellsWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsGramWater quality
A water purification system and method suitable for use in swimming pools, spas, hot tubs, water storage tanks, wells and water cooling towers employs a galvanic cell having a silver or copper or zinc anode electrically connected to a cathode made from a metal of still higher electrochemical potential, normally a platinum group metal and preferably palladium. A galvanic cell of some tens of square centimeters in size and some hundreds of grams in weight liberates sufficient silver or copper ions so as to treat a multi-thousand liter body of water, such as a swimming pool, for, typically under normal contamination, some months until the anode is consumed. Copper and / or silver ions liberated from the galvanic cell suppress bacterial, fungal and / or algae growth, thus, significantly reducing the amount of chlorine, bromine or other chemicals needed to maintain water quality. The invention operates on the current generated by the galvanic action between the dissimilar metals of the anode and cathode, and does not require external electrical power.
Owner:HRADIL GEORGE
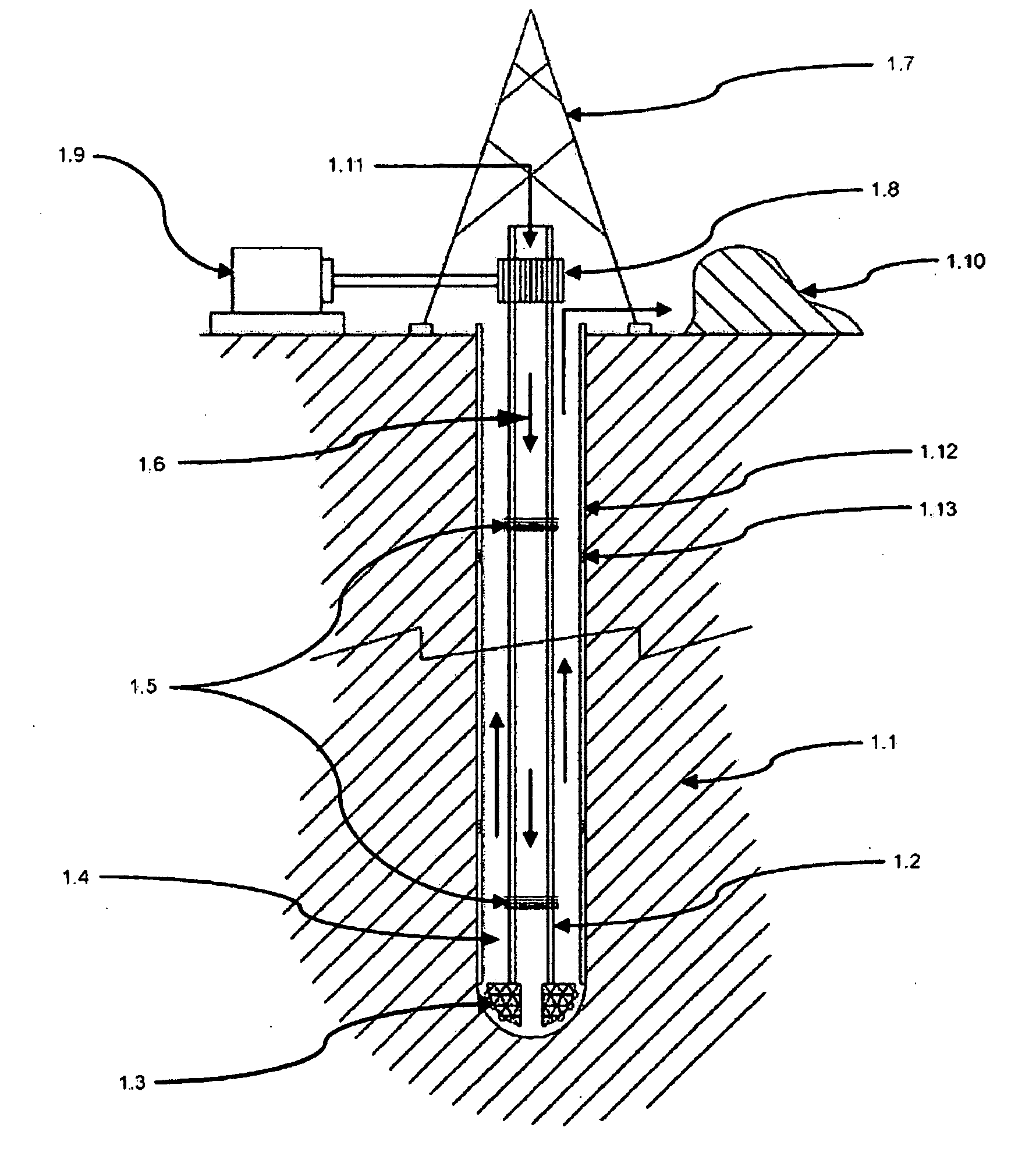
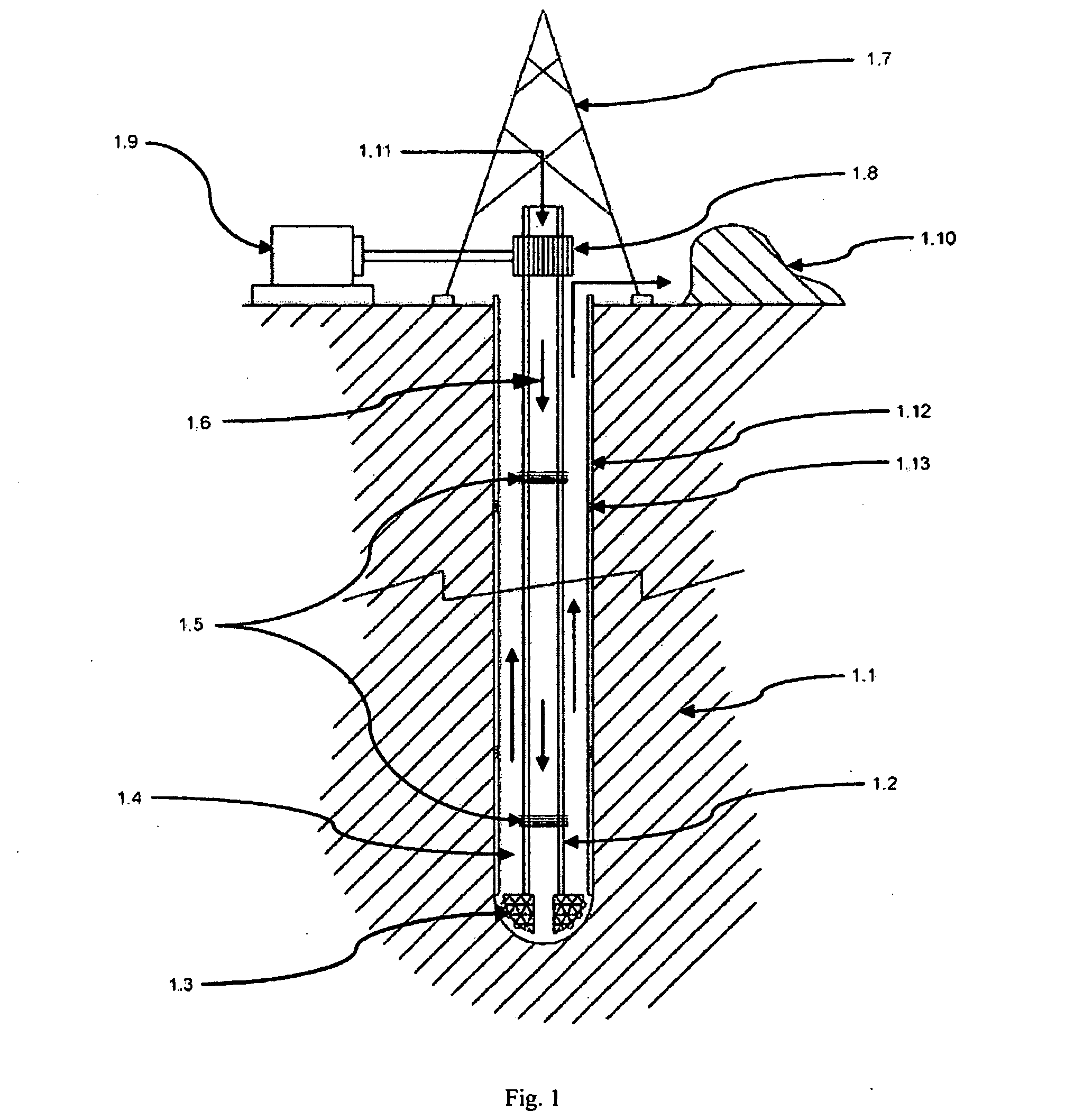
Equipment for excavation of deep boreholes in geological formation and the manner of energy and material transport in the boreholes
InactiveUS20100224408A1Considerable energy savingLarge boreholeDisloding machinesThermal drillingEngineeringEnergy depletion
Utilisation of geothermal energy in depths above 5 km could contribute considerably to resolving the global problems related to a lack of energy and to glasshouse gases from fossil fuels. The invention describes innovative equipment which makes deep holes in geological formations (rock) by disintegrating the soil into blocks carried to the land surface through the excavated hole filled with liquid, using transport modules yielded up by gas buoyancy interaction in the transport module utilising supercavitation. In an opposite direction—by help of negative buoyancy—the necessary energy carriers, materials and components, or entire devices required for rock excavation, are carried to the bottom. The opportunity to transport rock in entire blocks reduces energy consumption considerably, because the rock is disintegrated in the section volumes only. Some of the extracted rock and material carried from the surface is used to make a casing of the hole using a part of the equipment. The equipment also allows the generation of the necessary high pressure of liquid at the bottom of the hole, to increase permeability of adjacent rock. The equipment as a whole allows by its function that there is almost linear dependence between the price and depth (length) of the produced hole (borehole).
Owner:GA DRILLING AS
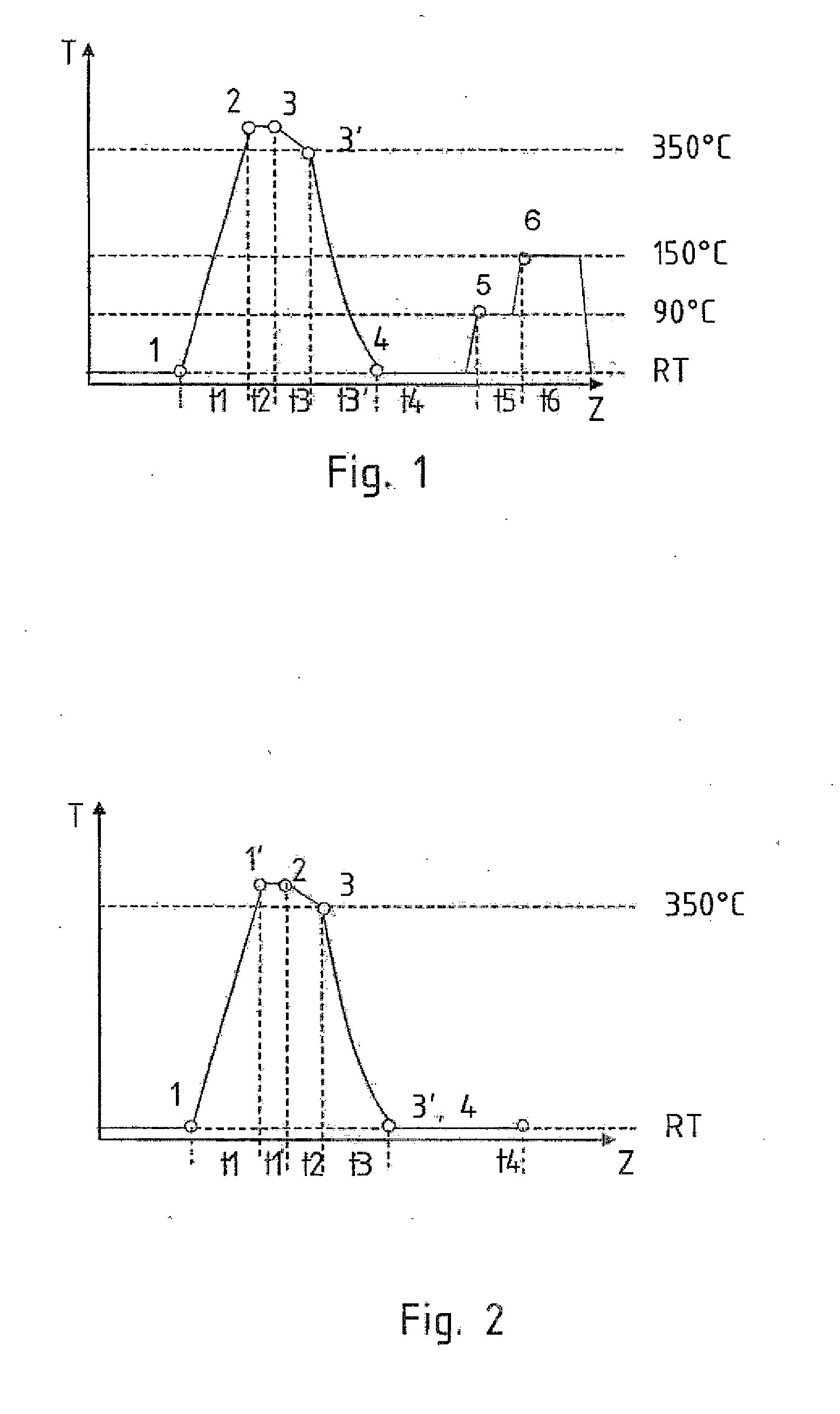
Method for producing a structural sheet metal component, and a structural sheet metal component
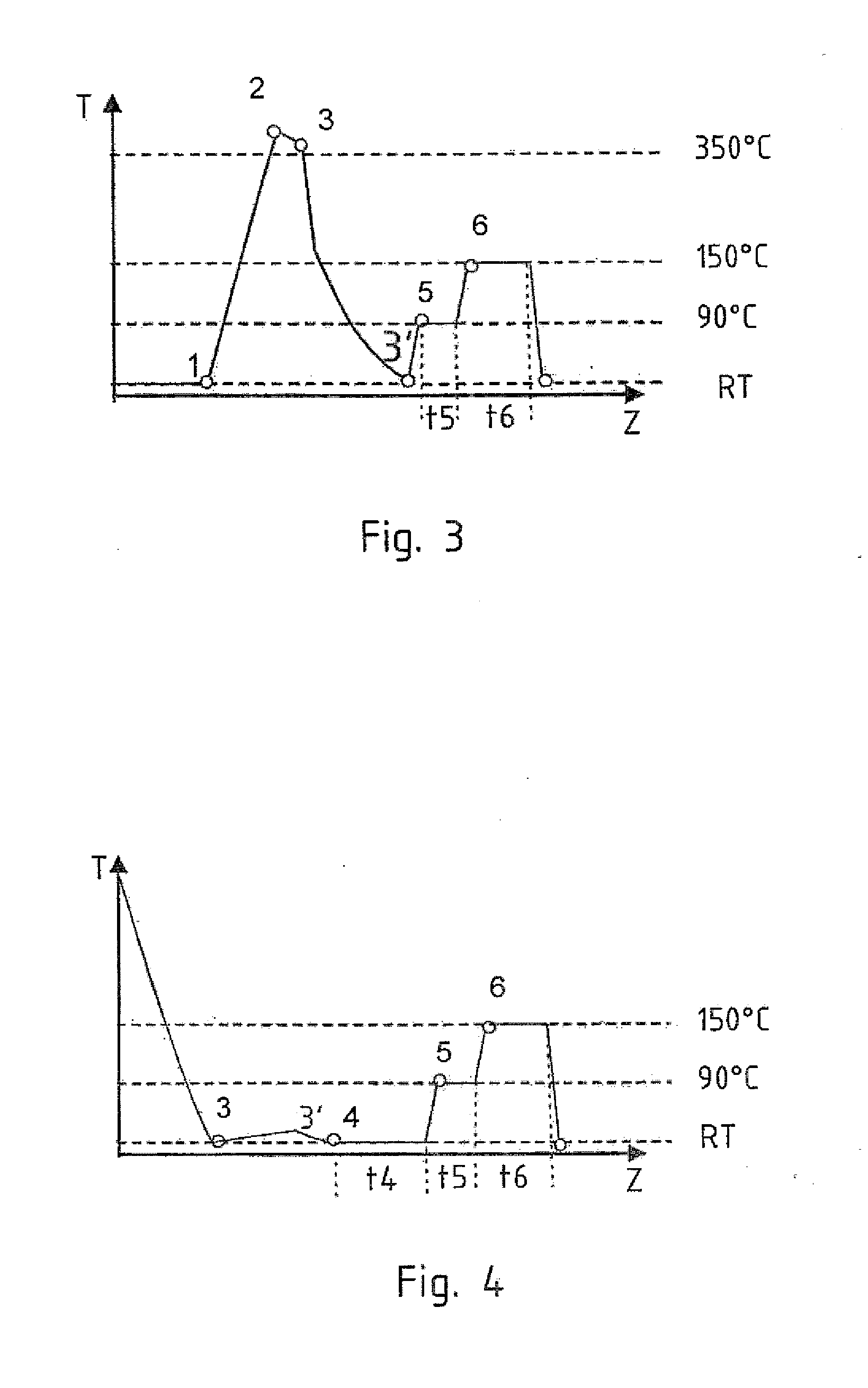
ActiveUS20120273098A1High hardnessHigh strengthShaping toolsOhmic-resistance heatingHeating temperatureMetal
A method for producing a structural sheet metal component formed from an aluminum alloy for a motor vehicle includes providing an aluminum sheet blank in a state T4 or T5 or T6 or T7, heating the aluminum sheet blank to a heating temperature between 100° C. and 450° C., forming the aluminum sheet blank to a structural sheet metal component, and heat post-treatment of the formed structural sheet metal component.
Owner:BENTELER AUTOMOBILTECHNIK GMBH
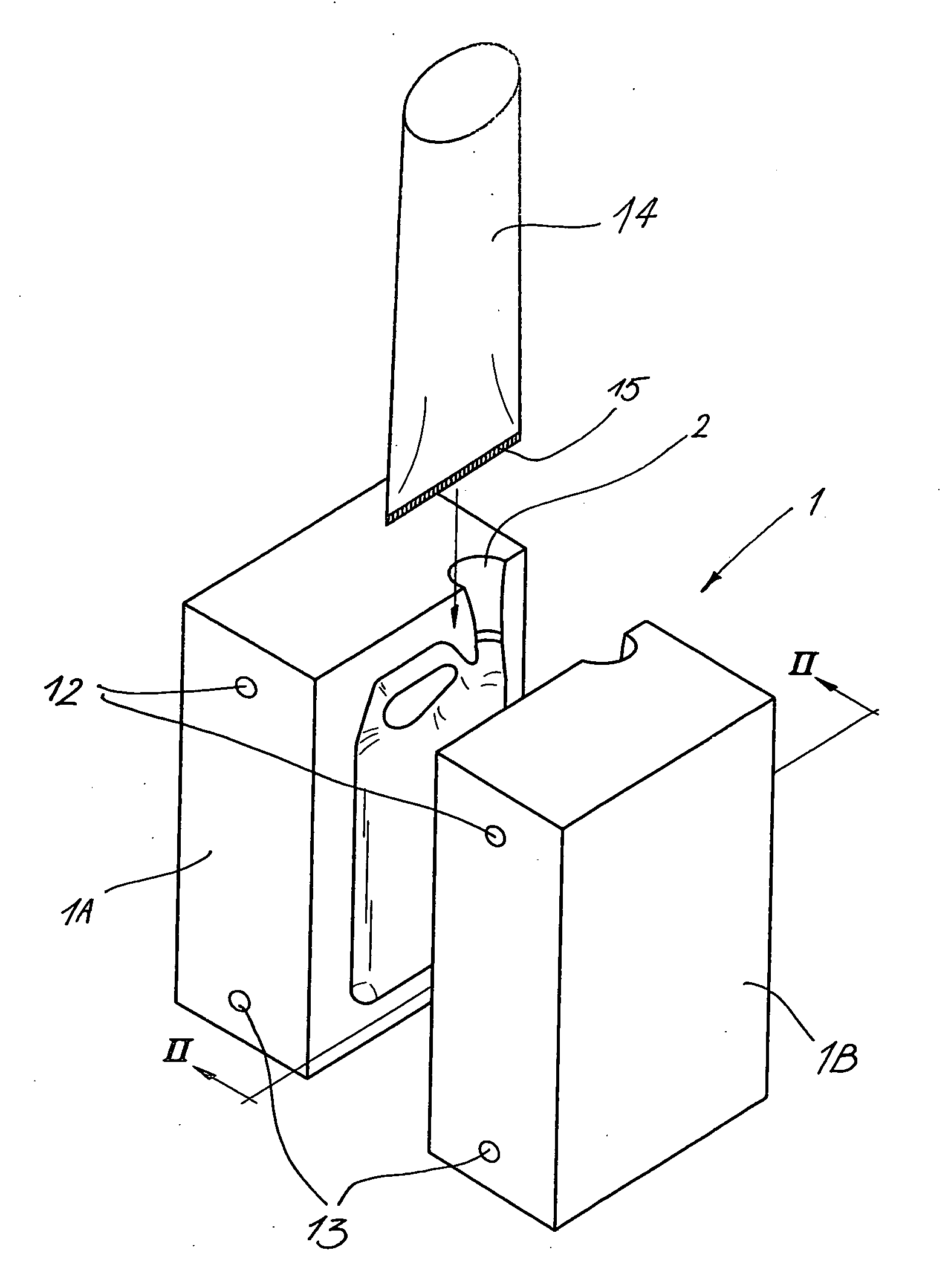
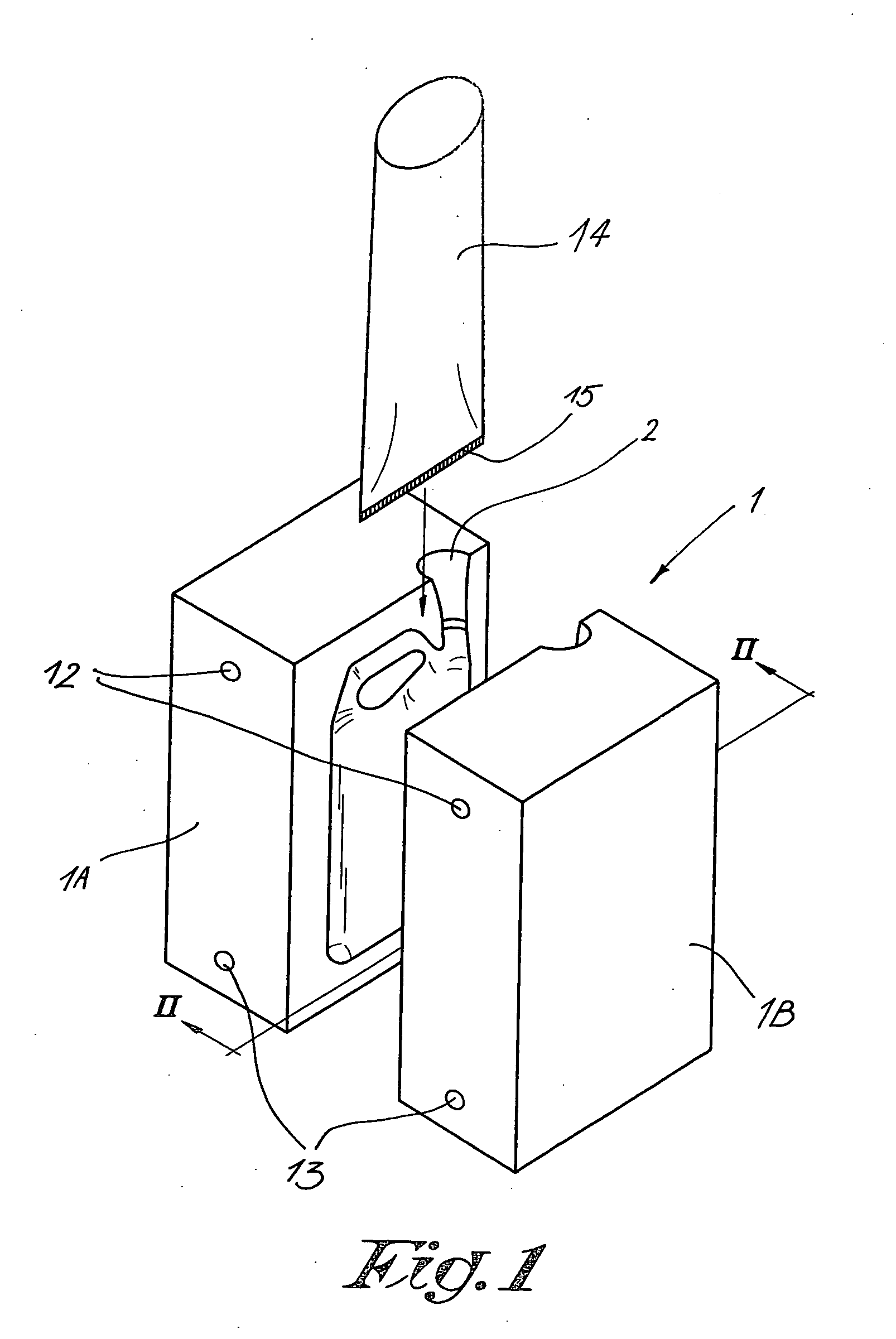
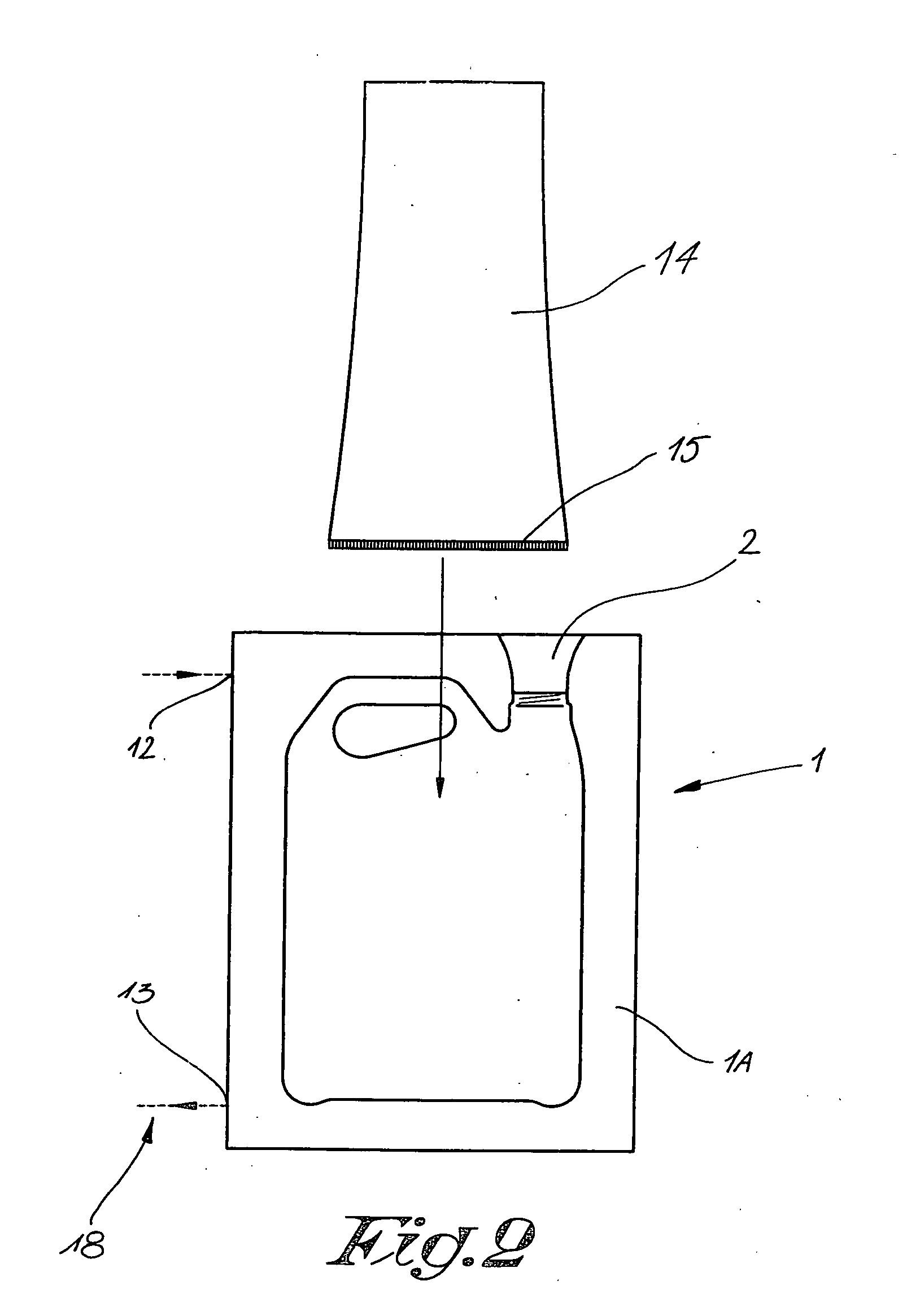
Method for blowing objects
InactiveUS20060012085A1Shorten cycle timeIncrease productivityHollow articlesEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
A method for blowing objects, in which the following steps are successively followed: providing a synthetic sleeve (14) in a mould (1); inflating this sleeve (14) by means of compressed air up to a maximum pressure; and scavenging the obtained object (4) by means of a compressed air flow, whereby the air in the object (4) is continuously refreshed, wherein the pressure of the compressed air varies from a start pressure to the atmospheric pressure according to an adjustable course which varies as a function of time.
Owner:DELTA ENG MET
Method of manufacturing a composite, especially a bulletproof composite, and composite obtained
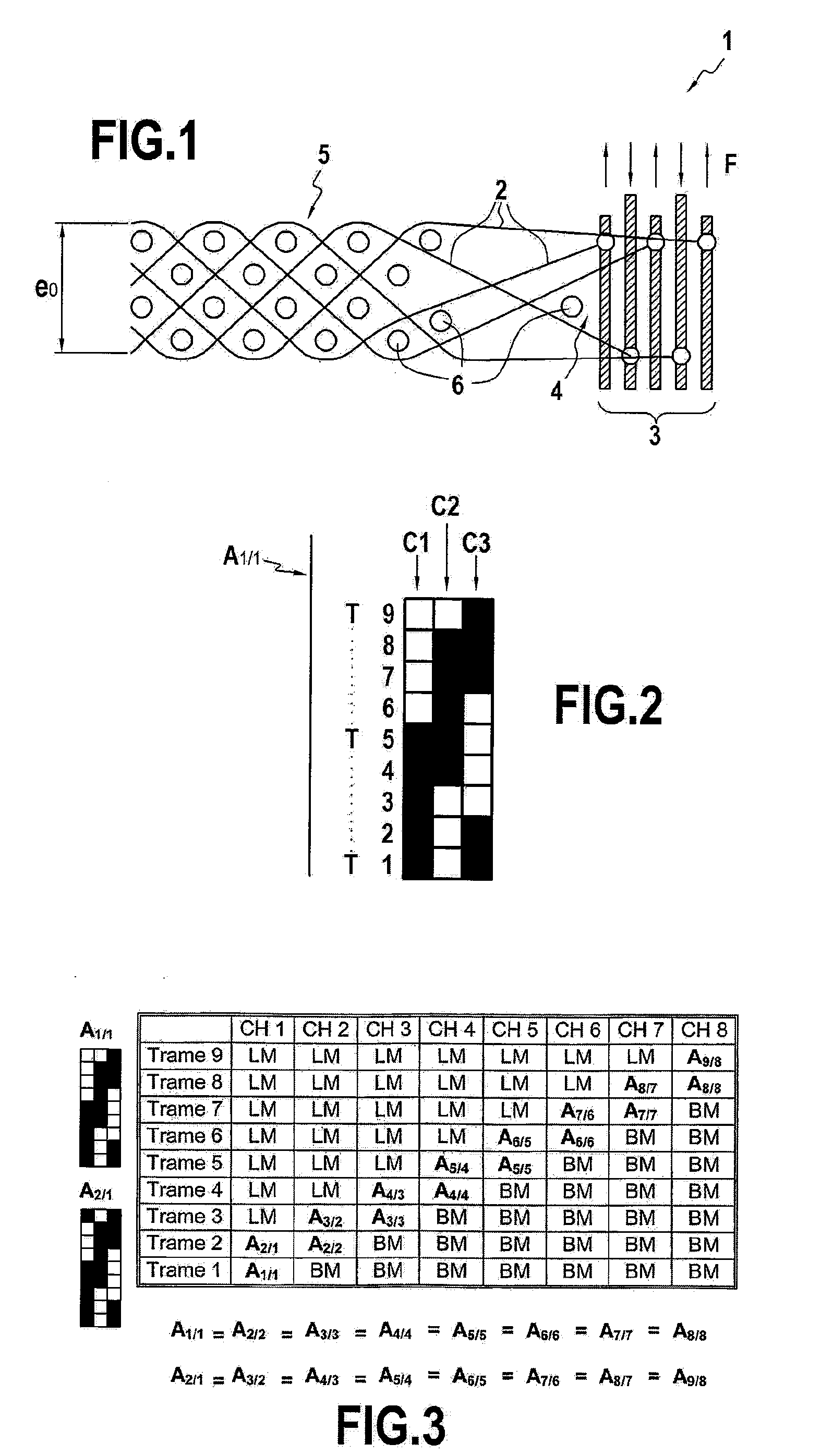
The subject of the present invention is a method of manufacturing a composite (8) comprising a textile reinforcement (7) and a polymer matrix, especially a bulletproof composite. Said method characteristically comprises: a step of forming the textile reinforcement (7) by 2.5D weaving of first yarns with second yarns in a defined weave (A1 / 1), said second yarns being of a thermosetting polymer and said first yarns being high-performance yarns, so as to obtain an interlock fabric (7); and then a heat treatment during which said interlock fabric (7) is subjected to specified temperature and pressure conditions so as to melt said second yarns in order to form the polymer matrix, without impairing the first yarns.
Owner:ENSAIT
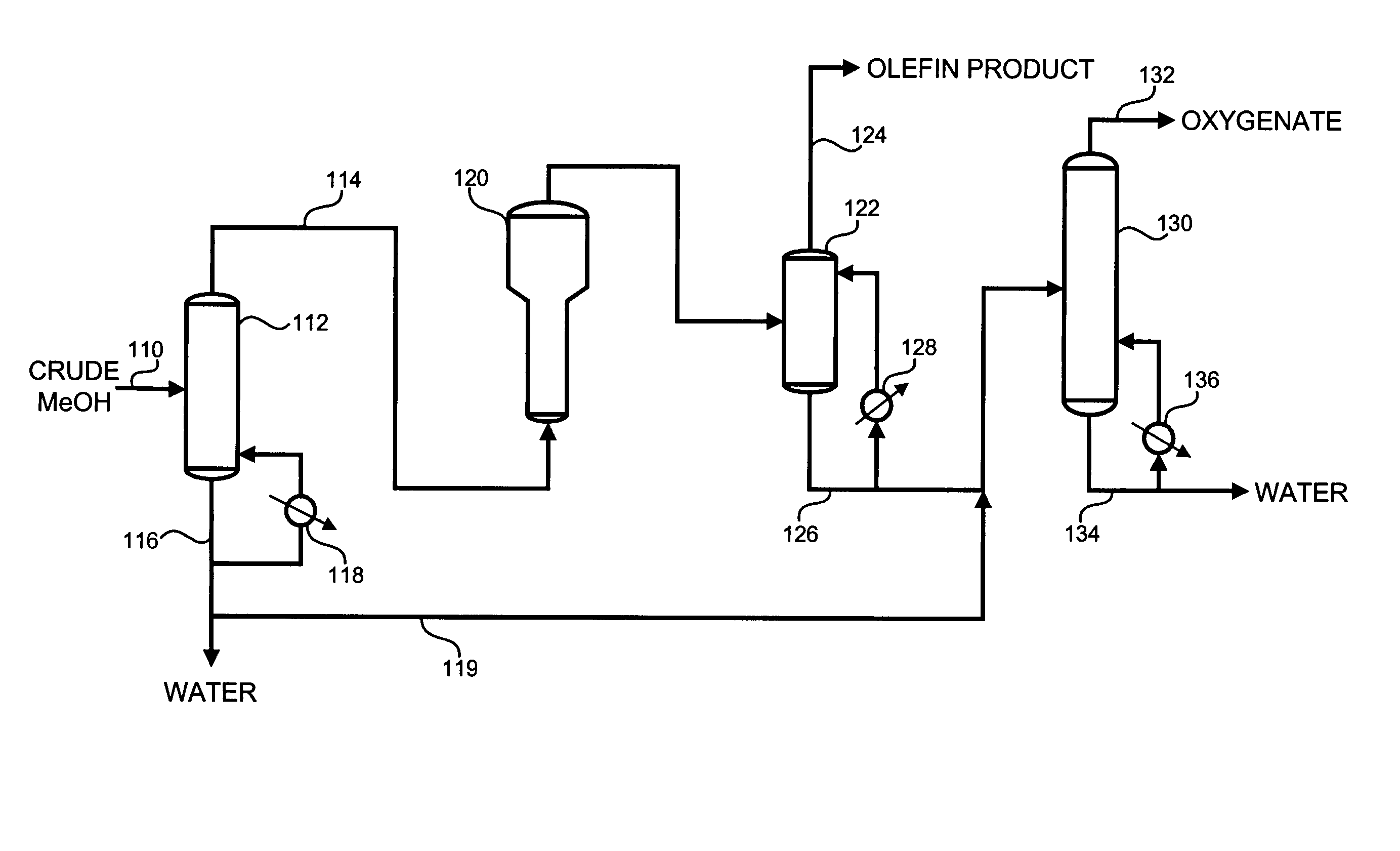
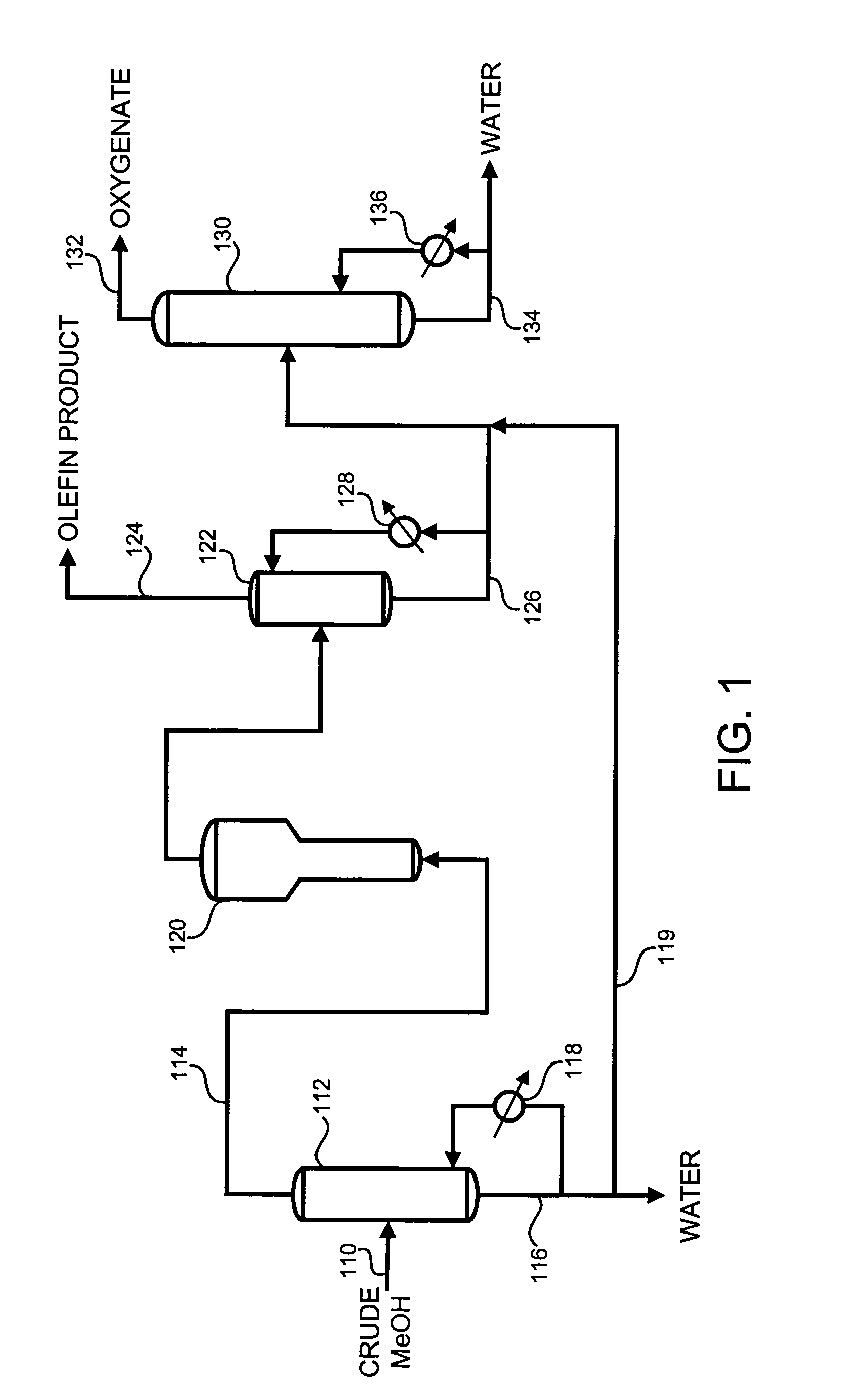
Oxygenate to olefin manufacture and recovery process
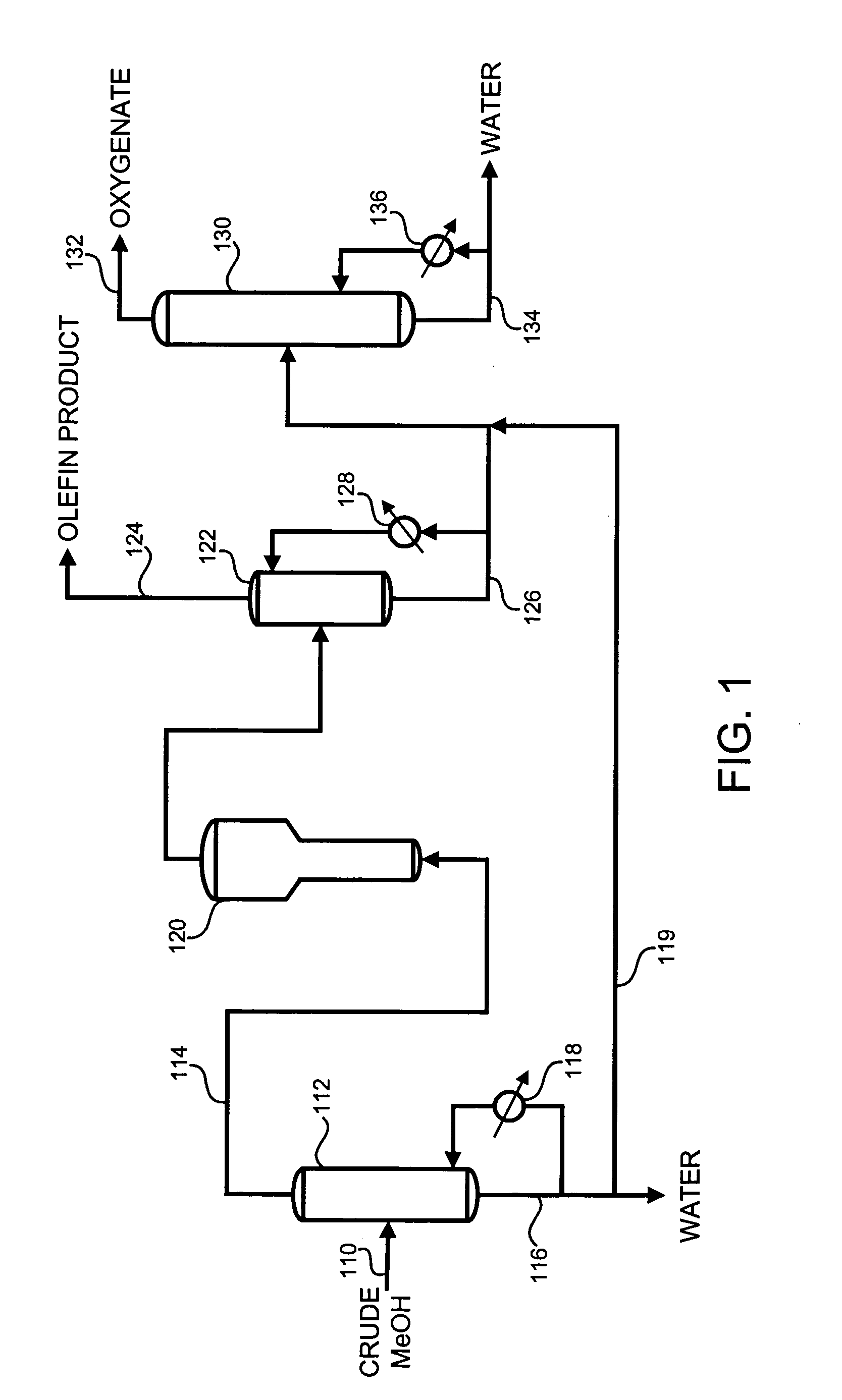
ActiveUS20060135632A1Reduce the amount requiredConsiderable energy savingOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOrganic compound preparationSolid componentDistillation
This invention is directed to methods for forming an olefin stream from a methanol stream. A lower grade methanol, such as chemical grade or crude methanol, can be used as feed to form the olefin stream. The process uses a relatively simple distillation type step to vaporize a portion of the methanol feed stream and send the resulting vapor stream to a reaction unit to form the olefin stream. In addition, the invention provides the ability to operate the downstream recovery units with reduced fouling or plugging due to the presence of fine solids components.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Waste heat recovery and optimized systems performance
ActiveUS9702634B1Considerable energy savingIncrease the effective surface areaFluid heatersEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingOperational costsEnergy expenditure
Energy systems in different industrial applications including automotive applications experience between 20 to 50 percent of raw energy input as waste heat. in the form of hot exhaust gases, hot cooling water and lost heat from hot equipment surfaces including heated products. Continued efforts to improve systems energy efficiency, recovering waste heat losses provide attractive opportunities for reduced emission and less costly energy resources. This invention introduces other methods for higher performance of existing energy consuming systems by optimizing the performance of some of the system modules that contributes to the waste energy. in turn reduce energy consumption of these systems, reduces its operating cost, damages to the population health by reducing pollution improving the environment quality, and also reduces the cost of health care. Improving efficiency of the module's' which contribute large percentage of waste energy as by-product from the operation of these systems can improve the system efficiency.
Owner:AMERICAN INNOVATION CORP
Apparatus and method for aeration/mixing of water
InactiveUS7644909B2Guarantee effective circulationImprove performanceFlow mixersLighting and heating apparatusAeration systemPropeller
The aeration system is for aeration and / or mixing of water, which system has at least one aeration unit that has a pump / propeller inside a feed pipe. The feed pipe, to which the water to be aerated, is sucked from beneath. The aeration system has the feed pipe expanding in the upper part of the aeration unit to a conical space working as a nozzle, via which the water continues its way to at least one annular opening.
Owner:WATERIX
High pressure lubricant pump for steelworks
ActiveUS20080095650A1Easily applicableEasily applicable to pumpCheck valvesCylindersPistonHigh pressure
The high pressure lubricant pump for steelworks comprises a body provided with at least one cylinder provided with a lubricant intake port and a lubricant delivery port. Within the cylinder a piston is movable to pressurize the lubricant. The cylinder and the piston define a pre-assembled pumping unit removably fixed into a seat of the body.
Owner:DROPSA
High bulk tissue product
ActiveUS9915034B2Less fiber materialConsiderable energy savingMechanical working/deformationPaper/cardboardEngineeringCalipers
Products having improved caliper, sheet bulk and absorbency and methods for making those products are described. The method comprises producing a multi-ply product having different emboss patterns on each ply where the emboss patterns are made up of emboss elements having an aspect ratio of from about 1 to about 2.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Method and device for filtering signals produced by an accelerometer of the piezo-electric type, and application to a portable object such as a watch
ActiveUS7143012B2Prolong lifeConsiderable energy savingTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksAccelerometerPiezo electric
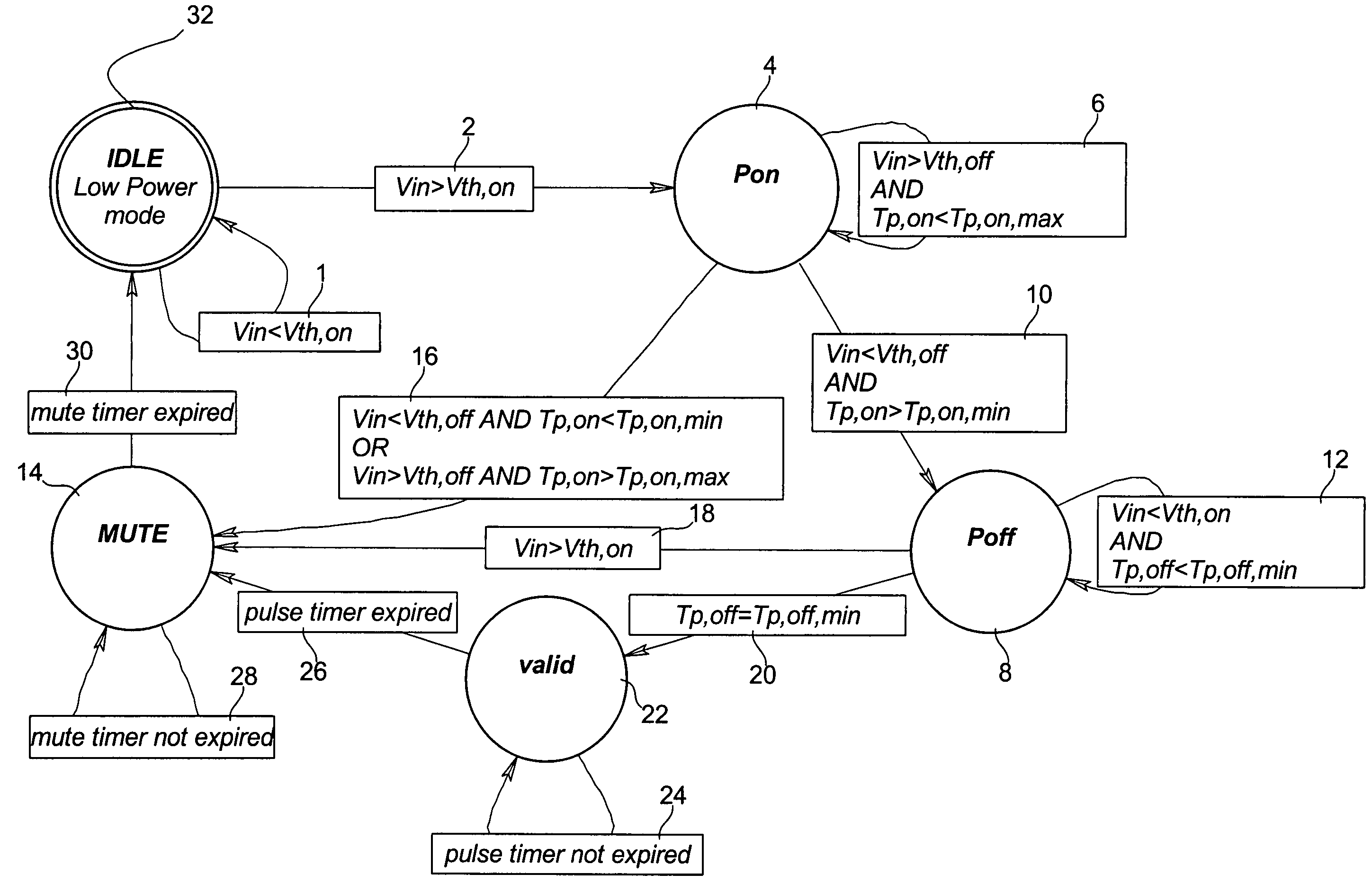
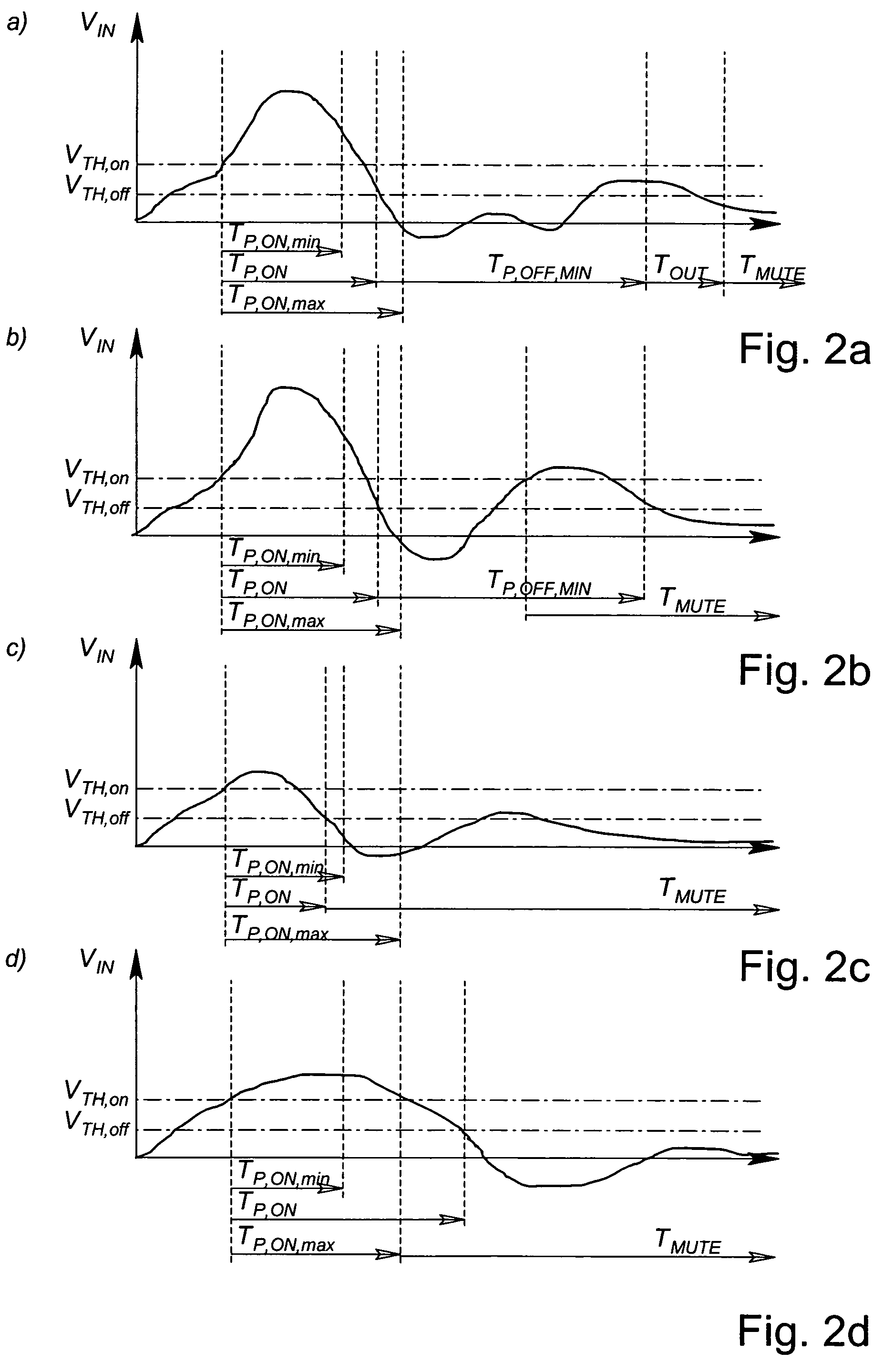
The invention concerns a method for filtering signals (Vin) generated by a piezo-electric type accelerometer in response to detection of a shock applied to an object to which the accelerometer is connected, this method characterised in that it ensures, during a particular step, that the signal (Vin) generated by the accelerometer, after having increased and exceeded a first threshold value (VTH,ON) decreases and becomes lower than a second threshold value (VTH,OFF) lower than the first threshold value (VTH,ON) after a period of time (TP,ON) greater than a minimum period of time (TP,ON,MIN) and less than a maximum period of time (TP,ON,MAX). The invention also concerns a device for filtering signals generated by an accelerometer in response to detection of a shock applied to an object connected to the accelerometer. Finally, the invention concerns a portable object such as a wristwatch including a detection device of this kind.
Owner:EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN
Method and Apparatus for High Temperature Heat Treatment of Combustible Material in Particular Waste
InactiveUS20080282946A1Considerable energy savingReduce pollutantsSolid fuel combustionAir/fuel supply for combustionProduct gasToxic material
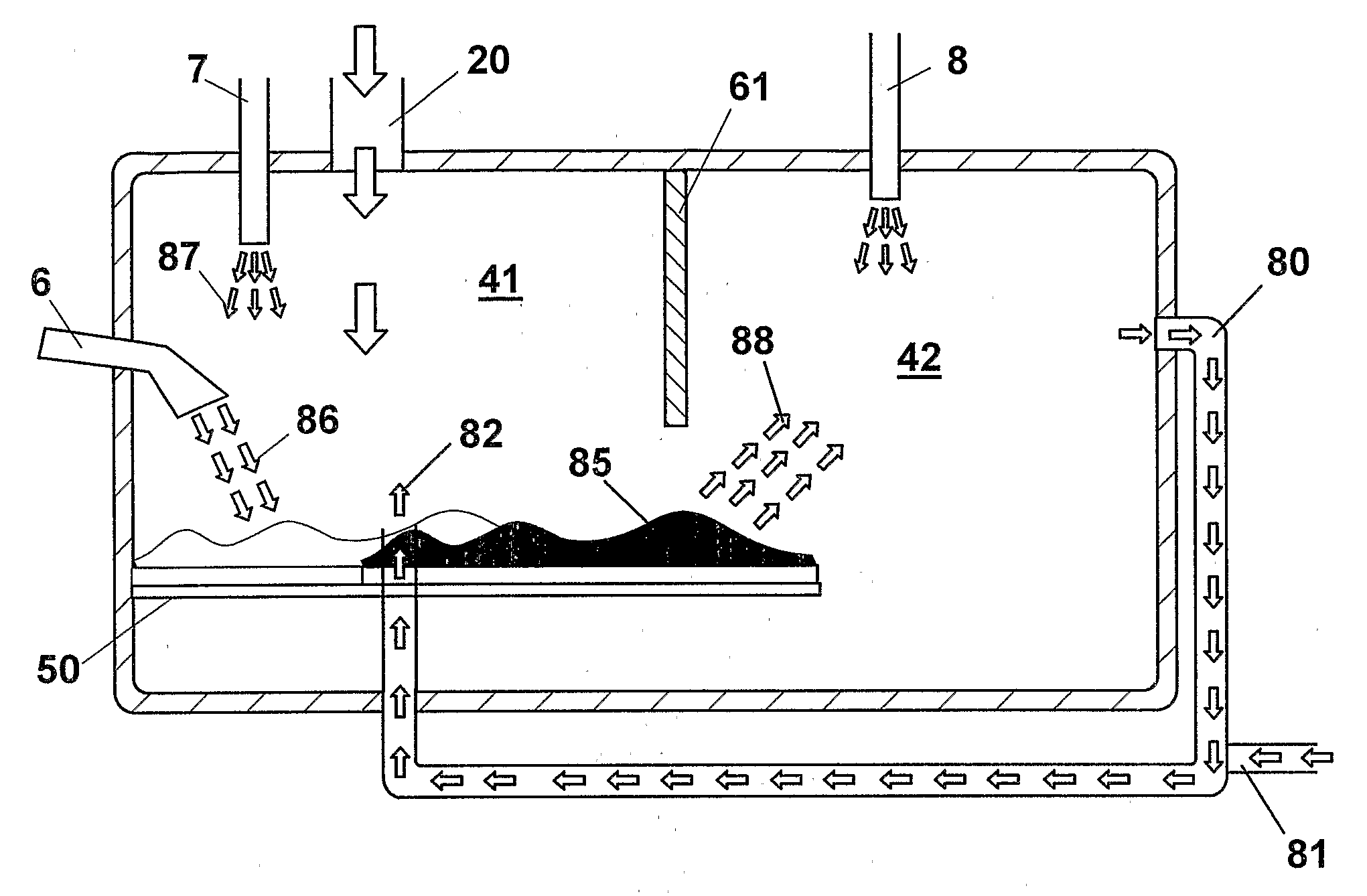
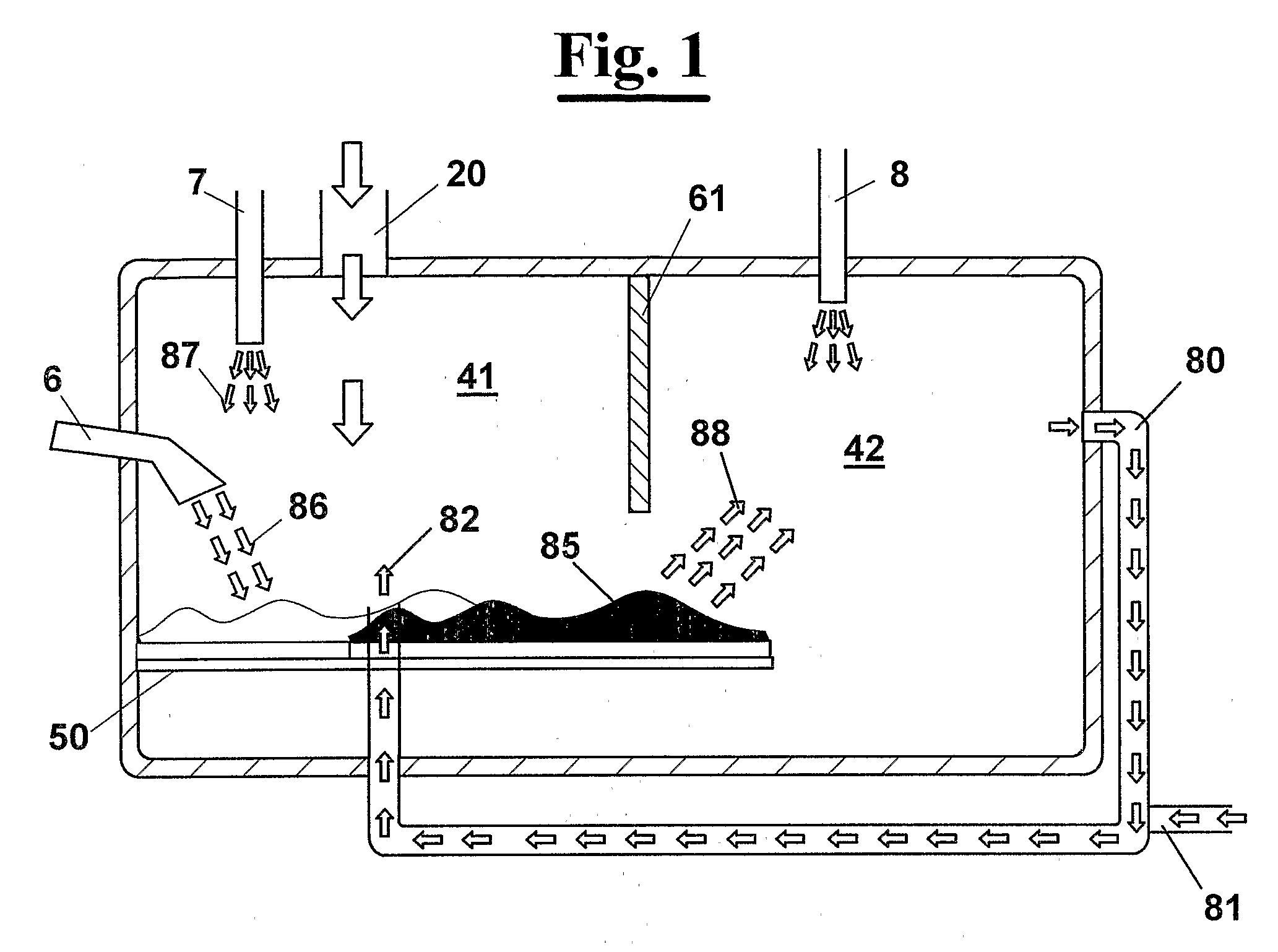
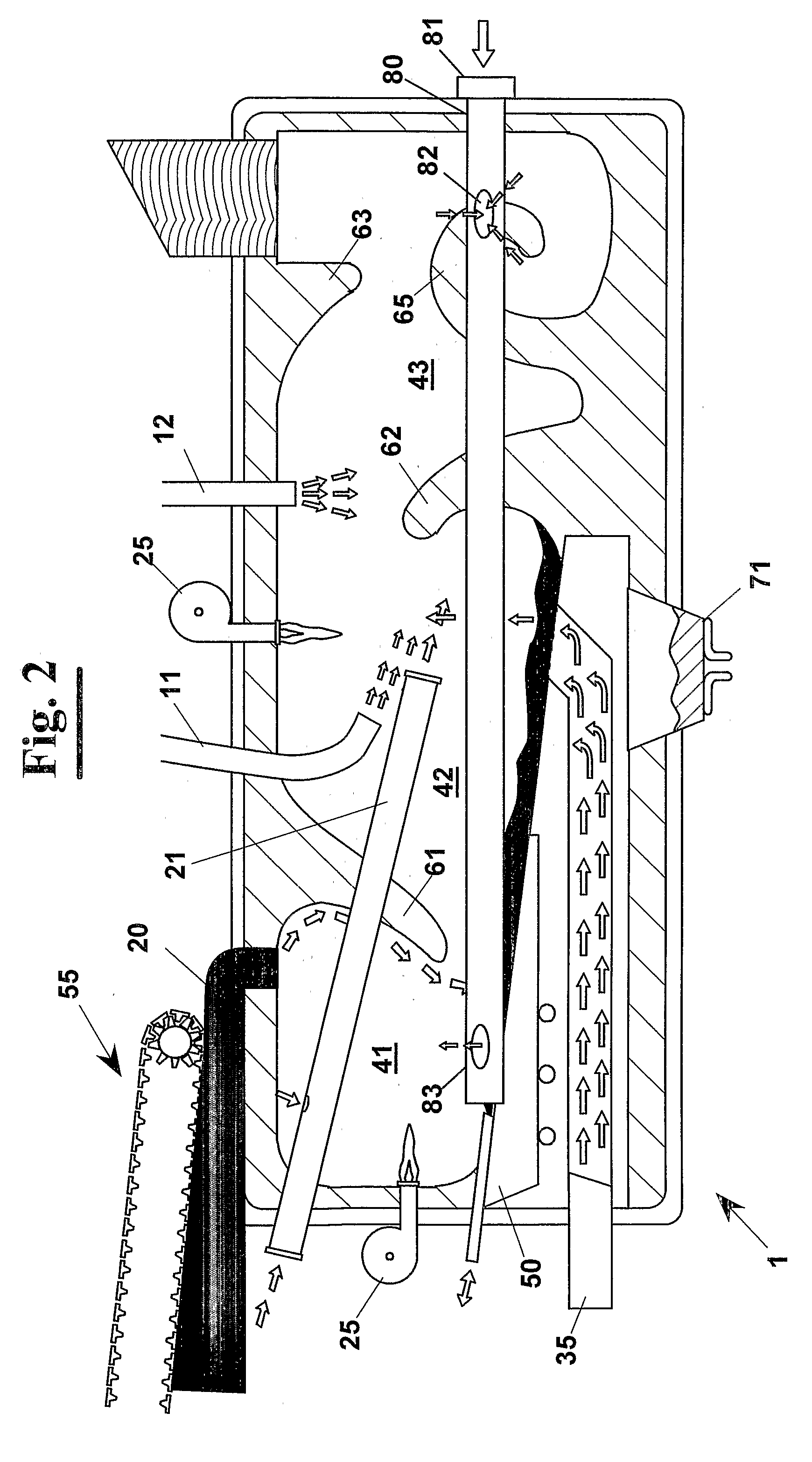
An apparatus (1) for high temperature heat treatment of combustible material comprising a pyrolysis chamber (41) and a combustion chamber (42). The full combustion of the combustible material produces gas at high temperature that is sent to the pyrolysis chamber in order to raise the temperature of pyrolysis. This associated to the introducing water vapour, through a duct (6), and of air, through a duct (7), in pyrolysis chamber (41) produce semiwater gas that is then burnt in combustion chamber (42) by feeding a current (8) of a fluid containing oxygen to raise the combustion temperature in order to carry out the process to temperature that assures the molecular break of the totality of the toxic substances.
Owner:SCOUTECH
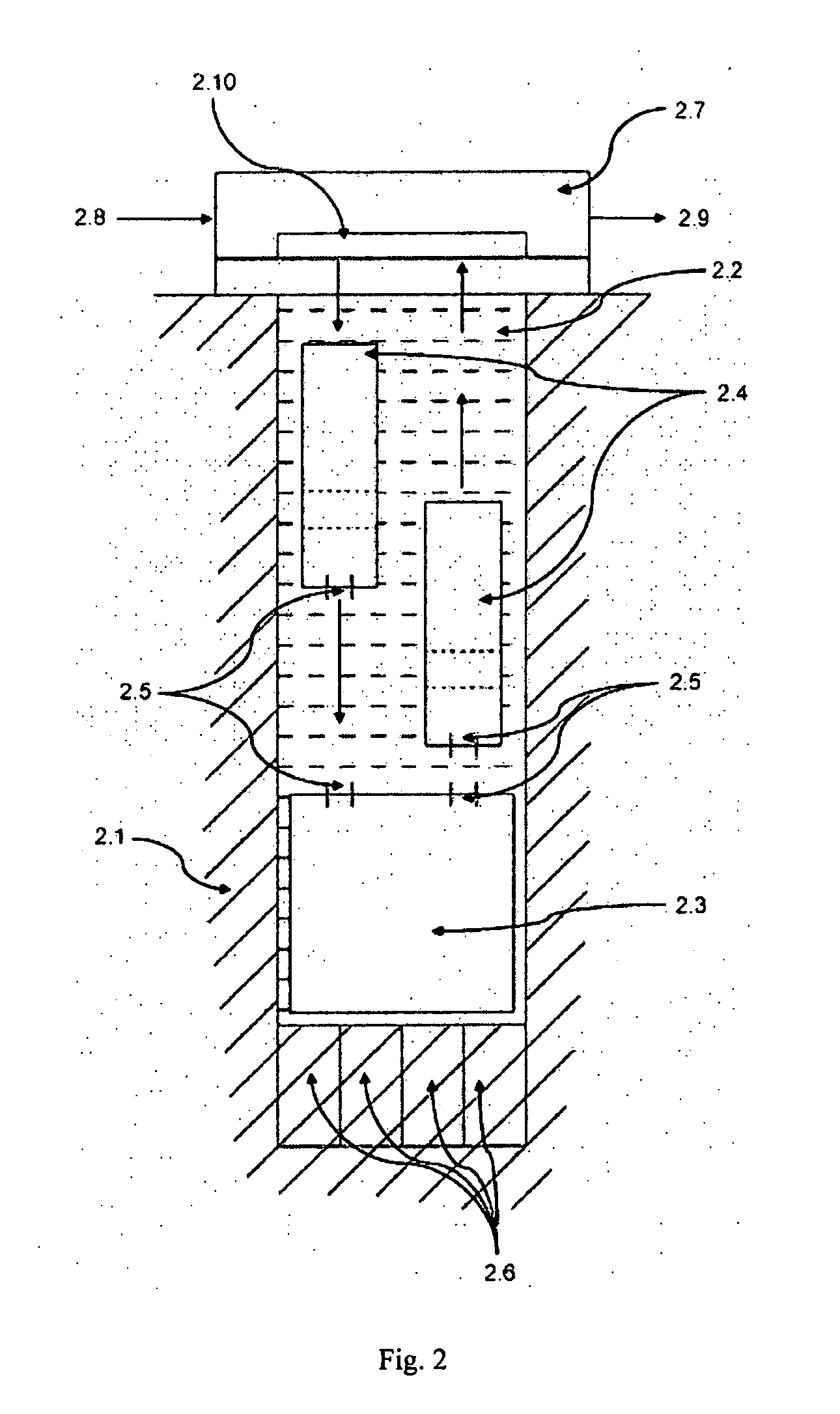
Device for controlling the temperature of objects
InactiveUS7260901B2Considerable energy savingMeet the construction conditionsDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials with heatTransport systemEngineering
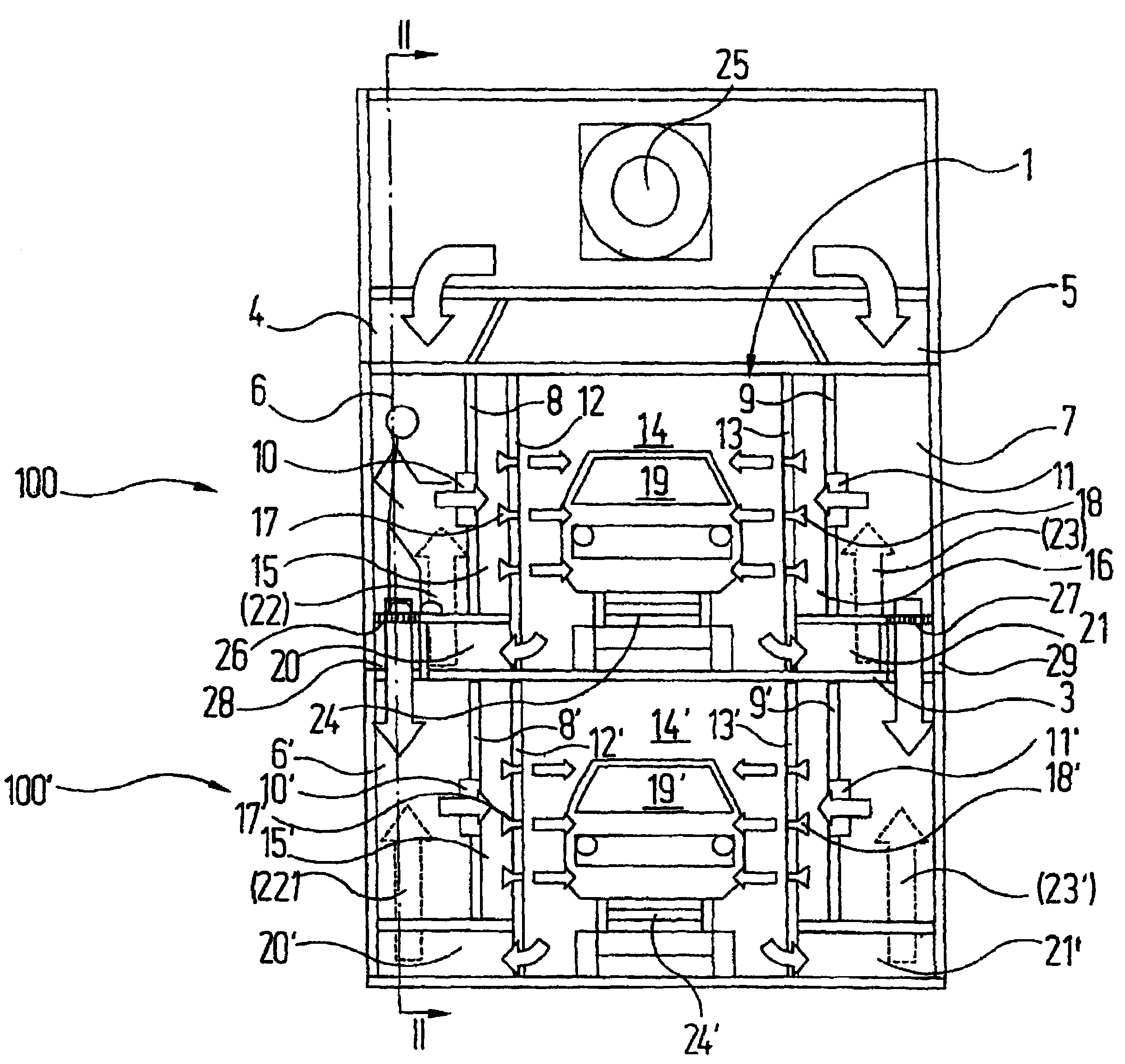
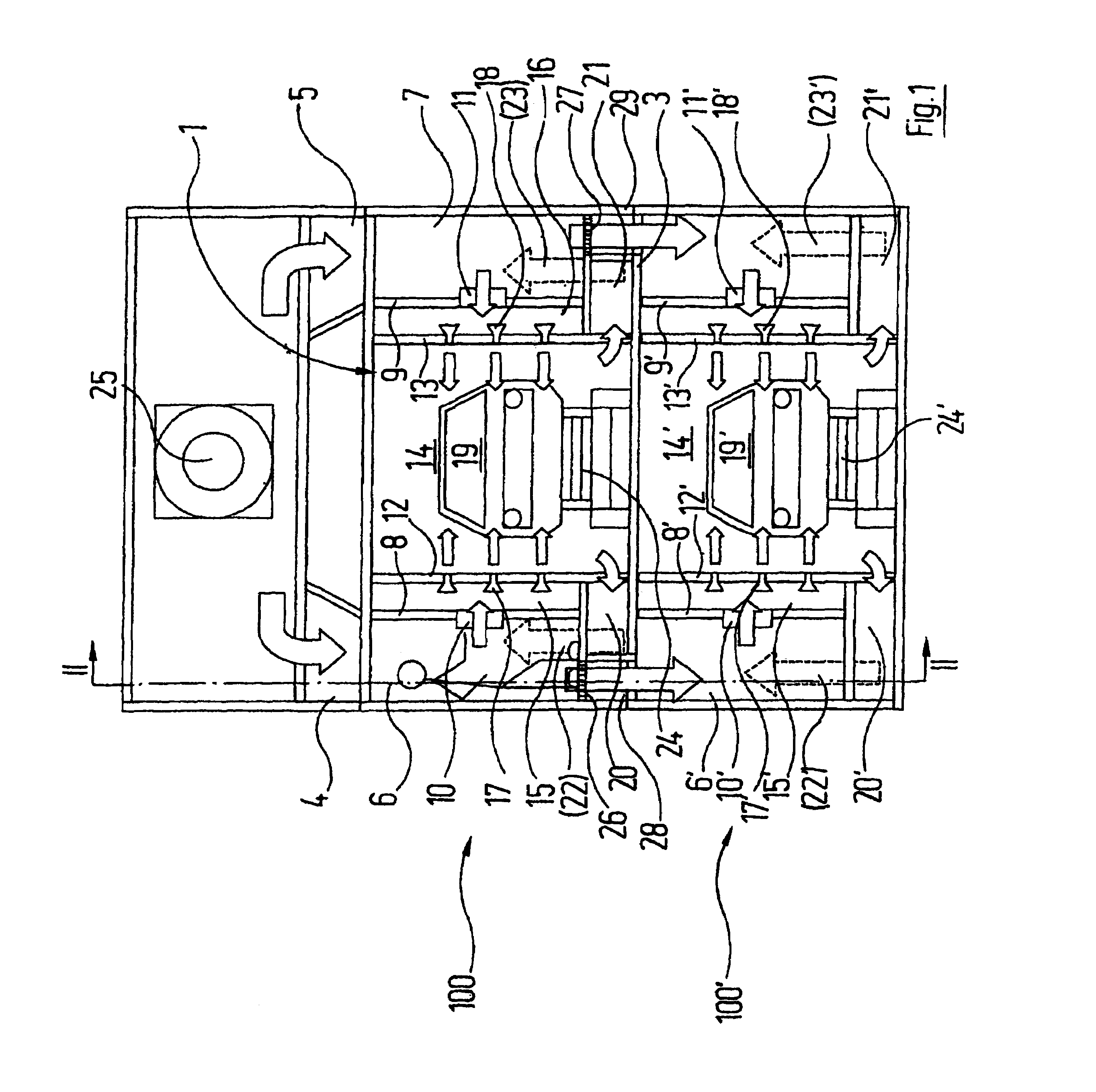
The invention relates to a device for controlling the temperature of objects, especially for drying or cooling objects, said device comprising a housing containing at least two tempering units which are arranged in a functionally parallel manner. Each tempering unit comprises a tunnel-type usable space in which tempered air is applied to the objects. Said objects can be displaced through the usable spaces by means of a respective transport system. According to the invention, the at least two tempering units are superimposed in the housing essentially above the same base surface.
Owner:EISENMANN AG
Air-drying system, in particular for rail vehicles
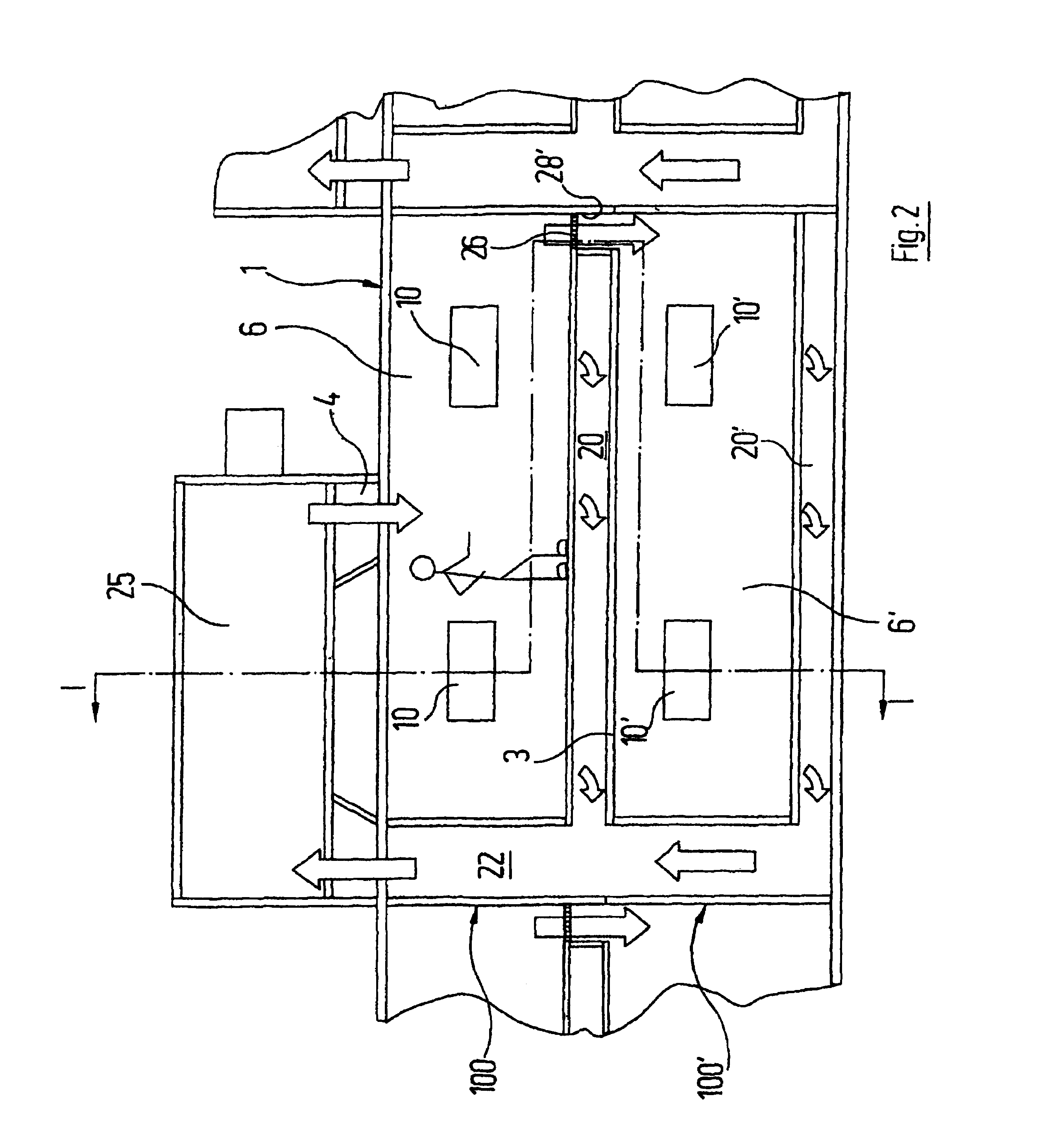
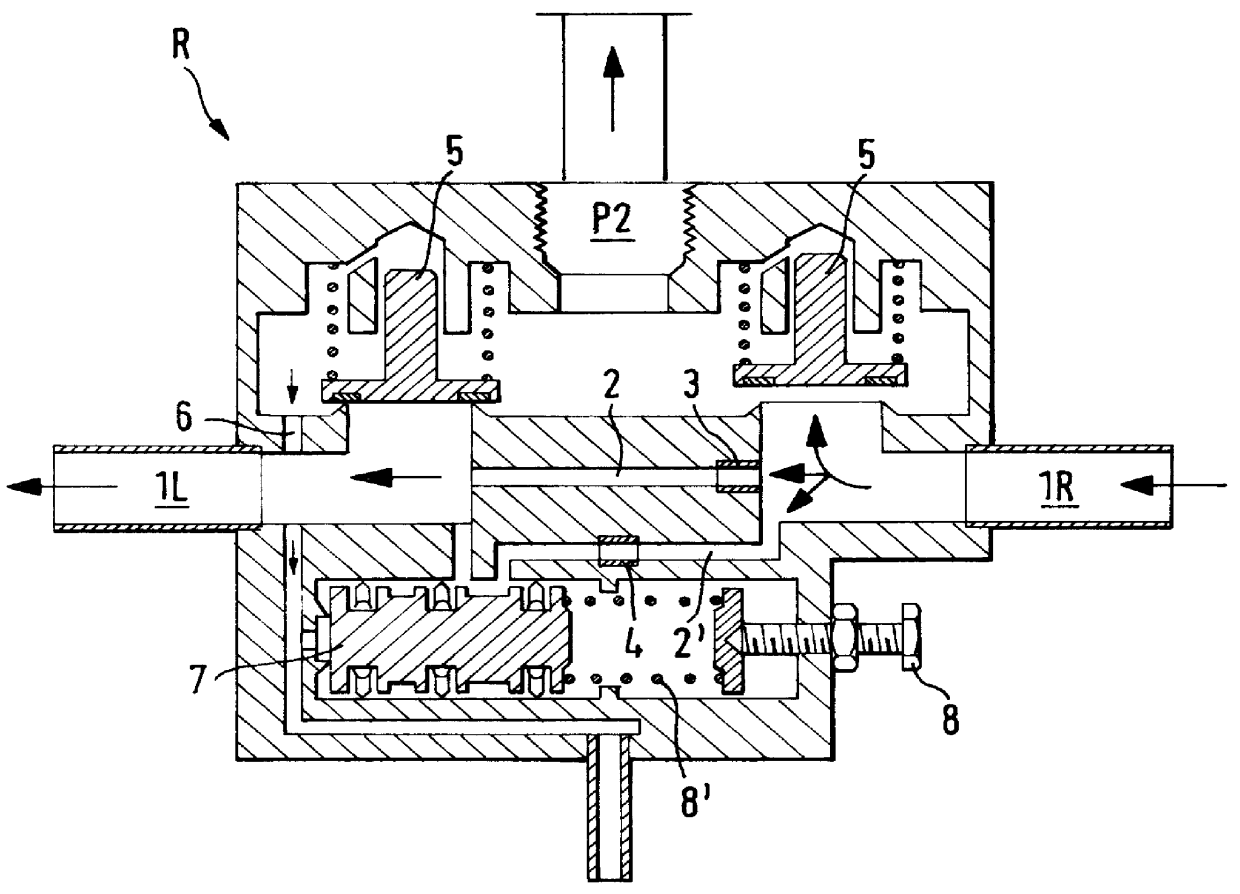
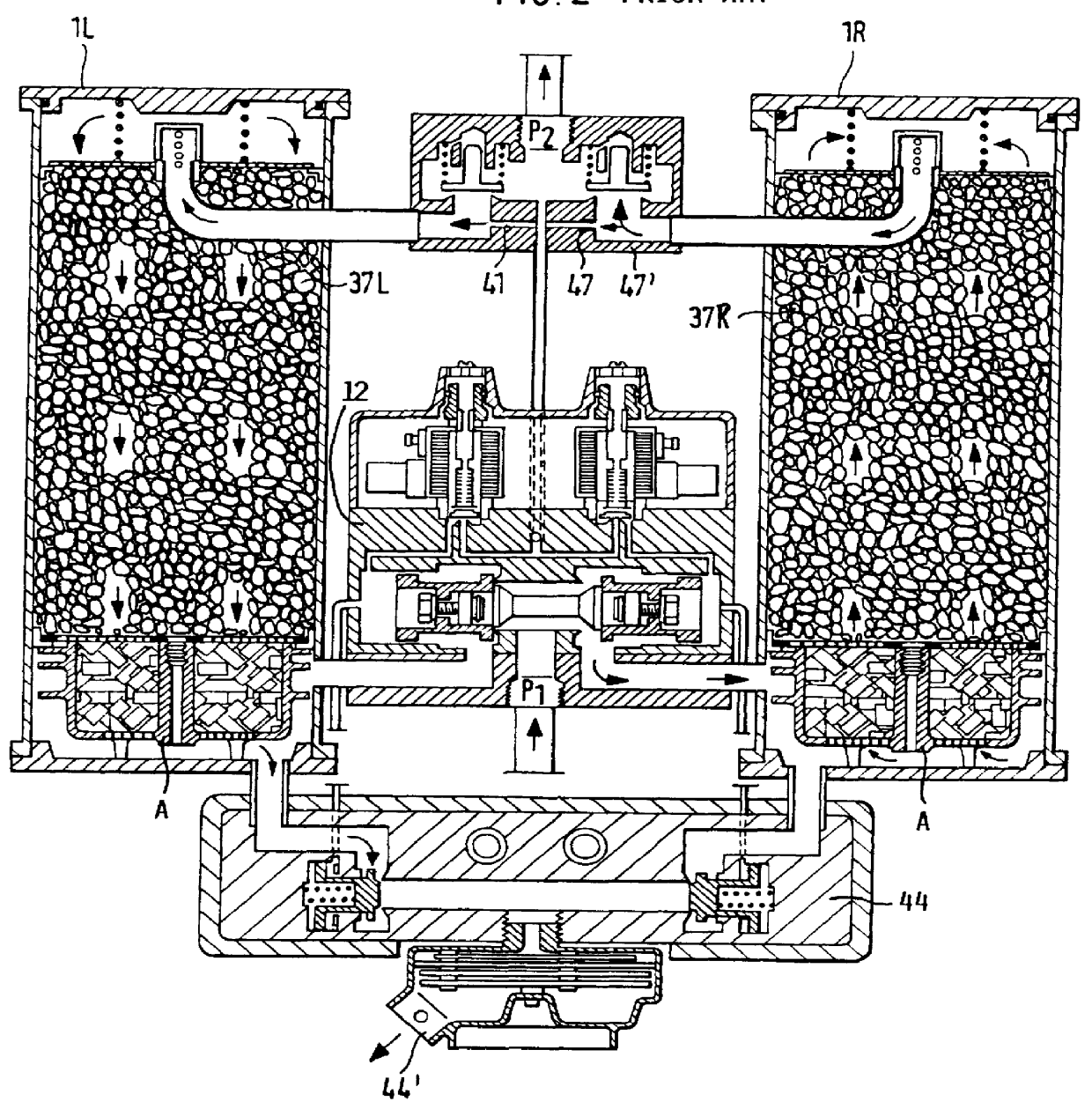
InactiveUS6042197AReduce air consumptionConsiderable energy savingApplication and release valvesAir treatment devicesEngineeringBraking system
PCT No. PCT / DE97 / 00487 Sec. 371 Date May 11, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 11, 1998 PCT Filed Mar. 11, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 42068 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 13, 1997An air-drying system, in particular for the pneumatic braking systems of rail vehicles, including at least two air-drying chambers (1L, 1R) interconnected with one another via first and second regeneration lines (2 and 2'). In a reversibly switchable manner one of the chambers is used for air drying and the respective other chamber is used for regeneration of the air-drying agent (adsorbate) contained in the chambers. The second regeneration line (2') can be switched on and off as necessary to provide two different flow rates of regeneration air.
Owner:KNORR BREMSE SYST FUR SCHIENENFAHRZEUGE GMBH
High pressure lubricant pump for steelworks
ActiveUS8257065B2Easily applicable to pumpConsiderable energy savingCheck valvesCylindersEngineeringHigh pressure
The high pressure lubricant pump for steelworks has a body provided with at least one cylinder, the cylinder having a lubricant intake port and a lubricant delivery port. Within the cylinder a piston is movable to pressurize the lubricant. The cylinder and the piston define a pre-assembled pumping unit removably fixed into a seat of the body.
Owner:DROPSA
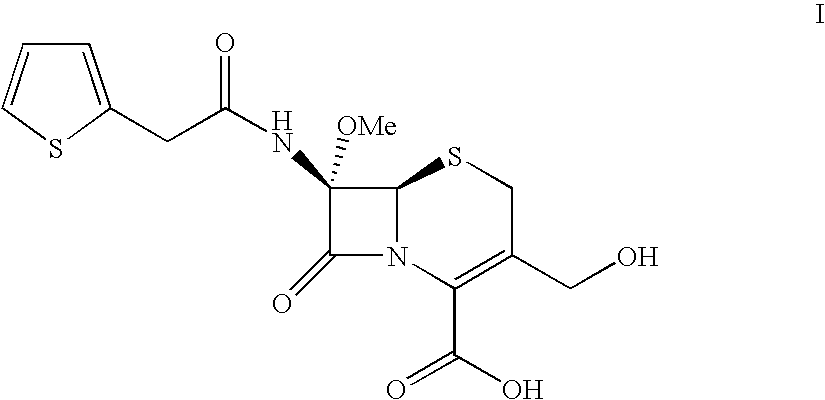
Process for producing 7-methoxy-3-desacetylcefalotin
ActiveUS20090093032A1Increase production capacityConvenience to workOrganic chemistryBacteriaCefoxitinHydrolysis
Process for producing 7-methoxy-3-desacetylcefalotin by a hydrolysis process which takes place in water and is catalyzed by an enzyme. Cefoxitin can be obtained from this compound by known methods.
Owner:ACS DOBFAR SPA
Magneto-inductive flow measuring device
InactiveUS8042410B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioGood reproducibilityVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersPhysicsMeasurement device
An apparatus for measuring volume- or mass-flow of a medium flowing through a measuring tube in the direction of the measuring tube axis, and includes: a magnet system, which produces a magnetic field passing through the measuring tube essentially transversely to the measuring tube axis; at least one measuring electrode, which contacts the medium in a defined surface region; and a control / evaluation unit, which provides information concerning volume- or mass flow of the medium in the measuring tube on the basis of a measurement voltage induced in the at least one measuring electrode. At least the medium-contacting surface region of the at least one measuring electrode is manufactured of a chemically inert and electrochemically and mechanically resistant material.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Hydraulic drive device having two pressure chambers and method for operating a hydraulic drive device having two pressure chambers
ActiveUS20110271667A1Energy-saving hydraulic operationLower energy requirementsServomotor componentsRotary clutchesHydraulic fluidHigh pressure
The invention relates to a hydraulic drive device, comprising a piston which is guided displaceably in a cylinder chamber along a working axis and adjoins a working pressure chamber that can be pressurized by hydraulic fluid, and comprising a control means that is guided in the piston at least in some sections between different control states in order to control the flow of the hydraulic fluid from a high pressure supply into the working pressure chamber to move the piston in the working direction and from the working pressure chamber to a return flow chamber, wherein the region of the piston facing away from the working pressure chamber delimits a low pressure chamber that is pressurized by a low pressure supply for hydraulic fluid during the operation of the device such that the piston is moved back against the working direction when the control means connects the working pressure chamber to the return flow chamber. The invention furthermore relates to a method for operating a hydraulic drive device.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Energy-saving type management controller for clean operation room purifying air-conditioning system
PendingCN111780280AShort lifeReduce replacement cycleMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsProcess engineeringCarbon dioxide sensor
The invention discloses an energy-saving type management controller for a clean operation room purifying air-conditioning system. The controller body is connected with a fresh air regulating valve, afresh air processing unit, a purifying air conditioning unit, an air supply regulating valve, a return air regulating valve and an exhaust fan of an operation room correspondingly. The controller bodyhas functions of direct starting up, appointed starting up and temperature and humidity setting. The actual value monitored by a temperature-humidity sensor and the set value can be utilized to makea comparison, and the opening degree of cold and heat source electrical valves of the fresh air processing unit and the purifying air conditioning unit is controlled. The controller body is equipped with a power-off self-purification function, direct self-purification or preset self-purification can be selected, and corresponding self-purification time is set. Besides, the controller body is further connected with a carbon dioxide sensor by which the carbon dioxide concentration inside the operation room can be monitored; and only when the self-purification time is out and the carbon dioxide concentration reaches the standard, purification air conditioning equipment related to the operation room stops running. By means of the energy-saving type management controller for the clean operationroom purifying air-conditioning system, accurate control over the air purification processing process of the operation room in stages such as a pre-operation stage, a post-operation stage and a during-operation stage can be achieved; and in addition, energy can be saved greatly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICAL COLLEGE +1
Oxygenate to olefin manufacture and recovery process
ActiveUS7879920B2Considerable energy savingSignificant energy savingOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOrganic compound preparationSolid componentDistillation
This invention is directed to methods for forming an olefin stream from a methanol stream. A lower grade methanol, such as chemical grade or crude methanol, can be used as feed to form the olefin stream. The process uses a relatively simple distillation type step to vaporize a portion of the methanol feed stream and send the resulting vapor stream to a reaction unit to form the olefin stream. In addition, the invention provides the ability to operate the downstream recovery units with reduced fouling or plugging due to the presence of fine solids components.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Energy saving and efficiency improving method for plunger pump
The invention relates to an energy saving and efficiency improving method for a plunger pump. The plunger pump adopts a linear piston reciprocating and direct electromagnetic driving mode for operation and employs a control box for controlling. An N-pole electromagnetic coil homonymic terminal, an electromagnetic coil ground terminal and an electromagnetic coil synonymic terminal are connected with corresponding terminals in the control box through a driving power cathode wire, a power ground wire and a driving power cathode wire respectively. A cylindrical piston cylinder is formed in spaces of a suction section, an intermediate section and a discharge section, between a suction-port valve and a discharge-port valve, of an inner cavity of a pump body. A suction-terminal valve, a permanent magnet N-pole terminal, a permanent magnet S-pole terminal and a discharge-terminal valve form a cylindrical piston through a linkage structure of a connecting rod and a connection frame; the piston is driven by a driving circuit through an N-pole electromagnetic coil and an S-pole electromagnetic coil. The driving circuit of the plunger pump includes driving signal generation, conversion and amplification and switch execution.
Owner:NANTONG MUTE BUILDING TECH CO LTD
Method for producing a structural sheet metal component, and a structural sheet metal component
ActiveUS10501829B2Well formedSave energyShaping toolsInduction heating apparatusHeating temperatureMaterials science
A method for producing a structural sheet metal component formed from an aluminum alloy for a motor vehicle includes providing an aluminum sheet blank in a state T4 or T5 or T6 or T7, heating the aluminum sheet blank to a heating temperature between 100° C. and 450° C., forming the aluminum sheet blank to a structural sheet metal component, and heat post-treatment of the formed structural sheet metal component.
Owner:BENTELER AUTOMOBILTECHNIK GMBH
Method of producing inorganic hydraulic binders
InactiveUS20110175258A1Production of building binders more effective and cheaperQuality improvementConstruction waste recoveryTransportation and packagingMetallurgical slagChemical reaction
Method of producing binders for building and building products consisting of a material of man-made and / or natural origin from solid products produced by burning of solid fuels, metallurgical slag, ground fire products, products from burnt out mining deep stock piles, glass production waste, ceramic production waste, brick and concrete construction waste, heat-activated clays, low-crystalline pyroclastic rocks, sedimentary laterite, bauxite, opalolite, allophanolite, diatomite rocks, limestones and claystones and clays. The material is subjected to physical treatment consisting in action of a power pulse, during which mechanical energy Etk is passed on to the particles of the material treated by acting of a force of the size from 50 to 3.105 N, related to 1 g of the treated material during a very short time in the range from 1.10−6 to 1.10−2 s or more. Subsequent pulses cause passing of mechanical energy Etk to grains of the material and / or passing of magnetic energy Etm to its grains together with passing of mechanical energy and / or after it by means of alternate and / or variable magnetic field having frequency from 15.101 to 15.106 Hz and intensity from 10−2 to 103 T. The energy acts on particles of the ferromagnetic substances if they are present in the treated material and / or on charges in defects of grains of the material. The defects were produced as a result of passing of mechanical energy. As a consequence the internal energy of the material treated increases and the particles become more fine at least to 200 micrometers. Re-aggregation of its particles is thus prevented and chemical reactivity of the material treated is increased to obtain dry binder and / or dry building material. Water is added in the quantity from 8.20 to 420% by weight, based on weight of the material treated to obtain formable wet binder and / or formable wet material, which can be formed to the desired form of products and / or hardened by autoclaving and / or dry warming up.
Owner:DASTIT MANAGEMENT SPOL S R O
Presence sensor-controlled lighting apparatus
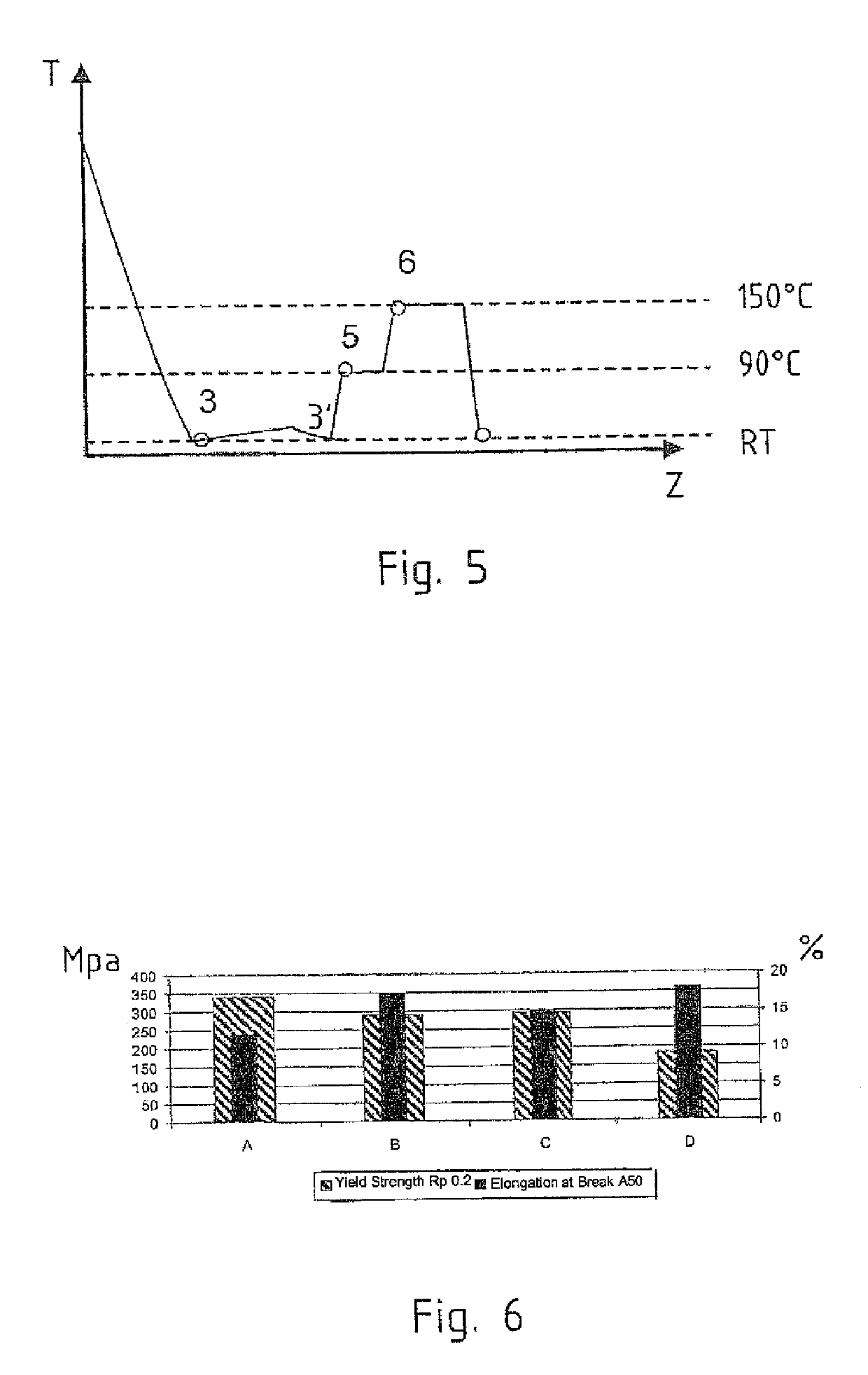
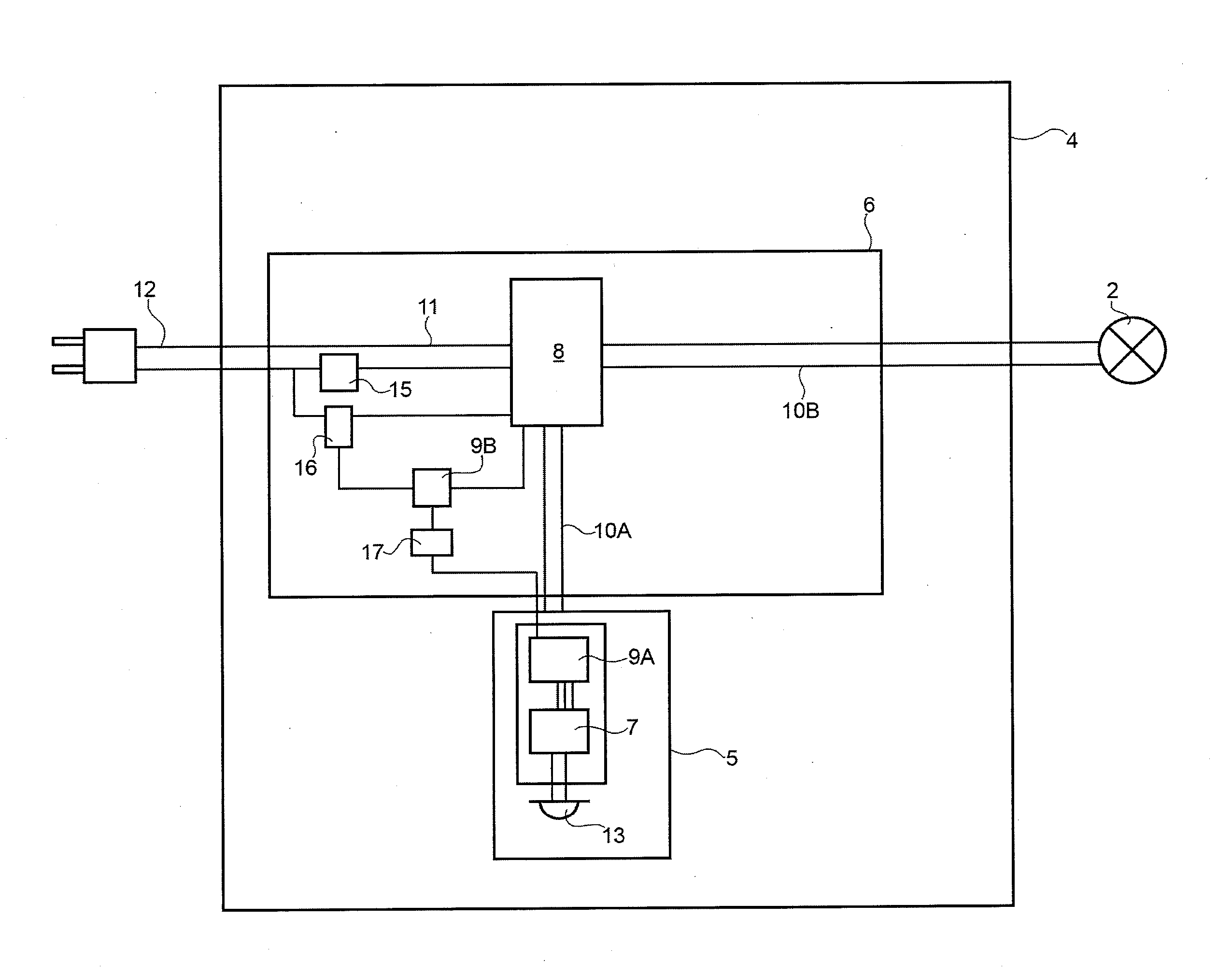
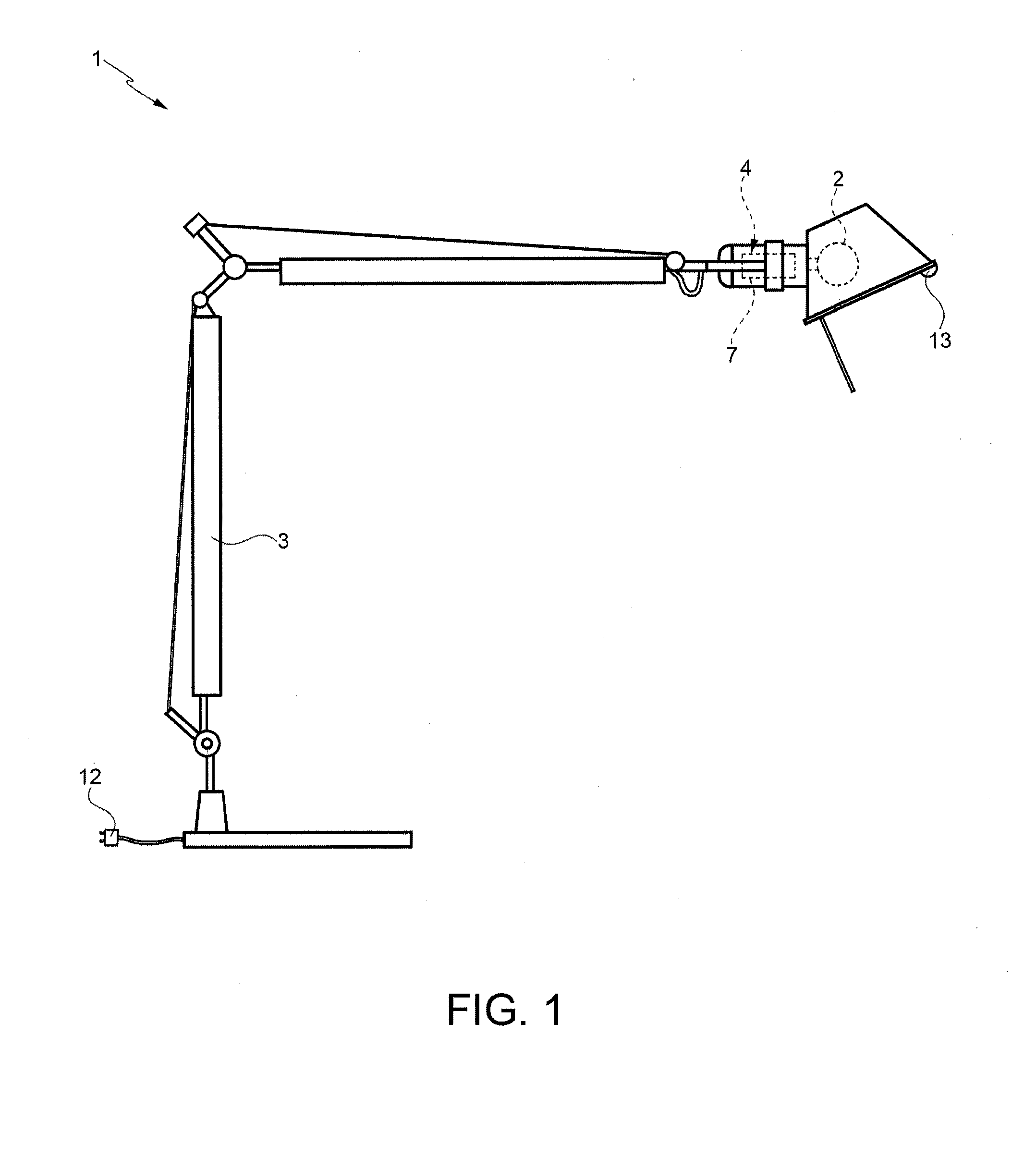
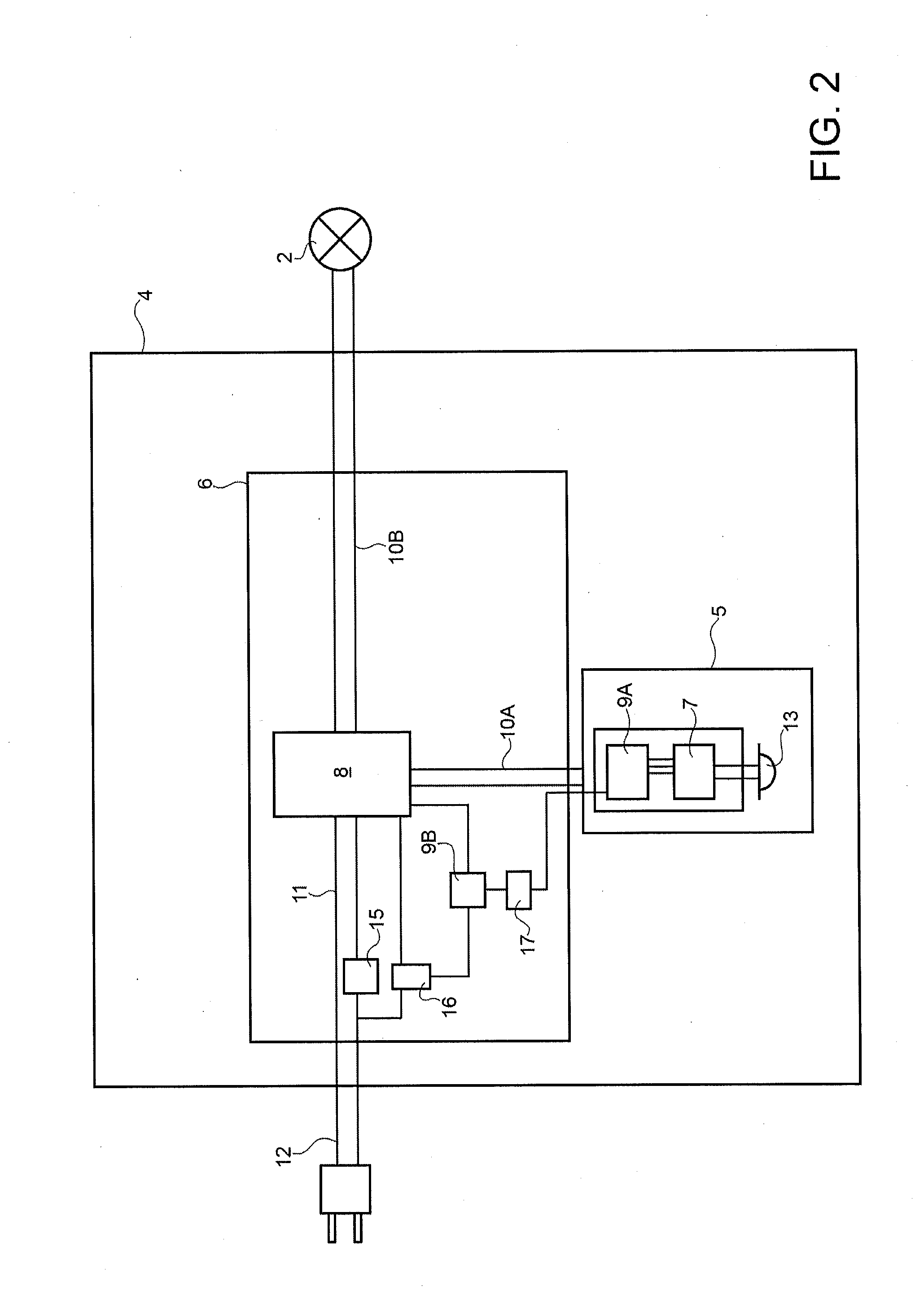
InactiveUS20140175991A1Easy to produceEasy to useElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementLight equipmentEffect light
A lighting apparatus, in particular a table lamp, includes a light source; a power and control device connected to the light source; and a power line for powering the light source and the power and control device by means of a power unit; the power and control device being designed: to turn the light source off after a first predetermined time interval in which the presence sensor detects no user presence; and to cut itself and any other electronic devices of the apparatus off from the power supply, by cutting off the power line, after a second predetermined time interval, longer than the first time interval, in which the presence sensor detects no user presence.
Owner:ARTEMIDE
Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and a method for preparation thereof
ActiveUS10726981B2Promote regenerationEfficient separationSemi-permeable membranesMembranesCarbon coatingPolymer science
The present disclosure relates to a method for manufacturing a covalently functionalized coated magnetic nanoparticle and to said particles and uses thereof. The preparation method includes forming a shell of a hydrophilic polymer coating layer on top of a magnetic metal core coated with a carbon coating. In the method a particle comprising a magnetic metal core coated with a carbon coating is provided. The surface of the particle is subjected to covalent functionalization by generating amino reactive groups via diazonium chemistry and subsequently an irreversible attachment of an atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) initiator is carried out on said surface. A hydrophilic polymer layer is formed) by a surface initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-ATRP) reaction with a monomer comprising N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM).
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Operating element with wake-up functionality
InactiveUS20080202903A1Reduce power consumptionConsiderable energy savingDashboard fitting arrangementsEmergency protective devicesMobile vehicleEngineering
An operating element with wake-up functionality for a motor vehicle is provided, wherein a setting of an operating element can be selected by means of a translationally and / or rotationally movable grip, having at least one wiper contact track divided into sectors, having a wiper contact connected directly or indirectly to the grip, wherein the wiper contact is movable over the at least one wiper contact track by means of the grip, having an electronic analysis unit that can be switched off, and having at least one switching means connected to the wake-up electronics unit by means of which the electronic analysis unit of the operating element can be activated, wherein the switching means can be actuated by means of the grip.
Owner:PREH GMBH
Active mechanical brake-force distribution with exclusive mechanical Anti-locking function
PendingUS20210387600A1Avoid it happening againEasy to brakeBraking element arrangementsElectrodynamic brake systemsGear wheelEngineering
An active mechanical brake-force distributor with exclusively mechanical anti-locking function, which is installable inside braking systems in the technical-engineering field, actuated by motors and / or generators of various types, characterized in that it is provided with at least one distribution free wheel and a plurality of interconnections consisting of gears or pulleys with belts, interconnection shafts and motion transmission, modulation and inversion devices or clutches adapted to provide rapid accelerations and equally efficient decelerations; the elements being operatively connected to one another to form the mechanical distributor, which is configured to optimize, in an exclusively mechanical and non-electronic manner, the controlled rotation under acceleration and deceleration of the vehicle wheels according to a mere rolling motion without slipping on any type of road surface, and to modulate the speed itself of the vehicle under acceleration and deceleration with full control of the directional stability thereof.
Owner:LAMBERTI LAMBERTO
Bar speed changing device
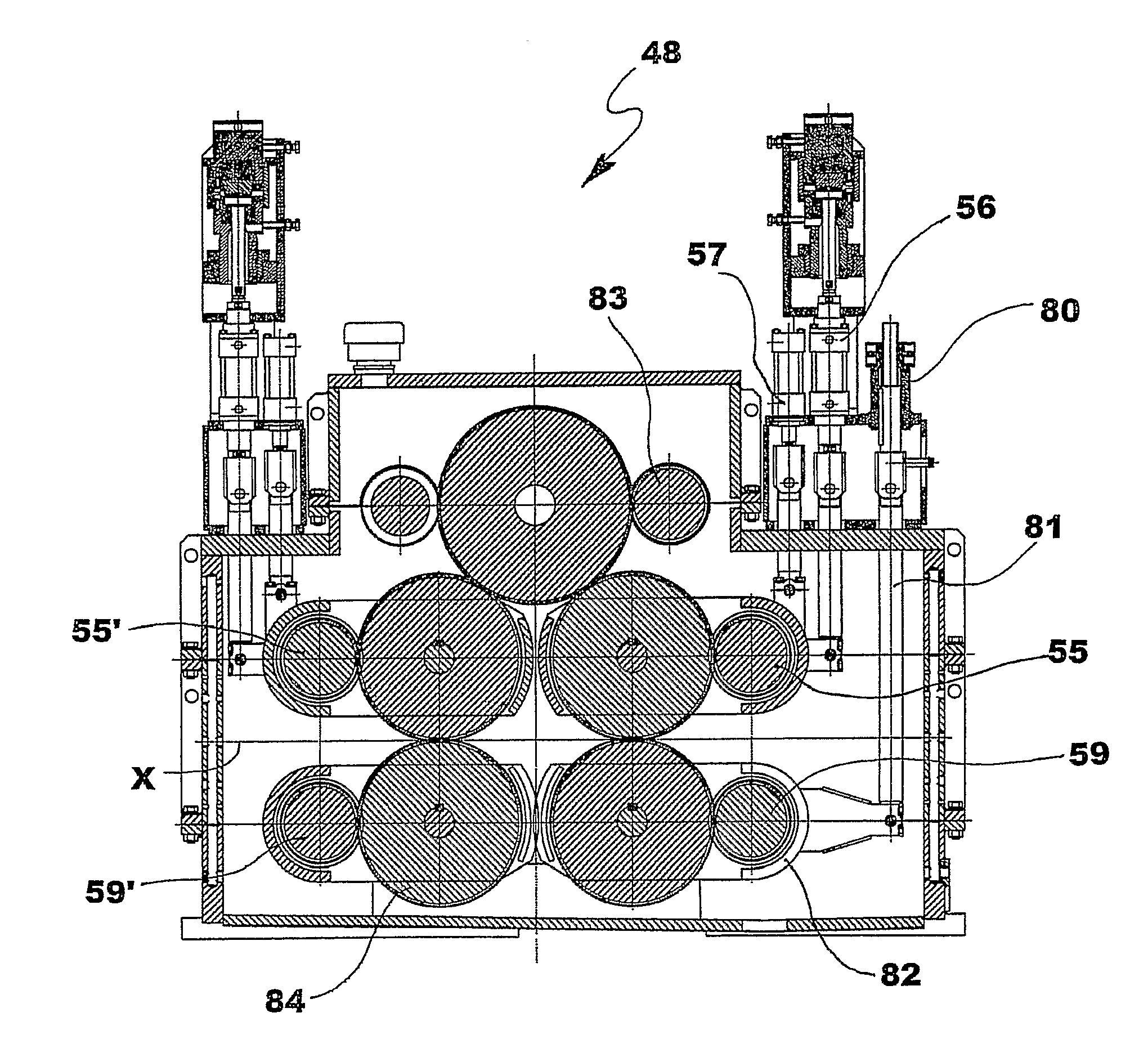
ActiveUS7559220B2Less powerConsiderable energy savingMetal rolling stand detailsGuiding/positioning/aligning arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:DANIELI & C OFF MEC SPA
Smoke exhaust backflash energy-saving device and method
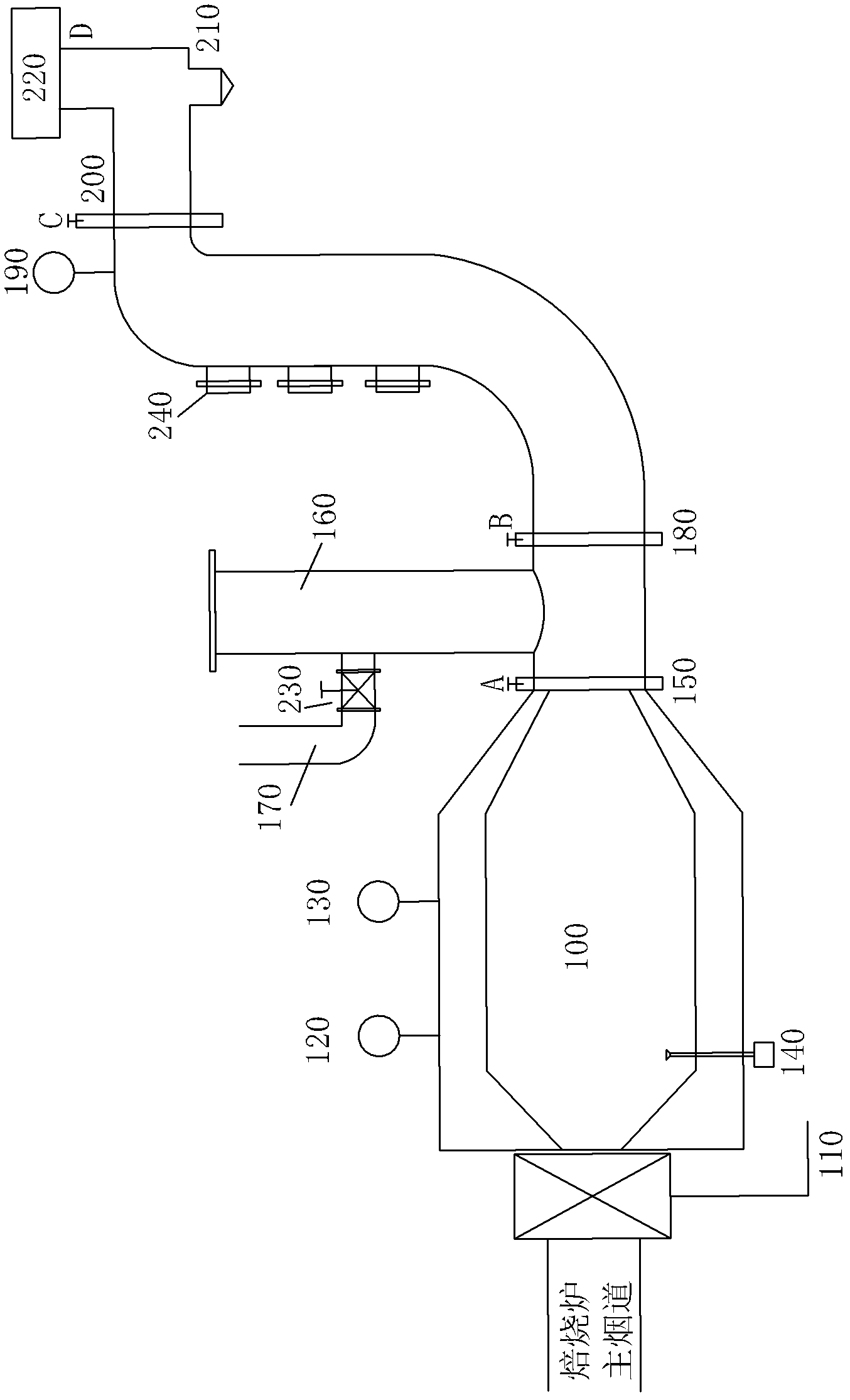
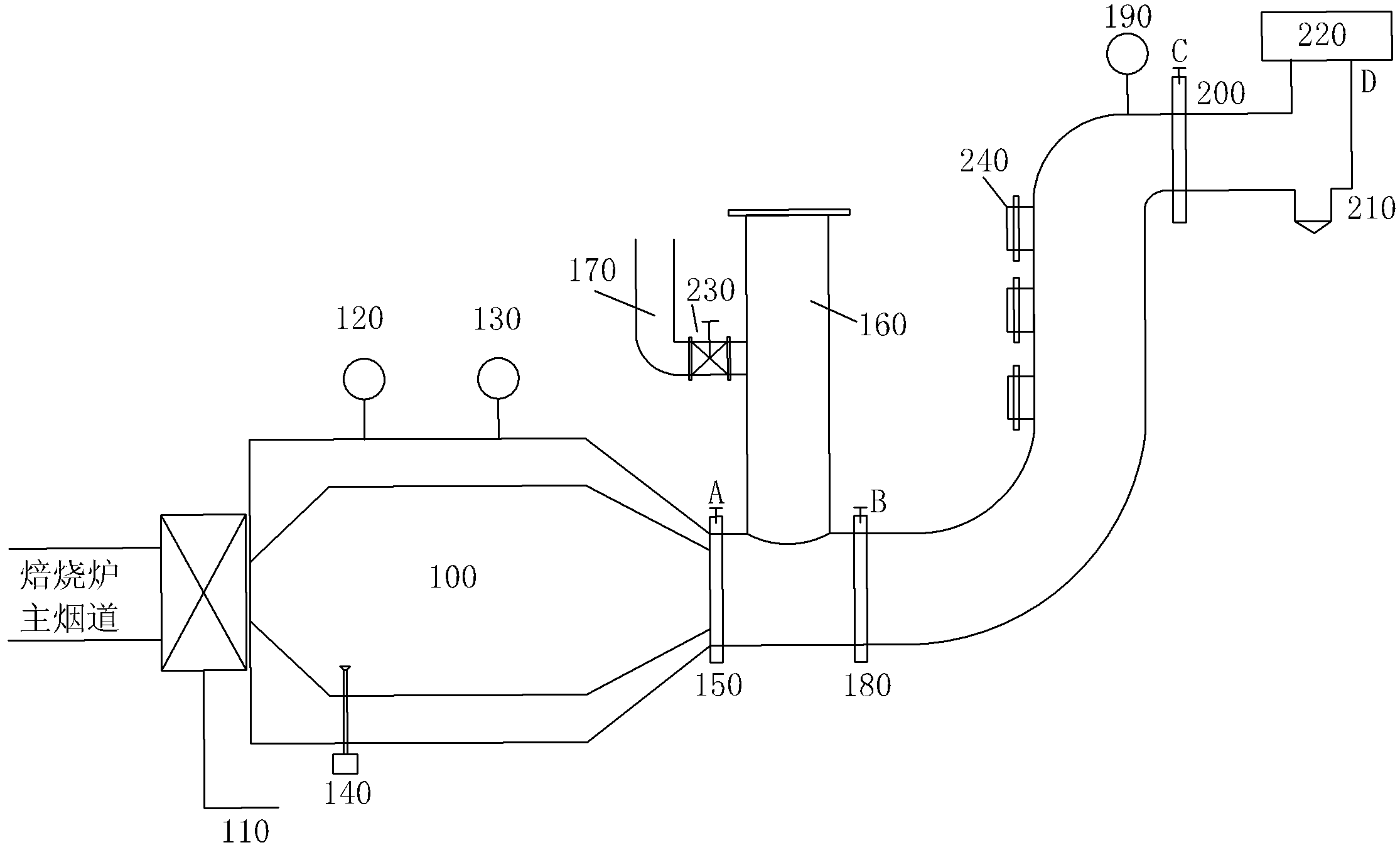
InactiveCN102538490AReduce dosageConsiderable energy savingIncreasing energy efficiencyIncinerator apparatusCooking & bakingAtmospheric air
The invention discloses a smoke tail gas backflash energy-saving device and a method, which belong to the filed of energy-saving devices, wherein a fan is arranged on a main flue outlet of a baking furnace, smoke tail gas in a main flue is lead into a burner by the fan, an outlet of the burner is connected with a first pipeline inlet, a first pipeline outlet is connected with a heat energy recover main pipeline inlet, a heat energy recover main pipeline outlet is connected with a smoke exhaust pipeline inlet, the side wall of the heat energy recover main pipeline is provided with a plurality of interfaces, and the interfaces are connected with a flue high temperature section of the baking furnace. The smoke tail gas backflash energy-saving device can reduce above 30 percent of gas dosage in the baking furnace, and smoke tail gas which is discharged into the atmosphere is superior to the national standard.
Owner:邹洪军
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com