Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
114results about How to "Guarantee effective circulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
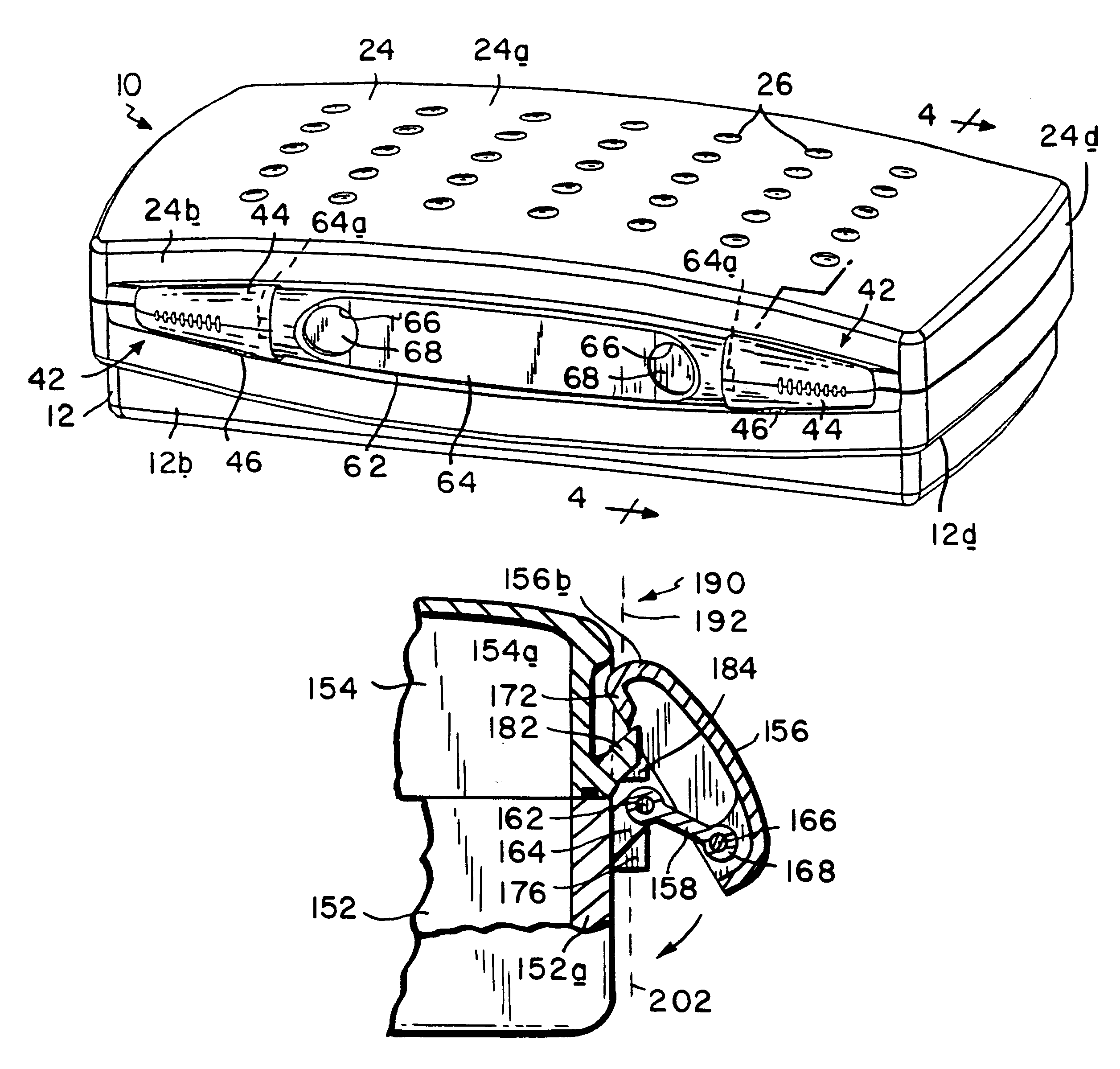
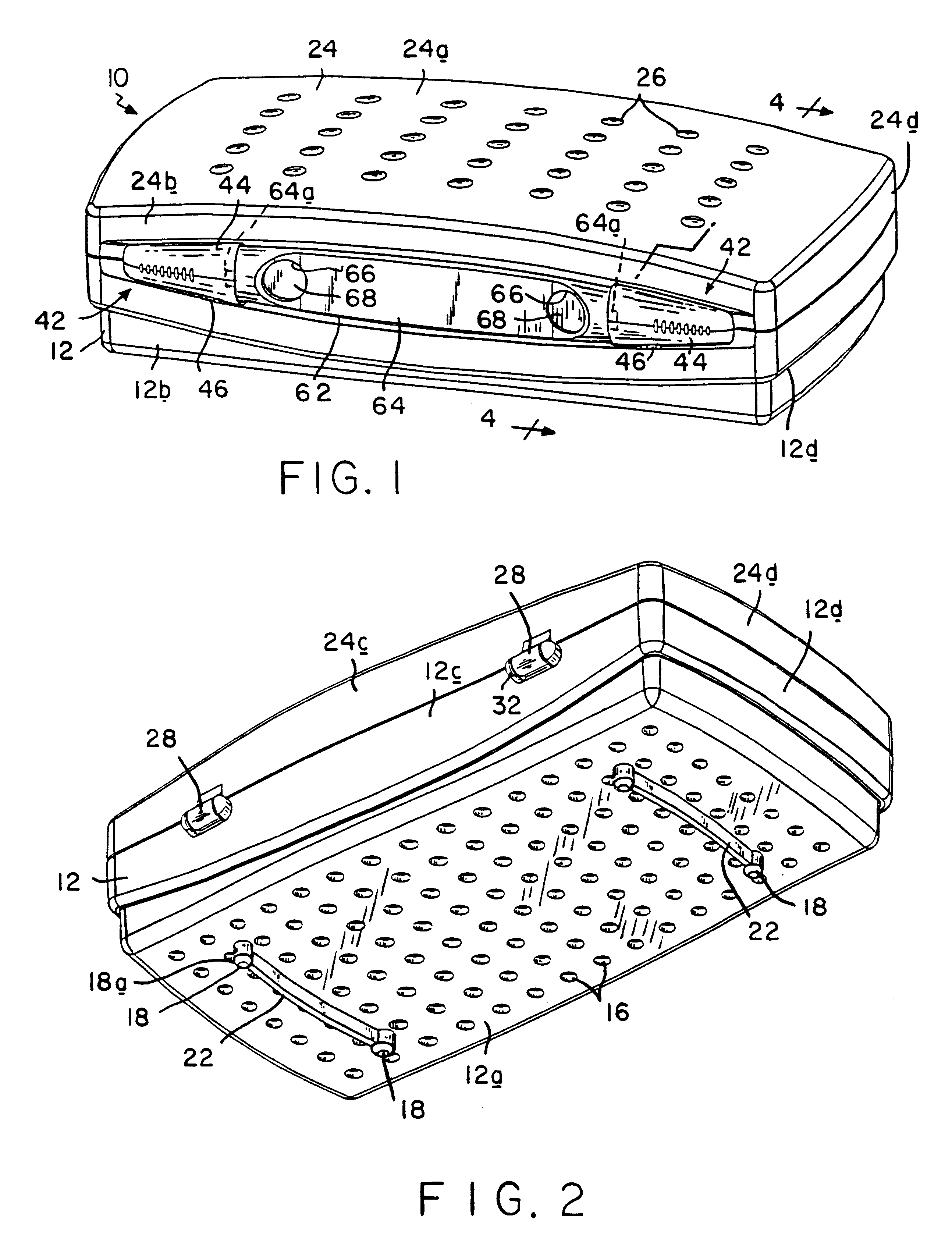
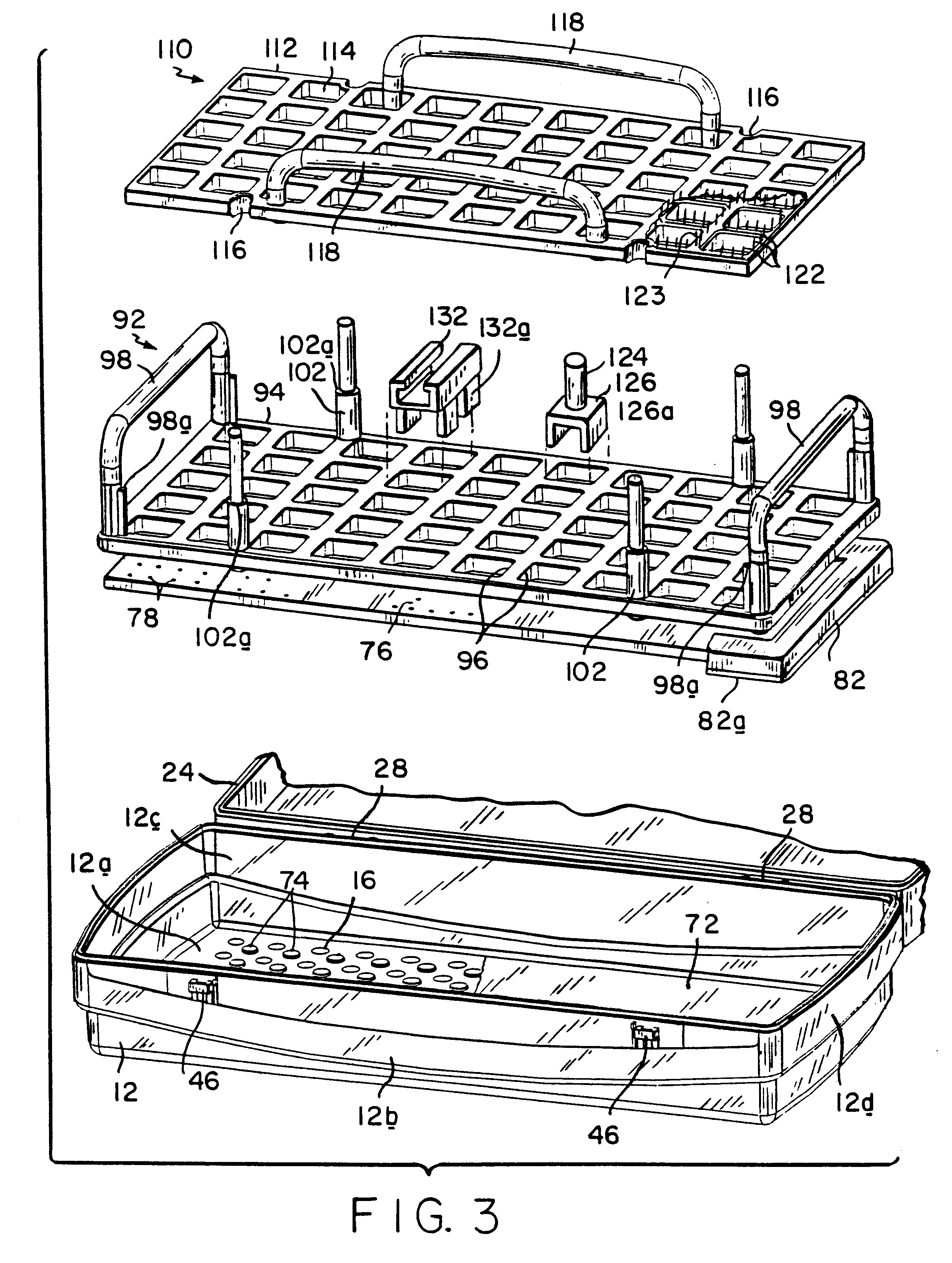
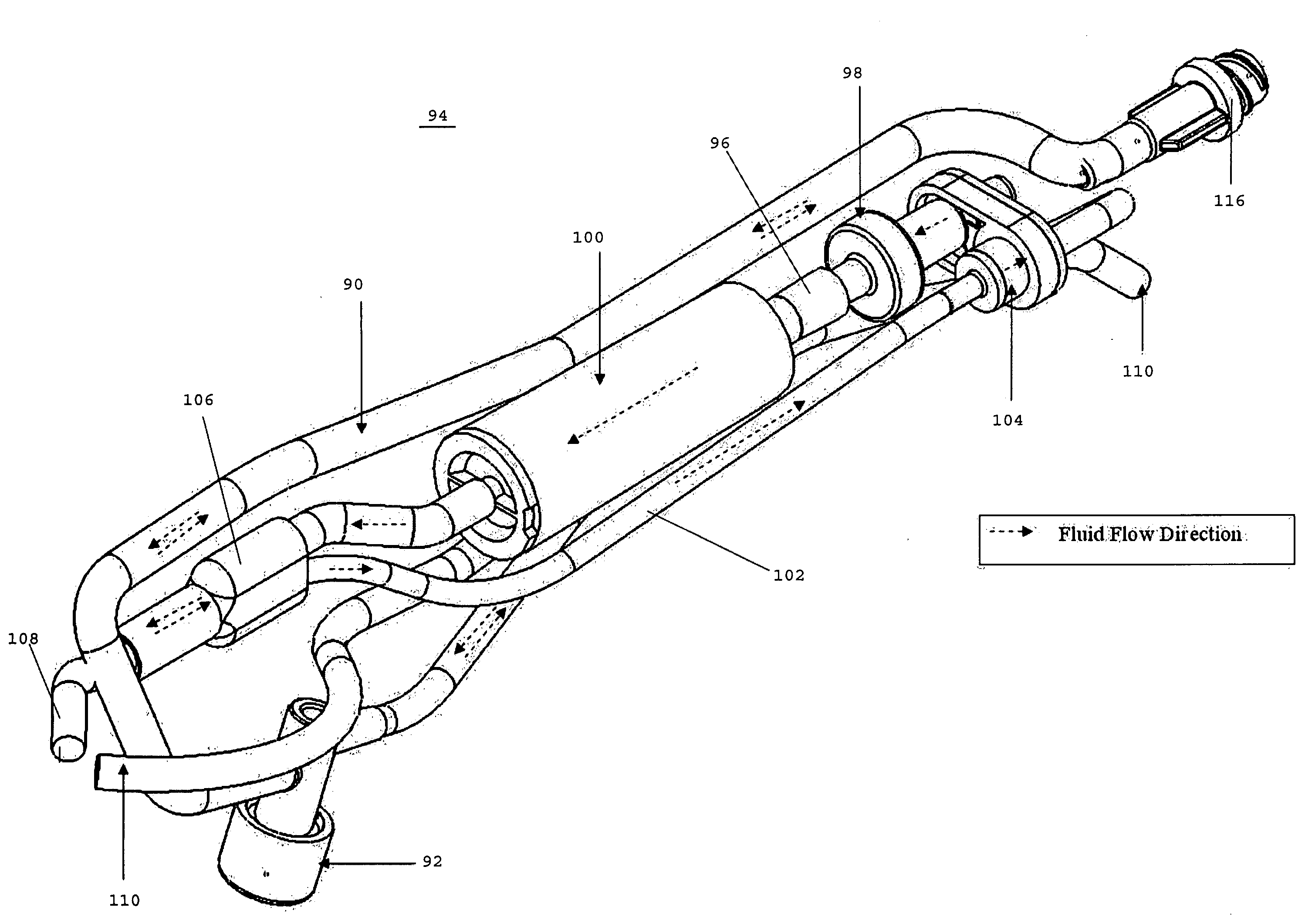
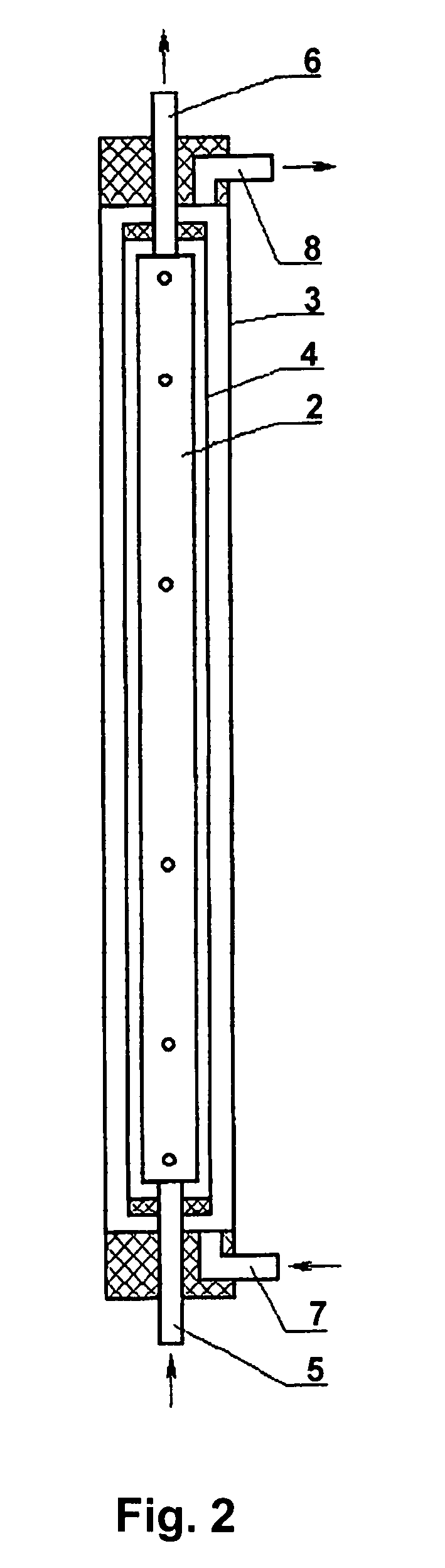
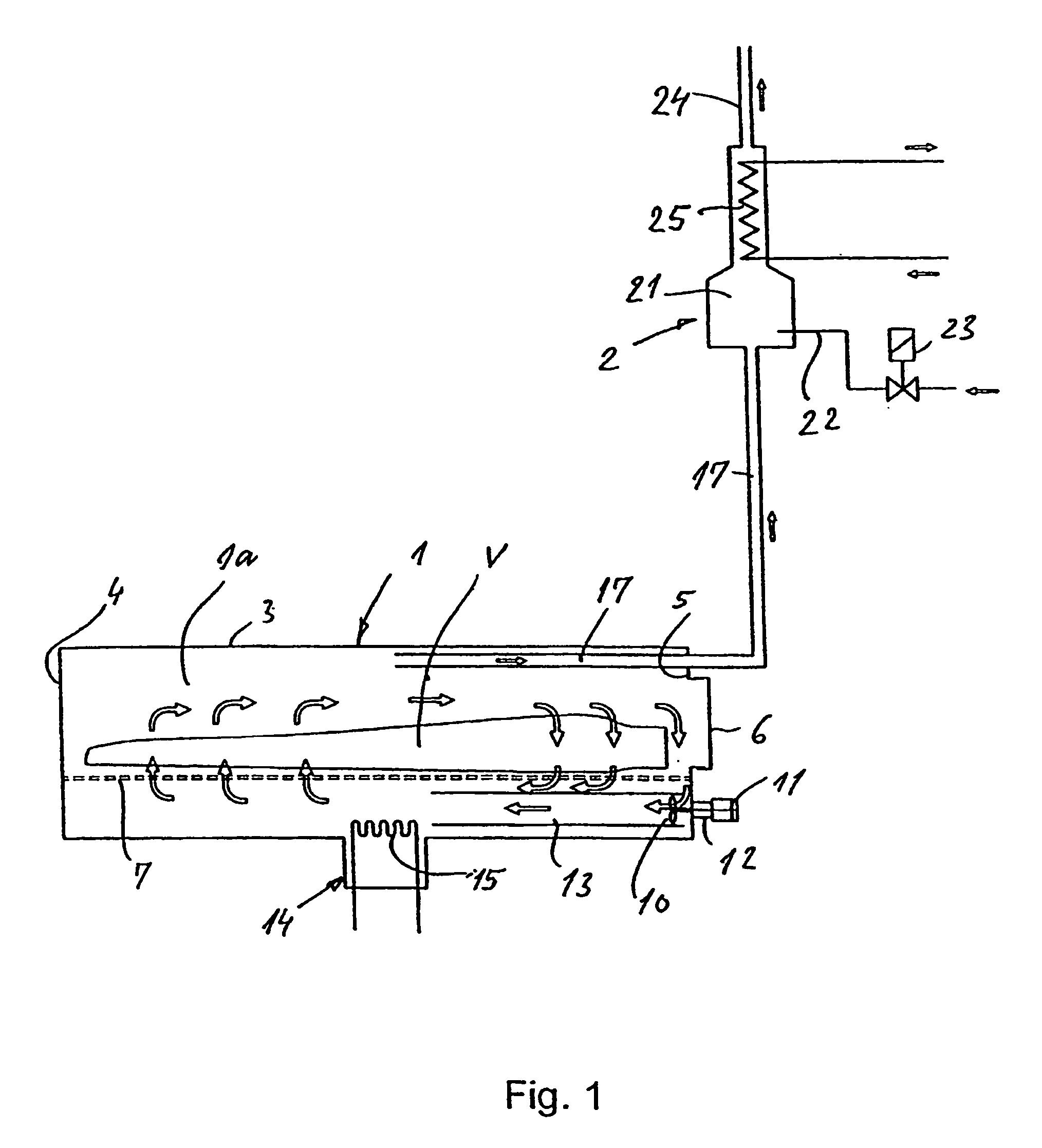
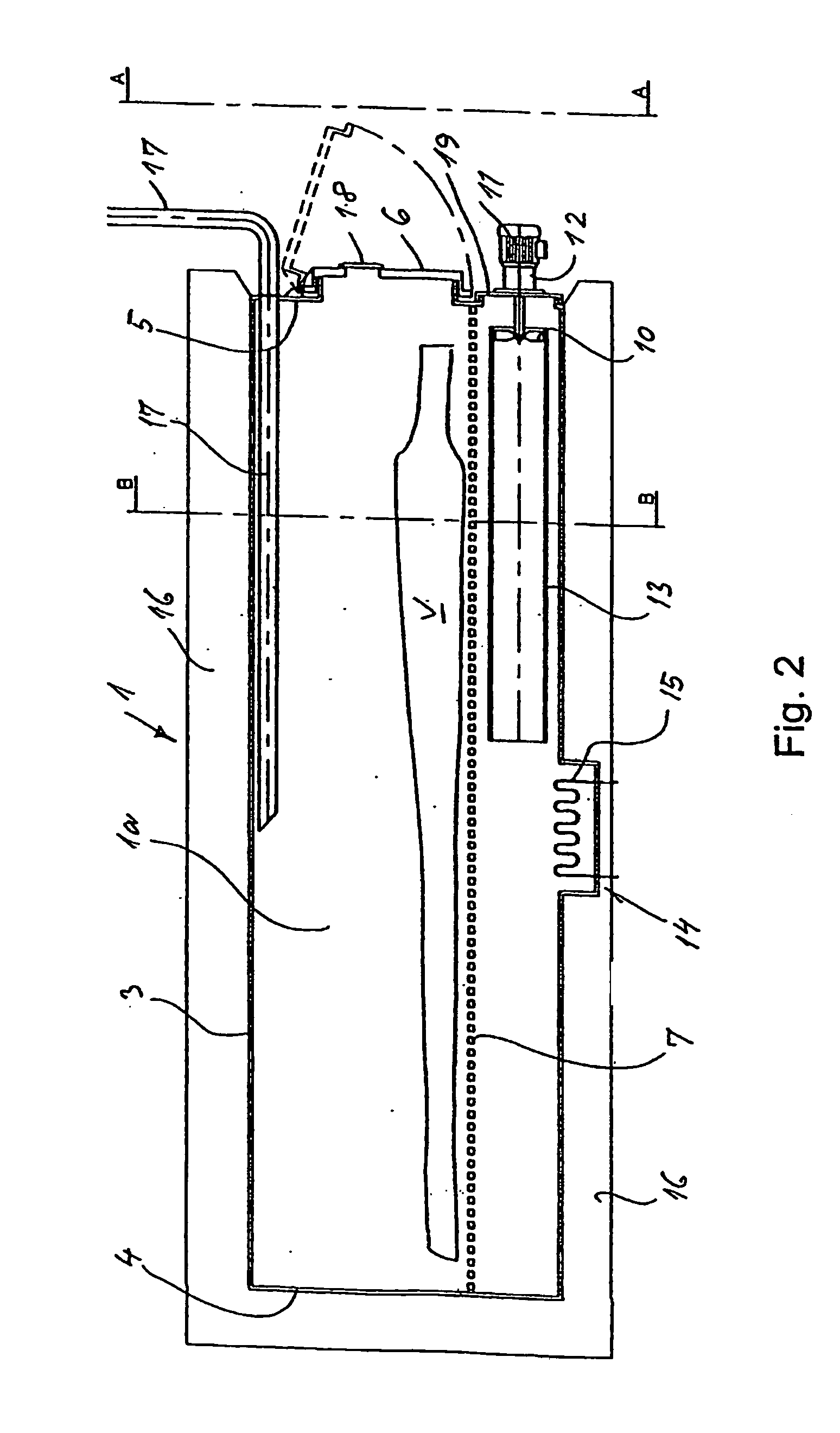
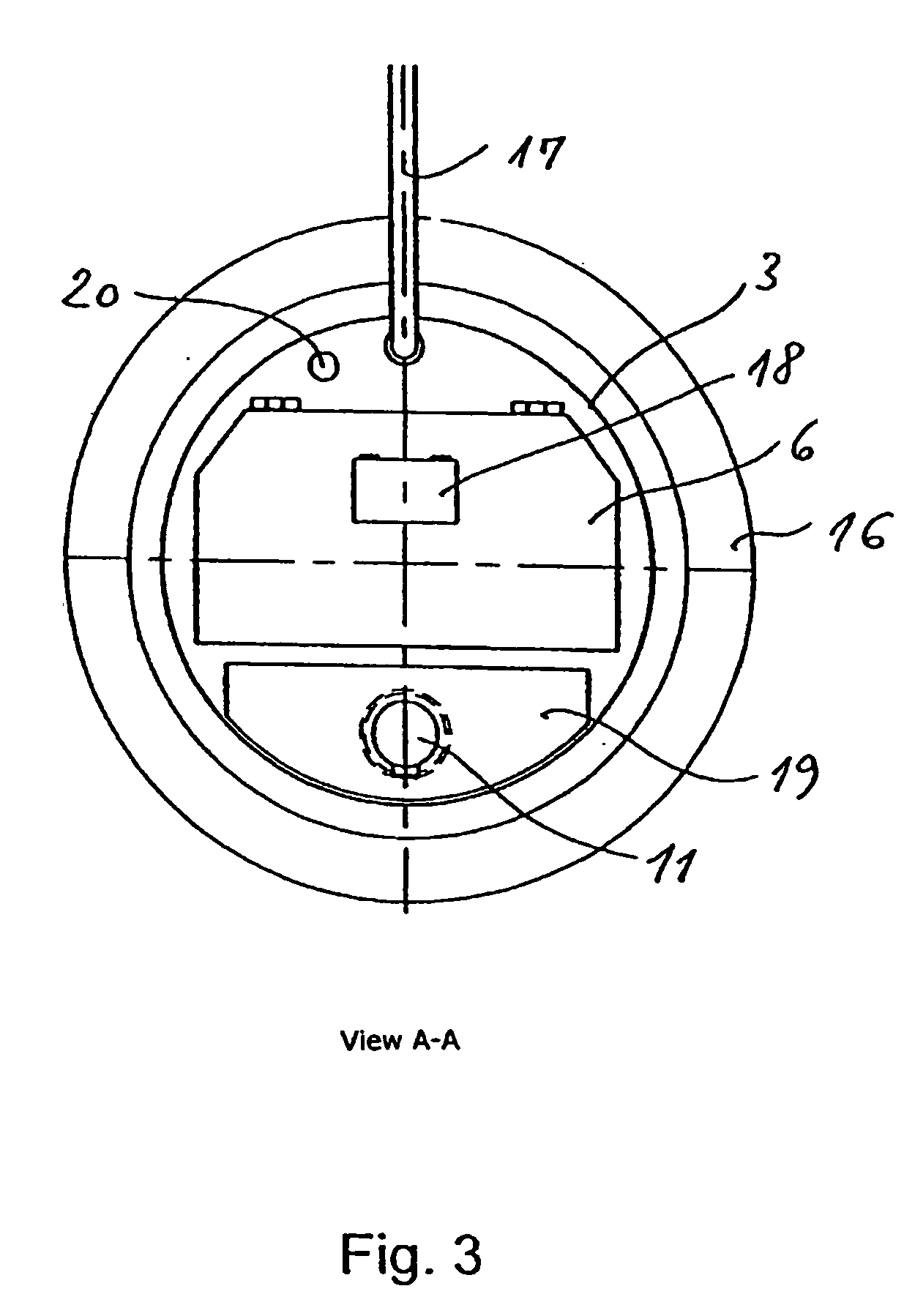
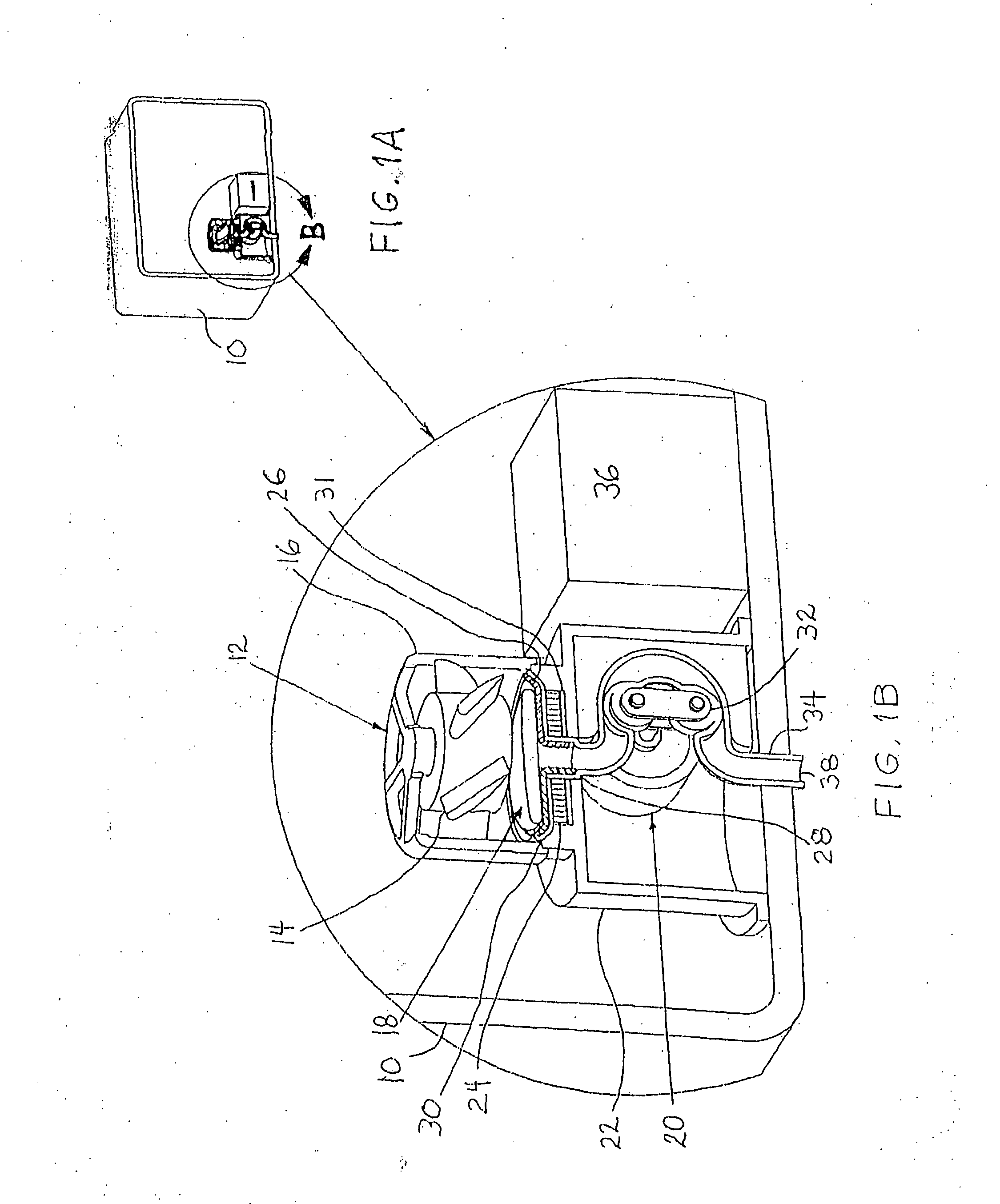
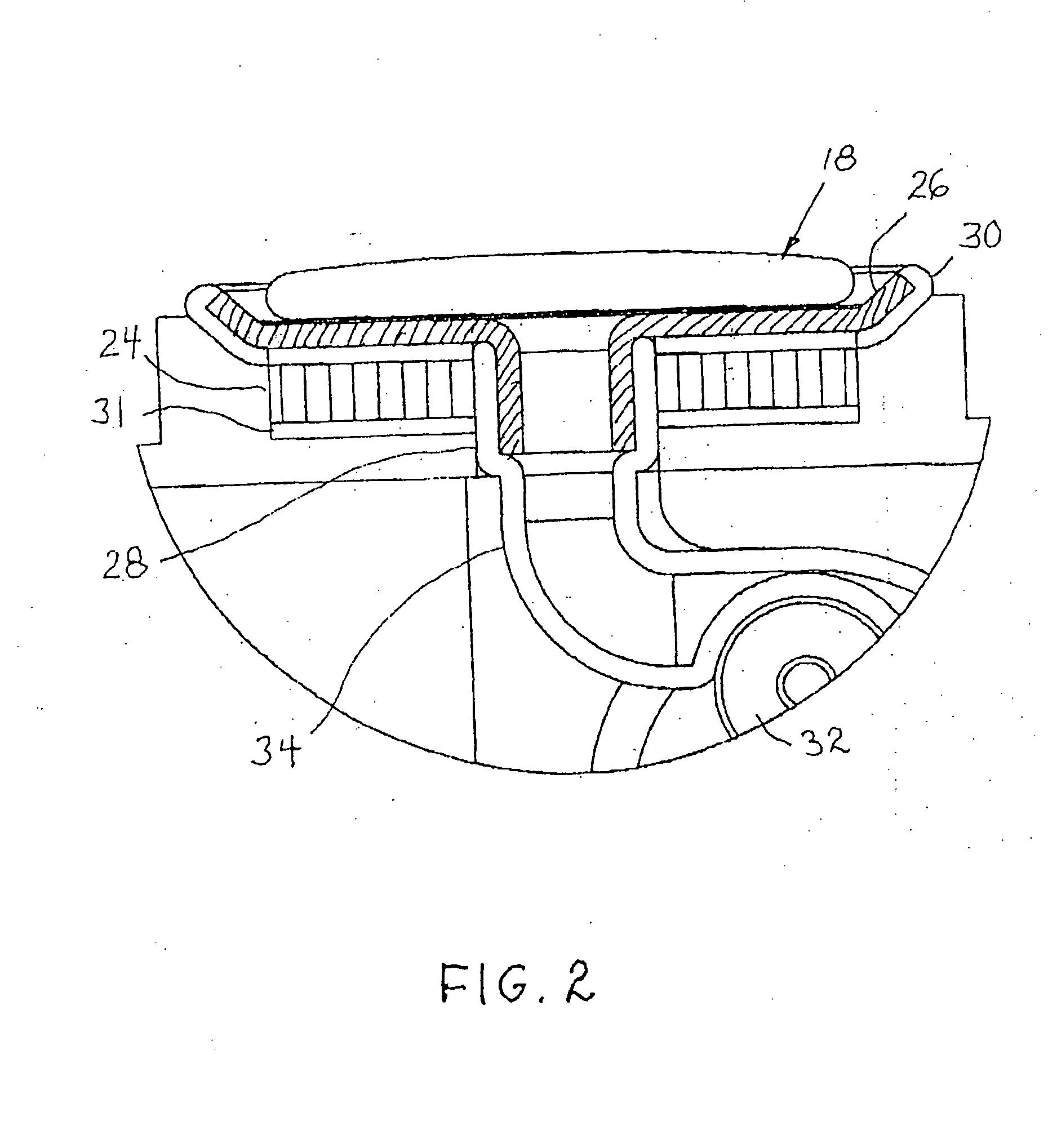
Sterilization container
InactiveUS6217835B1Improve sterilizationMinimum amount of timeCapsDispensing apparatusEngineeringMedical instruments
A sterilization container for medical instruments includes a receptacle with a bottom wall and an open top, there being a multiplicity of vent openings in the bottom wall. The receptacle has a cover movable between a closed position wherein the cover closes the open top of the receptacle and an open position wherein the cover is positioned to allow access to the interior of the receptacle. A filter sheet is positioned in the receptacle so as to cover the bottom wall and the vent openings therein and the receptacle contains one or more trays for supporting medical instruments above the filter sheet. A perforated highly thermally conductive plate is positioned between the trays and the filter sheet so that when steam enters the container through the vent openings during steam sterilization, it heats the plate to a temperature sufficient to revaporize steam condensate collecting on the plate. The internal structure of the container is also disclosed.
Owner:SYMMETRY MEDICAL MFG INC
Balloon catheter systems for treating uterine disorders having fluid line de-gassing assemblies and methods therefor
InactiveUS20100004595A1Effective heat absorptionEfficient heatingStentsBalloon catheterUterine DisorderDisease
A system for treating uterine disorders includes a catheter with a cannula having a proximal end and a distal end, and a degassing system in communication with the distal end of the cannula. The degassing system has a fluid insertion path having a first check valve and a gas filter, and a fluid extraction path that is separate from the fluid insertion path and includes a second check valve. The catheter may include an inflatable balloon secured to the distal end of the cannula with the degassing system in communication with the inflatable balloon. In one embodiment, a heating assembly is disposed inside the inflatable balloon for heating the fluid introduced into the balloon.
Owner:ETHICON INC
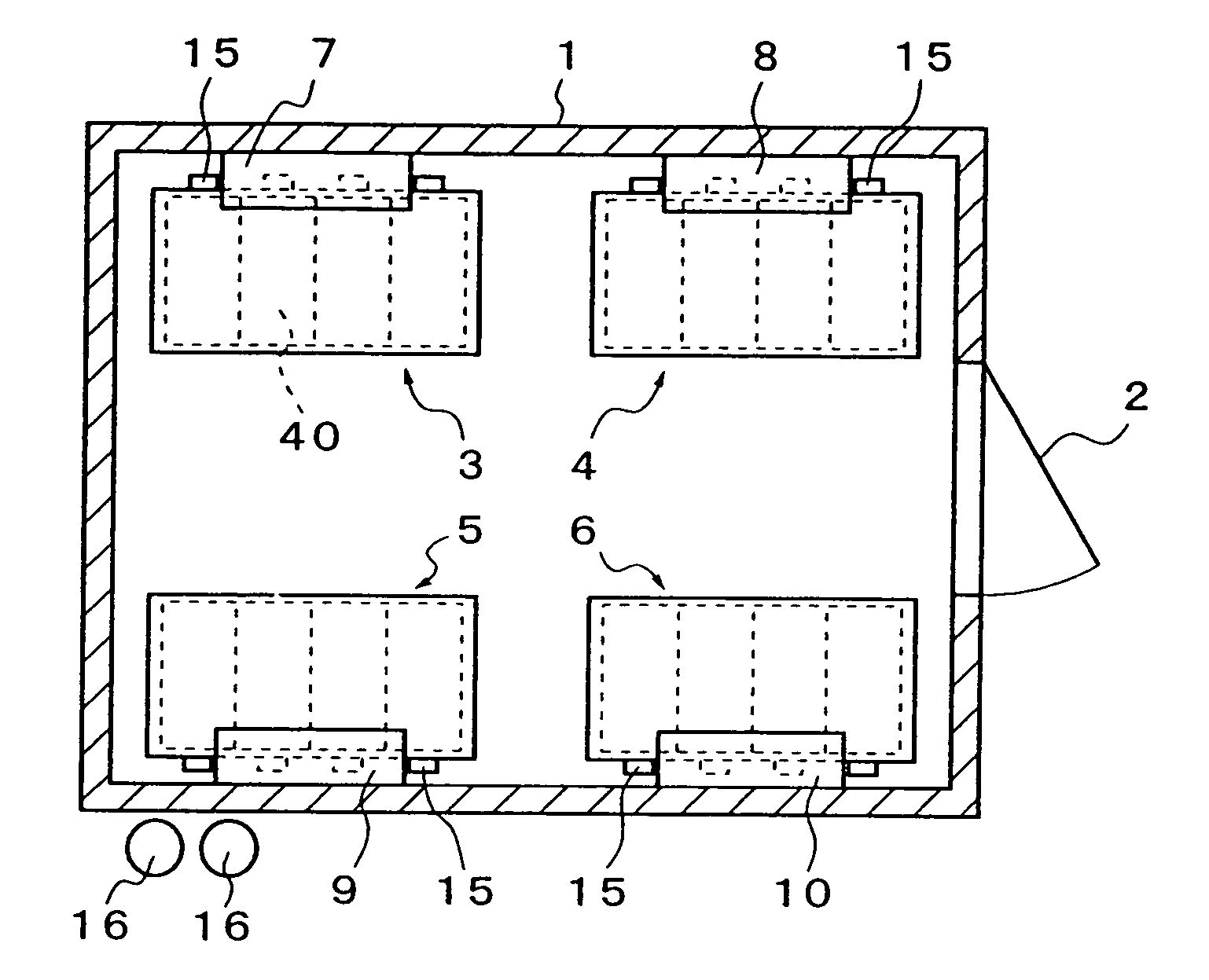
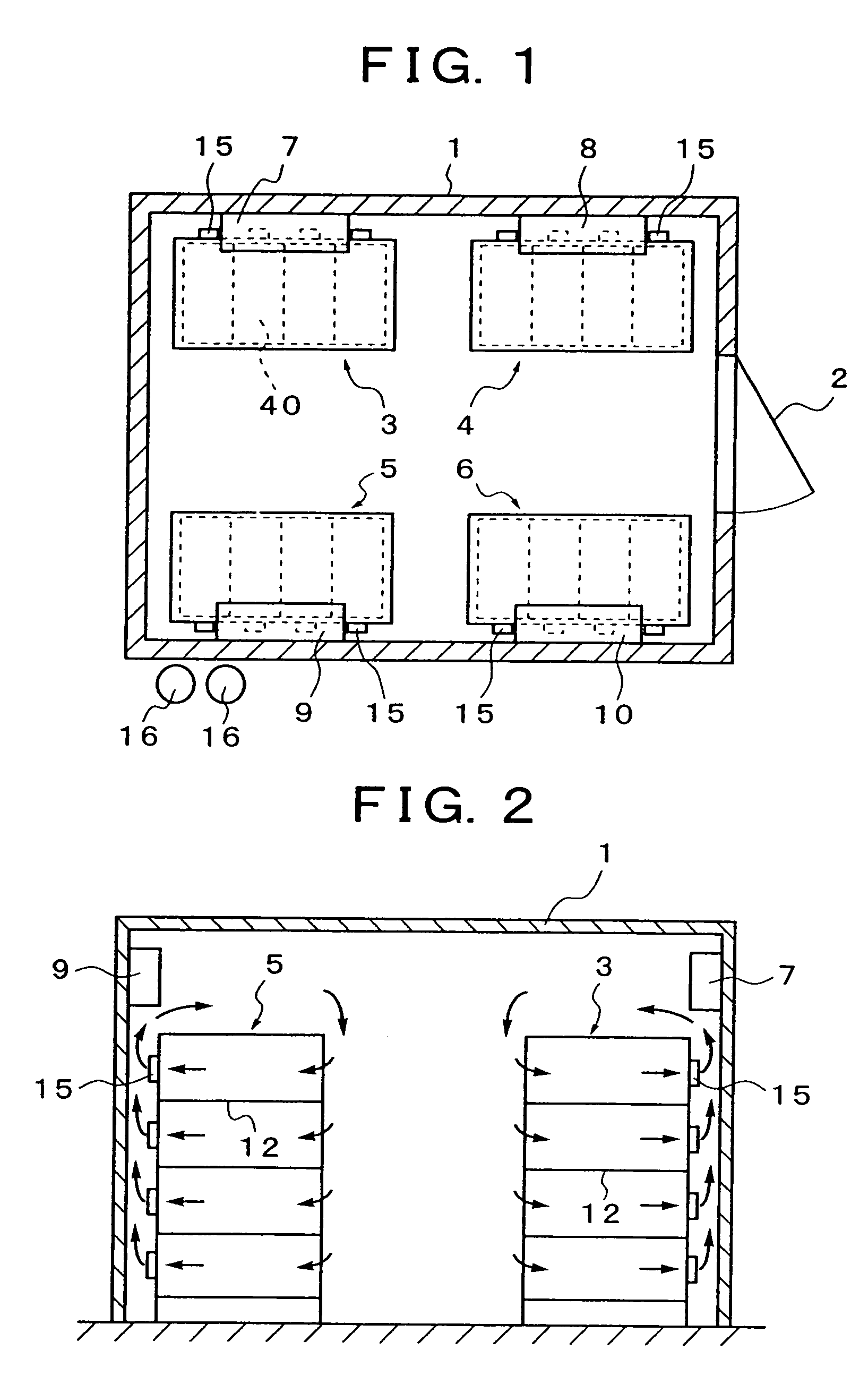
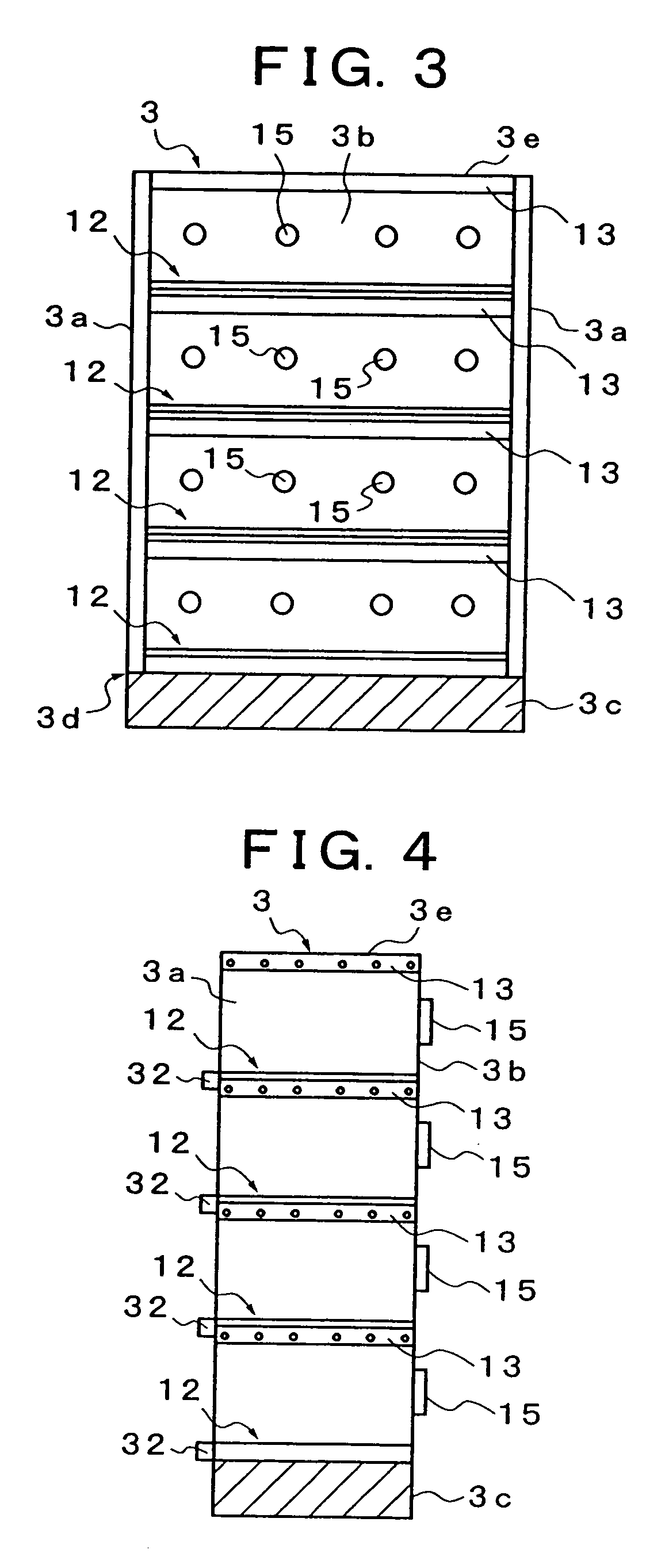
Battery assembly
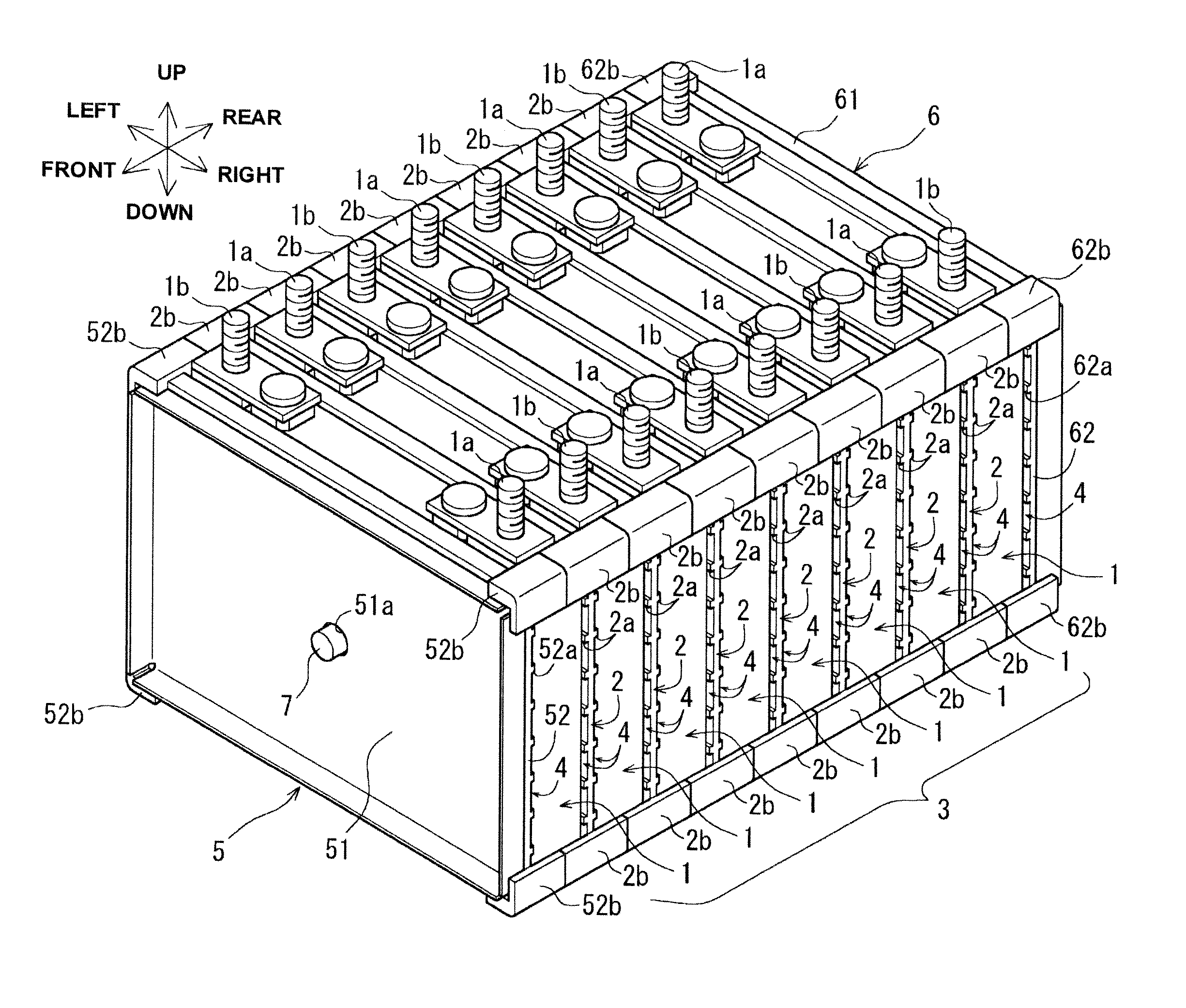
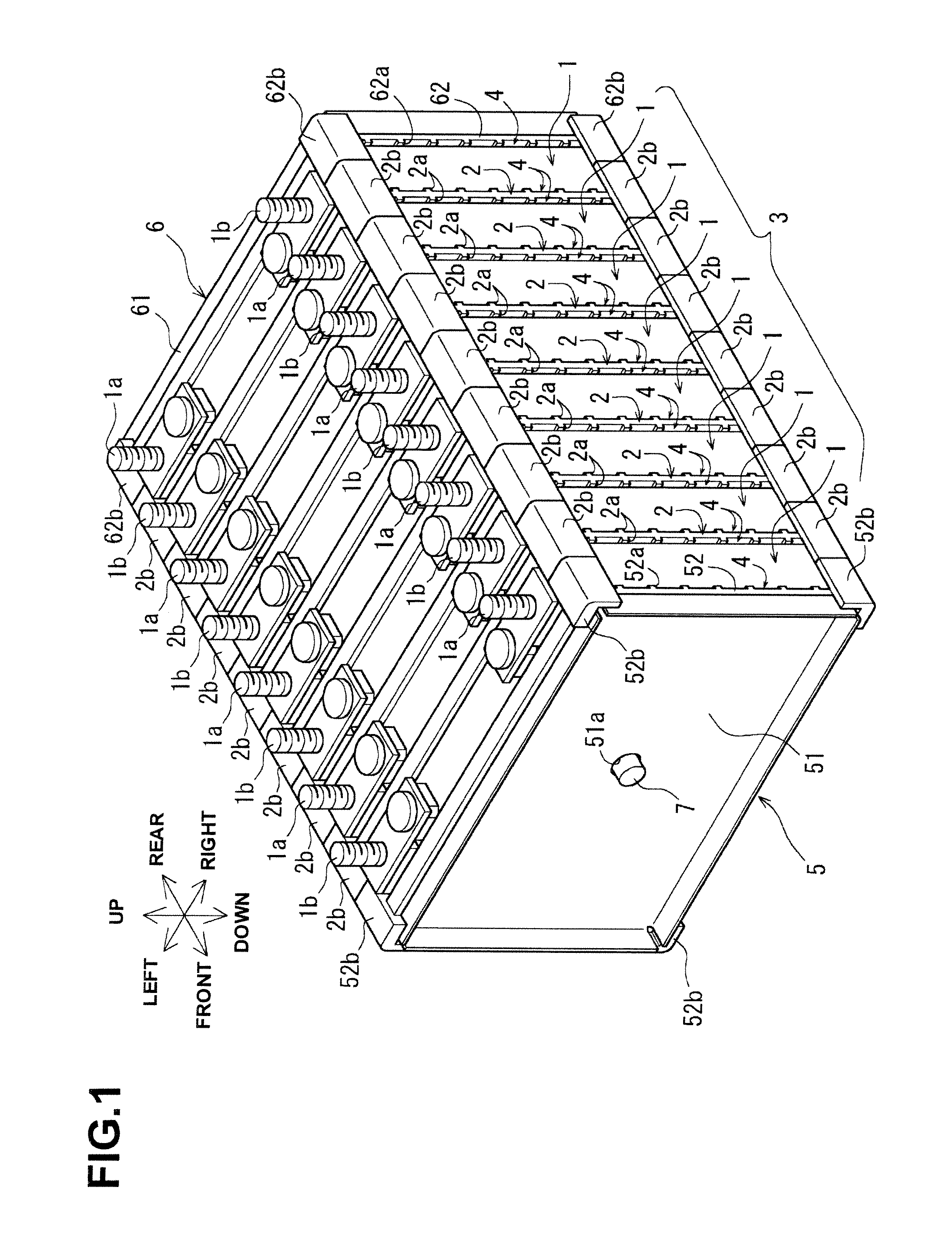
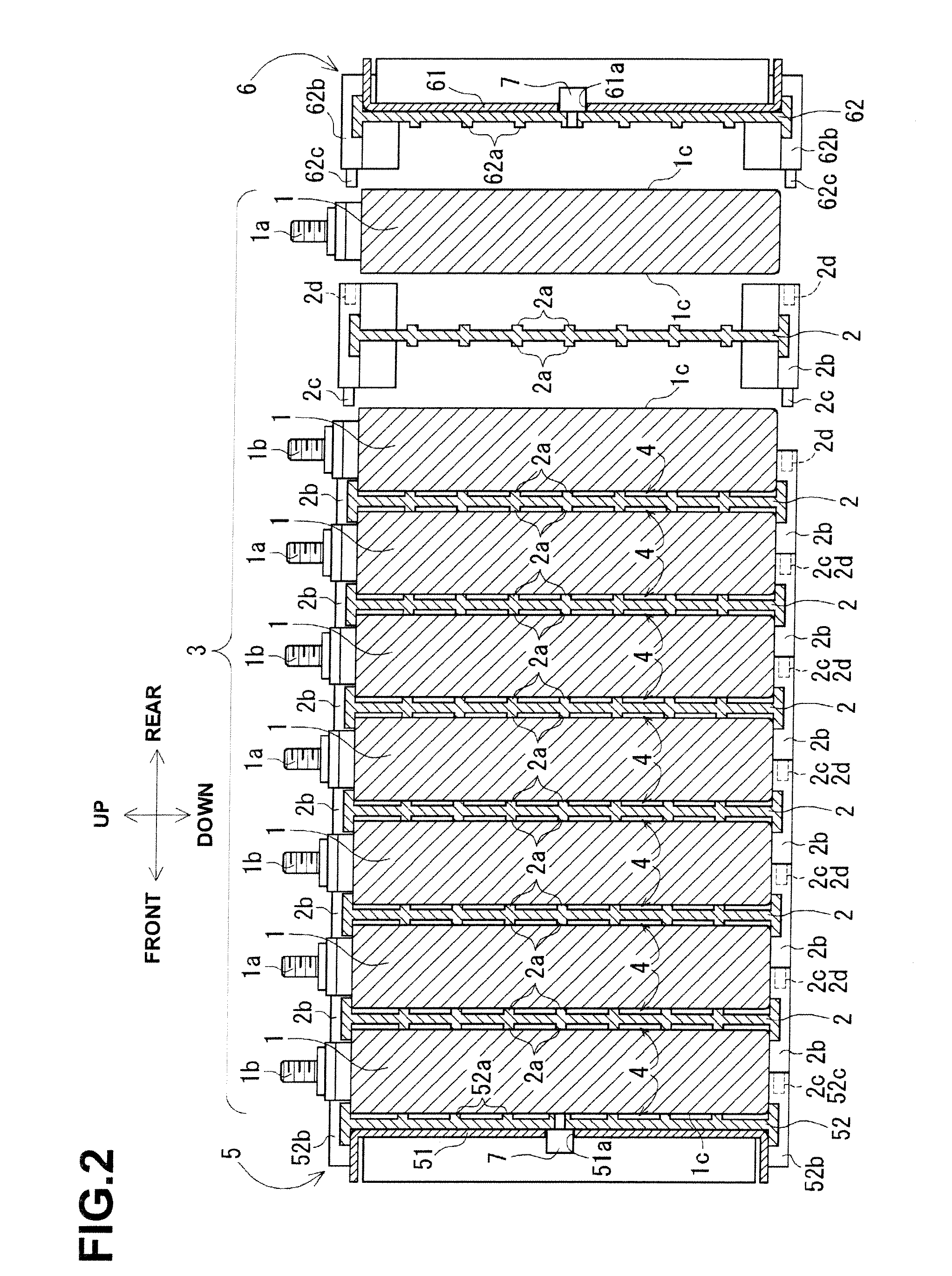
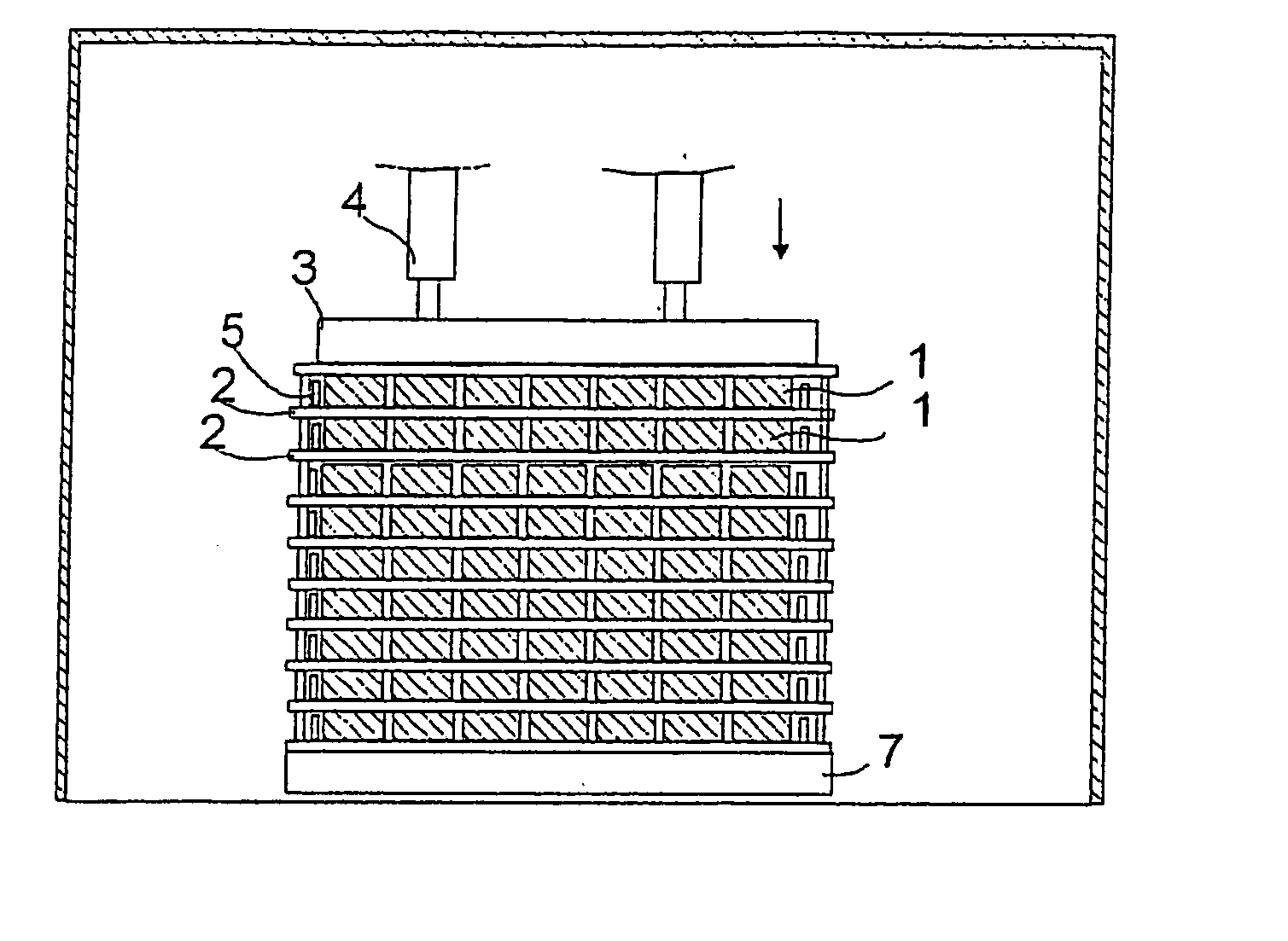
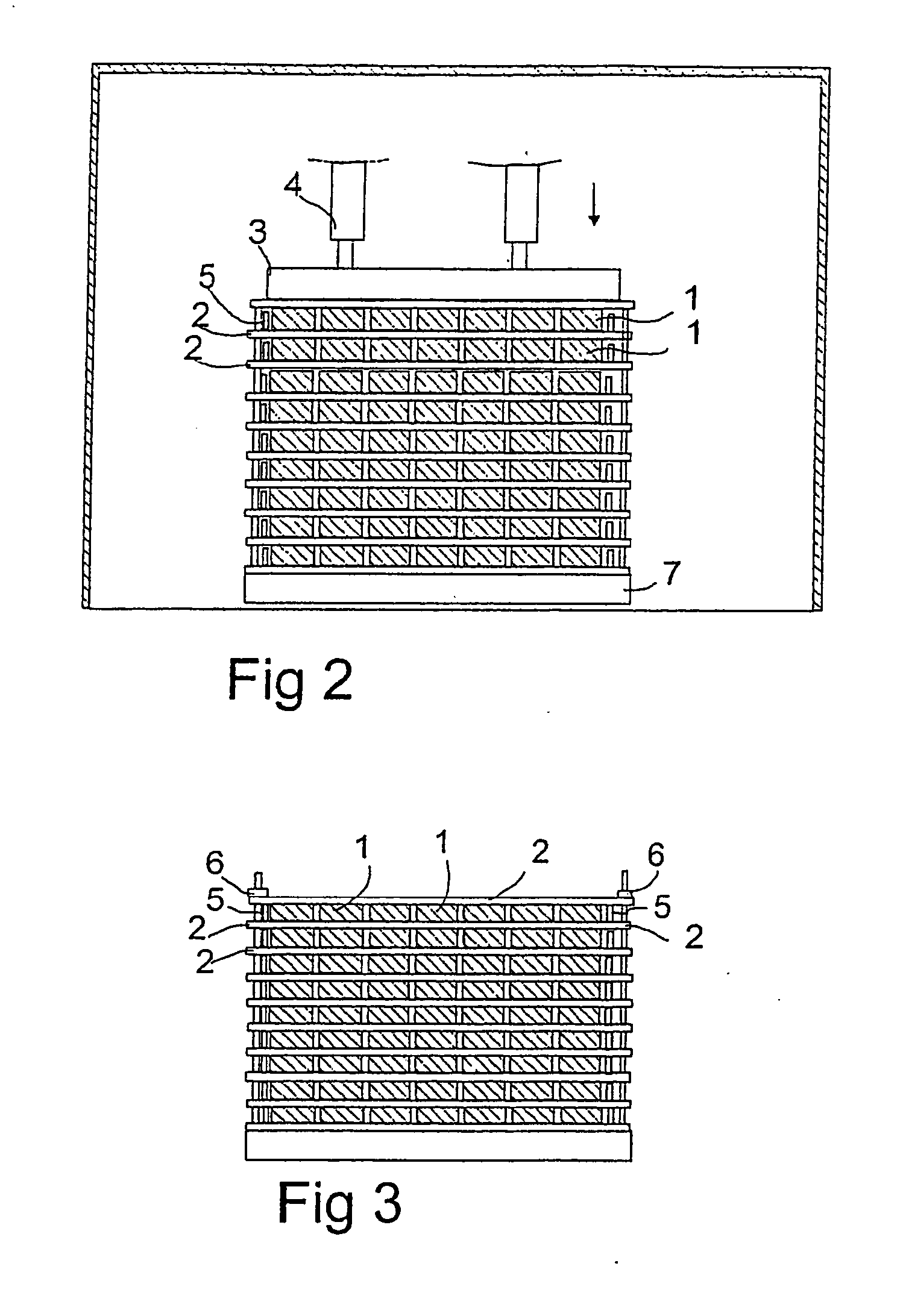
ActiveUS20120052359A1Reduce component countReduce in quantityPrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureEngineeringBattery cell
There is provided a battery assembly wherein assembly can be facilitated by reducing the number of components to be assembled, by integrally fixing resin plates (52, 62) on the inside of metal plates (51, 61) of end plates (5, 6). A laminated battery body (3) is constituted by adjacently arranging battery holders (2) made of resin forming cooling passages (4) between a plurality of batteries (1) and holding such batteries (1) on both sides between other batteries (1). The metal plates (51, 61) and resin plates (52, 62) that are integrally fixed on the inside of these metal plates are provided on the outside of the batteries (1) at both ends of the laminated battery body (3). Thus, the batteries (1) are held by the resin plates (52, 62), and the end plates (5, 6) are respectively arranged to form the cooling passages (4) between these batteries (1) and the metal plates (51, 61). The laminated battery body (3) is fixed in a clamped manner by fixing means clamping these end plates (5, 6).
Owner:GS YUASA INT LTD
Cleaning Apparatus
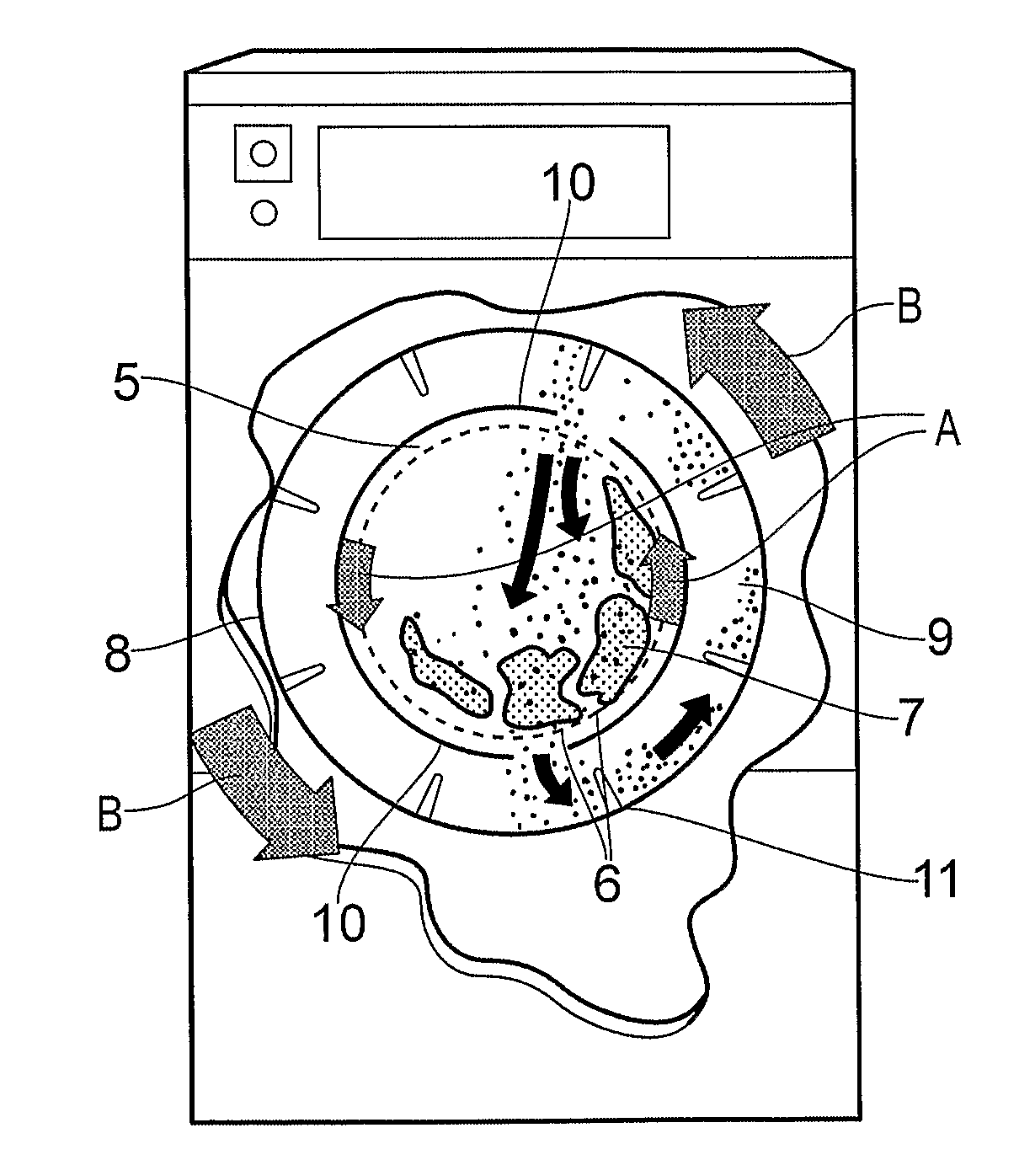
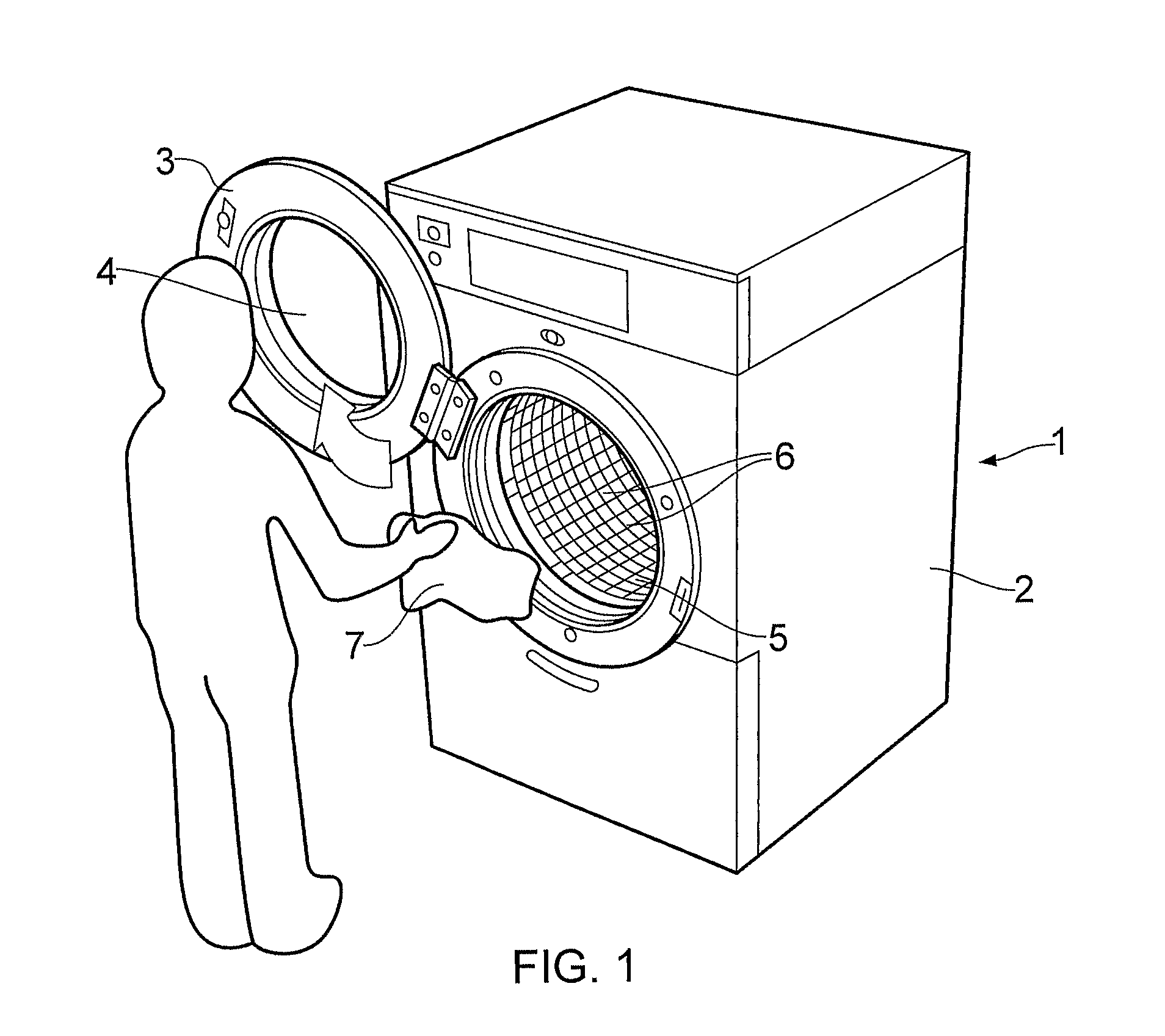
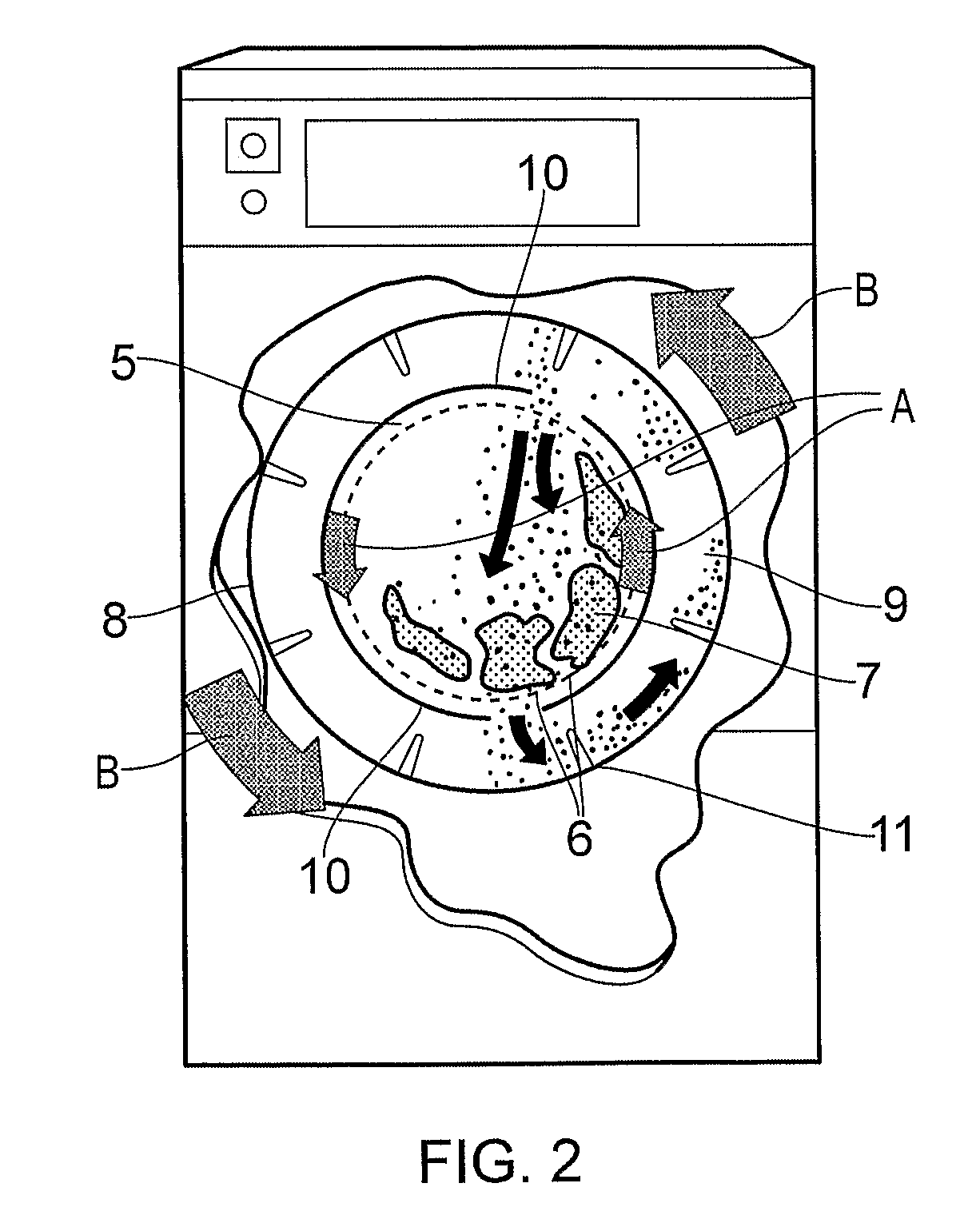
InactiveUS20110296628A1Guarantee effective circulationEasy to cleanOther washing machinesDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesEngineeringOrganic solvent free
The invention provides an apparatus and method for use in the cleaning of soiled substrates, the apparatus comprising a casing which contains a rotatably mounted cylindrical cage concentrically located within a rotatably mounted cylindrical drum having a greater diameter than the basket, wherein the cage and the drum are concentrically located within a stationary cylindrical drum having a greater diameter than the rotatably mounted drum, wherein the casing includes access means, allowing access to the interior of the cylindrical basket, and wherein the rotatably mounted cylindrical cage and the rotatably mounted cylindrical drum are adapted to rotate independently. The method involves cleaning the soiled substrate by treatment of the moistened substrate with a formulation comprising solid particulate cleaning material, the formulation being free of organic solvents, and the method being carried out using the apparatus of the invention, and the apparatus and method find particular application in the cleaning of textile fabrics.
Owner:XEROS LTD
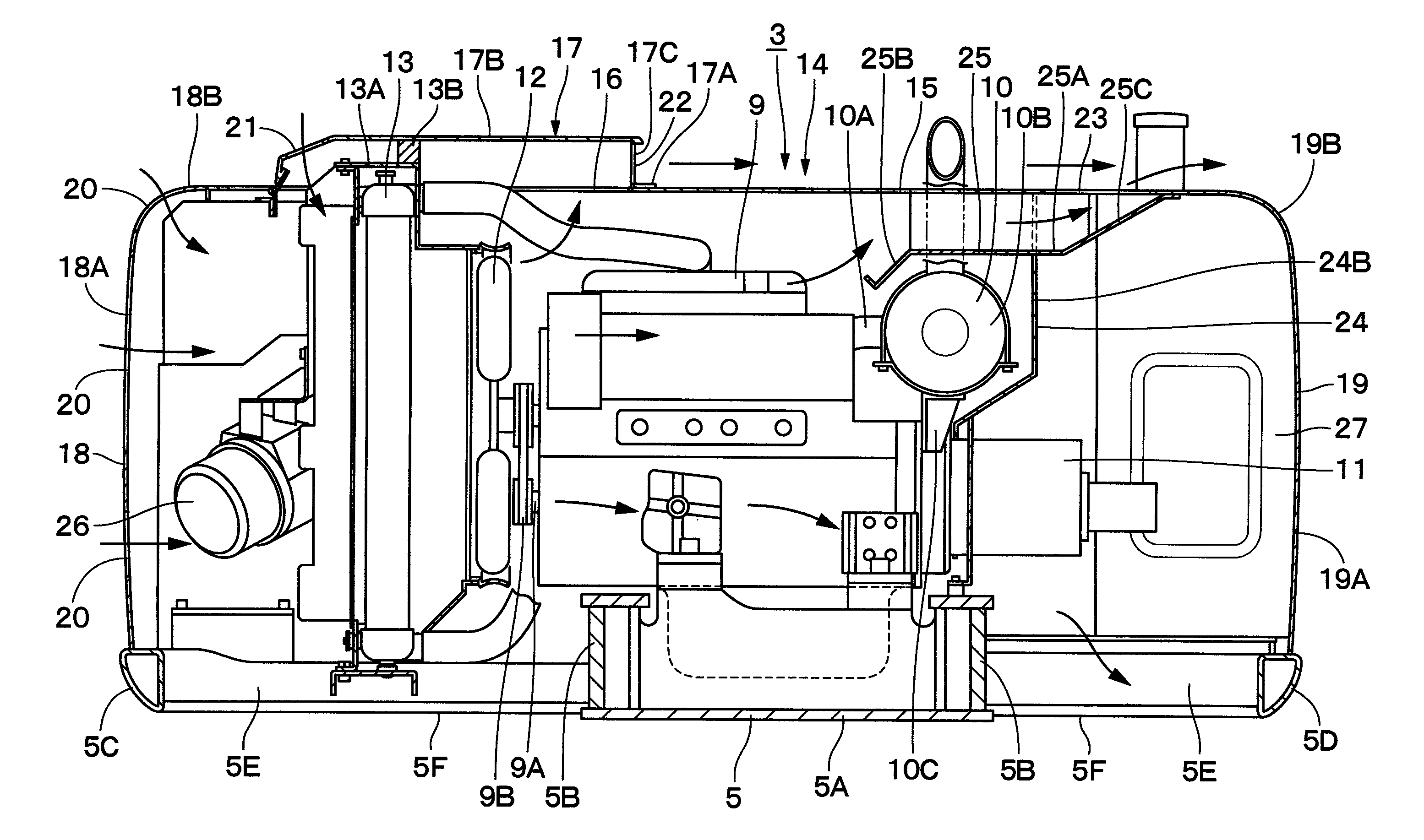
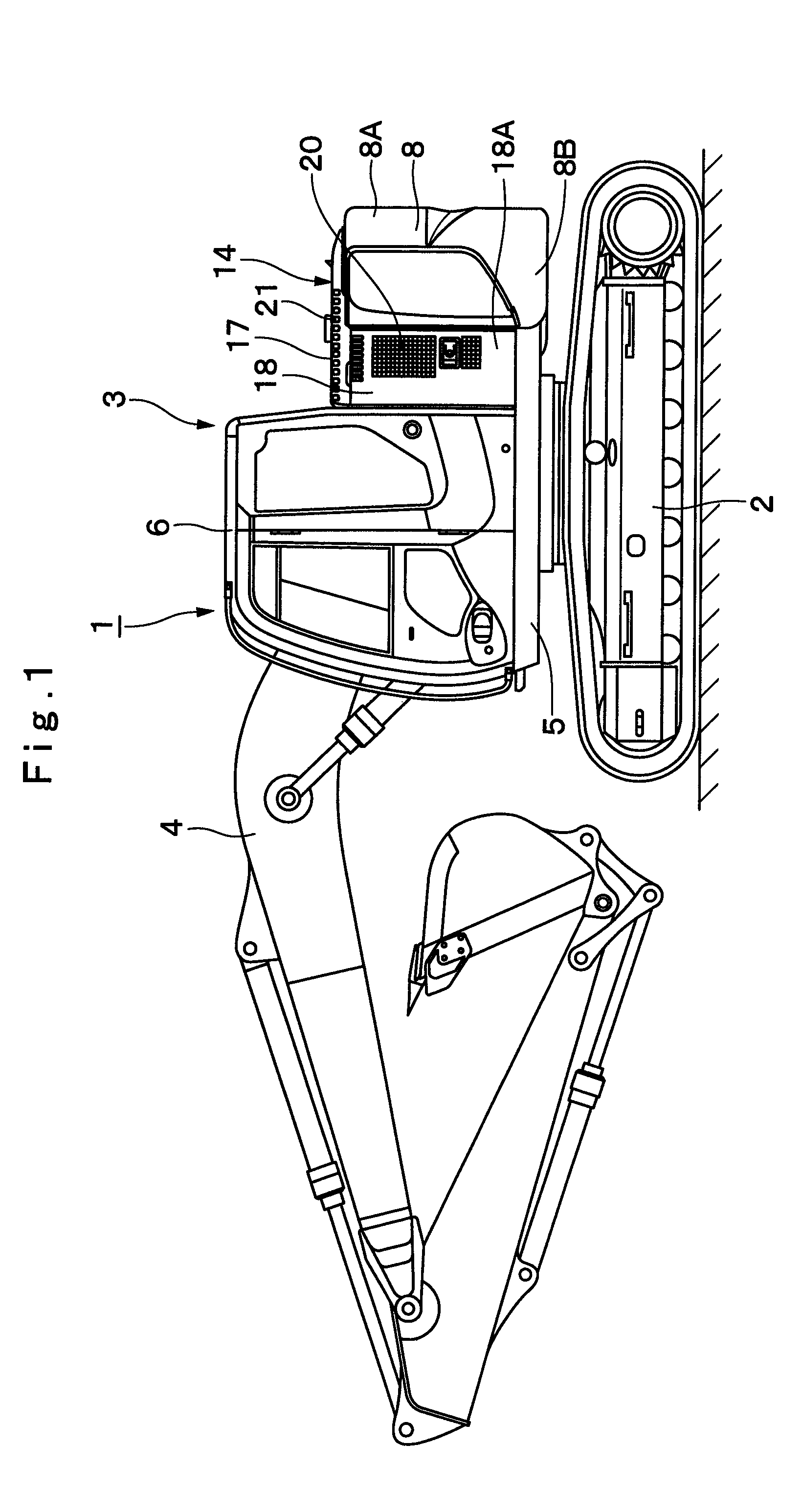
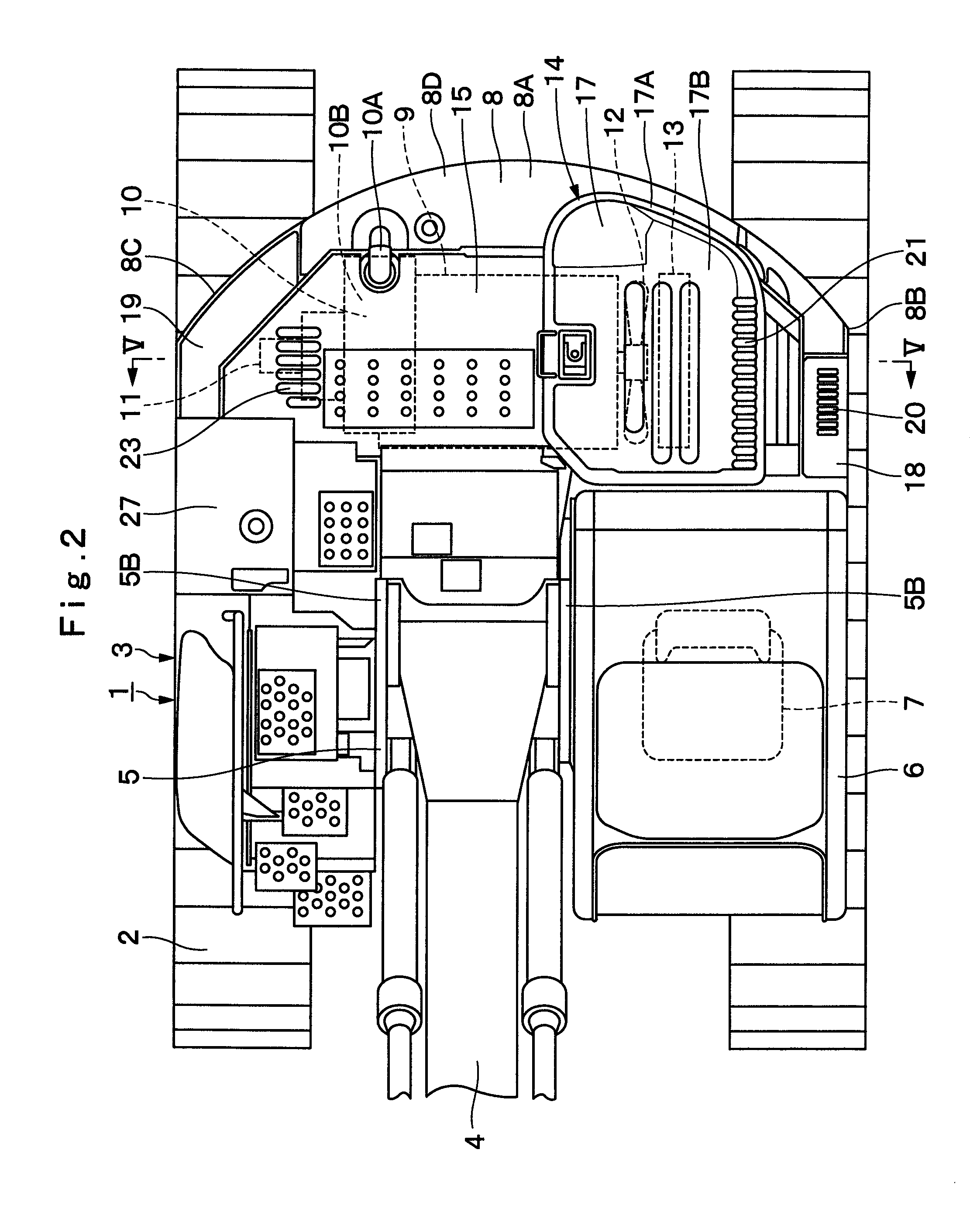
Construction machine
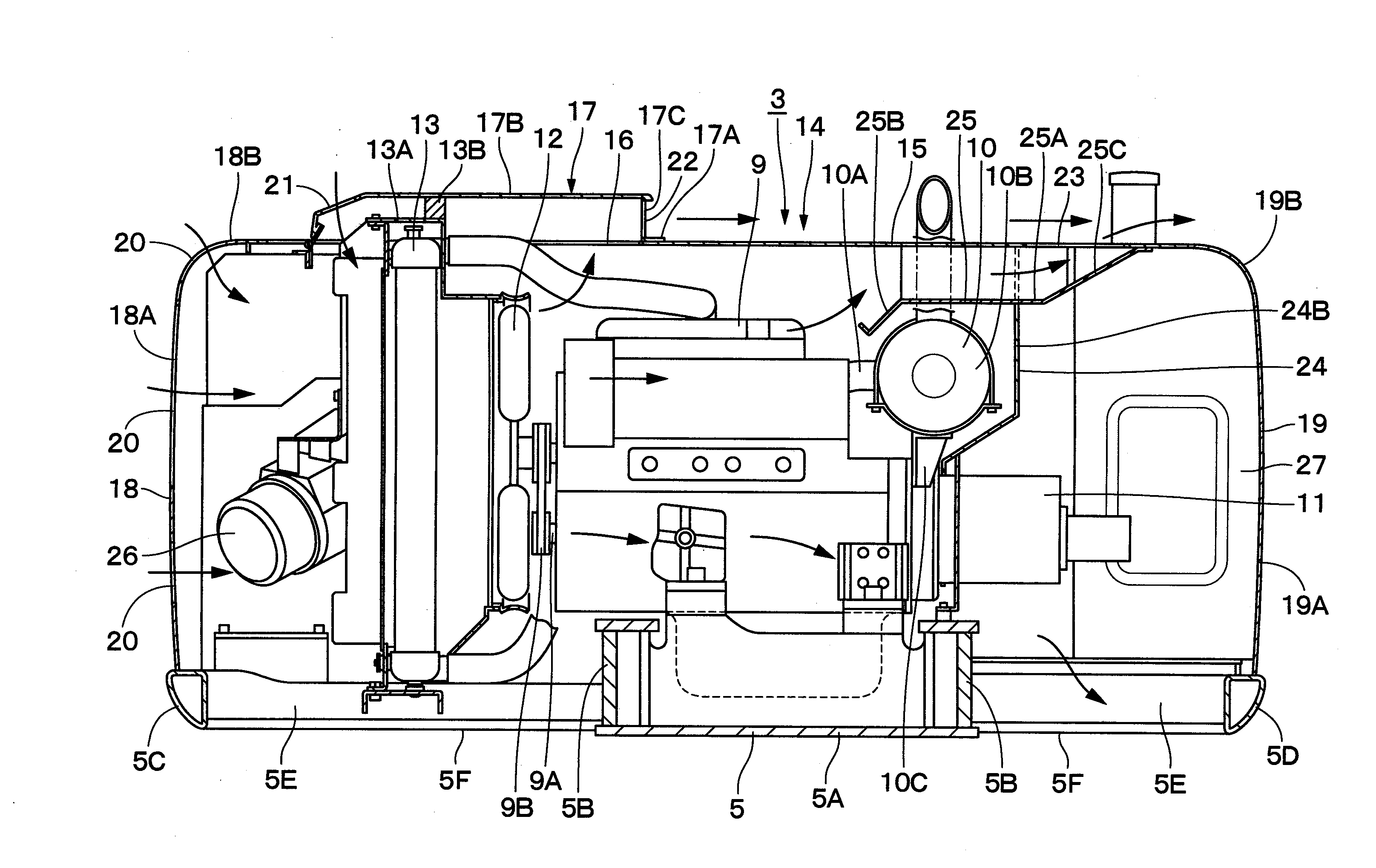
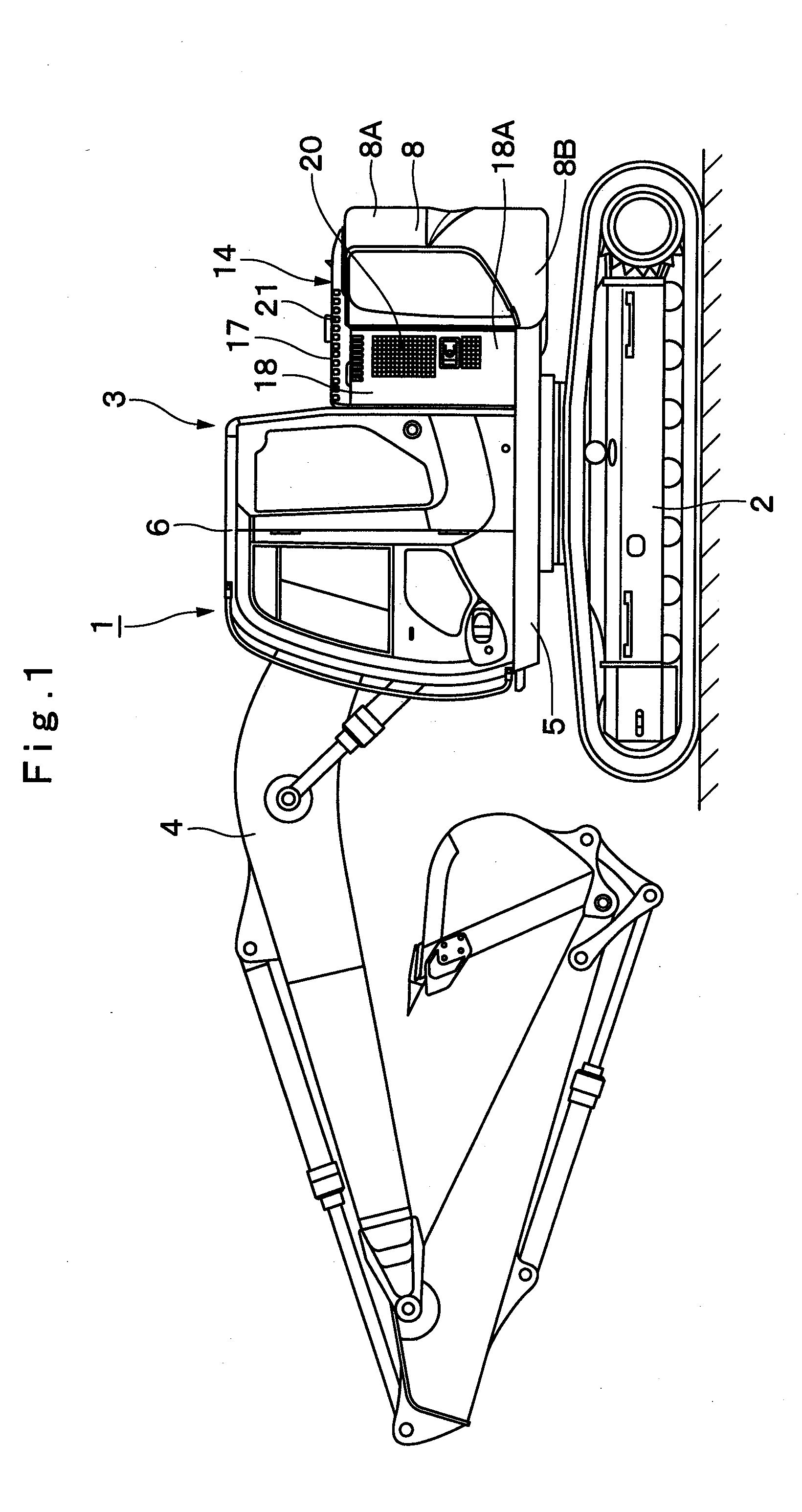
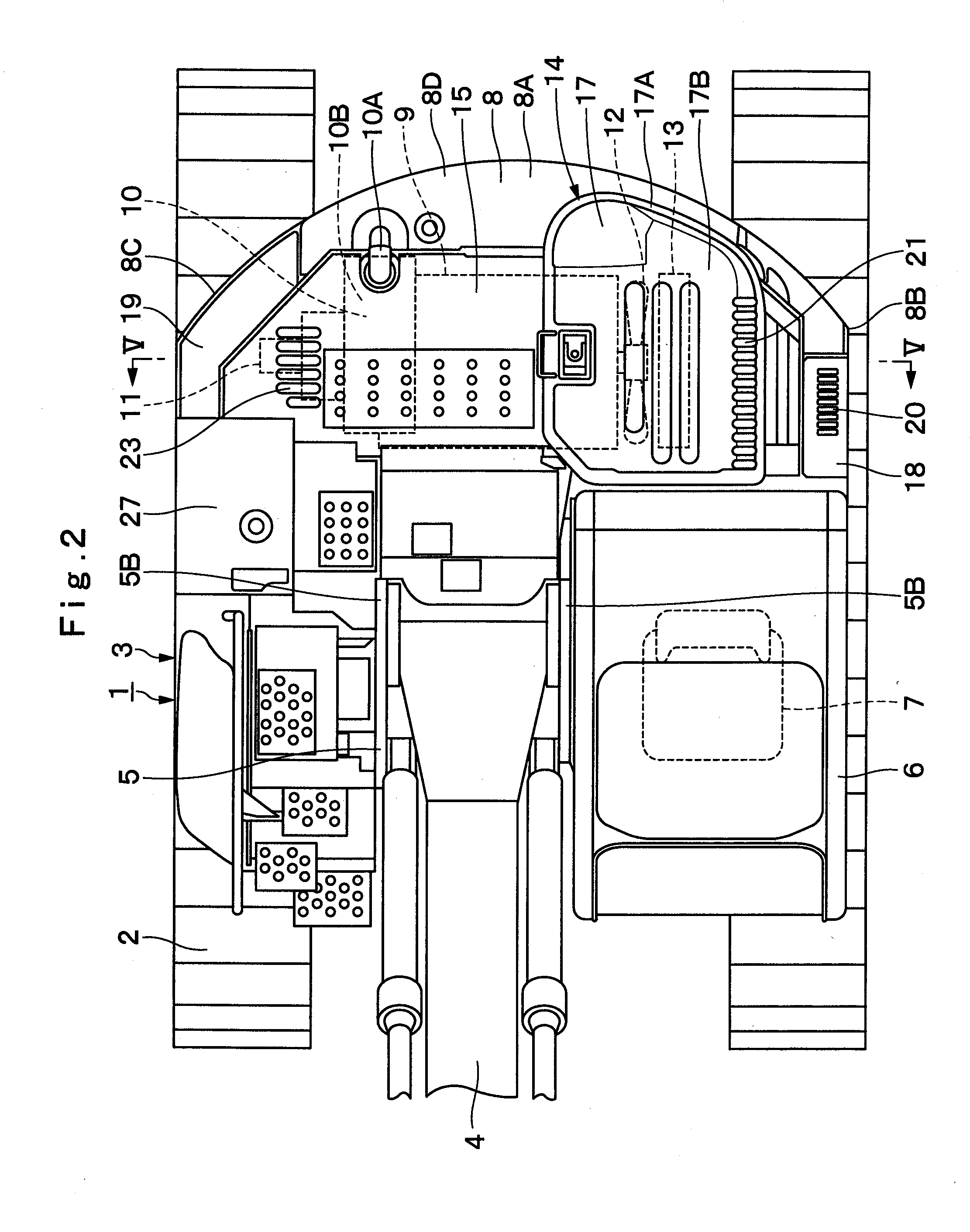
ActiveUS20100219008A1Improve cooling efficiencyGuarantee effective circulationElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingEngineeringHeat exchanger
In a heat exchanger cover (17) covering upper sides of heat exchanger (13), an inlet port (21) is provided on a left side which is an upstream side of cooling air, and one exhaust port (22) for exhausting the cooling air which has passed through the heat exchanger (13) is provided on a right side opposite to this inlet port (21). An engine cover (15) is provided with another exhaust port (23) at a position opposing the one exhaust port (22) in a left-right direction. The cooling air which has passed through the heat exchanger (13) can be exhausted horizontally from the exhaust port (22) provided in the heat exchanger cover (17) toward the exhaust port (23) provided in the engine cover (15).
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
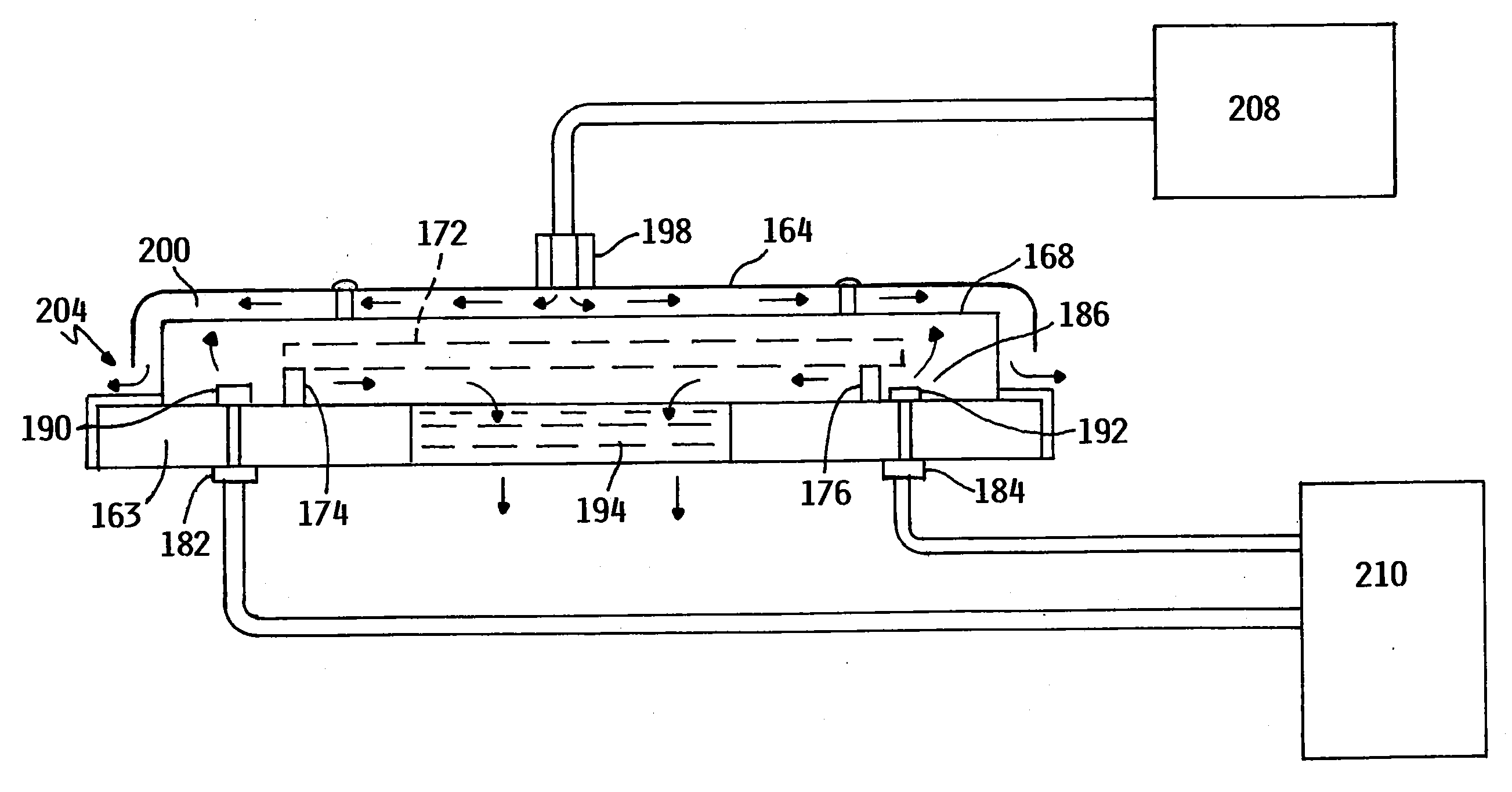
Device for producing anodic oxidaton products of an alkali or alkali-earth metal chloride solution
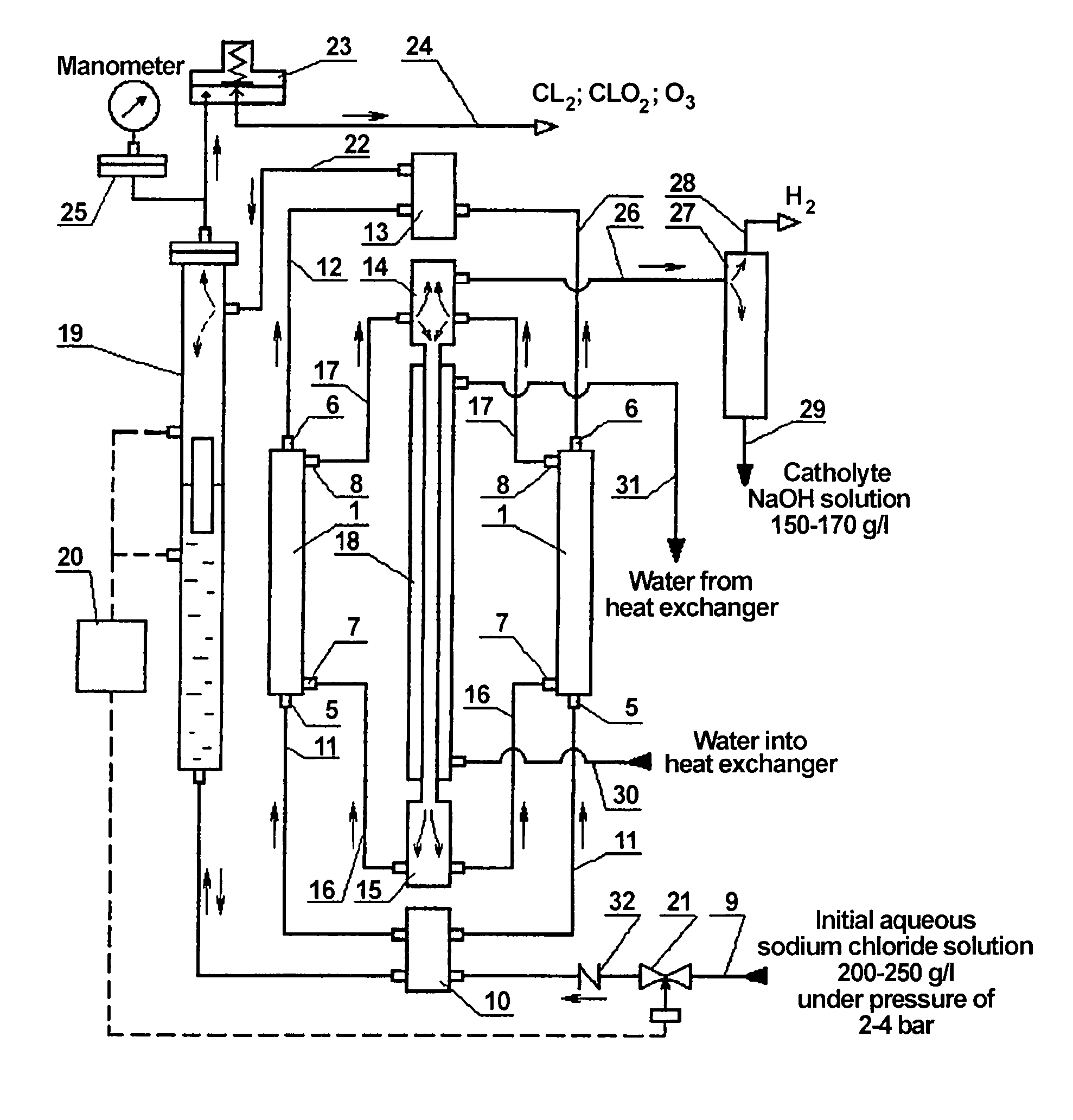
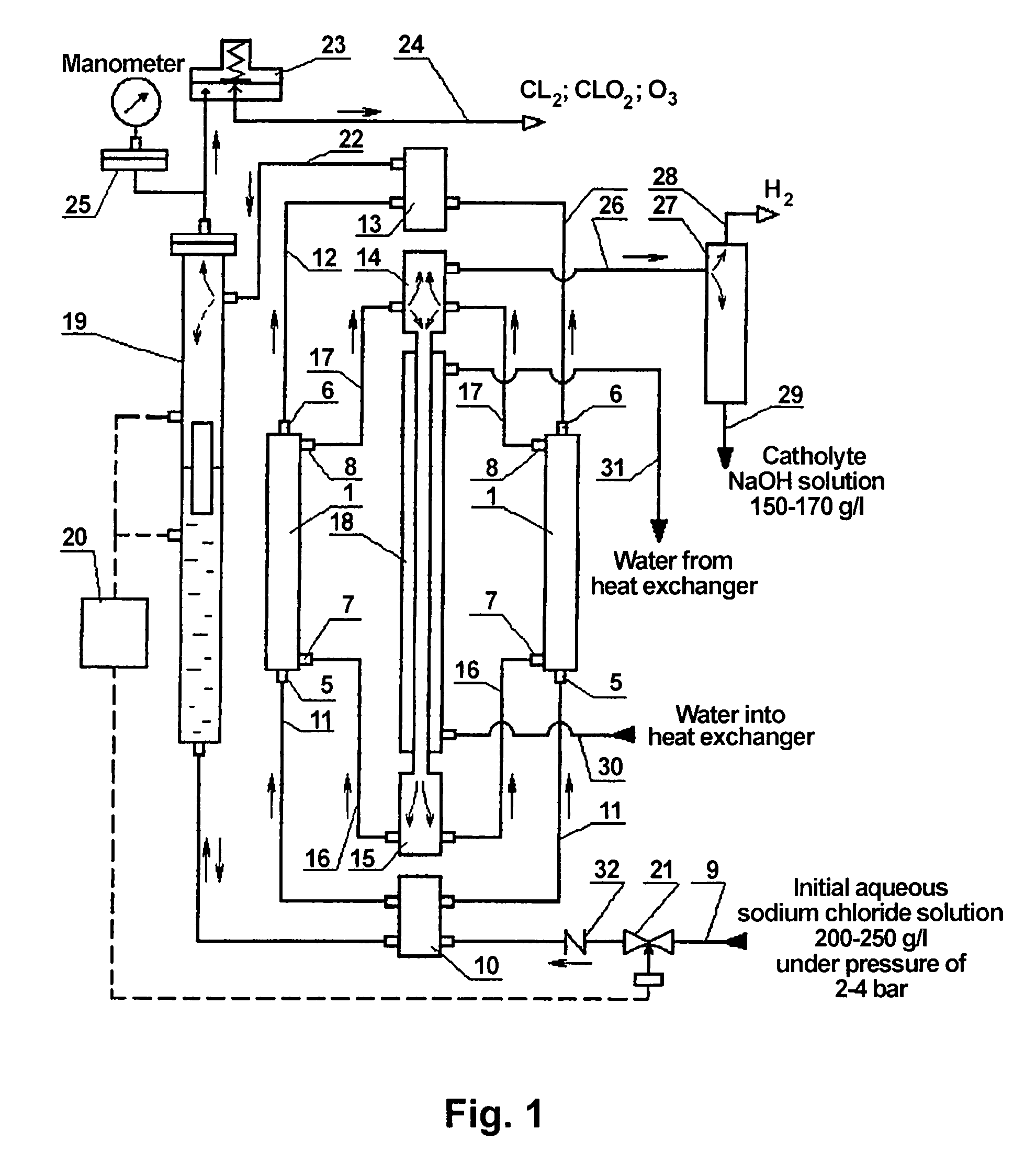
ActiveUS7897023B2Improve productivityReduce power consumptionCellsWater/sewage treatment apparatusElectrochemical responseElectrolysis
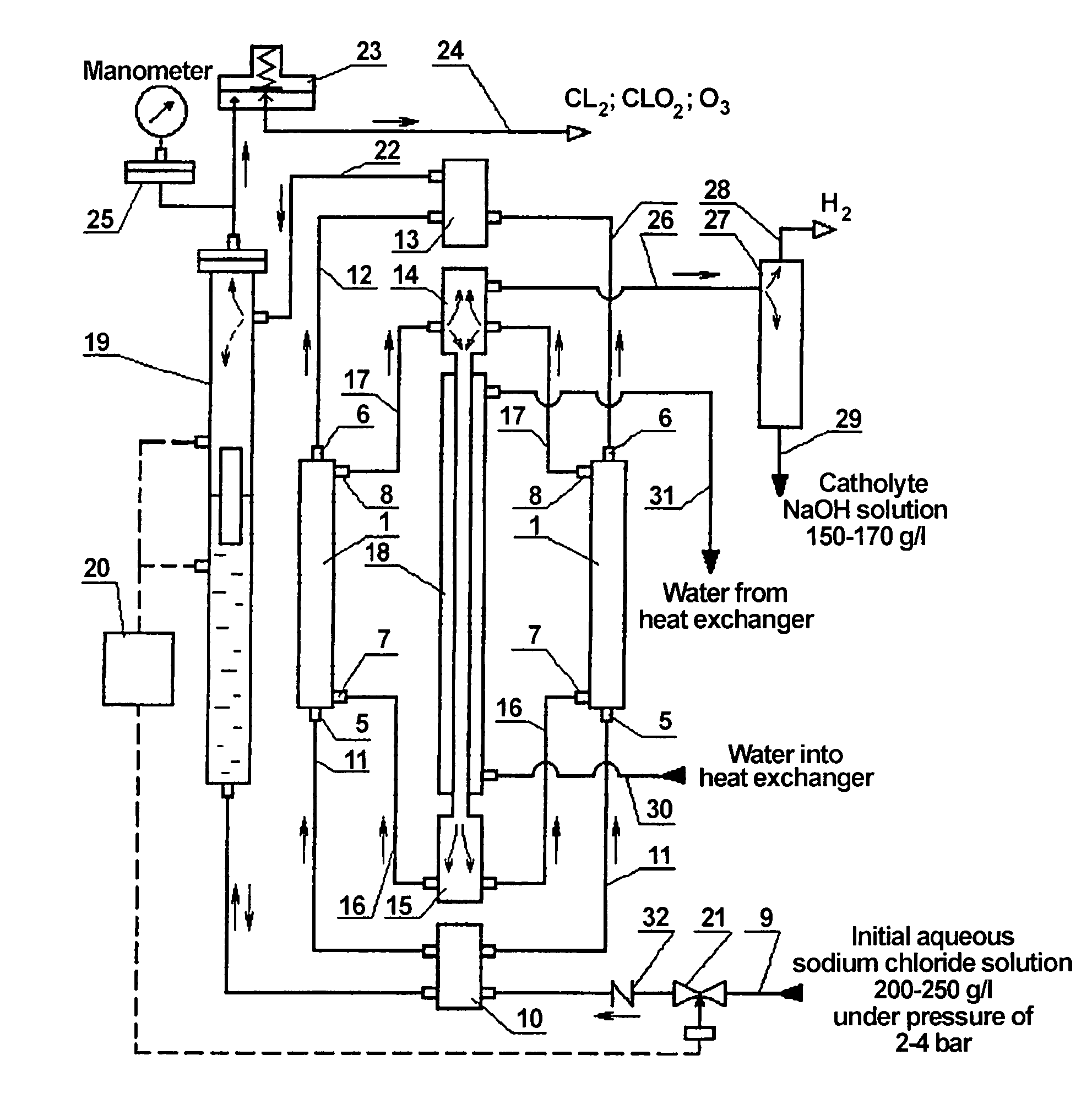
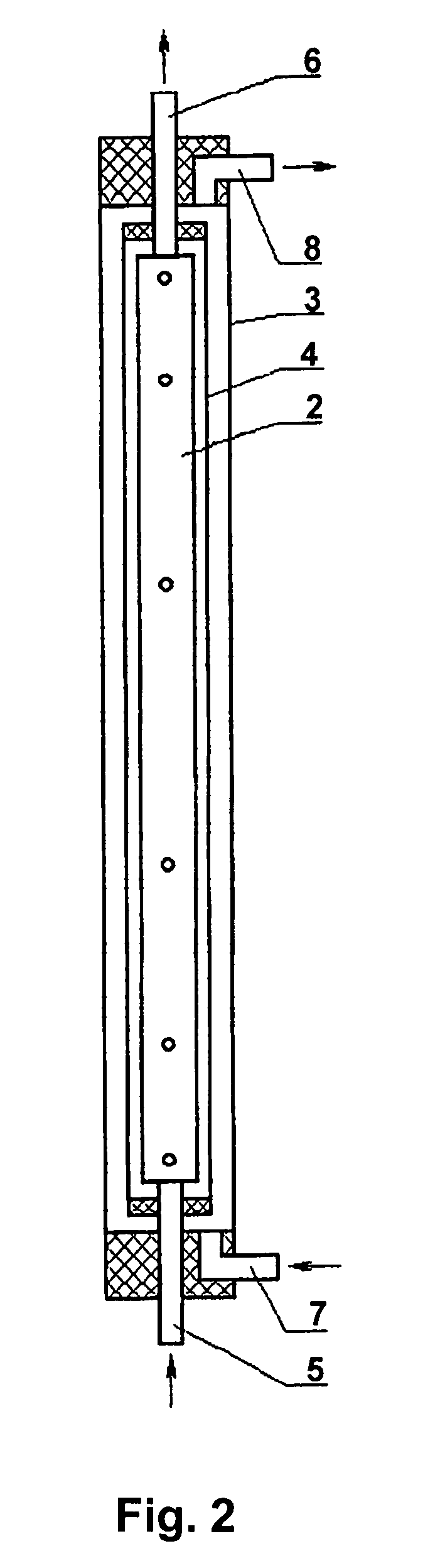
The invention relates to chemical engineering, in particular to devices for electrolyzing aqueous solutions of alkali or alkali-earth metal chlorides and for obtaining gaseous electrolytic products such as chlorine and oxygen. It can be used for water purifying and disinfecting processes and for electrochemically producing some chemical products. The inventive device includes at least one electrochemical reactor (1) comprising from 2 to 16 electrochemical cells. Lines for supplying and discharging cathode and anode chambers are embodied in the form of pipelines having an inner diameter equal to or less than 0.5 of the interelectrode distance and lengths which are equal to or greater than 2 Ld, wherein the interelectrode distance is an anode-to-cathode distance and Ld is the cathode length. A manifold for supplying an initial solution (10), a lower manifold of the cathode circulation circuit (15), a heat exchanger (18), an upper manifold of the cathode circulation circuit (14) and a manifold for collecting gaseous products of the anodic chamber cells (13) are arranged along the same vertical axis. The upper manifold of the cathode circulating circuit (14) is mounted at a height not less than then the distance equal to Ld from the cathode chamber output. The number of the inputs and outputs of the manifolds corresponds to the number of cells in the reactor, and said inputs and outputs are arranged symmetrically with respect to the vertical axis of symmetry of the manifold.
Owner:BAKHIR VITOLD MICHAILOVI +1
Methods and apparatuses for controlling contamination of substrates
InactiveUS20110114129A1Minimizing permeation of moistureImprove overall utilizationMechanical cleaningPressure cleaningProduct gasEnvironmental engineering
Components, systems, and methods for maintaining an extremely dry environment within substrate containers formed of polymers provides supplemental exterior gas washing of the substrate container to minimize permeation of moisture and oxygen through the polymer walls of the container and to control desorption of water entrapped in the polymer walls of the container.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Transplant production system
InactiveUS20060162246A1Efficient productionWeaken energyClimate change adaptationTransplantingTemperature controlInterior space
A system for transplant production comprising: at least one air conditioner installed in a completely light shielding closed structure surrounded by a thermally insulated wall, the air conditioner controlling the temperature and humidity of air in the closed structure; at least one box-shaped culturing module disposed in the internal space of the closed structure, the culturing module having a front face opening which is opened to the internal space of the closed structure; a plurality of transplant production shelves arranged vertically in multi-layer in the culturing module to form a transplant production space between the upper and lower transplant production shelves; a plurality of plug trays for holding a plant growing medium mounted on each transplant production shelf; a sub-irrigation unit capable of irrigation from the bottom of the plug trays mounted on each transplant production shelf; an artificial lighting unit provided on the back of each transplant production shelf, the artificial lighting unit irradiating light to the lower plug trays; and at least one air fan fixed to the back wall of each transplant production shelf of the culturing module. By sucking the air whose temperature and humidity have been controlled by the air conditioner using the air fan from the front face opening of the culturing module and sending the air to the rear of the back wall of each transplant production shelf, temperature-controlled and humidity-controlled air can be effectively generated.
Owner:MKV DREAM
Aquaculture rearing enclosure and circulation induction system
ActiveUS20150150223A1WithstandRobust designClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPipeflowWater flow
A system for efficiently circulating water in a large volume of rearing space for aquatic organisms, comprising an impervious enclosure for containing the water and aquatic organisms and a pump for pumping water from an intake duct through intake ducting to a flow diverter, which then directs a flow of water radially outward within the enclosure to directly induce a circulation of water within the enclosure. The ‘center drive’ circulation pattern is sufficiently uniform to provide optimum rearing conditions for cultured finfish, while also ensuring that solid wastes are swept toward the central drain, even in a very large tank.
Owner:AGRIMARINE HLDG INC
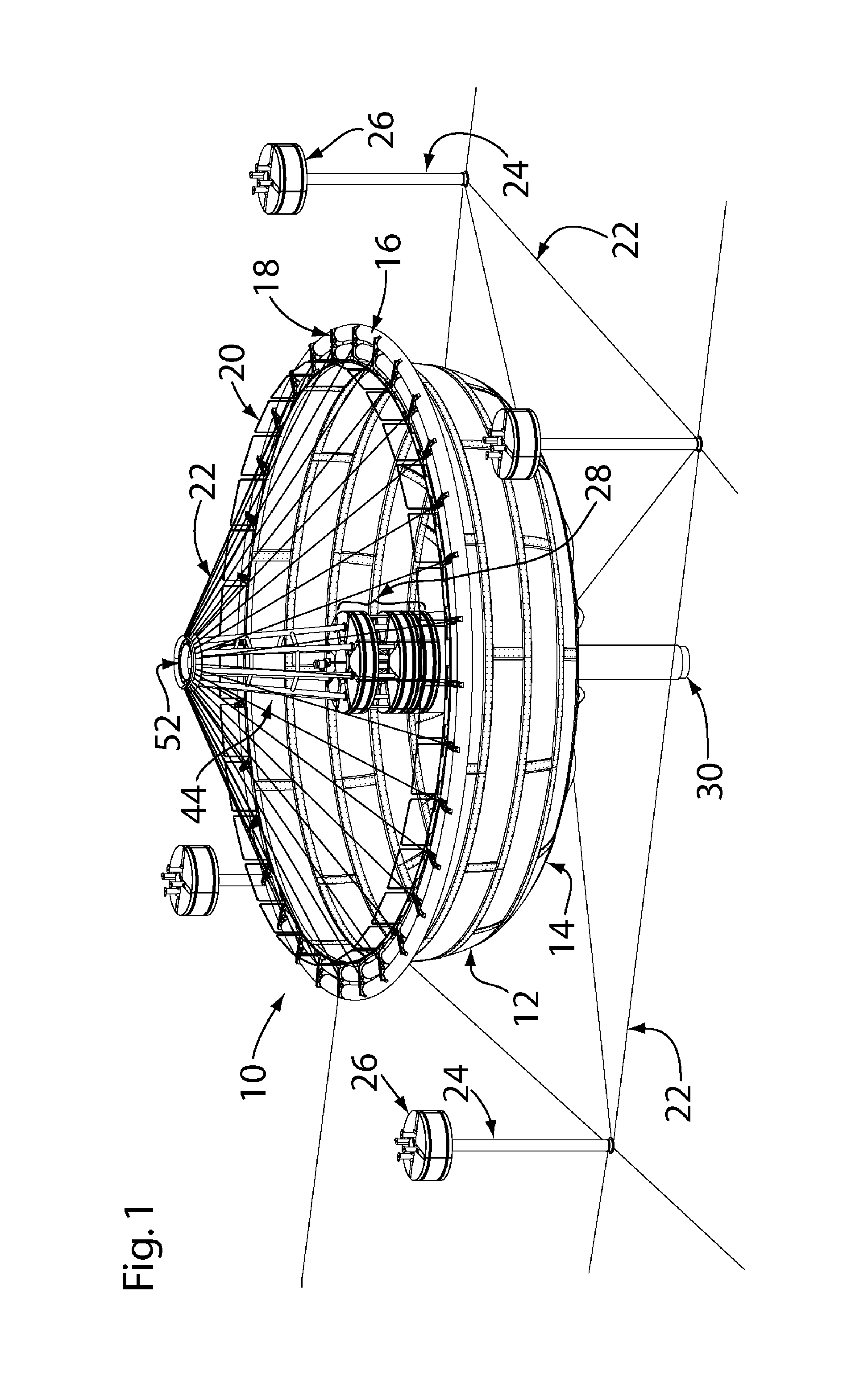
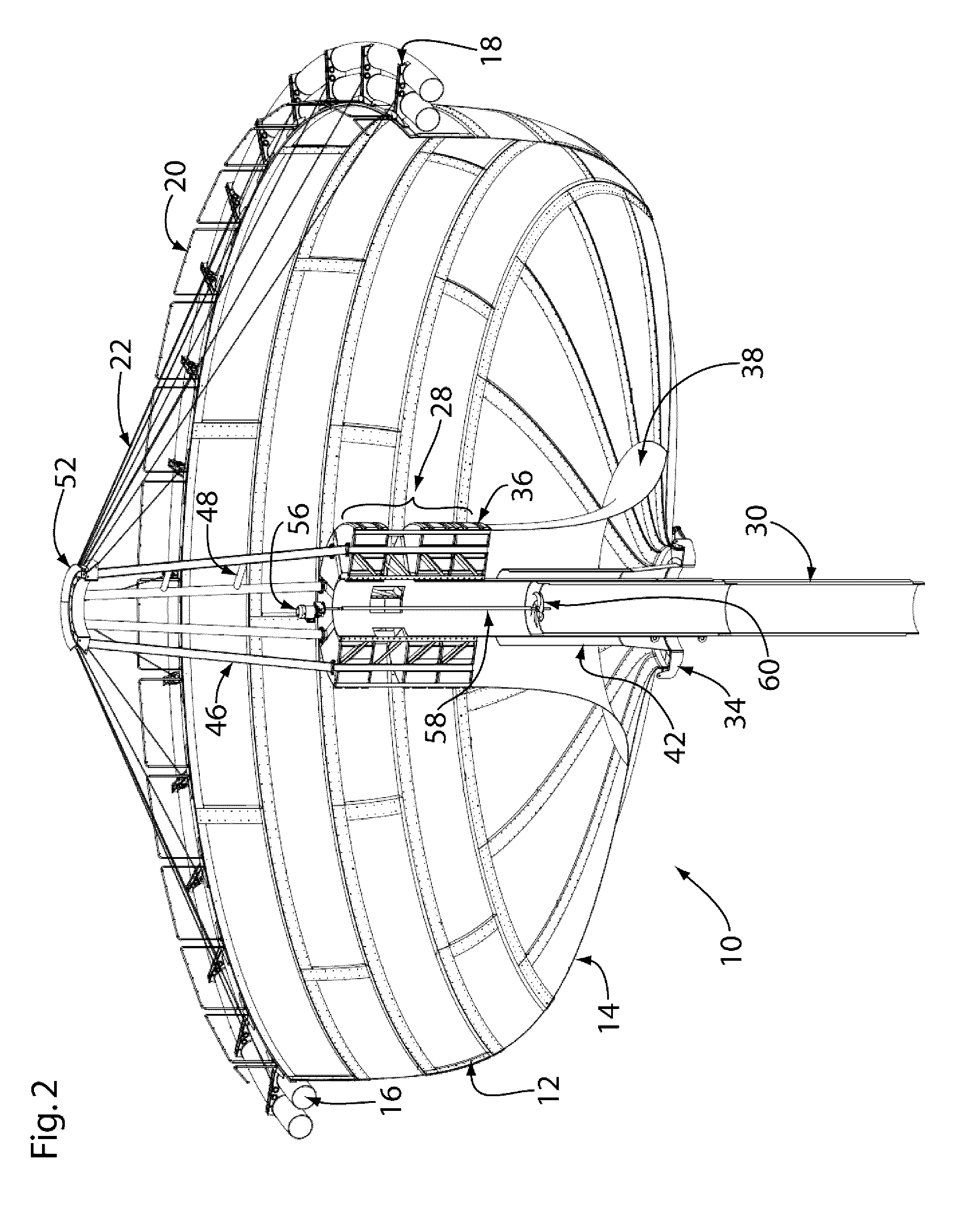
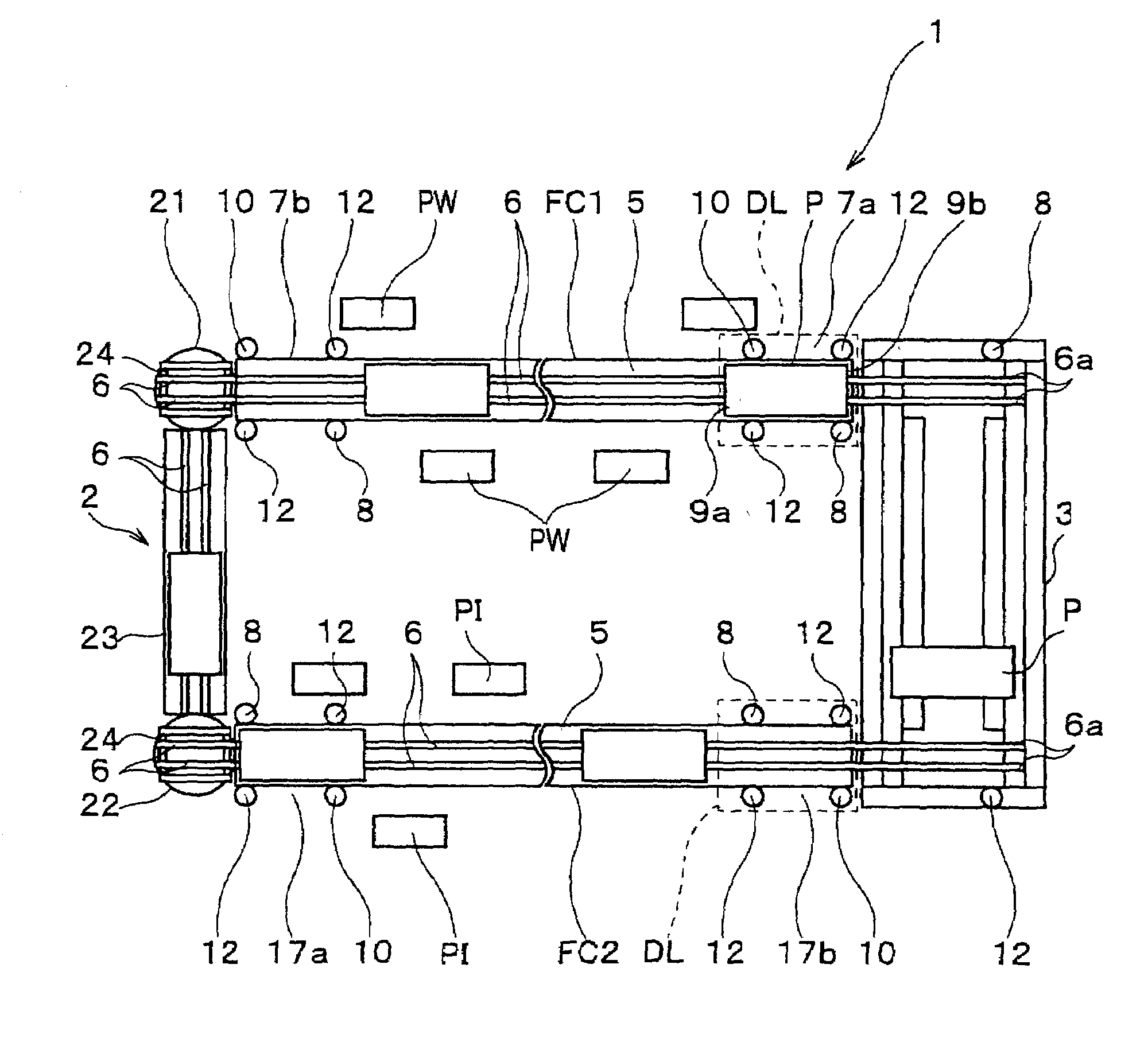
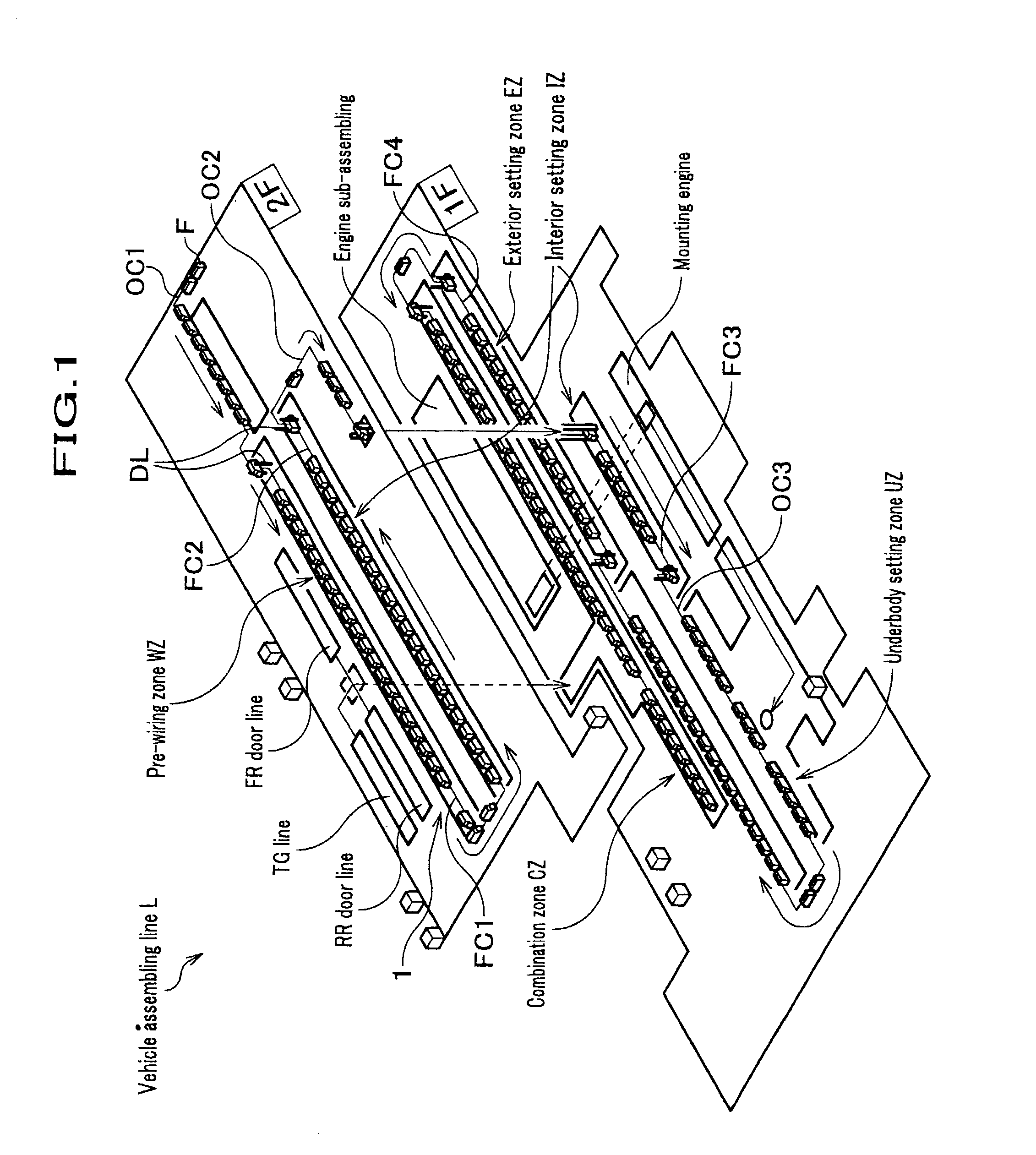
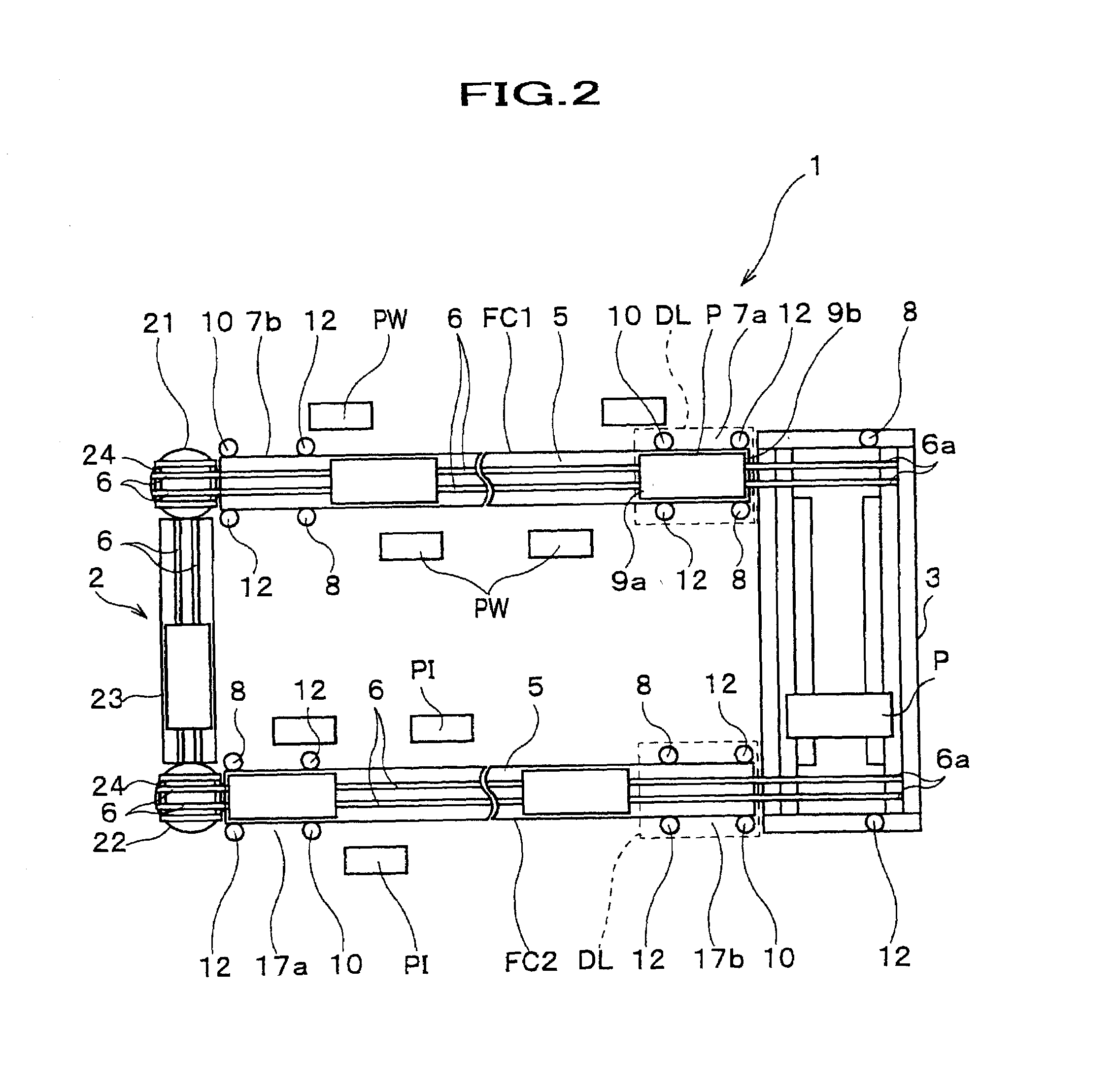
Palette conveyance mechanism and assembling line using it
InactiveUS7090068B2Fast circulationOptimization mechanismMonorailsCharge manipulationEngineeringFlange
It is the pallet conveying mechanism to move a pallet P arrived at an end point 17b of a friction conveyer FC2 to a starting point 7a of a friction conveyer FC1 in just as it is the direction without turning. The pallet conveying mechanism is comprised of rollers 34 having a flange portion 34a to contact with the pallet P by arranging along a main frame 31 provided so as to connect the friction conveyer FC 1 and FC 2 with each other and a drive mechanism 35 for driving rollers 34.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
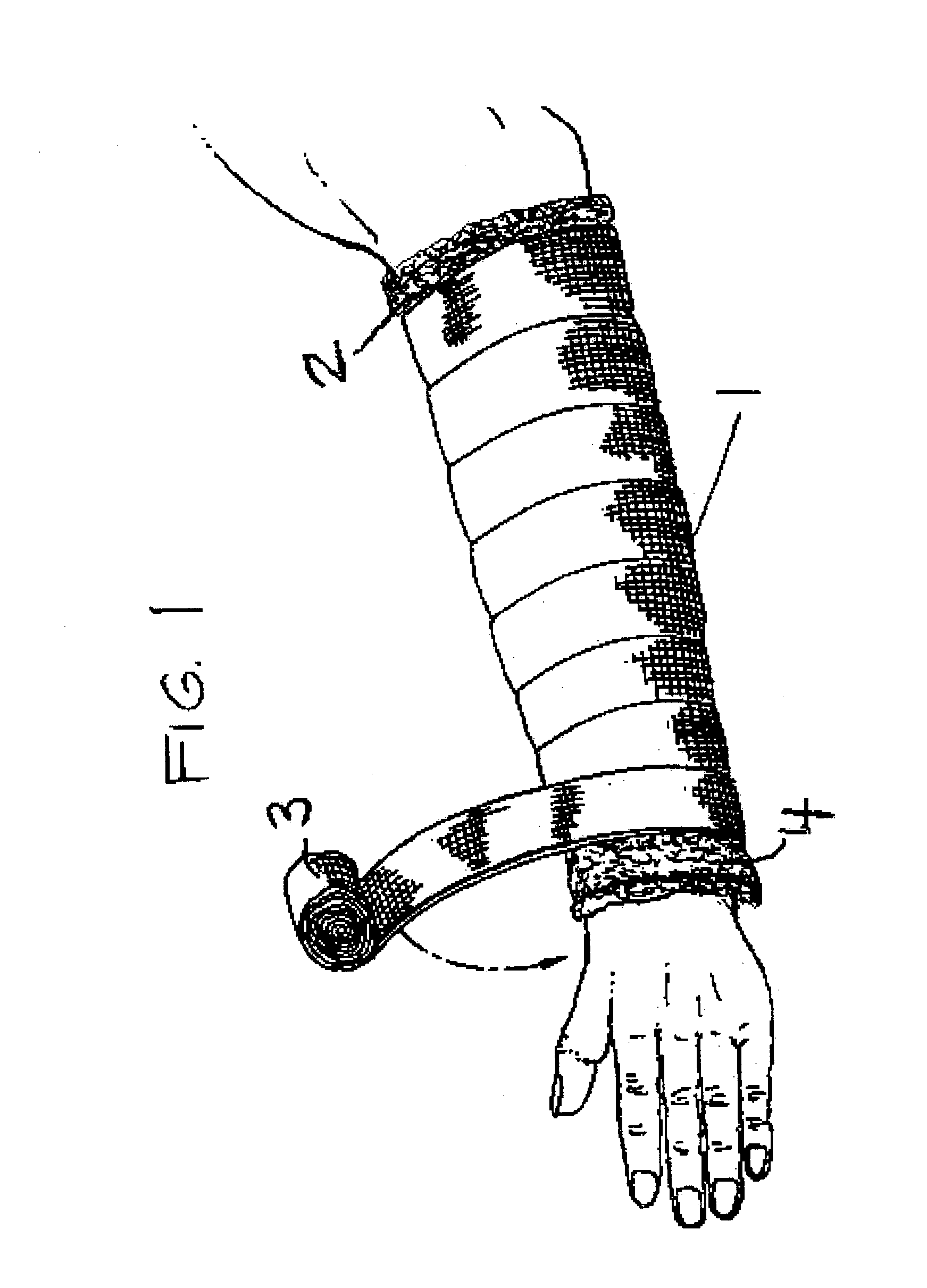
Fast drying, water permeable padding and immobilization apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS7311685B1Accelerated dryingCleanse the area beneath the paddingFinger bandagesTrousersSkin macerationMoisture
An immobilization apparatus incorporating a water permeable padding design that channels water away from the wearer and a method of preparing an immobilizing apparatus is described. In human or veterinary applications, the apparatus can be flushed with various solutions for cleansing of the limb beneath while avoiding the accumulation of excess moisture. The apparatus can be immersed in water then dried quickly in the open air. Subject invention allows for effective transfer of moisture away from the skin thereby avoiding skin maceration.
Owner:POLICASTRO JR THOMAS D
Thermoelectric conversion apparatus
InactiveUS20070235325A1Valid conversionEnergy efficiencyCellsFuel cell heat exchangeVapor–liquid separatorConcentration cell
A thermoelectric conversion apparatus has an evaporator for heating a working medium in liquid-phase to evaporate the working medium, an electric generator for forming a concentration cell for electric power generation when it is supplied with a reactive gas and the working medium evaporated by the evaporator, and a gas-liquid separator for being supplied with a mixed gas of the working medium and a cathode off-gas discharged from the electric generator and separating the mixed gas into the working medium and the reactive gas. The thermoelectric conversion apparatus also has an anode supply passage for supplying the reactive gas separated by the gas-liquid separator to the electric generator, and a cathode supply passage for supplying the working medium separated by the gas-liquid separator through the evaporator to the electric generator.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
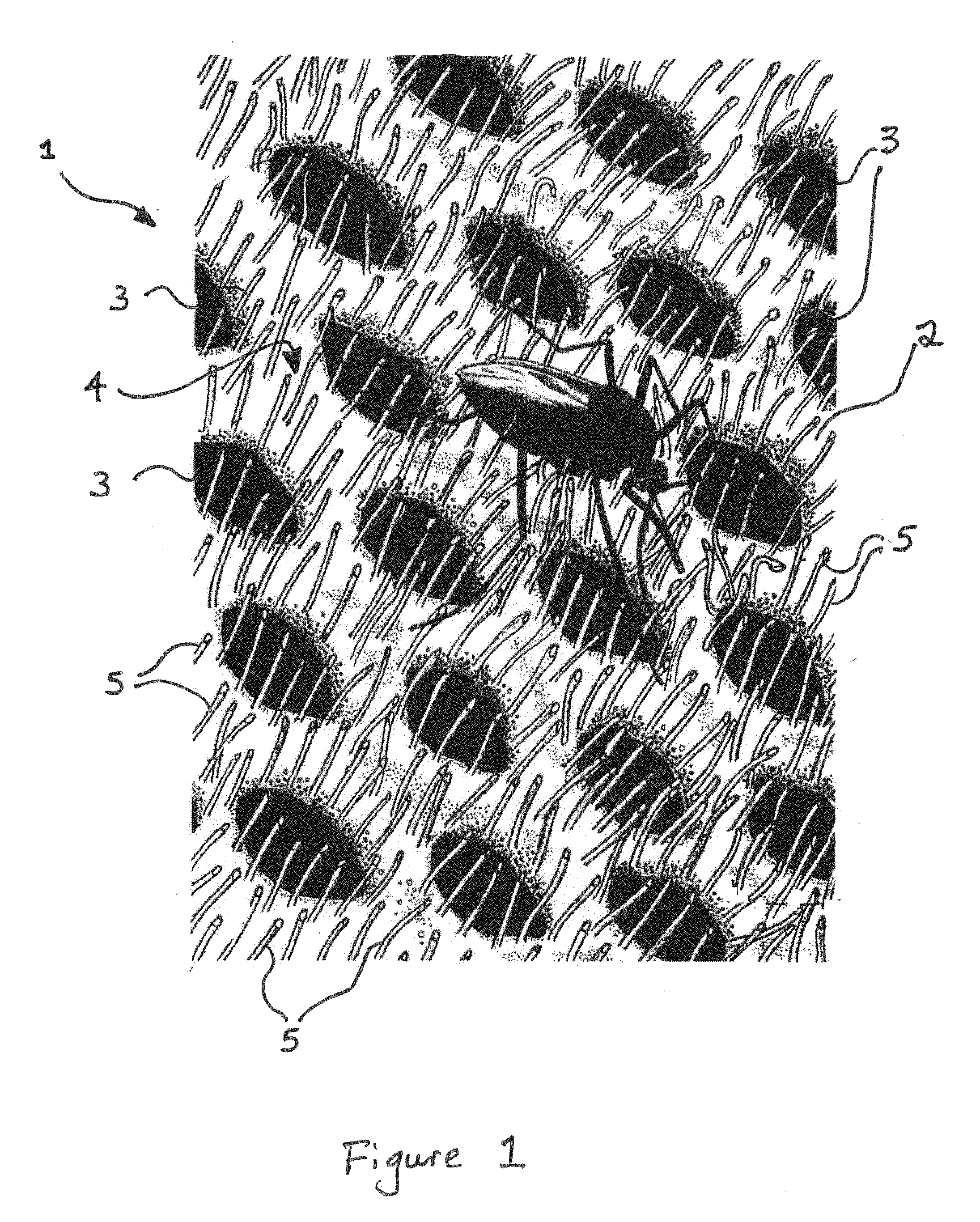
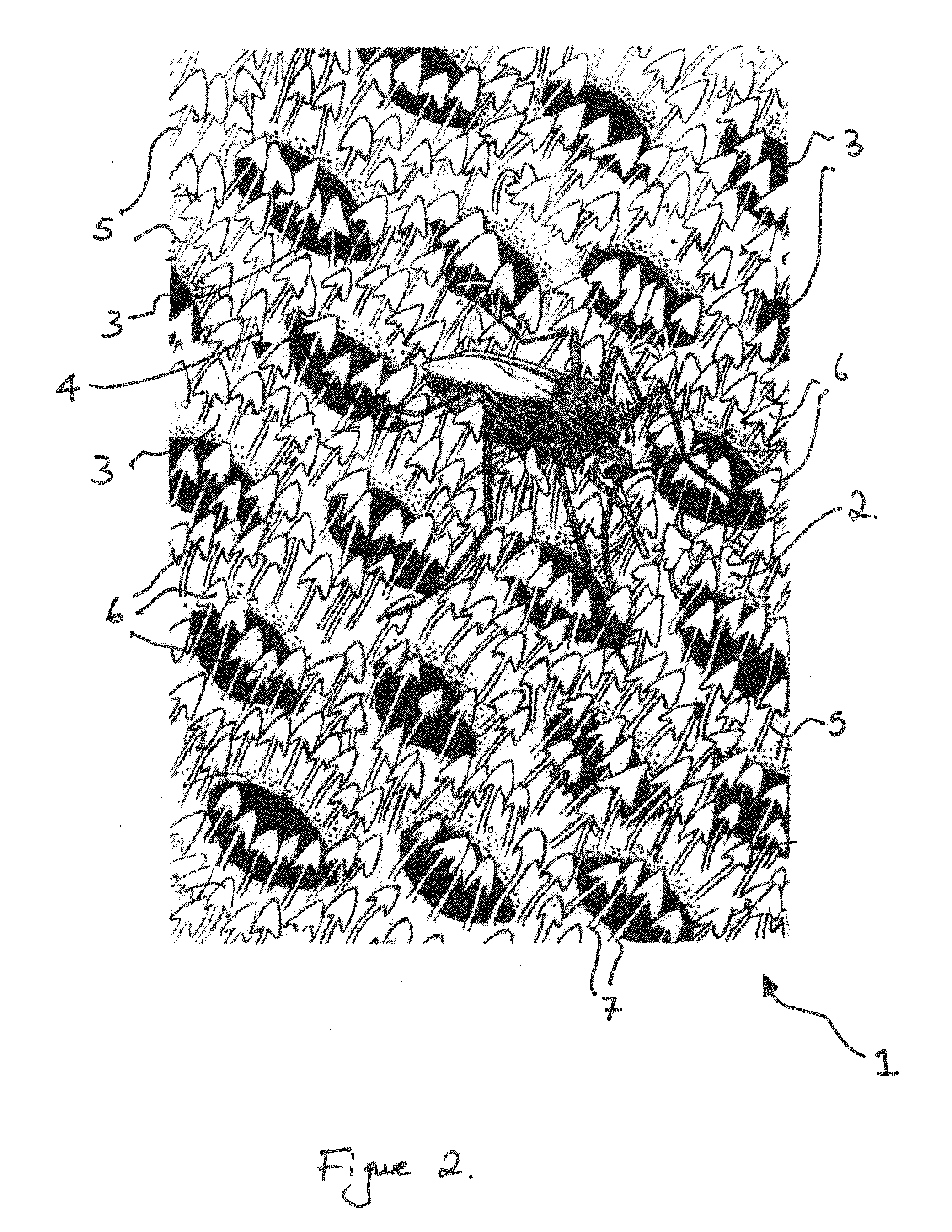
Pest control materials
InactiveUS20140041285A1Facilitate abrasionFacilitate mechanical interactionCrochetingTravelling sacksPaleontologyPest control
An open mesh insect control material is described which includes an insect contact surface, an internal surface, apertures communicating both surfaces and a plurality of filamentous projections protruding from the insect contact surface the projections at least partly occlude the apertures. The structure is suitable for use in pest control especially as a mosquito net.
Owner:INSECTSHIELD
Method for producing acrylic acid from glycerol
InactiveUS7910771B2Thermal equilibriumGood reaction selectivityPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationGas phaseGlycerol
The invention relates to a method for producing acrylic acid in one step by an oxydehydration reaction of glycerol in the presence of molecular oxygen. The reaction preferably carried out in gaseous phase in the presence of a suitable catalyst.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Elevation timing systems and methods for head up cpr
ActiveUS20170258677A1High outputIncrease pressureOperating tablesDiagnosticsElevation angleEmergency medicine
A method for performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) includes elevating the head, heart and shoulders of an individual from a starting elevation angle to a final elevation angle greater than zero degrees relative to horizontal while performing CPR by repeatedly compressing the chest. The method includes elevating the brain within a time period selected to be slow enough to permit a sufficient amount of blood to flow to the brain throughout the elevation time period. The method also includes regulating the intrathoracic pressure of the individual while performing CPR. The performance of chest compressions is stopped and after stopping the performance of chest compressions, the head, heart, and shoulders are promptly from the final elevation angle within a timeframe selected to prevent significant drainage of blood from the brain until the head, heart and shoulders are lowered.
Owner:LURIE KEITH G
Device for Producing Anodic Oxidaton Products of an Alkali or Alkali-Earth Metal Chloride Solution
ActiveUS20070261954A1Improve productivityReduce power consumptionCellsWater/sewage treatment apparatusElectrochemical responseAlkaline earth metal
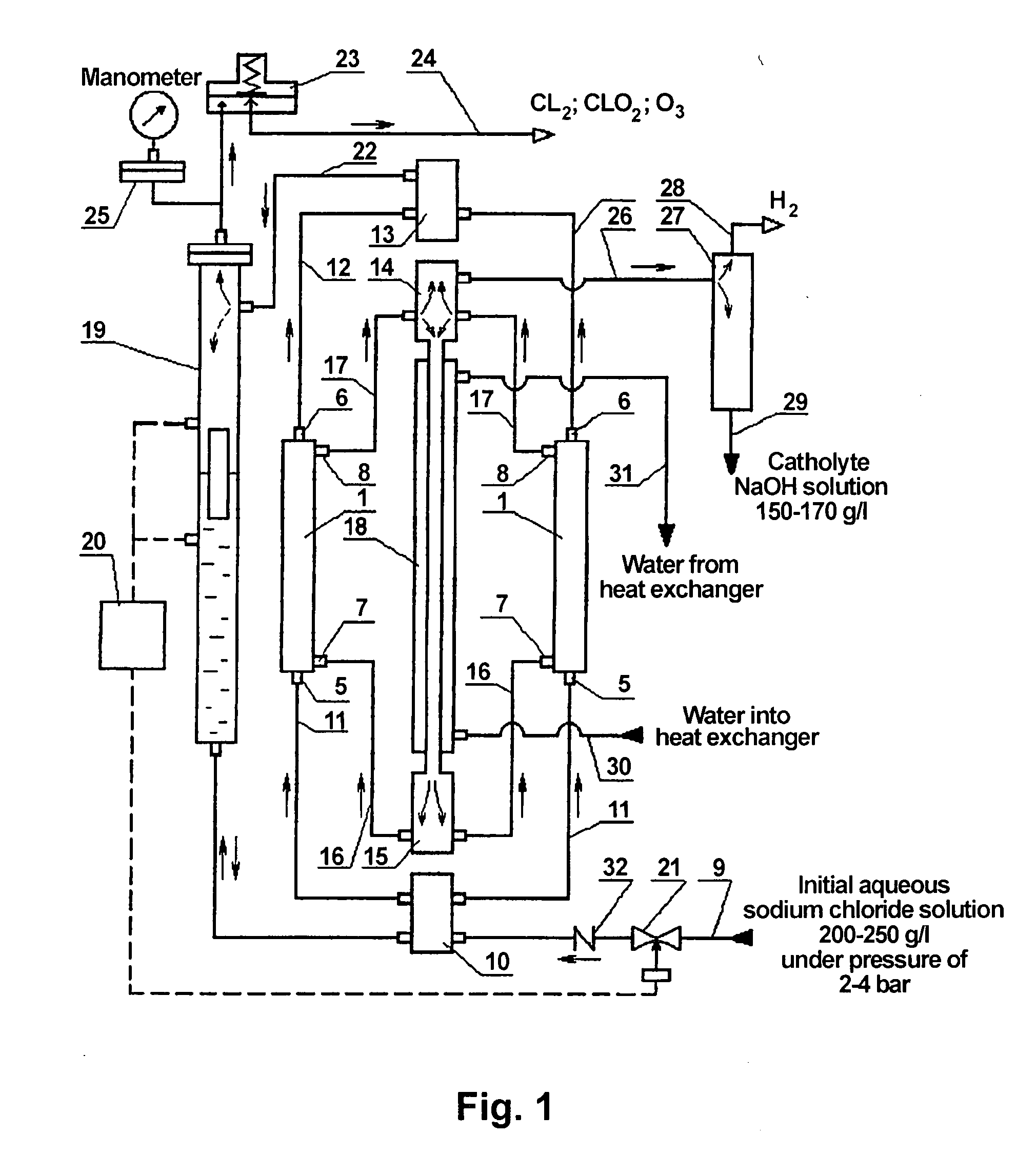
The invention relates to chemical engineering, in particular to devices for electrolyzing aqueous solutions of alkali or alkali-earth metal chlorides and for obtaining gaseous electrolytic products such as chlorine and oxygen. It can be used for water purifying and disinfecting processes and for electrochemically producing some chemical products. The inventive device includes at least one electrochemical reactor (1) comprising from 2 to 16 electrochemical cells. Lines for supplying and discharging cathode and anode chambers are embodied in the form of pipelines having an inner diameter equal to or less than 0.5 of the interelectrode distance and lengths which are equal to or greater than 2 Ld, wherein the interelectrode distance is an anode-to-cathode distance and Ld is the cathode length. A manifold for supplying an initial solution (10), a lower manifold of the cathode circulation circuit (15), a heat exchanger (18), an upper manifold of the cathode circulation circuit (14) and a manifold for collecting gaseous products of the anodic chamber cells (13) are arranged along the same vertical axis. The upper manifold of the cathode circulating circuit (14) is mounted at a height not less than then the distance equal to Ld from the cathode chamber output. The number of the inputs and outputs of the manifolds corresponds to the number of cells in the reactor, and said inputs and outputs are arranged symmetrically with respect to the vertical axis of symmetry of the manifold.
Owner:BAKHIR VITOLD MICHAILOVI +1
Construction machine
ActiveUS8550198B2Improve cooling efficiencyGuarantee effective circulationElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingEngineeringHeat exchanger
In a heat exchanger cover (17) covering upper sides of heat exchanger (13), an inlet port (21) is provided on a left side which is an upstream side of cooling air, and one exhaust port (22) for exhausting the cooling air which has passed through the heat exchanger (13) is provided on a right side opposite to this inlet port (21). An engine cover (15) is provided with another exhaust port (23) at a position opposing the one exhaust port (22) in a left-right direction. The cooling air which has passed through the heat exchanger (13) can be exhausted horizontally from the exhaust port (22) provided in the heat exchanger cover (17) toward the exhaust port (23) provided in the engine cover (15).
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
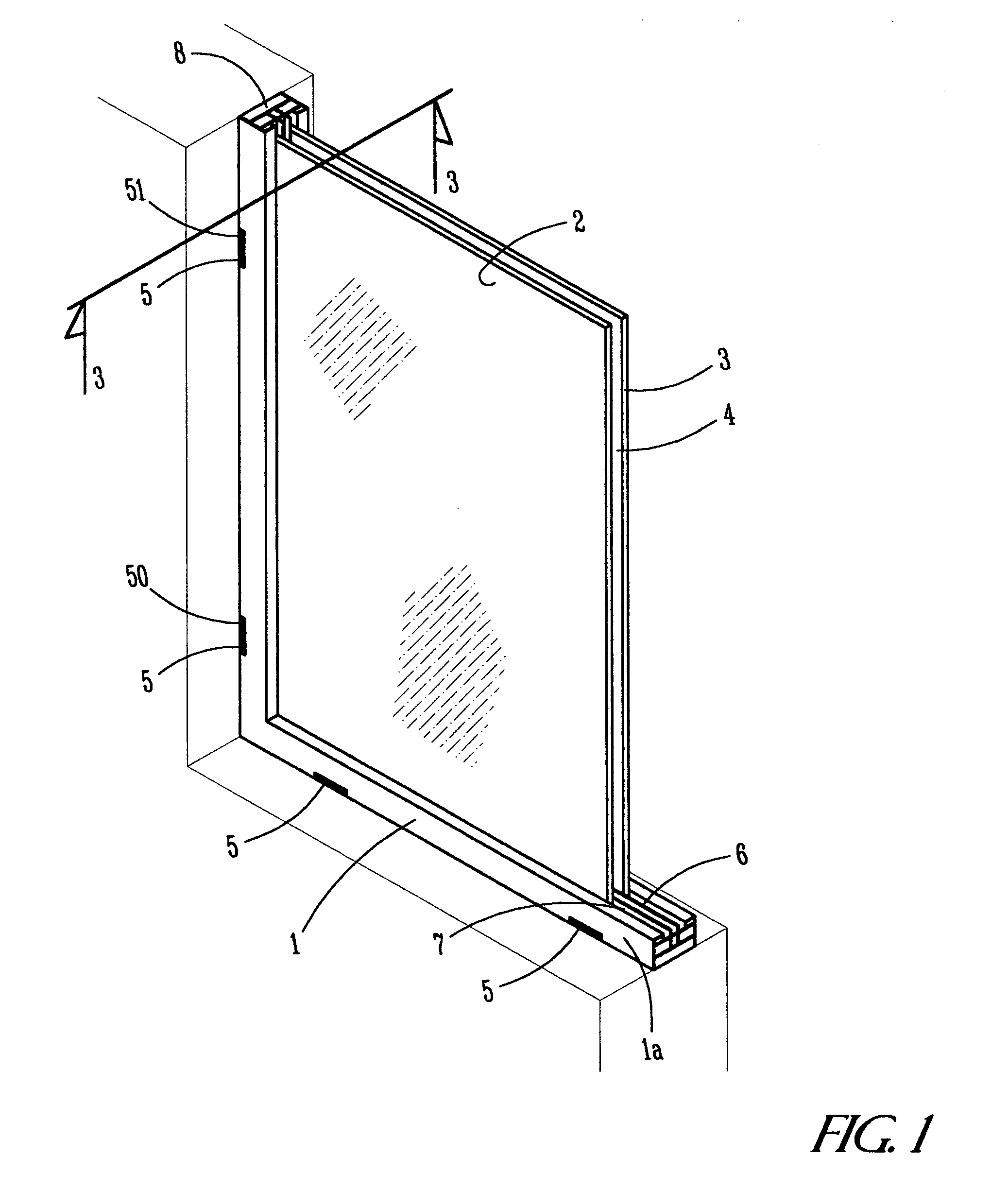
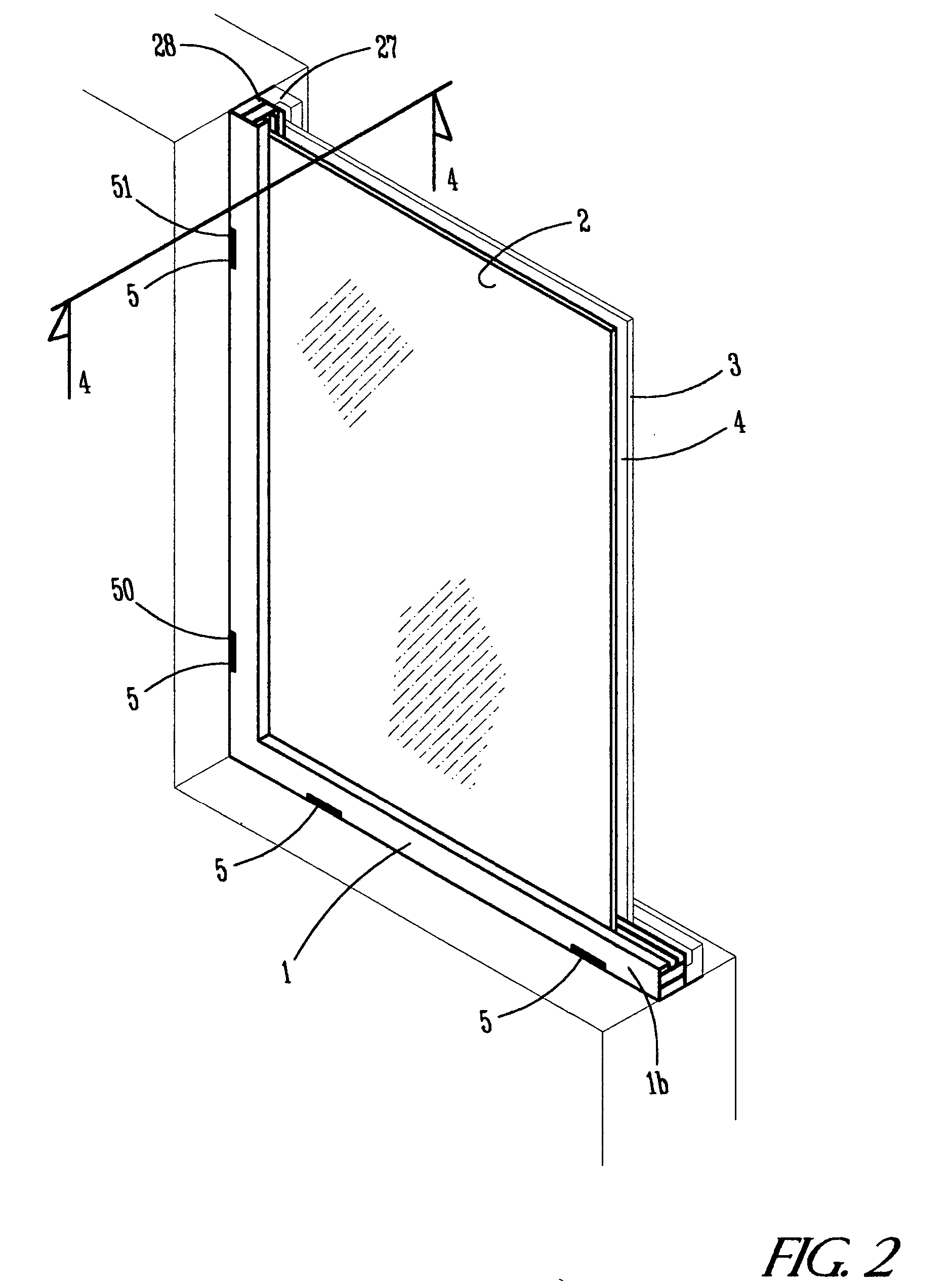
Apparatus for venting of protective panels
ActiveUS20050072076A1Efficient air circulationImprove ventilationLighting and heating apparatusVentilation arrangementEngineeringMoisture
The present invention provides an apparatus for venting an airspace formed between an ornamental window and a protective panel. The venting means includes at least one pair of vent openings, one for air to enter the airspace and one for air to exit. These vent openings include a path through the frame holding the protective panel to an interior opening which is to the airspace. The vent openings, the paths and the interior openings must be of adequate size to minimize the range of temperature and moisture within the airspace. It is recommended that effective vent openings are at least one square inch for every 2000-2500 square inches of ornamental window.
Owner:BOVARD STUDIO
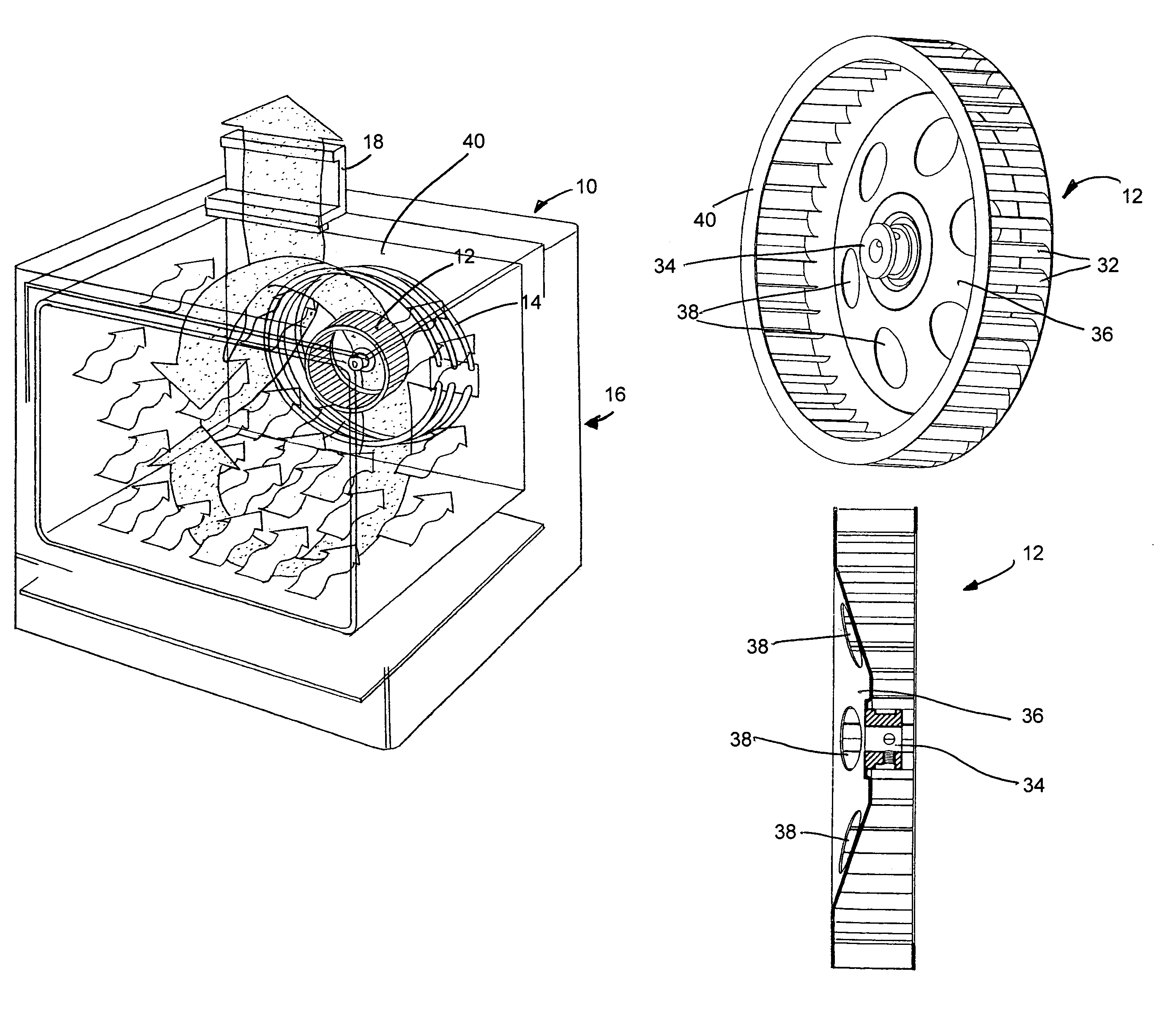
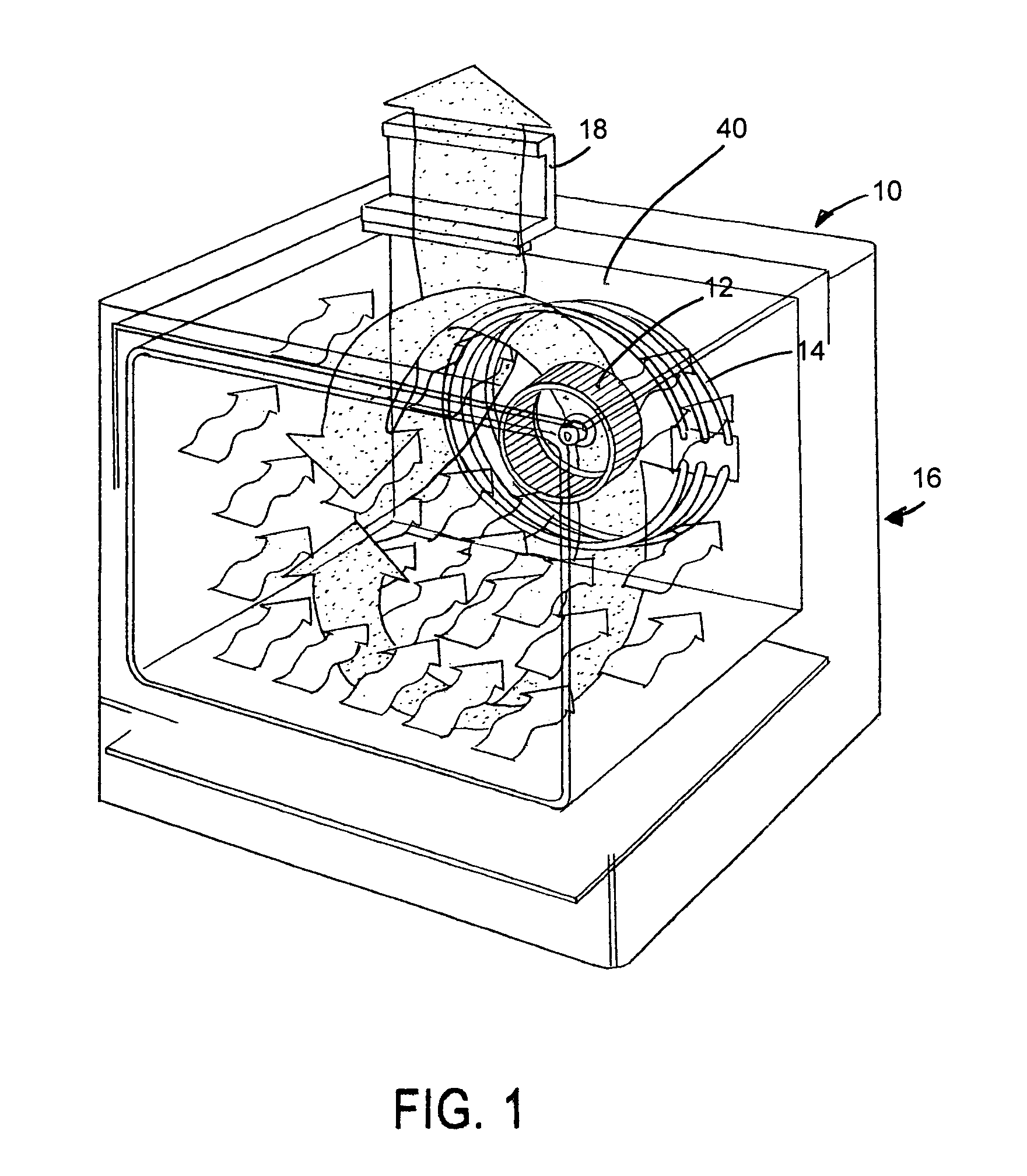
Electric convection oven
InactiveUS6933472B1Guarantee effective circulationAir-treating devicesDomestic stoves or rangesElectricityEngineering
An electric convection oven is provided wherein a squirrel cage fan is used to circulate air through a circular bank of heating coils surrounding the fan and into the oven. The coils wrap around the fan and are spaced from each other so that air from the fan will pass through the coils and into the oven. The fan is provided with a concave centrally located plate for drawing air from within the oven into the fan for recirculation through the heating coils and to return to the oven.
Owner:BLODGETT HLDG
Fluid filter separator and method
InactiveUS20090056542A1Efficient and inexpensiveGuarantee effective circulationDispersed particle filtrationRotary stirring mixersSyngasWaste management
A filter separator and method, including an annular microfilter and a separation chamber within the microfilter including a plurality of mixing blades circulating fluid upwardly and downward within the chamber. When the apparatus is used to purify syngas, adherent metal oxide particles are circulated in the chamber to adsorb waste oxides. The apparatus is purged by injecting hot CO2 free gas into the chamber through the filter and the filter pores may be expanded during purging.
Owner:CAREW BAYNE
Method and apparatus for the treatment of wood or wood products
InactiveUS20060278336A1Avoid large amounts of heatSave energyDrying using combination processesPlywood pressesPulp and paper industryWood product
A method for the treatment of wood or wood products, in which method moist wood or wood products (1) are dried by first pressing and further by heating so that a desired degree of dryness is reached. In a first stage, the wood or wood products (1) arranged between treating elements (2) are pressed between the treating elements (2) so that a considerable amount of water is removed from the wood being treated, next the treating elements (2) are locked so that the wood or wood products (1) remain compressed between the treating elements (2), and the combination of treating elements (2) and wood or wood products (1) between them thus formed is moved into a drying chamber (D), where the wood or wood products are dried further by applying heat. The invention also relates to an apparatus.
Owner:TEKNOCOMP
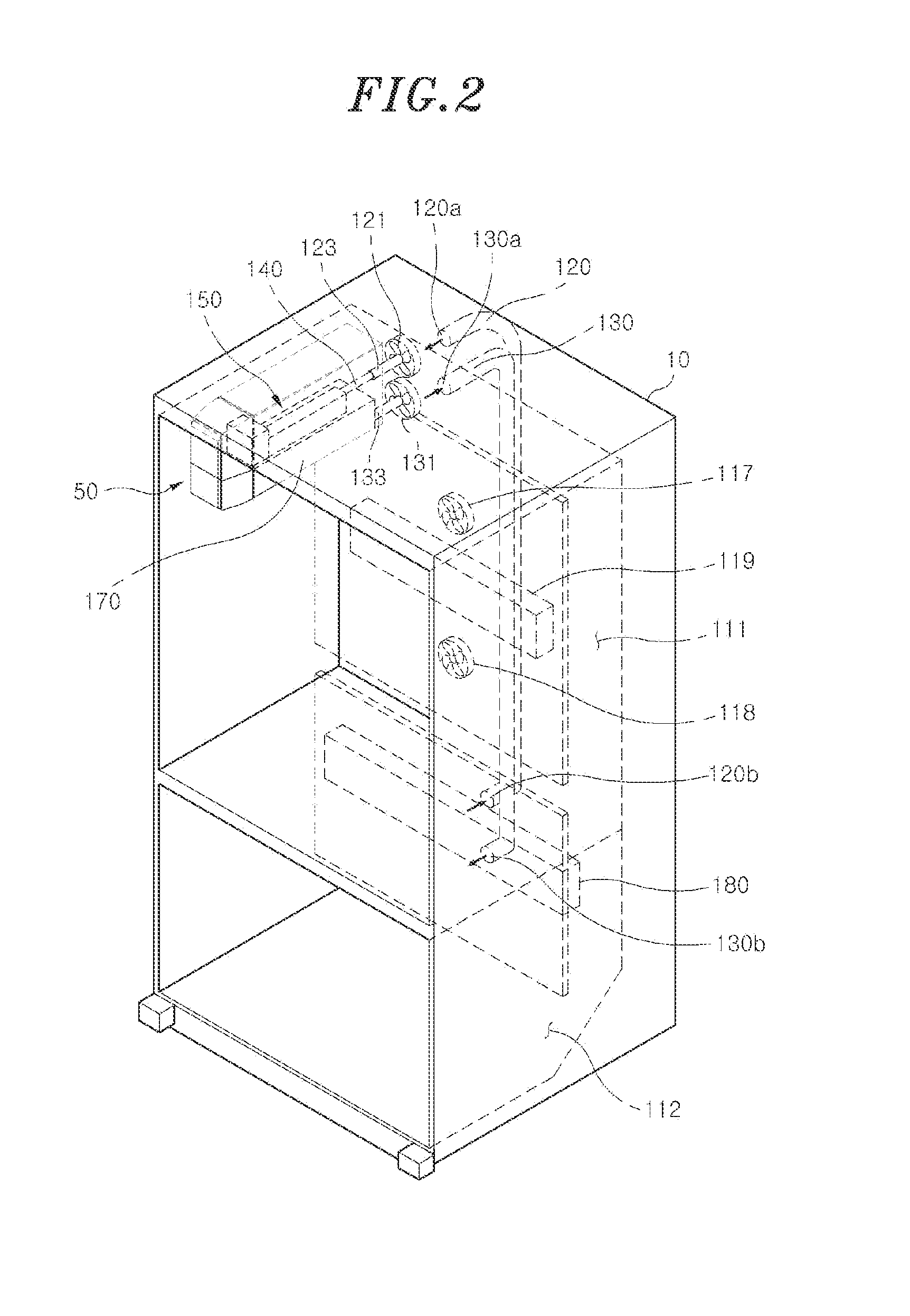
Cool air circulation structure of refrigerator and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS20160370091A1Enhance power efficiency and ice-making performanceCirculating cool air more efficientlyIce productionDomestic refrigeratorsEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
A refrigerator having a cool air circulation system capable of drawing cool air from a freezer to an ice machine disposed in a refrigerating space. The ice machine is removably installed in the refrigerating space. A cool air inlet duct is configured to supply cool air from an evaporator of the freezer into the ice machine provided in the refrigerating space. A cool air outlet duct is configured to return the cool air, used in the ice machine, from the ice machine to the freezer. After the ice machine is removed from the refrigerating space, cool air supplied from the cool air inlet duct is used to maintain a temperature in the refrigerating space.
Owner:DONGBU DAEWOO ELECTRONCIS CORP
Method for recycling composite materials
InactiveUS20040173239A1Prevent penetrationHigh rate of efficiencyElectrical coke oven heatingProductsPyrolysisNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a method for recovering the glass fibres from composite materials in connection with recycling. This is of particular importance in connection with recycling of glass fibre blades from wind turbines and other fibre reinforced composite materials of the type where glass fibre is embedded in a matrix of polyester, epoxy or a similar polymeric substance or a thermoplastic material. The method of the invention consists in a thermal process in which the material is pyrolysed at a relatively low temperature in a closed furnace chamber with an inactive atmosphere, for example in the form of nitrogen. The temperature and combustion conditions are chosen such that the matrix is glasified while the glass fibres remain intact, thus making recycling possible. The by-product of the pyrolysis is combustible gas, which is carried off from the furnace. The energy in the gas may be utilised for a number of objects, such as: propellant for gas engines in combined heat and power plants or storage for later use. Alternatively, the gas may be burned with a minimum of environmentally damaging wastes, if combustion takes place in the temperature range of 1000-1200° C.
Owner:REFIBER
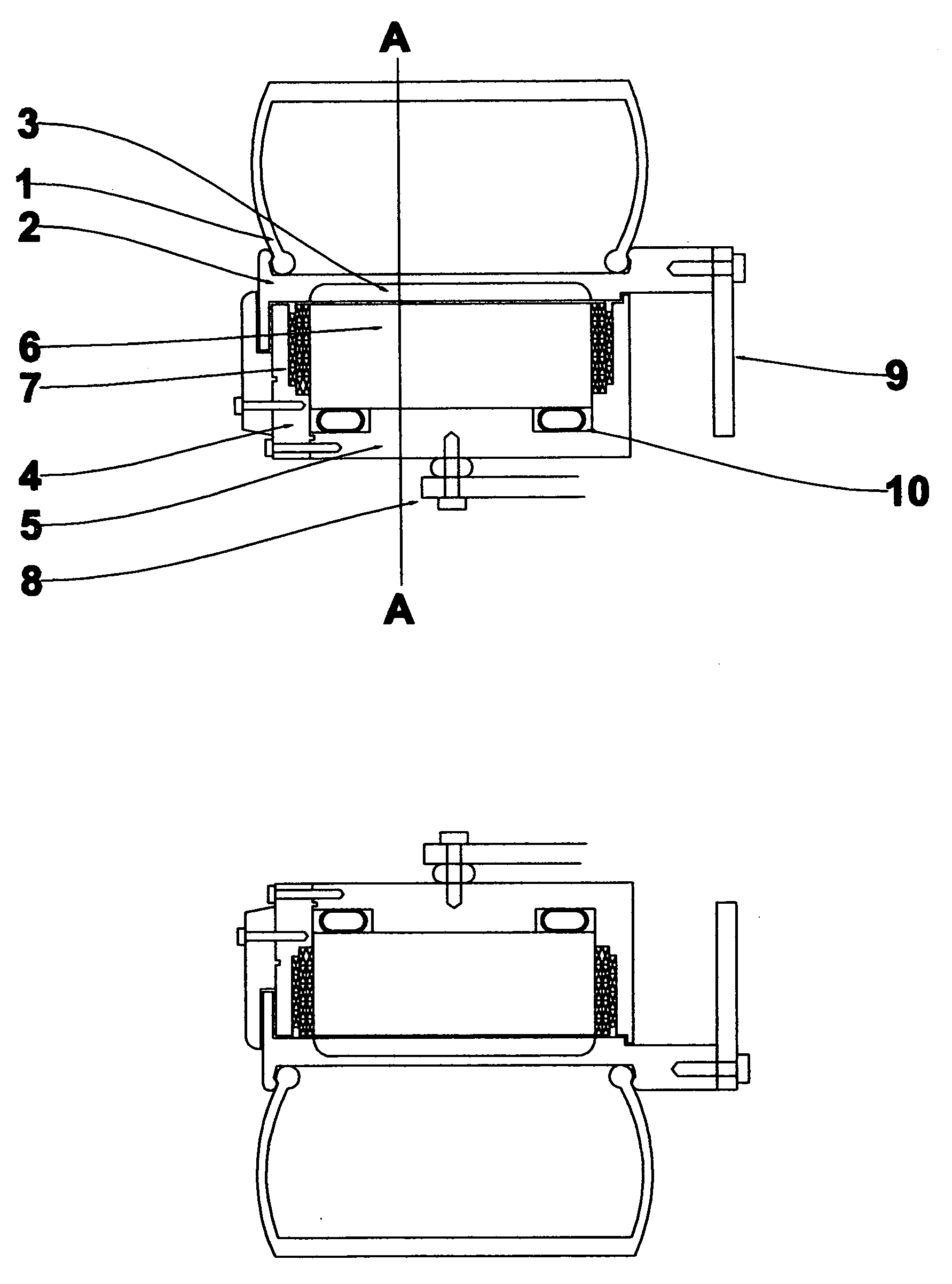
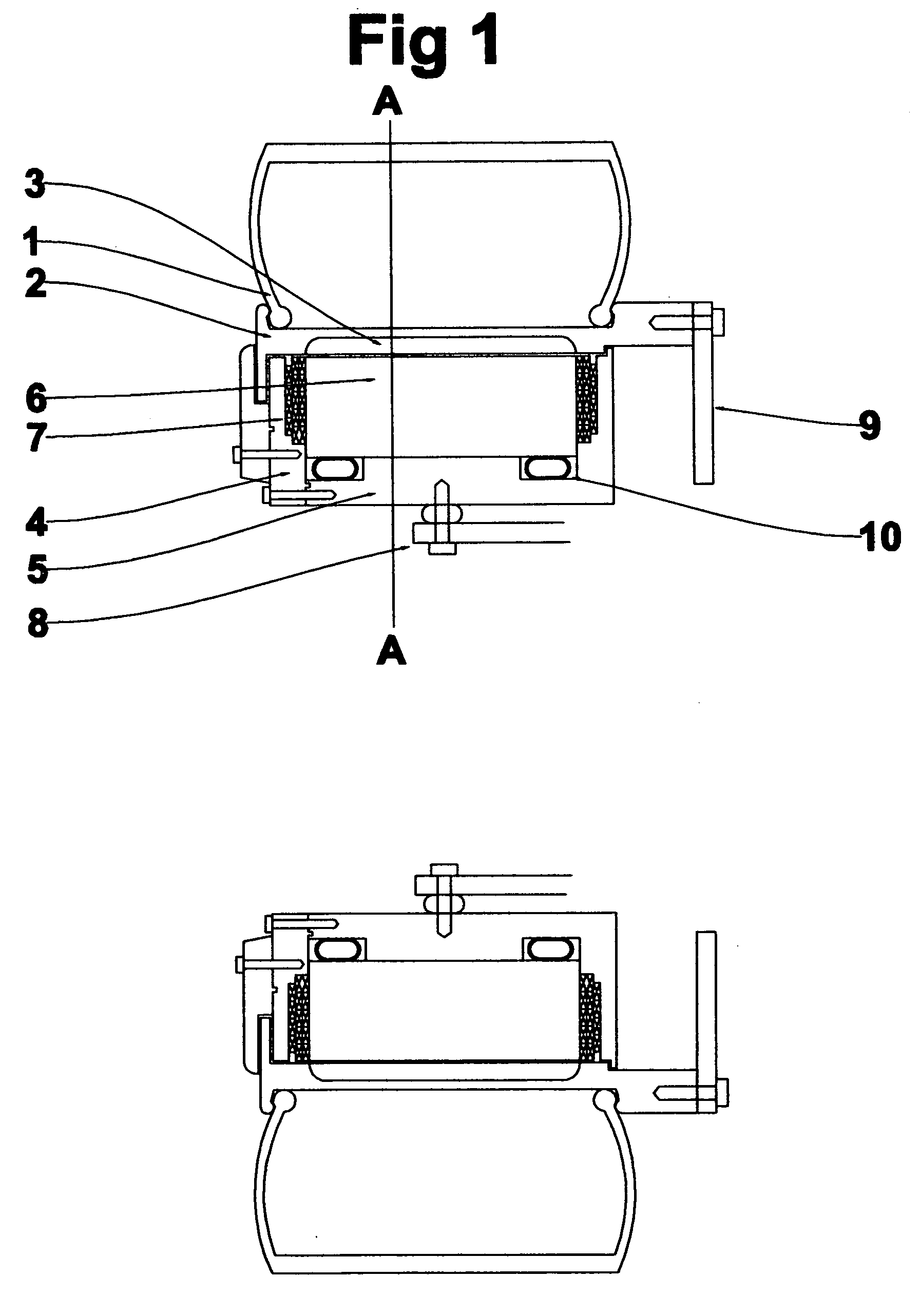
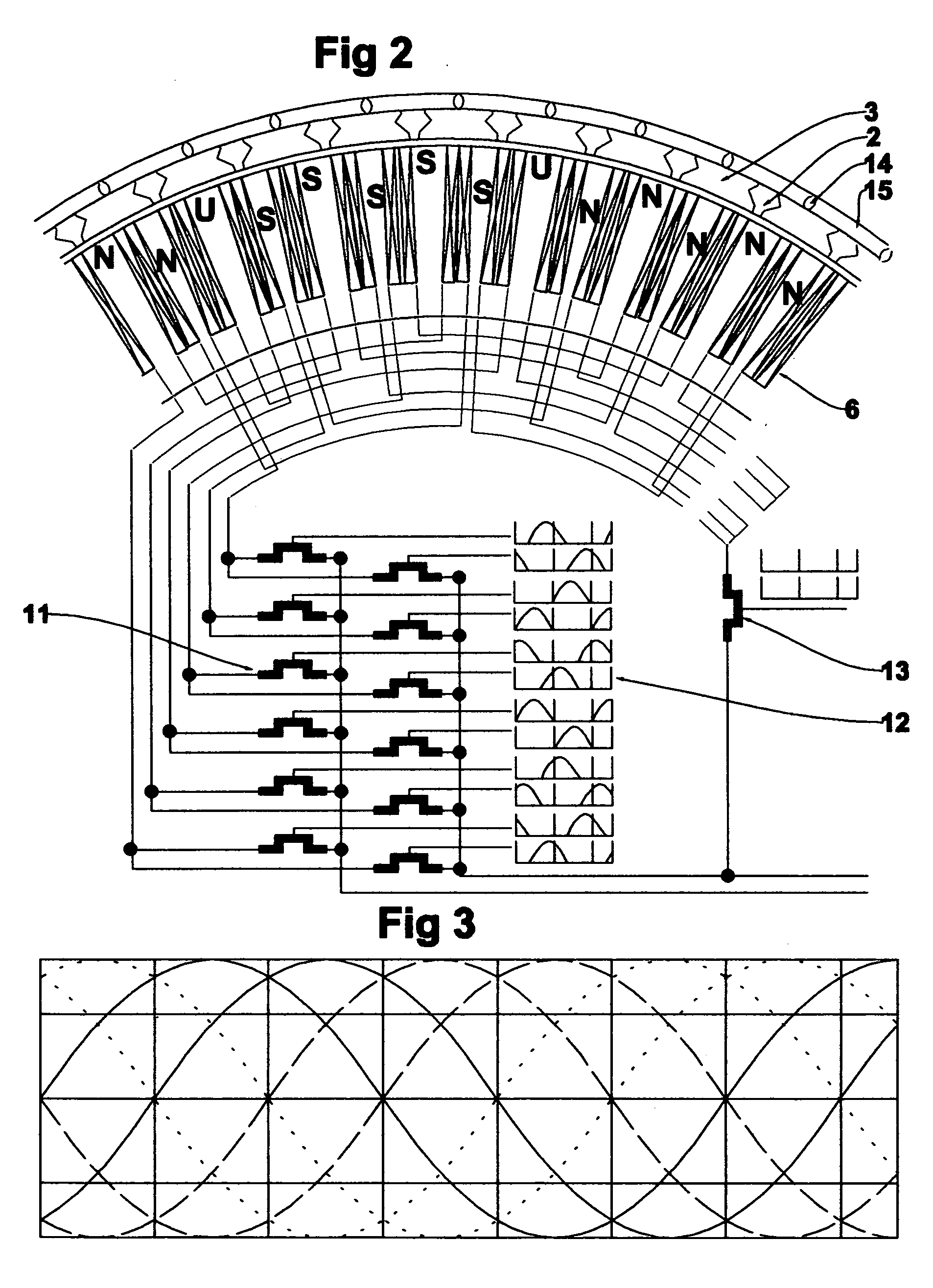
High power two speed electric motor
InactiveUS20050168090A1Guaranteed uptimeSuitable for operationDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesAsynchronous induction motorsElectric machineEngineering
This invention is a new dynamo electric machine of the alternating current type which provides for the entire stator winding to operate as an alternating current induction machine for relatively shorter periods of very high torque output operation, then provides for a portion of the stator winding to operate as a direct current exciter field winding while the balance of the stator operates as the armature windings of a high efficiency salient pole alternating current synchronous machine. The said machine or any electrical machine is further made more compact for a specific rate of output by providing stator winding insulation of an insulating material which provides for very high temperature operation and / or relatively high volume circulation of coolant throughout the porous winding insulation and potentially operates successfully at much higher temperatures than typical insulation systems. Also provided is a novel means of rotatably supporting a rotor of a dynamo electrical machine.
Owner:GOULD LEN CHARLES
Thermal management system for loudspeaker having internal heat sink and vented top plate
ActiveUS20070177756A1Increase air circulationEfficient air circulationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsDeaf-aid setsCooling effectEngineering
A thermal management system promotes cooling effects of a loudspeaker. The thermal management system includes an internal heat sink having a tubular shape and mounted between a pole piece and a magnet of the loudspeaker, the internal heat sink having pleat portions to form a plurality of air passages on an inner surface from top to bottom thereof; and a back plate connected to the pole piece and having ventilation holes that vertically penetrate through the back plate, the internal heat sink and the magnet being mounted on the back plate. A lower end of the air passage on the internal heat sink is positionally matched with an upper opening of the ventilation hole on the back plate, thereby allowing an air flow through the air passage and the ventilation hole.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
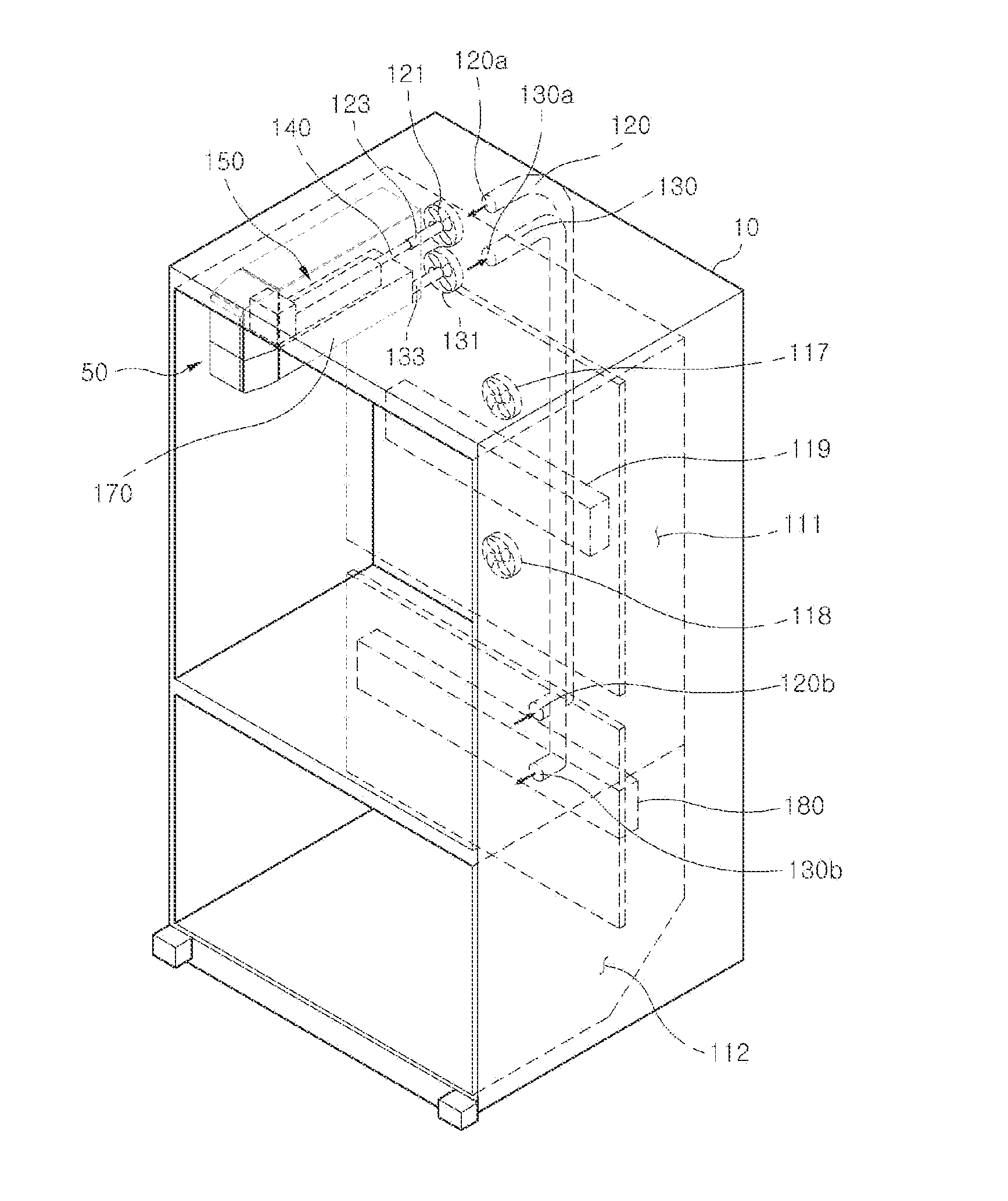
Water-cooling radiator unit and water-cooling module using same
ActiveUS20180092249A1Improved cooling fluid circulating efficiencyLower the volumeStationary conduit assembliesCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsEngineeringWater block
A water-cooling radiator unit and a water-cooling module using same are disclosed. The water-cooling radiator unit includes a main body divided into a first section, a second section and a transit zone, which are fluidly communicable with one another. The first section has a first flow passage system and an inlet formed thereon, the second section has a second flow passage system and an outlet formed thereon. The main body is internally filled with a cooling fluid, and the transit zone has a pump mounted therein. The water-cooling radiator unit can be fluidly connected to a water block via two tubes to form a water-cooling module. The pump drives the cooling fluid to circulate in the main body and between the water-cooling radiator unit and the water block, enabling the water-cooling module to provide upgraded heat-dissipation performance while the water block has a reduced volume.
Owner:ASIA VITAL COMPONENTS SHENZHEN CO LTD
Dehumidifier System Device and Method
InactiveUS20080282704A1Efficient air circulationRapid removal of moistureCondensate preventionUltrasonic humidifiersPeristaltic pumpAir pump
A dehumidifier system and device for maintaining a dry air environment in enclosures by extracting the water to outside the enclosure. The dehumidifier device comprises a condensation unit, typically a thermoelectric clement with a moisture collector, and a sealed pump, such as peristaltic pump, which pumps the condensed humidity out of the sealed enclosure, yet maintains the enclosure seal. The system is provided with a controller which alternately activates the thermoelectric element and the pump, in at least one mode: continuous, periodical, and programmable utilizing a humidity / relative humidity sensor. Optionally, in large-volume enclosures and containers, a fan assembly is connected to the controller so as to provide for rapid circulation of the air and removal of moisture.
Owner:SHALOM LEVIN
Developing device used in image forming device
ActiveUS7221892B2Guarantee effective circulationElectrographic process apparatusLatent imageImage formation
A developing device includes a removing roller positioned vertically above a supplying roller and in contact with a developing roller. Positively charged toner is supplied from the supplying roller to the developing roller and then supplied to a photosensitive drum for developing an electrostatic latent image thereon. Toner remaining on the developing roller that was not supplied to develop the latent image is removed by the removing roller. Some of the toner stripped by the removing roller falls down toward the supply roller and is again supplied to the developing roller.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
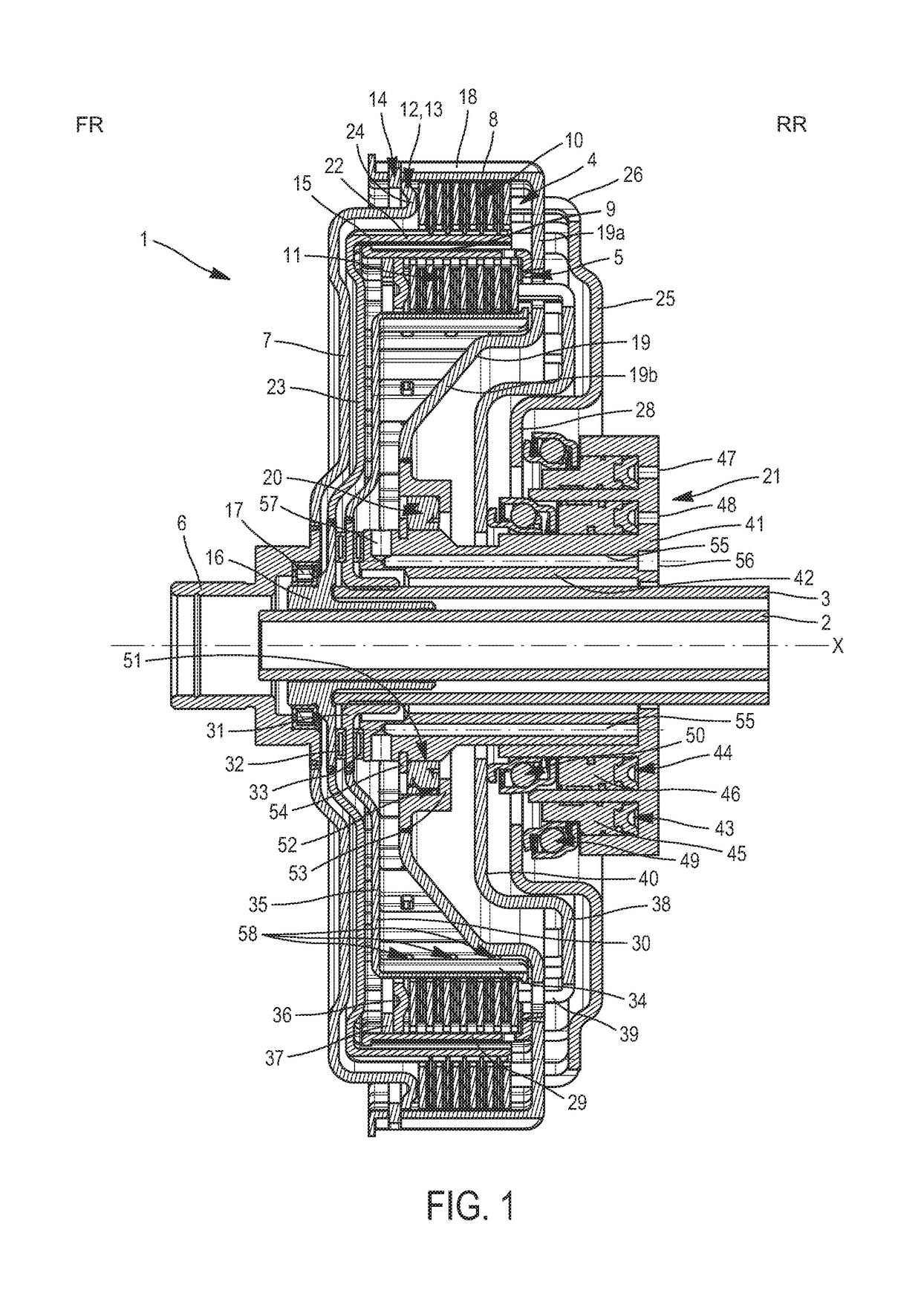
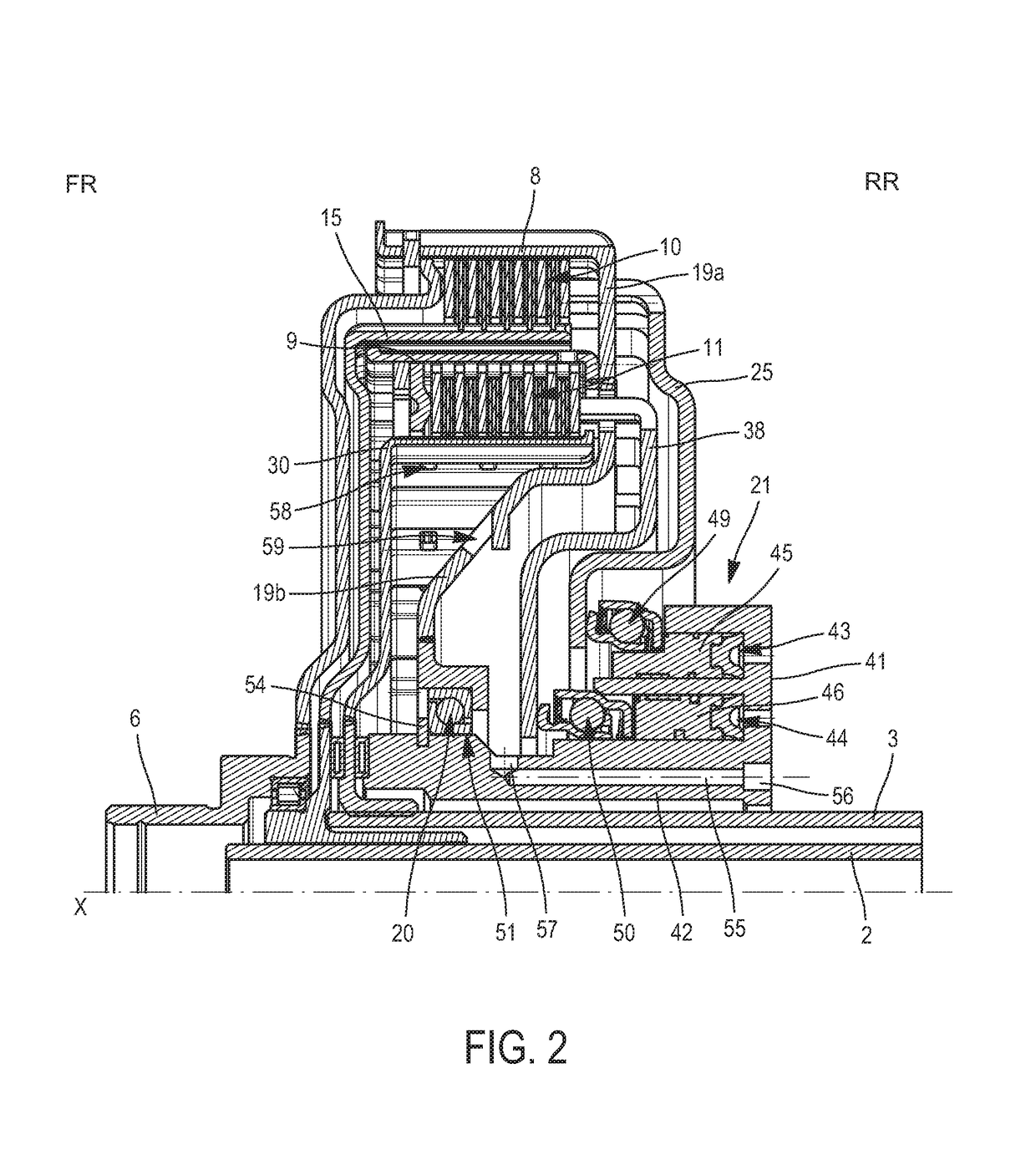
Hydraulic control system for a dual wet clutch
ActiveUS20170268580A1Eliminate disadvantagesReduce energy consumptionFluid actuated clutchesFriction clutchesInterior spaceControl system
The invention relates to a hydraulic control system (21) for a dual wet clutch (1), having:housing (41) having an internal tube (42) extending axially around the axis X and configuring an internal space intended for passage of the two input shafts (2, 3) of a gearbox, and a first and a second annular chamber (43, 44) concentric around the axis X and disposed radially around the internal tube (42);a first and a second annular piston (45, 46), which are respectively mounted axially slidingly inside the first and the second annular chamber (43, 44), the first and the second annular piston (45, 46) each carrying a rotating stop (49, 50);the internal tube (42) having at least one flow conduit (55) for a cooling fluid, intended to direct the cooling fluid to the clutches (4, 5).
Owner:VALEO EMBRAYAGES SAS
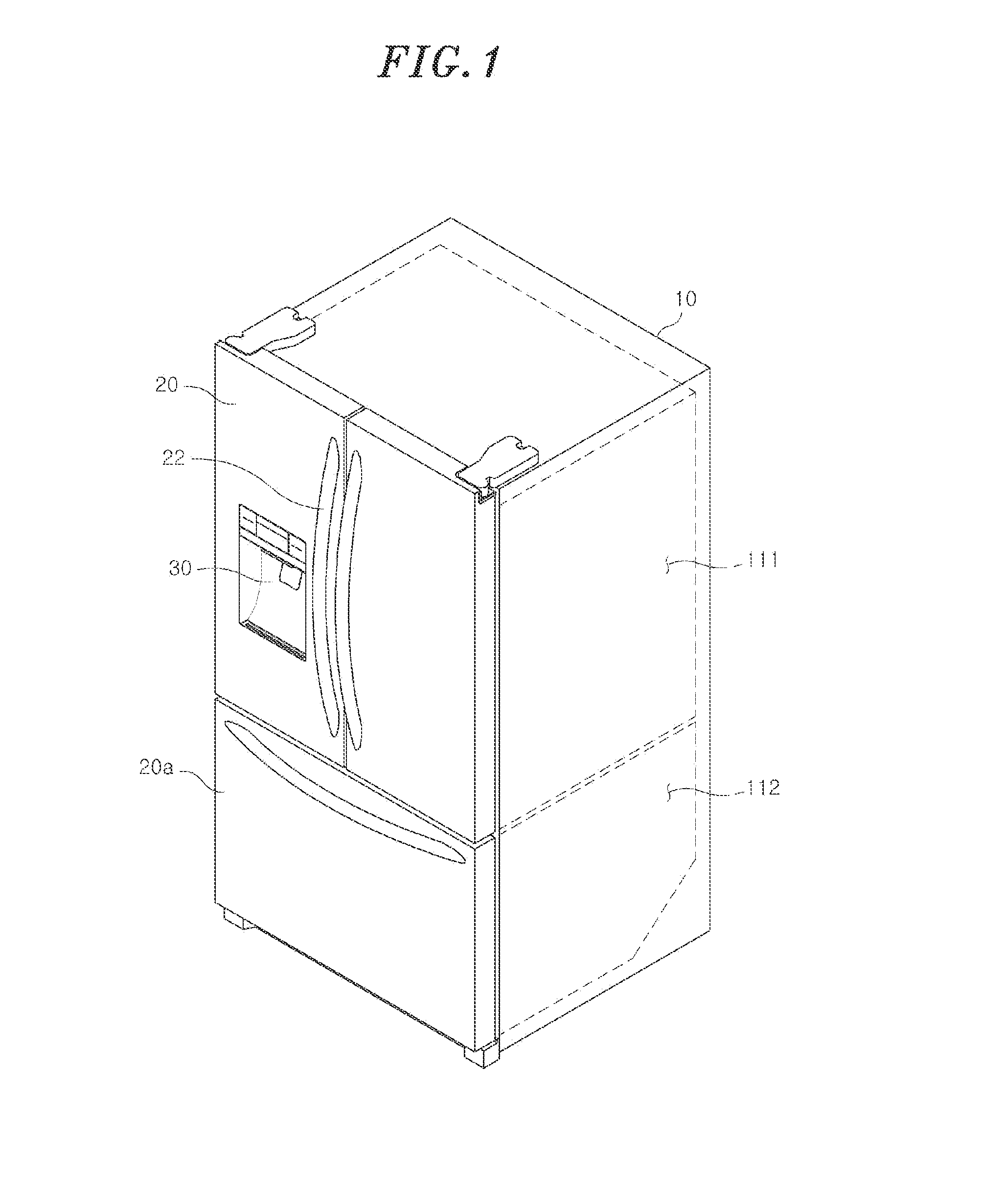
Refrigerator
ActiveUS10145605B2Improve user convenienceIncreased durabilityLighting and heating apparatusDrawersEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
The refrigerator includes item storage units arranged in multiple layers in a storage compartment, horizontal frames arranged in multiple layers, the horizontal frames respectively supporting the item storage units, a vertical frame coupled to each of the horizontal frames, the vertical frame extending vertically, first rail units arranged in multiple layers, the first rail units respectively supporting the horizontal frames so that the horizontal frames is movable in a front-to-back direction relative to the storage compartment, a link to connect any one of the horizontal frames arranged and the door to each other so as to move the horizontal frames in the front-to-back direction in response to rotation of the door, and a second rail unit located between the item storage unit and the horizontal frame arranged in the same layer so as to movably support the item storage unit in the front-to-back direction.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com