Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1599 results about "Control material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Materials control refers to managerial activities relating to giving instructions or directions to ensure maintaining adequate quality and quantity of materials for uninterrupted production process with the objective of minimizing material cost per unit. Both materials control and inventory control are not one and the same.
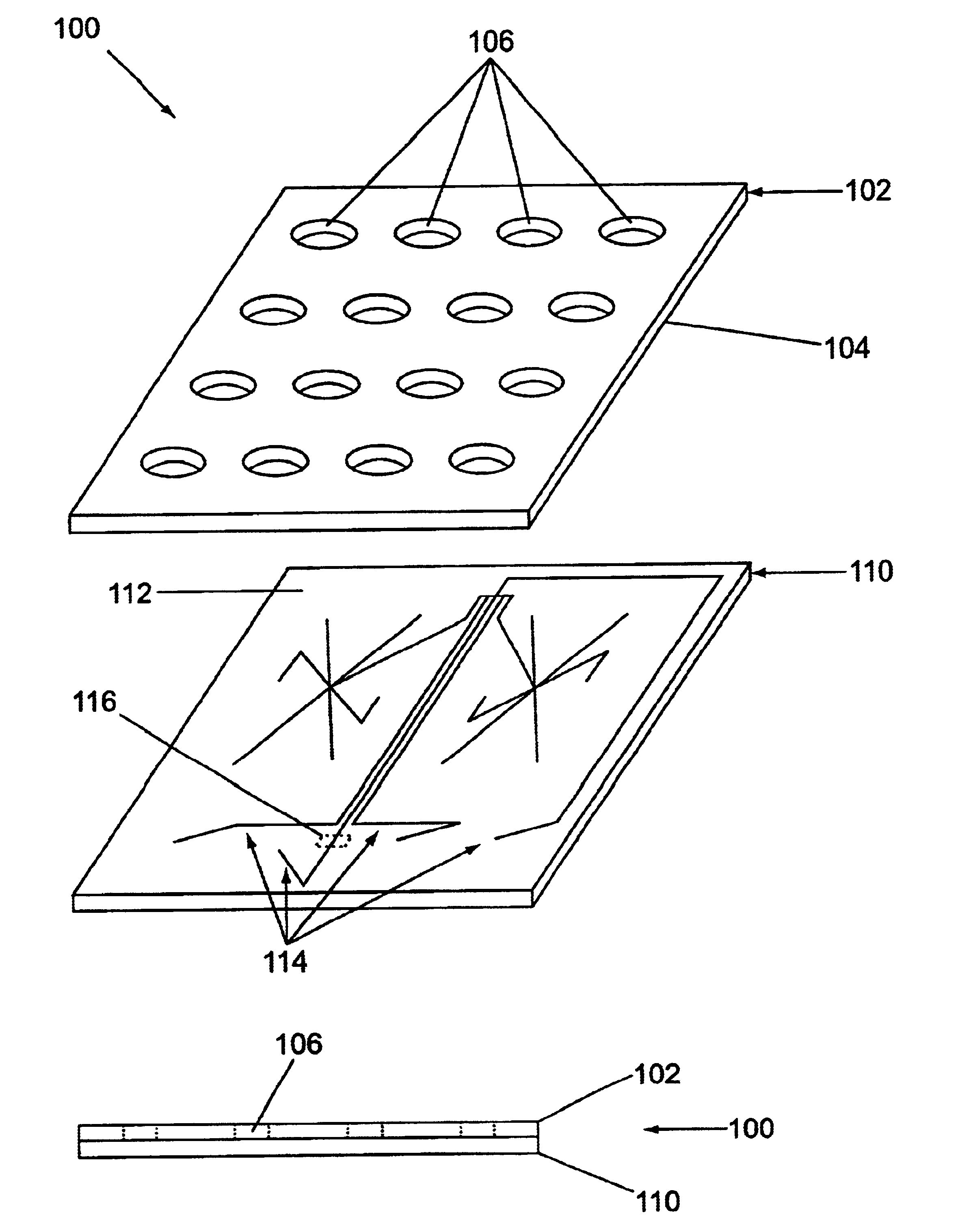
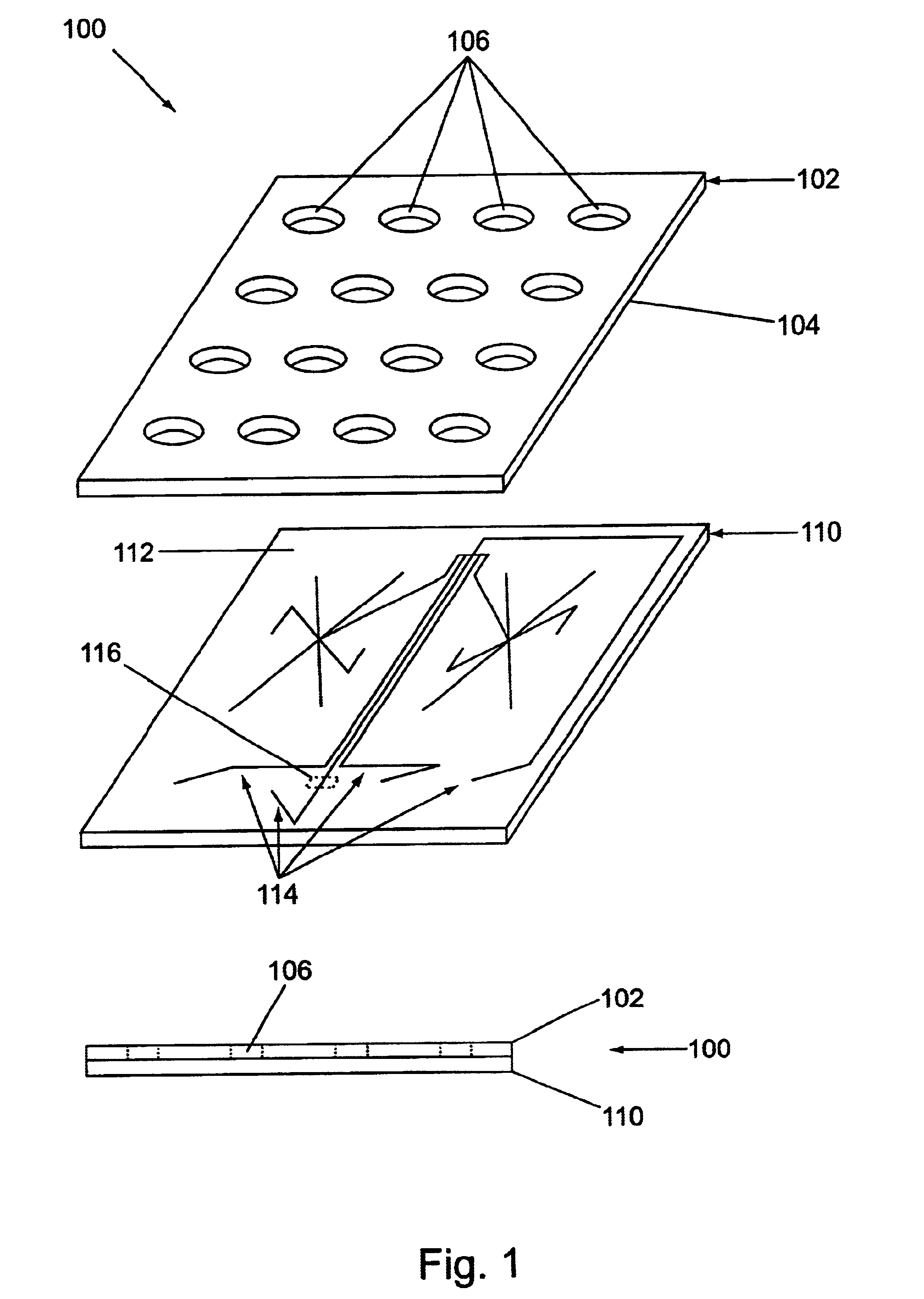
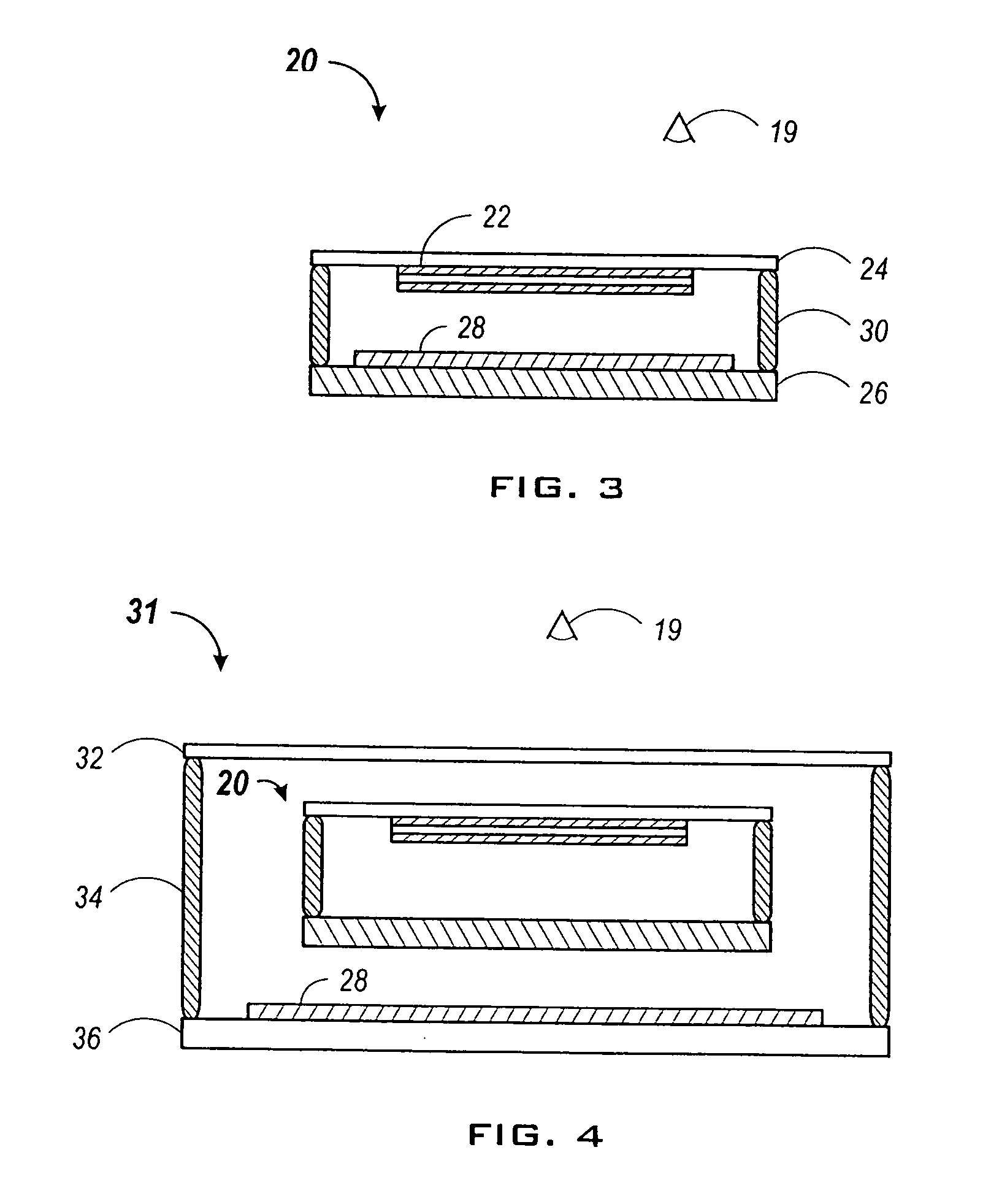
Microfluidic devices and systems incorporating cover layers
InactiveUS6756019B1Improved material handling characteristicReduce manufacturing costWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChannel networkConductive coating
The present invention provides microfluidic devices that comprise a body structure comprising at least a first microscale channel network disposed therein. The body structure has a plurality of ports disposed in the body structure, where each port is in fluid communication with one or more channels in the first channel network. The devices also include a cover layer comprising a plurality of apertures disposed through the cover layer. The cover layer is mated with the body structure whereby each of the apertures is aligned with a separate one of the plurality of ports. Rings are optionally disposed between the cover layer and the body structure and circumferentially around pairs of aligned apertures and ports. The devices also optionally include conductive coatings and membranes. The invention additionally provides methods of controlling the delivery of a composition of material into a microfluidic device.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
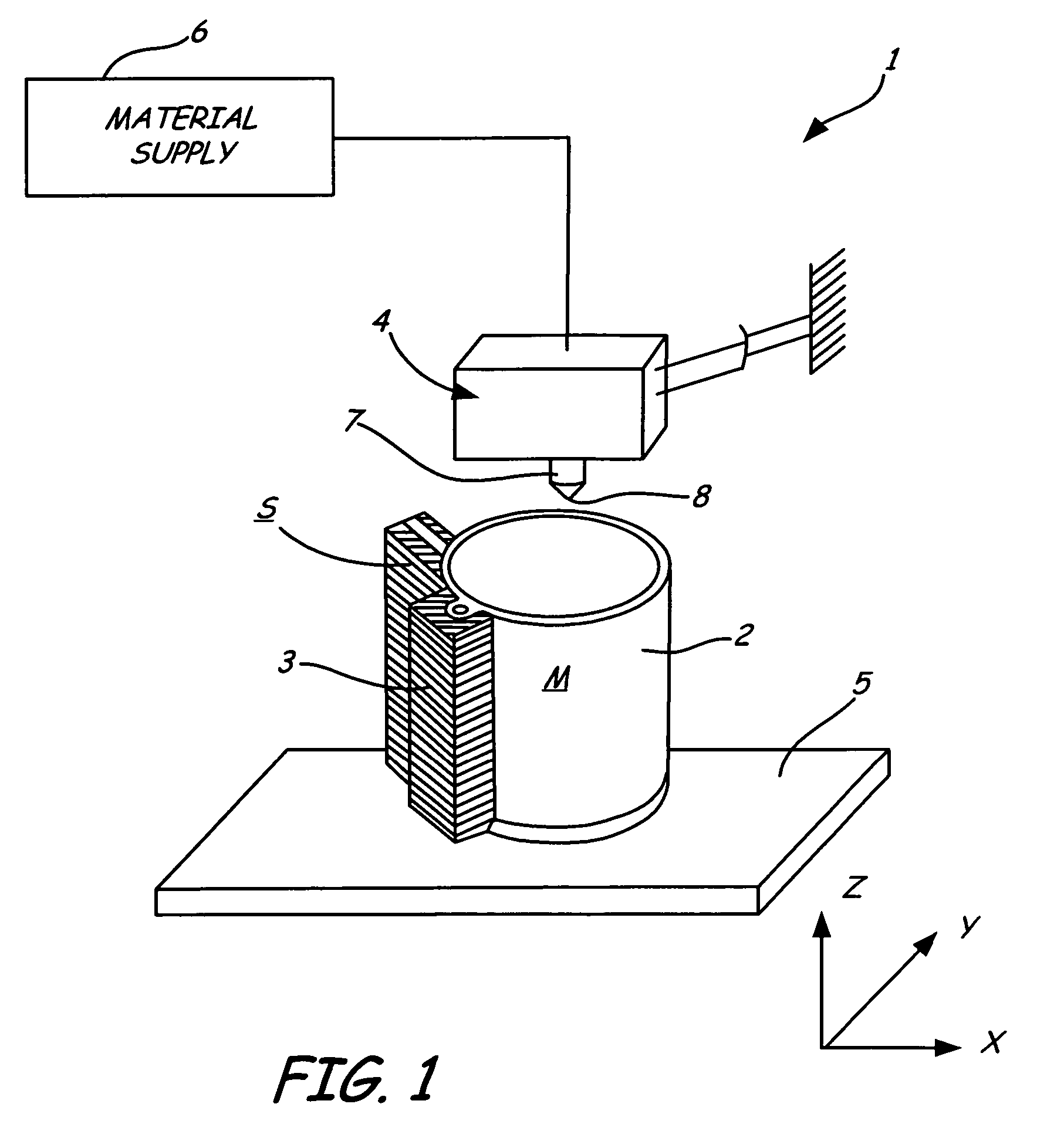
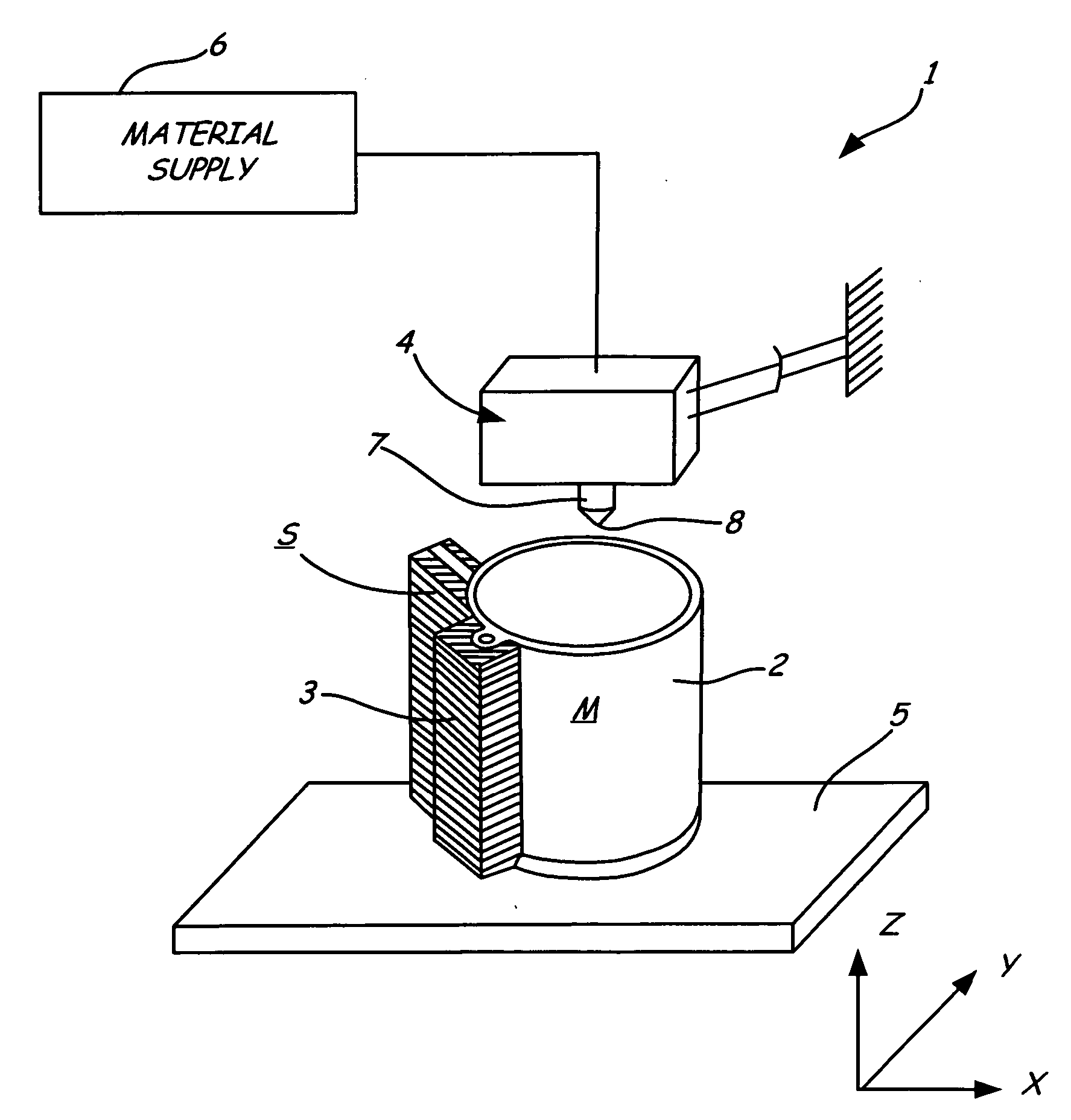
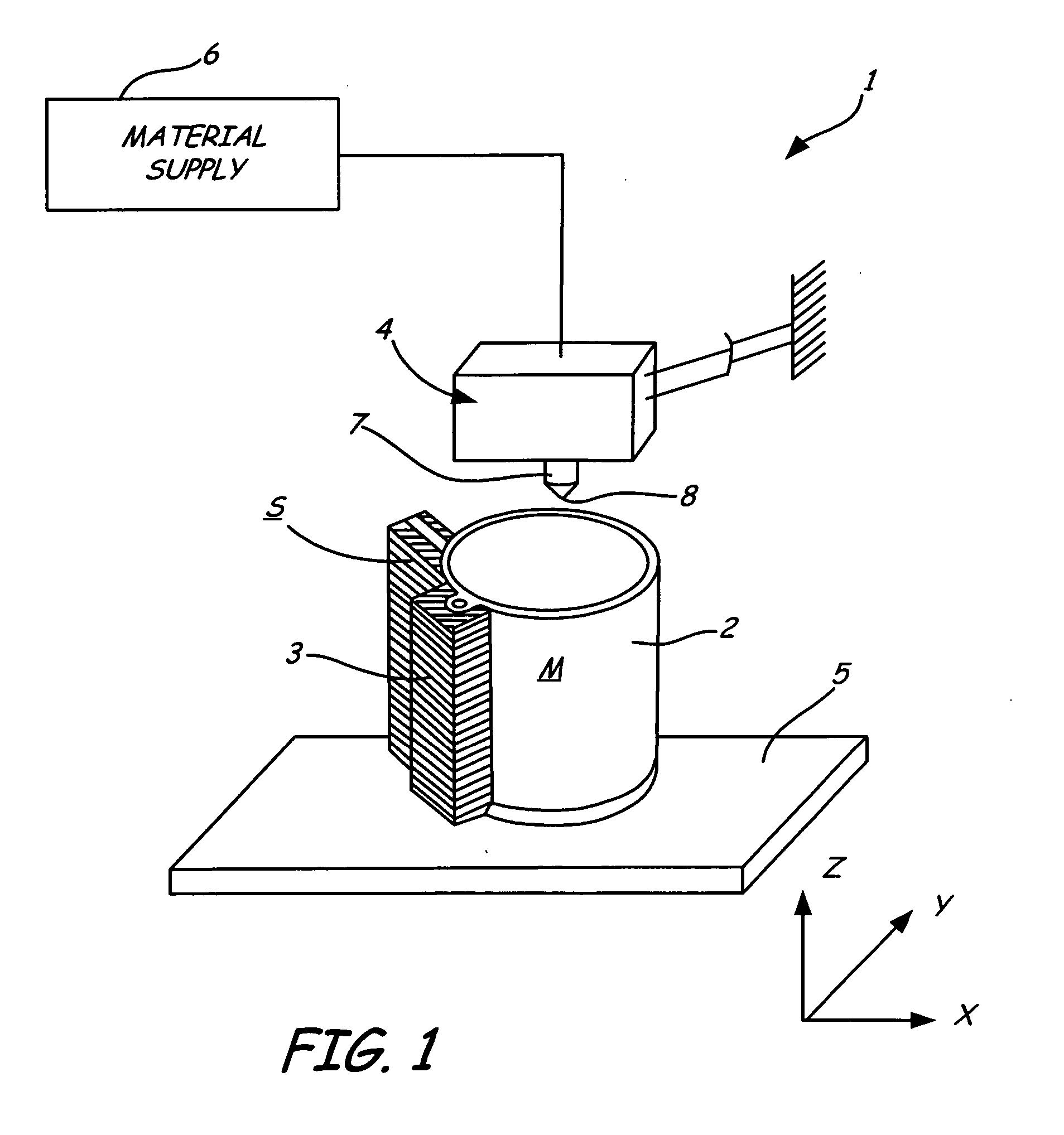
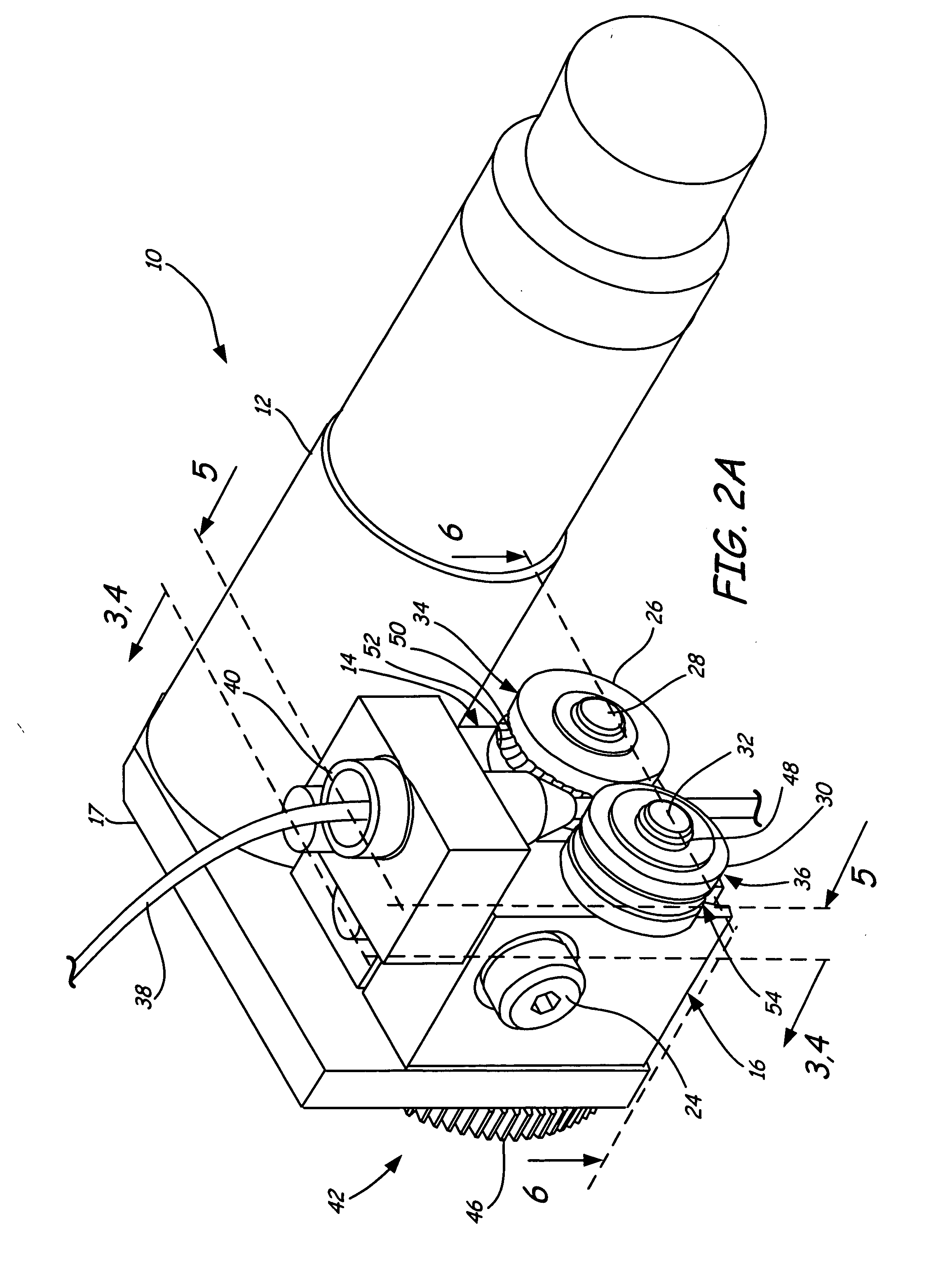
Rapid prototyping system with controlled material feedstock
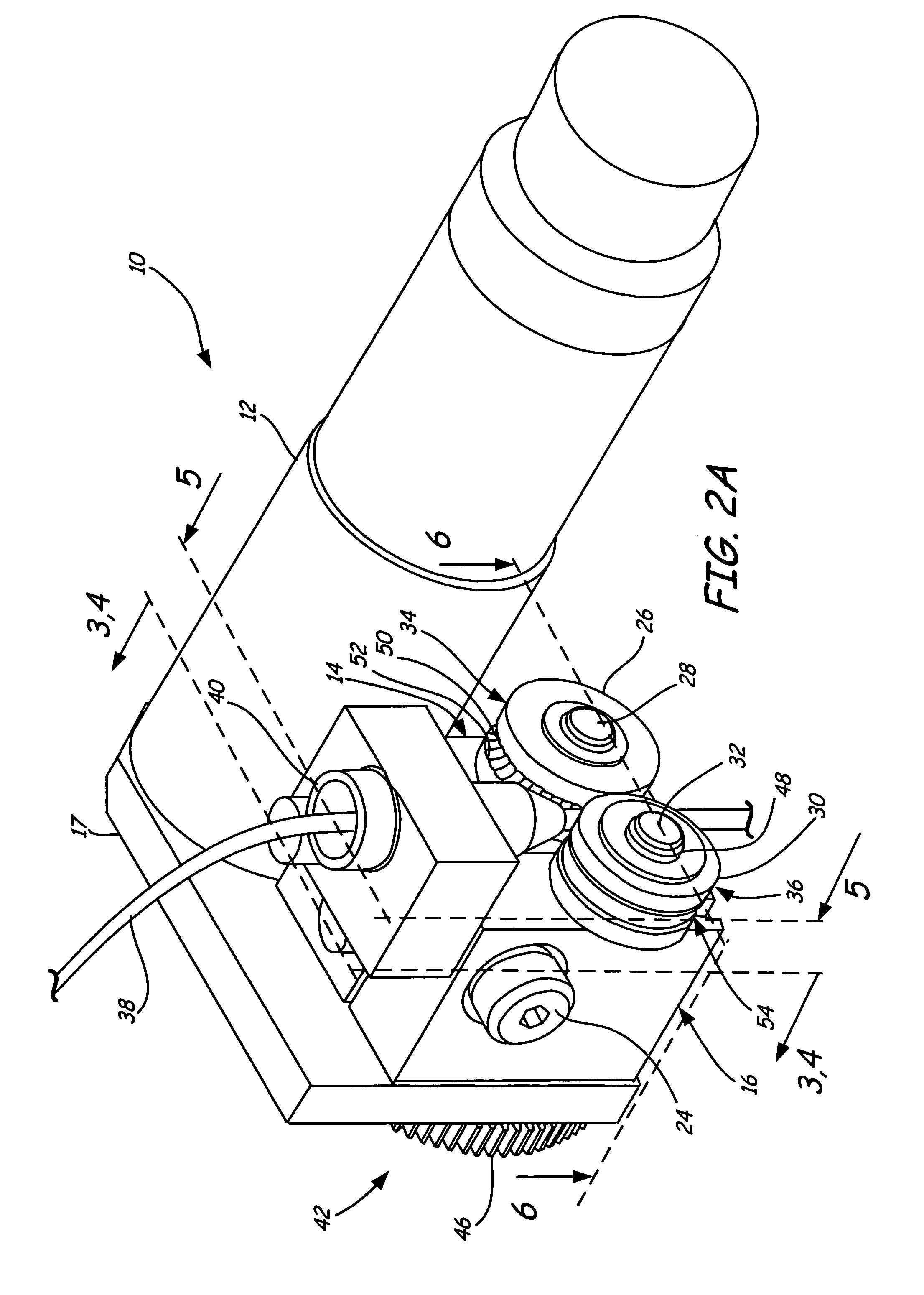
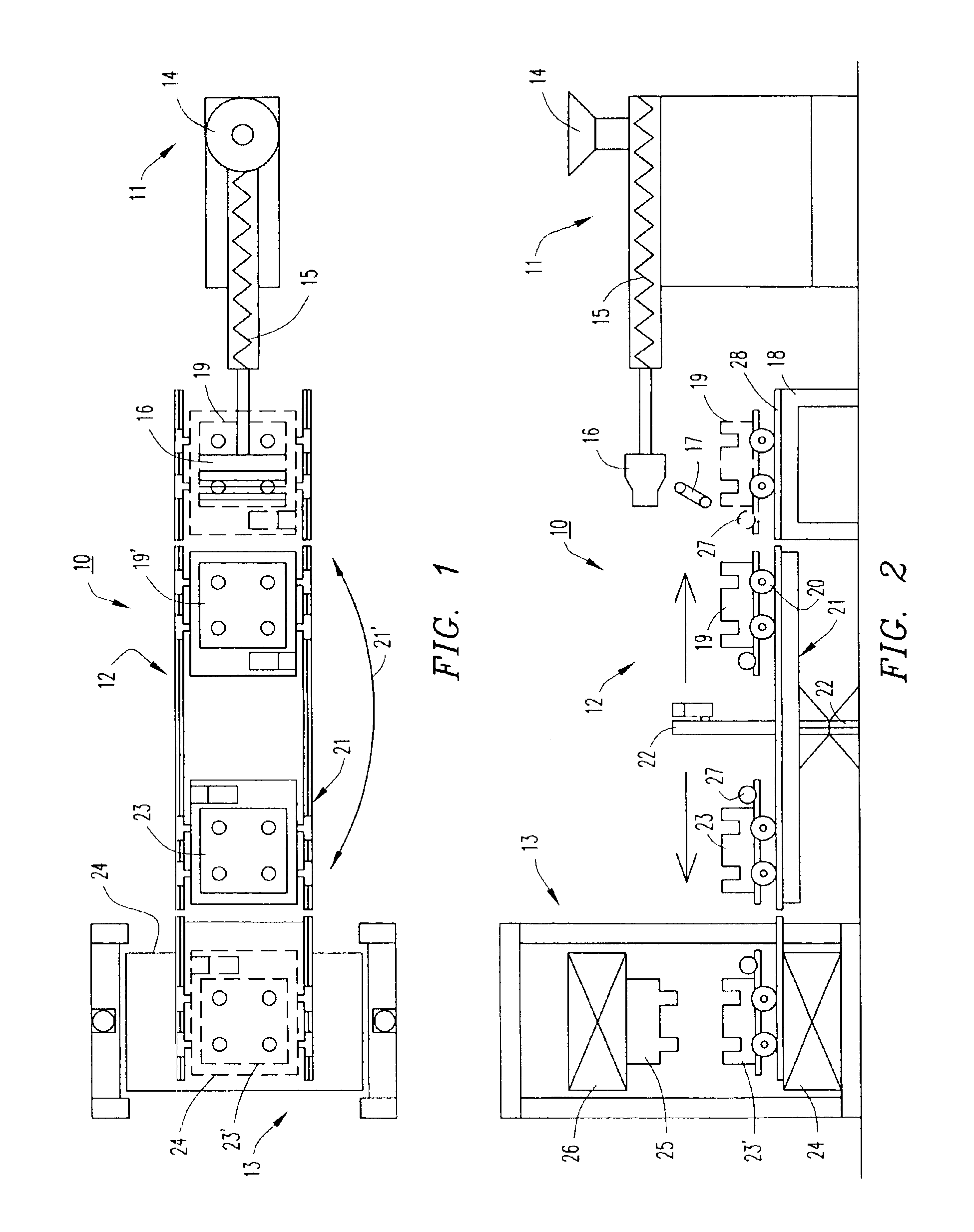
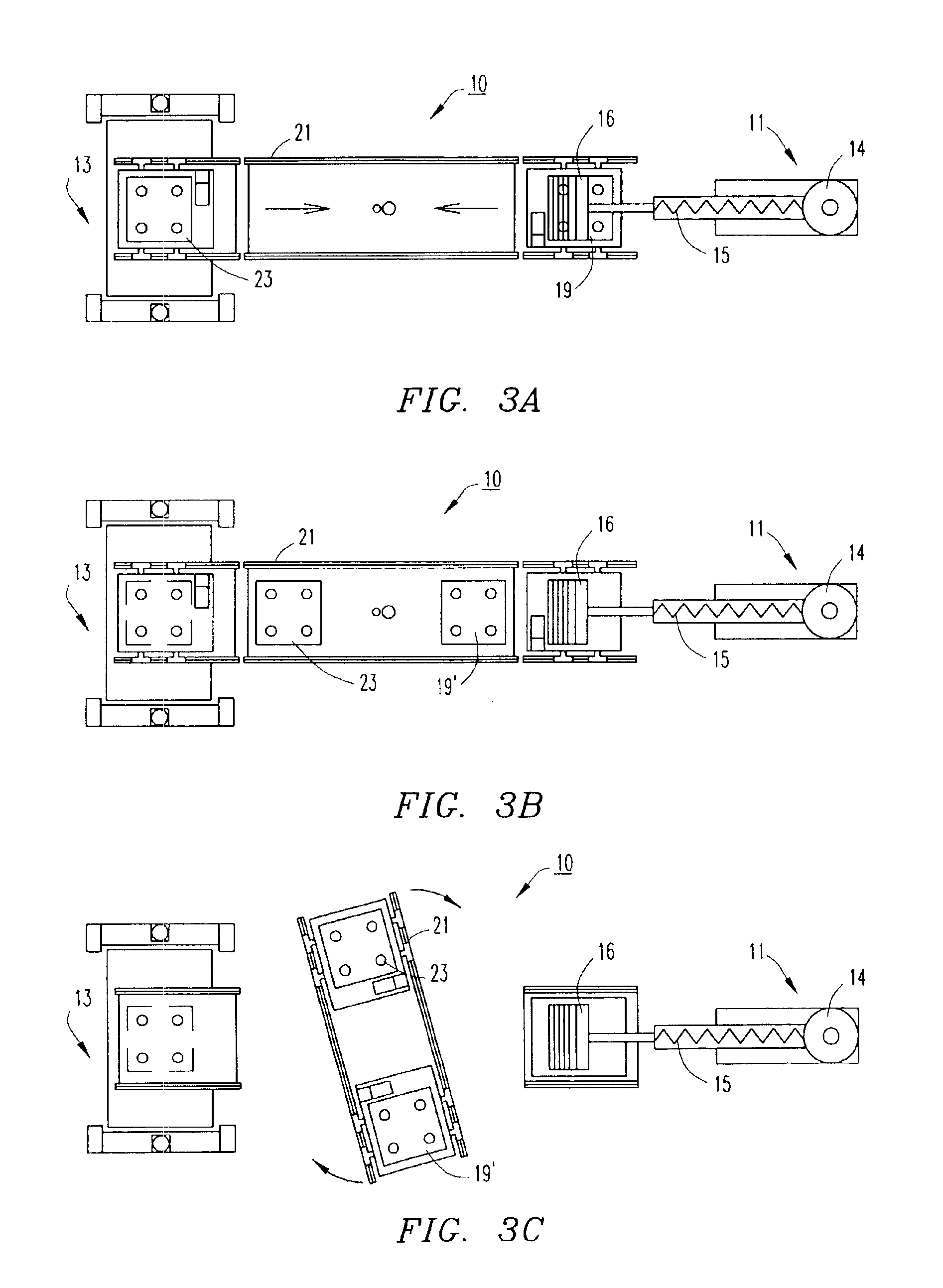
A deposition modeling system incorporates a drive mechanism to feed a strand of filament to create a model. The drive mechanism comprises a pivot block that is rotatably connected to a fixed block and a motor that rotates a drive shaft. A drive roller is connected to the drive shaft and an idler roller is connected to an idler axle that extends from the pivot block in a substantially perpendicular direction to the direction of rotation of the pivot block with respect to the fixed block and in a substantially parallel direction to the drive shaft.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
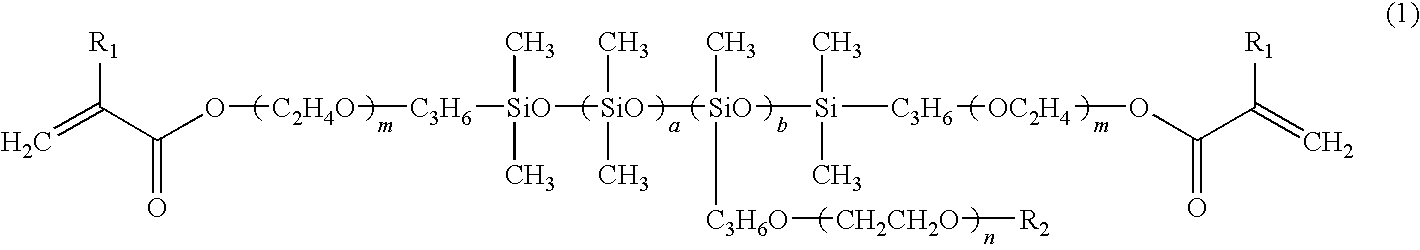
Hydrophilic Polysiloxane Macromonomer, and Production and Use of the same
ActiveUS20090234089A1Improve compatibilityHigh oxygen permeabilitySilicon organic compoundsOptical articlesSide chainHydrophile
Problem to be Solved To provide an ophthalmic lens, which can be more safely worn, that is, to provide a material, which is transparent and has high oxygen permeability and a high hydrophilic property, and to provide a novel monomer to be a raw material thereof.Solution A hydrophilic polysiloxane macromonomer contains polyoxyethylene as a hydrophilic side chains in a polysiloxane main chain, wherein transparency, oxygen permeability, and hydrophilic properties of the material are controlled by regulating the length of the polysiloxane main chain, the length of the hydrophilic polyoxyethylene side chains, and the number of the side chains.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Rapid prototyping system with controlled material feedstock
A deposition modeling system incorporates a drive mechanism to feed a strand of filament to create a model. The drive mechanism comprises a pivot block that is rotatably connected to a fixed block and a motor that rotates a drive shaft. A drive roller is connected to the drive shaft and an idler roller is connected to an idler axle that extends from the pivot block in a substantially perpendicular direction to the direction of rotation of the pivot block with respect to the fixed block and in a substantially parallel direction to the drive shaft.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Modular fabrication systems and methods
ActiveUS20130089642A1Improve throughputHigh-throughput applicationsReady-for-oven doughsAuxillary shaping apparatusEngineeringSystem controller
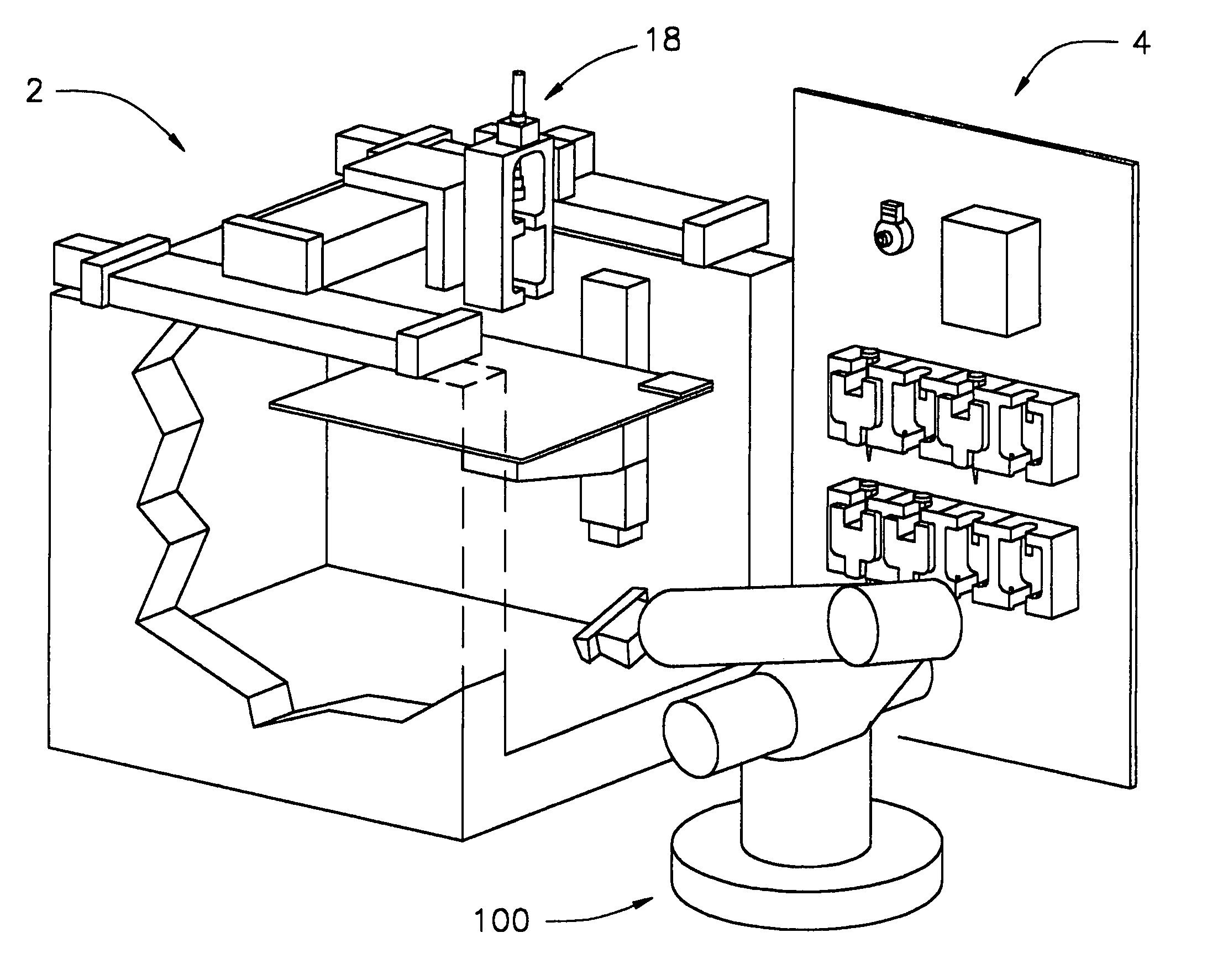
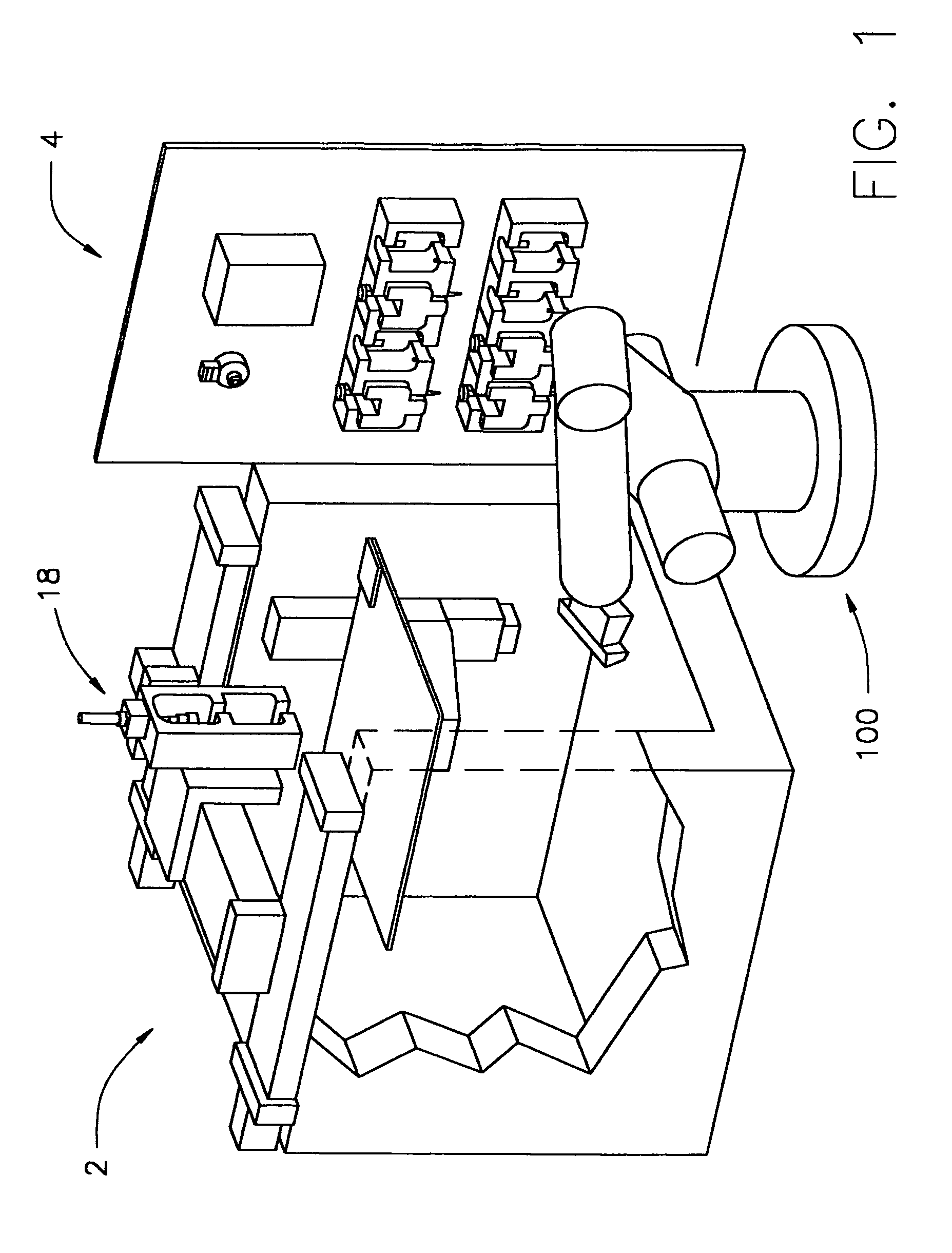
The present invention relates to an article fabrication system having a plurality of material deposition tools containing one or more materials useful in fabricating the article, and a material deposition device having a tool interface for receiving one of the material deposition tools. A system controller is operably connected to the material deposition device to control operation of the material deposition device. Also disclosed is a method of fabricating an article using the system of the invention and a method of fabricating edible foodstuffs.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Droplet deposition method for rapid formation of 3-D objects from non-cross-linking reactive polymers
InactiveUS20020111707A13D object support structuresSpecial data processing applicationsThermoplasticControl signal
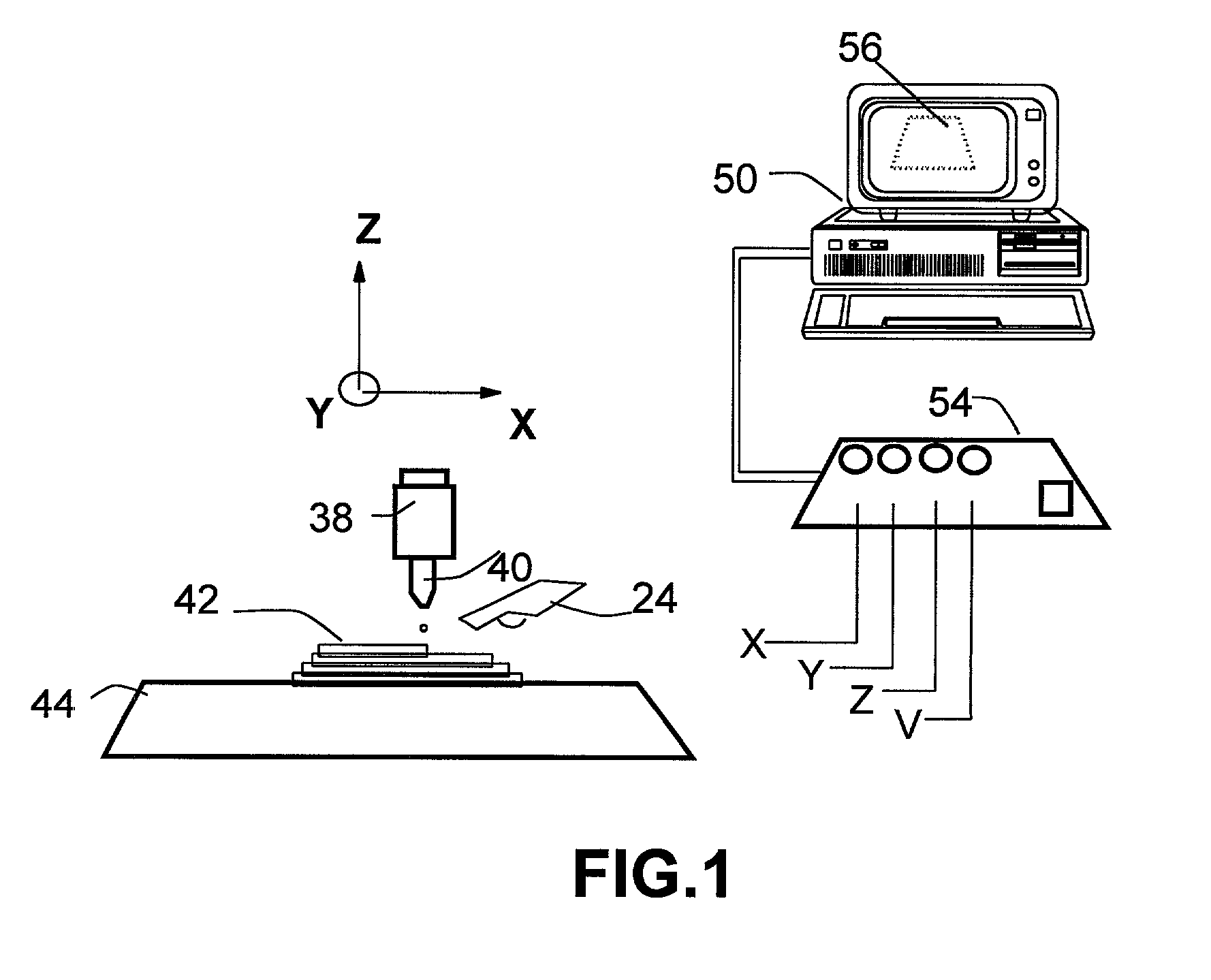
A droplet deposition-based freeform fabrication method for making a three-dimensional object from a design created on a computer, including (a) providing a support member; (b) operating a droplet dispensing head for dispensing droplets of a material composition in a fluent state at a first temperature onto the support member, the material composition including a reactive prepolymer with a melting point above 23° C. and the first temperature being greater than the prepolymer melting point; (c) operating material treatment devices for causing the material composition to rapidly achieve a rigid state in which the material composition is substantially solidified to build up the 3-D object, the material treatment devices also working to convert the reactive prepolymer to a higher molecular weight thermoplastic resin; and (d) operating control devices for generating control signals in response to coordinates of the object design to control the movement of the dispensing head relative to the support member and for controlling the droplet dispensing of the material composition to construct the 3-D object.
Owner:LI ZHIMIN +3
Modular fabrication systems and methods
ActiveUS7625198B2Improve throughputAdapt to a wide rangeLiquid surface applicatorsConfectioneryEngineeringSystem controller
The present invention relates to an article fabrication system having a plurality of material deposition tools containing one or more materials useful in fabricating the article, and a material deposition device having a tool interface for receiving one of the material deposition tools. A system controller is operably connected to the material deposition device to control operation of the material deposition device. Also disclosed is a method of fabricating an article using the system of the invention and a method of fabricating a living three-dimensional structure.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Powder feeder for material deposition systems
InactiveUS20050133527A1Small sizeEliminate warpingPower operated devices3D object support structuresSolid componentCoolant flow
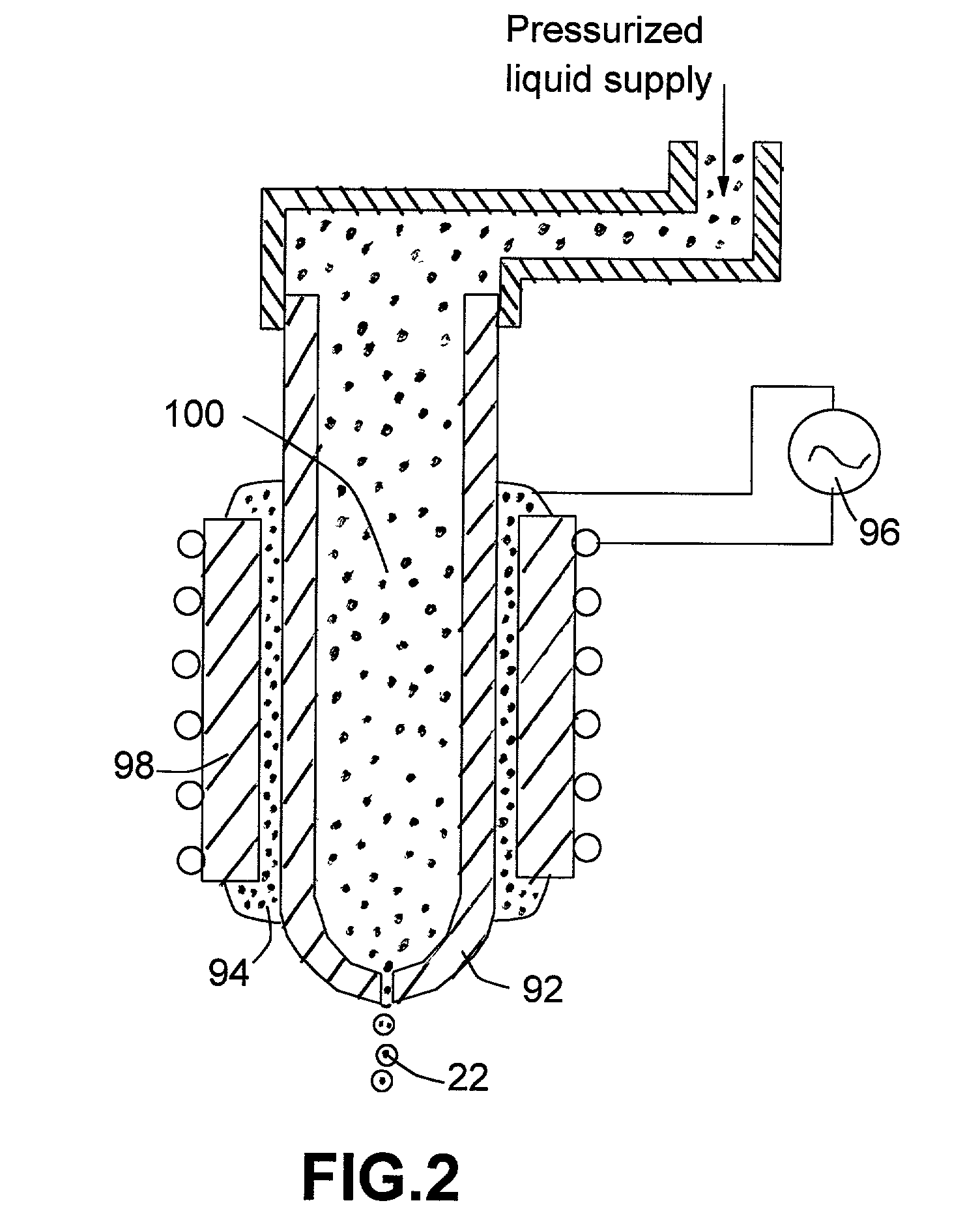
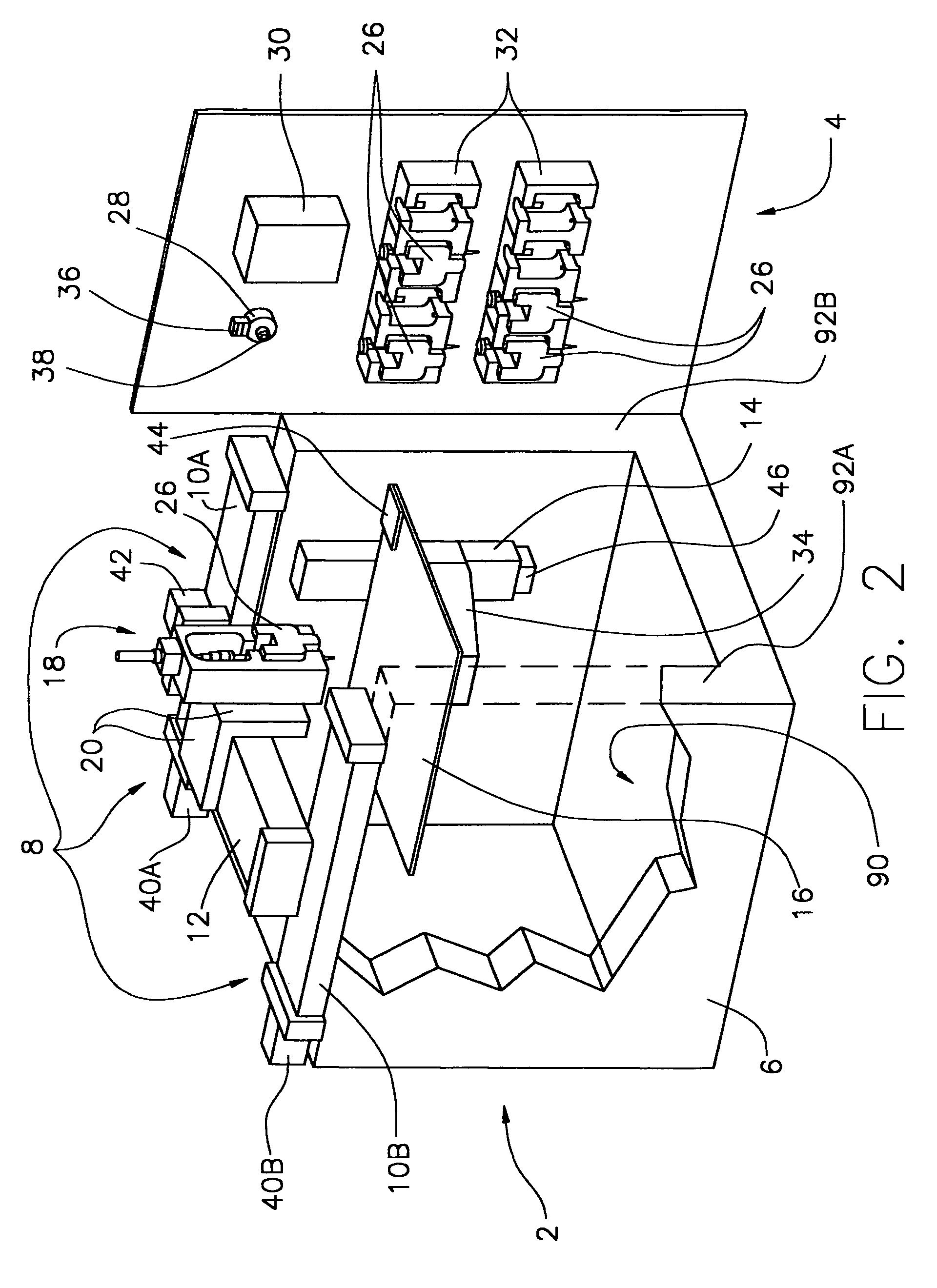
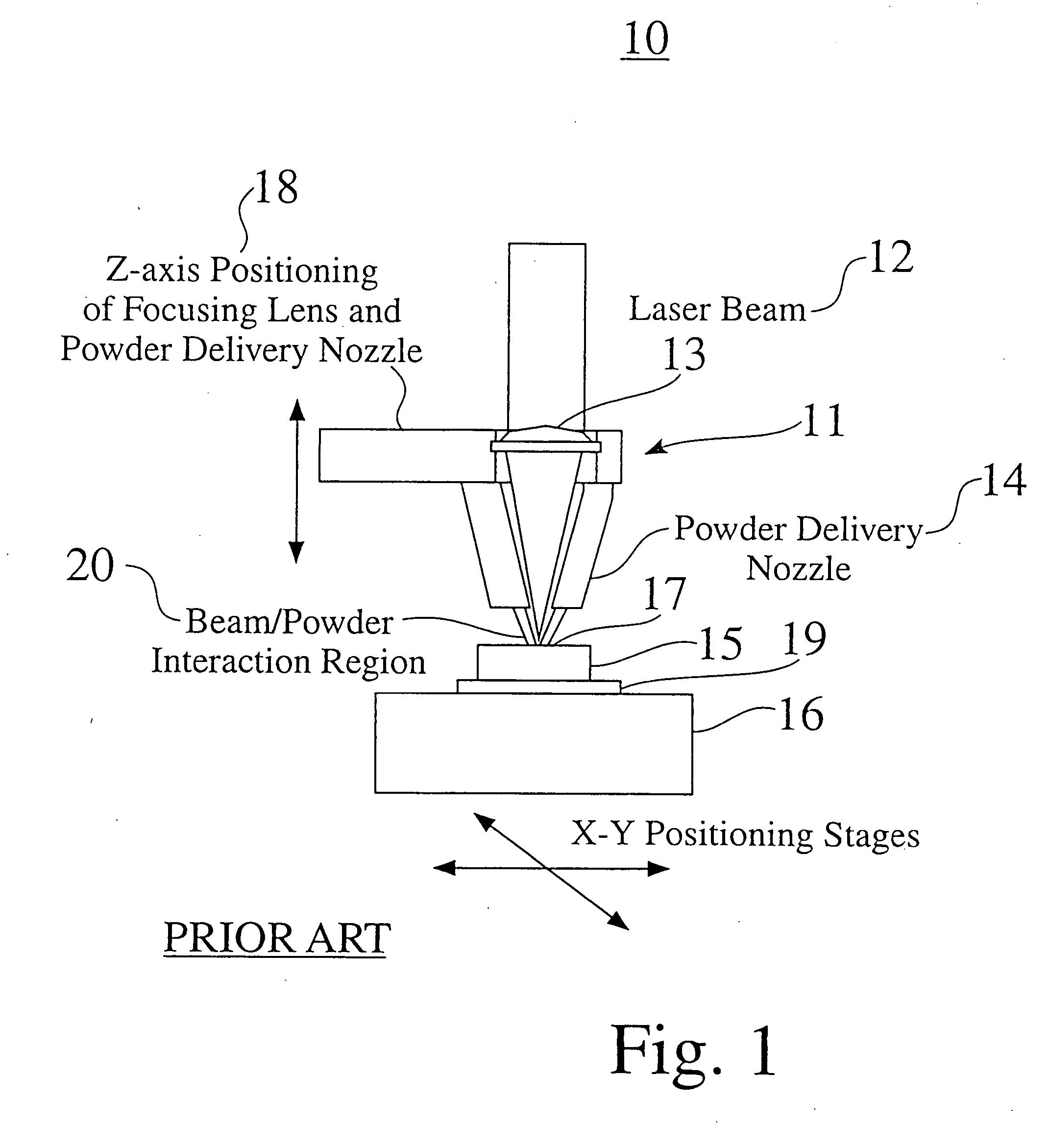
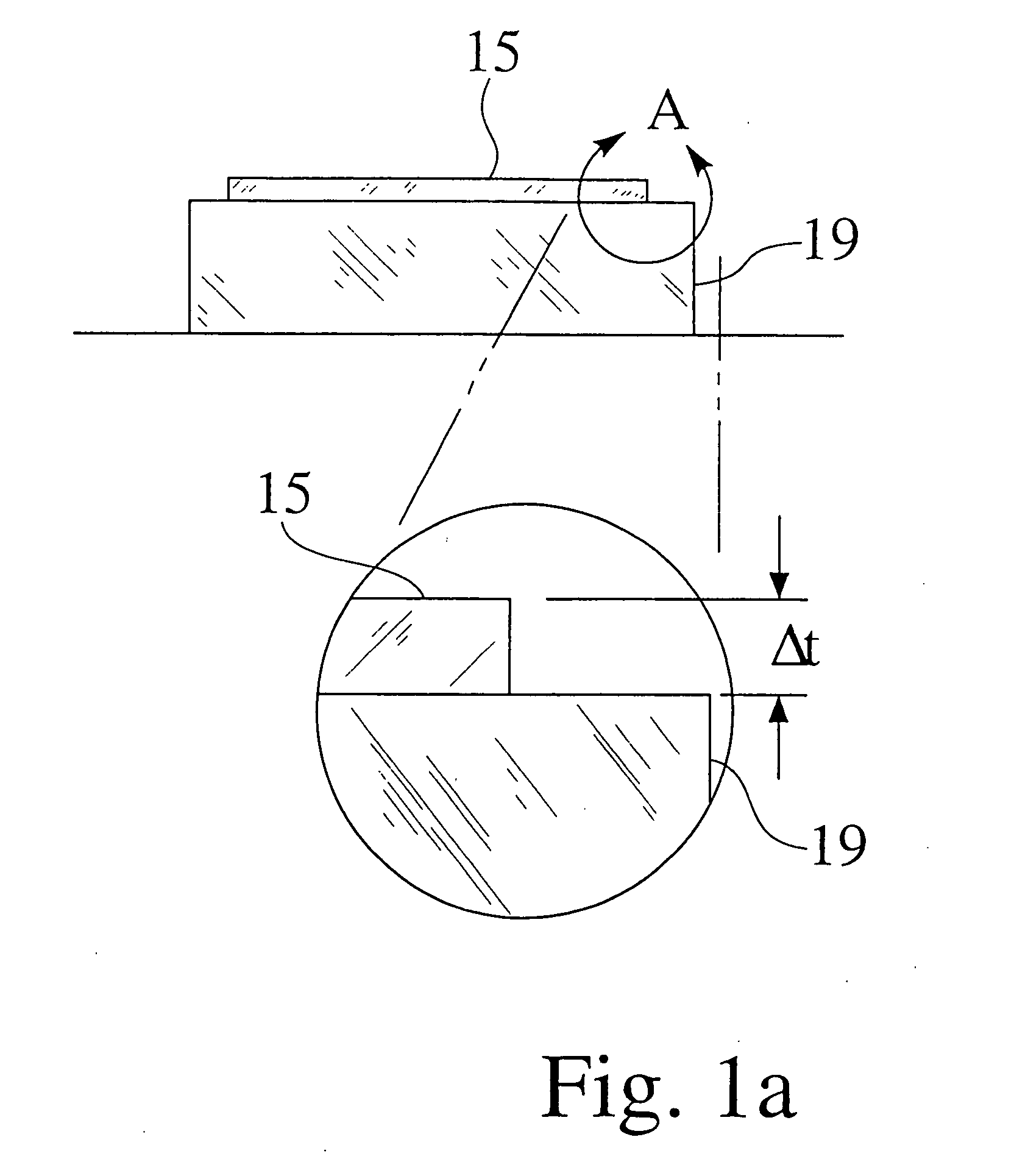
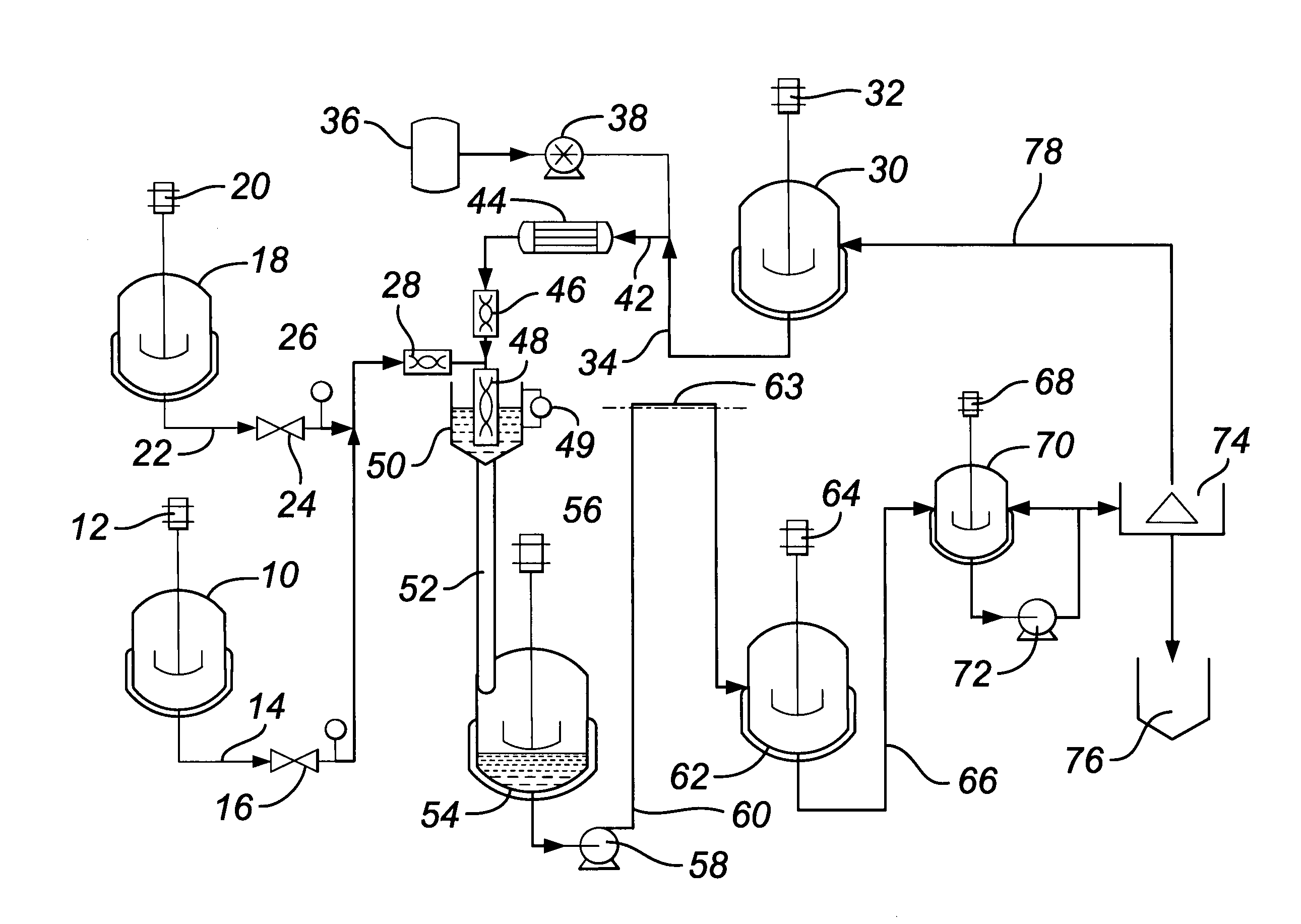
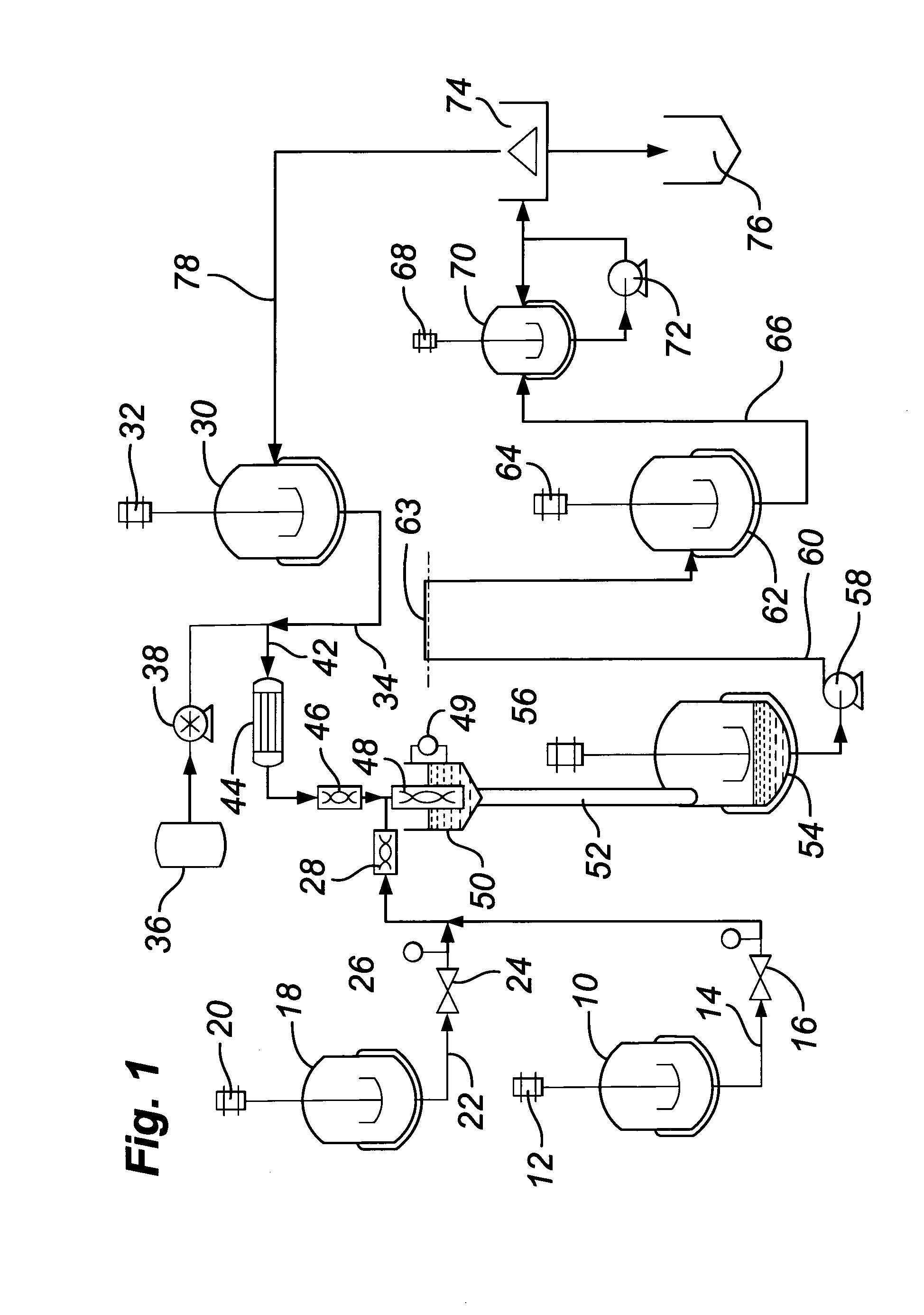
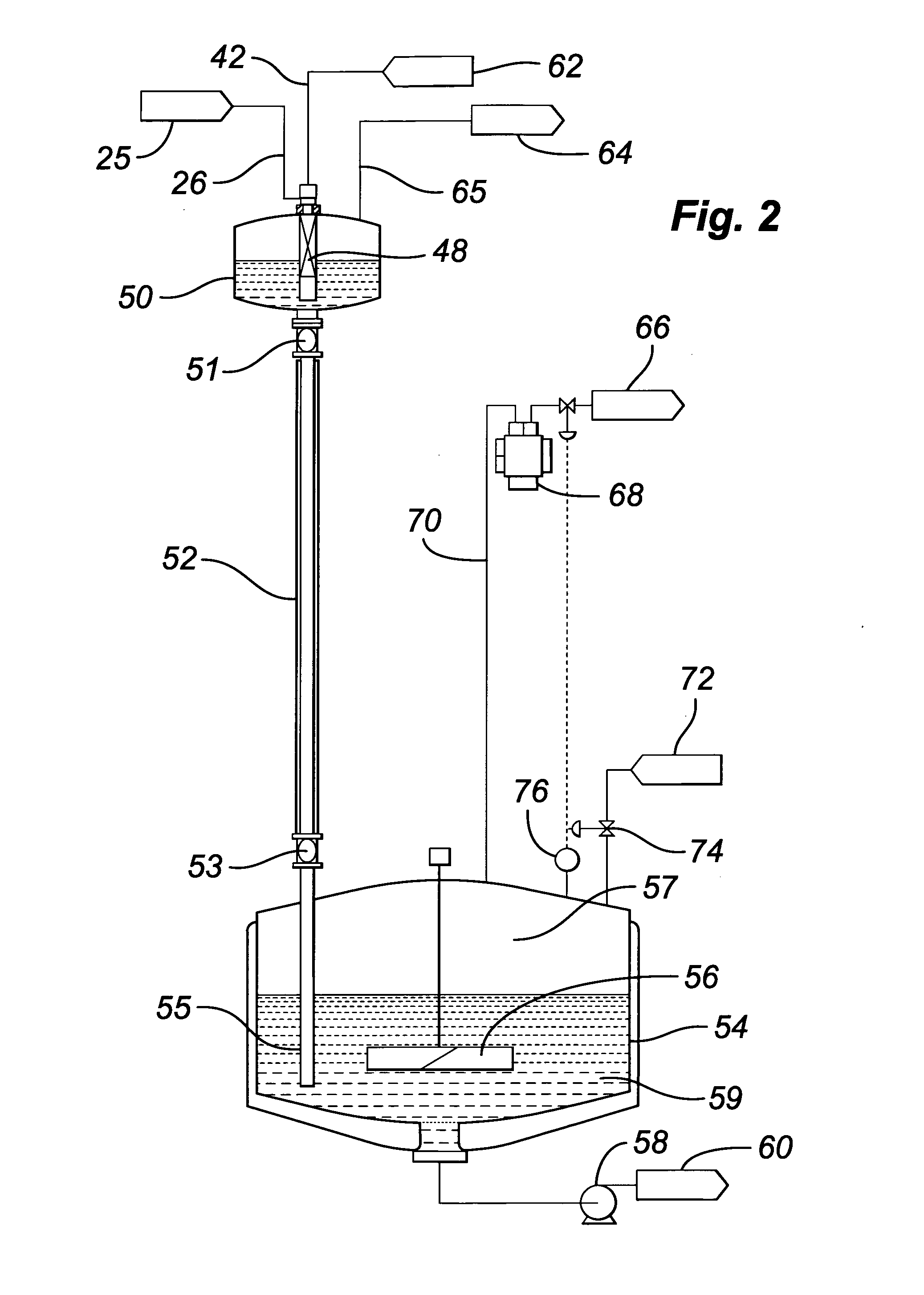
A method and apparatus for embedding features and controlling material composition in a three-dimensional structure (130) is disclosed. The invention enables the control of material characteristics, within a structure (130) made from a plurality of materials, directly from computer renderings of solid models of the components. The method uses stereolithography and solid model computer file formats to control a multi-axis head (480) in a directed material deposition process (123). Material feedstock (126, 127) is deposited onto a pre-heated substrate (19). Depositions (15) in a layer-by-layer pattern, defined by solid models (141, 146), create a three-dimensional article having complex geometric details. Thermal management of finished solid articles (250-302), not available through conventional processing techniques, is enabled by embedded voids (152) and / or composite materials (126, 127), which include dissimilar metals (210, 216). Finished articles control pressure drop and produce uniform coolant flow and pressure characteristics. High-efficiency heat transfer is engineered within a solid structure by incorporating other solid materials with diverse indexes. Embedding multi-material structures (132, 134) within a normally solid component (141) produces articles with diverse mechanical properties. Laser and powder delivery systems (420, 170) are integrated in a multi-axis deposition head (480) having a focused particle beam (502) to reduce material waste.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
Garment having an outer shell that freely moves in relation to an absorbent assembly therein
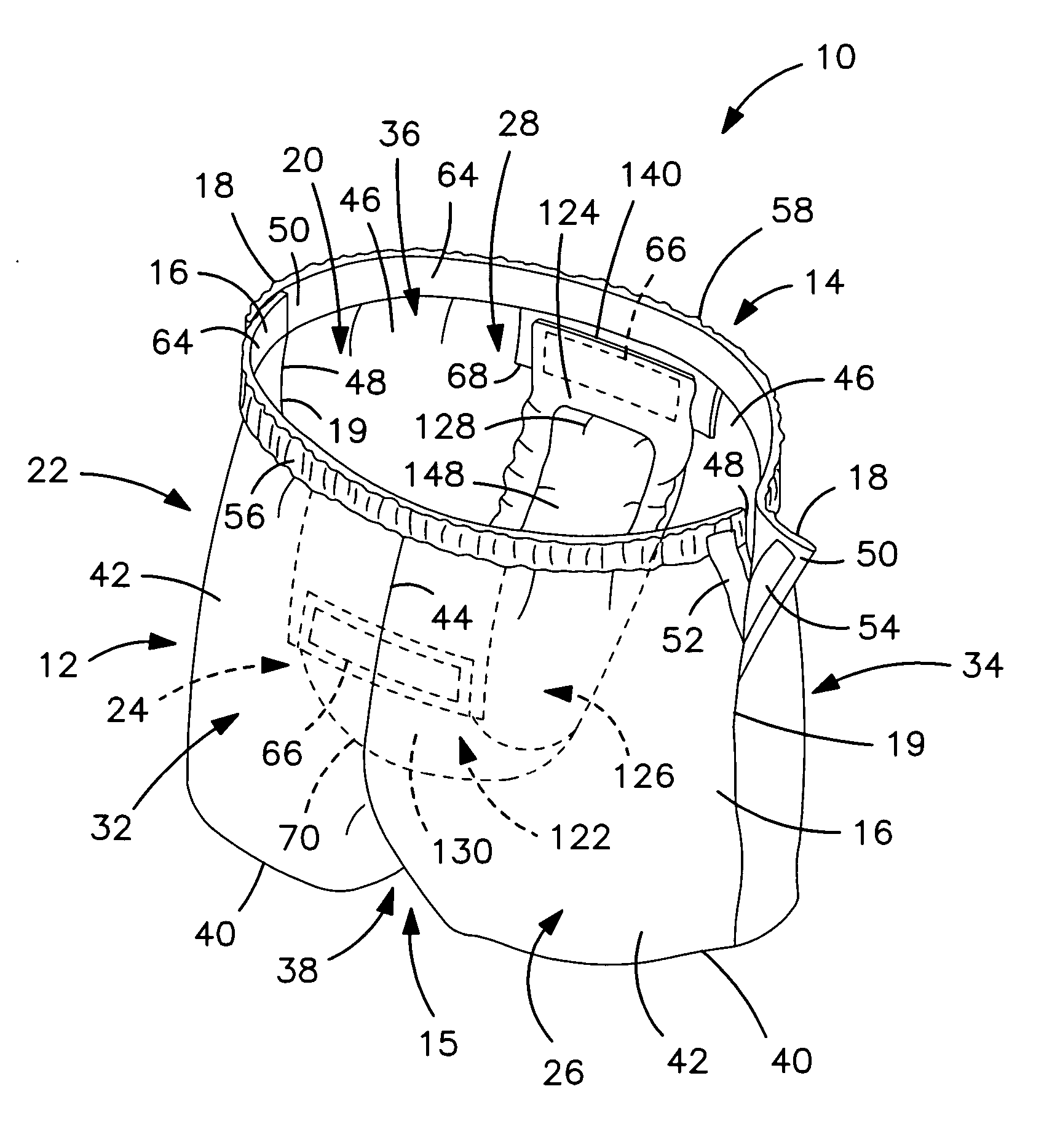
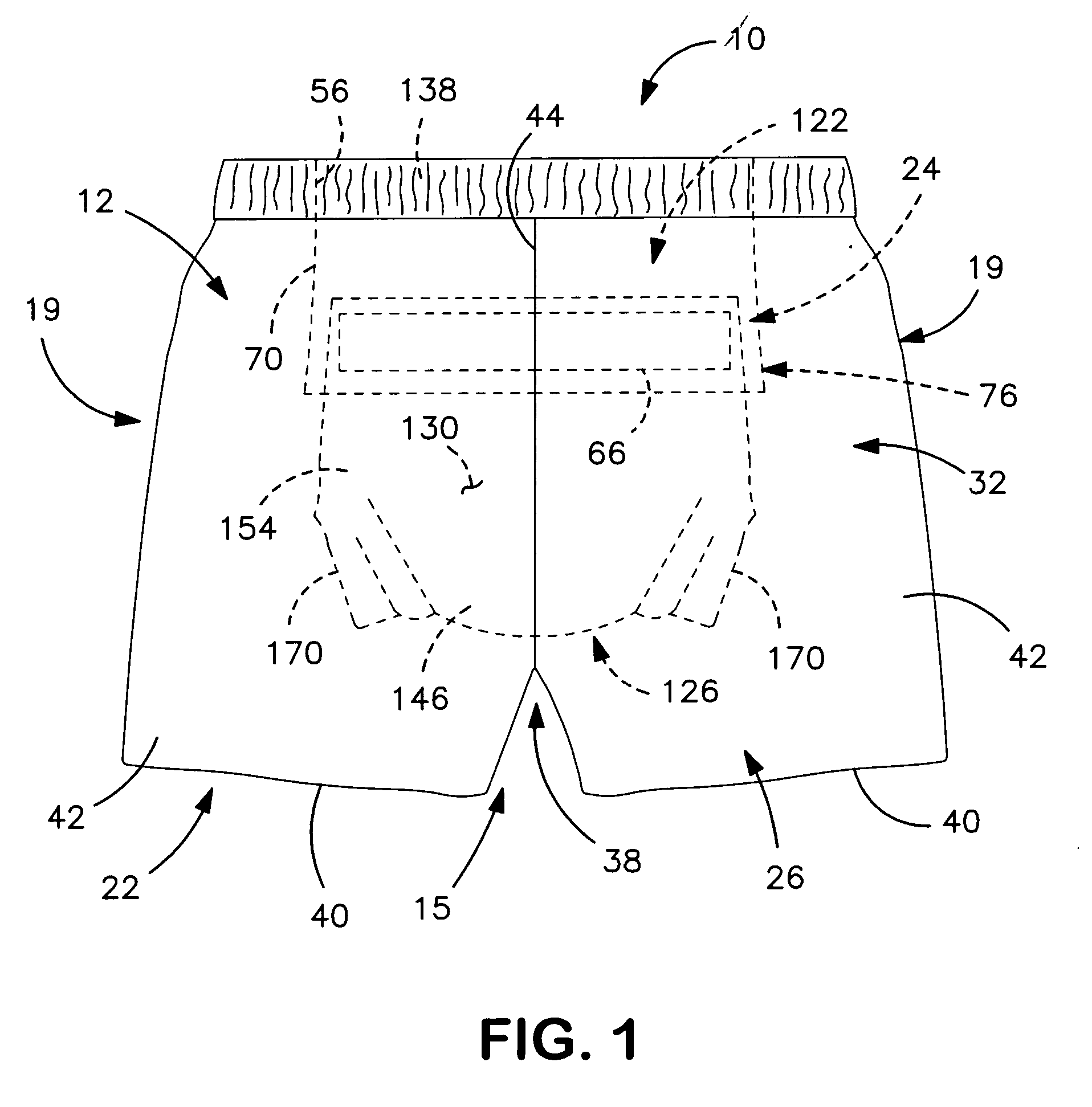
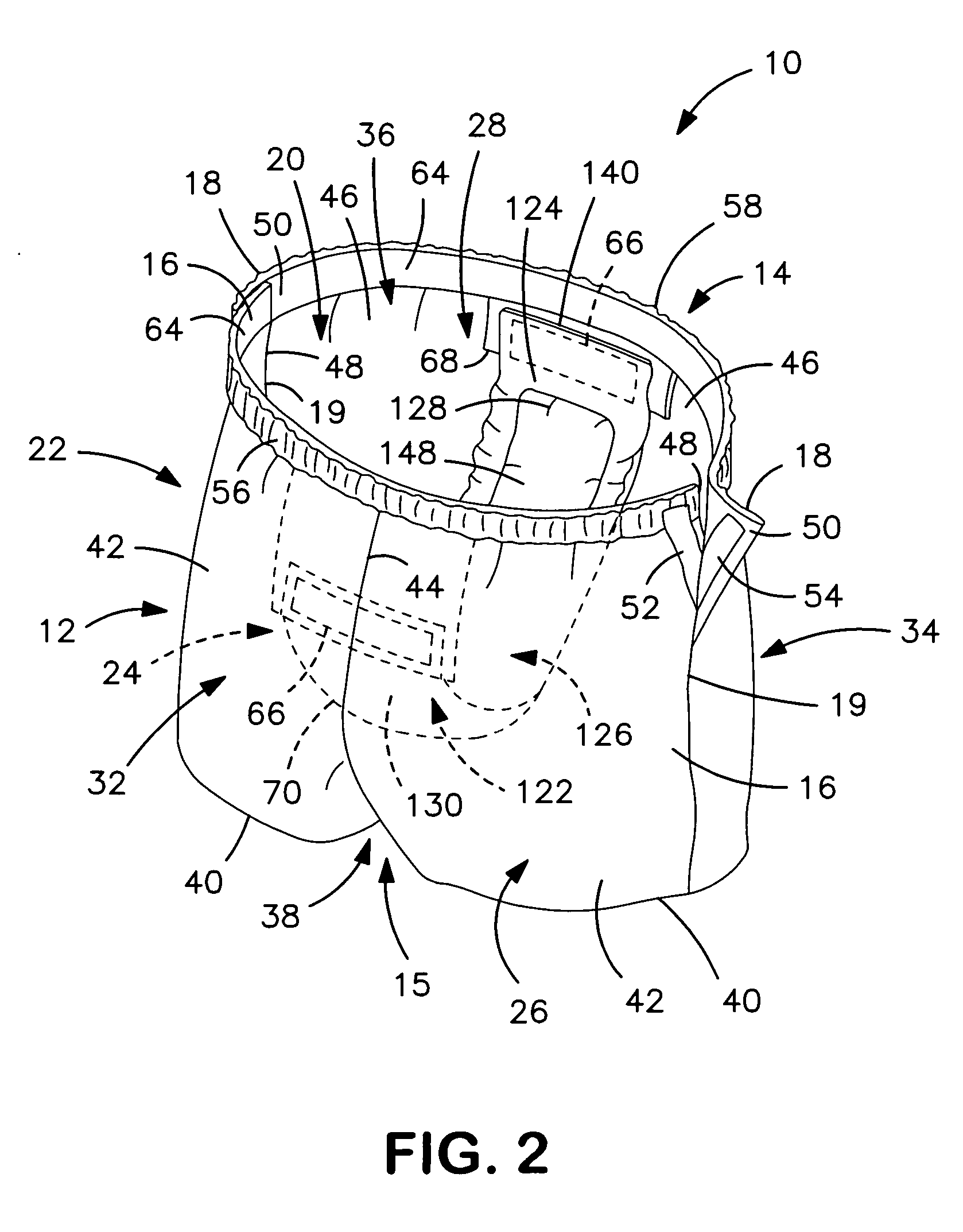
InactiveUS20060247599A1Prevent twisting and bunchingPrevents twisting and bunchingAbsorbent padsBaby linensStandard bedControl material
An absorbent garment having a garment-like outer shell and an absorbent assembly positioned therein as disclosed. In particular embodiments, the outer cover of the absorbent assembly has a relatively low coefficient of friction with the interior side of the garment shell. In one embodiment, the garment shell may be constructed such that the coefficient of friction between the garment shell and the outer cover of the absorbent assembly is less than, such as at least 15 percent less than the coefficient of friction between the exterior side of the garment shell and an adjacent material. The adjacent material may include, for instance, a standard bed sheet material. By carefully controlling the frictional properties of the materials as described above, problems associated with bunching and twisting of the garment are minimized.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Thermoplastic molding process and apparatus
InactiveUS6900547B2Promote formationLow rateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConfectioneryFiberLower upper
A system and method for forming an article from thermoplastic material and fiber. The method includes heating thermoplastic material to form a molten thermoplastic material for blending with the fiber. The molten thermoplastic material is blended with the fibers to form a molten composite material having a concentration of fiber by weight. The molten composite material may then be extruded through dynamic dies to deliver discrete controlled material that is gravitated onto a lower portion of a mold. The lower portion of the mold may be moved in space and time while receiving the flow of composite material to deposit a predetermined quantity of molten composite material thereon conforming to mold cavities of the lower and an upper portion of the mold. The upper portion of the mold may be pressed against the predetermined quantity of molten composite material and closing on the lower portion of the mold to form the article.
Owner:D&D MFG LLC
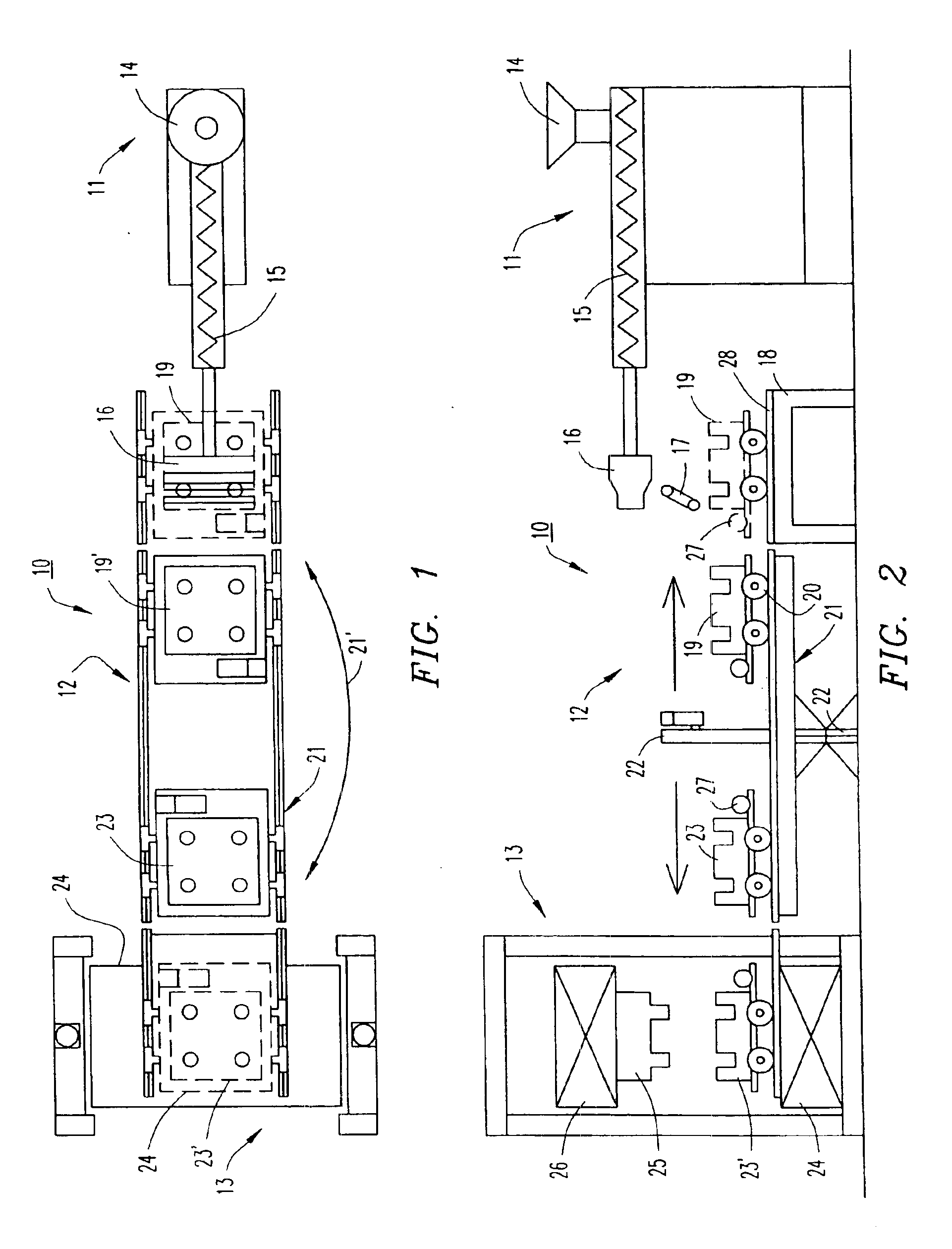
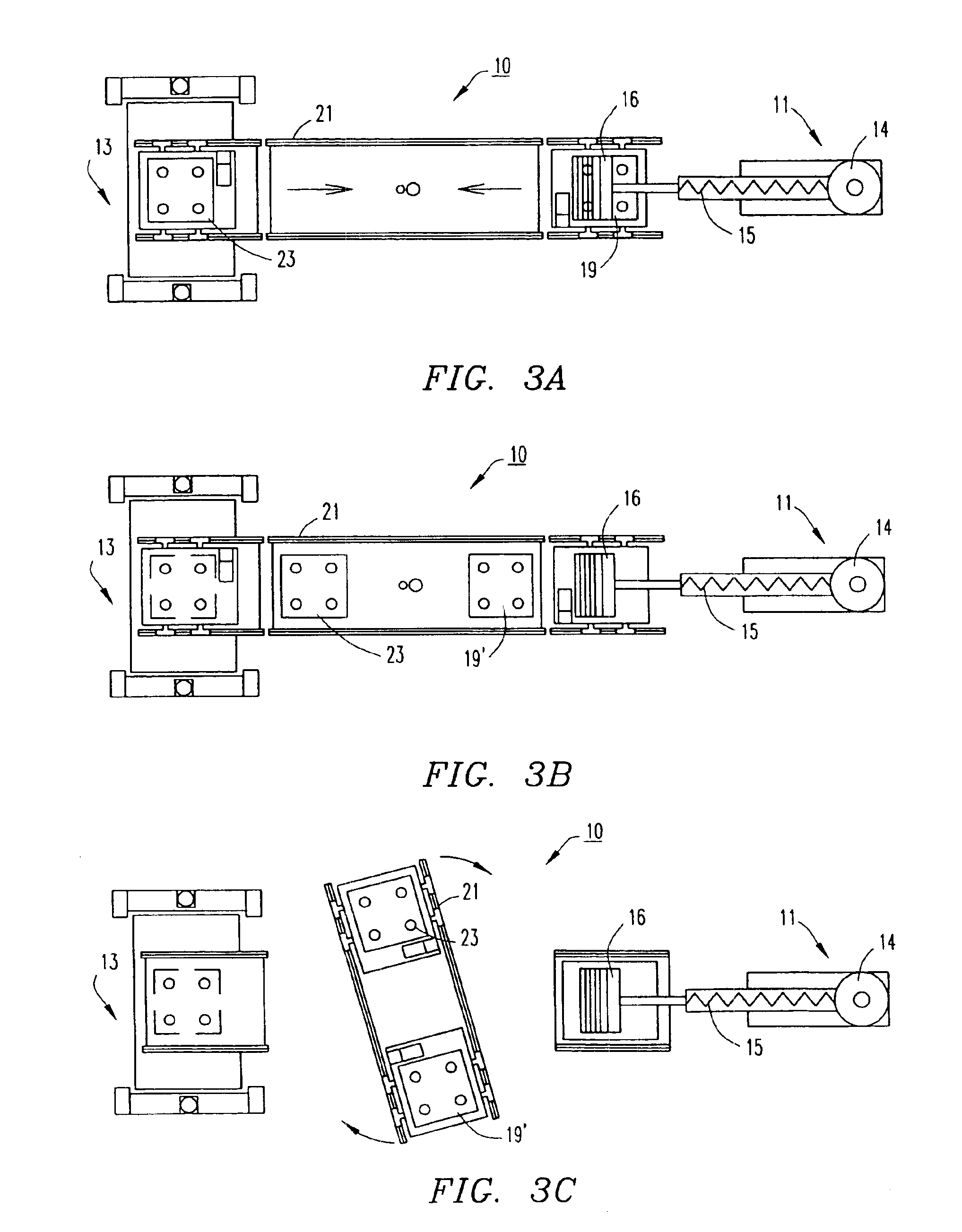
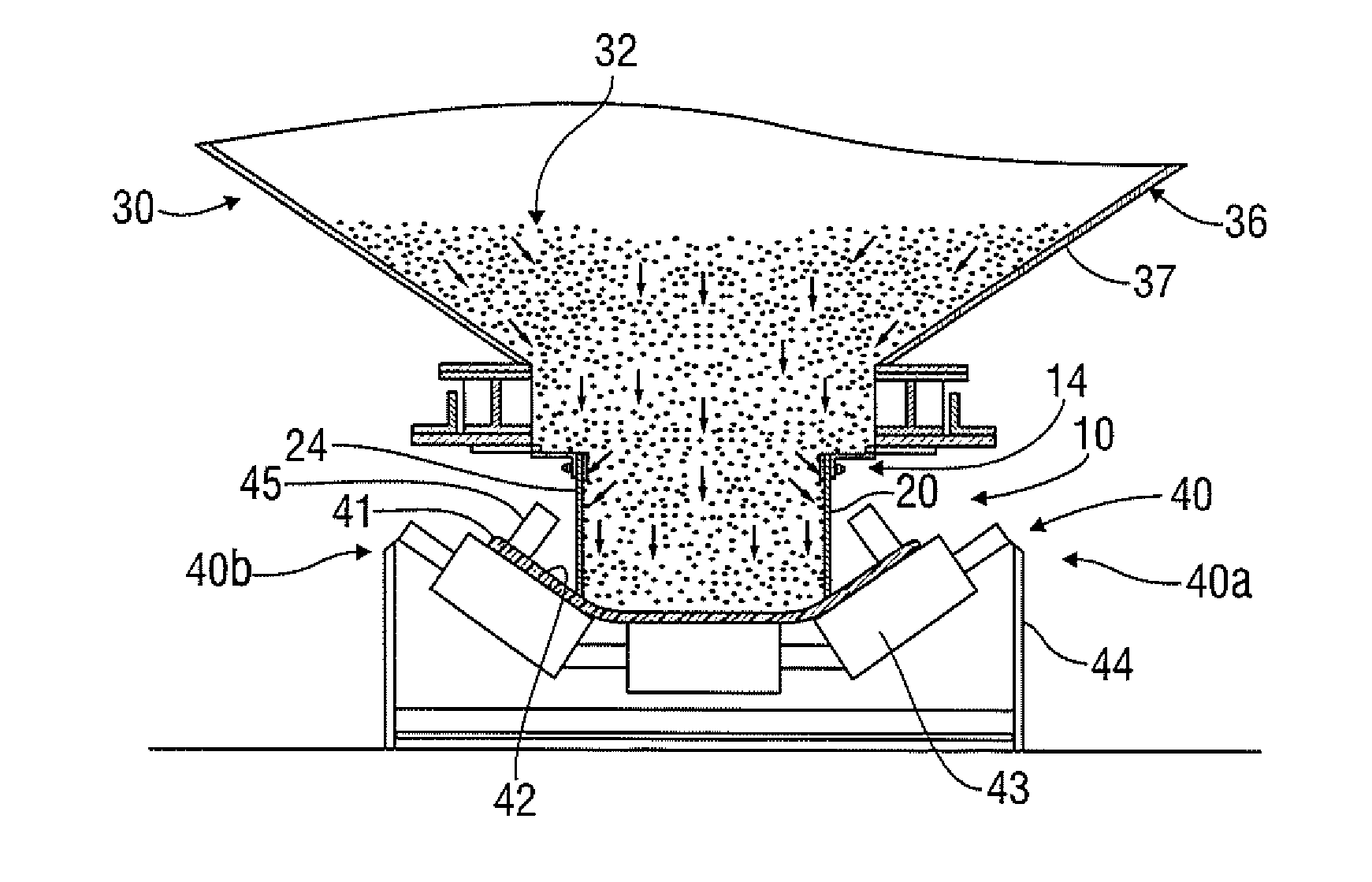
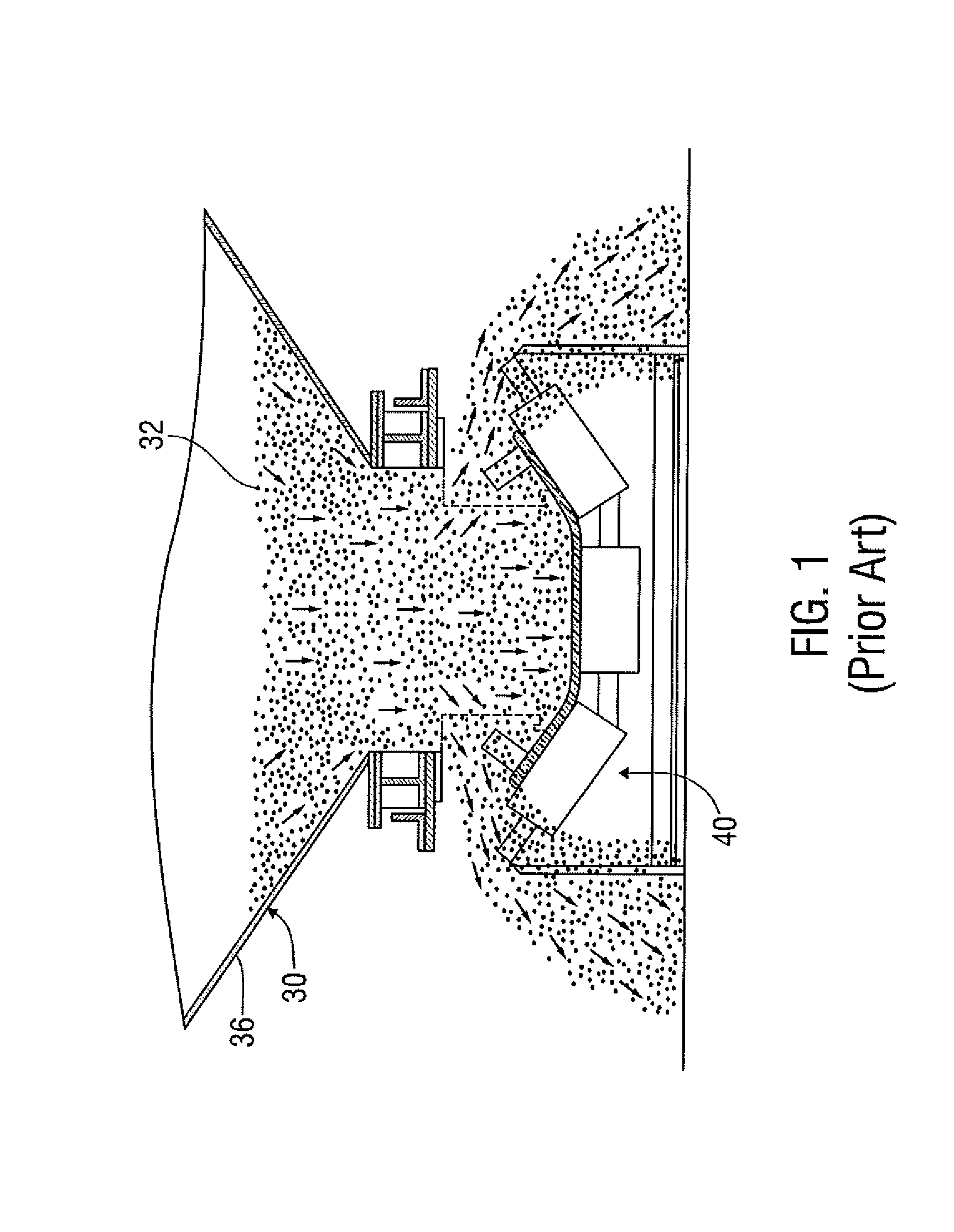
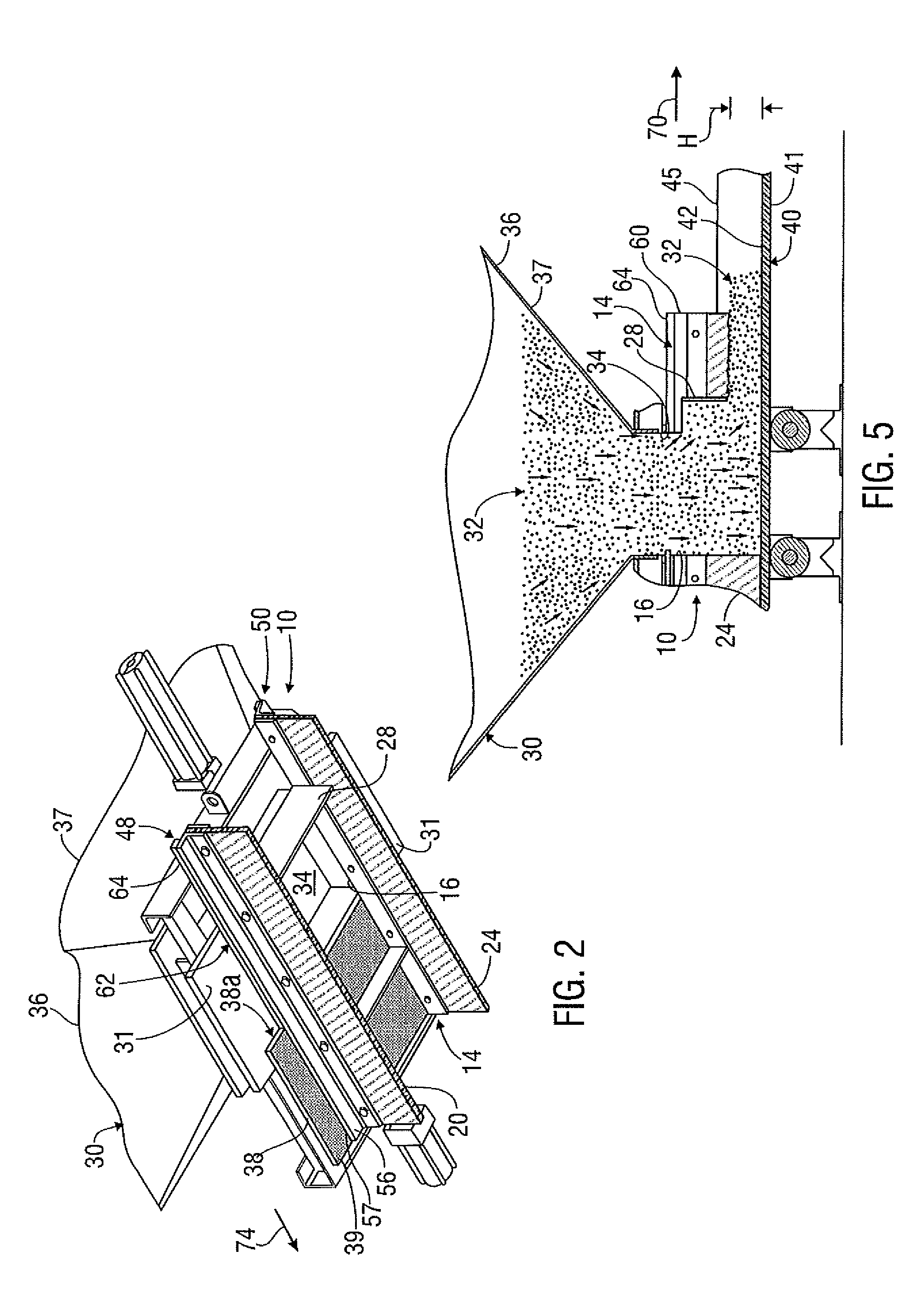
Apparatus and Methods for Assisting in Controlling Material Delivered on a Conveyor
ActiveUS20140044507A1Control devices for conveyorsWeighing apparatus for continuous material flowElectronic controllerConveyor belt
Method of controlling the amount of material delivered by conveyor belt includes measuring the speed of the conveyor belt or a drive pulley that drives the conveyor belt. A weighing device weighs material dispensed onto the conveyor belt from at least one material dispenser. Based at least in part upon such speed and weight measurements, an electronic controller maintains or changes the speed of the conveyor belt by dictating the output of at least one motor that drives the drive pulley.
Owner:BJ ENERGY SOLUTIONS LLC FORMERLY TES ASSET ACQUISITION LLC
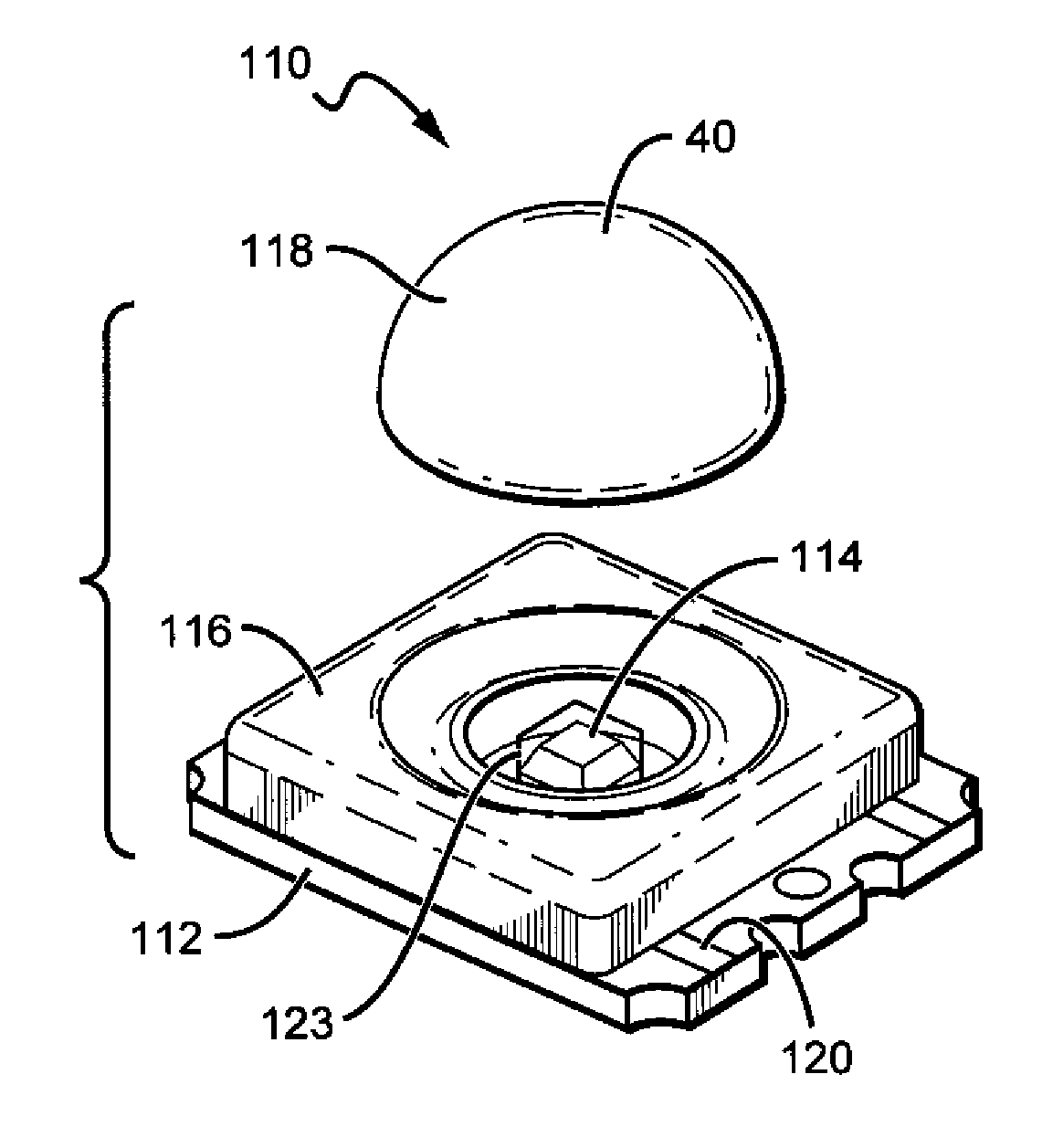
Light transmission control for masking appearance of solid state light sources
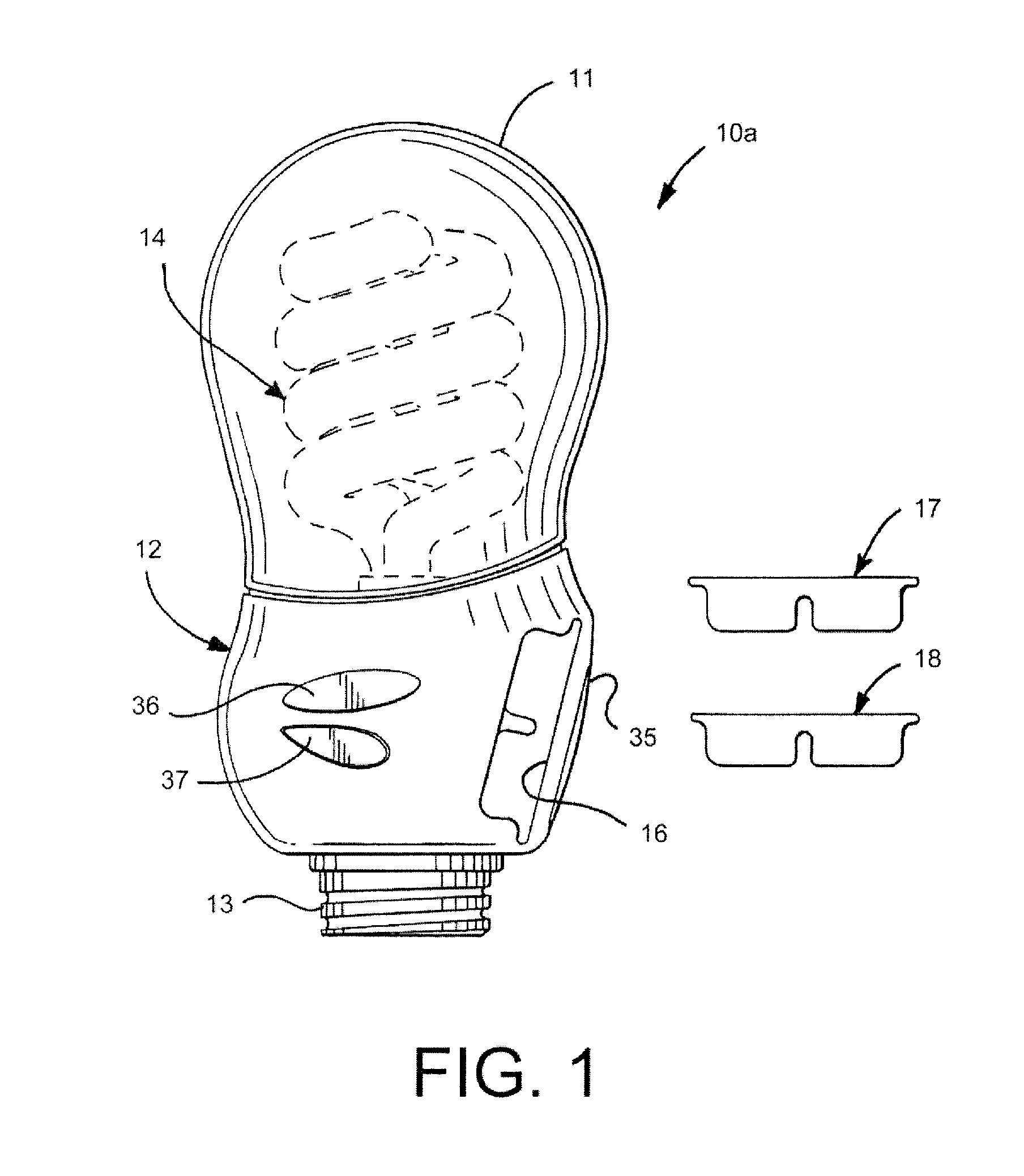
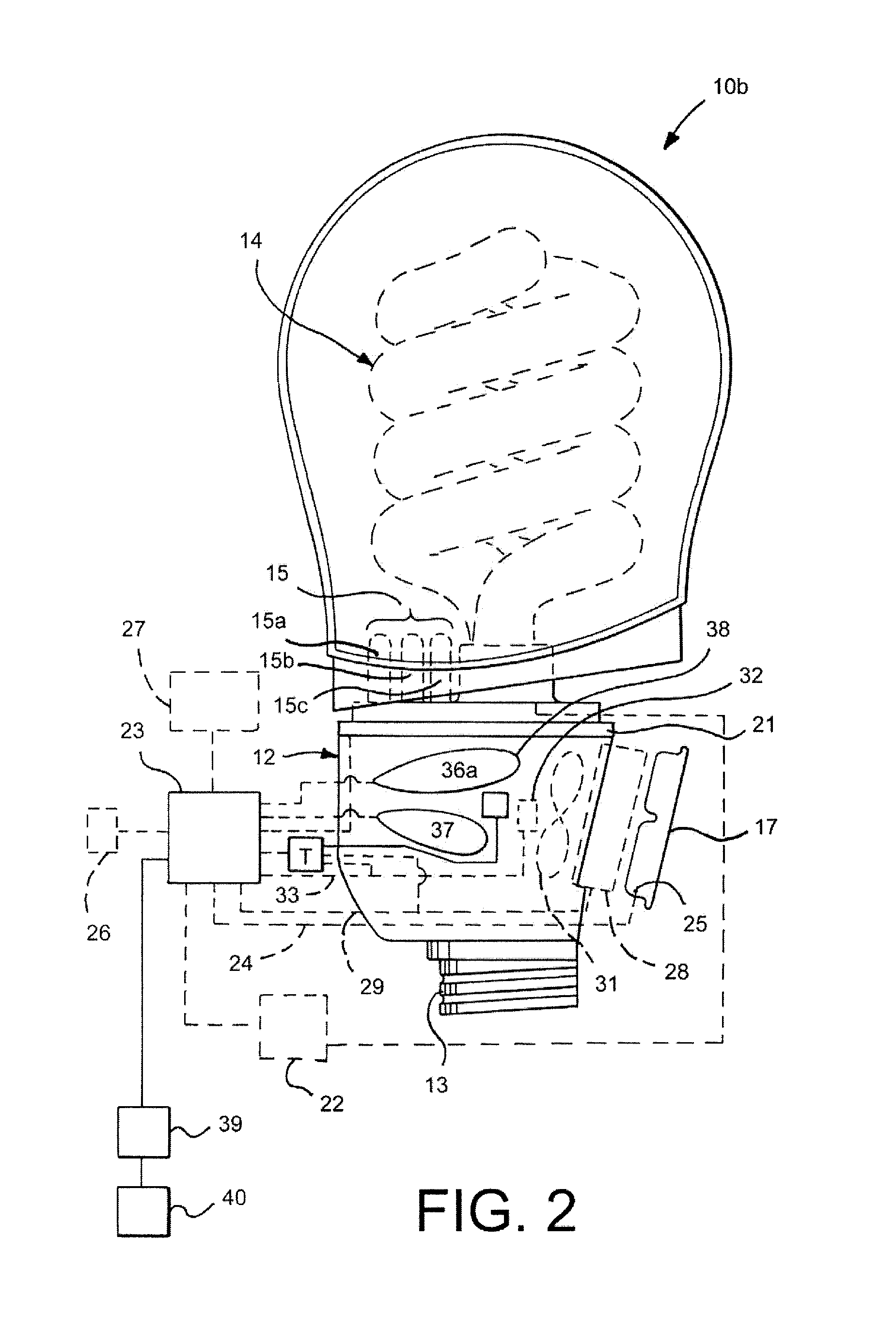
A light emitter device, package, or lamp that comprises and light emitter and a light transmission control material to mask the appearance of at least the light emitter. In one embodiment, a light emitting diode (LED) based lamp is disclosed, comprising an LED light source. A phosphor is arranged remote to the light source such that light emitted from the light source passes through this phosphor and is converted by this phosphor. A light transmission control material is applied at least partially outside the LED light source and the phosphor to reversibly mask the appearance of the LED light source and the phosphor. The light transmission control material is less masking when the LED light source is active. A method for masking the appearance of inactive light emitters is also disclosed that comprising providing at least one light emitter. Each of the at least one light emitters is provided with a light transmission control material over the light emitters to reversibly mask the appearance of the light emitters while the light emitters are inactive. The light transmission control material is less masking when the LED light source is active.
Owner:CREELED INC
Combination light device with insect control ingredient emission
InactiveUS7503675B2Coupling device connectionsLight source combinationsAdditive ingredientEngineering
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
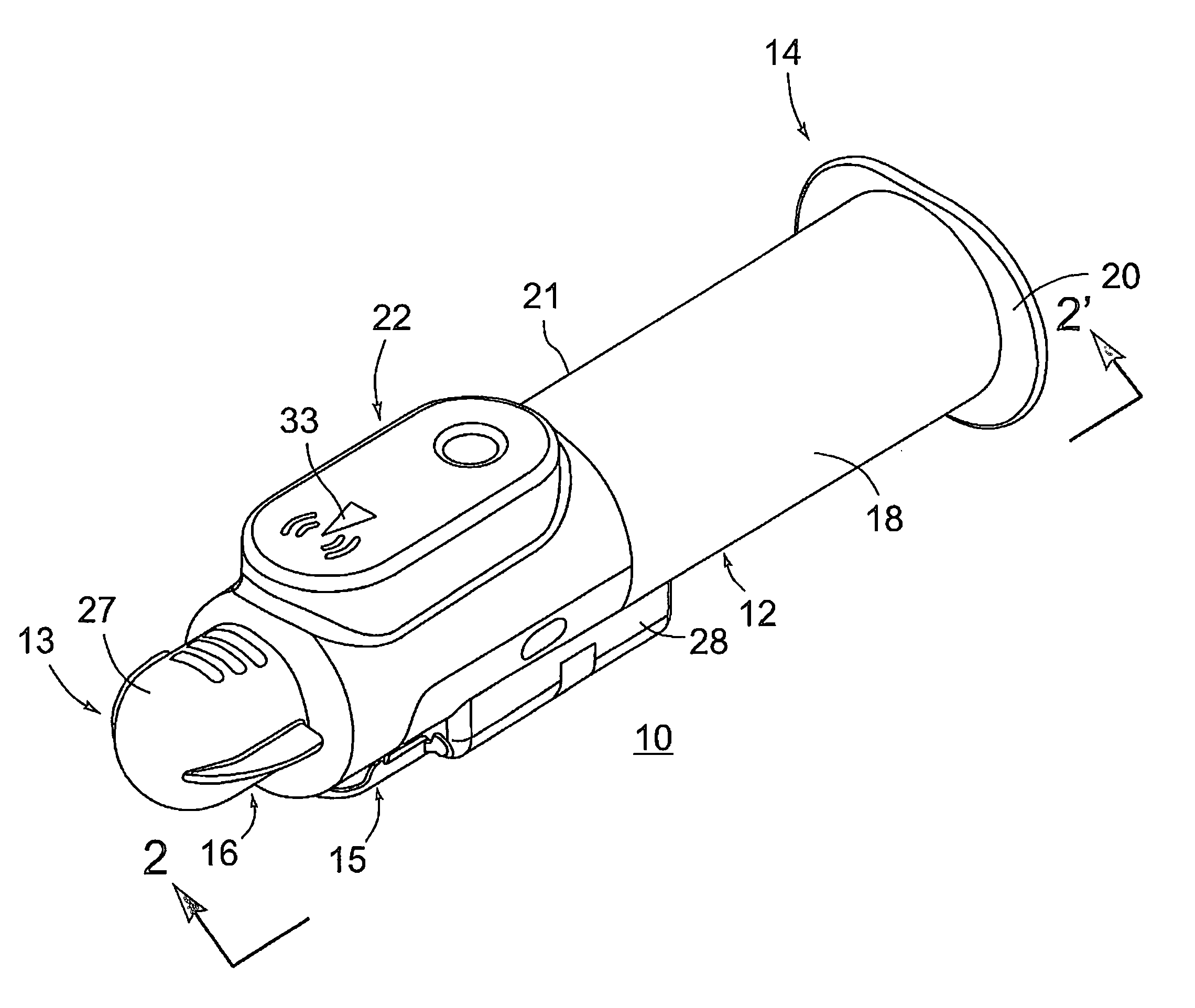
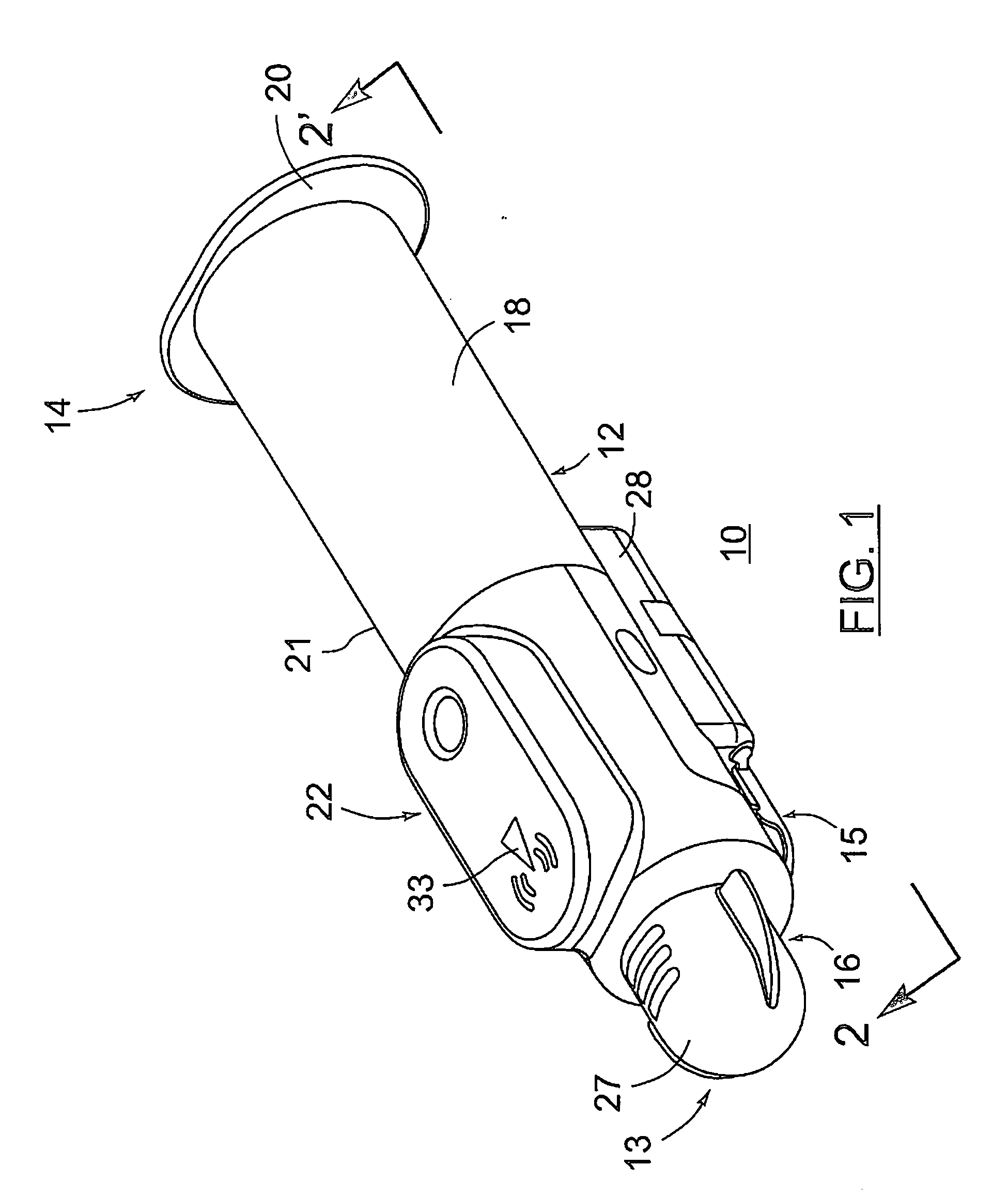
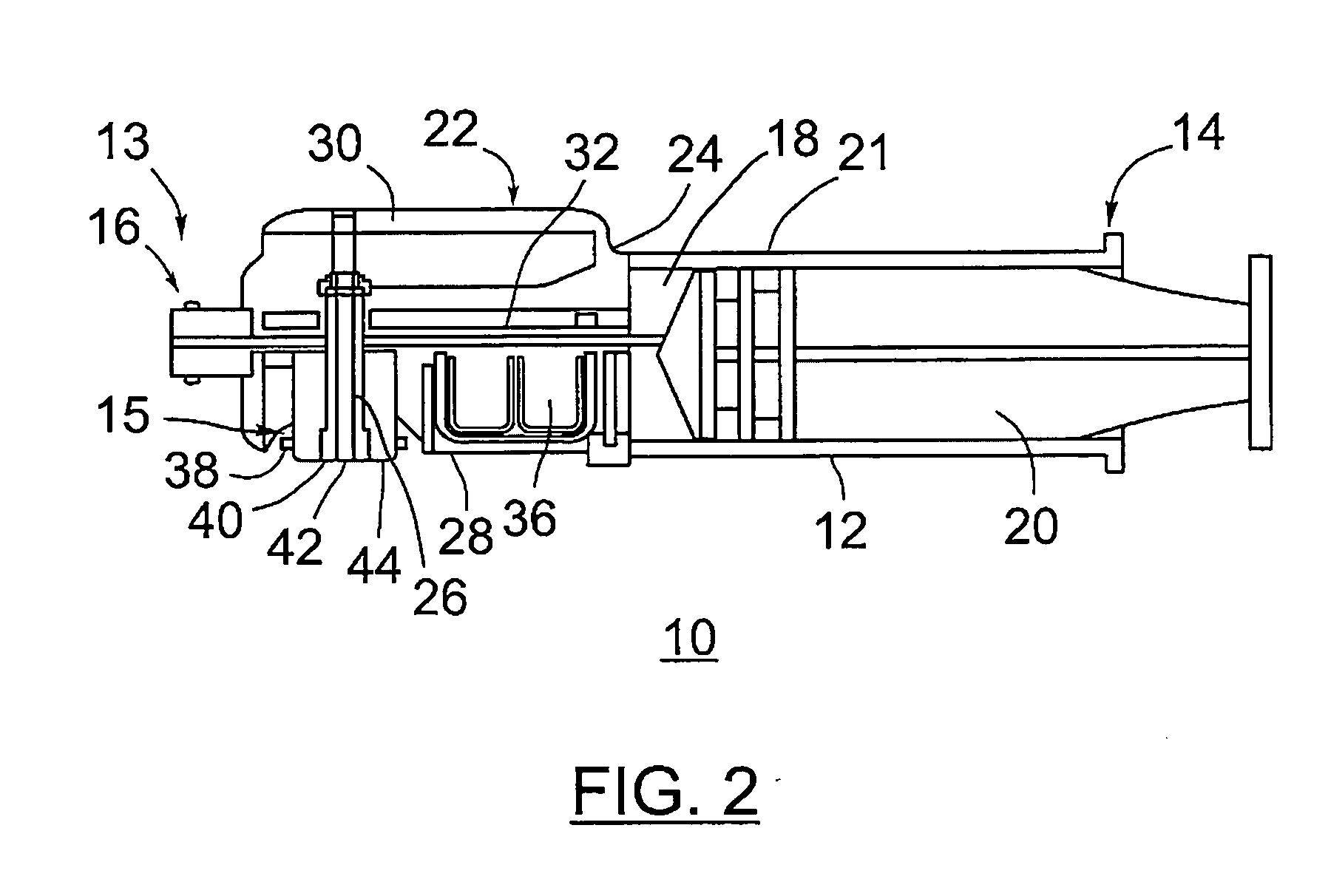
Product dispensing apparatus
A product dispensing apparatus for filling a container with product material has an enclosure for holding a supply of product material, a discharge outlet in the enclosure, and a gate device mounted adjacent the discharge outlet for controlling the flow of material through the outlet. The gate device is provided with a plate slidable across the discharge outlet between a fully closed position wherein the plate completely covers the discharge outlet and a maximum open position wherein the plate is generally clear of the discharge outlet and one or more partially open positions located between the maximum open and fully closed positions. The gate device is further provided with an actuator having a driven member connected to the plate for moving the plate among the closed, maximum open, and partially open positions, and stopping means adjacent the actuator for stopping the plate at the partially open positions.
Owner:INDAL PROCESS INNOVATIONS
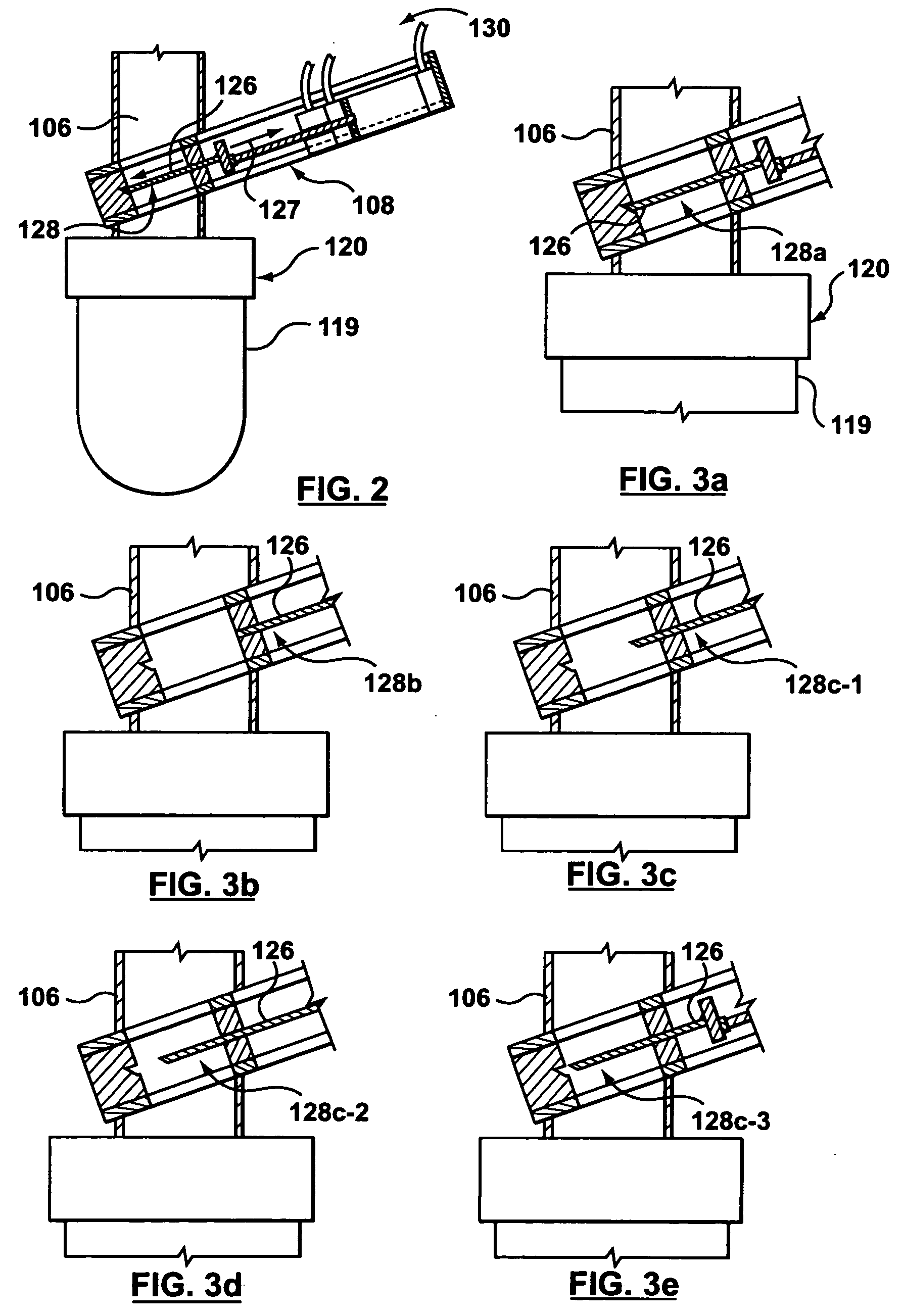
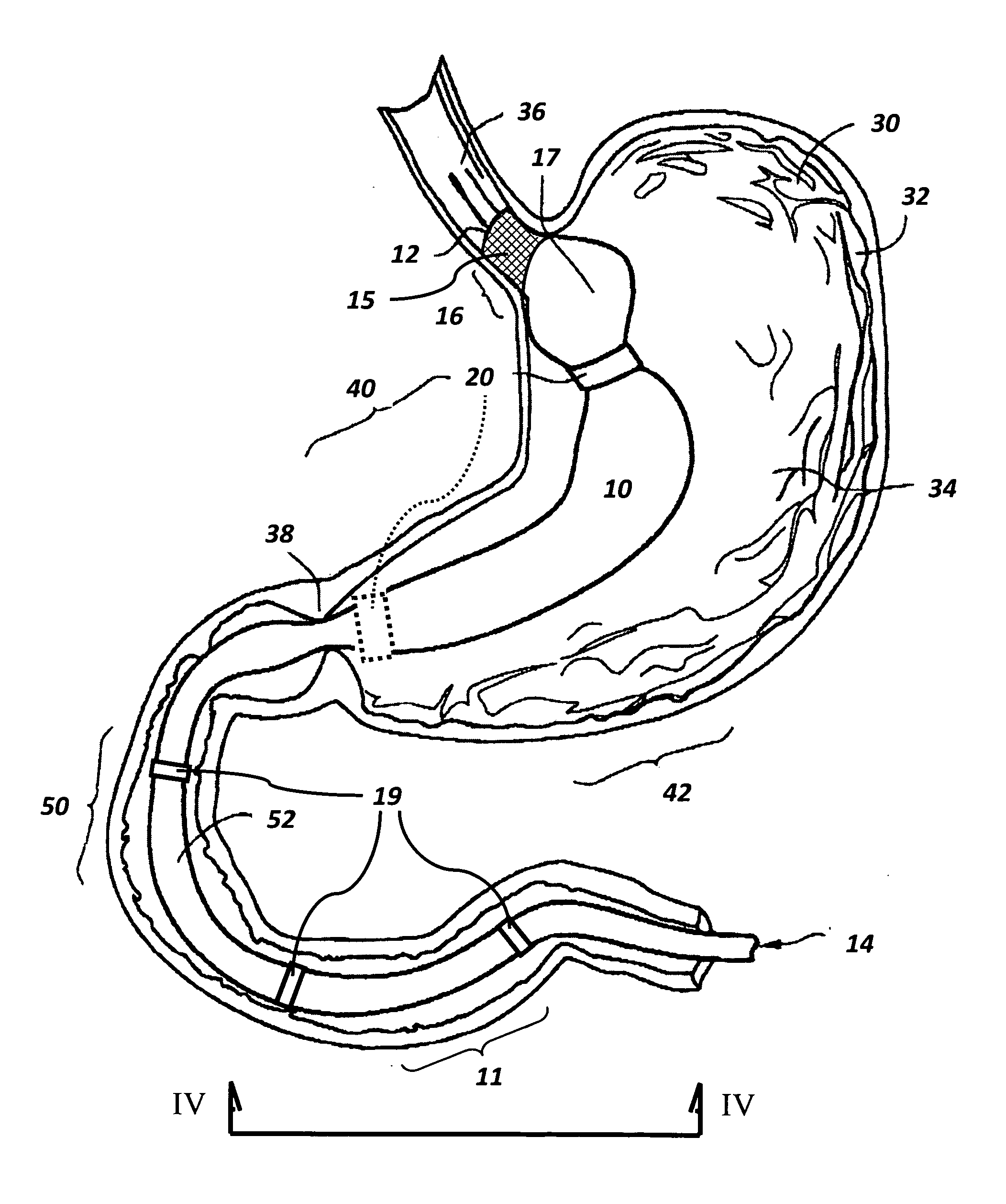
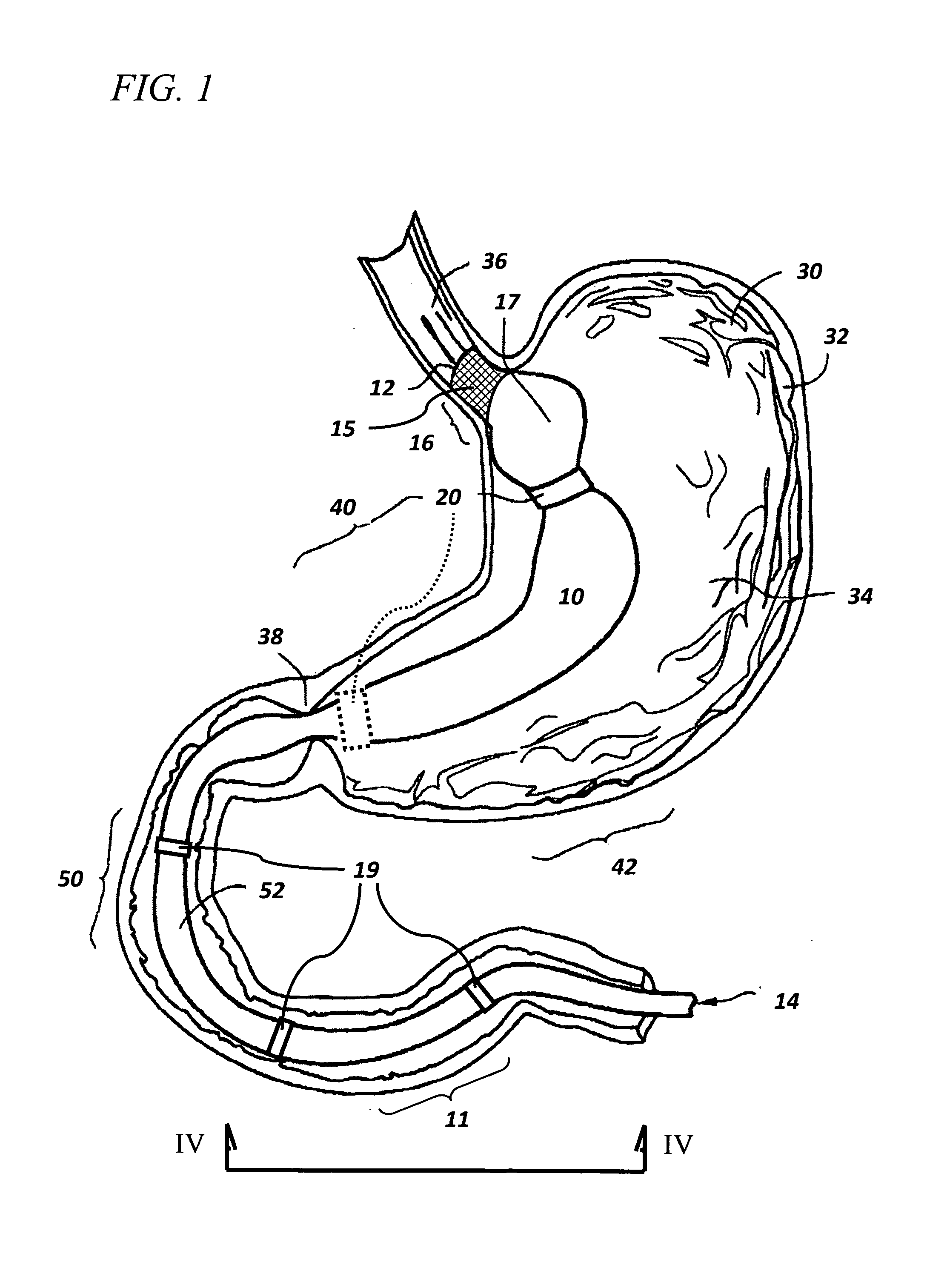
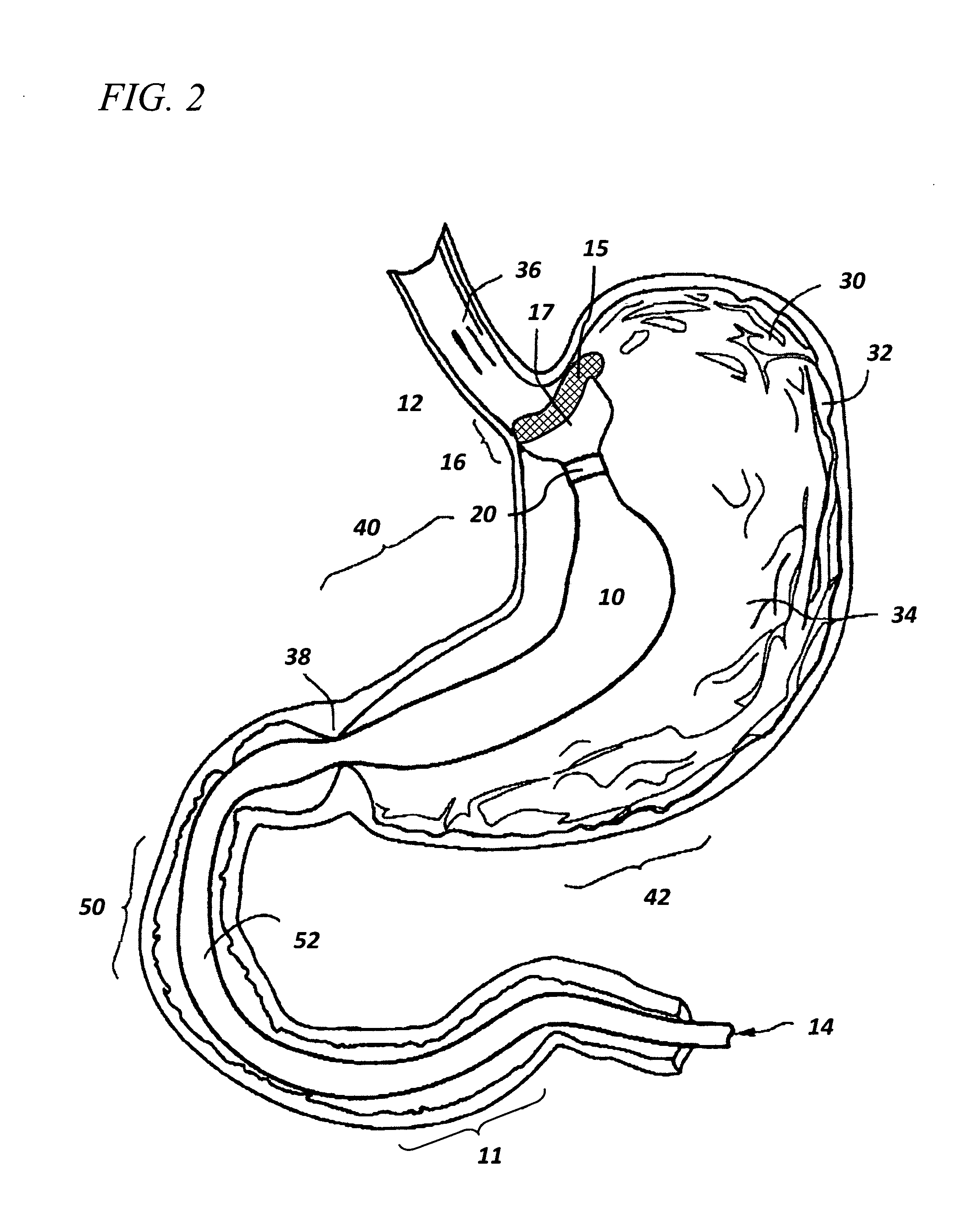
Devices and methods for endolumenal therapy
InactiveUS20090093767A1Promoting tissue in-growthAltering abilityDiagnosticsSurgeryGastrointestinal deviceLower esophagus
The present invention is directed generically to a means for altering the ability of the mammalian body to absorb nutritive content from ingested foodstuffs, and more specifically to an apparatus and method of use for an endolumenal sleeve (referred to also as an “intragastrointestinal device” or “gastrointestinal device”) positioned in the mammalian gastrointestinal (GI) tract. A suitable endolumenal sleeve is comprised of an anchor element and an opening at a proximal end, an elongate lumen or hollow open-ended tube having a transverse dimension, and a distal orifice. Optionally, an exterior aspect of the elongate lumen may include additional modes of attachment to the tissues walls of the GI tract through the use of one or more means for promoting tissue in-growth. The endolumenal sleeve is retained in the GI tract such that a substantial fraction of the food and liquids passing through the GI tract is channeled into the proximal opening and through an interlumenal space defined within the interior space of the endolumenal sleeve. Within the endolumenal sleeve there may be one or more restrictive means to constrain, impede or otherwise control the operative flow of material through the device. An individual restrictive means can either be of a fixed geometry or such means may include one or more elements which are adjustable in nature or function. The elongate lumen of the endolumenal sleeve is formed of a polymer composition suitable for controlled ingress of biological secretions, egress of certain selected nutritional elements, and may comprise either a single tubular structure or a multi-section (i.e. articulated and / or multiple lumen) assembly. When the endolumenal sleeve is in situ within the mammalian gastro-intestinal system, ingested foodstuffs are conveyed from the proximal end to said distal orifice. In typical applications, the proximal end of the endolumenal sleeve is positioned within the physiological region extending from the lower esophagus to the duodenum and the distal orifice is positioned within the physiological region extending from the upper duodenum to the lower jejunum, though further extension into the lower intestine is possible. Through proper selection of position for the endolumenal sleeve proximal and distal ends, combined by selection of the composition used in the fabrication of the elongate lumen, it is possible to finitely control the degree of nutritive absorption performed by the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:KELLEHER BRIAN
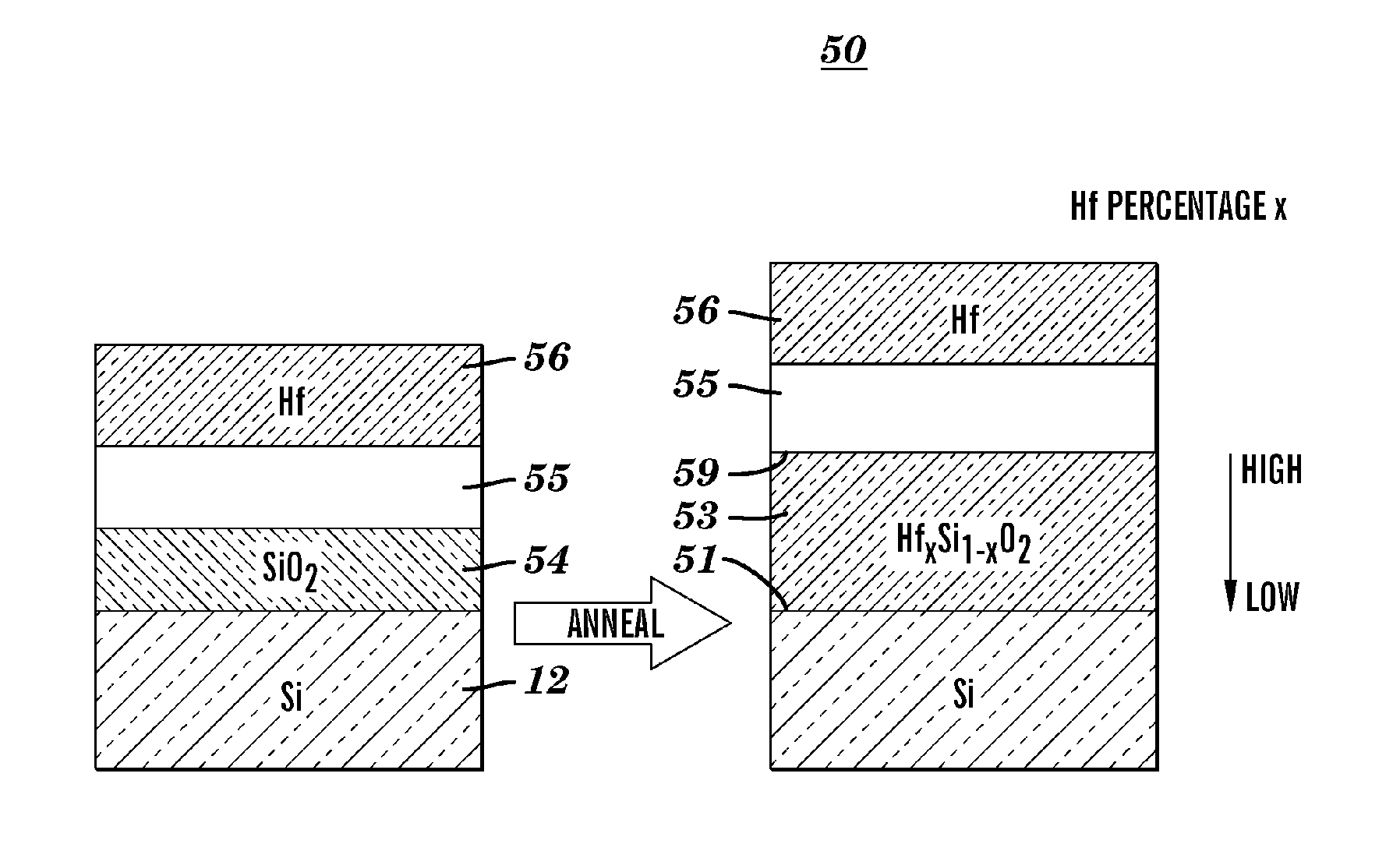
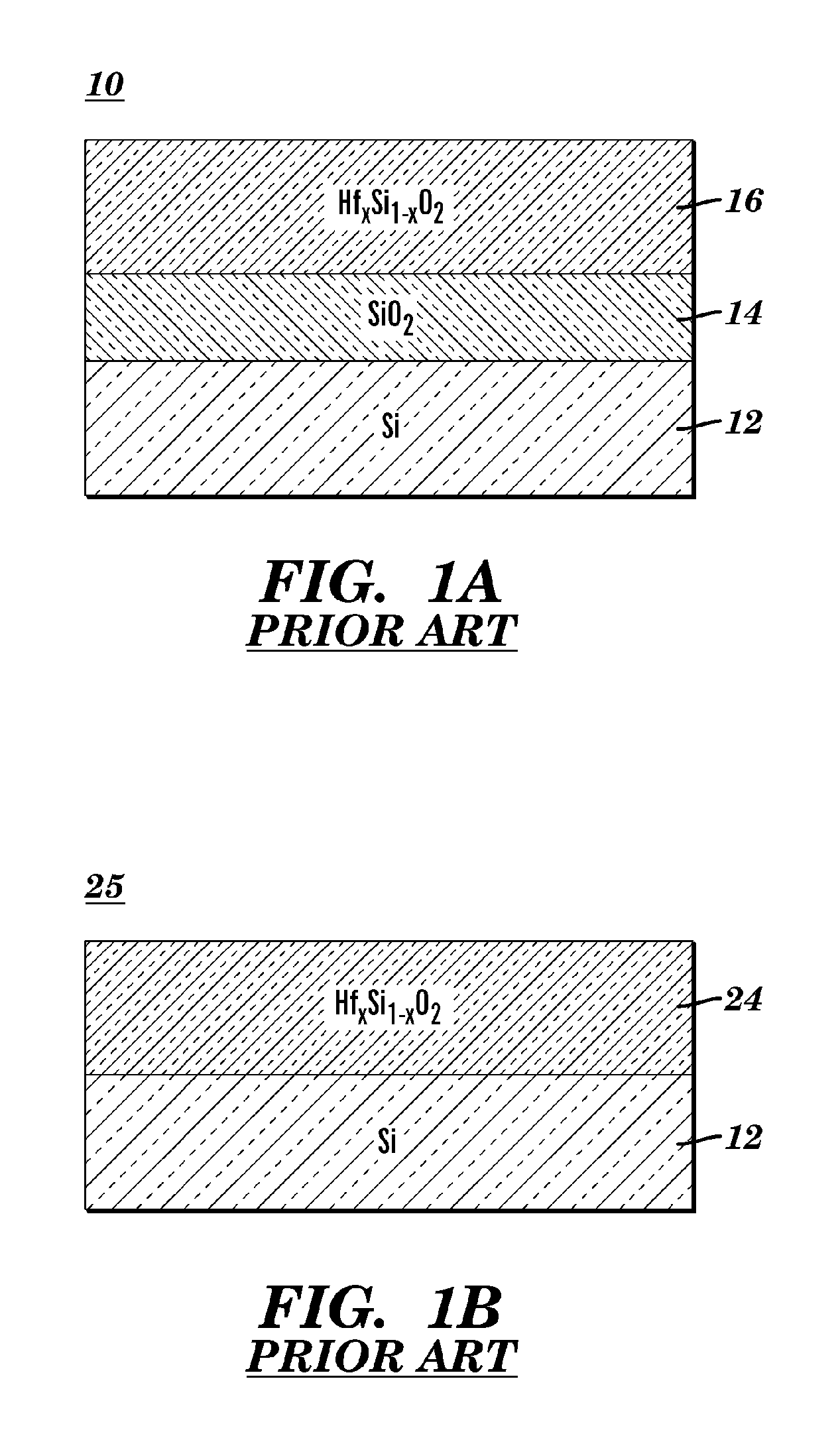
ULTRA-THIN Hf-DOPED-SILICON OXYNITRIDE FILM FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE CMOS APPLICATIONS AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURE
ActiveUS20060237803A1Improve device performanceImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSGate dielectric
A semiconductor structure and method of forming the same, comprising forming a uniform buffer layer of diffusion-controlling stable material on top of a base gate dielectric layer, and then forming a uniform layer which contains a source of transitional metal atoms, and then annealing the structure to diffuse the transitional metal atoms from their source through the diffusion-controlling material and into the base gate dielectric layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Pest control method for grass family plants using endophytic bacteria, pest control material, and seed bound to the pest control material
InactiveUS7037879B2Sharp reduction of pest occurrence prediction costReduce adverse influenceBiocideBacteriaChemical synthesisBacteroides
The objective of the present invention is to confer pest resistance to plants of Poaceae without using any chemically synthesized pesticides. The pest resistance can be conferred to plants of Poaceae by isolating from a natural plant an endophytic bacterium capable of expressing pest resistance, artificially culturing the endophytic bacterium, and introducing the bacteria to a Poaceae plant of interest.
Owner:SOC FOR TECHNO INNOVATION OF AGRI FORESTRY & FISHERIES +1
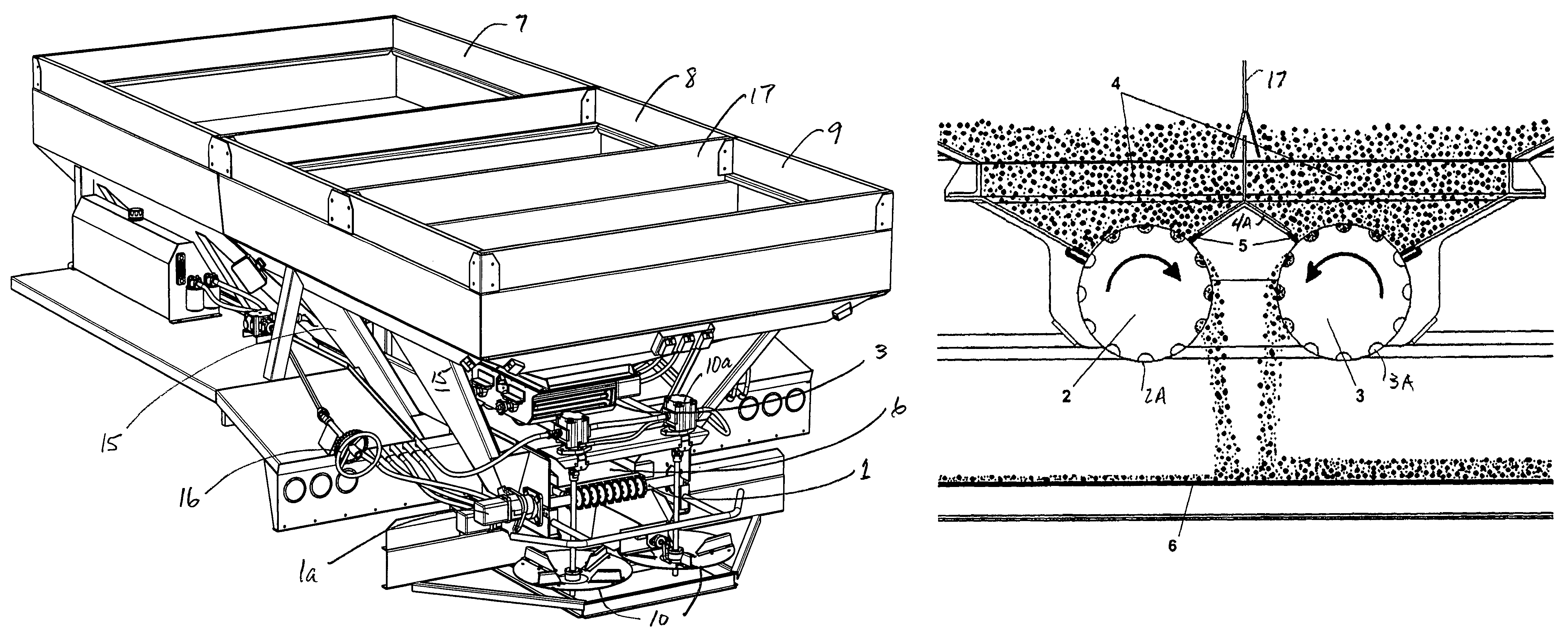
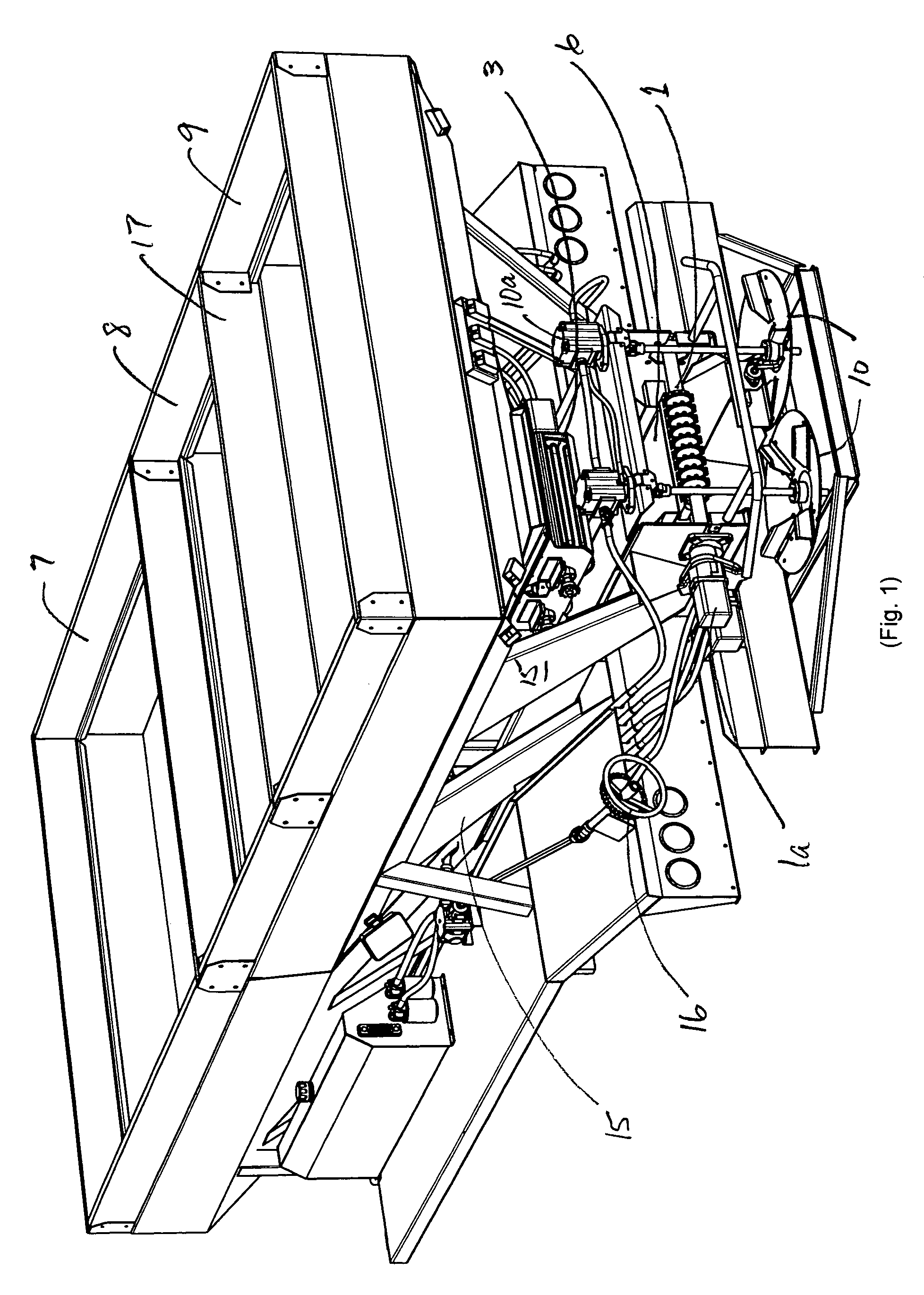
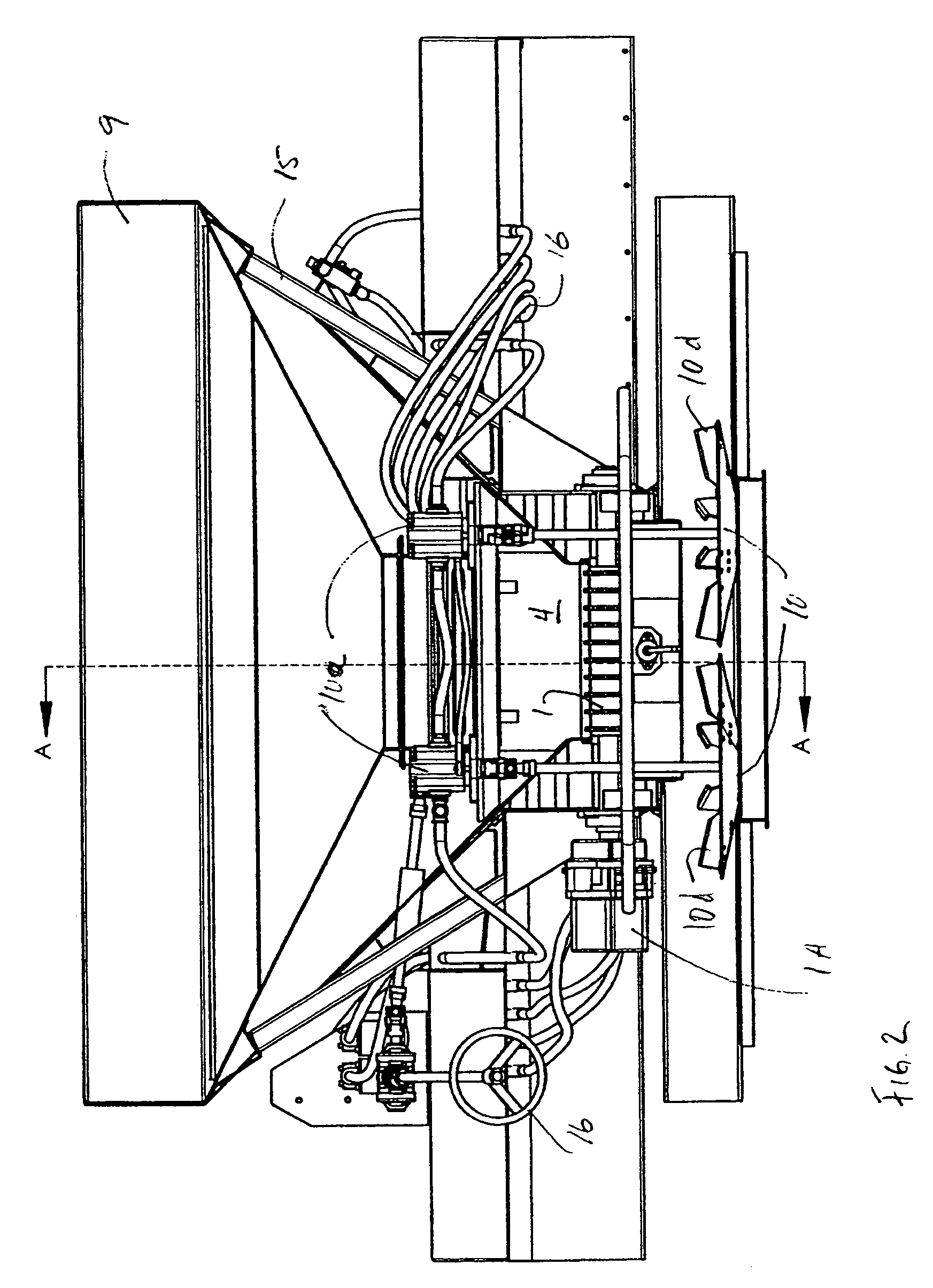
Plural bin metering system
ActiveUS7380733B2Low costLess-expensive to maintainFertiliser distributersCentrifugal wheel fertilisersOne passEngineering
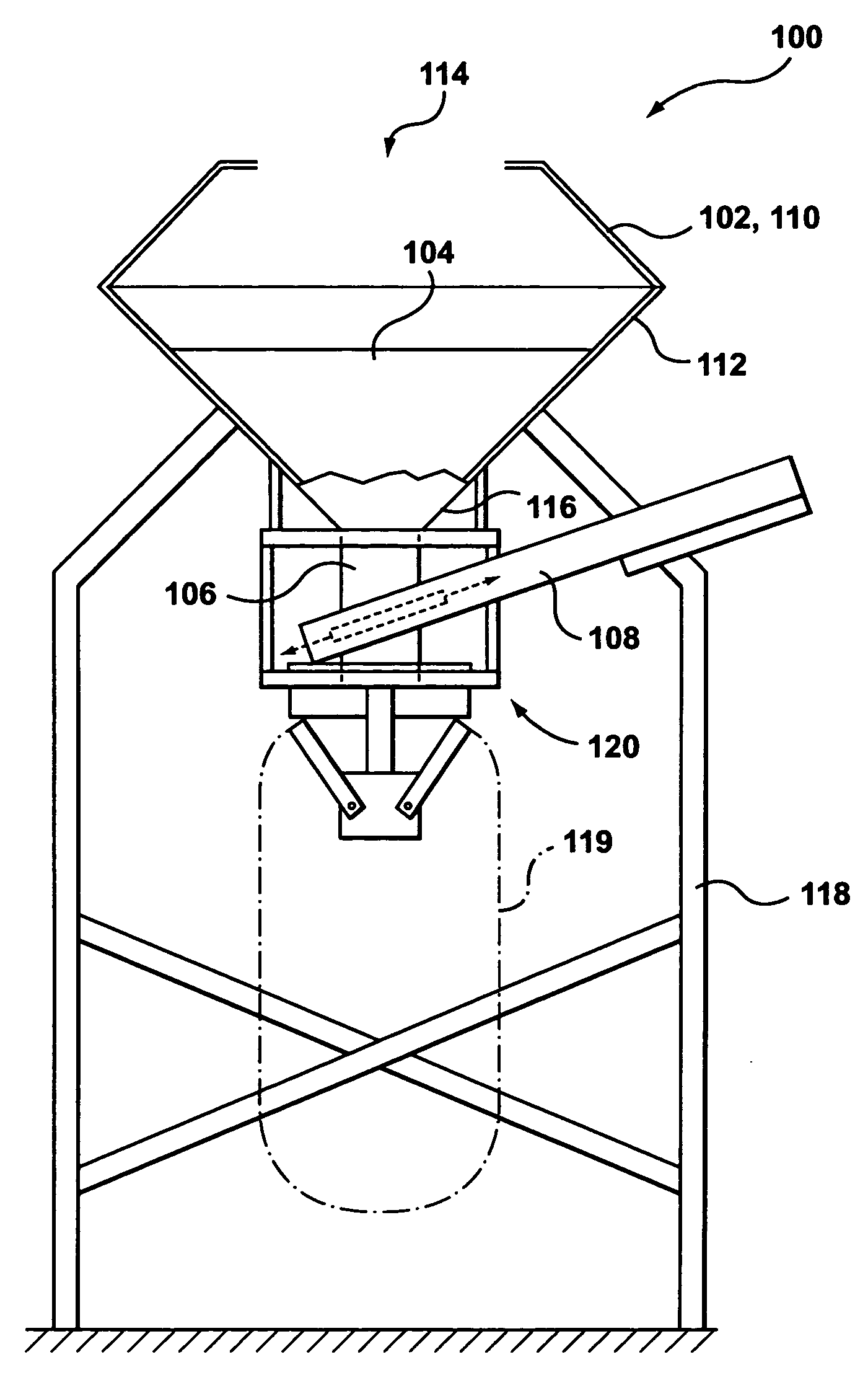
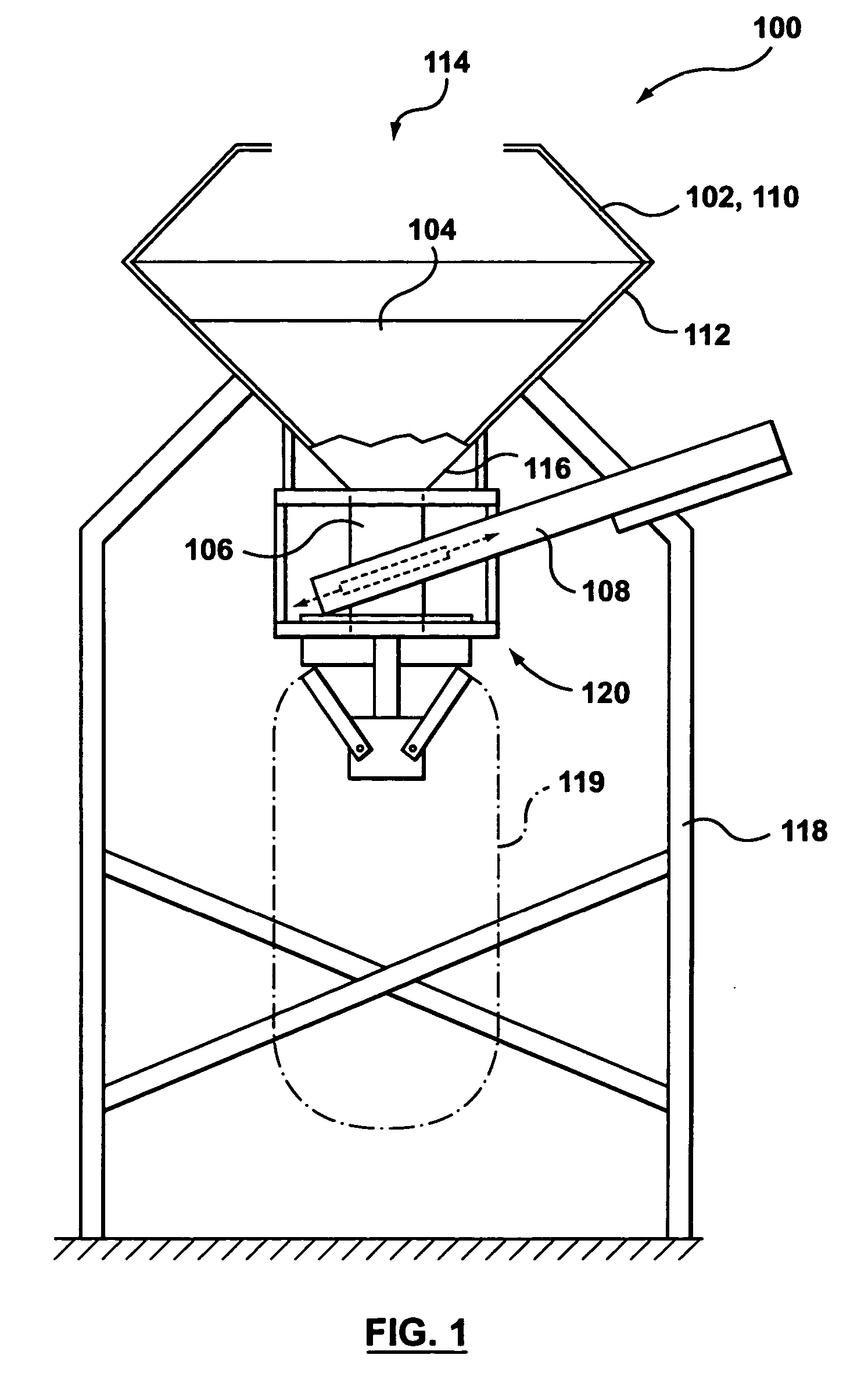
A plural bin metering system for broadcasting material ingredients contained therein over a ground surface. The system includes at least two material ingredient hoppers, each of the hoppers having a material ingredient discharge port. At least one of the material ingredient hoppers includes a variably controllable metering unit associated therewith for variably controlling the discharge of material ingredients therefrom independently from the rate of discharge of material ingredients from the other material ingredient hopper. A conveyor is disposed below the hoppers for receiving material ingredients discharged from the hoppers, and a material ingredient broadcasting device disposed off of one end of the conveyor for receiving material ingredients conveyed thereon, received from the hoppers, for broadcasting the material ingredients over a ground surface. The metering unit is capable of metering material ingredients from its associated hopper at ultra low rates. In a preferred embodiment the system has three hoppers for broadcasting, for example fertilizer across a field in one pass.
Owner:SALFORD BBI
Thermoplastic molding process and apparatus
A system and method for forming an article from thermoplastic material and fiber. The method includes heating thermoplastic material to form a molten thermoplastic material for blending with the fiber. The molten thermoplastic material is blended with the fibers to form a molten composite material having a concentration of fiber by weight. The molten composite material may then be extruded through dynamic dies to deliver discrete controlled material that is gravitated onto a lower portion of a mold. The lower portion of the mold may be moved in space and time while receiving the flow of composite material to deposit a predetermined quantity of molten composite material thereon conforming to mold cavities of the lower and an upper portion of the mold. The upper portion of the mold may be pressed against the predetermined quantity of molten composite material and closing on the lower portion of the mold to form the article.
Owner:D&D MFG LLC
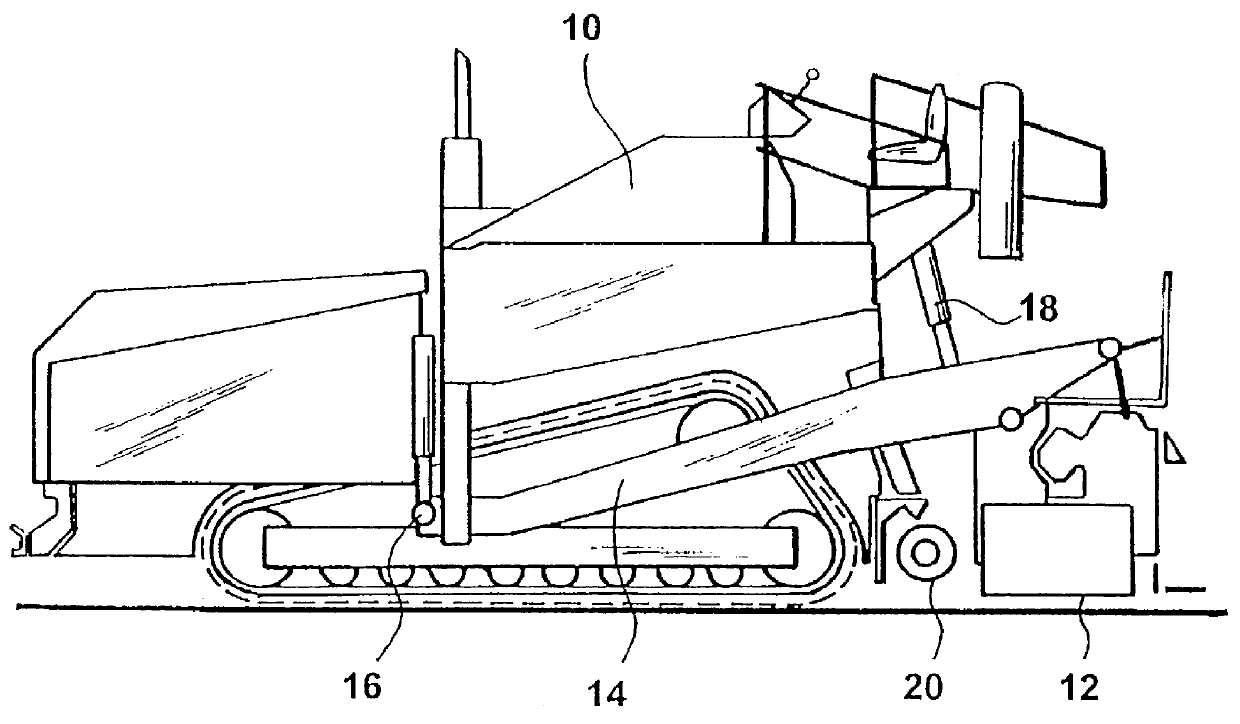
Device and method for controlling the application height of a road finisher
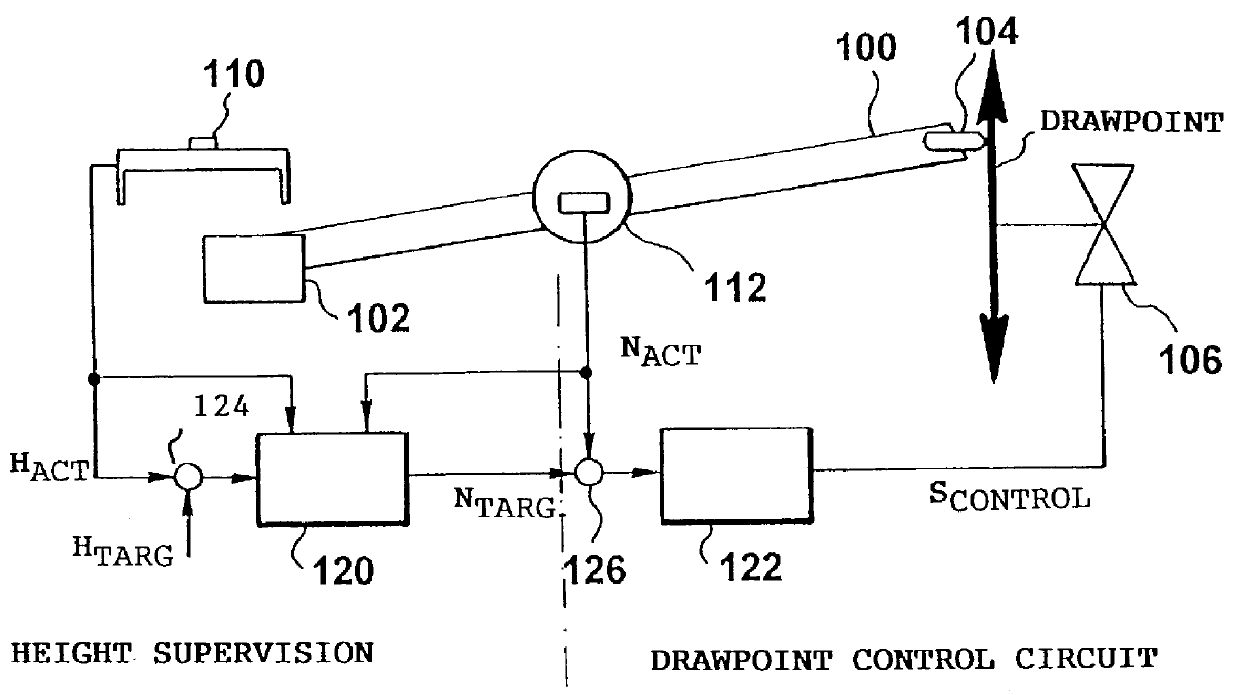
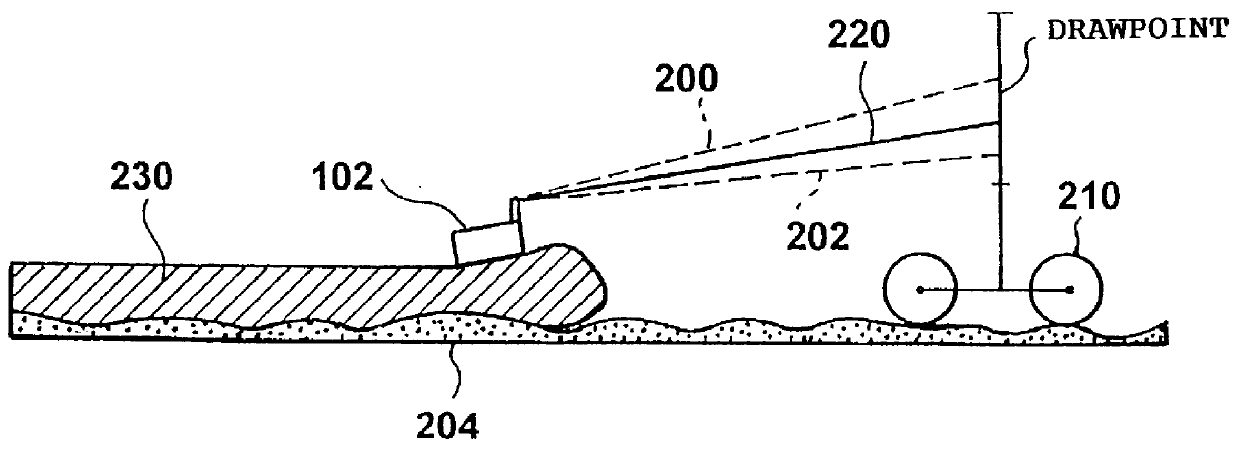
A control device for controlling the application of a material which is adapted to be applied to a subgrade by means of a road finisher, said road finisher comprising a tractor and a floating screed, which is attached by means of at least one drawarm to the tractor in such a way that said screed is arranged behind said tractor in the direction in which the road finisher is moving when in operation, a first end of said at least one drawarm being secured to the tractor by means of a vertically adjustable coupling device, and a second end of said at least one drawarm being rigidly secured to the floating screed, said control device comprising a device for detecting the height of a screed edge in relation to a reference height, said screed edge being the rear lower edge of the screed in the direction of movement. The control device further comprises a device for detecting the inclination of said at least one drawarm in relation to a reference plane. A device for controlling the height of the vertically adjustable coupling device controls the height of said vertically adjustable coupling device on the basis of the detected inclination and the detected height of the rear lower edge of the screed.
Owner:MOBA MOBILE AUTOMATION
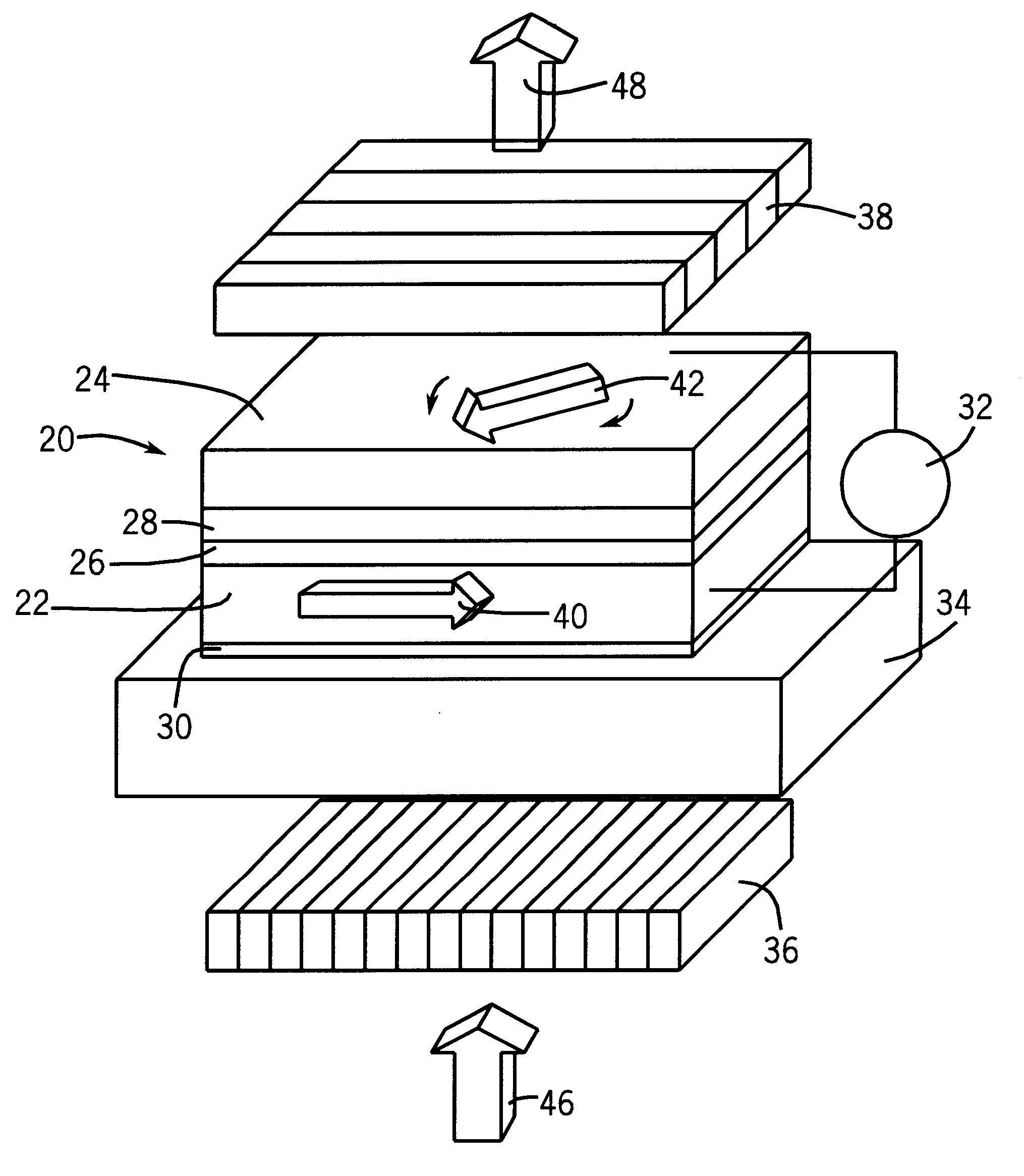
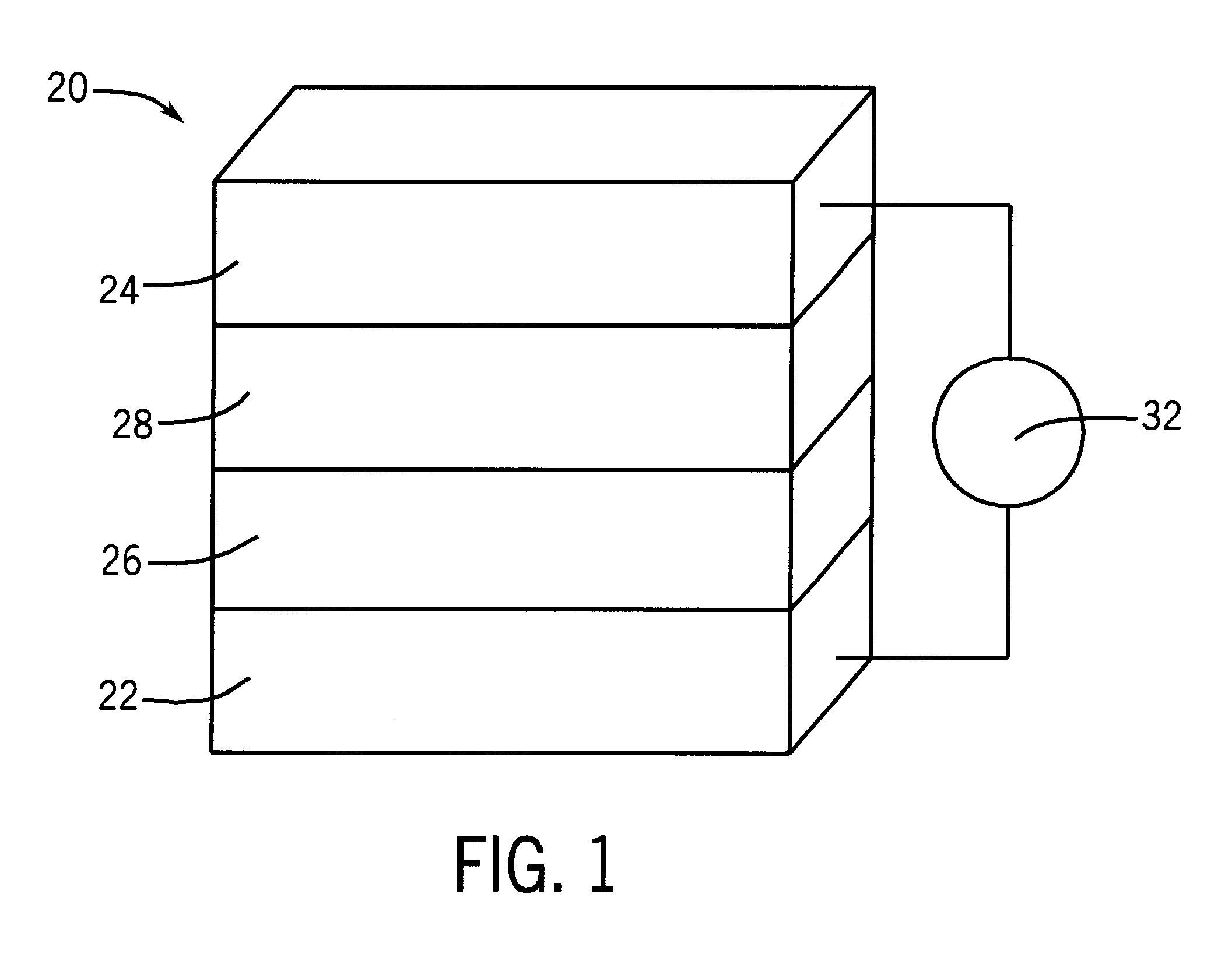
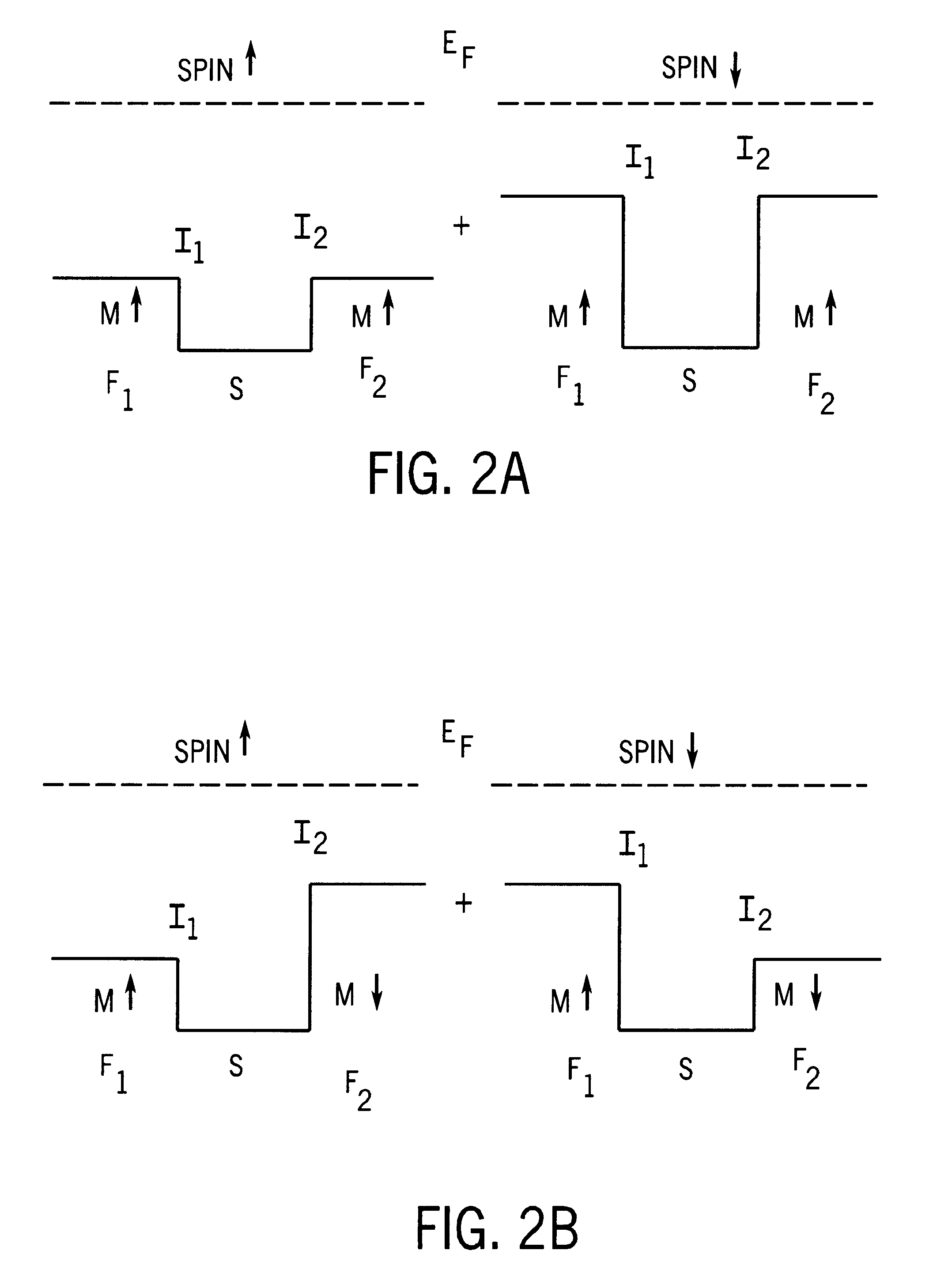
Control of magnetic direction in multi-layer ferromagnetic devices by bias voltage
A system for controlling the direction of magnetization of materials comprising a ferromagnetic device with first and second ferromagnetic layers. The ferromagnetic layers are disposed such that they combine to form an interlayer with exchange coupling. An insulating layer and a spacer layer are located between the first and second ferromagnetic layers. A direct bias voltage is applied to the interlayer exchange coupling, causing the direction of magnetization of the second ferromagnetic layer to change. This change of magnetization direction occurs in the absence of any applied external magnetic field.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
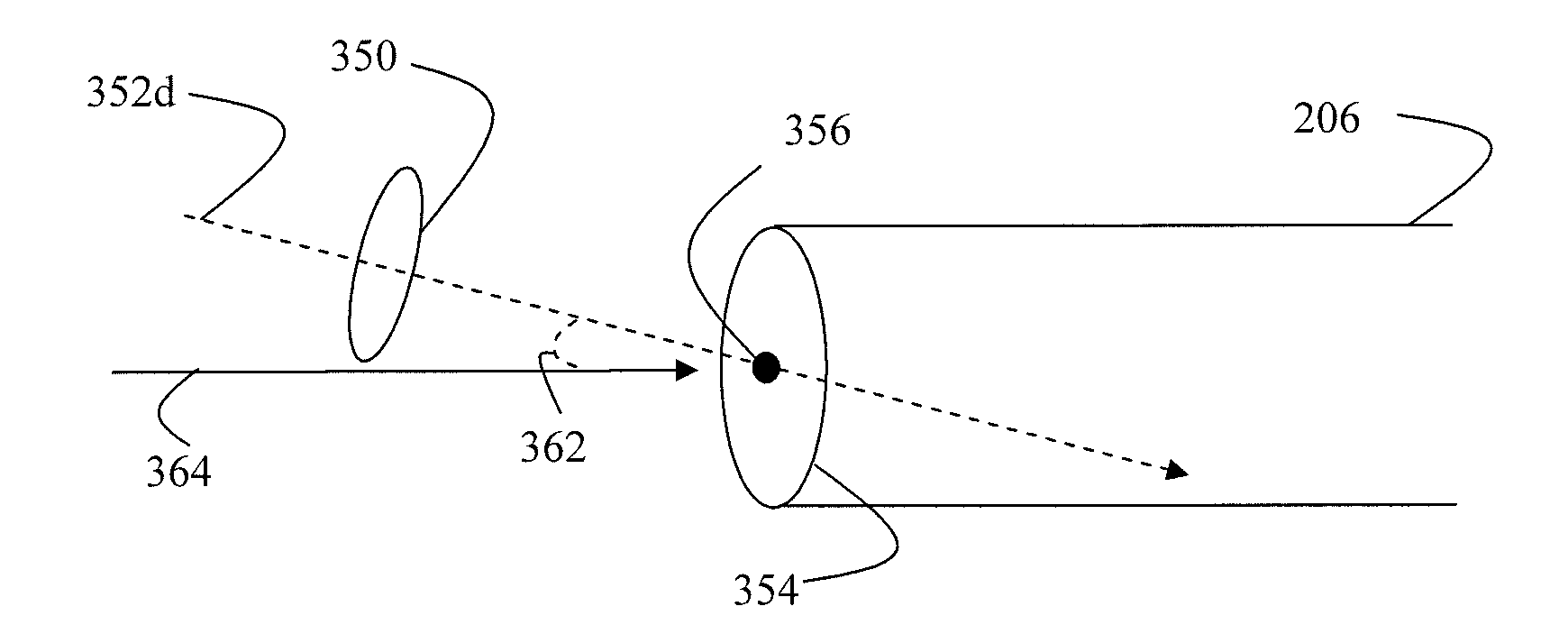
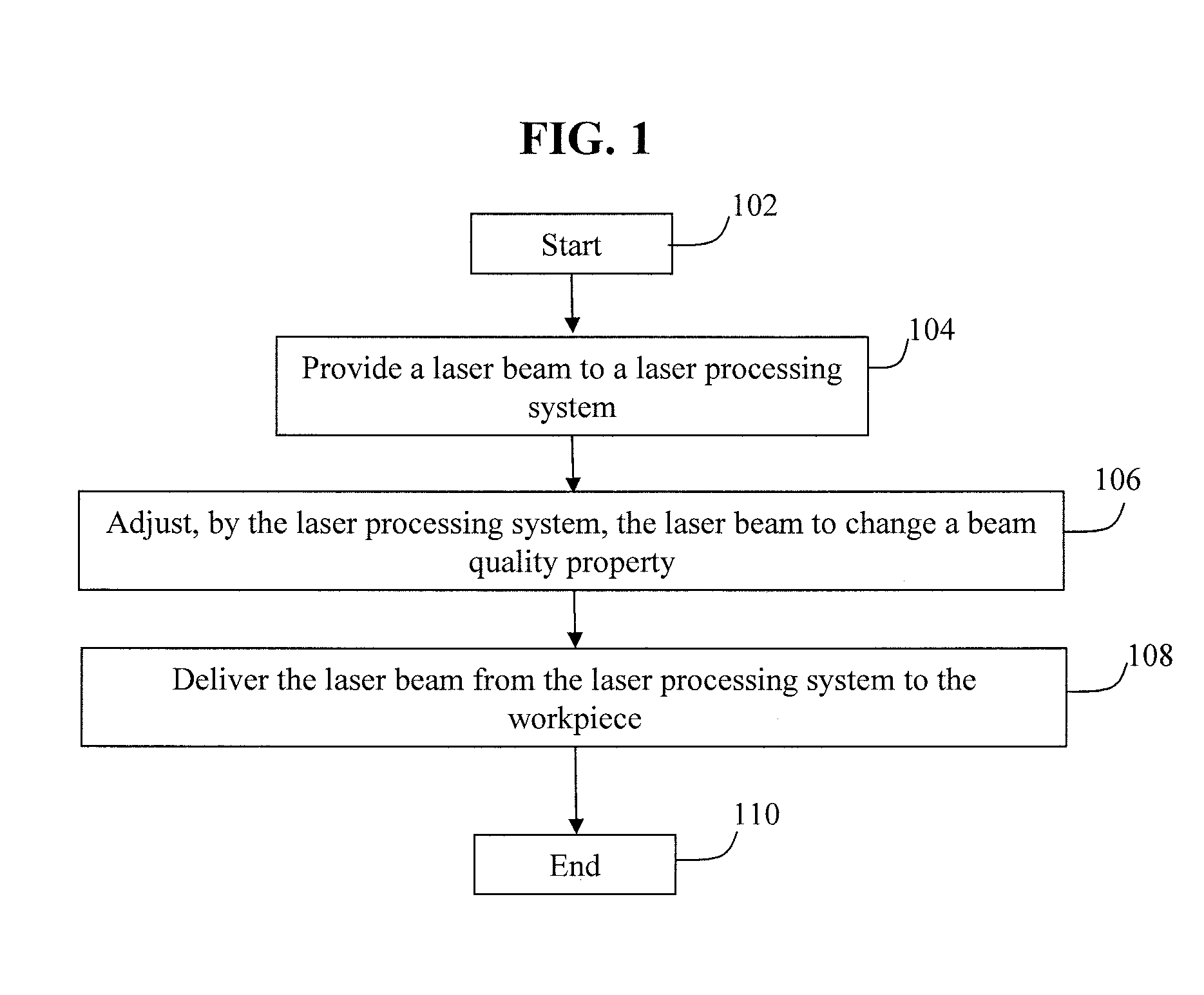
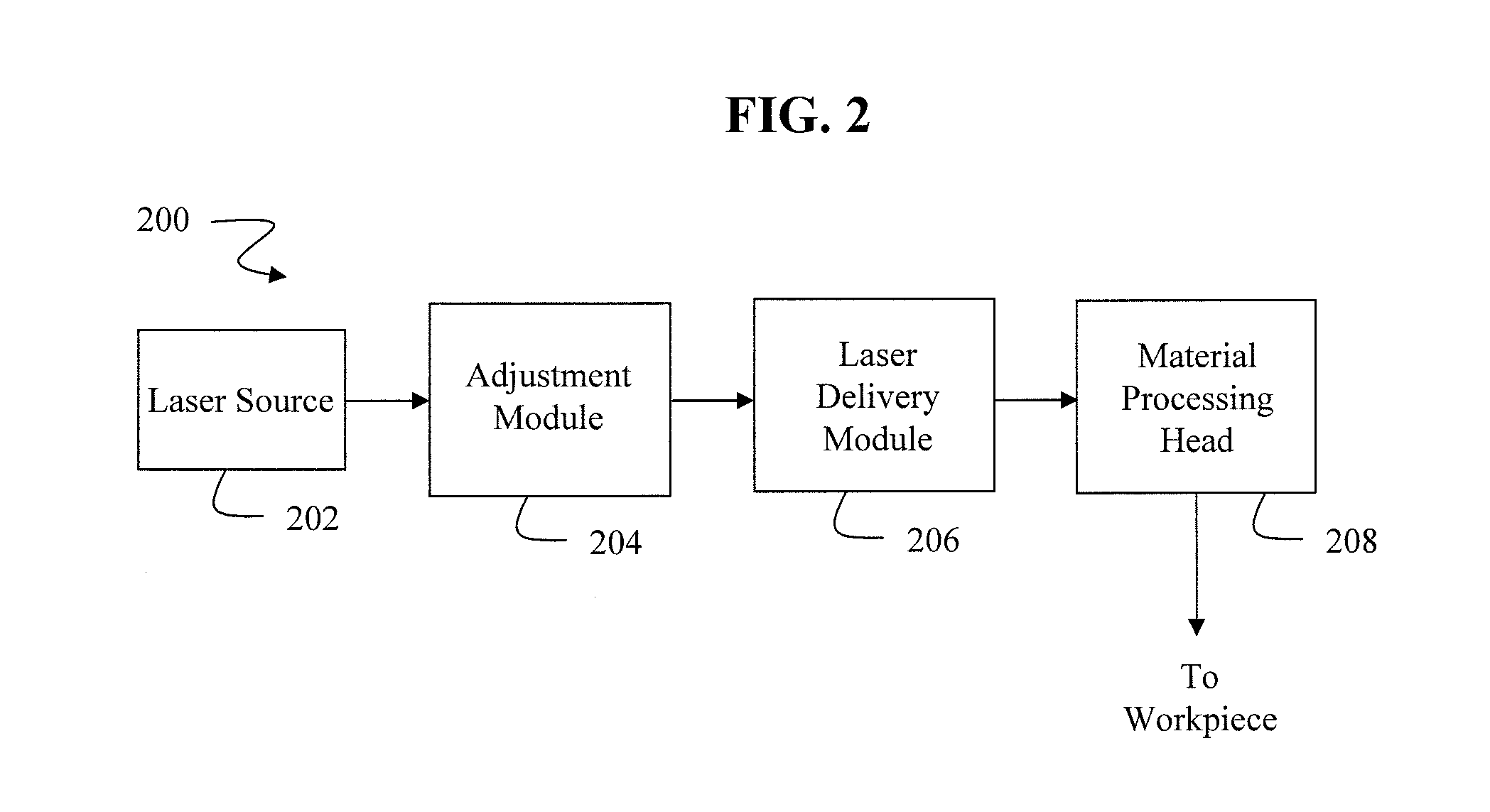
Optimization and control of beam quality for material processing
ActiveUS20130146569A1Enhancing beam quality propertyReduce thicknessOptical light guidesLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingLight beam
Systems and methods are provided for adjusting a laser beam applied to a workpiece in a processing operation. A laser processing system receives the laser beam that is associated with a beam quality property. The laser processing system adjusts the laser beam to change the beam quality property based on a characteristic of the workpiece, a characteristic of the processing operation, or a combination thereof. The adjusted laser beam can also be delivered to the workpiece.
Owner:HYPERTHERM INC
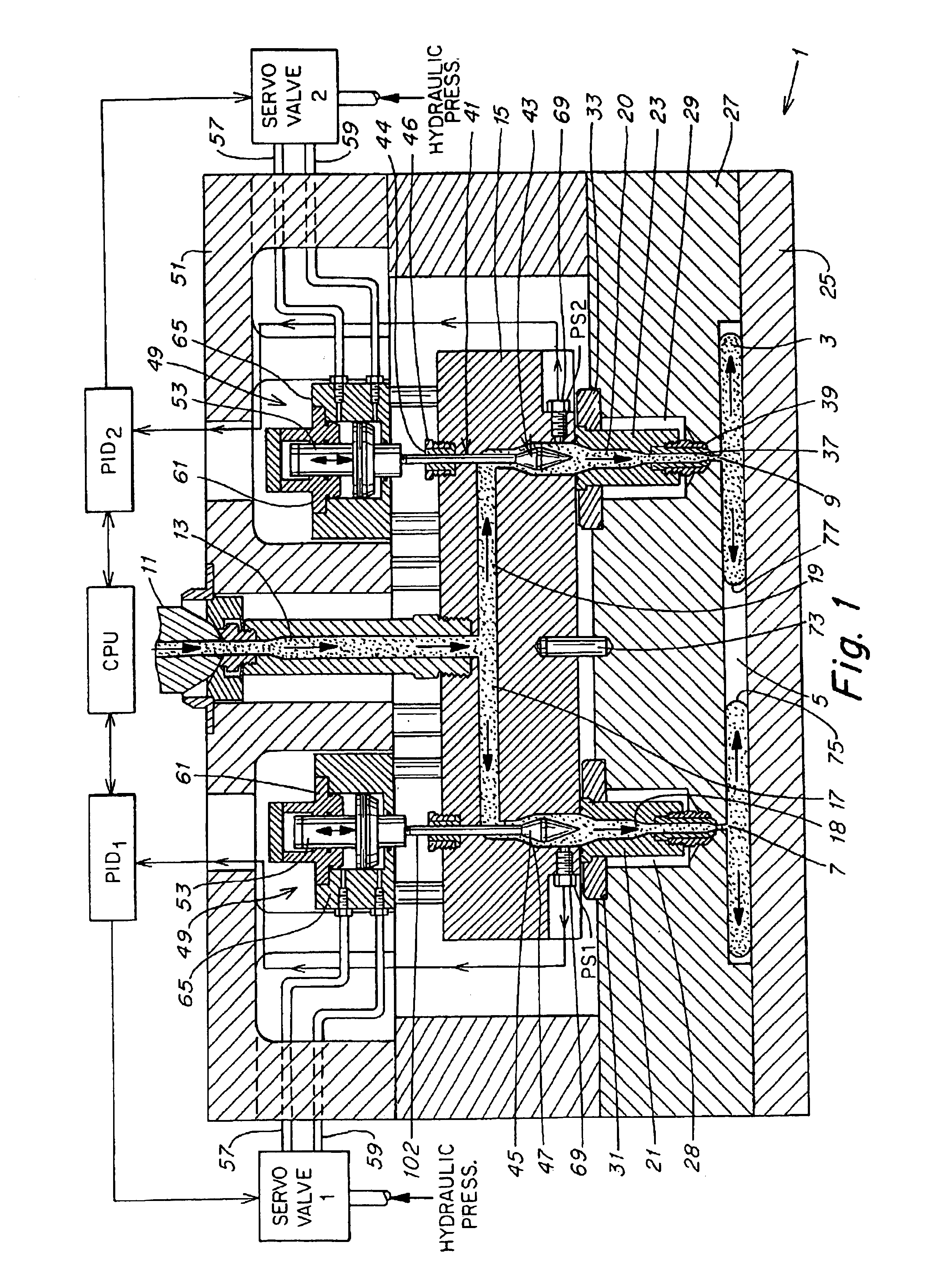
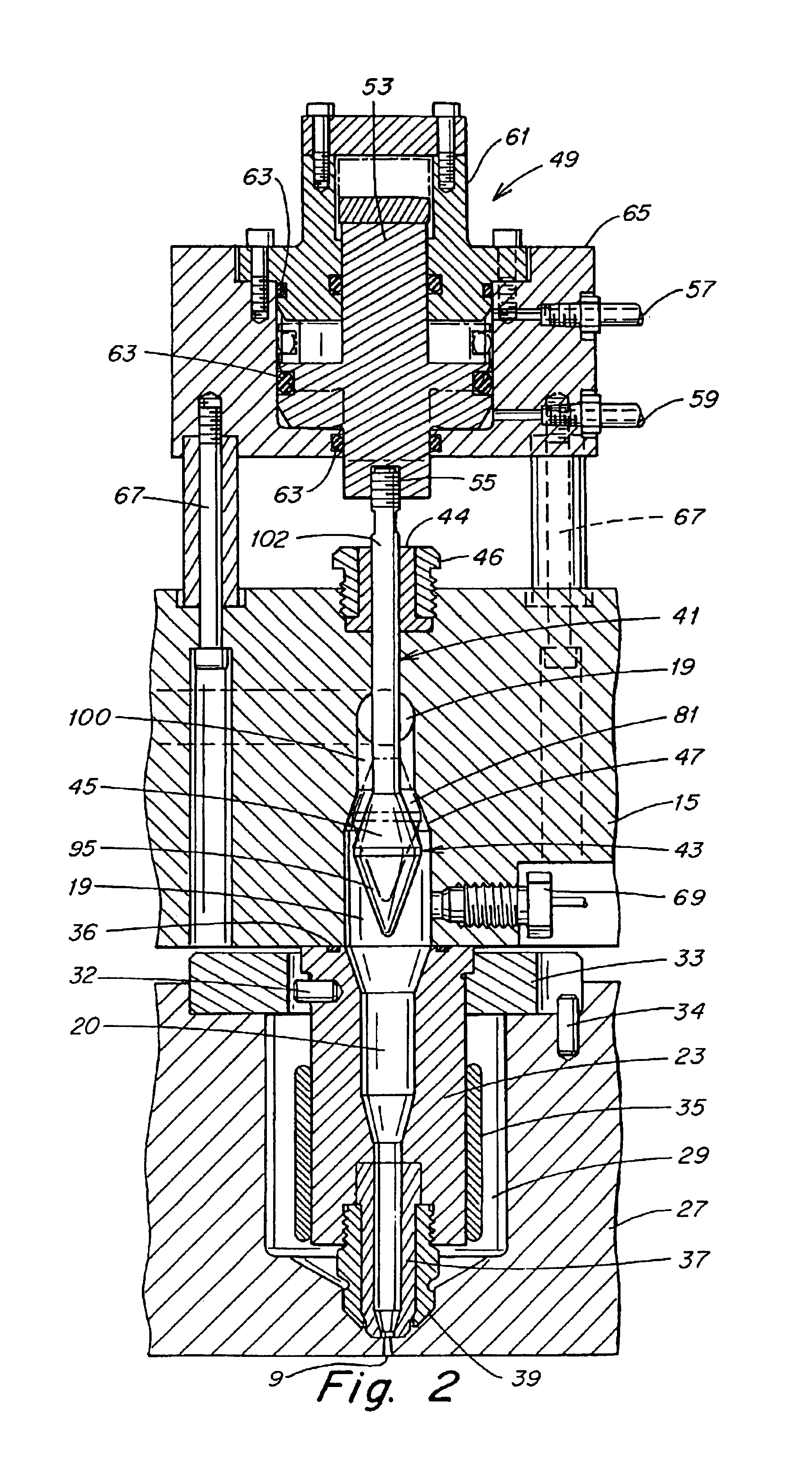
Apparatus for utilizing an actuator for flow control valve gates
Owner:SYNVENTIVE MOLDING SOLUTIONS INC
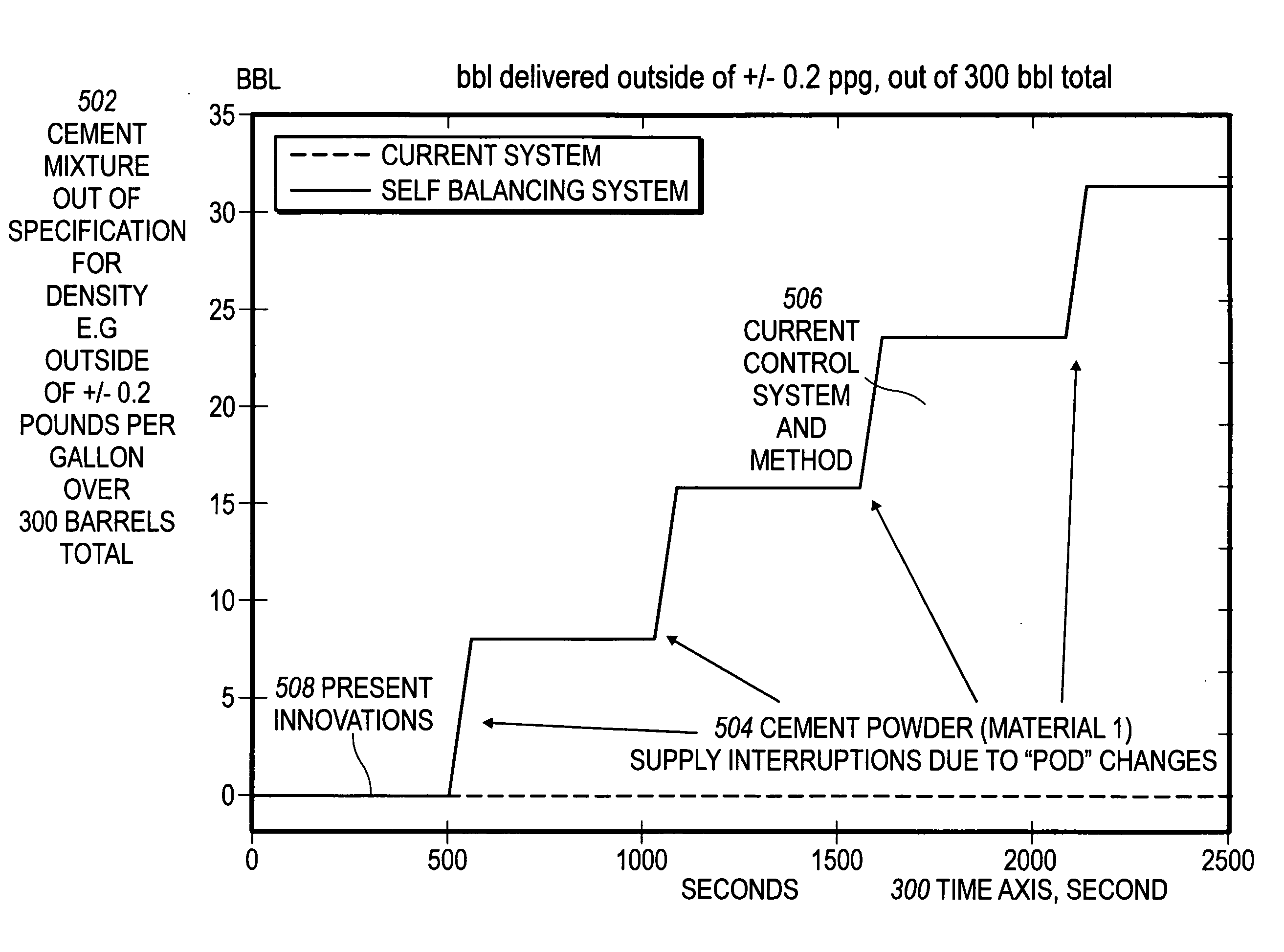
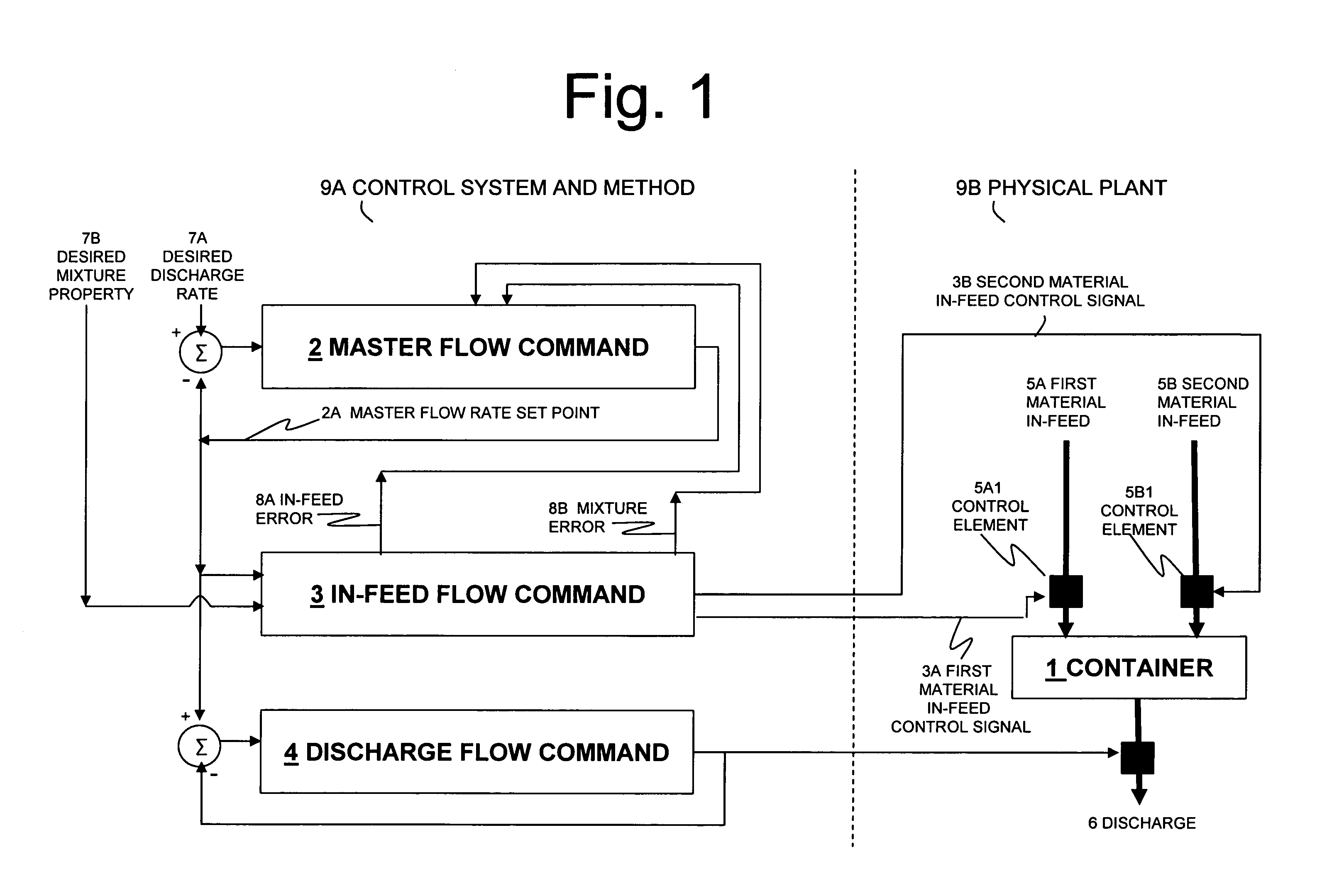
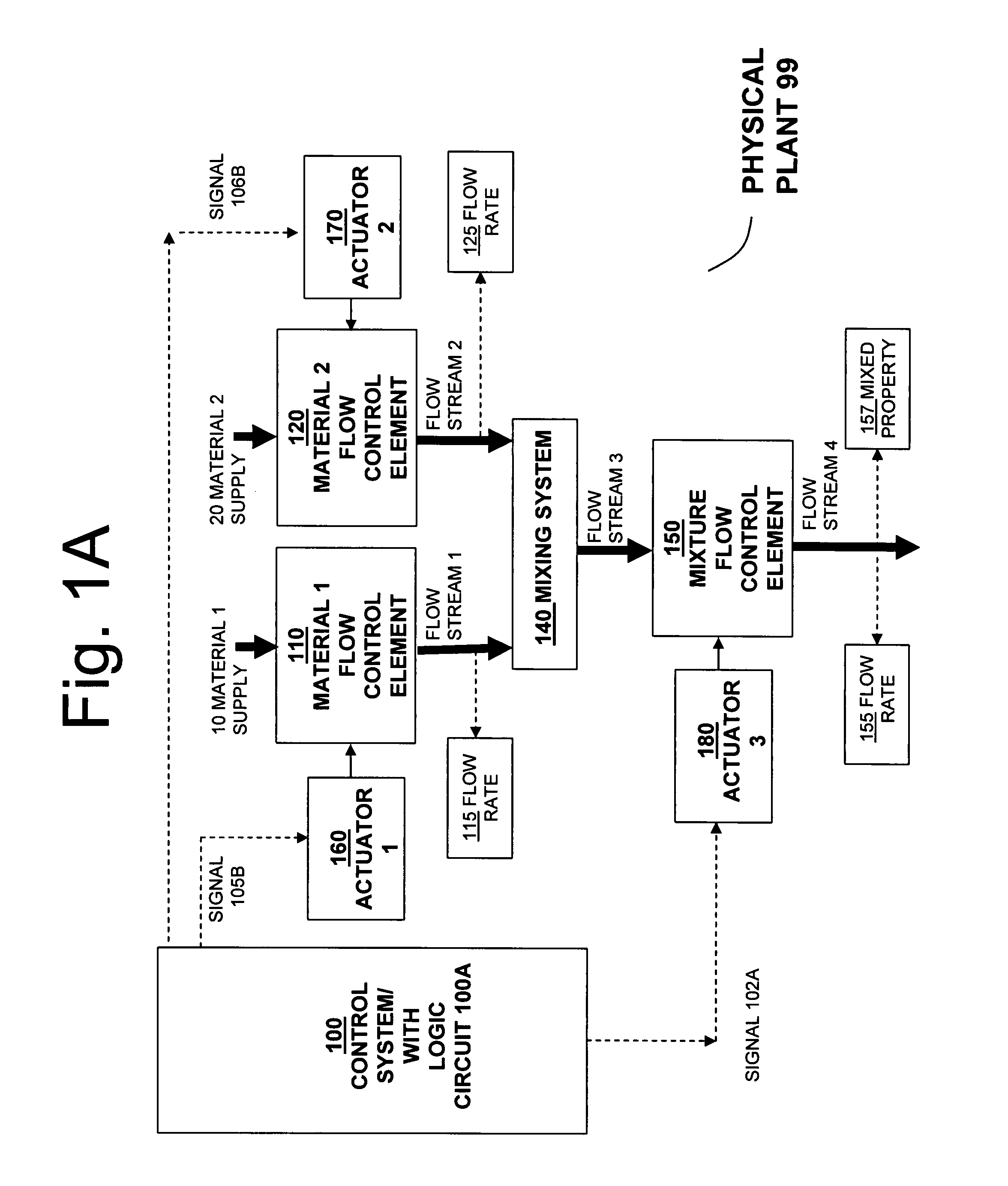
Systems for self-balancing control of mixing and pumping
ActiveUS20080165613A1Reduce needImprove consistencySampled-variable control systemsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsControl signalControl system
Systems for controlling the in-feed and discharge rates of materials flowing into and out of a mixing process where one priority is to achieve a target mixture flow rate from the mixing process and another priority can be to achieve a target value for a mixture property. Actuators can be operated to control material in-feed rates, the mixture composition, and discharge rate, and can maintain a hold-up of the mixture in the mixing process. A total flow rate controller provides a control signal to a controller acting on the discharge rate and a controller acting on the in-feed rates. The mixture discharge flow rate can be automatically reduced from its desired target when the commanded rate of at least one of the materials exceeds its available supply rate as inferred from an inability to maintain the targeted value for the mixture property.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
System and Method for Controlling the Presentation of Material and Operation of External Devices
Owner:READ ALOUD TECH
Carbonising and/or Activating Carbonaceous Material
A method is provided for carbonizing and activating carbonaceous material, which comprises supplying the material to an externally fired rotary kiln maintained at carbonizing and activating temperatures, the kiln having a downward slope to progress the material as it rotates, the kiln having an atmosphere substantially free of oxygen provided by a counter-current of steam or carbon dioxide, and annular weirs being provided at intervals along the kiln to control progress of the material. There may further be provided an externally fired rotary kiln for carbonizing and activating carbonaceous material having a hollow rotary body that has a downward slope towards a discharge end thereof, and which is provided at intervals along its length with annular weirs for controlling progress of the carbonaceous material. In embodiments, there is also provided a process is for producing discrete solid beads of polymeric material e.g. phenolic resin beads having a mesoporous structure, which may be useful as feedstock for the above mentioned carbonization / activation process or which may have other utility e.g. as ion exchange resins. The process may produce resin beads on an industrial scale without aggregates of resin building up speedily and interrupting production. The process comprises the steps of: (a) combining a stream of a polymerizable liquid precursor e.g. a novolac and hexamine as cross-linking agent dissolved in a first polar organic liquid e.g. ethylene glycol with a stream of a liquid suspension medium which is a second non-polar organic liquid with which the liquid precursor is substantially or completely immiscible e.g. transformer oil containing a drying oil; (b) mixing the combined stream to disperse the polymerizable liquid precursor as droplets in the suspension medium e.g. using an in-line static mixer; (c) allowing the droplets to polymerise in a laminar flow of the suspension medium so as to form discrete solid beads that cannot agglomerate; and (d) recovering the beads from the suspension medium. There is also provided apparatus for forming discrete solid beads of polymeric material, said apparatus comprising: a first line for conveying s stream of a polymerizable liquid precursor; a second line for conveying a stream of a dispersion medium with which the polymerizable liquid precursor is substantially or completely immiscible; an in-line mixer configured to receive a combined flow from the first and second lines and to disperse the polymerizable liquid precursor as droplets in the dispersion medium; a vertical polymerization column configured to receive the dispersion medium with the droplets dispersed therein and to permit the polymerizable liquid precursor polymerize while descending the column in a descending flow of polymerization medium; and a vessel at the base of the column for receiving the descending flow of dispersion medium and collecting polymerized solid beads.
Owner:BRITISH AMERICAN TOBACCO (INVESTMENTS) LTD
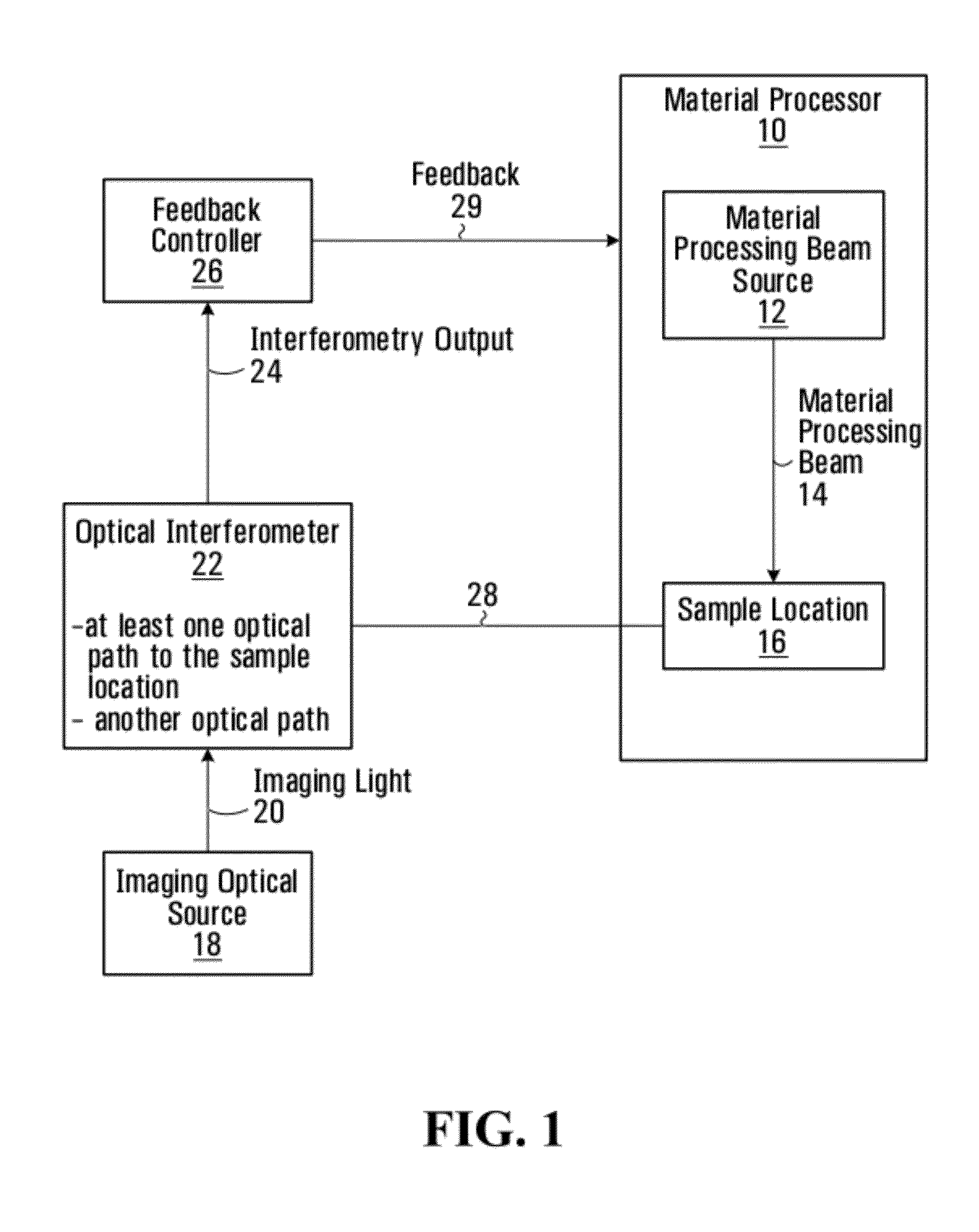
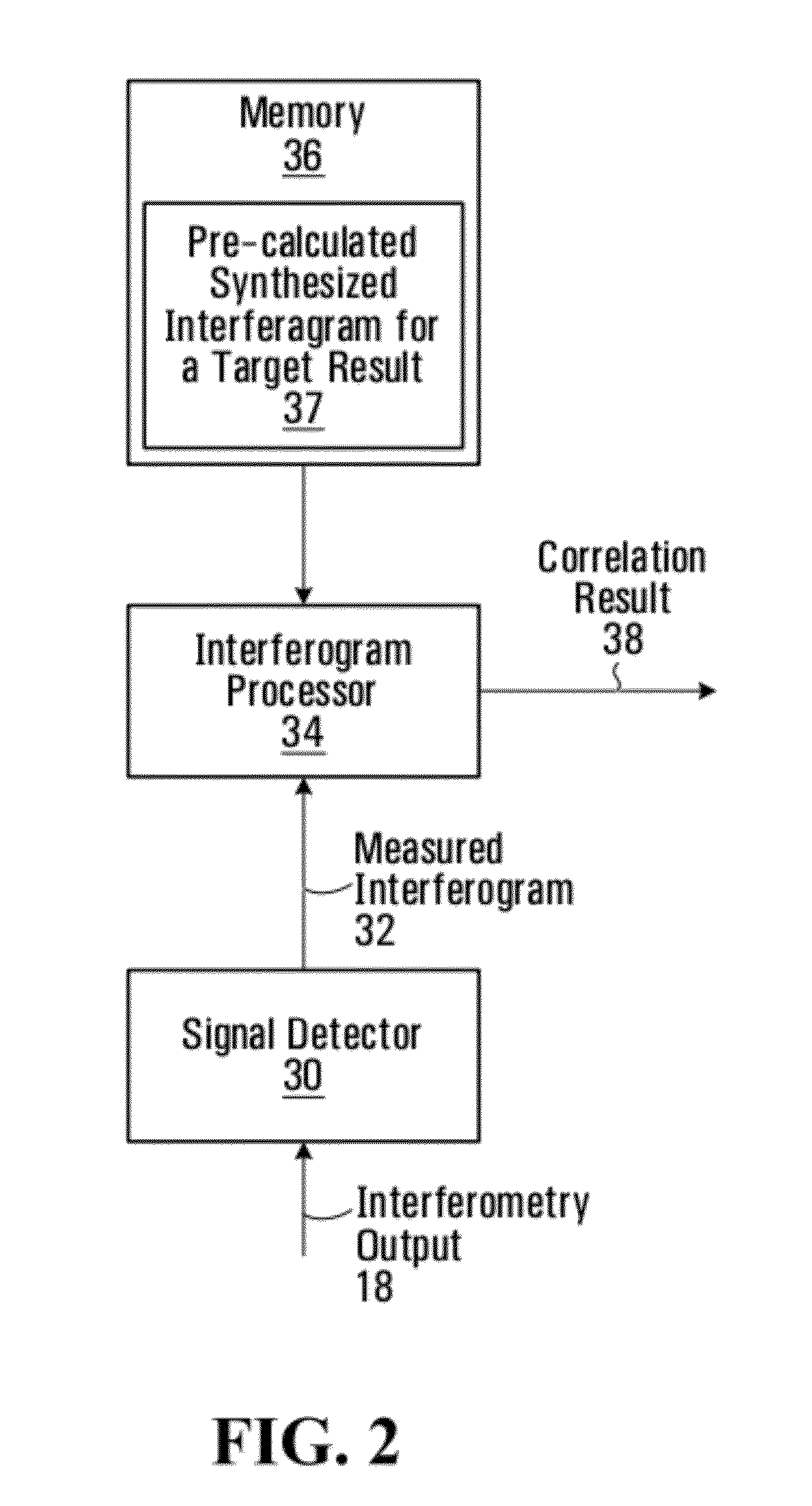
Methods and systems for coherent imaging and feedback control for modification of materials
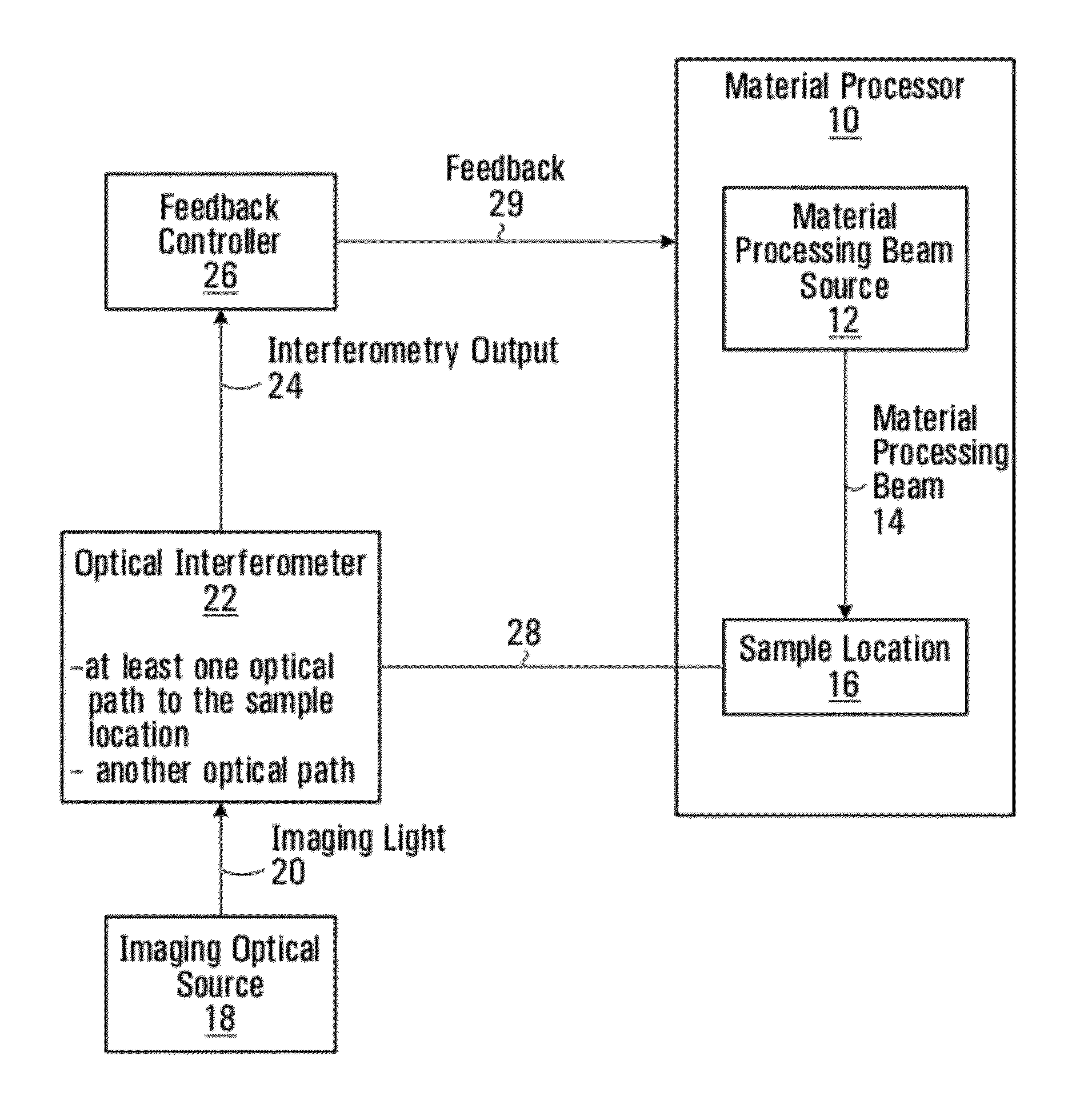
ActiveUS8822875B2Material analysis by optical meansArc welding apparatusFeedback controllerEngineering
Methods and systems are provided for using optical interferometry in the context of material modification processes such as surgical laser or welding applications. An imaging optical source that produces imaging light. A feedback controller controls at least one processing parameter of the material modification process based on an interferometry output generated using the imaging light. A method of processing interferograms is provided based on homodyne filtering. A method of generating a record of a material modification process using an interferometry output is provided.
Owner:LASER DEPTH DYNAMICS INC +1
Modifying the electro-mechanical behavior of devices
InactiveUS7161094B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOptical propertyEngineering
A MEMS device is packaged with a control material that is included in the package to affect an operation of a moveable element of the device. The control material may affect operational characteristics including actuation and release voltages and currents, mechanical affects including damping and stiffness, lifetime of the device, optical properties, thermal affects and corrosion. The control material may be inserted into the package as part of any of several structural components of the package or the MEMS device.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Material dispenser with a control valve
A syringe comprising a chamber and material transfer portion with a cavity in communication with an inlet portion and an outlet portion. The inlet portion includes an inlet valve means for controlling material flow therethrough, and the material transfer portion includes a control valve operable between a first position to control the inflow of material from the inlet portion to the material container portion, and a second position to control the flow of material from the chamber to the outlet portion, and the outlet portion includes a releasable lock means for allowing discharge the material through the outlet portion.
Owner:VASOGEN IRELAND LTD
Methods for controlling crystal growth, crystallization, structures and phases in materials and systems
InactiveUS20060037177A1Growth inhibitionExisting techniquePolycrystalline material growthOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxidePhase formationEnergy regulation
This invention relates to novel methods for affecting, controlling and / or directing various crystal formation, structure formation or phase formation / phase change reaction pathways or systems by exposing one or more components in a holoreaction system to at least one spectral energy pattern. In a first aspect of the invention, at least one spectral energy pattern can be applied to a crystallization reaction system. In a second aspect of the invention, at lest one spectral energy conditioning pattern can be applied to a conditioning reaction system. The spectral energy conditioning pattern can, for example, be applied at a separate location from the reaction vessel (e.g., in a conditioning reaction vessel) or can be applied in (or to) the reaction vessel, but prior to other (or all) crystallization reaction system participants being introduced into the reaction vessel.
Owner:GR INTELLECTUAL RESERVE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com