Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2535results about "Rotary clutches" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
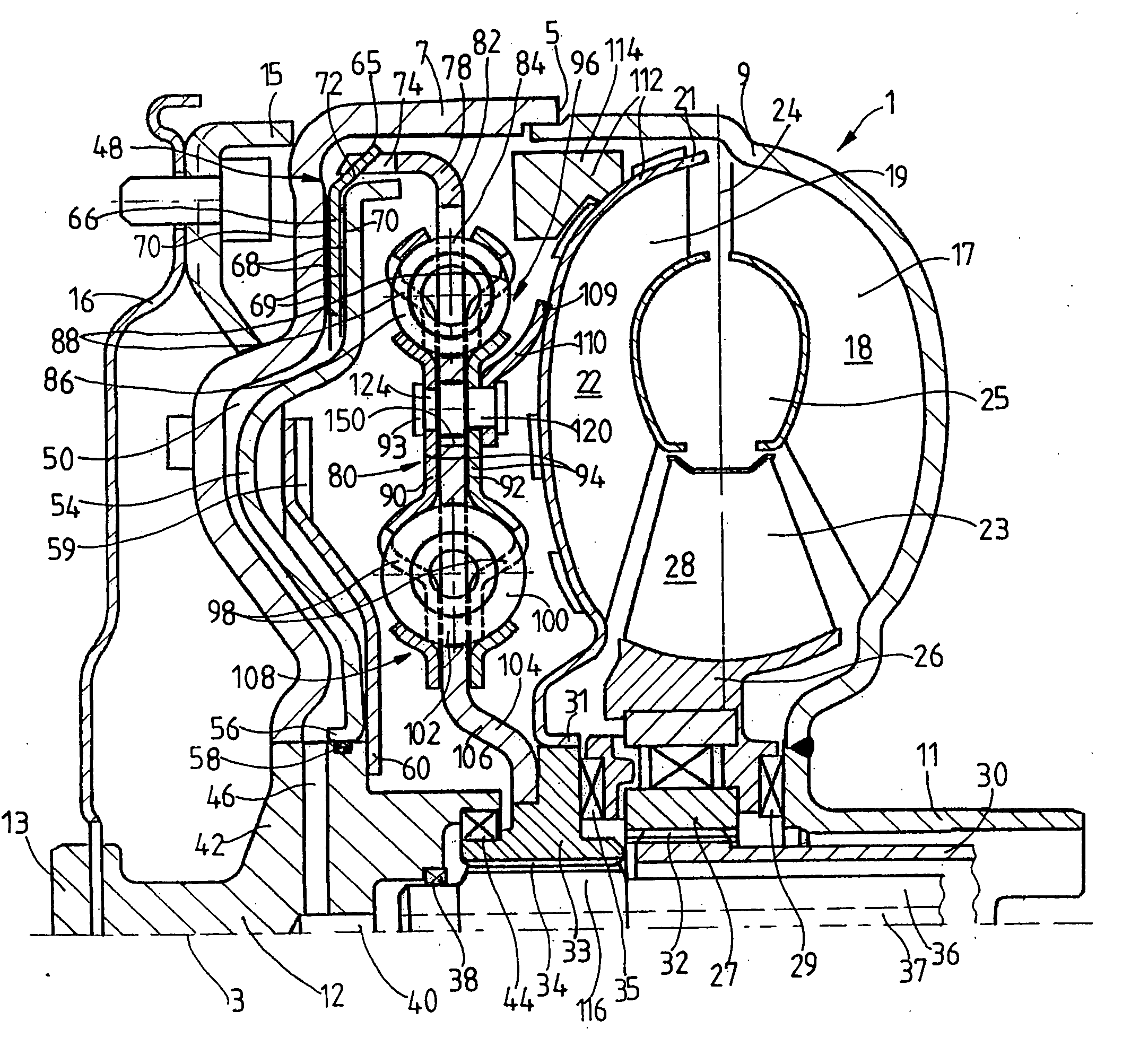
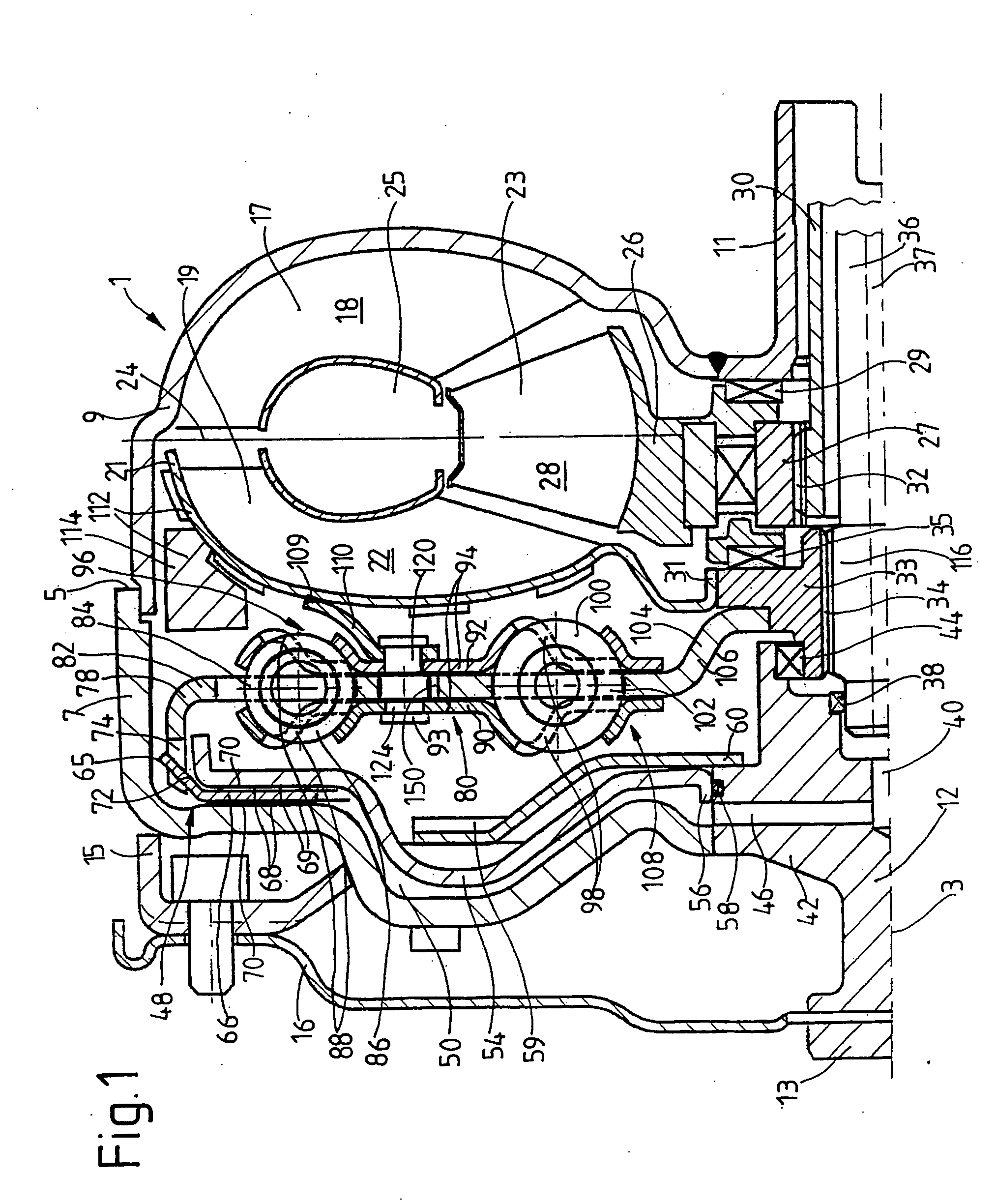
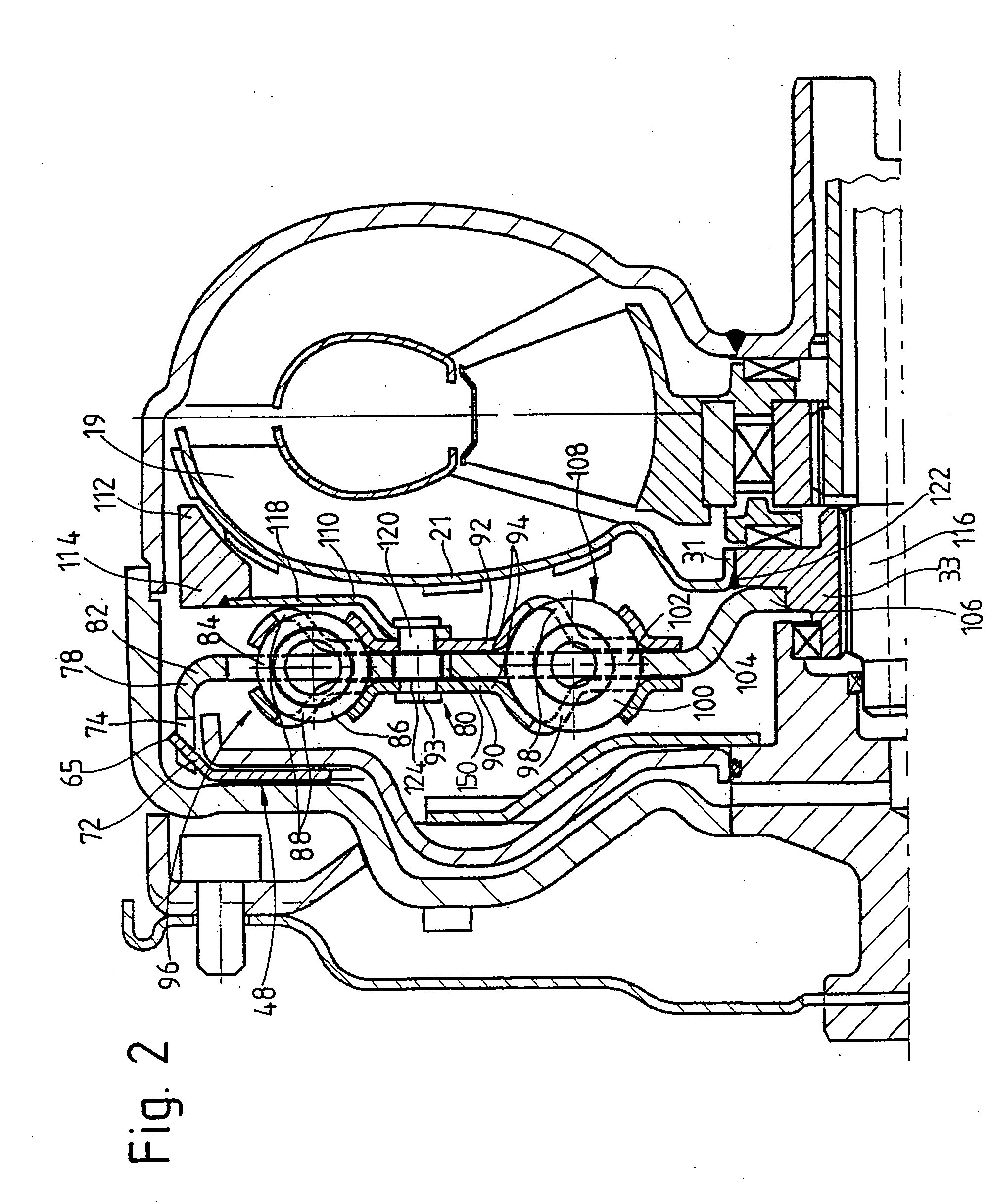
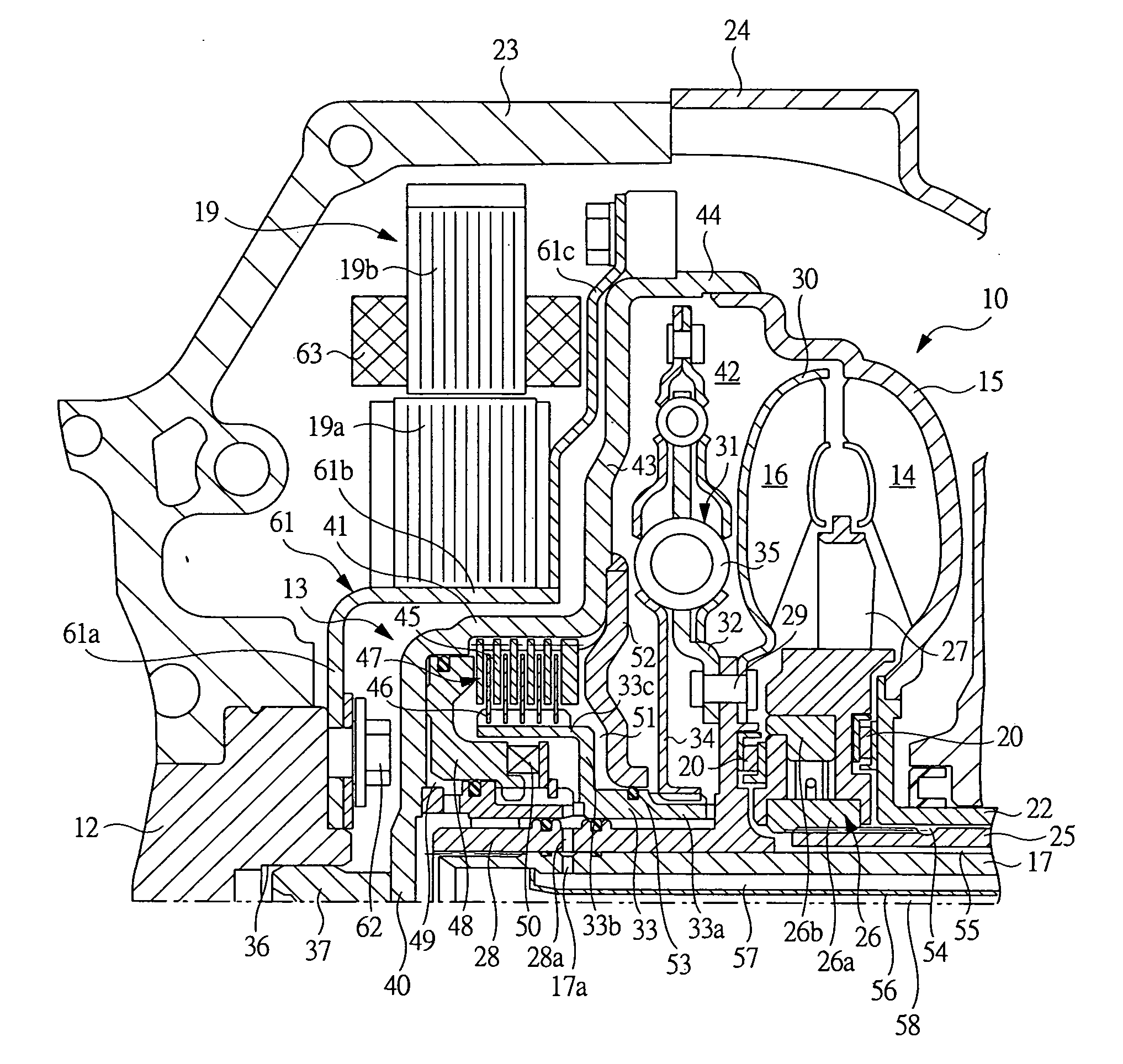
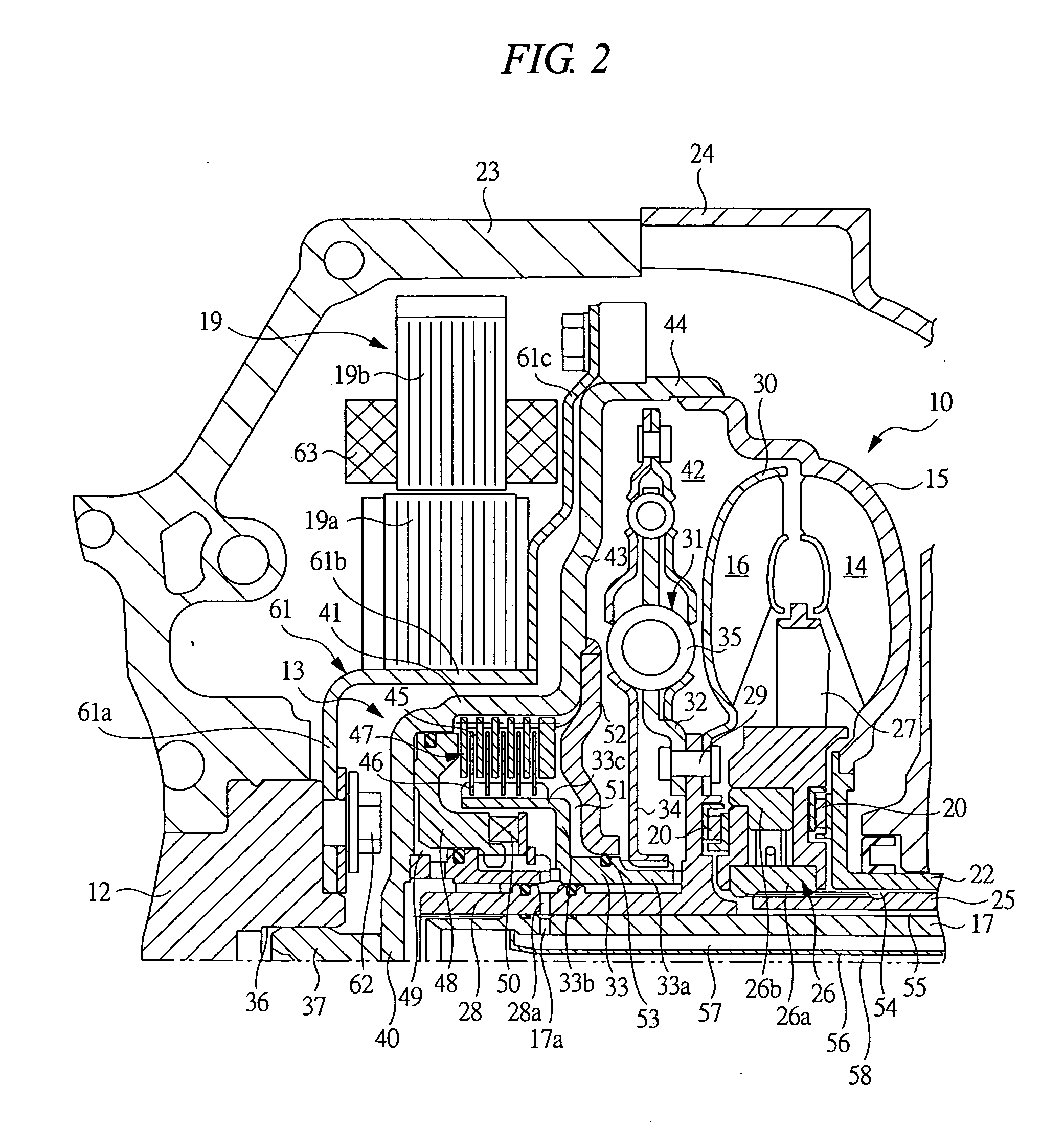
Electrochemical analyte sensor
InactiveUS7003340B2Avoid and reduce corrosionRotary clutchesMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrolysisAnalyte
An electrochemical analyte sensor formed using conductive traces on a substrate can be used for determining and / or monitoring a level of analyte in in vitro or in vivo analyte-containing fluids. For example, an implantable sensor may be used for the continuous or automatic monitoring of a level of an analyte, such as glucose, lactate, or oxygen, in a patient. The electrochemical analyte sensor includes a substrate and conductive material disposed on the substrate, the conductive material forming a working electrode. In some sensors, the conductive material is disposed in recessed channels formed in a surface of the sensor. An electron transfer agent and / or catalyst may be provided to facilitate the electrolysis of the analyte or of a second compound whose level depends on the level of the analyte. A potential is formed between the working electrode and a reference electrode or counter / reference electrode and the resulting current is a function of the concentration of the analyte in the body fluid.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
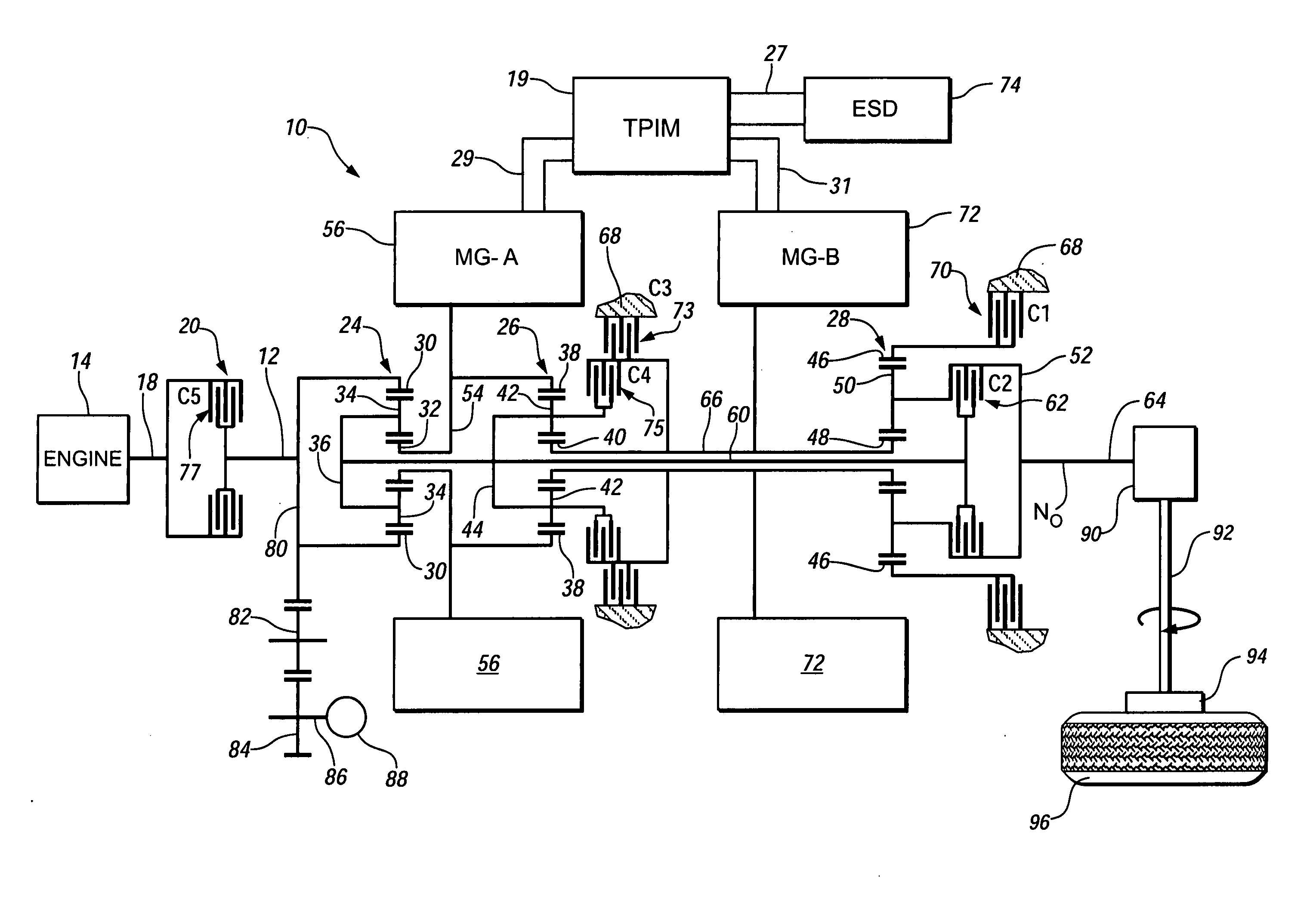
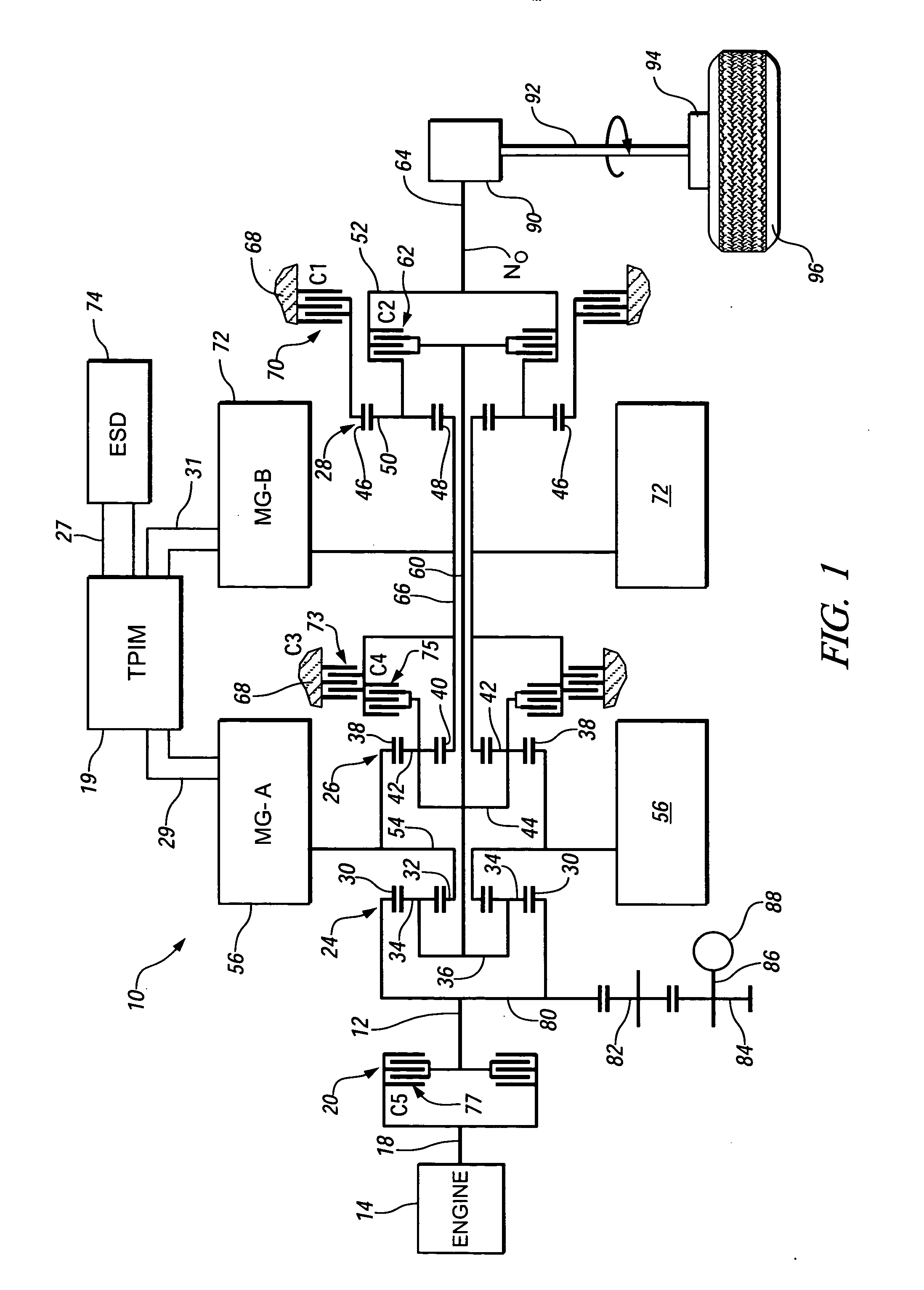
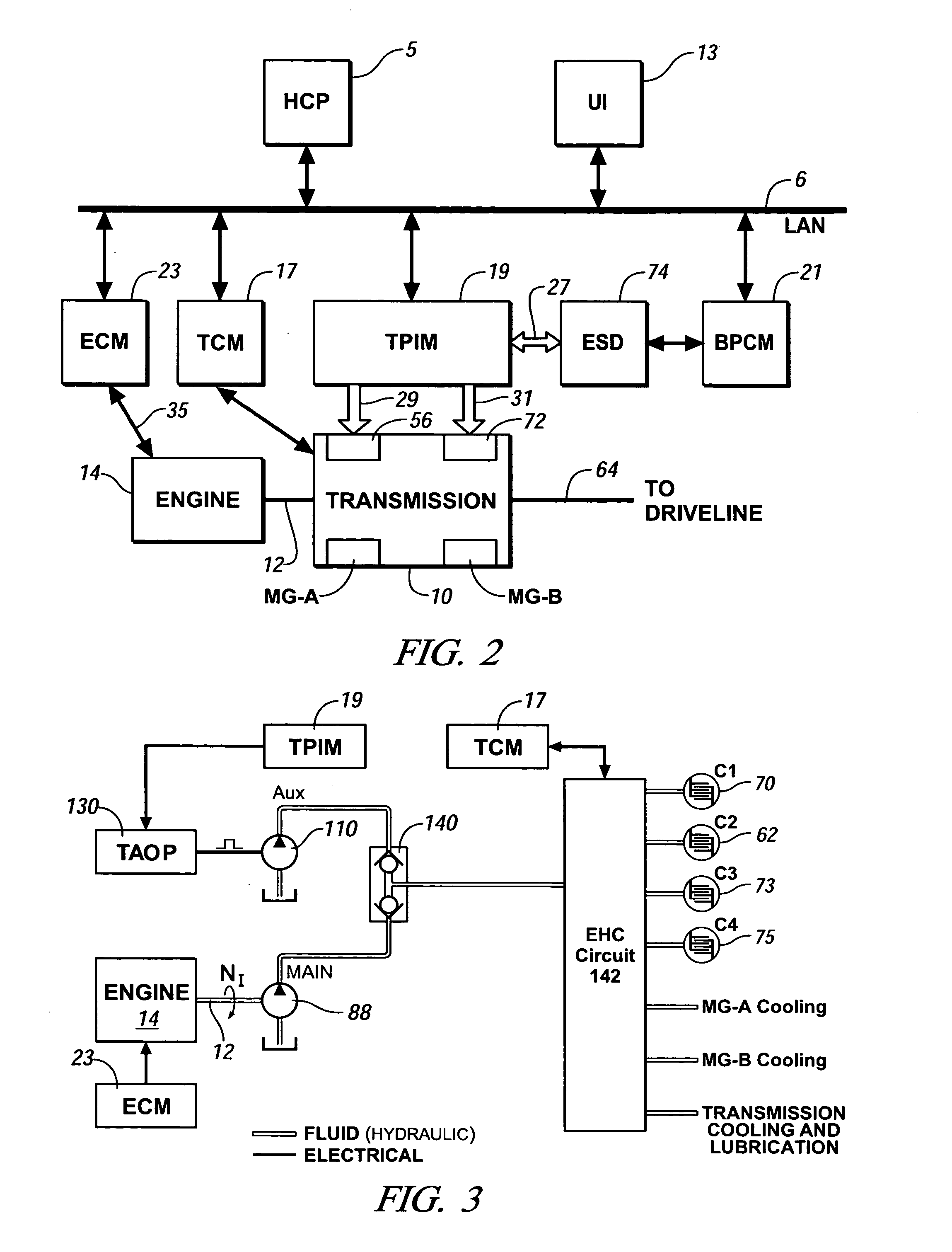
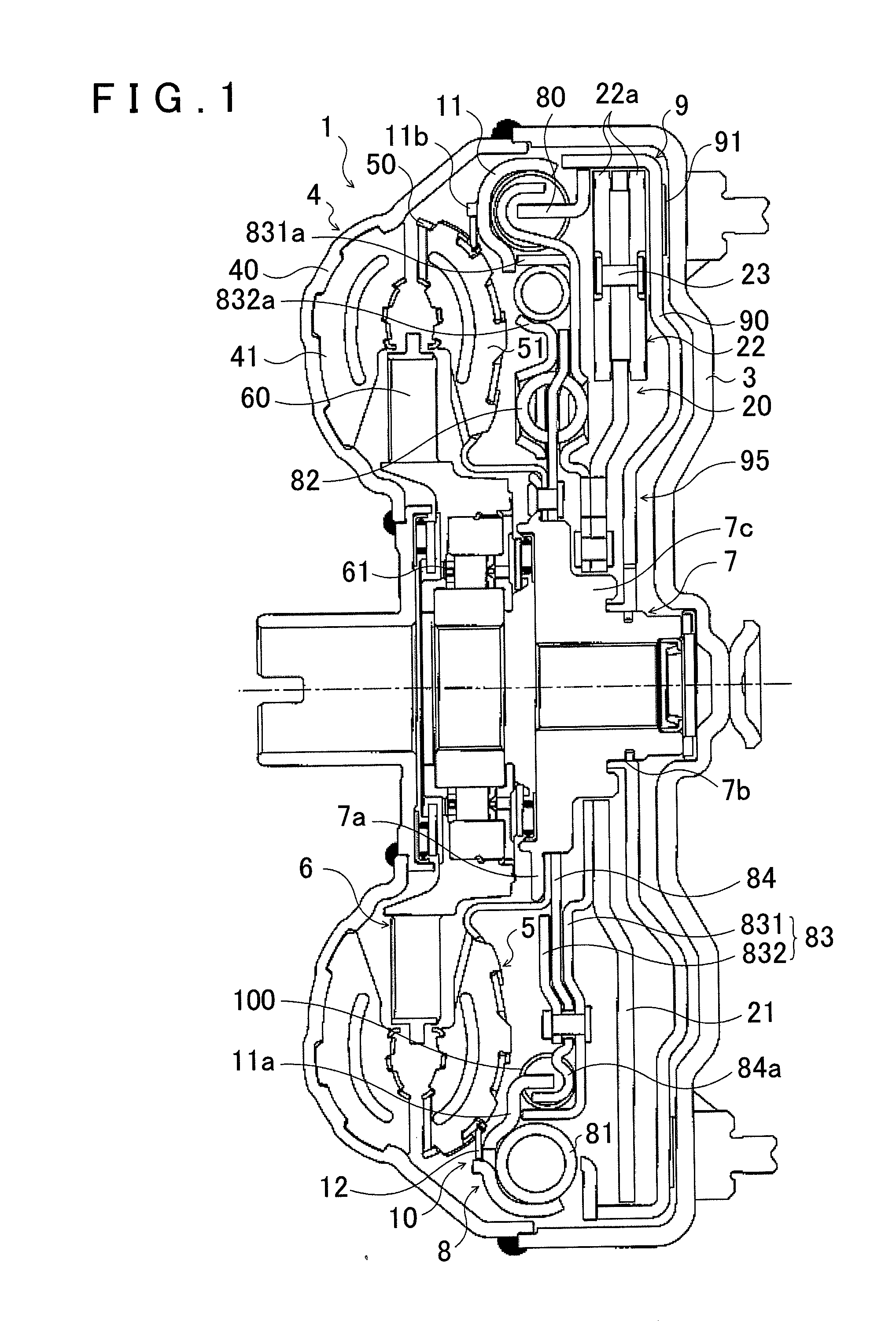
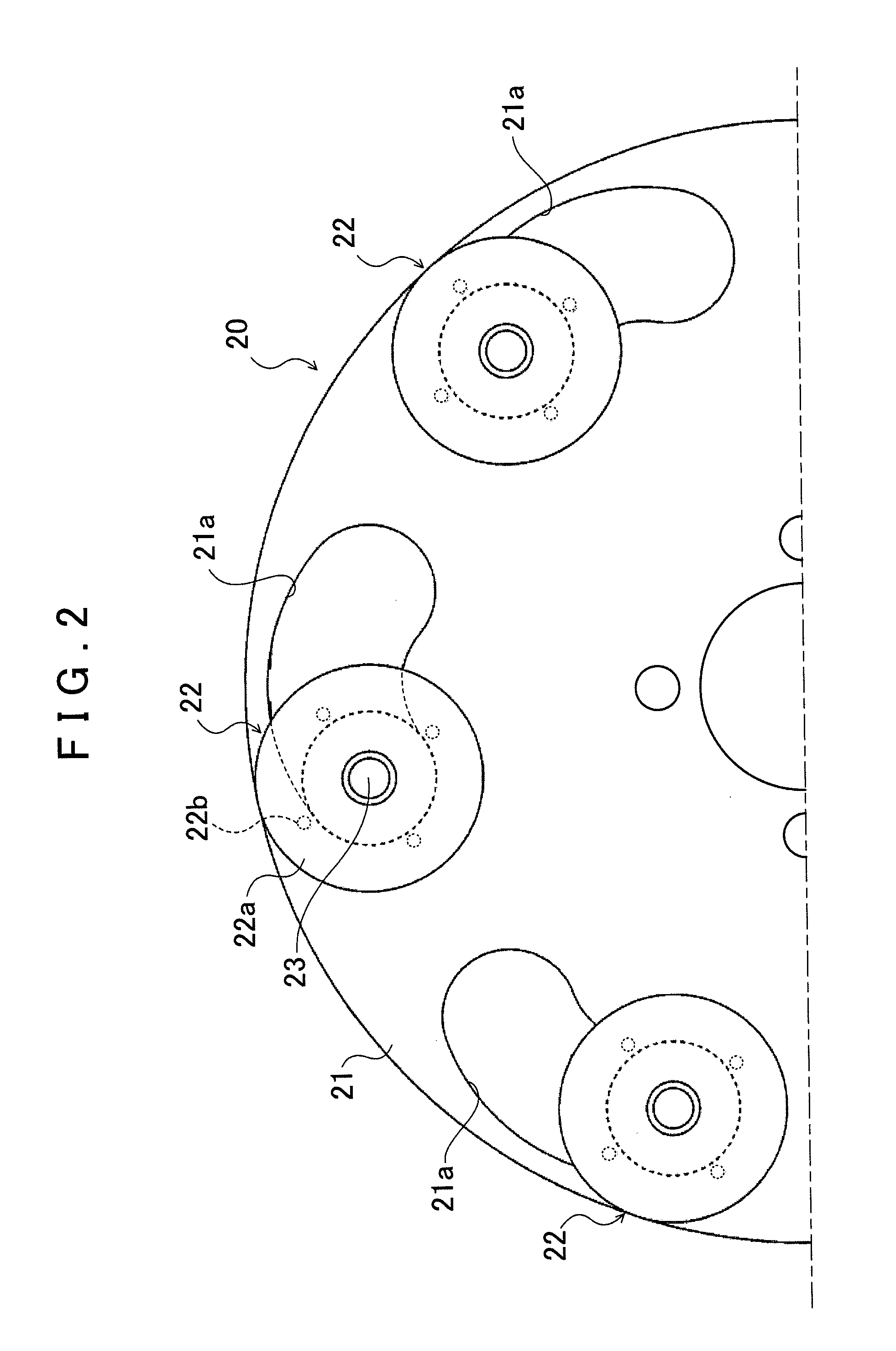
Method and apparatus to control hydraulic pressure in an electro-mechanical transmission
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Z-filter media with reverse-flow cleaning systems and methods
A method for cleaning a filter having Z-media includes providing a filter having Z-media and cleaning the media construction by directing a pulse of compressed gas into the media construction through the downstream flow face. Filter elements useable with such methods include elements made of Z-media. An example system utilizing the method includes a gas turbine air intake system.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
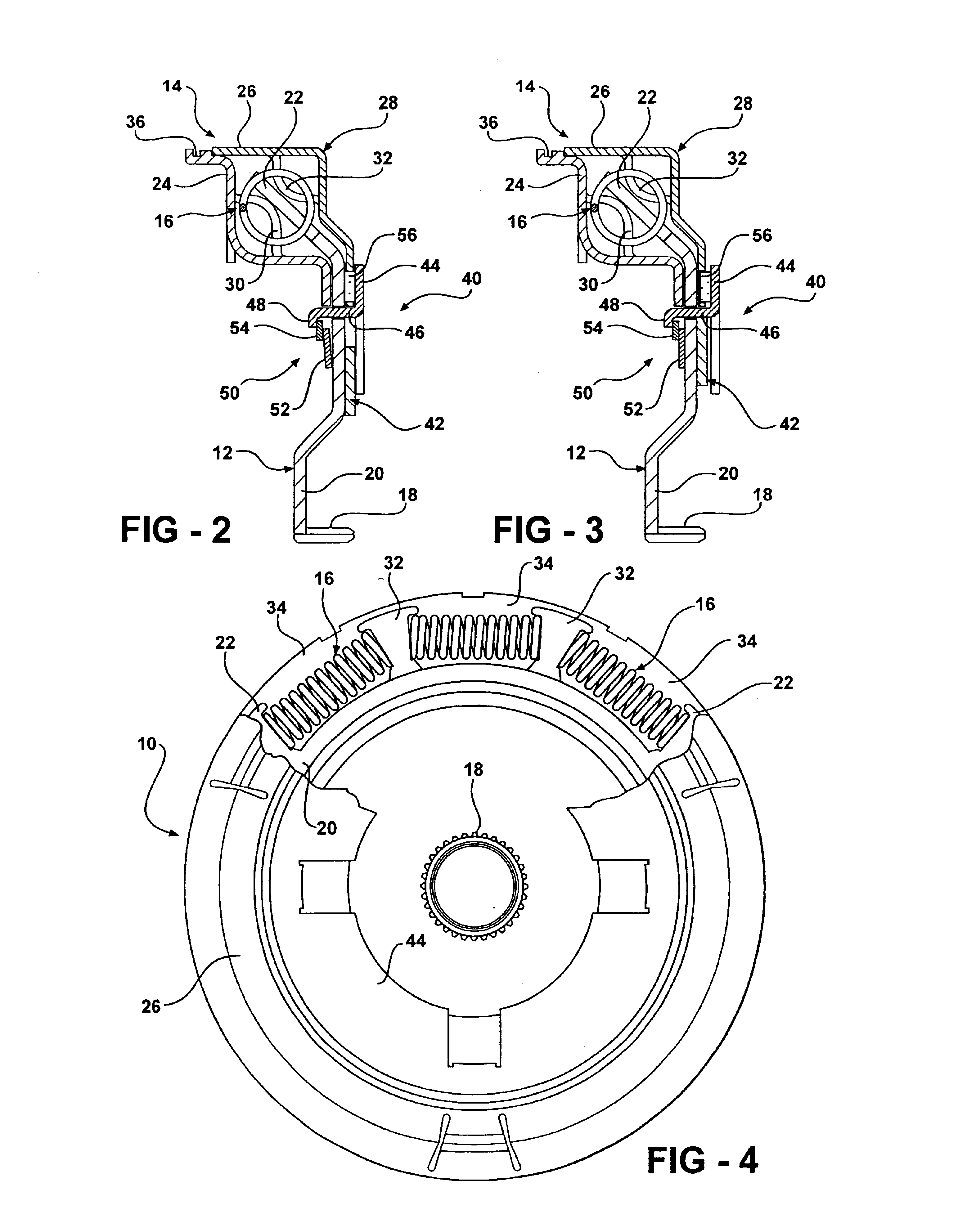
Torsional damper having variable bypass clutch with centrifugal release mechanism
InactiveUS6854580B2Restraint torsionReduce torqueYielding couplingRotary clutchesCentrifugal forceControl theory
A torsional damper (10) rotatably supported for translating torque between a prime mover and the input of a transmission including a torque input member (12) that is operatively connected for rotation with the power take-off of a prime mover, an output member (14) operatively connected for rotation with the input to a transmission and a plurality of damping elements (16) interposed between the input member and the output member. The damping members (16) act to translate torque between the input and output members and to dampen torsional forces generated between the prime mover and the transmission. A bypass clutch (40) acts to translate torque directly between the input and output members thereby providing a path for partial torque translation that bypasses the damping elements at low rotational speeds of the input and output members. In addition, the torsional damper (10) includes a clutch release mechanism (42) that is responsive to centrifugal forces acting on the torsional damper to disengage the bypass clutch (40) to reduce the torque translated directly between the input and output members at high rotational speeds.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
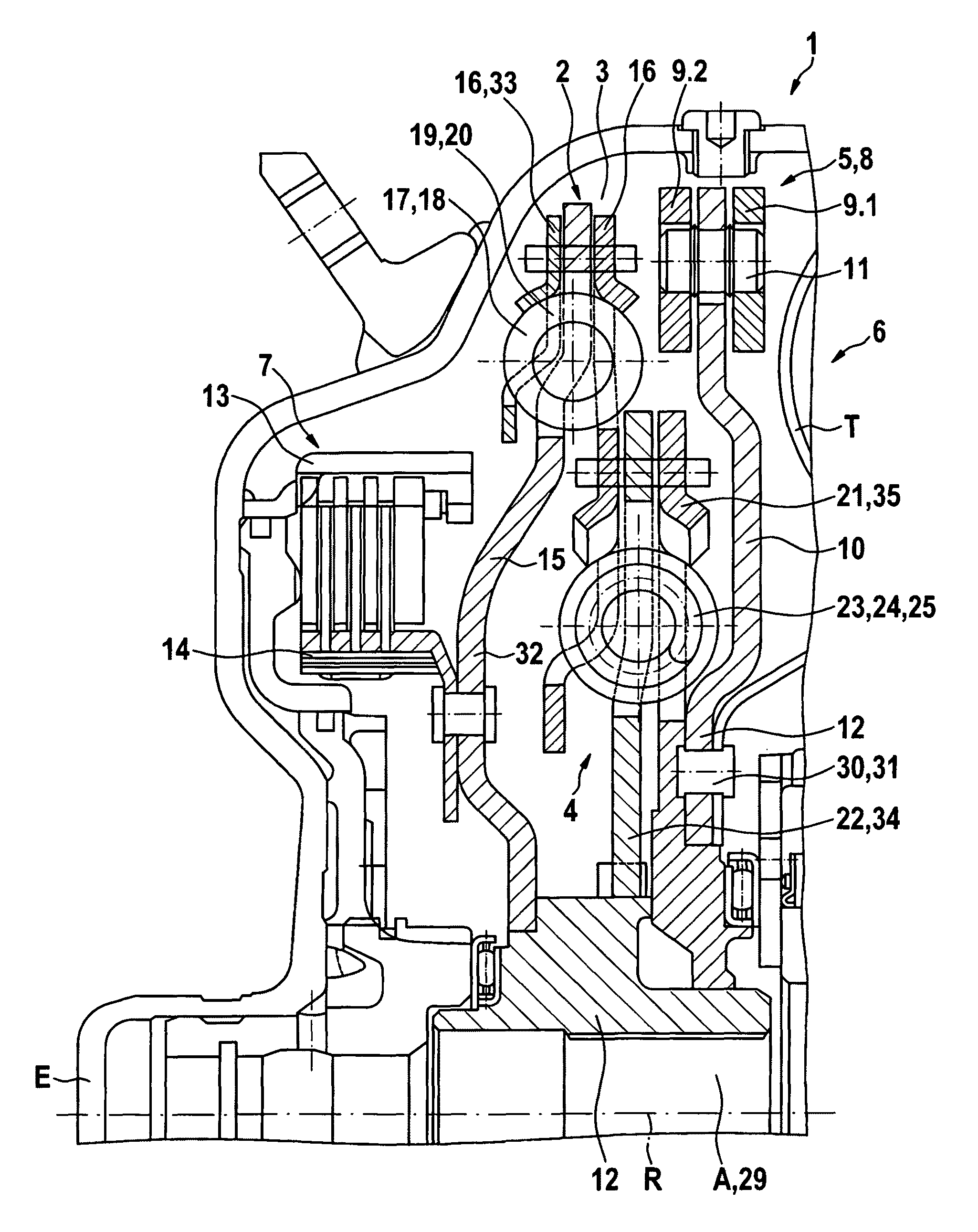
Force transmission device in particular for power transmission between a drive engine and an output
ActiveUS8161739B2Reduce variationEliminate variationRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingTuned mass damperSelf adaptive
A force transmission device, in particular or power transmission between a drive engine and an output, comprising a damper assembly with at least two dampers, which can be connected in series, and a rotational speed adaptive absorber, wherein the rotational speed adaptive tuned mass damper is disposed between the dampers at least in one force flow direction through the force transmission device.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Lockup clutch with a compensation flywheel mass at the torsional vibration damper
A lockup clutch at a hydrodynamic torque converter is constructed with a torsional vibration damper which has a drive-side transmission element and a driven-side transmission element which is rotatable relative to the latter. Both of the transmission elements are provided with driving devices for driving elastic elements of a damping device. A carrier for a compensation flywheel mass is associated with the driven-side transmission element, wherein the carrier is connected with the turbine wheel on the one hand and with the driven-side driving device of the elastic elements on the other hand so as to be fixed with respect to rotation relative thereto and is provided at least with a cutout for receiving the compensation flywheel mass. The cutout has a guide path at least in its area of contact with the compensation flywheel mass, which guide path allows a movement of the compensation flywheel mass with at least one component perpendicular to the radial direction at the carrier.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
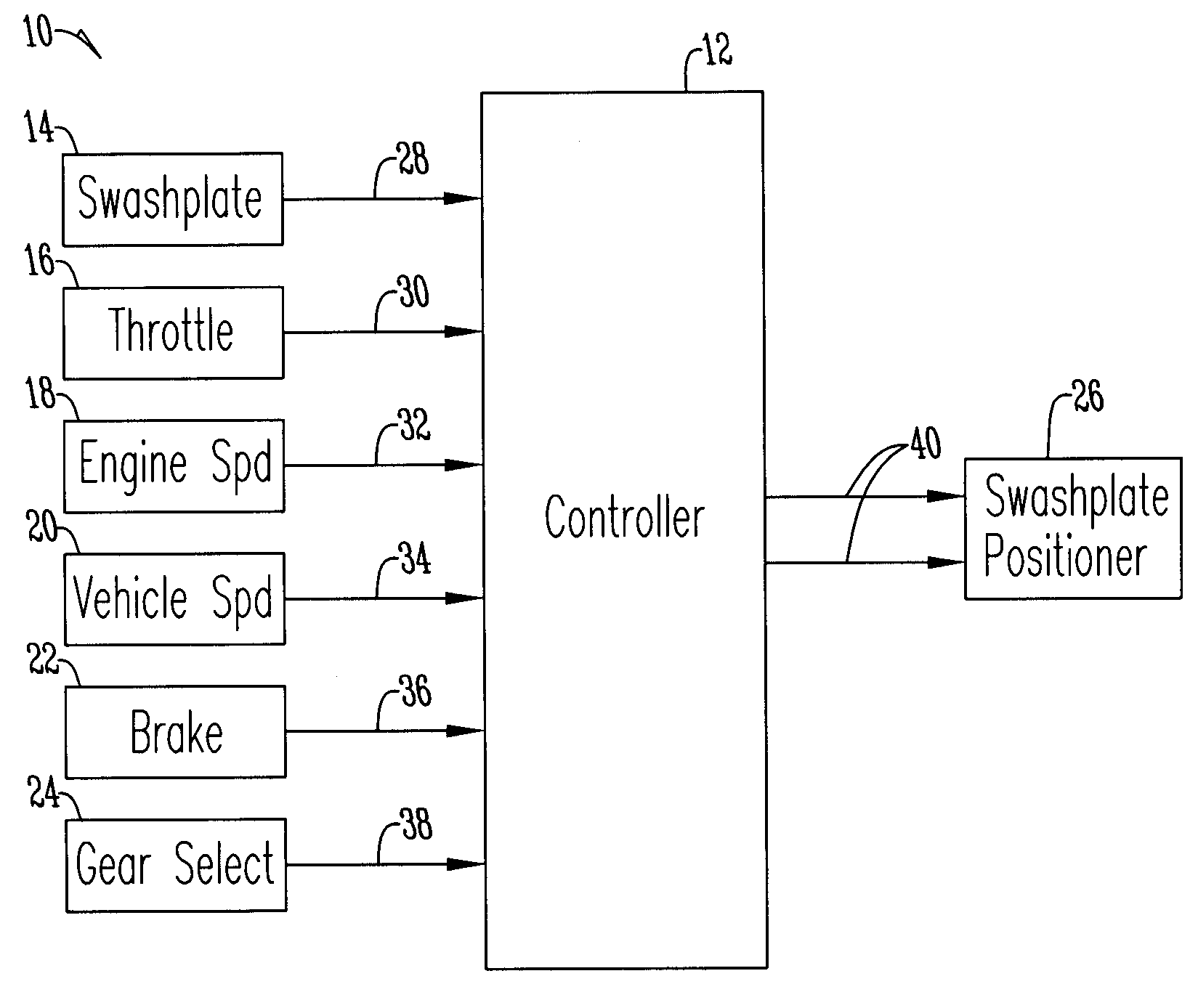
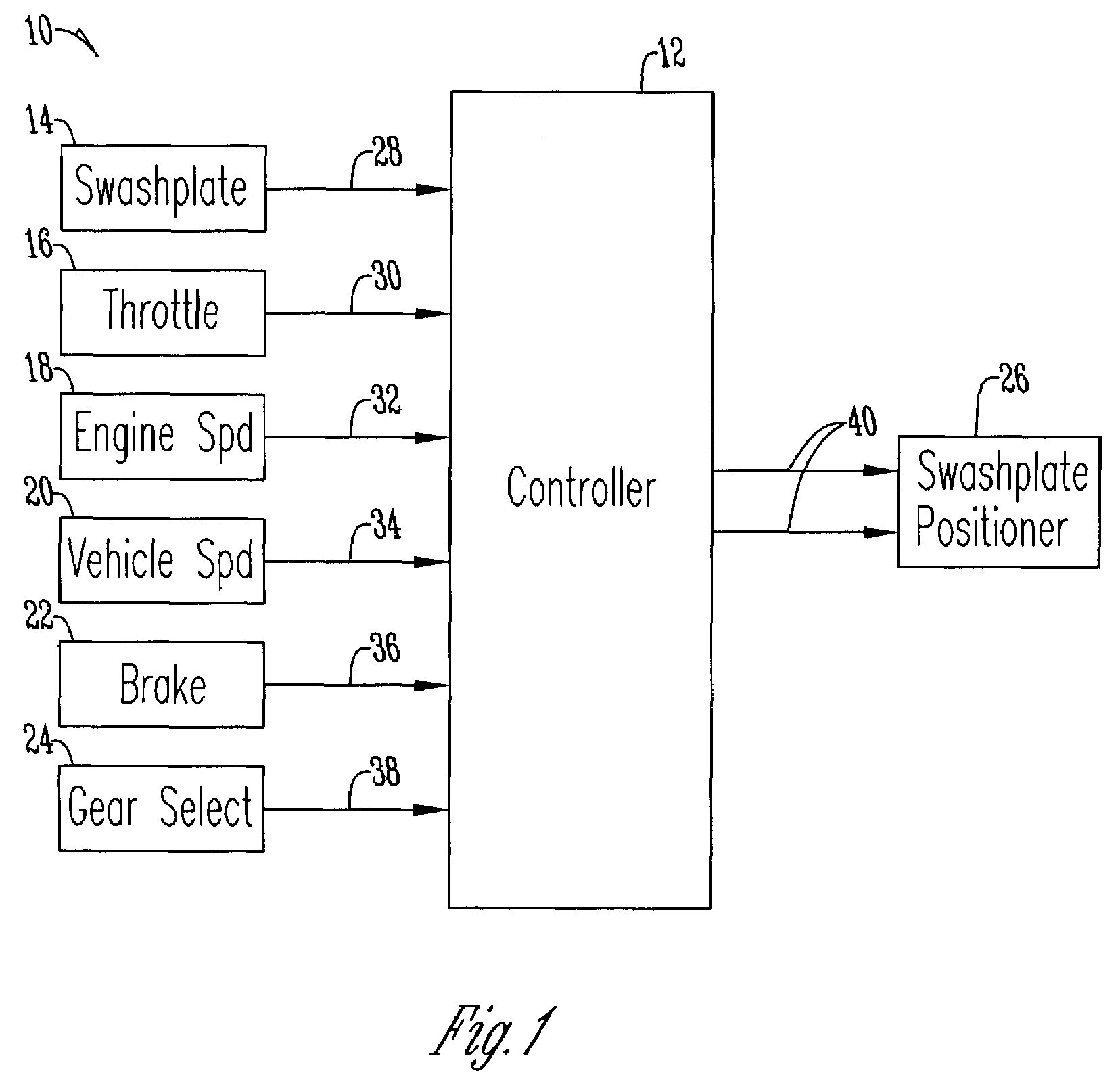
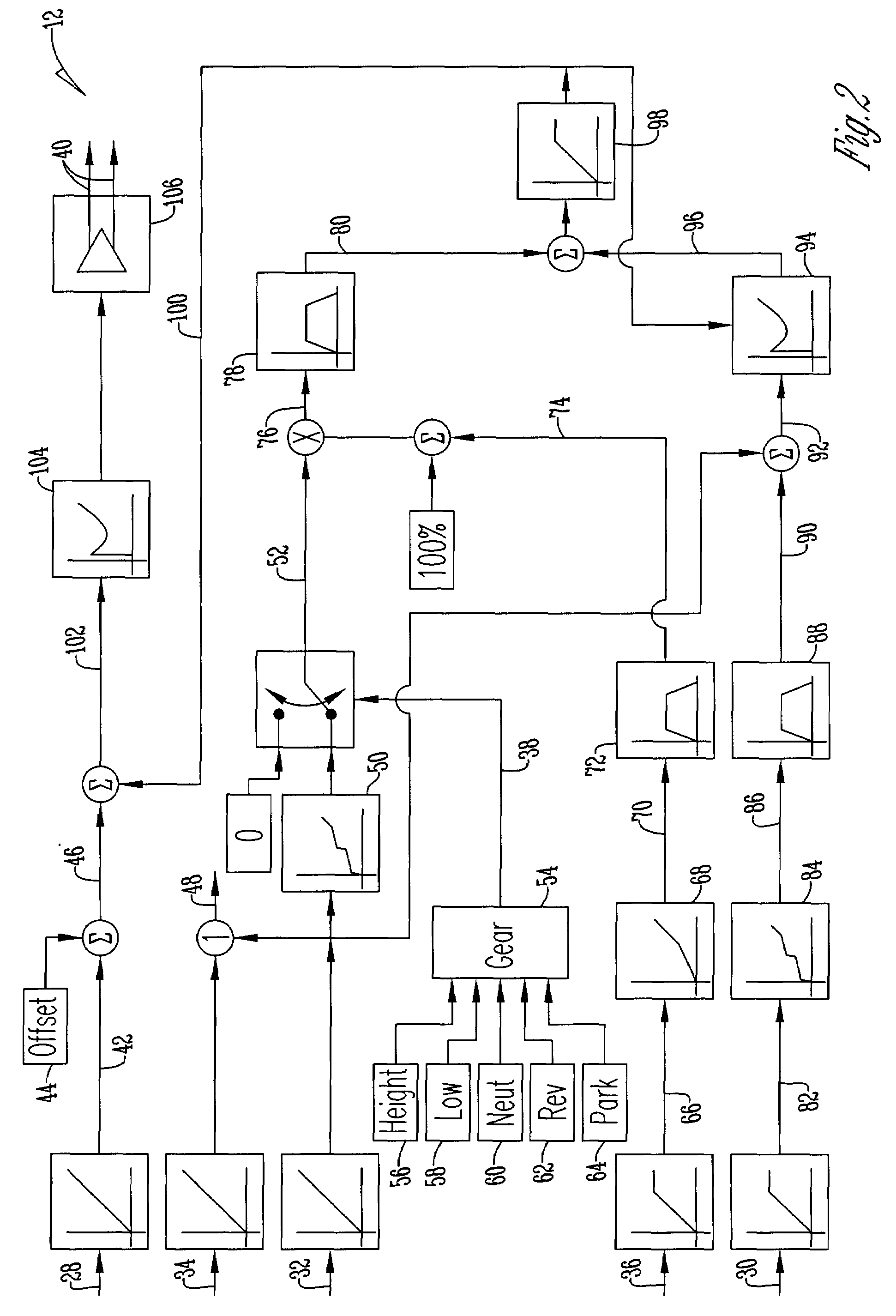
Engine speed control for a low power hydromechanical transmission
A method of operating a transmission of a vehicle. The method includes determining an open loop ratio percentage from an engine RPM input signal and a brake input signal using a first algorithm. Determining a closed loop ratio percentage from the engine RPM input signal, a vehicle RPM input signal and a throttle input signal using a second algorithm. Summing the open loop percentage and closed loop ratio percentage to calculate a ratio command percentage that is used to sum with a swashplate input to actuate a swashplate positioner and operate the transmission.
Owner:DANFOSS POWER SOLUTIONS INC
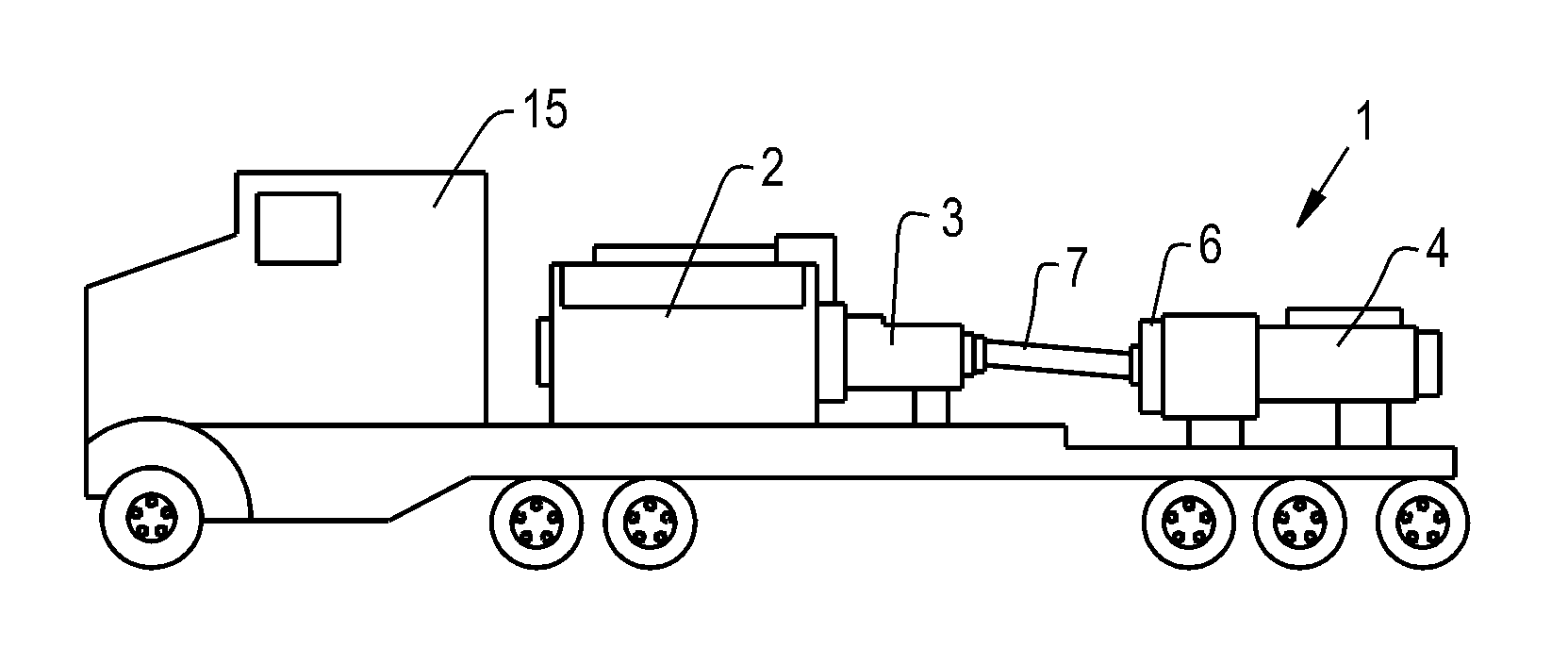
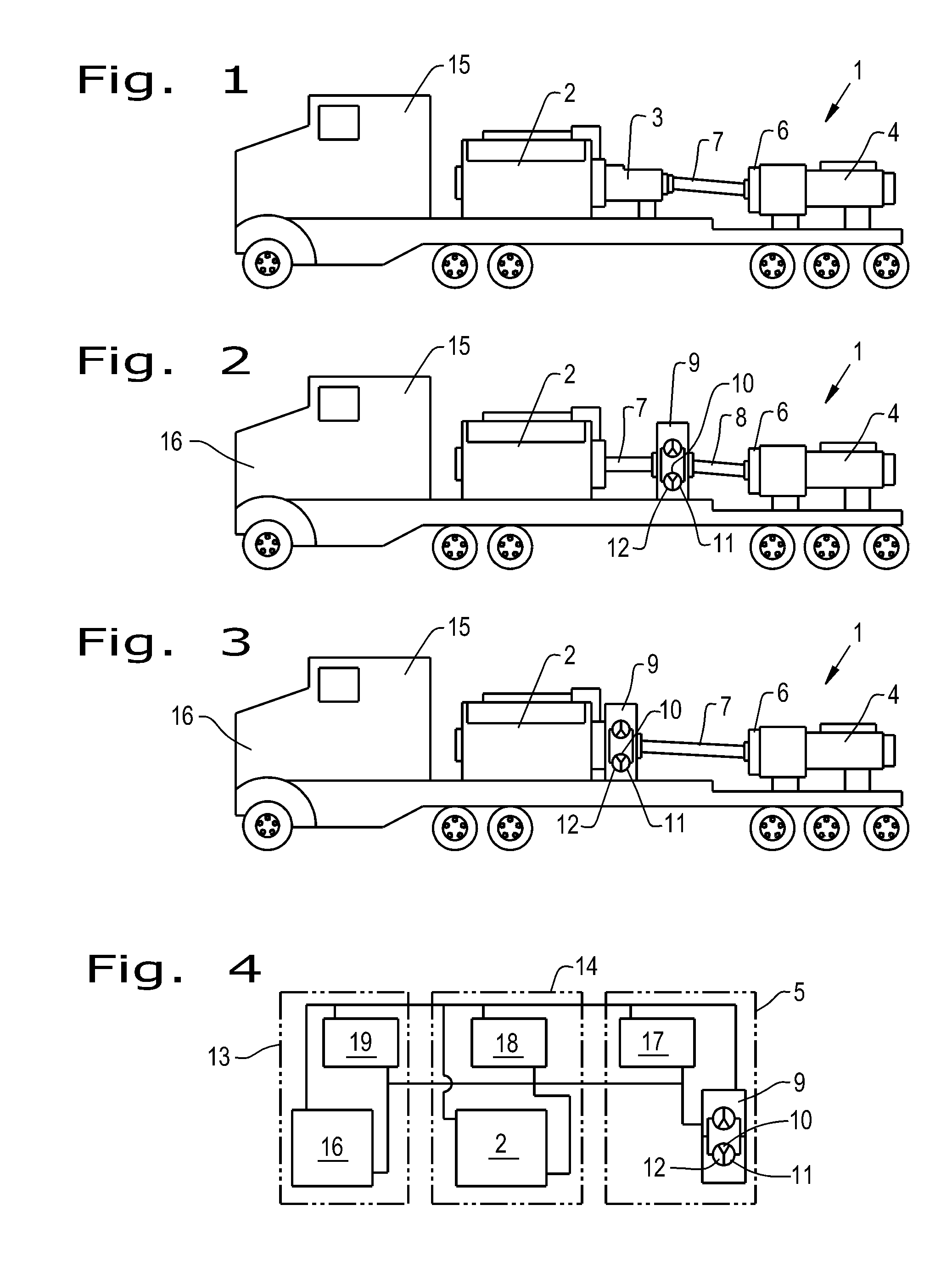
Pumping device
InactiveUS20150369351A1Shrink the necessary spaceEasy to adjustRotary clutchesFluid gearingsTorque converterFluid power
The invention relates to a pumping device for introduction of a fluid into a base layer, in particular into a base layer containing gas, for the production of gas-permeable structures in the base layer. The pumping device is arranged on a transportation vehicle having a separate drive unit, including a pump motor and a pump, whereby a speed / torque converter is arranged between pump and pump motor. A hydrodynamic device, in particular a hydrodynamic converter, is used in place of a transmission for speed / torque conversion.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
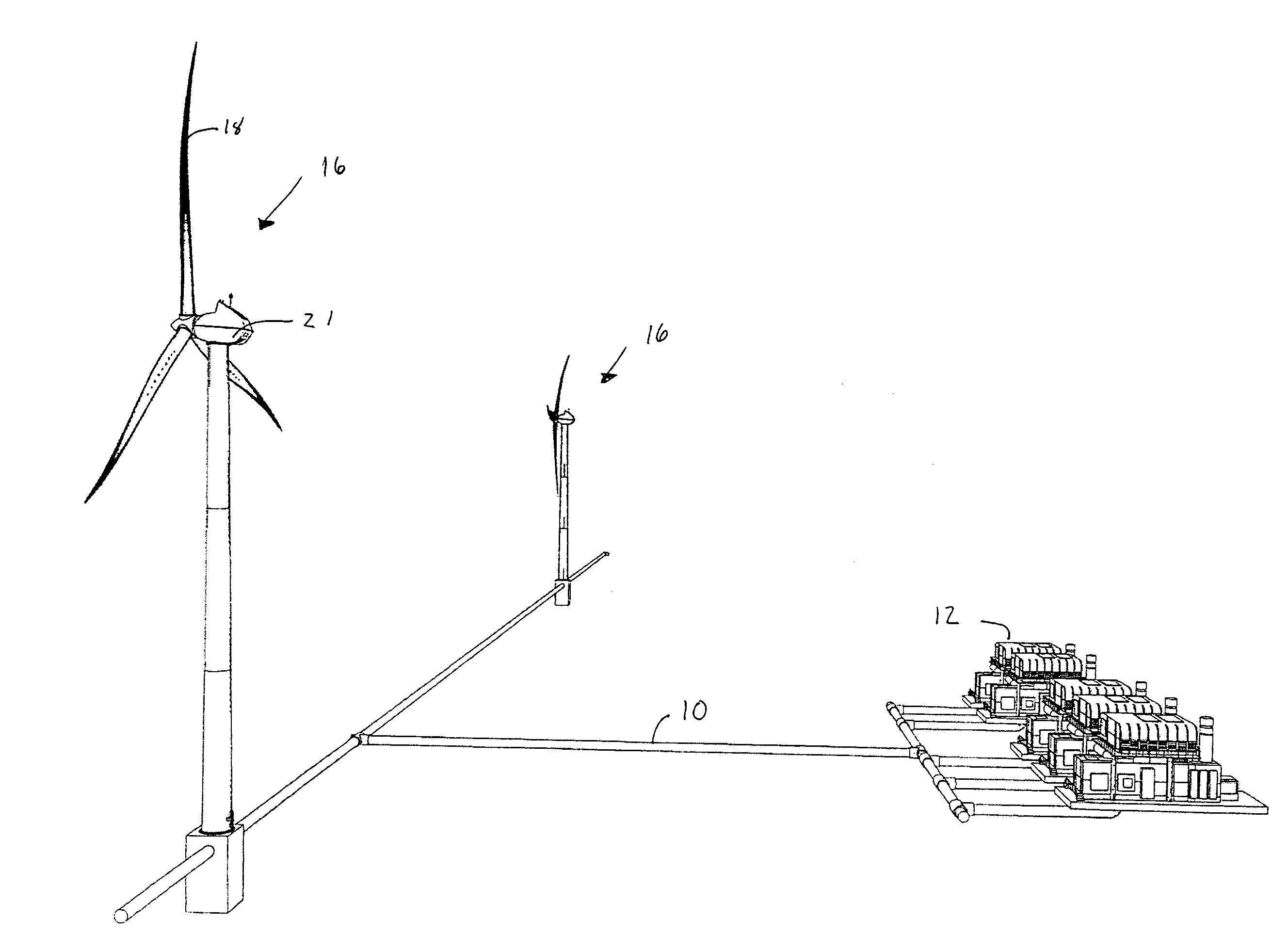
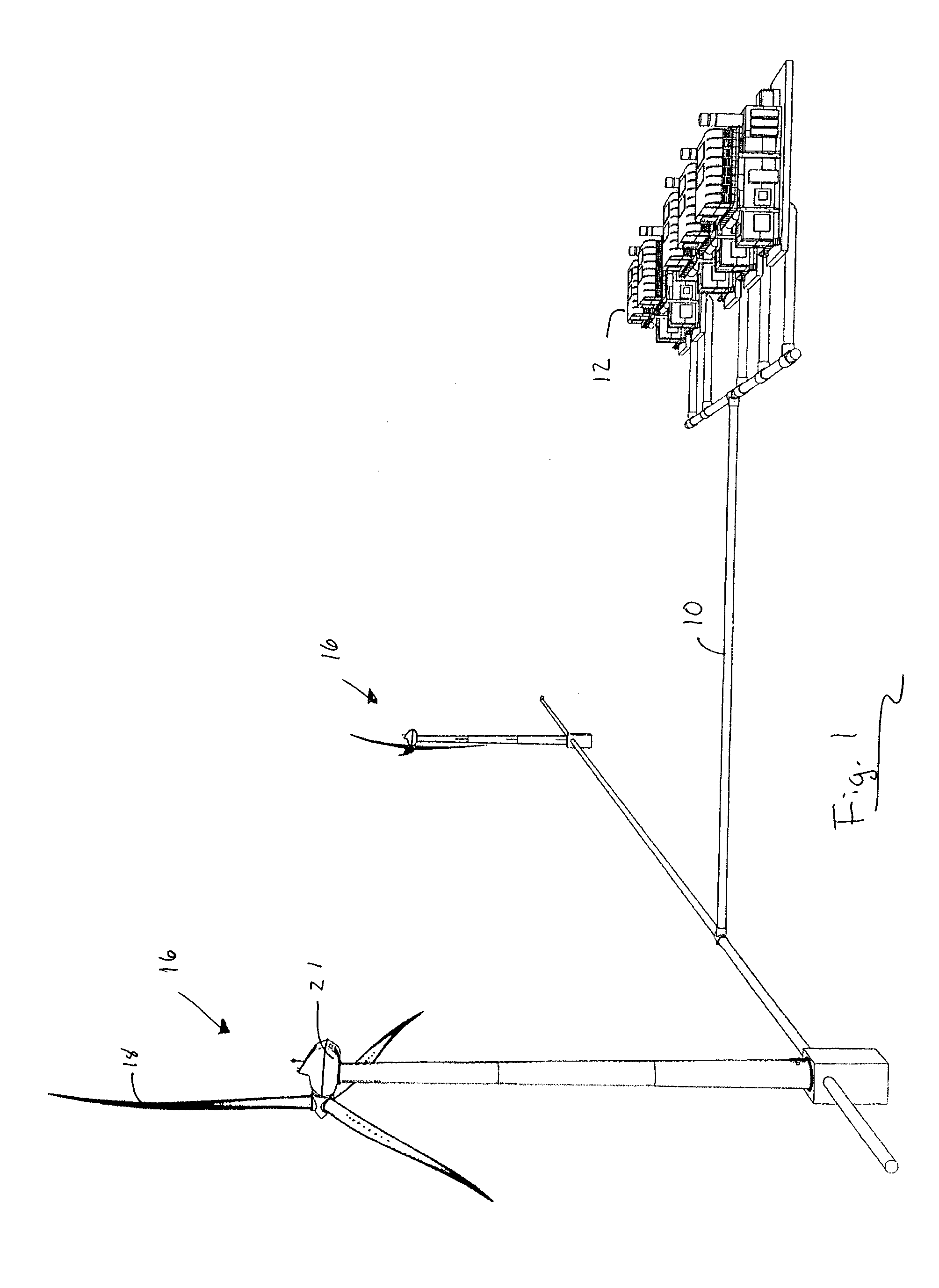
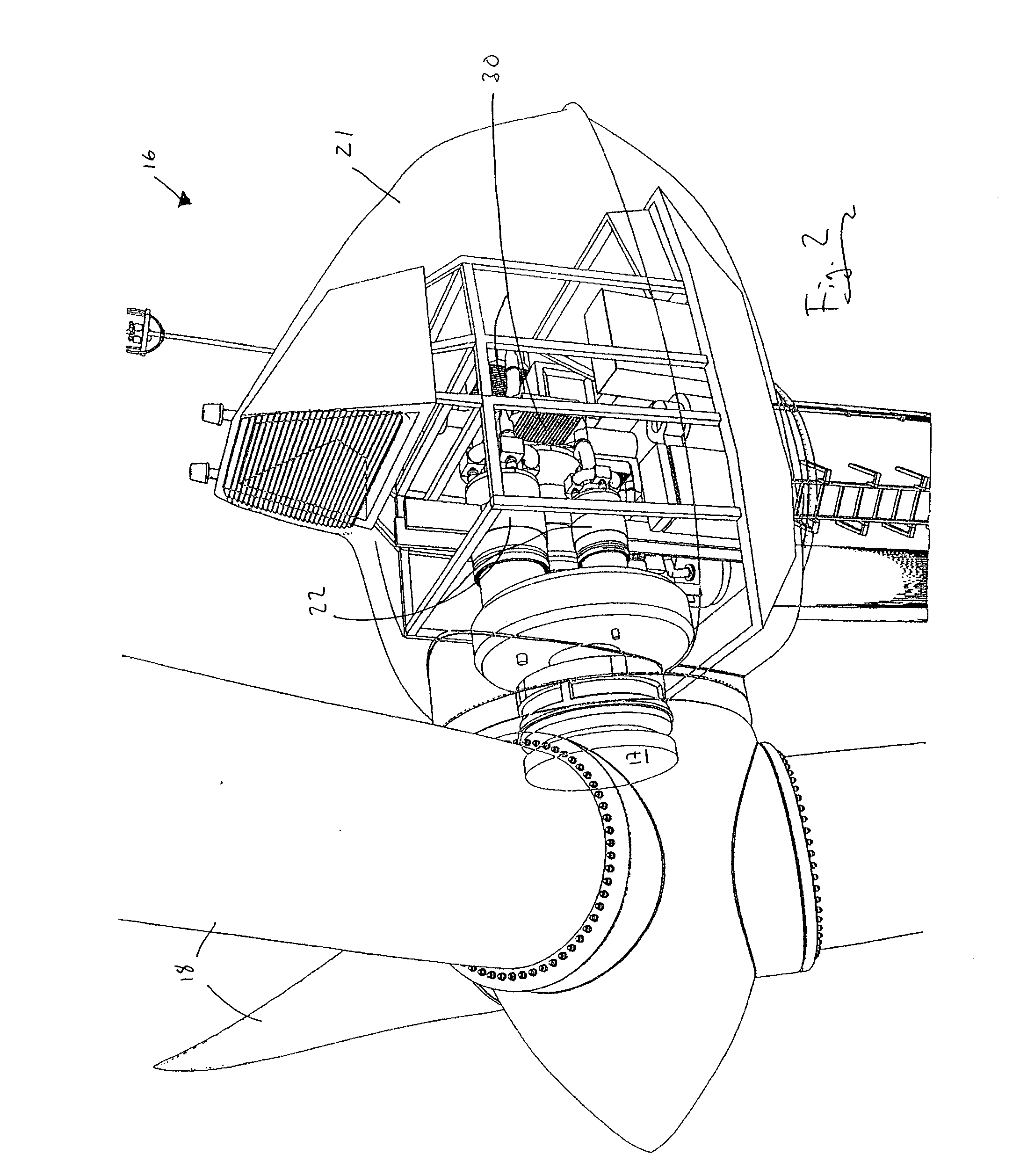
Wind turbine system
A wind turbine system for producing compressed air from wind energy. The wind turbine harvests energy from wind to produce mechanical energy. A compressor receives mechanical energy from the wind turbine to compress air to an elevated pressure. Thermal energy may be removed from the air, and the air is stored in a storage devices, such that the air may be released from the storage device on demand.
Owner:GENERAL COMPRESSION
Hydrodynamic torque converter
ActiveUS20100269497A1Improve insulation performanceCost-effective manufacturingRotary clutchesFluid gearingsImpellerSnubber
The invention relates to a hydrodynamic torque converter with an impeller connected on the drive side arranged in housing and a turbine driven by the latter, connected with the driven side of the torque converter, with a turbine damper actively disposed between the turbine and driven side. To improve the vibration damping on the driven side of the torque converter, it is proposed the turbine damper with a first damper part formed out of an input part connected with the turbine and an intermediate flange, limited and rotatable opposite and against the action of at least a first energy accumulator and a second damper part with the intermediate flange and an output part limited and rotatable oppositely and against the action of at least a second energy accumulator, wherein an adaptive-speed vibration absorber is arranged on the intermediate flange.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Overrunning coupling assembly
InactiveUS6116394AReduce wearEliminate lubrication control requirementRotary clutchesFriction clutchesCouplingTrunnion
An overrunning coupling assembly includes a notch plate and an annular coupling pocket plate positioned in face-to-face relationship with respect to each other along a common axis. The pocket plate includes strut pockets disposed at angularly spaced positions about the axis. The notch plate includes notch recesses at angularly spaced positions about the common axis and positioned in juxtaposed relationship with respect to the strut pockets. The notch plate includes an inner circumferential rail at a radially inward side of the notch recesses and an outer circumferential rail at a radially outward side of the notch recesses. Torque-transmitting struts are positioned in the strut pockets. Each strut has first and second ears at one edge thereof for enabling pivotal motion of the struts about an ear axis intersecting the ears. The opposite edge of each strut is engageable with one of the notch recesses whereby one-way torque transfer may occur between the plates. Each opposite edge has first and second corners. Each strut pocket is sufficiently enlarged to allow pivotal movement of each strut about a strut axis which is parallel with the common axis, thereby enabling one of the first and second corners to be selectively supported by one of the inner and outer circumferential rails to prevent the struts from slapping against the notch recesses as the notch plate and pocket plate are respectively counterrotated.
Owner:MEANS IND INC
Compressed air energy storage system utilizing two-phase flow to facilitate heat exchange
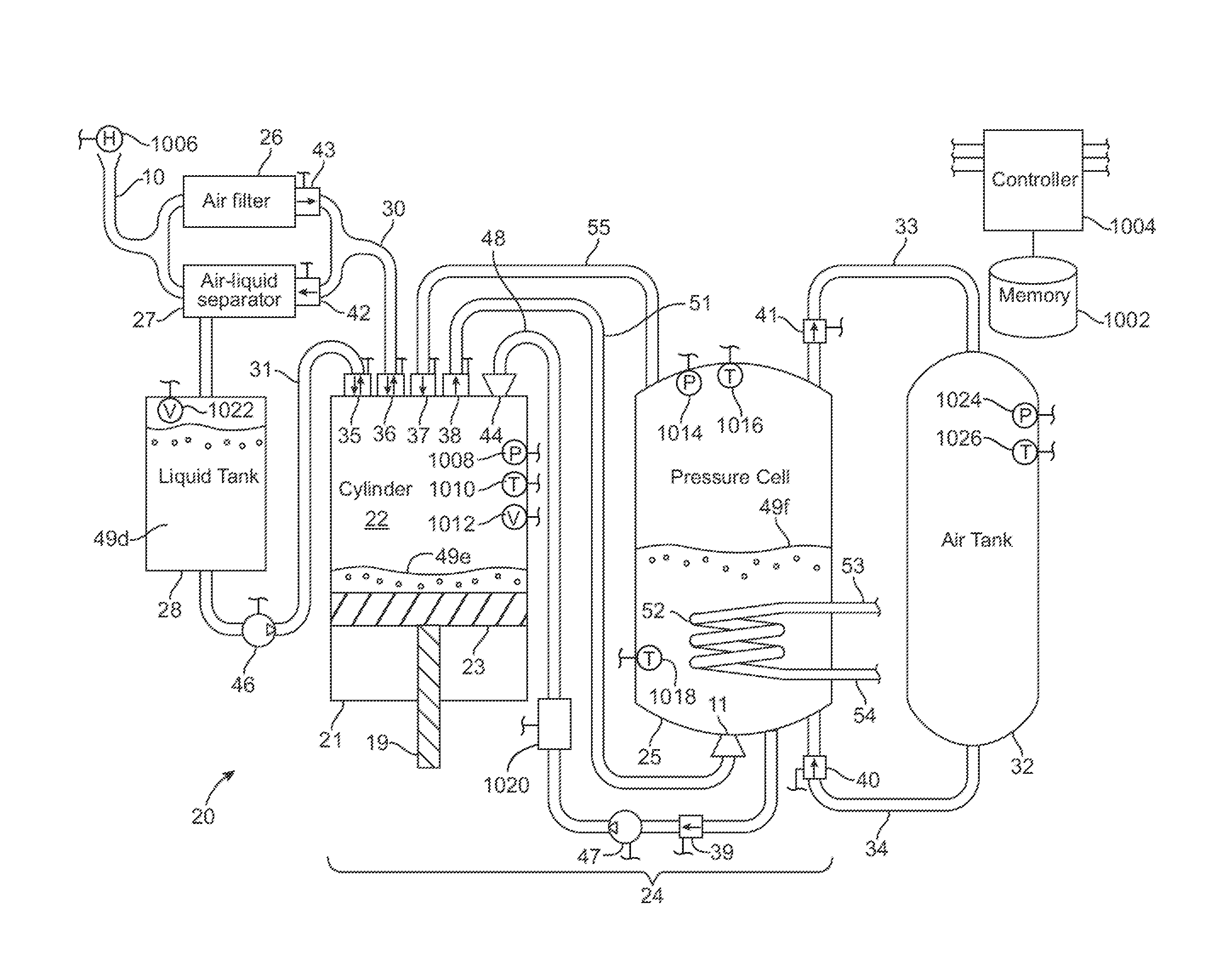
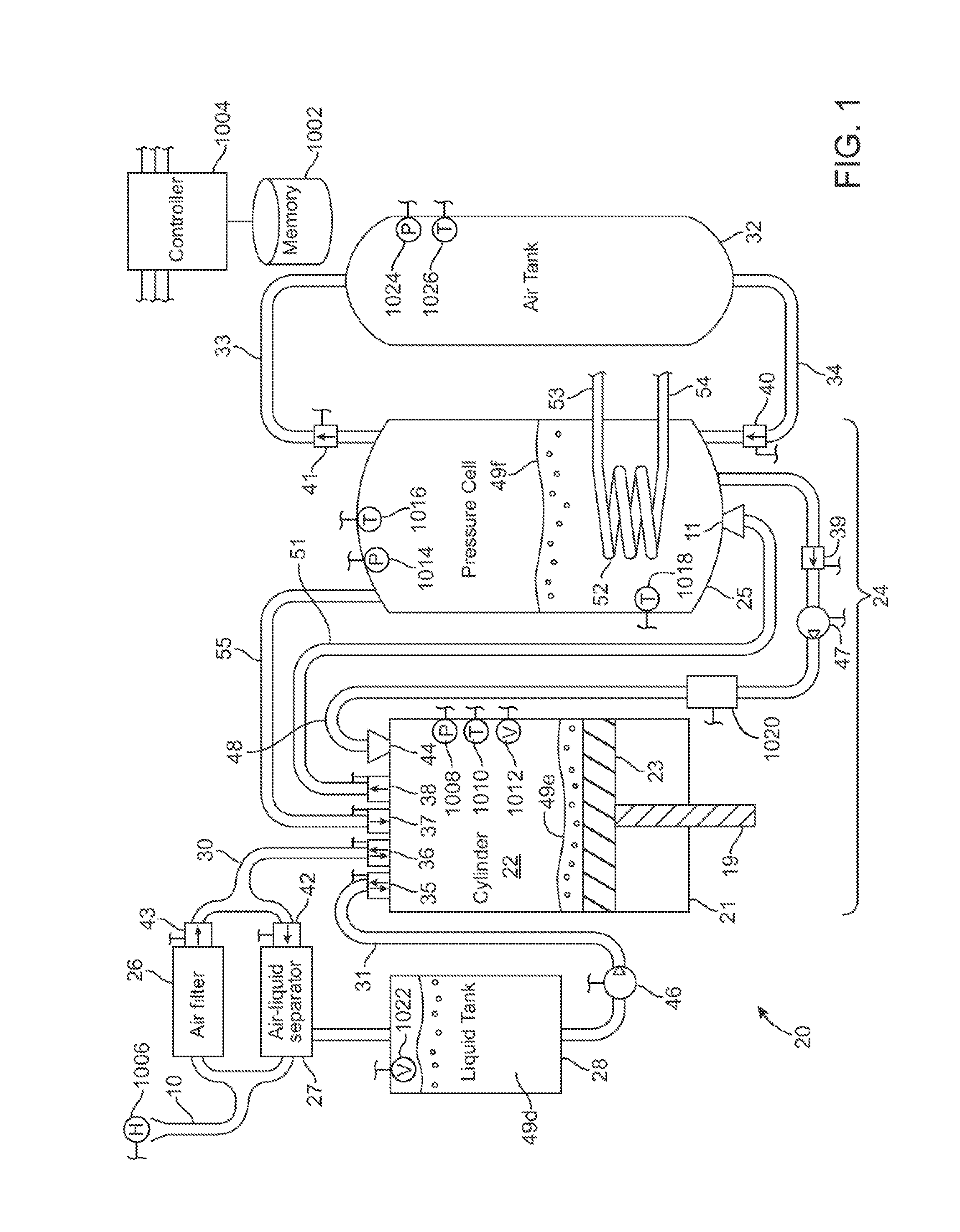
InactiveUS20100326062A1Facilitate heat exchangeImprove efficiencyElectrical storage systemServomotor componentsThermal energy storageEngineering
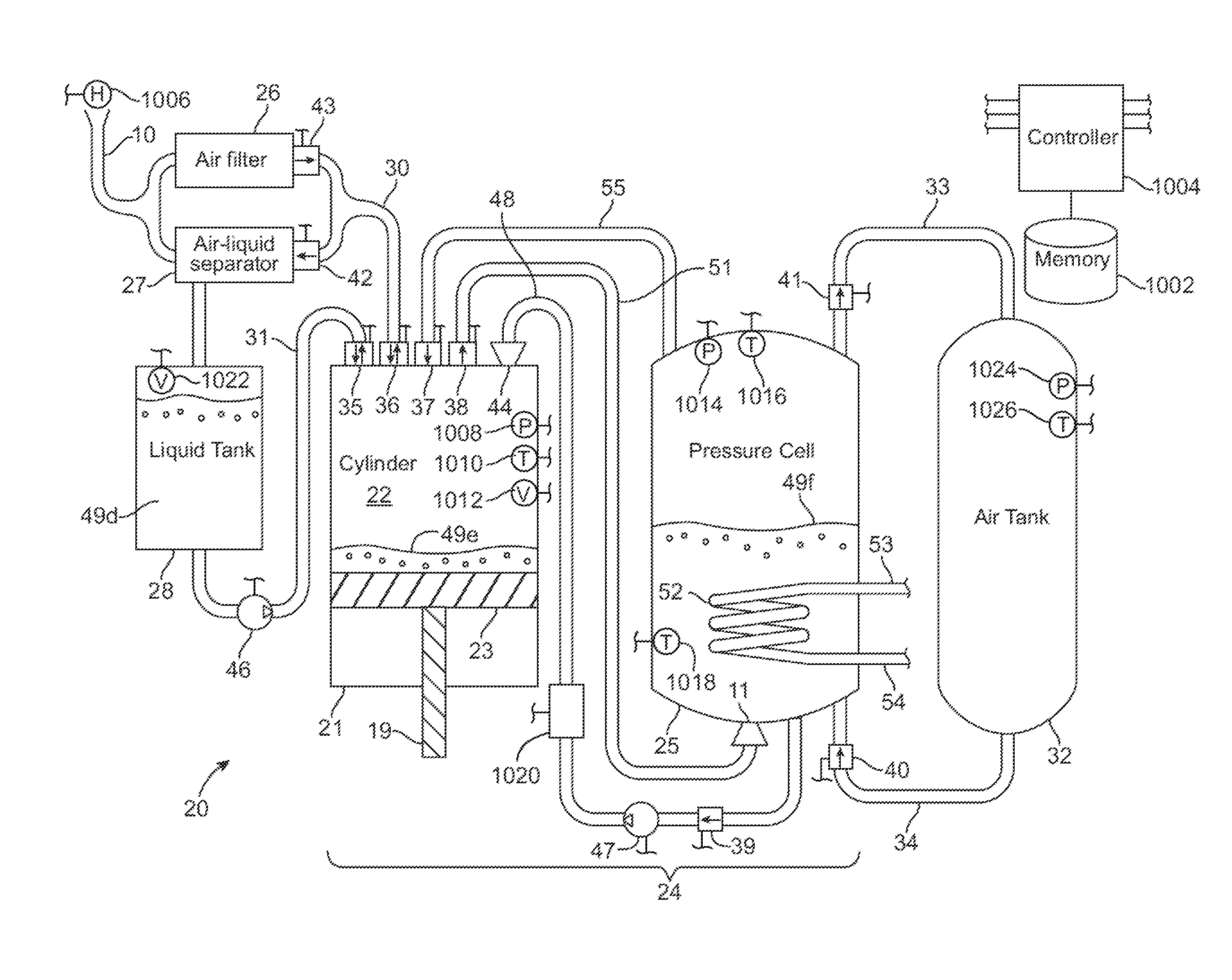
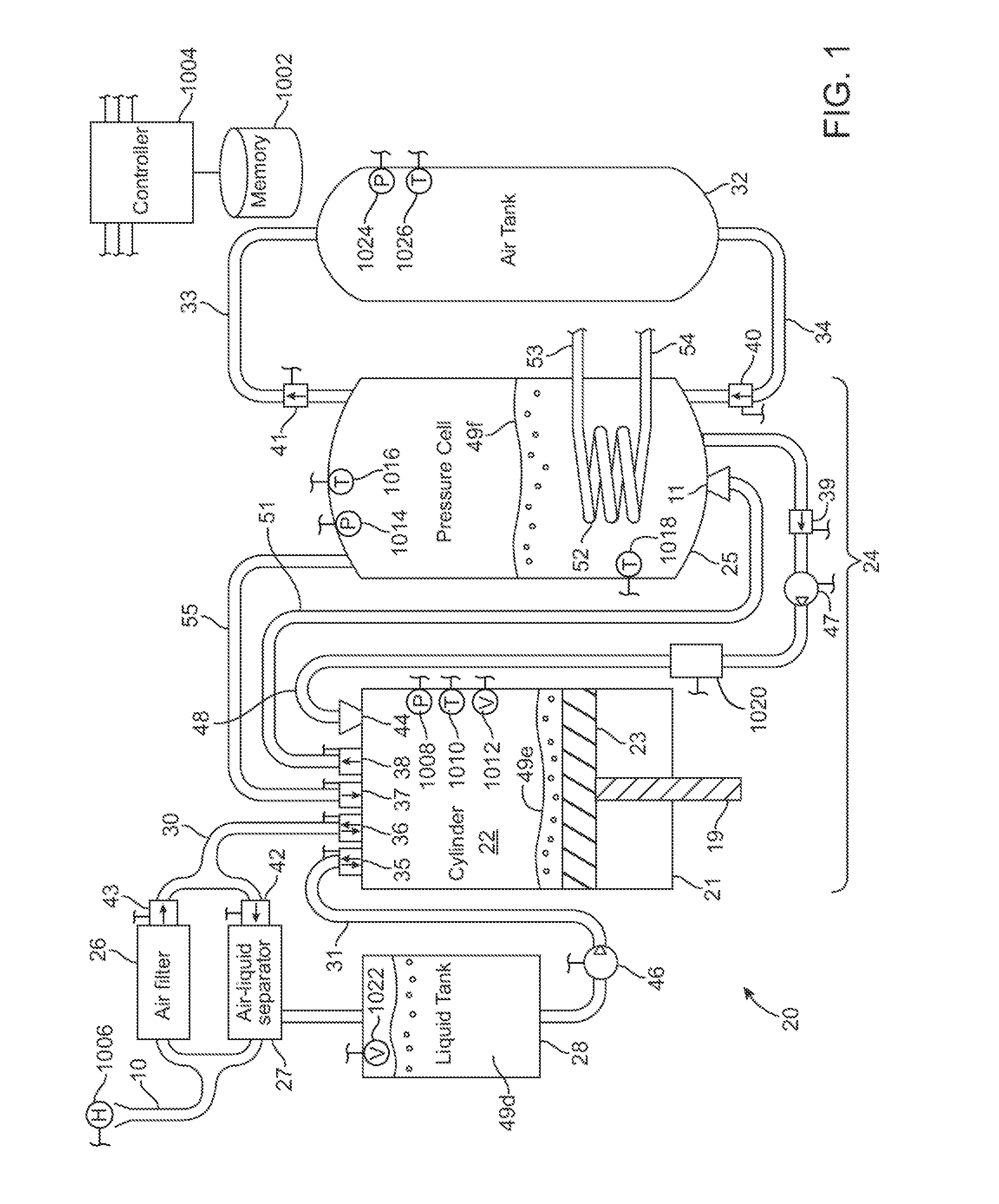
A compressed-air energy storage system according to embodiments of the present invention comprises a reversible mechanism to compress and expand air, one or more compressed air storage tanks, a control system, one or more heat exchangers, and, in certain embodiments of the invention, a motor-generator. The reversible air compressor-expander uses mechanical power to compress air (when it is acting as a compressor) and converts the energy stored in compressed air to mechanical power (when it is acting as an expander). In certain embodiments, the compressor-expander comprises one or more stages, each stage consisting of pressure vessel (the “pressure cell”) partially filled with water or other liquid. In some embodiments, the pressure vessel communicates with one or more cylinder devices to exchange air and liquid with the cylinder chamber(s) thereof. Suitable valving allows air to enter and leave the pressure cell and cylinder device, if present, under electronic control.
Owner:LIGHTSAIL ENERGY
Torque converter with turbine mass absorber
ActiveUS20090125202A1Simple designFlange mode is reducedRotary clutchesDigital data processing detailsFriction torqueSnubber
A torque converter having a first damper stage, a second damper stage, a floating flange torsionally connecting the first and second damper stages, an inertia element, and a tuned torsion damper. The torsion damper connects the inertia element and the flange. In a preferred embodiment, the inertia element is a turbine. In one embodiment, the first damper stage is a radially outer damper stage and the second damper stage is a radially inner damper stage. In another embodiment, the torsion damper generates a friction torque when rotated.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Hydraulic system
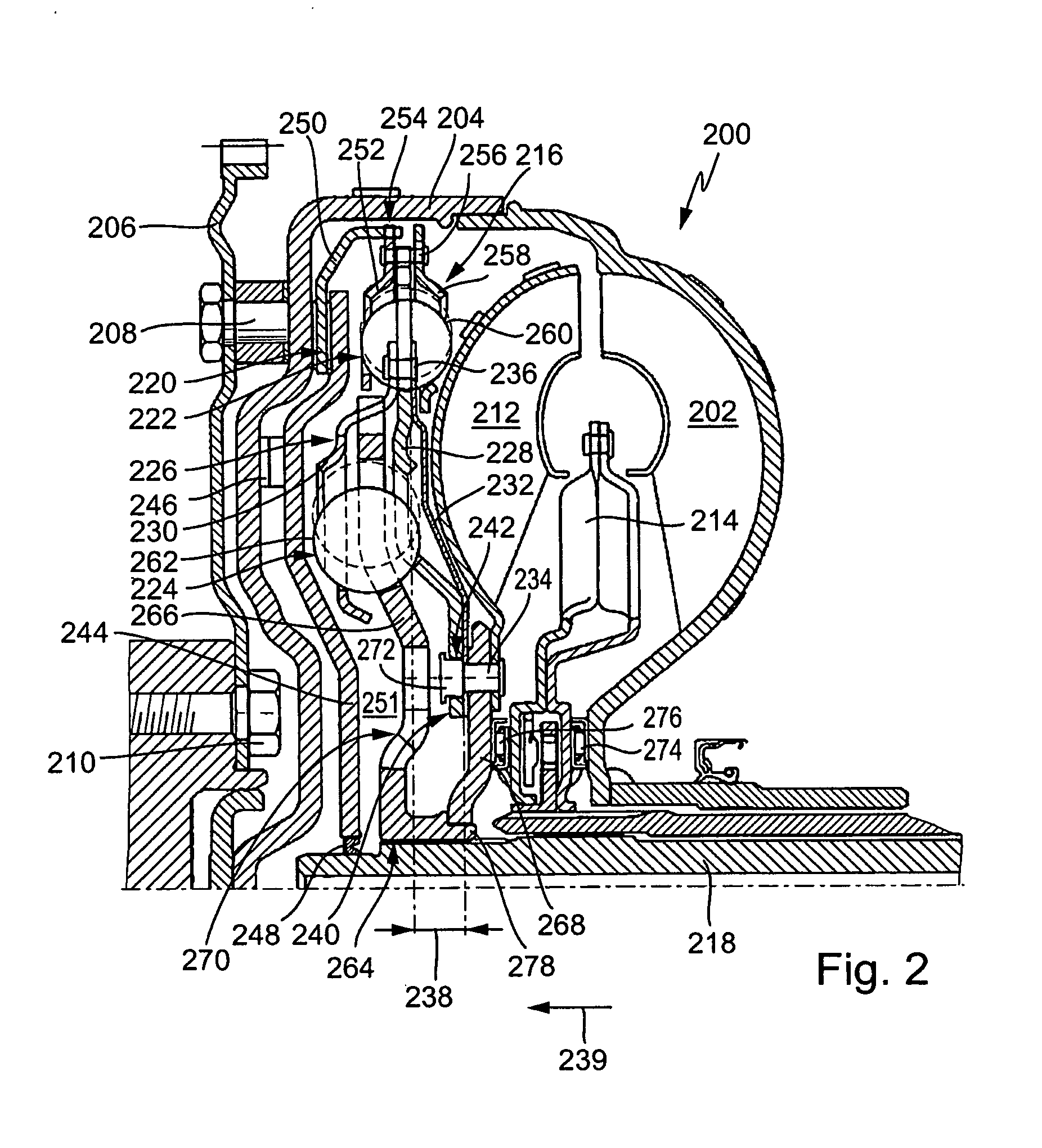
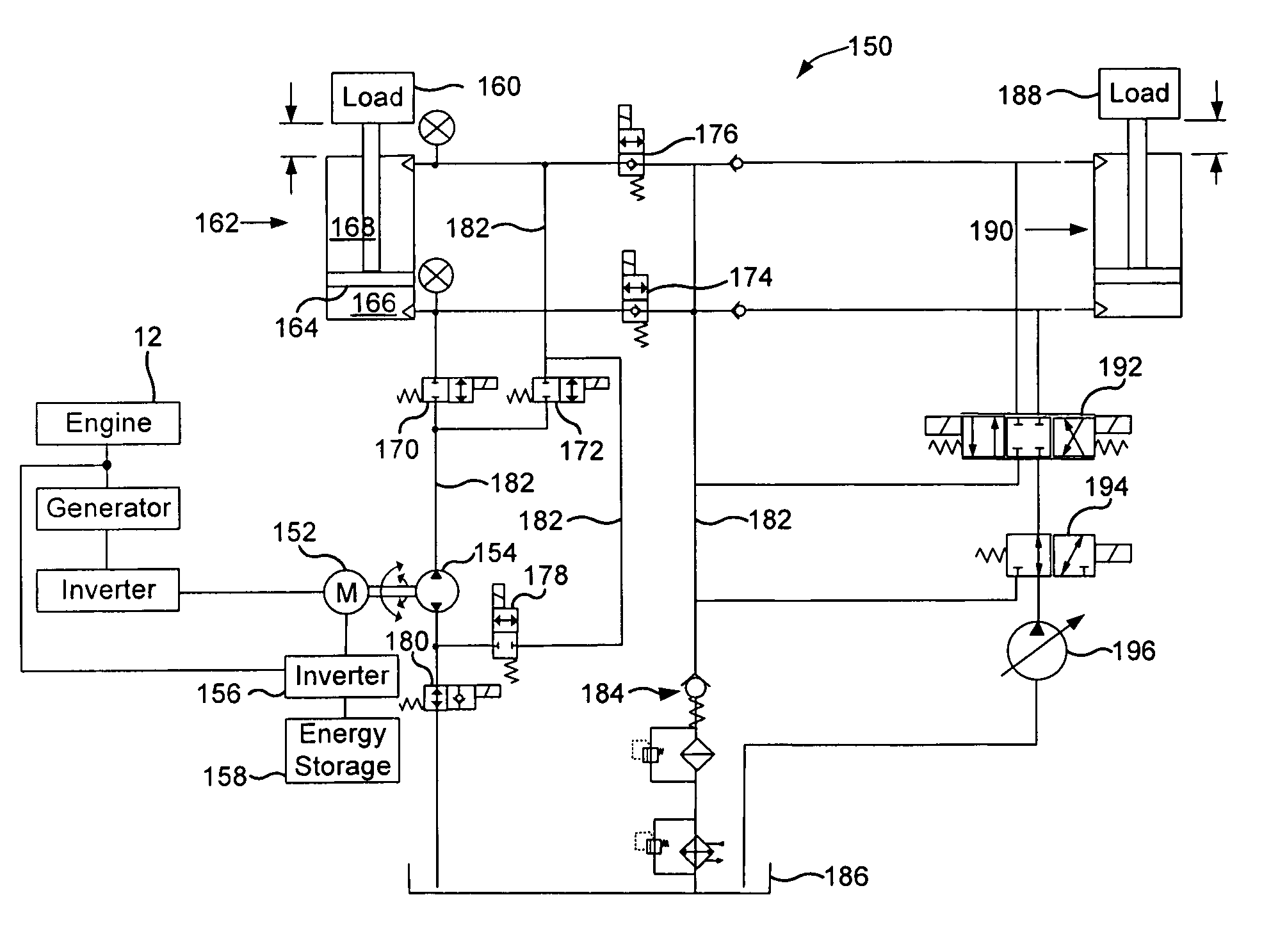
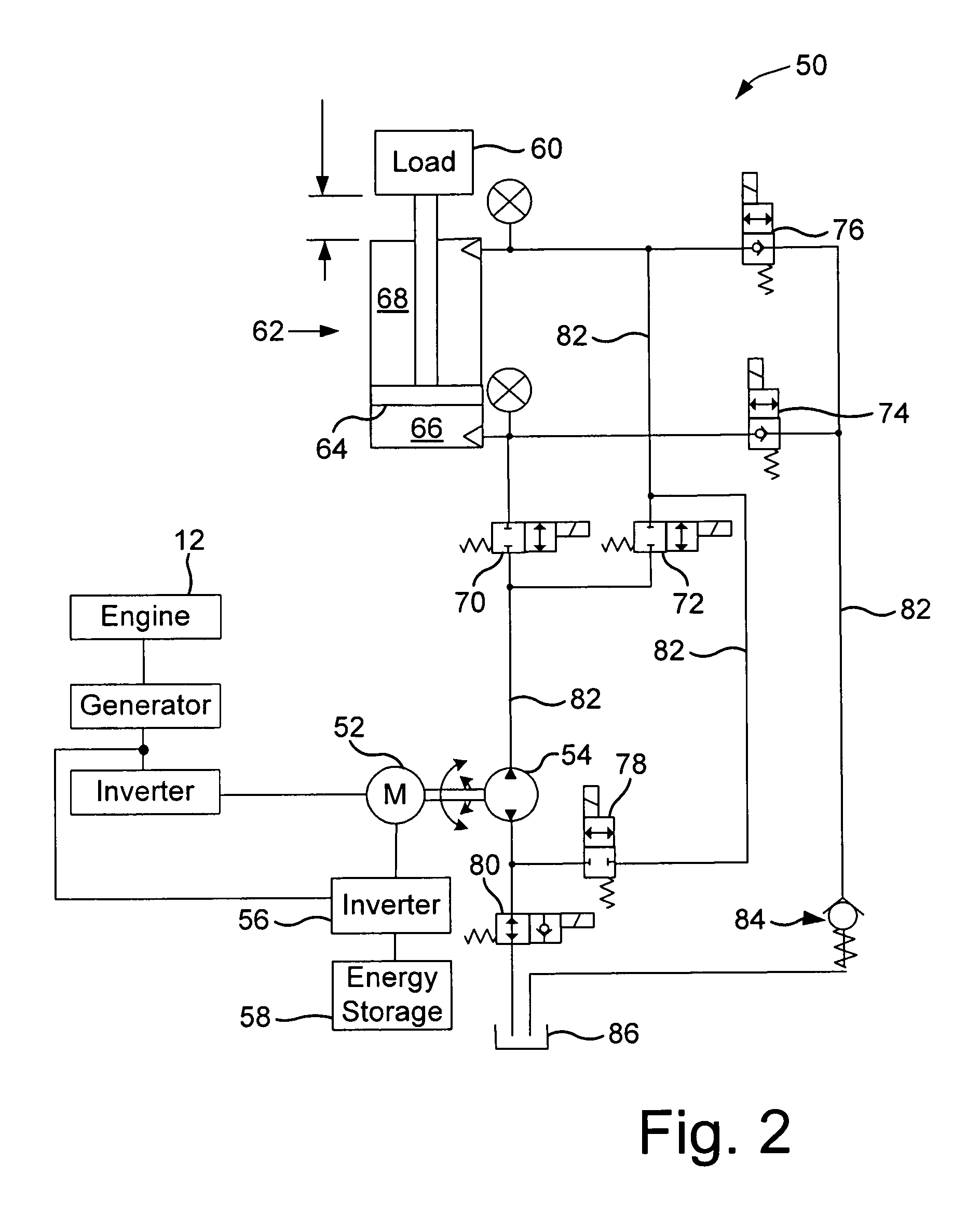
A ground engaging vehicle including a movable member, a hydraulically driven actuator, a hydraulic pump, a plurality of valves and at least one hydraulic conduit. The hydraulically driven actuator is coupled to the movable member and the actuator has a first chamber and a second chamber. The plurality of non-proportional valves include a first valve, a second valve, a third valve and a fourth valve. The at least one hydraulic conduit couples the pump with the first valve and the second valve. The first valve is in direct fluid communication with the first chamber. The second valve is in direct fluid communication with the second chamber. The third valve is in direct fluid communication with the first chamber and the fourth valve is in direct fluid communication with the second chamber. The first valve and the second valve each include an open position and a closed position.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Force transmission device with a rotational speed adaptive damper and method for improving the damping properties
The invention relates to a force transmission device for power transmission between an input and an output, comprising at least an input and an output, and a vibration damping device disposed in a cavity that can be filled at least partially with an operating medium, in particular oil, the vibration damping device coupled with a rotational speed adaptive absorber, wherein the rotational speed adaptive absorber is tuned as a function of an oil influence to an effective order qeff, which is greater by an order shift value qF than an order q of an exciting vibration of a drive system.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Method of and apparatus for transmitting torque in vehicular power trains
InactiveUS7286922B1Reduce capacityMechanical actuated clutchesDigital data processing detailsMobile vehicleAutomatic transmission
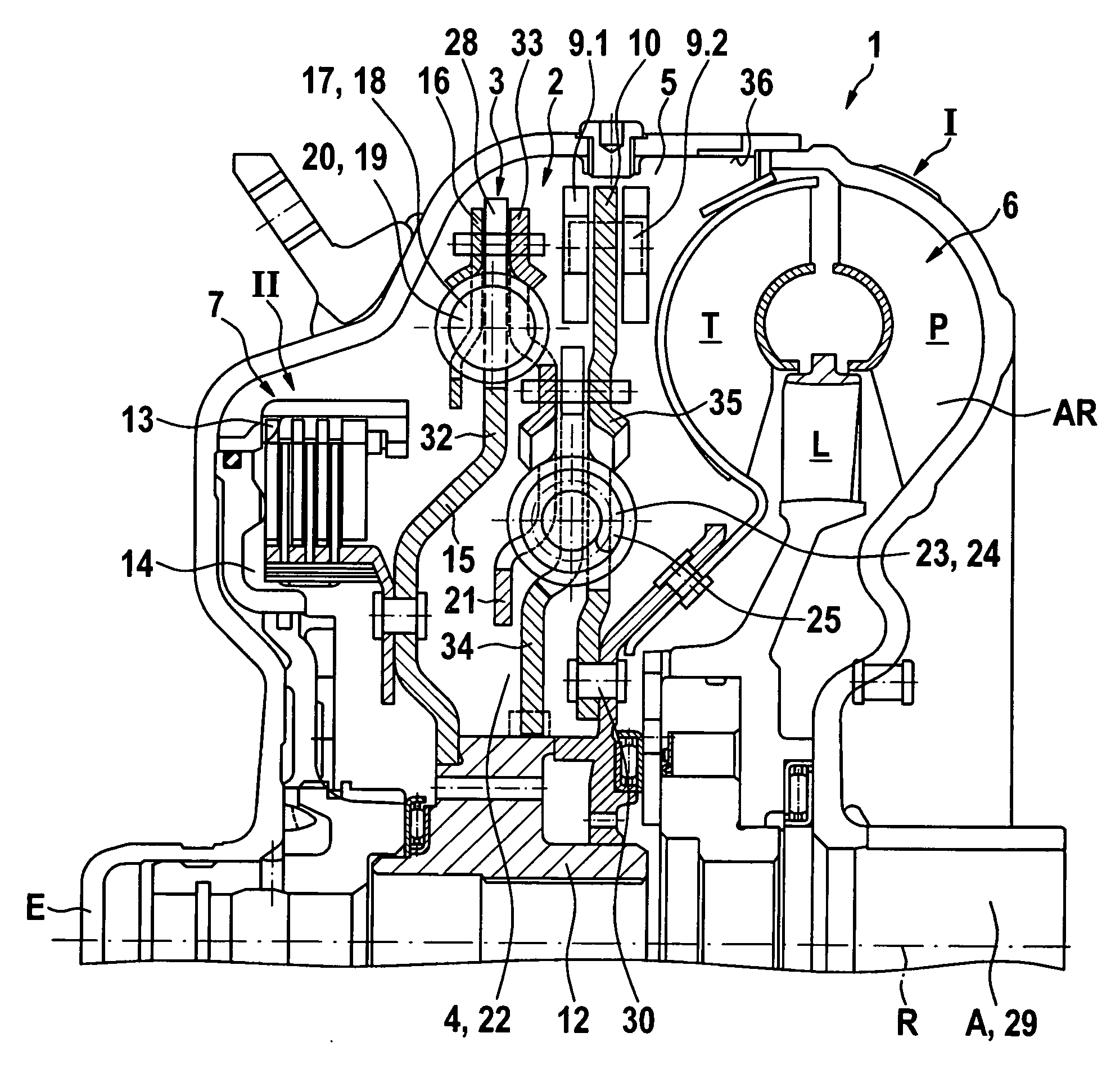
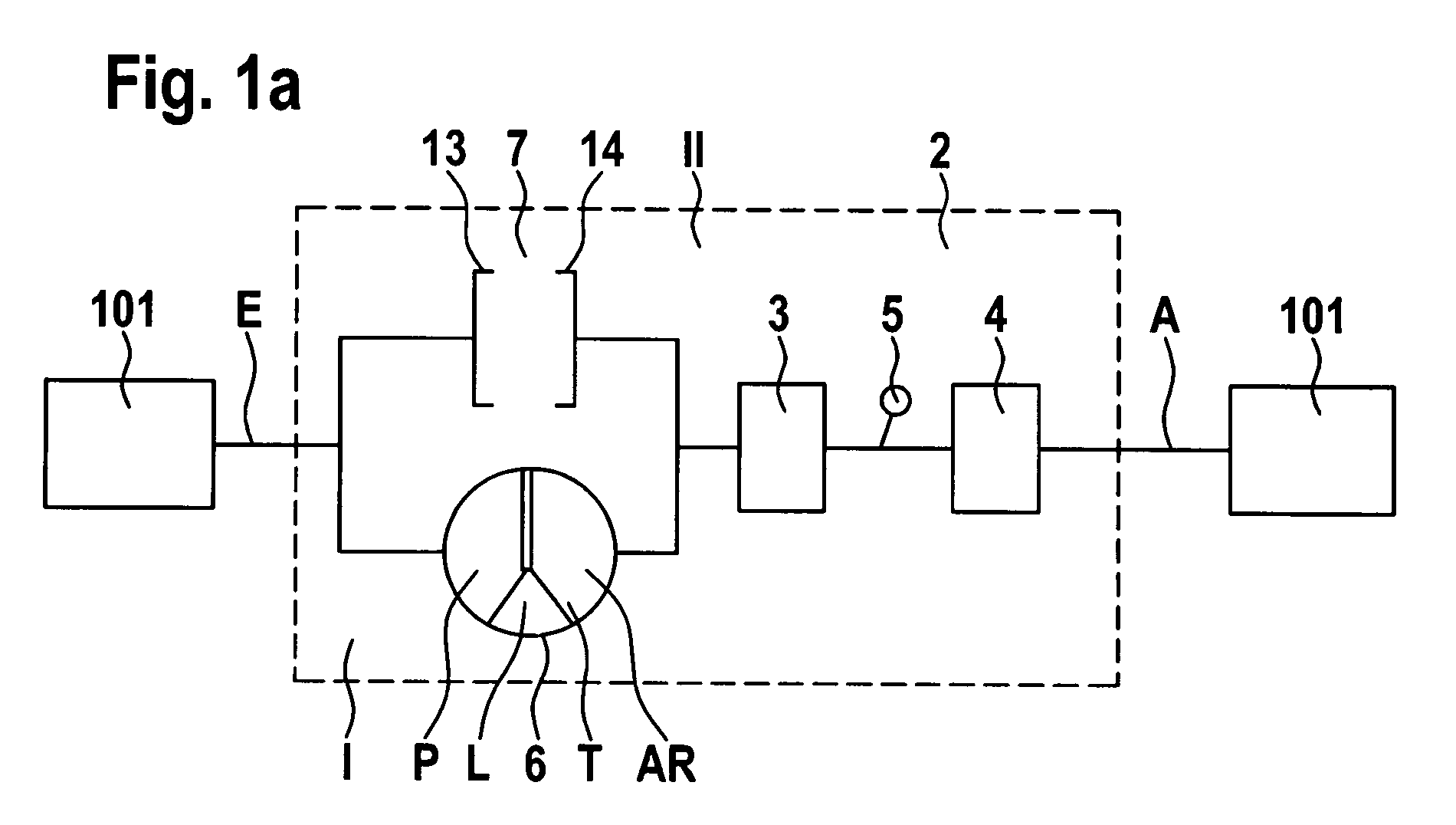
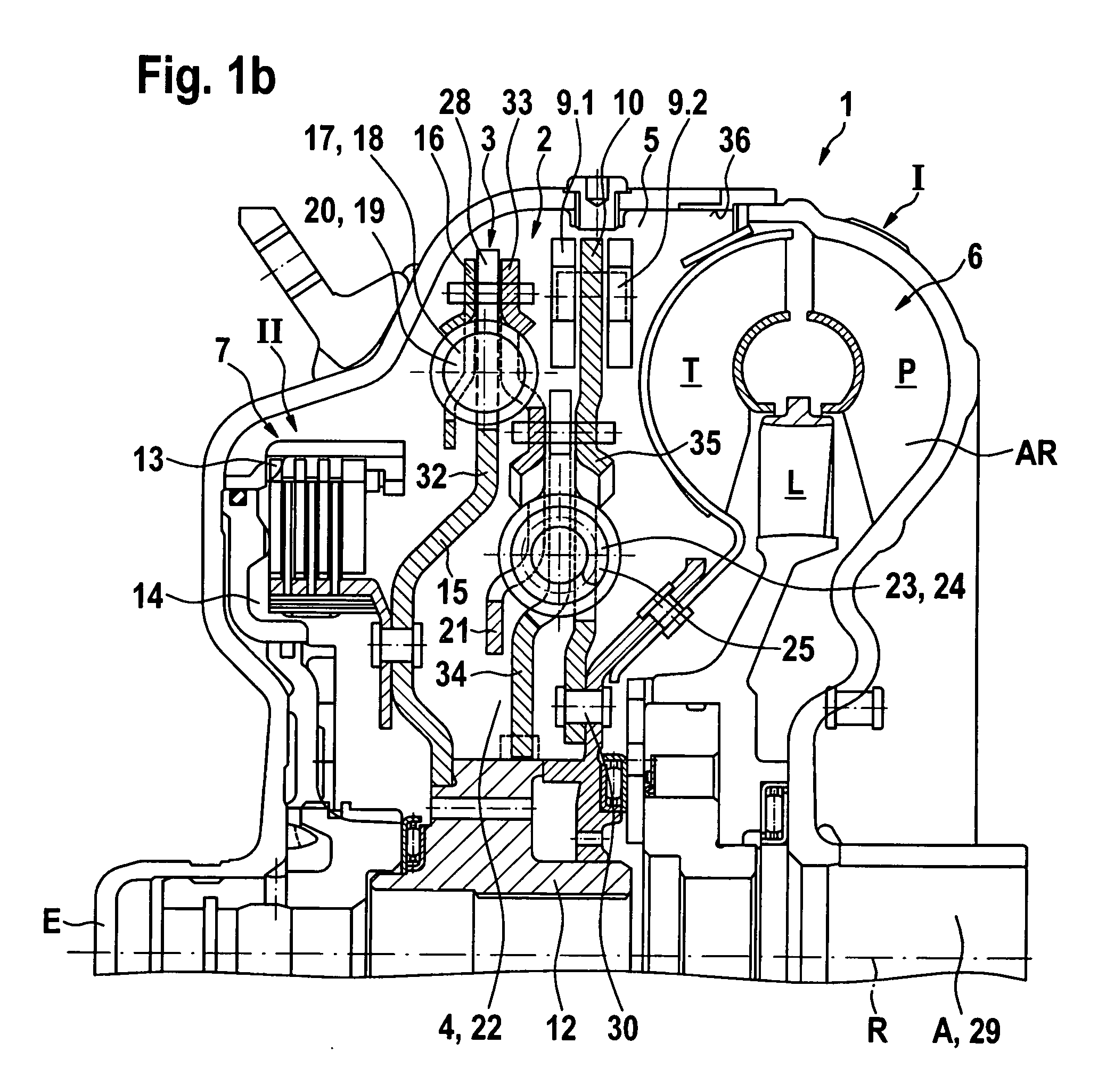
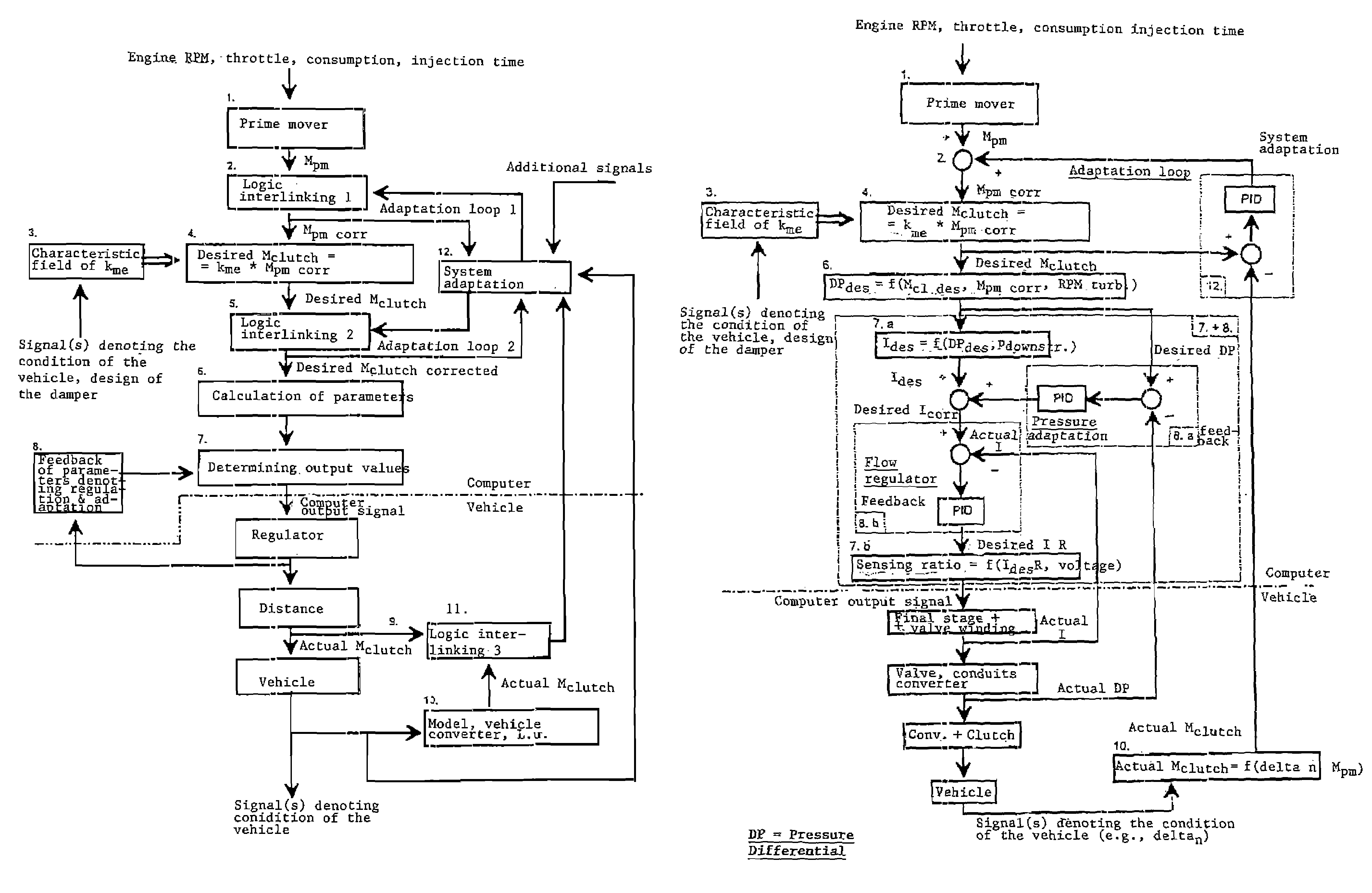
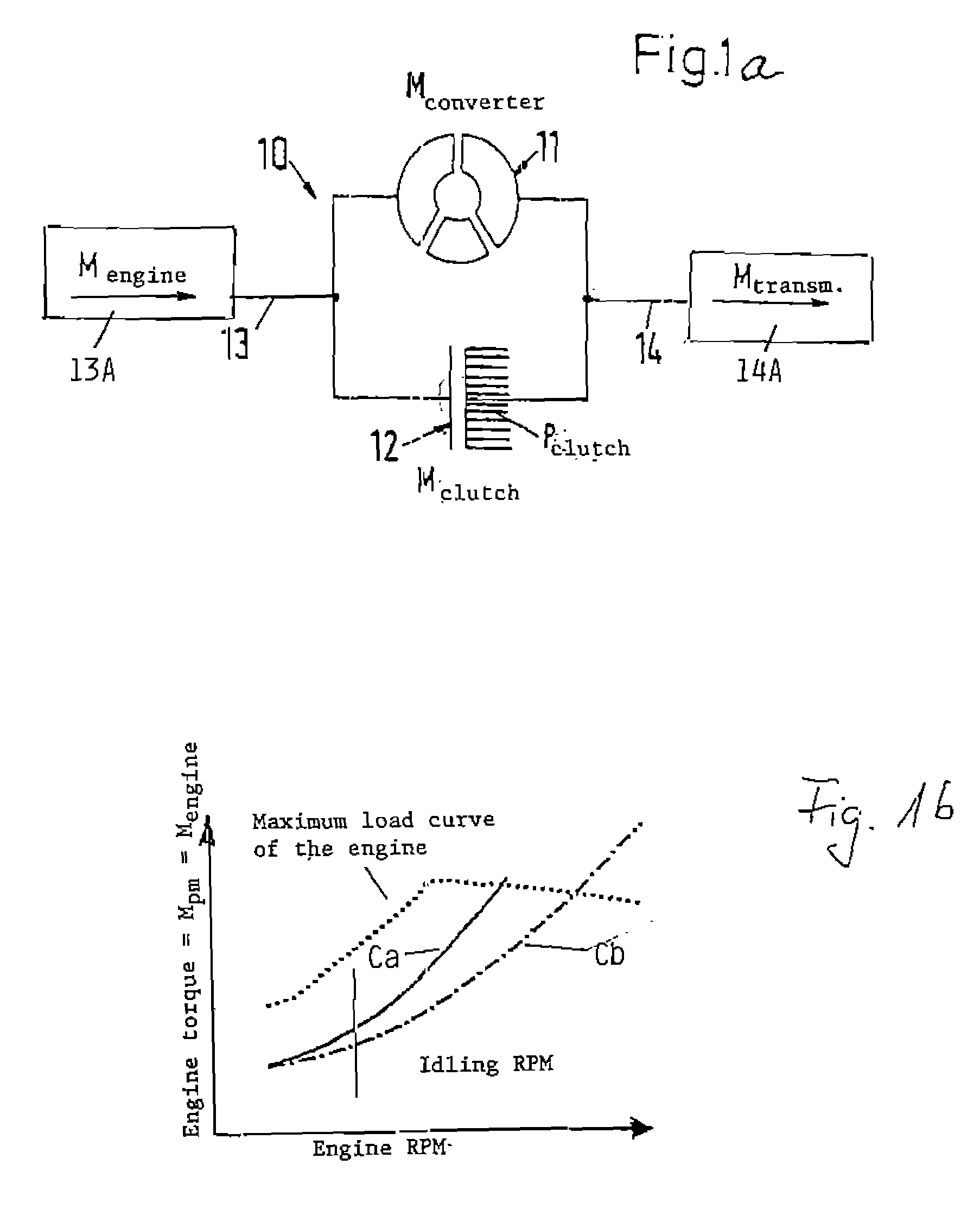
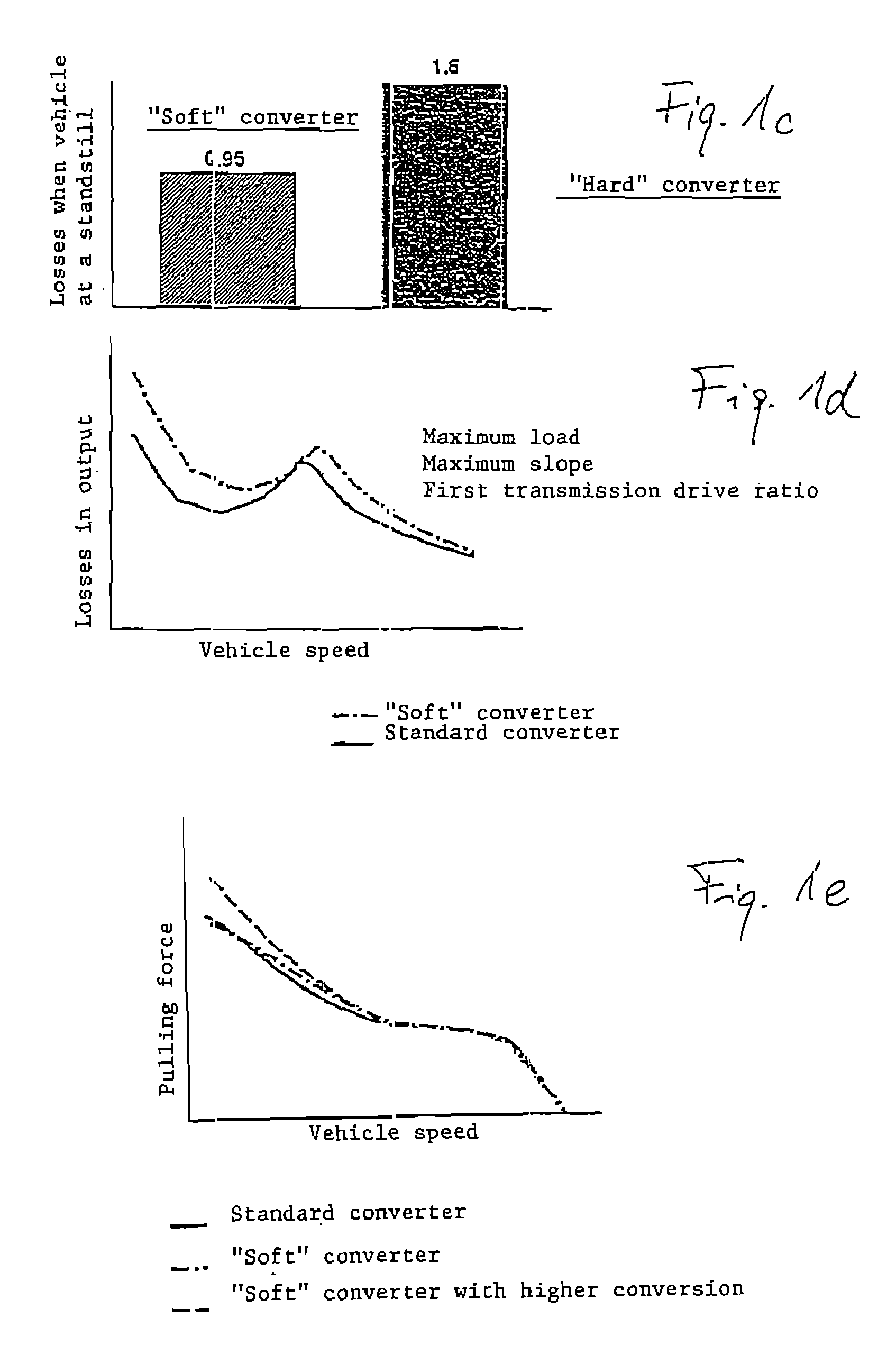
The magnitude of torque which can be transmitted by a bypass clutch between the housing and the turbine of a torque converter between a prime mover, such as an engine, and an automatic transmission in the power train of a motor vehicle is selectively regulatable by a computerized regulating unit. The regulation involves the transmission of torque by the clutch in dependency upon the magnitude of the torque being transmitted by the output element of the engine and ascertaining as well as adaptively applying to the clutch a variable force so that the clutch can transmit a predetermined torque. This entails automatic selection of a minimum slip between a torque receiving and a torque transmitting part of the power train. Compensation, particularly long-range compensation, is carried out for the existence of possible differences between the predetermined and actual torques being transmitted by the clutch.
Owner:LUK GETRIEBE SYST
Multiple-clutch device
InactiveUS6464059B1Reduced Tolerance RequirementsReduce dependenceRotary clutchesFluid actuated clutchesMobile vehicleDrivetrain
The invention is directed to a multiple-clutch device, such as a double-clutch device, for arranging in a drivetrain of a motor vehicle between a drive unit and a transmission, wherein the clutch device has a first clutch arrangement associated with a first transmission input shaft of the transmission and a second clutch arrangement associated with a second transmission input shaft of the transmission for transmitting torque between the drive unit and the transmission. It is suggested that a bearing arrangement is associated with at least one of the clutch arrangements, wherein the latter is supported or can be supported so as to be relatively rotatable by means of the bearing arrangement on at least one of the transmission input shafts, at least one of which is constructed as a hollow shaft and a shaft constructed as a hollow shaft encloses the other shaft, preferably at least at the radial outer transmission input shaft which is constructed as a hollow shaft.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG +1
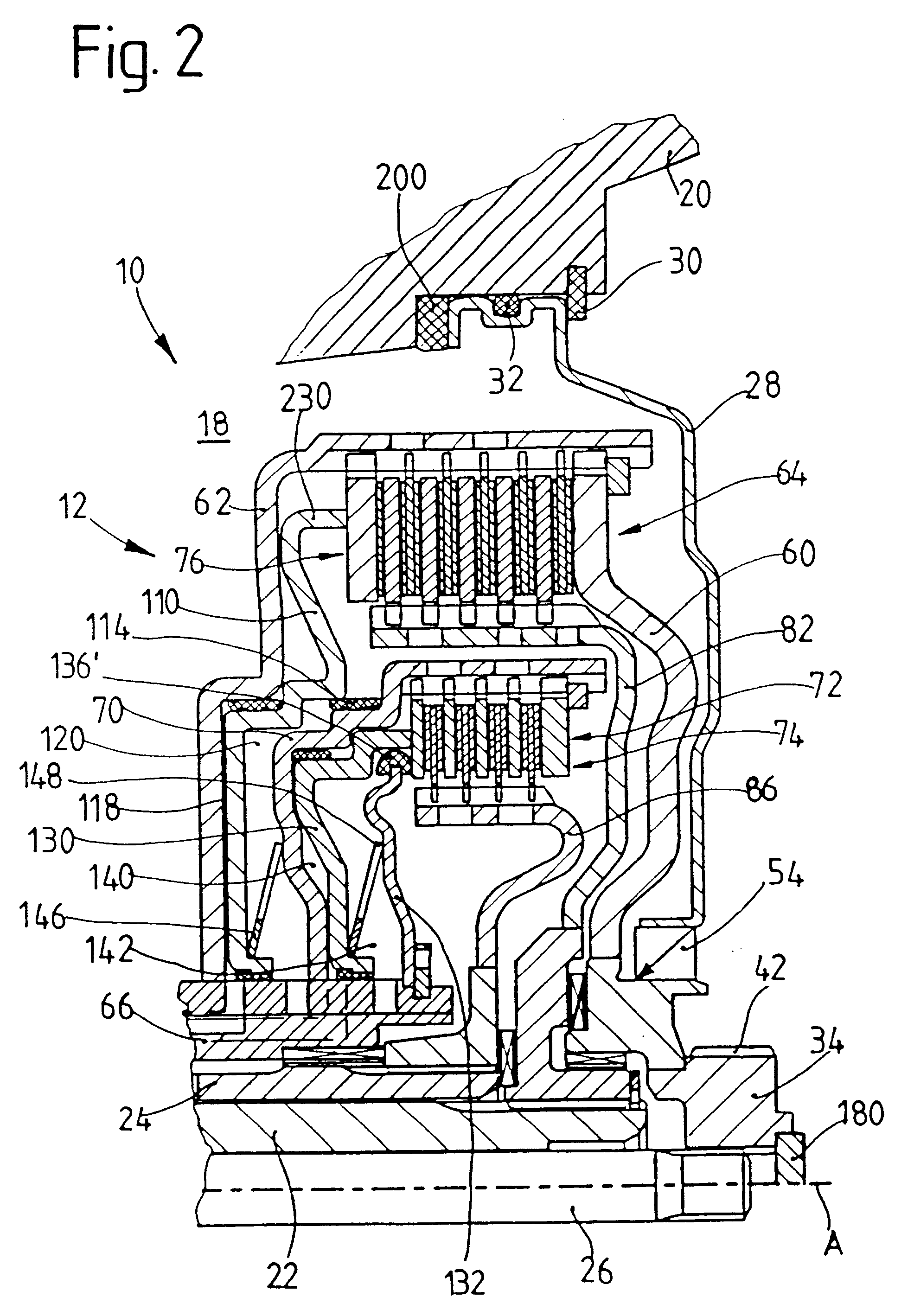
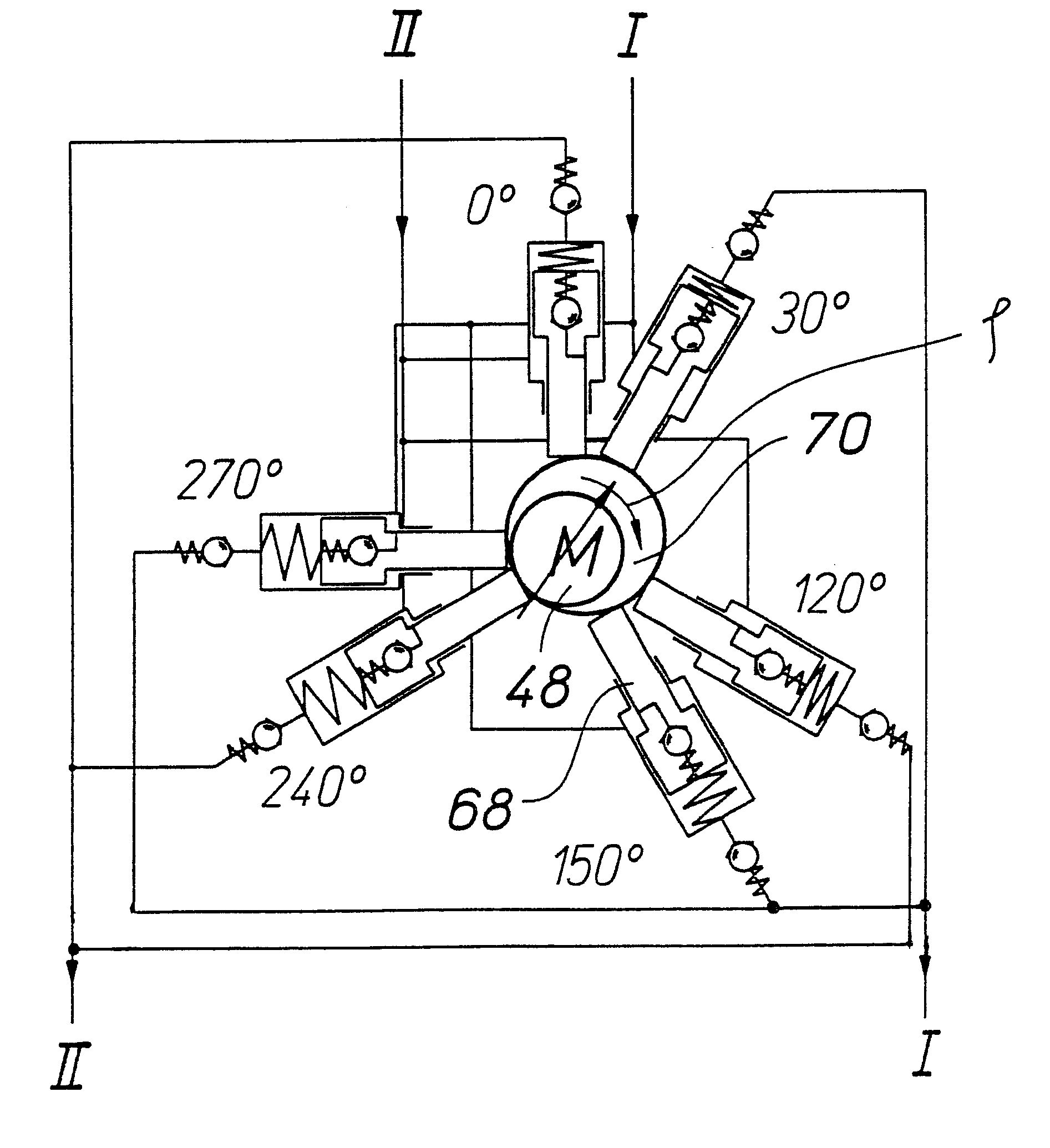
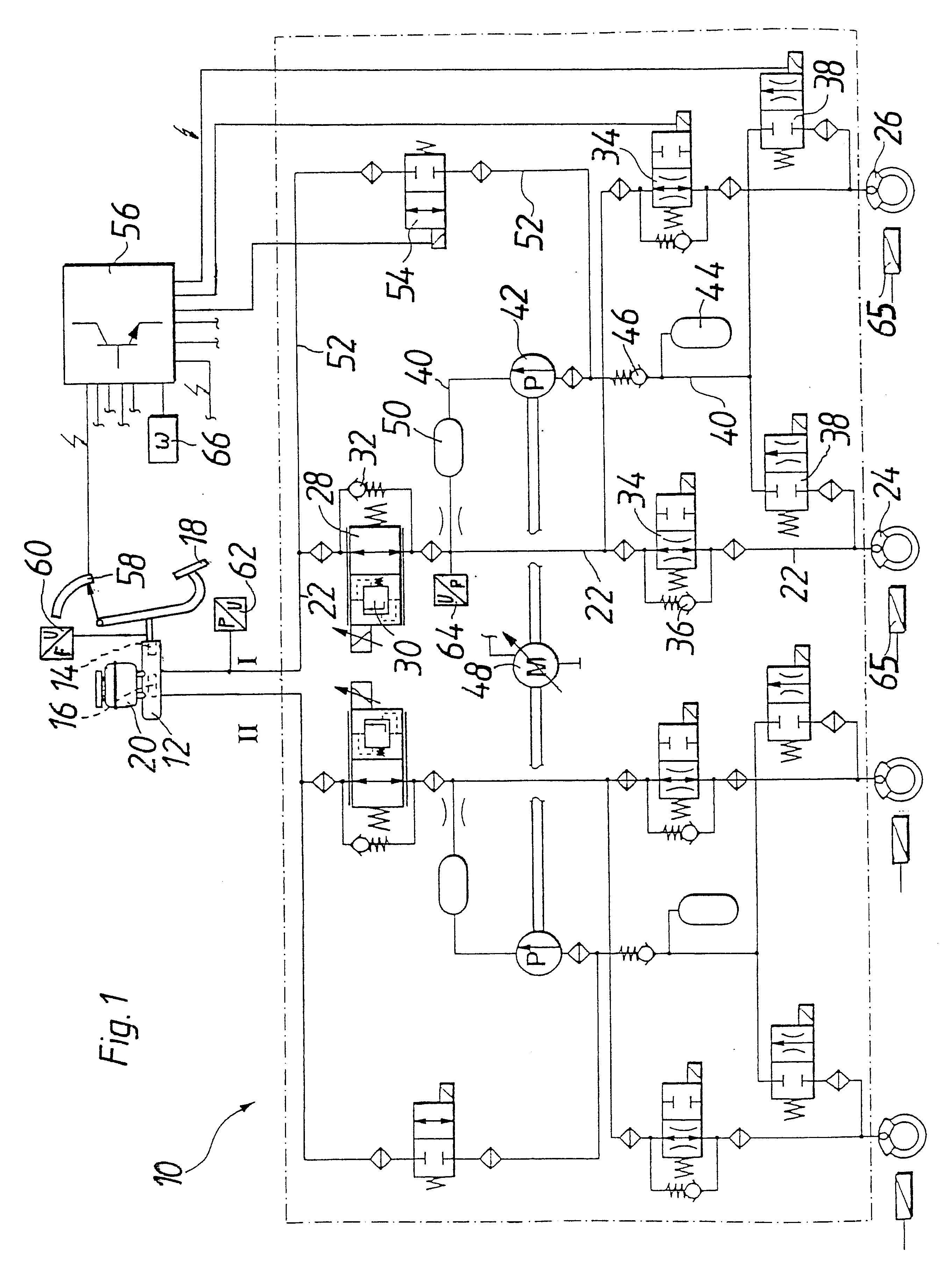
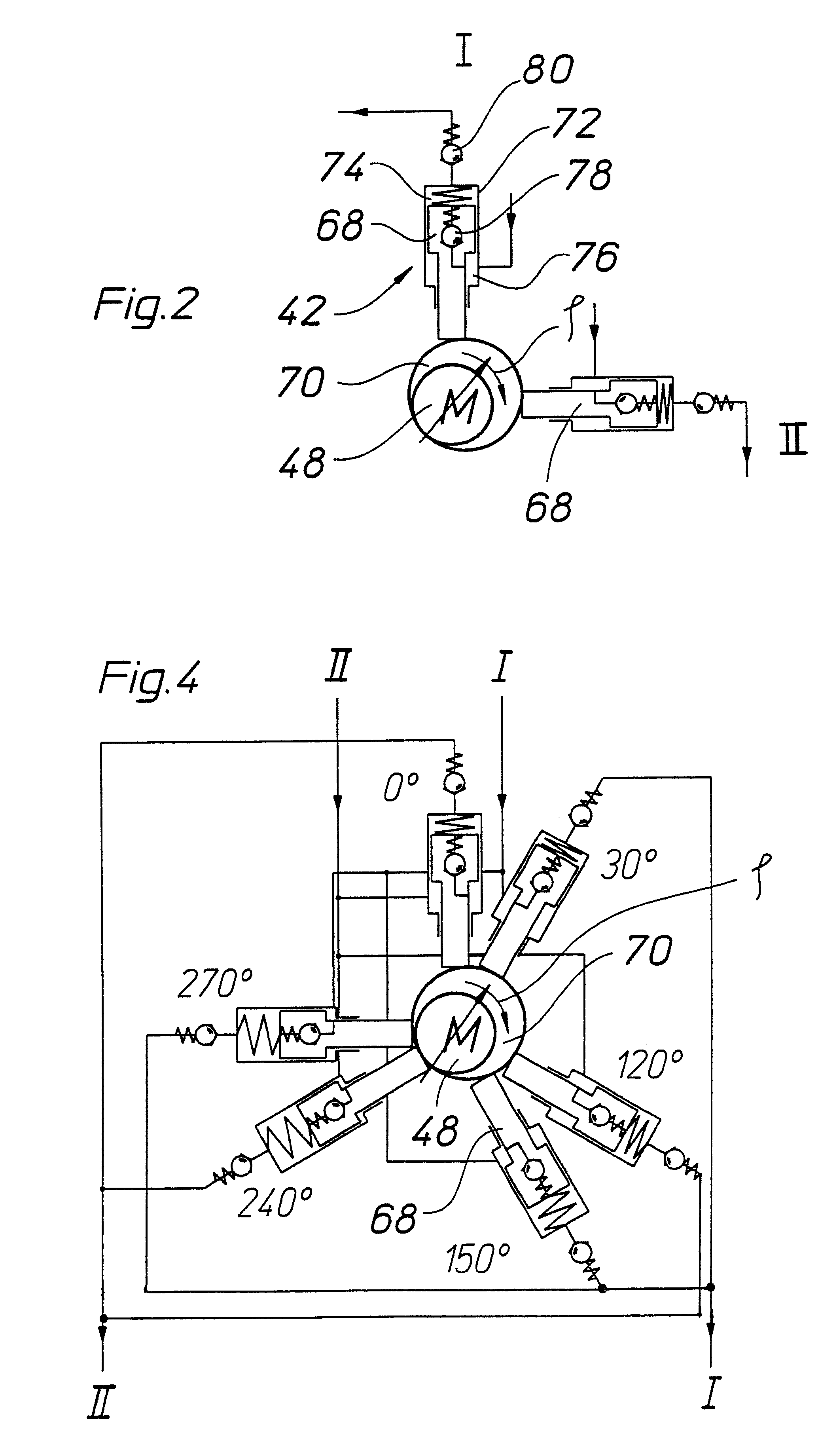
Hydraulic braking system for automobiles
The invention relates to a vehicle hydraulic brake system with electrohydraulic brake boosting by a piston pump. In order to reduce pressure pulsations on an intake side of the multi-piston pump, the brake system embodies a multi-piston pump, for example, as a six-piston pump with stepped pistons that are driven with an alternating phase shift of 30° and 90° in relation to one another. The phase shift of the drive of the stepped pistons is selected so that the intake volume flows have a uniform phase shift, by which the total intake volume flow of the multi-piston pump has a reduced amplitude of the pressure pulsation, which reduces the repercussions on a master cylinder.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electrically driven brake booster
InactiveUS6634724B2Reduce weightEasy constructionServomotor componentsRotary clutchesLinear motionMaster cylinder
An electrically driven brake booster (1) includes an input member (4) disposed in operative association with a brake pedal (12), an output member (5) disposed in operative association with the master cylinder (6), and drive transmitting device (10) for translating a rotating motion of a motor (9) into a linear motion to be transmitted to the output member (5). The drive transmitting device (10) comprises a rack (23) formed on the output member (5), and pinions (21, 22) disposed in operative association with the motor (9) and in meshing engagement with the rack (23). Also, reaction transmitting device (8) which transmits a brake reaction to the input member (4) and the output member (5) at a given proportion is provided. In comparison to conventional drive transmitting device, the drive transmitting device (10) of the present invention has a simple construction, a reduced weight and a better transmission efficiency. The provision of reaction transmitting device allows a correct brake control to be achieved on the basis of a brake reaction.
Owner:DIESEL KIKI CO LTD
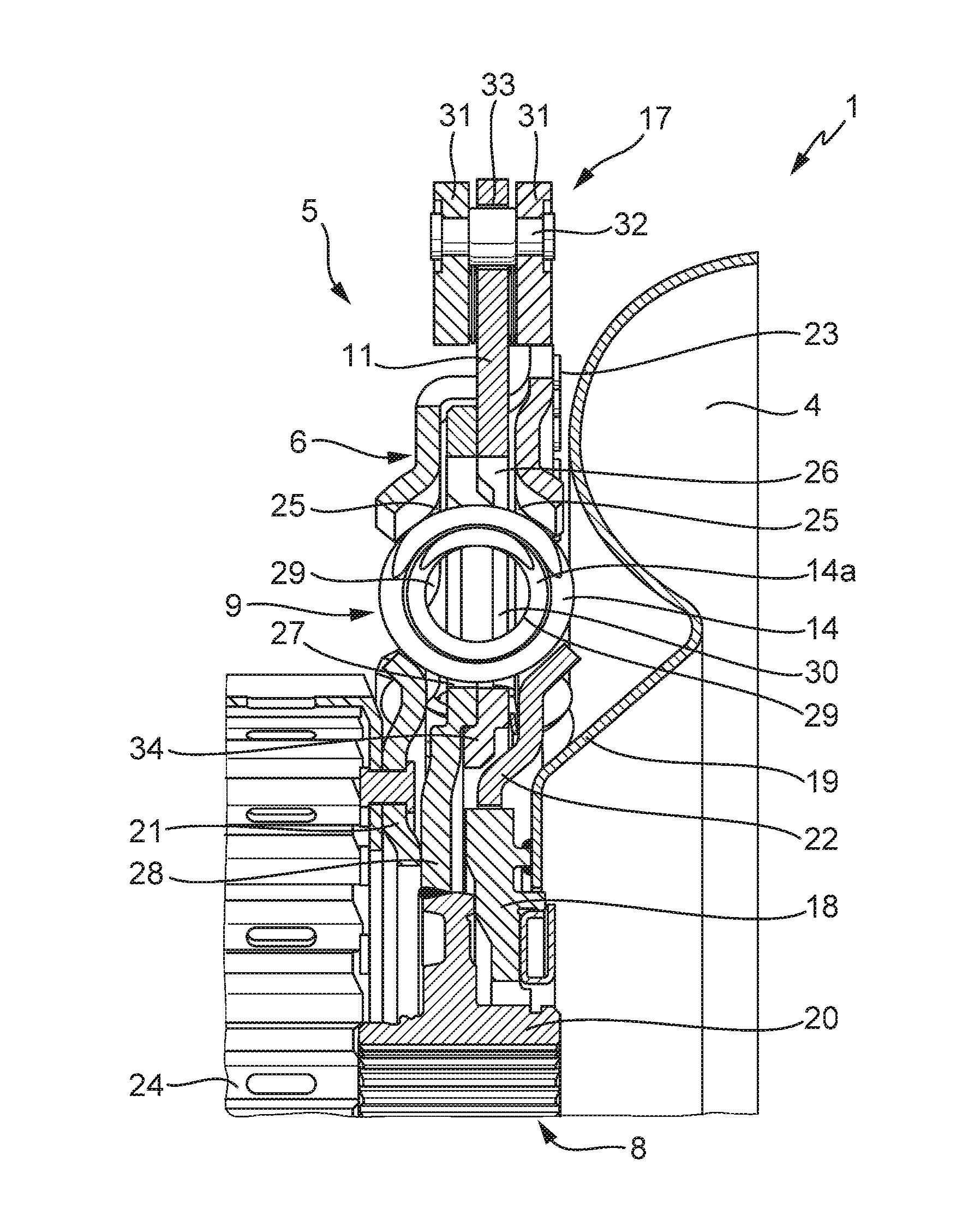
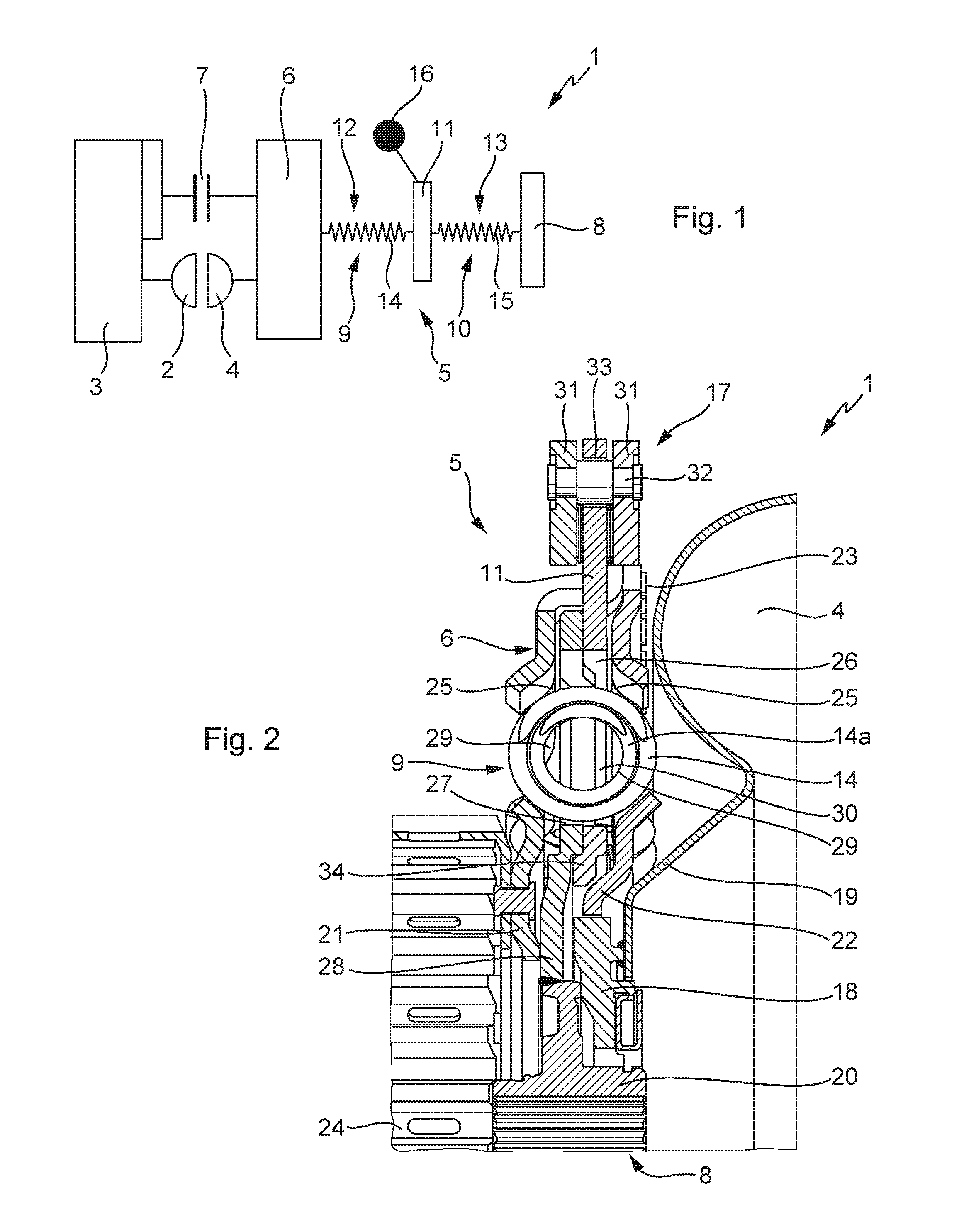
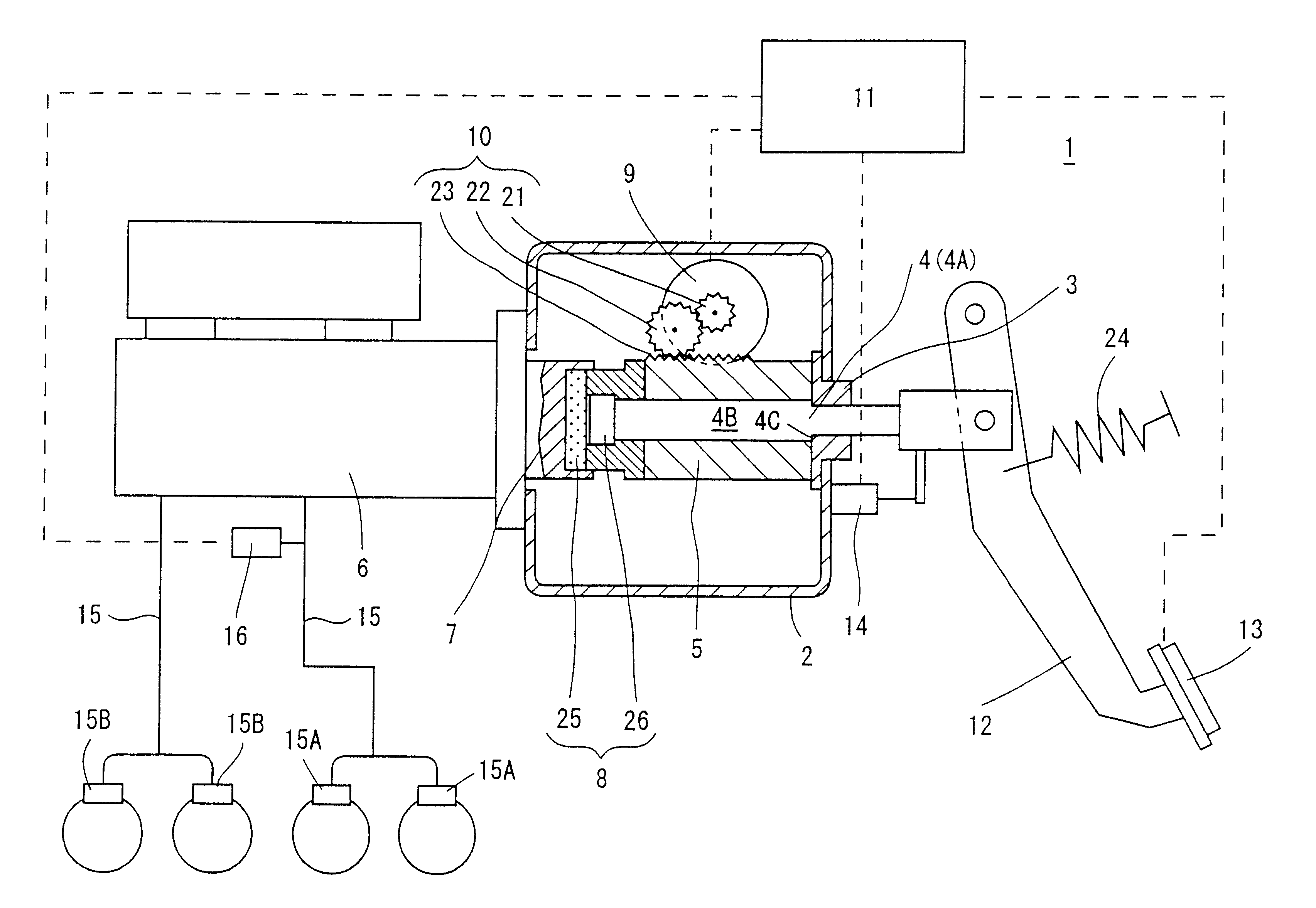
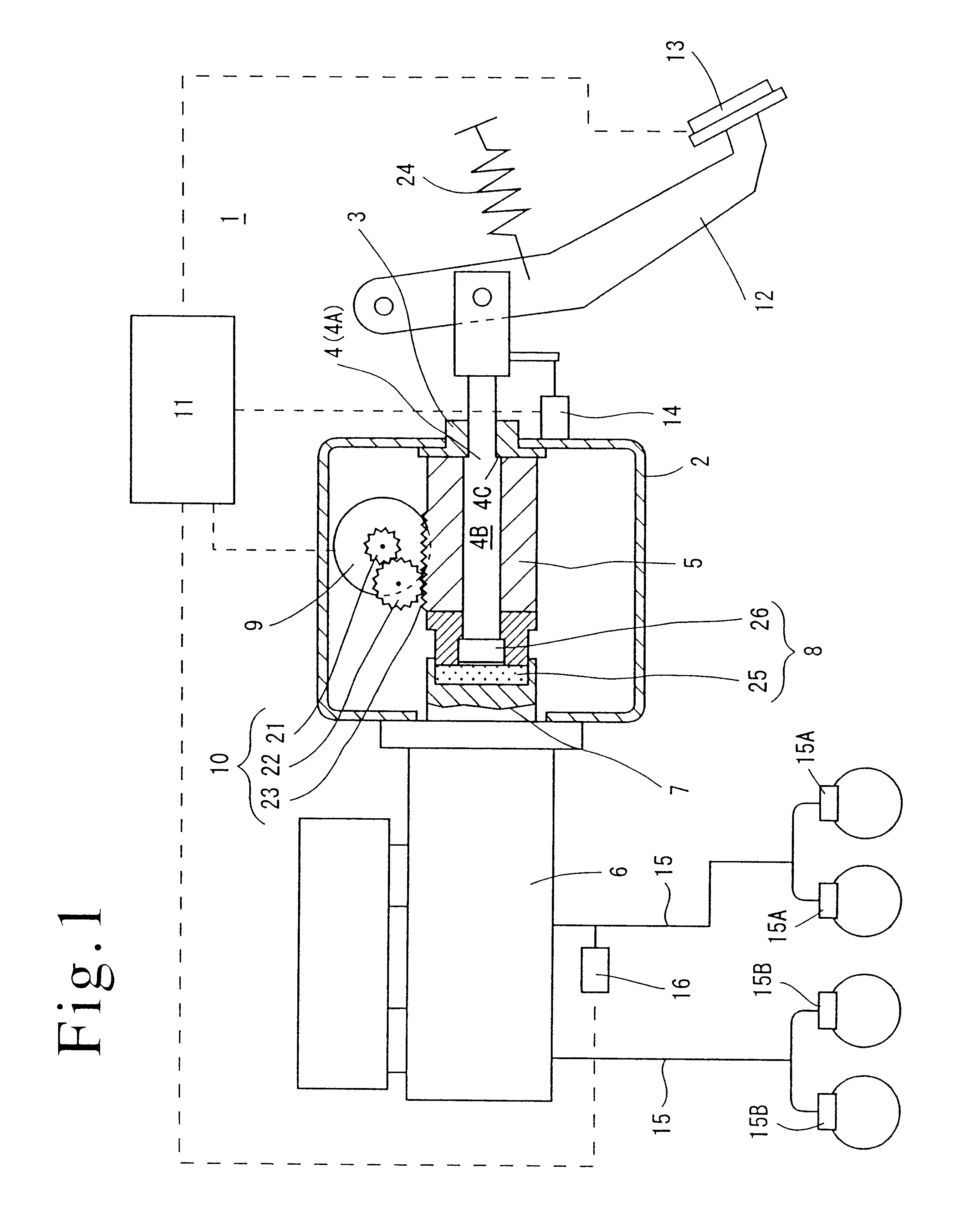
Starting apparatus
InactiveUS20120080281A1Reduce device sizeEasy to adjustRotary clutchesFluid gearingsElastomerEngineering
A starting apparatus including an input member coupled to a motor; a damper mechanism having an input element, an elastic body and an output element; a lock-up clutch mechanism for performing lockup where the input member is coupled to an input shaft of a transmission via the damper mechanism and for canceling lockup, and a dynamic damper including an elastic body and a mass body engaged with the elastic body. The mass body of the dynamic damper is an elastic body support member that is supported rotatably around an axis of the starting apparatus and that supports the elastic body of the damper mechanism. With this arrangement, the dynamic damper is easily adjustable while reducing the overall size of the starting apparatus.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Compressed air energy storage system utilizing two-phase flow to facilitate heat exchange
InactiveUS20100326064A1Facilitate heat exchangeImprove efficiencyElectrical storage systemServomotor componentsThermal energy storageEngineering
A compressed-air energy storage system according to embodiments of the present invention comprises a reversible mechanism to compress and expand air, one or more compressed air storage tanks, a control system, one or more heat exchangers, and, in certain embodiments of the invention, a motor-generator. The reversible air compressor-expander uses mechanical power to compress air (when it is acting as a compressor) and converts the energy stored in compressed air to mechanical power (when it is acting as an expander). In certain embodiments, the compressor-expander comprises one or more stages, each stage consisting of pressure vessel (the “pressure cell”) partially filled with water or other liquid. In some embodiments, the pressure vessel communicates with one or more cylinder devices to exchange air and liquid with the cylinder chamber(s) thereof. Suitable valving allows air to enter and leave the pressure cell and cylinder device, if present, under electronic control.
Owner:LIGHTSAIL ENERGY
Torsional vibration damper
A torsional vibration damper on the bridging clutch of a hydrodynamic clutch arrangement has a first connecting device, which can be brought into working connection with the clutch housing and with a drive-side transmission element. The drive-side transmission element is connected via first energy-storage devices to an intermediate transmission element. The torsional vibration damper also has a second connecting device for establishing a working connection via second energy-storage devices between the intermediate transmission element and a takeoff-side transmission element, which is connected to a takeoff-side component of the hydrodynamic clutch arrangement. The intermediate transmission element accepts a mass element, located operatively between the two connecting devices.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Rotating torque-transmitting apparatus
InactiveUS20050279605A1Reduce loadRotary clutchesFluid actuated clutchesTorque transmissionEngineering
A rotatable torque-transmitting apparatus includes a stationary piston and a rotatable apply plate. The rotatable apply plate is disposed adjacent a rotatable housing and separated therefrom by a return spring assembly which in a preload condition is trapped between the apply plate and the rotatable housing to limit the disengaged force which is transmitted between the rotatable housing and the stationary piston.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Torque converter
InactiveUS20050133328A1Preventing hydraulic pressureImprove cycle performanceRotary clutchesFriction clutchesCircular discImpeller
A torque converter which can prevent an engagement pressure of a lockup clutch from becoming very high. A converter chamber is formed between an outer disc portion of a front cover and an impeller shell. A partition wall separating a clutch chamber and a converter chamber is provided in the outer disc portion. A clutch chamber has a drive plate serving as an input side of an engine output, a driven plate serving as an output side, and a lockup piston forming an engagement oil chamber along with an inner disc portion of the front cover. Since the partition wall is provided, the lockup clutch can be engaged without being affected by the hydraulic pressure within the converter chamber.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
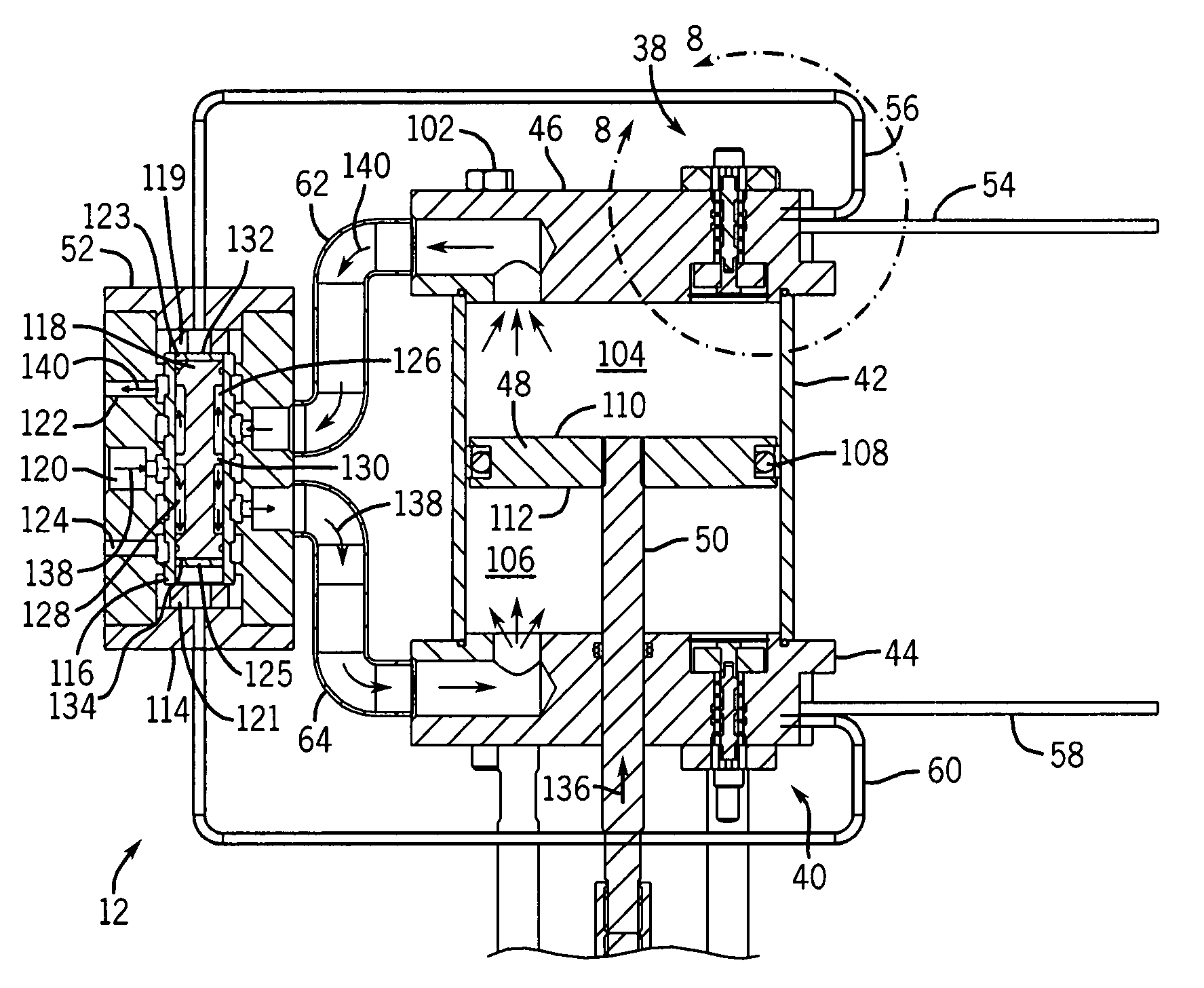
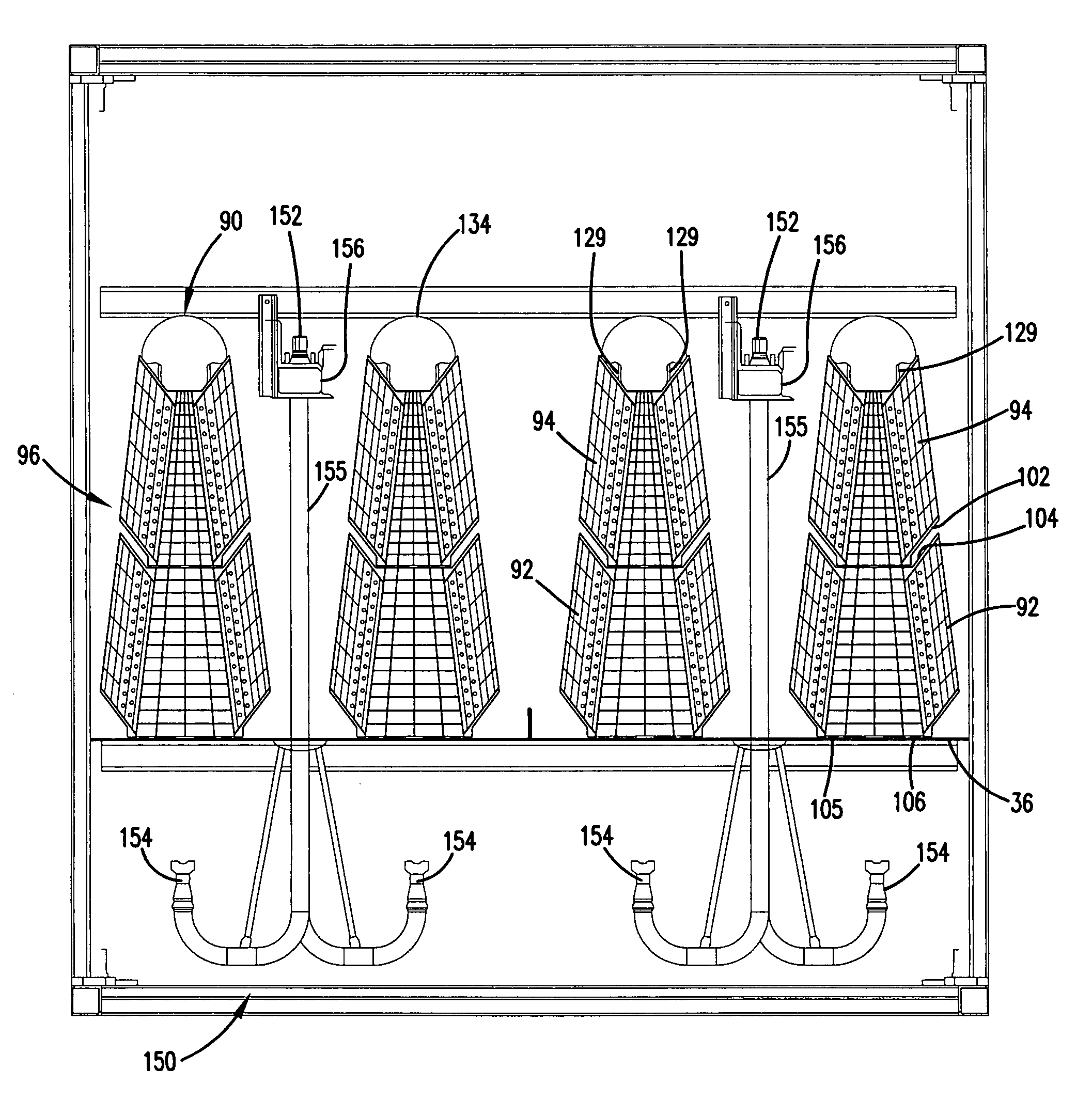
Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation
ActiveUS20110044824A1Reduce excessive wasteMaximizing membrane efficiencyFlexible member pumpsServomotorsHigh concentrationConcentration ratio
A method and apparatus for renewable power generation utilizes the chemical potential dissimilarity between solutions of differing ionic formulations. A train is formed by a sequentially ordered set of a plurality of cells in which each successive cell is related to the preceding cell. Each cell has pumping means and hydro-power generation turbine means to form a closed hydraulic loop configured for specified volumetric and flow capacity. Adjacent cells share semipermeable membranes. Each cell is charged with a brine of specified ionizable inorganic salt quantity and type with the brine being cycled in a controlled concentration-pressure loop, with each of the cells operating at progressively increasing concentration and osmotic pressure ratio. A continuous and constant flow rate of substantially salt-free permeate flux is maintained across each cell, the flux being osmotically induced from low salt concentration water being fed at the first cell in the train and exiting at the last cell along with the discarded high concentration water brine. The salt-free permeate flux is continuously induced, in symbiotic mode, through the shared membranes, driven by the chemical influence of concentration potential field bounded by water of low to no salt concentration on one end of the train and by brine of high salt concentration on the other end of the train with sufficient concentration difference to provide driving force for said plurality of cells, while maintaining adequate concentration difference between adjacent cells to enhance osmosis function, as well as defining a concentration ratio within each cell to ensure a net positive power generation.
Owner:KELADA MAHER ISAAC
Method of and apparatus for actuating the torque transmitting system and the transmission in the power train of a motor vehicle
PCT No. PCT / DE96 / 01755 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 23, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 23, 1997 PCT Filed Sep. 12, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 10456 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 20, 1997The friction clutch between the engine and an automated transmission in the power train of a motor vehicle are operated and controlled by an actuator which effects changes in the extent of engagement of the clutch as well as the selection of and shifting into particular gears. The actuator forms part of a unit which receives a pressurized hydraulic fluid from a source including an accumulator and a proportional valve which latter selects the fluid pressure necessary to shift the transmission into a selected gear.
Owner:LUK GETRIEBE SYST +3
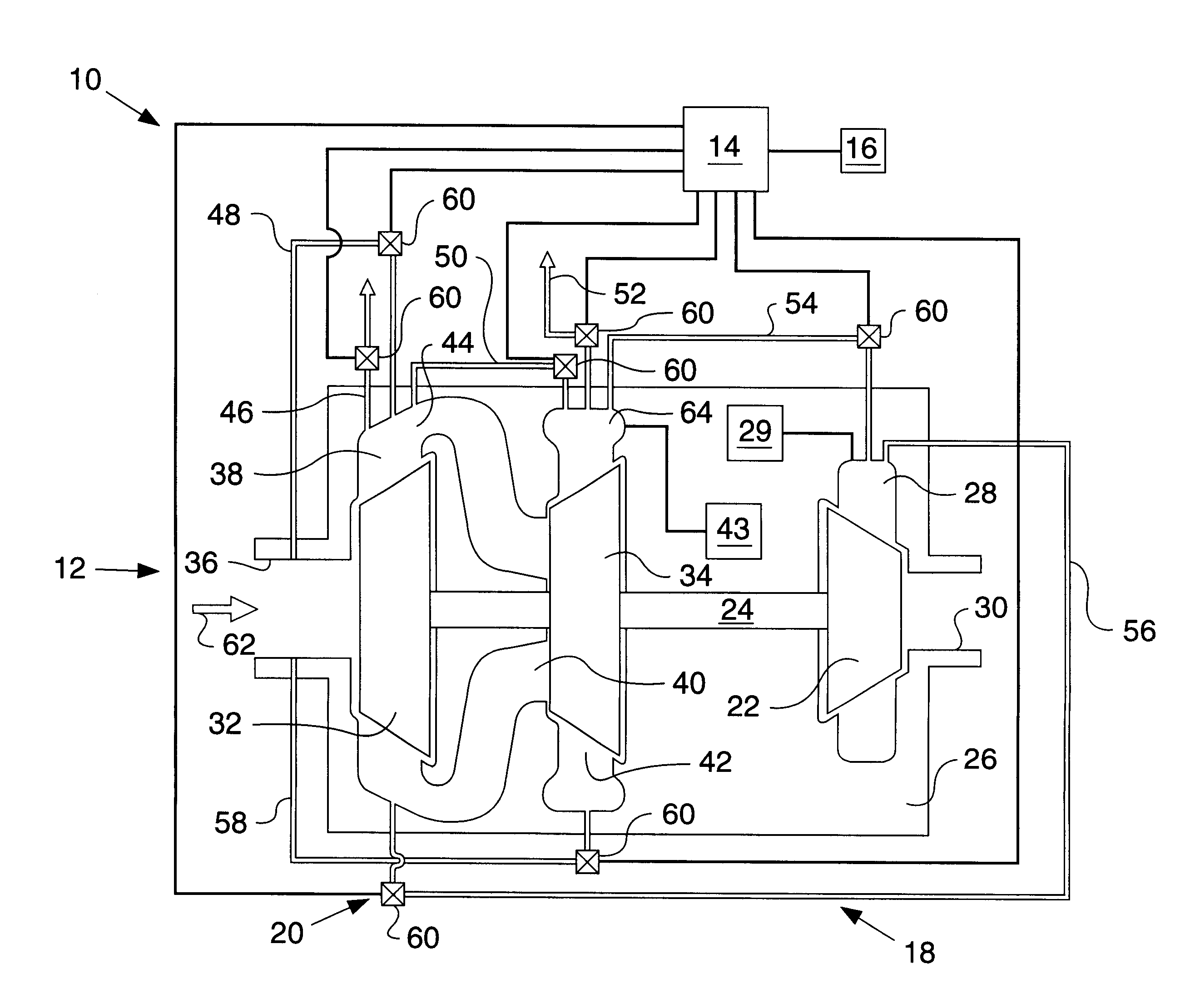
Turbocharger system to inhibit surge in a multi-stage compressor
A turbocharger system for an internal combustion engine is provided with at least one rotatable shaft and a multi-stage compressor. The multi-stage compressor includes a first compressor wheel carried by a corresponding shaft, an axially extending first inlet associated with the first compressor wheel, a radially extending first outlet associated with the first compressor wheel, a second compressor wheel carried by a corresponding shaft, an axially extending second inlet associated with the second compressor wheel, and a radially extending second outlet associated with the second compressor wheel. An interstage duct fluidly interconnects in series the first outlet associated with the first compressor wheel with the second inlet associated with the second compressor wheel. At least one bypass duct is provided, with each bypass duct fluidly interconnecting the first outlet with the first inlet; the first outlet with an ambient environment; and / or the second outlet with the first outlet. At least one valve is provided, each valve being positioned within a corresponding bypass duct. A controller is coupled with each valve and selectively actuates each valve.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Hydraulic pressurizer system
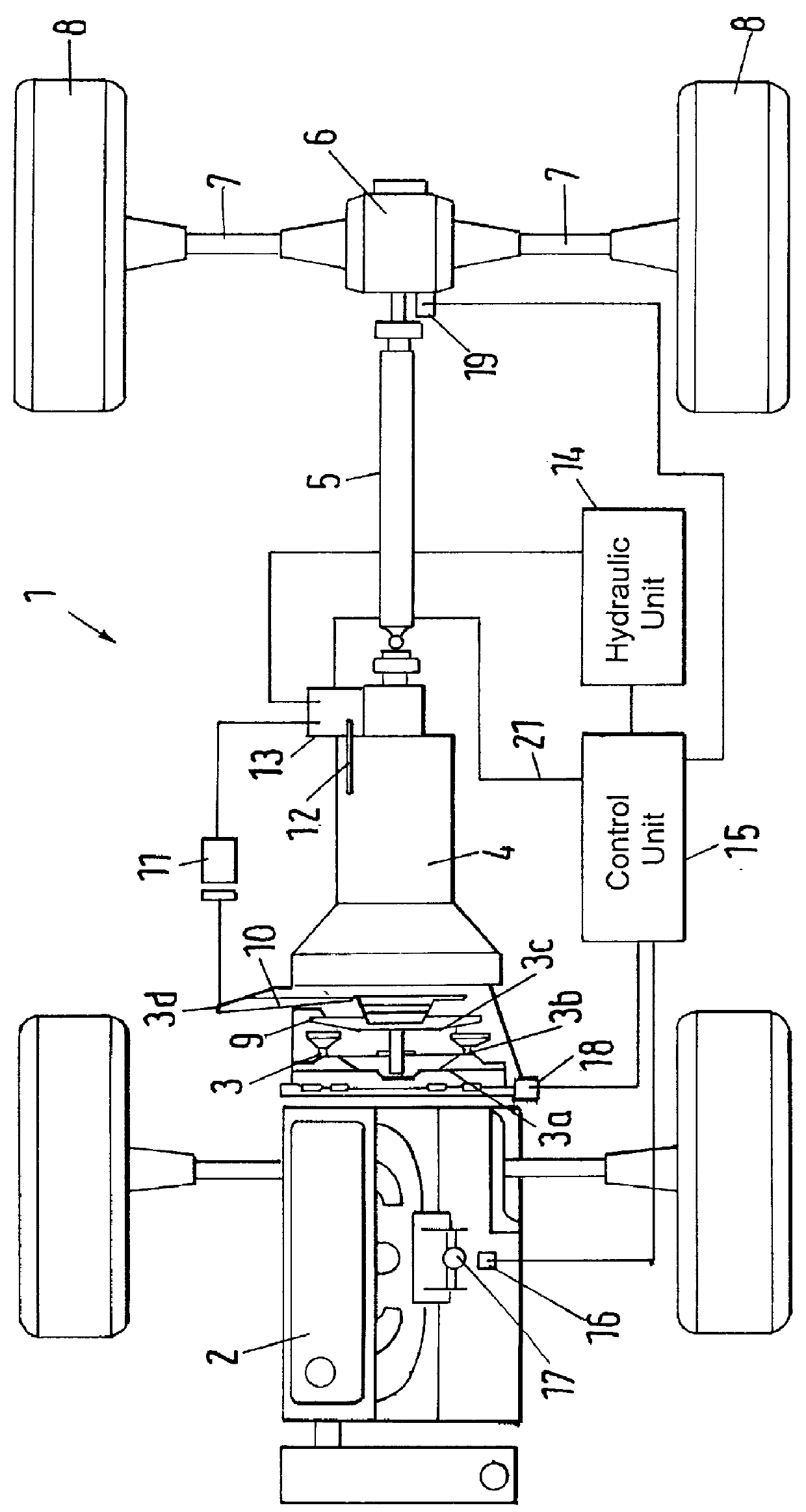
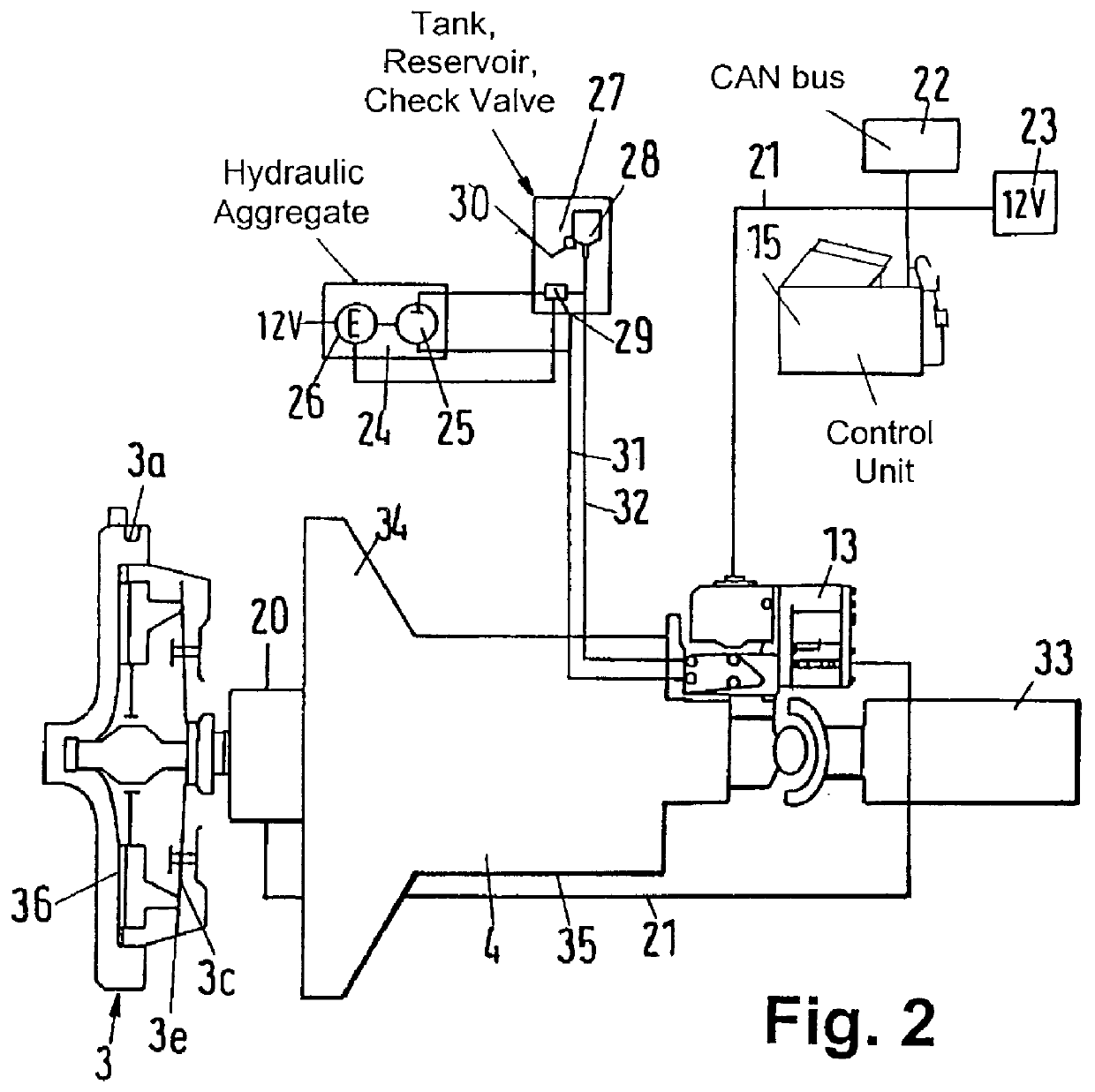
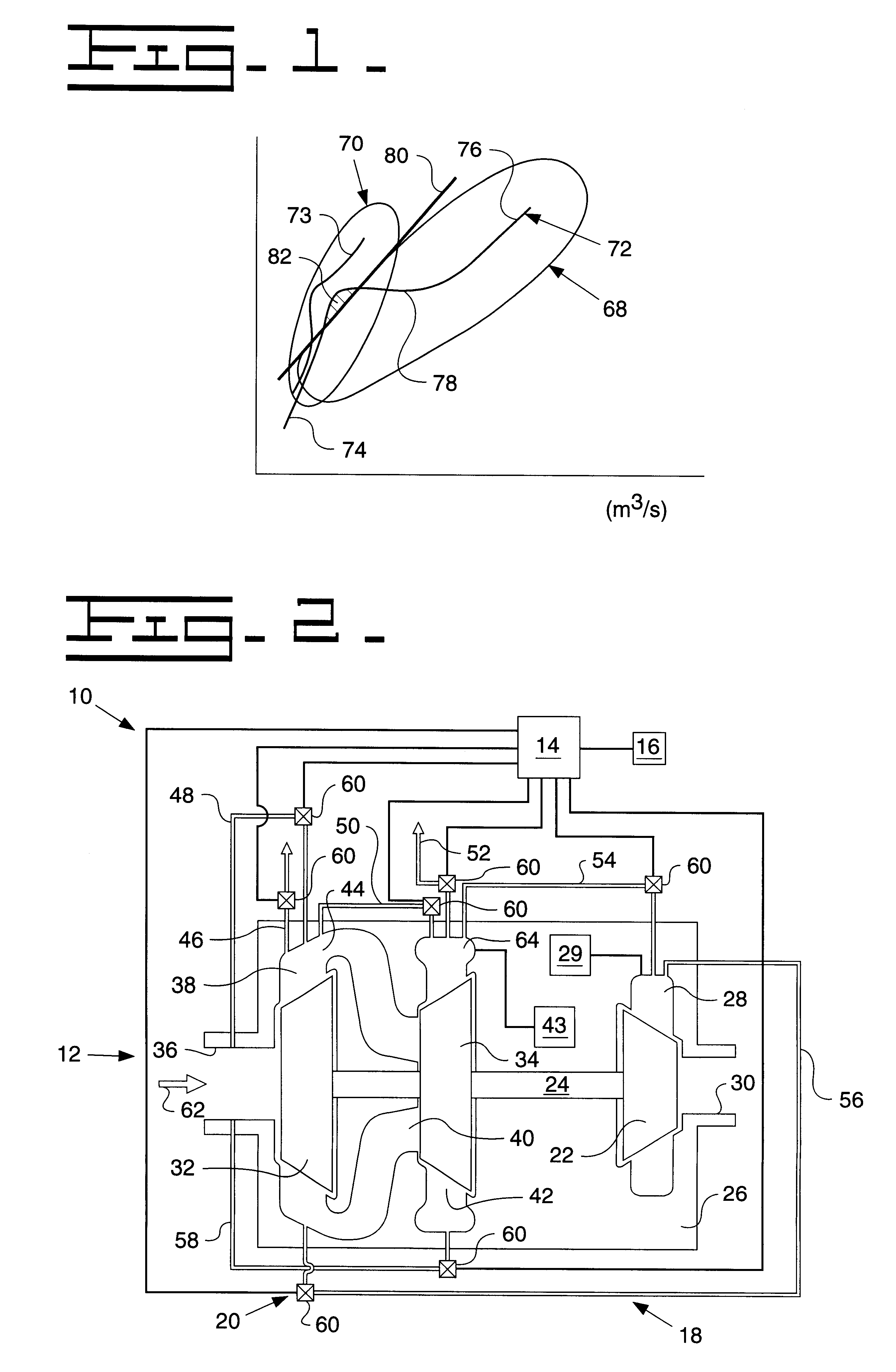
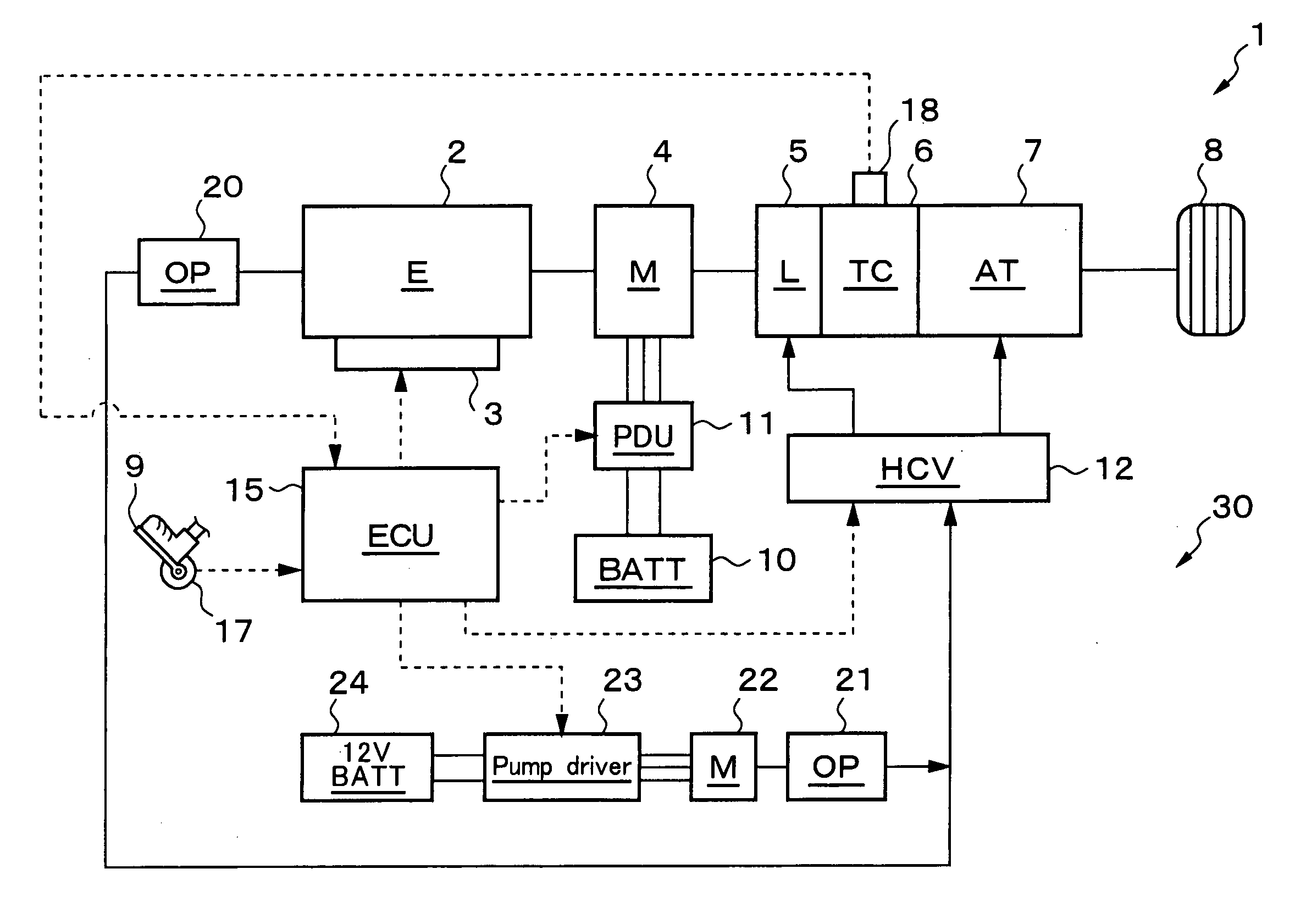
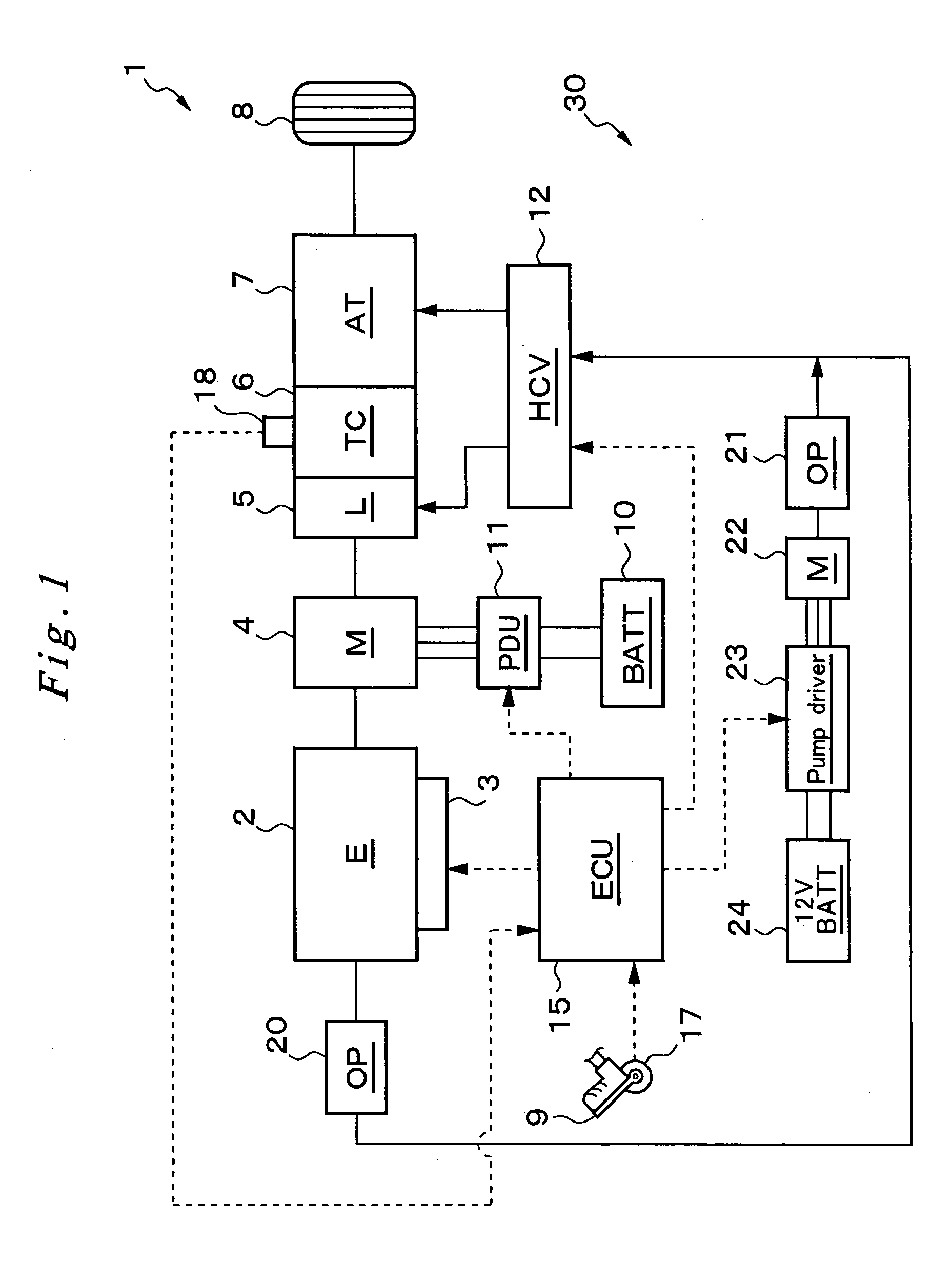
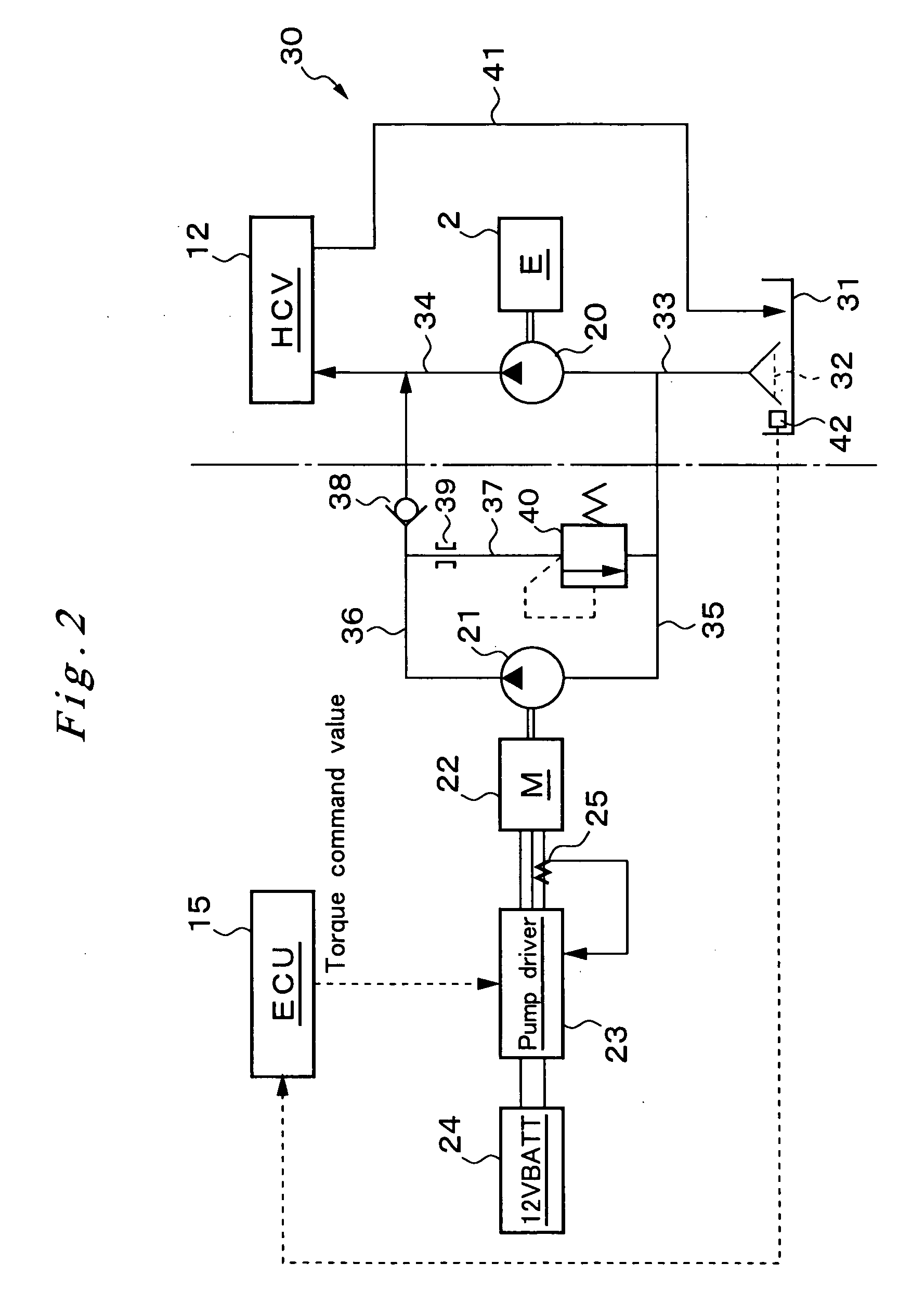
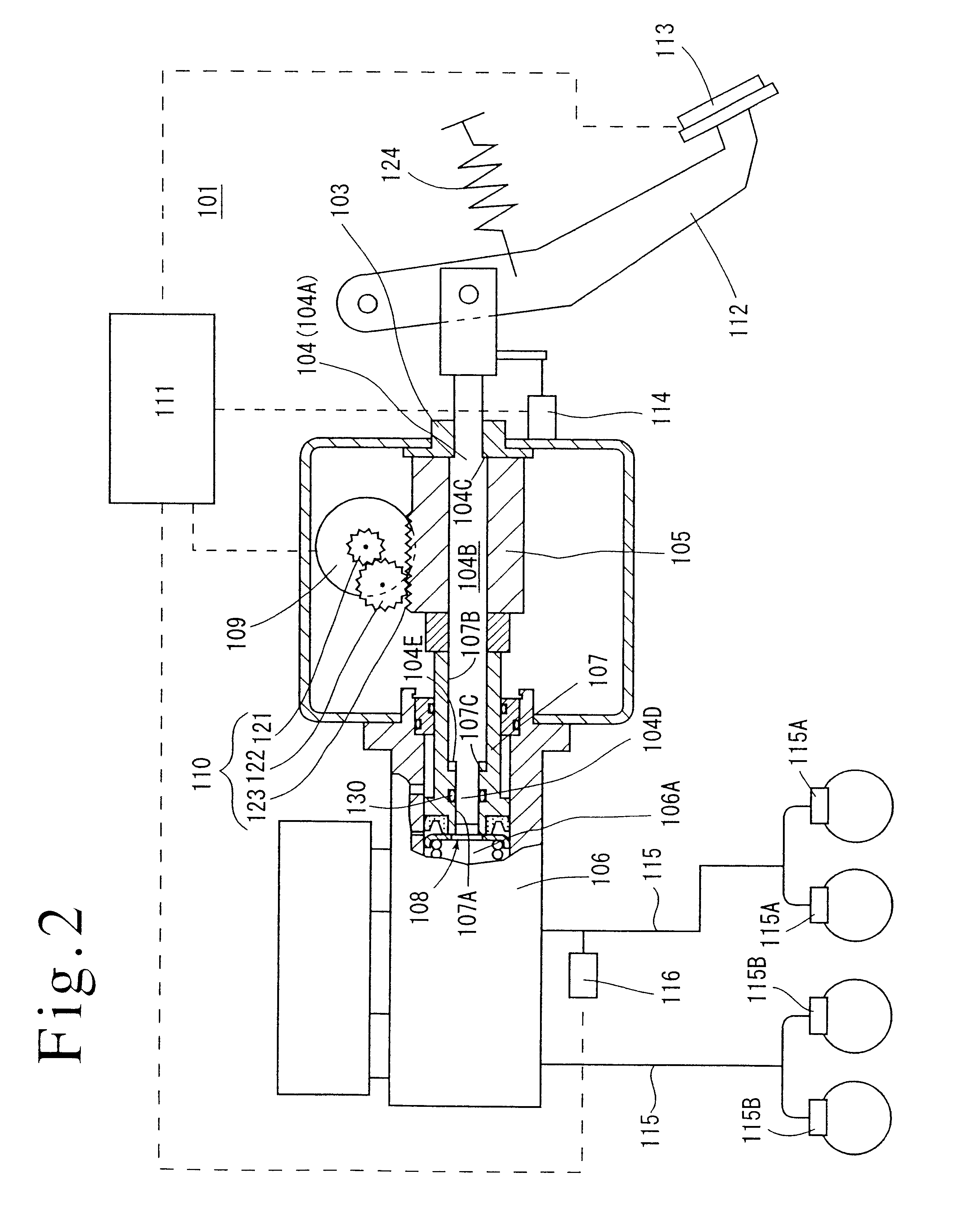
InactiveUS20060120876A1Maintain pressureCost-effective manufacturingRotary clutchesGearing controlHybrid vehicleMotor–generator
A hydraulic pressurizer system 30 comprises a drive source (an engine 2 and a motor generator 4), which drives a hybrid vehicle 1, a mechanical oil pump 20, which is driven by the drive source, an electrical motor 22, which is activated by a 12V battery 24, an electrical oil pump 21, which is driven by the electrical motor 22, and a control unit 15, which activates the electrical motor 22. The pressurizer further comprises a ratio-change mechanism 7, which is activated by hydraulic oil supplied by the mechanical oil pump 20 and by the electrical oil pump 21 to establish a speed change ratio, at which the rotational driving force of the drive source is transmitted to wheels 8 with a rotational speed change. The control unit 15 memorizes a characteristic value CV, which is specified from the temperature of the hydraulic oil and from the rotational speed of the electrical motor 22, and a threshold value NTH2 for the rotational speed Np of the electrical motor 22, which threshold value corresponds to the characteristic value CV. While the control unit 15 is executing a so-called idling-stop control, it cancels the idling-stop control if the rotational speed Np of the electrical motor 22 reaches the threshold value NTH2.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
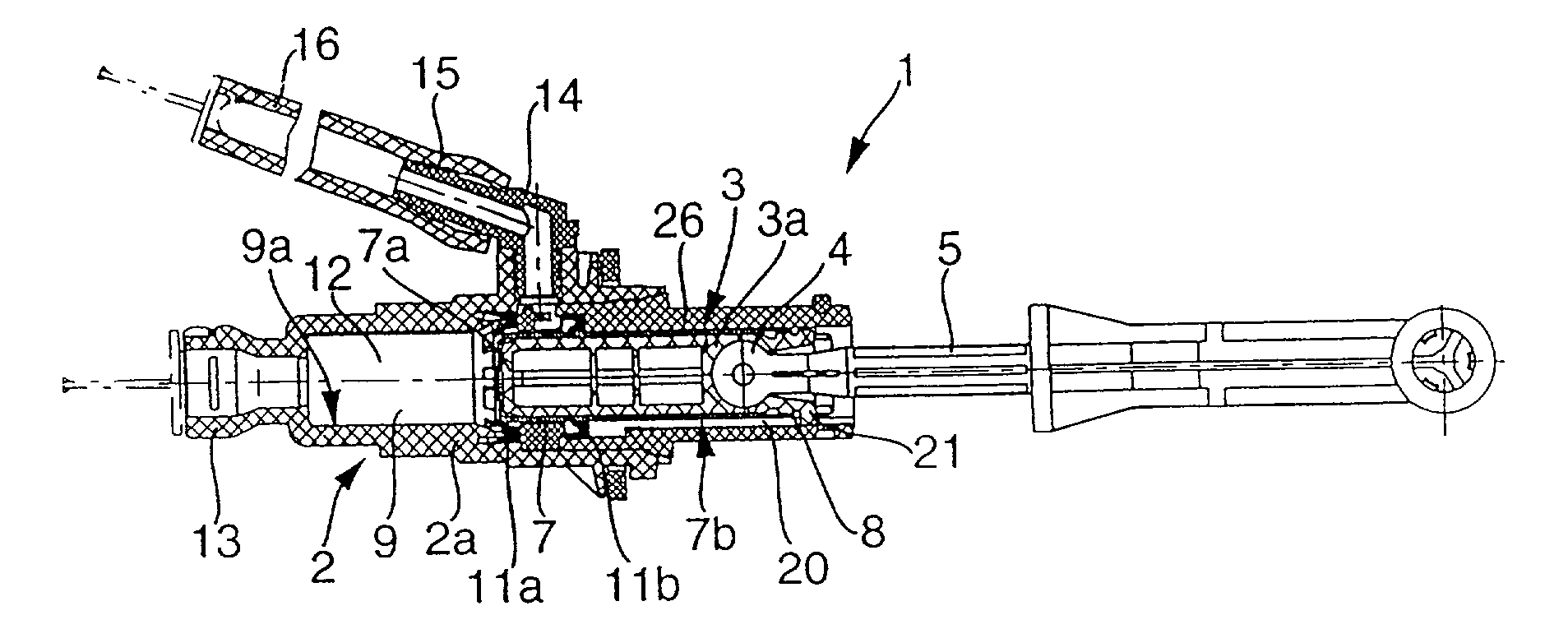
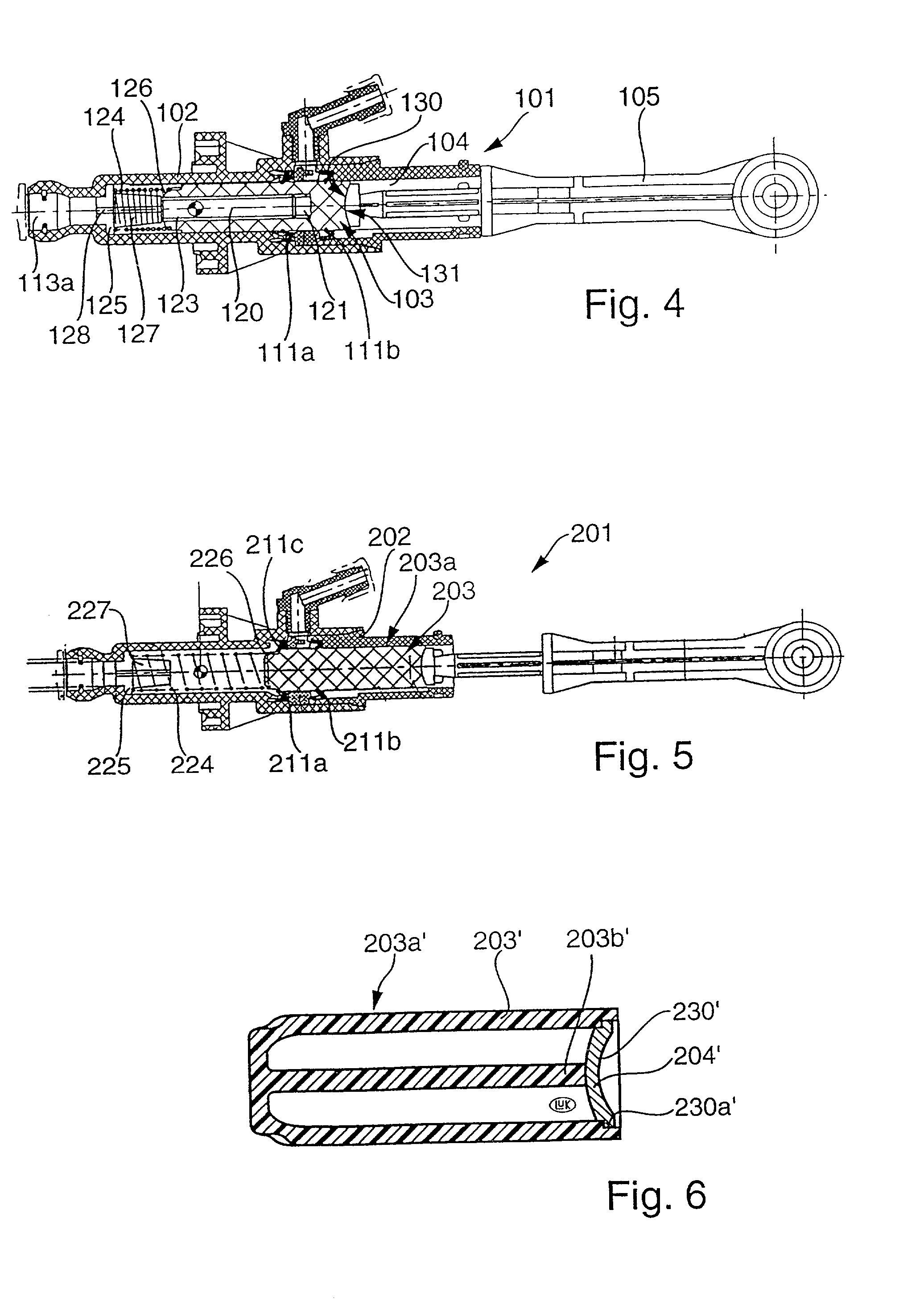
Master cylinder for use in power trains of motor vehicles
InactiveUS20020116924A1Satisfactory operationAvoid spreadingPiston ringsRotary clutchesMaster cylinderControl theory
A master cylinder for use in the power train of a motor vehicle to actuate the brakes or the friction clutch is designed to avoid the generation of screeching noise and / or the transmission of stray movements to the piston rod in response to shifting of the piston relative to the housing and relative to the sealing element(s) between the piston and the housing. This can be accomplished by causing the piston to turn relative to the housing and the sealing element(s) during axial movement in the housing and / or by installing one or more dampers between the piston and the housing and / or between the piston and the piston rod. The dampers can constitute separately produced parts and / or specially configured and / or finished surfaces provided on the piston and contacting the housing and / or the sealing element(s). The invention also relates to improvements in the configuration and / or the material(s) of the piston.
Owner:LUK LAMELLEN & KUPPLUNGSBAU BETEILIGUNGS KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com





![Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b4b27964-7dda-4348-9317-116c9790f6a1/US20110044824A1-20110224-D00000.png)
![Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b4b27964-7dda-4348-9317-116c9790f6a1/US20110044824A1-20110224-D00001.png)
![Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b4b27964-7dda-4348-9317-116c9790f6a1/US20110044824A1-20110224-D00002.png)