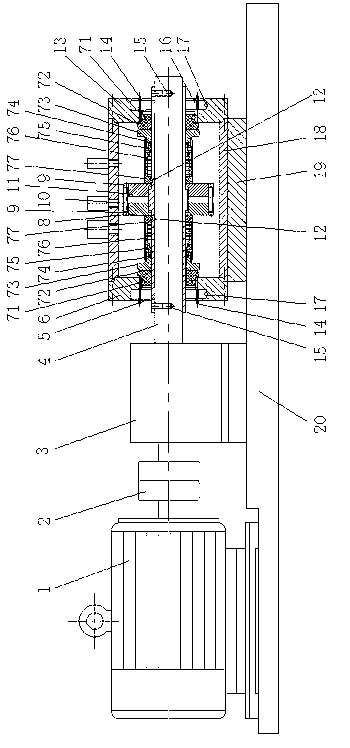
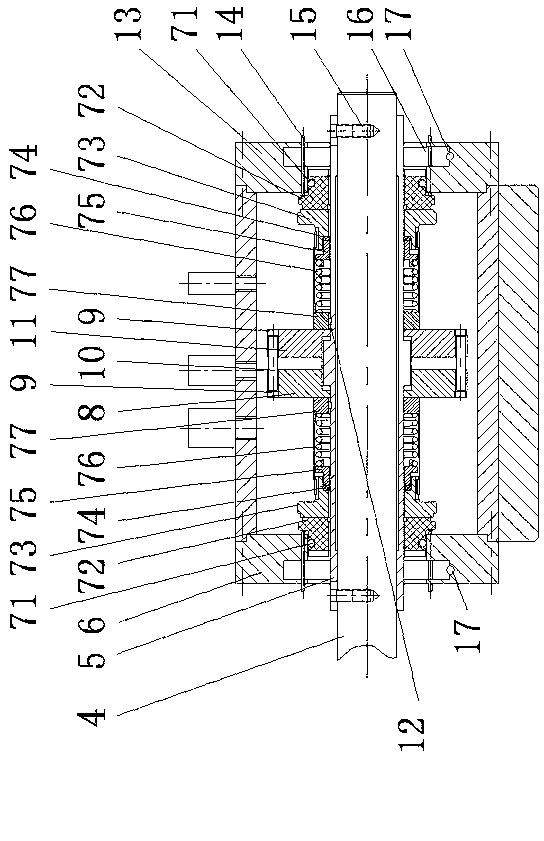
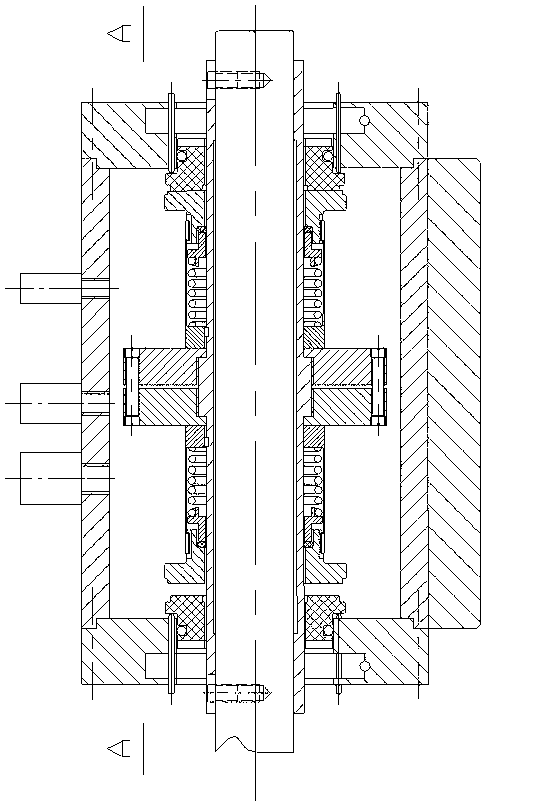
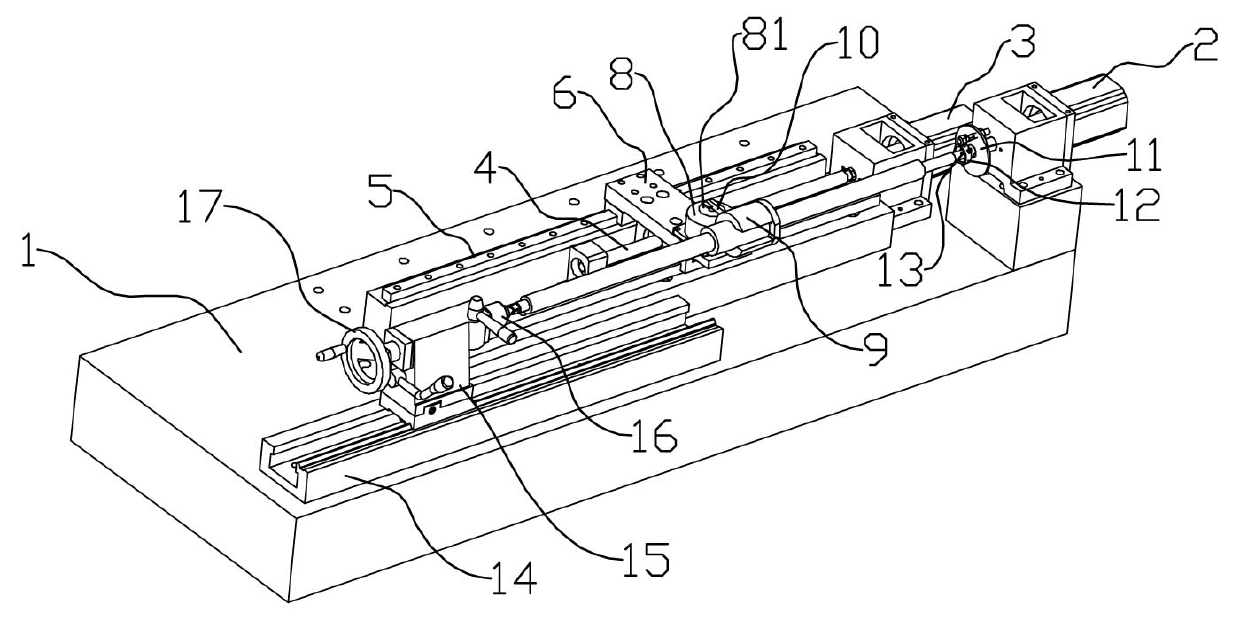
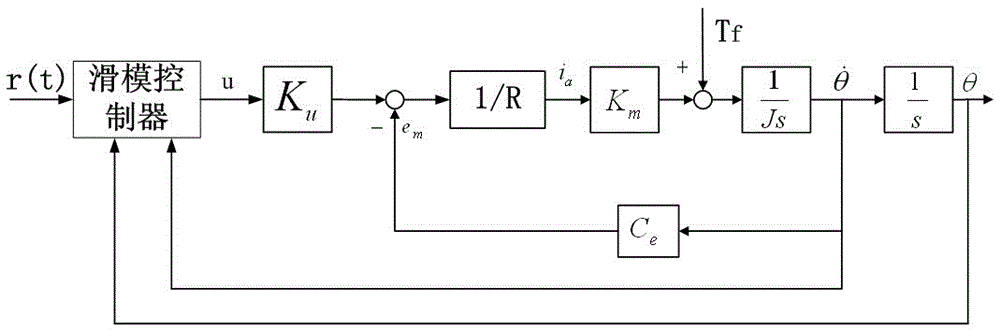
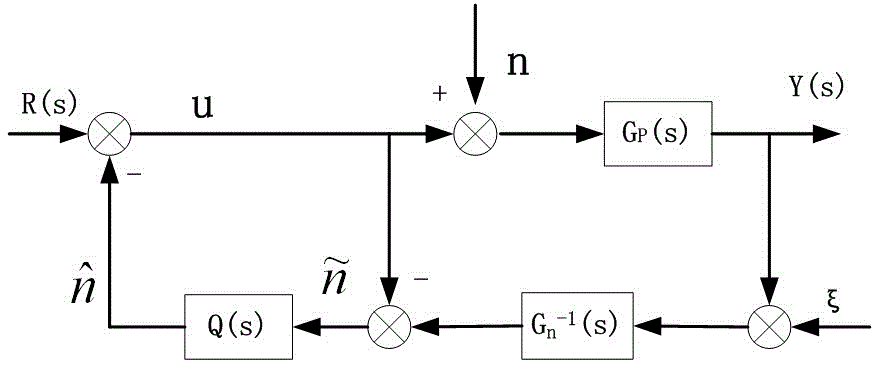
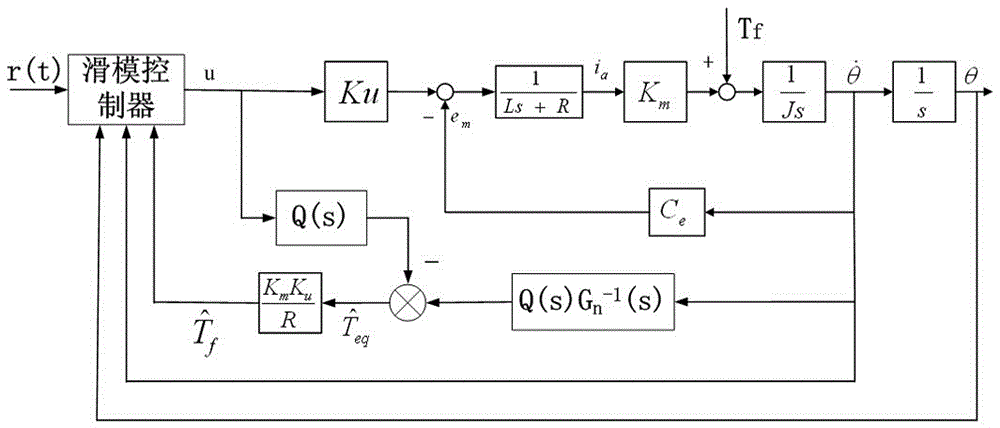
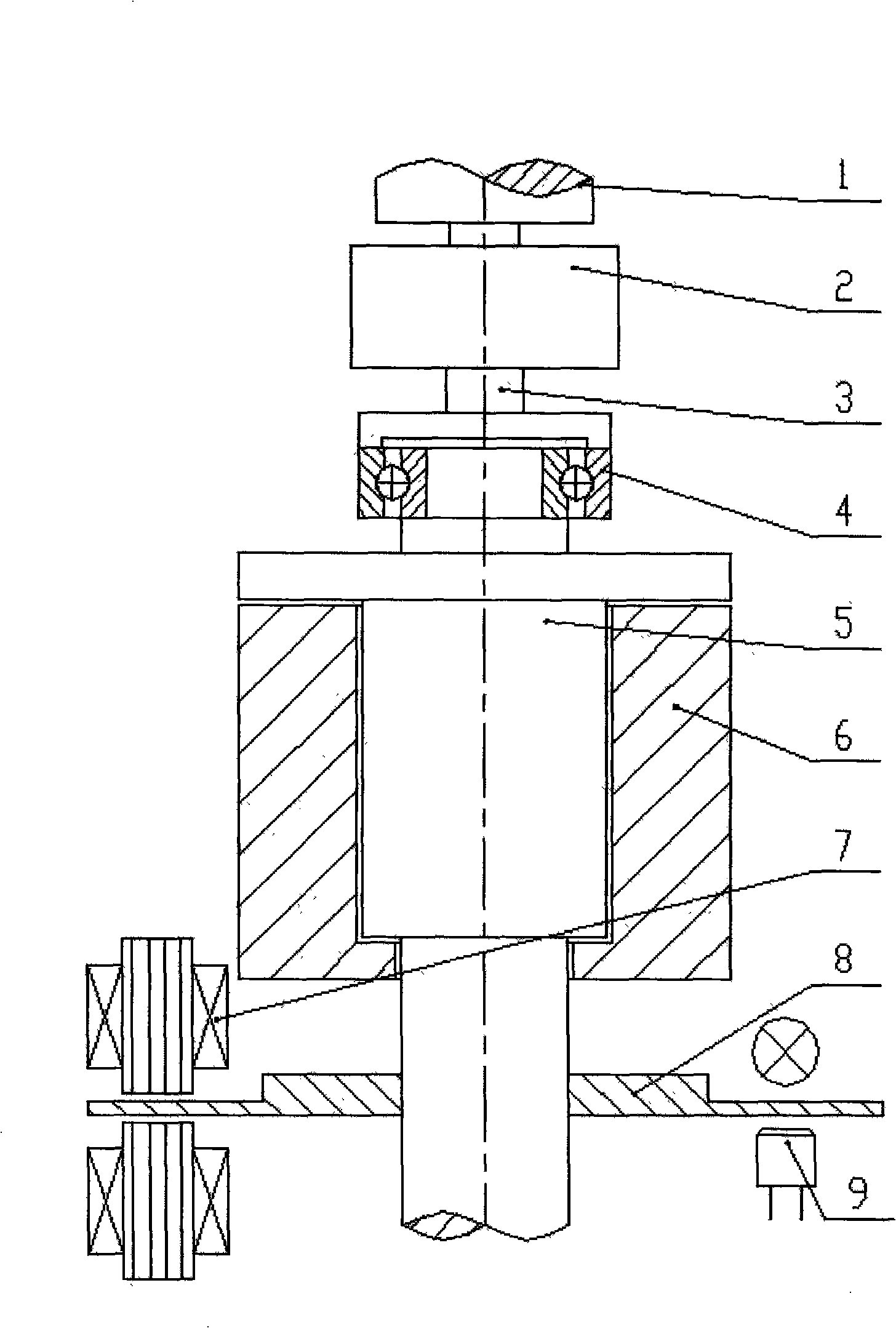
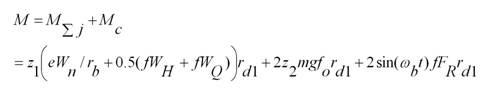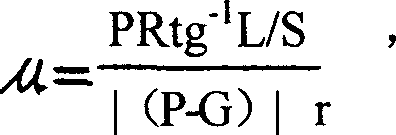Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1352 results about "Friction torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Friction torque is the torque caused by the frictional force that occurs when two objects in contact move. Like all torques, it is a rotational force which may be measured in newton metres or pounds-feet.
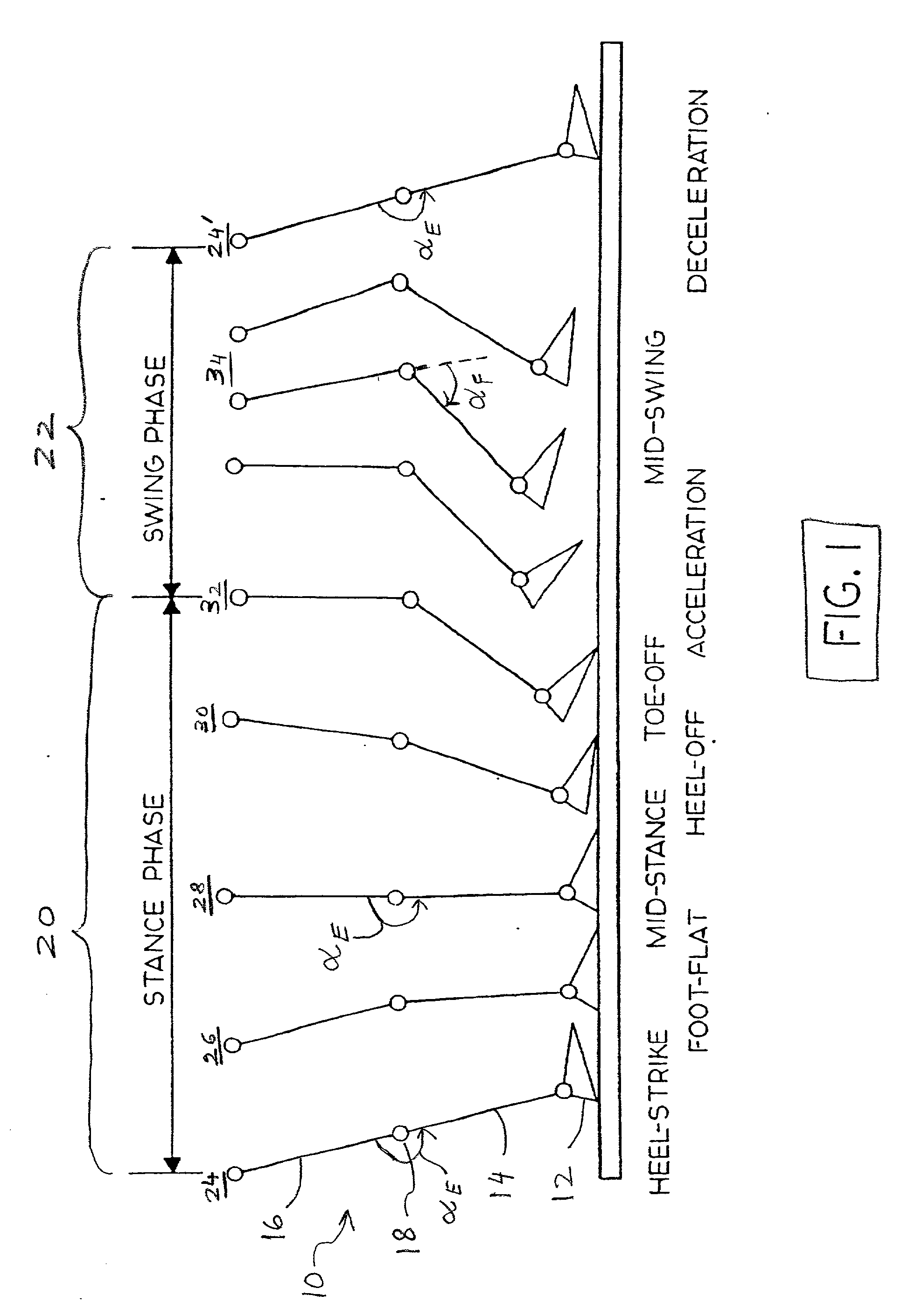
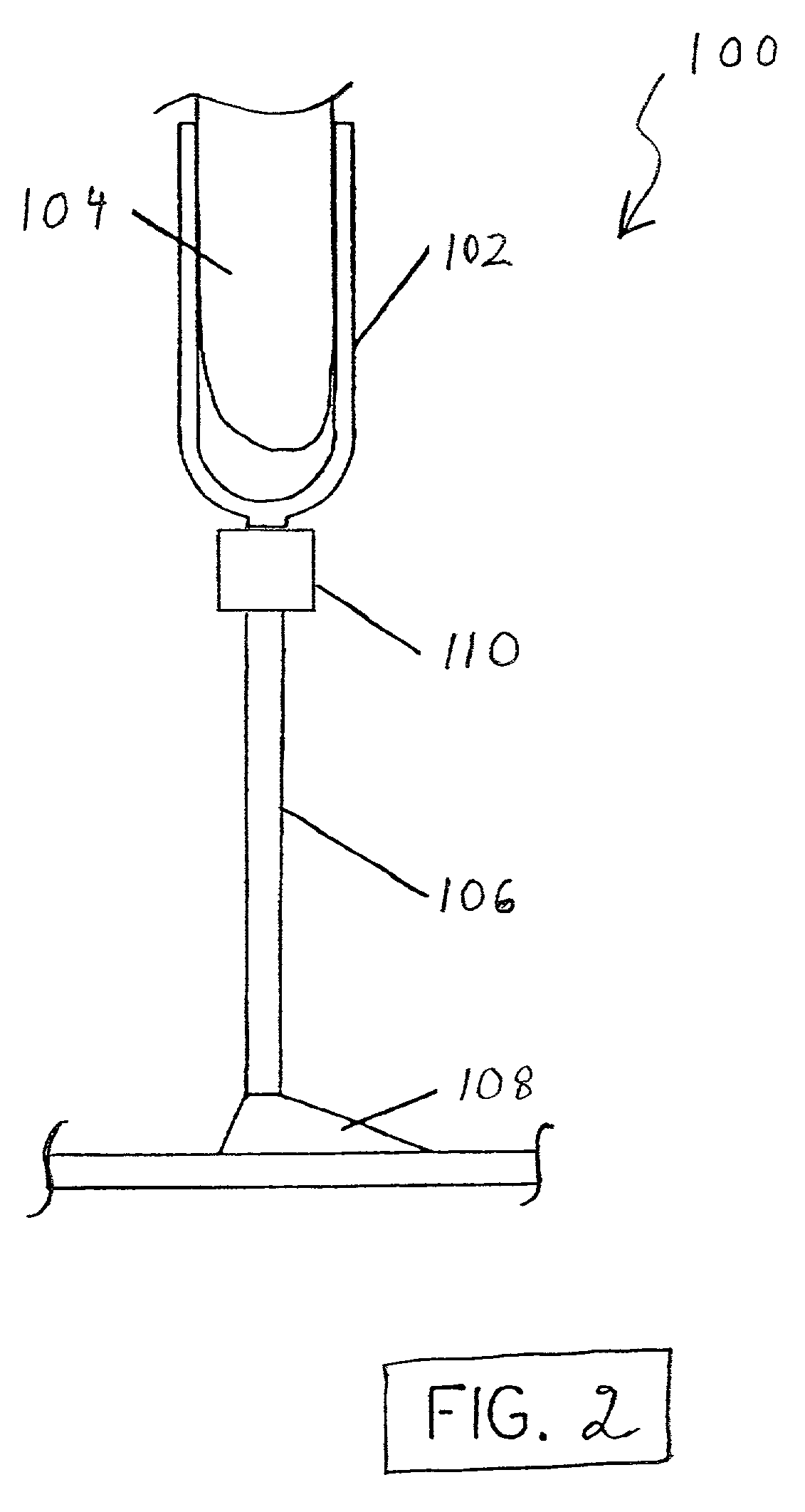
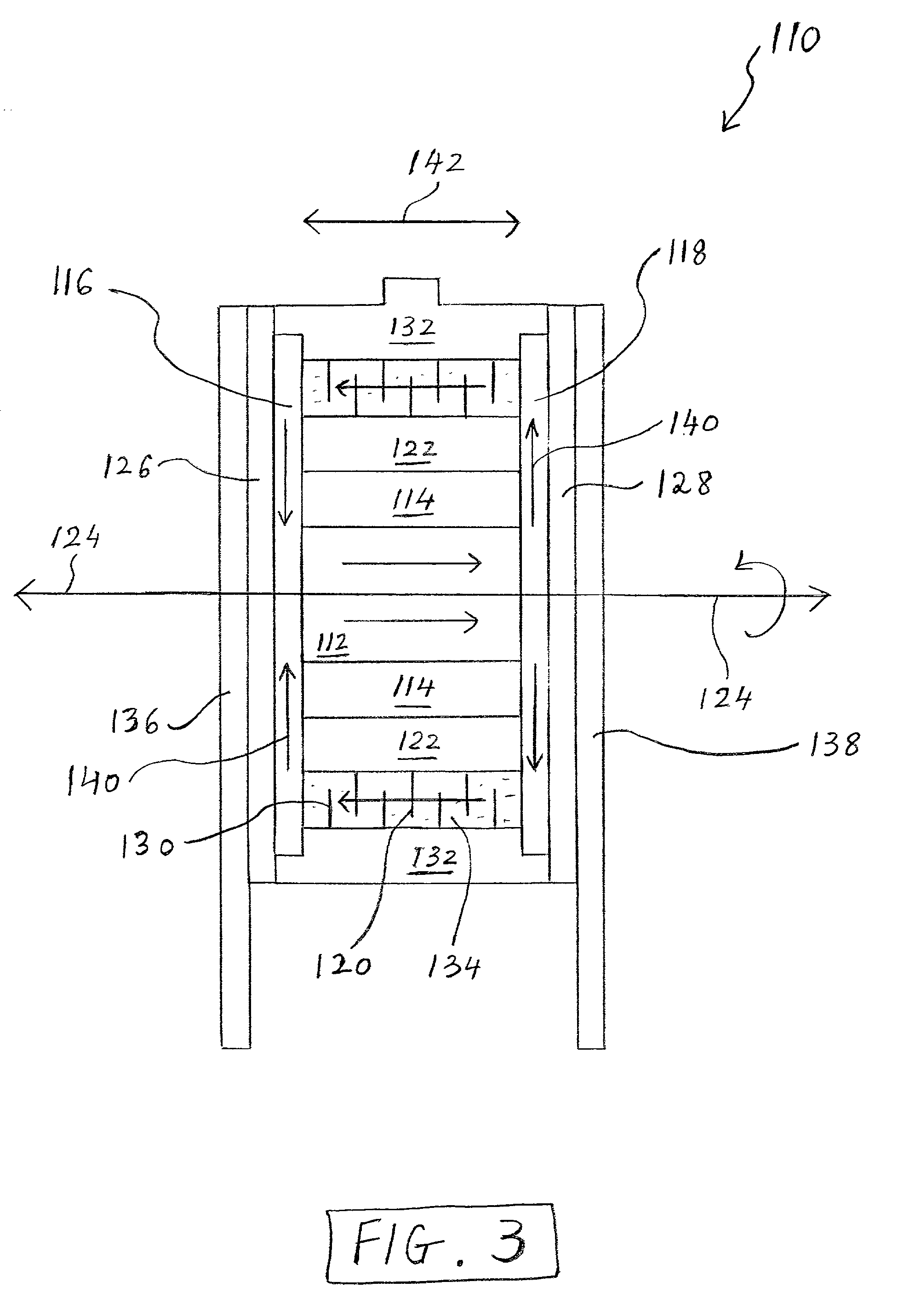
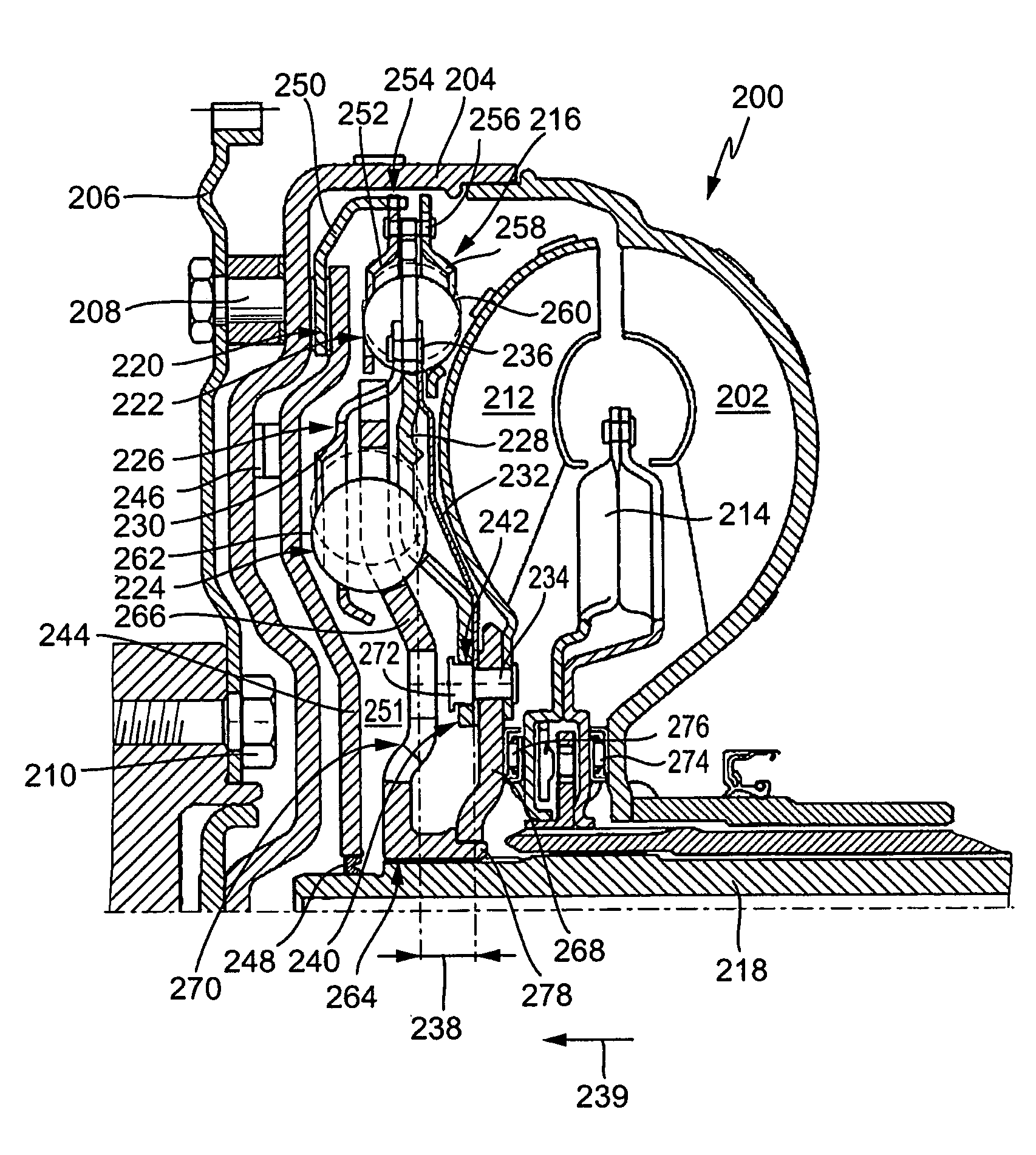
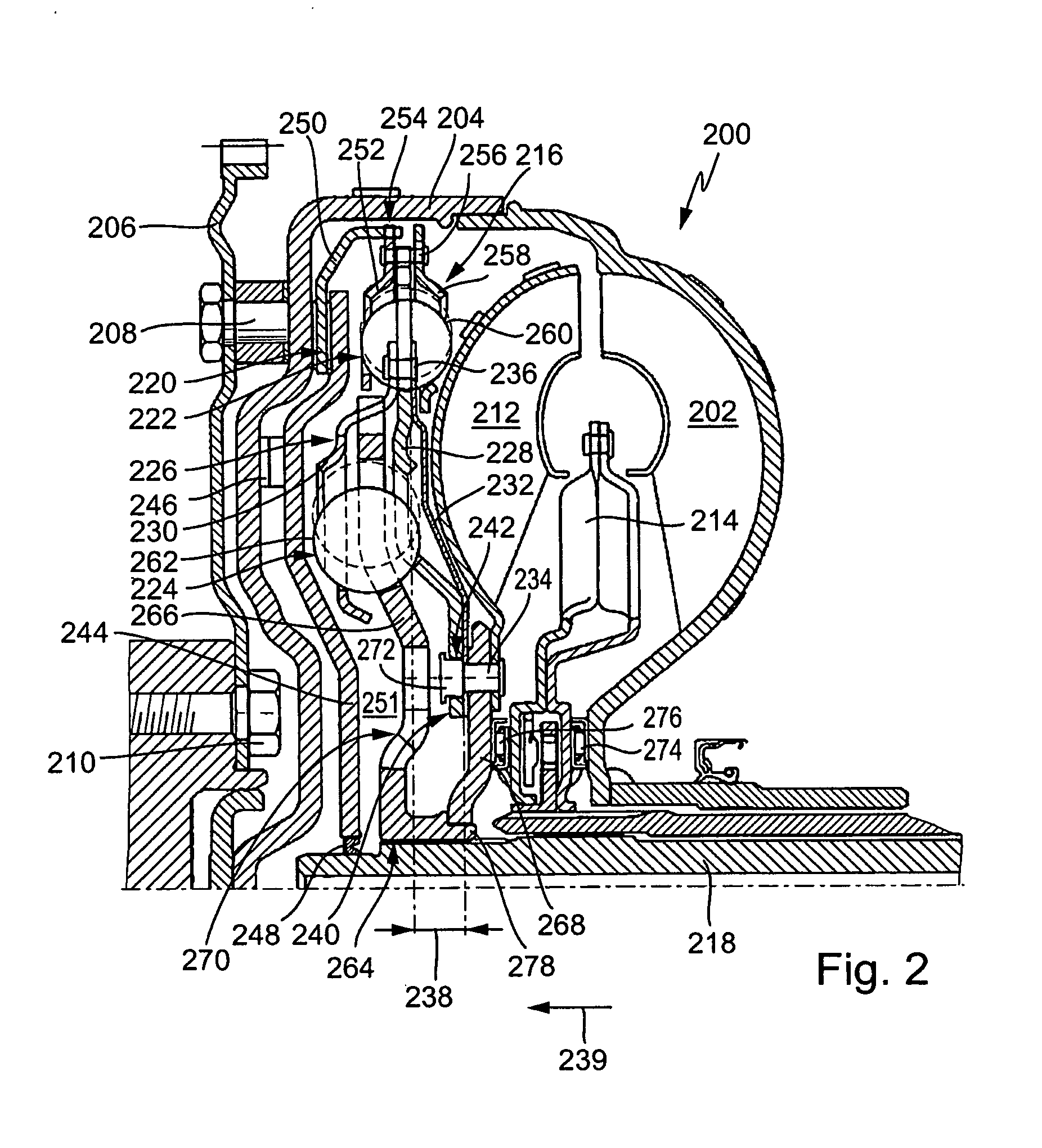
Electronically controlled prosthetic knee
InactiveUS20010029400A1Move and/or adapt comfortably and safelyImprove efficiencySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionFriction torqueMagnetorheological fluid
The present invention relates to a variable-torque magnetorheologically actuated prosthetic knee which utilizes a plurality of interspersed and alternating rotors and stators to shear magnetorheological fluid in gaps formed therebetween. Advantageously, by operating in the "shear mode" there is substantially no or negligible fluid pressure buildup or change. Moreover, the multiple MR fluid gaps or flux interfaces desirably allow for the production of a large torque at low speed-eliminating the need for a transmission-and also for a wide dynamic torque range. One embodiment of the invention allows the rotors and / or stators to close the gaps therebetween to create a frictional torque component, thereby forming a "hybrid" braking system which provides a total torque or damping which is a combination of viscous torque and frictional torque.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) servo system control method based on fuzzy and active disturbance rejection control
InactiveCN103401501AWide speed rangeImprove robustnessElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlDifferential coefficientFriction torque
The invention relates to a PMSM servo system control method based on fuzzy and active disturbance rejection control. A position signal is given by a differential tracker to arrange a transition process so that the contradiction between rapidness and overshoot of a system is solved, and uncertainty, friction torques and external disturbance due to modeling errors of the system are observed via an expansion state observer; according to the error between the differentials generated by the differential tracker and state variation generated by the expansion state observer, a fuzzy inference rule is obtained with application of experimental experience of technical staff, so that a fuzzy rule control table of an error proportion coefficient, a differential coefficient and an integration coefficient is established; accurate control amount is obtained after de-fuzzification, so that parameter self-adaptive adjustment of a nonlinear error feedback control law is realized; and compensation amounts of the nonlinear error feedback control law and the expansion state observer to the total disturbance forms the control amount, thereby realizing optimal control for an controlled object. The method of the invention improves both tracking precision and disturbance rejection capability of the system.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Torque converter with turbine mass absorber
ActiveUS20090125202A1Simple designFlange mode is reducedRotary clutchesDigital data processing detailsFriction torqueSnubber
A torque converter having a first damper stage, a second damper stage, a floating flange torsionally connecting the first and second damper stages, an inertia element, and a tuned torsion damper. The torsion damper connects the inertia element and the flange. In a preferred embodiment, the inertia element is a turbine. In one embodiment, the first damper stage is a radially outer damper stage and the second damper stage is a radially inner damper stage. In another embodiment, the torsion damper generates a friction torque when rotated.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Anti-lock braking system based on an estimated gradient of friction torque, method of determining a starting point for anti-lock brake control, and wheel-behavior-quantity servo control means equipped with limit determination means
An anti-lock braking system includes a friction torque gradient estimating unit for estimating, from a small number of parameters, the gradient of friction torque with respect to a slip speed, and controls a braking force acting on wheels on the basis of the friction torque gradient estimated by the friction torque gradient estimating unit. The friction torque gradient estimating unit may employ several types of estimating methods; e.g., a method of estimating the gradient of friction torque from only time-series data concerning a wheel speed; a method of estimating the friction torque gradient from time-series data concerning wheel deceleration as well as from braking torque or time-series data concerning physical quantities associated with the braking torque; or a method of estimating the friction torque gradient from micro-gains which are obtained when brake pressure is excited in a very small amount at the resonance frequency of a vibration system comprising a vehicle, wheels, and a road surface and which represent the characteristics of the vibration system. Further, there is also disclosed a method of determining, from the thus-estimated friction torque gradient, the limit of the characteristics of friction torque developed between the wheels and the road surface.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
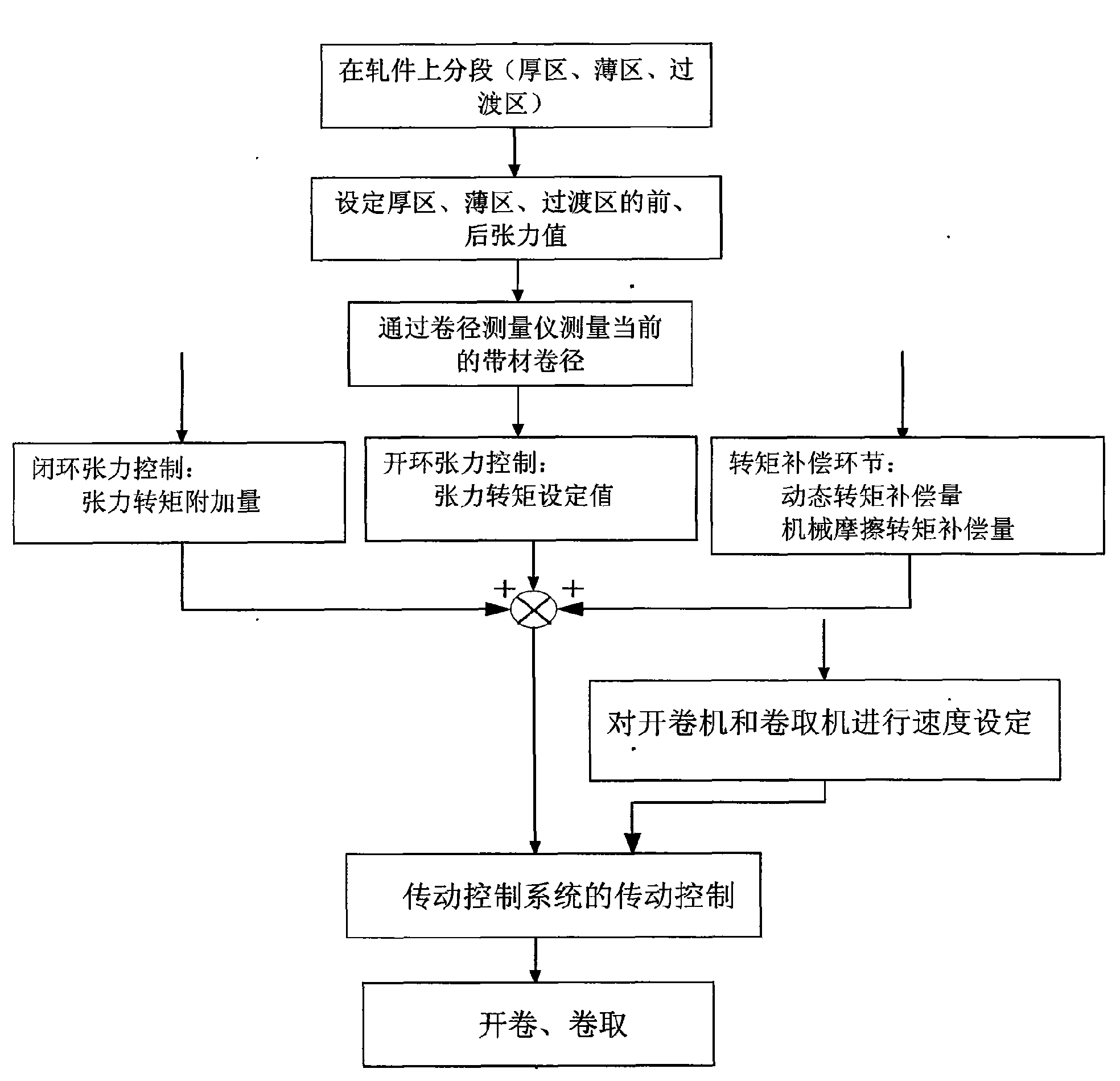
Control method and control system of tension in the process of rolling periodic variable-thickness strips
InactiveCN101602068AHigh precisionTension/compression control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsVariable thicknessMaximum torque
A control method and a control system of tension in the process of rolling periodic variable-thickness strips belong to the technical field of rolling. The method comprises the following steps: dividing segments on the rolled pieces, setting front and back tension values in each zone, realizing tension open-loop control and tension closed-loop control based on maximum torque limit and adding a dynamic torque compensation link and a mechanical friction torque compensation link; controlling torques of an uncoiler and a coiling machine motor and setting speed. The system comprises a rolling mill; coiling machines are arranged at both sides of the rolling mill respectively; length-measuring rollers are arranged between the coiling machines and the rolling mill; thickness gauges are arranged at both sides of the rolling mill respectively; coil diameter gauges are arranged on the coiling machines; a rolling force sensor and a hydraulic cylinder are arranged on the rolling mill; tensiometers are arranged below the length-measuring rollers and pulse coders are arranged on the length-measuring rollers; the thickness gauge, the coil diameter gauge, the rolling force sensor, a displacement sensor of the hydraulic cylinder, the tensiometer and the pulse coder are respectively connected with a computer control system.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Driving power control devices for hybrid vehicle
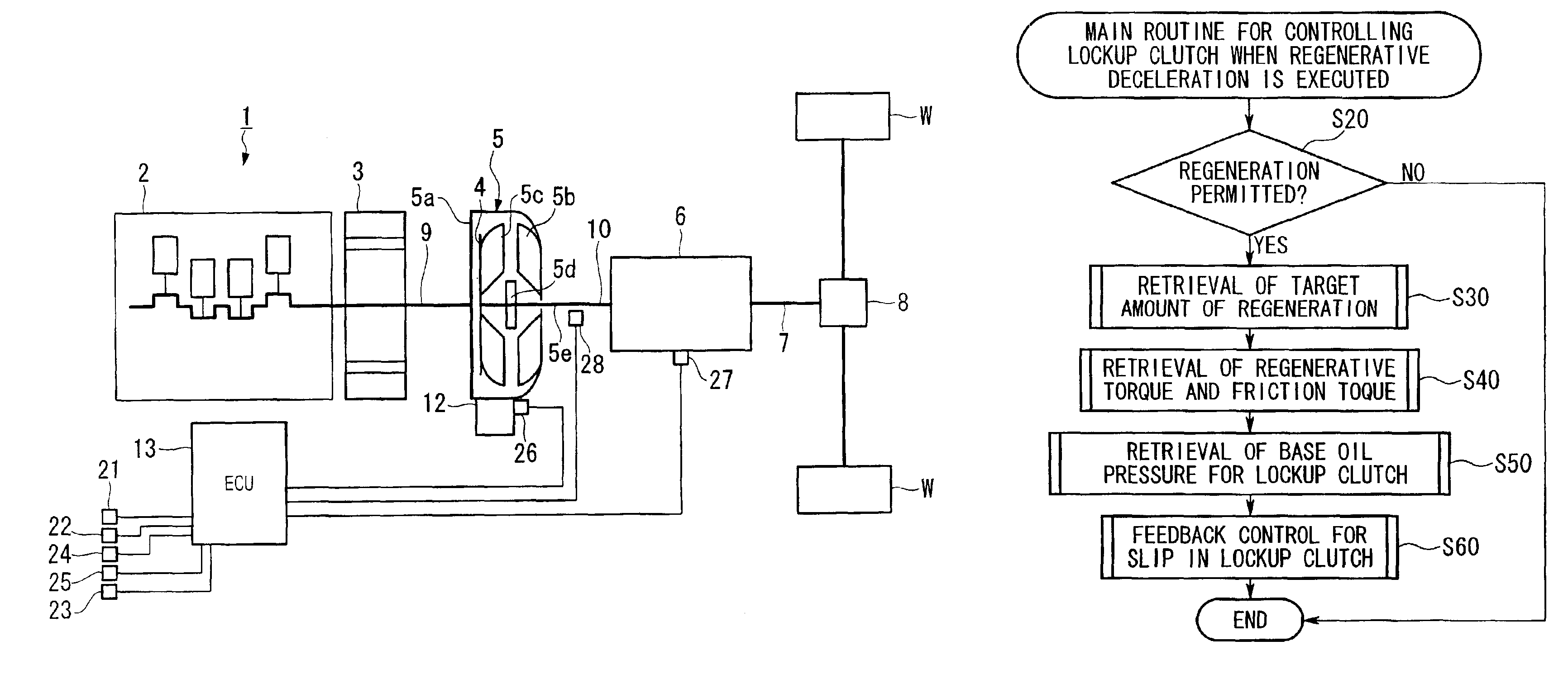
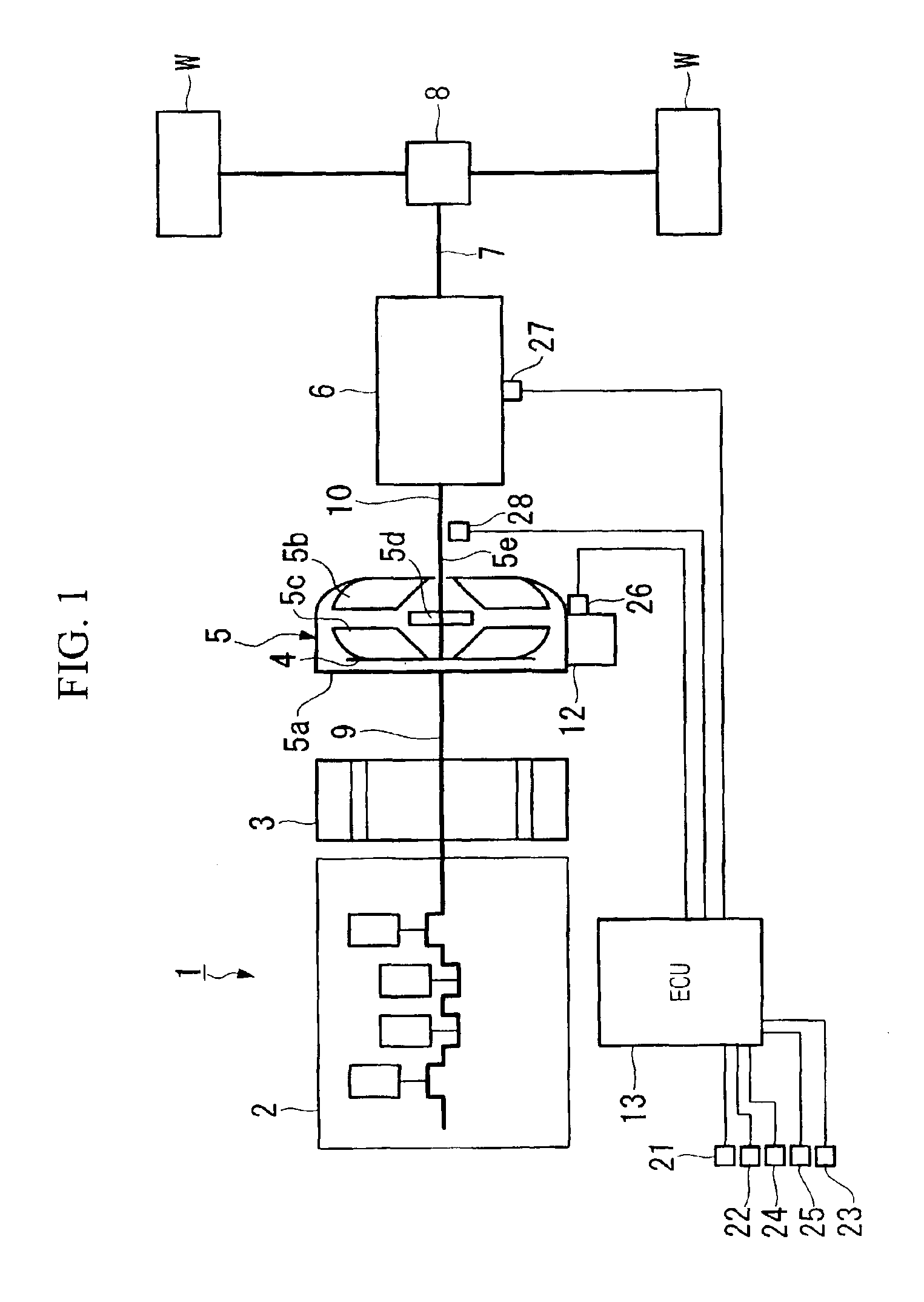
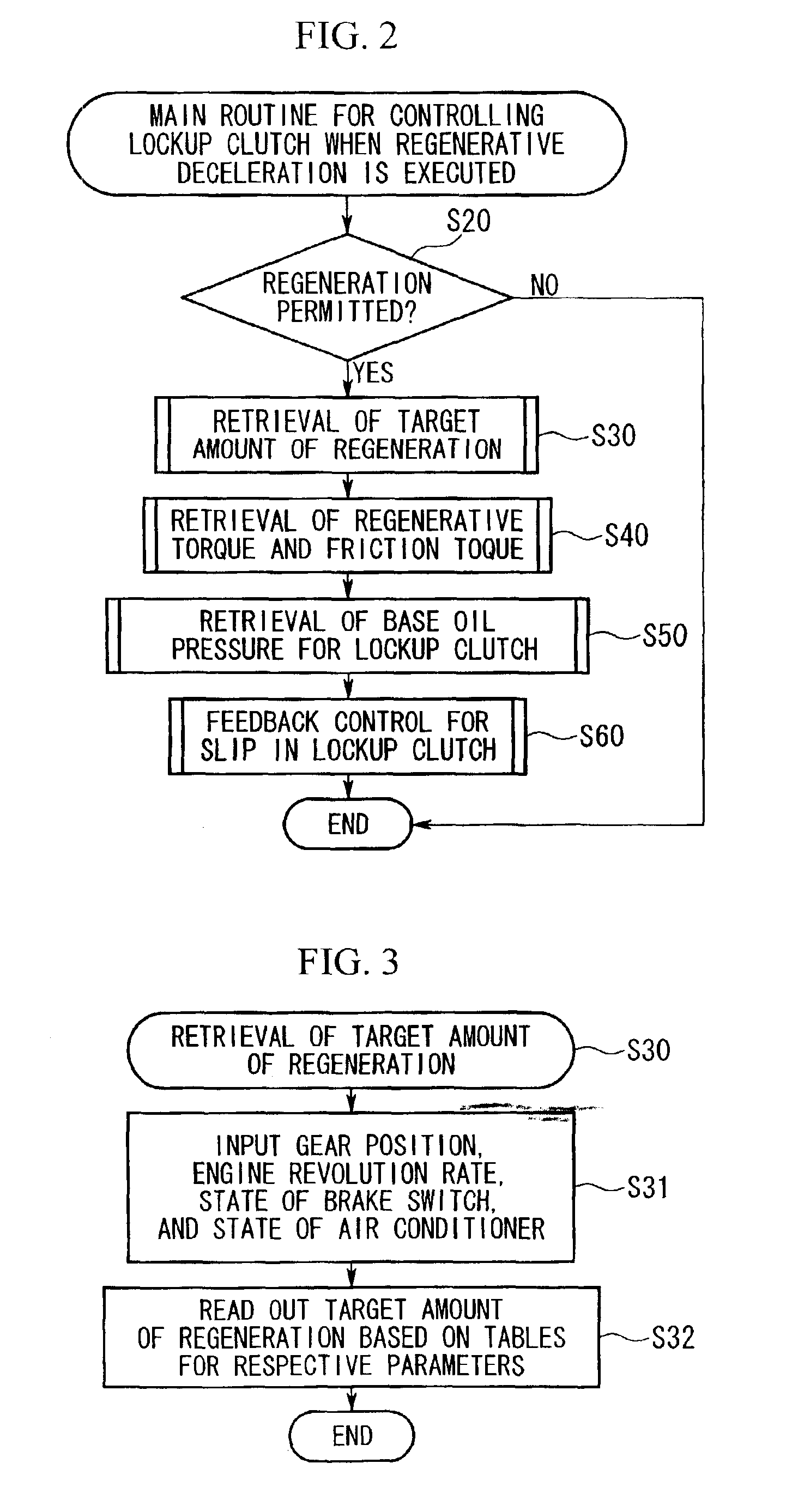
ActiveUS7100720B2High efficiency in regenerationImprove efficiencyGearing controlEngine controllersFriction torqueDrive wheel
A driving power control device for a hybrid vehicle controls the engagement state of a lockup clutch so that high efficiency in regeneration is obtainable. The driving power control device for a hybrid vehicle includes an engine and a motor-generator as power sources, an automatic transmission disposed between the power sources and driving wheels with an intervening torque converter having a lockup clutch, and an ECU for controlling selection of the power sources and for controlling a slip ratio of the torque converter. In this control device, a target slip ratio of the torque converter, which corresponds to a target amount of regeneration that is retrieved using regeneration amount determining factors, is obtained by executing a feedforward control operation using friction torque determining factors, and the slip ratio is controlled in a feedback manner based on the difference between the target slip ratio and the actual slip ratio.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
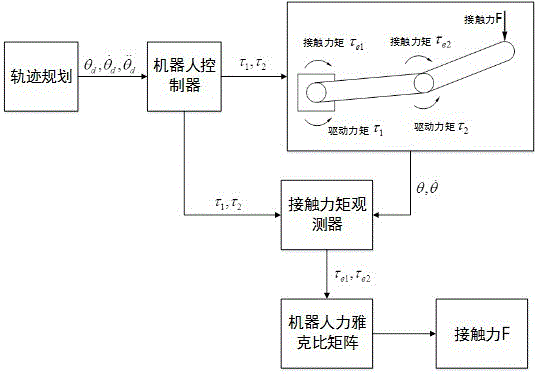
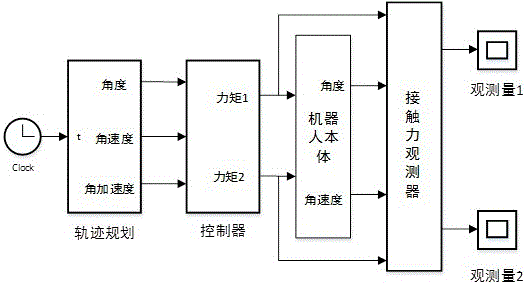
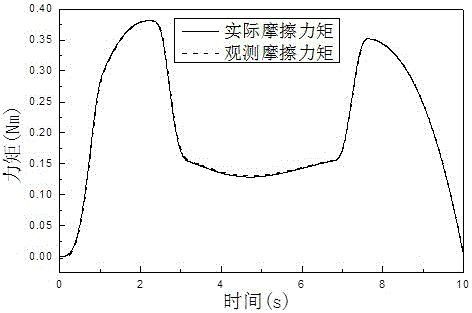
Robot contact force detecting method based on torque observation and friction identification
ActiveCN106426174AImprove detection accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorFriction effectFriction torque
The invention relates to a robot contact force detecting method based on torque observation and friction identification. A robot kinetic model and a generalized momentum are adopted to establish a joint torque observer for detecting joint torque change caused by a tail end contact force; a mode of combining an exponential friction model and a sine cosine function is adopted to describe the joint friction effect of a robot provided with a harmonic gear driving structure, a joint torque observation quantity is utilized to identify a joint friction parameter when an end effector of the robot has no contact force effect, and a joint friction torque is calculated according to the identified friction parameter; the torque observation quantity in a theoretical operating state of the robot sis regarded as a system model error, and an accurate joint contact torque observation quantity is finally obtained after the influences of friction and the system model error are considered, and finally a tail end contact force is calculated through a force Jacobian matrix of the robot.
Owner:SHANGHAI ROBOT IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
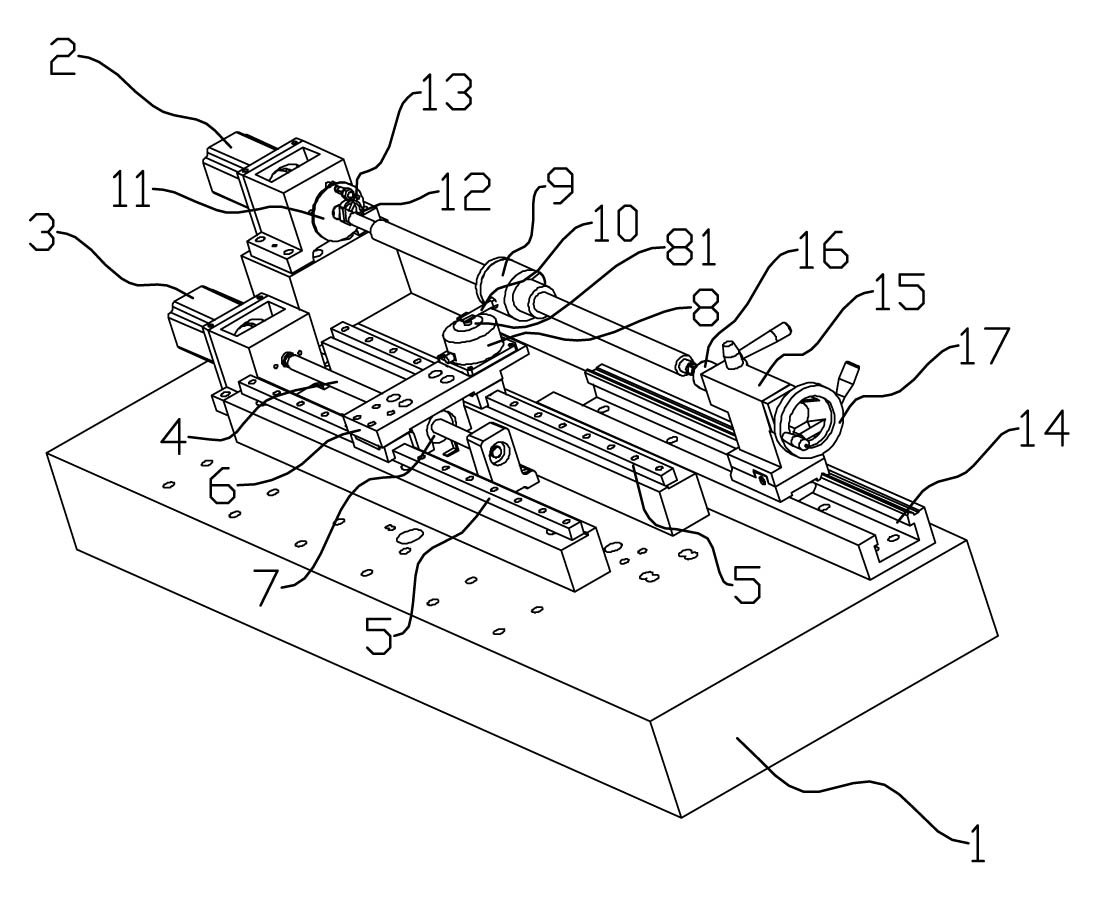
High-speed screw and screw pair comprehensive examination test bed
InactiveCN103543010ATake advantage of stabilityImprove economyMachine gearing/transmission testingDynamic stiffnessFriction torque
The invention discloses a high-speed screw and screw pair comprehensive examination test bed comprising a granite base, a floating guide rail and linear guide rails. The floating guide rail and the linear guide rails are arranged on the granite base parallelly. A linear guide rail holding plate is arranged on the linear guide rails, and the lower side of the linear guide rails is connected with a linear motor arranged on the granite base. A floating guide rail holding plate used for mounting a probe system is arranged on the floating guide rail and is connected with the linear guide rail holding plate through a connecting mechanism. By the aid of the test bed, a function of testing the features such as geometric accuracy, positioning accuracy, backlash, driving speed and acceleration, natural frequency, vibration mode, damping, and static and dynamic stiffness, friction torque and fatigue in the high-speed screw and screw pair and a function of testing stability in the high-speed screw and screw pair can be realized, and the rapid and accurate evaluation on most performance parameters of a precision ball screw can be given.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Space rolling bearing comprehensive performance experiment device
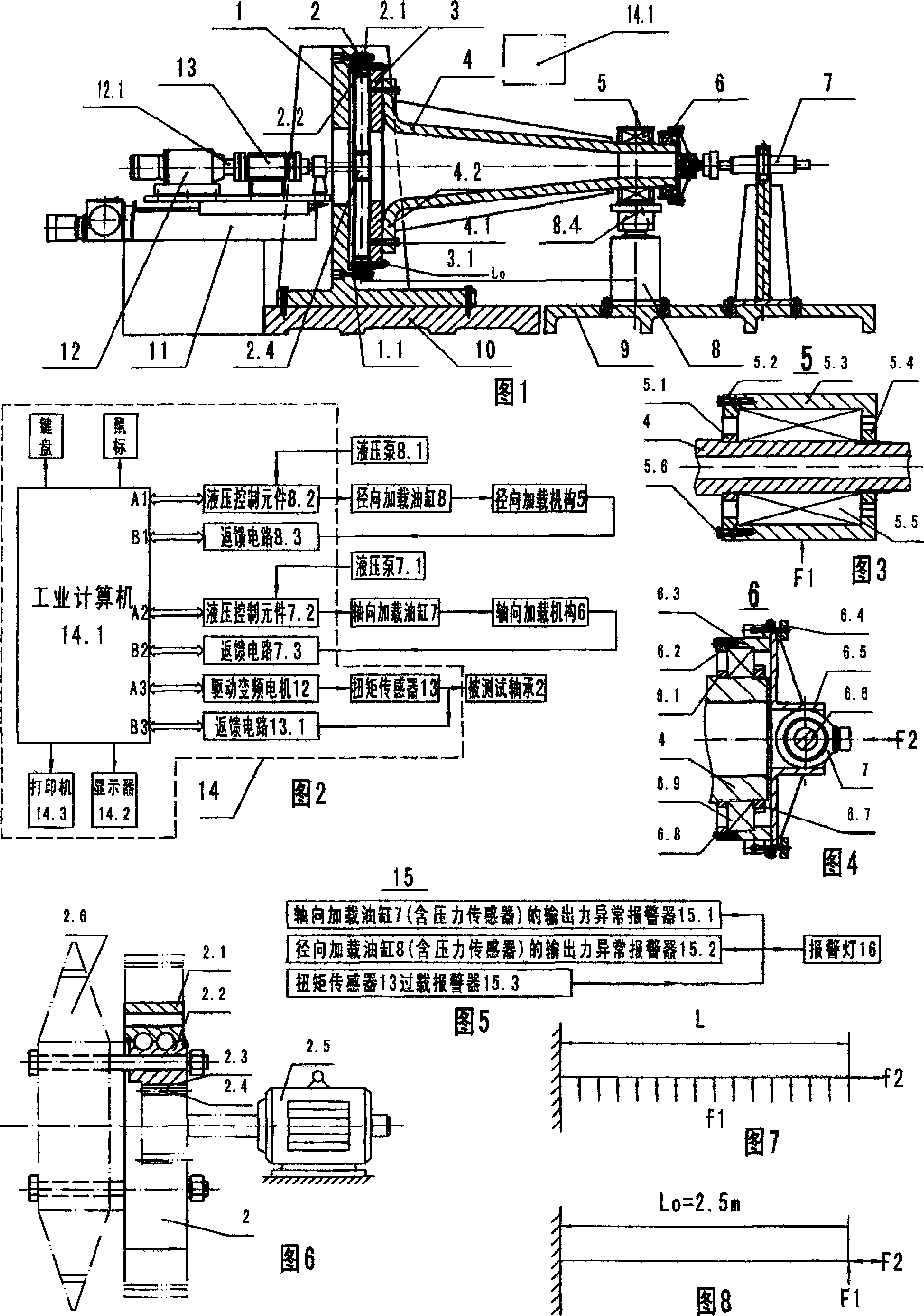
ActiveCN104568443ALoad accuratelyAccurate and stable loadingMachine bearings testingAviationFriction torque
The invention discloses a space rolling bearing comprehensive performance experiment device, relates to an experiment device and provides an experiment device capable of accurately measuring axial and redial united loads of a space rolling bearing and basic data including friction moment, bearing temperature rise, vibration and the like under different rotation speed working conditions. The space rolling bearing comprehensive performance experiment device can simultaneously conduct axial force and radial force accurate load on a measured bearing through an axial loading device and a radial loading device. A three-axis acceleration sensor is used for measuring radial, axial and peripheral vibration situations of the measured bearing. A temperature sensor is used for measuring the temperature rise situation of the measured bearing. A pressure sensor is used for measuring the friction moment of the measured bearing. An annular pressure sensor is used for measuring axial force borne by the measured bearing. Weights are used for marking radial force borne by the measured bearing. The space rolling bearing comprehensive performance experiment device can evaluate the comprehensive performance of the space rolling bearing and provide key scientific technical basis and test platform support for development of high-end bearings in the aerospace field of our country.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
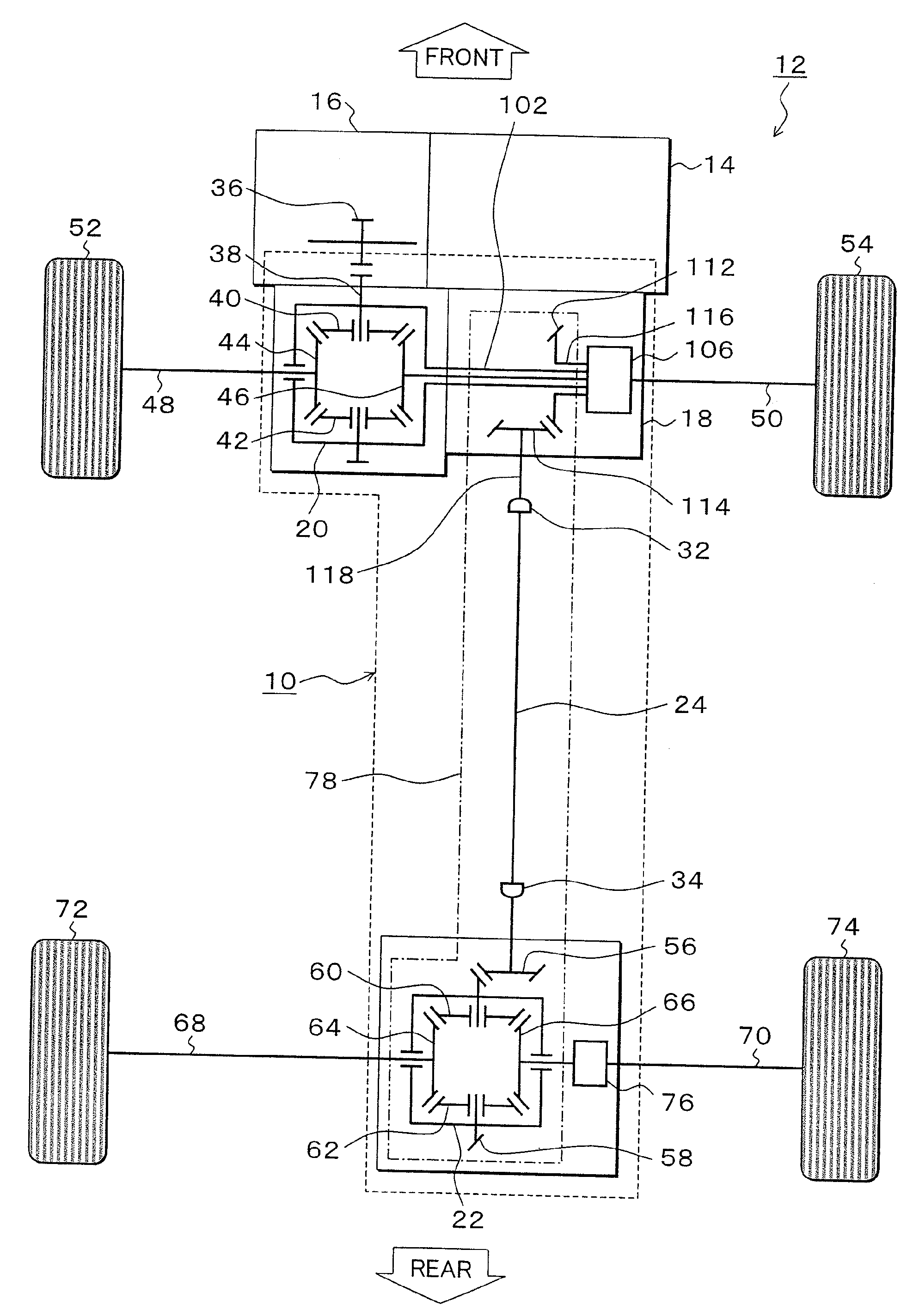
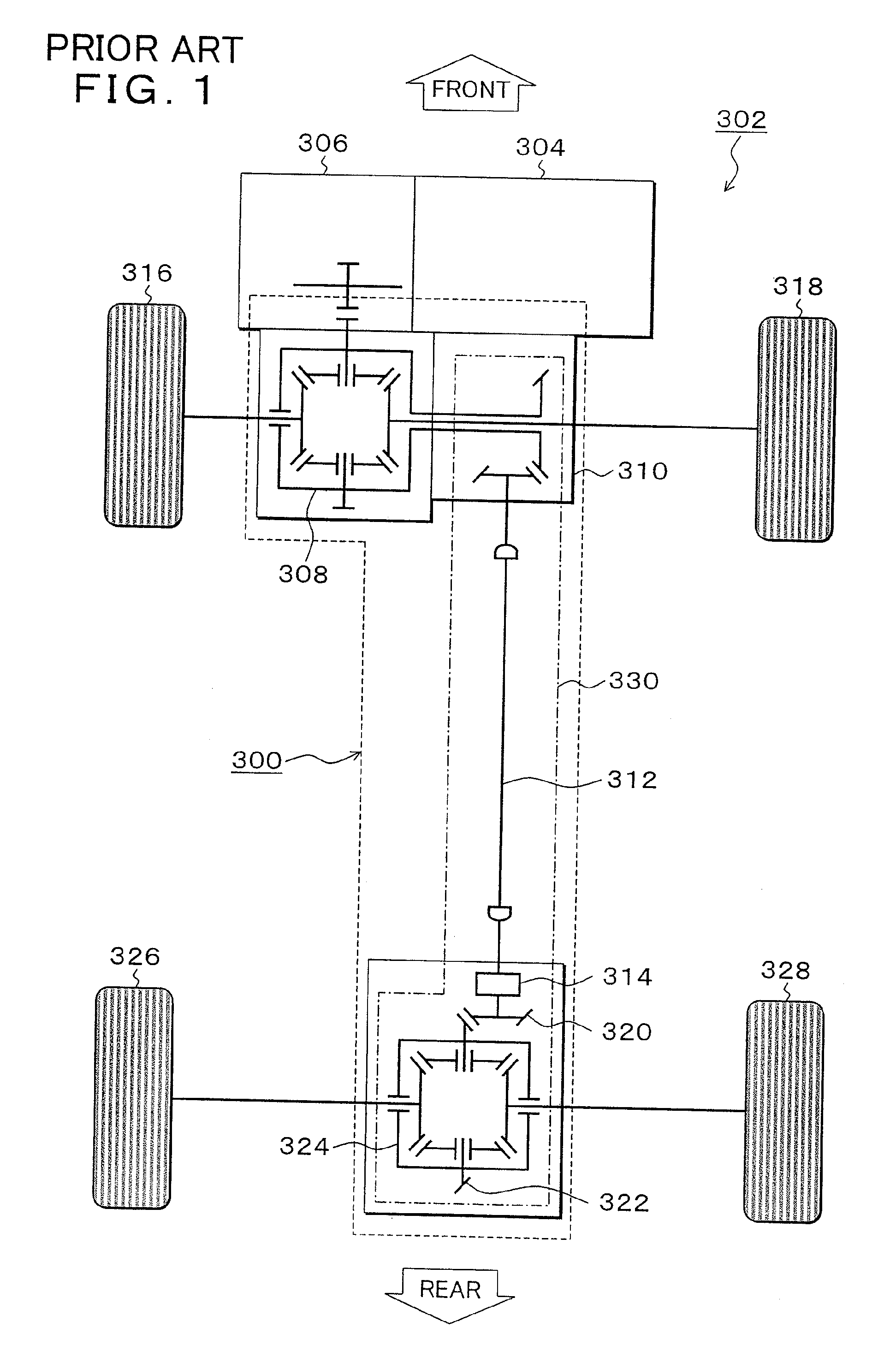
Driving-force transmitting apparatus for four-wheel-drive vehicle
InactiveUS20100274456A1Deterioration in fuel efficiency can be preventedFuel efficiencyManual control with multiple controlled membersDigital data processing detailsFriction torqueDrag torque
A transmitting apparatus includes a disengaging device that disengages a driving force from a front-wheel differential device to a first driving-force transmitting direction converting unit 20 and a multi-plate clutch mechanism provided between an output of a rear-wheel differential device and a right-rear wheel and capable of successively adjusting a fastening force. Drag torque when the fastening of the multi-plate clutch mechanism is released is set smaller than friction torque of a rear-wheel drive system between the first driving-force transmitting direction converting unit and a second driving-force transmitting direction converting unit. A controller unconnects the disengaging device and releases the fastening of multi-plate clutch mechanism when switching to a two-wheel drive mode, thereby stopping the rotation of the rear-wheel drive system.
Owner:UNIVANCE CORP
Mechanical seal performance testing device
ActiveCN103267613AAvoid axial forceRealize automatic adjustmentMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateWork measurementFriction torqueAxial force
Provided is a mechanical seal performance testing device. The mechanical seal performance testing device comprises a main shaft, a working cavity with end caps at two ends, and two sets of mechanical seals to be tested. A shaft sleeve and the main shaft are in clearance fit and penetrate through the end caps at the two ends of the working cavity together. U-shaped openings on the same generatrix are arranged in two ends, extending out of the end caps, of the shaft sleeve, and a transmission pin is arranged on a portion, corresponding to the U-shaped openings, of the main shaft; two sections of threads which are equal in thread pitch and opposite in screwing direction are arranged in the middle of the shaft sleeve, and movable ring bases in the two mechanical seals to be tested are arranged on the back sides of two nuts screwed on the threads respectively; the movable ring bases and the shaft sleeve slide in the axial direction and are located and connected in the circumferential direction; a radial force sensor used for measuring end face friction torque indirectly is arranged on the transmission pin, and an axial force sensor used for measuring end face specific pressure is arranged between the back side of a static ring and the end cap of the working cavity; the end cap is provided with an annular ring which is concentric with a center hole, and therefore a leakage cavity used for collecting leakage amount is formed. The mechanical seal performance testing device is suitable for mechanical seal performance tests of various pressure working conditions and various size series, including performance tests of high-pressure and large-diameter mechanical sealing.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Test bed for testing friction torque property of double ball screws
InactiveCN101769805AQuality improvementImprove dynamic performanceMeasurement of torque/twisting force while tighteningMachine gearing/transmission testingNumerical controlFriction torque
The invention discloses a test bed for testing friction torque property of double ball screws, which comprises a base, and first and second servo motors which are arranged on the base and controlled by a control system, wherein the first servo motor is used for driving a ball screw to be tested; the second servo motor is used for driving a reference ball screw; two sides of the reference ball screw are provided with a linear guide rail respectively, and the upper parts of the two linear guide rails are provided with a workbench; the workbench is fixed with a reference nut on the reference ball screw; the workbench is provided with a force measuring sensor and a nut sleeve which is arranged on a nut of the ball screw to be tested; and the nut sleeve is provided with a cantilever contacted with a detection end of the force measuring sensor. After the ball screw to be tested is connected with the first servo motor, the size of friction torque of a ball screw pair can be effectively measured by using a corresponding signal of the friction torque of the ball screw to be tested acquired by the force measuring sensor so as to improve the quality of a ball screw pair product and promote the dynamic performance of a numerical control machine.
Owner:WUYI UNIV
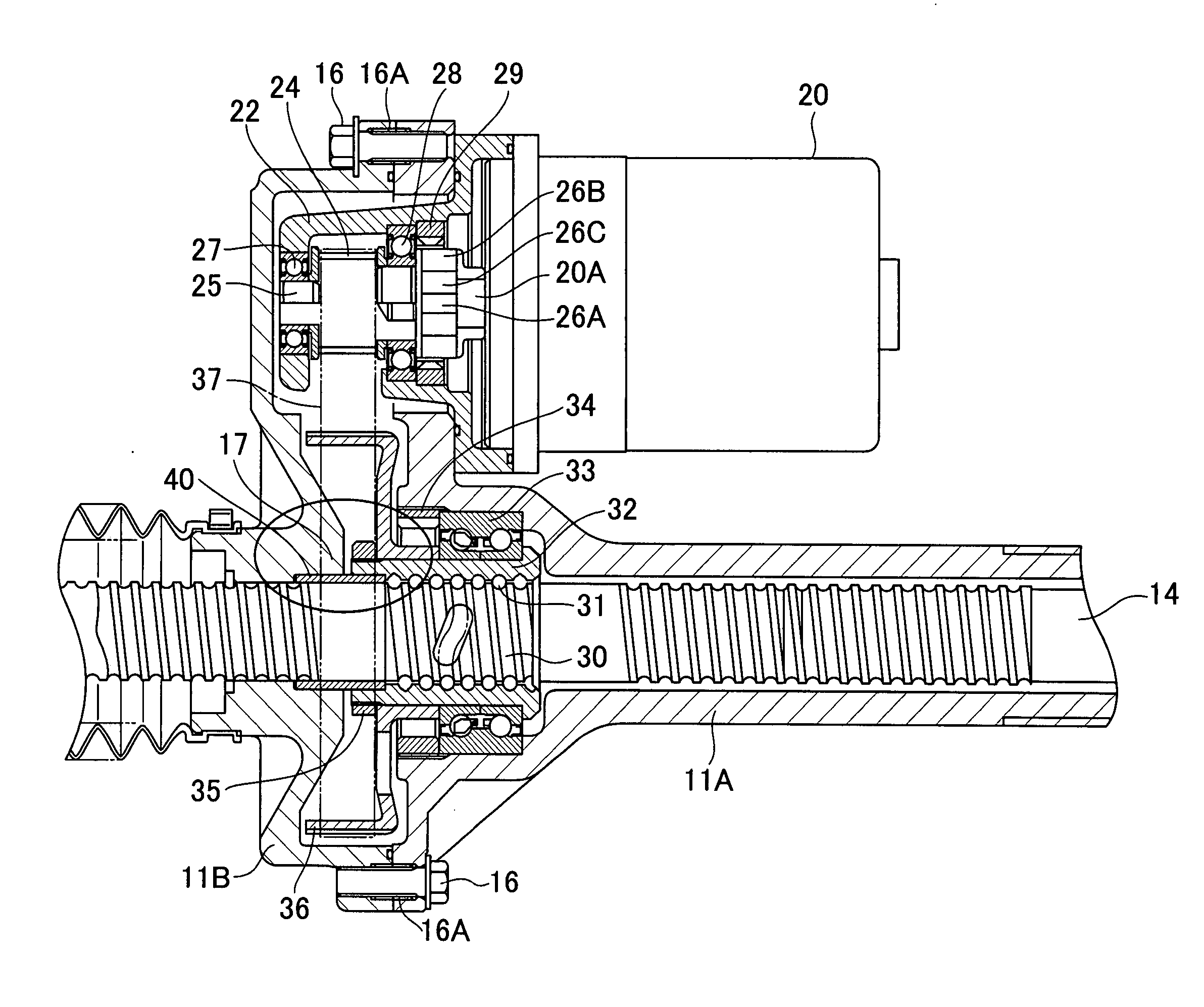
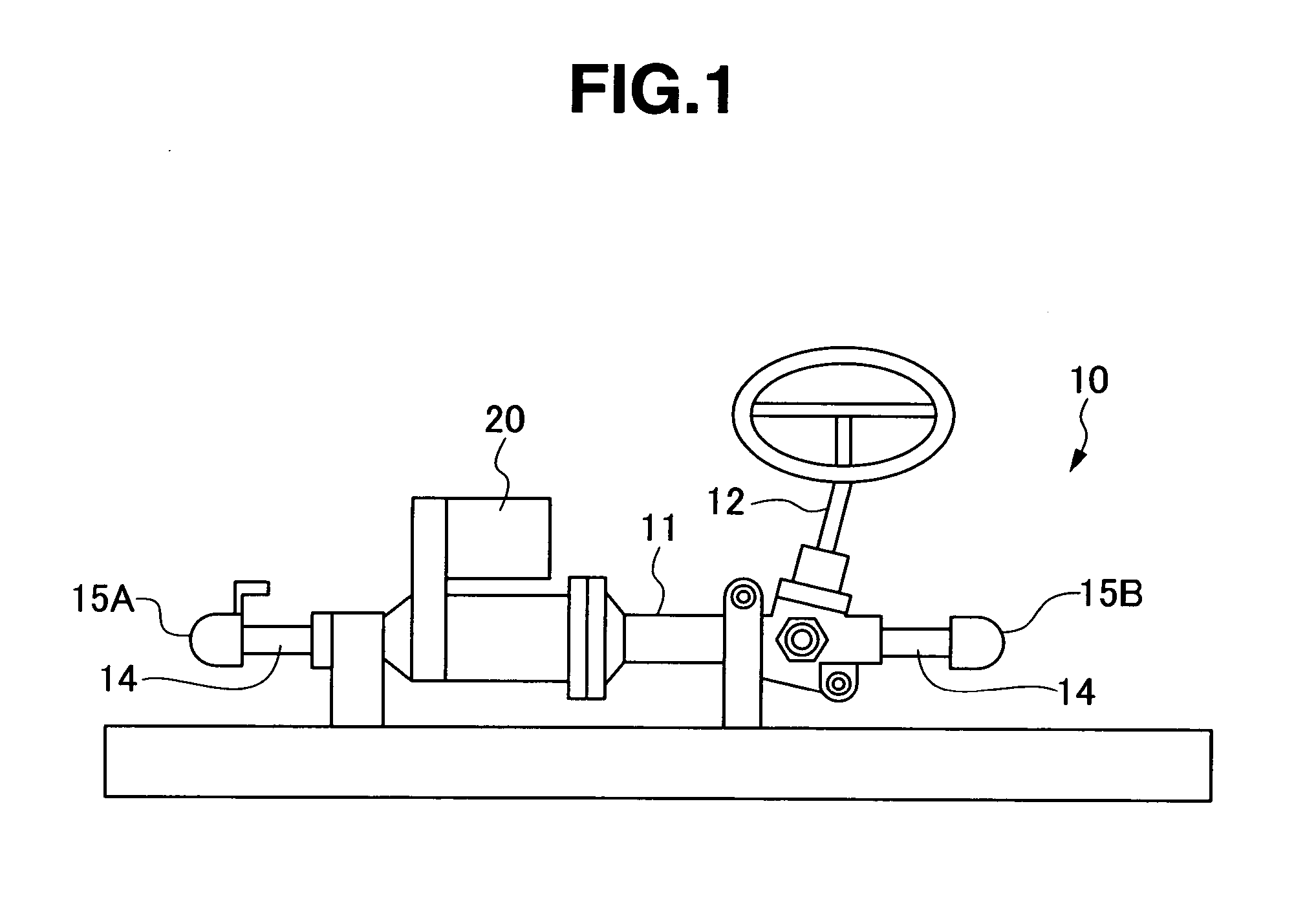
Motor-driven power steering apparatus
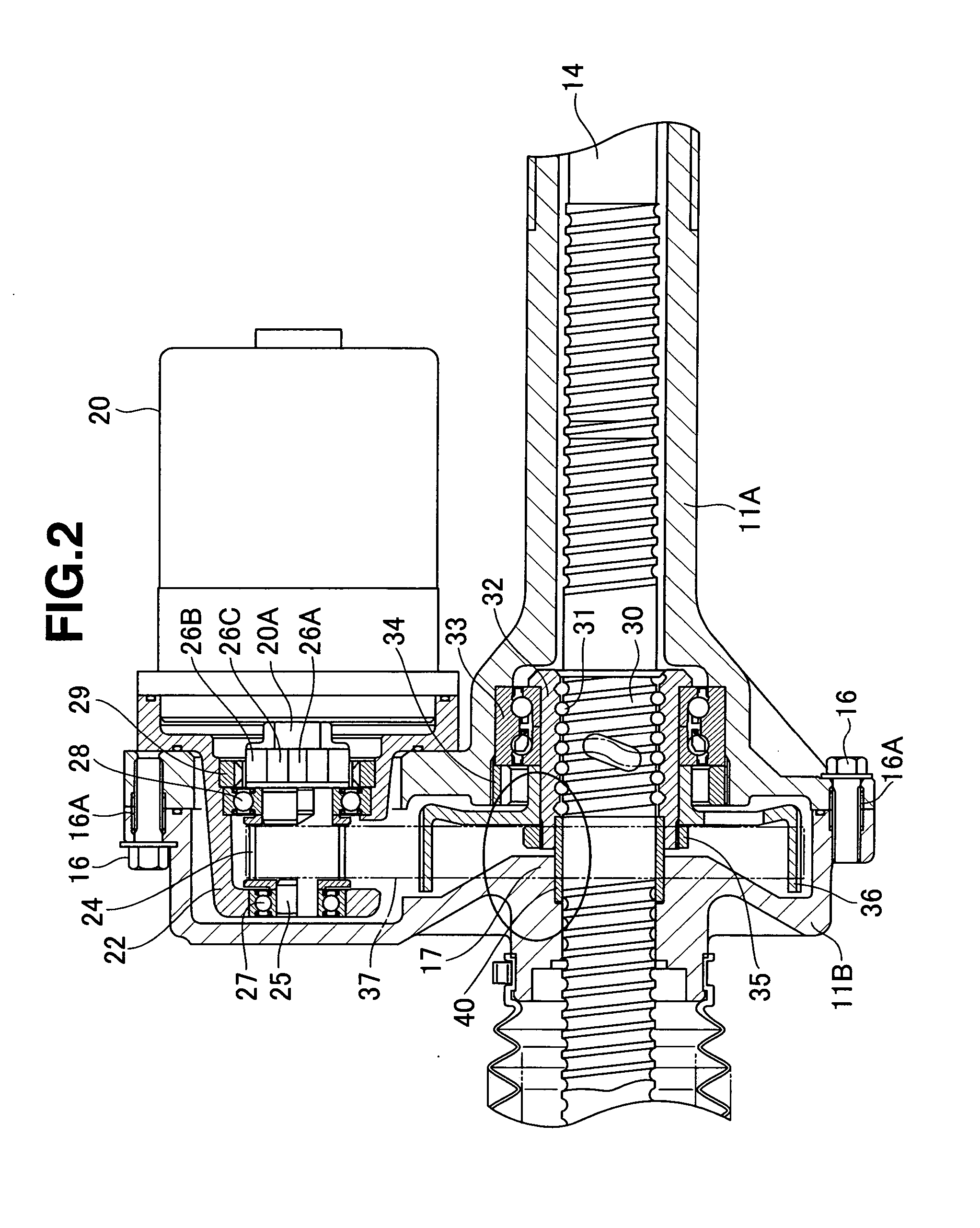
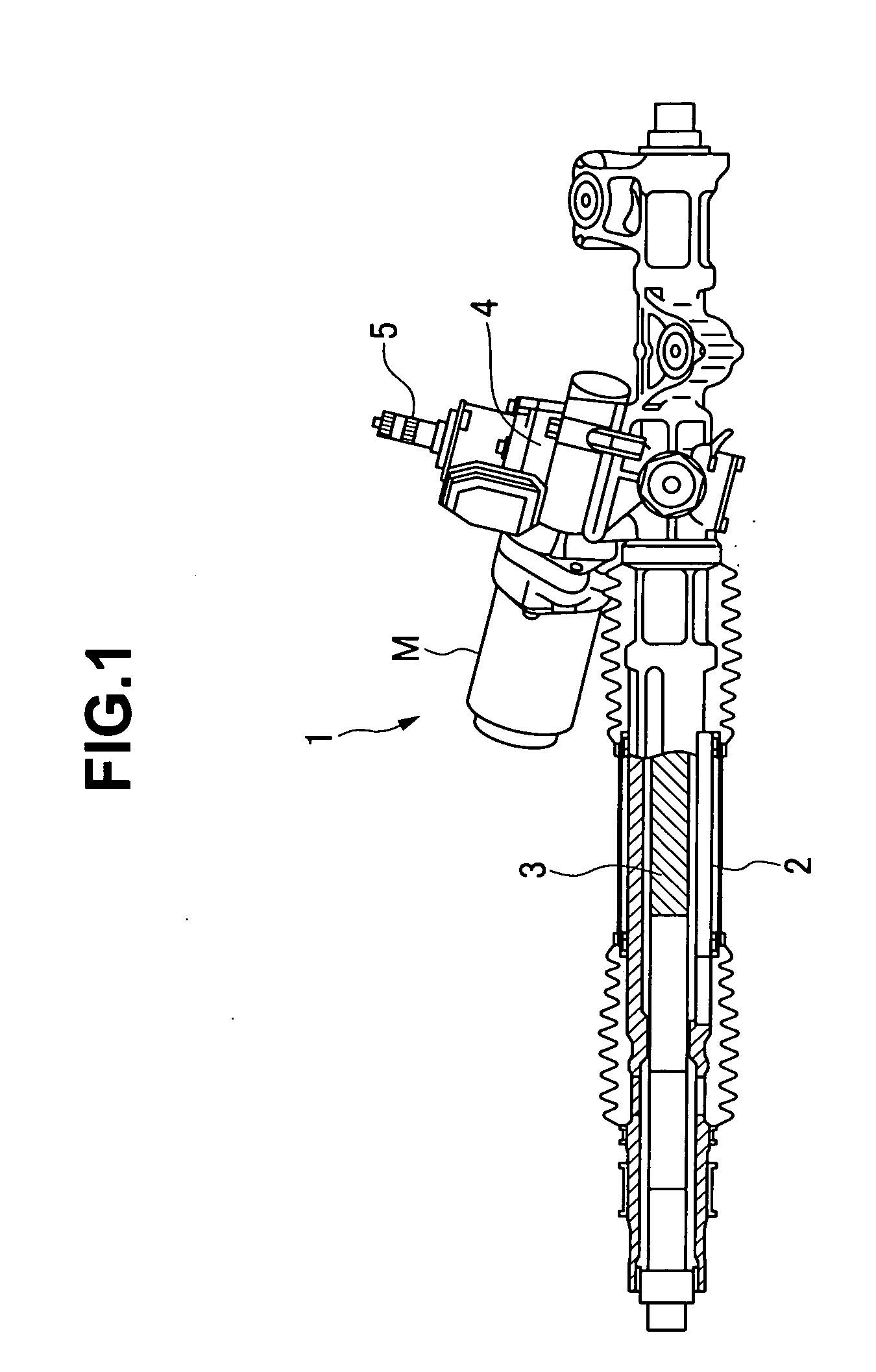
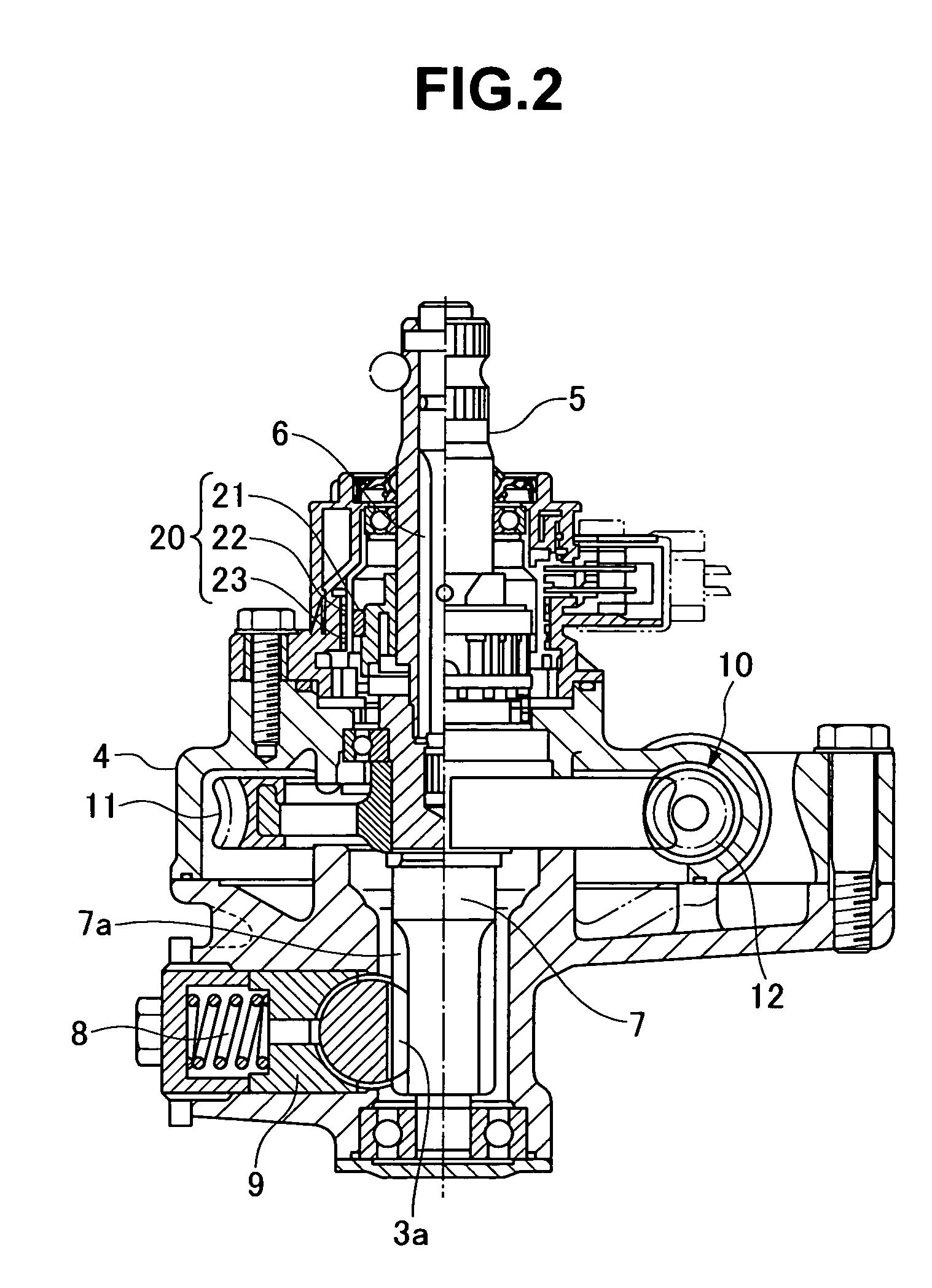
InactiveUS20060219470A1Reduce steering torque input requirementElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlElectric power steeringMotor drive
In a motor-driven power steering apparatus, the main coil winding and auxiliary coil winding are wound around the same slot of a stator core in a parallel manner, a motor drive means has a main driver feeding at least to the main coil windings, and an auxiliary driver feeding only to the auxiliary coil windings, the main driver being actuated so as to be capable of assisting the steering during normal conditions of a control system of an electric motor, and the auxiliary driver is actuated so as to execute an auxiliary assist corresponding to a motor friction torque under abnormal conditions of the control system of the electric motor.
Owner:SHOWA CORP
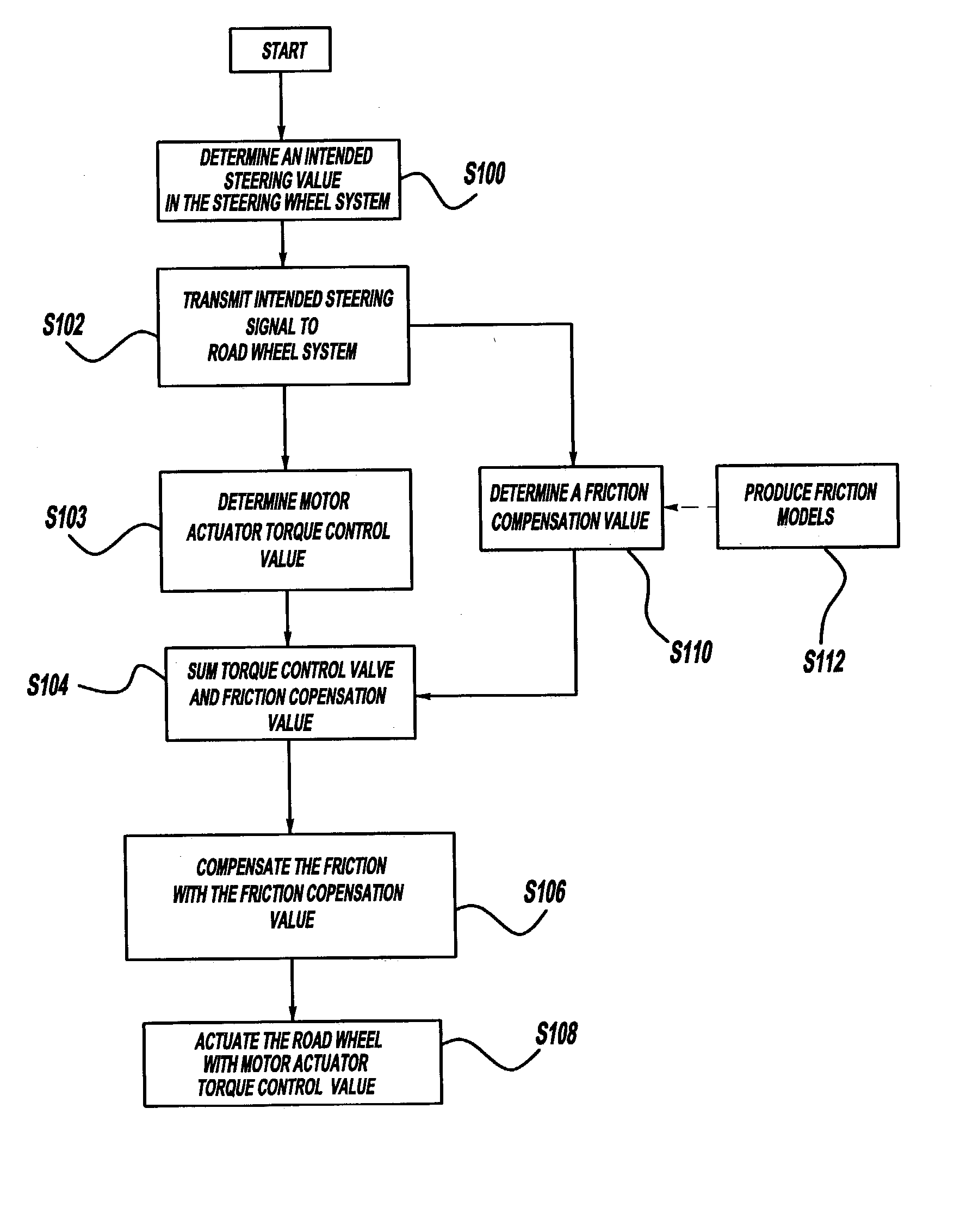
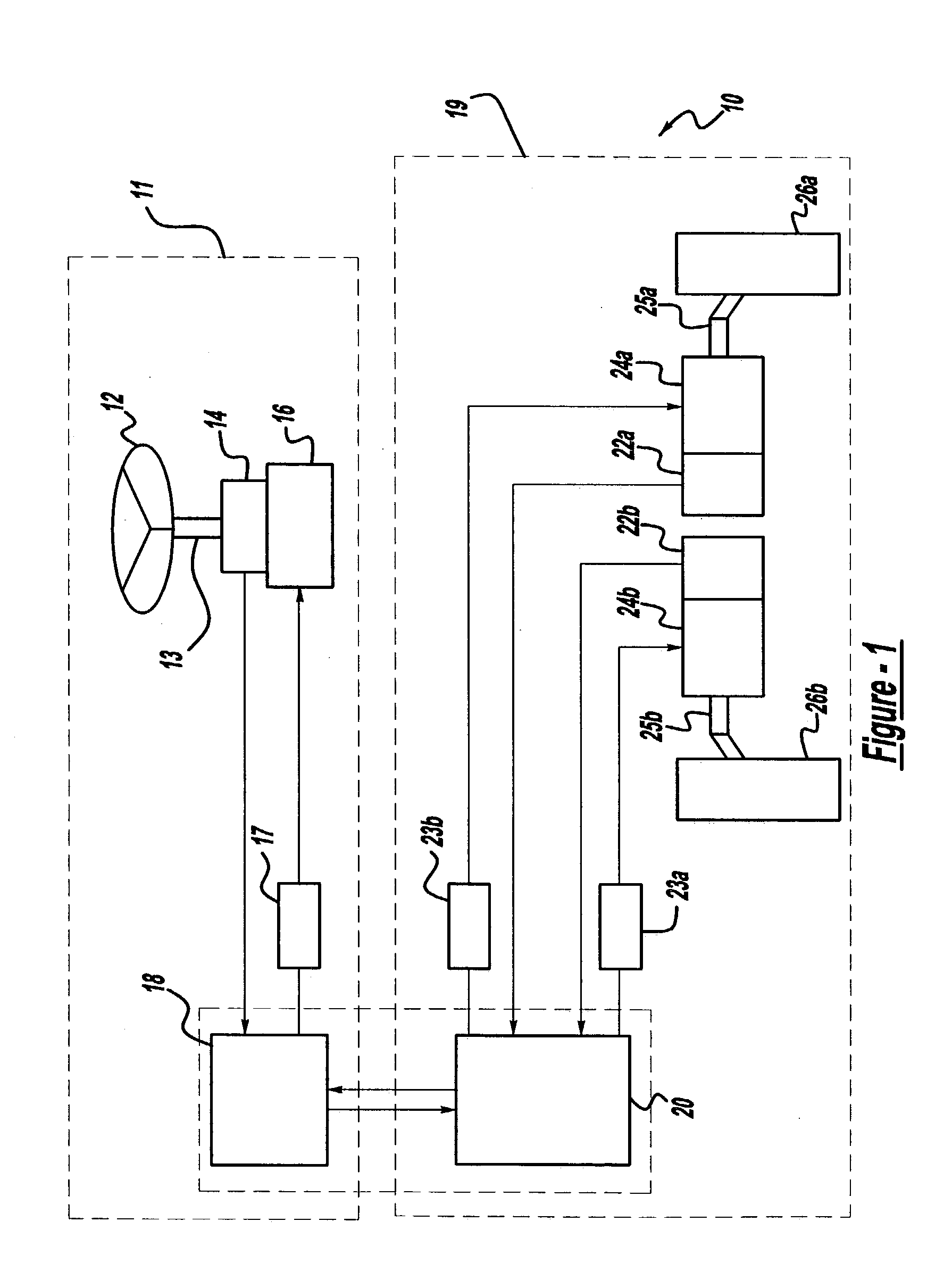
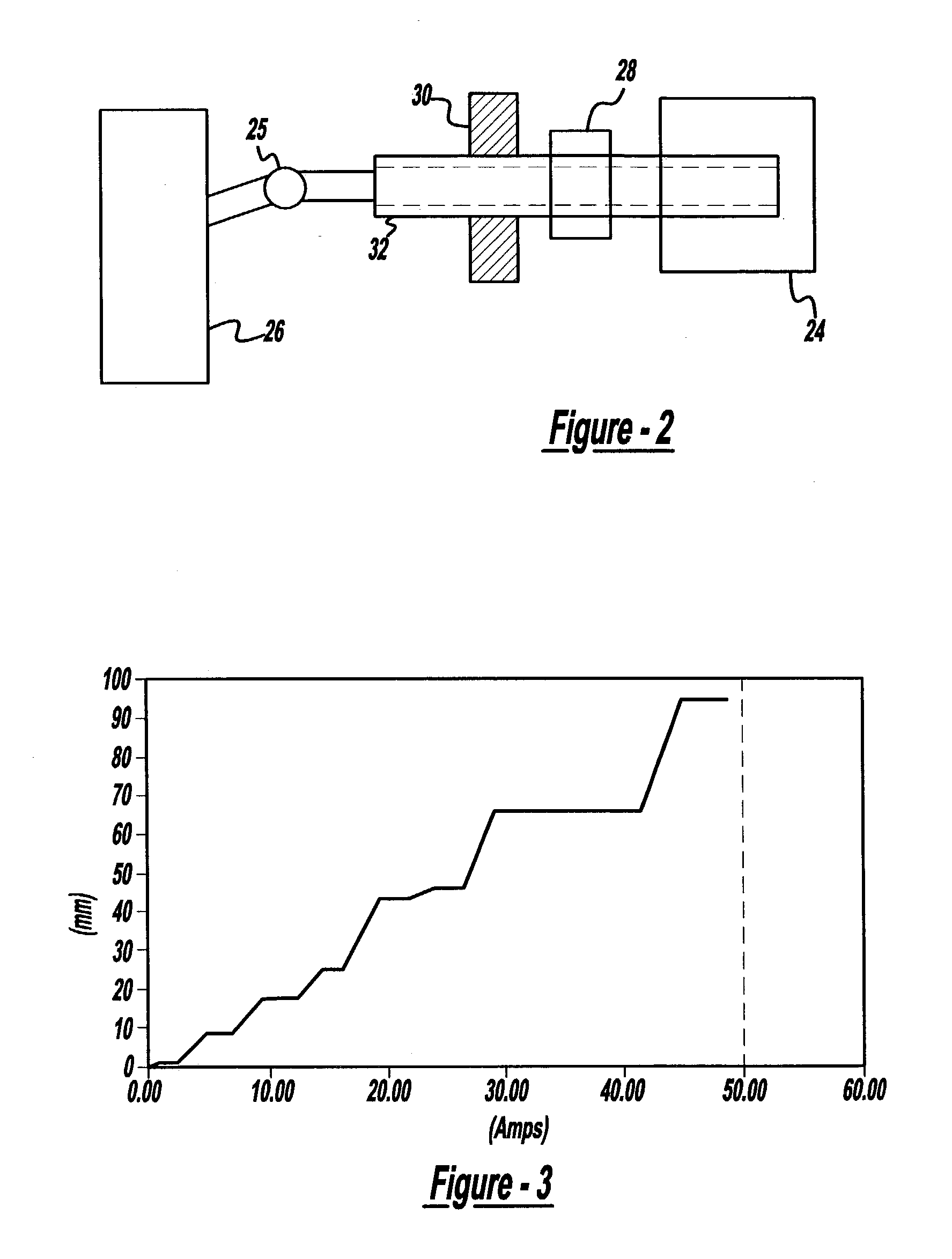
Friction compensation in a vehicle steering system
InactiveUS20040138797A1Eliminate the effects ofSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsFriction torqueControl signal
The present invention provides systems and methods of friction compensation in a steer-by-wire system or in a general electric steering system using control, estimation and modeling methodologies. A friction compensator in the steer-by-wire control system produces a friction compensating torque value equal and opposite in sign to the instantaneous friction torque. This compensating friction torque is added to the steering system control signal to eliminate the effects of friction present in the system such that the system performances are improved. The friction compensator produces the compensating friction torque according to one of two schemes: model-based or non-model based. The model-based scheme encompasses a number of different methods including a standard model-based scheme, a disturbance torque observer-based scheme, an adaptive friction compensation scheme, or a model reference adaptive control scheme. The non-model based scheme includes a fuzzy logic scheme.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
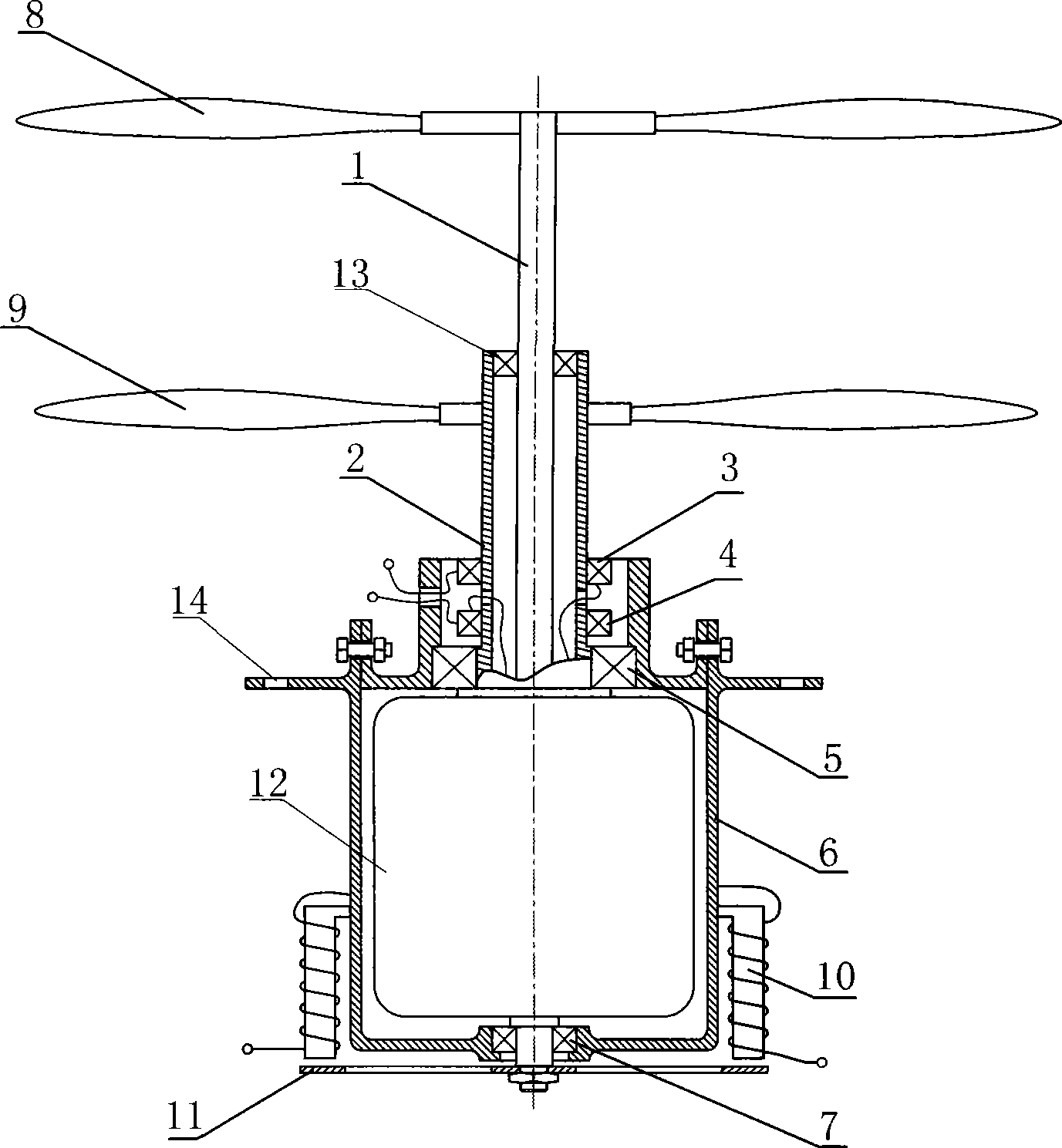
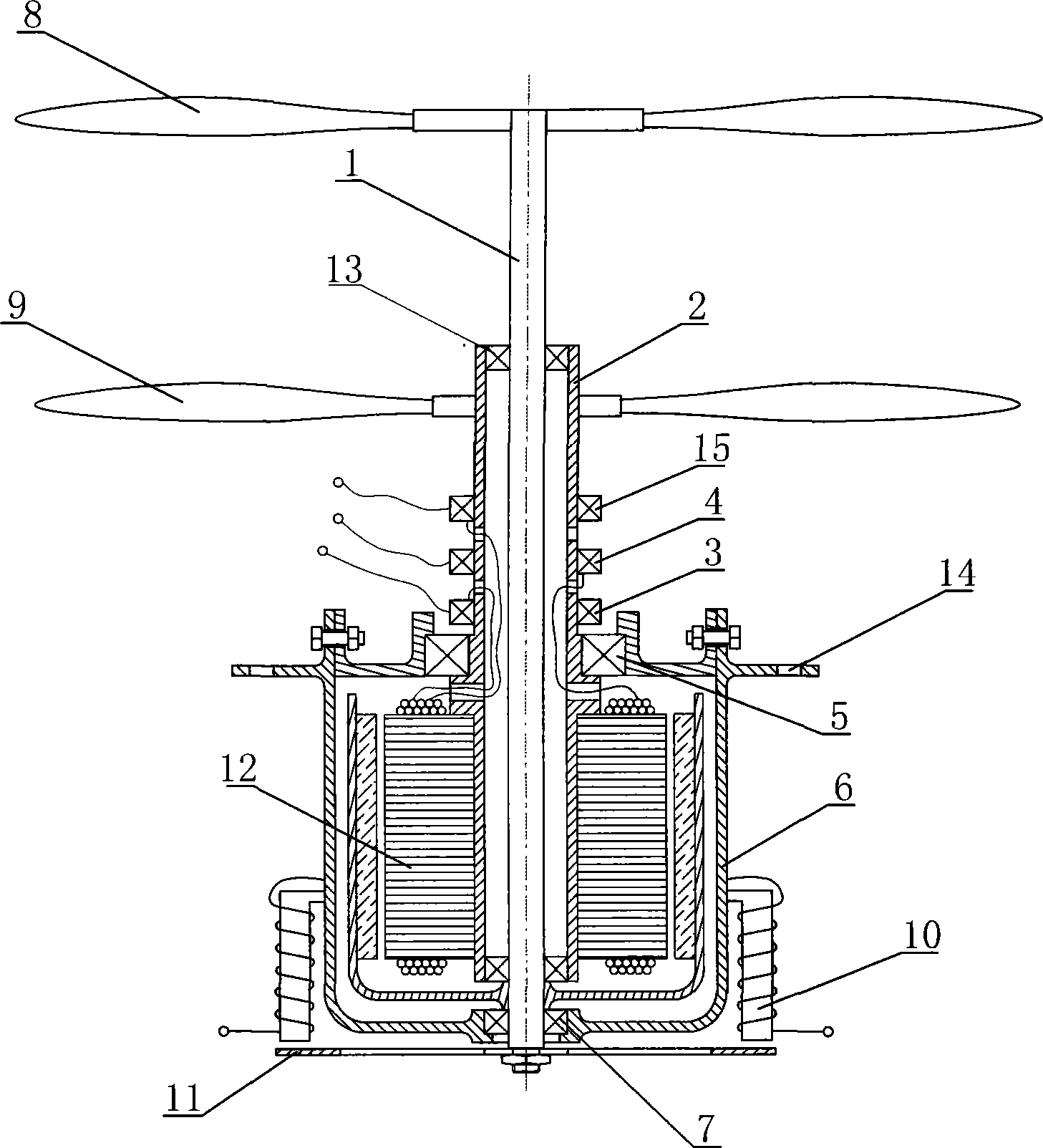
Power-driven system of aerial vehicle
InactiveCN101244762ASolve the steering problemMeet miniaturizationPropellersRotocraftFriction torqueFlight vehicle
The invention relates to a power driven system of the aircraft, which is characterized in that the power driven system comprises a power supply, a motor and a bearing support. The motor is vertically arranged in the bearing support by a bearing. Both the stator and the rotor of the motor are extending upwards and are respectively provided with propellers. The upper ends of the stator and the rotor where the propellers are arranged are coaxially sleeved, and the lower end of the rotor is fixed with a rotary disc after stretching out of the bearing support, an electromagnet with the magnetic pole part near the rotary disc is fixed-arranged outside the bearing support. When the motor is electrified, both the rotor and the stator drive the propellers to rotate to acquire power at the same time, and the power is transmitted to the frame by the bearing support to drive the aircraft to rise or advance. Meanwhile the electromagnetic moment between the electromagnet and the rotary disc is used to counteract the friction torque, and control the size of the electromagnetic moment to achieve the turning of the aircraft. The power driven system has the advantages of solving the problem of anti-torque of the propeller, satisfying the design requirements of miniature, simplification and lightness of the aircraft, and being beneficial to the popularization and manufacturing of the aircraft.
Owner:周公平
Twisting or micro-moving frictional wear test method and device thereof
InactiveCN101178345ANo wear and tearAccurately characterize kinetic propertiesStructural/machines measurementInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceLow speedFriction torque
The invention relates to a torsional fretting friction wear test method, the method is that: an upper testing part is clamped in an upper clamp, a lower clamp is fixed with a high-precision low-speed rotation table by a thread, a vertical central line of a holding cavity of the lower clamp is aligned with a rotating shaft of the high-precision low-speed rotation table, a spherical lower testing part is clamped by the lower clamp; the upper clamp is controlled for up and down movements by a data collection control system, the upper and lower testing parts are contacted and are exerted by a set load, at the same time, the lower clamp and the lower testing part clamped by the lower clamp are controlled by the data collection control system to carry out a plurality of times of reciprocating rotations by a set rotation speed and a rotation angle; at the same time, the friction torque is measured by a six-dimension force / torque sensor which is connected with the upper clamp and is sent to the data collection control system, and a torque-angular displacement curve under the set rotation speed and the load conditions can be obtained by analysis. The method can conveniently allow the materials to generate the small angle torsional fretting friction wear, the degree of the automation is high, the precision of the control and the test is high and the reproducibility of the test data is good.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
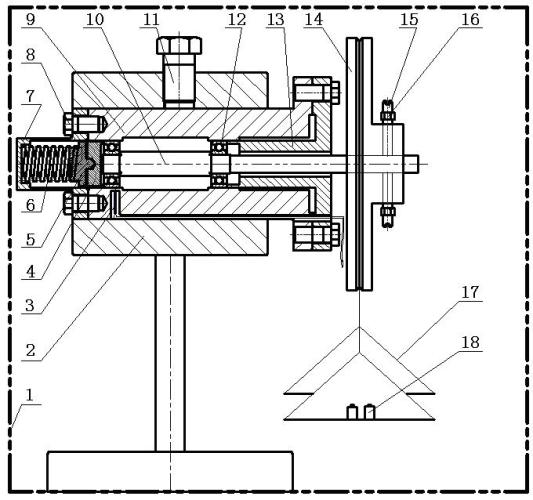
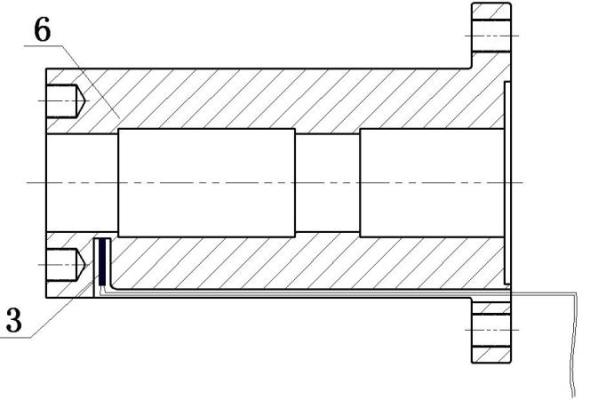
Friction torque testing device for rolling bearing at low temperature
InactiveCN102175369ASimple structureEasy to operateMachine bearings testingWork measurementSet screwTest performance
The invention relates to a friction torque testing device for a rolling bearing at low temperature. The friction torque testing device comprises a support and a pair of objective rolling bearings of same type, wherein the pair of objective rolling bearings of same type is mounted at two ends of a shaft so as to be placed in a sleeve, two ends of the sleeve are respectively located by a left end cover and a right end cover so as to be fixed on the support, and a temperature sensor is placed in a part of the sleeve near a drilling part of the objective rolling bearing so as to test the temperature variation of the bearing; an extending end of the shaft fixes a balance wheel through two set screws, two ends of each set screw are provided with two balance nuts to fine adjust the eccentricity of the balance wheel; a string comes around the balance wheel, and two trays are respectively hung on the two ends of the string; when weights are placed in the trays, a starting friction torque of the objective rolling bearing can be tested as soon as the balance wheel turns. The friction torque testing device for the rolling bearing at low temperature can effectively control certain pre-tightening force to test performance indexes of the friction torque of the bearing with different lubricants under different radial loads at low temperature; and the friction torque testing device is simple in structure, low in manufacturing cost and convenient to operate, and can repeatedly test the friction torque at harsh low temperature.
Owner:上海博高科技有限公司
Driving force transmitting device for four-wheel drive vehicle
InactiveUS20090229905A1Decreases oil viscosity resistanceDecreases friction lossFluid actuated clutchesRoad transportFriction torqueDrag torque
A driving force transmission device for four-wheel-drive vehicle based on the two-wheel drive of front wheels is provided. In the case of the two-wheel drive of front wheels, a multi-disc clutch mechanism for controlling the driving force distribution to a rear wheel output shaft, and a disconnection / connection mechanism for disconnecting and connecting a rear wheel differential and a right rear wheel drive shaft are provided, and in the two-wheel drive of front wheels, the dragging torque of the multi-disc clutch mechanism is made smaller than the friction torque of a rear wheel driving force transmission section, and the front wheel differential and the right rear wheel drive shaft are disconnected by the disconnection / connection mechanism, thereby the rotation of the rear wheel driving force transmission section is stopped.
Owner:UNIVANCE CORP
Robot arm control method and control device
By appropriately selecting a command value or an actually measured value as the angular velocity used for friction torque calculation, friction compensation can be effective in both cases when actively operating according to the angular velocity command and passively operating, that is, when being pushed by an external force . Also, after a collision is detected, when the motor rotation direction is opposite to the collision direction, the position control is switched to current control so that the motor generates torque in the opposite direction to the motor rotation direction, thereby reducing the motor rotation speed and weakening the collision energy. Thereafter, when the motor rotation speed becomes the set value or lower, the mode is set to flexible control, thereby eliminating deformation of the speed reduction device or the like caused by the collision. On the other hand, when the motor rotation direction and the collision direction are the same, the position control is directly transferred to the flexibility control without going through the current control. By performing operations according to the collision force, it is possible to weaken the collision torque.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Vehicular steering apparatus
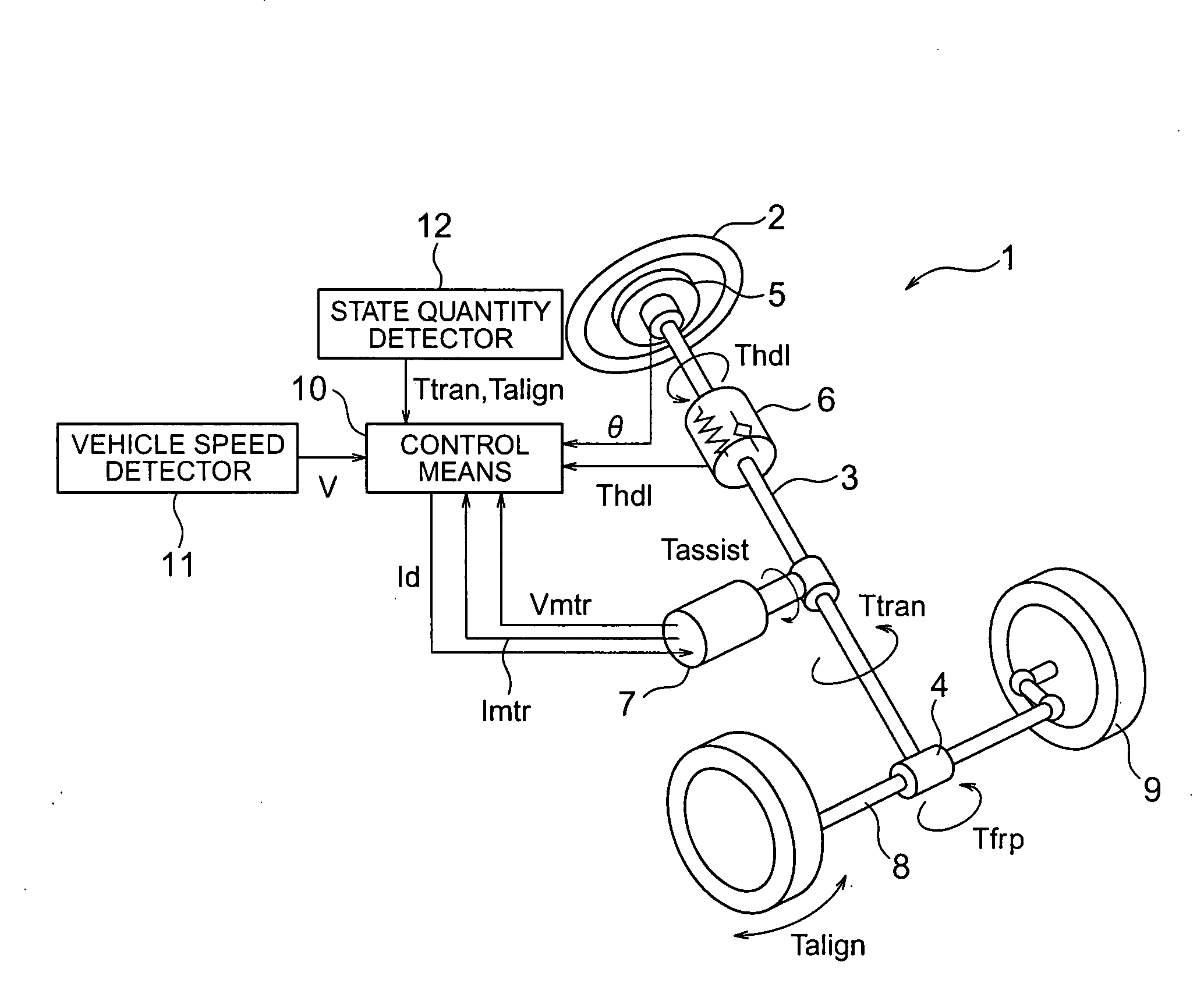
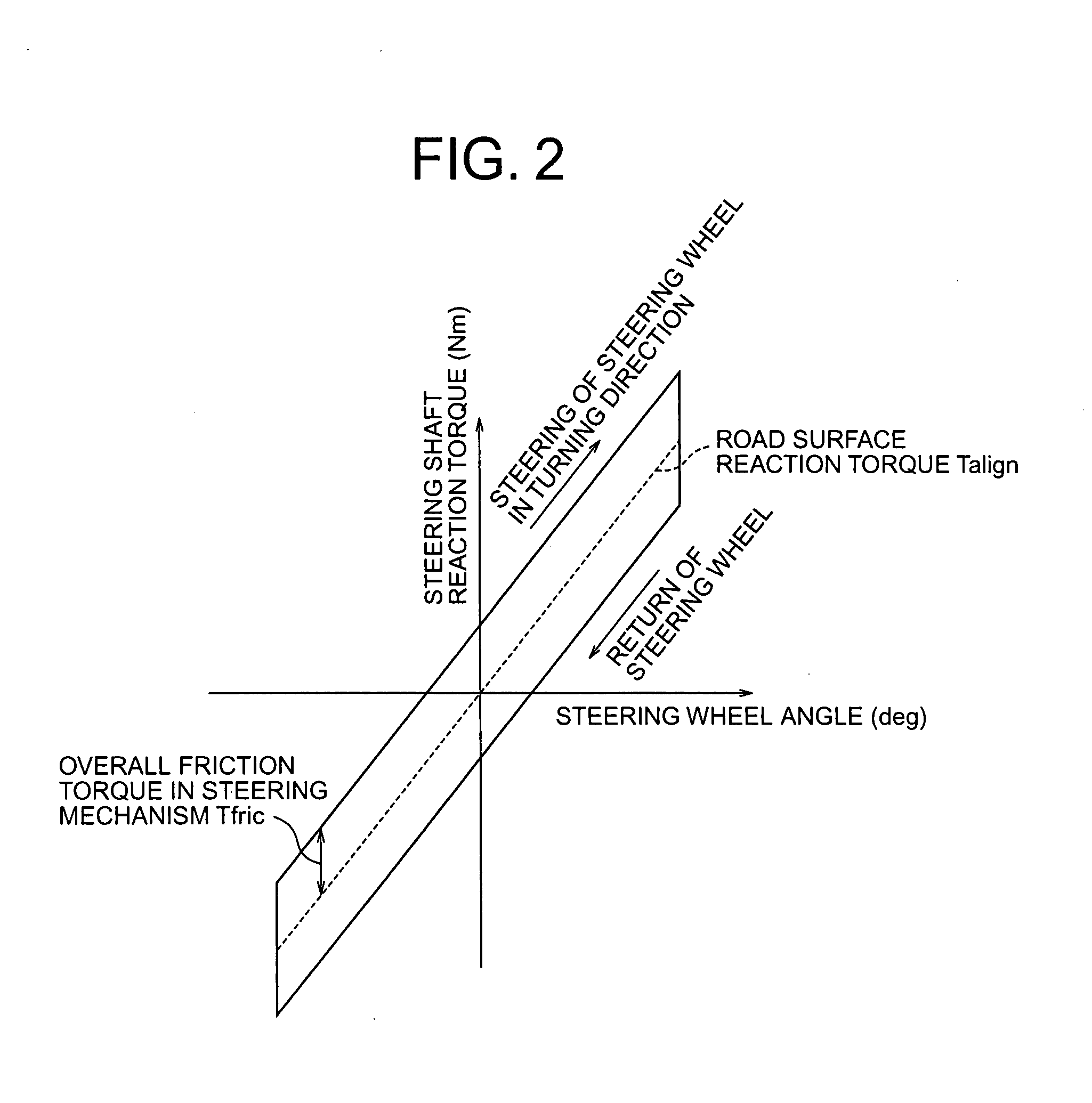
ActiveUS20080189014A1Feel goodLow costSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsFriction torqueRoad surface
Provided is a vehicular steering apparatus capable of improving a steering feeling and achieving a reduction in cost. The vehicular steering apparatus according to the present invention is equipped with an assist motor for generating an assist torque, a state quantity detector for detecting a steering shaft reaction torque and a road surface reaction torque, and a control unit for calculating a target current value of the assist motor. The control unit includes a friction compensation portion and a return compensation portion, which calculate a friction compensation torque for compensating for the assist torque and a return compensation torque for compensating for the assist torque from the steering shaft reaction torque and the road surface reaction torque respectively. The control unit compensates for an overall friction torque in a steering mechanism and a gradient of the road surface reaction torque, using the friction compensation torque and the return compensation torque.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Measuring for friction torque of bearing under micro-loading at different rotation rate and measuring apparatus therefor
ActiveCN1865878AThe principle is simpleSimple structureMachine bearings testingWork measurementObservational errorFriction torque
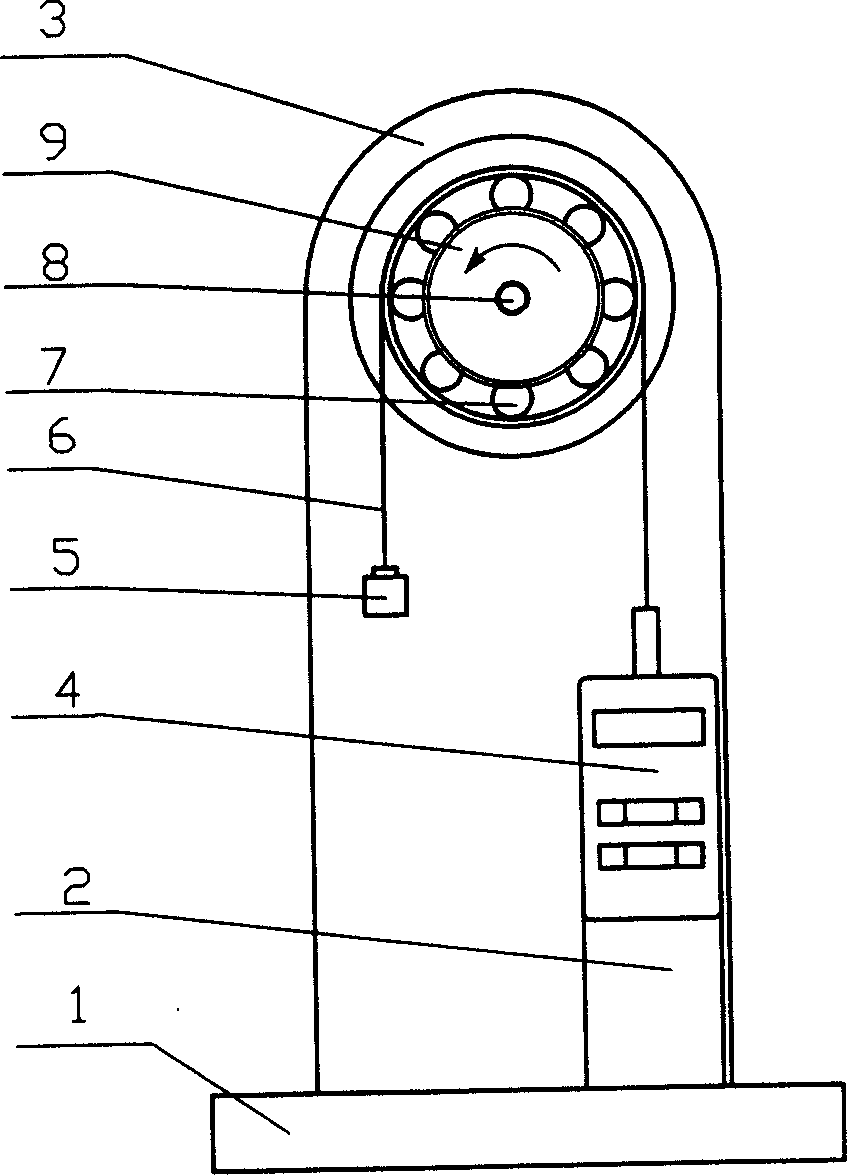
The disclosed measuring apparatus and method for frictional moment comprise: the target bearing with diameter as D is suspended a segment nylon wire with ends connected to weight and dynamometer respectively, when bearing static, the show value on dynamometer as A1 balances to the weight; if rotating toward one direction by some rate, the show value increases to A2, and the formula M=(A2-A1) .D / 2 can express the corresponding frictional moment. This invention is reliable, simple, and well practical.
Owner:CIXING GROUP
Measuring apparatus for frictional moment of bearing under different axial loads and rotation speeds
ActiveCN101487751AReduce rotation speedUnable to measure frictional torqueWork measurementTorque measurementHead pressingFriction torque
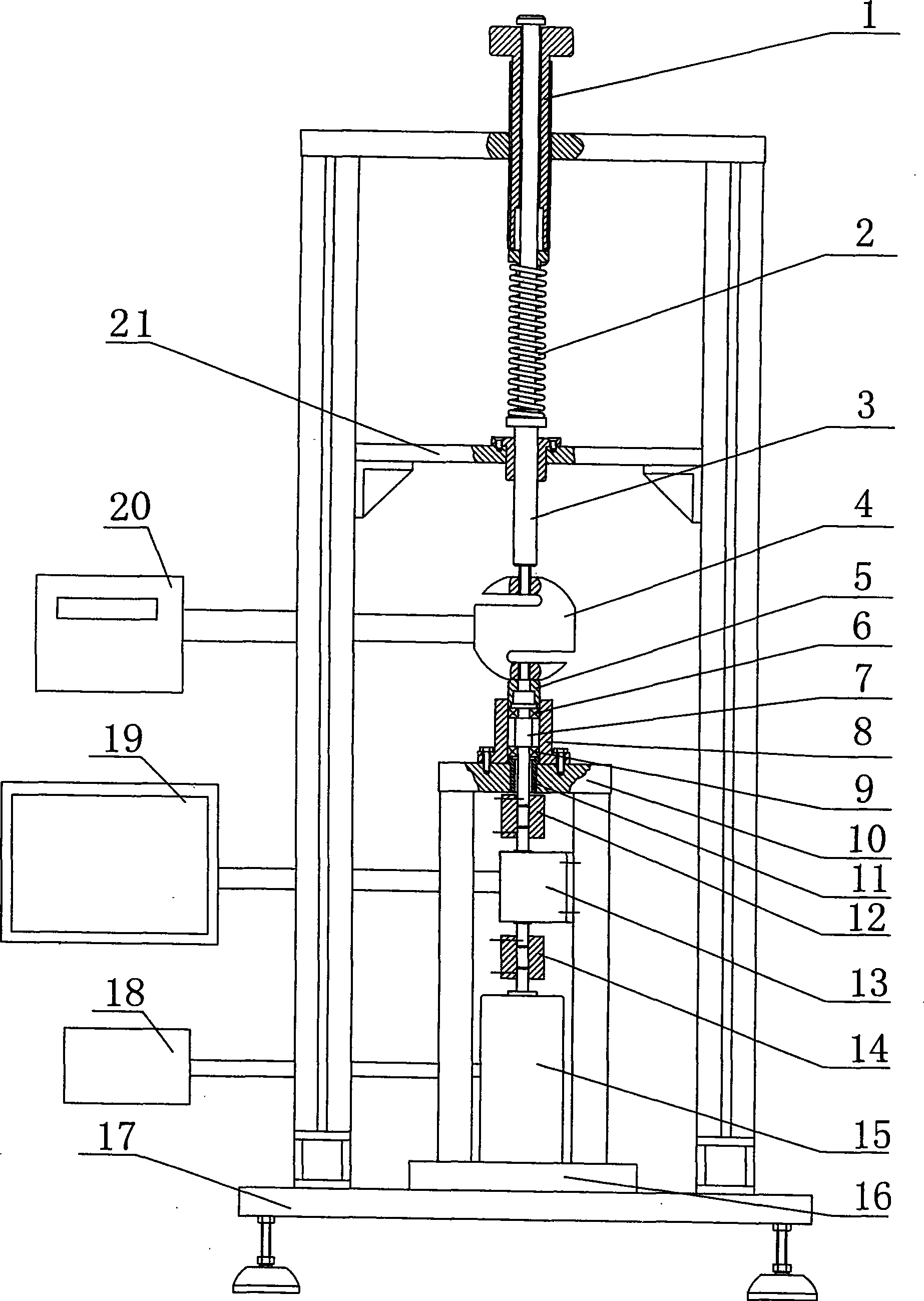
The invention relates to a device for measuring friction torque of a bearing under different axial load and revolution speed, comprising a fixing component, an axial loading component, a display component and a measurement component arranged on a stander base, wherein, the measurement component is arranged in a bearing support by an upper bearing and a lower bearing which are the same and fixed on a stander workbench, a bushing on the workbench supports the end face of the bearing outer ring of the lower bearing, so as not to contact the end face of the inner ring, and a loading head presses the end face of the bearing outer ring of the upper bearing. The two same bearings are used for measurement so that the axial load is not directly applied to a transmission shaft and a driving device to influence and damage the operation of the driving device. The voltage of a direct current motor is adjusted by a voltage regulator, so as to adjust the rotate speed of the motor. The axial load is adjusted by rotating a screw. The device can measure larger and different load and bearings with higher and different rotate speed, has wide measurement range which can be adjusted, can meet different requirements of users, and has the advantages of simple structure, easy fabrication, convenient, accurate and intuitive operation and use, wide universality and strong practicability.
Owner:NINGBO CIXING BEARING
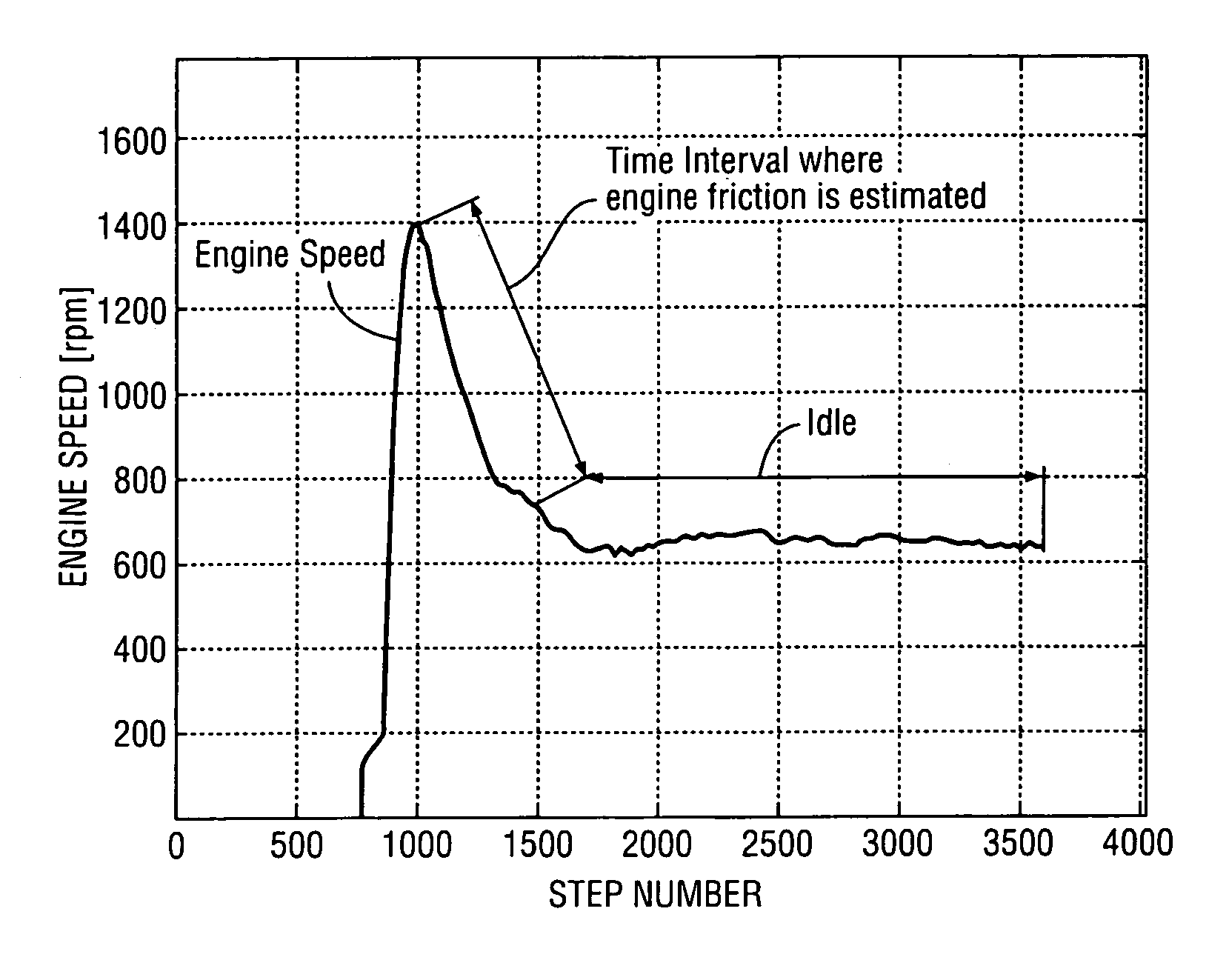
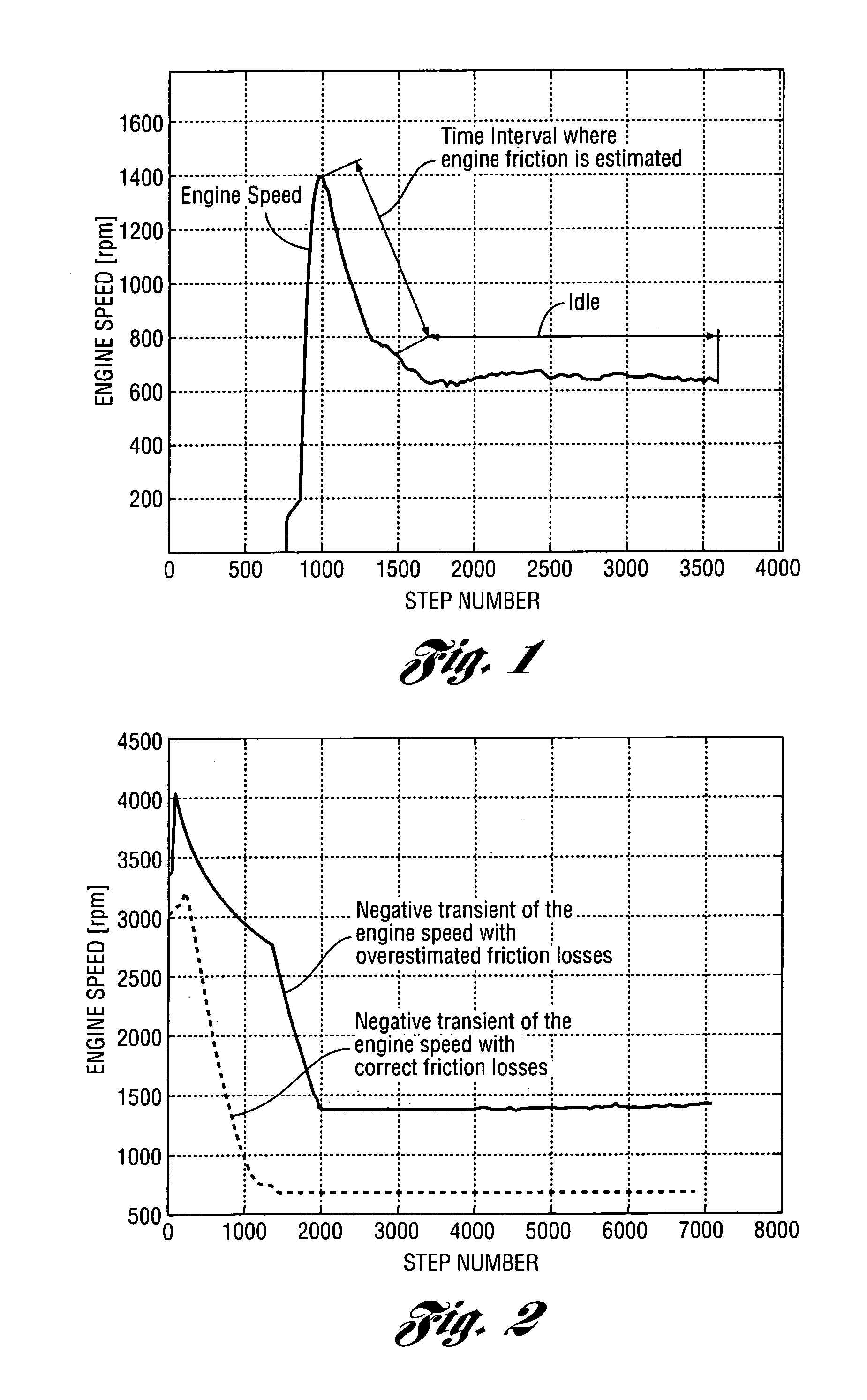
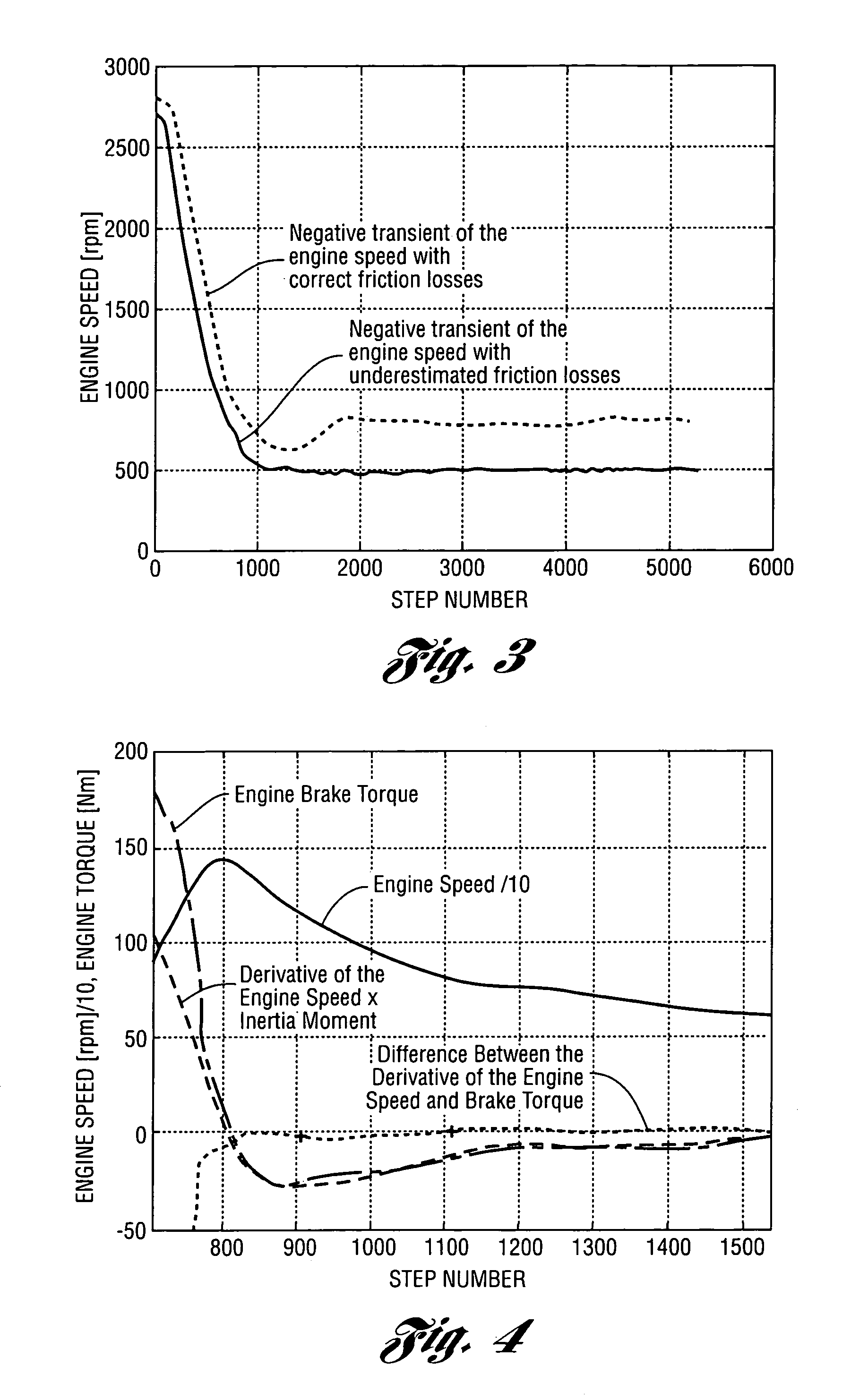
Method for estimating engine friction torque
ActiveUS7054738B1Lighten the computational burdenAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlFriction torqueEngineering
Algorithms for real-time estimation of the engine friction torque in a vehicle powertrain are disclosed. Engine friction torque is estimated at start and at engine idle. Recursive and computationally efficient algorithms allow prediction of friction torque for a wide range of speeds and loads even with few new measured points by taking into account physical dependencies used for adaptation of the sites of the look-up tables (static maps). The algorithms make it possible to avoid drivability problems that could result from errors in estimating engine friction torque.
Owner:VOLVO CAR CORP
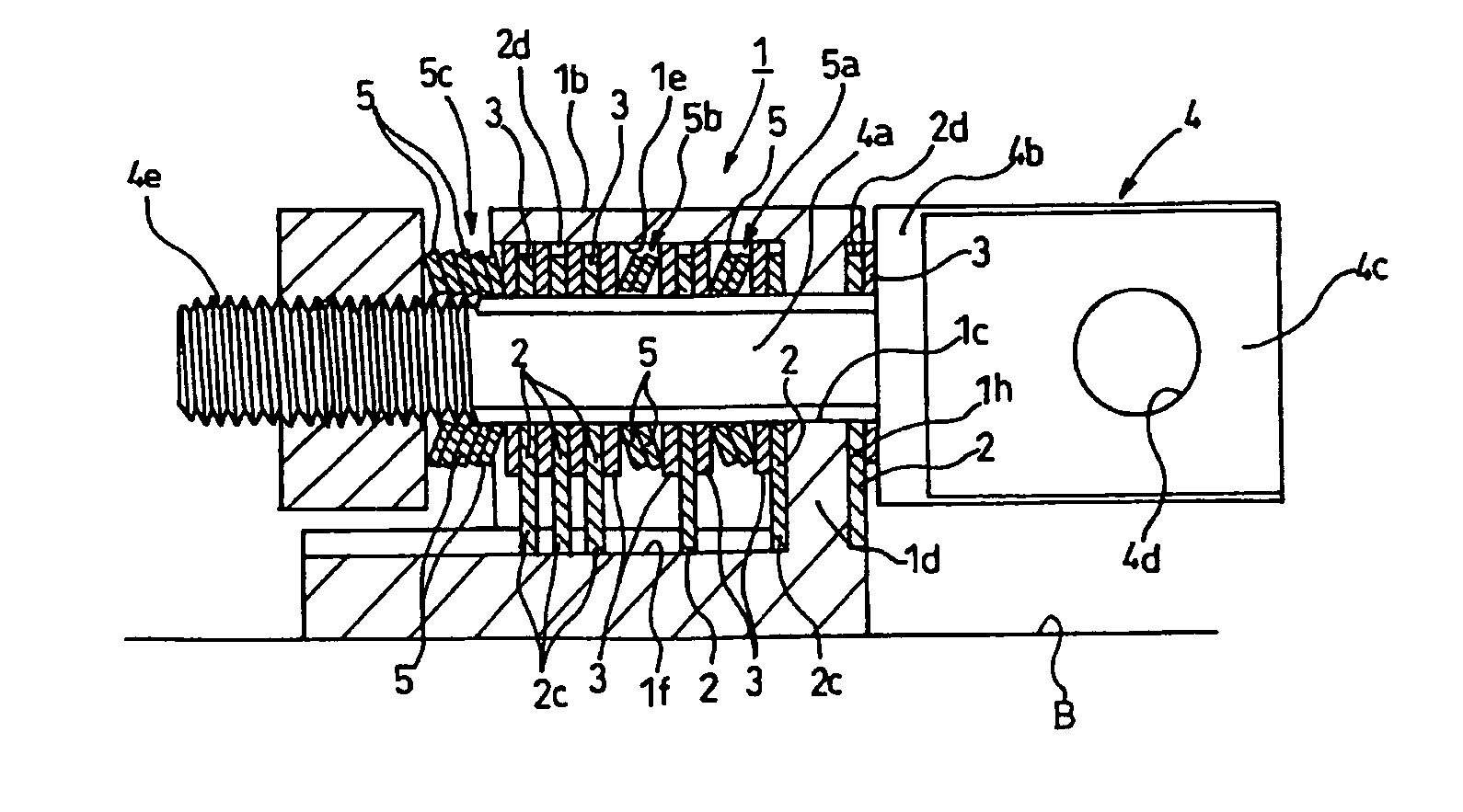
Tilt hinge
InactiveUS7143476B2Increase friction areaIncrease frictionWing fastenersDetails for portable computersFriction torqueEngineering
In order to provide a tilt hinge small in size and diameter capable of generating a stable friction torque of approximately 100 kgf / mm, a hinge friction-rotatably coupling a first member and a second member that are relatively opened / closed includes: a holder attached to one of the first member and the second member; a shaft attached to the other one of the first member and the second member to be rotatable relative to the holder and immovable in an axial direction; a plurality of first friction discs restrained by the holder to be rotatable and movable in the axial direction, with the shaft being inserted through insertion holes thereof; a plurality of second friction discs interposed between the first friction discs to be movable in the axial direction with rotation thereof restrained by the shaft; and a plurality of disc springs and / or spring washers attached to the shaft so as to bring the first friction discs and the second friction discs to be in contact with each other by pressing the first friction discs and the second friction discs in the axial direction, wherein the disc springs and / or the spring washers are provided outside the holder in which the first friction discs and the second friction discs are stacked on each other and inside the holder.
Owner:KATOH ELECTRIC MACHINERY
Design method for sliding mode disturbance observer used for servo system control
InactiveCN106067747AImprove shortcomingsReduce jitterDC motor speed/torque controlFriction torqueLow speed
The invention provides a design method for a sliding mode disturbance observer used for servo system control, and aims at the friction interference problem in low speed of a servo system and considers the error and uncertainty problem of system modeling. A common DC motor model is used, and a disturbance observer and sliding model variable structure control are combined so that the sliding mode disturbance observer is designed. Firstly the size of the friction torque is observed by using the disturbance observer, and then a sliding mode controller is designed according to the obtained friction torque. The switching item gain of the sliding mode controller can be reduced through observation of friction torque so that the buffeting phenomenon can be reduced. Suppression of the low speed servo system for dead zone, creeping, self-oscillation and other nonlinear phenomena can be realized through the sliding mode disturbance observer so that the requirements for the modeling precision can be reduced and the method has great robustness.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for measuring non-contact type bearing startup friction torque and measuring instrument thereof
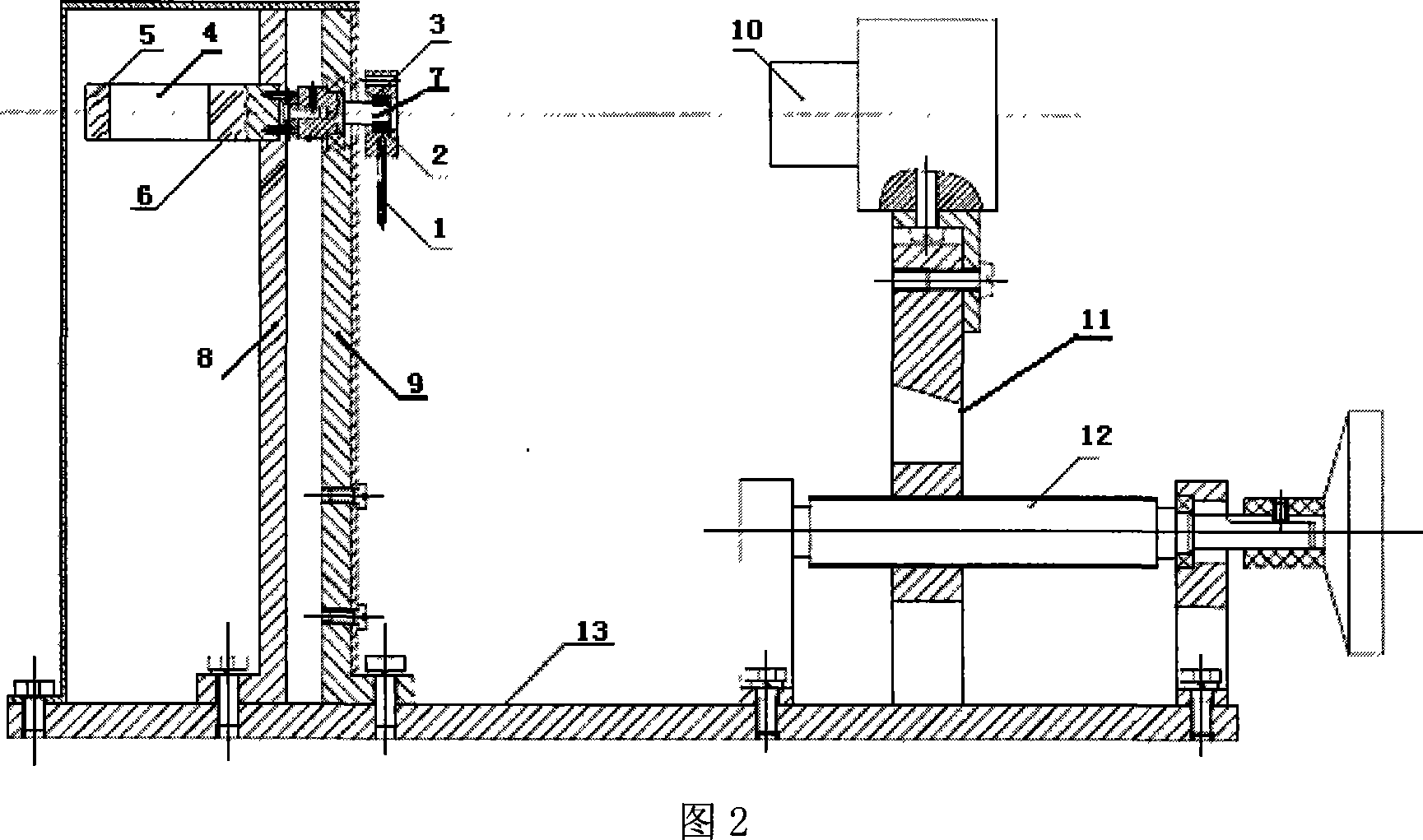
InactiveCN101303261ASolve the problem of starting friction torqueAutomatic monitoring of starting and running statusWork measurementTorque measurementAir bearingFriction torque
An apparatus for measuring non contact type bearing start friction torque, is composed mainly of a loading cylinder (1), a force transducer (2), a loading housing (3), an air main shaft (5), an air bearing (6), a torque generator (7), a disk drive (8), an optoelectric transducer (9), an electrical system. The torque generator generates induction electromagnetic torque as drive torque, the optoelectric transducer monitors bearing start running state automatically; when being measured, the measured bearing is installed on the air main shaft, the disk drive is linked with the air main shaft and placed in the torque generator, the electrical system applies input power to the torque generator step by step after throwing axial load, when the induction electromagnetism drives the air main shaft to rotate through the disk drive, the optoelectric transducer matching-installed by the disk drive monitors the measured bearing from static state to start running state, and outputs signal to stop applying input power, and records current power value which is the start friction torque value of the measured bearing.
Owner:LUOYANG BEARING SCI & TECH CO LTD
Motor-driven power steering apparatus
InactiveUS20070144824A1Feel stableDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsElectric power steeringSteering angle
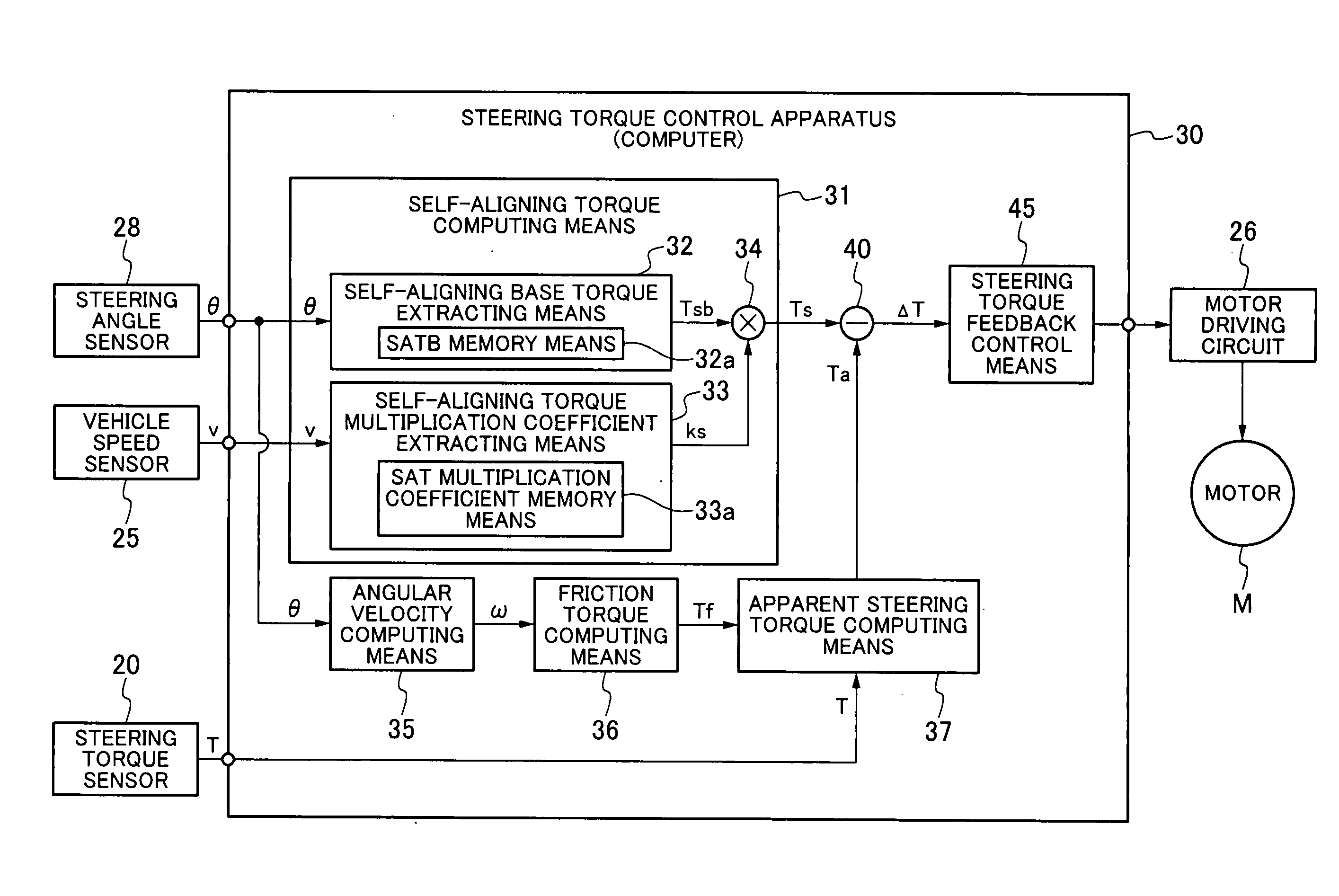
A motor-driven power steering apparatus is provided with a self-aligning torque computing means for computing a self-aligning torque based on of a steering angle and a vehicle speed, a friction torque computing means for computing a friction torque in accordance with a steering angle change from a steering angular velocity, an apparent steering torque computing means for computing an apparent steering torque from the friction torque and a steering torque, and a steering torque feedback control means for driving and controlling an assist motor in such a manner that a difference between the self-aligning torque and the apparent steering torque becomes 0.
Owner:SHOWA CORP
Megawatt level wind power generation oar-changing bearing friction torque numeric control testing machine and test approach
InactiveCN101256103ASmall sizeSimple structureMachine bearings testingEngine testingFriction torqueClosed loop
The invention provides a megawatt wind power generation adjustable blade bearing friction moment numerical control testing machine and a testing method. The tested bearing outer ring is fixed on the machine rack; a main axis is equipped, one end of the bearing inner ring is fixed on the bearing inner ring, the other end is equipped with a radial and axial loading mechanism, in which the radial and axial load cylinder are separately pressured, and is equipped with variable-frequency motor of torque sensor, the driving pinion is meshed with the tested bearing inner ring, which form the loading and transmission system. The testing machine is determined by force analysis and analog loading principle, which is reasonable and reliable, and has simple structure and small size. The closed-loop numerical control system, which is composed of an industrial computer, a hydraulic pressure control member, a hydro cylinder, a feedback element and other components, can realize overall monitor, data collection, analysis, process, and number and graph double output; the size, direction, variation period of the load are accurate, the curves of the load output and friction torque are intuitive, the testing process is highly automatic. And the invention can be matched with manual adjustment. The machine is shutdown automatically if any failure happens. The test provides data support for the bearing wind turbines, which assures that the machine can meet the test need after loading.
Owner:文鉴恒
Micro-bearing friction torgue measuring instrument
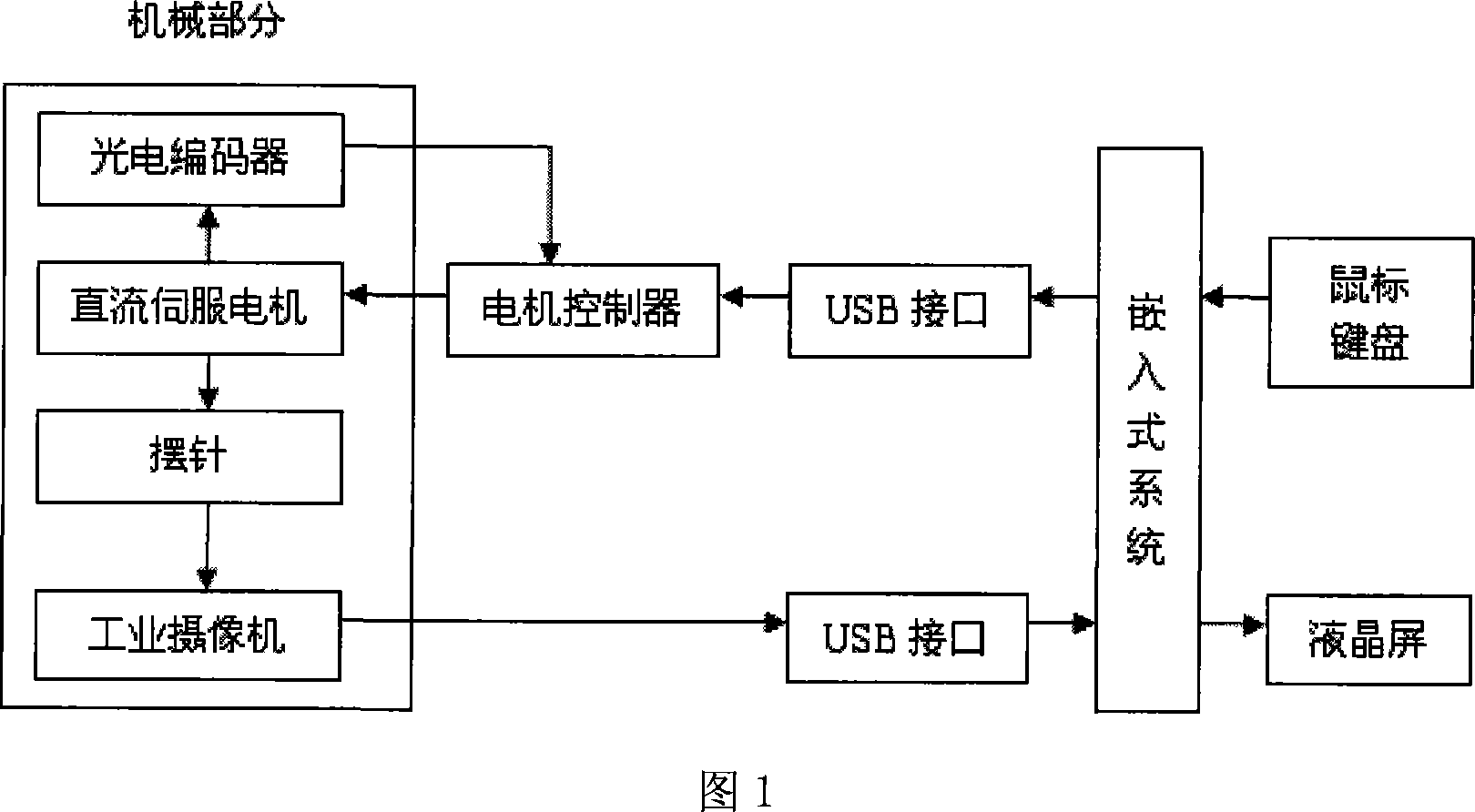
InactiveCN101067578AEliminate frictionEliminate distractionsMachine bearings testingForce measurement using counterbalancing forcesEmbedded technologyFriction torque
The invention is a microtype bearing friction moment measurer, belonging to the field of measuring and control technique. And the invention comprises: mechanical part, electrical part and embedded system, where the mechanical part is connected with the input end of the electrical part through lead wires and USB interface, and the input and output ends of the electrical part are connected the input and output ends of the embedded system, respectively. And the invention adopts digital image processing technique, embedding technique and auto control technique to be able to accurately measure friction moment of a microtype bearing. And the measurer has simple structure, operating convenience and high measuring accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
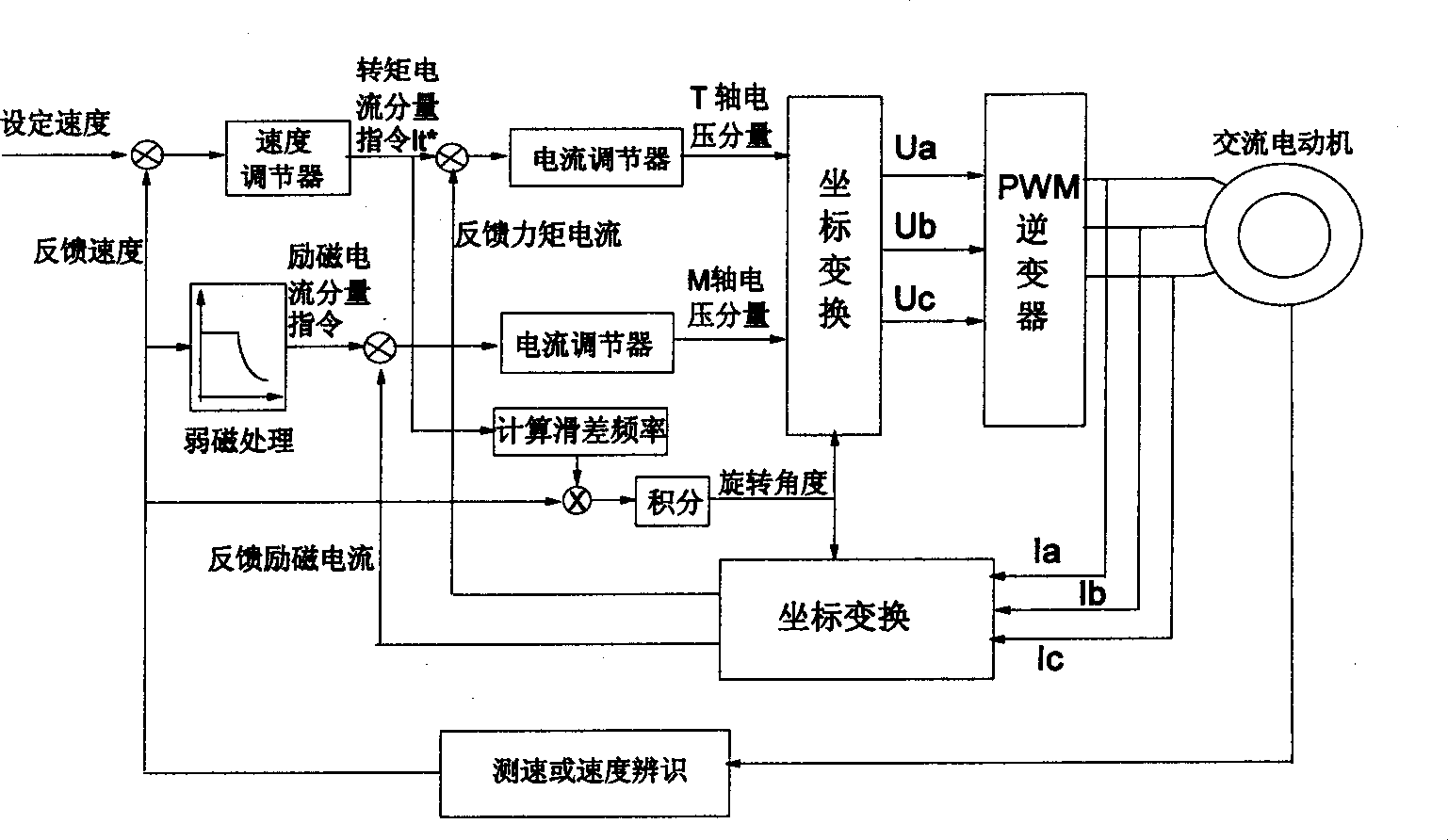
Non-synchronous motor rotary inertia identification method
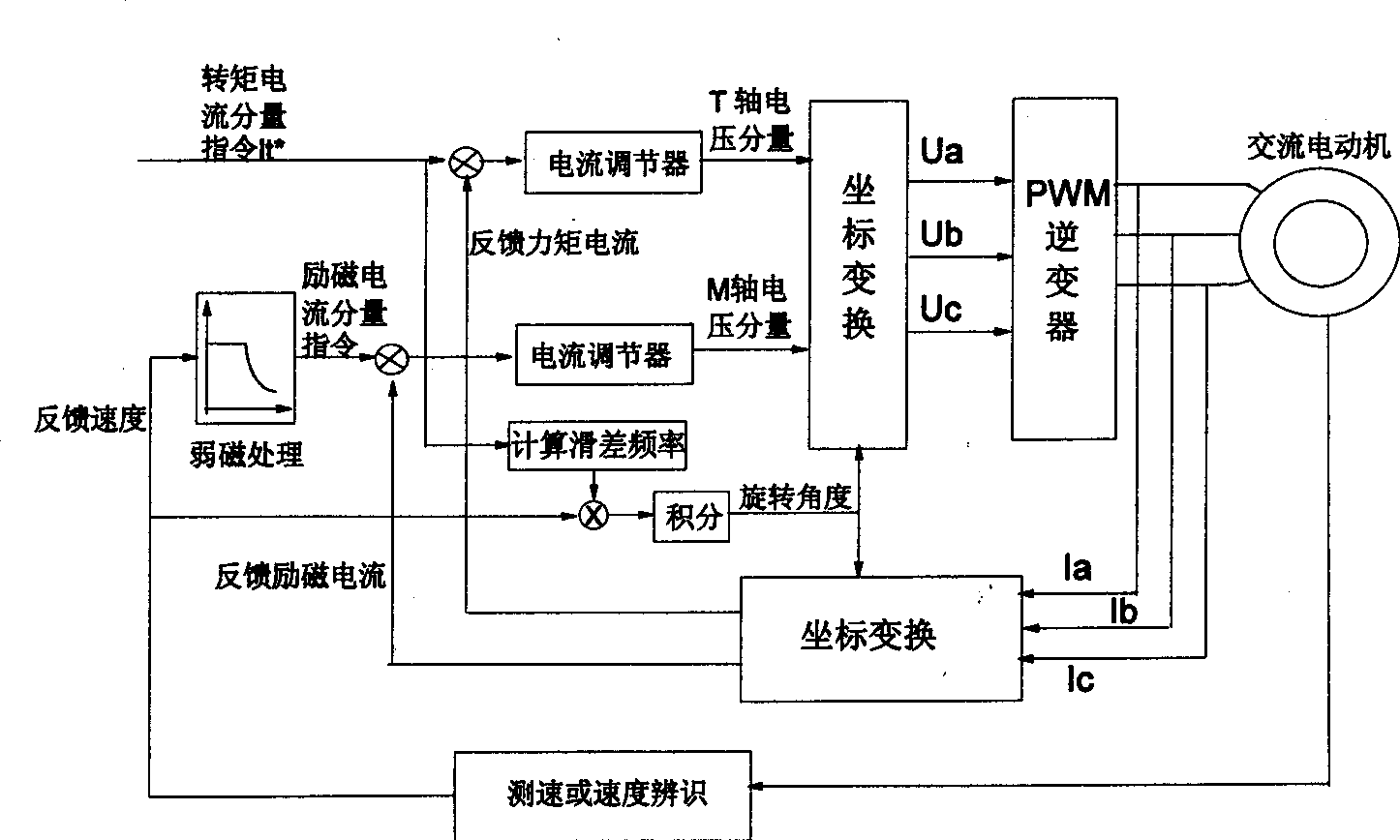
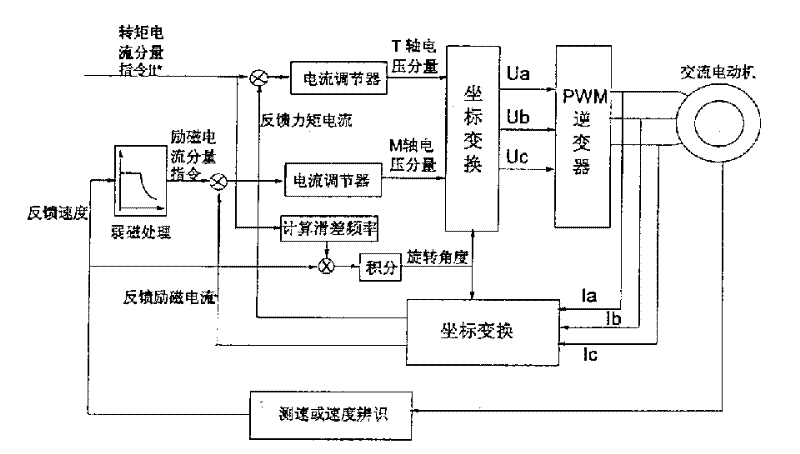
InactiveCN1354558AHigh accuracy of identification parametersImprove the performance of vector controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsFriction torqueSynchronous motor
The invention relates to a method for recognizing moment of inertia of asynchronous motor. For the purpose, following steps are taken. The electrical motor is controlled to run at constant acceleration from angular velocity omega 1 of no load operation to angular velocity omega 2 and recording the running time delta t by using control method of torque vector. By using control method of speed vector. The motor is controlled to run at constant angular velocity omega 3 of no load operation. The value of electromagnet torque is calculated based on the torque current component It at this time, so as to get the friction torque To of the motor. then based on the running time delta t and the friction torque Io, the moment of inertia Jo of the omtor is calculated. The invented method provides high accuracy for recognizing these parameters, thus improving the performance of the method of vector control.
Owner:SOMER LEROY ELECTRO TECH FUZHOU CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com