Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2550 results about "Moment of inertia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
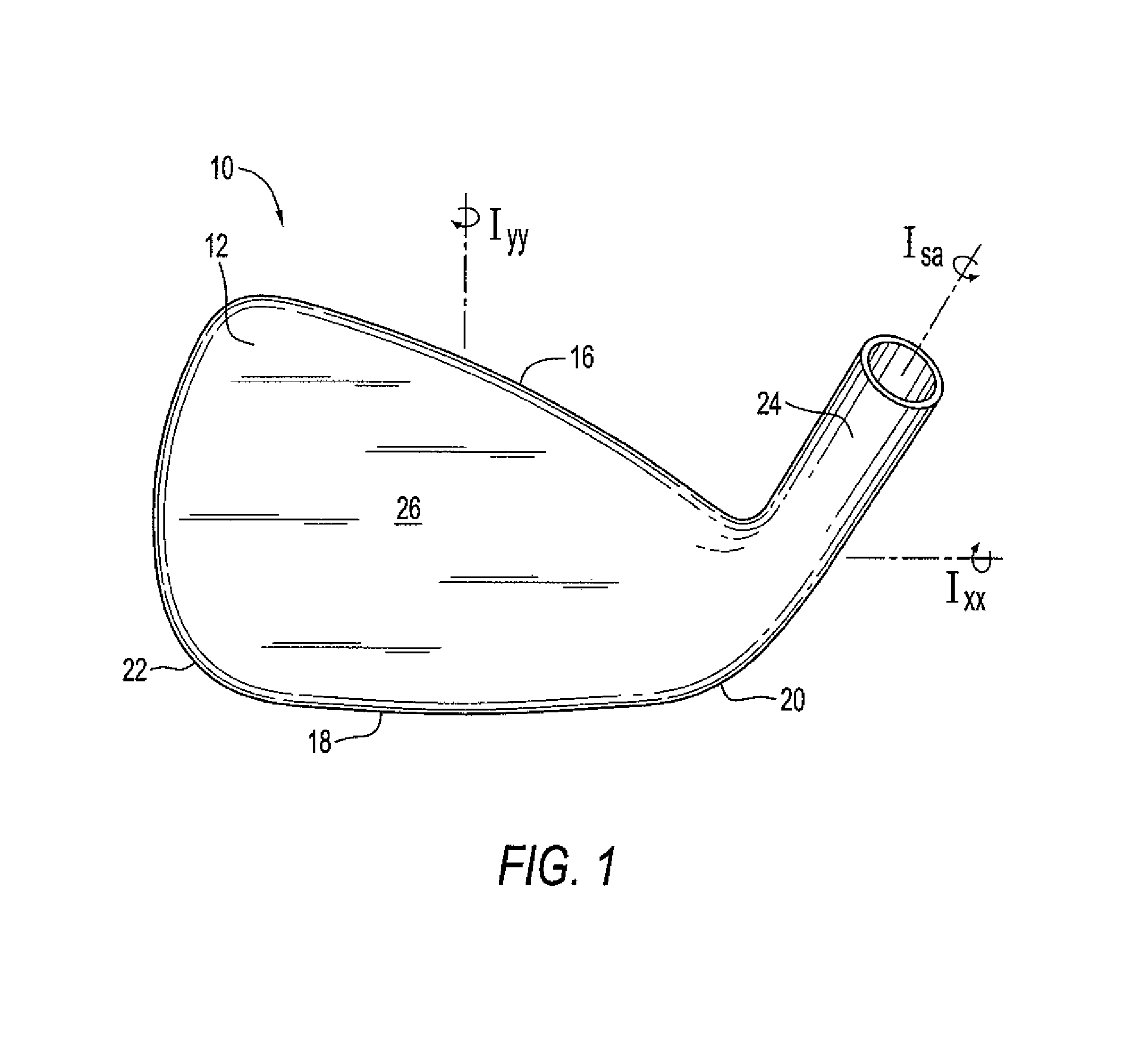
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the angular mass or rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis; similar to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rotation rate. It is an extensive (additive) property: for a point mass the moment of inertia is just the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the rotation axis. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis. For bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to the plane, a scalar value, matters. For bodies free to rotate in three dimensions, their moments can be described by a symmetric 3 × 3 matrix, with a set of mutually perpendicular principal axes for which this matrix is diagonal and torques around the axes act independently of each other.
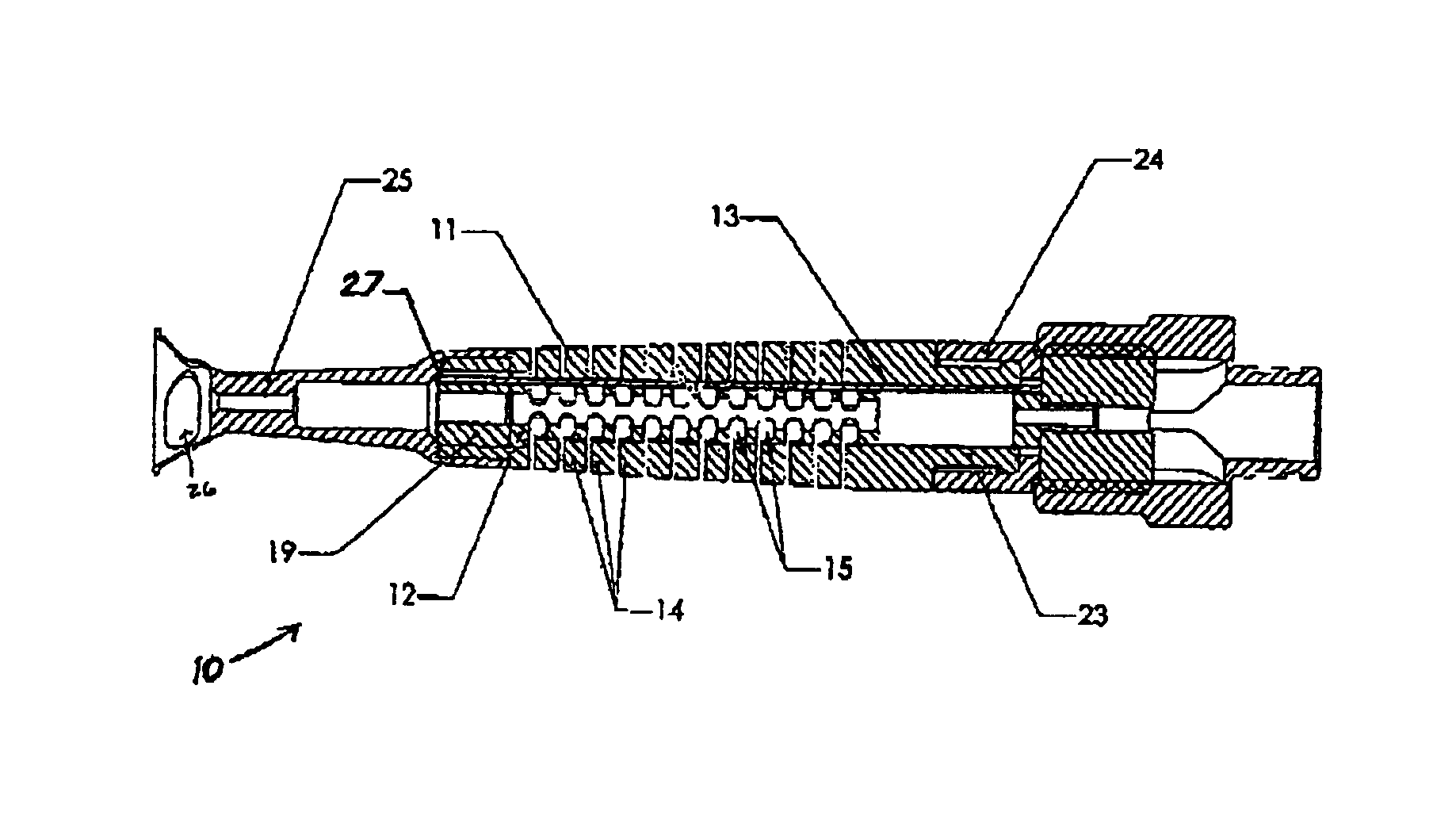
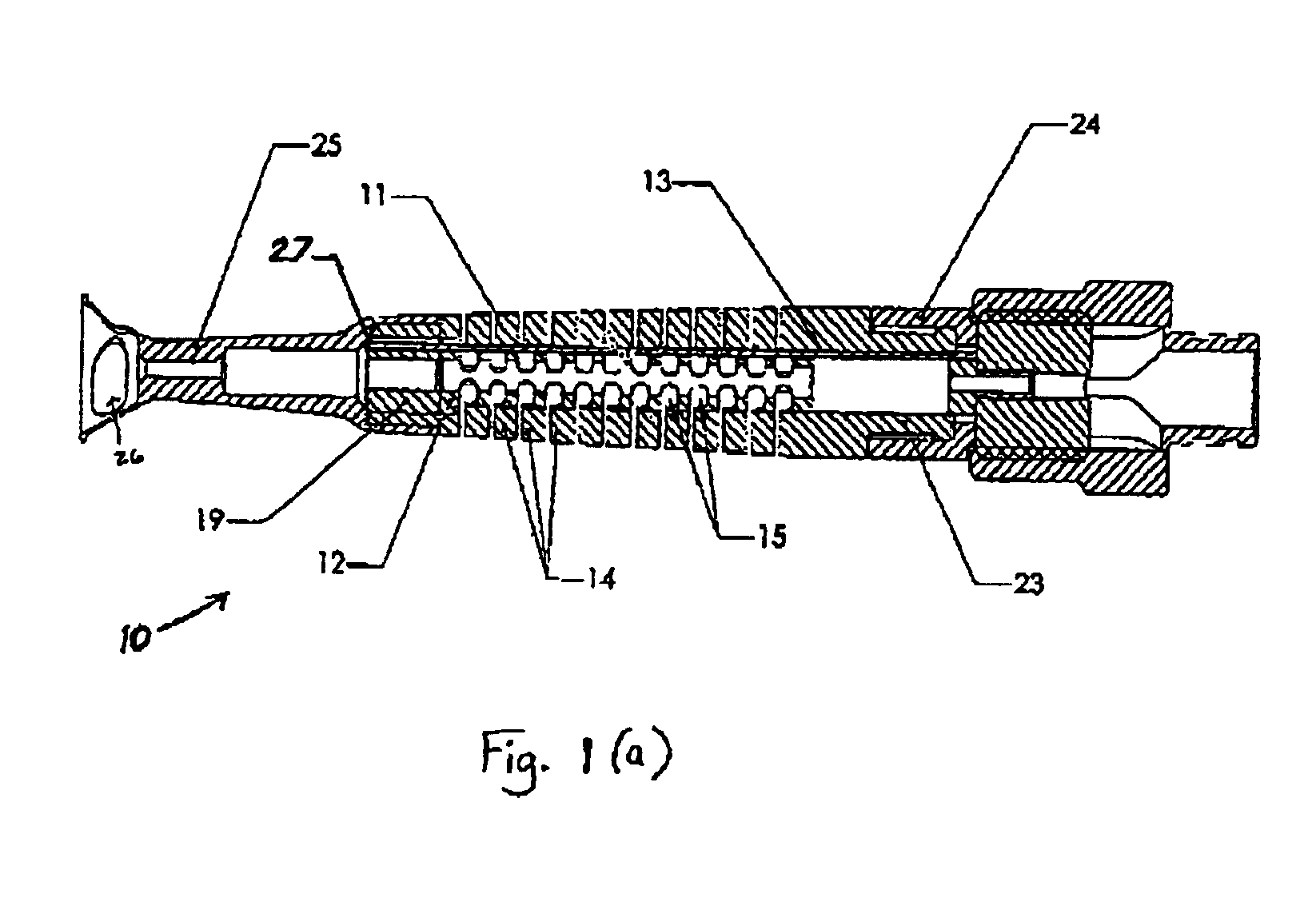
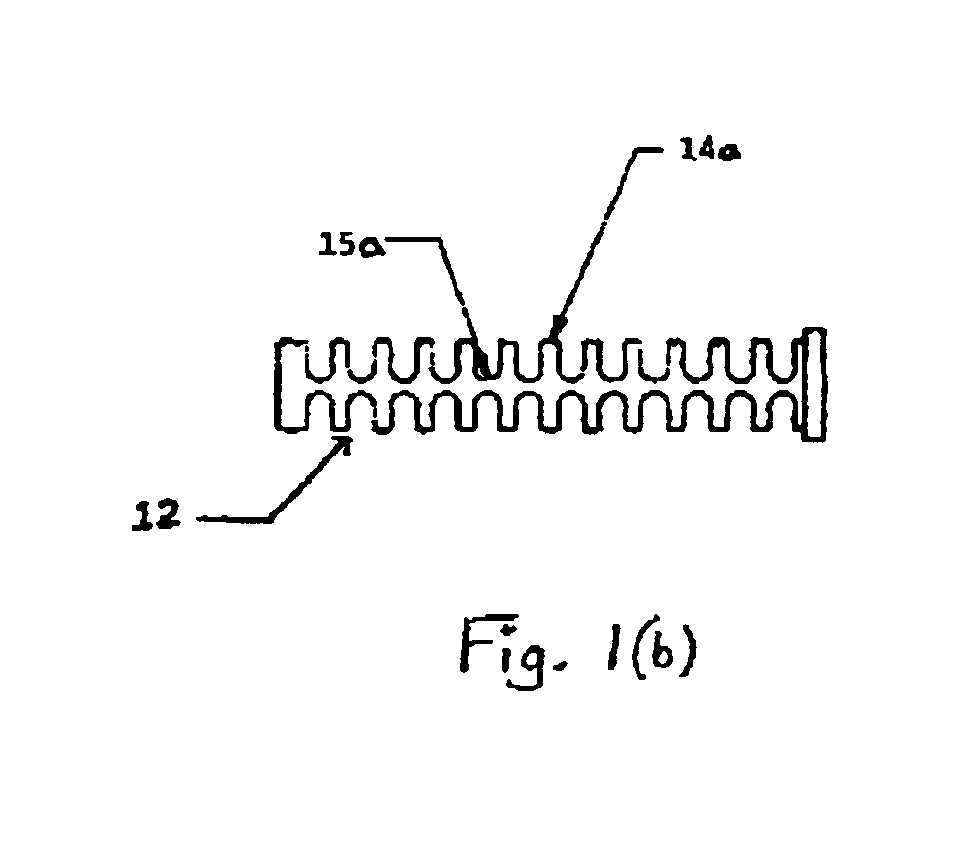
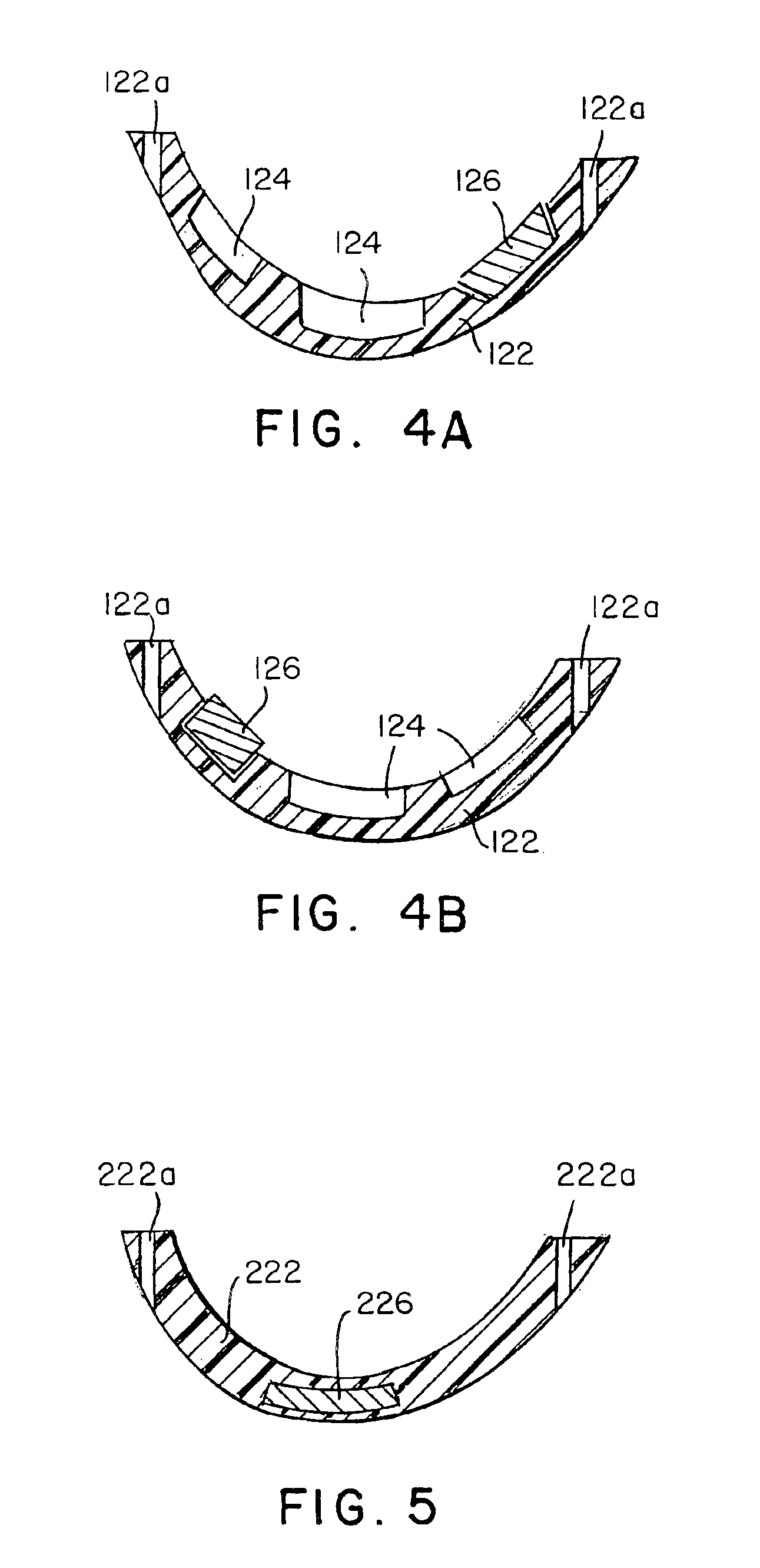
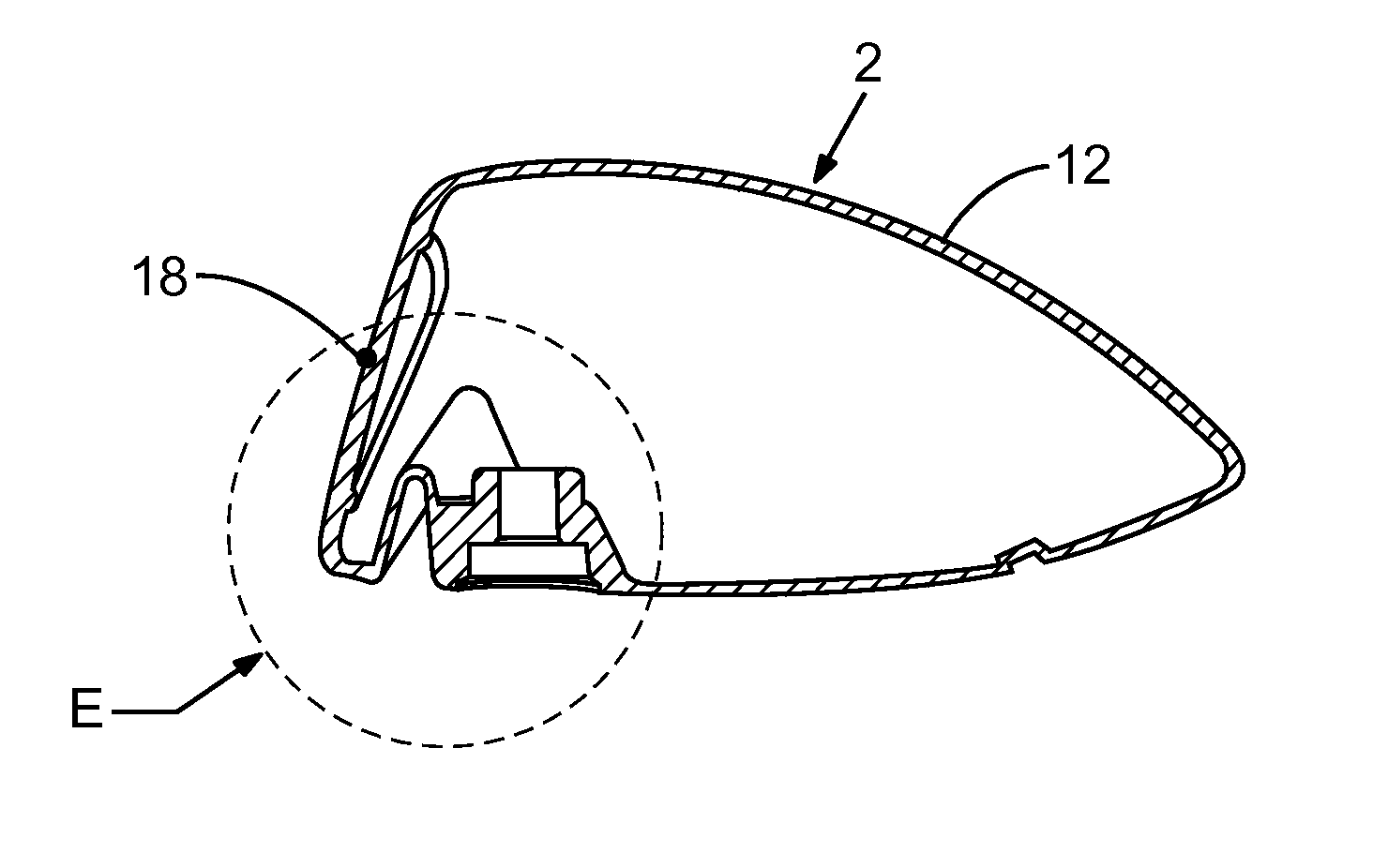
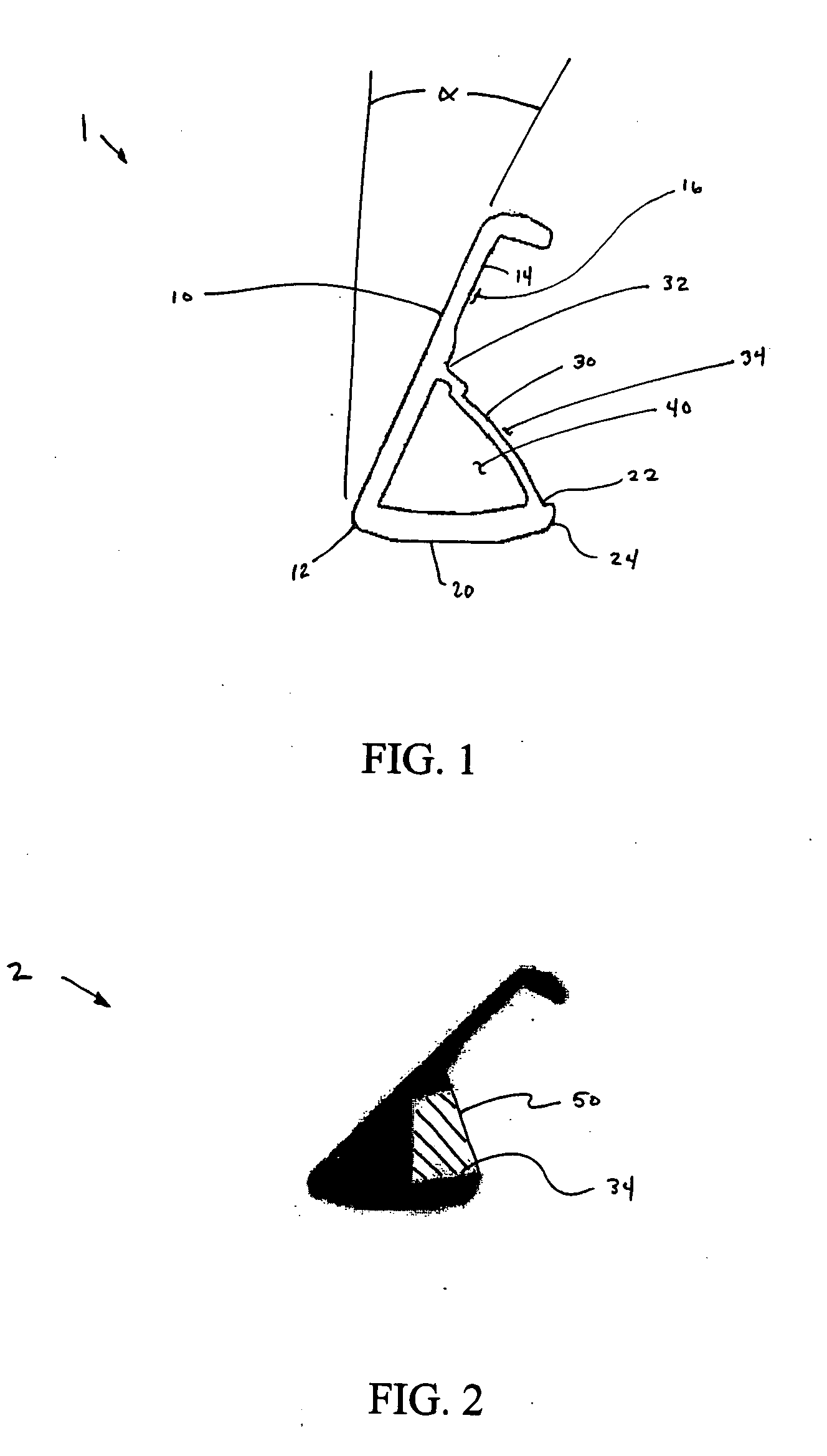
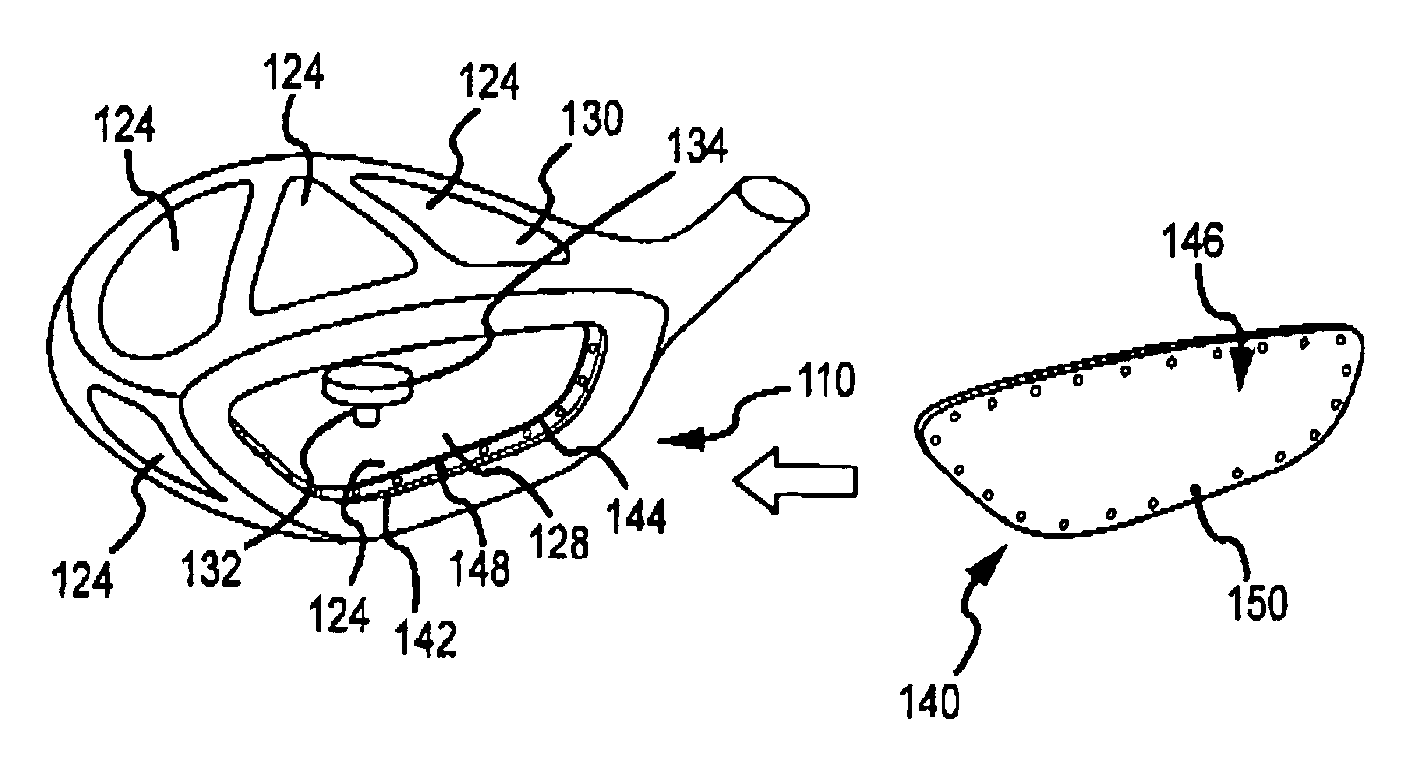
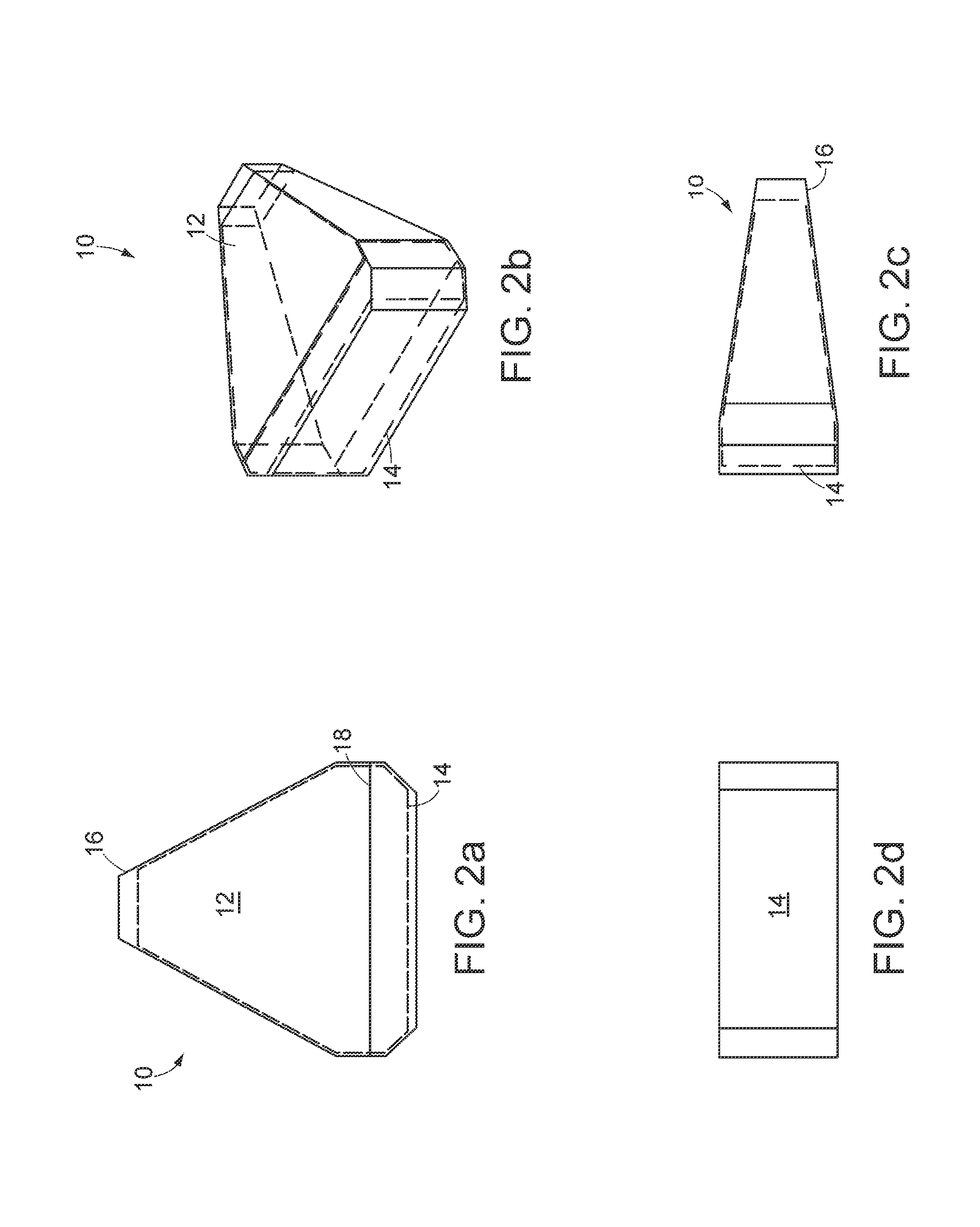
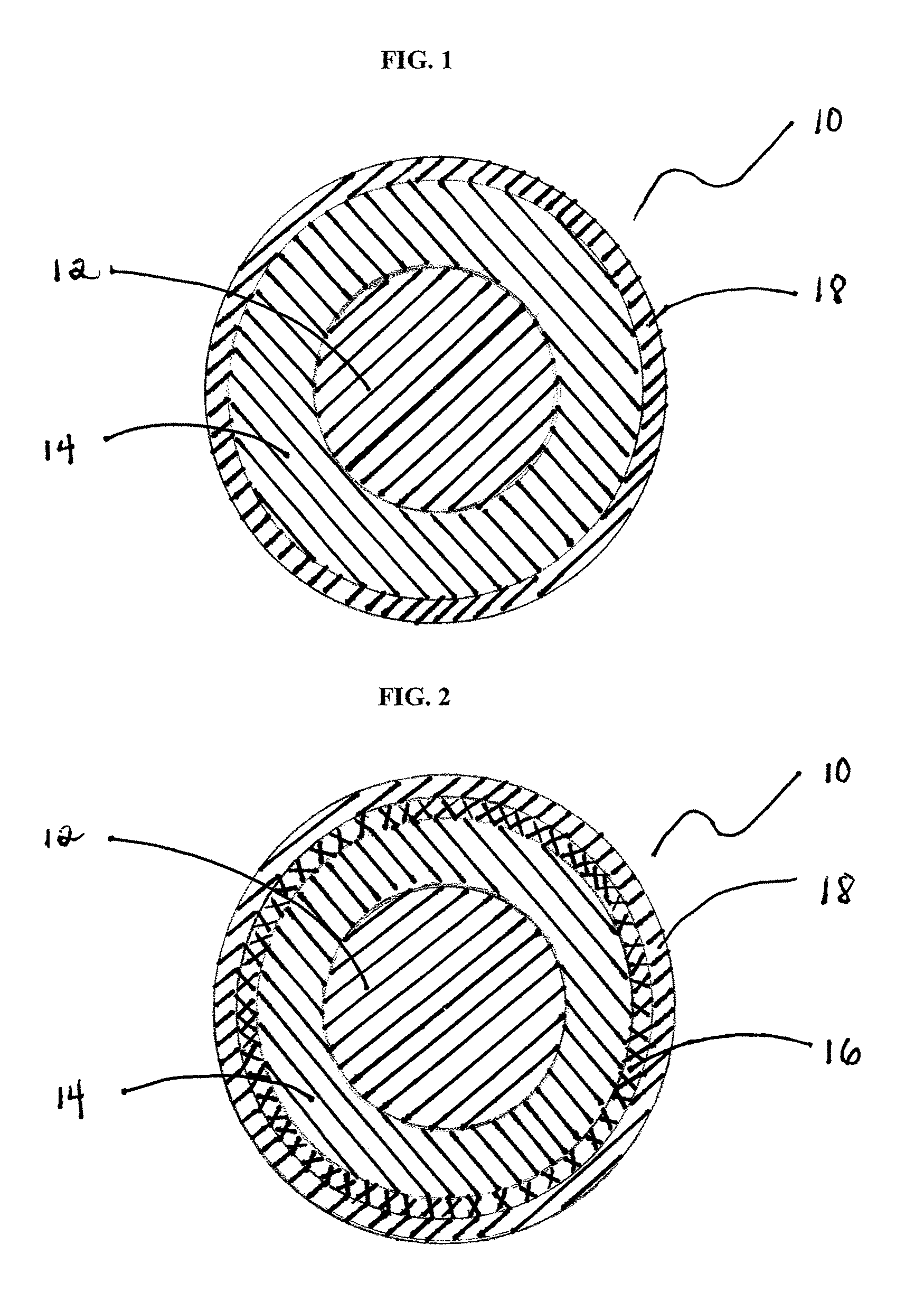
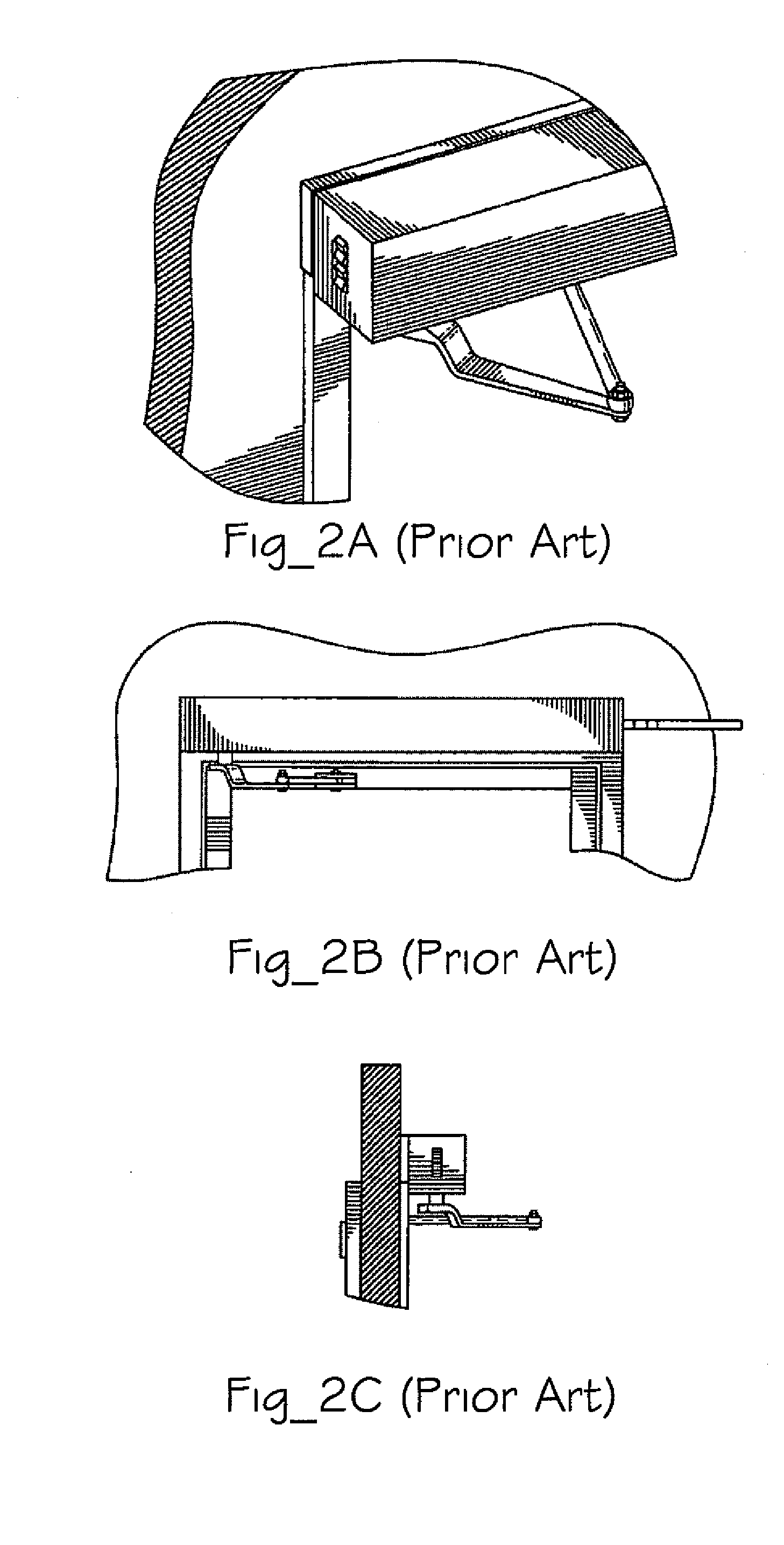
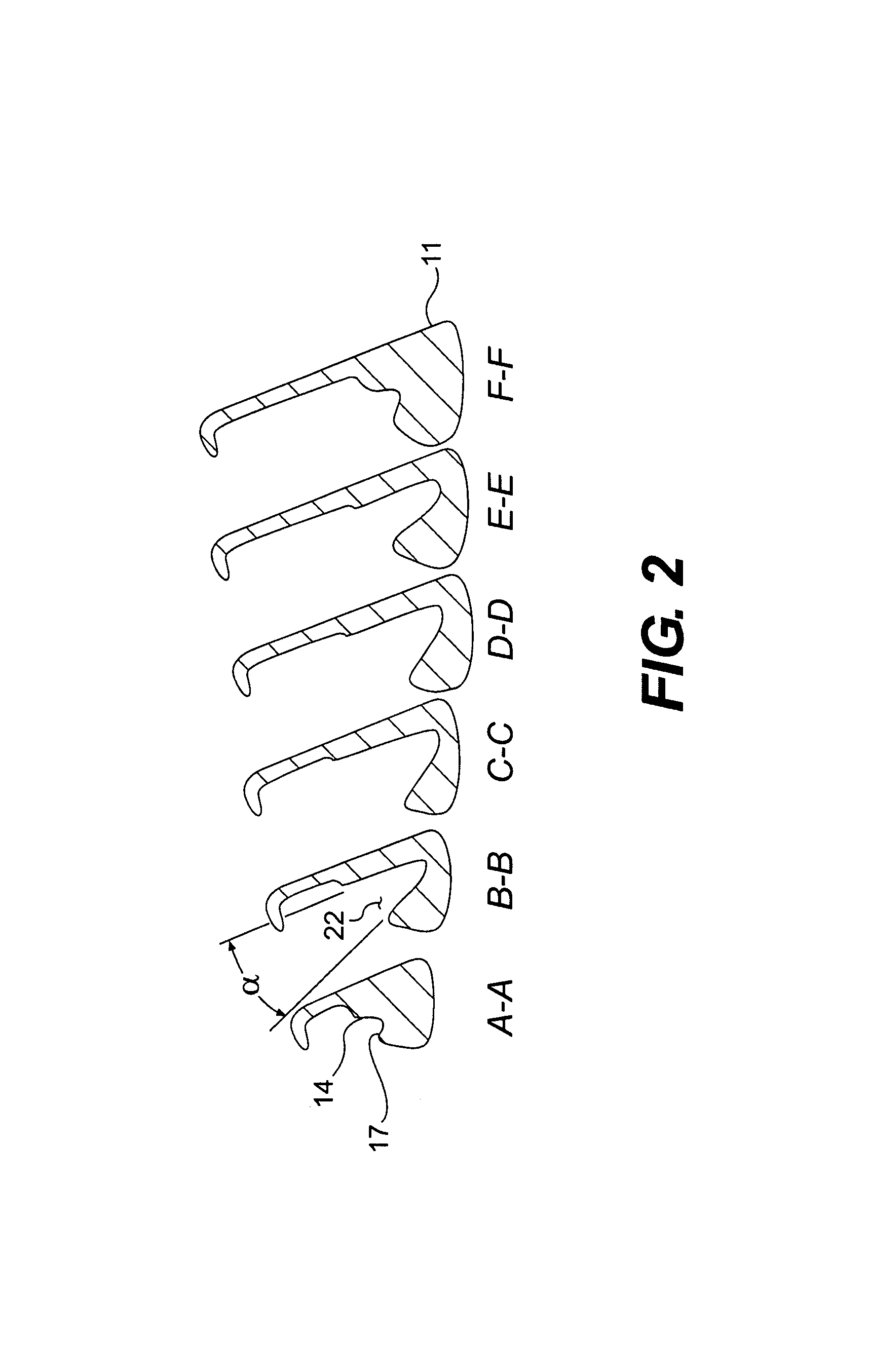
Articulation mechanism for medical devices
An improved articulating device for use with a medical insertion instrument comprising in part a first tube having a plurality of ribs defining a plurality of bending segments, a second tube axially disposed within the first tube, and means for transmitting an axial deflecting pull load. Such device has improved controlled for positioning an end of the device at a selected position within the body. The articulating device has a generally constant moment of inertia and a polar moment of inertia that generally decreases from its proximal to distal end.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
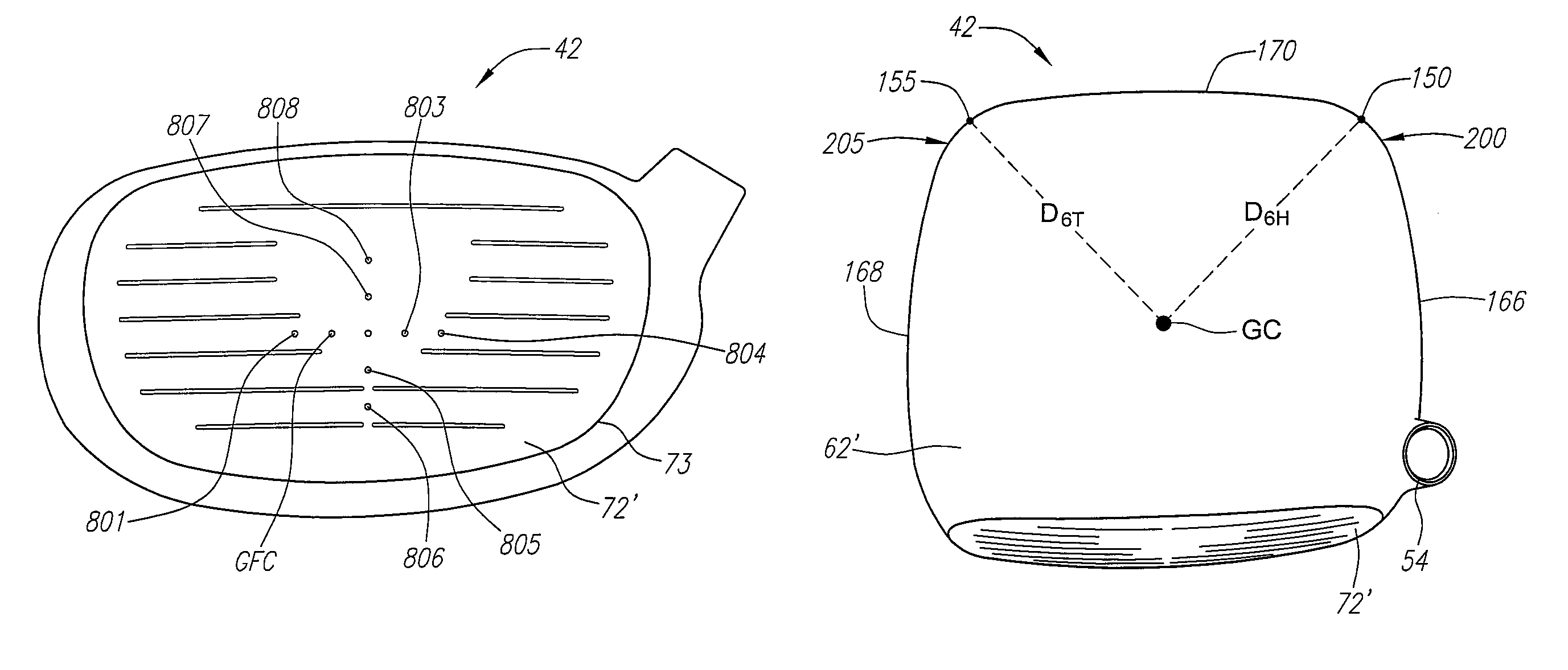
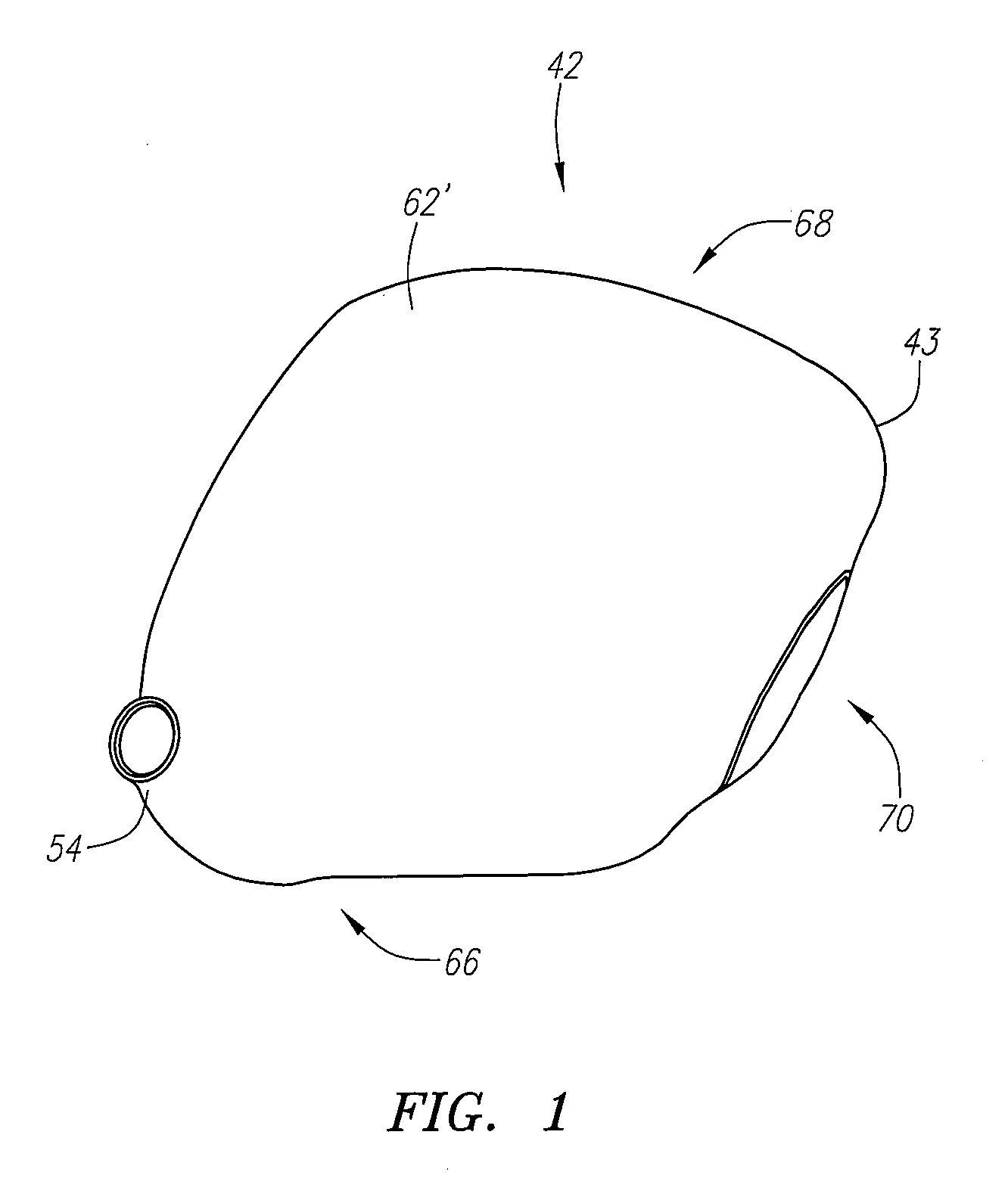
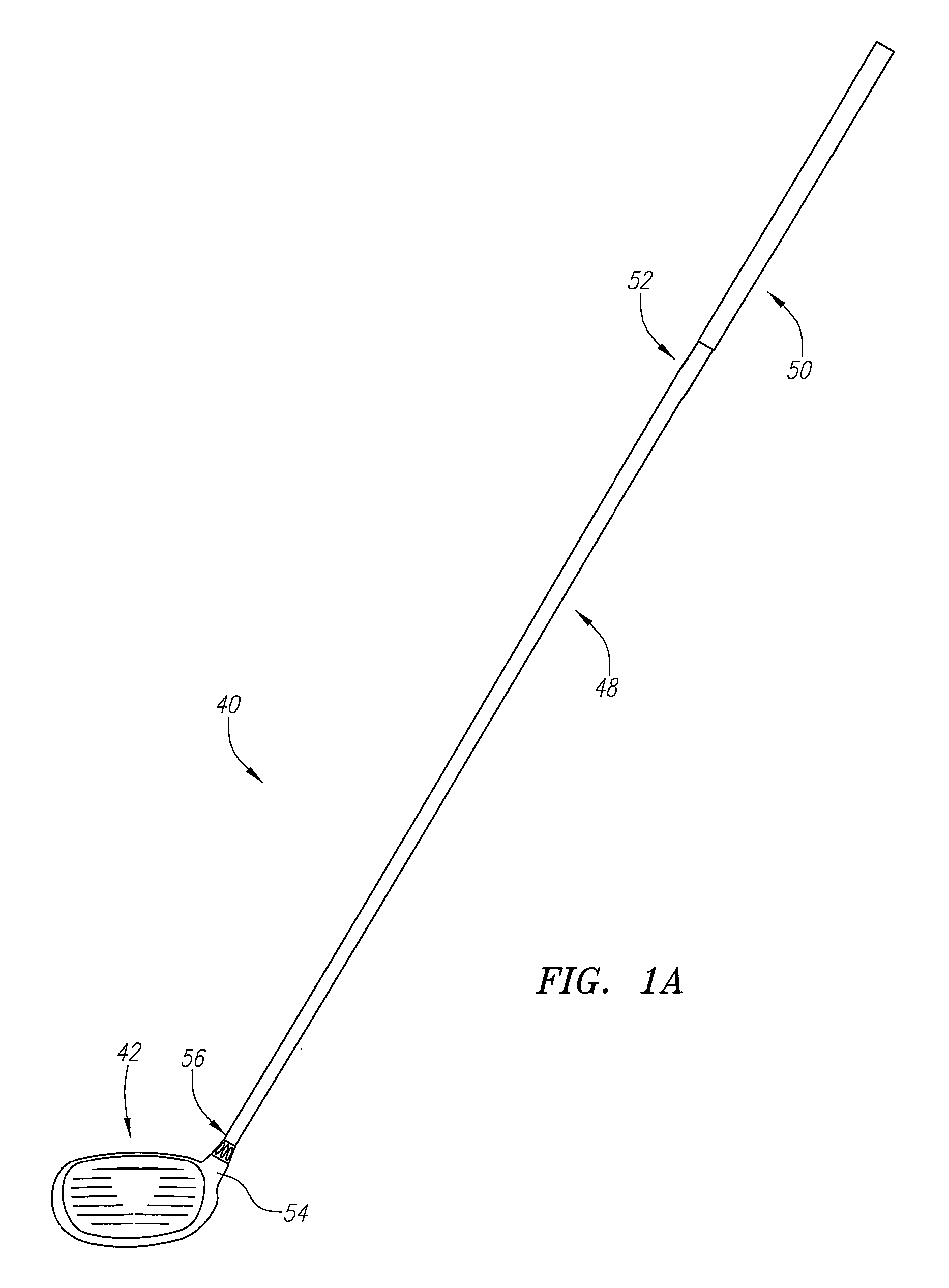
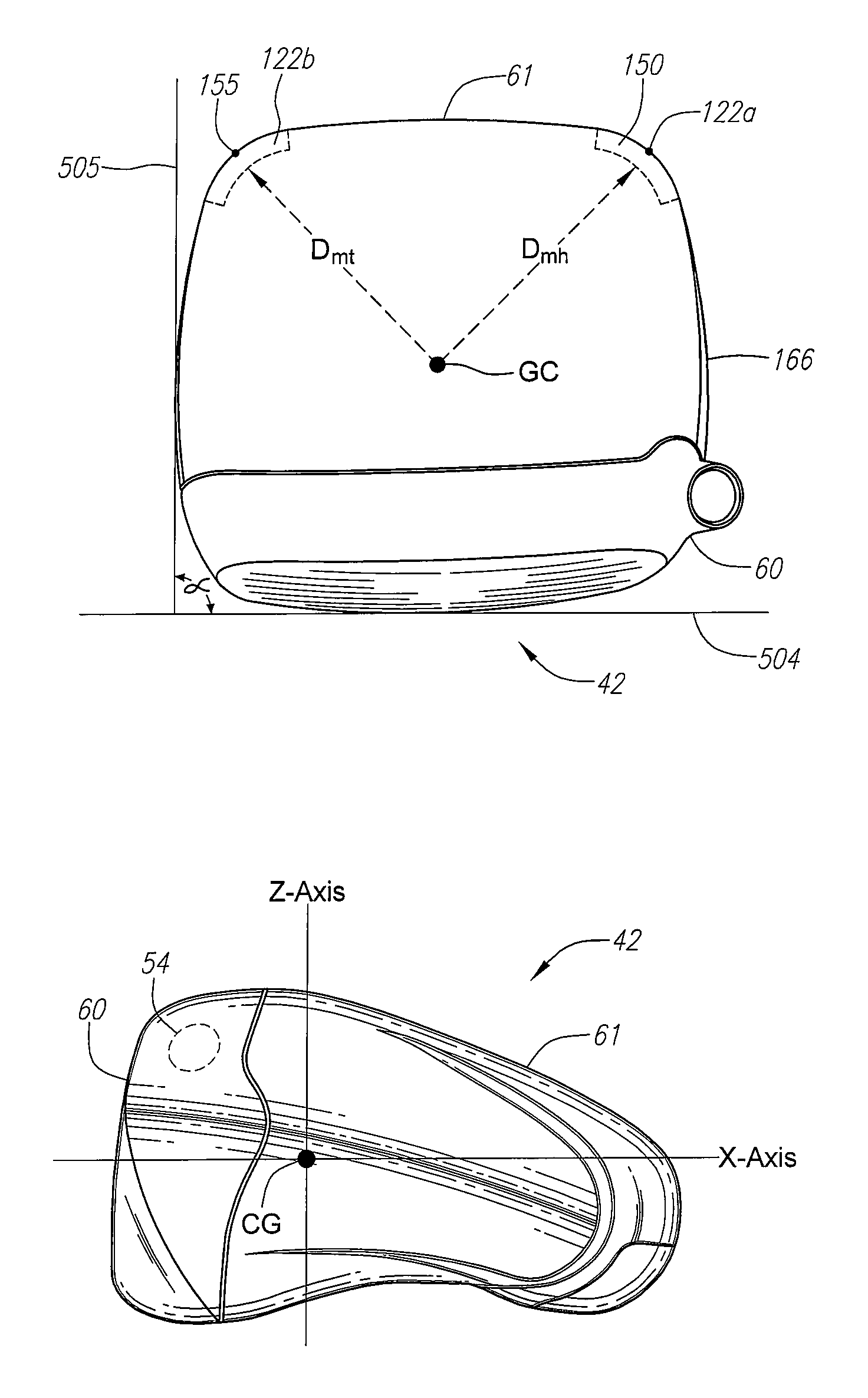
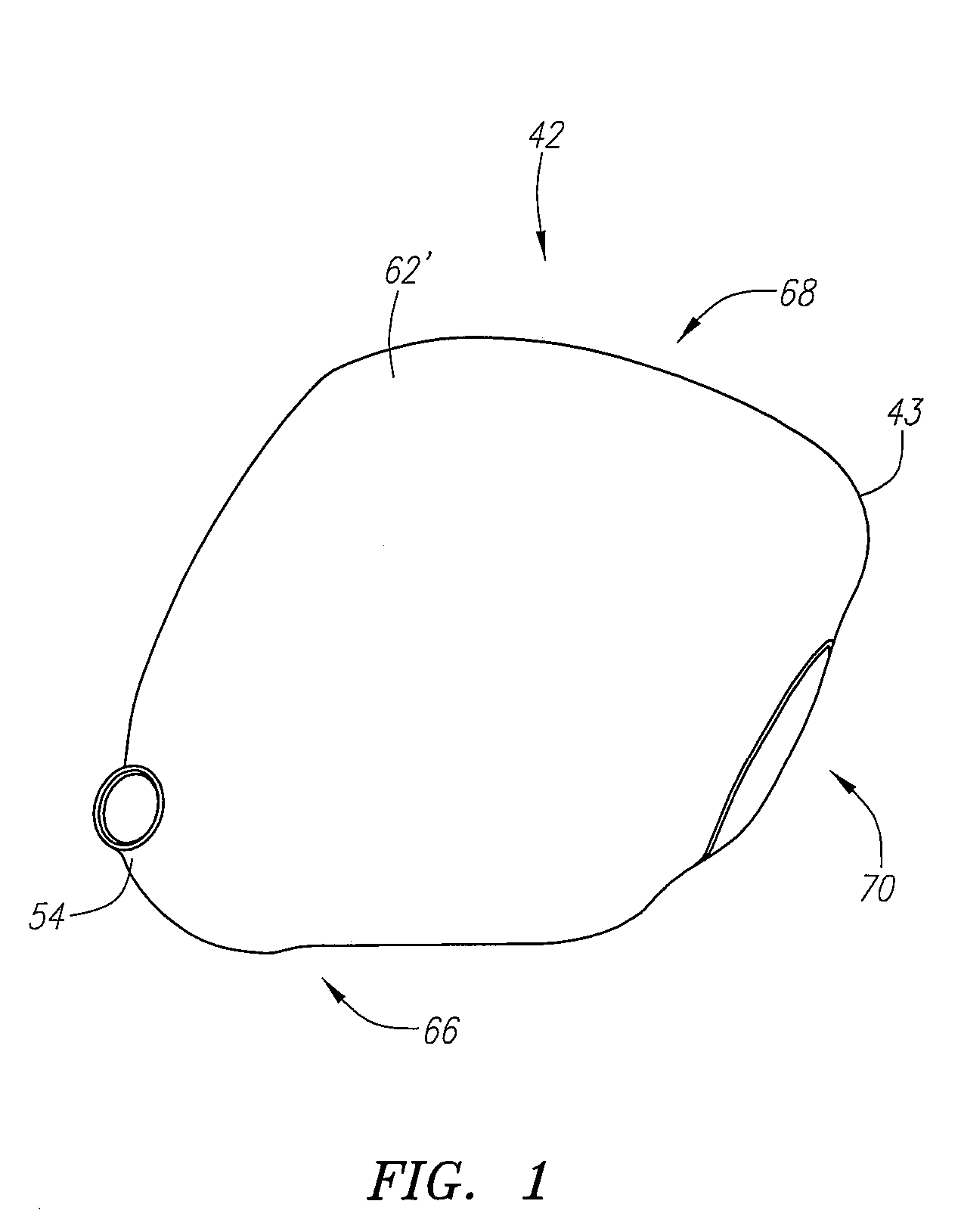
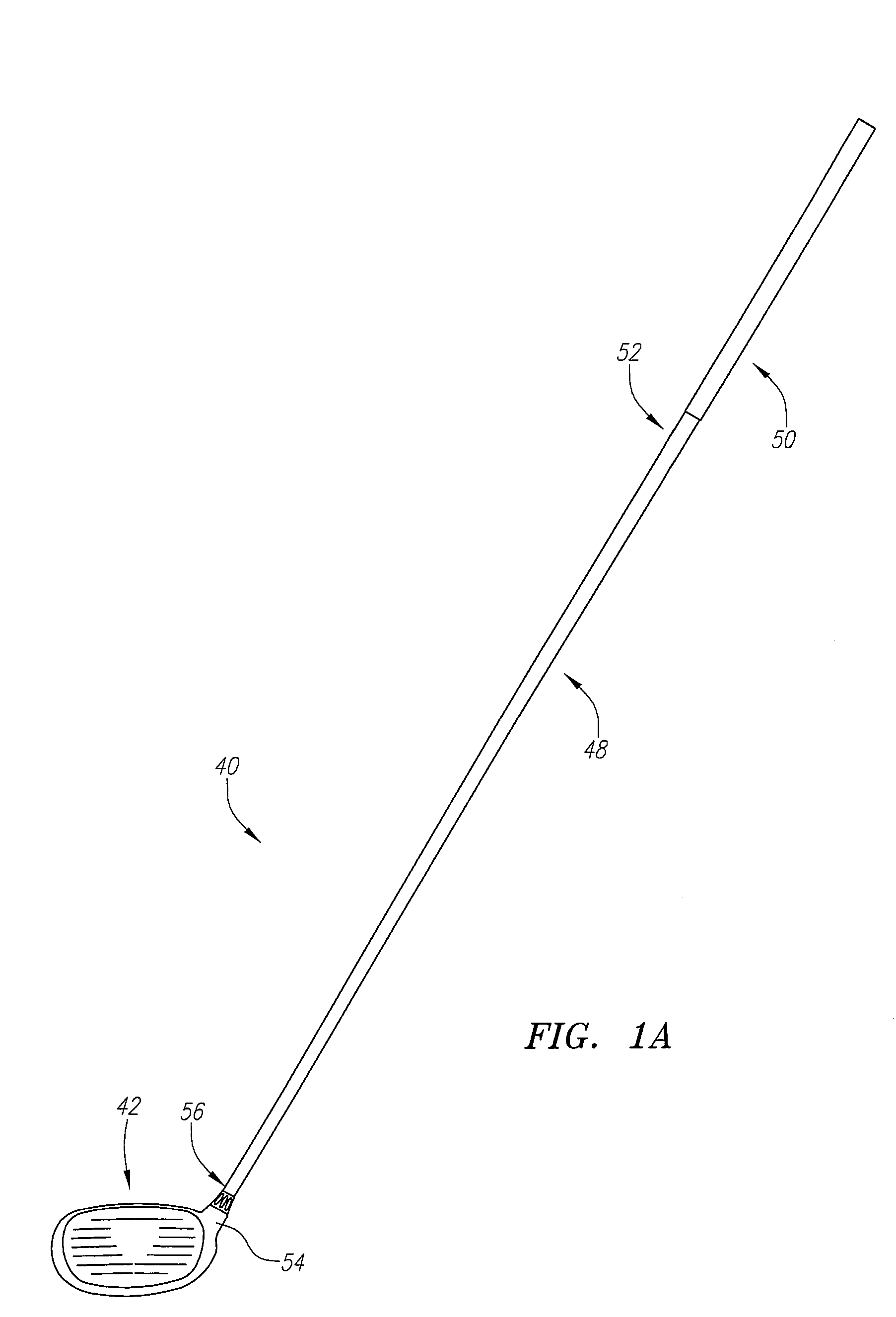
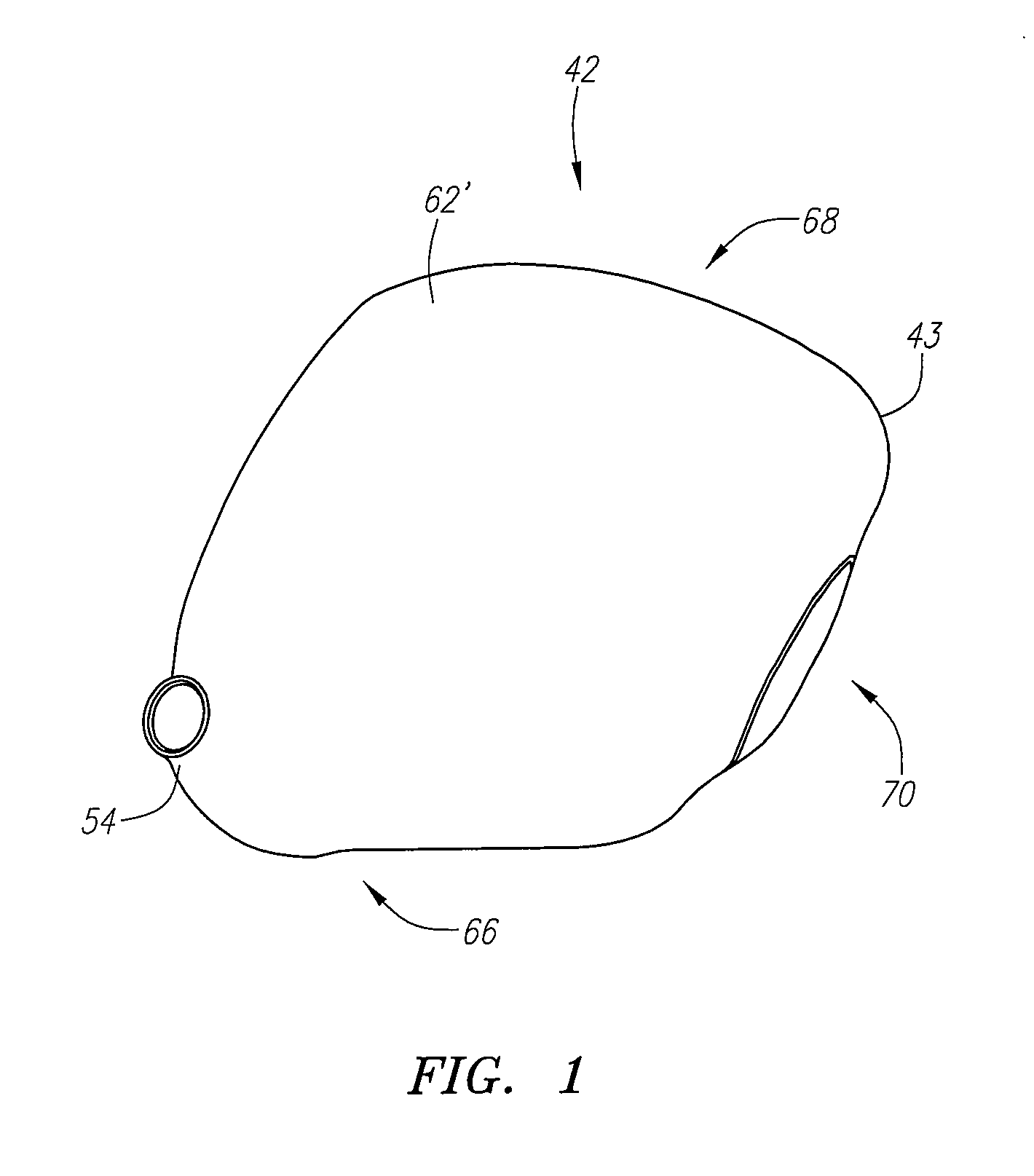
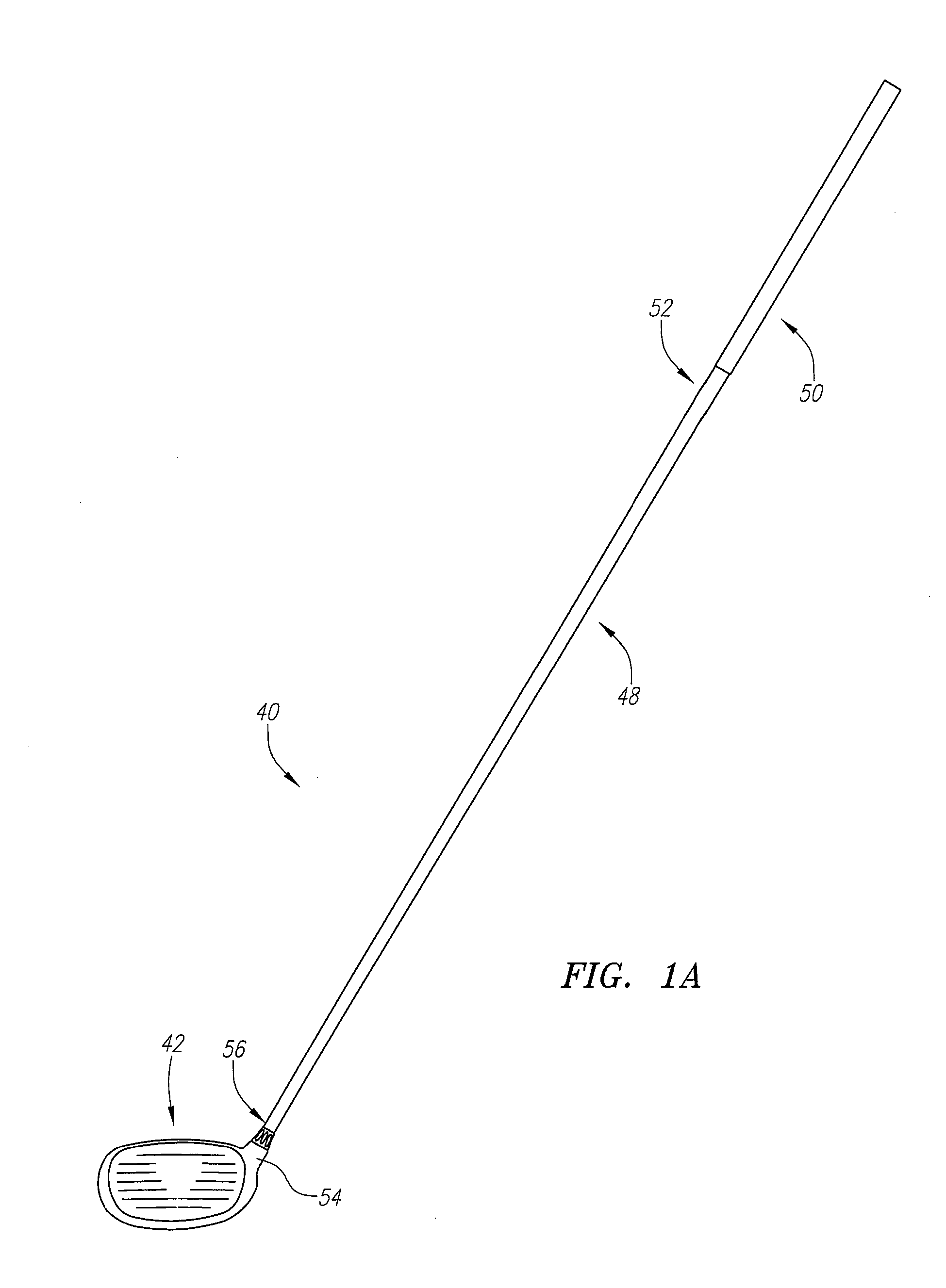
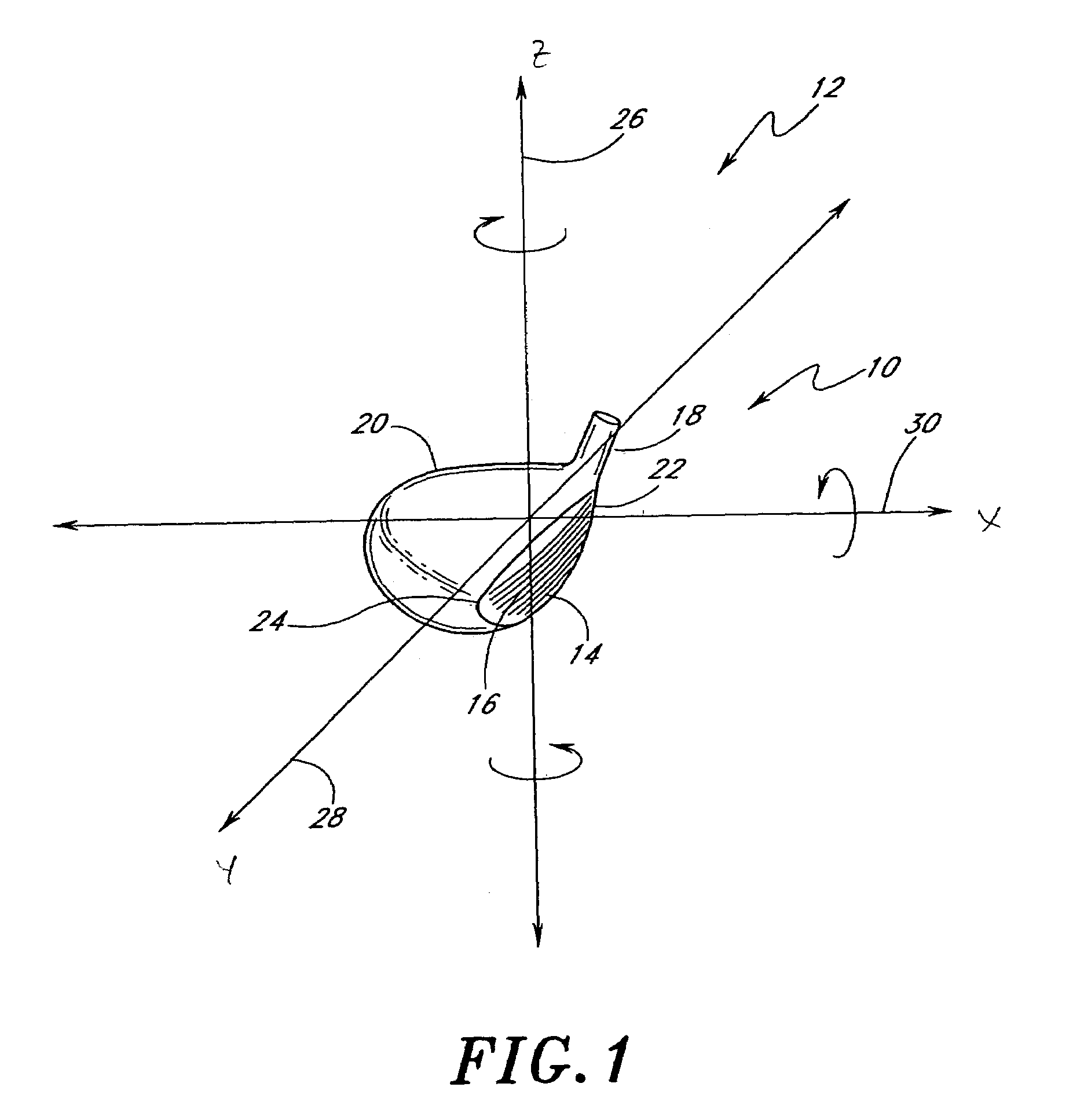
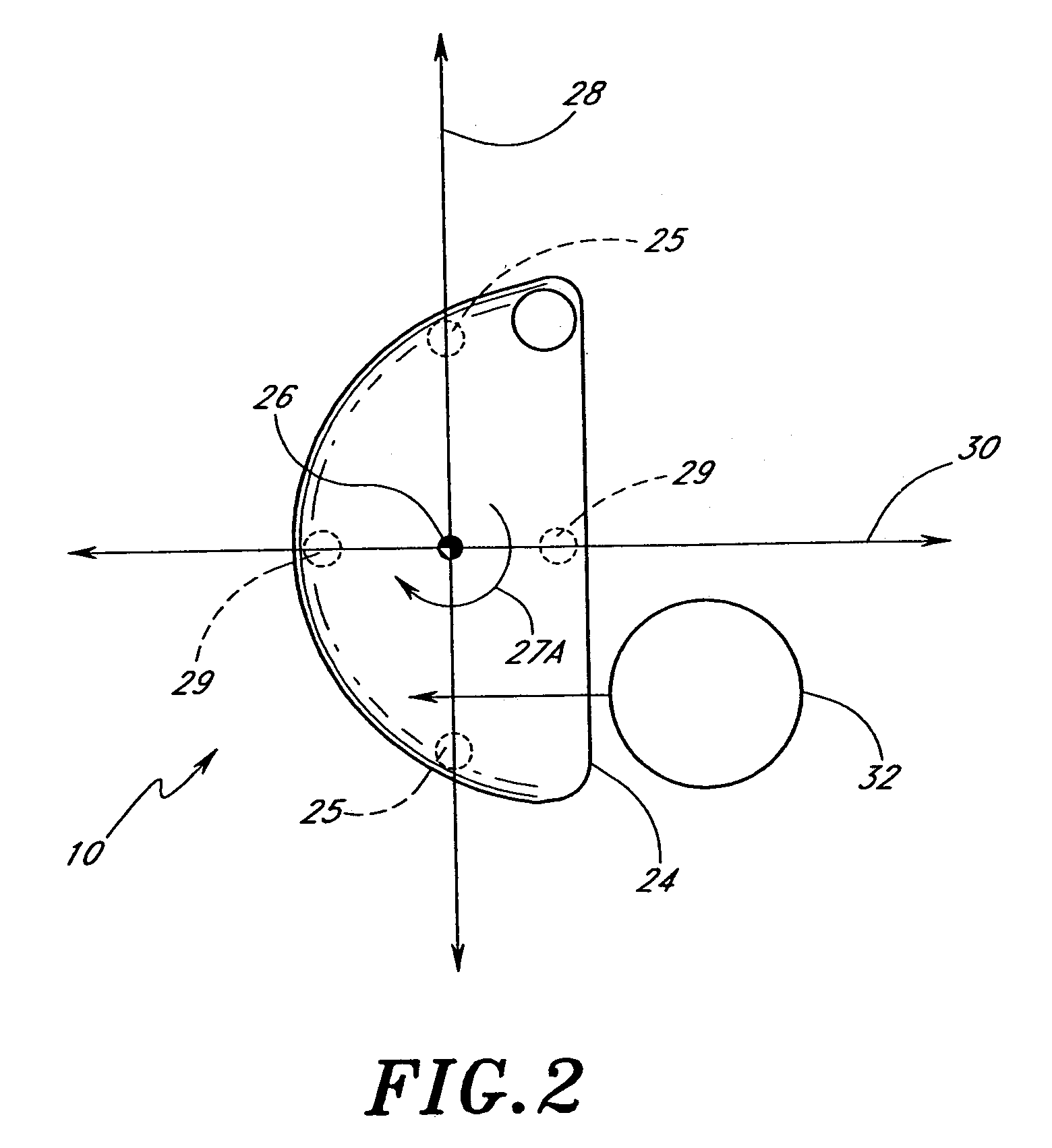
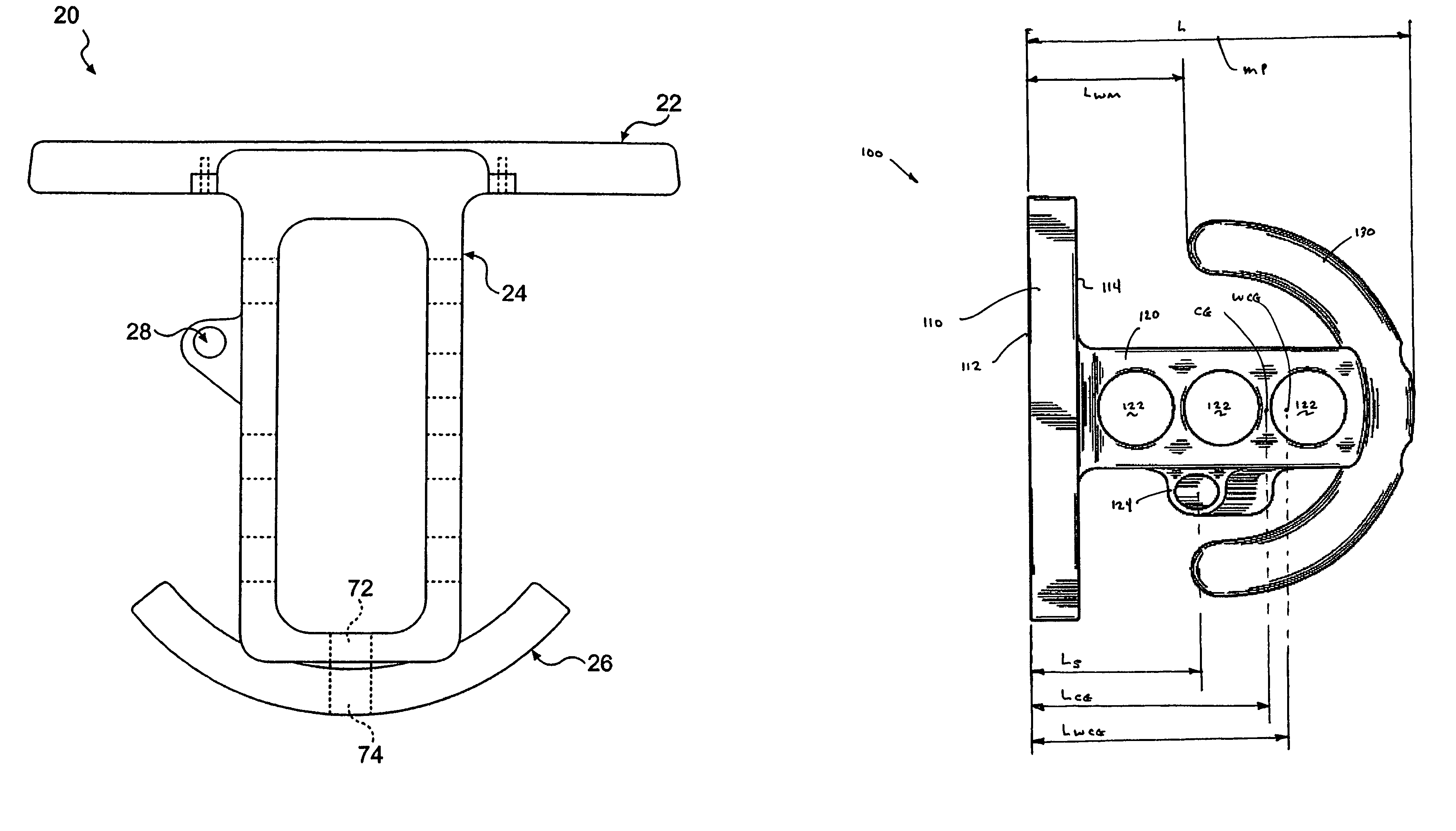
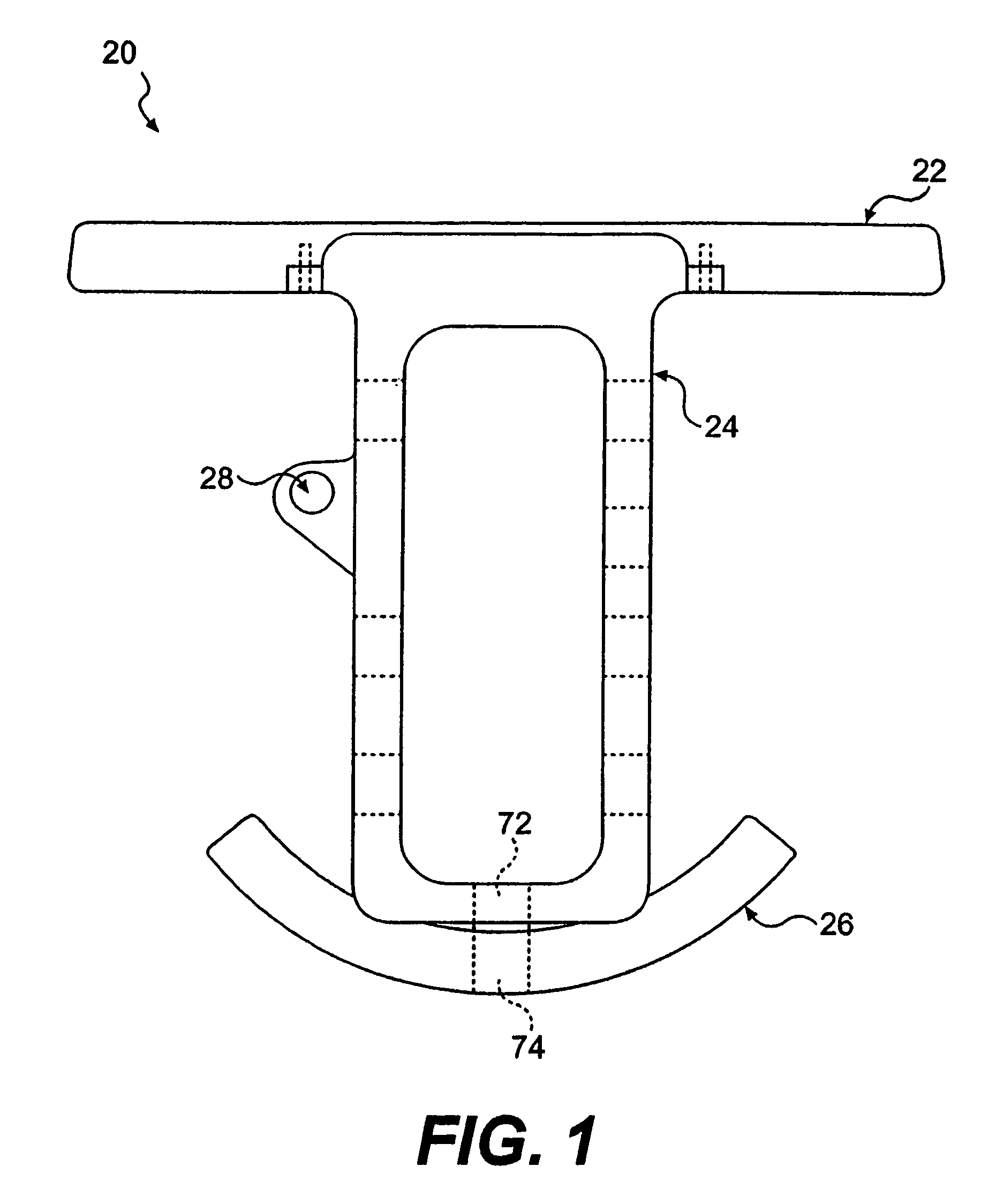
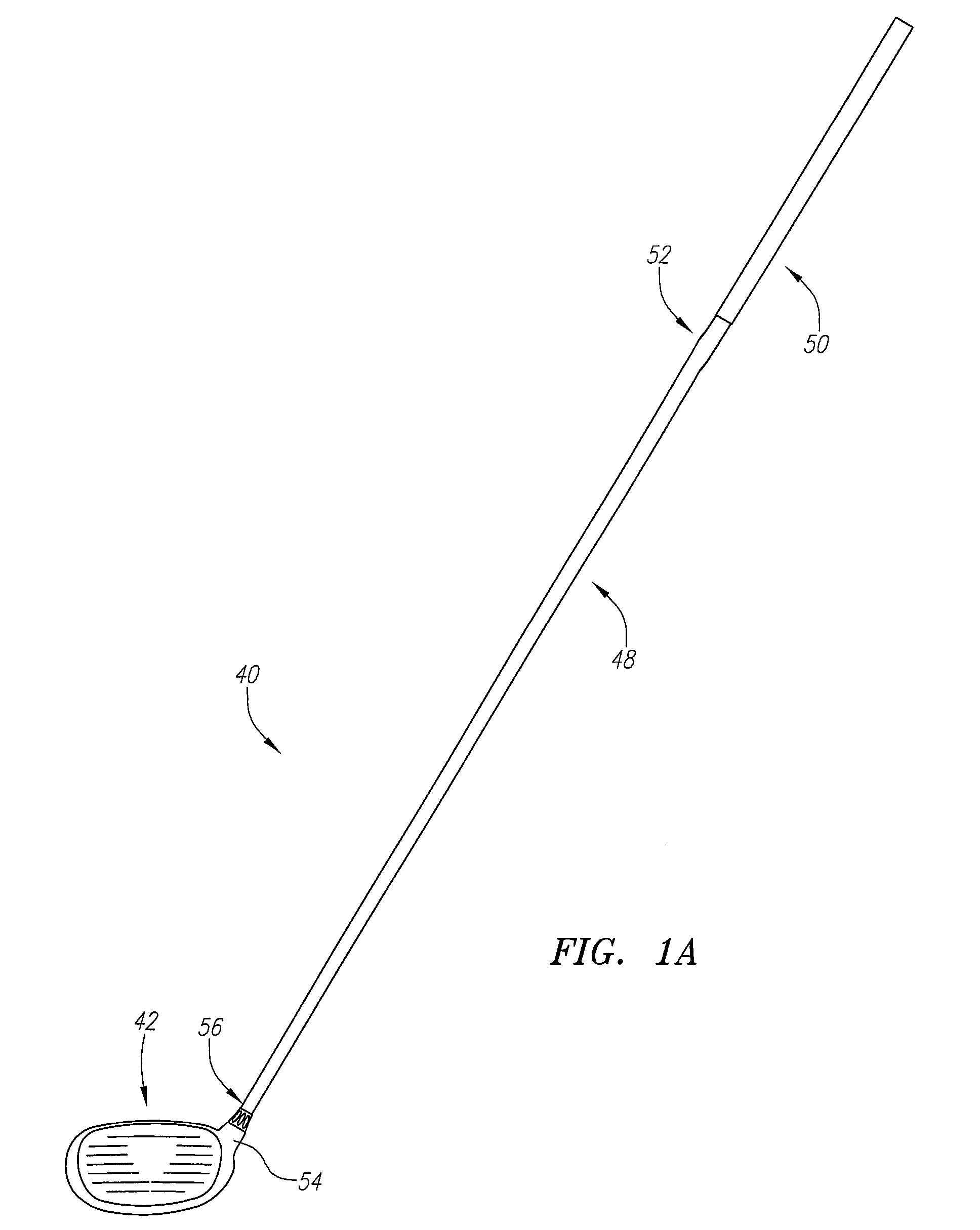
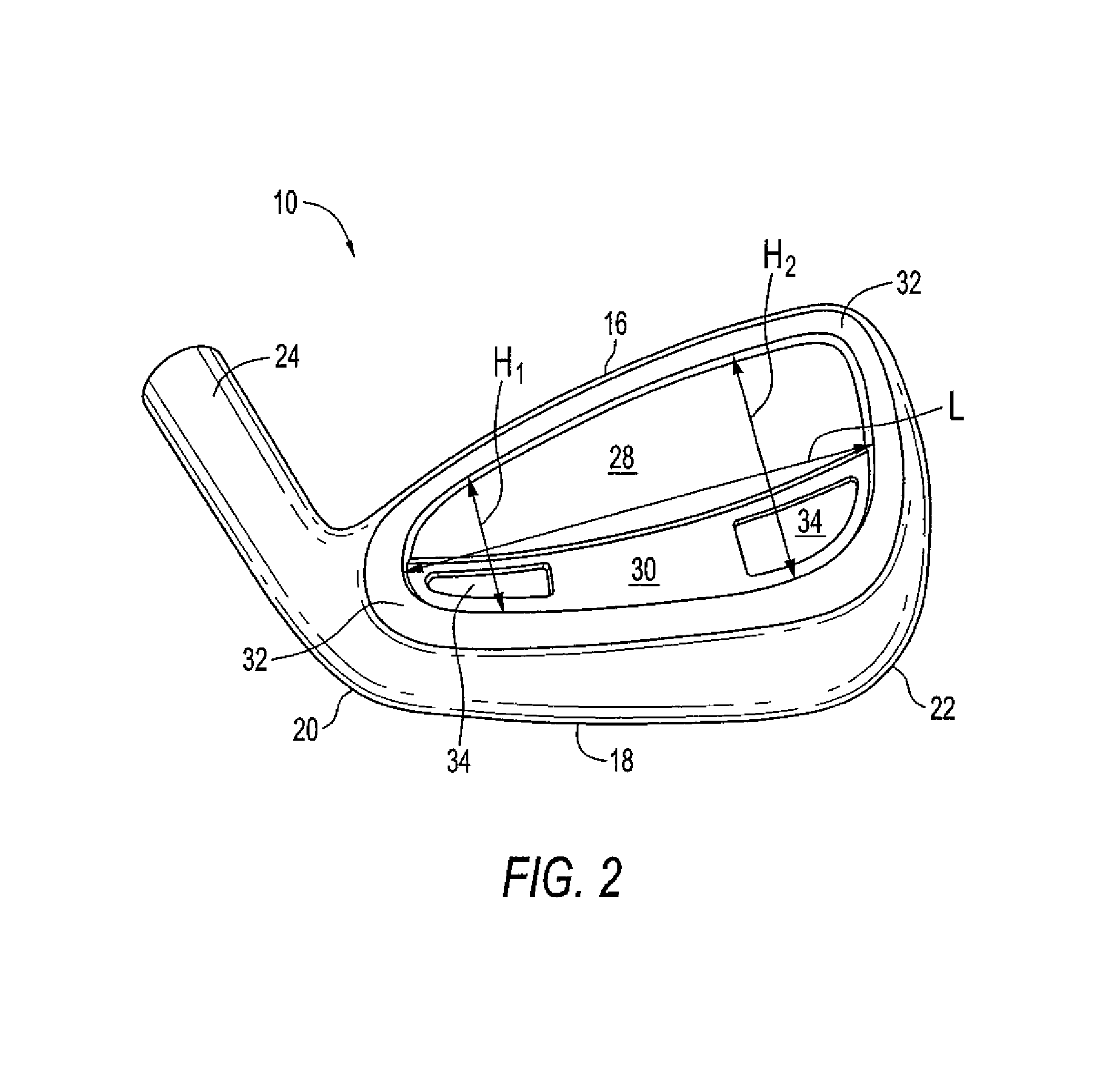
Golf club head
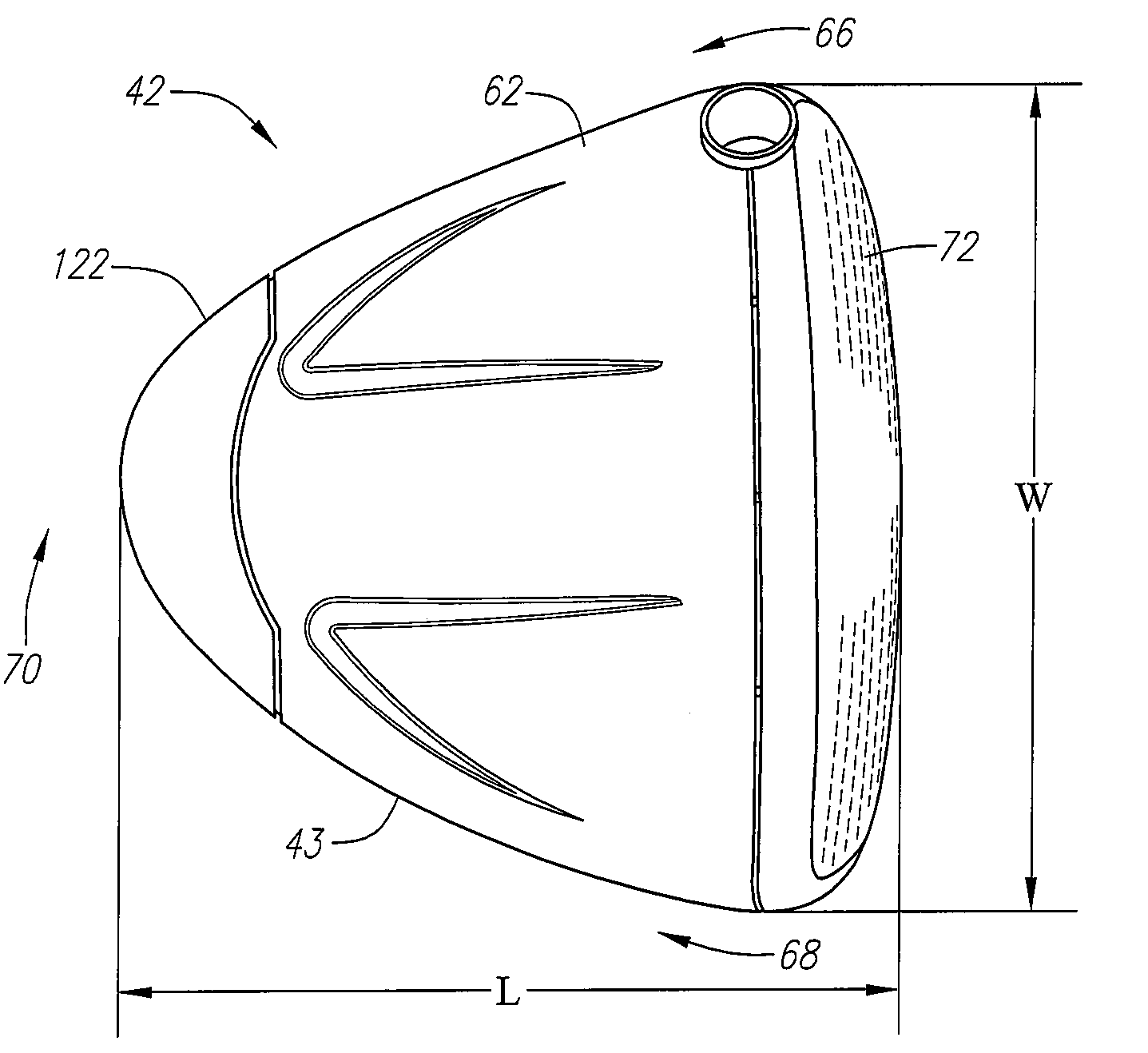
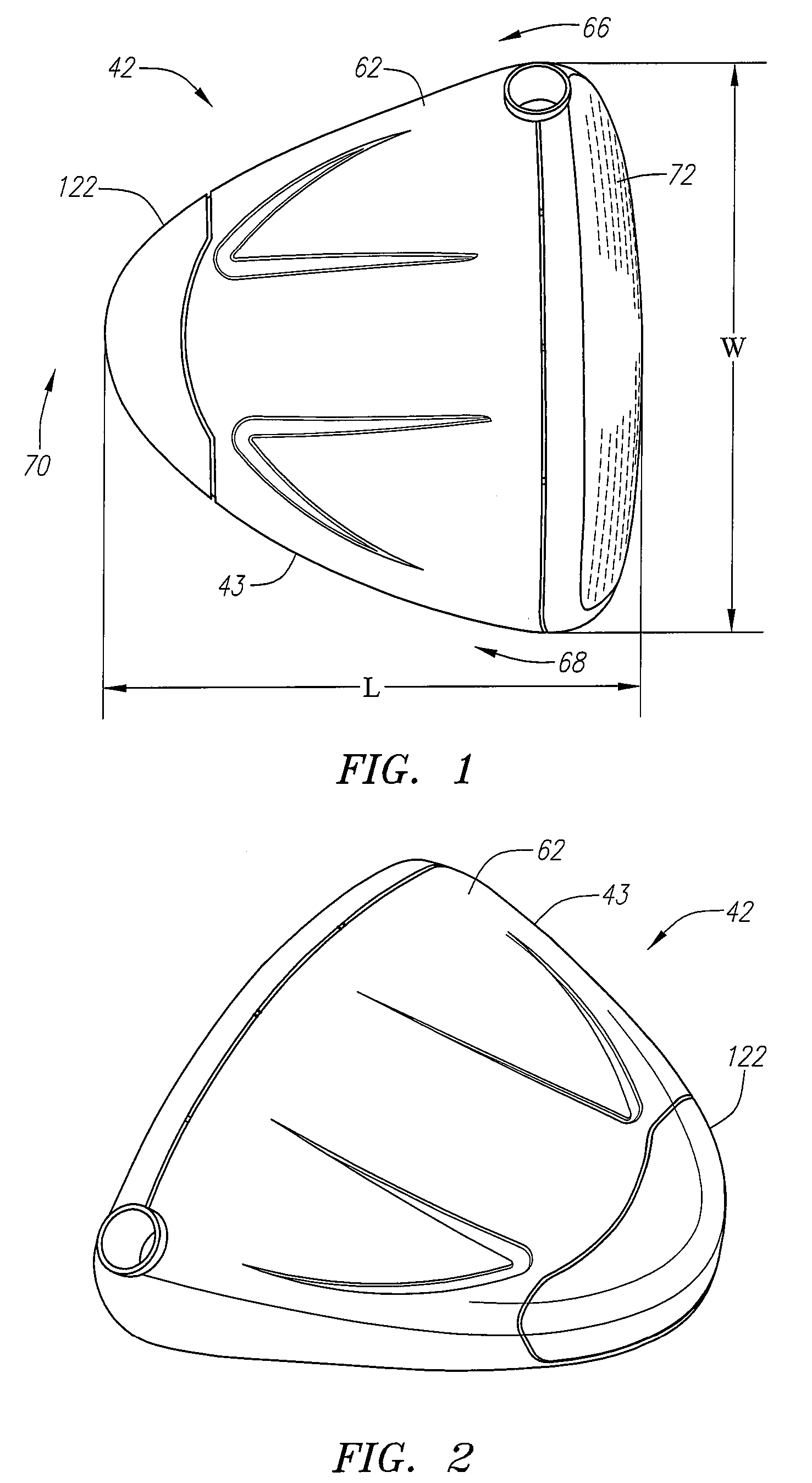
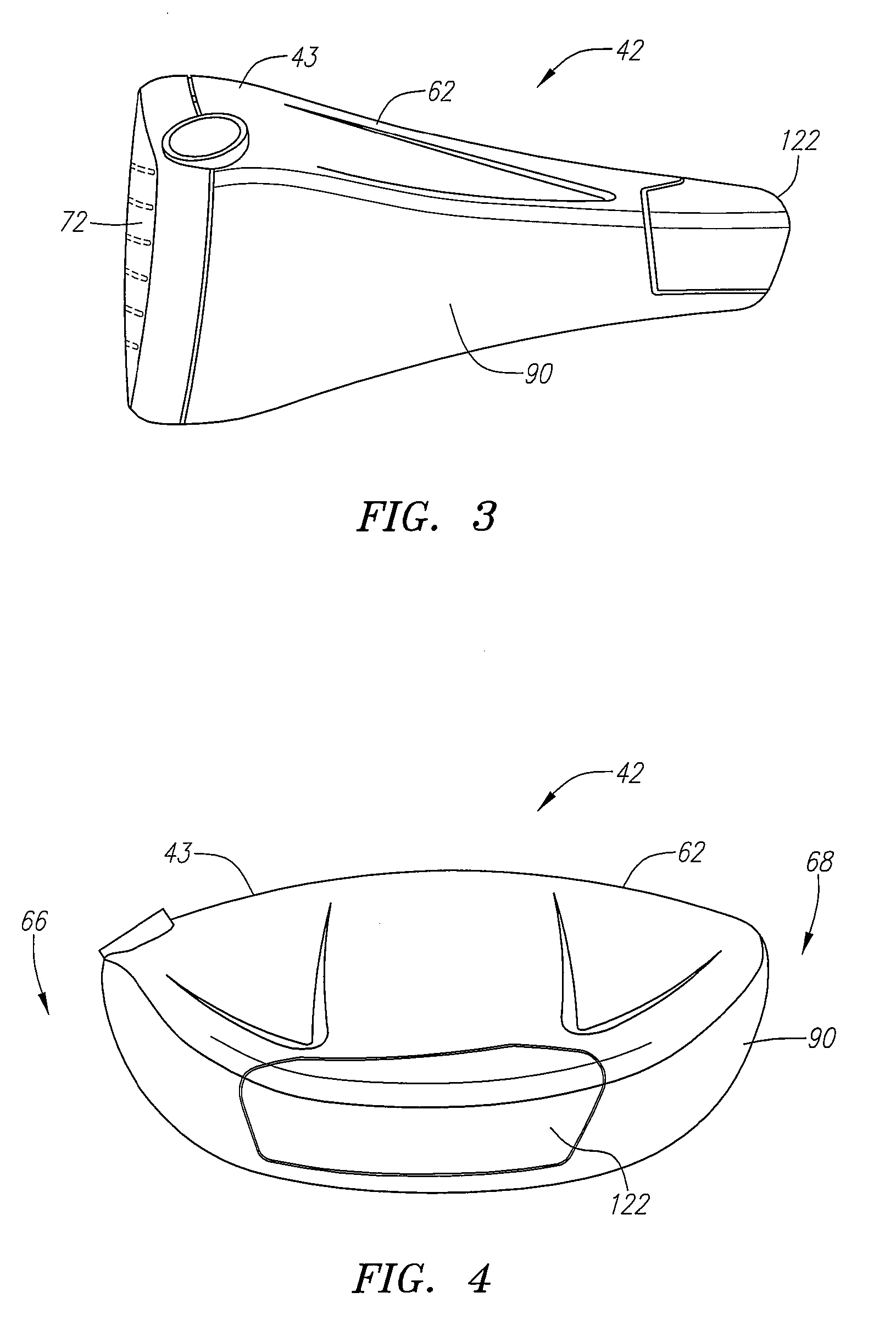
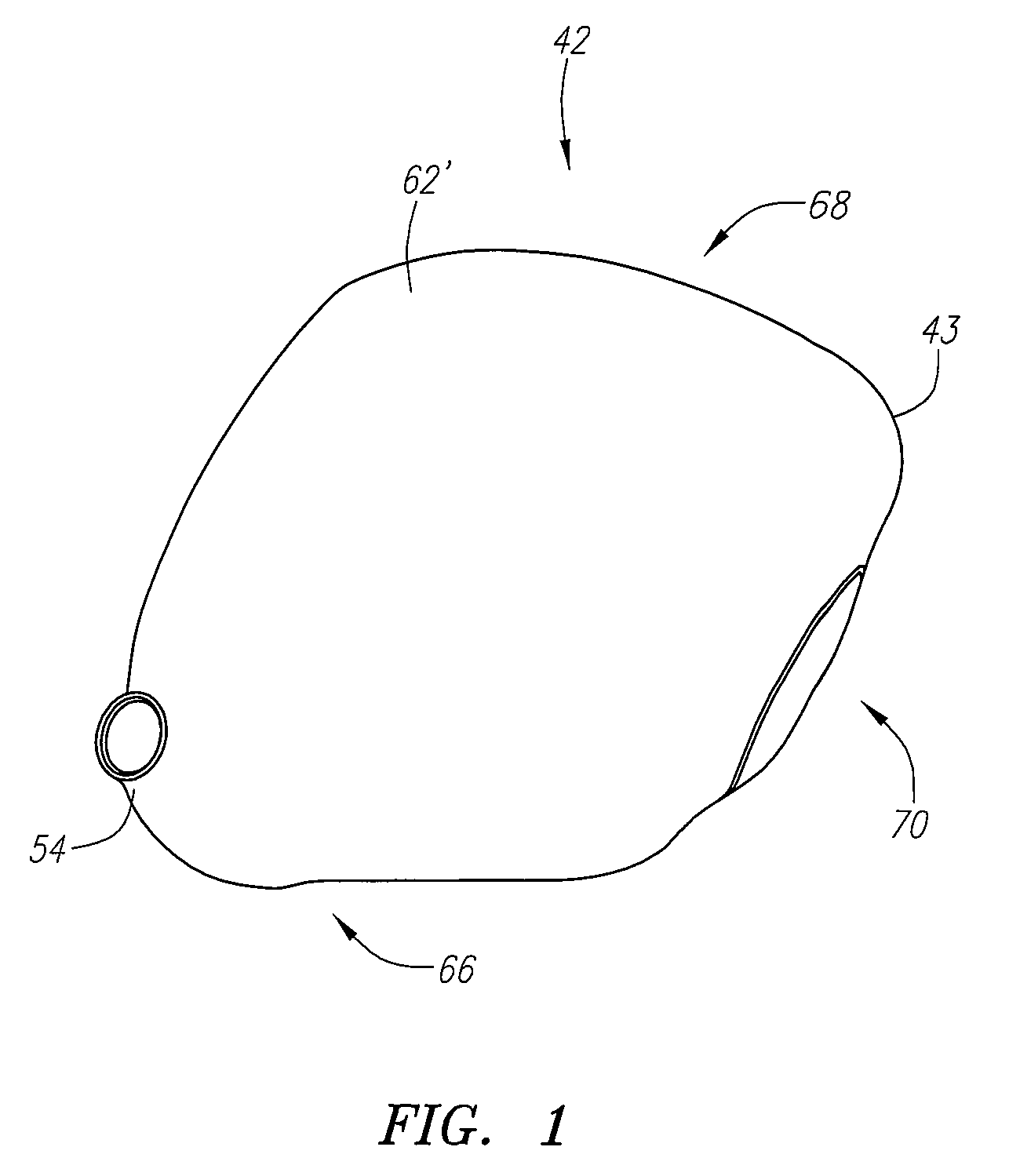
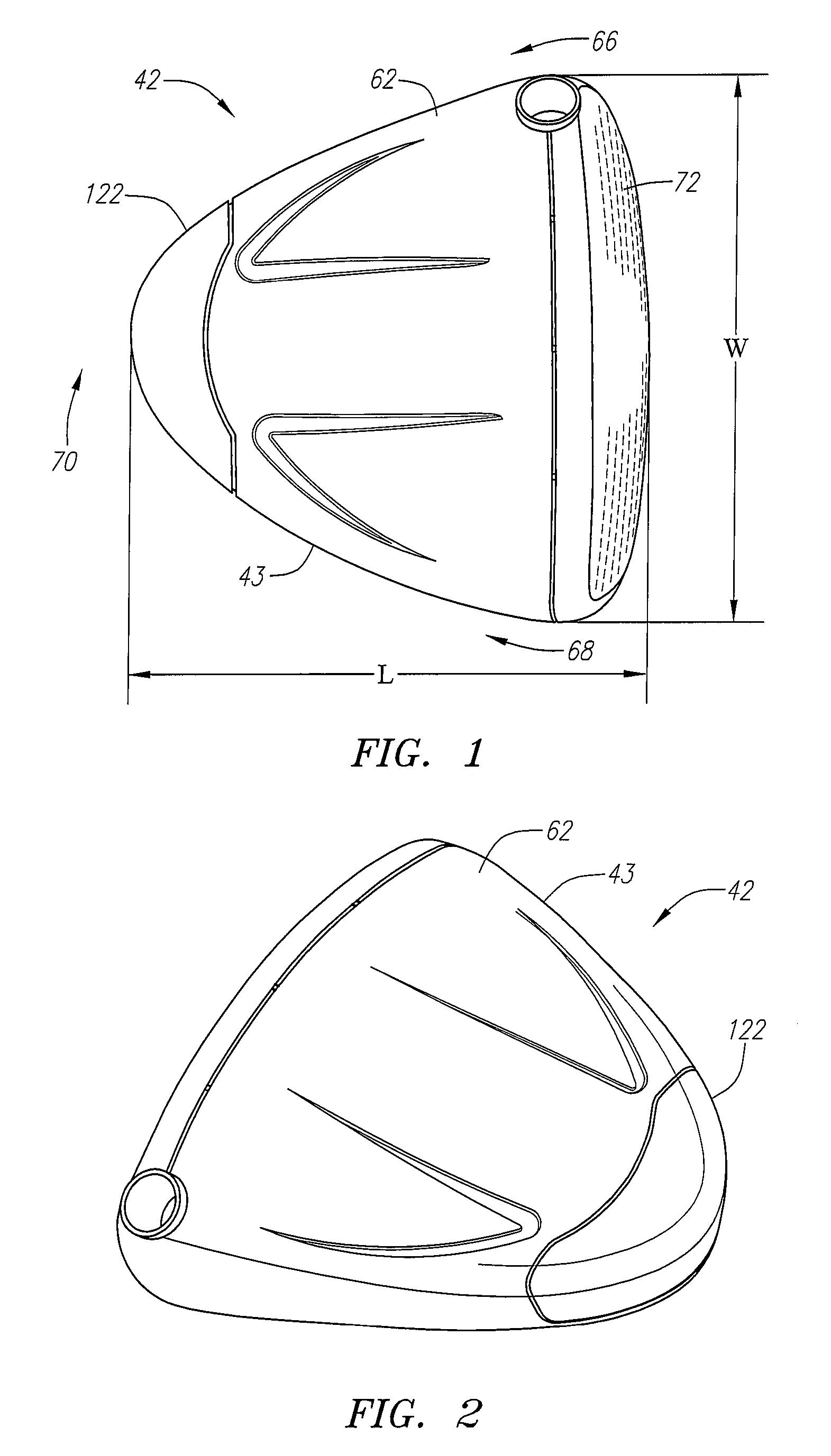
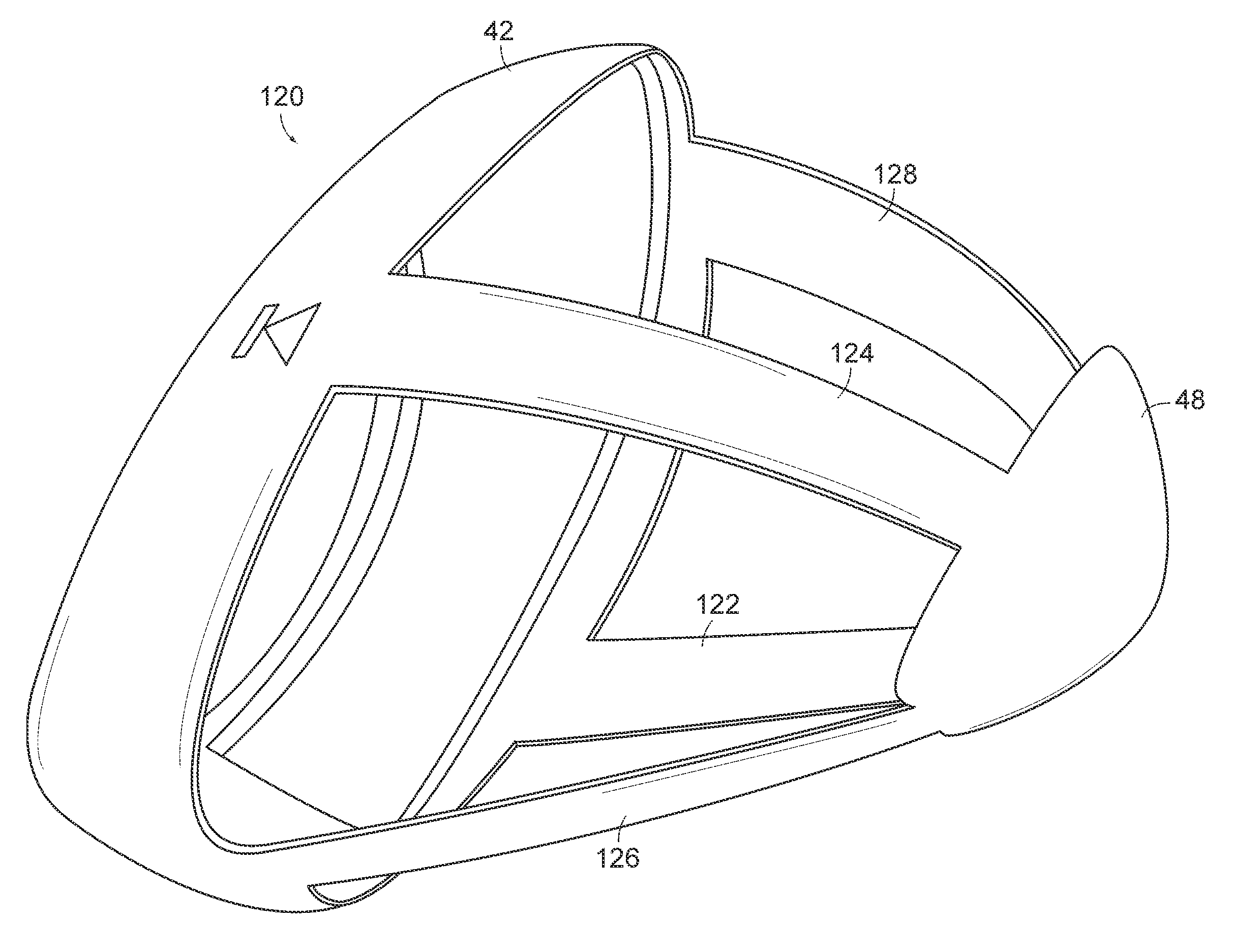
A golf club head (42) having a standard deviation of coefficient of restitution of less than 0.226 is disclosed herein. The golf club head (42) also preferably has a delta of the coefficient of restitution between a geometric face center of the face (72) and a location (806) 0.5 inch sole-ward from the face center that is less than 0.065. The golf club head (42) preferably has a volume ranging from 420 cubic centimeters to 470 cubic centimeters. The golf club head (42) preferably has a moment of inertia about the Izz axis through the center of gravity of the golf club head greater than 4000 grams-centimeters squared, and a moment of inertia about the Ixx axis through the center of gravity of the golf club head greater than 3000 grams-centimeters squared.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Golf club head
A golf club head (42) having a substantially square or rectangular body is disclosed herein. The golf club head (42) preferably has a volume ranging from 420 cubic centimeters to 470 cubic centimeters. The golf club head (42) preferably has a moment of inertia about the Izz axis through the center of gravity of the golf club head greater than 4000 grams-centimeters squared, and a moment of inertia about the Ixx axis through the center of gravity of the golf club head greater than 3000 grams-centimeters squared.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Golf club head
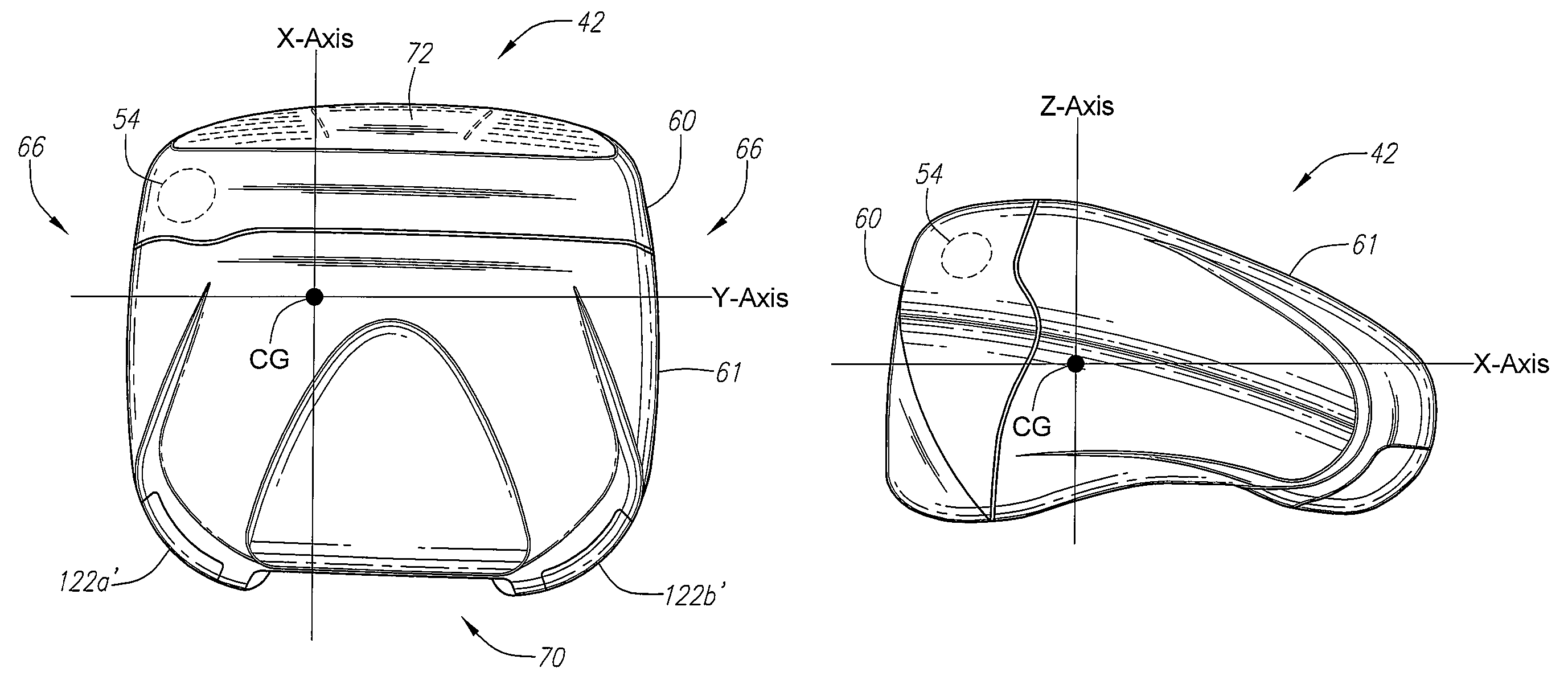
A club head for a golf club comprises a strike face and an outer shell. The strike face and the outer shell define a head volume of the club head. The club head has a first axis that extends generally horizontally and parallel to the strike face, a first moment of inertia about the first axis, a second axis that lies generally vertically and perpendicular to the first horizontal axis, a second moment of inertia about the second axis, and a center of gravity lying below a horizontal centerline of the club head. The first moment of inertia in units of kg-mm2 is greater than or equal to approximately 77 plus 0.46 times the head volume in units of cm3.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Golf club with adjustable center of gravity head
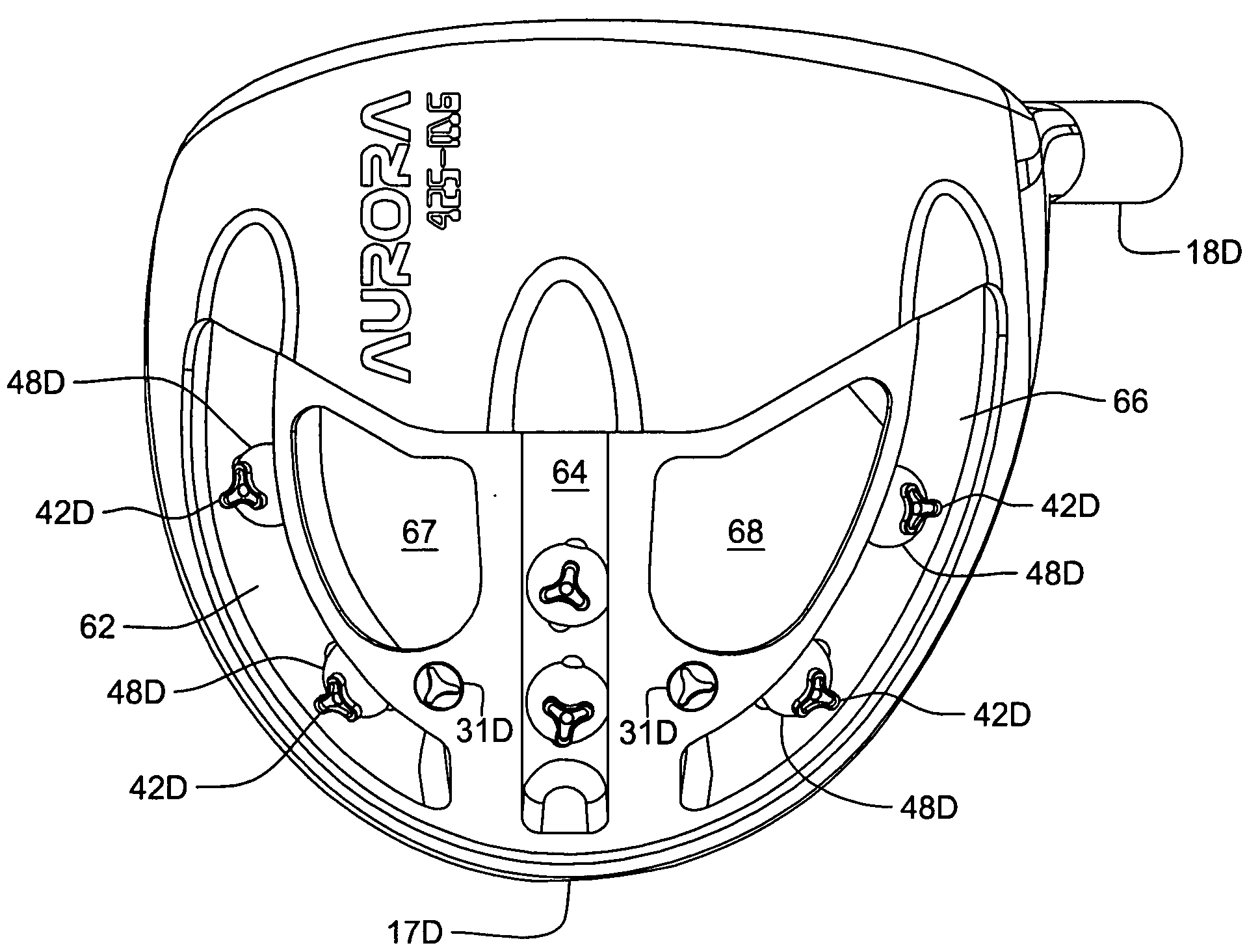
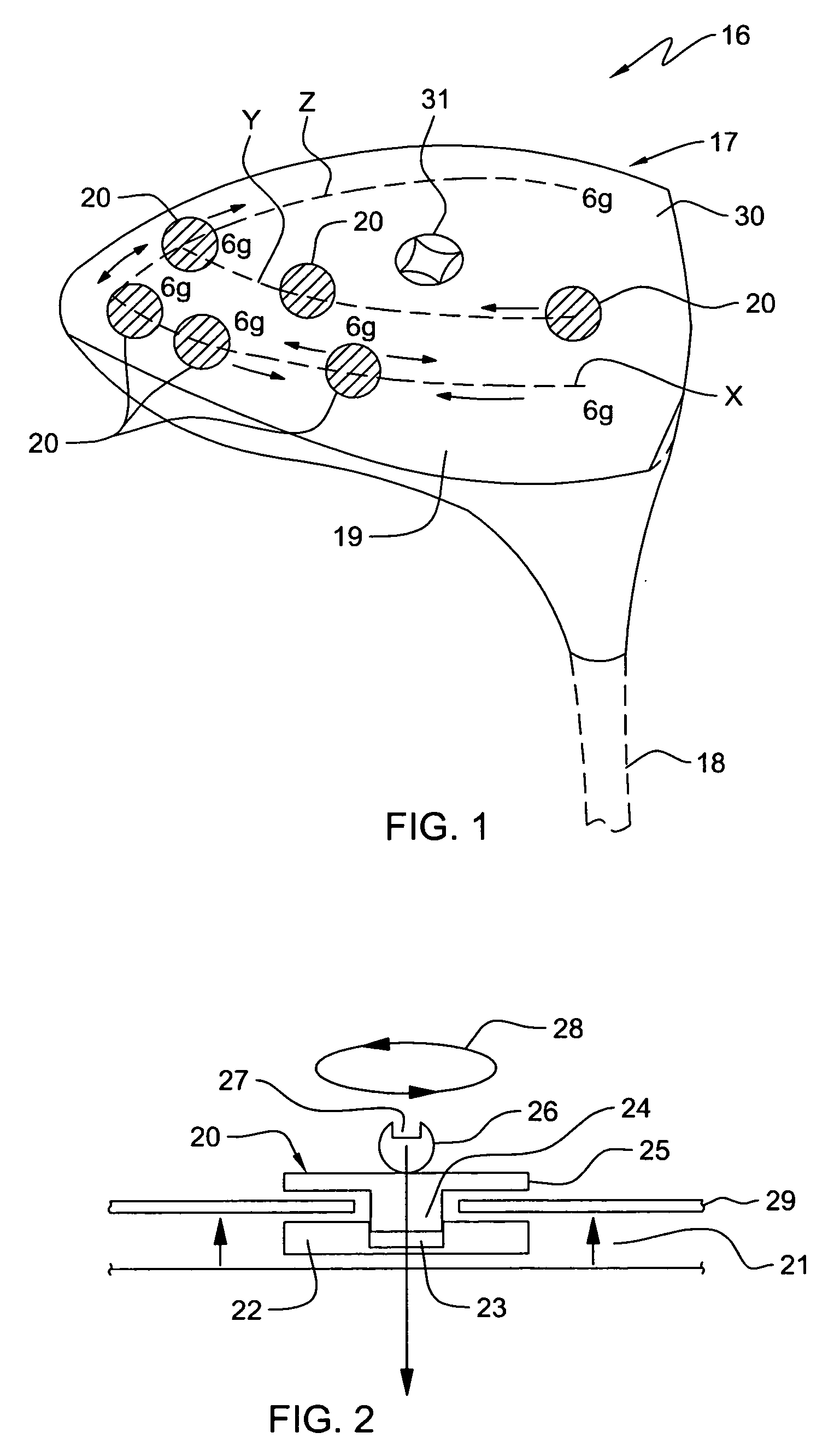
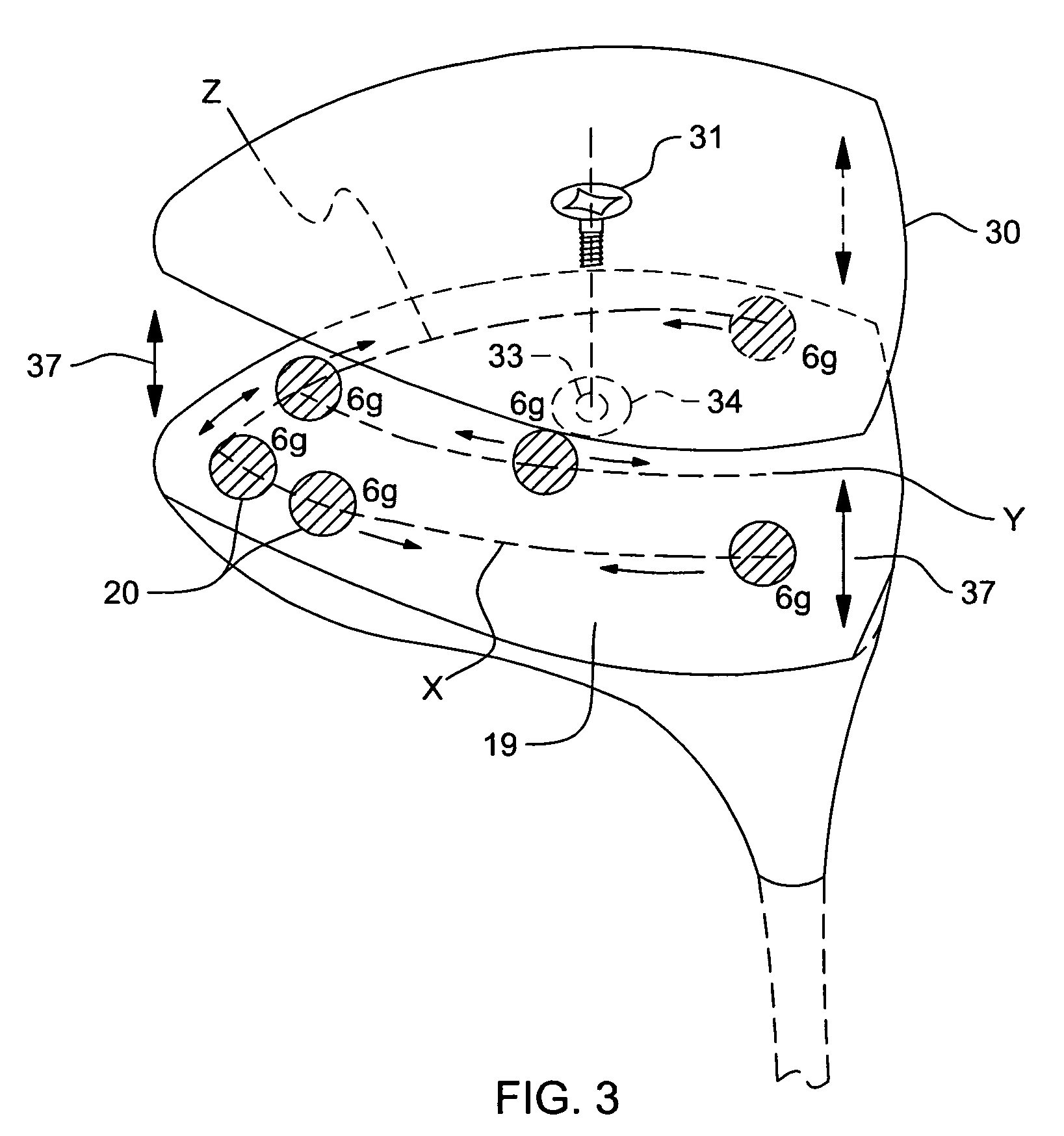
ActiveUS20080261715A1Easy to adjustDifficult to manipulateGolf clubsRacket sportsCouplingGravity center
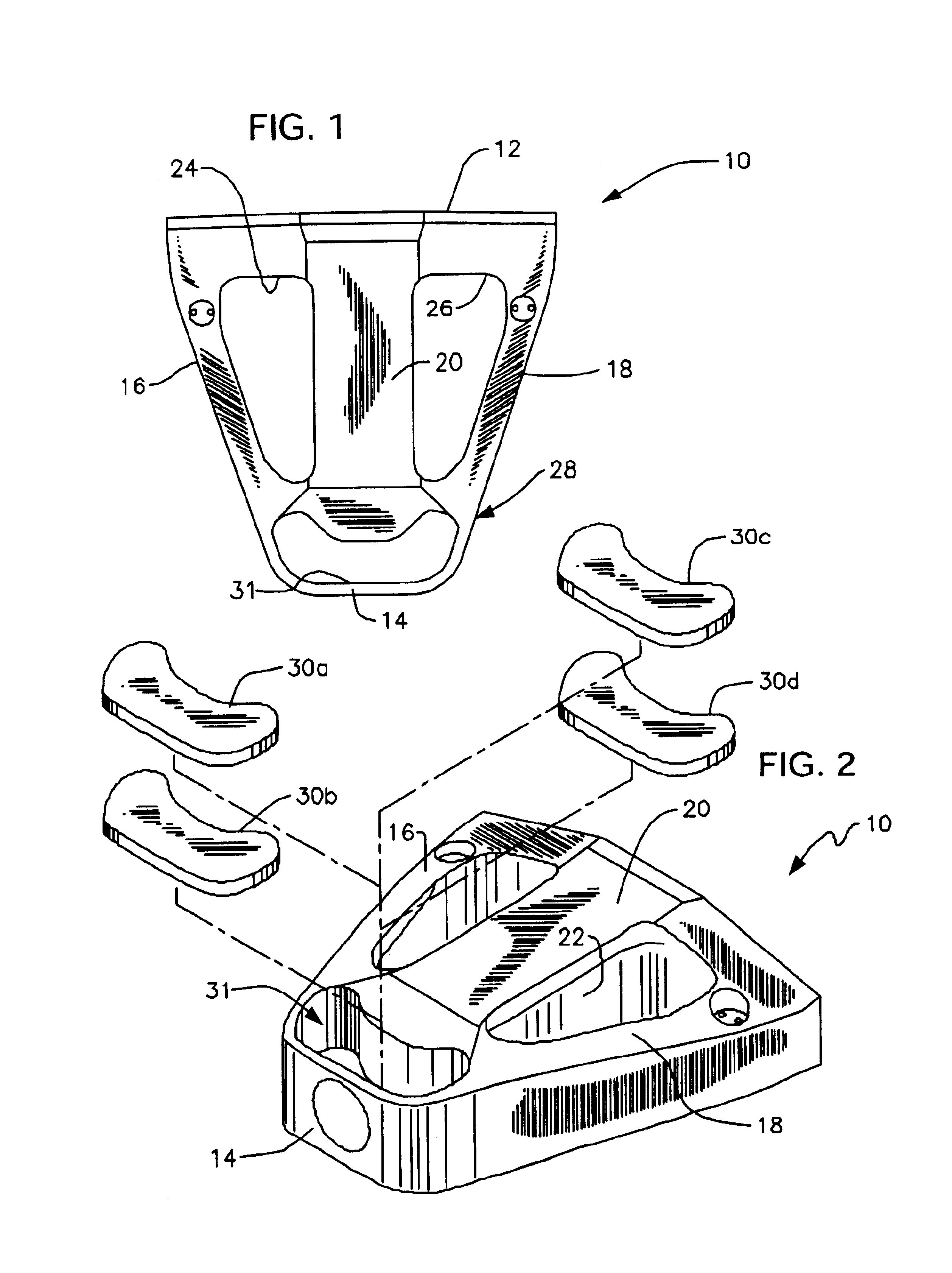
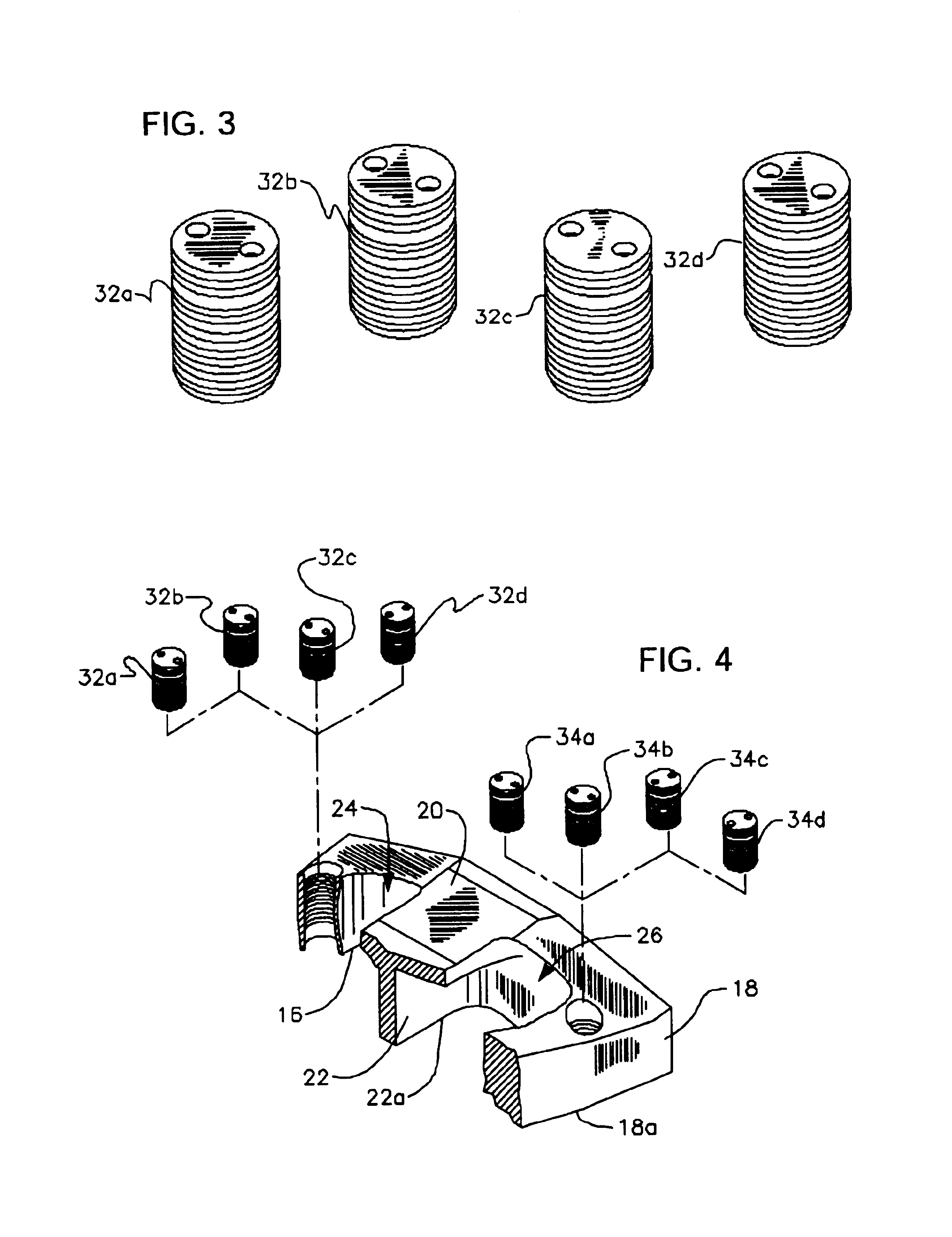
A golf club comprising a head having a series of tracks forming a three-dimensional pattern along a surface of the head; a plurality of weights for positioning along the channels; and a mechanism for securing the weights at arbitrary positions along the channels so as to customize at least one of center of gravity and moment of inertia of the head. The channels can all interconnect with one another to allow a weight to be moved from one to another. The golf club can further comprising a removable cover for at least a portion of the surface, the cover being for covering the channels and the weights positioned along the channels. The weights can comprise a spherical member disposed in a channel; an external member having a portion external to a surface of the head; and a coupling between the spherical member and the external member to allow the spherical member and the external member to securely capture between them a wall in which a track is formed. The channels may be in the removable cover, or below the removable cover, in the head.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Golf club head
A golf club head (42) having more than 50% of a volume forward of a center of gravity and more than 50% of a mass rearward of the center of gravity is disclosed herein. The golf club head (42) preferably has a volume ranging from 420 cubic centimeters to 470 cubic centimeters. The golf club head (42) preferably has a moment of inertia about the Izz axis through the center of gravity of the golf club head greater than 4000 grams-centimeters squared, and a moment of inertia about the Ixx axis through the center of gravity of the golf club head greater than 3000 grams-centimeters squared.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Golf club head with peripheral weighting
InactiveUS6890267B2Increase moment of inertiaVariable distributionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWound drainsMoment of inertiaGolf Ball
A golf club head with low peripheral and rearward weighting includes C-shaped and annular weights connected with at least one of the rear and bottom surfaces, respectively, of the head. The weighting within the peripheral weights is adjustable between the heel, rear, and toe portions of the head to customize the weight distribution of the head in accordance with a golfer's swing. The added weight and its orientation increases the moment of inertia of the head and reduces the rotation thereof.
Owner:THE TOP FLITE GOLF
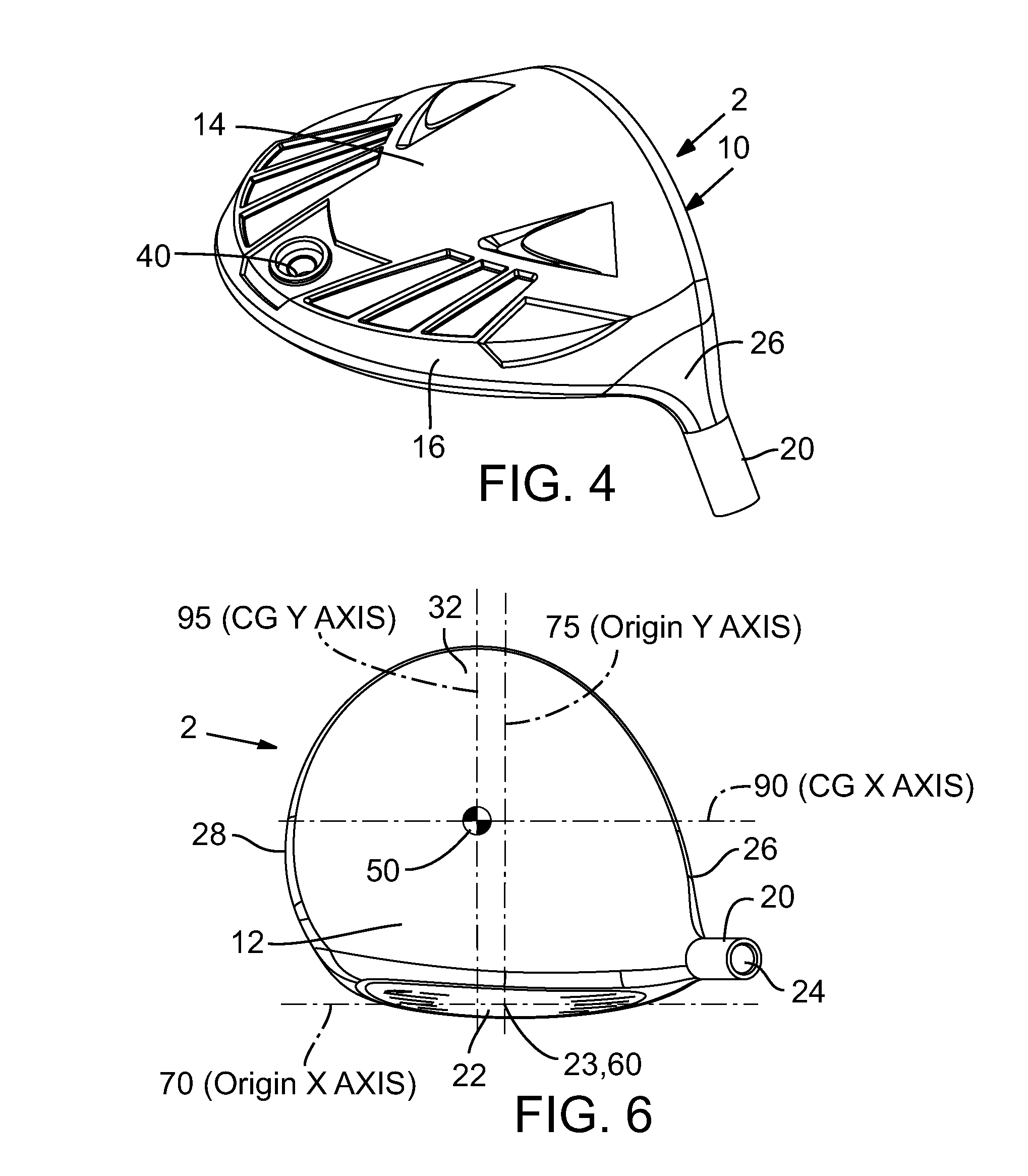
Golf club head
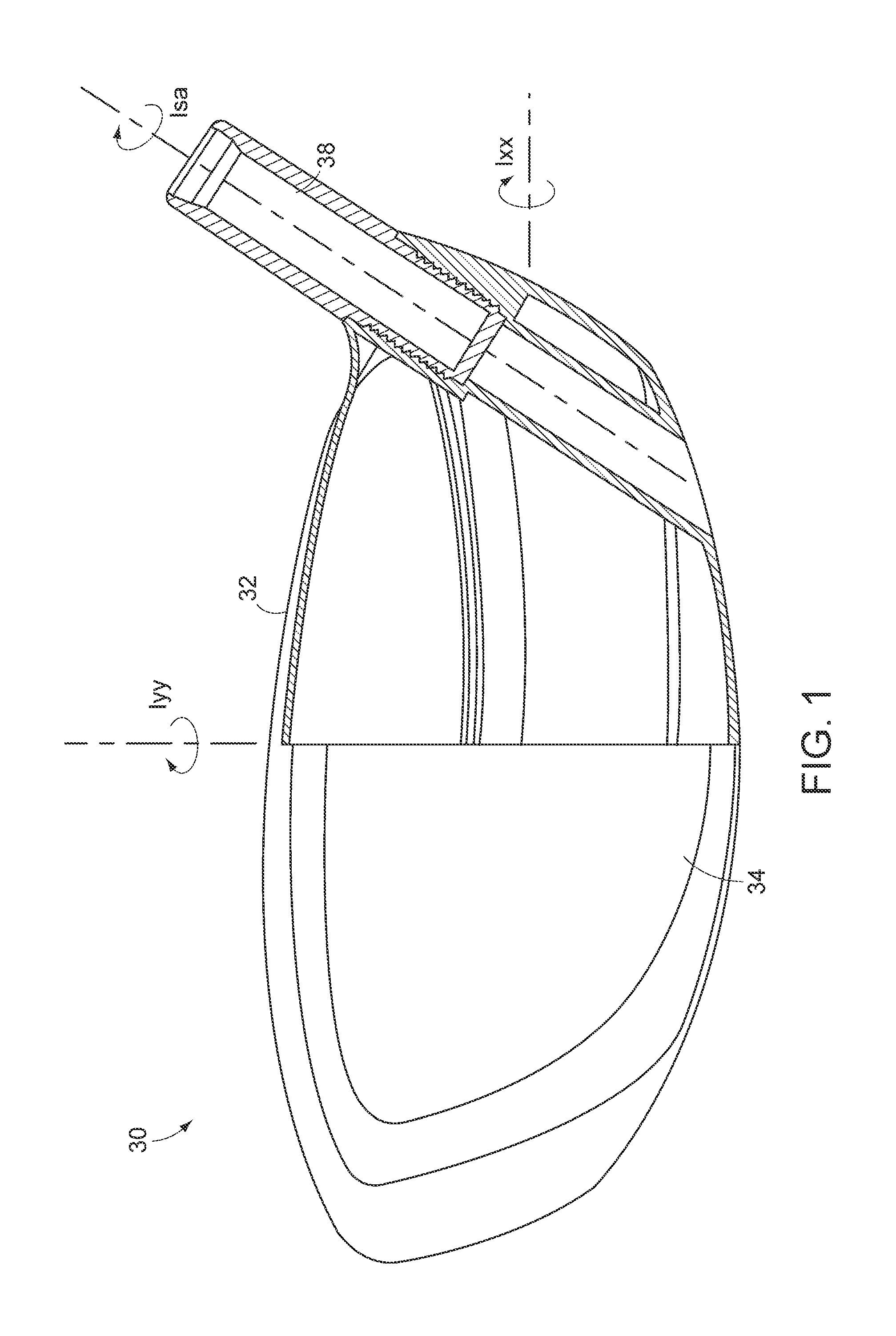
A golf club head comprising an outer shell and a strike plate having a strike face. The outer shell and the strike face define a club head volume. A heel / toe axis extends through the center of gravity of the club head. The heel / toe axis is generally parallel to the strike face and generally horizontal relative to a ground plane when the club head is at an address position. The rotational moment of inertia about the heel / toe axis is related to the club head volume by the equation Ixx ≧,46*HV+77, where Ixx is the rotational moment of inertia about the heel / toe axis in units of kg-mm2 and HV is the club head volume in units of cm3.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
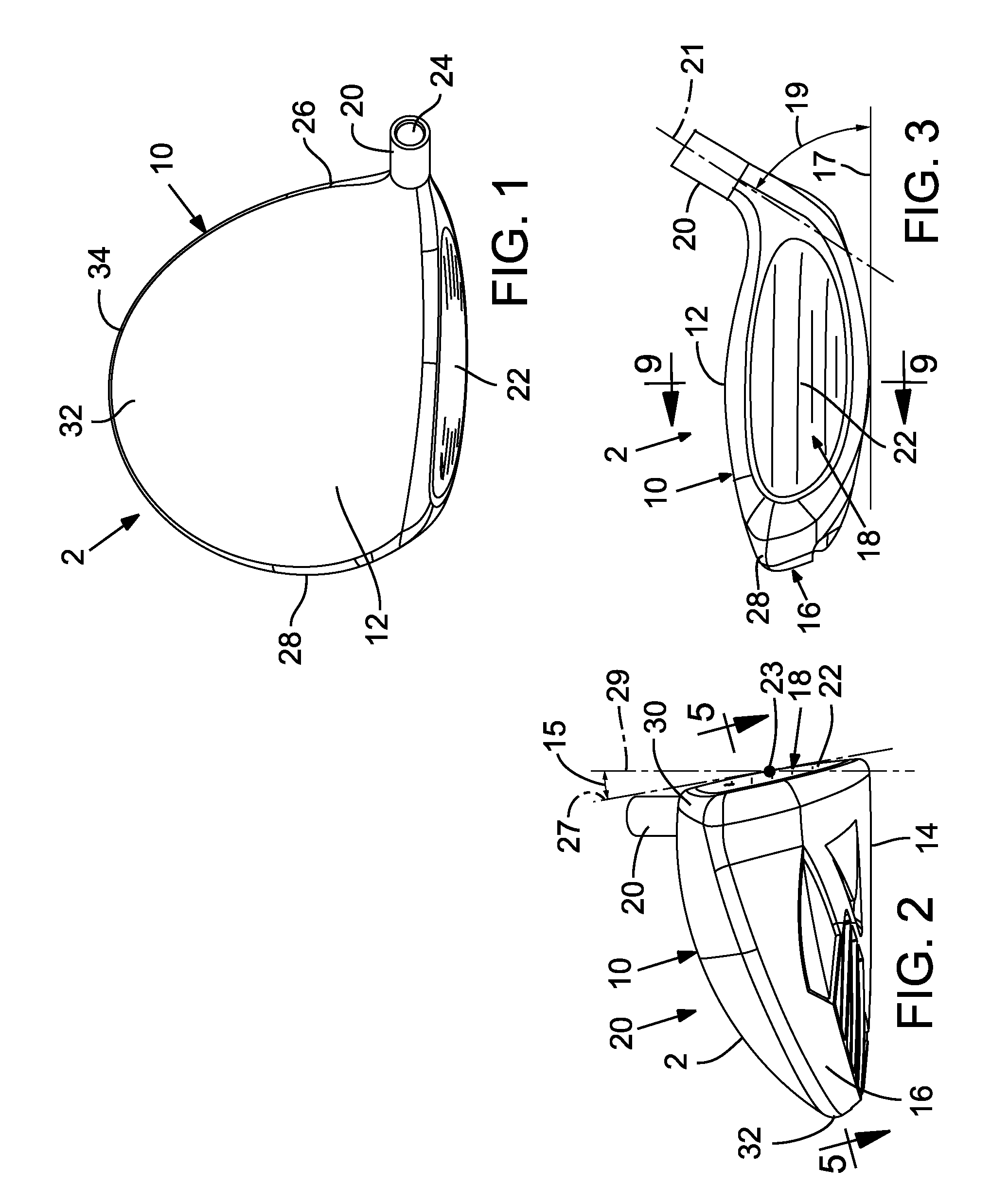
Fairway wood center of gravity projection
ActiveUS8900069B2Improved forgivenessImproved ballspeedGolf clubsRacket sportsCoefficient of restitutionGravity center
A golf club head includes a body defining an interior cavity. The body includes a sole positioned at a bottom portion of the golf club head, a crown positioned at a top portion, and a skirt positioned around a periphery between the sole and crown. The body has a forward portion and a rearward portion. The club head includes a face positioned at the forward portion of the body. The face defines a striking surface having an ideal impact location at a golf club head origin. Embodiments include club heads for a fairway wood that at least one of a high moment of inertia, a low center-of-gravity, a thin crown and a high coefficient of restitution.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Transitioning hollow golf clubs
The present invention relates to a set of golf club irons in which some of the club heads have a hollow space, and some of the club heads do not have a hollow space. The hollow space is preferably defined by a lower portion of the front face, a portion of the sole, and a rear wall. The presence of the hollow space moves the club head center of gravity back (away from the face) and down (toward the sole), making it easier to get a golf ball airborne. The volumes of the hollow spaces generally transition or get progressively smaller with an increase in the club loft angle, thus altering the center of gravity location and moments of inertia by different amounts for different clubs. The hollow spaces may be empty or filled, in whole or part.
Owner:COBRA GOLF
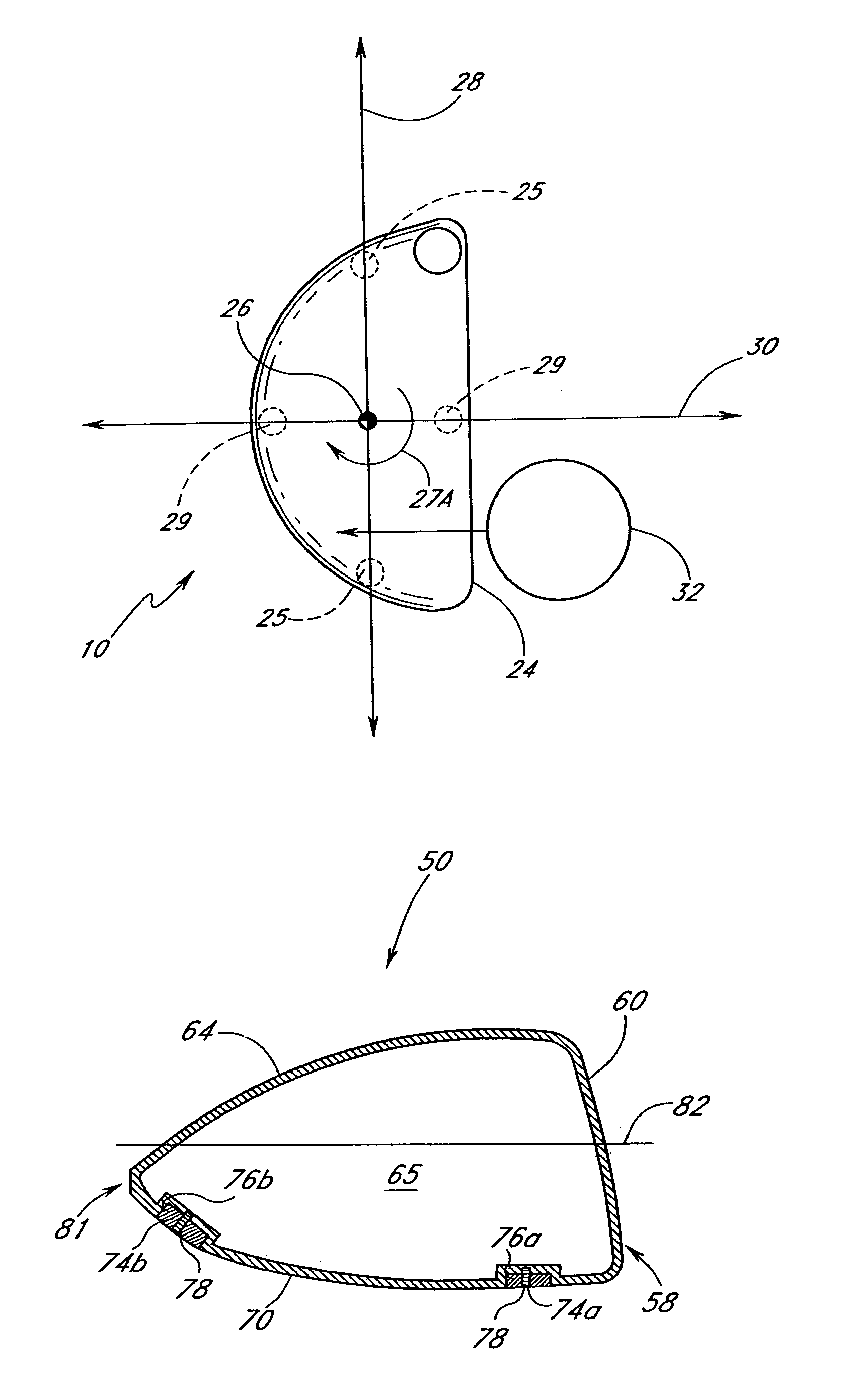
Putter
A golf putter head adapted for attachment to a club shaft is provided with a face member having a strike face and a cylindrical back cavity, and a body member configured to fit and rotate within the back cavity is disclosed. Selective rotation of the body member within the back cavity sets a loft of the putter head. The weighting of the putter is adjusted by securing a weight member to the body member. A golf putter head having an increased moments of inertia is also disclosed. The putter head includes a face member, a body member, and a weight member. Placement of the weight member is such that the moments of inertia are increased and the putter head is stable.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Golf putter with improved moment of inertia, aim and feel
InactiveUS7077758B2Maximizes clubhead planar moment of inertia (MOICH)Undesirable torsional vibrationGolf clubsRacket sportsVisibilityEngineering
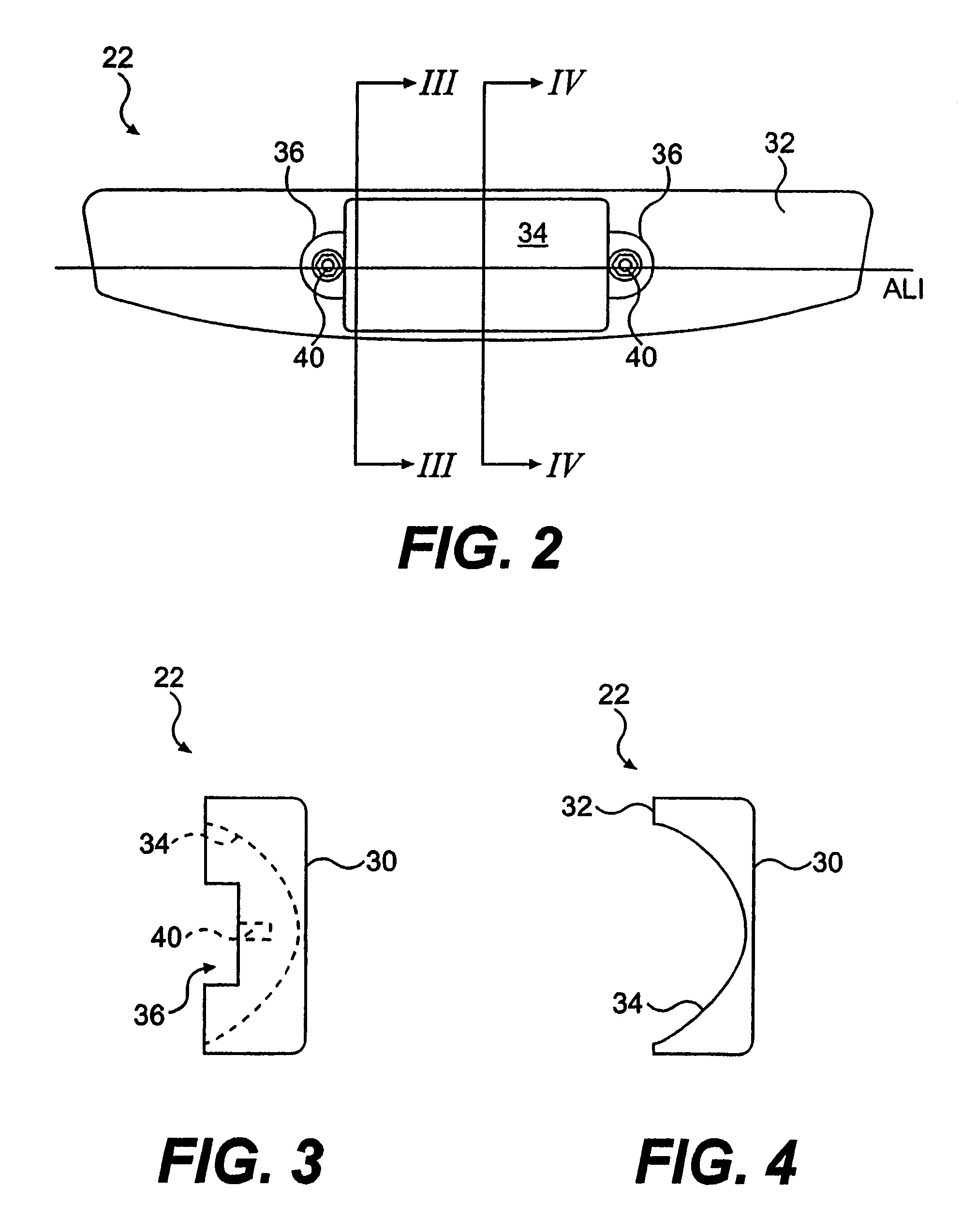
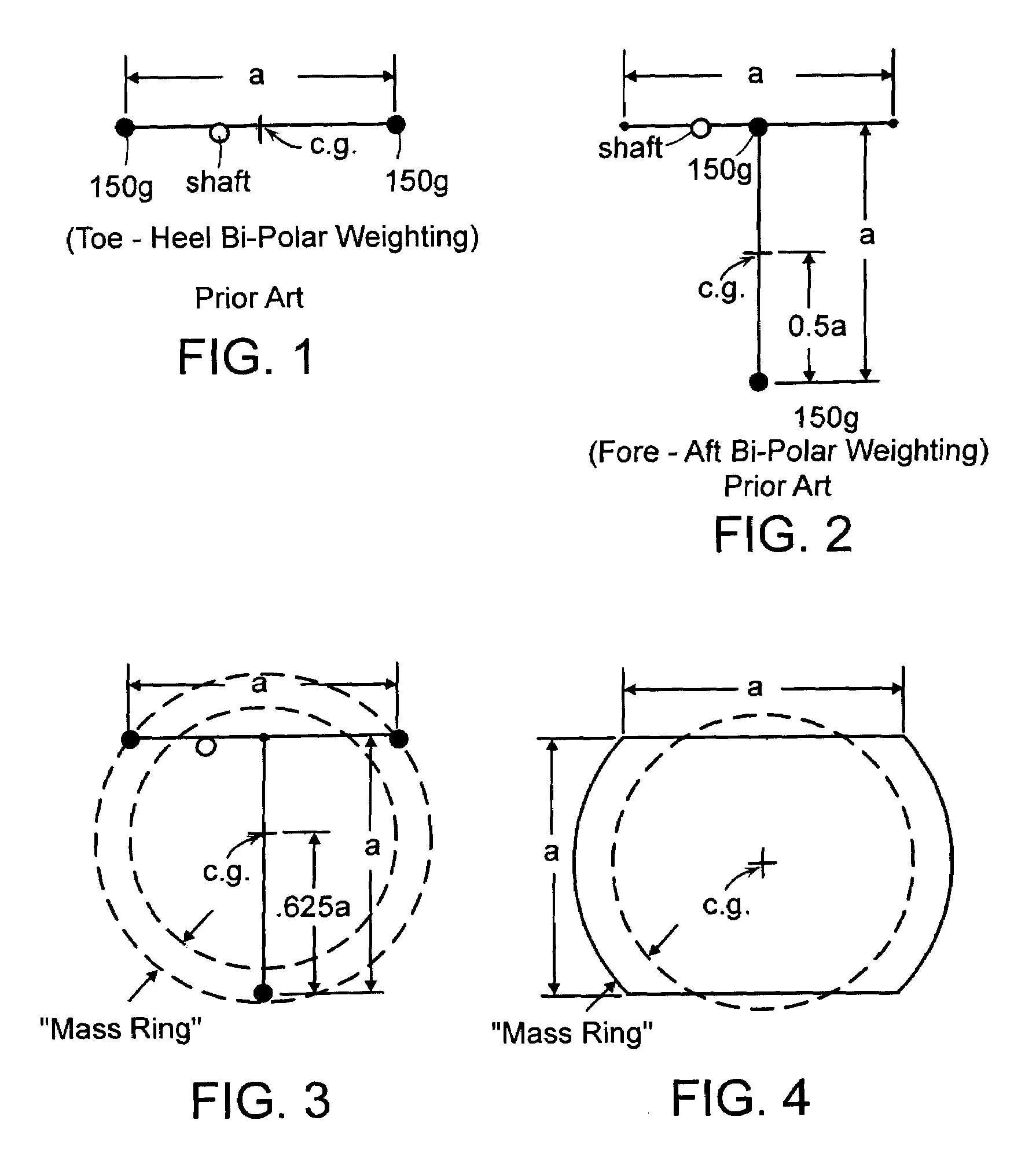
A golf putter in which most of the clubhead mass is distributed at three or more individual or one or more arcuate locations within a “Mass Ring” approximately equidistant from, and as remote as possible from, the clubhead planar center of mass with the clubshaft axis preferably forward of the clubhead center of mass thus maximizing both putter and clubhead planar moment of inertia for improved putter performance during mis-hits. Maximum remote mass is achieved by interconnecting the remote high mass areas (Mass Ring) with the putterface striking area and the putter shaft connection point with a light weight rigid open (see thru) truss system so arranged to enhance the visibility of the Sighting Field and / or aim or Sight Line on the putterhead while preventing undesirable vibration of individual clubhead members.
Owner:ROHRER TECH
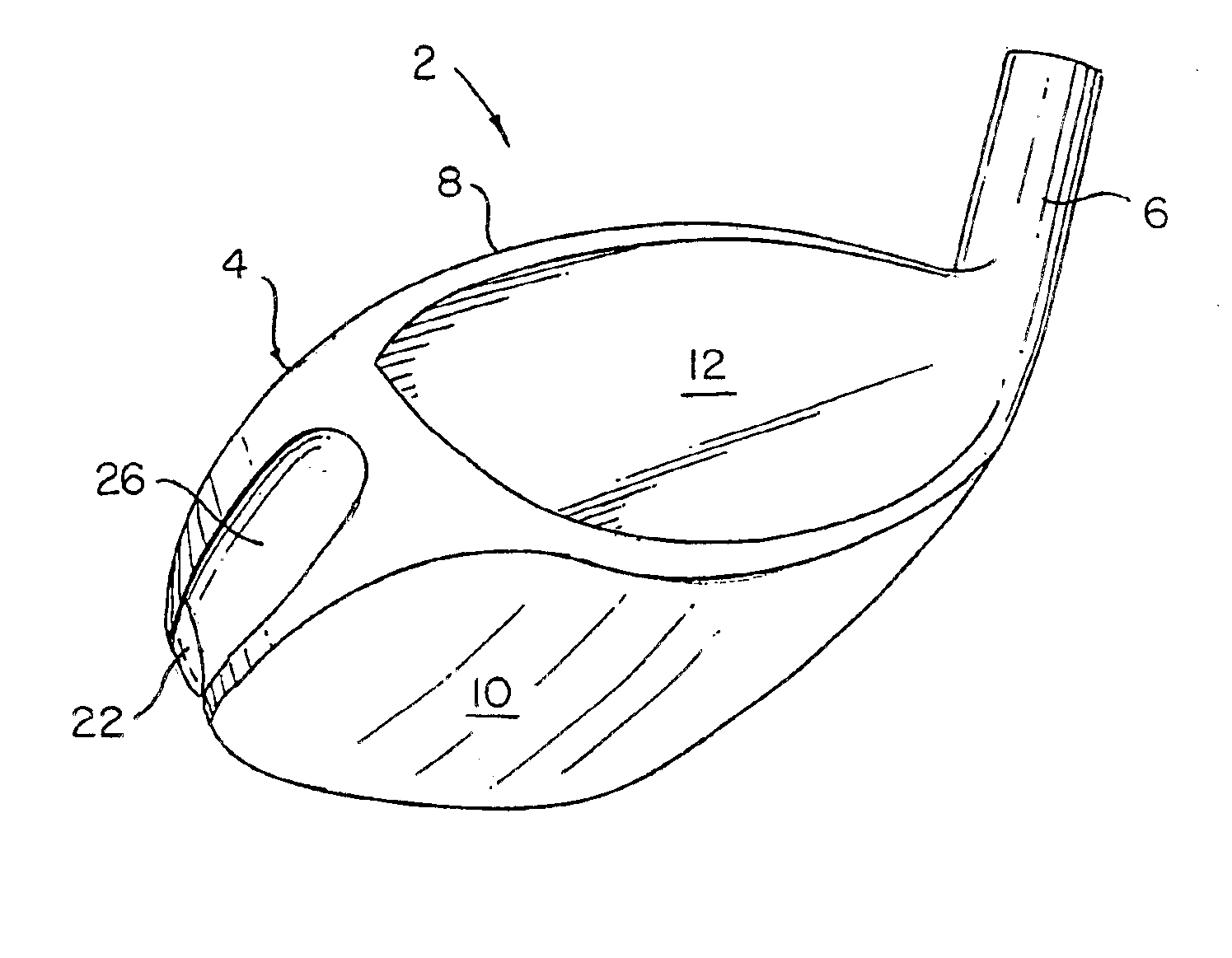
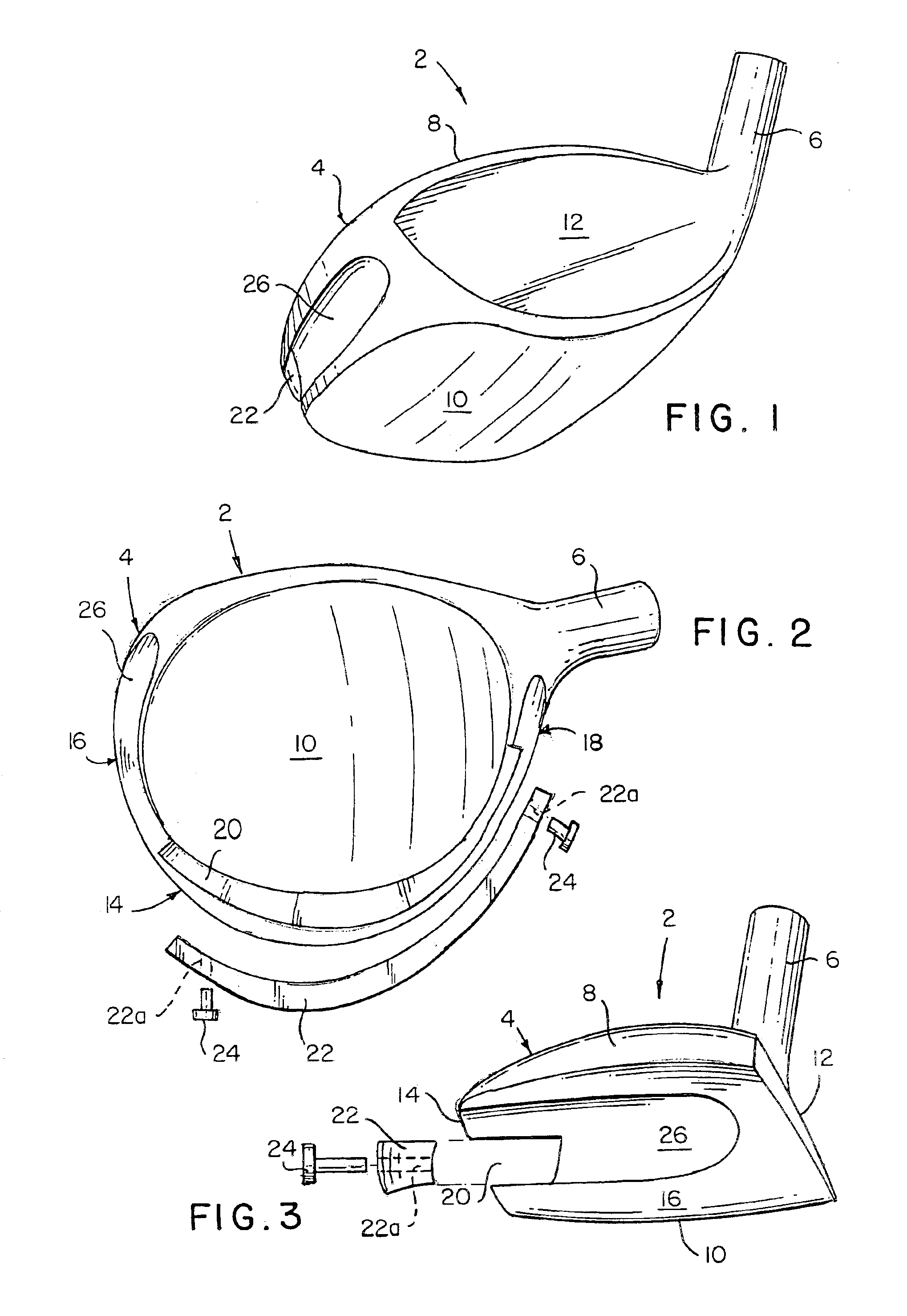
Golf club head with high moment of inertia
ActiveUS7413520B1Increase the areaHigh moments of inertiaGolf clubsRacket sportsMoment of inertiaGolf Ball
A golf club head having a high moment of inertia is disclosed herein. The golf club head preferably has a volume ranging from 450 cubic centimeters to 475 cubic centimeters, a mass ranging from 180 grams to 225 grams, and a length ranging from 4.0 inches to 5.0 inches. The golf club head preferably has a moment of inertia, Iyy, about the center of gravity of the golf club head greater than 4000 grams-centimeters squared. Preferably, the golf club includes a metal face component, a non-metal aft-body and a weight member attached to an inlaid portion of the non-metal aft-body.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
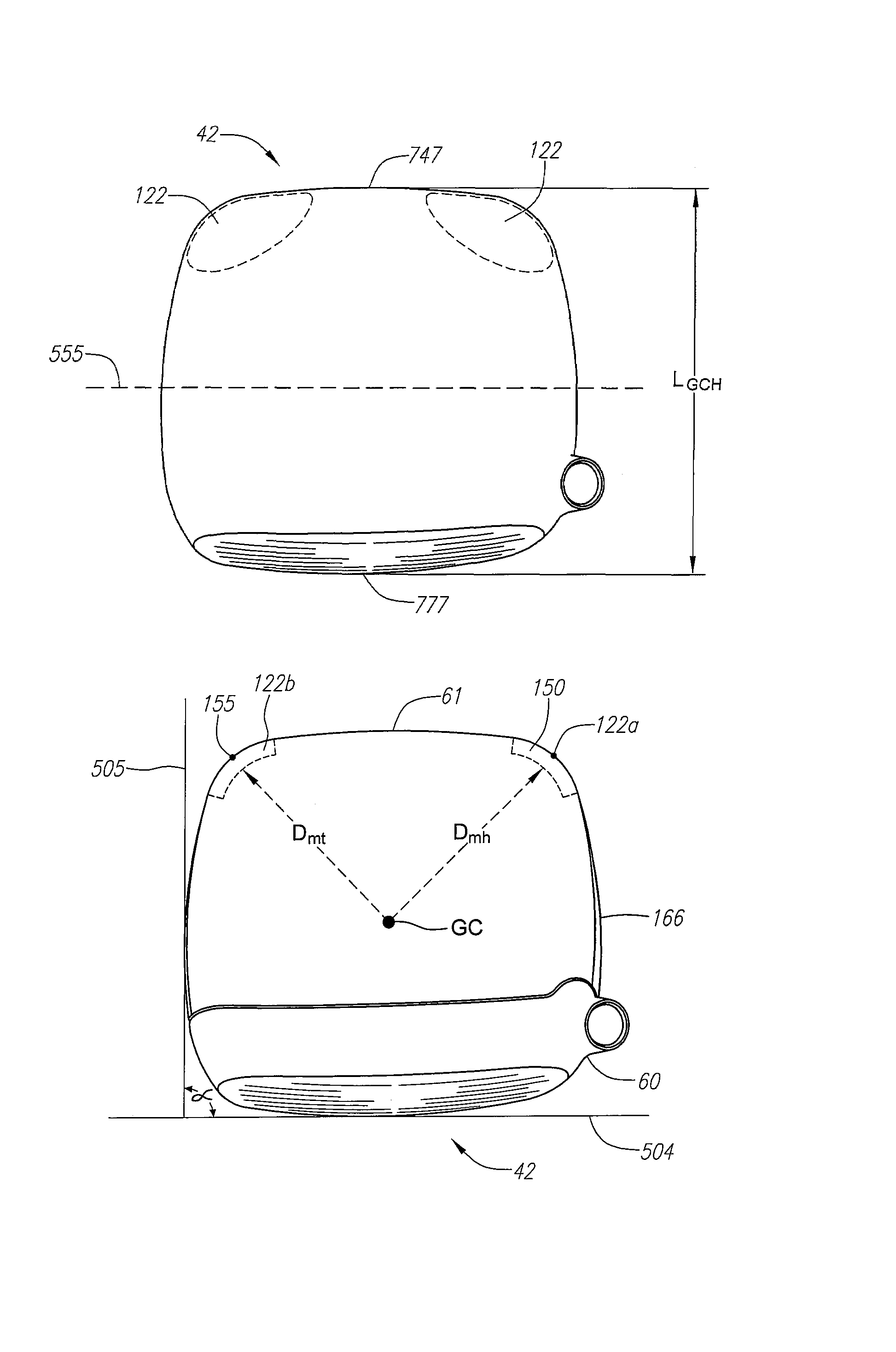
Golf club head
A golf club head (42) having a delta of the coefficient of restitution between a geometric face center of the face (72) and a location (806) 0.5 inch sole-ward from the face center that is less than 0.065. The golf club head (42) preferably has a volume ranging from 420 cubic centimeters to 470 cubic centimeters. The golf club head (42) preferably has a moment of inertia about the Izz axis through the center of gravity of the golf club head greater than 4000 grams-centimeters squared, and a moment of inertia about the Ixx axis through the center of gravity of the golf club head greater than 3000 grams-centimeters squared.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
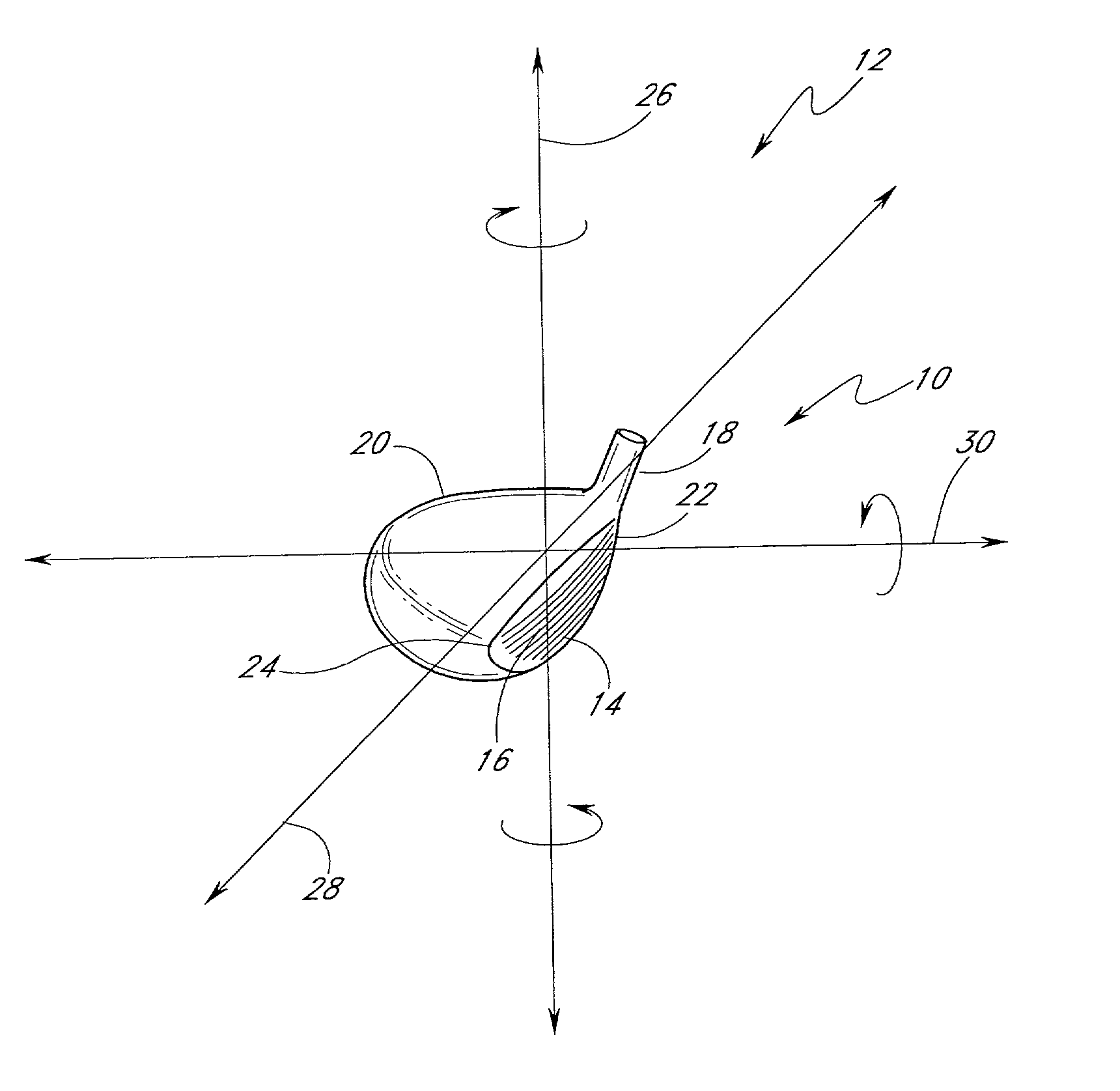
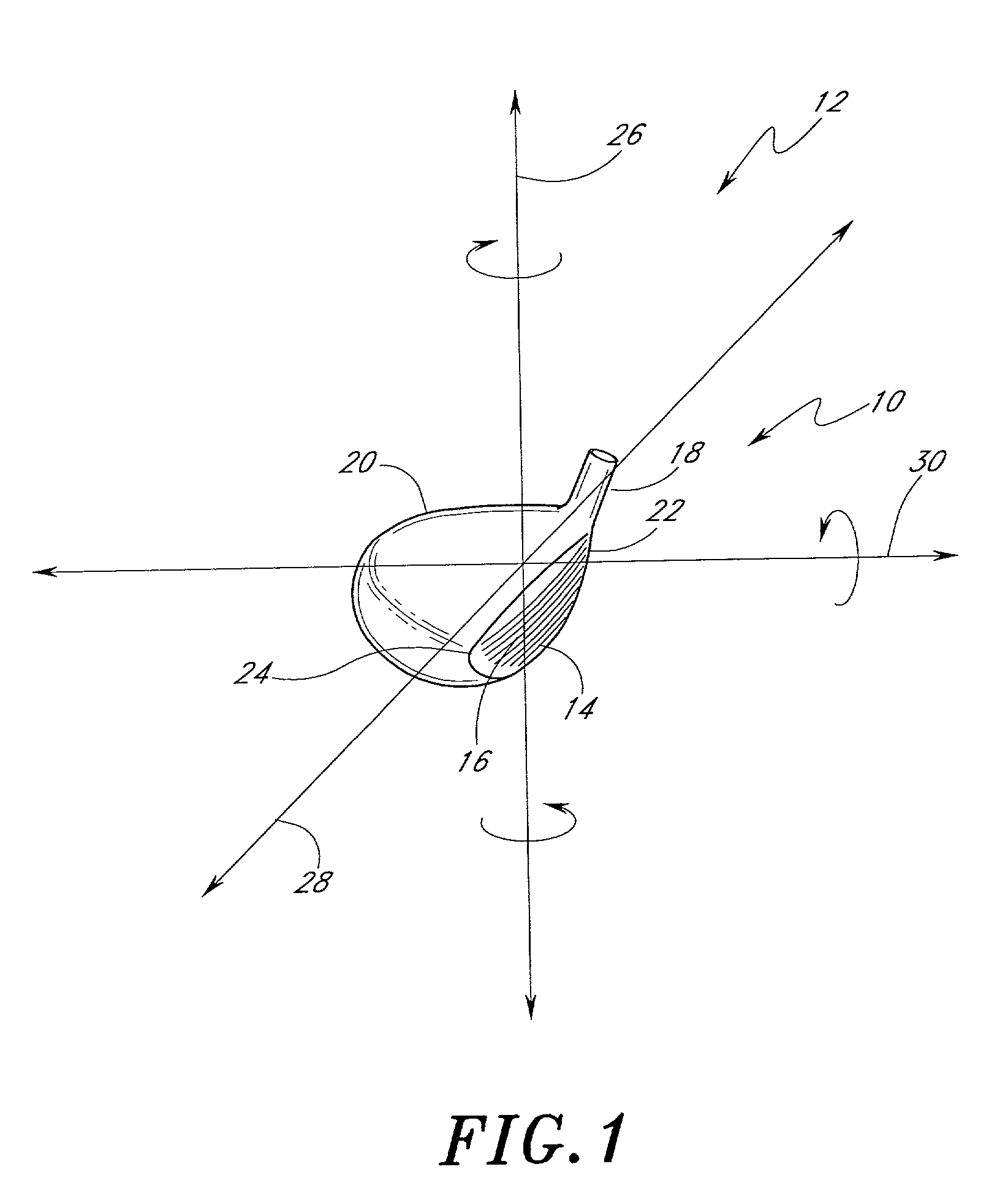
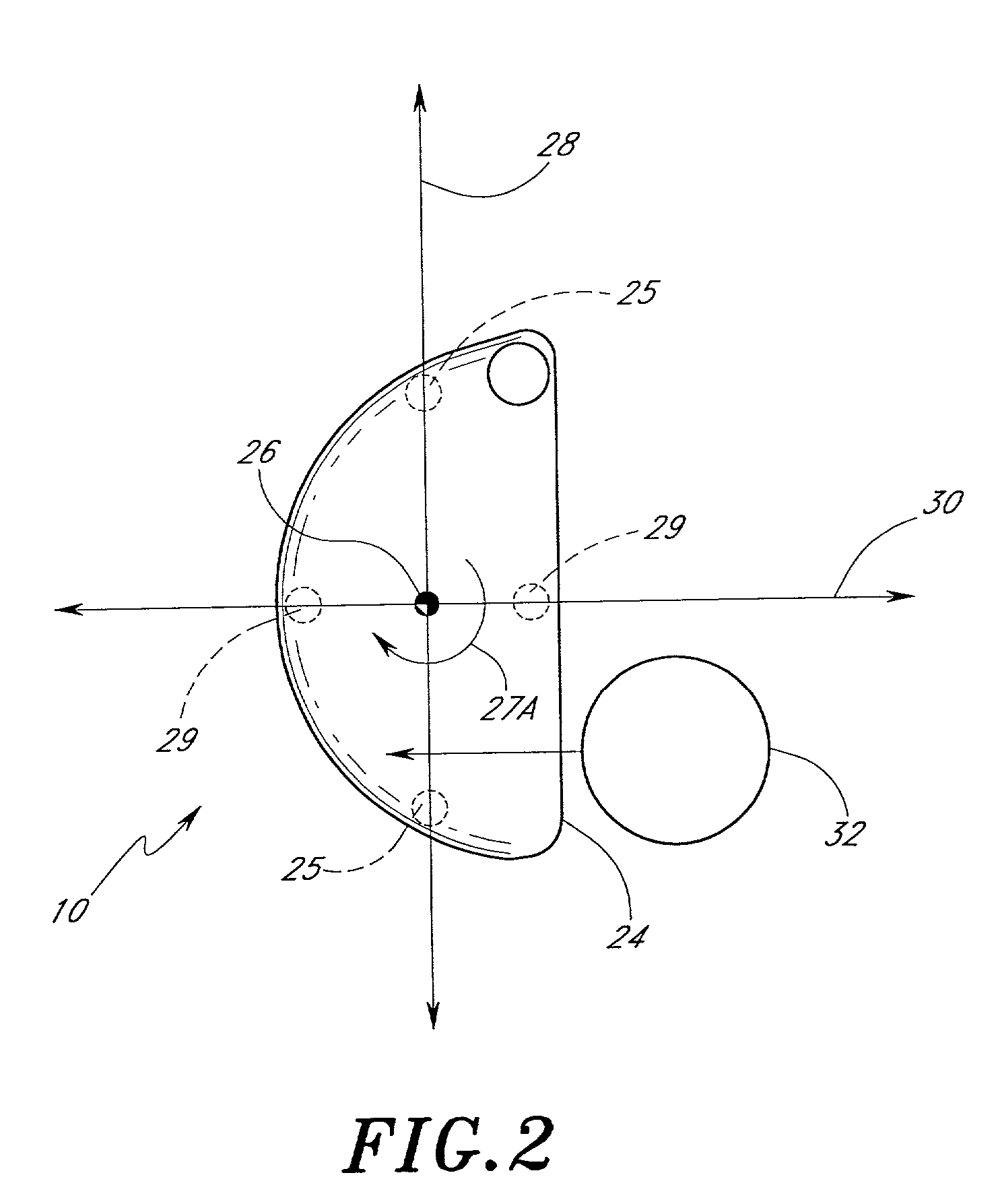
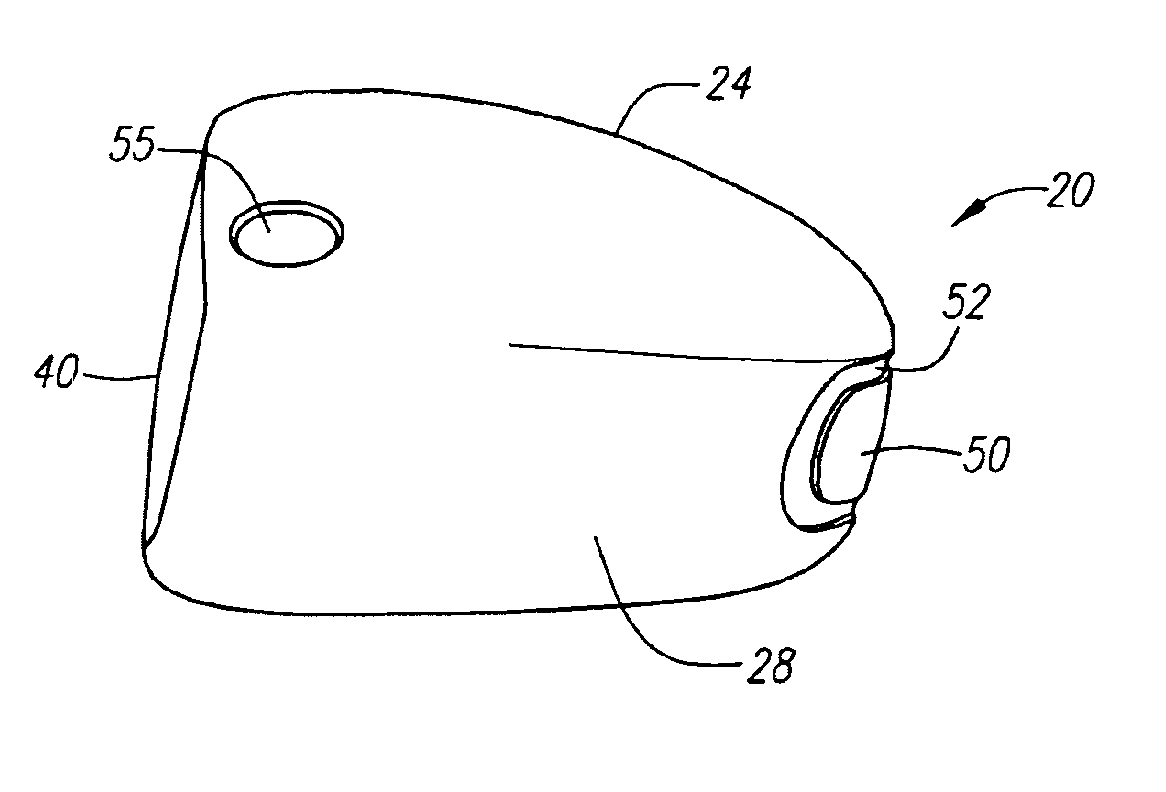
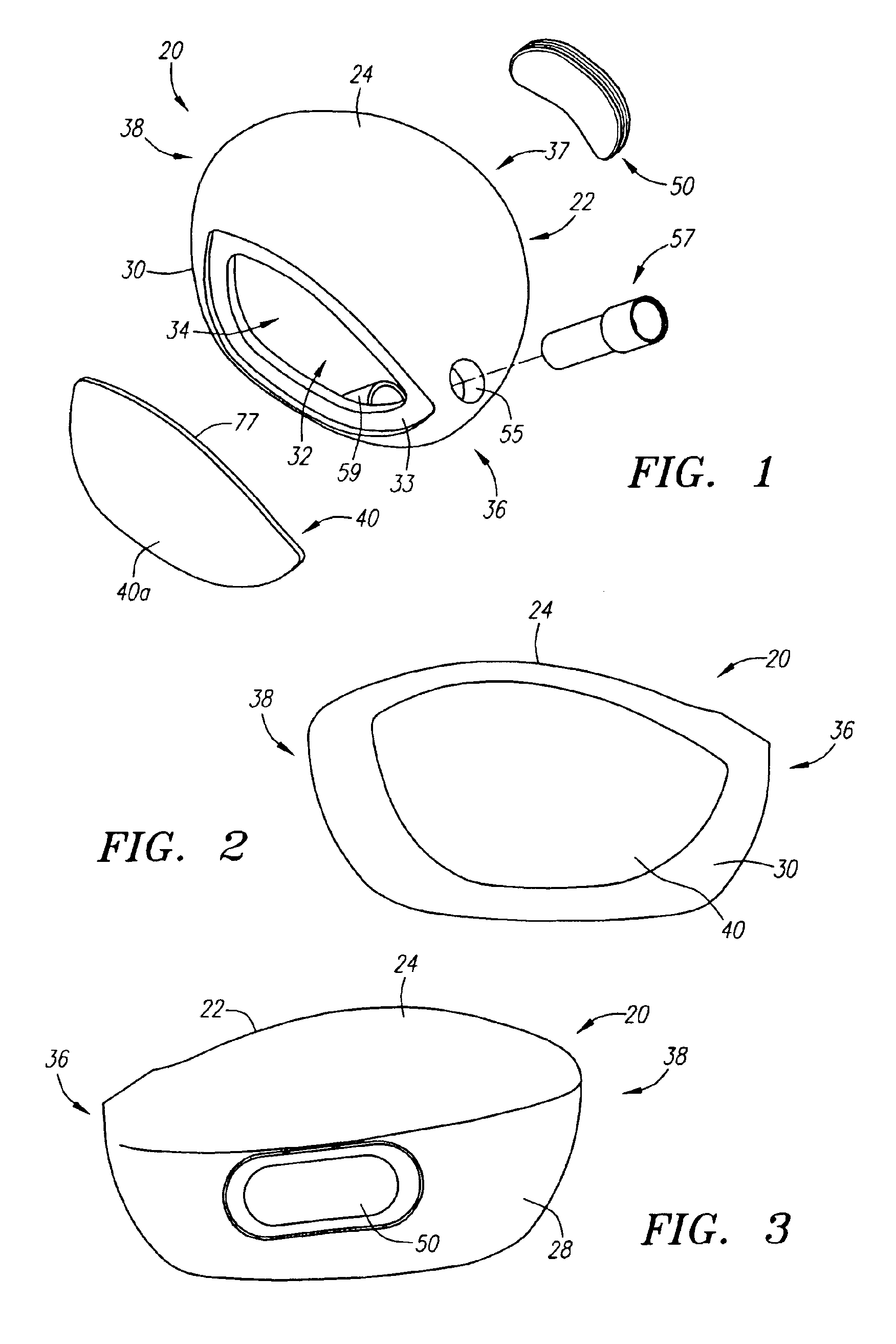
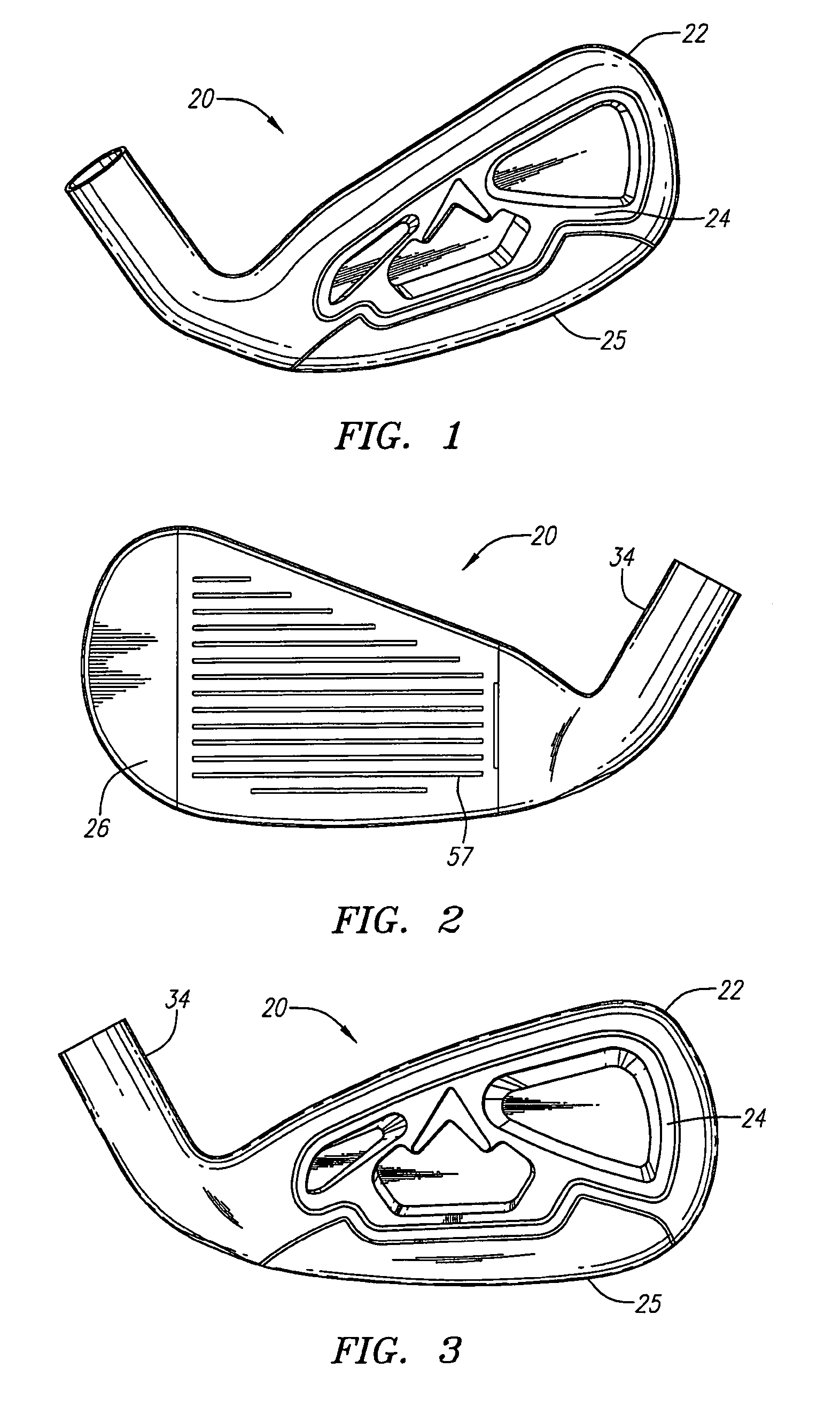
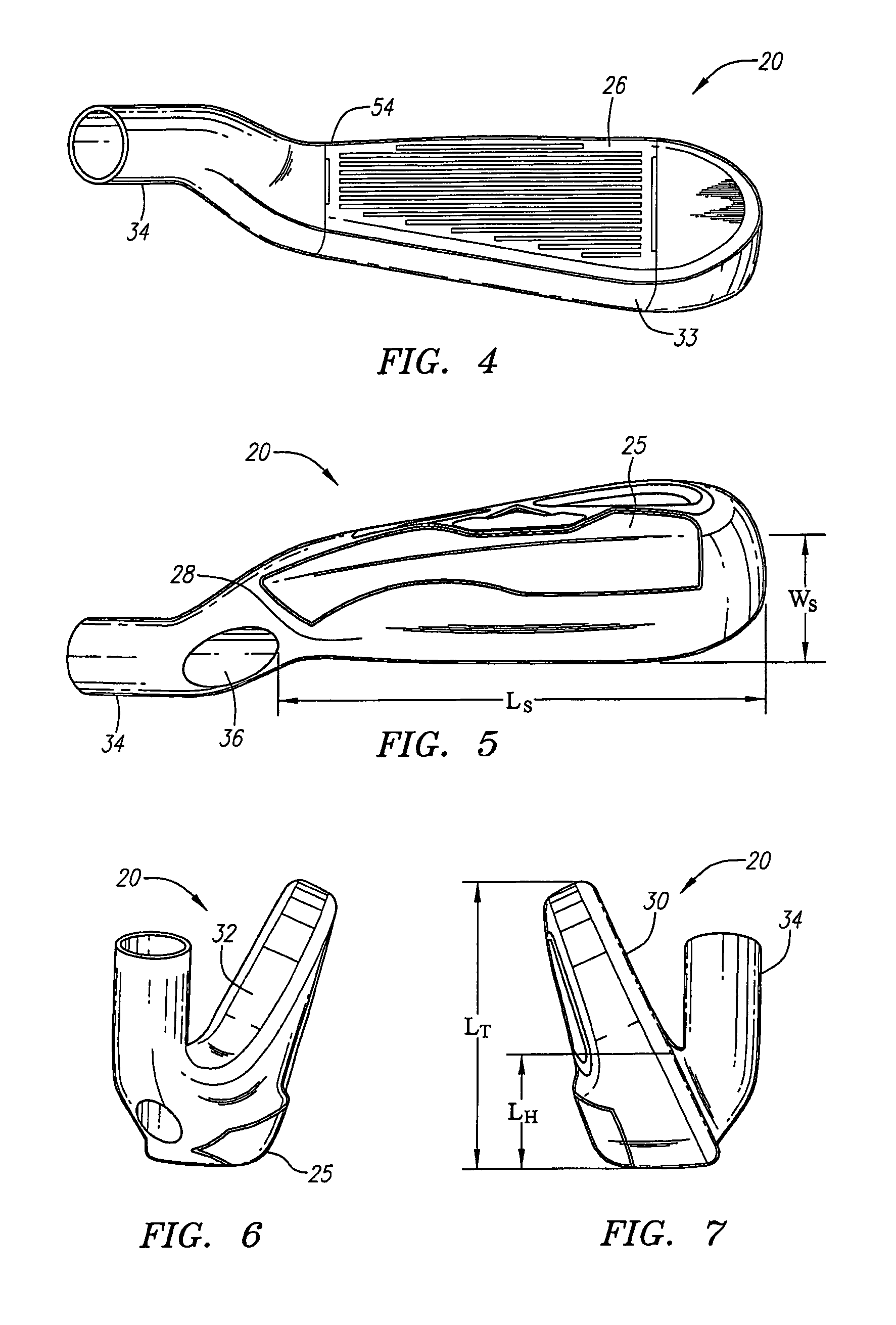
Golf club head (Corporate Docket PU2150)
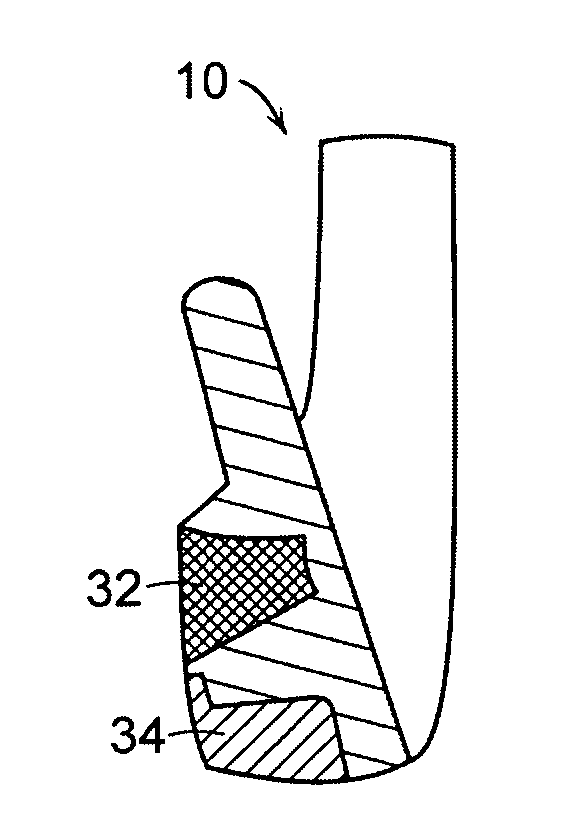
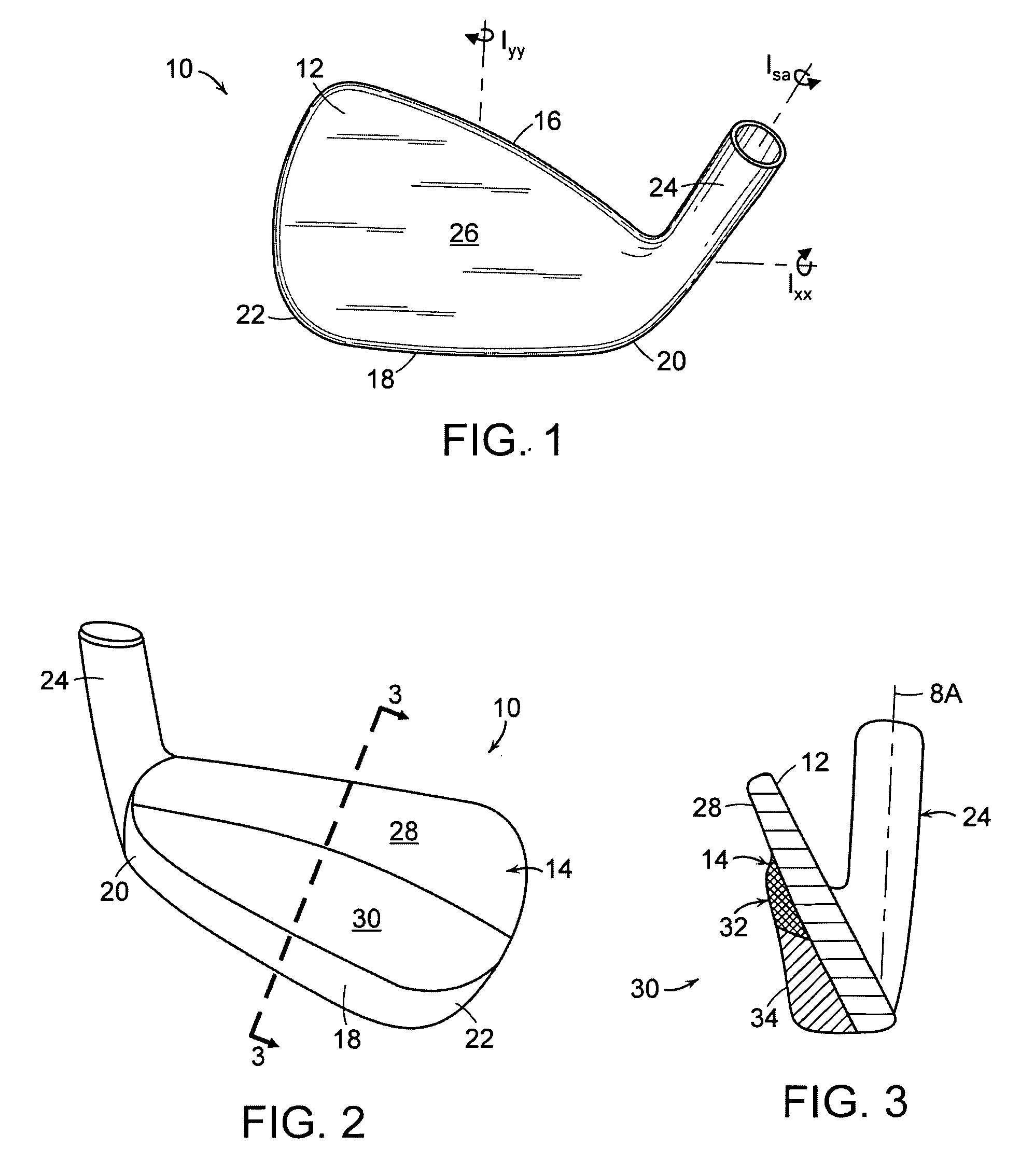
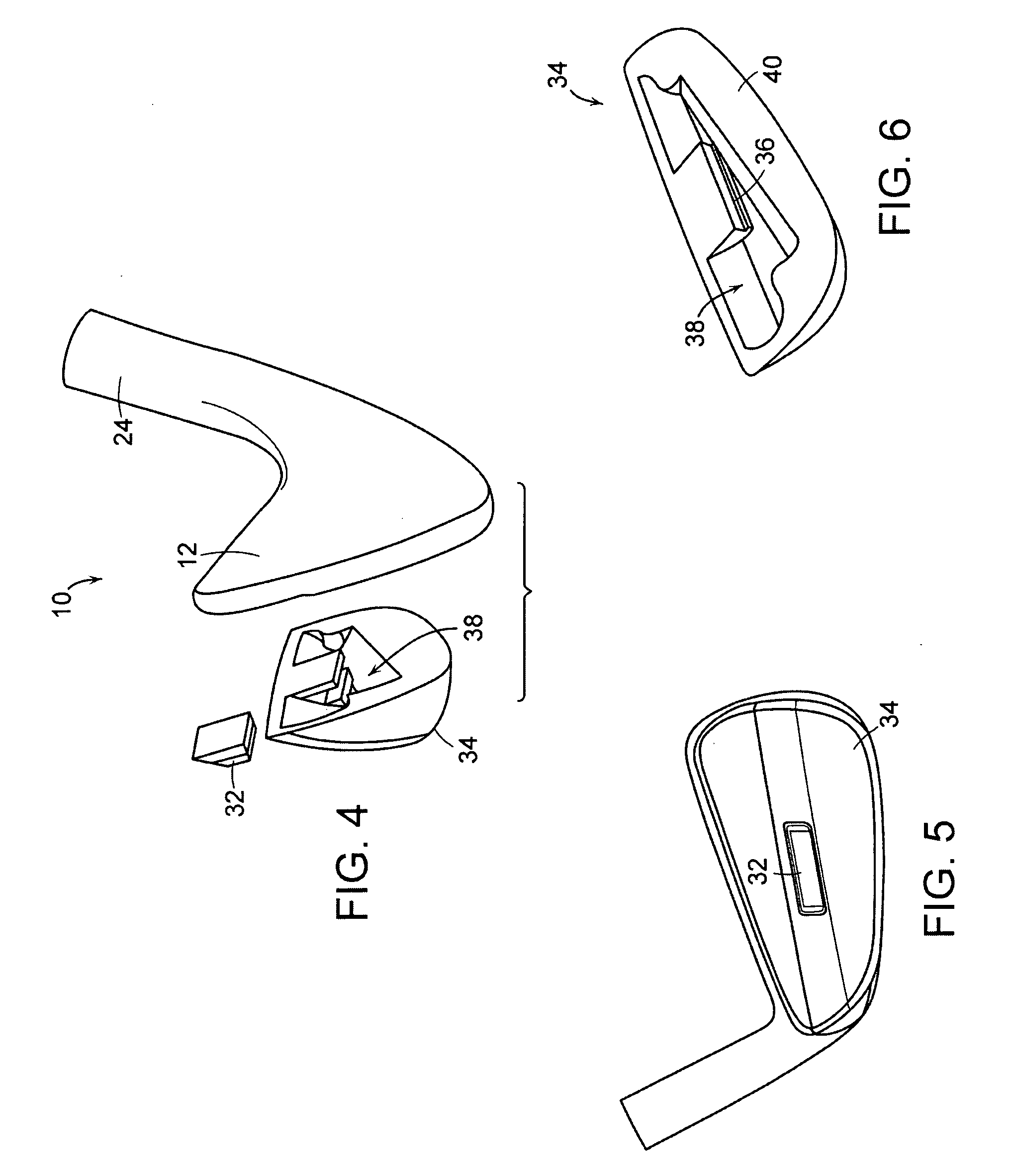
A golf club head (20) having a center of gravity located relatively forward toward the front wall (30) or striking plate (40) of the golf club head (20), and a relatively high moment of inertia about the Iyy axis through the center of gravity of the golf club head (20) is disclosed. The golf club head (20) preferably has a volume between 300 cubic centimeters and 500 cubic centimeters. The golf club head (20) preferably has a mass between 105 grams and 300 grams. The positioning of the of the center of gravity of the golf club head (20) and the relatively high moment of inertia Iyy through the center of gravity provide for a golf club with greater robustness and better performance.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
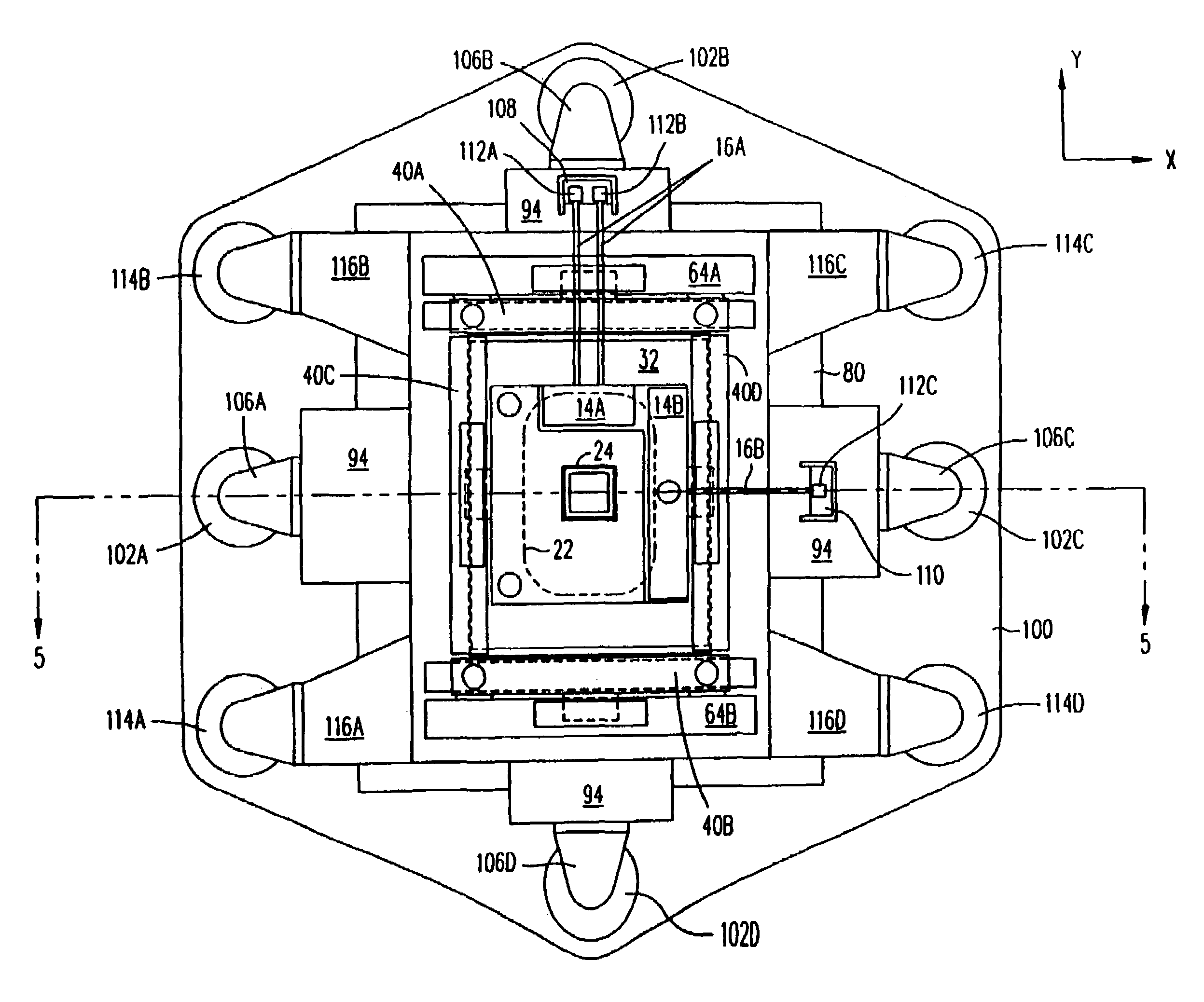
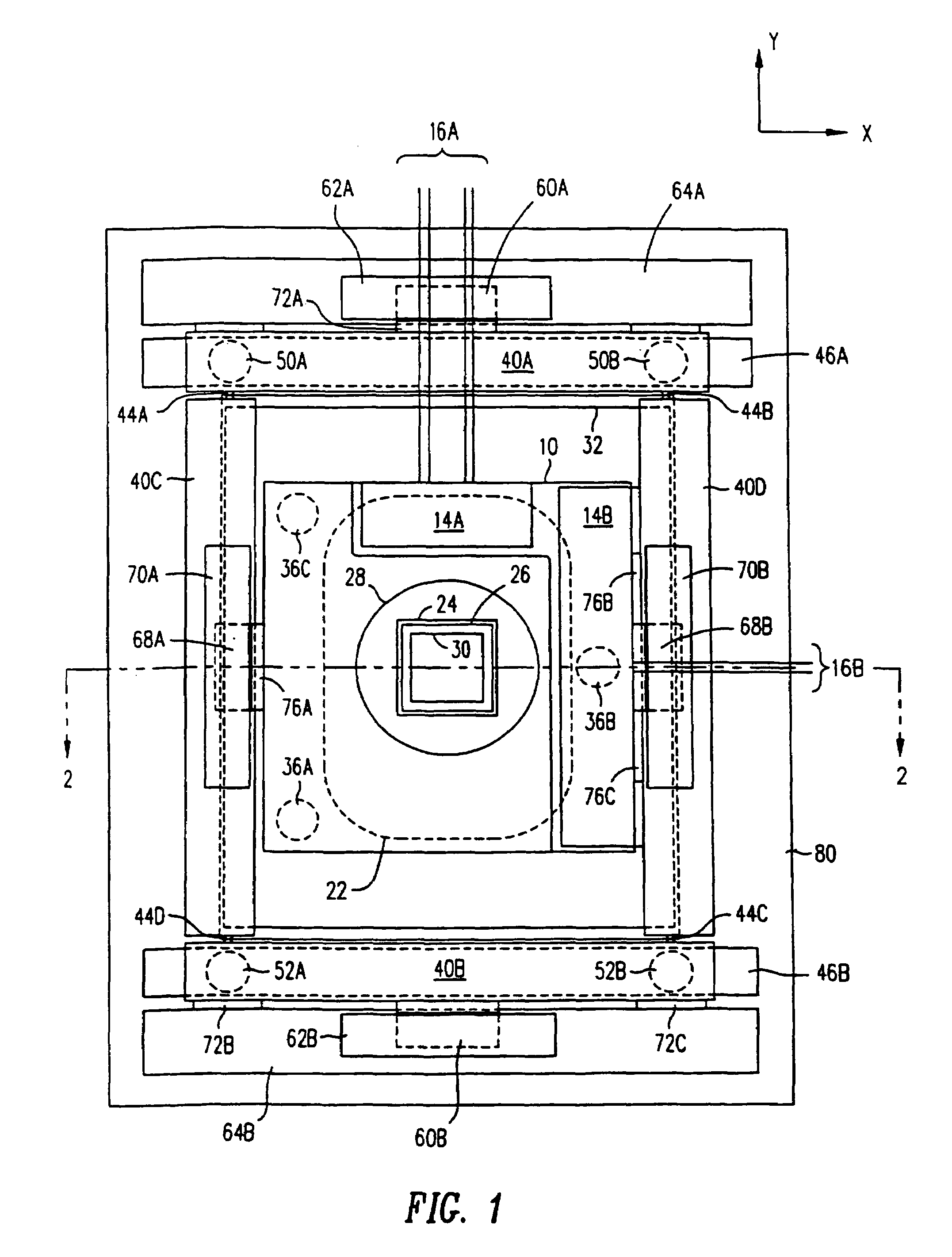
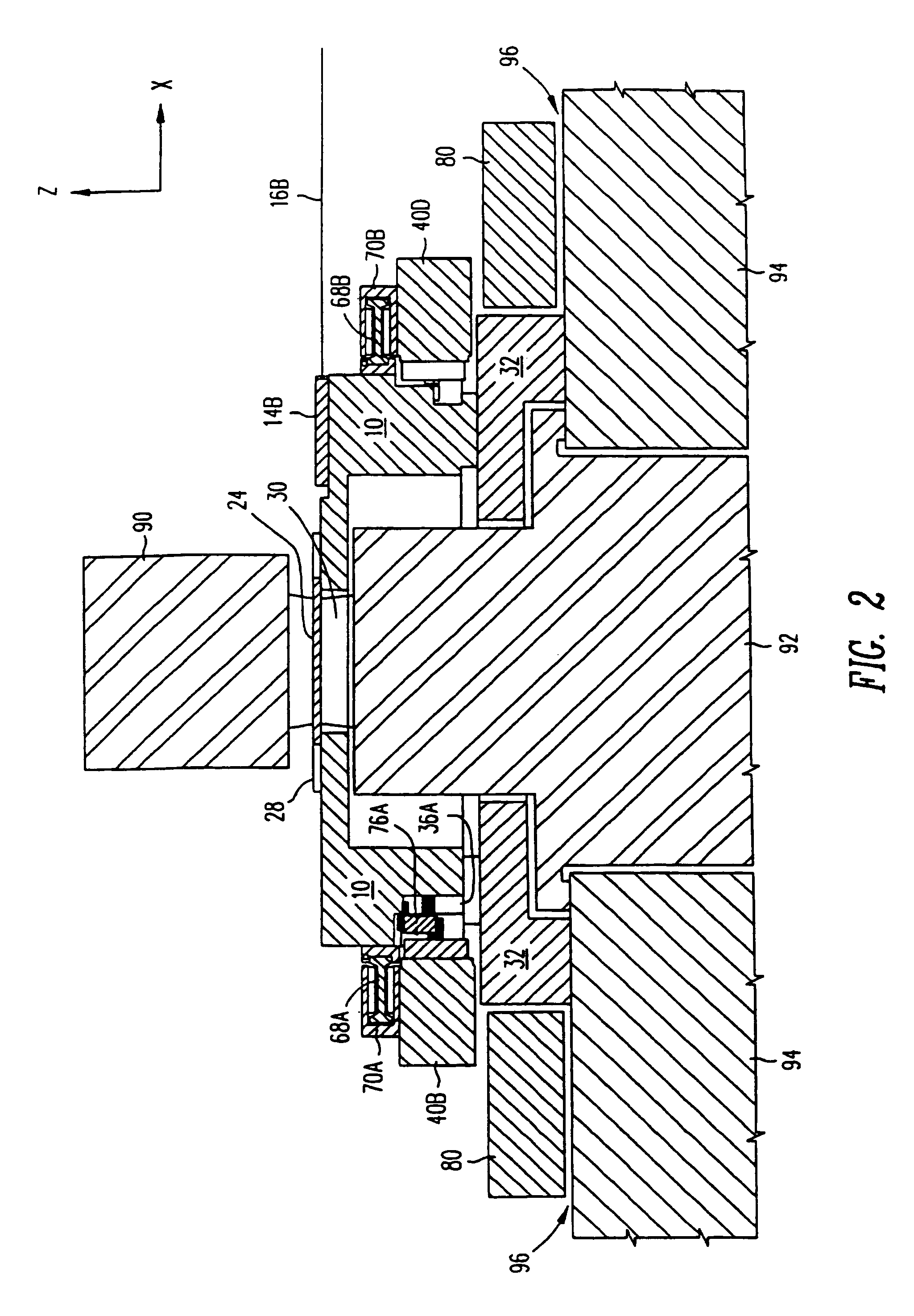
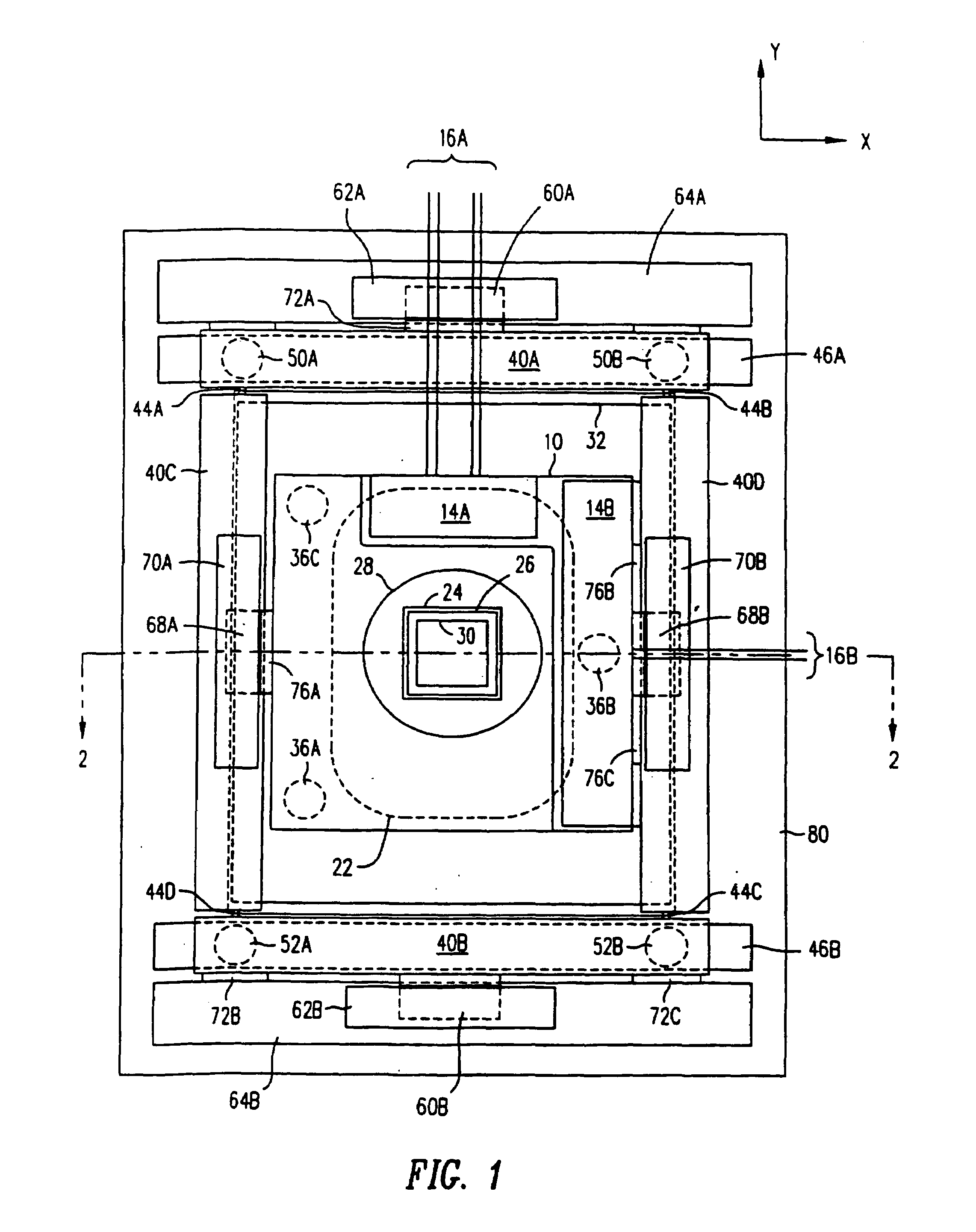
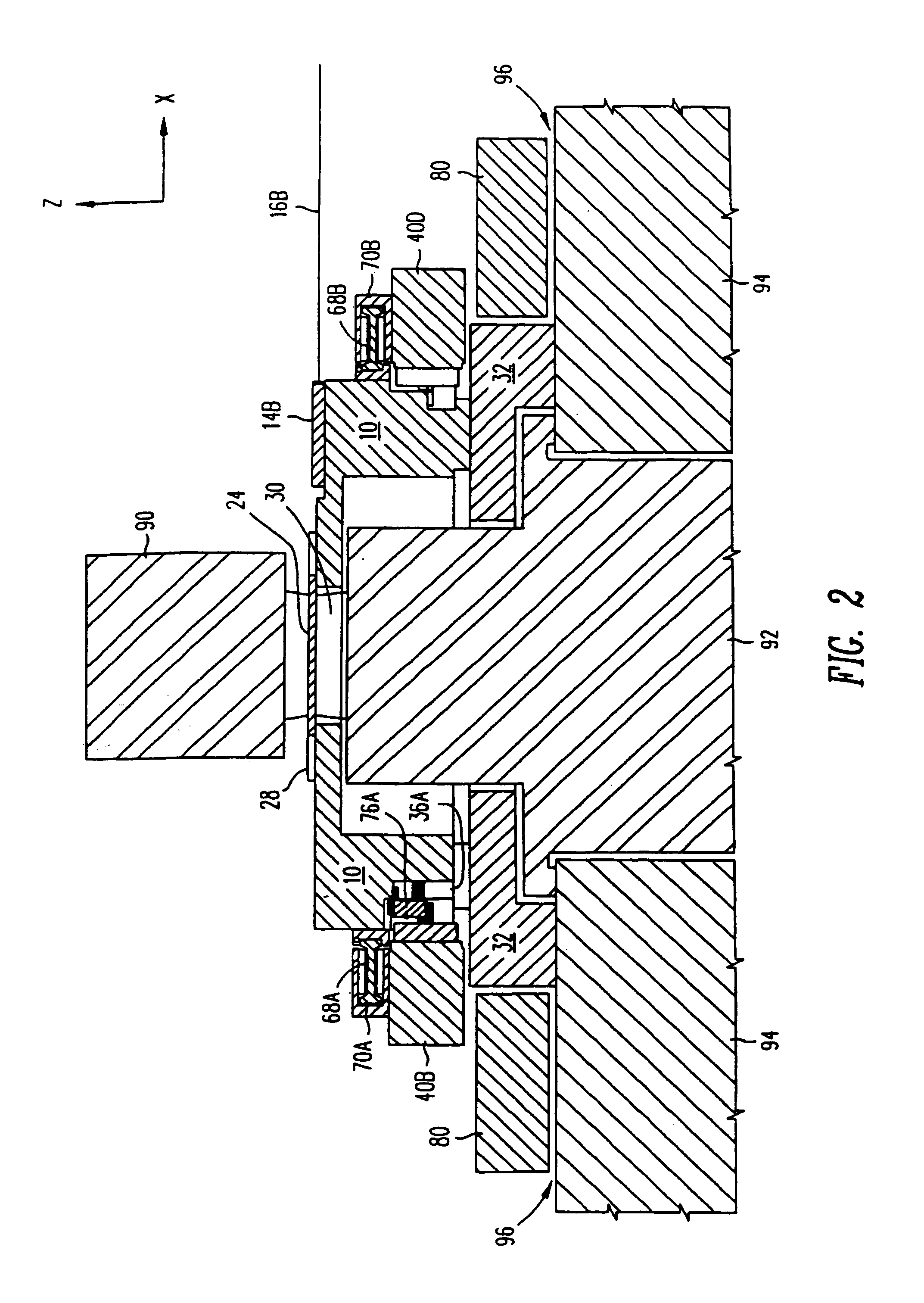
Positioning device having dynamically isolated frame, and lithographic device provided with such a positioning device
InactiveUS6989647B1Small distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDrive motorEngineering
A guided stage mechanism suitable for supporting a reticle in a photolithography machine includes a stage movable in the X-Y directions on a base. Laterally surrounding the stage is a rectangular window frame guide which is driven in the X-axis direction on two fixed guides by means of motor coils on the window frame guide cooperating with magnetic tracks fixed on the base. The stage is driven inside the window frame guide in the Y-axis direction by motor coils located on the stage cooperating with magnetic tracks located on the window frame guide. Forces from the drive motors of both the window frame guide and the stage are transmitted through the center of gravity of the stage, thereby eliminating unwanted moments of inertia. Additionally, reaction forces caused by the drive motors are isolated from the projection lens and the alignment portions of the photolithography machine. This isolation is accomplished by providing a mechanical support for the stage independent of the support for its window frame guide. The window frame guide is a hinged structure capable of a slight yawing (rotational) motion due to hinged flexures which connect the window frame guide members.
Owner:NIKON CORP
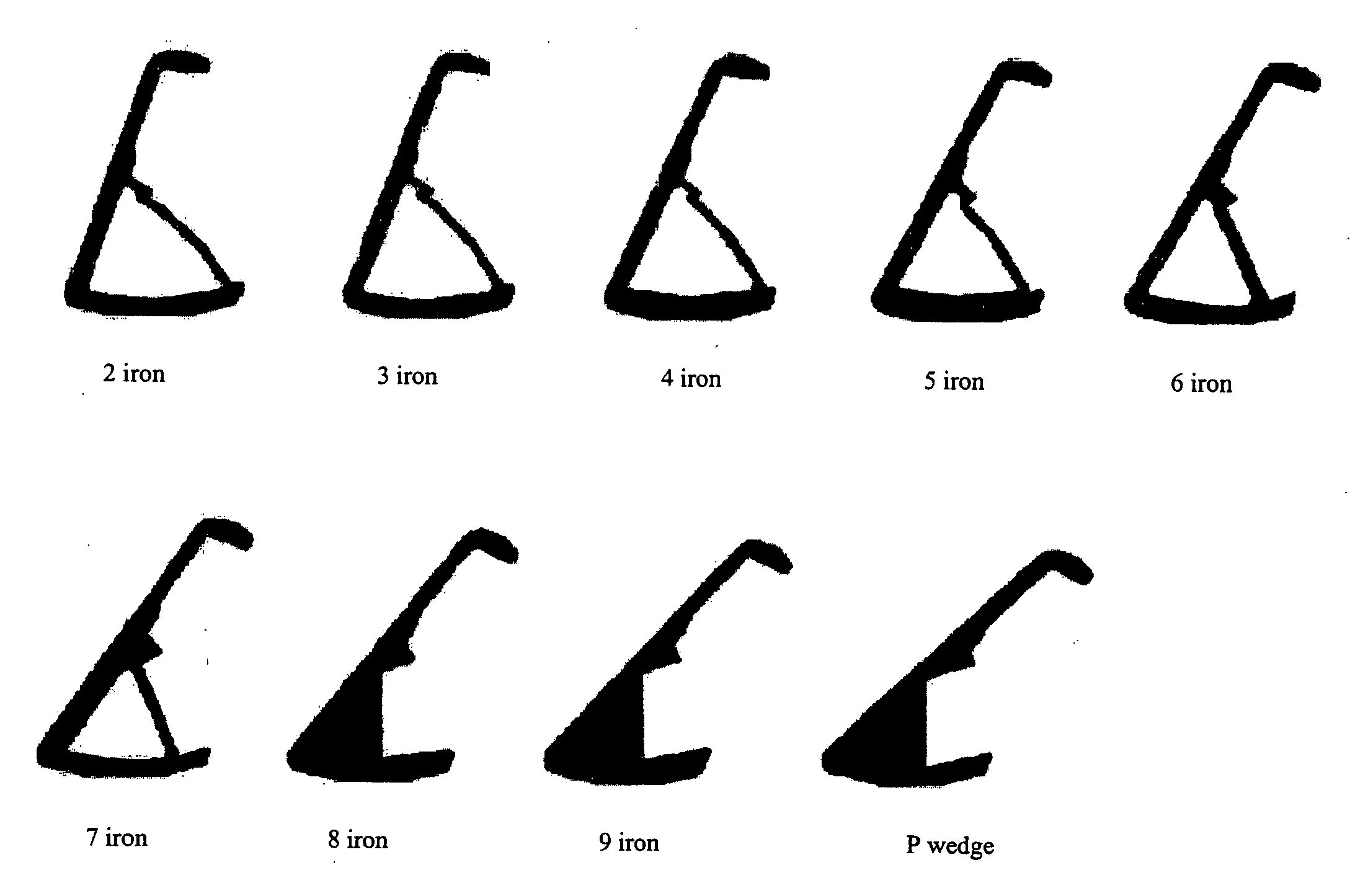
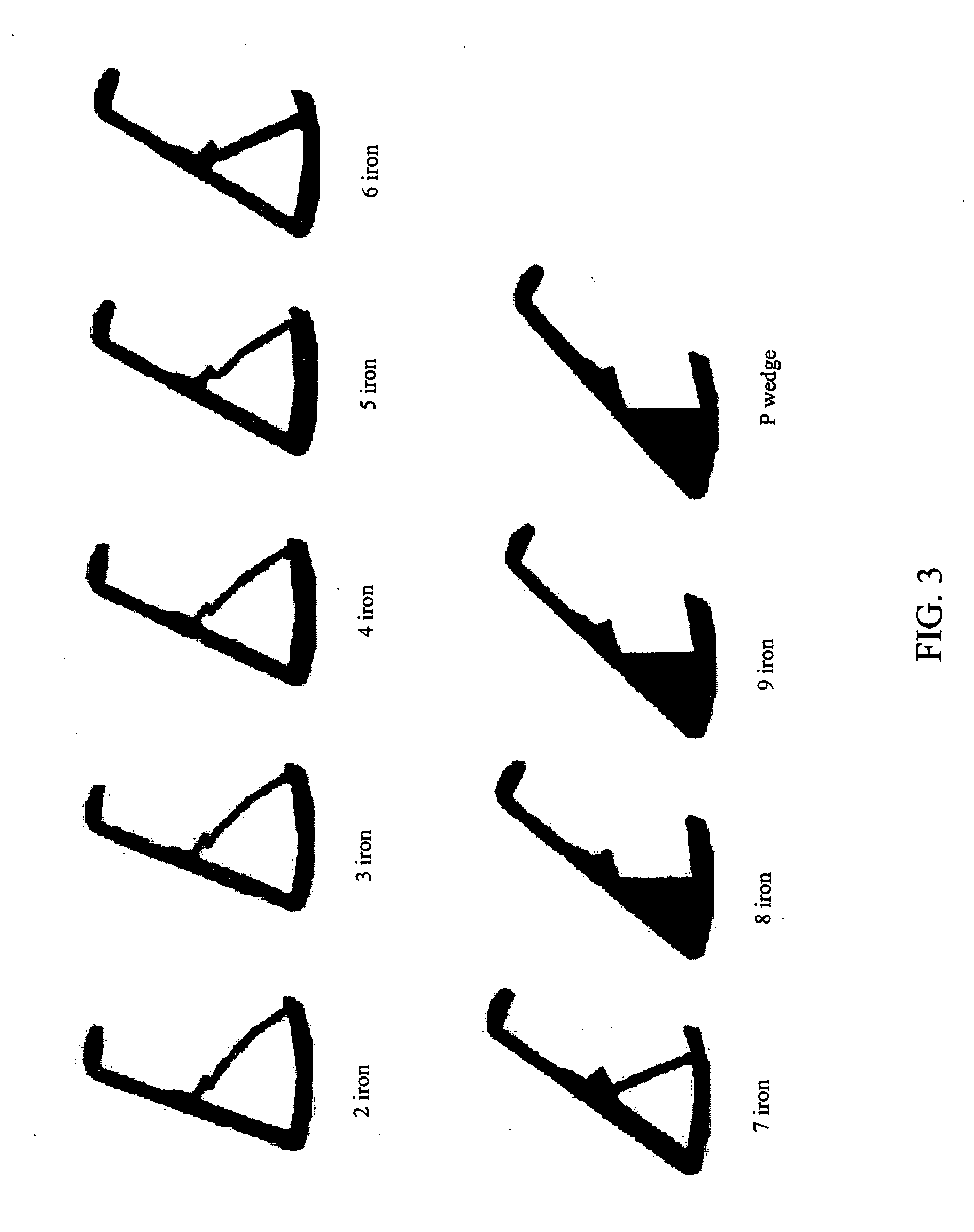
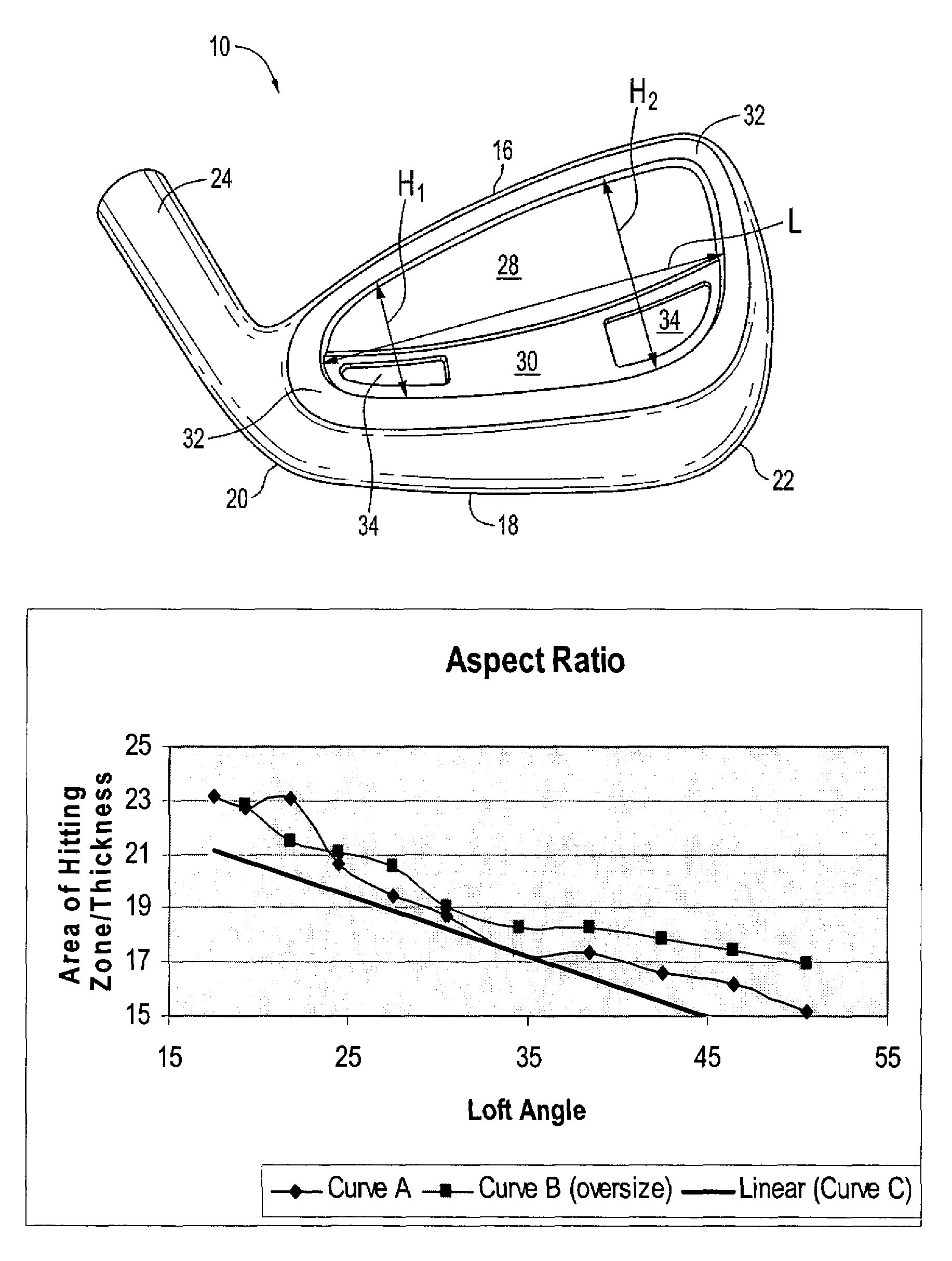
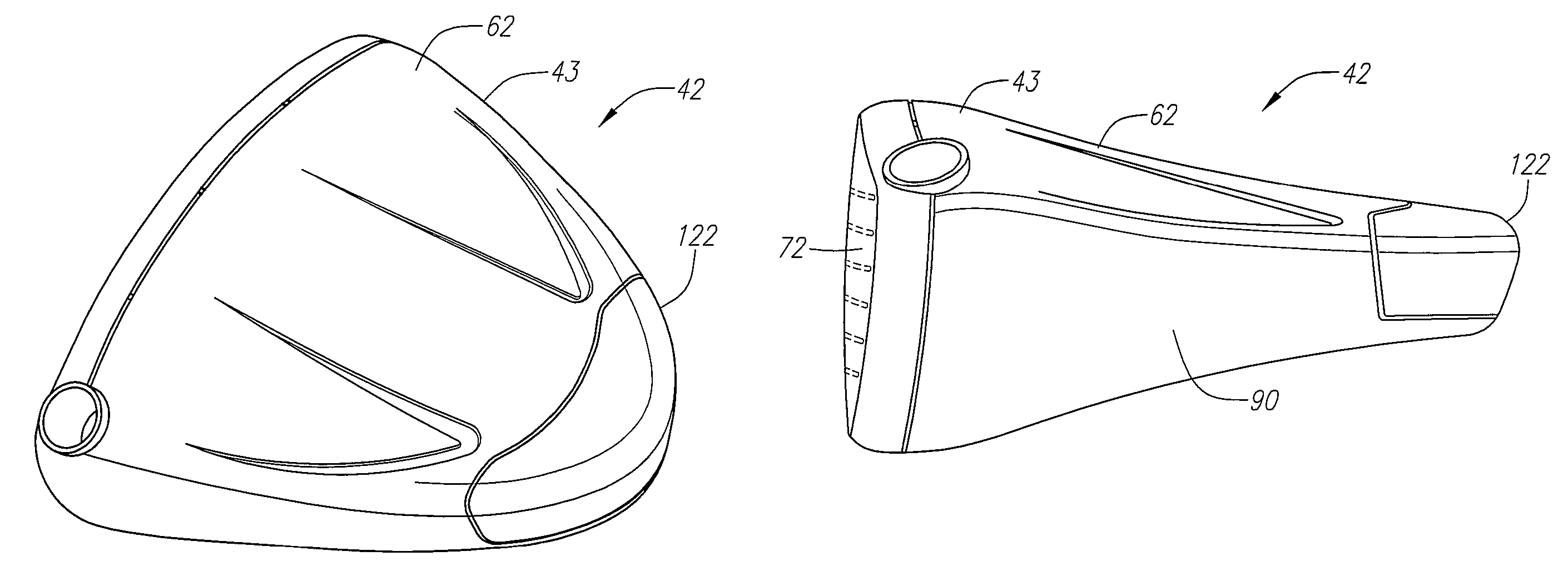
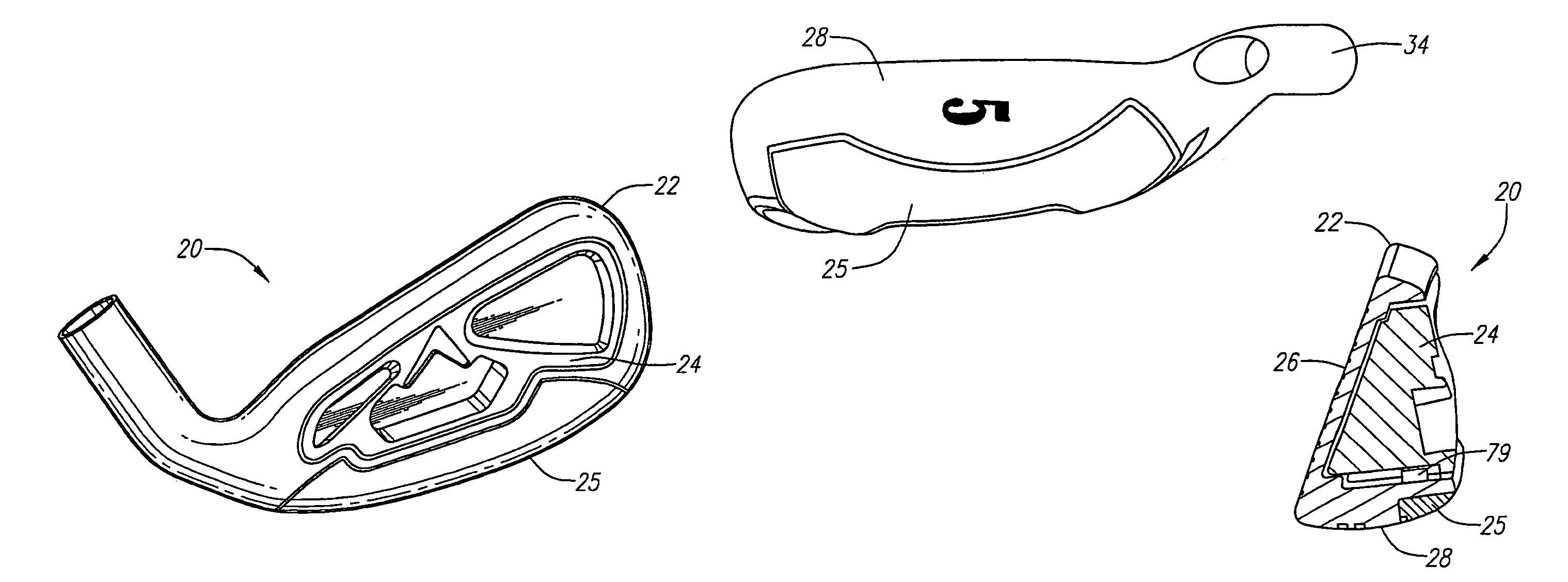
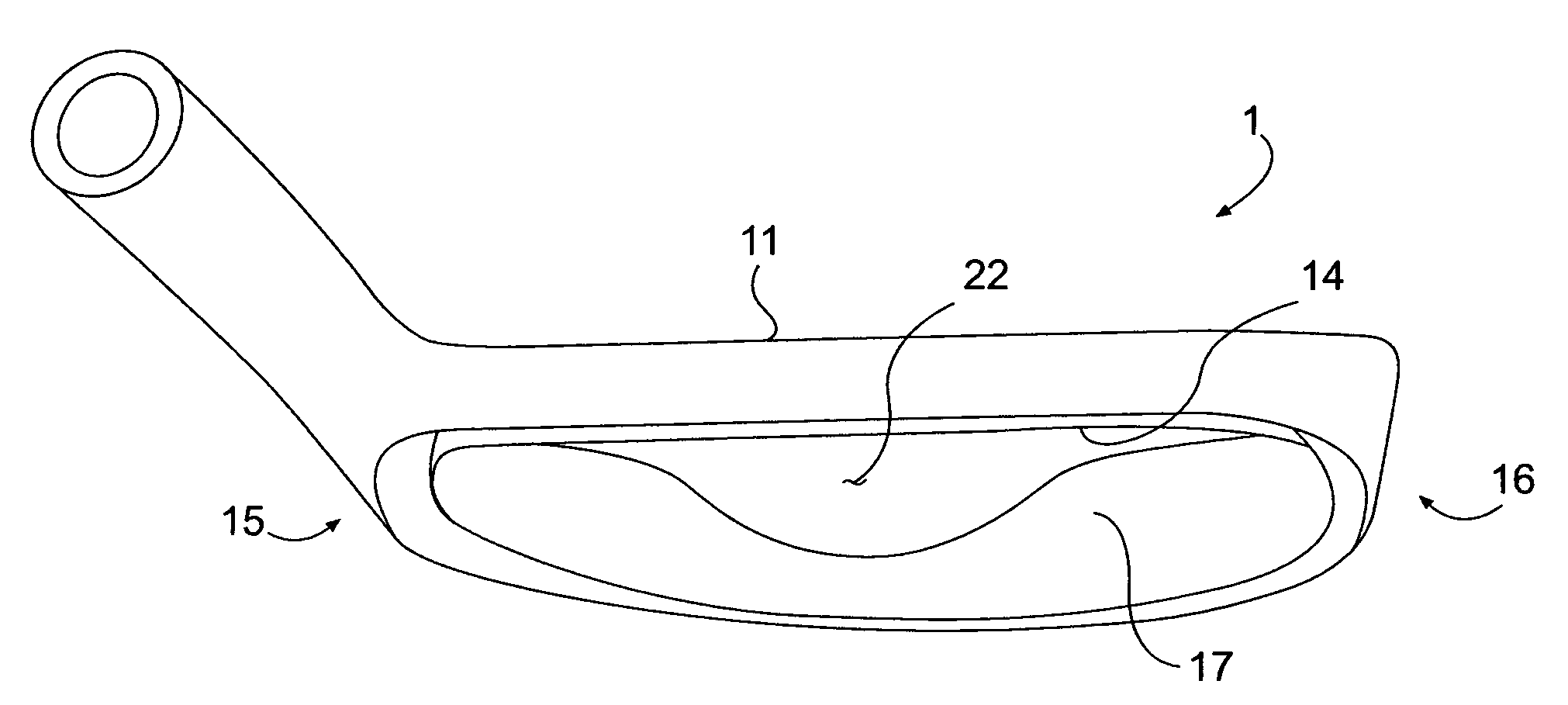
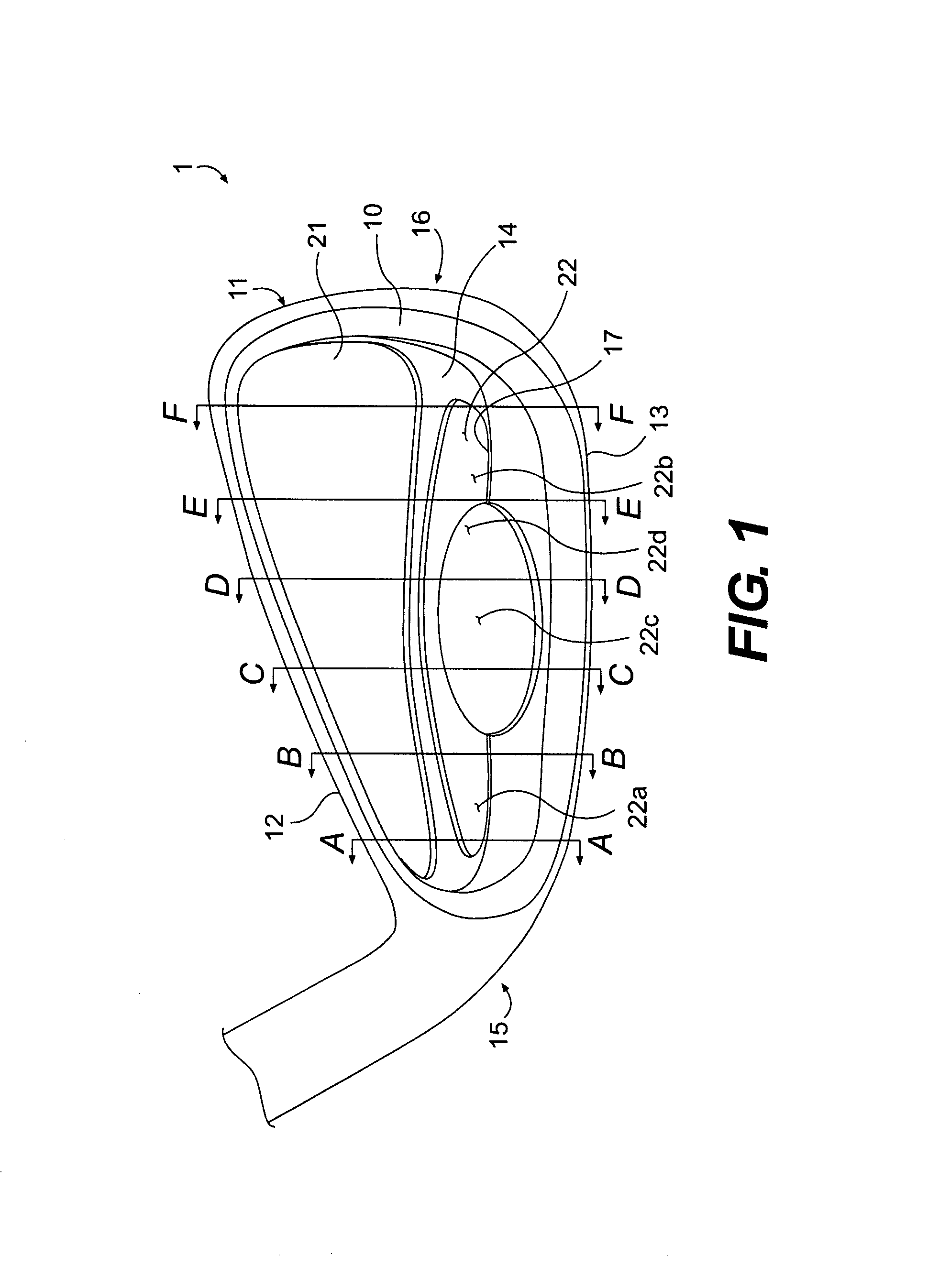
Forged iron-type golf clubs
Forged cavity back iron-type clubs and oversize clubs are disclosed. These forged clubs have thin, durable hitting face and relatively large cavity volumes. These clubs have high rotational moments of inertia to minimize distance and accuracy penalties associated with off-center hits. Long irons with hitting face of about 0.100 inch thick are achievable by the present invention. Also disclosed are forged irons made from stainless steels and annealed to achieve the desired hardness and ductility.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Positioning device having dynamically isolated frame, and lithographic device provided with such a positioning device
InactiveUS7365513B1Reduce torqueSmall distortionPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDrive motorEngineering
A guided stage mechanism suitable for supporting a reticle in a photolithography machine includes a stage movable in the X-Y directions on a base. Laterally surrounding the stage is a rectangular window frame guide which is driven in the X-axis direction on two fixed guides by means of motor coils on the window frame guide cooperating with magnetic tracks fixed on the base. The stage is driven inside the window frame guide in the Y-axis direction by motor coils located on the stage cooperating with magnetic tracks located on the window frame guide. Forces from the drive motors of both the window frame guide and the stage are transmitted through the center of gravity of the stage, thereby eliminating unwanted moments of inertia. Additionally, reaction forces caused by the drive motors are isolated from the projection lens and the alignment portions of the photolithography machine. This isolation is accomplished by providing a mechanical support for the stage independent of the support for its window frame guide. The window frame guide is a hinged structure capable of a slight yawing (rotational) motion due to hinged flexures which connect the window frame guide members.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Golf club head with high moment of inertia
ActiveUS7410428B1Improved off center ball speedIncrease the areaGolf clubsRacket sportsMoment of inertiaGolf Ball
A golf club head having a high moment of inertia is disclosed herein. The golf club head preferably has a volume ranging from 450 cubic centimeters to 475 cubic centimeters, a mass ranging from 180 grams to 225 grams, and a length ranging from 4.0 inches to 5.0 inches. The golf club head preferably has a moment of inertia, Iyy, about the center of gravity of the golf club head ranging from 2000 grams-centimeters squared to 4000 grams-centimeters squared. Preferably, a middle section of the golf club head has less than 20% of the mass of the golf club head.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Muscle-back iron golf clubs with higher moment of intertia and lower center of gravity
InactiveUS20070281796A1Improved mass propertyLower center of gravityGolf clubsRacket sportsMoment of inertiaEngineering
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
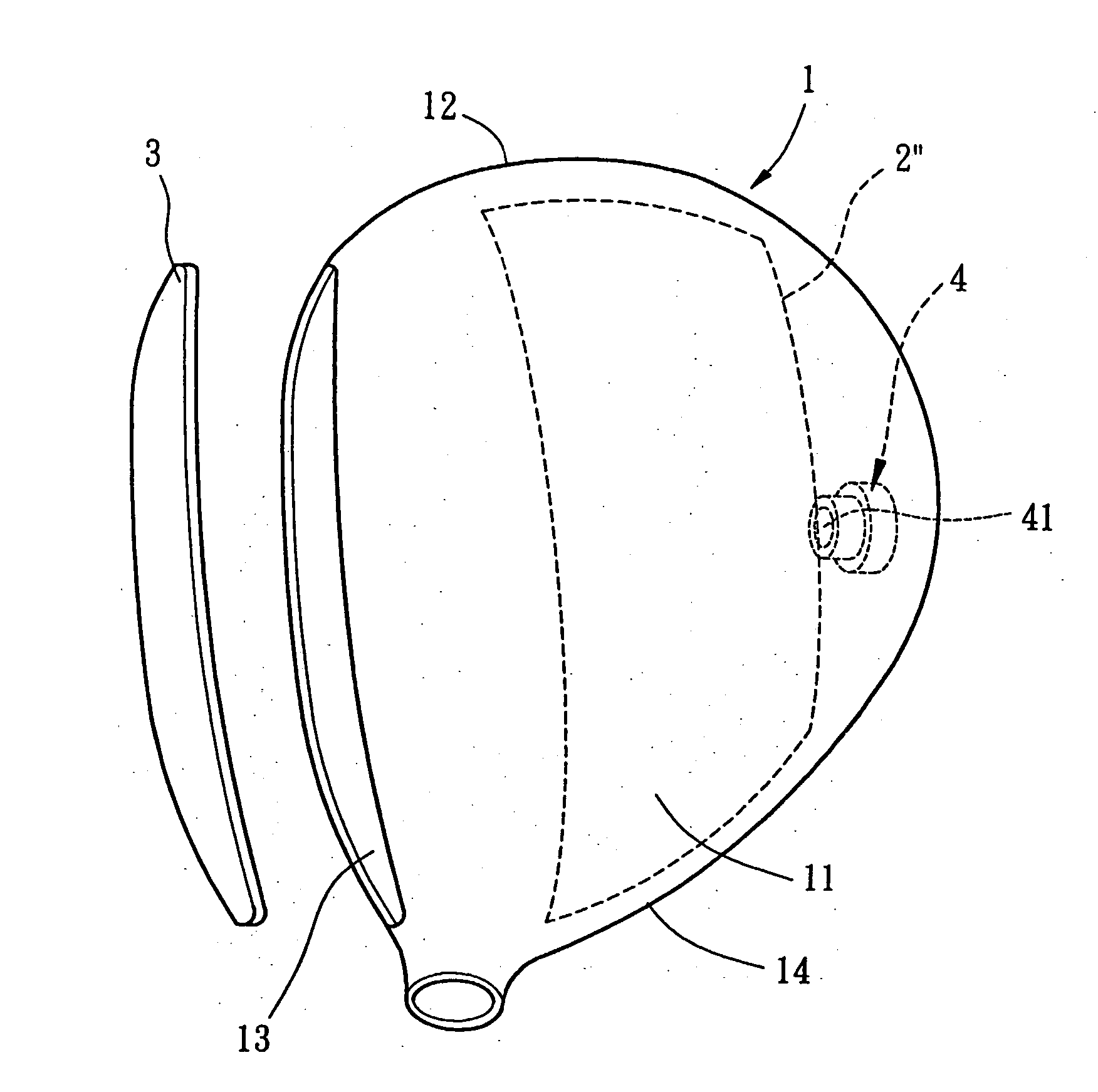
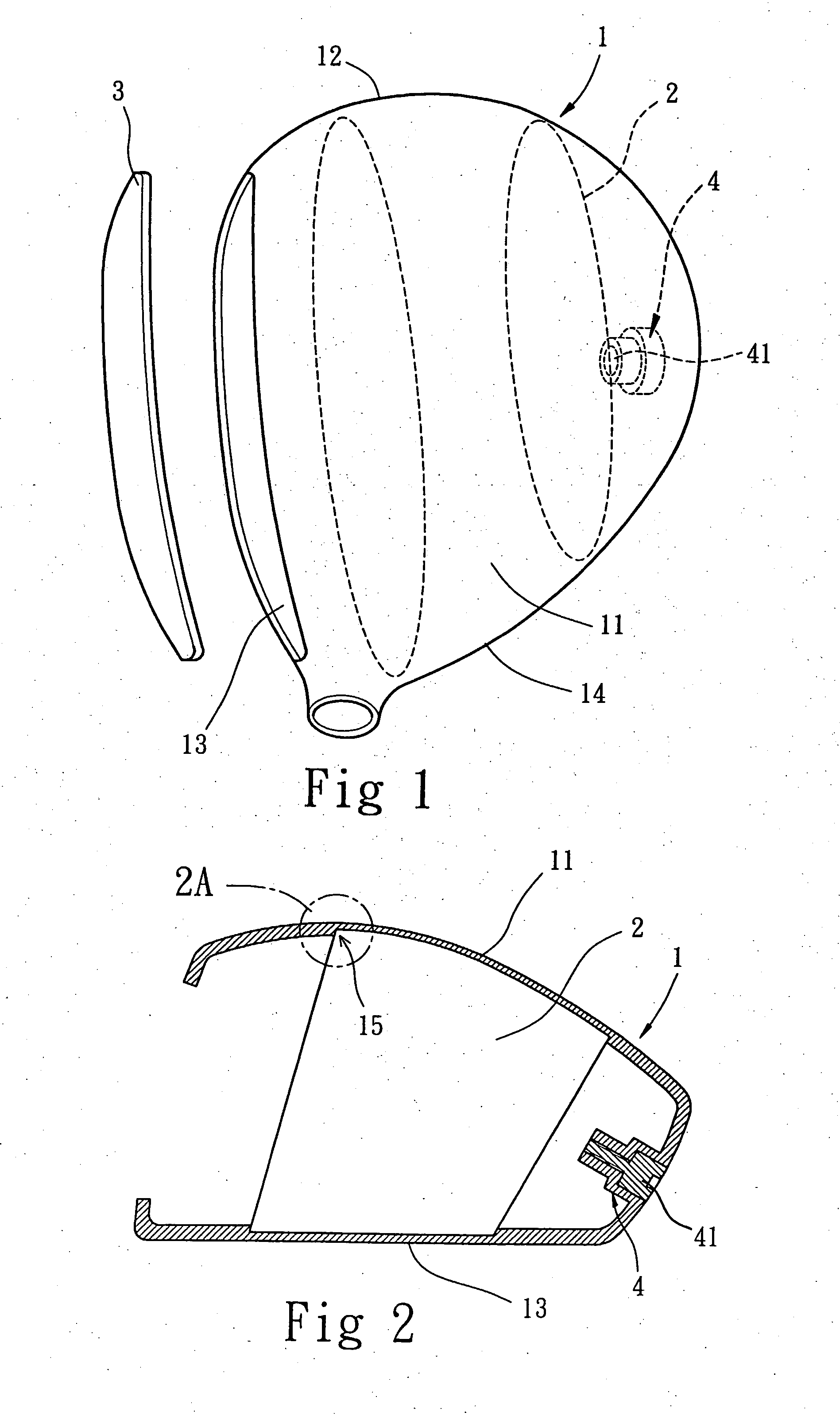
Wiper blade for windshields, especially automobile windshields, and method for the production thereof
InactiveUS6836926B1Improve wipe qualityEasy to produceWindow cleanersVehicle cleaningEngineeringMoment of inertia
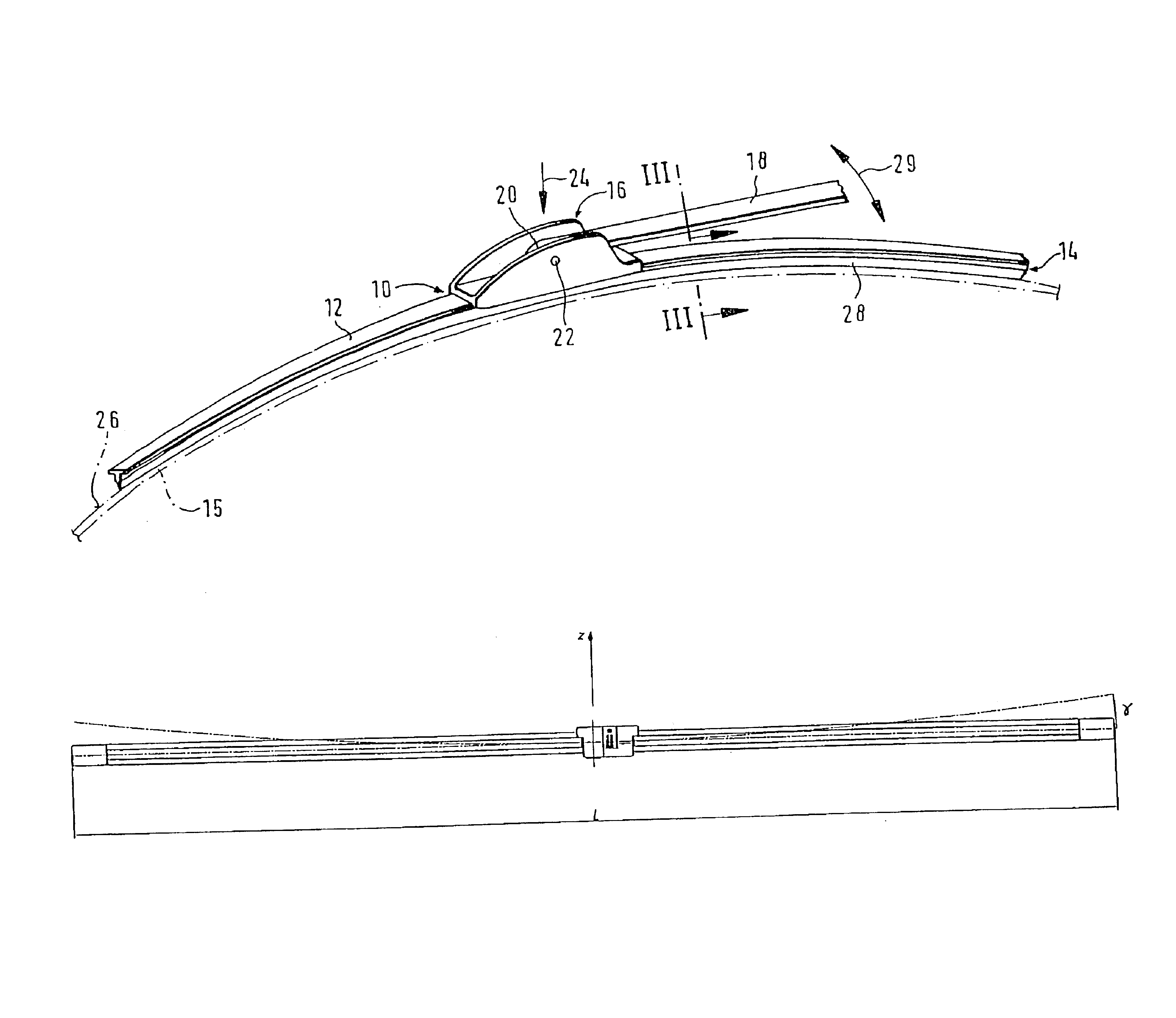
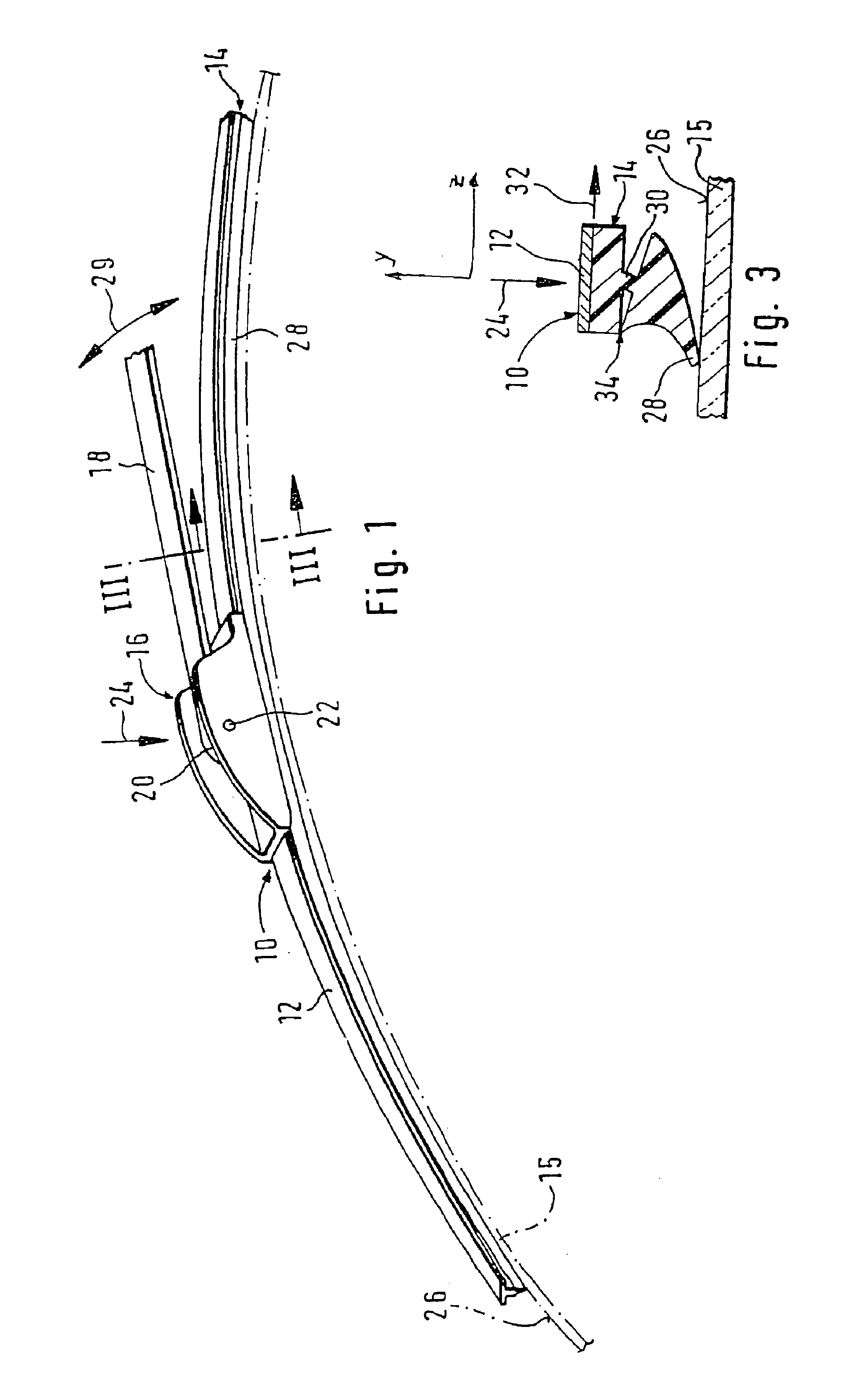
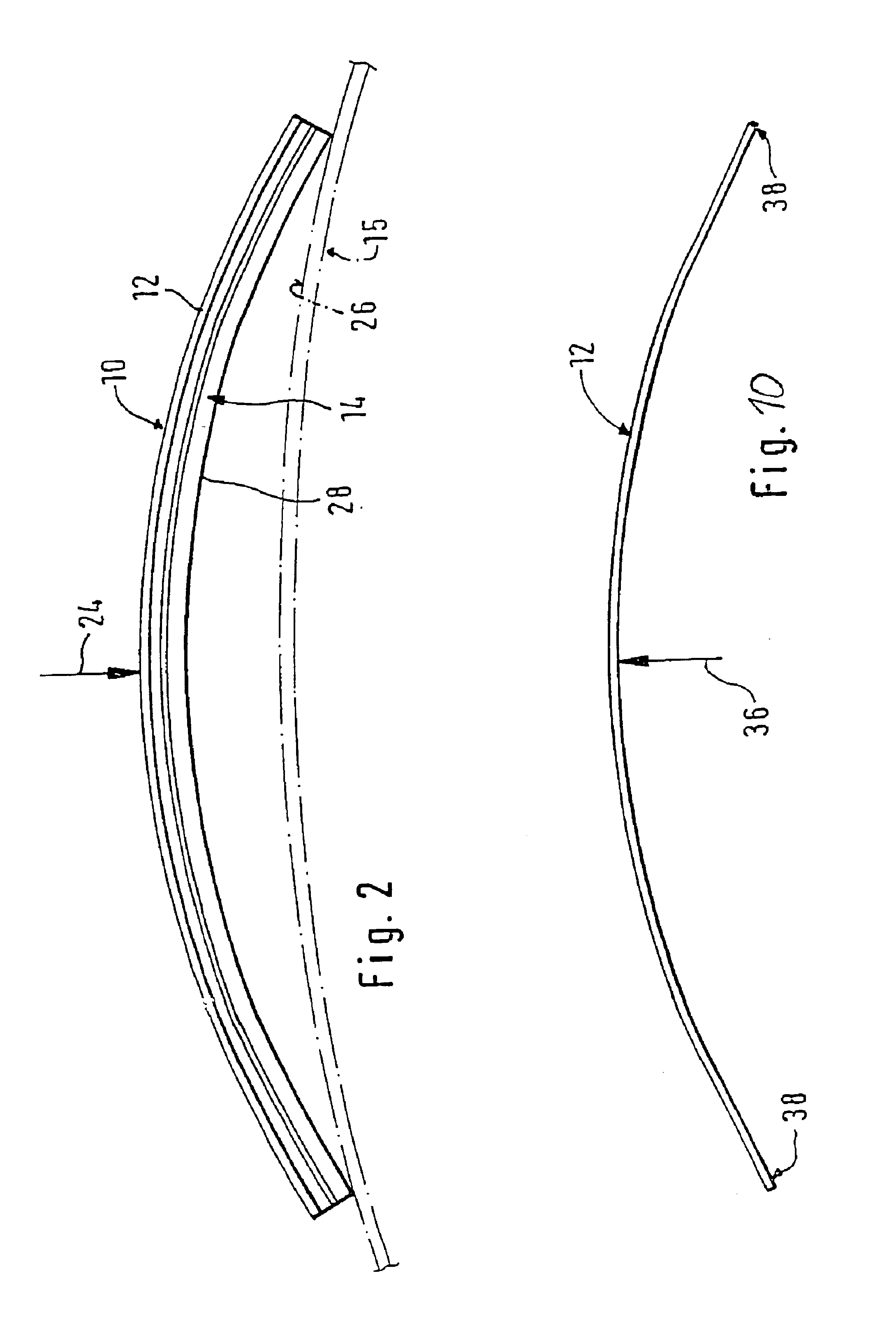
The invention relates to a wiper blade for windshields, especially automobile windshields, comprising at least one support element, a support element (12), a wiper strip (14) and connecting means (16) for a wiper arm (18). The support element (12) is a long flat rod to which the wiper strip (14) and the connecting means (16) are fixed. According to the invention, the flat rod has a cross-sectional profile (40), whereby Fwf*L2 / 48*E*Izz<0.009 when Fwf is the pressure force exerted on the wiper blade or the pressure force for which the wiper blade was originally intended, L represents the length of the wiper blade, E stands for the elasticity module of the flat rod material and Izz is the moment of inertia of the cross-sectional profile around the z axis (perpendicular to an s axis associated with the flat rod and perpendicular to the y axis).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP
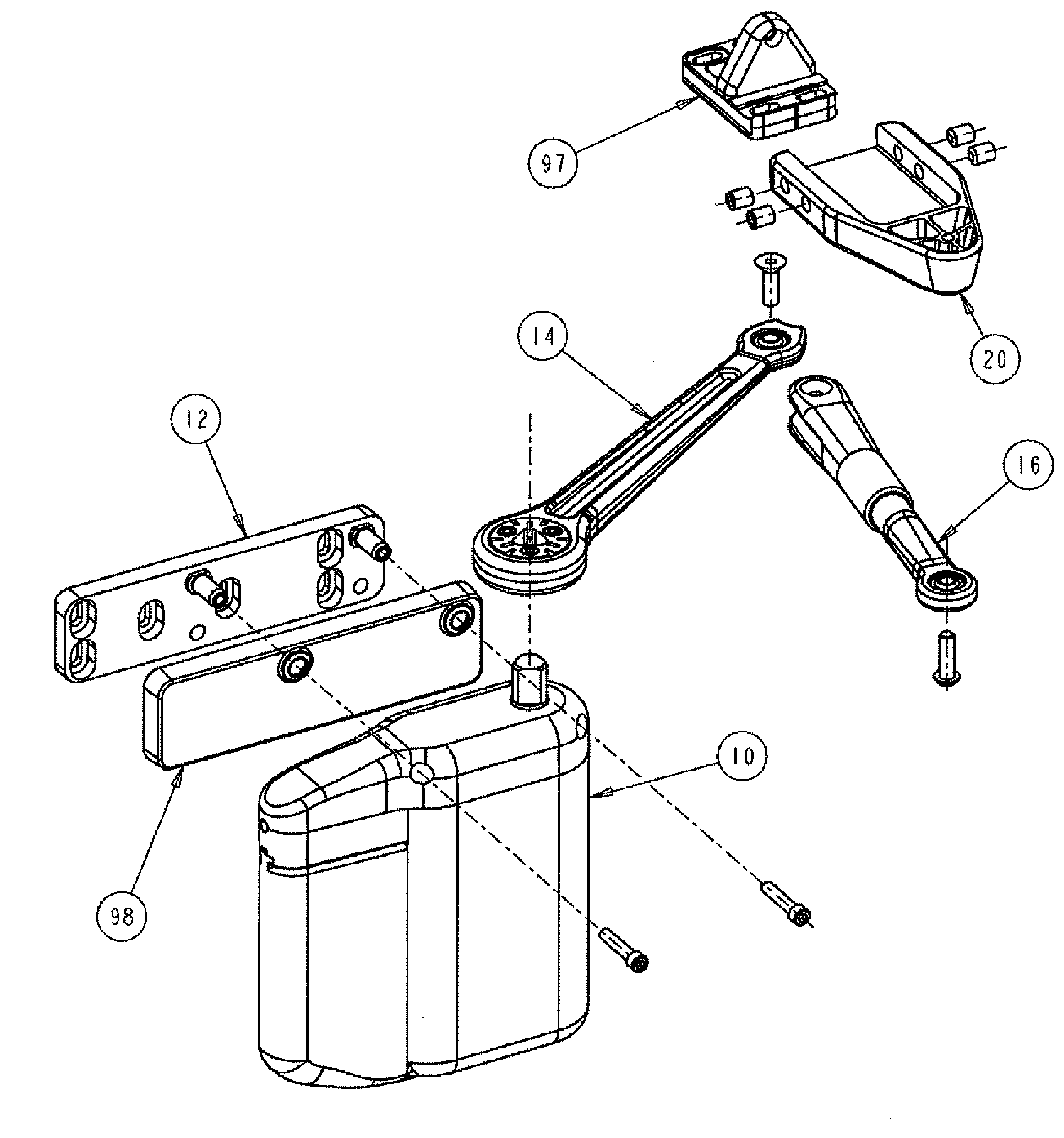
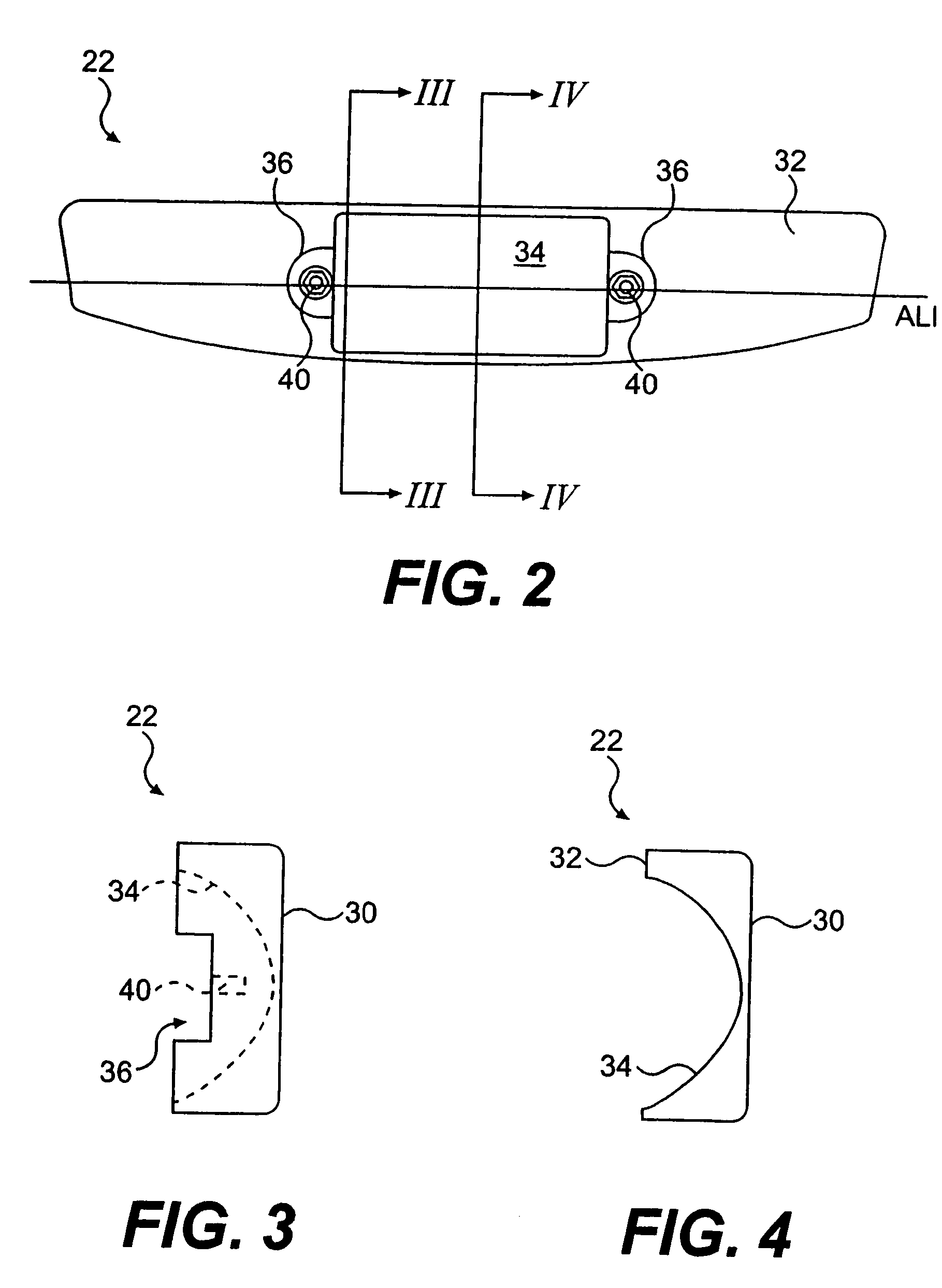
High moment of inertia putter having adjustable weights
InactiveUS6896625B2Avoid distortionRaises the swingweight of a low swingweight putterGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringMoment of inertia
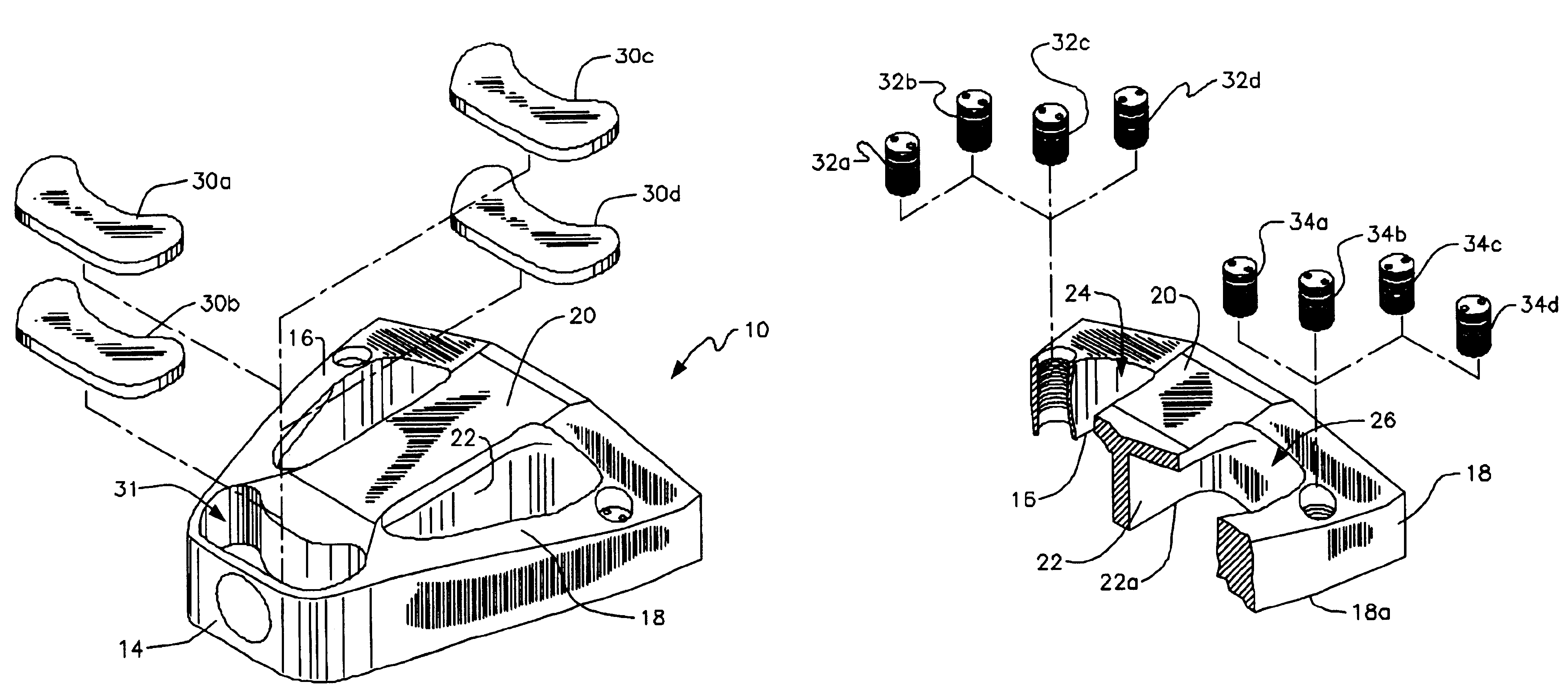
A golf putter head of triangular shape. A ball-striking leading wall has a first breadth greater than a second breadth of a trailing wall. The leading and trailing walls are interconnected at their respective opposite ends by sidewalls that converge toward one another. A web interconnects the leading and trailing walls along a longitudinal axis of the golf putter head. A first embodiment may include a trailing copper weight and side wall aluminum weights. A second embodiment may include three copper weights, a third embodiment may include three copper-tungsten weights, and a fourth embodiment may include three tungsten weights. The weights are removable so that a putter having a low swingweight or a high swingweight can be brought up to or down to a standard swingweight. The weights may also be mixed in the second, third, and fourth embodiments.
Owner:MACGREGOR GOLF
Multi-material golf club head
ActiveUS7338390B2Increase volumeStrong characteristicGolf clubsRacket sportsMulti materialMoment of inertia
A golf club head in accordance with various aspects of the present invention, may have a higher volume and / or higher strength. The golf club head may comprise a frame structure with a composite matrix. The golf club head may also comprise a detachable face, allowing various faces of differing materials to be attached to the body. A detachable face further allows the head to be tuned via placement / rearrangement of weights within the head to change the center of gravity and moment of inertia.
Owner:DICK'S SPORTING GOODS
Iron golf club
InactiveUS7338387B2Lower center of gravityHigh moment of inertiaGolf clubsRacket sportsHigh densityMetallic materials
The iron golf club head (20) of the present invention is preferably composed of three main components: a main body (22), a central member (24) and a mass member (25). The Mass member (25) is preferably composed of a high density material such as a nickel-tungsten alloy. The central member (24) is preferably composed of a lightweight, non-metal material. The main body (22) is preferably composed of a titanium alloy material. The iron golf club head (20) preferably has high moments of inertia Izz and Ixx, and a low center of gravity.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Golf club head having a high-degree elastically deformable structure
InactiveUS20070082751A1Increase elasticityImprove elastic deformation abilityGolf clubsRacket sportsThin layerEngineering
A golf club head includes a golf club head body, an elastically deformable thin layer, a striking plate and a club weight portion. The golf club head body includes a crown portion, a toe-side wall portion, a sole portion and a heel-side wall portion. The elastically deformable thin layer is provided on the golf club head body and arranged between the toe-side wall portion and the heel-side wall portion. The elastically deformable thin layer has a thickness thinner than that of other portions of the golf club head body. Mounted on a front portion of the striking plate is the striking plate along which the elastically deformable thin layer has a direction of extension so as to absorb a striking stress transmitted from the striking plate. The club weight portion is arranged on the golf club head body to adjust the center of gravity and the moment of inertia.
Owner:FUSHENG IND CO LTD
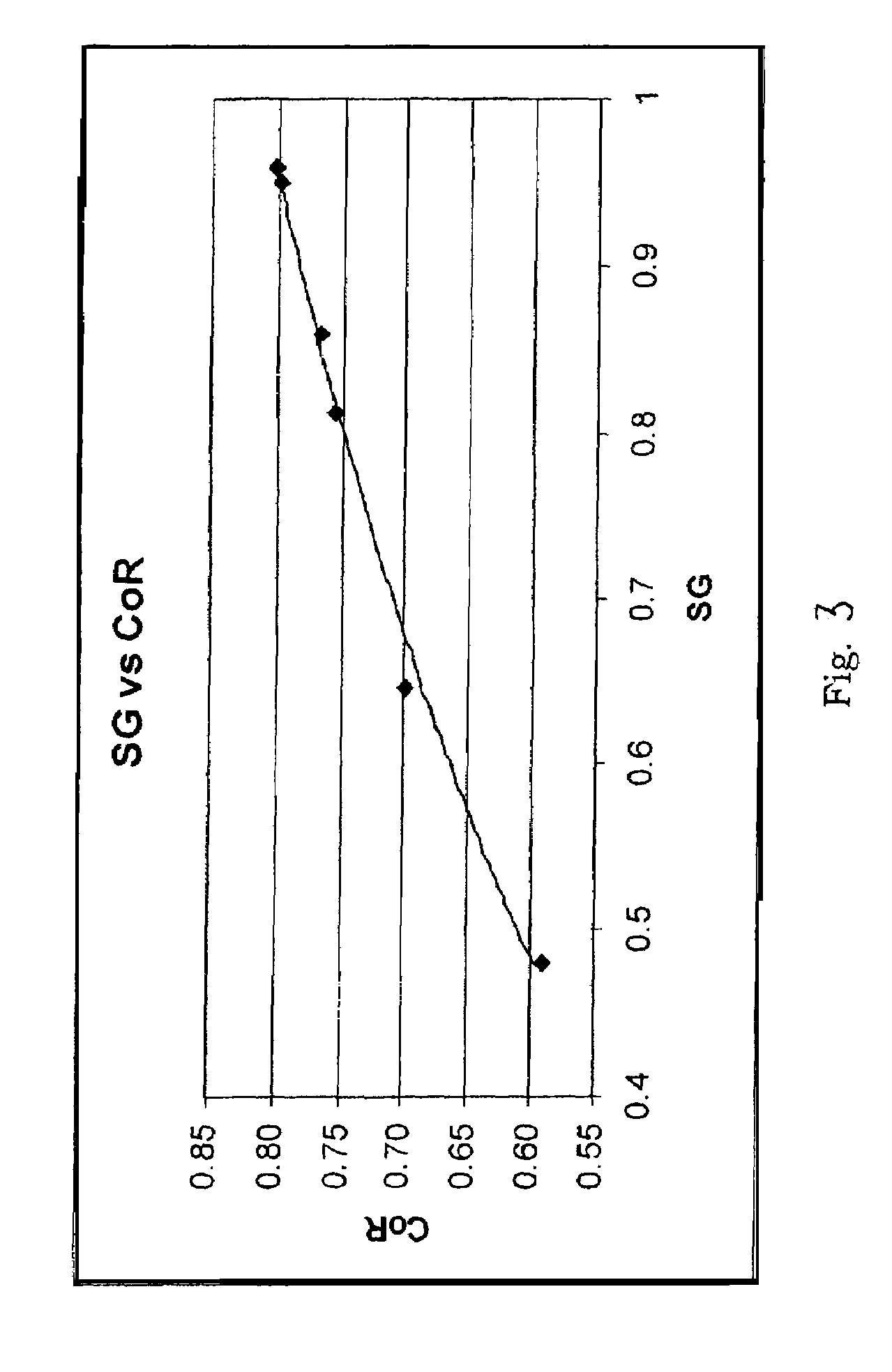
Foam-core golf balls
A golf ball with a controlled moment of inertia and controlled spin rate is disclosed. The ball has an intermediate layer positioned between the core and the cover and the intermediate layer has a reduced specific gravity. Preferably, this reduction is less than about 30% in specific gravity and the reduction in the coefficient of restitution is less than about 2%.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Door Operator for Controlling a Door and Method of Same
ActiveUS20090265992A1Minimize error signalDC motor speed/torque controlBuilding braking devicesRechargeable cellSpring force
A door operator for controlling operation of a door, the door operator having a motor to open the door against a spring force, the door operator further comprising a door position sensor for transmitting a signal indicative of door position; and among other things, calculates a door moment of inertia based on a net torque and the time for the door to reach a predetermined angle from the closed position. Also provided is a door operator that compares door speed to a desired door speed based on a door speed-position profile and generates a door speed error signal and minimizes the door speed error signal by adjusting the braking load resulting from charging a chargeable battery using the motor as a generator.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY ACCESSORIES & DOOR CONTROLS GRP INC
Putter
InactiveUS20060094535A1Reduce groundingGolf clubsRacket sportsMoment of inertiaBiomedical engineering
A golf putter head adapted for attachment to a club shaft is provided with a face member having a strike face and a cylindrical back cavity, and a body member configured to fit and rotate within the back cavity is disclosed. Selective rotation of the body member within the back cavity sets a loft of the putter head. The weighting of the putter is adjusted by securing a weight member to the body member. A golf putter head having an increased moments of inertia is also disclosed. The putter head includes a face member, a body member, and a weight member. Placement of the weight member is such that the moments of inertia are increased and the putter head is stable.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Golf club head with undercut
ActiveUS7238119B2Enlarges the club sweet spotIncreases the moment of inertiaGolf clubsRacket sportsMoment of inertiaGolf Ball
A golf club head having an undercut is disclosed. The club head includes a body defining a striking face, a top line, a sole, a back, a heel, and a toe. The back contains a cavity that extends in a direction substantially perpendicular to the face. A recesses is provided within the cavity, with the recess extending away from the cavity and toward the sole. The recess causes more of the club head mass to be oriented towards the perimeter of the club head. This enlarges the club sweet spot and increases the moment of inertia, producing a more forgiving club. The recess may have a varying depth and / or a varying draft angle. A rear wall of the recess may be provided with a cutout to further reposition mass toward the club head perimeter. An insert, such as a vibration dampening member, may be provided within the recess. The insert may contain secondary inserts, such as weight members, therein in strategic locations. The insert may completely fill the recess, or may fill only a portion thereof.
Owner:COBRA GOLF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com