Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1346 results about "Current regulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
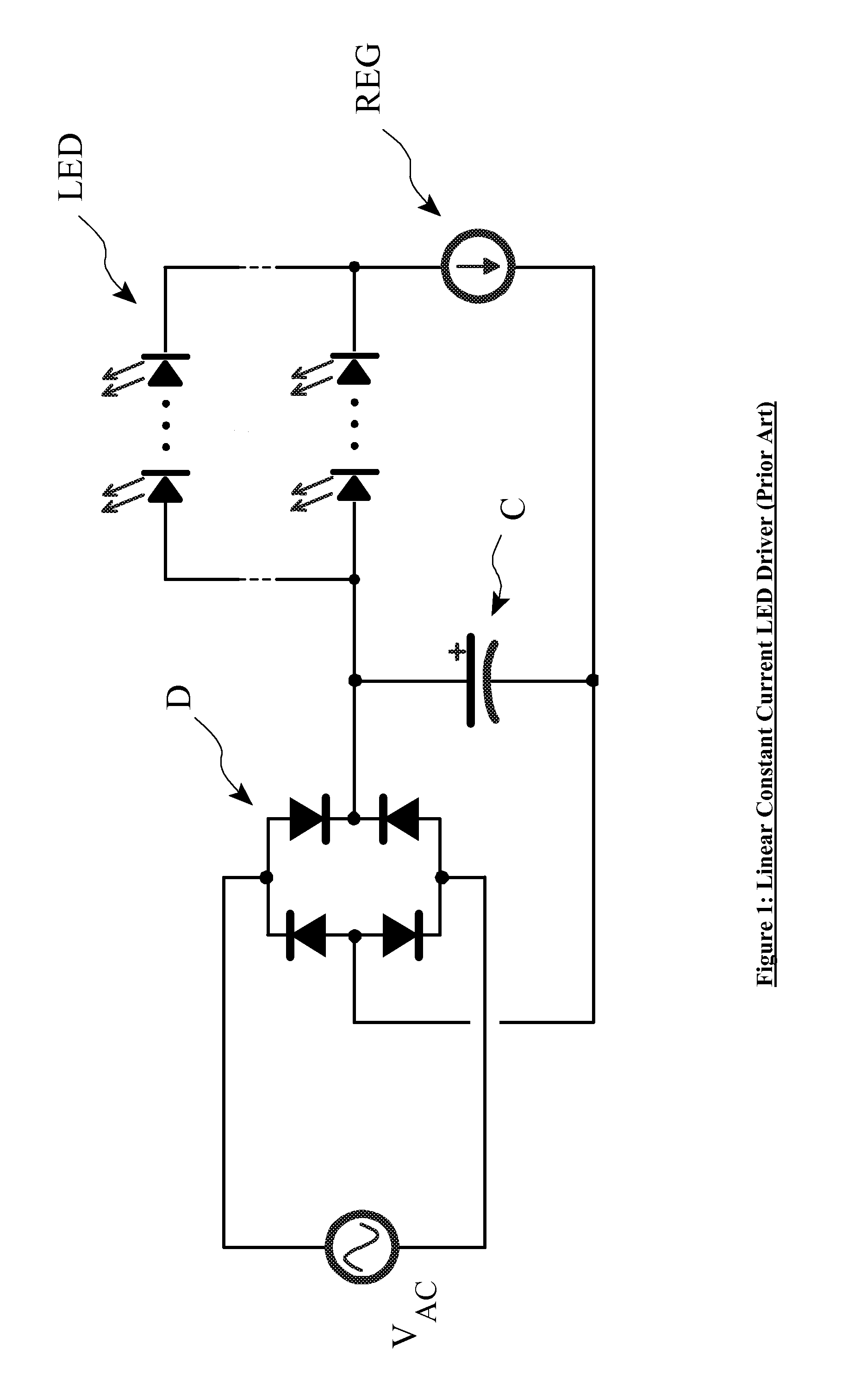
Current regulator is a device that provides a constant current regardless of change in load or supply.
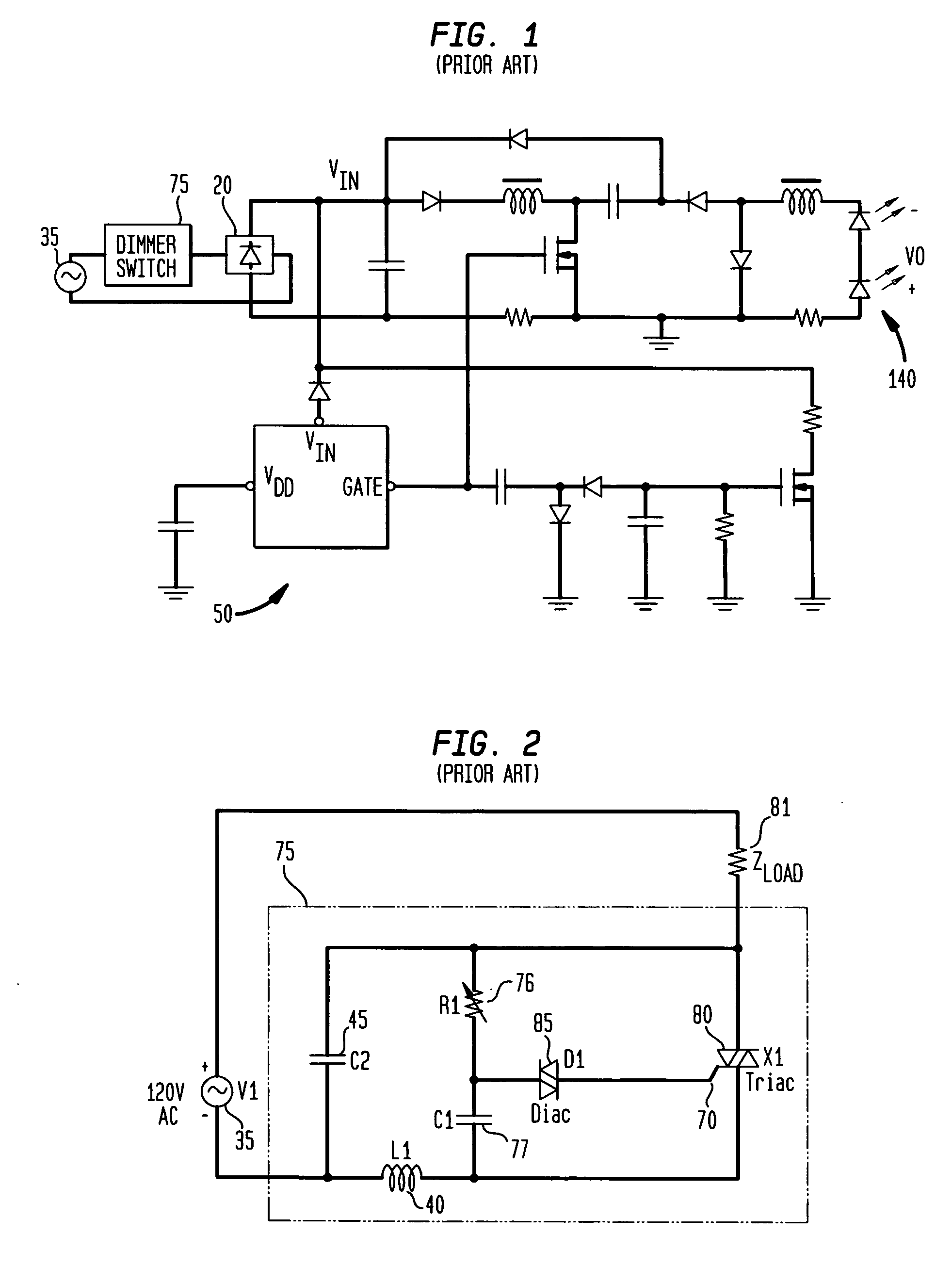
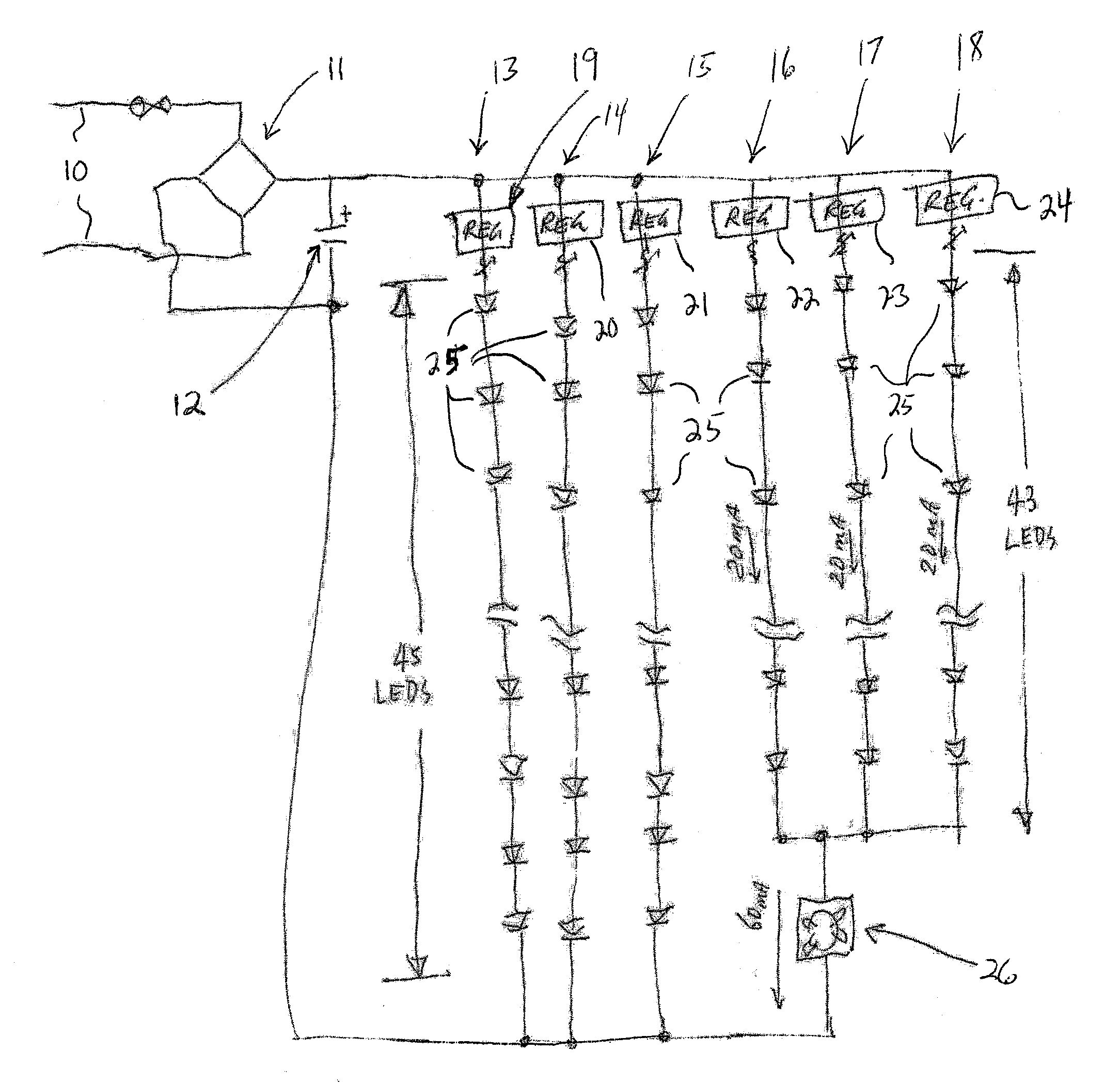
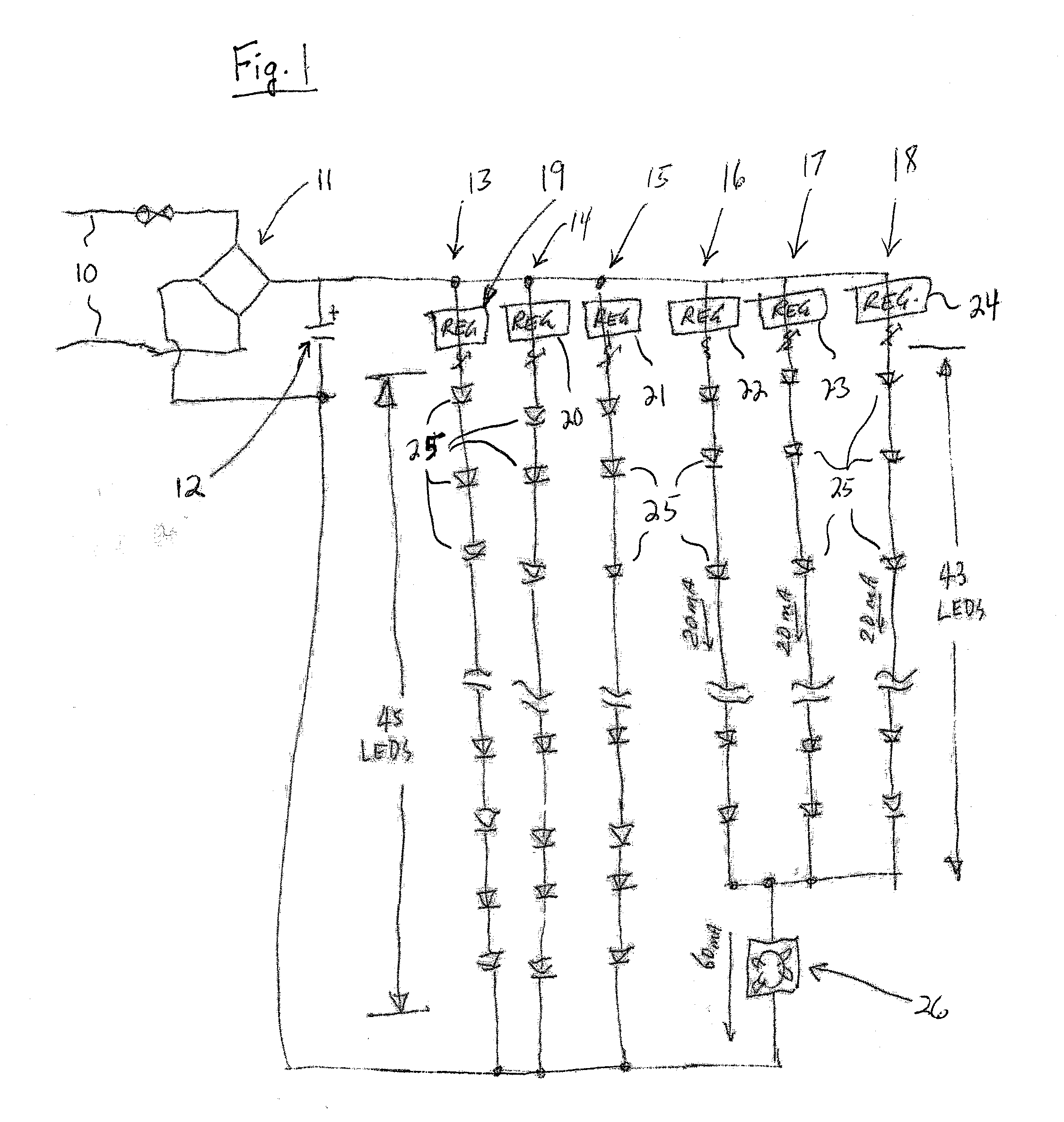
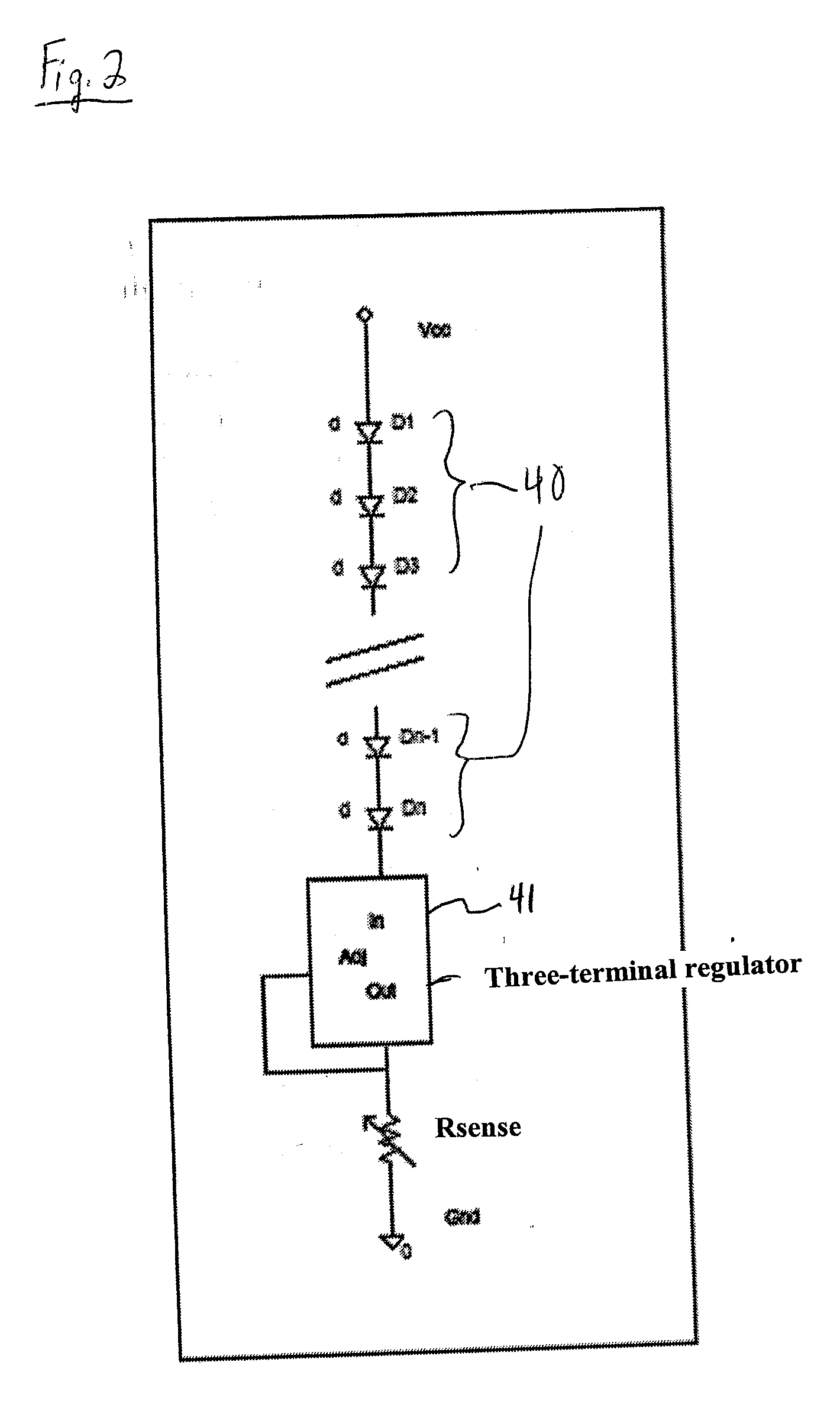
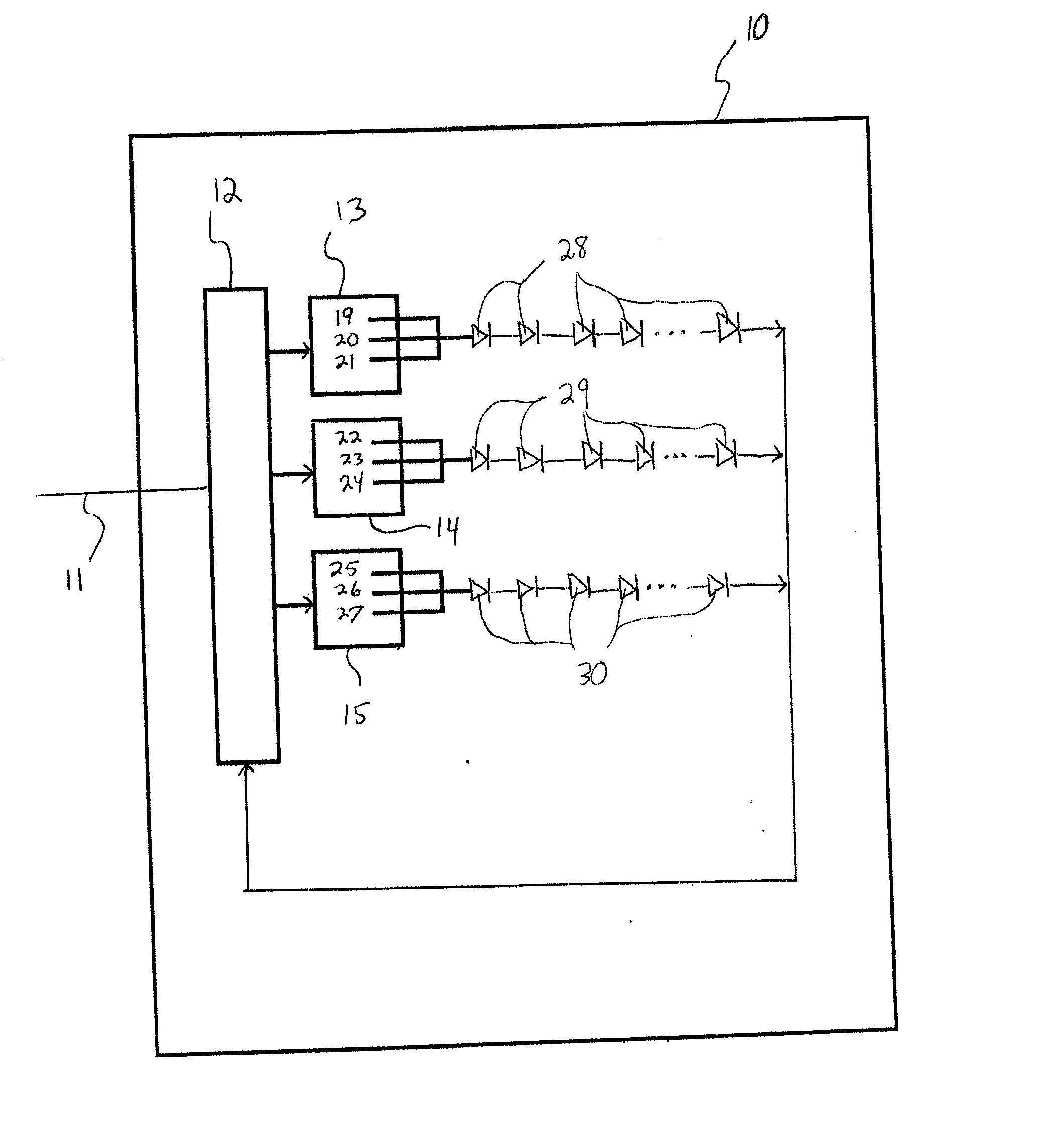
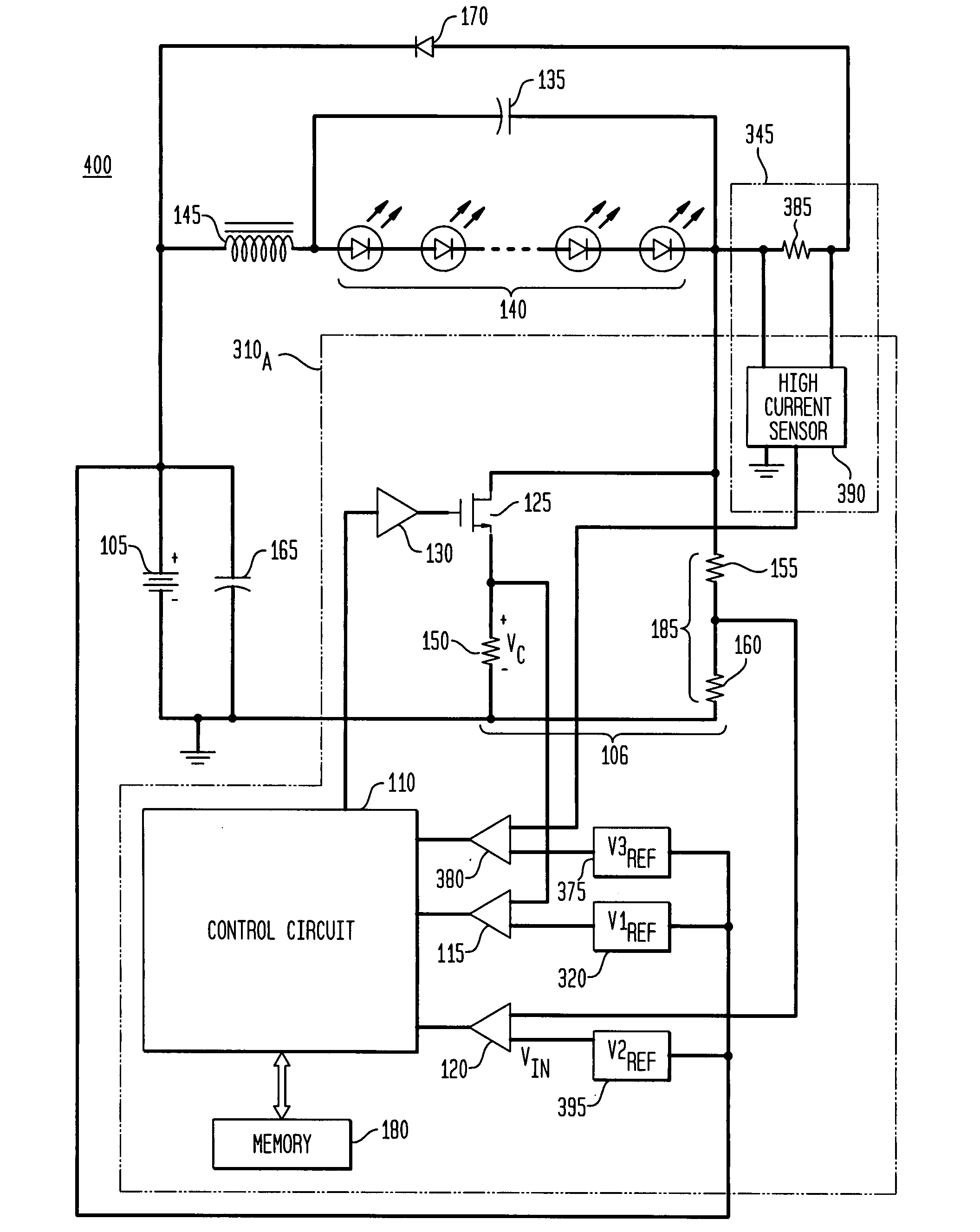
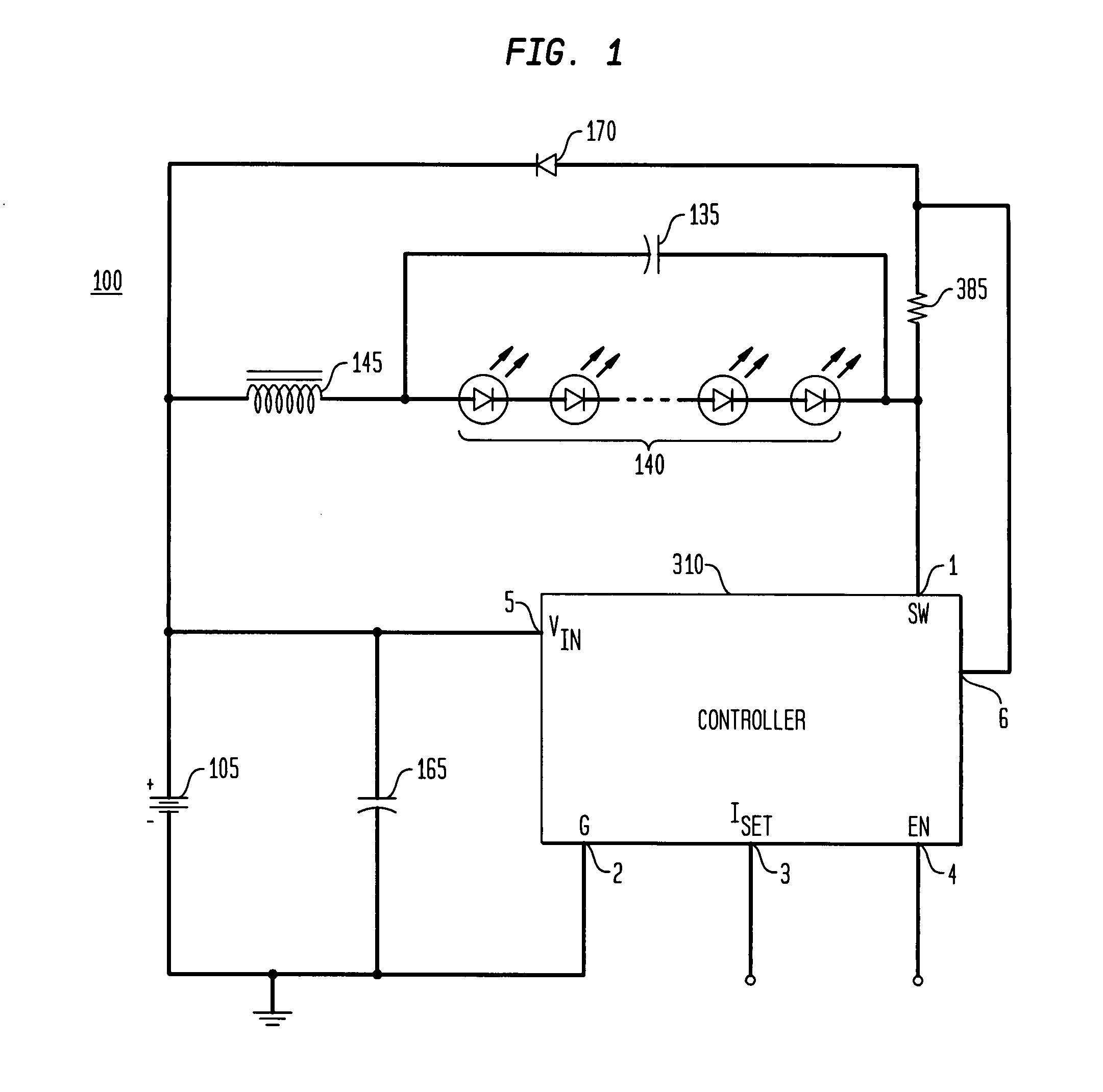
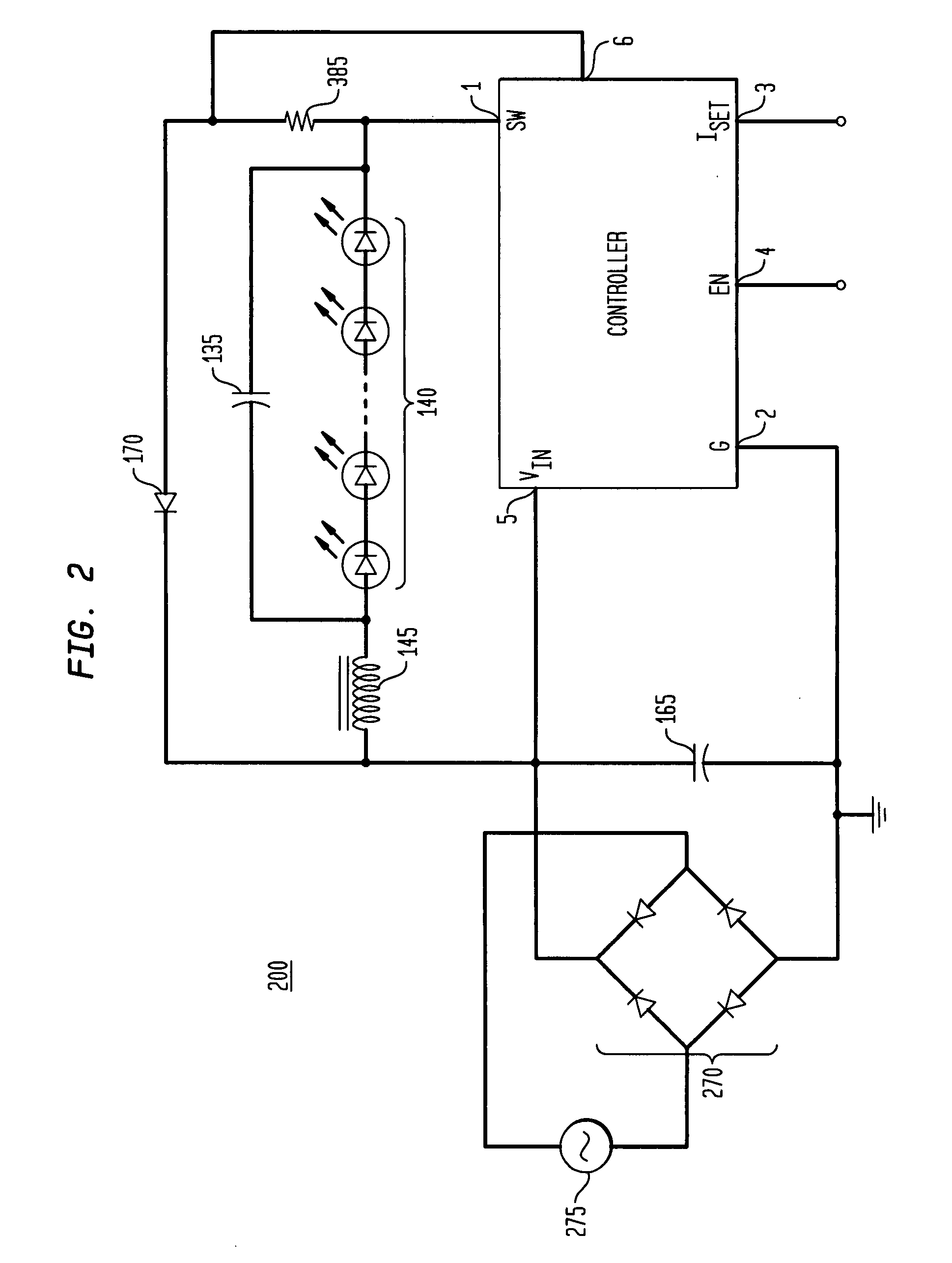
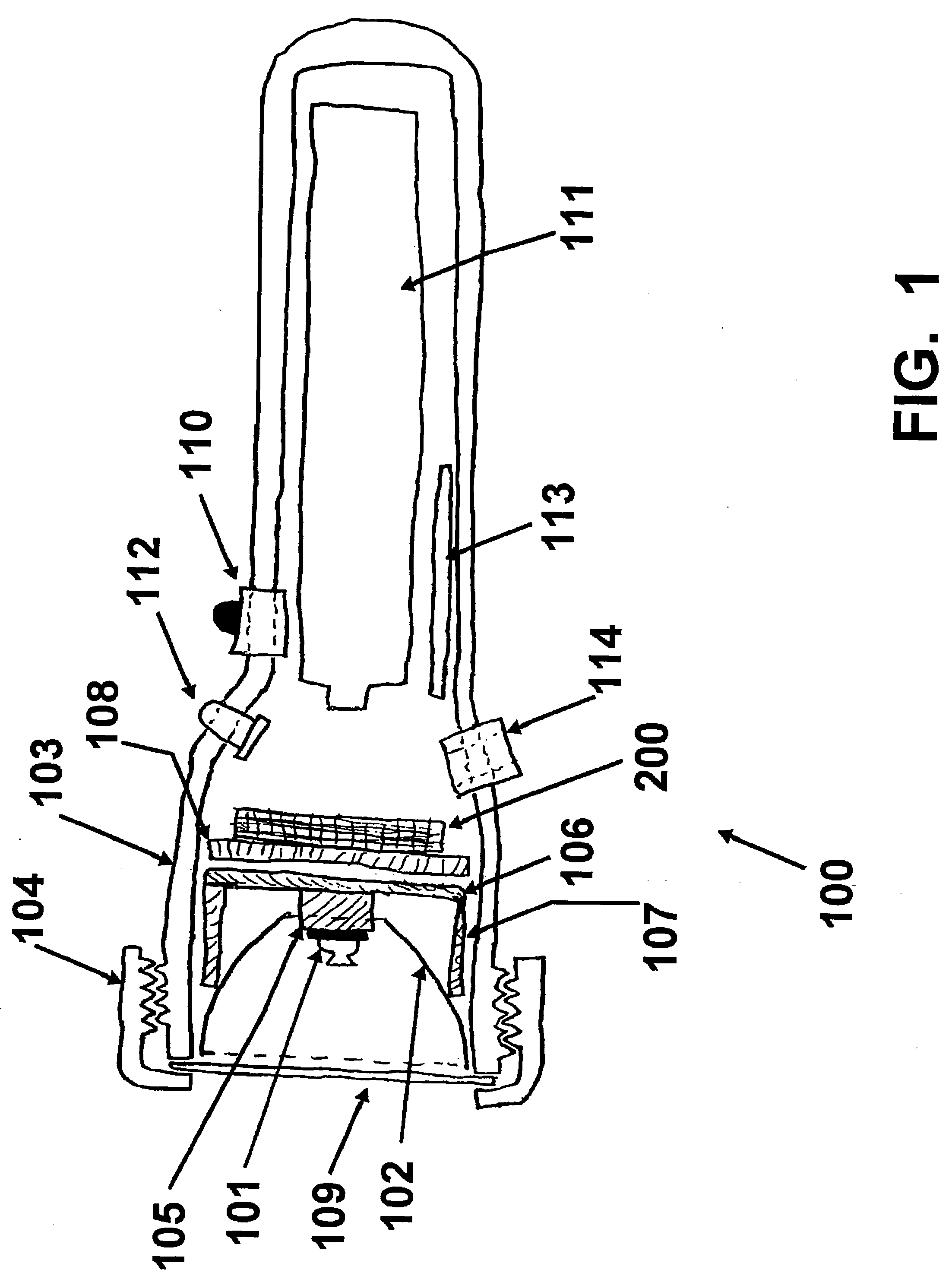
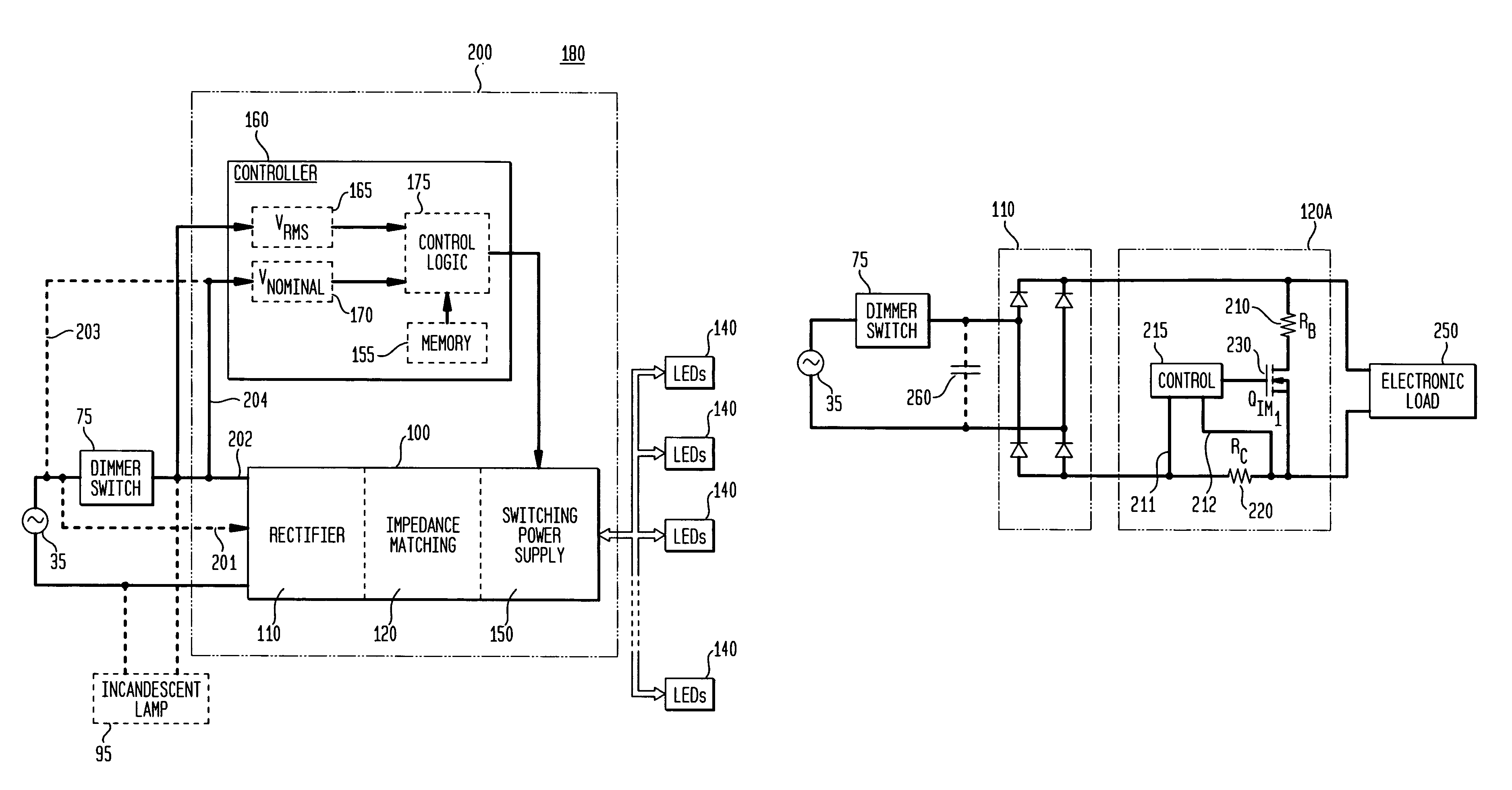
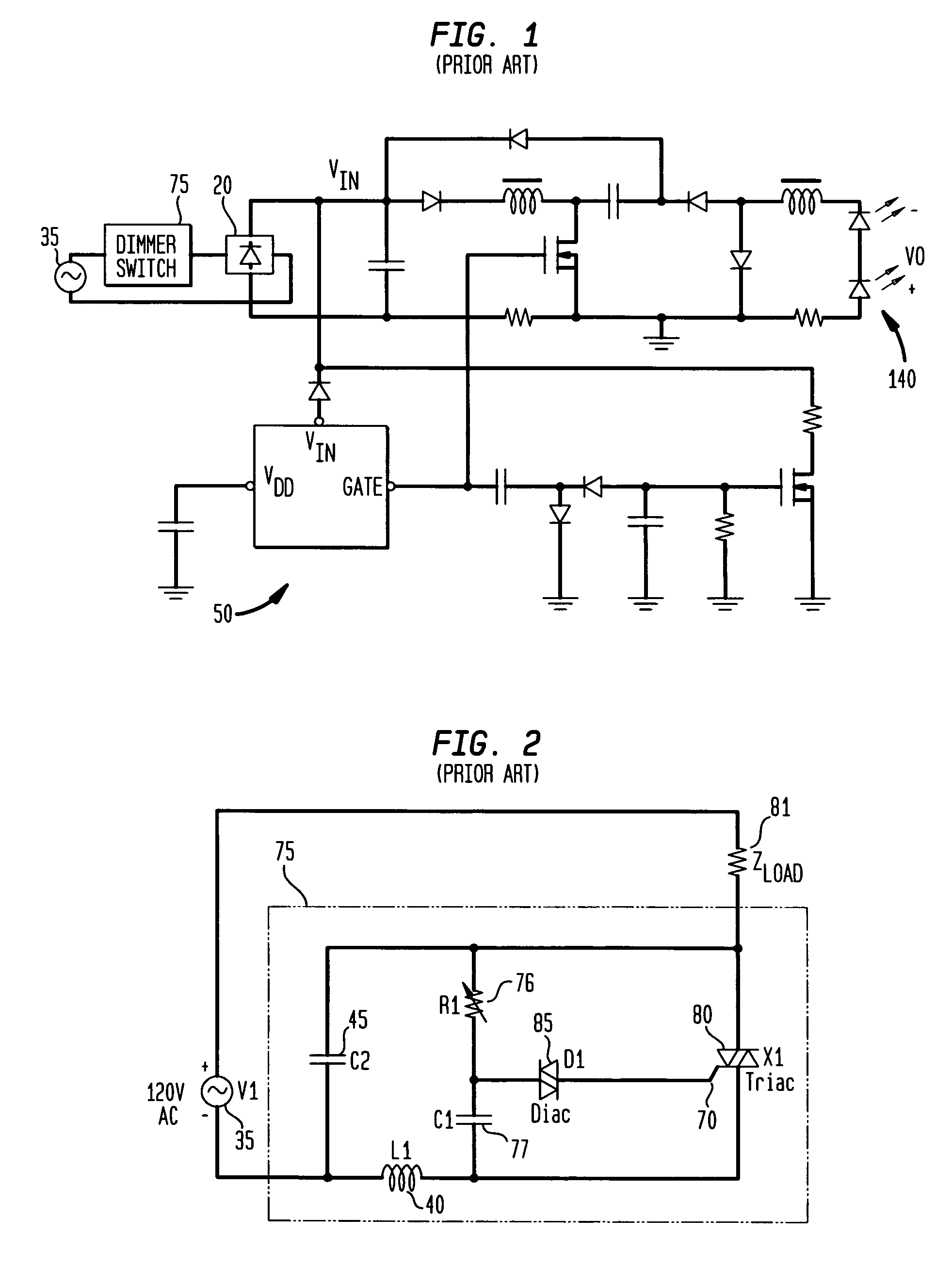
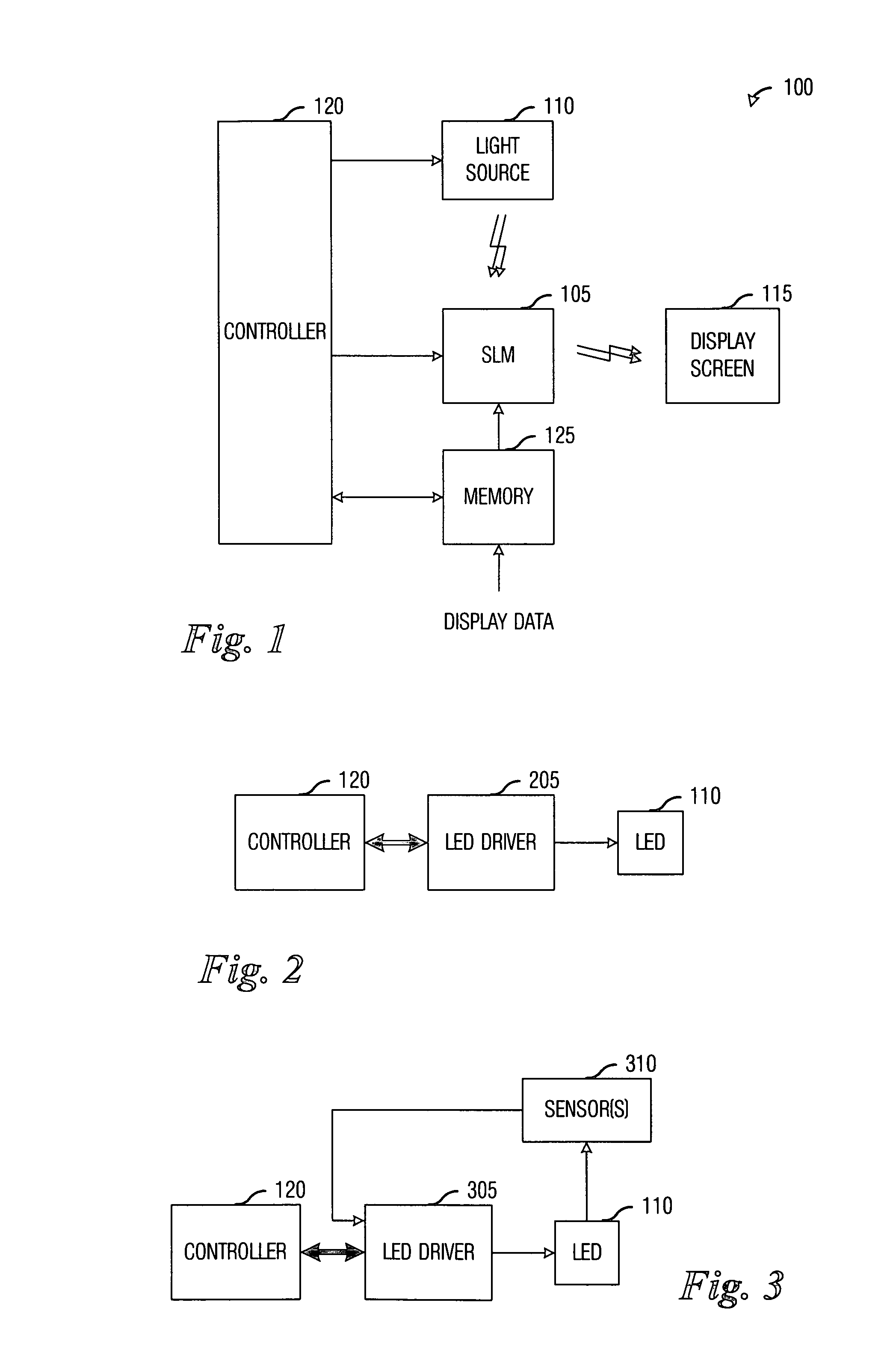
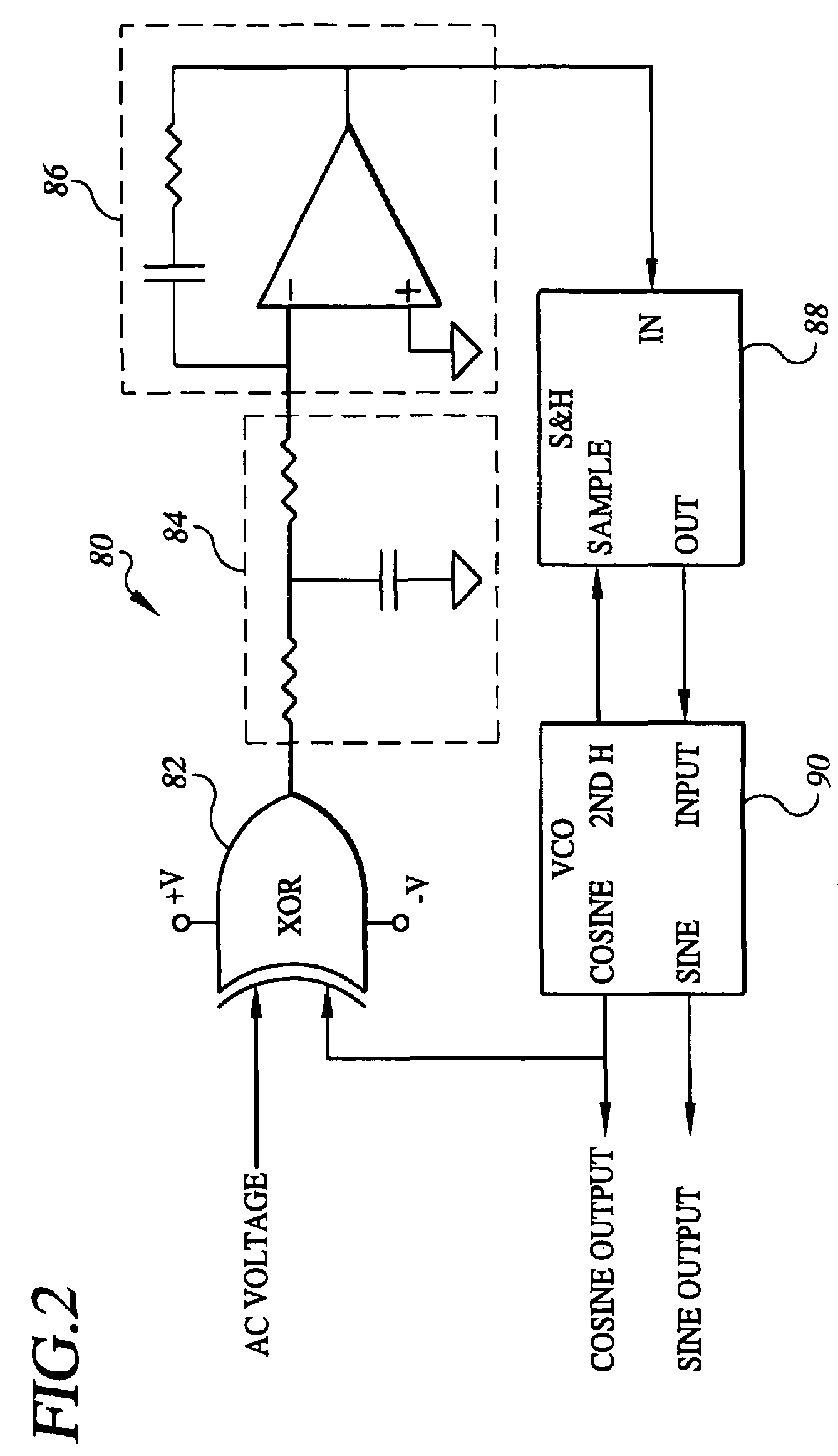
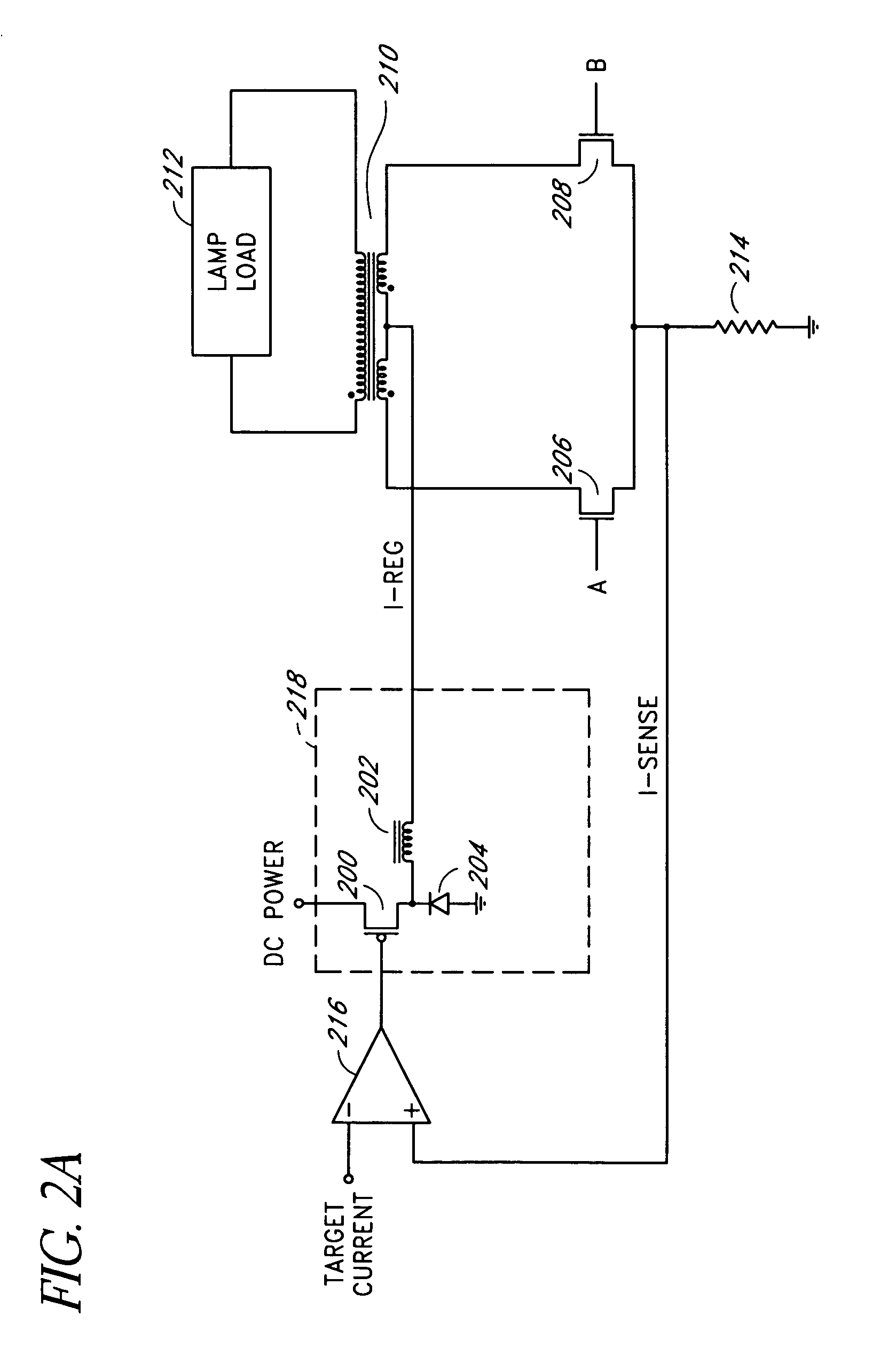
Apparatus, Method and System for Providing AC Line Power to Lighting Devices
ActiveUS20120081009A1Reduction in size and costImprove Utilization and EfficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentVoltage regulation
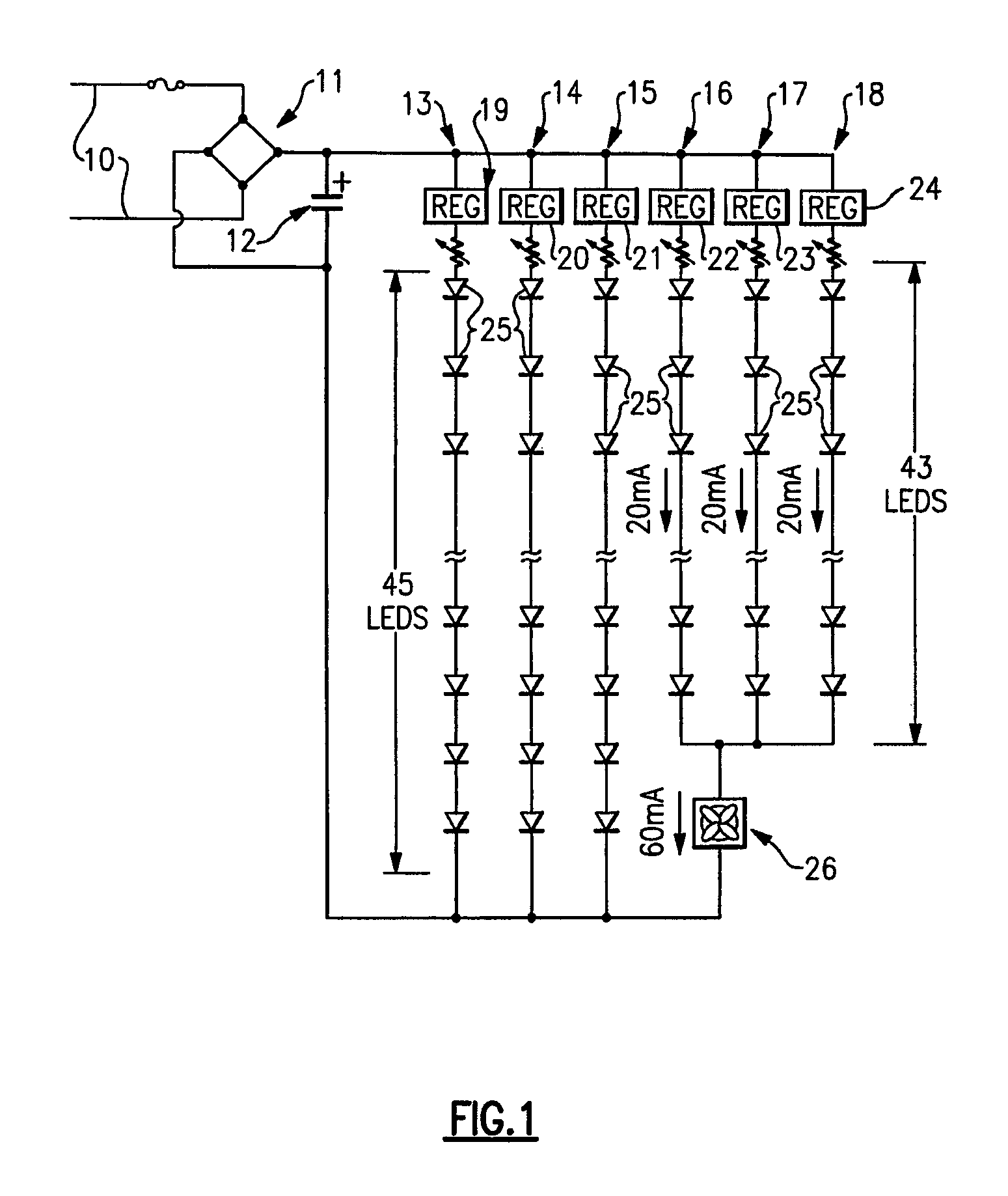
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed for providing AC line power to lighting devices such as light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary apparatus comprises: a plurality of LEDs coupled in series to form a plurality of segments of LEDs; first and second current regulators; a current sensor; and a controller to monitor a current level through a series LED current path, and to provide for first or second segments of LEDs to be in or out of the series LED current path at different current levels. A voltage regulator is also utilized to provide a voltage during a zero-crossing interval of the AC voltage. In an exemplary embodiment, first and second segments of LEDs are both in the series LED current path regulated at a lower current level compared to when only the first segment of LEDs is in the series LED current path.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Current regulator for modulating brightness levels of solid state lighting
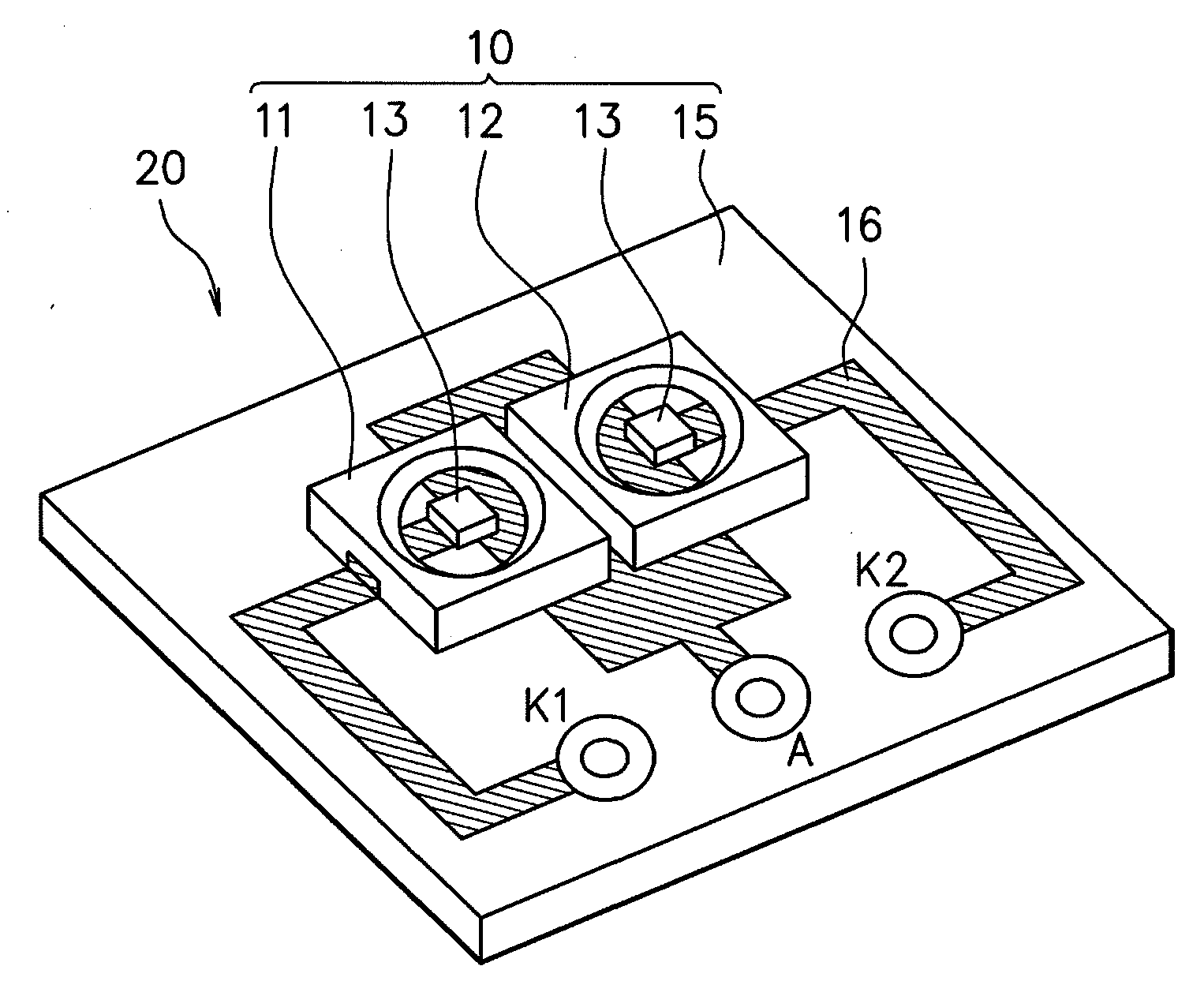
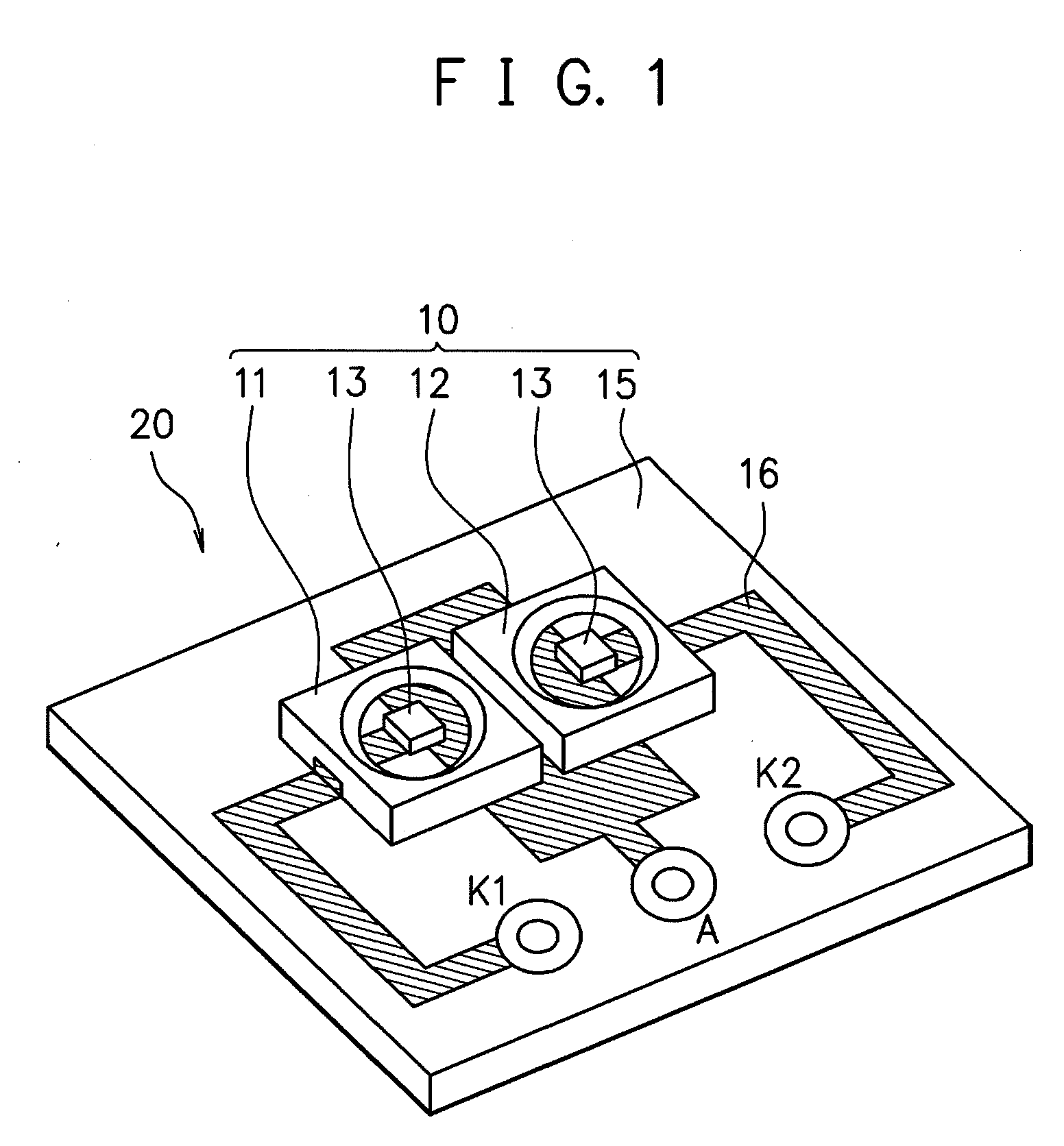
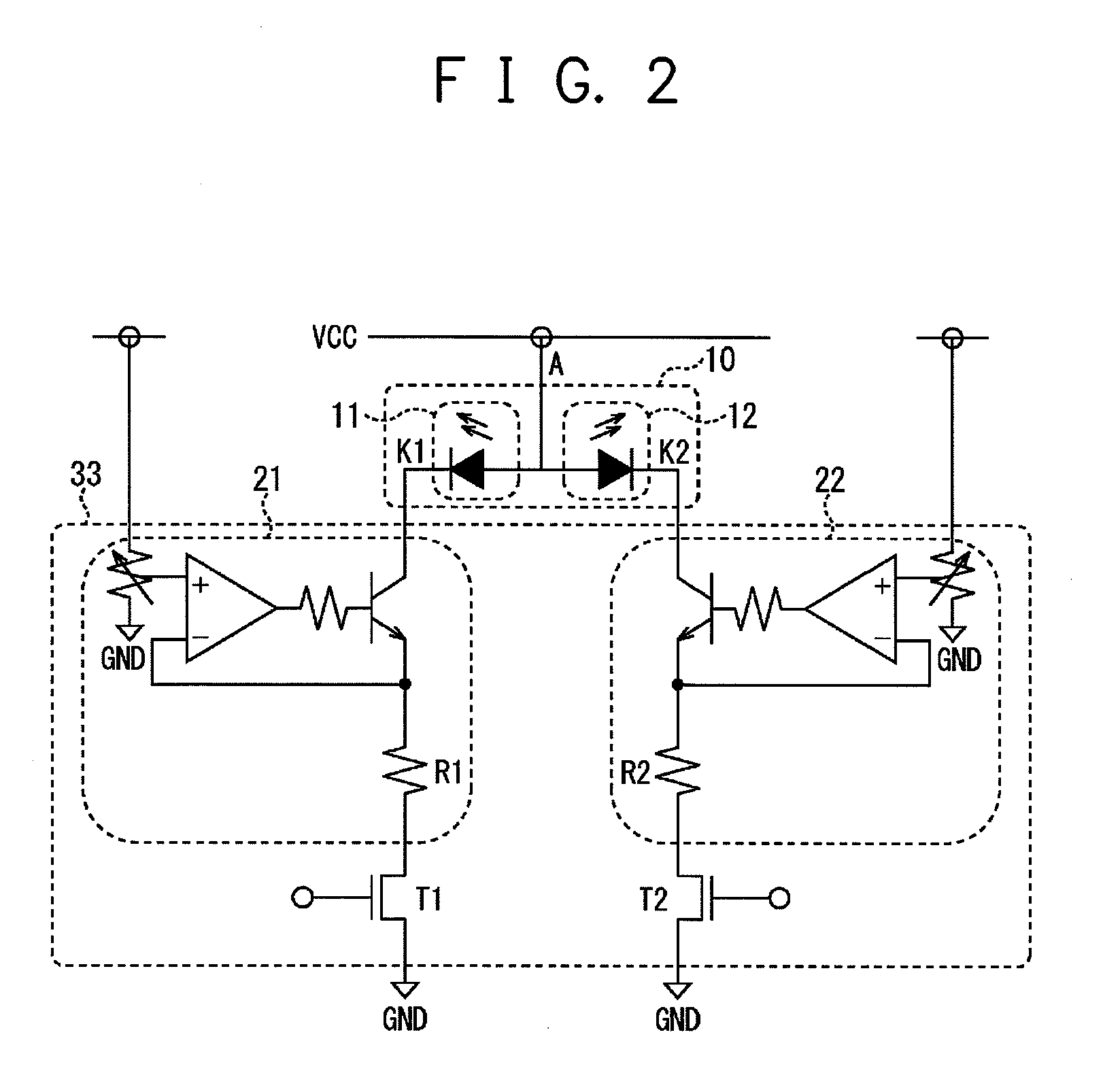
ActiveUS20070182338A1Low component requirementsElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesImpedance matchingRoot mean square
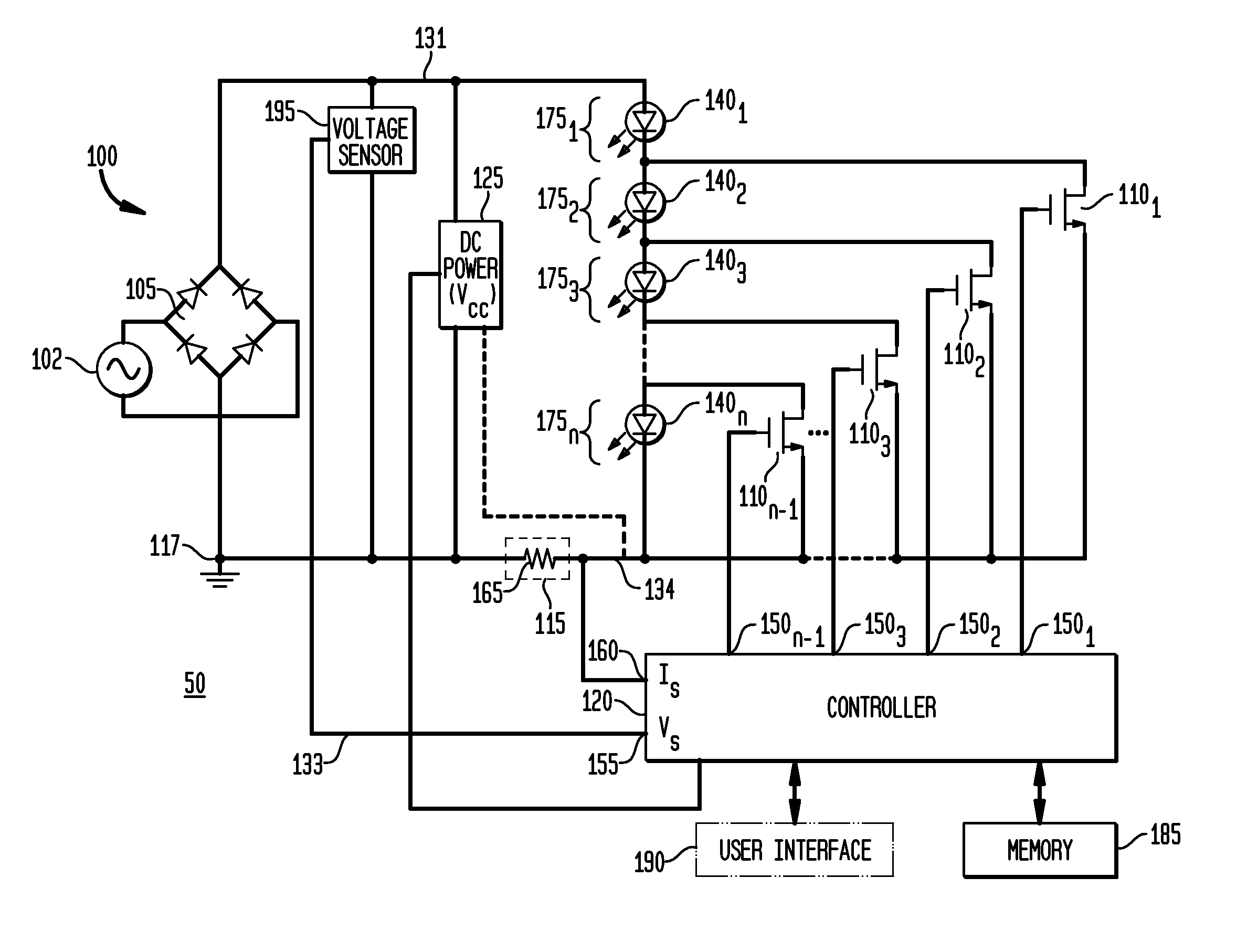
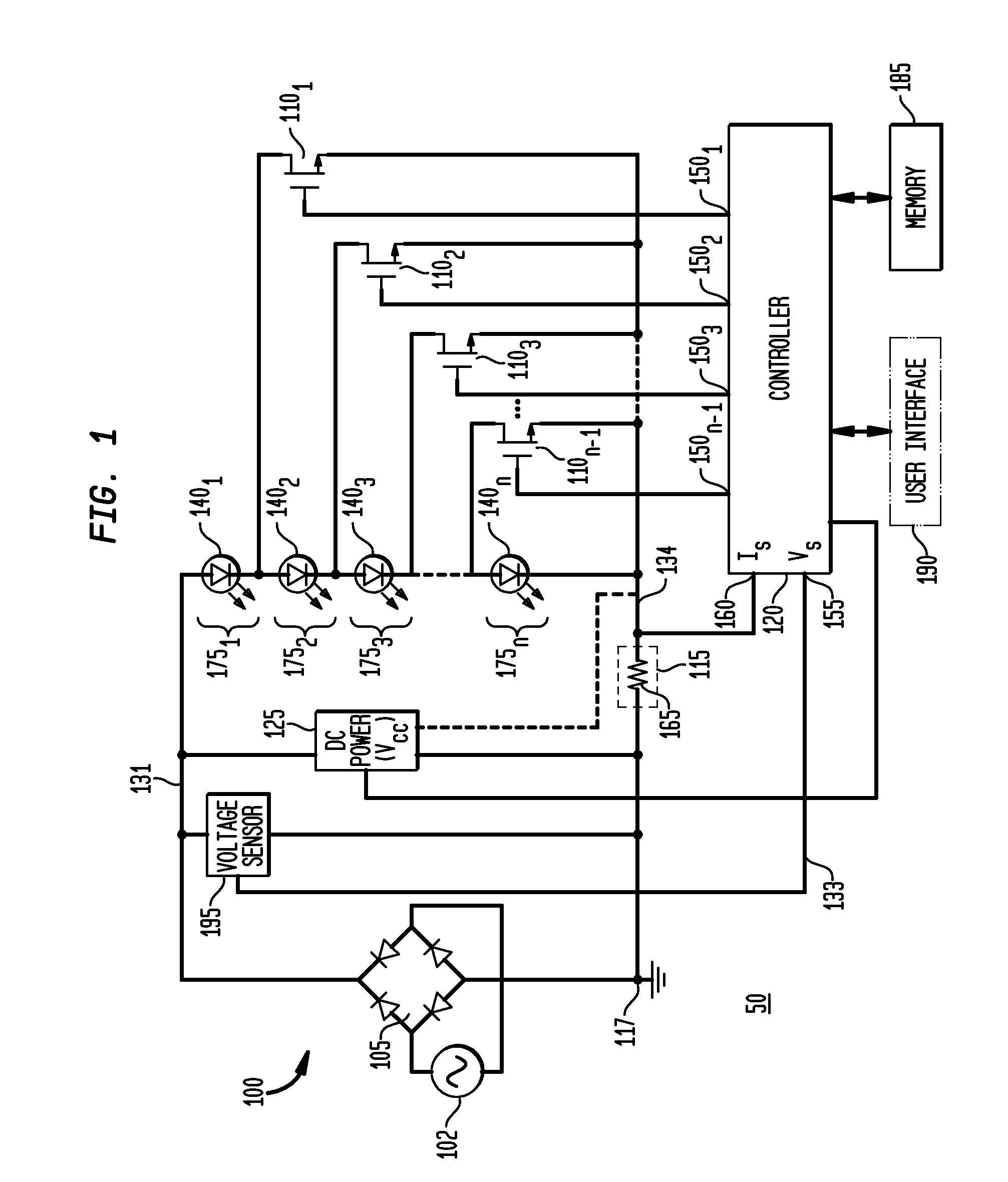
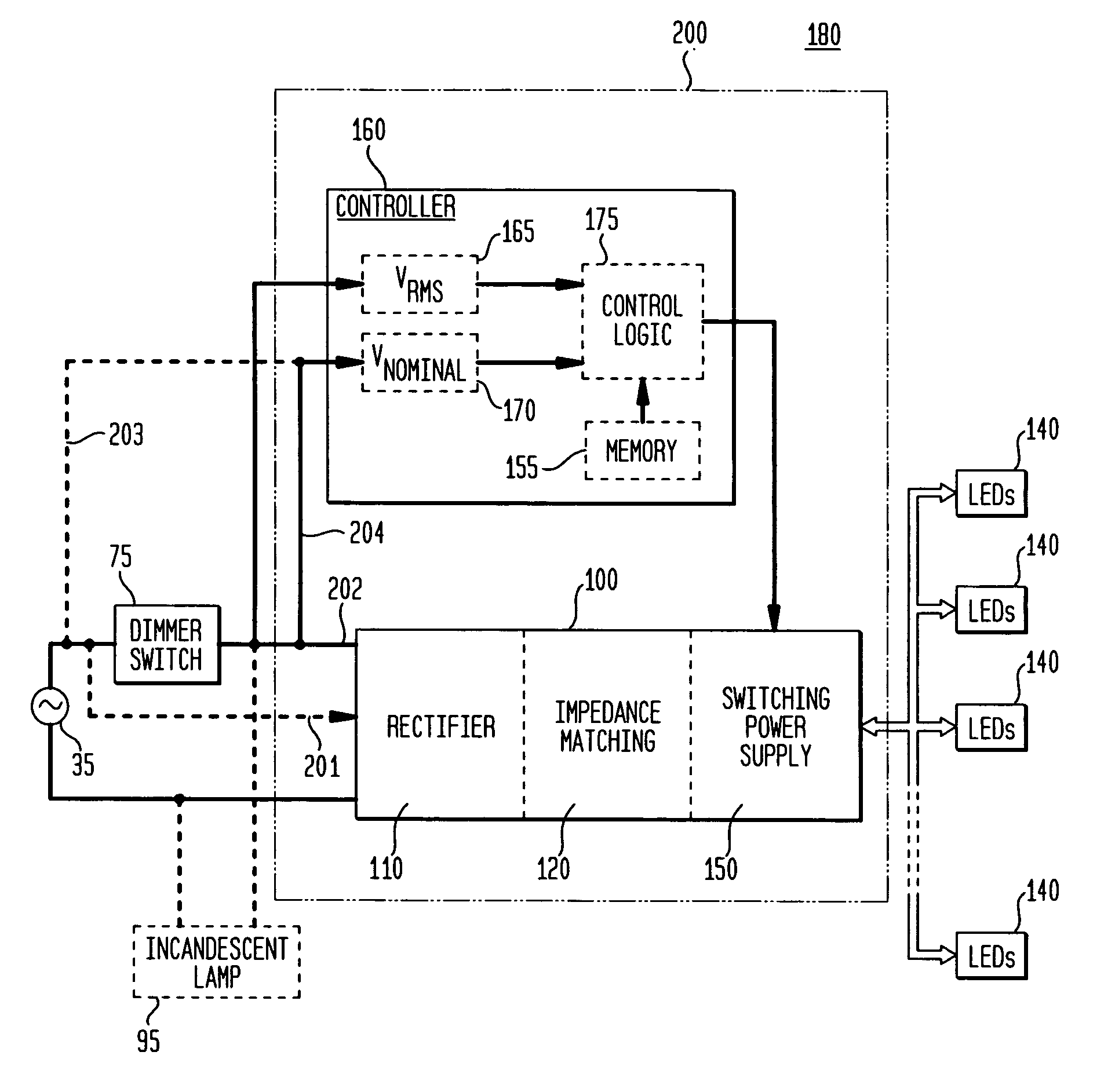
An exemplary embodiment provides a current regulator for controlling variable brightness levels for solid state lighting. The current regulator is couplable to a phase-modulating switch, such as a dimmer switch, which is coupled to an AC line voltage. An exemplary current regulator includes a rectifier; a switching power supply providing a first current; an impedance matching circuit; and a controller. The impedance matching circuit is adapted to provide a second current through the phase-modulating switch when a magnitude of the first current is below a first predetermined threshold, such as a holding current of a triac of the phase-modulating switch. The controller is adapted to determine a root-mean-square (RMS) voltage level provided by the phase-modulating switch from the AC line voltage and to determine a duty cycle for pulse-width current modulation by the switching power supply in response to the comparison of the RMS voltage level to a nominal voltage level.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
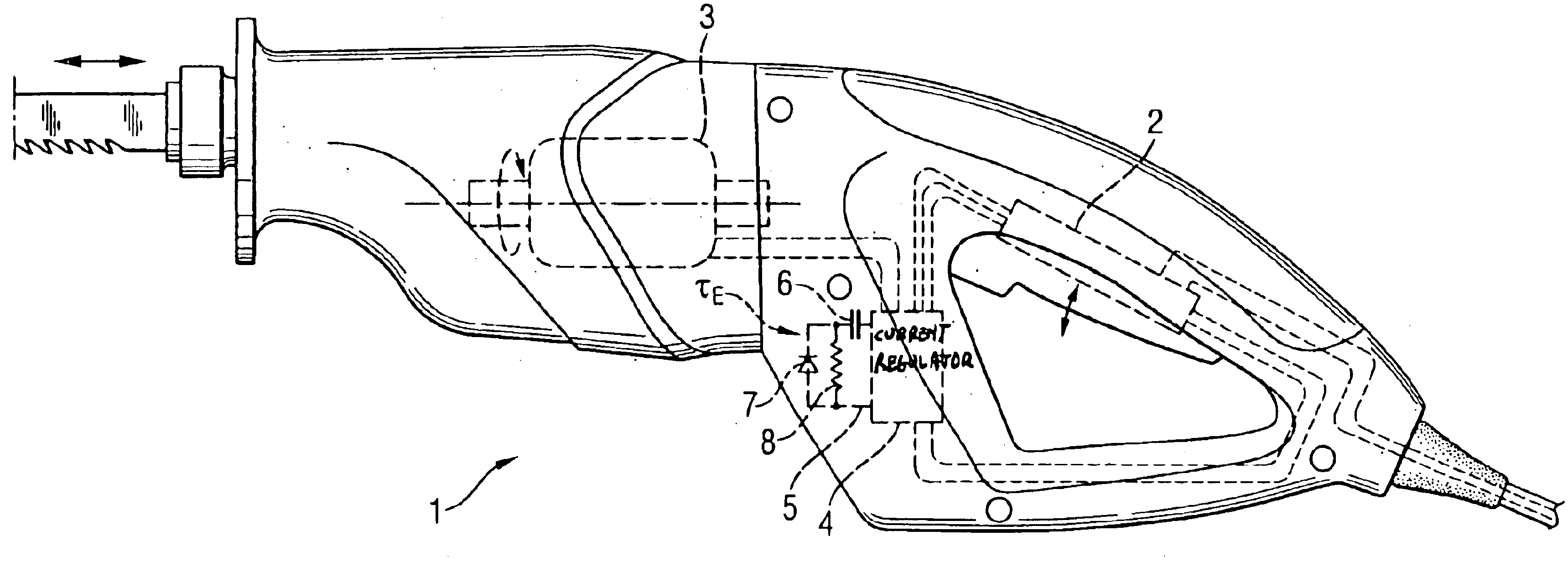
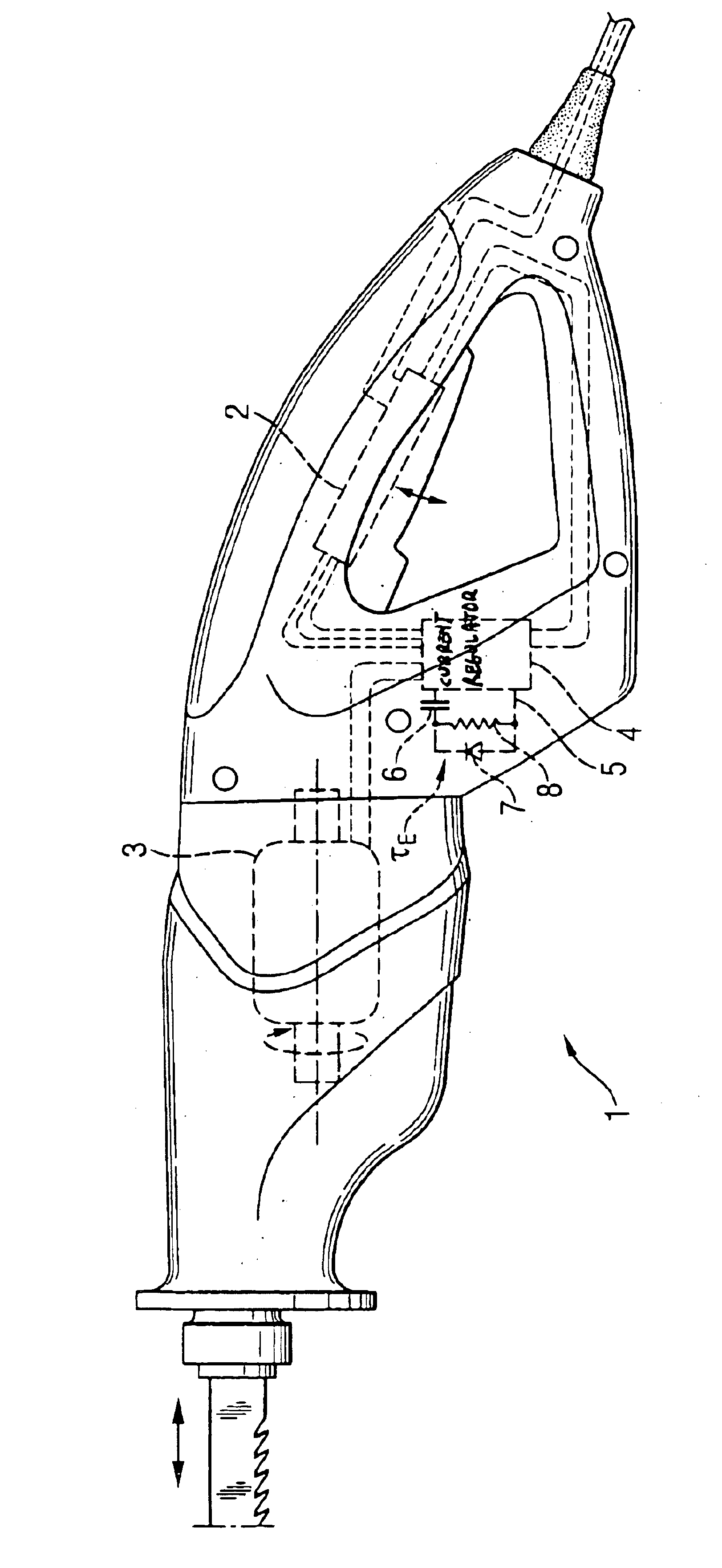
Electrical hand tool machine with soft-start
An electrical hand tool machine (1) having a motor switch (2) configured as a button and a current regulator (4) disposed in the current circuit of an electrical motor (3), having a soft-start input (5), in whose branch current a timing capacitor (6) is arranged. A current-direction-dependent element (7) is arranged between the soft-start input (5) and the capacitor (6).
Owner:HILTI ELLSCHAFAT
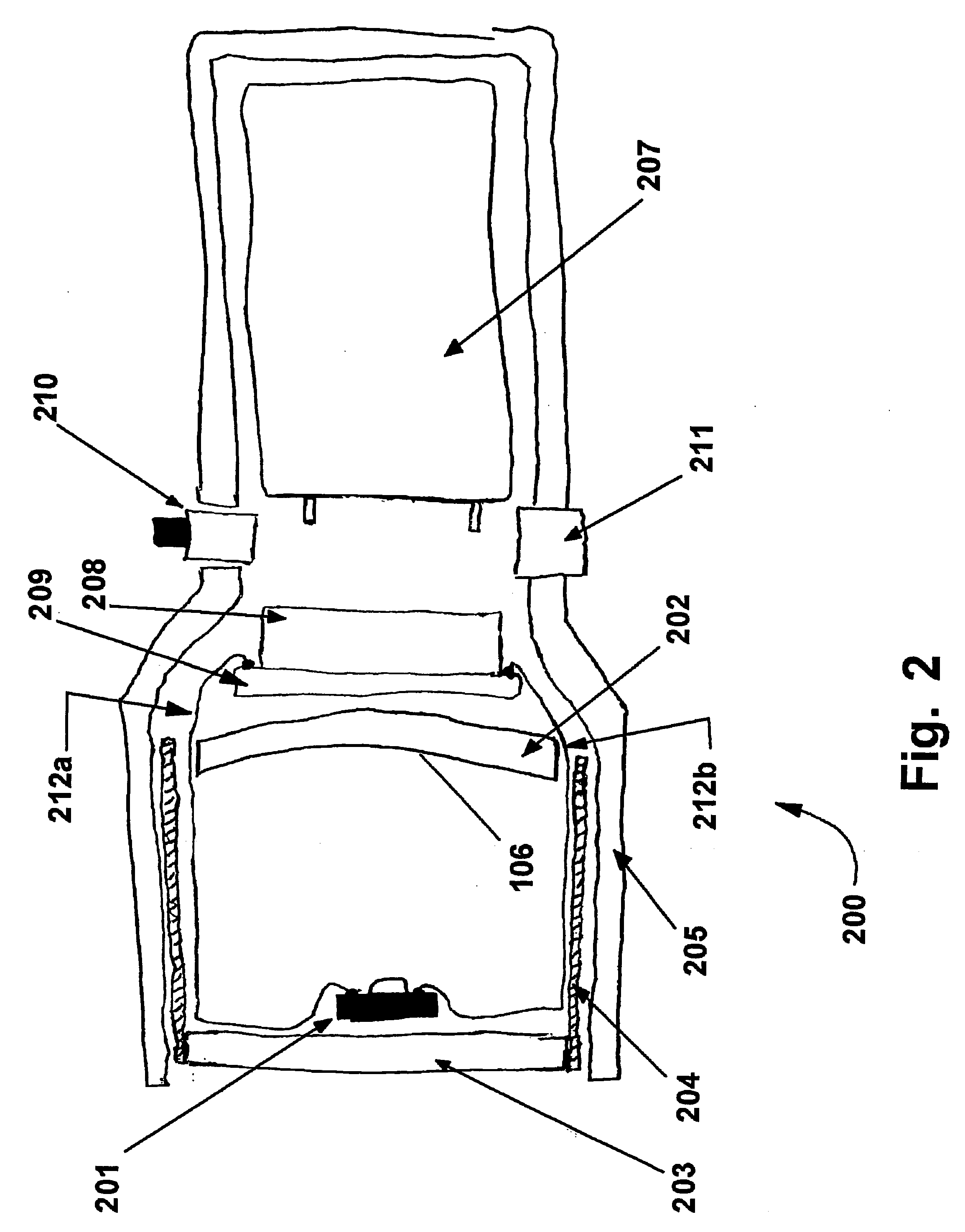
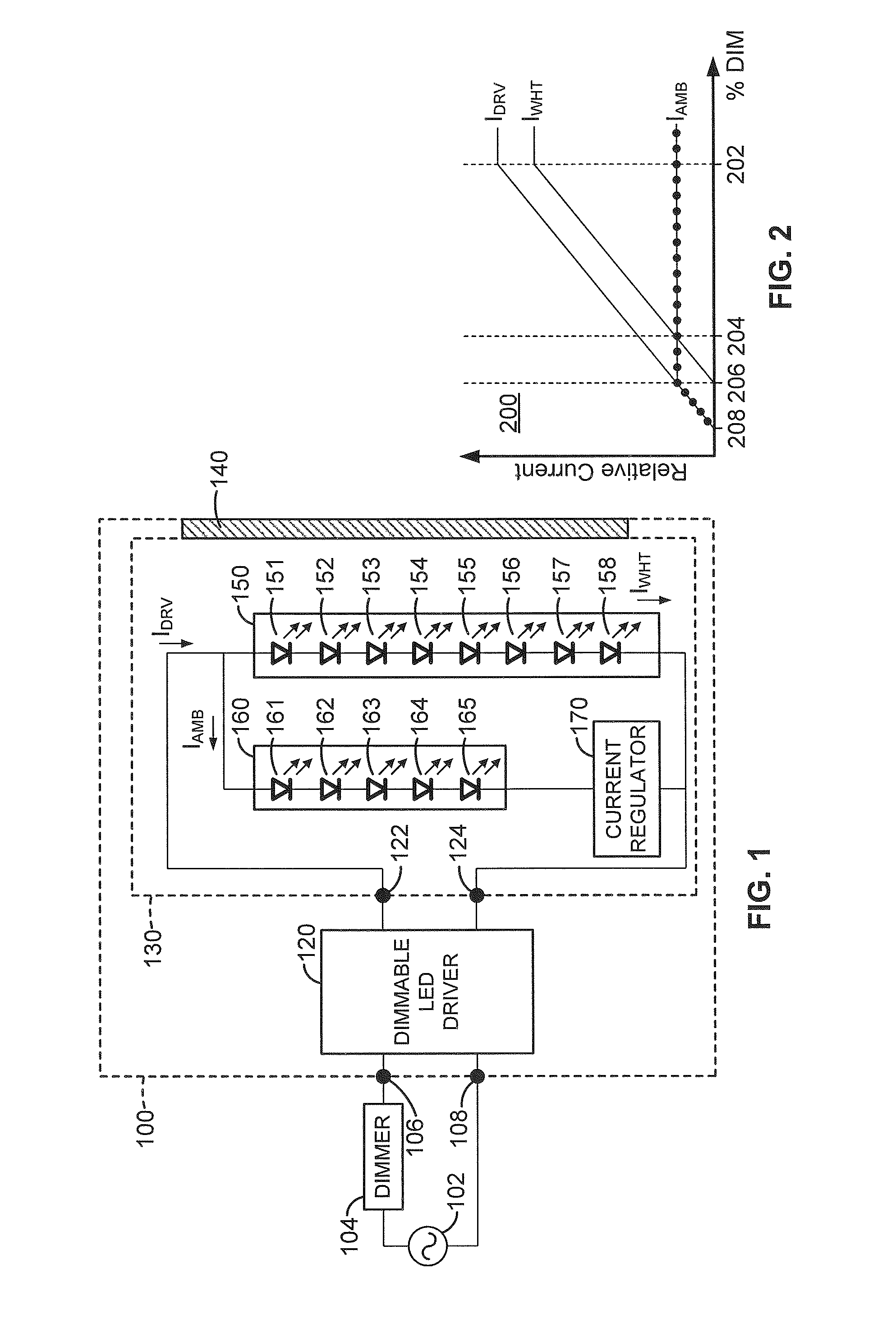
Circuit for lighting device, and method of lighting
ActiveUS20070171145A1Minimize amount of power lostImprove efficiencyElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesElectricityEffect light
A circuit for a lighting device comprises a sub-circuit which comprises a series current regulator and a group of solid state light emitters. The current regulator and the solid state light emitters are arranged in series. In some embodiments, the circuit further comprises a fan electrically connected in series in the sub-circuit. In some embodiments, the circuit further comprises a second sub-circuit which comprises a second series current regulator and a second group of solid state light emitters, the first sub-circuit and the second sub-circuit being arranged in parallel. In some embodiments, an anode of the series current regulator is electrically connected to a cathode of one of the solid state light emitters. Also, methods of lighting wherein a sum of voltage drops across light emitters and a current regulator is in the range of from 1.2 to 1.6 times the line voltage.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
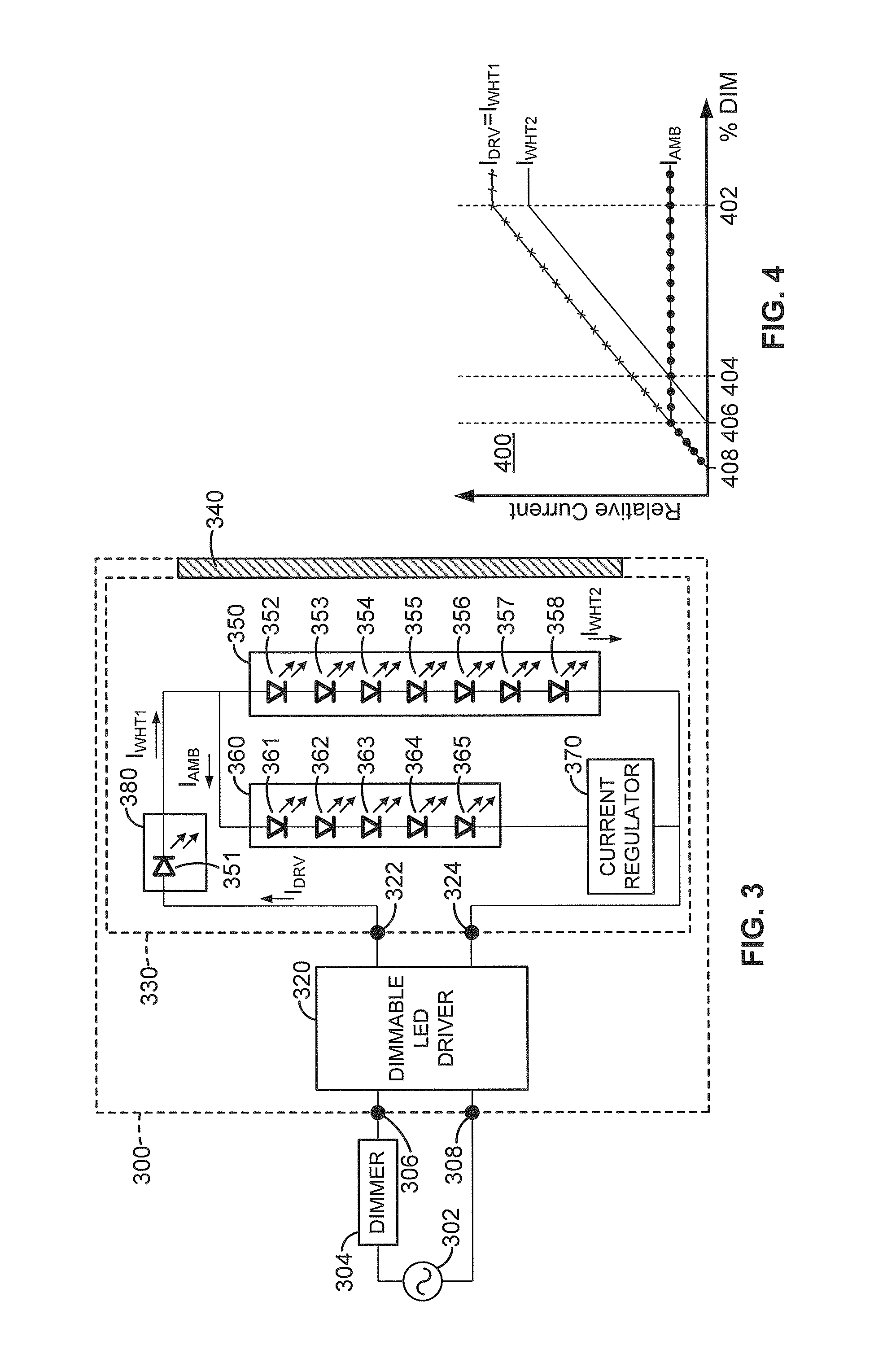
Lighting device and method of lighting
A lighting device, comprising at least first and second current regulators, each switchable among two settings, and at least first and second groups of solid state light emitters. If the first regulator is in a first setting, a first current is supplied to the first group and a second current is supplied to the second group, and if the first regulator is in a second setting, a third current is supplied to the first group and a fourth current is supplied to the second group. In some embodiments, a ratio of the third current divided by the first current differ's from a ratio of the fourth current divided by the second current by at least 5 %. Also, a method comprising substantially simultaneously adjusting current supplied to a first group, and adjusting a current supplied to a second group.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Driver that efficiently regulates current in a plurality of LED strings
InactiveUS20090187925A1Minimize output voltageImprove performanceElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesLinear regulatorMOSFET
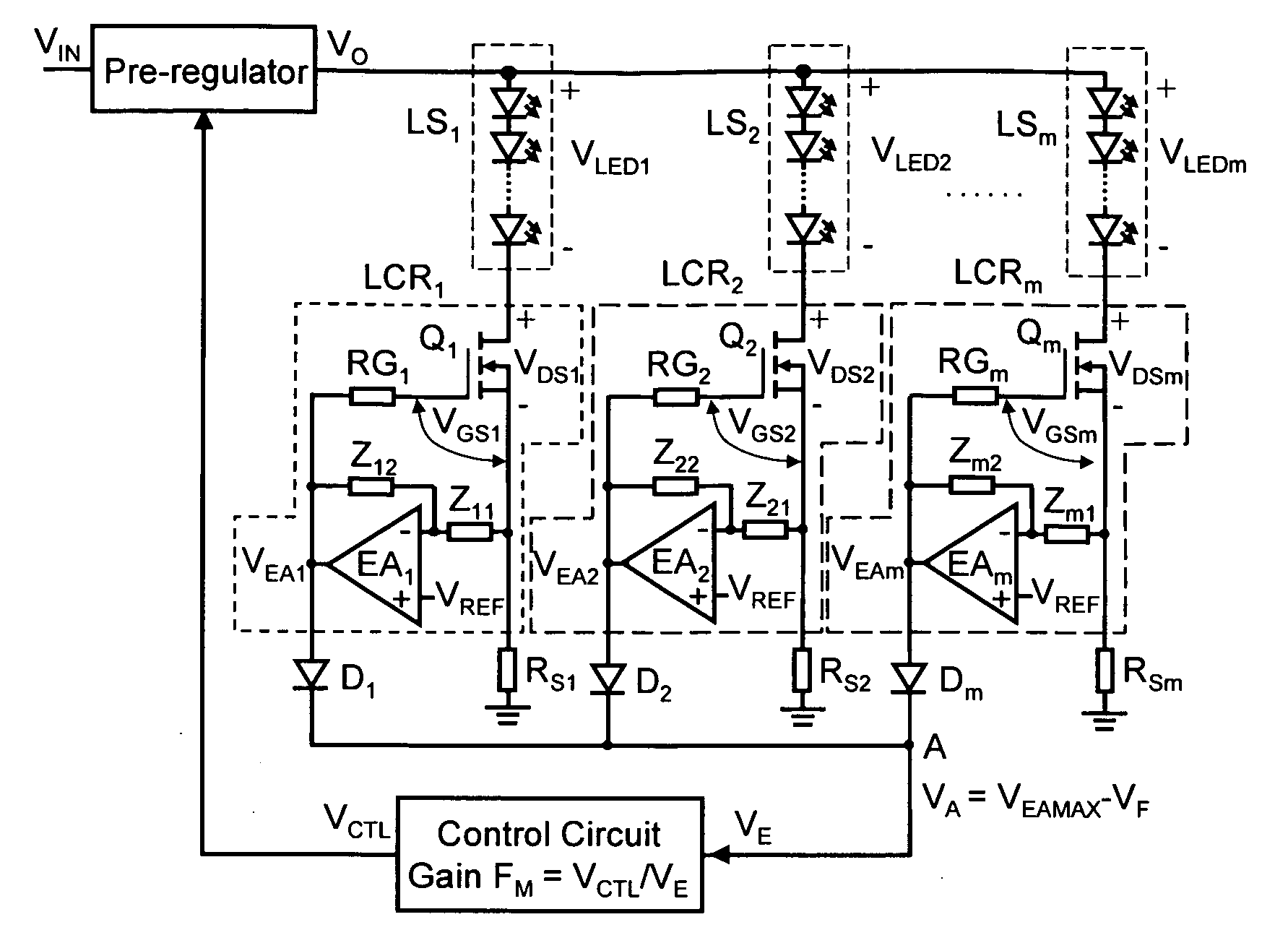
A light-emitting diode (LED) driver according to the present invention consists of a voltage pre-regulator and multiple linear current regulators with an adaptively-controlled drive voltage. In this LED driver, the efficiency maximization is achieved by eliminating the sensing of the voltage drops across the linear regulators, i.e., by removing the external voltage feedback for the adjustment of the output voltage of the pre-regulator. In the LED driver of the present invention, the self-adjustment of drive voltage is achieved by relying on a relatively strong dependence between the gate-to-source and drain-to-source voltages of a current-regulating transistor, e.g., a MOSFET, operating in the linear region. The driver powers all LEDs in a string with a constant current and provides consistent illumination and optimum operating efficiency at low cost over a wide range of input / output voltage and temperature.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Digitally controlled current regulator for high power solid state lighting
InactiveUS20070267978A1Improve efficiencyLow costElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesCurrent meterAverage current
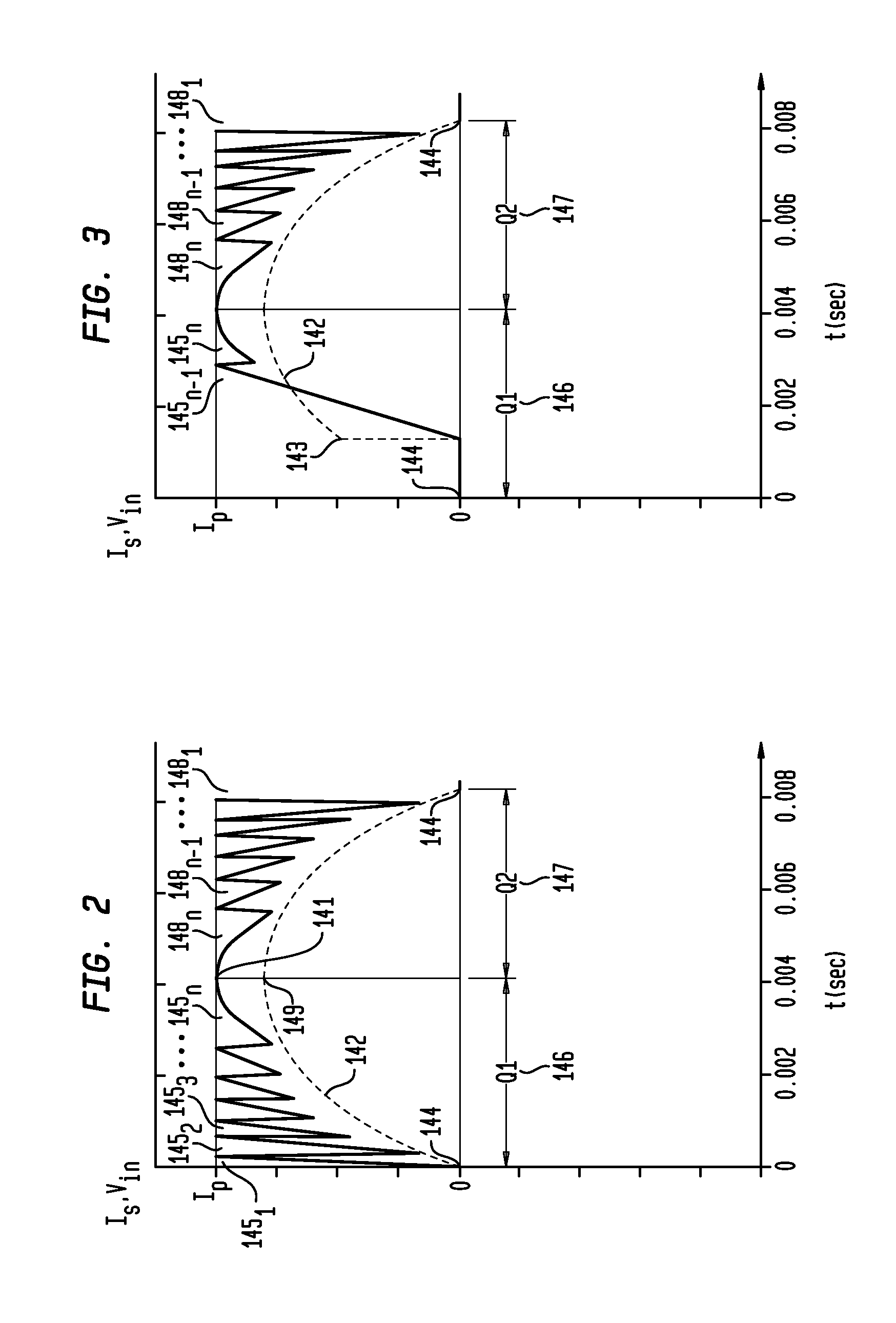
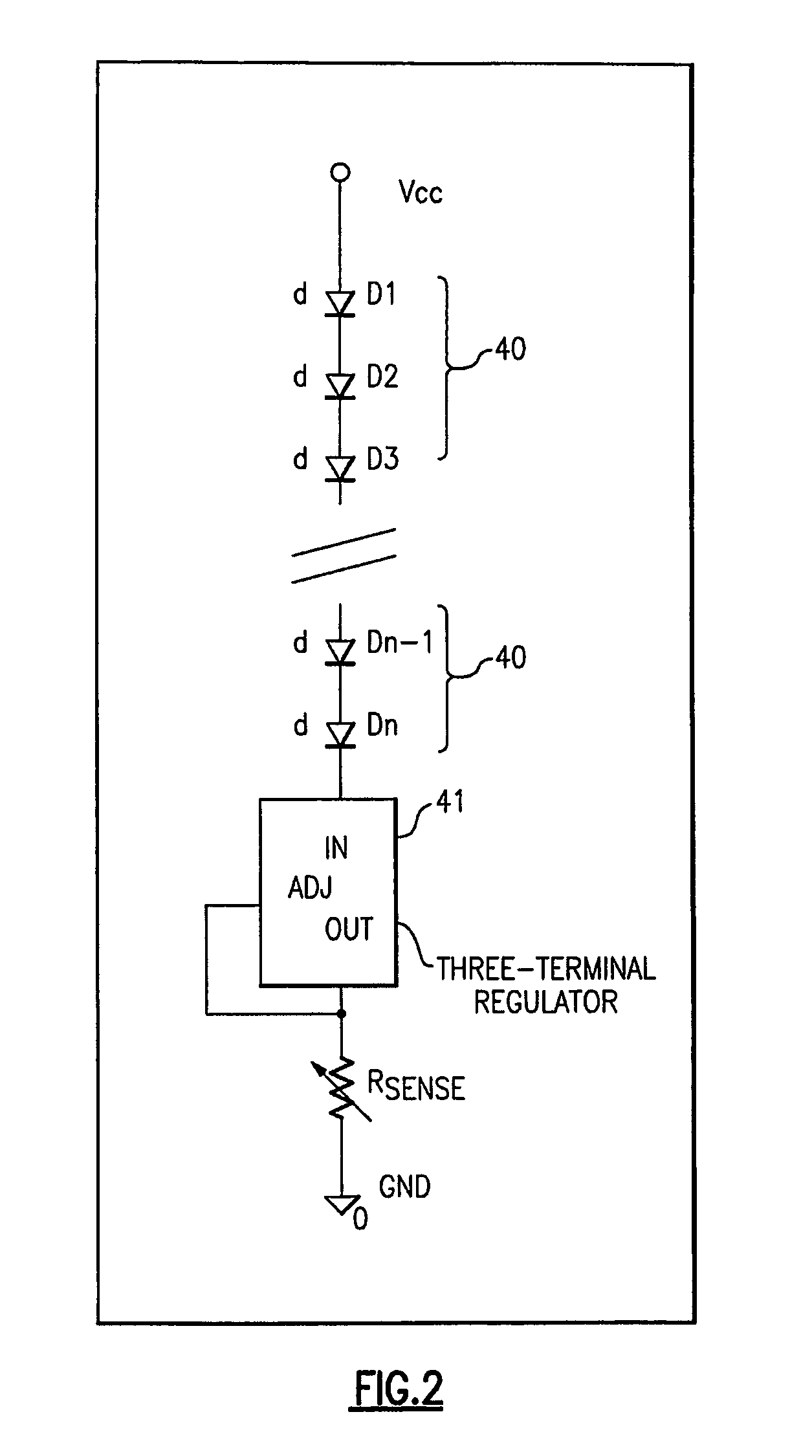
An exemplary apparatus embodiment provides for controlling current supplied to solid state lighting, such as light emitting diodes. An exemplary apparatus comprises a memory adapted to store a plurality of current parameters; and a control circuit adapted to modulate an energizing cycle time period for providing a substantially constant DC average current to the solid state lighting in response to a selected current parameter of the plurality of current parameters. In an exemplary embodiment, the control circuit modulates a current provided to the solid state lighting in response to a predetermined minimum current level (IMIN) parameter and a predetermined peak current level (IP) parameter, such that the DC average current level (IO) is substantially proportional to one-half of a sum of a predetermined peak current level (“IP”) and a predetermined minimum current levelIM(IO∝IP+IMIN2).
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
LED lamps and LED driver circuits for the same
ActiveUS20050007777A1Assist in detectingLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceLight beamEngineering
LED lamp has LEDs aimed rearwards with either a concave mirror to the rear of each LED, or one concave mirror to the rear of two or more LEDs, collecting the light from the LEDs to form a forward projecting beam. LEDs may be high power types that require heatsinking. LED lamp may have a lens forward of each LED to collimate the radiation produced by the LEDs into a beam, where at least one lens has at least one aspheric curved surface. LED lamp may have a transparent reflective optic to collimate the radiation produced by each LED into a beam. For an inspection lamp, the LEDs typically have a peak wavelength of 395 to 415 naometers for seeing the area being irradiated but not so visible as to overwhelm fluorescence of fluorescent materials to be detected. Other wavelengths may be used. LED inspection lamp has a combination of LEDs of different wavelengths or a combination of at least one LED and at least one other light source such that the lamp produces radiation suitable for detection of materials to be detected and adequately illuminates the area being irradiated. LED lamp has LEDs that produce a beam of suitable radiation with a width of 10 degrees or less without additional optics. LED inspection lamp has head attached to a flexible member, with head serving as heatsink for one or more high power LEDs. Current regulator circuits are also disclosed.
Owner:ALLTEMP PROD CO LTD
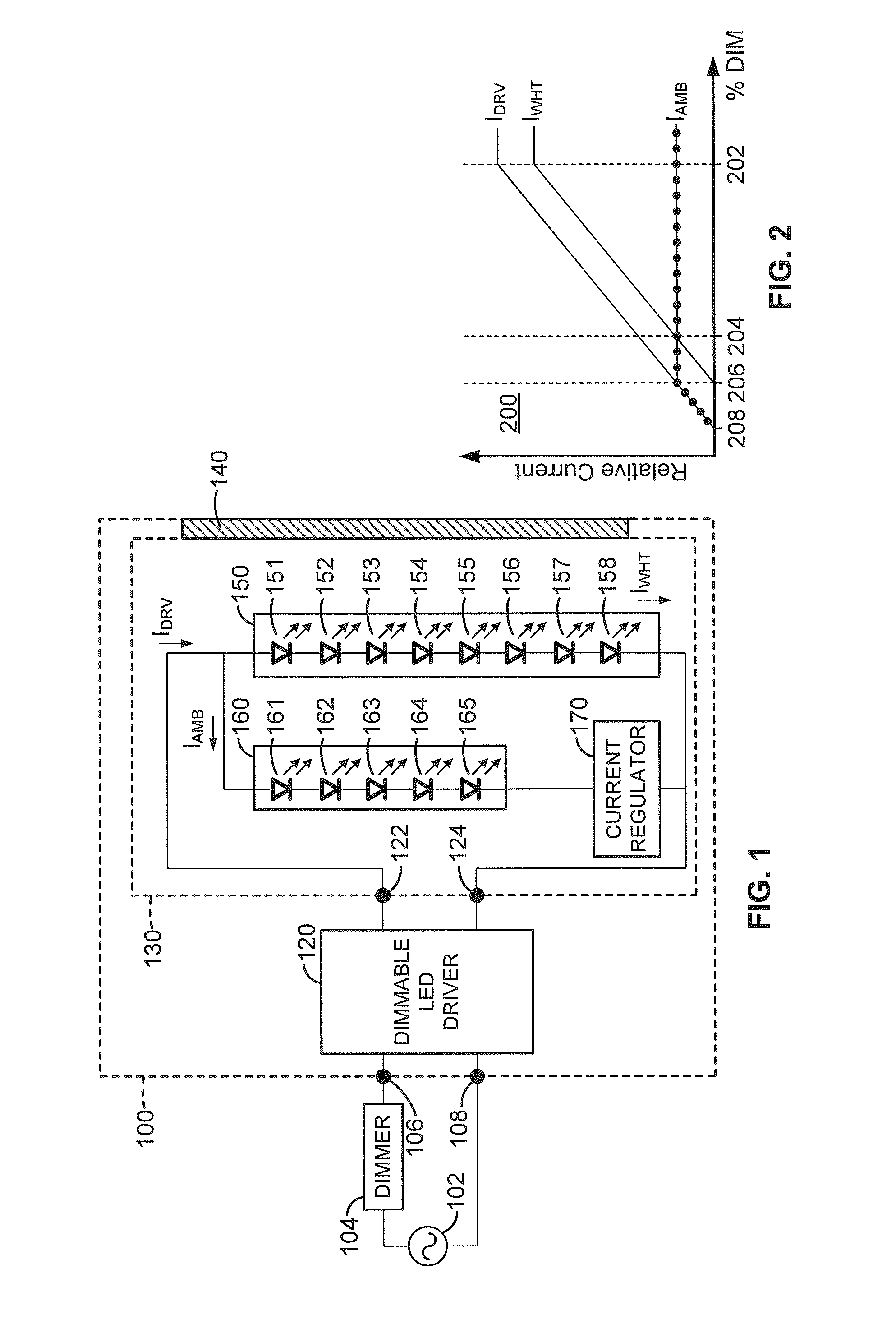
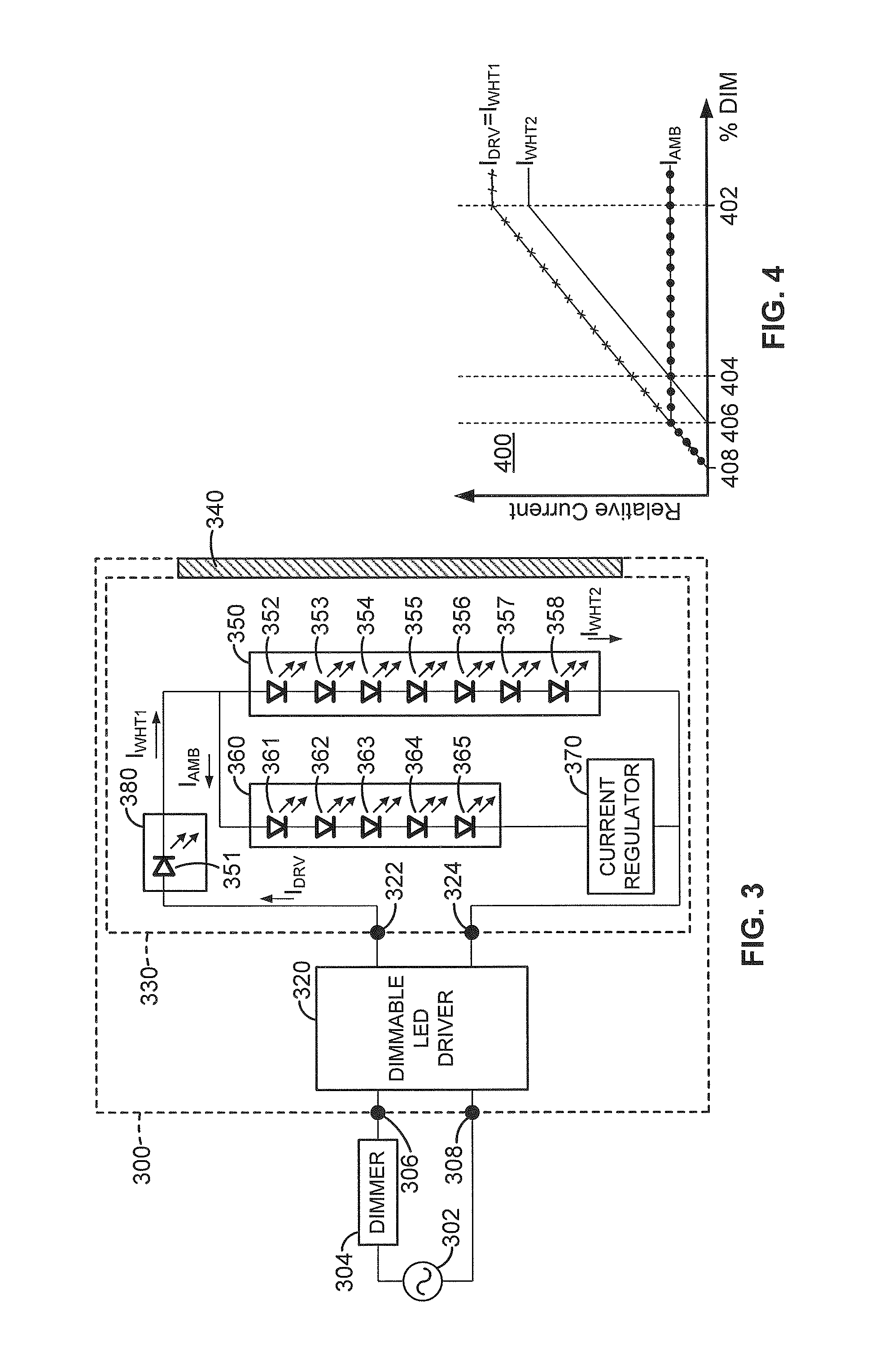
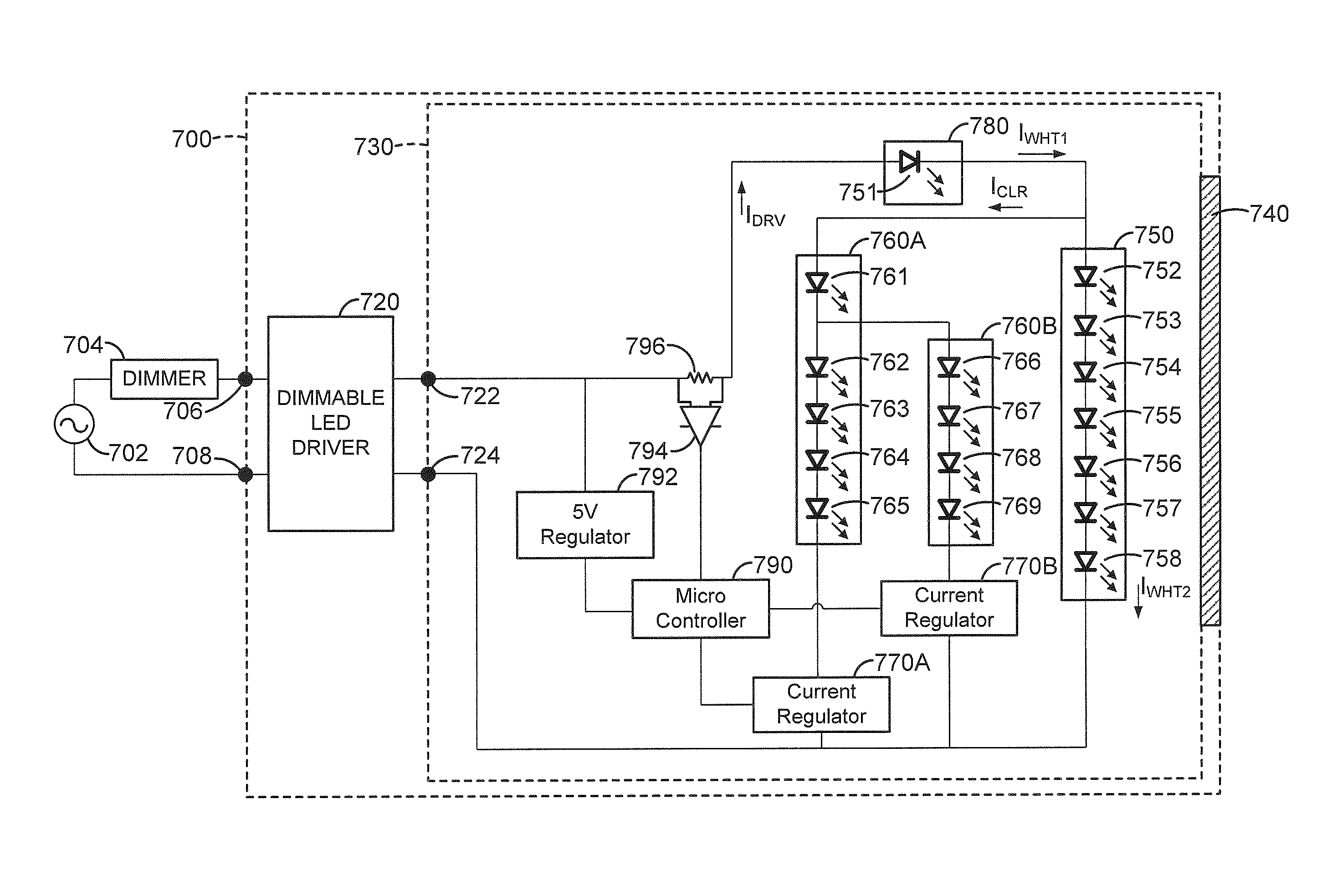
Dimmable LED light fixture having adjustable color temperature
ActiveUS20130063035A1Easy to controlSimulation is accurateElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDc currentEngineering
Electronic circuitry for color-mixing in an LED light fixture during AC power dimming is disclosed to achieve adjustable color temperature. According to one embodiment, a dimmable LED light fixture has first, second, and third LED light sources, the first and second LED light sources producing white light, the third LED light source producing colored light, the LED driver configured to power the LED light sources by providing a single-channel variable-DC current source having two output terminals, and a current regulator for maintaining the current in the third LED light source path substantially constant as the LED driver output current is decreased when the AC power is reduced by the dimmer module, thereby altering the color of the light produced by the combination of the LED light sources.
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
White light emitting apparatus and line illuminator using the same in image reading apparatus
InactiveUS20100320928A1Low costReduce the number of productsMechanical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesOptical axisColor mixing
A white light emitting apparatus includes a light source section in which a first white LED that emits white light whose chromaticity deviates to a blue side from a predetermined white region of a CIE chromaticity diagram and a second white LED that emits white light whose chromaticity deviates to a yellow side from the predetermined white region are adjacently disposed so as to emit light with optical axes in substantially the same direction, and a current regulator that independently drives the blue LED chip in the first and second white LEDs, respectively. A color mixture of lights emitted from the first and second white LEDs is adjusted to a chromaticity of the predetermined white region using the current regulator.
Owner:CANON COMPONENTS INC
Current regulator for modulating brightness levels of solid state lighting
ActiveUS7902769B2Low component requirementsElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesImpedance matchingRoot mean square
An exemplary embodiment provides a current regulator for controlling variable brightness levels for solid state lighting. The current regulator is couplable to a phase-modulating switch, such as a dimmer switch, which is coupled to an AC line voltage. An exemplary current regulator includes a rectifier; a switching power supply providing a first current; an impedance matching circuit; and a controller. The impedance matching circuit is adapted to provide a second current through the phase-modulating switch when a magnitude of the first current is below a first predetermined threshold, such as a holding current of a triac of the phase-modulating switch. The controller is adapted to determine a root-mean-square (RMS) voltage level provided by the phase-modulating switch from the AC line voltage and to determine a duty cycle for pulse-width current modulation by the switching power supply in response to the comparison of the RMS voltage level to a nominal voltage level.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
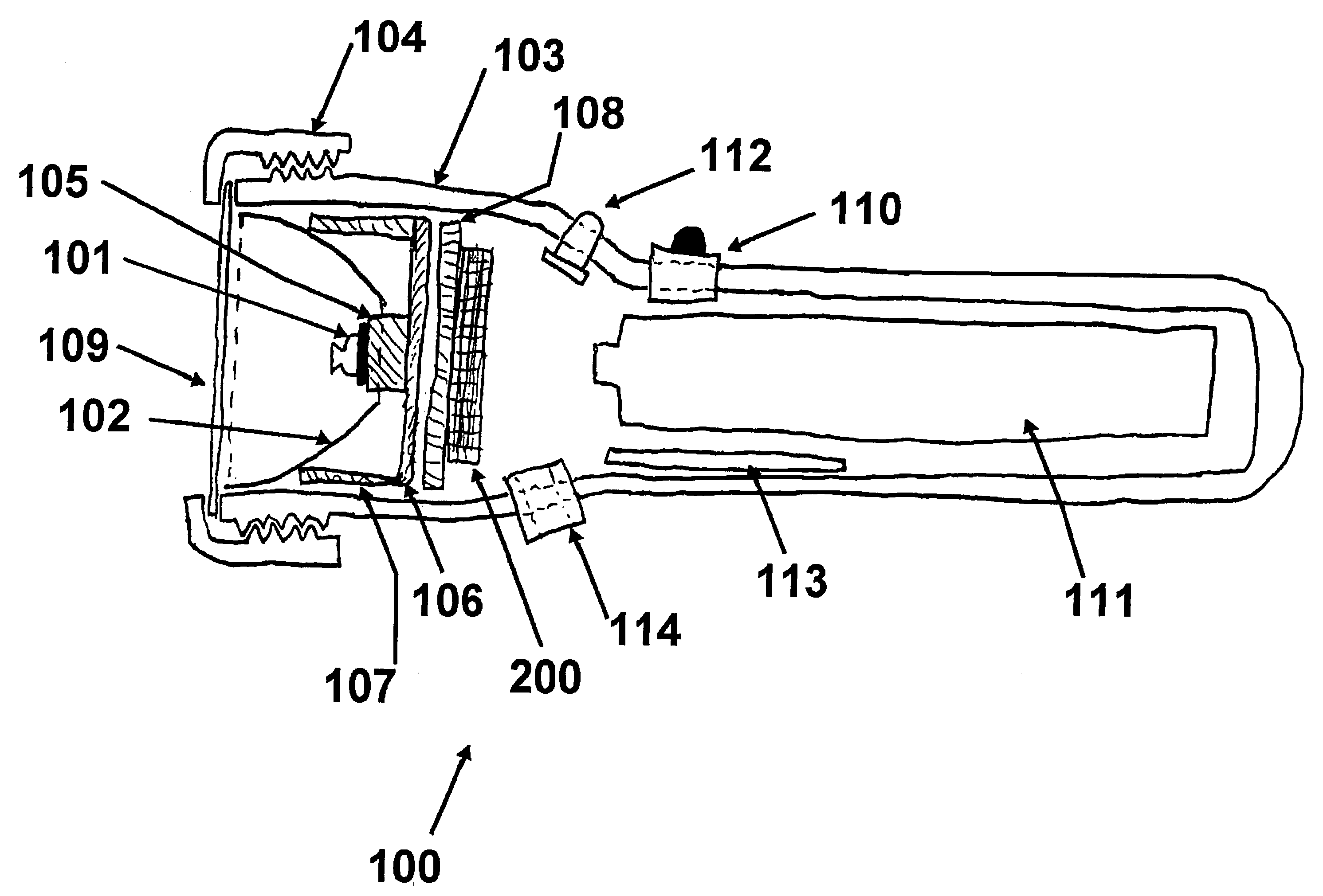
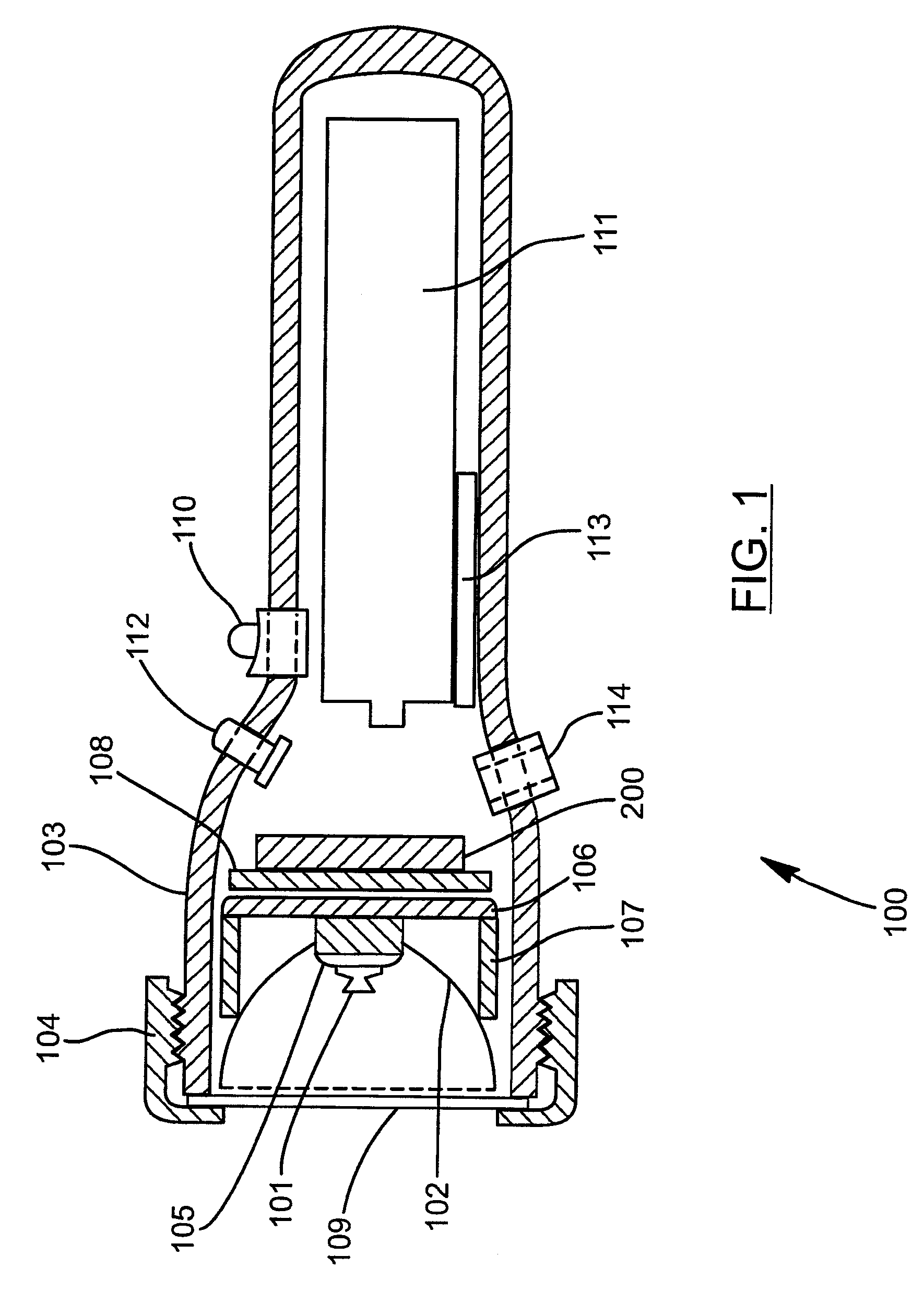
UV LED Curing Apparatus with Improved Housing and Switch Controller
InactiveUS20110277338A1Improve securityImprove reliabilityDrying solid materials with heatElectric circuit arrangementsAutomatic controlEngineering
The present invention is related to an UV LED curing apparatus, and more particularly, to an UV LED curing apparatus with improved housing and switch controller. The UV LED curing apparatus of the present invention is preferably provided for curing UV hardening gel applied onto the nails of multiple fingers or toes all at once and with automatic controls; the UV LED curing apparatus comprises a light reflective inner casing enclosing a curing chamber having a front opening, an outer casing detachably attached to the inner casing and an UV LED light source disposed on the inner casing and capable of providing an illumination covering a large space in the curing chamber. The automatic controls of the apparatus may be achieved by a switch controller having a photo interrupter, timer and current regulator such that the UV light from the UV LED light source is triggered to an on-state by the sensor of the photo interrupter and switched to an off-state by the timer and current regulator with reference to a preset curing time automatically. The UV LED light source is preferably to be of a wavelength between 360 nm and 460 nm. The light reflective inner casing is preferably provided as an effective UV light reflector and as a supporting substrate of the UV LED light source while being capable of transmitting heat from the UV LED light source away for further heat dissipation to the ambient by the outer casing. The outer casing is detachably attached to the inner casing and allows a greater user interaction for decorative and entertainment purposes while also being a protective and heat dissipation means.
Owner:NAIL ALLIANCE
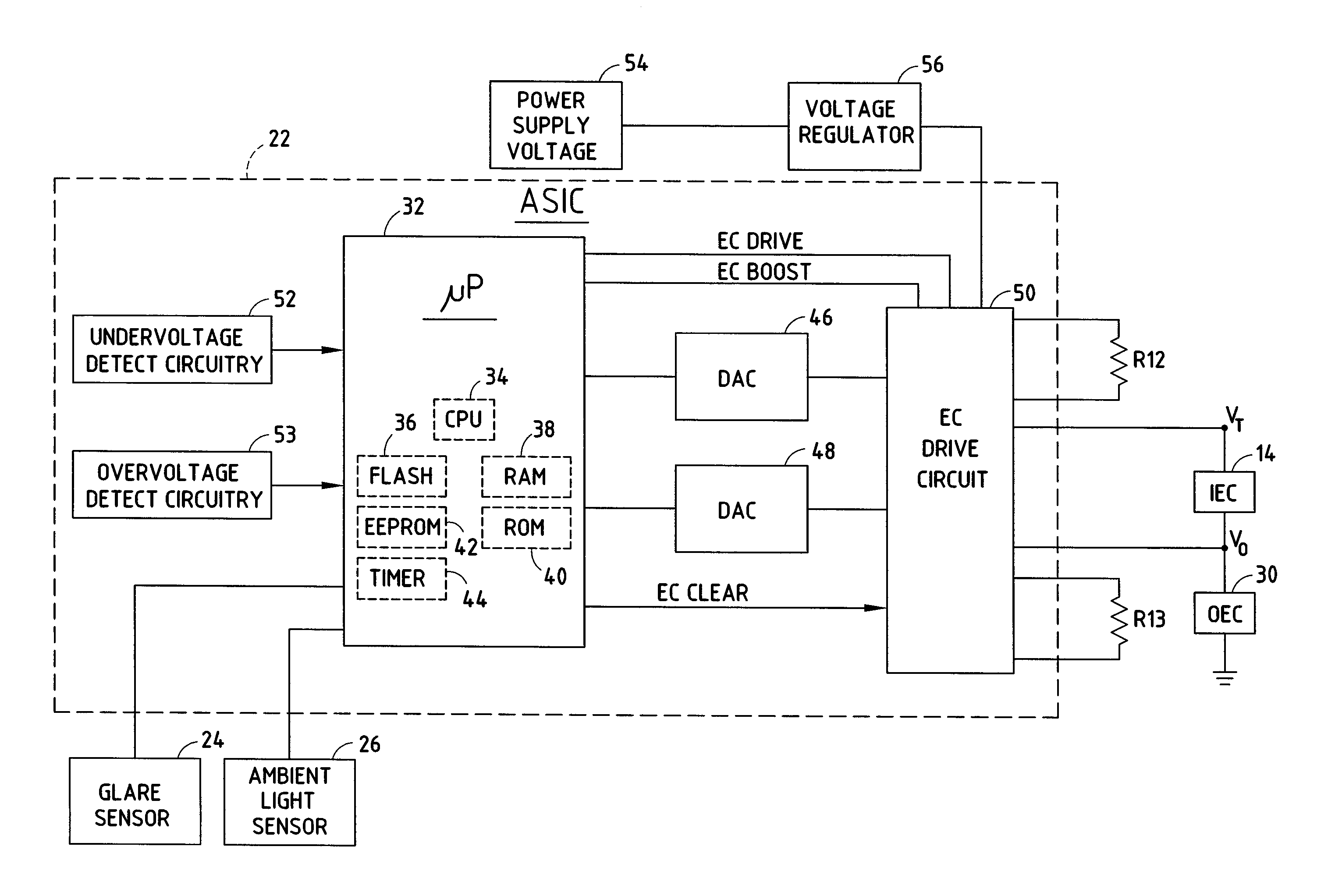
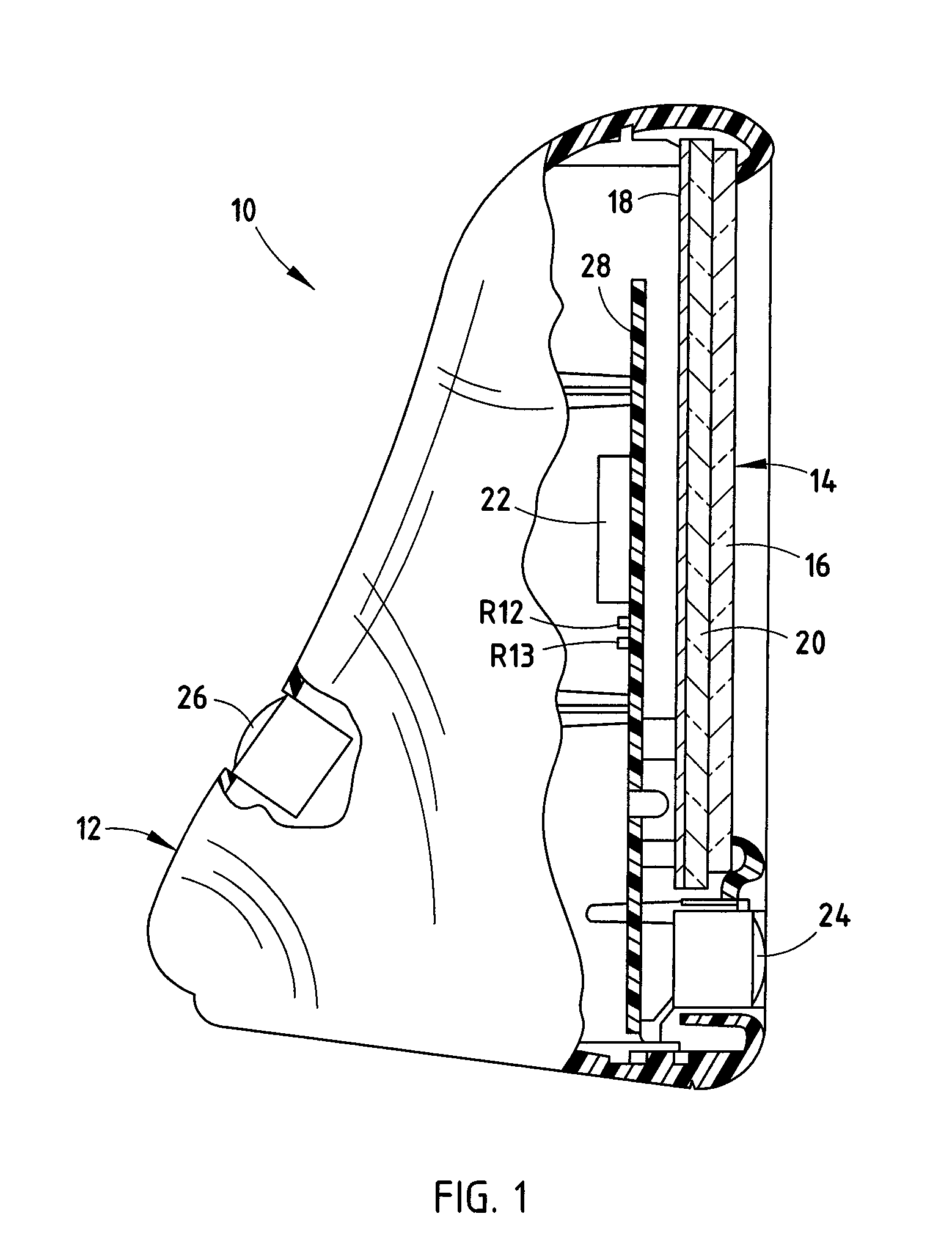
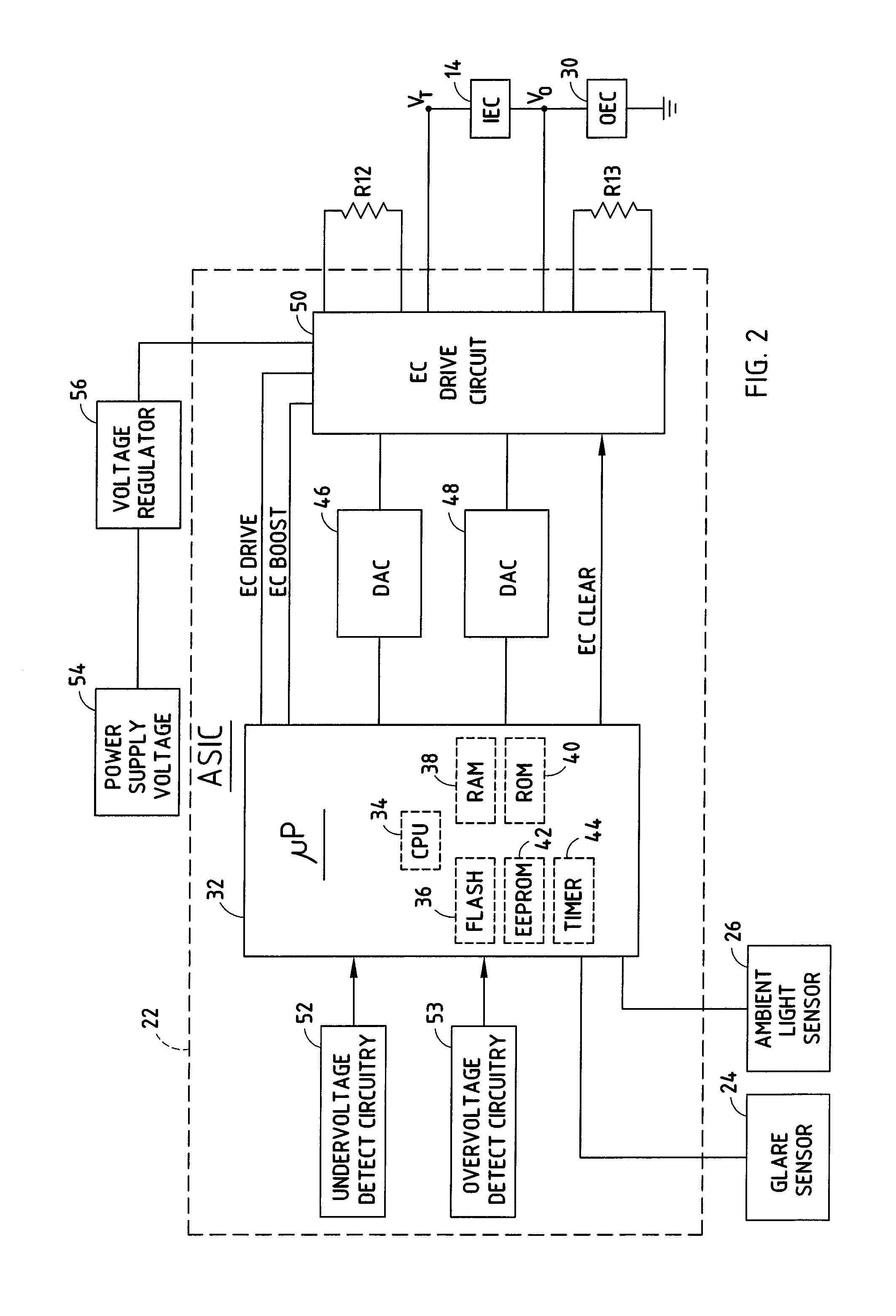
Electrochromic element drive control circuit
InactiveUS7215318B2Dissipate thermal energyDissipate energyCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
A drive control circuit for controlling an electrochromic element is substantially integrated into an integrated circuit, with the exception of resistive elements for dissipating heat away from the integrated circuit. The drive control circuit includes a current regulator for generating a select one of at least two discrete amounts of current to drive the electrochromic element. Further, a control system individually controls a plurality of electrochromic elements and includes shunts coupled in parallel with the individual electrochromic elements. The control system controls the ratio of the reflectance of the individual electrochromic elements as a function of sensed glare.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
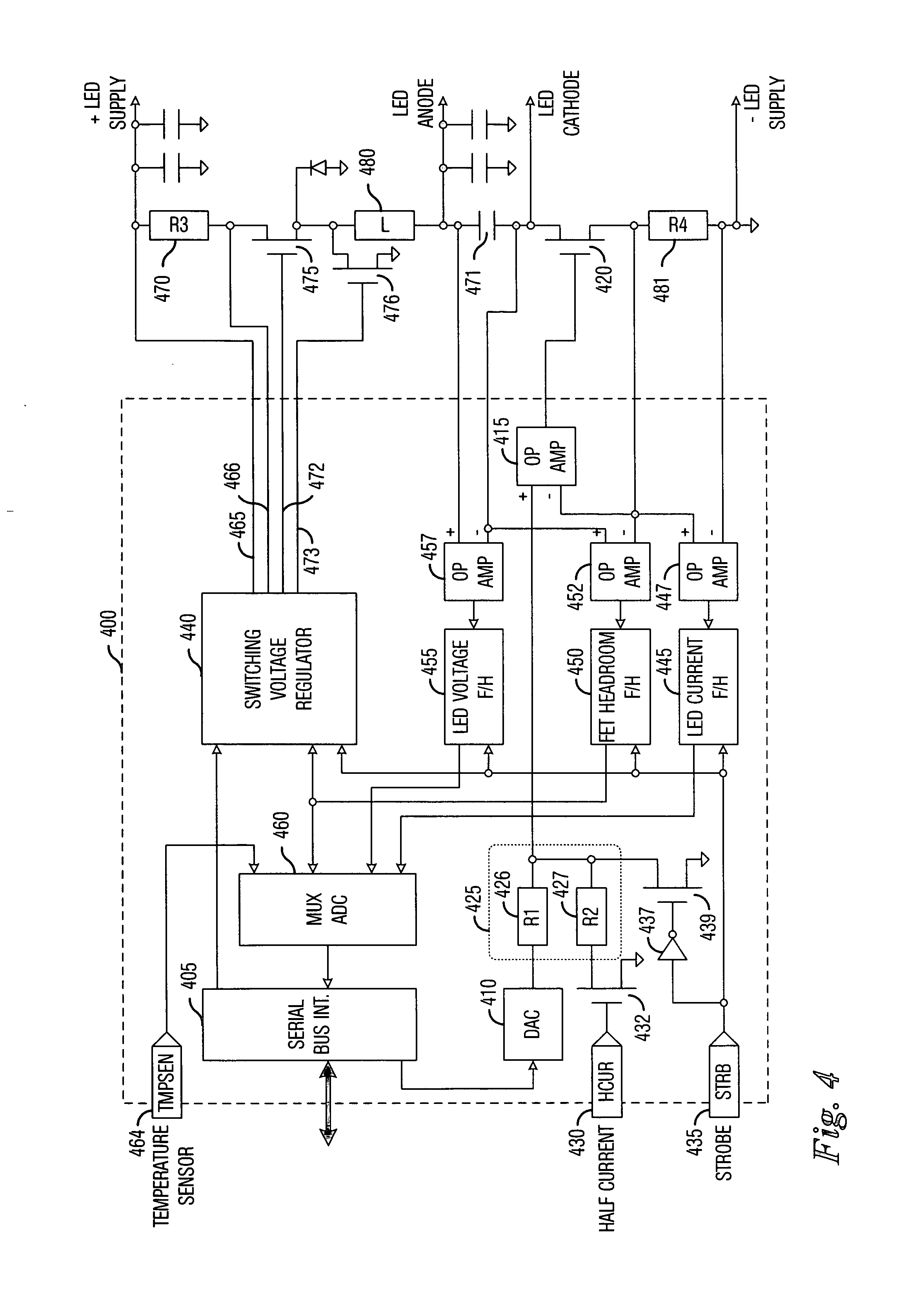
High efficiency power supply for LED lighting applications
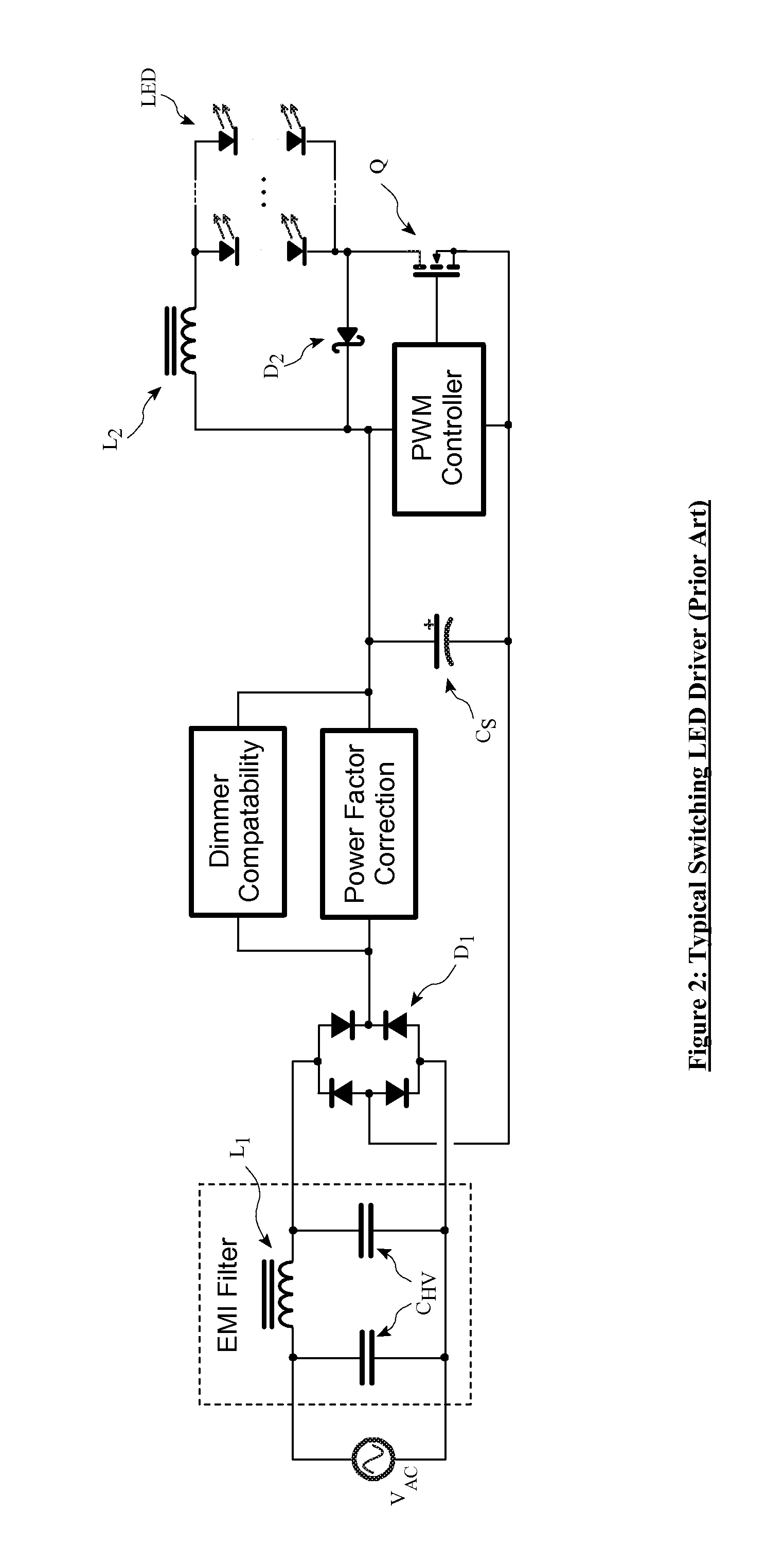
InactiveUS20070120506A1Accurate current regulationHigh efficiency operating pointElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesVoltage regulationEffect light
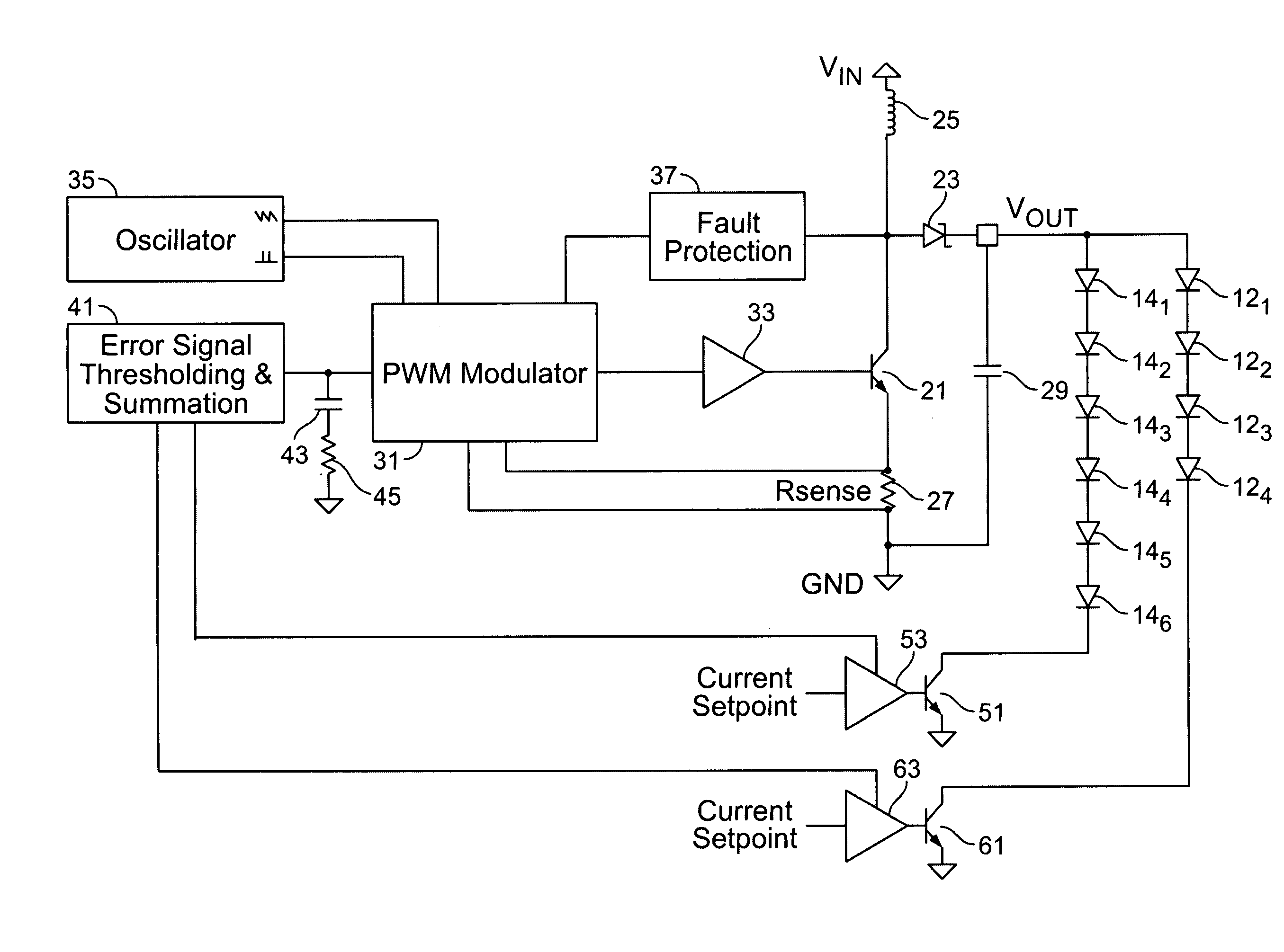
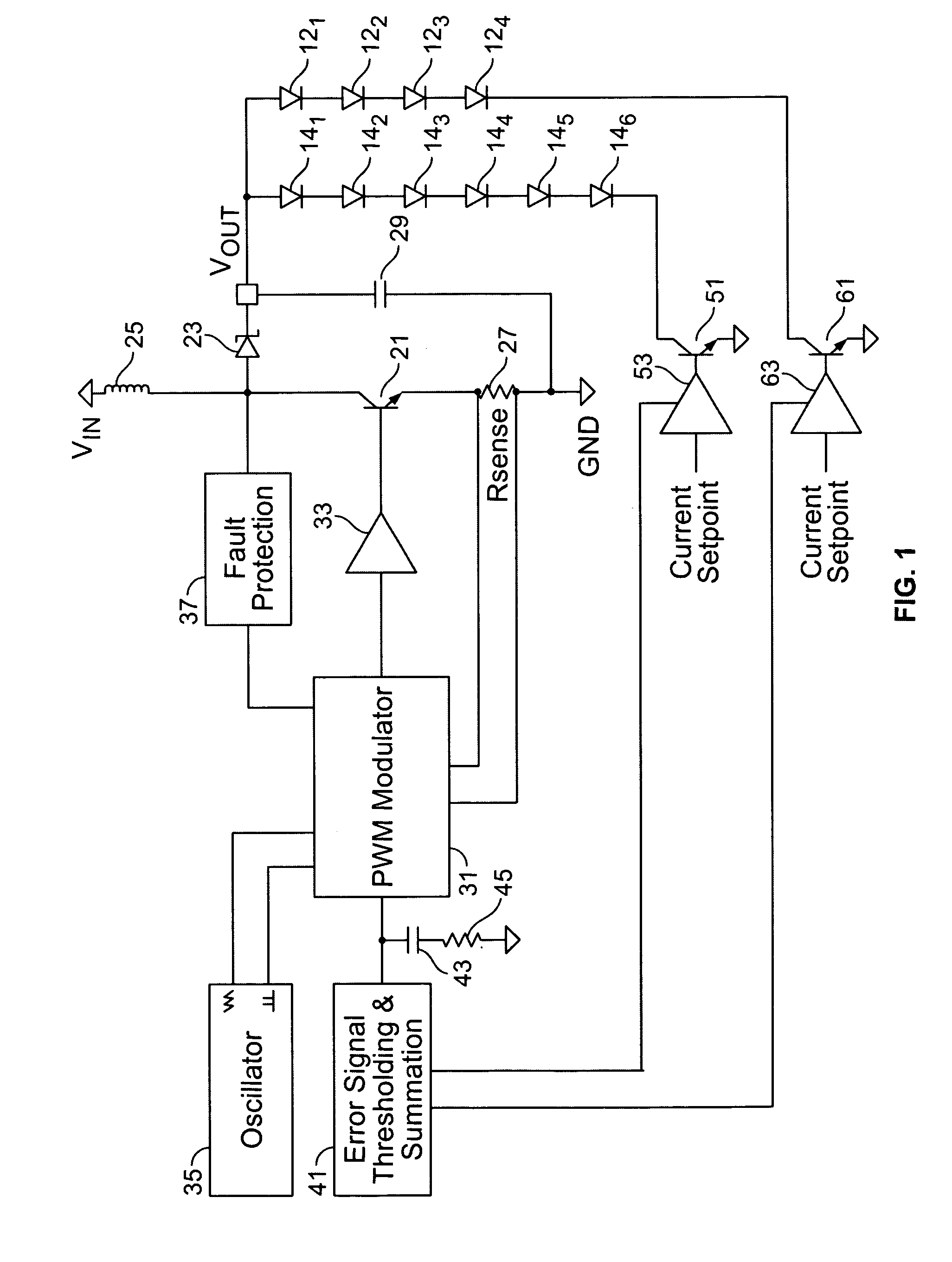
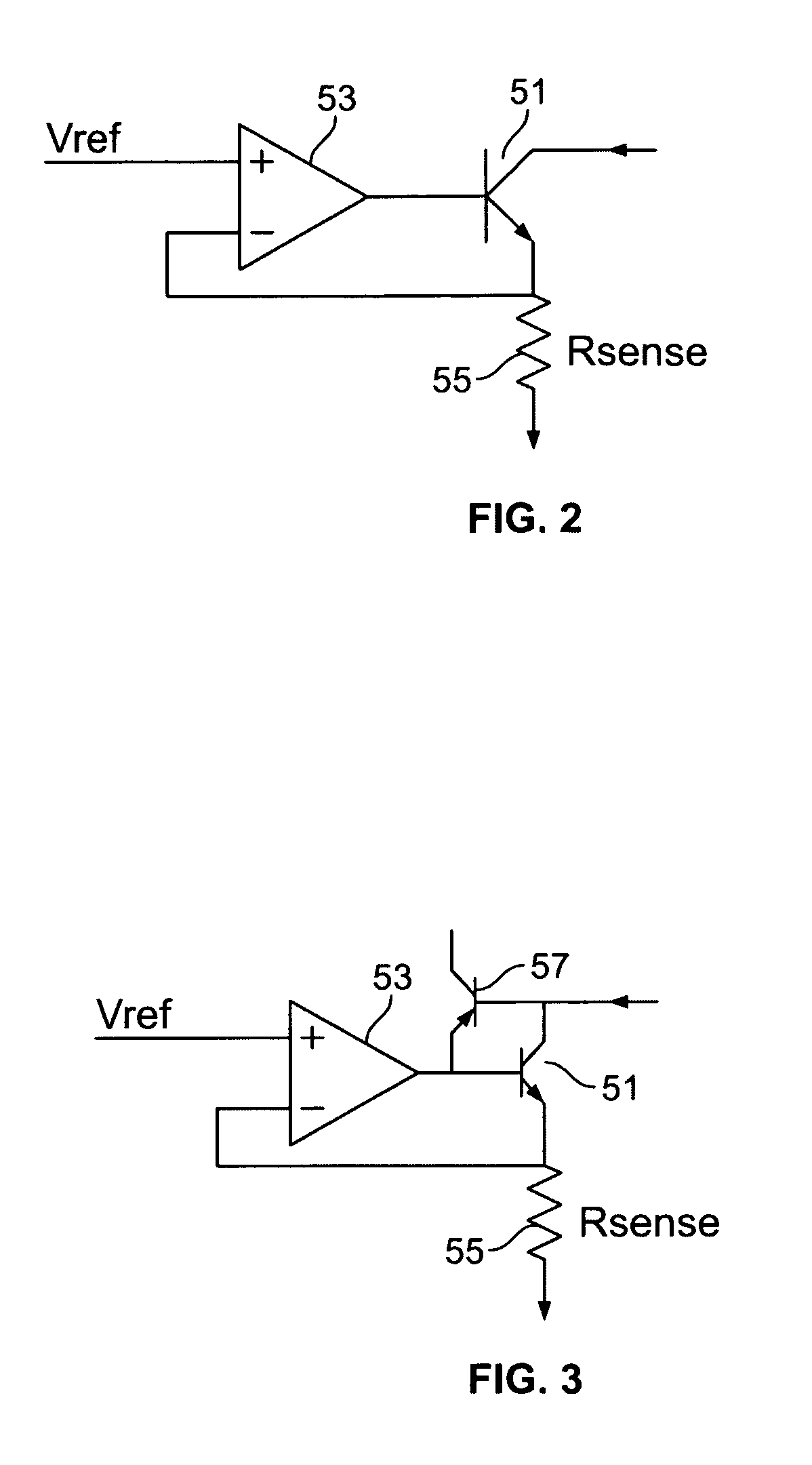
A power supply for plural loads coupled in parallel comprises a voltage regulator, a plurality of current regulators, and an error control circuit. The voltage regulator provides a common output voltage to the plural loads. The voltage regulator comprises a sensor circuit providing a voltage sense signal corresponding to the output voltage, which provides feedback to regulate the output voltage at a selected level. The plurality of current regulators are coupled to respective ones of the plural loads. Each of the plurality of current regulators regulates current drawn by respective ones of the plural loads to within a desired regulation range. The plurality of current regulators each further provide a respective error signal corresponding to an ability to remain within the desired regulation range. The error control circuit is operatively coupled to the voltage regulator and to the plurality of current regulators. The error control circuit receives the error signals from the plurality of current regulators and provides a common error signal to the voltage regulator. The voltage regulator thereby changes the selected level of the output voltage in response to the common error signal. Accordingly, the selected level of the output voltage remains at a minimum voltage necessary to keep the plural loads in the desired regulation range.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
LED lamps and LED driver circuits for the same
LED lamp has LEDs aimed rearwards with either a concave mirror to the rear of each LED, or one concave mirror to the rear of two or more LEDs, collecting the light from the LEDs to form a forward projecting beam. LEDs may be high power types that require heatsinking. LED lamp may have a lens forward of each LED to collimate the radiation produced by the LEDs into a beam, where at least one lens has at least one aspheric curved surface. LED lamp may have a transparent reflective optic to collimate the radiation produced by each LED into a beam. For an inspection lamp, the LEDs typically have a peak wavelength of 395 to 415 naometers for seeing the area being irradiated but not so visible as to overwhelm fluorescence of fluorescent materials to be detected. Other wavelengths may be used. LED inspection lamp has a combination of LEDs of different wavelengths or a combination of at least one LED and at least one other light source such that the lamp produces radiation suitable for detection of materials to be detected and adequately illuminates the area being irradiated. LED lamp has LEDs that produce a beam of suitable radiation with a width of 10 degrees or less without additional optics. LED inspection lamp has head attached to a flexible member, with head serving as heatsink for one or more high power LEDs. Current regulator circuits are also disclosed.
Owner:ALLTEMP PROD CO LTD
Dc-link voltage balancing system and method for multilevel converters
ActiveUS20110141786A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionReference currentControl system
A control system for a multilevel converter includes a differential mode current regulator, a neutral point (NP) controller and a PWM controller for generating switching pulses for the multilevel converter. The differential mode current regulator generates reference voltage command signals based on a difference between reference current command signals and actual current command signals, and the NP controller determines a modified neutral point current signal in response to a DC link voltage unbalance. The NP controller utilizes the modified neutral point current signal to generate a common mode reference voltage signal. The switching pulses are generated by the PWM controller based on the reference voltage command signals and the common mode reference voltage signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for driving light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
ActiveUS20070035538A1Minimum heat dissipationEfficient power supplyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesSwitched currentControl signal
System and method for improving efficiency in driving LEDs. A preferred embodiment comprises a switch current regulator coupled to a current control signal input, the switch current regulator to control an amount of current provided to the LED based upon a magnitude of a voltage on the current control signal input, a switching voltage regulator coupled to the switch current regulator and the LED, the switching voltage regulator to provide current to the LED, and a sensor coupled to the switch current regulator, the LED, and a signal feedback circuit, the sensor to measure status information regarding the switch current regulator and the LED and provides the information to a controller, wherein the status information can be used to adjust the current on the current control signal input.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
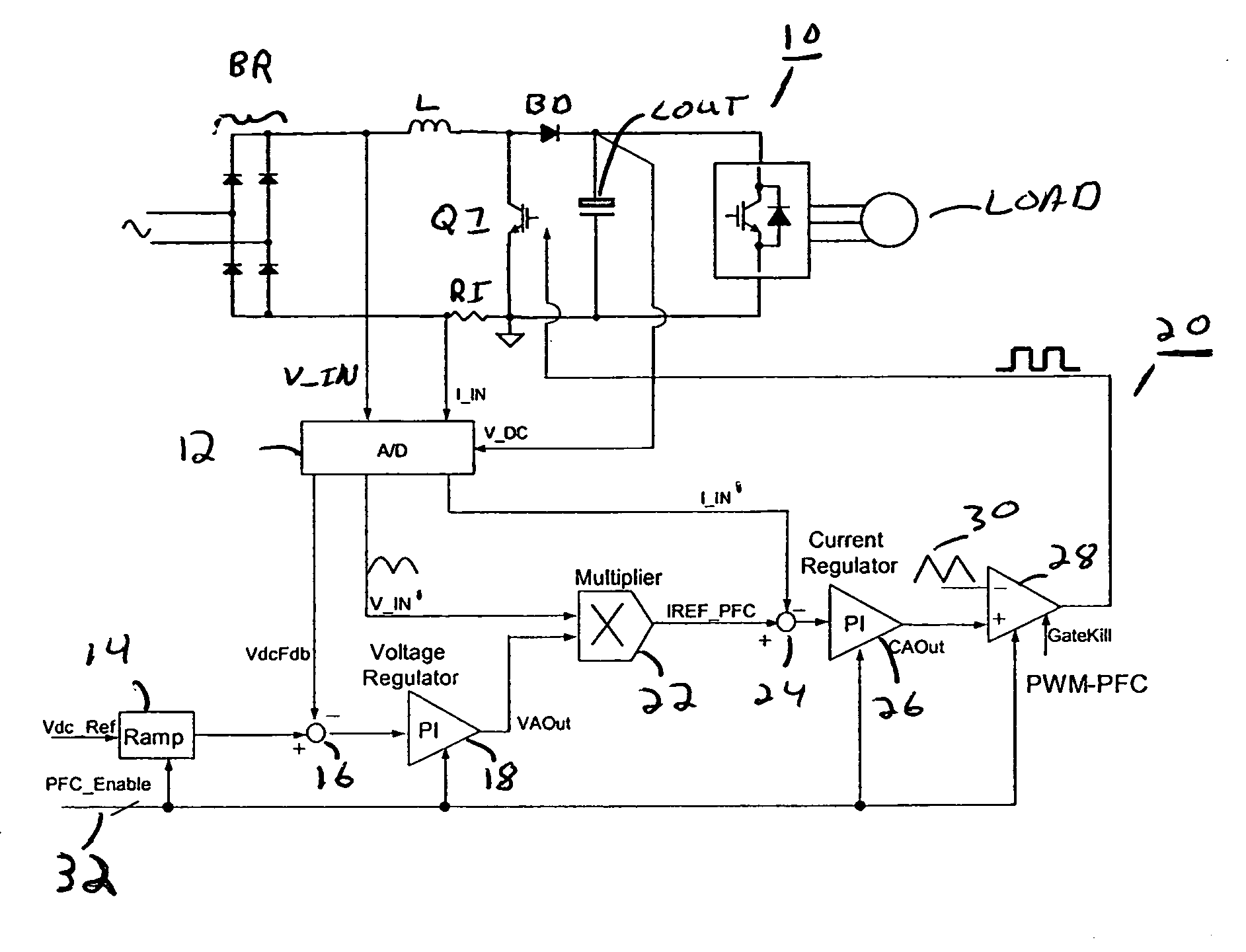
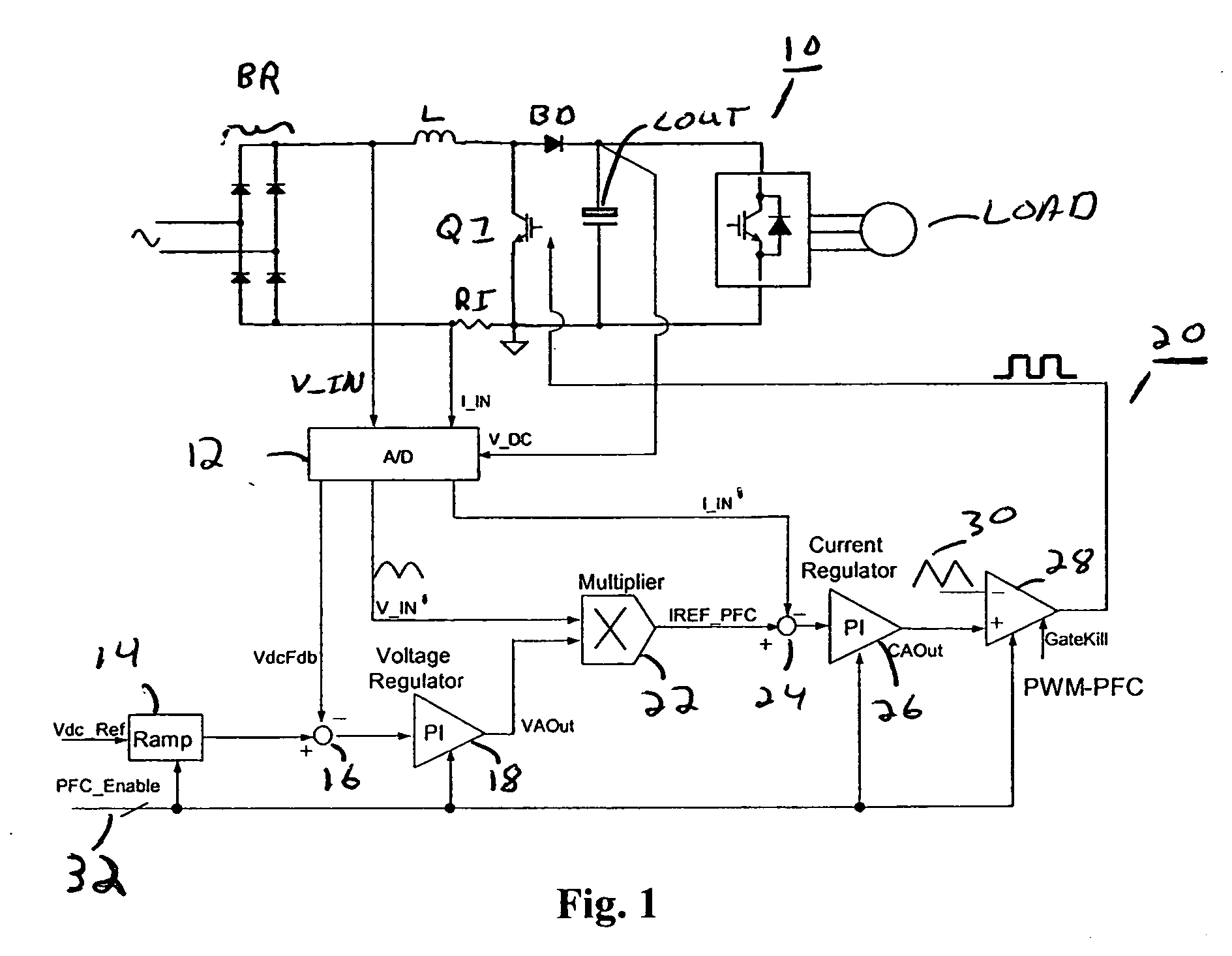
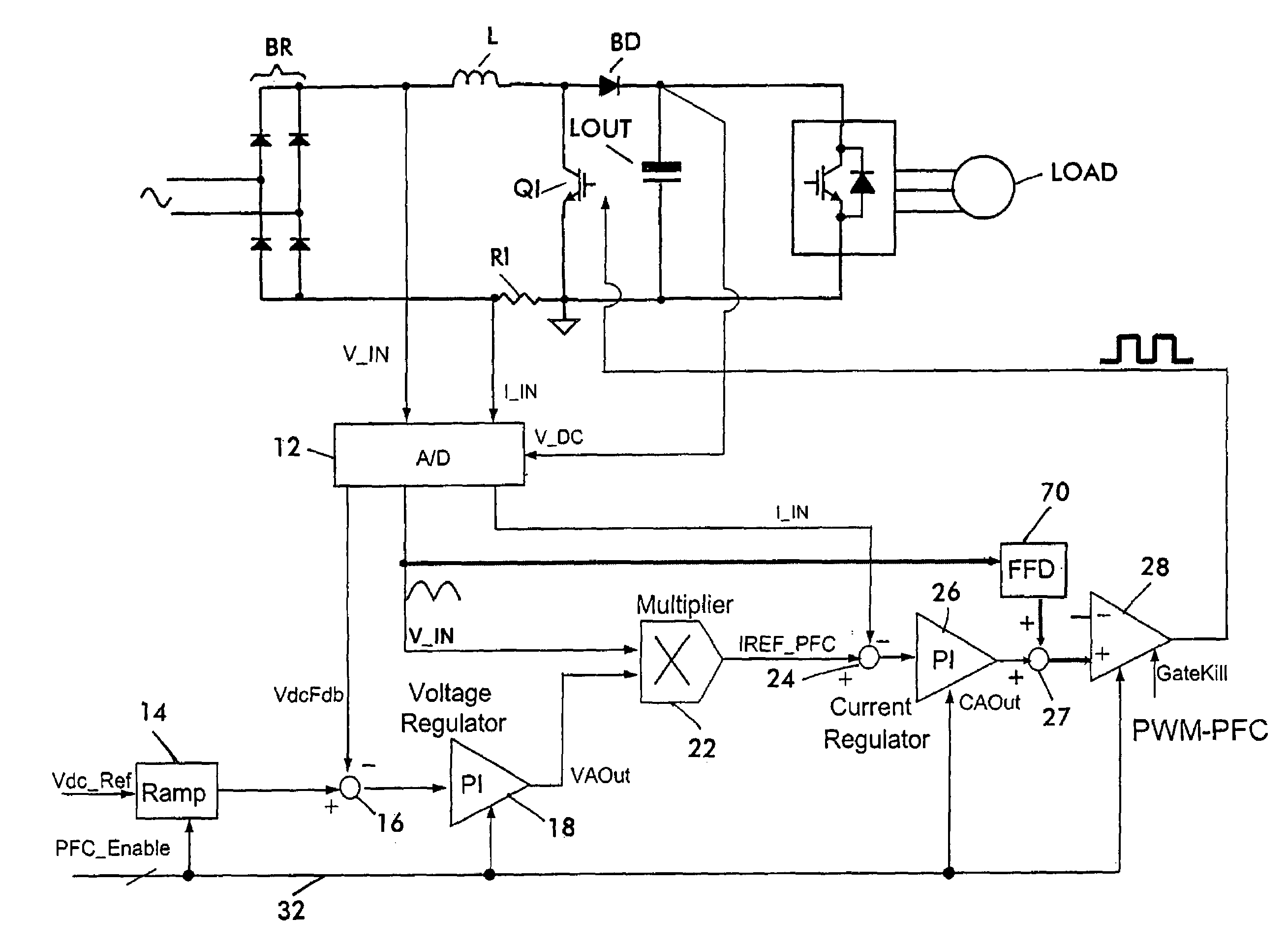
Digital implementation of power factor correction
InactiveUS20060245219A1Avoid problemsAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionControl signalEngineering
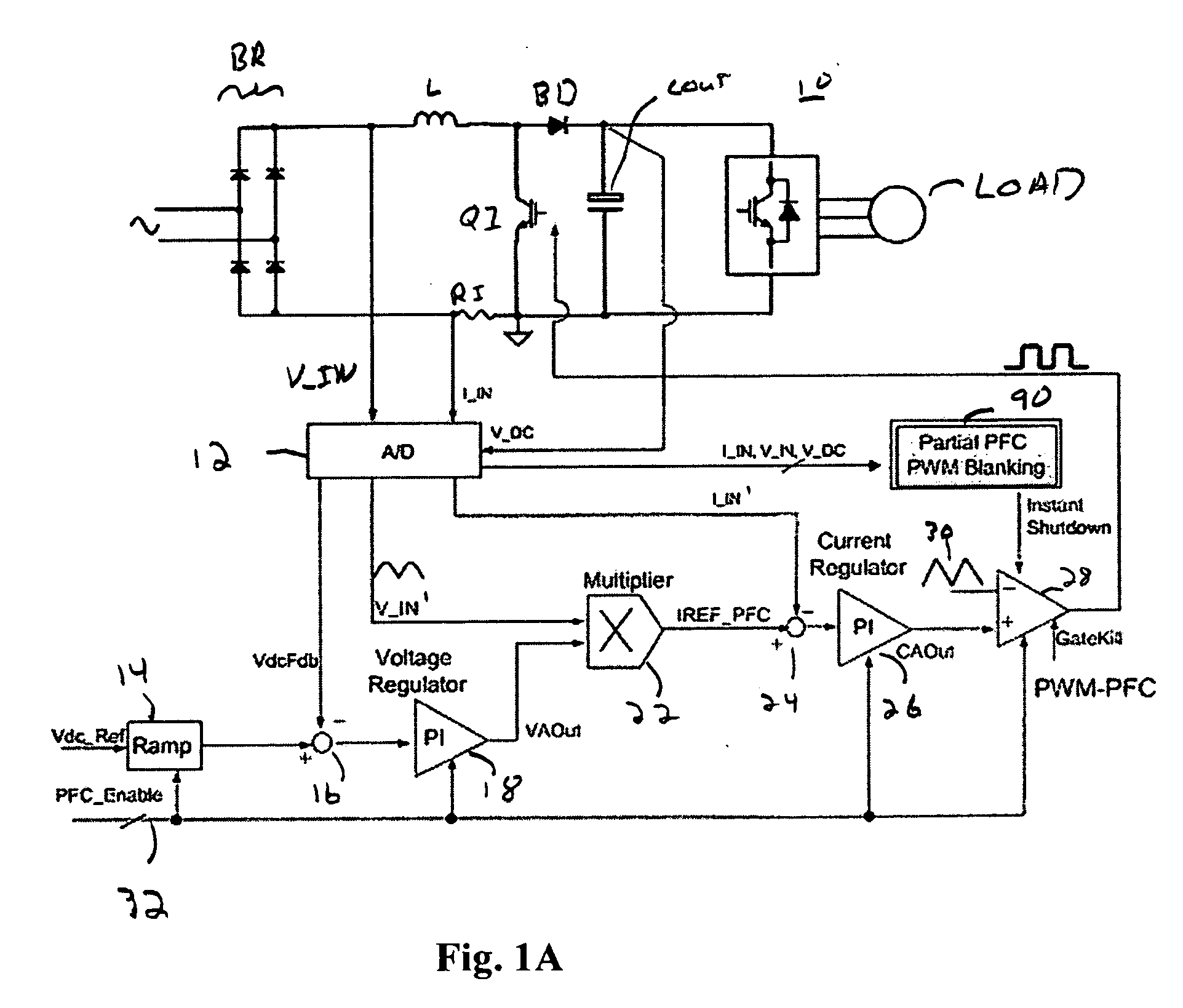
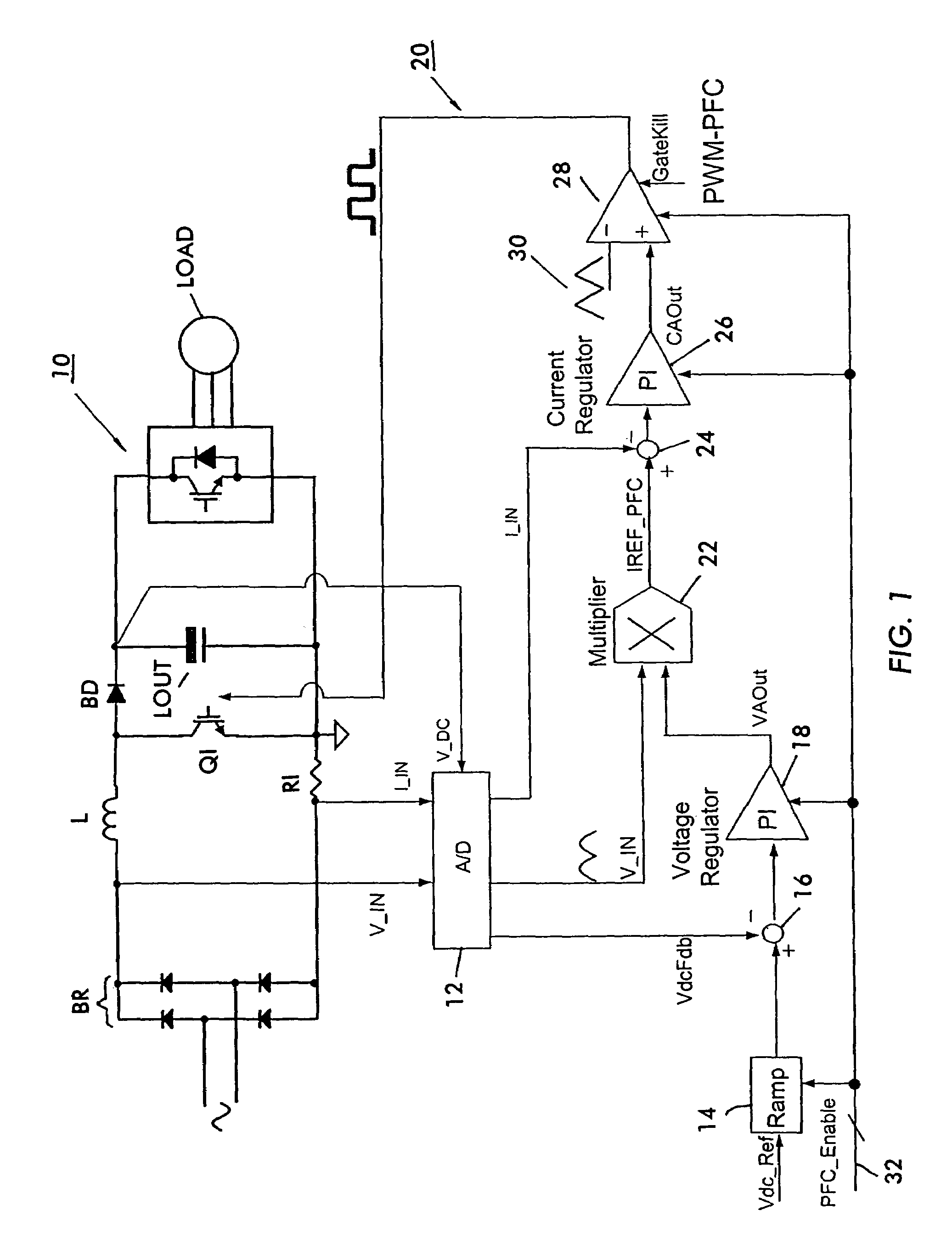
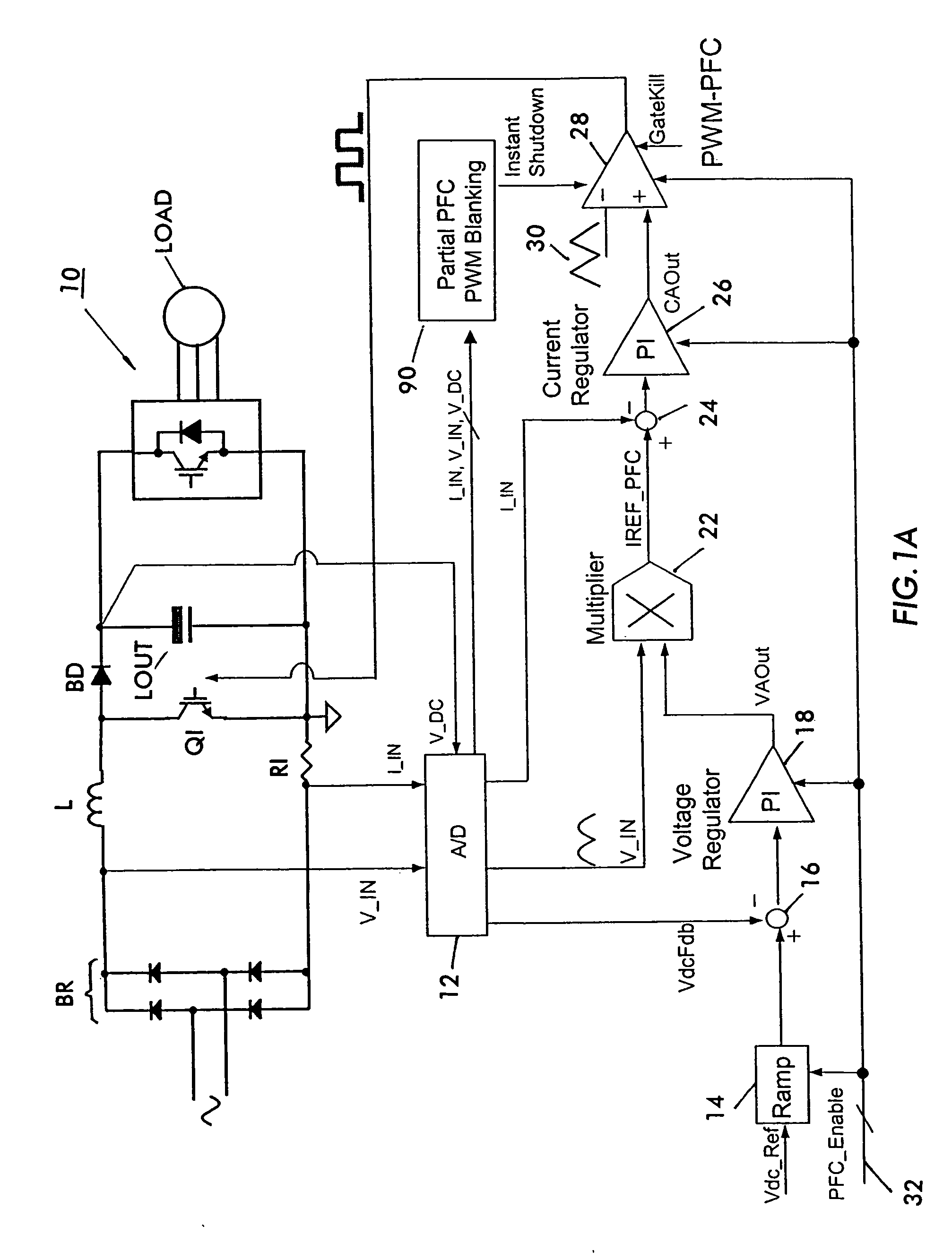
A circuit for providing power factor correction in accordance with an embodiment of the present application may include a boost converter circuit and a control circuit receiving as inputs a rectified AC input voltage from a rectifier, a signal proportional to current through the boost inductor and the DC bus voltage across the capacitor of the boost converter. The control circuit provides a pulse width modulated signal to control the on time of a PFC switch. The control circuit further includes a voltage regulator and a current regulator. The current regulator includes a difference device operable to subtract a signal proportional to the inductor current from the current reference signal, a PI controller adapted to receive the output of the difference device and provide a first control signal, a feed forward device operable to receive the rectified AC input voltage and to provide a second control signal with a smaller dynamic range than the AC input voltage, and an adder operable to add the first control signal to the second control signal to provide a PWM reference signal for generating the pulse width modulated signal. A zero crossing detector and vector rotator may be provided to provide a clean sinusoidal reference to the current regulator. A partial PFC regulator may be provide to provide partial mode PFC if desired.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
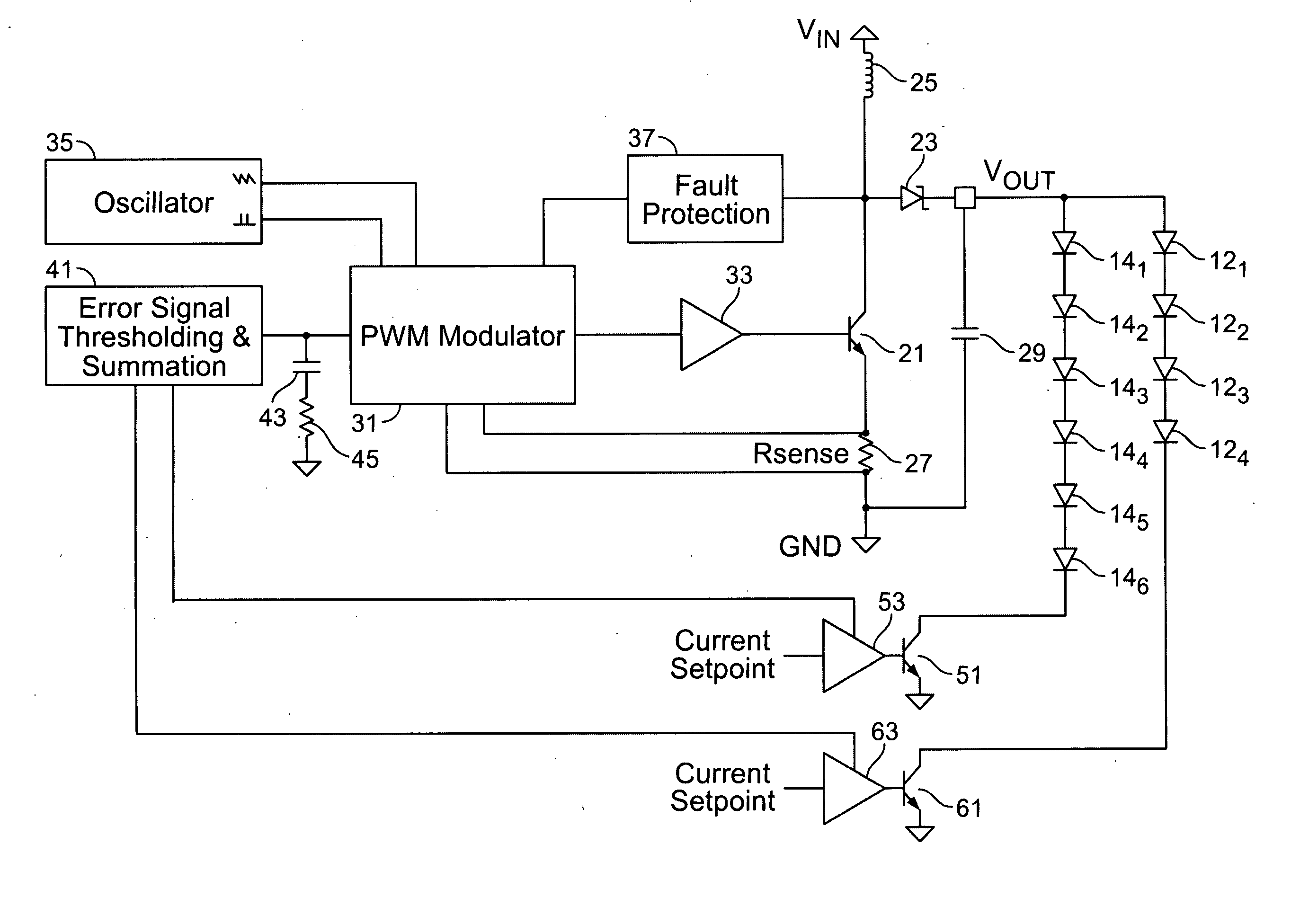
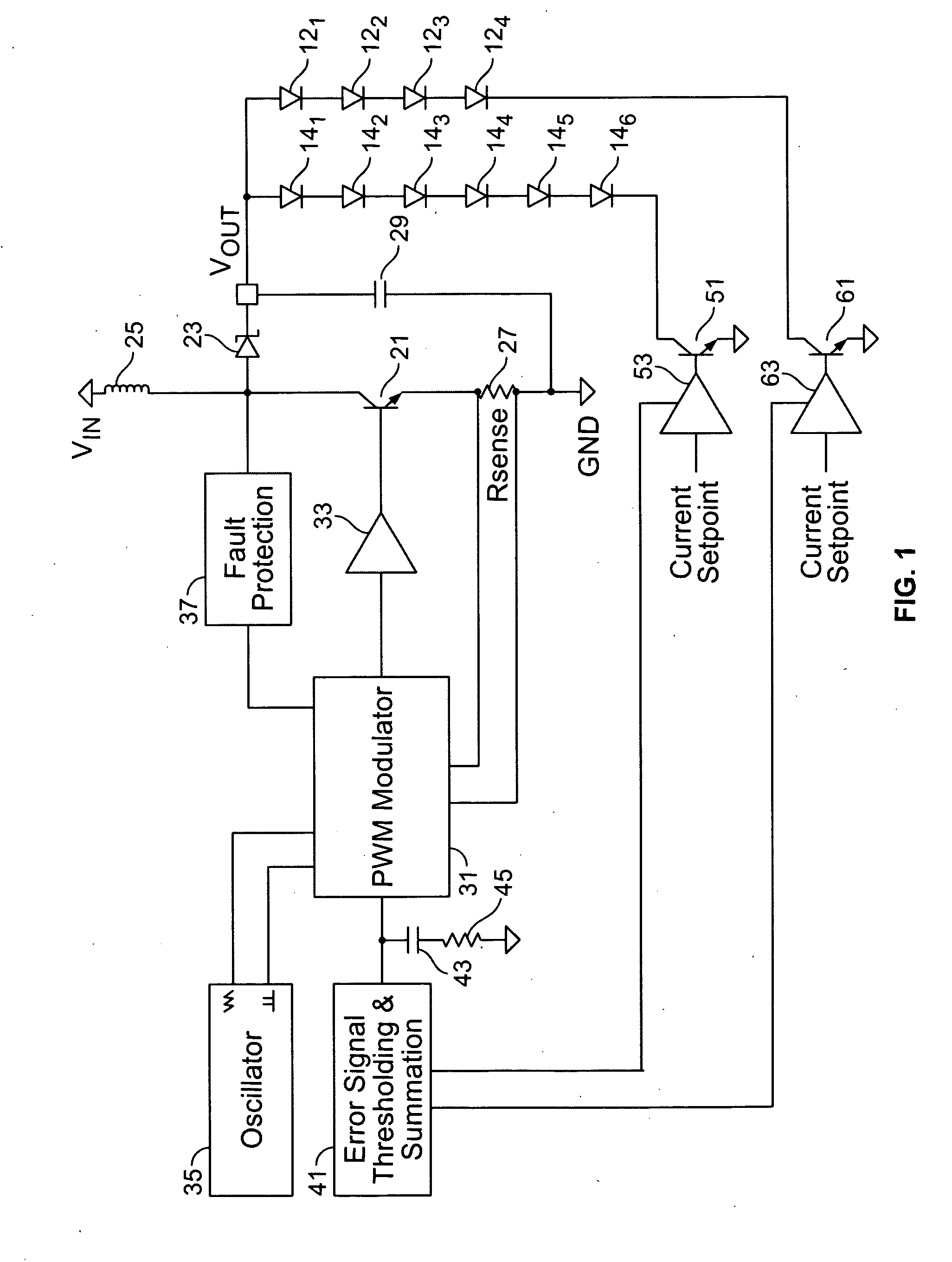
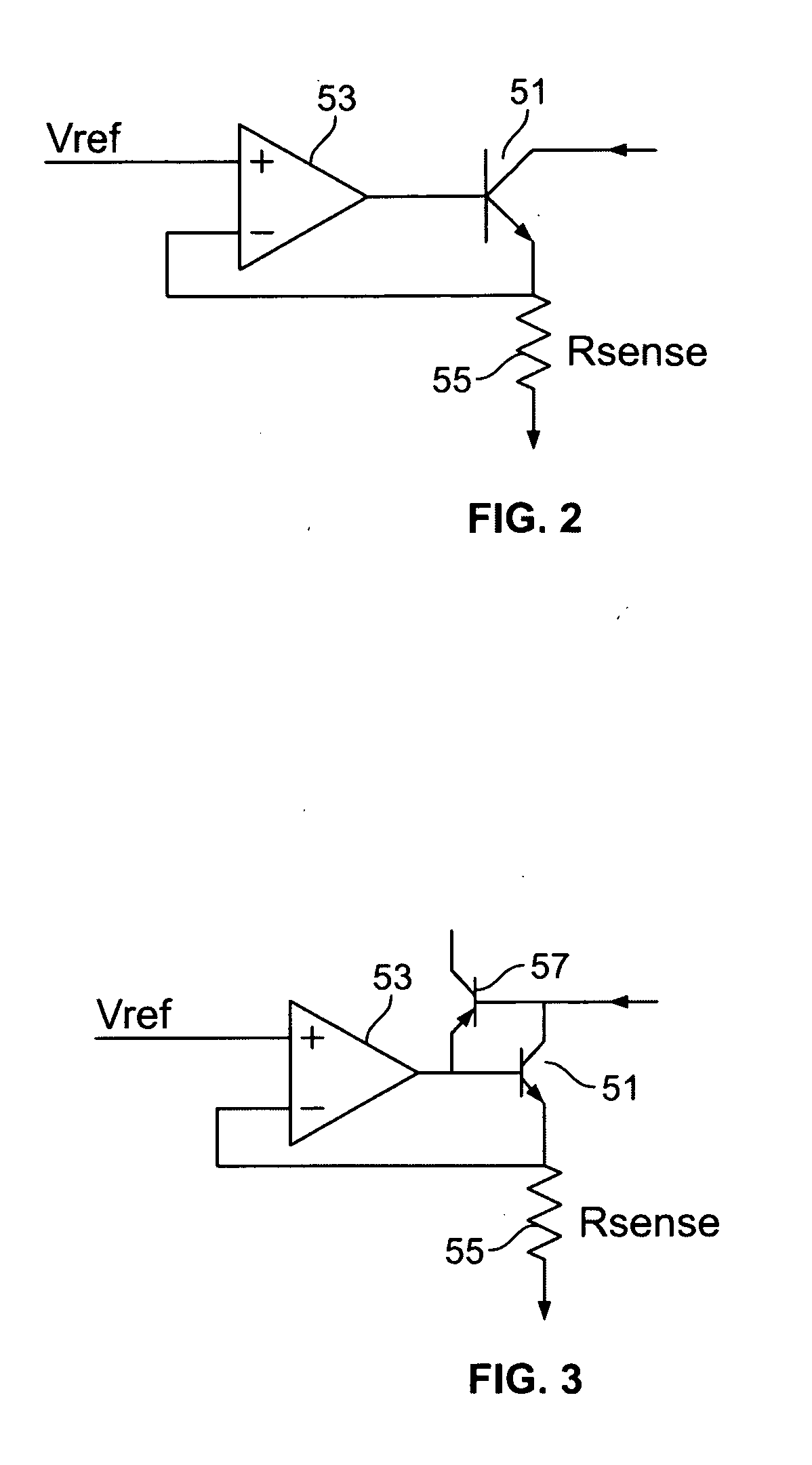
Multiple stage sequential current regulator
ActiveUS20120262075A1Eliminate needDc network circuit arrangementsElectroluminescent light sourcesPower factorEngineering
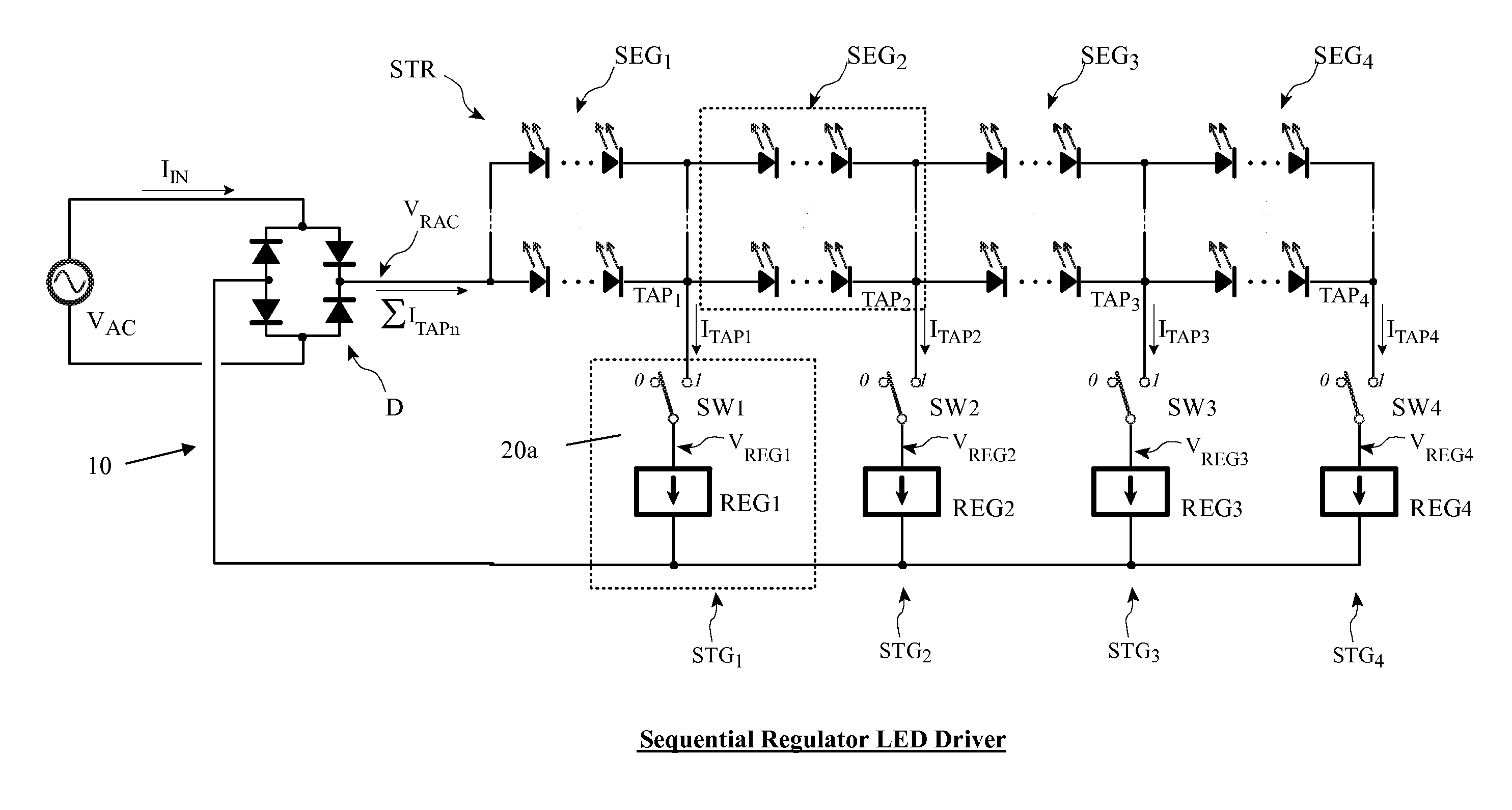
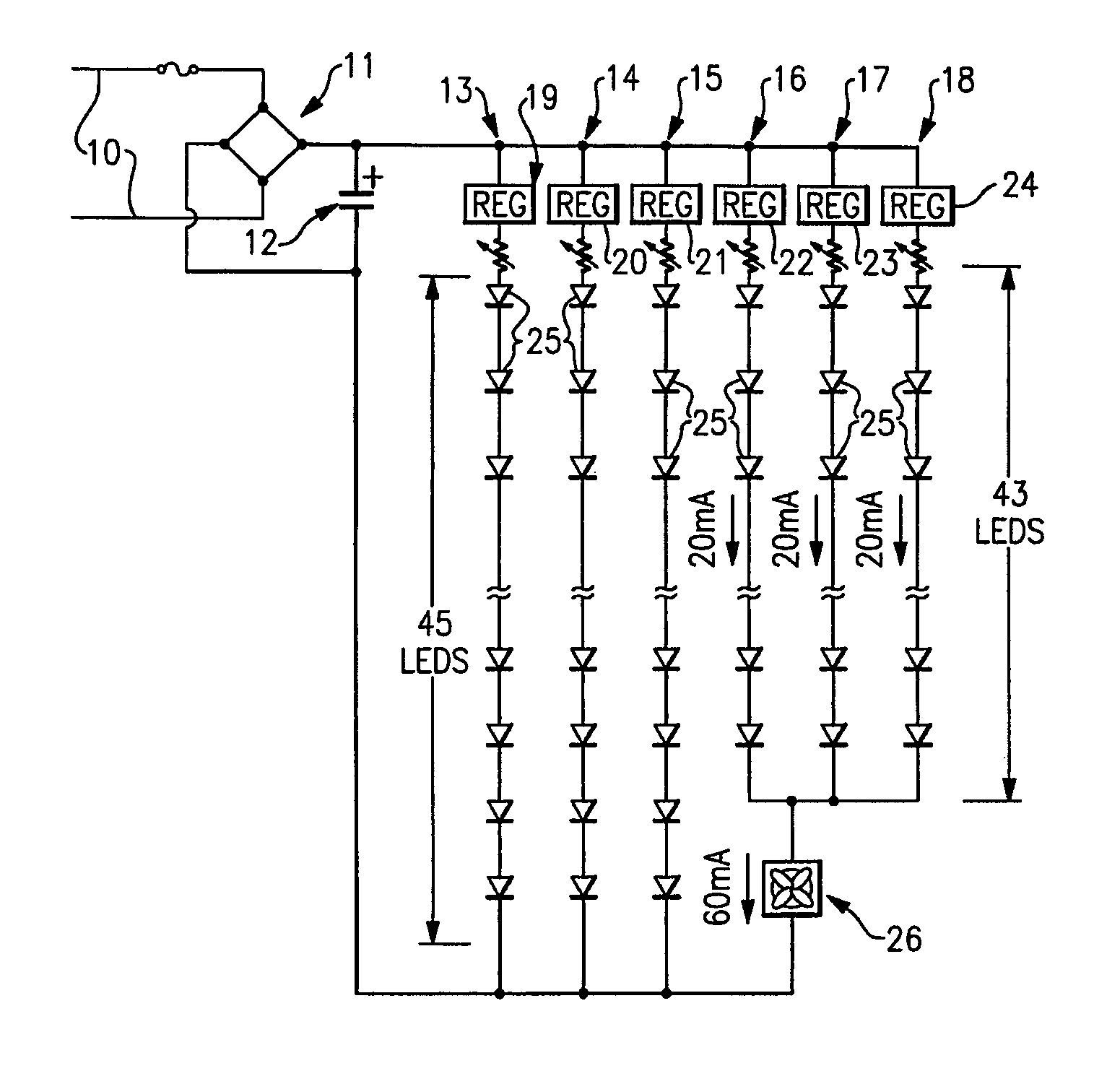
An LED driver circuit operating from the AC power line providing high efficiency, good line and load regulation, high power factor, low line current harmonics, low conducted EMI, high LED utilization, and lamp dimming compatibility, while consisting of a minimal number of components. No inductors, nor capacitors (including electrolytics), nor high current switching transistors are employed. The top of a string of series connected LED segments is connected to the output of a rectifier, which in turn is connected to an AC sine wave power source. The string is tapped at various locations, including the bottom of the string. Each segment can consists of any number of serial or parallel connected LEDs. Current control elements or regulators sink current at each tap and are sequentially turned on and off one at a time, tracking the rectified sine wave voltage. Voltage across each regulator and current when conducting is individually controllable. Power loss in the regulators is minimized by keeping regulator voltage to a minimum. The regulators may control current in a multitude of ways, including a constant current, or a current dependent on voltage across the regulators including a resistor, or a combination. The driver is self-commutating, with the sequencing of the current control elements an inherent feature closely integrated with the current control elements and providing optimal performance over variable operating conditions. Given the large number of design variables, the driver circuit can be optimized for various performance criteria including input voltage range, line / load regulation, output power / current, efficiency, power factor, line current harmonics, dimmer compatibility, and LED utilization.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
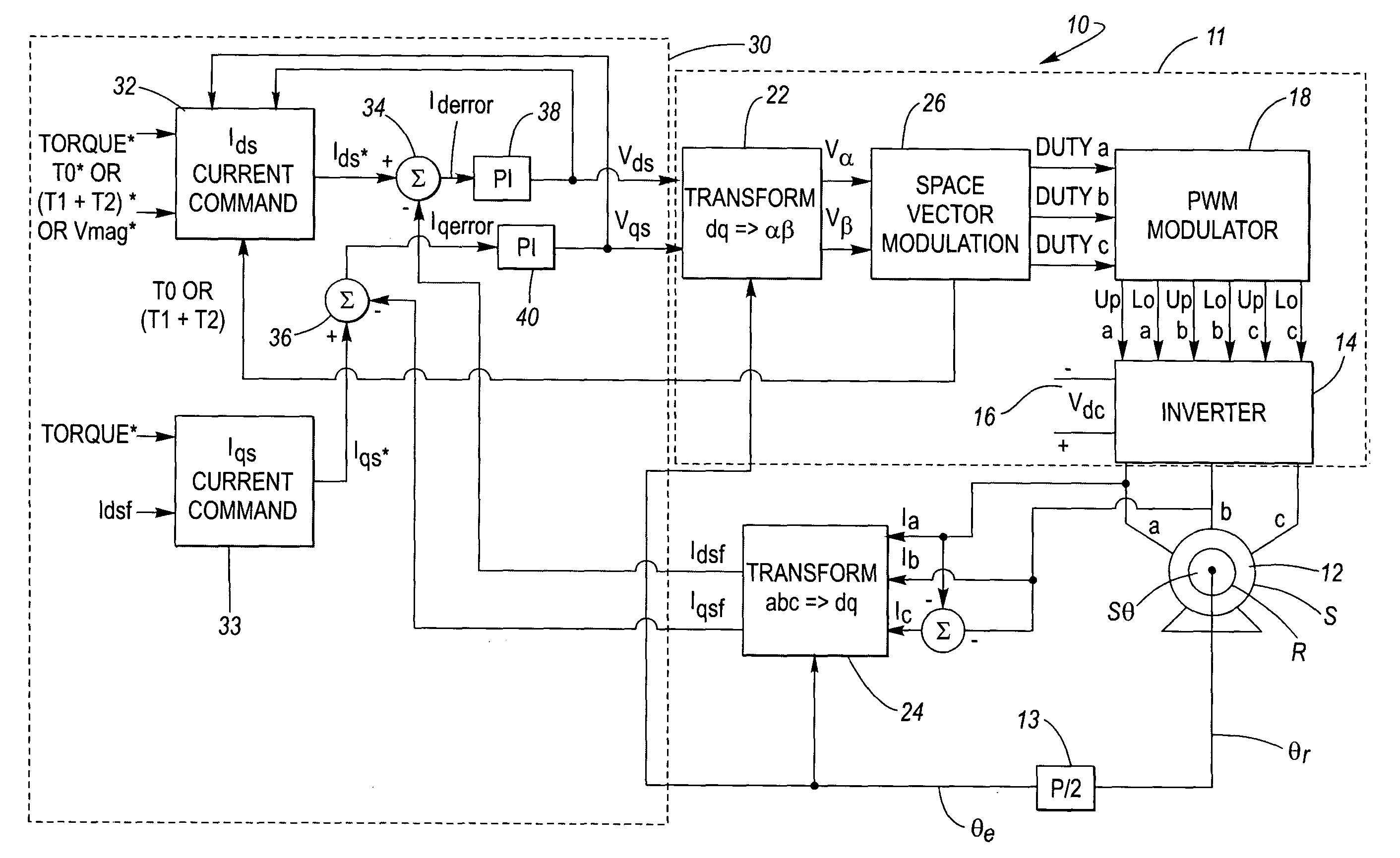
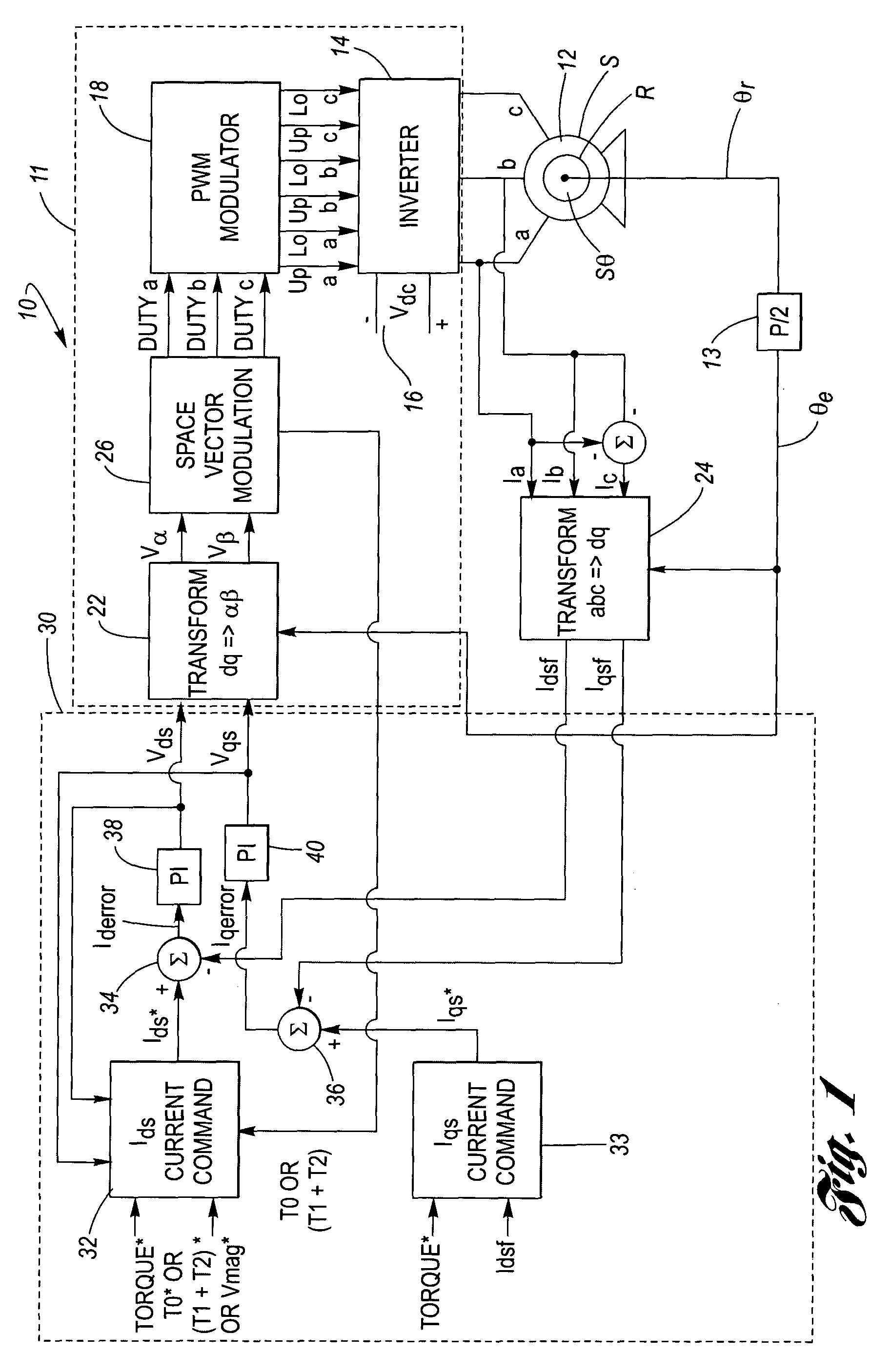
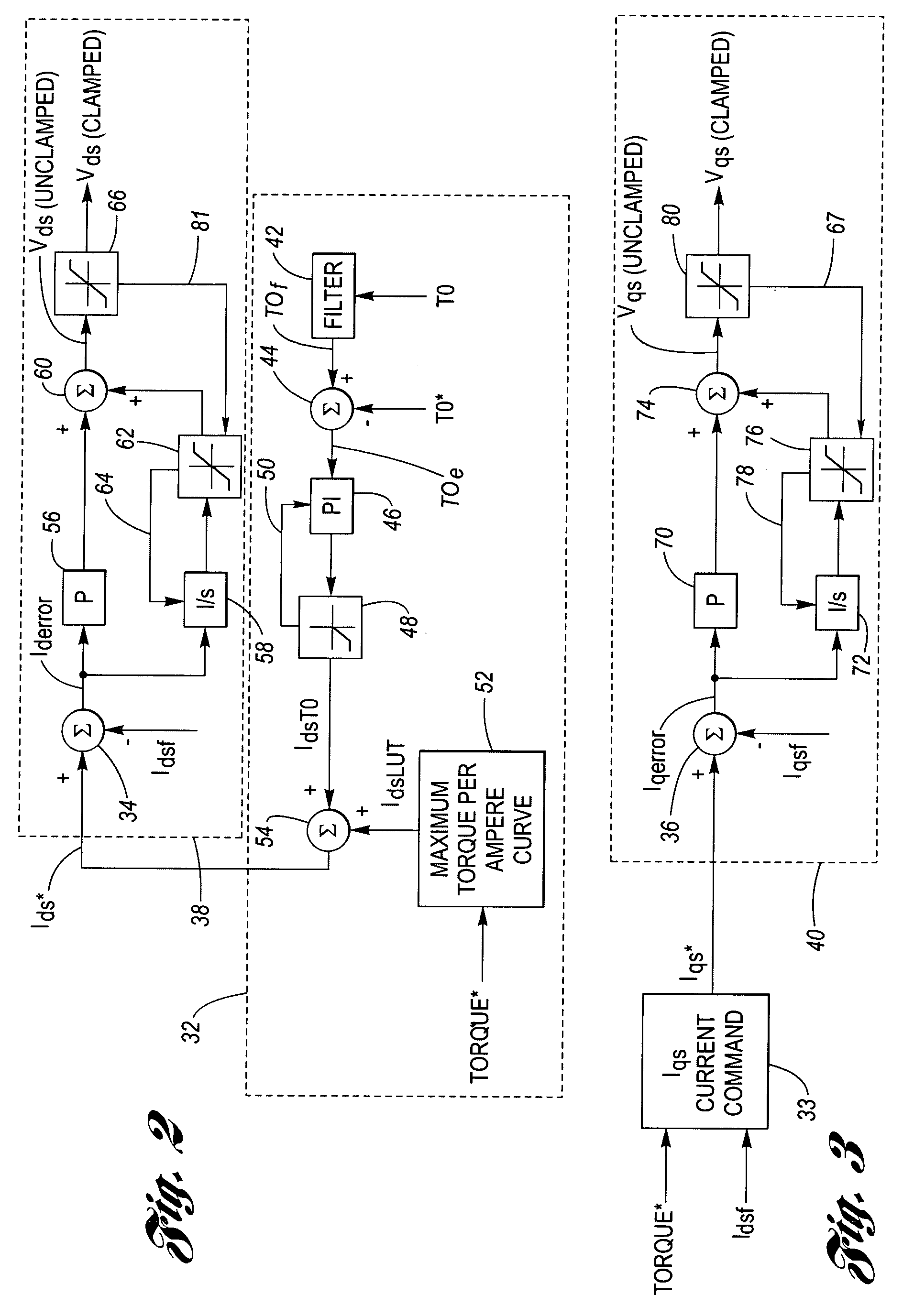
System and method for clamp current regulation in field-weakening operation of permanent magnet (PM) machines
ActiveUS20050046370A1Maximize processing efficiencyMaximum possible torqueAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlPhase currentsIntegrator
A device to regulate current produced by a permanent magnet machine responsive to a plurality of phase current signals. The motor produces torque for application on a shaft. A processing and drive circuit responsive to a direct current command signal and a quadrature current command signal produces phase current signals for input to the motor. A command circuit responsive to the phase current signals, an angular position of said shaft, and a voltage input command signal to produce a direct current error signal and a quadrature current error signal. A control circuit responsive to the direct and quadrature current error signals produces the direct voltage signal command and the quadrature voltage signal command. The control circuit has a direct and quadrature proportional gain, integrator and clamp circuits. An algorithm produces limited or clamped voltage modulation index signals to obtain maximum efficiency and maximum torque per ampere in the speed range. The algorithm ensures that the current regulator does not run out of voltage by limiting the voltage vector to the achievable voltage vector range that provides maximum torque per ampere and maximum efficiency.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Digital implementation of power factor correction
InactiveUS7359224B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitanceControl signal
A circuit for providing power factor correction in accordance with an embodiment of the present application may include a boost converter circuit and a control circuit receiving as inputs a rectified AC input voltage from a rectifier, a signal proportional to current through the boost inductor and the DC bus voltage across the capacitor of the boost converter. The control circuit provides a pulse width modulated signal to control the on time of a PFC switch. The control circuit further includes a voltage regulator and a current regulator. The current regulator includes a difference device operable to subtract a signal proportional to the inductor current from the current reference signal, a PI controller adapted to receive the output of the difference device and provide a first control signal, a feed forward device operable to receive the rectified AC input voltage and to provide a second control signal with a smaller dynamic range than the AC input voltage, and an adder operable to add the first control signal to the second control signal to provide a PWM reference signal for generating the pulse width modulated signal. A zero crossing detector and vector rotator may be provided to provide a clean sinusoidal reference to the current regulator. A partial PFC regulator may be provide to provide partial mode PFC if desired.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Current-mode direct-drive inverter
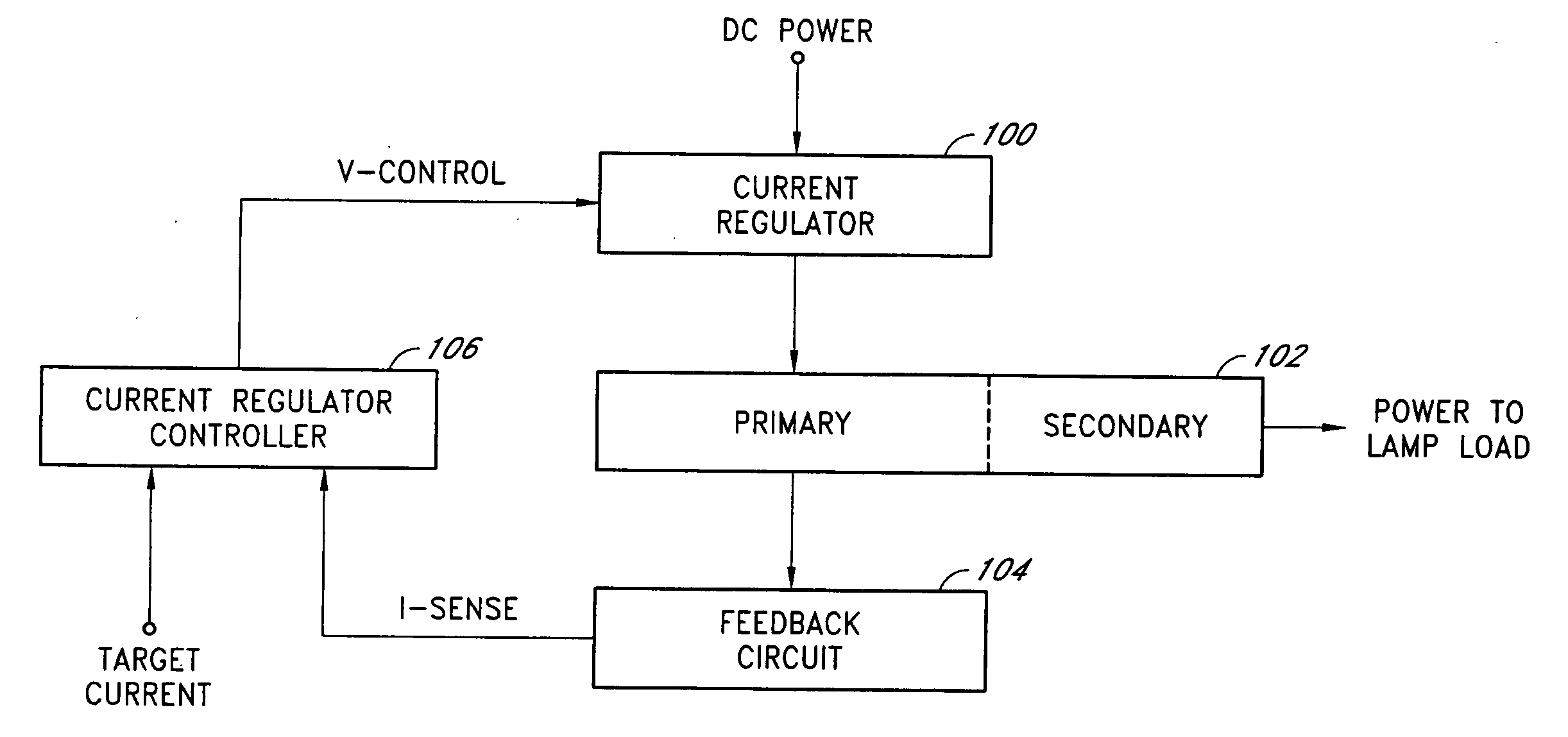
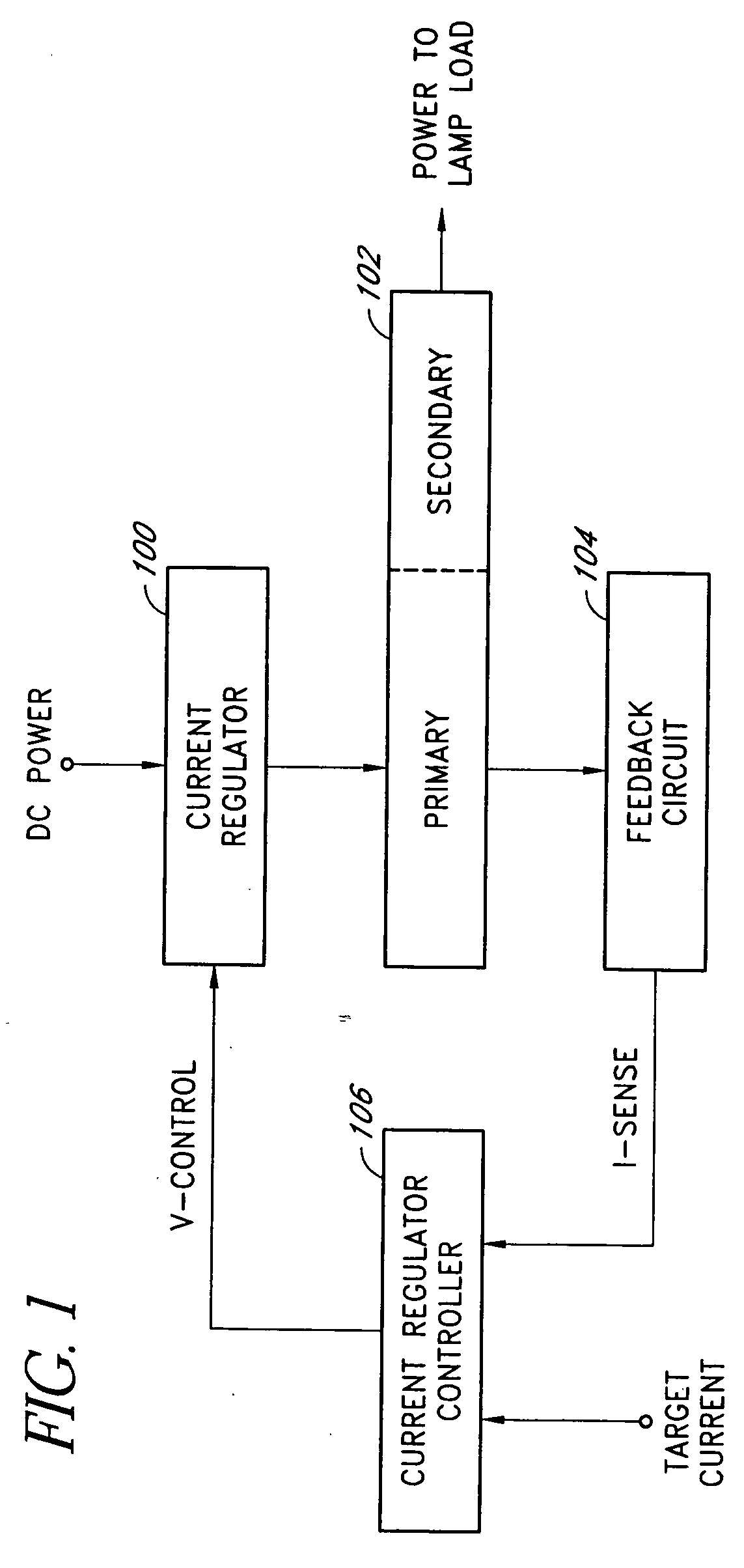
InactiveUS20050162098A1Increased operating lifeStable light outputElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageOutput transformerTime-sharing
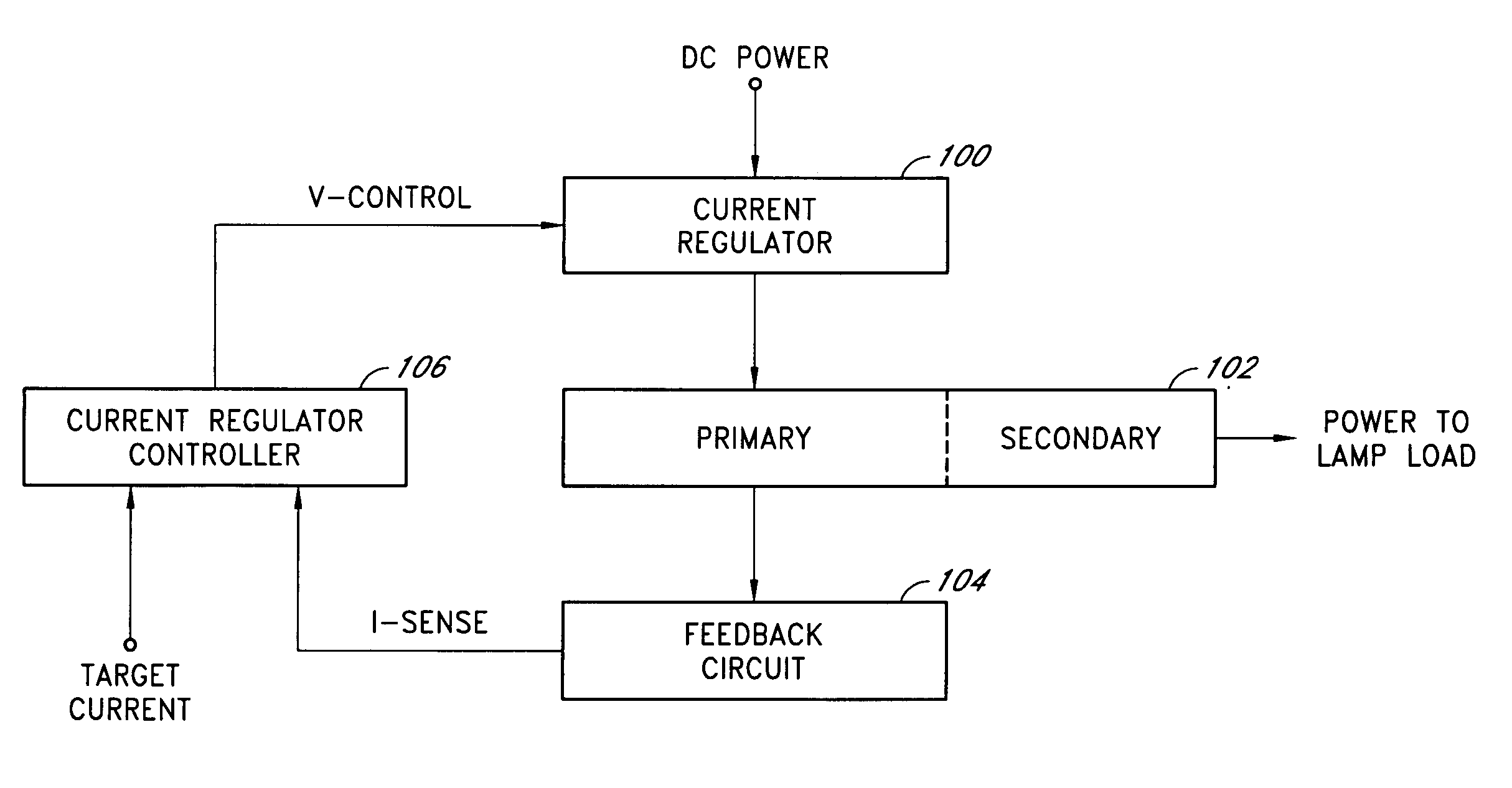
An efficient and flexible current-mode driver delivers power to one or more light sources in a backlight system. In one application, the current-mode driver is configured as an inverter with an input current regulator, a non-resonant polarity-switching network, and a closely-coupled output transformer. The input current regulator can output a regulated current source in a variety of programmable wave shapes. The current-mode driver may further include a rectifier circuit and a second polarity-switching network between the closely-coupled output transformer and a lamp load. In another application, the current-mode driver delivers power to a plurality of light sources in substantially one polarity by providing a regulated current to a network of time-sharing semiconductor switches coupled in series with different light sources coupled across each semiconductor switch.
Owner:POLARIS POWERLED TECH LLC
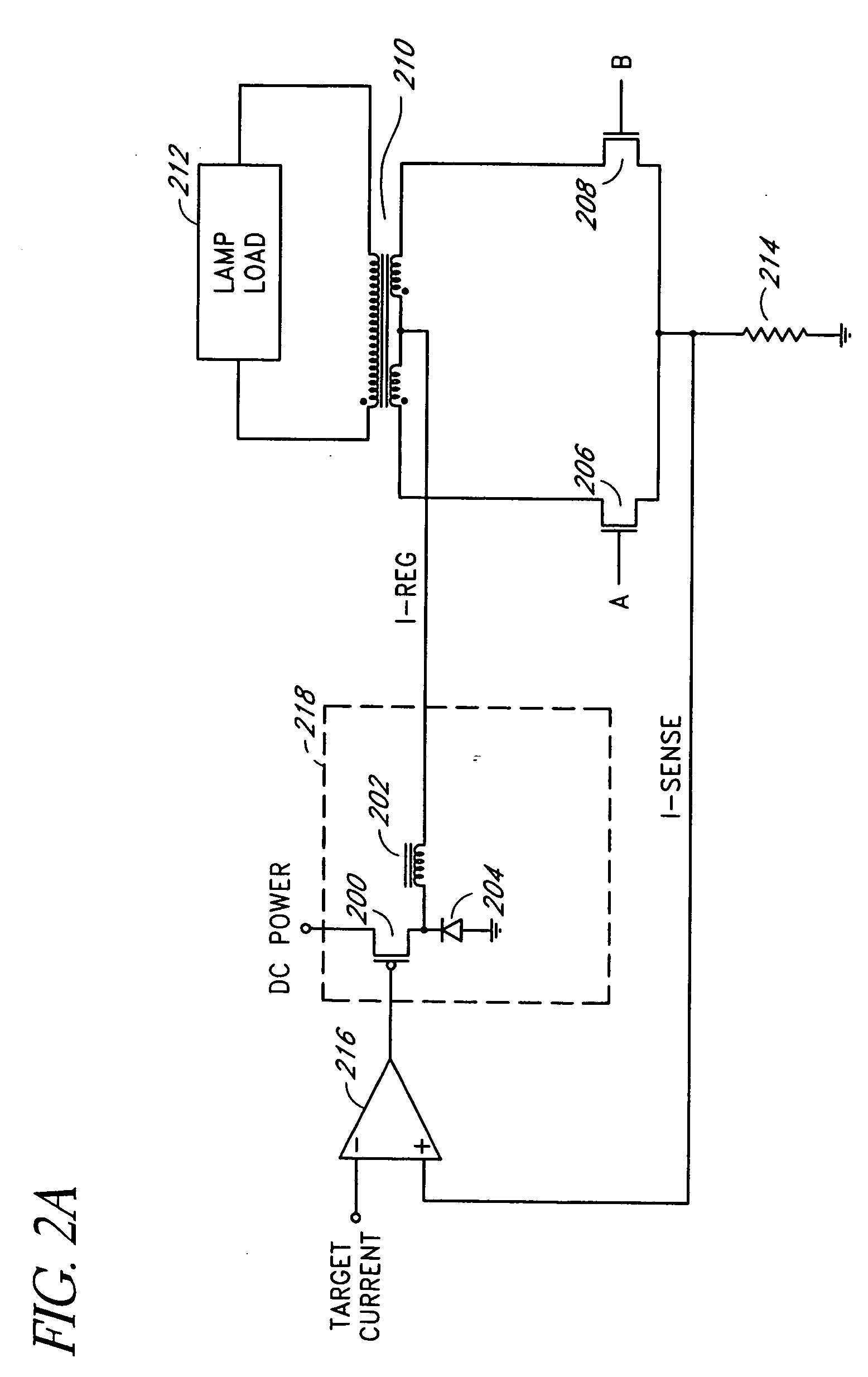
Voltage/current regulator improvements for an implantable medical device
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
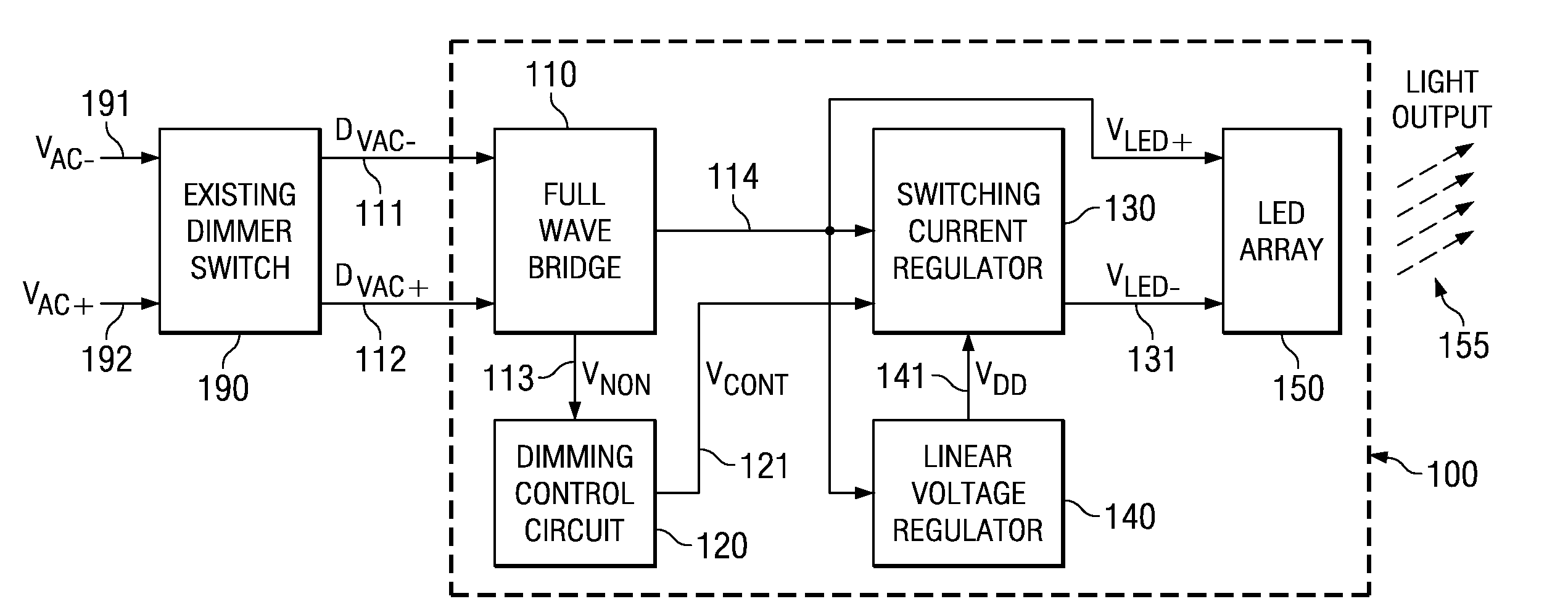
Systems and methods for LED based lighting
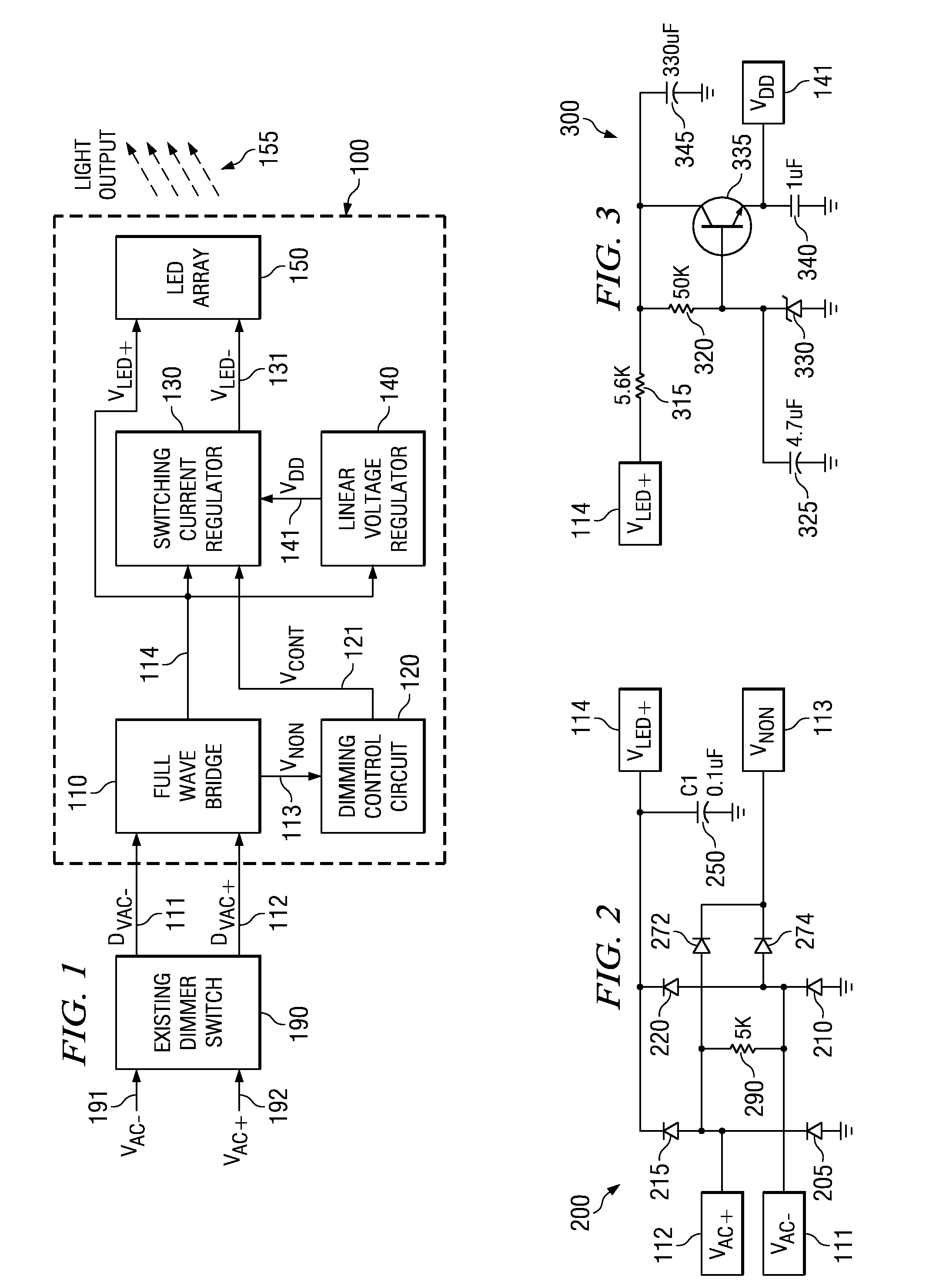
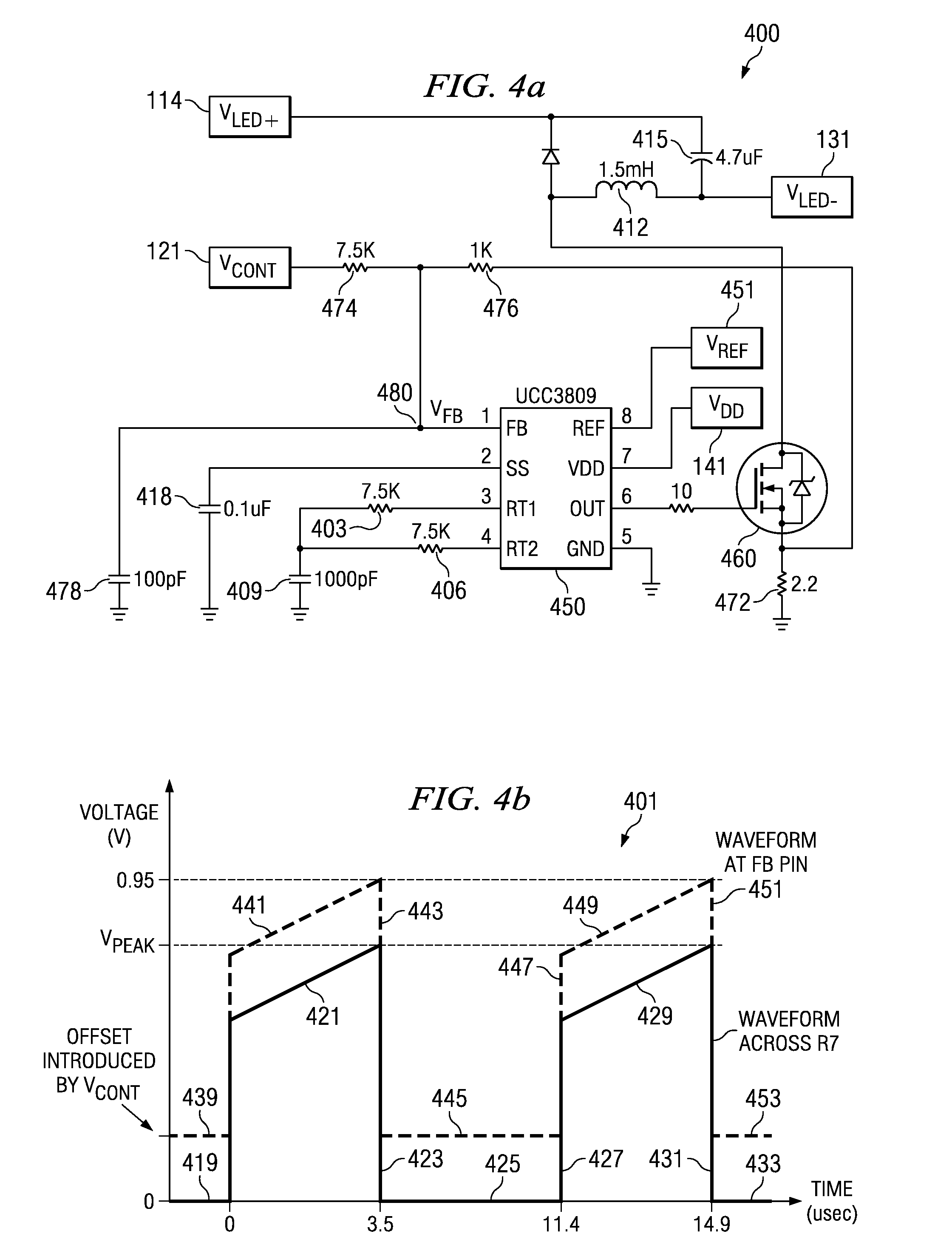
Various systems and methods for lighting are disclosed. For example, some embodiments of the present invention provide methods for retrofitting lights. The methods include providing a solid state light bulb. The solid state light bulb includes: an LED array, a dimming control circuit, and a current regulator. The current regulator provides an LED current to the LED array. The LED current varies based on a control from the dimming control circuit. The methods further include, electrically coupling the solid state light bulb to an existing incandescent dimmer switch, and adjusting the existing incandescent dimmer switch such that the intensity of light emitted from the LED array is adjusted in proportion to the adjustment of the existing incandescent dimmer switch.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Parallel-connected inverters with separate controllers having impedance current regulators
InactiveUS7145266B2Batteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalElectric power systemElectric network
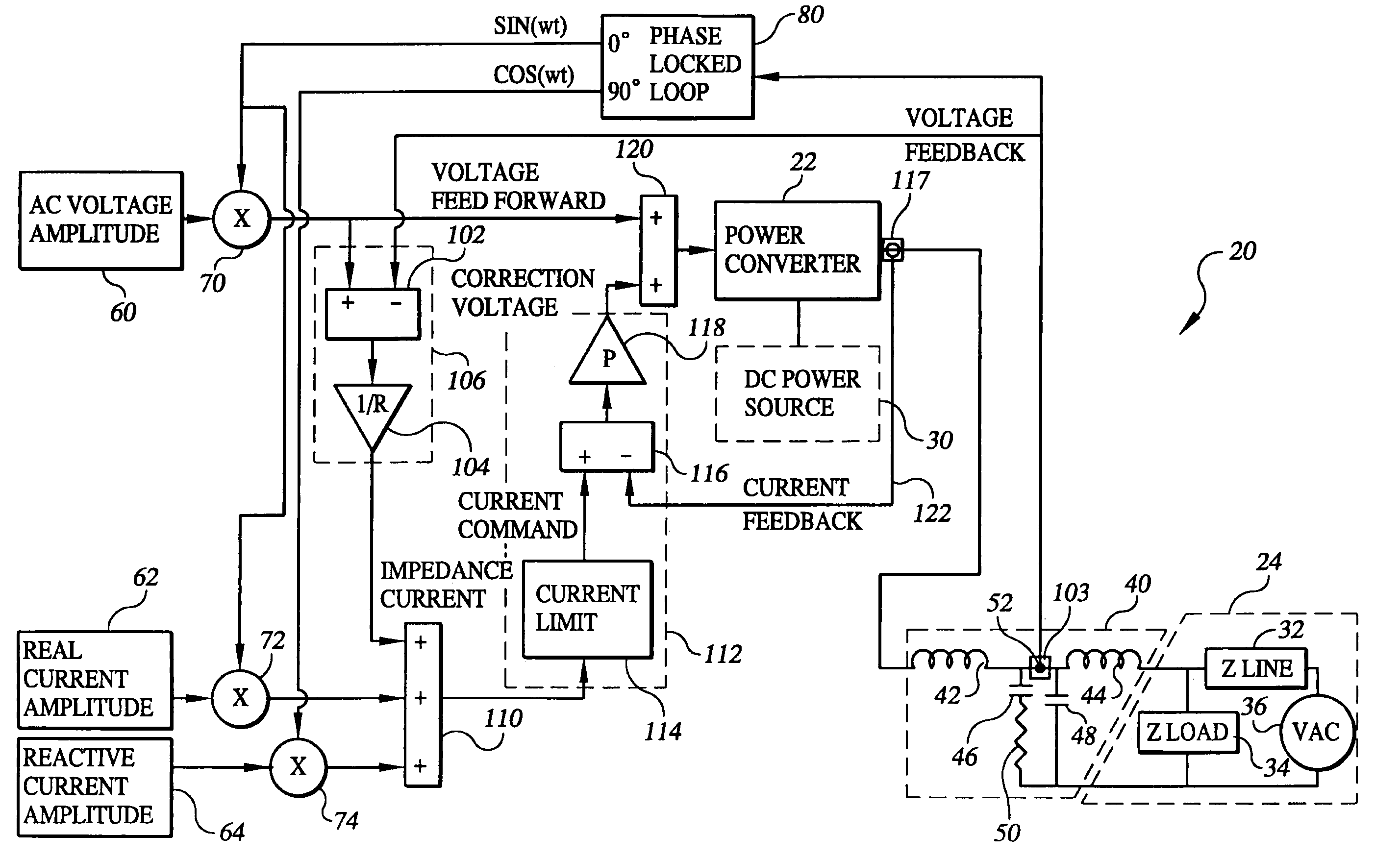
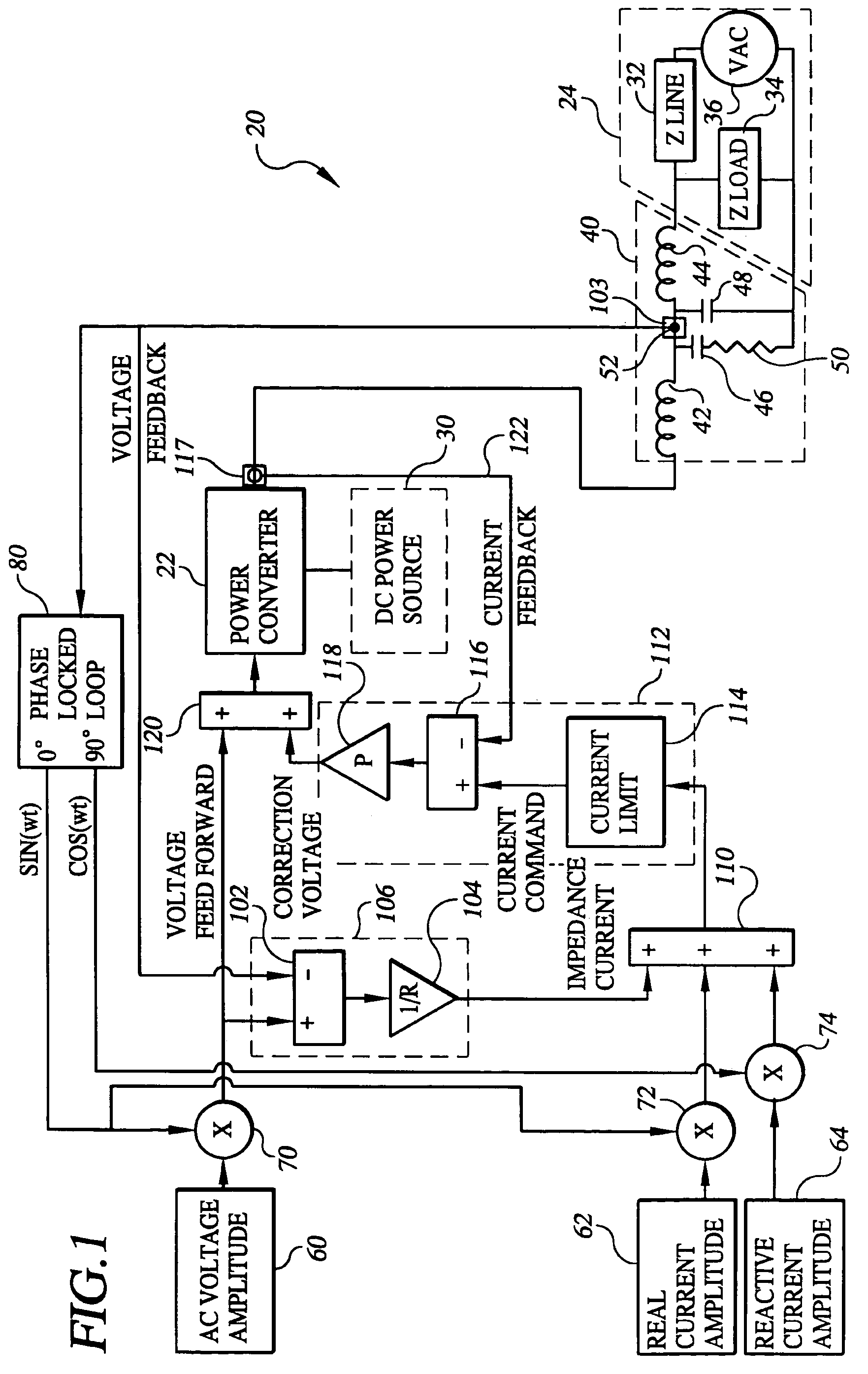
A control system (20) for a power converter (22) designed to convert DC power from a source (30) such as a battery, flywheel or fuel cell into AC power. The control system includes an impedance current regulator (106) for providing an impedance current signal to a summing unit (110) where it may be combined with real and reactive current command signals provided from respective sources (62, 64). The resultant current signal provided by the summing unit is provided to a voltage correction unit (112) that uses the resultant current signal in developing a correction voltage signal provided to the power converter. The correction voltage signal contains information used by the power converter in adjusting the real and reactive currents in its output AC power based on the ability of the AC power network to accept changes in current. Multiple power converters having the control system of the present invention may be connected in parallel to a single AC load or multiple AC loads, without the need for a separate control system interconnecting the power converters. The control system may be advantageously incorporated into a distributed generation network and in uninterruptible power systems, whether or not such systems are included in a distributed generation network.
Owner:WEG ELECTRIC CORP
Dimmable LED light fixture having adjustable color temperature
ActiveUS8710754B2Easy to controlSimulation is accurateElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDc currentEngineering
Electronic circuitry for color-mixing in an LED light fixture during AC power dimming is disclosed to achieve adjustable color temperature. According to one embodiment, a dimmable LED light fixture has first, second, and third LED light sources, the first and second LED light sources producing white light, the third LED light source producing colored light, the LED driver configured to power the LED light sources by providing a single-channel variable-DC current source having two output terminals, and a current regulator for maintaining the current in the third LED light source path substantially constant as the LED driver output current is decreased when the AC power is reduced by the dimmer module, thereby altering the color of the light produced by the combination of the LED light sources.
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
High efficiency power supply for LED lighting applications
InactiveUS7265504B2Accurate currentEffective pointingElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEffect lightVoltage regulation
A power supply for plural loads coupled in parallel comprises a voltage regulator, a plurality of current regulators, and an error control circuit. The voltage regulator provides a common output voltage to the plural loads. The voltage regulator comprises a sensor circuit providing a voltage sense signal corresponding to the output voltage, which provides feedback to regulate the output voltage at a selected level. The plurality of current regulators are coupled to respective ones of the plural loads. Each of the plurality of current regulators regulates current drawn by respective ones of the plural loads to within a desired regulation range. The plurality of current regulators each further provide a respective error signal corresponding to an ability to remain within the desired regulation range. The error control circuit is operatively coupled to the voltage regulator and to the plurality of current regulators. The error control circuit receives the error signals from the plurality of current regulators and provides a common error signal to the voltage regulator. The voltage regulator thereby changes the selected level of the output voltage in response to the common error signal. Accordingly, the selected level of the output voltage remains at a minimum voltage necessary to keep the plural loads in the desired regulation range.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
Lighting device circuit with series-connected solid state light emitters and current regulator
ActiveUS7852009B2Improve efficiencyLow efficiencyElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesElectricityEffect light
A circuit for a lighting device comprises a sub-circuit which comprises a series current regulator and a group of solid state light emitters. The current regulator and the solid state light emitters are arranged in series. In some embodiments, the circuit further comprises a fan electrically connected in series in the sub-circuit. In some embodiments, the circuit further comprises a second sub-circuit which comprises a second series current regulator and a second group of solid state light emitters, the first sub-circuit and the second sub-circuit being arranged in parallel. In some embodiments, an anode of the series current regulator is electrically connected to a cathode of one of the solid state light emitters. Also, methods of lighting wherein a sum of voltage drops across light emitters and a current regulator is in the range of from 1.2 to 1.6 times the line voltage.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Lamp current control using profile synthesizer
InactiveUS20050156539A1Increased operating lifeStable light outputElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageOutput transformerWave shape
An efficient and flexible current-mode driver delivers power to one or more light sources in a backlight system. In one application, the current-mode driver is configured as an inverter with an input current regulator, a non-resonant polarity-switching network, and a closely-coupled output transformer. The input current regulator can output a regulated current source in a variety of programmable wave shapes. The current-mode driver may further include a rectifier circuit and a second polarity-switching network between the closely-coupled output transformer and a lamp load. In another application, the current-mode driver delivers power to a plurality of light sources in substantially one polarity by providing a regulated current to a network of time-sharing semiconductor switches coupled in series with different light sources coupled across each semiconductor switch.
Owner:POLARIS POWERLED TECH LLC
Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) AC servo system
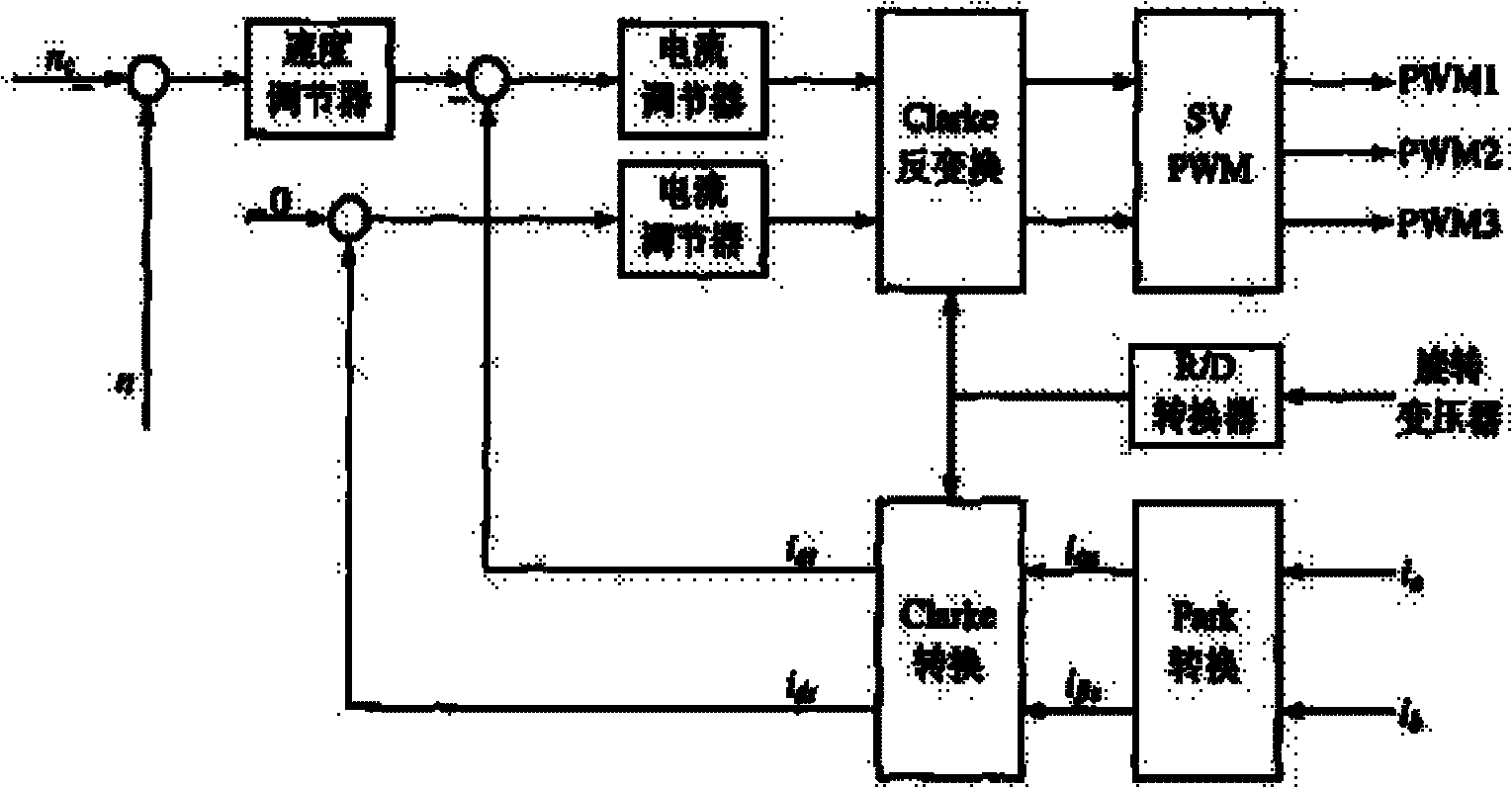
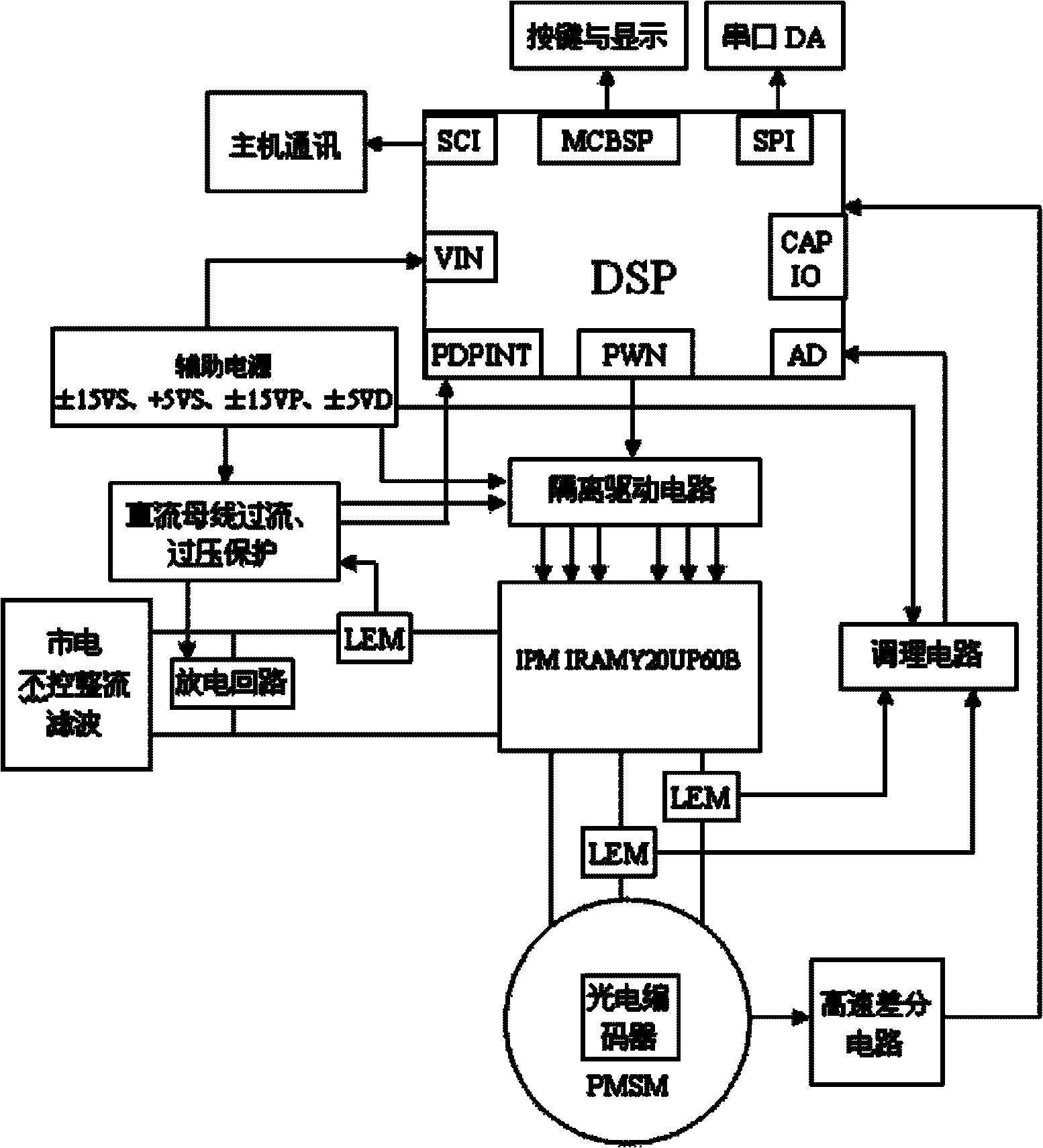
InactiveCN101867343AEliminate fluctuationsReduce harmonic lossElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsOvervoltagePermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention relates to a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) AC servo system, which is composed of a DSP control panel, a rotary transformer, a main power circuit and a conditioning and protecting circuit, a motor body consists of an armature winding and a permanent magnet core rotor, wherein the motor is excited by a permanent magnet, and the DSP is used for realizing an field-orientated control algorithm, communication, sampling calculation of current and configuration output of a drive; the output of the rotary transformer enables data to be transmitted to the DSP via four-path DA transform chips and SPI of the DSP or multi-channel buffering; the DSP outputs pulse width modulation, is connected with voltage signals output by a current regulator, and is connected with a PWM1-PWM3 drive inverter which can convert the voltage signals into three-phase switch signals by CLARK inverse transformation, and the inverter outputs to the armature winding so as to control the armature winding of the motor to generate a rotary round magnetic field; and the main power circuit is composed of a direct current detection circuit with controllable rectification, an inverter, a current detection circuit, an overvoltage discharging circuit, a protection circuit and a driving circuit. The invention adopts the field-orientated control algorithm which can control the torque, speed and position state of the motor in real time and has good control performance.
Owner:南京大桥机器有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com