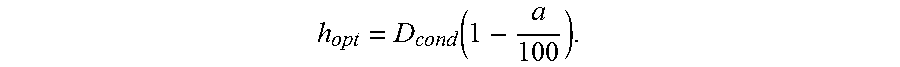Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Assist in detecting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
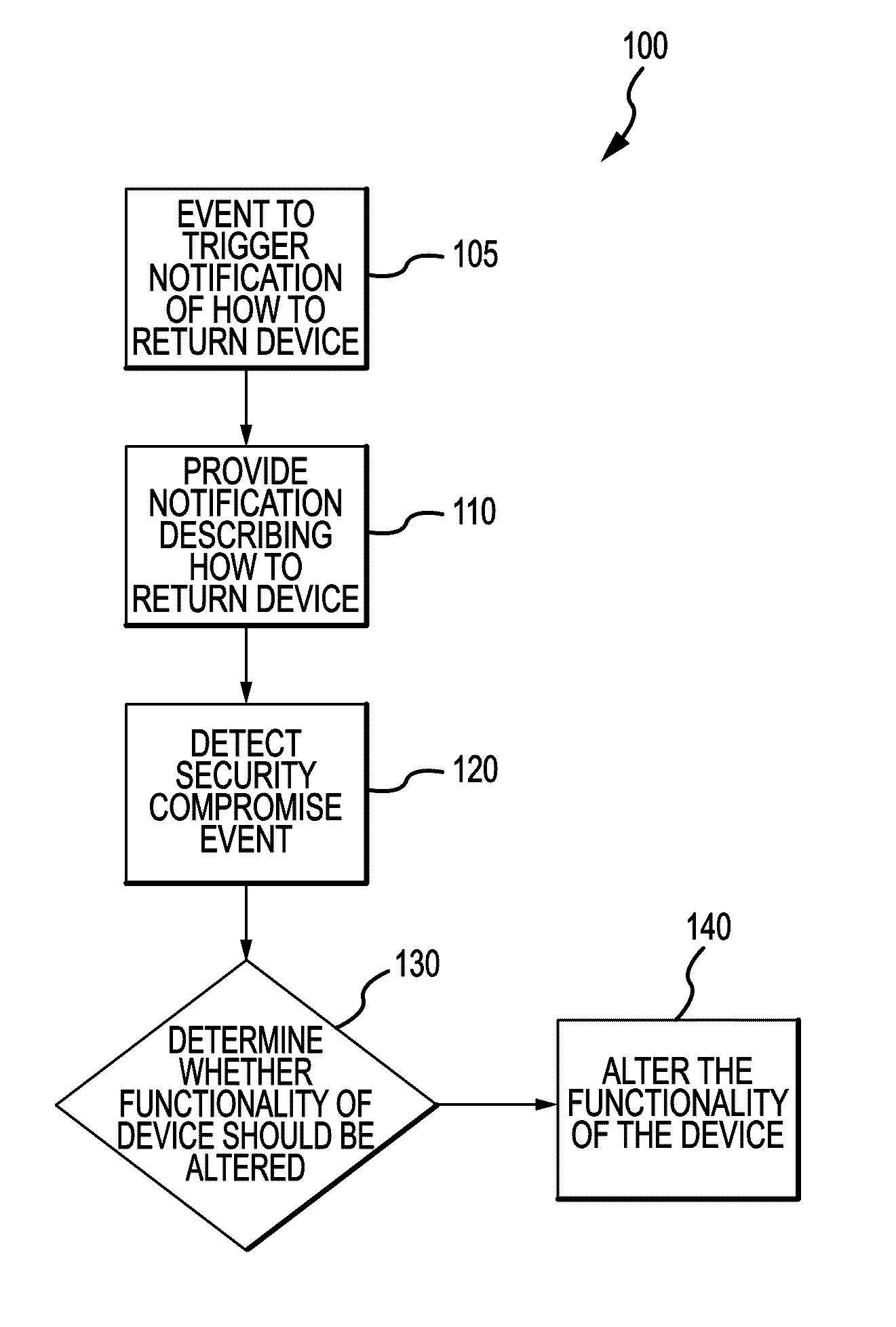
Systems and methods for dynamically assessing and mitigating risk of an insured entity
InactiveUS20140200929A1Assist in detectingRisk minimizationFinanceNetwork traffic/resource managementPosition dependentMobile device
Embodiments of the present invention delineate systems and methods for dynamically assessing and mitigating risk of an insured entity. An entity that provides insurance may, in various embodiments, use applications installed on mobile devices to monitor information that may reduce or mitigate fraudulent insurance claims. Additional embodiments of the present invention delineate systems and methods for providing a user of a mobile device with information relevant to a position of a mobile device, wherein such information may describe one of a risk and an opportunity within a predetermined distance of a location for the mobile device.
Owner:BLANCCO TECH GRP IP OY
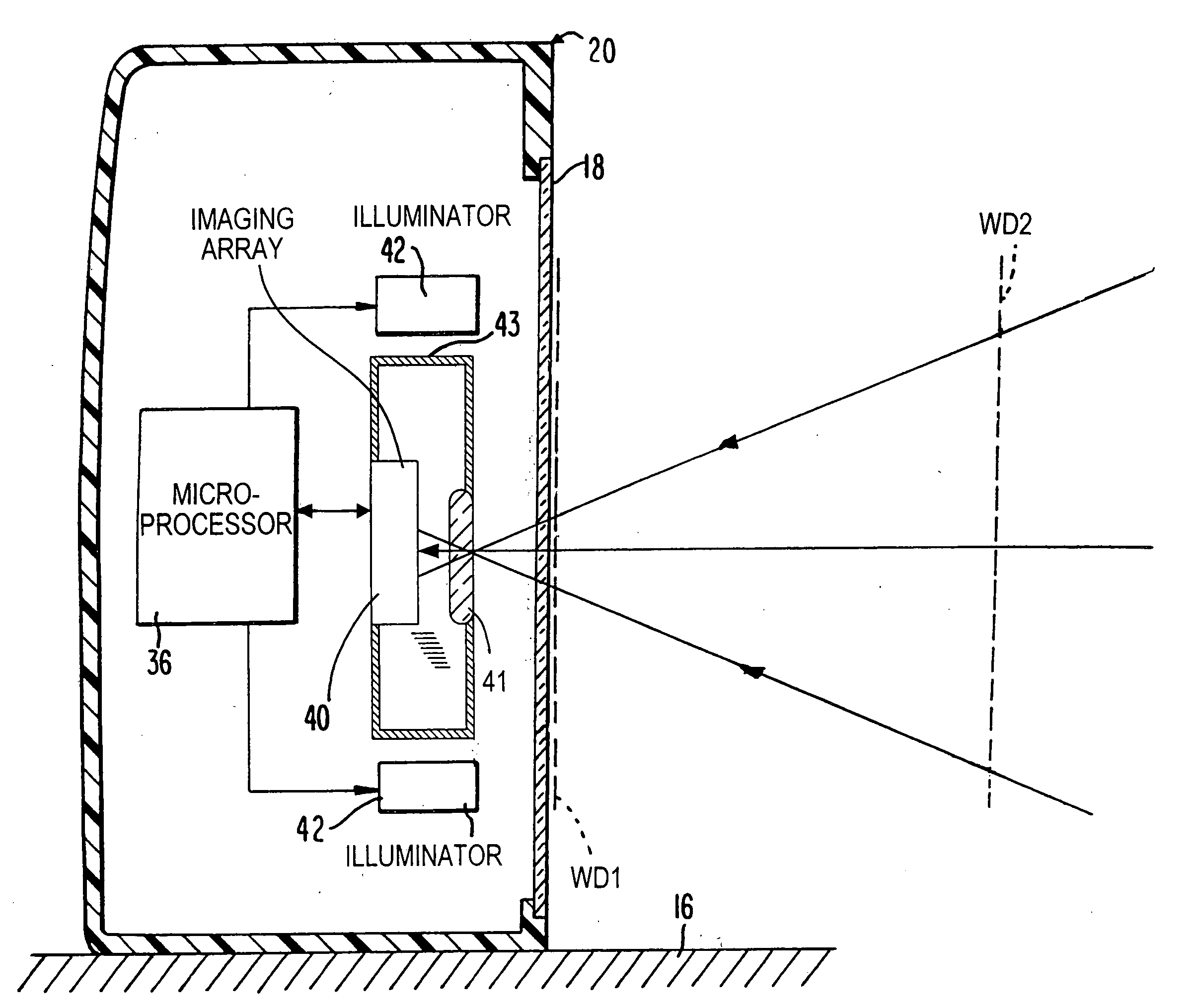
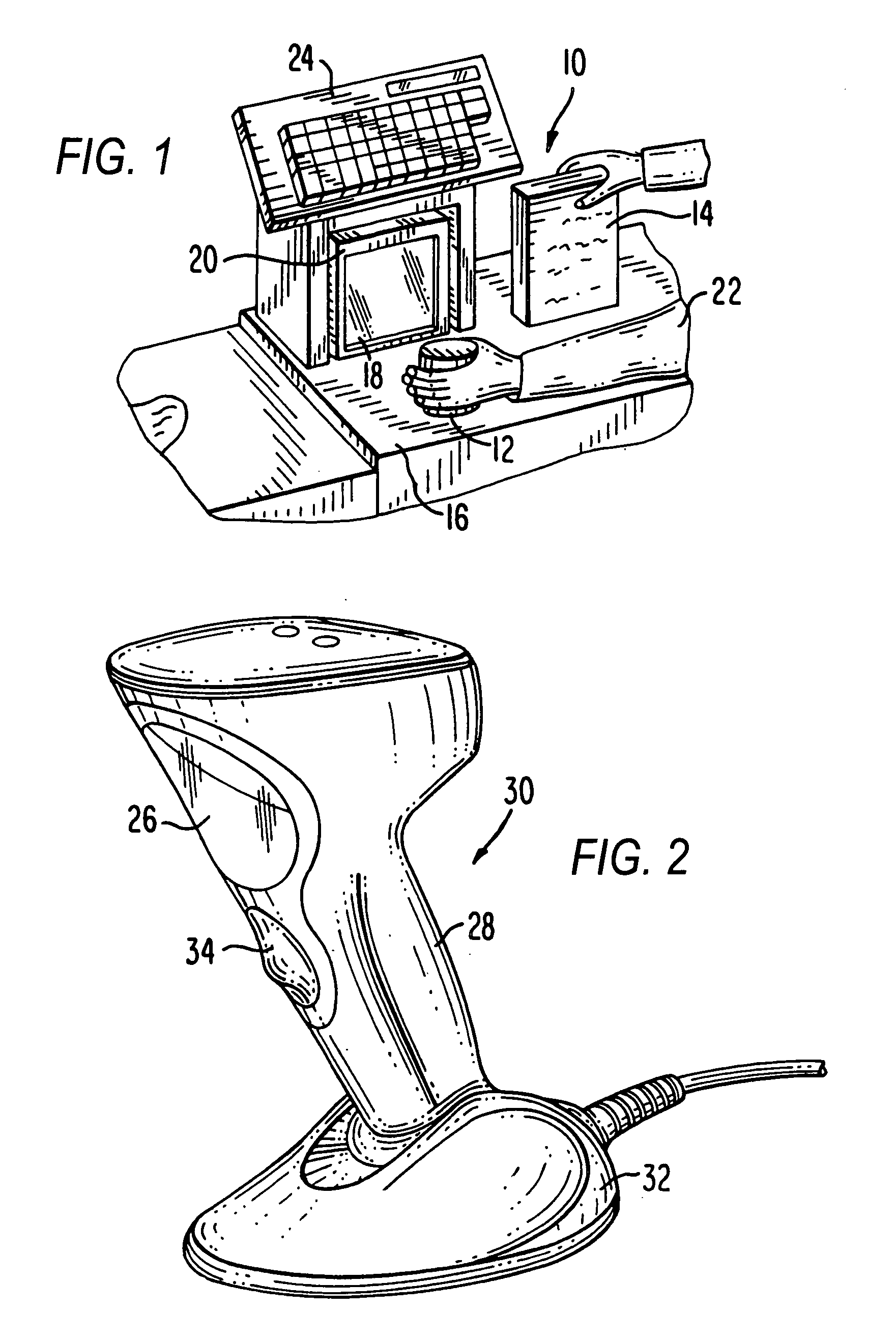
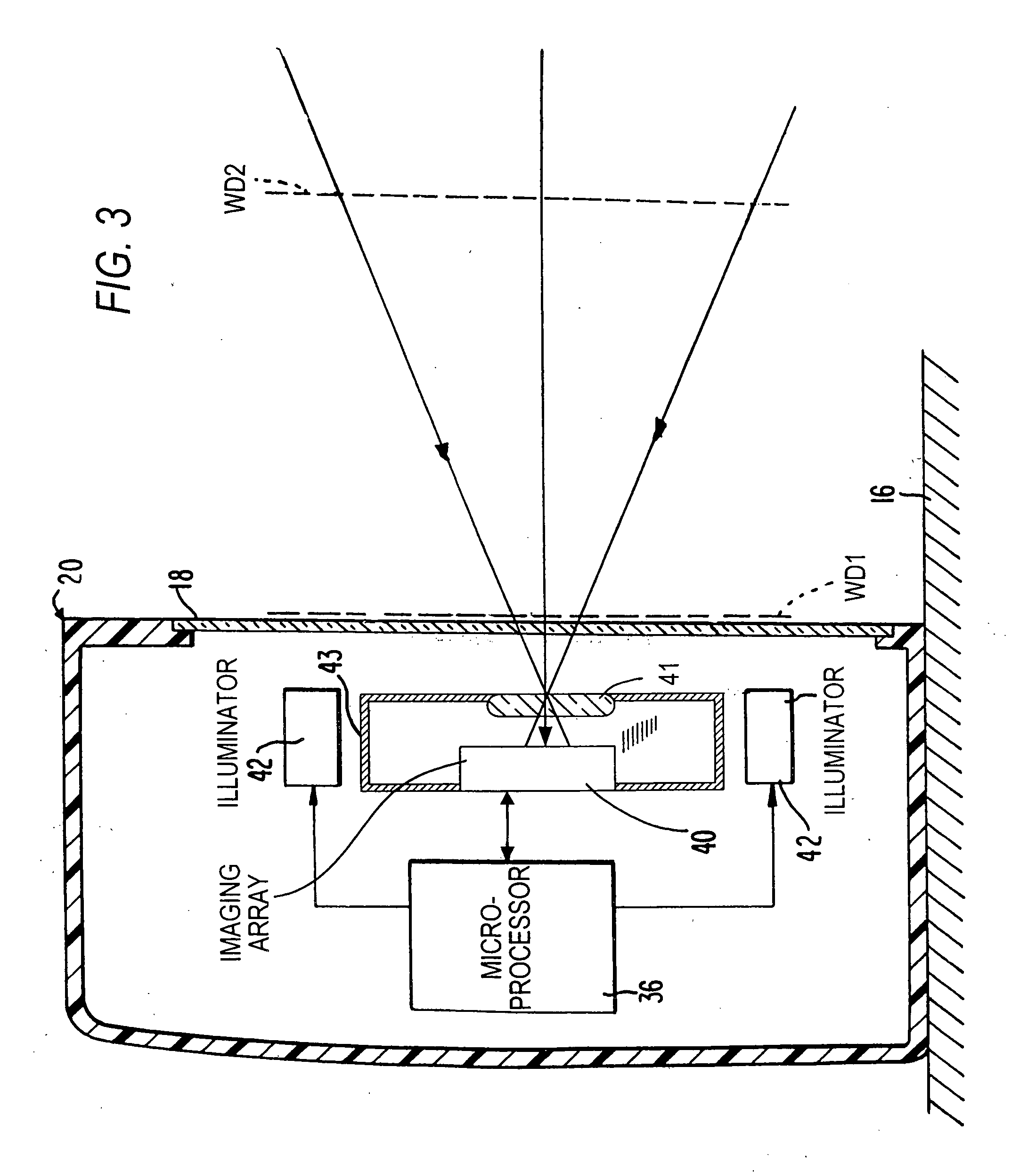
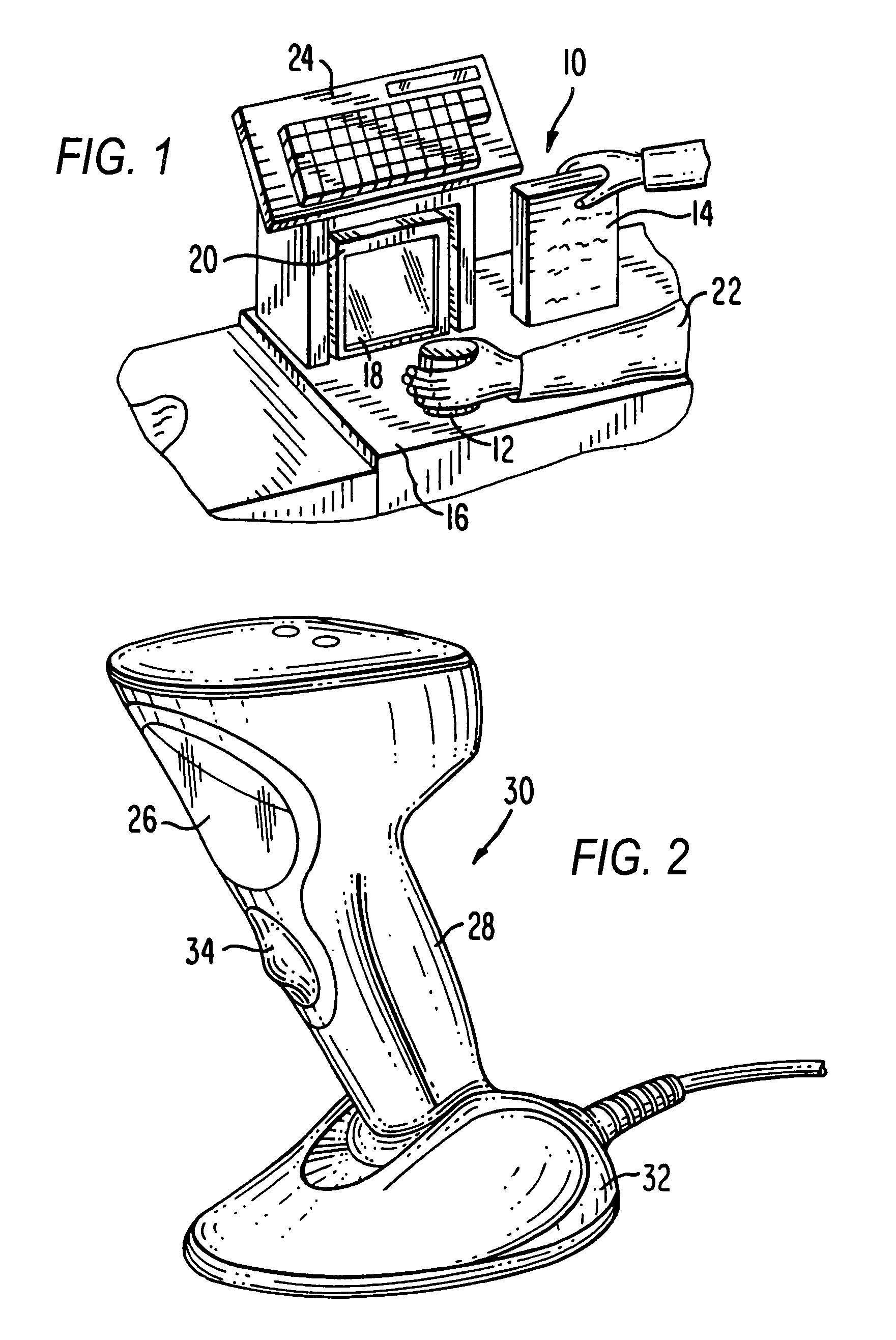
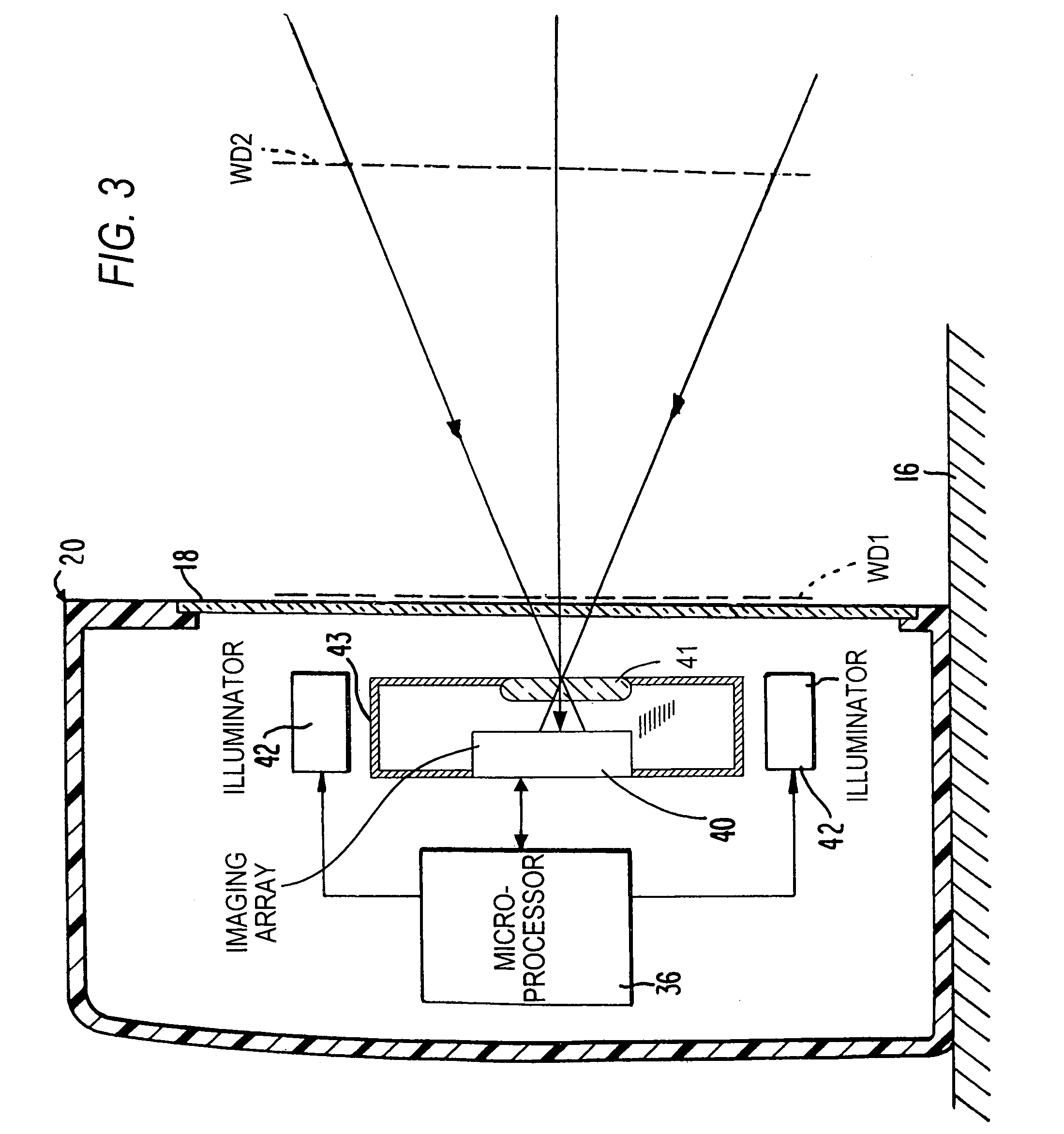
Imaging reader with target proximity sensor
ActiveUS20080023556A1Increased power consumptionEfficient and rapid detectionSensing by electromagnetic radiationIlluminanceProximity sensor
An illuminator illuminates a symbol with a low level of illumination in a detection mode of operation to enable an imager to detect the symbol in a working range and in a field of view of the imager in an imaging reader, and also illuminates the symbol with a high level of illumination in a reading mode of operation to enable the imager to read the symbol.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Method to detect bacteria
InactiveUS6461833B1Reduce populationReduce needMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDrugBacilli
The present invention relates to a method for enhancing the time of response of an assay for a first bacterium, wherein: a) the first bacterium is exposed to infection by phage particles to which the first bacterium is permissive; b) the infected bacterium is treated to inactivate exogenous phage particles; c) the treated bacterium is cultivated in the presence of a second bacterium which is permissive to infection by the phage or its replicand and which has a doubling rate greater than the effective doubling rate of the first bacterium; and d) assessing the extent of plaque formation and / or of second bacterium growth in the cultivated second bacterium cells. The method can be used to assess the presence of first bacterium in a sample, notably where the first bacterium is a slow growing bacterium, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, where the method enables an operator to detect the presence of low amounts of the bacterium in sample within days instead of weeks as required by conventional cultivation techniques. The invention can also be used to assess the effect of a drug or other treatment on a bacterium or on a virus. The invention also provides a diagnostic kit for use in the method of the invention.
Owner:BIOTEC LAB
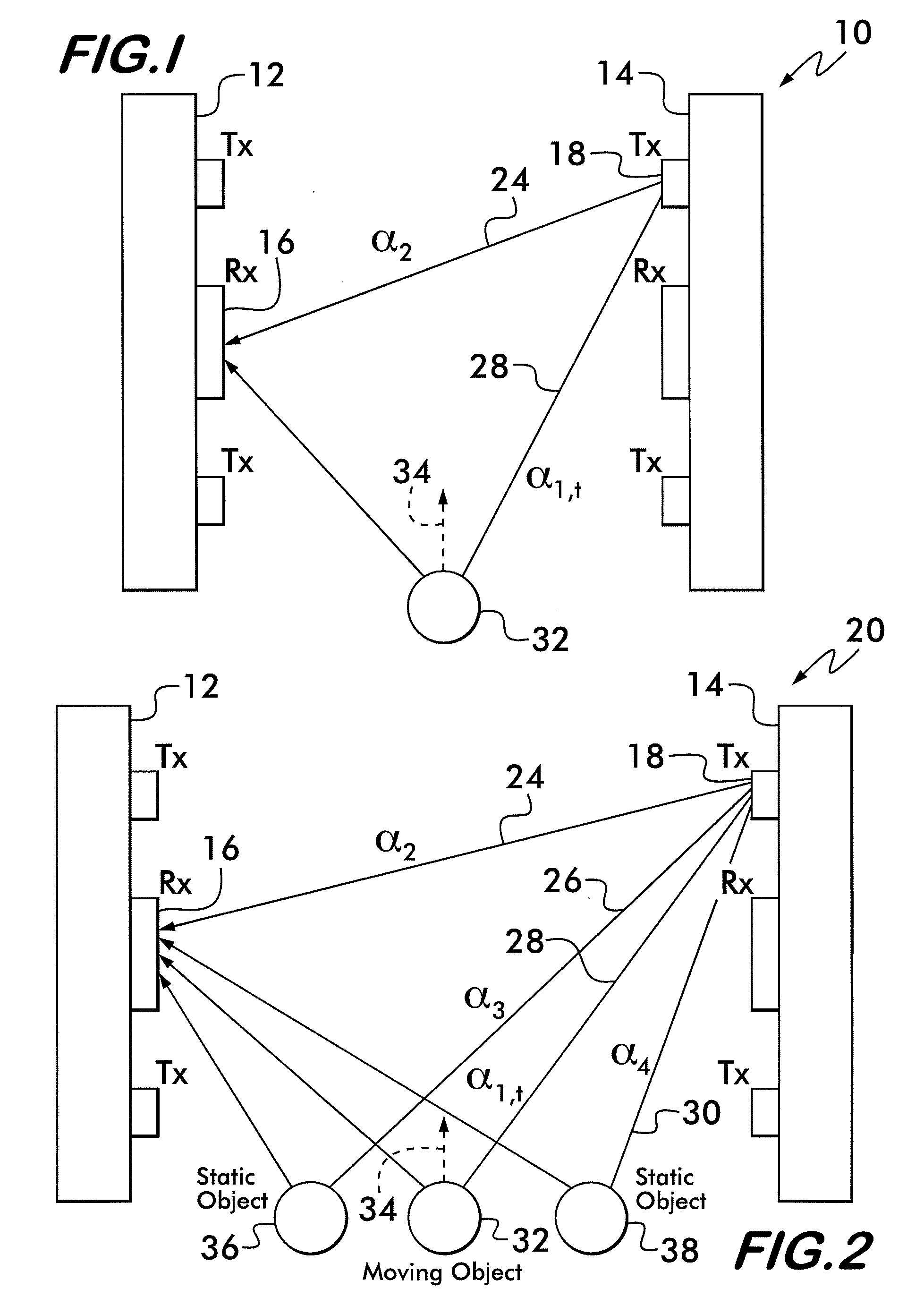
Background Object Sensor
ActiveUS20120319819A1Assist in detectingDetect presenceSensing detailsPosition fixationTransceiverRadio frequency signal
An RFD reader includes a transceiver configured to receive a first radio frequency signal reflected off at least one surface to provide baseline signal information and a second radio frequency signal reflected off the at least one surface and an object to provide further signal information. A comparator is configured to compare the baseline signal information and the further signal information to provide a signal comparison. A processor is configured to detect the presence of the object in accordance with the signal comparison. A determination is made whether the object is in motion in accordance with the signal comparison. The determination whether the object is in motion is made in accordance with a continuous fluctuation of the second radio frequency signal. A determination whether the object is no longer in motion is made in accordance with an ending of the continuous fluctuation of the second radio frequency signal.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
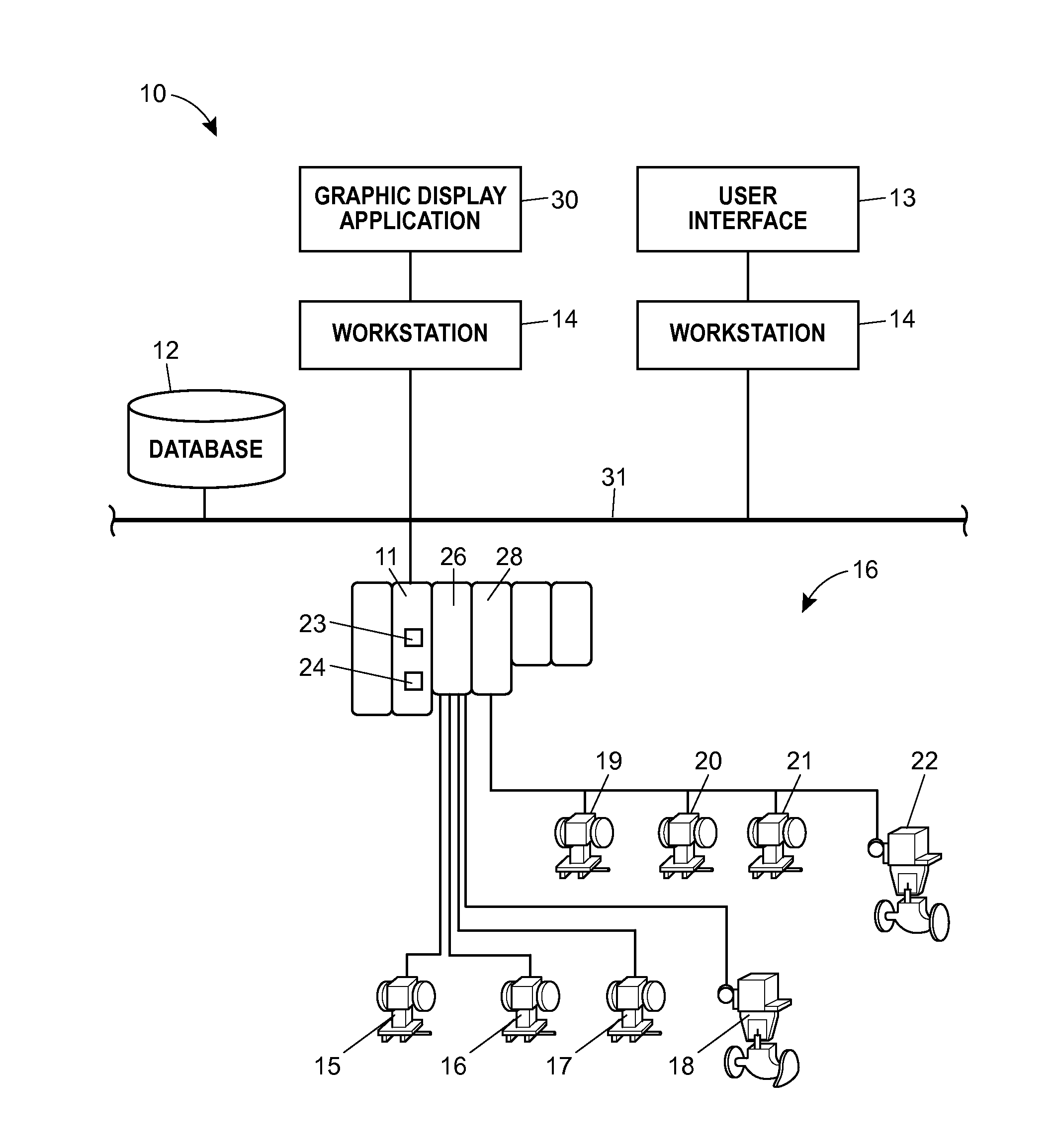
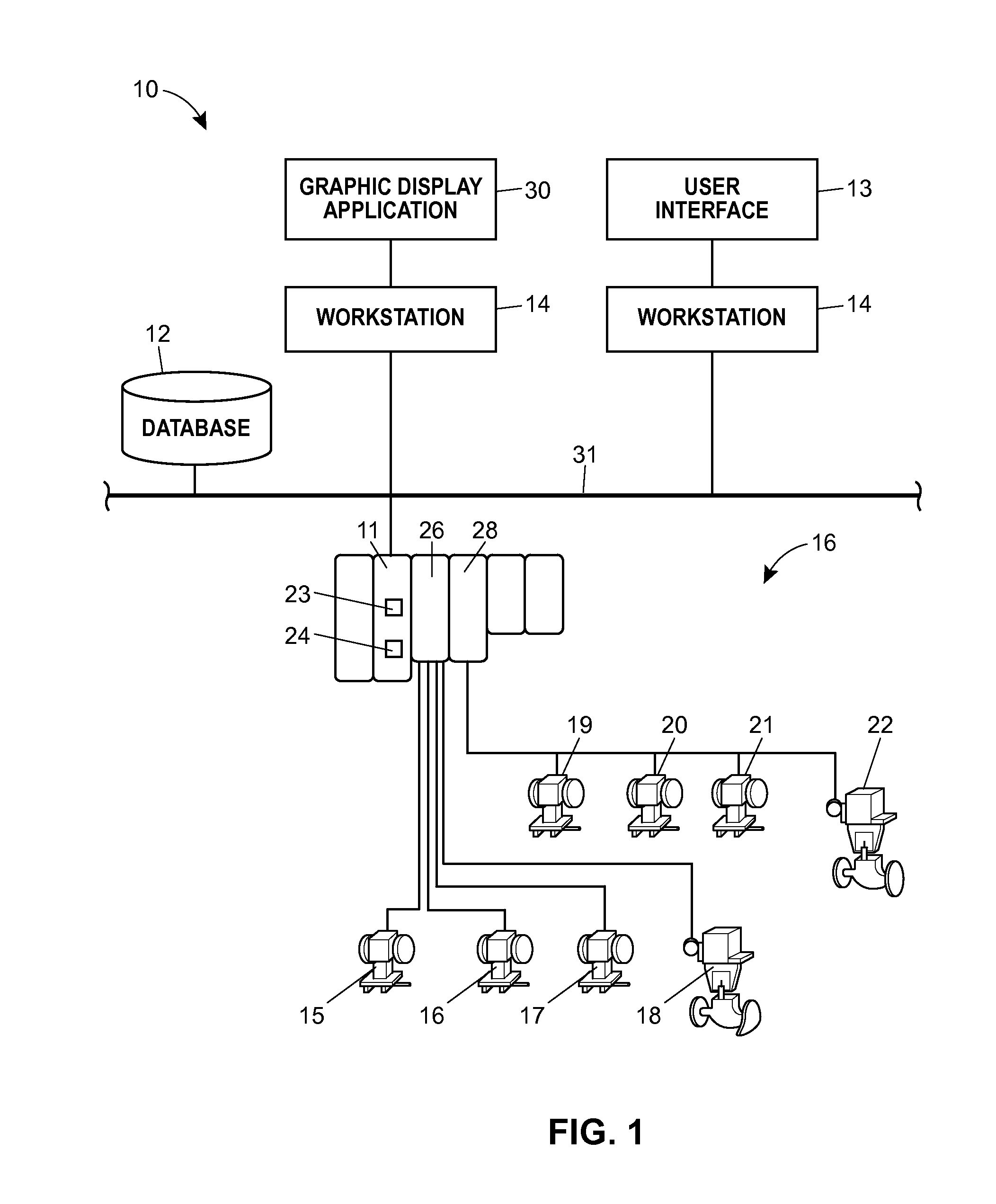
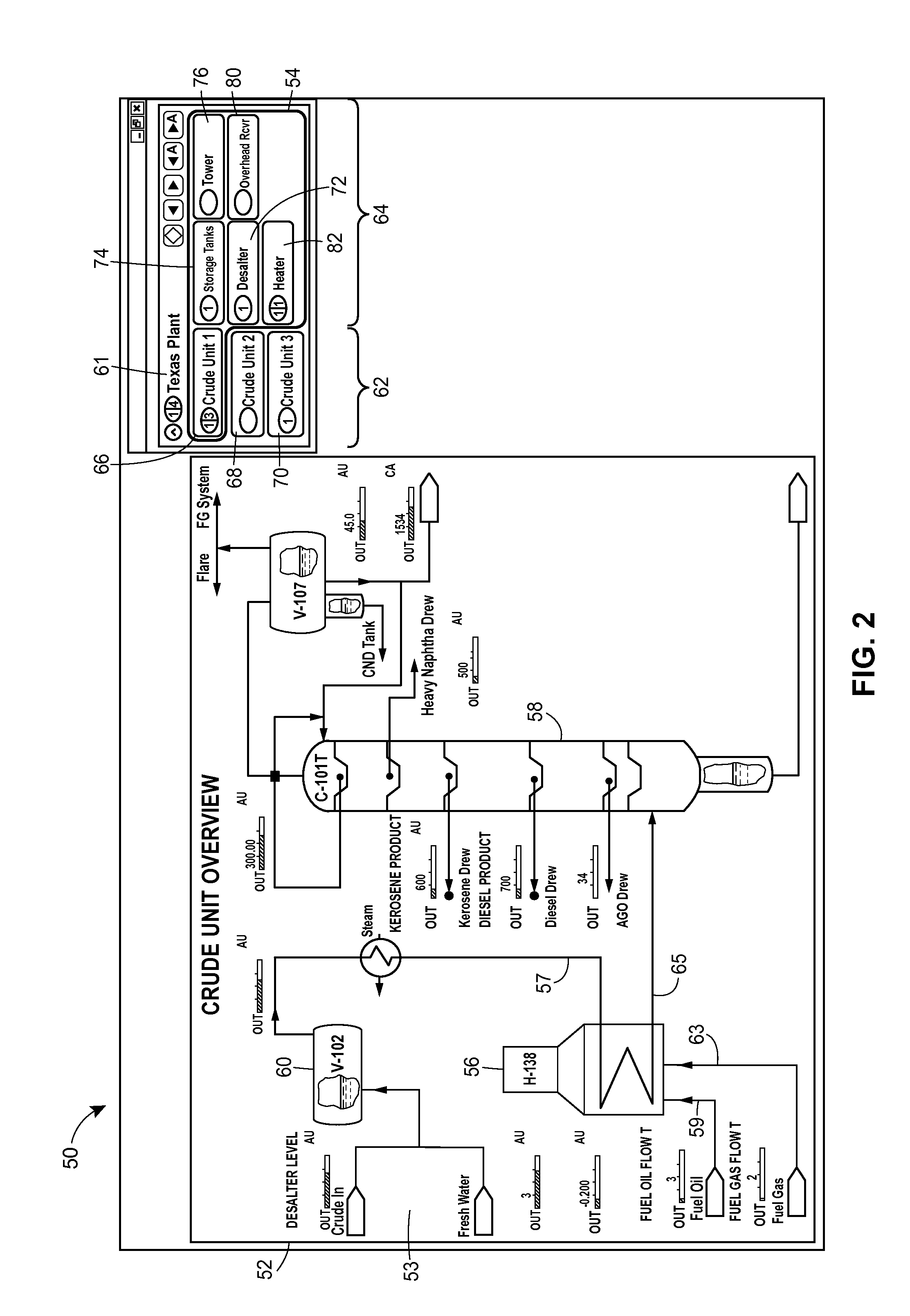
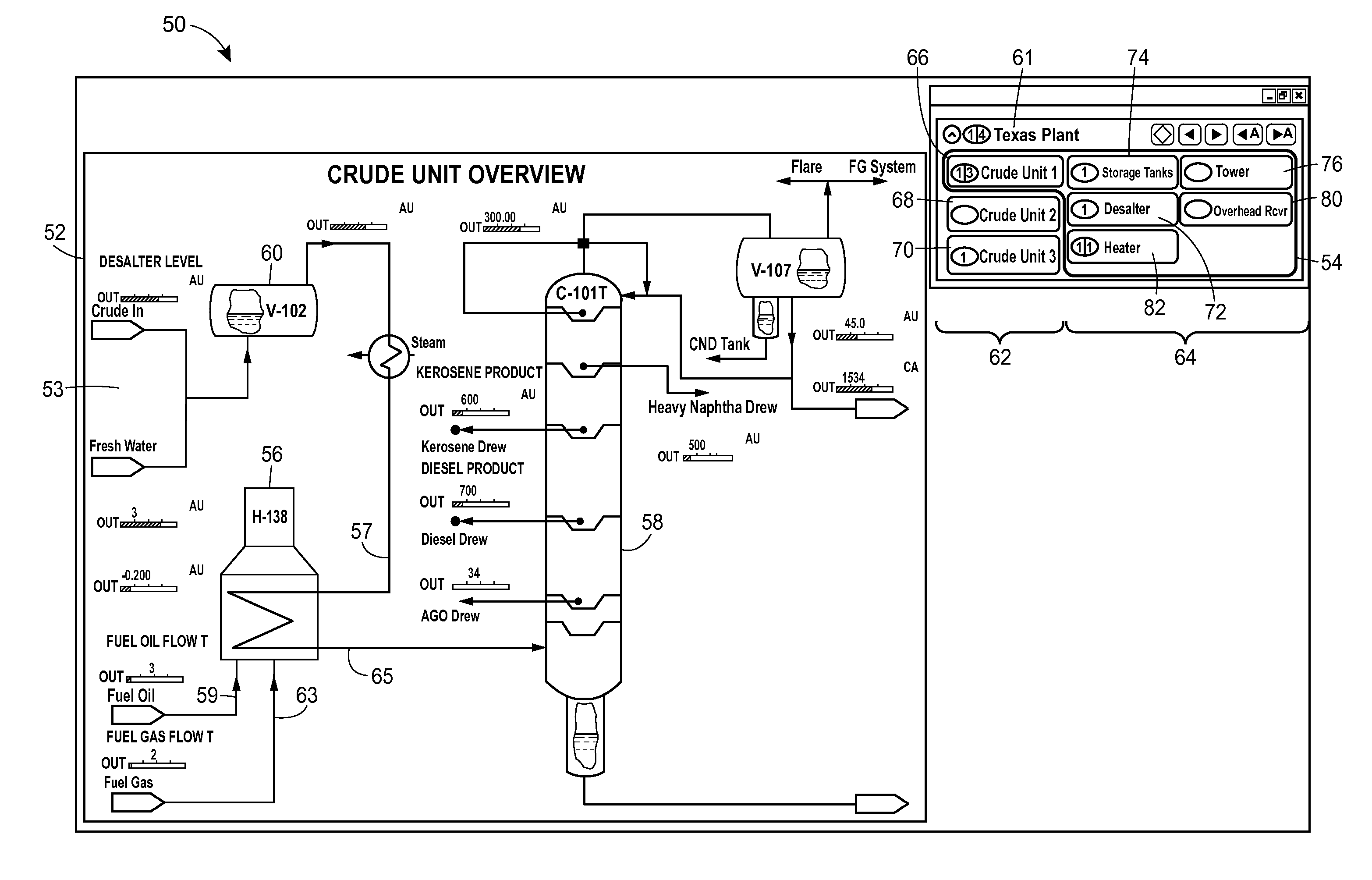
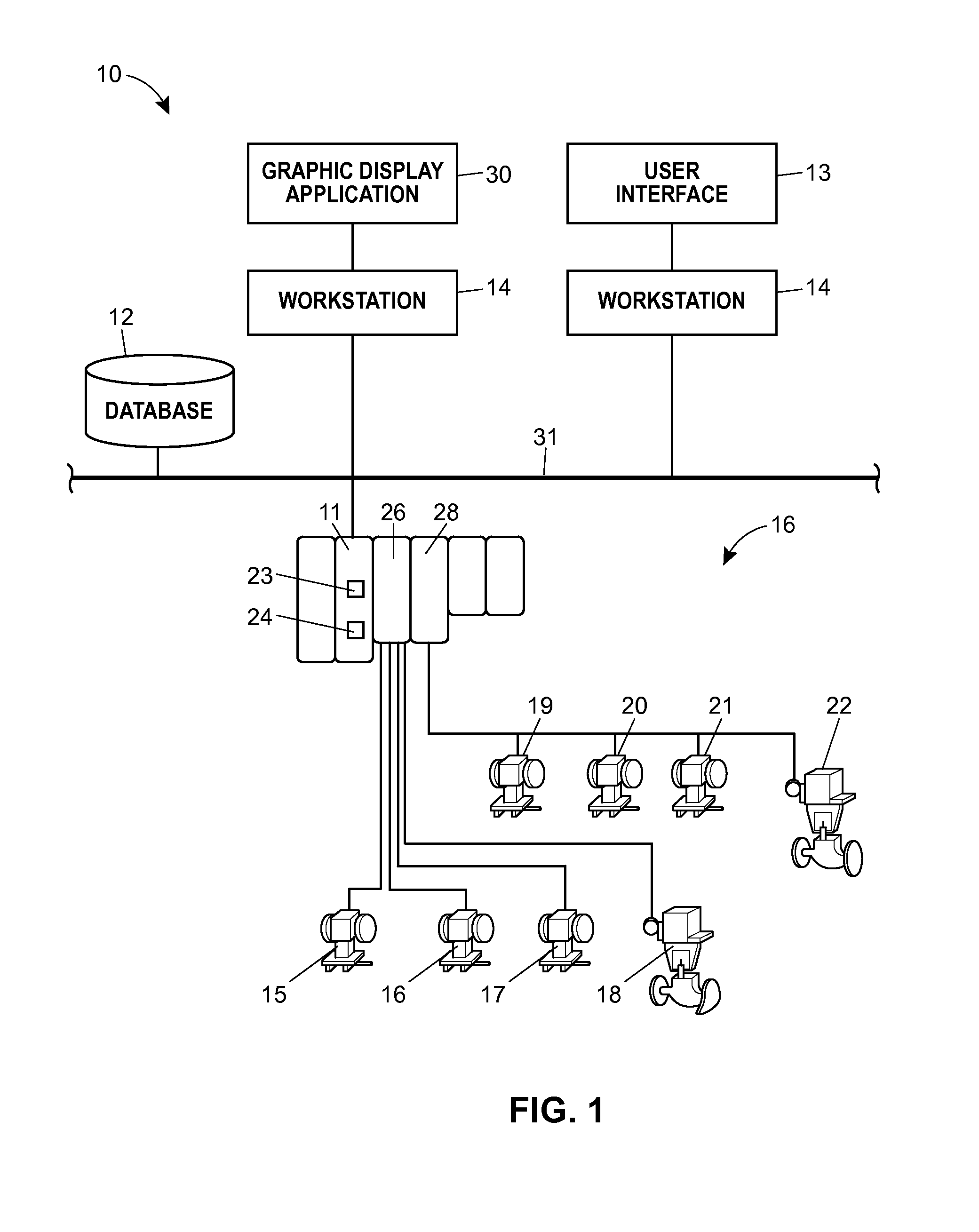
Graphical Process Variable Trend Monitoring, Predictive Analytics and Fault Detection in a Process Control System
ActiveUS20160042541A1Assist in detectingEasy to distinguishDrawing from basic elementsTesting/monitoring control systemsProblem identificationTrend monitoring
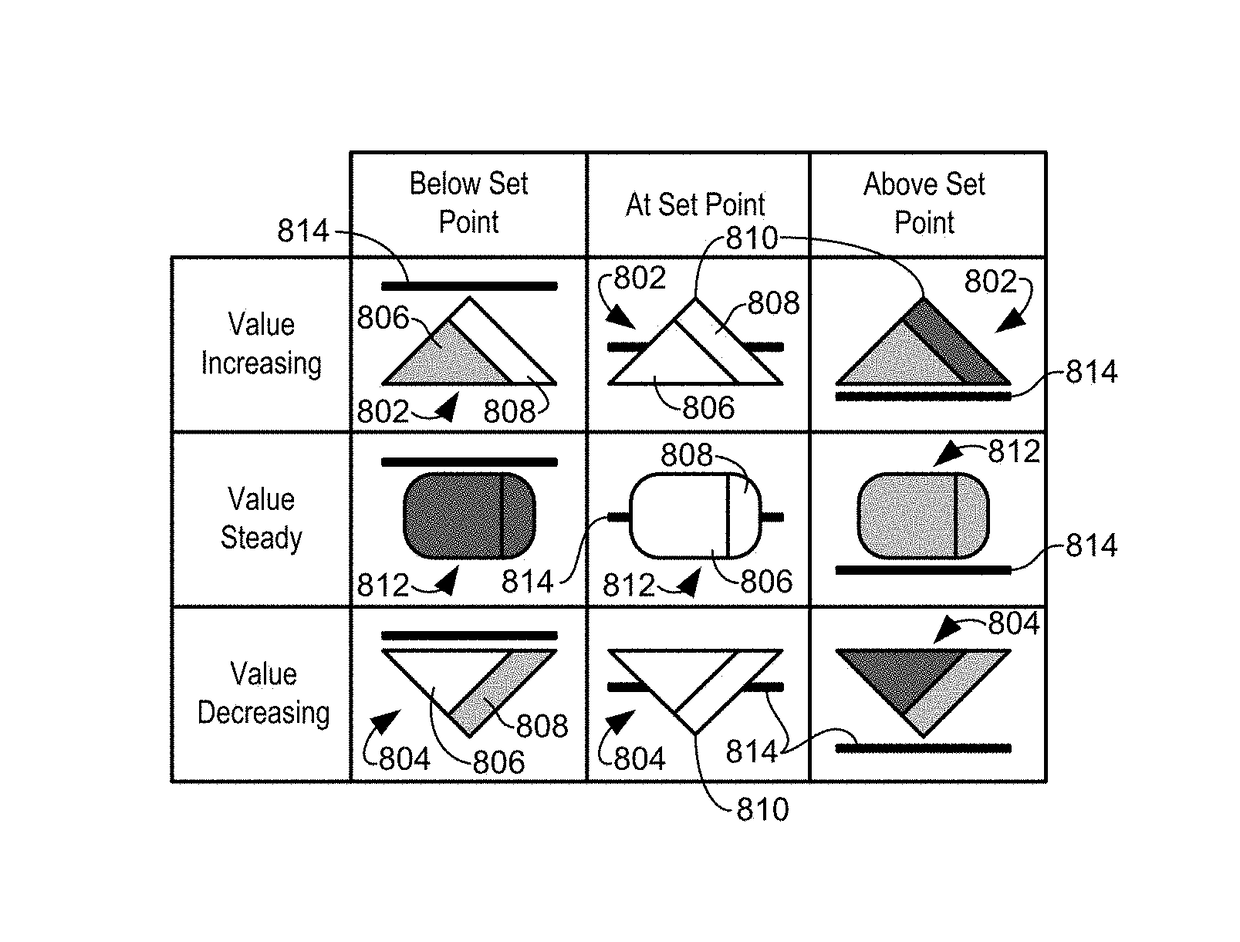
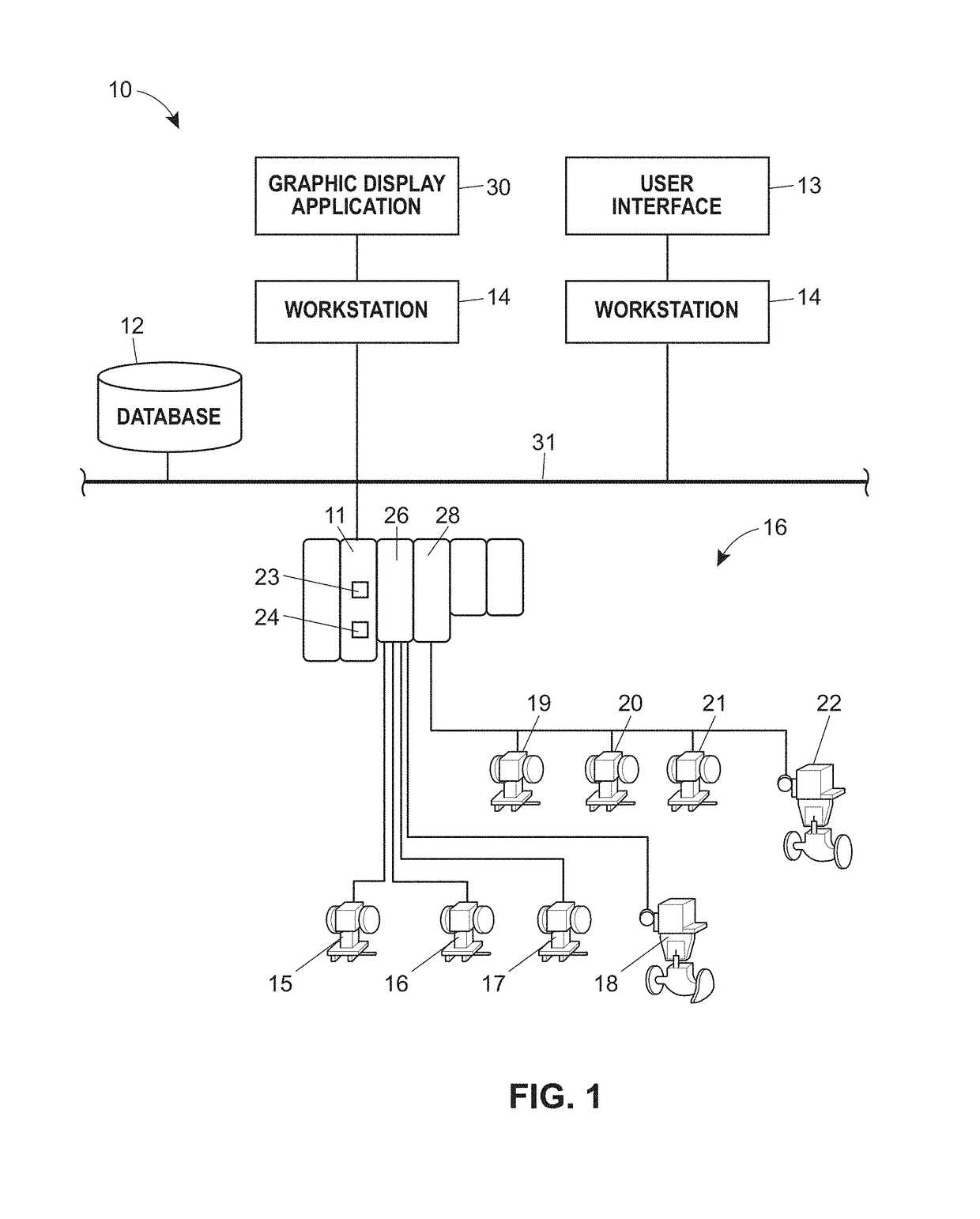
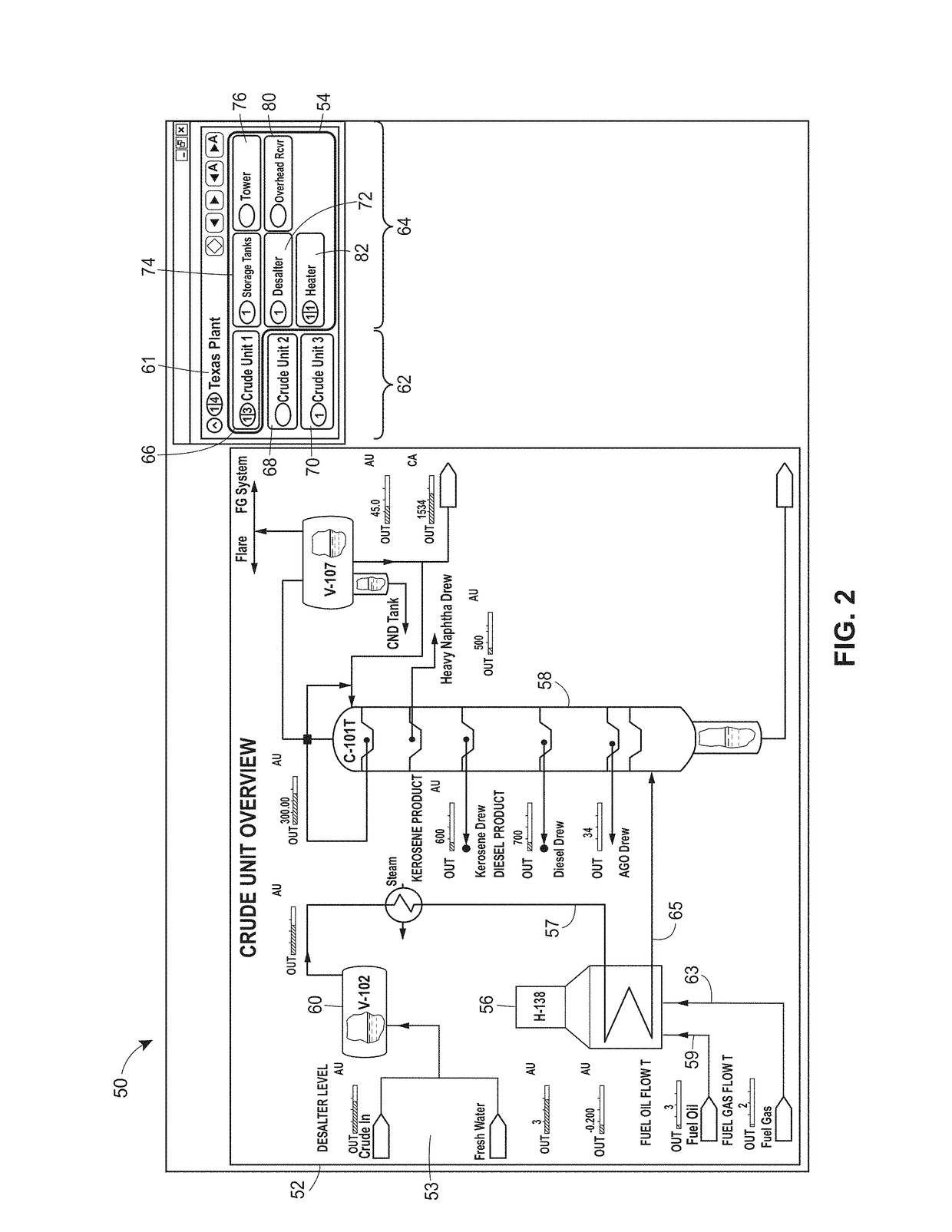
A process control monitoring system for a process control plant uses graphic trend symbols to assist in detecting and monitoring trends of process variables within the process control plant. A graphic display application within the process control monitoring system may implement and display each graphic trend symbol to graphically indicate or encapsulate current trend and value information of a process variable within the process control plant. The graphic display application may display the graphic trend symbol in a spatially realistic location within a graphical representation of the process control plant while maintaining the hierarchical structure or each hierarchical level of the process plant. The graphic display application may also include a navigation pane and a zoom feature that enable a user to quickly drill down through tend data to obtain more information and to support problem identification and diagnosis tasks.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Graphical process variable trend monitoring in a process control system using a navigation pane
ActiveUS20140277619A1Assist in detectingEasy to distinguishProgramme controlComputer controlGraphicsDrill down
A process control monitoring system for a process control plant uses graphic trend symbols to assist in detecting and monitoring trends of process variables within the process control plant. A graphic display application within the process control monitoring system may implement and display each graphic trend symbol to graphically indicate or encapsulate current trend and value information of a process variable within the process control plant. The graphic display application may display the graphic trend symbol in a spatially realistic location within a graphical representation of the process control plant while maintaining the hierarchical structure or each hierarchical level of the process plant. The graphic display application may also include a navigation pane and a zoom feature that enable a user to quickly drill down through tend data to obtain more information and to support problem identification and diagnosis tasks.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
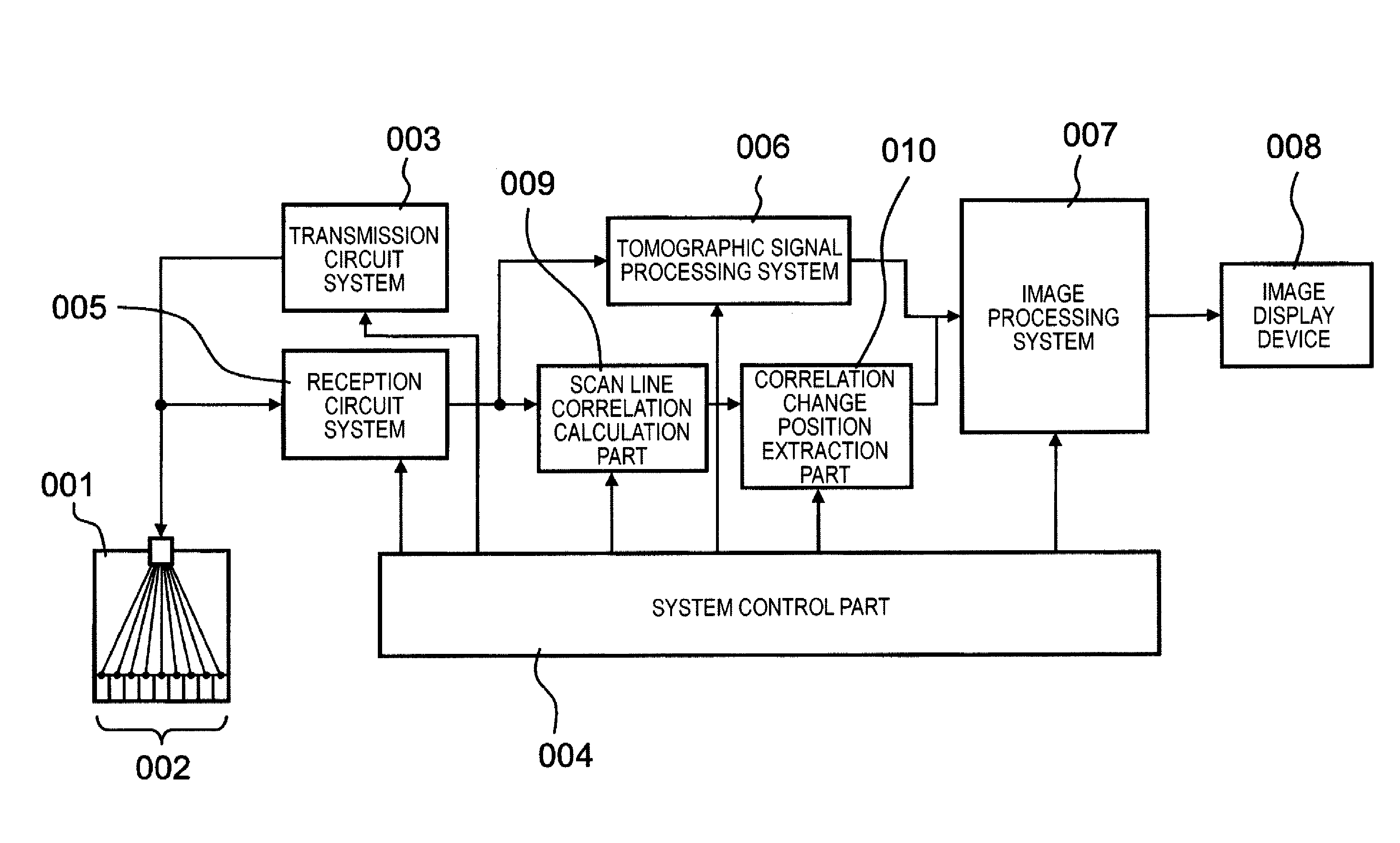
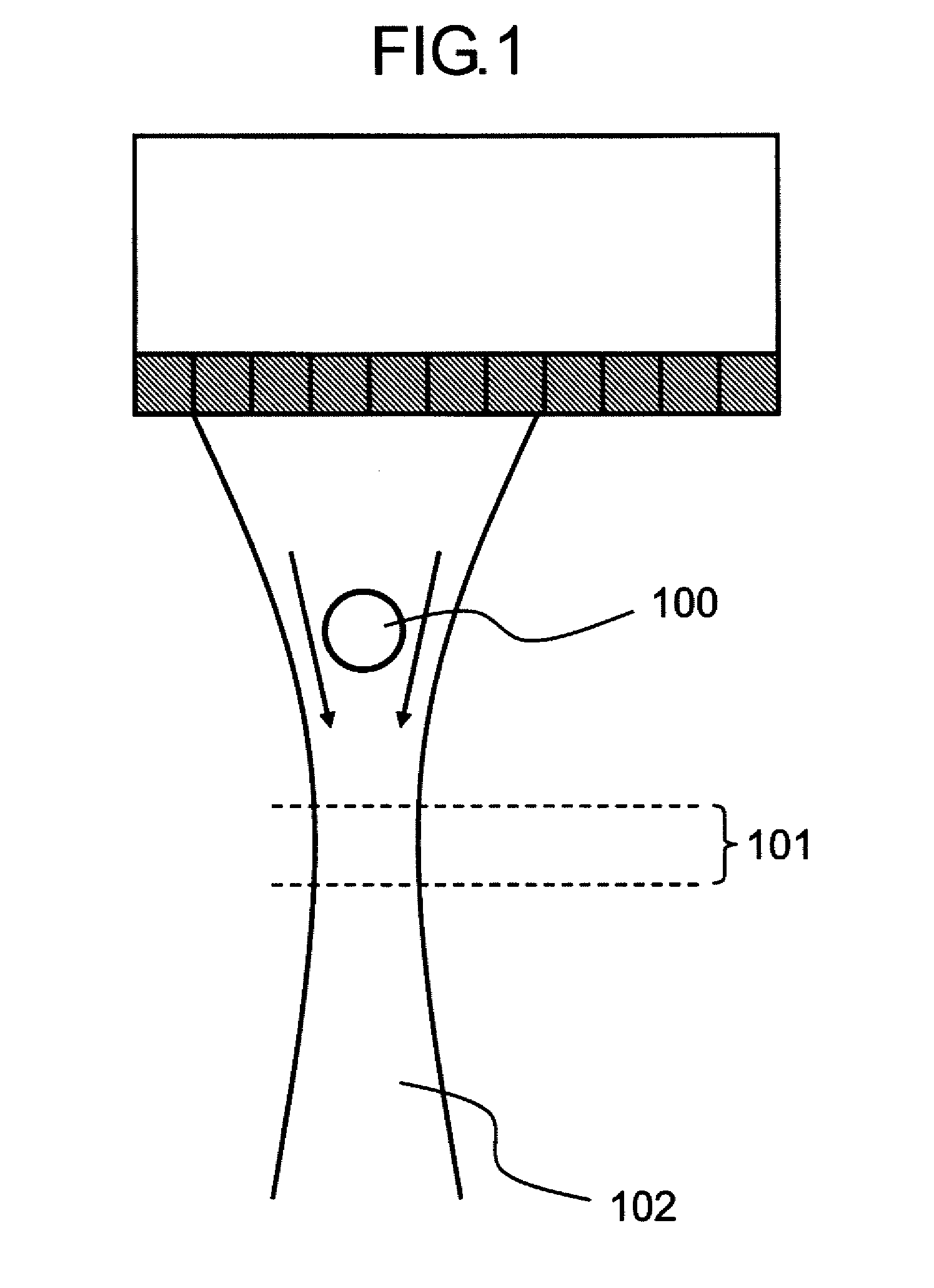
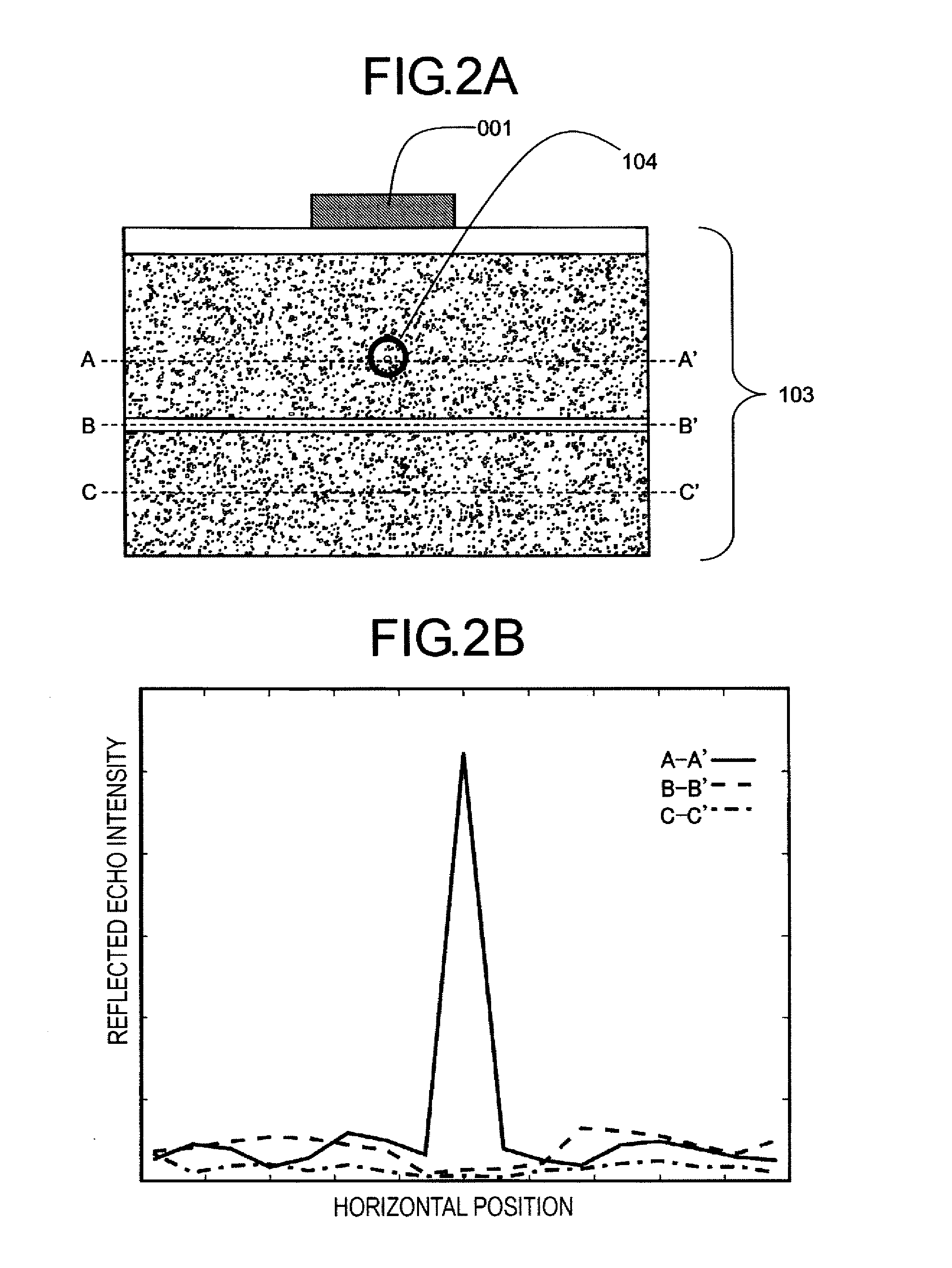
Signal processing apparatus, ultrasonic apparatus, control method for signal processing apparatus, and control method for ultrasonic apparatus
ActiveUS20110083511A1Improve resolutionDetection signal be so smallUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTomographic imageUltrasound
A signal processing apparatus scans a beam of elastic waves into an object to be examined, acquires received waveform data of a plurality of scan lines, and performs signal processing to form a tomographic image of said object to be examined from the received waveform data of the plurality of scan lines. The signal processing apparatus includes a scan line correlation calculation part (009) that calculates a correlation value of received waveform data between a first scan line and a second scan line that has a prescribed correlation with the first scan line, for a plurality of positions on the scan lines, and a correlation change position extraction part (010) that extracts, from among the plurality of positions on said scan lines, a position at which the correlation value becomes a value different from a prescribed value as a position at which a unique region can exist.
Owner:CANON KK
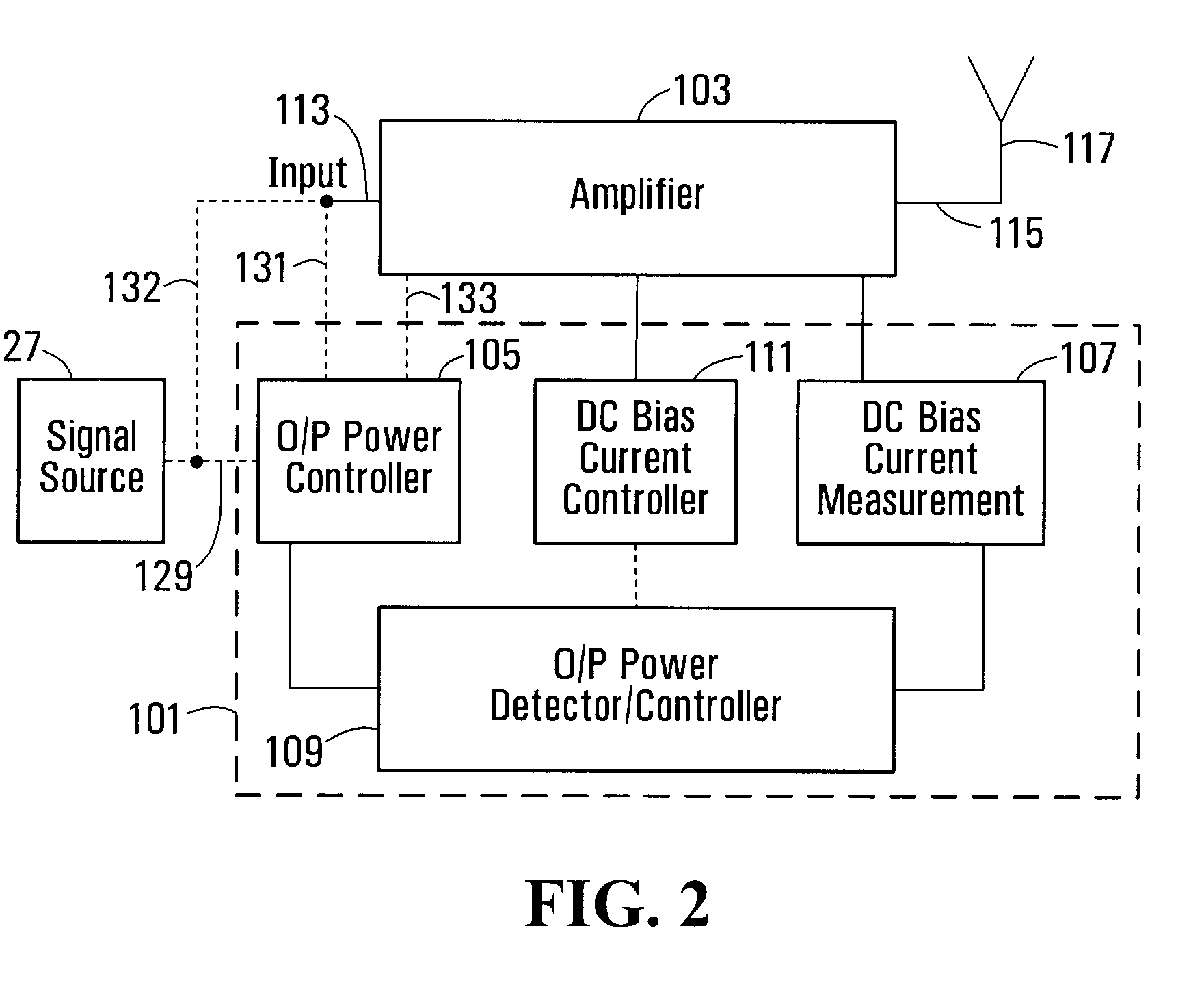
Apparatus and Method for Detecting Output Power From an Amplifier
InactiveUS20090021300A1Easy to detectAssist in detectingElectric devicesCurrent/voltage measurementAudio power amplifierEngineering
An apparatus for detecting output power from an amplifier (103) comprises a first controller (105) for controlling output power of a signal from the amplifier (103), a device (107) for measuring dc bias current / voltage at an output (115) of the amplifier (103), second controller (109) operative to set the first controller (105) to a setting corresponding to an output power at a finite level, and a detector (109) for determining whether or not there is output power from the amplifier based on the measured dc bias current / voltage at the setting of the first controller (105). In one embodiment, the first controller (105) is set at a setting corresponding to an output power level which is sufficient to at least partially saturate the amplifier (103).
Owner:DRAGONWAVE
Wireless network assisted GPS system
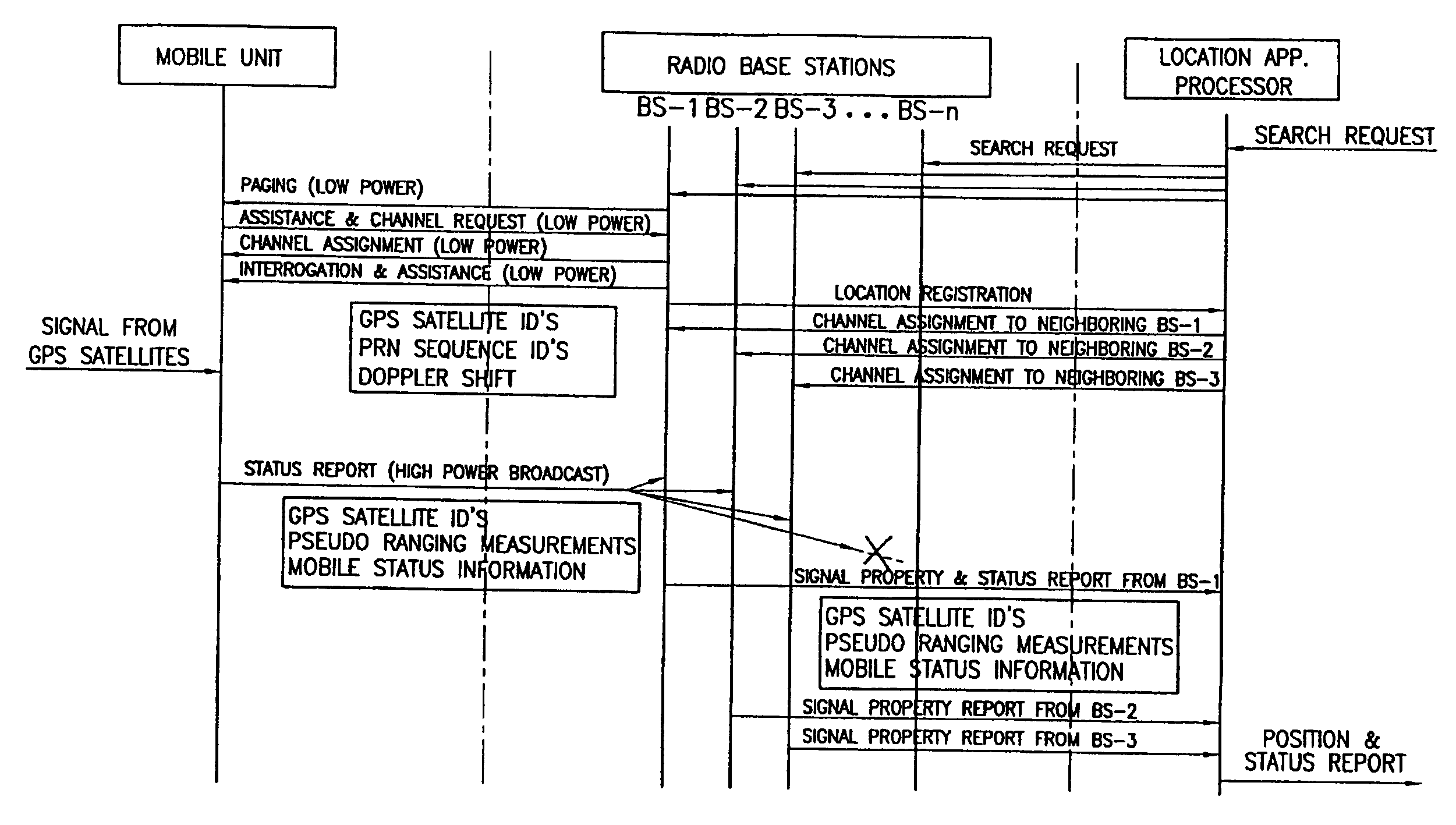
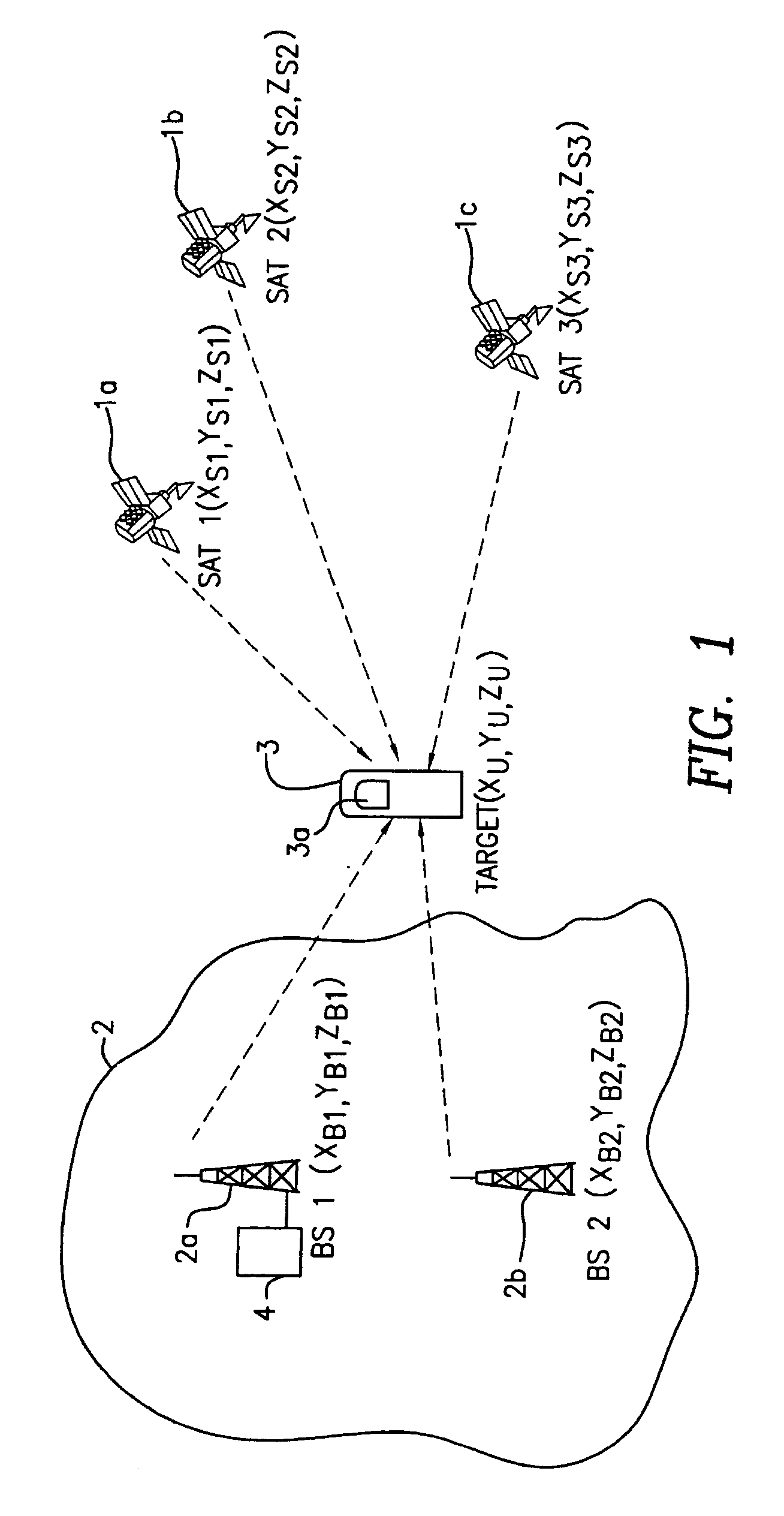
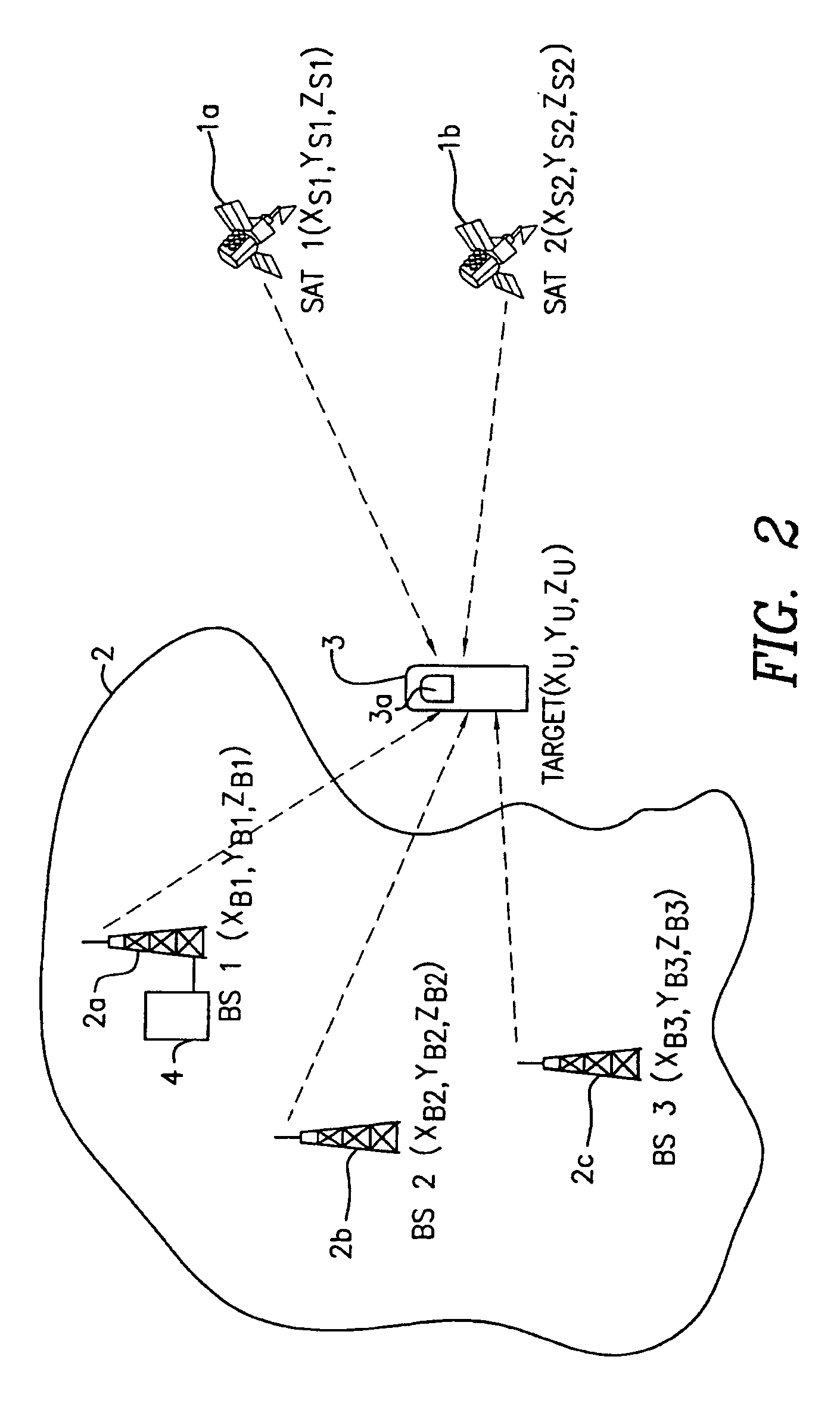
ActiveUS7215281B2Minimize consumptionSignal minimizedPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsCellular telephoneCommunication device
A method and apparatus for locating a mobile communications device such as a cell phone includes apparatus for communicating with base stations and apparatus for communicating with satellites. Signals received from satellites and the base stations are combined to provide the necessary information to calculate the location of the mobile communications device.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Graphical process variable trend monitoring with zoom features for use in a process control system
ActiveUS20140277620A1Assist in detectingEasy to distinguishProgramme controlComputer controlDrill downTrend monitoring
A process control monitoring system for a process control plant uses graphic trend symbols to assist in detecting and monitoring trends of process variables within the process control plant. A graphic display application within the process control monitoring system may implement and display each graphic trend symbol to graphically indicate or encapsulate current trend and value information of a process variable within the process control plant. The graphic display application may display the graphic trend symbol in a spatially realistic location within a graphical representation of the process control plant while maintaining the hierarchical structure or each hierarchical level of the process plant. The graphic display application may also include a zoom feature that enables a user to quickly drill down through tend data to obtain more information and to support problem identification and diagnosis tasks.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
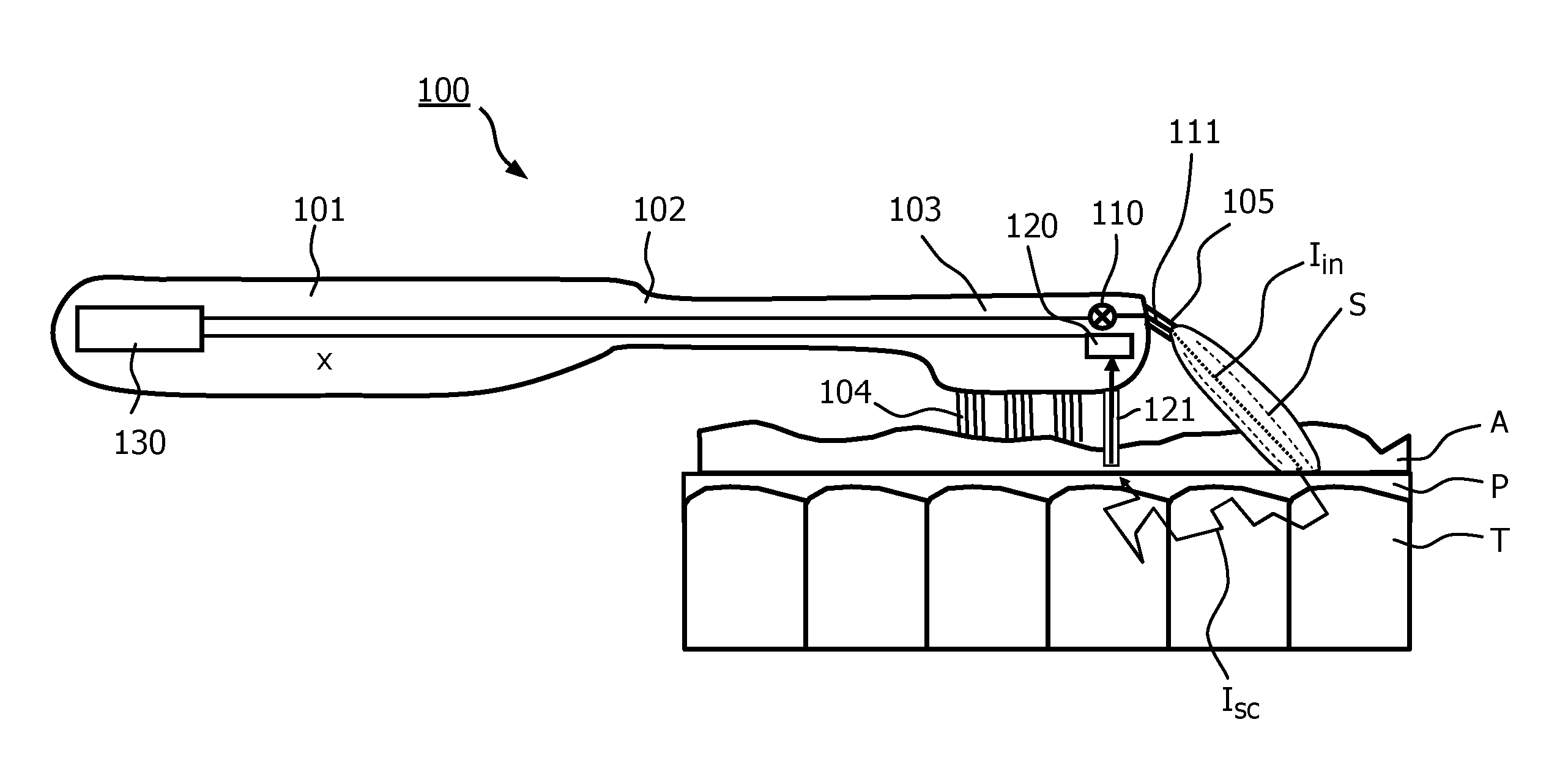
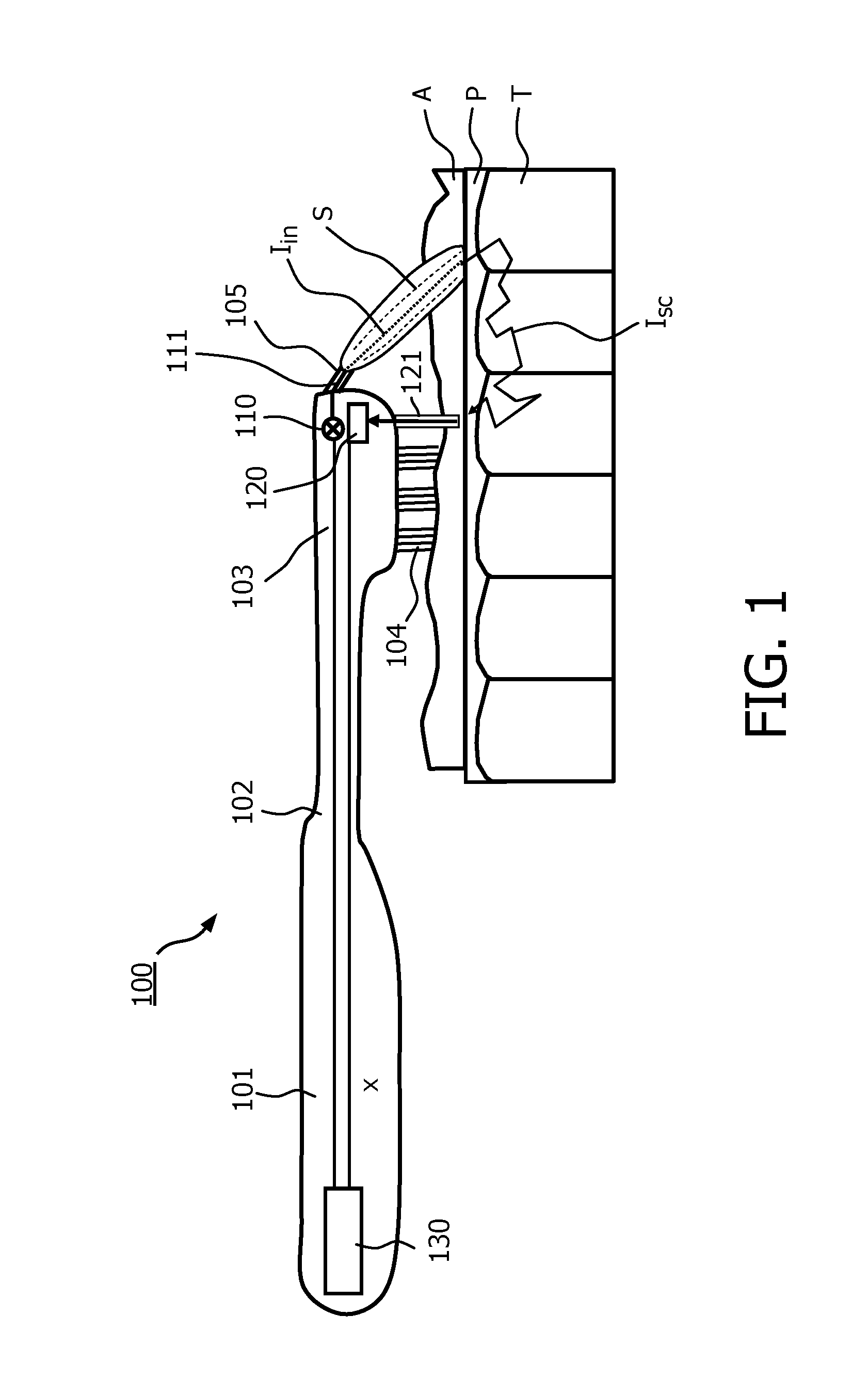
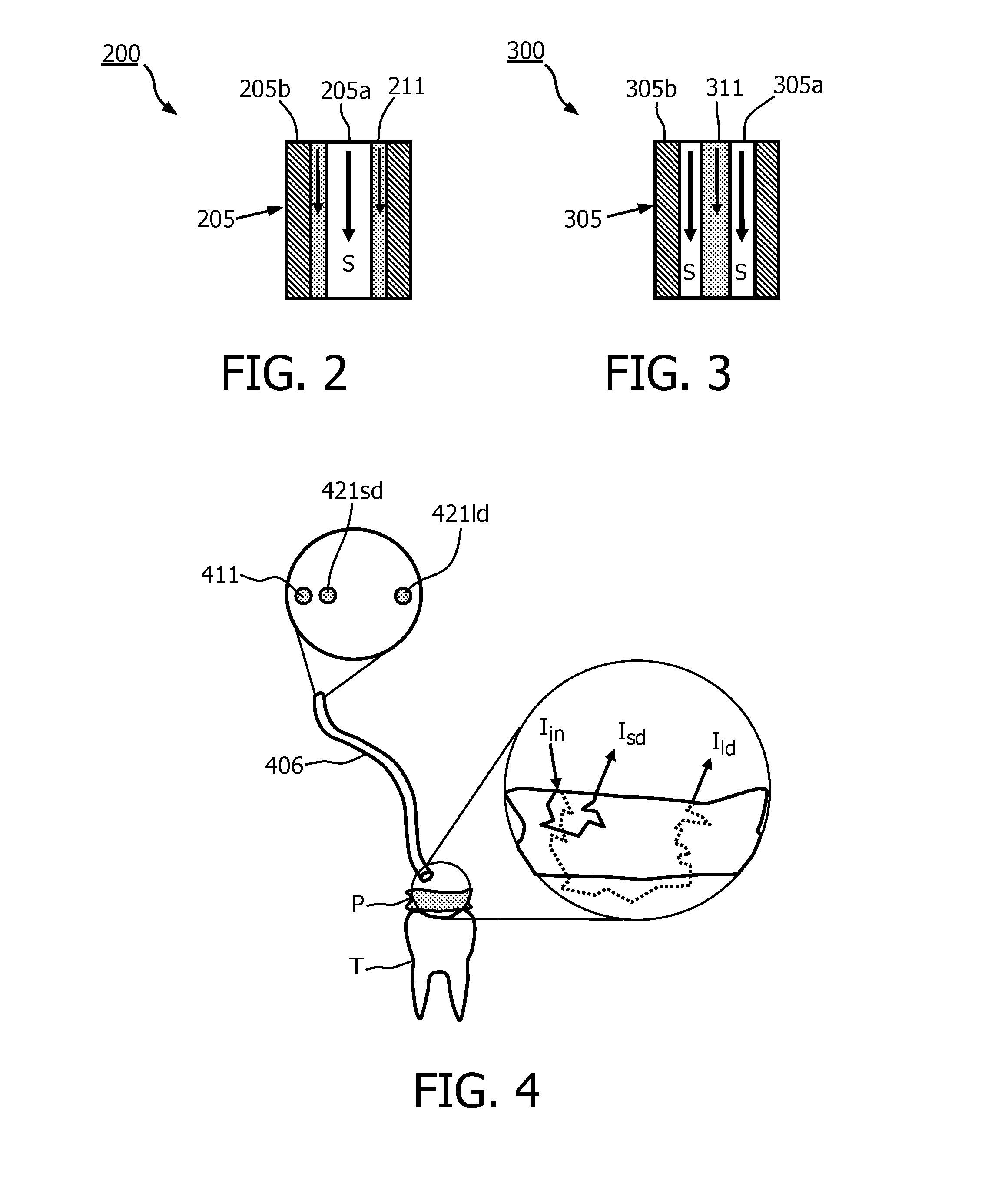
Device for dental plaque detection
InactiveUS20160242652A1Convenient treatmentImprove efficiencyMedical imagingDiagnostics using spectroscopySpeckle patternDental plaque
The invention relates to a device (100) for detection of plaque (P) on teeth (T). According to a preferred embodiment, light (Im) is emitted towards the teeth (T), and a part thereof as scattered from the surface of the teeth (T) and plaque (P) which may be present on the teeth (T) is recollected by a light receiving element (121). The received light (Isc) is provided to a light detector (120) for generating a detection signal (x) that represents at least one property of the light (Isc), which is then evaluated with respect to the presence of plaque (P) by determining at least one scattering-related quantity. The quantity may for example be a ratio or coefficient to be calculated from the spectrum of the received light (Isc), or the temporal development of a speckle pattern.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Medical device for discreetly performing a routine vaginal examination
The invention is a system for performing a routine vaginal examination. The examination is carried out using a medical imaging device that is optimally shaped to match the shape of the vaginal canal and comprises an imaging sensor, wide field of view optics, illumination means, electronic circuitry, and communication means. In addition a medical image and analysis (MIUA) unit comprising a processor and a dedicated MIUA algorithm is provided, either as part of the device or as a separate unit. The system is characterized in that the dedicated MIUA algorithm compares the acquired images to a predefined standard of quality and verifies that sufficient images of a predefined region of interest (ROI) have been obtained; saves the acquired images that meet the predefined standard and also show the ROI; and signals the user carrying out the examination when a sufficient number of images having sufficient image quality and taken at appropriate viewing angles of the area being examined have been acquired. The device and MIUA unit enable routine examination of the vagina to be carried out at any location by untrained persons, preferably by the woman herself in the privacy of her own home. The images acquired by the camera are transmitted to an authorized center where trained medical personnel view, analyze, and interpret them.
Owner:WAVE GROUP +1
Method and system for employing automatic reply systems to detect e-mail scammer IP addresses
ActiveUS7917593B1Assist in detectStable deliveryMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsIp addressElectronic mail
A method and apparatus for employing automatic reply systems to detect e-mail scammer IP addresses whereby a decoy system to receive illegitimate e-mails, also known as a “honeypot” is established. E-mails sent to the honeypot decoy e-mail addresses are initially scanned and preliminarily identified as scam e-mails and the fact that the scammer must make contact with the intended user / victim is exploited by analyzing the scam e-mail to identify one or more e-mail addresses in either the header or the body of the preliminarily identified scam e-mail. The one or more identified e-mail addresses are then extracted and fabricated reply e-mails are generated that include one or more mechanisms for ascertaining the IP address of the scammer. The fabricated reply e-mails are then sent to the one or more identified e-mail addresses and when the scammer takes the necessary action, the IP address and browser information associated with scammer is obtained.
Owner:NORTONLIFELOCK INC
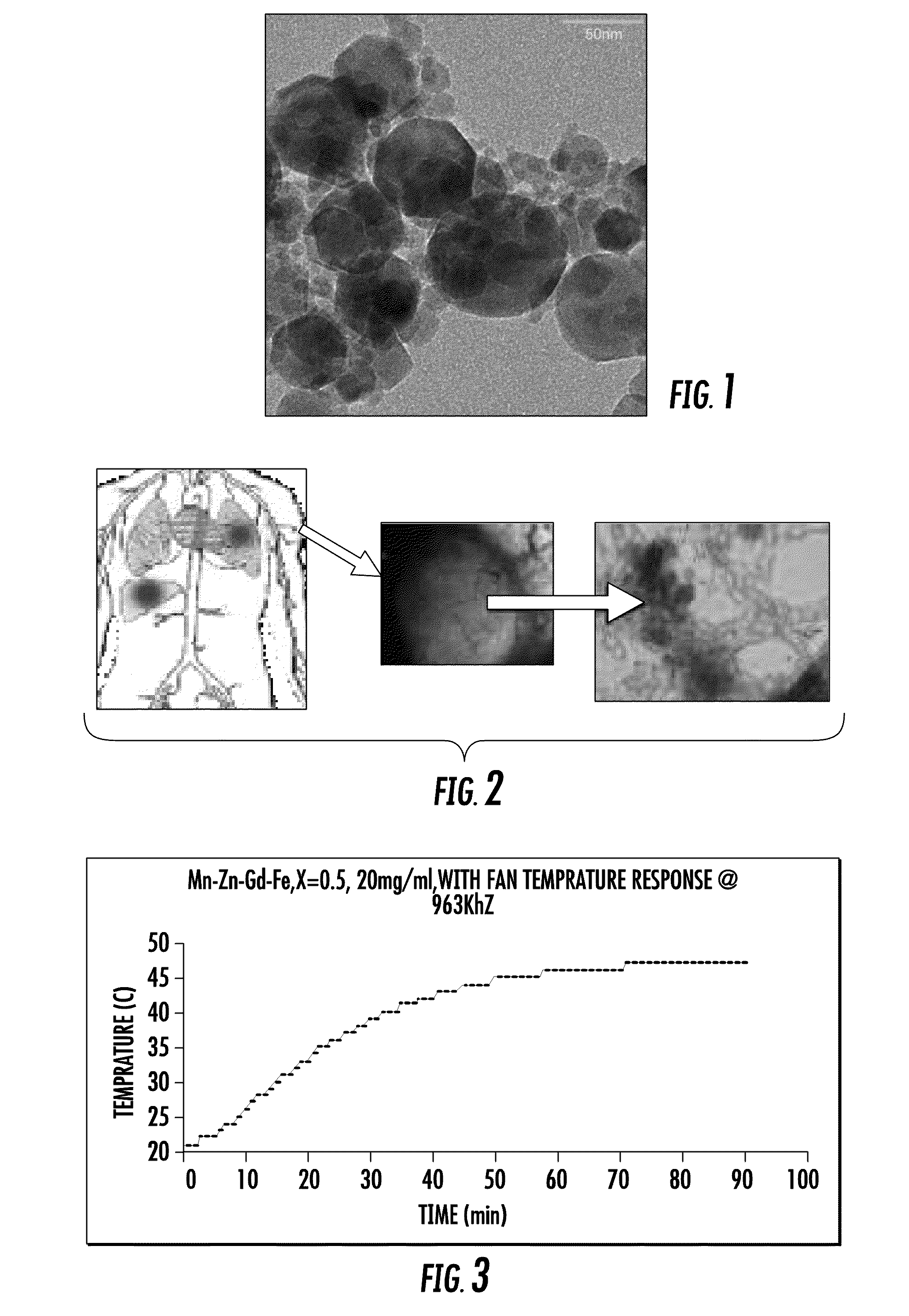
Magnetic Nanoparticles for Imaging
InactiveUS20090068112A1Reduction of septic shock potentialReduced virulenceNanomedicineNMR/MRI constrast preparationsTumor siteAttenuated strain
A medical imaging system that enables the discovery of malignant tissue utilizing contrast agents and heating agents made of magnetic nanoparticles that are delivered to tumor sites utilizing attenuated strains of bacteria that seek and reside at tumor sites is disclosed. The thermal contrast agents may be temperature self-controlled magnetic nanoparticles that may be encapsulated in a biocompatible coating. The thermal contrast agents may be uploaded into attenuated strains of bacteria that seek and reside in tumor tissue when placed into a bloodstream of a patient. An alternating magnetic field device with a prescribed frequency range may be used to induce heating of the magnetic nanoparticles in the patient, and a thermal scan may be utilized to identify tumors. In another embodiment, the contrast agent may be formed from magnetic nanoparticles having distinct magnetic moment profiles, and a MRI system may be utilized to identify tumors with such contrast agent.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT GREENSBORO
Accelerometer with Offset Compensation
ActiveUS20150122024A1Assist in detectingAcceleration measurementTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesAccelerometerEngineering
An accelerometer has a movable mass suspended above a substrate, and a variable acceleration capacitor supported by the substrate. The movable mass has a mass anchor securing the mass to the substrate, while the acceleration capacitor has both a stationary finger extending from the substrate, and a movable finger extending from the movable mass. The accelerometer also has a variable stress capacitor, which also includes the stress finger, for determining movement of the mass anchor relative to the substrate.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
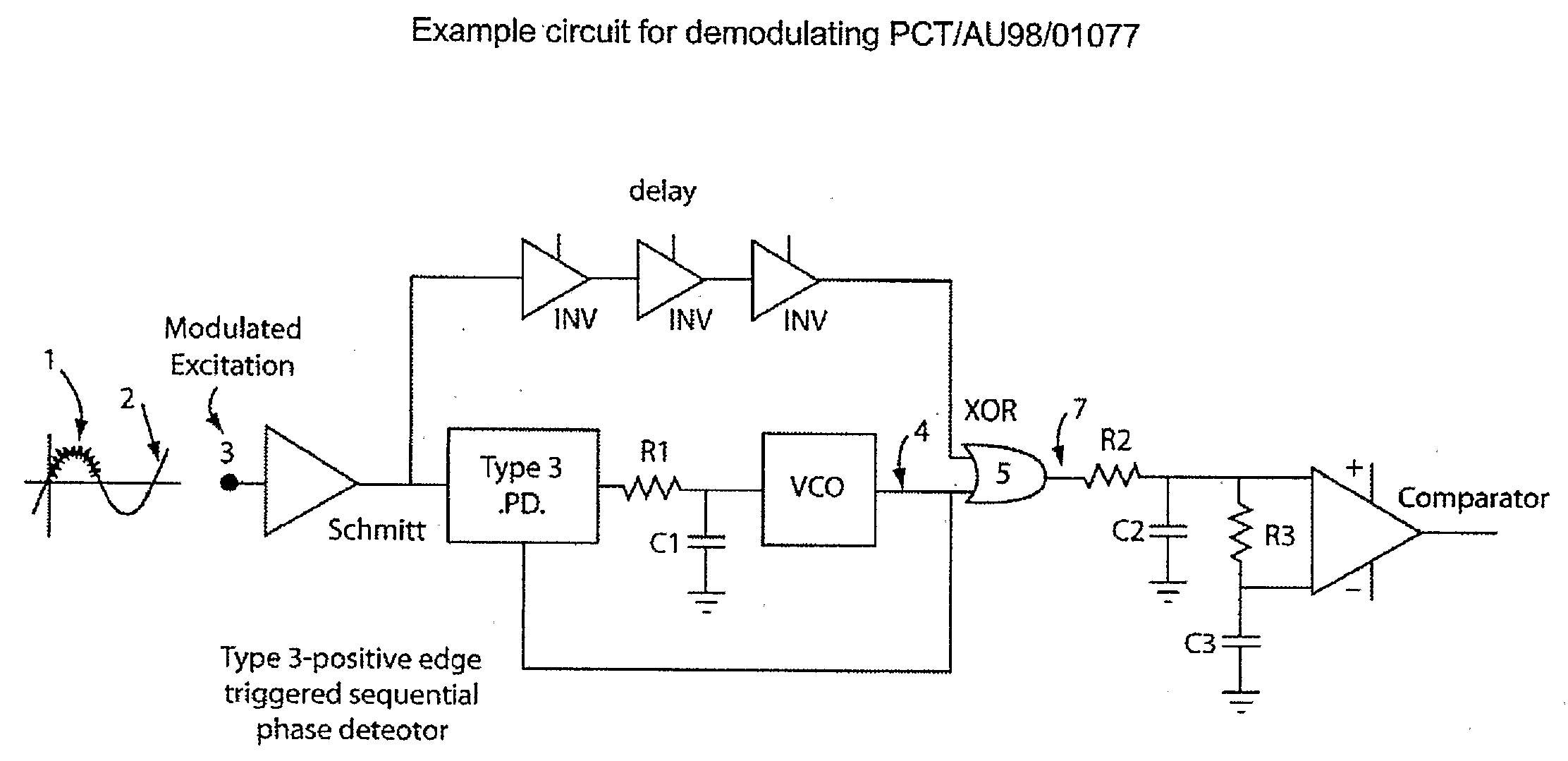
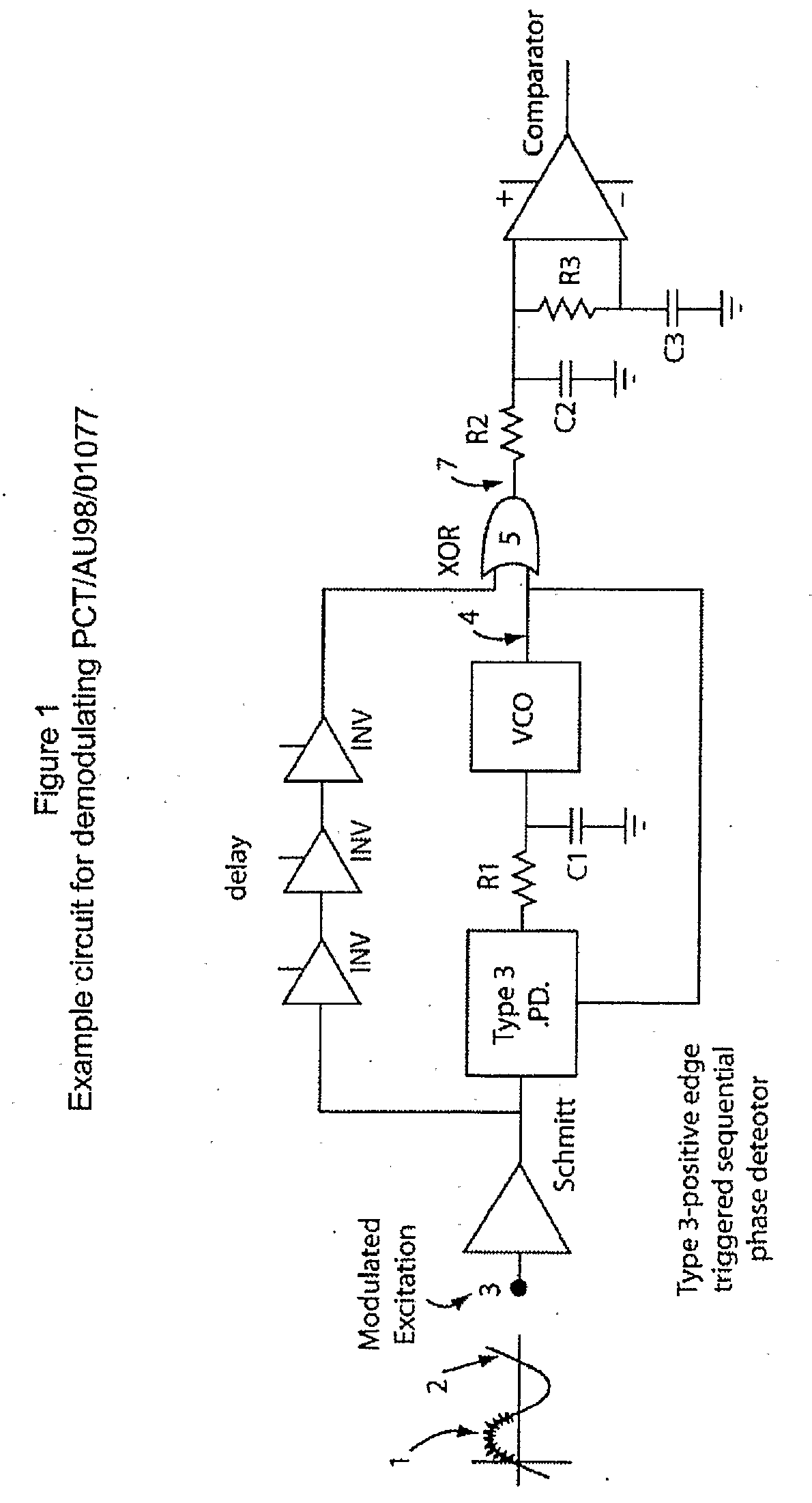
Method and Apparatus Adapted to Demodulate a Data Signal
ActiveUS20080267331A1Narrow bandwidthIncrease data rateElectric signal transmission systemsNear-field transmissionData transmissionRadio-frequency identification
The present invention relates to the field of receiving data and / or demodulating a data transmission signal. The present invention provides a method of and / or device for determining a data signal imposed on a phase jitter modulation signal. In one form, the invention relates to the field of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), and the transmission of data between a tag and an interrogator.
Owner:SATO HLDG CORP
Vehicle monitoring apparatus, fraud detection server, and control methods
ActiveUS20190371085A1Assist in detectingFinanceRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesReal-time computing
A vehicle monitoring apparatus includes: a first communicator that receives specifying information for specifying a target vehicle from a server; and an acquirer that acquires driving information from the target vehicle, the driving information being information regarding driving of the target vehicle specified by the specifying information received by the first communicator. The first communicator transmits the driving information acquired by the acquirer to the server. For example, the acquirer may acquire the driving information obtained from the target vehicle through communication.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Signal processing apparatus, ultrasonic apparatus, control method for signal processing apparatus, and control method for ultrasonic apparatus
ActiveUS8784317B2Promote generationSpeed up extractionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScan lineChange positions
A signal processing apparatus scans a beam of elastic waves into an object to be examined, acquires received waveform data of a plurality of scan lines, and performs signal processing to form a tomographic image of said object to be examined from the received waveform data of the plurality of scan lines. The signal processing apparatus includes a scan line correlation calculation part (009) that calculates a correlation value of received waveform data between a first scan line and a second scan line that has a prescribed correlation with the first scan line, for a plurality of positions on the scan lines, and a correlation change position extraction part (010) that extracts, from among the plurality of positions on said scan lines, a position at which the correlation value becomes a value different from a prescribed value as a position at which a unique region can exist.
Owner:CANON KK
Computer-based apparatus system for assessing, predicting, correcting, recovering, and reducing risk arising from an operator?s deficient situation awareness
InactiveUS20200241525A1Reduce lossReduce riskInput/output for user-computer interactionElectroencephalographyAutopilotSituation awareness
A computer-based apparatus system for assessing, predicting, correcting, recovering, and reducing risk arising from an operator's deficient situation awareness (SA). This system identifies operator situation awareness by computer-apparatus and method that utilizes neurogenic-psychophysiological-neurocognitive-artificial intelligence processes. This system is configured to receive psychophysiological data from the operator via the neurogenic sensor(s) and configured to be loaded with data corresponding to the operator's baseline SA capacity and / or possesses AI algorithms to learn and calibrate the operator's baseline SA capacity and sound a warning in response if an SA deficiency threshold has been exceeded. Optionally, an autopilot / auto-driver / auto-operator / auto-worker / student alert / player & coach alert interface is configured to activate an autopilot / auto-driver / auto-operator / auto-worker command in response an SA deficiency threshold has been exceeded.
Owner:HUMAN AUTONOMOUS SOLUTIONS LLC
Background object sensor
ActiveUS8890684B2Assist in detectingDetect presenceDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationTransceiverRadio frequency signal
An RFD reader includes a transceiver configured to receive a first radio frequency signal reflected off at least one surface to provide baseline signal information and a second radio frequency signal reflected off the at least one surface and an object to provide further signal information. A comparator is configured to compare the baseline signal information and the further signal information to provide a signal comparison. A processor is configured to detect the presence of the object in accordance with the signal comparison. A determination is made whether the object is in motion in accordance with the signal comparison. The determination whether the object is in motion is made in accordance with a continuous fluctuation of the second radio frequency signal. A determination whether the object is no longer in motion is made in accordance with an ending of the continuous fluctuation of the second radio frequency signal.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
Wireless network assisted GPS system
ActiveUS20050052320A1Assist in detectingMinimize consumptionPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsWireless mesh networkCellular telephone
A method and apparatus for locating a mobile communications device such as a cell phone includes apparatus for communicating with base stations and apparatus for communicating with satellites. Signals received from satellites and the base stations are combined to provide the necessary information to calculate the location of the mobile communications device.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Accelerometer with offset compensation
ActiveUS9927459B2Assist in detectingAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesAccelerometerEngineering
An accelerometer has a movable mass suspended above a substrate, and a variable acceleration capacitor supported by the substrate. The movable mass has a mass anchor securing the mass to the substrate, while the acceleration capacitor has both a stationary finger extending from the substrate, and a movable finger extending from the movable mass. The accelerometer also has a variable stress capacitor, which also includes the stress finger, for determining movement of the mass anchor relative to the substrate.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Imaging reader with target proximity sensor
ActiveUS7597263B2Less electric powerAssist in detectingSensing by electromagnetic radiationIlluminanceProximity sensor
An illuminator illuminates a symbol with a low level of illumination in a detection mode of operation to enable an imager to detect the symbol in a working range and in a field of view of the imager in an imaging reader, and also illuminates the symbol with a high level of illumination in a reading mode of operation to enable the imager to read the symbol.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Safety detection in sealed vehicle spaces
InactiveUS20180261069A1Increased accuracy levelImprove accuracyAcoustic signal devicesOptical signallingMotor vehicle drivingCarbon dioxide sensor
A safety alert system for use in a motor vehicle cabin. A temperature sensor and a carbon dioxide sensor operate in conjunction to detect the presence of a person within the sealed vehicle cabin in unsafe circumstances. Based upon preset parameters, a local alarm or notification or operator notification can be triggered in the vicinity of the vehicle if an alert condition exists, or in some embodiments remote alert notifications can be triggered to vehicle owners or safety authorities. An auxiliary carbon dioxide sensor could be located within the trunk of the vehicle in addition to within the vehicle cabin. A video capture subsystem could also be included, to capture video of the cabin of the vehicle on detection of the alert condition, and the video could be archived or transmitted to safety personnel. The method of detection of a human in an unsafe vehicle environment is also disclosed.
Owner:HONEY JONES DAVID
System Event Analyzer and Outlier Visualization
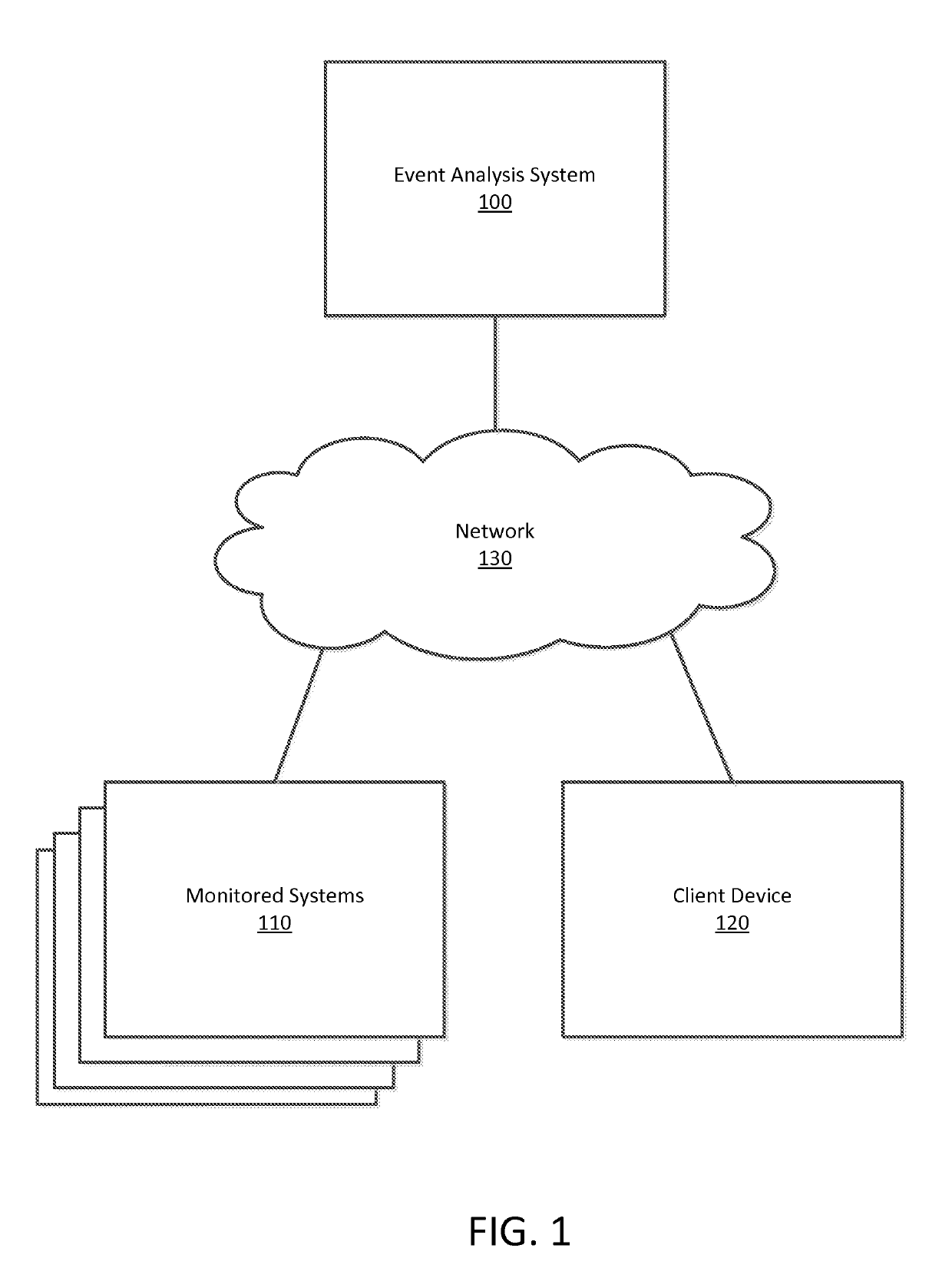
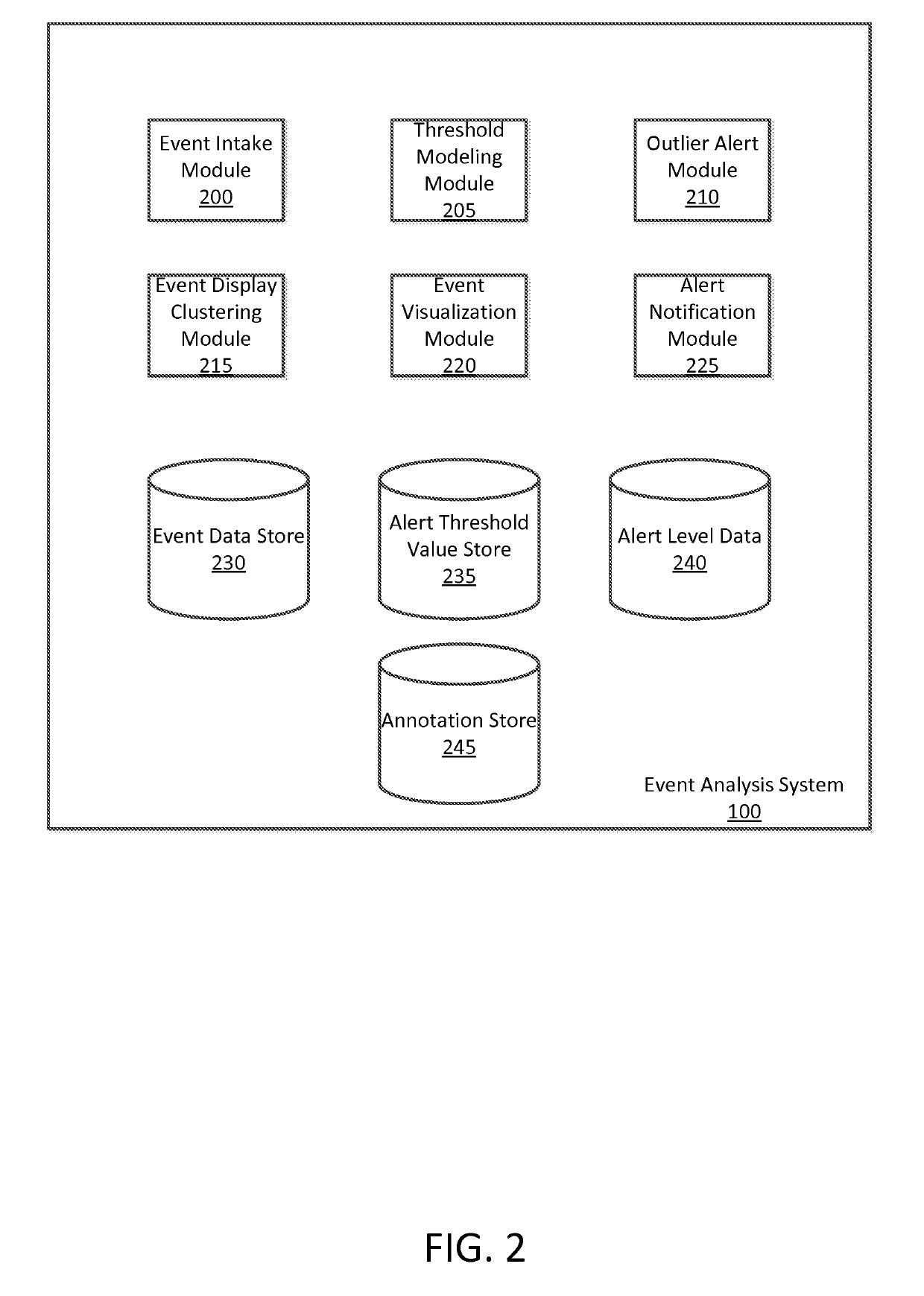
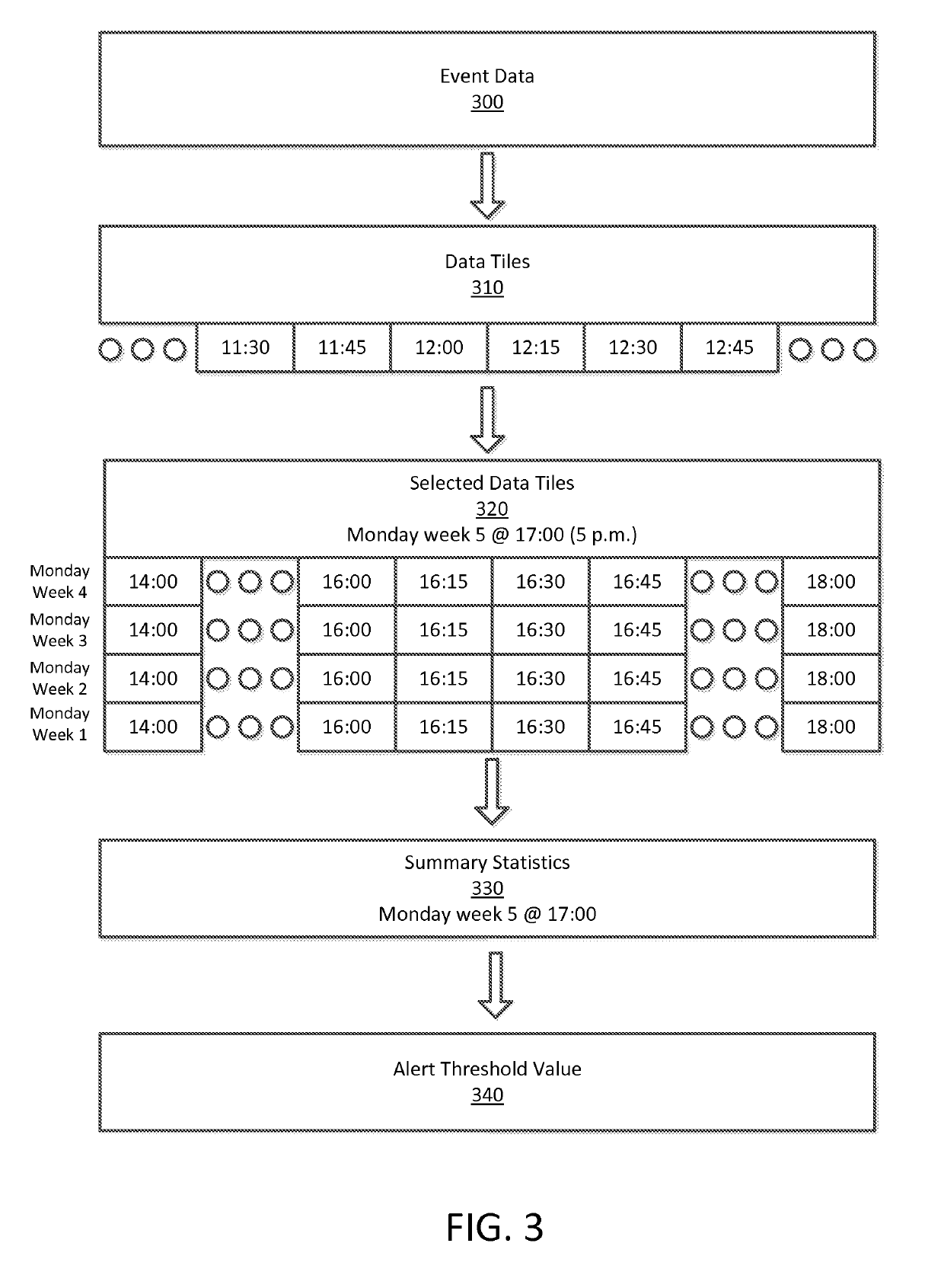
ActiveUS20190222503A1Weight increaseIncrease and decrease notification thresholdData switching networksEvent typeMonitoring system
An event analysis system receives events in a time-series from a set of monitored systems and identifies a set of alert threshold values for each of the types of events to identify outliers in the time-series at an evaluated time. Portions of historic event data is selected to identify windows of event data near the evaluated time at a set of seasonally-adjusted times to predict the value of the event type. The alert threshold value may also account for a prediction based on recent, higher-frequency events. Using the alert threshold values for a plurality of event types, the event data is compared with the alert threshold values to determine an alert level for the data. The event data types are also clustered and displayed with the alert levels to provide a visualization of the event data and identify outliers when the new event data is received.
Owner:UBER TECH INC
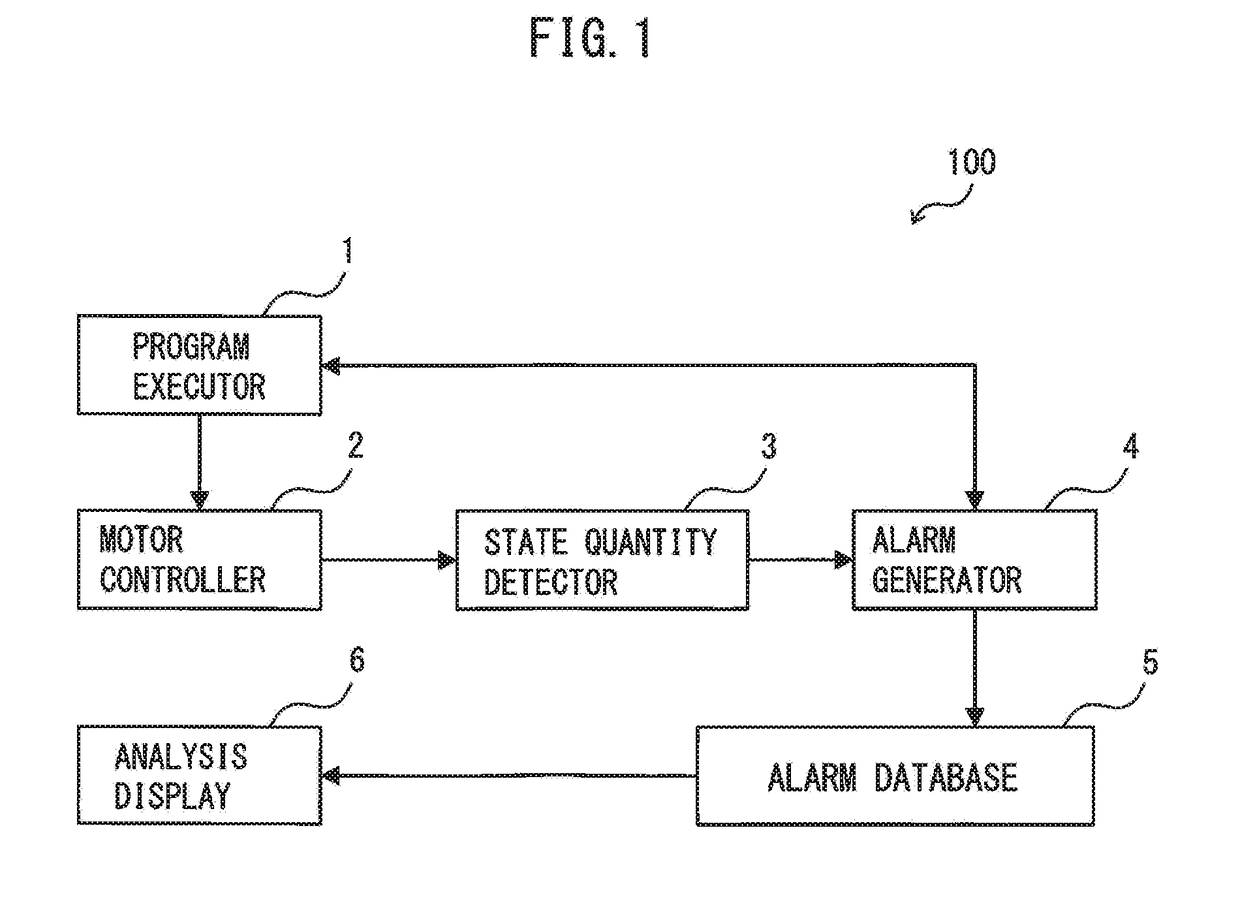
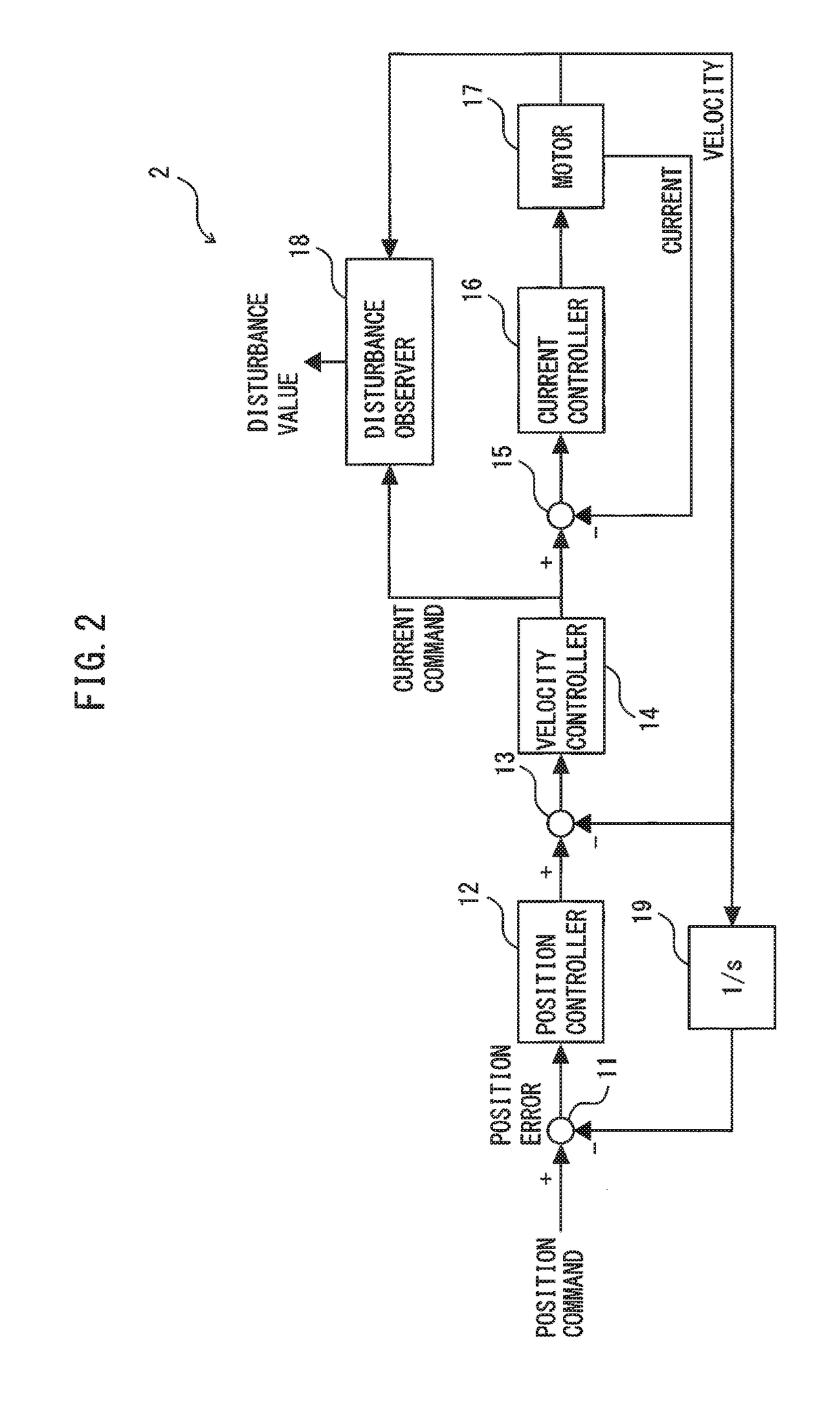
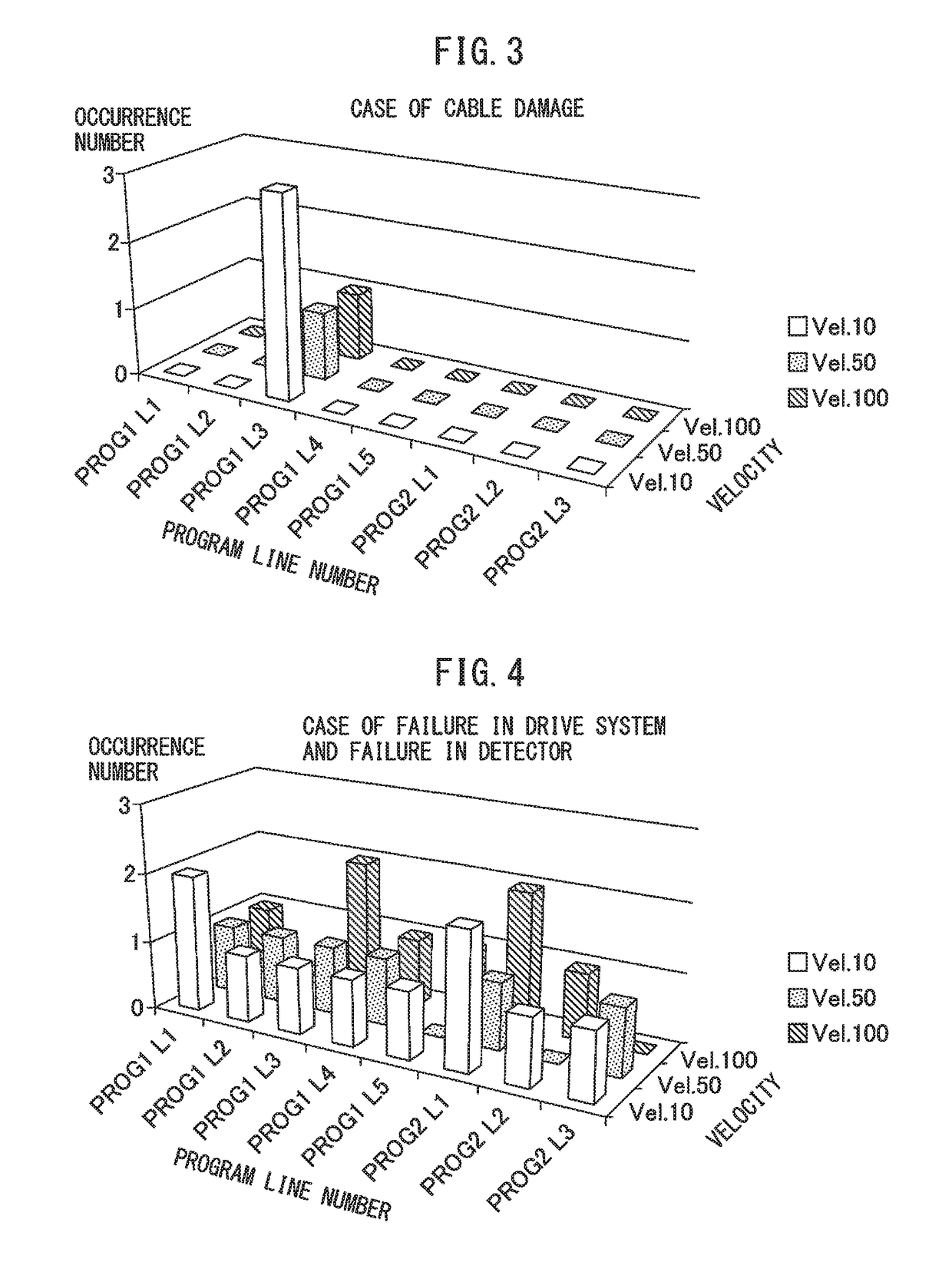
Cable damage detection assistance apparatus and cable damage detection assistance method in robot mechanism
ActiveUS20180354134A1Assist in detectingProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorDrive motorMotor controller
A cable damage detection assistance apparatus in a robot mechanism includes a program executor for executing a program to operate a robot, a plurality of times, while changing velocity for driving motors whenever the program is executed; a motor controller for controlling the motors; a state quantity detector for detecting a state quantity indicating an operation state of the robot during the execution of the program; an alarm generator that, when the state quantity exceeds a threshold value, generates an alarm and outputs information about a line number at that time; an alarm database for counting the number of occurrence of alarms on each line number on which the alarm has occurred, and storing the alarm occurrence number on each line number on a velocity-by-velocity basis; and an analysis display for displaying the relationship between the alarm occurrence number and the velocity on each line number.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Conductive adhesives
ActiveUS20150175851A1Not to failAssist in detectingLamination ancillary operationsControlling laminationAnisotropic conductive adhesiveComputational physics
A conductive adhesive, such as an anisotropic conductive adhesive, comprising a population of conductive particles and a population of signal particles in an adhesive; wherein both the conductive particle population and the signal particle population have an average particle diameter of <200 μm with a coefficient of variance of <10%; wherein the signal particles are arranged to provide an indication when they are deformed to a pre-determined height; and wherein the conductive particles are arranged such that they will not fail, e.g. crack or fracture, when deformed to a height larger than or equal to the pre-determined height at which the signal particles are arranged to provide the indication.
Owner:CONPART
Graphical process variable trend monitoring for a process control system
ActiveUS10013149B2Assist in detectingEasy to distinguishElectric testing/monitoringInput/output processes for data processingProblem identificationApplication software
A process control monitoring system for a process control plant uses graphic trend symbols to assist in detecting and monitoring trends of process variables within the process control plant. A graphic display application within the process control monitoring system may implement and display each graphic trend symbol to graphically indicate or encapsulate current trend and value information of a process variable within the process control plant. The graphic display application may display the graphic trend symbol in a spatially realistic location within a graphical representation of the process control plant while maintaining the hierarchical structure or each hierarchical level of the process plant. The graphic display application may also include a zoom feature that enables a user to quickly drill down through tend data to obtain more information and to support problem identification and diagnosis tasks.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Wireless Network Assisted GPS System
ActiveUS20070159389A1Minimize consumptionSignal minimizedPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsRadio Base StationCellular telephone
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Distributed optical fibre sensor
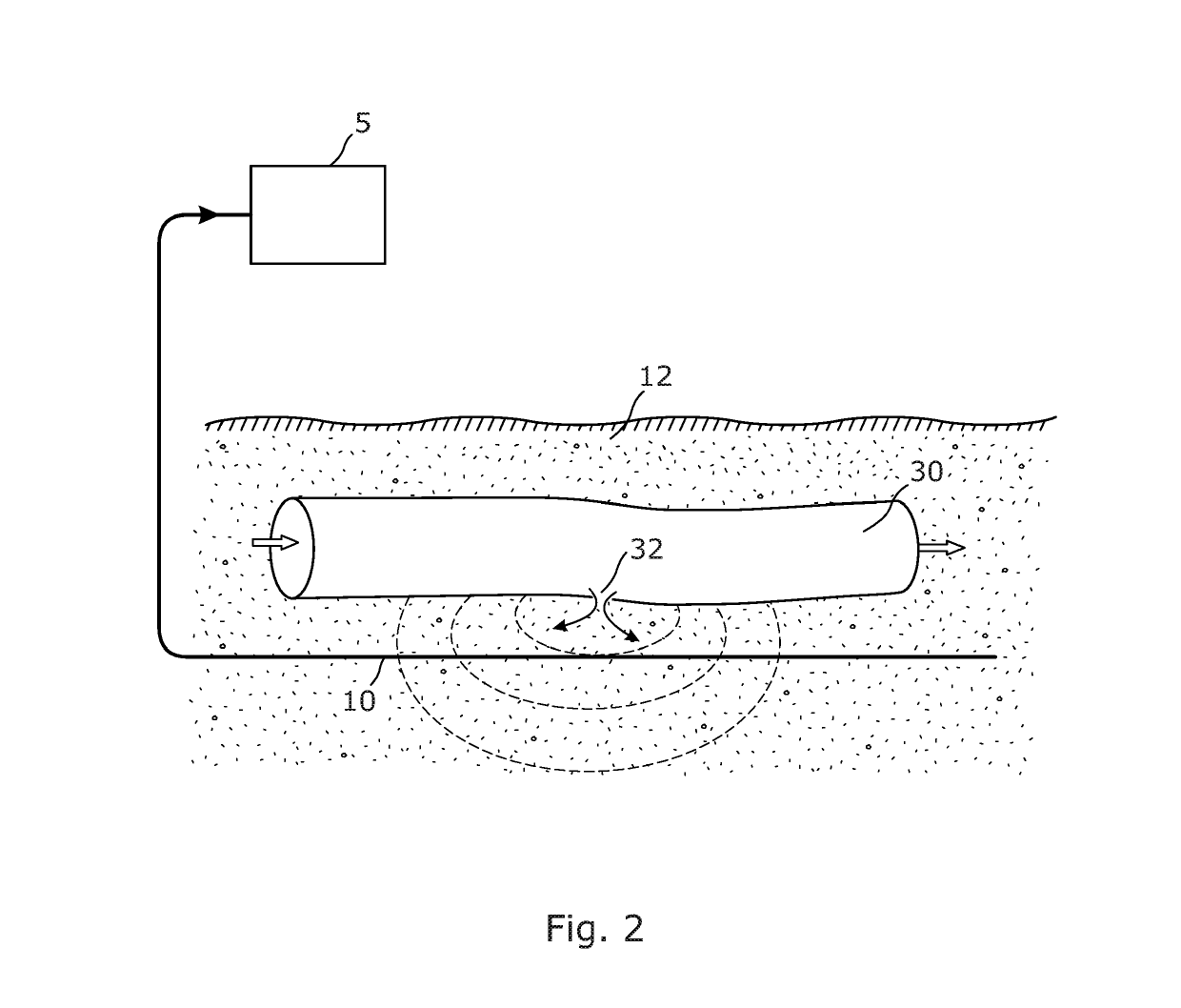
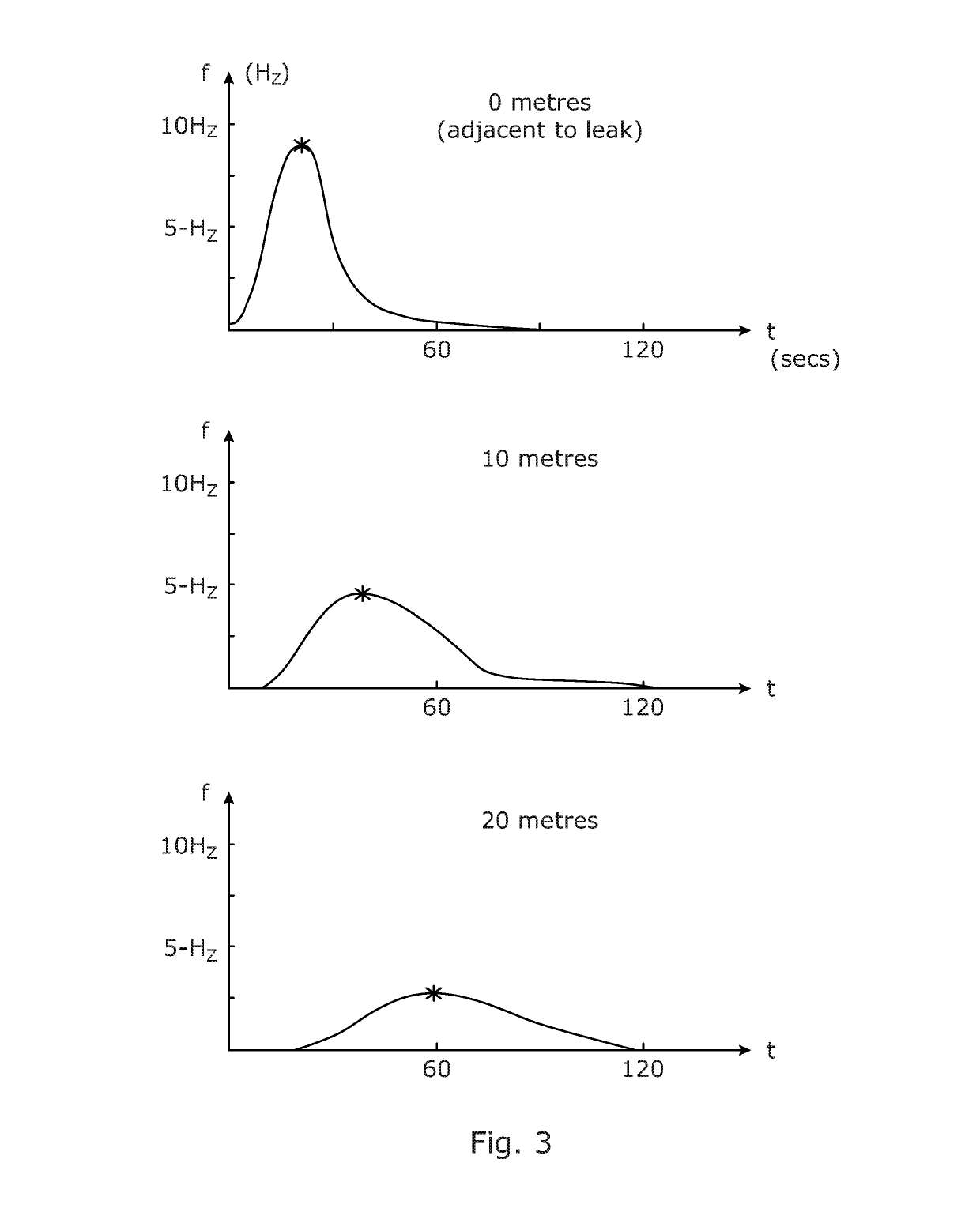
ActiveUS10281300B2Assist in detectingSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansOptical fiber cableFiber optic sensor
The disclosure relates to distributed optical fiber sensors arranged to detect coherent Rayleigh backscatter from a sensing optical fiber disposed in an environment, and to determine an infrasonic signal in the backscatter, or to determine a change in the environment within an infrasonic frequency range from the backscatter.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com