Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3793 results about "DC-BUS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
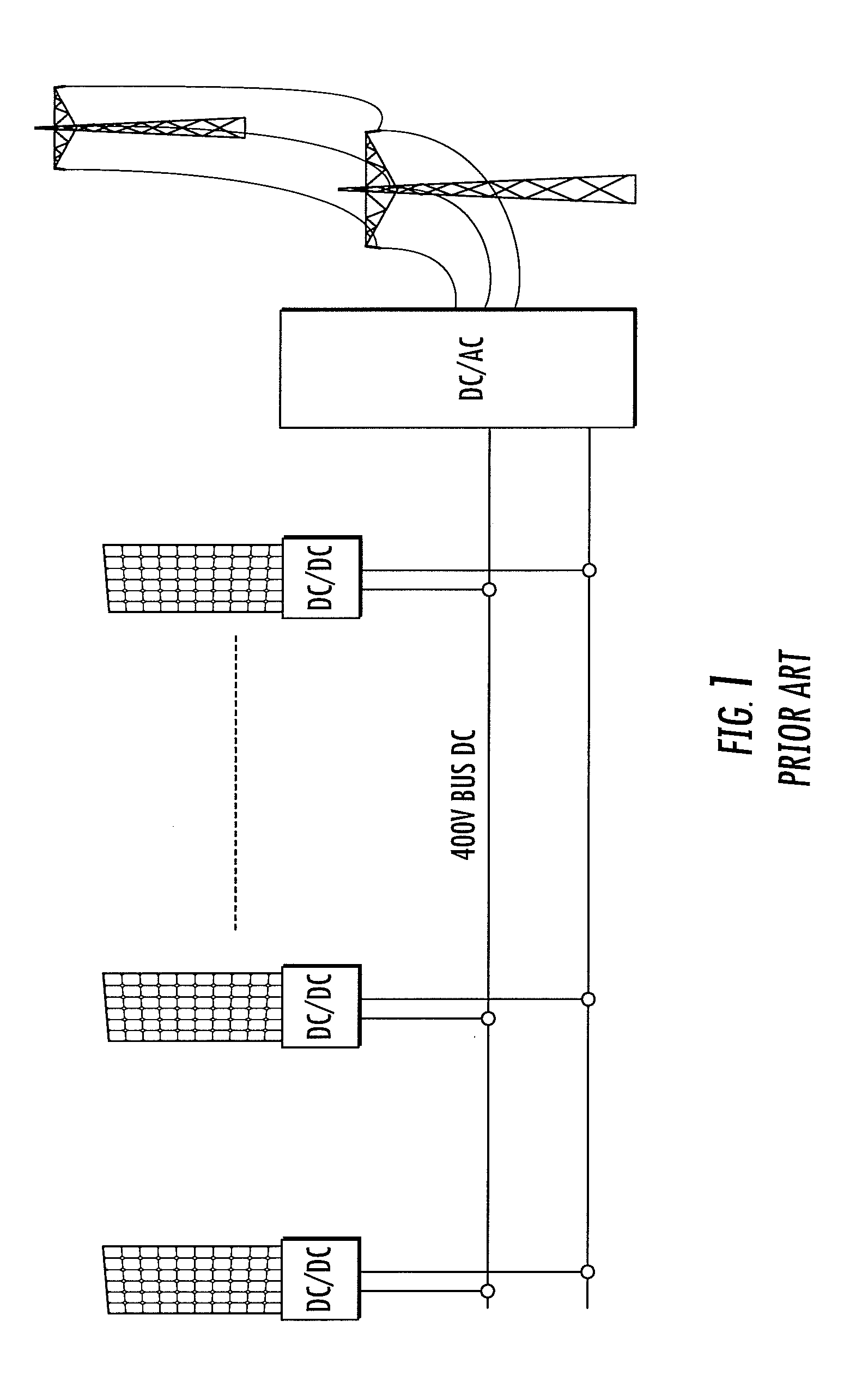
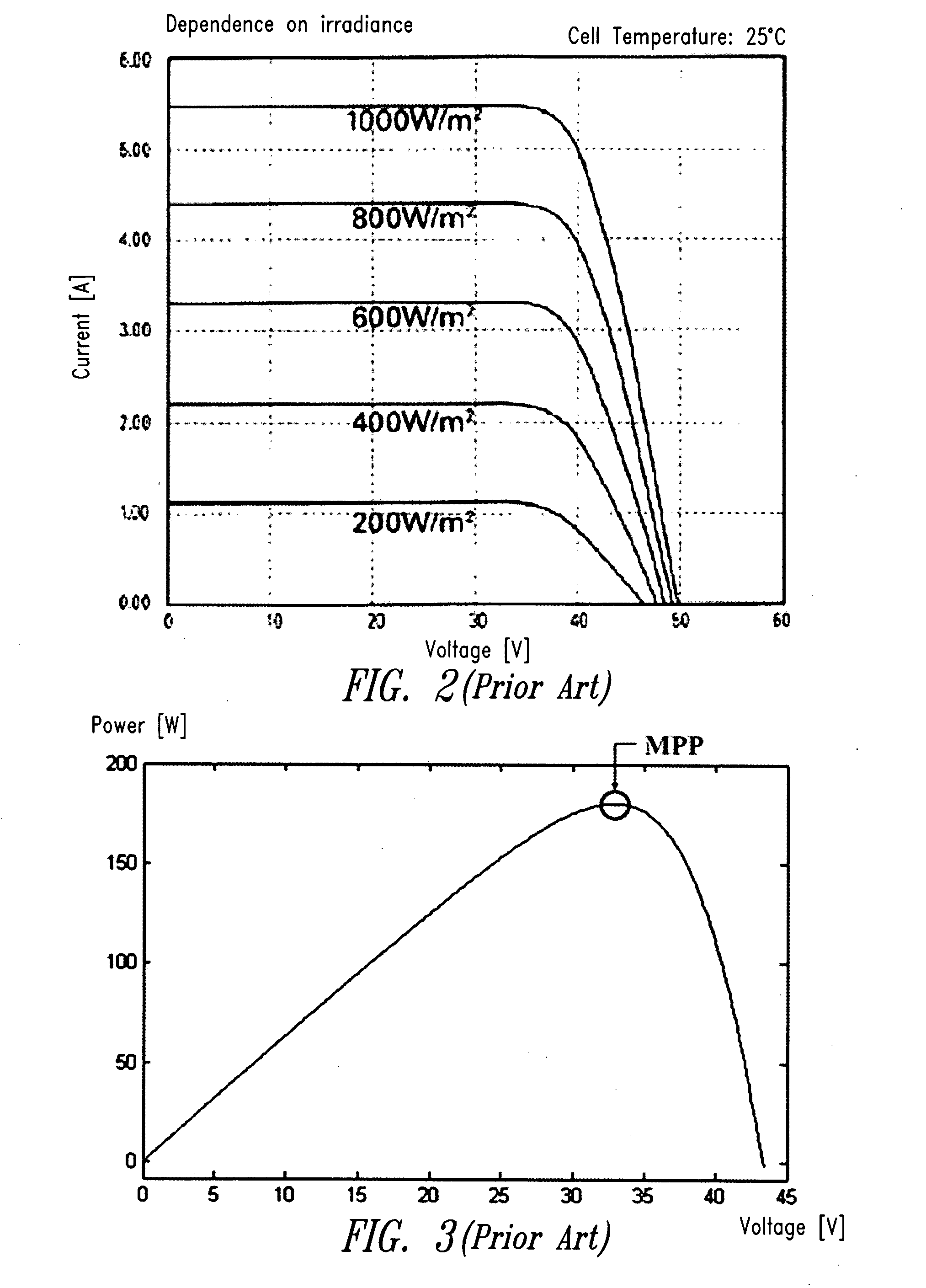
DC-BUS is technology for reliable and economical communication over noisy DC or AC power lines. The DC-BUS was originally developed by Yamar Electronics Ltd. together with the DC-BUS Alliance, for low cost sub-networks in vehicles, using the battery lines for in-vehicle data communication. The DC-BUS converts the digital input data into phase modulated signals, protected against errors generated by noise over the powerline. On the receiving side, the received signal is demodulated into the original digital data. Gradually it became a popular means of communication in a plurality of applications within aerospace, automotive, solar energy management and lighting. It is also used as an alternative to RS-232 and RS-485 networks in some cases. The common goal for all these applications is reducing wires, saving space, lowering cost and increasing reliability.
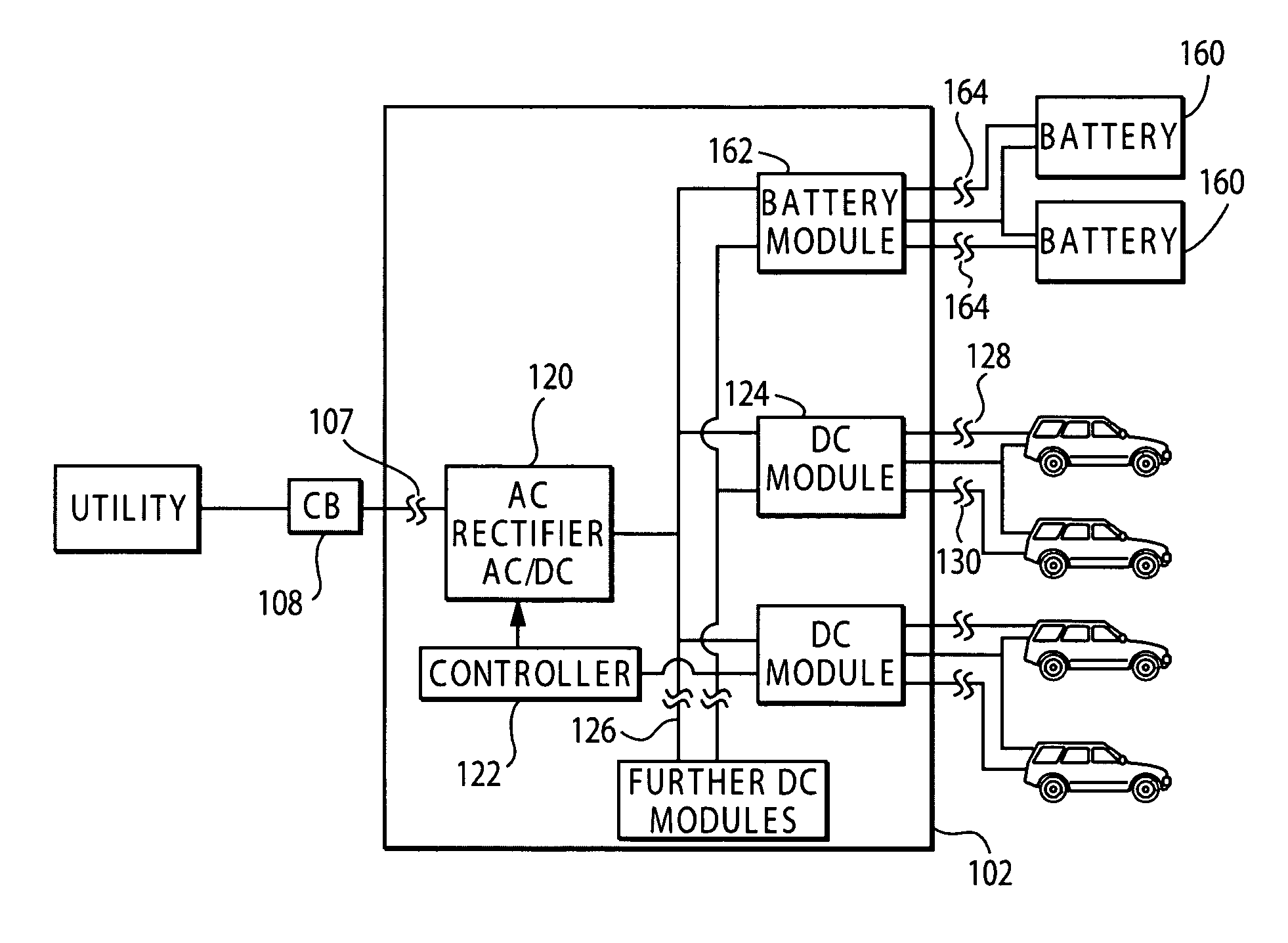
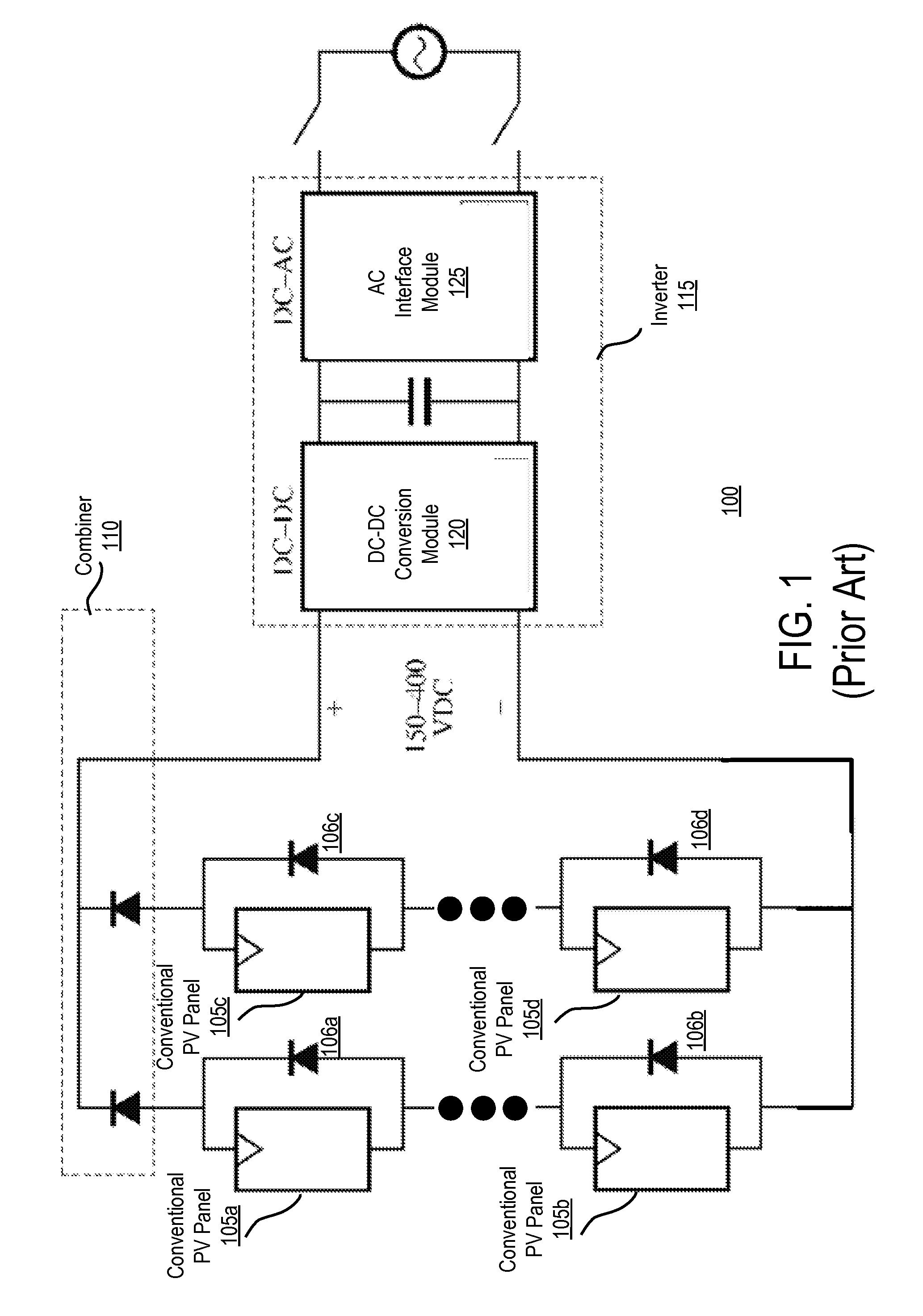
Battery charging system and method
InactiveUS7256516B2Meet system requirementsMeet power requirementsLoad balancing in dc networkDc source parallel operationEngineeringAC power
A charging system for simultaneously charging the batteries of a plurality of battery powered vehicles. The charging includes one or more DC-DC power converters having one or more charging ports configured to plug into the batteries. The DC-DC power converters are each configured to selectively connect to more than one charging port to selectively provide for higher port power levels. The DC-DC power converters connect to an AC rectifier through a DC bus. The AC rectifier connects to an AC power source having a limited power rating. The AC charging system also has a controller that controls the operation of the DC-DC power converters such that the total power draw on the AC rectifier does not exceed the power rating. The system is further configured such that the DC-DC power converters can drain selected batteries to obtain power for charging other batteries, thus allowing for batteries to be cycled.
Owner:WEBASTO CHARGING SYST INC
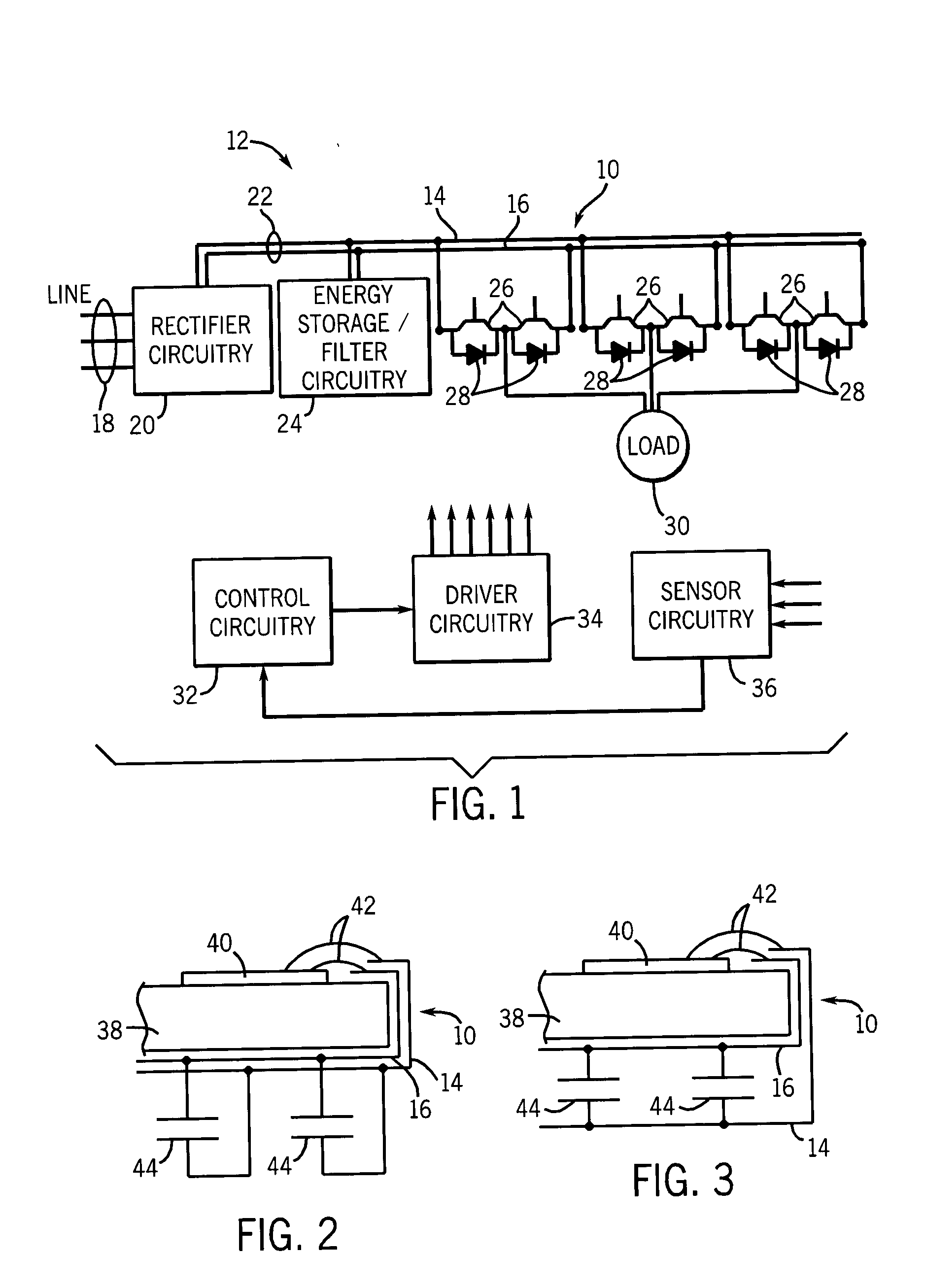
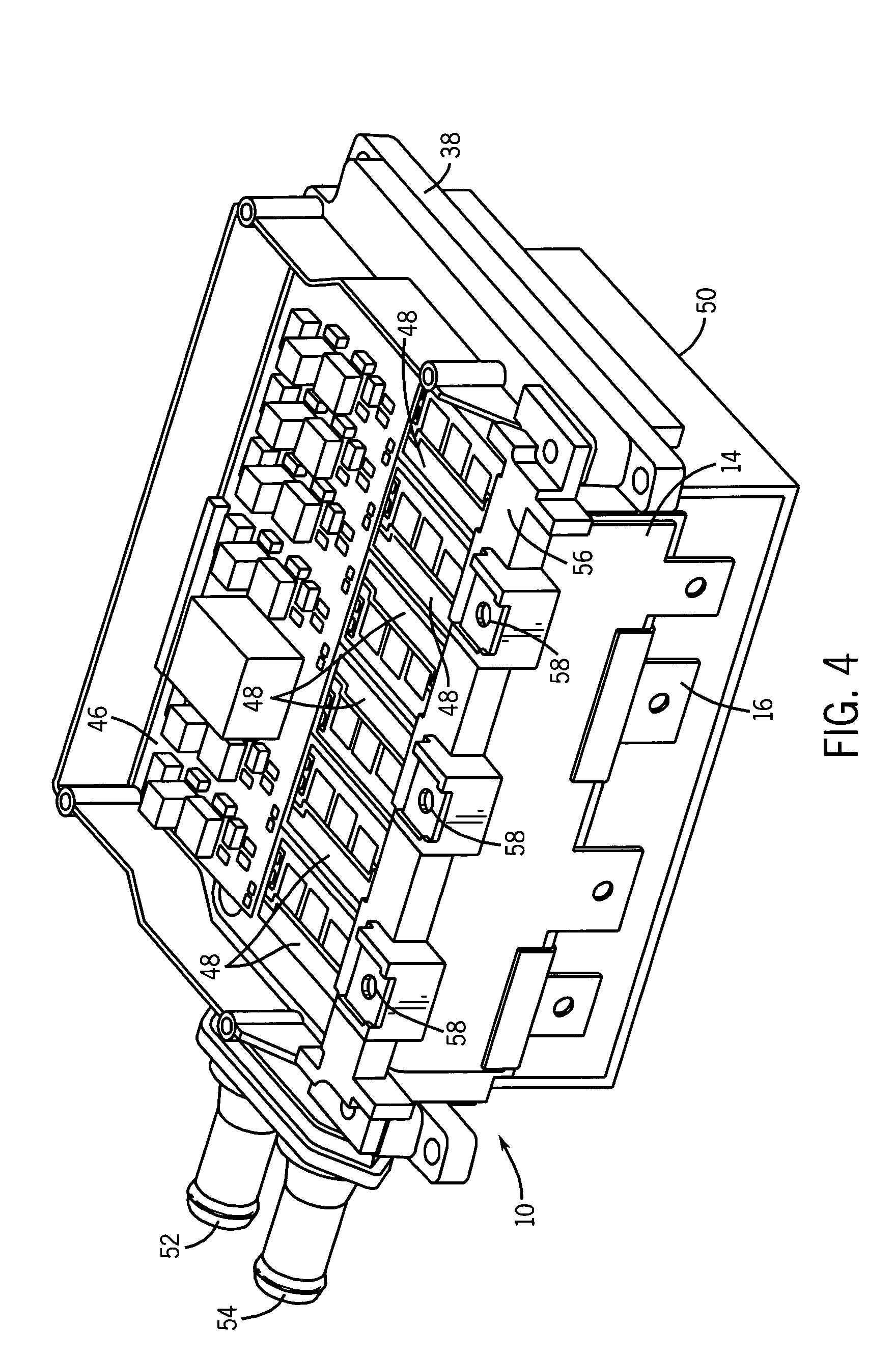
Bus structure for power switching circuits
ActiveUS20050068820A1Easy to optimizeReduction in parasitic conductanceBus-bar/wiring layoutsConversion constructional detailsElectricityPower switching
A bus system is disclosed for use with switching devices, such as power electronic devices. The system includes generally parallel bus elements that define electrical reference planes, such as for a dc bus. The bus elements are separated from one another by insulative layers, with additional insulative layers being available for separating the system from other circuit components. Portions of the bus elements are extended or exposed to permit connection to the circuit elements, including packaged switching circuits and energy storage or filtering circuits. The bus system may be conformed to a variety of geometric configurations, and substantially reduces parasitic inductance and total loop inductance in the resulting circuitry.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH +1
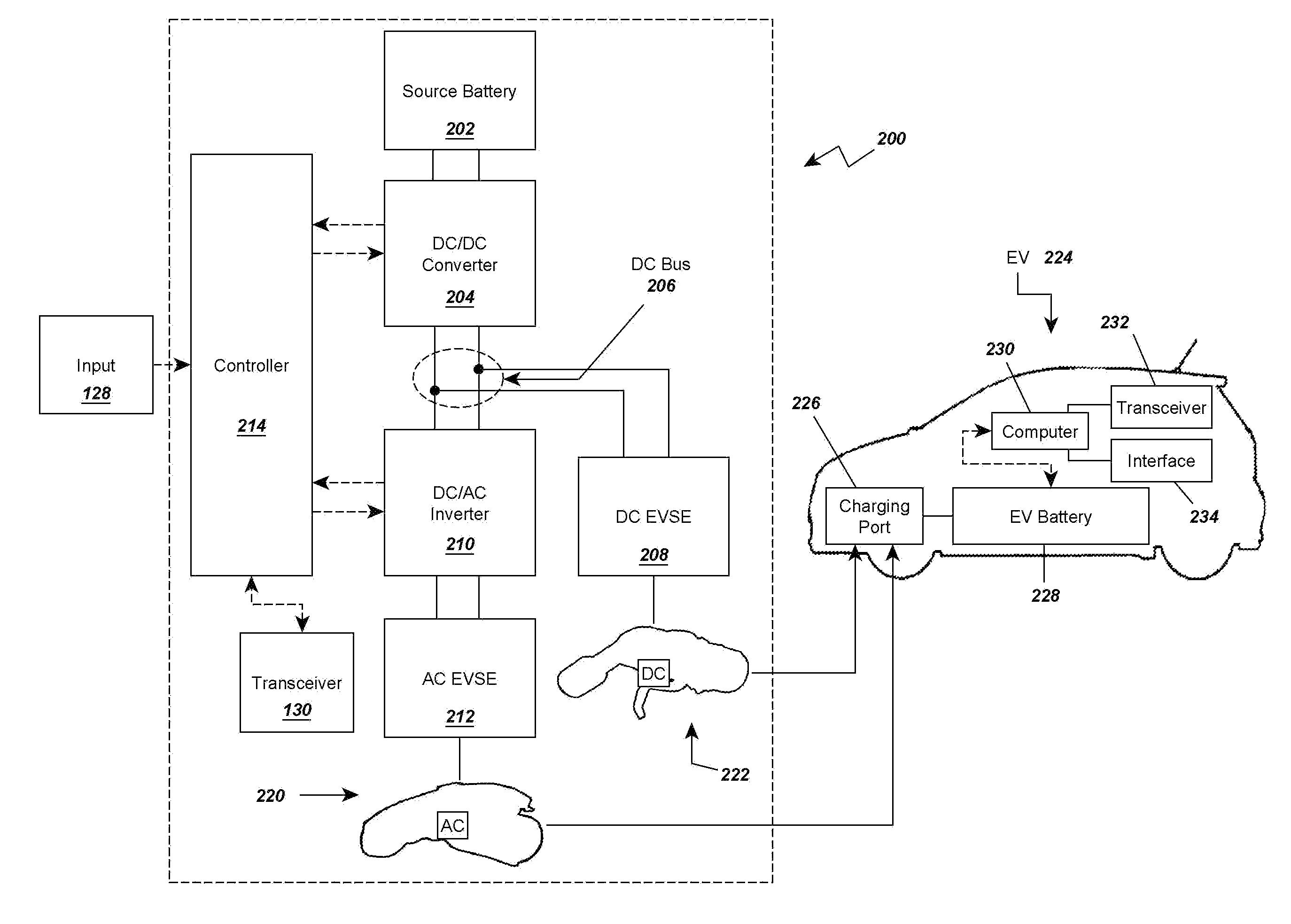
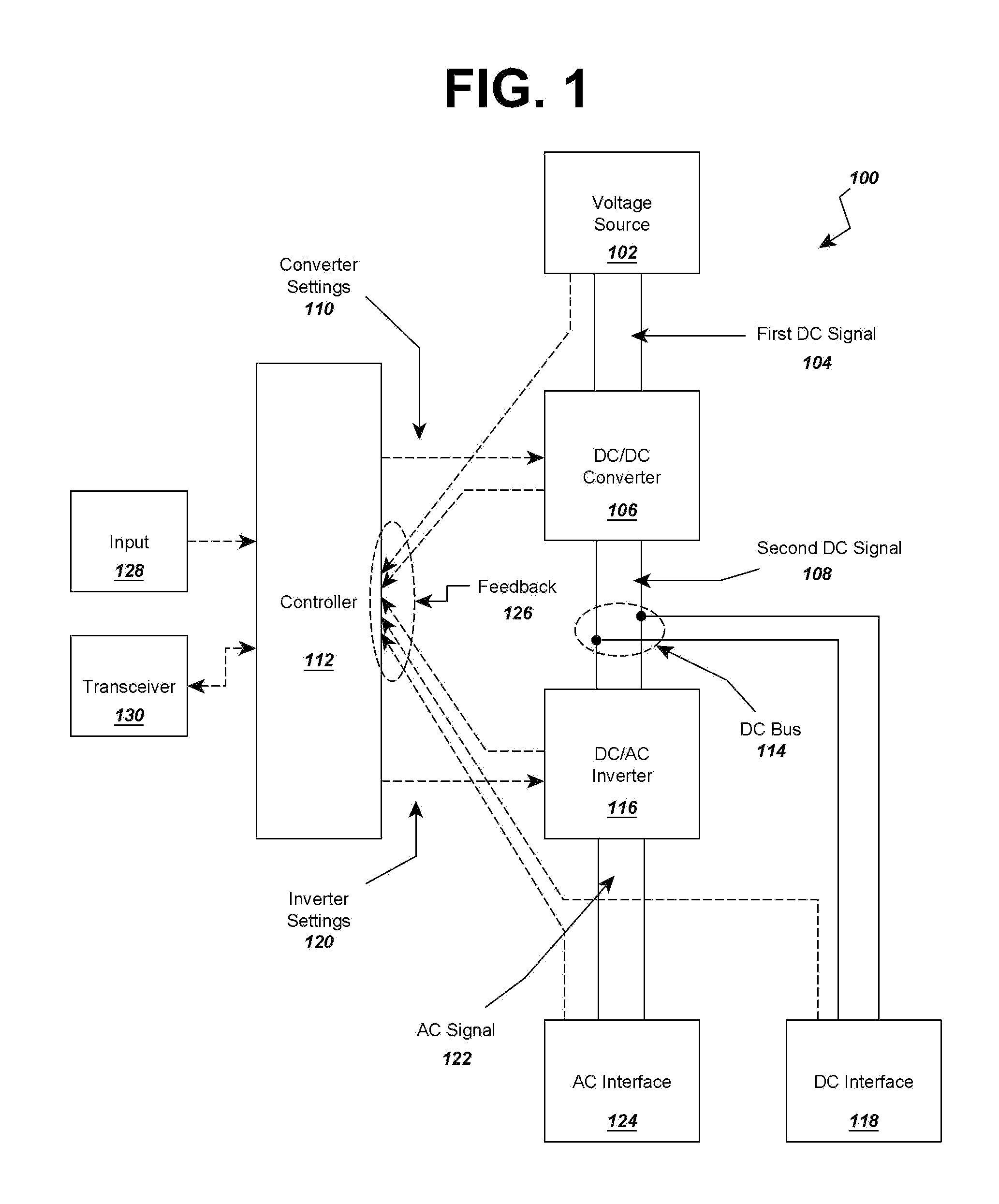
Multi-Mode Electric Vehicle Charging Station
InactiveUS20130020993A1Low costReduce equipment costsCircuit authenticationCharging stationsElectricityReduced size
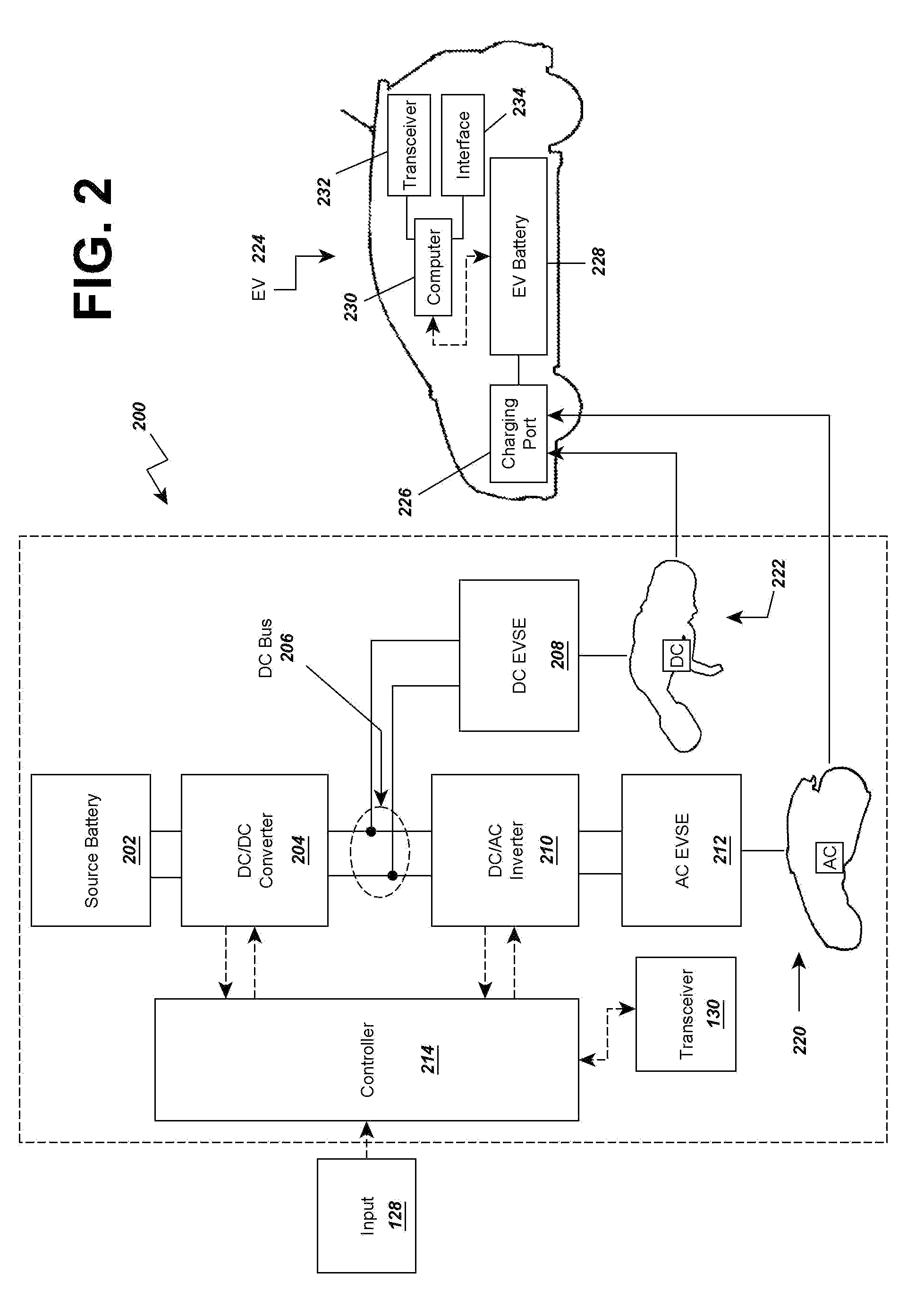
A reduced size and complexity multi-mode electric vehicle charging station is provided which allows a user to select AC and DC powerform output and may provide those outputs to connectors for charging electric vehicles. A voltage source is provided to a DC converter that then outputs to a DC bus or electrical connection. The DC bus may be accessed by DC charging equipment or a DC-AC inverter that is connected to AC charging equipment, thereby providing DC and AC charging ability. In one aspect, the multi-mode electric vehicle charging station is used in a rescue vehicle for charging stranded EVs via multiple charging standards without requiring the rescue vehicle to carry independent charging systems for each charging standard. In another aspect, the charging station is used in a stationary charging station to reduce cost and complexity of using multiple independent charging systems.
Owner:GREEN CHARGE NETWORKS
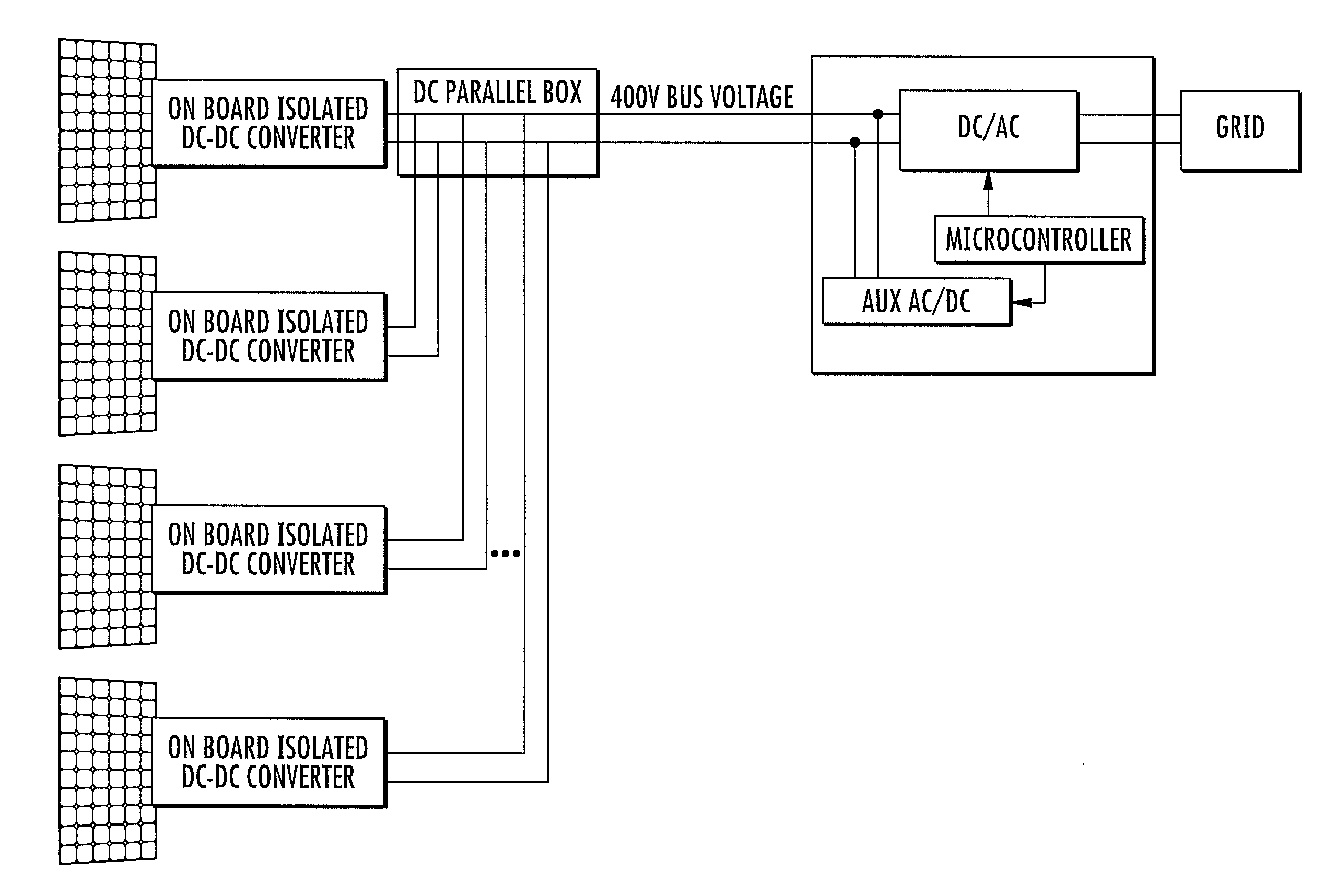
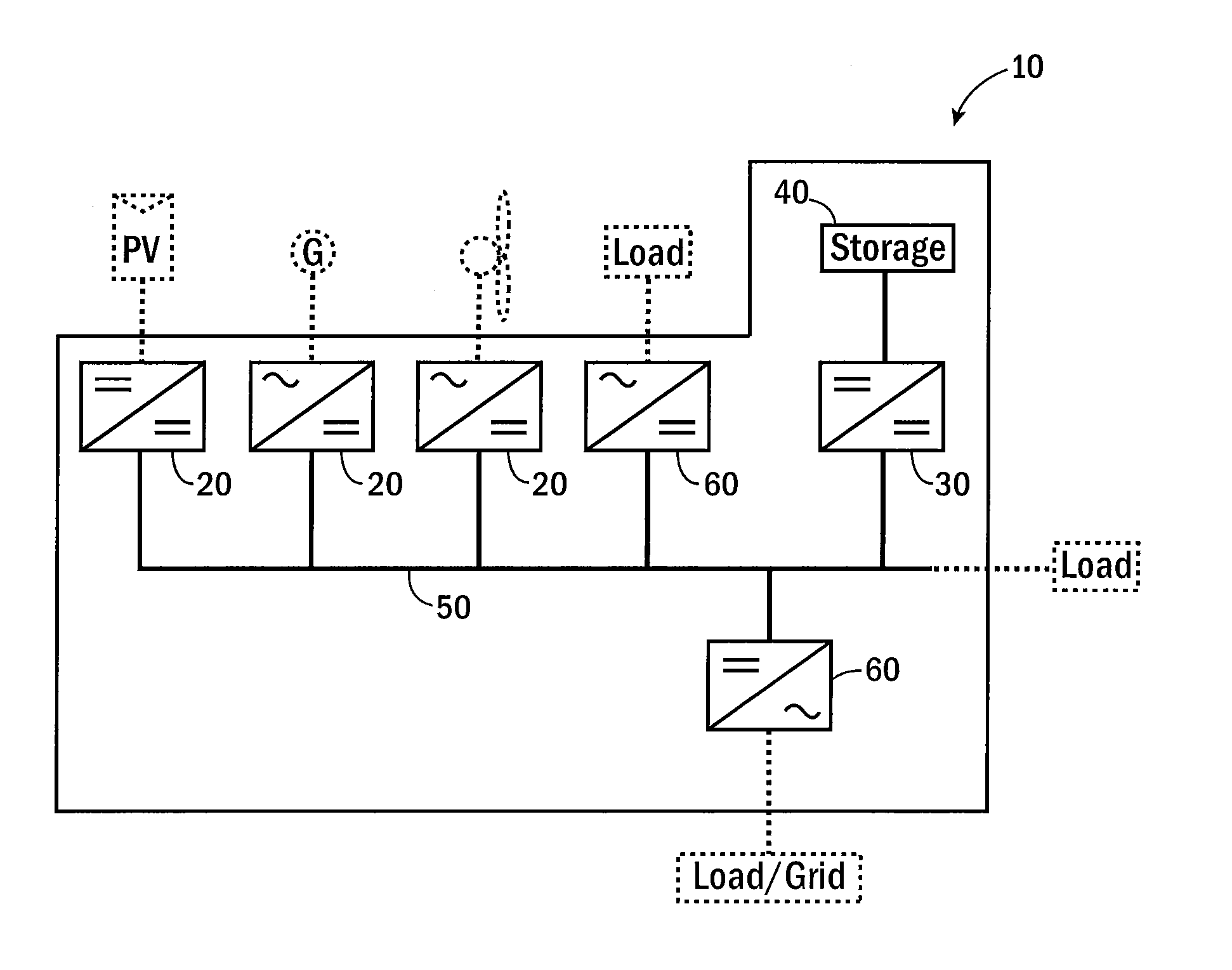
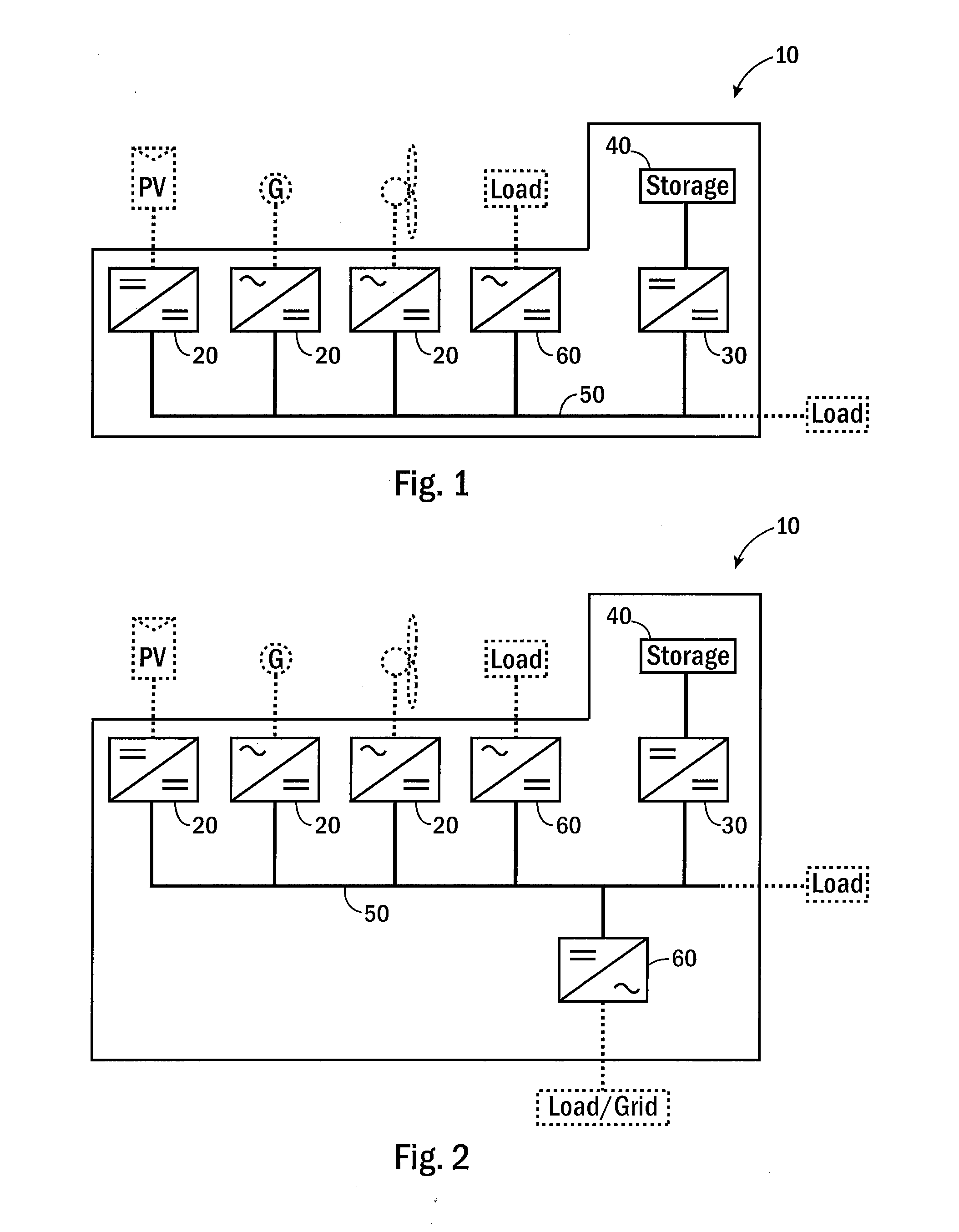
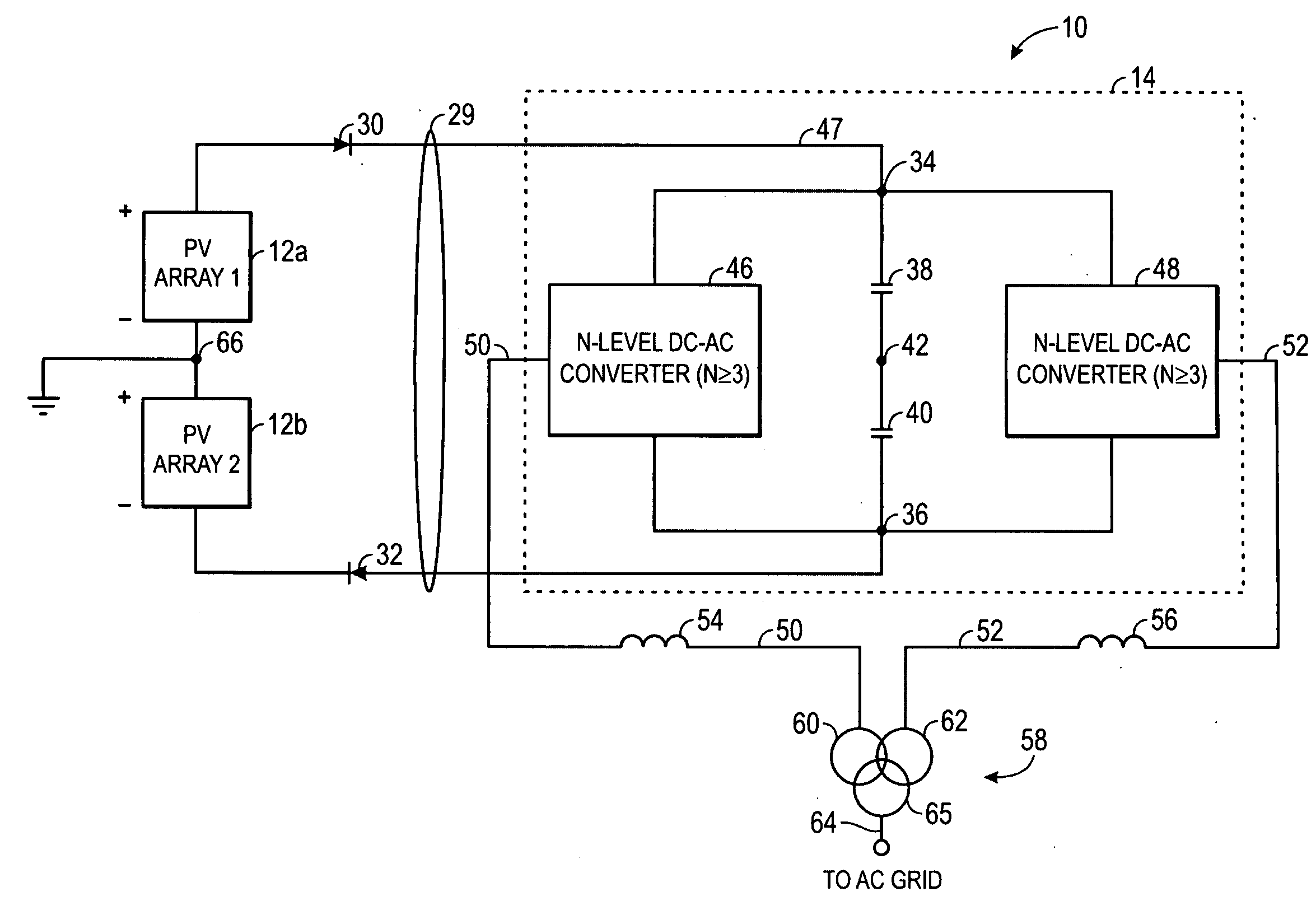
Systems to connect multiple direct current energy sources to an alternating current system
ActiveUS8058747B2Dc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHigh-voltage direct currentEngineering
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
Electrical starting, generation, conversion and distribution system architecture for a more electric vehicle
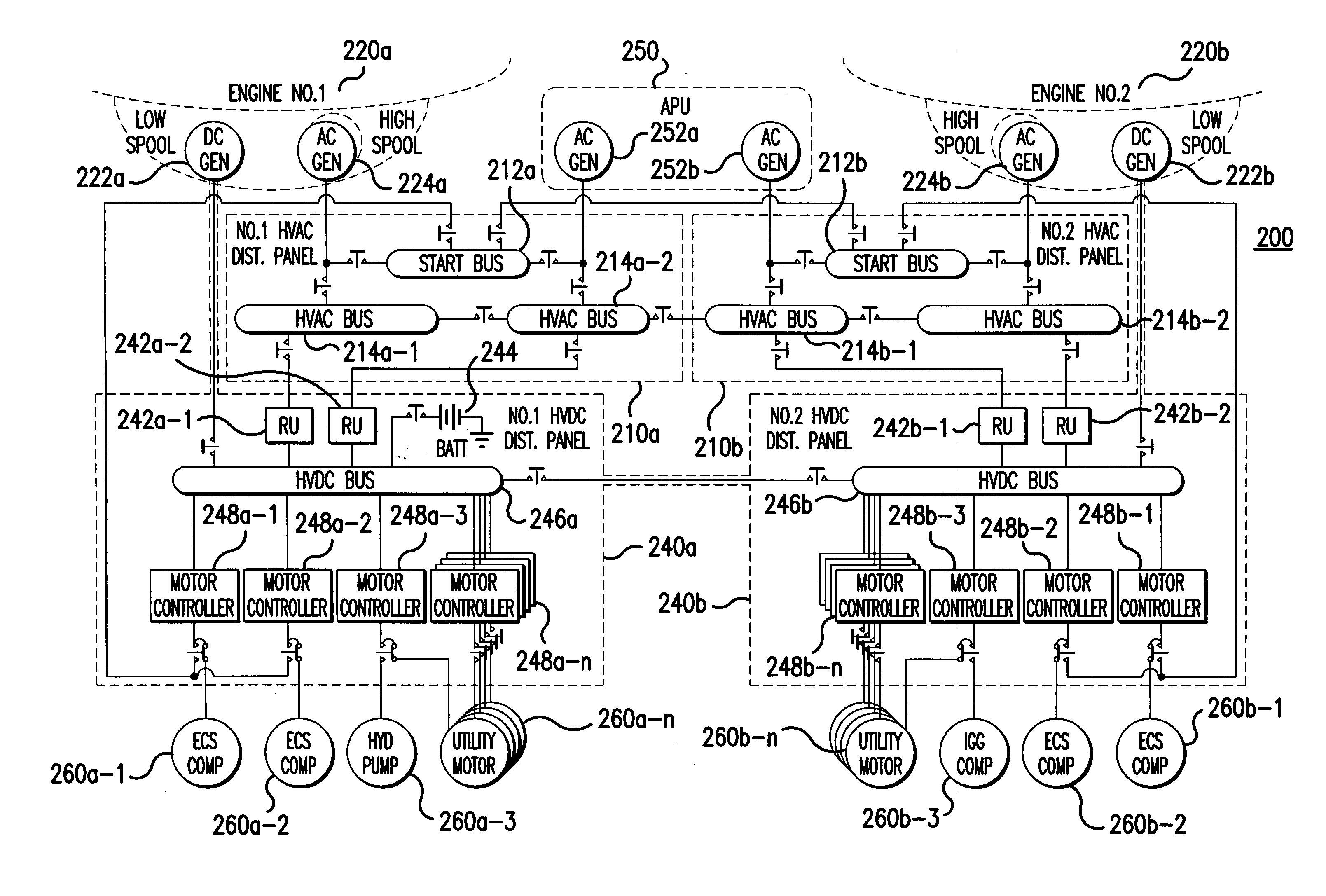
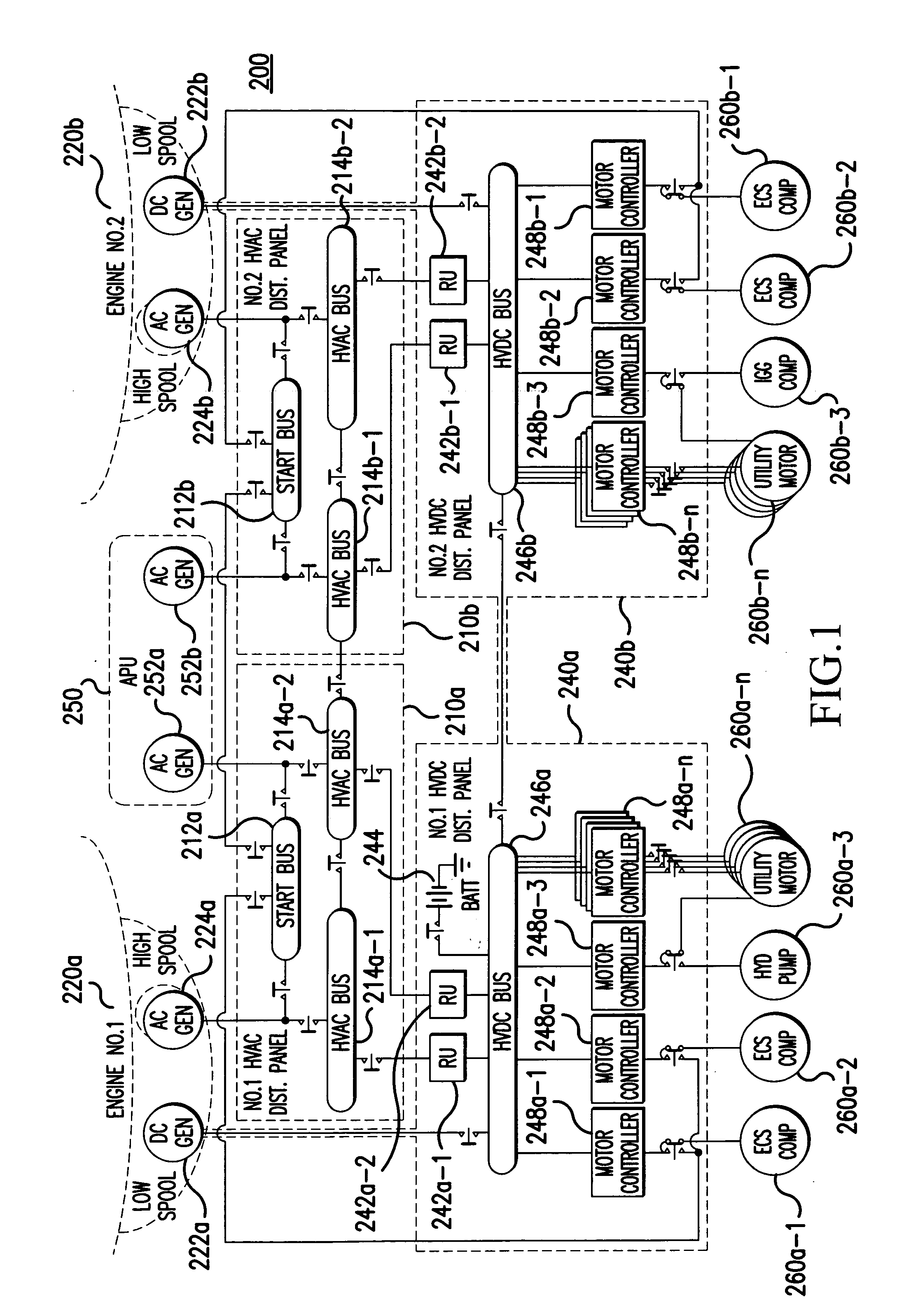
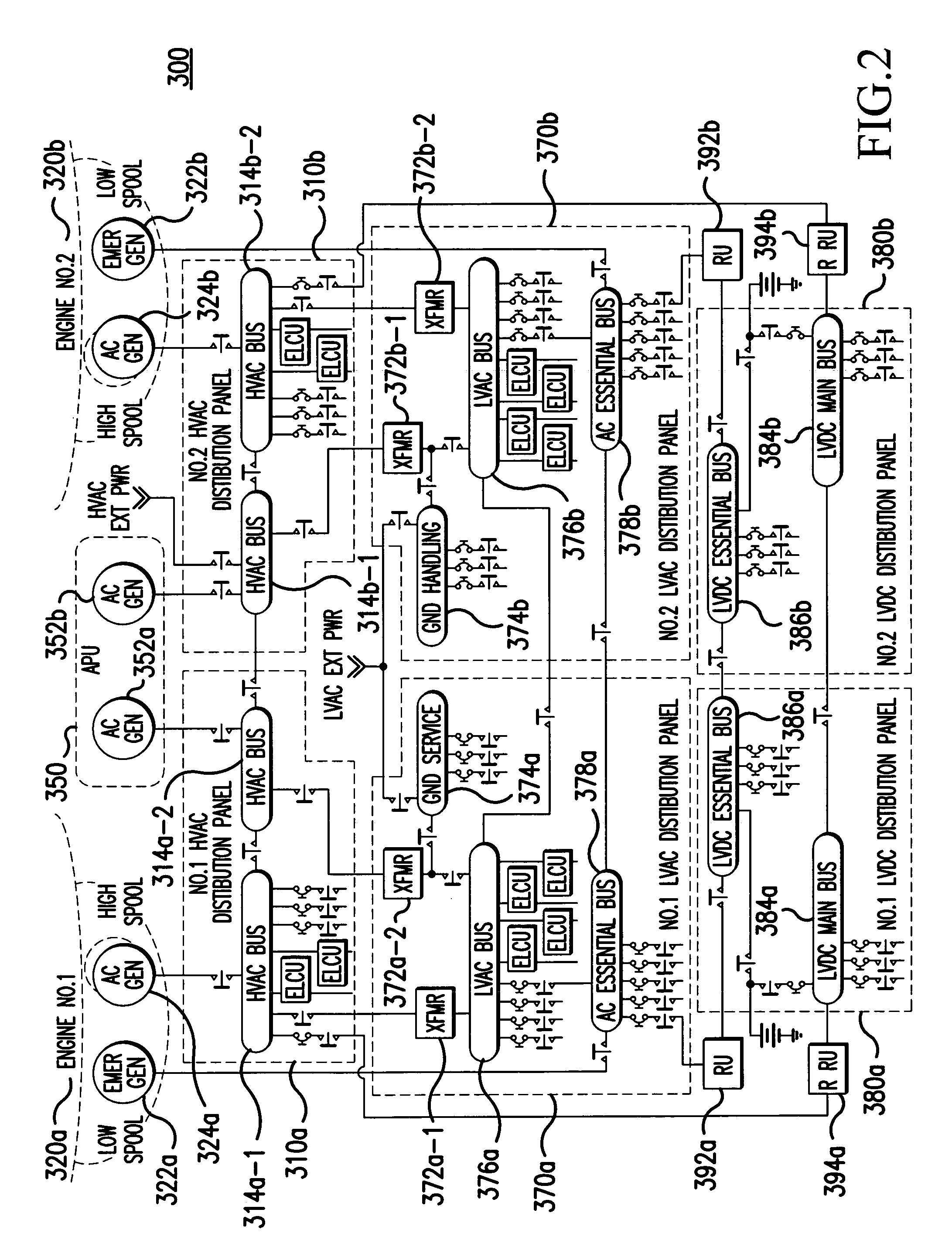
InactiveUS20060061213A1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectric power distributionElectricityDistribution system
A system (200) for distributing electrical power, includes: a first high voltage AC power distributing unit (210a) including a first high voltage AC bus (214a-1, 214a-2), which is selectively connected to a first high voltage AC generator (224a), and a first start bus (212a); a second high voltage AC power distributing unit (210b) including a second high voltage AC bus (214b-1, 214b-2), which is selectively connected to a second high voltage AC generator (224b), and a second start bus (212b); a first high voltage DC power distributing unit (240a) including, a first high voltage DC bus (246a), and a second high voltage DC power distributing unit (240b) including a second high voltage DC bus (246b). The first high voltage AC bus (214a-1, 214a-2) is selectively connectable to the second high voltage AC bus (214b-1, 214b-2), such that the system (200) provides redundancy for high voltage power distribution.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
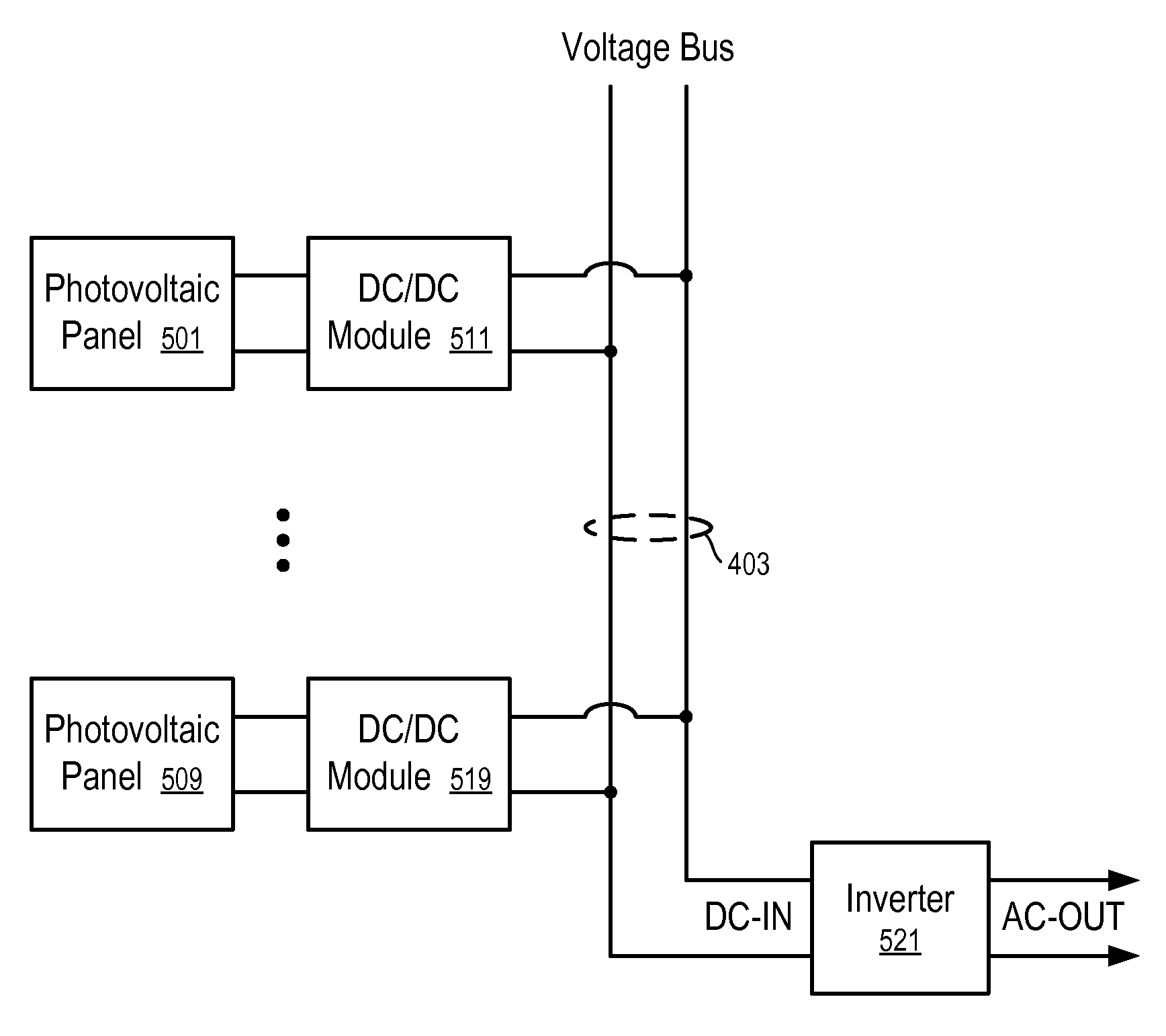
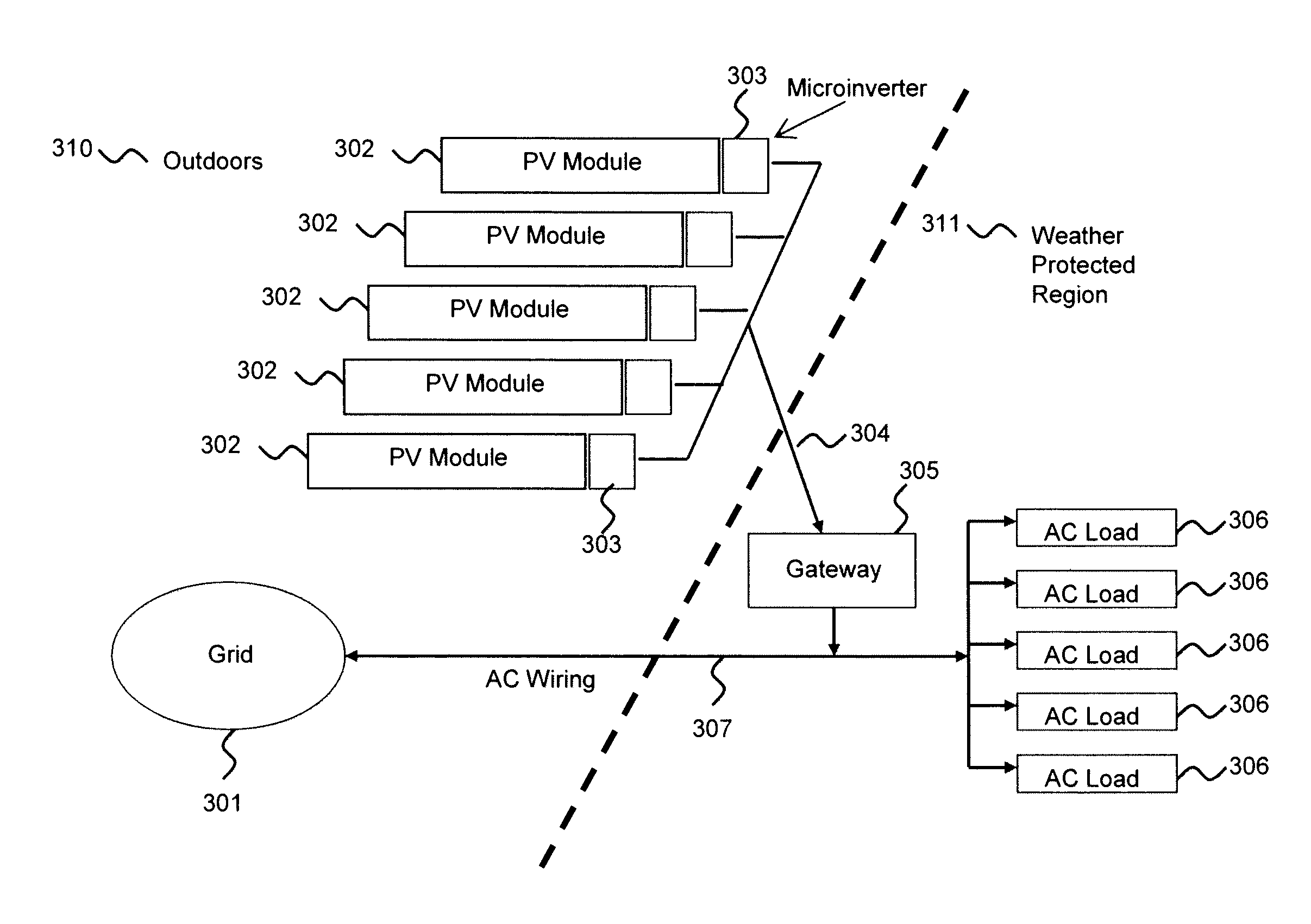
Automatic system for synchronous enablement-disablement of solar photovoltaic panels of an energy production plant with distributed dc/dc conversion
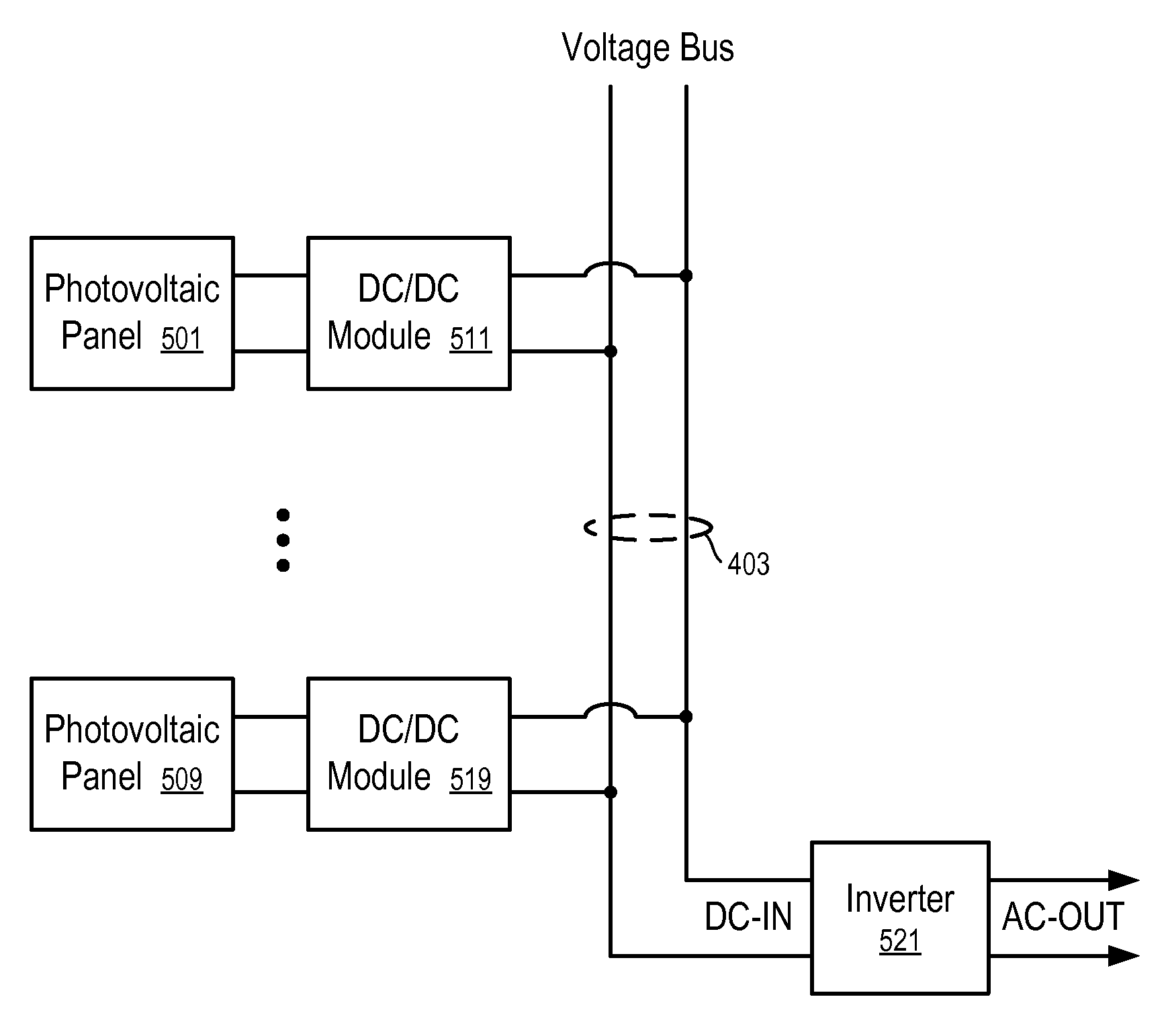
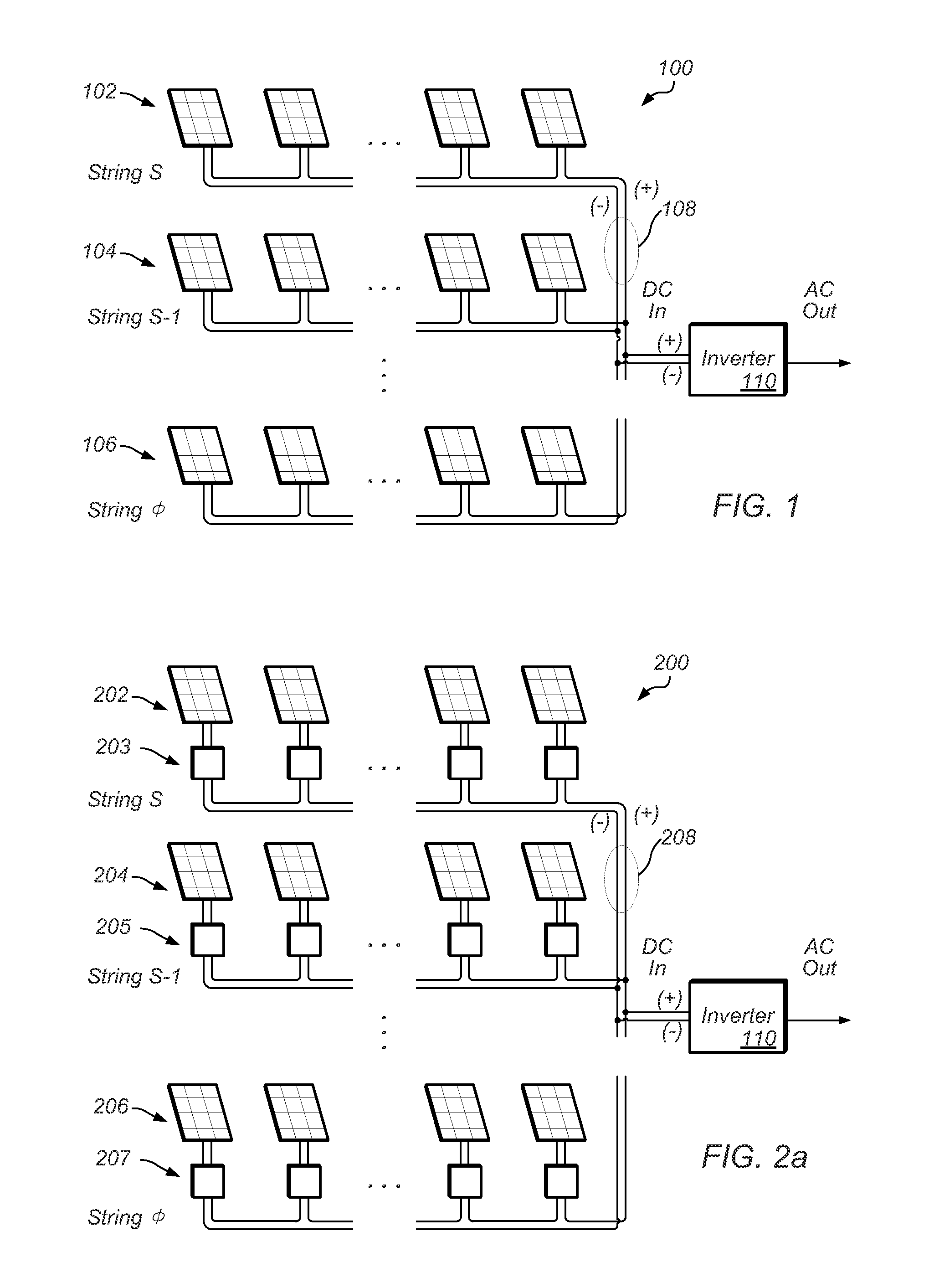
ActiveUS20120091810A1Low costEliminate riskDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsParasitic capacitanceDC-BUS
A solar energy plant may include a DC bus, photovoltaic panels coupled in parallel to the DC bus, each photovoltaic panel having a DC / DC converter, and a first controller controlling the DC / DC converter depending on whether a voltage on the DC bus is equal to or greater than a first threshold and lower than or equal to a second threshold. The solar energy plant may include a DC / AC inverter coupled to the DC bus and outputting an output AC voltage, an auxiliary start-up power supply charging a parasitic capacitance on the DC bus up to the first threshold, and a second controller turning on the auxiliary start-up power supply based upon a start command, and turning off the auxiliary start-up power supply and simultaneously turning on the DC / AC inverter.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
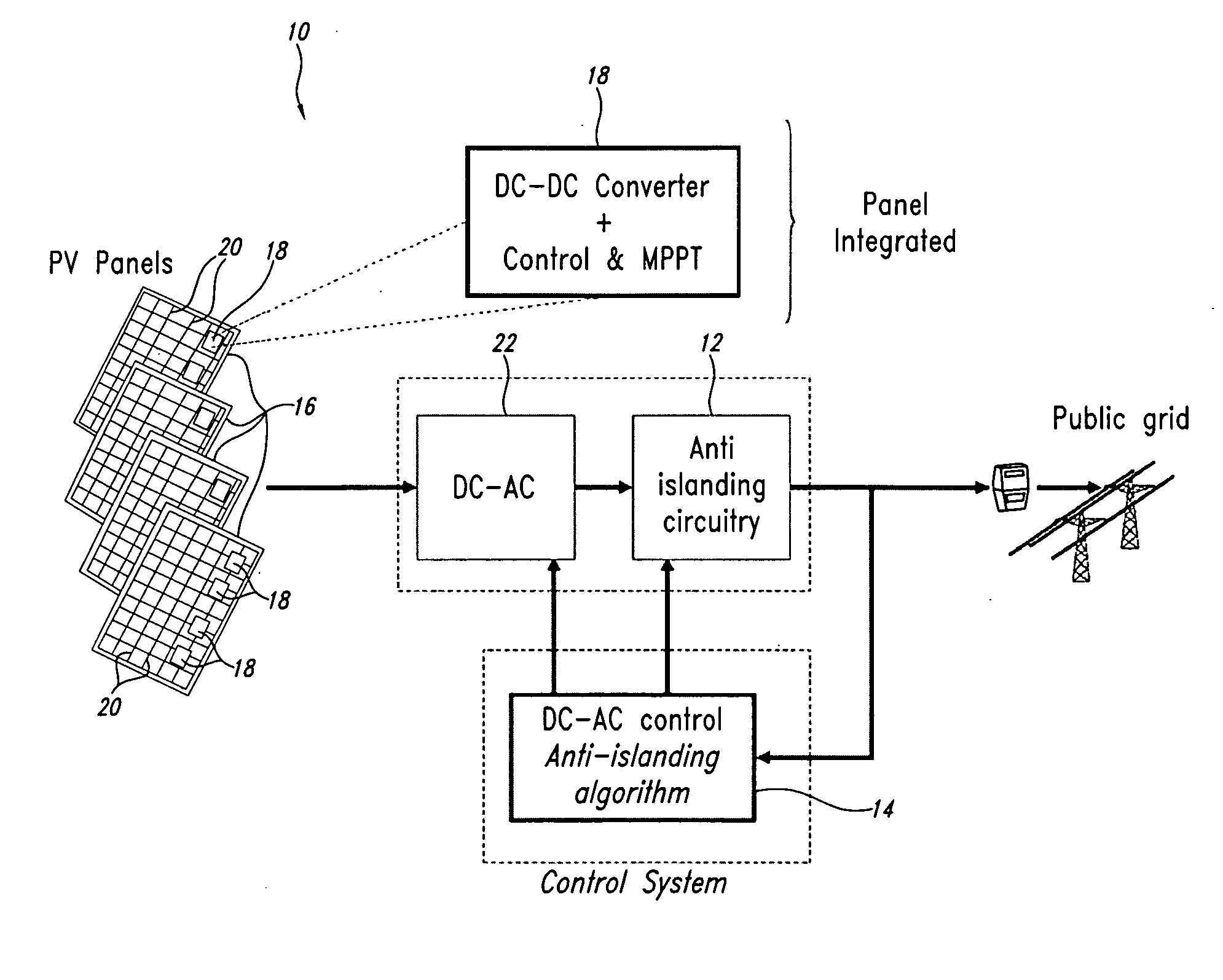
Multi-cellular photovoltaic panel system with dc-dc conversion replicated for groups of cells in series of each panel and photovoltaic panel structure
ActiveUS20090179500A1Improve efficiencySimple processClimate change adaptationDc source parallel operationDc dc converterMppt algorithm
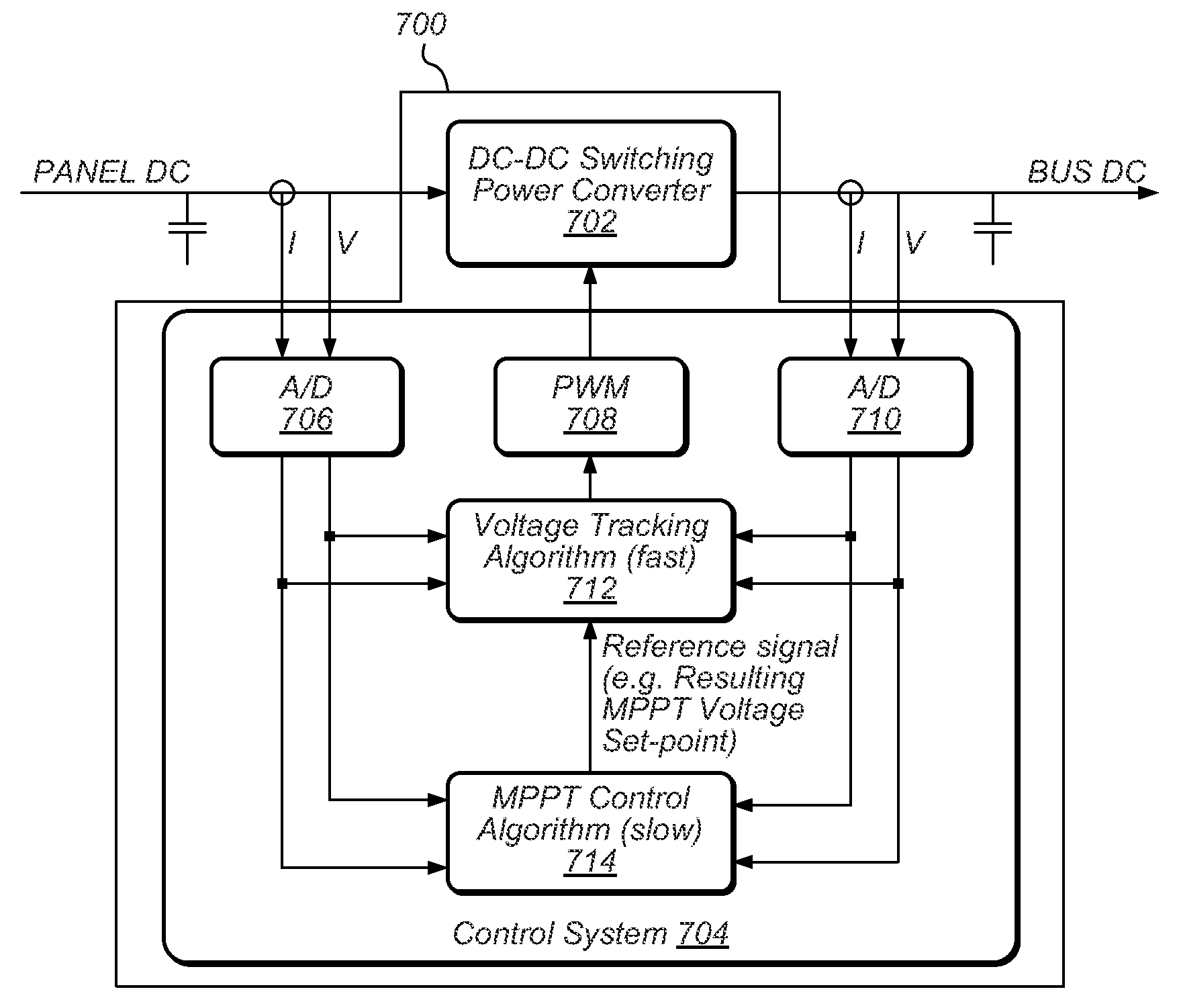
A photovoltaic energy conversion system includes a distributed control structure for groups of cells of each multi-cellular panel, the components of which are entirely physically integrated in the photovoltaic panel. Each multi-cellular photovoltaic panel has a DC bus, supplied in parallel by a plurality of DC-DC converters, each provided with a controller that controls the working point of the photovoltaic cells coupled to the input of the DC-DC converter for a maximum yield of electric power by implementing a relatively simple MPPT algorithm. The controller includes a logic circuit and A / D converters of analog signals representing the input voltage and the input current generated by the group of cells that is coupled to the input of the DC-DC converter and optionally also of the output voltage of the converter, and a relatively simple D / A converter of the drive control signal of the power switch of the DC-DC converter.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Systems to Connect Multiple Direct Current Energy Sources to an Alternating Current System
ActiveUS20100026097A1High voltage outputLower breakdown voltageDc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHigh-voltage direct currentComputer module
High voltage direct current systems to connect direct current energy sources to an alternating current system. In one aspect, a system includes a plurality of direct current modules having variable direct current inputs; an inverter; and a direct current bus to connect the direct current modules to the inverter, where the bus is configured to operate at a nominal voltage higher than 100 volts and to operate within 10 percent of the nominal operating voltage.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
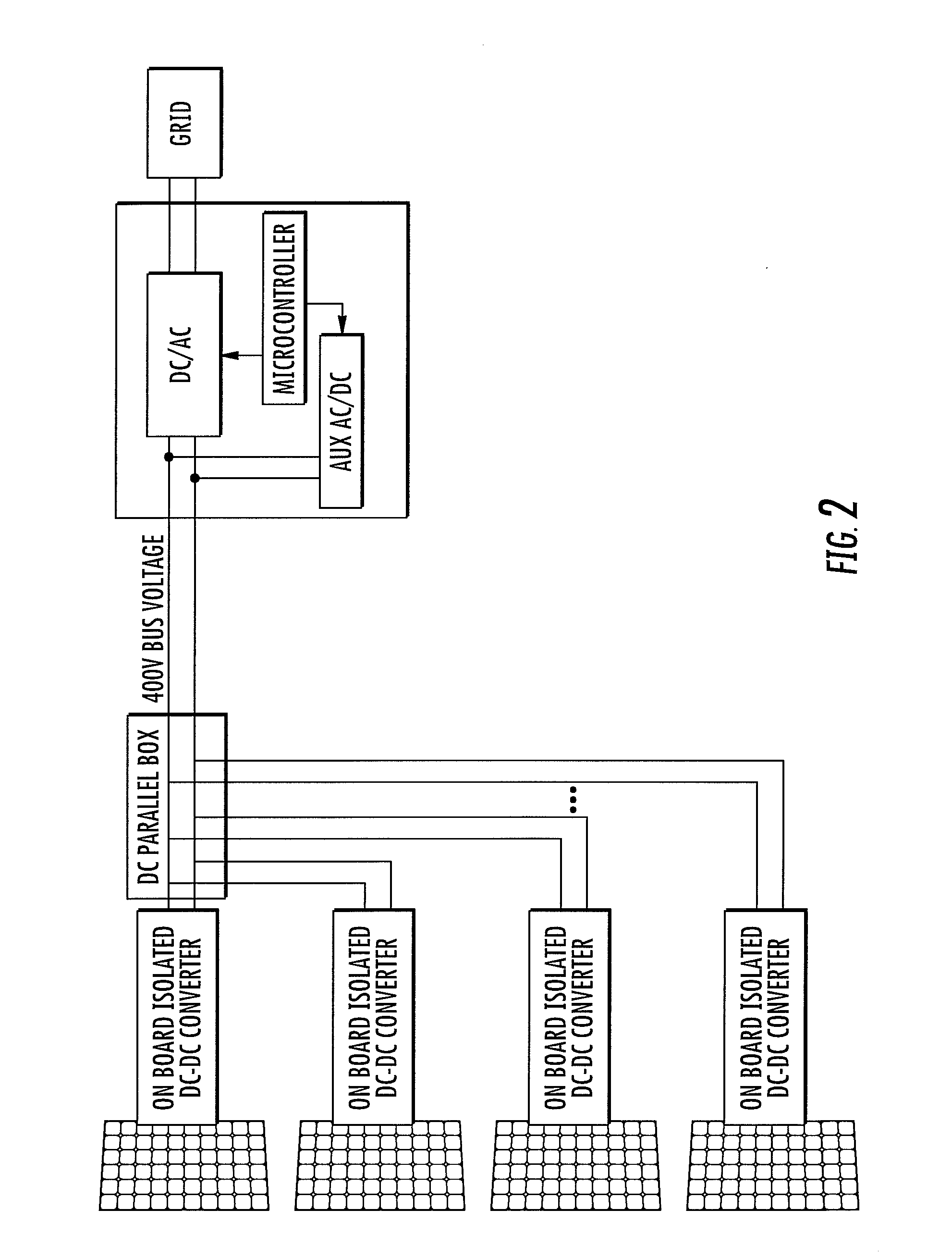
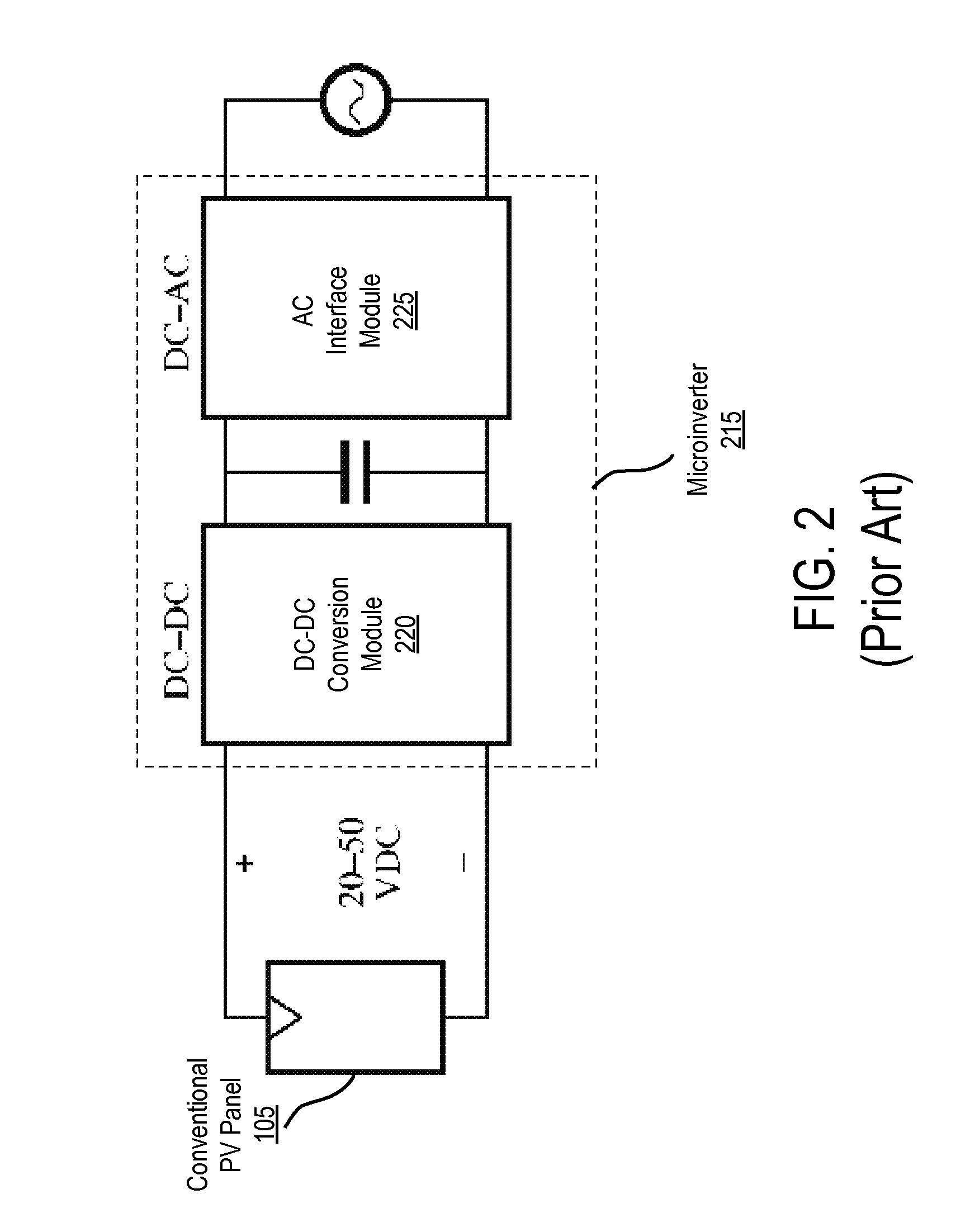
Distributed inverter and intelligent gateway
ActiveUS8581441B2Improve reliabilityLong lastingBatteries circuit arrangementsPower distribution line transmissionPower inverterComputer module
A system and apparatus for generating power. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises a power module for coupling to a DC power source via a DC bus, wherein the power module (i) converts a first power from the DC power source to a second power, and (ii) comprises a maximum power point tracking module unit for dynamically adjusting a load voltage of the DC power source; an AC bus; and a controller, physically separate from the power module and coupled to the power module via the AC bus, for operatively controlling the power module.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
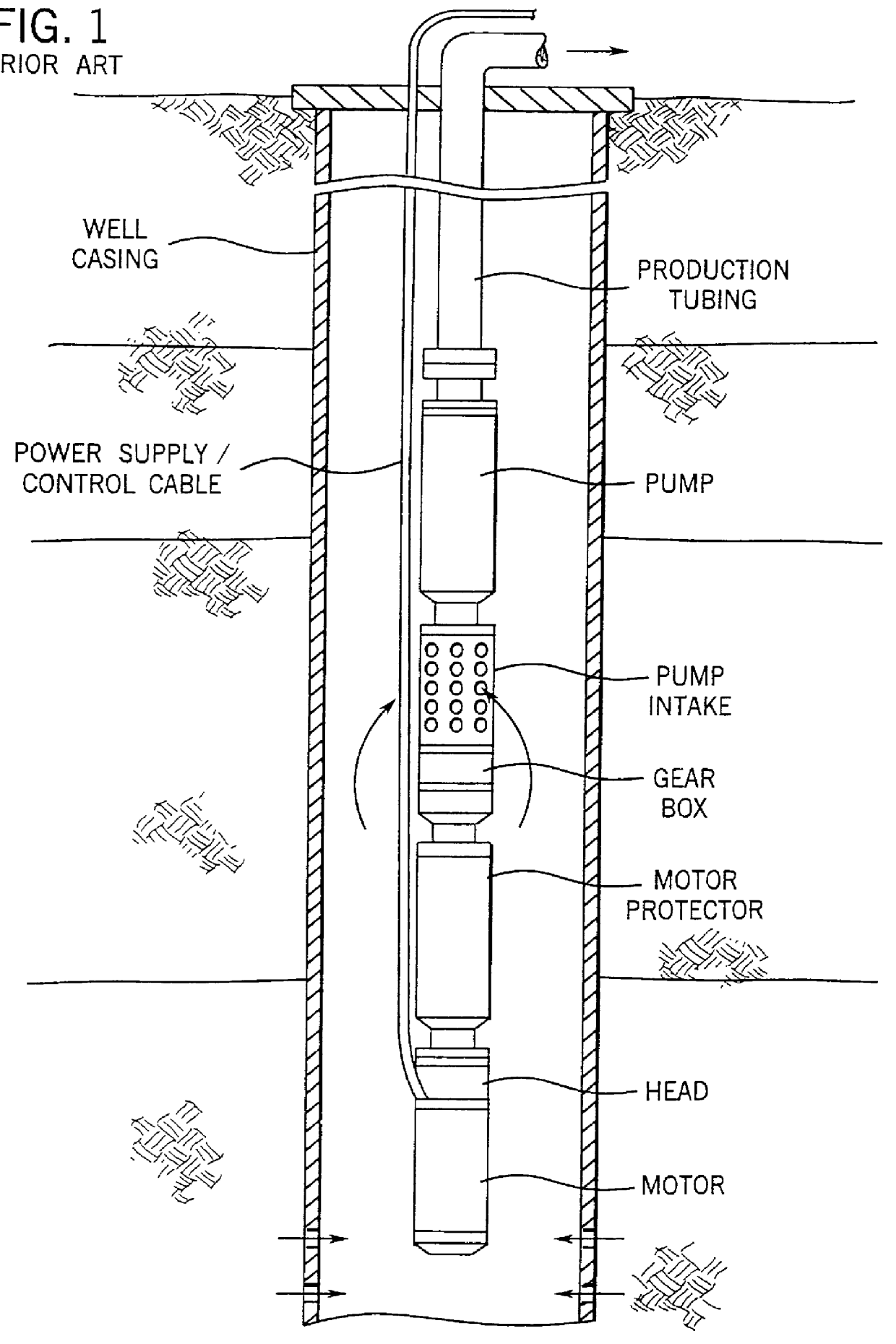
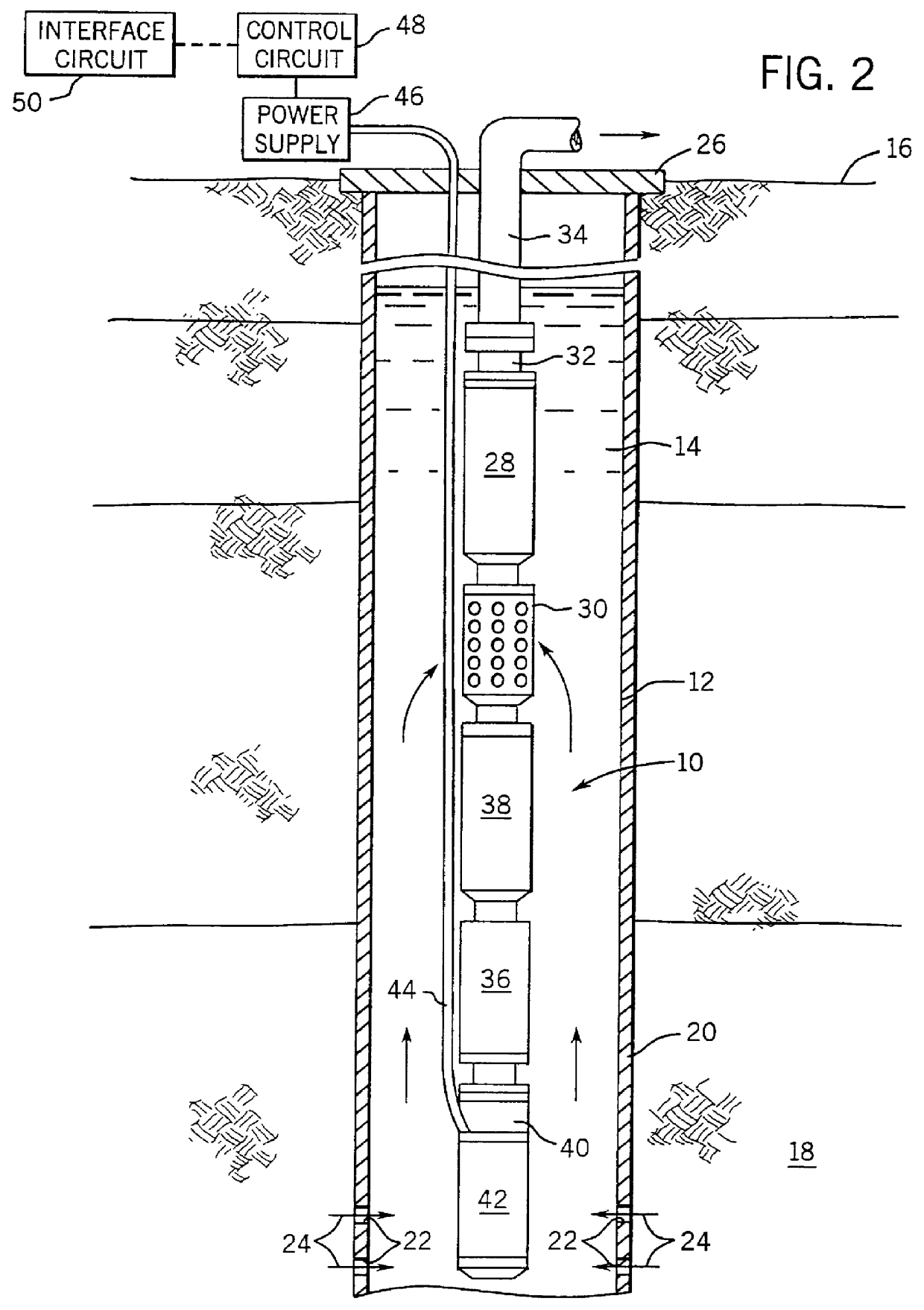
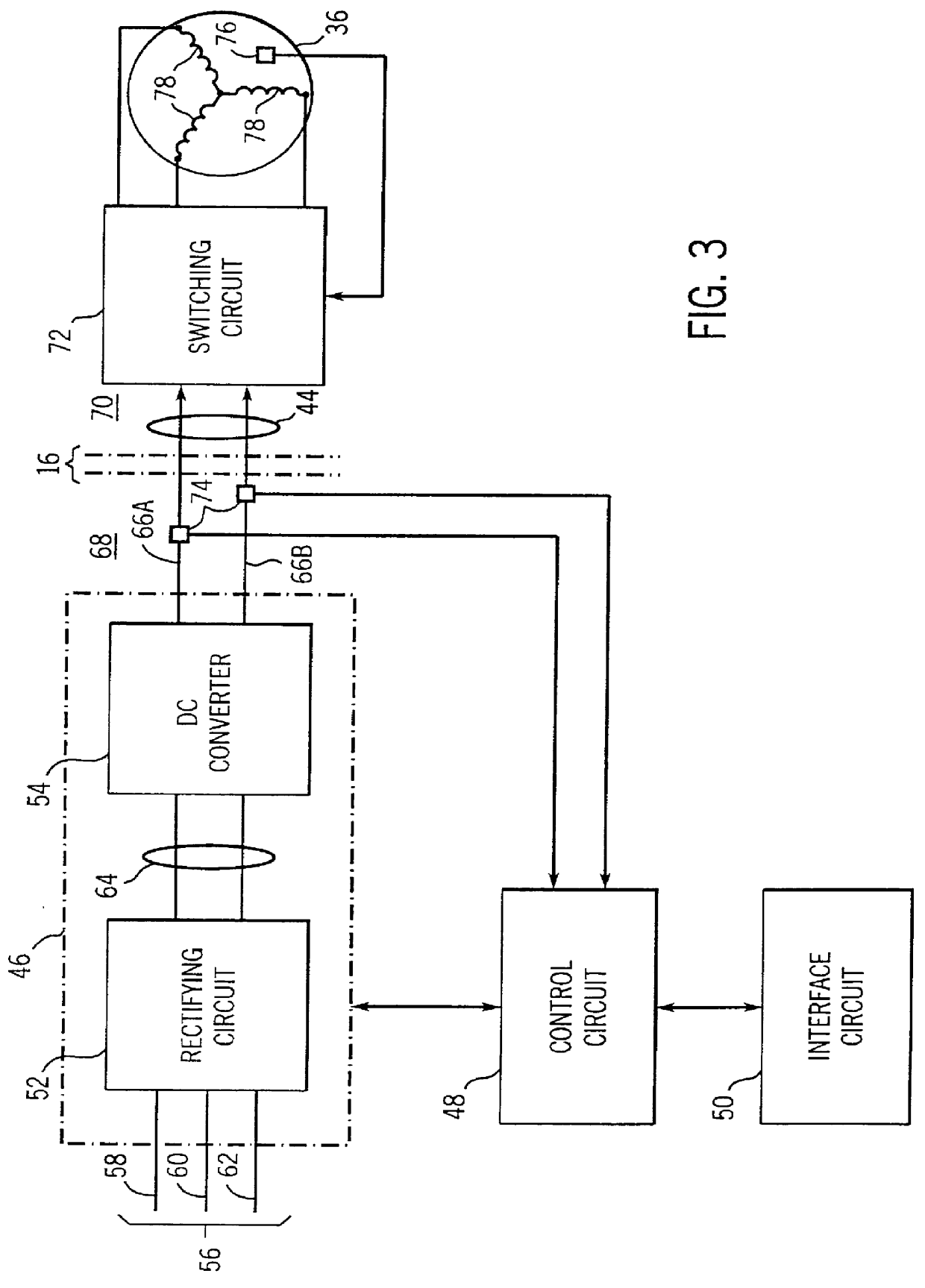
Method and apparatus for controlling a submergible pumping system
A submergible pumping unit for raising viscous fluids from a well is driven by an electronic drive and control system, a first portion of which is located above the well, and a second portion of which is coupled to the submergible pumping unit. The drive and control system includes a power supply circuit located above the well for converting AC power from a source to DC power having current and voltage levels. The DC power is transmitted to the pumping unit via a two-conductor DC bus cable. The pumping unit includes a switching circuit which receives the DC power for driving a submergible motor, such as a permanent magnet brushless motor. The speed of the motor, and of a pump coupled thereto, is proportional to the voltage of the DC power applied to the pumping unit. The pump is preferably a progressive cavity pump, and the drive and control circuitry provides sufficient torque to start the pump from a static condition. A control circuit is provided for transmitting configuration and desired flow rate and speed data to the power supply.
Owner:CAMCO INT
Method and Apparatus for Controlling a Hybrid Power System
ActiveUS20110273022A1Simple power controlSimple methodBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy industryPower inverterDC-BUS
The present invention provides a simplified method of controlling power among the various sources and loads in a power system. Power generating sources are each connected to a common DC bus through a converter. The converter selectively transfers energy to the DC bus at a maximum rate or at a reduced rate according to the level of the DC voltage present on the DC bus. At least one storage device is preferably connected to the common DC bus through a power regulator. The power regulator selectively transfers energy to or from the DC bus as a function of DC voltage level present on the DC bus. Further, an inverter may be provided to bidirectionally convert between the DC voltage and an AC voltage for connection to a customer load or the utility grid. Each power conversion device is independently controlled to provide a modular and simplified power control system.
Owner:FAITH TECH INC
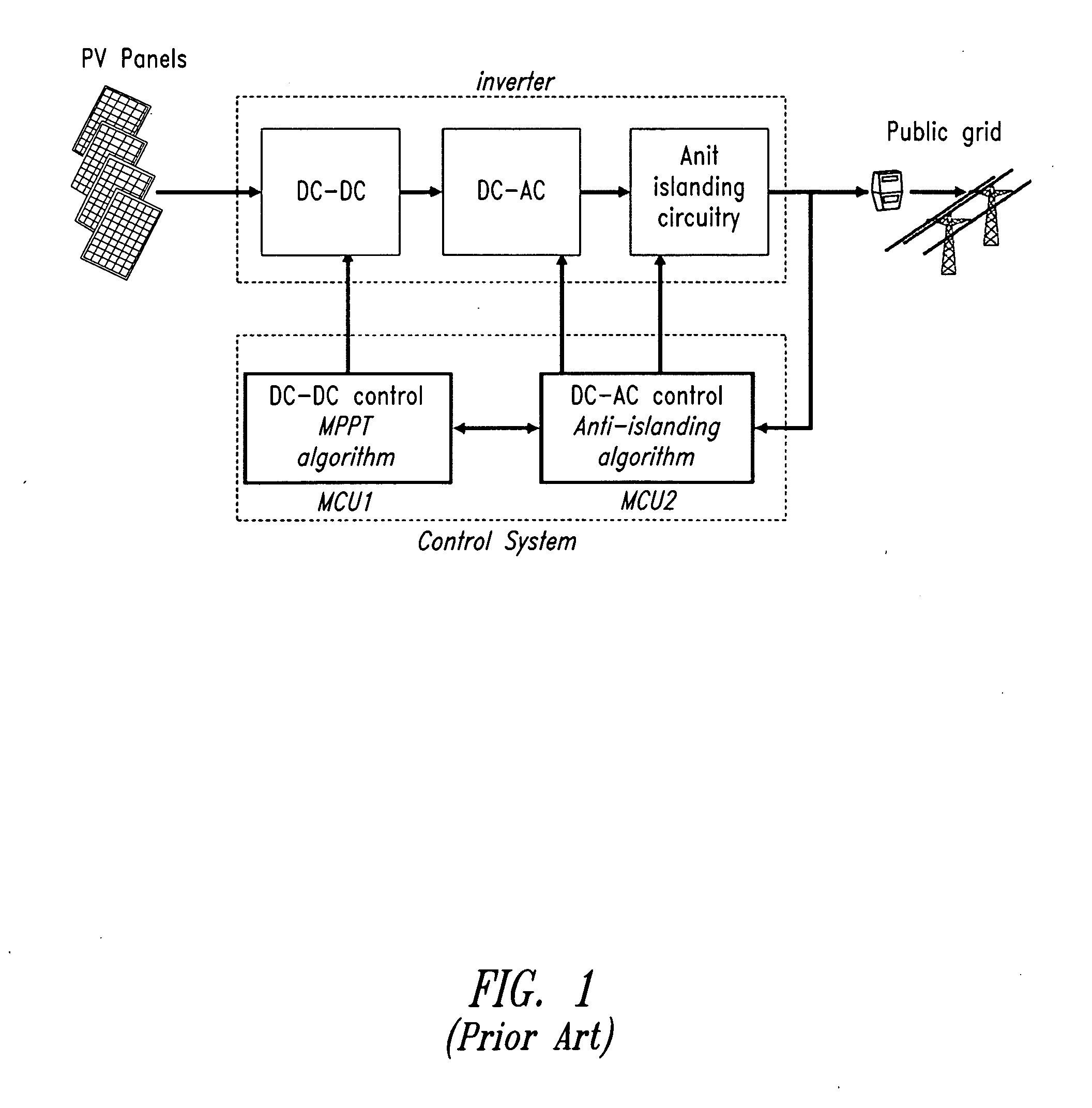
Dc-to-ac power conversion system and method
ActiveUS20100141041A1Dc network circuit arrangementsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionLevel converterAC power
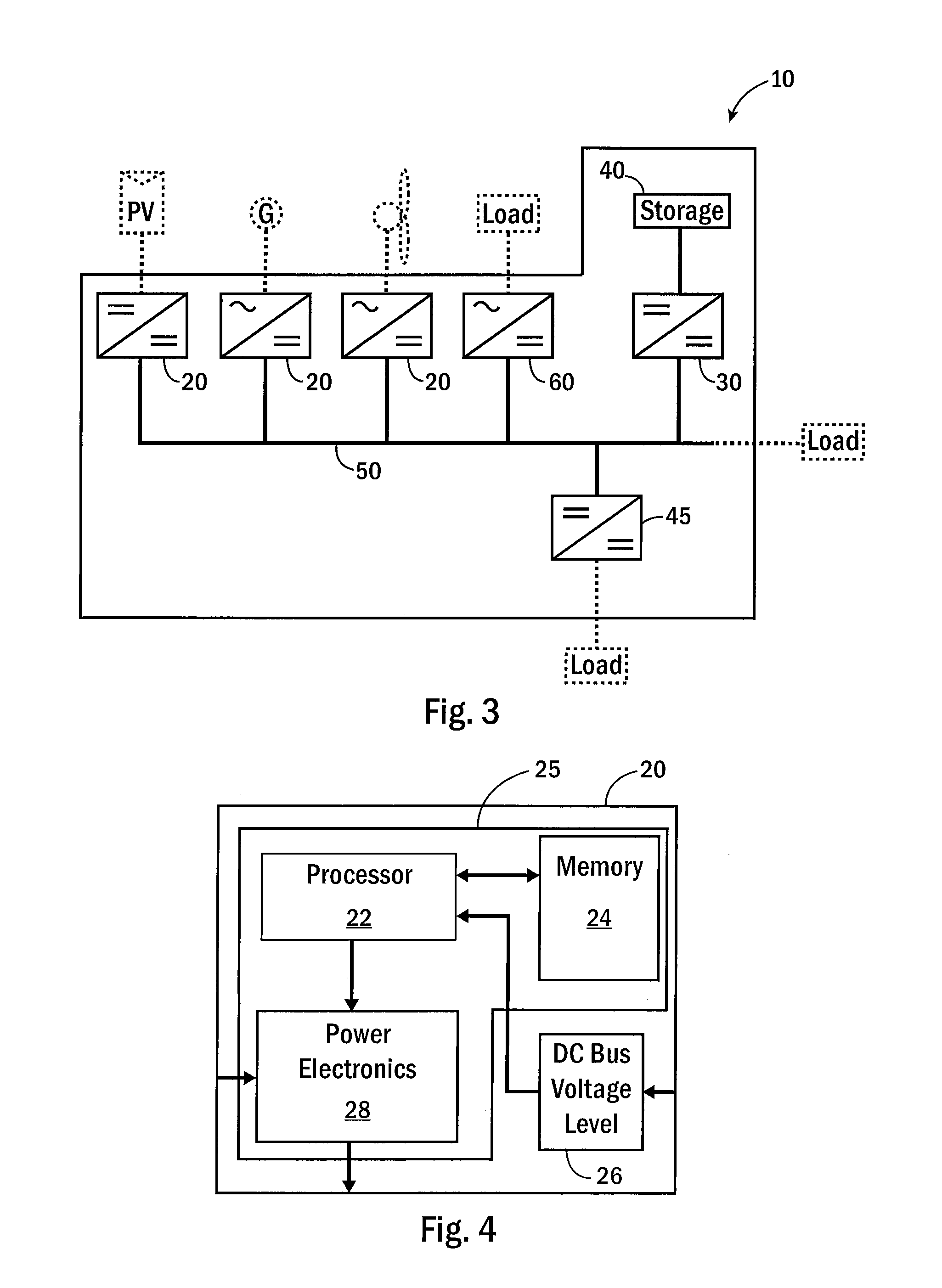
A system, in one embodiment, includes a photovoltaic power converter. The photovoltaic power converter includes one or more photovoltaic arrays configured convert solar energy into a DC signal and two or more N-level converters coupled to a common DC bus (N being an integer greater than 2).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
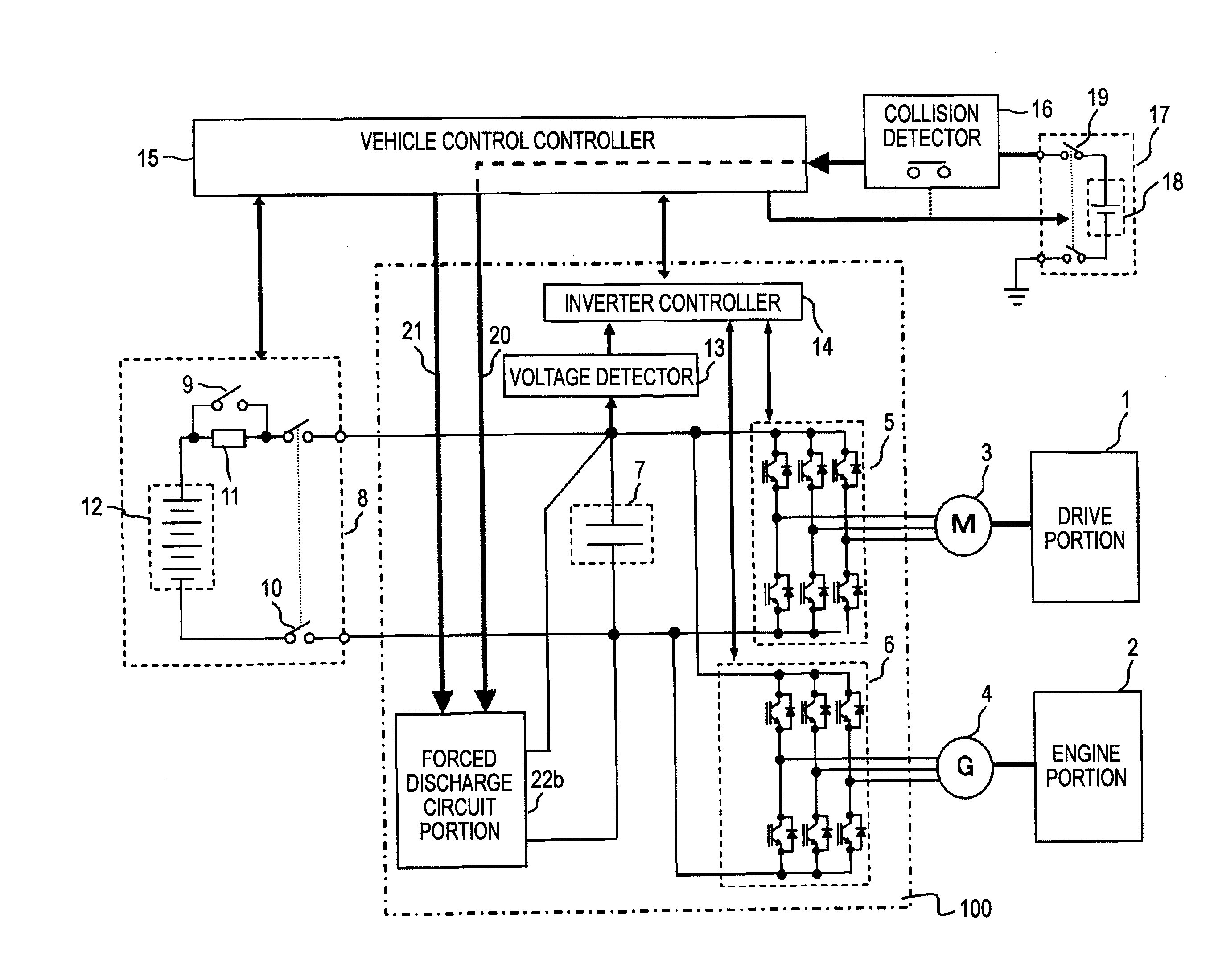
Electric vehicle inverter apparatus and protection method therefor
InactiveUS20100214055A1Improve design flexibilityIncrease flexibilityBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesElectrical batteryHigh voltage battery
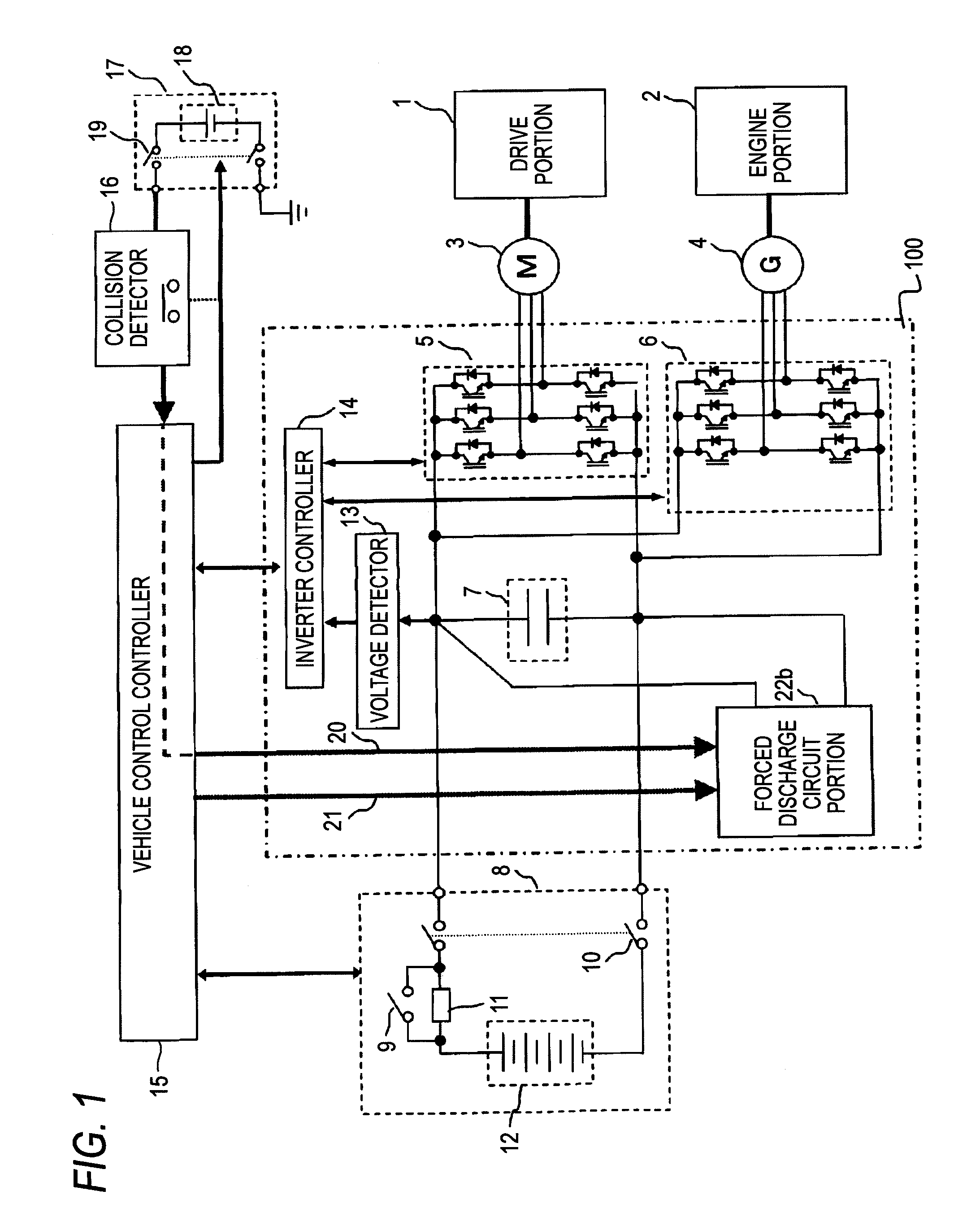
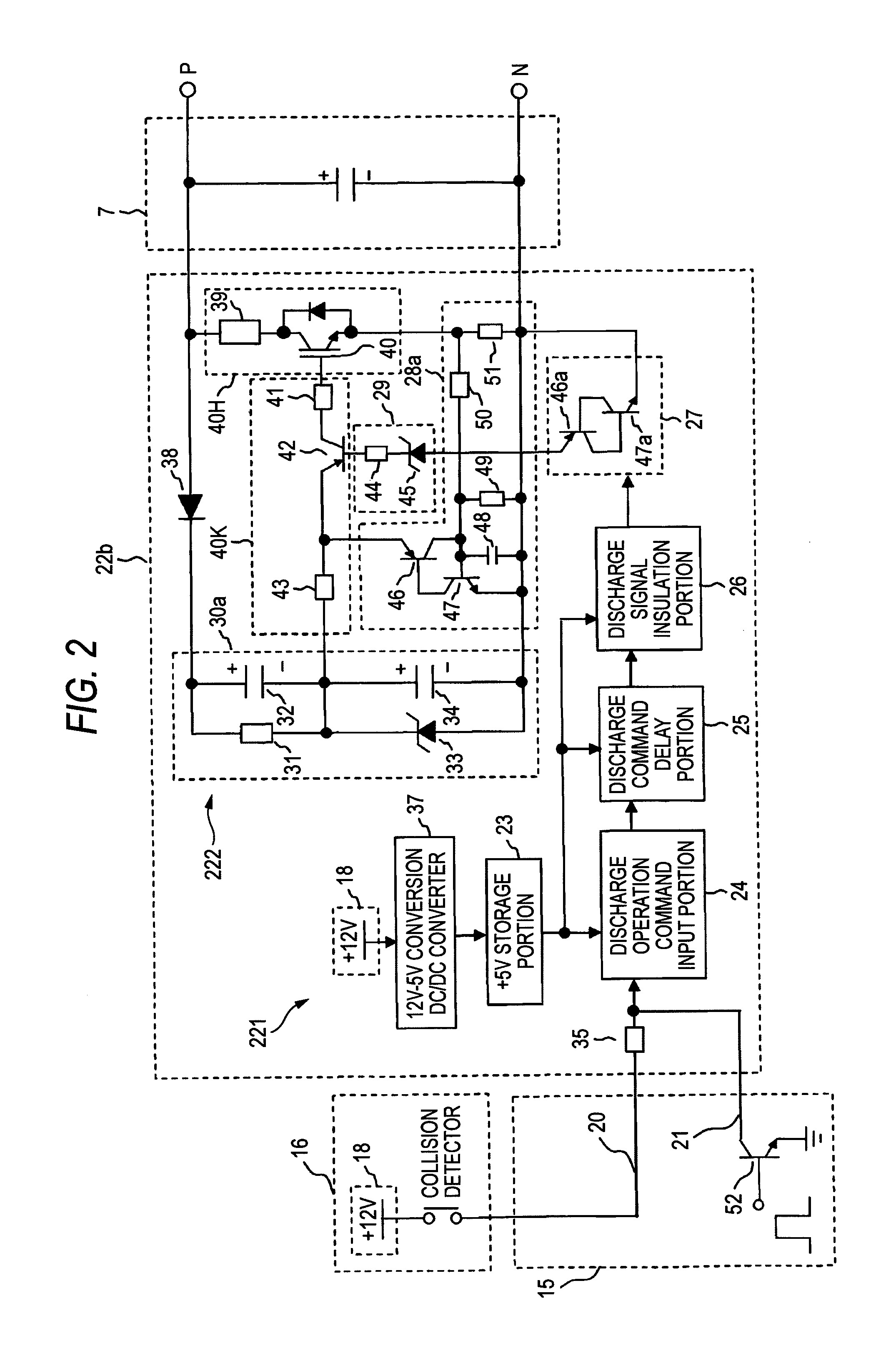
In an electric vehicle inverter apparatus 100, a vehicle control controller 15 detects a switch open signal output from a collision detector 16 when the collision detector 16 is caused by a collision between electric vehicles to operate. Then, an inverter main circuit connection switch 10 of a high-voltage battery unit 8 is put into an open state. Thus, the direct-current power supply from a high-voltage battery 12 to a DC bus portion is interrupted. In addition, electric charges charged into a main circuit capacitor 7 are discharged by a forced discharge circuit portion 22b.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK +1
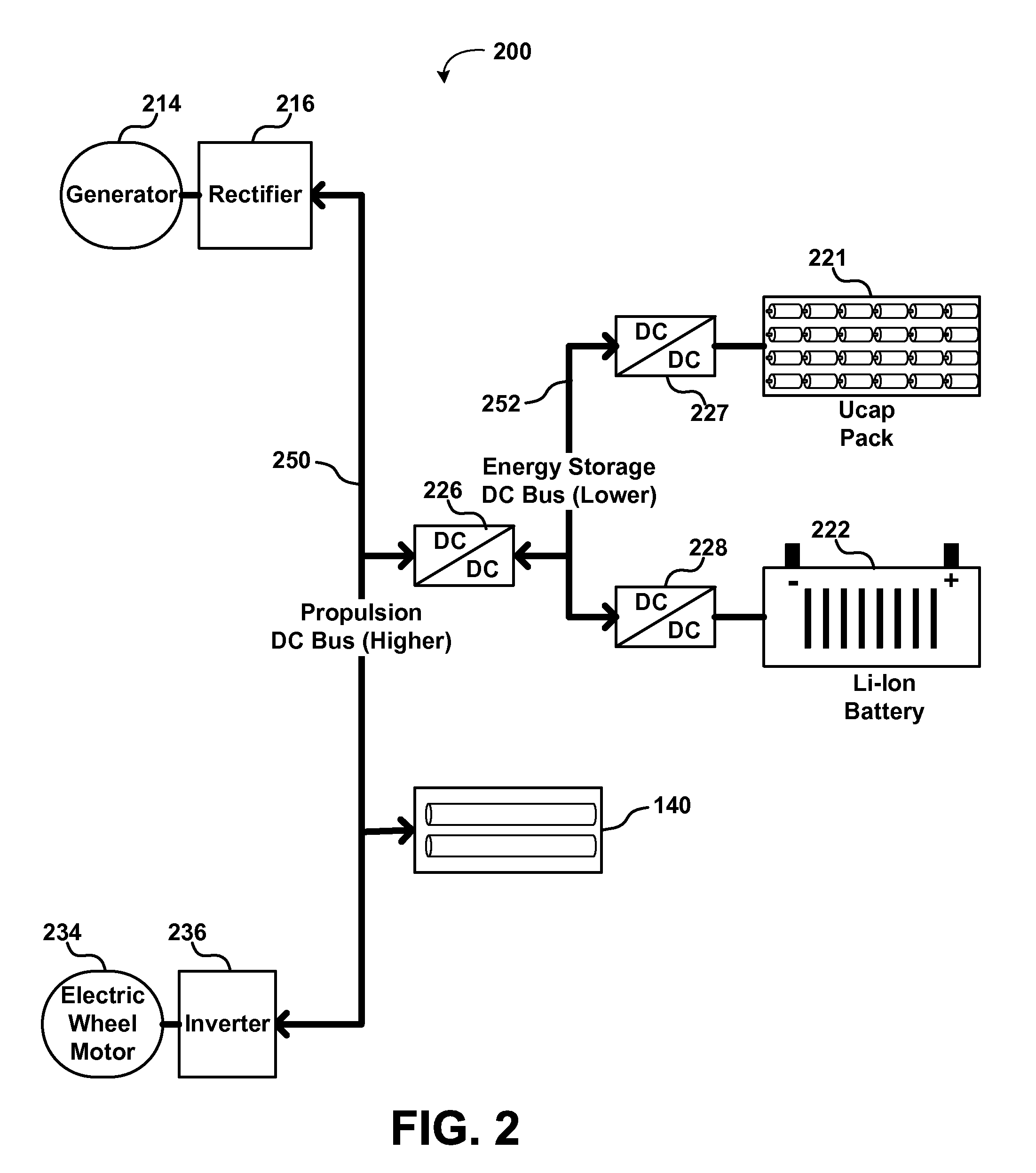
Propulsion Energy Storage Control System and Method of Control
InactiveUS20110100735A1Efficient and inexpensive and reliableElectrodynamic brake systemsPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectricityControl system
A propulsion energy storage control system and method of control interspersed between a heavy duty hybrid-electric drive system and its propulsion energy storage. The control system having an energy storage DC bus, electrical interfaces to the drive system and a plurality of propulsion energy storage subsystems, DC-to-DC converters at each interface, and a controller configured to operate each DC-to-DC converter independently such that power flow may charge, discharge, and shuttle between the plurality of propulsion energy storage subsystems.
Owner:SHEPPARD MULLIN RICHTER & HAMPTON
Inverter system
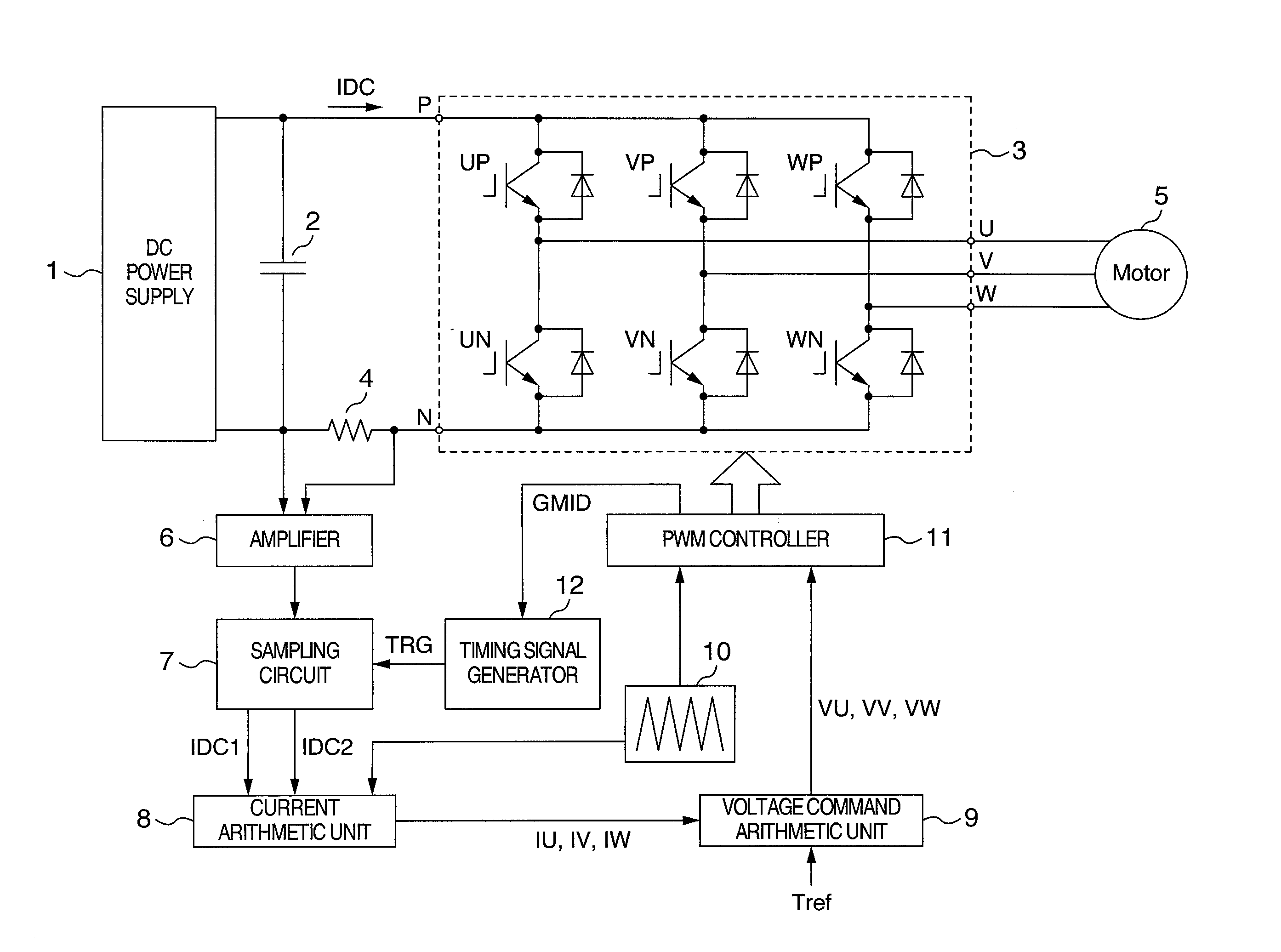
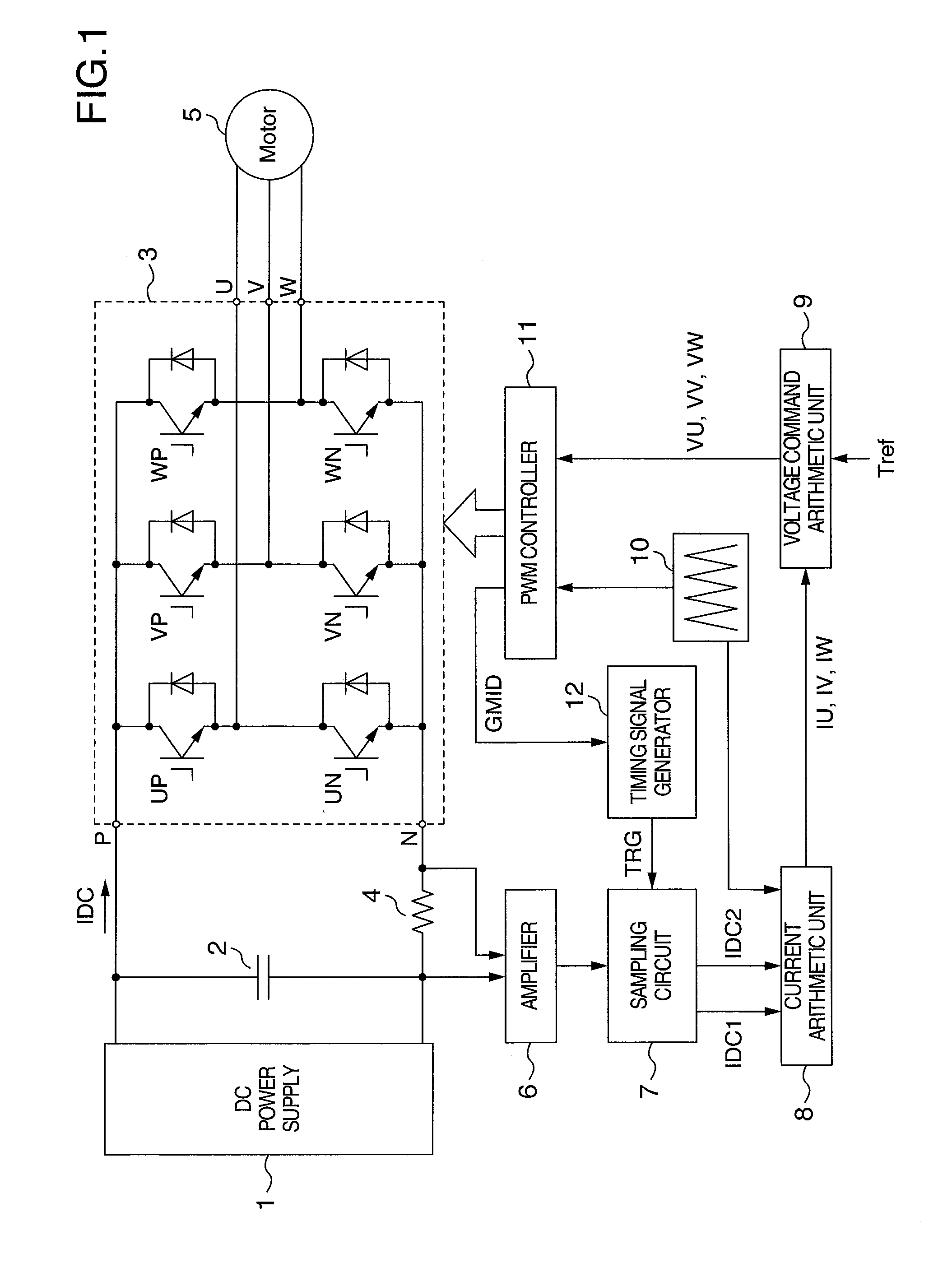
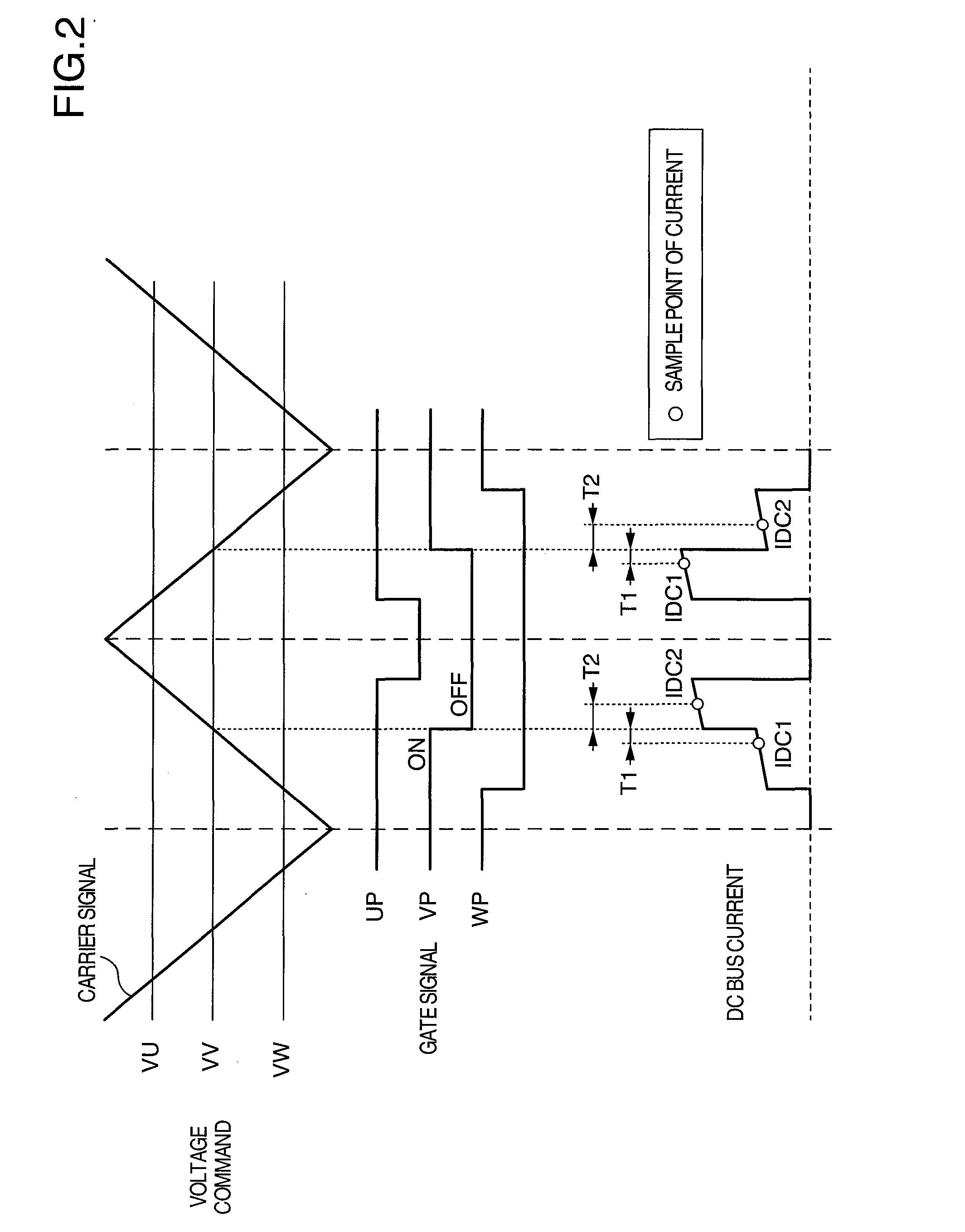
InactiveUS20070241720A1High precisionEfficient processElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlCurrent sampleCarrier signal
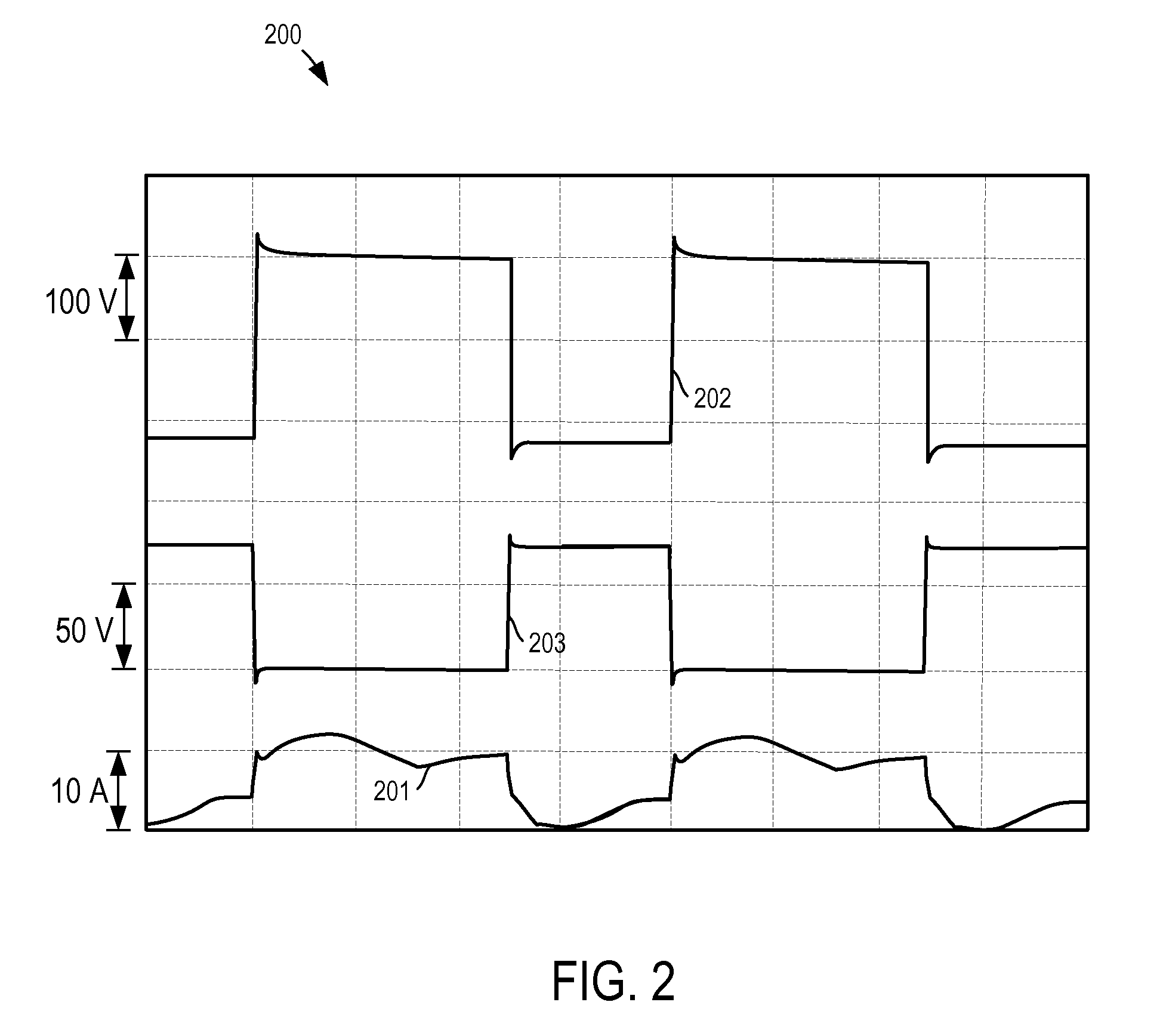
When finding a current on an AC side of an inverter by observing that on a DC side, a current that is not affected by pulsating components contained in the AC current must be detected. Timing of change of a gate signal for driving a switch element of a phase having an intermediate magnitude among three-phase voltage command signals to ON / OFF is used as a reference time point for DC bus current detection. DC bus currents sampled T1 before and T2 after the reference time point are designated as IDC1 and IDC2, respectively. A detected current value of a maximum voltage phase is computed by using IDC2 and IDC1 respectively in an increase period and a decrease period of a carrier signal alternately. A detected current value of a minimum voltage phase is computed by using IDC1 and IDC2 respectively in an increase period and a decrease period alternately.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP +1
Integrated photovoltaic module
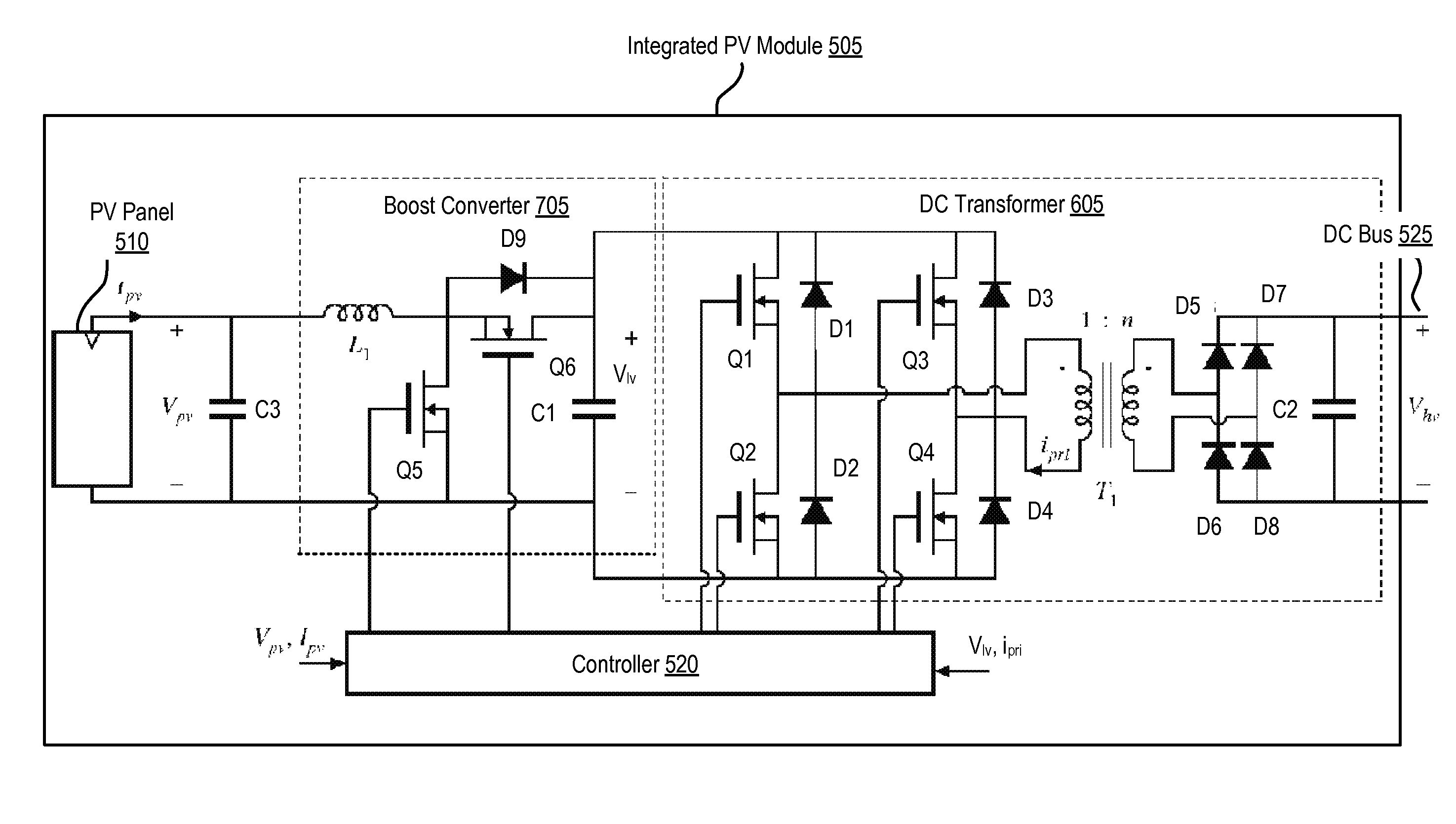
InactiveUS20120042588A1Easy wiringPhotovoltaic supportsRoof covering using slabs/sheetsSystems designDc dc converter
The disclosed embodiments increase the power generated by a photovoltaic (PV) array, when the PV panels within the PV array are not uniformly illuminated or oriented or when PV panels are mismatched (e.g., have varying performance characteristics) and / or operate at non-uniform temperatures. It also provides simpler interconnection and wiring of the elements (e.g., PV panels) of the array. A dc-dc converter comprised of a DC transformer is coupled to each PV panel in a photovoltaic array to generate an increased dc voltage from a lower dc voltage produced by the PV panel. The outputs of the dc-dc converters are connected in parallel to a dc bus, which distributes the resulting voltage. As a result, the energy generated by the PV array is increased, the costs of system design and installation are reduced, and it becomes feasible to install PV arrays in new locations such as on gabled or non-planar roofs.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
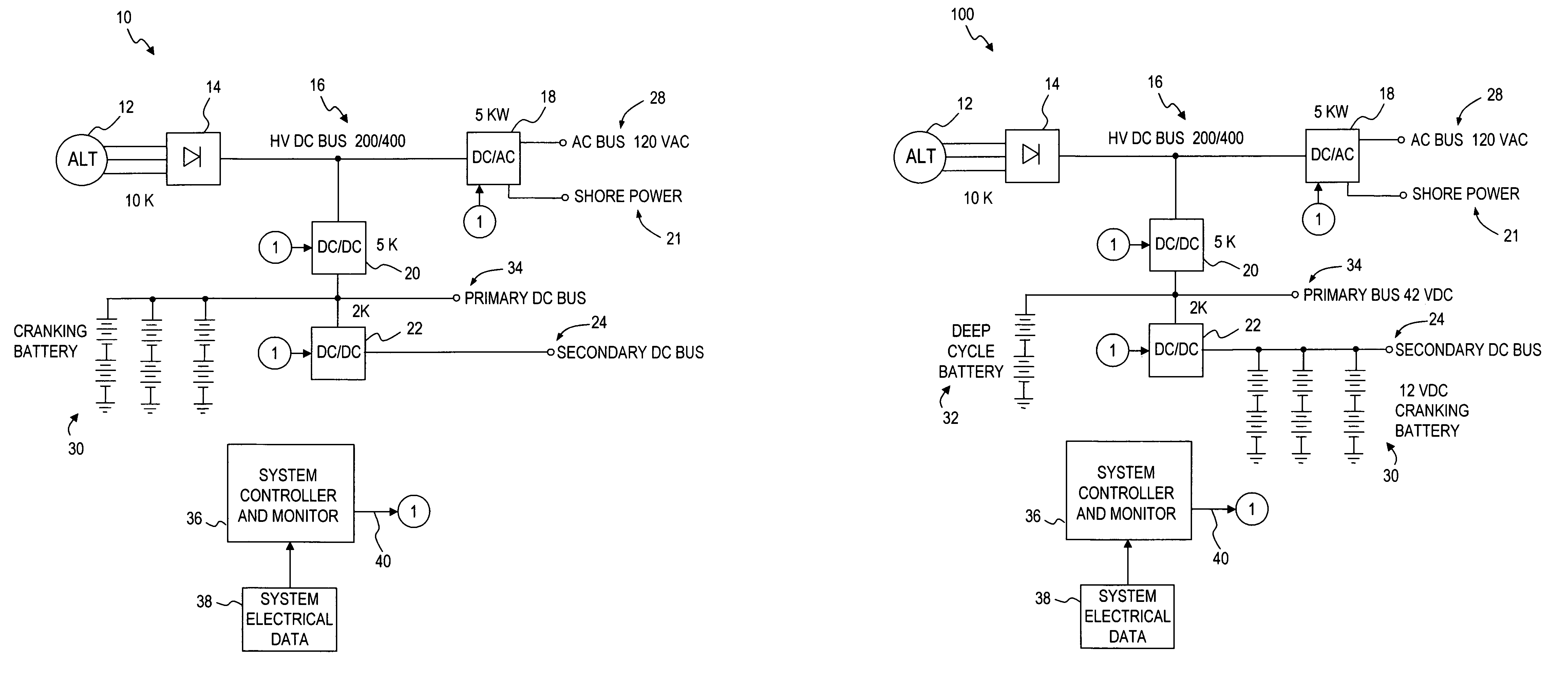
Power management system for vehicles
InactiveUS7057376B2Ac-dc network circuit arrangementsThree-or-more-wire dc circuitsPower inverterEngineering
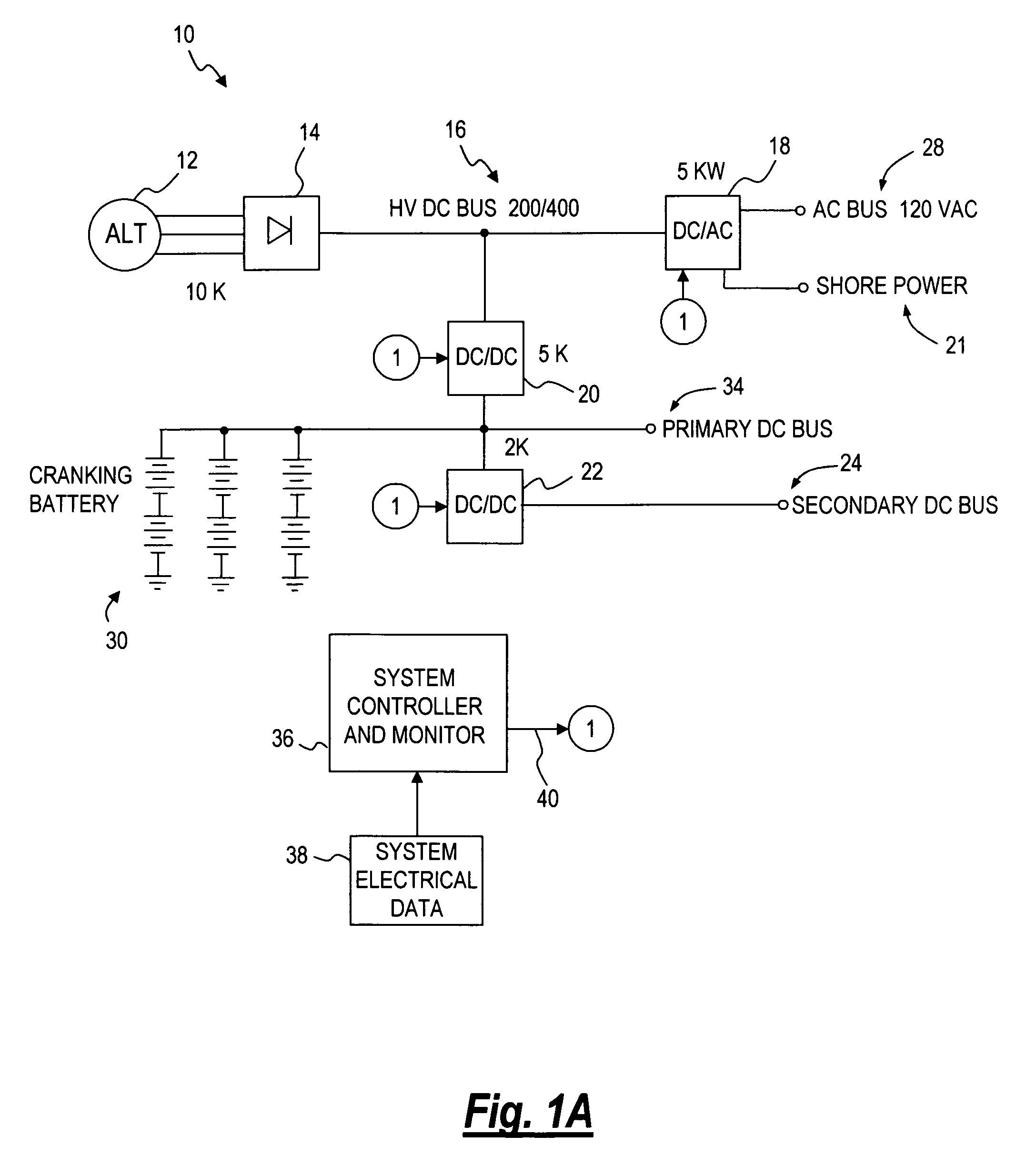
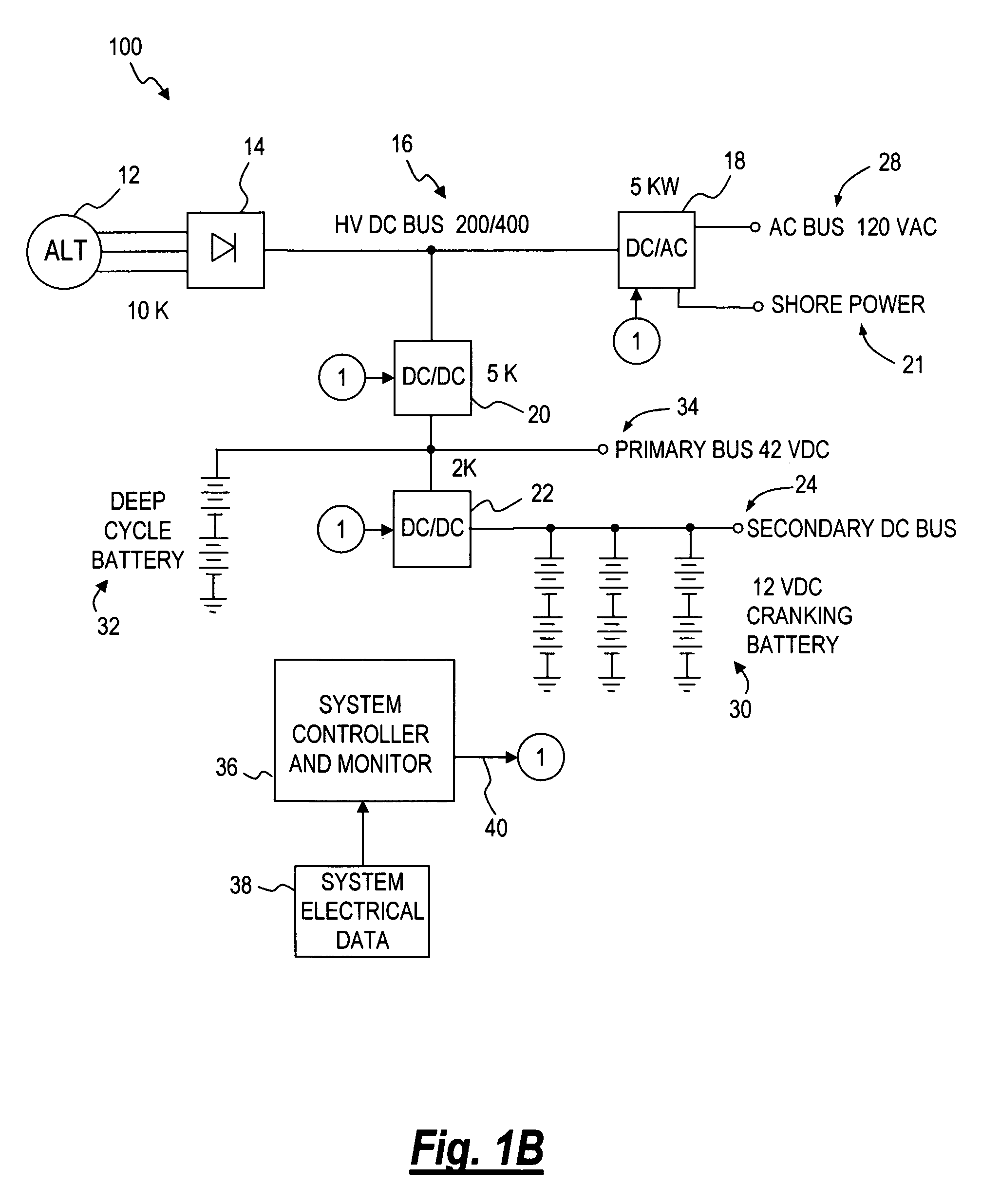
A power management system for a vehicle. The system may be flexibly configured using various arrangements of DC to AC inverters, DC to DC converters AC to DC converters, DC to AC converters and AC to AC converters, one or more batteries, and a control portion to provide an AC bus, a primary DC bus and a secondary DC bus. The control portion monitors the status of the buses, inverters and converters and controls the operation of the inverters and converters to supply and regulate the power supplied by the buses. The inverters and converters may be bidirectional, allowing power to be transferred between buses.
Owner:VANNER
Emergency power supply apparatus
ActiveUS20110187197A1Extended run timeBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerReconfigurabilityVirtualization
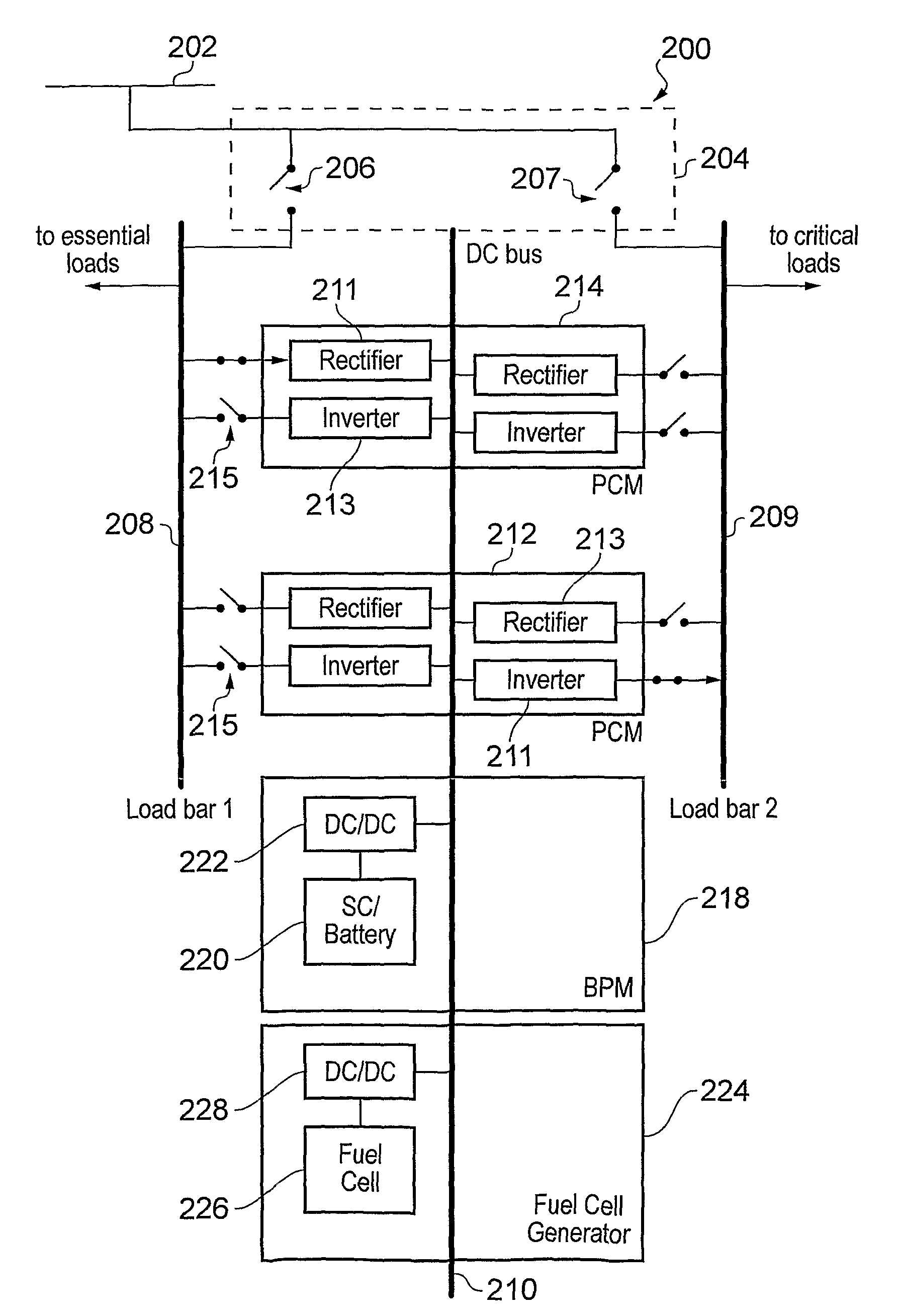
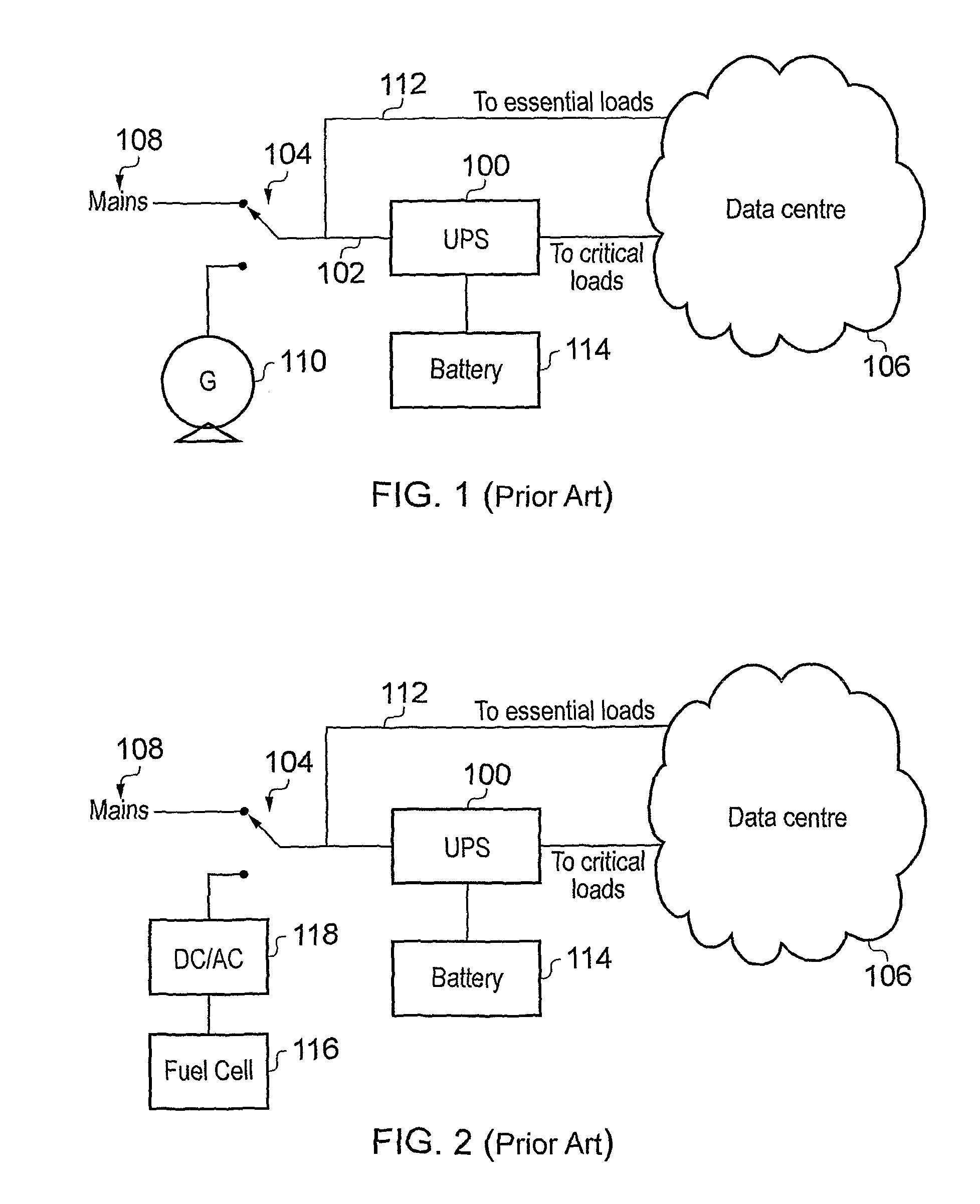
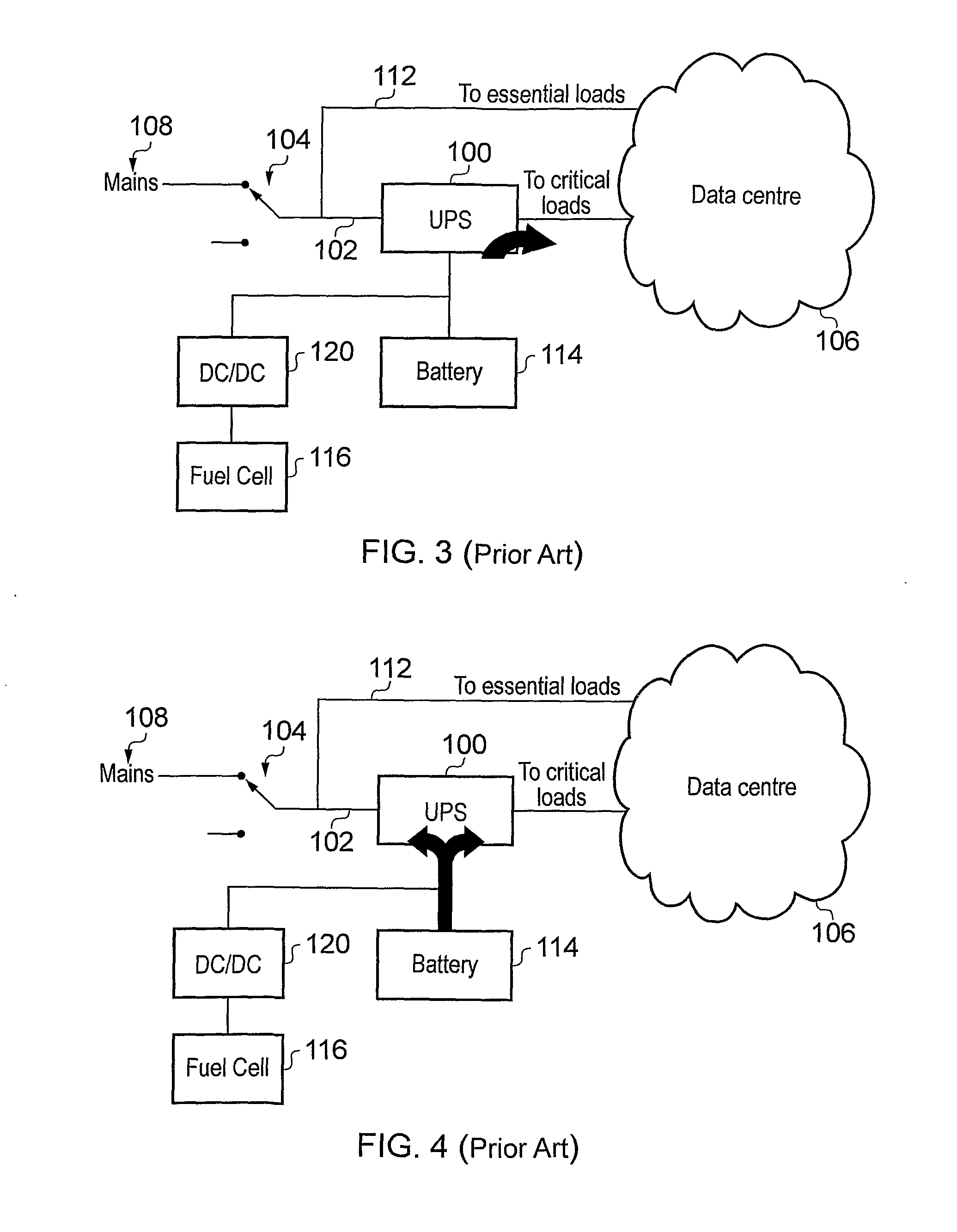
A modular emergency power system architecture (200) with a plurality of output power supply lines for feeding power to a destination, in which the operational status of each output power supply line is configurable. The architecture comprises a plurality of load bars (208, 209) from which power is delivered to the destination. The load bars (208, 209) are selectively connectable to send power to or receive AC power from a mains supply (202) and / or a DC bus (210) via one or more AC / DC power conversion modules (212, 214). The DC bus (210) is connected to receive a secondary (e.g. emergency) power supply (218, 224). The architecture may provide redundancy and on-the-fly reconfigurability to complement changes in the physical location of critical components in the destination, e.g. caused by virtualisation, zoning or repair. The architecture is operable as a stand-alone uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or as an extended runtime generator for an existing UPS.
Owner:LEANECO APS
Hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20140244082A1Wide constant power rangeLow costHybrid vehiclesAC motor controlCapacitanceExternal combustion engine
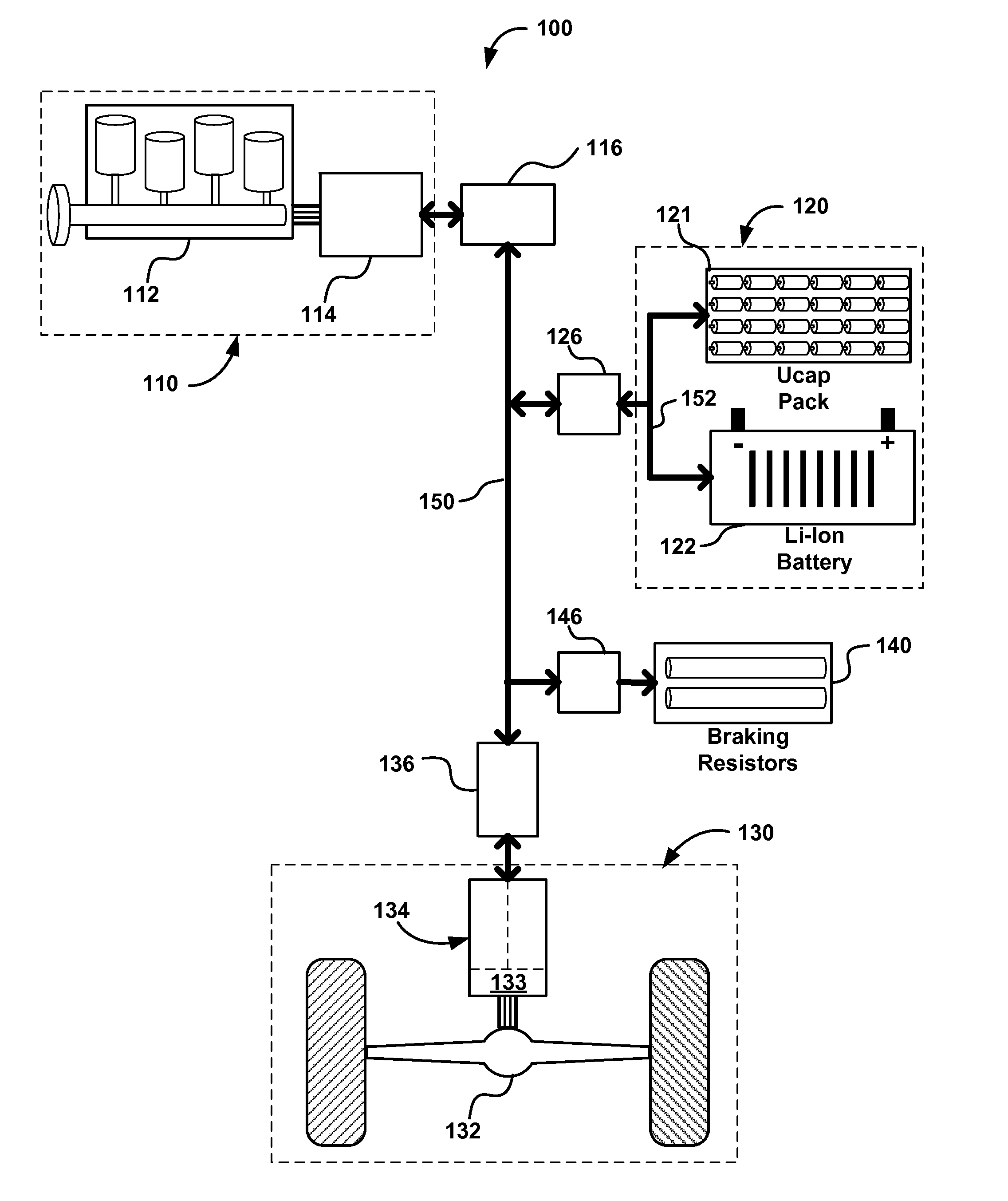
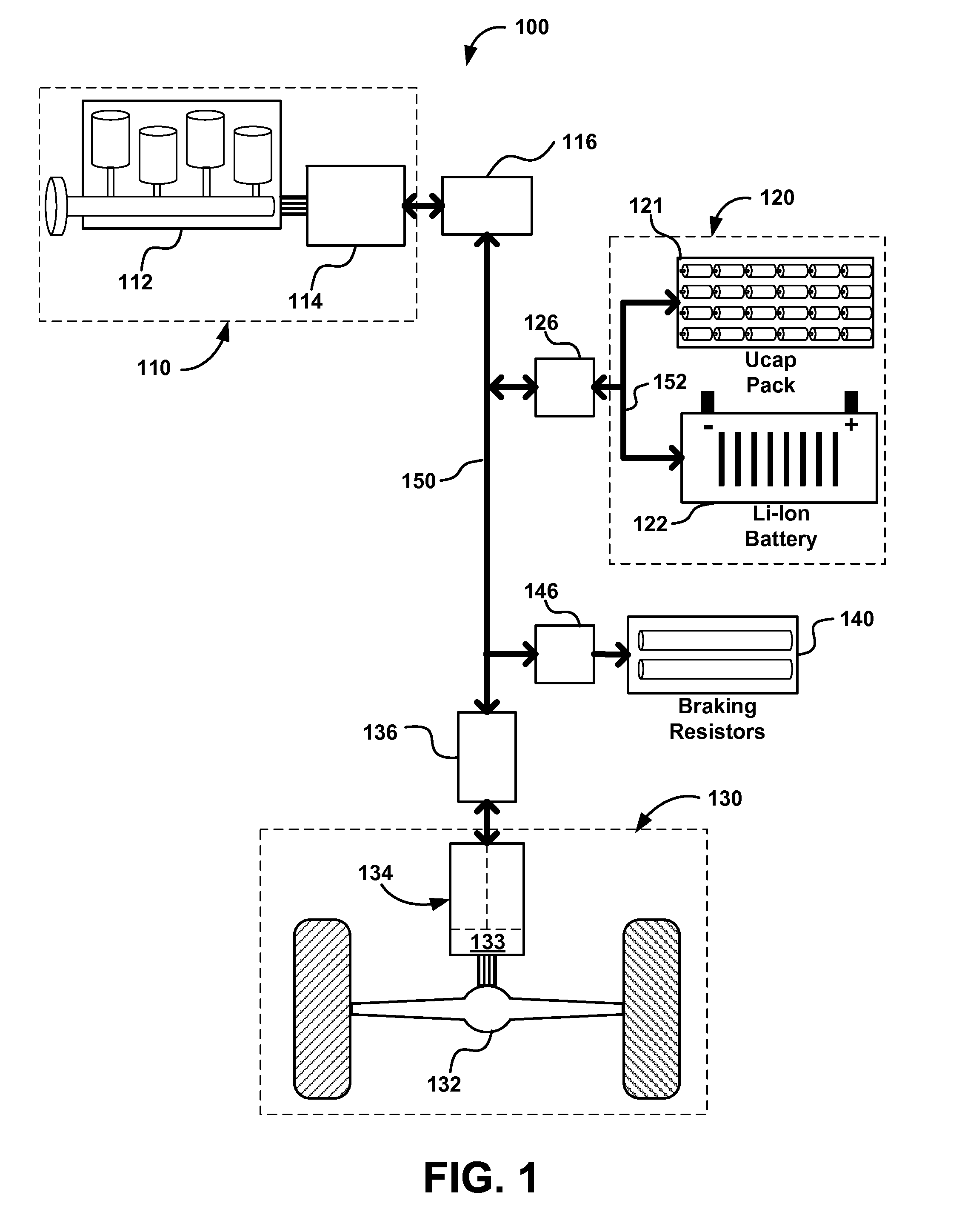
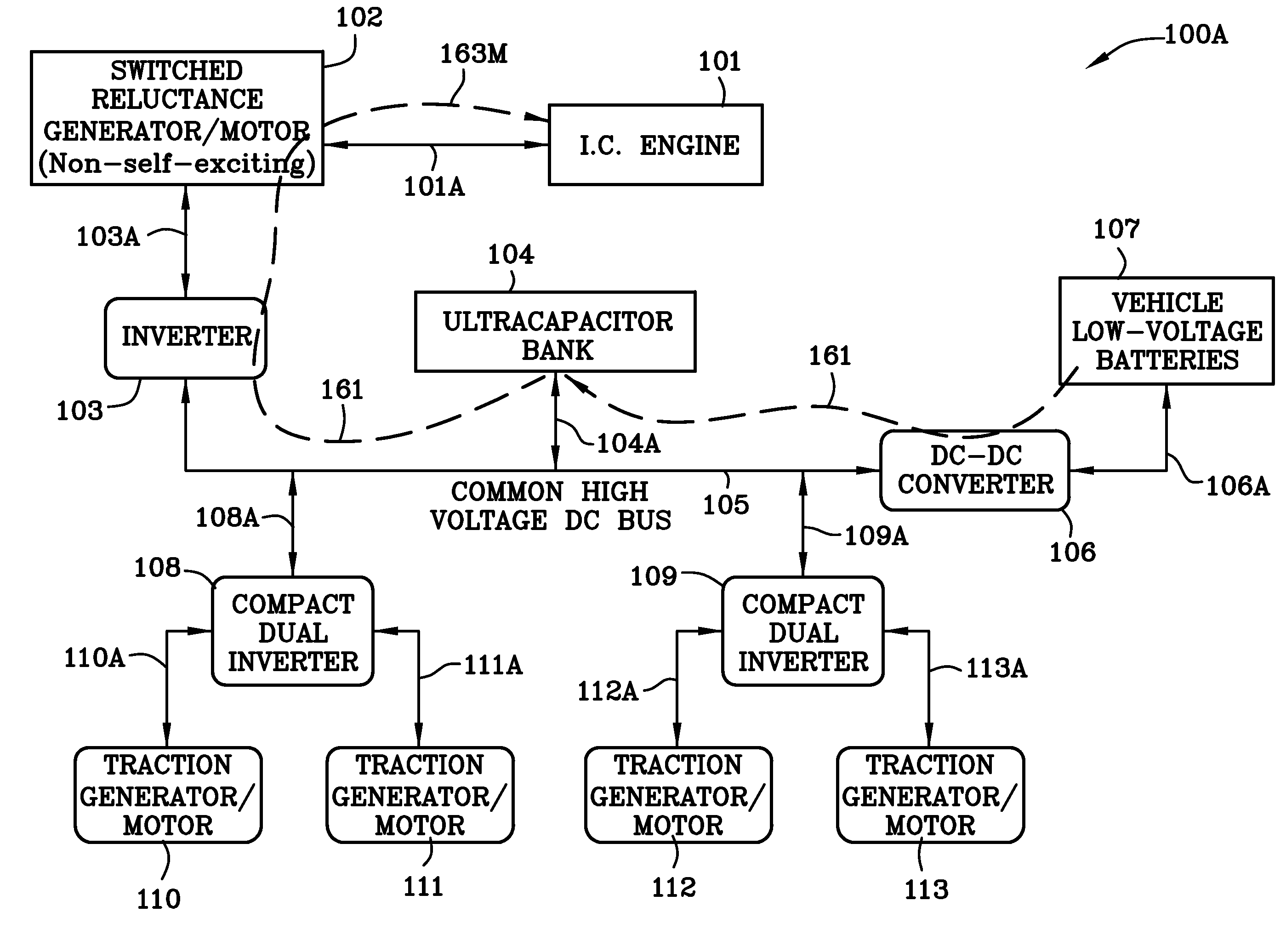
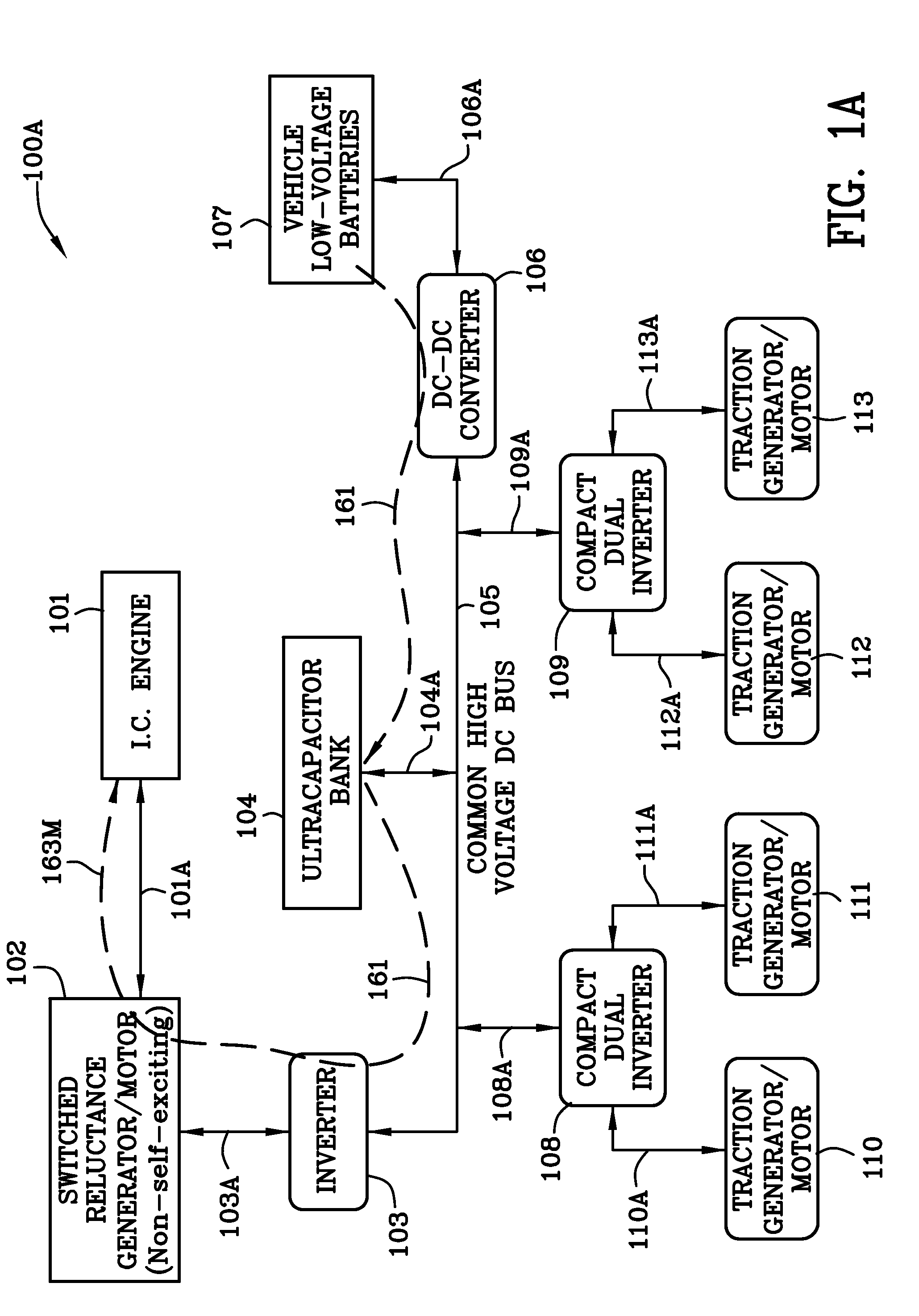
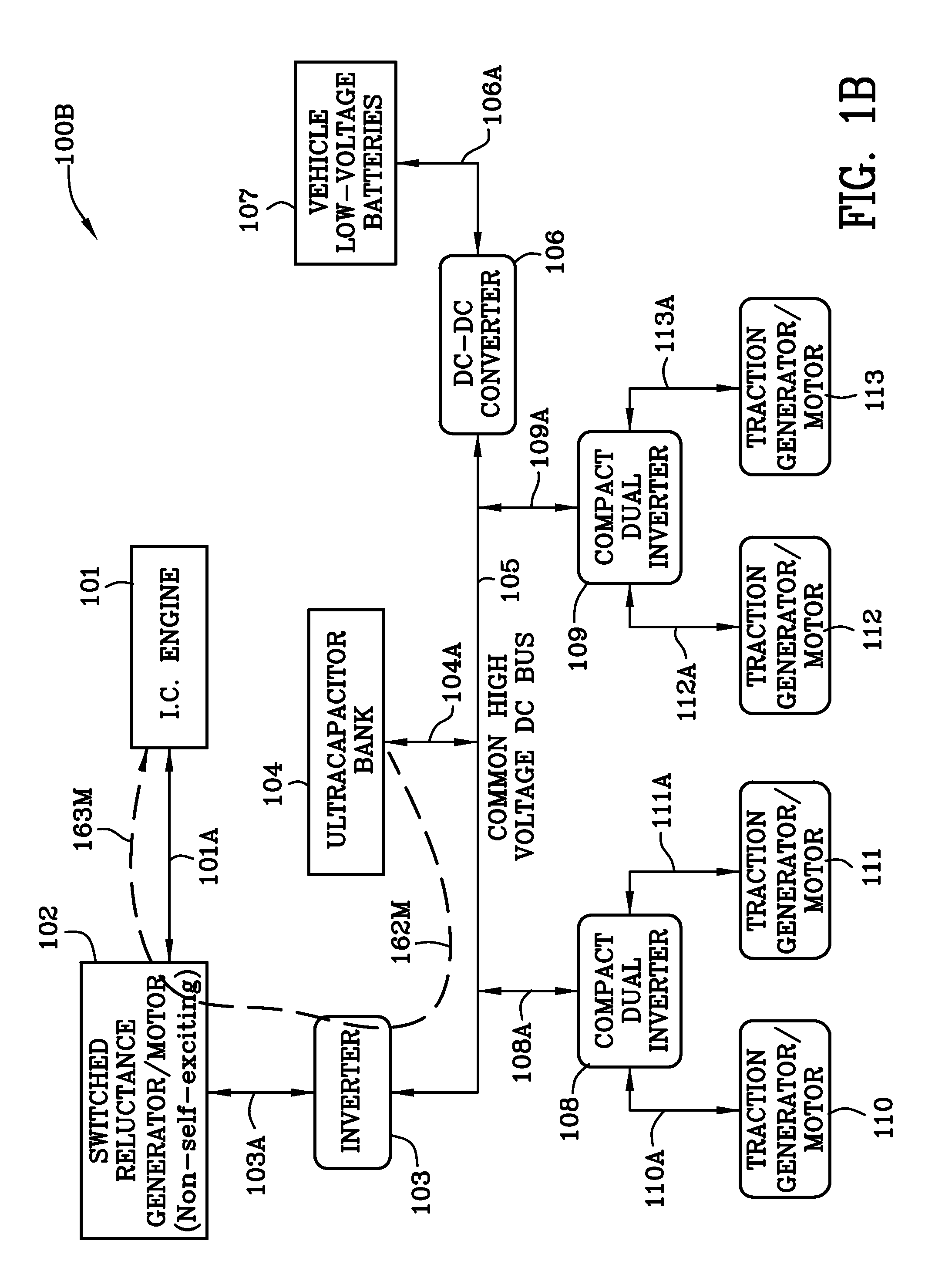
A hybrid electric vehicle includes a high voltage DC bus and an internal combustion engine. The internal combustion engine is mechanically coupled to a non self-excited generator / motor which is preferably a switched reluctance machine. A power inverter electrically and bidirectionally couples the high voltage DC bus to the non self-excited switched reluctance generator / motor. Front and rear axle dual DC-AC inverters electrically and bidirectionally couple two traction AC non self-excited switched reluctance motors / gear reducers to the high voltage DC bus for moving the vehicle and for regenerating power. An ultracapacitor coupled to the high voltage DC bus. A bidirectional DC-DC converter interposed between a low voltage battery and the high voltage DC bus transfers energy to the high voltage DC bus and ultracapacitor to ensure that the non self-excited switched reluctance generator / motor operating in the motor mode is able to start the engine.
Owner:FAIRFIELD MFG CO INC
Control method for grid-connected power generation system of optical storage microgrid
ActiveCN104810858AImprove power qualityReduce power consumptionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentPower qualityGrid-tie inverter
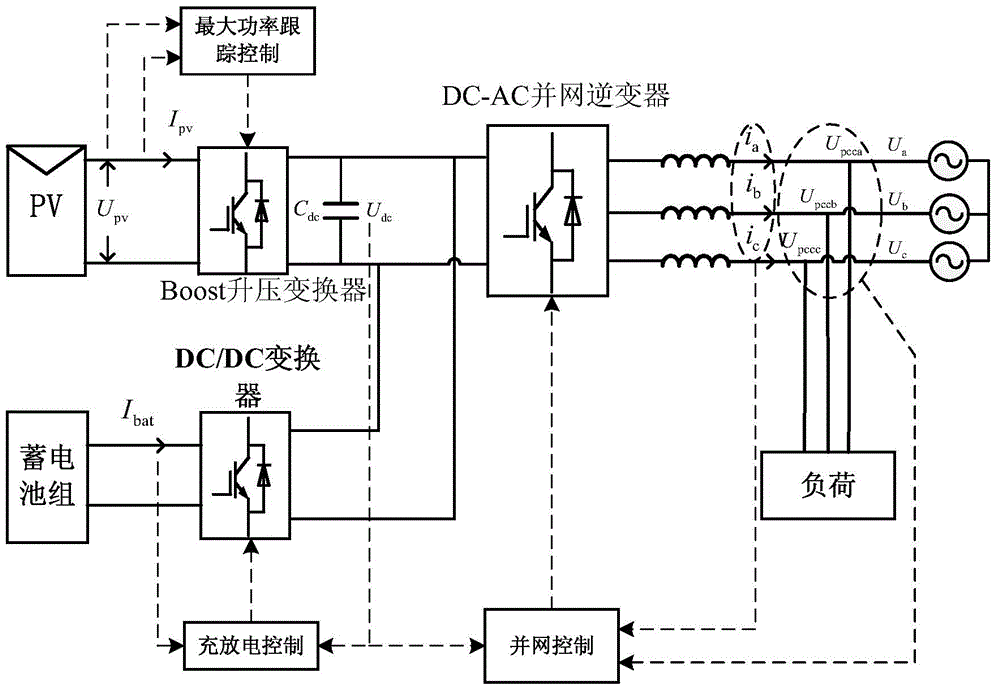
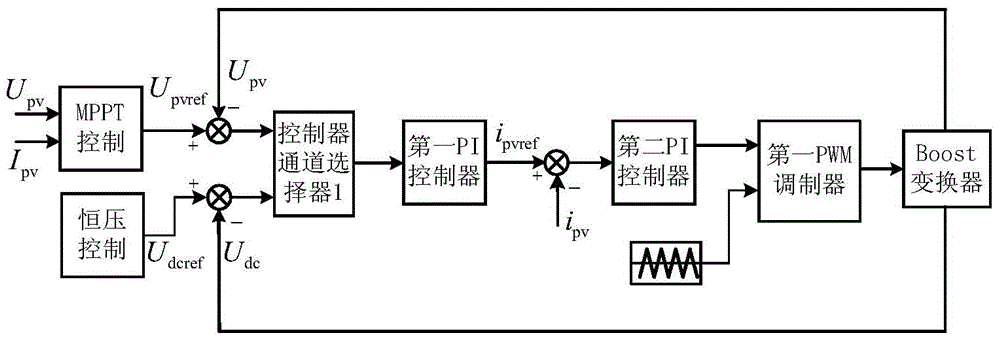
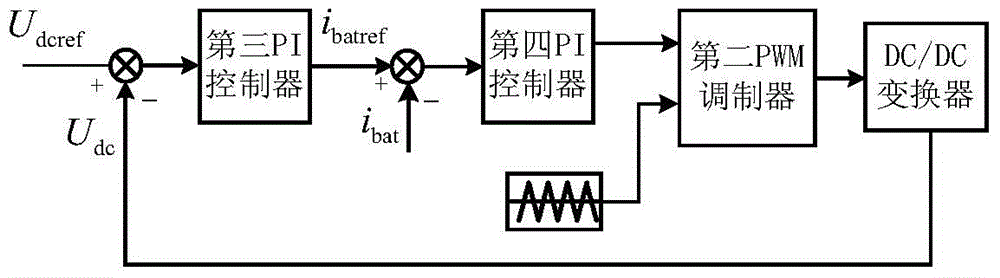
The invention discloses a control method for a grid-connected power generation system of an optical storage microgrid. According to the method, a photovoltaic power generation power supply is connected with a direct-current (DC) bus through a boost converter, and an energy storage module is connected with the DC bus through a bidirectional DC-DC converter; a DC side of a DC-AC (Alternating Current) grid-connected inverter is connected with the DC bus, and an AC side of the DC-AC grid-connected inverter passes through a filtering inductor and then is connected with a power grid and a load respectively; the photovoltaic power generation power supply is subjected to maximum power tracking control and constant-voltage control respectively through a boost converter control strategy according to the charging state of the energy storage module, the output power of the photovoltaic power generation power supply, the voltage drop conditions of grid connected points and the reactive power demand set value of the power grid, the charging and discharging of the energy storage module are controlled through a bidirectional DC-DC converter control strategy, and the voltage of the grid connected points is stabilized through a DC-AC grid-connected inverter control strategy. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the stable grid connection of the optical storage microgrid is guaranteed, and the quality of electric power of the power grid is improved; the multi-functionalization of the grid-connected inverter is realized, and the cost is reduced; the new energy absorption capacity of the power grid is enhanced, so as to meet the demands of the power grid.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
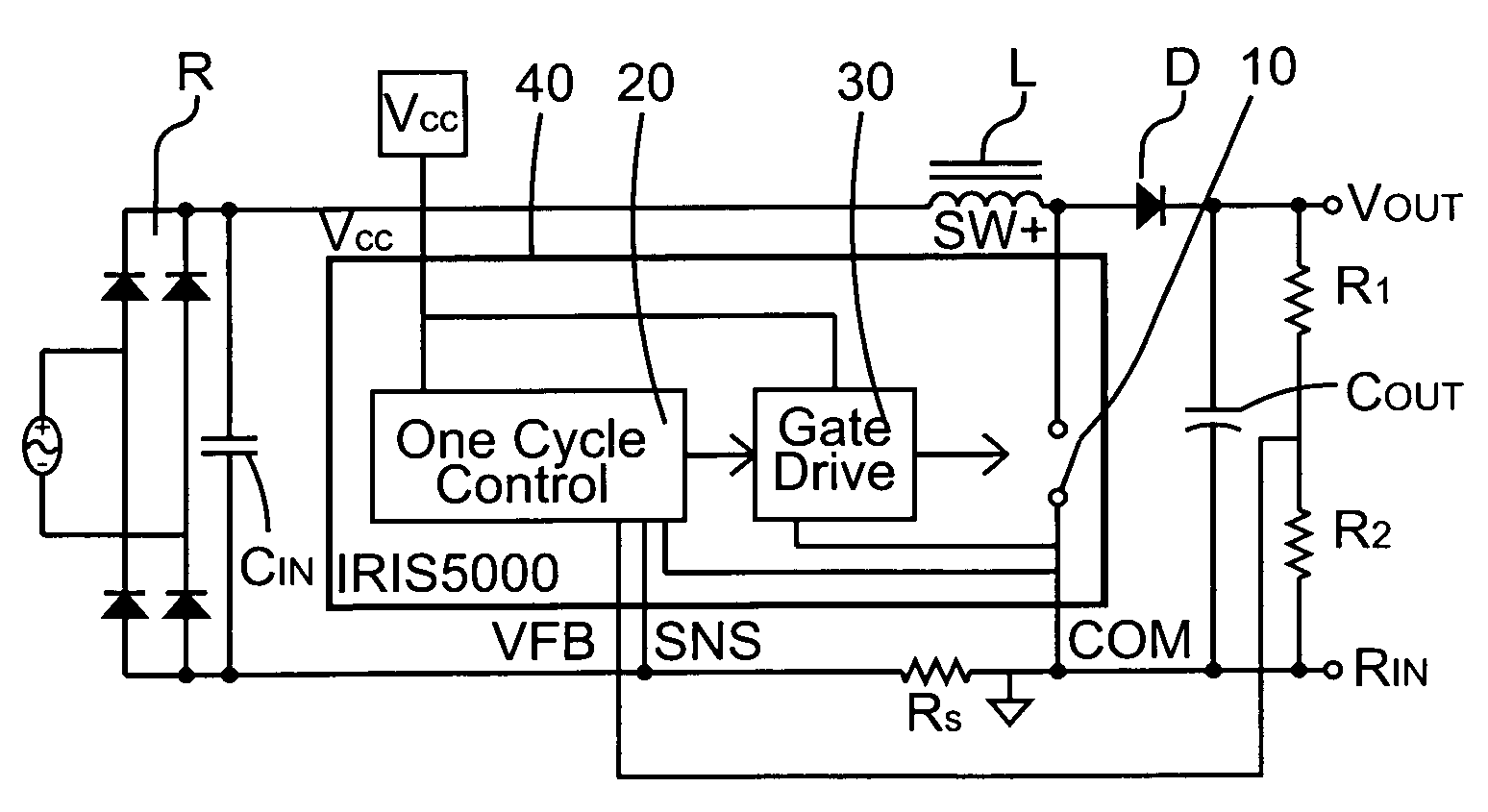
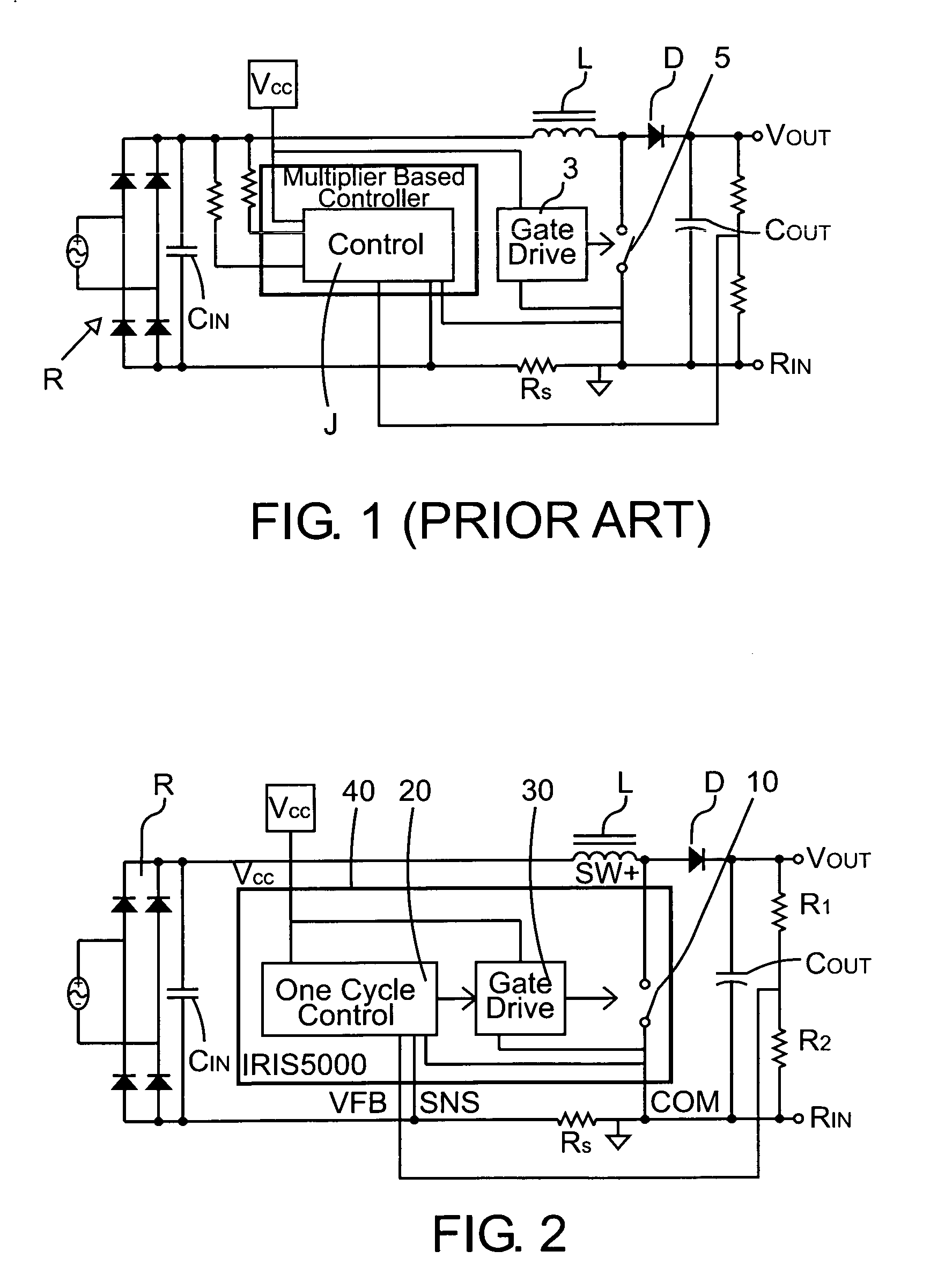
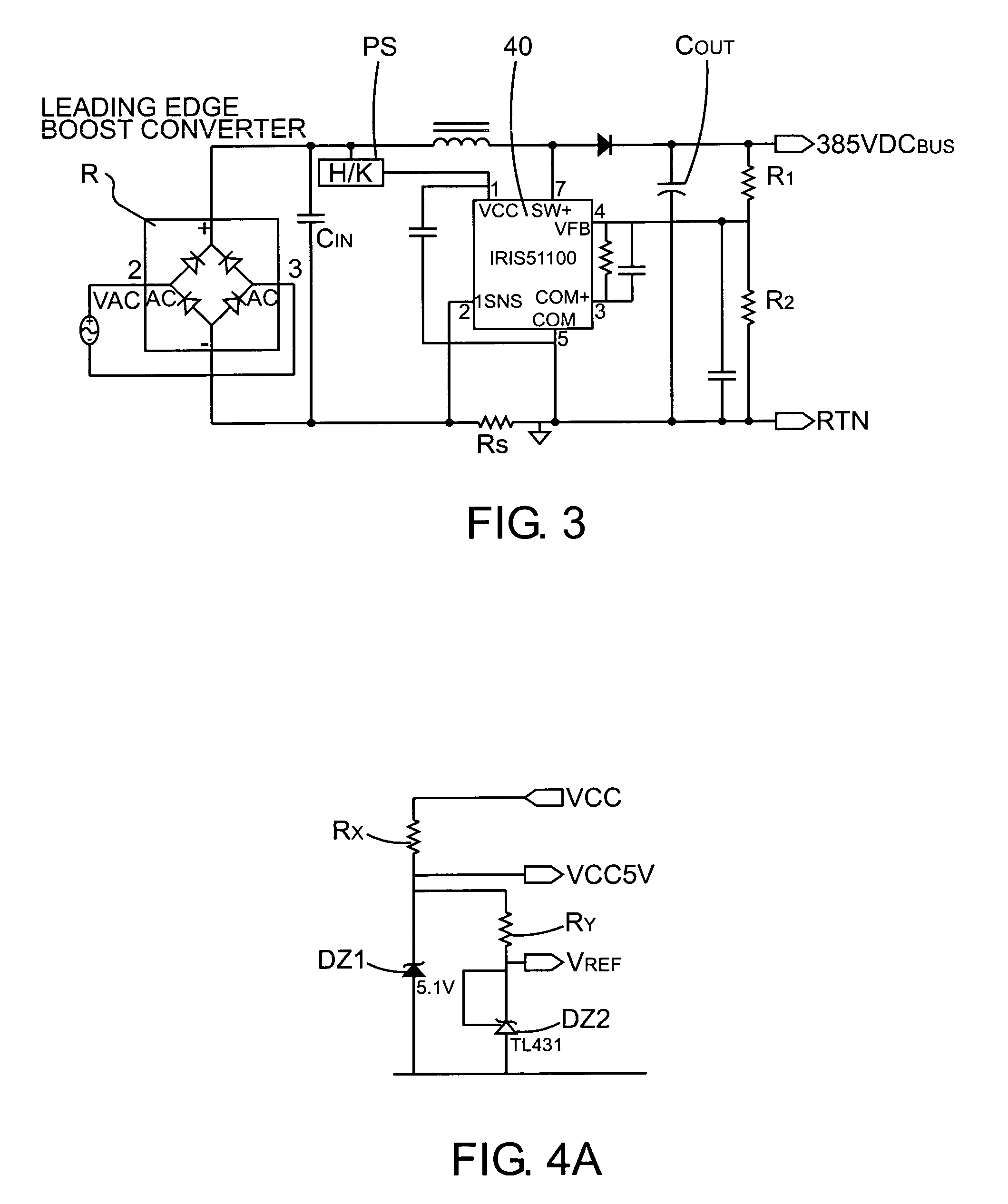
One cycle control PFC boost converter integrated circuit with inrush current limiting, fan motor speed control and housekeeping power supply controller
ActiveUS7068016B2Eliminating redundant switching circuitsSimplifies inclusionBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionMotor speedCycle control
A power factor corrected boost converter circuit includes a rectifier connectable to an ac input and having a rectified dc output provided across a dc bus, an inductor having first and second terminals connected in one leg of the dc bus, an integrated circuit comprising a control circuit for controlling a switch, the integrated circuit including a housing enclosing the control circuit, the integrated circuit having a power terminal, a ground terminal, a first control input terminal coupled to an output of the converter circuit, and a second control input terminal coupled to a sensor for sensing current in the dc bus and further having an output terminal connected to the switch, a boost rectifier diode having a first terminal, the diode coupled to the inductor, and a storage capacitor connected to the diode. The control circuit comprises a one cycle control circuit having an integrator reset by a clock signal for each cycle of the clock signal. The circuit further includes any or all of an inrush current limiting circuit for limiting the current through the inductor to a value below a predetermined level, a fan motor speed controller and a housekeeping power supply controller.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
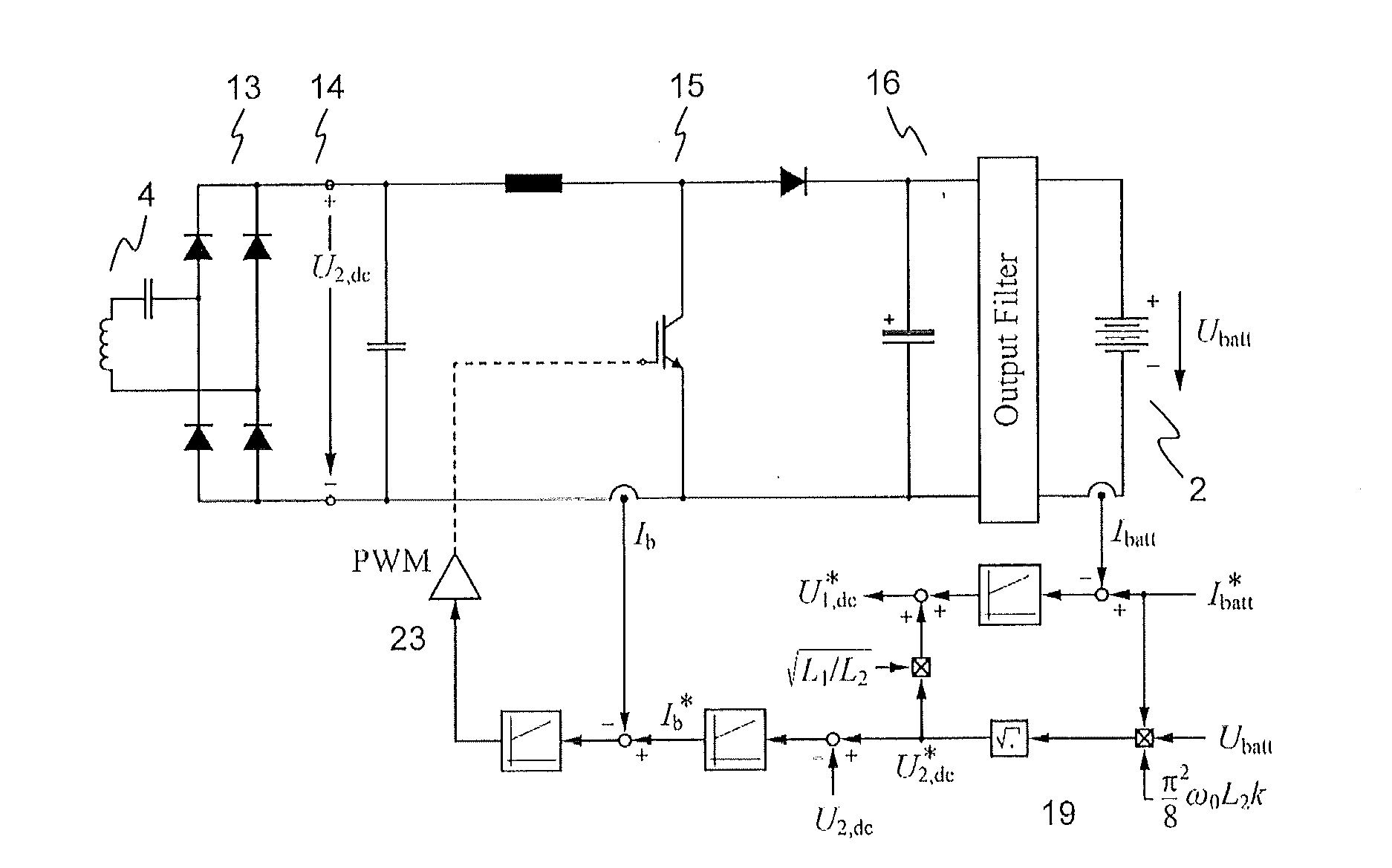
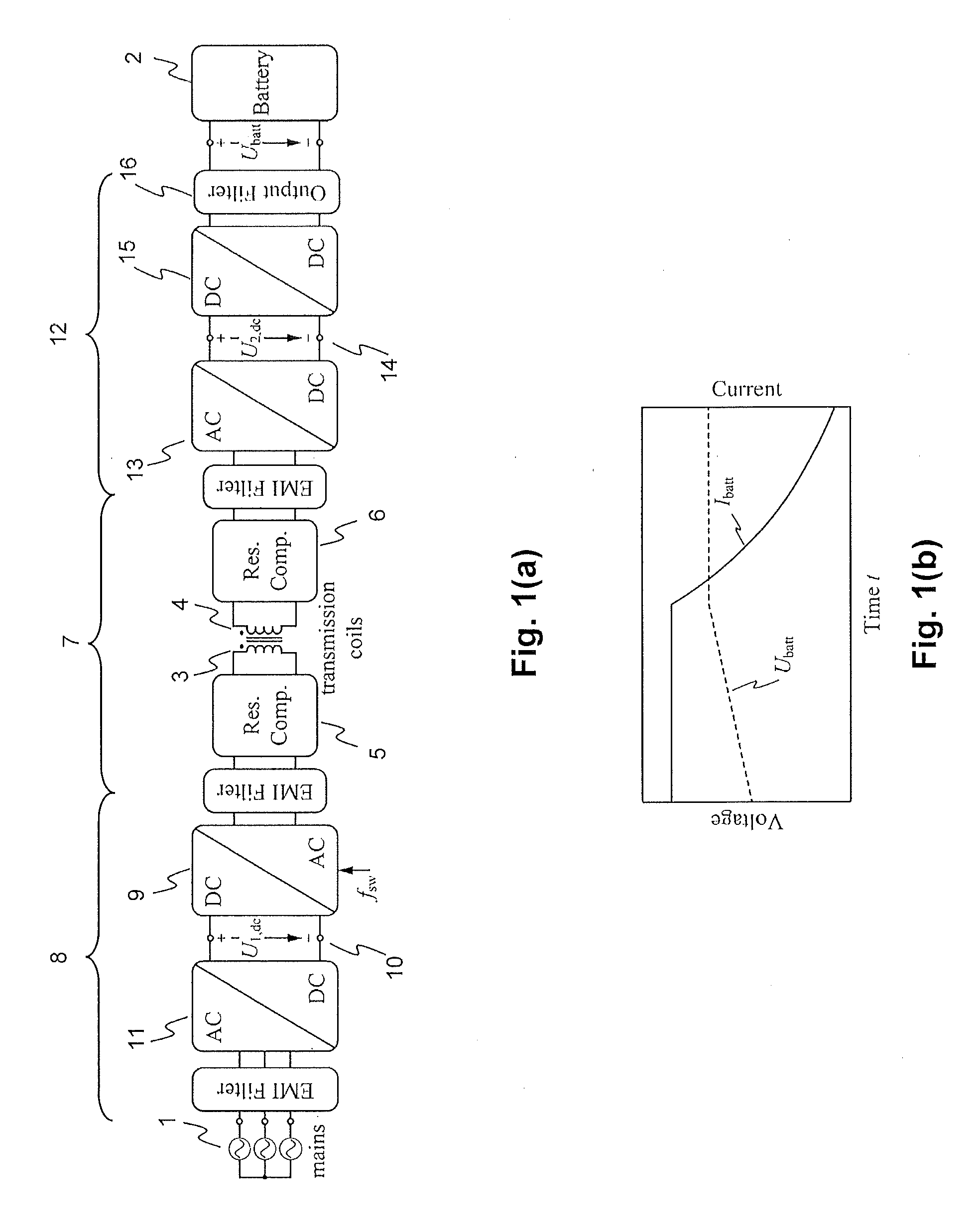
Inductive power transfer system and method for operating an inductive power transfer system
InactiveUS20150280455A1Minimize switching lossesBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsTransmitter coilEngineering
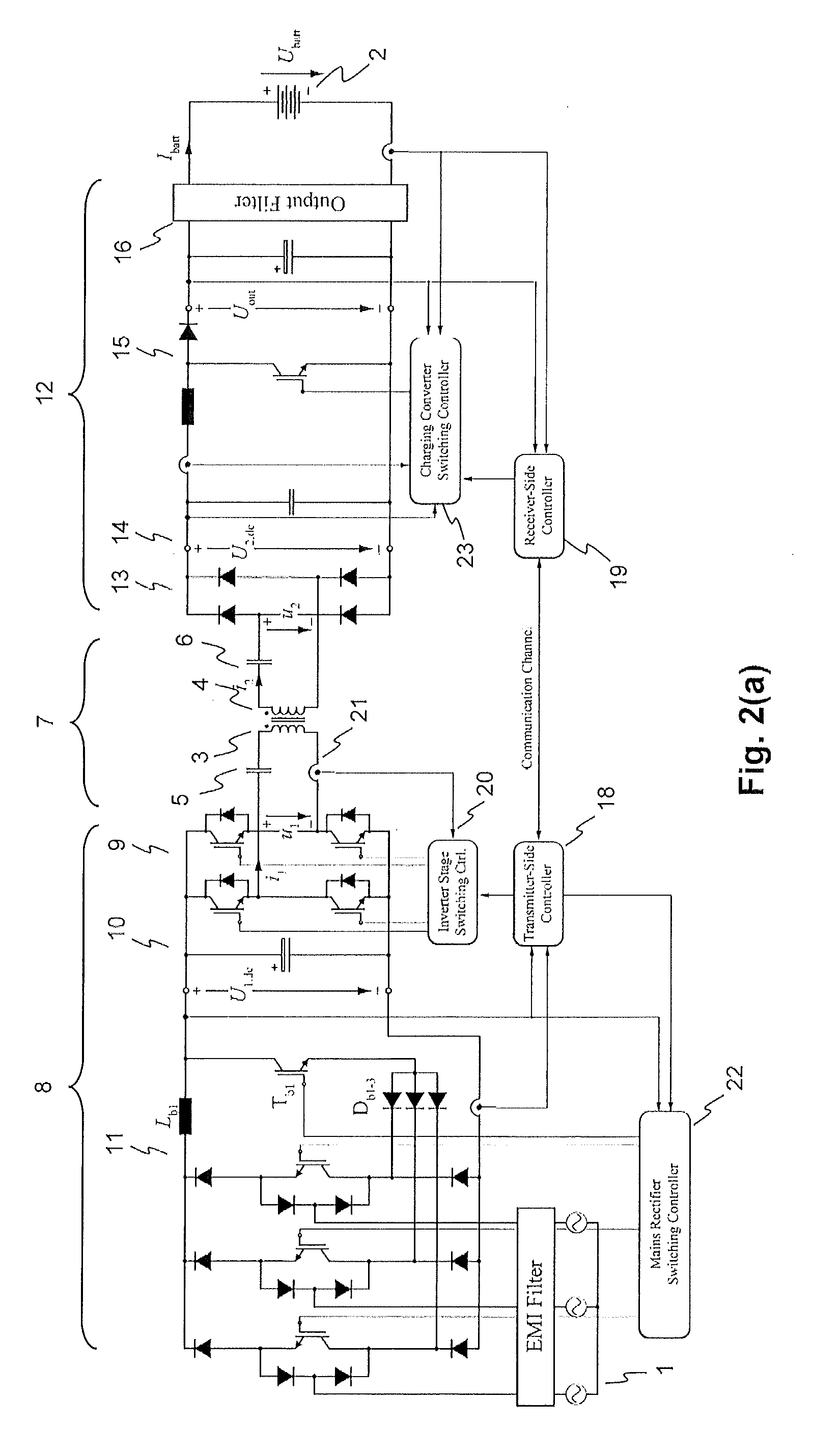
An exemplary inductive power transfer system having a transmitter coil and a receiver coil. A transmitter-side power converter having a mains rectifier stage powering a transmitter-side dc-bus and controlling a transmitter-side dc-bus voltage U1,dc. A transmitter-side inverter stage with a switching frequency fsw supplies the transmitter coil with an alternating current. A receiver-side power converter having a receiver-side rectifier stage that rectifies a voltage induced in the receiver coil and powering a receiver-side dc-bus and a receiver-side charging converter controlling a receiver-side dc-bus voltage U2,dc. Power controllers that determine from a power transfer efficiency of the power transfer, reference values U1,dc*, U2,dc* for the transmitter and receiver side dc-bus voltages. An inverter stage switching controller controls the switching frequency fsw to reduce losses in the transmitter-side inverter stage.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Active power filter including power unit and its control method
InactiveCN101051751ASolve control problemsSolve the inrush currentActive power filteringAc-dc conversionCapacitanceEngineering
The power unit includes H bridge inverter circuit, capacitance in DC section connected to DC bus in inverter circuit, and control circuit for controlling operation of the power unit. The power unit also includes a clipping energy consumption circuit. Combining a small quantity of active power absorbed by active electric power filter, the method realizes controlling DC bus voltage of power unit. The active electric power filter includes following parts: inverter with each phase including at least one power unit; voltage detection circuit, central control system, filtering circuit, precharge circuit, income line switch, interface and communication circuit, and cooling unit etc.
Owner:上海艾帕电力电子有限公司
Protection for permanent magnet motor control circuits
InactiveUS20080304189A1DC motor speed/torque controlAsynchronous induction motorsPermanent magnet motorMotor control
Methods and apparatus are provided for protecting a motor control circuit in a permanent magnet electric motor system. The permanent magnet electric motor system includes a permanent magnet electric motor having a predetermined number of windings corresponding to the phases of the permanent magnet electric motor and a direct current (DC) bus coupled to a power source for providing operational power for the electric motor system. A motor control circuit is connected to the DC bus for receiving the operational power therefrom and is connected to the windings of the permanent magnet electric motor for controlling the permanent magnet electric motor. A protection circuit is connected to the DC bus for receiving the voltage therefrom for operation of the protection circuit and for detecting predetermined motor control circuit fault conditions from voltage sensed on the DC bus and in response thereto providing protection for the motor control circuit.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method of controlling power to a non-motor load
ActiveUS20070007929A1Single-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlDC-BUSVoltage sensor
A motor drive for conditioning power to be delivered to a non-motor load includes a voltage feedback circuit that monitors a DC bus voltage and, based on changes in the DC bus voltage, adjusts a power conditioning scheme such that near steady-state load conditions are maintained in response to a transient load condition. The voltage feedback circuit has a voltage sensor that provides voltage feedback to a controller that determines what changes in power conditioning are needed in response to a transient load condition that manifests itself in a change in DC bus voltage.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
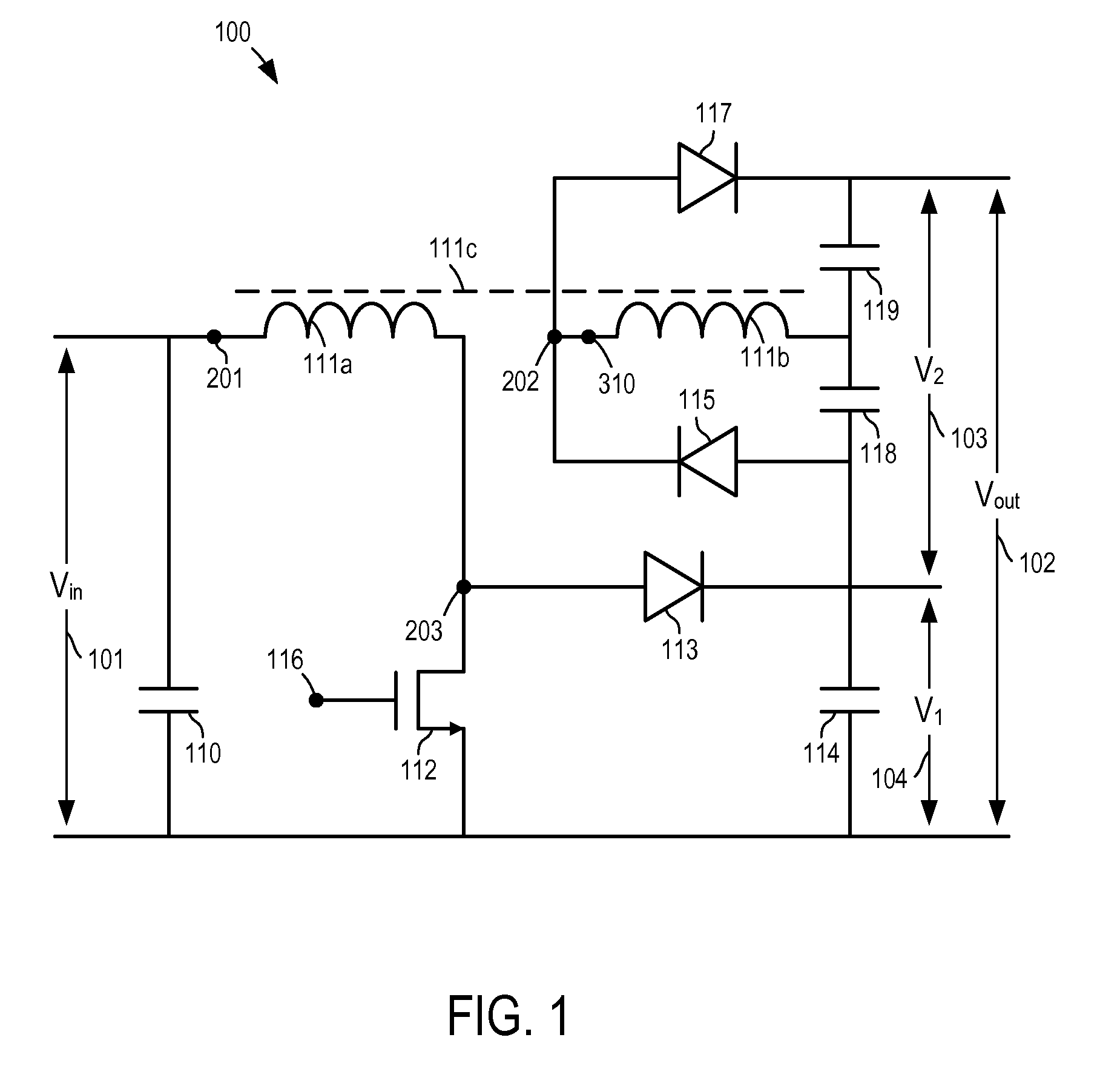
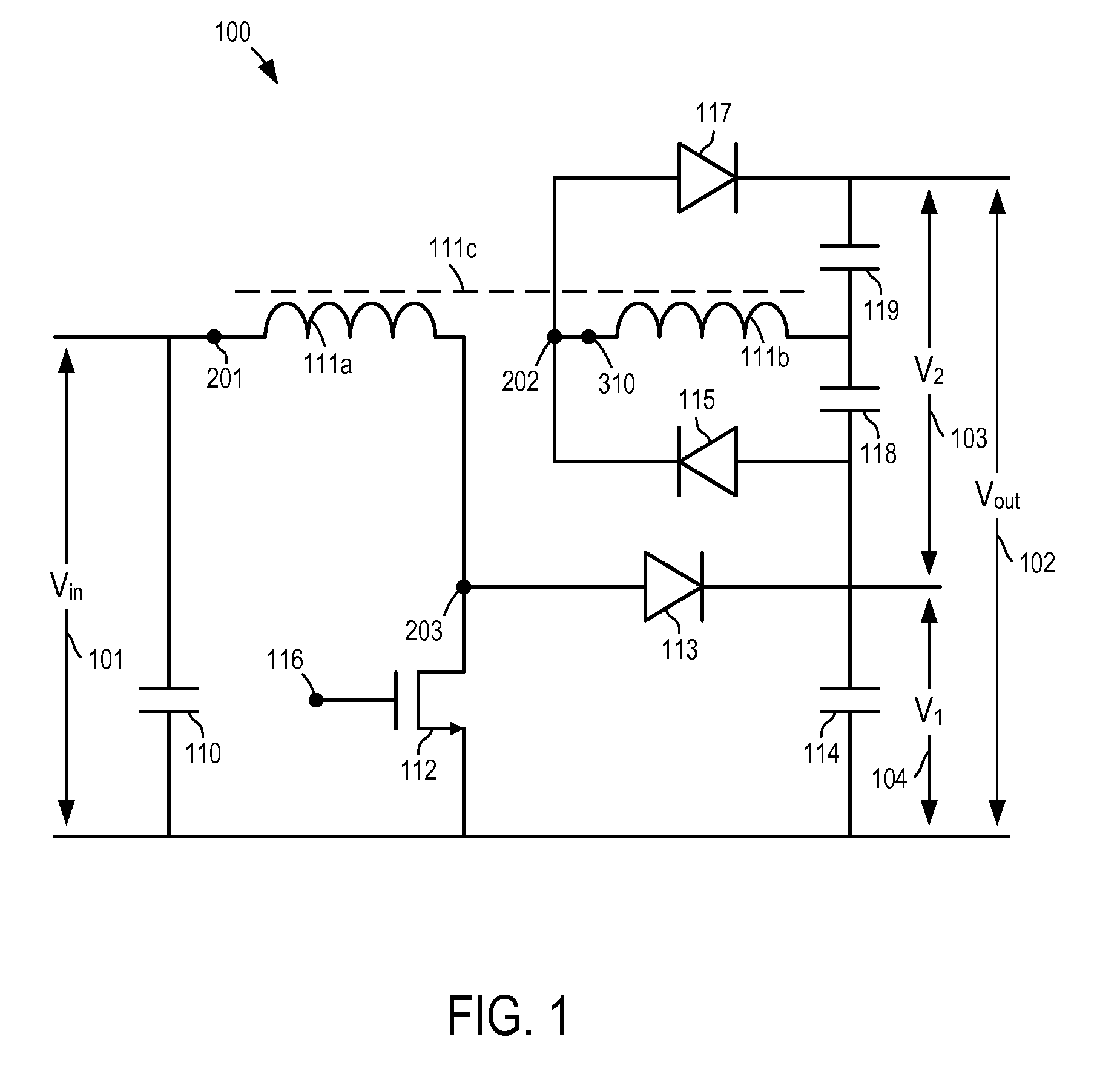
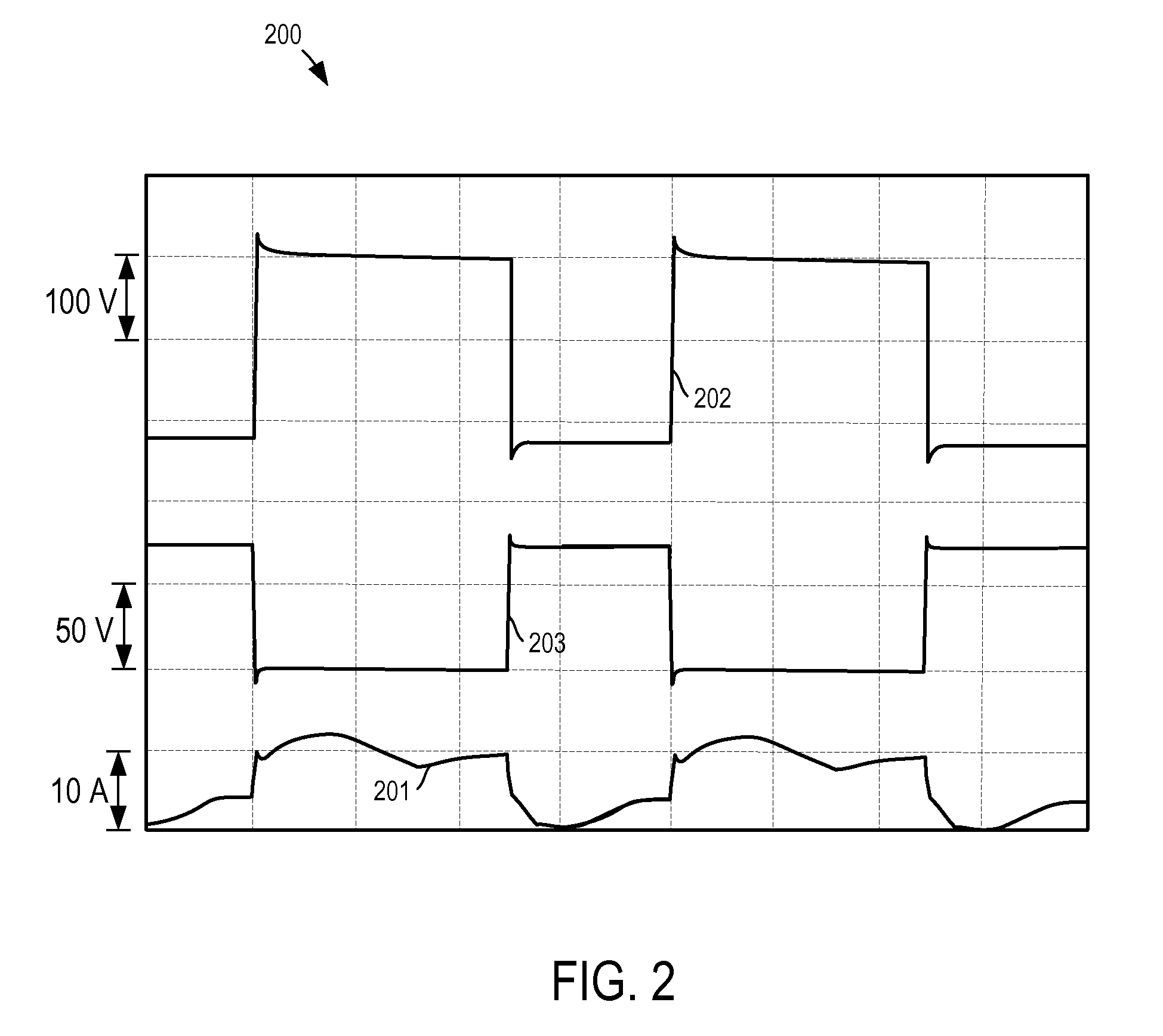
Multi-level dc bus inverter for providing sinusoidal and PWM electrical machine voltages
InactiveUS6969967B2Shorten the counting processAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlMachine controlFull bridge
A circuit for controlling an ac machine comprises a full bridge network of commutation switches which are connected to supply current for a corresponding voltage phase to the stator windings, a plurality of diodes, each in parallel connection to a respective one of the commutation switches, a plurality of dc source connections providing a multi-level dc bus for the full bridge network of commutation switches to produce sinusoidal voltages or PWM signals, and a controller connected for control of said dc source connections and said full bridge network of commutation switches to output substantially sinusoidal voltages to the stator windings. With the invention, the number of semiconductor switches is reduced to m+3 for a multi-level dc bus having m levels. A method of machine control is also disclosed.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Grid-Connected Power Conditioner and Grid-Connected Power Supply System
InactiveUS20090086520A1Reduce power lossIncrease power storageAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionPower conditionerGround failure
During charging operations of a power storage unit, a voltage converting unit converts a voltage received from direct-current buses and supplies it to power storage unit, whereas during discharging operations of power storage unit, voltage converting unit converts a voltage received from power storage unit and outputs it to direct-current buses. In voltage converting unit, a side connected to power storage unit and a side connected to direct-current buses are insulated from each other. As a result of this, if a ground failure occurs in power storage unit, its effects on an inverter circuit, a commercial power system and the like are prevented. A grid-connected power conditioner with high safety can thus be obtained.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and Apparatus for Controlling a Hybrid Power System
ActiveUS20100181837A1Simple control systemPrevent further power flowDc network circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower flowPower control system
The present invention provides a simplified method of controlling power among the various sources and loads in a power system. Power generating sources are each connected to a common DC bus through a converter designed to optimize power flow to the DC bus. A DC storage device is connected to the common DC bus through a power regulator designed to maintain a constant voltage on the DC bus. Further, an inverter may be provided to convert the DC voltage to an AC voltage for a customer load or for connection to the utility grid. Each power conversion device is independently controlled to provide a modular and simplified power control system.
Owner:FAITH TECH INC
Regulation of Inverter DC Input Voltage in Photovoltaic Arrays
ActiveUS20120205974A1Batteries circuit arrangementsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringDC-BUS
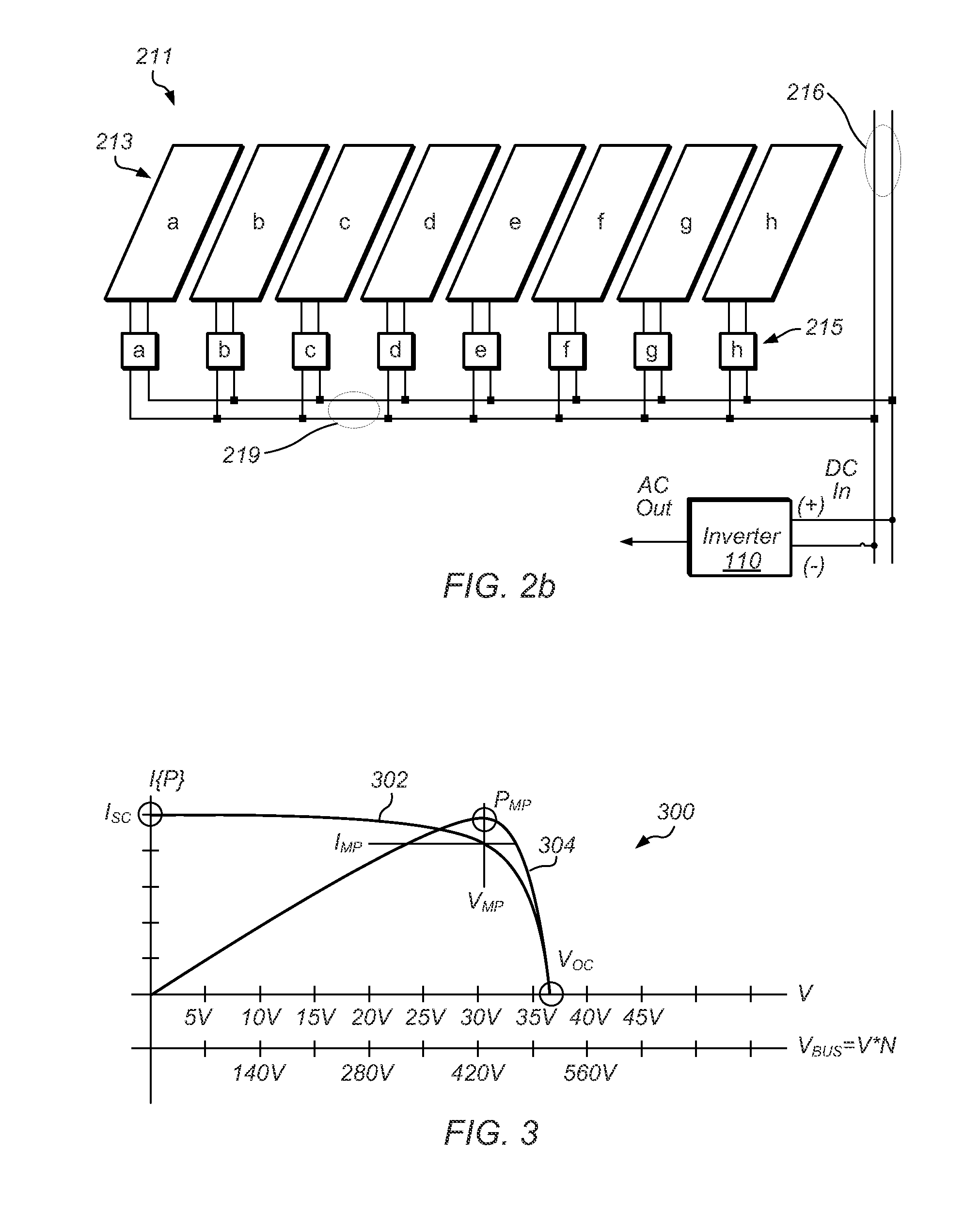
A converter unit configured to couple to a photovoltaic panel (PV) may include a controller to sense an output voltage and output current produced by the photovoltaic panel, and manage the output voltage of a corresponding power converter coupled to a DC bus to regulate the resultant bus voltage to a point that reduces overall system losses, and removes non-idealities when the panels are series connected. The controller may also adapt to output condition constraints, and perform a combination of input voltage and output voltage management and regulation, including maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for the PV. The output voltage and output current characteristic of the power converter may be shaped to present a power gradient—which may be hysteretically controlled—to the DC bus to compel an inverter coupled to the DC bus to perform its own MPPT to hold the DC-bus voltage within a determinate desired operating range.
Owner:BLUED ACQUISITION CORP
Aging status diagnostic apparatus for power conversion system, and method their of
InactiveUS20100161259A1Easy to installAchieve reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitor testingPower inverterHarmonic
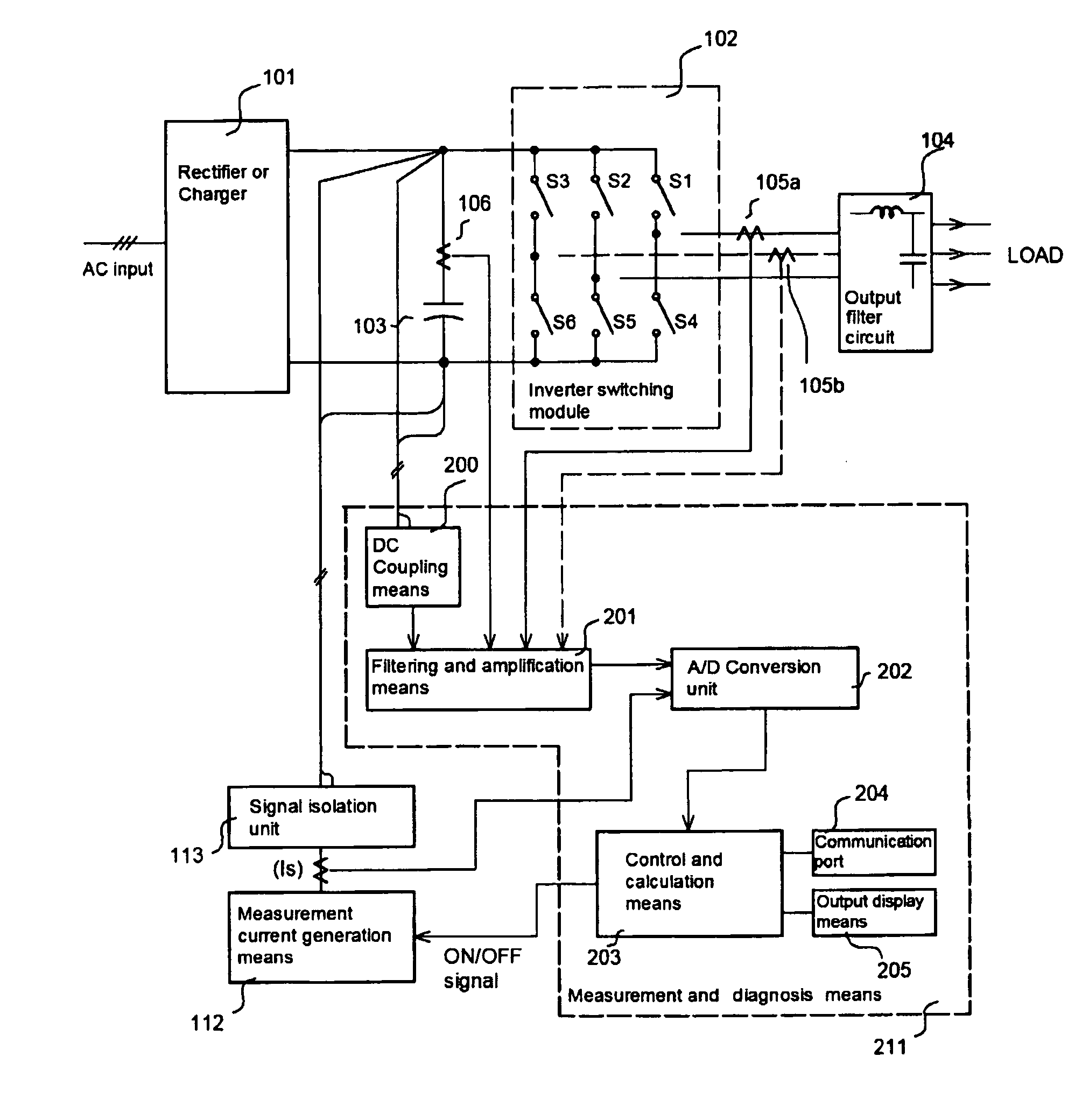
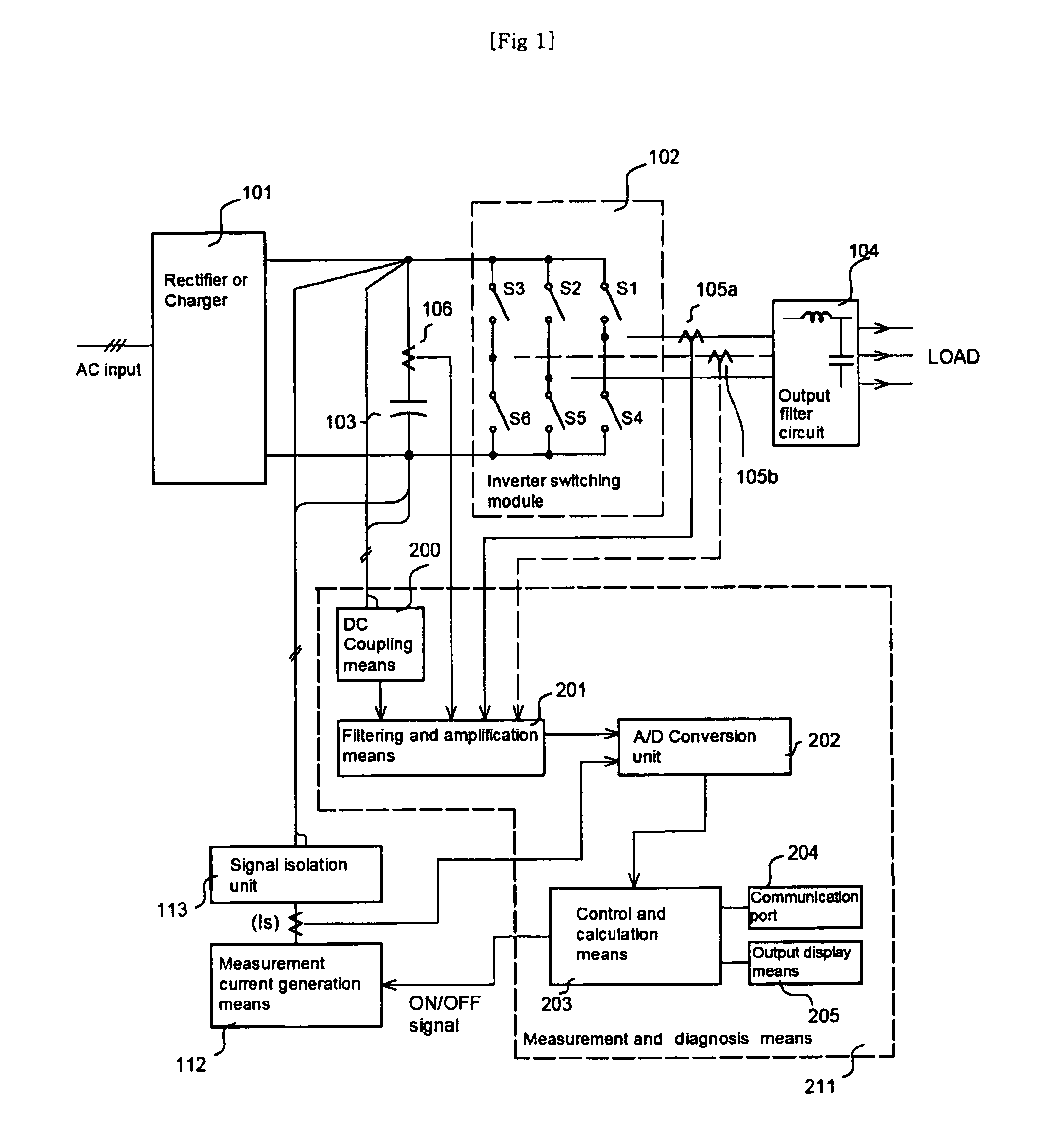
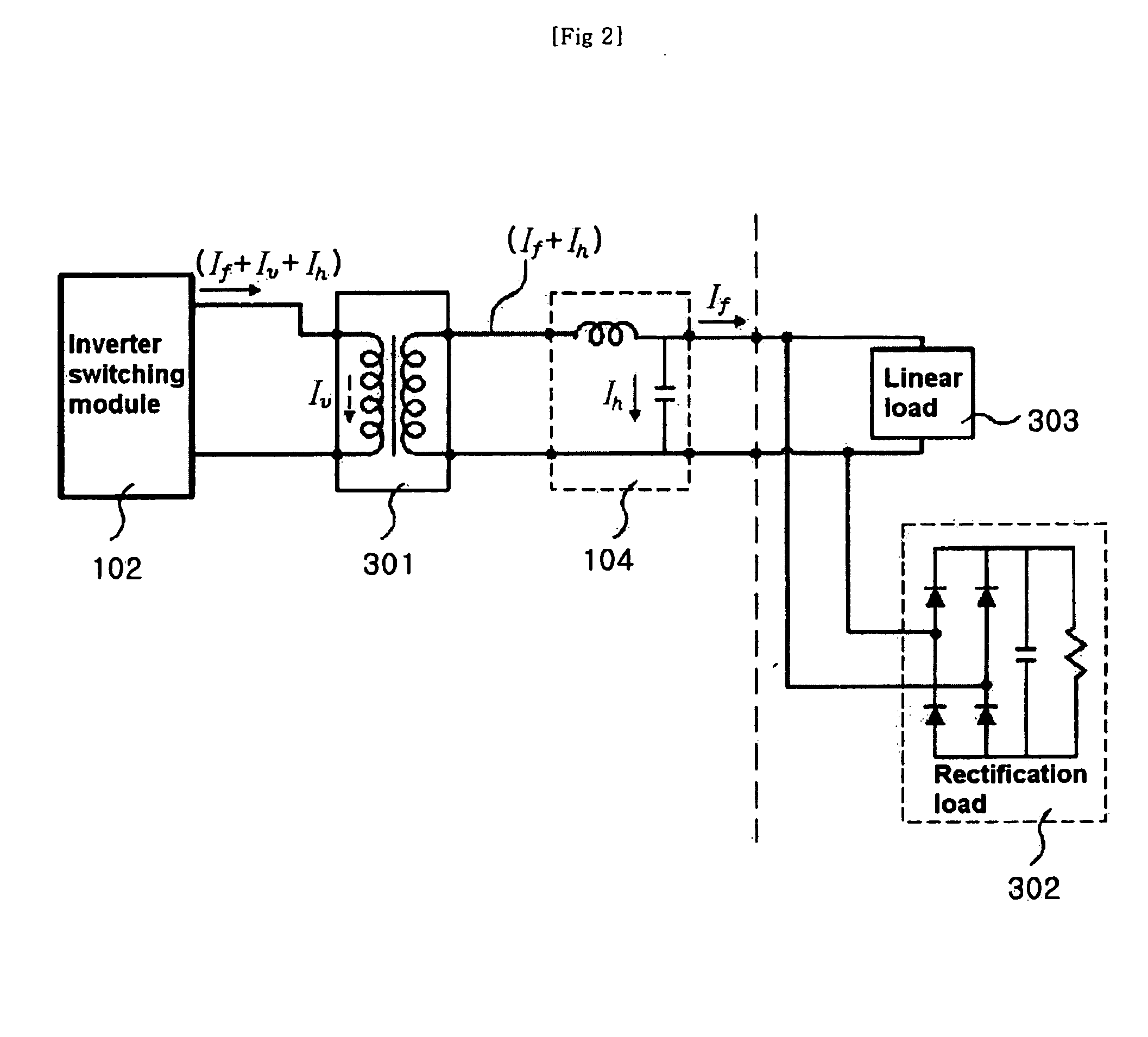
The present invention relates to an apparatus capable of diagnosing the aging state of a power conversion system at ordinary times and its diagnosing method to ensure the reliability of a power conversion system. The apparatus includes a current sensing means for detecting the output current of a inverter switching module or an electrolytic capacitor, and measurement and diagnosis means for extracting elements related to the aging status of the power conversion system by receiving the output current waveform of the inverter switching module and magnitude of each harmonic or an impedance voltage signal of the electrolytic capacitor. Furthermore, it is preferable that the apparatus further includes a measurement current generation means for generating measurement current to be supplied to the electrolytic capacitor. By analyzing an average value or the magnitude of harmonics by FFT analysis of the output current waveform of the inverter switching module and measuring an ESR value or a loss angle tan δ of a DC bus of the power conversion system, the present invention is able to monitor and diagnose the abnormal state attributable to the aging or degradation of the power conversion system in advance.
Owner:POWERTRON ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com