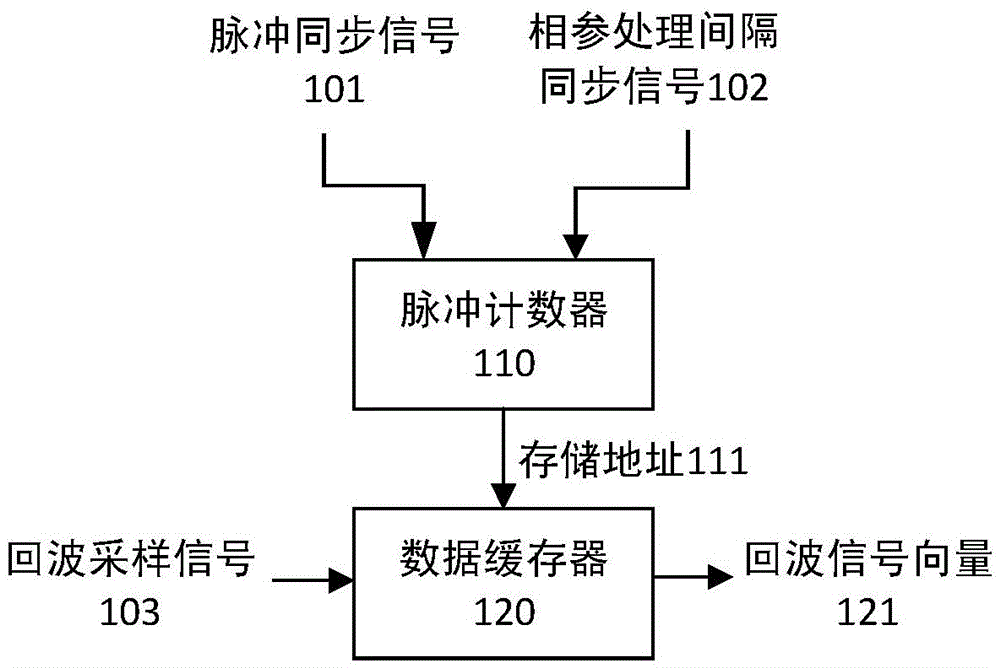
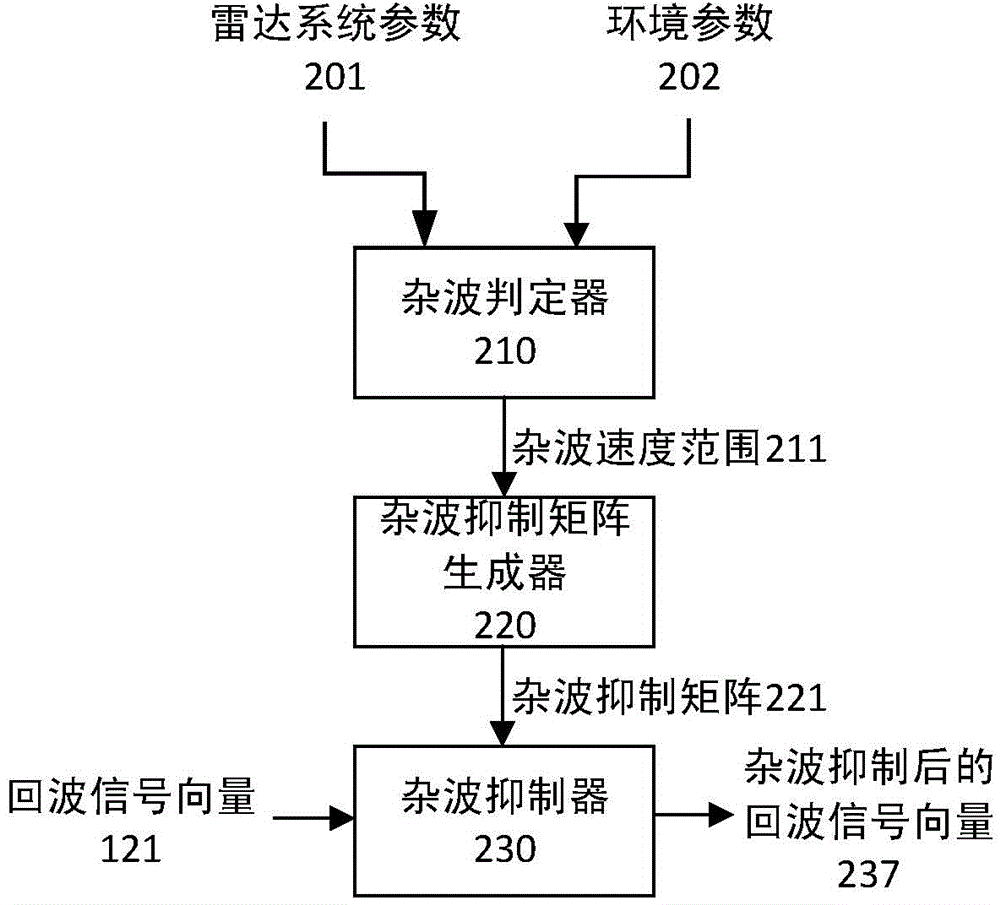
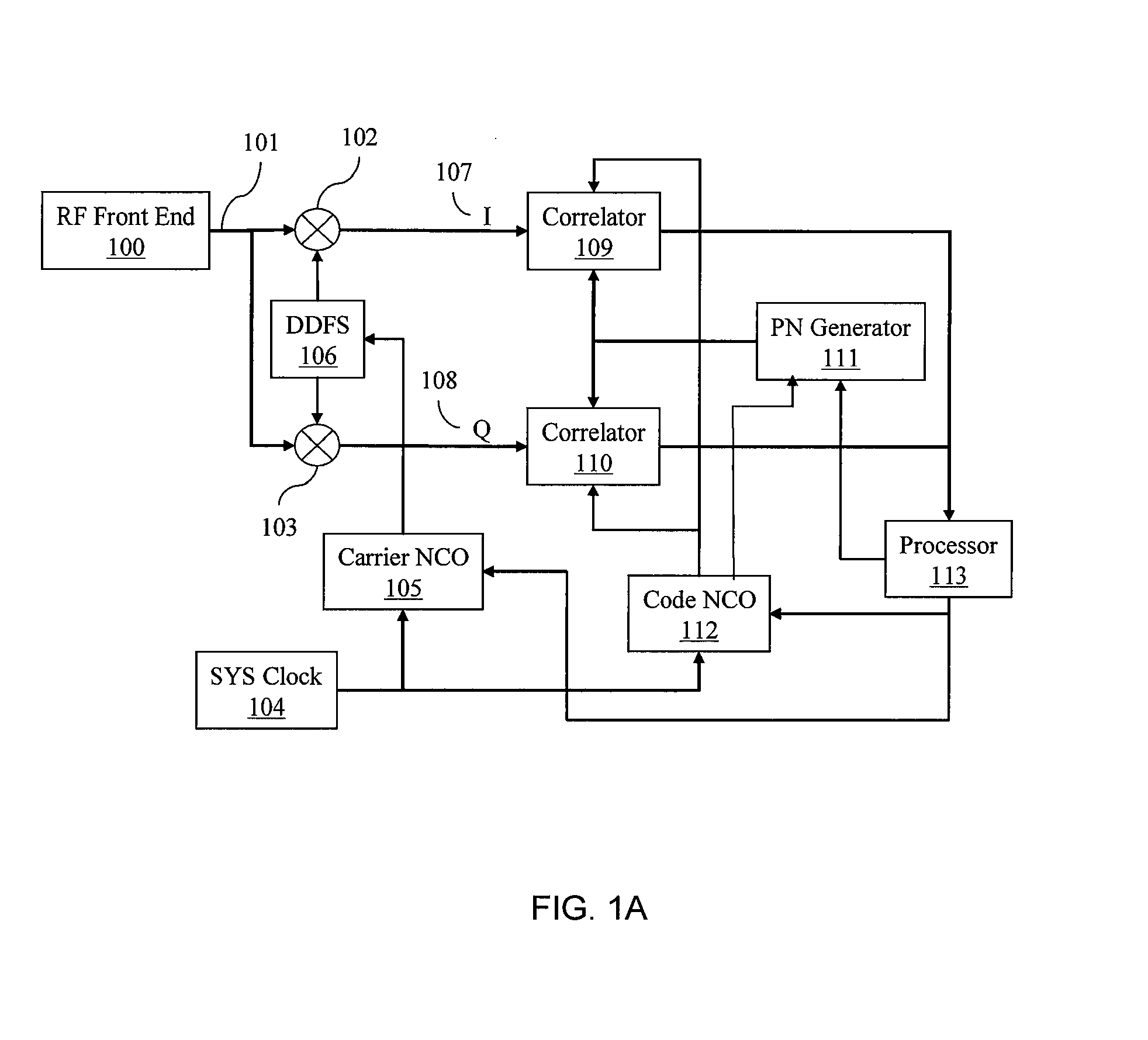
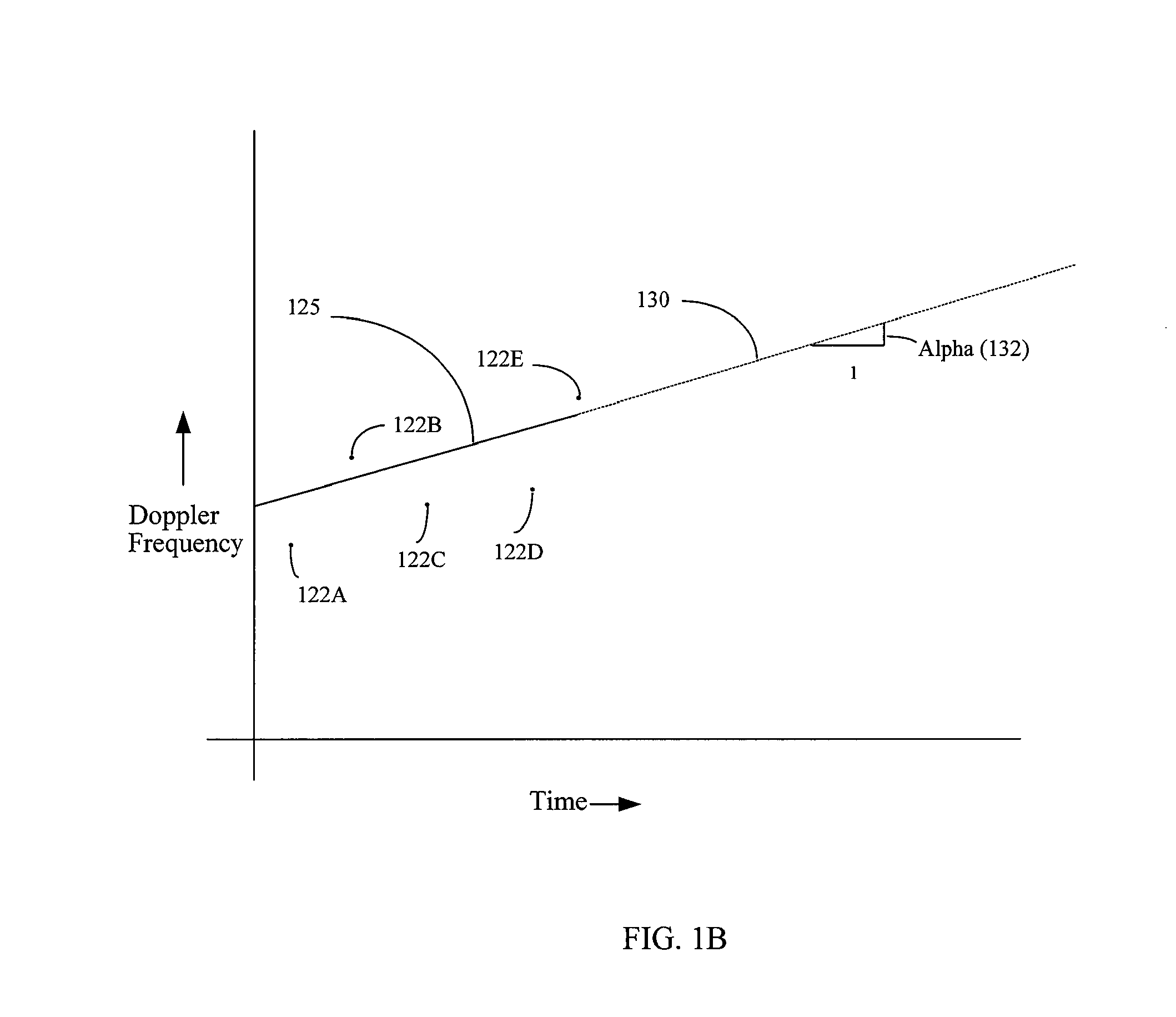
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
379 results about "Coherent integration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
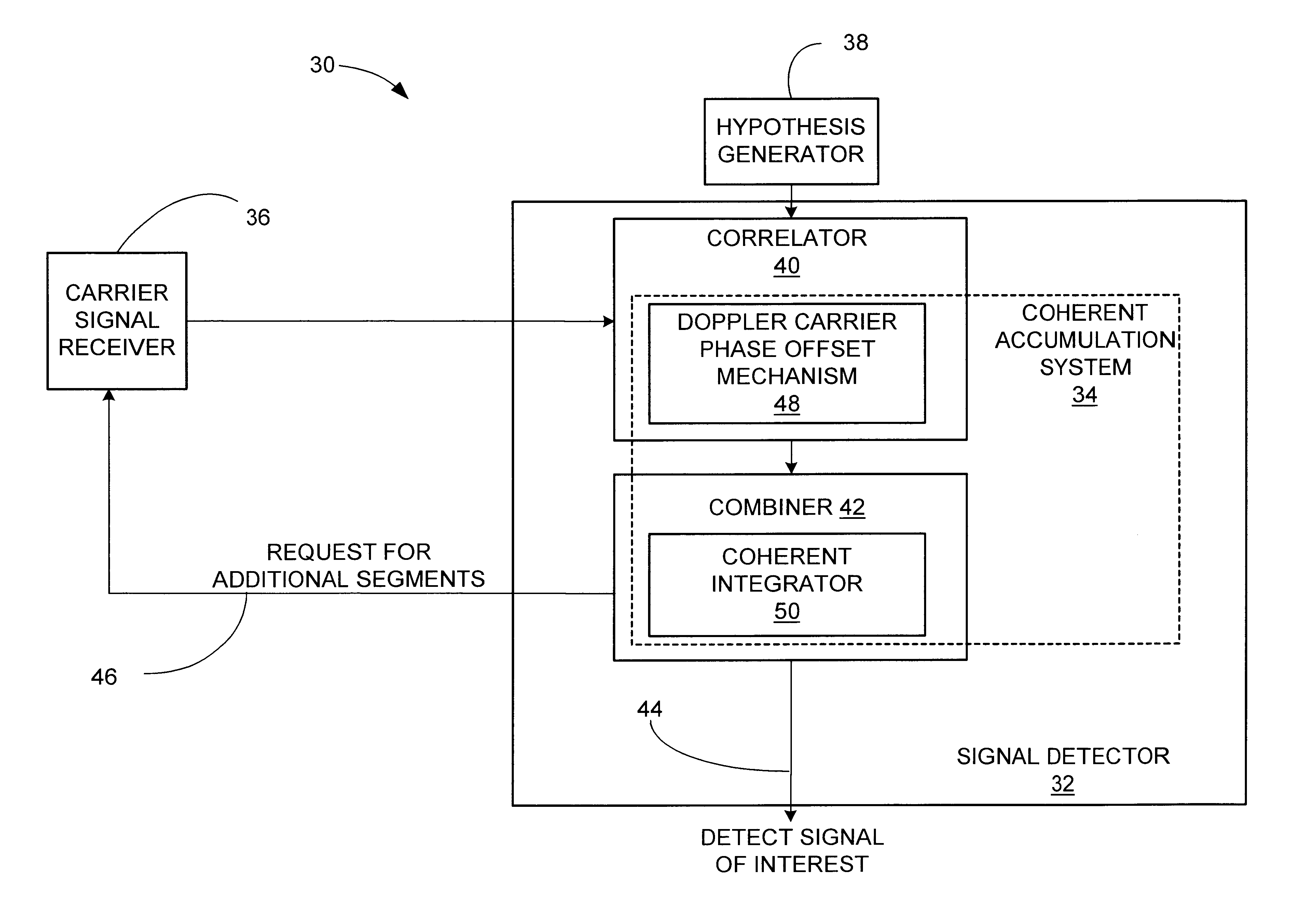
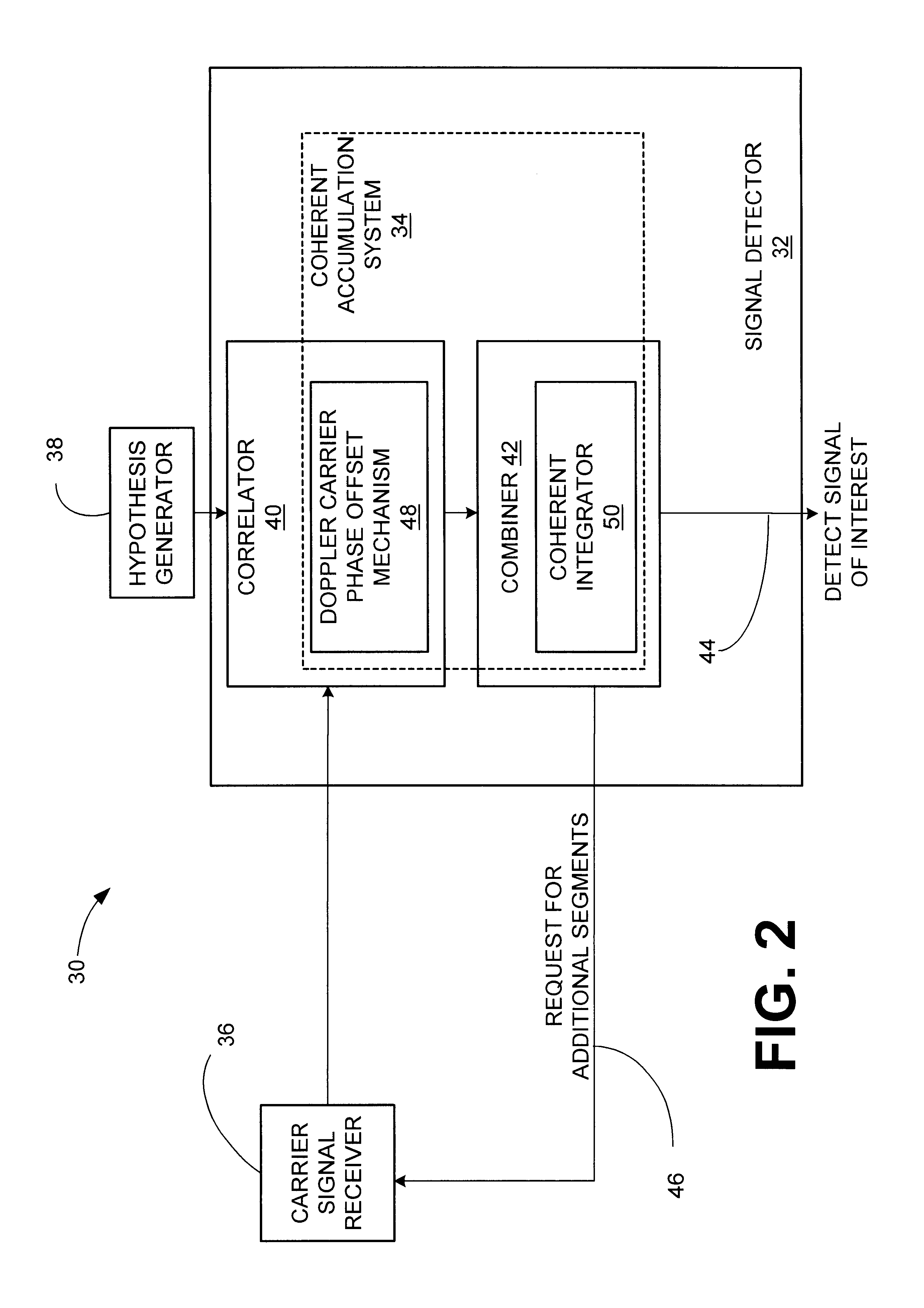
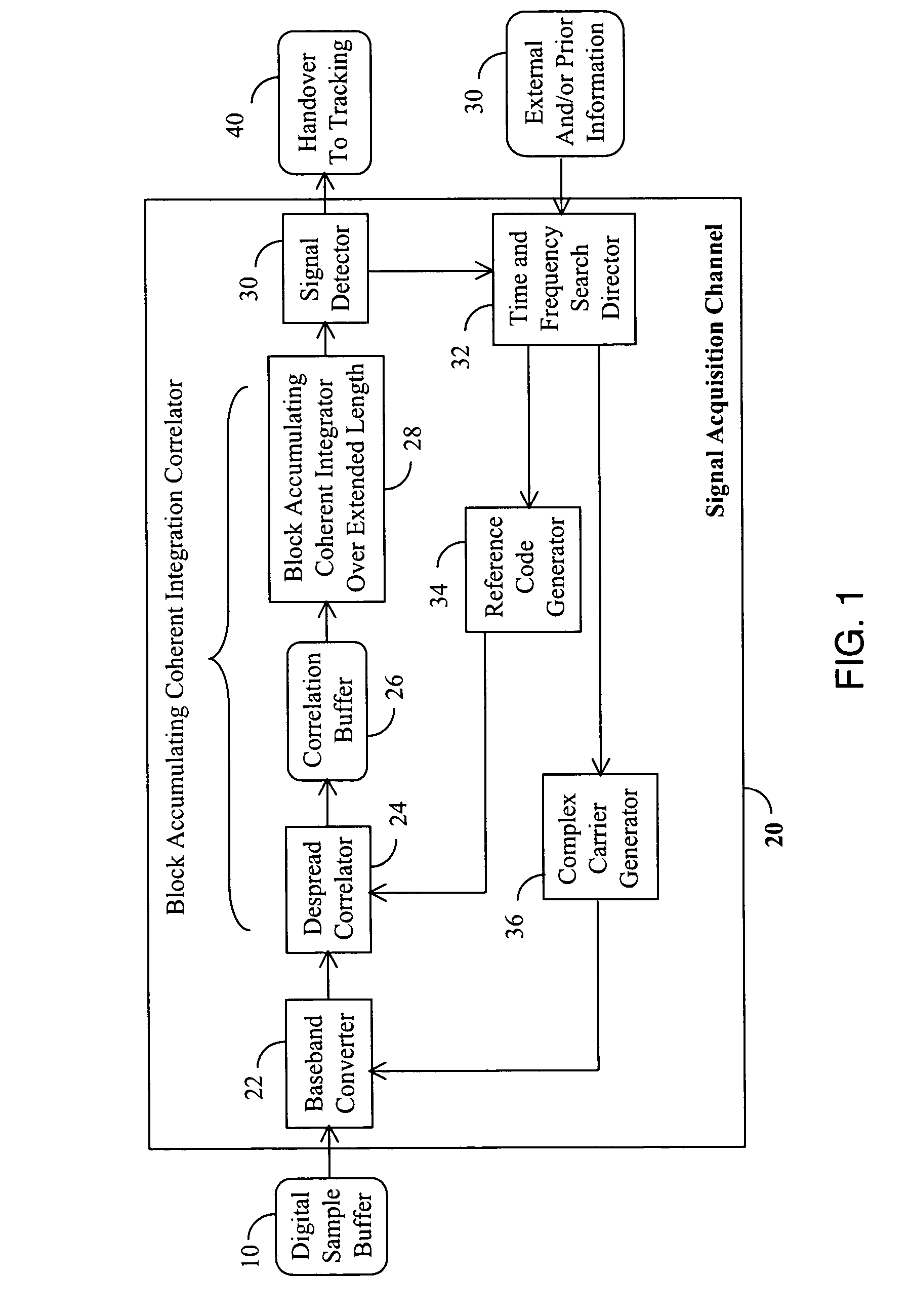
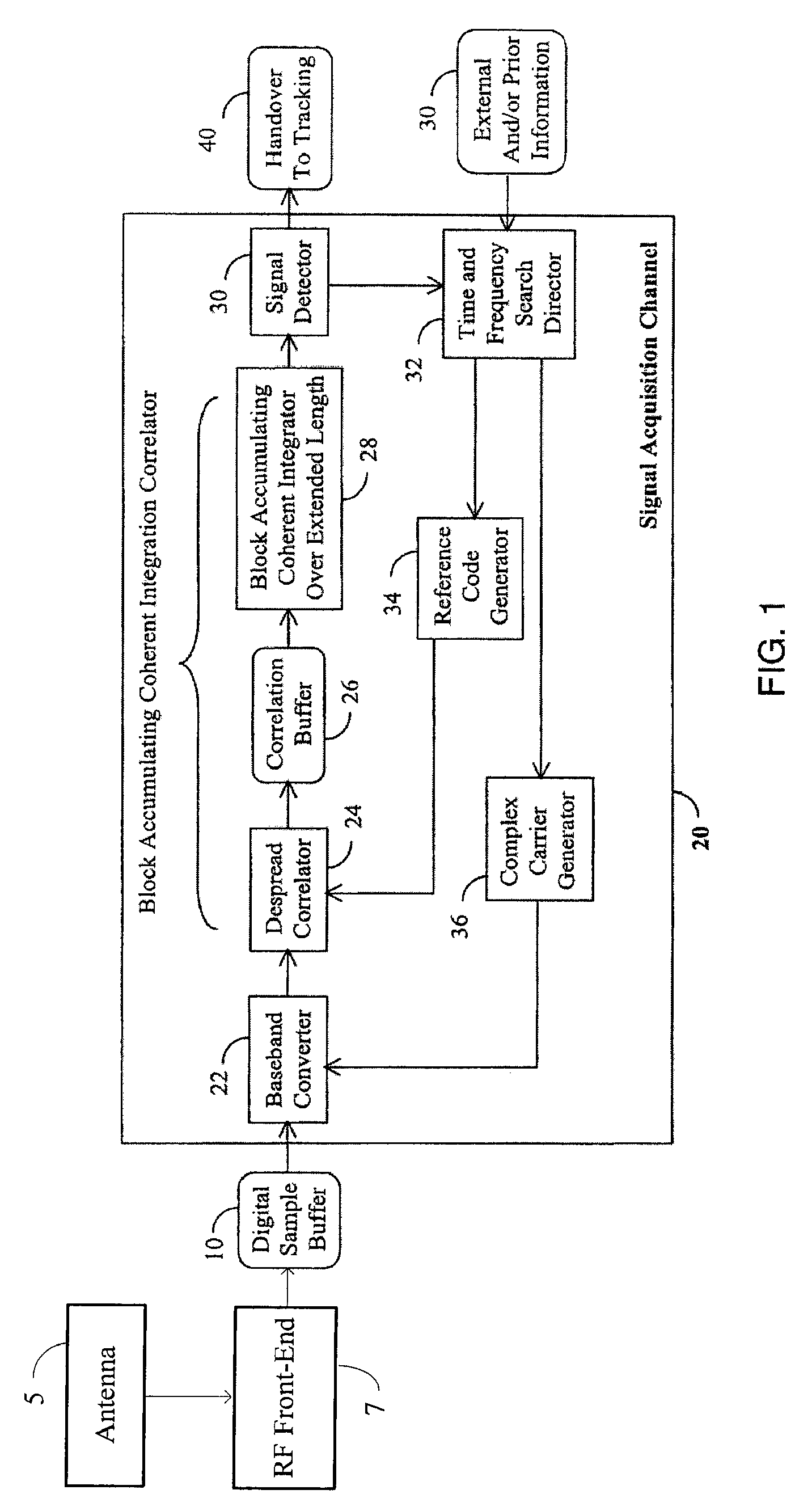
Signal detector and method employing a coherent accumulation system to correlate non-uniform and disjoint sample segments
InactiveUS6850557B1Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsModulated-carrier systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Time segment
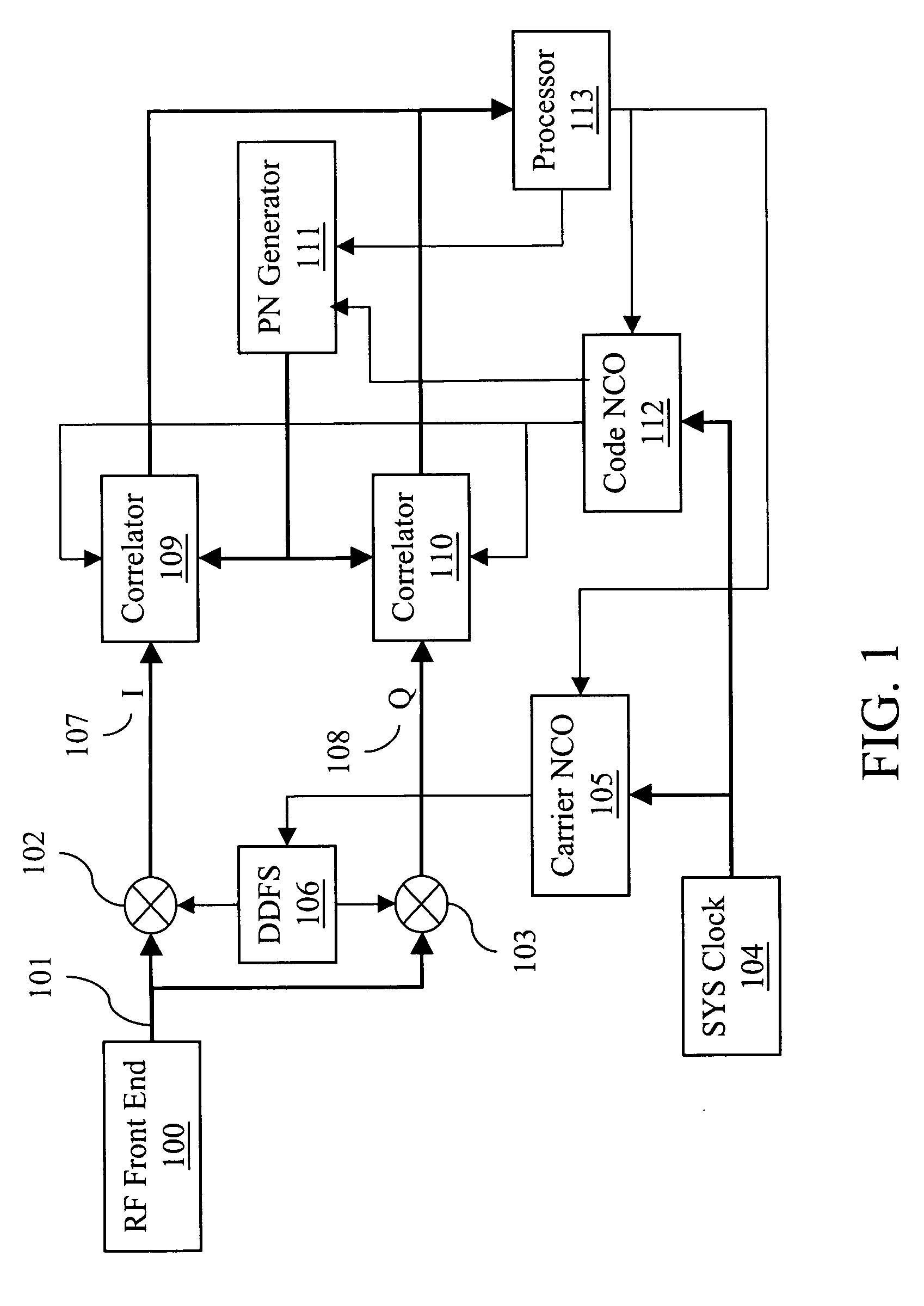
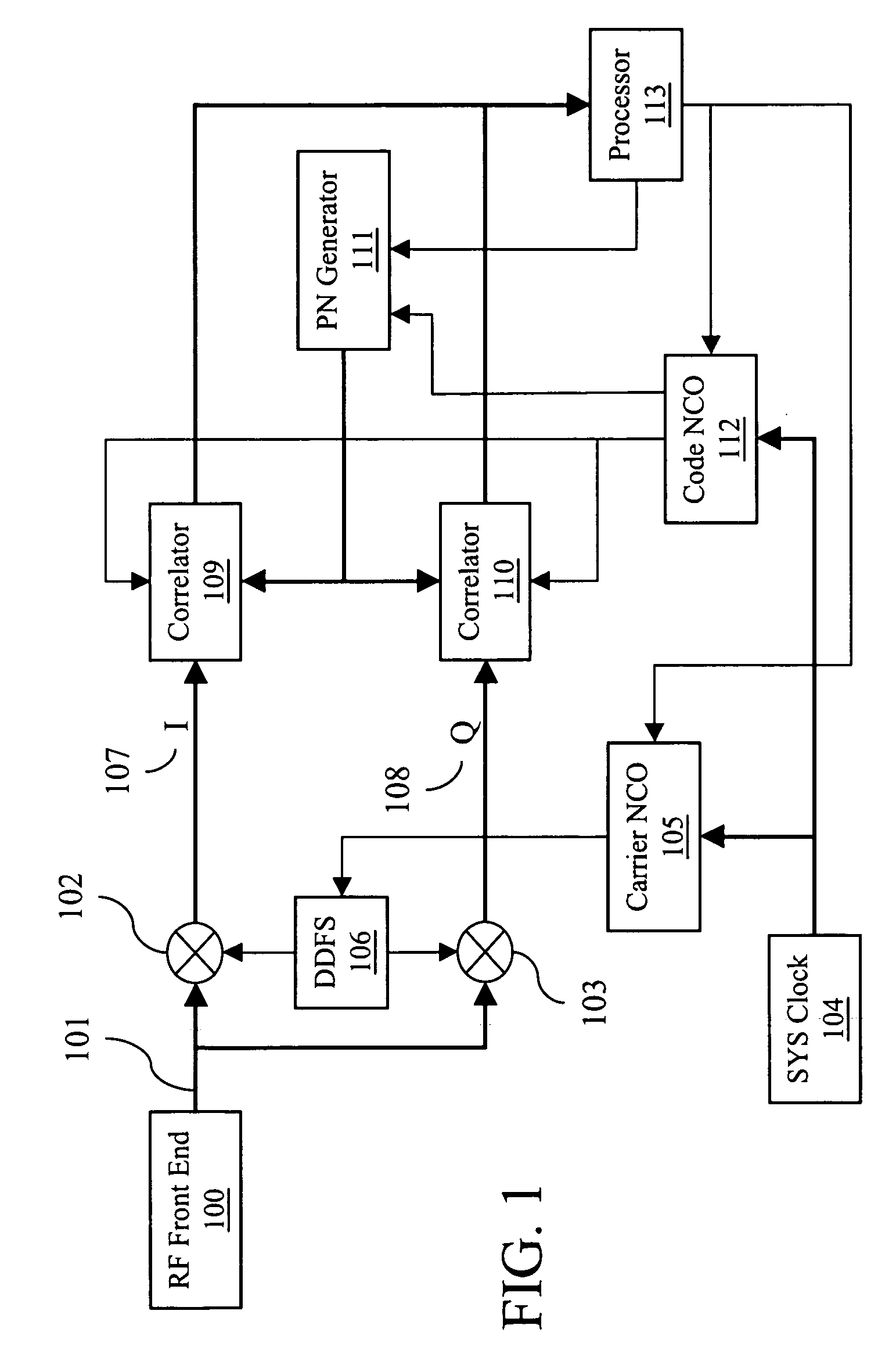
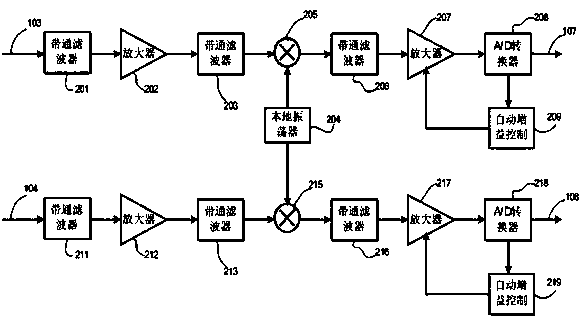
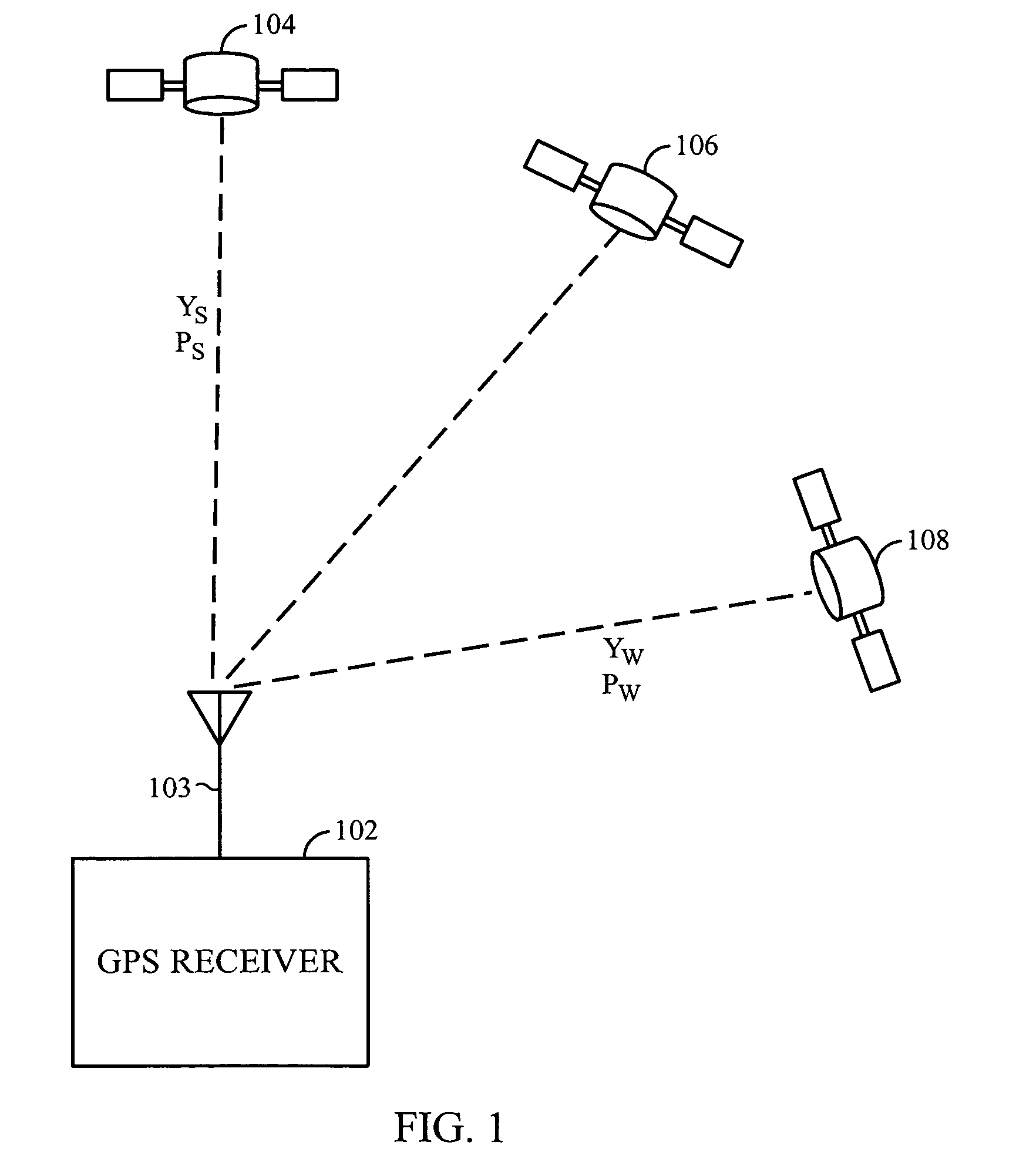
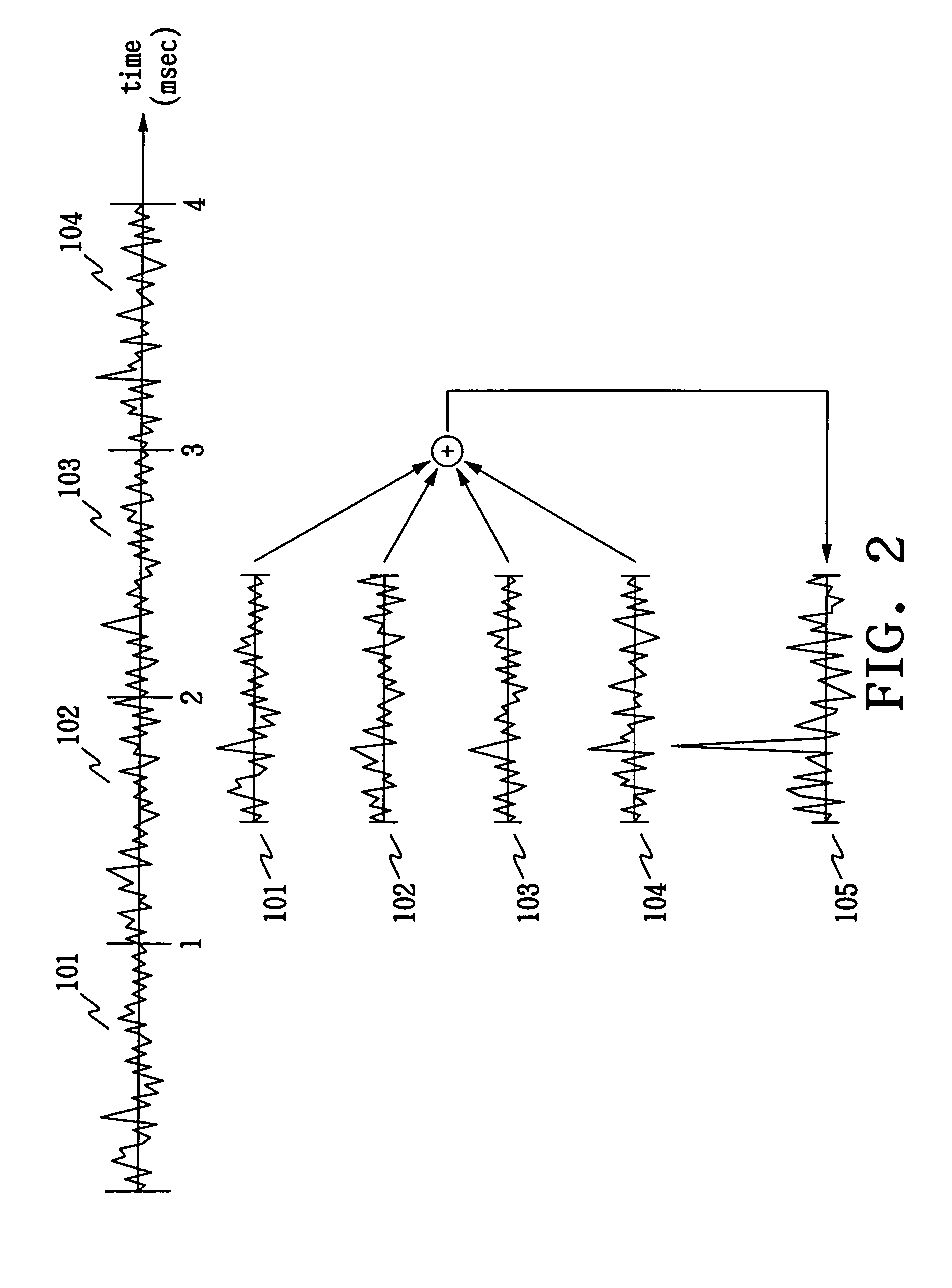
A signal detector employs a coherent accumulation system that coherently combines the correlation results derived from segments of samples of a received signal. The segments may have non-uniform lengths and may have been obtained over different and non-overlapping time periods. The segments are obtained during sampling windows of arbitrary length and at arbitrary times, and the results of processing the segments are successively combined in a coherent manner (separate magnitude and phase accumulation) until a threshold signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) has been achieved. Coherent integration is enabled by introducing a carrier phase offset as well as a code phase offset, so that different segments are aligned in carrier phase as well as code phase. Although not limited to this application, in one implementation example, the signal detector is used in connection with and as part of a global positioning system (GPS) receiver.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
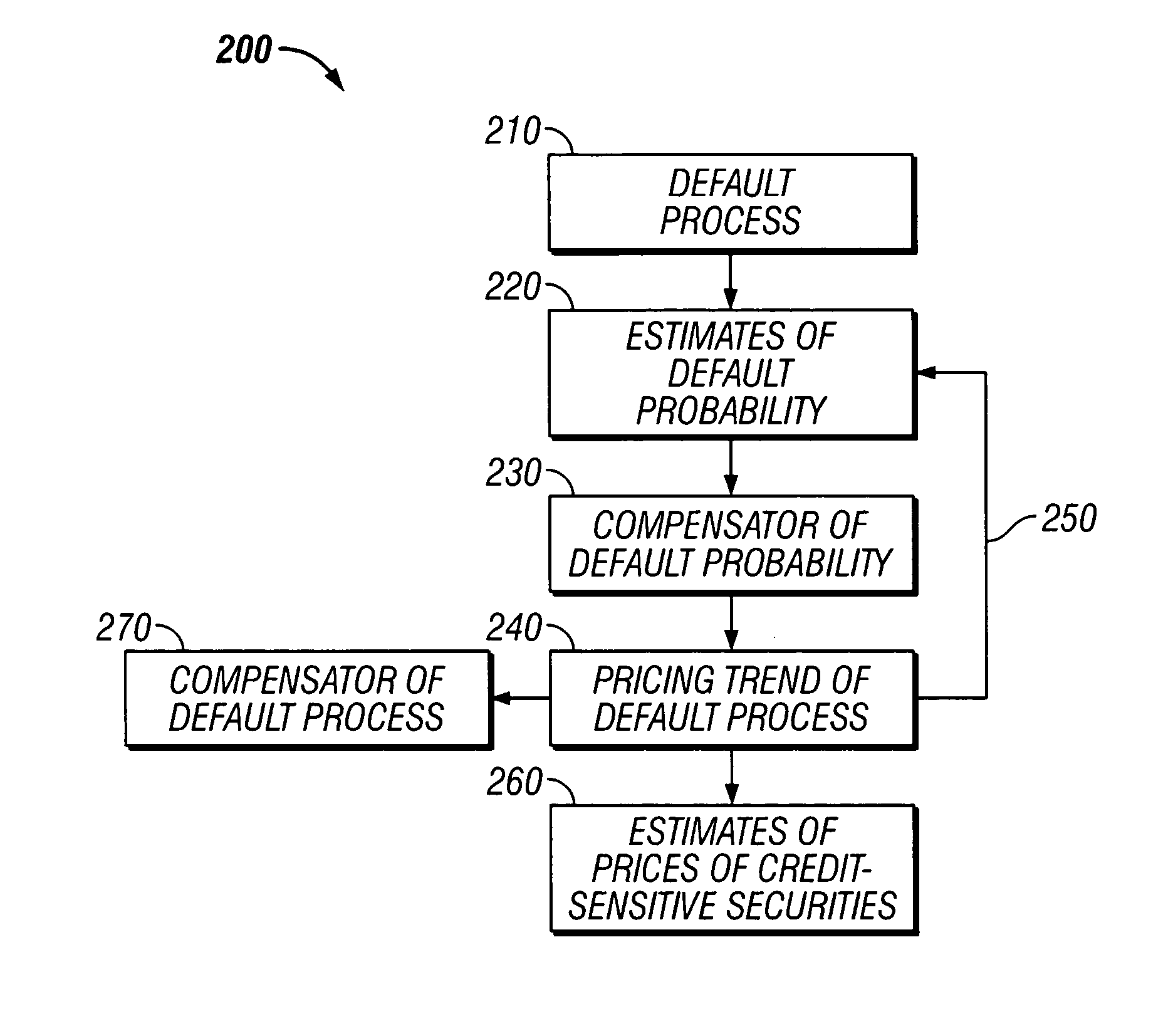
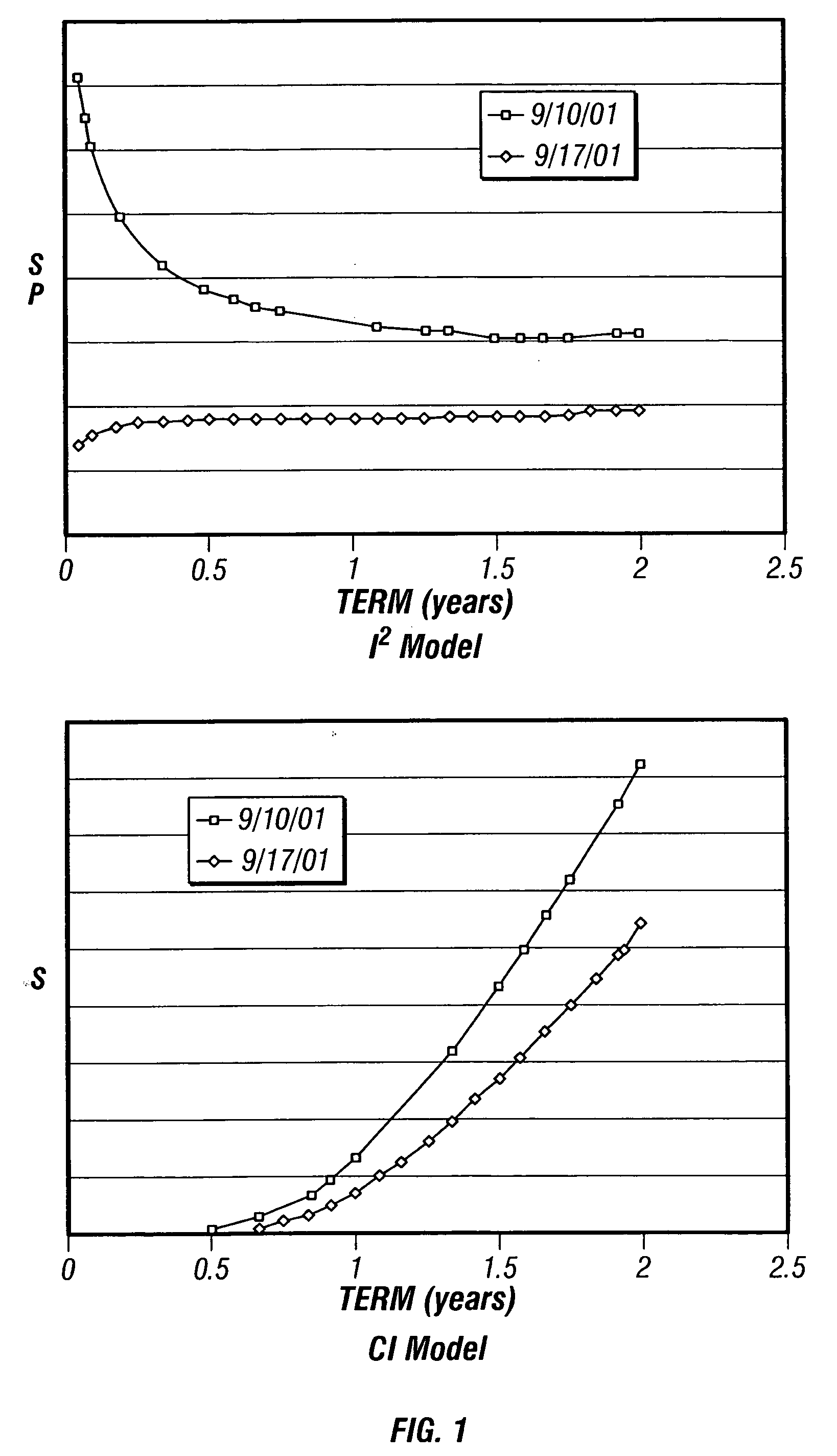
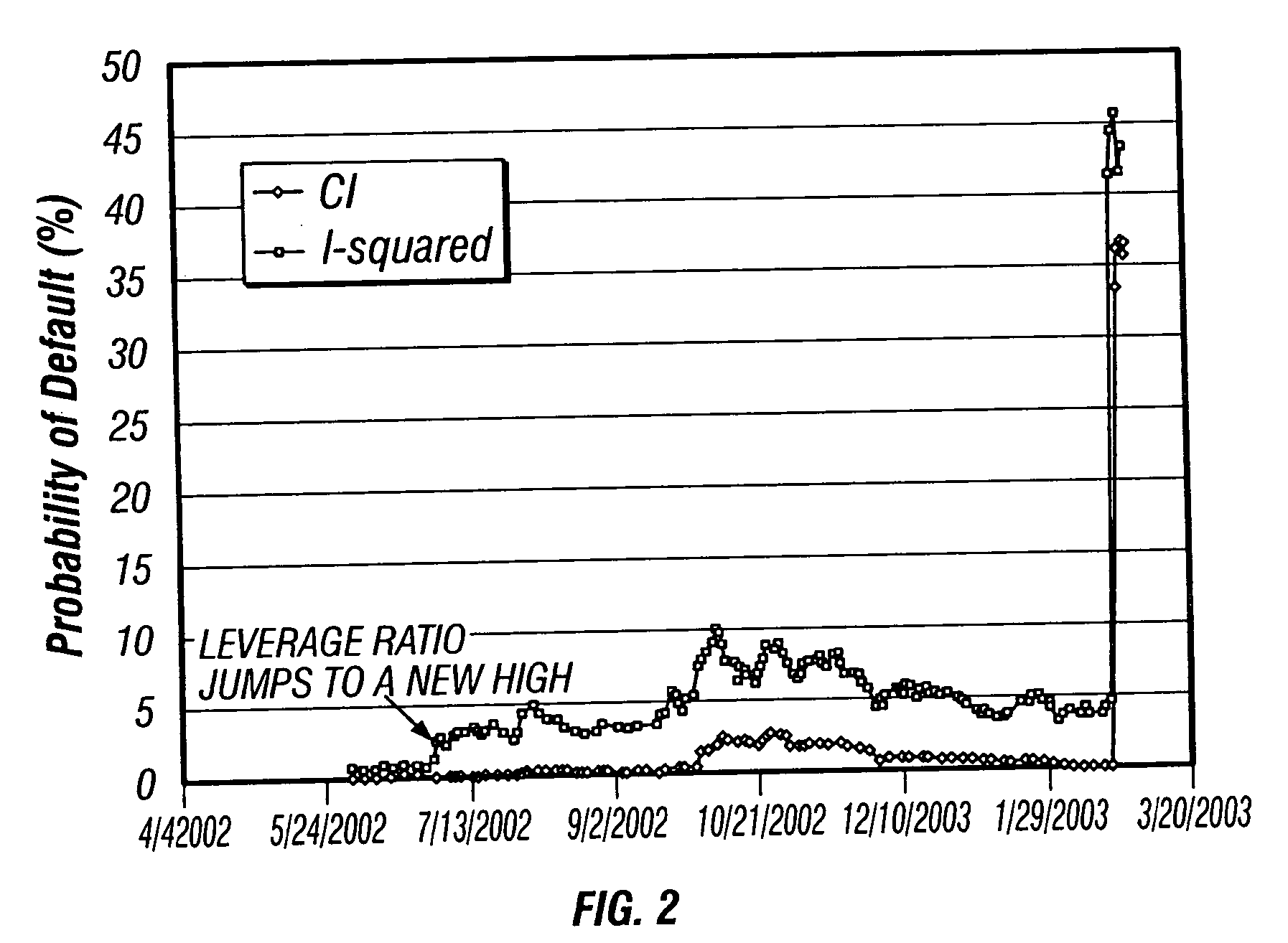
Method and apparatus for an incomplete information model of credit risk
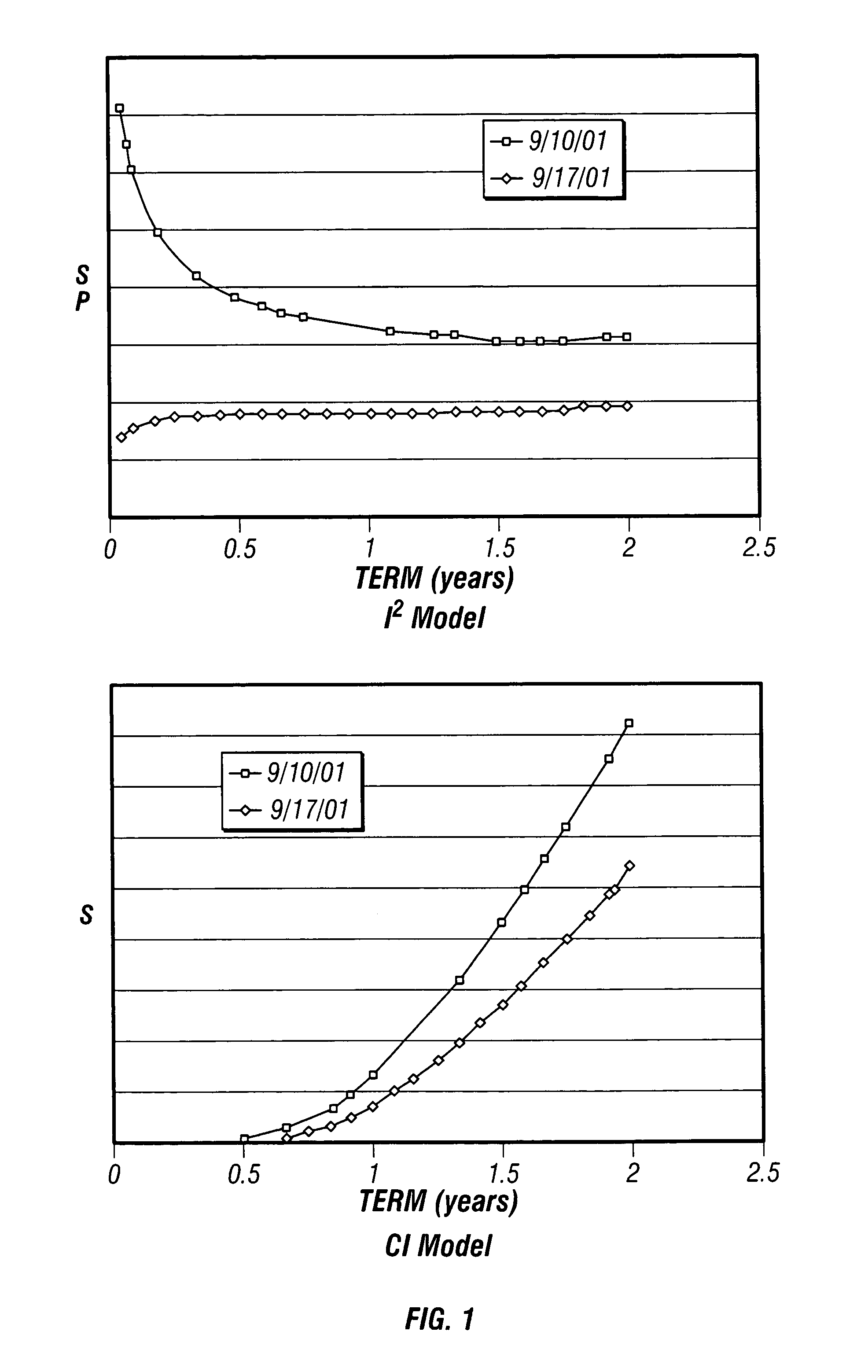
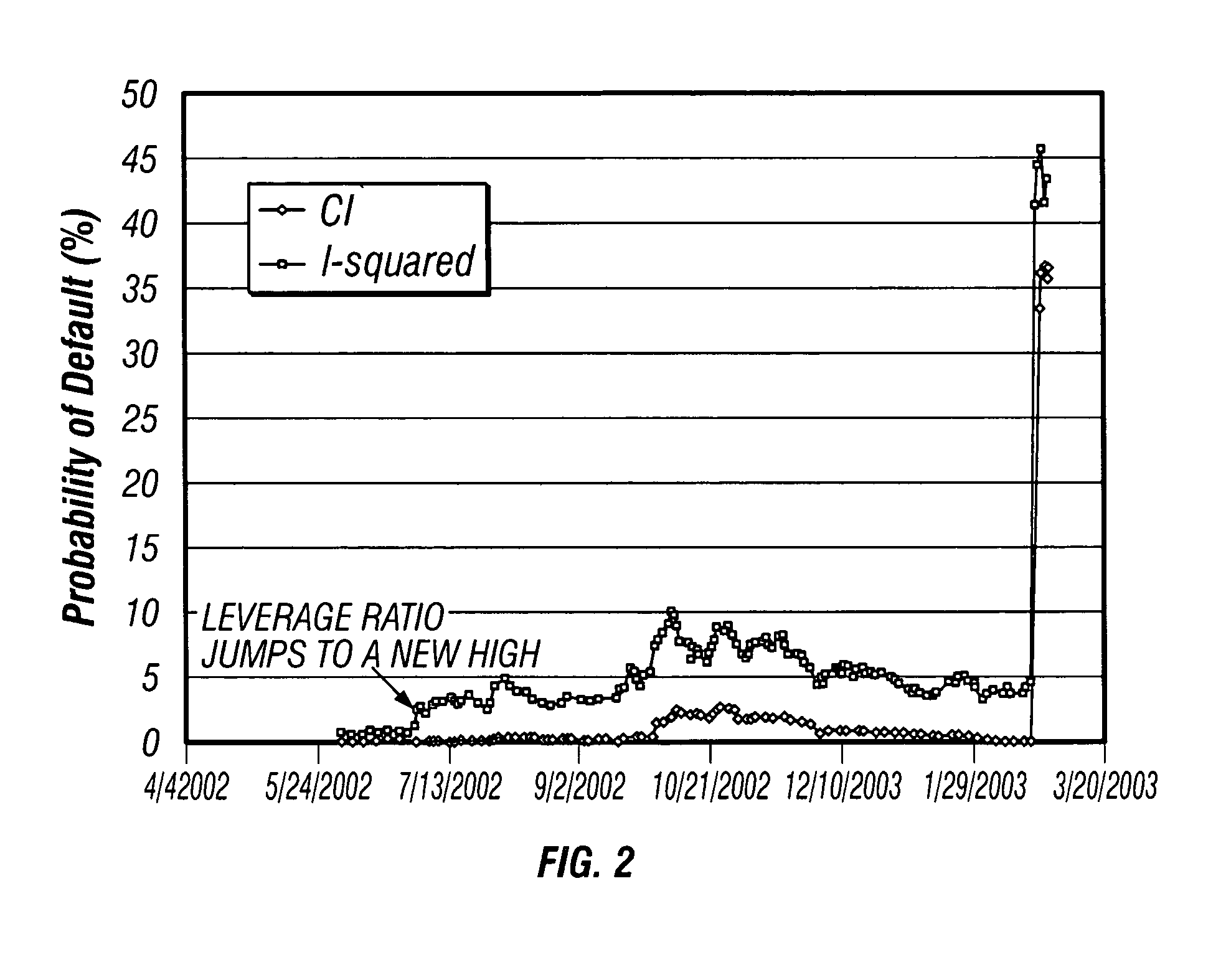
A method and apparatus for developing a structural model of credit risk that incorporates the short-term uncertainty inherent in default events is disclosed. The model is based on the assumption of incomplete information, taking as premise that bond investors are not certain about the true level of a firm's value that may trigger default. In addition, the coherent integration of structure and uncertainty is facilitated with compensators. Compensators form the infrastructure of a class of credit models that is broad enough to include traditional structural models, intensity-based models, and a great deal more. Several empirical examples are provided that compare default probabilities and credit yield spreads forecast by the incomplete information model to the output of a Black and Cox (1976) model. It is found that the incomplete information model reacts more quickly and, unlike traditional structural models, forecasts positive short-term credit spreads for firms that are in distress. It is also demonstrated that while the model is predicated on the surprise nature of default, it does not have conditional default rate.
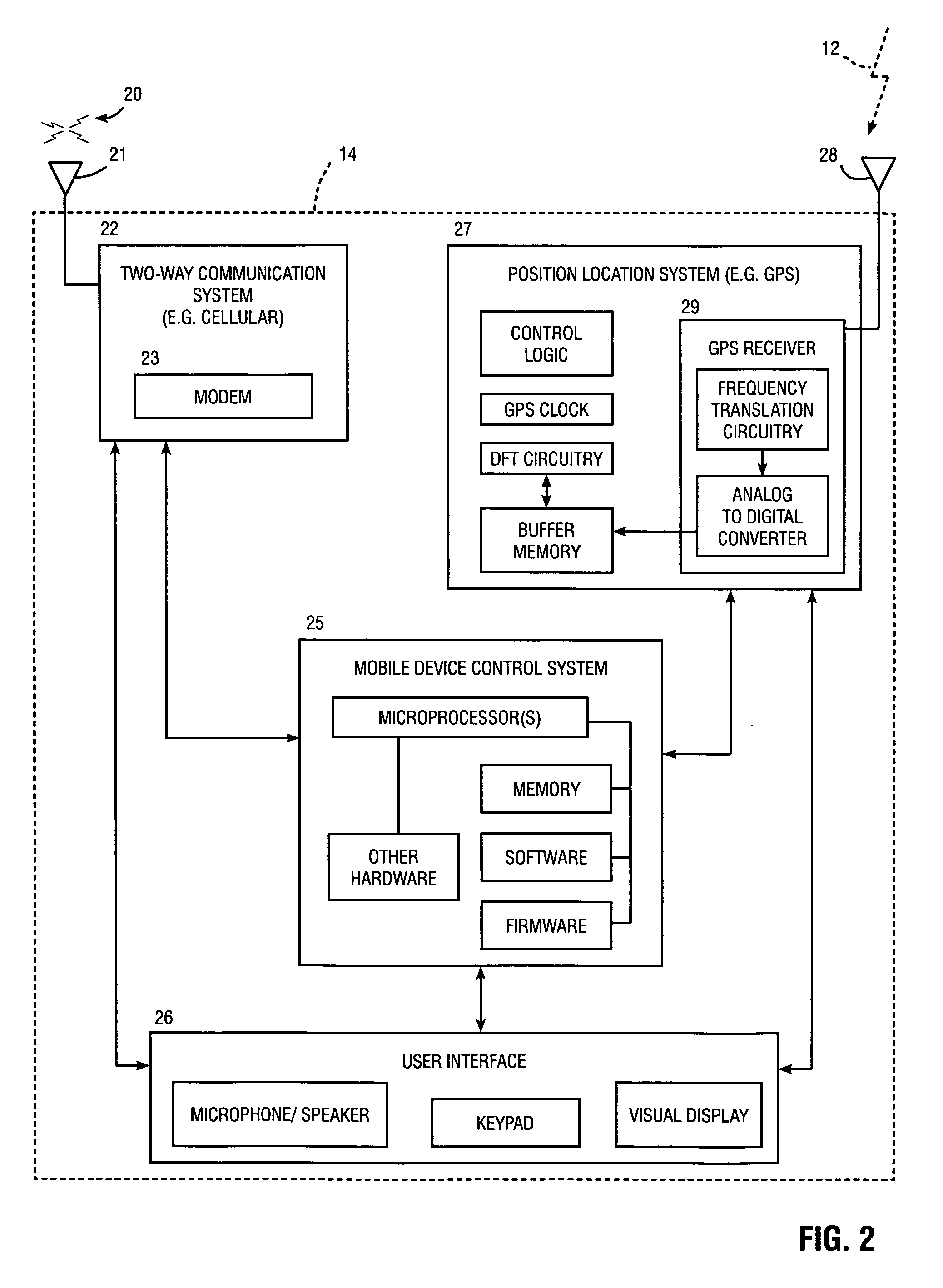
Owner:BARRA
Signal detector employing coherent integration
InactiveUS6577271B1Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsBeacon systems using radio wavesGps receiverSignal detector
A signal detector is provided in which complex samples of a received signal are multiplied by data representative of a hypothesis, and the resulting product data is coherently integrated over a desired duration to provide correlation data representative of the level of correlation between the hypothesis and the signal. In one embodiment, the signal detector is part of a GPS receiver.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
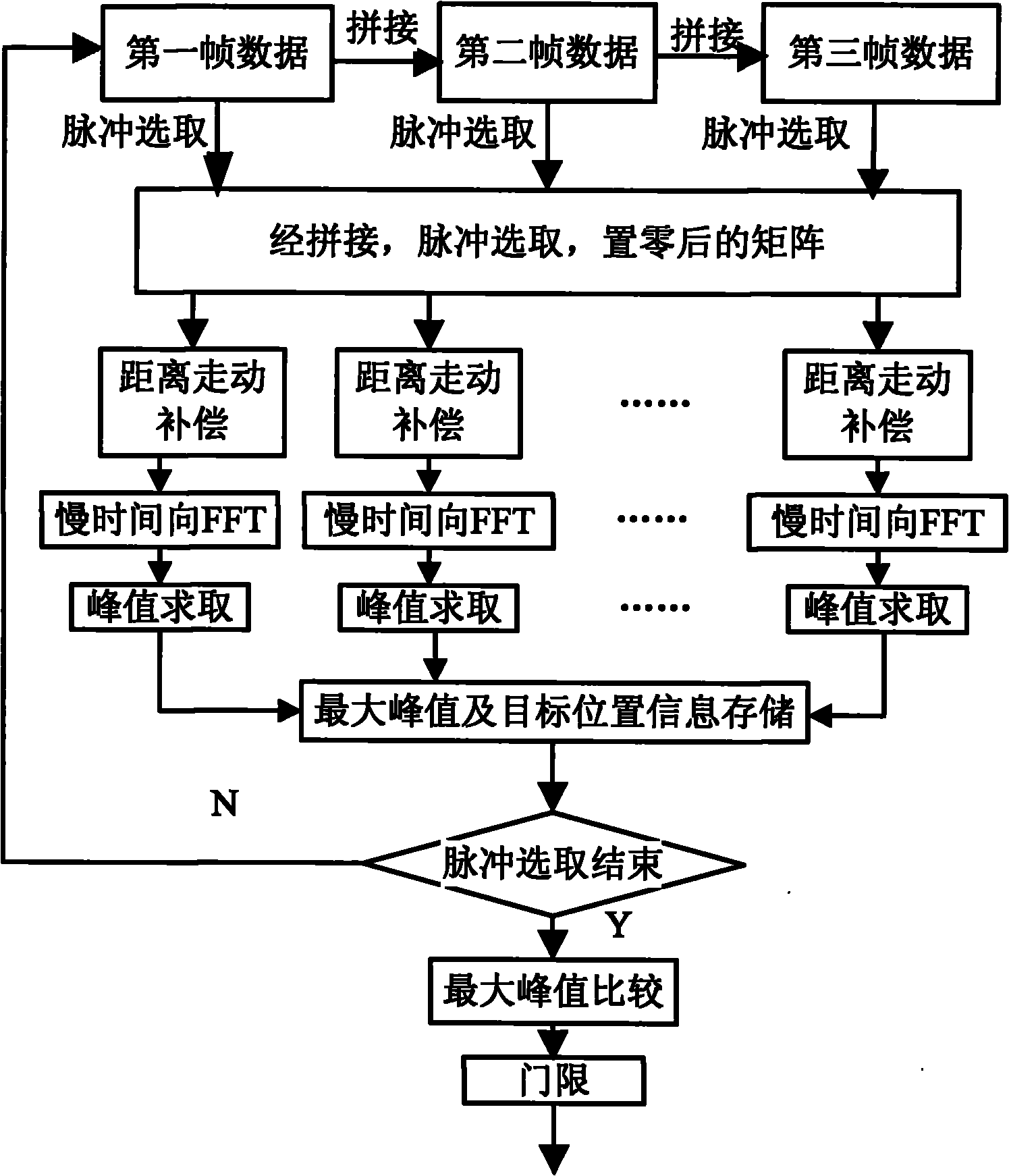
Target track-before-detect (TBD) method based on multi-frame coherent integration
InactiveCN102313884ARealize detectionImplement trackingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTrack-before-detectSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
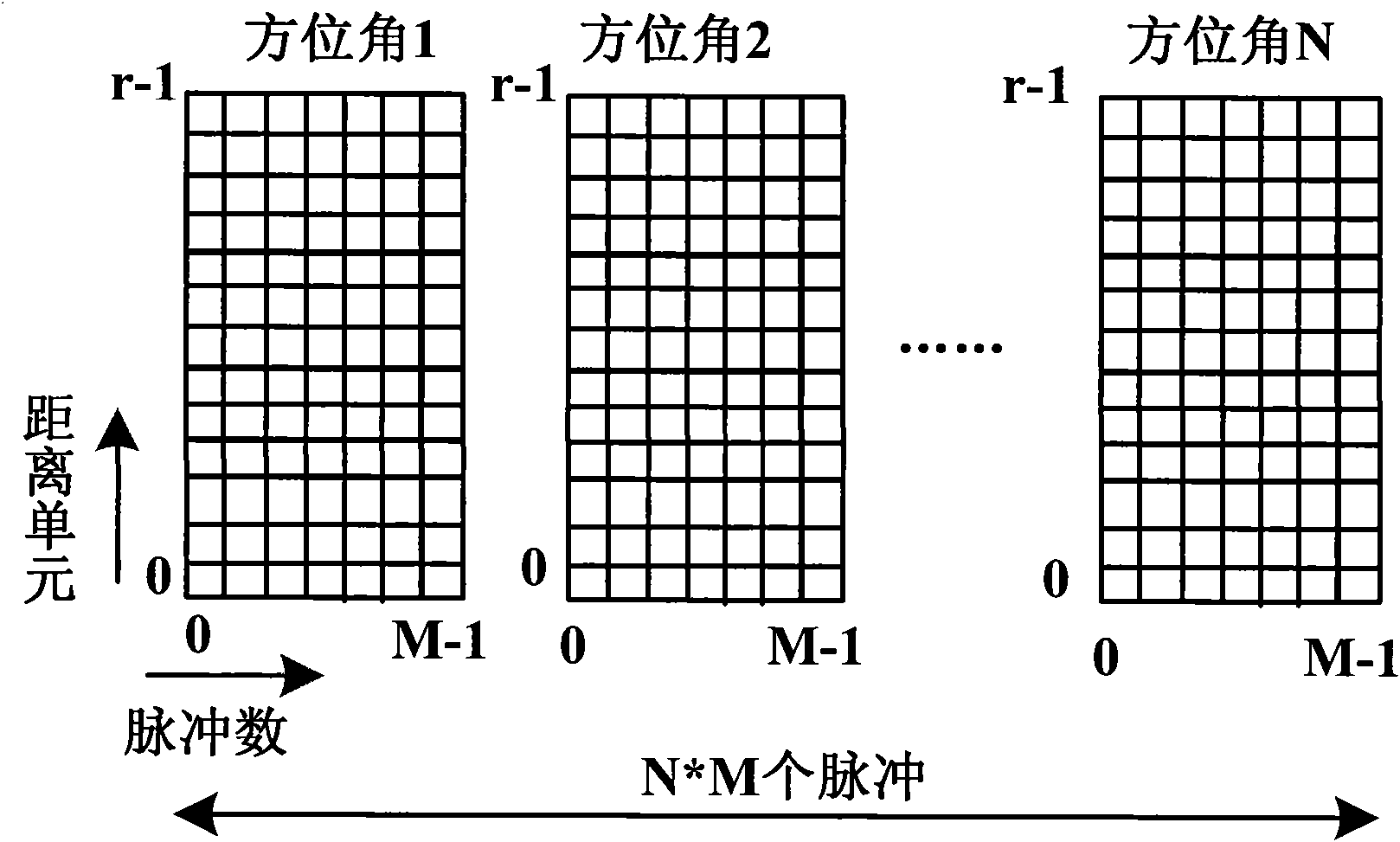
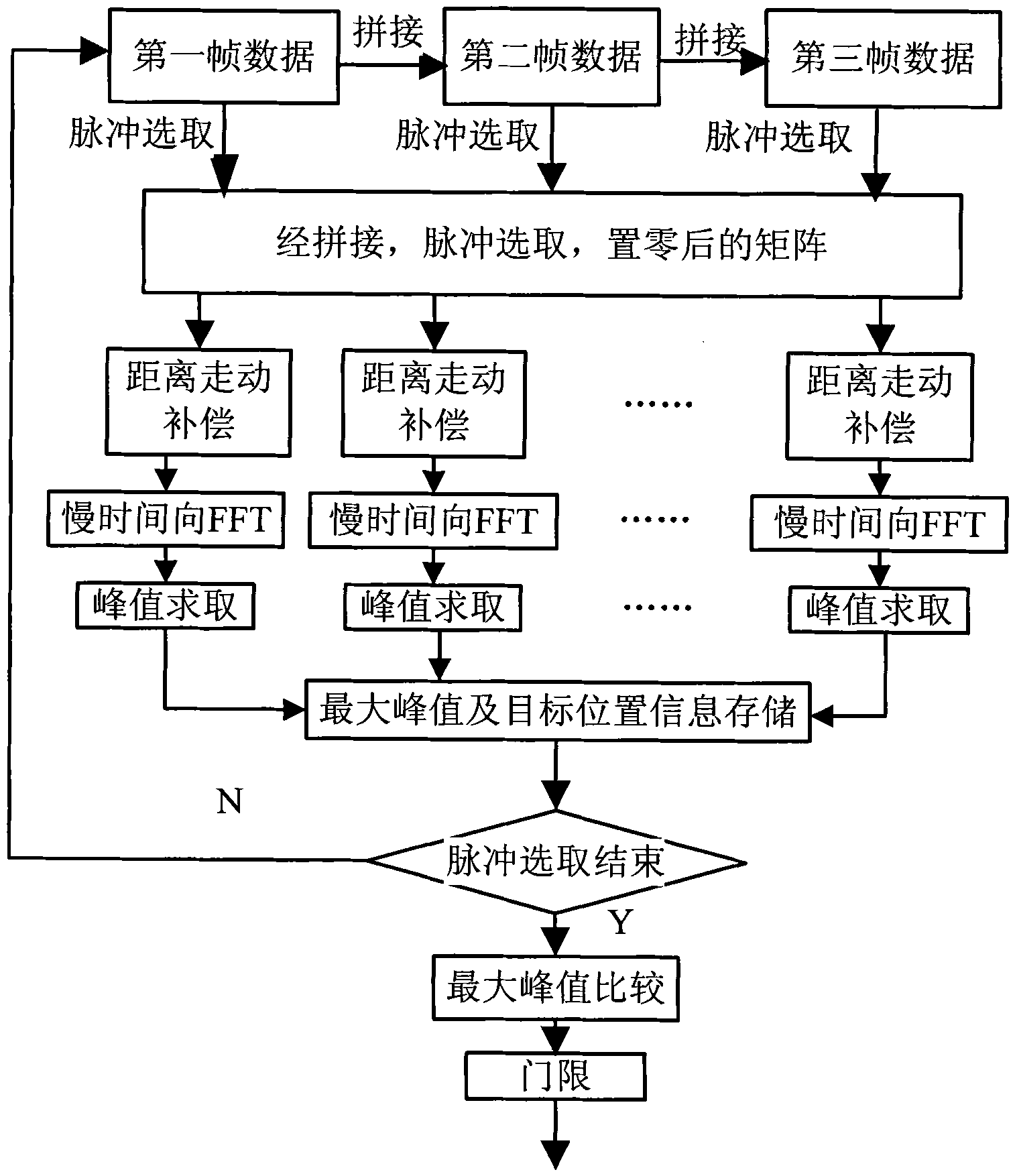
The invention provides a target track-before-detect (TBD) method based on multi-frame coherent integration. The method is characterized in that a new TBD method is provided aiming at the fact that when multi-frame integration is carried out, the phase information of target echo is not utilized in the traditional TBD method. According to the method provided by the invention, a signal to noise ratio is improved through multi-frame echo coherent integration by utilizing the phase information of the target echo; and by using the method in the invention, the detection of a weak target can be effectively achieved under the condition of less echo data frame numbers, the detection efficiency is improved, and the position speed information of the target is provided while detecting so as to realizethe track of the target.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and device for acquiring weak global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals
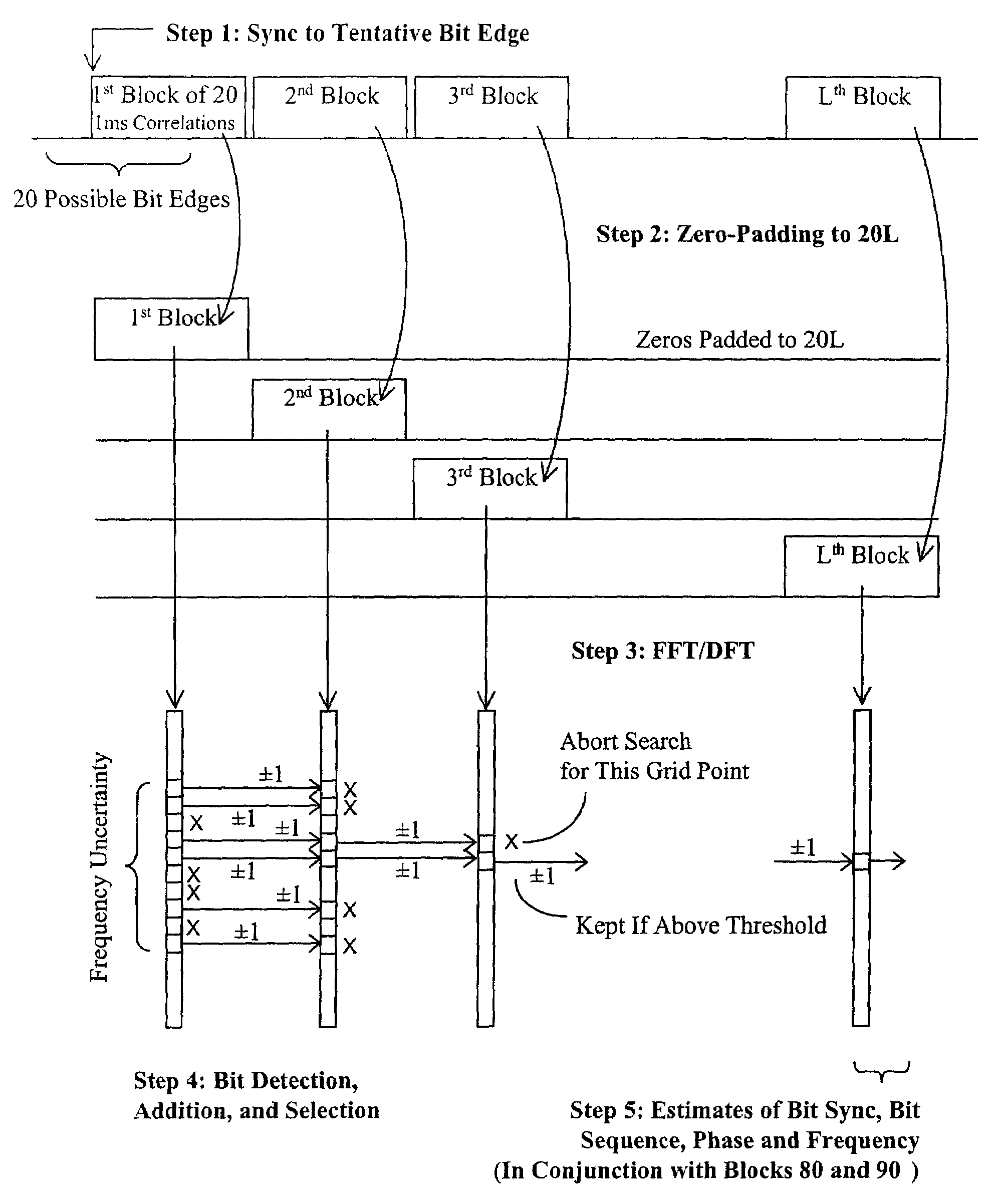
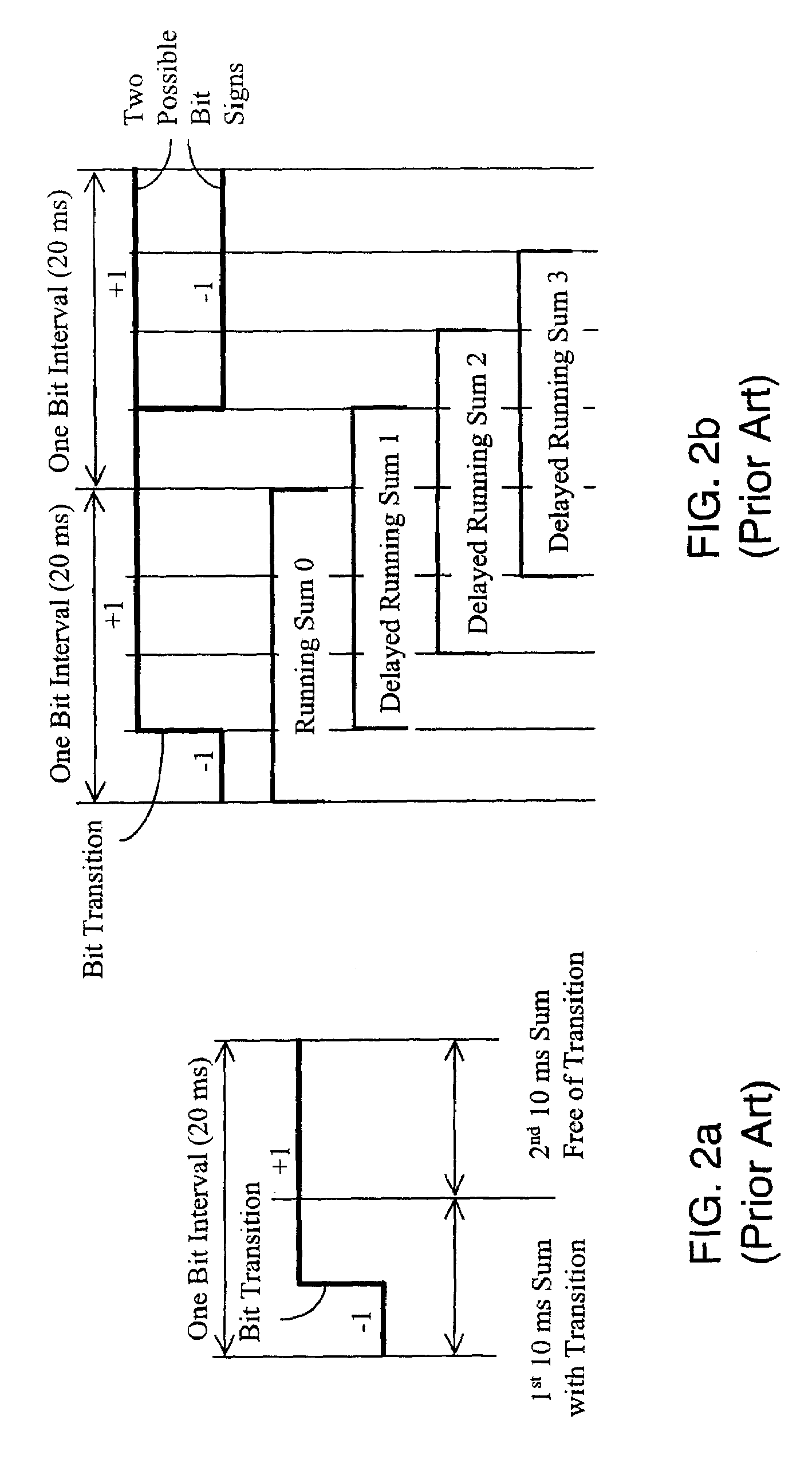
InactiveUS20070008217A1Reduces time and frequency uncertainty spaceWeak signalPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingBandpass filteringSignal tracking
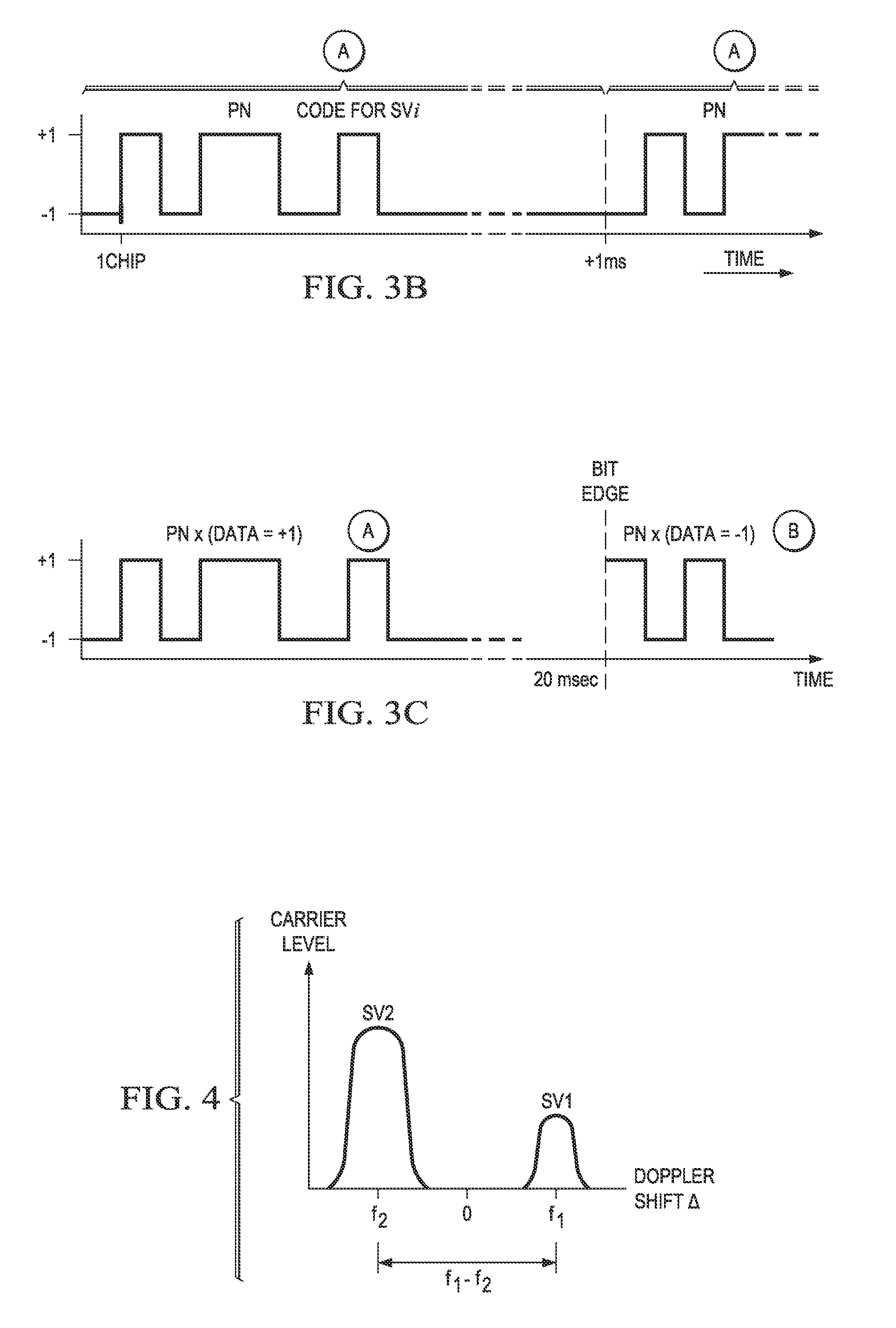
A Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and associated method capable of acquiring weak GNSS signals from a plurality of GNSS satellites produces a GNSS signal's code time, carrier frequency, and data bit transition parameters for subsequent signal tracking and position fixing. The GNSS receiver includes a baseband signal processor with special functionalities for acquiring weak signals. In a preferred embodiment, the time and frequency uncertainty space is reduced using available information and then special techniques are used to rapidly search the remaining uncertainty space. Successive reversal of short-length correlations within a data bit interval (a block) enables data bit transition detection and data bit sign correction prior to coherent integration. Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is applied as a bank of bandpass filters to coherently accumulate blocks of short-length correlations over extended coherent integration intervals to boost the signal power while averaging noise out despite unknown data bit transitions.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
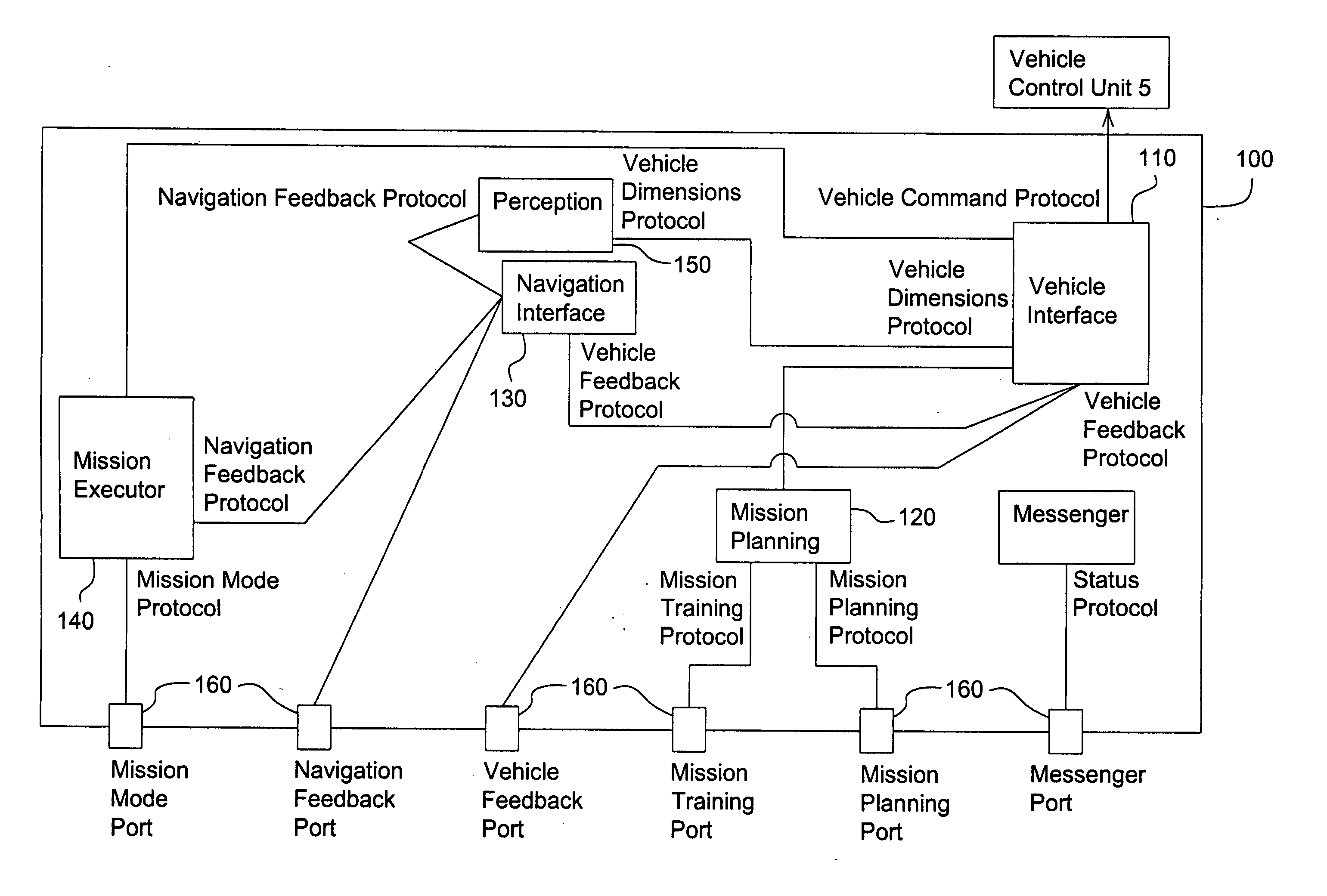
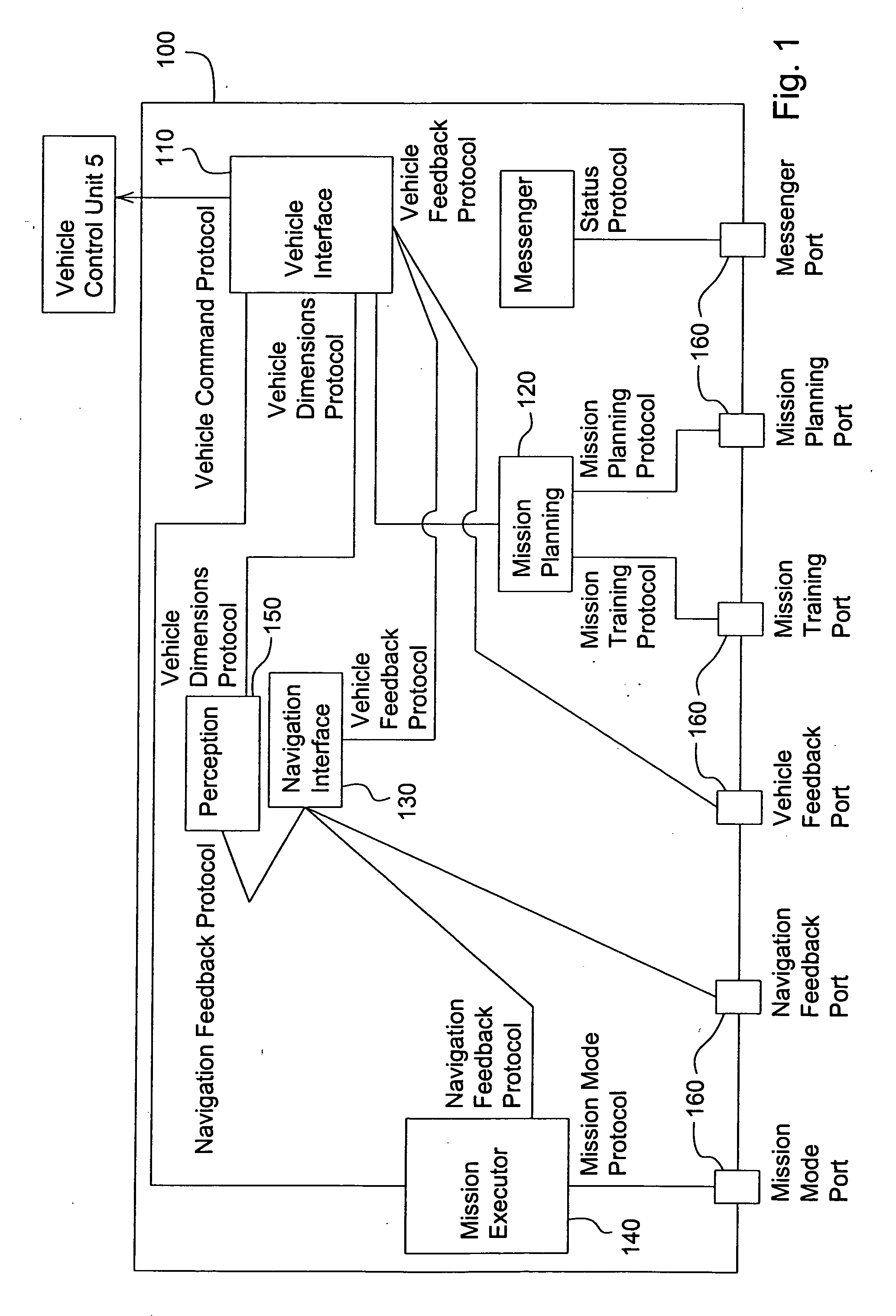
Method and system for modular data processing for a vehicle control system
InactiveUS20070061053A1Easy to adaptEasy to modifyAutonomous decision making processDigital data processing detailsHuman interactionSoftware system
The present invention is for a modular, extensible software system for use with multi-modal, autonomous, or semi-autonomous vehicles. The design of the present invention involves the coherent integration of modules with responsibilities for human-interaction, training, path planning, mission execution, navigation, and safety to develop and complete missions. The present invention provides a modular software system that expresses vehicle behaviors through numerous small-grain elements to complete a mission. The system can be easily adapted or modified by adding new software modules or modifying existing modules as missions change or expand, with the smaller-grain modules being easier to adapt and reuse.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Method and device for acquiring weak global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals
InactiveUS7522100B2Reduces time and frequency uncertainty spaceWeak signalBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingBandpass filteringFast Fourier transform
A Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and associated method capable of acquiring weak GNSS signals from a plurality of GNSS satellites produces a GNSS signal's code time, carrier frequency, and data bit transition parameters for subsequent signal tracking and position fixing. The GNSS receiver includes a baseband signal processor with special functionalities for acquiring weak signals. In a preferred embodiment, the time and frequency uncertainty space is reduced using available information and then special techniques are used to rapidly search the remaining uncertainty space. Successive reversal of short-length correlations within a data bit interval (a block) enables data bit transition detection and data bit sign correction prior to coherent integration. Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is applied as a bank of bandpass filters to coherently accumulate blocks of short-length correlations over extended coherent integration intervals to boost the signal power while averaging noise out despite unknown data bit transitions.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
System and method for generating image shadows with ray-coherent integration of extruded transparency maps
ActiveUS7675518B1Calculation is complexFast integrationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Coherent integration
System and method for generating hard and soft extruded image shadows with ray-coherent integration of extruded transparency maps. The ends of rays are positioned along a set of spokes radiating from the background point to be illuminated. In some embodiments, the weighted sum of integrals along a dense cone of rays from each point on the background is computed to determine the fraction of light obscured by the extruded artwork. The end points of the rays may be placed on lines that converge to the background point, according to some embodiments. Thus, intermediate line integrals of the alpha matte may be used to compute values for multiple rays. In other words, since the endpoints of multiple rays are placed along a single line, the results of computing the weighted sums for shorter rays may be used when calculating the sums for longer rays.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Cross-correlation mitigation method and apparatus for use in a global positioning system receiver
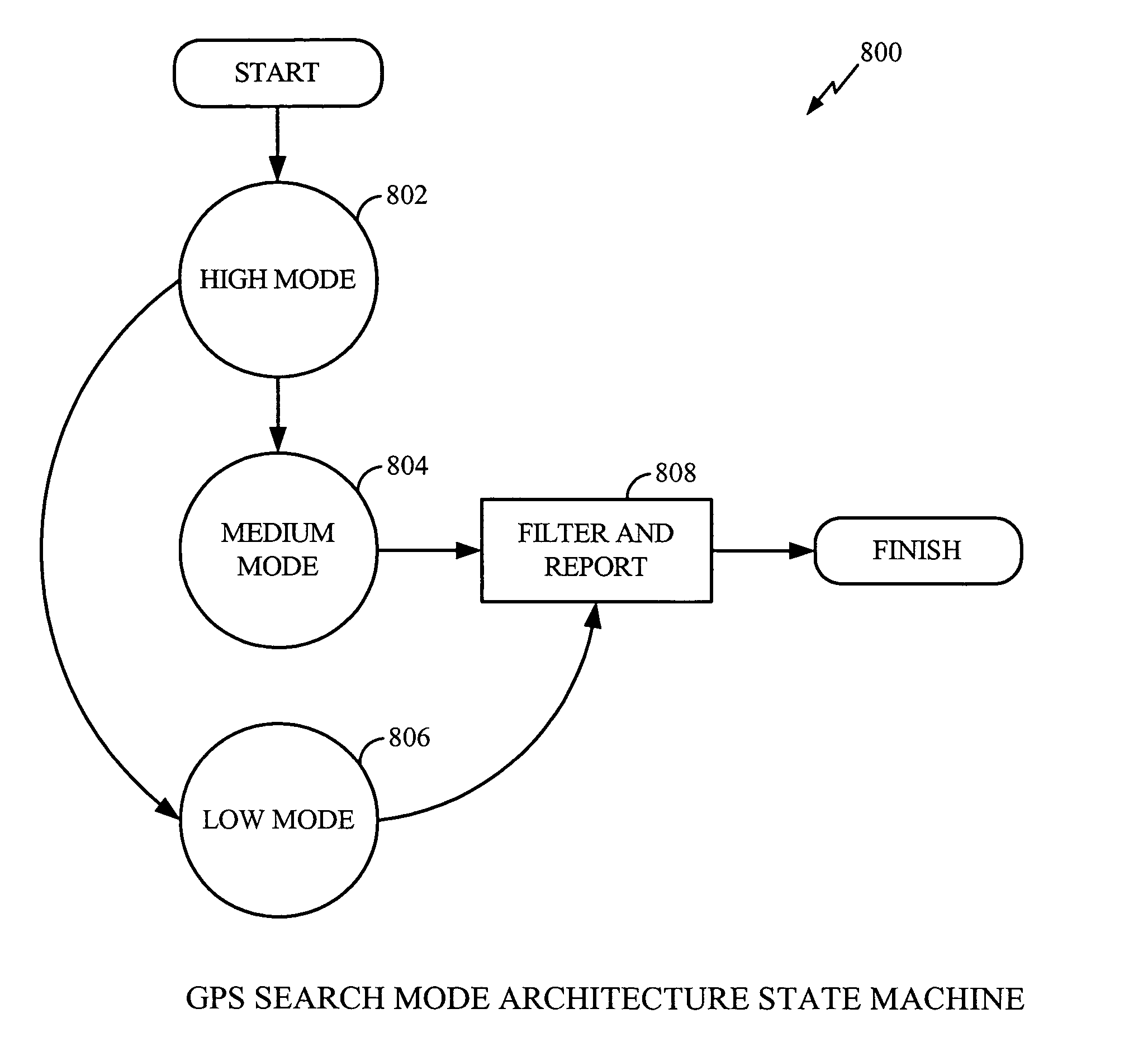
A method and apparatus mitigating the effects of cross-correlation signals on received satellite signals in a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver is described. MS-Assisted and MS-Based cross-correlation detection and mitigation methods and apparatus are described. A GPS search mode architecture is used to detect SV signals and identify potential cross-correlations. The GPS search modes have different coherent integration lengths and different degrees of sensitivity. After detection, measurements are logged into a database for further processing. Several cross-correlation tests are described. For example, a “Mainlobe” cross-correlation test is described that identifies the most significant cross-correlations that occur when the Doppler difference between the interfering SV signal and the target SV signal is nonzero and a multiple of 1 kHz. Appropriate C / No and Doppler thresholds, or masks, are selected and used to identify the mainlobe cross-correlations. A wide Doppler mask is used to account for the effects on cross-correlations caused by BPSK data bit modulation. Appropriate MS-Assisted and MS-Based cross-correlation masks are described. Other cross-correlation tests include “variable C / No”, “strong”, “wide Doppler” and “pre-emptive” cross-correlation detection tests.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Beidou signal capturing method in weak signal environment
ActiveCN103645483AReduce squared lossImprove signal-to-noise ratioSatellite radio beaconingIntermediate frequencyCarrier signal
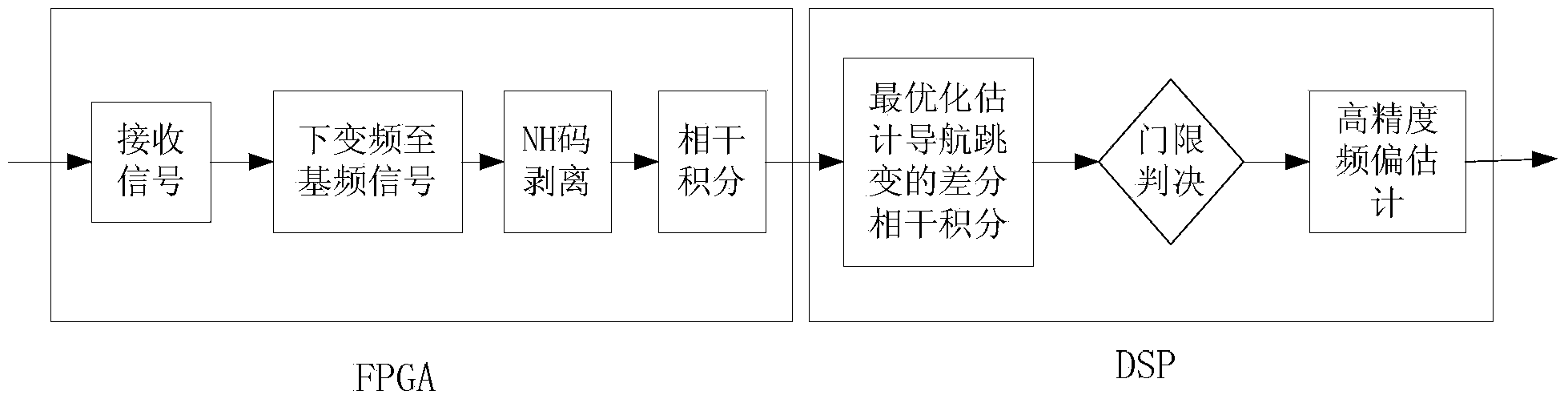
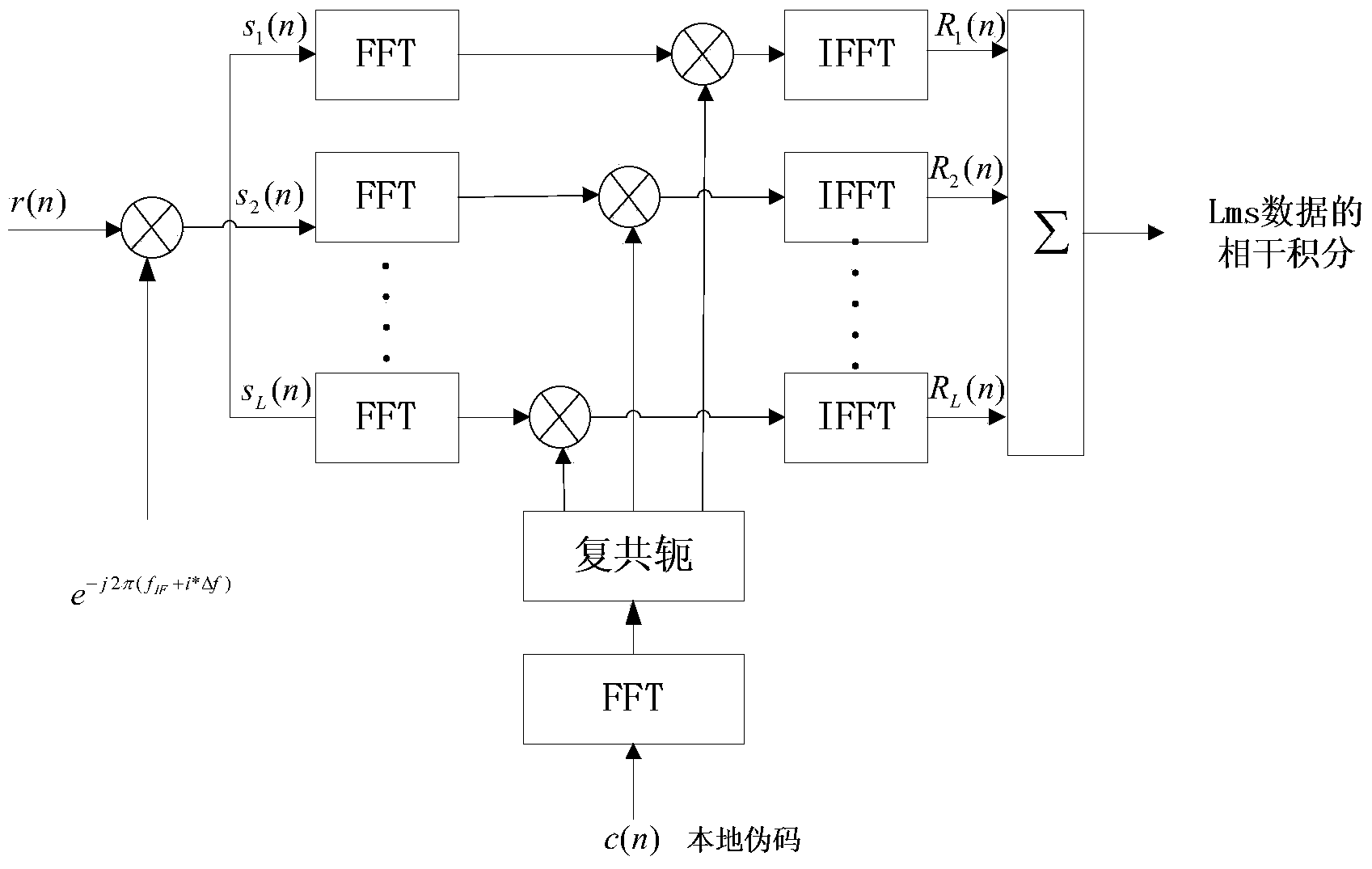
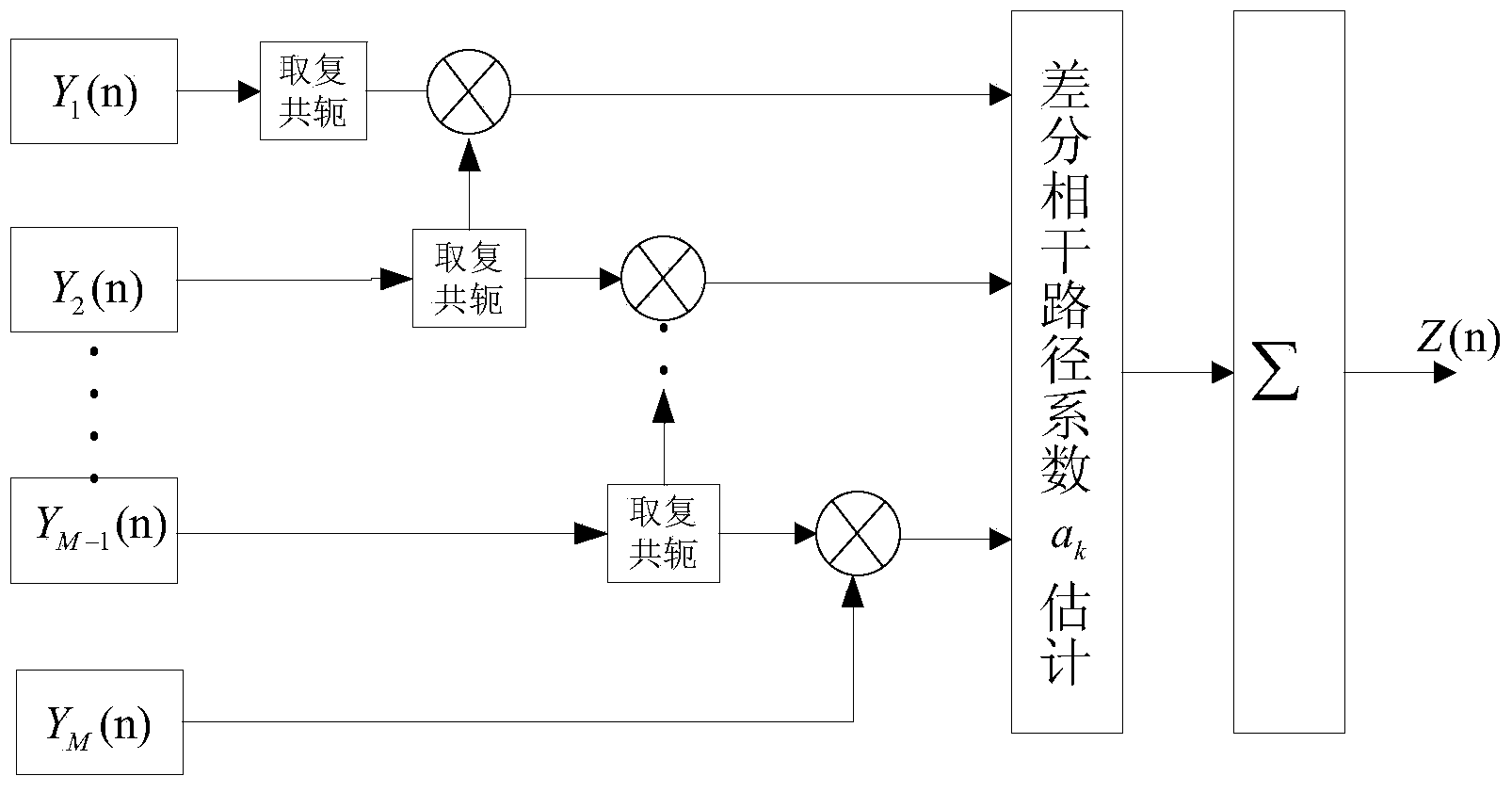
The invention relates to a Beidou signal capturing method in a weak signal environment. The method comprises the following steps: S1, arranging a down-conversion unit and carrying out down conversion processing on a received intermediate-frequency sampling signal; S2, carrying out NH code stripping on the received signal respectively, carrying out transformation into a frequency domain signal, carrying out multiplying with a multiplexing sum of a local code frequency domain value and then carrying out inverse transformation into a time domain; S3, carrying out conjugate multiplication on a coherent accumulation value at current time and a coherent accumulation value at previous time and carrying out summation; and S4, carrying out taylor series expansion on an amplitude difference value of two-side spectral lines of the peak value of the coherent integration result, deriving a quasi-linear relation of a frequency value and the amplitude difference value, and solving a frequency estimation value by using the linear relation. According to the invention, correlation calculation can be carried out on coherent values corresponding all code phases by one time; the signal to noise ratio is improved and the detection efficiency is improved; and the squaring loss of the non-coherent integration can be reduced. A problem of bit flipping caused by navigation data modulation can be solved, thereby improving the detection probability; the code phase and carrier wave frequency-offset estimation precision is enhanced; and the calculating speed and the calculating precision are guaranteed and the good stability and practicability are realized.
Owner:西安电子科技大学昆山创新研究院 +1
Fast fourier transform with down sampling based navigational satellite signal tracking
InactiveUS20070046536A1High frequency resolutionReduce computing needsPulse automatic controlPosition fixationFast Fourier transformImage resolution
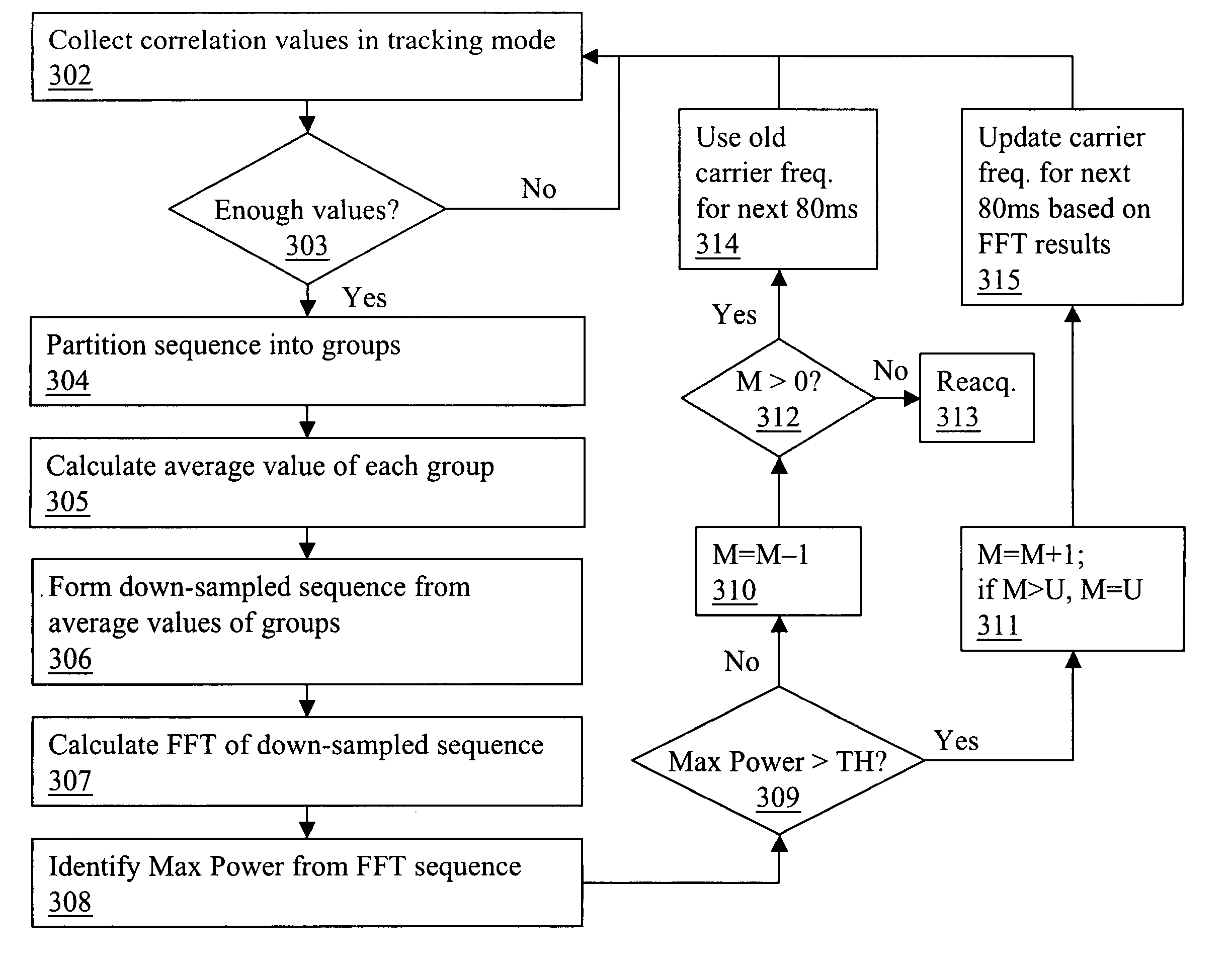
A method and device to track navigational satellite signals, are claimed. In this invention, a combination of down-sampling and frequency domain transformation are used to track the navigational satellite signals under dynamic environment. A Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) with long coherent integration has been employed to determine the varying frequency components with high resolution. By representing a number of correlation values with their average value, it is possible to represent a long sequence of input values by a smaller number of values and a relatively short length FFT can reveal the low frequency components that are present in the signal during tracking operation. A large reduction in the computational load may be achieved using this down-sampling method without compromising on the frequency resolution.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Continuous integration based satellite navigational signal acquisition
InactiveUS20070013583A1Less computing powerReduce computing loadPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingContinuous integrationAmbiguity
A method and device to acquire navigational satellite signals combines non-coherent and coherent integrations and can efficiently acquire both strong and weak signals. Successive steps eliminate lower powered and less likely combinations of code offsets and carrier frequencies or dwells of a given satellite signal. Only remaining dwells then are correlated and integrated over larger time duration to obtain the most probable dwell or dwells, which results in reduced computational load. The selection of most likely dwells is based on Parseval's theorem on equivalence of power in time and frequency domains. An optimal estimator algorithm efficiently estimates the probable navigation data bits embedded in the received signal. In case of an ambiguity due to several possible dwells, the steps are repeated with a new set of signal samples.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Method and system for rapidly capturing relay satellite measurement and control system signal
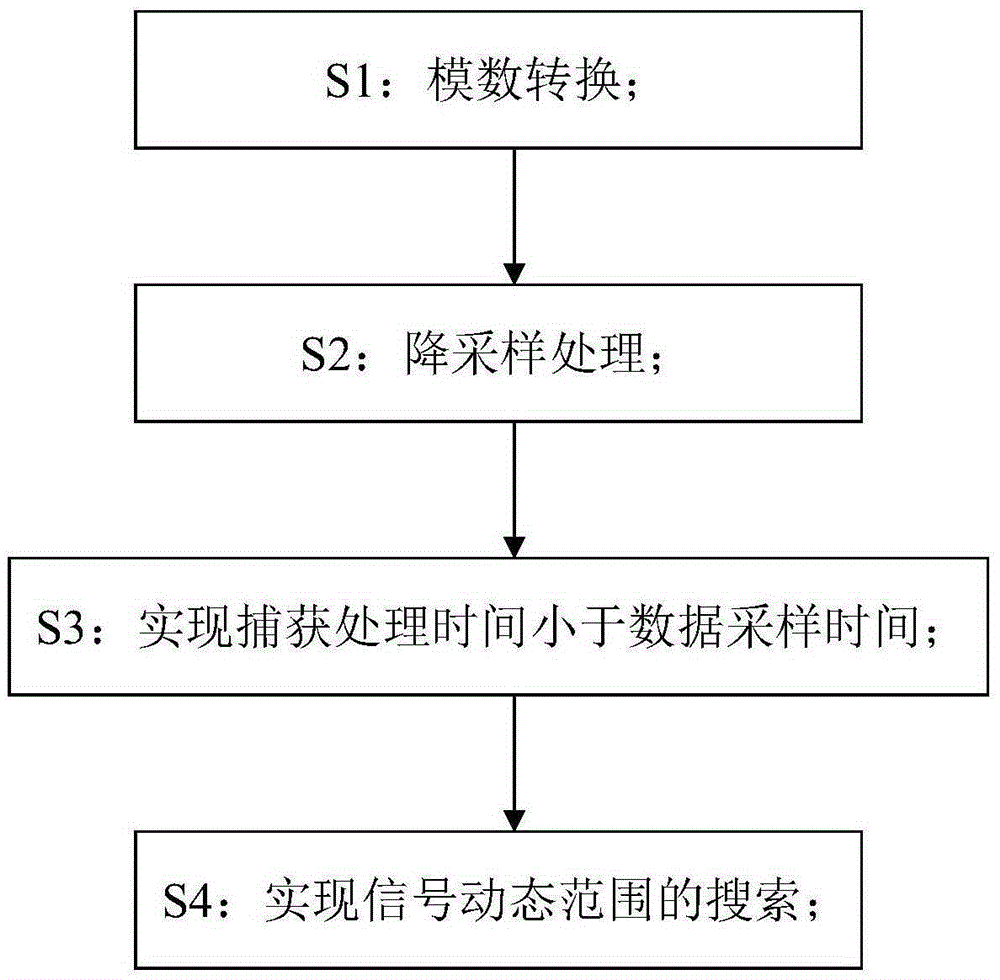
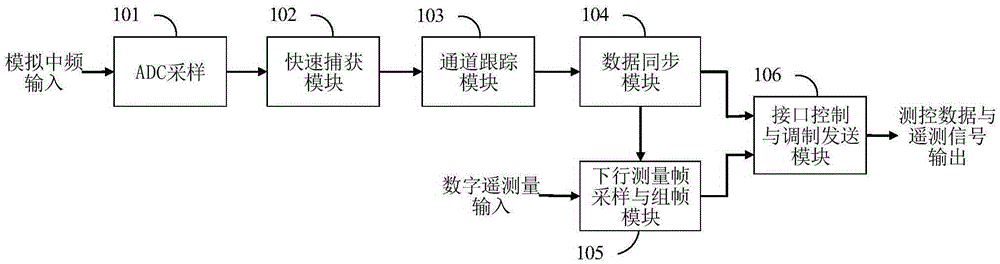
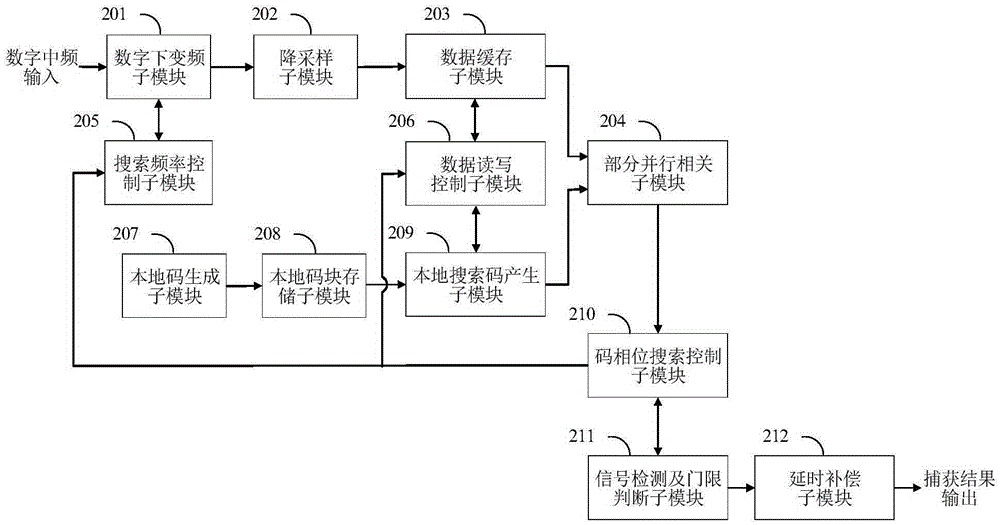
ActiveCN105306095ASmall capture processing timeSmall loss of signal-to-noise ratioRadio transmissionData streamCoherent integration
The invention discloses a method and a system for rapidly capturing a relay satellite measurement and control system signal. The method comprises the following steps: S1, analog-to-digital conversion: performing band-pass sampling on an analog intermediate-frequency signal through a high-speed analog-to-digital converter by comprehensive digital baseband equipment to obtain a digital intermediate-frequency signal; S2, down-sampling processing; S3, implementation of a capturing time shorter than a data sampling time: controlling two memories to implement seamless caching of data streams, wherein a caching depth is a sampling number of coherent integration, and a switching interval between the two memories is a sampling time of captured data; and S4, implementation of a search of a signal dynamic range: converging a Doppler frequency range by adopting a two-round frequency search according to a speed of outputting a frequency search unit result in a data sampling period, and obtaining a code phase offset of cached data in a third-round phase search. The system is used for implementing the method. The method and the system have the advantages of easiness in implementation, high accuracy, capability of satisfying a current engineering condition, and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and apparatus for an incomplete information model of credit risk
A method and apparatus for developing a structural model of credit risk that incorporates the short-term uncertainty inherent in default events is disclosed. The model is based on the assumption of incomplete information, taking as premise that bond investors are not certain about the true level of a firm's value that may trigger default. In addition, the coherent integration of structure and uncertainty is facilitated with compensators. Compensators form the infrastructure of a class of credit models that is broad enough to include traditional structural models, intensity-based models, and a great deal more. Several empirical examples are provided that compare default probabilities and credit yield spreads forecast by the incomplete information model to the output of a Black and Cox (1976) model. It is found that the incomplete information model reacts more quickly and, unlike traditional structural models, forecasts positive short-term credit spreads for firms that are in distress. It is also demonstrated that while the model is predicated on the surprise nature of default, it does not have conditional default rate.
Owner:BARRA
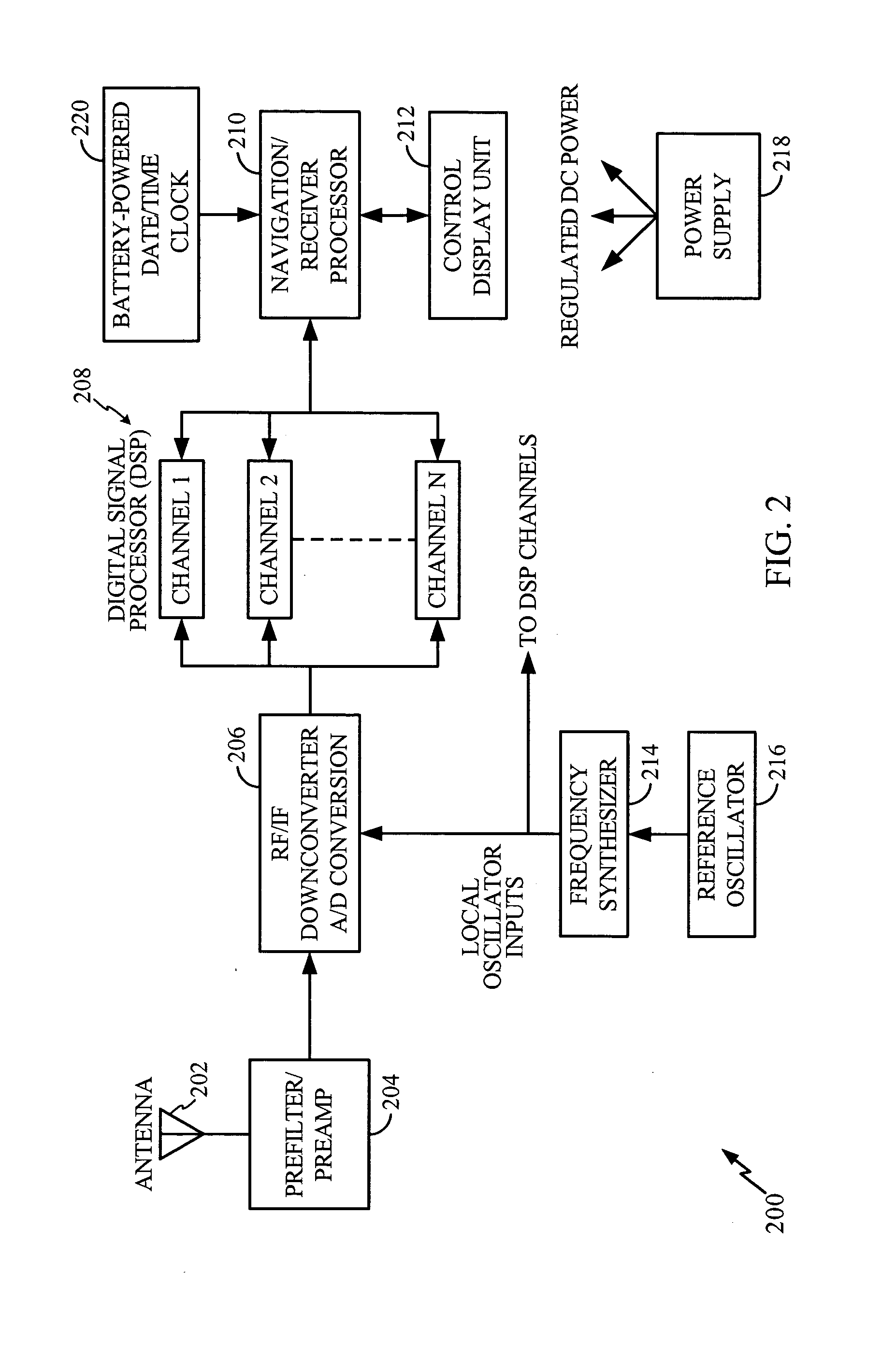
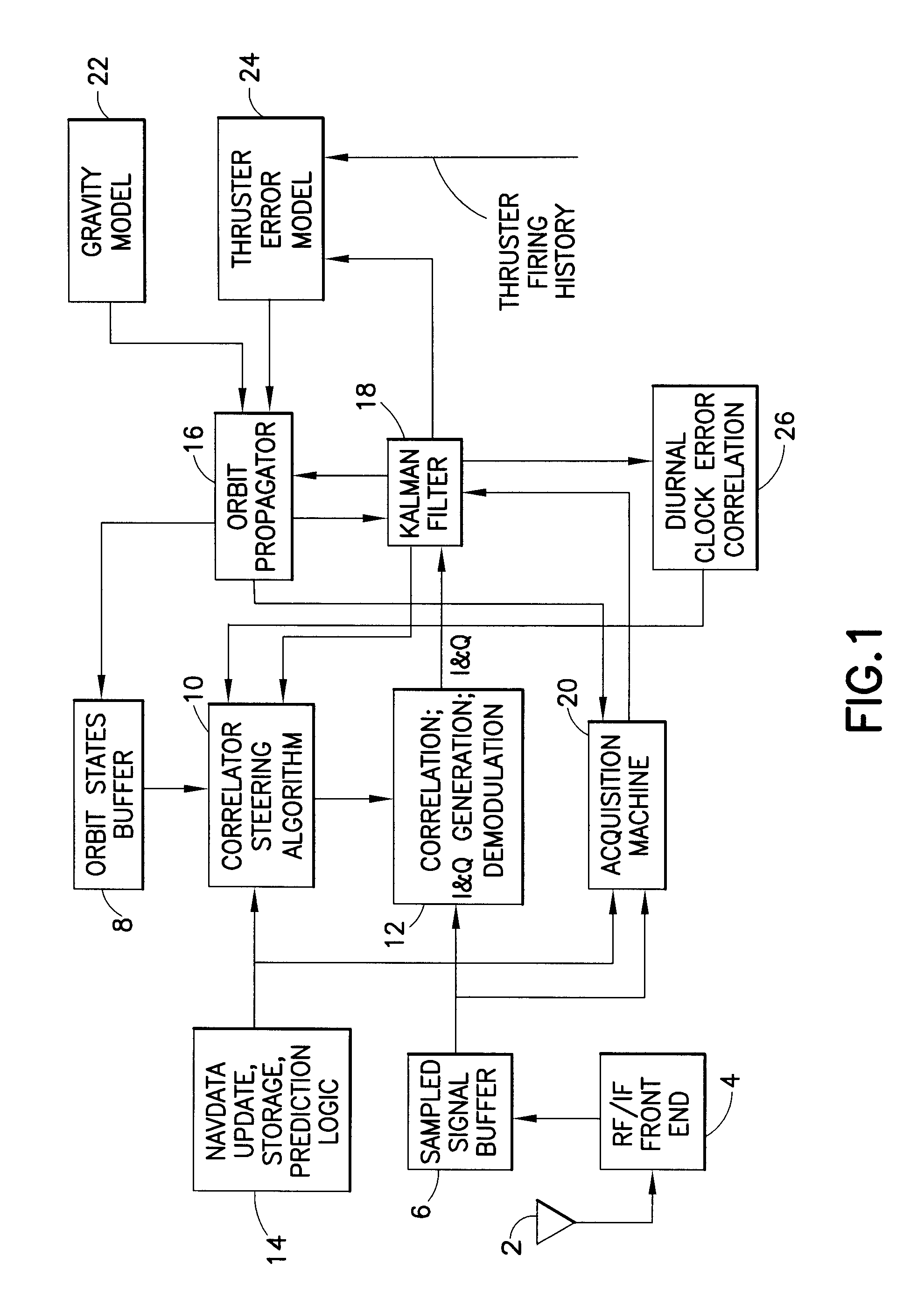
Software GNSS Receiver for High-Altitude Spacecraft Applications
ActiveUS20110254734A1Longer coherent integrationMinimization requirementsSatellite radio beaconingLow speedDelayed time
A system that provides GPS-based navigation / orbit determination capabilities for high-altitude spacecraft. The system uses an existing spacecraft processor and an easy-to-space-qualify minimum-hardware front end to minimize the need for new space-qualified hardware. The system also uses coherent integration to acquire and track the very weak GPS signals at high altitudes. The system also uses diurnal thermal modeling of a spacecraft clock and precision orbit propagation to enable longer coherent integration, a special Kalman filter to allow weak signal tracking by integrated operation of orbit determination and GPS signal tracking, and a segment-by-segment, post-processing, delayed-time approach to allow a low-speed spacecraft processor to provide the software GPS capability.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
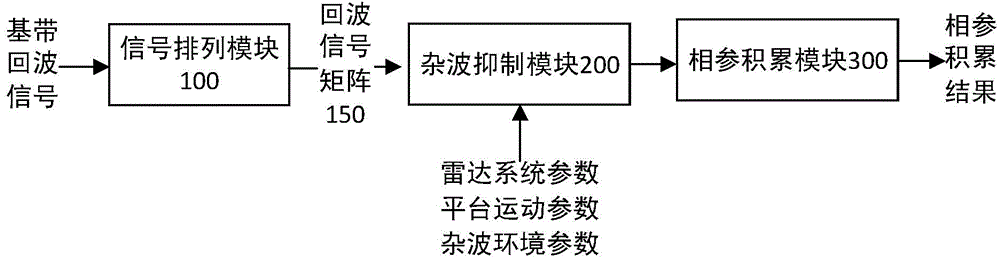
Coherent agile frequency radar clutter inhibition method and system
ActiveCN104931938AHigh speedAvoid missing targetsWave based measurement systemsRadial motionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a coherent agile frequency radar clutter inhibition algorithm, comprising: arranging radar base-band echo signals to perform clutter inhibition and coherent integration in an echo signal matrix; calculating the matrix to inhibit clutter components in the echo signals and reserve signal components in a movable target; and performing coherent integration on the echo signals after clutter inhabitation. The invention also discloses a coherent agile frequency radar clutter inhibition system corresponding with the algorithm, comprising a signal arrangement module, a clutter inhibition module and a coherent integration module. The algorithm can effectively inhibit clutter energy, obtain radial motion speed information of a target at the same time of detecting a movable target, and meanwhile obtain a high resolution range profile of the target so as to realize simultaneous high resolution detection of speed and range of the target; the algorithm has lower calculated amount, and can inhibit clutter components in signals, increase a signal to noise ratio of the target, and obtain speed information and high resolution images of the target.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods and systems for acquisition, reacquisition and tracking of weak navigational signals
ActiveUS20080180321A1High sensitivityHighly accurate reference signalBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationFourier transform on finite groupsEphemeris
Provided herein are systems and methods for achieving long coherent integration in a navigational receiver to improve the sensitivity of the receiver and enable the receiver to acquire, reacquire and track signals under very weak signal conditions. In an embodiment, phase compensation is computed based on estimated Doppler frequency, rate of change of the Doppler frequency with time, and second order rate of change of the Doppler frequency. The Doppler frequency may be computed from an orbital model or ephemeris. This phase compensation is used to compensate samples of the input signal for changes in the phase due to the Doppler frequency. Frequency components of the phase-compensated samples are then computed using a frequency analysis such as a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). The maximum frequency component is taken as an error frequency and used to compensate the samples of the input signal for residual frequency error.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Method and system for adaptively cancelling clutter from the sidelobes of a ground-based radar
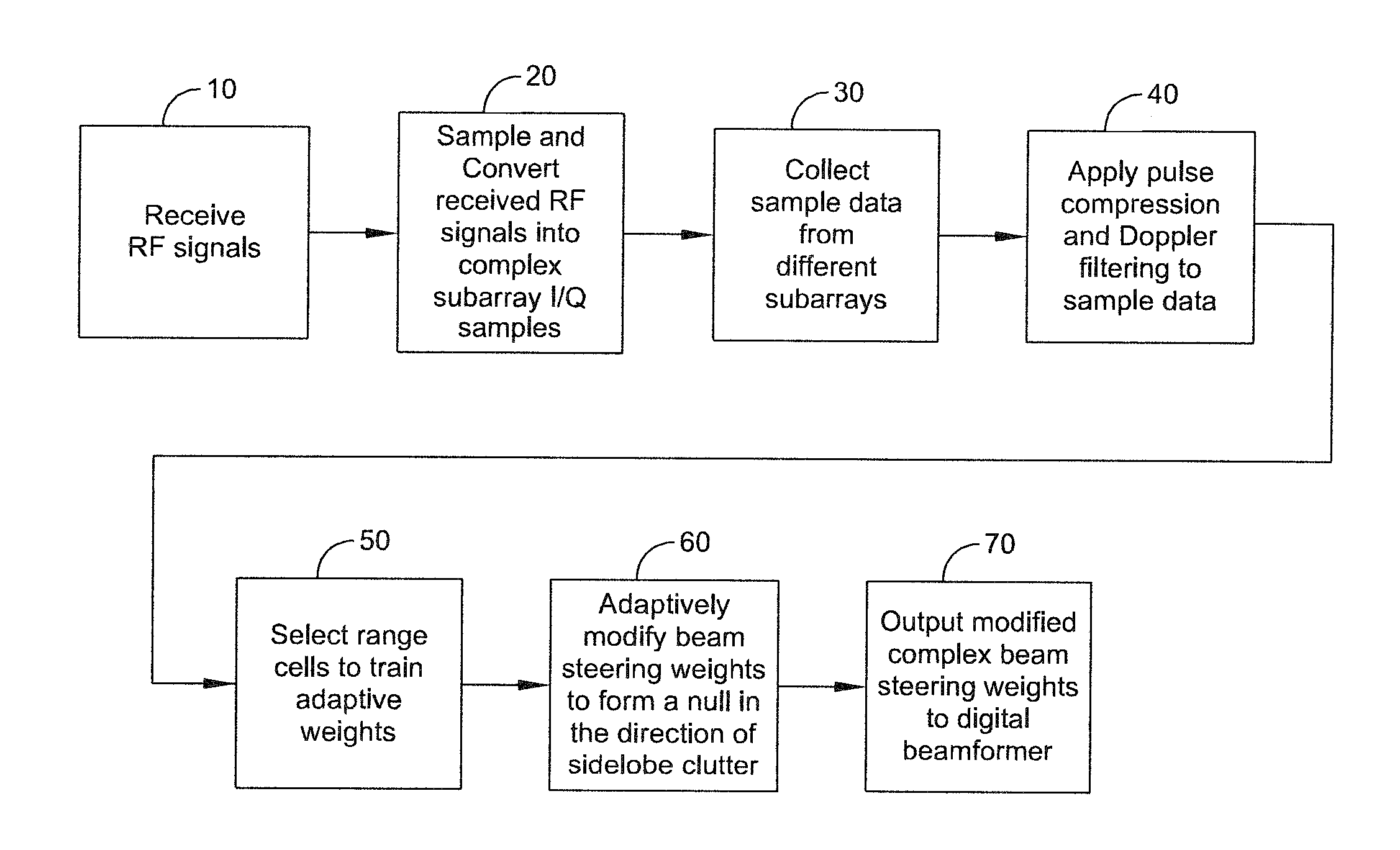
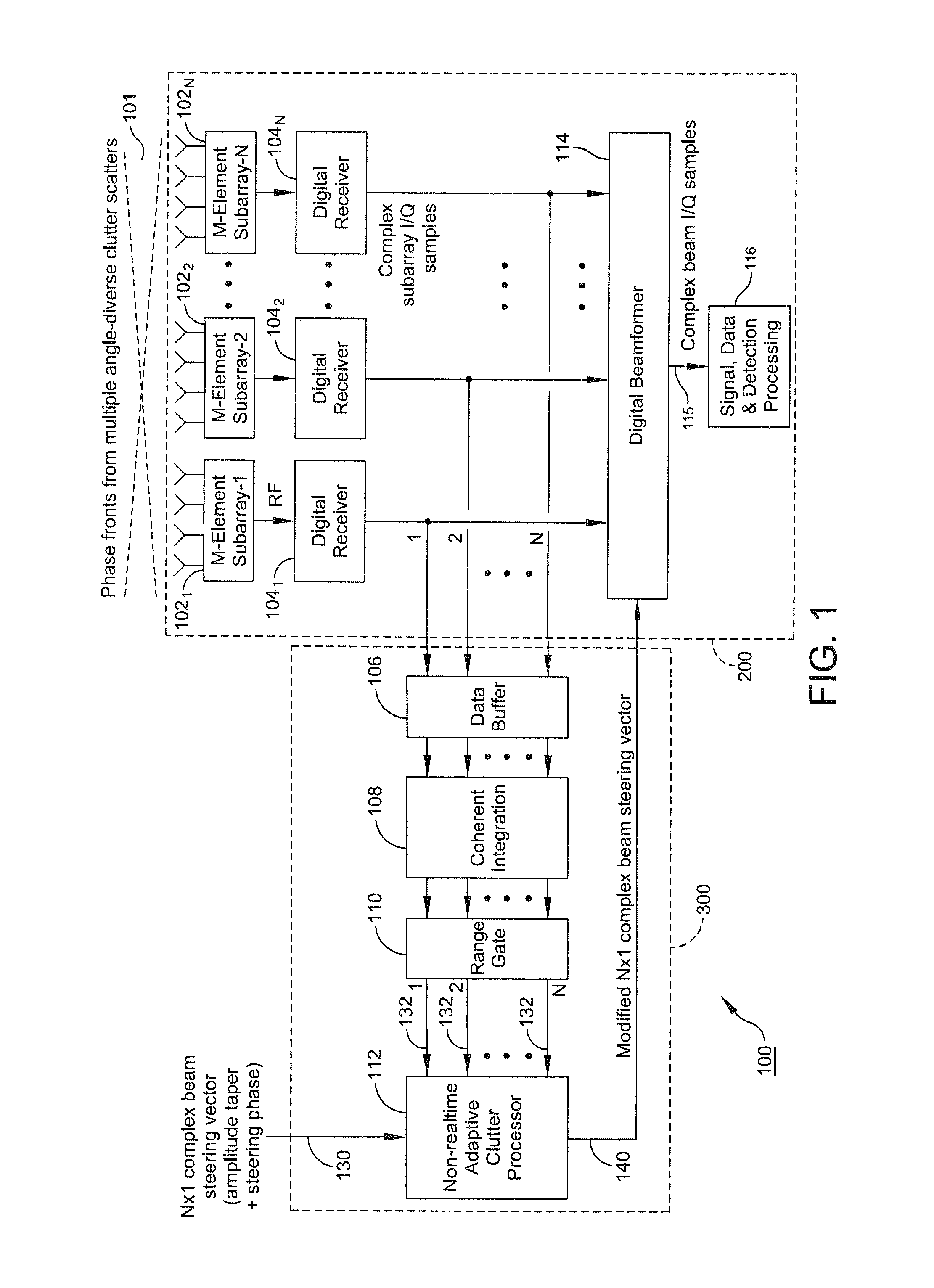
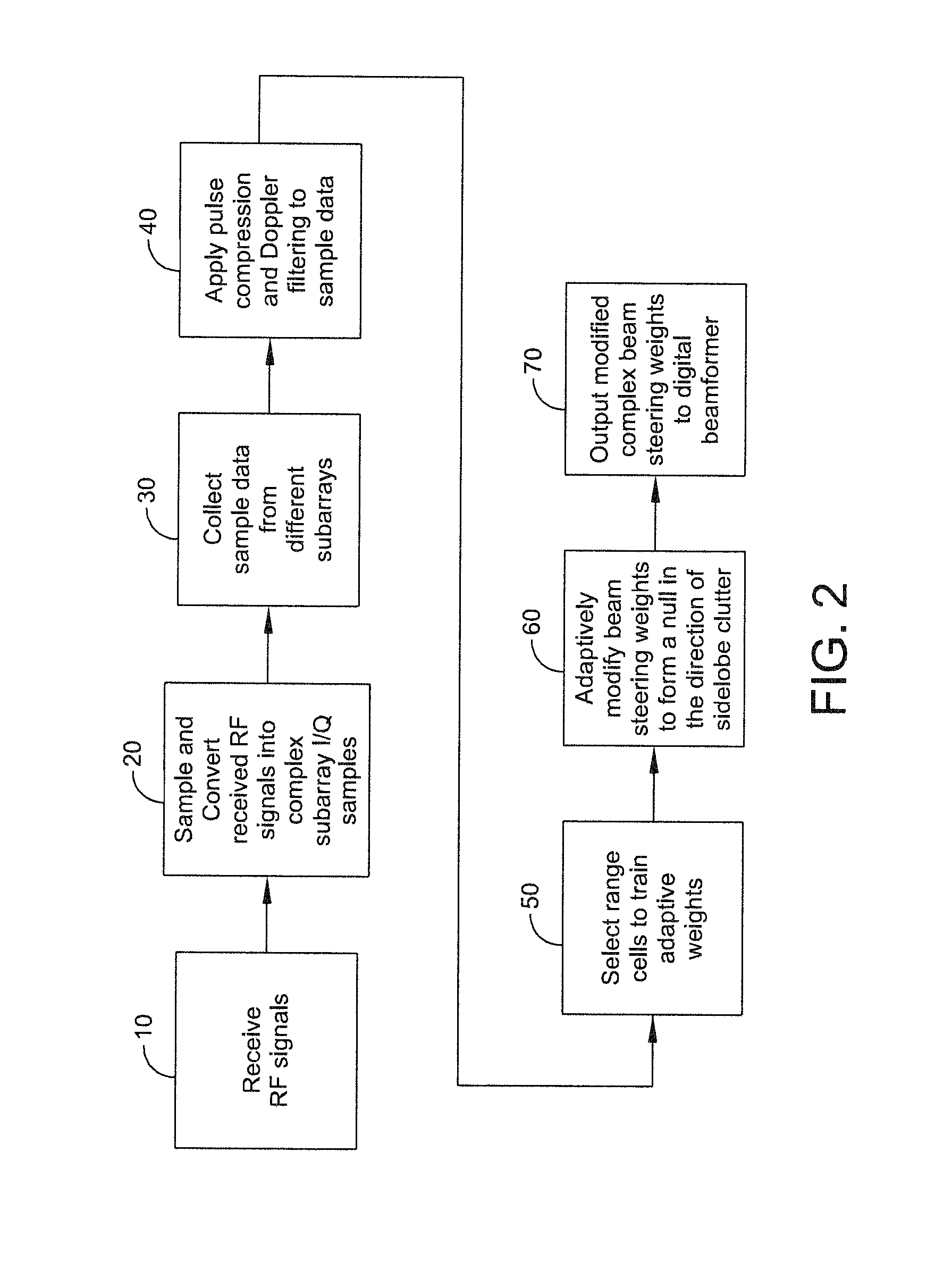
ActiveUS8947294B1Enhance clutter-to-noise ratioReduced sidelobe gainAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGround based radarHorizon
A system and method of providing to a beamformer a modified complex beam steering vector includes collecting subarray I / Q samples from a plurality of subarrays receiving clutter, performing coherent integration of the subarray I / Q samples to increase the CNR, adaptively modifying a complex beam steering vector to form a null in the direction of the received clutter, and outputting to a beamformer the modified complex beam steering vector. The beamformer receives complex I / Q data samples representing a radar signal containing near-horizon clutter and applies the modified beam steering vector to generate a beamformed signal having an elevated mainlobe and a spatial sidelobe null in the direction of the received clutter.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Double-antenna A-GNSS receiving machine system
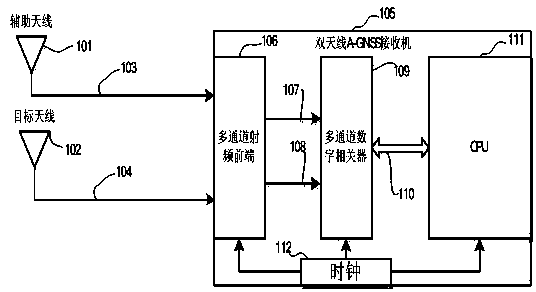
ActiveCN103728634AImprove capture speedHigh sensitivitySatellite radio beaconingPhase detectorCarrier signal
The invention discloses a double-antenna A-GNSS receiving machine system. The double-antenna A-GNSS receiving machine system utilizes double antennae to perform positioning, the auxiliary antenna is arranged in the open sky to be positioned so as to extract code phases and carrier wave Doppler values in satellite signal digital channels, calculating satellite signal navigation message information and then utilizing the auxiliary information to assist baseband processing of a target antenna receiving signal. In the baseband processing process of the target antenna receiving signal, the code phase values and the carrier wave Doppler values are set according to the auxiliary information, the capture process and the frequency pulling process of a receiving machine system can be omitted, and tracking process is directly performed after code phase pulling. The coherent integration time is prolonged by eliminating the bit influence during tracking, the tracking accuracy and the sensitivity are improved by adopting pure phase-locked loop phase discriminator and other modes, and the positioning speed and positioning performance are finally improved in the weak-signal and complicated-signal environments.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Circuits, devices, and processes for improved positioning satellite reception and other spread spectrum reception
ActiveUS20130136154A1Improve performancePromote disseminationTransmissionHypothesisCoherent integration
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for increasing coherent integration length while receiving a positioning signal
ActiveUS20060114984A1Increase the lengthAvoid short lengthPosition fixationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsHypothesisWave shape
A receiving method and apparatus for increasing coherent integration length while receiving a positioning signal from transmitters such as GPS satellites. In order to compensate for frequency drifts that may occur in the positioning signal, a hypothesis is made as to the frequency drift, which is inserted into the receiving algorithm. Advantageously, the length of coherent integration can be increased at the expense of reducing the length of incoherent integration while keeping the total integration length the same, the net effect of which is an increase in signal detection sensitivity. The frequency drift hypothesis has any appropriate waveform; for example, approximately linear or exponential. The hypothesized frequency drift can be inserted into the receiver algorithm in any suitable place; for example, the data block may be adjusted for the hypothesized frequency drift, alternatively the reference signal may be adjusted, or the frequency samples of either the data block or the reference signal may be adjusted.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Cross-correlation mitigation method and apparatus for use in a global positioning system receiver
A method and apparatus mitigating the effects of cross-correlation signals on received satellite signals in a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver is described. MS-Assisted and MS-Based cross-correlation detection and mitigation methods and apparatus are described. A GPS search mode architecture is used to detect SV signals and identify potential cross-correlations. The GPS search modes have different coherent integration lengths and different degrees of sensitivity. After detection, measurements are logged into a database for further processing. Several cross-correlation tests are described. For example, a “Mainlobe” cross-correlation test is described that identifies the most significant cross-correlations that occur when the Doppler difference between the interfering SV signal and the target SV signal is nonzero and a multiple of 1 kHz. Appropriate C / No and Doppler thresholds, or masks, are selected and used to identify the mainlobe cross-correlations. A wide Doppler mask is used to account for the effects on cross-correlations caused by BPSK data bit modulation. Appropriate MS-Assisted and MS-Based cross-correlation masks are described. Other cross-correlation tests include “variable C / No”, “strong”, “wide Doppler” and “pre-emptive” cross-correlation detection tests.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for integrally detecting and tracking motorized dim target based on information mutual feedback
ActiveCN102628936AImprove adaptabilityAdaptableWave based measurement systemsCoherent integrationSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a method for integrally detecting and tracking a motorized dim target based on information mutual feedback. The conventional method has low requirements on detection signal-noise ratio, and is complex for implement. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a pulse compression output signal of a radar echo signal in a beam residence time interval, feeding target Doppler estimation obtained by performing integral detection and tracking in the beam residence time interval to a signal accumulating end, and determining maximum allowed coherent integration timeunder the condition that a target does not perform cross-unit walking together with pulse repeating frequency, beam residence time and a bandwidth; comparing the maximum allowed coherent integration time with the single frame processing time of a detection and tracking integral method; performing coherent or segmental coherent integration on a pulse compression output signal respectively according to a comparison result; and performing one-stage low-threshold constant false alarm processing on an integration result. The self-adaptability of the method is enhanced, the problems of mass calculation and storage caused by the use of an exhaust algorithm are avoided, and the practicability is enhanced.
Owner:盐城市凤凰园科技发展有限公司
Apparatus and method for acquiring spread-spectrum signals
ActiveUS20050254560A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioBeacon systems using radio wavesCode division multiplexFrequency mixerSoftware engineering
An apparatus for acquiring spread-spectrum signals includes a mixer for generating an in-phase signal and a quadrature signal from the spread-spectrum signal, a decimator for subsampling the in-phase signal and the quadrature signal, a correlation engine for producing an in-phase correlation between the subsampled in-phase signal and a PN code and producing a quadrature correlation between the subsampled quadrature signal and the PN code, a first coherent integrator for accumulating a plurality of in-phase correlations to produce an in-phase coherent integration, a second coherent integrator for accumulating a plurality of quadrature correlations to produce a quadrature coherent integration, an incoherent integrator for accumulating the in-phase coherent integrations and the quadrature coherent integrations to produce an incoherent integration, and a signal detector for checking the presence of the spread-spectrum signal based on the incoherent integration.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method for capturing weak signals of Big Dipper D1 satellite navigation system
ActiveCN102928853ACapture meetIncrease processing gainSatellite radio beaconingWeaknessNavigation system
The invention discloses a method for capturing weak signals of a Big Dipper D1 satellite navigation system. The method comprises the steps of: a. estimating a signal-to-noise ratio of a signal; b. utilizing the signal-to-noise ratio to set a signal detection threshold value and judging the weakness; c. selecting an NH secondary coding sequence and carrying out two-dimensional capturing processing of a CA code phase and a Doppler frequency; d. utilizing lms coherent integration and collecting twenty integration results; e. selecting a first type of the NH secondary coding sequence and gradually multiplying with the twenty integration results; f. carrying out non-coherent integration and storing the result; g. repeating the steps c-d until the twenty types of NH secondary codes are traversed; h. selecting the maximum value of the twenty types of integration and comparing the maximum value with a set signal detection threshold value to obtain whether a positioning satellite signal exists in a received signal or not; i. if so, positioning; when the signal is not found, replacing Doppler frequency sections until all the Doppler frequency sections are traversed; and j. replacing a satellite and repeating the steps c-i. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the NH secondary codes can be stripped to obtain a high-integration gain, so that the weak signals of the Big Dipper D1 satellite navigation system are captured.
Owner:SHANGHAI CYGNUS SEMICON CO LTD
Apparatus and method for acquiring spread-spectrum signals
An apparatus for acquiring spread-spectrum signals includes a mixer for generating an in-phase signal and a quadrature signal from the spread-spectrum signal, a decimator for subsampling the in-phase signal and the quadrature signal, a correlation engine for producing an in-phase correlation between the subsampled in-phase signal and a PN code and producing a quadrature correlation between the subsampled quadrature signal and the PN code, a first coherent integrator for accumulating a plurality of in-phase correlations to produce an in-phase coherent integration, a second coherent integrator for accumulating a plurality of quadrature correlations to produce a quadrature coherent integration, an incoherent integrator for accumulating the in-phase coherent integrations and the quadrature coherent integrations to produce an incoherent integration, and a signal detector for checking the presence of the spread-spectrum signal based on the incoherent integration.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Cell search circuit for CDMA
InactiveUS6088382AReduce search timeOptimized in conformity with loadCode division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationControl signalCell search
Owner:NEC CORP
System and method for acquiring weak signals in a global positioning satellite system
InactiveUS20070046534A1Overcomes shortcomingImprove receiver sensitivityPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingCoherent integrationCircular correlation
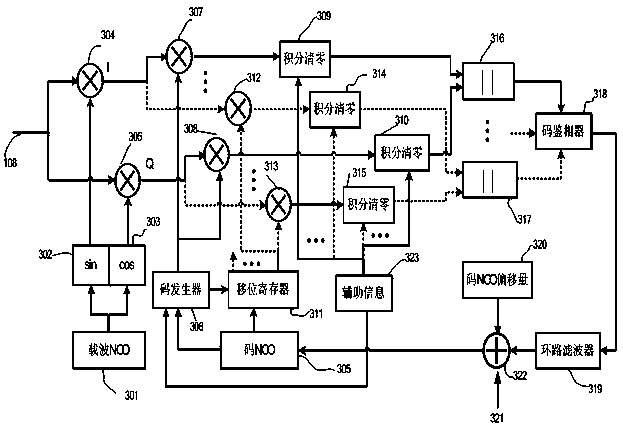
A method of acquiring a weak signal includes selecting a first predetection integration time (PIT) interval for processing a digital intermediate frequency (IF) signal, selecting a number of data bit edges within the PIT, computing a plurality of coherent integrations for each data bit edge, selecting a coherent integration, which corresponds to a most likely data combination for each data bit edge, from the plurality of coherent integrations, updating an incoherent integration total for each data bit edge with the coherent integration corresponding to the selected most likely data bit combination for each data bit edge, comparing the incoherent integration total for each data bit edge with a threshold after a predetermined number of steps of the coherent integration computations and incoherent integration total updates, and identifying a code delay from the incoherent integration. The method may also include determining a code delay from an estimated Doppler shift corresponding to the identified code delay. In this method, the coherent integrations are computed using a circular correlation technique that is performed in a manner so the coherent integrations are not independent from one another in successive steps. Thus, computational efficiencies may be gained from subsequent uses of coherent integrations computed during previous steps. The circular correlation is preferably performed over intervals corresponding to the separation between data bit edges.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Coherent integration method based on dynamic programming and back image projection algorithm
InactiveCN102608590AImprove detection rateEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsTime domainTrack-before-detect
The invention discloses a tracing accumulation method of coherent detection based on dynamic programming and a back image projection algorithm, comprising the following steps of: obtaining a predication track of a target through the dynamic programming; and then carrying out energy accumulation through the back image projection algorithm to improve an output signal to noise ratio, so as to realize the detection on a low observable target. Compared with a non-coherent TBD (Track Before Detect) algorithm, the method uses phase information of an echo signal when inter-frame accumulation is carried out, and coherent accumulation is carried out on a multi-frame echo to improve an output signal to noise ratio and further improve the detection efficiency; a distance migration compensation is directly carried out on a time domain, so that approximate unfolding of a target distance does not need to be carried out, and Doppler migration of a target is not considered; and therefore, an accumulation error is reduced, the detection possibility and the detection precision are improved, and the false alarm probability is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for MIMO radar system angle estimation based on fast Fourier transformation
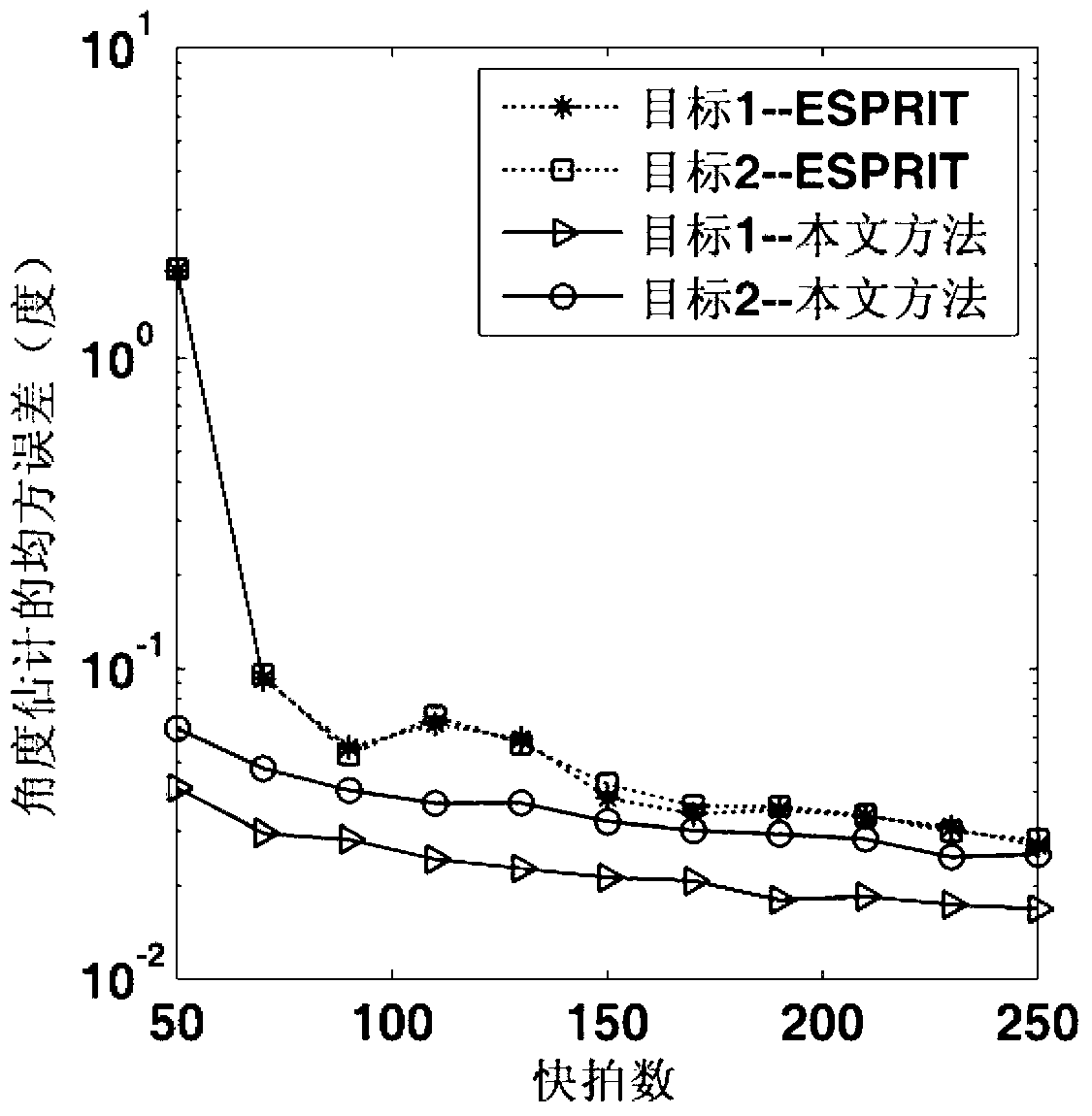
The invention discloses a method for MIMO radar system angle estimation based on fast Fourier transformation. The method for MIMO radar system angle estimation based on fast Fourier transformation comprises the steps that a data matrix received by a first pulse of the radar system is evenly divided and divided signals are expressed in the description, new signals are divided by the four matrix blocks defining; bi-dimensional fast Fourier transformation is respectively conducted to the signals shown in the description; coherent integration is conducted on F11(l), F12(l), F21(l) and F22(l), a peak point shown in the description and the corresponding subscript ix and the corresponding subscript iy are recorded, points corresponding to the subscript ix and the subscript iy are respectively obtained from the F11(l), the F12(l), the F21(l) and the F22(l), so that the vector of f(1) belonging to C4*1 is established; the covariance matrix of the f(1) is calculated according to the sampling covariance matrix inversion principle, characteristic decomposition is conducted on the covariance matrix, and a noise projection matrix pn can be obtained through a noise sub space un; a transmitting oriented vector and a receiving oriented vector br(theta) are obtained according to a receiving data matrix Y(1) and the leaving angle and the reaching angle are estimated through the MUSIC arithmetic.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com