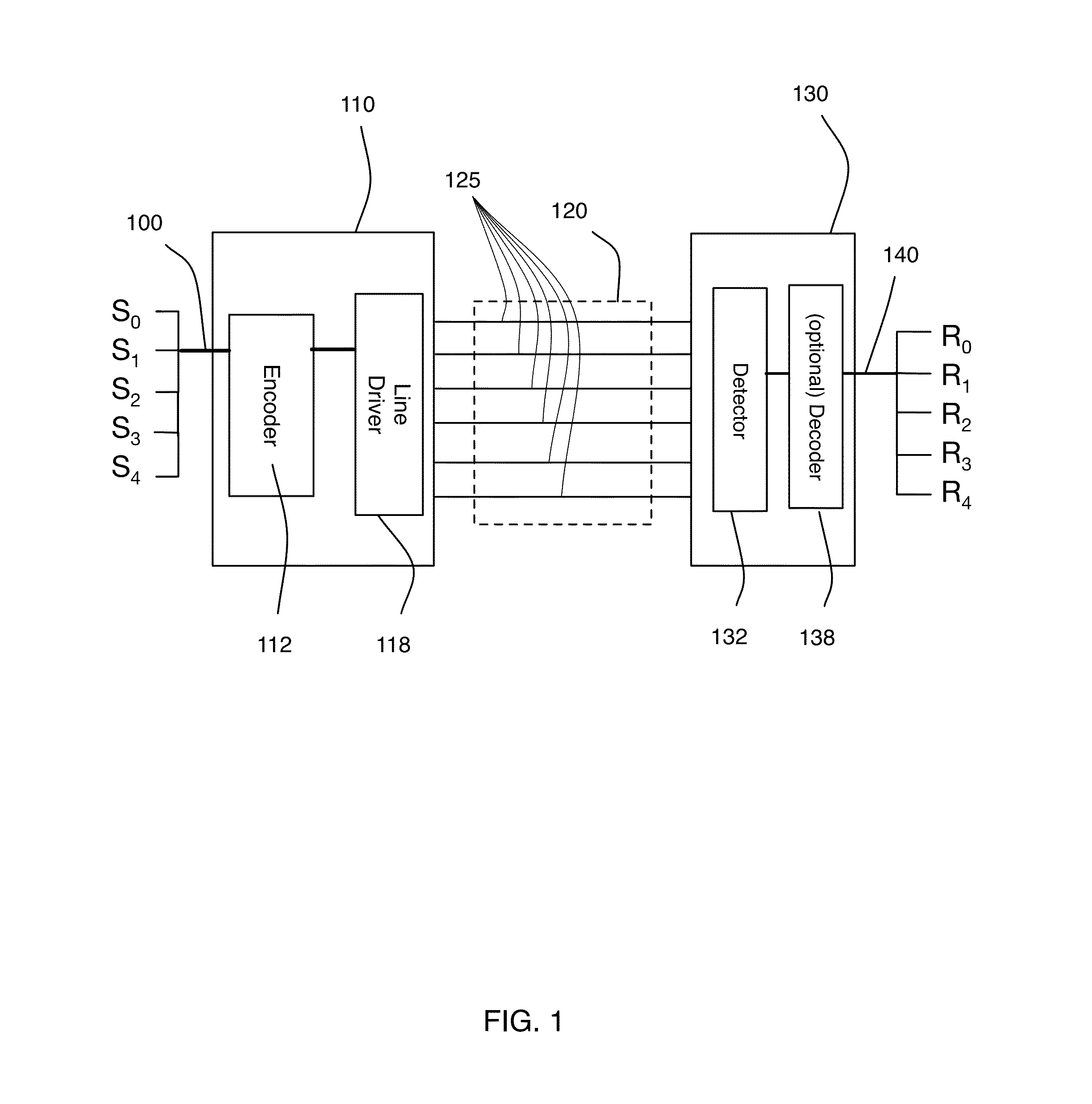
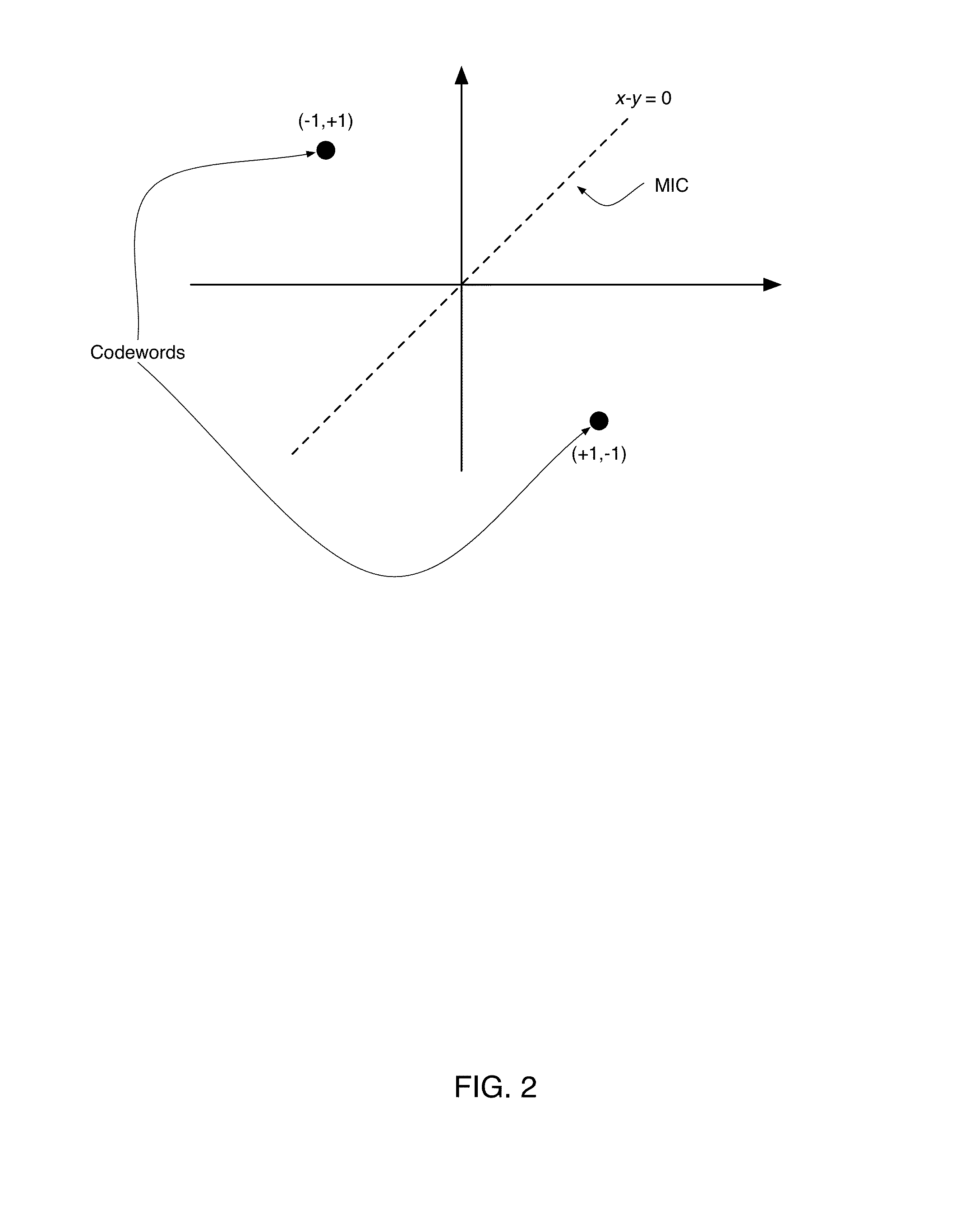
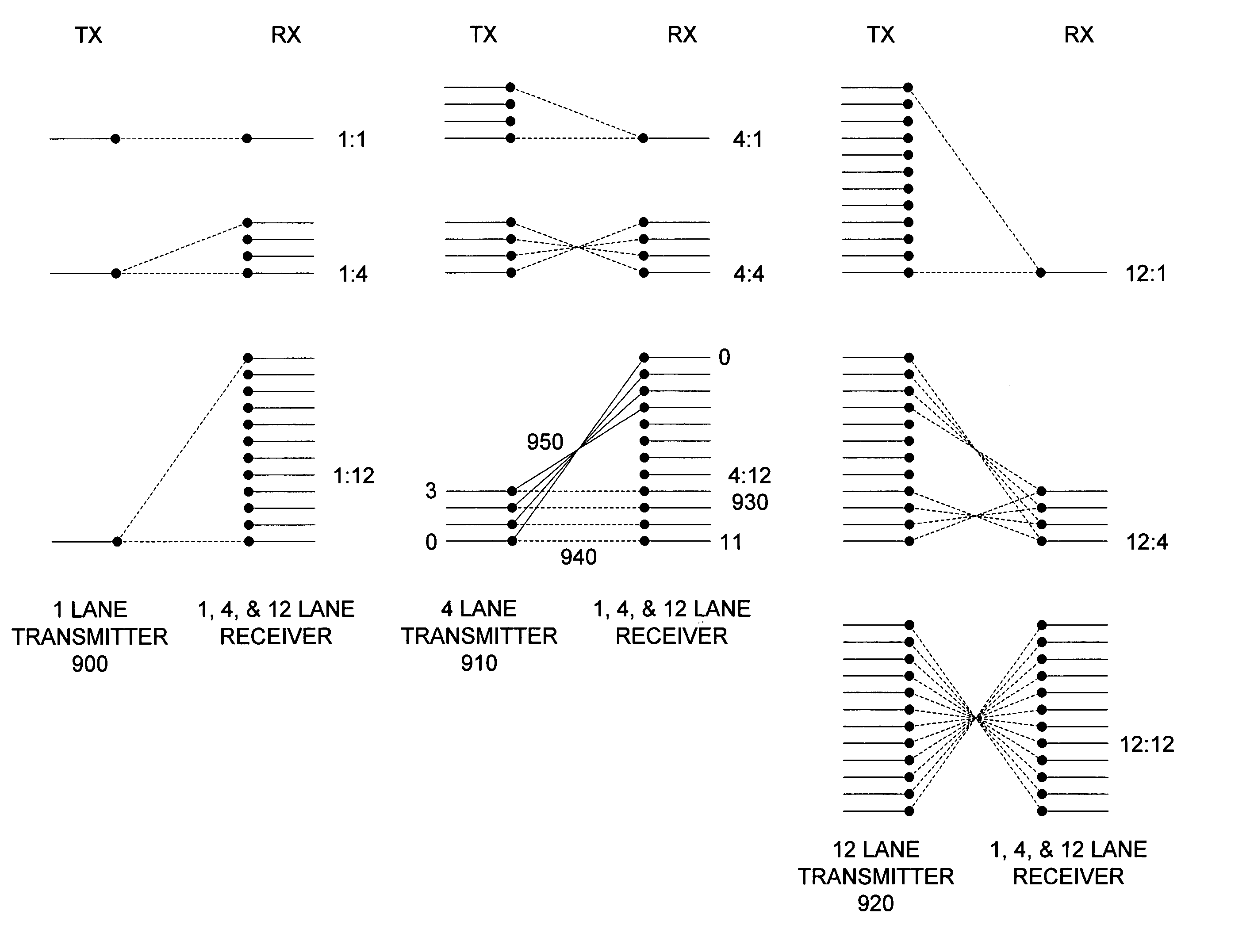
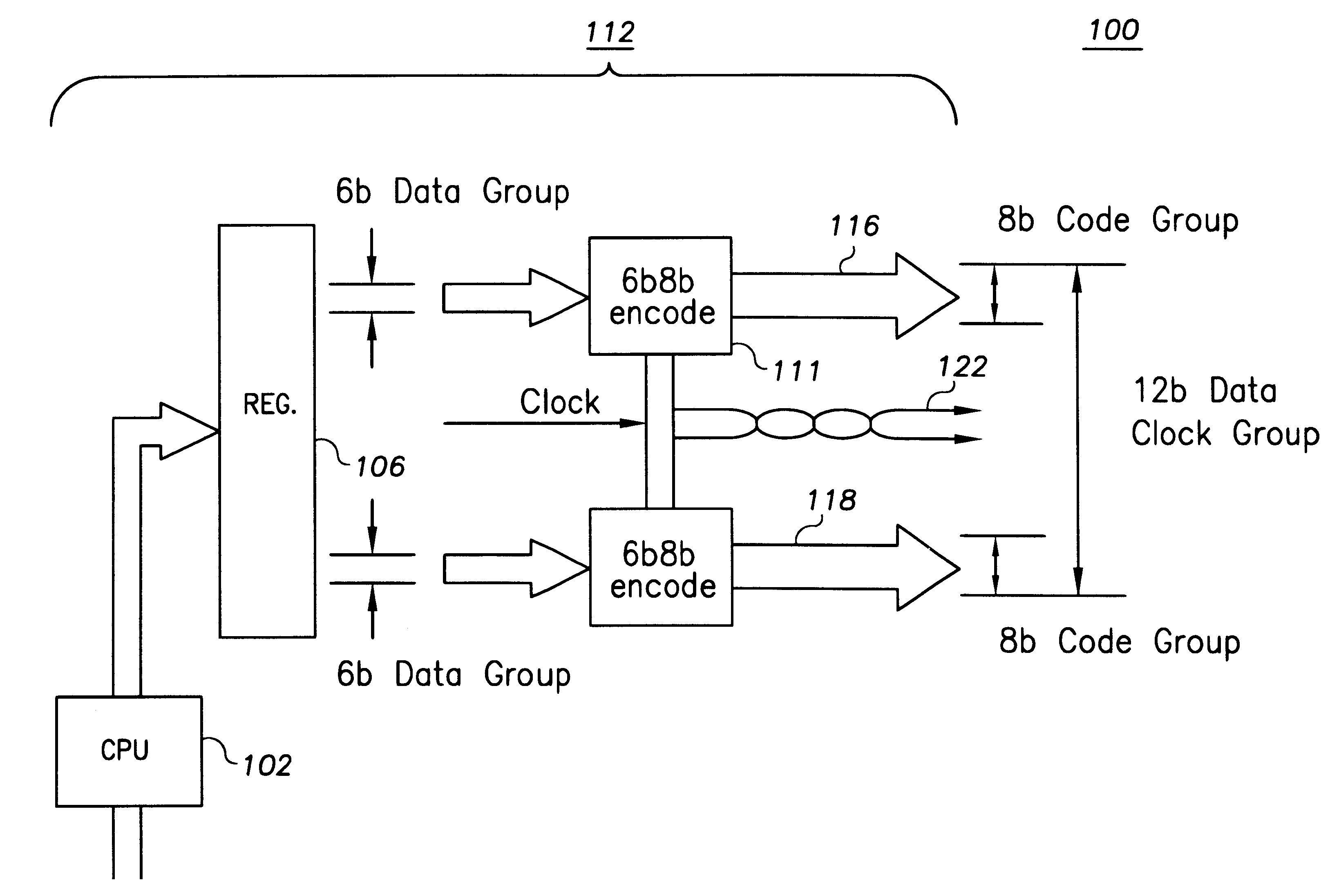
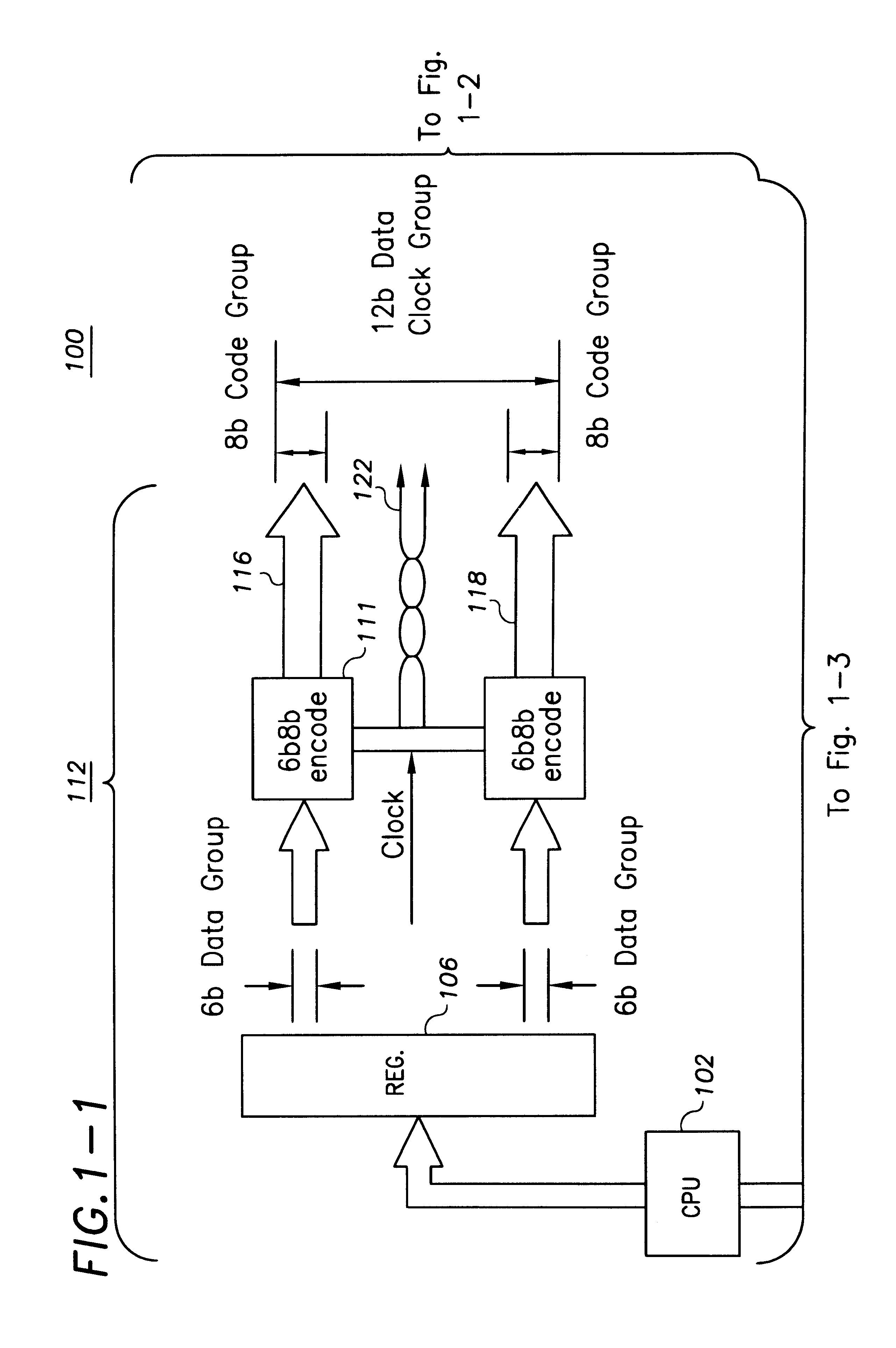
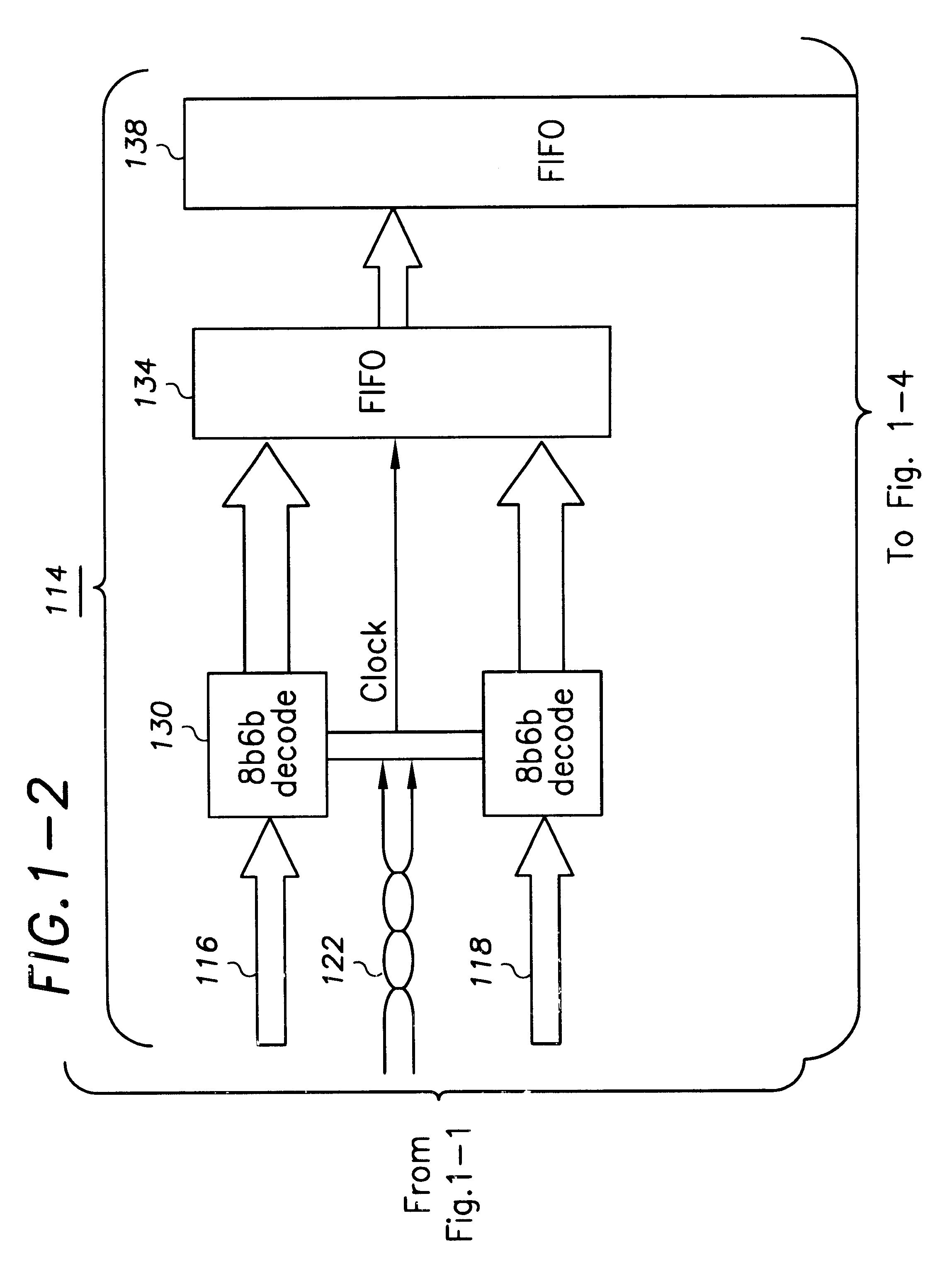
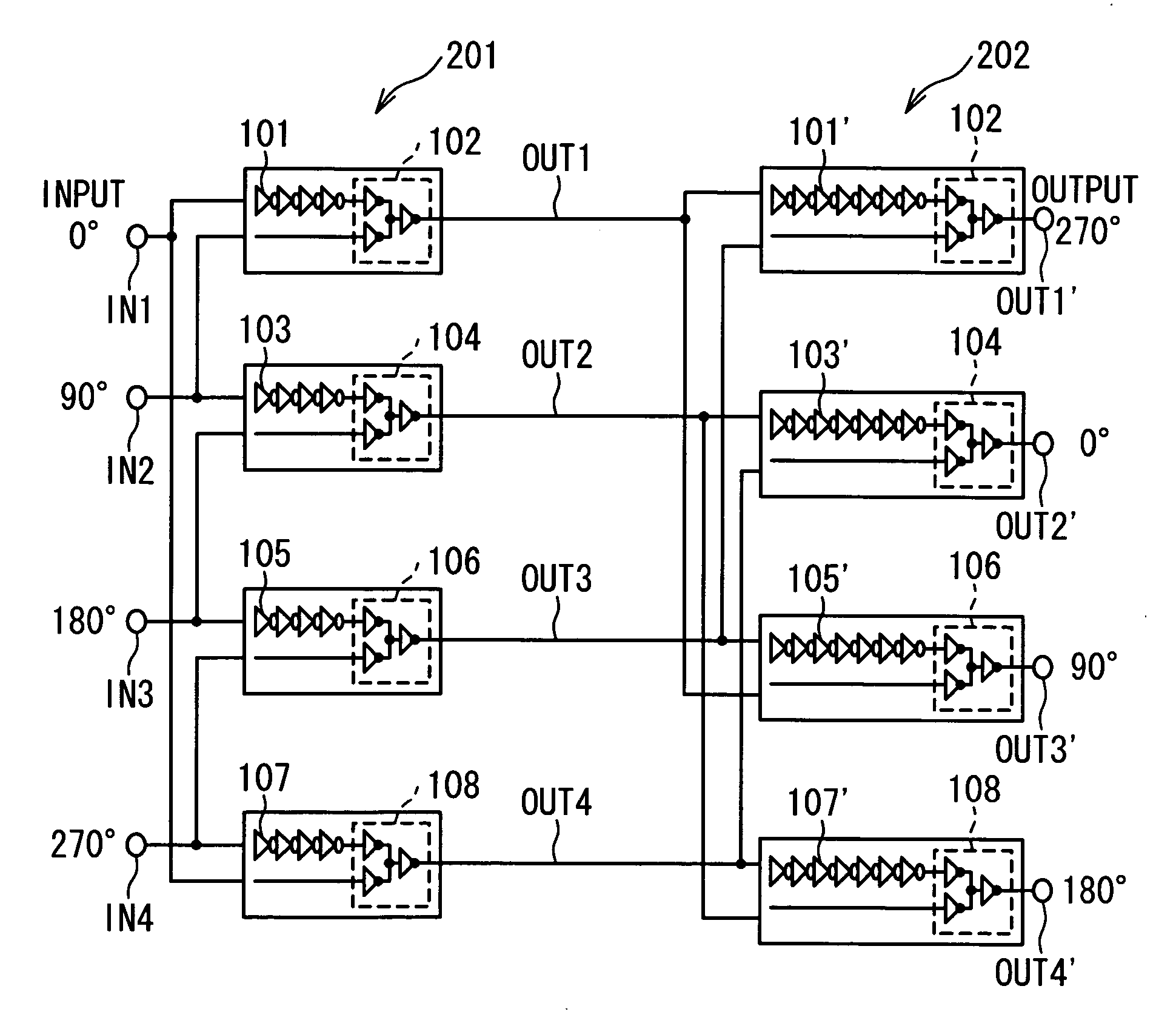
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
777results about "Channel dividing arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
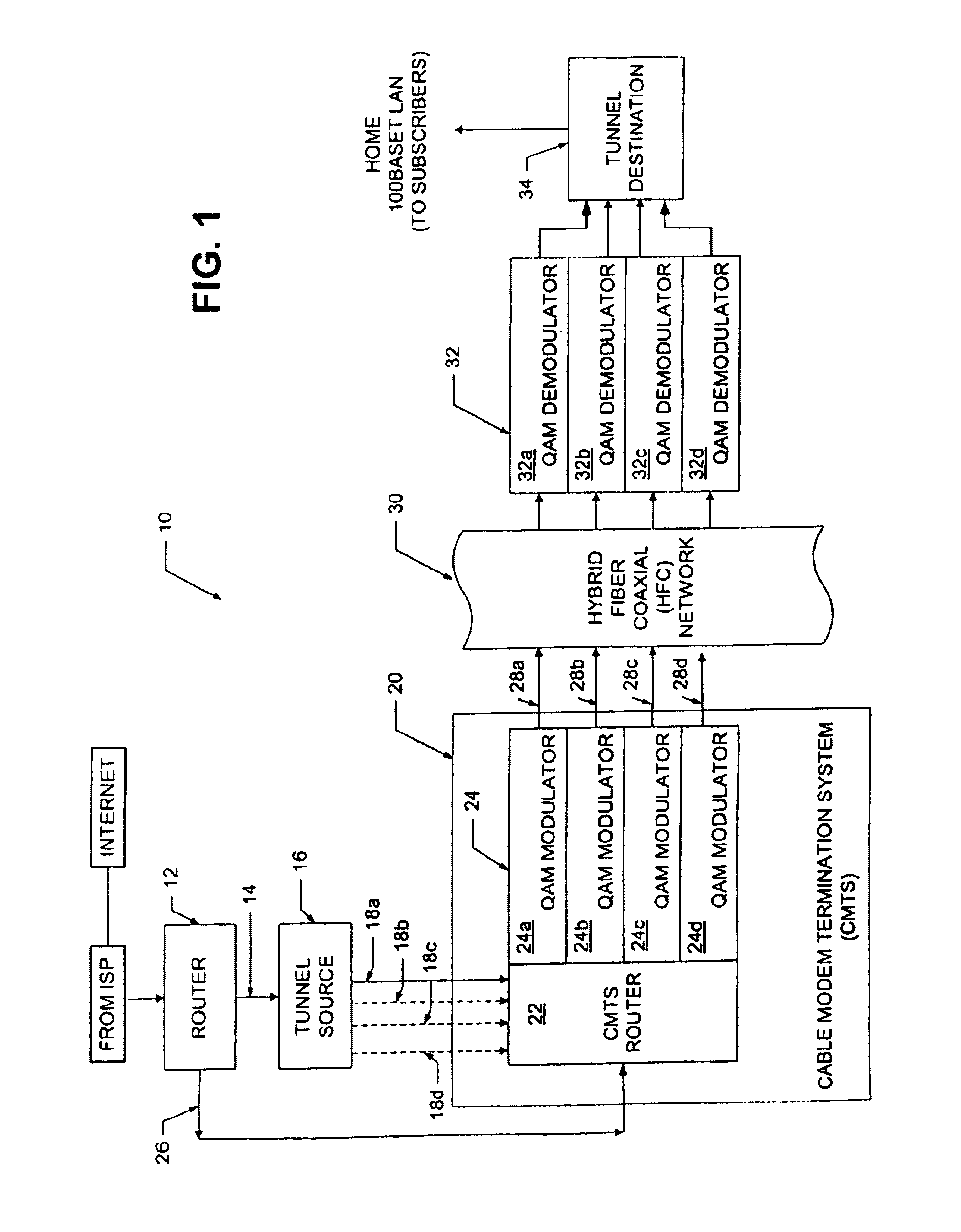
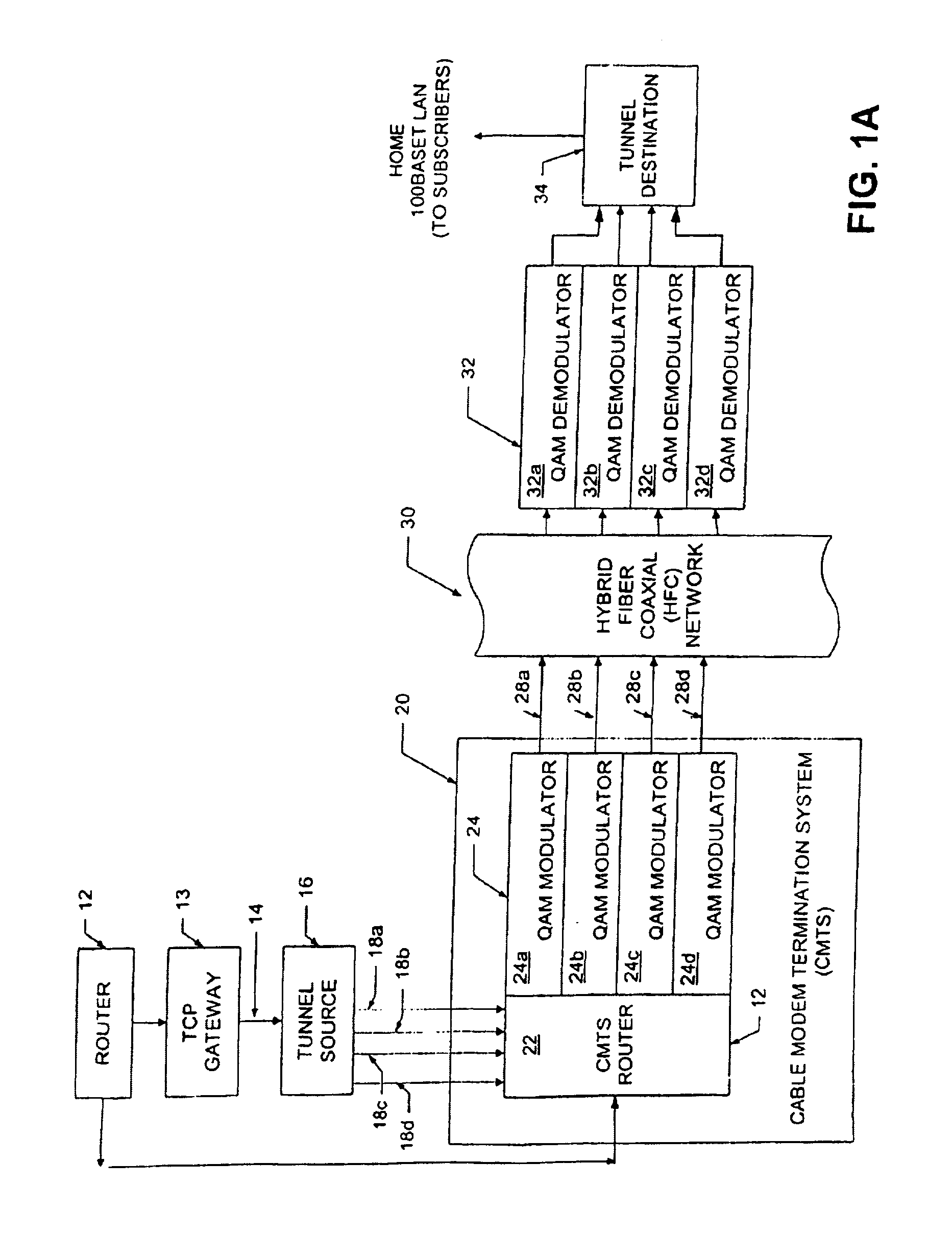
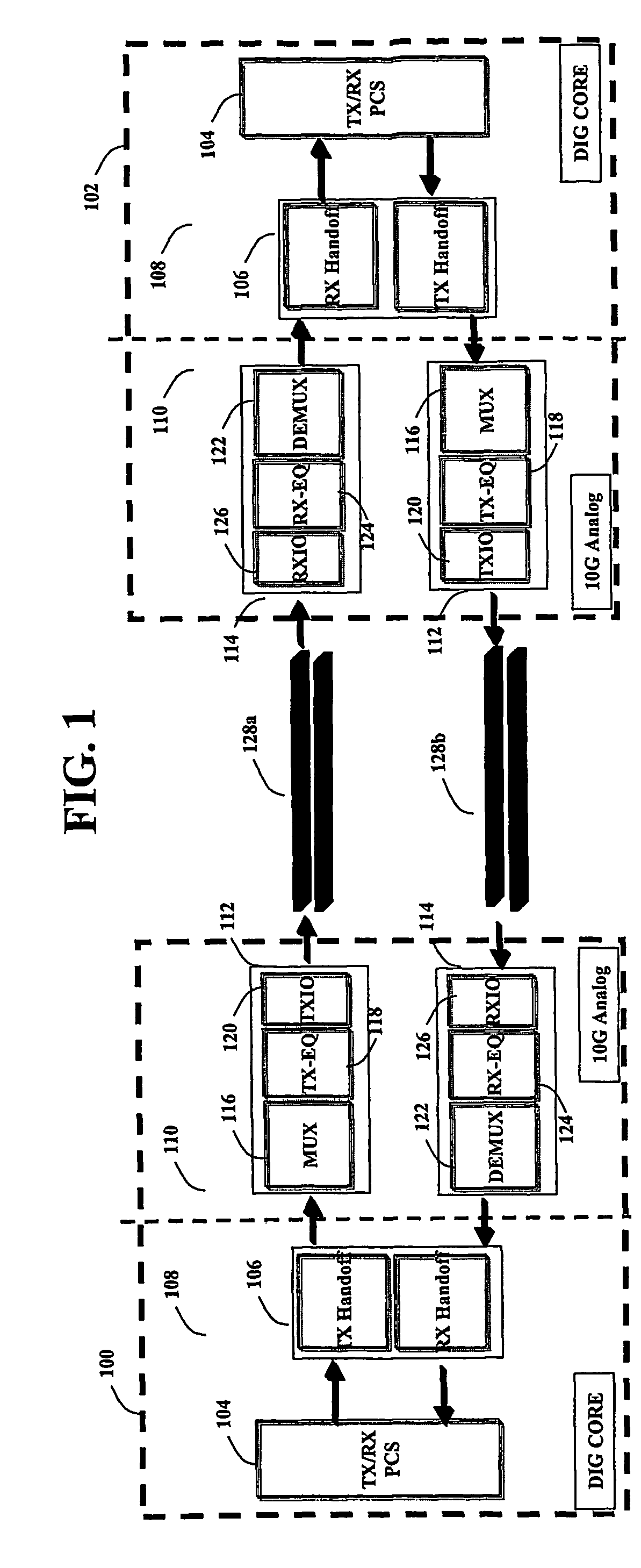
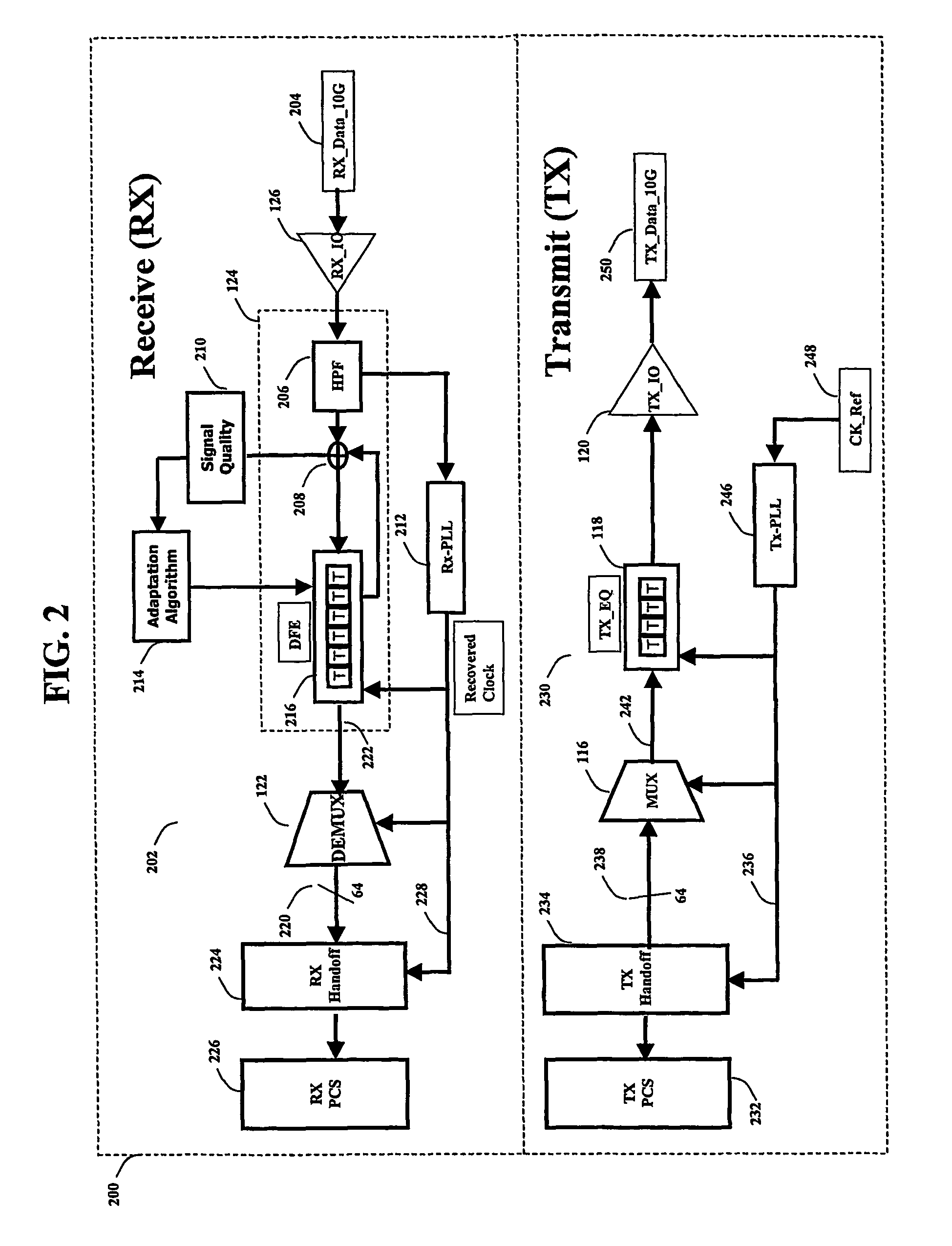
Channel equalization system and method
InactiveUS6904110B2Increase high performance and data rate capacityLow costMultiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsFiberEngineering
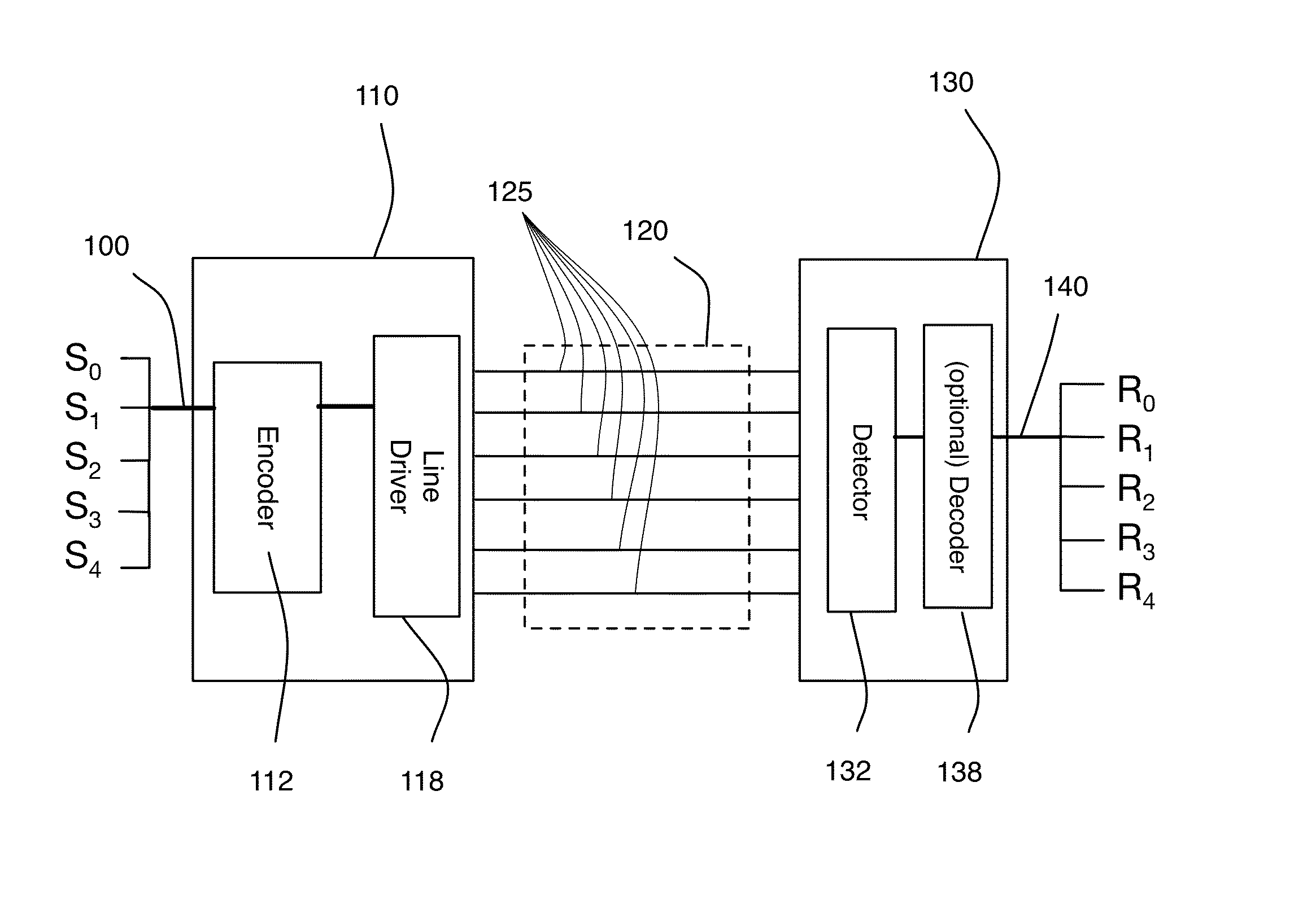
A system and method for delivering increases speed, security, and intelligence to wireline and wireless systems. The present invention increases channel capacity by using a parallel or multi-channel structure in such wireless and wireline at the edge or the core of. This new architecture of the present invention uses parallel bitstreams in a flexible way and distributed switching / routing technique, is not only to avoid the potential bottlenet of centralized switches, but also to increase speed with intelligence that is seamlessly integrating into the Fiber Optic Backbone such as WDM and SONET of the MAN / WAN network with a Real-time guarantees, different types of traffic (such as Stringent synchronous, isochronous, and asynchronous data messages) with different demands, and privacy & security of multi access and integrated services environment.
Owner:B C LEOW
Channel adaptive equalization precoding system and method
InactiveUS20030086515A1Increase high performance and data rate capacityLow costChannel dividing arrangementsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPrecodingOperational system
A system and method for delivering increased speed, security, and intelligence to wireline and wireless systems. The present invention includes a new generation Fast Circuit Switch (packet / circuit) Communication processors and platform which enables a new Internet Exchange Networking Processor Architecture at the edge and core of every communication system, for next generation Web Operating System or Environment (WOE) to operate on with emphasis of a non-local processor or networking processor with remote web computing capabilities.
Owner:TRANS FRANCOIS +1
Method for code evaluation using ISI ratio
ActiveUS9100232B1Fast communication speedReduce power consumptionChannel dividing arrangementsCode division multiplexComputer architectureCode assessment
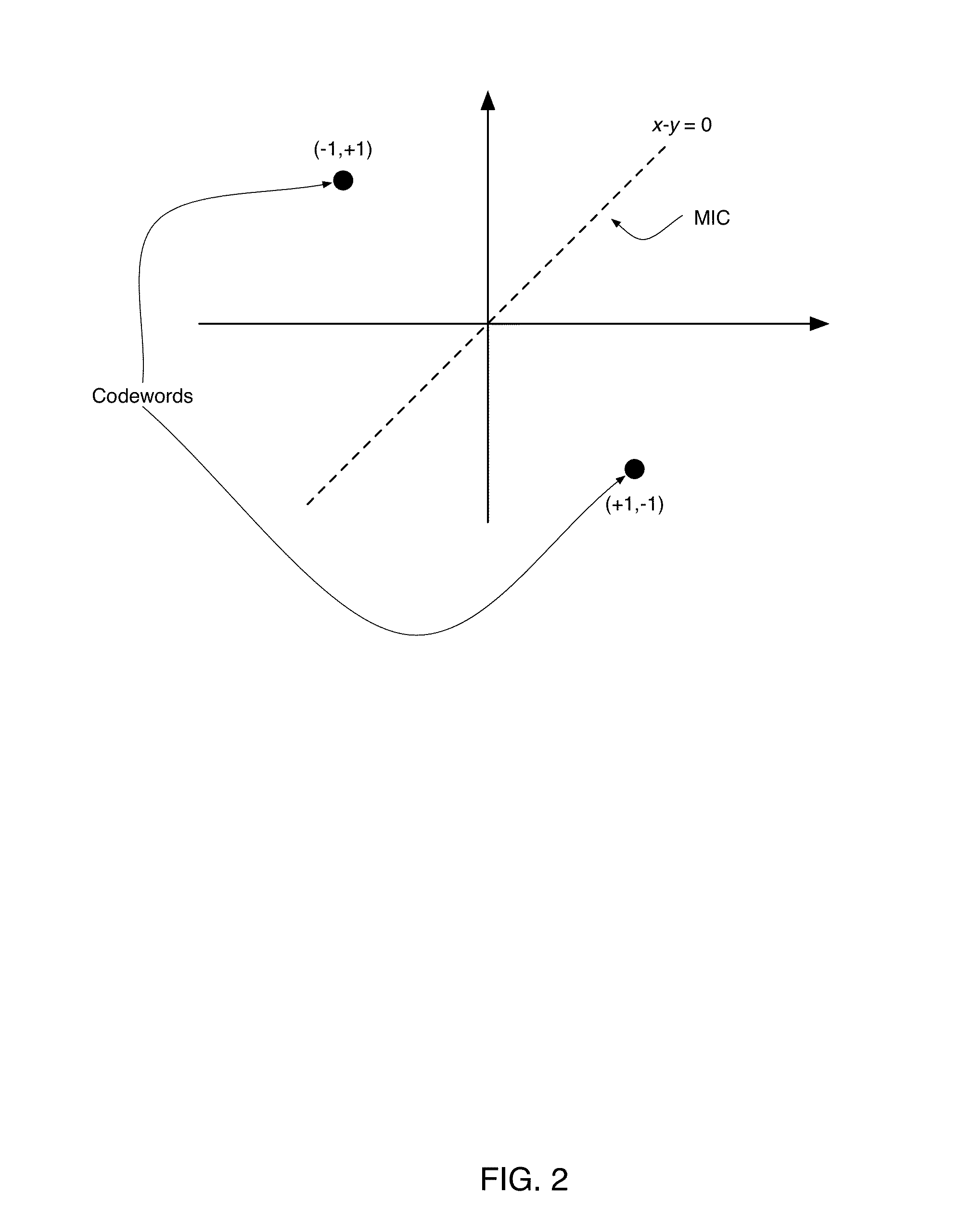
An efficient communications apparatus is described for a vector signaling code to transport data and optionally a clocking signal between integrated circuit devices. Methods of designing such apparatus and their associated codes based on a new metric herein called the “ISI Ratio” are described which permit higher communications speed, lower system power consumption, and reduced implementation complexity.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
Finite state encoders and decoders for vector signaling codes
ActiveUS8718184B1Channel dividing arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemComputer science
In a chip-to-chip communication system and apparatus, a set of physical signals to be conveyed over a communication bus is provided, and mapped to a codeword of a vector signaling code using the physical signals and a state information, wherein a codeword is representable as a vector of plurality of real-valued components, and wherein a vector signaling code is a set of codewords in which the components sum to zero and for which there is at least one component and at least three codewords having different values in that component; and wherein the state information is a plurality of information present in continuous or discrete form which may have been obtained from previous codewords transmitted over the communication bus.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
Method for Code Evaluation Using ISI Ratio
ActiveUS20150222458A1Fast communication speedReduce power consumptionChannel dividing arrangementsCode division multiplexComputer architectureTelecommunications equipment
An efficient communications apparatus is described for a vector signaling code to transport data and optionally a clocking signal between integrated circuit devices. Methods of designing such apparatus and their associated codes based on a new metric herein called the “ISI Ratio” are described which permit higher communications speed, lower system power consumption, and reduced implementation complexity.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
High-speed interconnection link having automated lane reordering
A multi-lane link that automatically detects if the lanes in the link have been reordered and corrects the order of the lanes. In one embodiment, the link includes a transmitter and a receiver. The receiver is configured to receive a plurality of lanes and includes a receiver logic circuit configured to receive signals from each of the plurality of lanes. Lane misordering is corrected during a training sequence in which a first training sequence and a second training sequence are bilaterally transmitted between the transmitter and receiver. The receiver monitors the training sequence for symbols that are unique to each lane and if an unexpected symbol is detected in the lane, the receiver logic circuit will correct the order of the lanes. The link further comprises a transmitter logic circuit configured to transmit signals to the lanes. The transmitter logic circuit is configured to reorder the sequence of the signals transmitted to the lanes if the transmitter does not detect a response from the receiver. The transmitter logic circuit may consist of a bank of multiplexers configured to transmit a selected one of two input signals to be transmitted through a lane. Similarly, the receiver logic circuit may comprises a bank of multiplexers configured to transmit a selected one of two input signals received from a lane. The unique lane identifiers symbols are preferably insensitive to binary inversion and are preferably 10-bit symbols compatible with an 8B / 10B encoding scheme.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
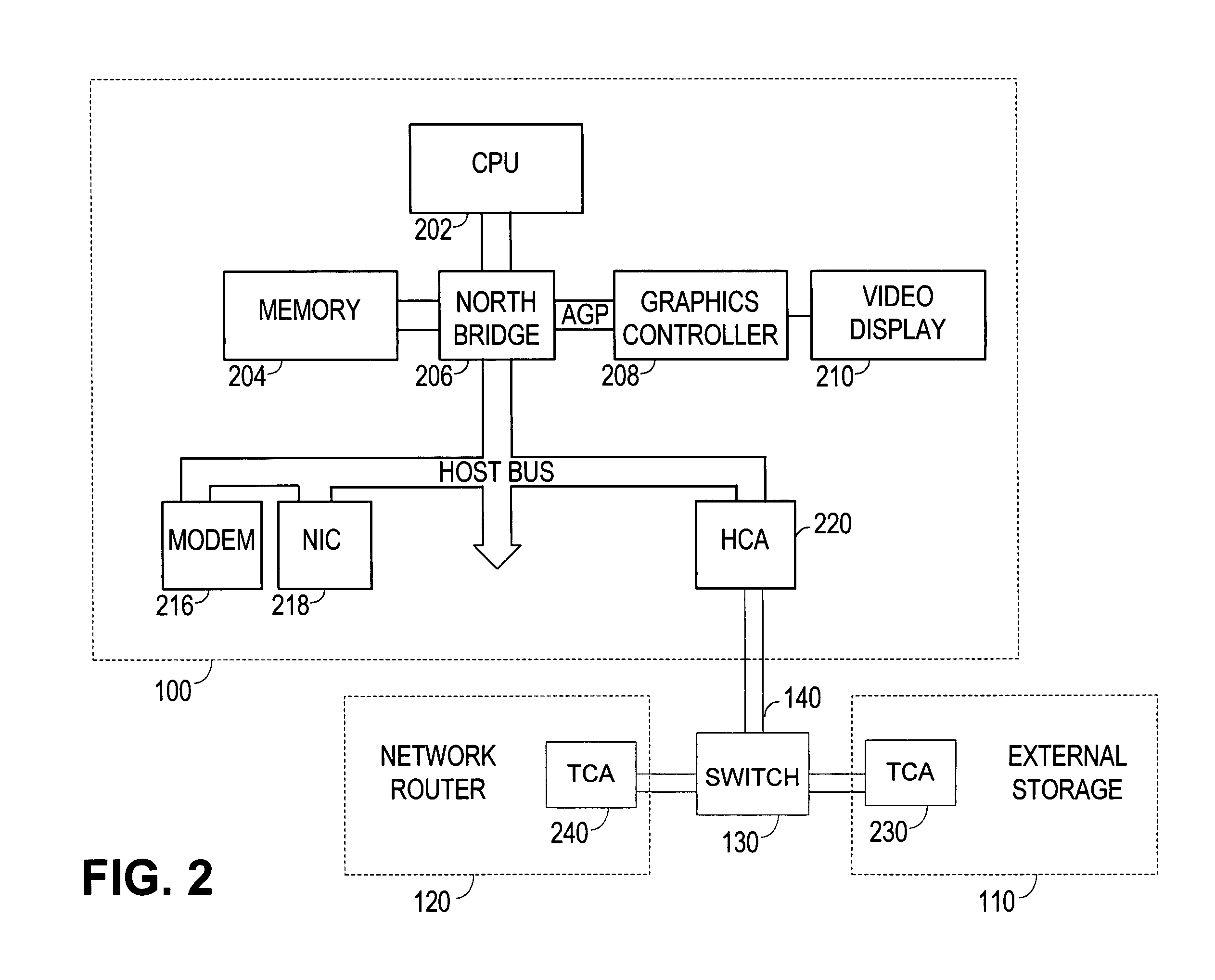
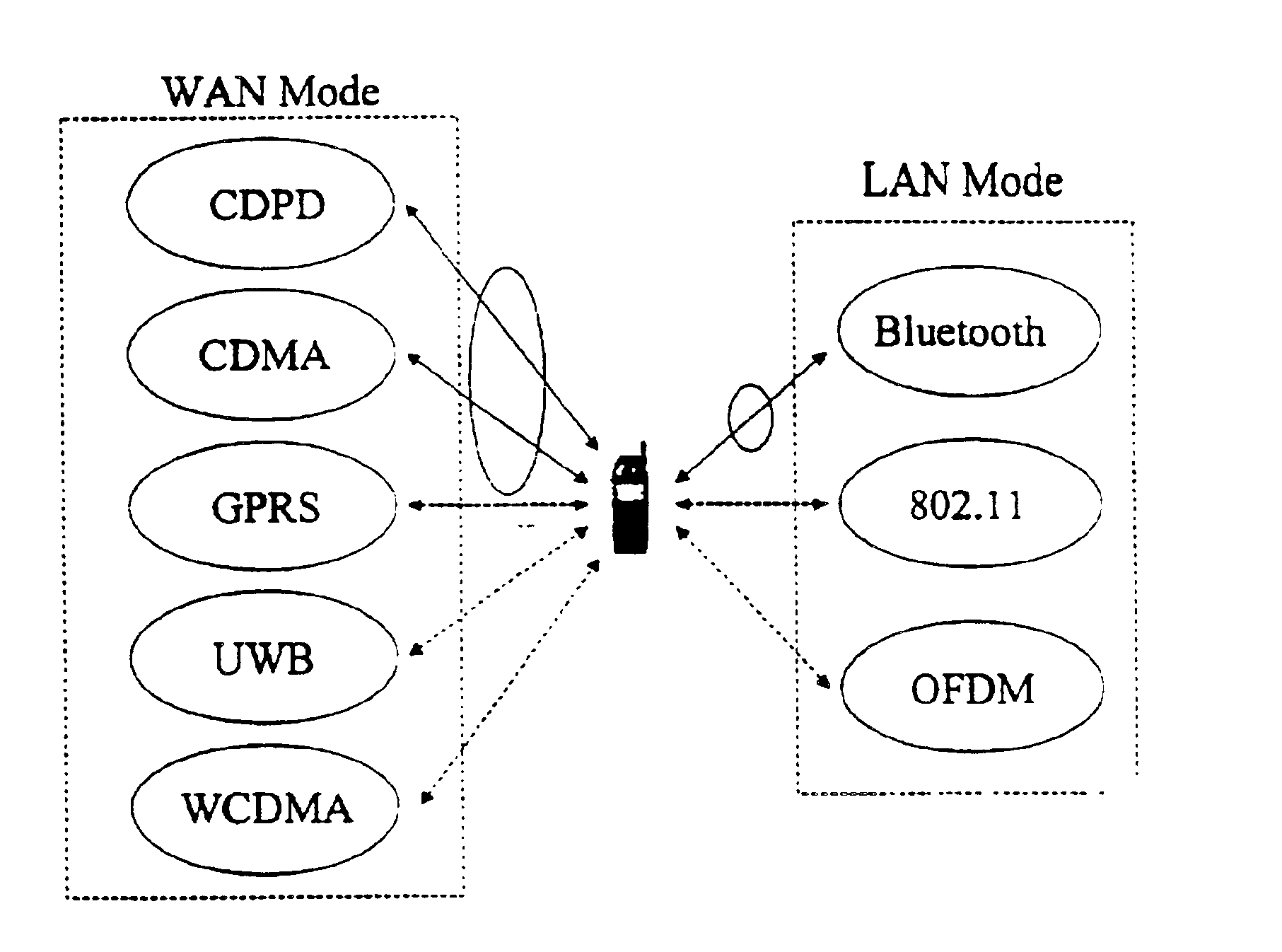
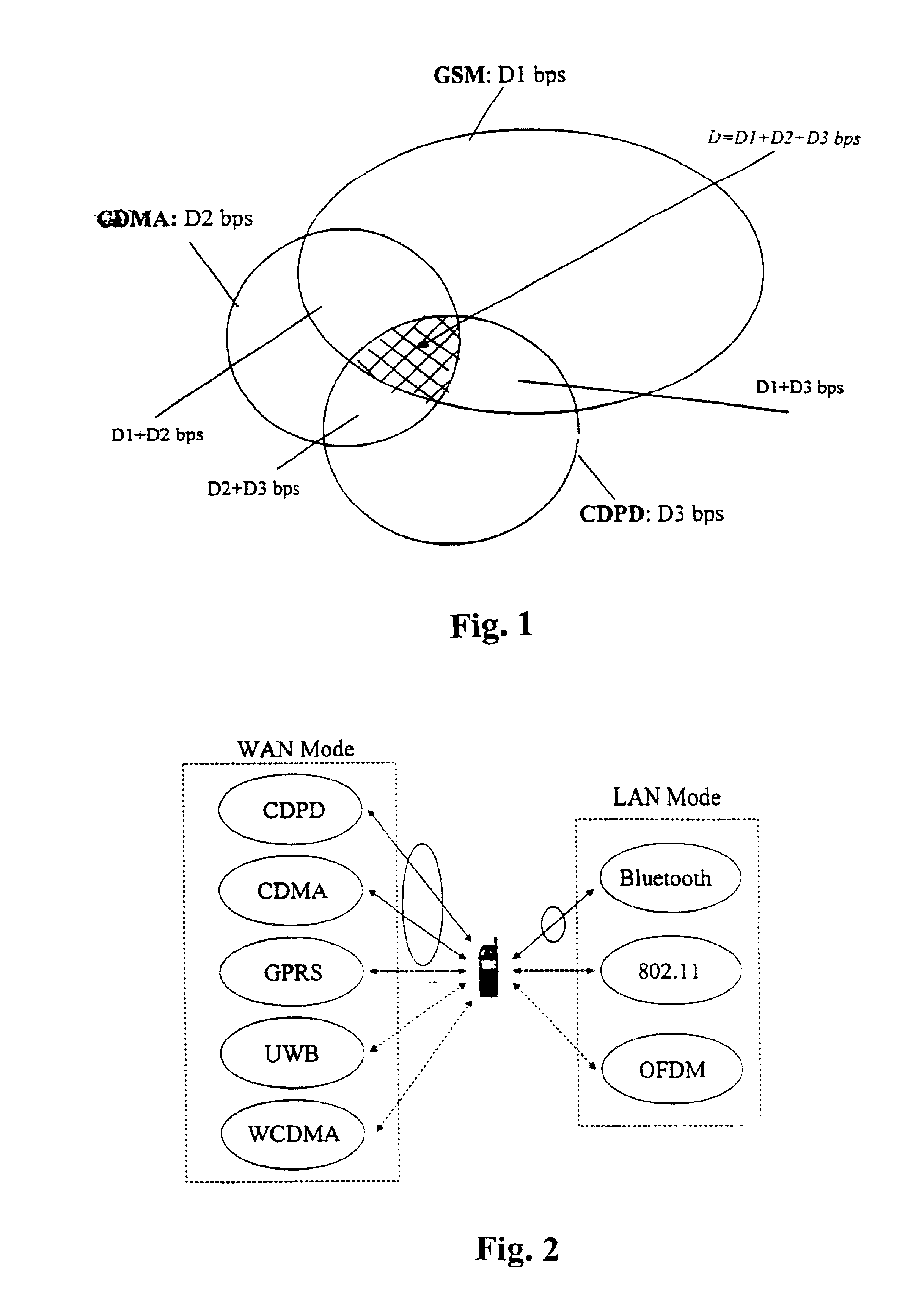
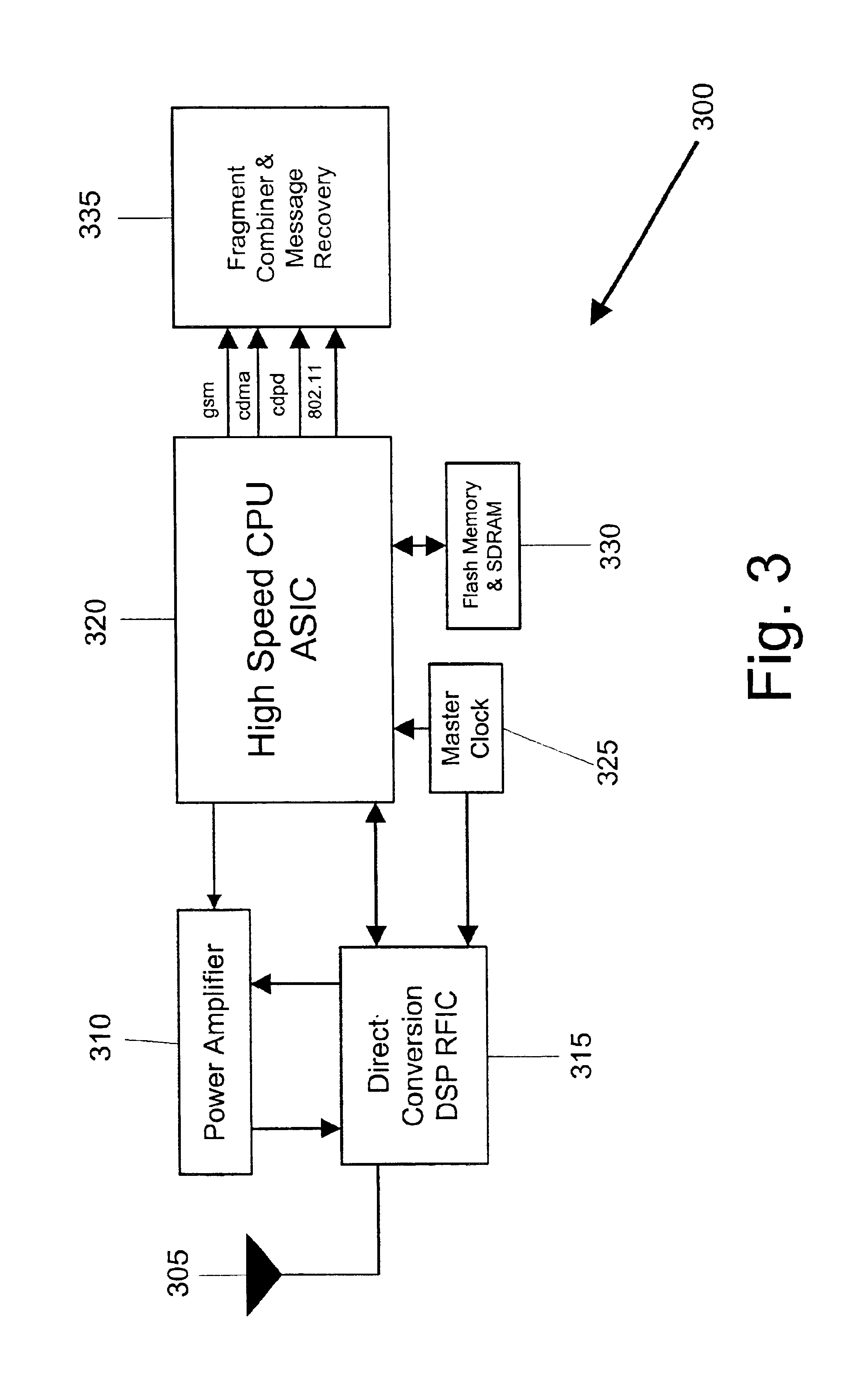
Method and apparatus for distributed data transfer over multiple independent wireless networks
ActiveUS7224964B2Maximum efficiencyHigh bandwidthChannel dividing arrangementsWave amplification devicesModem deviceRadio frequency
The present invention provides for methods and apparatus for fragmenting a single message and sending the message fragments over multiple independent networks to a single receiving unit. The receiving unit then reassembles the message fragments to generate the original message. The preferred apparatus embodiment is a wireless radio frequency modem that can both receive and transmit fragmented messages over multiple independent networks.
Owner:NOVATEL WIRELESS
Pair-swap independent trellis decoder for a multi-pair gigabit transceiver
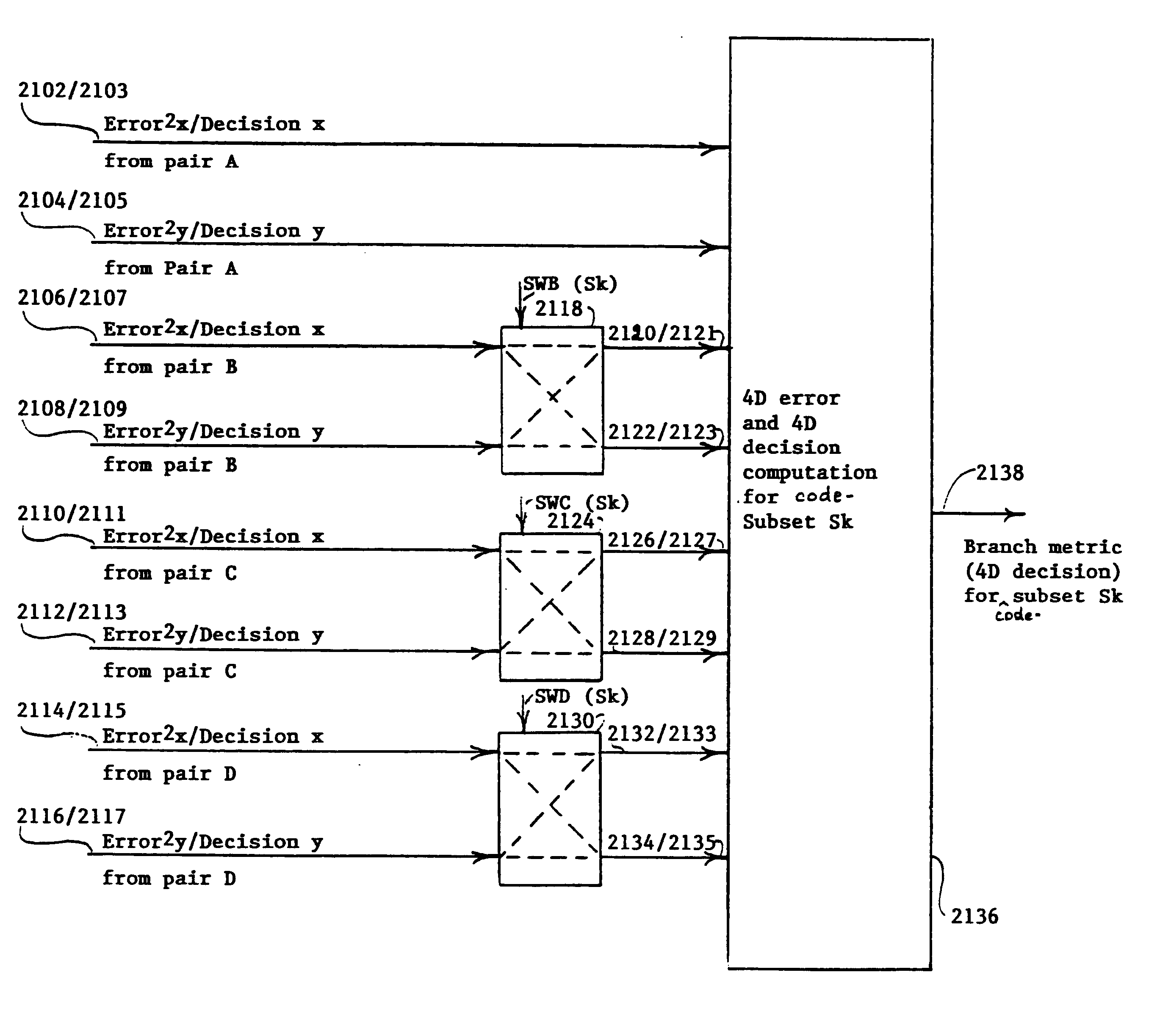
InactiveUS6865234B1Channel dividing arrangementsDigital circuit testingGigabitMulti-gigabit transceiver
A method and a system for compensating for a permutation of L pairs of cable such that the compensation is localized in a trellis decoder of a receiver. The L pairs of cable correspond to L dimensions of a trellis code associated with the trellis decoder. The trellis code includes a plurality of code-subsets. The permutation of the L pairs of cable is determined. A plurality of sets of swap indicators based on the permutation of the L pairs of cable is generated. Each of the sets of swap indicators corresponds to one of the code-subsets. The code-subsets are remapped based on the corresponding sets of swap indicators.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
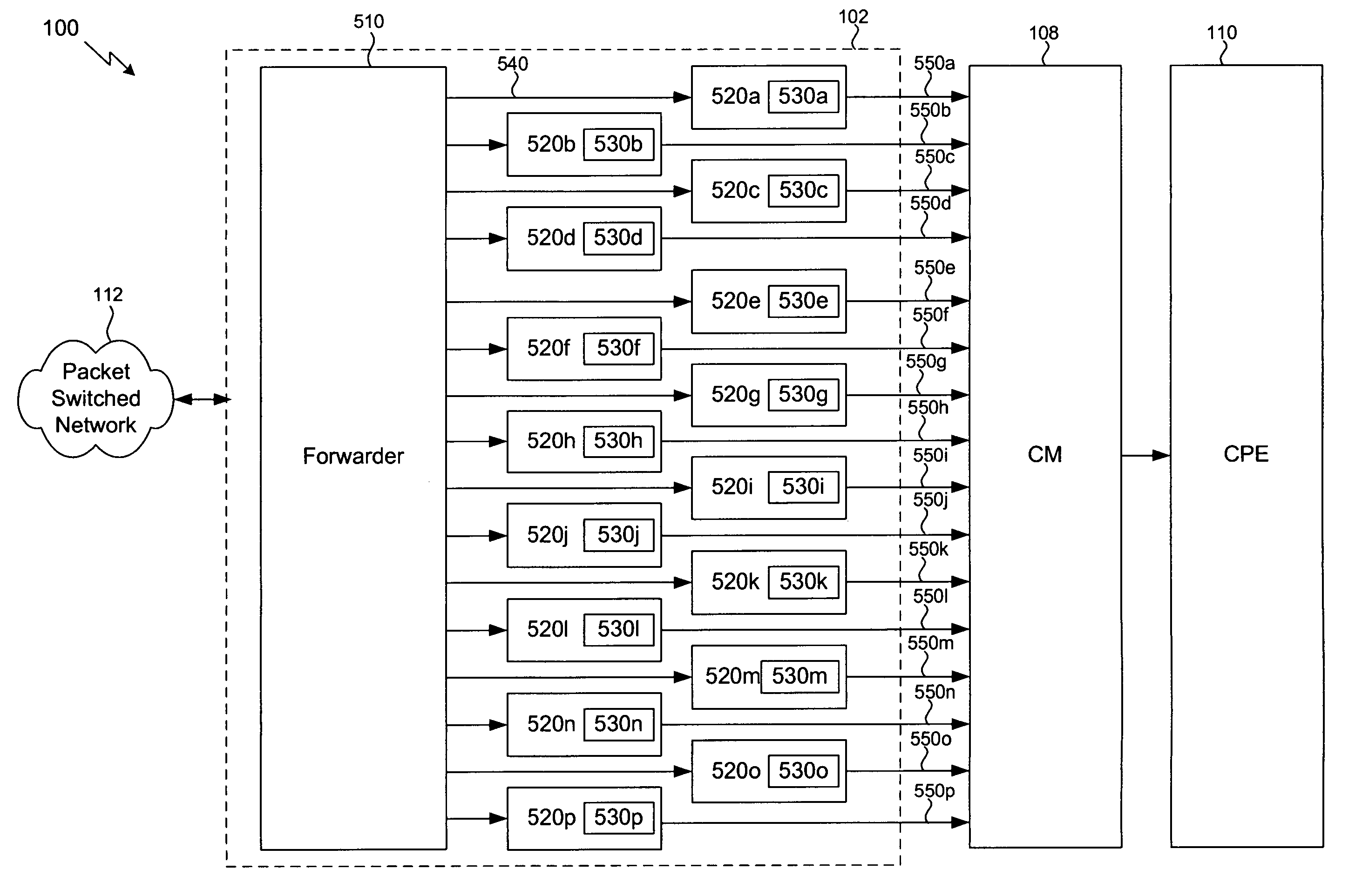
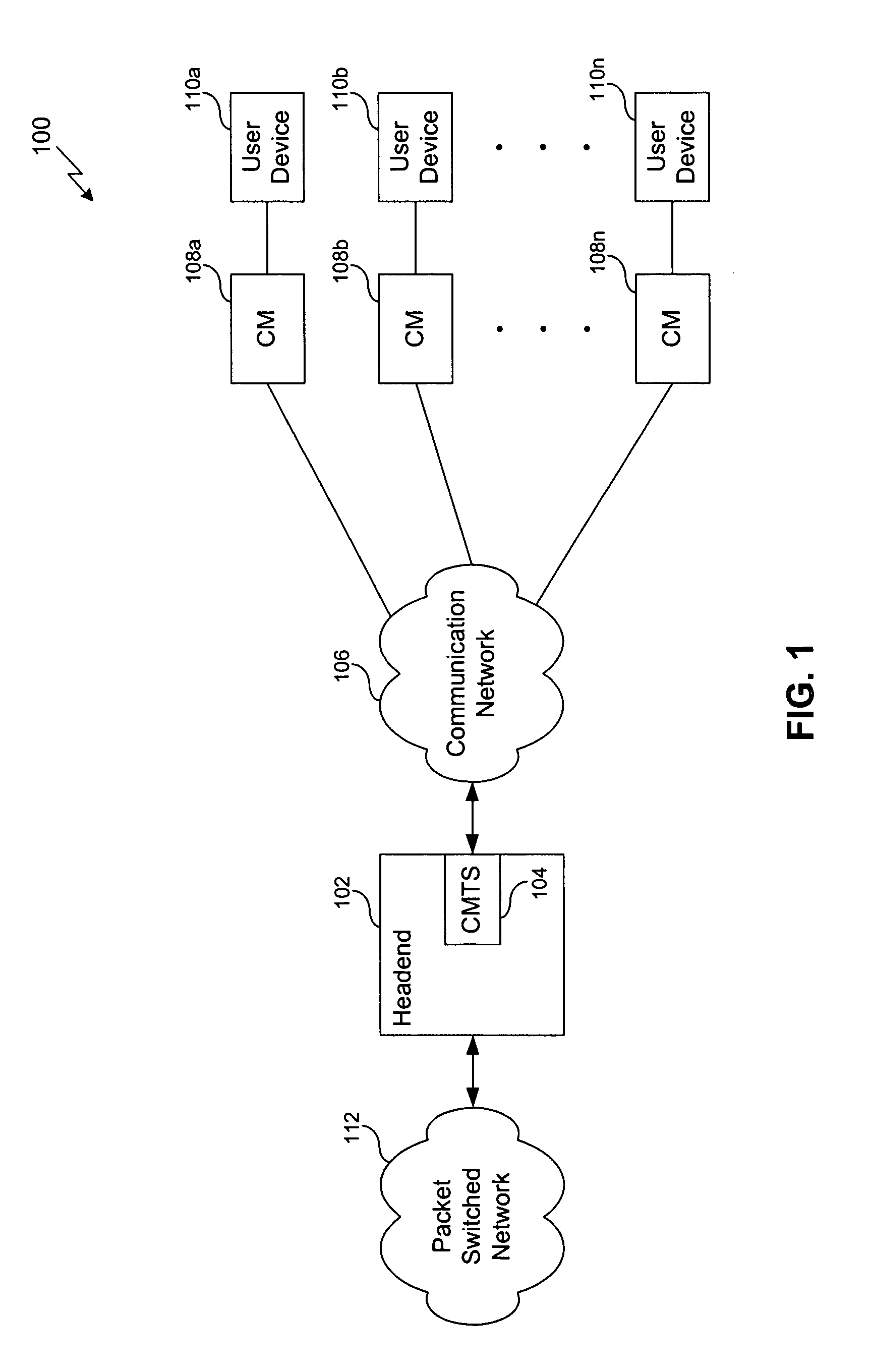
Hierarchical flow-level multi-channel communication
InactiveUS20070098007A1Improve network performanceImprove throughputEnergy efficient ICTChannel dividing arrangementsCommunications systemEngineering
A communication system that includes a supervisory node (e.g., a headend) and one or more remote nodes (e.g., cable modems). Packets are transmitted between the supervisory node and the one or more remote nodes via RF channels. A plurality of the RF channels are bonded, such that packets may be transmitted via any one or more of the RF channels that are bonded. Bonding may include higher-layer bonding and / or lower-layer bonding. In higher-layer bonding, the communication system further includes a forwarder and a plurality of edge modulators. Each edge modulator is connected to a different RF channel or group of RF channels. The forwarder determines to which edge modulator one or more packets or flows are to be transmitted. In lower-layer bonding, a packet is split into pieces. The pieces are assigned to respective RF channels that are associated with an edge modulator for transmission to a remote node.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for multi-point HSDPA communication utilizing a multi-link PDCP sublayer
InactiveCN103201977AError prevention/detection by using return channelChannel dividing arrangementsTelecommunicationsRadio networks
A method and apparatus for wireless communication may provide a multi-link PDCP sublayer (710) in a radio network controller (702) capable of allocating PDCP PDUs among a plurality of RLC entities (712) for use in a multi -point HSDPA network. Some aspects of the disclosure address issues relating to out-of-order delivery of the PDCP PDUs to a UE (610), such as unnecessary retransmissions. That is, the disclosed multi-link PDCP (710) may be capable of distinguishing between sequence number gaps that are caused by physical layer transmission failures and those caused merely by skew.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Flexible ethernet client multi-service and timing transparency systems and methods
A node configured to support multi-service with Flexible Ethernet (FlexE) includes circuitry configured to receive a client signal, wherein the client signal is different from a FlexE client; and circuitry configured to map the client signal into a FlexE shim. A method, implemented in a node, for supporting multi-service with Flexible Ethernet (FlexE) includes receiving a client signal, wherein the client signal is different from a FlexE client; and mapping the client signal into a FlexE shim.
Owner:CIENA
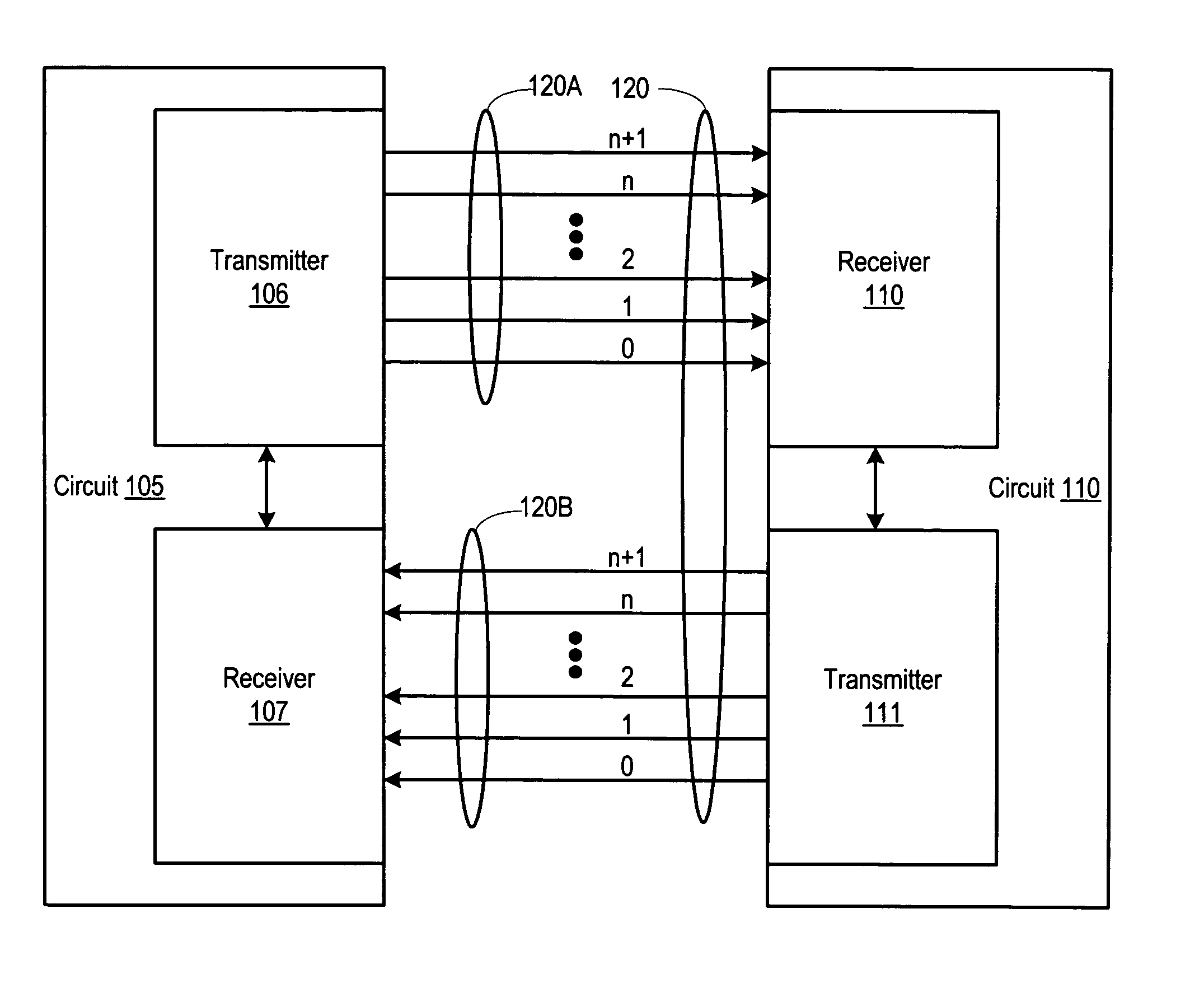
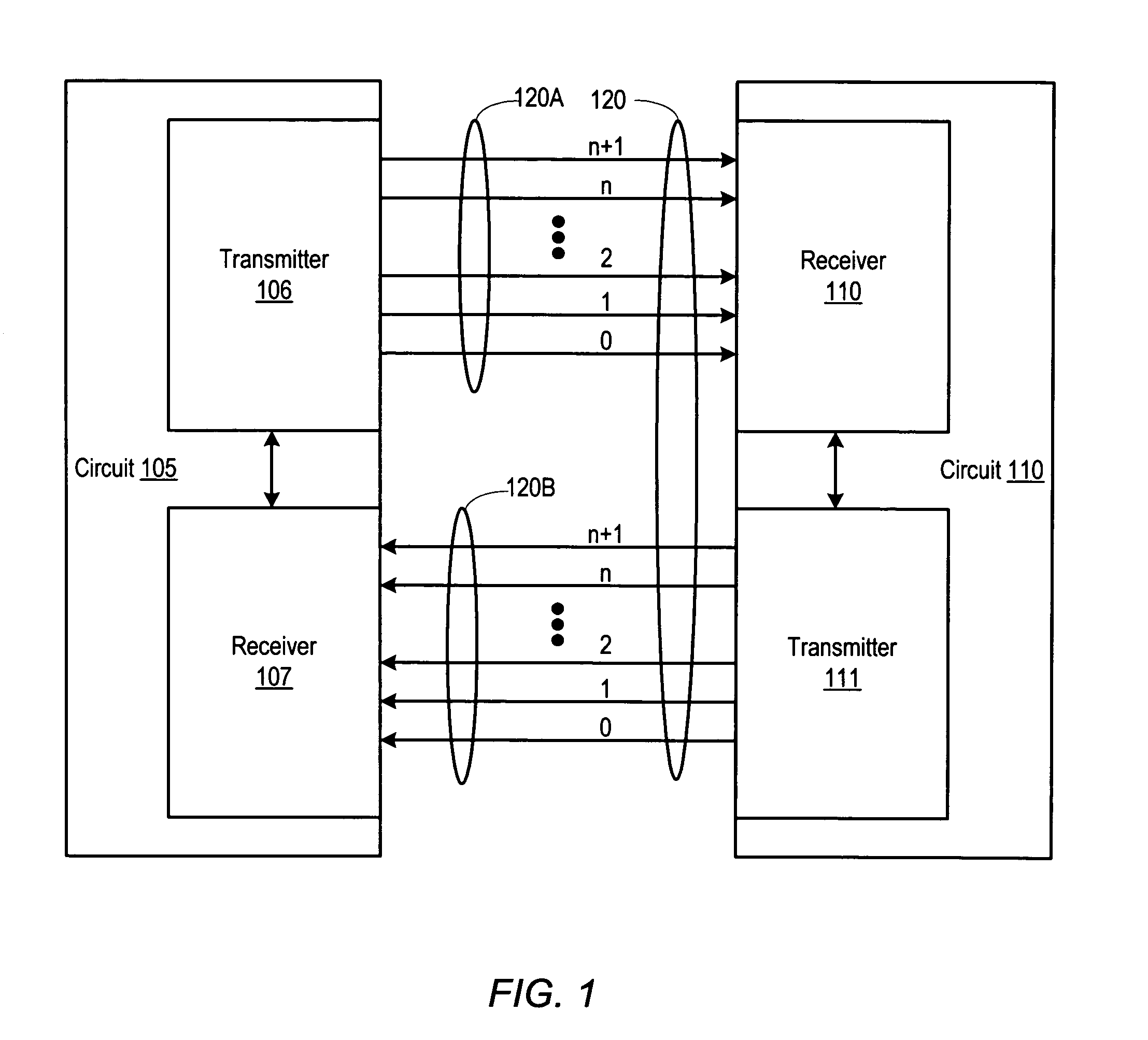
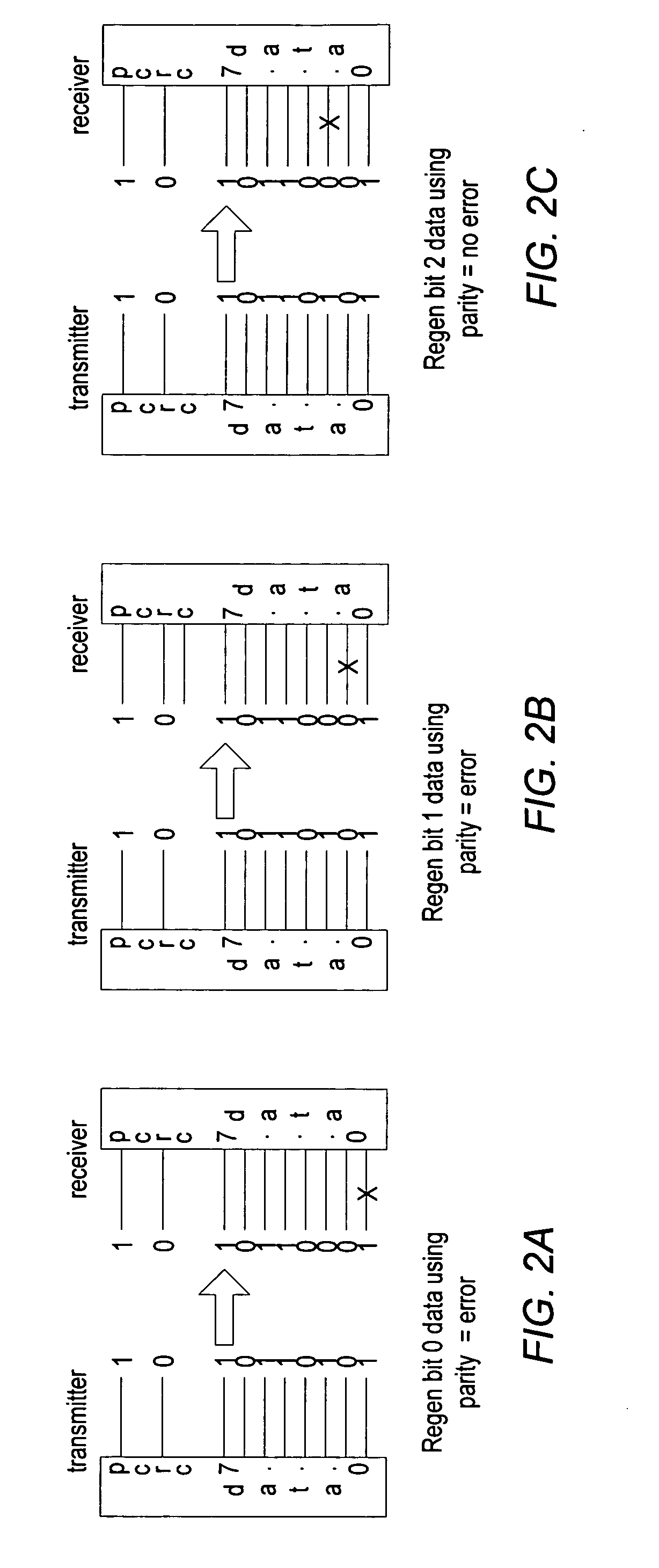
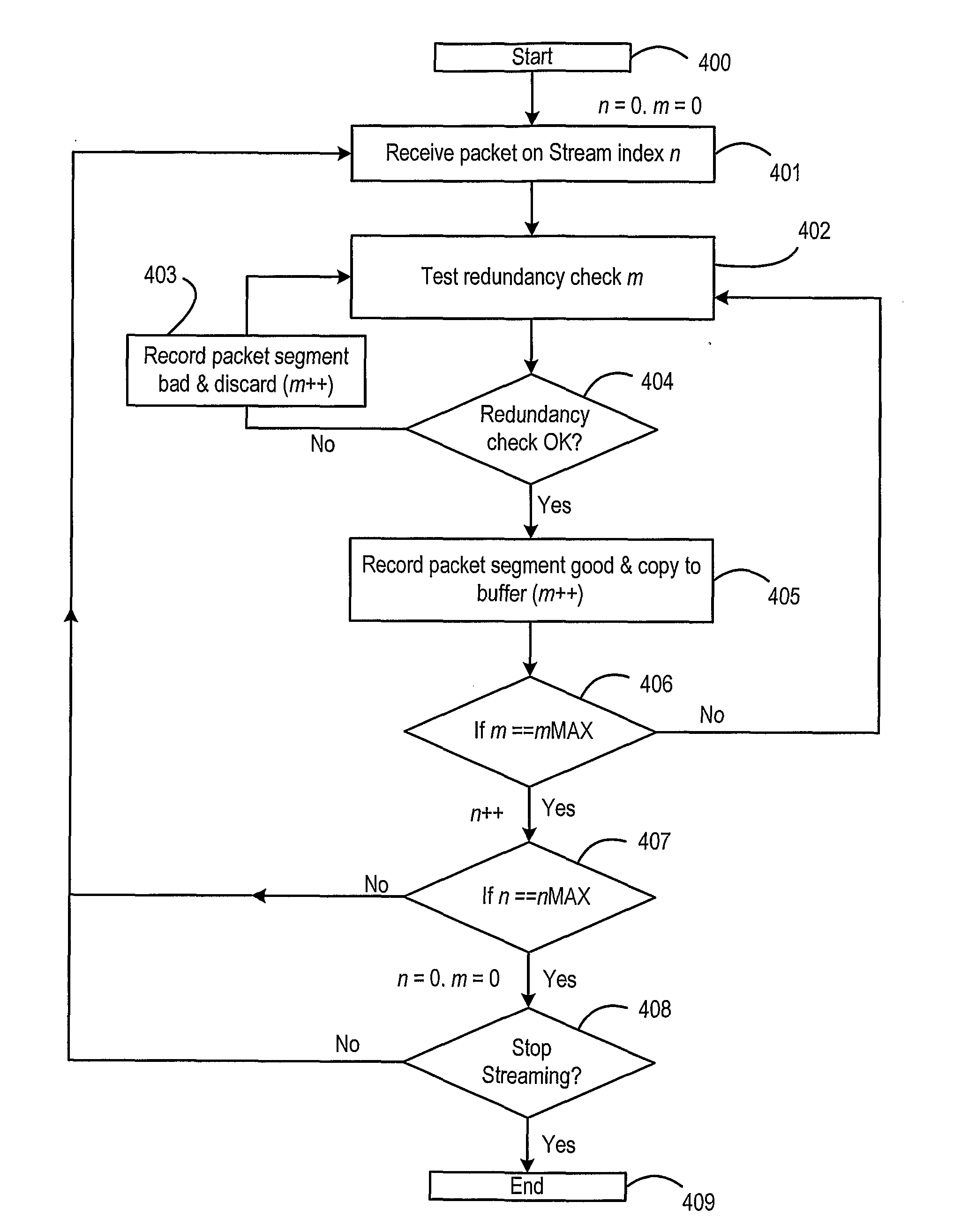
System and method for tolerating communication lane failures
ActiveUS20060212775A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelChannel dividing arrangementsTelecommunications linkData segment
A system for tolerating communication lane failures includes a transmitter configured to transmit a segment of data, an error detecting code, and redundant information. The system also includes a receiver coupled to the transmitter via a communication link including a plurality of bit lanes. Each bit of the segment of data may be conveyed to the receiver serially via respective single-bit lanes. The segment of data, the redundant information, and the error detecting code may be accumulated within the receiver over a plurality of clock cycles. The receiver may detect an error in the segment of data using the error detecting code. In addition, the receiver may, in response to detecting the error, regenerate the segment of data using the redundant information. Further, the receiver may determine whether a resulting regenerated bit, along with remaining bits, of the segment of data are correct using the error detecting code.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
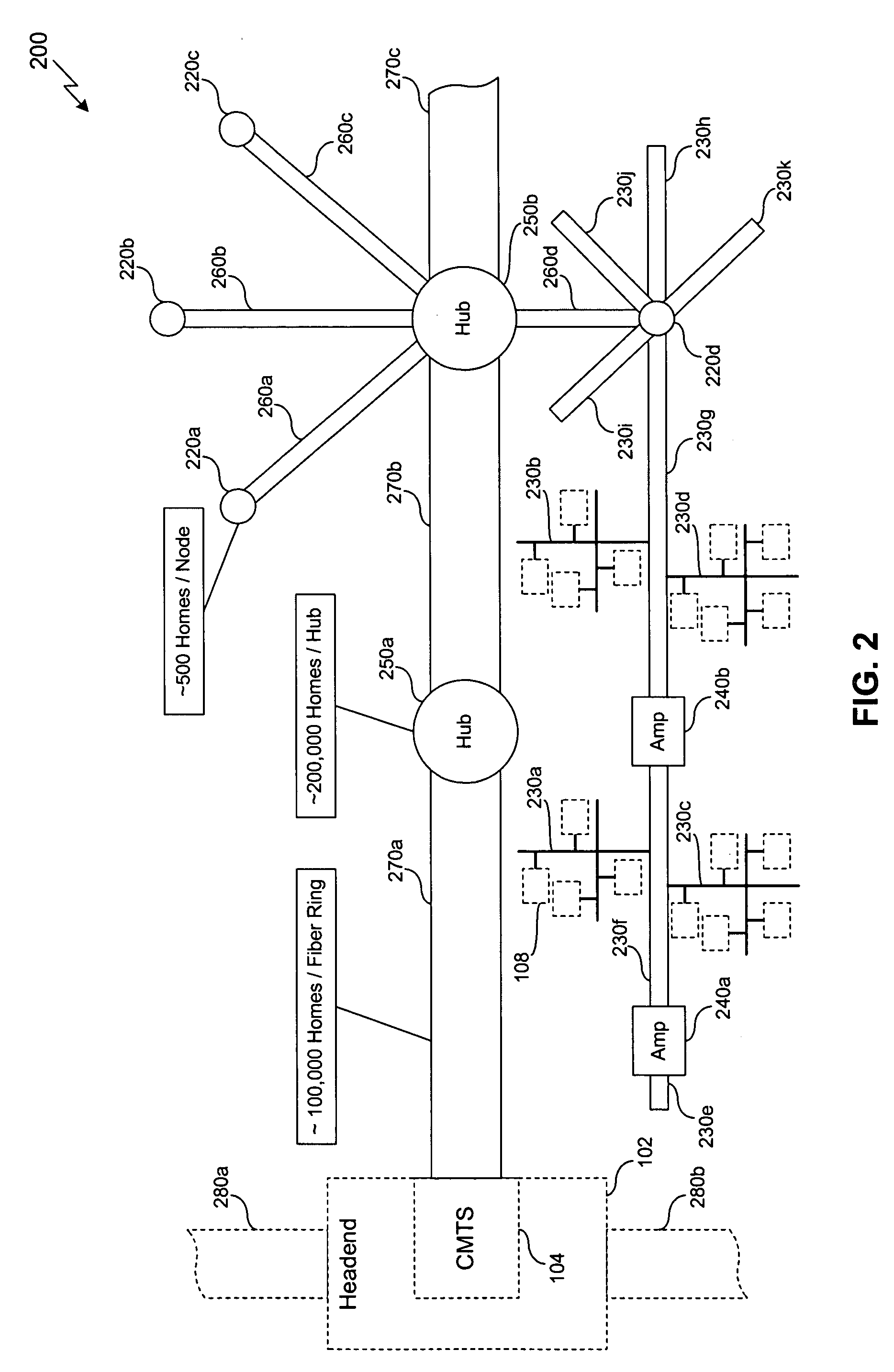
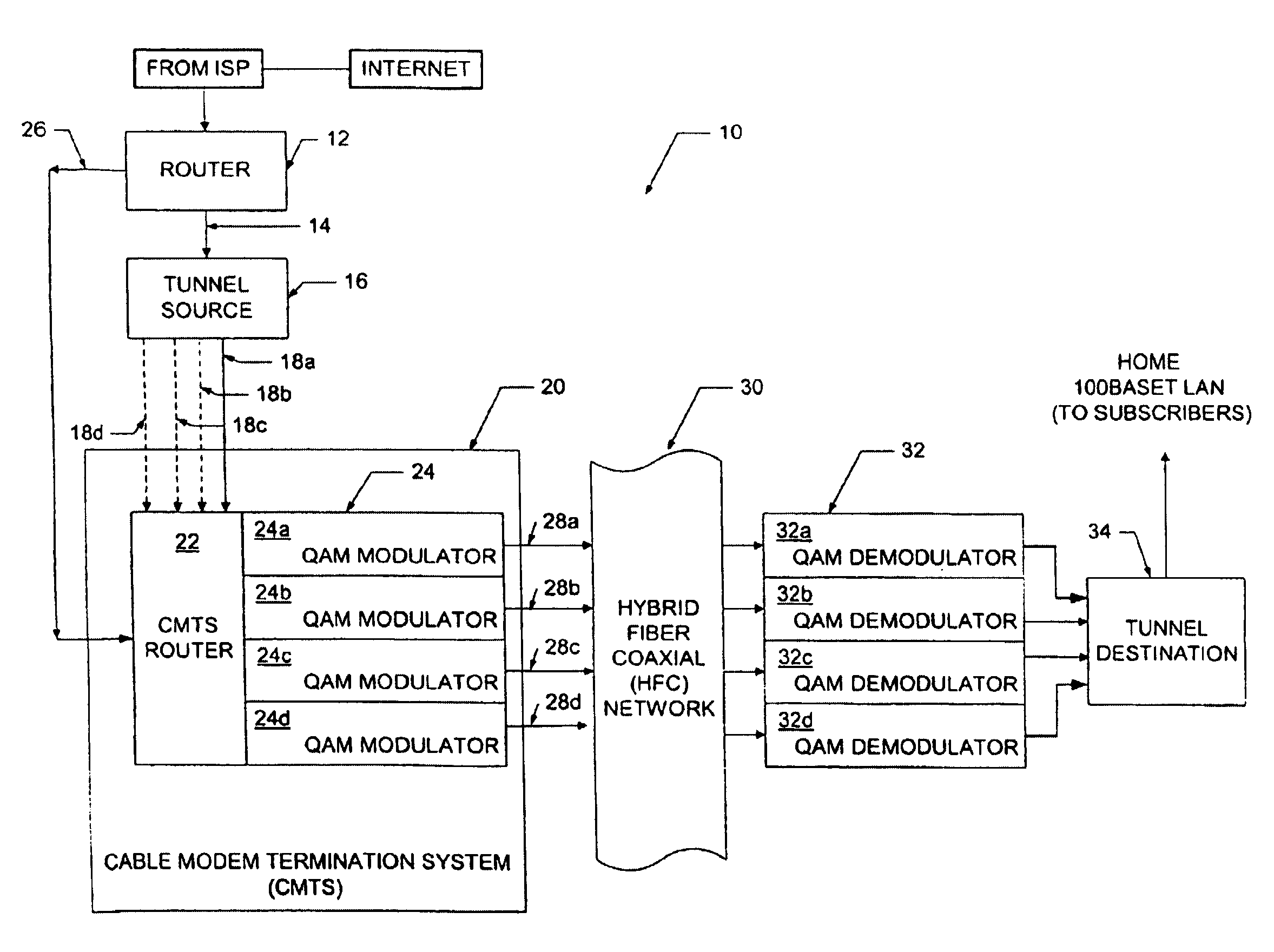
Cable data service method
InactiveUS6993353B2Increase peak rateSimple to provideChannel dividing arrangementsBroadband local area networksData streamBit rate
A method for sending data from a transmit site to a receive site which includes dividing a transmit data stream having a first bit rate into multiple data streams with each of the multiple data streams having a bit rate which is lower than the first bit rate, transmitting each of the multiple data streams over a plurality of RF channels and recombining the multiple data streams at the receive site to provide a receive data stream having a bit rate equal to the first bit rate.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
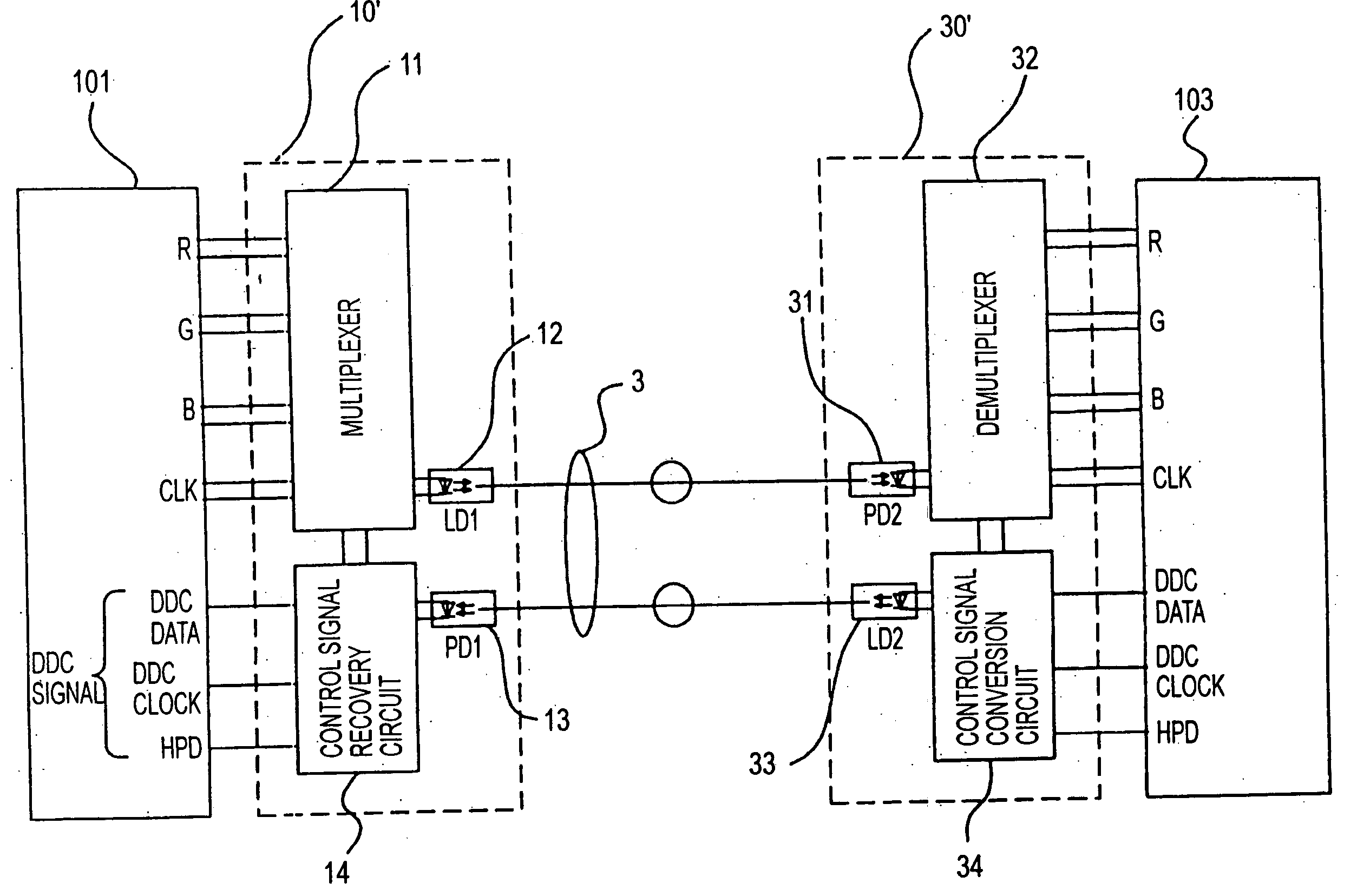
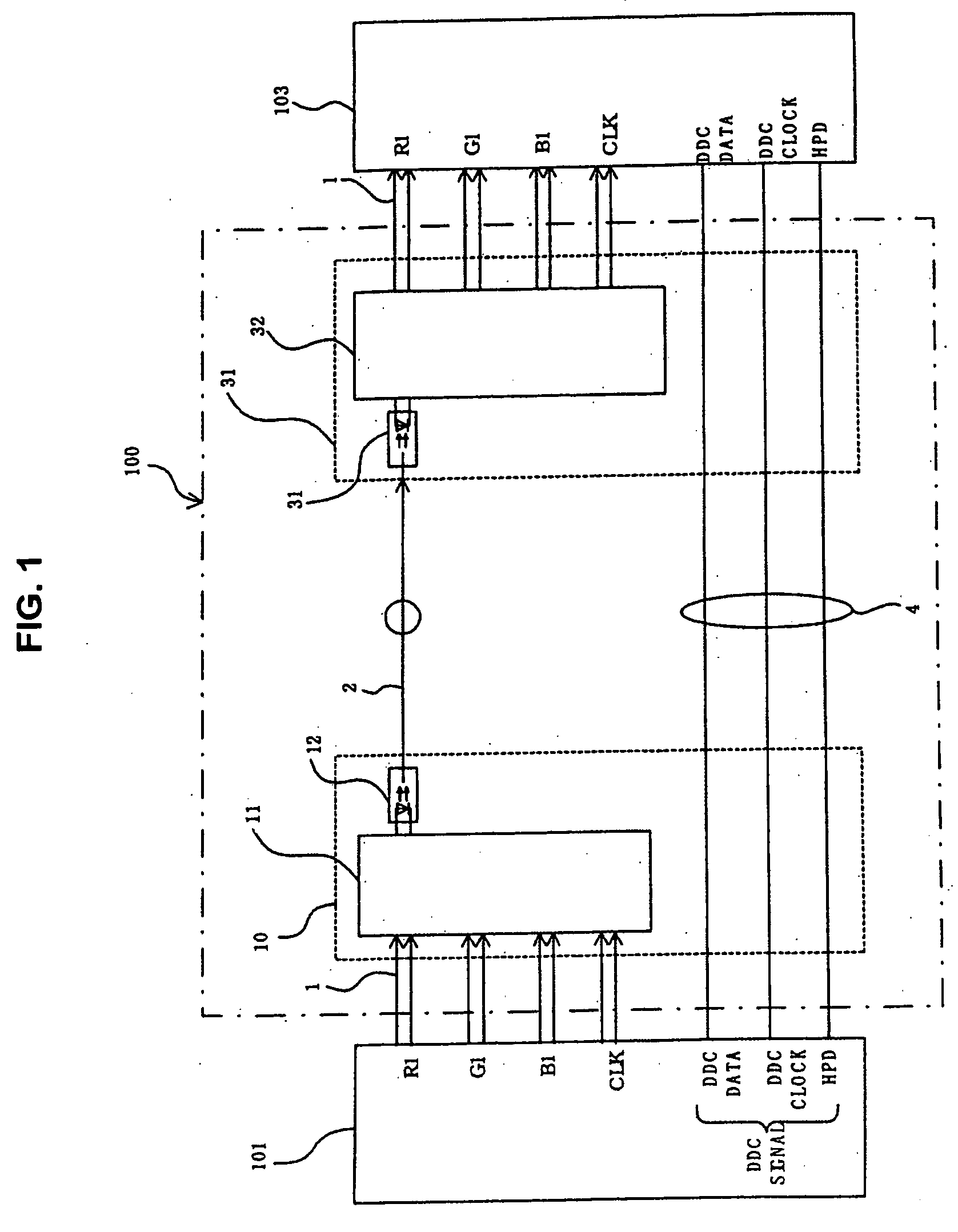
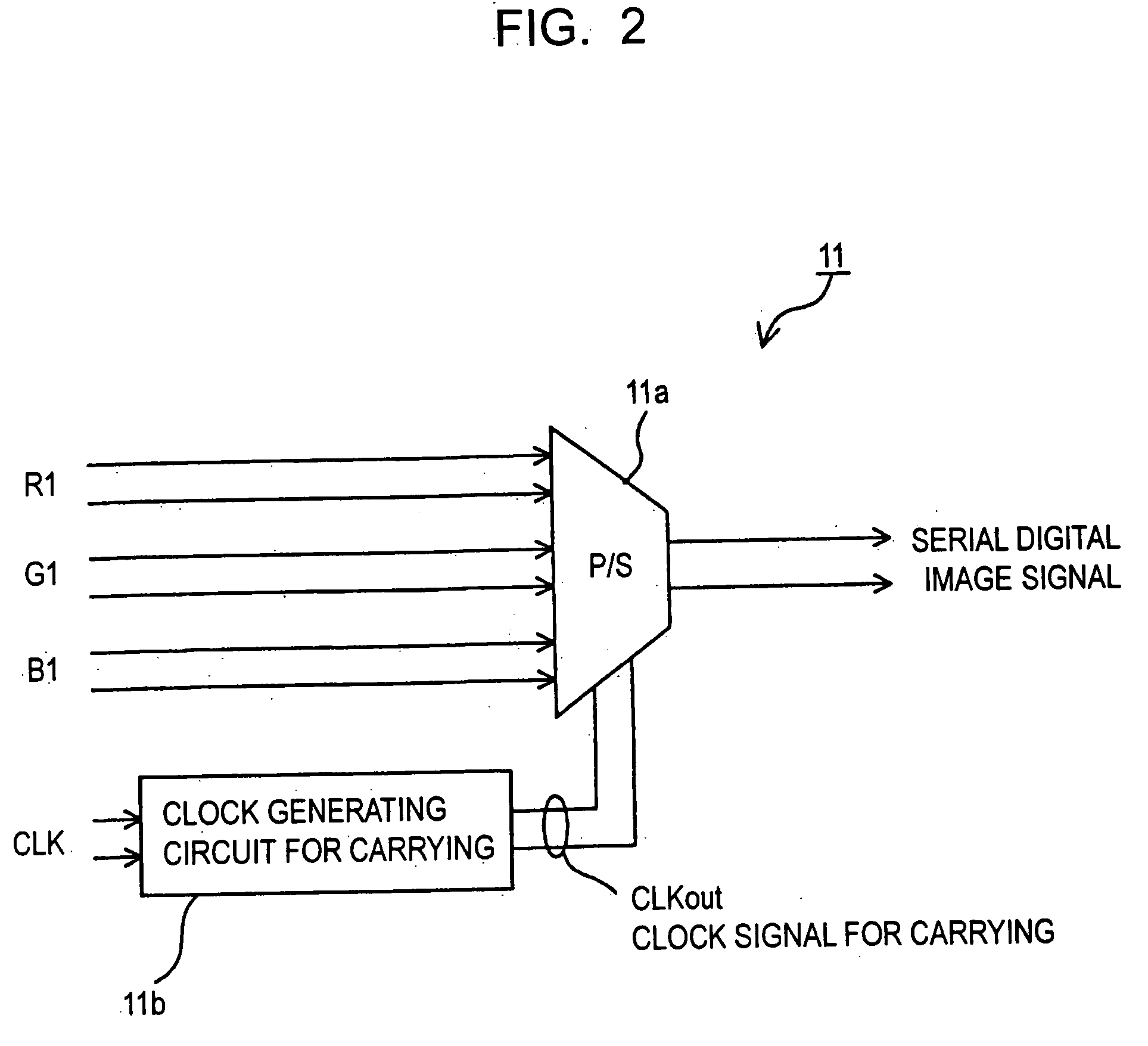
Method for transmitting digital image signal, digital image transmitting device, digital image sending device and digital image receiver
InactiveUS20050063707A1Quality improvementIncrease costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMultiplexerSignal on
A multiplexer of a transmission section generates a clock signal by multiplying a reference clock signal of a digital image signal by a predetermined number ‘K’. A parallel digital image signal is converted into a serial digital signal on the basis of the clock signal, and the serial digital signal is converted into an optical signal in an optical transmission section for transmitting. A demultiplexer extracts a reception clock signal from a serial digital reception signal which is converted into an electric signal in an optical reception section of a reception section, the serial digital reception signal is converted into a parallel signal and a signal corresponding to the parallel digital image signal on the basis of the reception clock signal, and a clock signal corresponding to the reference clock signal is recovered by multiplying the reception clock signal by ‘1 / K’.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Signal transmission circuit and method for equalizing disparate delay times dynamically, and data latch circuit of semiconductor device implementing the same
InactiveUS7085336B2Accurate compensationKeep in syncChannel dividing arrangementsError preventionDelayed timeDatapath
A signal transmission circuit and a method equalize differential delay characteristics of two signal transmission lines. A controllable delay unit is connected serially to the second line, so as to compensate by adding its internal delay. An auxiliary signal transmission line replicates the second transmission line, while it processes the input signal of the first. A controlling unit compares the output signal of the first transmission line and the of the auxiliary signal transmission line, and adjusts dynamically the internal delay of the controllable delay unit, to attain continuous synchronization. A data latch circuit synchronizes the delays of data paths by having one controllable delay units in each of the data paths.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
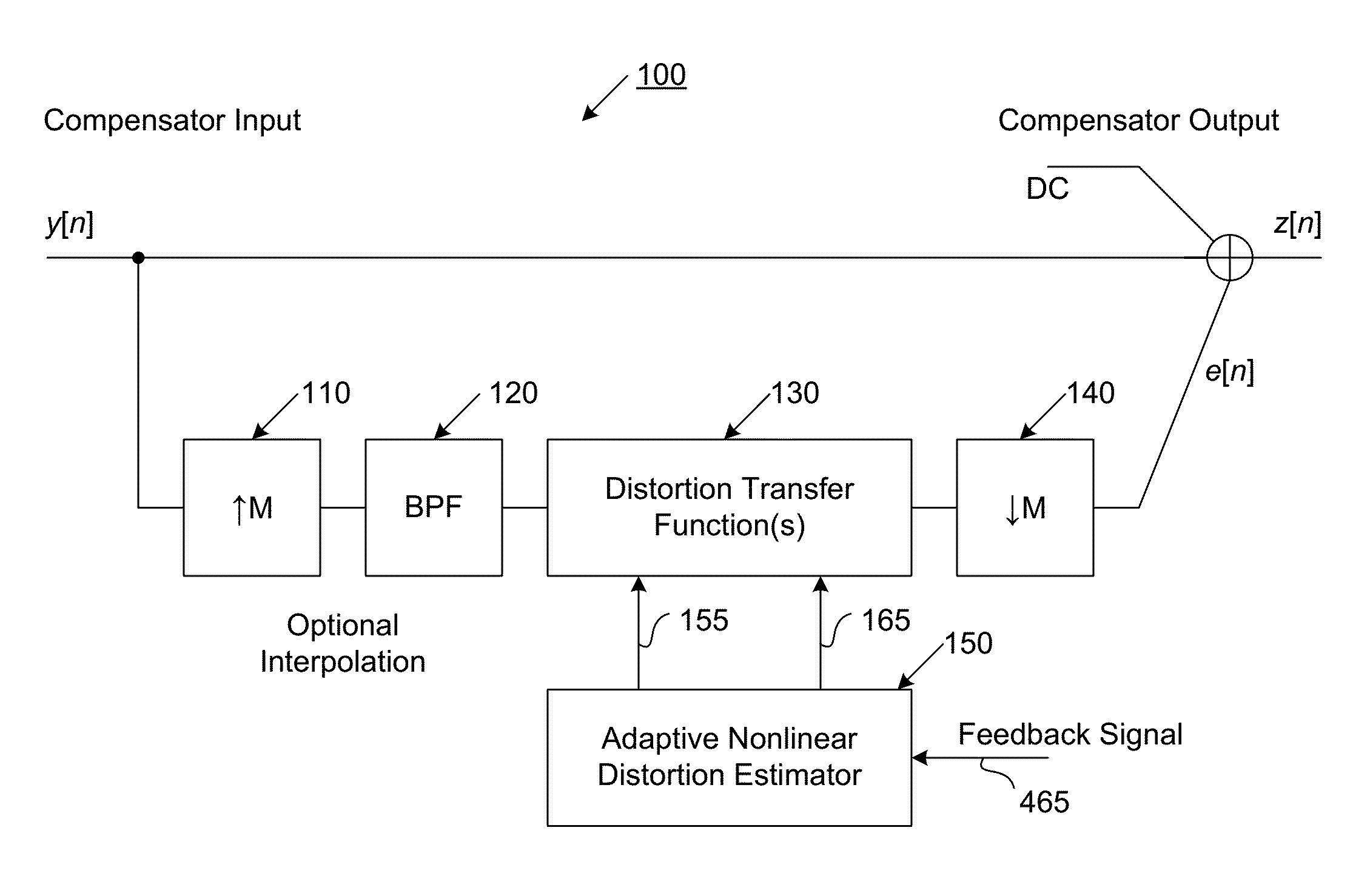
Compensator for removing nonlinear distortion
ActiveUS20160191020A1Easy to processReduce complexityChannel dividing arrangementsElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionComputation complexity
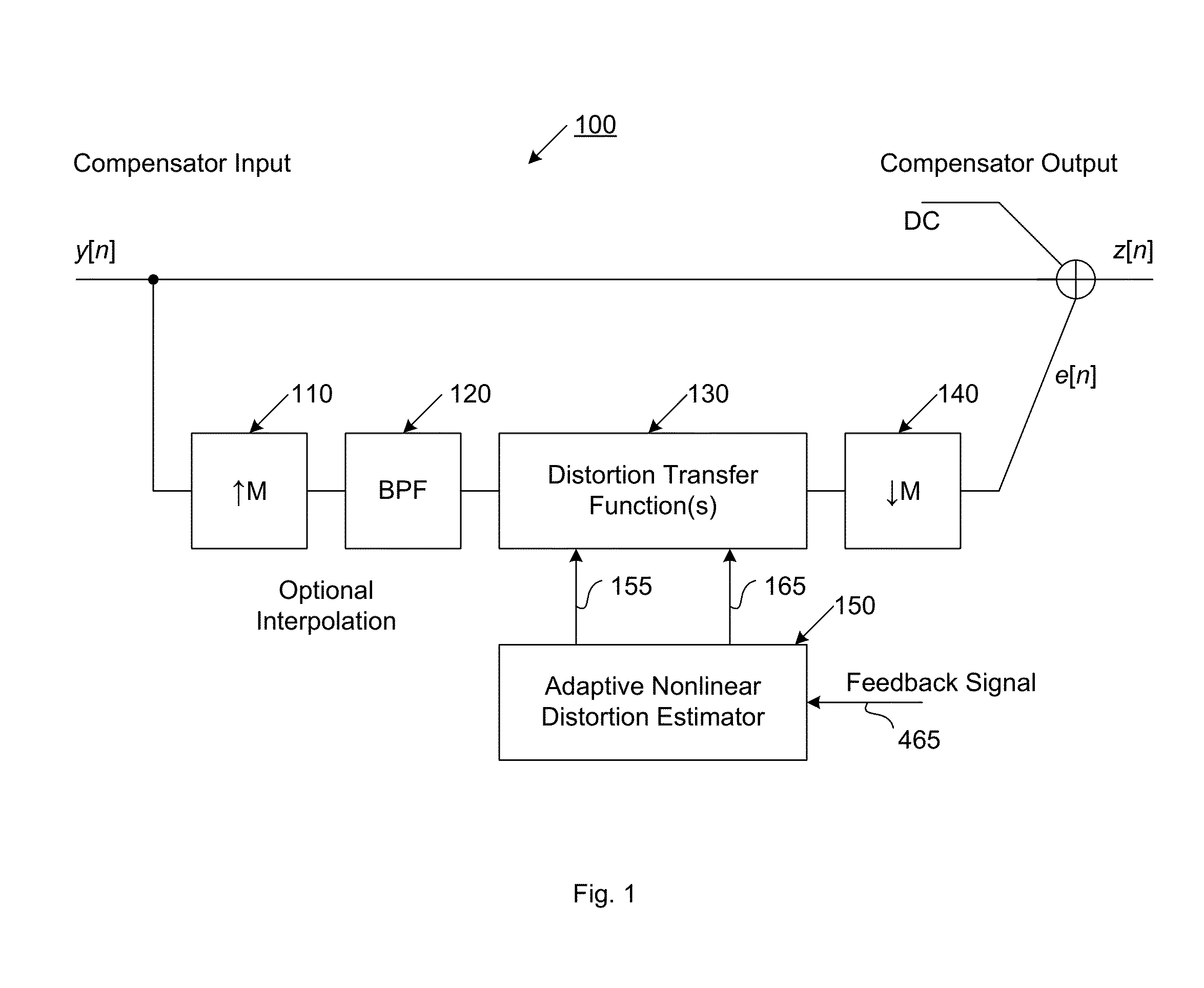
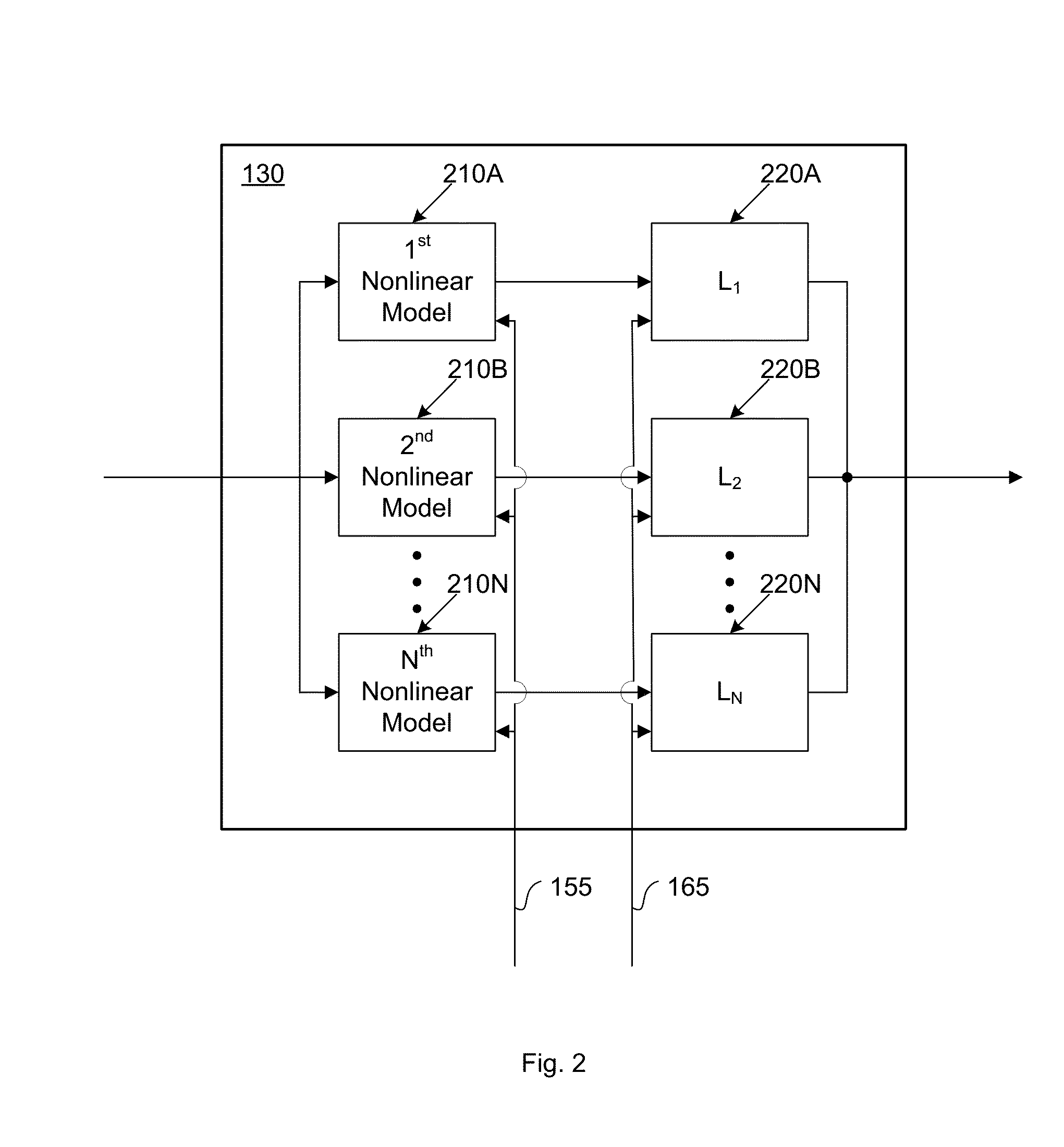
The present invention is a computationally-efficient compensator for removing nonlinear distortion. The compensator operates in a digital post-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as analog-to-digital converters and RF receiver electronics. The compensator also operates in a digital pre-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as digital-to-analog converters, RF power amplifiers, and RF transmitter electronics. The compensator effectively removes nonlinear distortion in these systems in a computationally efficient hardware or software implementation by using one or more factored multi-rate Volterra filters. Volterra filters are efficiently factored into parallel FIR filters and only the filters with energy above a prescribed threshold are actually implemented, which significantly reduces the complexity while still providing accurate results. For extremely wideband applications, the multi-rate Volterra filters are implemented in a demultiplexed polyphase configuration which performs the filtering in parallel at a significantly reduced data rate. The compensator is calibrated with an algorithm that iteratively subtracts an error signal to converge to an effective compensation signal. The algorithm is repeated for a multiplicity of calibration signals, and the results are used with harmonic probing to accurately estimate the Volterra filter kernels. The compensator improves linearization processing performance while significantly reducing the computational complexity compared to a traditional nonlinear compensator.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
Flow control and quality of service provision for frame relay protocols
InactiveUS20030185249A1Energy efficient ICTChannel dividing arrangementsTraffic capacityQuality of service
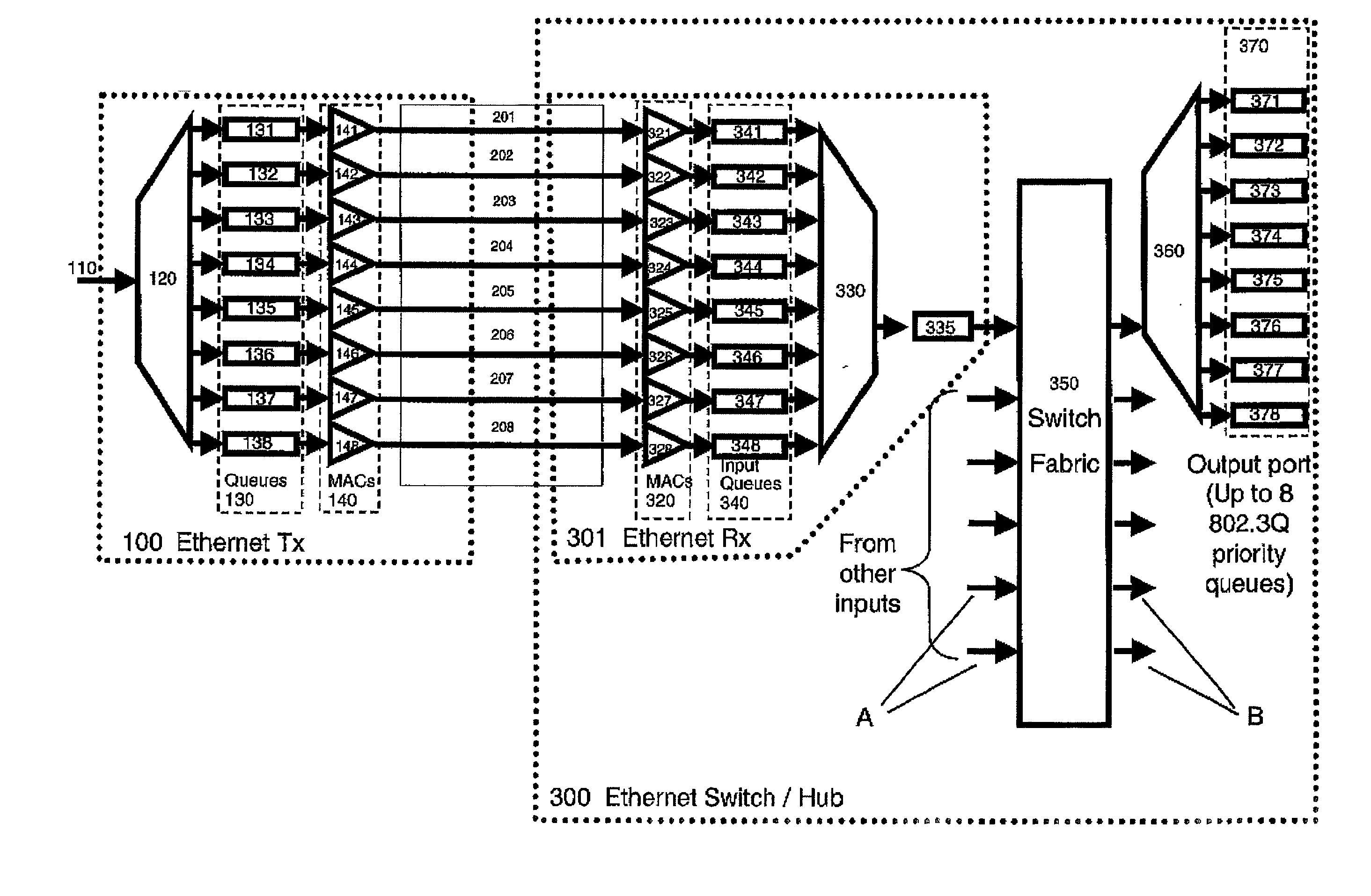
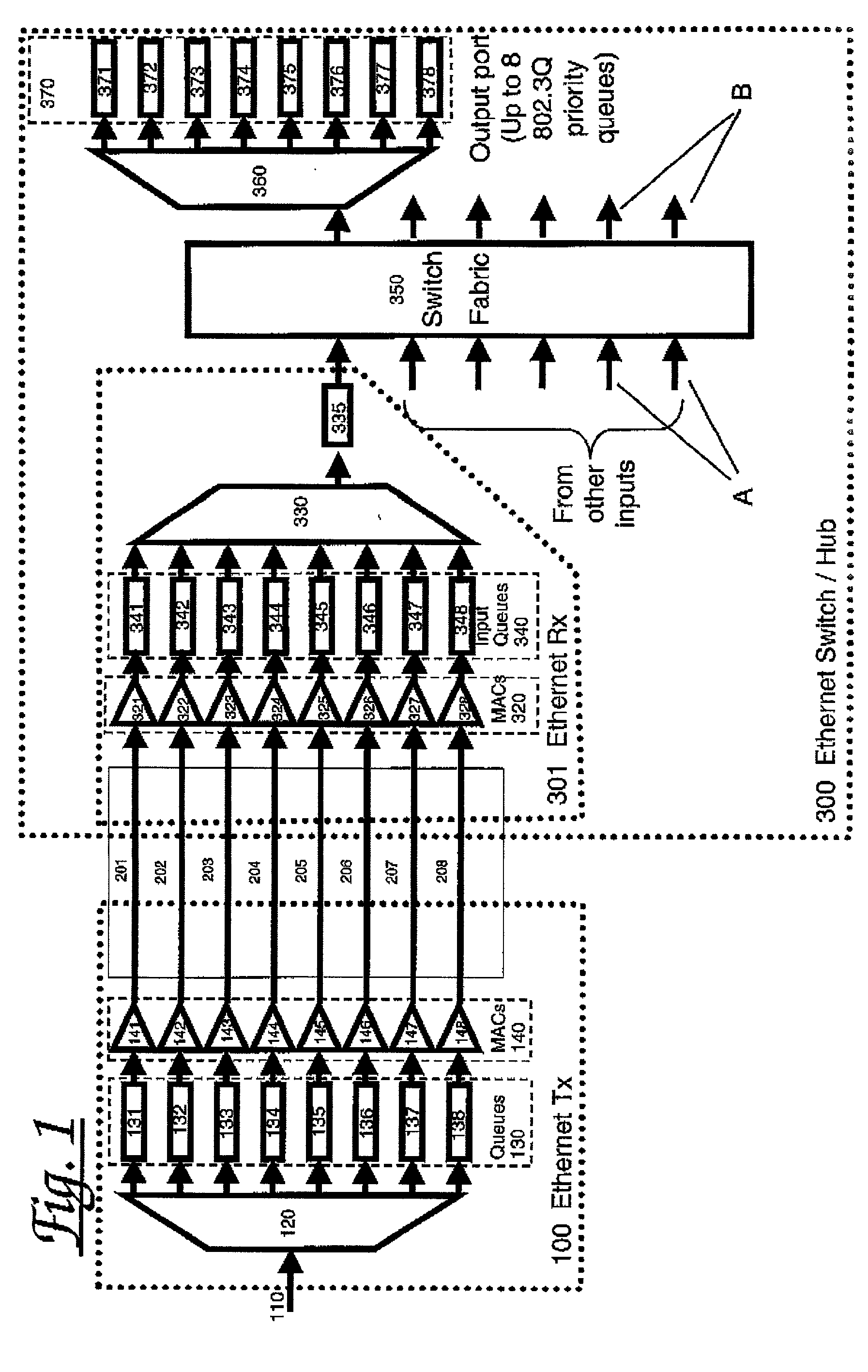
Apparatus and method for providing controlled Quality of Service over Ethernet-like links. Prioritised frames are allocated to transmission queues responsive to their priorities. Each queue has an associated subsidiary Ethernet MAC which transmits frames from its queue subject to a scheduler which selects from the set of MAC's according to a pre-determined algorithm. The multiple logical paths between corresponding pairs of transmitter and receiver subsidiary MAC's are preferably multiplexed over a single physical channel. If congestion occurs at the receiver, then Ethernet PAUSE frames may be sent back to the transmitter, directed to specific subsidiary MAC's-typically those with lower priority-to suspend transmission from the corresponding queue for a time period indicated in the PAUSE frame. In this way back pressure flow control may be applied selectively to so that large amounts of low priority traffic do not cause unnecessary delays to higher priority traffic.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Communications system and method
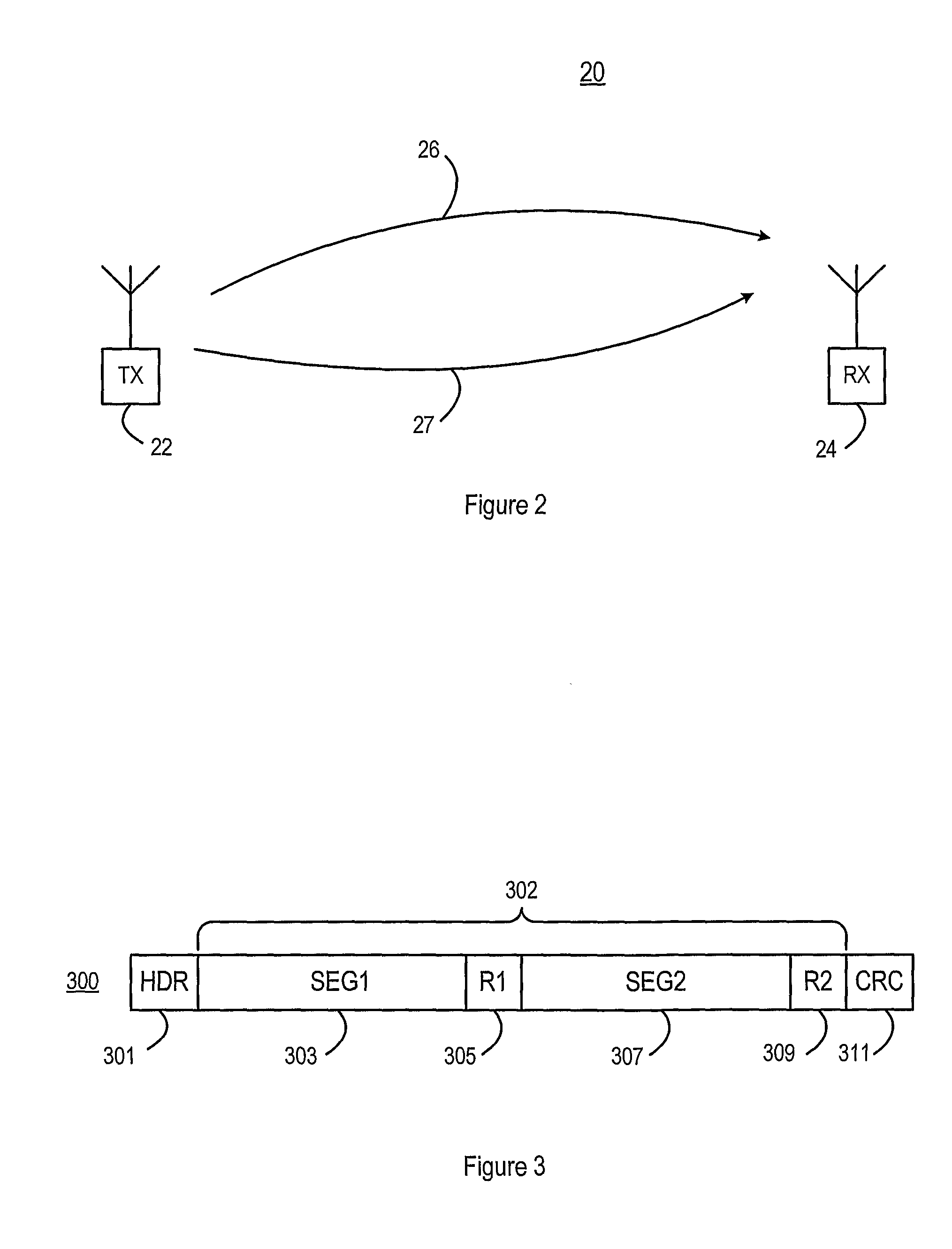
InactiveUS20100085964A1Channel dividing arrangementsData switching by path configurationCommunications systemData segment
A method for transmitting data using data packets includes dividing a data portion of the data packet into two or more data segments, each having a corresponding check portion. The data packet may also be communicated over two or more logical communication channels. The order of data portions in one communication channel may differ from the order of data portions in a second communication channel. Identical or different check portions may be assigned to respective data portions.
Owner:ITI SCOTLAND
Processing high-speed digital signals
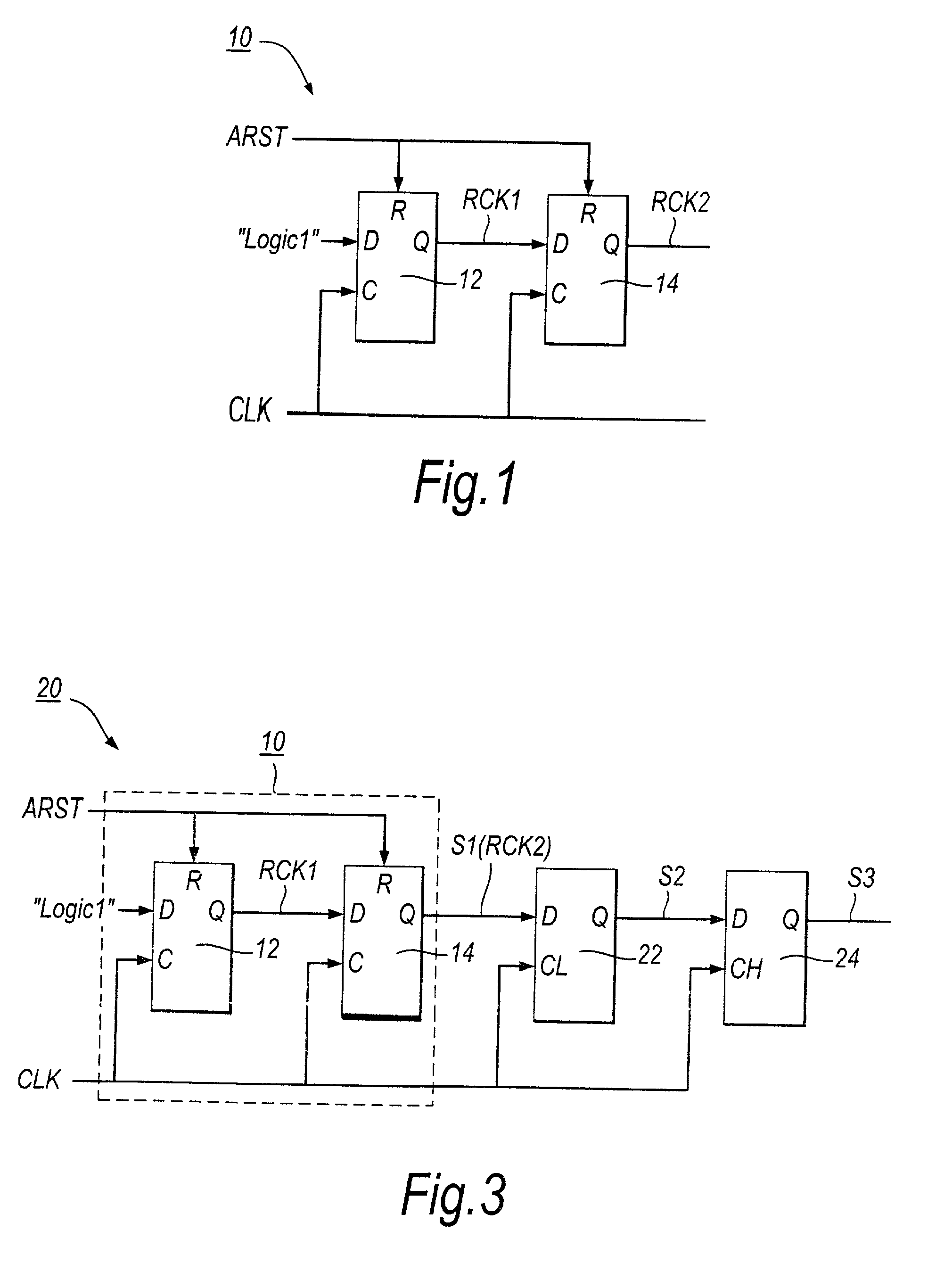
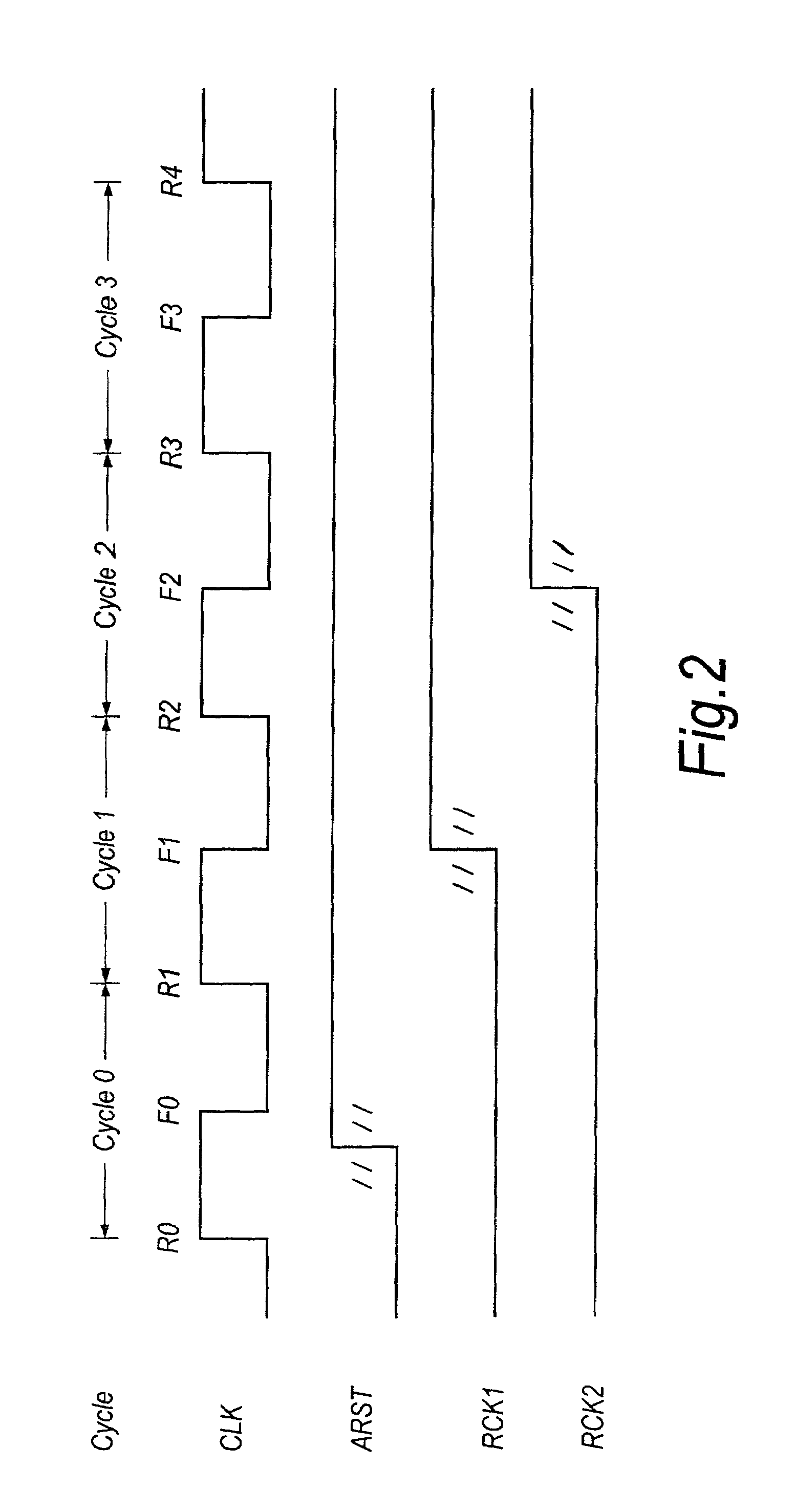
ActiveUS7187738B2Reduce controlMeet high-speed operationChannel dividing arrangementsPulse automatic controlData synchronizationData stream
A first transparent latch receives a first synchronised signal changing its logic state synchronously with respect to a clock signal. A second transparent latch receives a second synchronised signal output by the first latch. When the clock signal has a first logic state the first latch has a non-responsive state and the second latch has a responsive state, and when the clock signal has a second logic state the first latch has the responsive state and the second latch has the non-responsive state. The change in logic state of a third synchronised signal output by the second latch is guaranteed to occur in a particular half-cycle of the clock signal, irrespective of process / voltage / temperature (PVT) variations of the circuitry. Clock recovery circuitry may have rising-edge and falling-edge latches; circulating control pattern verification circuitry; data synchronising circuitry for converting parallel data clocked by a first clock signal into serial data clocked by a second clock signal asynchronous with the first clock signal; and data recovery circuitry for producing an offset clock signal which suits a data eye shape of a received serial data stream.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
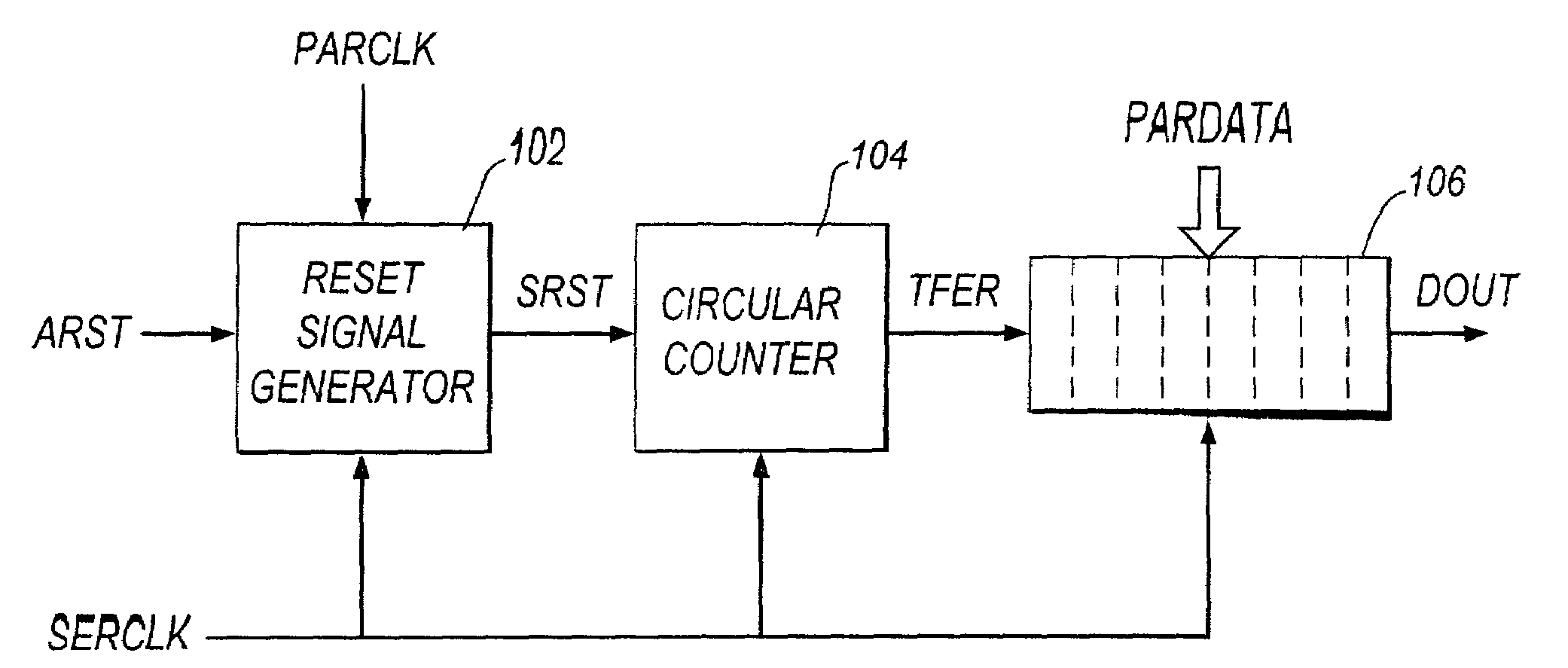
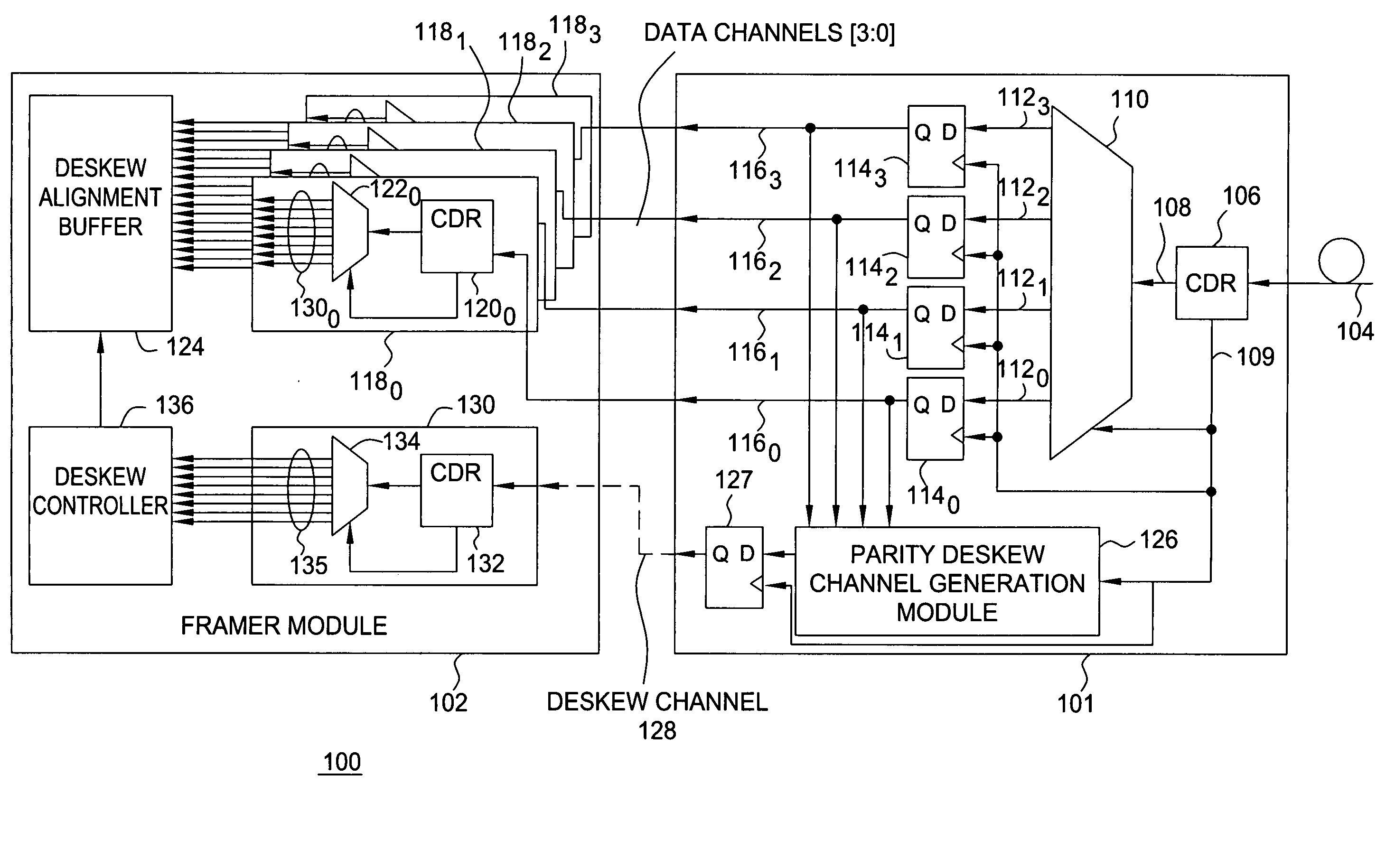
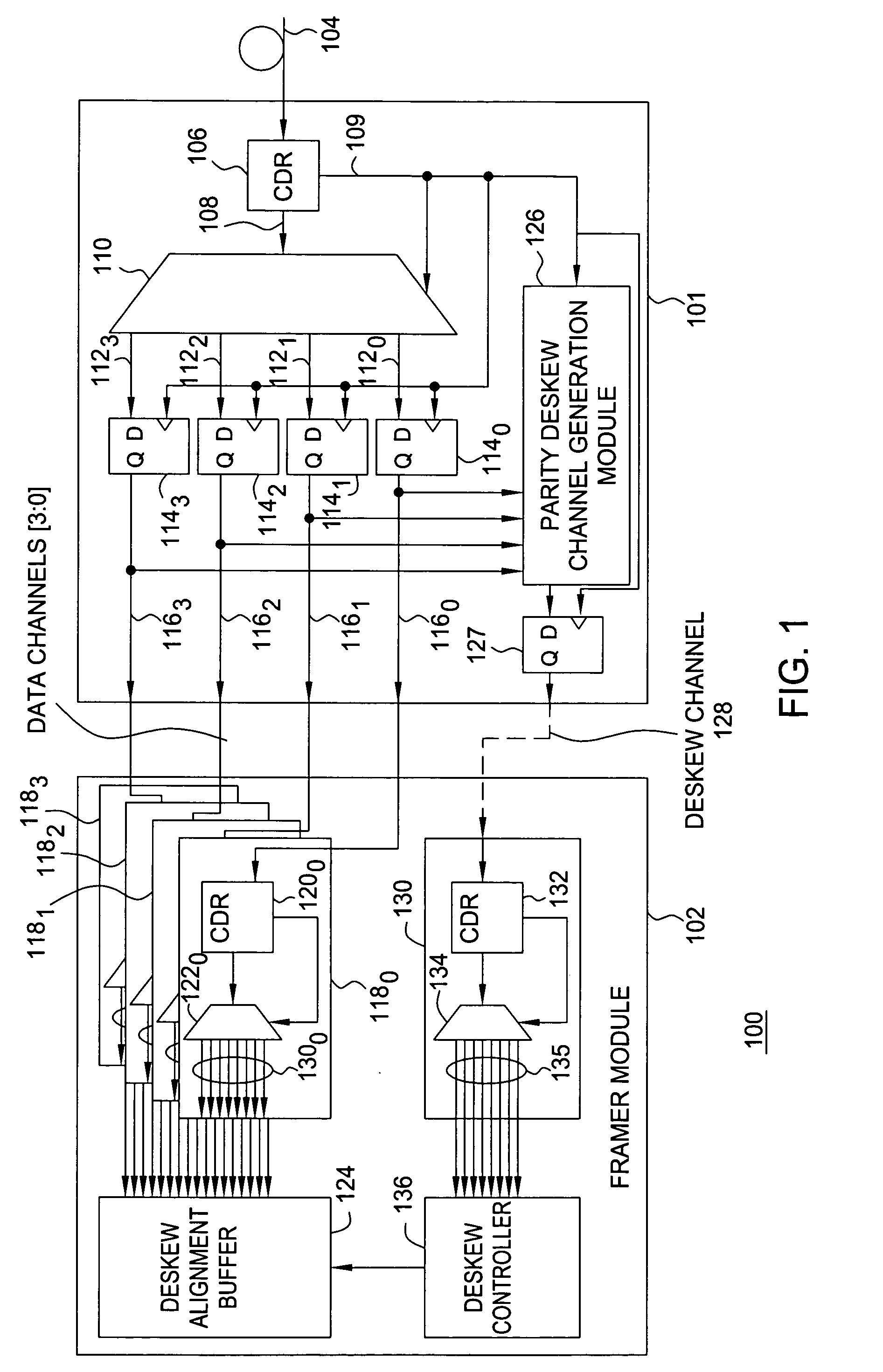
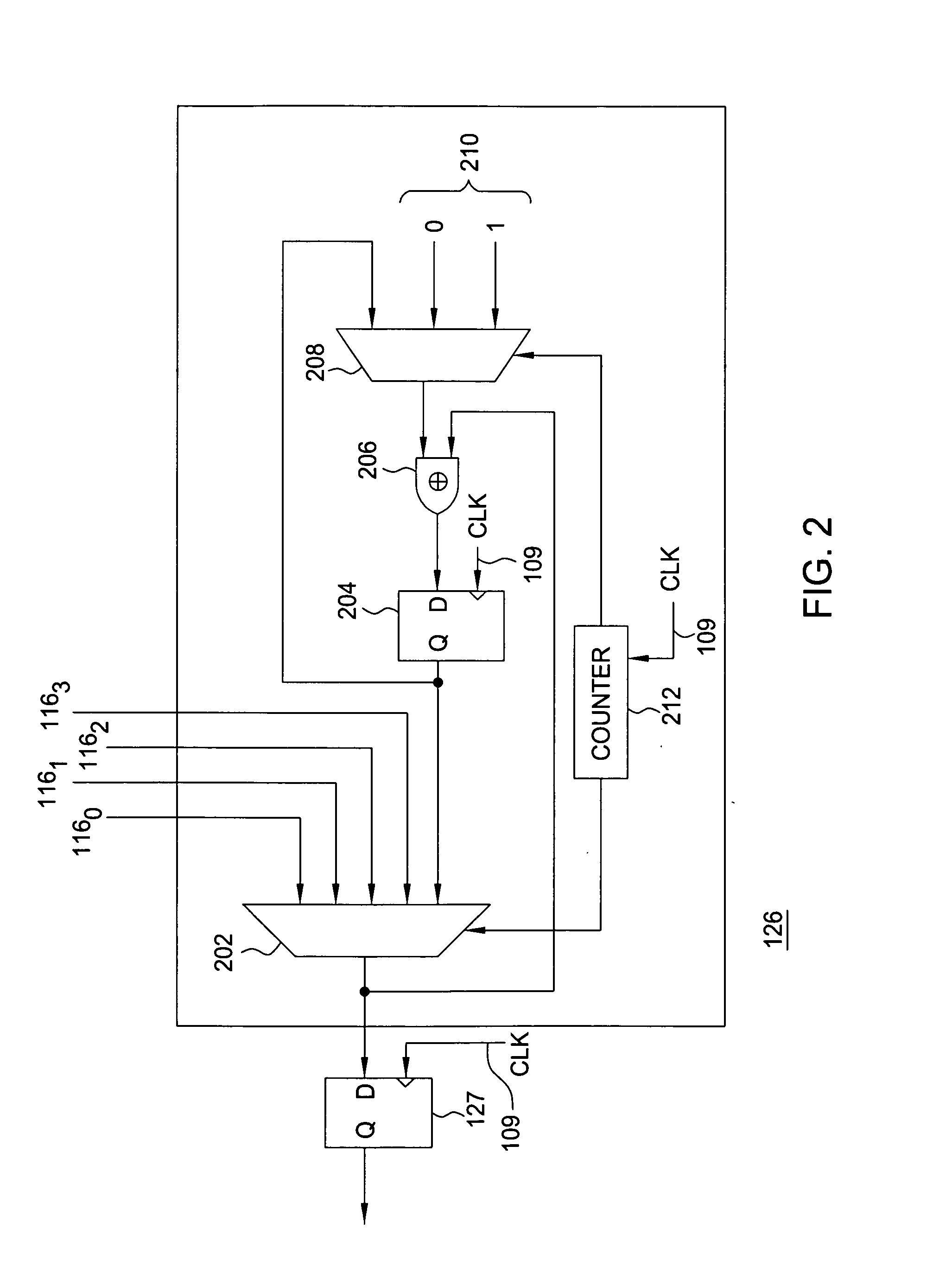
Method and apparatus for synchronizing data channels using an alternating parity deskew channel
ActiveUS20070006053A1Reduce skewSimpler and efficient and reliable and cost-effectiveChannel dividing arrangementsError detection/correctionChannel useParity bit
The invention includes a method and apparatus for aligning a plurality of data channels using a deskew bitstream. The method includes receiving the deskew bitstream, identifying an aligned deskew frame by processing the deskew bitstream, identifying a data channel alignment position associated with each of the plurality of data channels by comparing a deskew channel comparison bit from the aligned deskew frame to a data channel comparison bit from each of the plurality of data channels, and selecting the plurality of data channel alignment positions associated with the respective plurality of data channels for aligning the plurality of data channels. The plurality of data channels are aligned in a manner for substantially reducing skew associated with the data channels. The deskew bitstream comprises a plurality of data bits associated with the data channels and a plurality of parity bits generated using at least a portion of the data bits.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Spacial derivative bus encoder and decoder
InactiveUS7167523B2Reduce noiseReduce power consumptionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsChannel dividing arrangementsData signalBus encoding
A method and apparatus for providing efficient and accurate electronic data transmission of information on a data bus in the presence of noise. Data signals are received on a plurality of input lines by a spacial derivative encoder. The spacial derivative encoder encodes the signals and transmits them to a receiver having a spacial derivative decoder. The spacial derivative decoder then decodes the signals. Minimal overhead is required as for n input lines only n+1 lines are needed to transmit each of the encoded signals.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
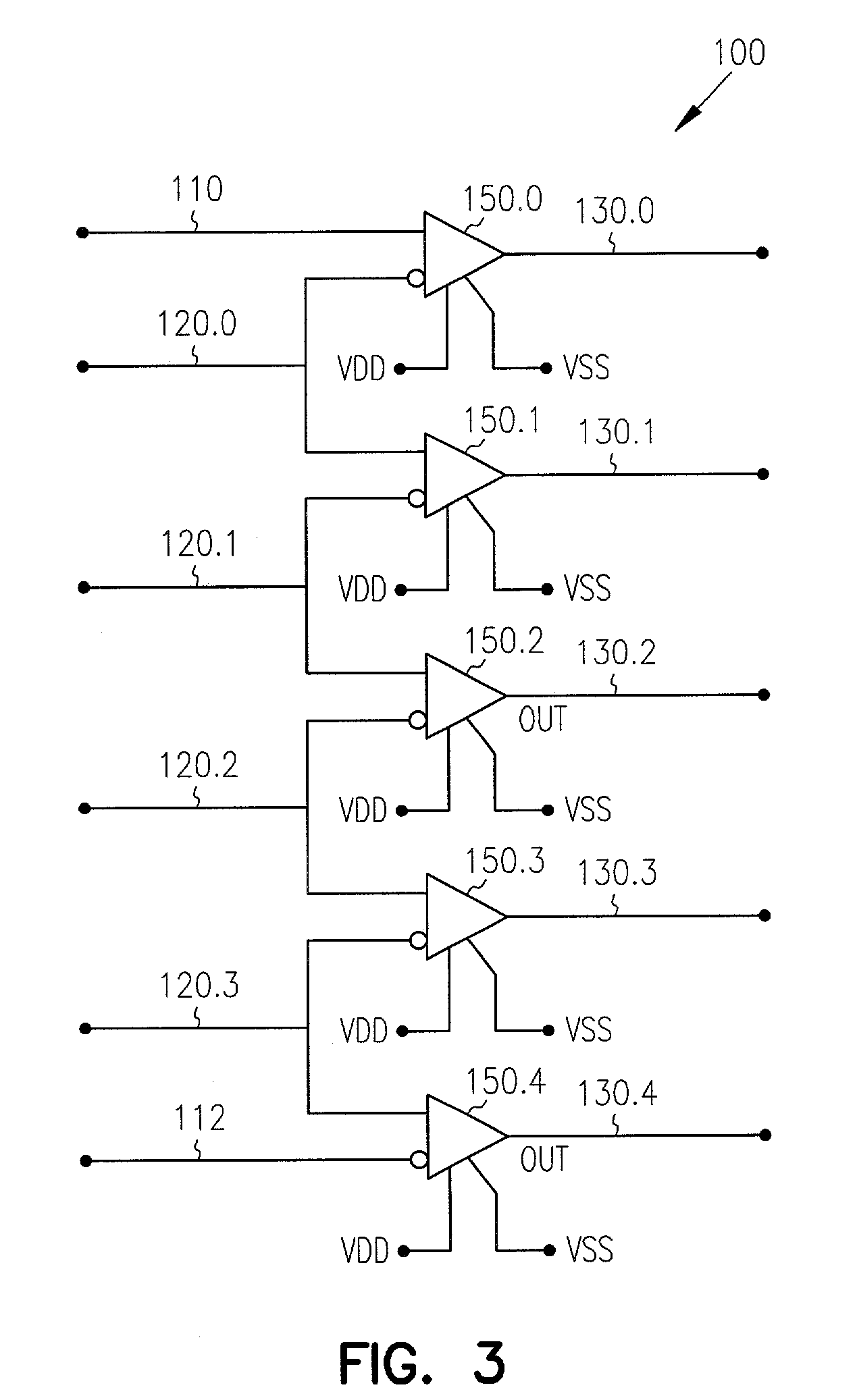
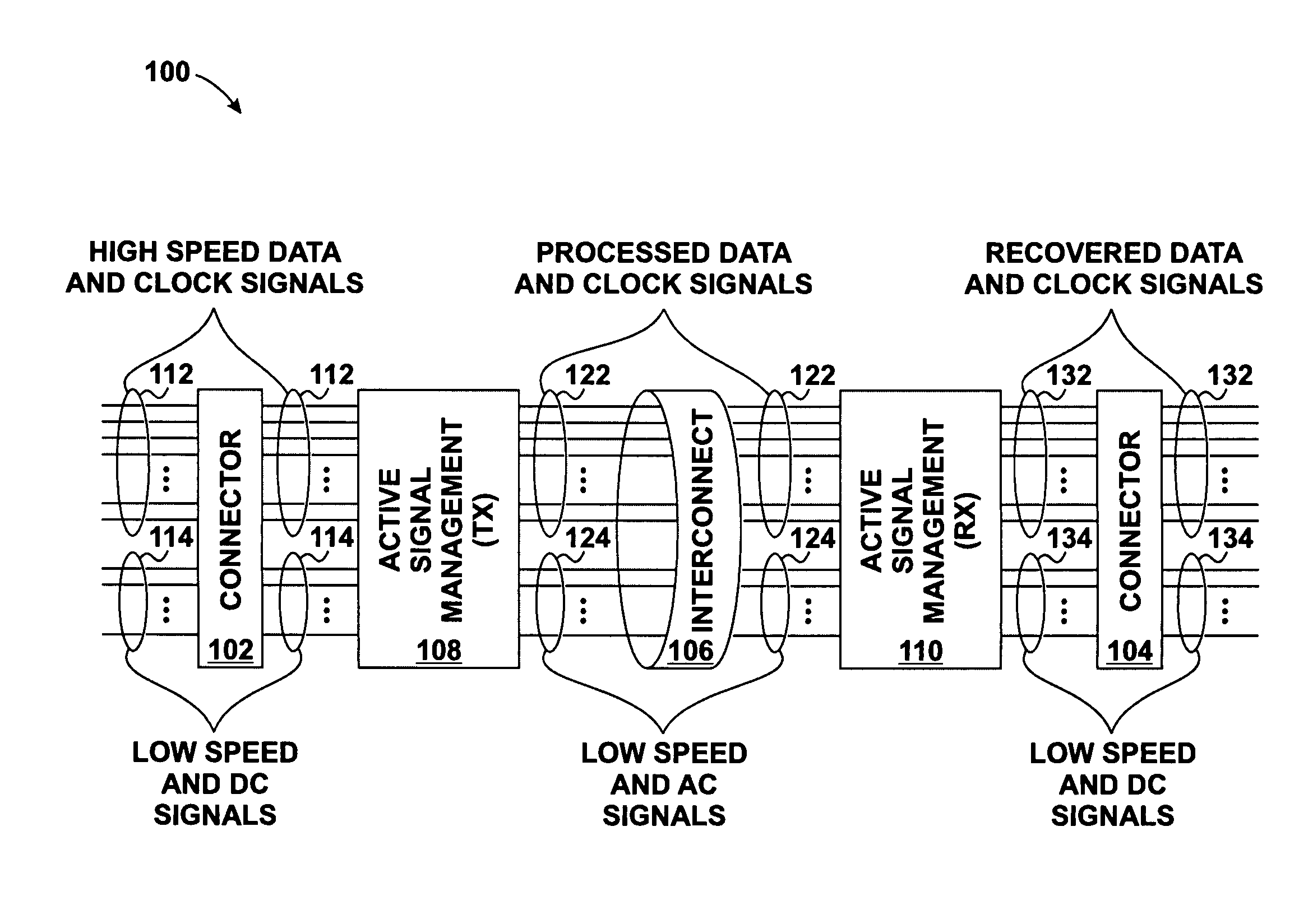
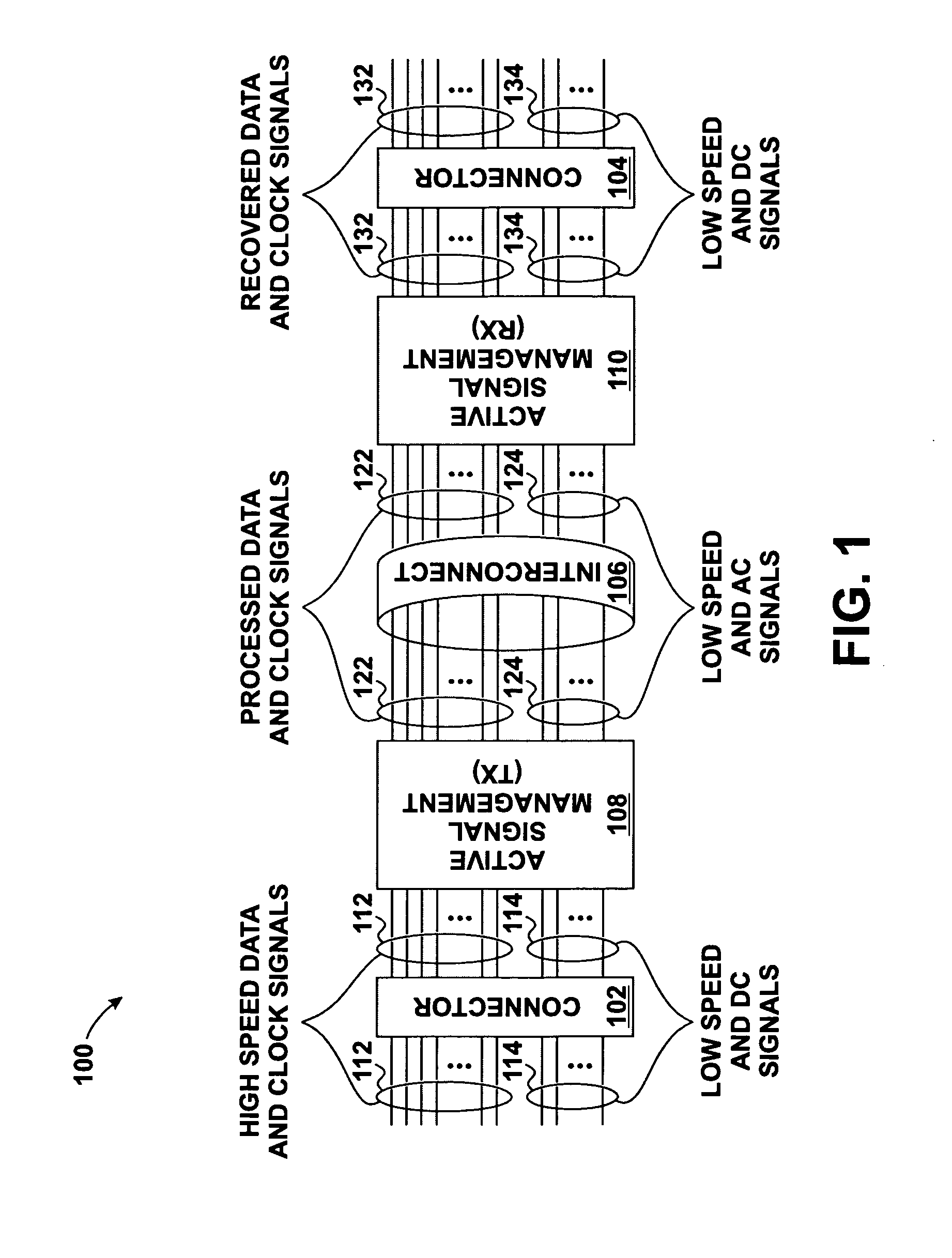
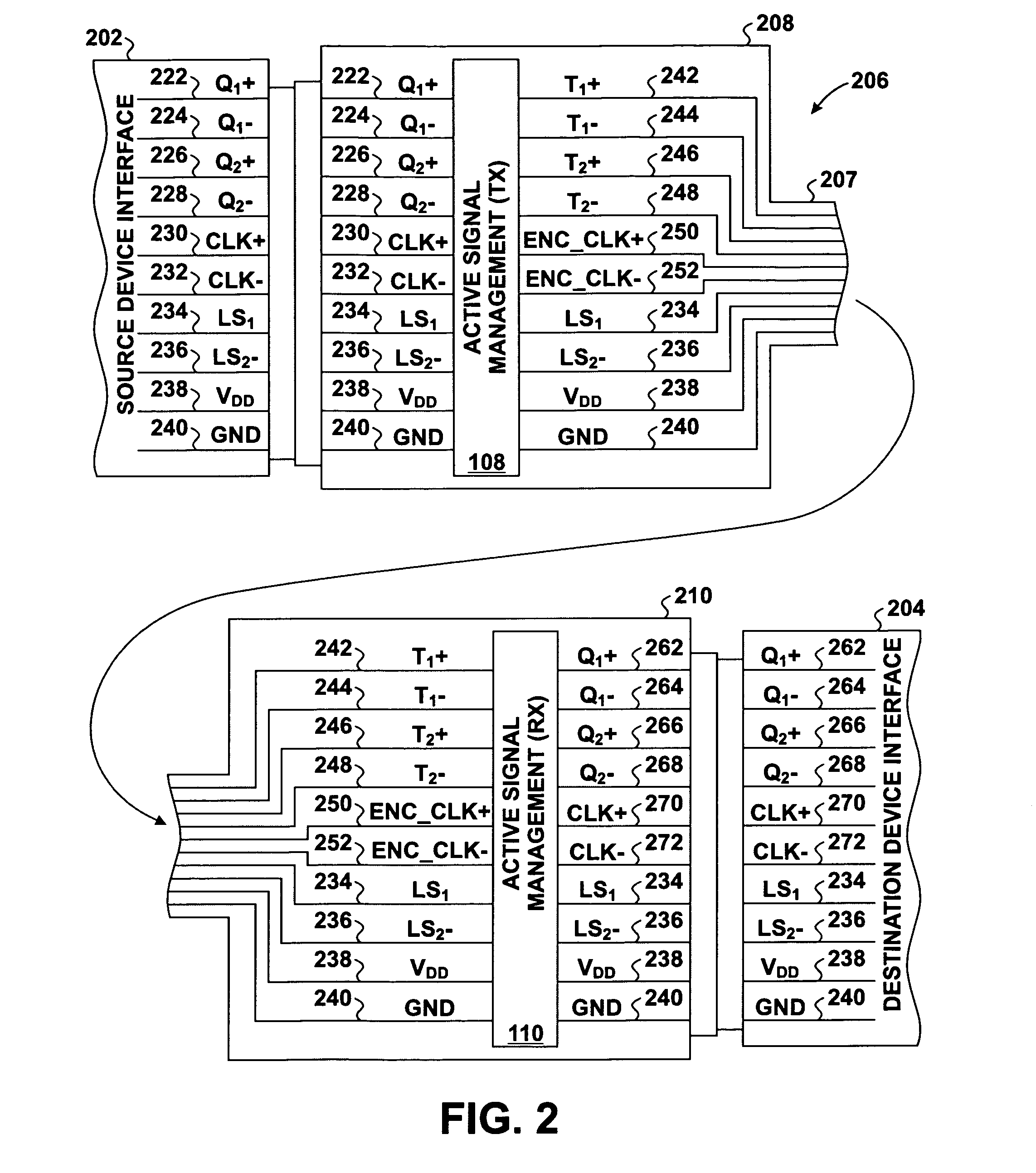
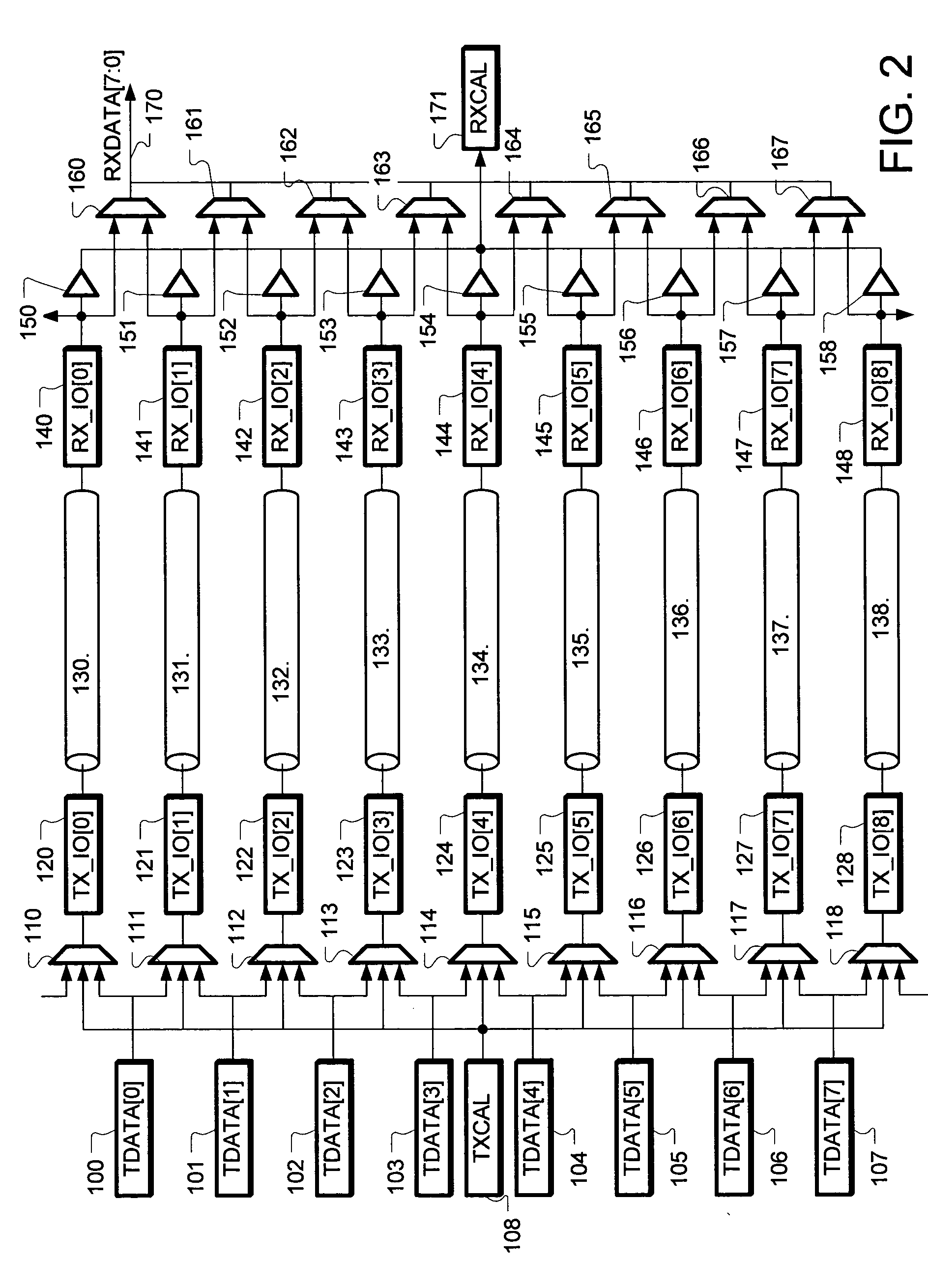
Skew management in cables and other interconnects
InactiveUS20070206643A1Channel dividing arrangementsParallel/series conversionManagement processEngineering
Transmit-side active signal management circuitry applies one or more active signal management processes to a digital signal at a transmit side of an interconnect. At the receive side of the interconnect, receive-side active signal management circuitry applies one or more corresponding active signal management processes, as appropriate, to the received digital signal to recover the information represented by the original digital signal. The interconnect can include a cable used to transmit the signals between a source device and a destination device, whereby one or both of the transmit-side active signal management circuitry and the receive-side active signal management circuitry is implemented at a corresponding cable receptacle of the cable. Alternately, one or both of the transmit-side active signal management circuitry and the receive-side active signal management circuitry can be implemented at a cable adaptor, thereby permitting the use of a passive cable interconnect to transmit the signal.
Owner:XEMI
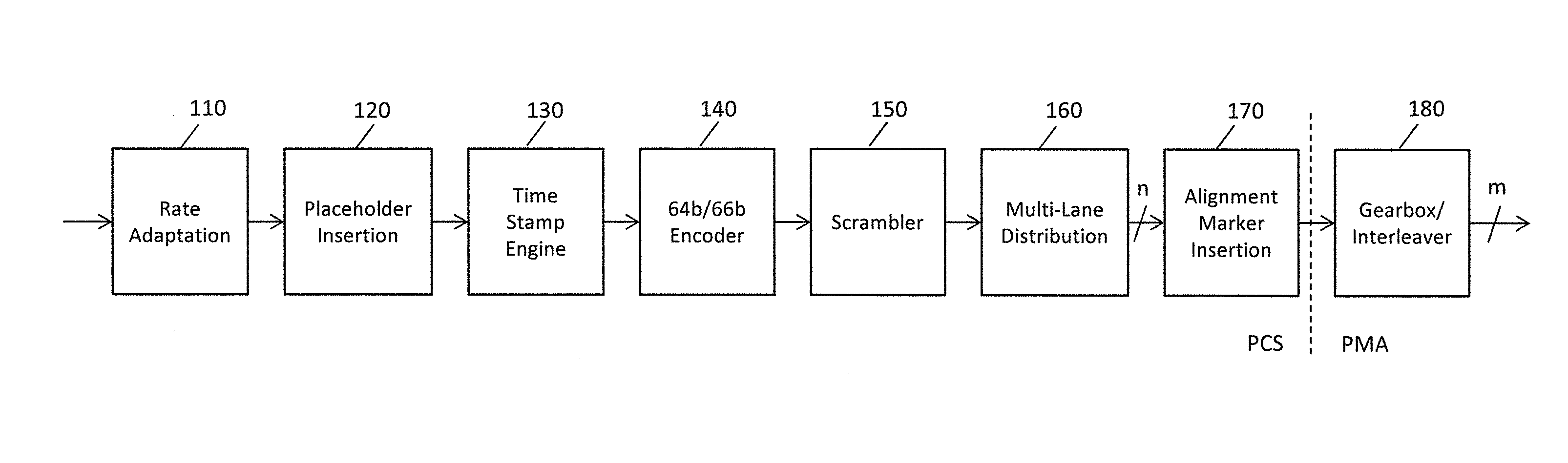
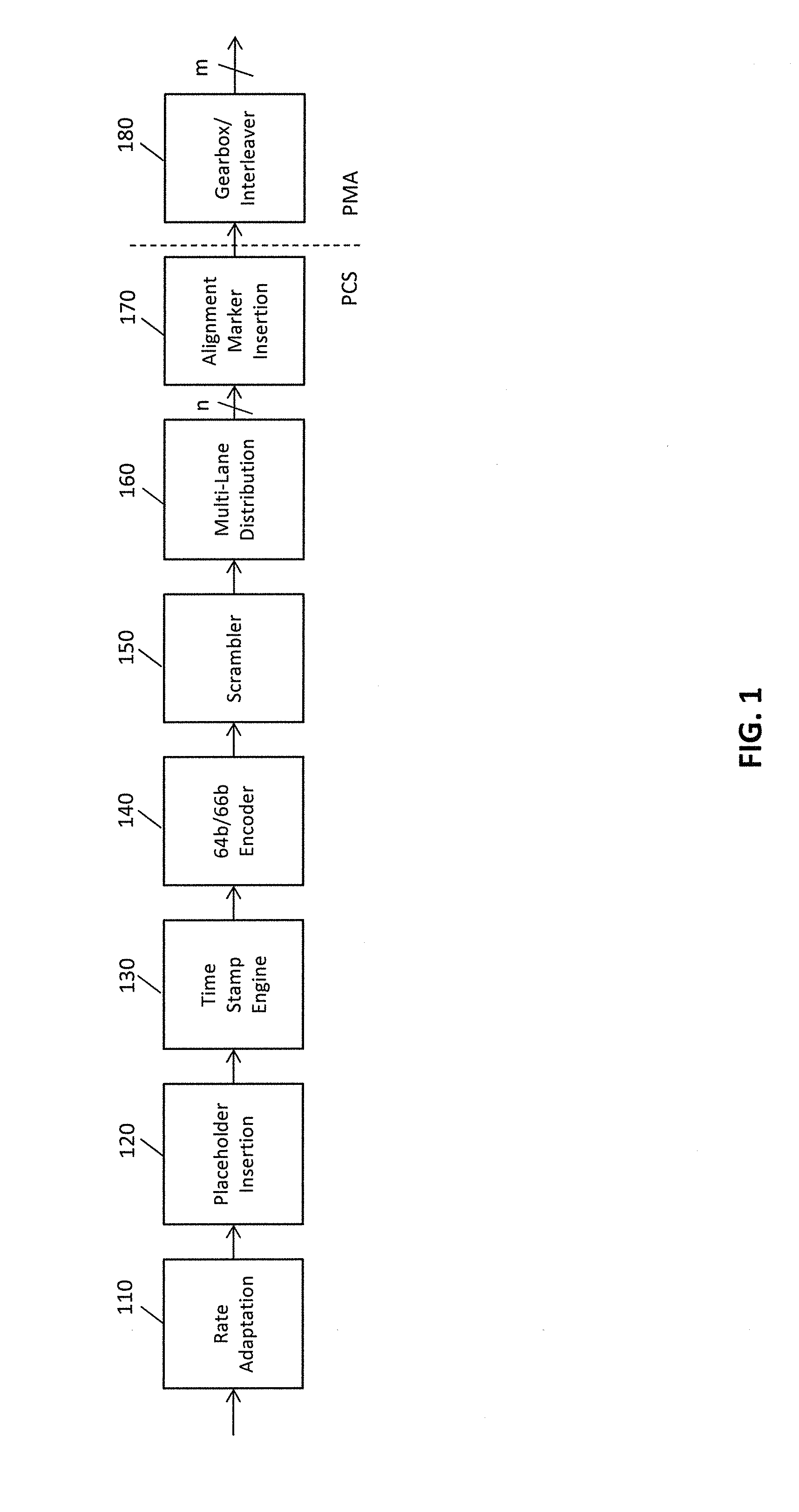
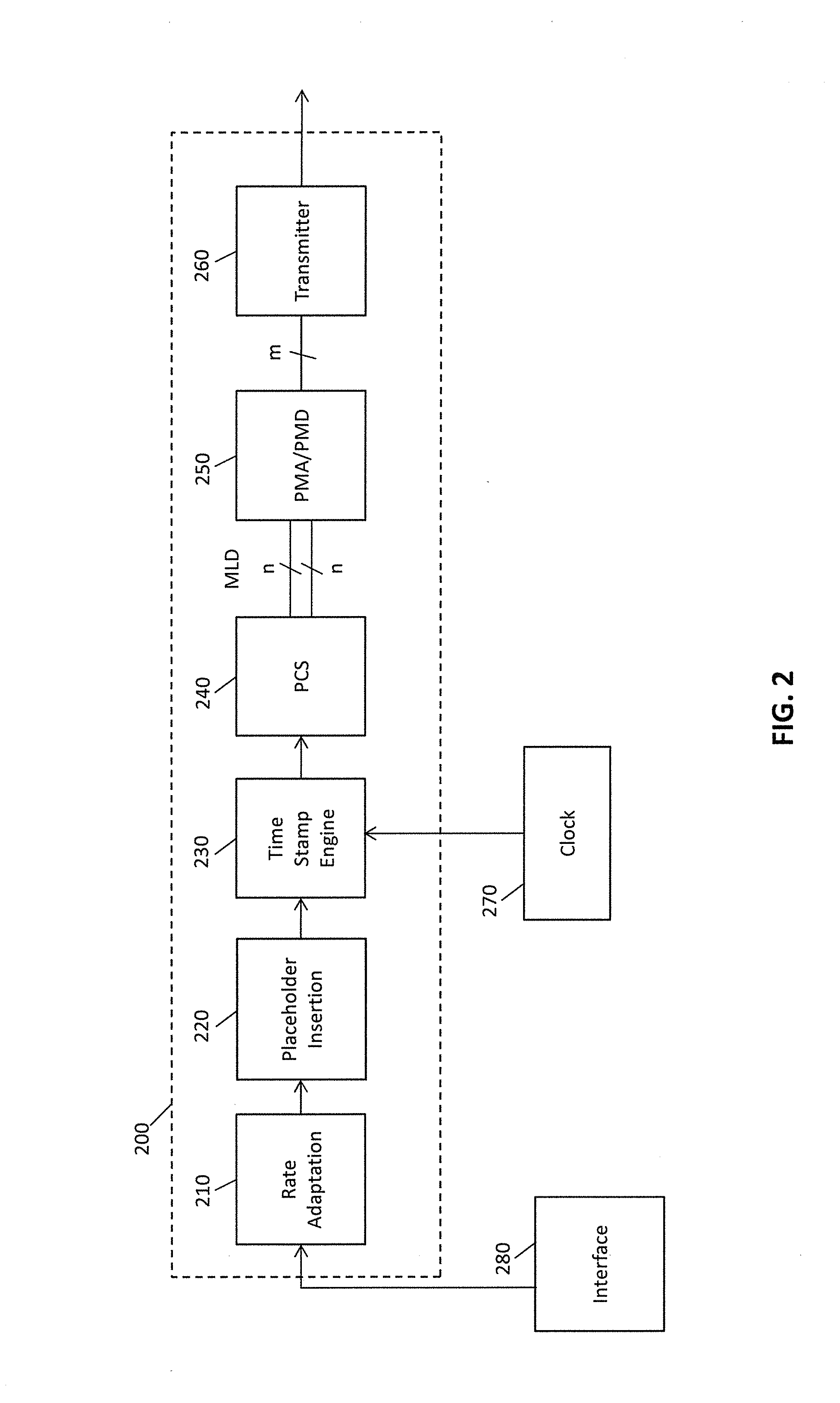
High accuracy 1588 timestamping over high speed multi lane distribution physical code sublayers
ActiveUS20140092918A1Fully comprehendedChannel dividing arrangementsError preventionTight frameReal-time computing
A physical layer device provides for synchronization of clocks in a communication network. A place holder for an alignment marker is inserted into a frame to be transmitted. Once the placeholder alignment marker is inserted into the frame, no additional data is added to the frame. Transmission of the frame including the placeholder alignment marker may also be delayed to allow data processing in subsequent blocks within a transmit block to complete prior to further processing of the frame including the placeholder alignment marker (e.g., timestamping, MACSec, etc.) to improve timing accuracy with a multi lane distribution environment.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
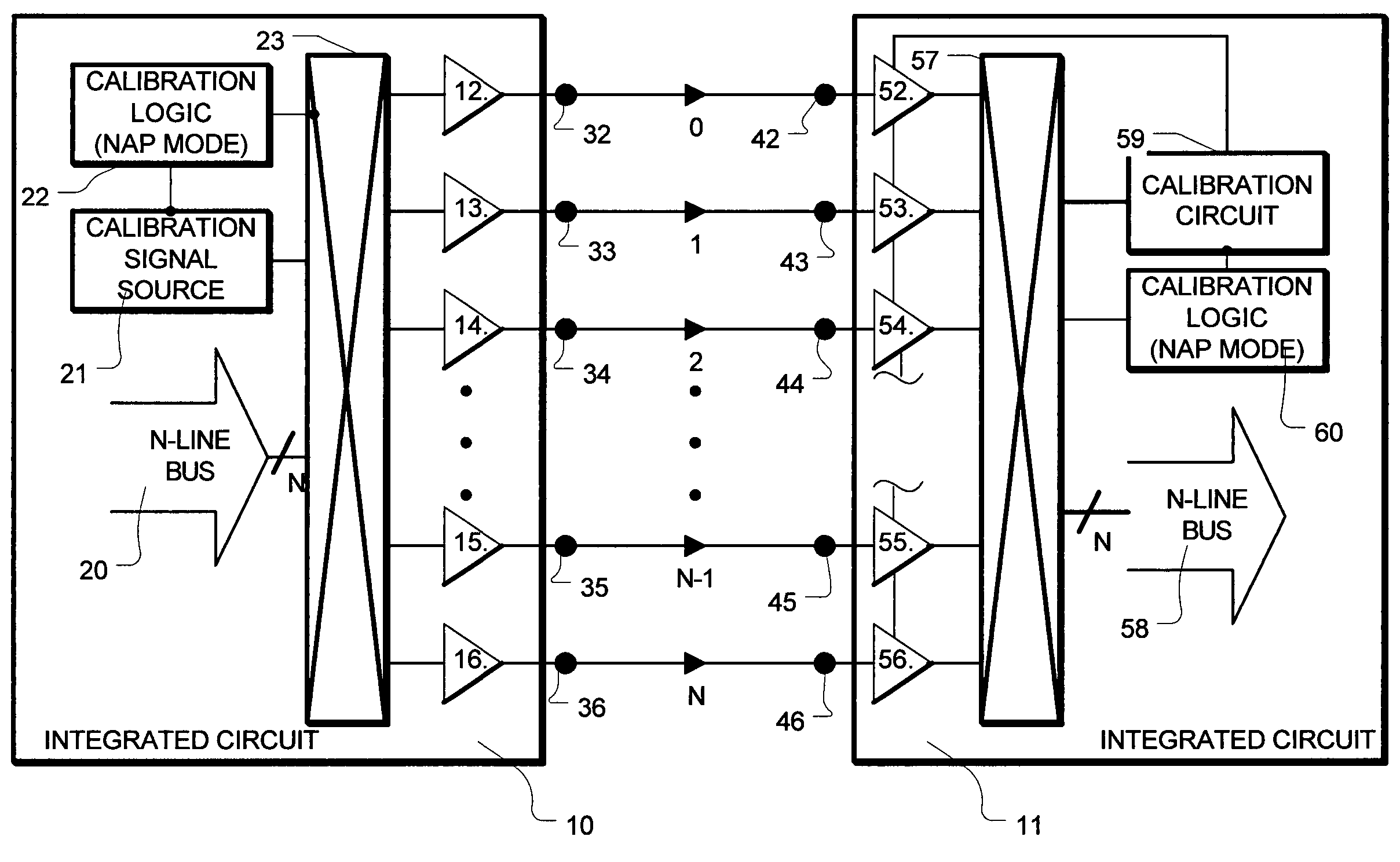
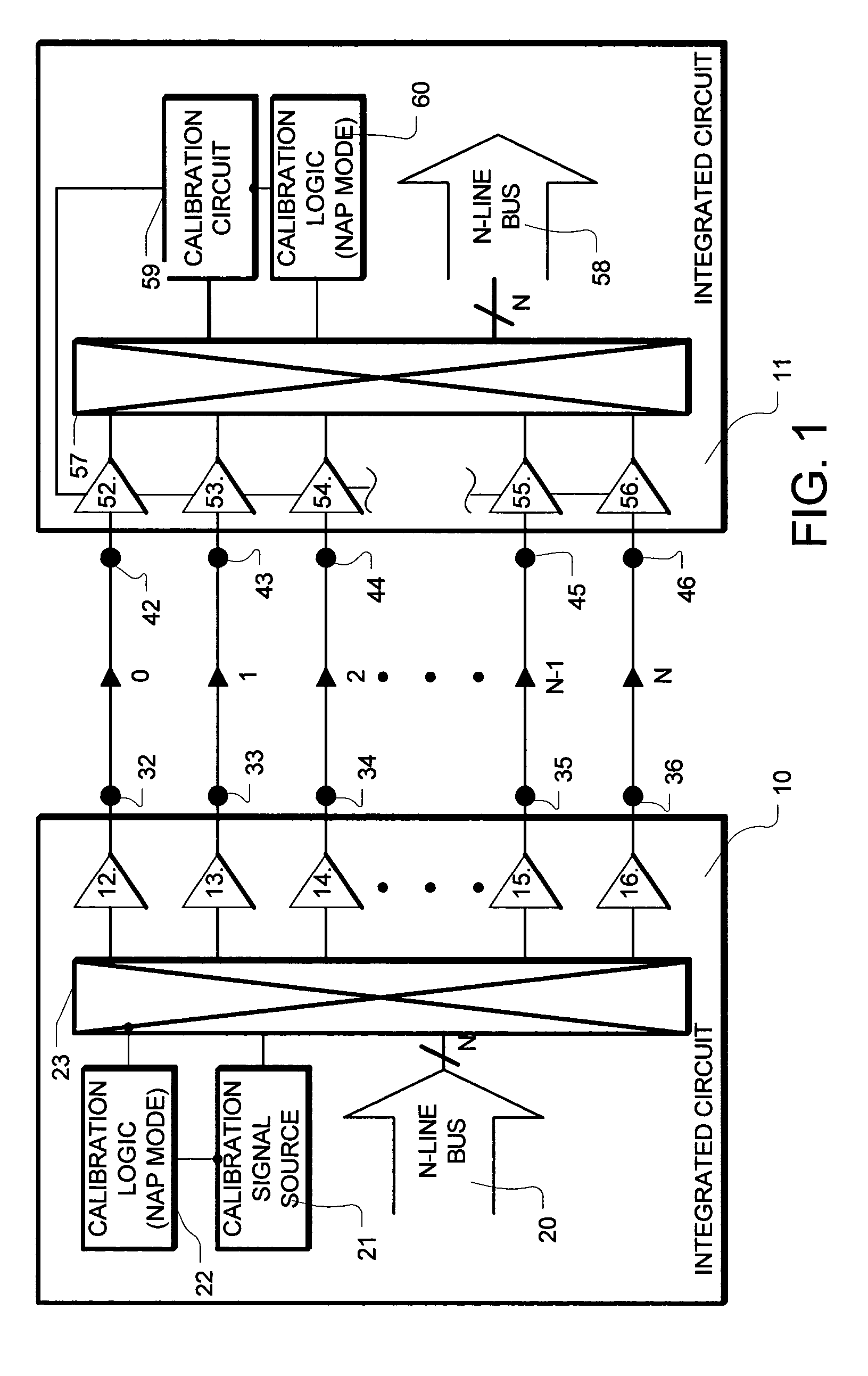
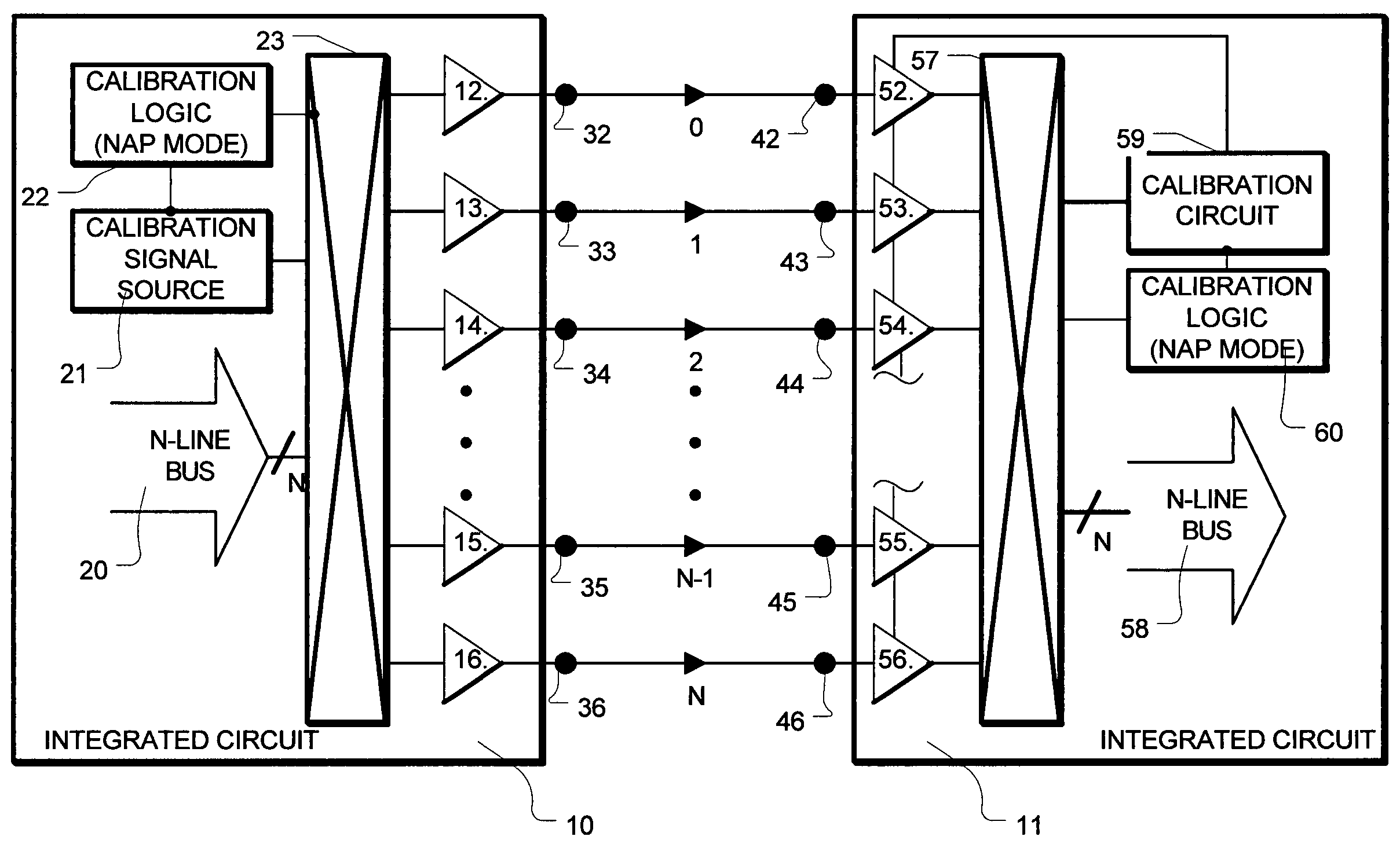
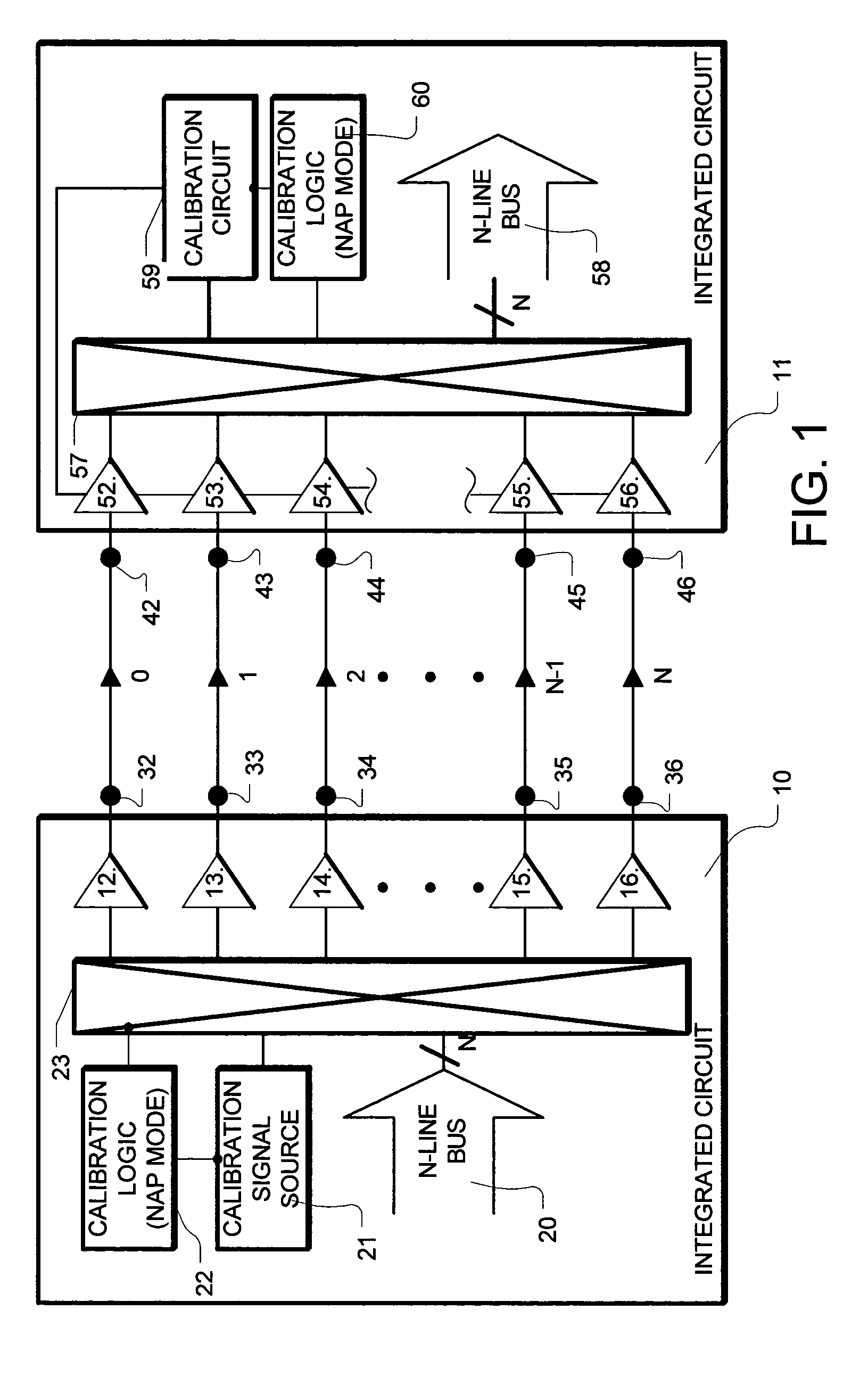
Periodic interface calibration for high speed communication
InactiveUS7072355B2Channel dividing arrangementsParallel/series conversionCommunication interfaceEngineering
A high-speed communication interface manages a parallel bus having N bus lines. N+1 communication lines are established. A maintenance operation is performed on one of the N+1 communication lines, while N of the N+1 communication lines is available for data from the N line bus. The communication line on which the maintenance operation is performed, is changed after the operation is complete, so that all of the N+1 communication lines are periodically maintained, without interfering with communications on N of the N+1 communication lines.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
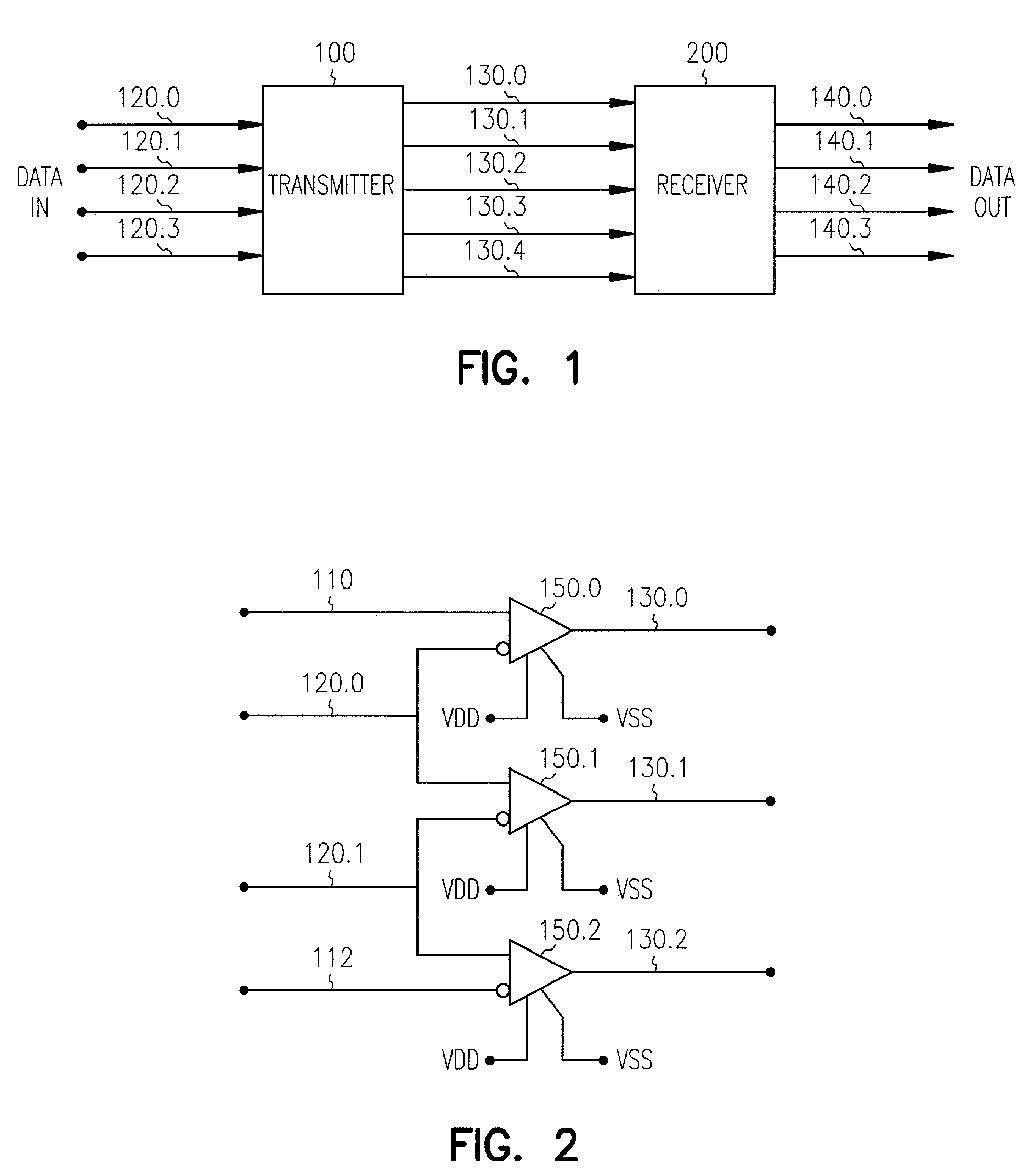
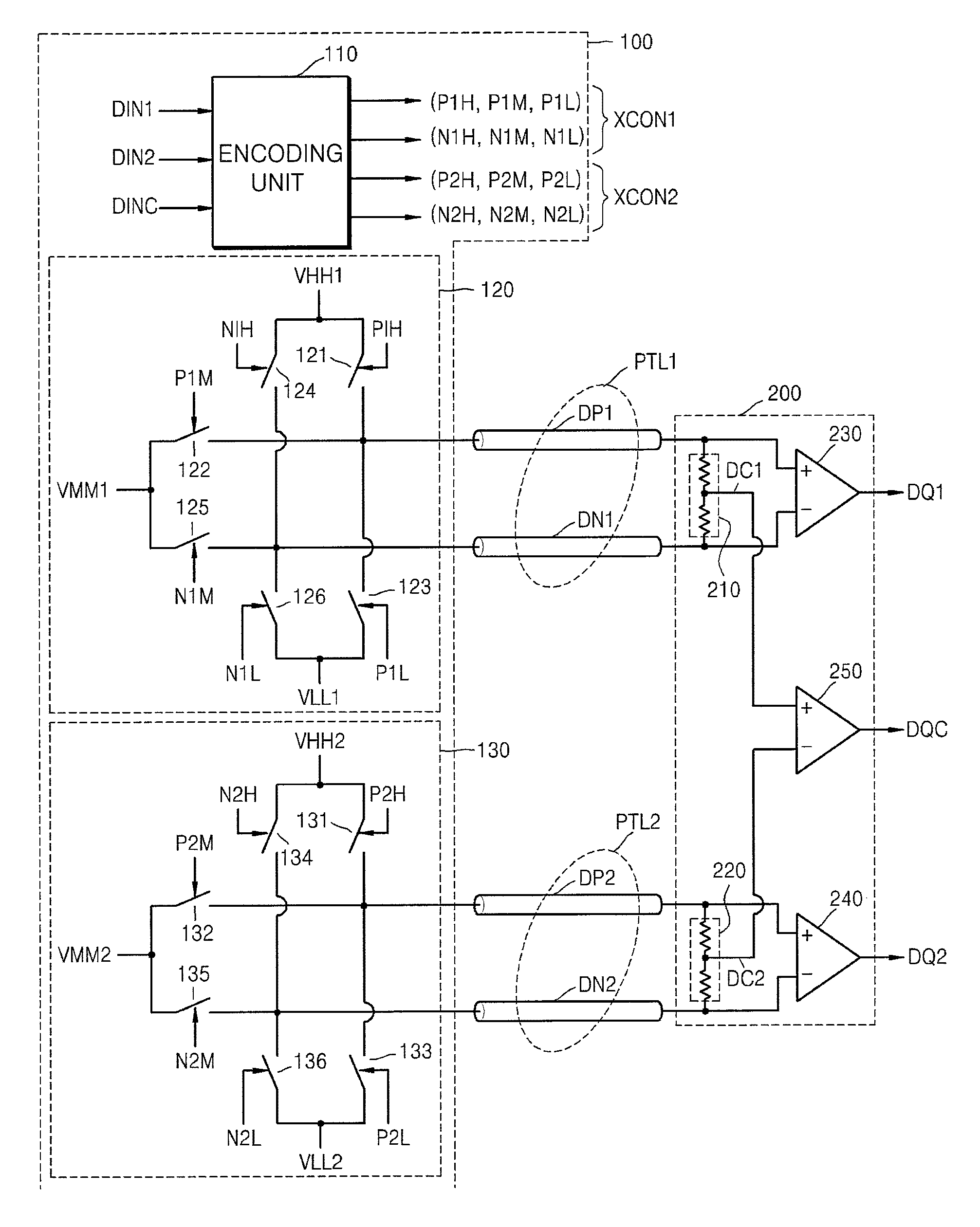
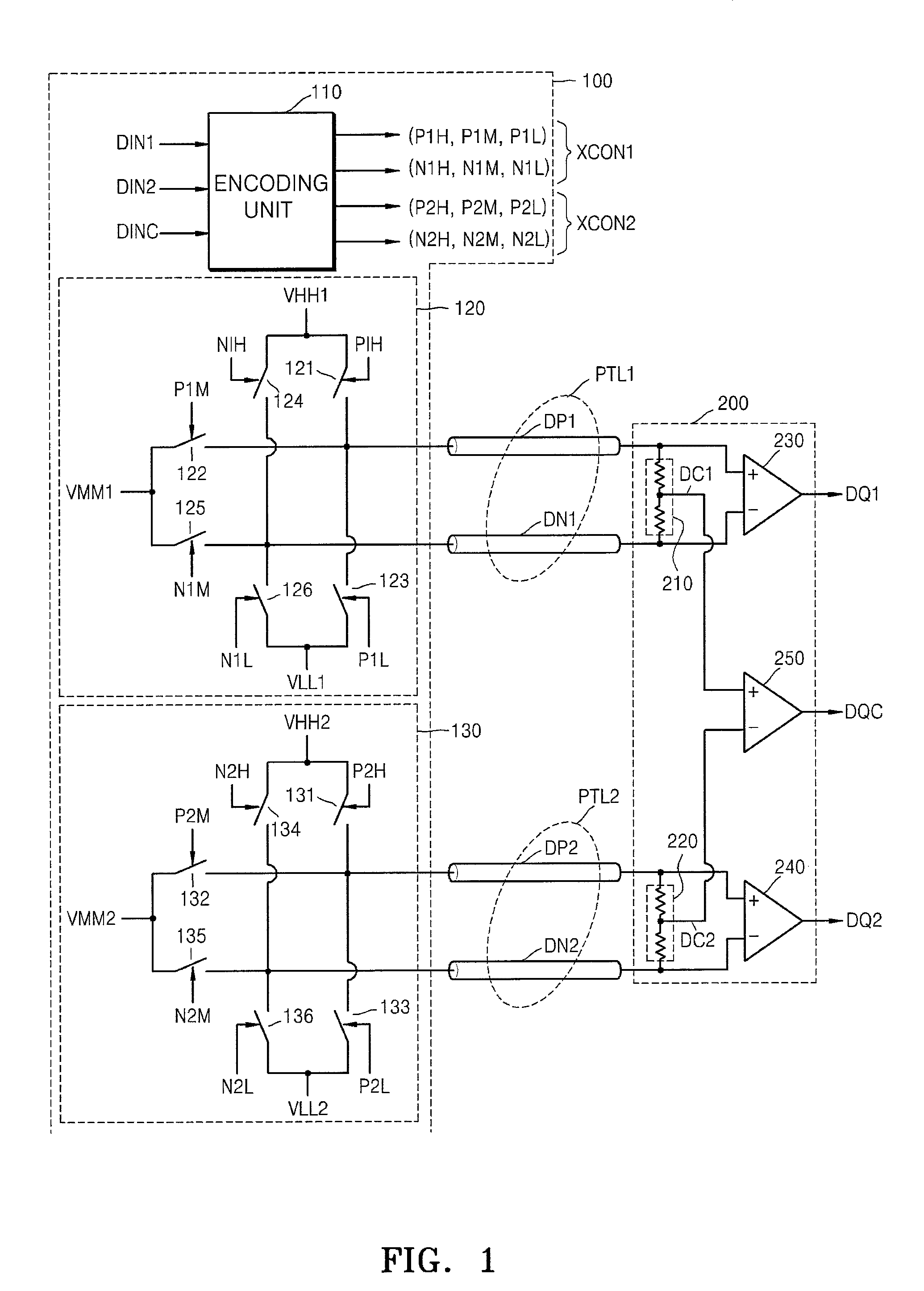
Differential data transferring system and method using three level voltages
ActiveUS8284848B2Improve efficiencyChannel dividing arrangementsTransmission line coupling arrangementsThree levelTransfer system
Owner:TLI
Parallel data communication having multiple sync codes
InactiveUS6920576B2Channel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsDigital dataData file
A high-speed parallel-data communication approach overcomes skewing problems by transferring digital data with automatic realignment. In one example embodiment, a parallel bus has parallel bus lines adapted to transfer digital data from a data file, along with a synchronizing clock signal. To calibrate the synchronization, the sending module transfers synchronization codes which are sampled and validated according to an edge of the clock signal by a receiving module and then used to time-adjust the edge of the clock signal relative to the synchronization codes. The synchronization codes are implemented to toggle the bus lines with each of the synchronization codes transferred.
Owner:FUTURE LINK SYST
Phase interpolator circuitry for reducing clock skew
InactiveUS20050024117A1Reduced clock skewsImprove smoothnessChannel dividing arrangementsSingle output arrangementsConstant current sourceEngineering
A phase interpolator circuitry is composed of a delay line, and a phase blender circuit. The delay line delays a first input clock signal to develop a delayed clock signal. The phase blender circuit includes a first inverter receiving the delayed clock signal, and a second inverter receiving a second input clock signal phased away from the first input clock signal. The outputs of the first and second inverters are commonly coupled together. The phase interpolator circuitry additionally includes at least one of constant current sources: first one connected between a power terminal of the first inverter and a power supply, second one connected between a ground terminal of the first inverter and ground, third one connected between a power terminal of the second inverter and a power supply, and fourth one connected between a ground terminal of the second inverter and ground.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
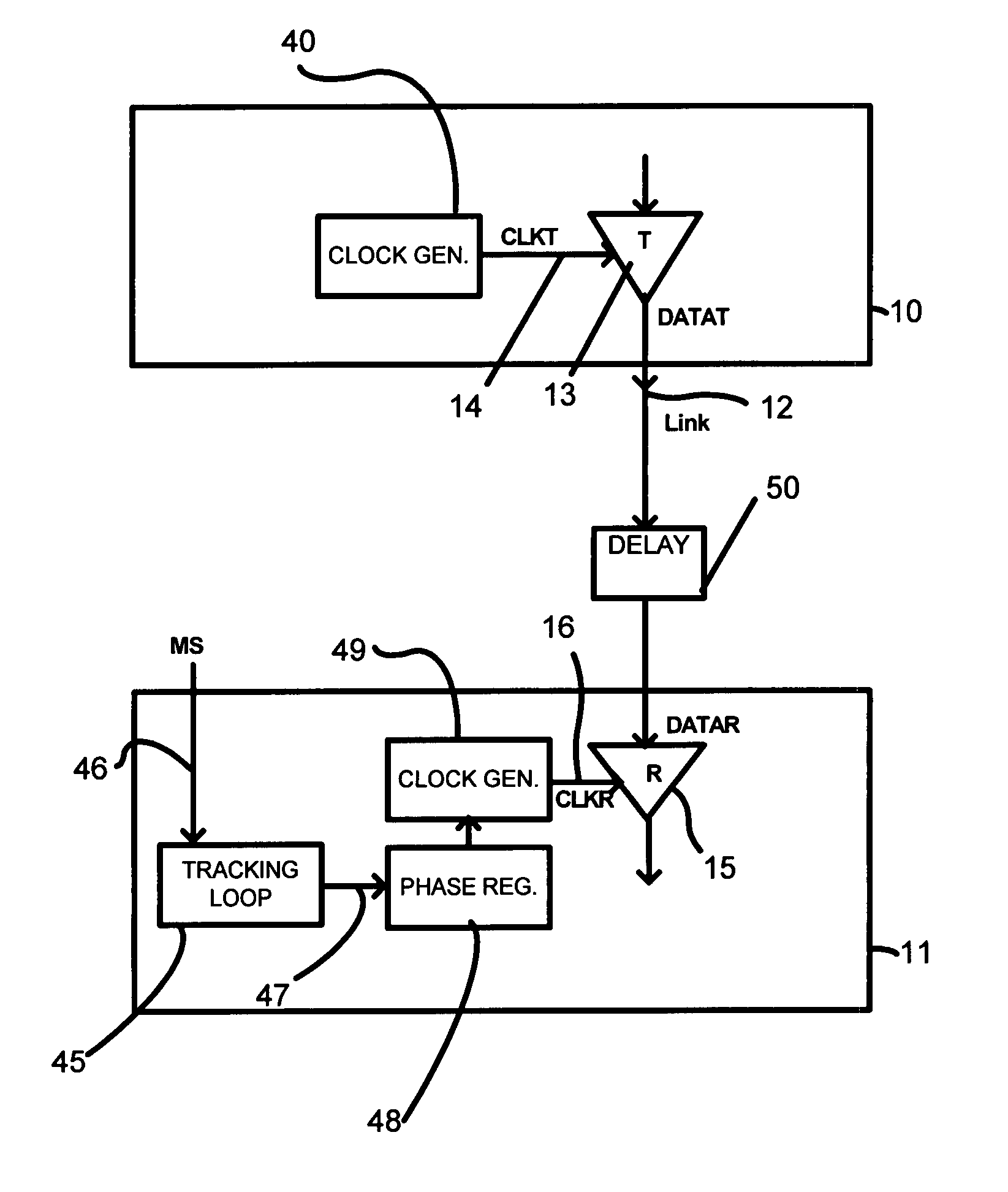
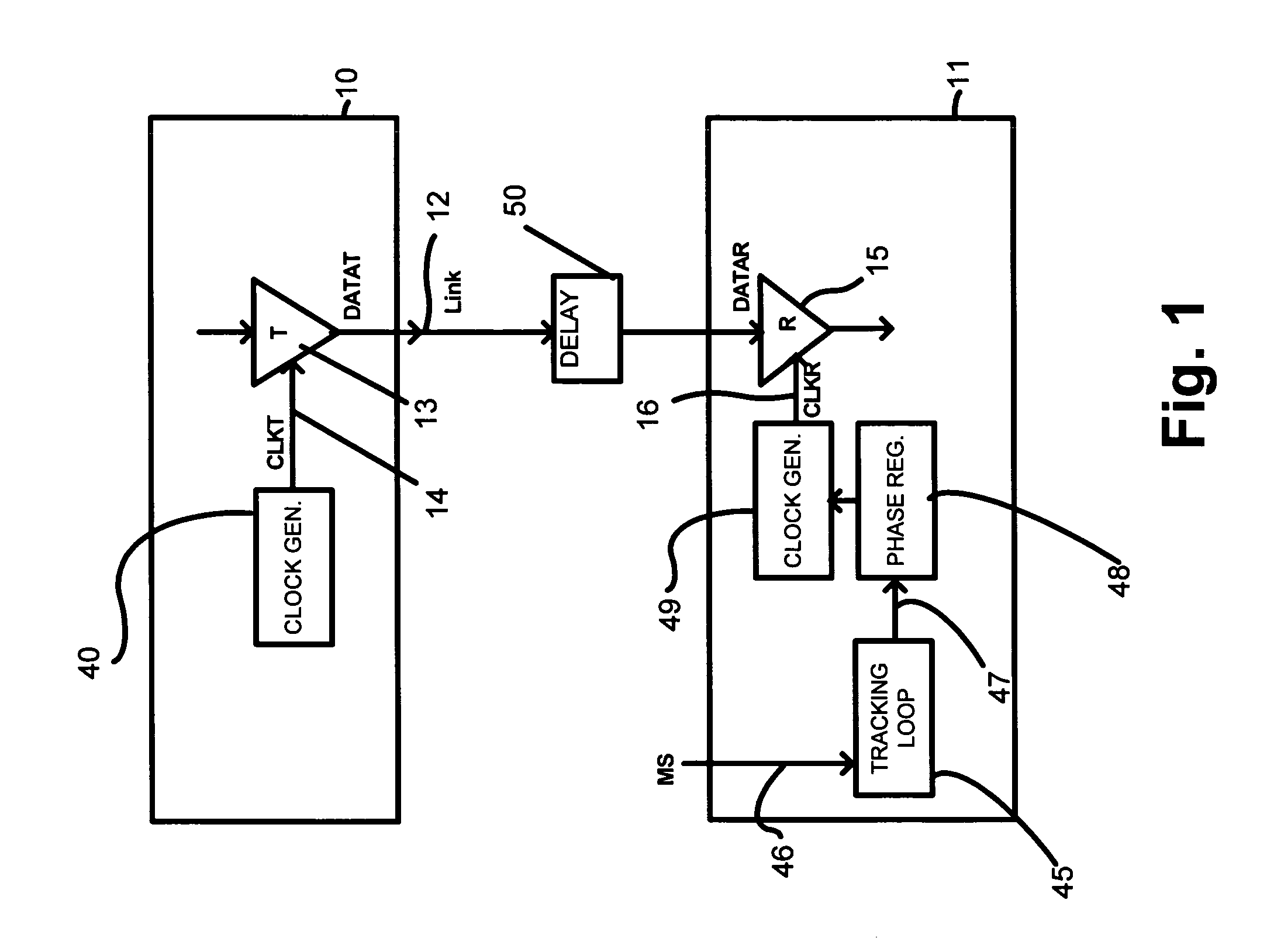
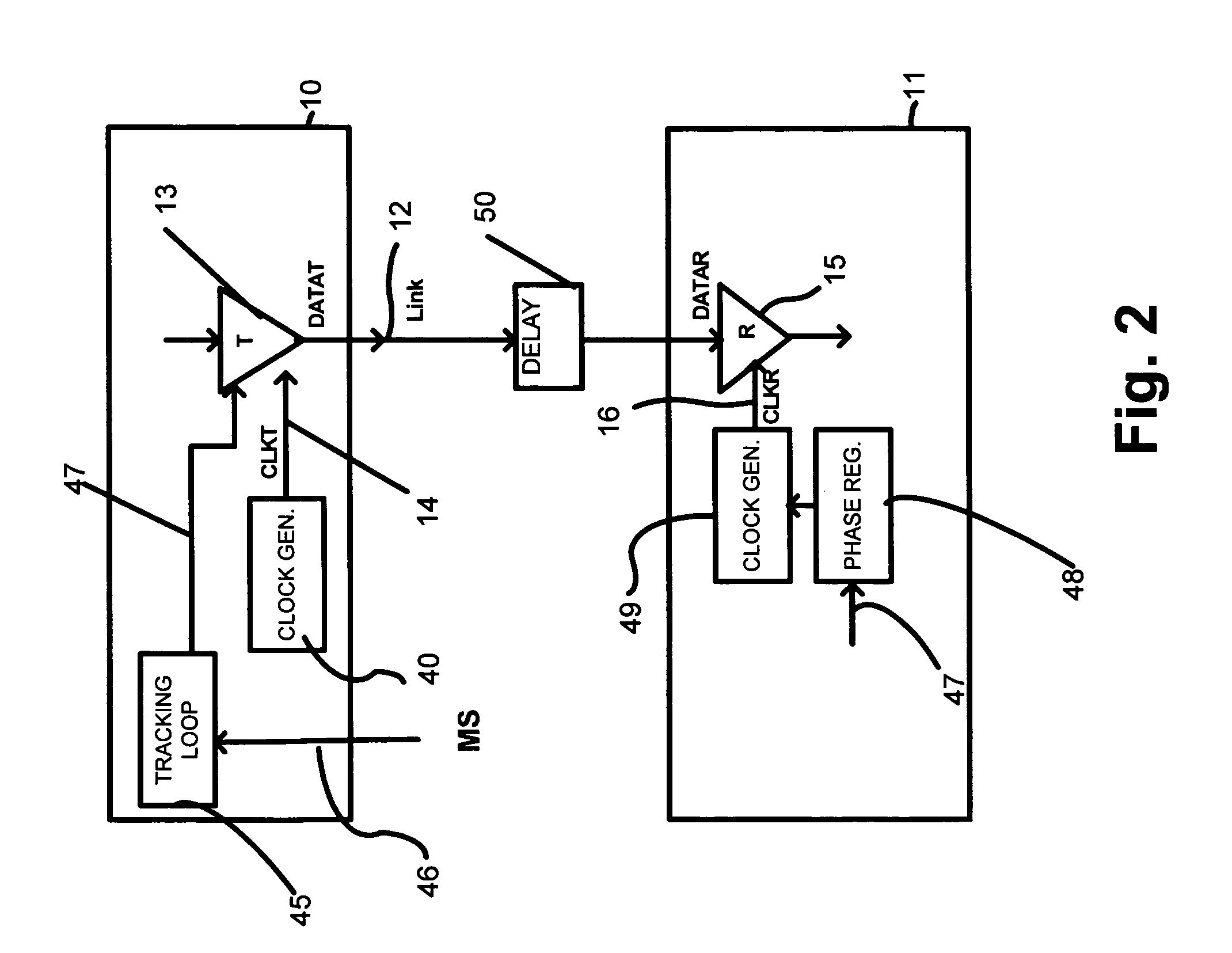
Drift tracking feedback for communication channels
ActiveUS6961862B2Efficiently tracking drift of property of channelReceiver initialisationChannel dividing arrangementsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A communication channel includes a first component having a transmitter coupled to a normal signal source, and a second component having a receiver coupled to a normal signal destination. A communication link couples the first and second components. Calibration logic provides for setting an operation value for a parameter of the communication channel, such as by executing an exhaustive calibration sequence at initialization of the link. A tracking circuit, including a monitoring function, tracks drift in the parameter by monitoring a feedback signal that has a characteristic that correlates with drift in the communication channel, and updates, or indicates the need for updating of, the operation value of the parameter in response to the monitoring function.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Periodic interface calibration for high speed communication
InactiveUS20050041683A1Continuous operationChannel dividing arrangementsParallel/series conversionCommunication interfaceEngineering
A high-speed communication interface manages a parallel bus having N bus lines. N+1 communication lines are established. A maintenance operation is performed on one of the N+1 communication lines, while N of the N+1 communication lines is available for data from the N line bus. The communication line on which the maintenance operation is performed, is changed after the operation is complete, so that all of the N+1 communication lines are periodically maintained, without interfering with communications on N of the N+1 communication lines.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
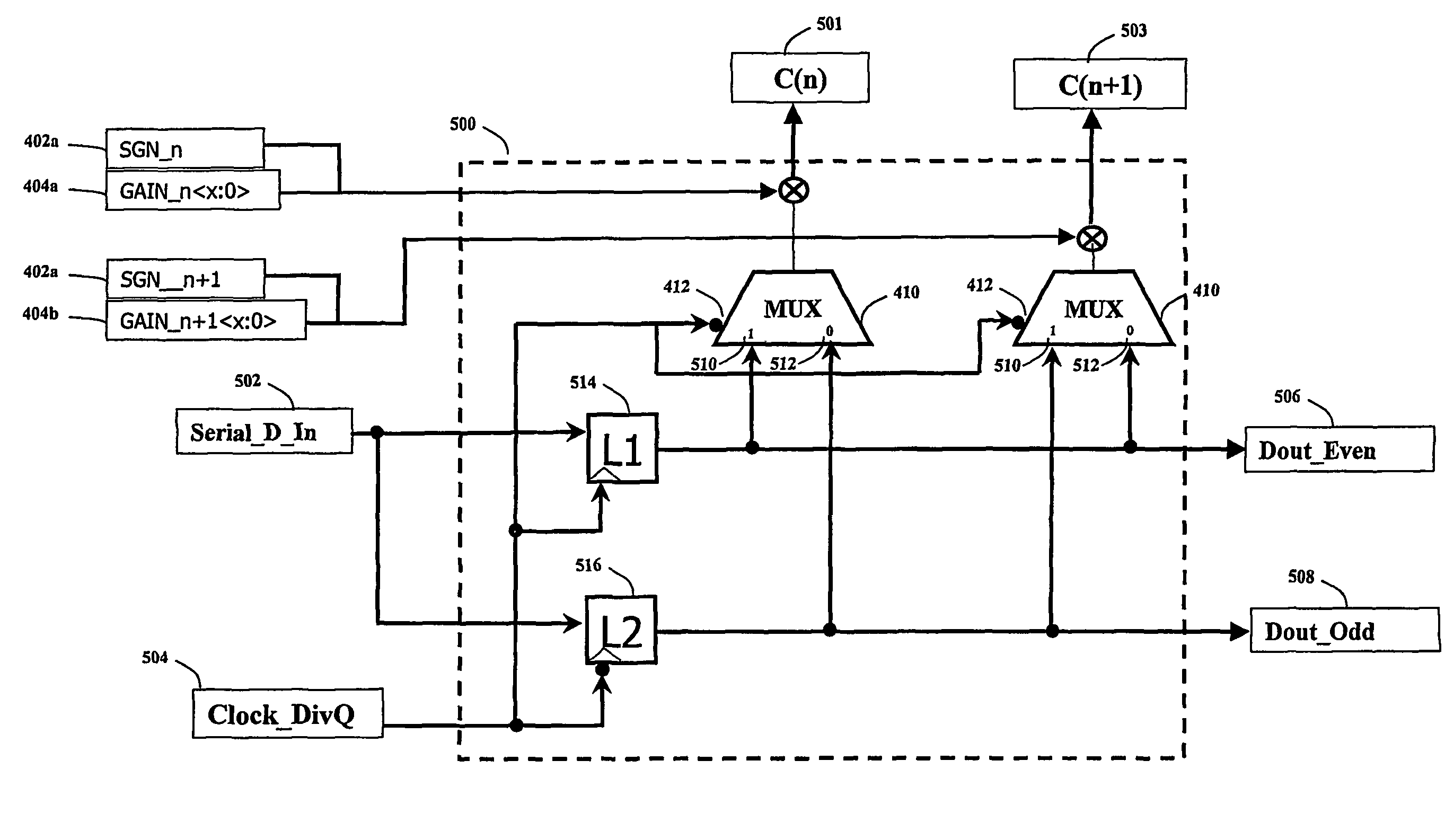
Operating frequency reduction for transversal FIR filter
InactiveUS7889786B2Reduce operating frequencyMore powerMultiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsFinite impulse responseShift register
A method and system for reducing the frequency of operation for a transversal Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter is disclosed. In the preferred embodiment, the transversal filter operates in such a way that it has an even and odd row of data, which are latched on rising and falling edges of the clock respectively. This allows the clock frequency to be reduced by a factor of 2, and thus allows the use of more power efficient latches. A reduction in the frequency of operation causes the high speed latches within the transversal filter to hold the data bits twice as long as is required, which changes the desired impulse response of the FIR filter. A circuit is required to select the appropriate data bits from the output of the appropriate half-speed latch, and subsequently scale it to apply the co-efficient gain. Each of the subsystems is analog, and operates in accordance with a synchronous clock system. In a more general embodiment of the invention, the data is provided to Q shift registers that operate at a clock rate which is reduced by a factor of Q.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com