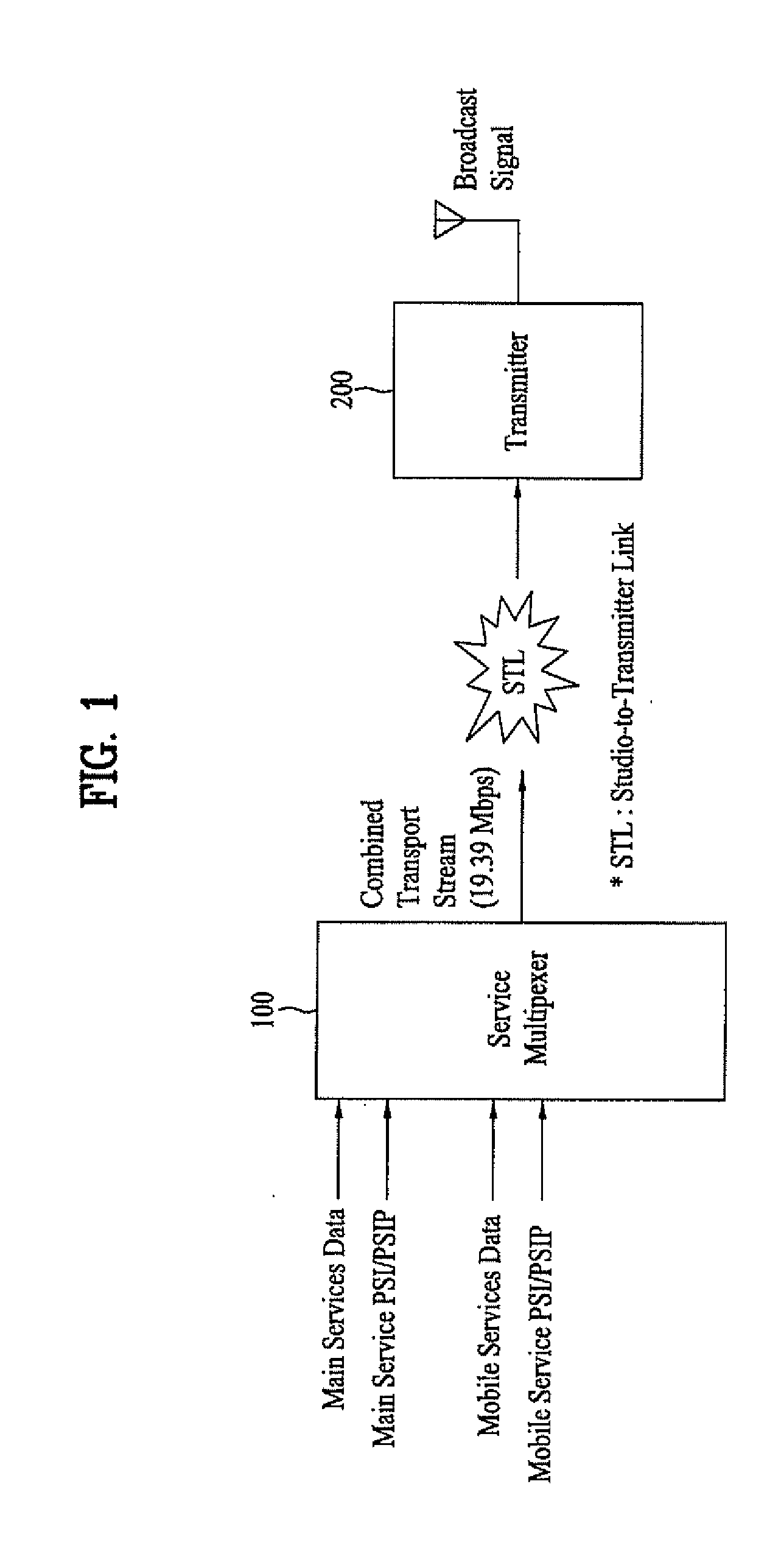
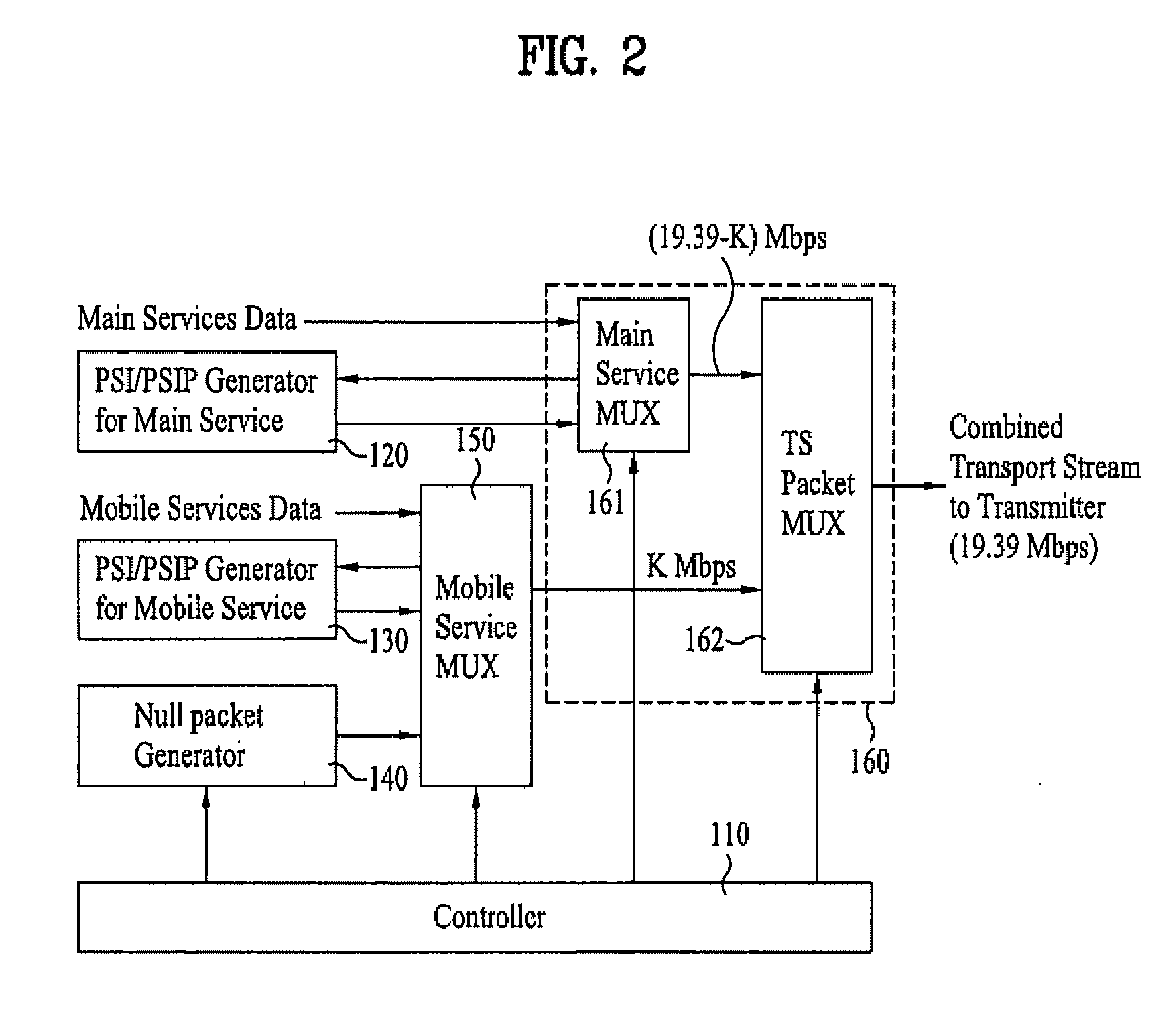
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3243results about "Delay line applications" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
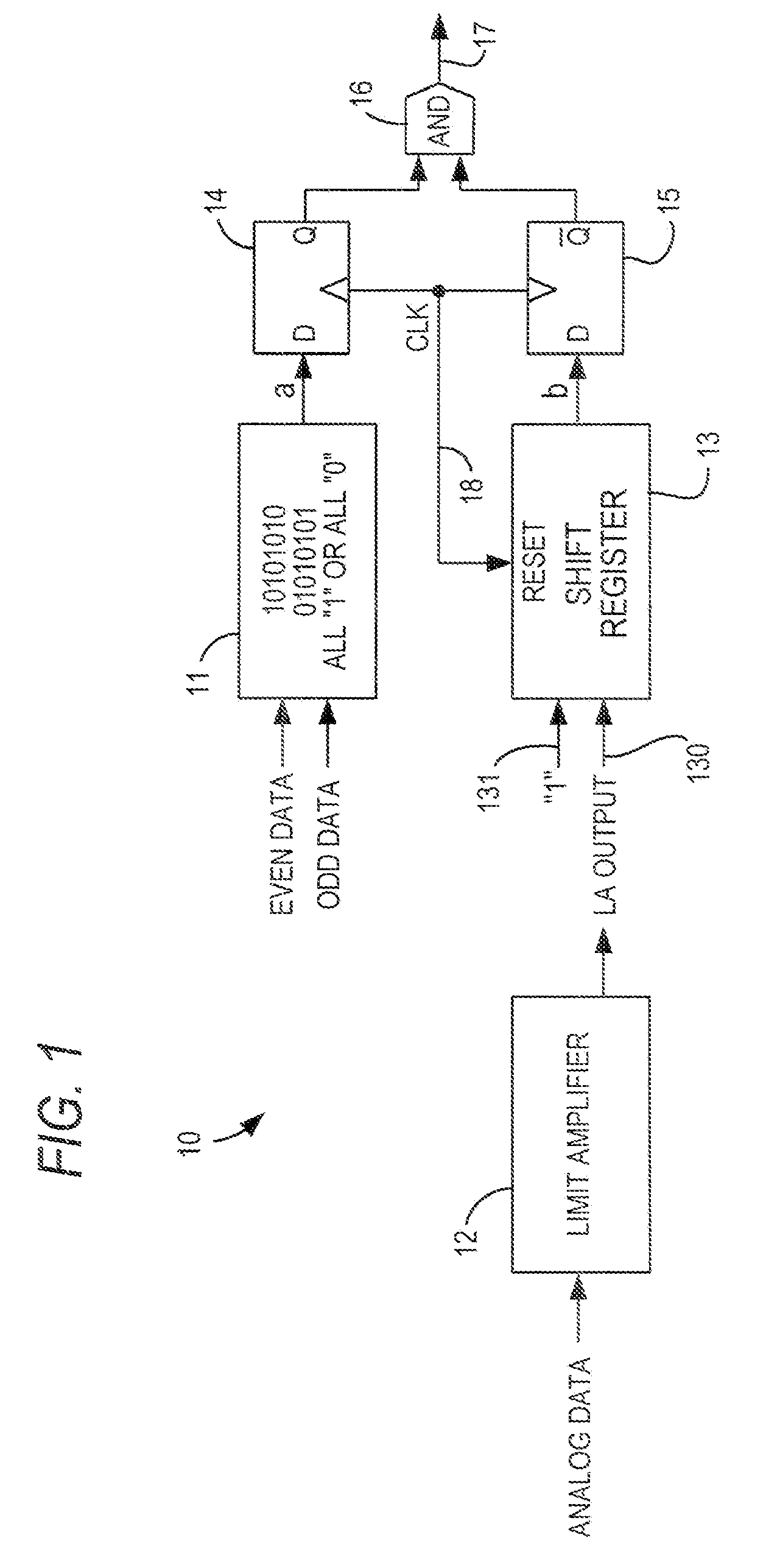
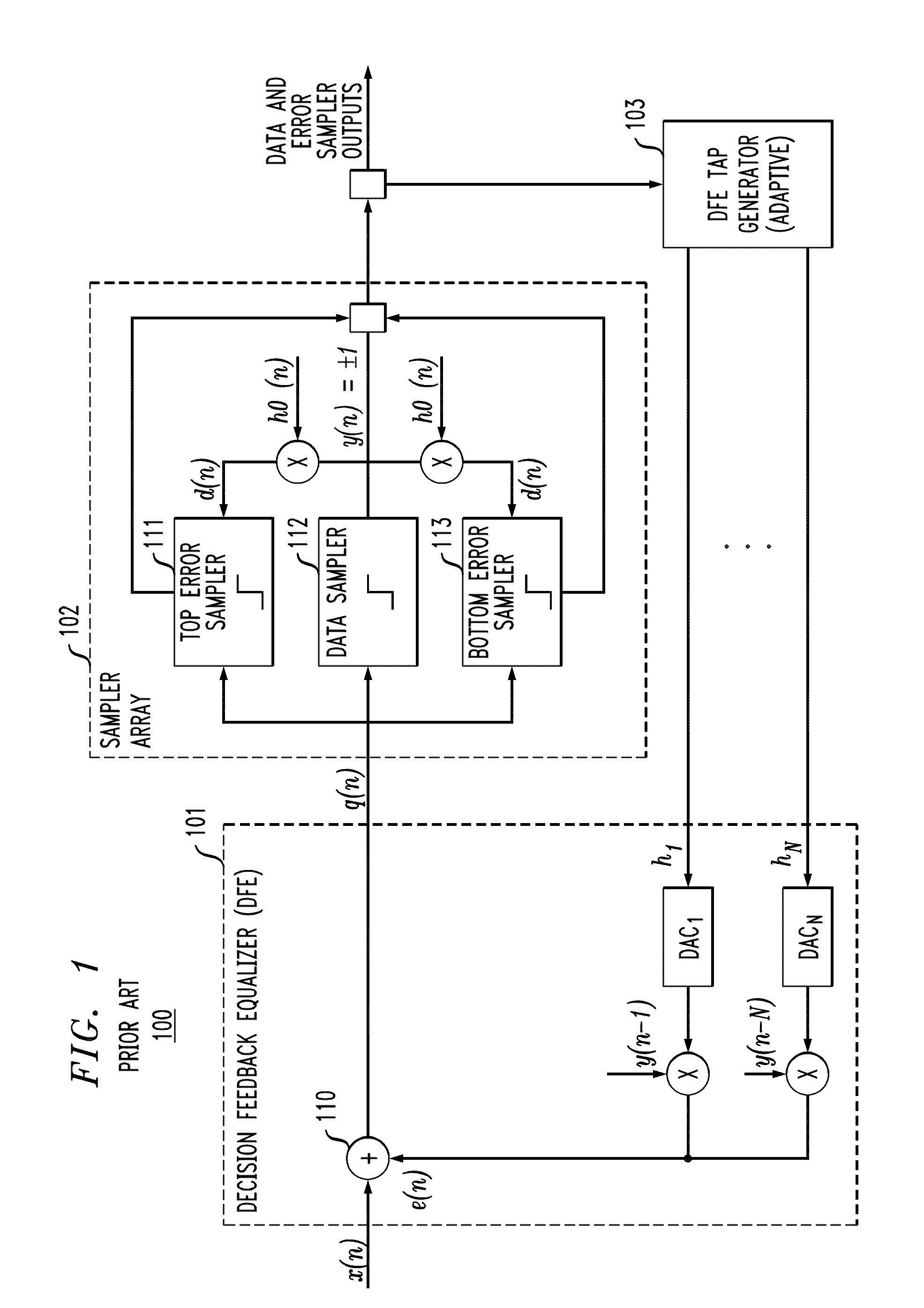
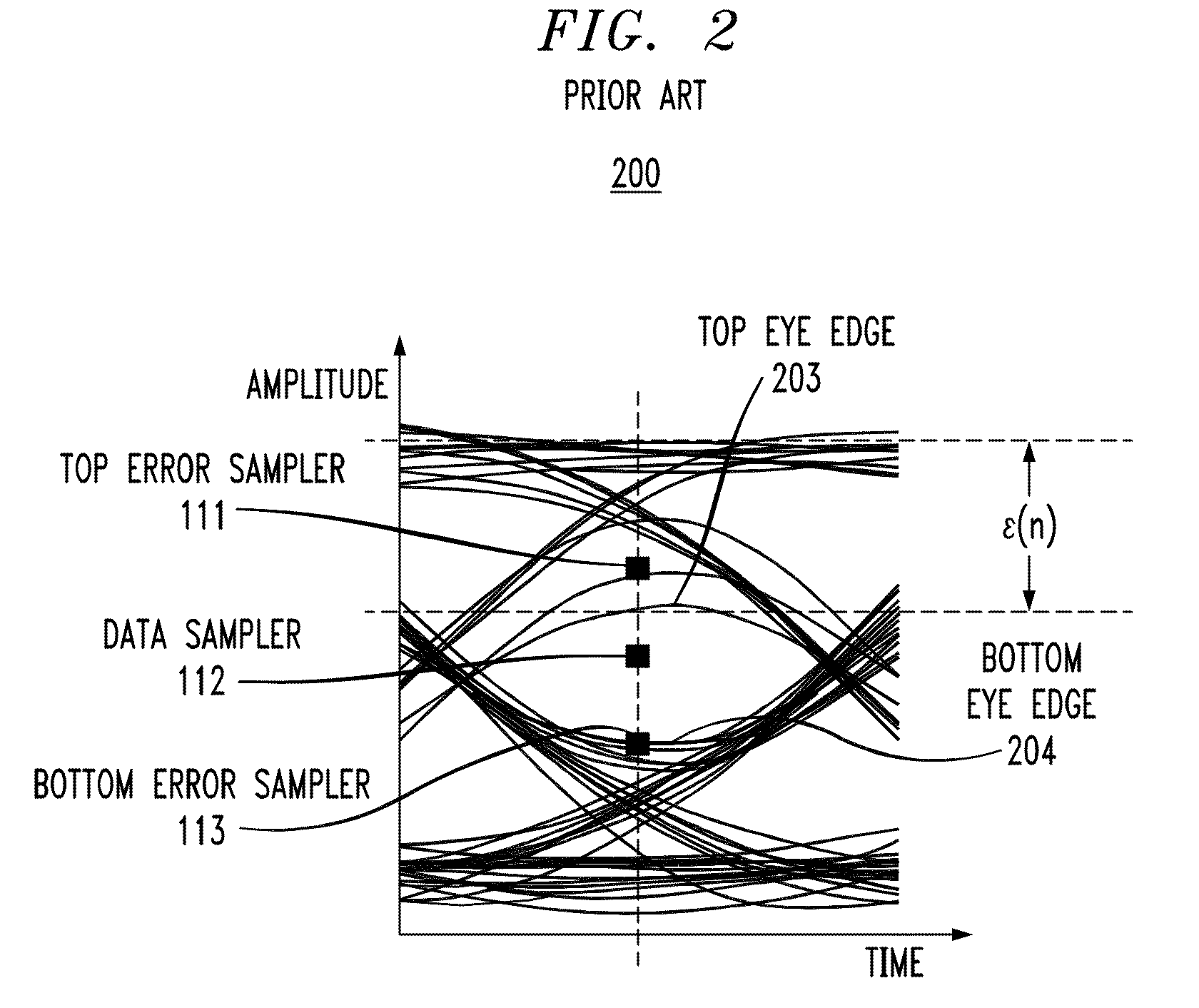
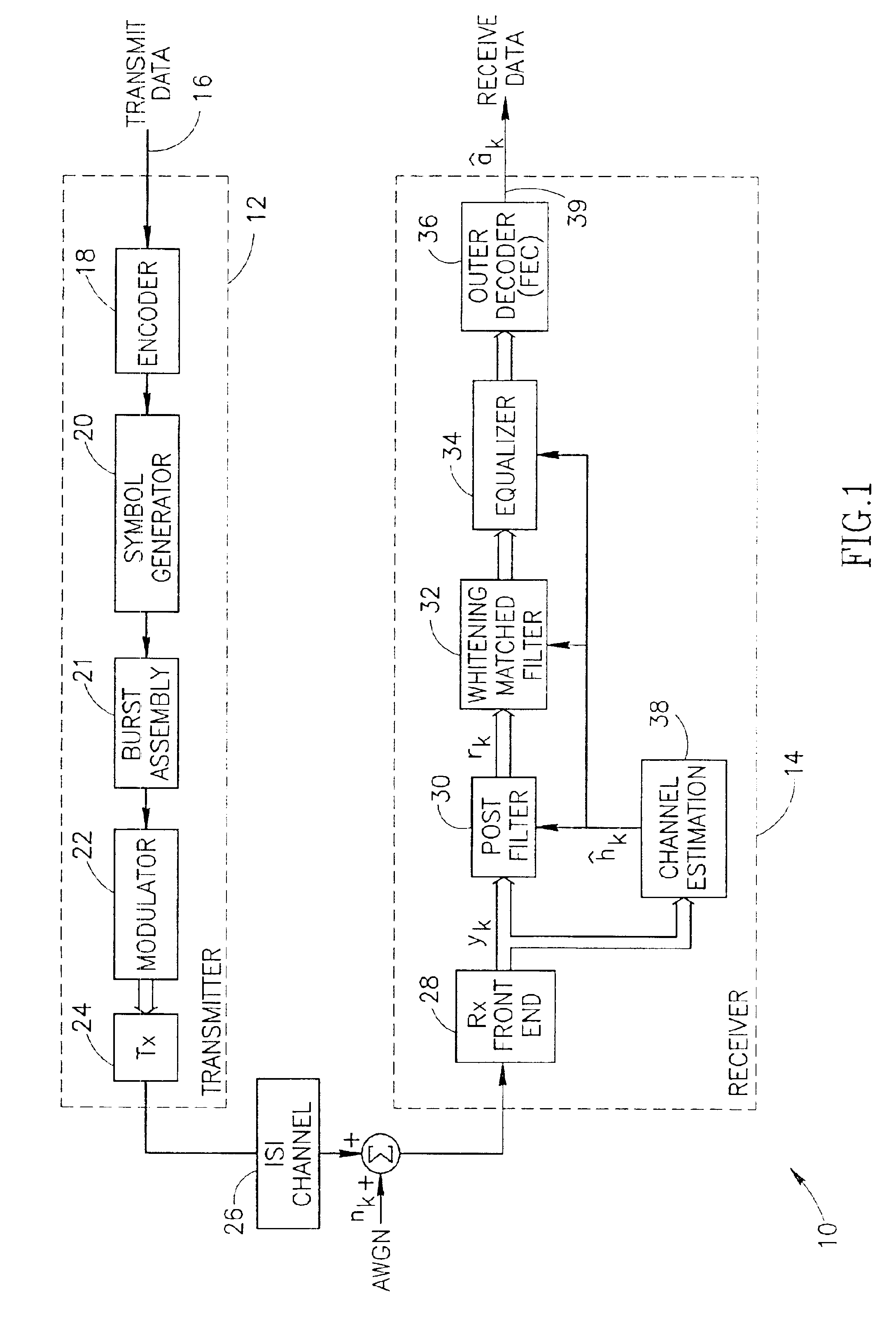
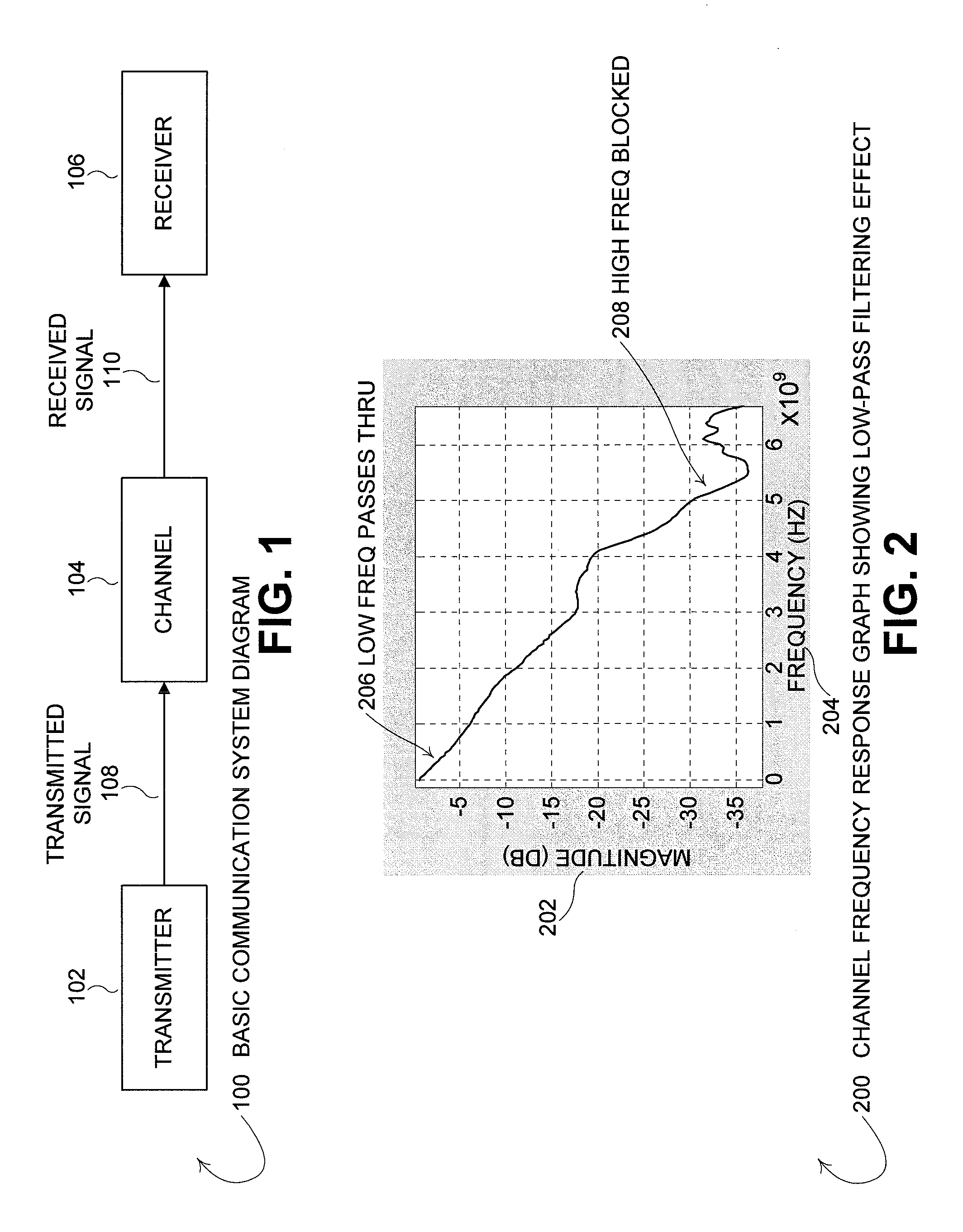
Channel equalization system and method
InactiveUS6904110B2Increase high performance and data rate capacityLow costMultiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsFiberEngineering
A system and method for delivering increases speed, security, and intelligence to wireline and wireless systems. The present invention increases channel capacity by using a parallel or multi-channel structure in such wireless and wireline at the edge or the core of. This new architecture of the present invention uses parallel bitstreams in a flexible way and distributed switching / routing technique, is not only to avoid the potential bottlenet of centralized switches, but also to increase speed with intelligence that is seamlessly integrating into the Fiber Optic Backbone such as WDM and SONET of the MAN / WAN network with a Real-time guarantees, different types of traffic (such as Stringent synchronous, isochronous, and asynchronous data messages) with different demands, and privacy & security of multi access and integrated services environment.
Owner:B C LEOW
Signal loss detector for high-speed serial interface of a programmable logic device
InactiveUS7996749B2Multiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionPattern matchingProgrammable logic device
Owner:ALTERA CORP
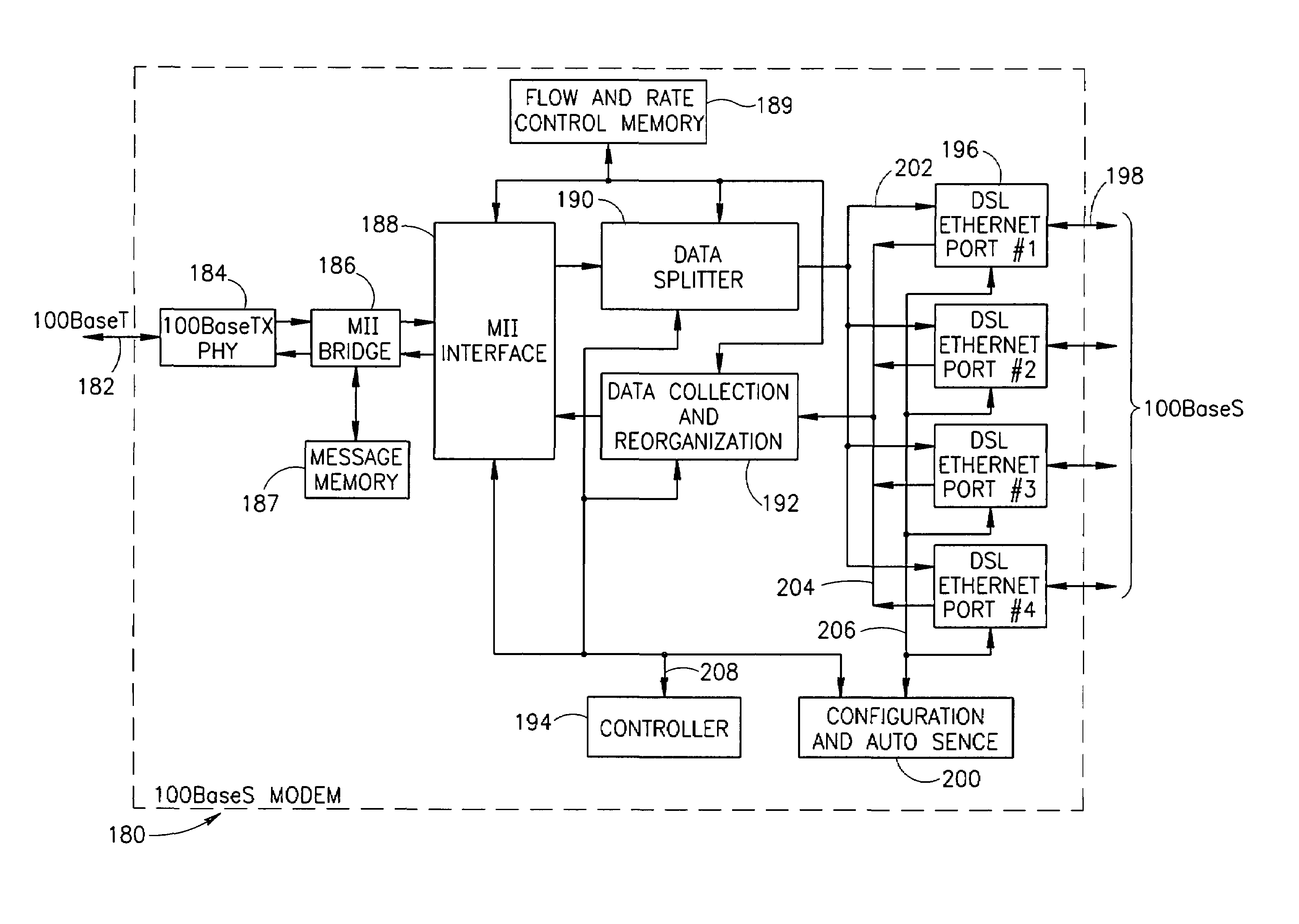
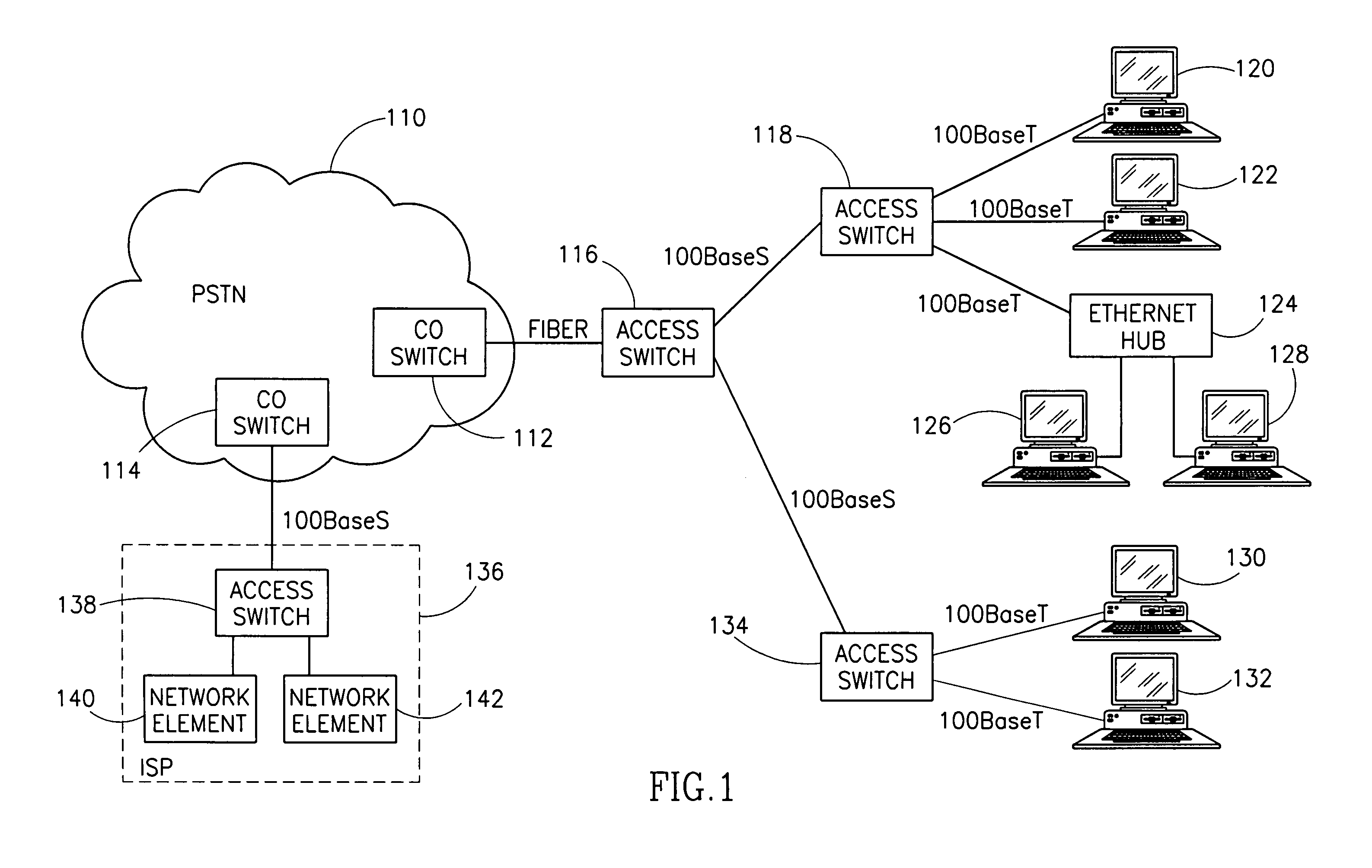
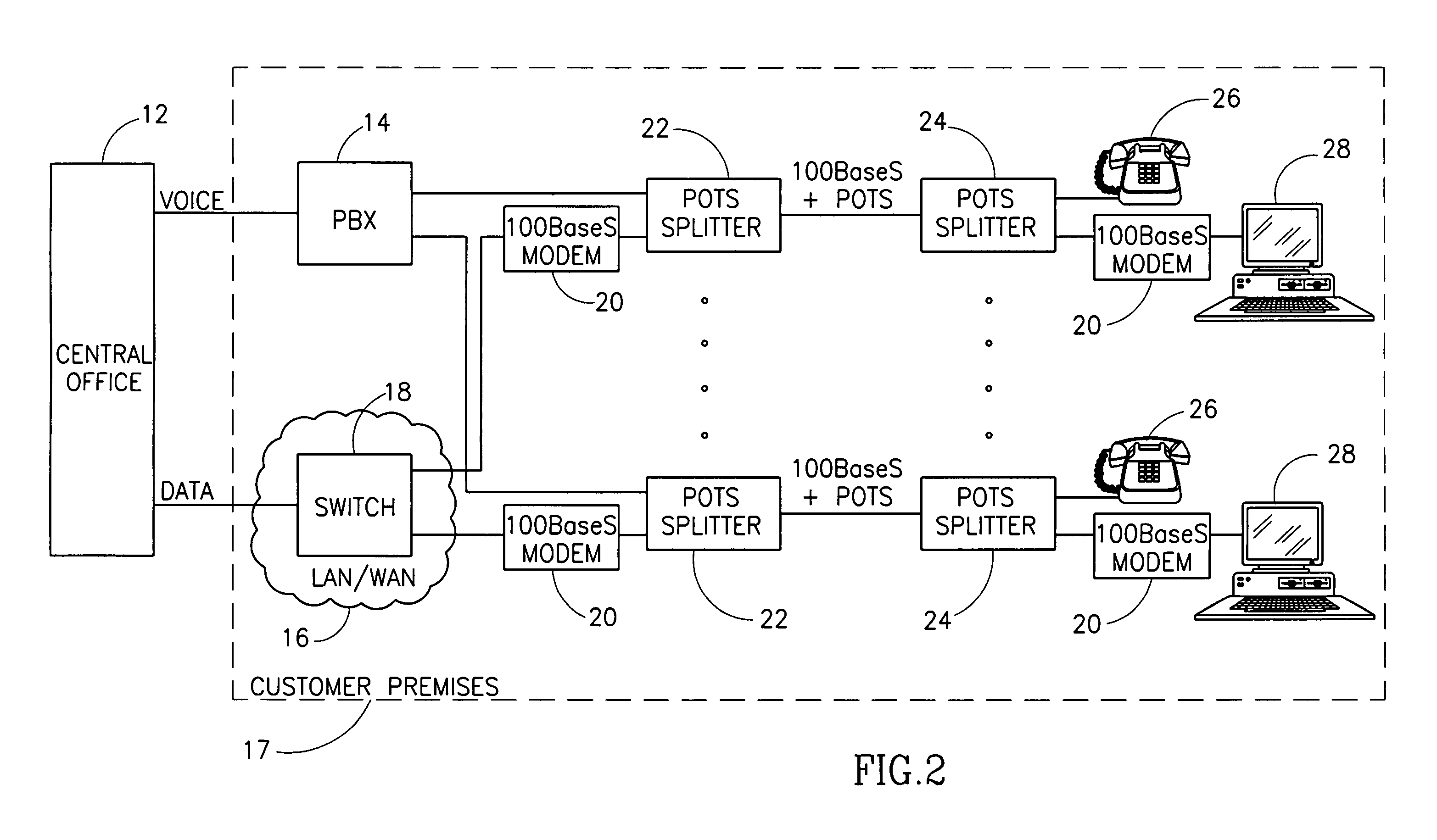
High data rate ethernet transport facility over digital subscriber lines
InactiveUS7054376B1Simple and cost-effectiveIncrease transfer speedMultiple-port networksError preventionTransport systemModem device
A facility transport system for transporting high speed Ethernet data over digital subscriber lines. The system, referred to as 100BaseS, is capable of transmitting 100 Mbps Ethernet over existing copper infrastructure up to distances of approximately 400 meters. The system achieves bit rates from 25 to 100 Mbps in increments of 25 Mbps with each 25 Mbps increment utilizing a separate copper wire pair. Each pair used provides a bidirectional 25 Mbps link with four copper wire pair connections providing 4×25 Mbps downstream channels and 4×25 Mbps upstream channels. The system utilizes framing circuitry to adapt the 100BaseT input data signal to up to four separate output signals. A DSL Ethernet Port card couples the modem to each twisted pair used. Each DSL Ethernet Port card comprises modem transmitter and receiver circuitry for sending and receiving 100BaseS signals onto twisted pair wires. The system utilizes QAM in combination with frequency division multiplexing (FDM) to separate downstream channels from upstream channels and to separate both the downstream and the upstream channels from POTS and ISDN signals.
Owner:LANTIQ BET GMBH & CO KG
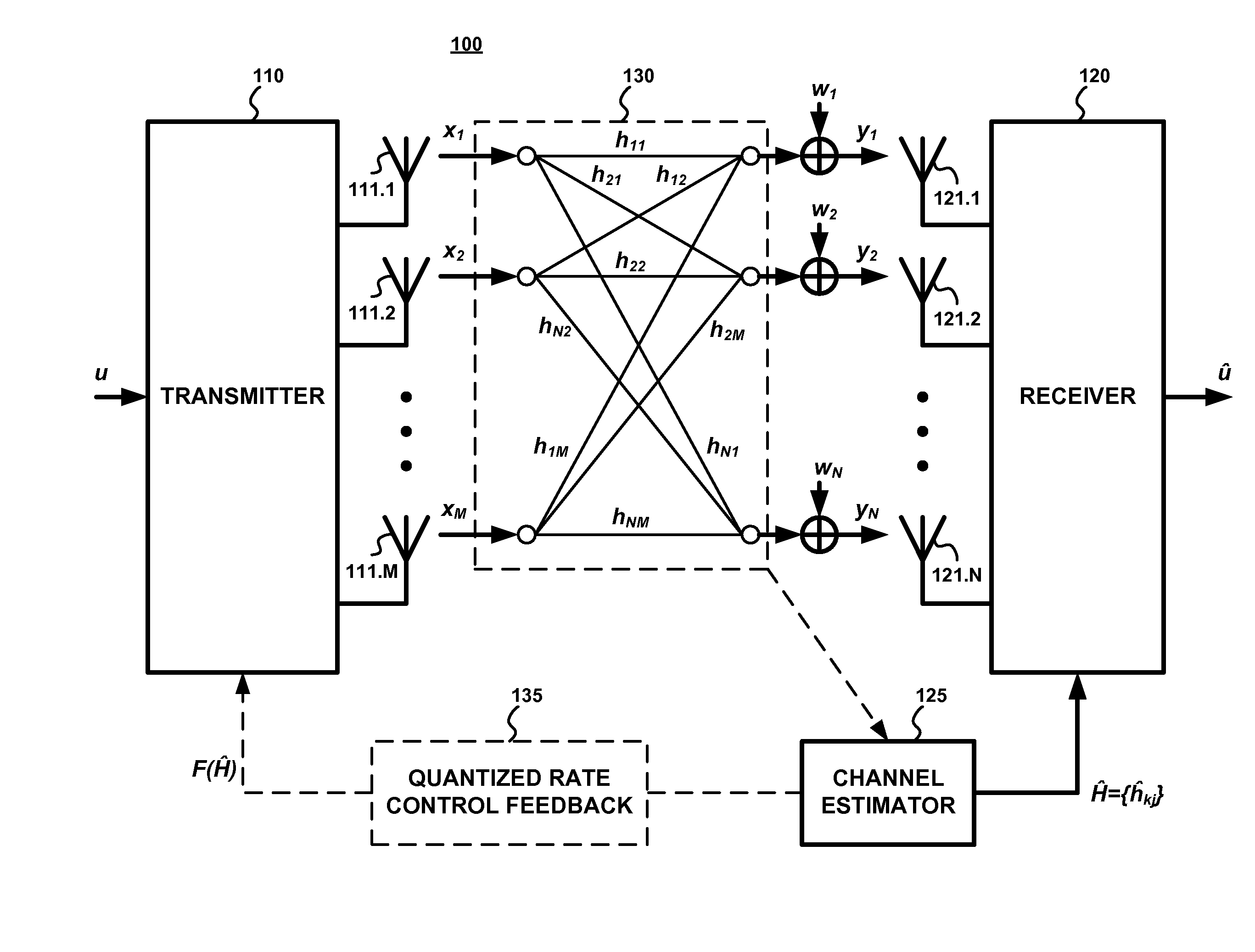
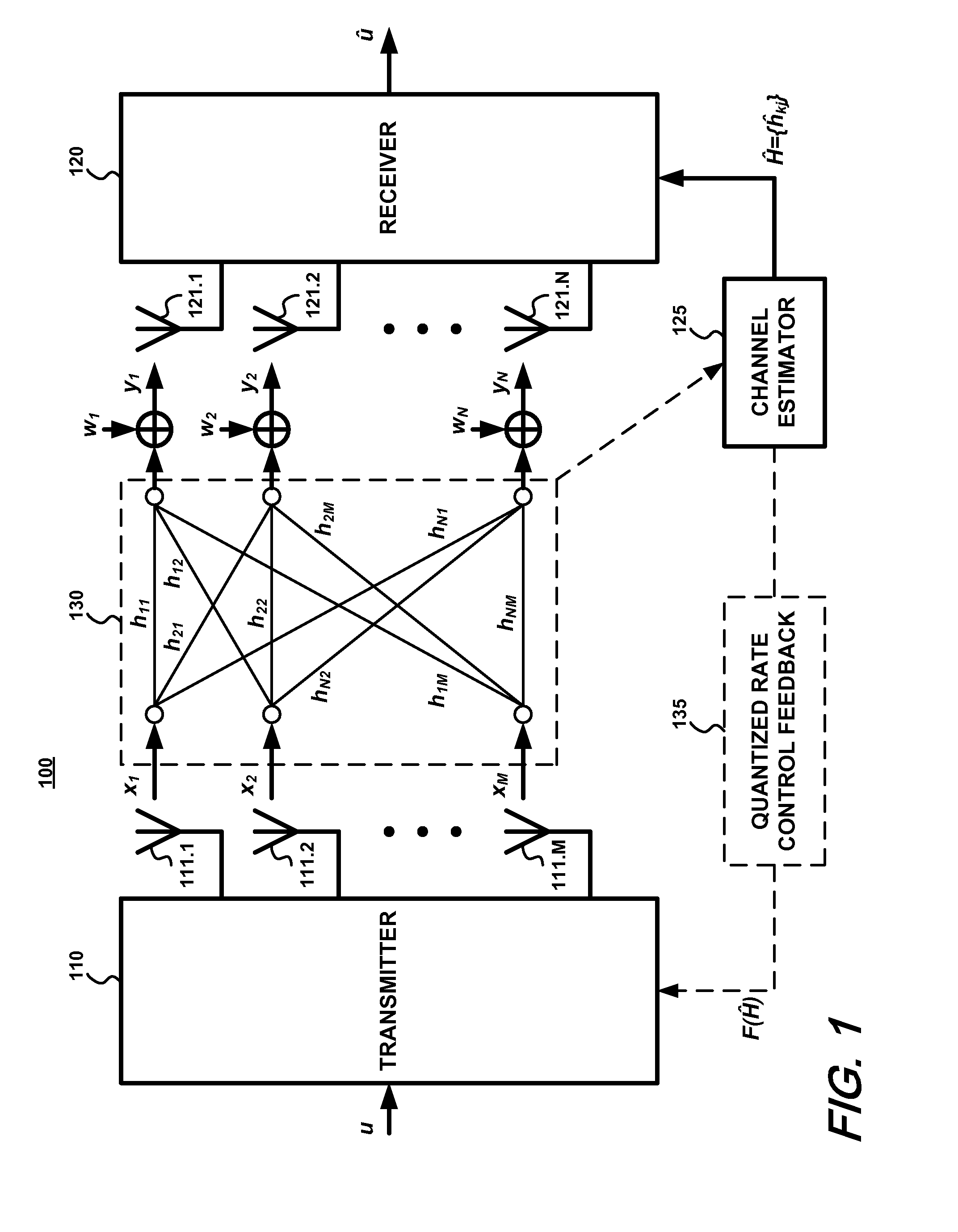
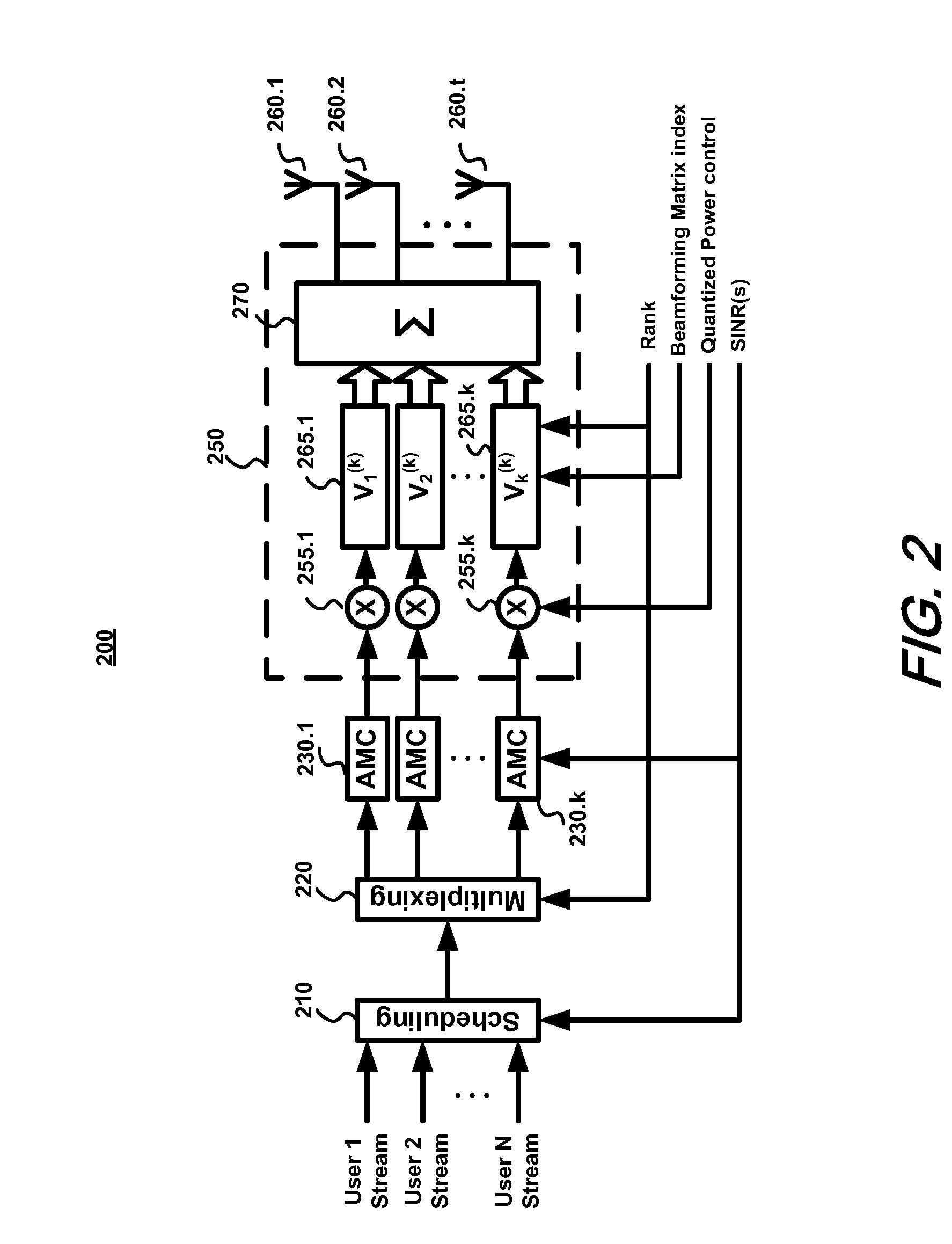
Structured codebook and successive beamforming for multiple-antenna systems
ActiveUS20070191066A1Reduce complexityLow feedback rateMultiple-port networksPower managementTransmitted powerUser equipment
A quantized multi-rank beamforming scheme for multiple-antenna systems such as a multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) wireless downlink. User equipment (UE) estimates downlink channel and transmit power and determines rank and power allocations. A quantized beamforming matrix is then determined by the UE using successive beamforming. The UE also determines channel quality indices (CQI) which it feeds-back to the wireless downlink base station along with the index of the quantized beamforming matrix. The base station uses the CQI information to select a UE for scheduling of downlink transmission and the quantized beamforming matrix index received from the selected UE to beamform the downlink transmission to the UE. Base station overhead and is minimized while providing near-optimal performance given the constraints of a limited feed-back channel and computational complexity of the UE.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus of codebook-based single-user closed-loop transmit beamforming (SU-CLTB) for OFDM wireless systems
ActiveUS20090041150A1Improve throughputMaximize signal to noise ratioMultiple-port networksAntenna arraysCommunications systemClosed loop
A method includes broadcasting, at a transmitter, messages comprising antenna configuration, antenna spacing and a number of antenna of the transmitter and reference signals; generating, at a receiver, a codebook comprising a plurality of antenna beams based on the broadcasted messages; receiving, at the receiver, the broadcasted reference signals; selecting, at the receiver, an antenna beam among the plurality of antenna beams within the codebook in dependence upon a predetermined performance criteria of a data communication system and in dependence upon the broadcasted reference signals; feedbacking to the transmitter, at the receiver, information comprising the antenna beam selected by the receiver; optimizing, at the transmitter, a beamforming process by utilizing the feedback information from the receiver; transmitting, at the transmitter, data signals by utilizing the optimized beamforming process; and receiving and processing, at the receiver, the data signals in dependence upon the selected antenna beams within the codebook.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
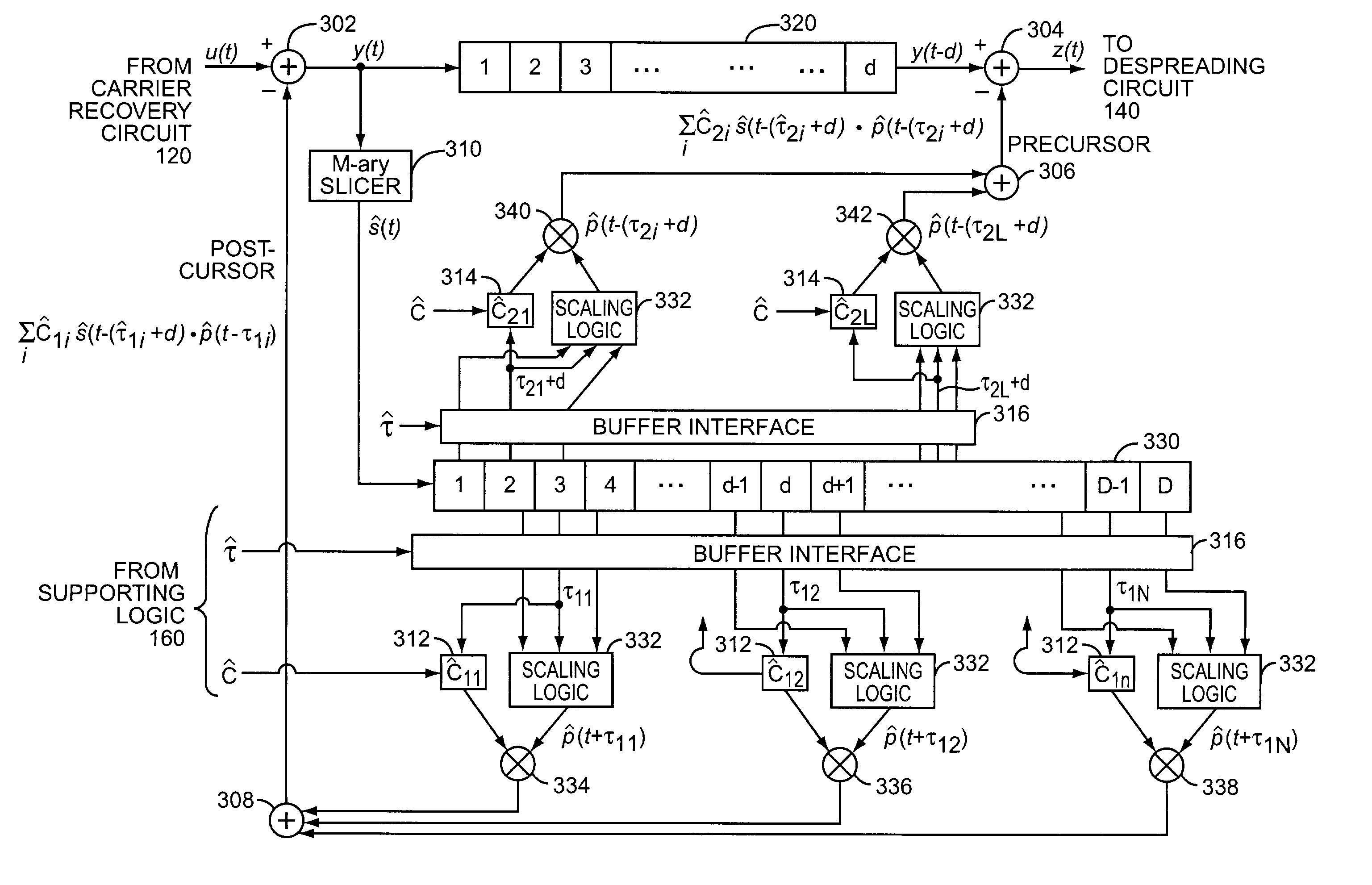
Method and apparatus for multipath signal compensation in spread-spectrum communications systems
ActiveUS7054396B2Effective multipath signal compensationChange effective lengthMultiple-port networksError preventionCommunications systemImage resolution
The equalizer of the present invention operates on input multipath signal samples, preferably at chip or sub-chip resolution, to remove or substantially cancel the effects of one or more secondary signals from the main path signal. Using predetermined path information for one or more of the secondary path signals, including magnitude, phase, and time offset relative to the main path signal, the equalizer compensates input multipath signal samples by subtracting estimated secondary signal values from the input samples. For each input sample, the equalizer forms a sliced sample, where the sliced sample represents a nominal phase value defined by the modulation scheme used in the original chip or symbol transmission that is closest in value to the actual phase of the input sample. These sliced samples are held in a running buffer and used, in combination with the predetermined path information and scaling logic, to form the estimated secondary signal values for compensating the input samples.
Owner:QORVO US INC
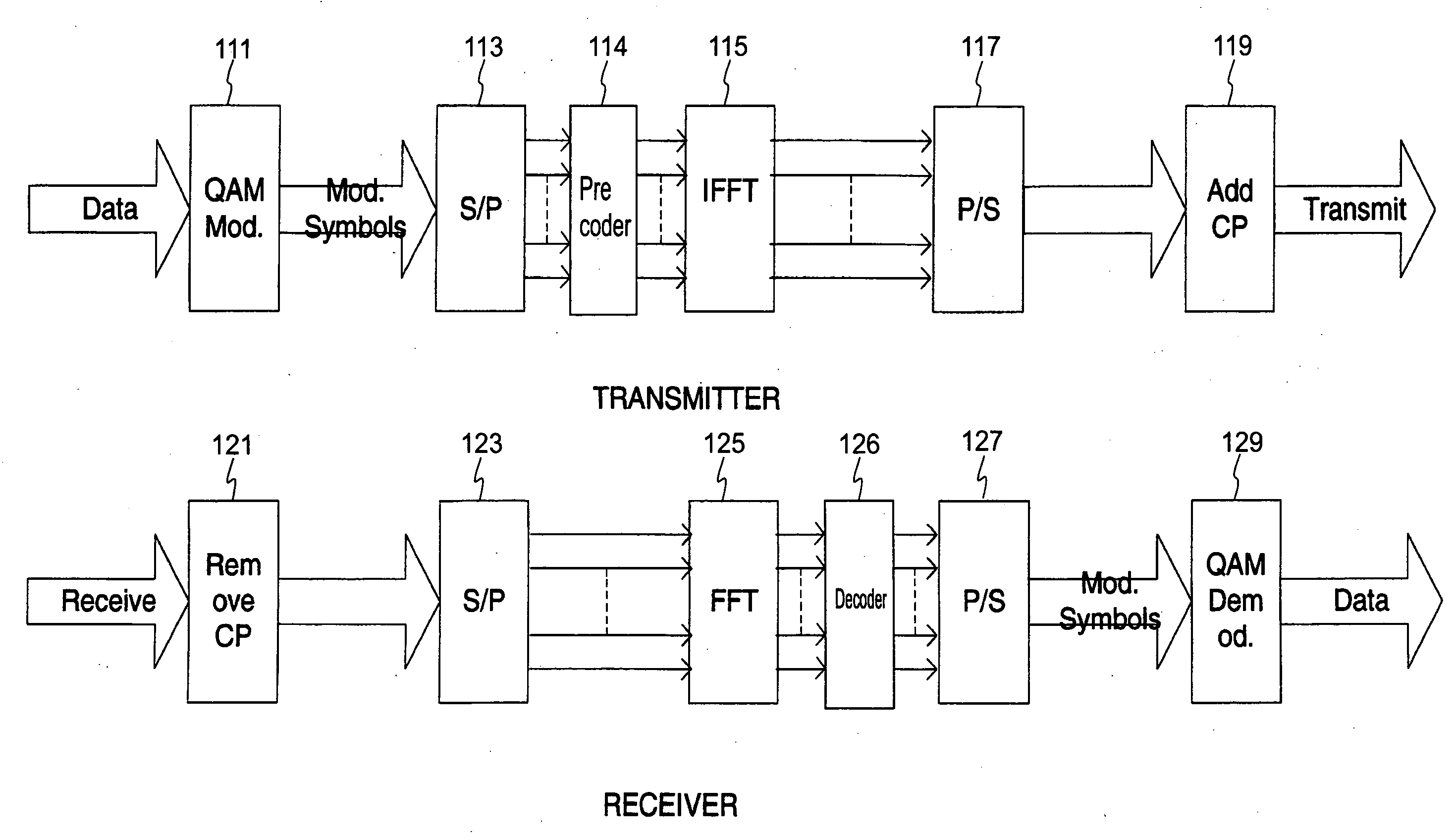
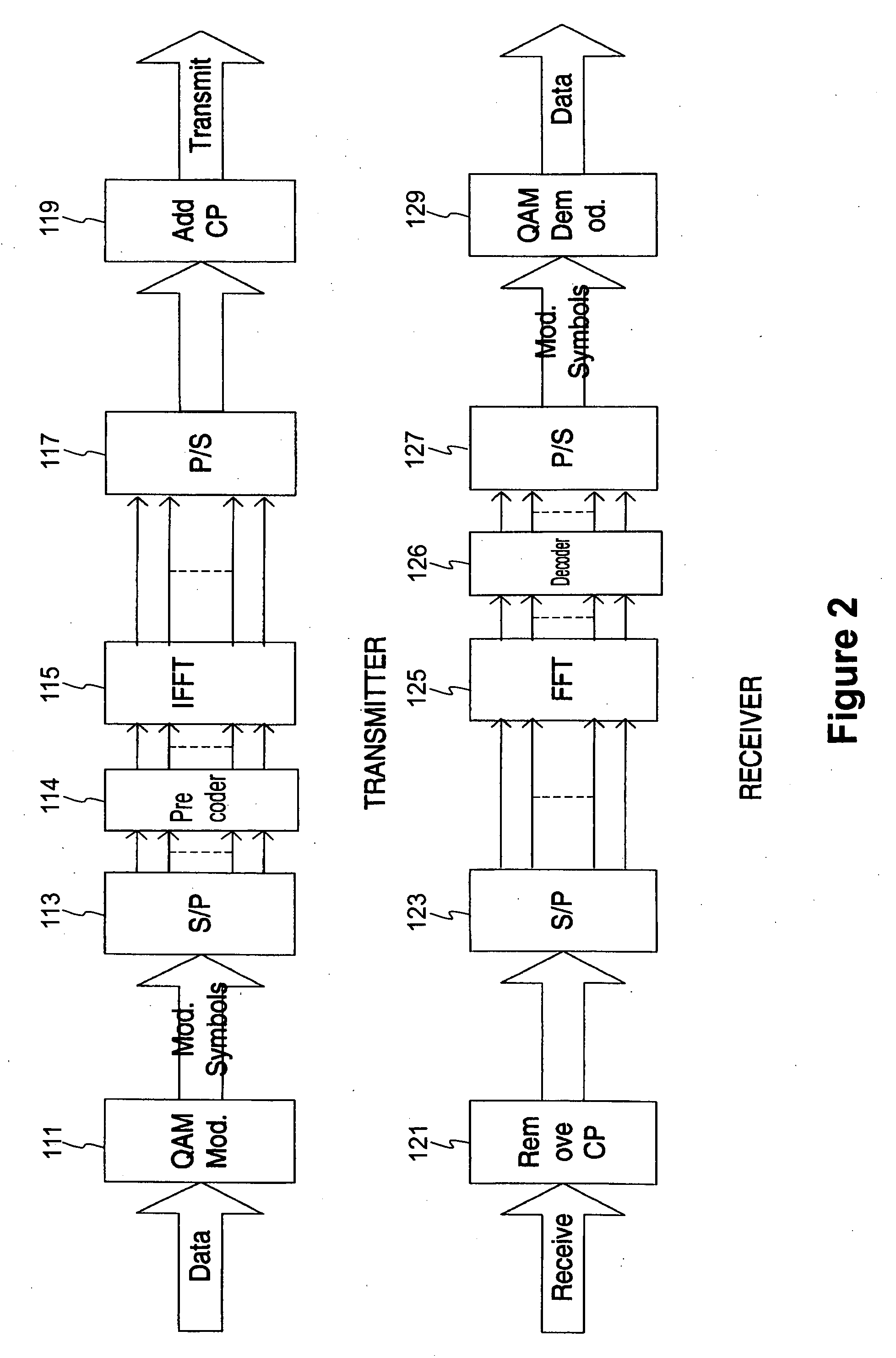
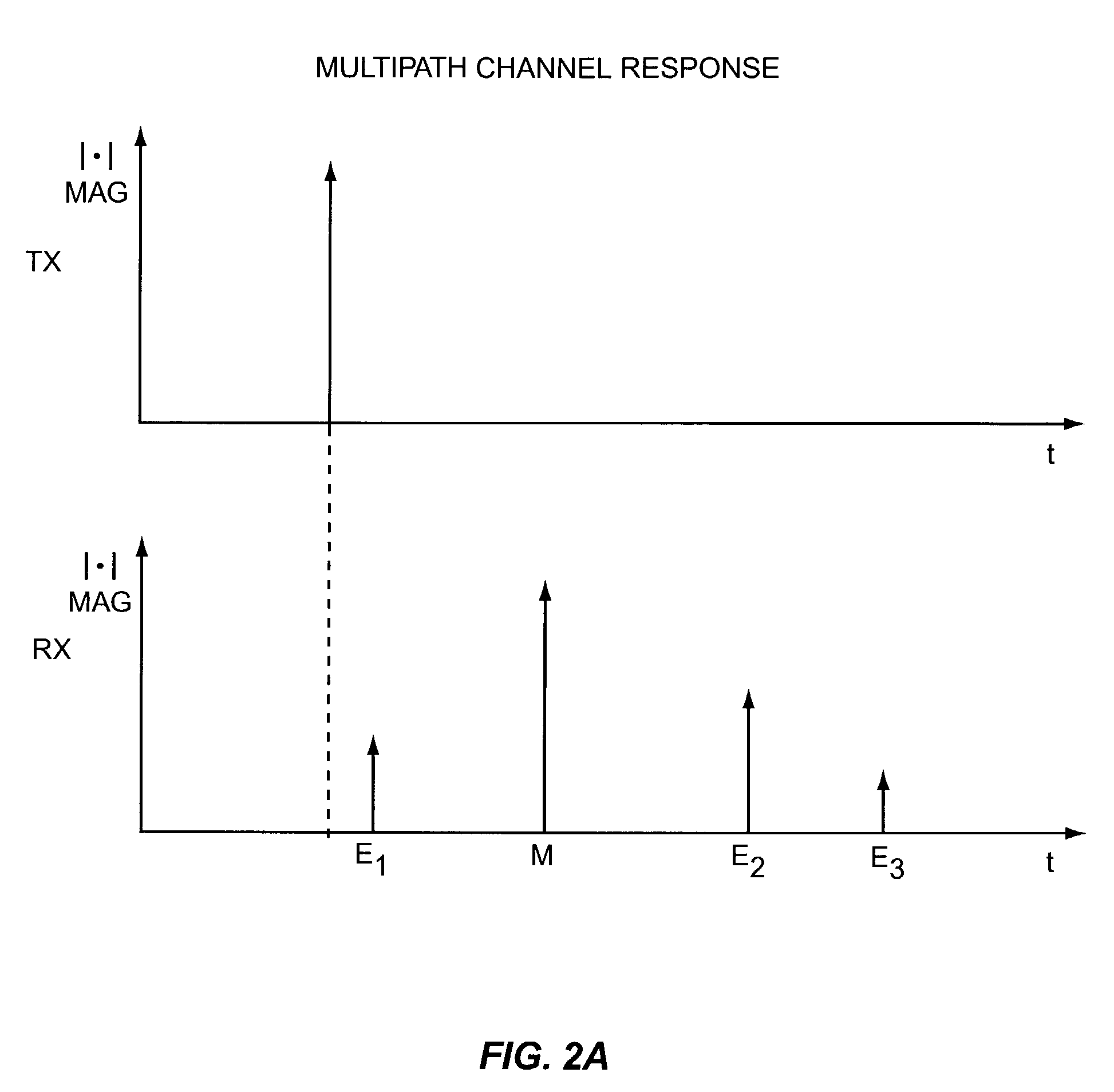
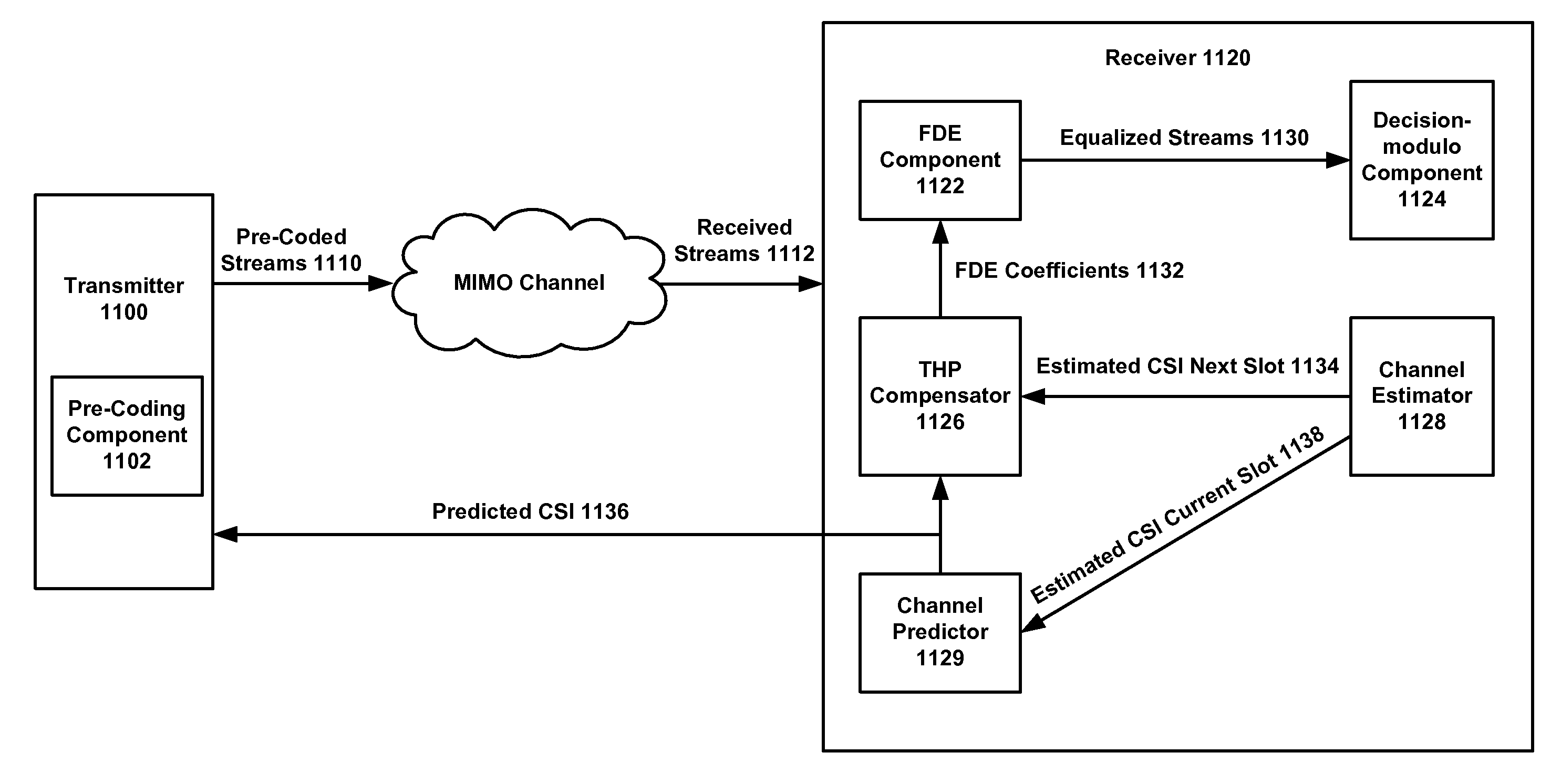
Frequency domain equalization with transmit precoding for high speed data transmission
InactiveUS20090122854A1Avoid error problemsMaximum performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMIMOSC-FDE
Various embodiments of multi input multi output (MIMO) communication systems include a transmit Tomlinson-Harashima Precoding (THP) technique and a single carrier frequency domain equalization (SC-FDE) technique. Parallel THP-FDE and successive THP-FDE are proposed based on the minimum mean square error (MMSE) criterion. For the successive THP-FDE technique, where all transmit streams are subsequently precoded, both suboptimal and optimal MMSE ordering algorithm are set forth. Since the feedback processing is performed at the transmitter, no error propagation problem exists in the THP-FDE MIMO techniques, yielding significant performance improvements over conventional FDE MIMO techniques. Applying channel prediction and THP compensation techniques can also further enhance performance.
Owner:YIM TU INVESTMENTS
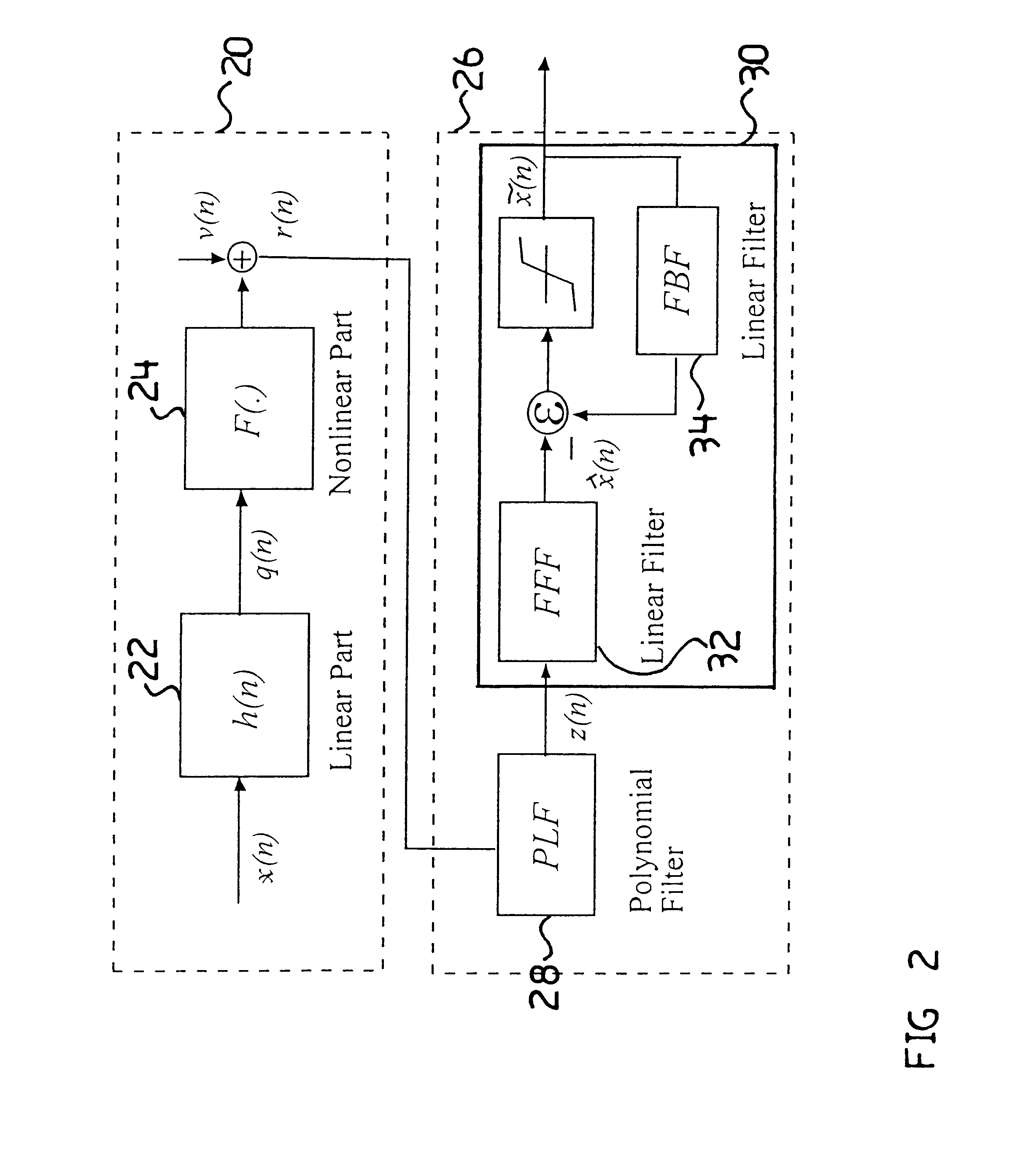
Method and apparatus for adaptively compensating channel or system variations in precoded communications system
InactiveUS6400761B1Reduce distractionsImprove performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPrecodingCommunications system
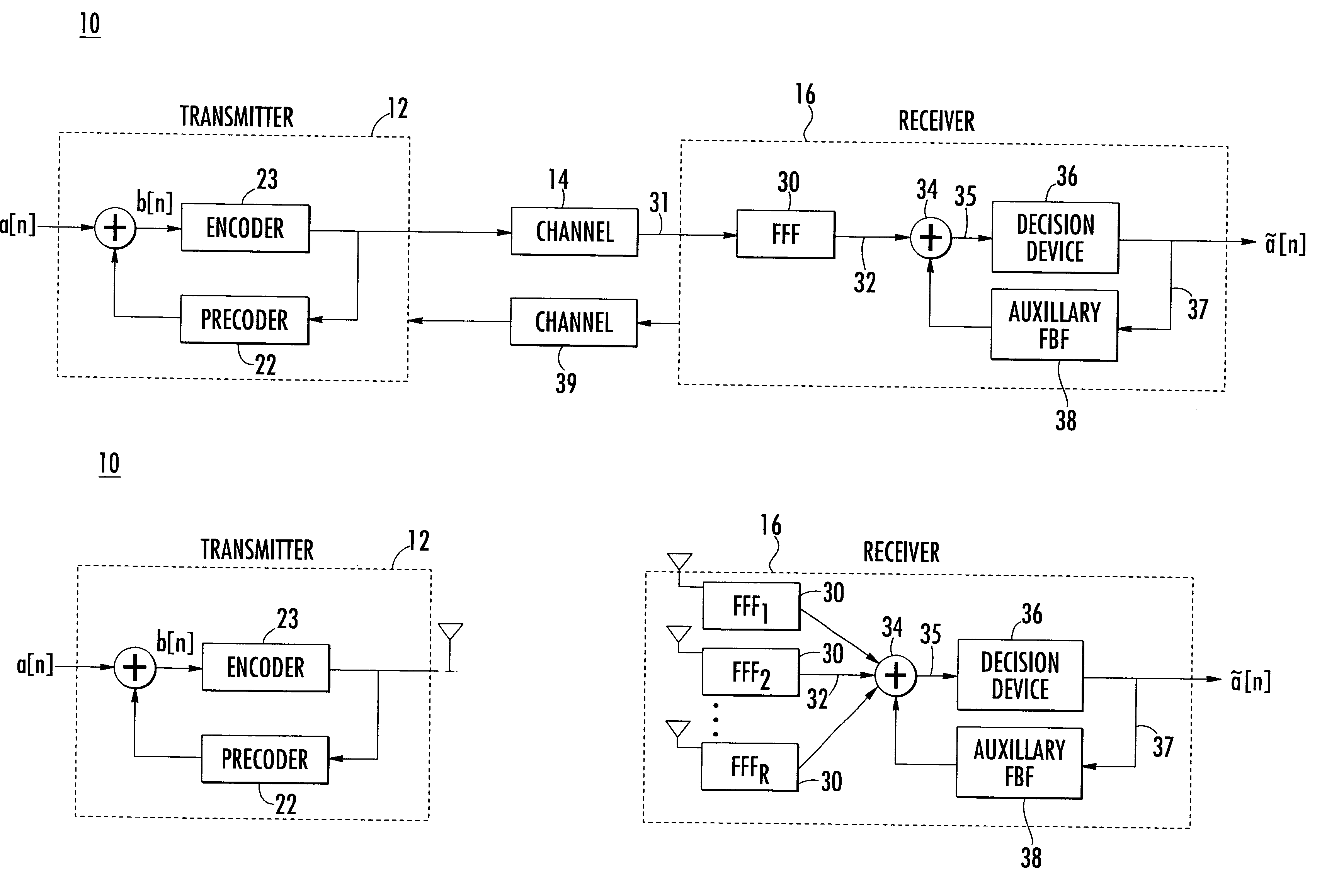
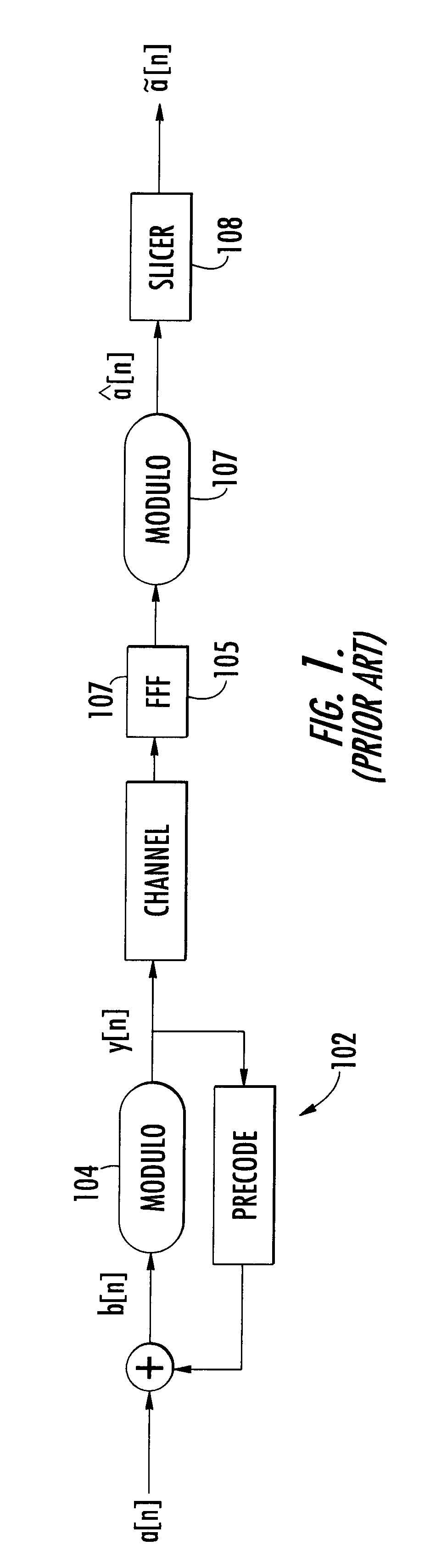
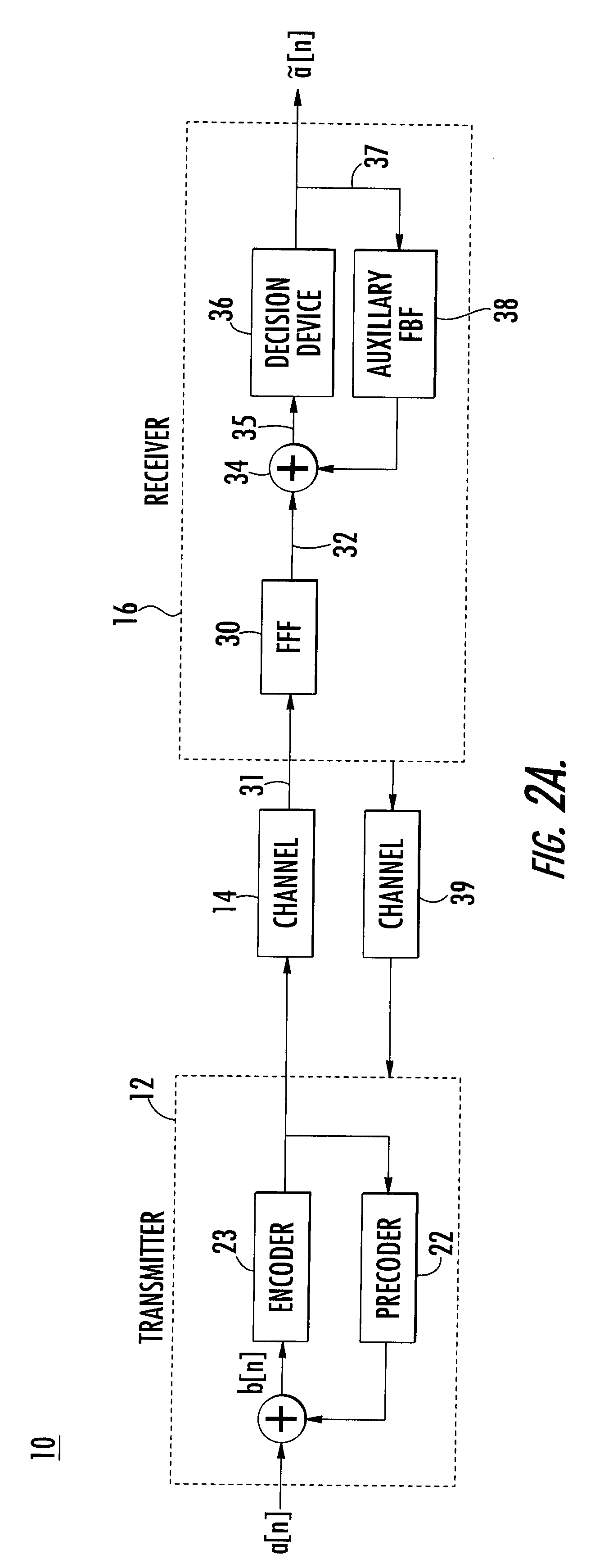
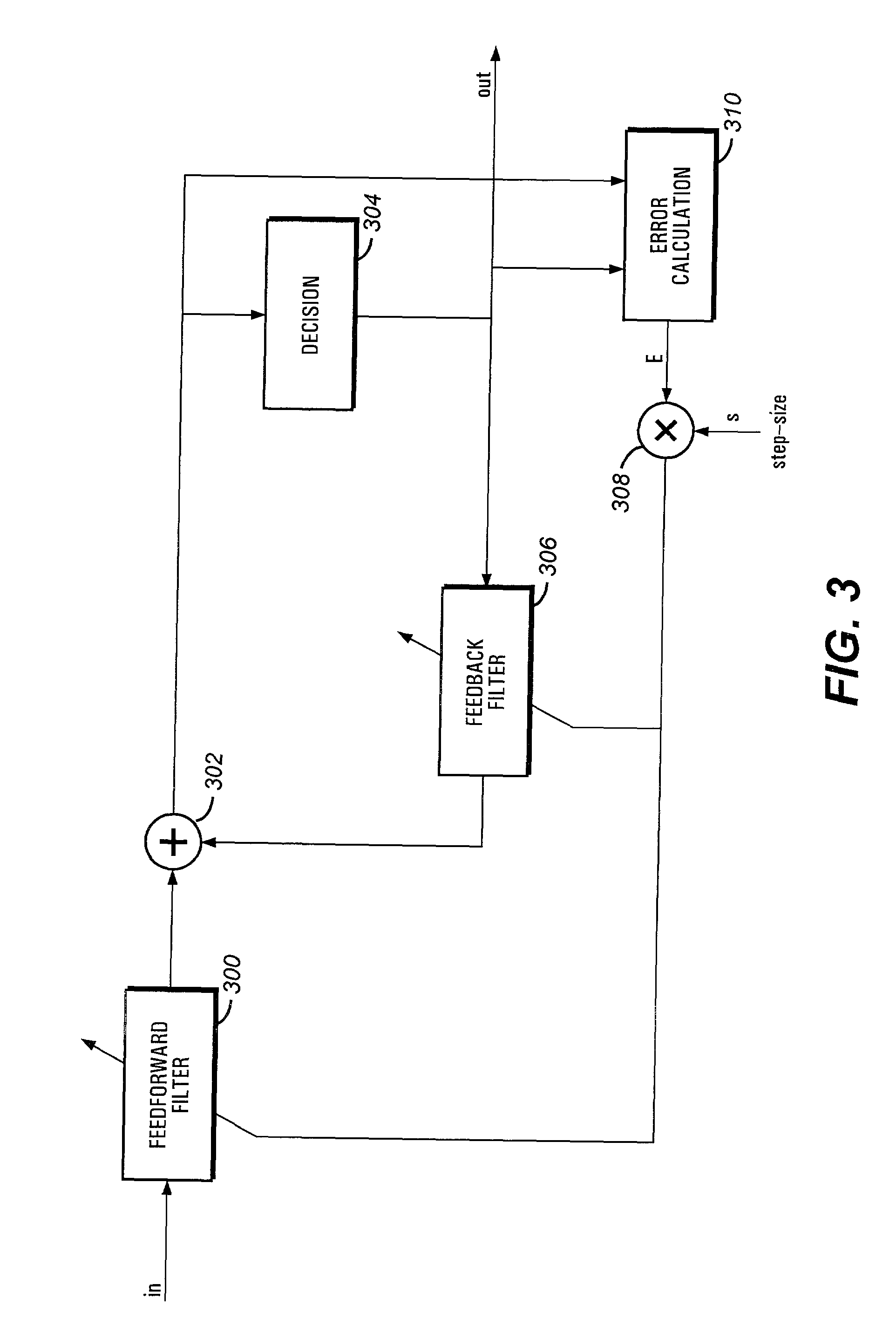
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for adaptively compensating for channel or system variations in which adaptive compensation is used in the receiver of a digital communication system. The transmitter of the digital communication system includes precoding. The adaptive receiver compensation mitigates the interferences not removed by the transmitter precoder. In an embodiment of the invention, the adaptive compensation can be performed using an adaptive feedforward filter (FFF) and a feedback filter (FBF) in the receiver. The FBF output is generated based on previous values of estimates of the transmitted precoded sequence. The determined value of the FBF coefficients can be periodically relayed to the transmitter to update the precoder coefficients of the transmitter. Alternatively, the value of the FBF coefficients can be relayed to the transmitter after the value of the coefficients exceeds a predetermined threshold. Accordingly, the receiver adaptively and automatically compensates for misadjustments of the fixed transmitter precoder with respect to the actual channel at a given point in time.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Statistically-Adapted Receiver and Transmitter Equalization
InactiveUS20100329325A1High error rateReduce error rateMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTraining periodData integrity
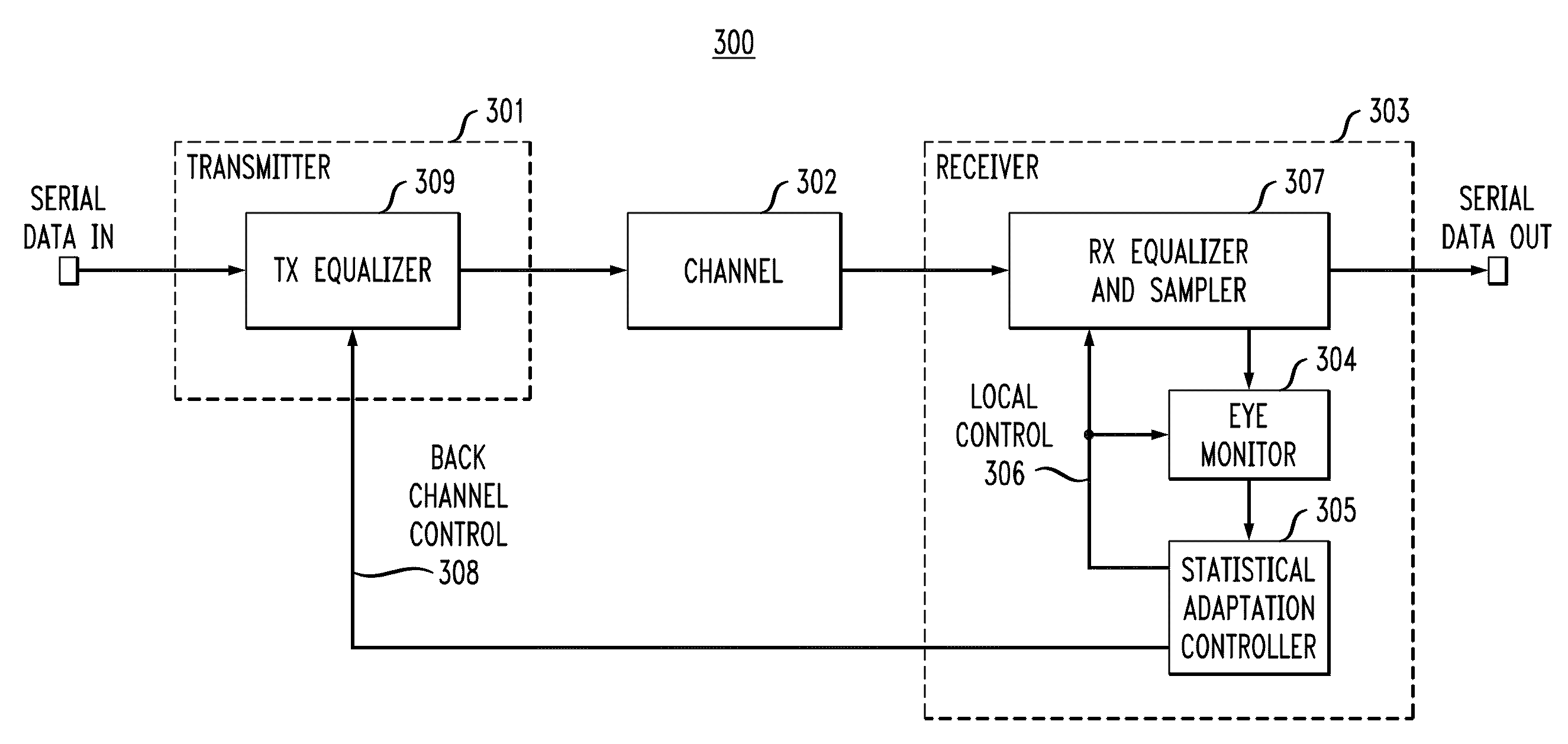
In described embodiments, adaptive equalization of a signal in, for example, Serializer / De-serializer transceivers by a) monitoring a data eye in a data path with an eye detector for signal amplitude and / or transition; b) setting the equalizer response of at least one equalizer in the signal path while the signal is present for statistical calibration of the data eye; c) monitoring the data eye and setting the equalizer during periods in which received data is allowed to contain errors (such as link initiation and training periods) and periods in which receive data integrity is to be maintained (such as normal data communication).
Owner:LSI CORPORATION
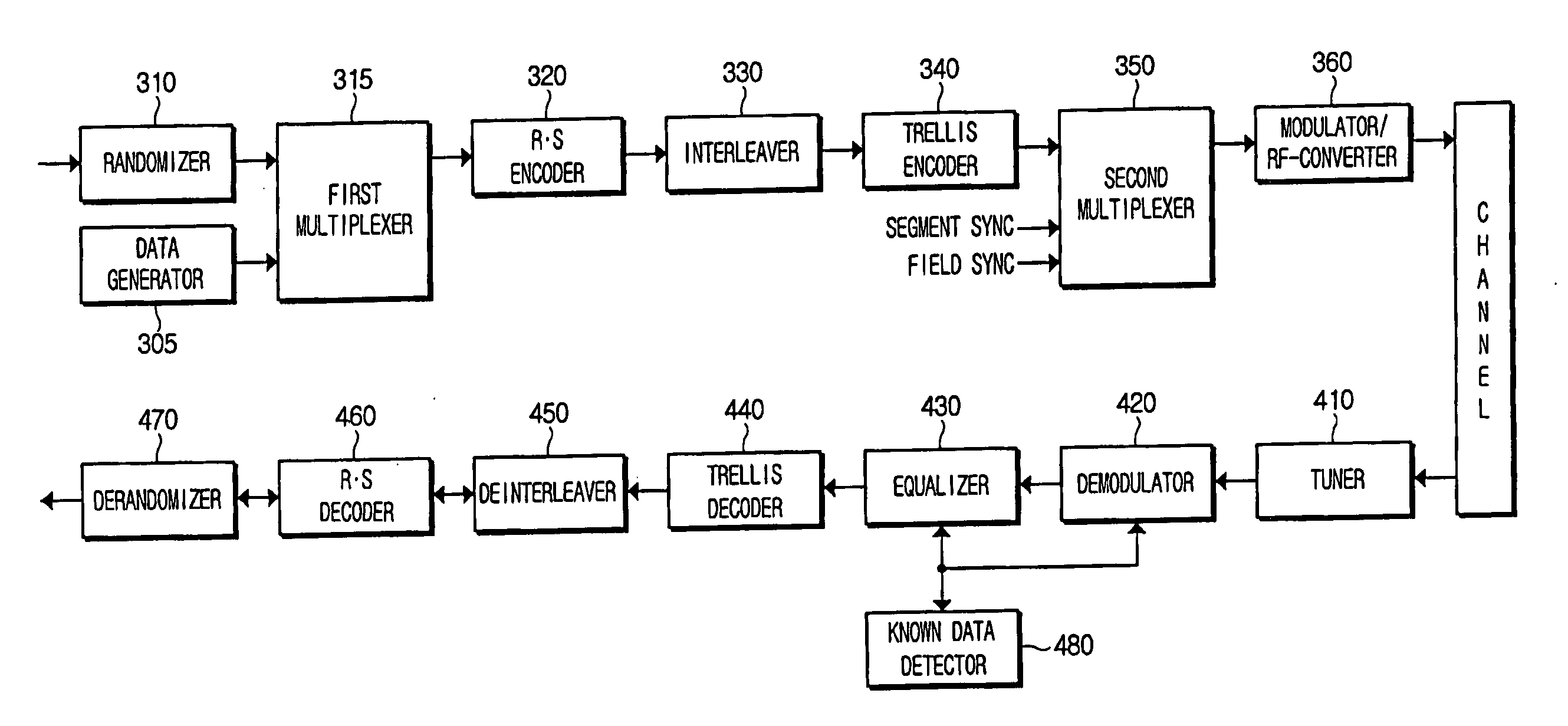
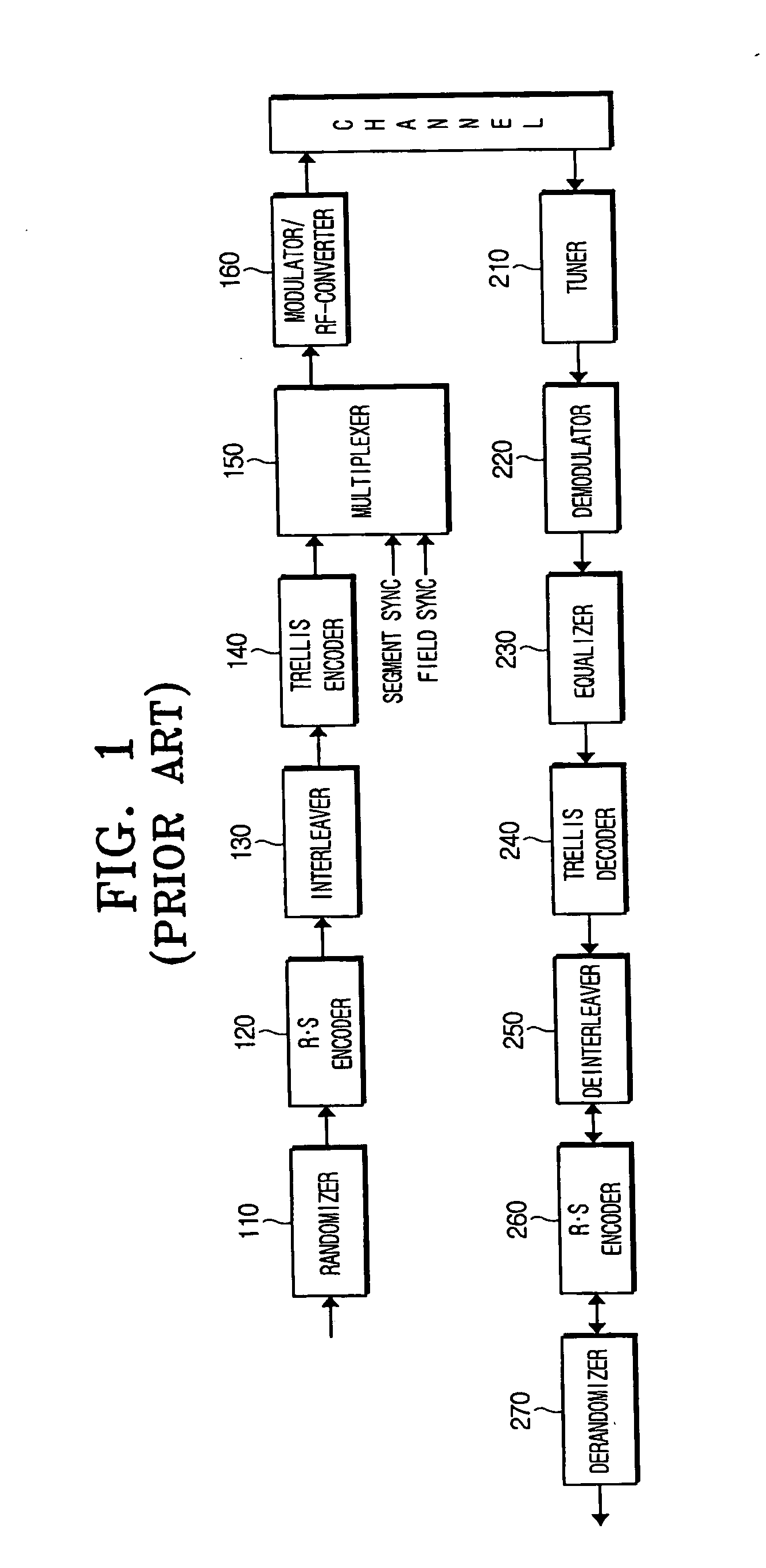
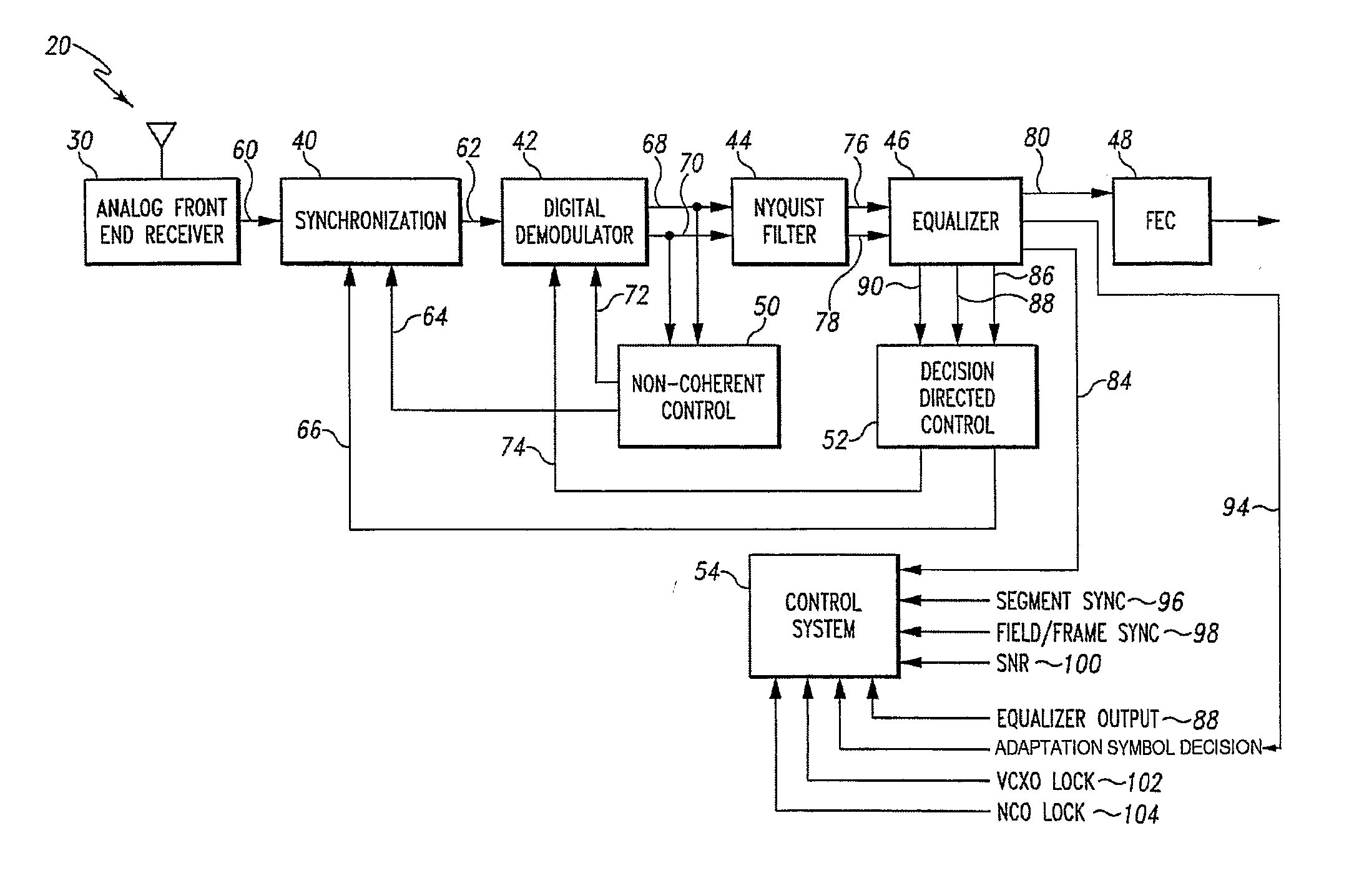
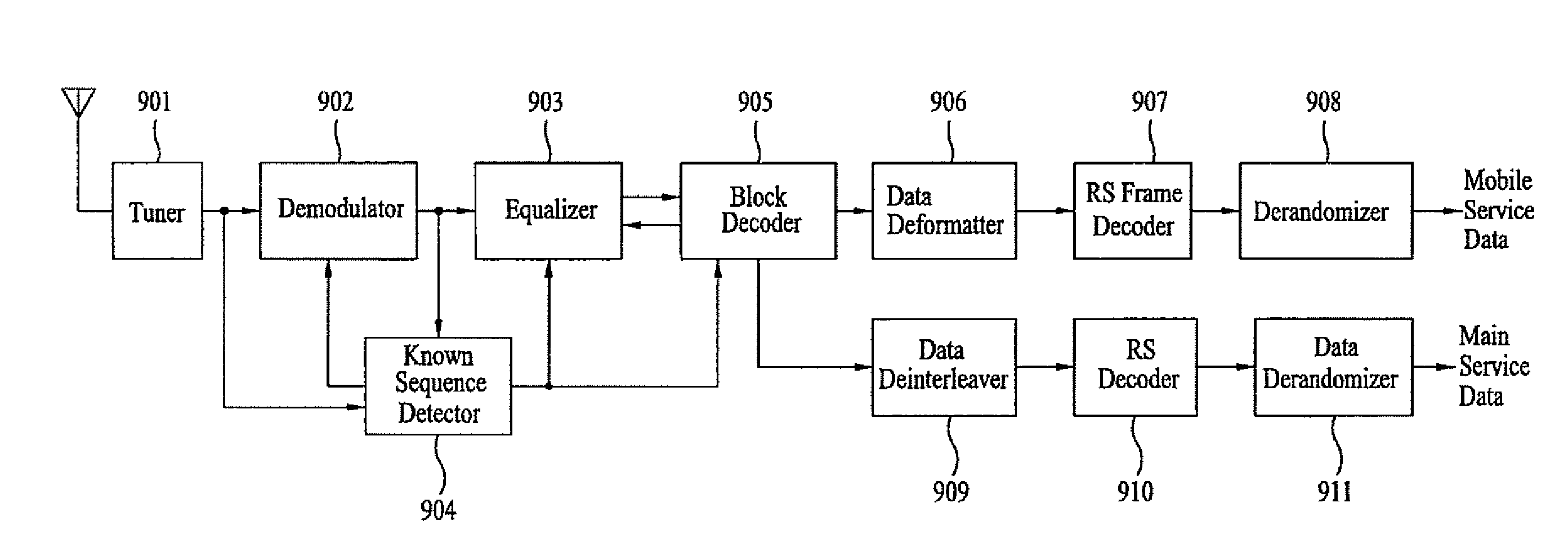
Digital broadcast transmitting/receiving system having an improved receiving performance and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS20050162886A1Improve reception performanceMultiple-port networksError preventionData streamMultiplexer
A digital broadcast transmitting / receiving system and a signal processing method thereof that can improve the receiving performance of the system. A digital broadcast transmitter has a randomizer to randomize an input data stream which has null bytes being inserted at a specified position, a multiplexer to output a data stream formed by inserting specified known data into the position of the null bytes of the randomized data stream, an encoder to encode the data stream outputted from the multiplexer, and a modulator / RF-converter to modulate the encoded data, RF-convert the modulated data and transmit the RF-converted data. The receiving performance of the digital broadcast transmitting / receiving system can be improved even in a multi-path channel by detecting the known data from the received signal and using the known data in synchronization and equalization in a digital broadcast receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
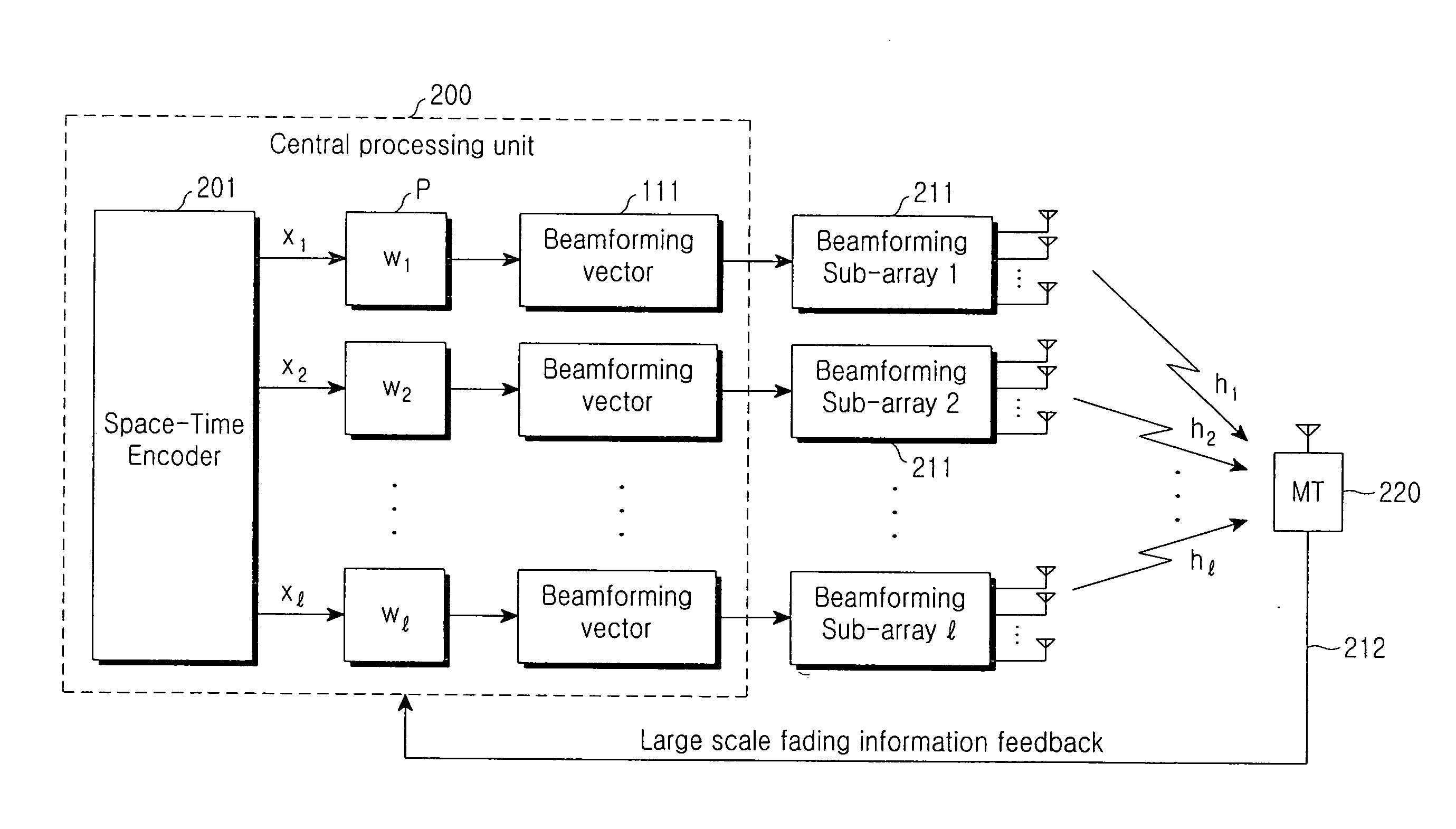
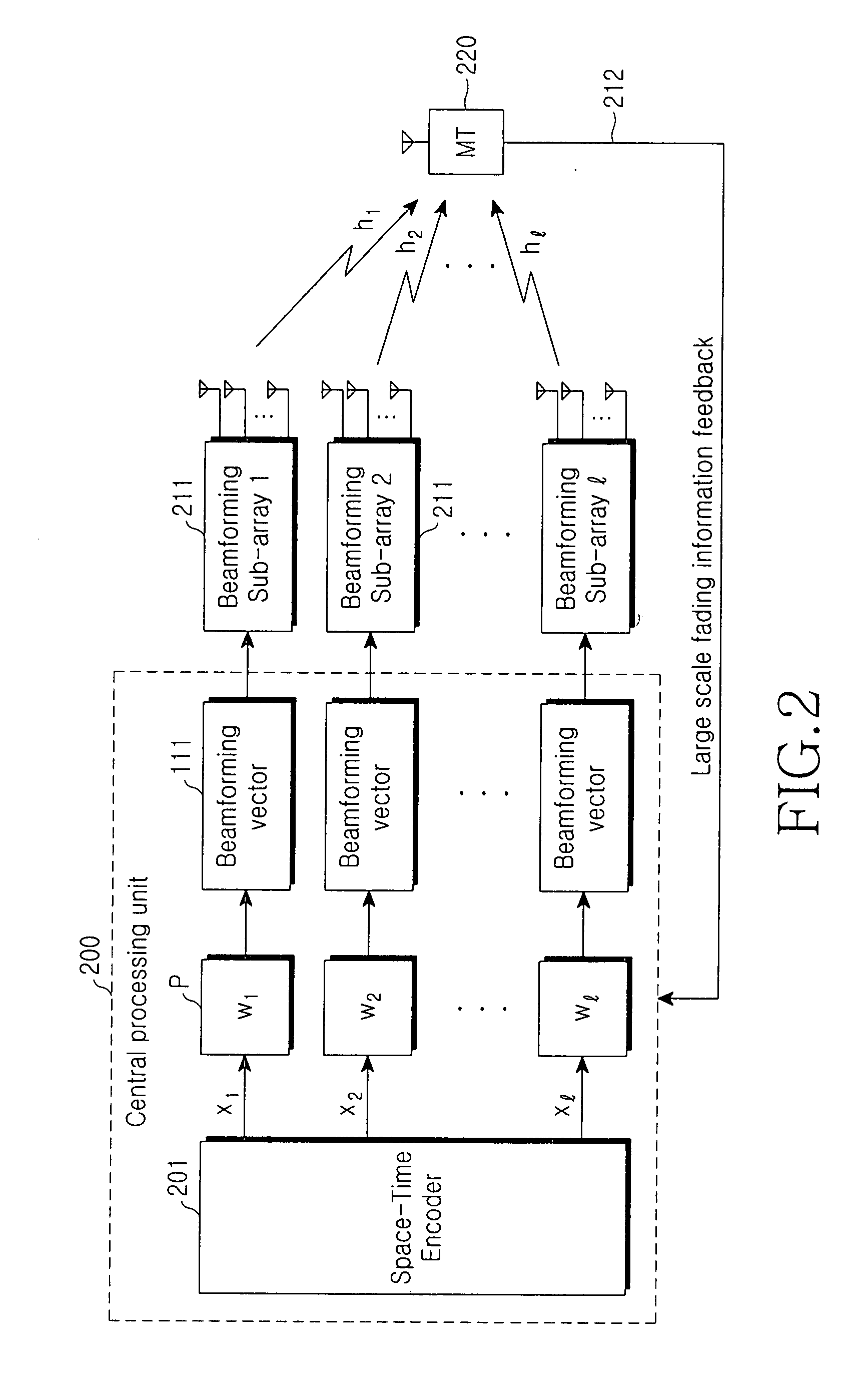
Method and apparatus of adaptively allocating transmission power for beamforming combined with orthogonal space-time block codes based on symbol error rate in distributed wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080117961A1Minimizing symbol error rateImprove performanceMultiple-port networksPower managementCommunications systemSymbol error rate
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for adaptively allocating transmission power for beamforming combined with orthogonal space-time block codes (OSTBC) in a distributed wireless communication system, the apparatus comprising: a plurality of sub-arrays for beamforming, which are geographically distributed and each of which comprises a plurality of distributed antennas placed in random groups; and a central processing unit for identifying performances of subsets by applying a predetermined power allocation scheme according to subsets which can be obtained by combining the sub-arrays, by means of a Nakagami fading parameter and information about large-scale fading of each of the sub-arrays, fed back from a receiving party, for determining a subset having a best performance as an optimal subset according to the identified performances, and for performing power allocation based on the subset set as the optimal subset.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
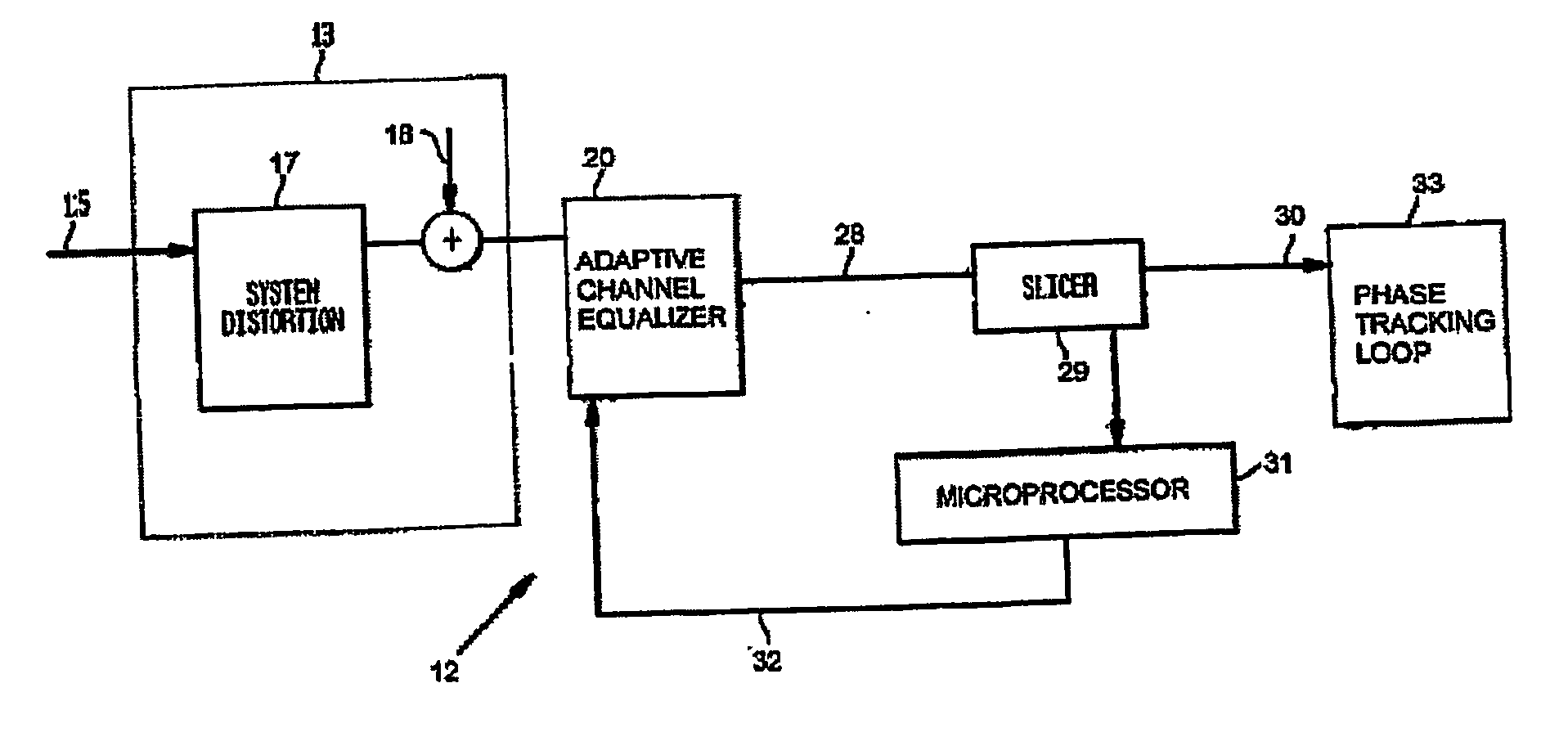
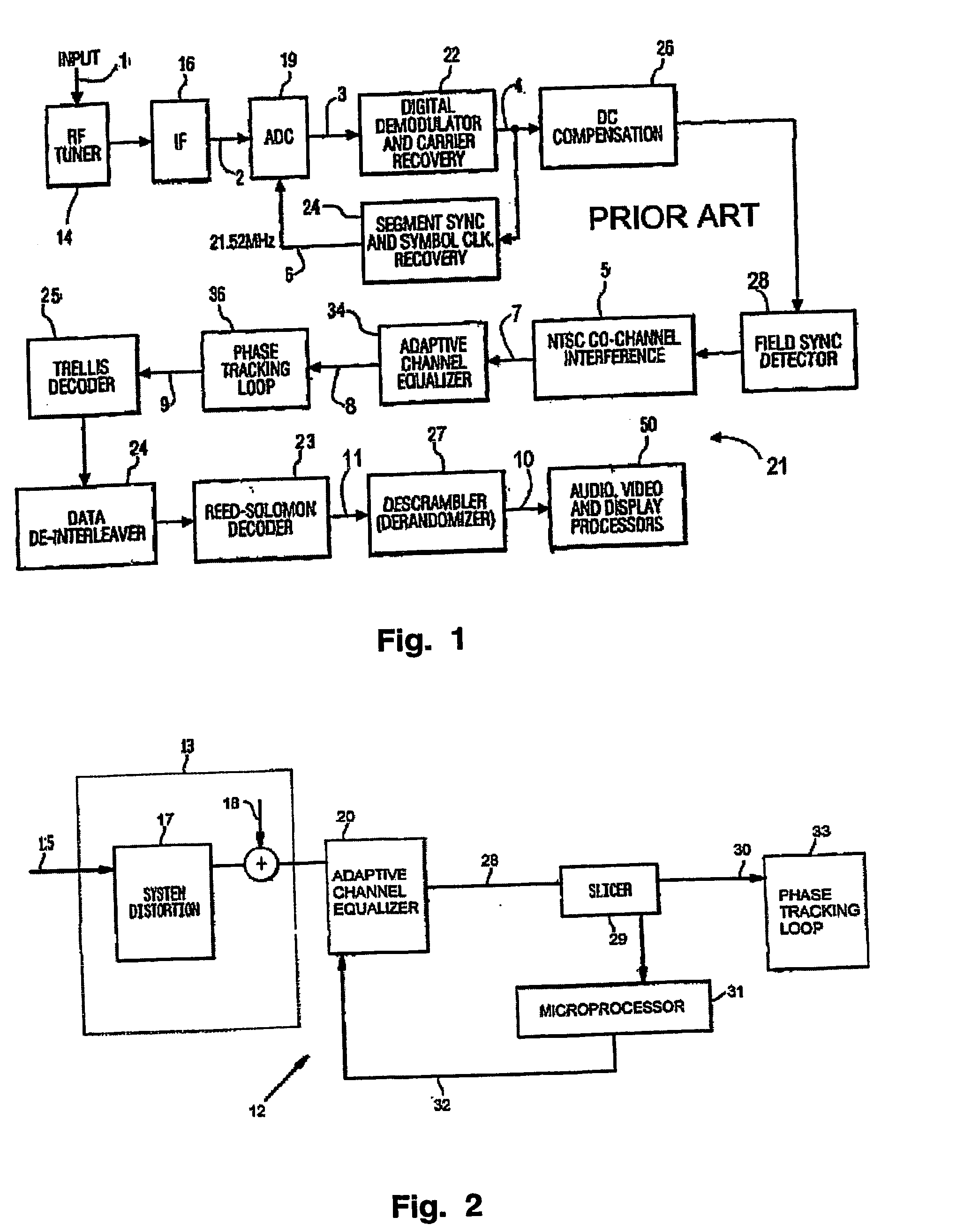
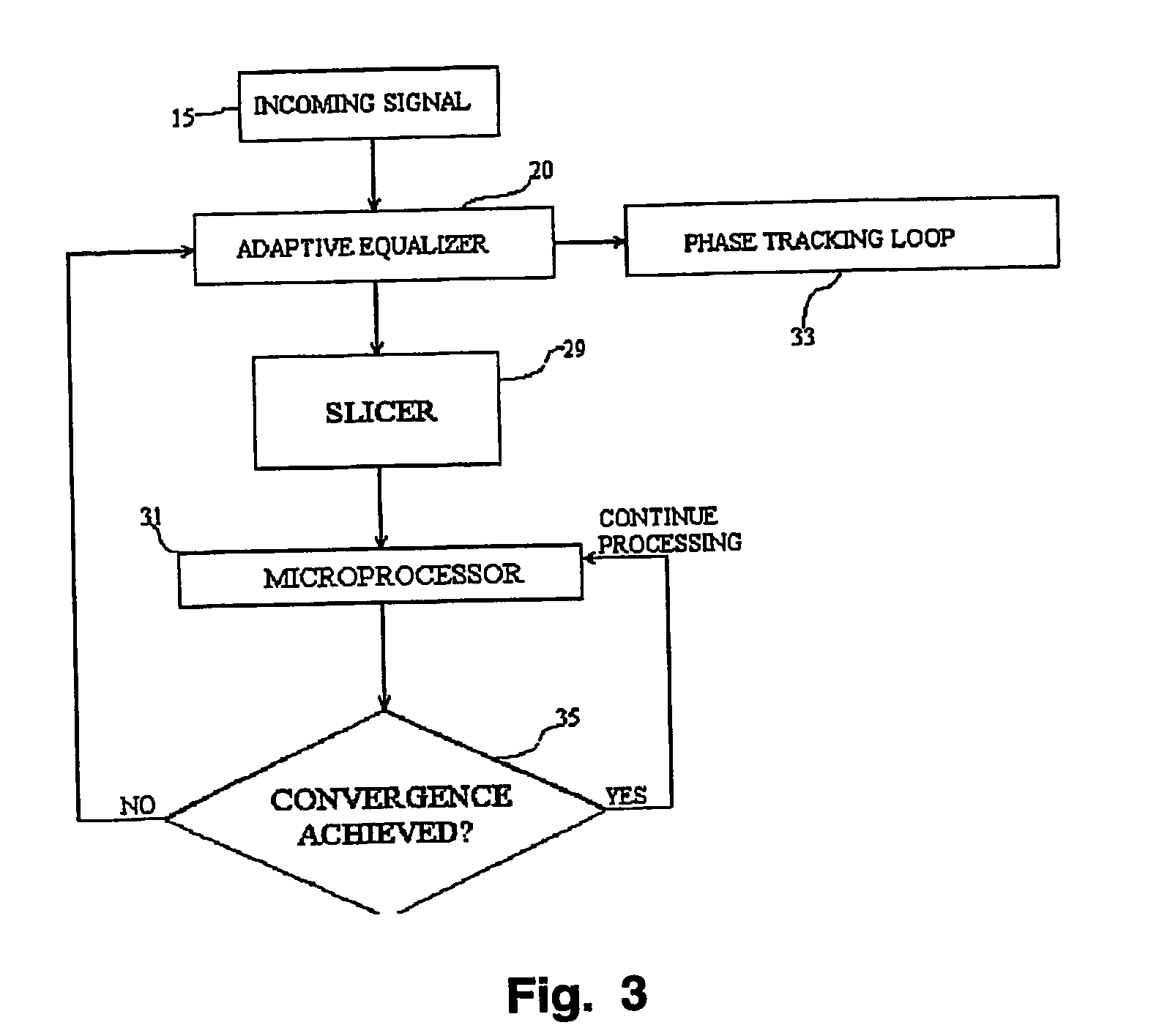
Equalizer status monitor
InactiveUS20050175080A1Reduce complexityThe testing process is simpleTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksEngineeringSelf adaptive
A system for monitoring the output of an adaptive channel equalizer in order to determine if convergence has been achieved. A slicer samples data from the equalizer during a predetermined period. The output data from the slicer is forwarded to a microprocessor in order to apply a test standard to the slicer data. For example, if one of every possible transmitted symbol is detected by the microprocessor, convergence is assumed to have occurred. If the test criterion is not met, a reset signal is sent to the equalizer.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
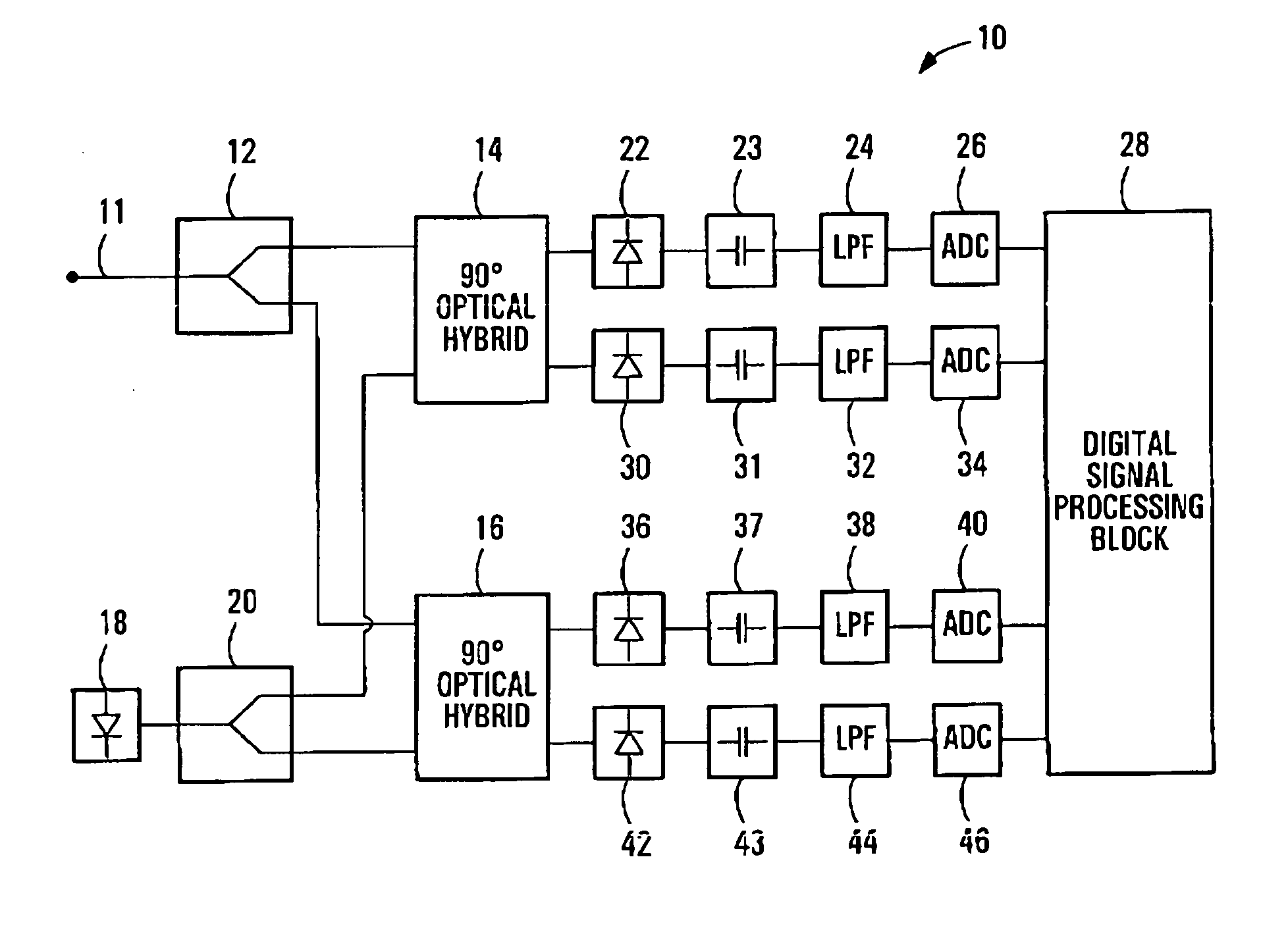
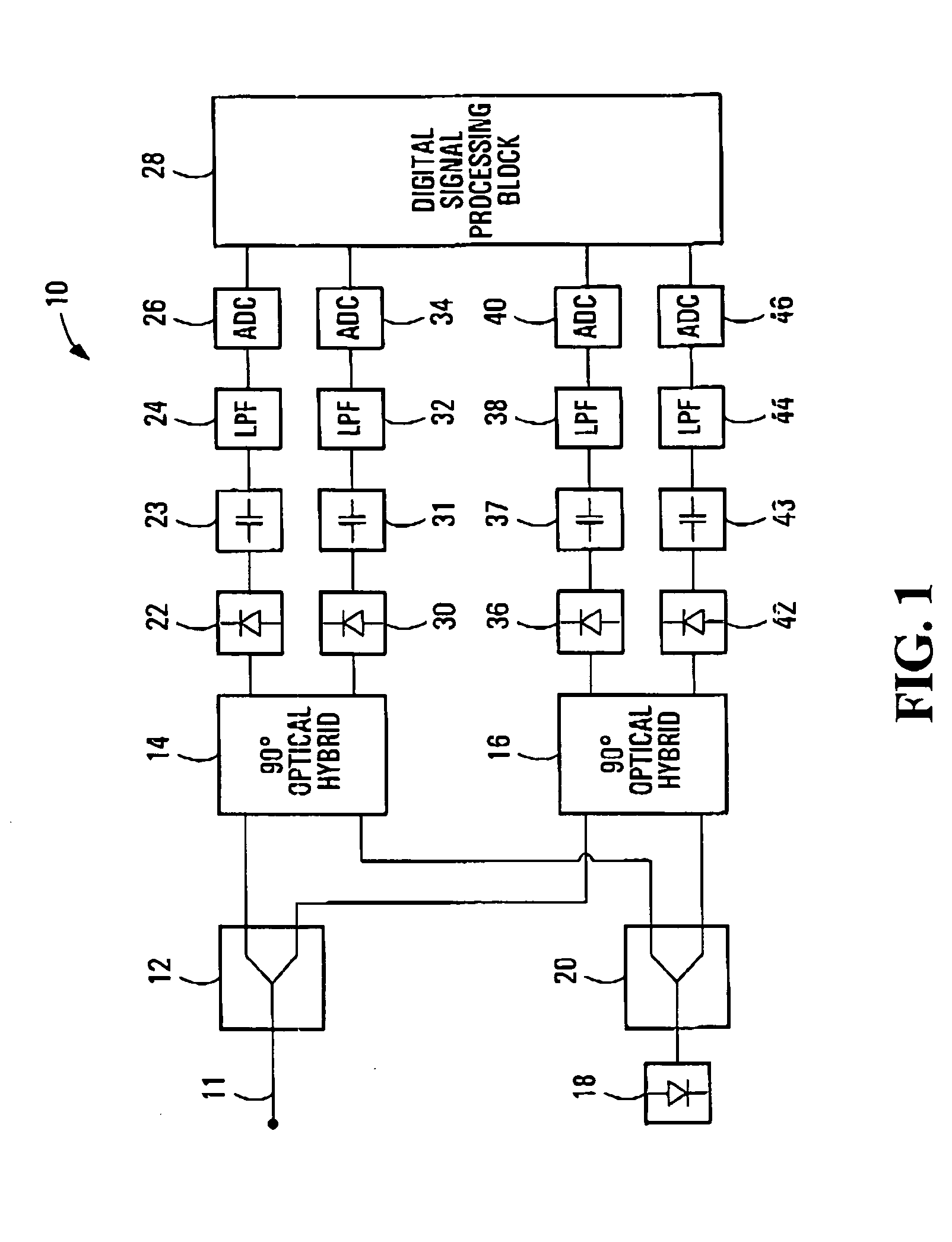
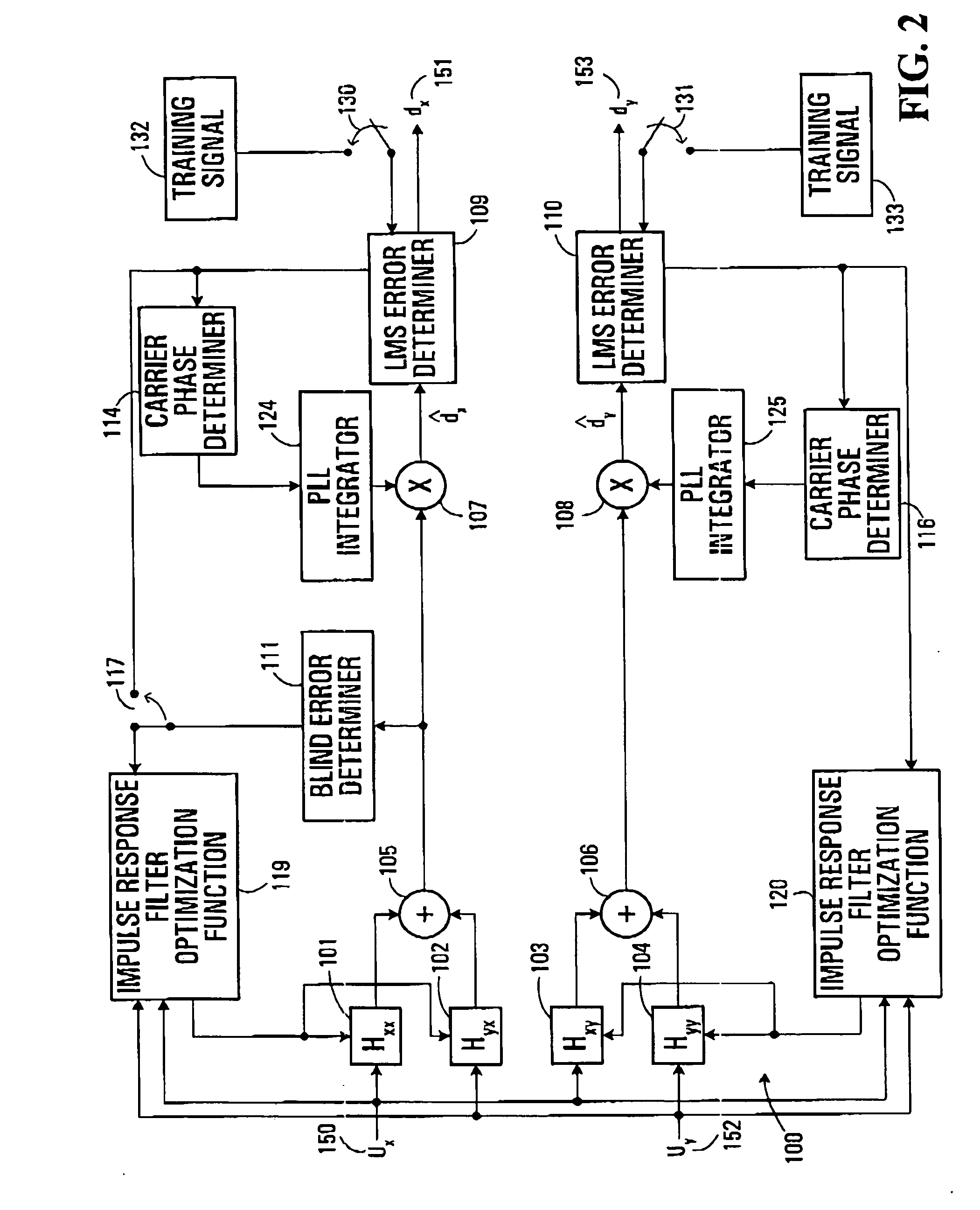
Equalization strategy for dual-polarization optical transport system
ActiveUS20050196176A1Avoid convergencePrevent degradationMultiple-port networksError preventionDigital signal processingSelf recovery
A method is provided for an equalization strategy for compensating channel distortions in a dual-polarization optical transport system wherein the received signal includes a complex signal of a first transmitted polarization component and a complex signal of a second transmitted polarization component. In a first step, a blind self-recovery mode used a blind adaptation algorithm in calculating and modifying multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of only the complex signal of the first transmitted polarization component. By recovering only a single polarization component in the first step the degenerate case of recovering only a single transmitted signal at both polarization component outputs of an equalizer is prevented. In a second step, equalization is performed in a training mode for calculating and modifying the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. In a third step, equalization is performed in a data directed mode for continuing to calculate and modify the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to ensure continued recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. The method is suited for a digital signal processing implementation in a coherent receiver when a modulation scheme used on a transmitted signal is quadriphase-shift keying (QPSK). In other embodiments, the method can be used with modulation schemes such as binary PSK, M-ary PSK where M>4, or Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM).
Owner:CIENA
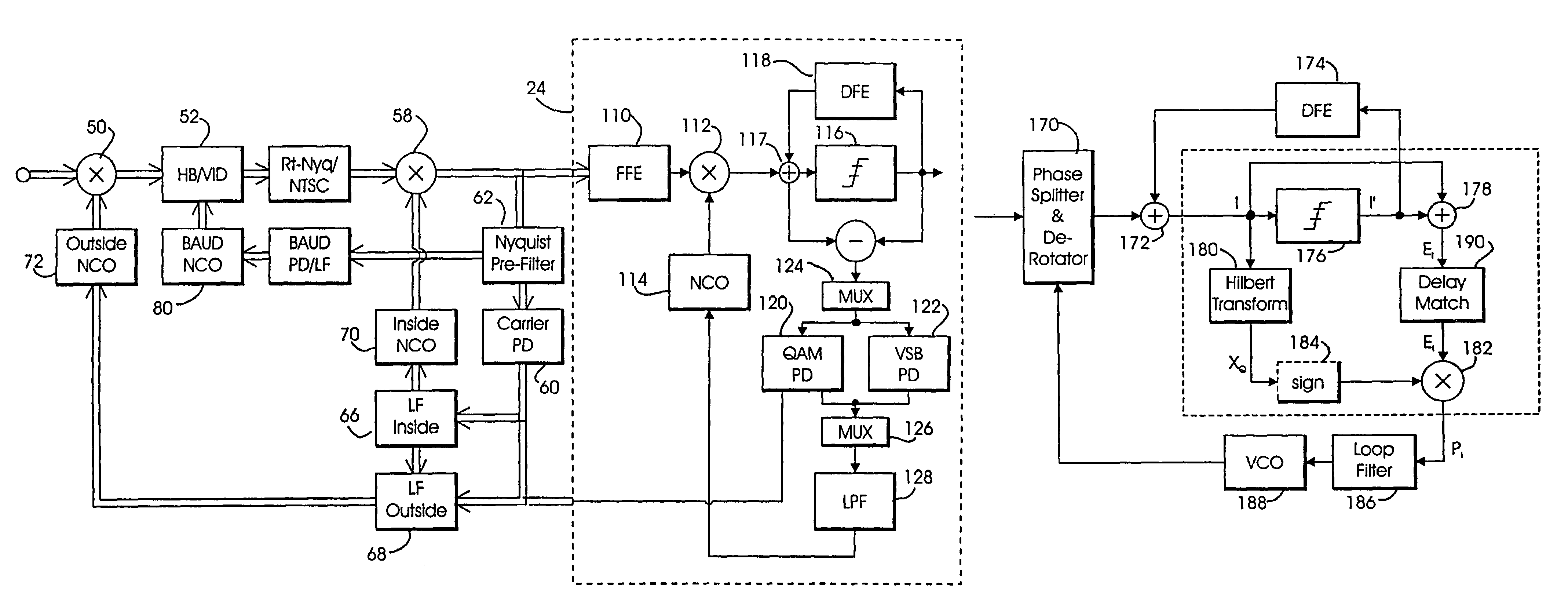
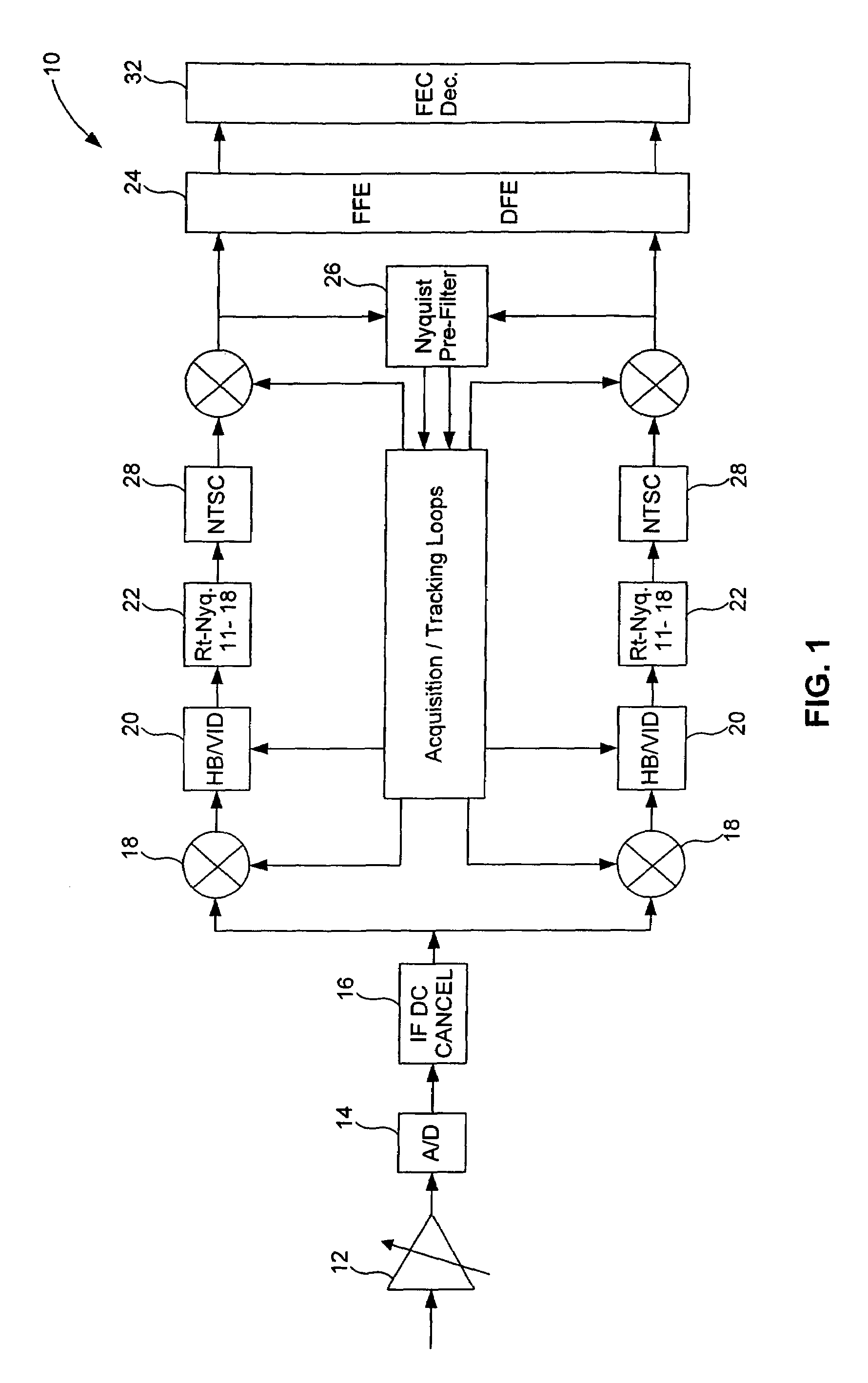
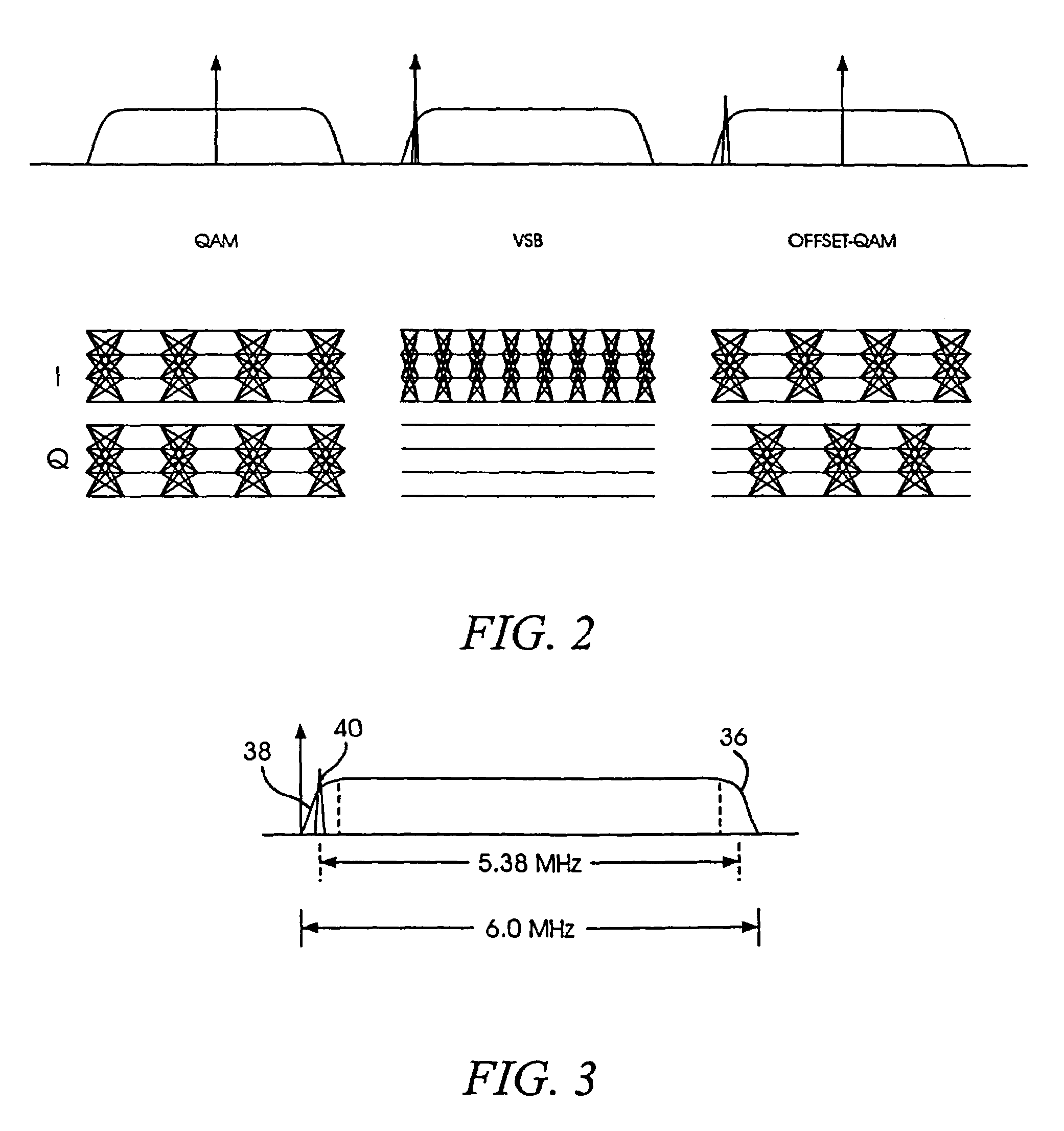
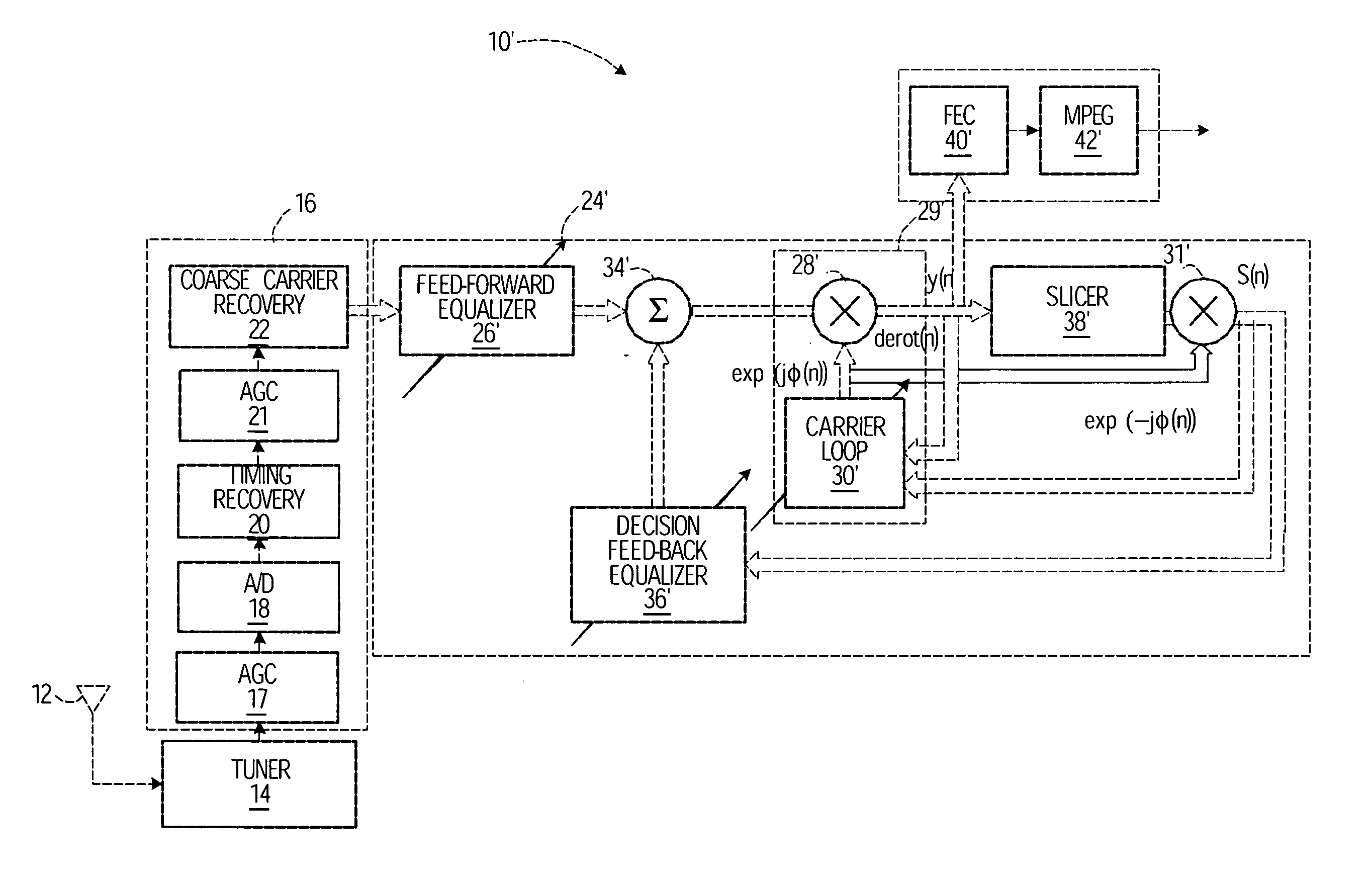
Equalization and decision-directed loops with trellis demodulation in high definition TV
InactiveUS7474695B2Improve reliabilityIncrease delay timeTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksHigh definition tvHigh-definition television
Improved decision feedback equalizer and decision directed timing recovery systems and methods suitable for use in connection with a dual mode QAM / VSB receiver system are disclosed. A trellis decoder operates in conjunction with a decision feedback equalizer circuit on trellis coded 8-VSB modulated signals. The trellis decoder includes a 4-state traceback memory circuit outputting a maximum likelihood decision as well as a number of intermediate decisions based upon the maximum likelihood sequence path. Any number of decisions, along the sequence, may be provided as an input signal to timing recovery system loops, with the particular decision along the sequence chosen on the basis of its delay through the trellis decoder. Variable delay circuitry is coupled to the other input of the timing recovery system loops in order to ensure that both input signals bear the same timestamp. Final decisions are output from the trellis decoder to a DFE in order to enhance the DFE's ability to operate in low SNR environments. A decision sequence estimation error signal is also generated and used to drive the tap updates of both the DFE and an FFE portion of the equalizer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
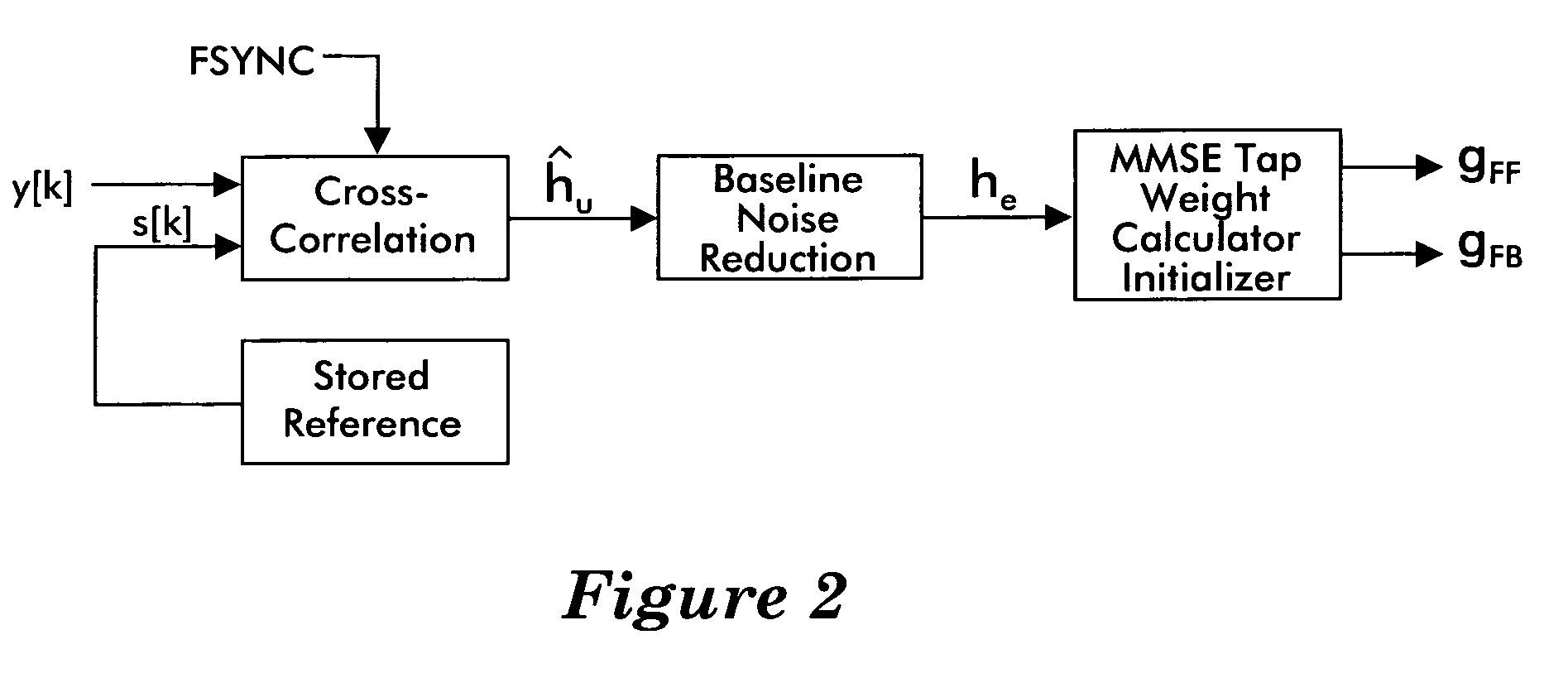
Adaptive equalizer
ActiveUS20060039460A1Improve accuracyMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsChannel impulse responseEngineering
A channel impulse response is determined from a cross-correlation of a received training sequence and a stored version of the transmitted training sequence. The channel impulse response is iteratively cleansed of noise caused by the finiteness of the cross-correlation. Initial values of the tap weights for the taps of an equalizer such as a decision feedback equalizer may be determined based on the cleansed channel impulse response.
Owner:ZENITH RADIO CORP
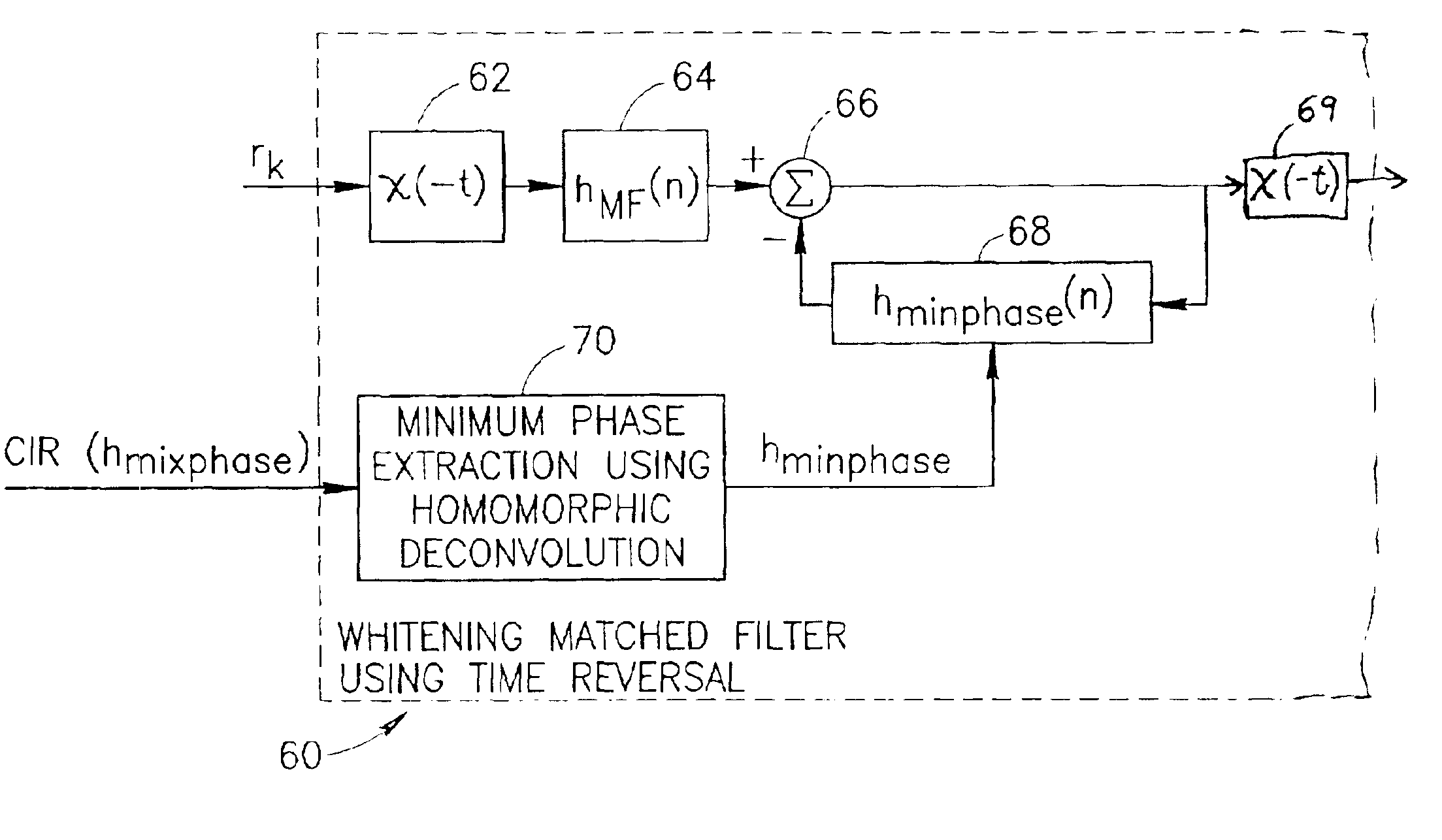
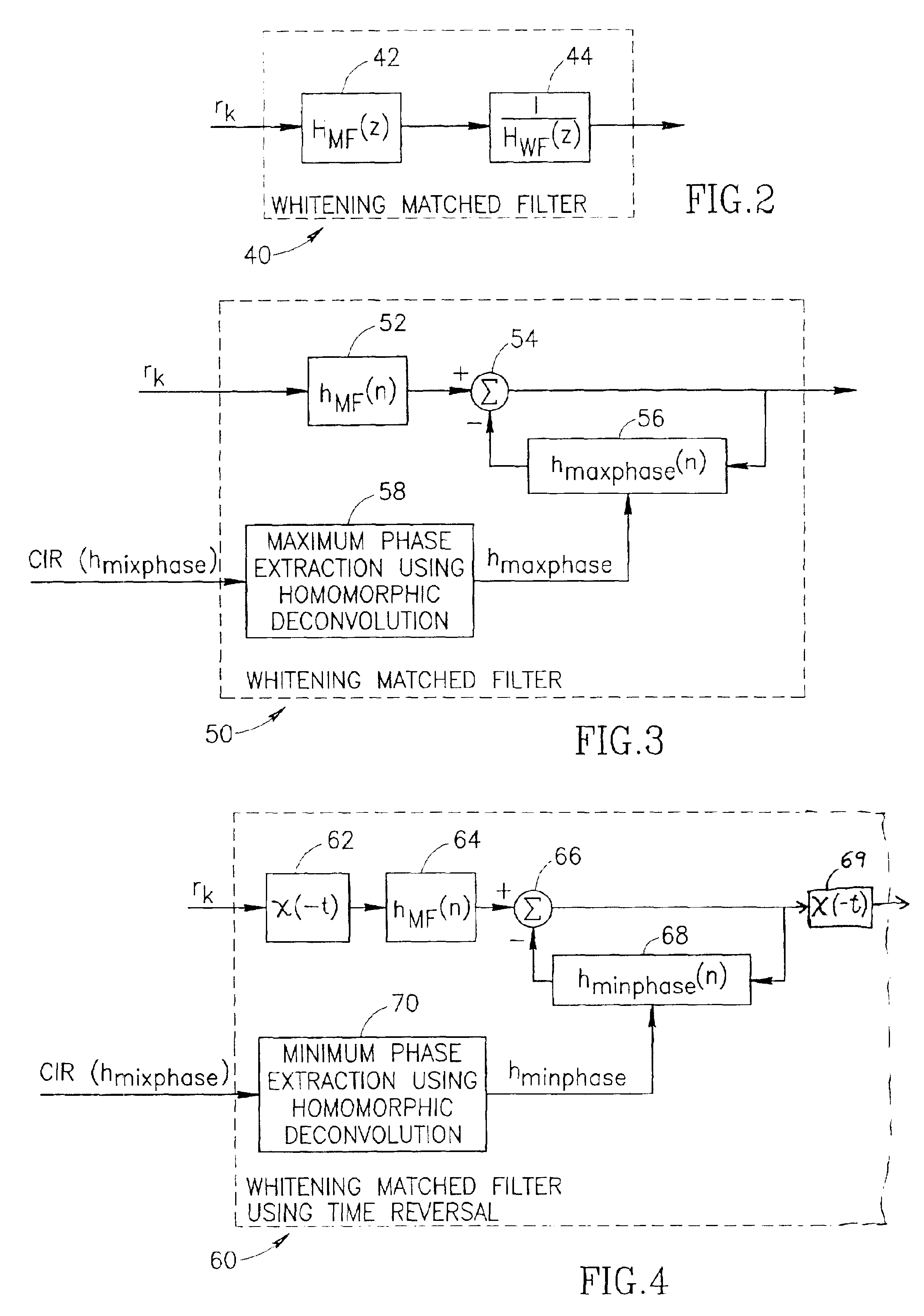
Whitening matched filter for use in a communications receiver
InactiveUS6862326B1Improve performanceMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkIir filteringChannel impulse response
A novel and useful whitening matched filter (WMF) for use in a communications receiver. The WMF is constructed by cascading a matched filter and a noise-whitening filter. The response of the matched filter is derived from the time reversed complex conjugate of the channel impulse response. The whitening filter is derived by extracting the minimum phase portion of the mixed phase channel impulse response using homomorphic deconvolution. The whitening filter is implemented using either an FIR or IIR filter adapted to process the data received before and after the training sequence using a minimum phase system in a direction in time opposite to that of the direction of corresponding data sample processing performed by the equalizer.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
Digital receiver having adaptive carrier recovery circuit
InactiveUS20050157820A1Reduce instabilityCompensation deviationMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsInstabilityEngineering
A digital receiver, that may be used to receive VSB / QAM digital television signals, includes an adaptive fine carrier recovery circuit that compensates for deviations in the carrier frequency or phase. The carrier recovery circuit de-rotates a signal including phase errors. Estimations of phase errors are filtered using a filter whose gain and bandwidth are adjusted adaptively. This allows the carrier recovery circuit to track phase / frequency offset without introducing significant jitter. In one embodiment, the receiver includes a DFE, and the adaptive carrier recovery circuit mitigates instability that might be associated with the DFE.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
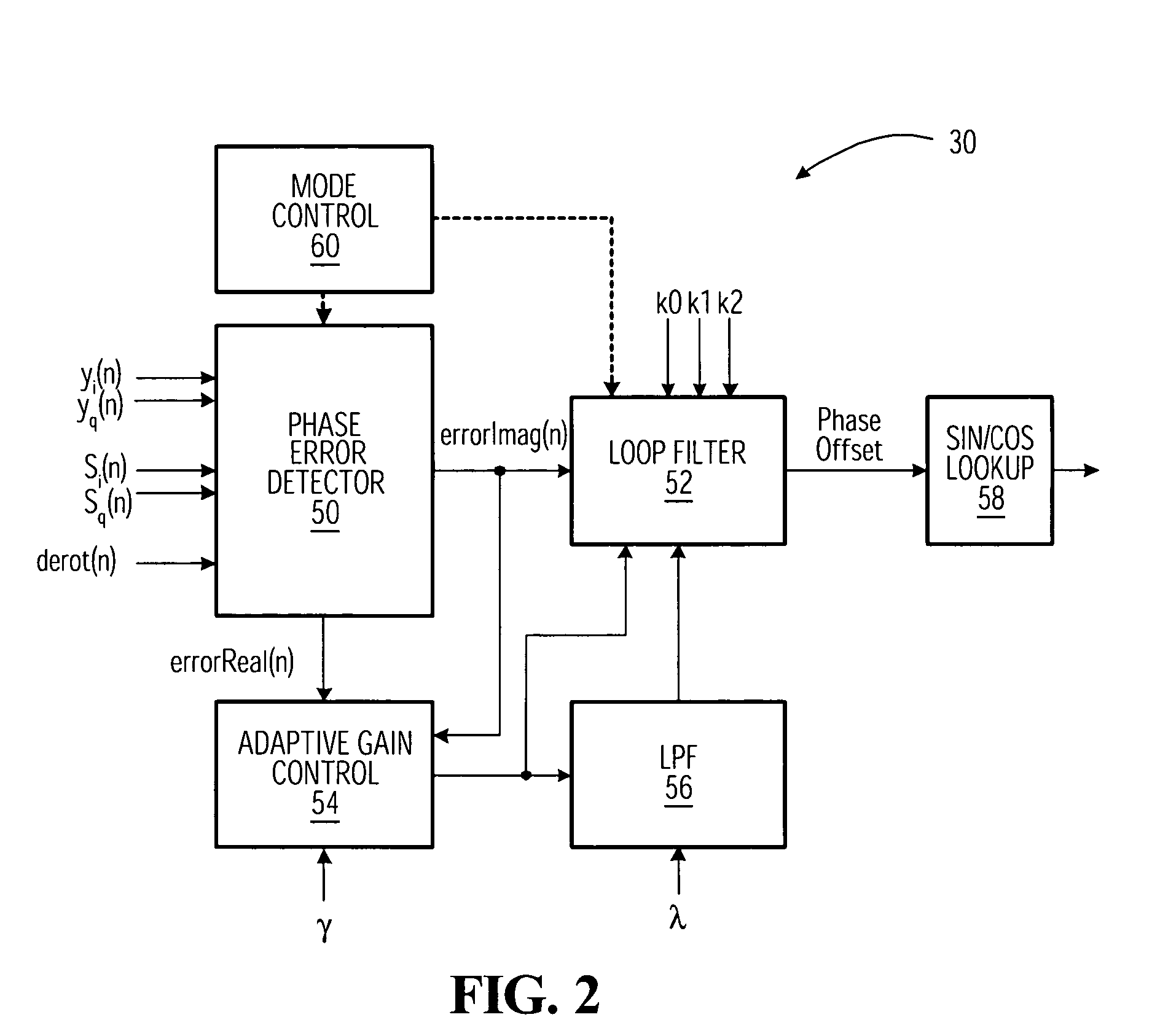
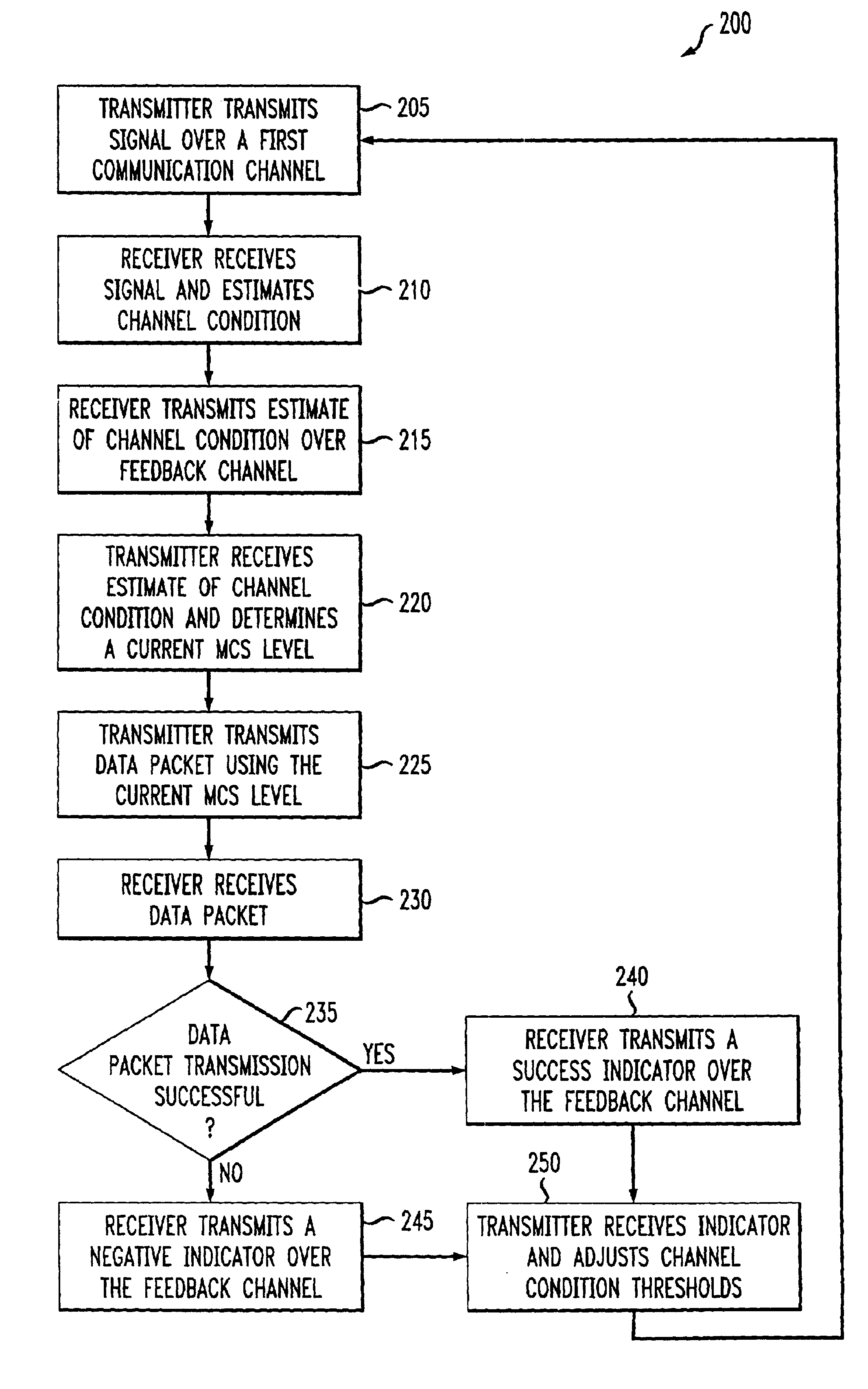
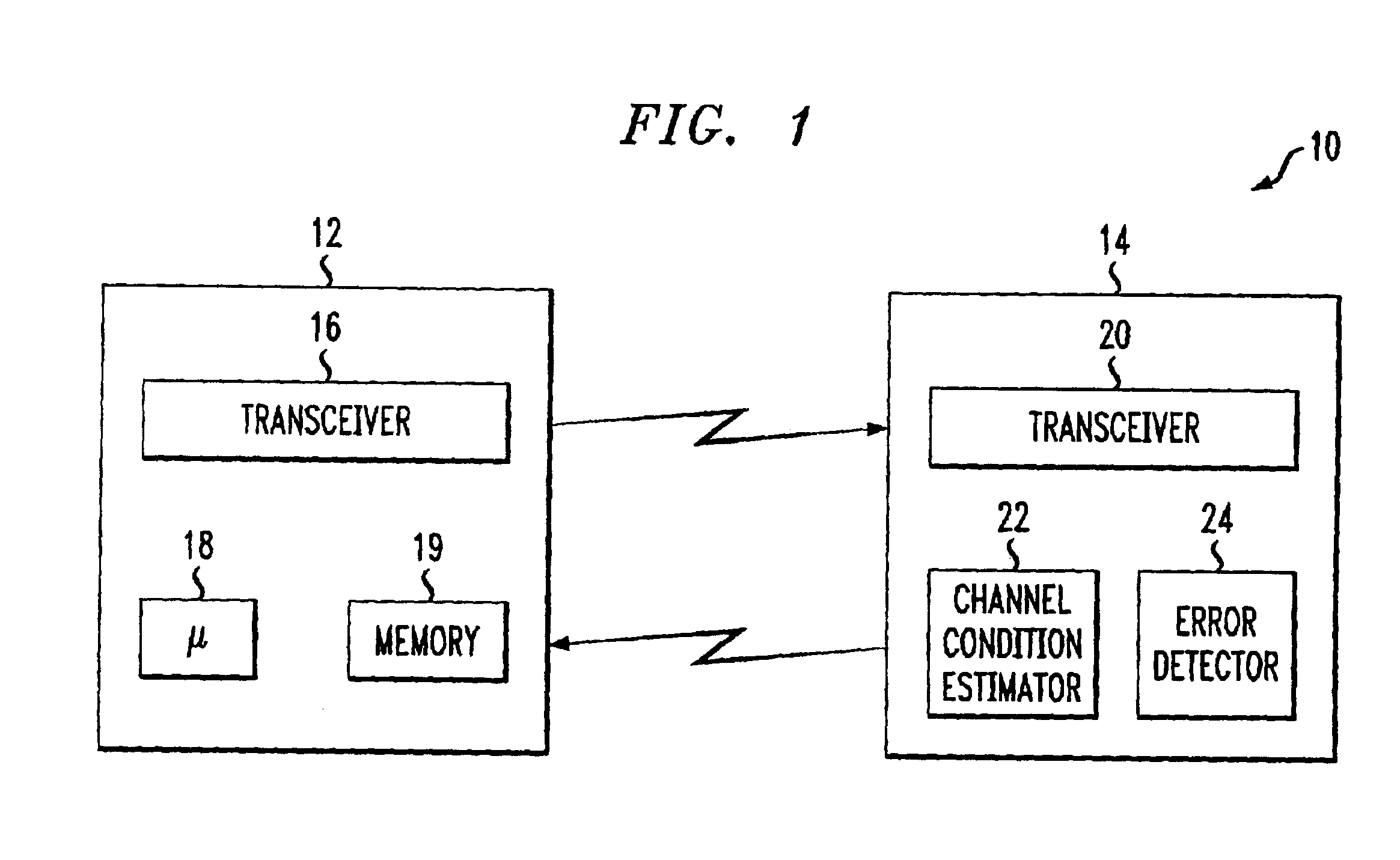
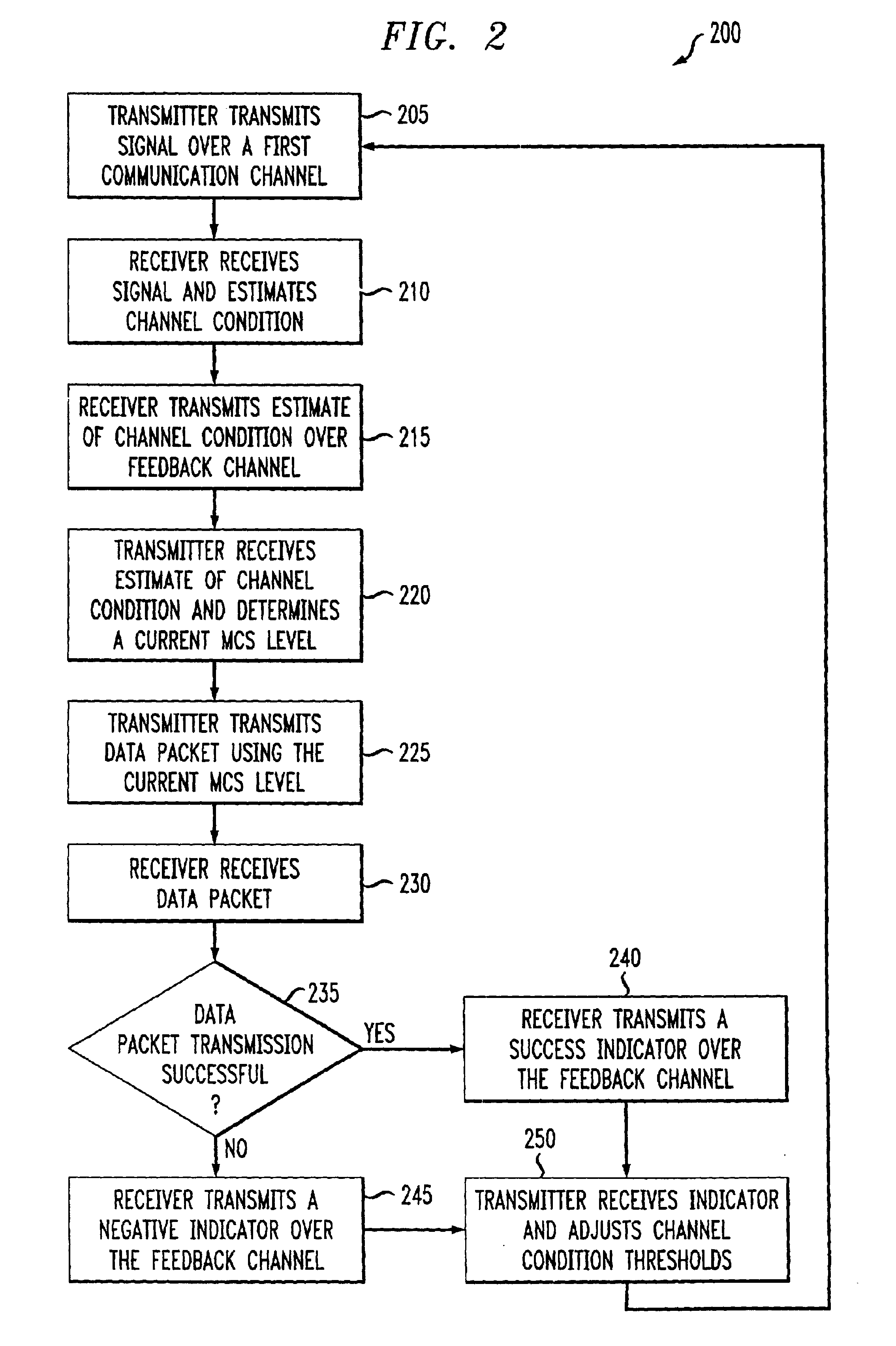
Delay sensitive adaptive quality control loop for rate adaptation
InactiveUS6915477B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelMultiple-port networksCommunications systemRate adaptation
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation that selectively adjusts channel condition thresholds based on delay sensitivity of data packets being transmitted. For wireless communication systems incorporating an error correction scheme using re-transmissions, the quality control loop adaptively adjusts channel condition thresholds more frequently for delay sensitive data packets, such as video, and less frequently for delay insensitive data packets, such as text messaging. Channel condition thresholds may be adjusted using fixed or variable steps based on error detection results.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
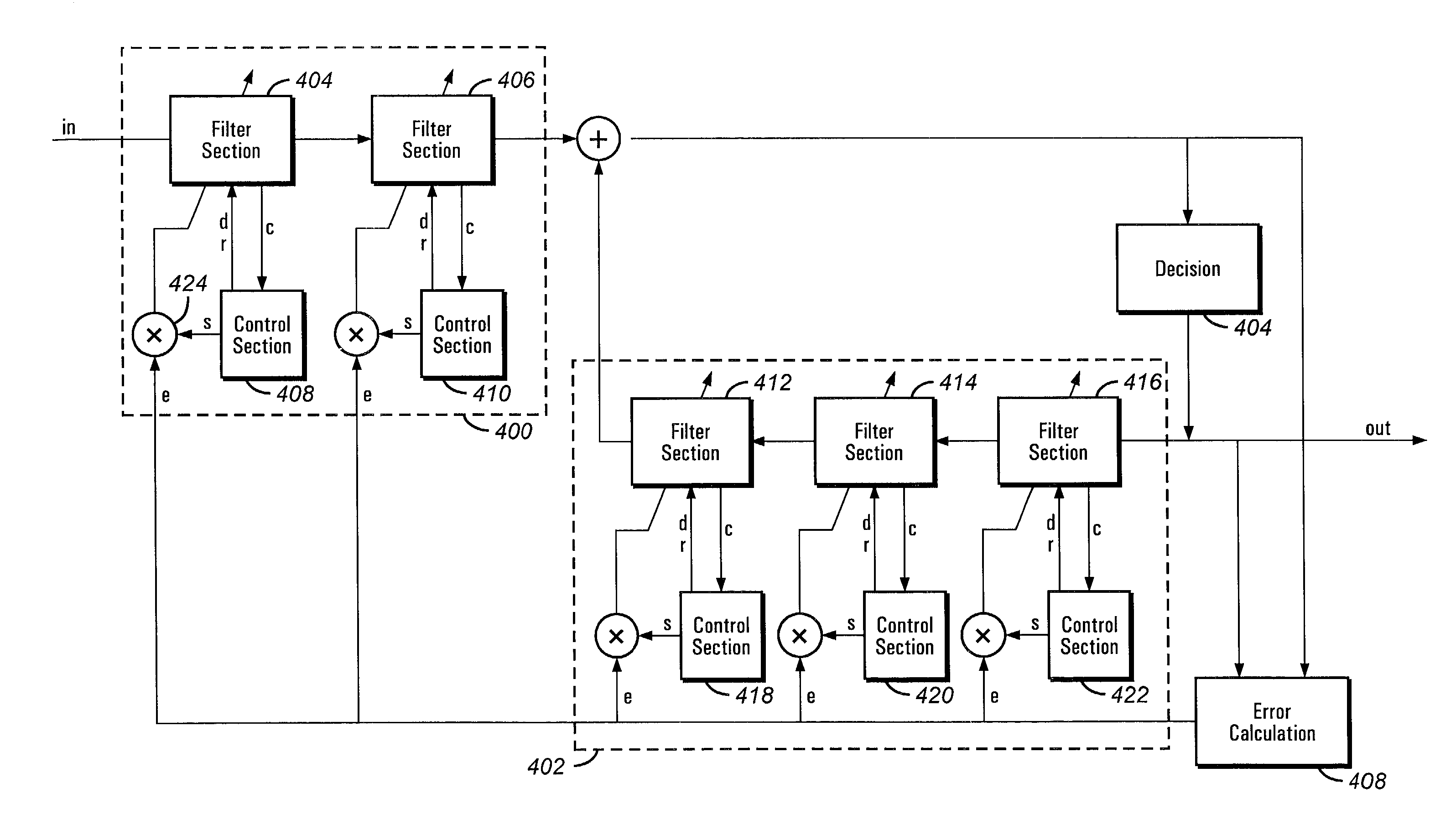
Convergence speed, lowering the excess noise and power consumption of equalizers
An equalizer for equalizing channel multi-path distortion includes digital filters. To improve the convergence speed and tracking ability of the equalizer while lowering noise and power consumption, the digital filters are divided into sections. Various parameters of the sections, such as step-size, shutdown and update rates can be controlled. Control of the various parameters can be realized either in software on an embedded or external processor or by dedicated hardware.
Owner:CONEXANT SYST INC
Optical fiber based on wireless scheme for wideband multimedia access
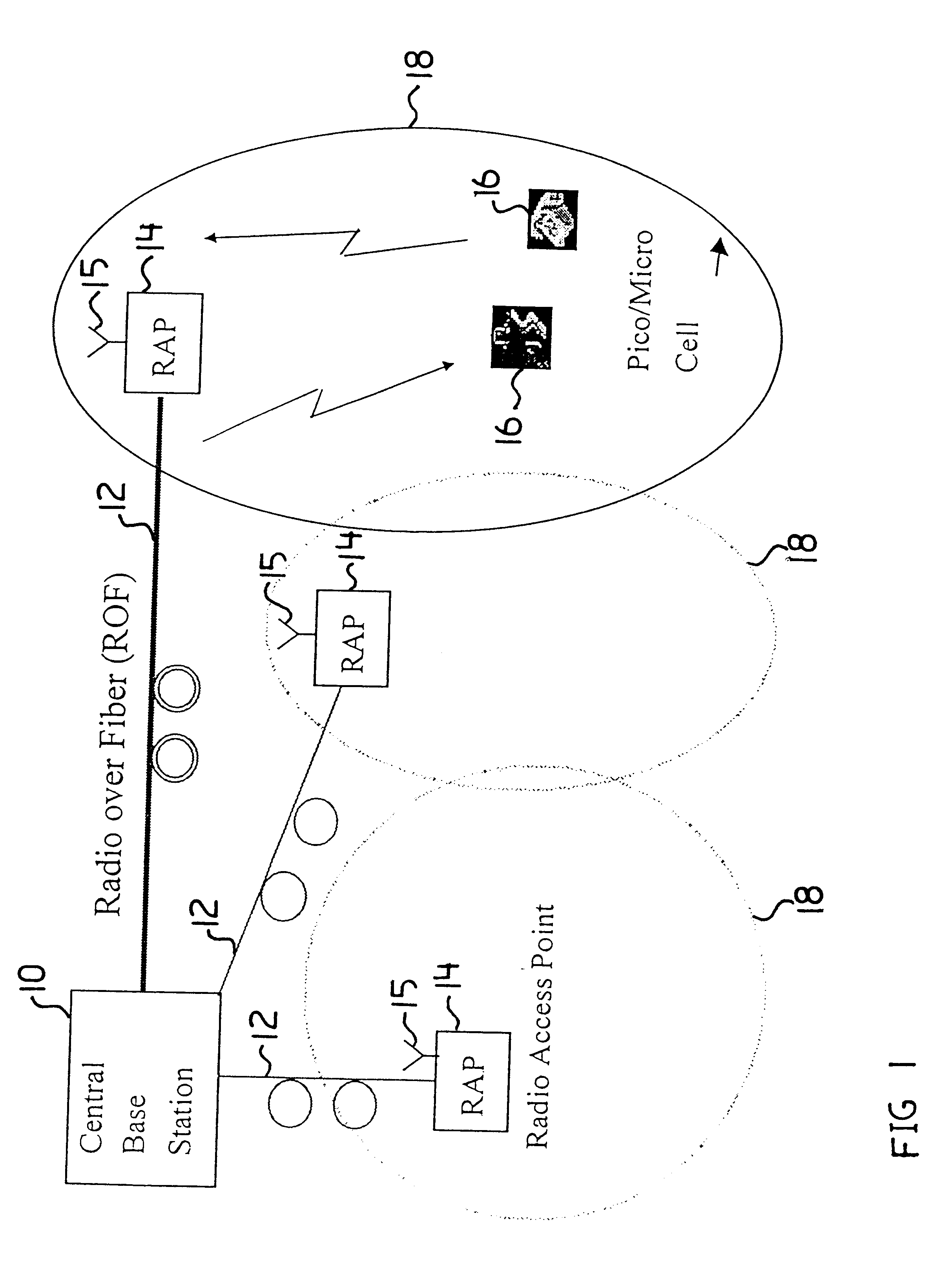
InactiveUS6889060B2Good compensationLess complexMultiple-port networksError preventionNonlinear distortionRadio over fiber
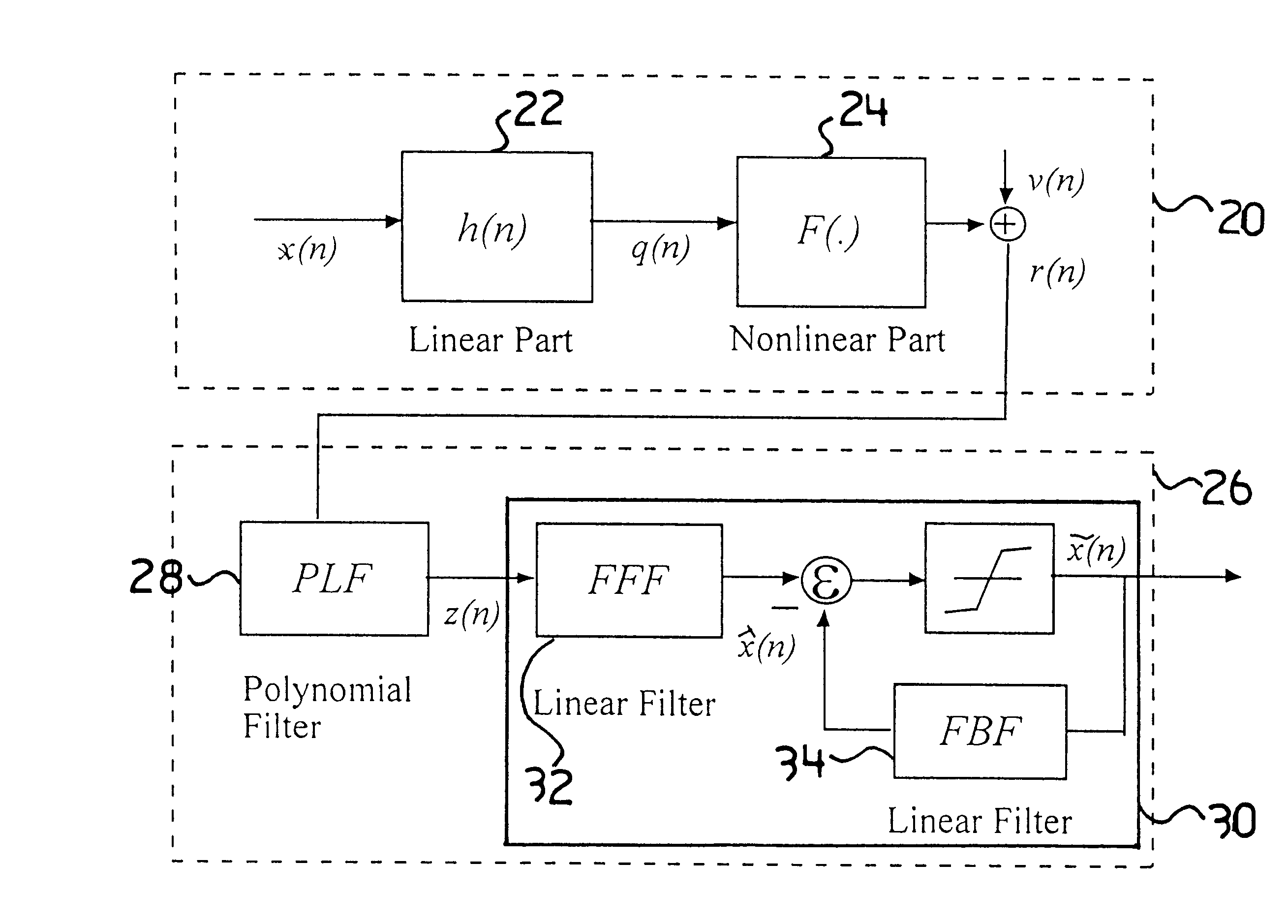
A Fiber-wireless uplink consists of a wireless channel followed by a radio-over-fiber (ROF) link. Typically, nonlinear distortion of the ROF link is the major concern when the radio frequency is only a few GHz. This especially severe in the uplink, because of the multipath fading of the wireless channel. A Hammerstein type decision feedback equalizer is described for the fiber wireless uplink, that compensates for nonlinear distortion of the ROF link as well as linear dispersion of the wireless channel. Since the linear and nonlinear parts of the receiver are separated, tracking the fast changing wireless channel is virtually independent of compensating for the relatively static nonlinearity. Analytical results show that the receiver provides excellent compensation with notably less complexity.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
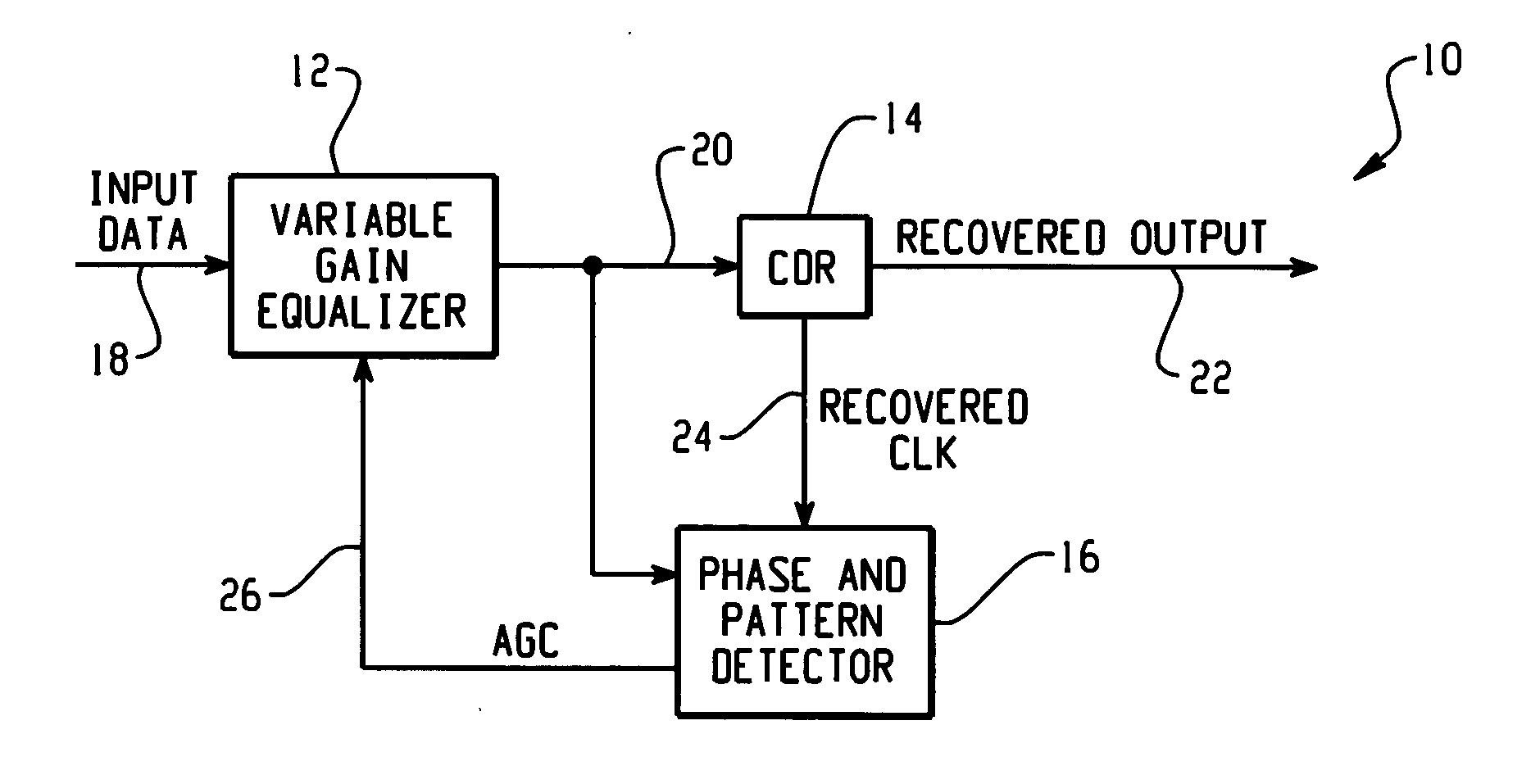
Precision adaptive equalizer
InactiveUS20050047500A1Multiple-port networksAdaptive networkDetector circuitsAutomatic gain control
In accordance with the teachings described herein, systems and methods are provided for a precision adaptive equalizer. A variable gain equalizer may be used to apply a variable gain to an input signal to generate an equalized output signal. A phase and pattern detector circuit may be coupled in a feedback loop with the variable gain equalizer. The phase and pattern detector circuit may be used to identify a high frequency data pattern in the equalized output signal and compare the high frequency data pattern with a clock signal to detect a high frequency phase error. The phase and pattern detector circuit may be further operable to generate an automatic gain control signal as a function of the high frequency phase error, the automatic gain control signal being fed back to the variable gain equalizer to control the variable gain applied to the input signal.
Owner:SEMTECH CANADA
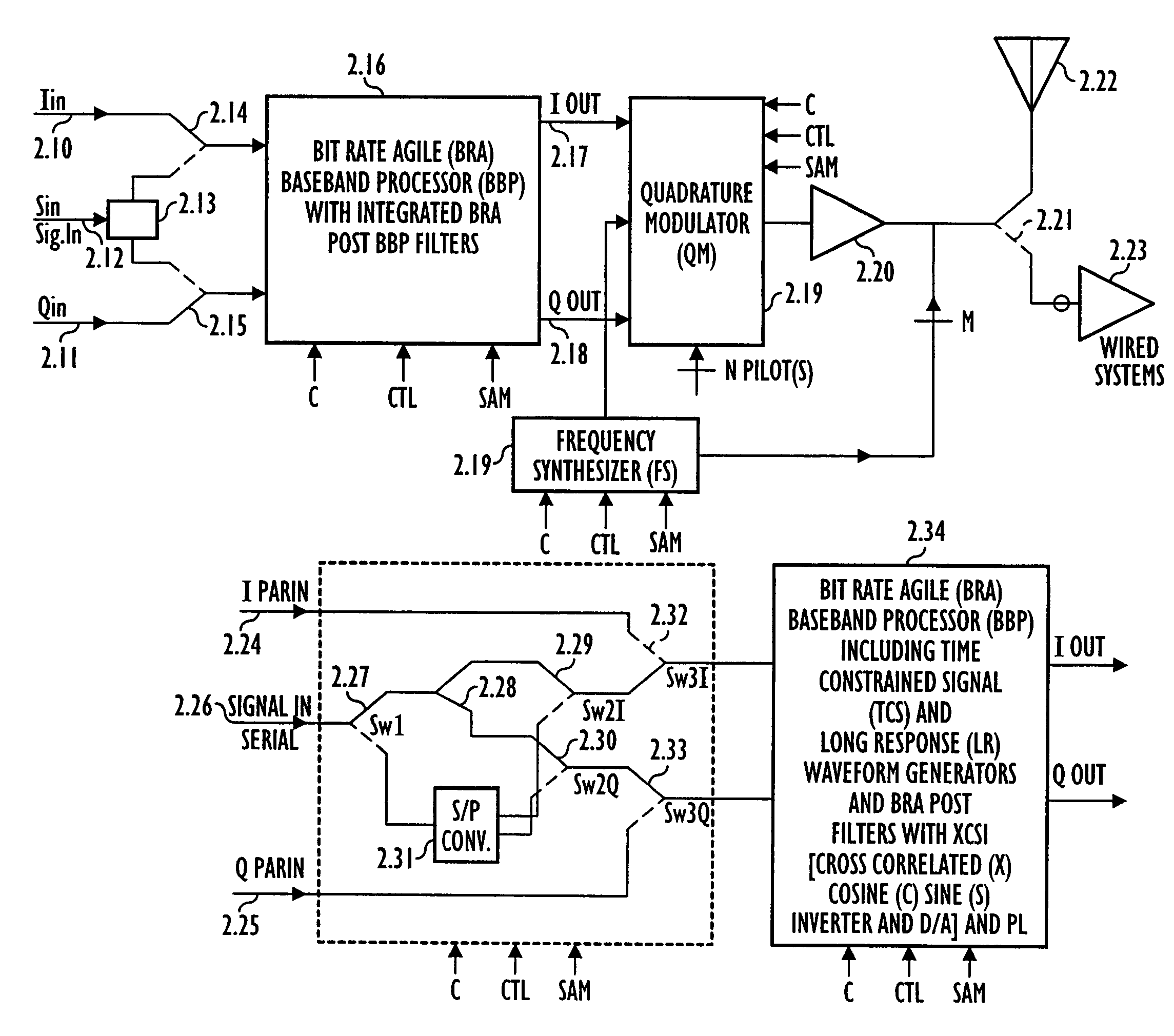
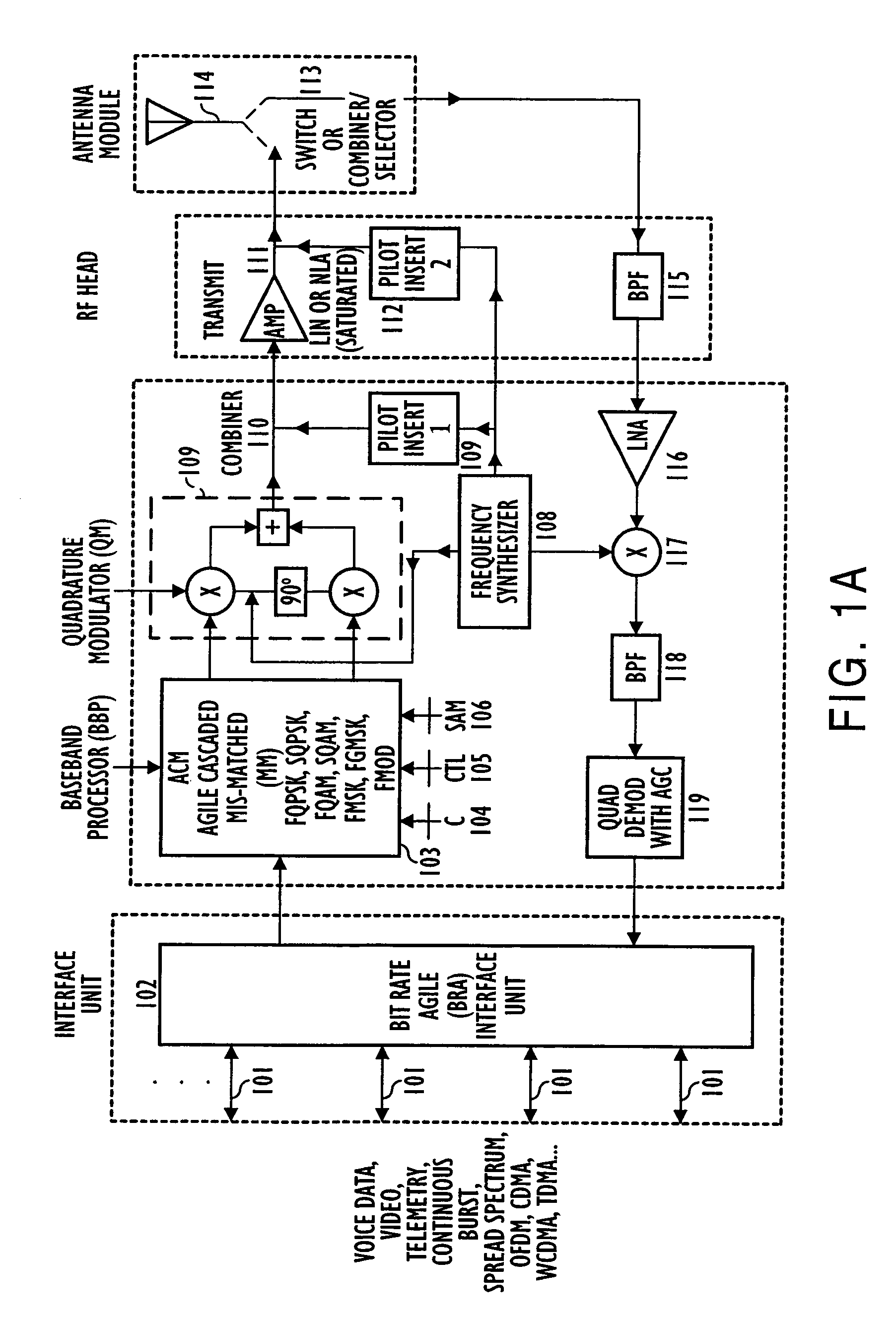
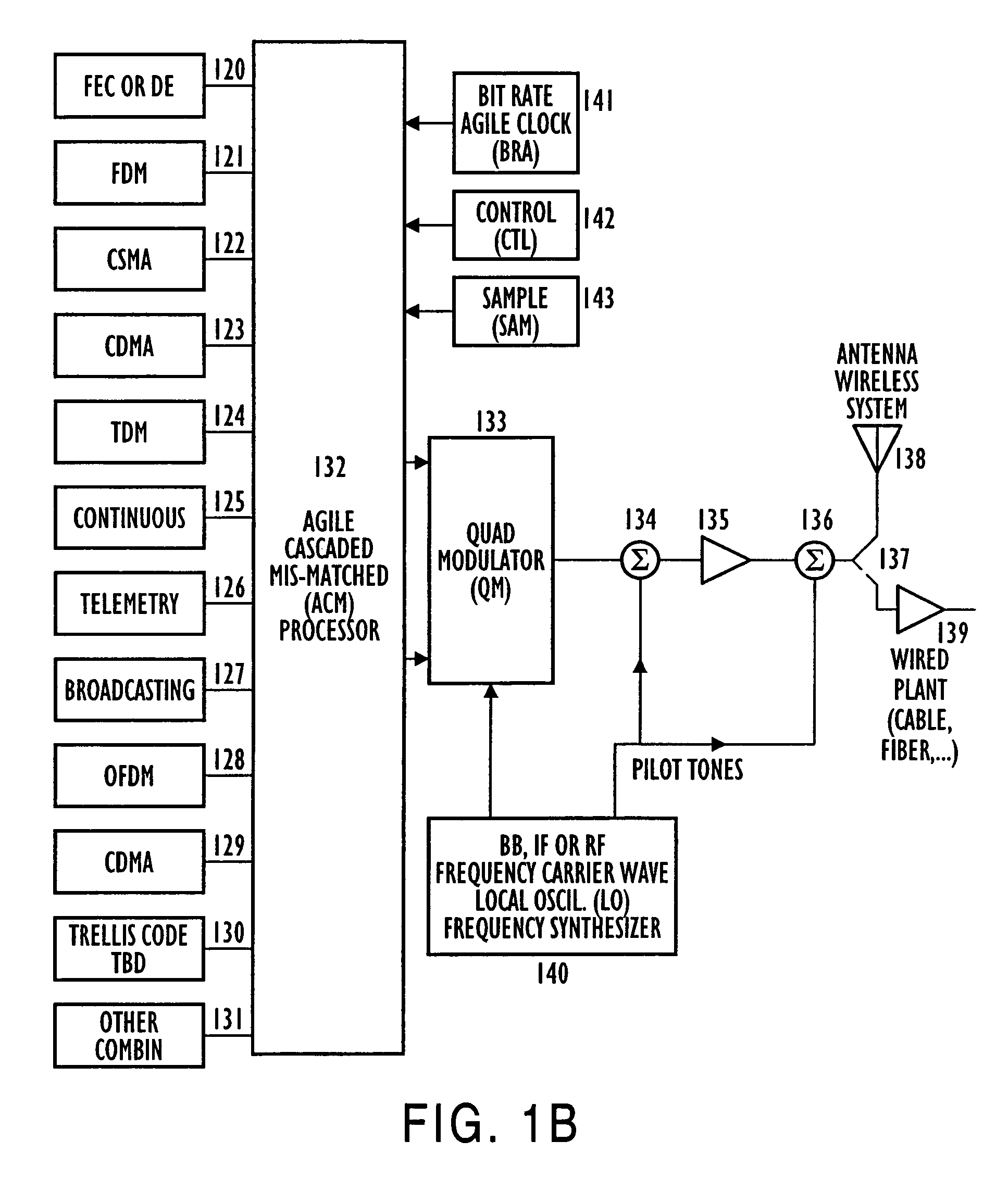
Adaptive receivers for bit rate agile (BRA) and modulation demodulation (modem) format selectable (MFS) signals
InactiveUS7376180B2Improve performanceSignificant spectral saving advantageMultiple-port networksSecret communicationModem deviceThird generation
Systems, apparatus, and methods for new generations of wireless systems, including multiple standard, interoperable Third-Generation (3G) and Second-Generation (2G), Spread Spectrum CDMA, WCDMA, GSM, Enhanced GSM systems and CSMA, TDMA and OFDM. Bit Rate Agile (BRA), Modulation and Code Selectable processing techniques of Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK), Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM), and of Mis-Matched demodulator filters in which the demodulator filter set is mismatched to the filter set of the signal modulator.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
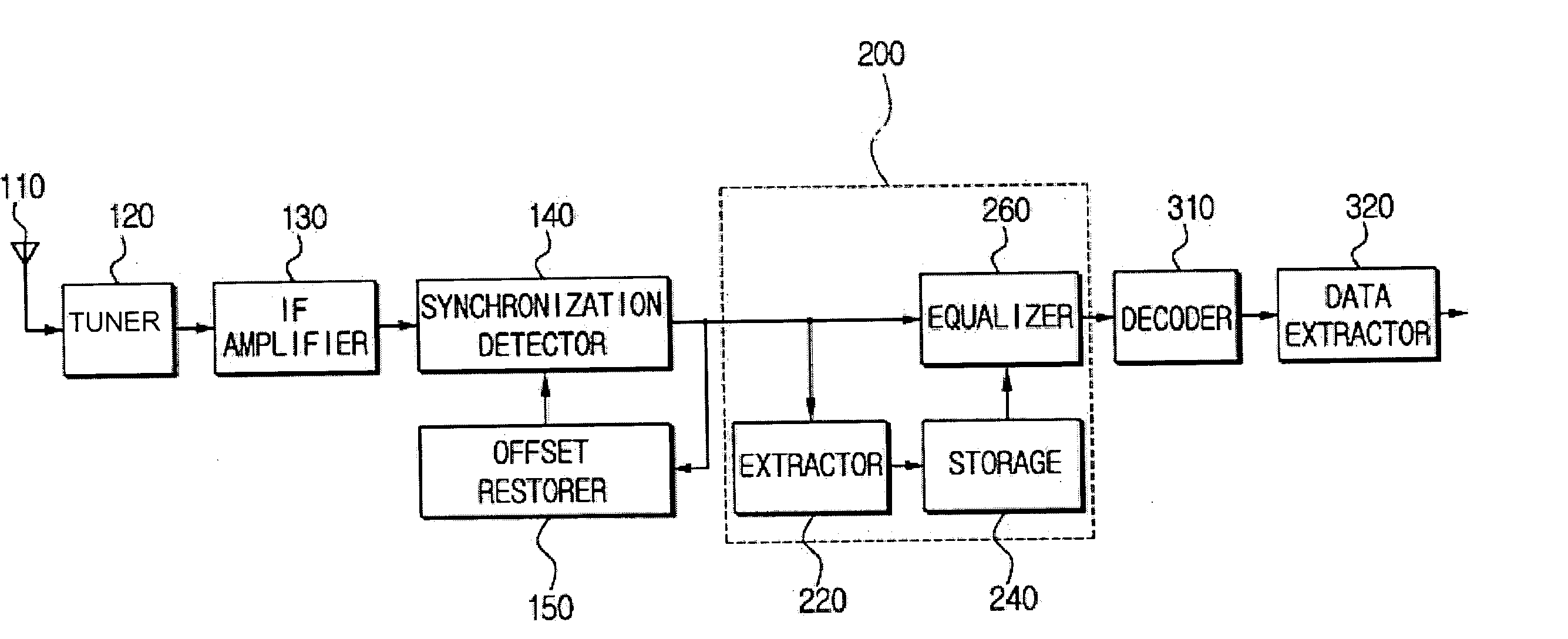
Equalizer for a VSB receiver enabling equalizations using segment synchronization information
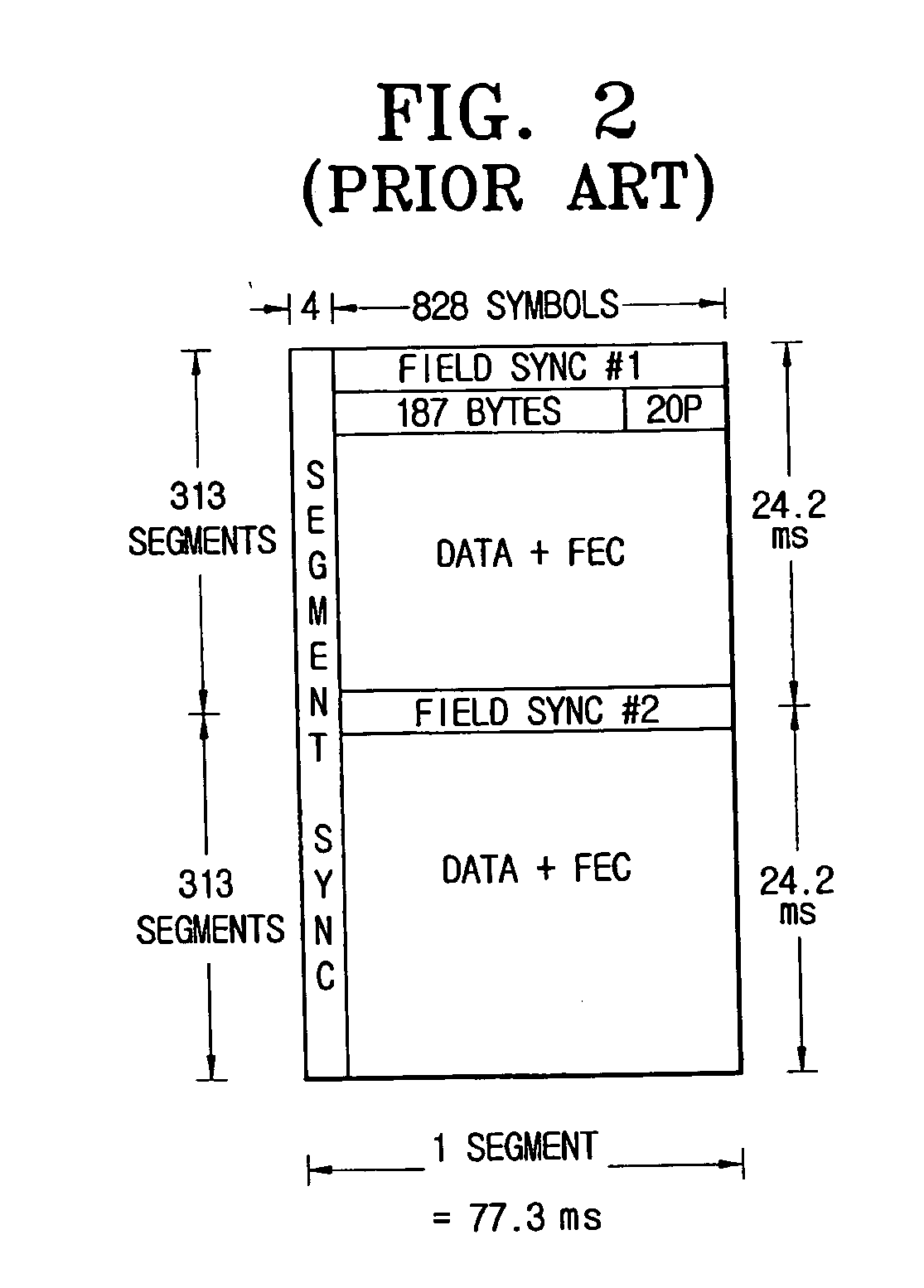
InactiveUS20030223519A1Improve uniformityTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksData segmentEqualization
An equalizer for a VSB receiver, which enables equalizations using segment synchronization information, has an extraction unit extracting the segment synchronization information included in the VSB broadcast signal, a storage unit storing the extracted segment synchronization information, and an equalization unit equalizing the VSB broadcast signal based on the segment synchronization information stored in the storage unit. The storage unit stores the segment synchronization information extracted from the extraction unit by field unit or by unit of N data segments within the field according to a channel state. More stable equalizations can be carried out in channel environment changes by storing segment synchronization information by the predetermined number of data segments and equalizing data within a corresponding data segment in a training mode while using the segment synchronization information every matching number of data segments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
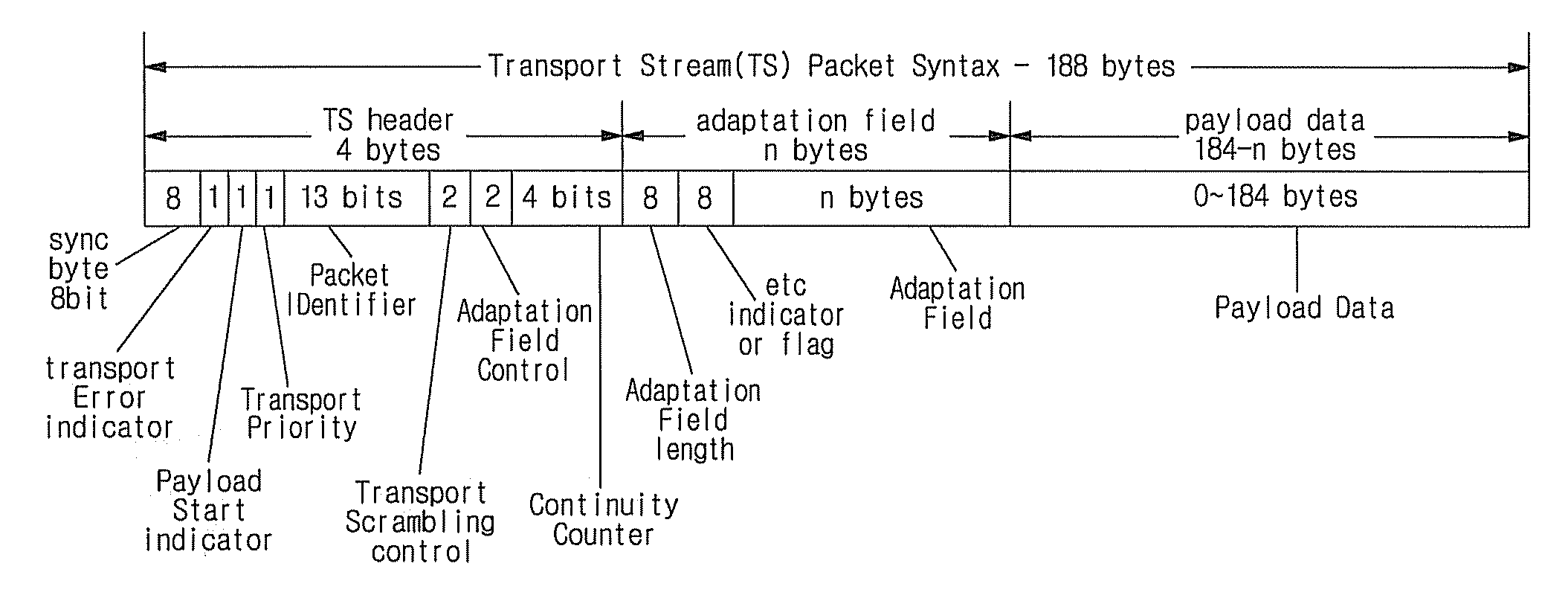
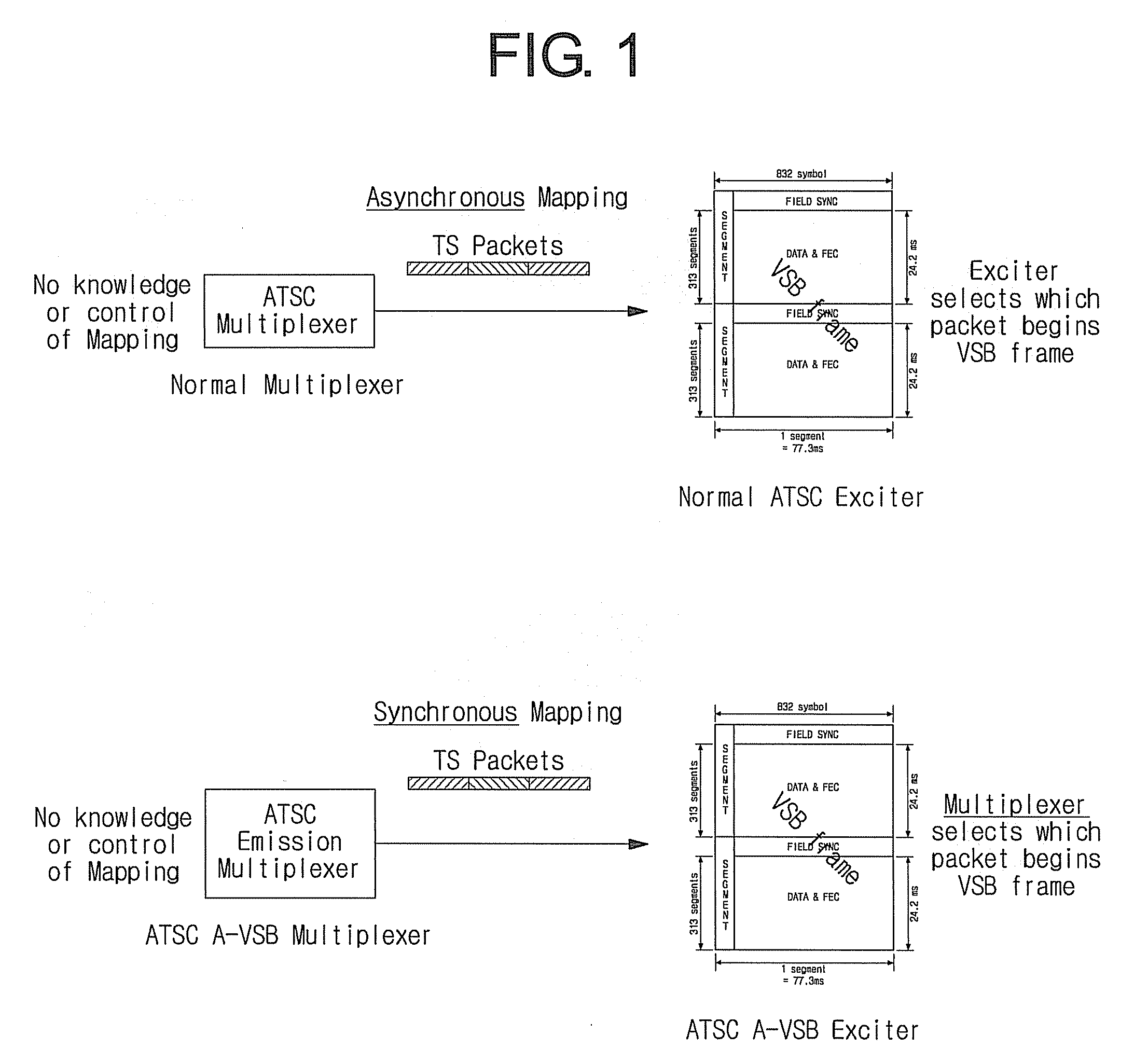
Method of and apparatus for transmitting digital broadcasting signal in advanced-vsb (a-vsb) system in which transport packet without adaptation field is provided at fixed location in data field slices
A method of processing a digital broadcasting signal includes generating a transport stream including a plurality of transport packets; selecting one of the transport packets as a starting packet to be mapped into a first data segment of an encoded data frame; and constructing deterministic data frames in the transport stream beginning with the starting packet; wherein at least one of the 52 transport packets does not have an adaptation field; wherein all remaining ones of the 52 transport packets do have an adaptation field; and wherein the at least one transport packet that does not have an adaptation field is provided at a fixed location in each of the slices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
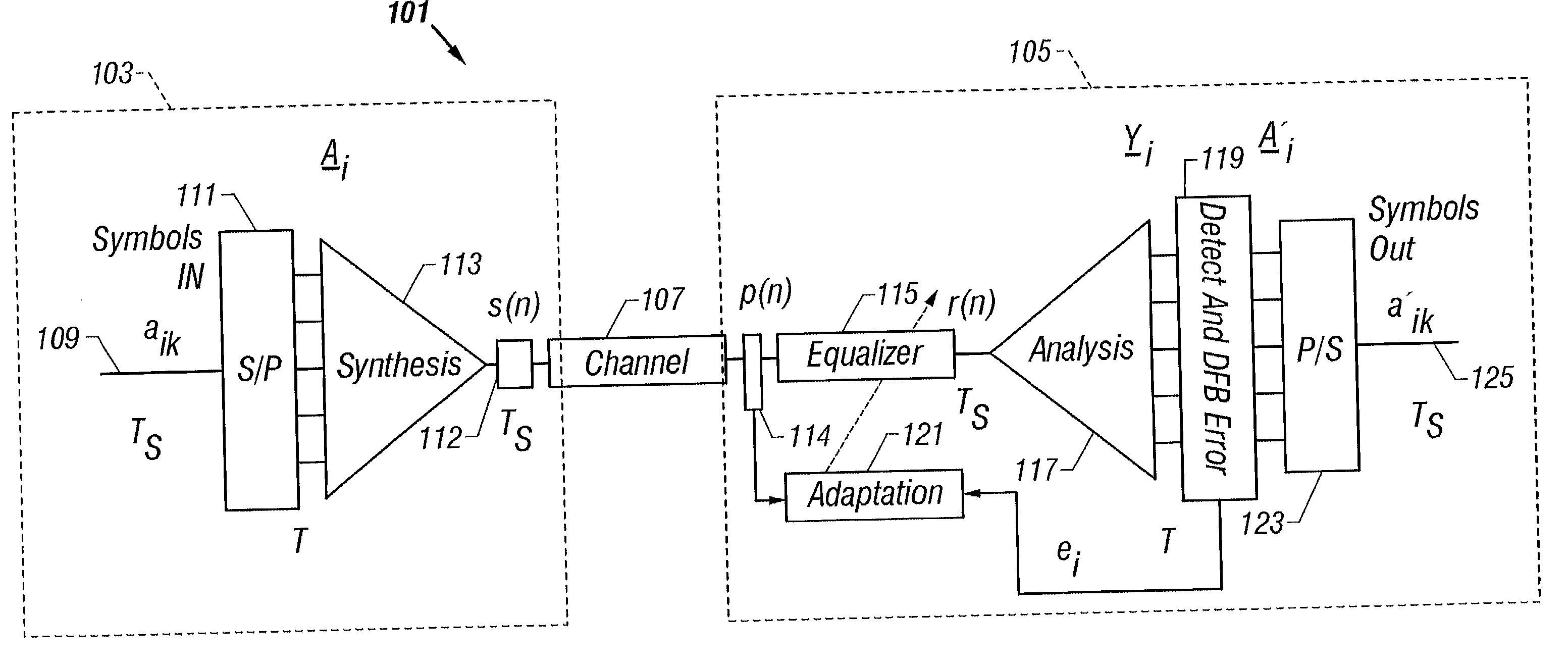
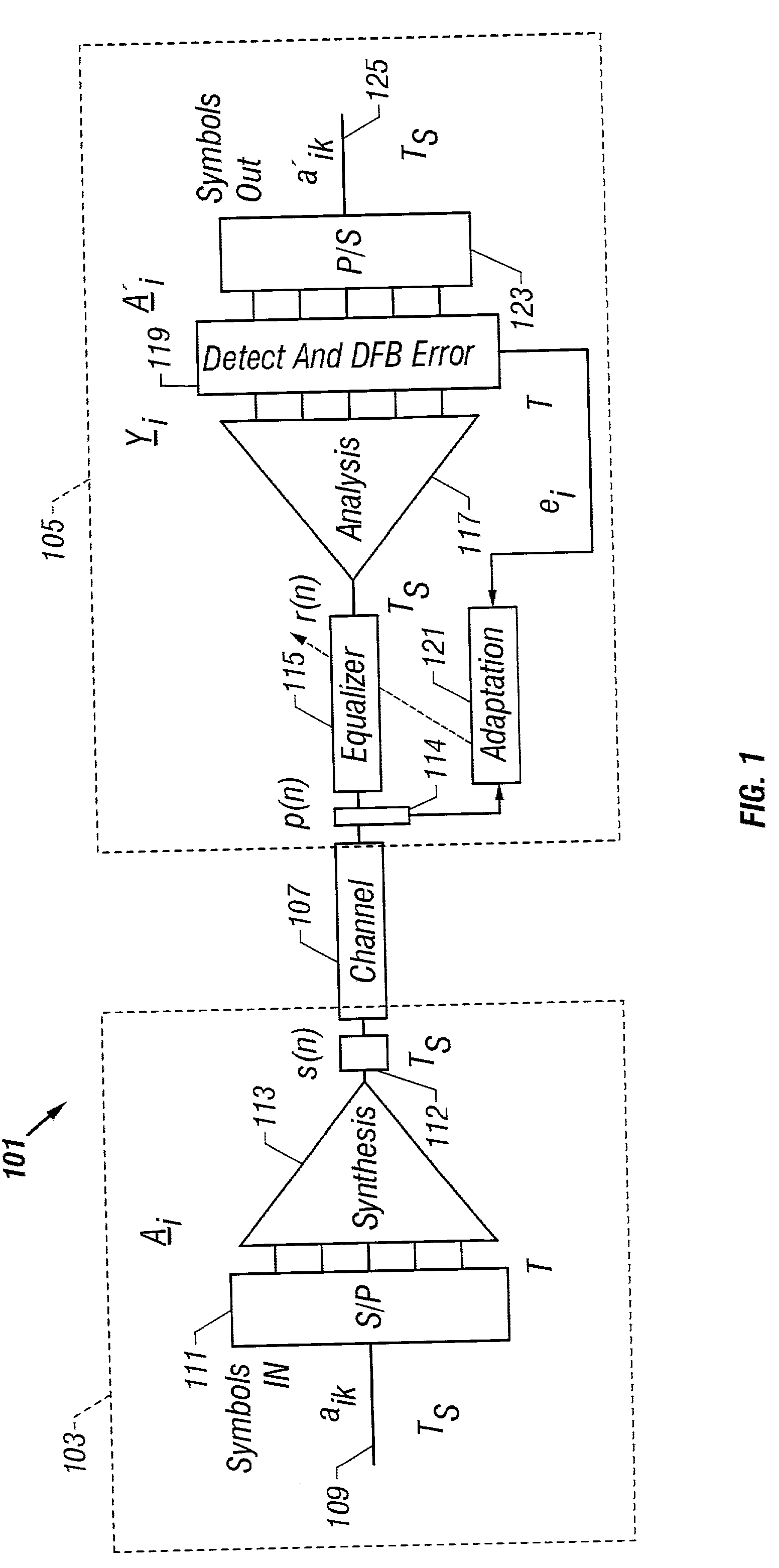
Communication system using orthogonal wavelet division multiplexing (OWDM) and OWDM-spread spectrum (OWSS) signaling
InactiveUS20020181388A1Multiple-port networksPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMultiplexingBroadband pulse
An orthogonal wavelet division multiplexing (OWDM) communication system including a synthesis section and a channel interface. The synthesis section includes a filter pair bank with multiple inputs and an output that provides an OWDM signal. Each input receives a corresponding symbol of a supersymbol, where the symbols are from a selected modulation scheme. The synthesis section generates the OWDM signal as a combination of weighted OWDM pulses, where each weighted OWDM pulse represents of a symbol of the supersymbol. An OWDM Spread Spectrum (OWSS) communication system that uses broad-time and broadband pulses generated from a family of OWDM pulses together with a set of orthogonal PN code vectors. The OWSS pulses are mutually orthogonal and allow multi-user operation. Each user is assigned an OWSS pulse corresponding to a particular PN code. OWSS enables high rate operation for wireless channels with the use of an equalizer with FE and DFE sections.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +2
Method and apparatus for implementing precision time delays
Owner:TDC ACQUISITION HLDG
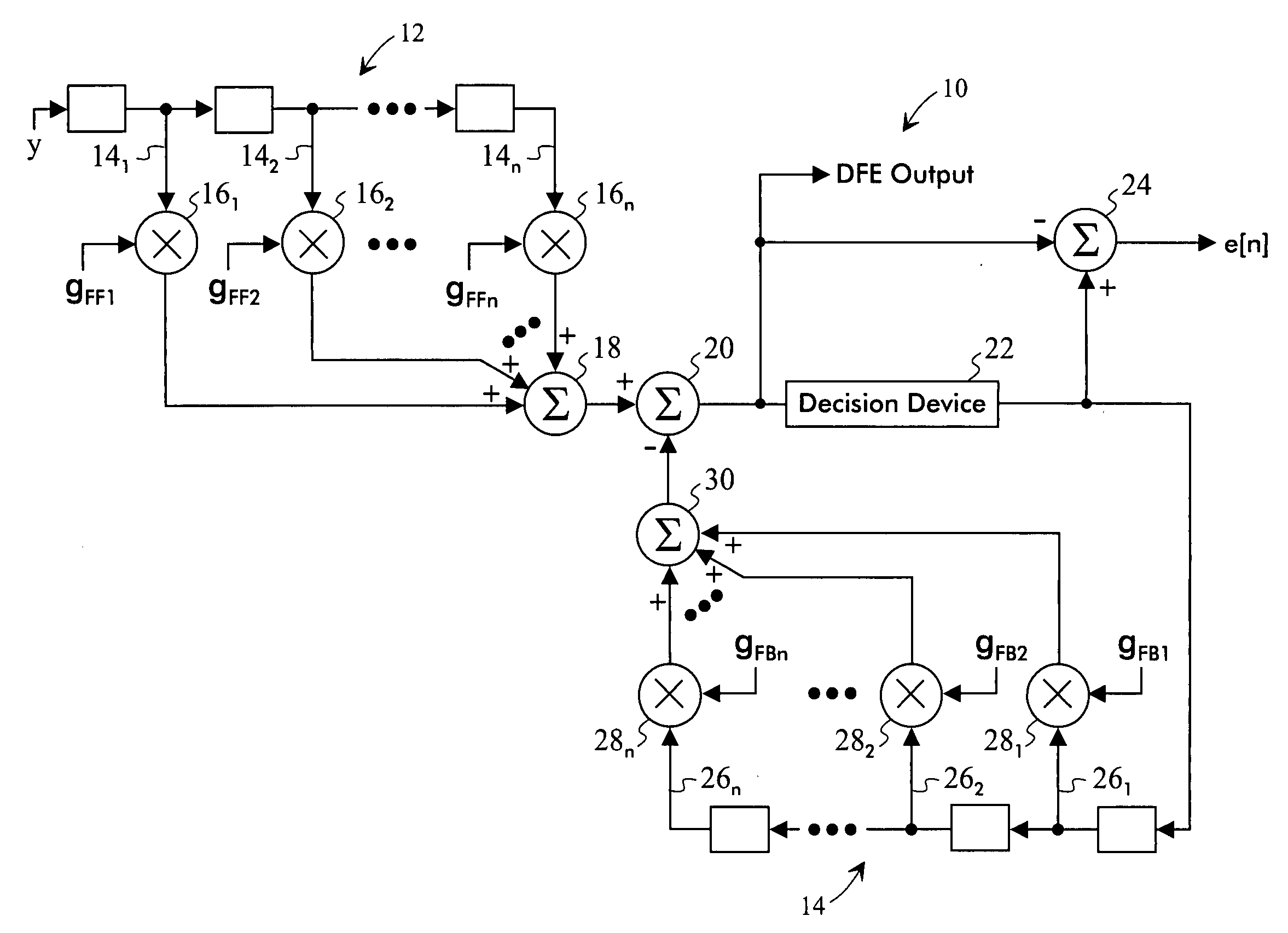
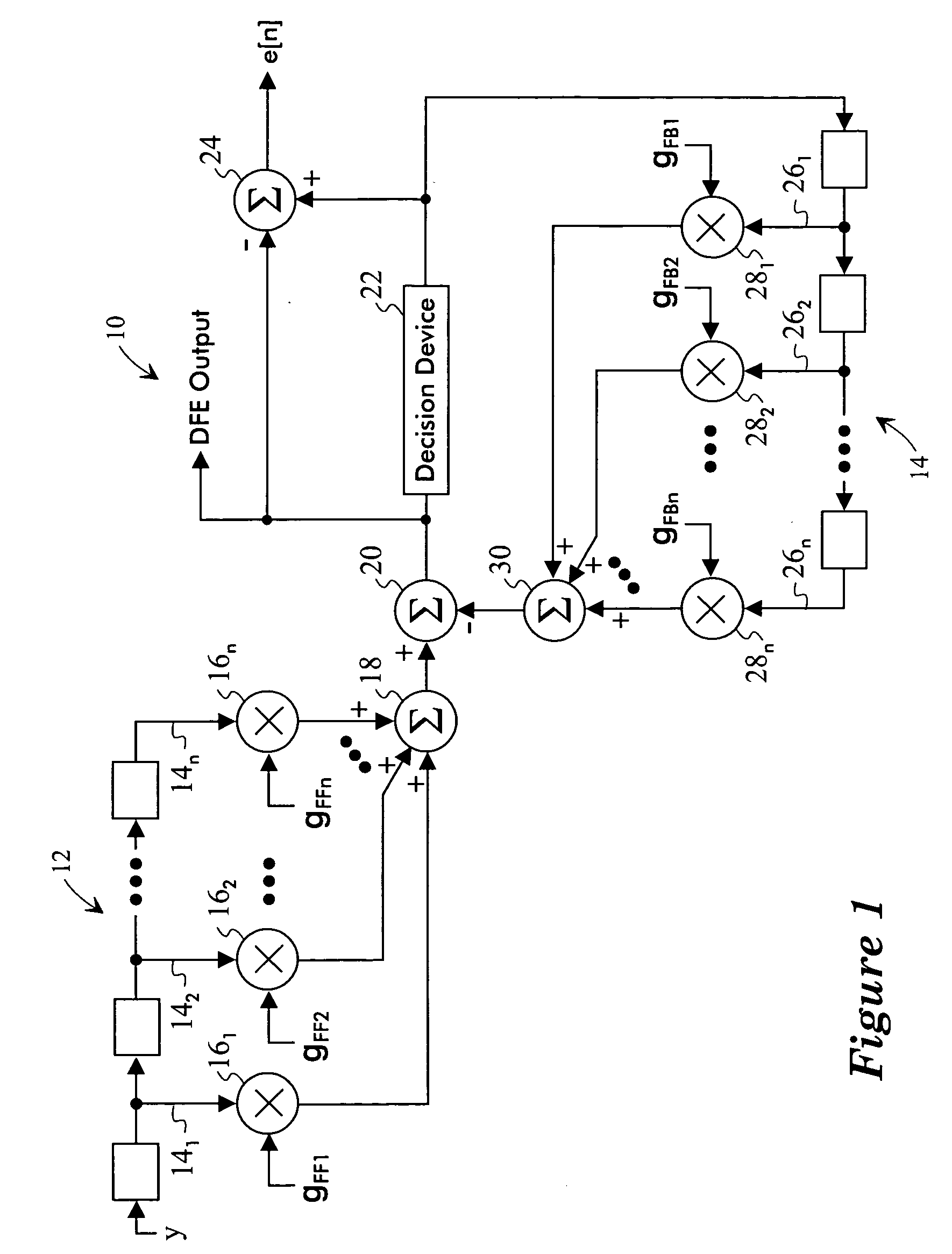
Apparatus For And Method Of Controlling A Feedforward Filter Of An Equalizer
InactiveUS20070201544A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPhase correctionComplex representation
A method of controlling a feedforward filter of an equalizer includes the steps of generating a complex representation of an output of the feedforward filter and generating a representation of a decision from an output of the equalizer. The complex representation and the decision representation are correlated to obtain a phase error estimate. A phase correction value is generated based on the phase error estimate and used to adjust the phase of the output of the feedforward filter.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
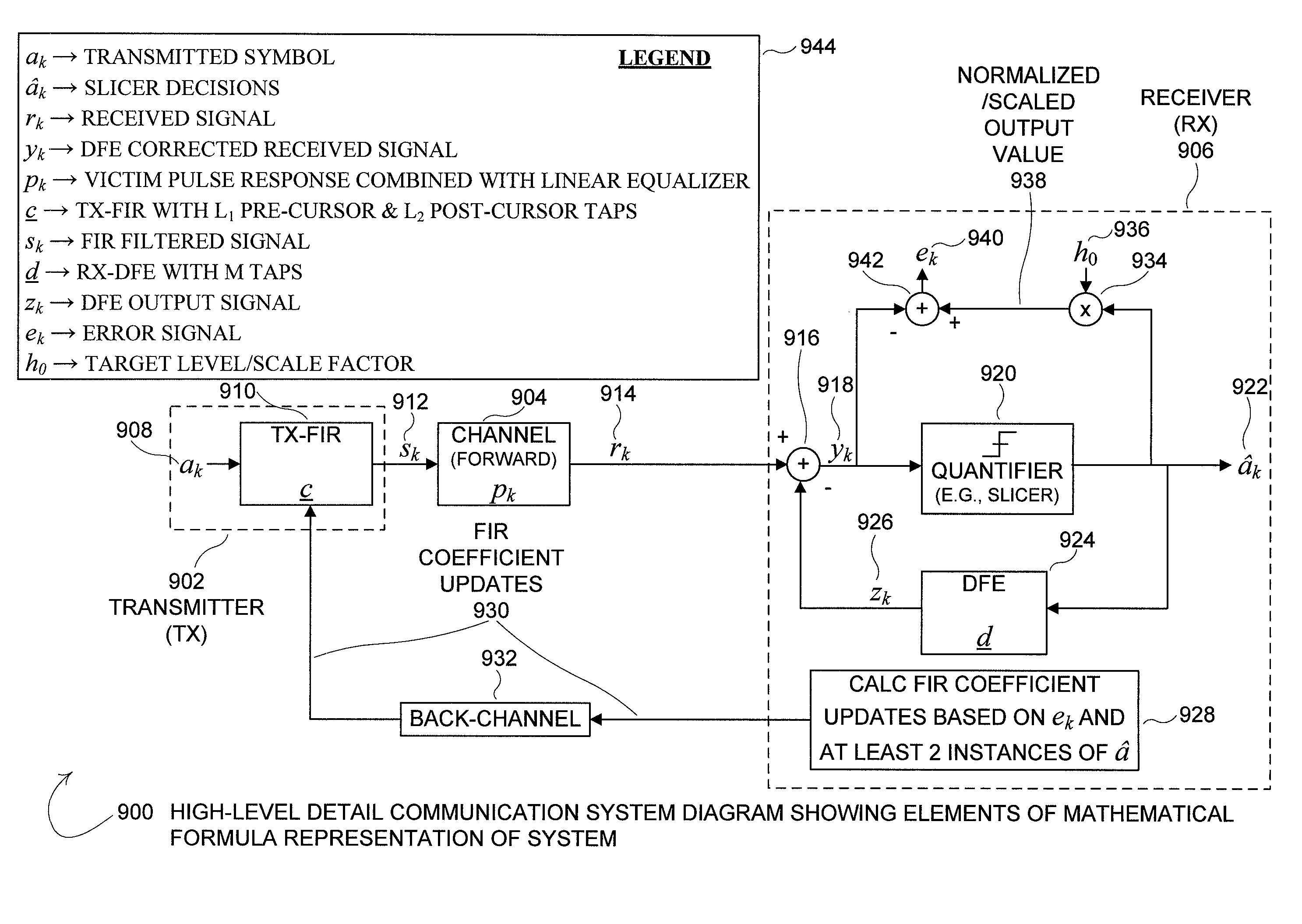
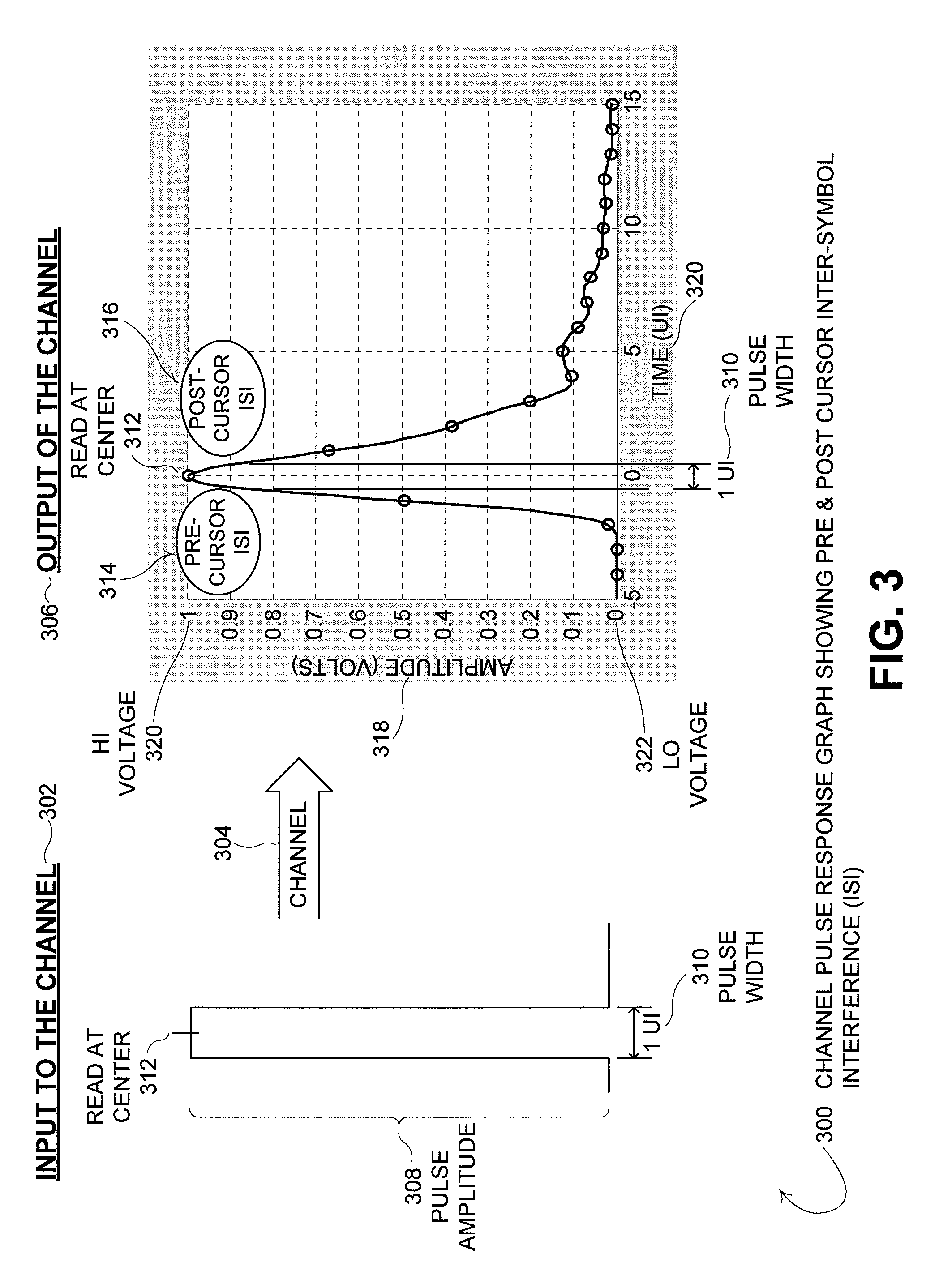
TX back channel adaptation algorithm
ActiveUS8472513B2Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFinite impulse responseCommunications system
Disclosed is a method and system that adapts coefficients of taps of a Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter to increase elimination of Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI) introduced into a digital communications signal due to distortion characteristics caused by a real-world communications channel. In the communications system there is a Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter. The FIR filter has at least one pre and / or post cursor tap that removes pre and / or post cursor ISI from the signal, respectively. The pre / post cursor taps each have pre / post cursor coefficients, respectively, that adjusts the effect of the pre / post cursor portion of the FIR filter. The FIR filtered signal is transmitted over the channel which distorts the signal due to the changing and / or static distortion characteristics of the channel. The channel distorted signal is received at a receiver that may pass the channel distorted signal through a quantifier / decision system (e.g., a slicer) as the quantifier input signal to quantify the quantifier input signal to one of multiple digital values. The channel distorted signal may be further adjusted by summing the channel distorted signal with the output of a Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) filter to create a DFE corrected signal which then becomes the quantifier input signal. An error signal is determined by finding the difference between the scaled quantifier decision and the quantifier input signal. The pre / post cursor coefficient values that adjust the effects of the pre / post cursor taps of the FIR filter are updated as a function of the error signal and at least two quantifier decision values, and update coefficient values, may be sent over a communications back-channel to the FIR filter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
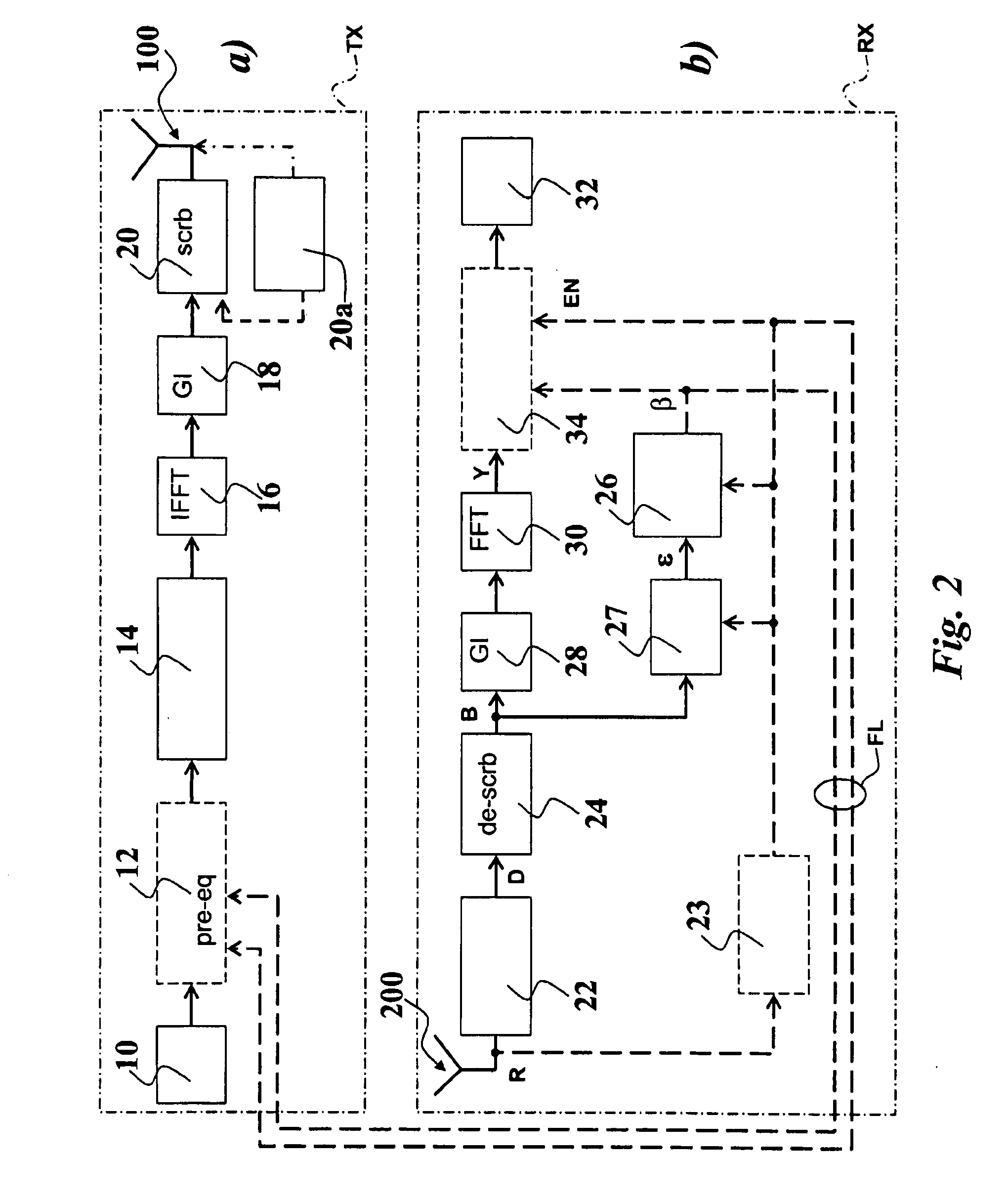
Scrambled multicarrier transmission
InactiveUS20100027608A1Easy to useImprove carrier-to-noise ratioMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainGuard interval
Signals (typically in the form of OFDM signals) are transmitted between one or more transmitting antennas and one or more receiving antennas. The signals transmitted are subject to addition of a guard interval before scrambling in the time domain, while the signals received are subject to removal of the guard interval after scrambling in the time domain. Preferably time-scrambling of the OFDM signal being transmitted occurs after IFFT processing and guard interval insertion, while time de-scrambling of the signal being received occurs before both guard interval removal and FFT processing. Optionally, unscrambled pilot symbols (e.g. in the form of a training sequence), can be present at regular intervals inside the signal structure. At the receiver, equalization is carried out preferably in the frequency domain.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data
InactiveUS20080240293A1Improve reception performanceMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsDigital broadcastingComputer science
A digital broadcast system and method of processing data are disclosed. A channel equalizer includes a frequency domain converter receiving a known data sequence, when the known data sequence is periodically inserted and transmitted in general data, and converting the received data to frequency domain data, a CIR estimator using the data being received during a known data section and known data generated by a receiving system, so as to estimate a CIR, a CIR calculator interpolating or extrapolating the CIR estimated by the CIR estimator in accordance with characteristics of the general data being received, a coefficient calculator converting the CIR being outputted from the CIR calculator to a frequency domain CIR and calculating and outputting an equalization coefficient, and a distortion compensator multiplying the equalization coefficient calculated by the coefficient calculator with the data converted to frequency domain data by the frequency domain converter, thereby compensating channel distortion.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Popular searches
Error detection/prevention using signal quality detector Transmission path division Line-faulsts/interference reduction Transmitter/receiver shaping networks Duplex signal operation Pulse slope modification Synchronisation information channels Cross-talk reduction Time-division multiplex Amplitude demodulation details
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com