Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
986 results about "Packet communication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
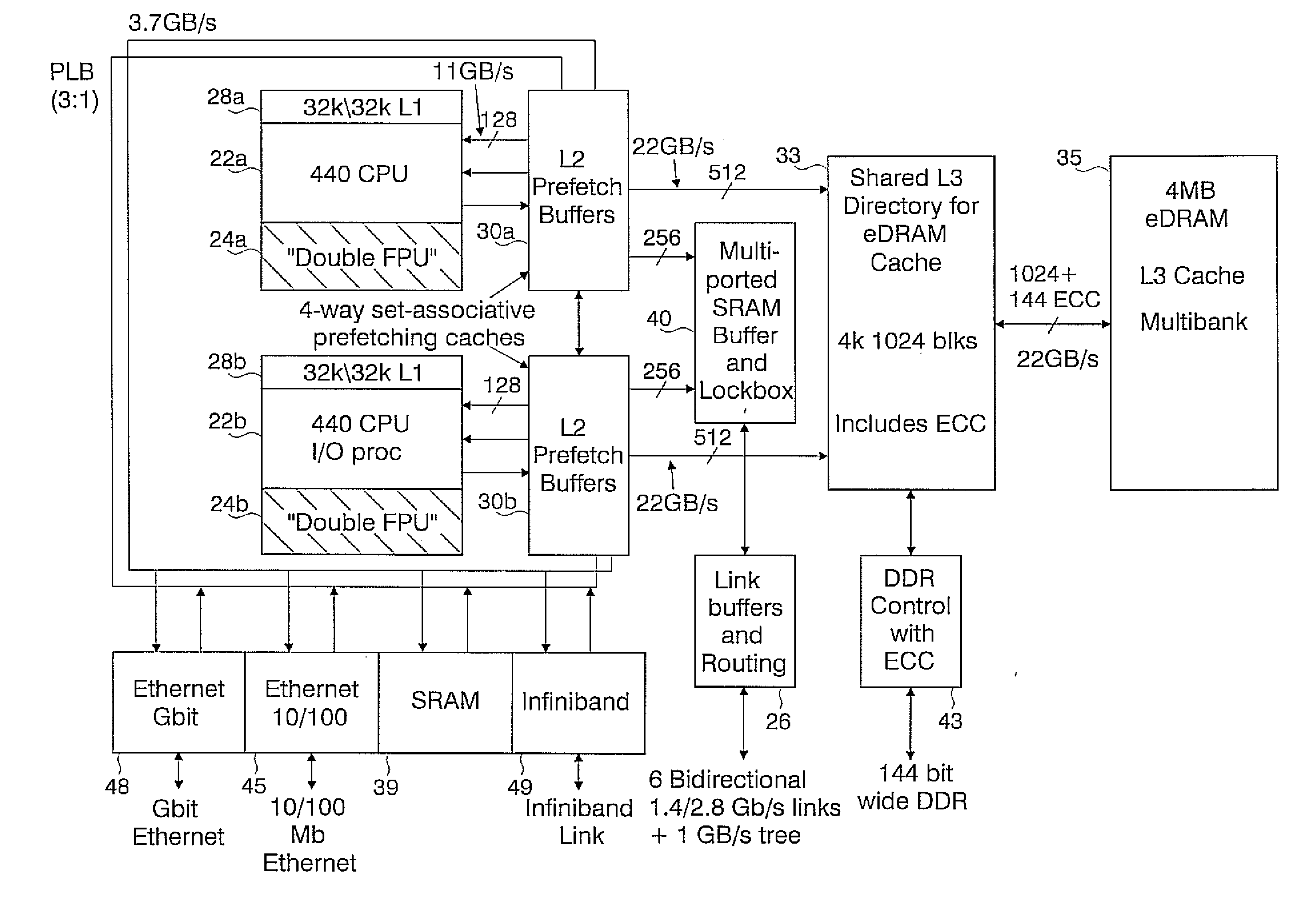
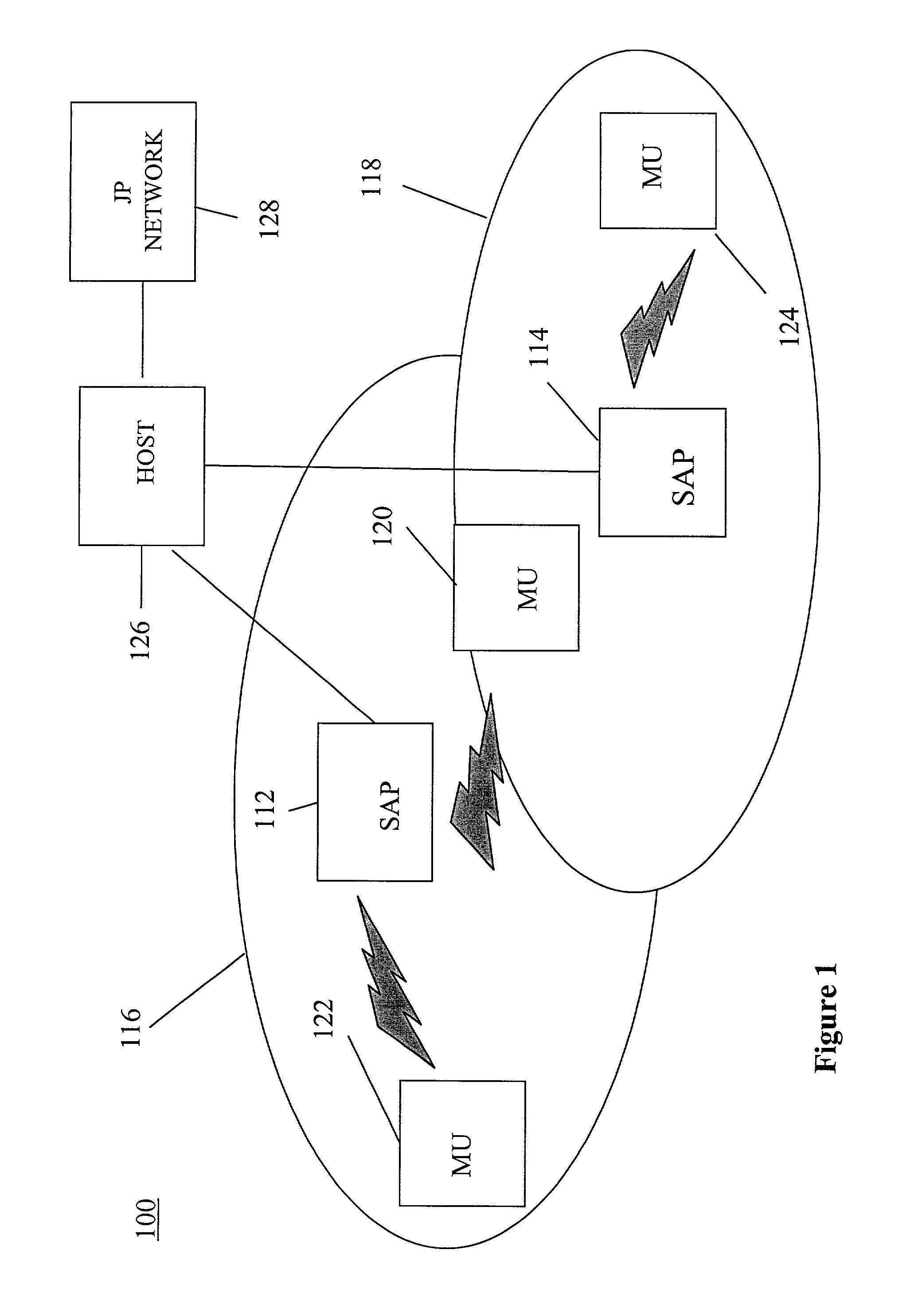
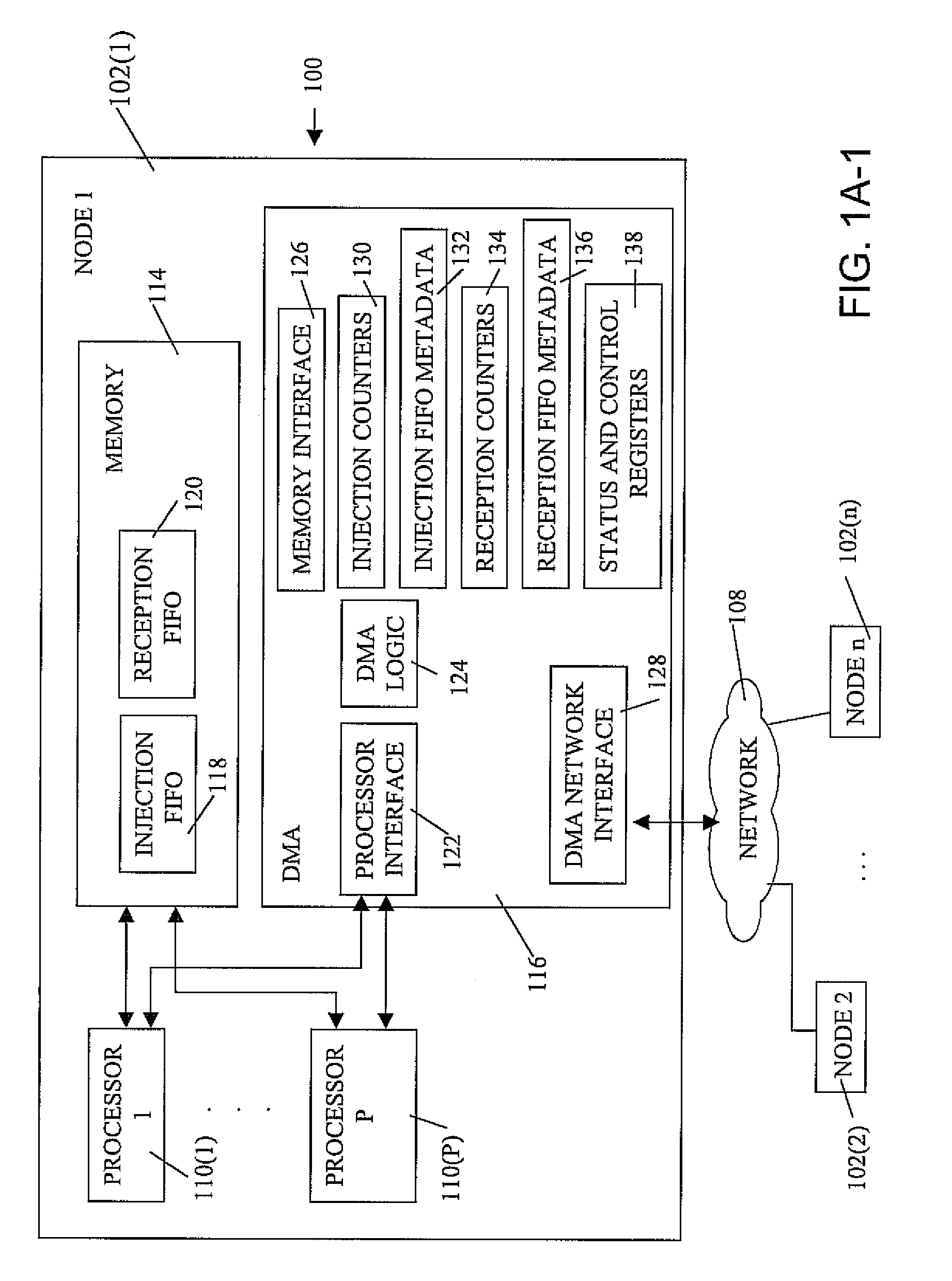
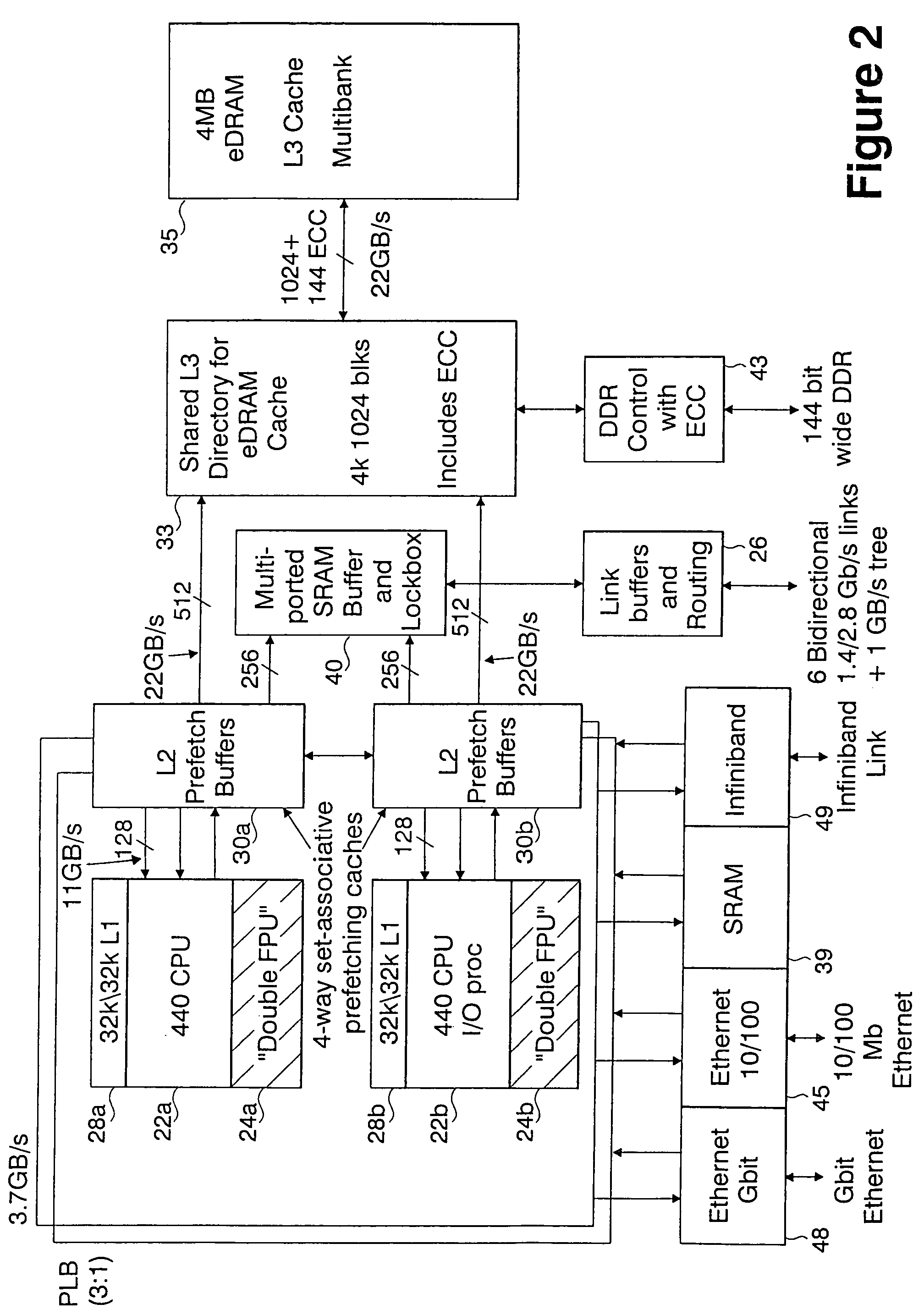
Novel massively parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS20090259713A1Low costReduced footprintError preventionProgram synchronisationSupercomputerPacket communication
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
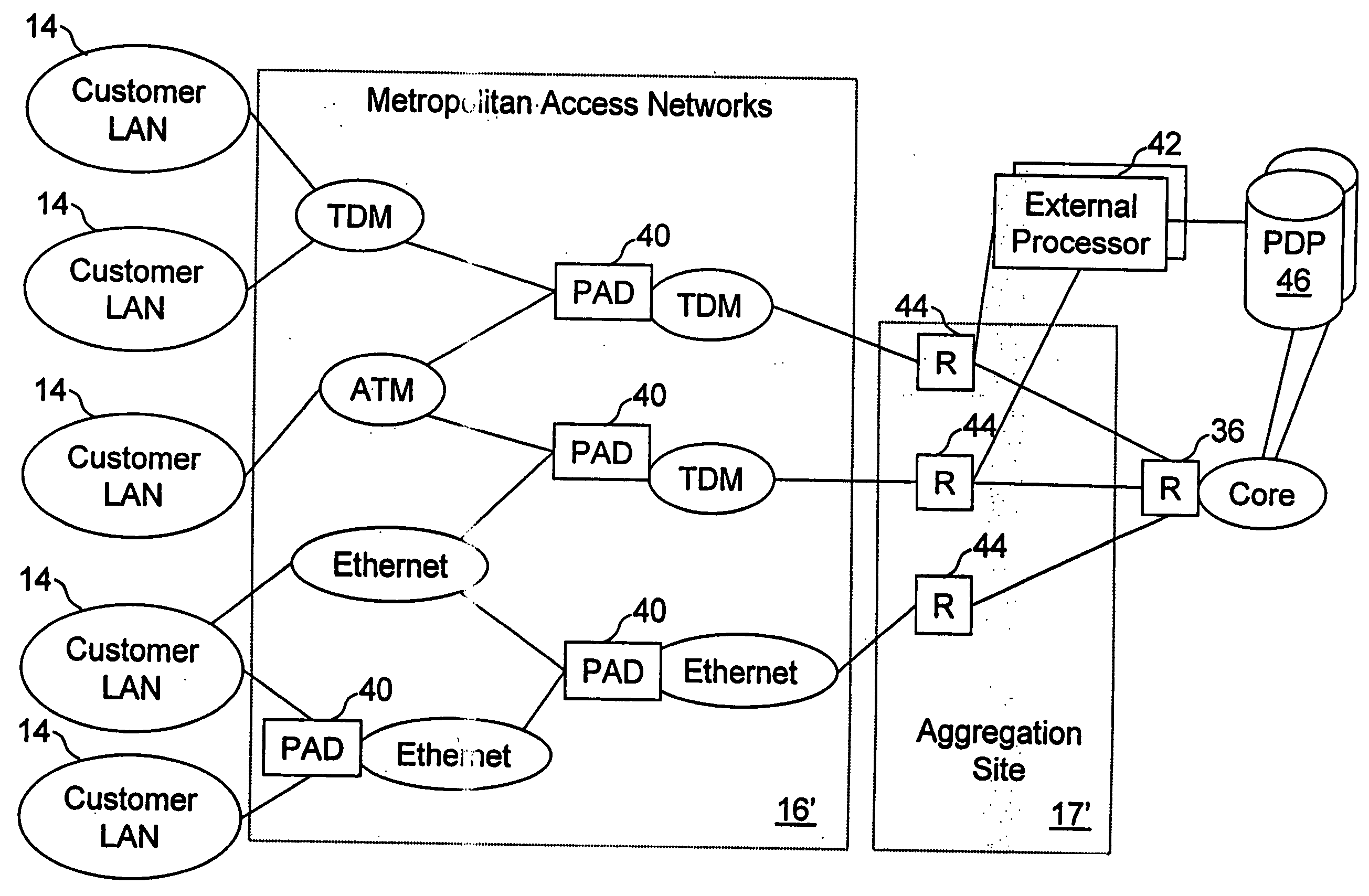
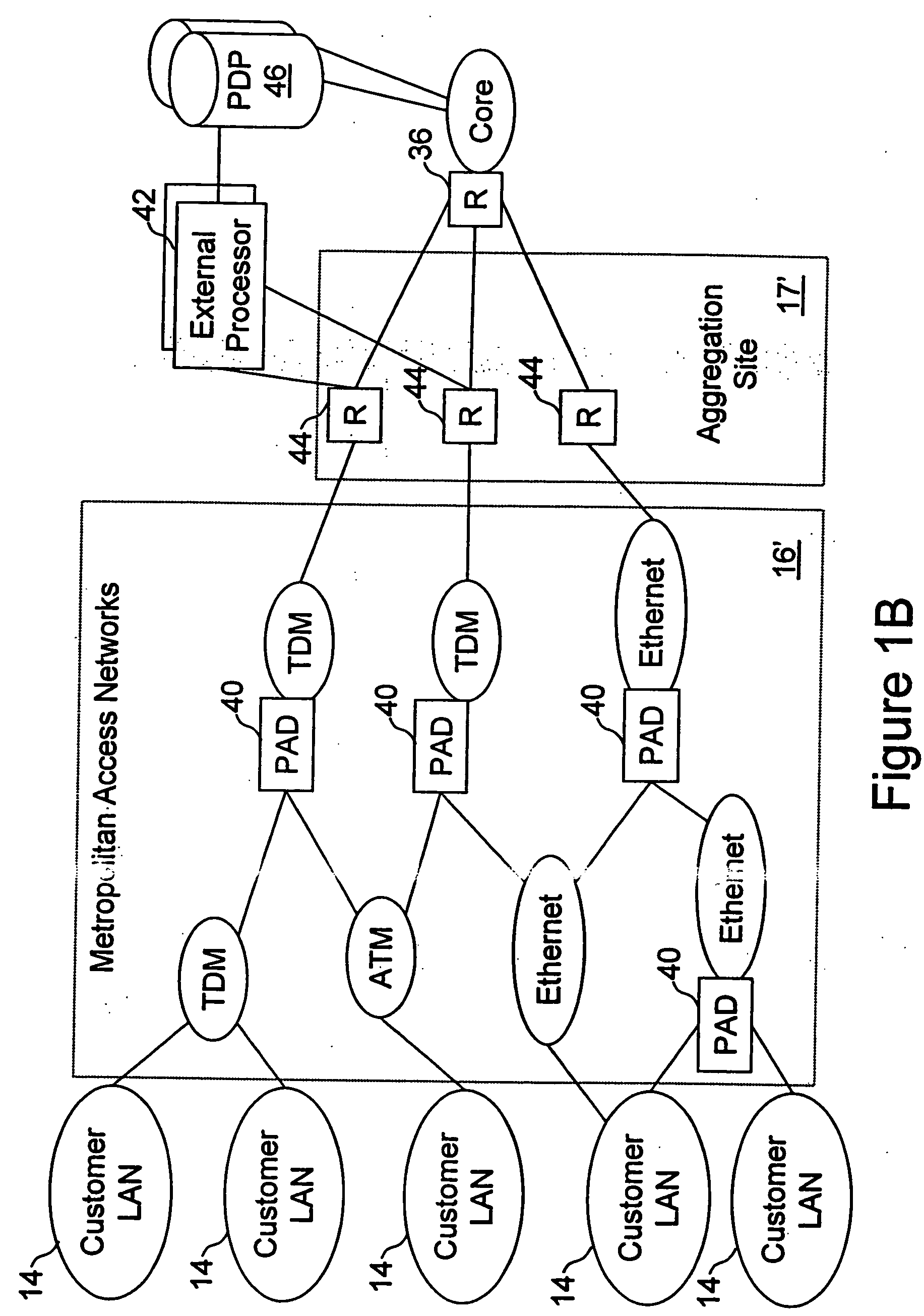
Network access system including a programmable access device having distributed service control
InactiveUS20050117576A1Good extensibilityIncrease flexibilityData switching by path configurationPacket communicationService control
A distributed network access system in accordance with the present invention includes at least an external processor and a programmable access device. The programmable access device has a message interface coupled to the external processor and first and second network interfaces through which packets are communicated with a network The programmable access device includes a packet header filter and a forwarding table that is utilized to route packets communication between the first and second network interfaces. In response to receipt of a series of packets, the packet header filter in the programmable access device identifies messages in the series of messages upon which policy-based services are to be implemented and passes identified messages via the message interface to the external processor for processing. In response to receipt of a message, the external processor invokes service control on the message and may also invoke policy control on the message.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
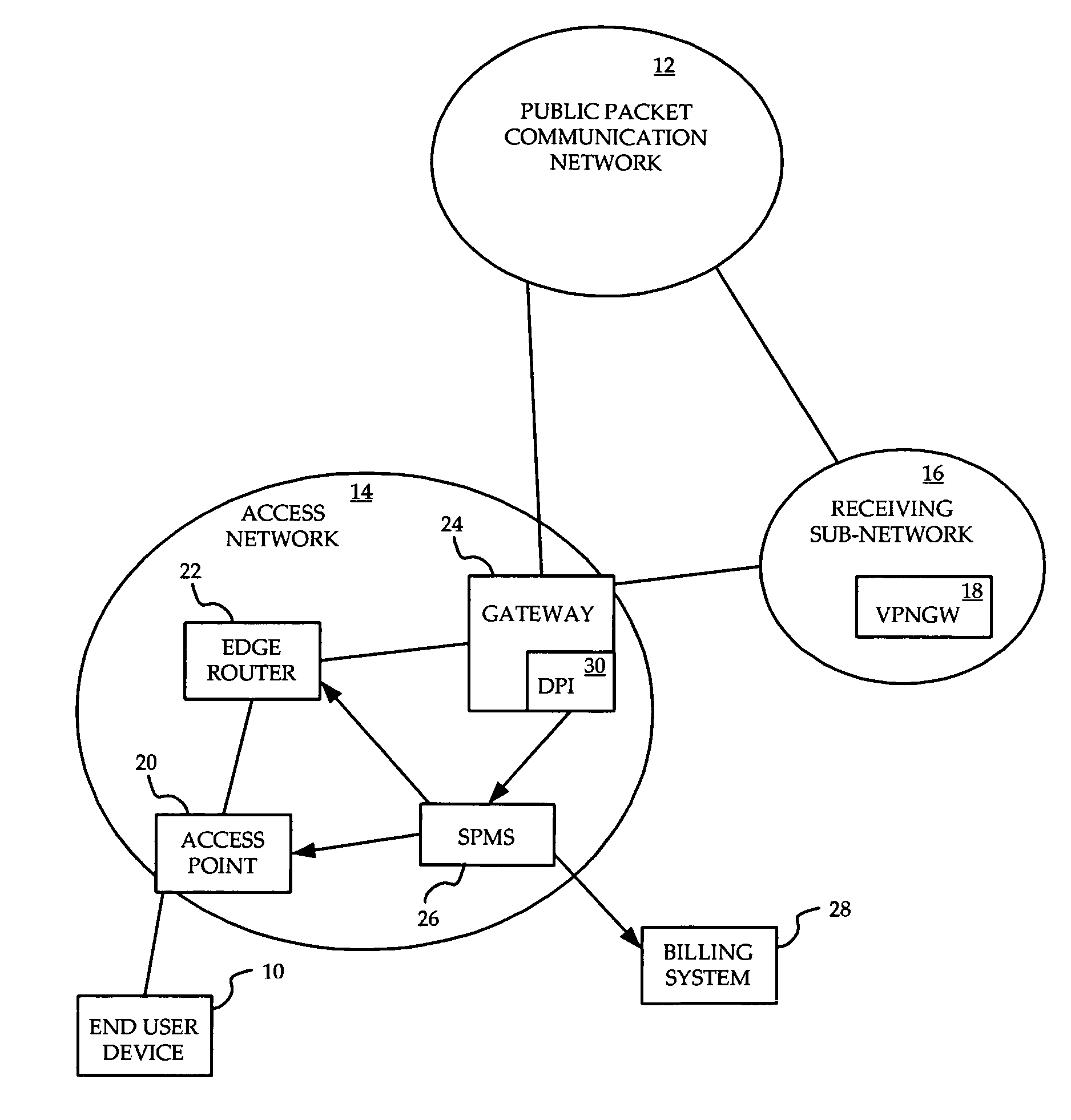
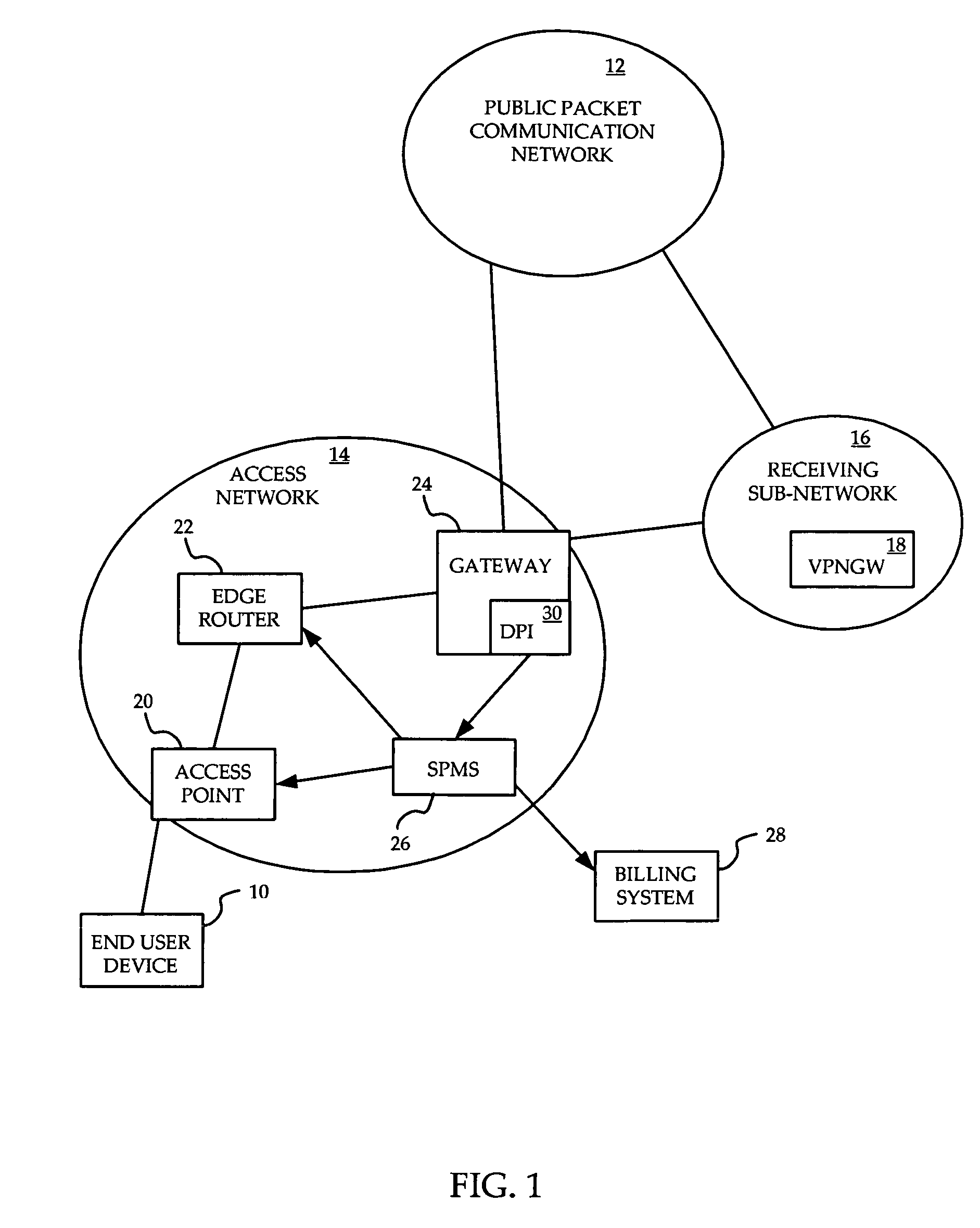
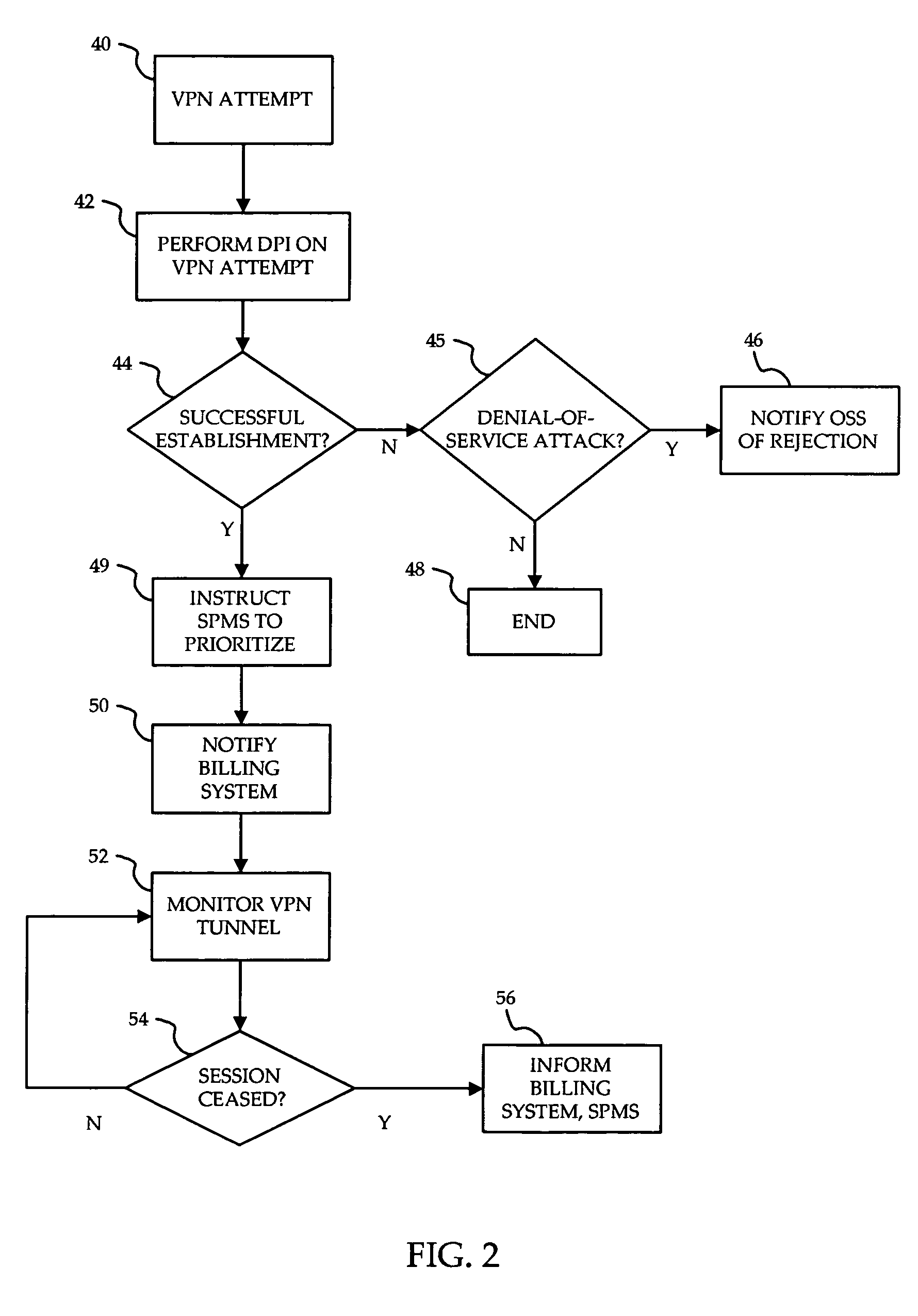
System and method for prioritization of traffic through internet access network
InactiveUS7881199B2Avoid allocation problemsRaise priorityError preventionTransmission systemsPacket communicationTraffic capacity
A method is provided for ensuring that specific traffic flows are adequately prioritized in a public packet communication network even when the network is heavily congested. Per-flow QoS capability is added to VPN tunnels. Connection requests are routed through a specific port in an access provider's network to designated VPN gateway. Deep packet inspection is performed on traffic through the port in an attempt to determine whether the connection request was accepted. If the connection request was accepted, the traffic flows associated with that session may be given a specific priority of QoS level when transiting a packet access network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
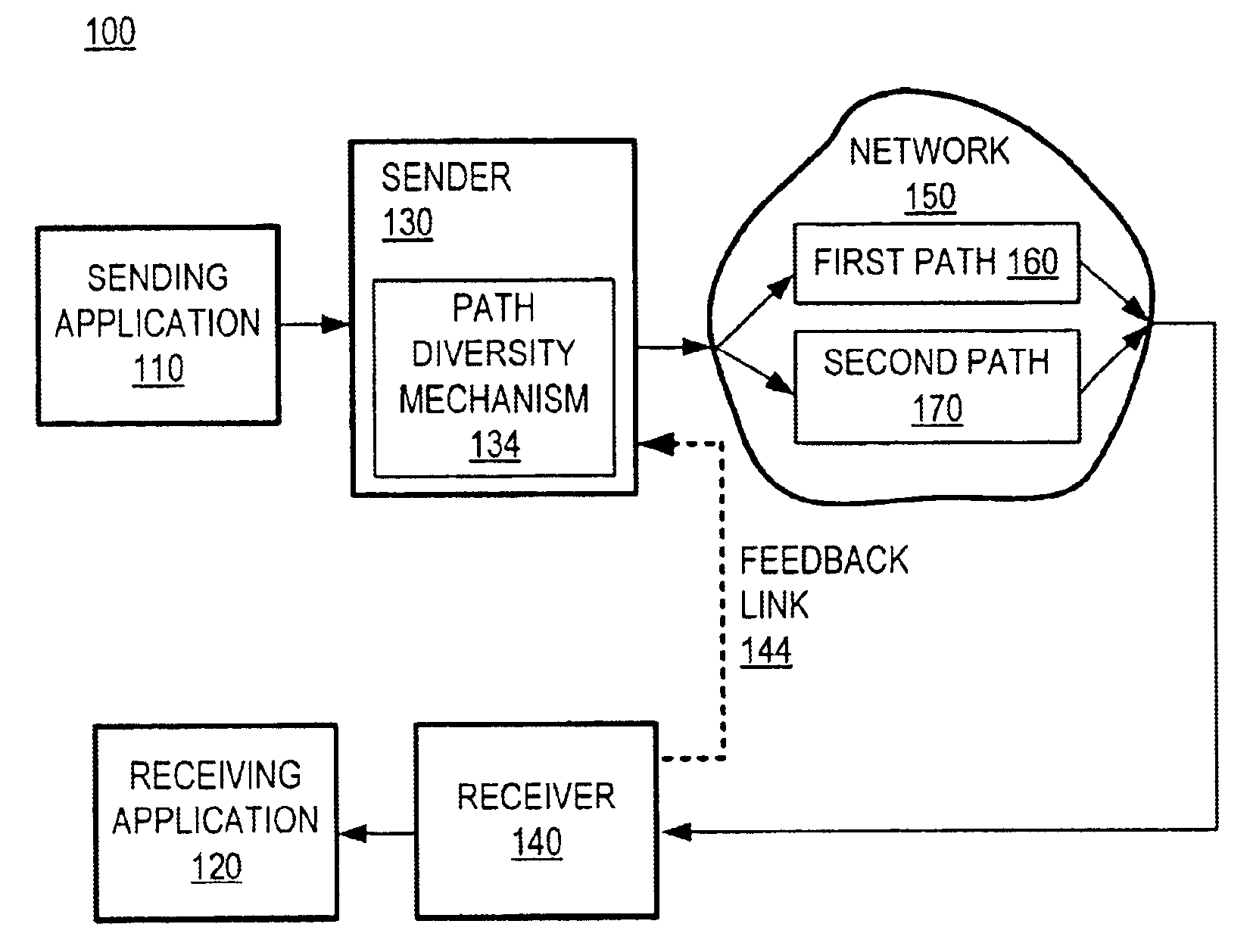
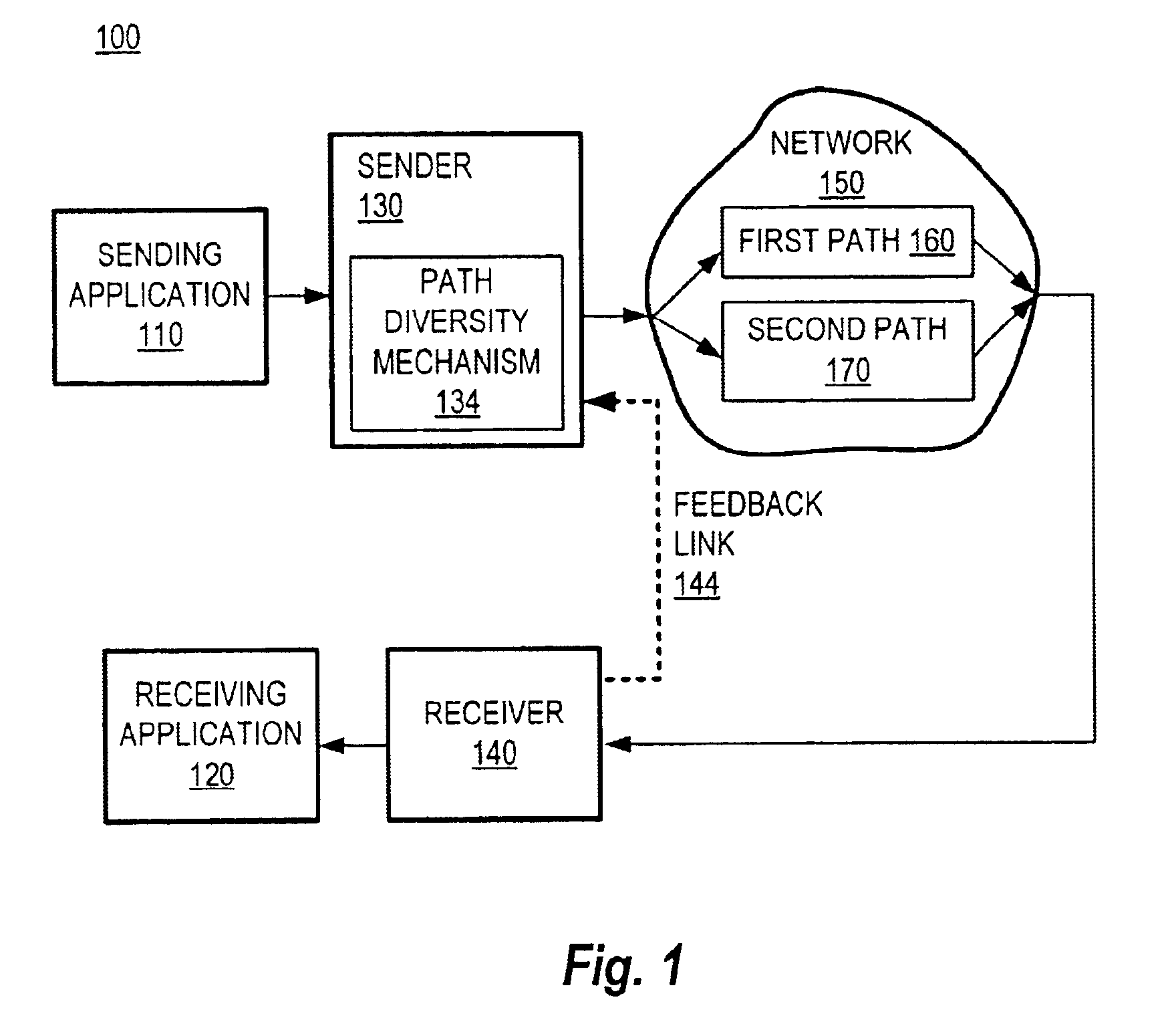
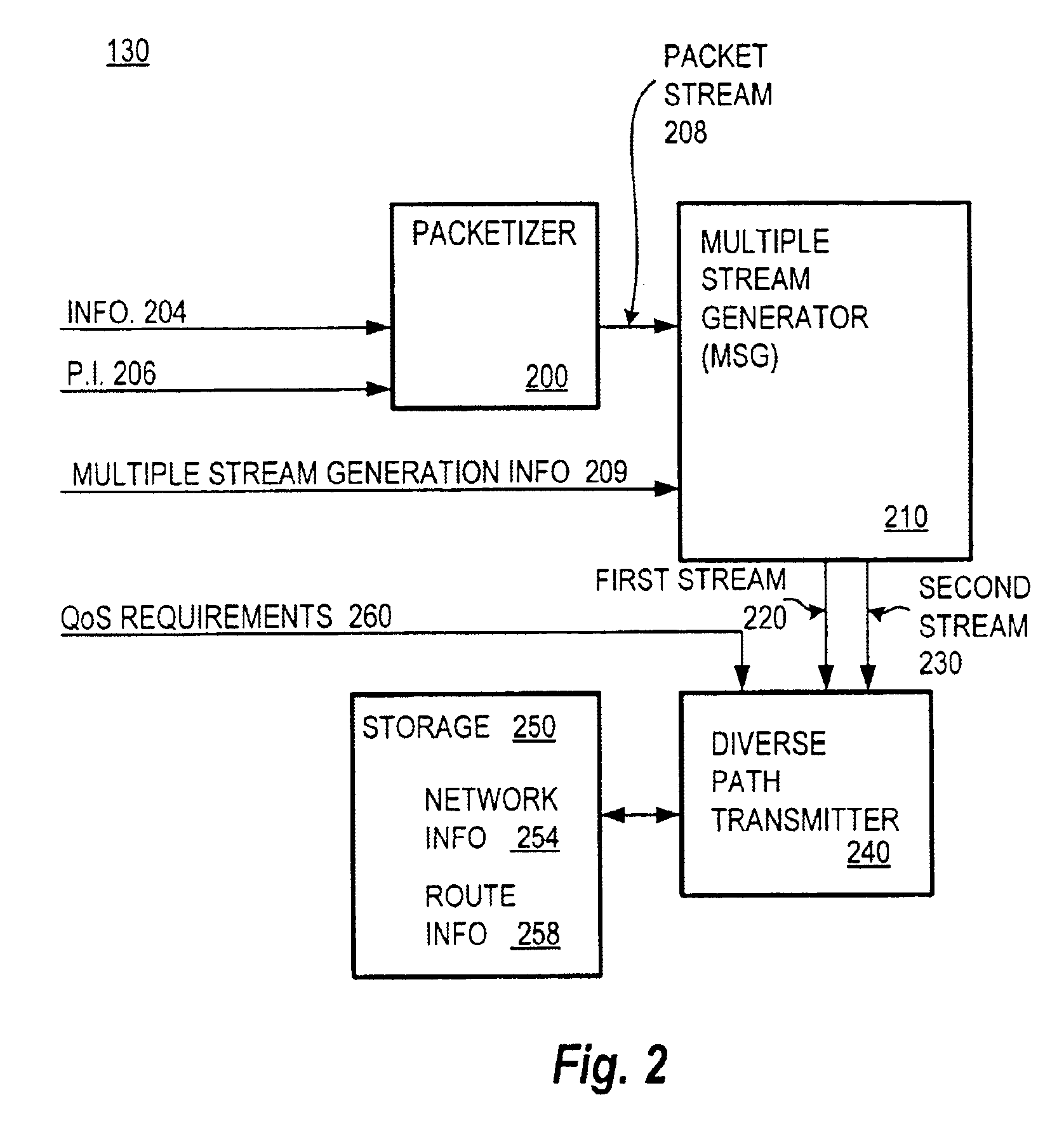
Method and system for packet communication employing path diversity
InactiveUS6868083B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationPacket loss
Communication over lossy packet networks such as the Internet is hampered by limited bandwidth and packet loss. The present invention provides a path diversity transmission system for improving the quality of communication over a lossy packet network. The path diversity transmission system explicitly sends different subsets of packets over different paths, thereby enabling the end-to-end application to effectively see an average path behavior. Generally, seeing this average path behavior provides better performance than seeing the behavior of any individual random path. For example, the probability that all of the multiple paths are simultaneously congested is much less than the probability that a single path is congested. The resulting path diversity can provide a number of benefits, including enabling real-time multimedia communication and simplifying system design (e.g., error correction system design). Two exemplary architectures for achieving path diversity are described herein. The first architecture is based on source routing, and the second architecture is based on a relay infrastructure. The second architecture routes traffic through semi-intelligent nodes at strategic locations in the Internet, thereby providing a service of improved reliability while leveraging the infrastructure of the Internet.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
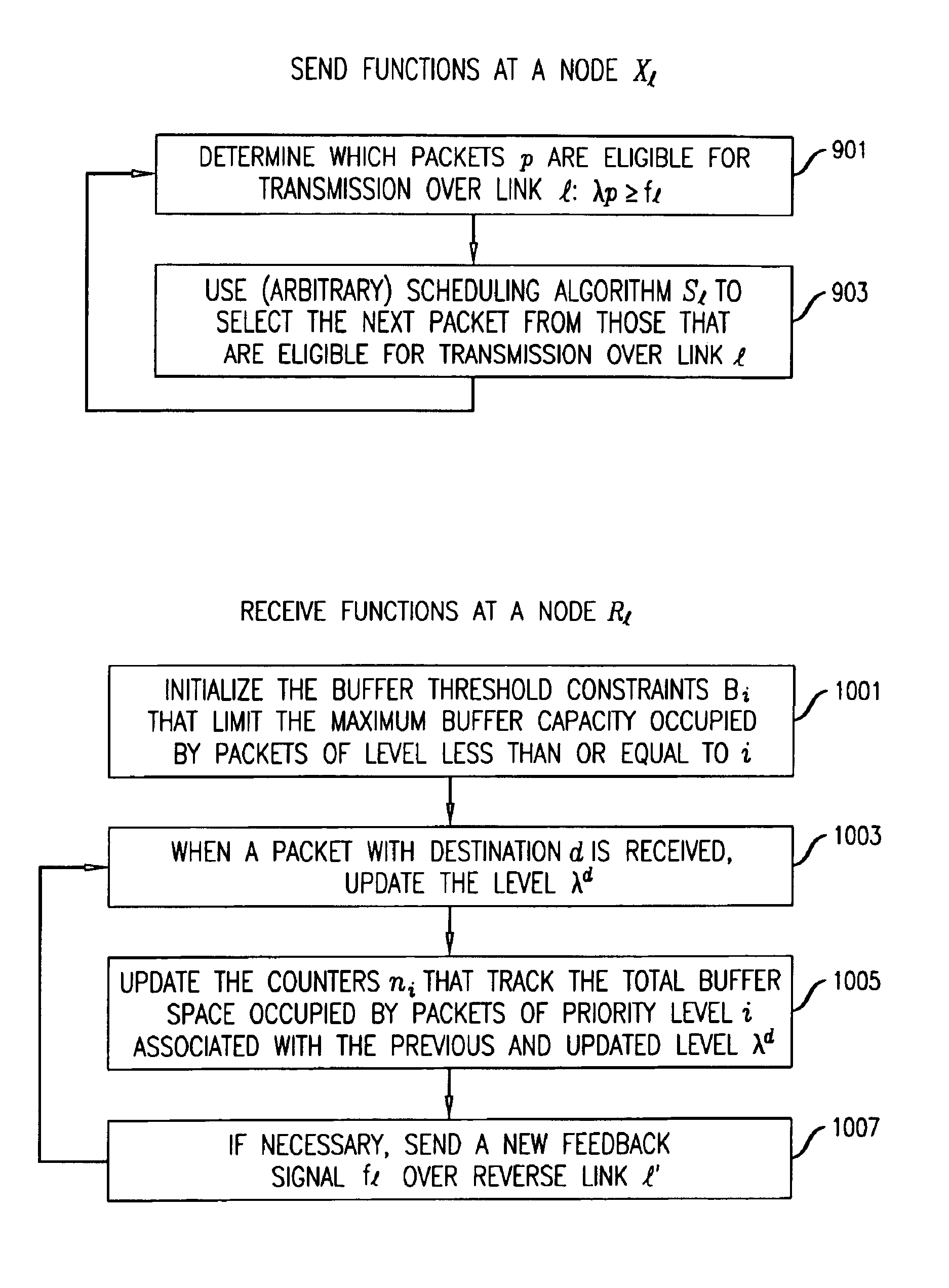
Prevention of deadlocks and livelocks in lossless, backpressured packet networks
InactiveUS6859435B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationComputer network
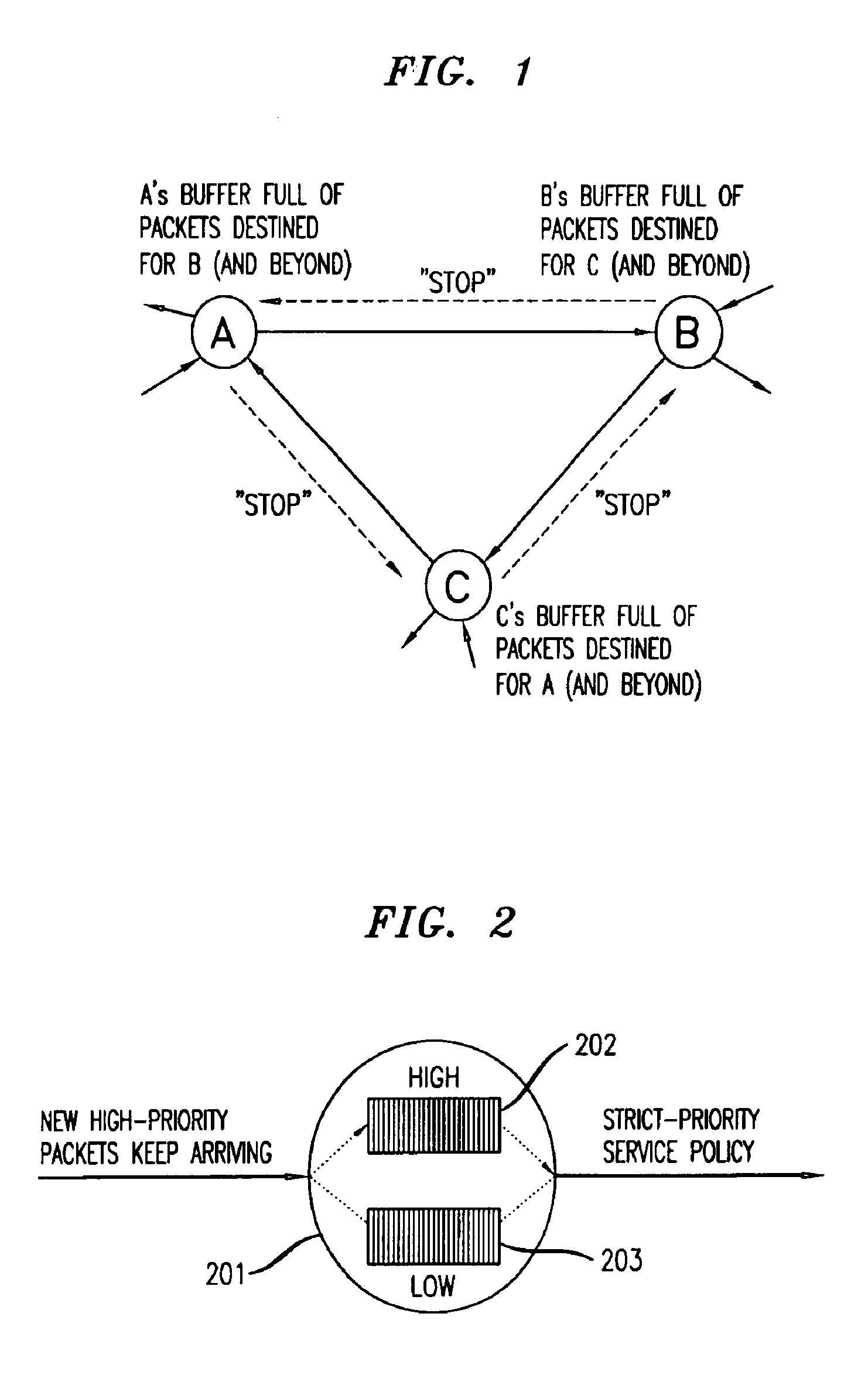
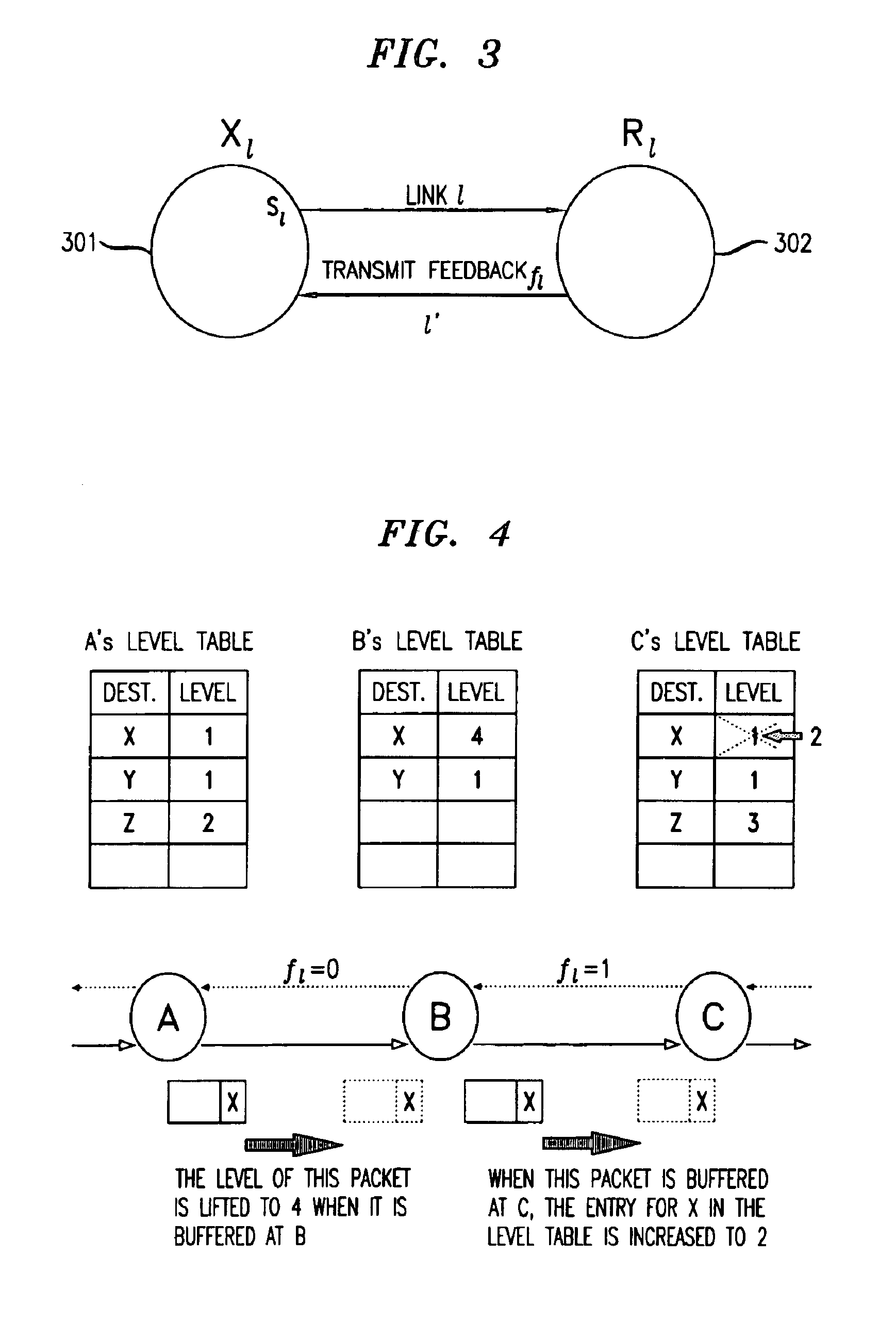
A packet communication network is arranged so that a backpressure or feedback signal is sent from a receiving node to a node having packets to send to the receiving,node, selectively allowing only certain packets to be considered eligible for transmission. The backpressure is arranged to be lossless, and to avoid network deadlocks and livelocks. The transmission of a packet p from a sending node Xl to a receiving node Rl, via a link l, is controlled by (a) sending from the receiving node Rl to the upstream node Xl a feedback value fl that assures that there will be room in the buffer in the receiving node Rl to store packets subsequently received from the upstream node Xl; (b) assigning a priority level λp to packets stored in the buffer of the receiving node Rl; and (c) transmitting from the sending node Xl to the receiving node Rl, only those stored packets at Xl whose priority level λp exceeds the feedback value fl received from the receiving node Rl.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
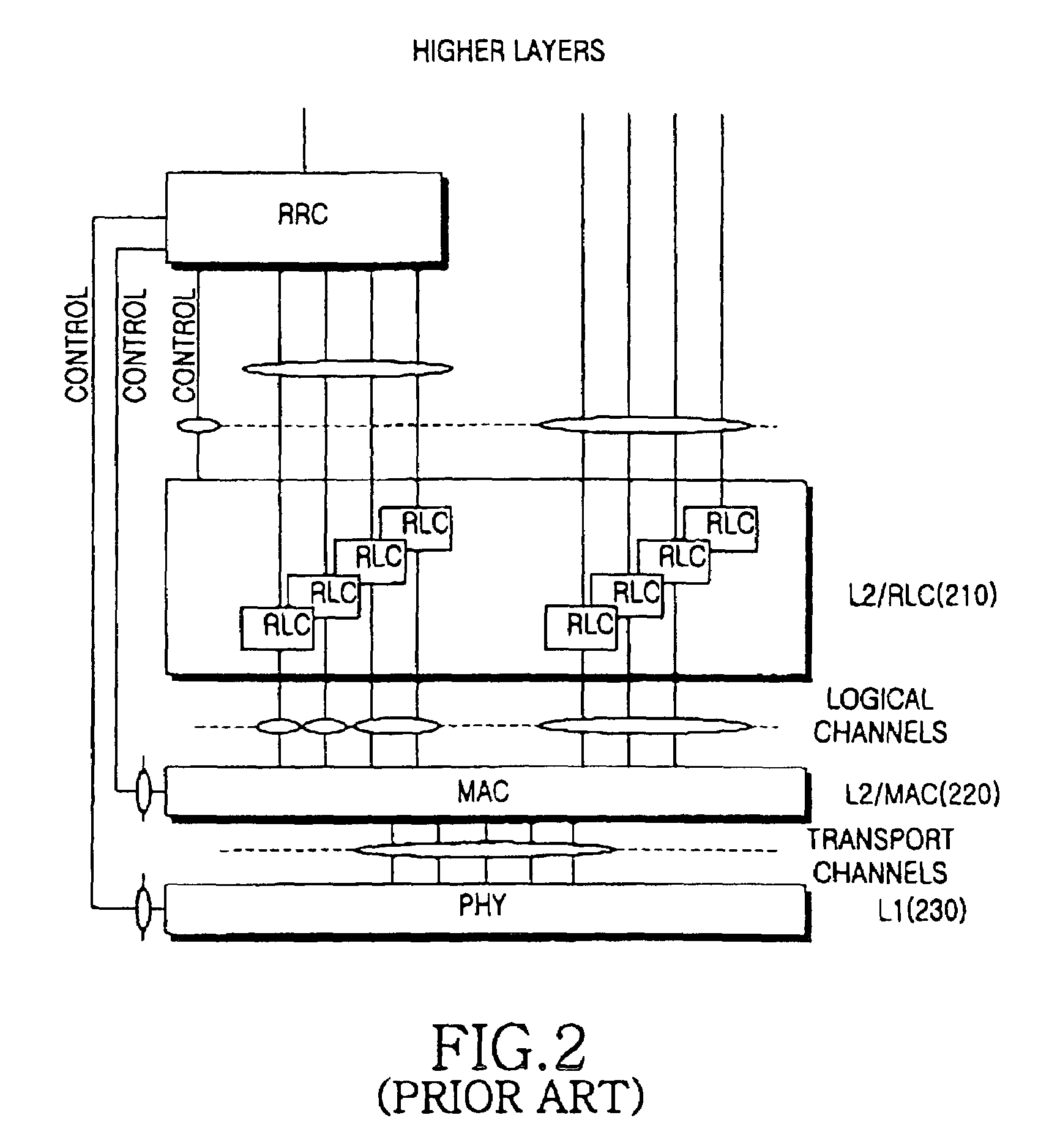
Signaling method between MAC entities in a packet communication system
ActiveUS7359345B2Power managementError prevention/detection by using return channelPacket communicationMedia access control
A signaling method between a MAC (Medium Access Control) layer entity of a transmission apparatus and a MAC layer entity of a reception apparatus in a packet communication system including the transmission apparatus and the reception apparatus wherein upon receiving a signaling request, the MAC layer entity of the transmission apparatus transmits a MAC signaling message including control information and a signaling indication indicating transmission of the control information and the MAC layer entity of the reception apparatus determines whether the MAC signaling message includes the signaling indication, and receives the control information included in the MAC signaling message, if the MAC signaling message includes the signaling indication.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
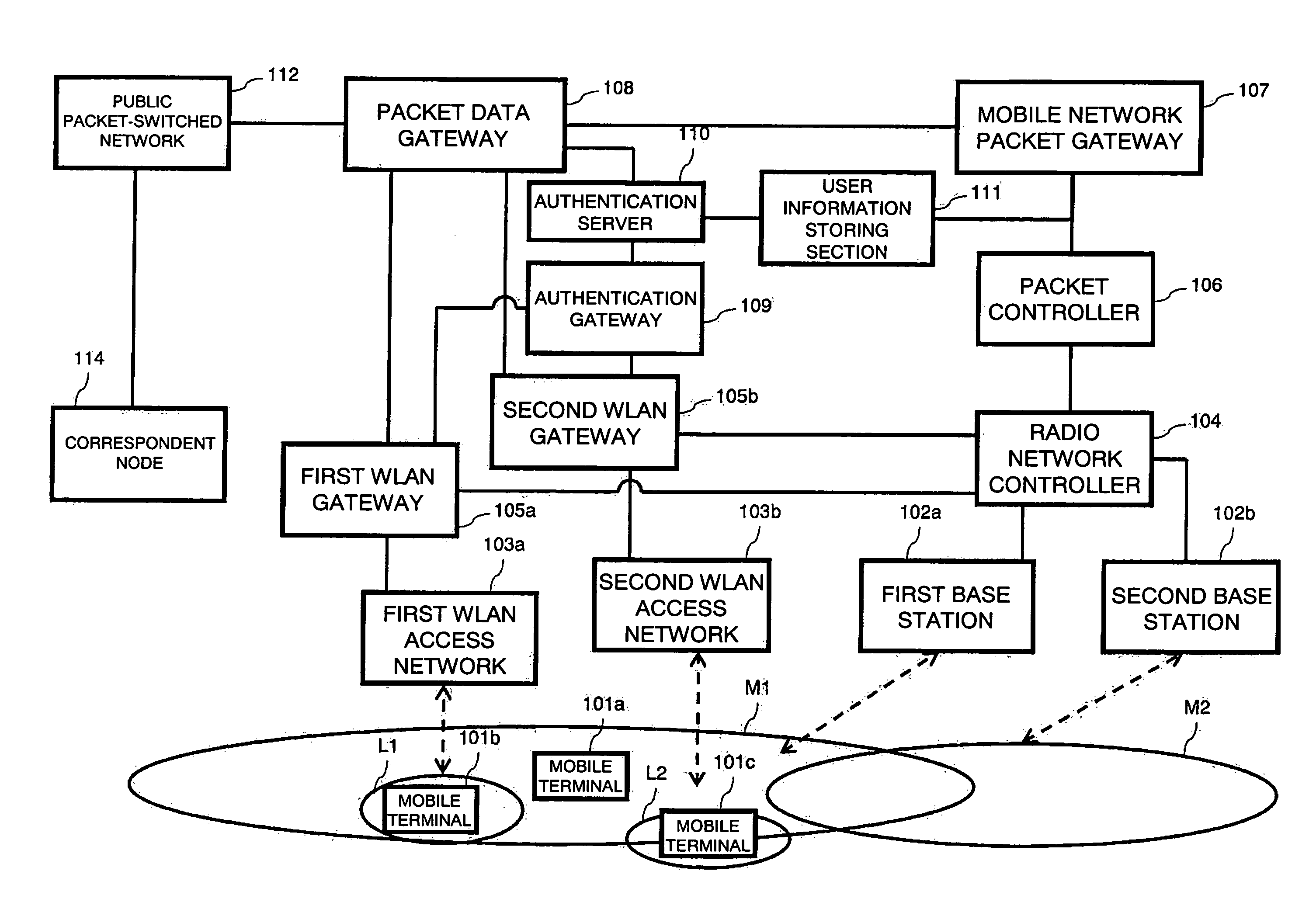
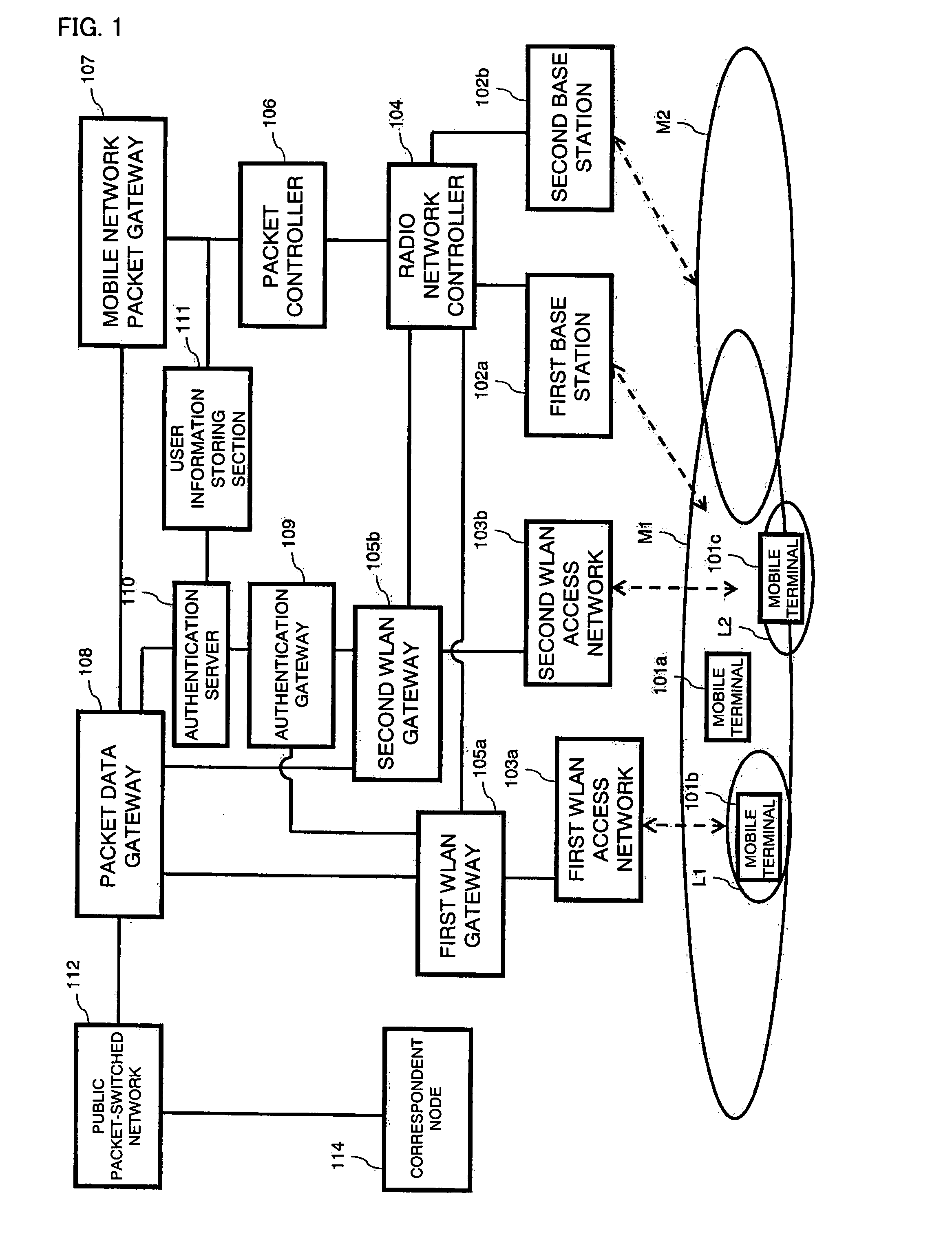
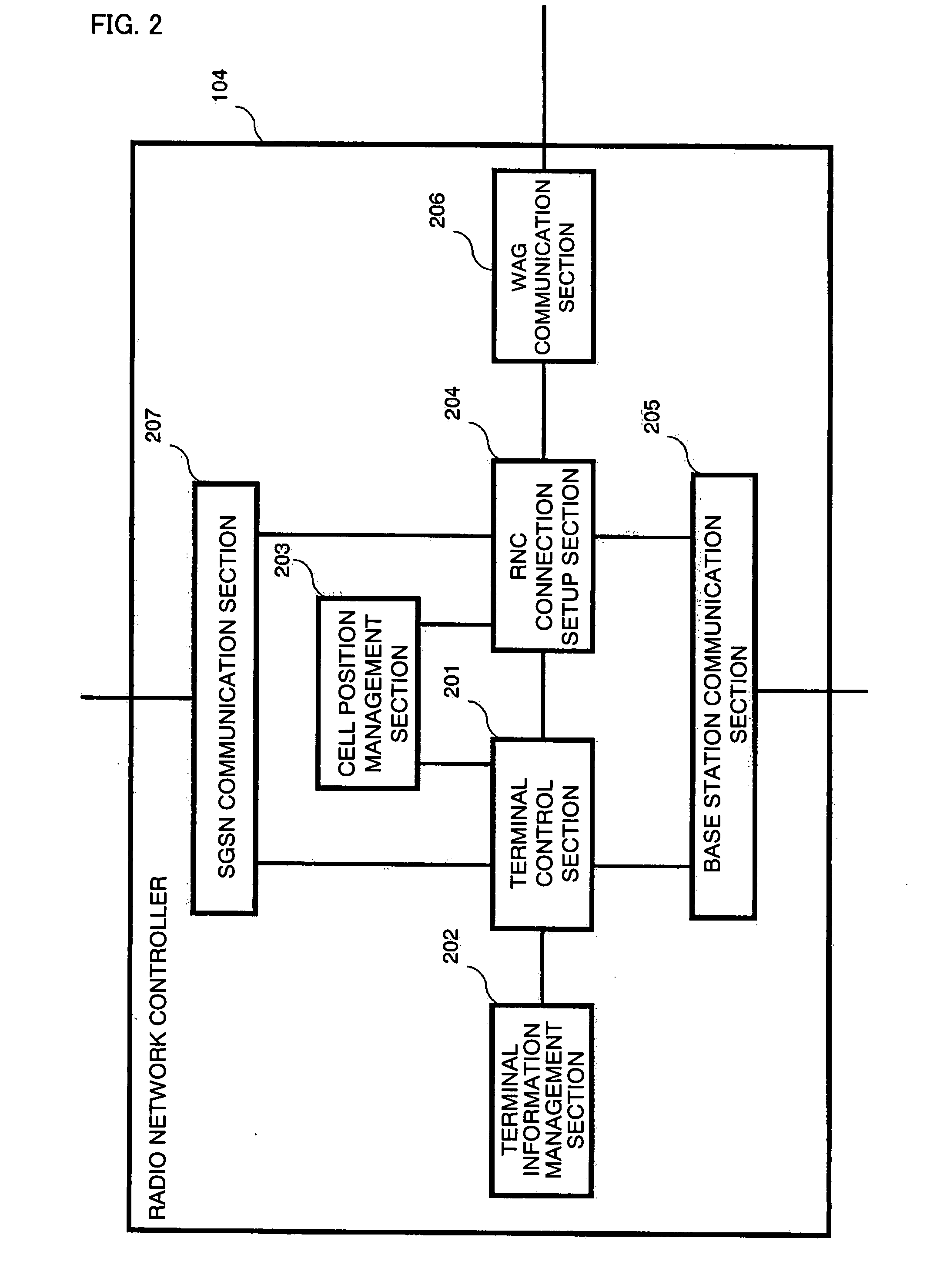
Radio Network Controller, Wireless Access Gateway, Radio Communication System, and Communication Method for Radio Communication System
ActiveUS20080117884A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionPacket communicationCommunications system
A radio network controller (104) according to the present invention outputs a context required for a terminal (110a) capable of communicating with a mobile communication network and a wireless local area network to communicate with the wireless local area network to the terminal (110a) among pieces of information input from wireless access gateways (105a, 105b) that control connection with one or more wireless local area networks (103a, 103b) and provide seamless handover of packet communication between the mobile communication network and the wireless LAN.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
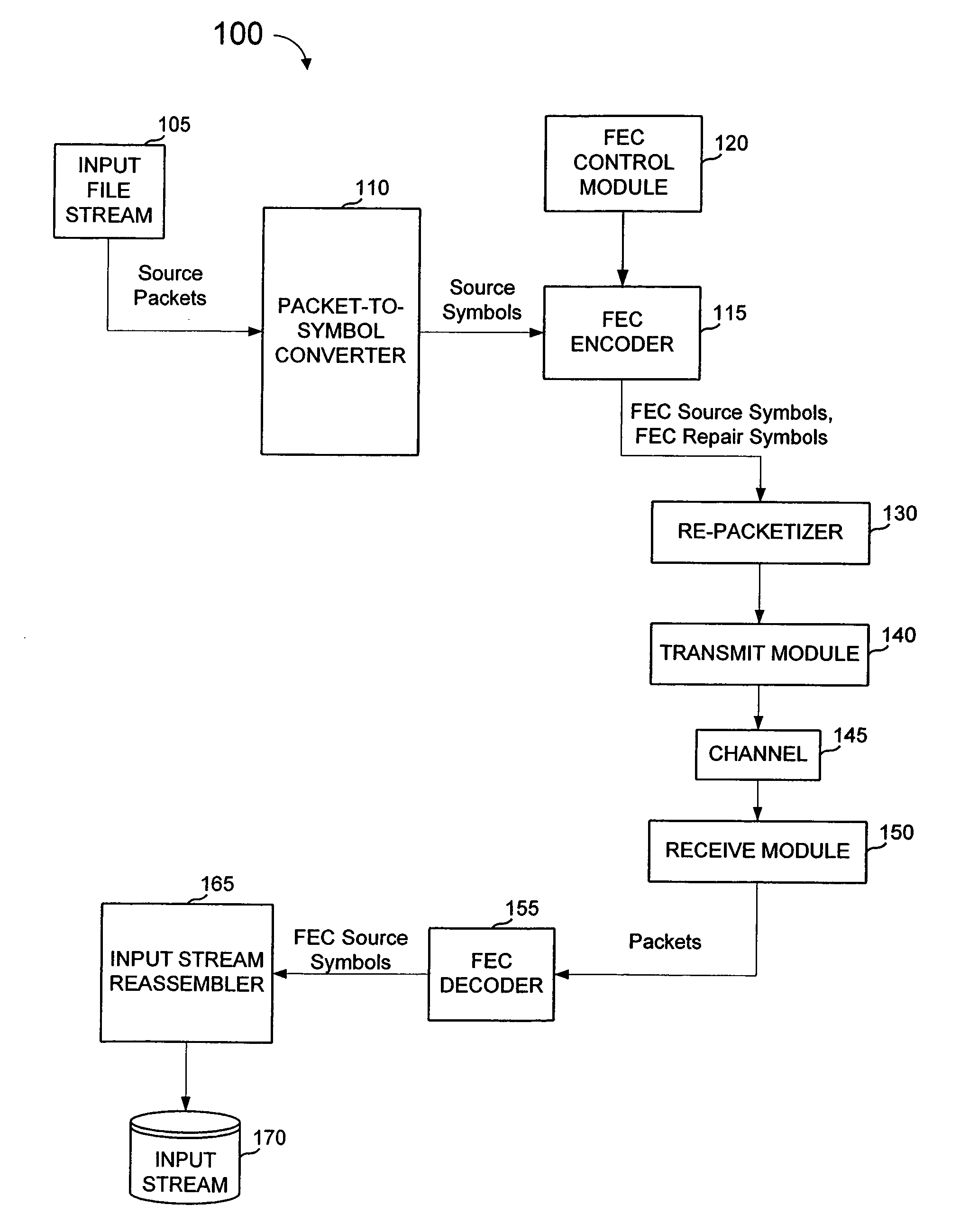
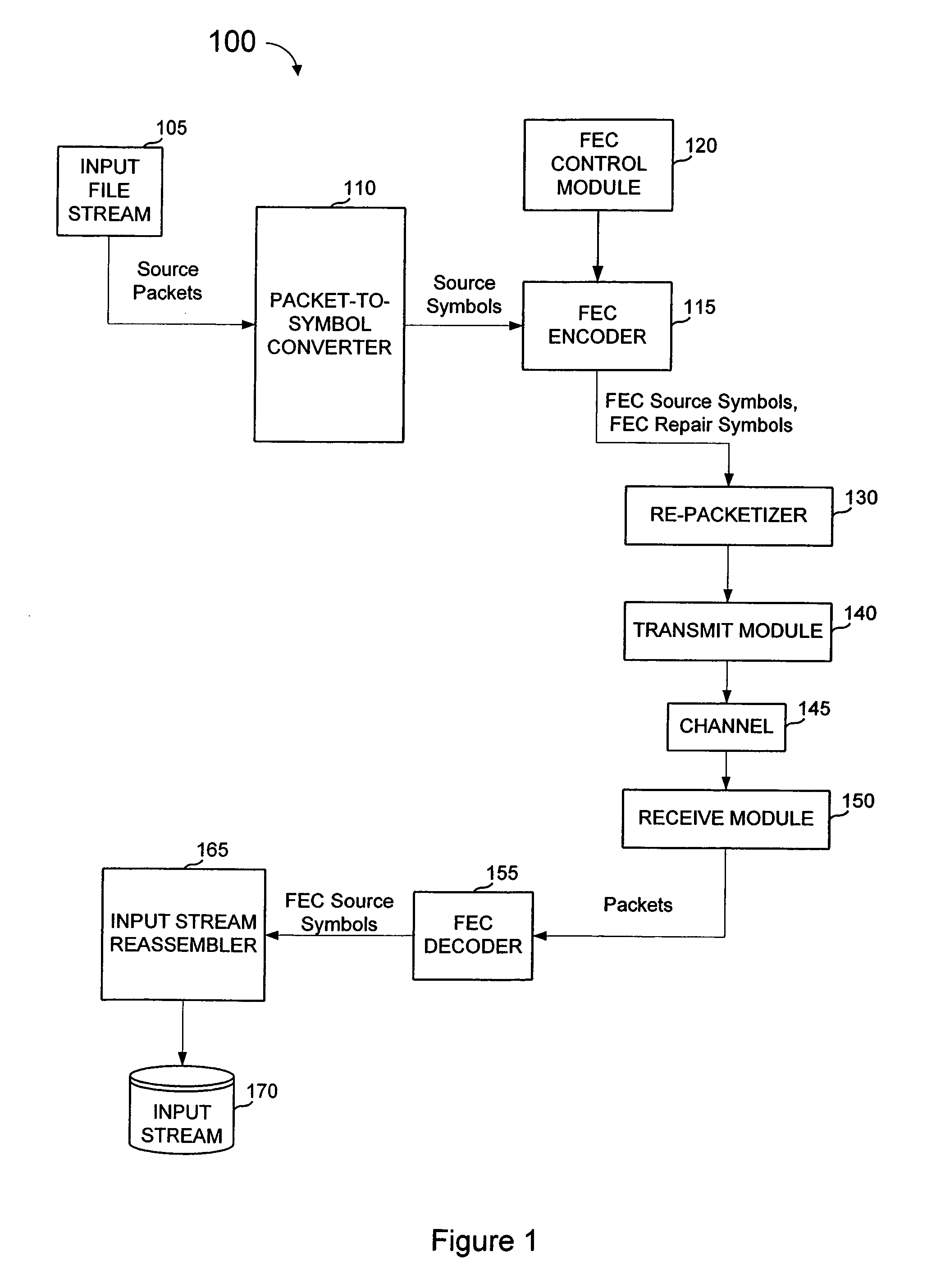
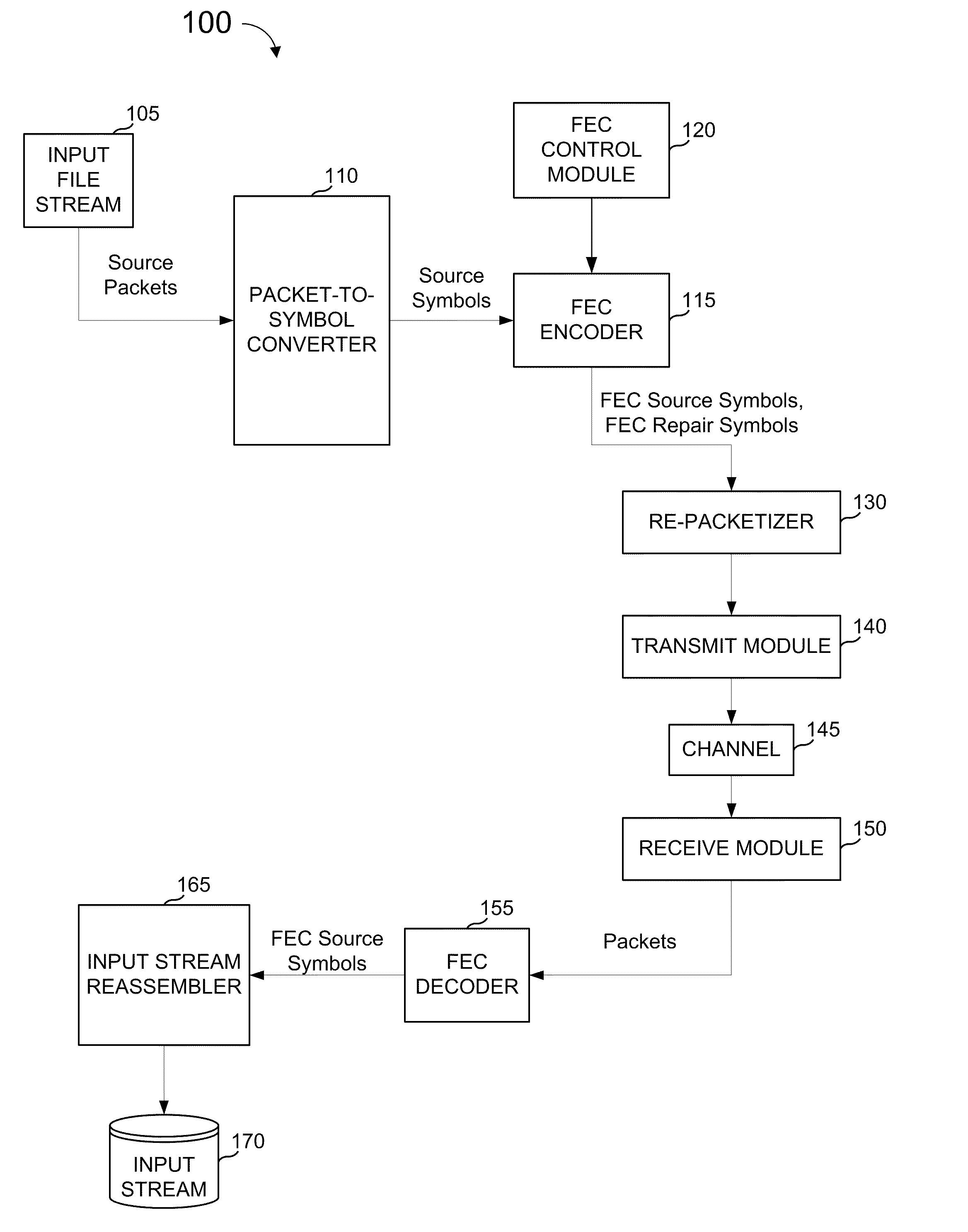
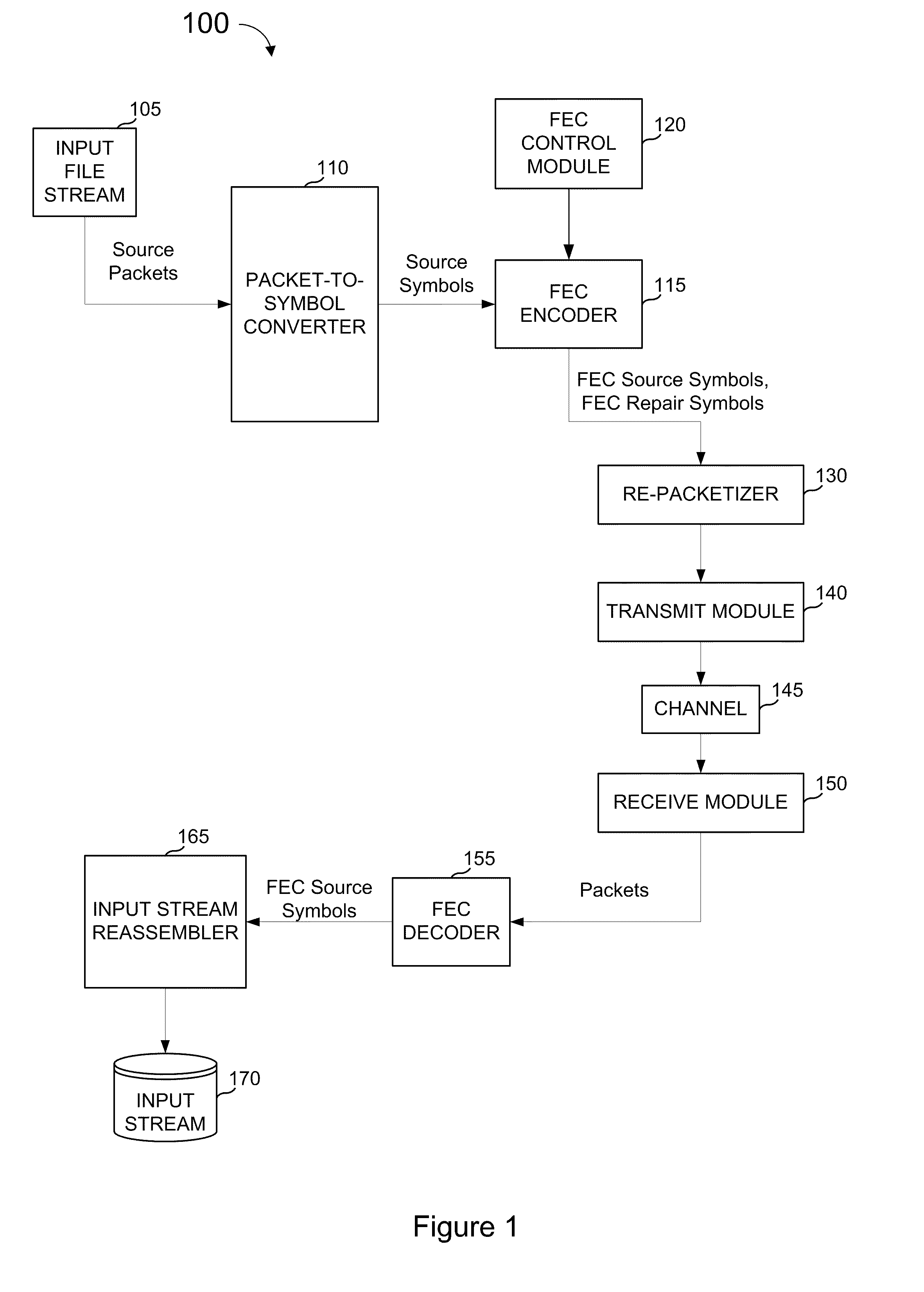
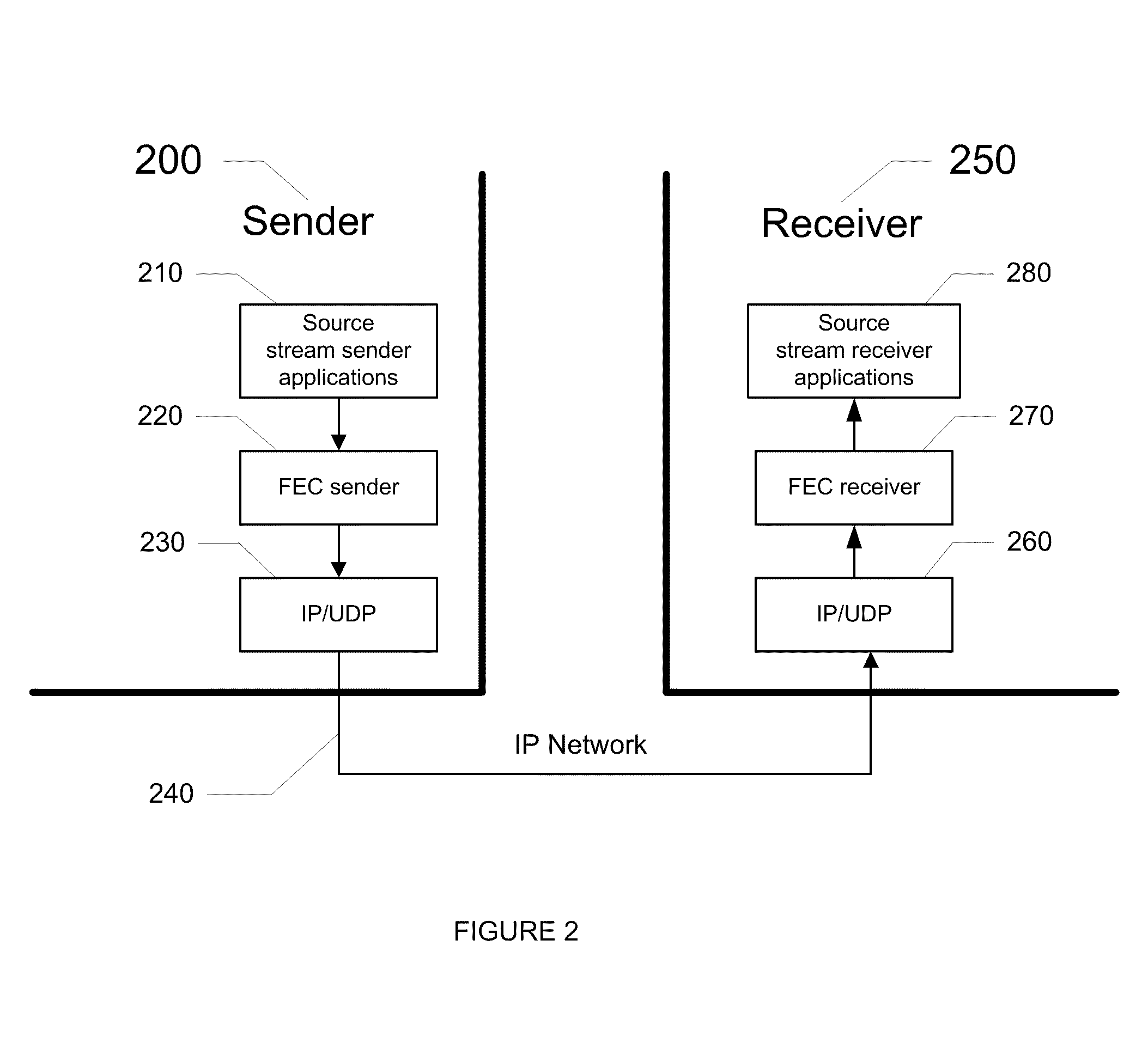
FEC architecture for streaming services including symbol-based operations and packet tagging
ActiveUS7660245B1Loss of protectionEfficiently recreateTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationStreaming data
In a packet communications system stream data is transported over a channel over which packet loss or corruption is possible, with forward error correction (“FEC”) information. A transmitter receives source packets comprising source data, generates FEC source packets formatted to allow for identification of lost or corrupted source packets at a receiver, arranges source data from the source packets into a plurality of source symbols wherein at least one source packet is arranged into more than one source symbol, associates a plurality of source symbols with a source block, generates a plurality of repair symbols from the source block according to a predetermined FEC encoding process and groups the plurality of repair symbols into one or more FEC repair packets associated with the source block. A receiver can use the FEC repair symbols from the FEC repair packets to recover source symbols, as needed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
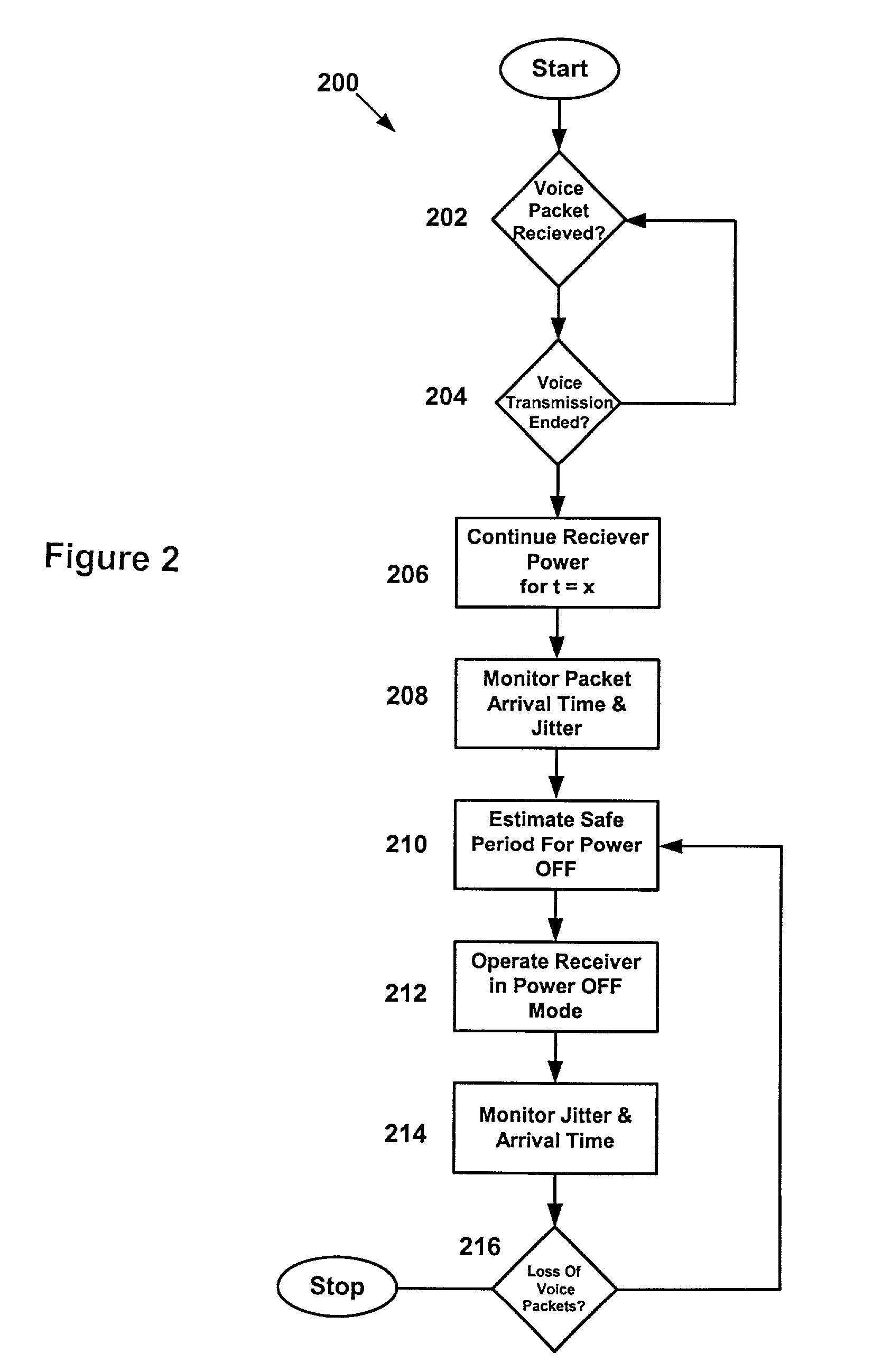
Power saving function for wireless LANS: methods, system and program products
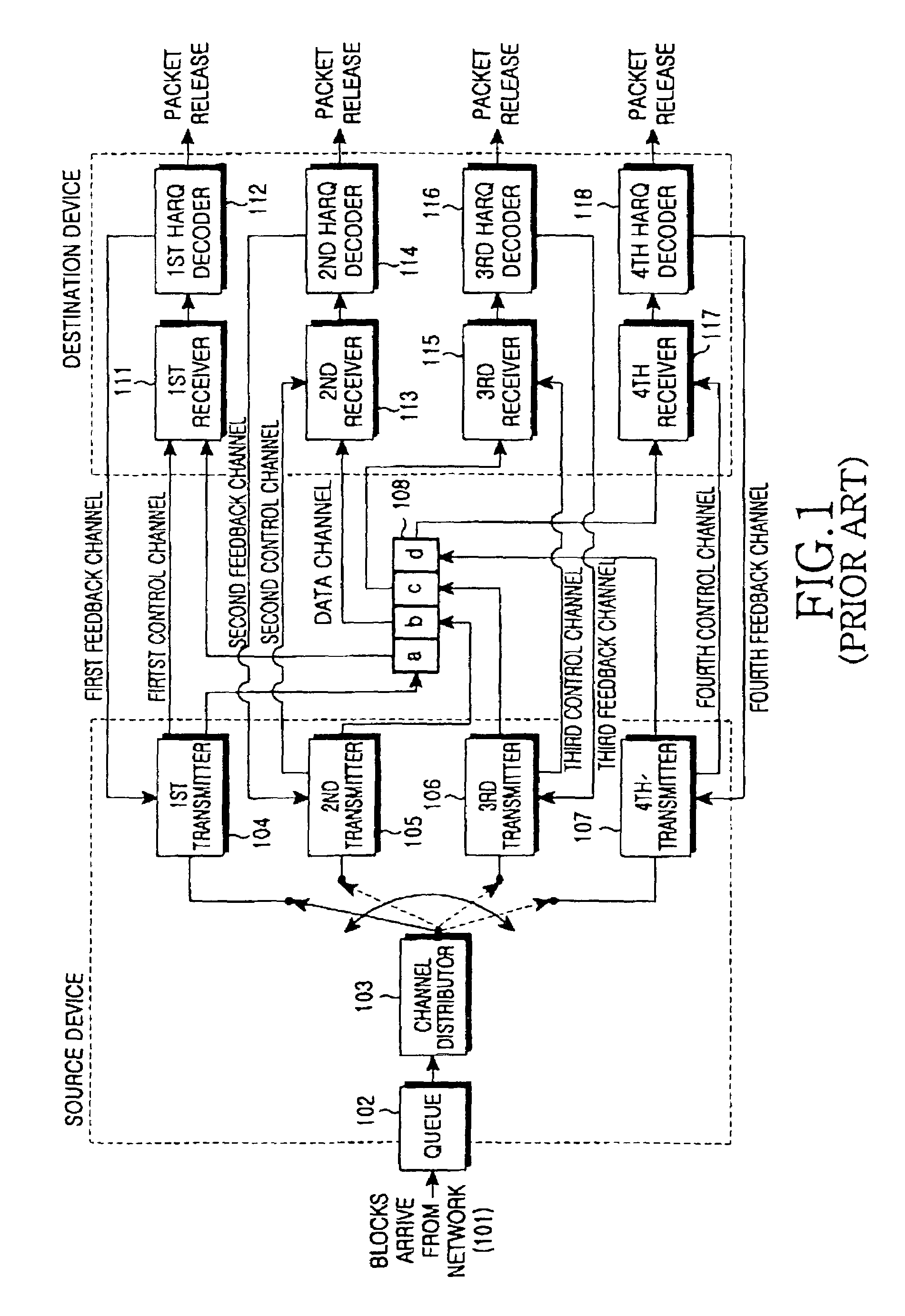
ActiveUS7126945B2Function increaseShorten closing timePower managementError preventionPacket arrivalPacket communication
A wireless data communication system has a first station or mobile unit is linked to a second station configured as an access unit to support packet communication, voice or data, where the voice packets are transmitted in the Continuously Aware Mode (CAM) mode while other packets are buffered by the access point and held until asked for by the first station when in a Power Saving-Poll (PSP) mode. A monitoring apparatus at the access point monitors all transmitted packets and sorts the packets to the mobile unit according to CAM or PSP mode. Voice packets are sent out immediately to the mobile unit. Other packets are stored at the access point. The packet arrival rate may vary during transmission and due to random packet delays introduced by propagation characteristic and processing apparatus. The packet arrival rate and delays are taken into account by the first station in an algorithm to determine and extend the normal safe period in which the station receiver may be powered off.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
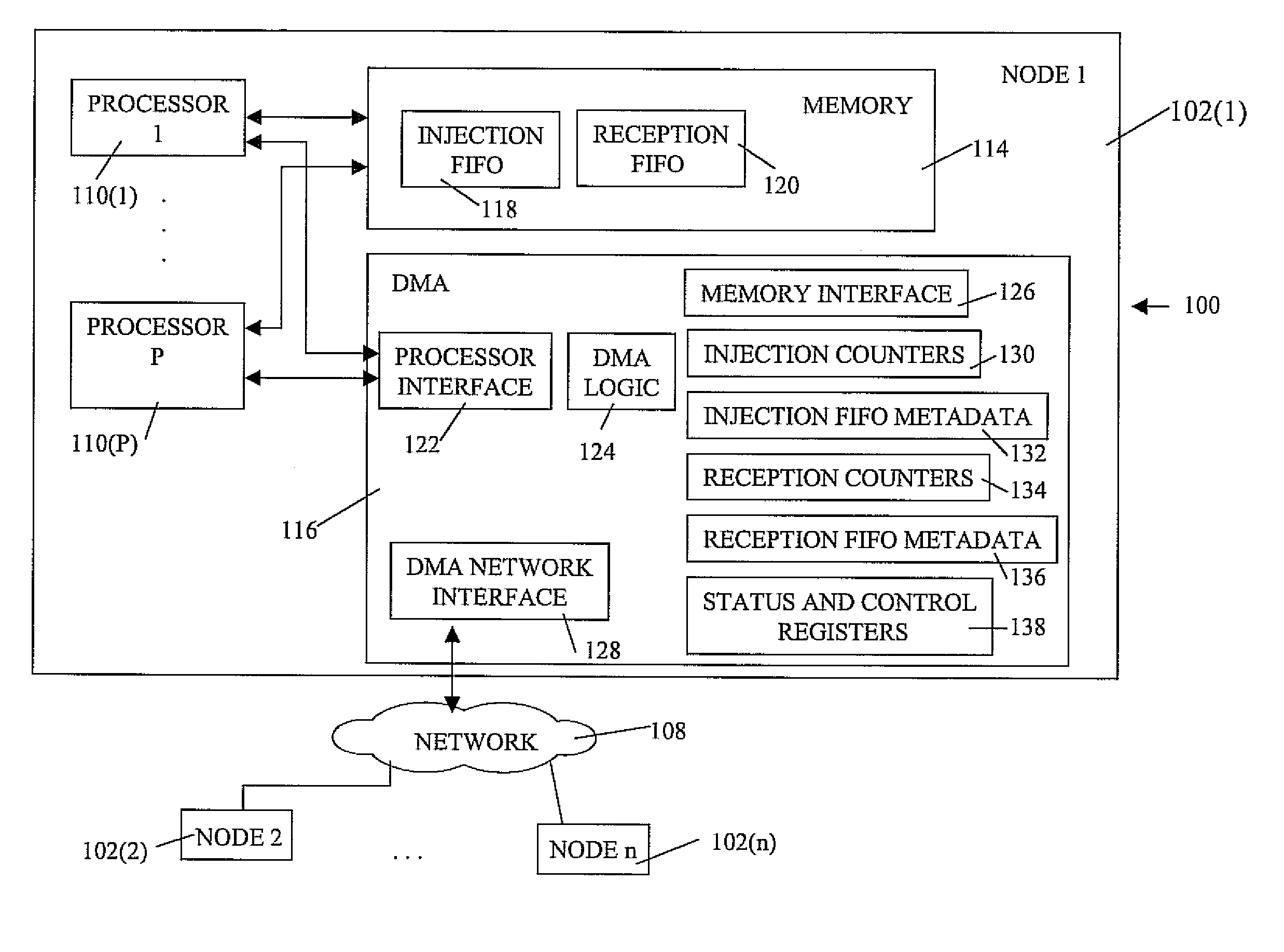
Ultrascalable petaflop parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS7761687B2Maximize throughputDelay minimizationGeneral purpose stored program computerElectric digital data processingSupercomputerPacket communication
A massively parallel supercomputer of petaOPS-scale includes node architectures based upon System-On-a-Chip technology, where each processing node comprises a single Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) having up to four processing elements. The ASIC nodes are interconnected by multiple independent networks that optimally maximize the throughput of packet communications between nodes with minimal latency. The multiple networks may include three high-speed networks for parallel algorithm message passing including a Torus, collective network, and a Global Asynchronous network that provides global barrier and notification functions. These multiple independent networks may be collaboratively or independently utilized according to the needs or phases of an algorithm for optimizing algorithm processing performance. The use of a DMA engine is provided to facilitate message passing among the nodes without the expenditure of processing resources at the node.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Terminal -to-terminal communication connection control method using IP transfer network
InactiveUS20020009073A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationPacket communicationSignaling system
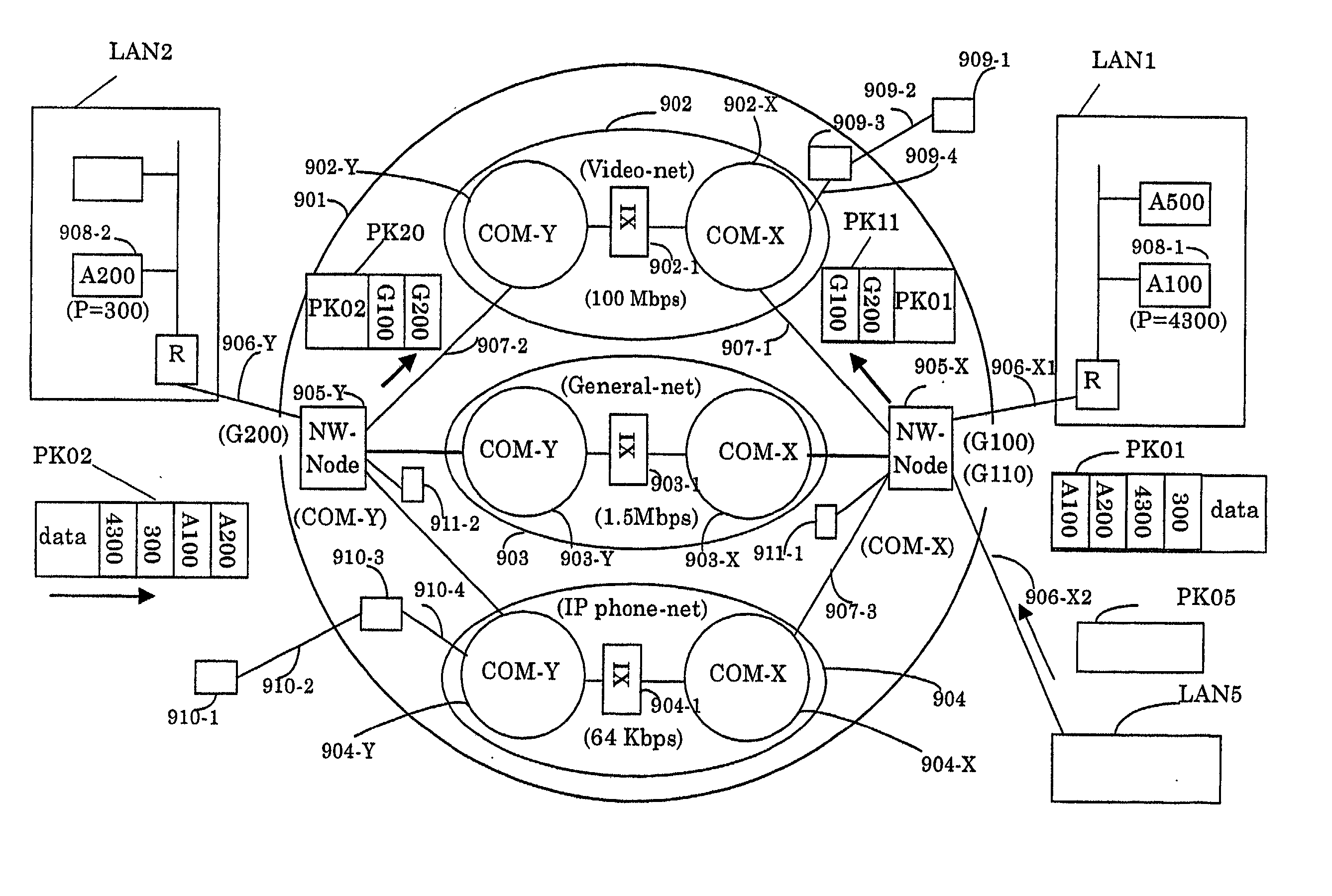
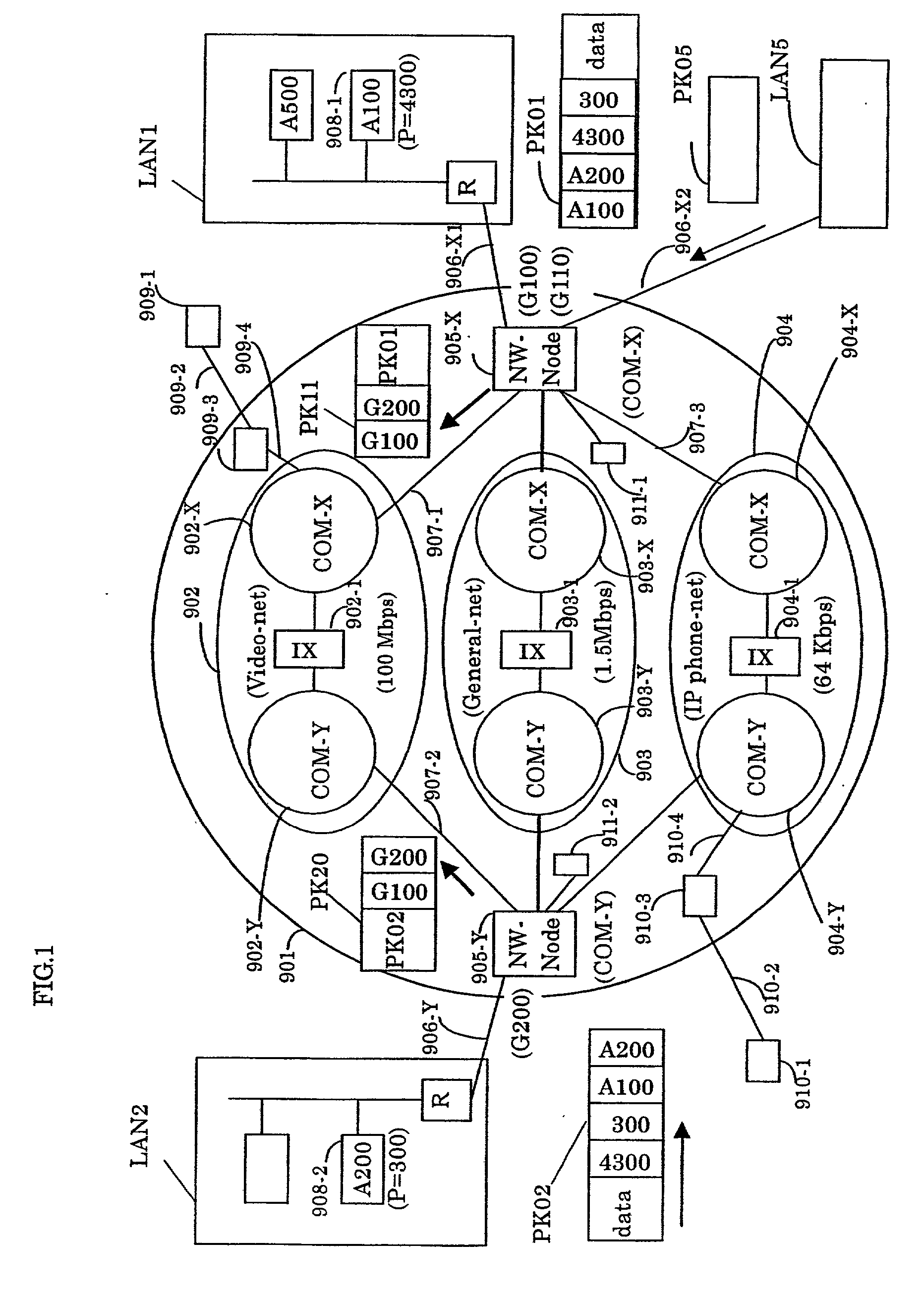
Both a connection server and a relay connection server are installed in an IP transfer network; a function similar to a line connection control of a subscriber exchanger is applied to a connection server; a function similar to a line connection control of a relay exchanger is applied to the relay connection server; and a terminal-to-terminal communication connection control method with using the IP transfer network is realized in such a manner that a telephone set and a terminal such as an IP terminal and a video terminal transmit / receive an initial address message, an address completion message, a call pass message, a response message, a release message and a release completion message, which can be made in a 1-to-1 correspondence relationship with line connection control messages of the common line signal system. Furthermore, while an address administration table is set to a network node apparatus of an IP transfer network, means for registering addresses of the terminals into this address administration table is employed, so that an IP packet communication by a multicast manner can be realized with improving information security performance.
Owner:DISTRIBUTION SYST RES INST THE AN UNDIVIDED 60 INTEREST +1
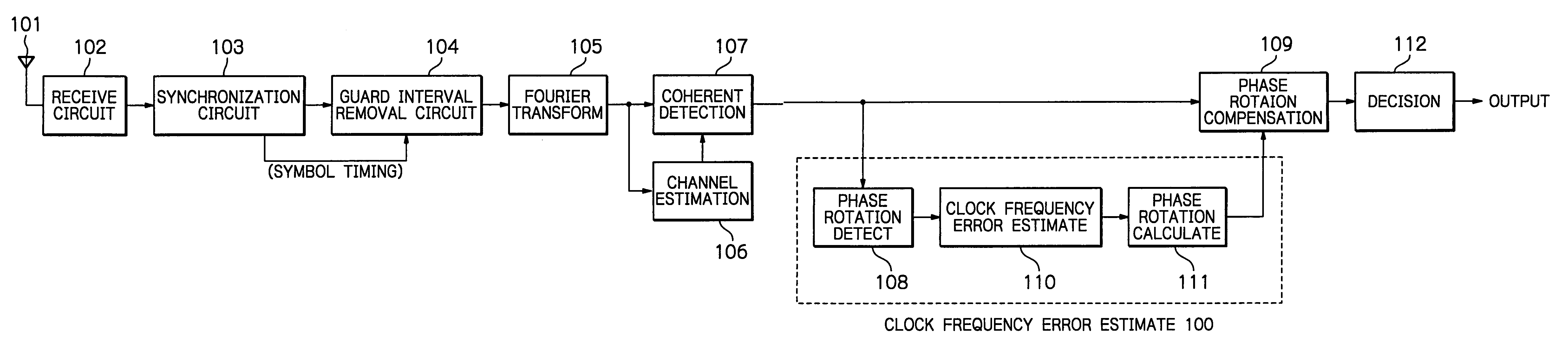
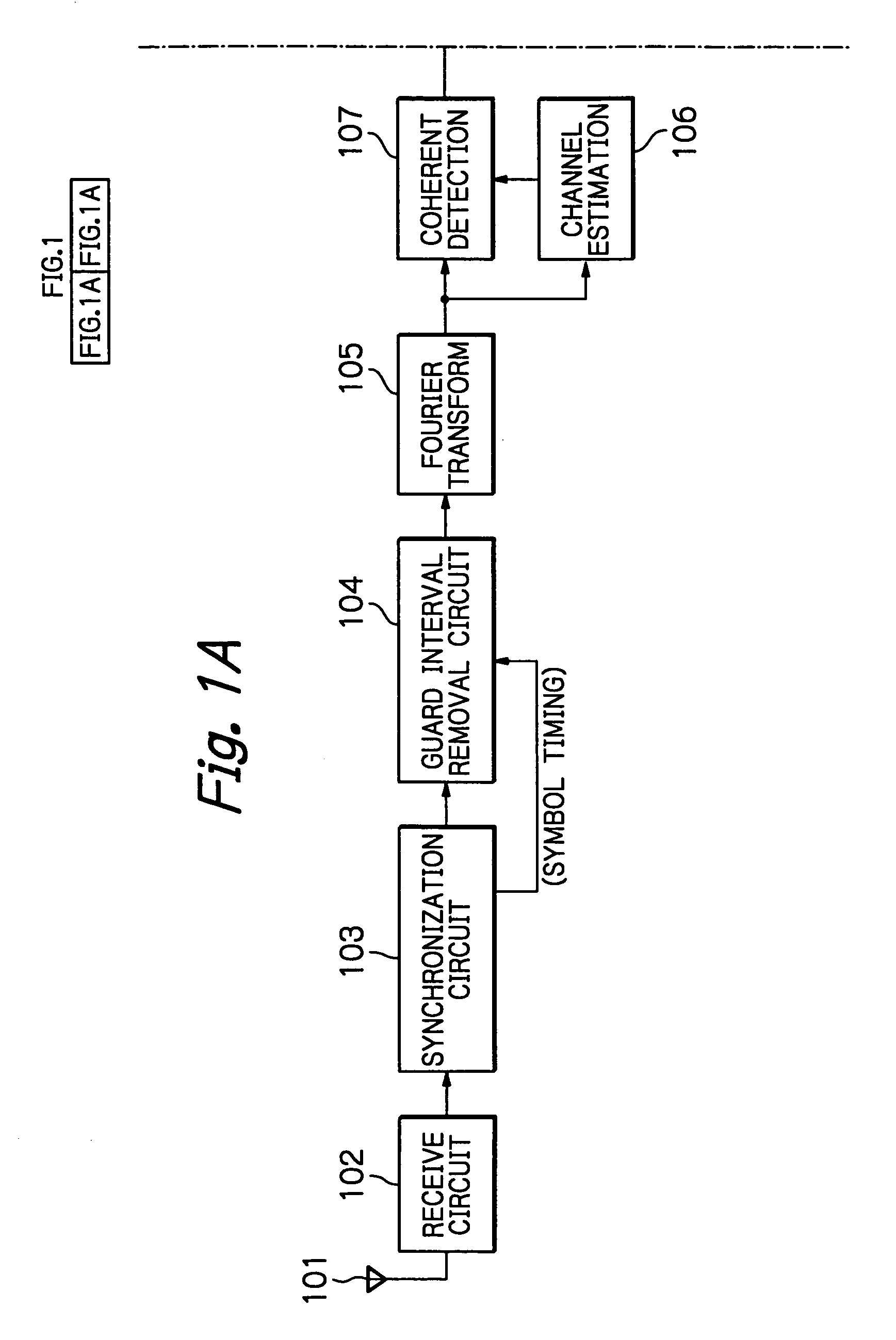
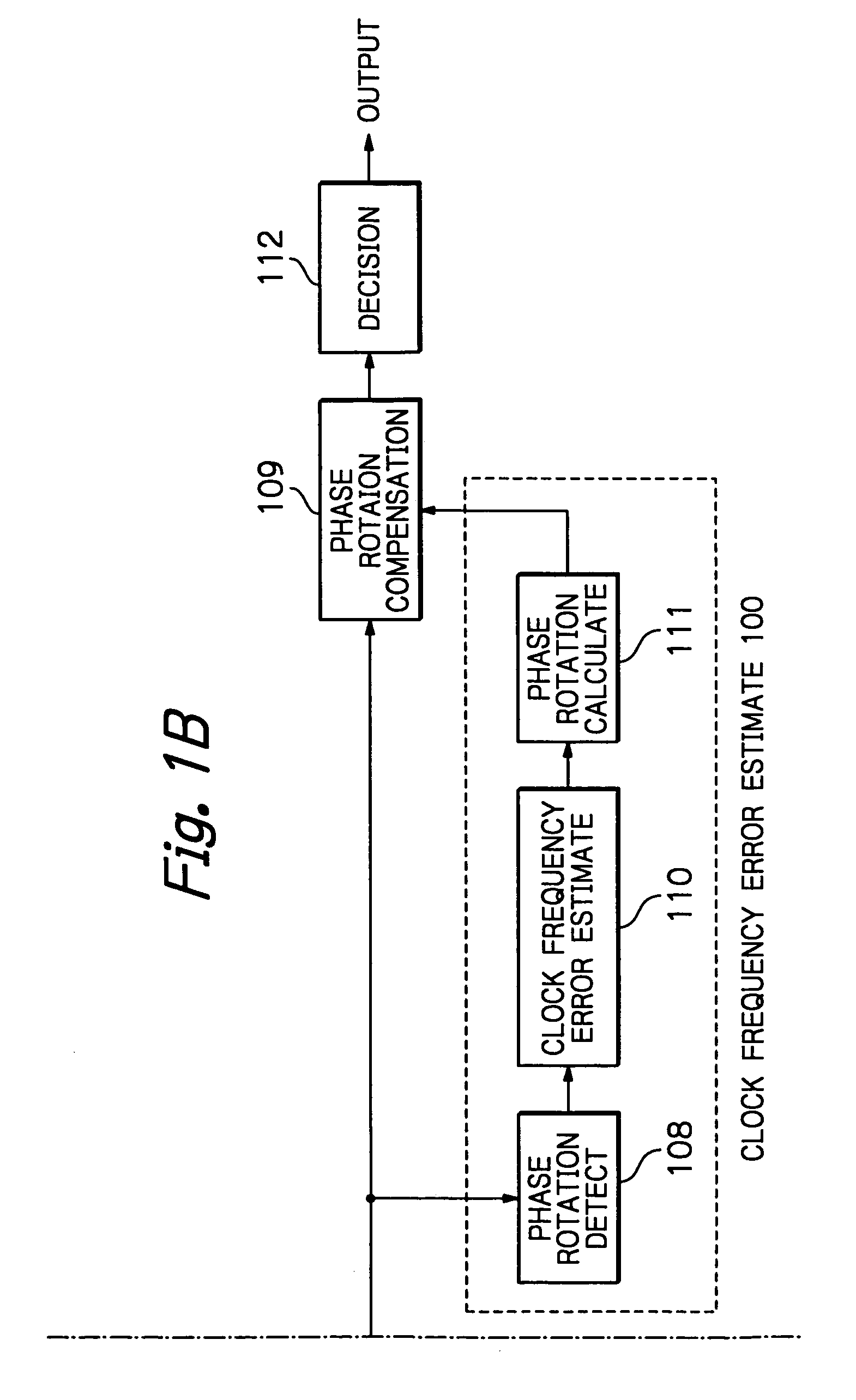
OFDM packet communication receiver
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
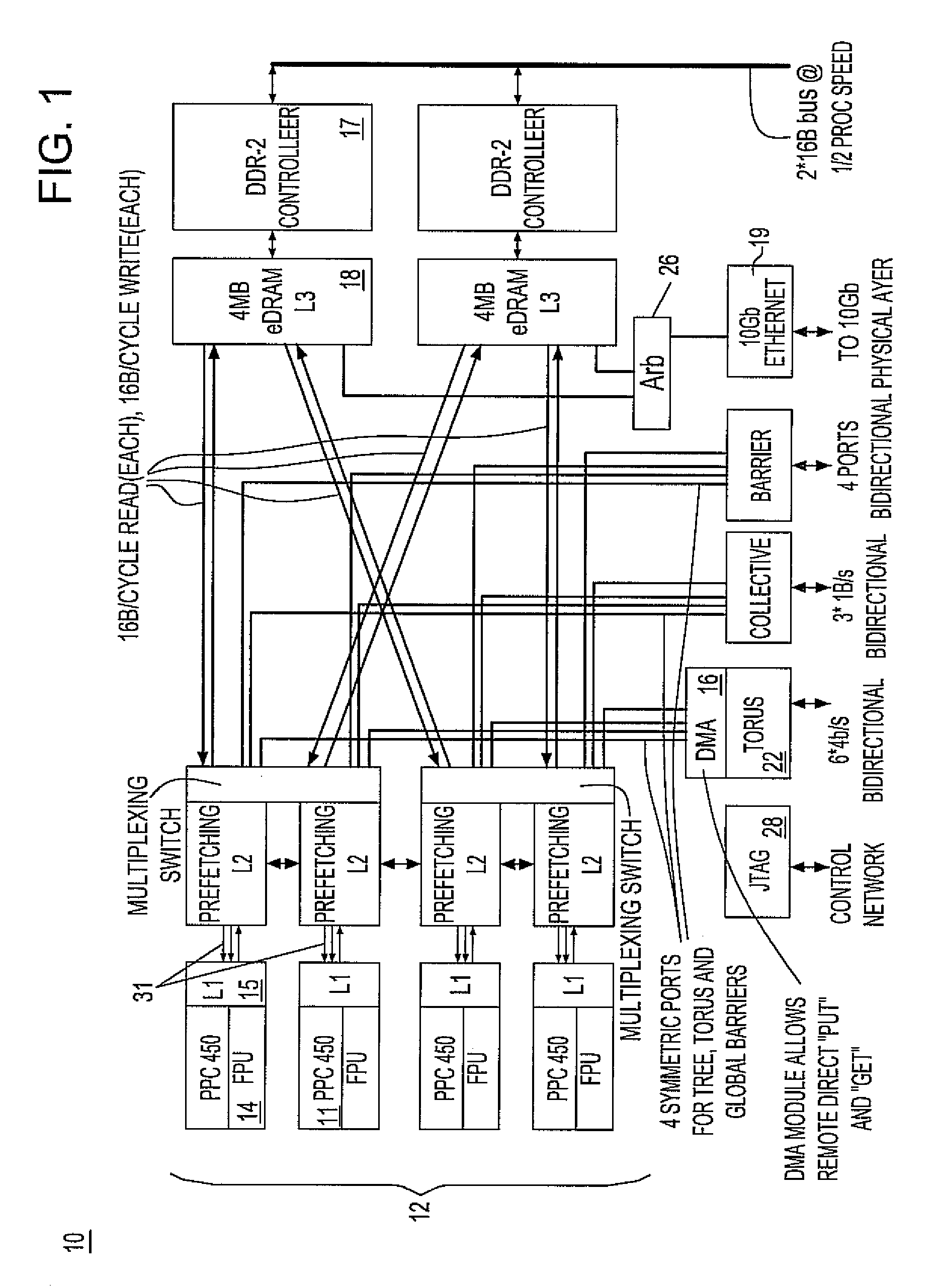
Massively parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS7555566B2Massive level of scalabilityUnprecedented level of scalabilityError preventionProgram synchronisationPacket communicationSupercomputer
A novel massively parallel supercomputer of hundreds of teraOPS-scale includes node architectures based upon System-On-a-Chip technology, i.e., each processing node comprises a single Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC). Within each ASIC node is a plurality of processing elements each of which consists of a central processing unit (CPU) and plurality of floating point processors to enable optimal balance of computational performance, packaging density, low cost, and power and cooling requirements. The plurality of processors within a single node may be used individually or simultaneously to work on any combination of computation or communication as required by the particular algorithm being solved or executed at any point in time. The system-on-a-chip ASIC nodes are interconnected by multiple independent networks that optimally maximizes packet communications throughput and minimizes latency. In the preferred embodiment, the multiple networks include three high-speed networks for parallel algorithm message passing including a Torus, Global Tree, and a Global Asynchronous network that provides global barrier and notification functions. These multiple independent networks may be collaboratively or independently utilized according to the needs or phases of an algorithm for optimizing algorithm processing performance. For particular classes of parallel algorithms, or parts of parallel calculations, this architecture exhibits exceptional computational performance, and may be enabled to perform calculations for new classes of parallel algorithms. Additional networks are provided for external connectivity and used for Input / Output, System Management and Configuration, and Debug and Monitoring functions. Special node packaging techniques implementing midplane and other hardware devices facilitates partitioning of the supercomputer in multiple networks for optimizing supercomputing resources.
Owner:IBM CORP
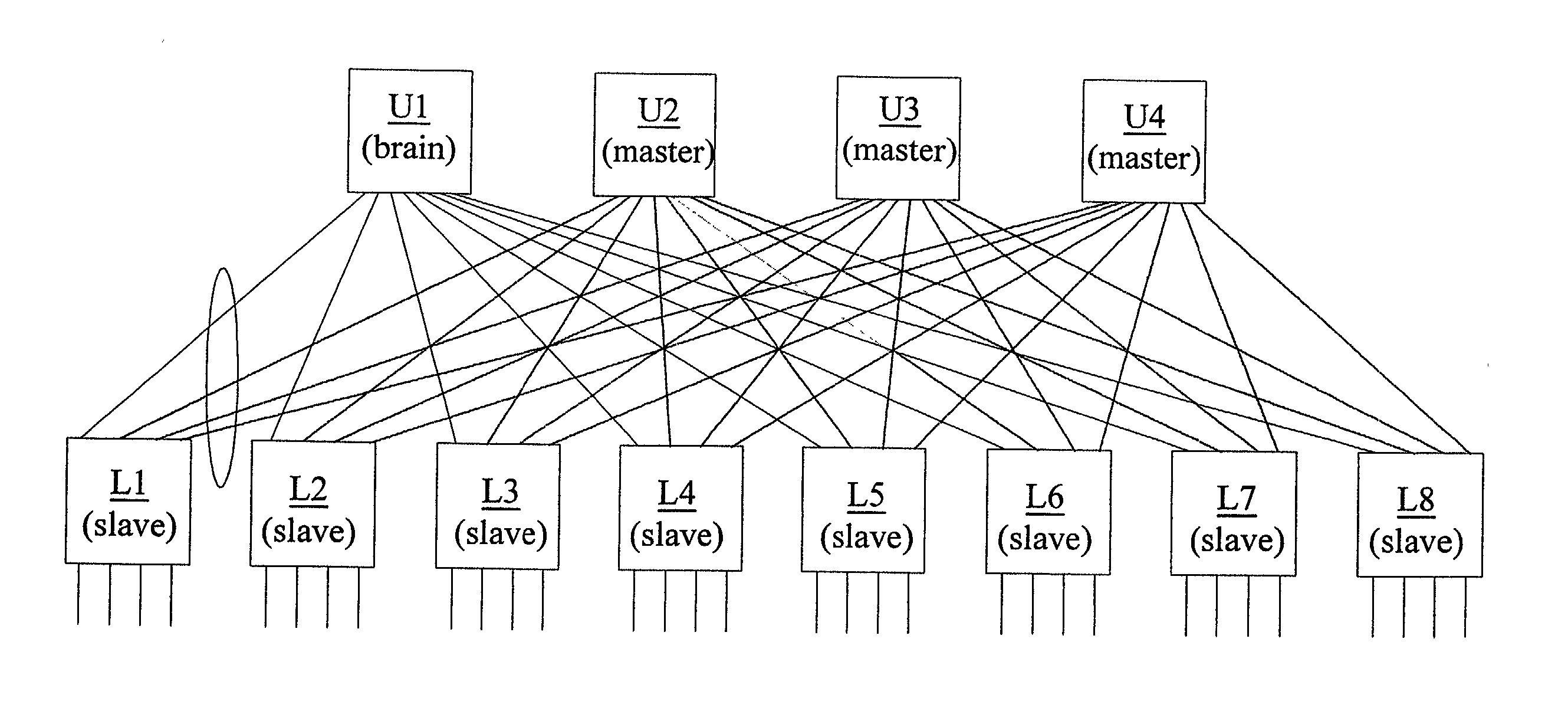
System and method of stacking network switches
ActiveUS20030169734A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexPacket communicationTelecommunications
A network switch system that includes a plurality of first-level switches operating in a slave mode, the first-level switches providing a plurality of local ports for receiving and sending network packets, and a plurality of second-level switches operating in one of brain mode or master mode, wherein, the first-level switches includes a plurality of upward ports connecting to the second-level switches, each of the first-level switches and the second-level switches having a forwarding database, wherein the first-level switches sends the refresh packets to the second-level switches for synchronizing the forwarding databases of the second-level switches, wherein the second-level switches providing packet communications among the first-level switches, and wherein a second-level switch operating in the brain mode providing refresh packets to the first-level switches for synchronizing the forwarding databases of the first-level switches.
Owner:A10 NETWORKS
Process and apparatus for the operation of virtual private networks on a common data packet communication network
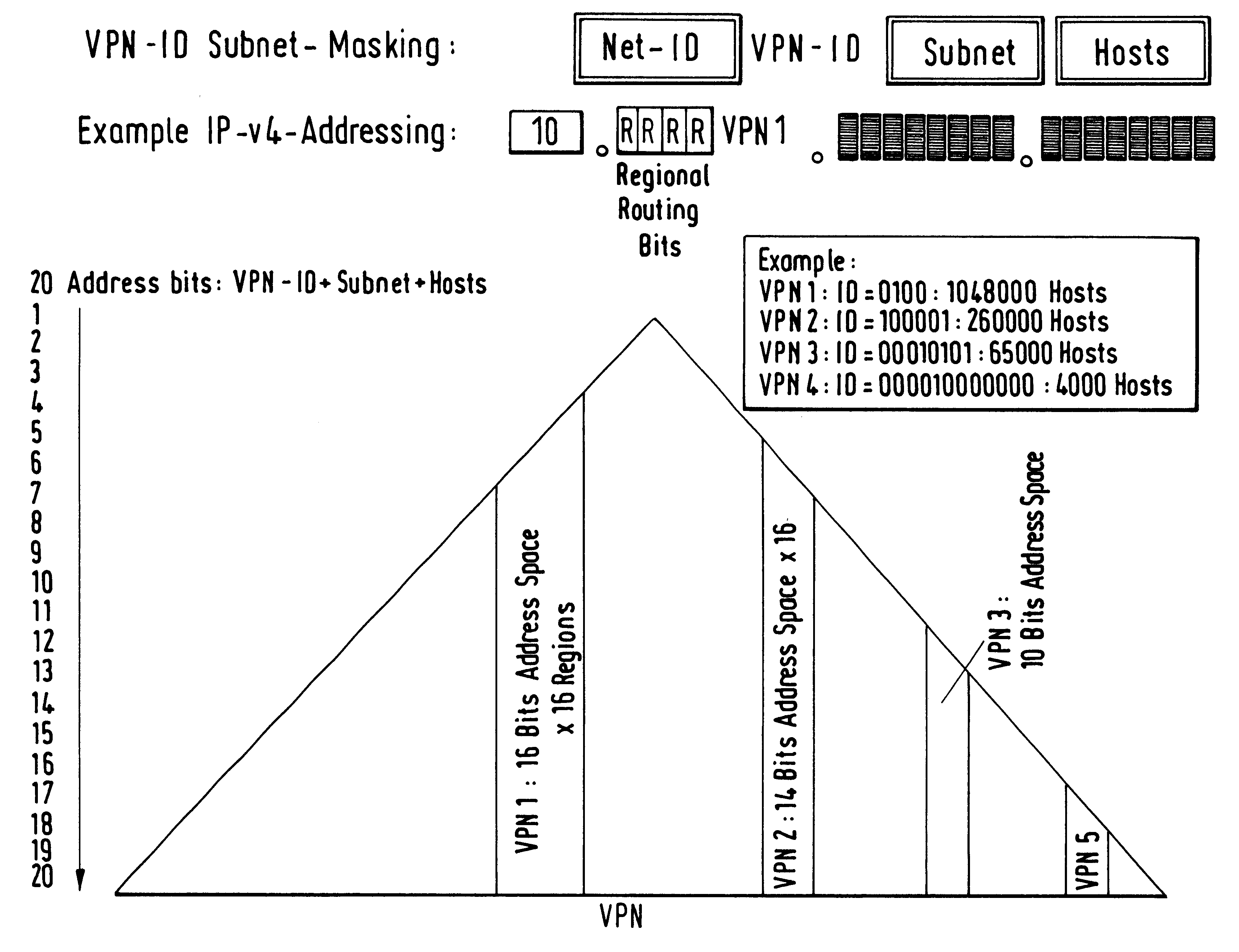
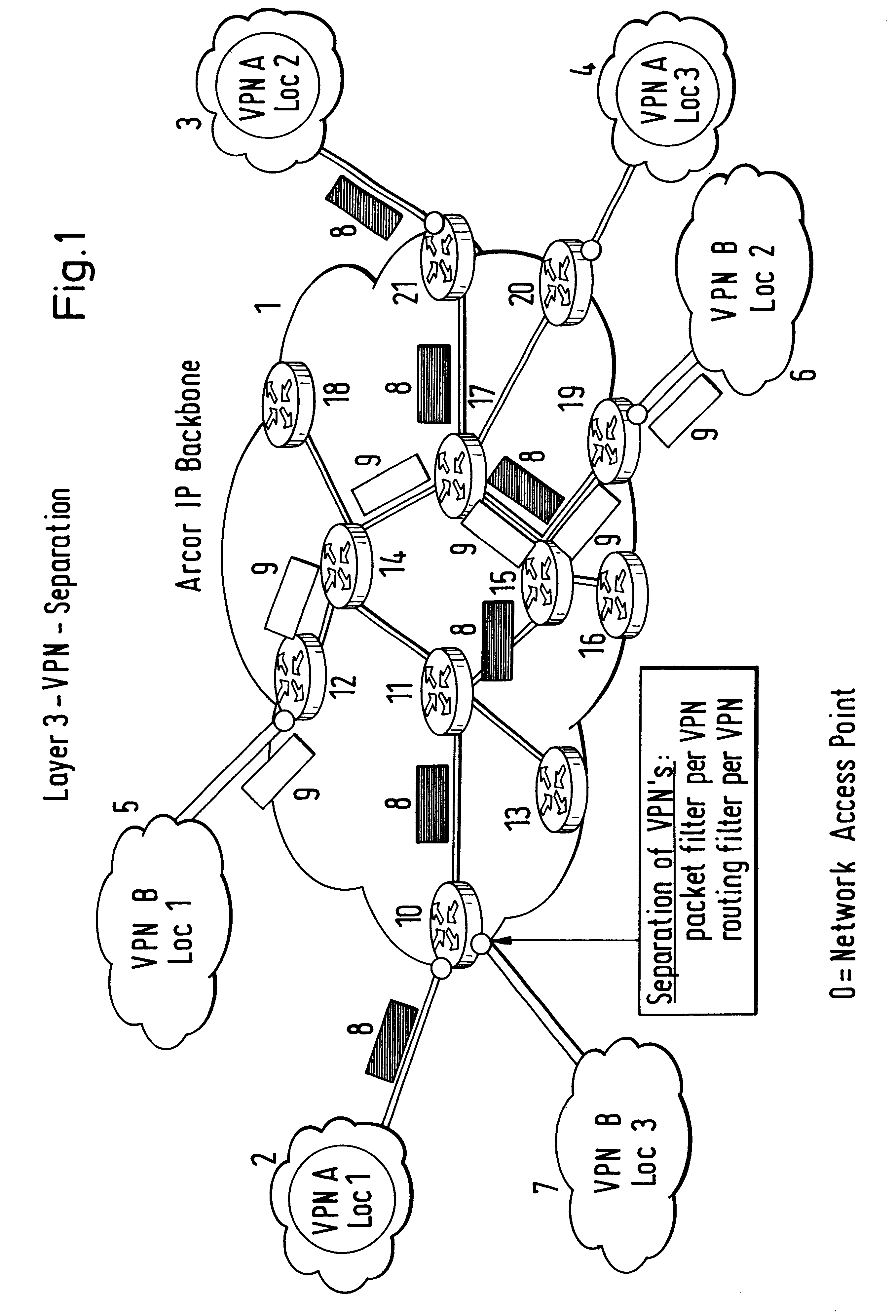
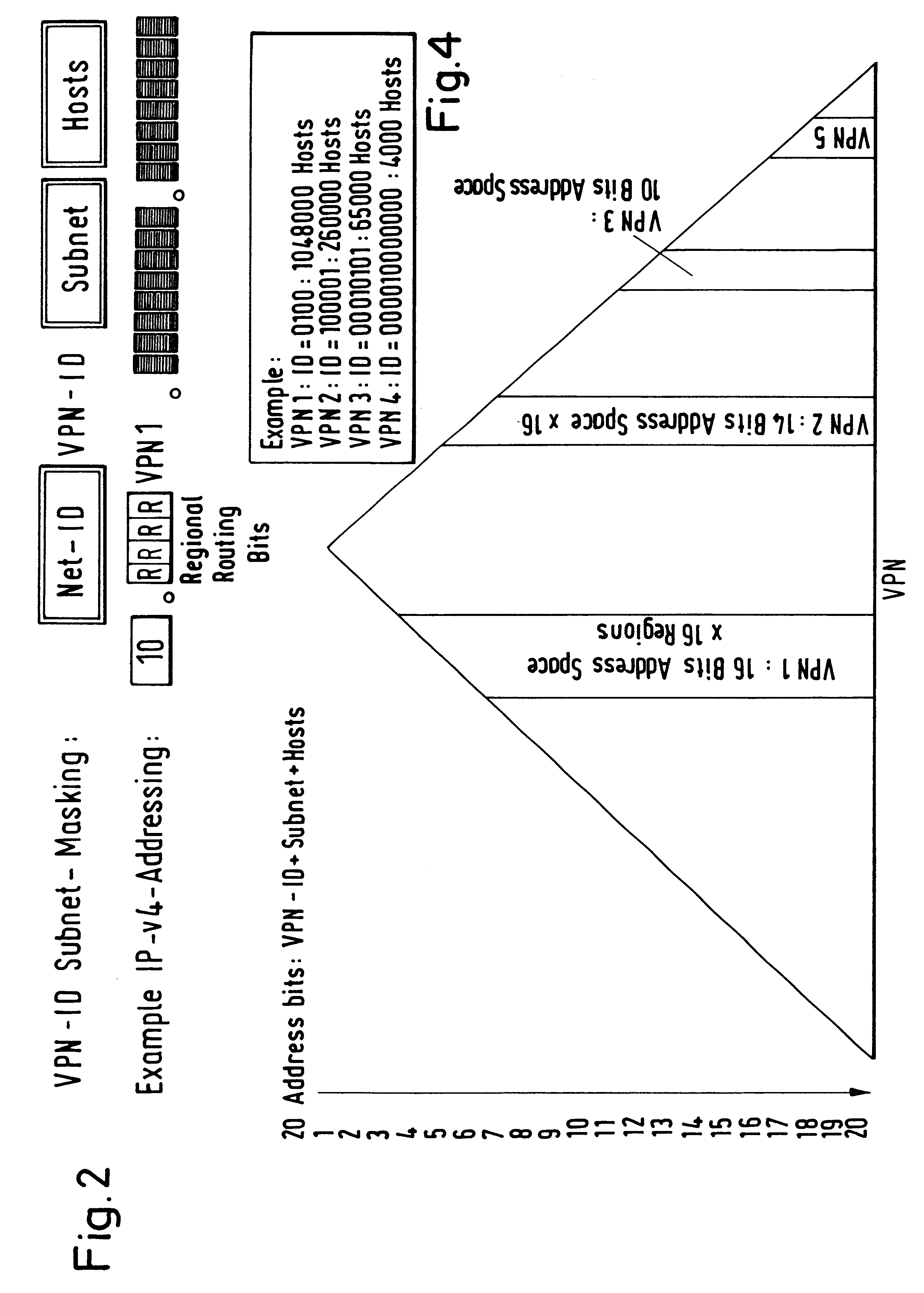
Economical and dependable networking of spatially separated branches of an organization is made possible for a plurality of individual subscribers with spatially separated branches by means of an arrangement and process for the operation of layer-3 virtual private networks (VPN A, VPN B) on a common data packet.communication network (e.g. OSI L3 data packet communication network 1). A logical separation of the layer-3 VPNs (VPNA, VPNB) is accomplished by allocating disjoint partial address spaces of a given homogeneous total address space to these L3 VPNs. A virtual private network identification number VPN ID is assigned to each L3 VPN and used to identify the disjoint partial address space by forming a part of the address. The VPN ID characterizing the L3 VPN starts at a fixed bit position in the individual subscriber address of each individual subscriber of the L3 VPN and may have a variable or a fixed length. Secure separation of the L3 VPNs is implemented by filtering of routing information and / or data packets based on the VPN ID.
Owner:MANNESMANN AG
Minimum latency cut-through switch fabric
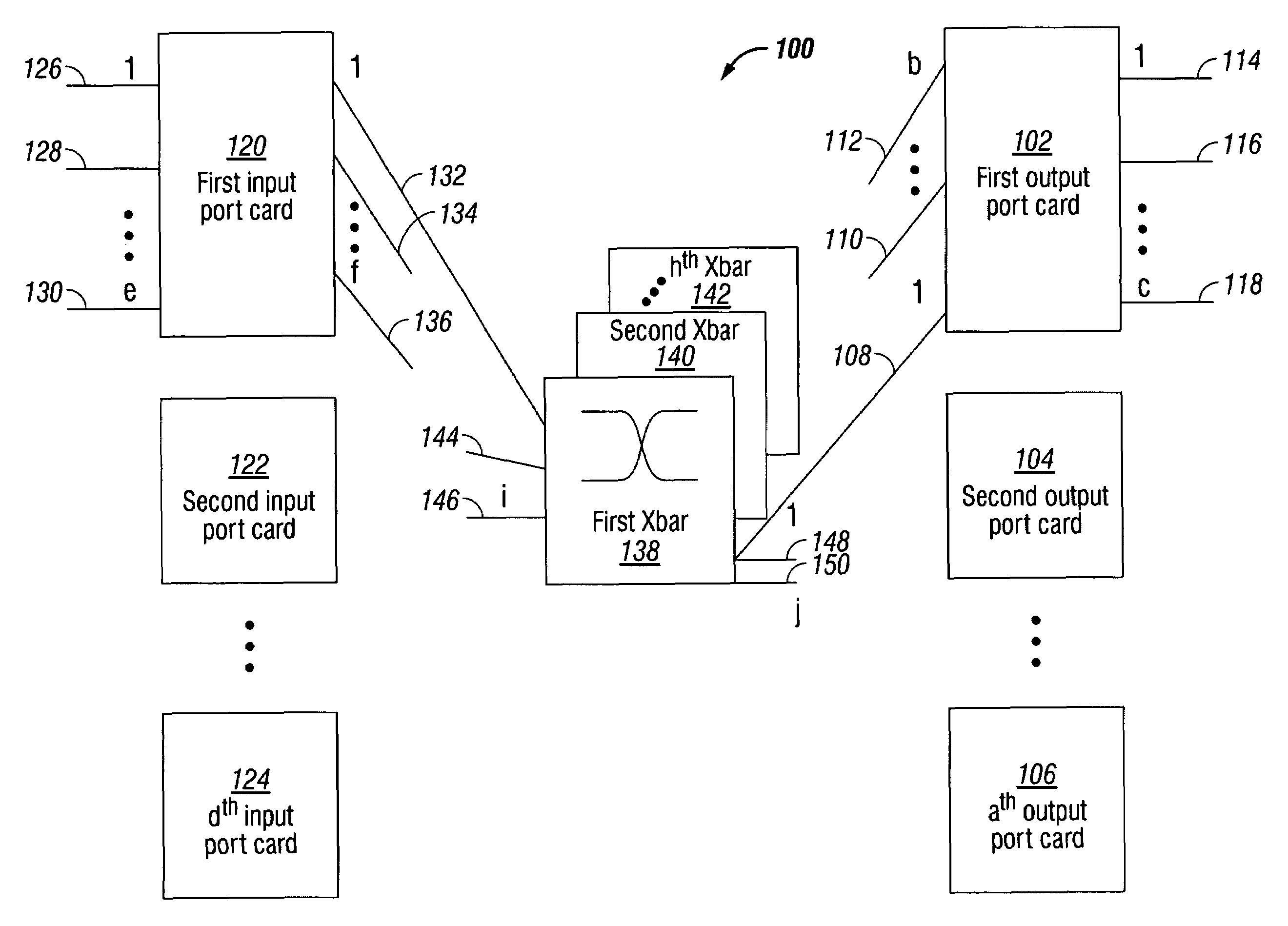
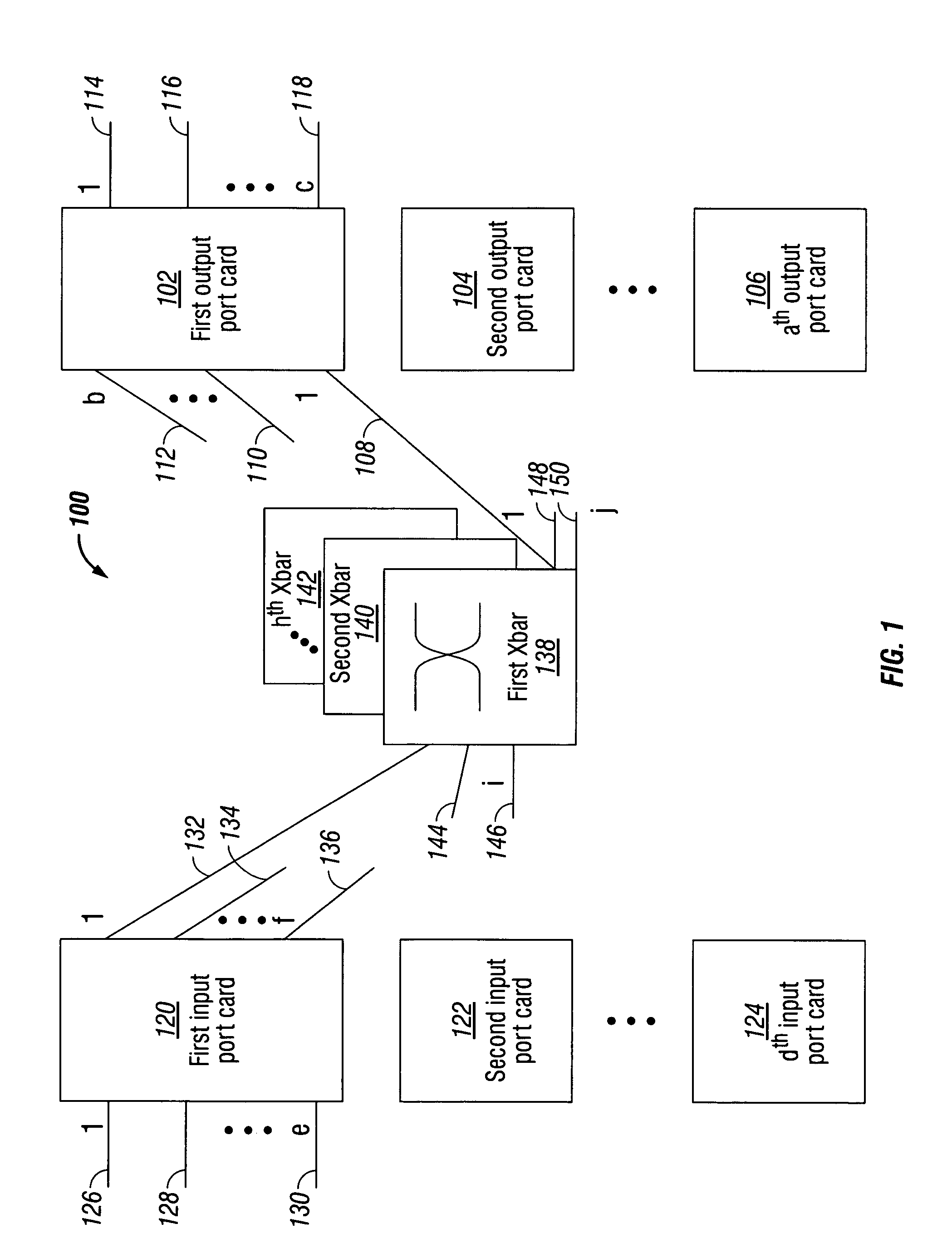
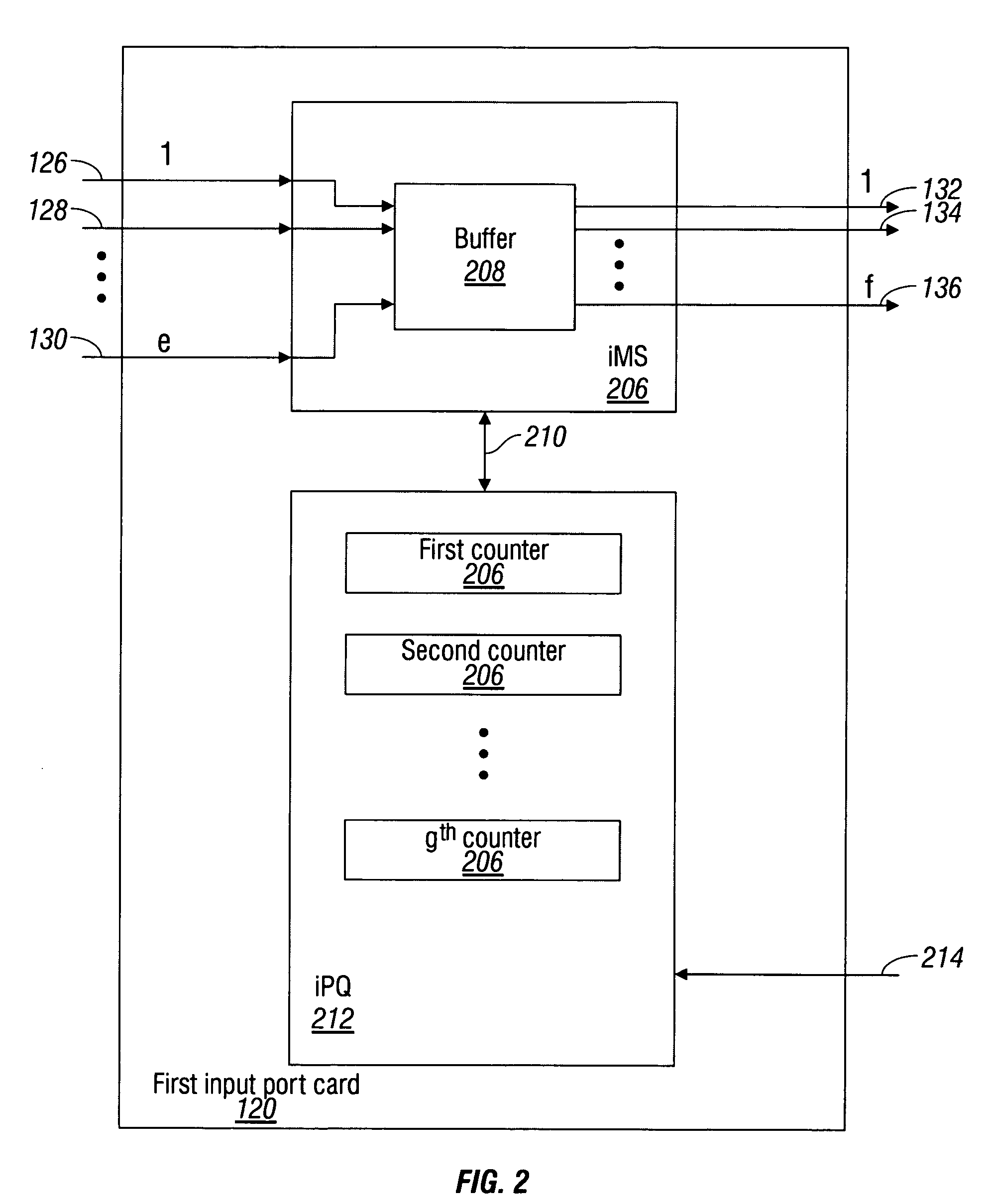
InactiveUS7230947B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationPacket communicationCut-through switching
A system and method are provided for cut-through packet routing in a packet communications switch fabric. The method comprises: accepting information packets addressed to a plurality of output port card egress ports at an input port card ingress port; routing information packets between port cards on backplane data links through an intervening crossbar; maintaining a credit counter for each port card egress destination, at the input port card; decrementing the counter in response to transmitting cells in a packet from the input port card; and, incrementing the counter in response to transmitting cells from the packet at the output port card. In some aspects of the method, accepting information includes buffering the packets in an ingress memory subsystem (iMS). Routing information includes the iMS transmitting buffered packets on a selected backplane data link. Decrementing the counter includes the iMS communicating with the iPQ in response to transmitting a cell.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
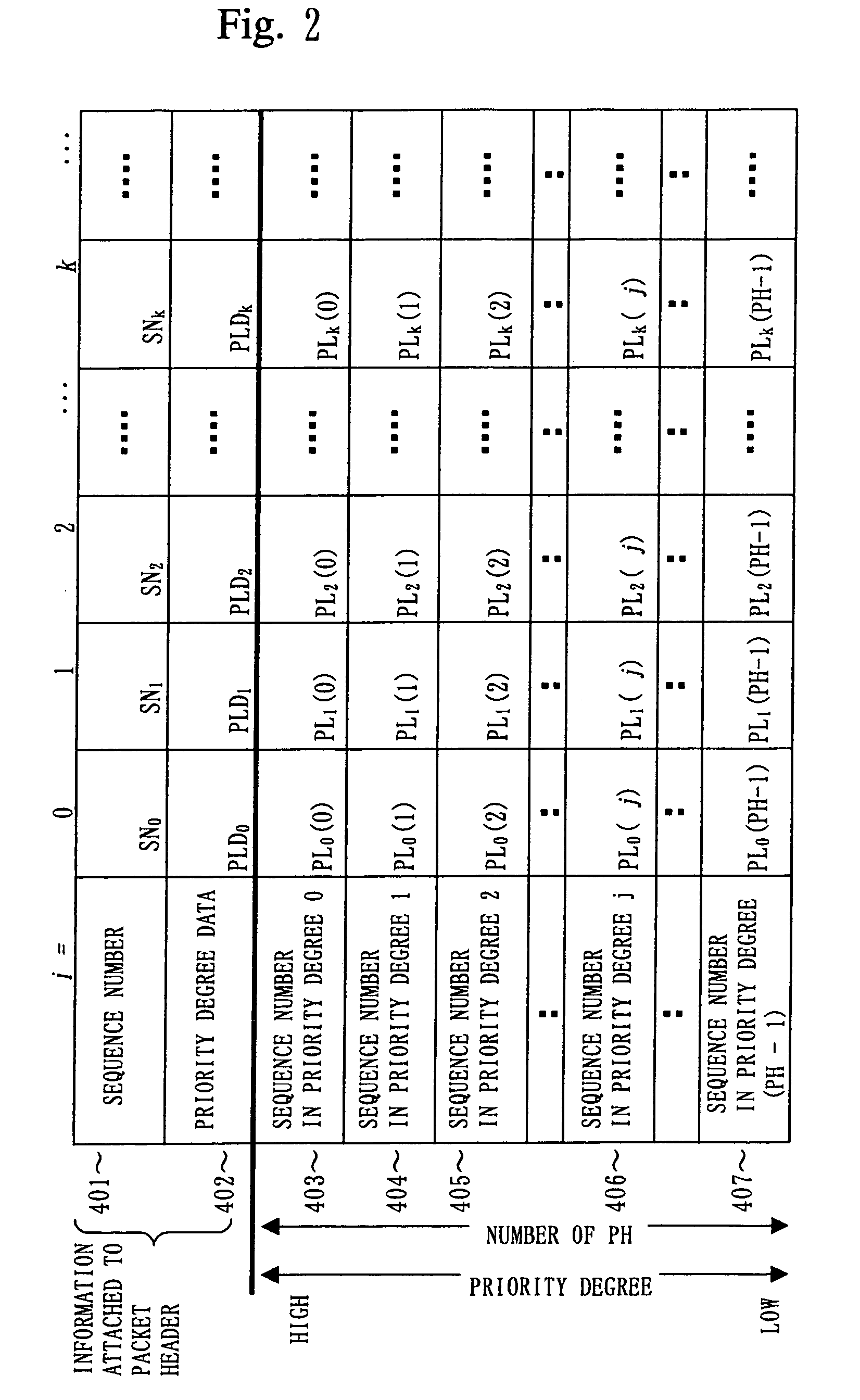
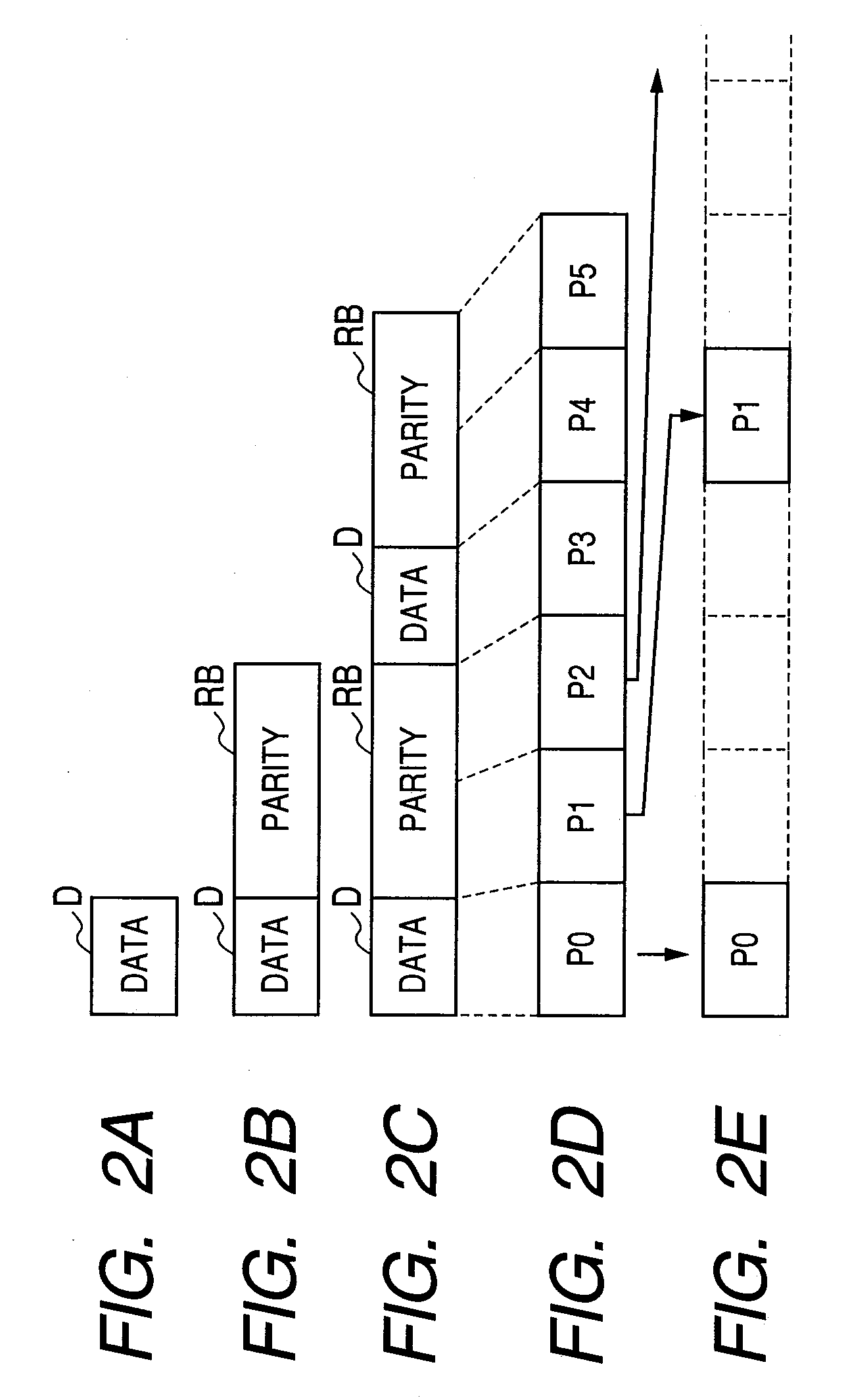
Packet retransmission system, packet transmission device, packet reception device, packet retransmission method, packet transmission method and packet reception method
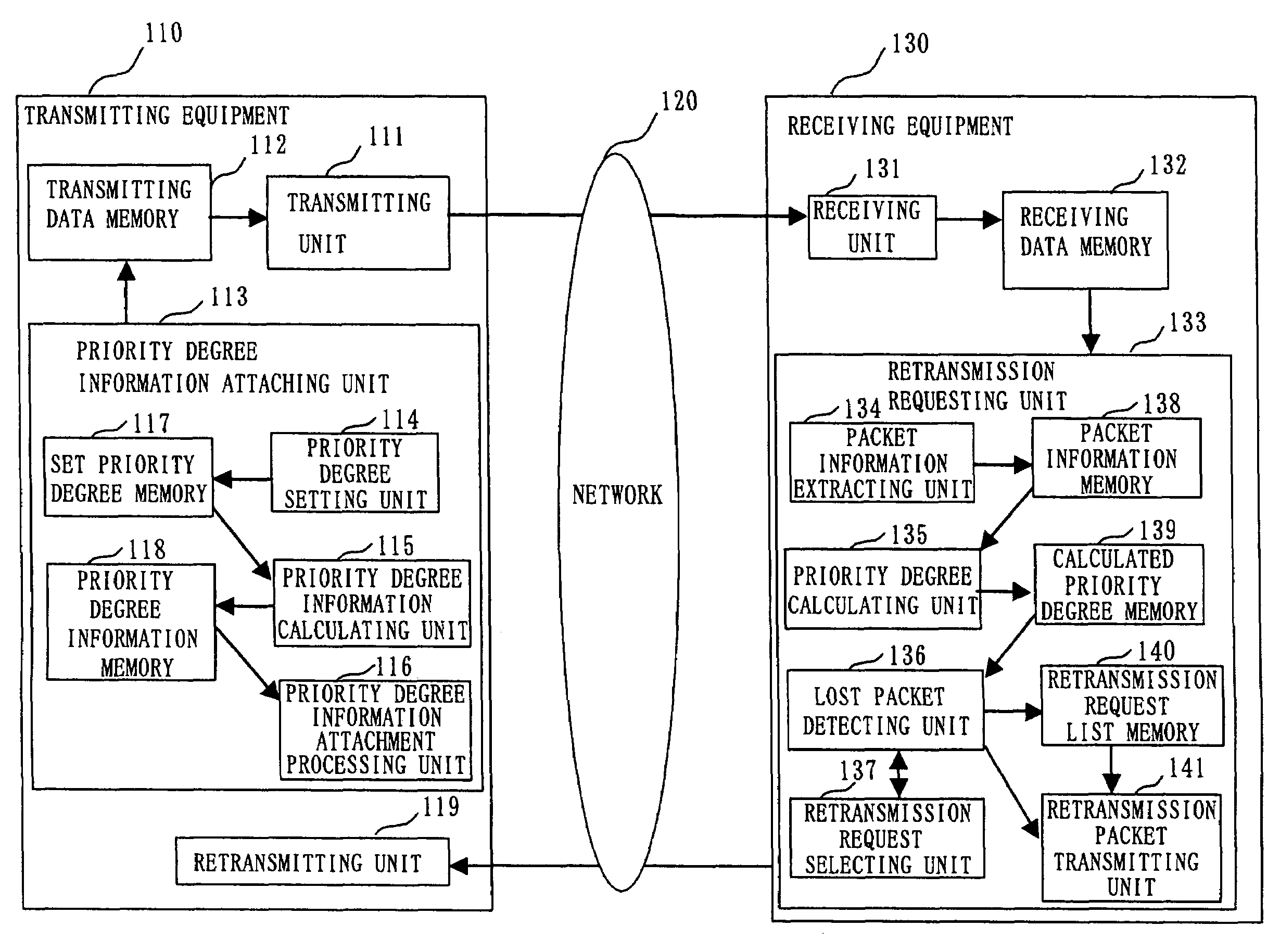
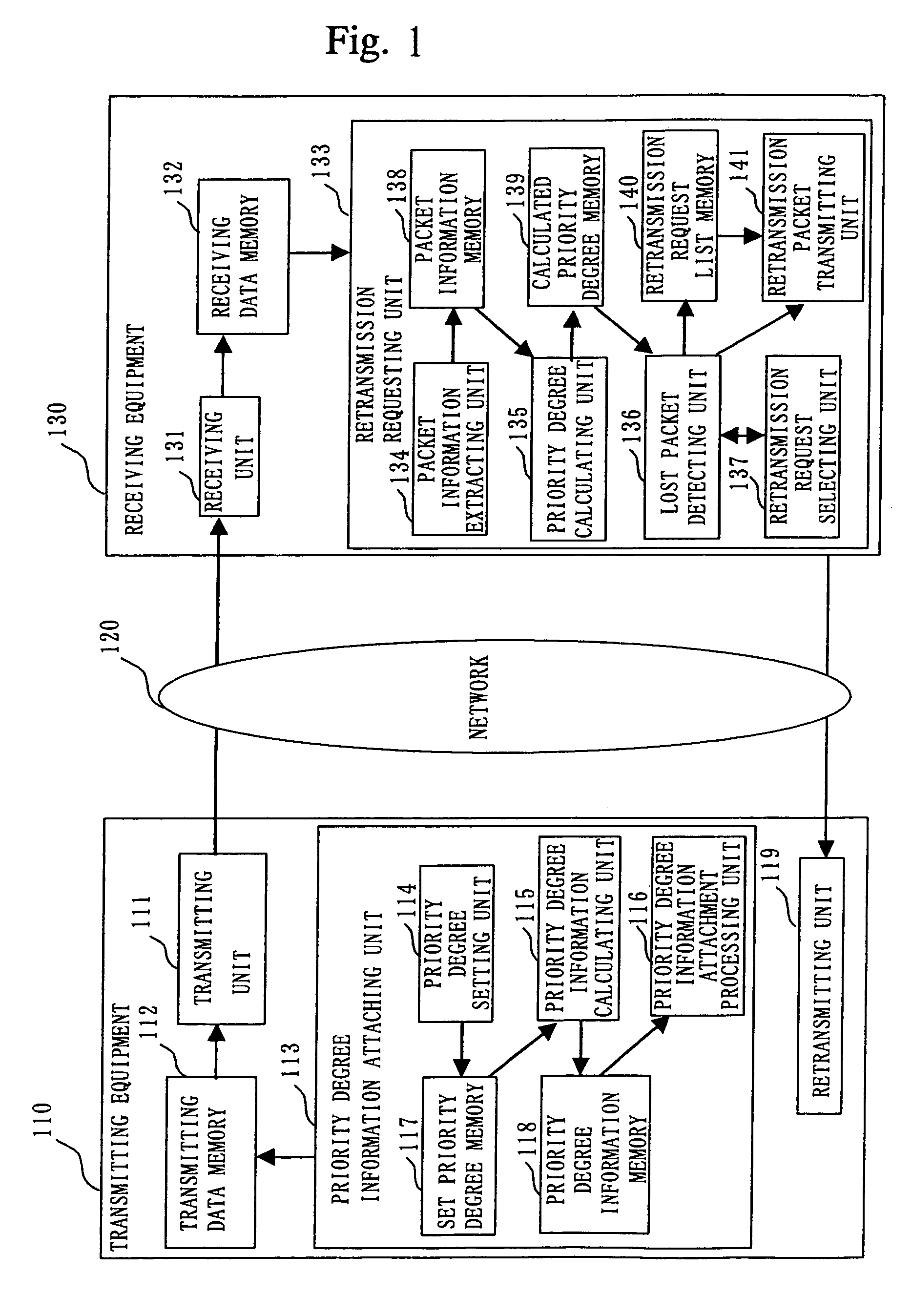
InactiveUS7114002B1Increase valueError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching by path configurationPacket communicationPacket reception
In a packet retransmitting system for retransmitting a packet including a sequence number in a packet header, which is lost during packet communication, a transmitting equipment (110) includes a priority degree information attaching unit (113) for defining a plurality of priority degrees, setting an importance degree of each of the plurality of priority degrees for a packet, producing priority degree information by using the plurality of priority degrees, and attaching the priority degree information to the packet header included in the packet repeatedly for each of the plurality of packets, a transmitter (111) for transmitting the plurality of packets, and a retransmitting unit (119) for receiving a retransmission request packet and retransmitting a packet of which retransmission is requested in the retransmission request packet received. A receiving equipment (130) includes a receiving unit (131) for receiving the plurality of packets and a retransmission requesting unit (133) for extracting a plurality of sequence numbers and a plurality of priority degree information from the packet header, detecting lost packets based on the plurality of sequence numbers and the plurality of priority degree information extracted, detecting an important packet among the lost packets, and requesting retransmission of the packet.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Fec architecture for streaming services including symbol based operations and packet tagging
ActiveUS20100050057A1Easy to useFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsPacket communicationGroup communication systems
In a packet communications system stream data is transported over a channel over which packet loss or corruption is possible, with forward error correction (“FEC”) information. A transmitter receives source packets comprising source data, generates FEC source packets formatted to allow for identification of lost or corrupted source packets at a receiver, arranges source data from the source packets into a plurality of source symbols wherein at least one source packet is arranged into more than one source symbol, associates a plurality of source symbols with a source block, generates a plurality of repair symbols from the source block according to a predetermined FEC encoding process and groups the plurality of repair symbols into one or more FEC repair packets associated with the source block. A receiver can use the FEC repair symbols from the FEC repair packets to recover source symbols, as needed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Multi-channel adapative quality control loop for link rate adaptation in data packet communications
InactiveUS20030123598A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission monitoringPacket communicationRate adaptation
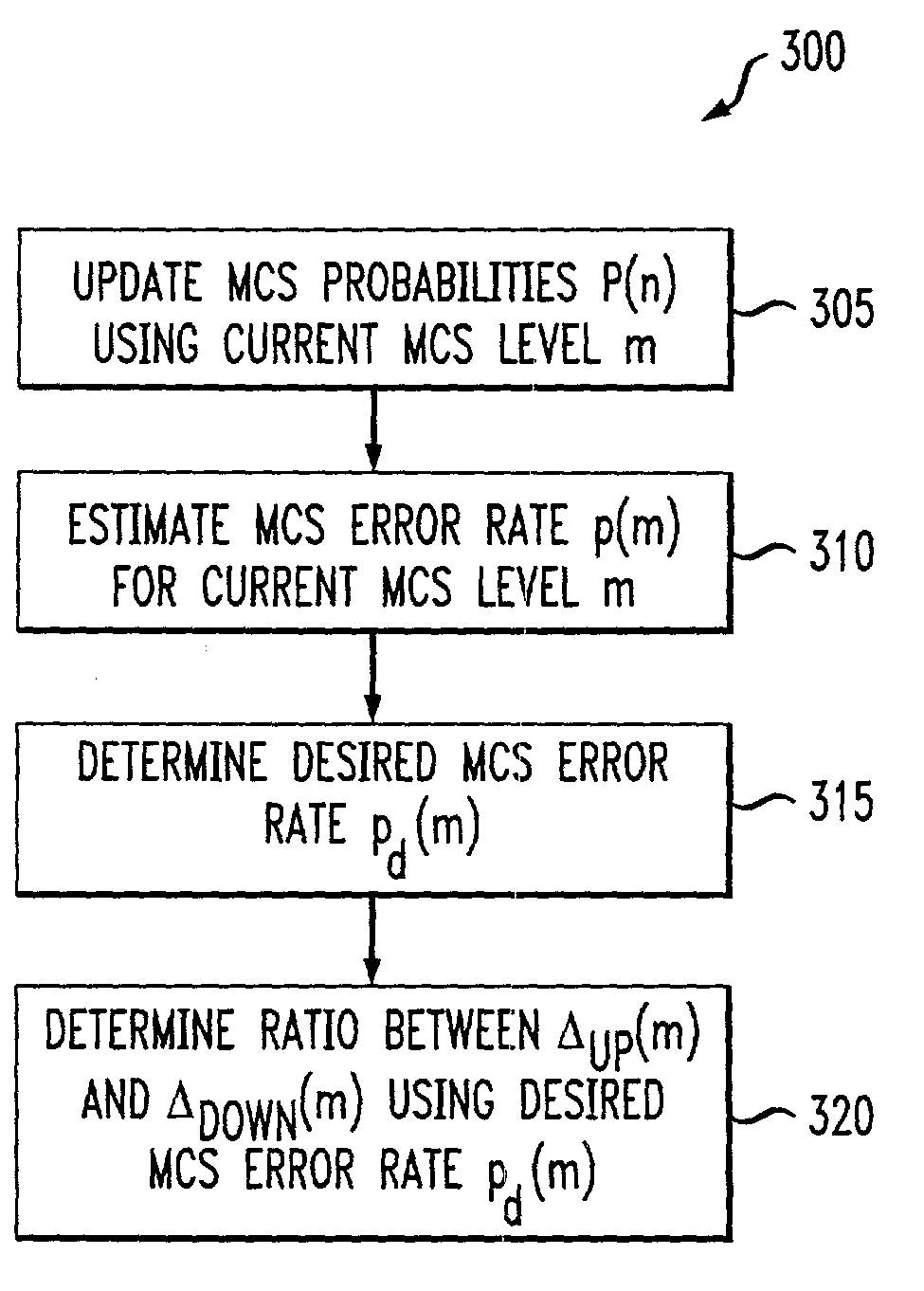
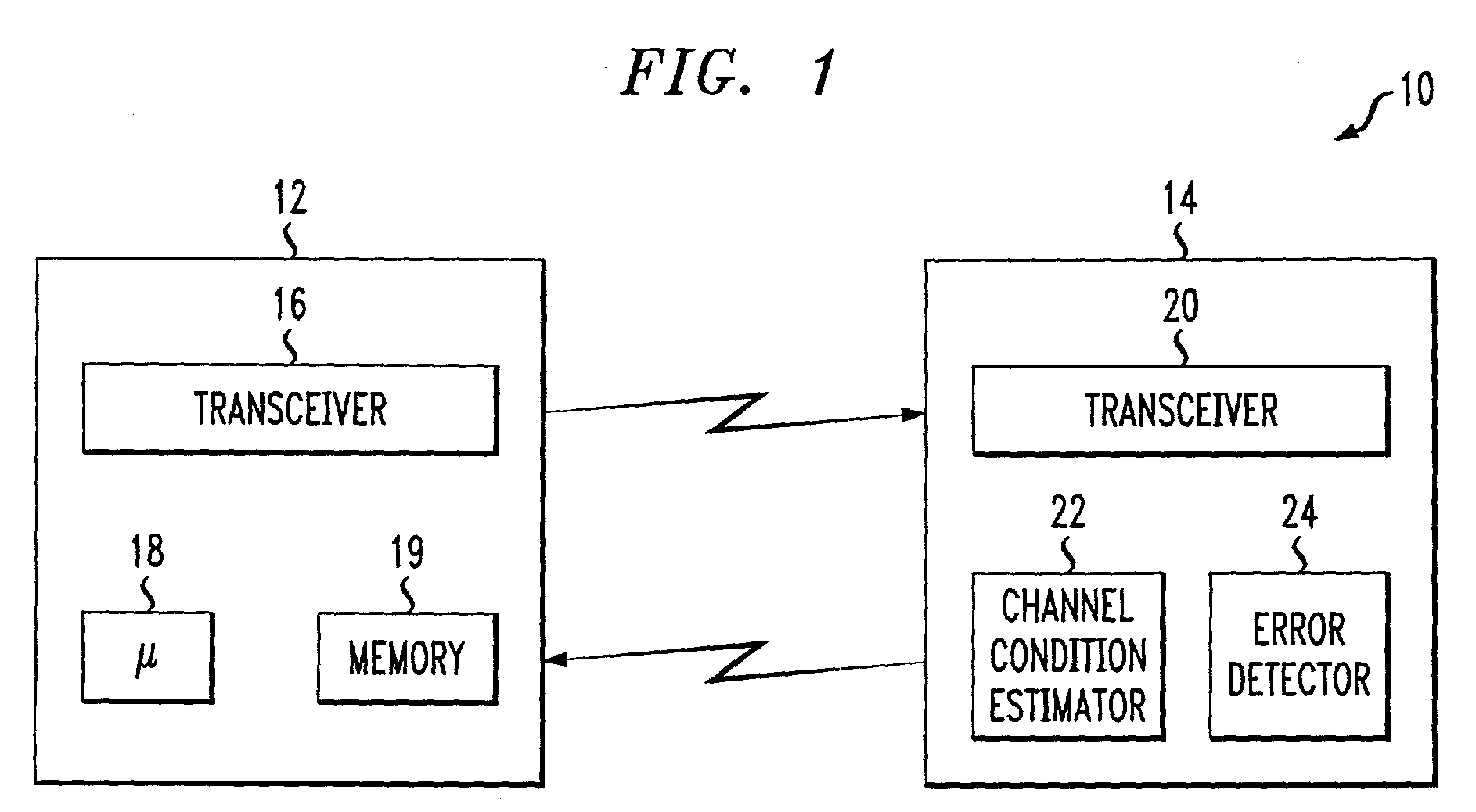
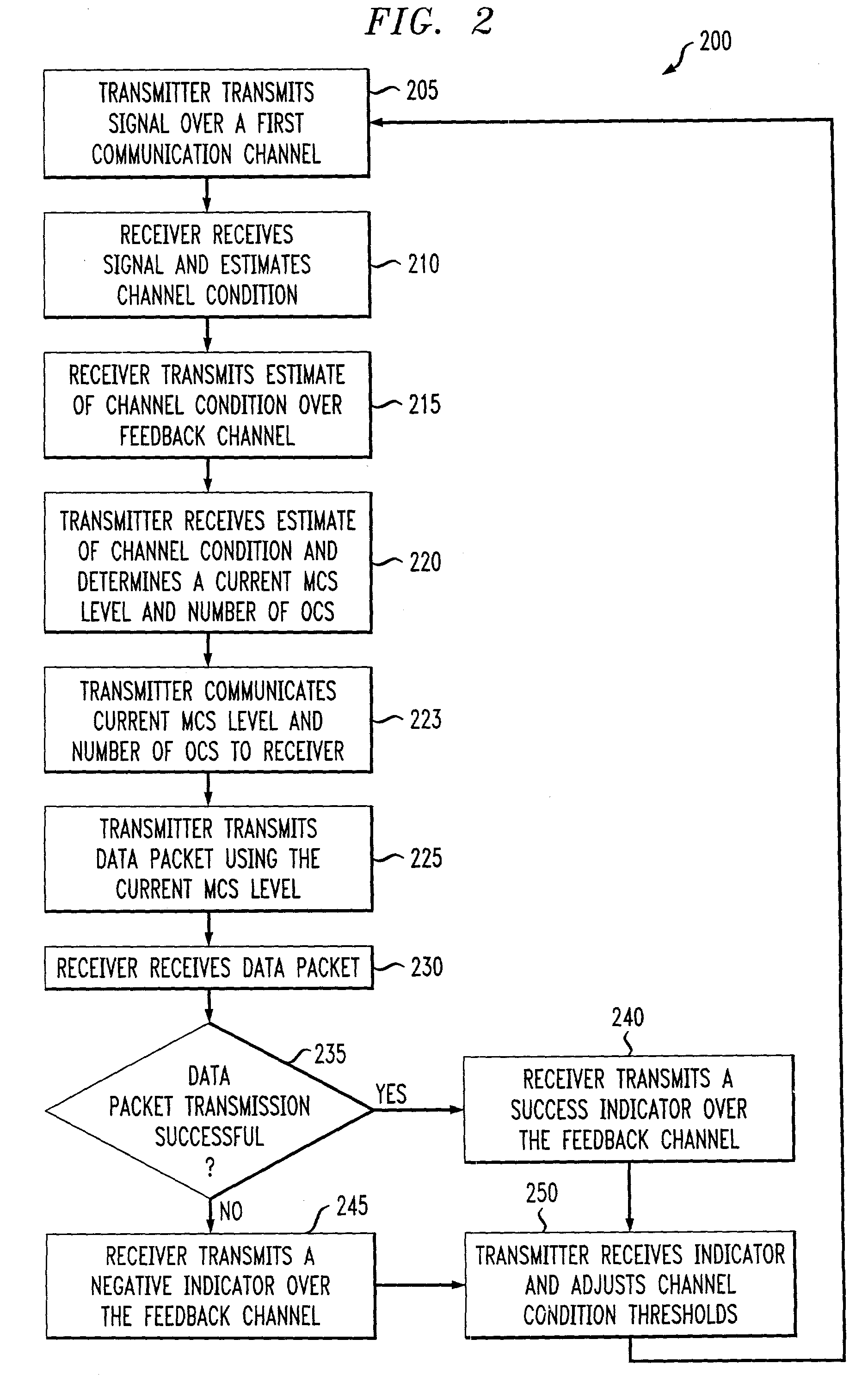
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation based on modulation and / or coding schemes (also referred to as "MCS levels") and one or more spreading codes that adaptively selects channel condition thresholds in real-time without measuring all the factors that affect selecting optimal channel condition thresholds. The adaptive quality control loop involves adjusting the channel condition thresholds with variable up and down steps based on target quality metrics along with measurements such as error detection results, relative frequencies of visiting each MCS level, and transmitted data rates, wherein the target quality metrics can be a block error rate or bit error rate target criterion. If the target quality metric is a block error rate target criterion, the variable step is determined using a desired MCS error rate based on MCS probabilities, MCS error rates and the block error rate target criterion. If the target quality metric is a bit error rate target criterion, the variable step is determined using a desired MCS error rate based on MCS probabilities, MCS error rates, average rate of bit errors, data rate, and the bit error rate target criterion.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
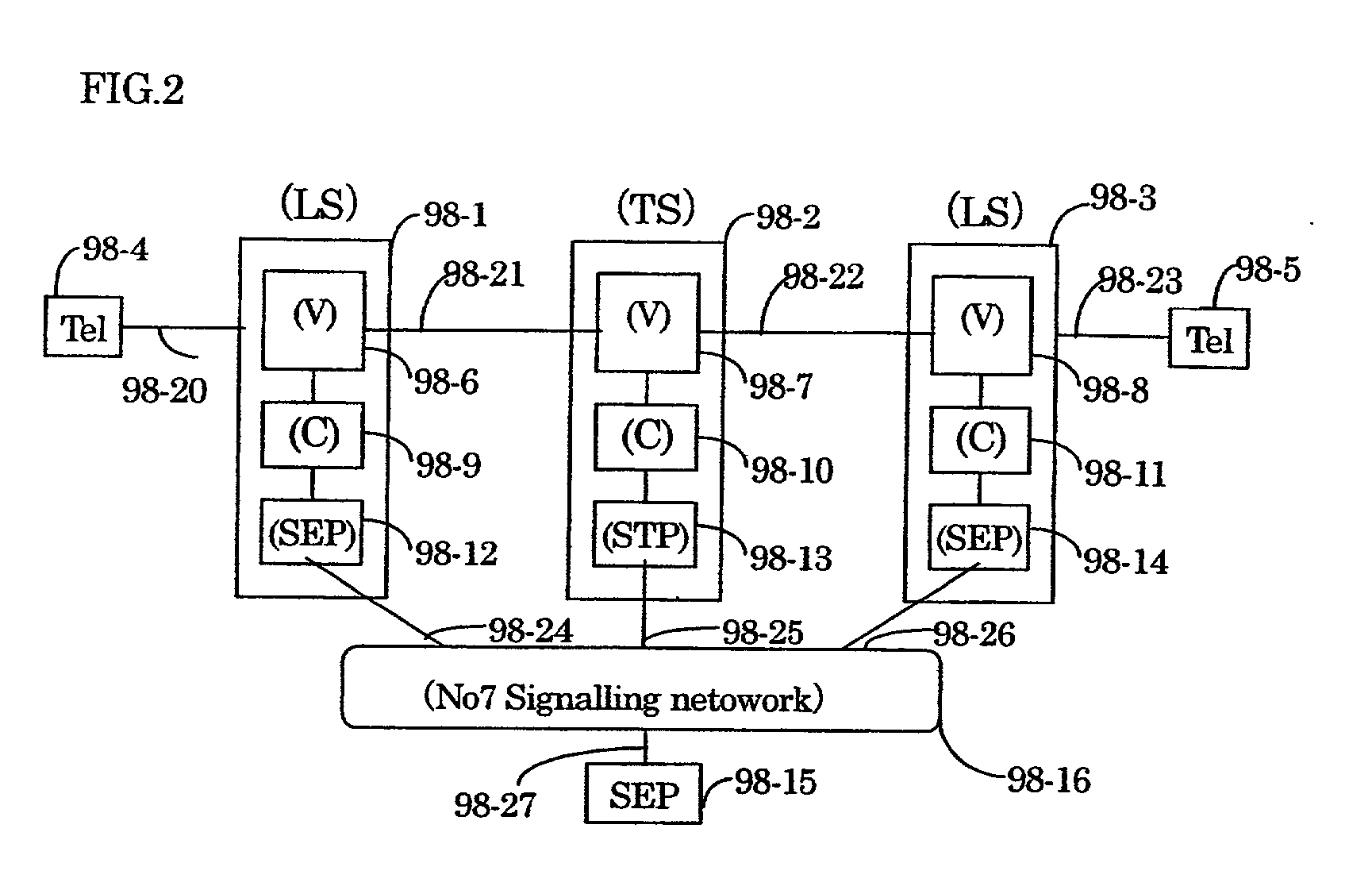
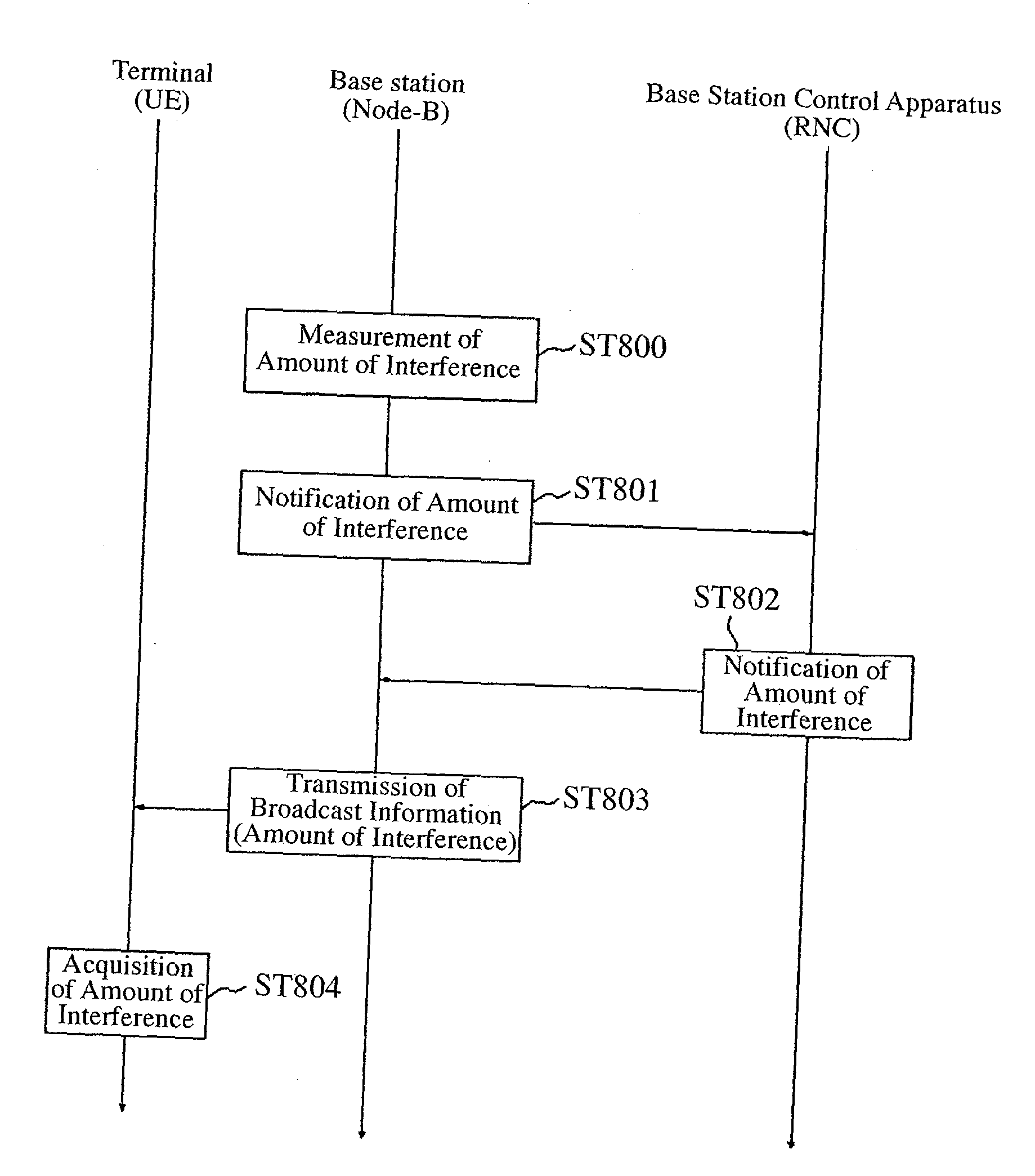
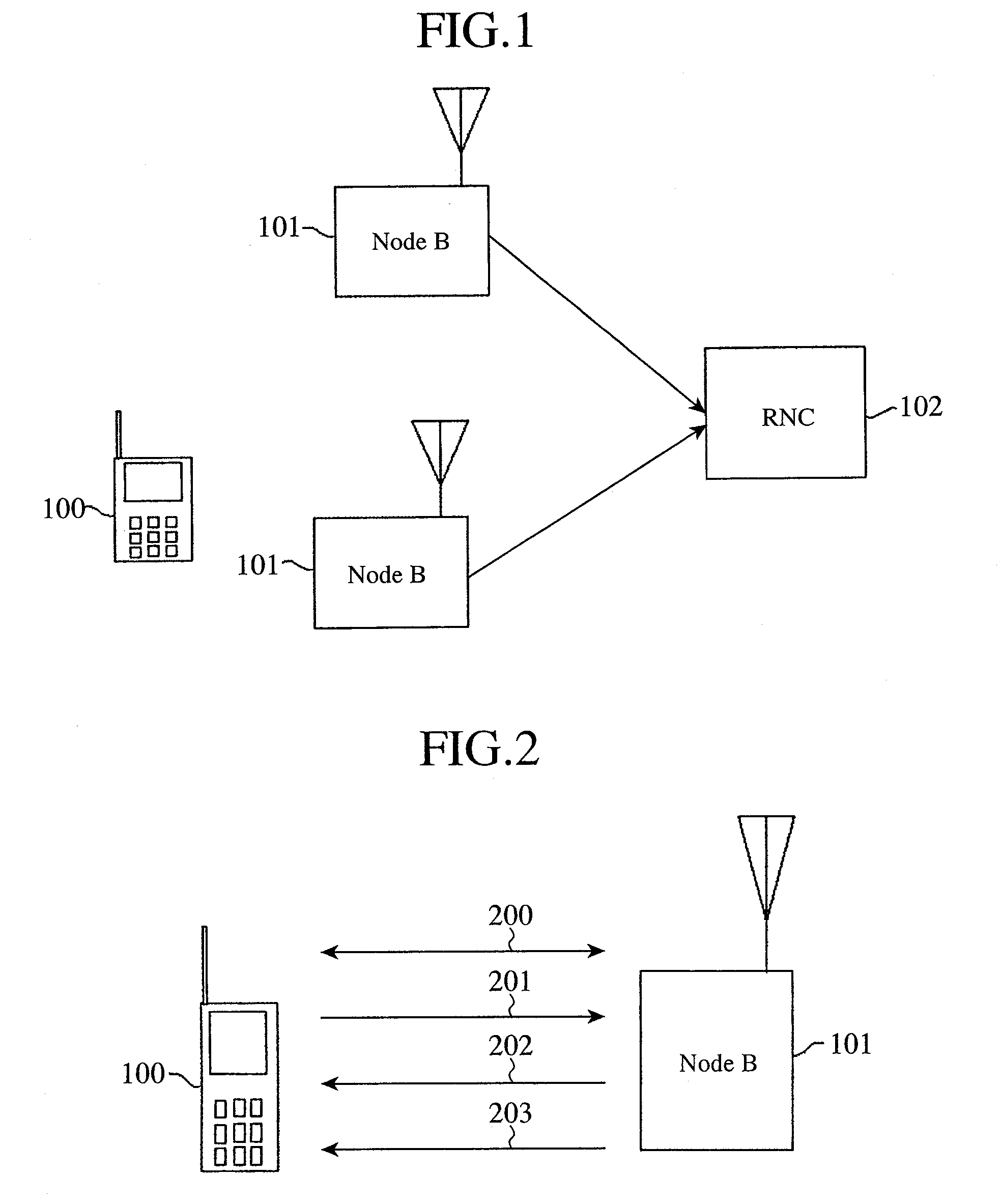
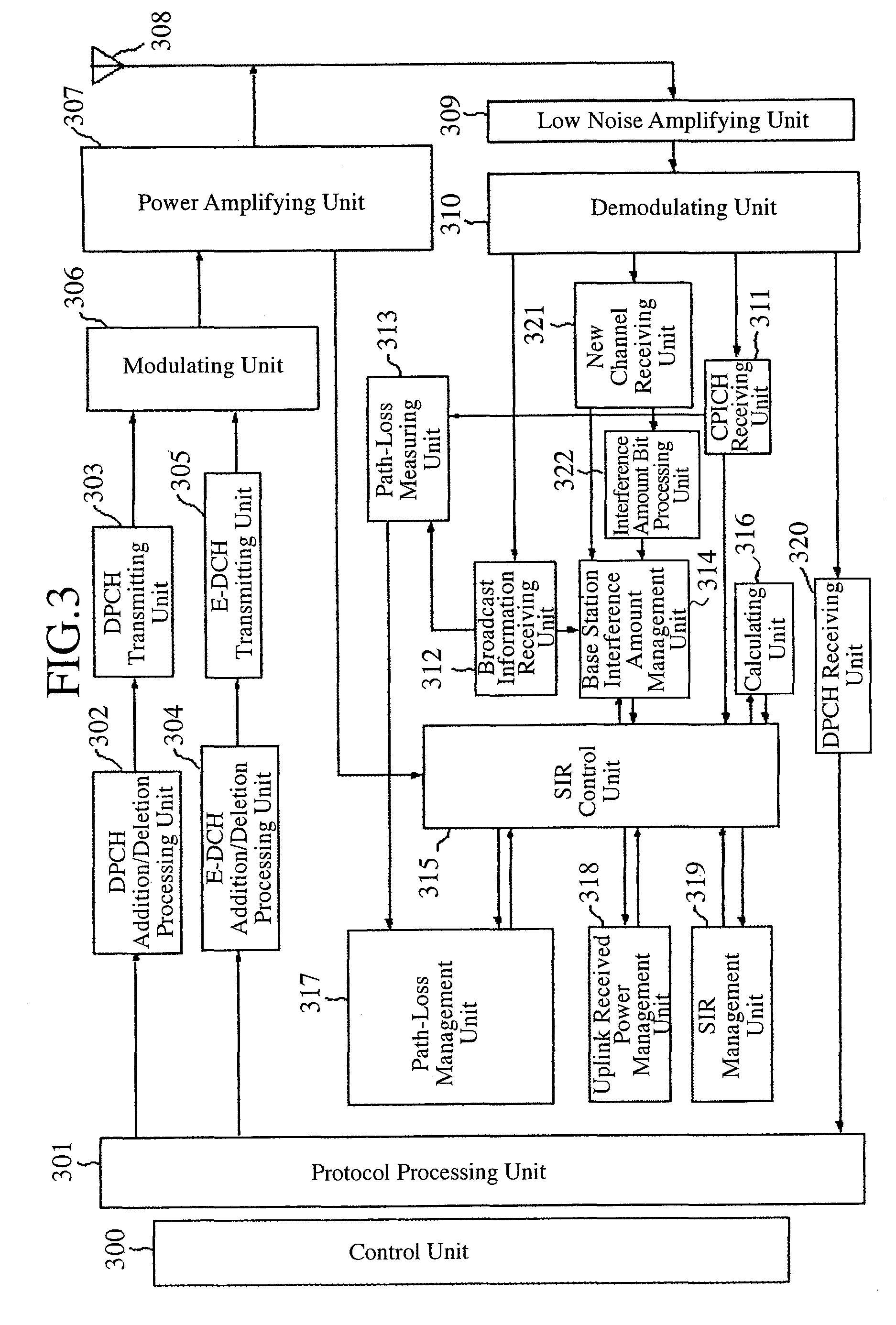
Communication Quality Judgment Method, Mobile Station, Base Station, and Communications System
In order to carry out high-speed packet communications using a large-volume transmission channel like an E-DCH, uplink communication quality must be good. However, in a state in which a link imbalance occurs, a mobile station cannot estimate the uplink communication quality from downlink communication quality. Therefore, the mobile station calculates a path loss from the setting power of a common pilot channel which is notified from a base station, and the received power of the common pilot channel received thereby, and also estimates the received power in the base station on the basis of this path loss. The mobile station further judges the uplink communication quality by estimating the SIR in the base station by using the interference power notified from the base station and the estimated received power.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
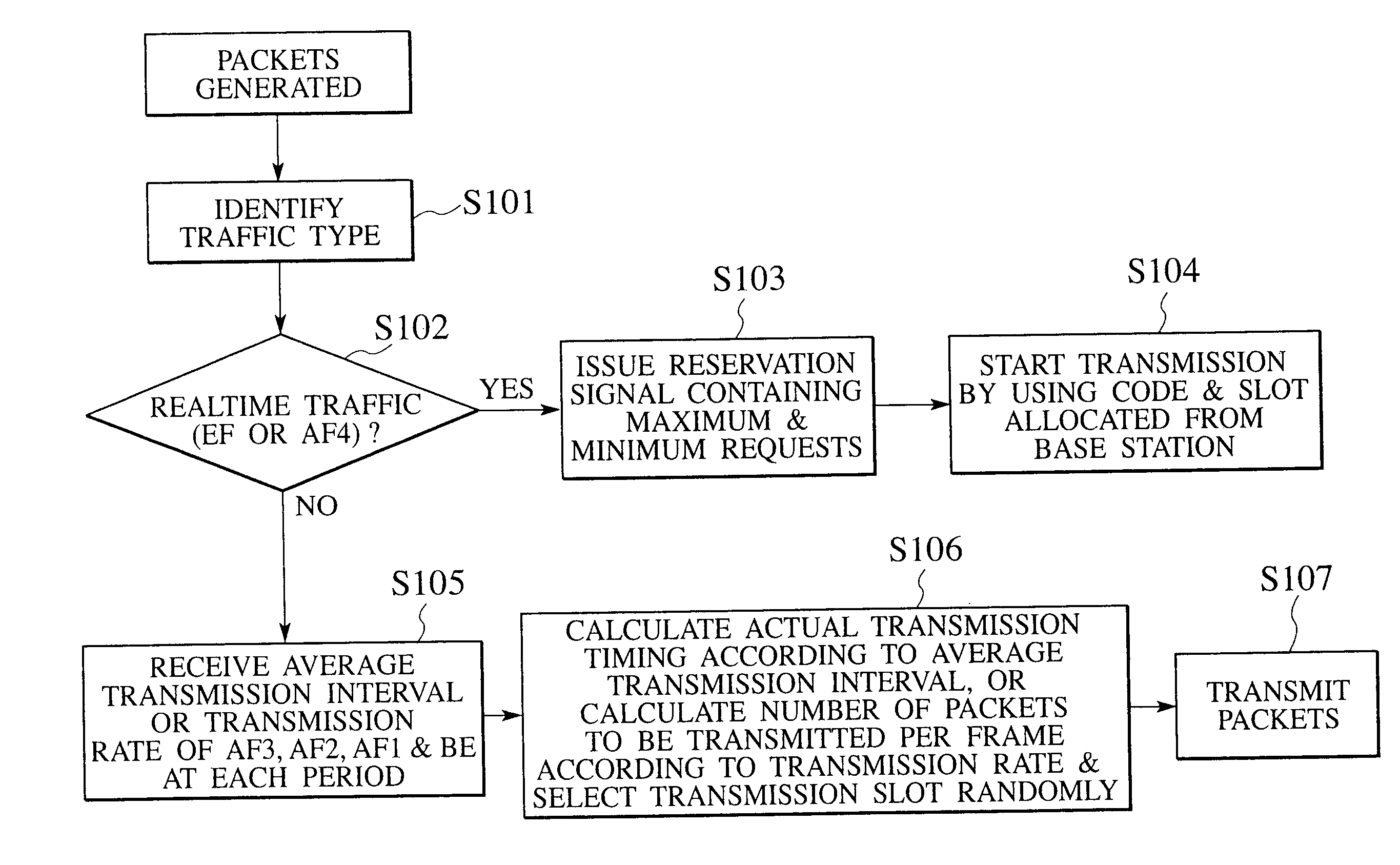
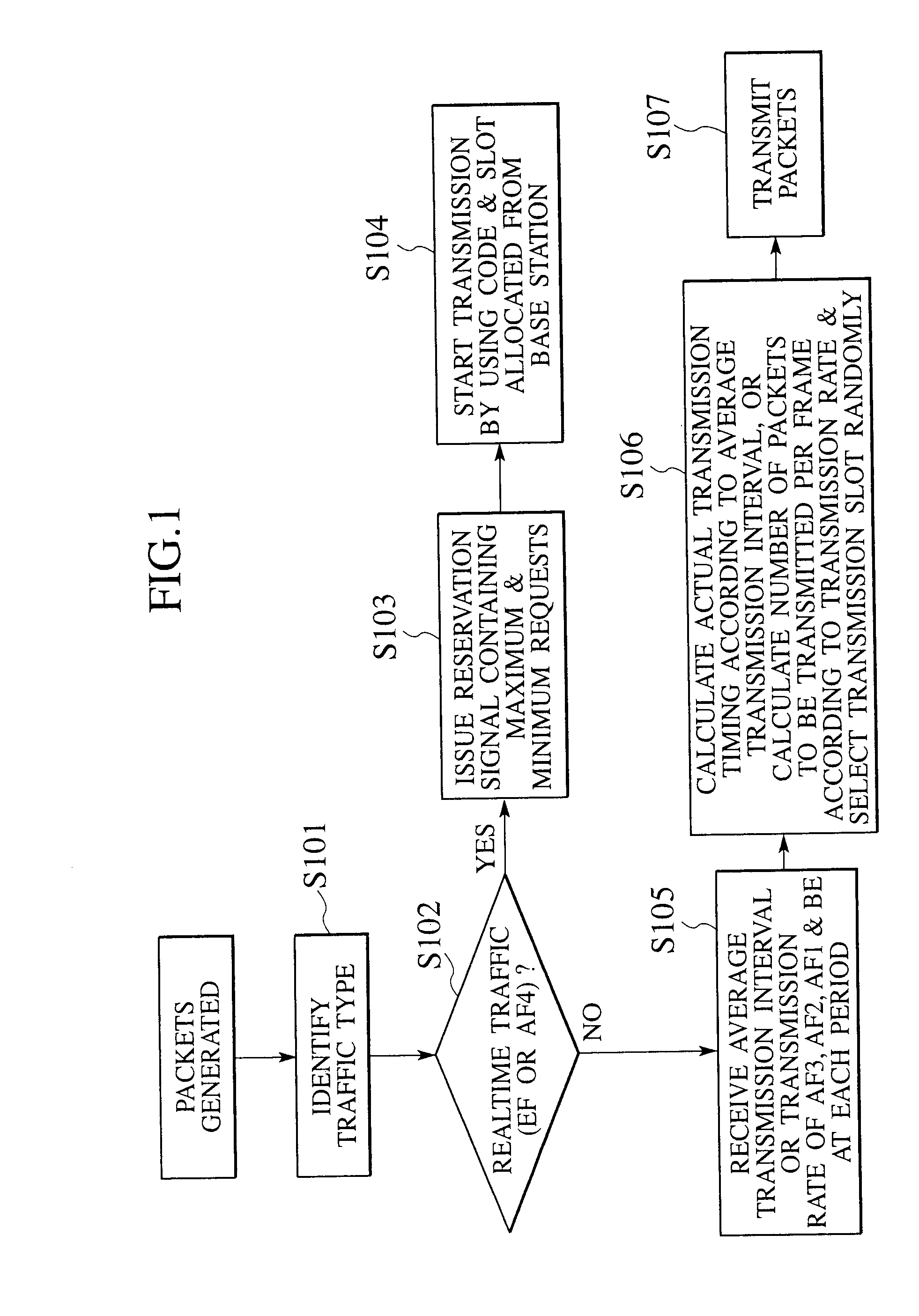
Communication control system, communication control method, base station device and mobile terminal device
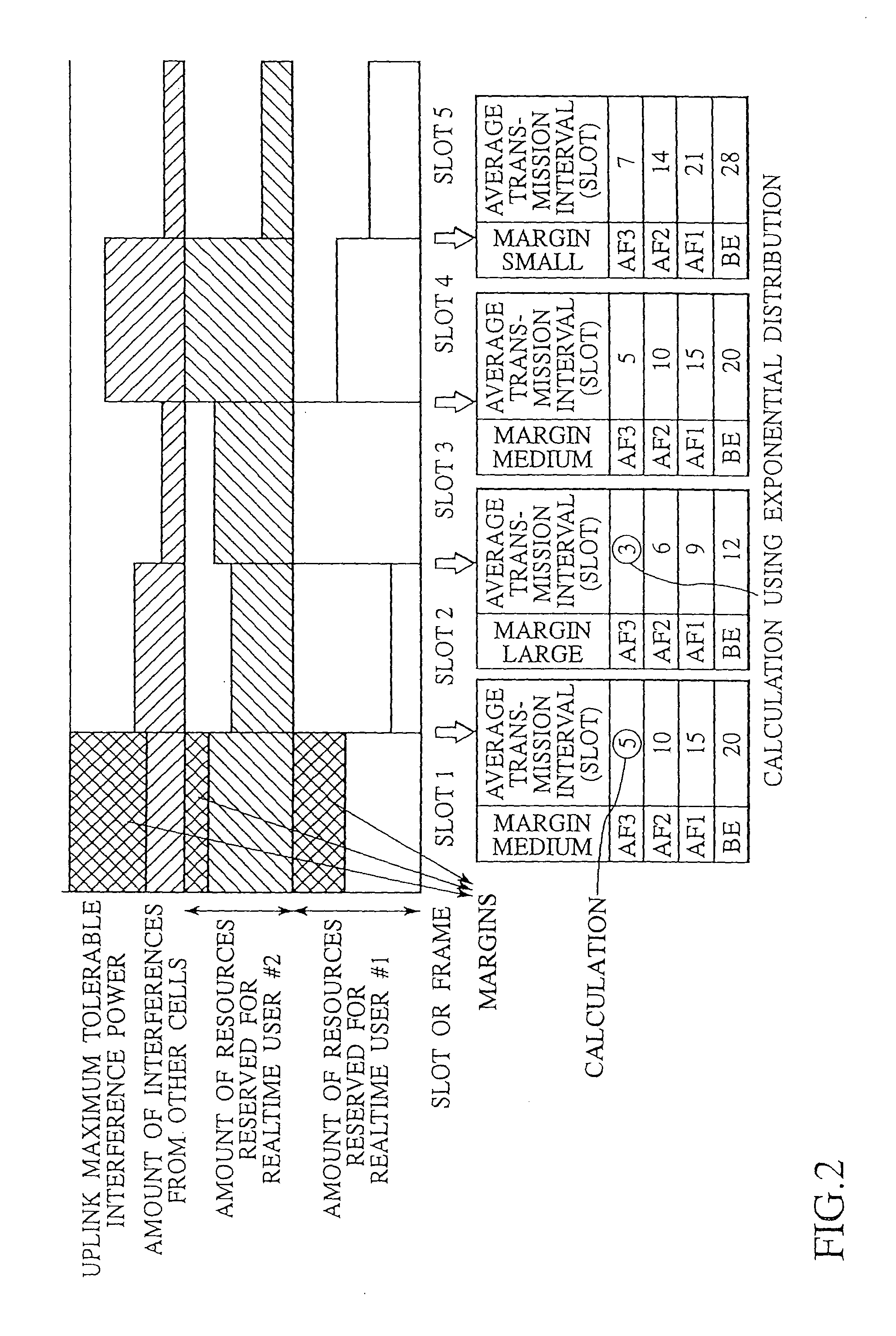
InactiveUS20100254263A1Efficient use of resourcesImprove service qualityError preventionTransmission systemsPacket communicationResource utilization
In packet communications between a mobile terminal and a base station, the mobile terminal checks a priority level of a traffic and judges a type of the traffic, and transmits a reservation signal for a transmission request to the base station when the type of the traffic is a high priority level or realtime type, and does not transmits it when the type of the traffic is a low priority level or non-realtime type, while the base station determines a resource amount to be reserved for packet transmission according to a resource utilization state and the reservation signal for the traffic of the high priority level or realtime type, or an average transmission interval or transmission rate for the traffic of the low priority level or non-realtime type according to margins in remaining resources, and notifies the resource amount or the average transmission interval or transmission rate to the mobile terminal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
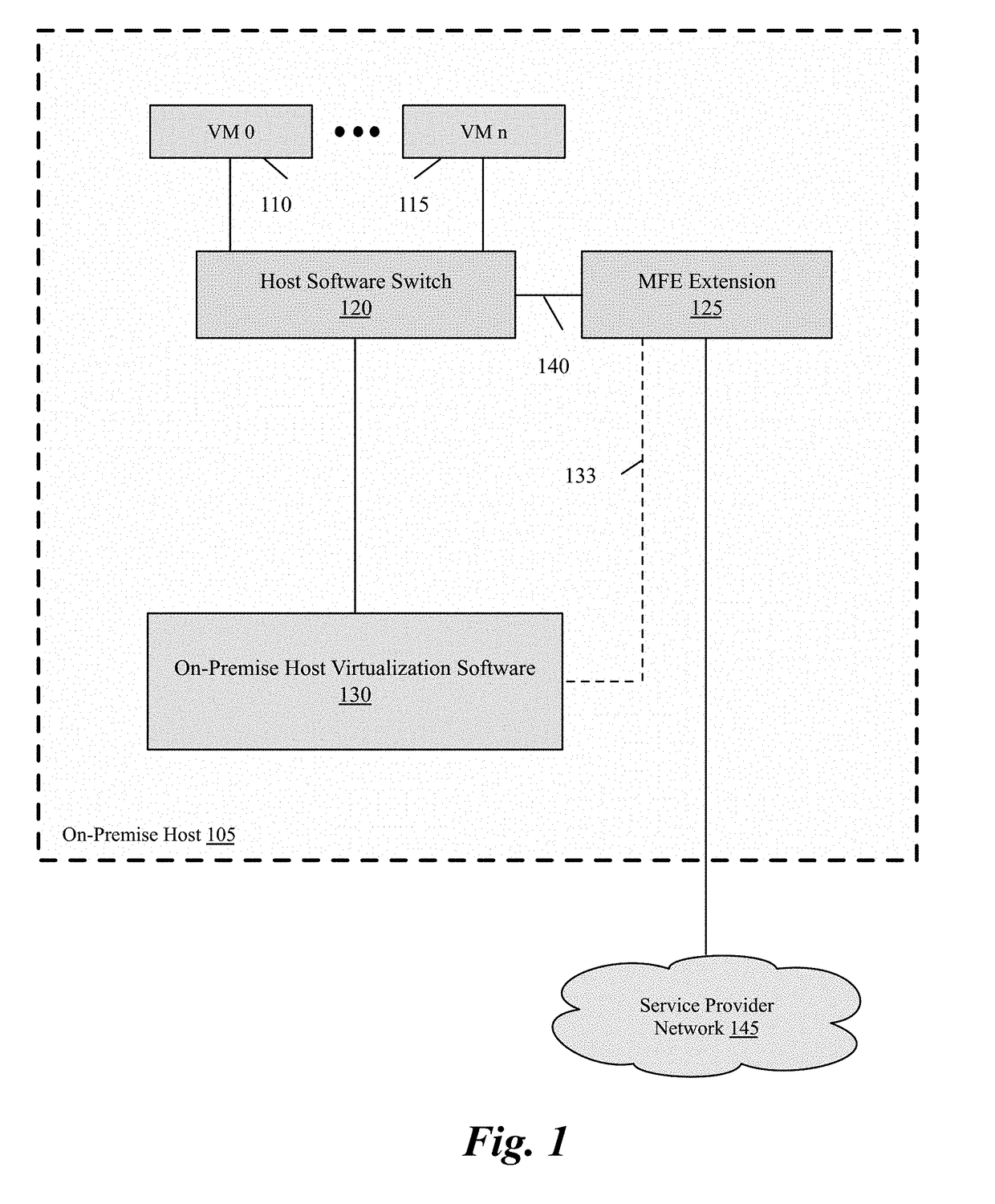
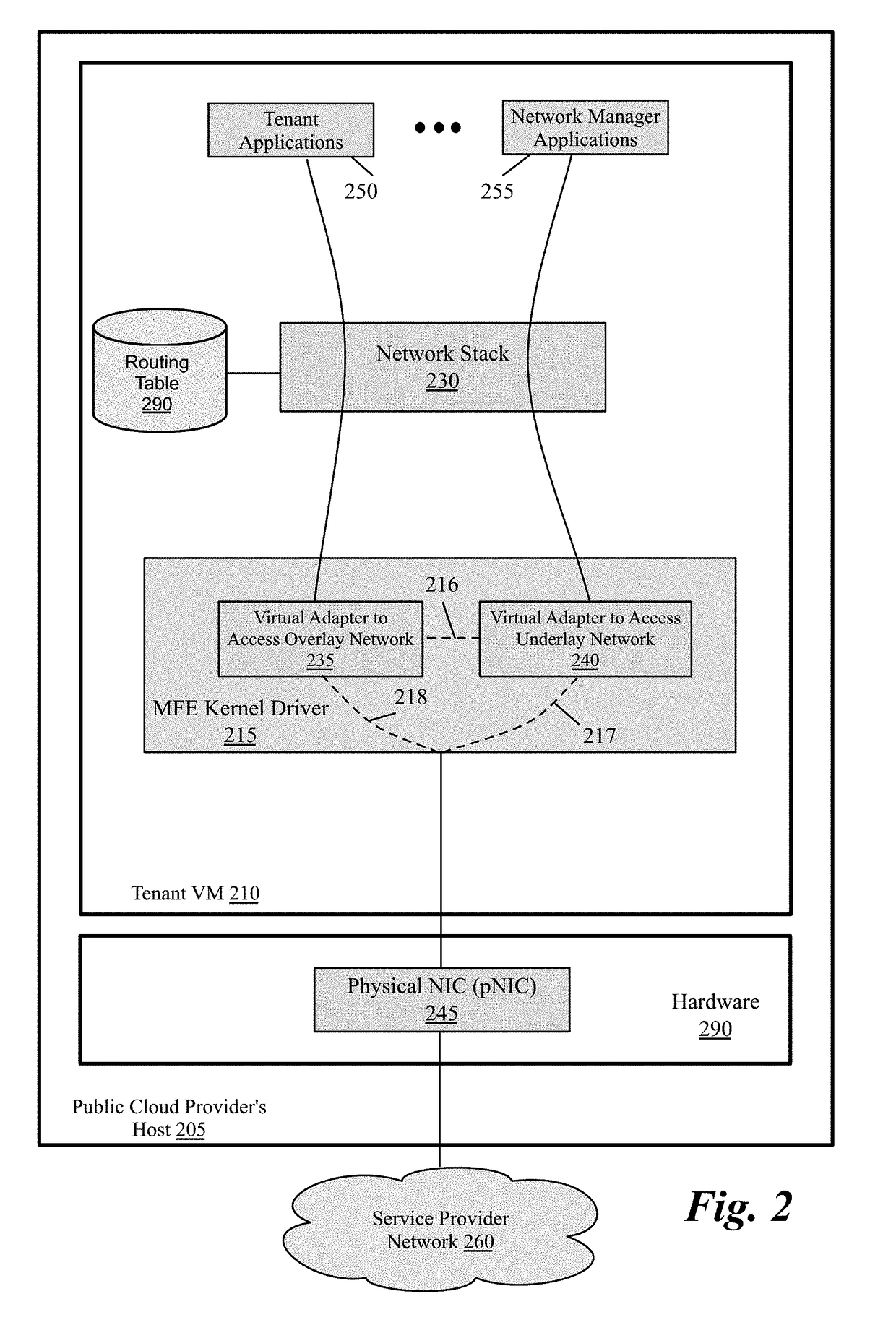
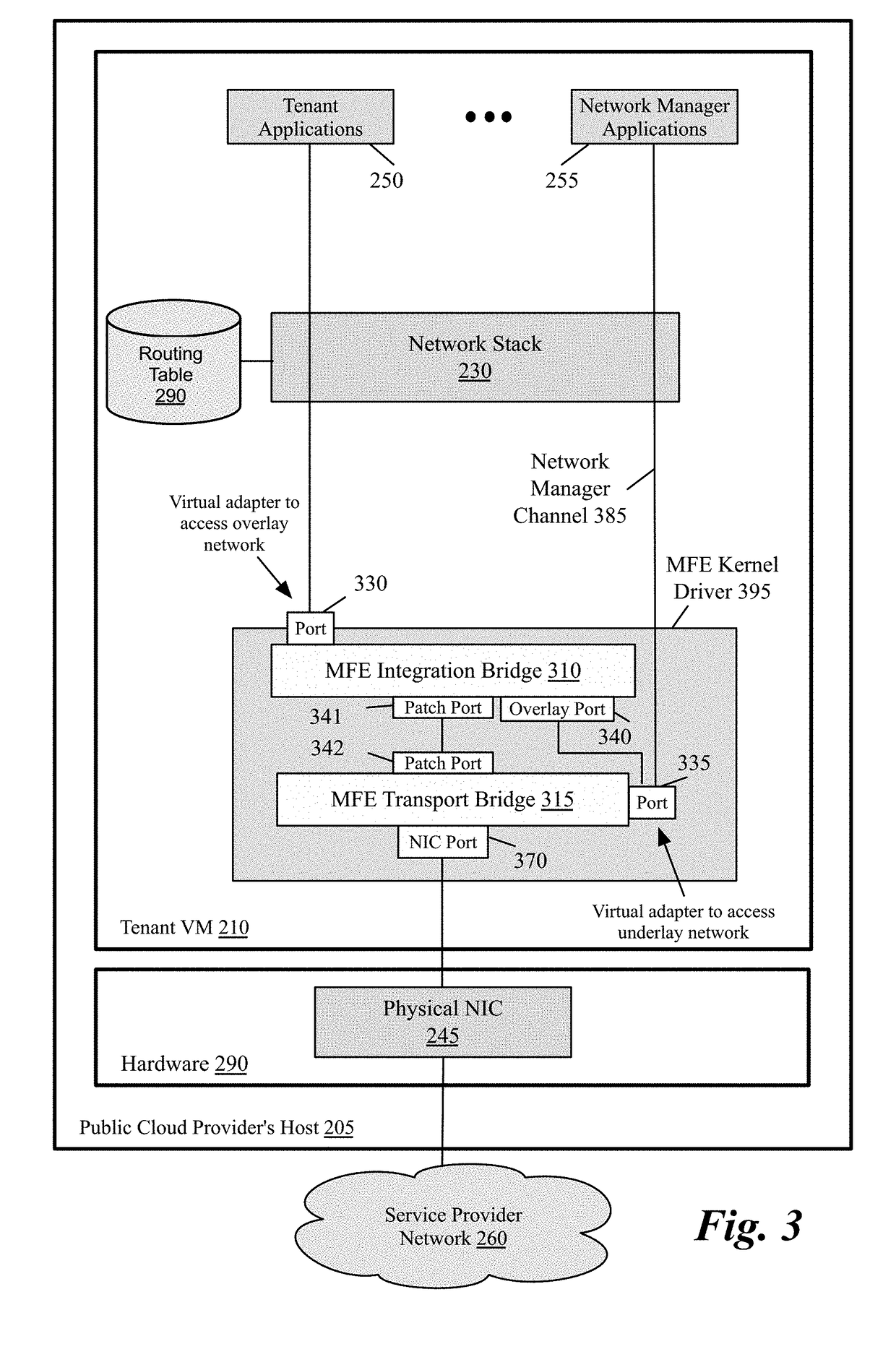
Packet communication between logical networks and public cloud service providers native networks using a single network interface and a single routing table
A data compute node executes (i) a set of tenant applications connected to a third party overlay network, (ii) a set of network manager applications, and (iii) a managed forwarding element that includes a pair of overlay and underlay network virtual adapters. A packet that is received from a network manager application and addressed to an underlay network destination is sent to the underlay network destination address through a physical NIC of the host without network address translation or encapsulation. A packet that is received from a tenant application and addressed to an underlay network destination is subject to SNAT and is sent to the underlay network destination address. A packet that is received from a tenant application and is addressed an overlay destination address is encapsulated with the header of the overlay network and is sent to the overlay network destination address through the underlay virtual adapter.
Owner:NICIRA
Customer billing in a communications network
InactiveUS20030152039A1Improved billing arrangementImprove methodAcutation objectsTelephonic communicationPacket communicationComputer network
In a packet communications network, e.g. a third generation wireless network, combined billing of a user is provided for the delivery of communications services to that user and for the on-line purchase of goods and services by the user via the communications network. A set of rules is provided and a respective billing tariff and account is determined from the rules and each packet address. Credit transfers are made between user accounts and the accounts of goods / services supplies held in a common database.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
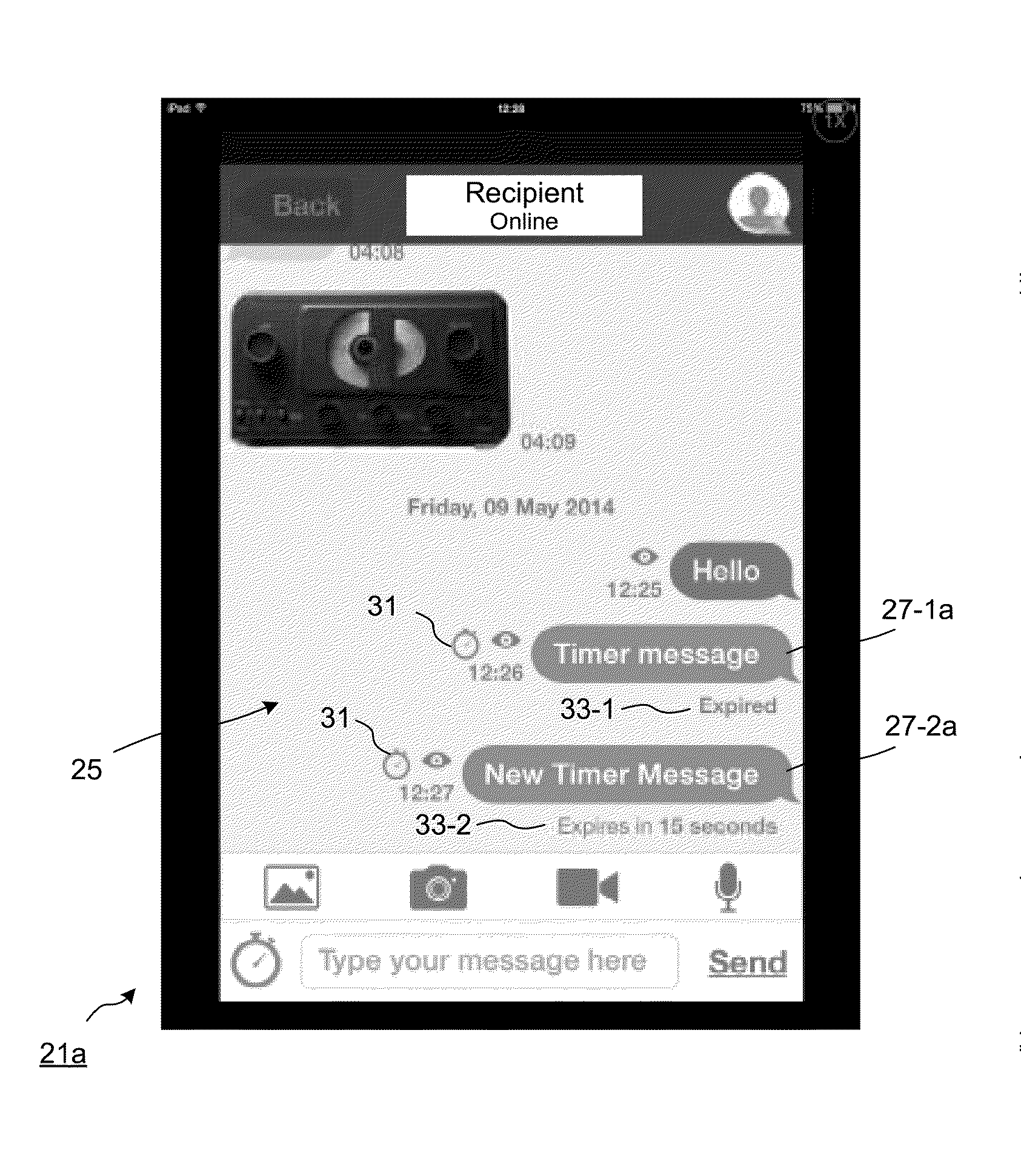
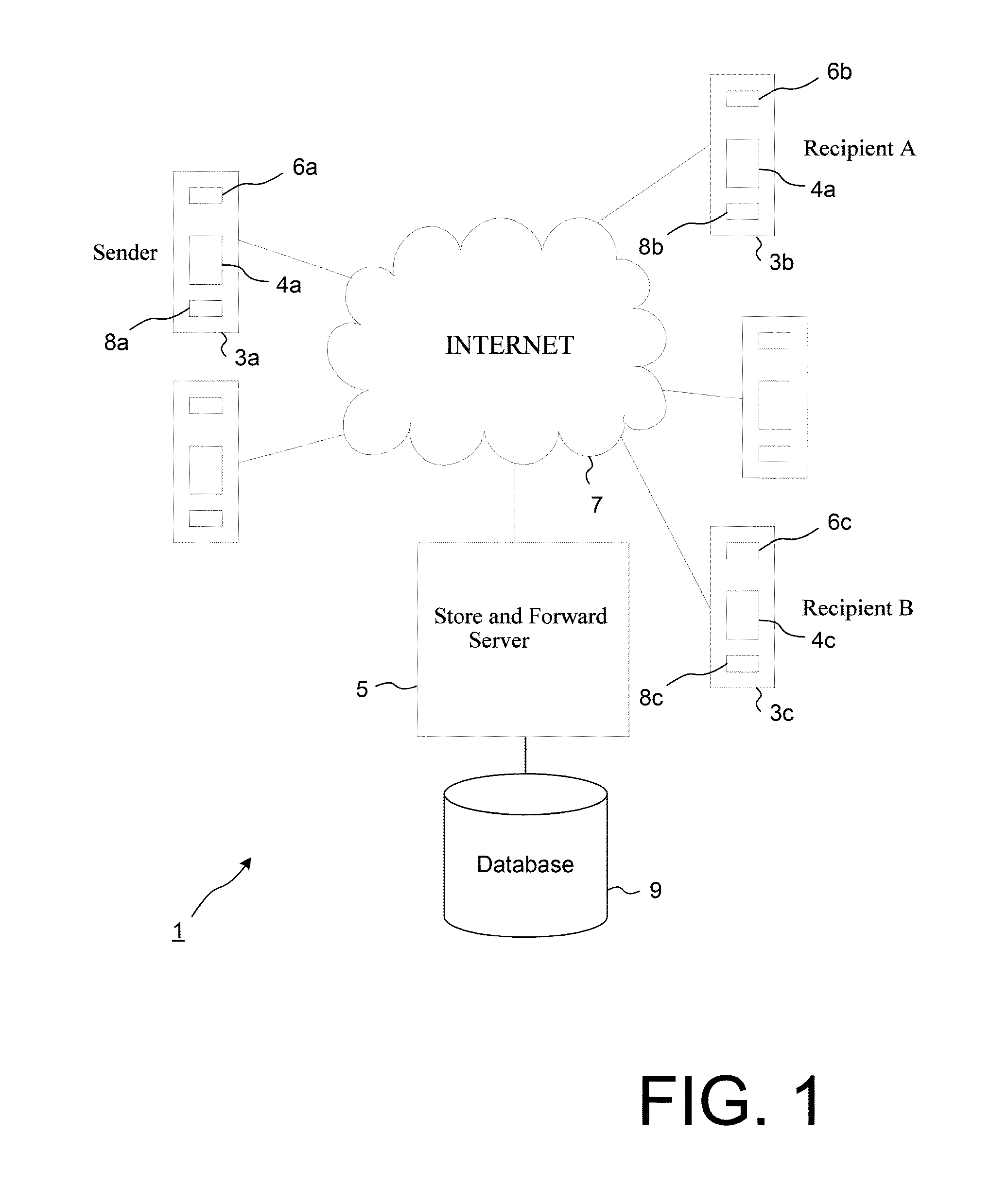
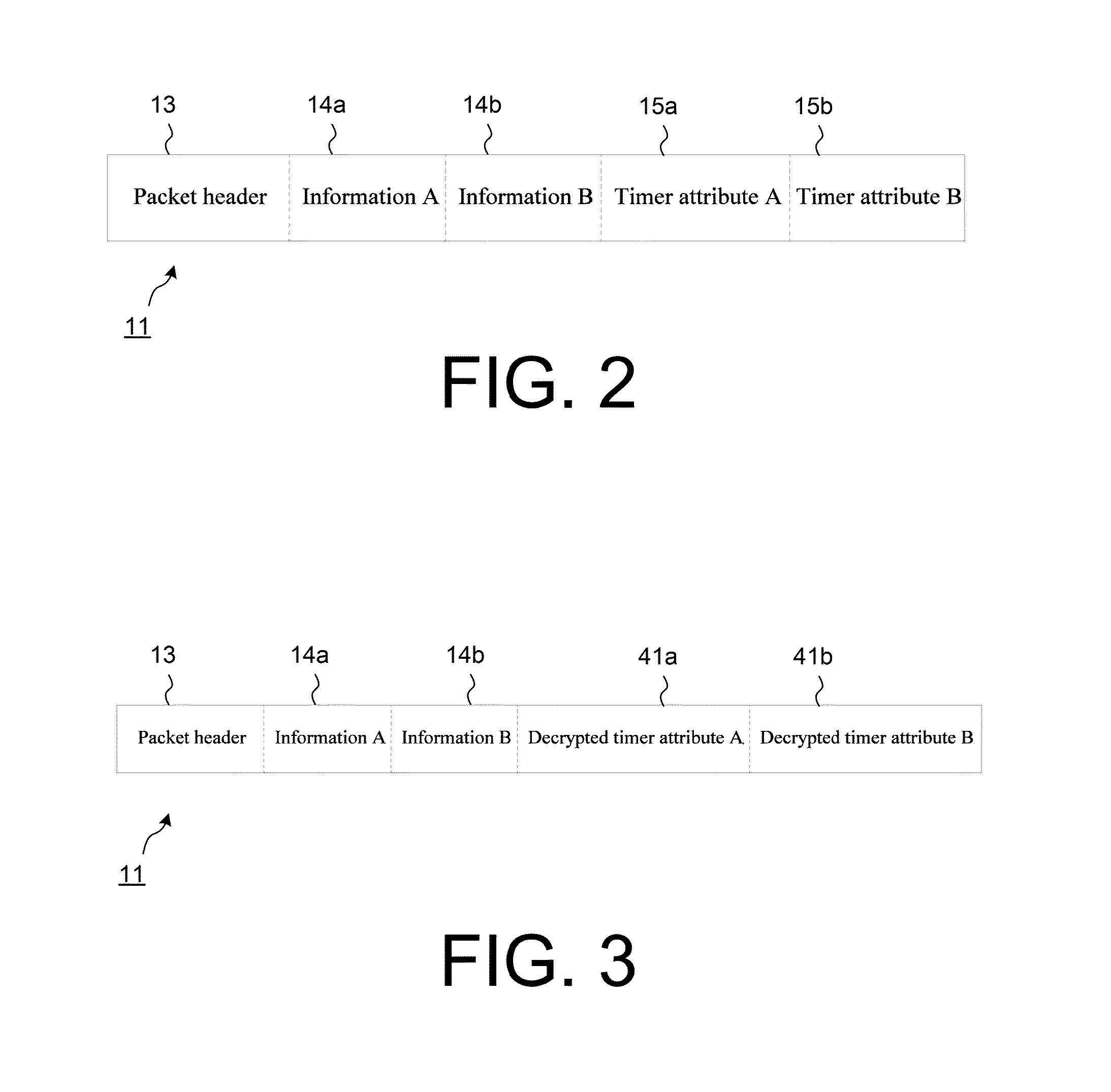
Method and Apparatus for Time Limited Messages in Packet Communications
ActiveUS20150326510A1Robust transmissionData switching networksPacket communicationStore and forward
The present disclosure includes systems and methods for direct packet communications and store and forward packet communications including packets which have attributes which determine the lifetime of the packet contents and these lifetimes are optionally a function of the recipient. Example methods are given featuring the transmission of packets with limited lifetime, the storing and retransmission of packets to one or more recipients and confirmation of deletion of packet contents. It is also shown that cryptography may be employed to ensure that timed presentation of packet contents to recipients takes place and is authenticated by the sender.
Owner:PQ SOLUTIONS LTD
Customer billing in a communications network
InactiveUS20040125755A1Improved billing arrangementImprove methodMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationPacket communicationComputer network
In a packet communications network, e.g. a third generation wireless network, combined billing of a user is provided for the delivery of communications services to that user and for the on-line purchase of goods and services by the user via the communications network. A set of rules is provided and a respective billing tariff and account is determined from the rules and each packet address. Credit transfers are made between user accounts and the accounts of goods / services supplies held in a common database.
Owner:APPLE INC
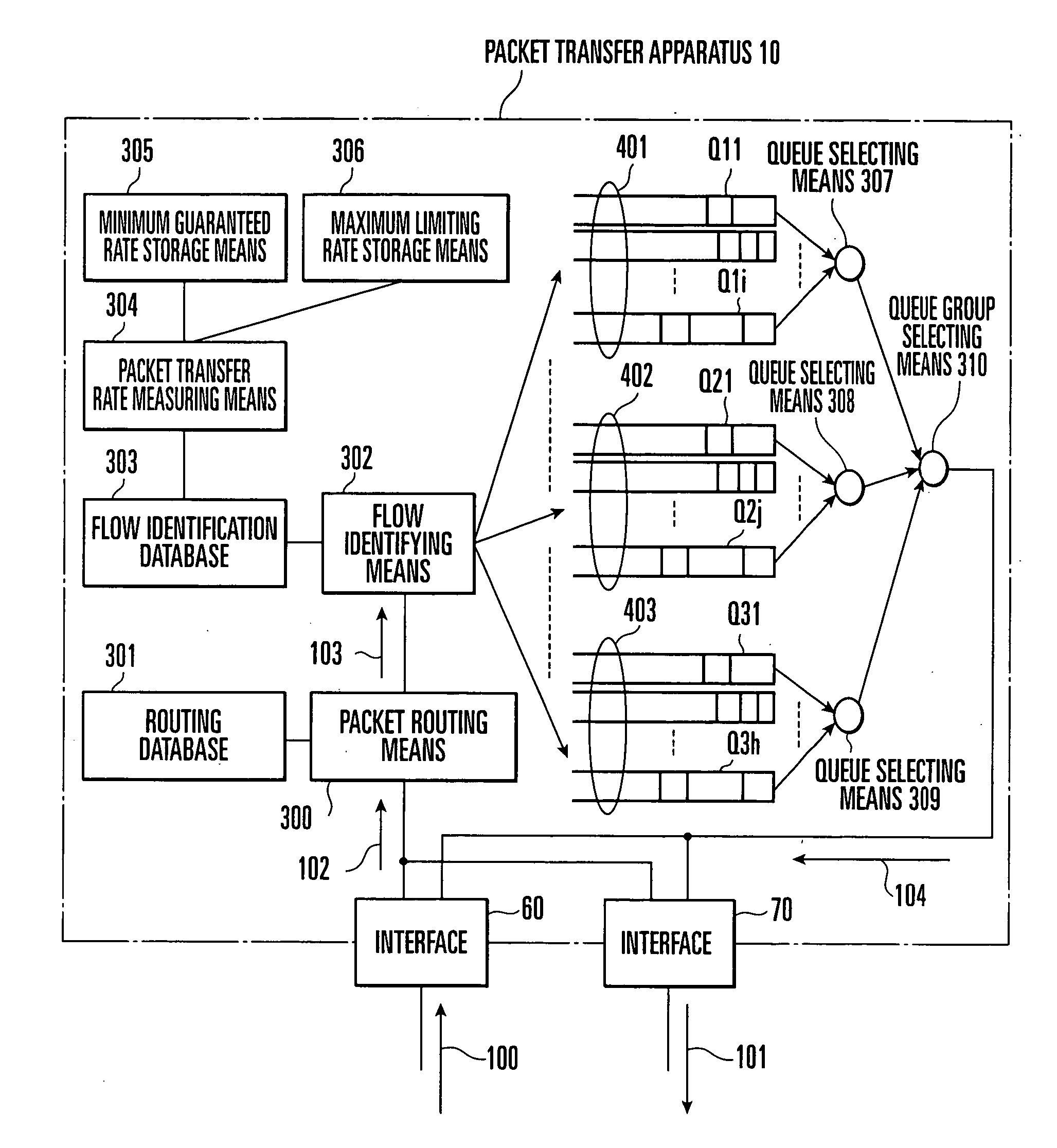
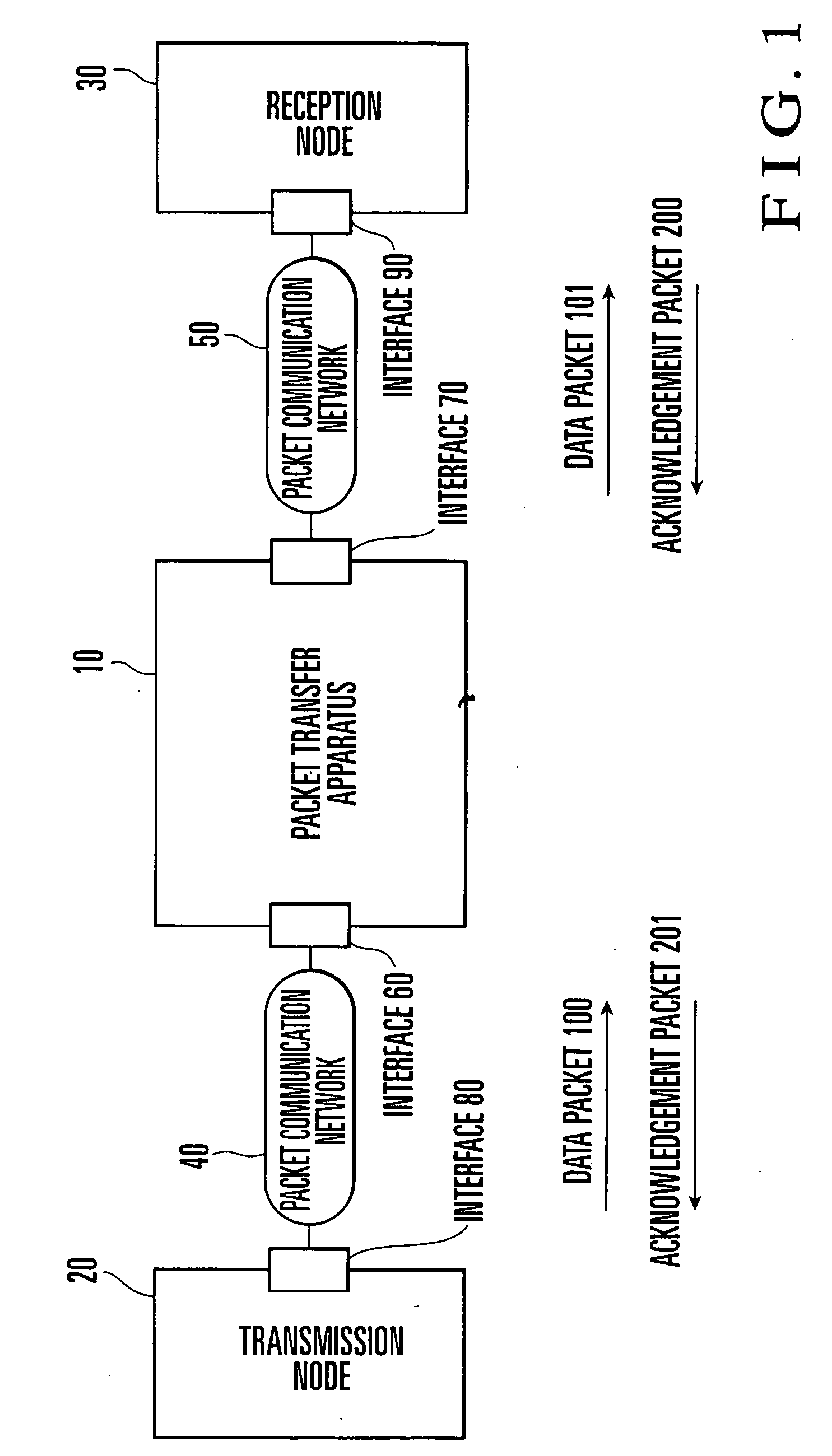
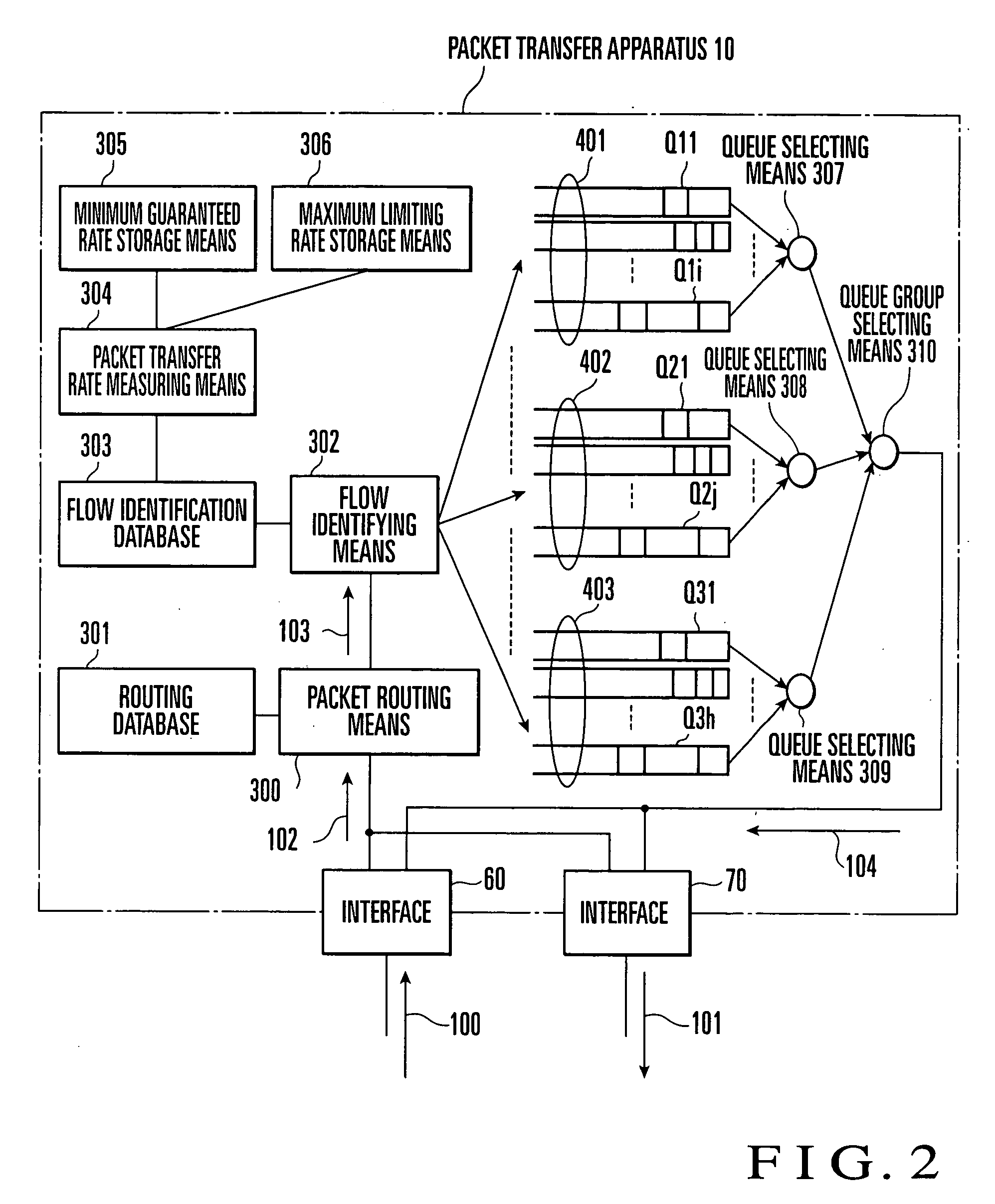
Packet transfer rate monitoring control apparatus method and program
InactiveUS20040066746A1Improve transfer rateGuaranteed rateError preventionTransmission systemsPacket communicationReal-time computing
In a packet communication network in which the minimum guaranteed rate and maximum limiting rate of packet transfer are contracted for each service, this invention classifies flows corresponding to received packets into group 1 to which a flow whose packet transfer rate is less than the minimum guaranteed rate belongs, group 2 to which a flow whose packet transfer rate is equal to or higher than the minimum guaranteed rate and less than the maximum limiting rate belongs, and group 3 to which a flow whose packet transfer rate exceeds the maximum limiting rate belongs. A packet received in relation to a flow which belongs to group 1 is preferentially transferred before a packet received in relation to a flow which belongs to group 2, and a packet received in relation to a flow which belongs to group 2 is preferentially transferred before a packet received in relation to a flow which belongs to group 3. This allows easy and fair redistribution of an extra band, while a packet transfer rate equal to or higher than the minimum guaranteed rate is ensured, even when traffic has increased.
Owner:NEC CORP
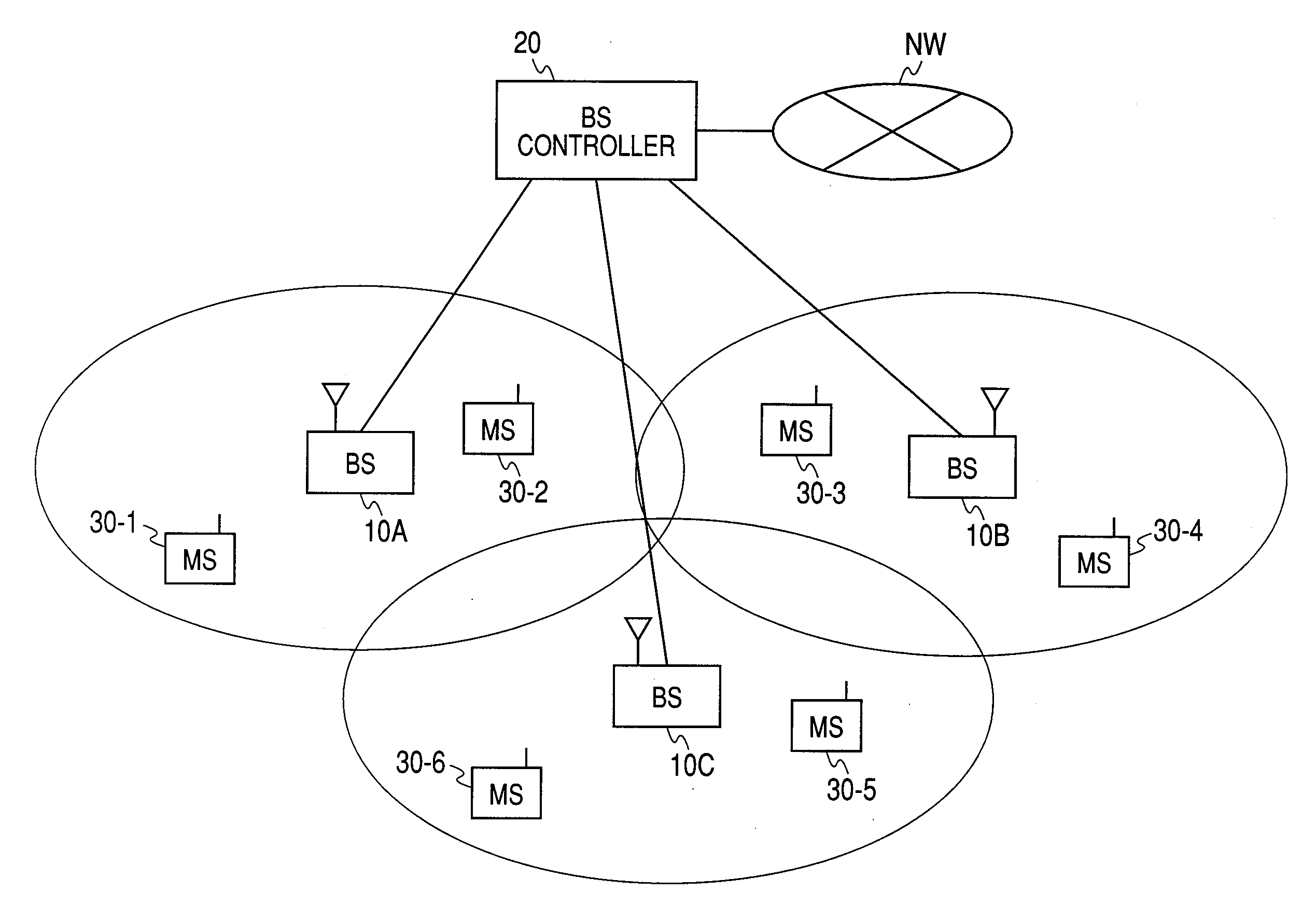
Radio communication system, mobile station, and radio base station
InactiveUS20090016265A1Shorten transmission intervalReduce transmission delayError preventionSecret communicationPacket communicationCommunications system
A radio communication system of an HARQ method that makes an HARQ transmission interval of subpackets appropriate and reduces data transmission delay resulting from subpacket retransmission. In the radio communication system in which a packet is transmitted and receives with the HARQ method between a base station and multiple radio mobile stations, each of the base station and the multiple radio mobile stations has: a packet transmission circuit for transmitting subpackets in predetermined intervals; a packet reception circuit for repeating decoding processing by combining a newly received subpacket and a previously received former subpacket until an original packet is successfully decoded; and a HARQ control equipped with a function of, for packet communication whose data length is short, transmitting a subpacket or response from the packet transmission circuit in an HARQ transmission interval that is shortened from the HARQ transmission interval of the normal mode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
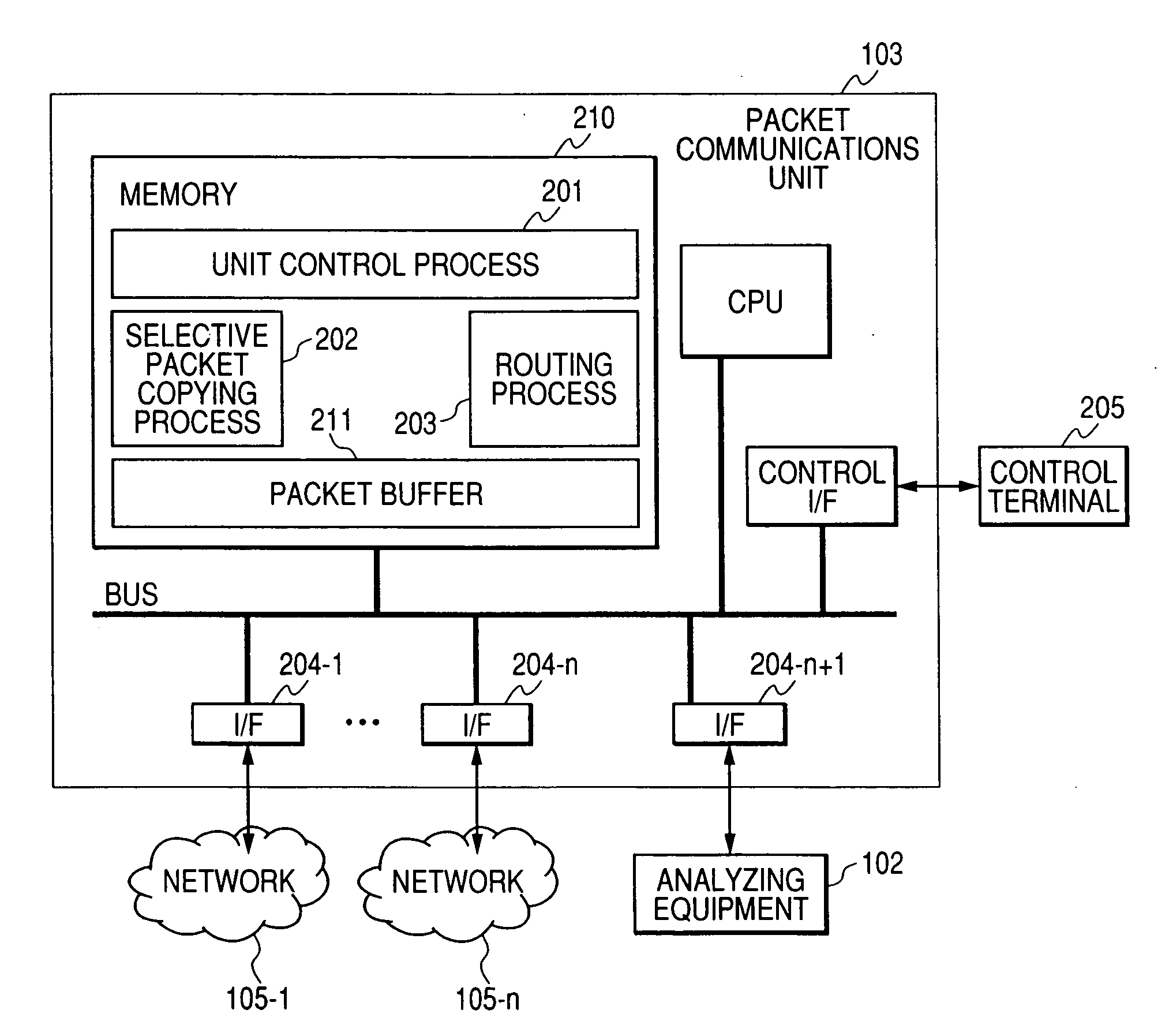
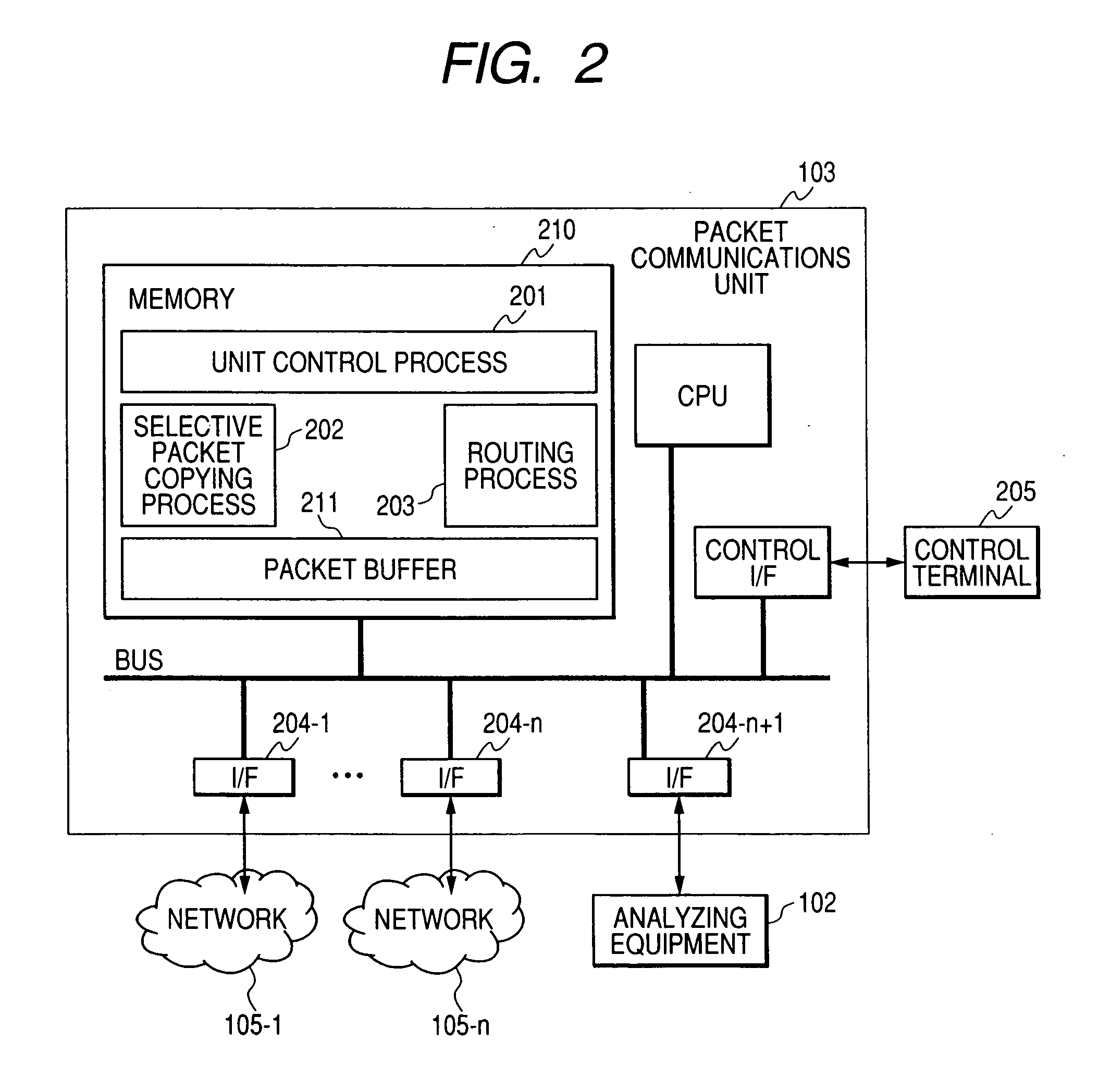
Packet communications unit
InactiveUS20070160073A1Reduce analysisTraffic can be can be increased and reducedError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationTraffic capacity
To analyze traffic at an application level, a stream according to TCP or SCTP is required to be reconstructed and to be analyzed. When a packet is transferred to analyzing equipment using a port mirroring function with which a router and a switch are provided, transferred traffic volume increases and exceeds the throughput of the analyzing equipment. As only a part of packets configuring a stream is transferred to the analyzing equipment in transfer to the analyzing equipment using a packet sampling function, analysis at the application level is impossible. To solve the problem, when a packet communication unit recognizes a stream start packet, samples a stream initiated by the packet on a condition and at a rate respectively determined beforehand and generates a condition for copying the packet based upon information of both ends of the stream included in the packet, packets sampled in units of stream can be transferred to the analyzing equipment.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
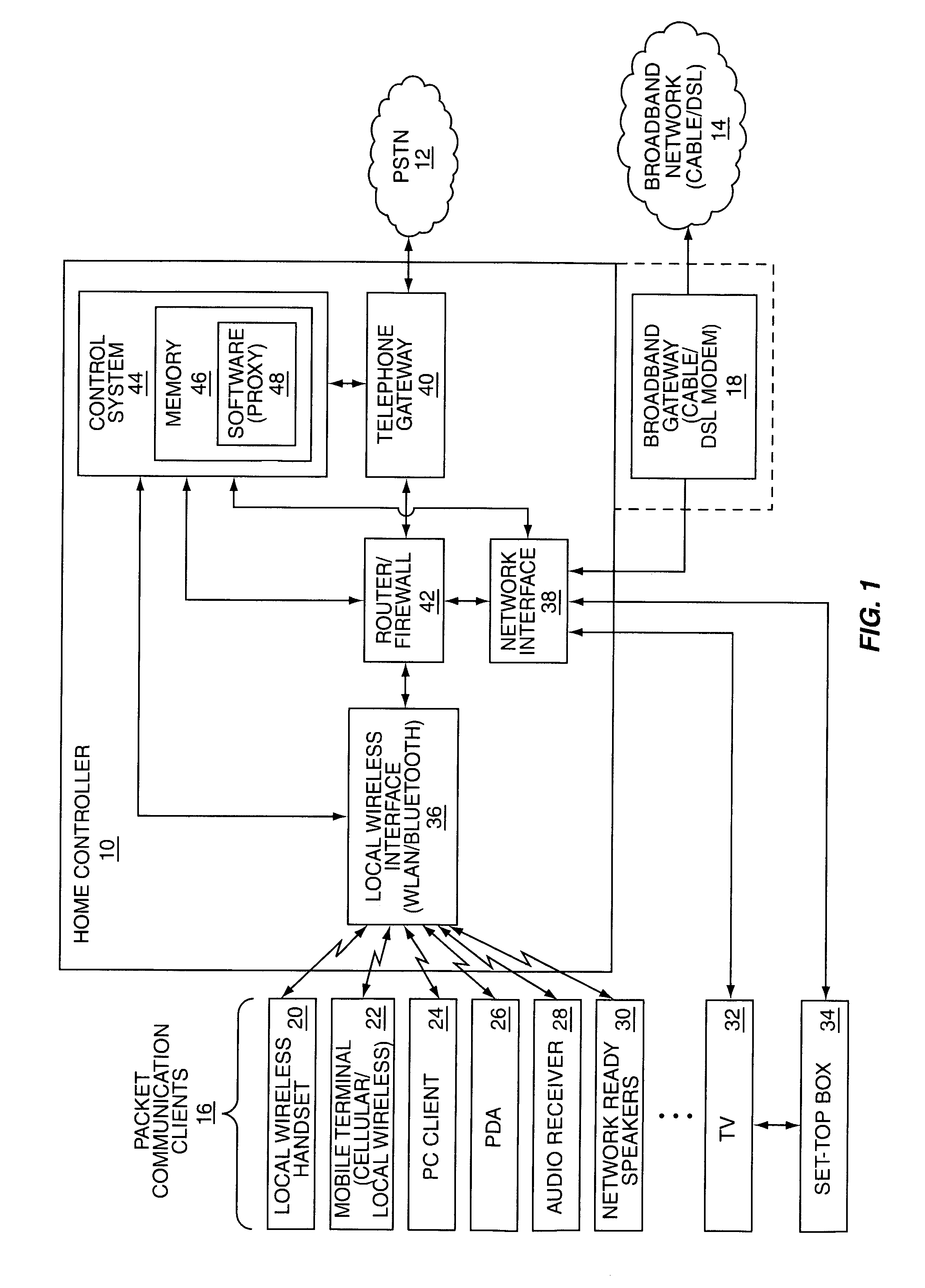
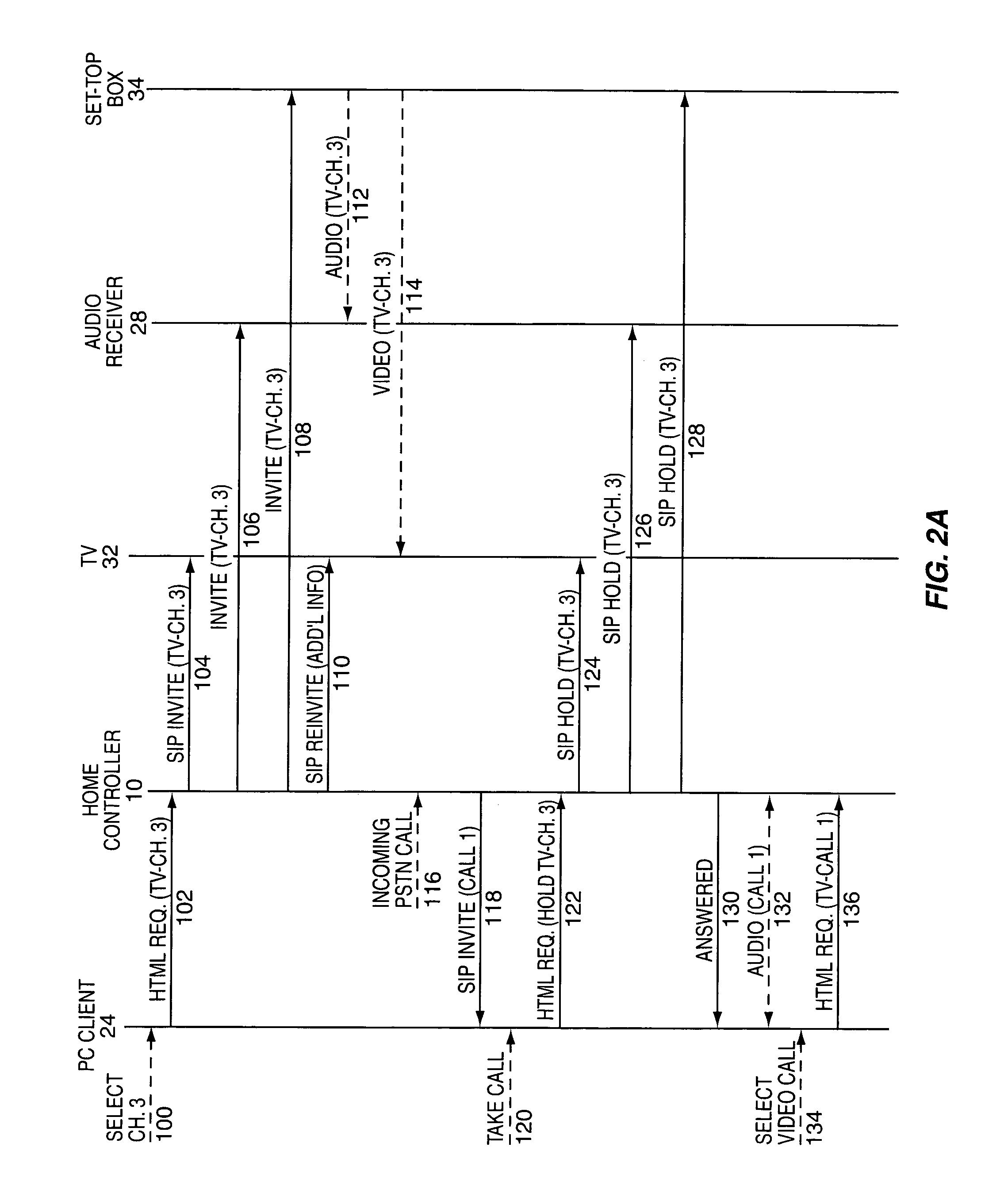
Integrated home service network
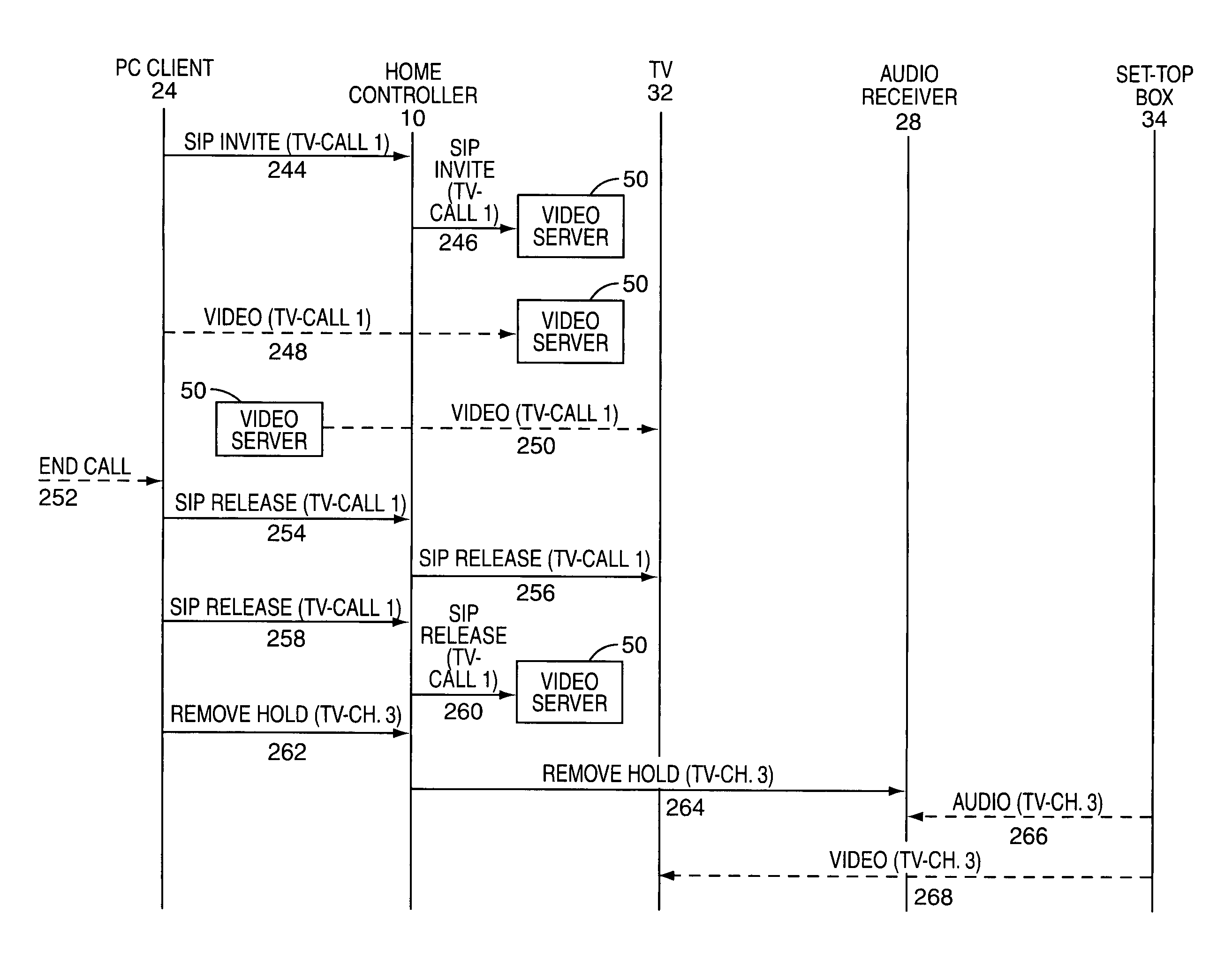
ActiveUS7957326B1Effective controlEasy to operateSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsPacket communicationClient-side
The present invention provides a centralized home controller that is used to coordinate a plurality of associated packet communication clients. The home controller provides a centralized and unified control and messaging system for the various packet communication clients. The home controller also allows the packet communication clients to establish and control packet sessions among the associated packet communication clients, as well as between any one of the packet communication clients and remote clients. The packet communication clients are provided in consumer electronics devices, and the associated packet sessions support data, voice, audio, or video content. In one embodiment, the home controller acts as a proxy for the various communications between the packet communication clients.
Owner:APPLE INC
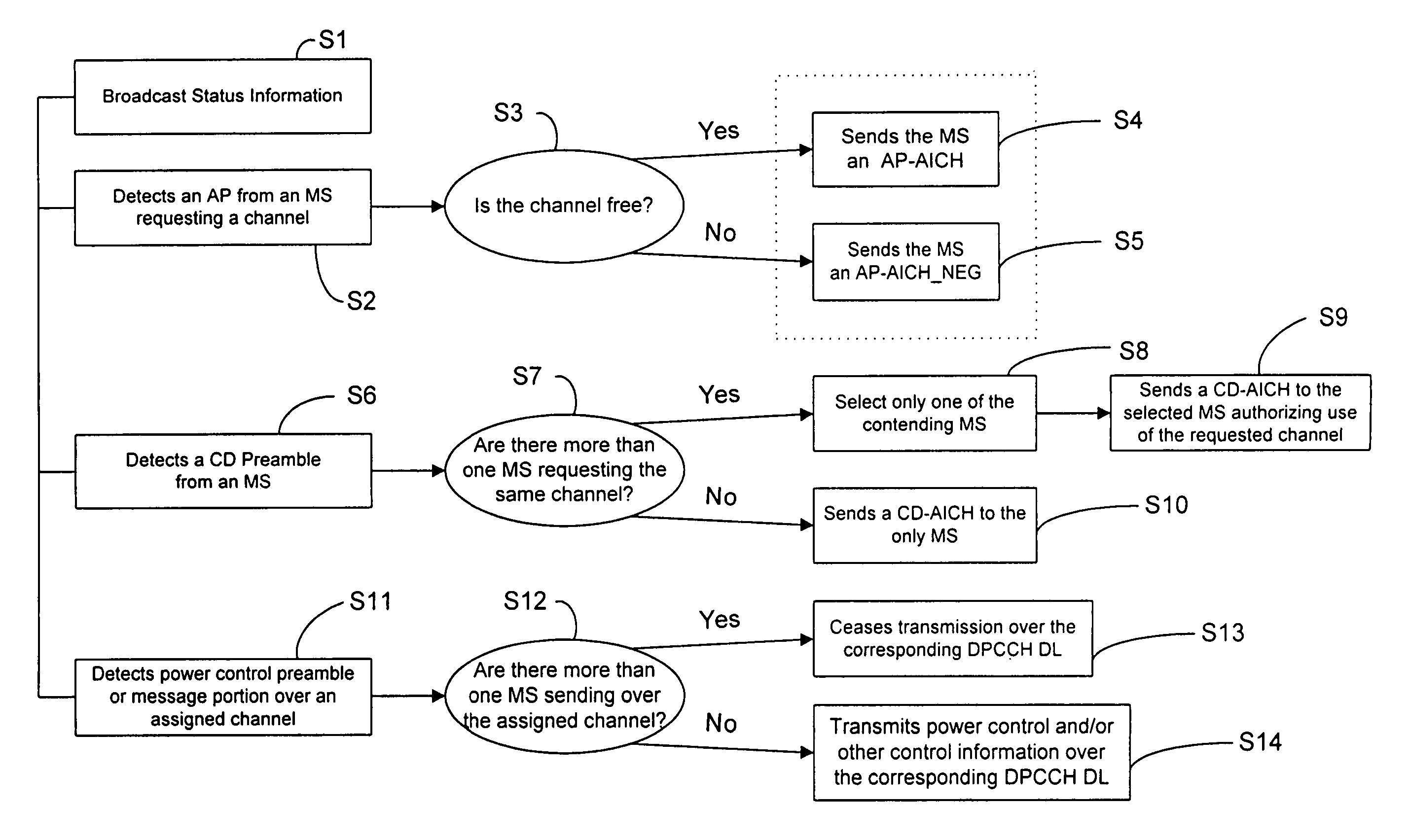
Hybrid DSMA/CDMA (digital sense multiple access/code division multiple access) method with collision resolution for packet communications
InactiveUS7075971B2Avoid collisionEffective distributionPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelPacket communicationTime division multiple access
A hybrid DSMA-CR / CDMA methodology provides efficient access to one of a group of packet channels in a spread spectrum wireless communication network. The base station broadcasts status information as to the availability and / or available data rates for each packet channel or group of channels. Each mobile station uses the status information to select an available channel and / or a channel with sufficient data rate. The mobile station then starts transmission of a series of access preambles, each of which contains a signature corresponding to the selected channel. The mobile station transmits the preambles at increasing power levels. When the base station detects a preamble transmission, the base station responds with a corresponding acknowledgement essentially permitting the mobile station to send its packet data along with any closed-loop power control information over the selected channel.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com