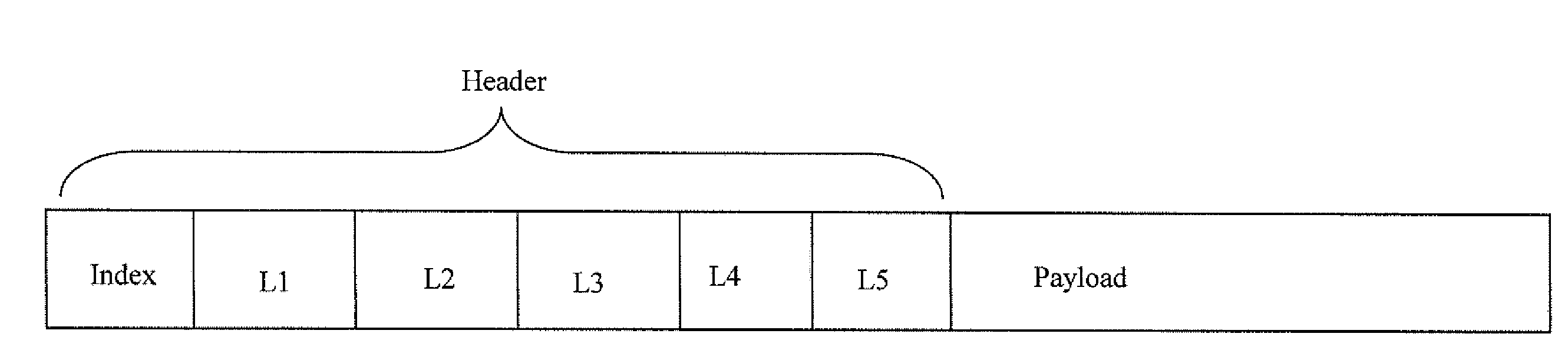
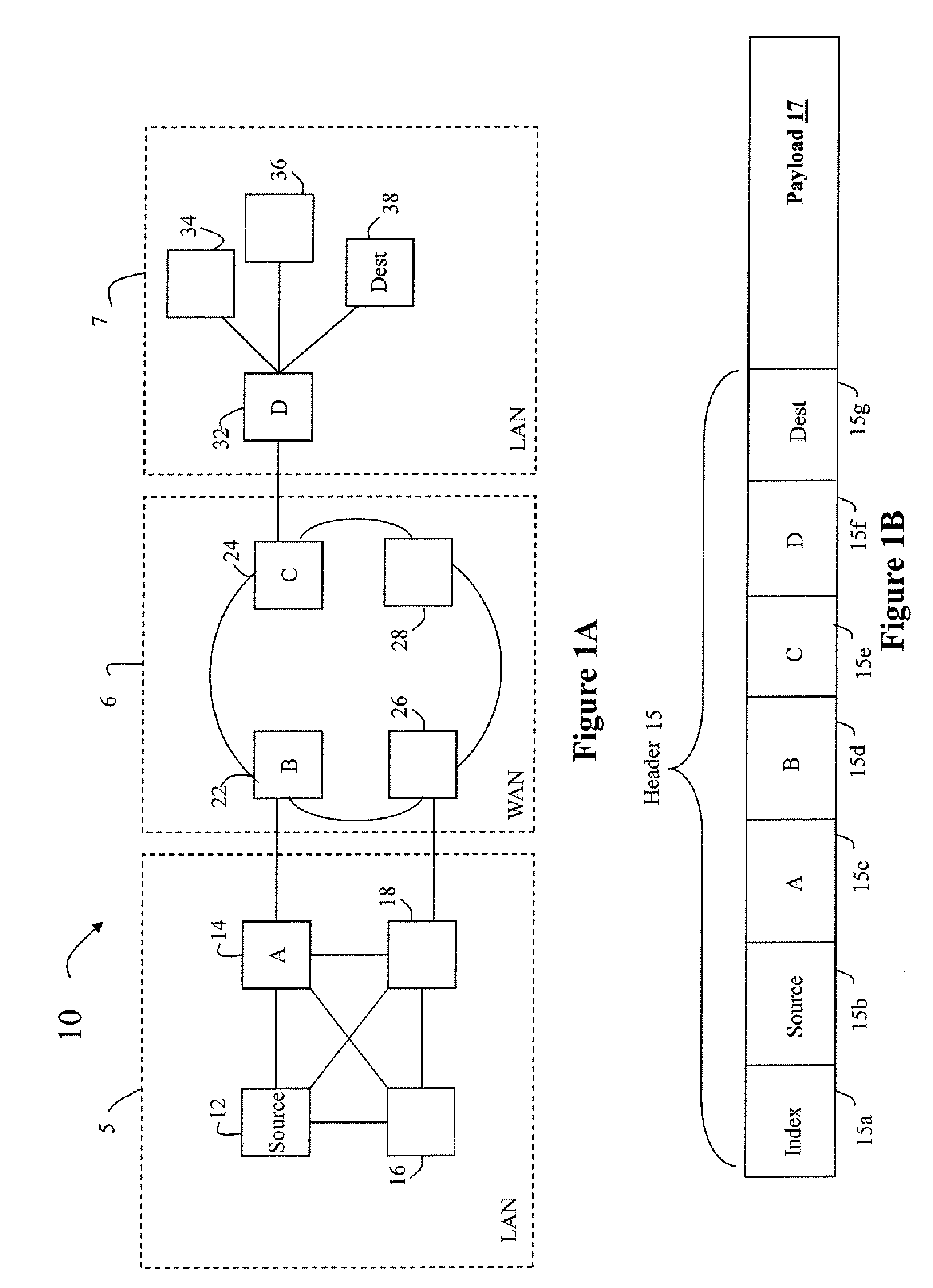
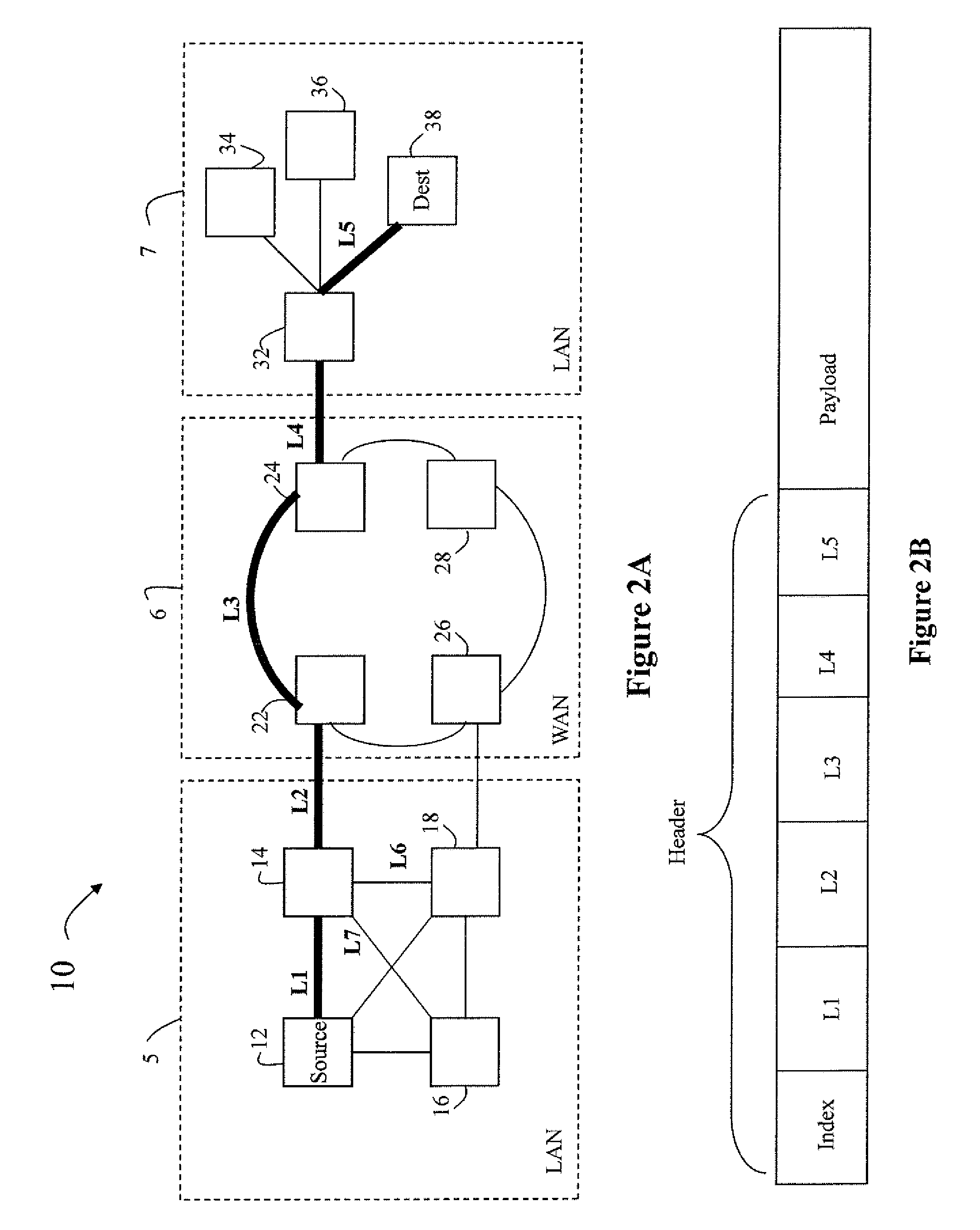
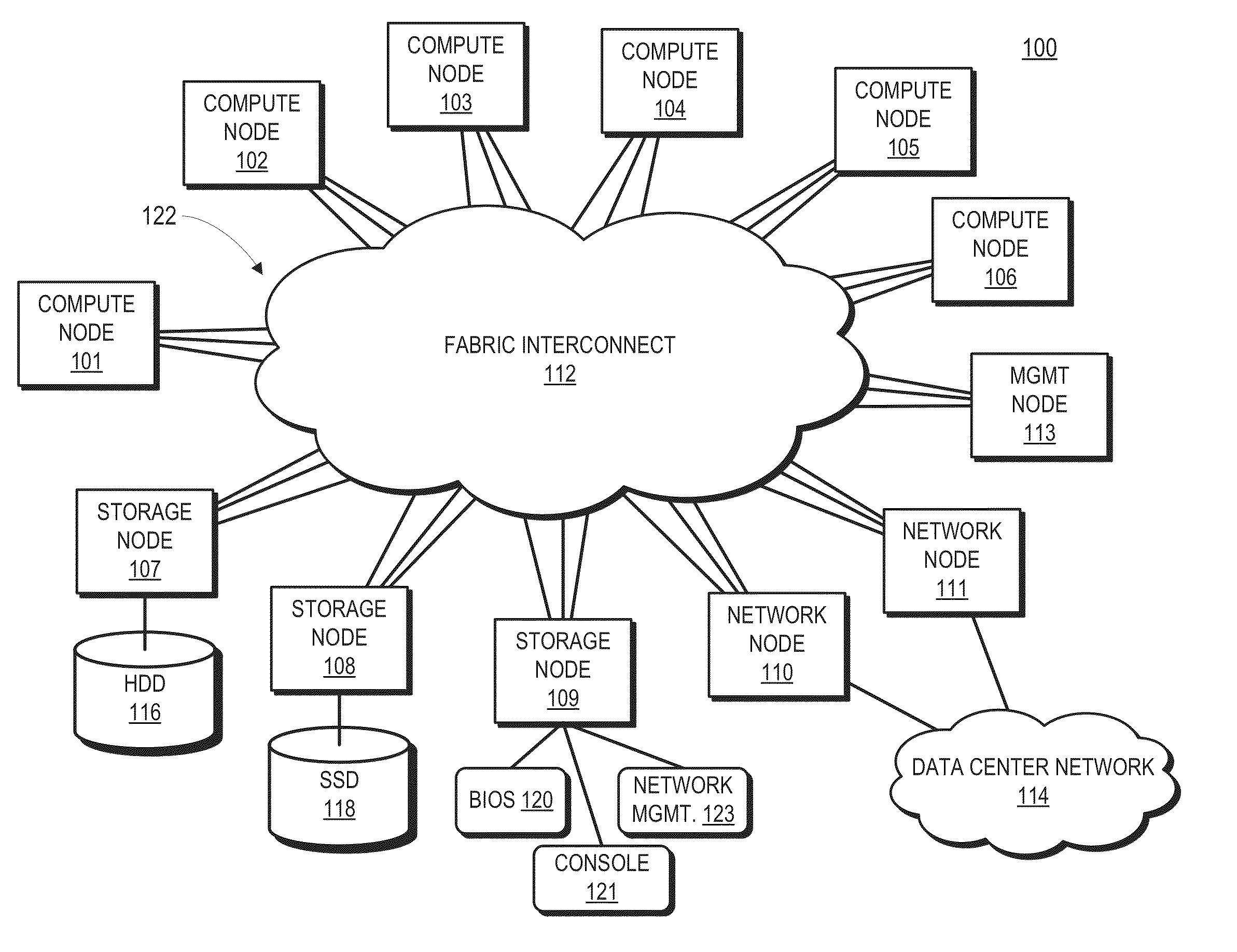
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
219 results about "Source routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
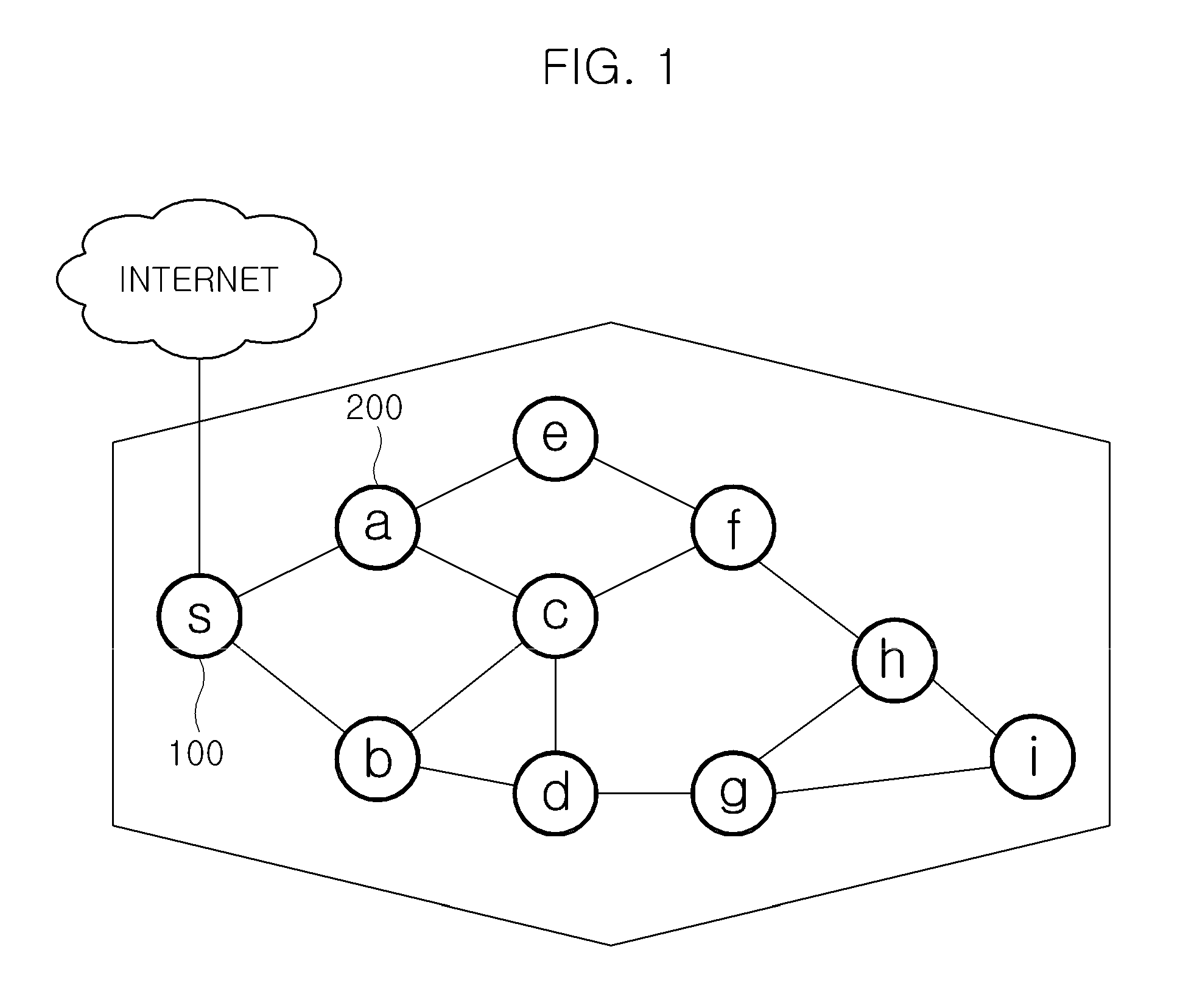
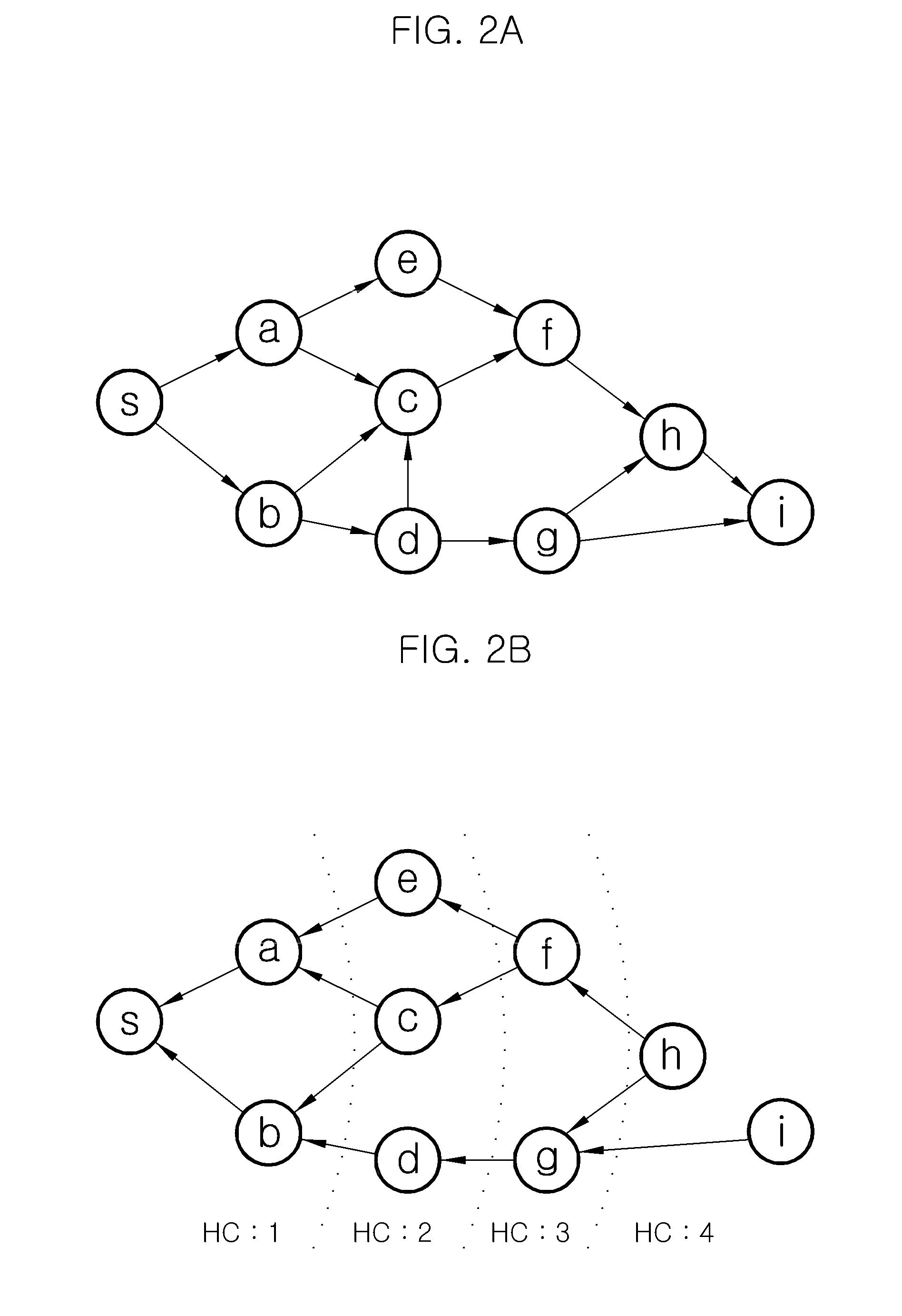
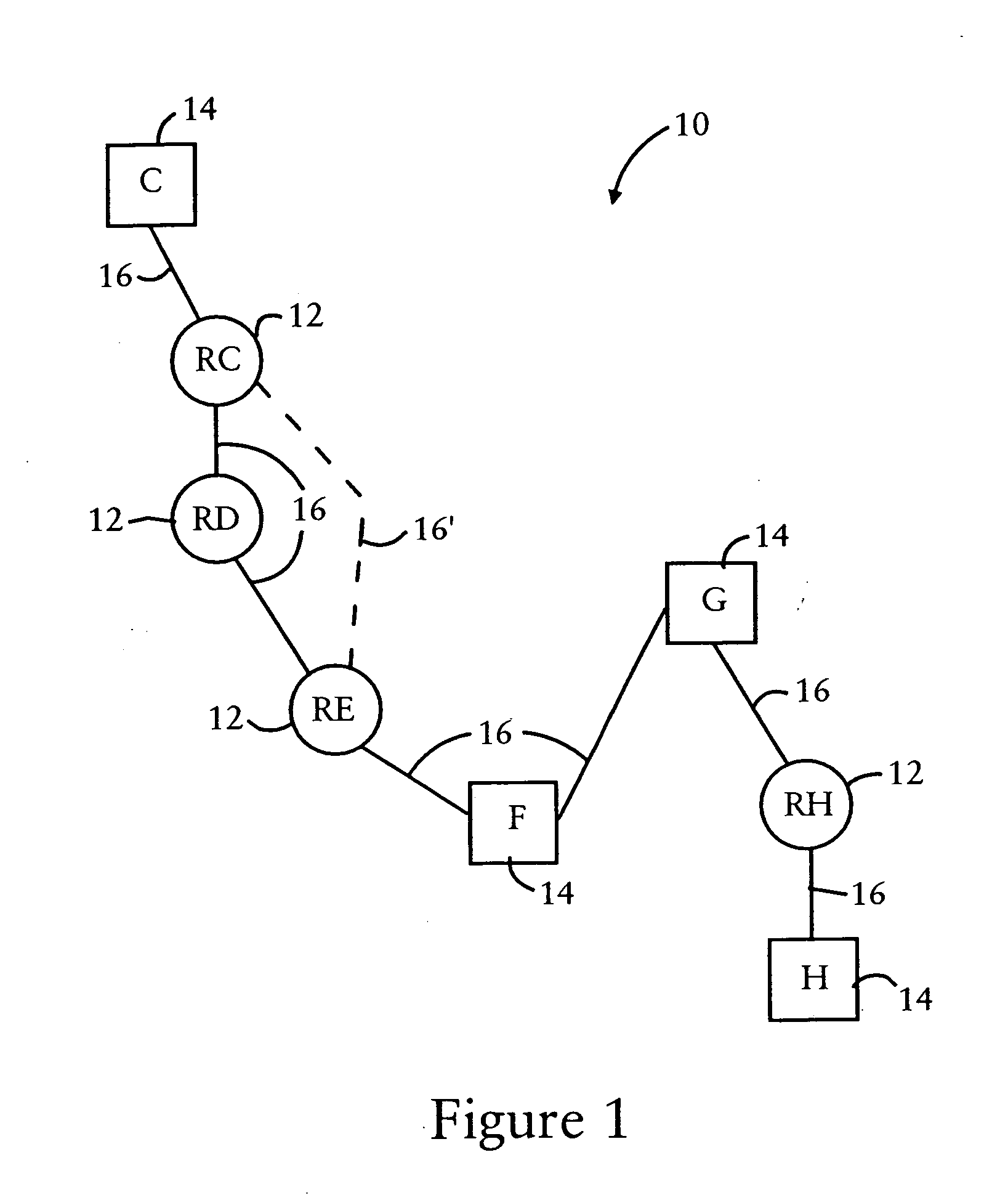
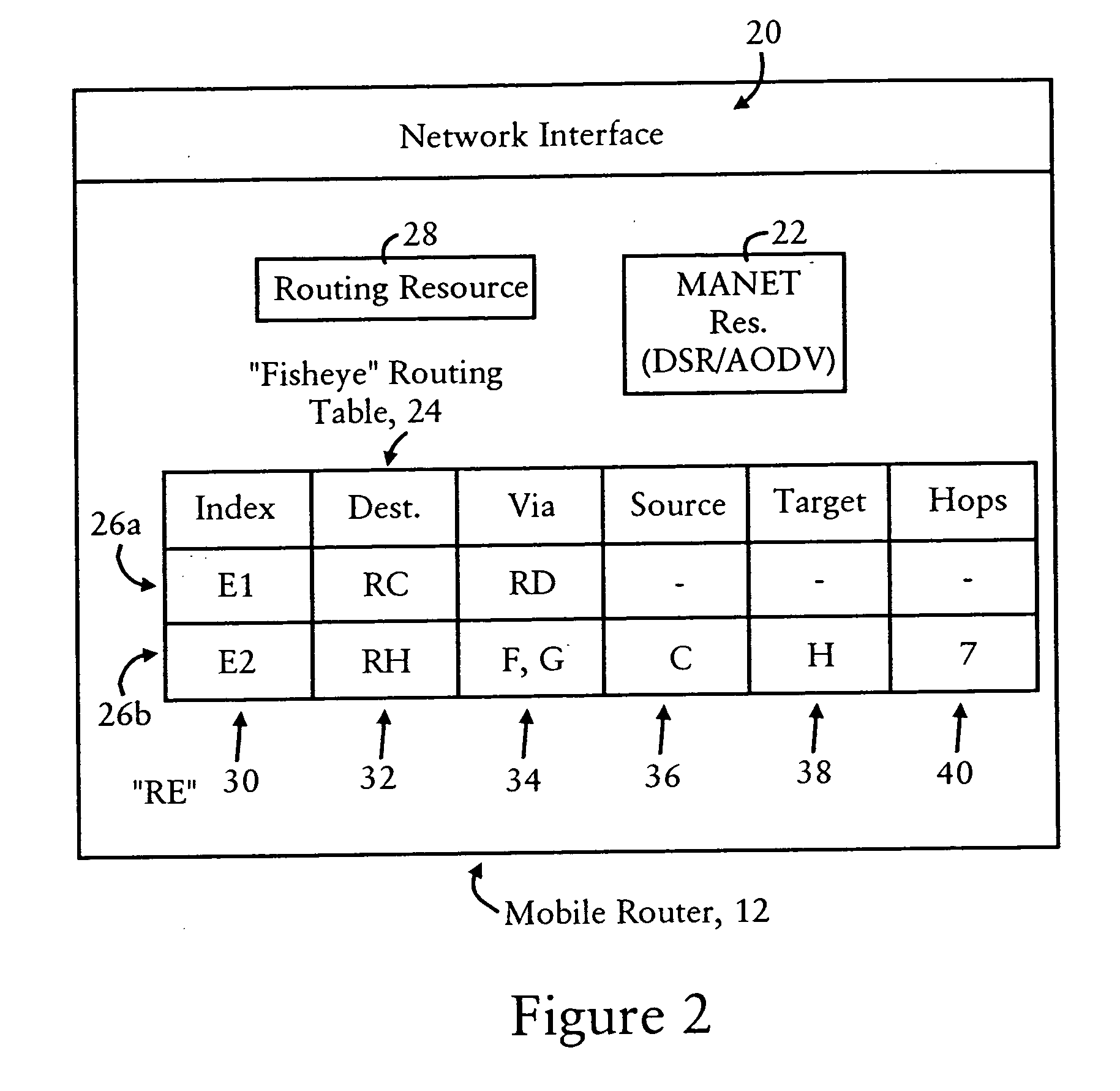
In computer networking, source routing, also called path addressing, allows a sender of a packet to partially or completely specify the route the packet takes through the network. In contrast, in conventional routing, routers in the network determine the path incrementally based on the packet's destination. Another routing alternative, label switching, is used in connection-oriented networks such as X.25, frame relay, ATM and MPLS.
Method and system for packet communication employing path diversity
InactiveUS6868083B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationPacket loss
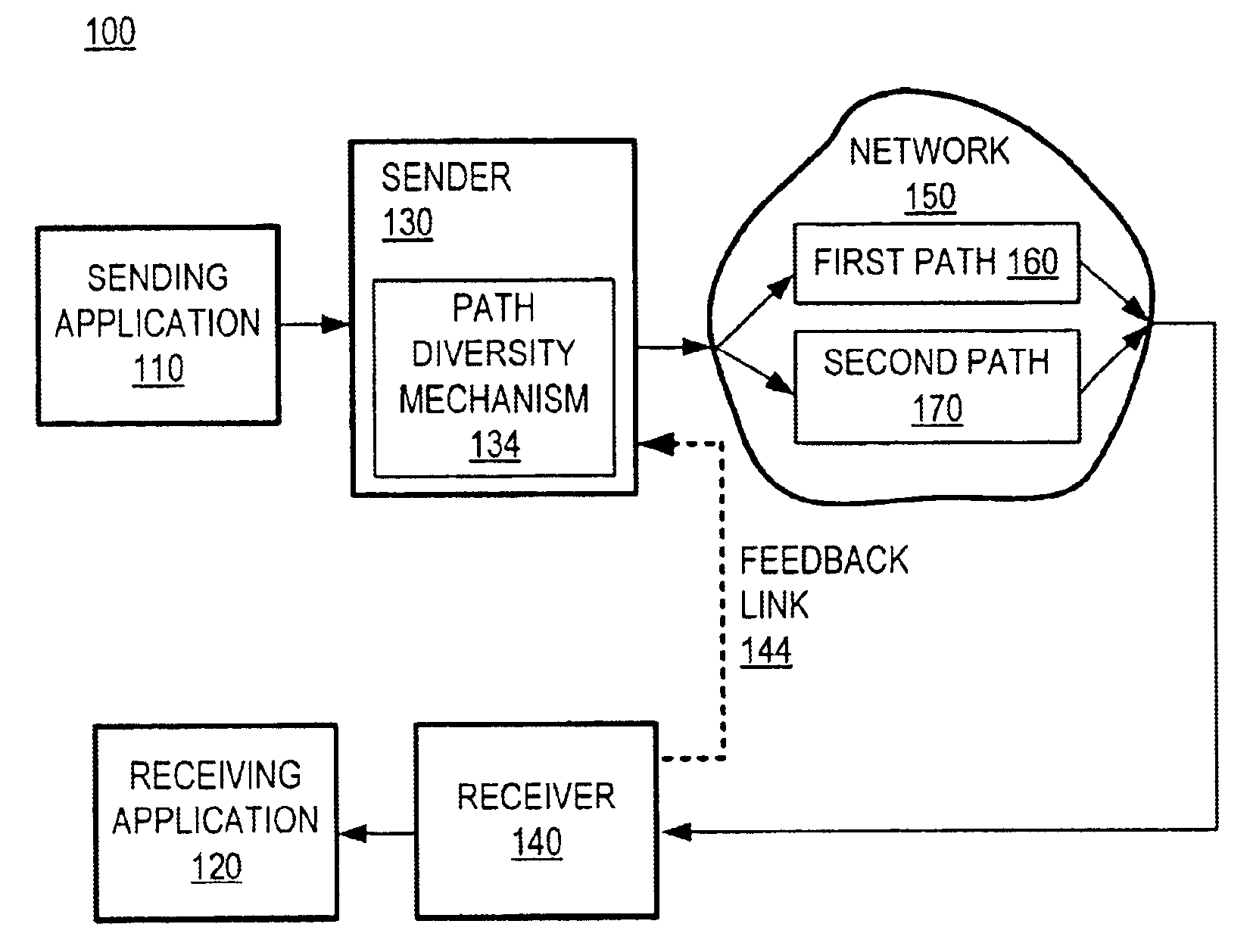
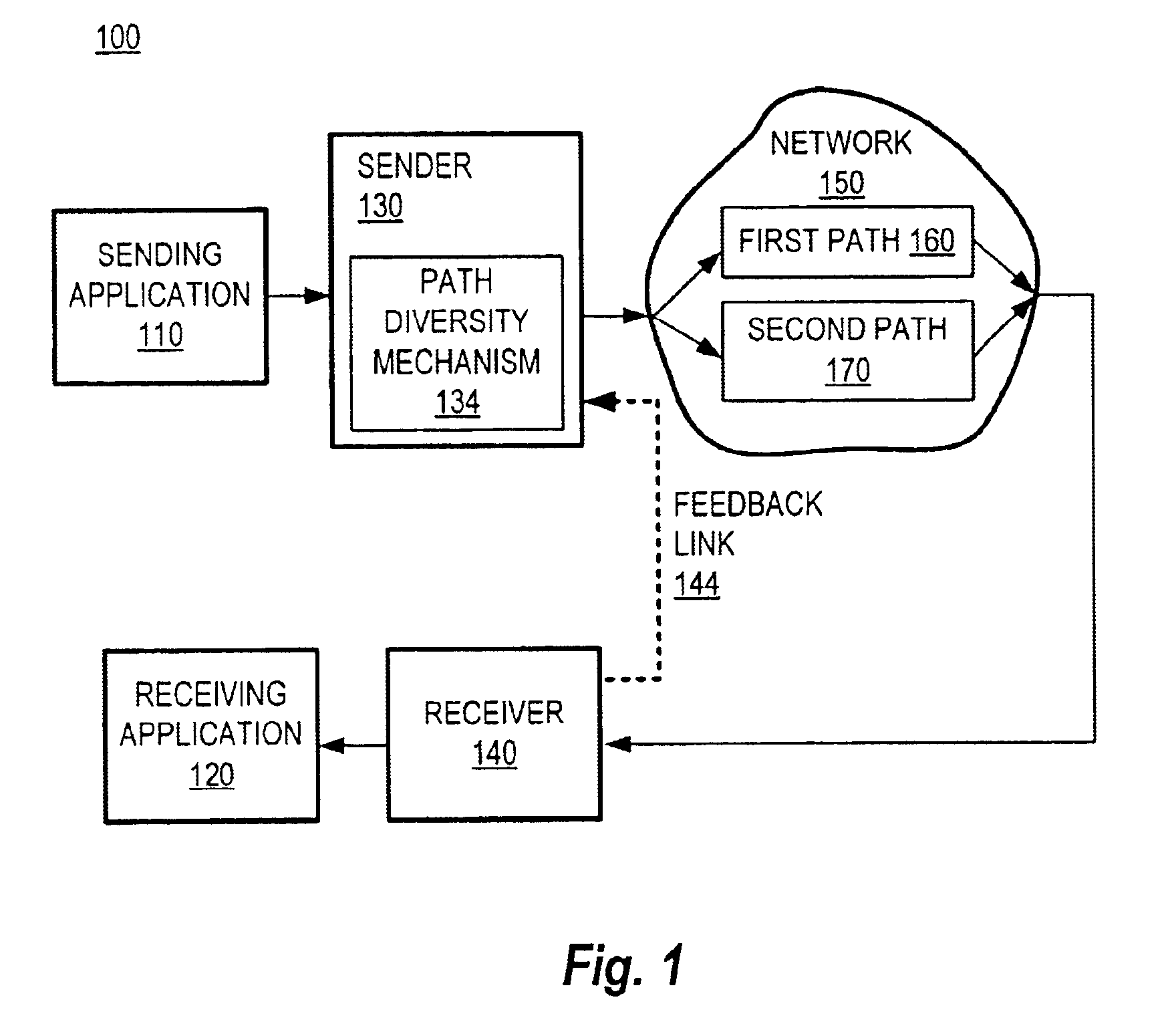
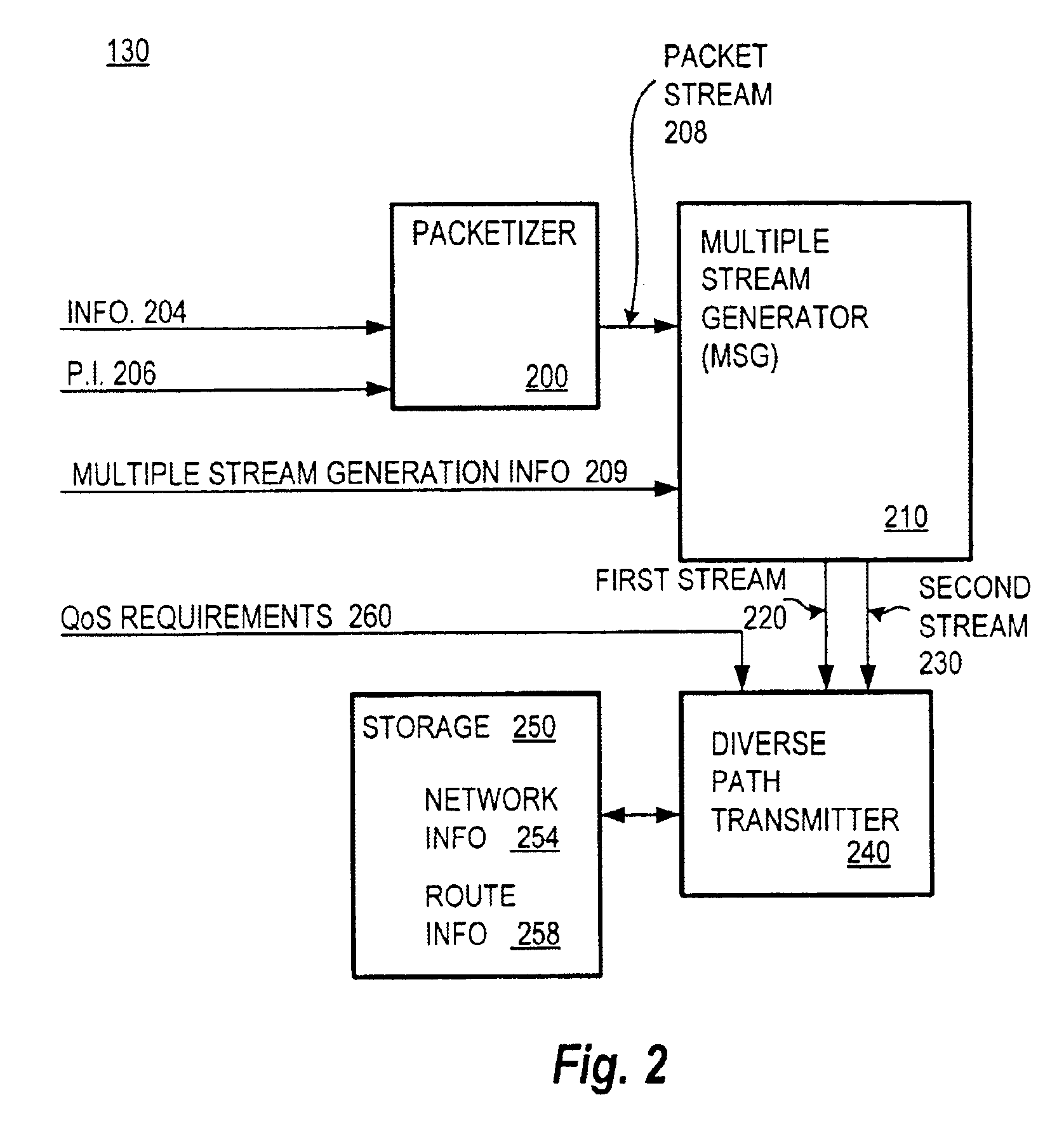
Communication over lossy packet networks such as the Internet is hampered by limited bandwidth and packet loss. The present invention provides a path diversity transmission system for improving the quality of communication over a lossy packet network. The path diversity transmission system explicitly sends different subsets of packets over different paths, thereby enabling the end-to-end application to effectively see an average path behavior. Generally, seeing this average path behavior provides better performance than seeing the behavior of any individual random path. For example, the probability that all of the multiple paths are simultaneously congested is much less than the probability that a single path is congested. The resulting path diversity can provide a number of benefits, including enabling real-time multimedia communication and simplifying system design (e.g., error correction system design). Two exemplary architectures for achieving path diversity are described herein. The first architecture is based on source routing, and the second architecture is based on a relay infrastructure. The second architecture routes traffic through semi-intelligent nodes at strategic locations in the Internet, thereby providing a service of improved reliability while leveraging the infrastructure of the Internet.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
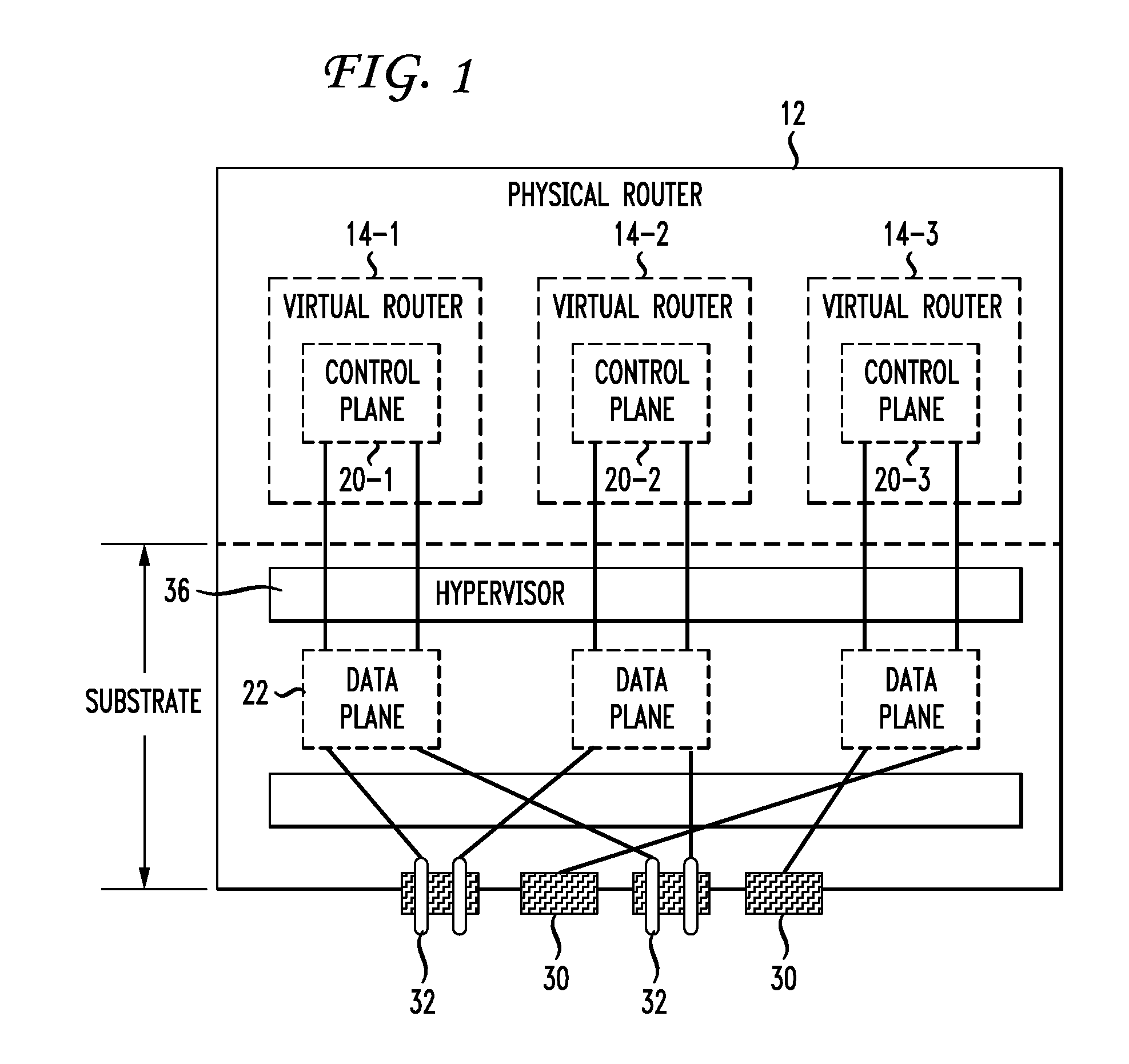
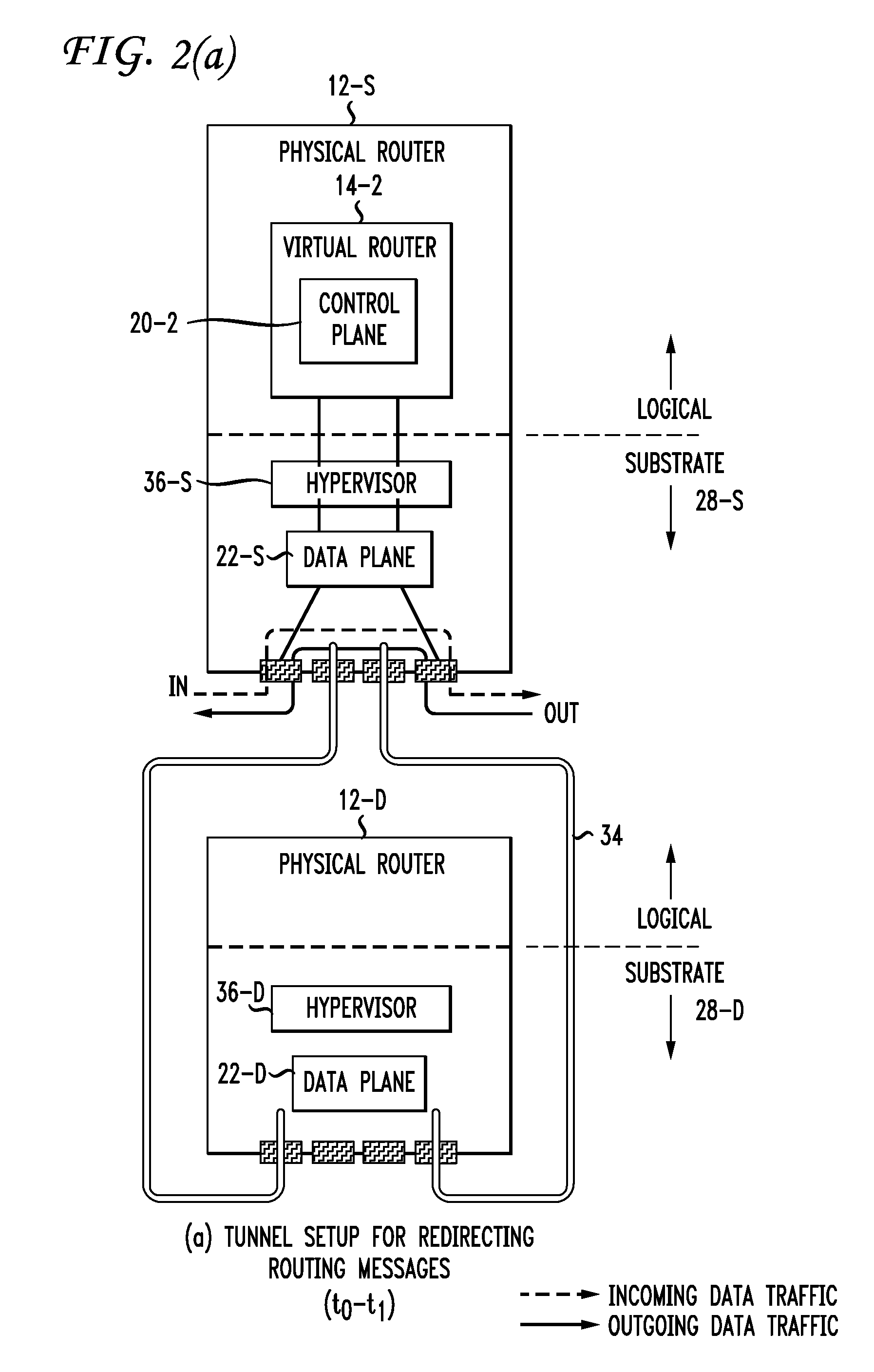
Live Router Migration
InactiveUS20110032830A1Easily and quickly migrateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData trafficReal time routing
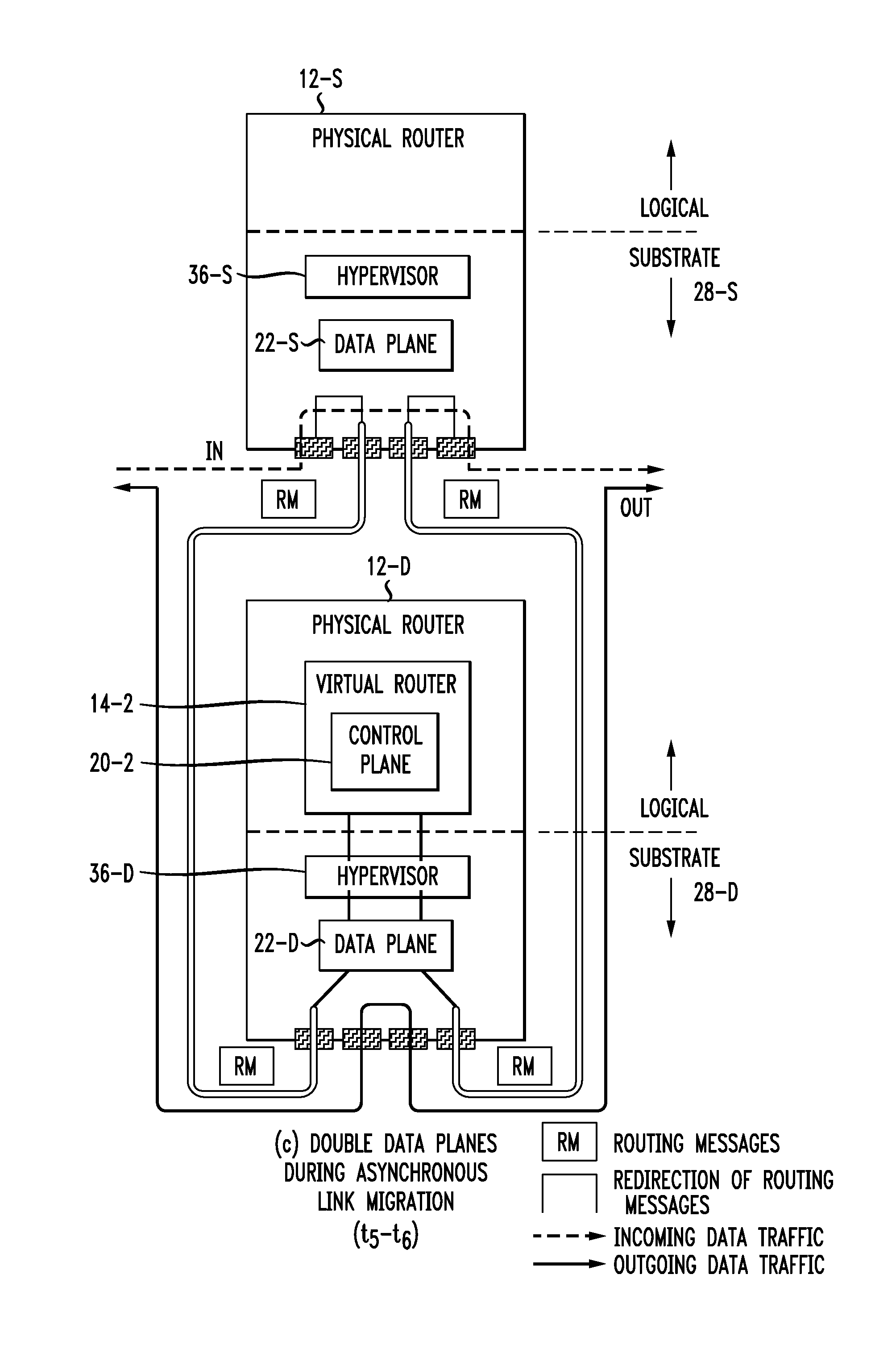
Live router migration is implemented by separating the logical features of a virtual router from its physical features. Tunnels are established between a source (physical) router and a destination (physical) router, allowing the control plane of the virtual router being migrated to send and receive messages from the destination router. The control plane information is then transferred to the destination router, which functions to clone the data plane at the destination router. Outgoing links from the destination router are then be established. The double appearance of the data plane at both the source and destination routers allows for the data plane information to be transferred asynchronously over to the destination router. Once all of the data plane information has been transferred, incoming data traffic links at the destination router can be established and the tunnels between the routers taken down.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
System and method for link quality source routing
InactiveUS20050185632A1Data switching by path configurationWireless communicationKnowledge gainNetwork packet
Systems and methods for routing packets by nodes in an ad hoc network in accordance with a link quality source routing protocol are disclosed. Route discovery, route maintenance, and metric maintenance are designed to propagate and keep current link quality measurements. Metric maintenance includes a reactive approach for links that a node is currently using to route packets, and a proactive mechanism for all links. Nodes are configured to include a send buffer, a maintenance buffer, a request table, link quality metric modules, and preferably a neighbor cache and a link cache. The invention allows for asymmetric links in the network. The invention may be implemented within a virtual protocol interlayer between the link and network layers. The invention may employ any particular link quality metrics, including metrics based on probing techniques as well as metrics based on knowledge gained in other ways.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Source routed multicast LSP
Source routed multicast LSP is described herein. In one embodiment, when a first node receives a first packet having a label stack including a plurality of labels compatible with MPLS (multi-protocol label switching), in response to a first label on a top of the label stack, the first packet is duplicated into a second packet. In addition, at least two labels are popped from the top of the label stack of the second packet forming a third packet. Thereafter, the first and third packets are processed based on a label on the top of the label stack of the first and third packets respectively. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
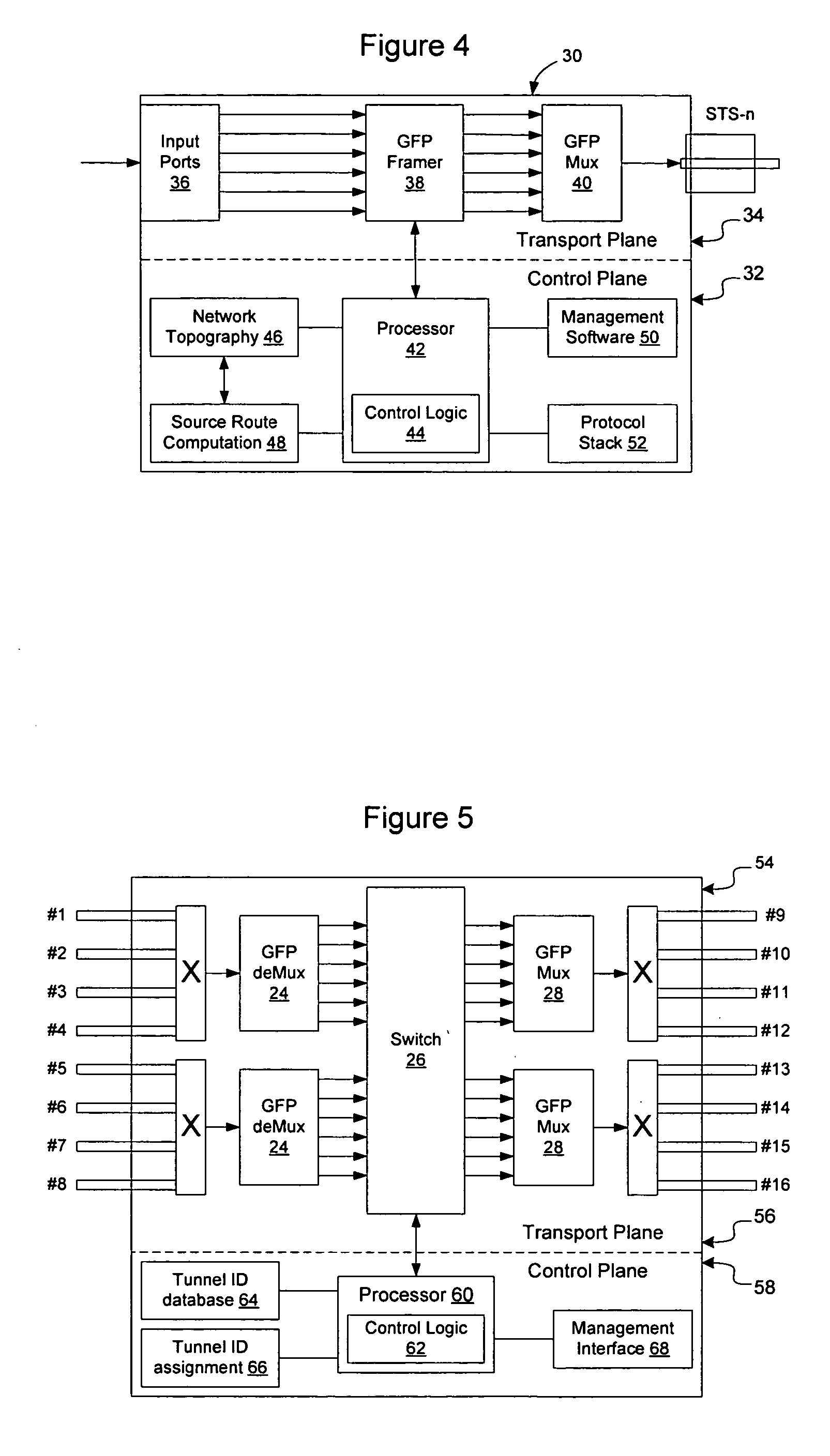
Method and apparatus for implementing link-based source routing in generic framing protocol
InactiveUS20060002304A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTopographyNetwork topology
Link-based source routing may be implemented using generic framing protocol (GFP) to enable GFP frames to contain a switching context that will allow them to be forwarded on a network without requiring state information to be distributed to interior network elements on the network. Source routes may be computed from network topography information obtained using OSPF or ISIS. An extension header type is added to the GFP frames to signal to the network elements that the GFP frame contains a link-based source route. The source route contains a vector of tunnel IDs and a pointer to the current hop, to enable the current tunnel ID to be determined. The tunnel IDs have local significance only, and hence state information is not required to be distributed on the network. A return route may be built by index substitution as the frame traverses the network.
Owner:CIENA
Adaptive source routing and packet processing
Paths for packets traveling through a distributed network fabric are chosen using information local to the source of packets. The system allows resequencing of packets at their destination and detecting out-of-order and missing packets.
Owner:AVICI SYST
System and methods for improved network routing
ActiveUS20150236945A1Facilitate easy transitionData switching networksSelf adaptiveLink-state routing protocol
Known intra-domain routing methods (e.g., OSPF and IS-IS) are link-state routing protocols with hop-by-hop forwarding that sacrifice optimal traffic engineering for ease of implementation and management. Known optimal traffic engineering procedures are either not link-state methods or require source routing—characteristics that make them difficult to implement. Certain embodiments of the present invention include a fully distributed, adaptive, link-state routing protocol with hop-by-hop forwarding configured to achieve optimal traffic engineering. Such embodiments facilitate significant performance improvements relative to known intra-domain routing methods and decrease network infrastructure requirements.
Owner:CORNELL UNIV CENT FOR TECH LICENSING CTL AT CORNELL UNIV
System and methods for improved network routing
ActiveUS9521067B2Facilitate easy transitionData switching networksSelf adaptiveLink-state routing protocol
Known intra-domain routing methods (e.g., OSPF and IS-IS) are link-state routing protocols with hop-by-hop forwarding that sacrifice optimal traffic engineering for ease of implementation and management. Known optimal traffic engineering procedures are either not link-state methods or require source routing—characteristics that make them difficult to implement. Certain embodiments of the present invention include a fully distributed, adaptive, link-state routing protocol with hop-by-hop forwarding configured to achieve optimal traffic engineering. Such embodiments facilitate significant performance improvements relative to known intra-domain routing methods and decrease network infrastructure requirements.
Owner:CORNELL UNIV CENT FOR TECH LICENSING CTL AT CORNELL UNIV
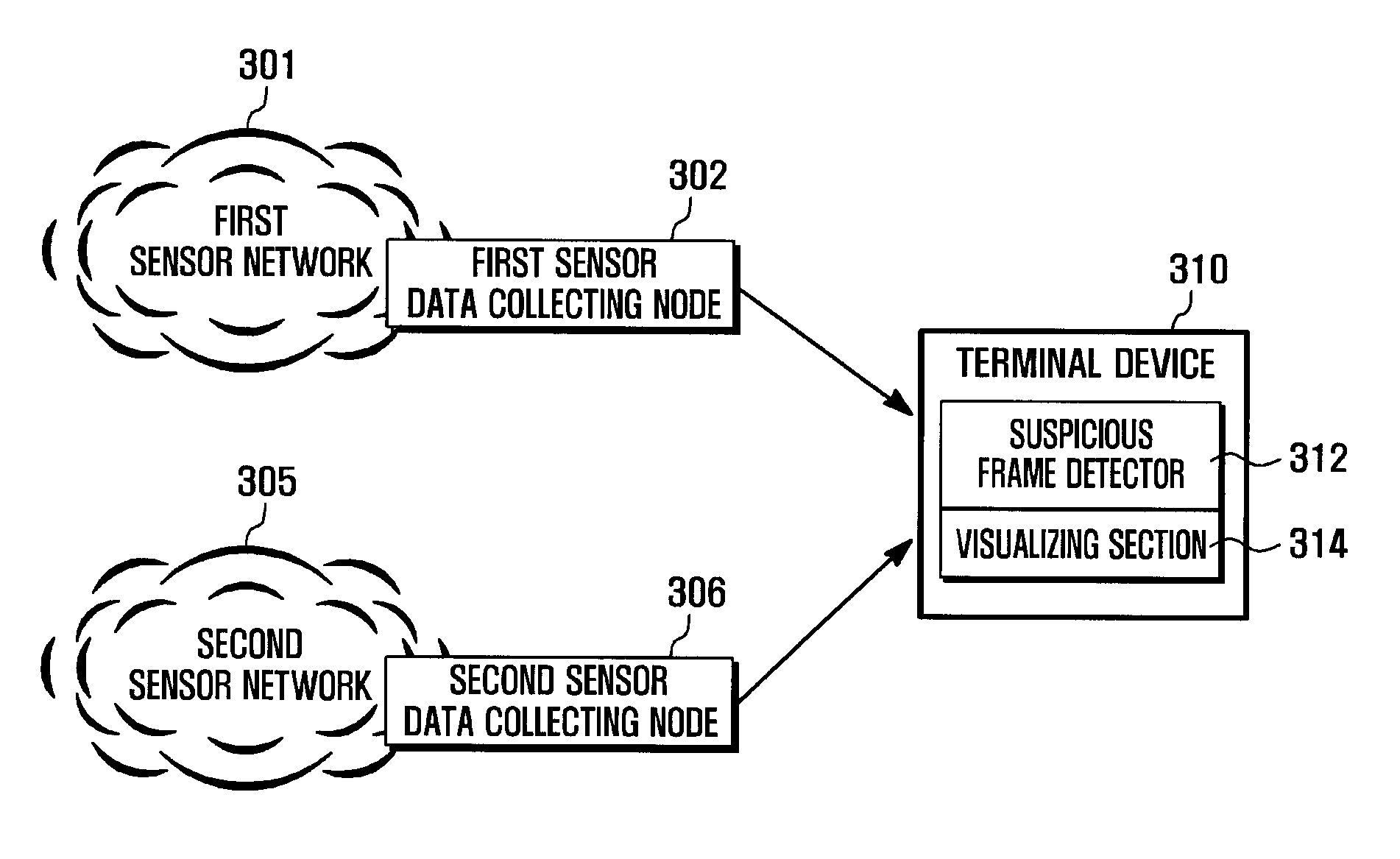
Method and system for detecting suspicious frame in wireless sensor network
ActiveUS20090133122A1Quick fixImprove user convenienceMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSensing dataLine sensor
A method and system for detecting a suspicious frame in a wireless sensor network that includes: a plurality of sensor nodes, for sending sensed data and data regarding an upper-level node and cluster head node. A data collecting node receives data from the sensor nodes, sends information, and extracts data received from the sensor nodes. A first probability of occurrence of the routing path is computed with respect to training frames, and a second probability of occurrence of a source routing path is computed using the first probability. The second probability is compared with a reference value, and displays an indication notifying an abnormality of the source node according to when the second probability and the reference value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for indicating congestion in a source routed network
InactiveUS20120147752A1Full bandwidth potentialError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetDistributed computing
A packet header in a source routed network is augmented to include, with each hop identifier, at least one bit for indicating congestion at the particular hop. As the packet traverses from the source to the destination, when congestion is detected at a hop, a congestion bit associated with the hop is set in the header. At the destination, when another packet is forwarded from the destination to the source on the same path, the congestion bits are reflected back to the source. When the source receives the congestion bits, it has the option of re-routing subsequent communications between the source and destination nodes by generating a new hop list, which routes around one or more of the congested hops.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Distributed packet switching in a source routed cluster server
A cluster compute server includes nodes coupled in a network topology via a fabric that source routes packets based on location identifiers assigned to the nodes, the location identifiers representing the locations in the network topology. Host interfaces at the nodes may be associated with link layer addresses that do not reflect the location identifier associated with the nodes. The nodes therefore implement locally cached link layer address translations that map link layer addresses to corresponding location identifiers in the network topology. In response to originating a packet directed to one of these host interfaces, the node accesses the local translation cache to obtain a link layer address translation for a destination link layer address of the packet. When a node experiences a cache miss, the node queries a management node to obtain the specified link layer address translation from a master translation table maintained by the management node.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Methods of and systems for remote outbound control
InactiveUS20060072543A1Fast dataQuick updateData switching by path configurationData transmissionType of service
The present invention is directed to a system for and a method of selecting a combination of resources for transmitting data from a remote site to a destination site. The method comprises generating a list of combinations of resources at a regional site and transmitting the list to the remote site. Data is transmitted from the remote site to the regional site using each combination of resources and statistics for each transmission are stored. Metrics, based on the application at hand, are computed for each set of statistics corresponding to each transmission, and a preferred combination of resources is selected at the regional site based on the metrics. The regional site then transmits to the remote site information corresponding to the preferred combination of resources. The remote site is then configured to transmit data to the destination site using the selected combination of resources. Resources include links with a specified bandwidth, VPN and GRE tunnels, and routers configured to perform MPLS switching, type-of-service routing, and source routing.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Data routing
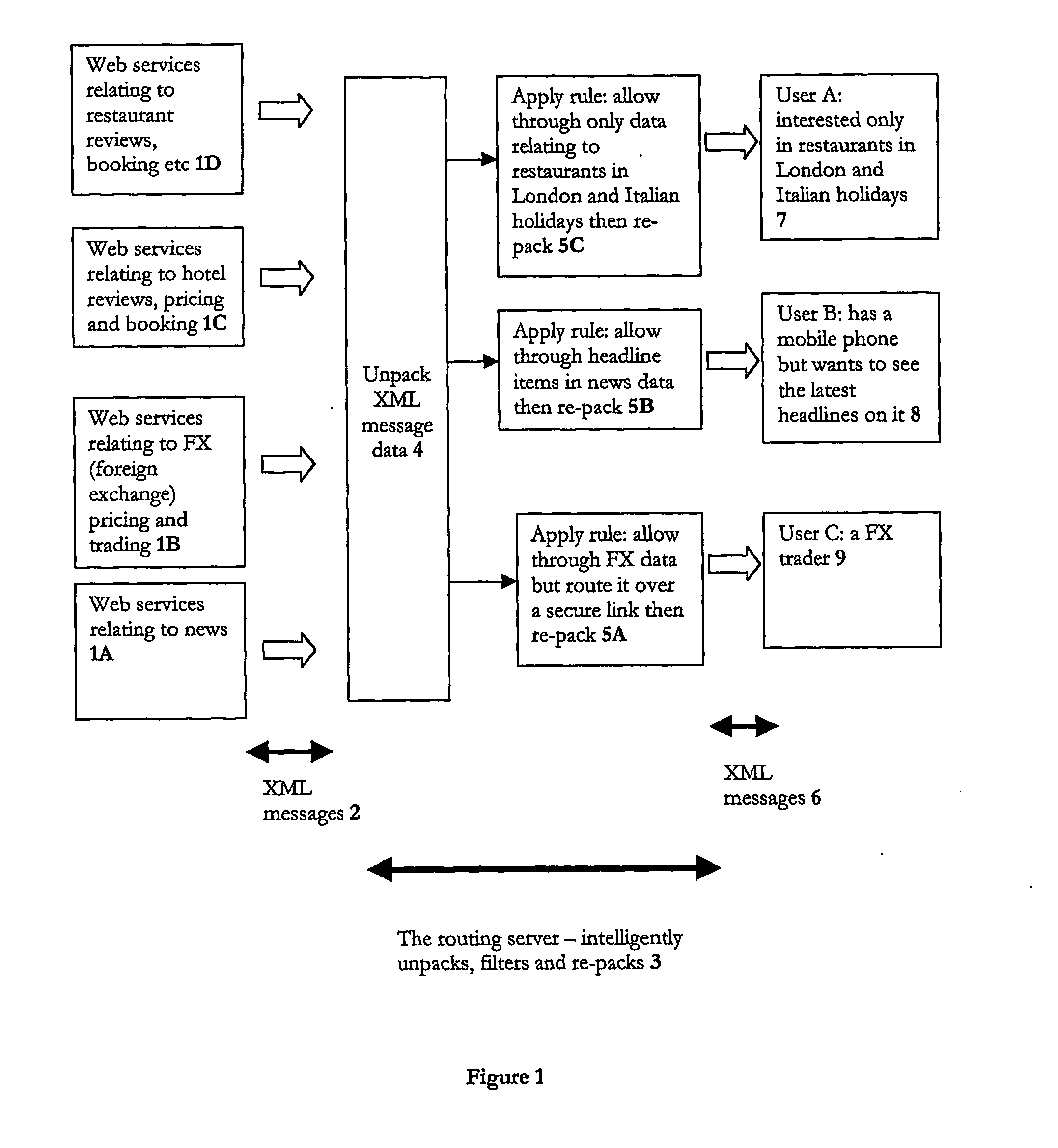
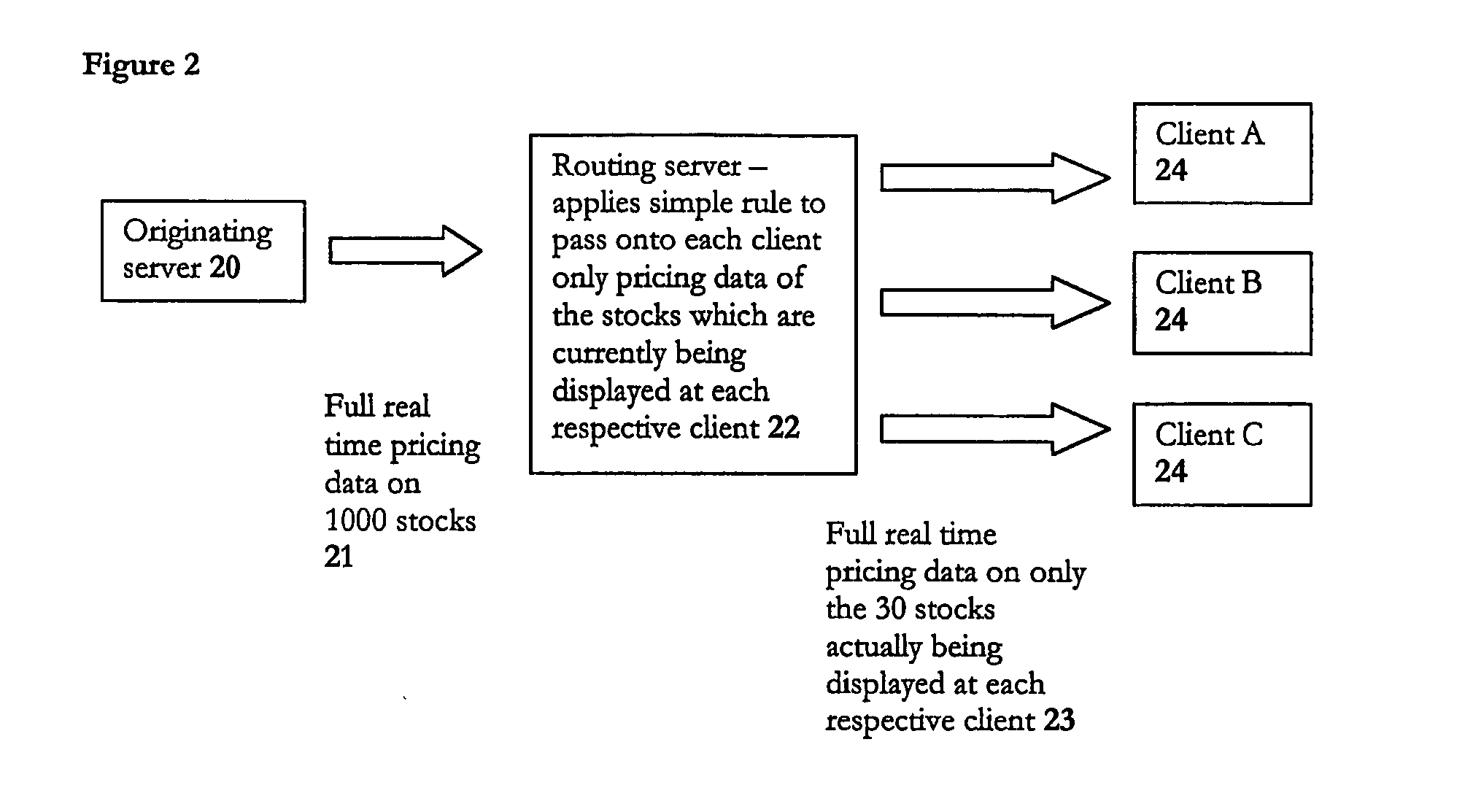
ActiveUS20050021838A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksDatabaseDistributed computing
A method of routing data from a source to one or more clients over a network, where the data conforms to a structured meta-language; in which the routing is performed by a server applying rules to the data itself, and not any address accompanying the data, to determine where to route that data to. The present invention is predicated on the counter-intuitive insight that data does not need to be concealed within a data envelope and given an address label in order to be routed effectively and efficiently. Instead, routing can be performed on the actual content of a message by applying simple routing rules to the data itself by intelligent ‘routing’ servers within the network which can unpack data from their message envelopes and intelligently filter / combine them with data unpacked from other messages to achieve a routing function.
Owner:INTEGRA
Method for multi-path source routing in sensor network
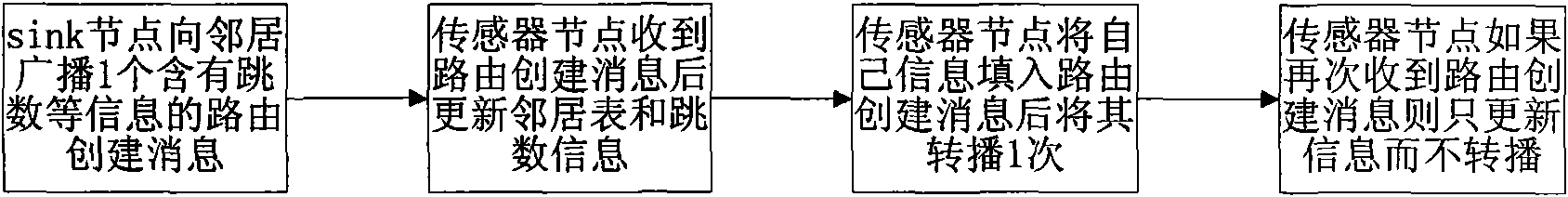
InactiveUS20090296704A1Improve fault toleranceControl message overheadEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationSensor nodeMulti path
A method for a multi-path source routing in a sensor network. In the sensor network including a sink node and a plurality of sensor nodes, the sensor network transmits data packets through a downlink route set based on a routing table generated by collecting uplink neighbor information of each sensor node from a control message for initializing a network and an uplink route formed by using uplink neighbors of each sensor node. Uplink neighbors for transmitting data from each sensor node to the sink node by performing a network initialization process and acquires the information in the sink node to generate the multi-path is maintained. As a result, it has advantages of reducing a control message overhead while using the multi-path and increasing scalability and energy efficiency by keeping a routing table small in the sensor node regardless of the size of the network.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Packet transfer apparatus
InactiveUS20050207411A1Reduce the probability of packet lossSave packetNetworks interconnectionWide area networksTraffic capacityPacket communication
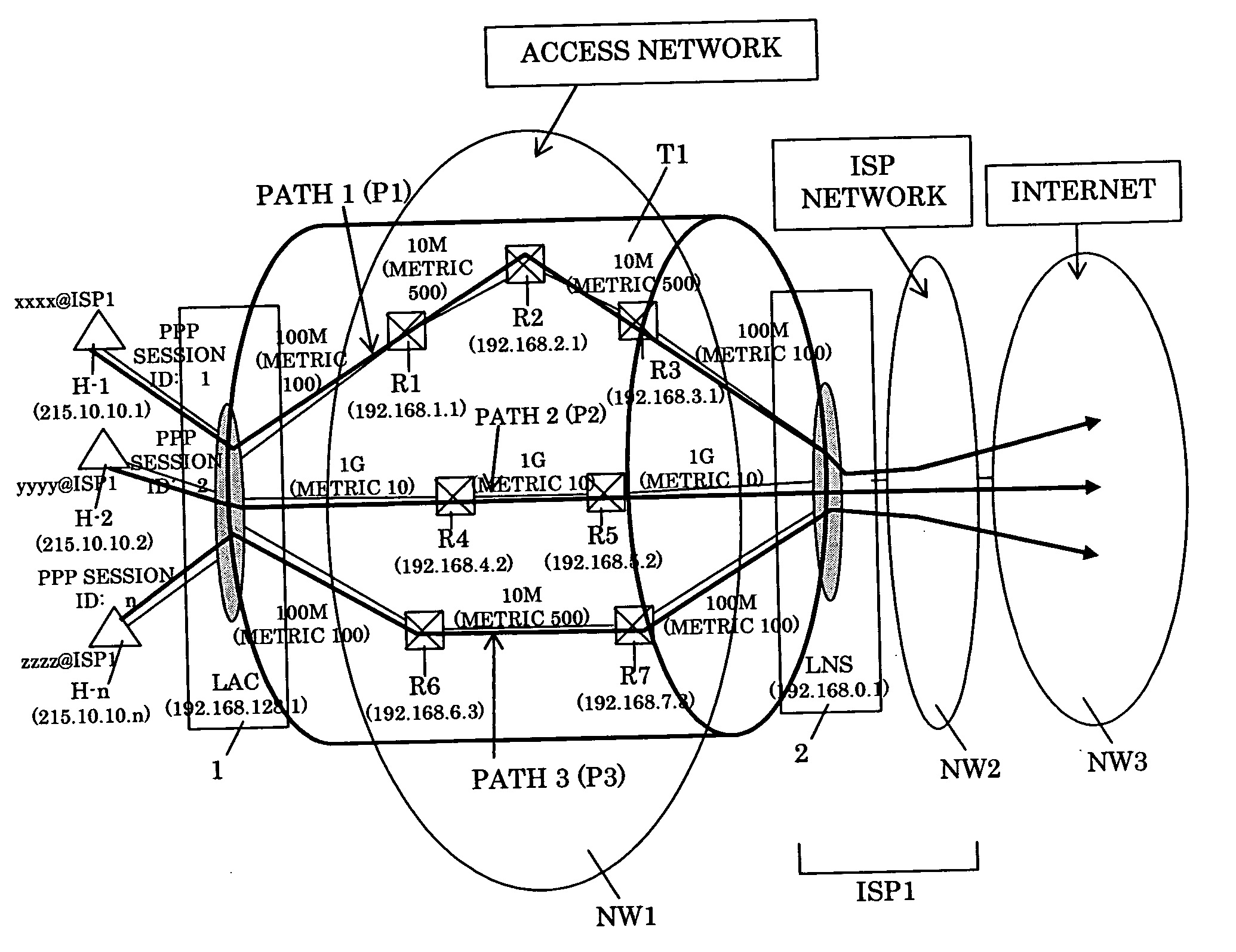
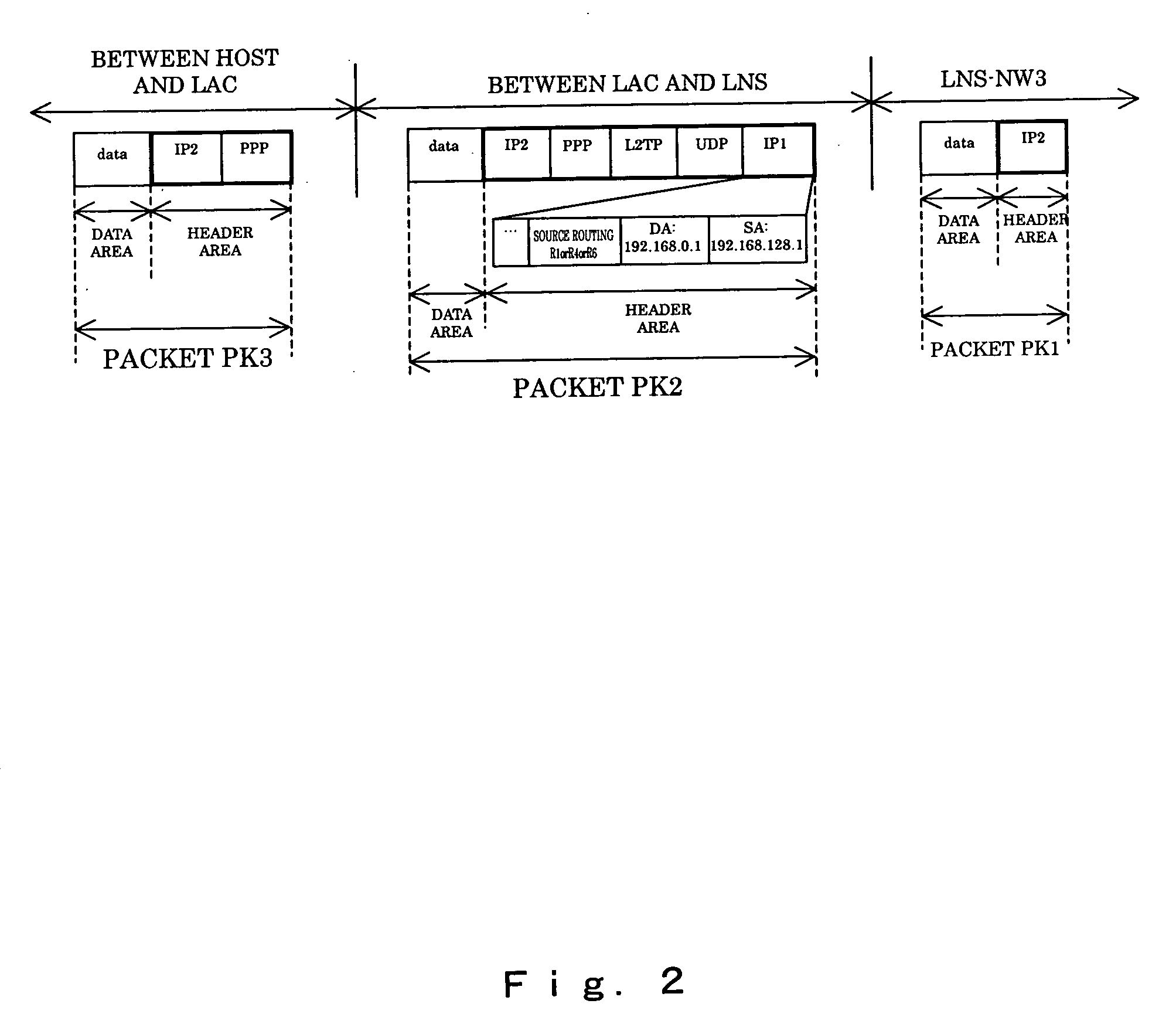
A packet transfer apparatus which can switch a communication path for each of a plurality of users using the same L2TP tunnel is provided. Packet transfer apparatuses terminating L2TP contain a table specifying a flow threshold level and a priority level of each subscriber; the amount of packet flow of each subscriber is measured in accordance with the information in the table; if the threshold level is exceeded, the packet communication path is switched in accordance with the priority level specified for each subscriber. The OSPF protocol is used to manage the path information, and the information of a plurality of paths to a destination is stored in a path management table. The path is switched by specifying destination routers with the source routing option in the IP header of a packet after L2TP encapsulation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Source routing in multicast transmissions
ActiveUS20150049760A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationDistribution treeComputer network
The subject technology provides configurations for receiving, at a first network device, a multicast packet of a multicast transmission from a multicast source. A header is inserted including one or more fields of information for a multicast distribution tree into the multicast packet in which the fields of information include a root level node field indicating a root node of the multicast distribution tree and one or more second level fields indicating one or more child nodes of the root node of the multicast distribution tree. In one example, the fields of information are not duplicative of routing information, stored by the first network device, corresponding to the one or more child nodes. The subject technology then forwards the multicast packet including the inserted header to respective network devices corresponding to the one or more child nodes based on the one or more fields of information from the inserted header.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
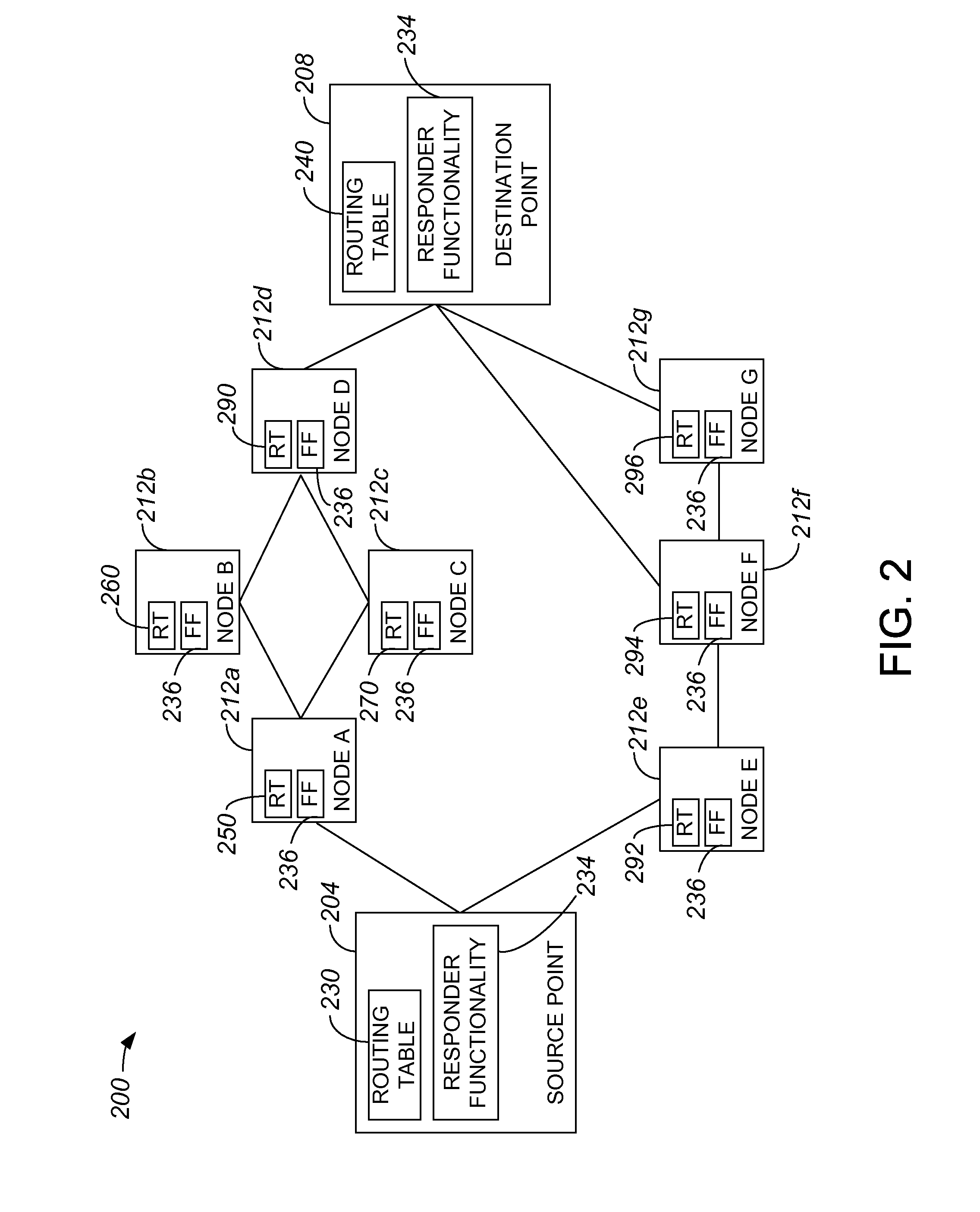
Source routing approach for network performance and availability measurement of specific paths
In one embodiment, a method includes obtaining a first packet that has a first payload. The first payload identifies a first path between endpoints traversed by the first packet, and identifying information associated with a first node associated with the first path traversed by the first packet. The identifying information includes an arrival time that identifies approximately when the first packet arrived at the first node and a leaving time that identifies approximately when the first packet left the first node. A first service level agreement (SLA) parameter of the first path is determined by analyzing the arrival time and the leaving time, comparing the first SLA parameter with a second SLA parameter associated with a second path traversed by a second probe packet, and selecting the first path for sending packets if the first SLA parameter indicates a higher SLA level than indicated by the second SLA parameter.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
End-to-end service quality using source-routed probes
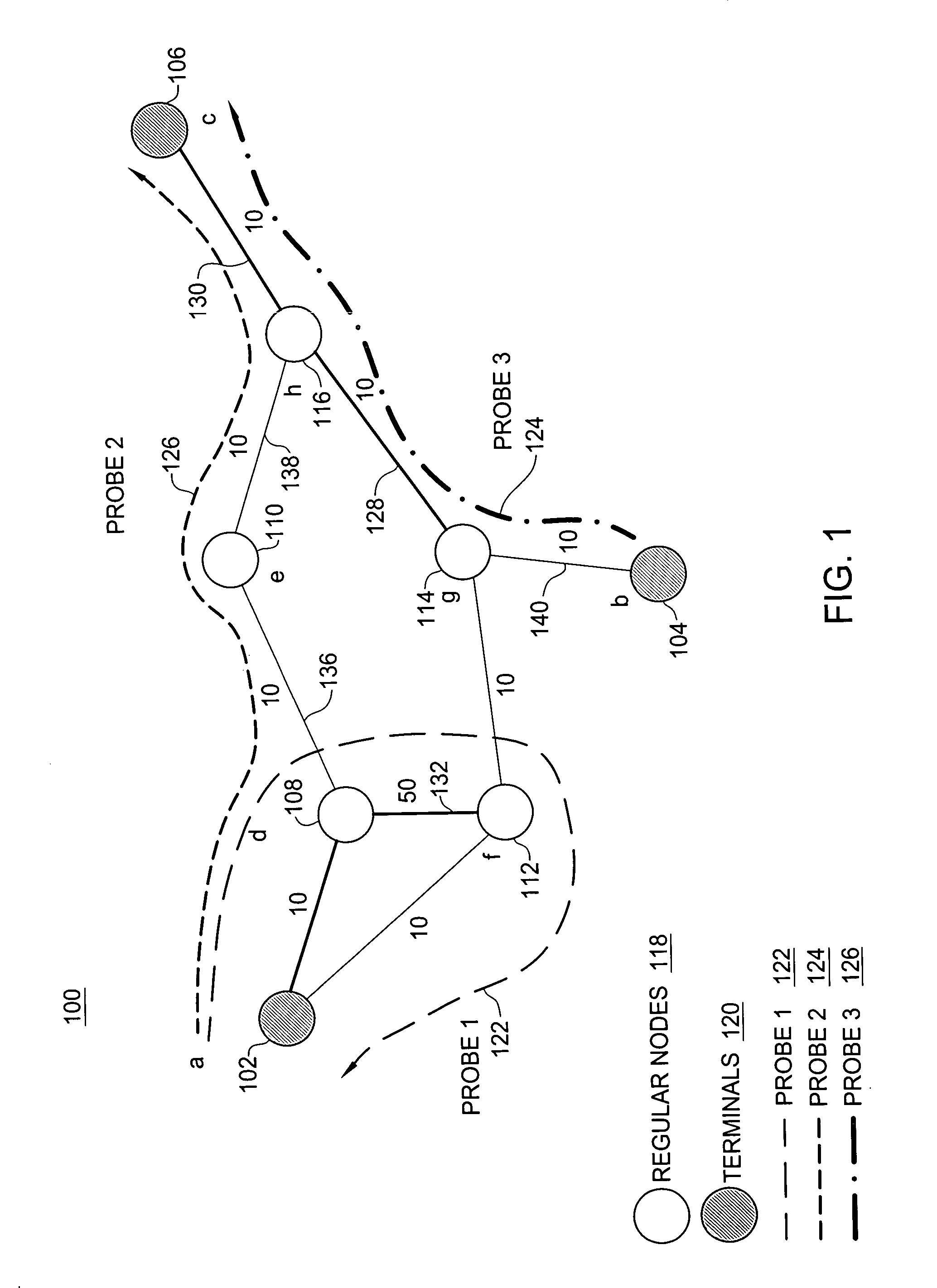
InactiveUS20070177518A1Low costError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
The need to monitor real time network services has prompted service providers to use new measurement technologies, such as service-specific probes. A service-specific probe is an active probe that closely mimics the service traffic so that it receives the same treatment from the network as the actual service traffic. Service-specific probes are end-to-end and their deployment depends on solutions that address questions such as minimizing probe traffic, while still obtaining maximum coverage of all the links in the network. A polynomial-time probe-path computation algorithm is provided as well as a 2-approximate solution for merging probe paths when the number of probes exceeds a required bound k. The algorithms are evaluated using ISP topologies generated via Rocketfuel. For most topologies, it is possible to cover more than about 98% of the edges using just about 5% of the nodes as terminals.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
MAC address population protocol
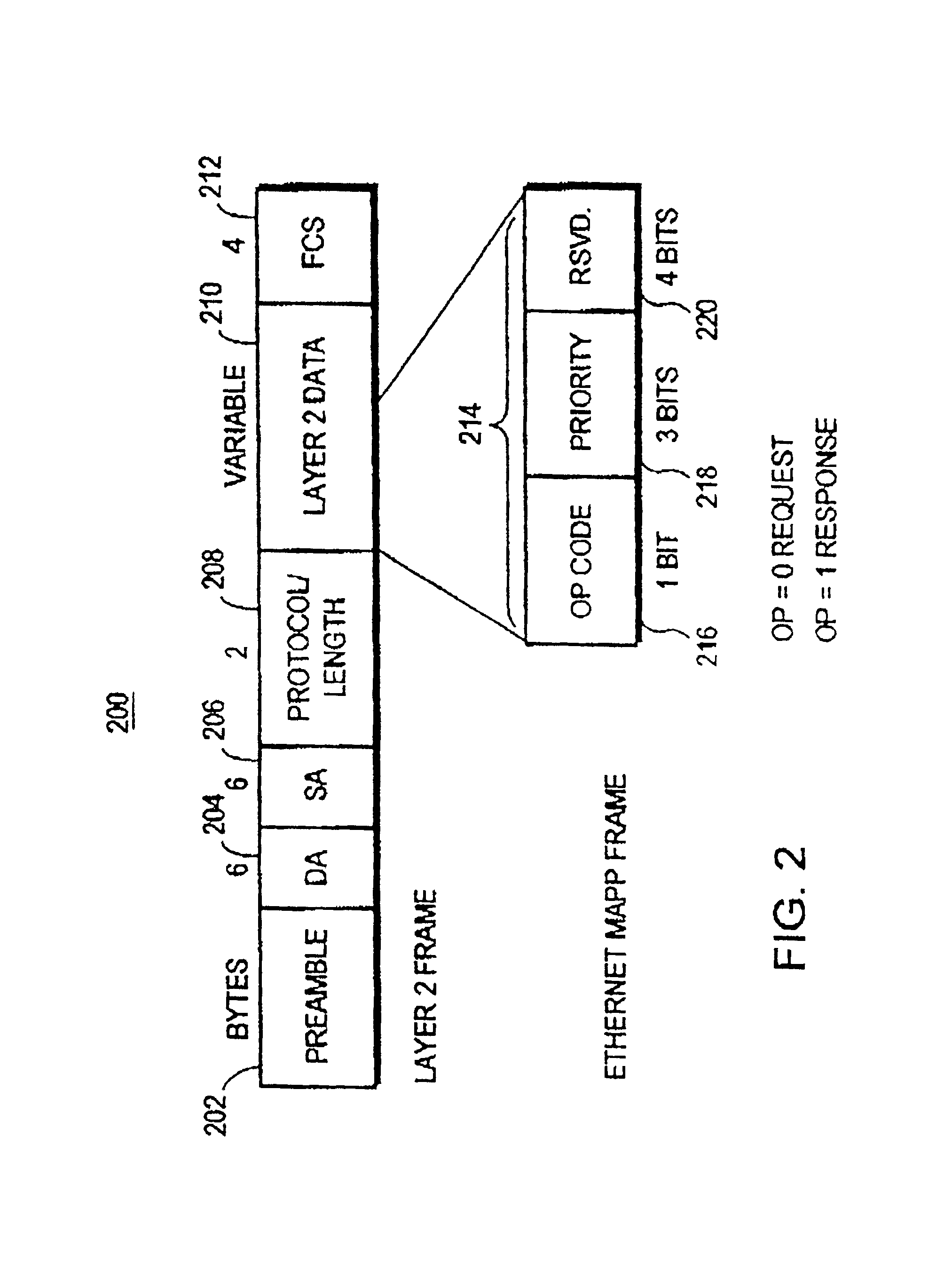
InactiveUS6873603B1Reduce network bandwidth consumptionNo need to waste bandwidthTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionPopulation protocolEthernet lan
A new search protocol uses a message which a router periodically transmits onto the local LANs connected to its ports, and in response to the new protocol, all end stations receiving the message transmit their addresses to the router. The addresses transmitted to the router comprise the addresses and any other information needed by the router to reach the end station. For example, for an Ethernet LAN the layer 2 or MAC layer address of the end station is transmitted to the router. In the event that the protocol of the LAN uses source routing, the information transmitted to the router includes both the MAC address and the Route Information Field of the end station. In any event, the router uses the information received from the end stations to build its routing table. Then, upon receipt of the next CANUREACH message from a peer router, the desired destination end station will appear in the router's routing table, and there will be no need to waste bandwidth by transmitting search messages looking for the end station. The new protocol messages are transmitted periodically in order to keep the routing tables current is as the network changes dynamically.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Routing method and routing path recovery mechanism in wireless sensor network environment
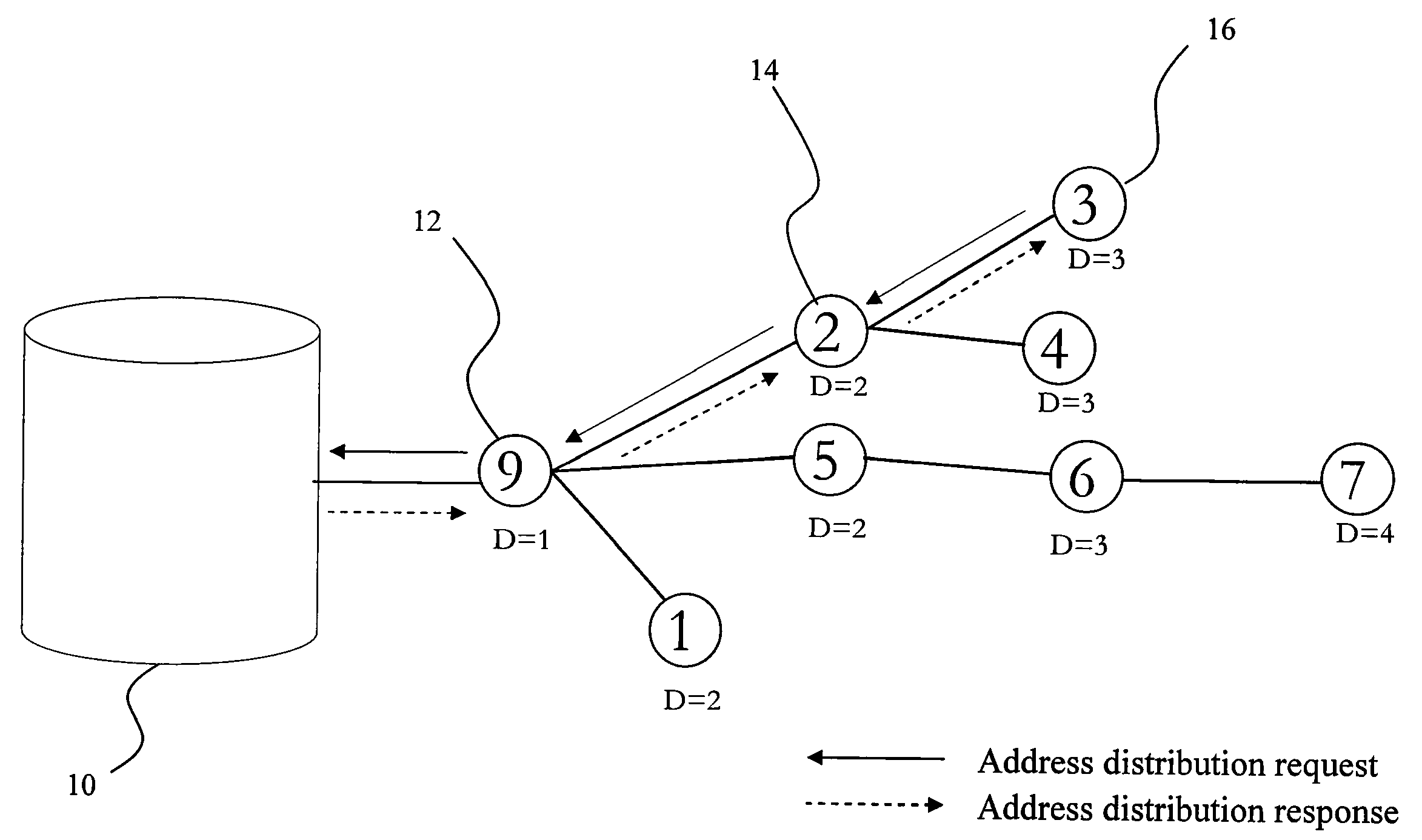
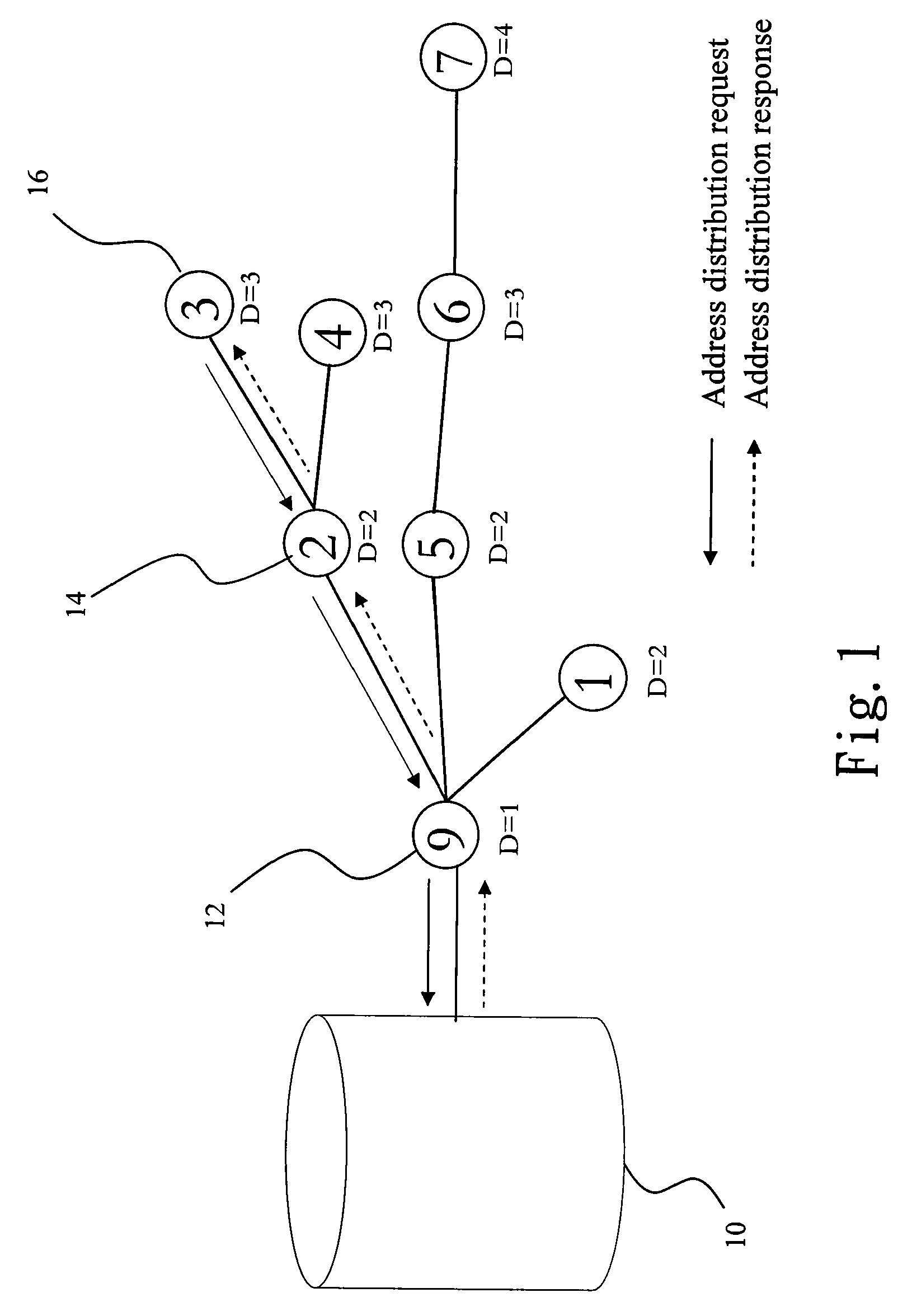
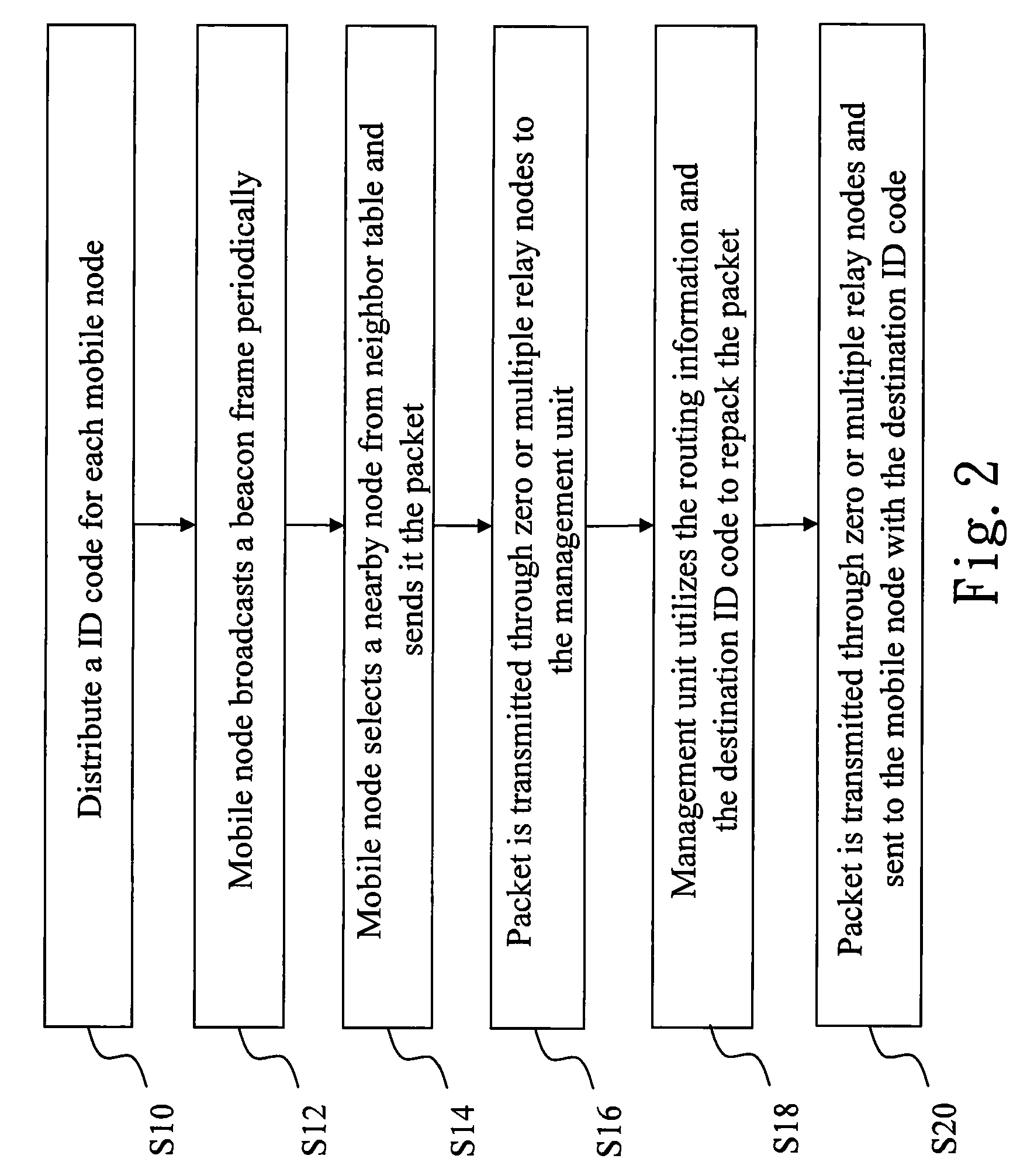
InactiveUS20100260071A1Quick buildFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexManagement unitWireless sensor networking
The present invention discloses an asymmetric routing method and routing path recovery mechanism. The wireless sensor network environment includes at least a management unit, at least a gateway, and mobile nodes. When joining, each mobile node obtains an unique ID code and, additionally, a depth as the gradient to the management unit. Accordingly, a mobile node sends an uplink packet via a nearby node with lower depth to the management unit; while the management unit transmits a downlink packet to a mobile node by utilizing the source route method. When the parent node of a mobile node is damaged or moves to another position or said mobile node with its sub-tree descendants changes their position together, the uplink routing path is recovered via selecting a nearby node of the sub-tree as relay node and the downlink routing path is recovered via sending a control message to the management unit.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Compression of a routing header in a packet by a mobile router in an ad hoc network
ActiveUS20070153764A1Data switching by path configurationWireless communicationComputer scienceMobile ad hoc network
Each mobile router in a mobile ad hoc network is configured for identifying routes to nearby nodes that are within a prescribed distance, based on storage of explicit paths specified within routing headers of packets transmitted from a host node to a destination node. Each mobile router also can selectively compress the routing header, based on the storage of the explicit path, resulting in a loose source route type routing header in the packet output from the mobile router. In addition, a routing header of a received packet can be expanded based on the mobile router inserting the explicit path, enabling mobile hosts in the explicit path to forward the packet according to strict source routing. The storage and compression of explicit paths also can be applied to packets specifying reverse routing headers, minimizing the size of the reverse routing headers.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
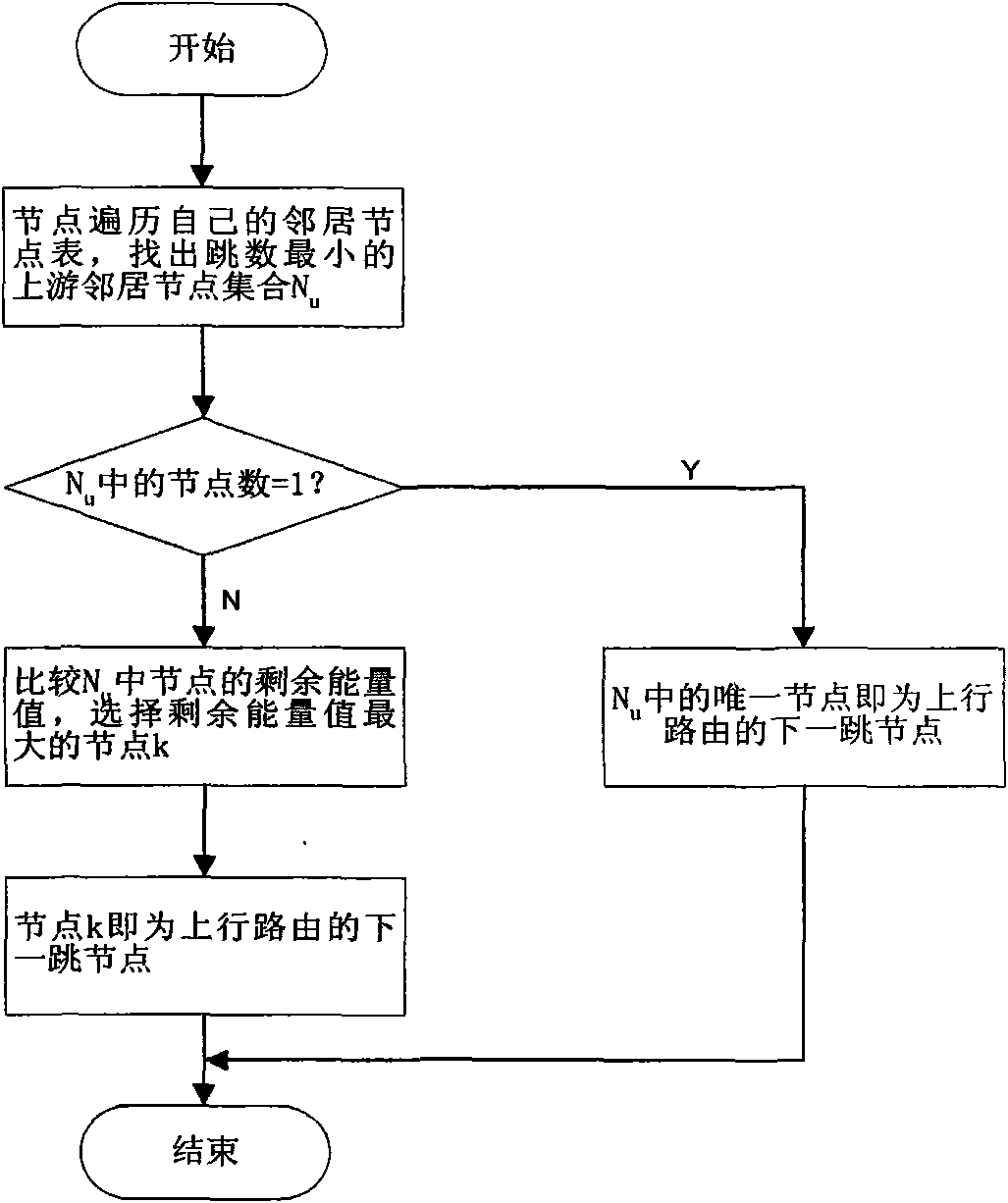
Cross-layer and bi-directional routing method based on hop number and energy in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101562861AImprove bandwidth utilizationExtend your lifeEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesLine sensorRest energy
The invention asks for protecting a cross-layer and bi-directional routing method in a wireless sensor network and relates to the technical field of communication. The existing wireless sensor network has the disadvantages that no downlink route is established in route establishing process, function of inquiring a sink node can not be supported, extra-cost occurs when energy information is updated by adopting node energy as the routing standard, and the cost of controlling the system is slightly larger. The method adopts source routing and cross-layer information share manner and uses smaller cost to establish the downlink route from the sink node to a sensor node without using special control group, the function of inquiring the sink node is added, and regular acquiring, releasing and updating of the rest energy information of the node are realized, when routing, the hop number and the rest energy of the node are both used as the measure standards, the energy consumption when forwarding the node is balanced when reducing the node energy and the network bandwidth consumption, and the service life of the wireless sensor network can be prolonged, and the network bandwidth utilization rate is increased.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Routing traffic in a communications network
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
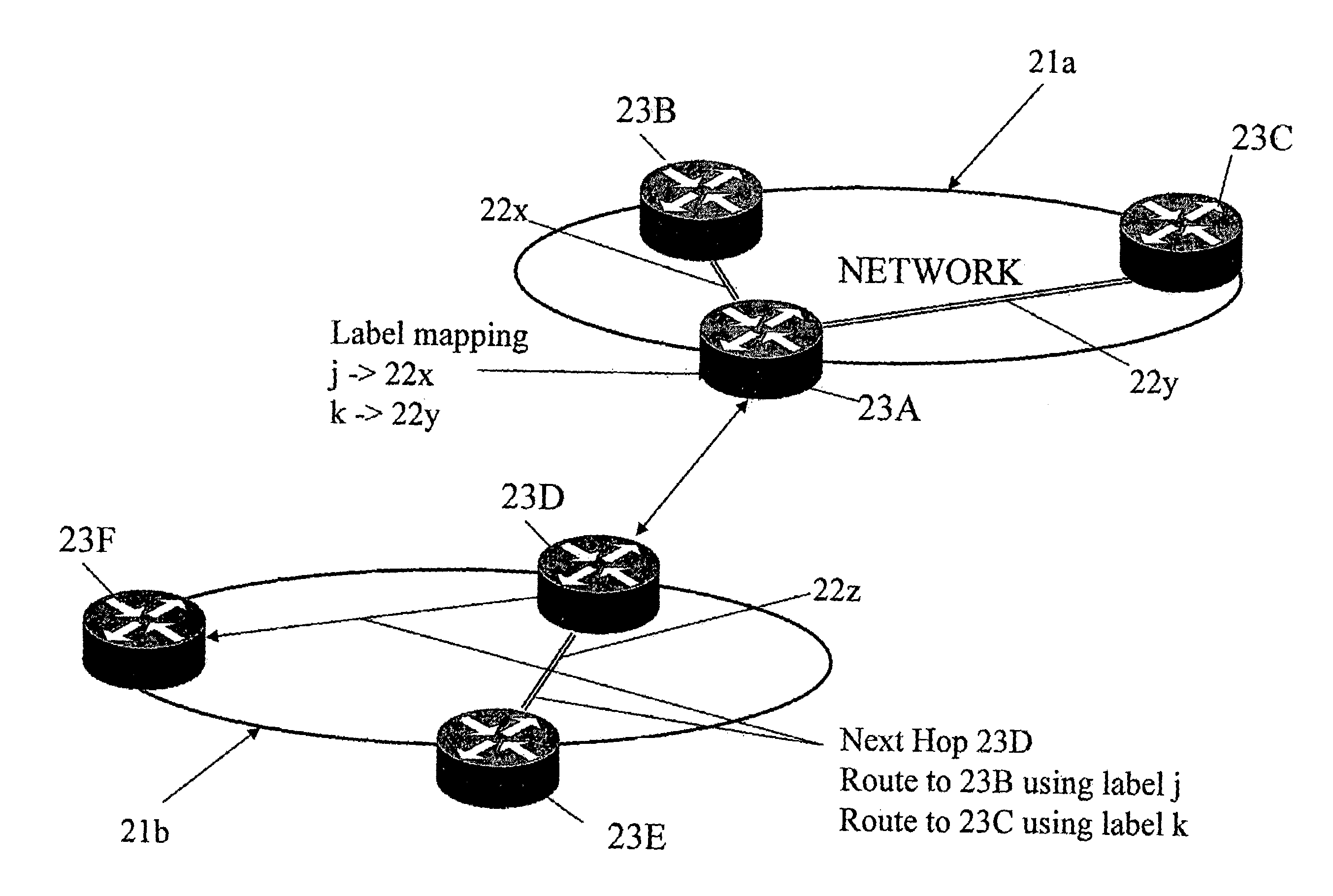
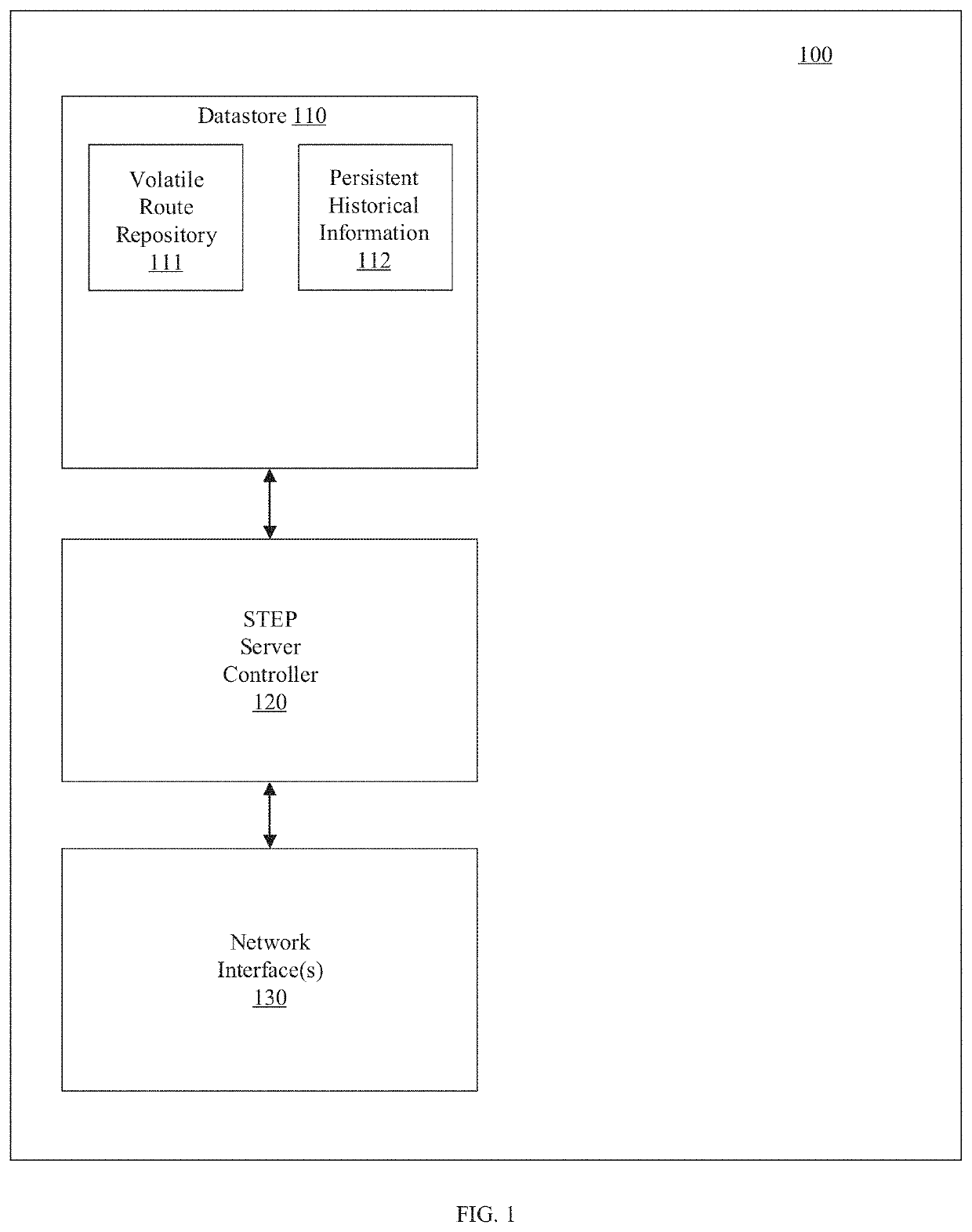
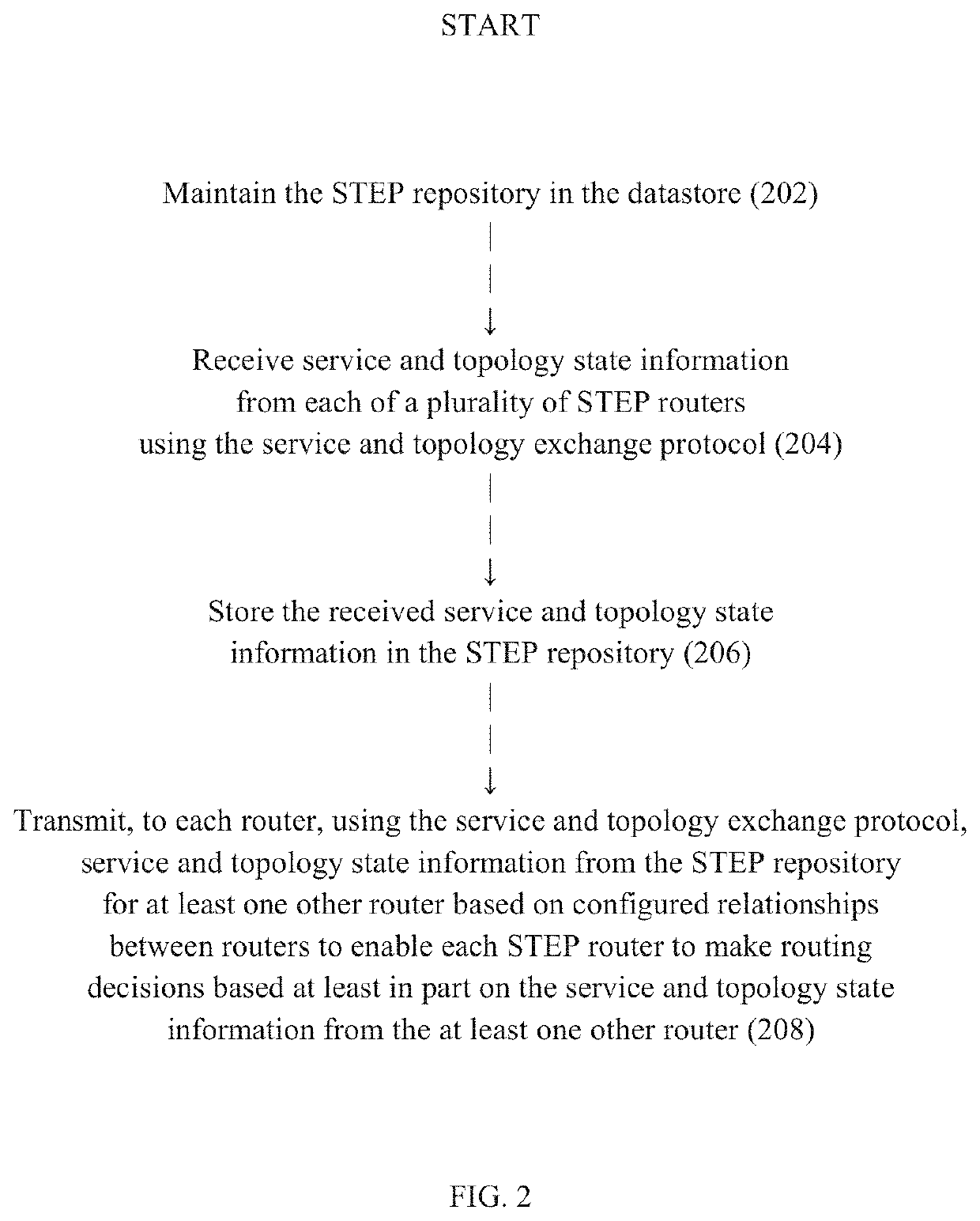
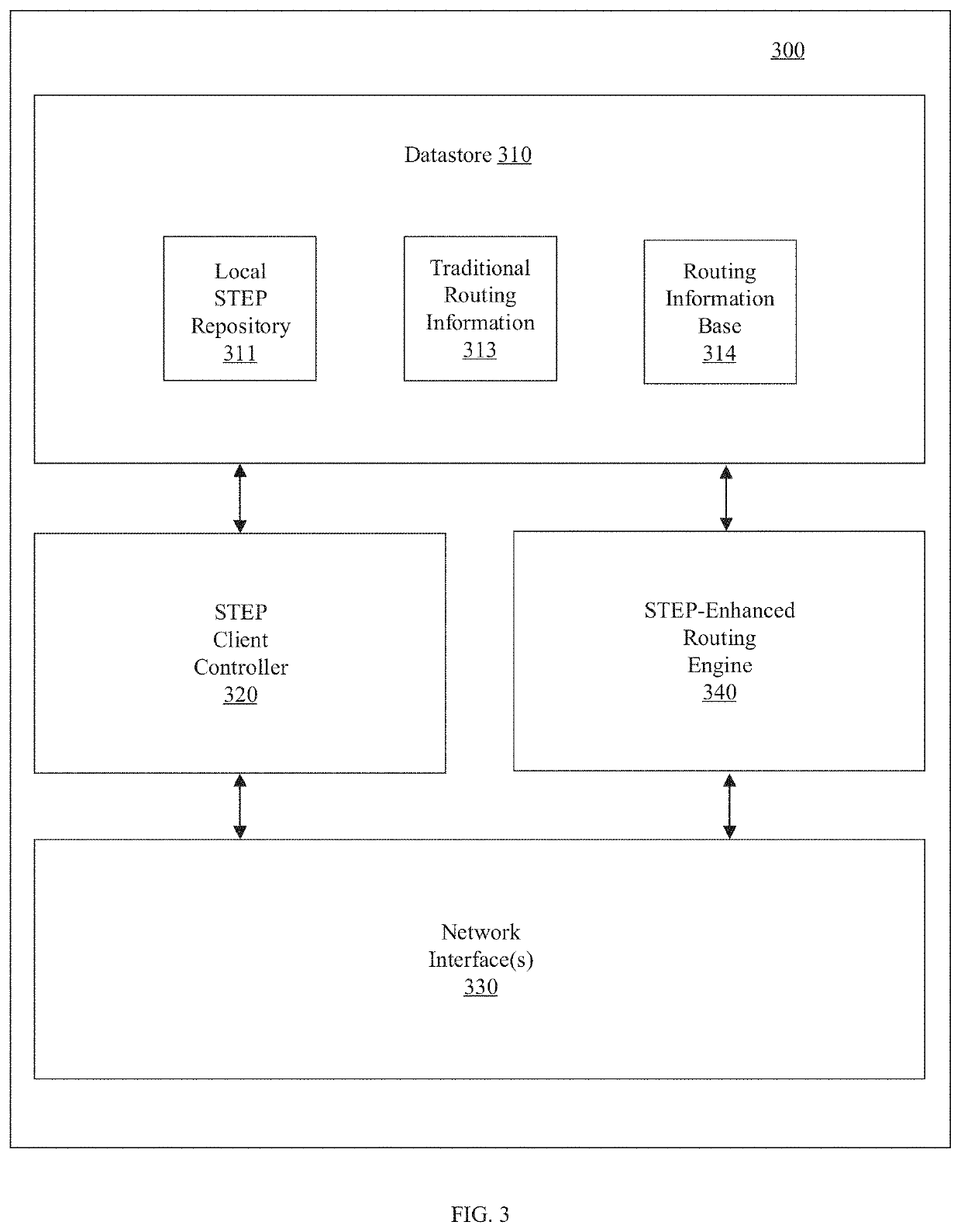
Source-based routing
A routing system for routing packets for a route or service comprises a plurality of routers including a source router, wherein the source router is configured to receive, using a service and topology exchange protocol, service and topology state information from a STEP repository for at least one other router based on configured relationships between routers; determine a first path to a destination for a route or service based on the service and topology state information, the first path including an ordered list of successive routers to receive a packet associated with the route or service starting with a first successive router and ending with a destination router; and transmit a packet toward the first successive router with first metadata including a list of at least one remaining router of the ordered list of routers to receive the packet associated with the route or service. Each successive router, starting with the first successive router, is configured to receive a packet and determine if the router is the destination router based on metadata associated with the received packet, and when the router is not the destination router, forward the packet toward a next successive router in the ordered list of routers.
Owner:128 TECH
Carrier aggregation
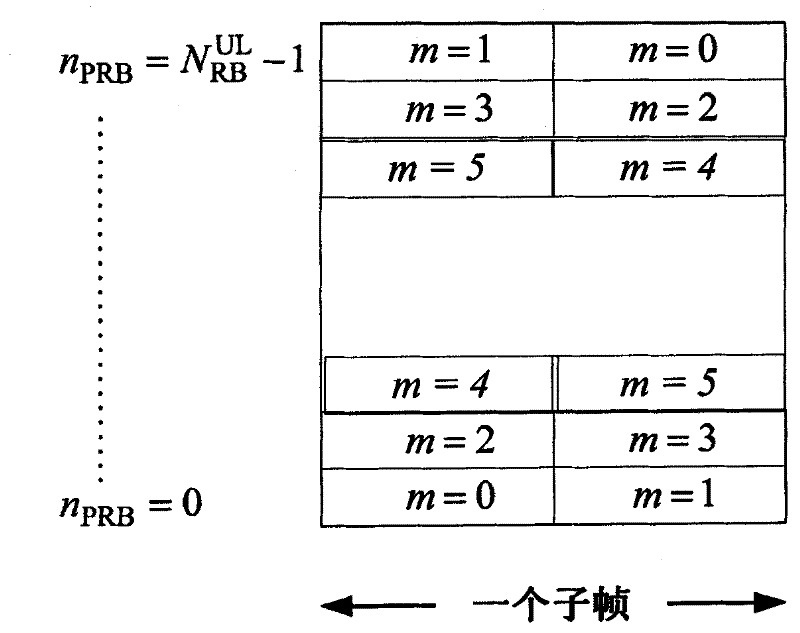
ActiveCN102187726ASite diversityTransmission path divisionTelecommunicationsSounding reference signal
A method and apparatus for transmitting uplink control information (UCI) for Long Term Evolution-Advanced (LTE-A) using carrier aggregation is disclosed. Methods for UCI transmission in the uplink control channel, uplink shared channel or uplink data channel are disclosed. The methods include transmitting channel quality indicators (CQI), precoding matrix indicators (PMI), rank indicators (RI), hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) acknowledgement / non-acknowledgement (ACK / NACK), channel status reports (CQI / PMI / RI), source routing (SR) and sounding reference signals (SRS). In addition, methods for providing flexible configuration in signaling UCI, efficient resource utilization, and support for high volume UCI overhead in LTE-A are disclosed.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Distributed denial of service attack defense method and device
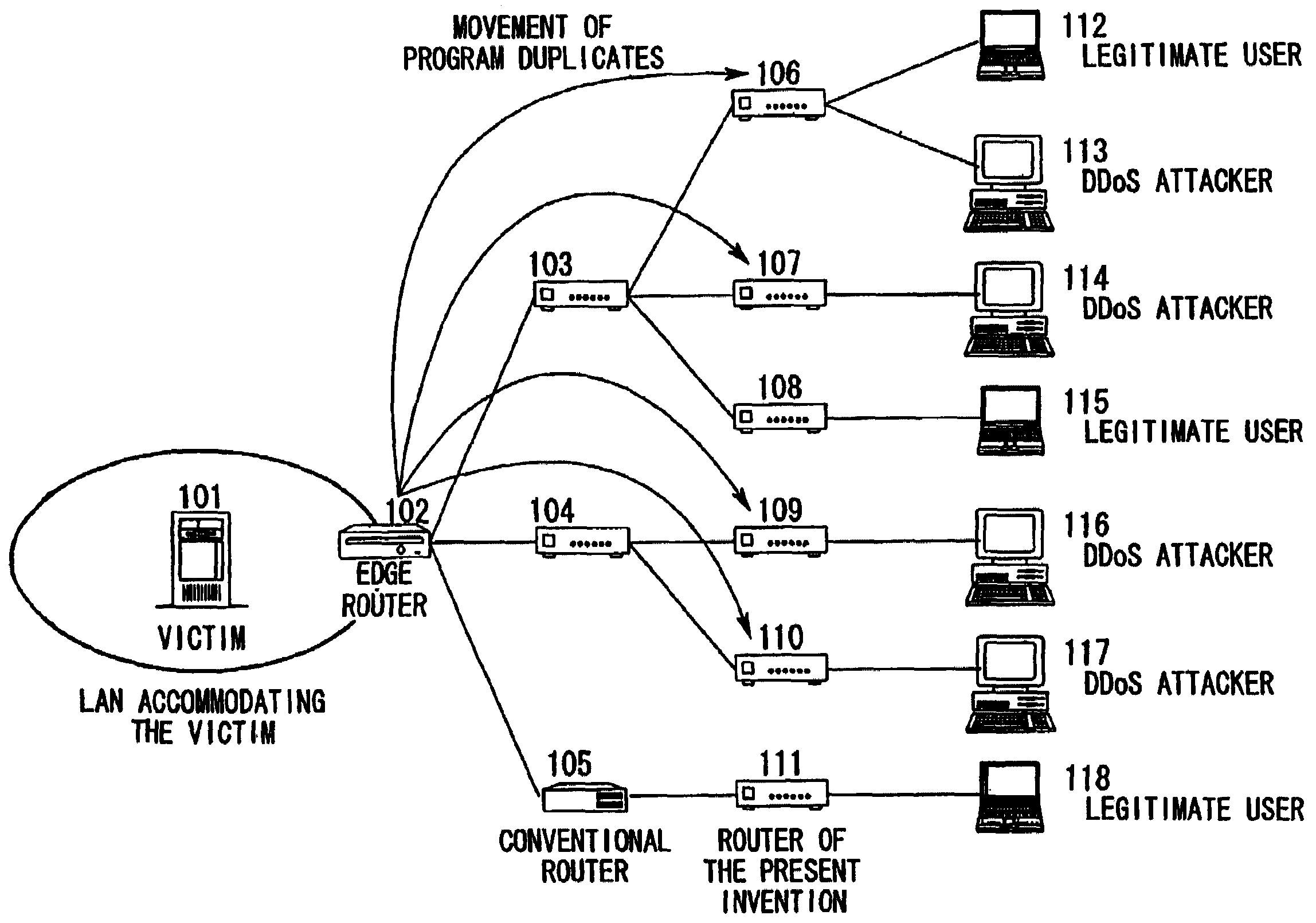
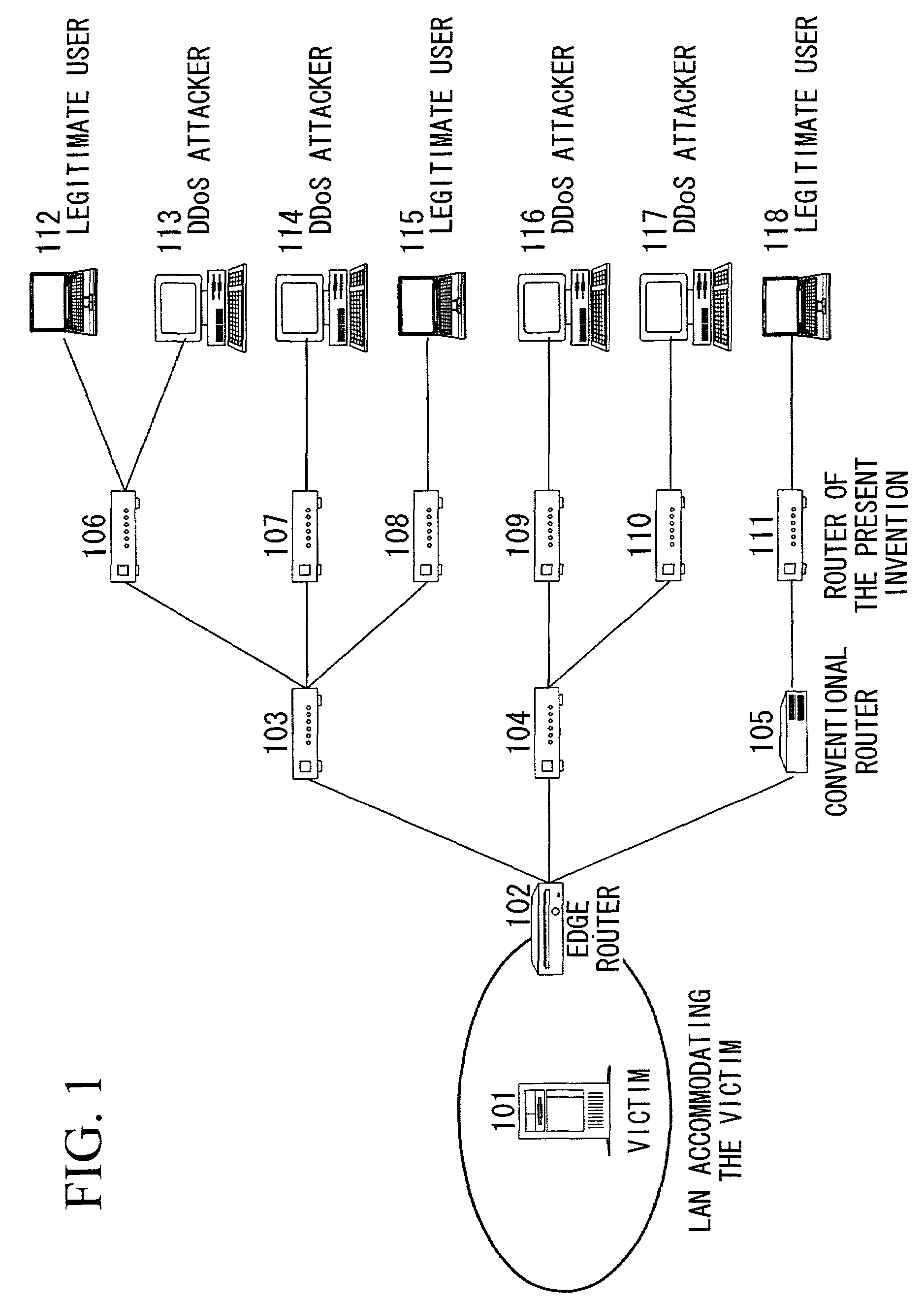
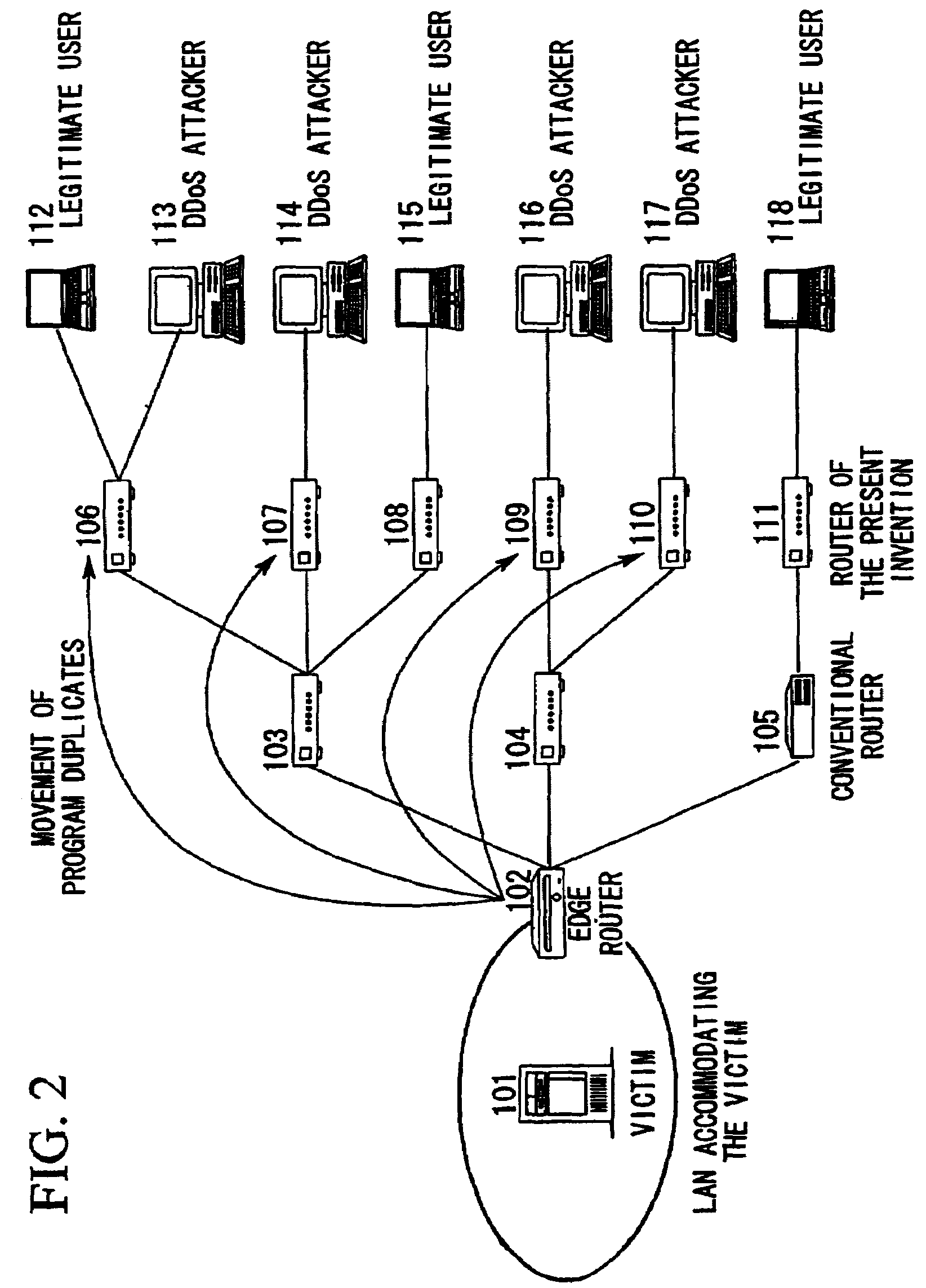
InactiveUS7188366B2Simplify protection algorithmImprove securityMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsNetwork packetDenial-of-service attack
When DDoS attack packets are transmitted from the attacker to the victim's server, the attack packets are detected in the edge router of the LAN accommodating the server. These packets are then destroyed, the address of the upstream routers close to the attack source are retrieved, and attack source retrieval modules are transmitted from the edge router to all the upstream routers. By executing the retrieval modules in the upstream routers, verification is performed as to whether the attack packets are passing through those upstream routers. The results are notified to the transmission source router and if the attack packets are passing through, the retrieval modules are transmitted to routers at the upper stream. When the router at the uppermost stream is reached, a protection module is executed to destroy the attack packets. When the attacks cease, the protection module deletes itself and the protection process is ended.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Source-implemented constraint based routing with source routed protocol data units
ActiveUS20050135330A1Overcomes drawbackEliminate needData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityA domain
Source-implemented constraint-based routing with source routing enables traffic engineering to be performed and reservations to be made within a domain without requiring constraint information and reservation information to be disseminated to all nodes in the domain. In one embodiment, a focal node maintains a table containing metrics of links and connection reservations through the domain. When a connection is to be added, the focal node determines a path, given the constraints reflected in the table, and allocates resources on the links forming the path. The table is updated, and the path is used to generate headers for traffic associated with the connection. Traffic from the nodes toward the focal point follow the reverse path. If a node or link fails, connections carried through the failure are identified, reservations on links associated with the connections are released, and new reservations are made taking into account the new network topology.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
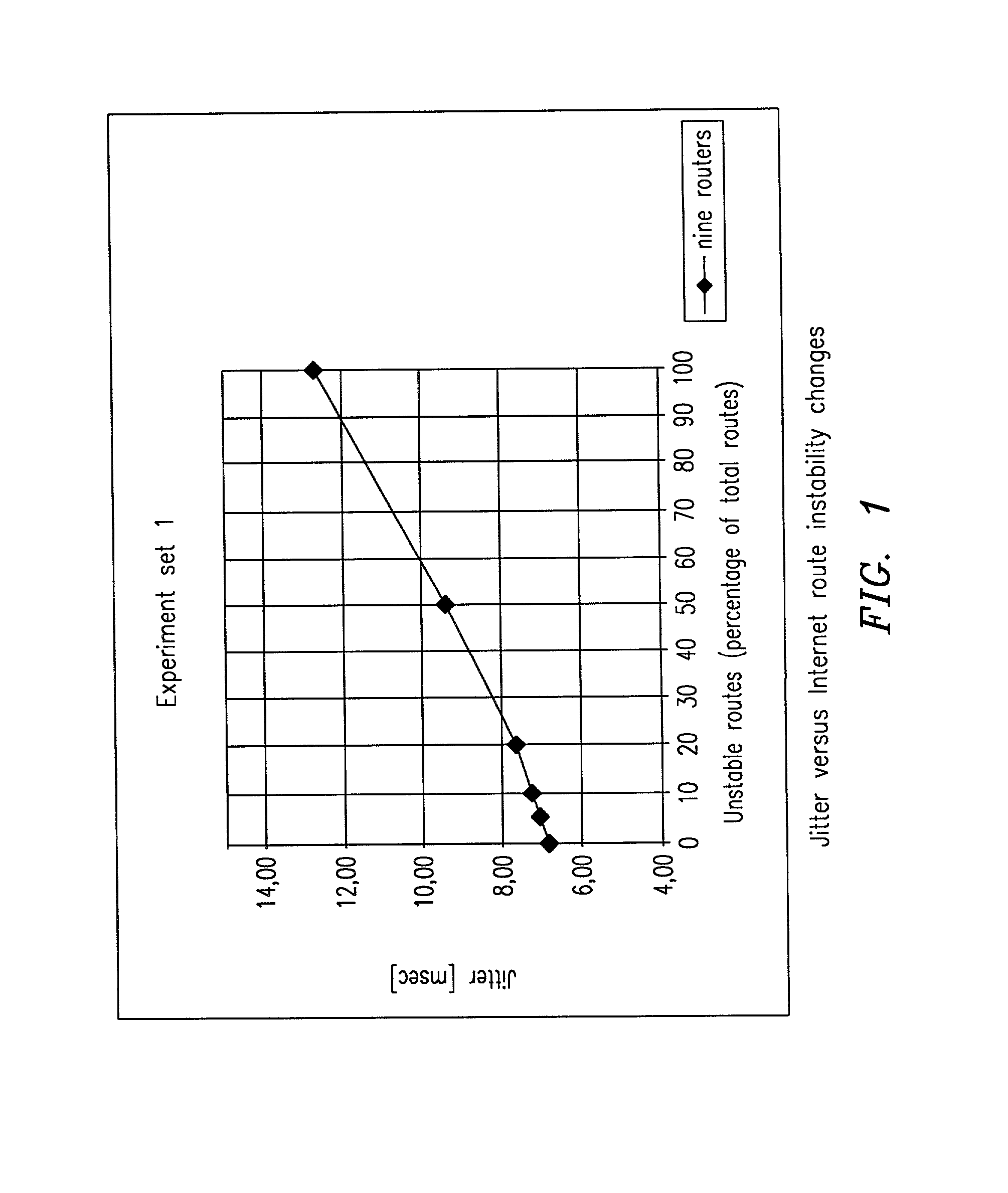
Jitter reduction in Differentiated Services (DiffServ) networks
InactiveUS20020024974A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsDifferentiated servicesPathPing
A method and a computer program for reducing jitter in IP packet transmission in a Diffserv network having ingress and egress Border Routers and using premium service, expedited forwarding and source route option, recognize incoming packets which have firm jitter requirements. The program verifies if a recognized packet has an entry in the forwarding cache for its IP destination address. If affirmative, the identified packet is sent to the next hop. If not, the program checks to see if a route table entry exists for the specified destination address. If affirmative, the route table entry is stored in the forwarding cache, and the packet is sent on its way. Otherwise, the program uses special filters to extract and select the shortest and fastest path to an egress border router to match the destination address; a list of selected router addresses is inserted as part of a source route option. All intermediate routers receiving a packet with the strict source route option set will forward the packet to the first address in the strict source option list. Subsequent packets which follow after the recognized packet and are bound to the same destination address will be sent in the same path as the identified first packet with the source route option turned off. The method ensures reduced jitter for packets having firm jitter requirements in a network using either static or dynamic routing. The invention also teaches a memory and an algorithm using the method.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Routing method for a wireless multi-hop network
InactiveUS20130215739A1Reduce decreaseSolve the real problemError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityBroadcasting
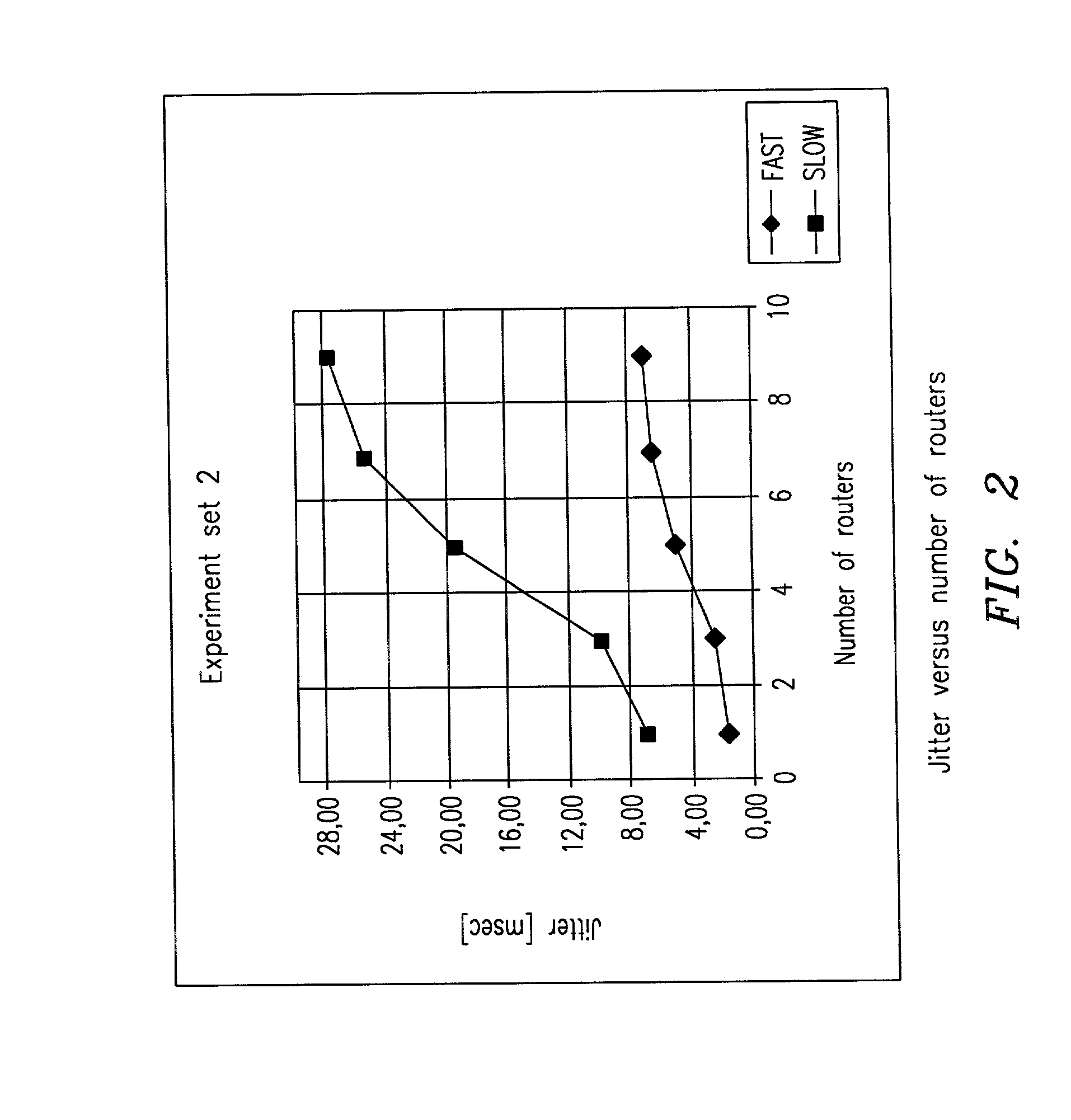
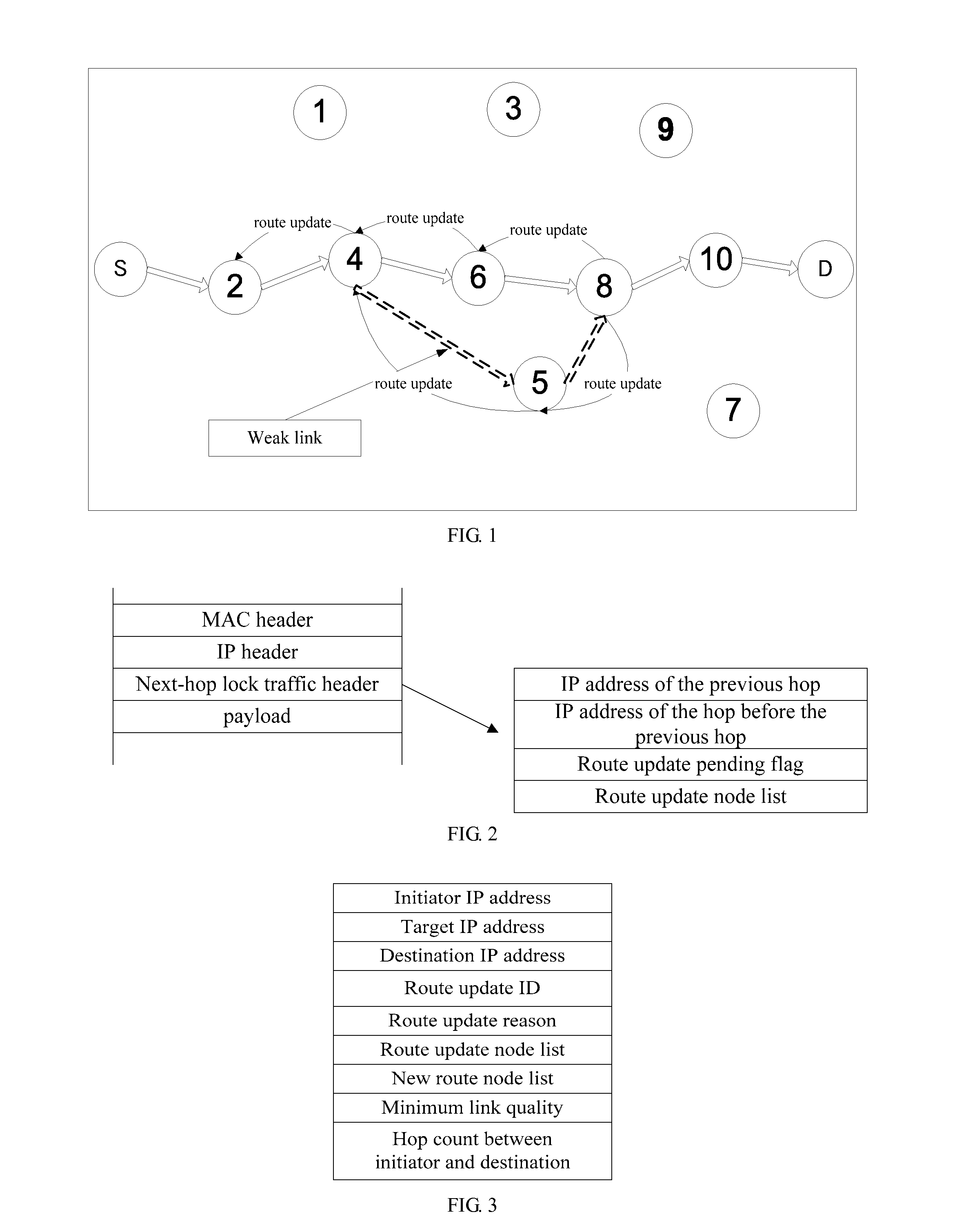
Disclosed is a routing method named lock routing for a wireless multi-hop network, which can be based on next-hop routing and source routing and named next-hop lock routing and source lock routing respectively. The routing method utilizes traffic packets to monitor the link quality and utilizes local broadcast to help a source node keep track of the varying network topology in order to update a route path to a destination node. In local broadcast, routing control messages can be forwarded by path nodes and neighbors of an old route path, which reduces the routing control overhead and enhances the network scalability. A route update process can be triggered by the link quality and the path node state and is used to maintain ongoing traffic flows and extend the network lifetime.
Owner:ZHANG YIKUN
Method of device-to-device communications in hybrid distributed device control networks
InactiveUS7058055B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationEngineering
The present invention comprises a method of source routing to implement device-to-device communications across a hybrid distributed device control network. The method is based in packet communications in which packets are structured so that they can be readily converted between communications protocols, and in which packets enclose routing information and parameters.
Owner:SMARTMATIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com