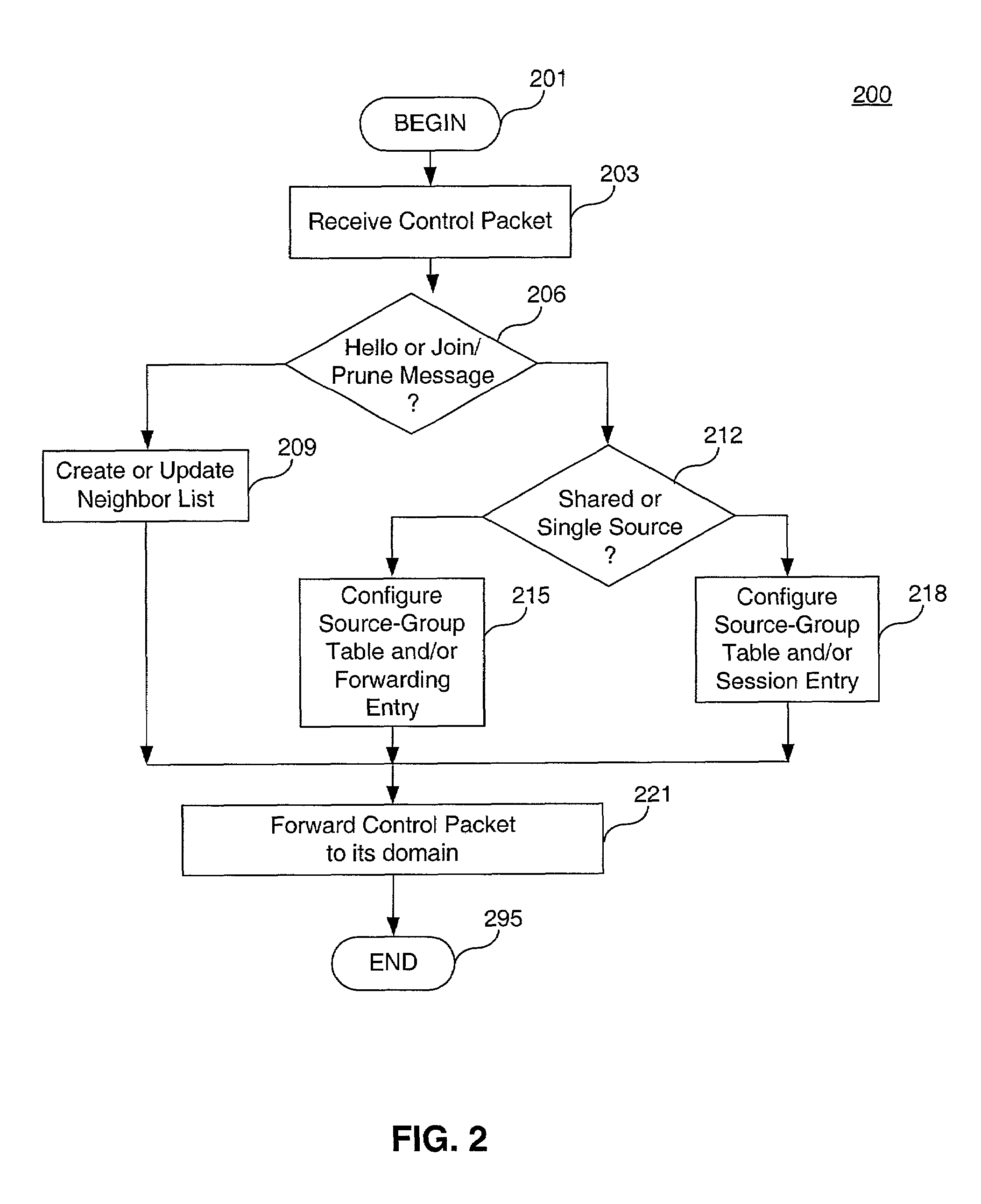
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
248 results about "Distribution tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
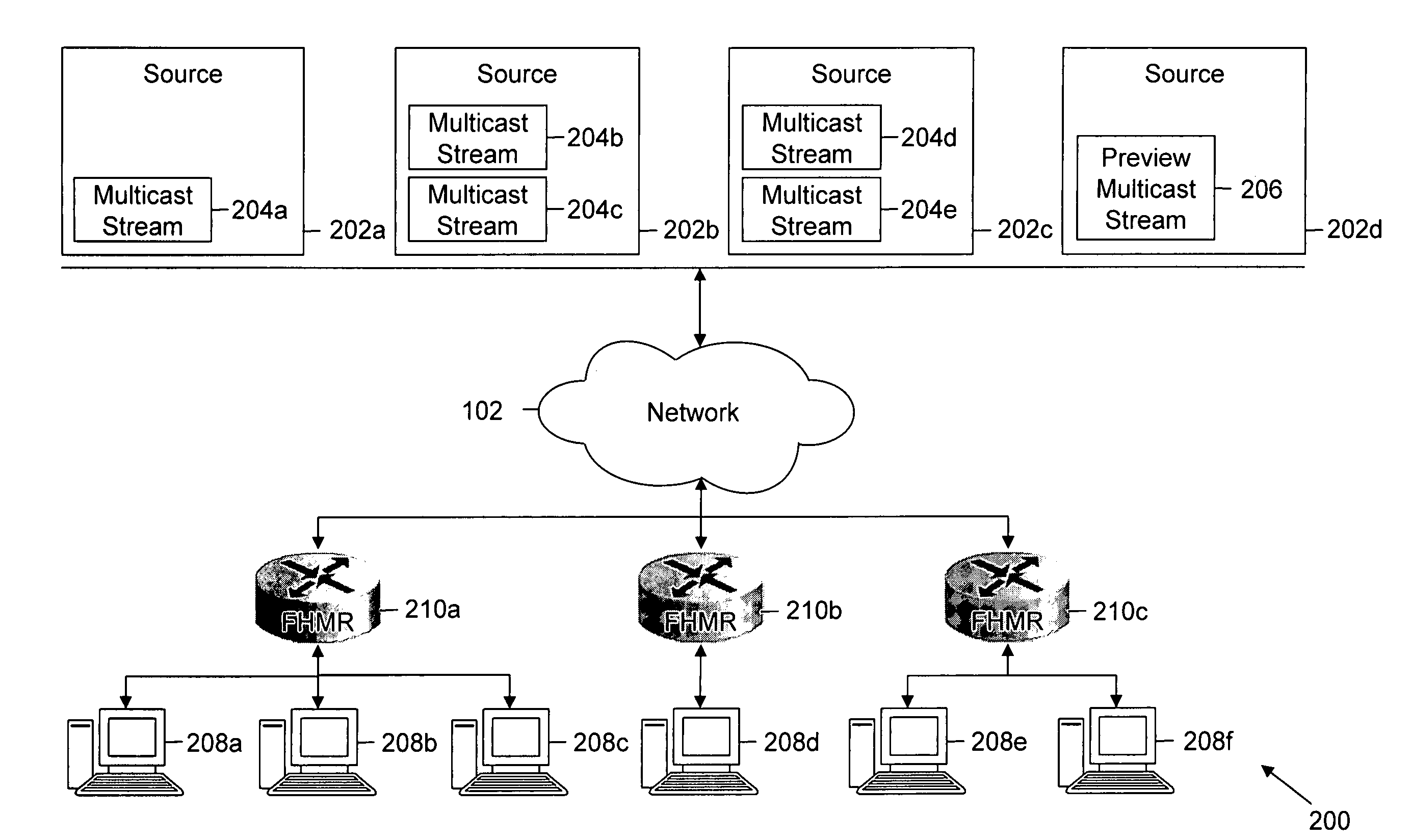
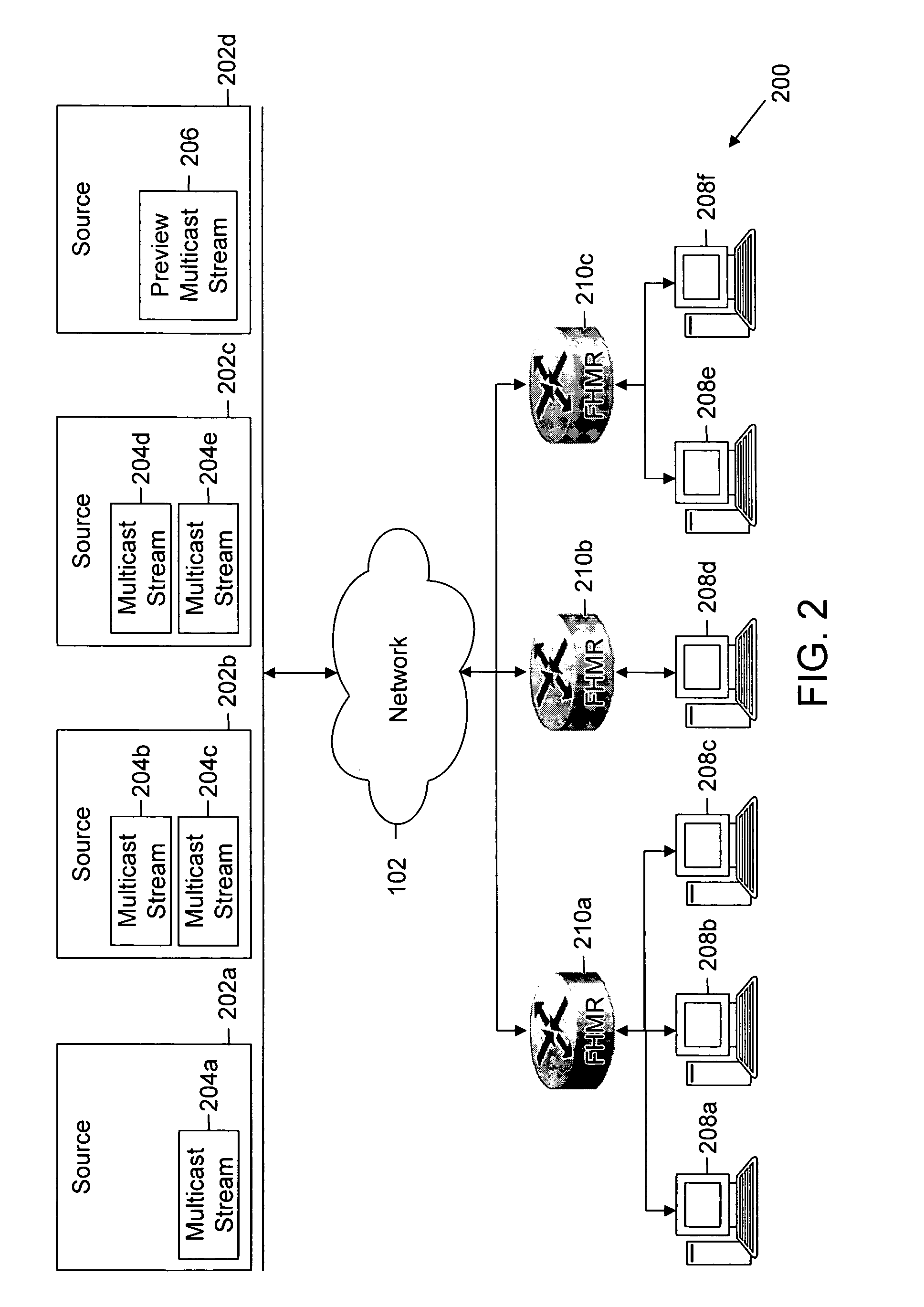
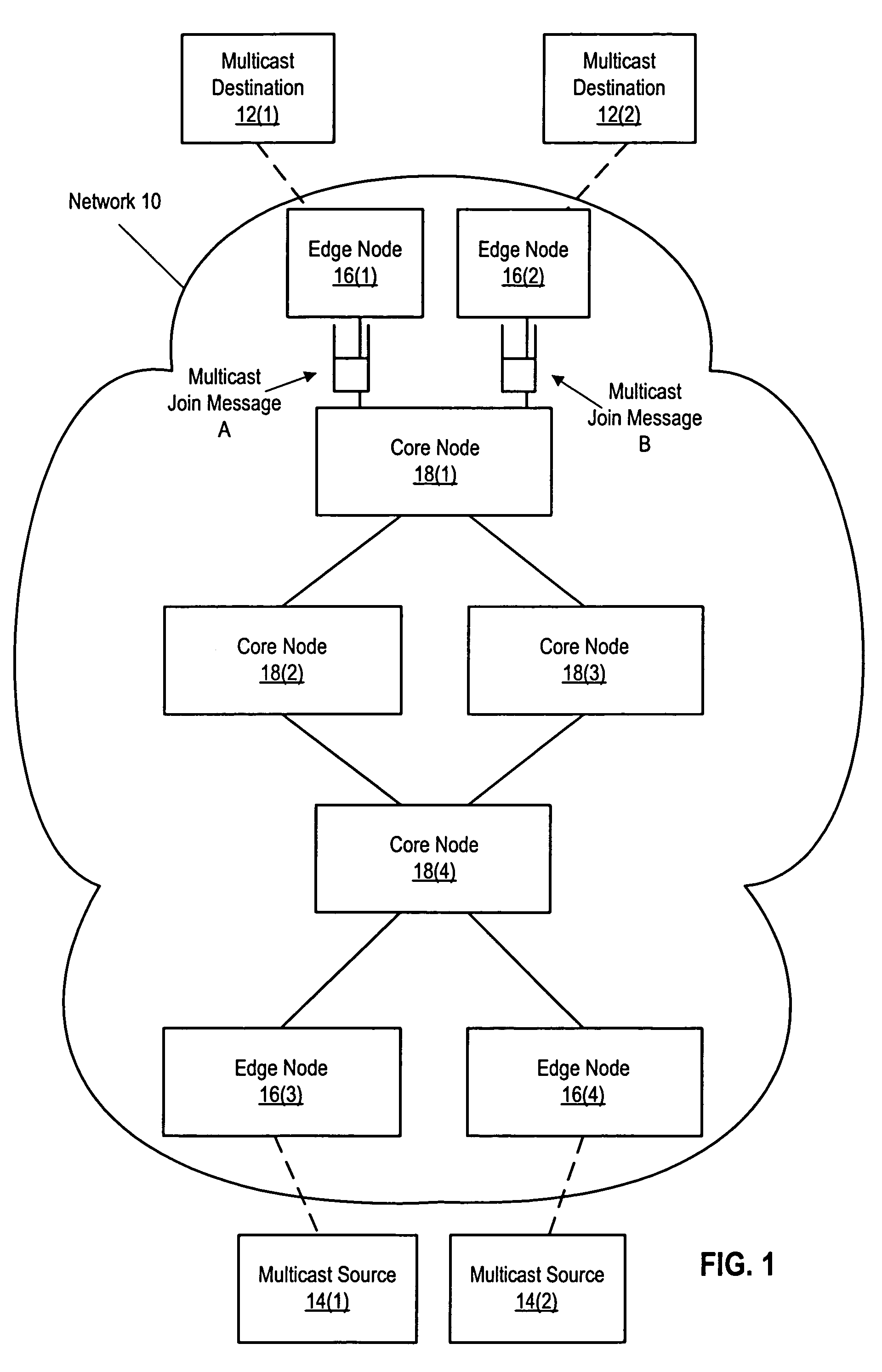
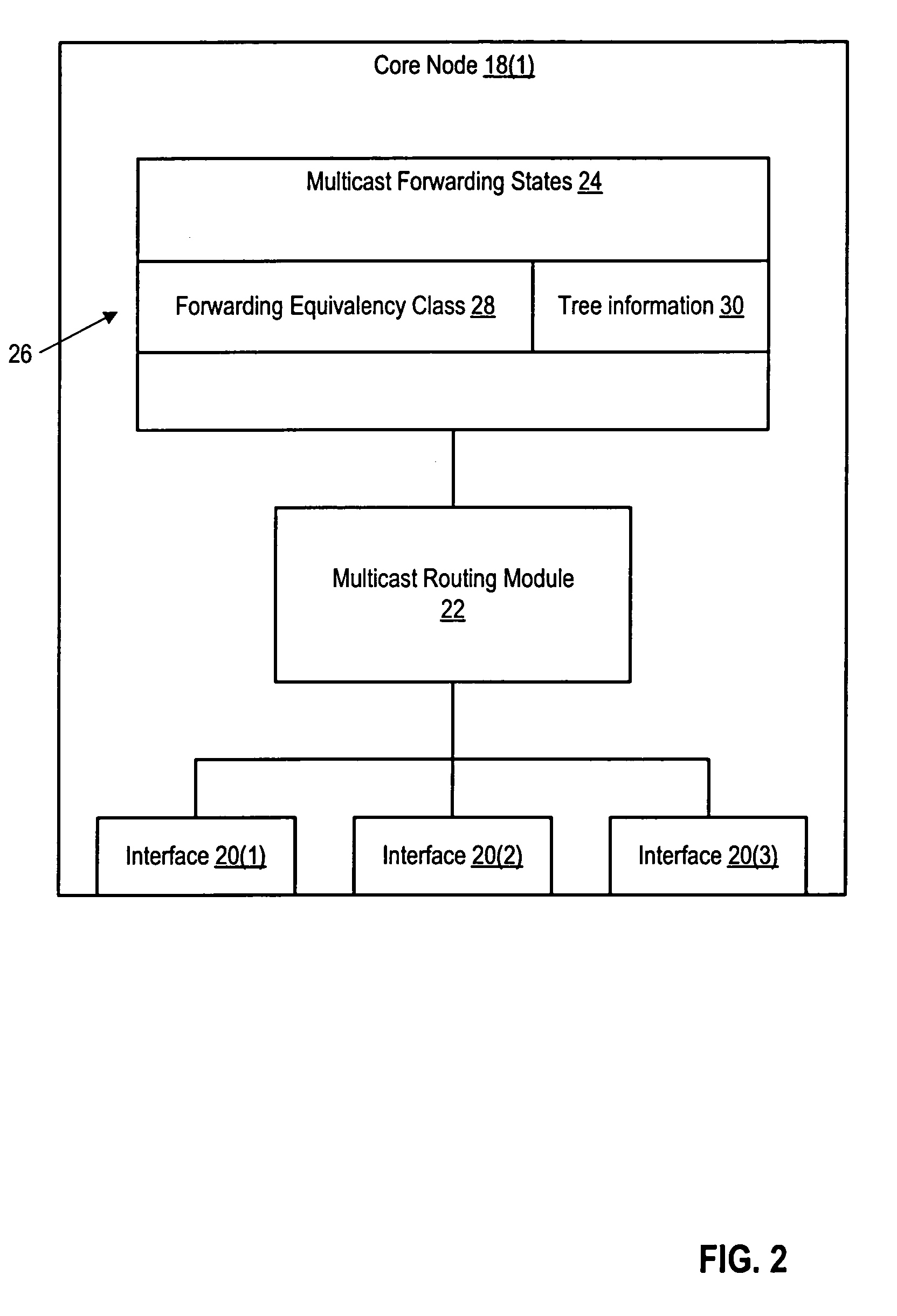
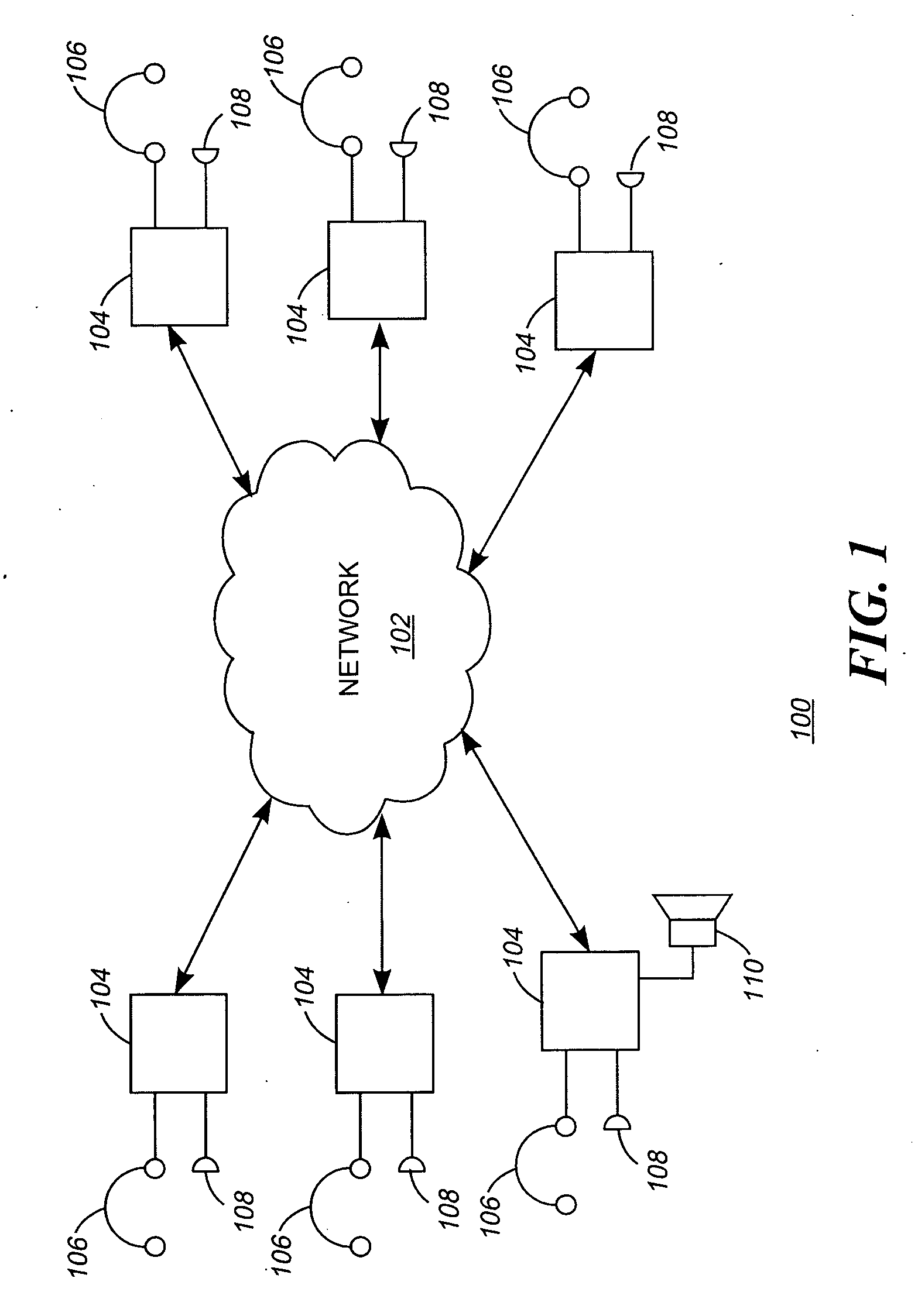
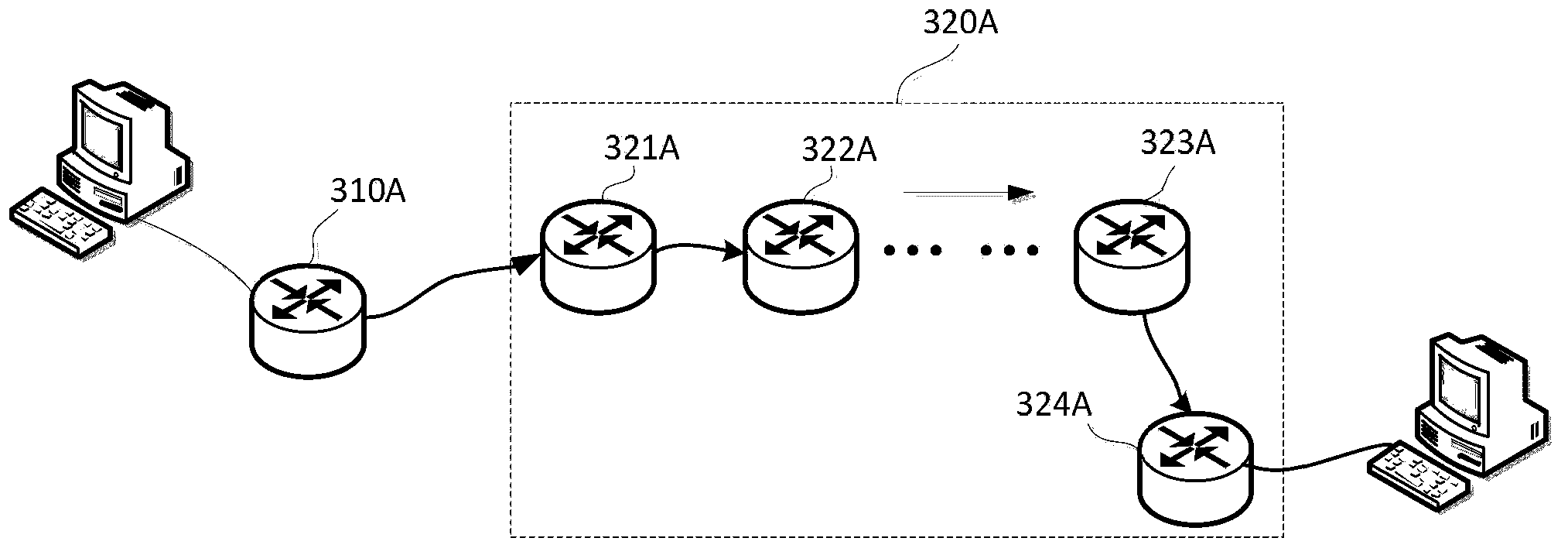
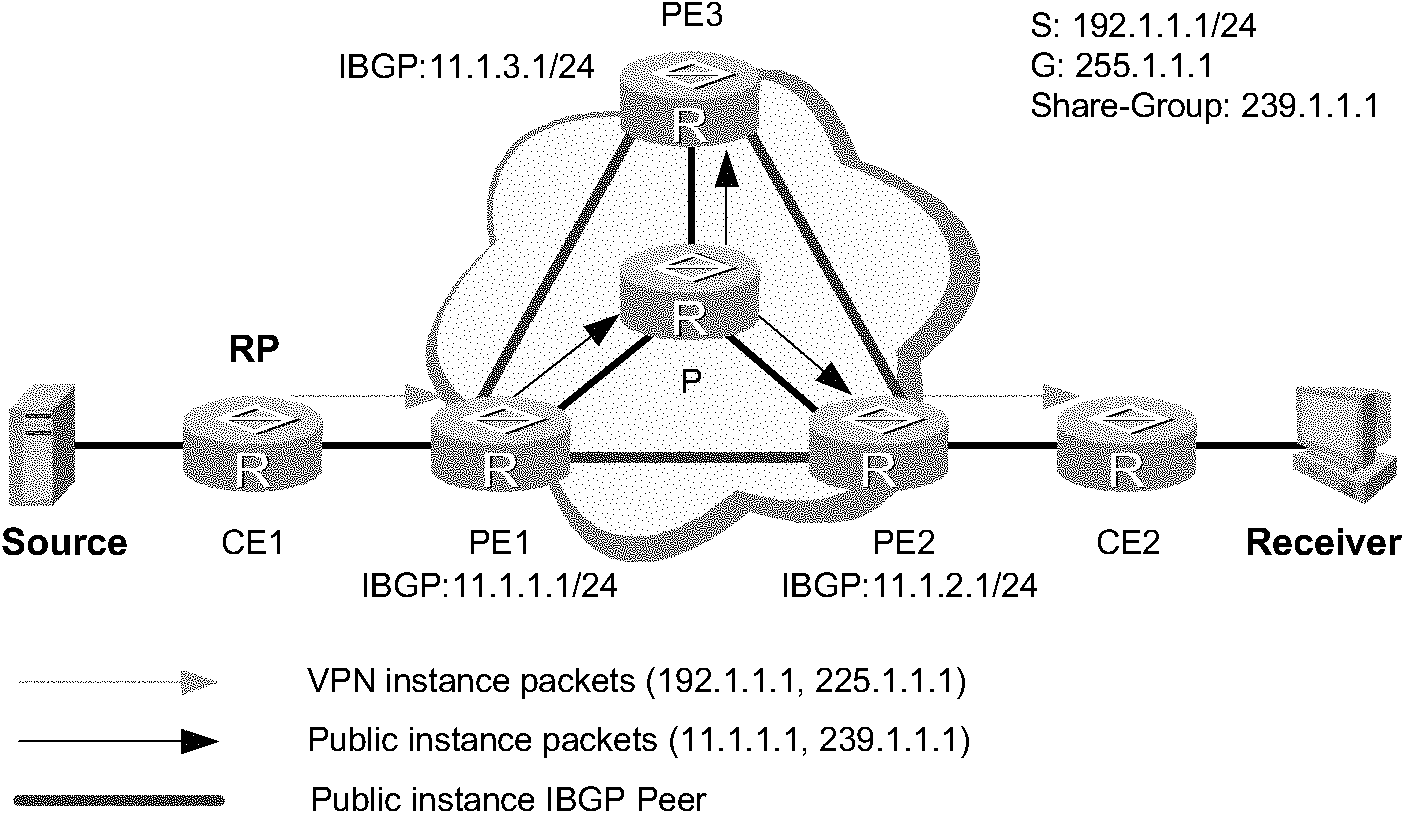
Method and system for reducing latency in a multi-channel multicast streaming environment in content-delivery networks
ActiveUS20080025304A1Lower latencyDelay minimizationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDistribution treeWaiting time
Methods, systems and apparatus for reducing apparent latency in content-delivery networks are provided. Sources multicast certain ‘preview multicast streams’ to multiple subscribers. These preview multicast streams provide pre-recorded content of multicast streams. When a subscriber switches to a desired multicast stream, pre-recorded content of the desired multicast stream is reconstructed from a preview multicast stream. Thereafter, the pre-recorded content is played during the setup of the new multicast distribution tree to minimize latency. Once the distribution tree is setup, live content of the desired multicast stream is made available to the subscriber.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
PIM sparse-mode emulation over MPLS LSP's
ActiveUS20060221958A1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexDistribution treeNetwork packet
An apparatus and method for emulating a shared or source distribution tree within an MPLS network. In one embodiment of the method, a router receives a multicast data packet. The router transmits the multicast data packet to a first router via a first point-to-point label switched path (LSP). The router replicates the multicast data packet to produce a replicated multicast data packet. Then the router transmits the replicated multicast data packet to a second router via a second point-to-point LSP. The first point-to-point LSP is distinct from the second point-to-point LSP.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Efficient multipoint distribution tree construction for shortest path bridging
InactiveUS20090080345A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationDistribution treeComputer network
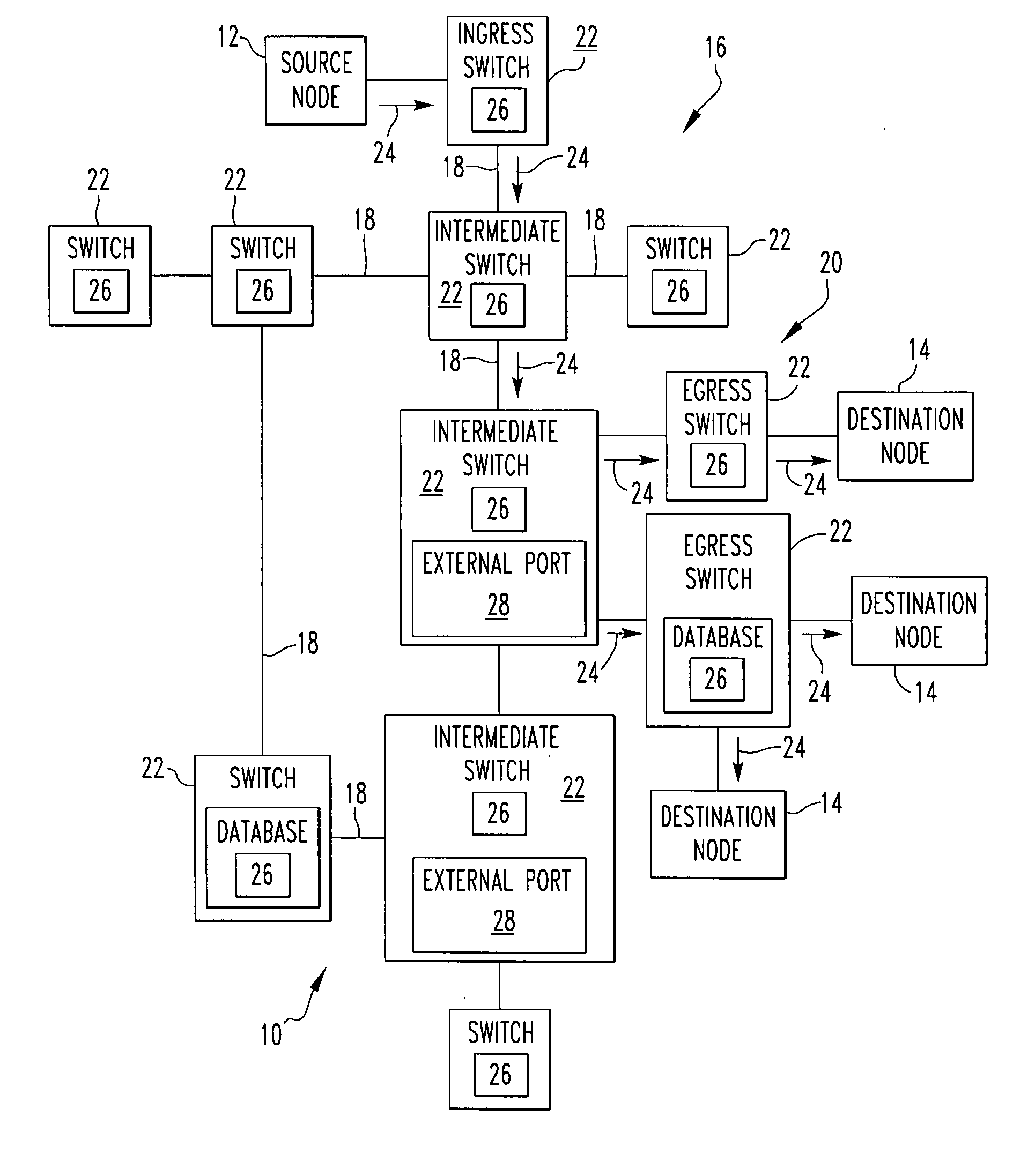
A telecommunications system includes a source node. The system includes a plurality of destination nodes. The system includes a network having links and end stations. The system includes a plurality of switches that create paths along links between the source nodes and the destination nodes where there is 100% efficiency along the paths with the paths traversing any link only once to the corresponding destination node from the source node, and the path being a shortest path between the source node and the destination node, where each switch has a Dijkstra computation complexity of O(N) in regard to forming the shortest paths. A method for telecommunications includes the steps of creating paths with a plurality of switches along links of a network between a source node and a plurality of destination nodes where there is 100% efficiency along the paths with the paths traversing any link only once to the corresponding destination node from the source node, and each path being a shortest path between the source node and the destination node, where each switch has a Dijkstra computation complexity of O(N) in regard to forming the shortest paths. There is the step of delivering with the switches frames from the source node to the destination nodes along the shortest paths.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multicast operations using prioritized state information
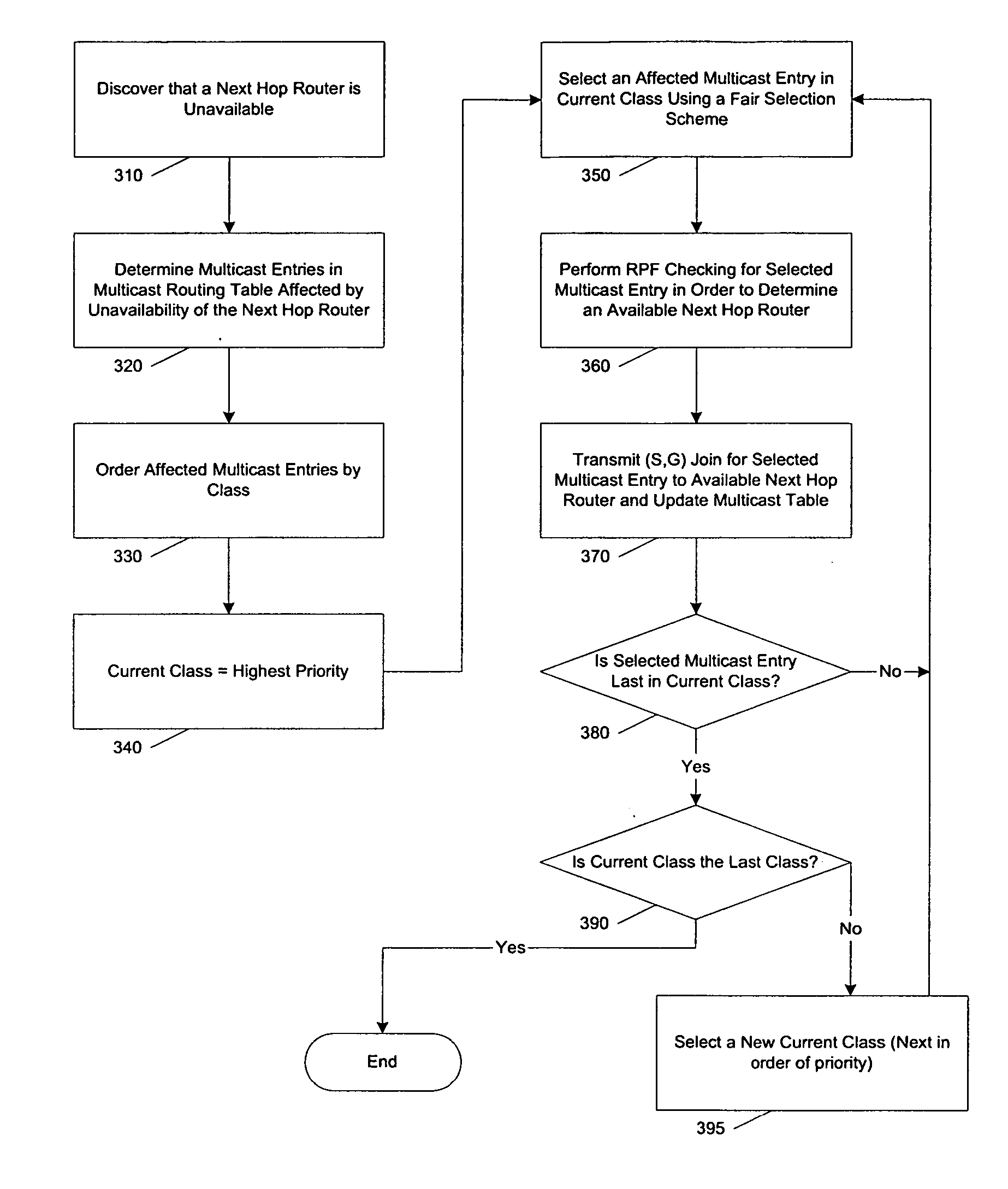
ActiveUS20070140107A1Special service provision for substationError preventionDistribution treeUnavailability
A classification mechanism to allow selected classes of multicast entries to be acted upon in a chosen order of priority during multicast distribution tree convergence is provided. Such prioritization allows for the designation of customers, networks or multicast groups to receive faster convergence of multicast distribution trees to modified multicast distribution trees in response to unavailability of an upstream router, and in performing other multicast-related tasks (e.g., PIM joins and prunes). One aspect of the present invention provides for multicast entries (also called multicast states) that are at a same priority level to be acted upon in a fair manner, thereby avoiding having certain multicast entries and their associated users from being acted upon consistently last.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System, device, and method for controlling access in a multicast communication network
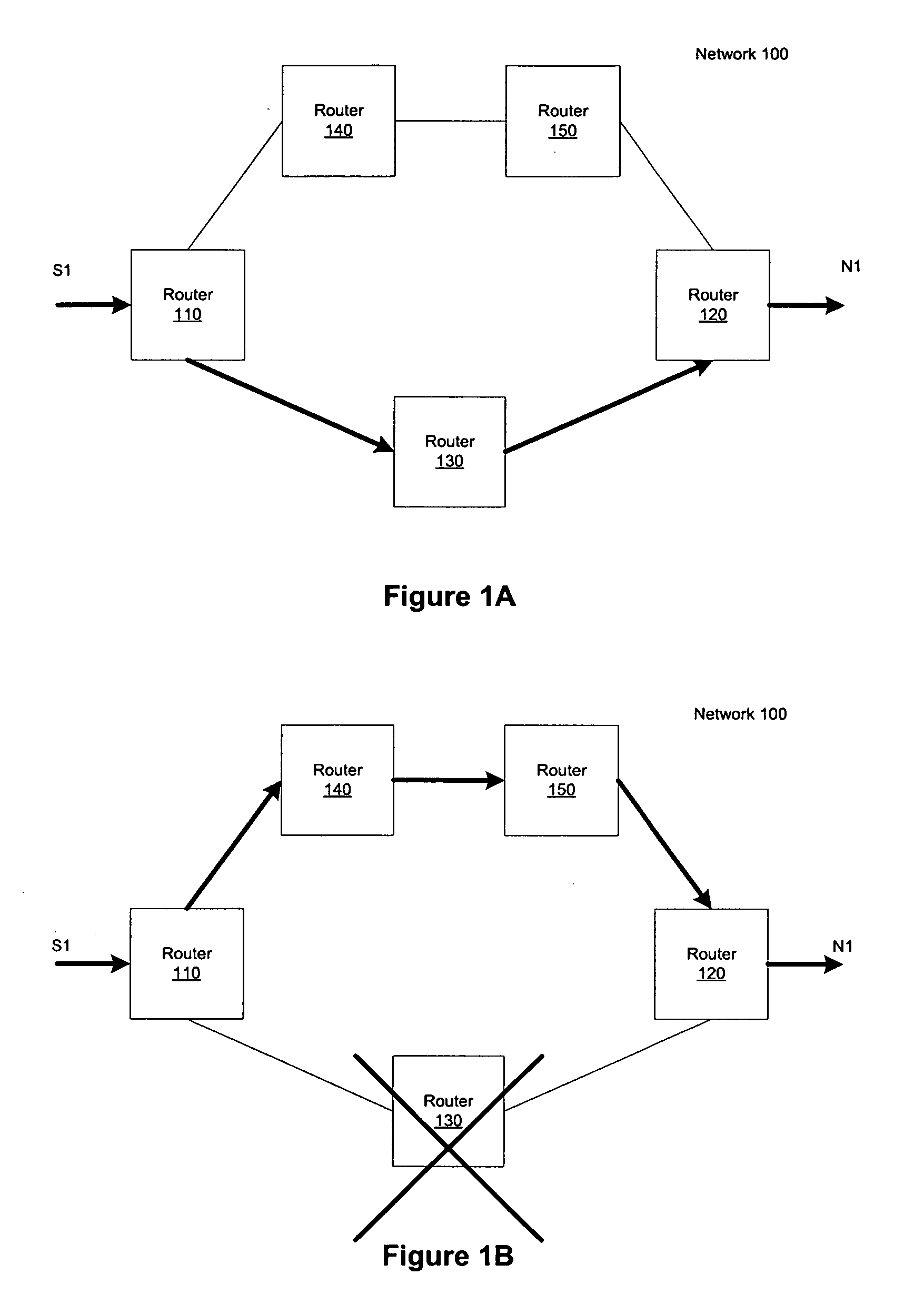
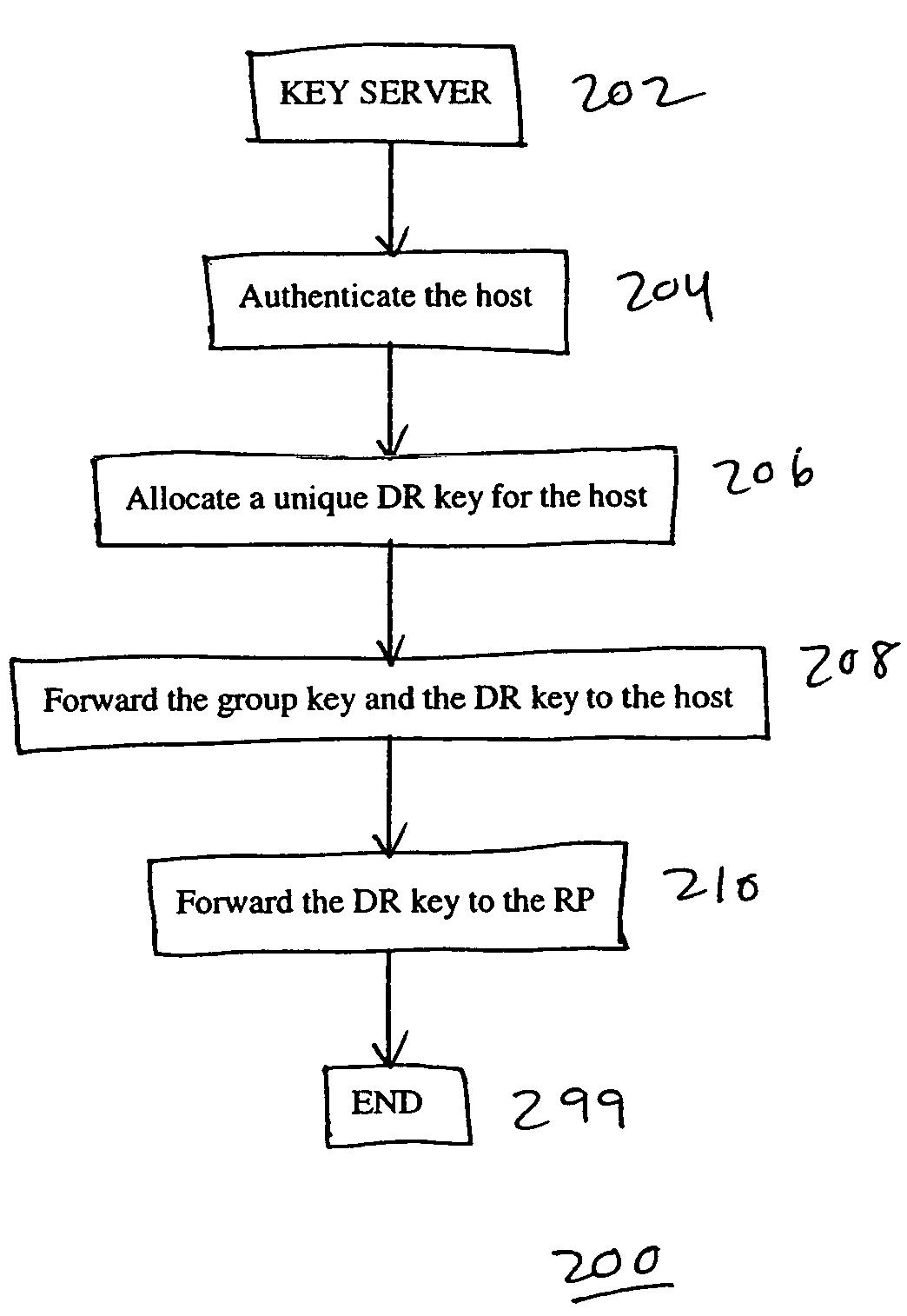
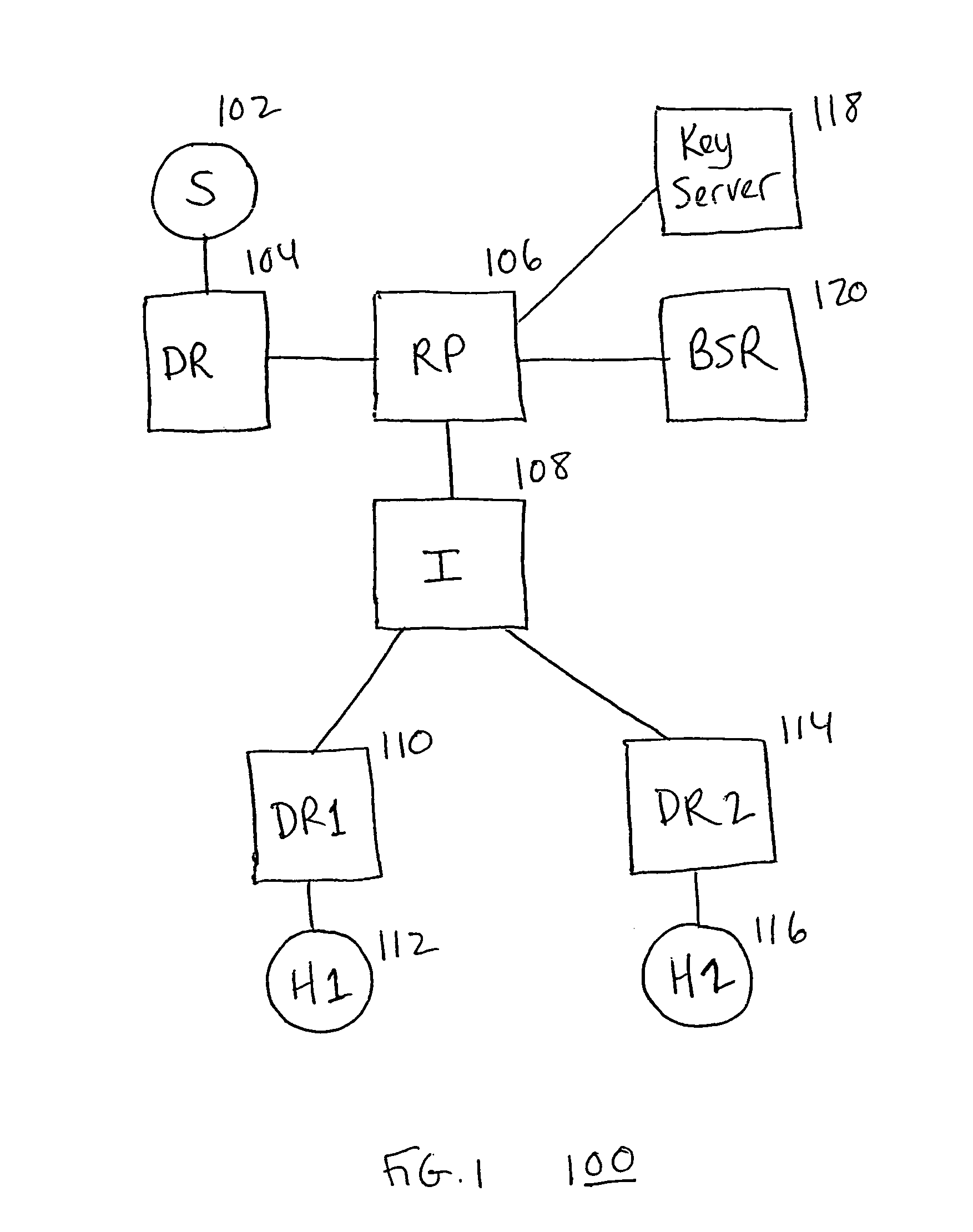
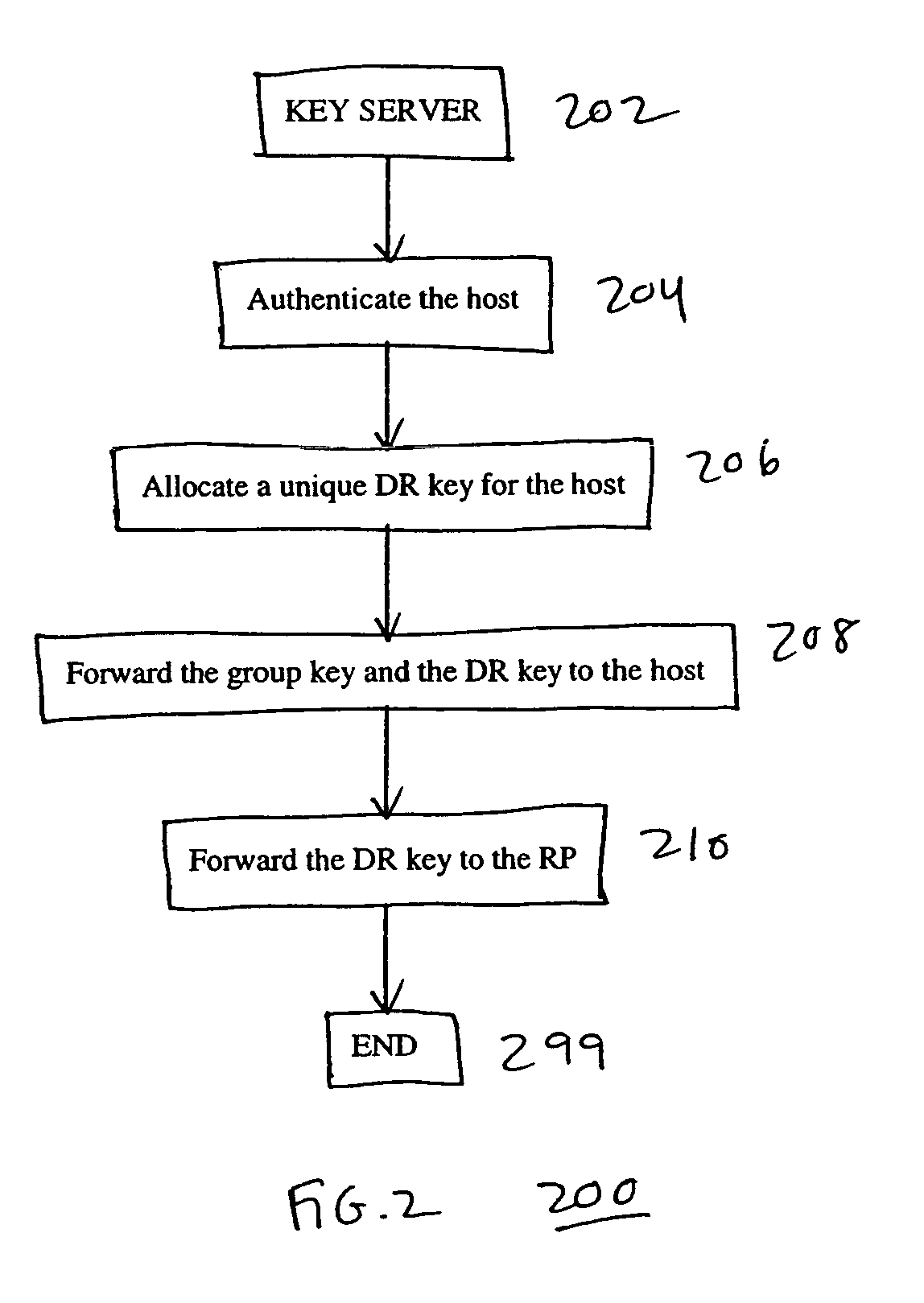
InactiveUS7360084B1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsDistribution treeNetwork packet
A system, device, and method for controlling access in a multicast communication network uses a centralized host authentication scheme to prevent unauthorized hosts from joining a shared multicast distribution tree. Each authorized host is allocated a unique authentication key, which is used by the designated router to encode the PIM join message and by the rendezvous point router to authenticate the PIM join message. If the PIM join message is authentic, then each PIM router from the rendezvous point router to the designated router establishes appropriate multicast routes to route multicast packets to the host. If the PIM join message is not authentic, then multicast packets are prevented from reaching the host.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
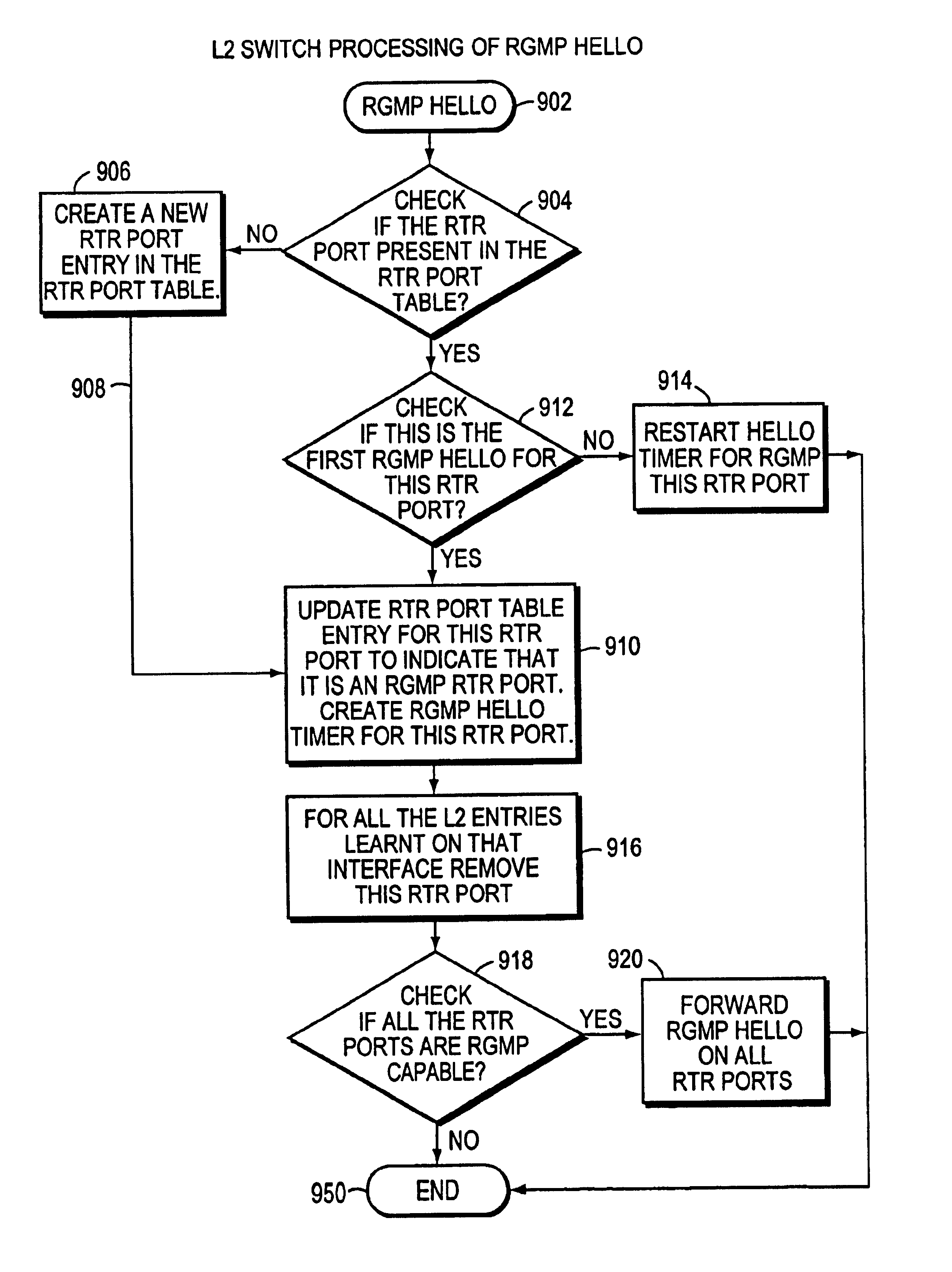
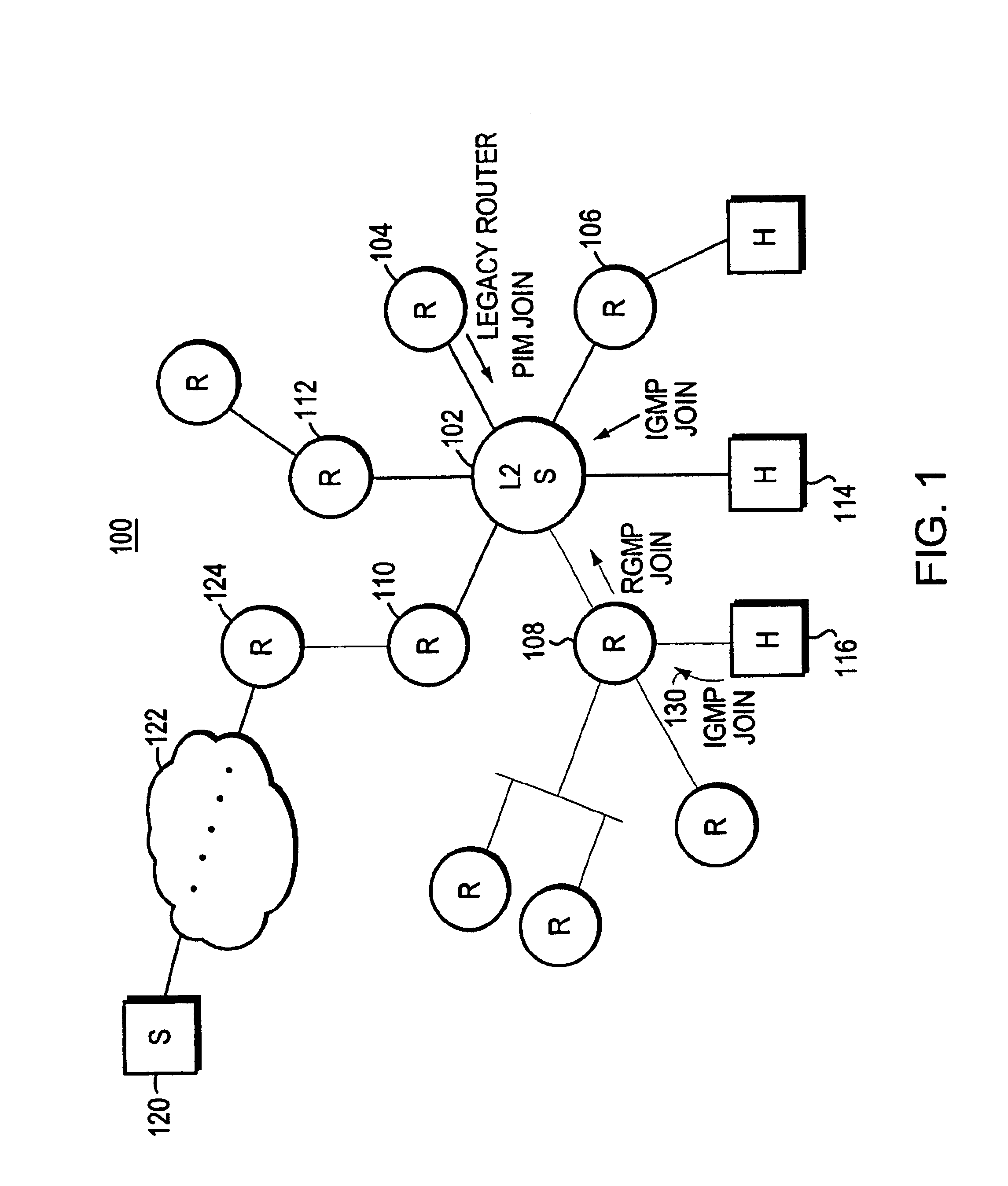
Multicast system for forwarding desired multicast packets in a computer network
InactiveUS6847638B1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationDistribution treeIP multicast
A method and apparatus for a router to inform a Layer 2 switch by use of packets of a new router group port management protocol (RGMP) that the layer 2 switch is to forward multicast packets of a specified group to the router. First the router transmits a RGMP HELLO packet to the layer 2 switch to inform the switch that the router is a multicast router implementing the invention. Then, in the event that the router receives an IGMP packet from an end station requesting multicast packets of a particular group, in response the router sends an RGMP JOIN packet to the layer 2 switch. The RGMP JOIN packet requests that the layer 2 switch forward only multicast group packets, of the group whose group number is written into a field of the RGMP JOIN packet, to the router. Also, the router sends a prior art PIM JOIN packet to other multicast routers in order to be placed on the multicast distribution tree for that group. The layer 2 switch builds a forwarding table for multicast groups listing ports connected to routers having sent a RGMP JOIN for that group. When a multicast group packet arrives at the layer 2 switch, the switch uses the forwarding table to forward the packet only to those routers requesting that group.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and systems for streaming data
InactiveUS20050185578A1Minimize impactSpecial service provision for substationError preventionData packDistribution tree
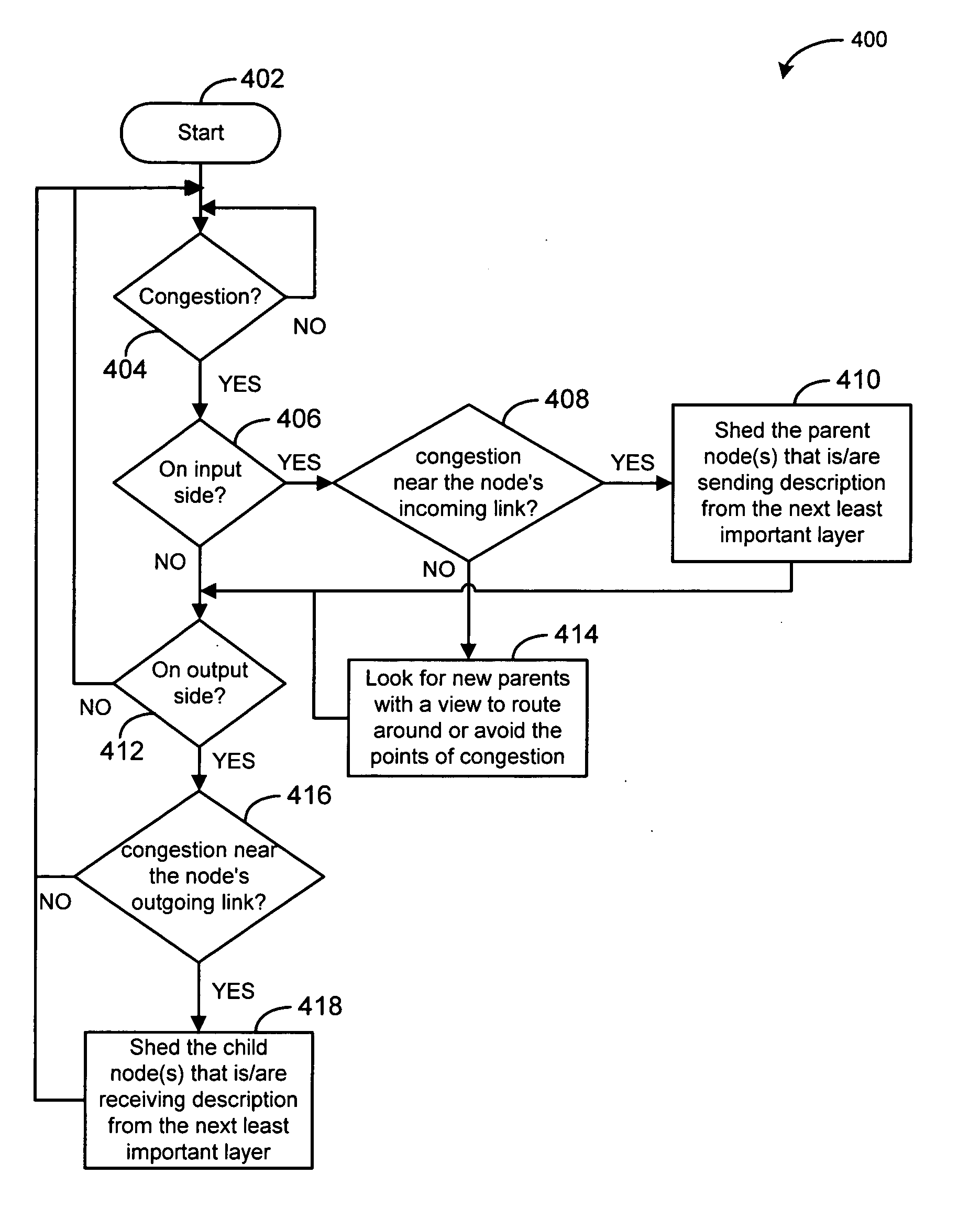
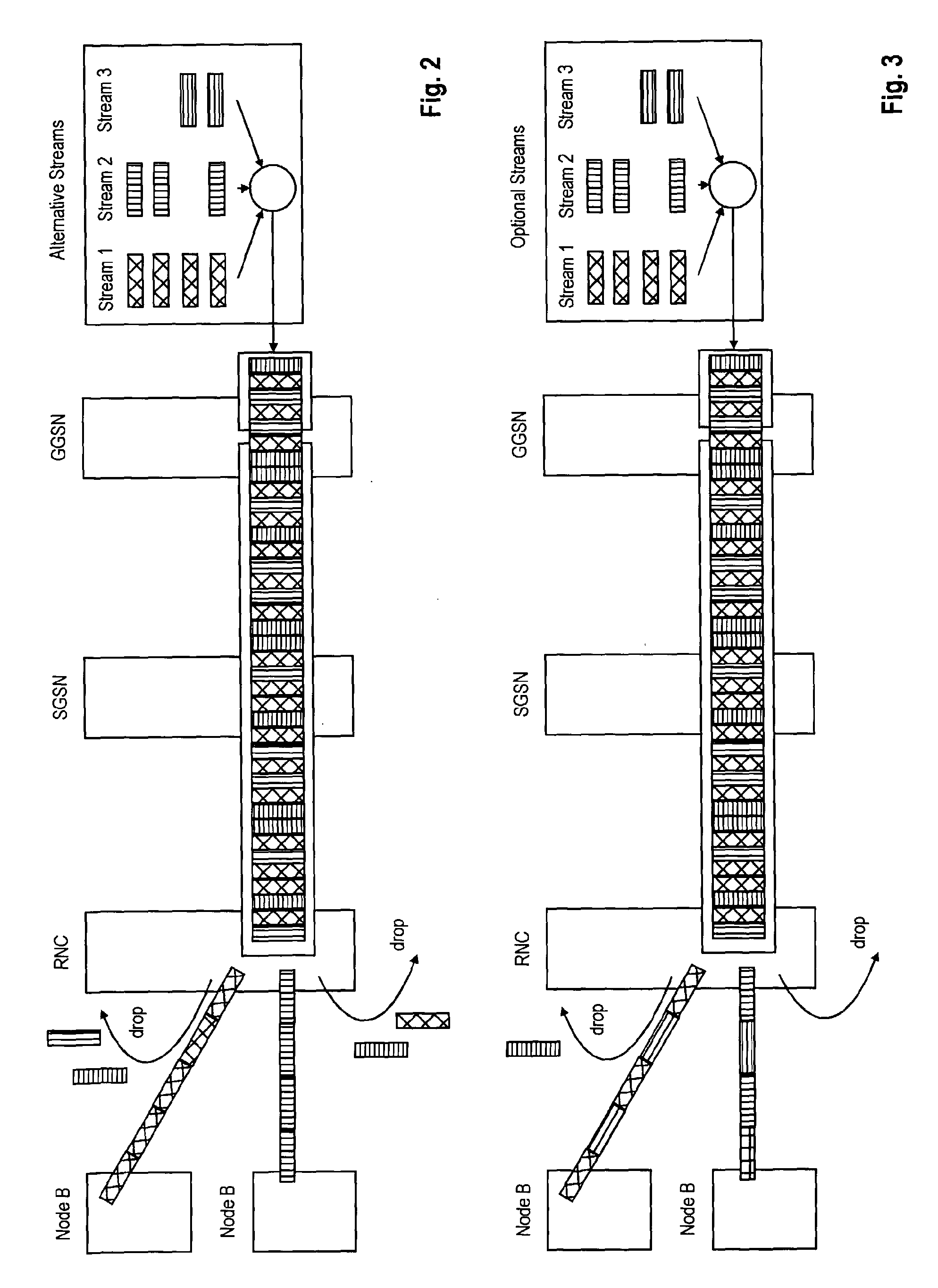
A technique is disclosed that can efficiently control congestion, while supporting heterogeneity for streaming data among multiple computers in a network. A plurality of nodes is divided into a plurality of distribution trees within a computer network, wherein the data is divided into a plurality of prioritized layers. When a node experiences packet loss, the location of the congestion is inferred. If the congestion is at or near the outgoing link, outgoing traffic is shed to alleviate the congestion by shedding child node(s) receiving descriptions in the least important layer of data that the child node(s) are receiving. Similarly, if the congestion is at or near the incoming link, incoming traffic is shed by shedding parent nodes that are sending descriptions in the least important layer of data that the node is receiving. Nodes with available bandwidth are further instructed to subscribe to additional descriptions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
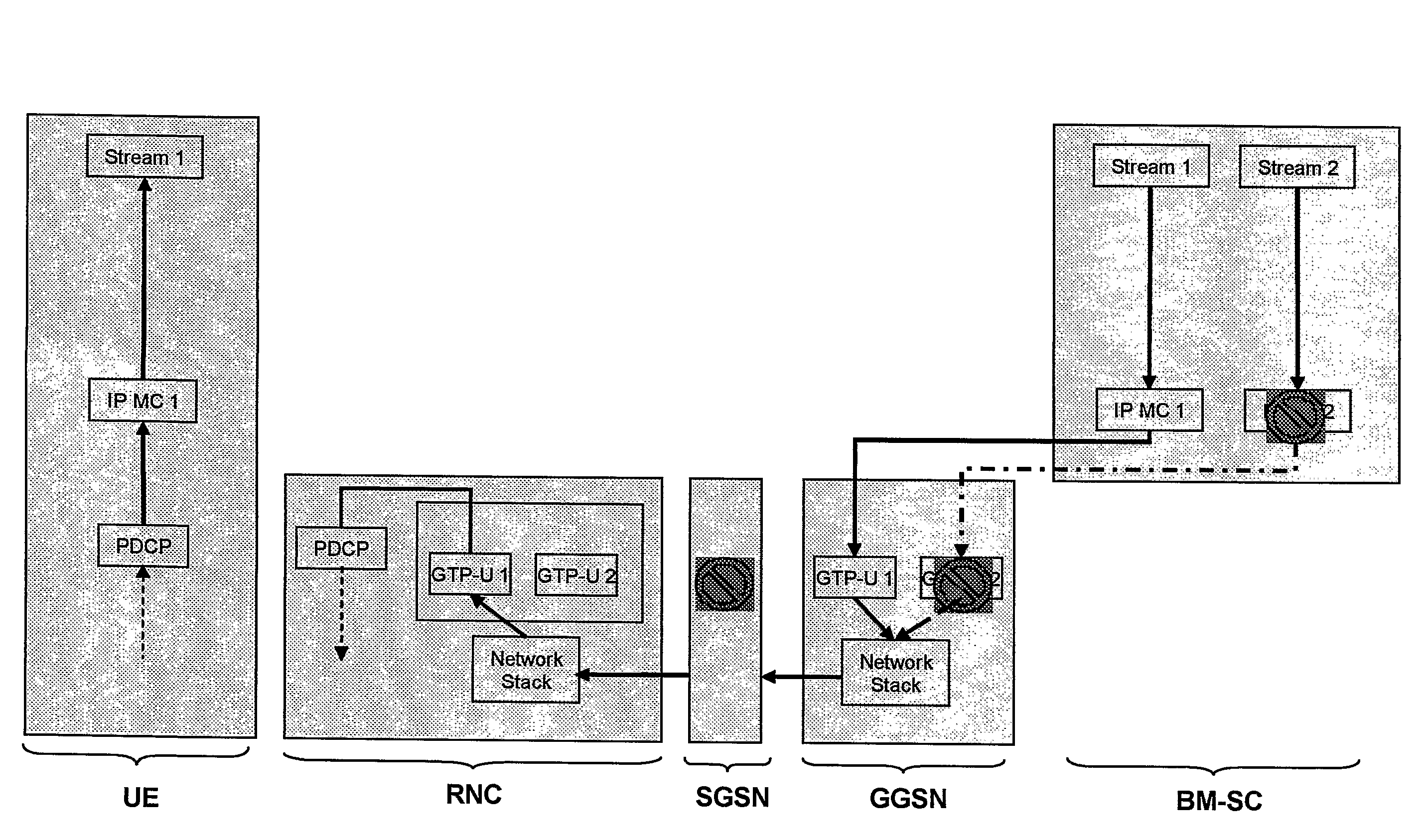
Adaptive and Scalable Qos Architecture for Single-Bearer Multicast/Broadcast Services
ActiveUS20080212583A1Increase the number ofImprove service qualitySpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementDistribution treeQuality of service
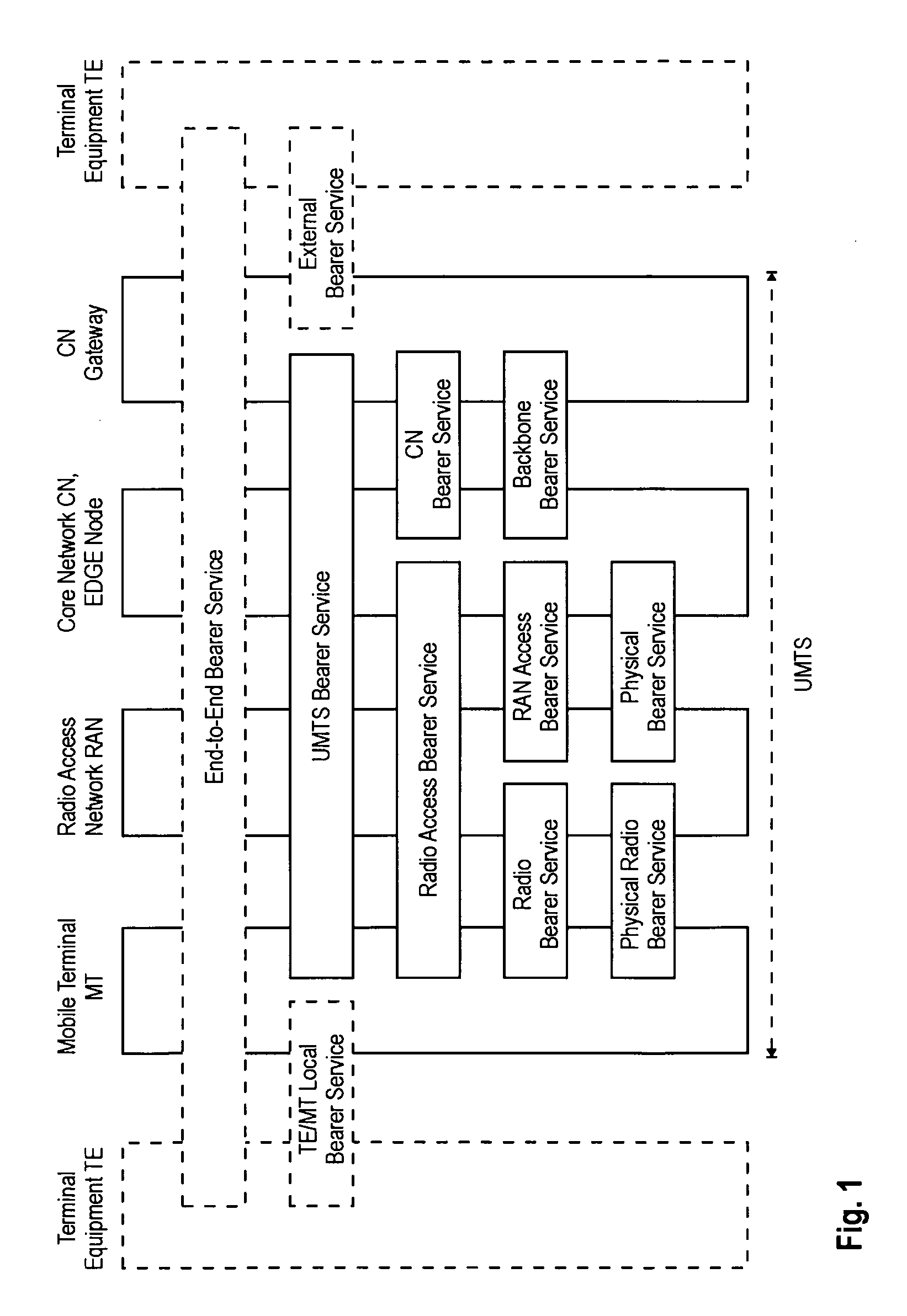
The present invention relates to a method for filtering a multiplexed packet stream in a network entity of the core network or the radio access network of a mobile communication system. The multiplexed packet stream provides a multicast or broadcast service and is delivered from a service center via the network entity to a mobile terminal. Further, the network entity comprises a service manager providing a quality-of-service management function. The invention further relates to a network entity provided with filtering capabilities, as well as to a communication system comprising the network entity. To provide an adaptive multimedia broadcast / multicast service QoS architecture that is scalable to a great number of users the invention suggests providing the service in form of a multiplexed packet stream via a single bearer service an equipping nodes within the distribution tree of the service filter capability allowing to filter the multiplexed stream based on the downlink quality-of-service constraints obtained from a service manager.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Router-assisted multicast congestion control
InactiveUS7035217B1Convenient and expandable methodError preventionTransmission systemsLoss rateDistribution tree
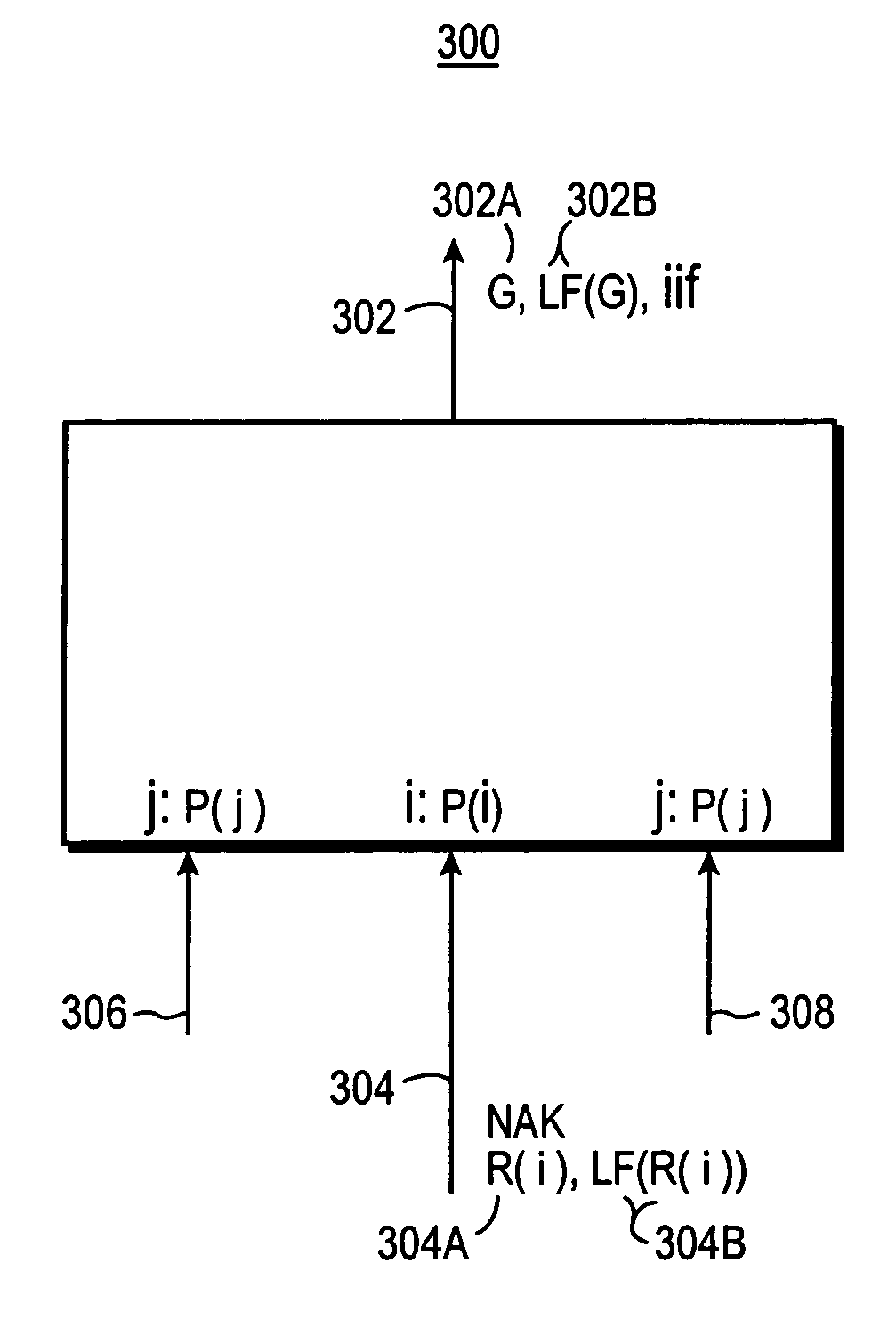
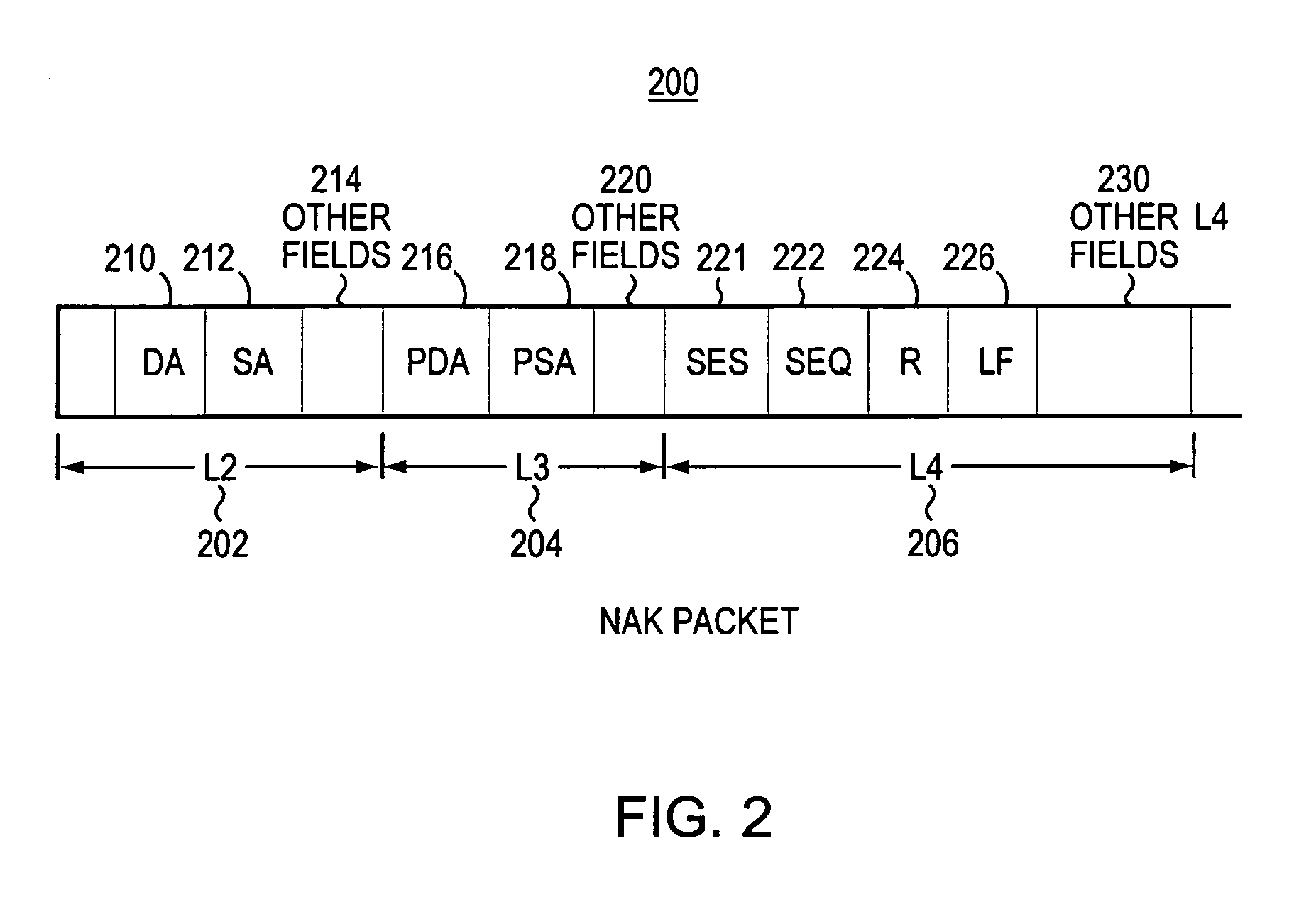
The invention provides a convenient and expandable method for transmitting one or more loss rate statistics determined in a distributed manner from a multicast distribution tree to a source computer. First, the loss rate statistics are collected in a distributed manner from target receiver stations, and from routers in the multicast distribution tree. Second, there is a distributed calculation of statistics on loss rate by routers in the multicast distribution tree. Third, there is transportation of the loss rate statistics back to the source computer in reverse along the multicast distribution tree. For example, congestion information is collected by routers, and the congestion information is sent upstream to the multicast source station in fields of NAK messages. A router may receive a NAK packet in transit from an intended destination station to a source station, the NAK packet indicating loss of a data packet. The router writes a loss rate statistic determined by the router into a “loss rate field” of a message to be sent upstream along the reverse of the distribution tree. The router determines the loss rate statistic to be written into the loss rate field of the message, in response to: analyzing the loss rate statistics on each of its links; the loss rate reported by the incoming NAK packet; and, the elapsed time from the time stamp showing when the various loss rate statistics were determined.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
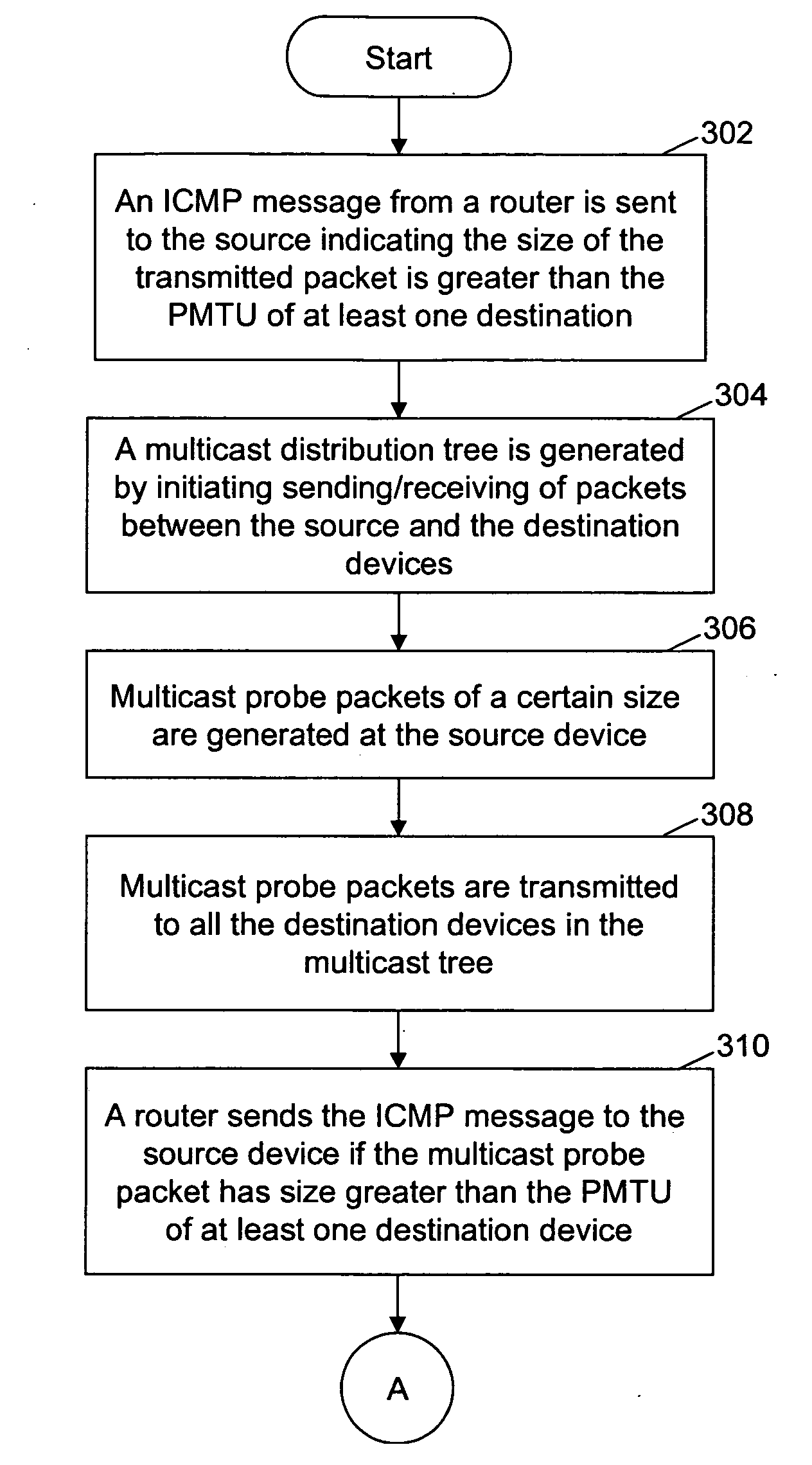
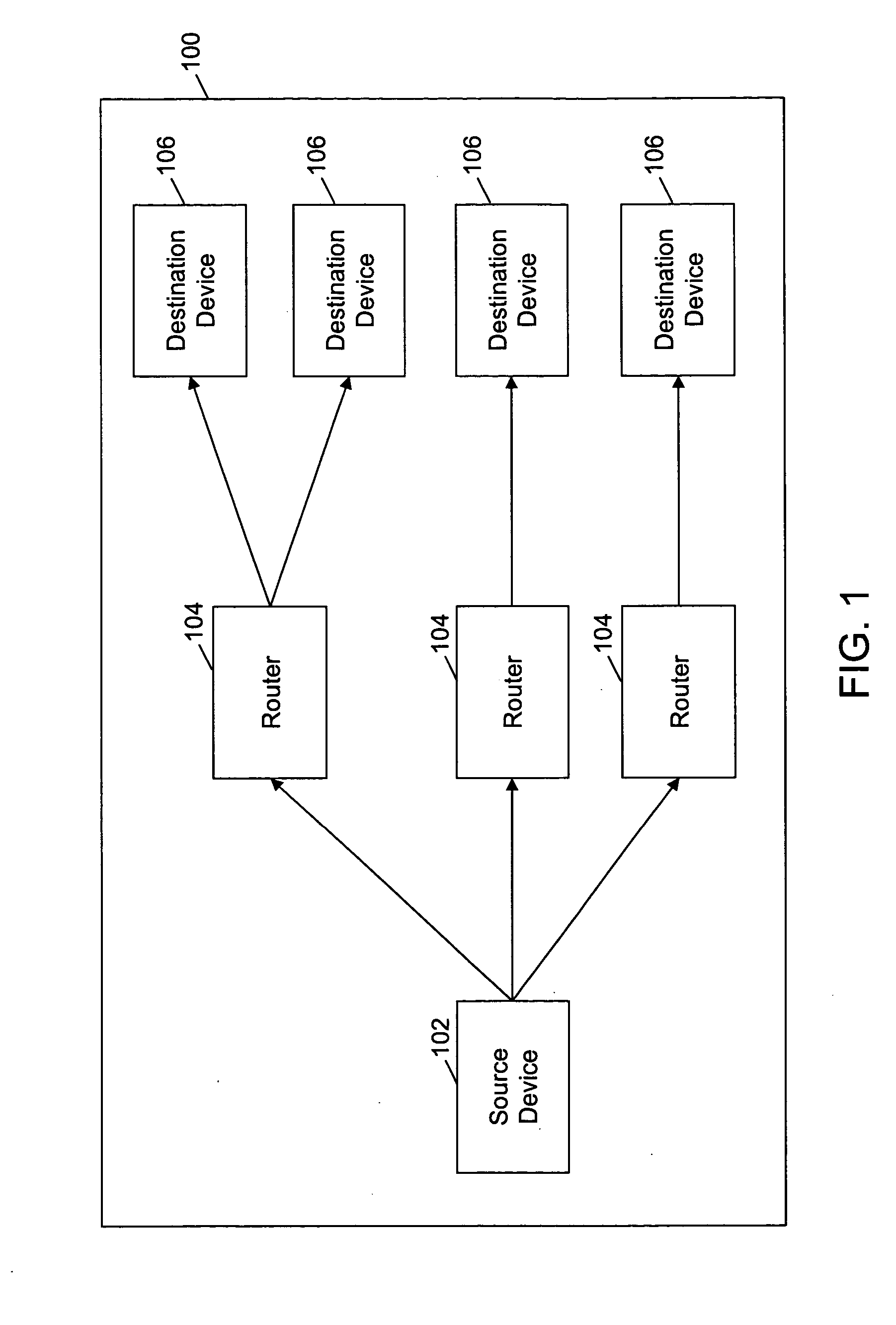
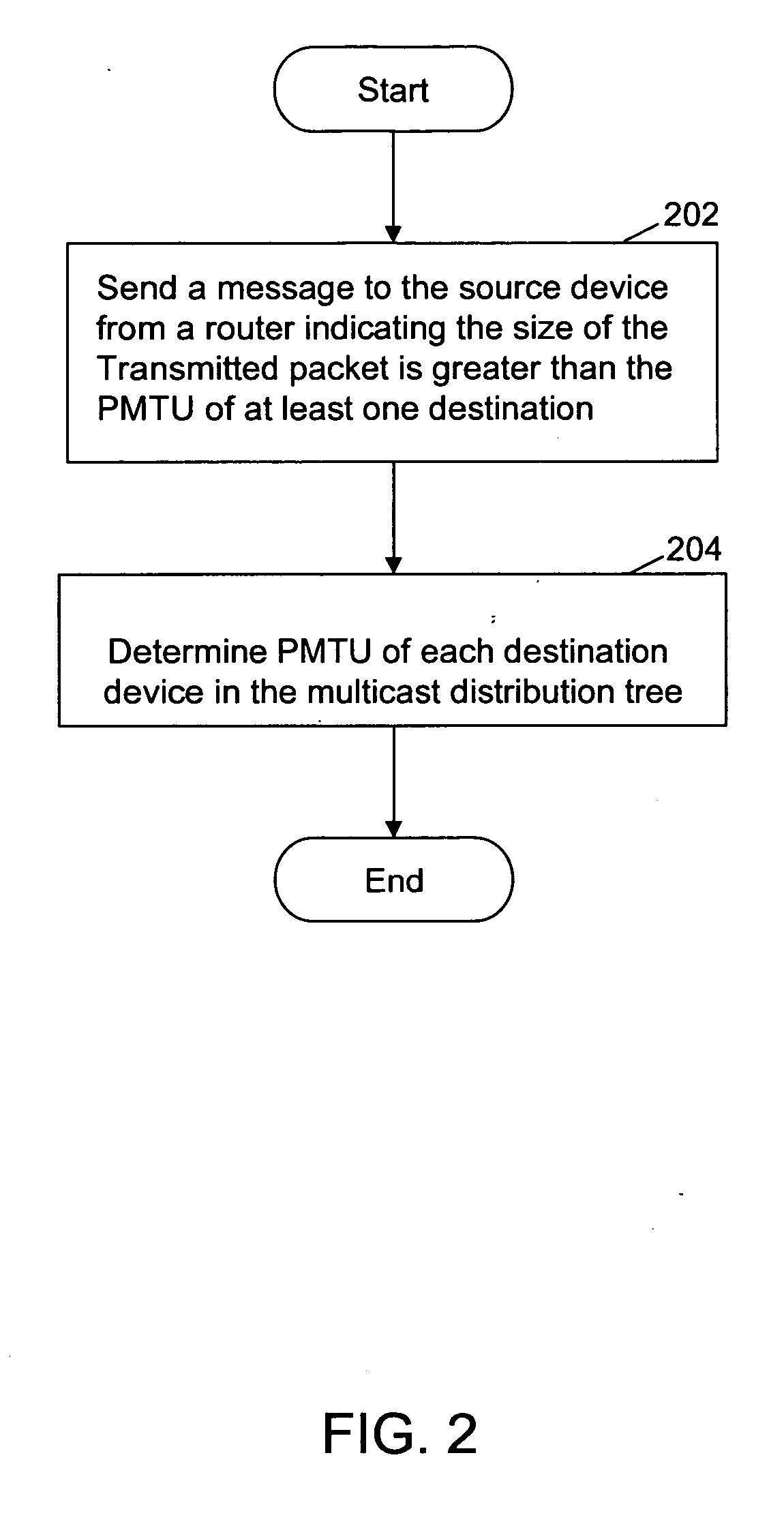
Method and system for determining path maximum transfer unit for IP multicast
InactiveUS20060221844A1Special service provision for substationError preventionTraffic capacityDistribution tree
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Source routing in multicast transmissions
ActiveUS20150049760A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationDistribution treeComputer network
The subject technology provides configurations for receiving, at a first network device, a multicast packet of a multicast transmission from a multicast source. A header is inserted including one or more fields of information for a multicast distribution tree into the multicast packet in which the fields of information include a root level node field indicating a root node of the multicast distribution tree and one or more second level fields indicating one or more child nodes of the root node of the multicast distribution tree. In one example, the fields of information are not duplicative of routing information, stored by the first network device, corresponding to the one or more child nodes. The subject technology then forwards the multicast packet including the inserted header to respective network devices corresponding to the one or more child nodes based on the one or more fields of information from the inserted header.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Method and system for intelligently forwarding multicast packets
ActiveUS7389359B2Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexDistribution treeNetwork packet
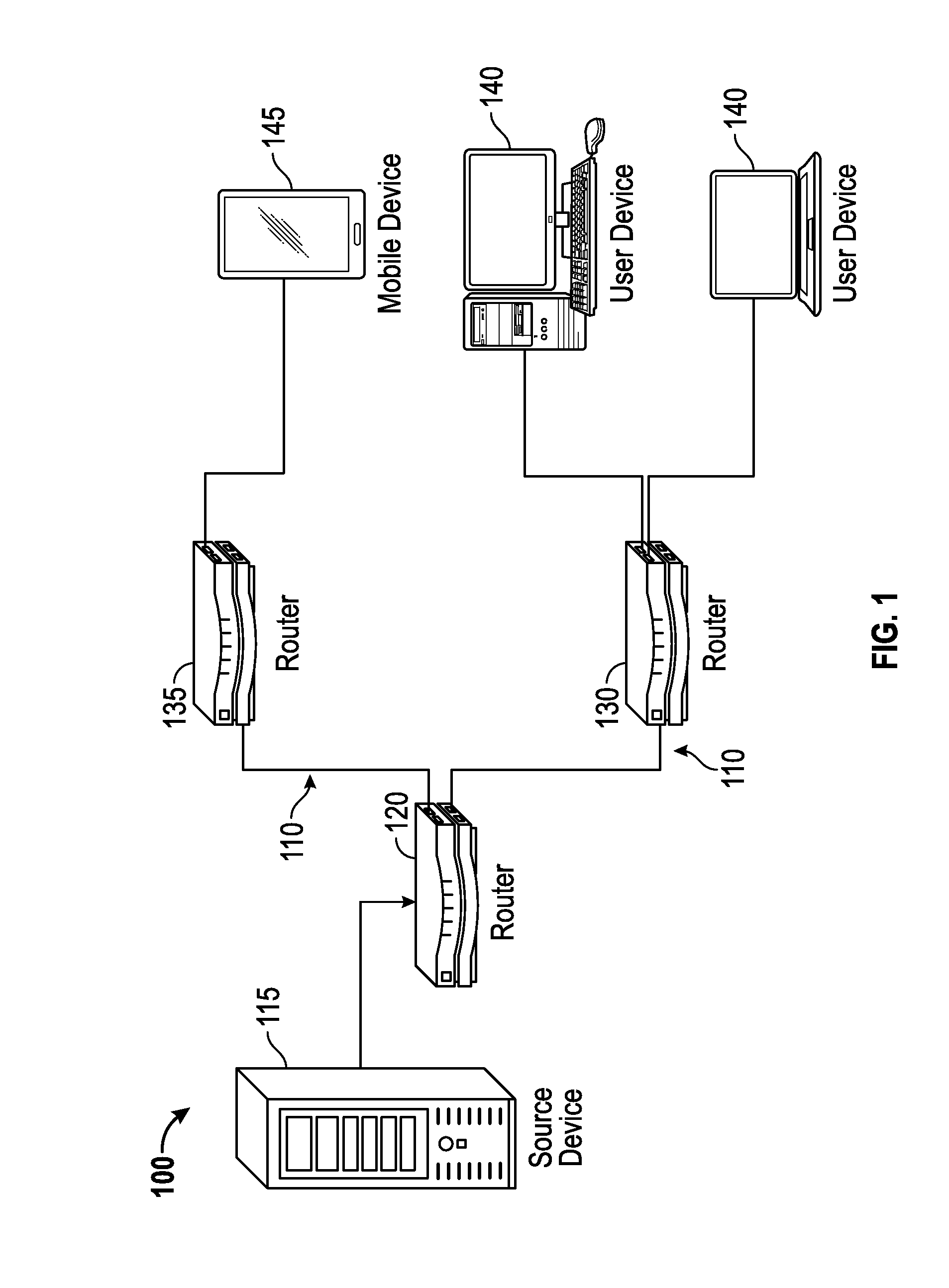
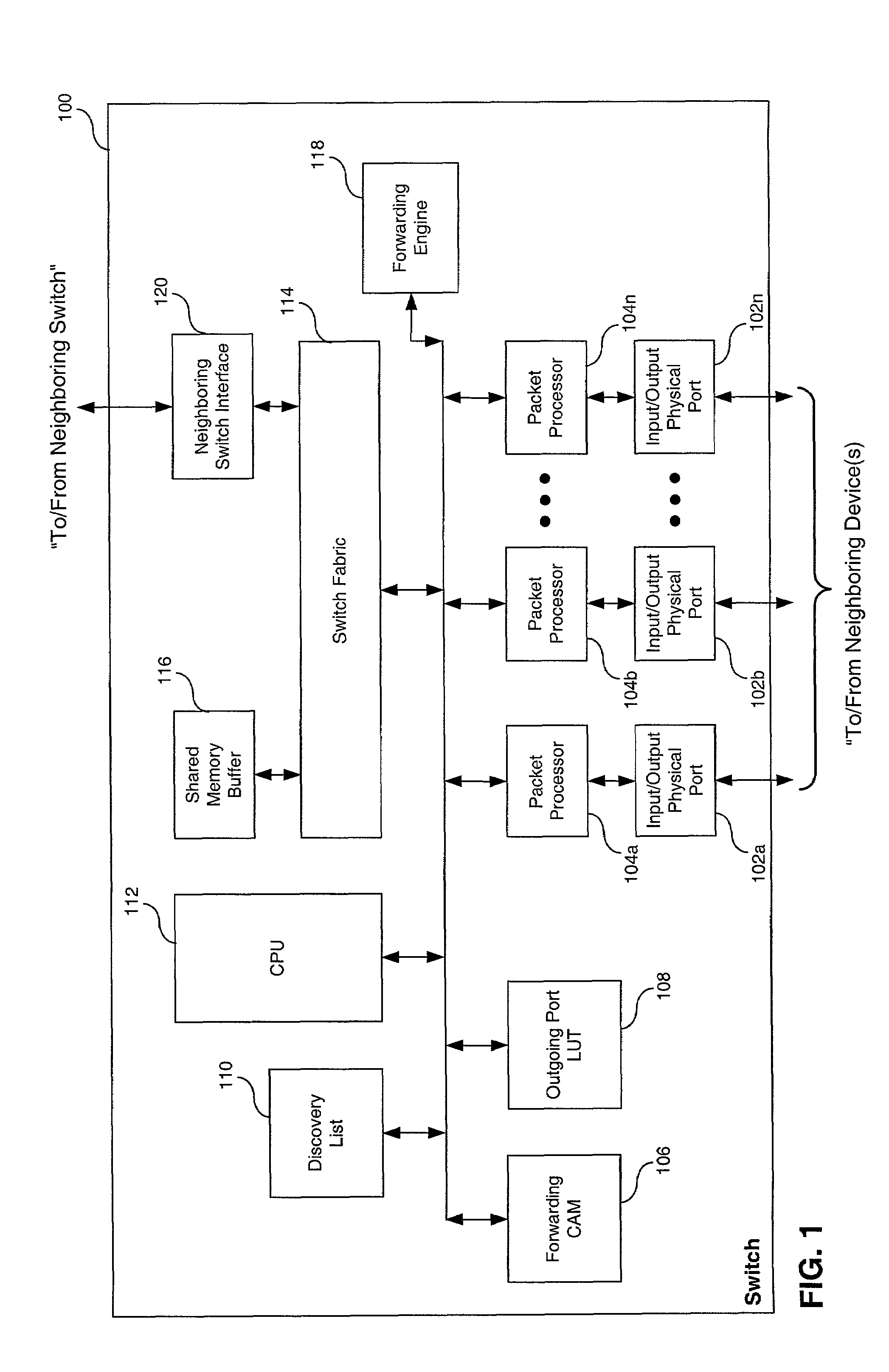
A routing system utilizes a layer 2 switch interconnecting several routers to intelligently forward multicast packets throughout an internet exchange carrying multicast content. The layer 2 switch performs protocol snooping to extract a lookup key that is based on network layer protocol information. The lookup key is uniquely formulated to support either shared or explicit source distribution trees. The lookup key is used to query a forwarding memory that returns an outgoing port index. The outgoing port index points to one or more outgoing ports that are eligible to receive the multicast packet. The outgoing ports are also connected to the neighboring device(s) that are designated to receive the multicast packet. The routing system also supports real time maintenance and updating of the forwarding memory based on the periodic exchange of control messages. The routing system is configured to support PIM routers operating in PIM SM or PIM SSM modes. However, the routing system can also support other multicast protocols and / or standards.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
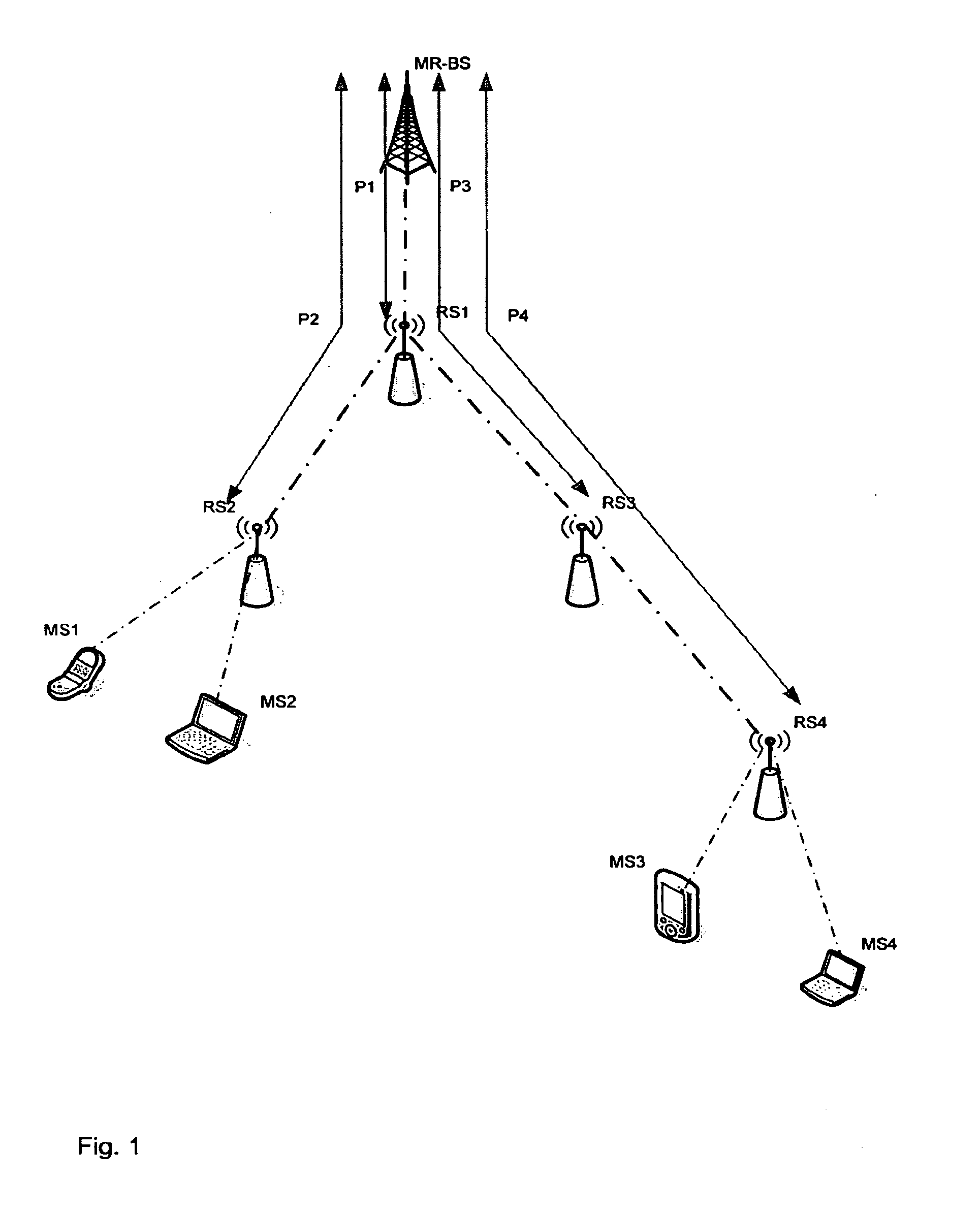
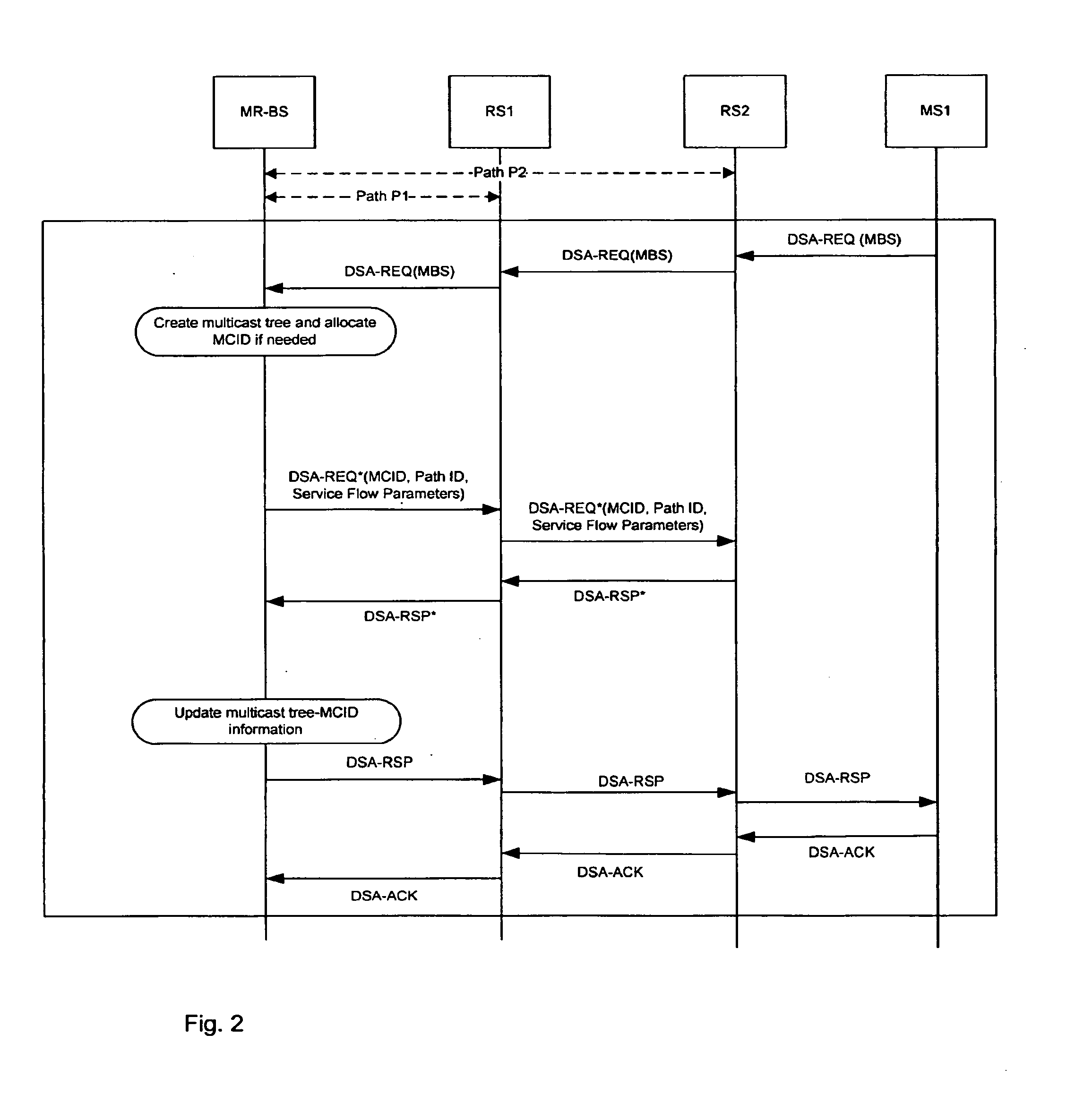
Multicast distribution tree establishment and maintenance in a wireless multi-hop relay communication system
ActiveUS20100046400A1Effective distributionNetwork topologiesBroadcast transmission systemsDistribution treeMulti hop relay
A method and apparatus for multicast communications in a multi-hop relay network are described including sending an extended request message, wherein the request message includes a multicast connection identification, multicast distribution tree information and a path identification and receiving an extended response message. Correspondingly, a method and apparatus for multicast communications in a multi-hop relay network are described including receiving an extended request message, wherein said request message includes a multicast connection identification, multicast distribution tree information and a path identification and sending an extended response message.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
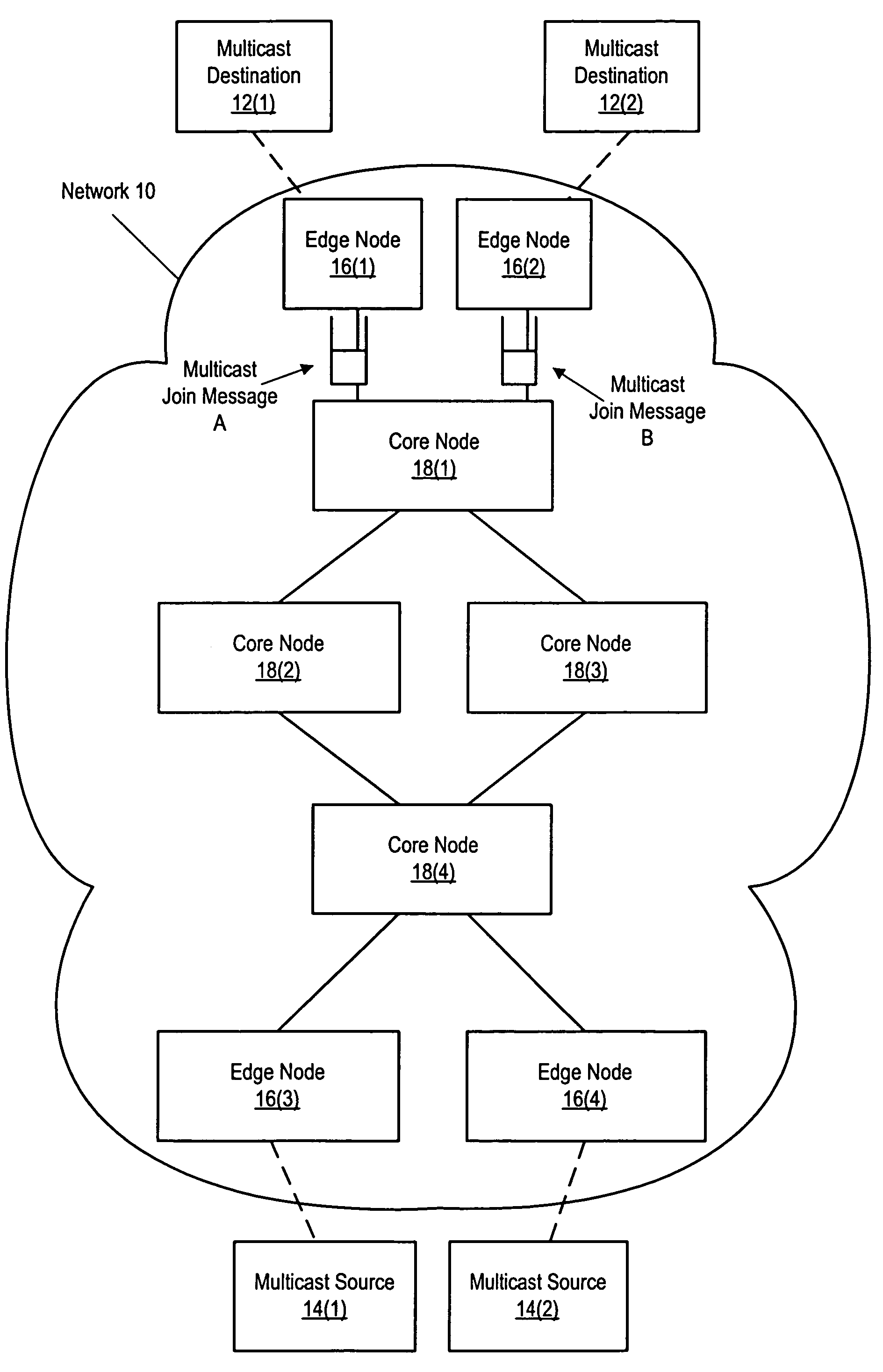
System and method for resolving conflicts in proxy routing information associated with multicast distribution trees
A first message, received from a first device, identifies a multicast distribution tree and includes first information associated with a route leading to a root of the multicast distribution tree. A second message, received from a second device, also identifies that tree, but the second message includes second information, which conflicts with the first information. In one embodiment, the conflict is resolved by building a first version of the tree based on the first information and building a second version of the tree based on the second information. The first version is used to forward multicast packets to the first device, while the second version is used to forward multicast packets to the second device. In another embodiment, the conflict is resolved by selecting either the first information or the second information, based on a policy, and then building a single version of the tree corresponding to the selected information.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
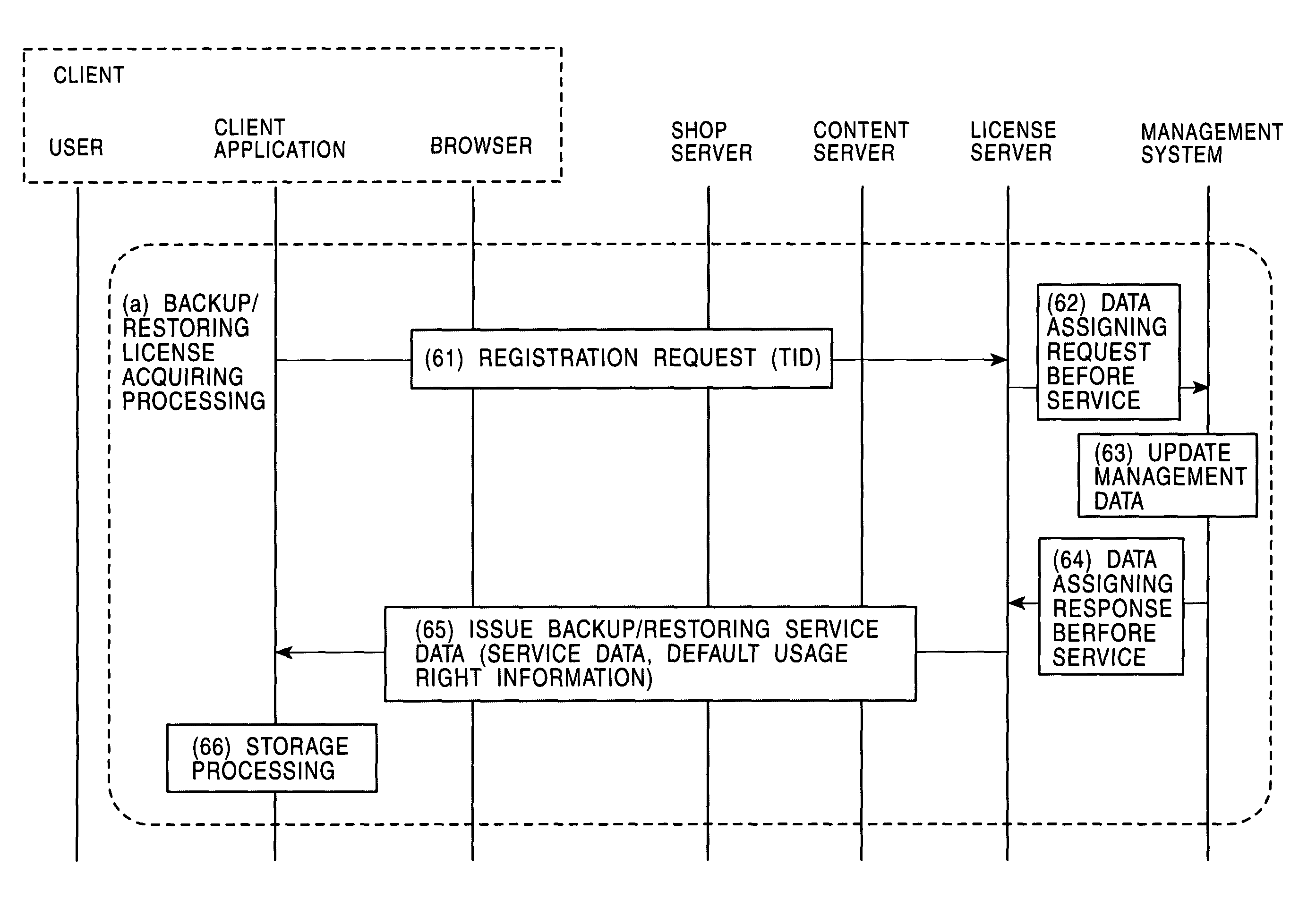
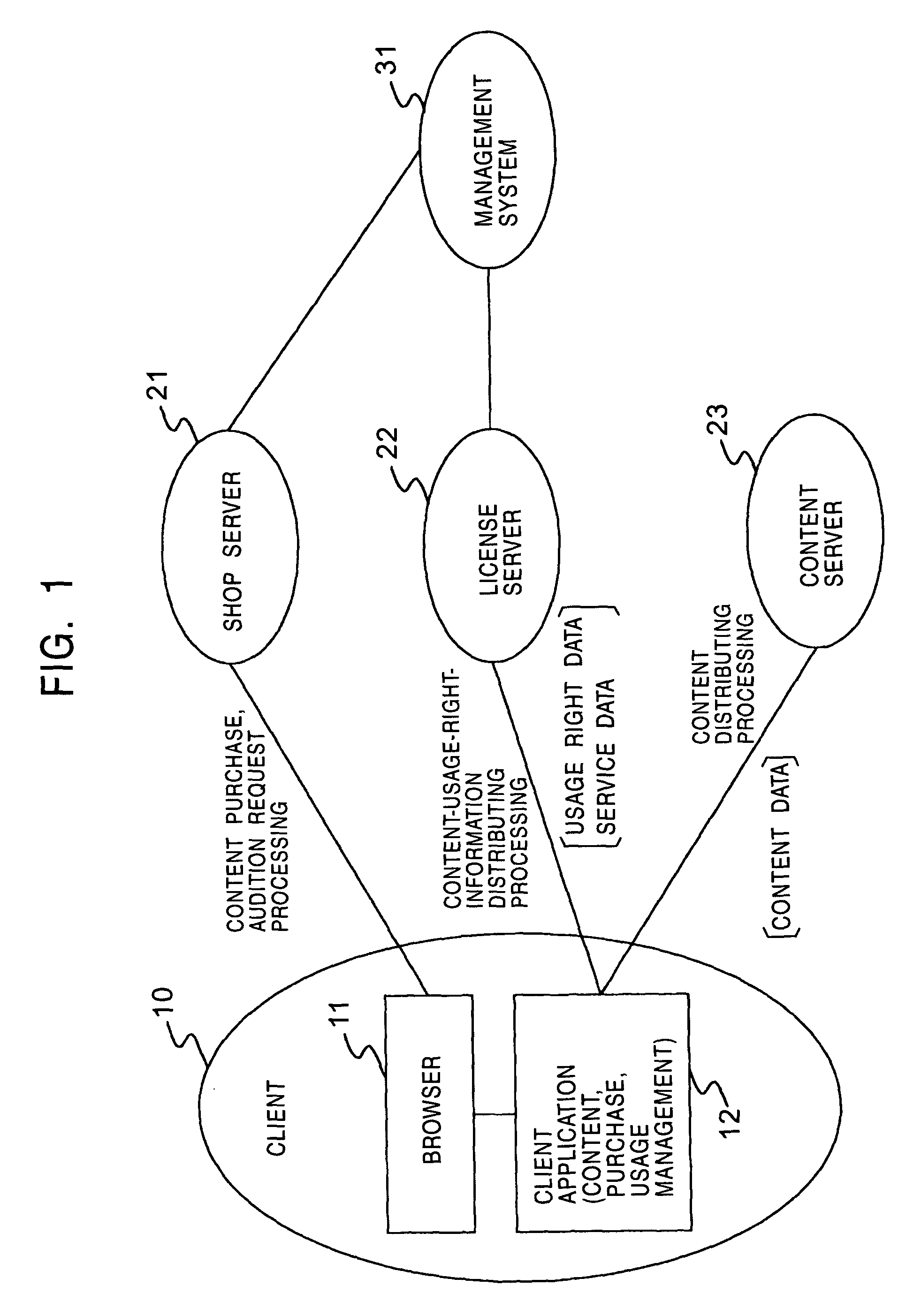
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and computer program used therewith
InactiveUS7836311B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsInformation processingDistribution tree
Service data or usage right information, used as purchased content or license information, is set so as to be re-acquired on condition that an acquirer is an authorized content-purchasing client. A leaf ID as a client identifier in an enabling-key-block distribution tree, and a restoring-processing requesting file including verification data for the leaf ID are used as client identifying data, whereby it is ensured that an authorized content-purchasing client is verified.
Owner:SONY CORP
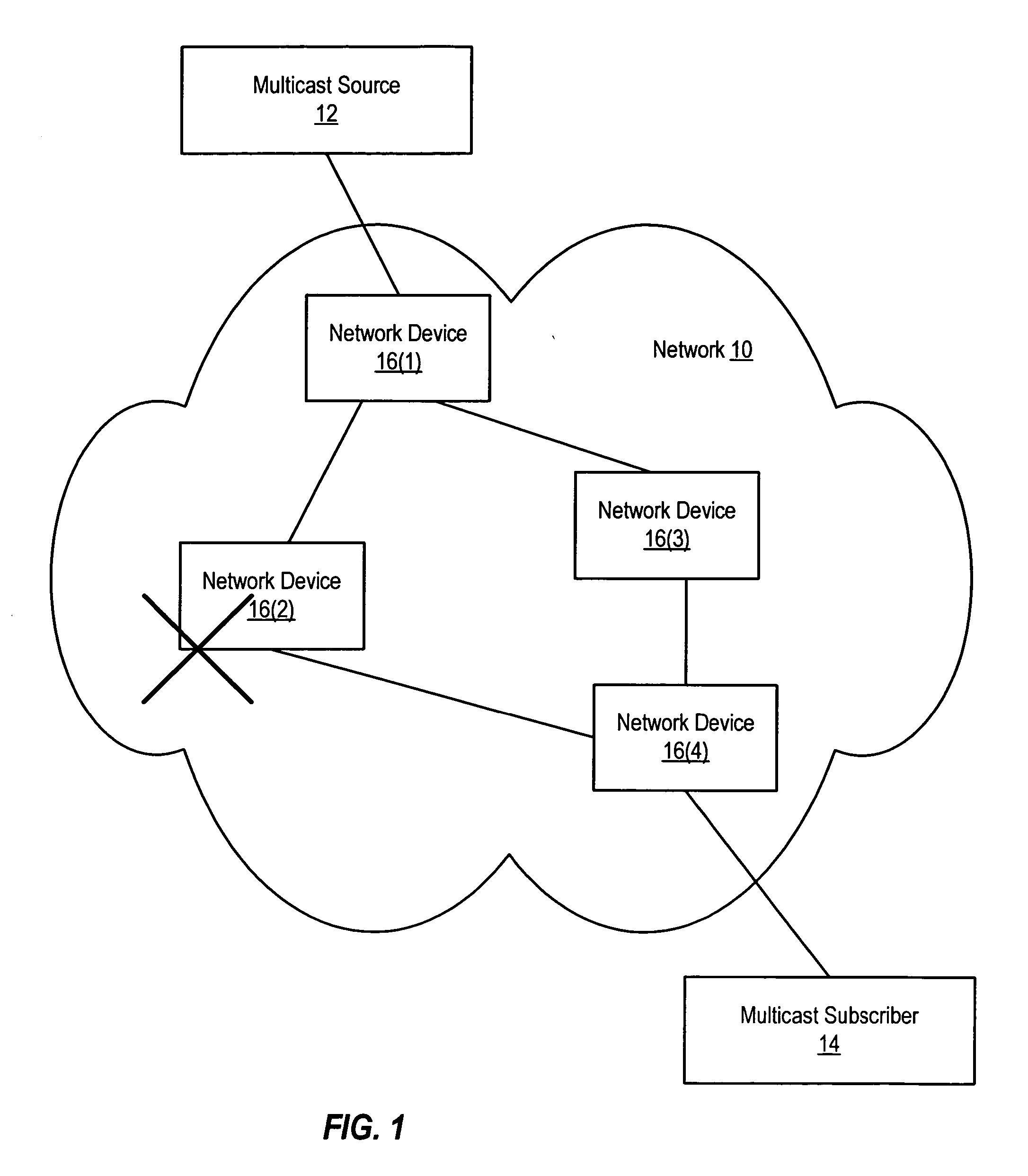
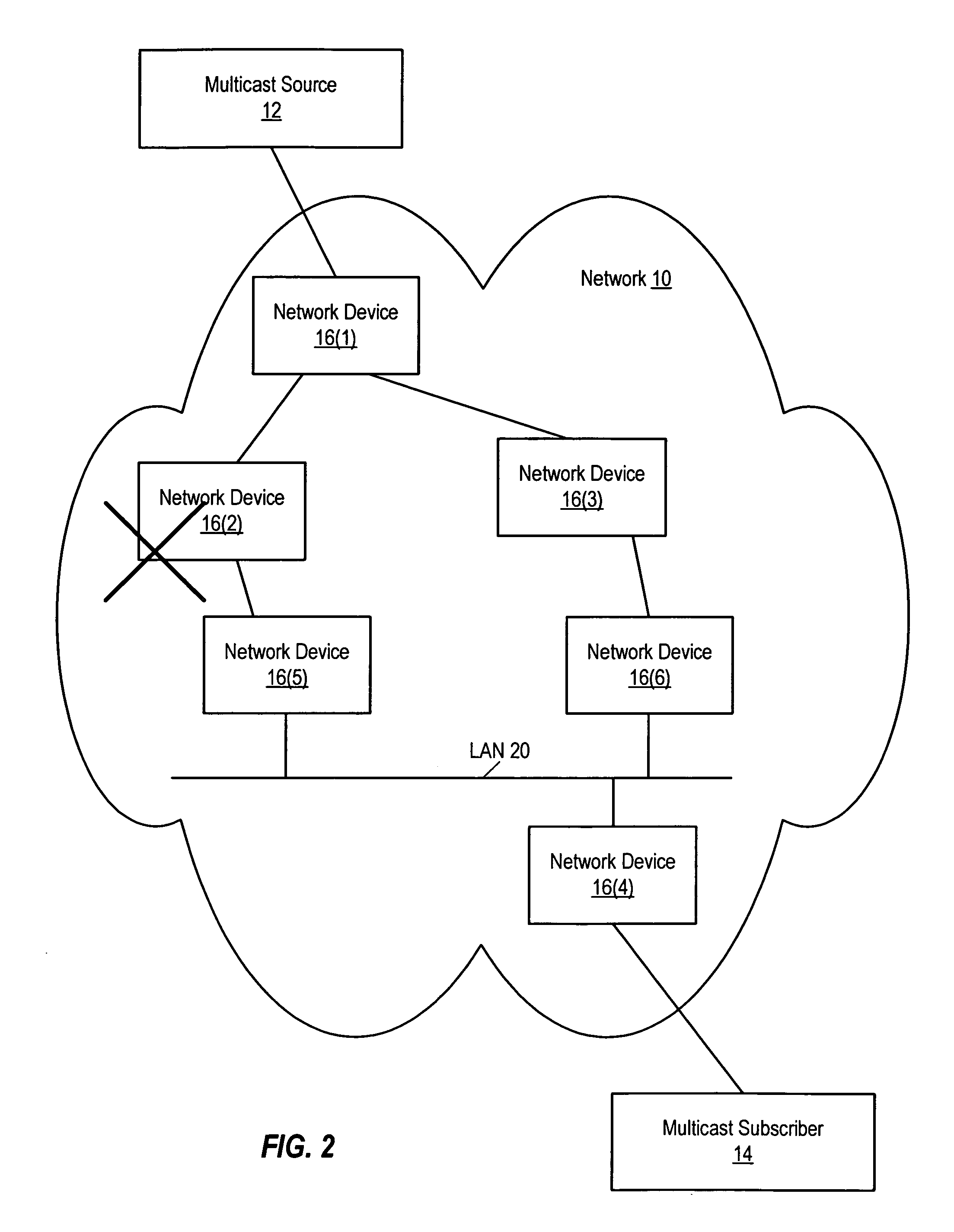
Rerouting multicast traffic in response to detecting imminent network disruption
Various systems and method for rerouting multicast traffic in response to detecting imminent network disruption are disclosed. One method involves detecting an imminent topology change and, in response, identifying a new multicast distribution tree for a multicast group. A join message for the multicast group is then sent towards a root of the new multicast distribution tree. Multicast traffic addressed to the multicast group continues to be forwarded via the current multicast distribution tree, subsequent to sending the join message. The multicast traffic is not forwarded via the new multicast distribution tree until one or more multicast data packets have been received via the new multicast distribution tree.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for multicast cloud with integrated multicast and unicast channel routing in a content distribution network
InactiveUS7373394B1Faster and efficientLess efficientData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsDistribution treeContent distribution
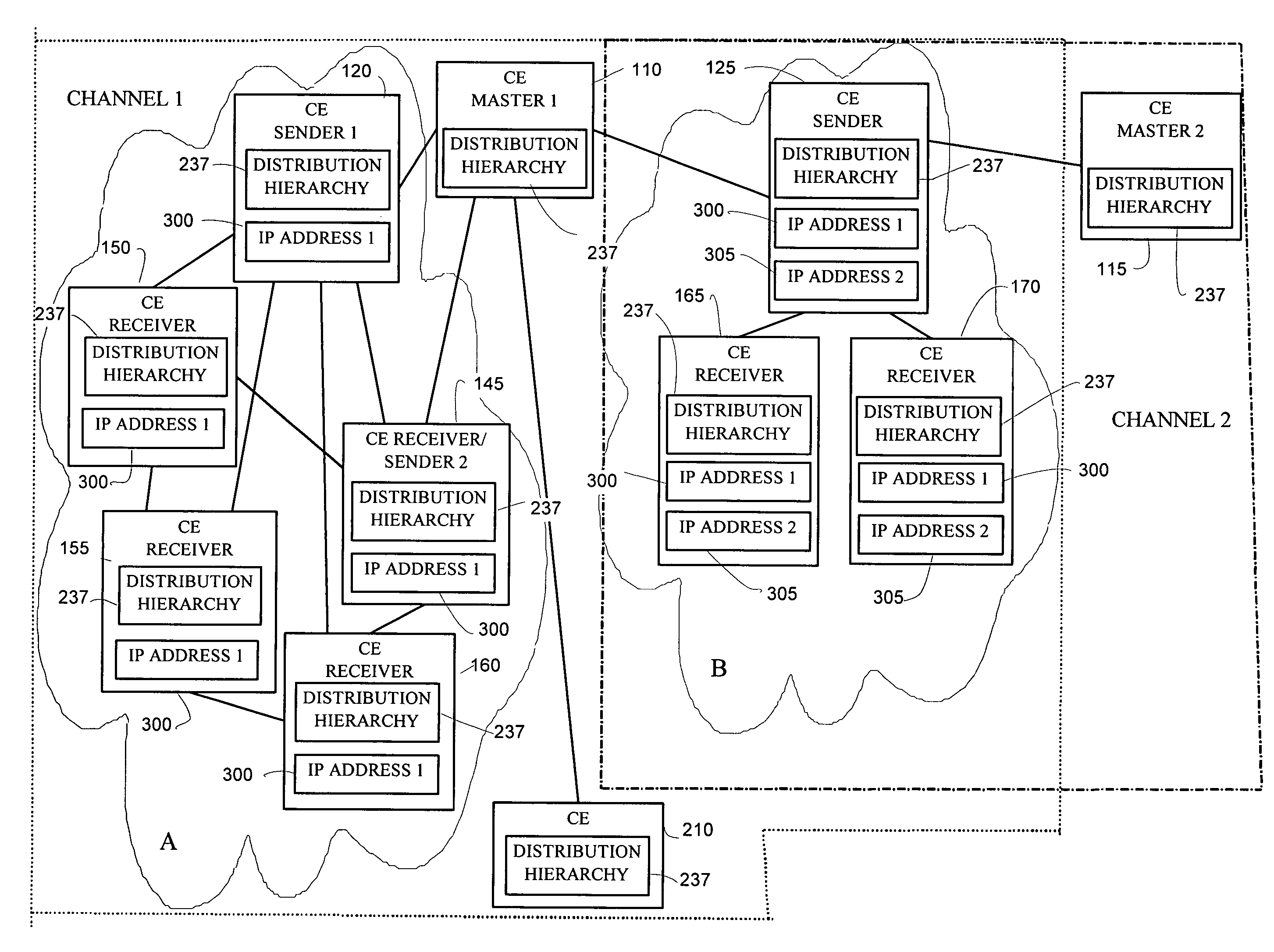
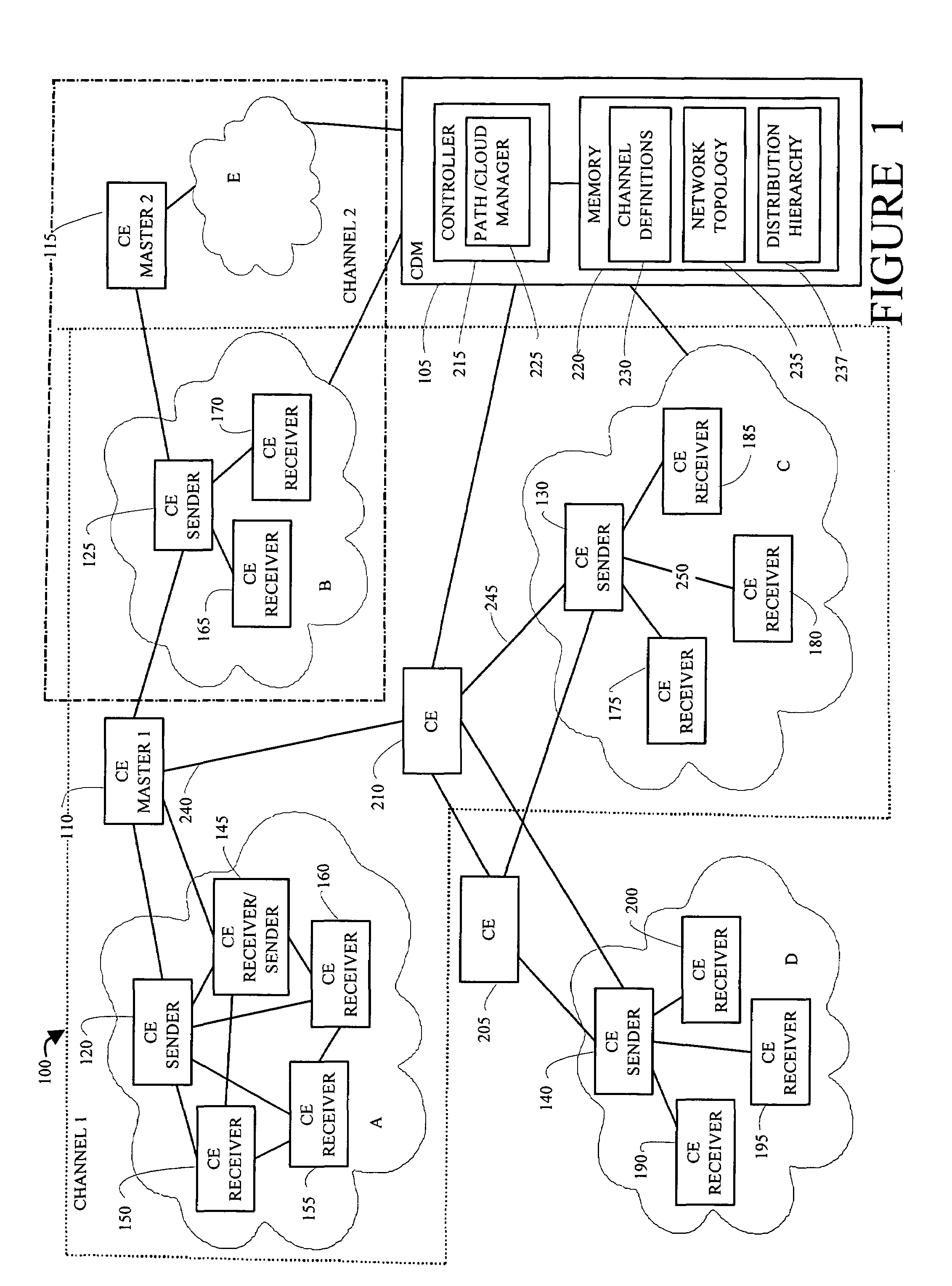
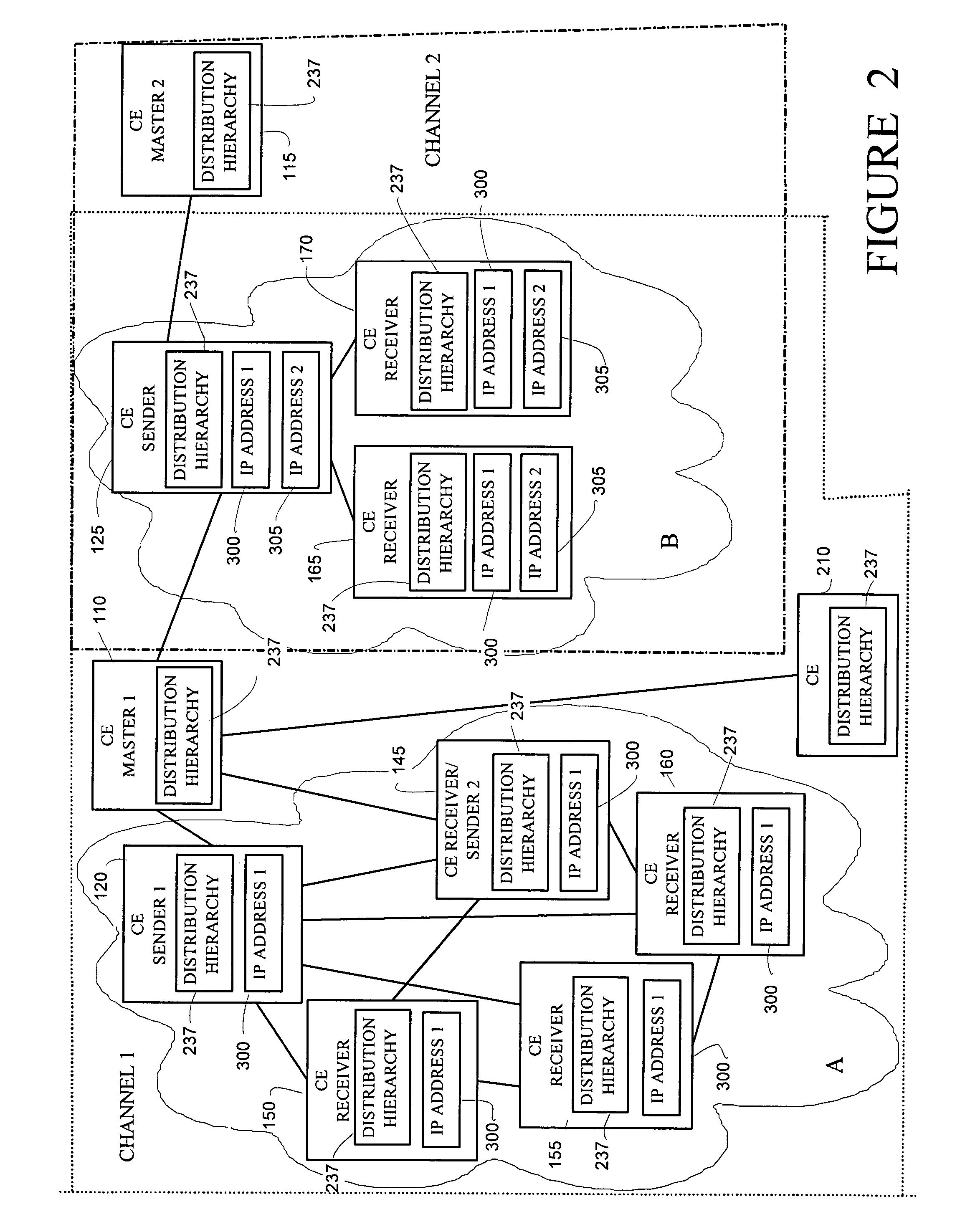
An apparatus and method for defining content distribution paths in a content distribution network integrate unicast and multicast connections. Content engines in the content distributed network are organized into channels with a master content engine maintaining specific content. The content distribution network is further organized into a distribution hierarchy based on network topology and channel definitions, first by establishing unicast paths through the content distributed network and then by integrating multicast paths into the unicast hierarchy. The further organization of the content distribution network establishes distribution trees from the channel masters to the network edges.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for peer-to-peer multi-party voice-over-IP services
A system, method, and computer program product for establishing multi-party VoIP conference audio calls in a distributed, peer-to-peer network where any number of nodes are able to arbitrarily and asynchronously start or stop producing audio output to be mixed into a single composite audio stream that is distributed to all nodes. A single distribution tree is used that has optimal communications characteristics to distribute the composite audio signal to all nodes. An audio mixing tree is established and maintained by adaptively and dynamically adding and merging intermediate mixing nodes operating between user nodes and the root of the single distribution tree. The intermediate mixing nodes and the root of the single distribution tree are all hosted, in an exemplary embodiment, on user nodes that are endpoints of the distribution tree.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
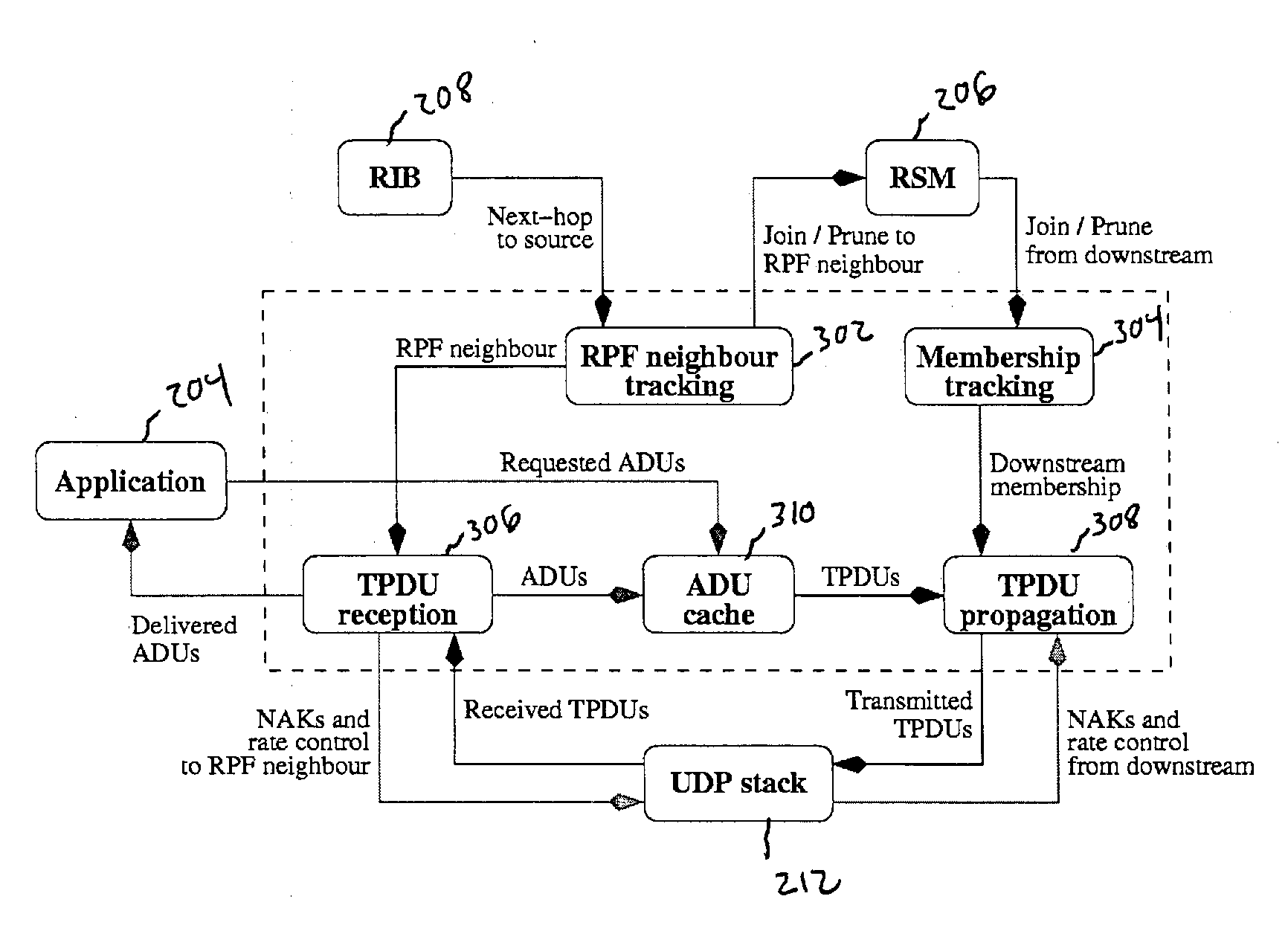
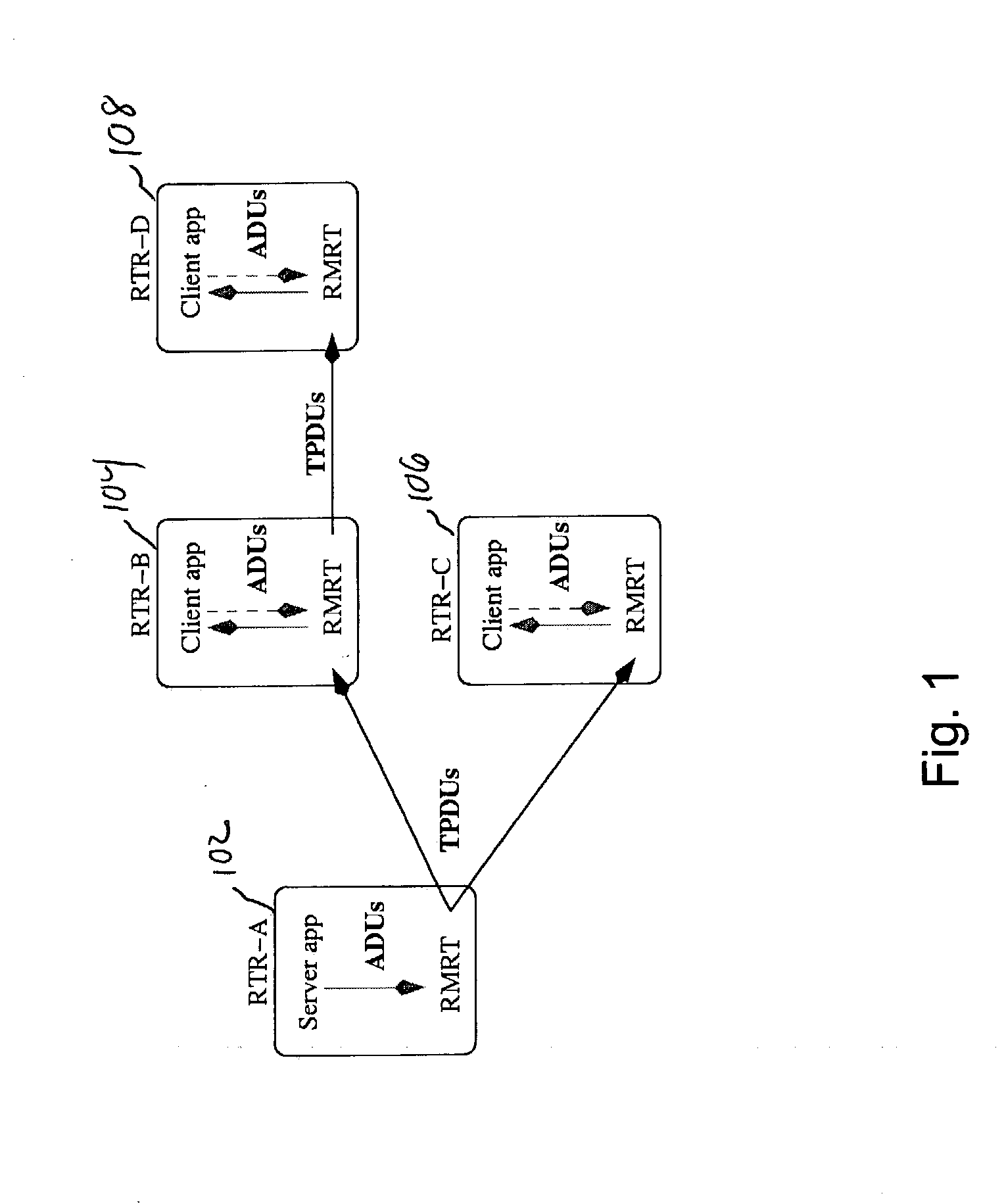
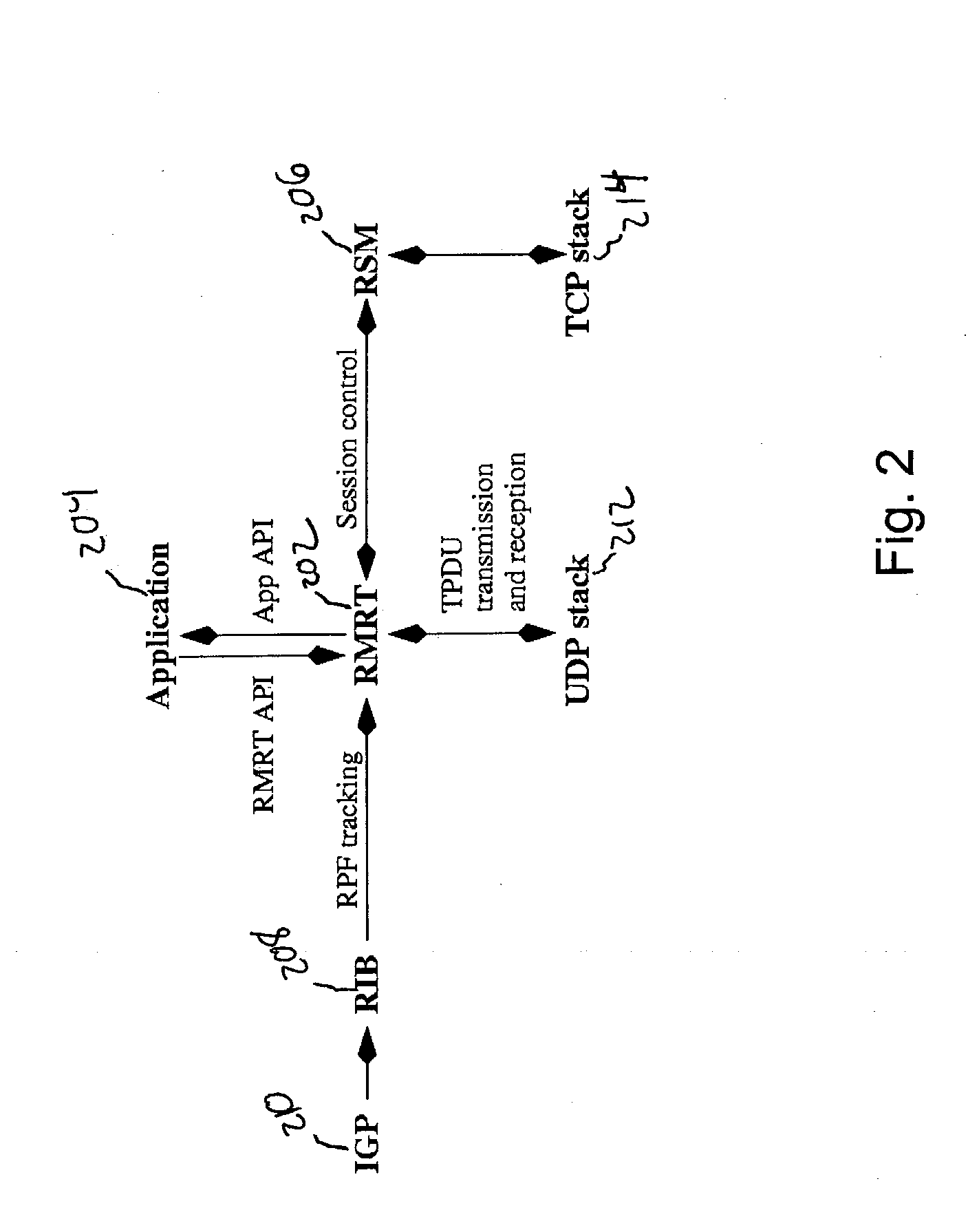
RPF multi-party reliable transport
InactiveUS20080077710A1Special service provision for substationData processing applicationsSingle sessionTransmission protocol
A multi-party reliable transport protocol for use by a higher layer application. A single session source distributes database updates to multiple receivers via a distribution tree. A node desiring to join a session selects a directly-connected node on a path upstream to a source by accessing unicast routing protocol information and sends a “Join” message to this upstream neighbor. Each node participating in the scheme handles retransmission requests from its directly-connected downstream neighbors. A supported application provides storage of previously transmitted information for potential retransmission.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
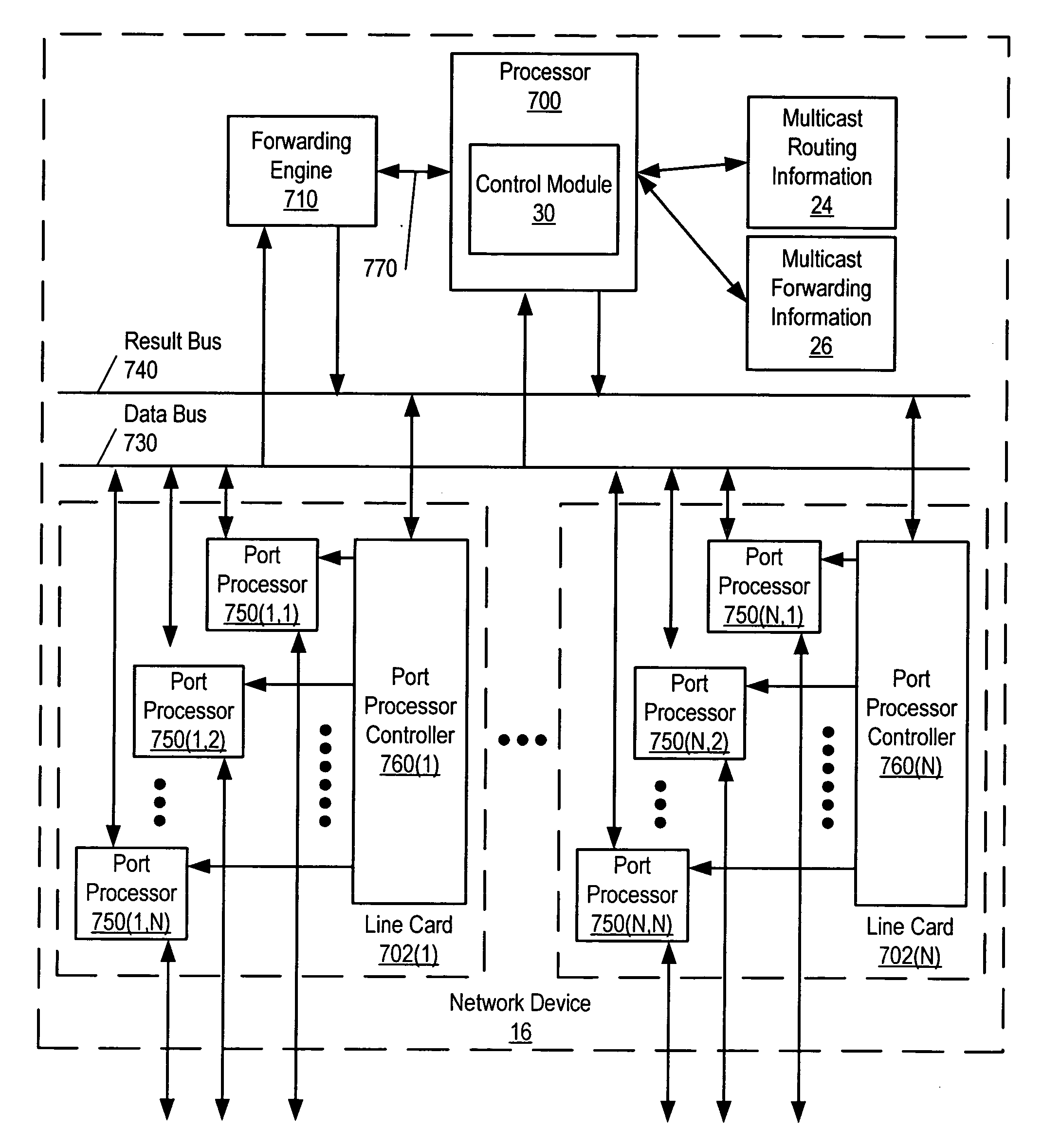
IP multicast over multi-chassis trunk
In embodiments of the present invention, multicast traffic is simultaneously routed via all switches participating in the trunk (can be referred to as partner switches). A respective partner switch synchronizes the local multicast state information with all other partner switches. For a respective multicast group, a plurality of partner switches can be the part of the corresponding multicast distribution tree and obtain multicast traffic from uplink sources. For the multicast group, only one partner switch is elected as the primary forwarder which forwards the multicast traffic via the trunk. Another partner switch can become the primary forwarder for the multicast traffic of another multicast group and provide load sharing of multicast traffic between partner switches. Furthermore, because the partner switches have the multicast traffic and state readily available, in the event of a switch or link failure to the primary forwarder, another partner switch can readily become the primary forwarder.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
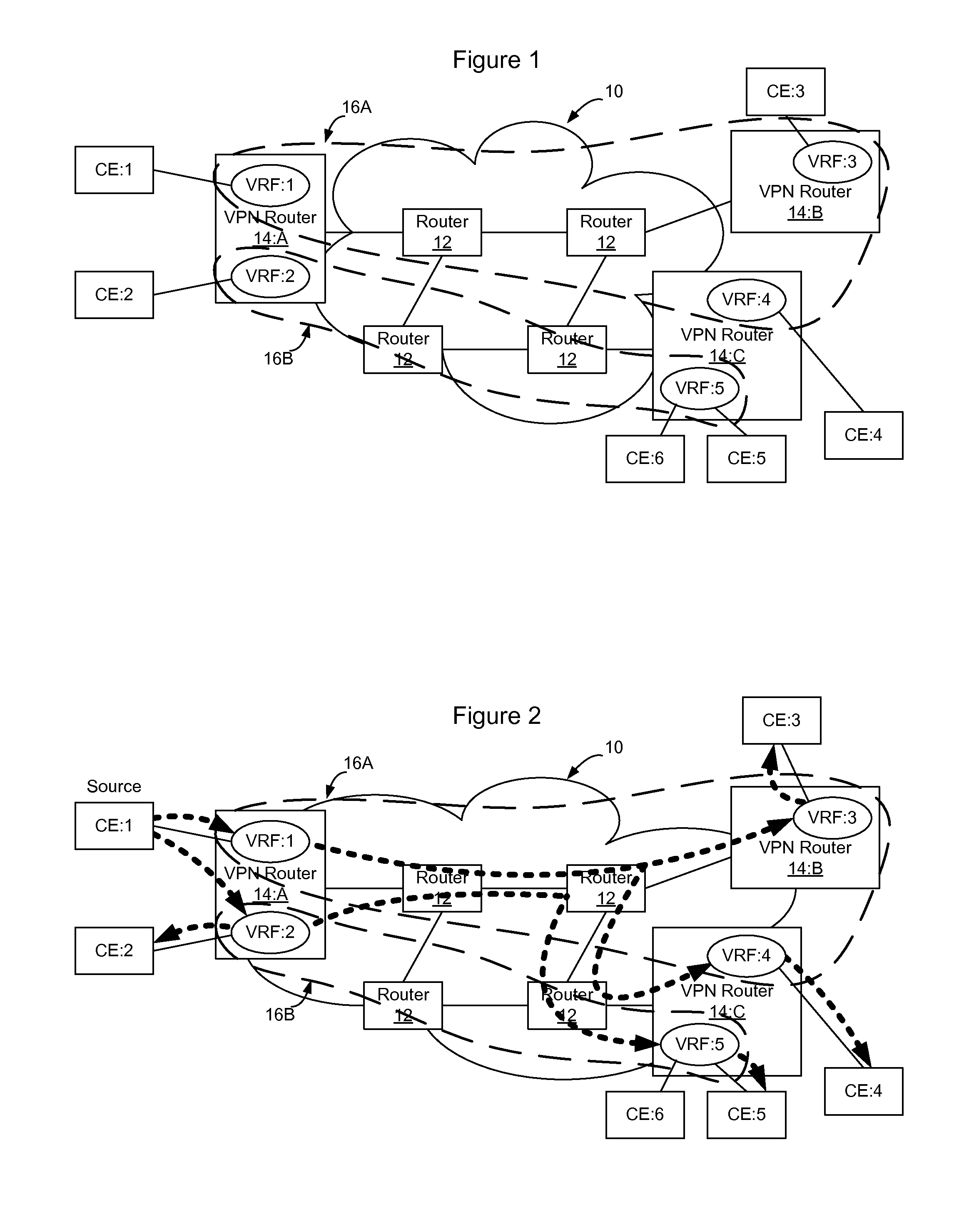
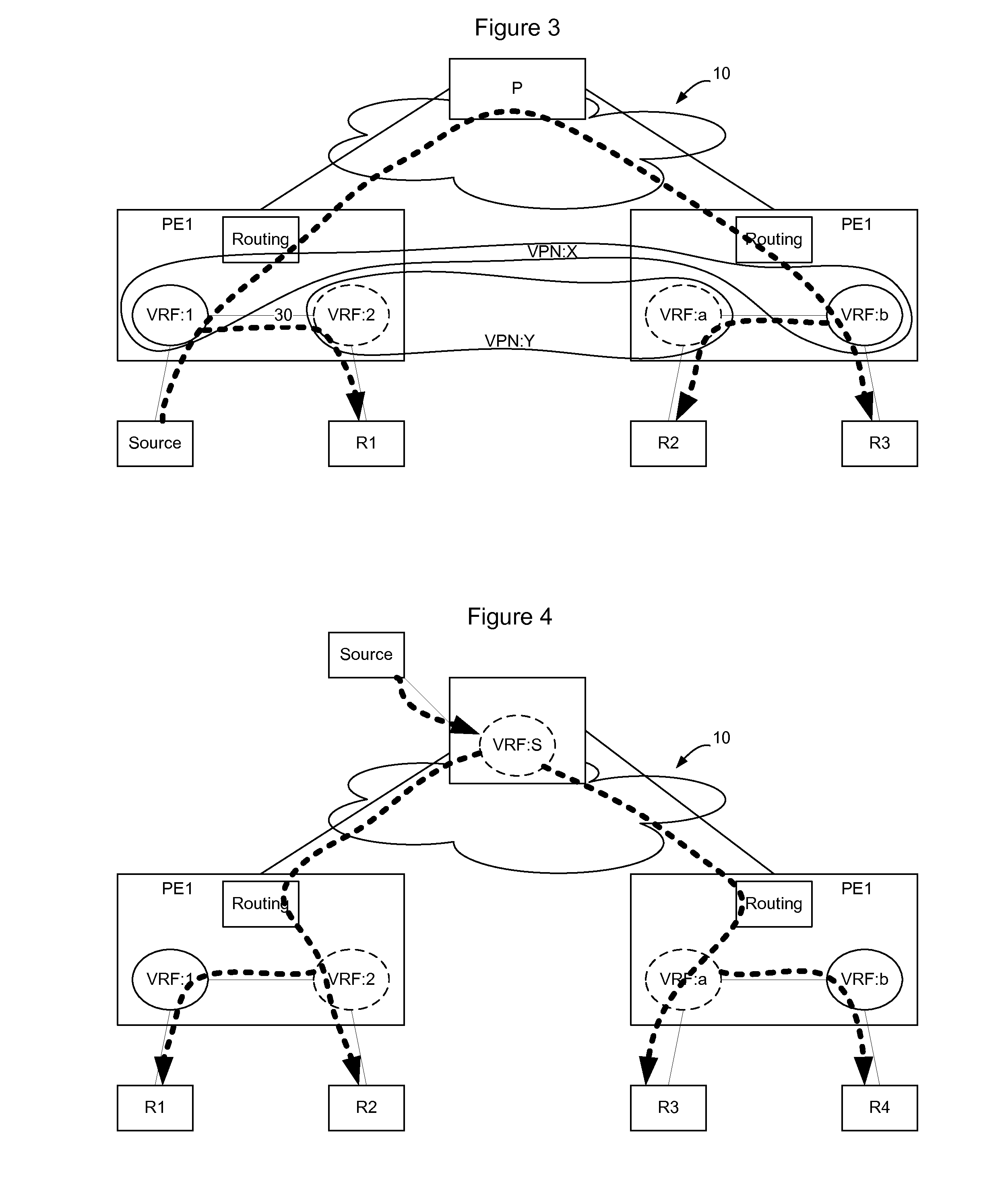
Method and Apparatus for Enabling Multicast Route Leaking Between VRFs in Different VPNs
InactiveUS20100329252A1Efficient processEfficient IP multicastSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationDistribution treeIP multicast
Multicast route leaking between VRFs in different VPNs enables receivers in different VPNs to subscribe to the same IP multicast so that an efficient IP multicast distribution tree can be built to include subscribers in multiple VPNs. VRFs are administratively configured to implement multicast route leaking and each such configured VRF brings up an internal connectionless IP interface. The VRFs then enable the multicast routing protocol (e.g. PIM) on the internal IP interface to establish PIM neighborships with each other. When a VRF receives an IGMP join from a receiver, it uses PIM to join the receiver to the multicast over the internal IP interface. This enables receivers outside of a VPN but associated with VRFs that are co-located on the same PE to join multicasts established within the VPN so that separate multicast distribution trees are not required for each VPN.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Connectivity detection method, device and system
The invention discloses connectivity detection method, device and system, which belongs to the technical field of communication. The connectivity detection method comprises the steps that connectivity detection request information is received; according to the identifiers of target nodes, whether the node which receives the connectivity detection request information is one of the target nodes is judged; if the node is one of the target nodes, connectivity detection response information is sent to a source node; and if the node is not one of the target nodes, corresponding processing is carried out according to the value of hop count and the condition whether the node is on the path between the source node in a multicast distribution tree to any target node. According to the invention, connectivity detection and fault diagnosis can be carried out for a number of specified target nodes, so that the source node only receives the feedback of nodes on a real path and path identification is easy.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Adaptive and Scalable Qos Architecture for Multi-Bearer Multicast/Broadcast Services
ActiveUS20080293428A1Increase the number ofUnnecessary resource reservation by unused links may be preventedSpecial service provision for substationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceDistribution tree
The invention relates to a method for filtering and a network entity of the core network or the radio access network of a mobile communication system filtering streams belonging to a single user service. The packet streams, each being transported by a bearer service, provide a multicast or broadcast service and is delivered from a service center via the network entity to a mobile terminal. The network entity comprises a service manager providing a quality-of-service management function. The invention further relates to a communication system comprising the network entity. To provide an adaptive multimedia broadcast / multicast service QoS architecture that is scalable to a great number of users, the invention suggests providing the service in form of a packet streams, each being provided via a single bearer service, and equipping nodes within the distribution tree of the service filter capability allowing to (de)register bearer services providing the service based on the downlink quality-of-service constraints obtained from a service manager.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
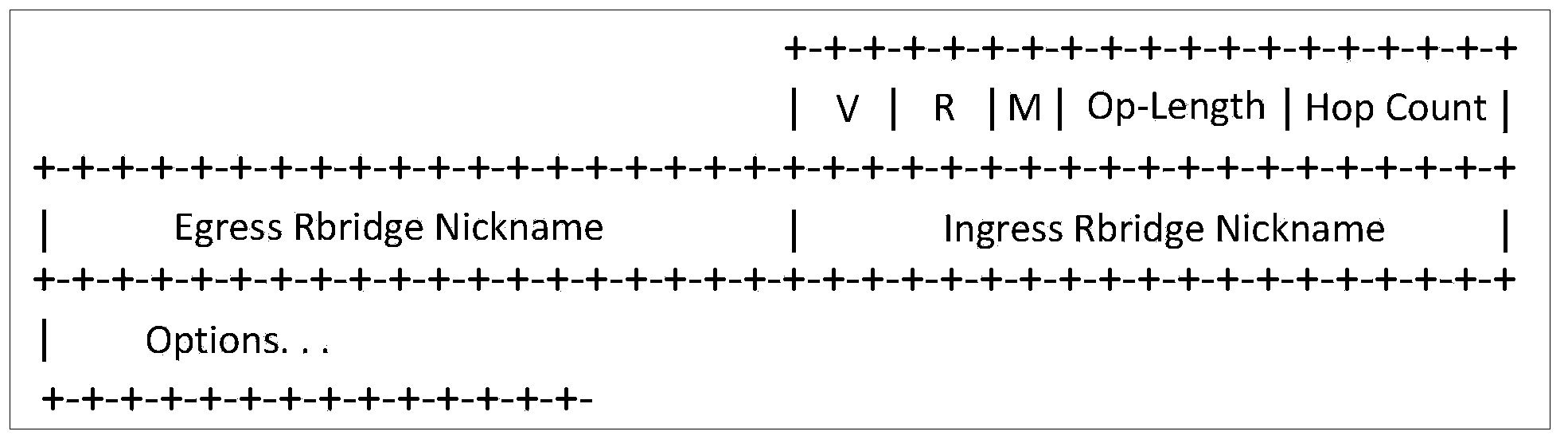
Multi-link transparent interconnection multicast frame transmission method and system
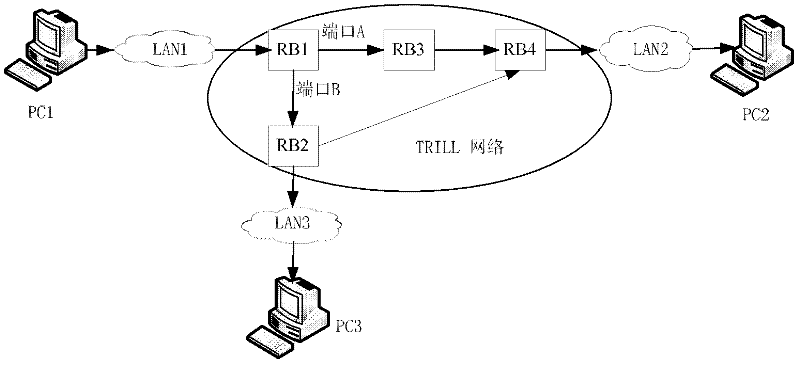
ActiveCN102299845AGuaranteed smooth scalingReduce missing reportsData switching networksDistribution treeData center
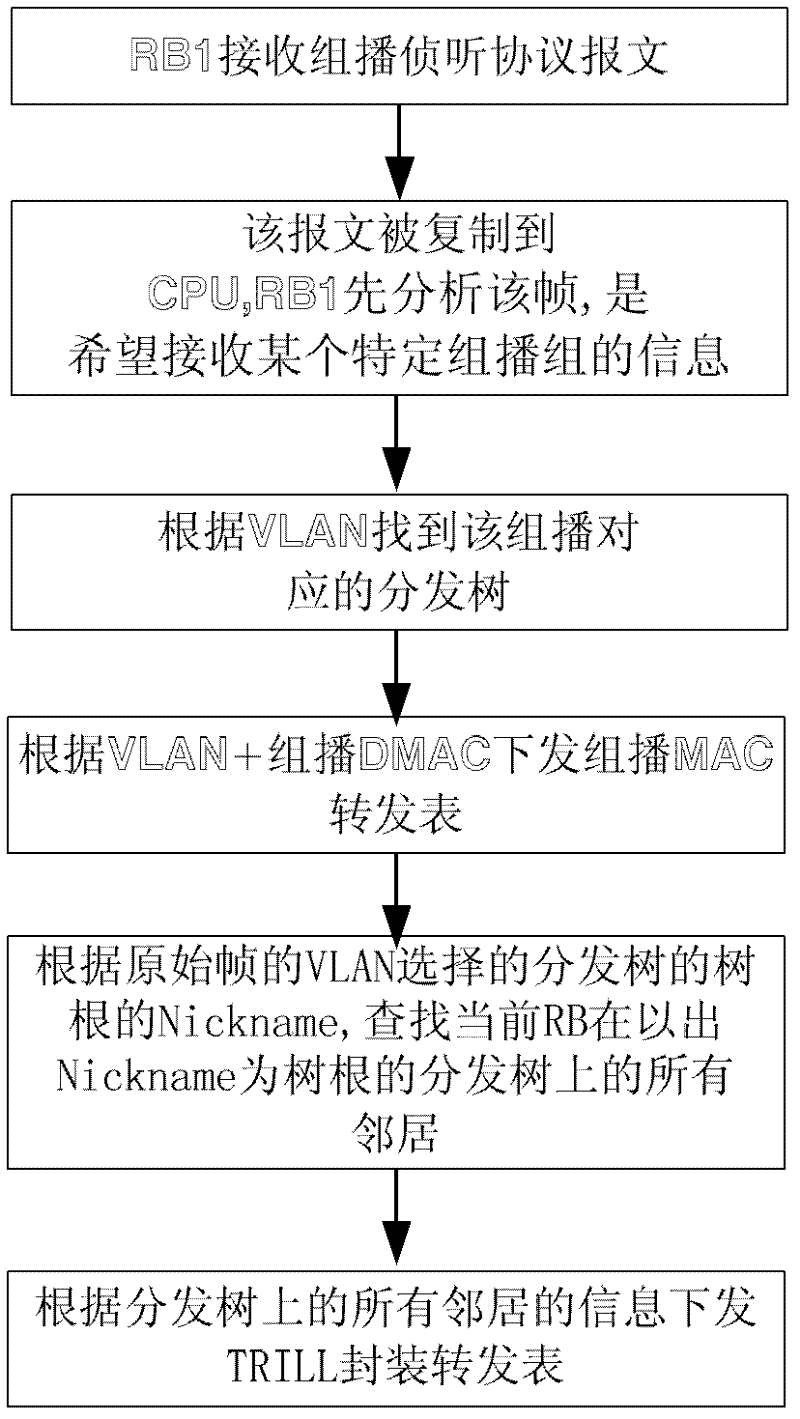
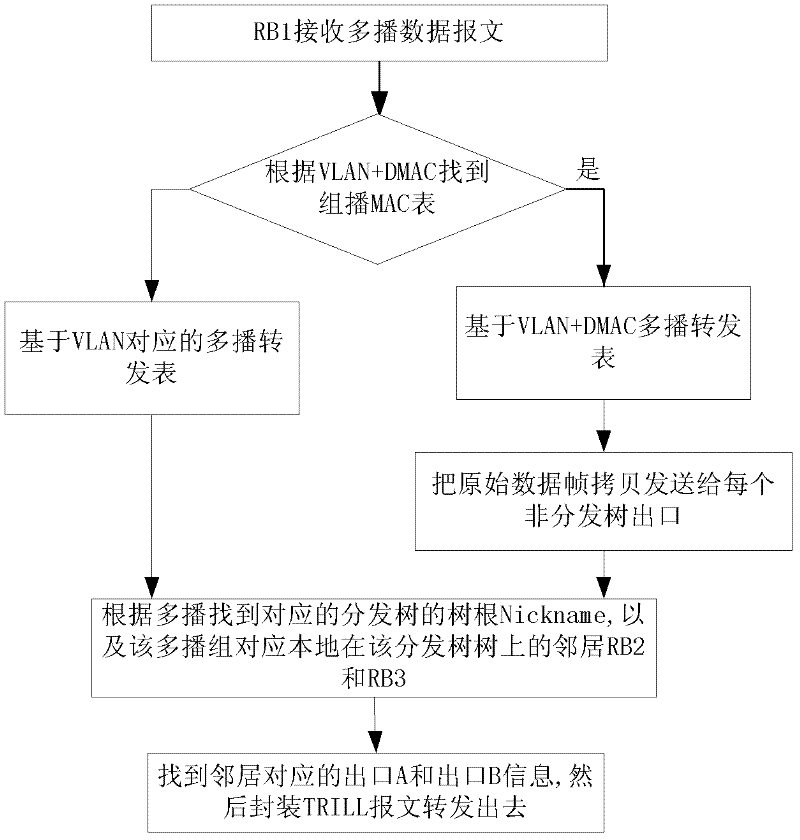
The invention discloses a multi-link transparent interconnection multicast frame transmission method and system, which recognizes the topology of the TRILL network through the link state protocol and generates a distribution tree; according to the received multicast listening protocol message and the route of the RB The forwarding table information generates a multicast TRILL forwarding table; when the RB receives a VLAN broadcast frame or multicast frame, the RB encapsulates the data frame as a TRILL data frame and sends it to the TRILL network; when a fault is detected, the channel status is changed to allow the TRILL data Packet smooth switching and forwarding. Adopting the technical solution of the present invention effectively guarantees the transmission of multicast messages in the TRILL network, fully utilizes the bandwidth and effectively prevents broadcast storms, well supports the rapidly increasing horizontal traffic between servers, and ensures the smooth expansion of the two-layer network , effective hierarchical MAC address, providing guarantee for virtualized data center business expansion.
Owner:武汉神州数码云科网络技术有限公司
IP multicast layered distribution method and system
InactiveUS20140376366A1Throughput lowTransmission performance lowSpecial service provision for substationError preventionDistribution treeLinear network coding
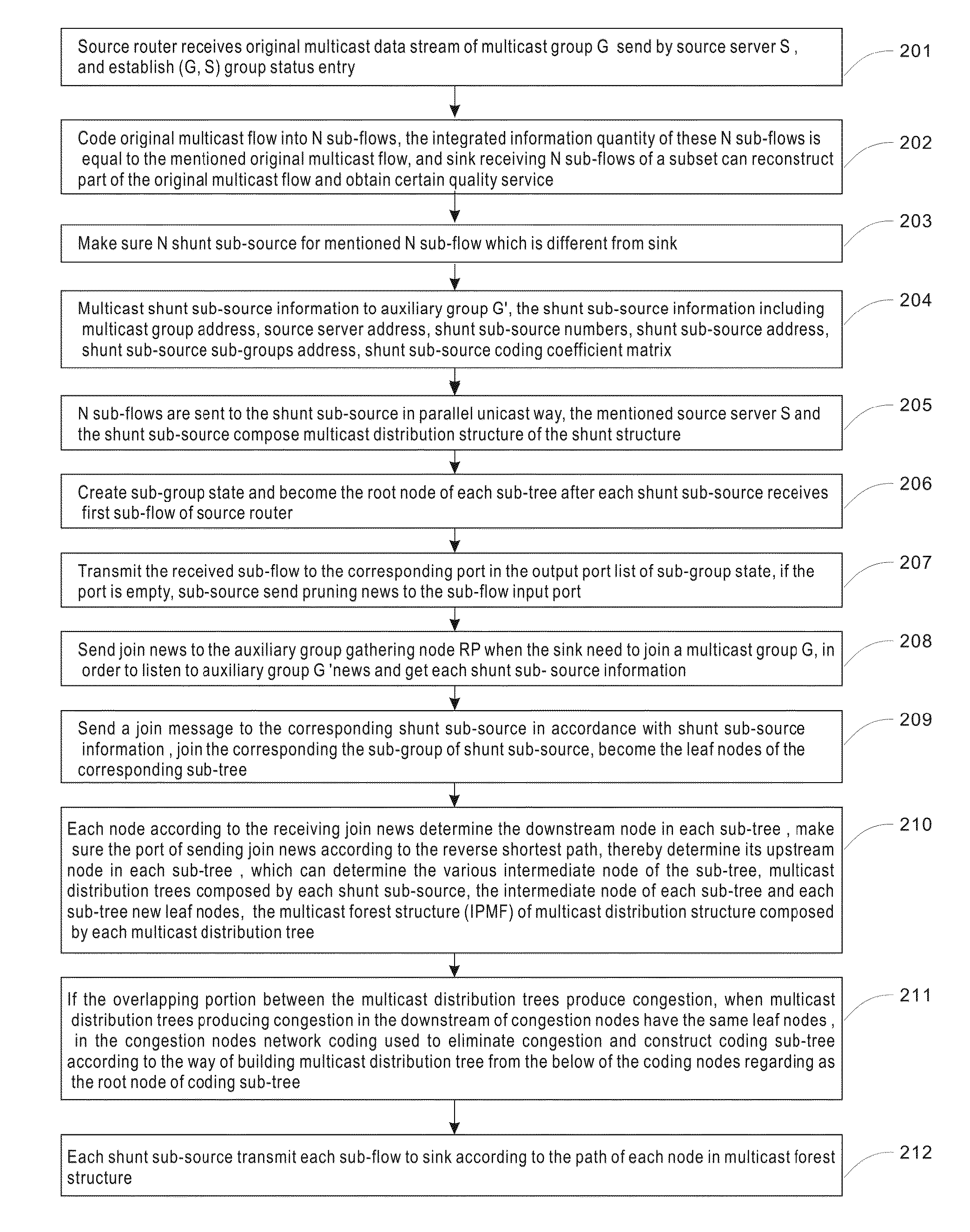
The present invention relates to IP network communication technology. It provides a kind of IP multicast data layer distribution method and system. The method includes: first code original multicast data into multiple sub-flow, separately specify different shunt sub-source for every sub-flow, distribute sub-group address, create sub-group state, etc, form shunt structure. Then the sink send join news to each shunt sub-source, join each shunt sub-source sub-group and become the leaf node of each sub-tree. And then each shunt sub-source determine the intermediate node according to the port receiving join news and construct multicast distribution-tree. If the overlapping portion between the multicast distribution trees produce congestion, in the congestion nodes network coding is used to eliminate congestion and construct coding sub-tree according to the way of building multicast distribution tree from the below of the coding nodes.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +2
Distributing system, method and device for group key control message
InactiveCN101022333AImprove usabilityImprove acceleration performanceKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationDistribution treeComputer hardware
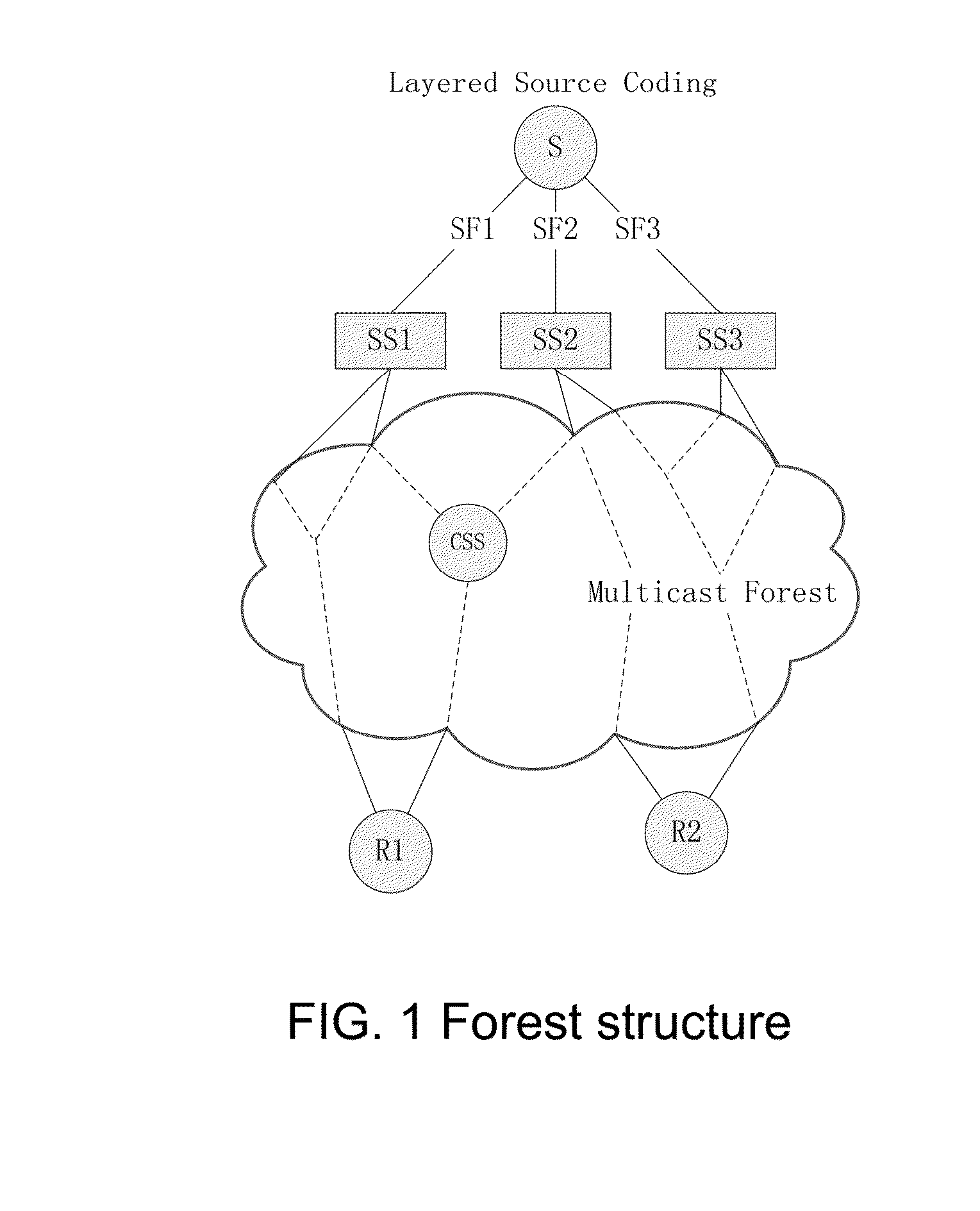
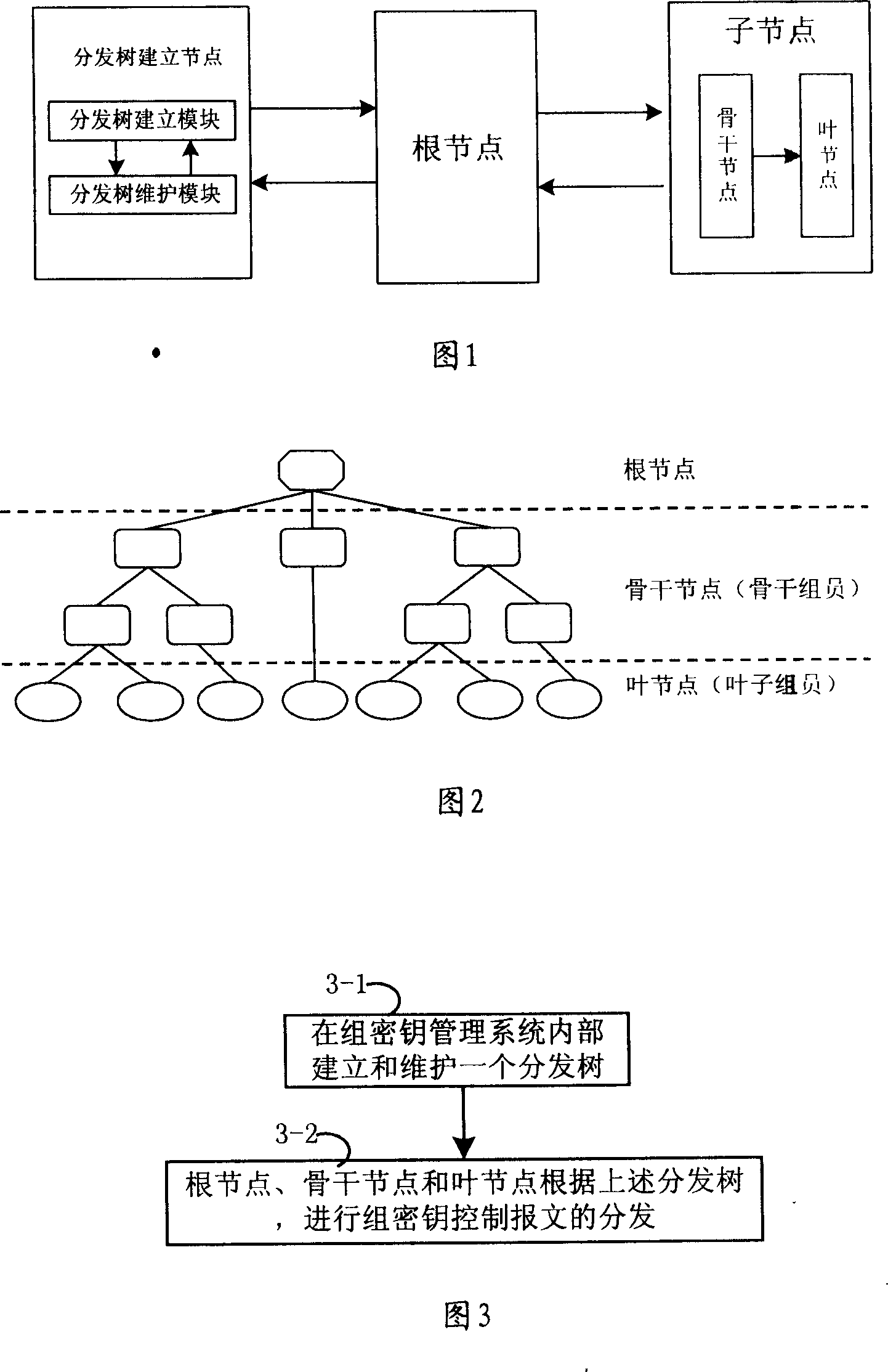
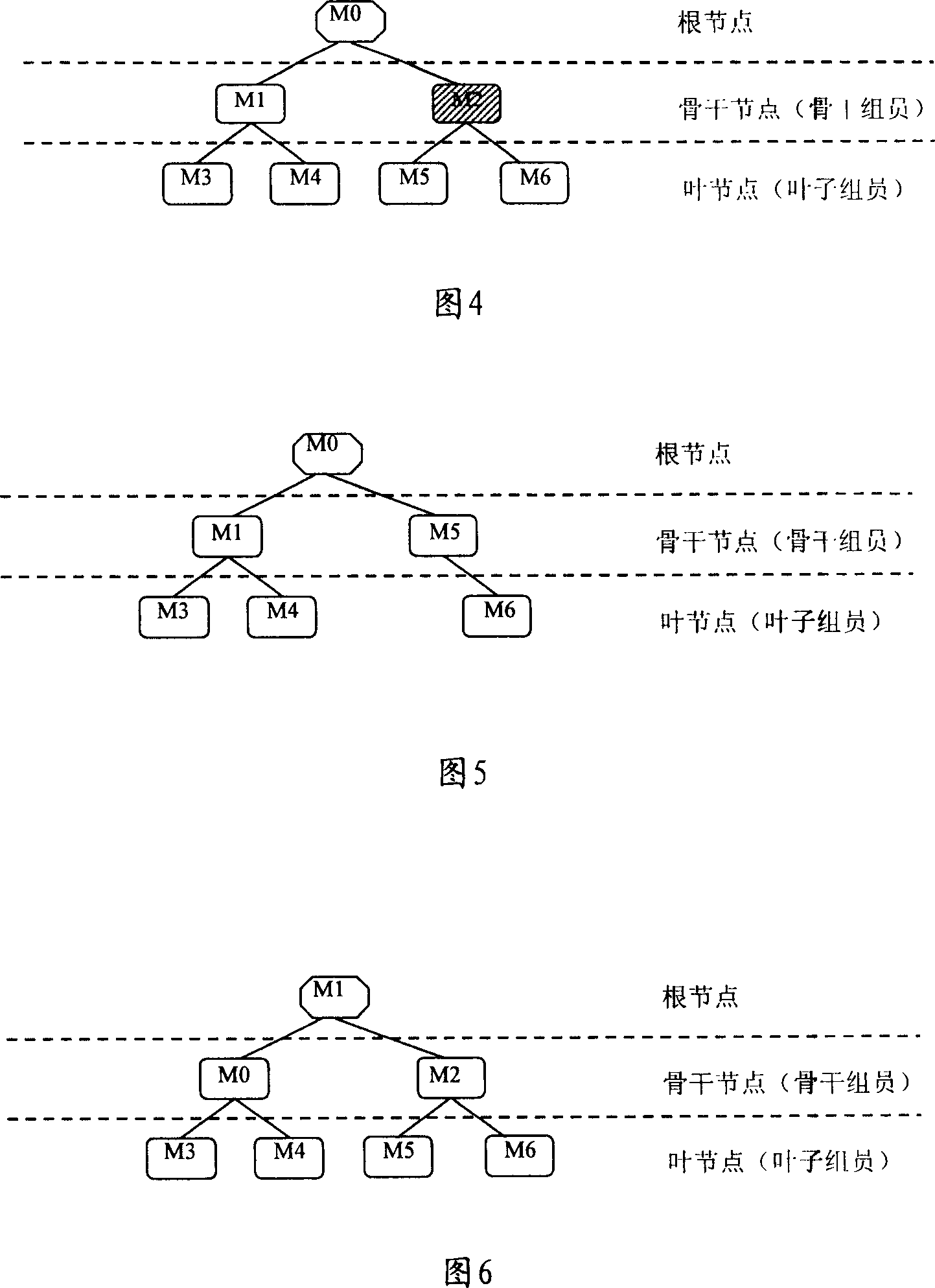
A method for distributing composite cipher key control message includes setting up distribution tree of composite cipher key control message in composite cipher key management unit, down-sending composite cipher key control message to sub-node by root-node according to distribution tree, carrying out relevant retransmission or local treatment on received composite cipher key control message by sub-node. The system and device used for realizing said method are also disclosed.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for scalable virtual private network multicasting
ActiveUS20060133375A1Quantity minimizationBroadcast with distributionTime-division multiplexDistribution treeData stream
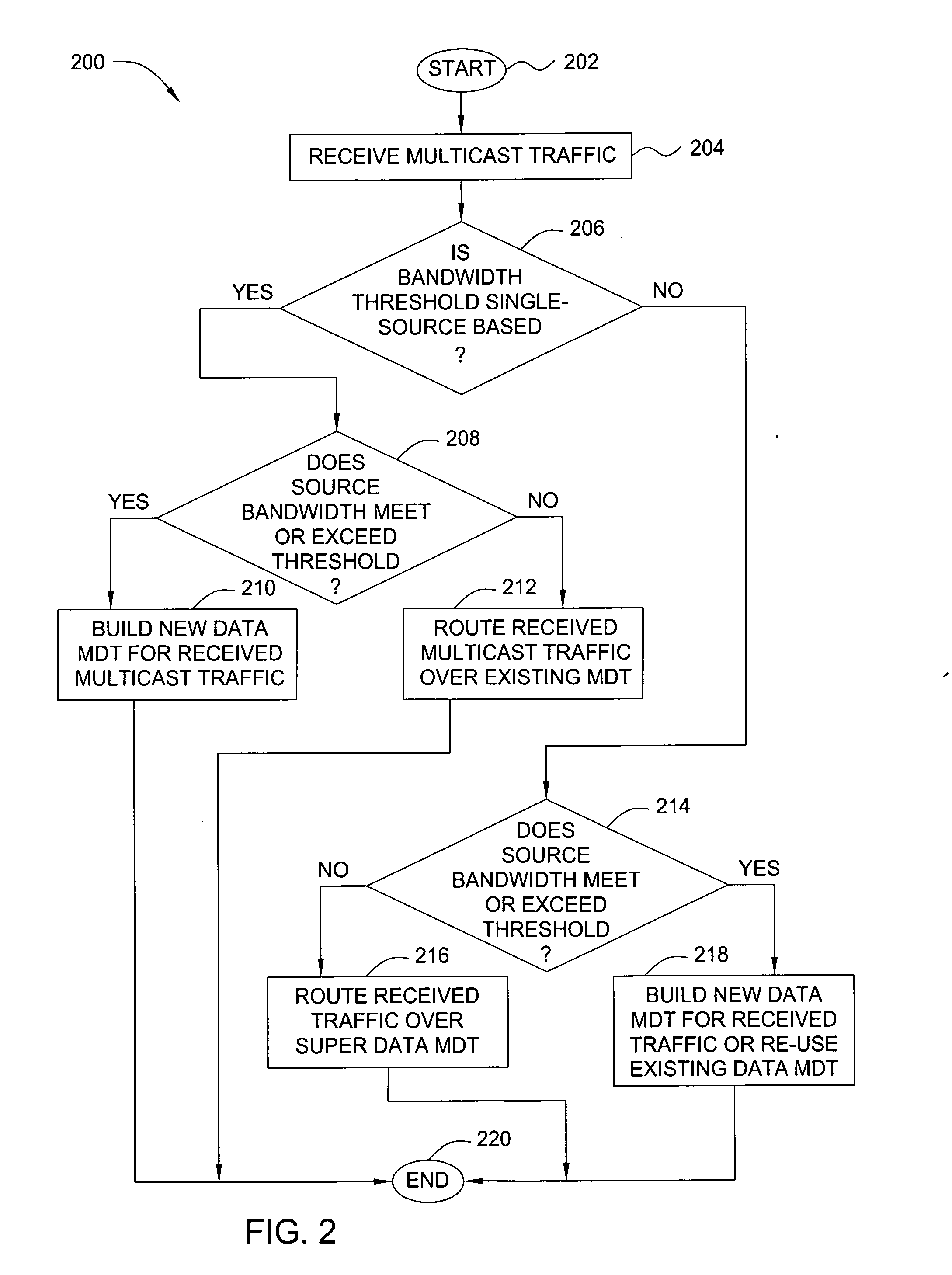
In one embodiment, the present invention is a method and apparatus for scalable virtual private network multicasting. In one embodiment a service network builds a new data multicast distribution tree for each high-bandwidth multicast data flow (e.g., multicast data flows that require an amount bandwidth meeting or exceeding a predefined threshold). However, if the multicast data flow is a low-bandwidth flow (e.g., if the required amount of bandwidth falls below the predefined threshold), the multicast data flow is routed over an existing multicast distribution tree in order to minimize an amount of state information that must be maintained by service provider core routers in the backbone network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method, device and system for establishing switching multicast distribution tree
ActiveCN102137000AThere will be no problem of packet lossSpecial service provision for substationNetworks interconnectionDistribution treePacket loss
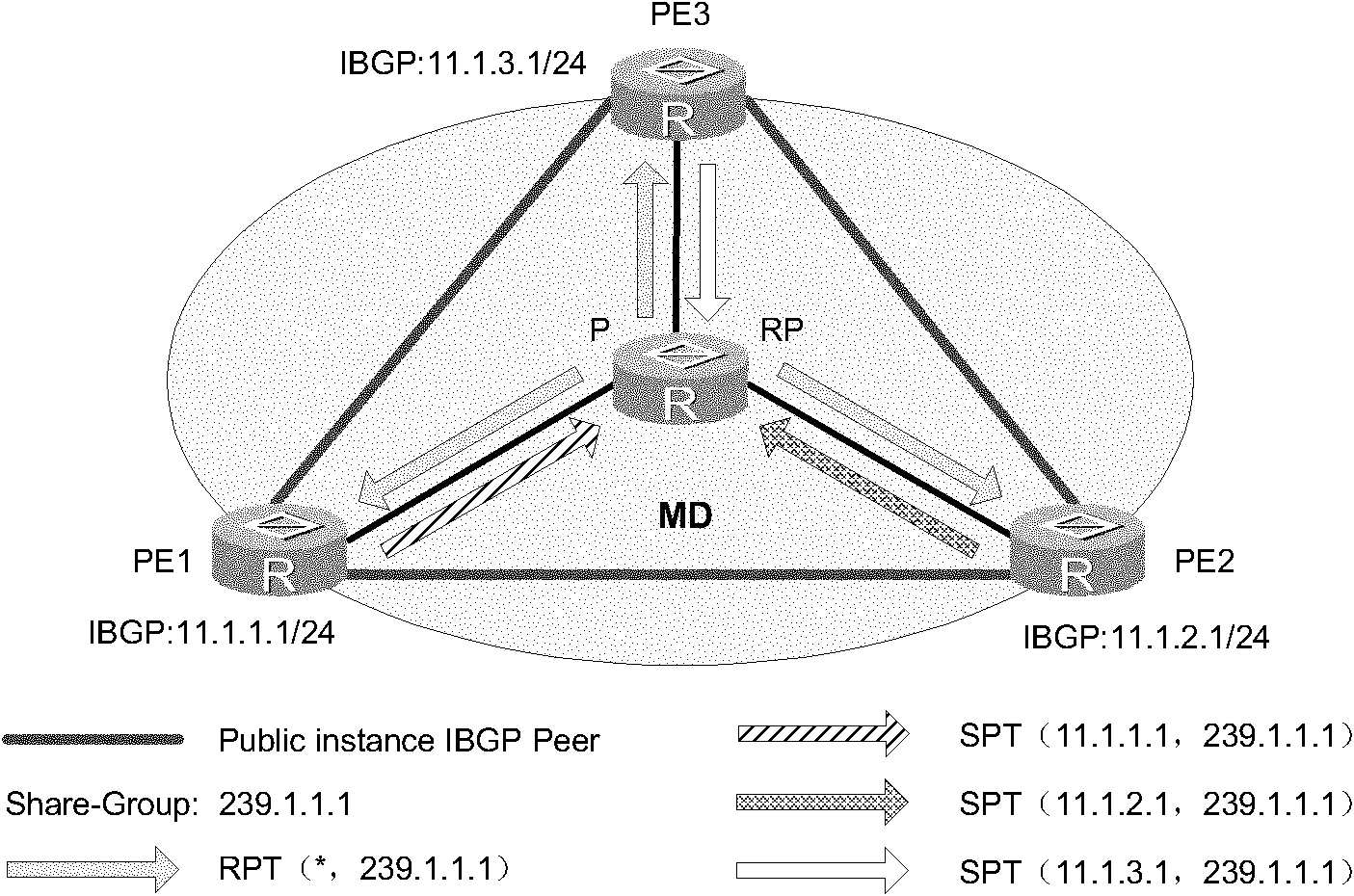
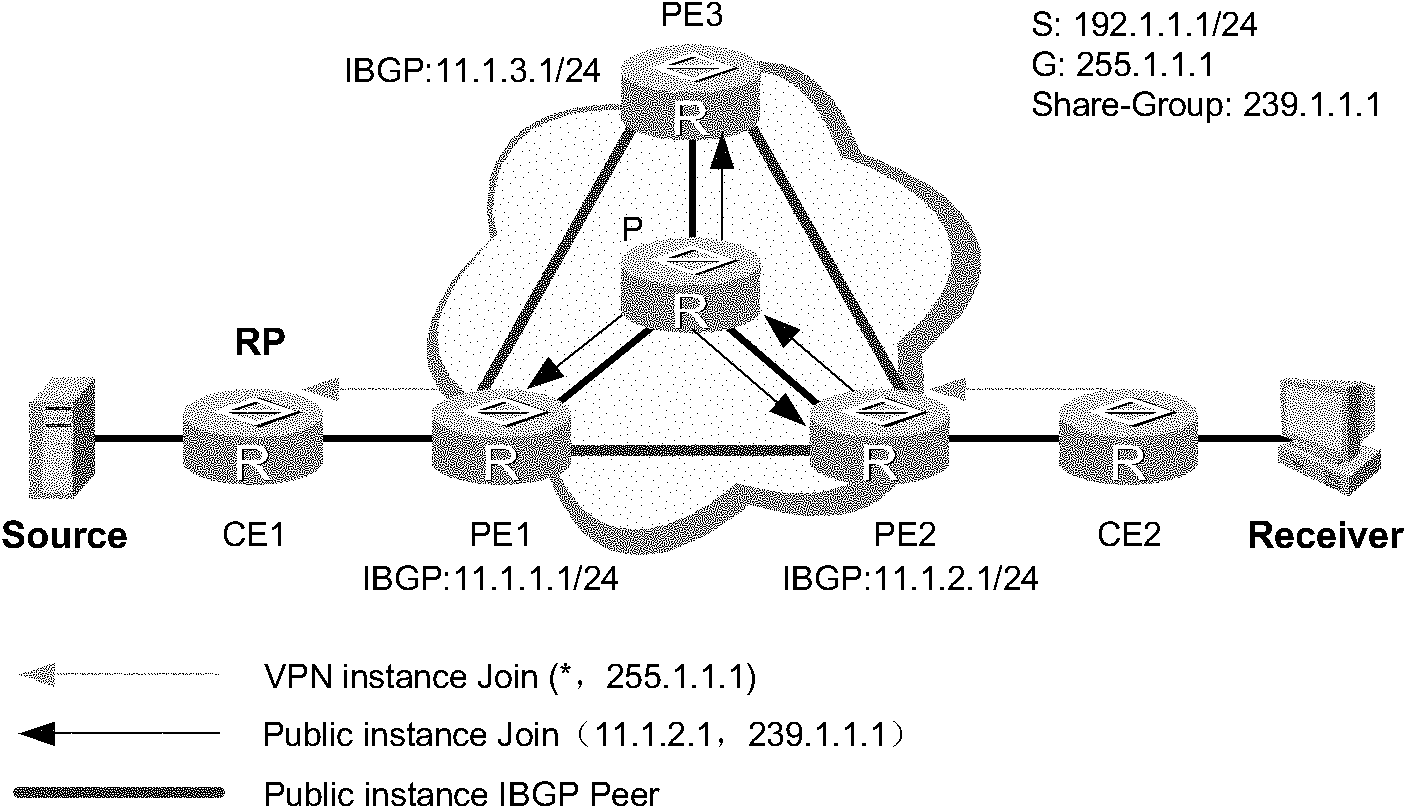
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for establishing a switching multicast distribution tree (a public network forwarding tunnel) in a multicast virtual private network (VPN). In the method, a provider edge (PE) at a source end sends a switching message containing a switching group address to a downlink PE along a share-multicast distribution tree (share-MDT), wherein the switching message is used for establishing the switching multicast distribution tree; and a register message is sent to a rendezvous point (RP) in a public network before multicast streaming on the share-MDT starts to switch so as to trigger the RP in the public network and the PE at the source end to establish the switching multicast distribution tree with a PE at a receiving end. The embodiment of the invention also provides a corresponding device and system. By using the method, the switching multicast distribution tree can be established before the multicast streaming is switched to the switching multicast distribution tree from the share-MDT, thus the problem of packet loss of the multicast steaming can be avoided in the process of switching the multicast streaming to the switching multicast distribution tree from the share-MDT.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
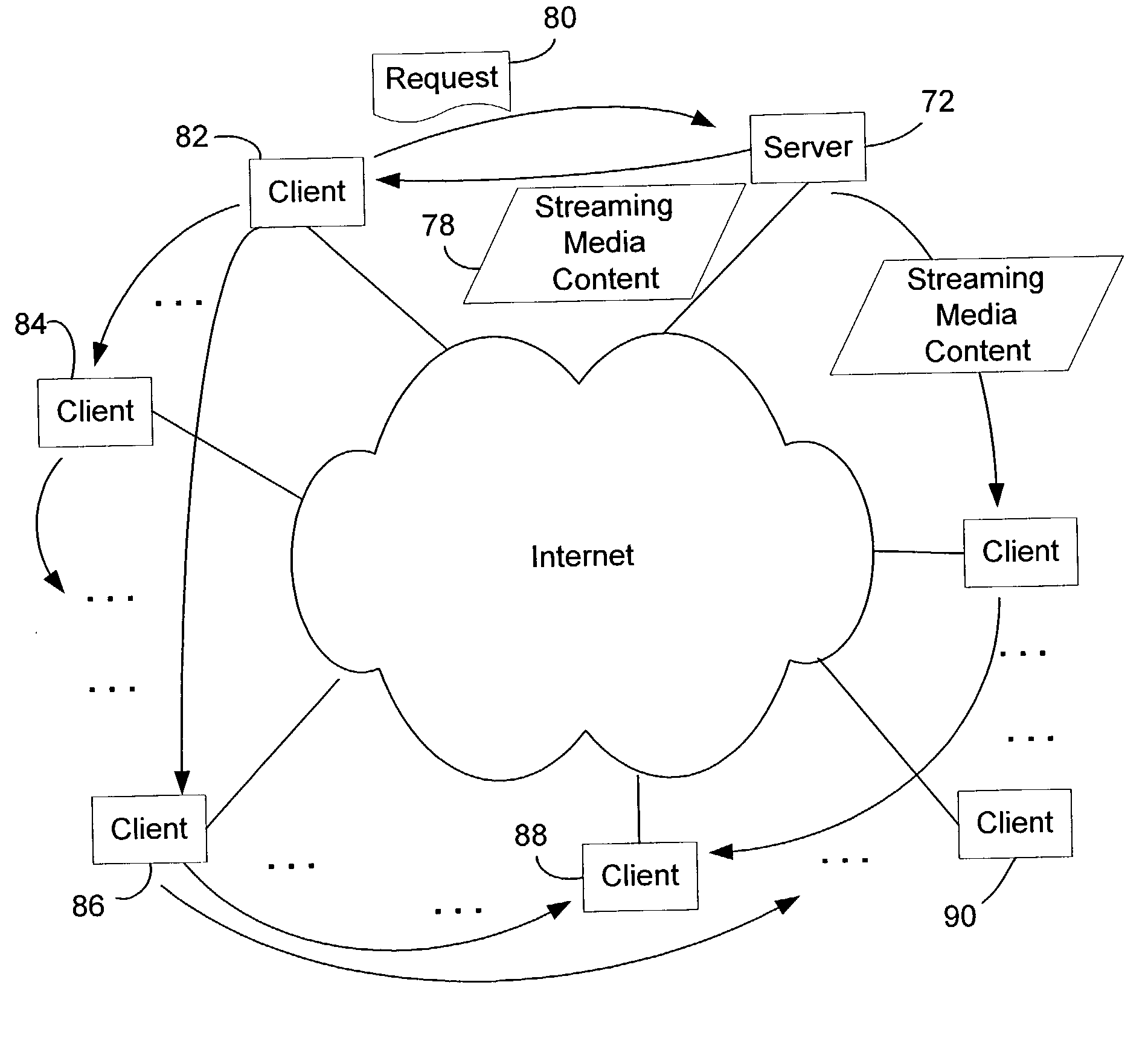
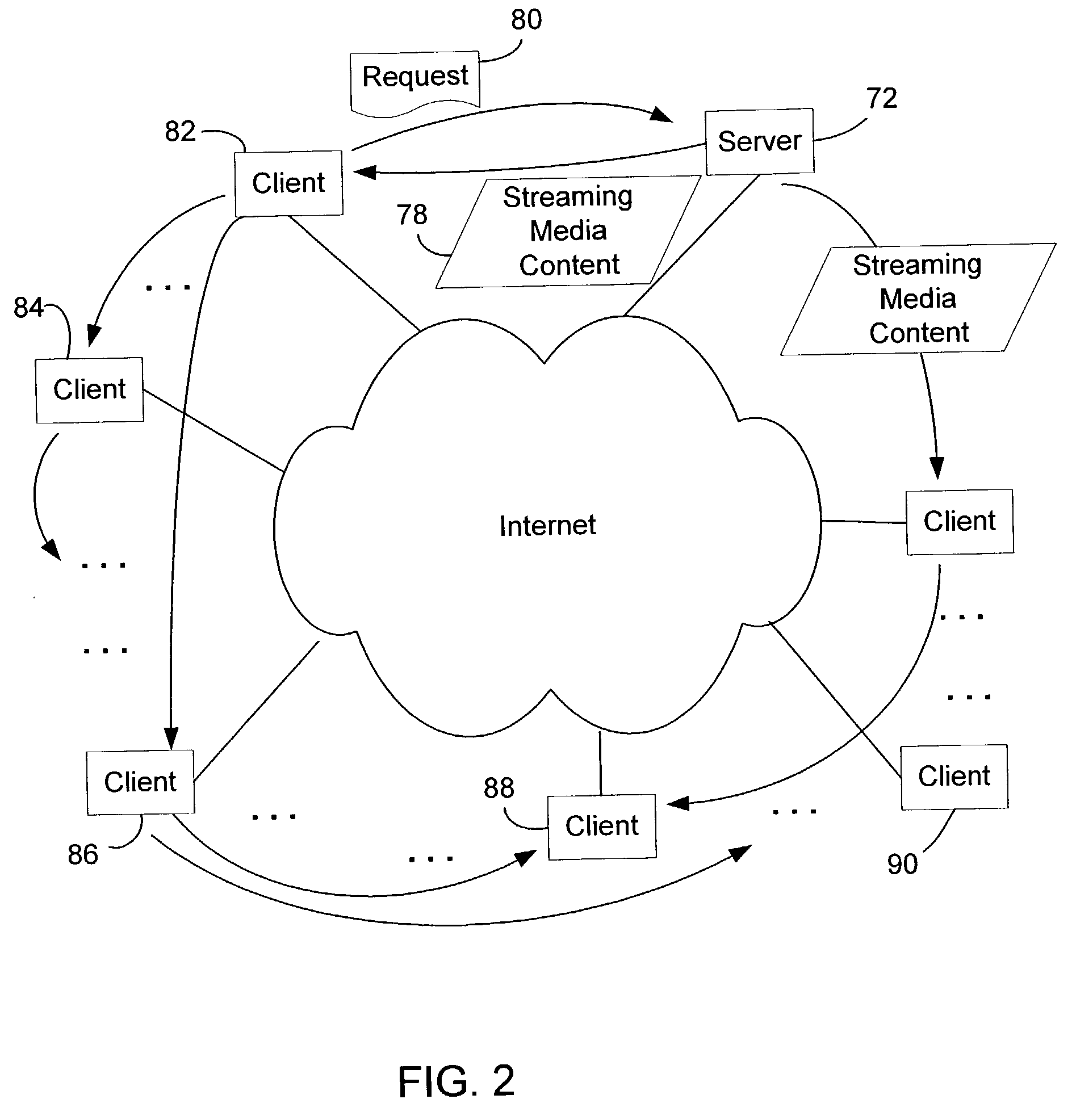
System and method for distributing streaming content through cooperative networking
InactiveUS7792982B2Reduce loadEasy to handleMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDistribution treeComputer network
A system and method for distributing streaming content data from a server to multiple clients enables the server to handle transient surges of requests by having the clients cooperate with the server and other clients to distribute content, thereby alleviating the load on the server. The server divides the streaming content into multiple sub-streams (e.g., by using multiple description coding), and constructs multiple distribution trees with itself at the root and each client as a node in each of the trees. Each sub-stream is transmitted down a corresponding one of the distribution trees. Clients that receive sub-streams from its parent nodes in the distribution trees in turn forward the sub-streams to their child nodes in the trees.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Inter-Domain Group-Communications
ActiveUS20080298294A1Improve resource utilizationBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexDistribution treeComputer network
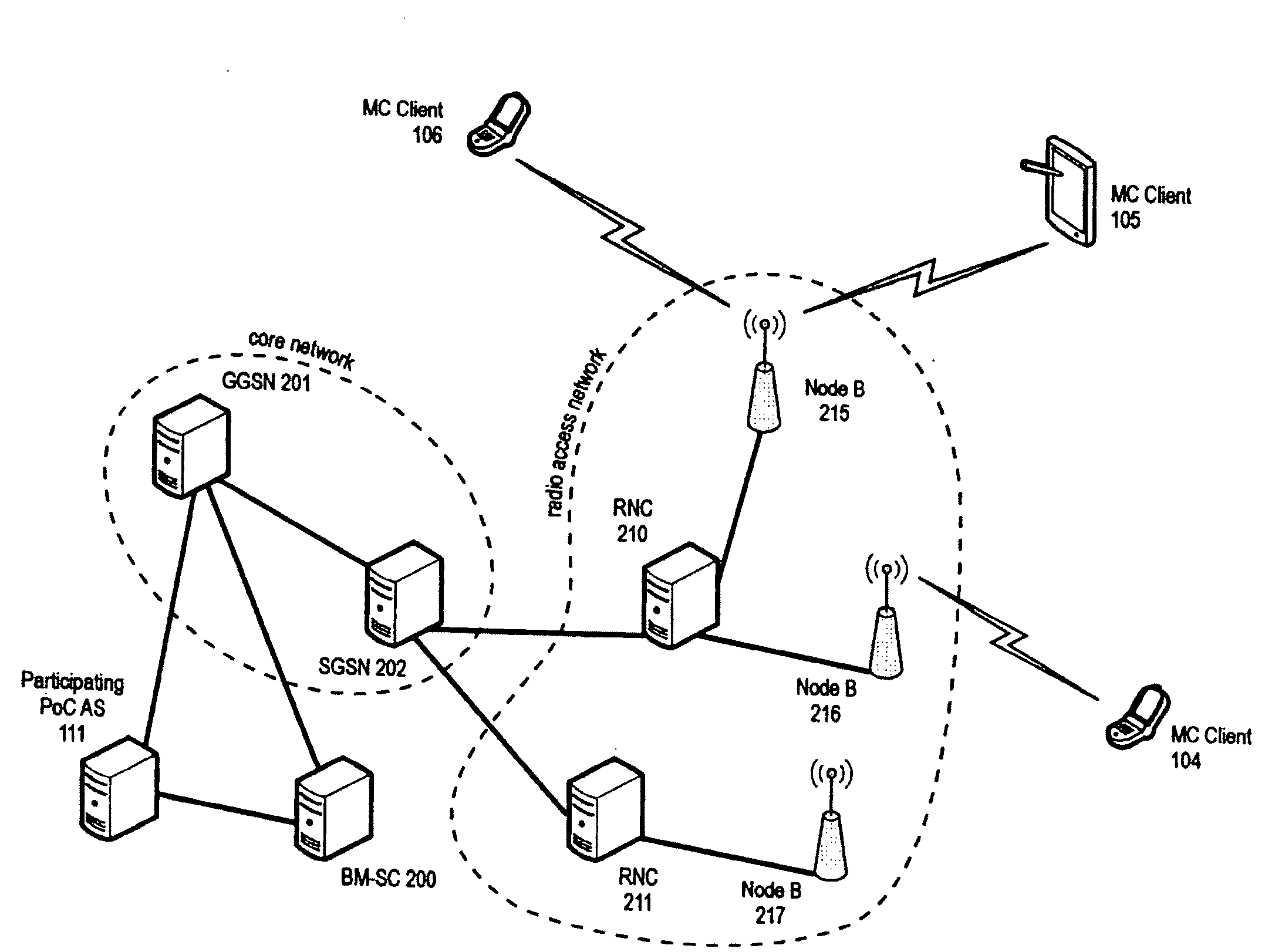
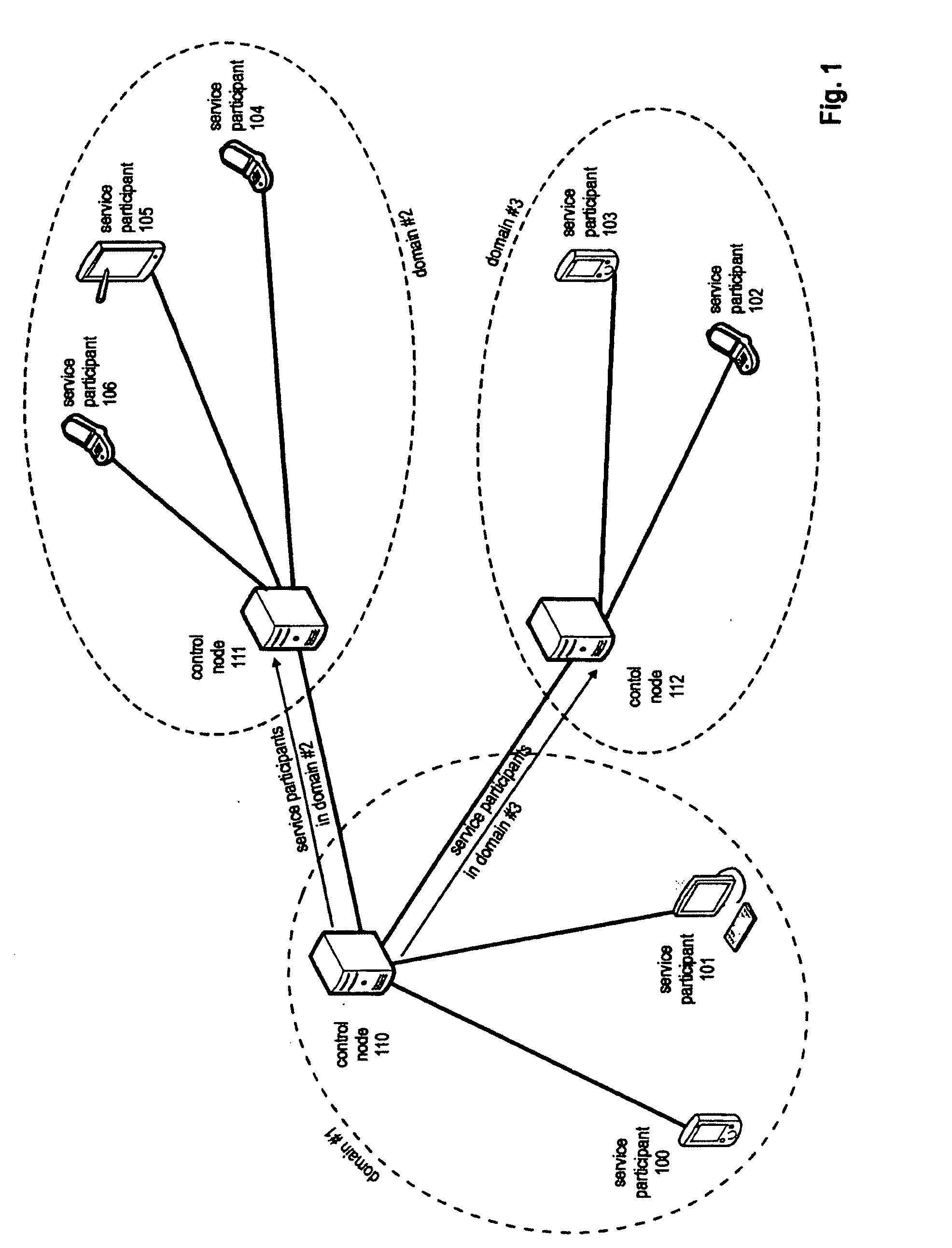
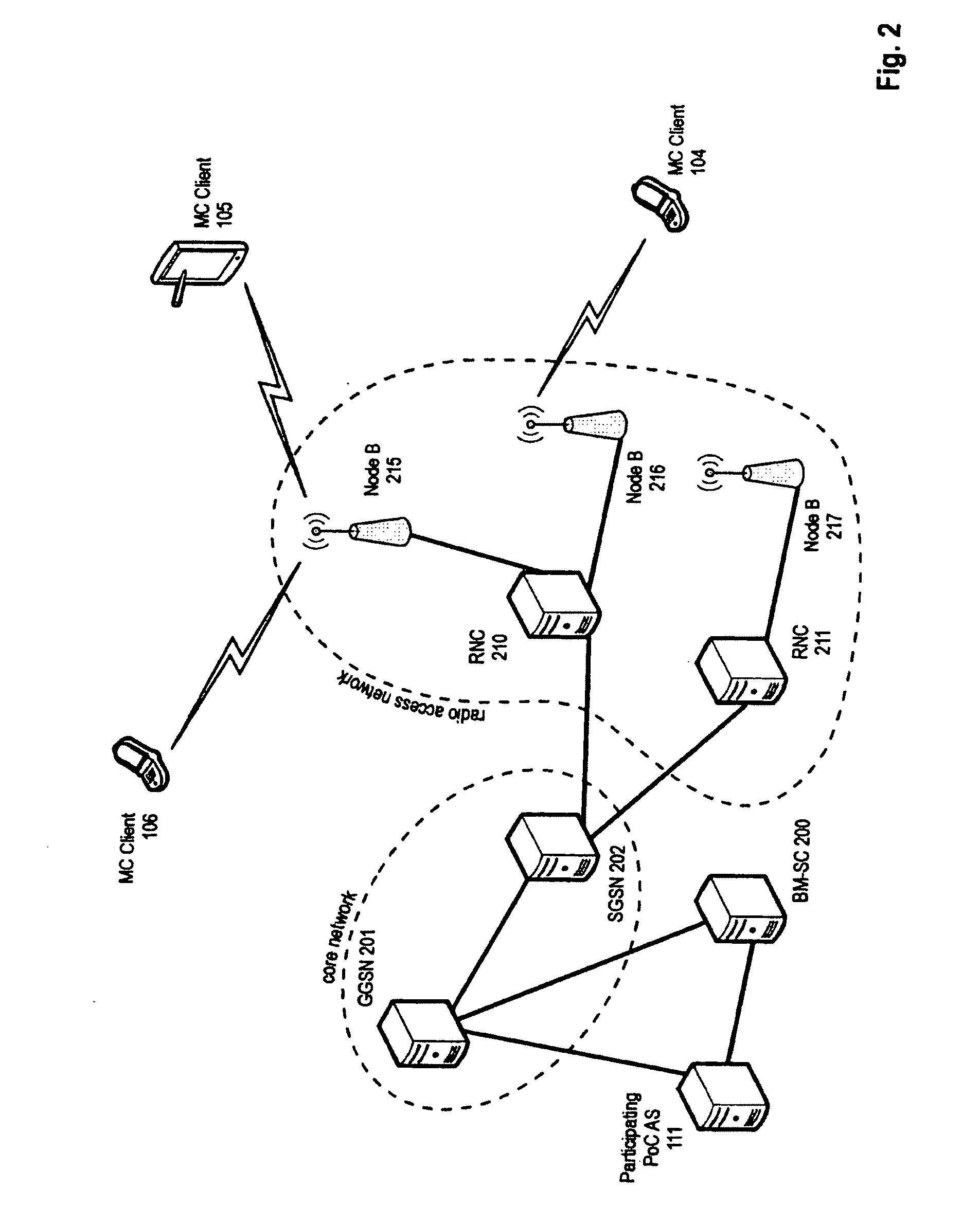
The invention relates to group communication services, i.e. communication services involving two or more users (or service participants). The invention provides a method for distributing multicast data of a multicast service to different domains and a method for distributing multicast data to service participants in a domain. Further, the invention relates to a control node and system implementing the respective methods. To improve resource utilization when providing a multicast service, including inter alia PoC services, to service participants the invention provides mechanisms to avoid unnecessary multiplication of multicast data in the distribution tree for multicast services with service participants of different domains. For this purpose the controlling node that is initiating the multicast service upon request determined to which domains the multicast data is to be provided and only forwards the multicast data on a per-domain basis. Another aspect of the invention is the avoidance of unnecessary duplications of multicast data within individual domains.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com