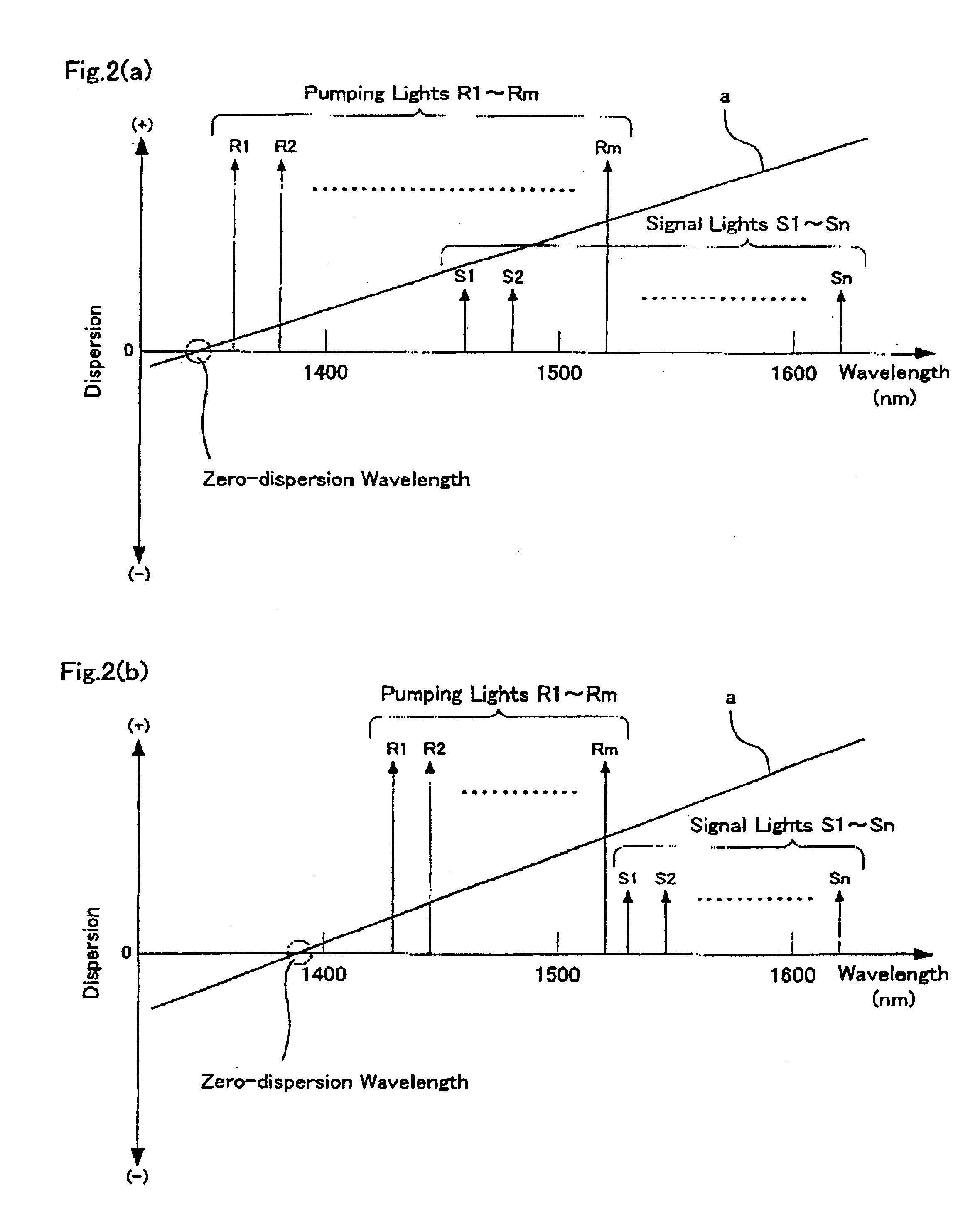
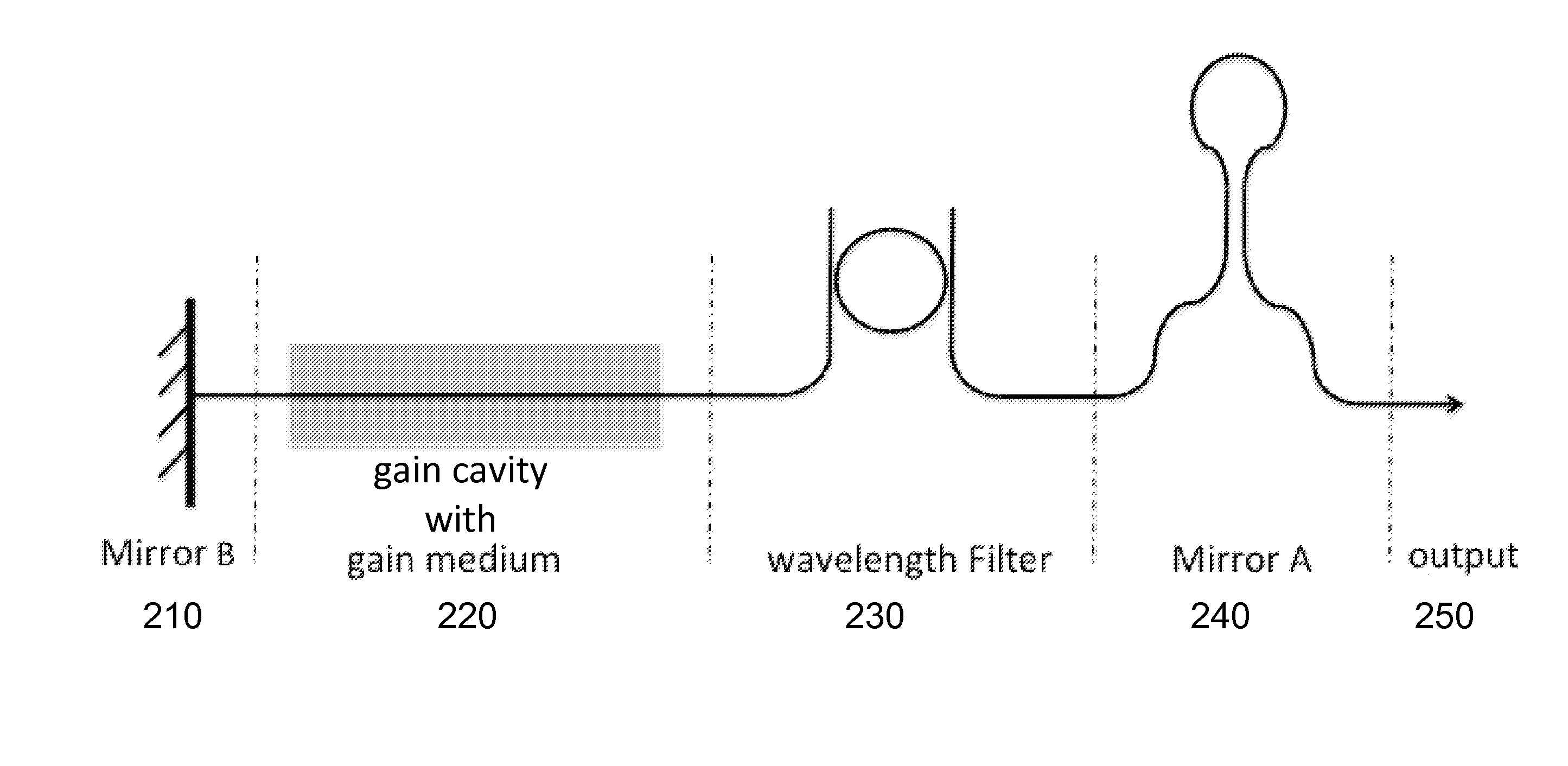
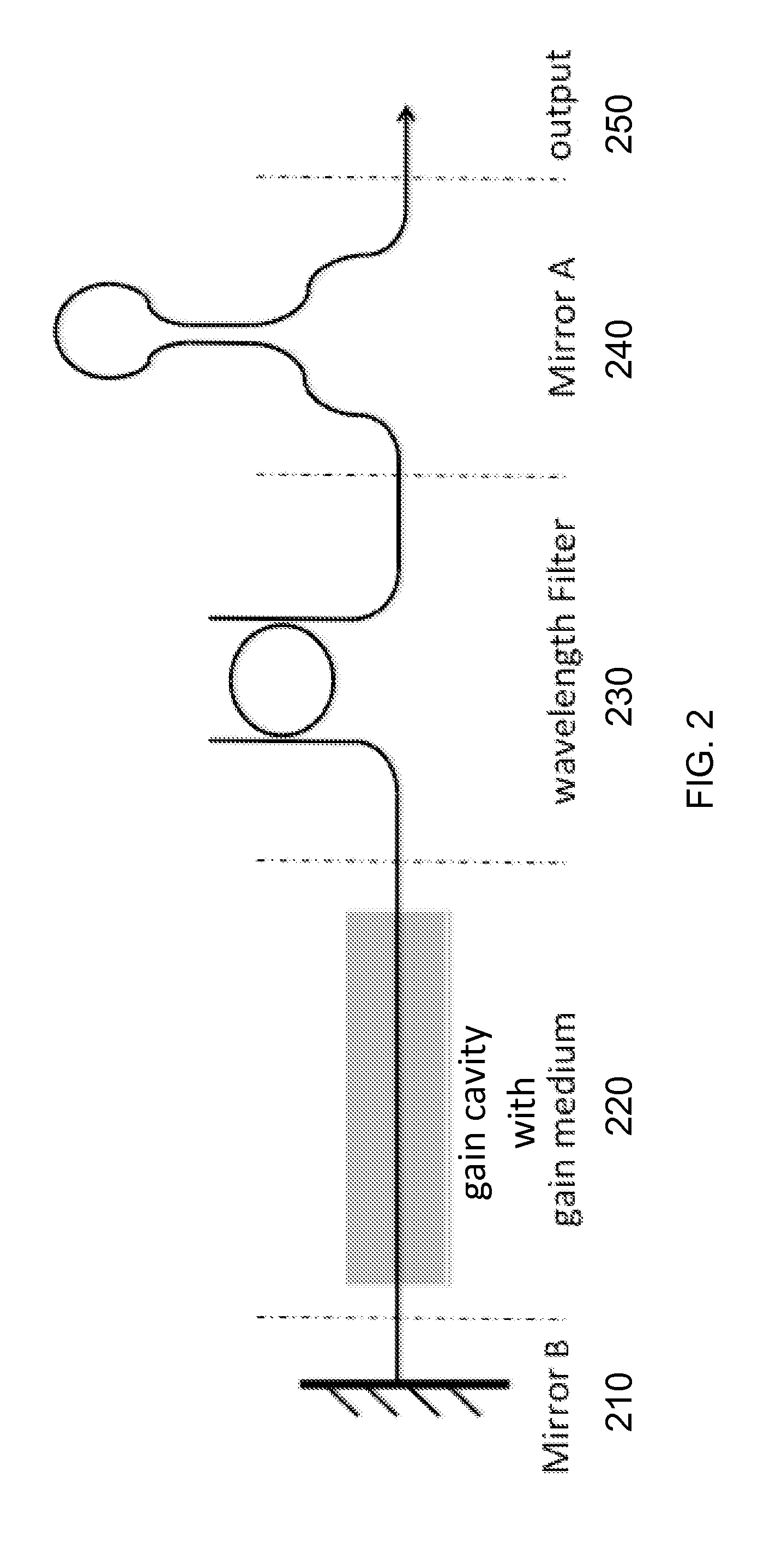
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
85 results about "Wdm transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
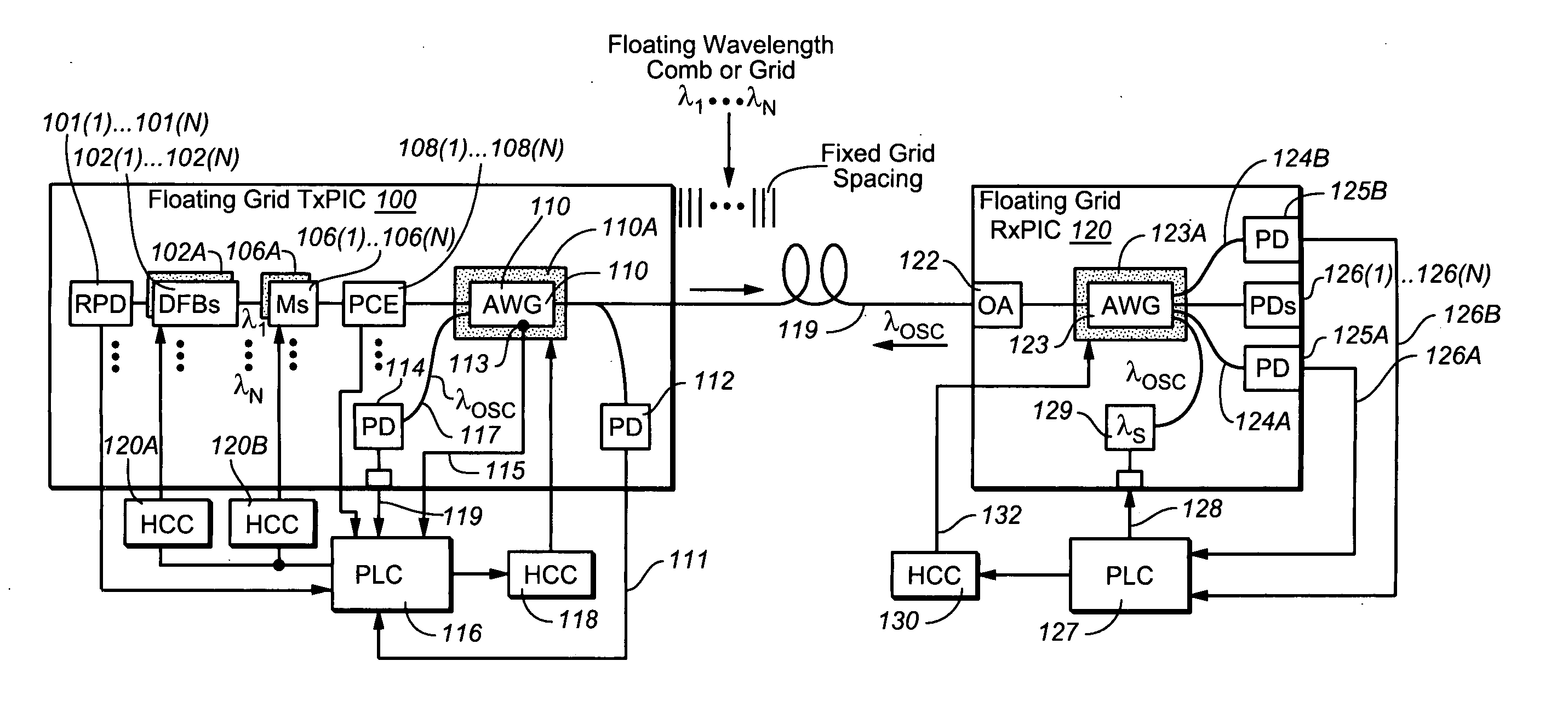
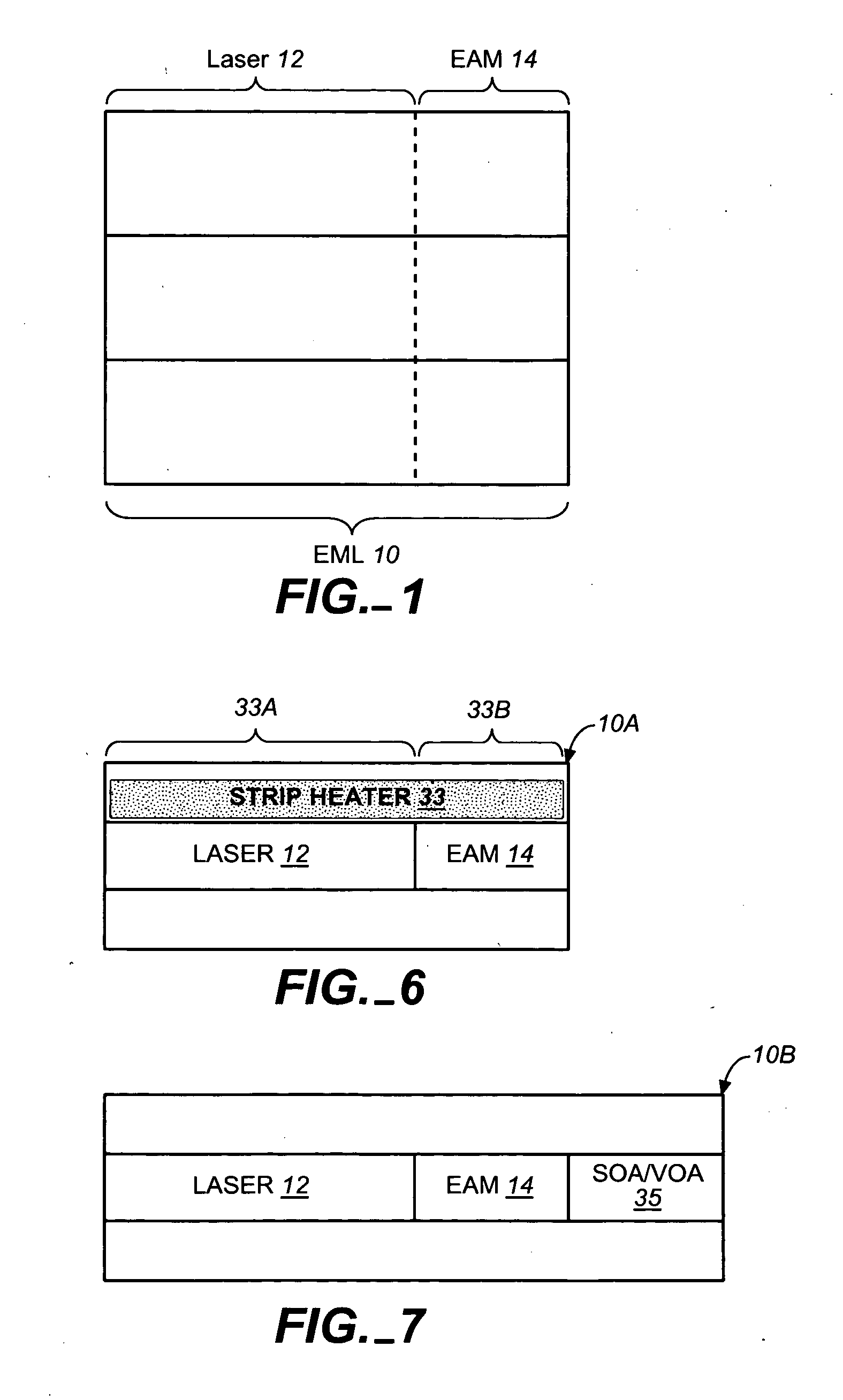
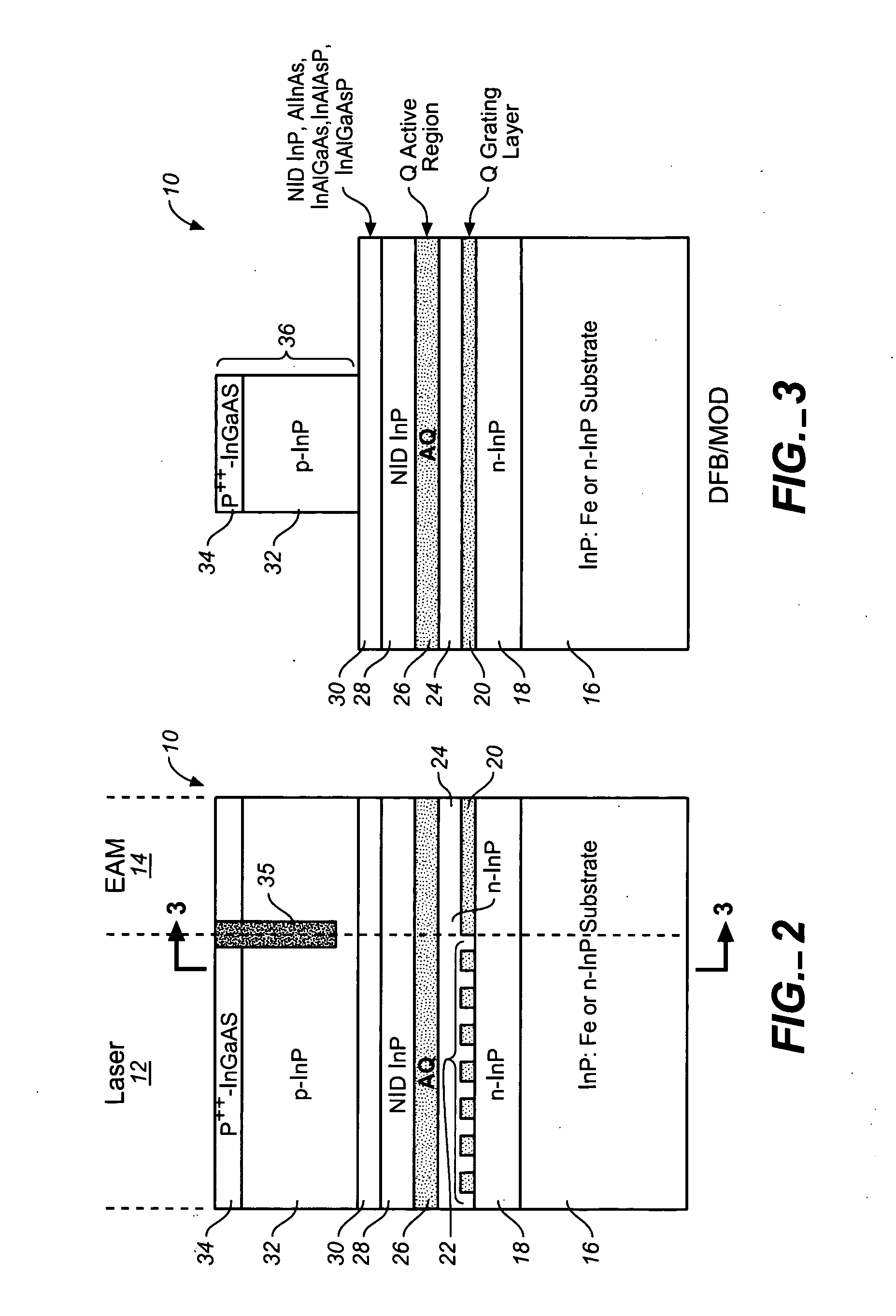
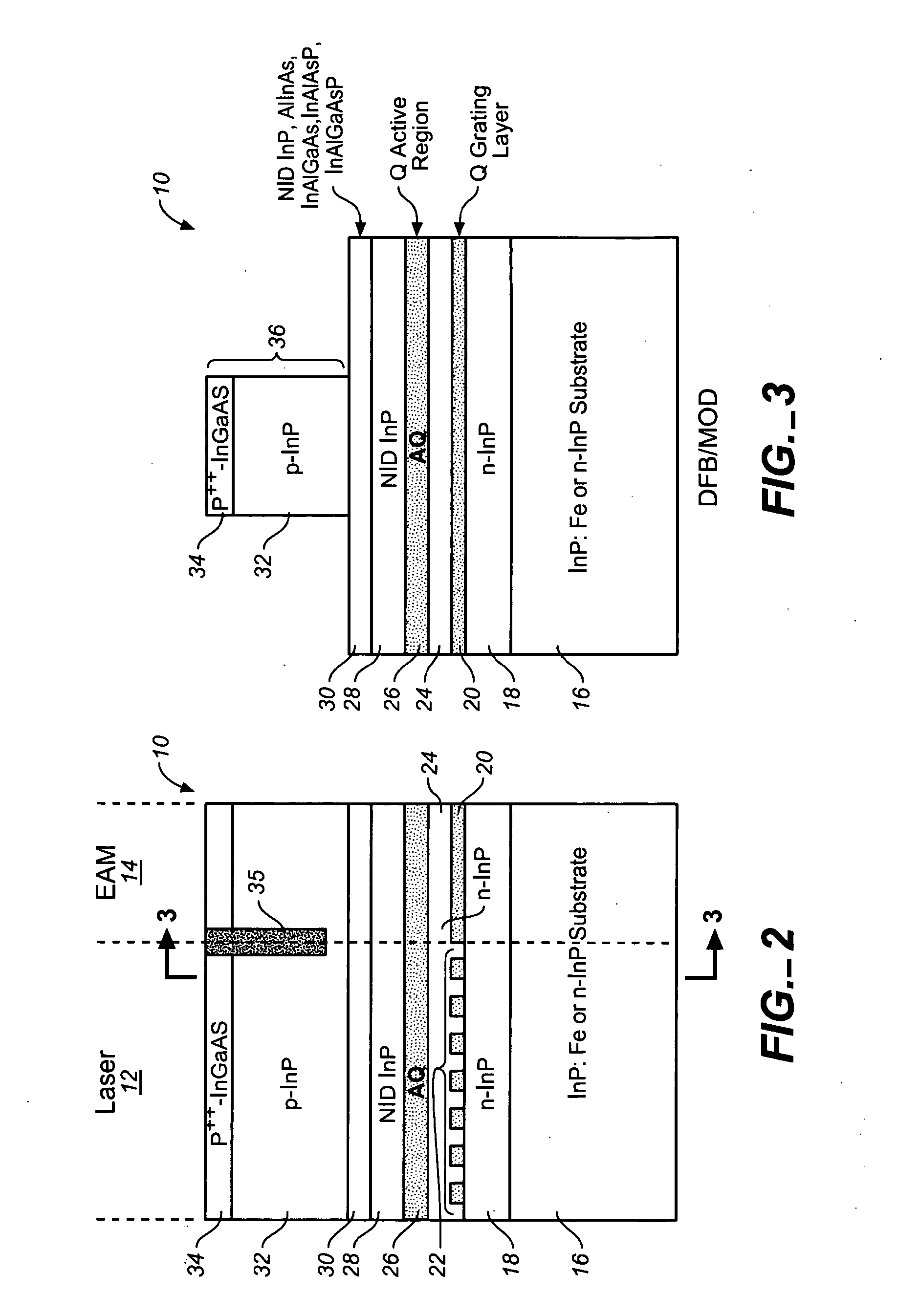
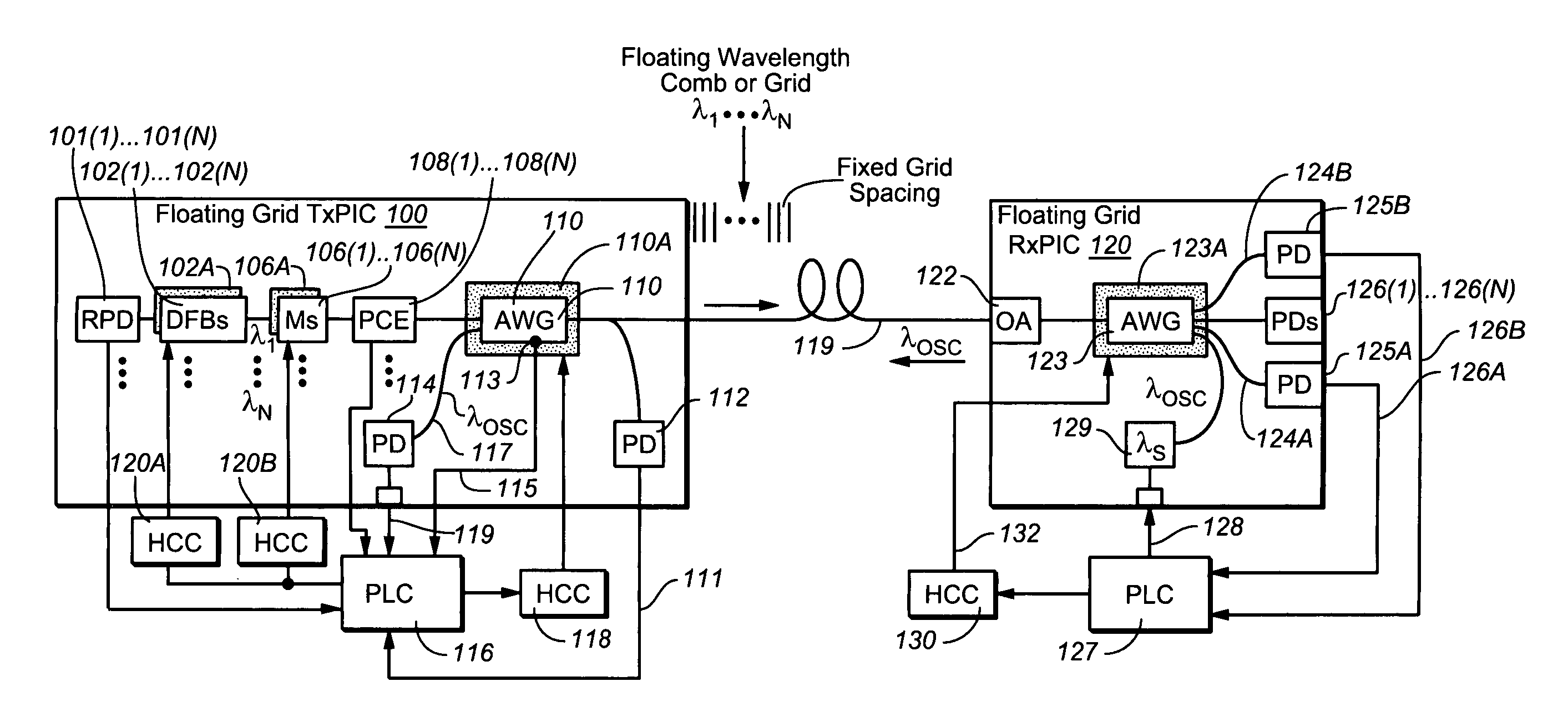
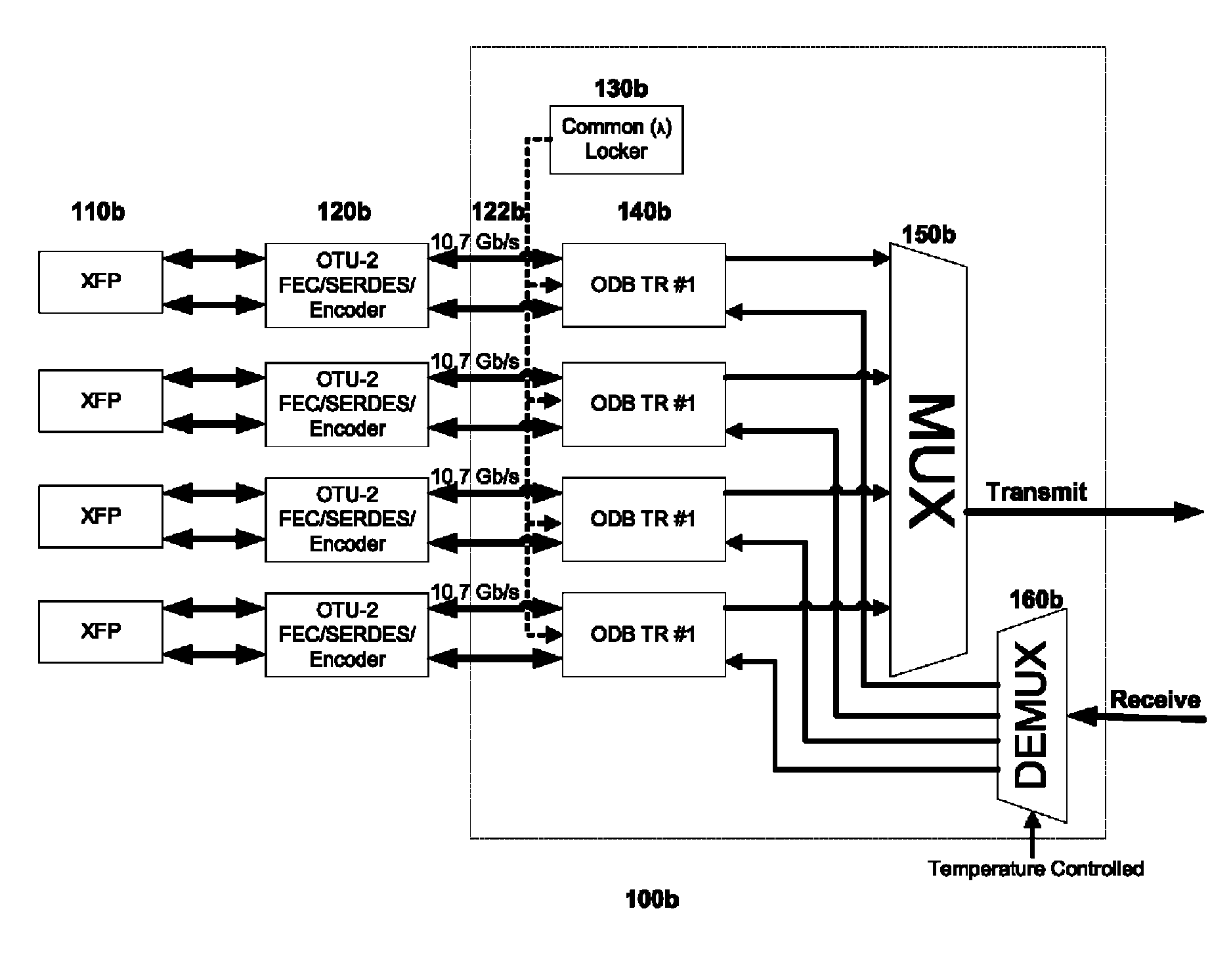
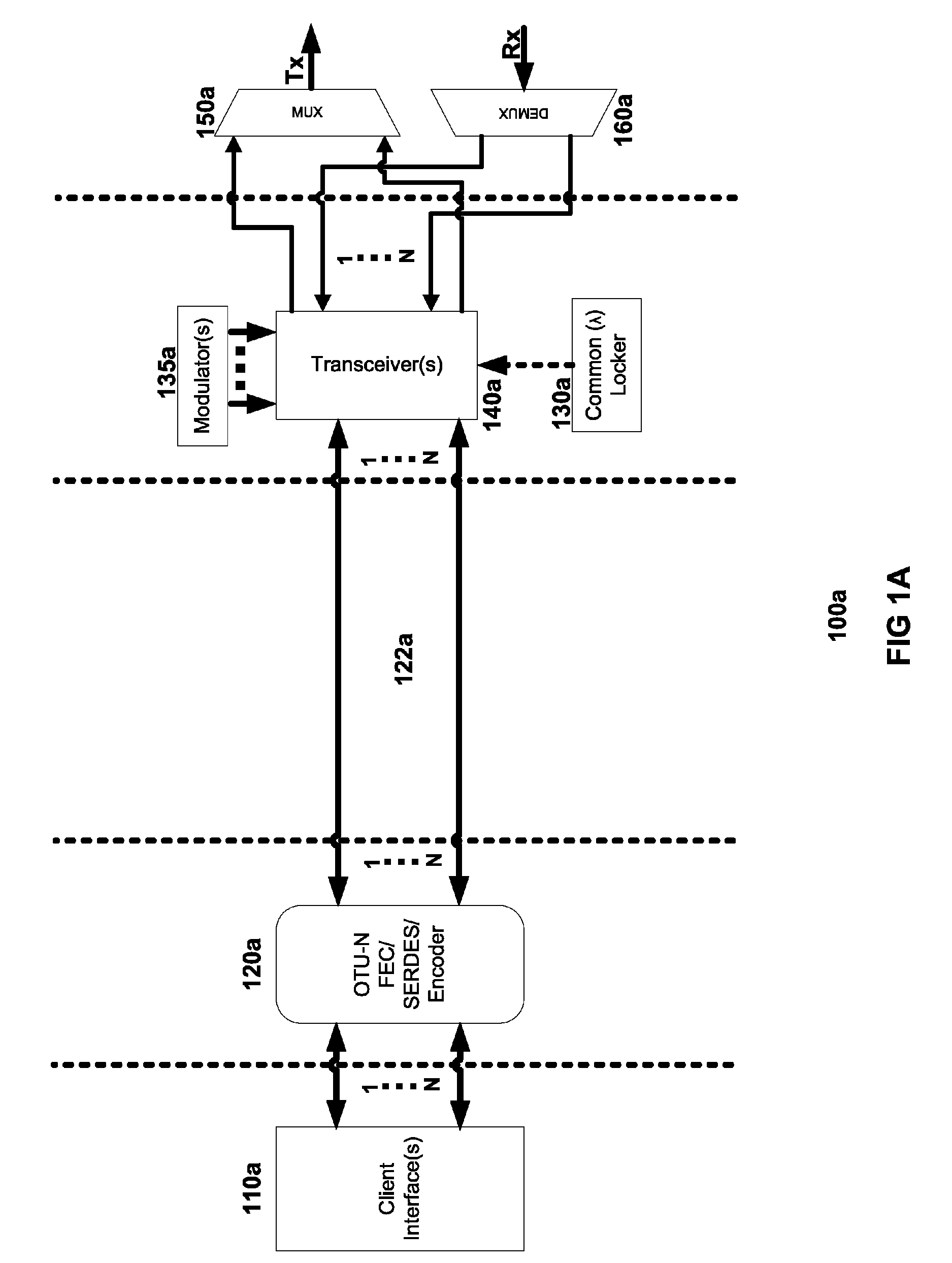
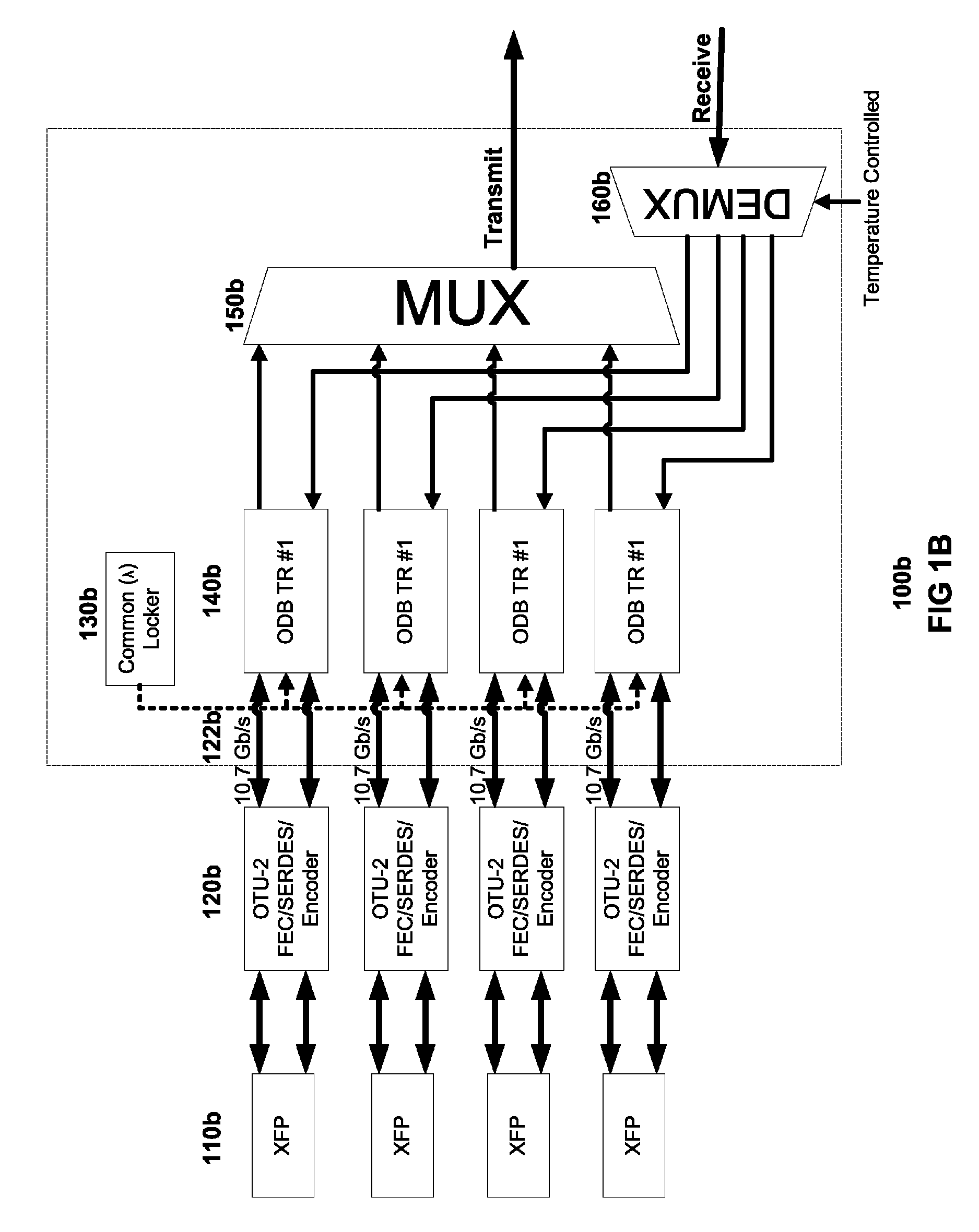
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
ActiveUS20050249509A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedEasy to controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorHermetic packaging
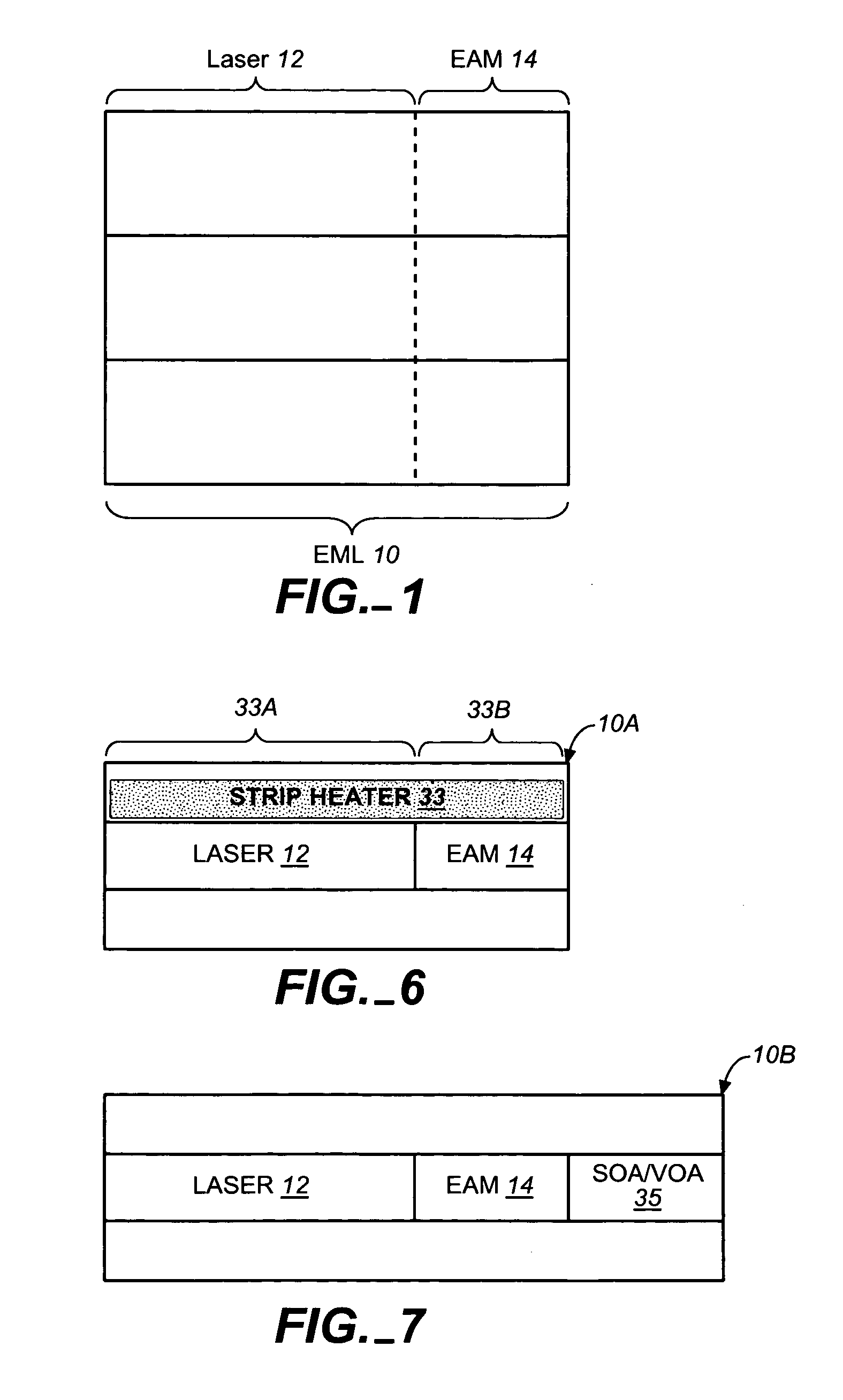
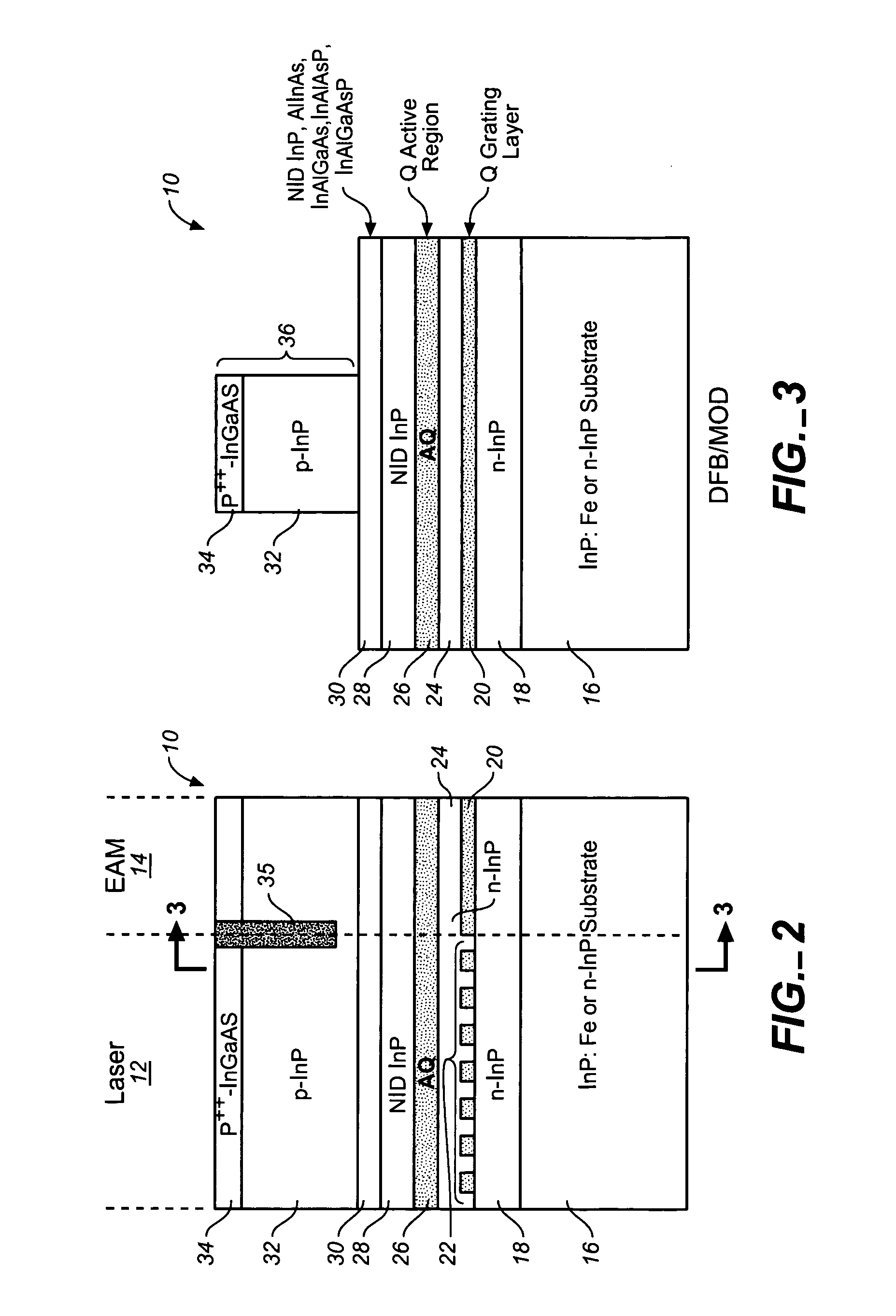
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Subchannel security at the optical layer
InactiveUS20140193154A1Facilitate decision-makingMinimize network congestionWavelength-division multiplex systemsSecret communicationComputer scienceConcatenation
The present invention includes various novel systems and methods for dynamically modifying WDM transmission and receive steps (individually or in combination), including encoding client signals, mapping them to subchannels within or across ITU channels, modulating them onto subcarrier frequencies, and multiplexing them together for optical transmission. By dynamically modifying one or more of these processing steps over time (as well as encrypting underlying client signals), additional security is provided at the physical (optical) layer of an optical network, thereby greatly enhancing overall network security. Tunable lasers are employed to generate respective subcarrier frequencies, which represent subchannels of an ITU channel to which client signals are mapped. Client circuits are divided and combined with one another before being mapped to individual subchannels within and across ITU channels, thereby facilitating desired optical routing, switching, concatenation and protection of the client circuits mapped to those subchannels across the nodes of a WDM network.
Owner:SONUS NETWORKS
COOLERLESS PHOTONIC INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (PICs) FOR WDM TRANSMISSION NETWORKS AND PICs OPERABLE WITH A FLOATING SIGNAL CHANNEL GRID CHANGING WITH TEMPERATURE BUT WITH FIXED CHANNEL SPACING IN THE FLOATING GRID
ActiveUS20100166424A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorPeak value
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Optical fiber having a lower bending loss
ActiveUS6901196B2Bending lossSuppressing transmission loss increaseGlass optical fibreGlass making apparatusHydrogenRelative refractive index
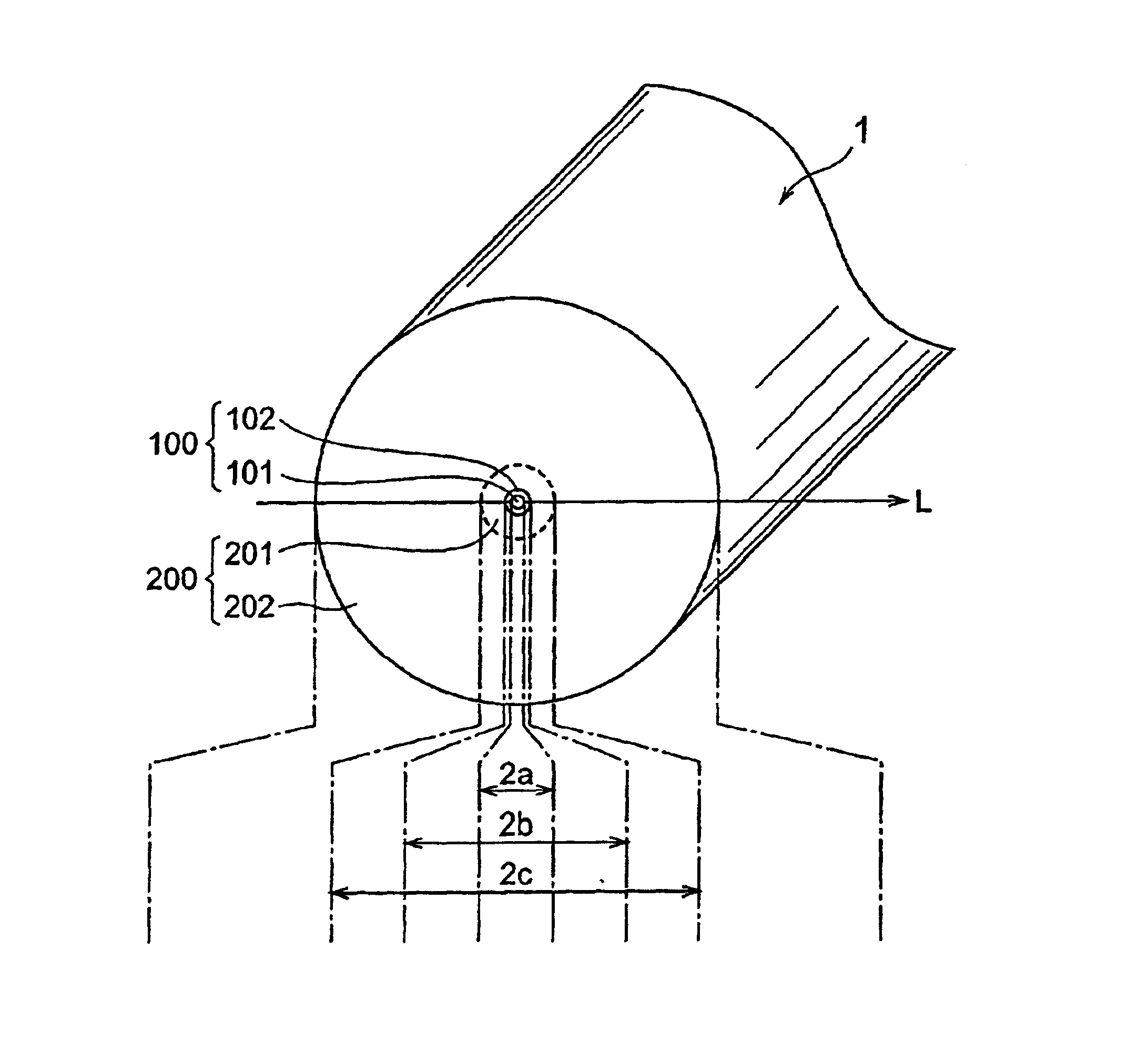
An optical fiber includes a first core having a relative refractive index difference of larger than 0.36%, and a cladding. The optical fiber has fiber cut-off wavelength λc of more than 1350 nm, cable cut-off wavelength λcc of less than 1285 nm, bending loss at a wavelength of 1625 nm of not more than 10 dB / km when wound at a diameter of 20 mm, transmission loss at a wavelength range of 1285 to 1625 nm of not more than 0.40 dB / km, transmission loss at a wavelength of 1383 nm less than transmission loss at a wavelength of 1310 nm, and difference in transmission loss at a wavelength of 1383 nm of not more than 0.04 dB / km before and after exposure to hydrogen. The lower bending loss of the optical fiber provides an optical fiber cable for use in a WDM transmission in wavelength range of 1285 to 1625 nm.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
ActiveUS7636522B2Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorPeak value
Owner:INFINERA CORP
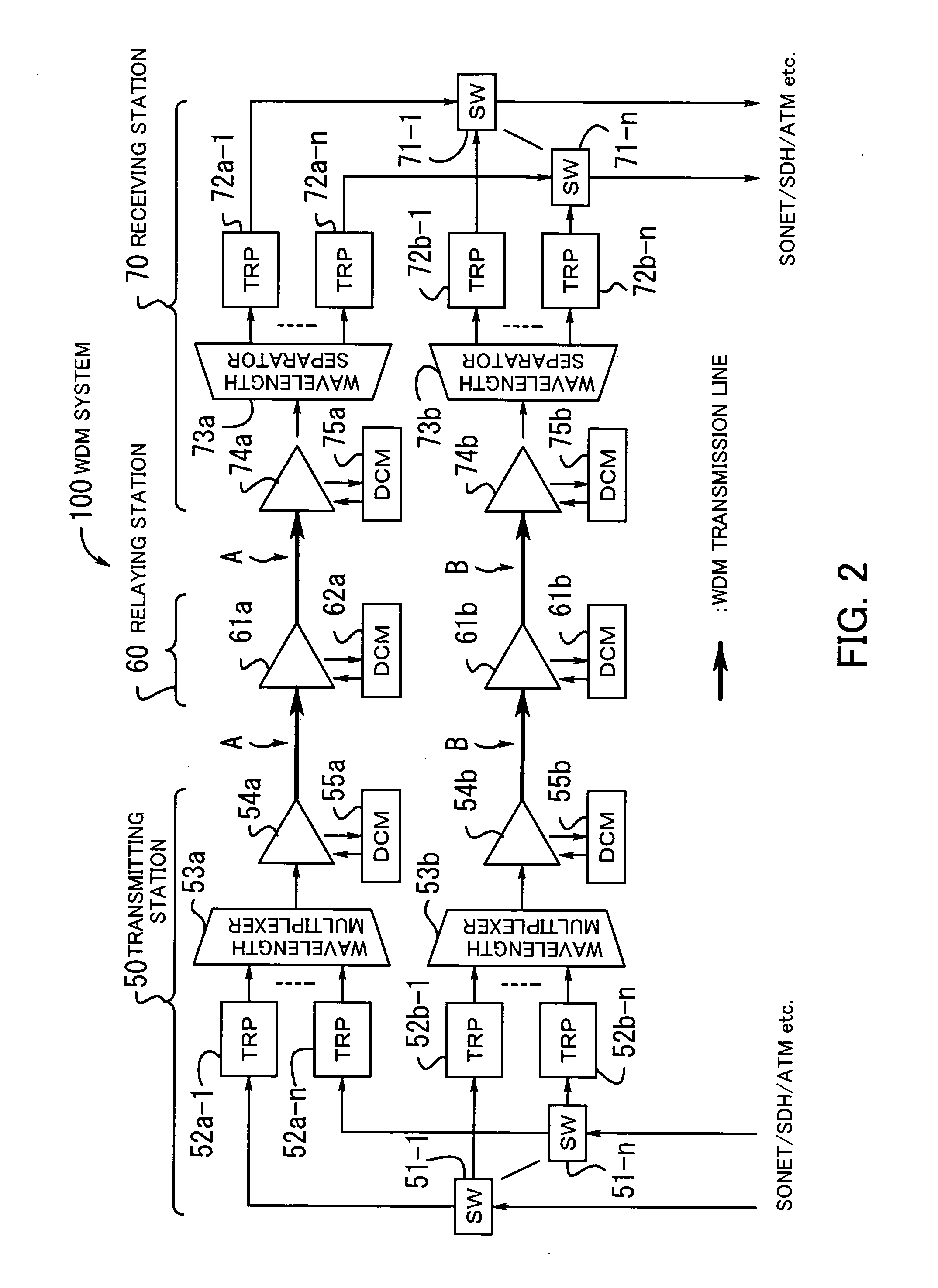
Optical wavelength multiplexing transmission apparatus and optical output control method for optical wavelength multiplexing transmission apparatus
InactiveUS20030035171A1Improve transmission qualityEasy to adjustLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignal lightLength wave
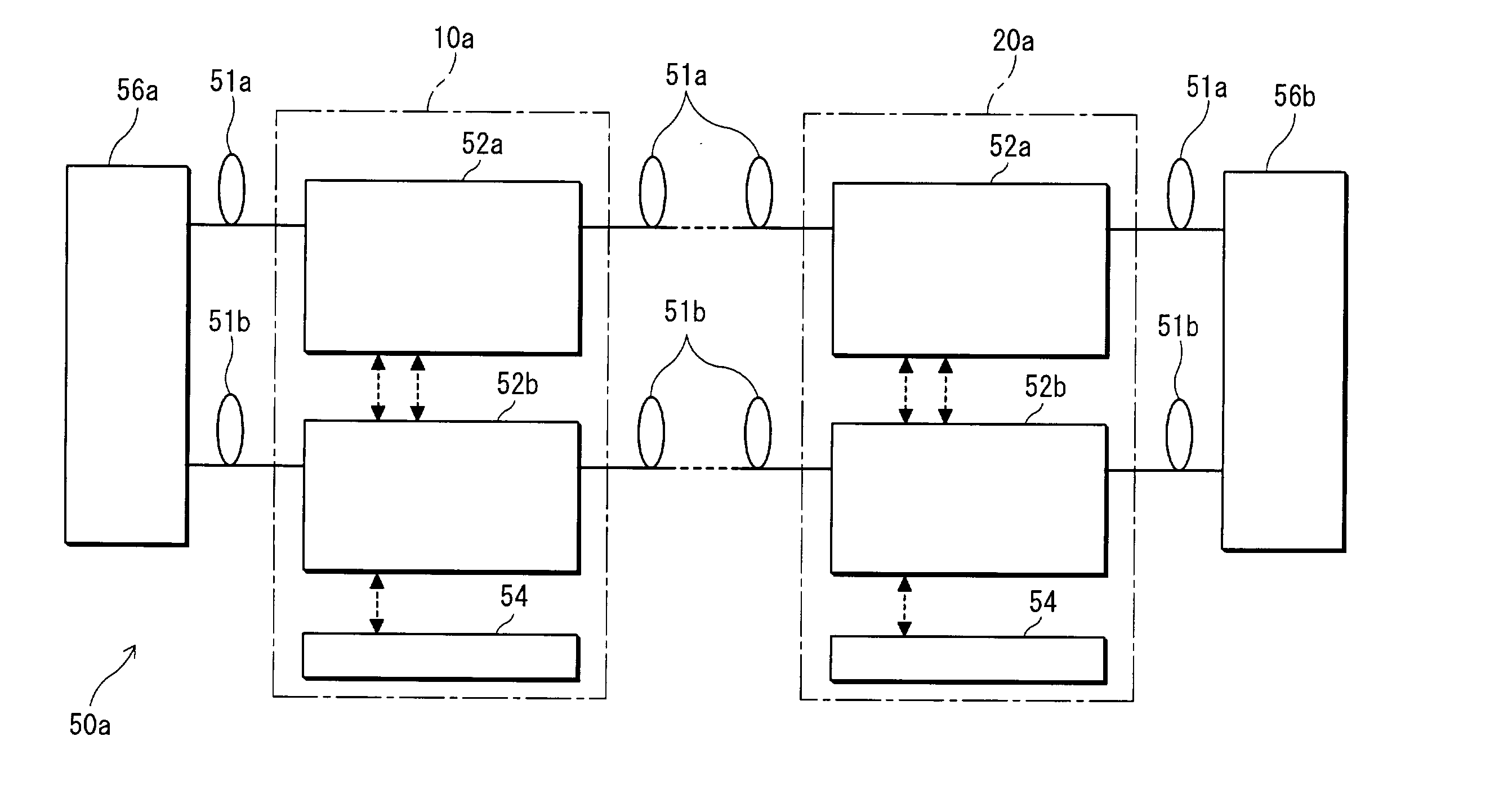
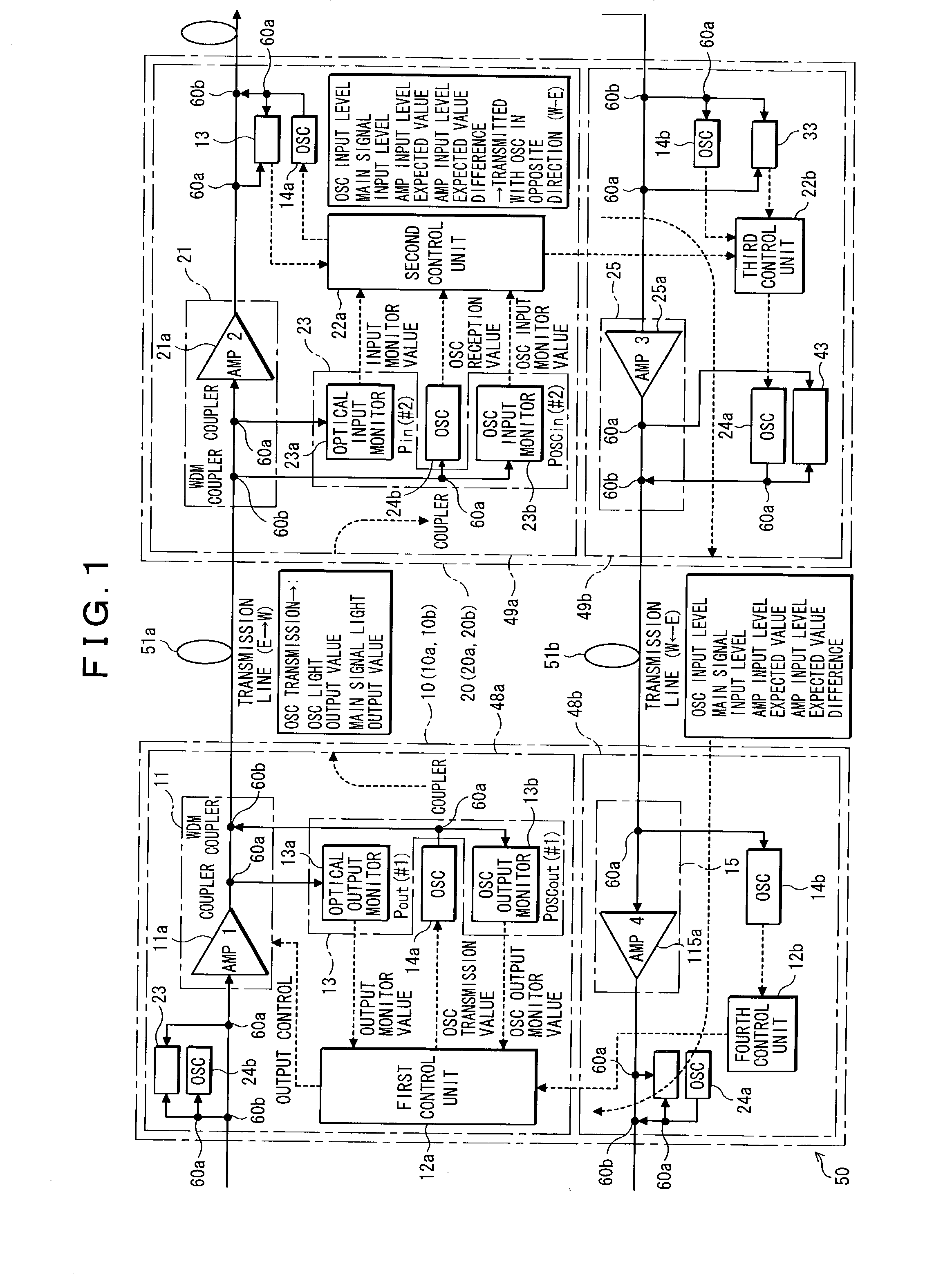
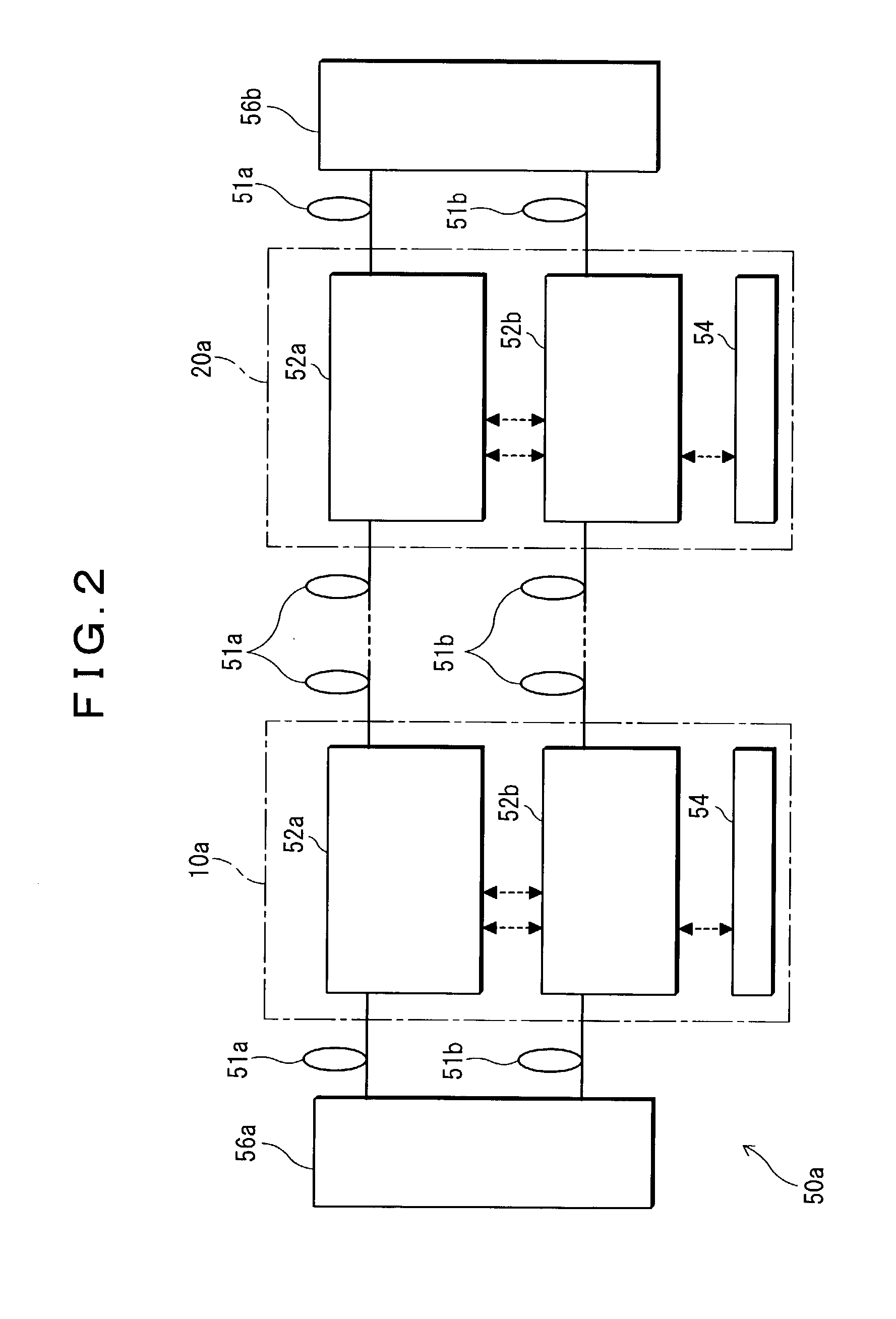
The present invention provides an optical wavelength multiplexing transmission apparatus and an optical output control method for an optical wavelength multiplexing transmission apparatus in an optical wavelength multiplexing transmission system using a main signal light and an OSC light. The optical wavelength multiplexing transmission apparatus (10a) is made up of a first transmitting / receiving section (52a) a second transmitting / receiving section (52b) and an apparatus supervisory control unit (54). This can not only achieve quick restoration from troubles, but also stably calculate an optical output level even if a change of the number of wavelengths to be multiplexed takes place in a main signal light, and even save troublesome adjustments for the improvement of reliability of a transmission line while eliminating the need for a signal source for the adjustment of a receive optical level at the initial installation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical fiber and optical transmission line and optical communication system including such optical fiber
InactiveUS6856744B2Improve power generation efficiencyHigh strengthOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesCommunications systemRelative refractive index
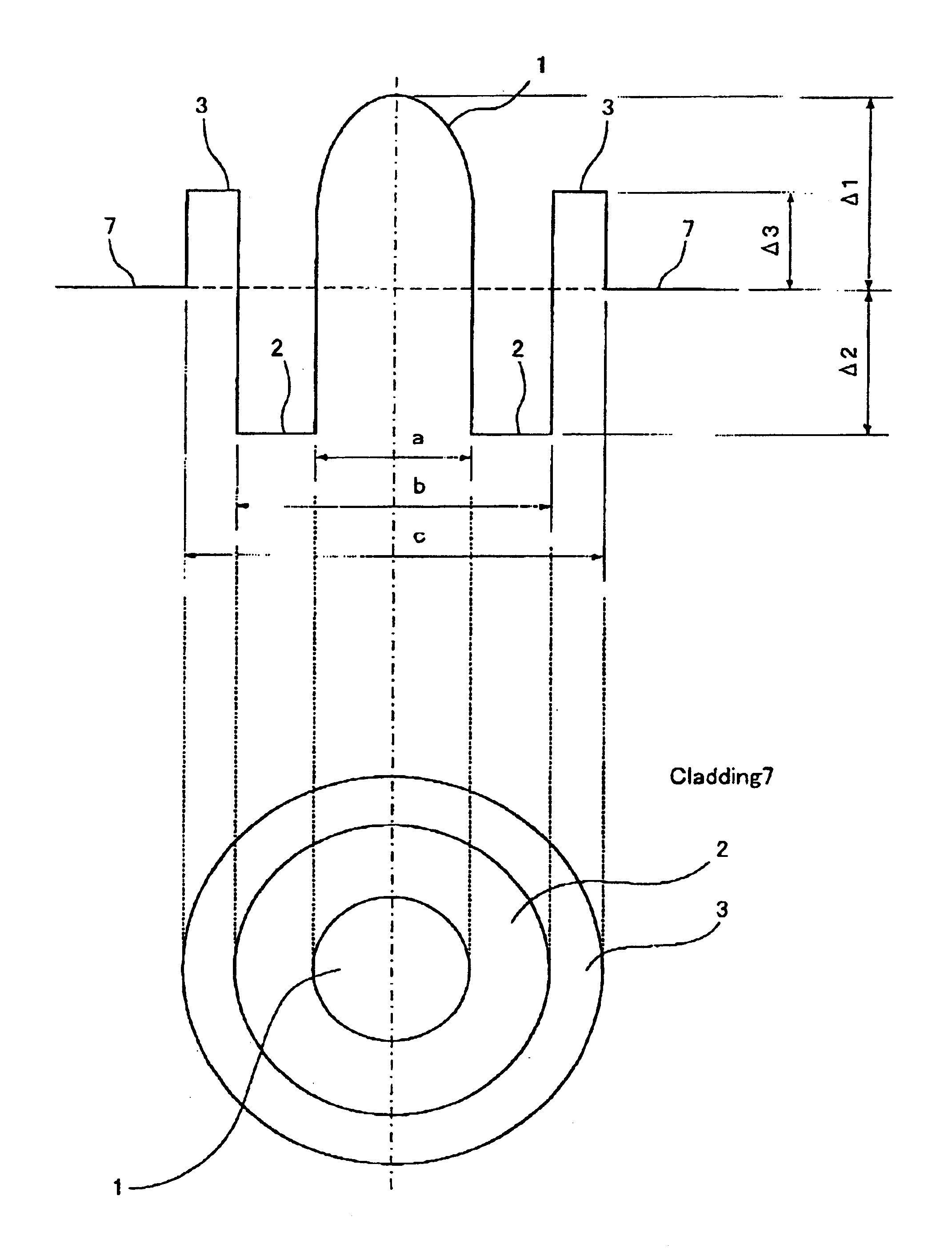
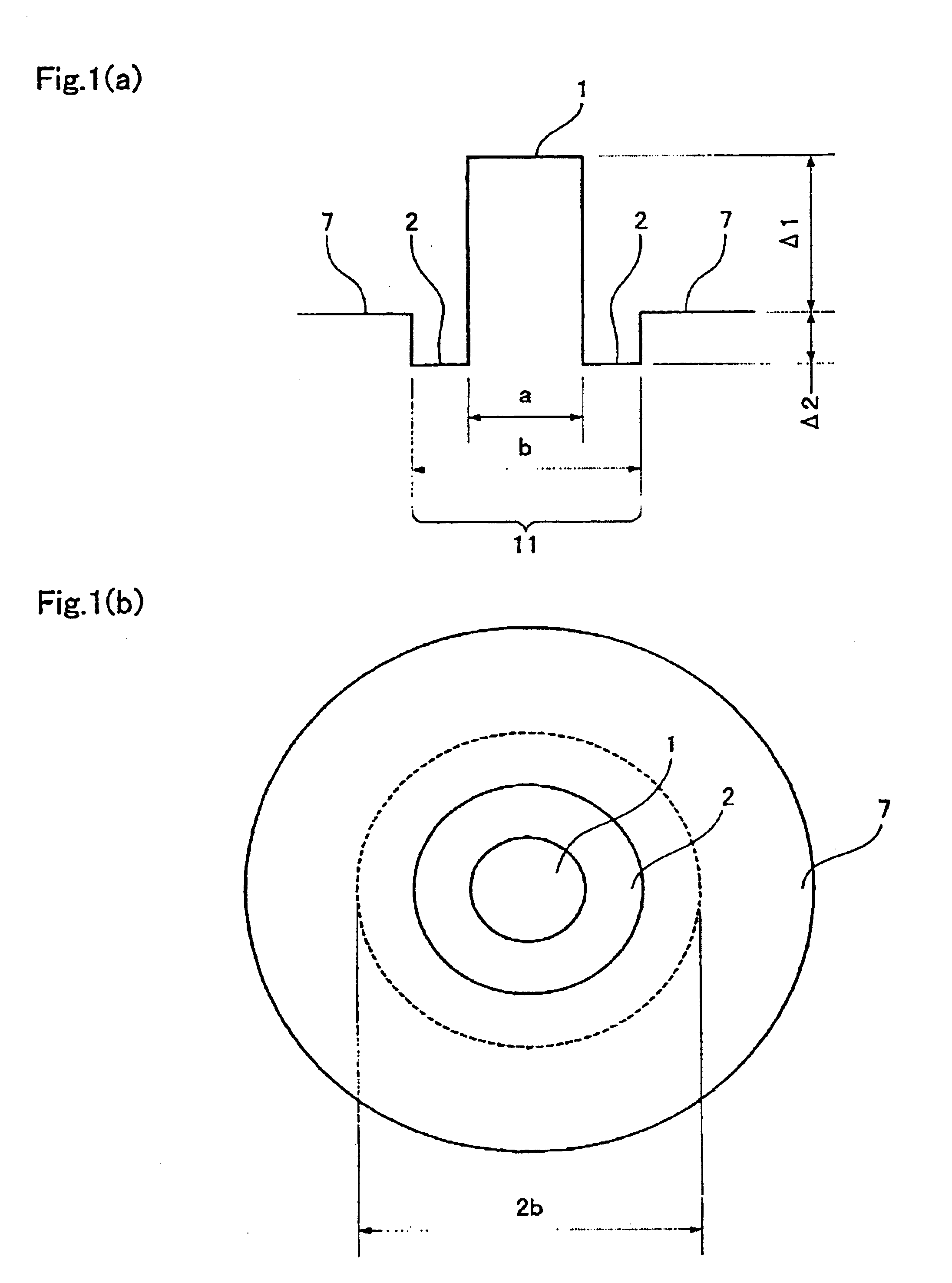
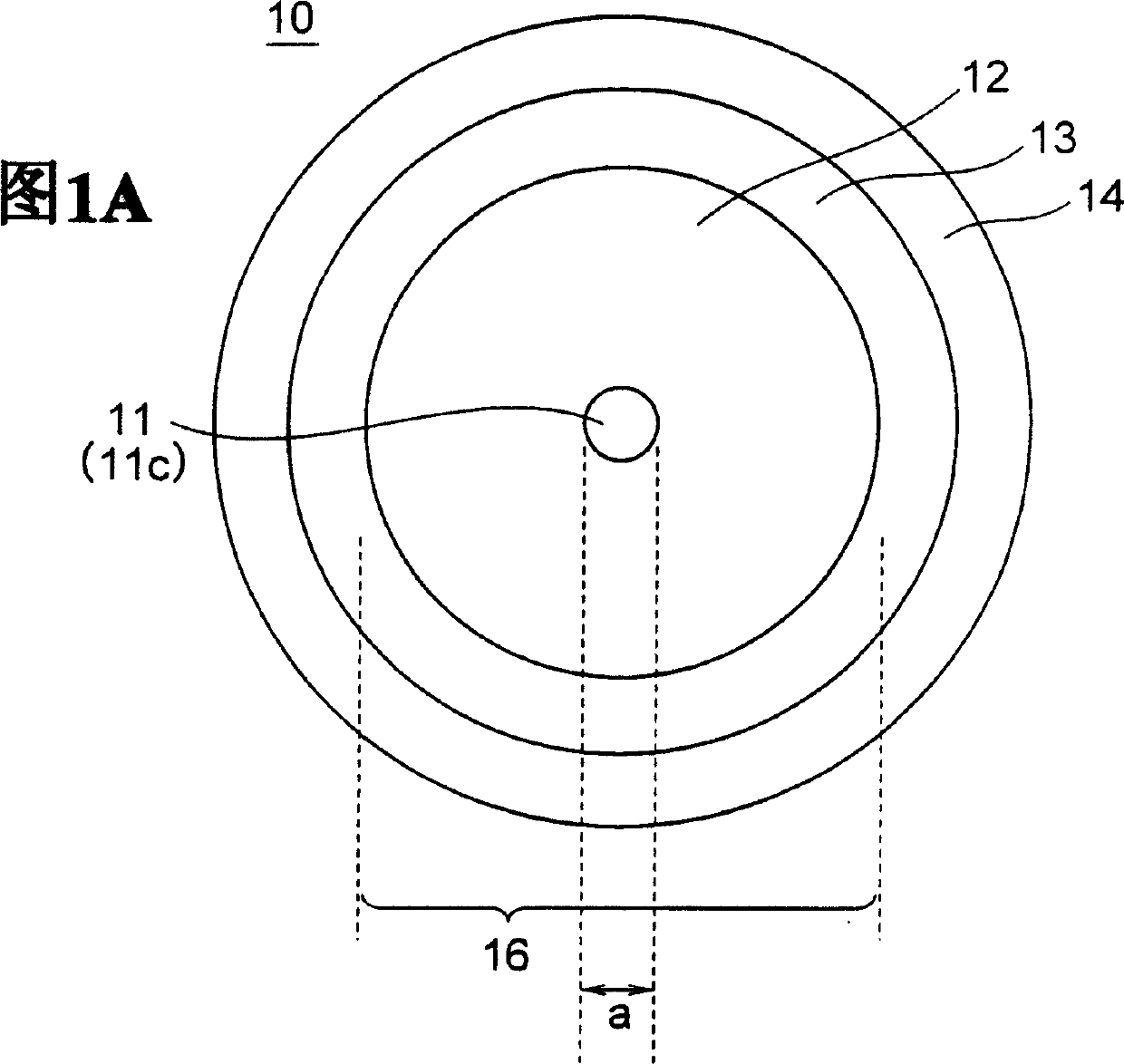
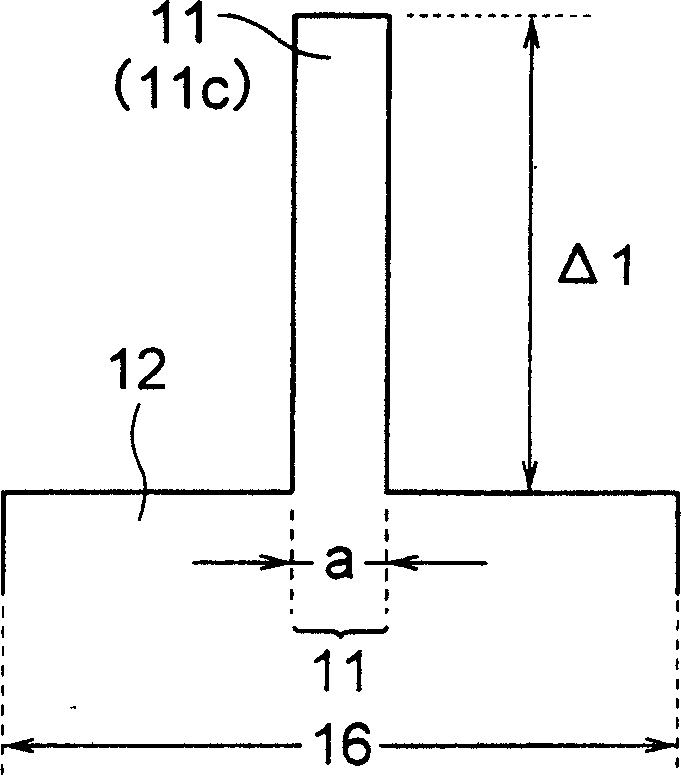
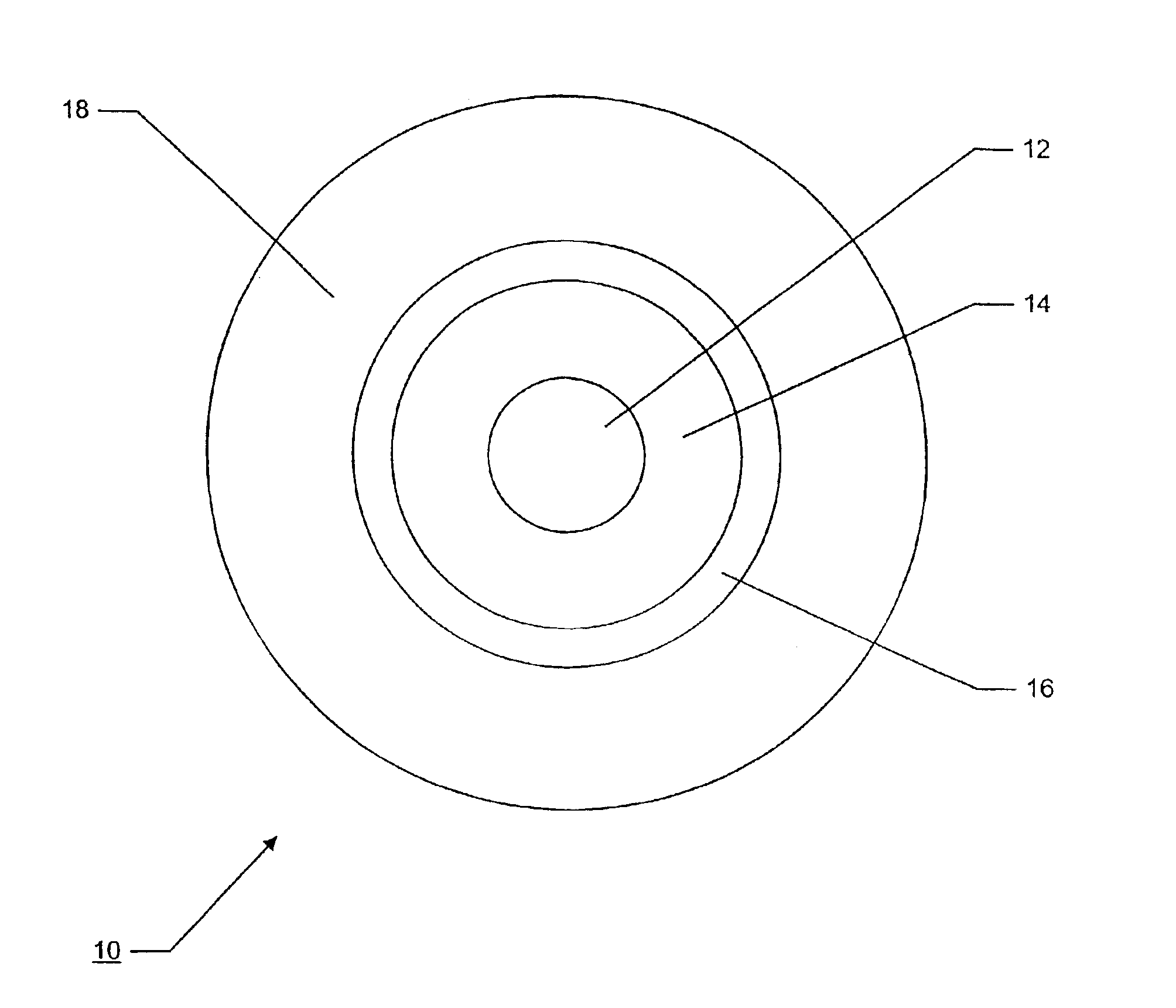
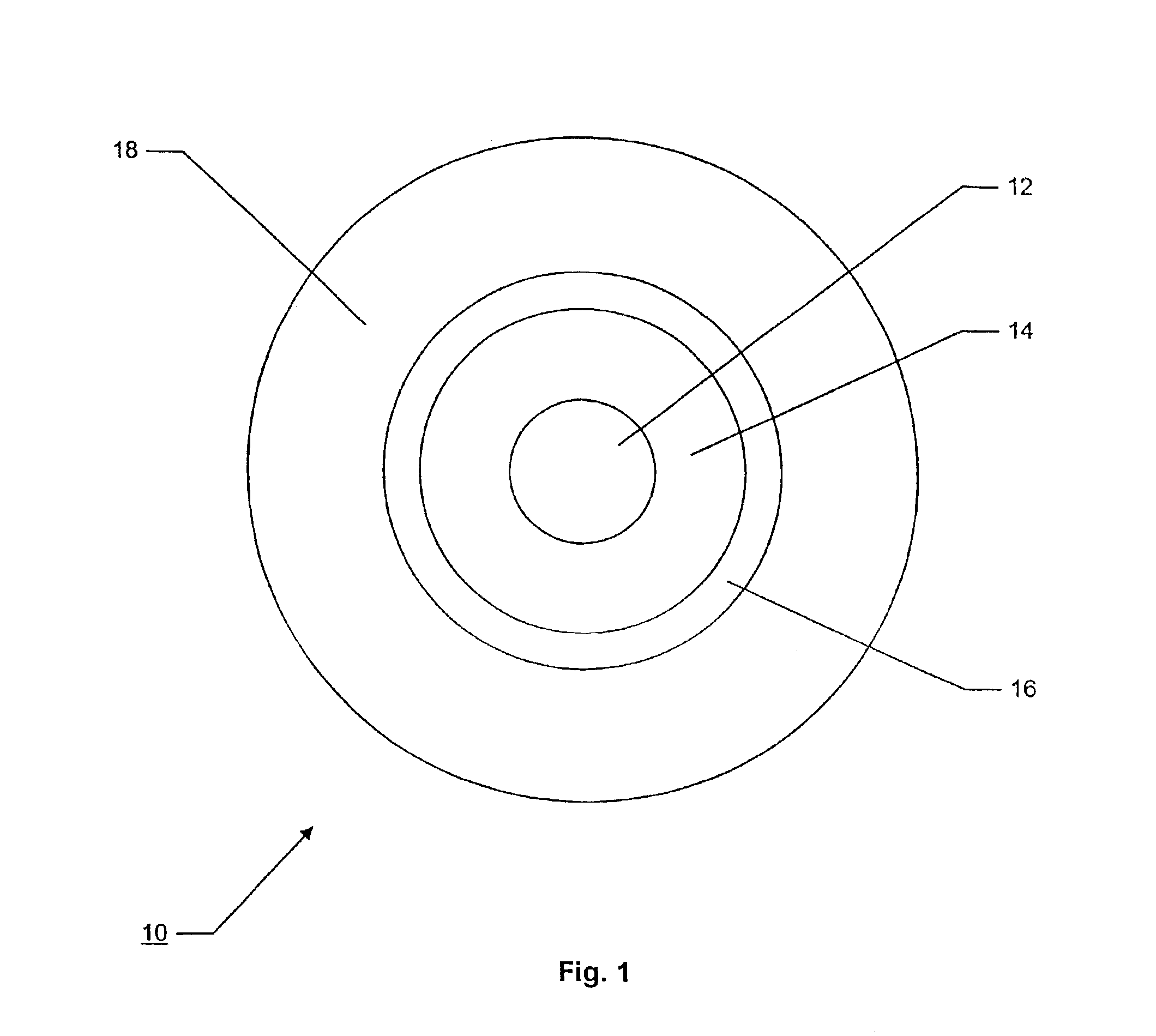
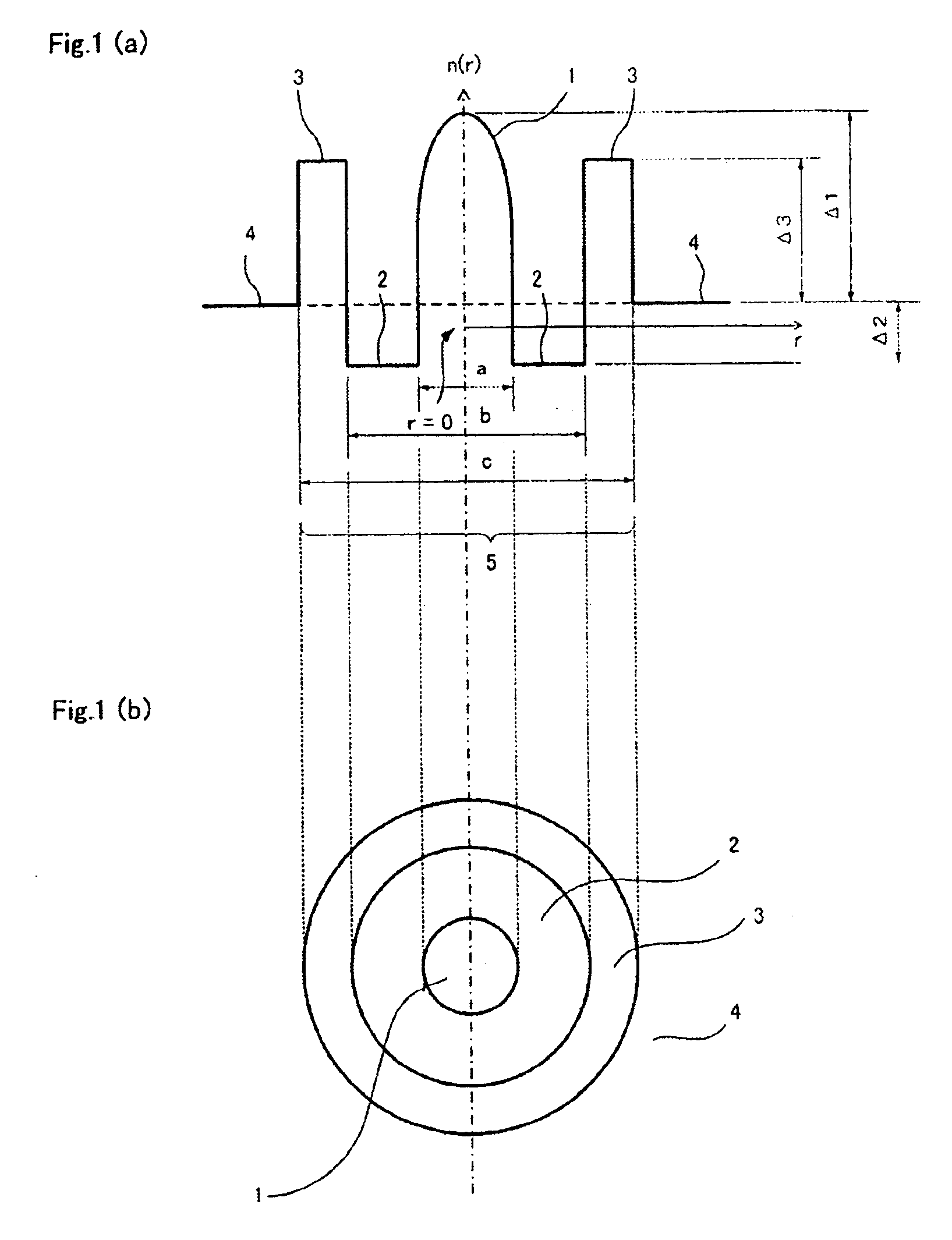
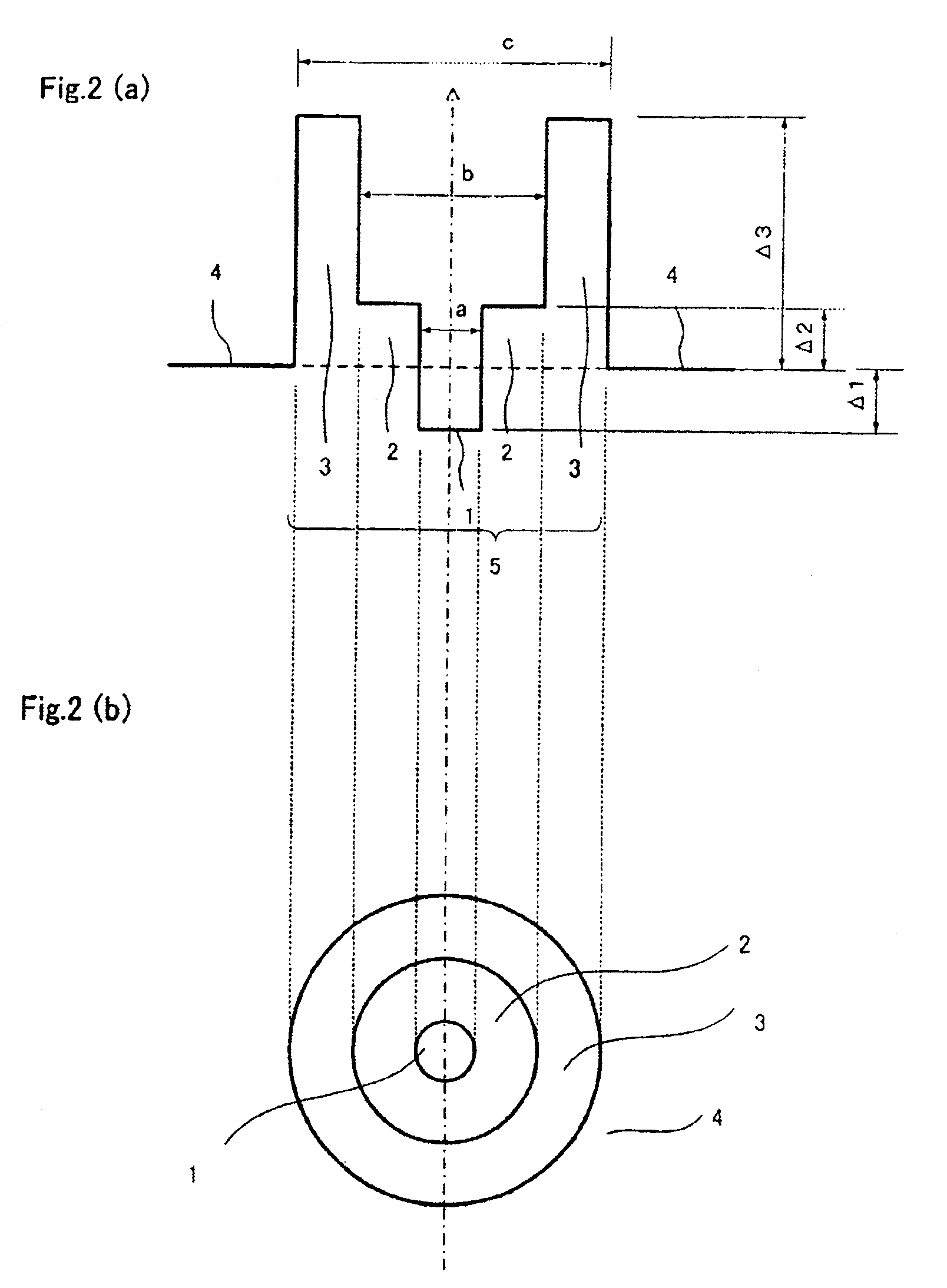
Optical fibers to form an optical transmission line suitable for WDM transmission in a wide-spreading wavelength band, having the following characteristics and parameters: a dispersion in absolute value of 0.5 ps / nm / km to 9 ps / nm / km in a wavelength band of 1430 nm to 1625 nm, a dispersion slope in absolute value of 0.04 ps / nm2 / km or less at a wavelength of 1550 nm, a mode field diameter of 7 μm or less at a wavelength of 1550 nm and a cable cutoff wavelength of less than 1430 nm; core 11 surrounded by cladding 7, core 11 being at least two-layered (first layer 1 at the center and second layer 2 surrounding the first layer; relative refractive index of glass layer Δ1 with reference to the cladding being adjusted to not less than 0.6 but not more than 1.6%, relative refractive index of second layer Δ2 with reference to the cladding being adjusted to a negative value.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
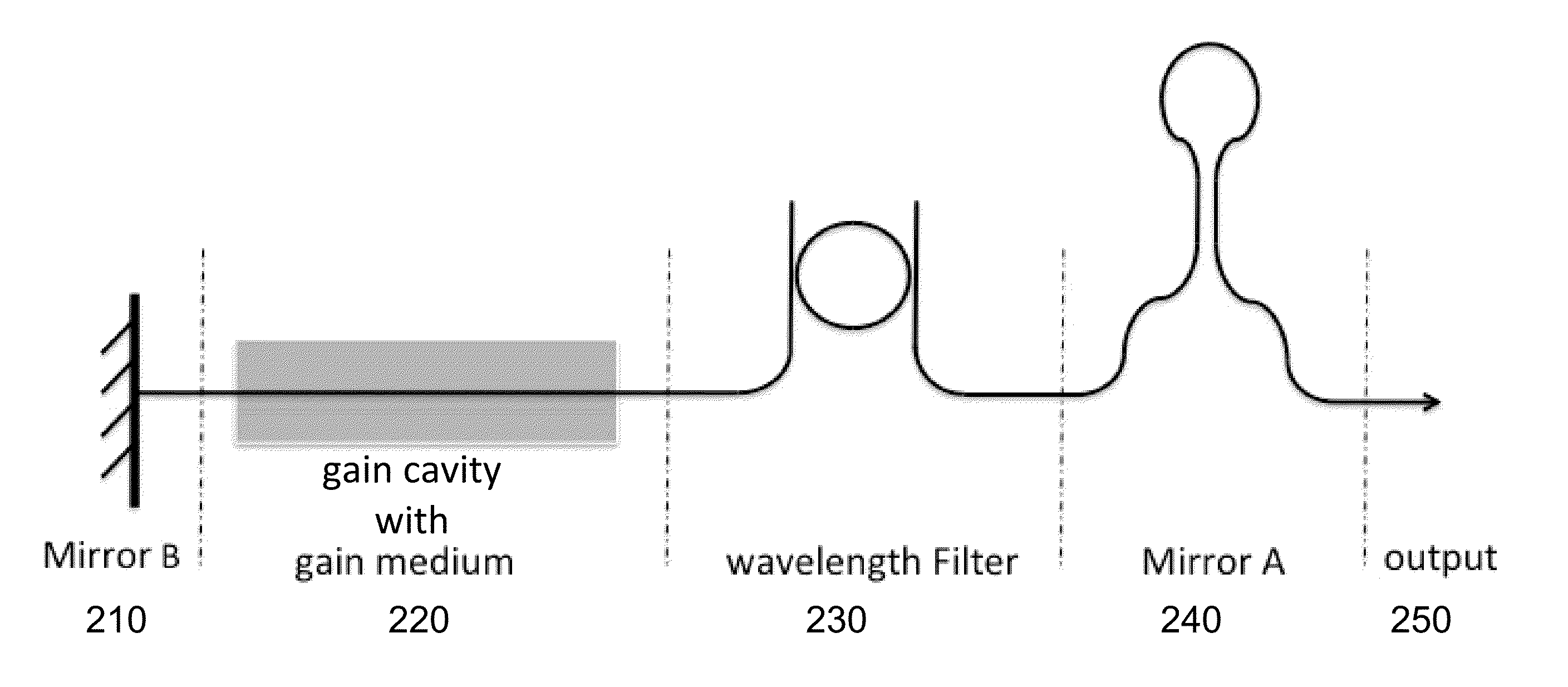
Quantum dot soa-silicon external cavity multi-wavelength laser
ActiveUS20150180201A1Hermetic sealLaser optical resonator constructionLaser active region structureSilicon photonicsQuantum dot
A hybrid external cavity multi-wavelength laser using a QD RSOA and a silicon photonics chip is demonstrated. Four lasing modes at 2 nm spacing and less than 3 dB power non-uniformity were observed, with over 20 mW of total output power. Each lasing peak can be successfully modulated at 10 Gb / s. At 10−9 BER, the receiver power penalty is less than 2.6 dB compared to a conventional commercial laser. An expected application is the provision of a comb laser source for WDM transmission in optical interconnection systems.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Optical fiber for a flat-gain optical amplifier
InactiveUS6175445B1Reduce background noiseAcceptable output powerLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantAudio power amplifier
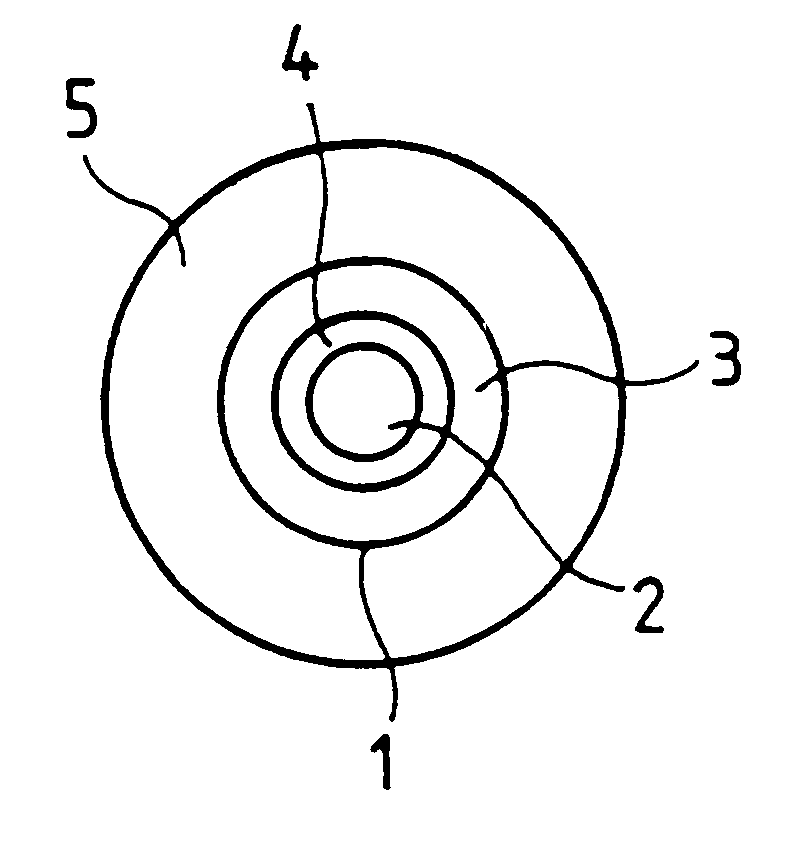
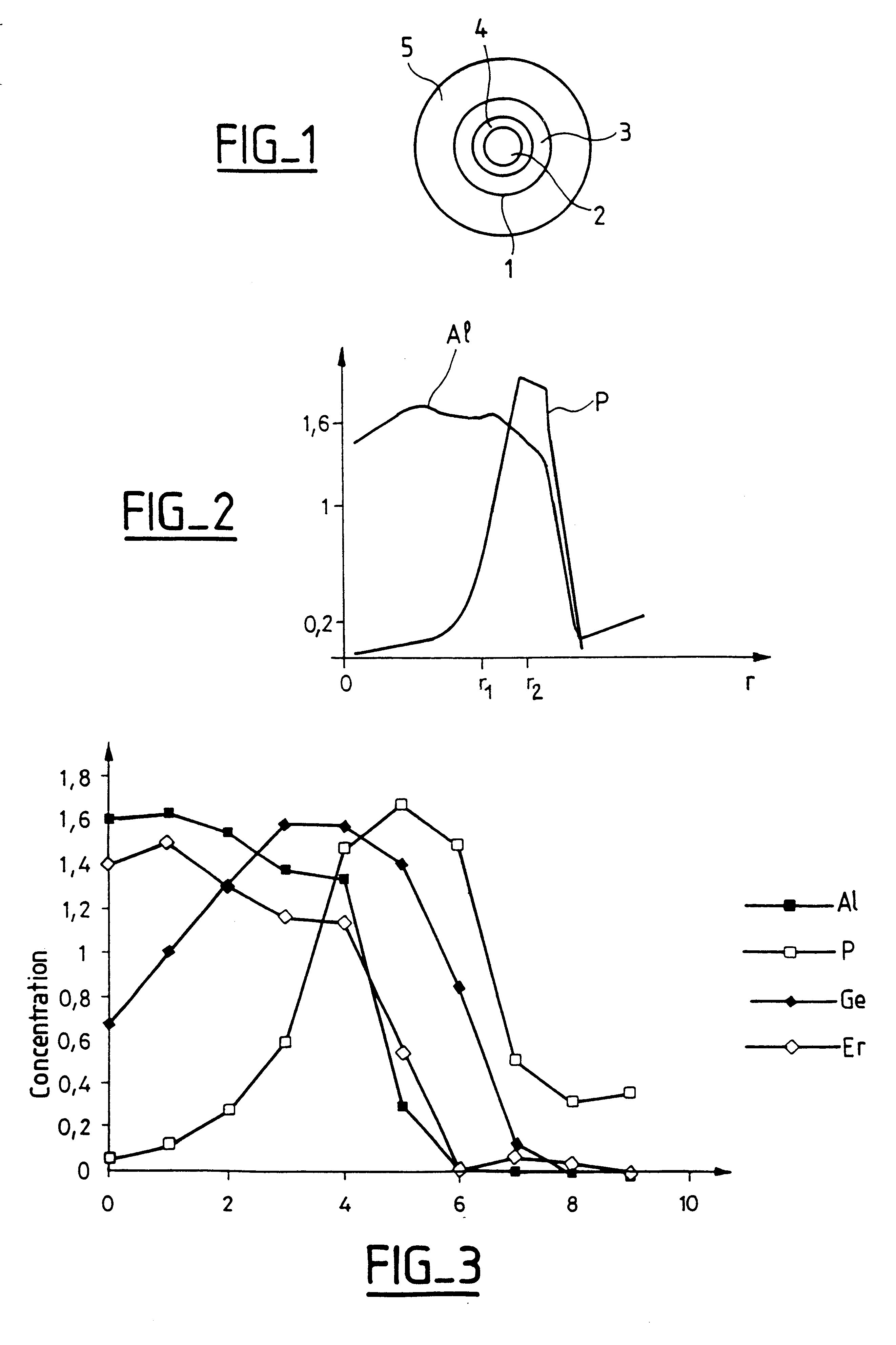
The invention relates to an optical fiber having a core based on silica with at least one fluorescent dopant distributed over the entire section of the core, a central zone co-doped with a co-dopant chosen from Al and P, and a peripheral zone co-doped with the other co-dopant chosen from Al and P. The invention can be used in an optical fiber amplifier, and it guarantees good amplifier gain flatness over a wavelength band suitable for WDM transmission.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Quantum dot SOA-silicon external cavity multi-wavelength laser
ActiveUS9450379B2Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsSilicon photonicsQuantum dot
A hybrid external cavity multi-wavelength laser using a QD RSOA and a silicon photonics chip is demonstrated. Four lasing modes at 2 nm spacing and less than 3 dB power non-uniformity were observed, with over 20 mW of total output power. Each lasing peak can be successfully modulated at 10 Gb / s. At 10−9 BER, the receiver power penalty is less than 2.6 dB compared to a conventional commercial laser. An expected application is the provision of a comb laser source for WDM transmission in optical interconnection systems.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
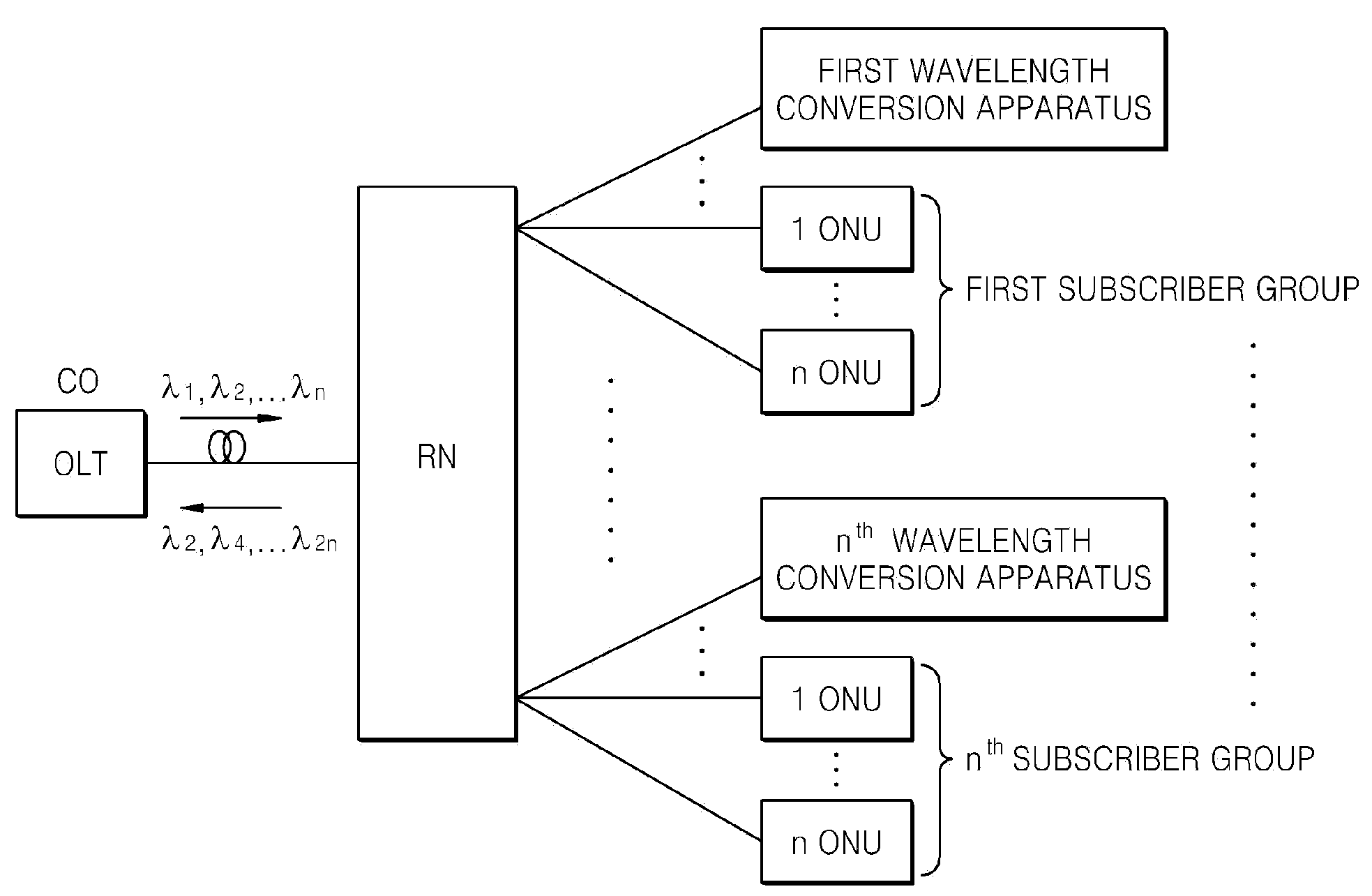
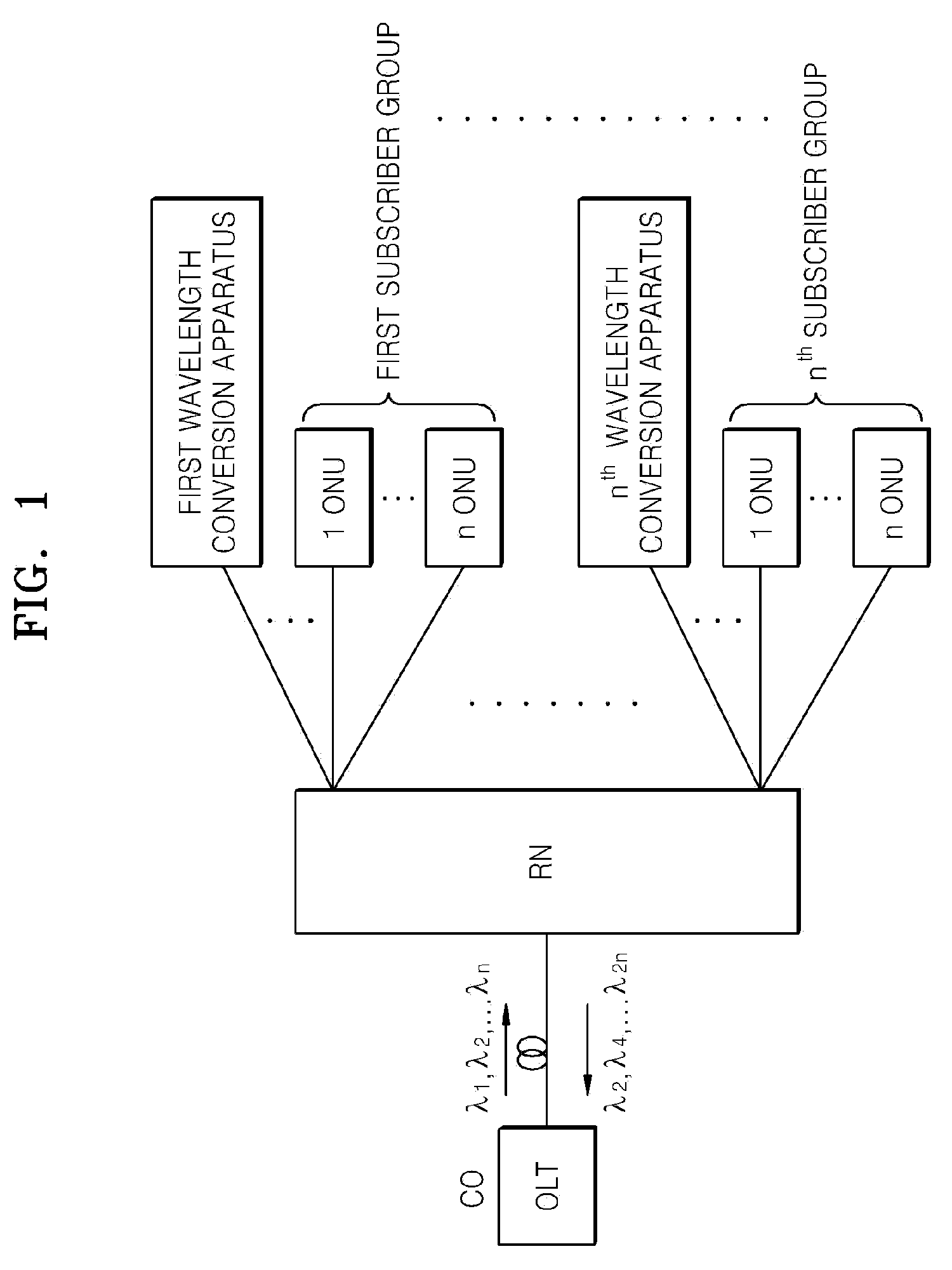
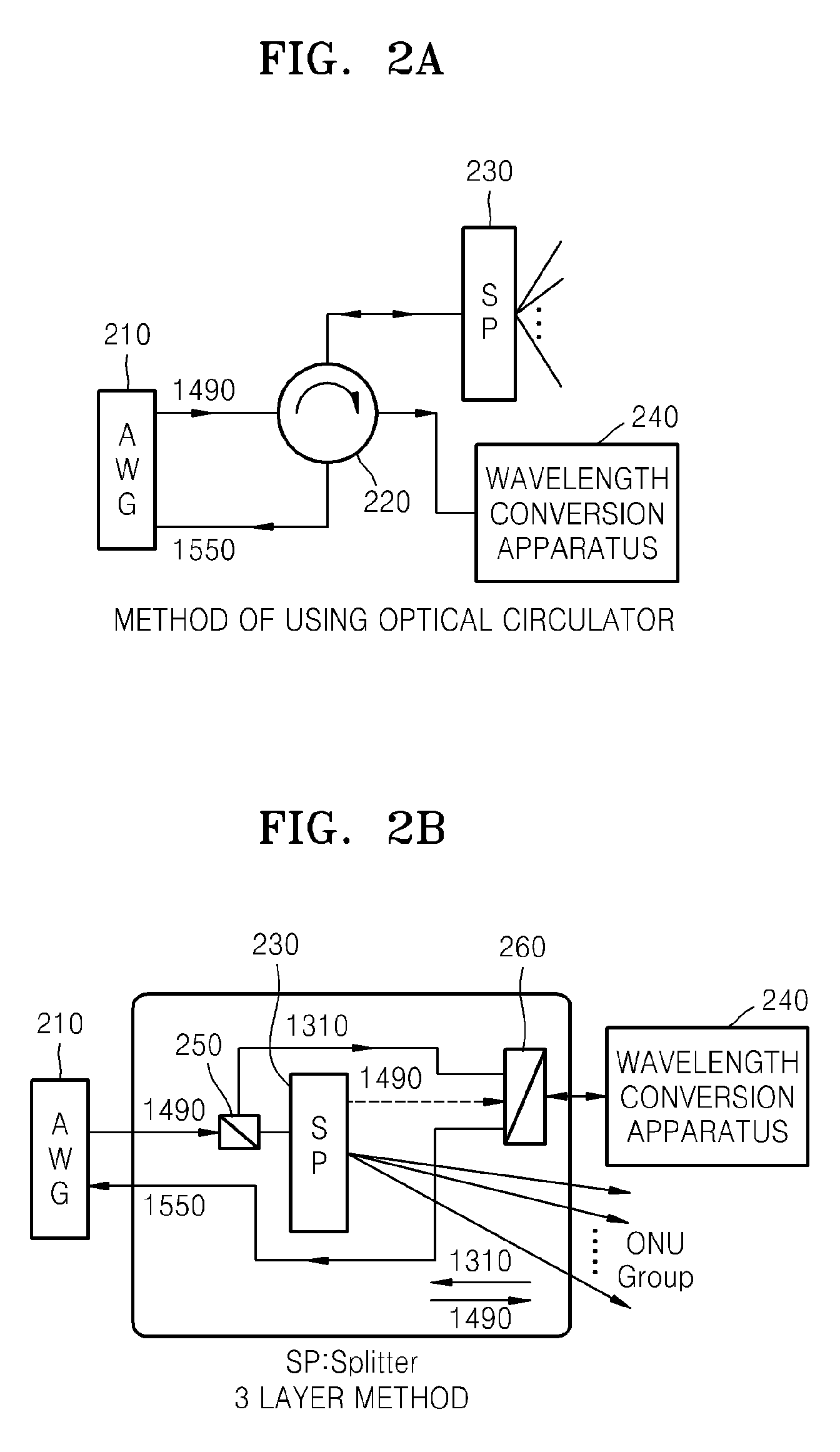
Wavelength conversion apparatus in time division multiplexing -passive optical network sytem based on wavelength division multiplexing system, and optical transmission apparatus and method using the same
InactiveUS20080138073A1Reduce in quantityIncrease the number ofWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionSignal routingOptical power
Provided are a wavelength conversion apparatus in a Time Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network (TDM-PON) system based on a Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) system, and an optical transmission method using the wavelength conversion apparatus. Each subscriber does not need to have its own wavelength but transmits an uplink signal using a wavelength band used in the TDM-PON system and routs optical network unit (ONU) uplink signals belonging to the same ONU to a wavelength conversion apparatus positioned in a subscriber area. The wavelength conversion apparatus converts the ONU uplink signals into wavelengths and uplinks the wavelengths of an optical line terminal (OLT) of a central office (CO) so as to enable a WDM transmission. Thus, a method of constituting a wavelength conversion apparatus and a remote node (RN) using the wavelength conversion apparatus can be suggested to realize a hybrid-PON system into which TDM-PON system and WDM systems are combined. In the hybrid-PON system, an ONU uses a wavelength used in the TDM-PON system and requires a lower optical power than an ONU of the TDM-PON system. Therefore, the WDM system can be easily applied in an area in which the TDM-PON system is installed.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
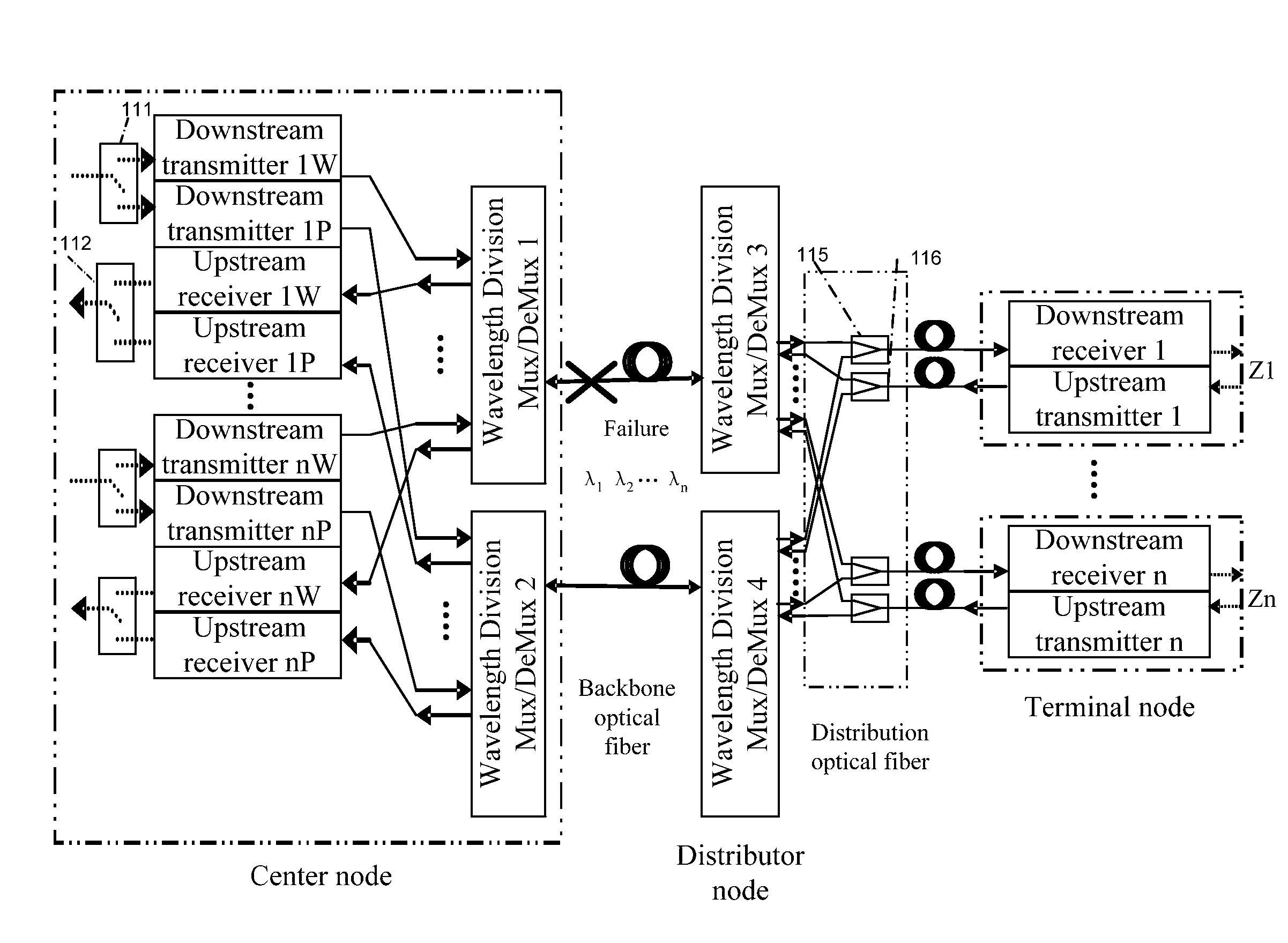
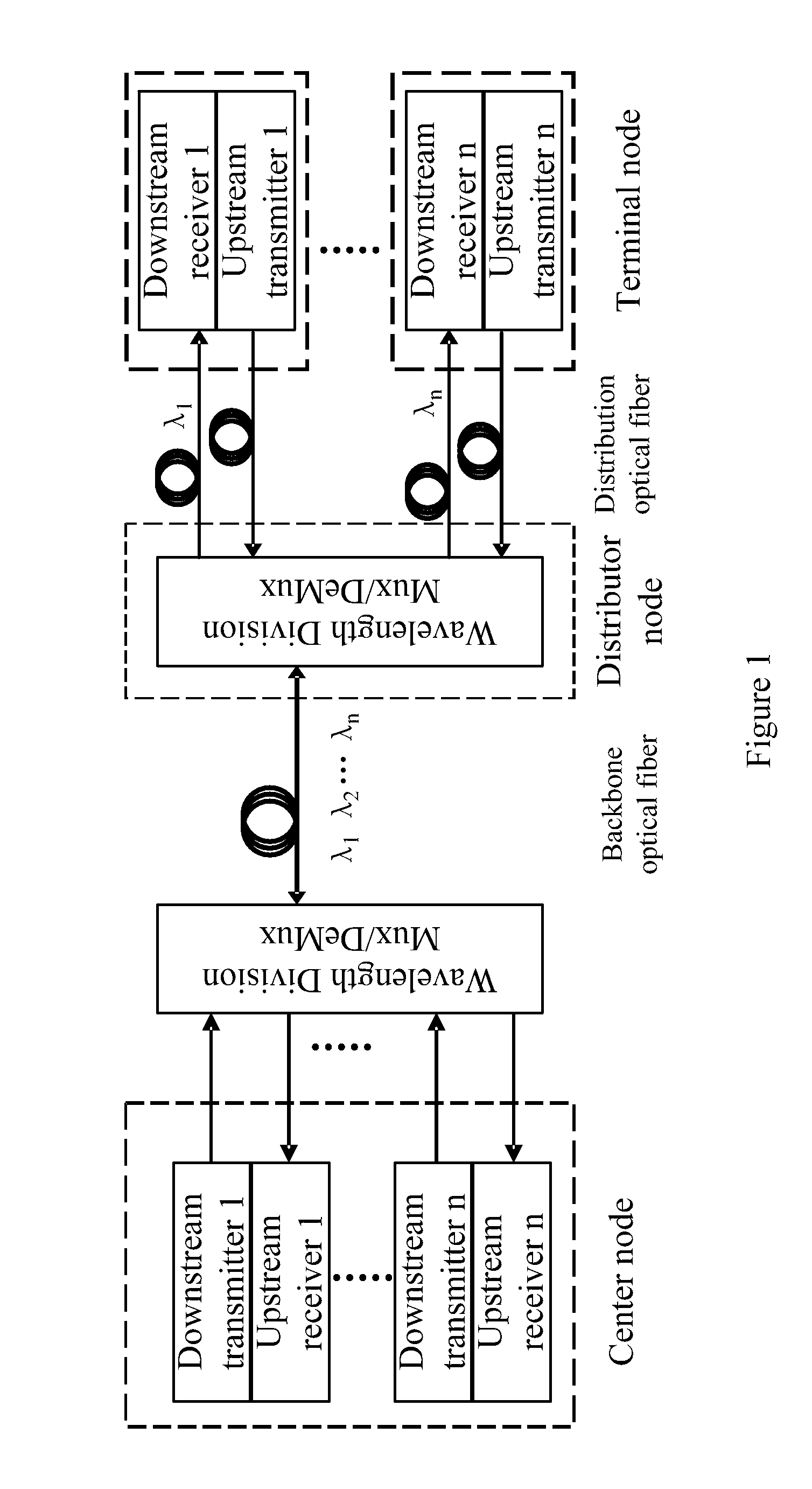
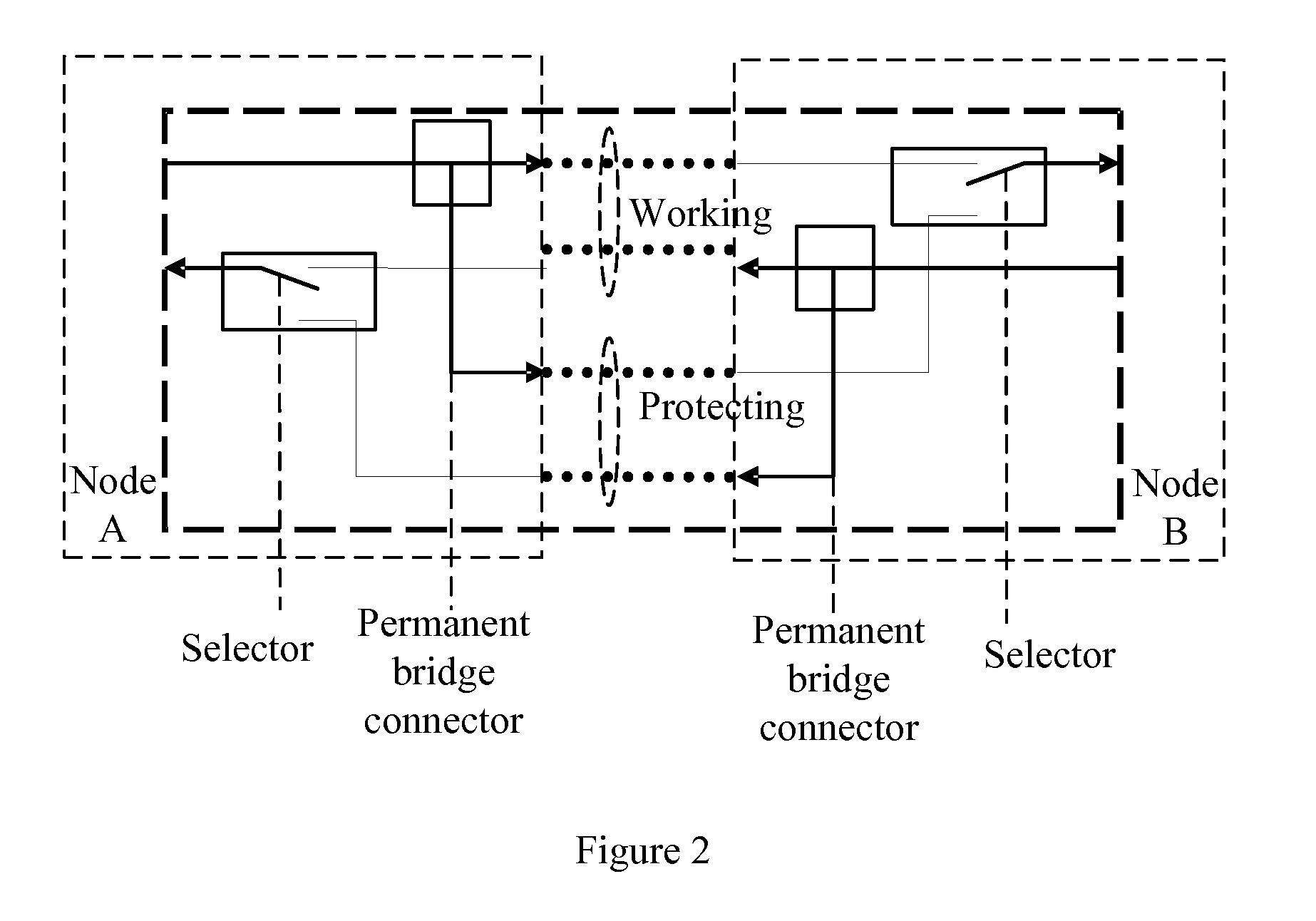
Method, system and apparatus for protecting wavelength division multiplex transmission
InactiveUS20090169200A1Low costReduce construction costsLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringLength wave
A method for protecting WDM transmission. On the first transmission direction, the first node implements service transmission to the second node by selecting one from the two transmission paths protected by each other, the second node implements two-path reception based on the two transmission paths; on the second transmission direction contrary to the first transmission direction, the second node implements two-path service sending via the two transmission paths protected by each other, the first node implements reception by selecting one from the two transmission paths. A system for implementing the WDM transmission protection and an apparatus thereof.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
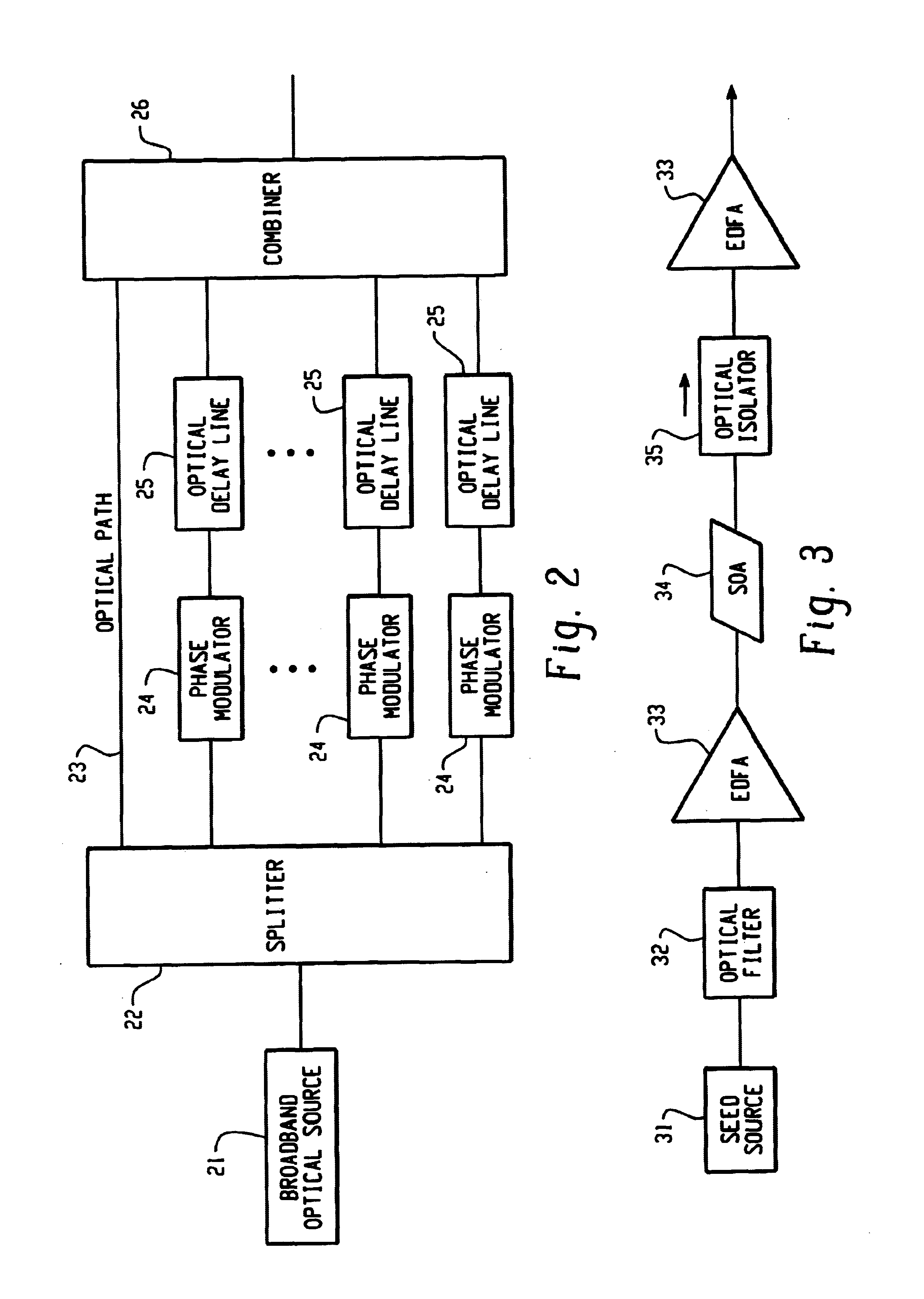
Multichannel optical communication system and method utilizing wavelength and coherence division multiplexing
InactiveUS7061657B1Raise countVary numberTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
Method and system thereof for transmission of several coherence division multiplexed (CDM) optical signals via one wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) transmission channel of a multichannel WDM telecommunication system to extend the network capacity to a theoretical limit. A broadband optical source generates light within the spectral range of at least one WDM transmission channel. Several CDM channels share this spectral range to transmit and detect phase modulated optical signals through optical fiber links.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
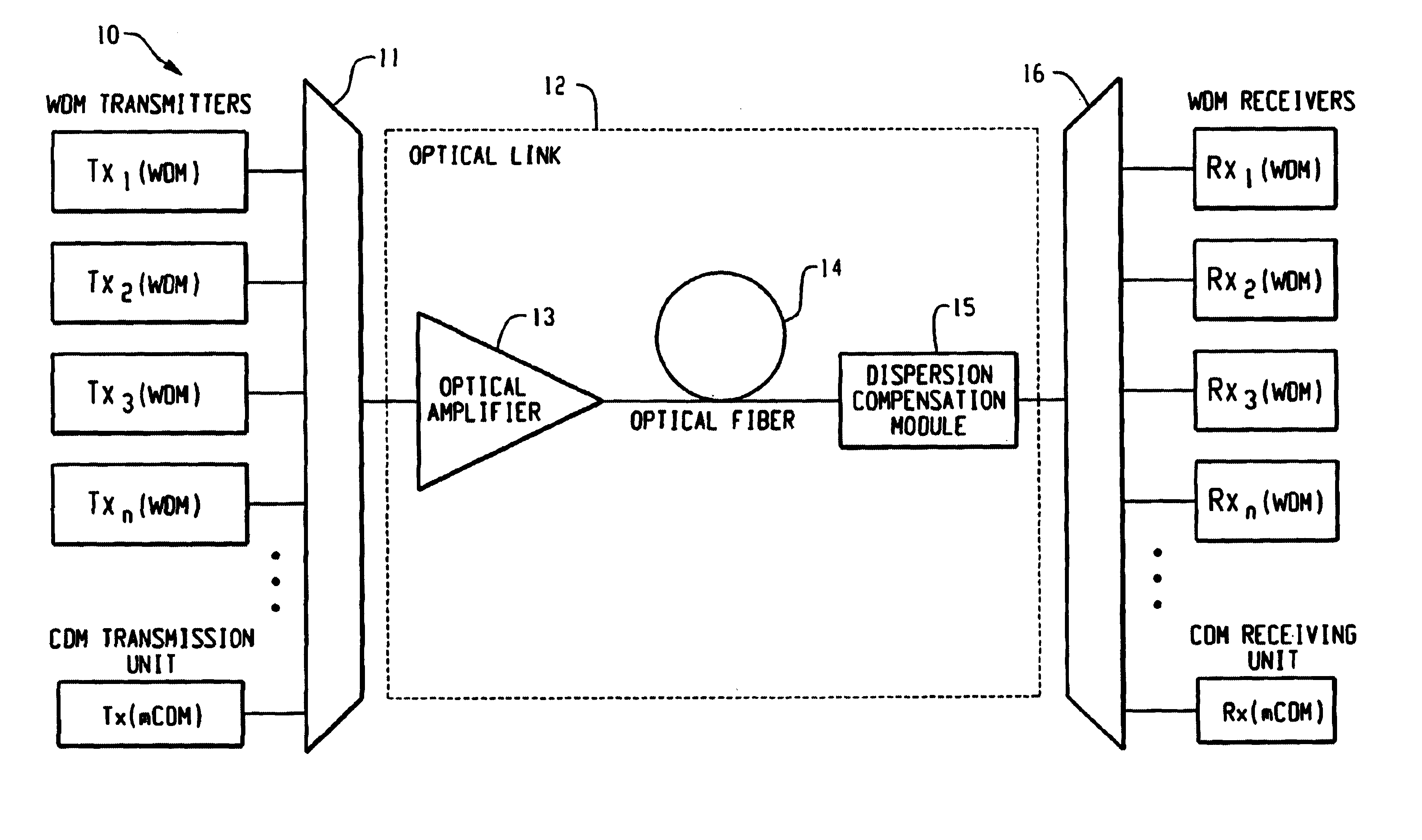
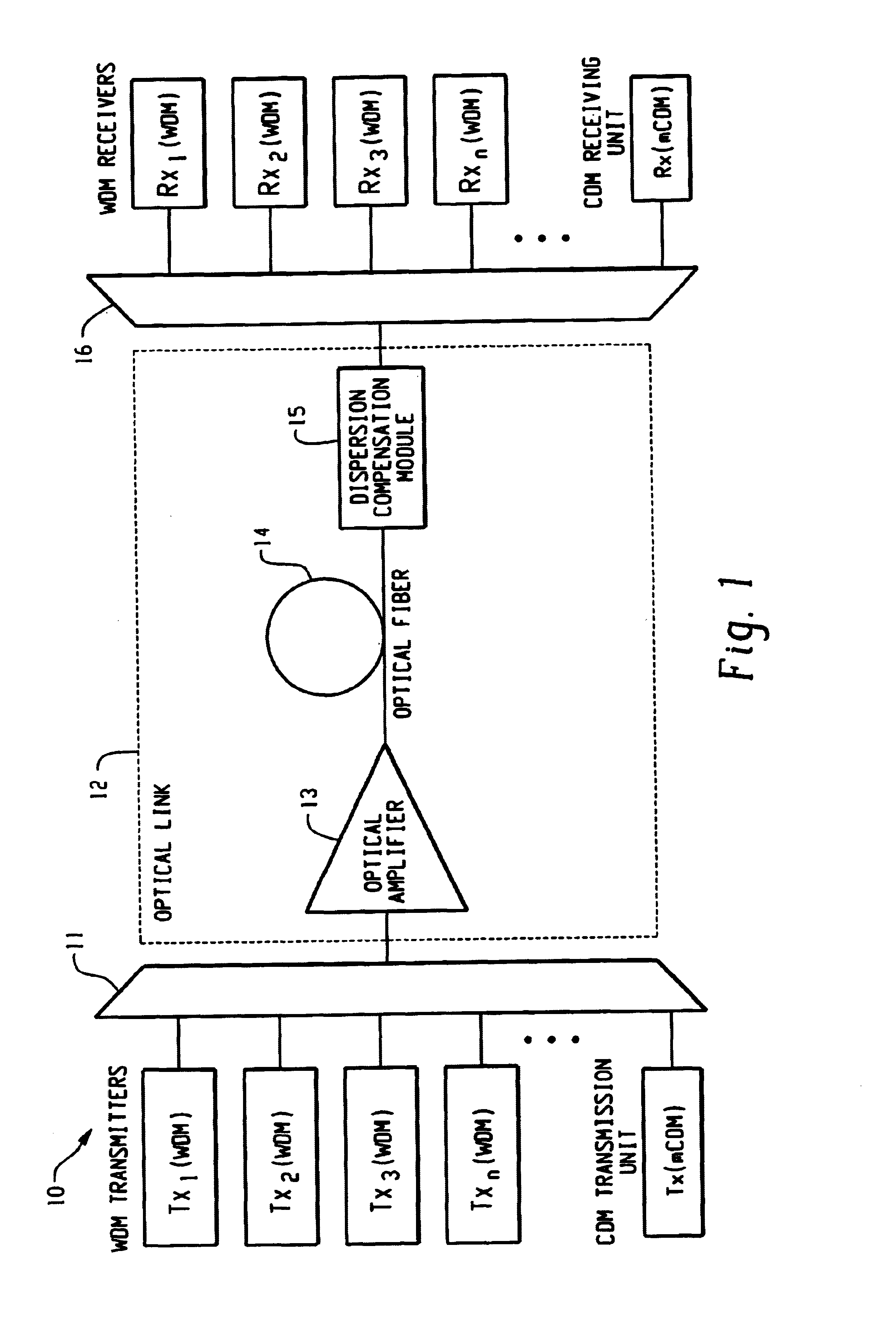
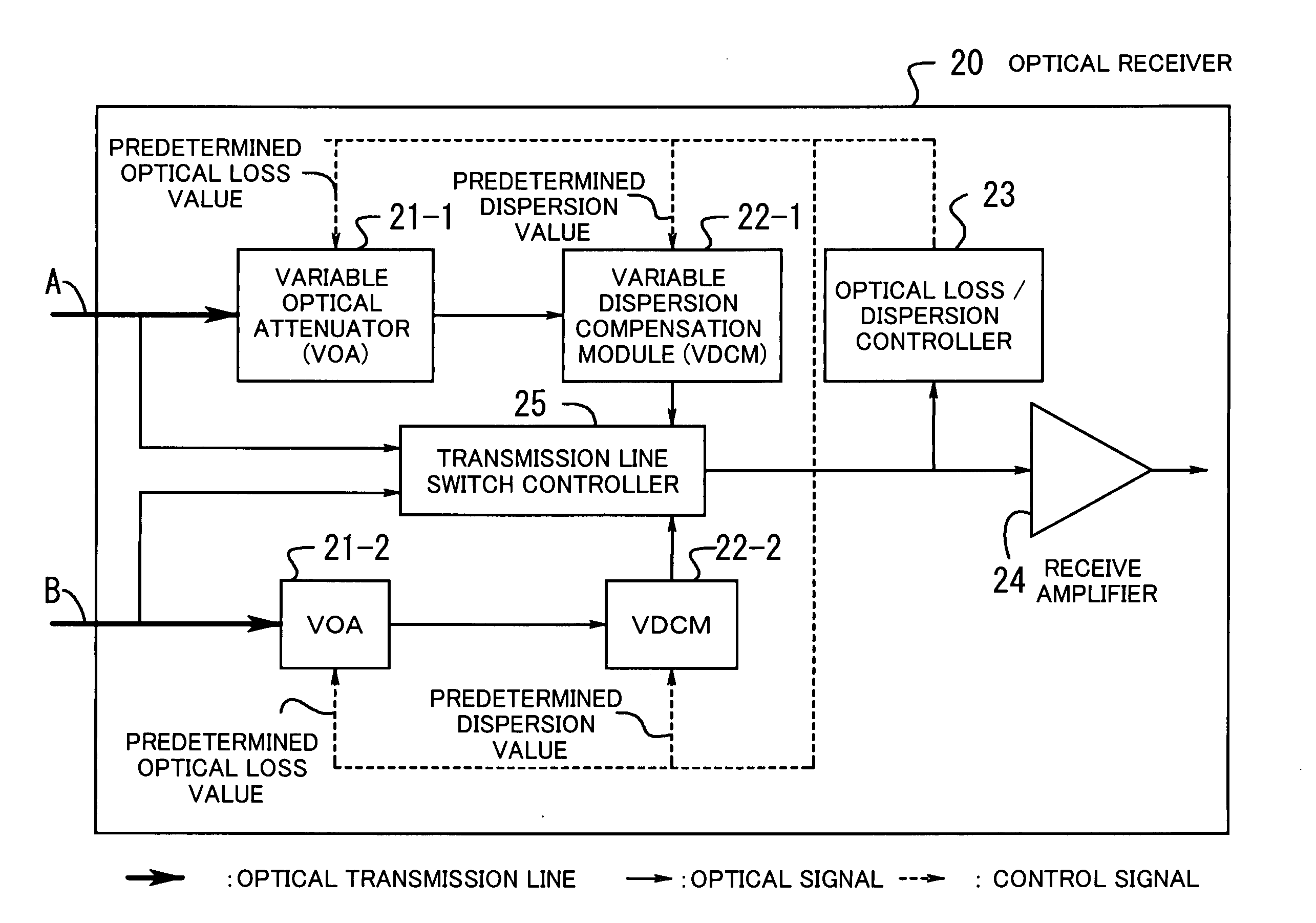
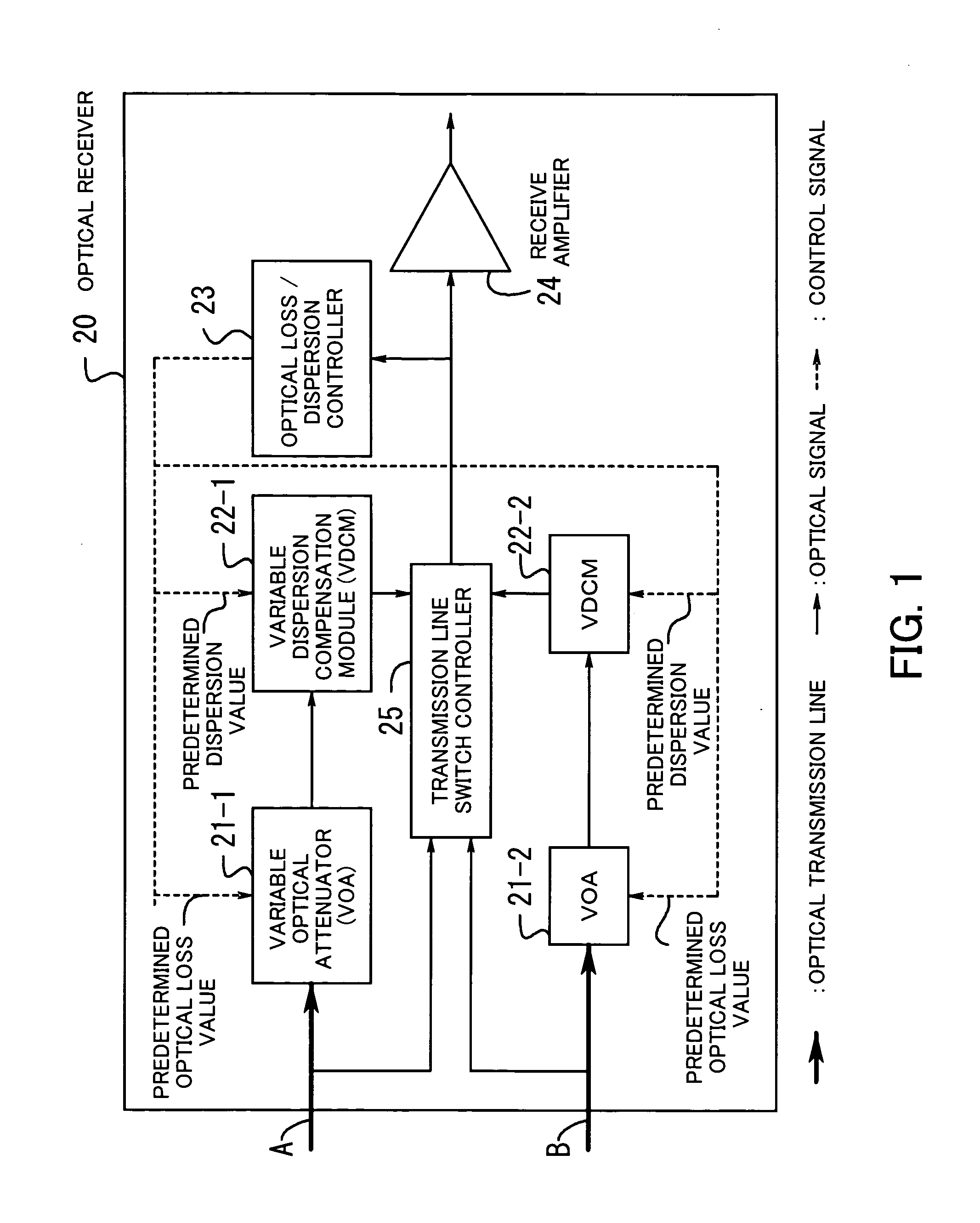
Optical receiver
InactiveUS20050123305A1Quality improvementSuppress transmissionLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAudio power amplifierOptical attenuator
An optical receiver is provided for reducing in scale the overall system for wavelength division multiplex transmission lines configured redundantly and improving the quality of transmission when the line is switched. The optical receiver includes a variable optical attenuator for controlling an optical loss value for each optical transmission line based on a predetermined optical loss value. A variable dispersion compensation module is also provided for controlling a wavelength dispersion value for each optical transmission line based on a predetermined dispersion value. An optical loss / dispersion controller is also provided for measuring the optical loss value and the wavelength dispersion value of every optical transmission line, outputting the predetermined optical loss value and dispersion value so that the optical loss values and the wavelength dispersion values are equal in all the optical transmission lines, and controlling the variable optical attenuator and the variable dispersion compensation module based on the outputted predetermined values. A receive amplifier is also provided for receiving the optical signal whose light level is kept constant and amplifying the signal. Also, a transmission line switch control module is provided for switching a working transmission line into a protection line if the optical signal level of the working line is lower than a threshold value.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
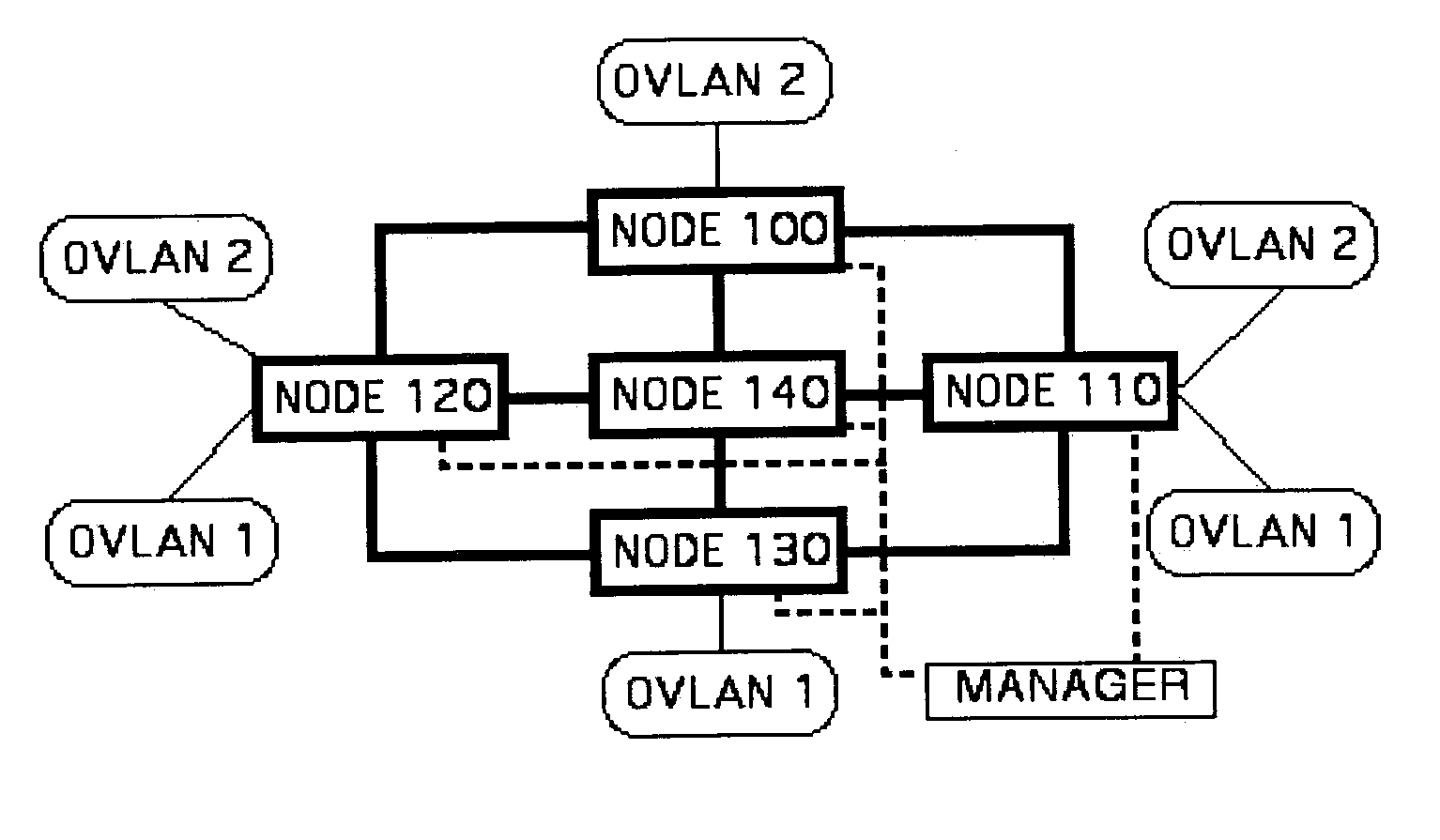
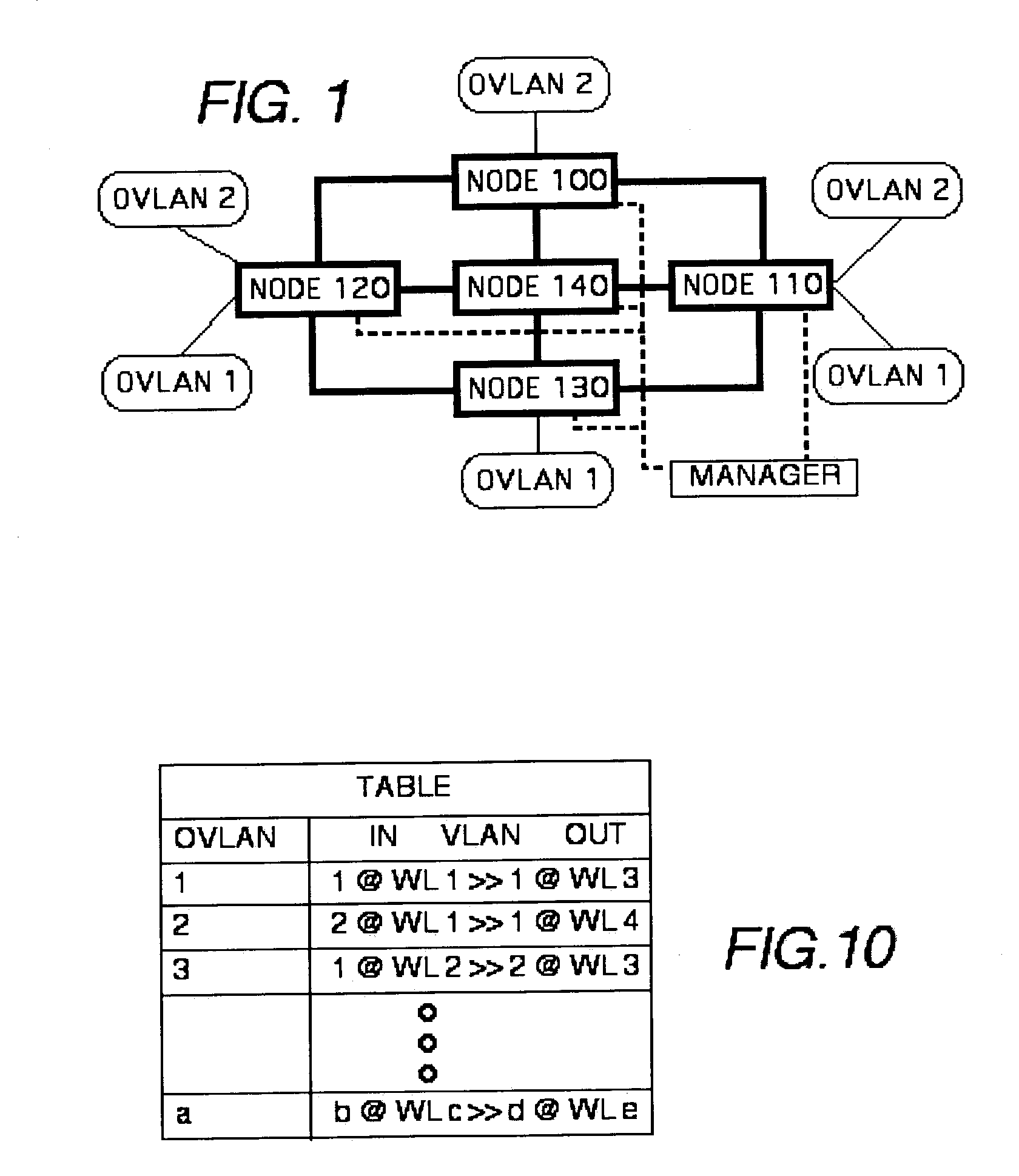
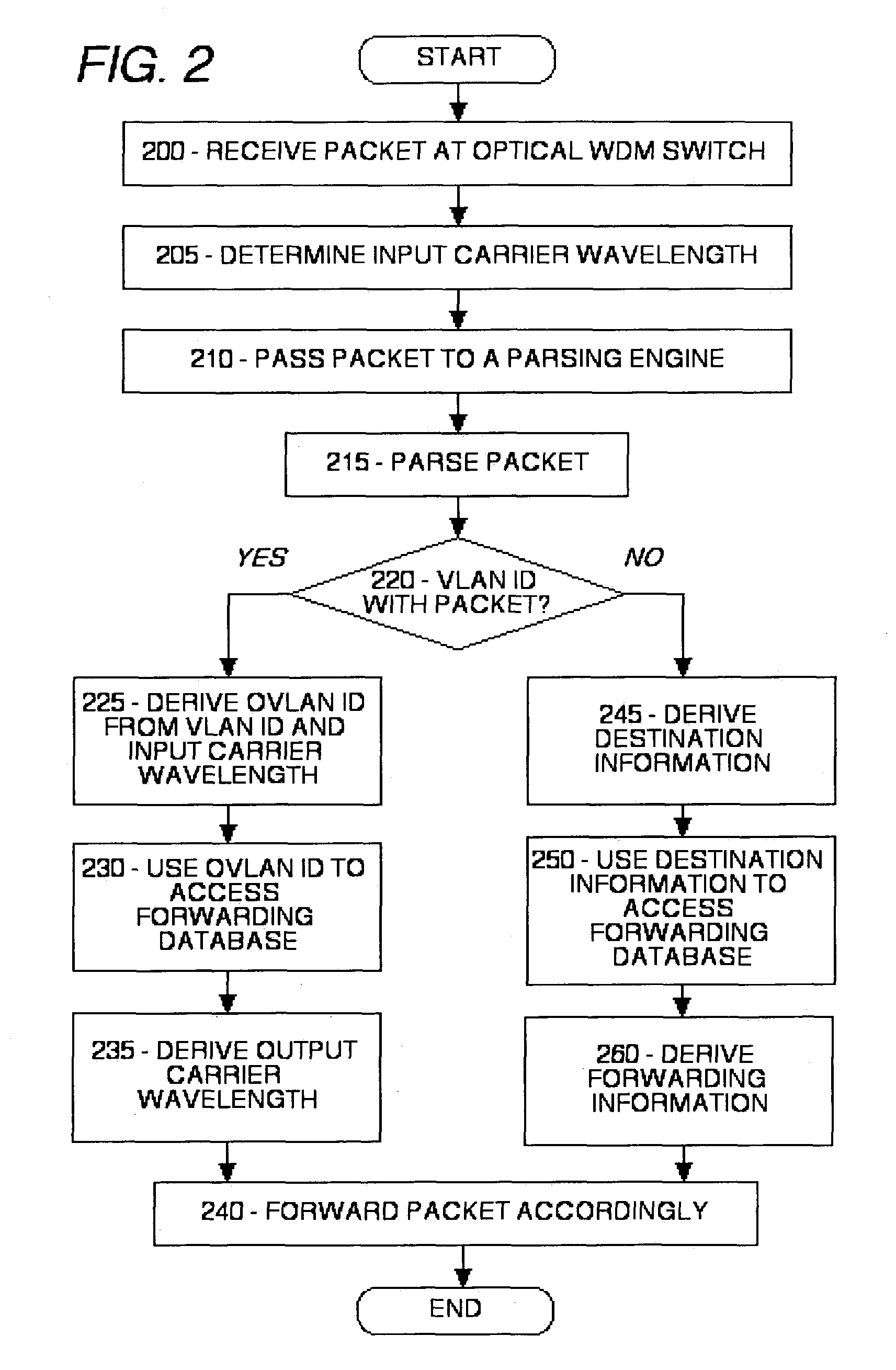
Optical virtual local area network
InactiveUS7283746B2Increase the number ofEasy data transferElectromagnetic network arrangementsOptical multiplexVirtual LANLength wave
The maximum number of virtual local area networks (VLANs) is increased beyond the number provided solely with the VLAN ID, by a factor related to the number of wavelengths of a Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) used by a network switching. An optical VLAN number (OVLAN ID) is a combination of the VLAN ID from the packet header and a path or wavelength ID (WL ID) that identifies a selected one of available wavelengths of a WDM transmission line. An Optical VLAN (OVLAN) conversion table stores data of the OVLAN ID, the VLAN ID and optical path ID, for an optical VLAN node.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
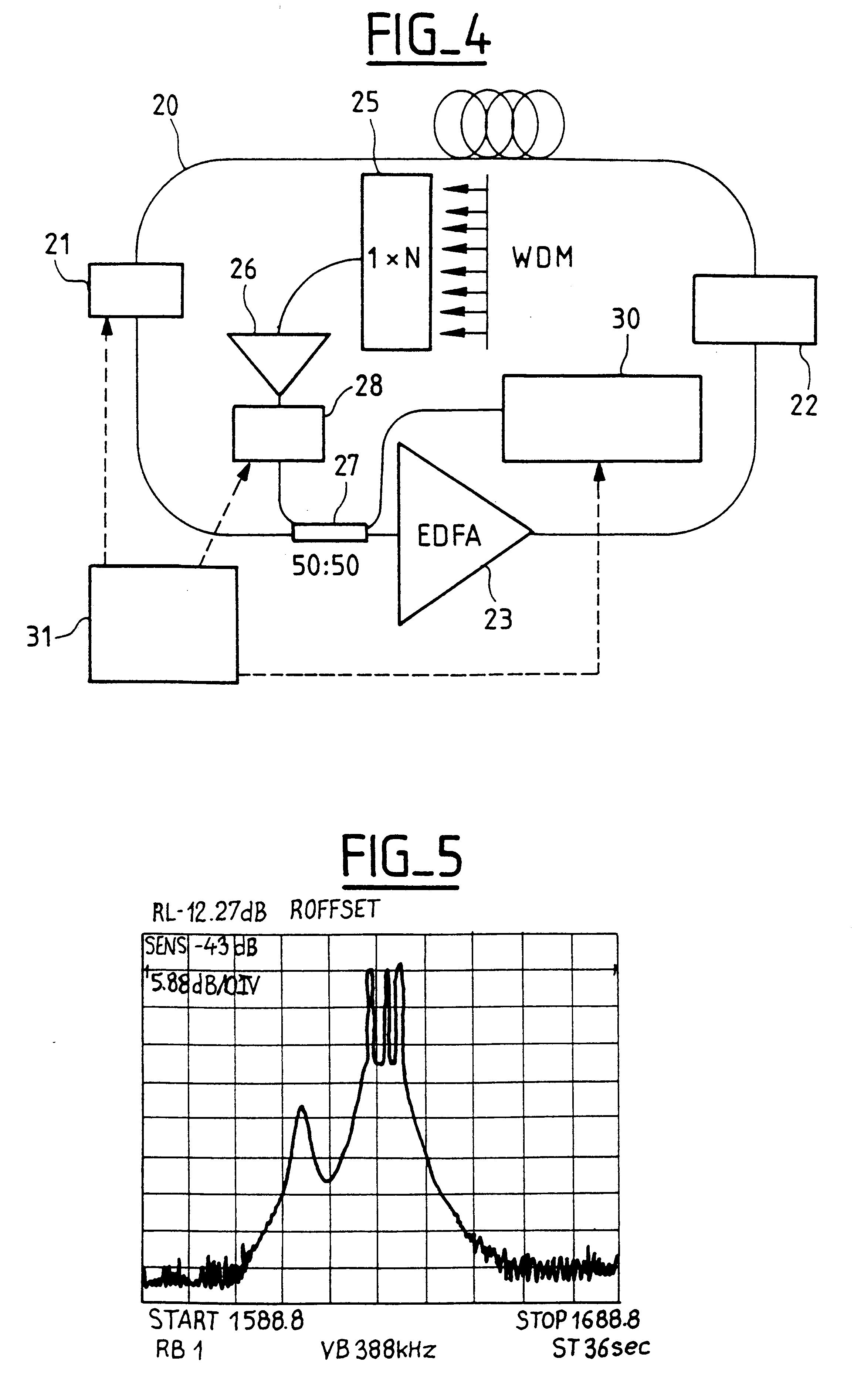
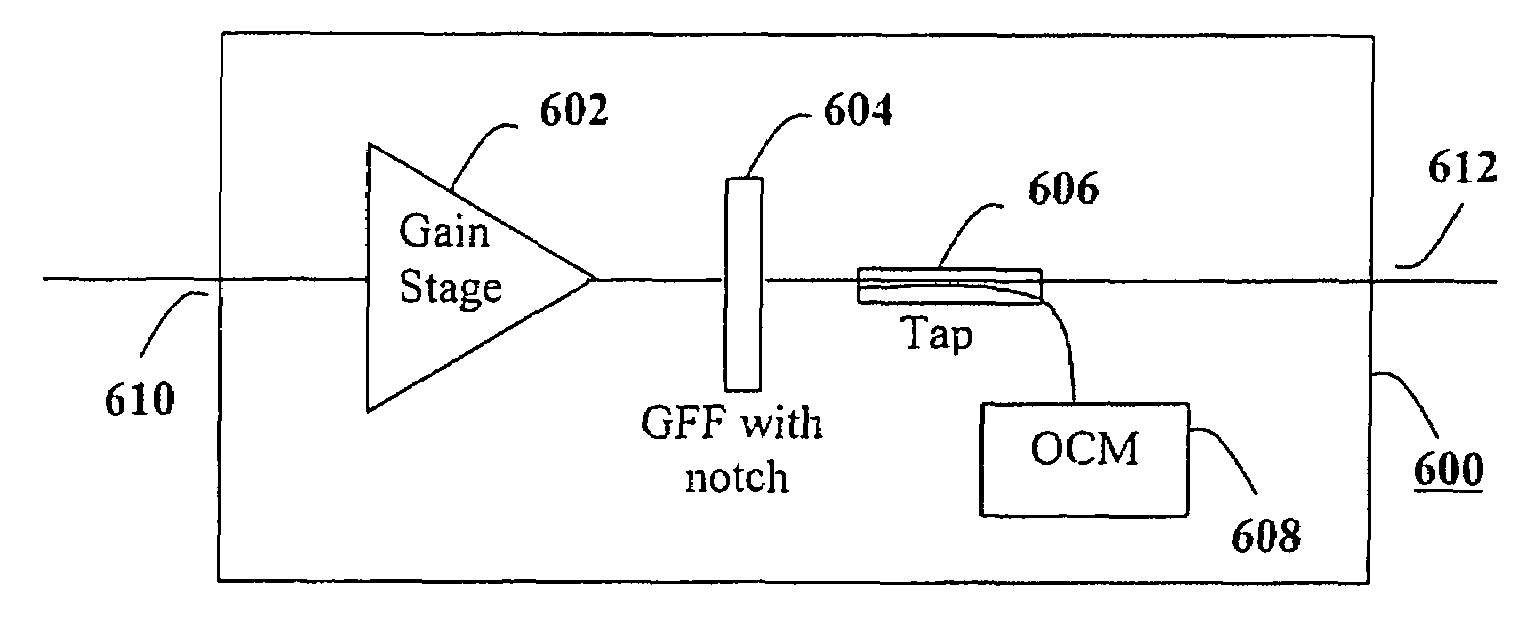
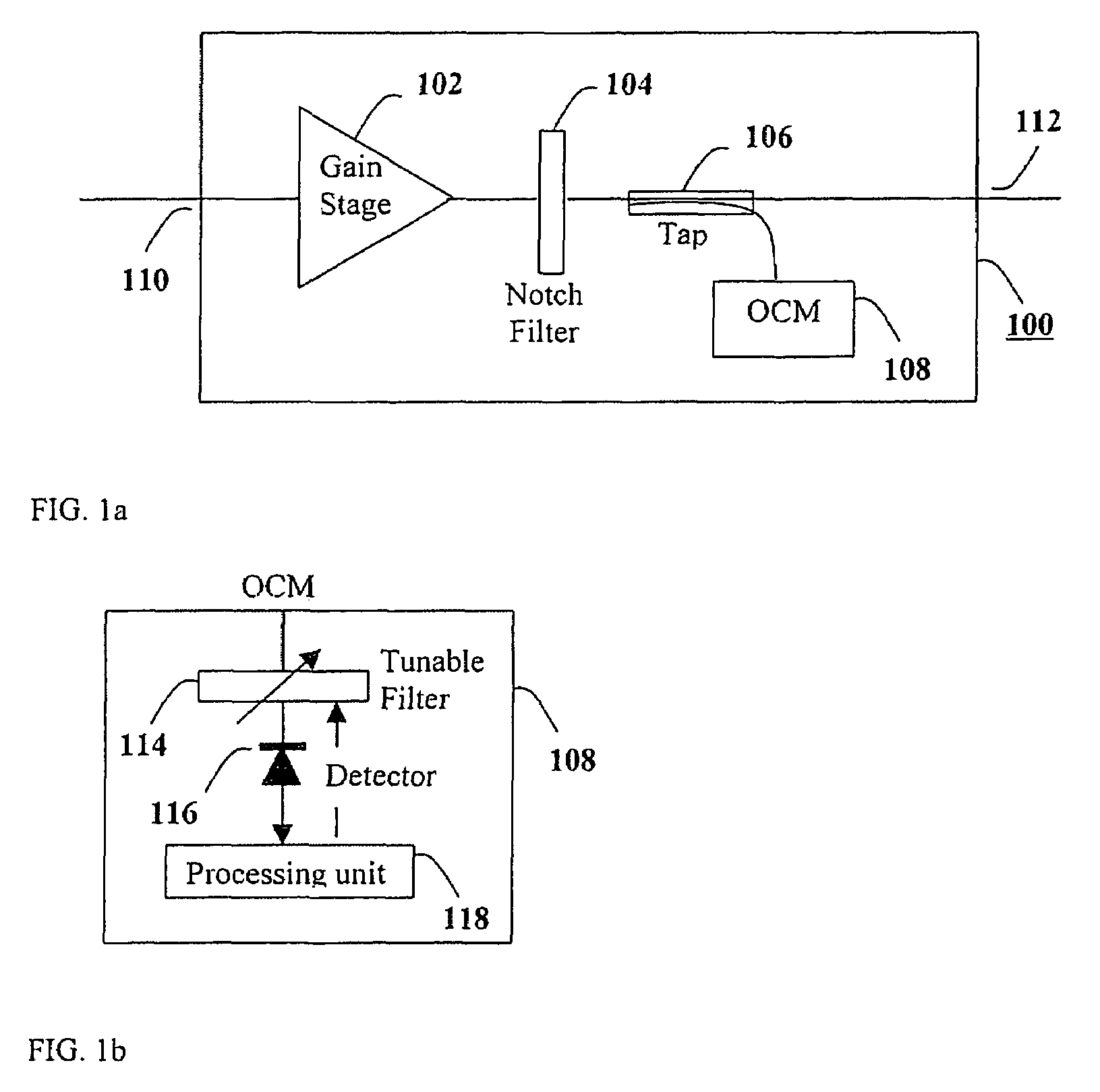
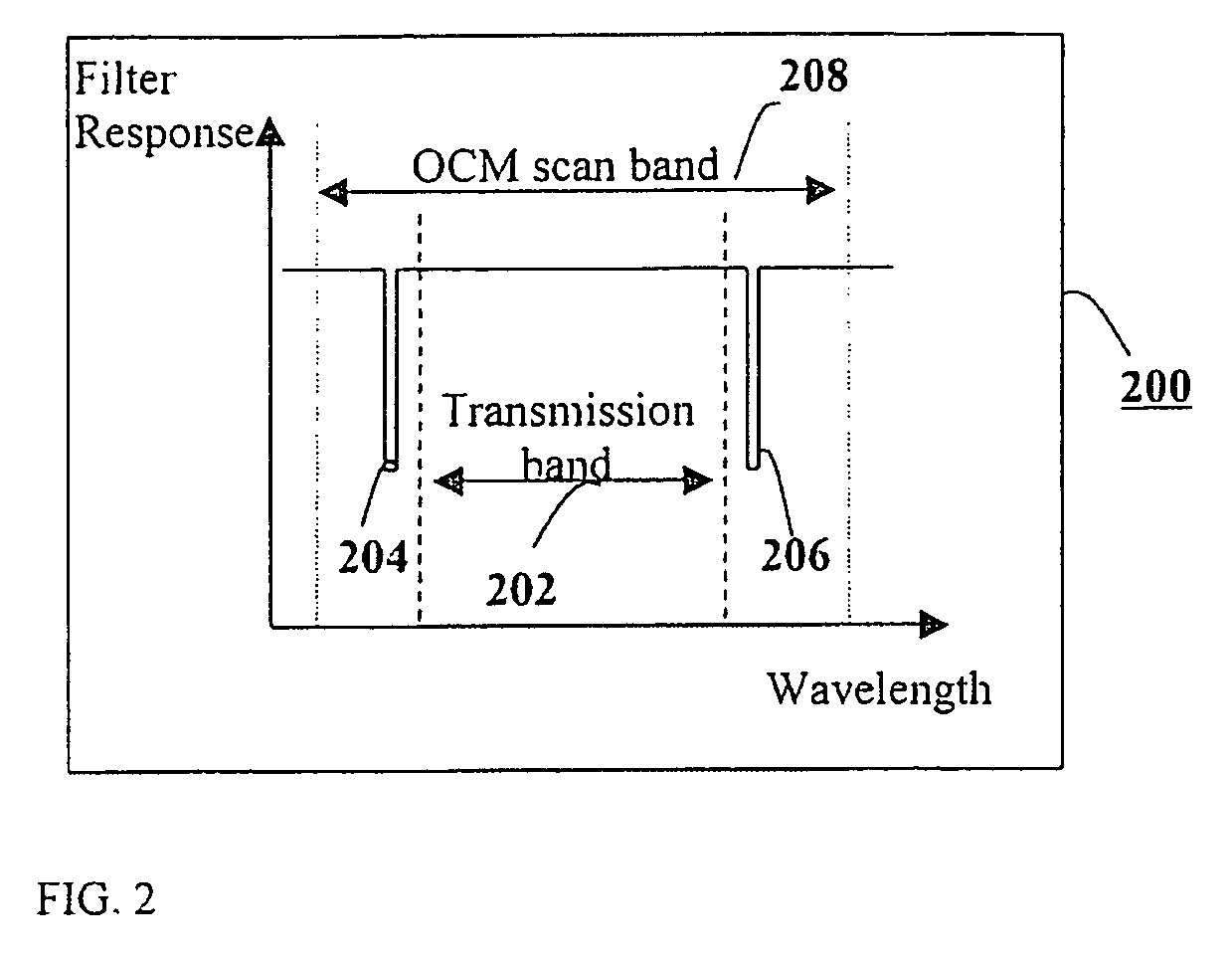
Efficient wavelength referencing in a combined optical amplifier-optical channel monitor apparatus
InactiveUS7385754B2Efficient calibrationEasy and efficient referenceLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFrequency spectrumAudio power amplifier
Efficient wavelength calibration in a WDM optical amplifier that includes an optical channel monitor (OCM) is obtained by introducing a notch into the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) noise spectrum of the amplifier outside a WDM transmission band, and having the OCM detect the notch and use the notch as a reference to calibrate the wavelength measurement. The notch is introduced into the ASE noise spectrum using a notch filter, which is preferably incorporated in a gain flattening filter (GFF).
Owner:RED C OPTICAL NETWORKS +1
Optical fiber having a lower bending loss
InactiveCN1576916ALow bending lossSuppresses increase in transmission lossGlass optical fibreGlass making apparatusRelative refractive indexTransmission loss
An optical fiber includes a first core having a relative refractive index difference of larger than 0.36%, and a cladding. The optical fiber has fiber cut-off wavelength lambdac of more than 1350 nm, cable cut-off wavelength lambdacc of less than 1285 nm, bending loss at a wavelength of 1625 nm of not more than 10 dB / km when wound at a diameter of 20 mm, transmission loss at a wavelength range of 1285 to 1625 nm of not more than 0.40 dB / km, transmission loss at a wavelength of 1383 nm less than transmission loss at a wavelength of 1310 nm, and difference in transmission loss at a wavelength of 1383 nm of not more than 0.04 dB / km before and after exposure to hydrogen. The lower bending loss of the optical fiber provides an optical fiber cable for use in a WDM transmission in wavelength range of 1285 to 1625 nm.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
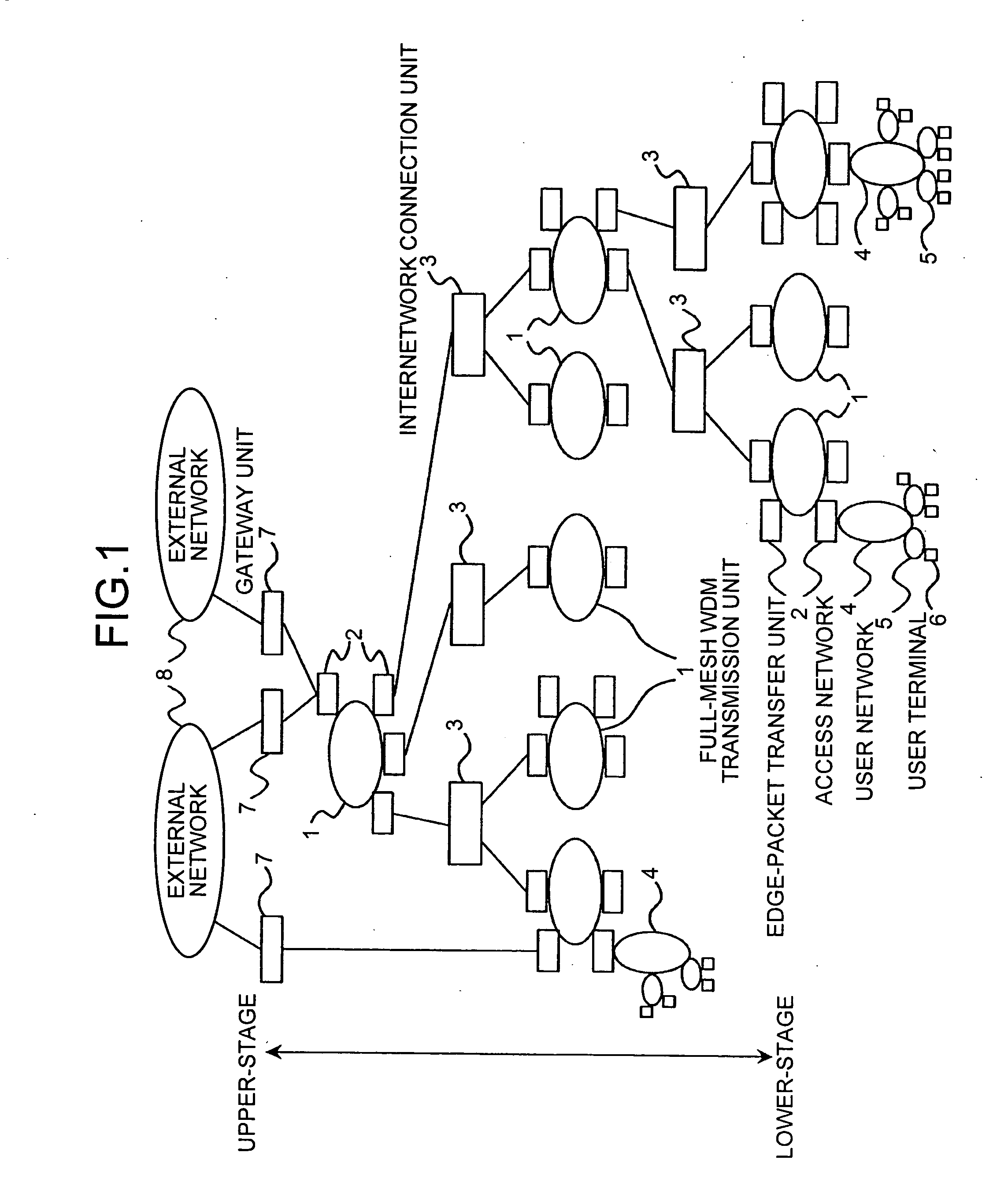
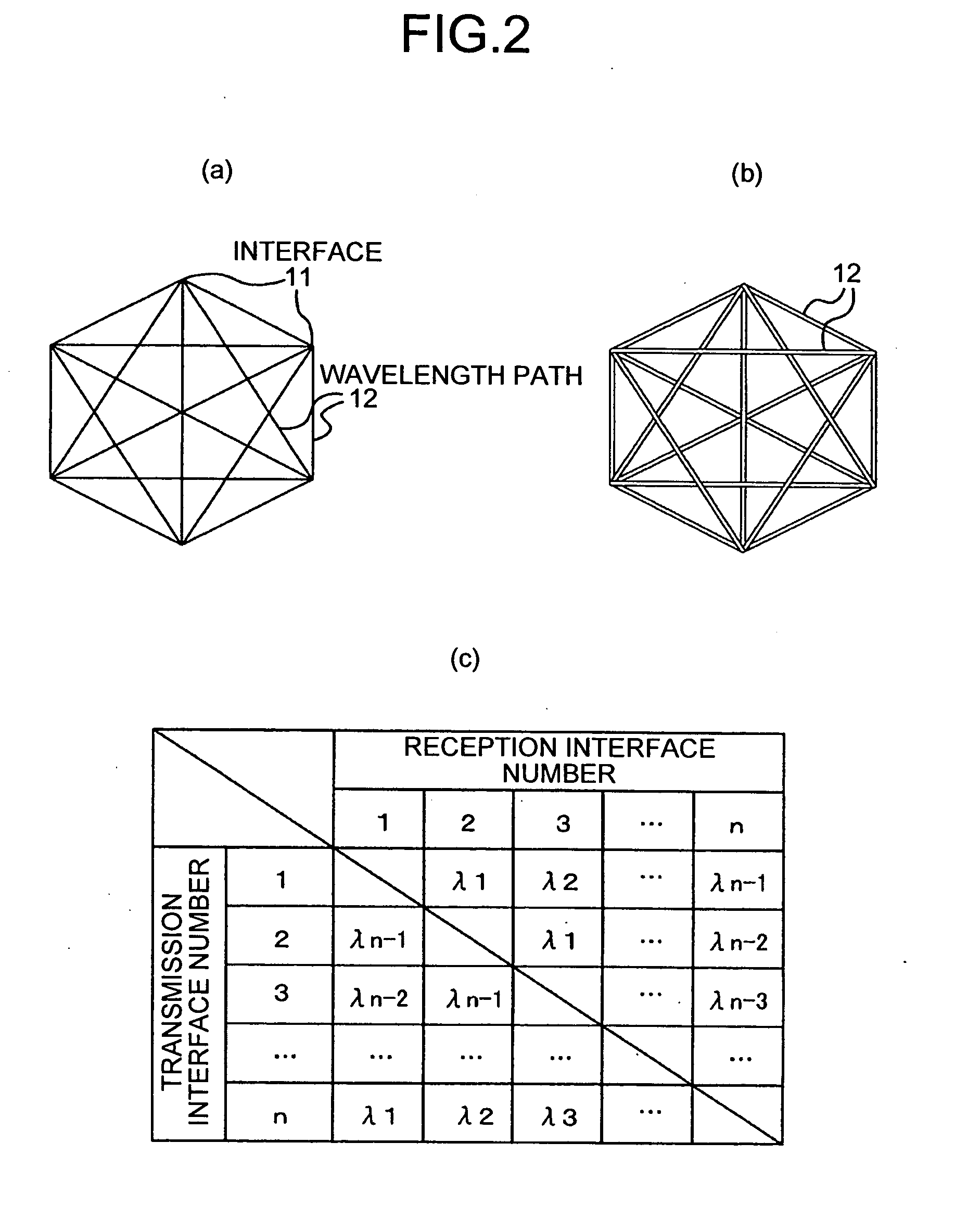
Packet Communication Network and Packet Communication Method
InactiveUS20070242684A1Easy to identifyRouting management can beMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPacket communicationTelecommunications
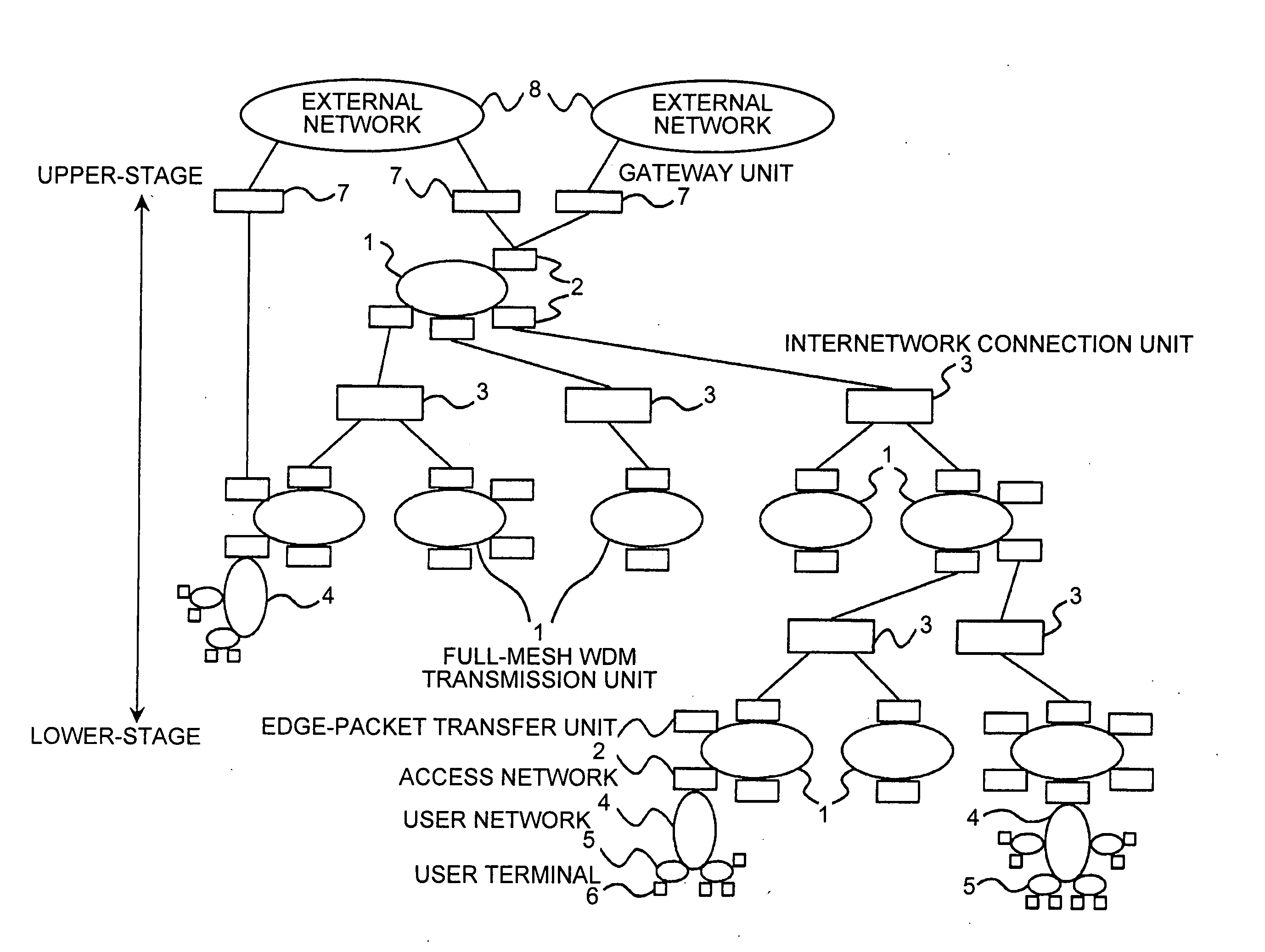
Full-mesh WDM transmission units, each of which includes n number of interfaces and is capable of establishing a bidirectional full-mesh communication between all of the interfaces using wavelength paths based on a wavelength division multiplexing technique, are connected in a multistage tree-shaped structure by internetwork connection units through edge-packet transfer units connected to the respective interfaces. Therefore, it is possible to hold a direct communication between user terminals connected to the edge-packet transfer units of the same full-mesh WDM transmission unit, and to realize scalability by a multistage connection configuration.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
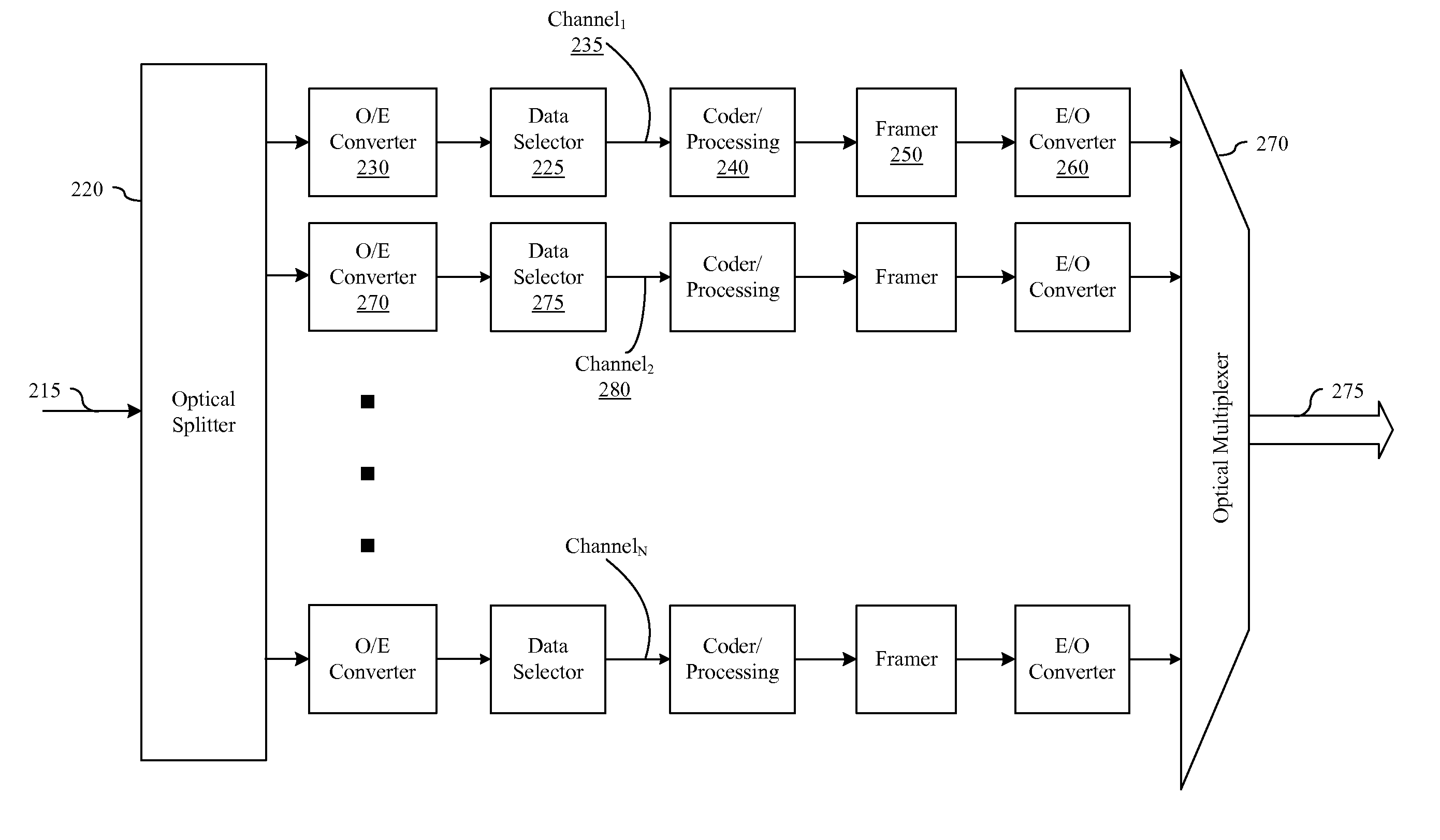
Mapping a Client Signal into Transport Frames
ActiveUS20090245793A1Time-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm transmissionWeb transport
Embodiments of the present invention provide a systems, devices, and methods in which a client signal is divided into a plurality of channels, mapped within transport frames, and combined into a WDM transport signal. These embodiments include intra-nodal redundancy that protects against failure events within the transport transmitter. In particular, redundancy is provided within a network transport transmitter such that redundant paths are available so that electrical channels may be routed around a malfunctioning component within the transmitter.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
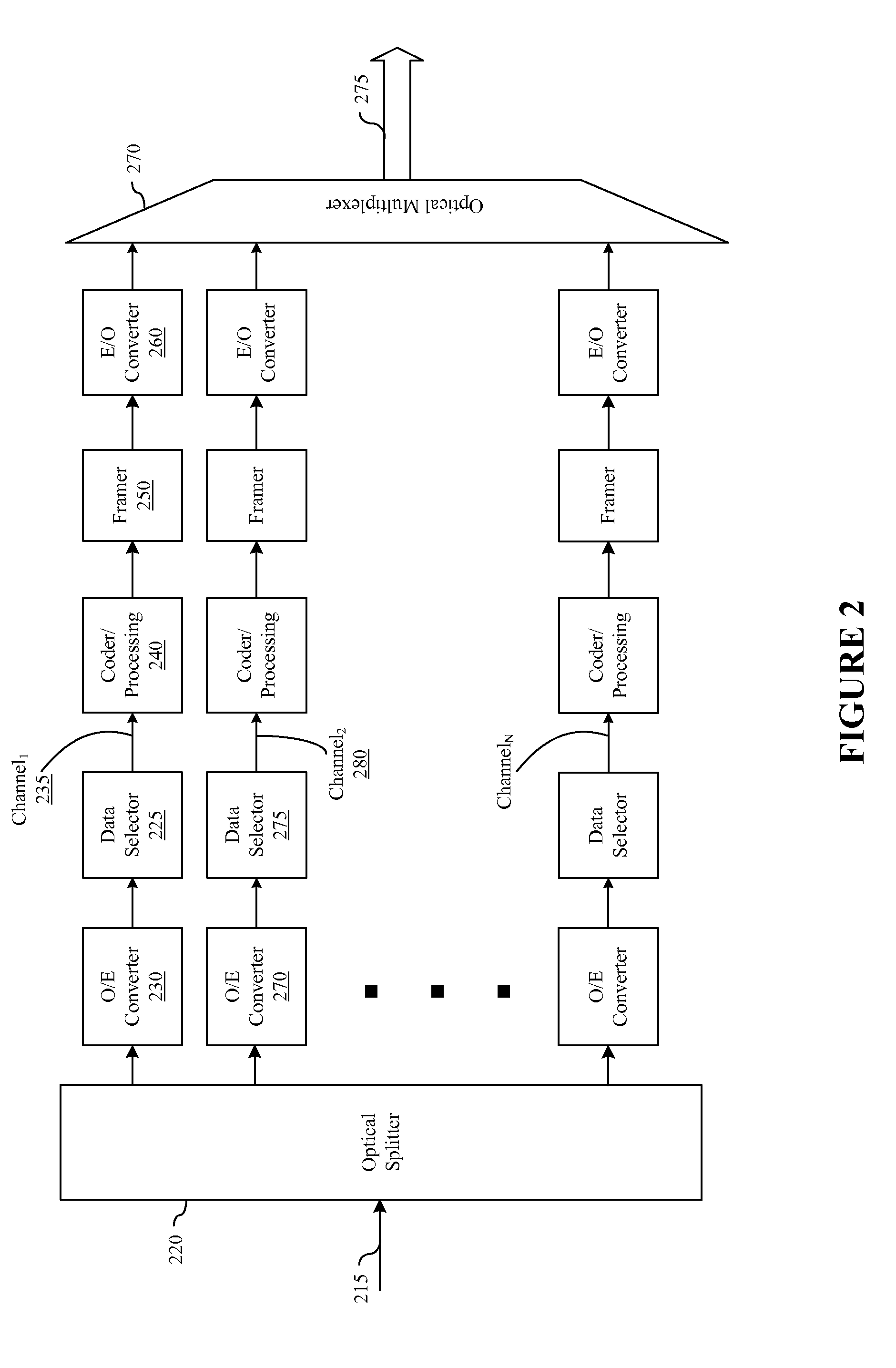
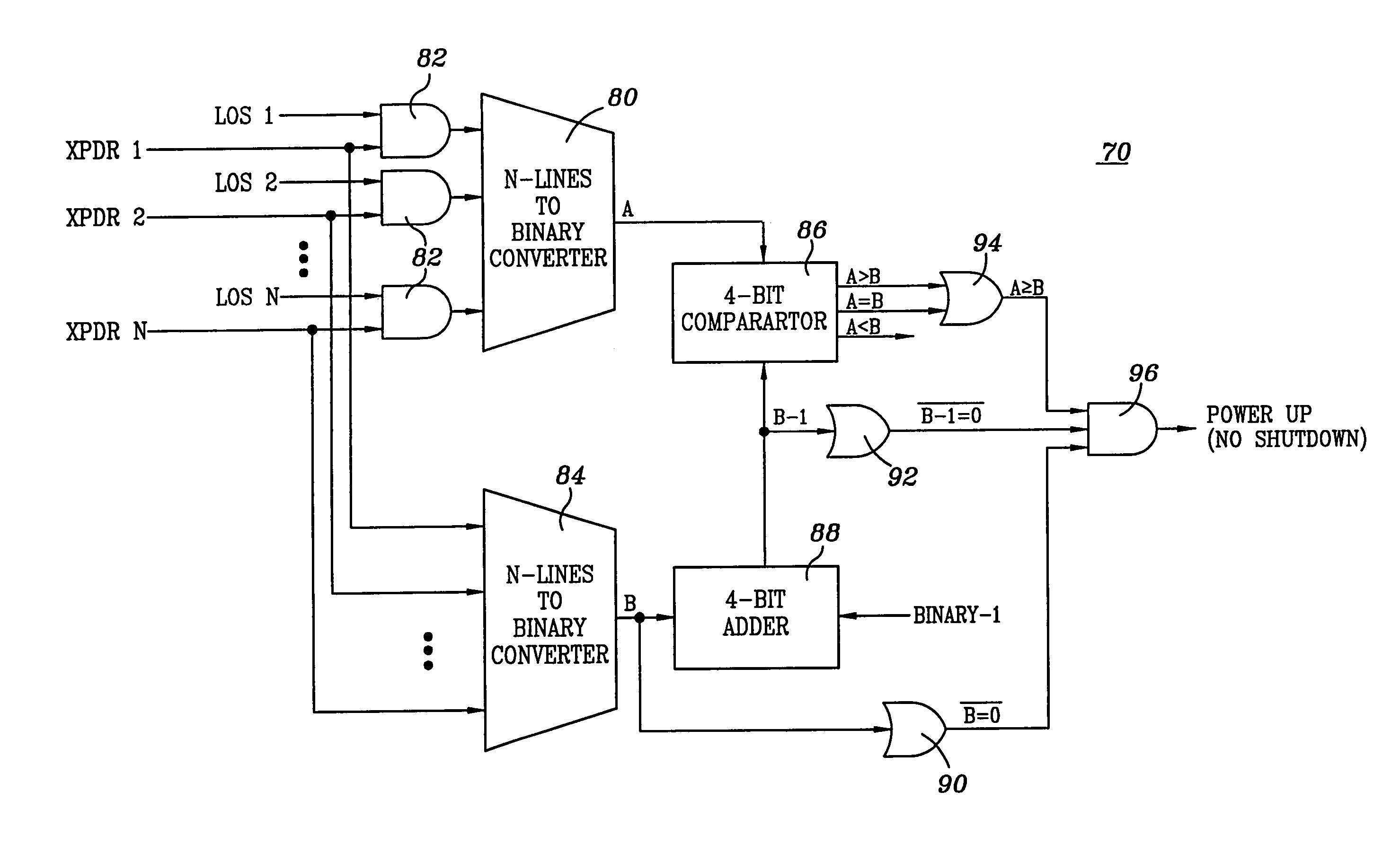
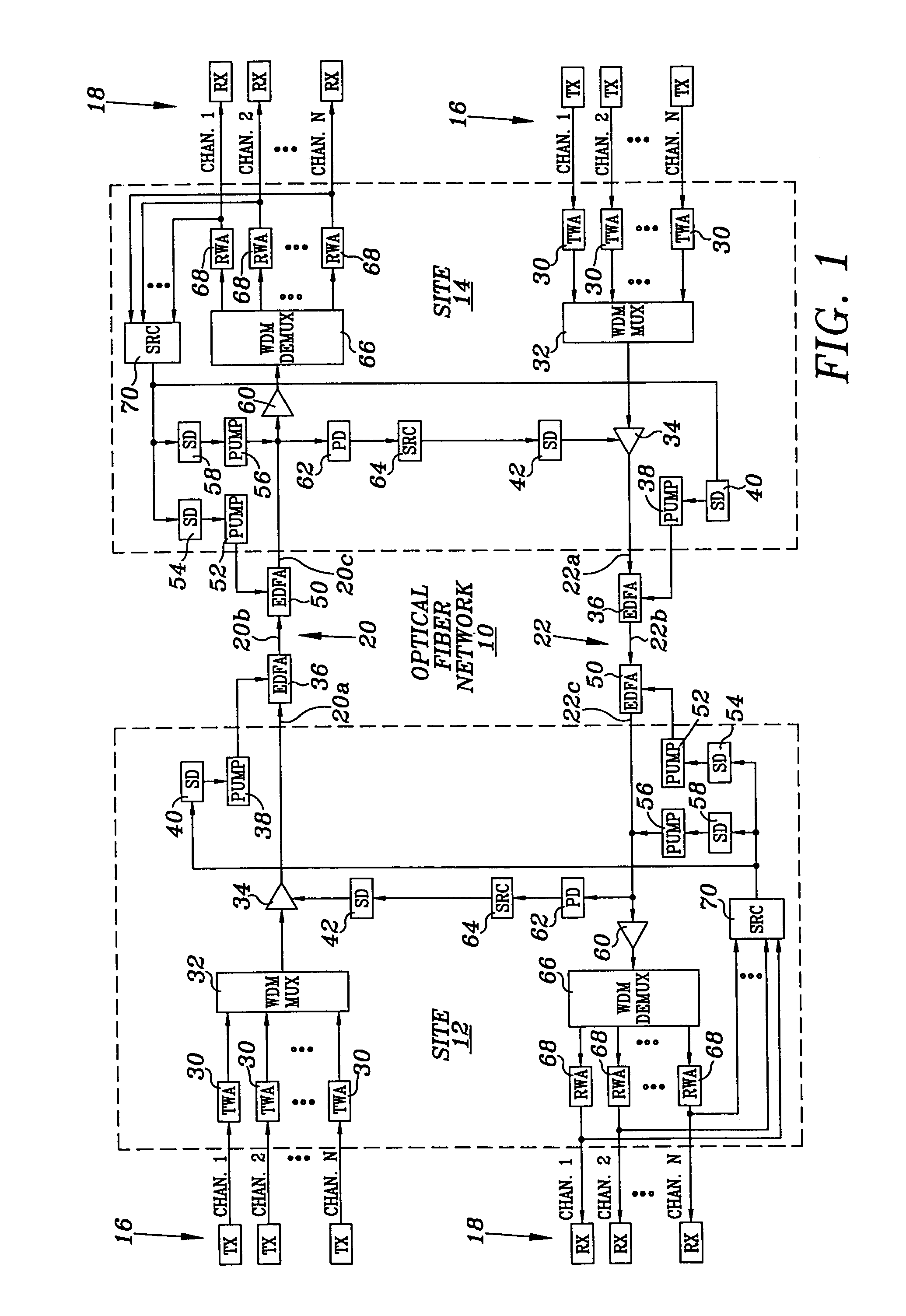
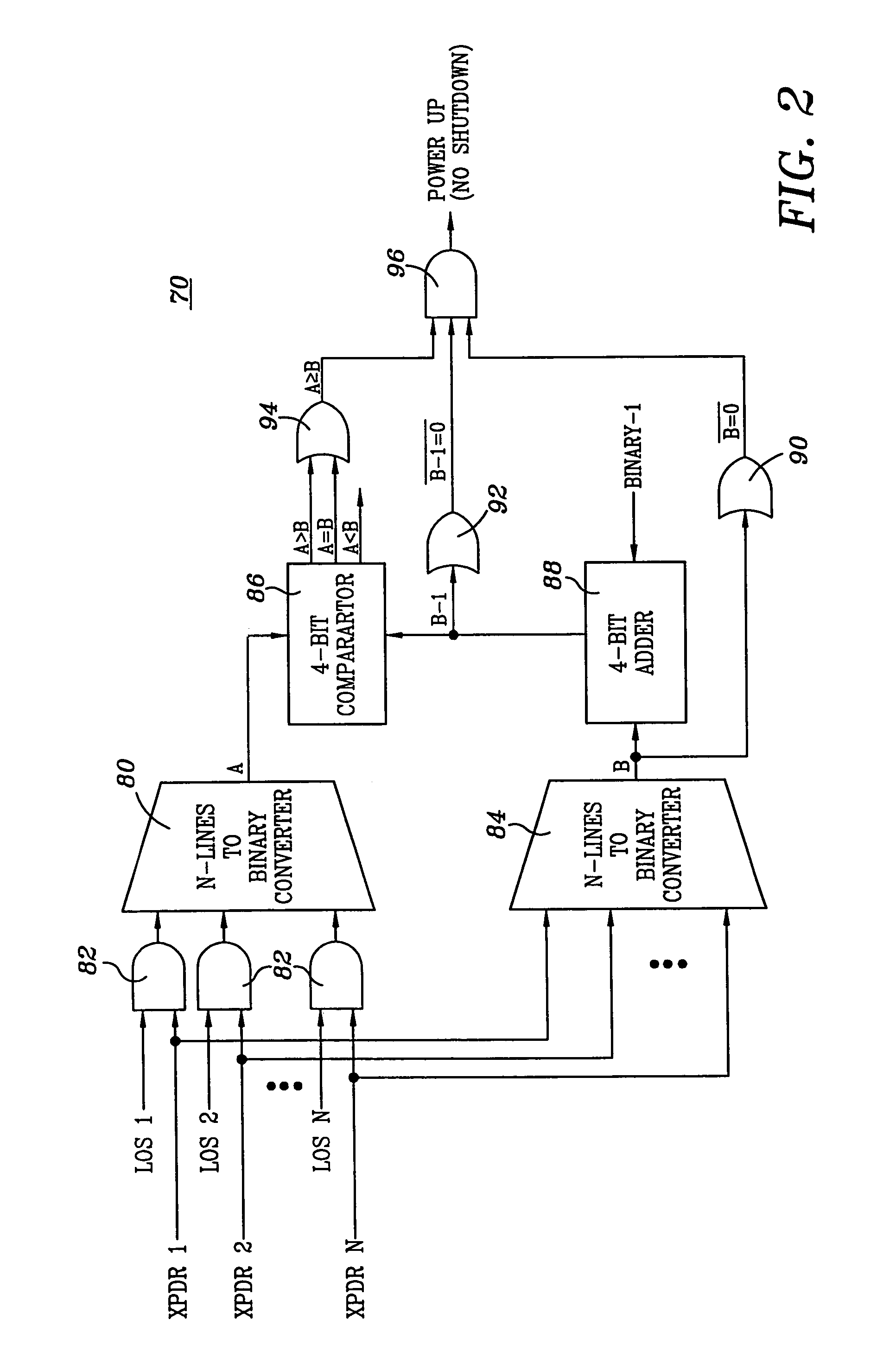
Safety shutdown system for a WDM fiber optic communications network
InactiveUS7130537B1Low failure rateEliminates failure probability factorTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsFiberTerminal equipment
A fiber optic communications network includes multiple transmitters and multiple receivers connected by an optical WDM transmission link, the receivers having output channels for providing signals to terminal devices, each receiver including a demodulator to detect and recover a received signal, and the network includes at least one optical amplifier having a shutdown input for actuating the safety shut down of the network upon detecting a disconnect in the transmission line. The system includes circuitry connected to the output of each of the demodulators for sensing the presence of a valid signal and for determining whether a predetermined number of valid signals are present at the demodulators. If the number of valid signals detected is less than the predetermined majority number, the safety shutdown function is actuated.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Optical fiber having low non-linearity for WDM transmission
InactiveUS6922514B2High refractive indexLow refractive indexLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingDopantEngineering
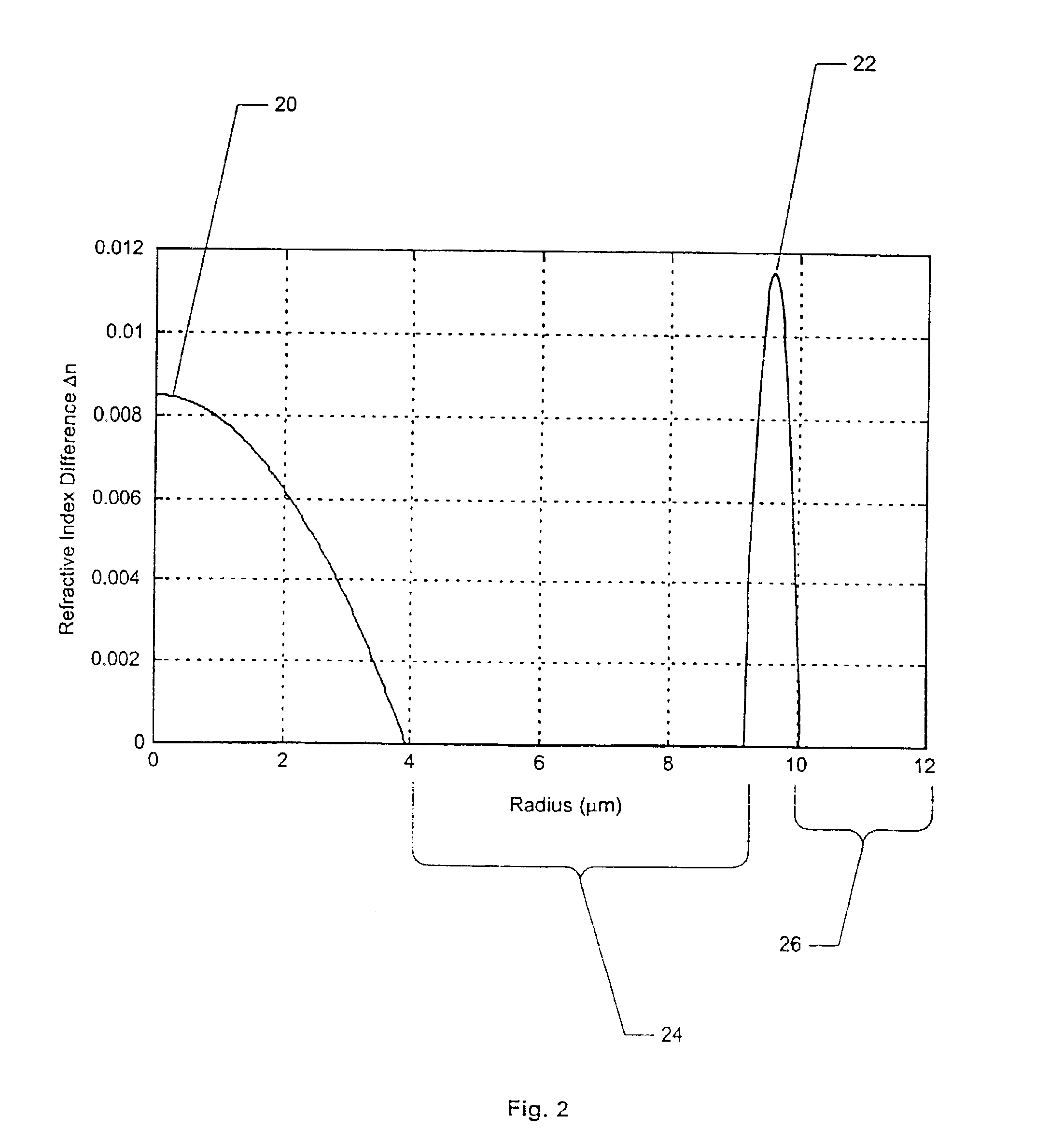
An optical transmission fiber has a refractive index profile with an area of increased index of refraction at the inner core of the fiber, an annular region positioned radially outward from the inner core with an index of refraction exceeding the index of the inner core, and at least a low dopant content region in a cross-sectional region between the inner core and the annular region. A low loss cladding layer surrounds the core region. The optical transmission fiber with this segmented core profile provides a high effective area, low non-linearity coefficient, nonzero dispersion, and relatively flat dispersion slope.
Owner:PRYSMIAN CAVI E SISTEMI ENERGIA
Optical fiber and optical transmission system using such optical fiber
InactiveUS6983094B2Large capacityShorten the lengthOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideLength waveOptical fiber cable
An optical fiber comprising a core and a cladding characterized by a dispersion of 0 to 17 ps / nm / km, an effective area (Aeff) of 130 μm2 or more, a bending loss of 10 dB / m or less in a diameter of 20 mm, a dispersion slope of 0 ps / nm2 / km to 0.08 db / nm2 / km at a wavelength of 1550 nm, and a cutoff wavelength λc of a 2 m length of fiber of 1700 nm or shorter, is provided. The optical fiber and an optical transmission system of the present invention are suitable for the WDM transmission.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
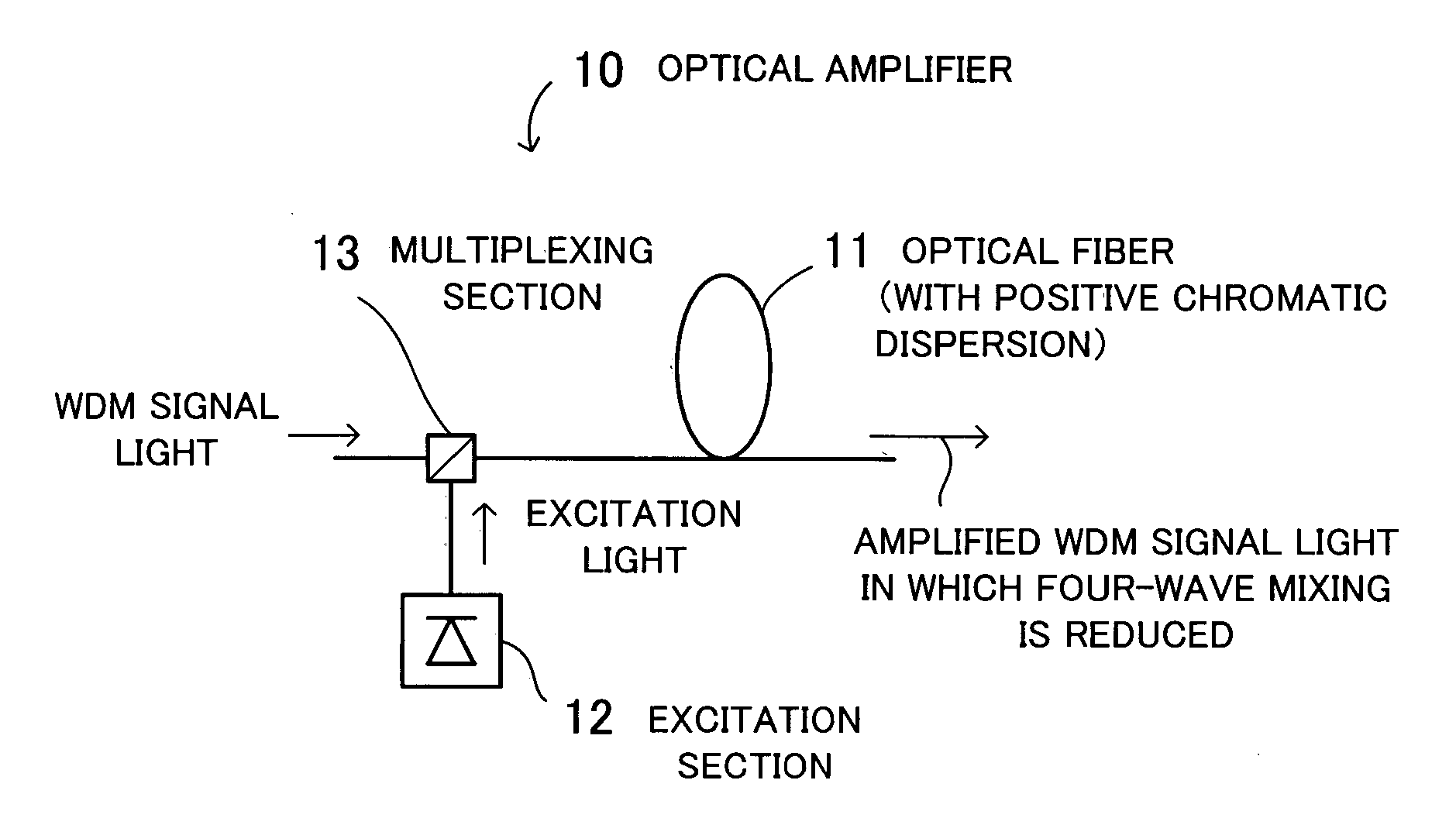
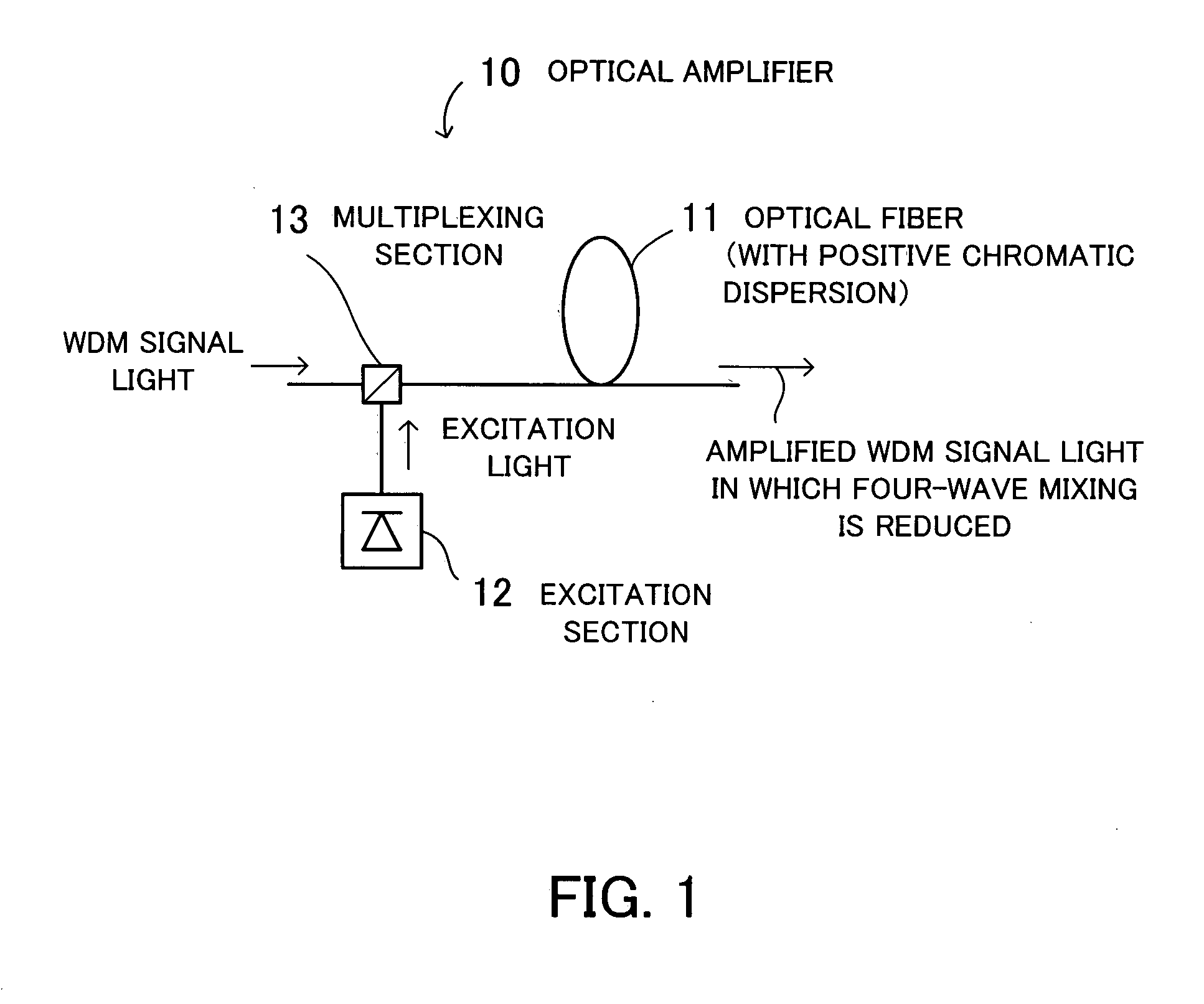
Optical amplifier and optical fiber
InactiveUS20060291036A1Reduce mixImprove reliabilityLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLength waveWdm transmission
An optical amplifier that improves the quality of WDM transmission by reducing four-wave mixing. An optical fiber has positive chromatic dispersion in a signal band and is used as an optical amplification medium for amplifying a wavelength division multiplex signal. An excitation section inputs excitation light to the optical fiber. In order to actualize mismatching of phases of optical signals with different wavelengths to be propagated, the optical fiber has positive chromatic dispersion in a signal band by which there is a great difference between a signal frequency, being a frequency of a signal to be amplified, and a zero-dispersion frequency, being a frequency at which chromatic dispersion is zero. As a result, the optical fiber functions as an optical amplification medium in which four-wave mixing is suppressed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
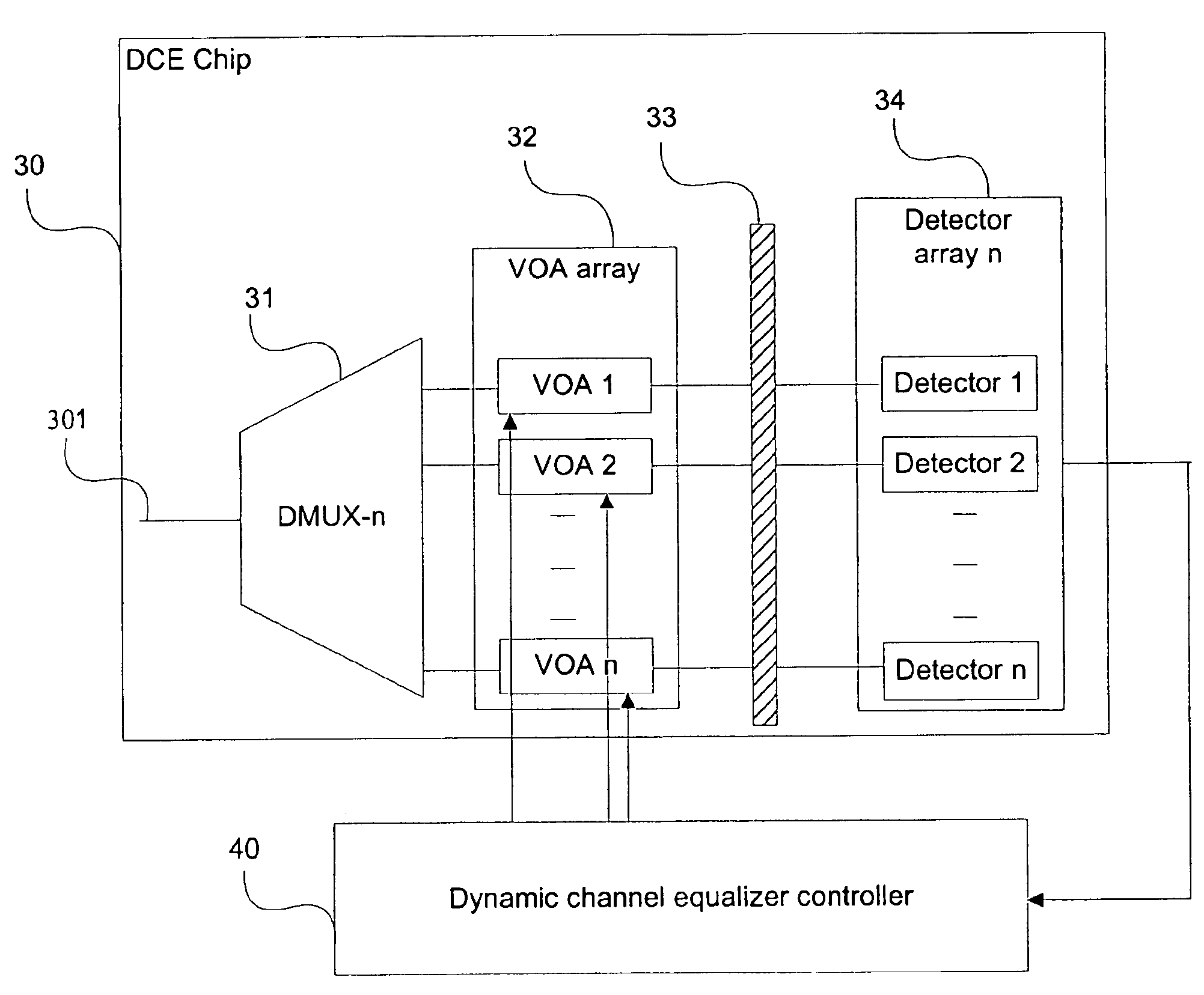
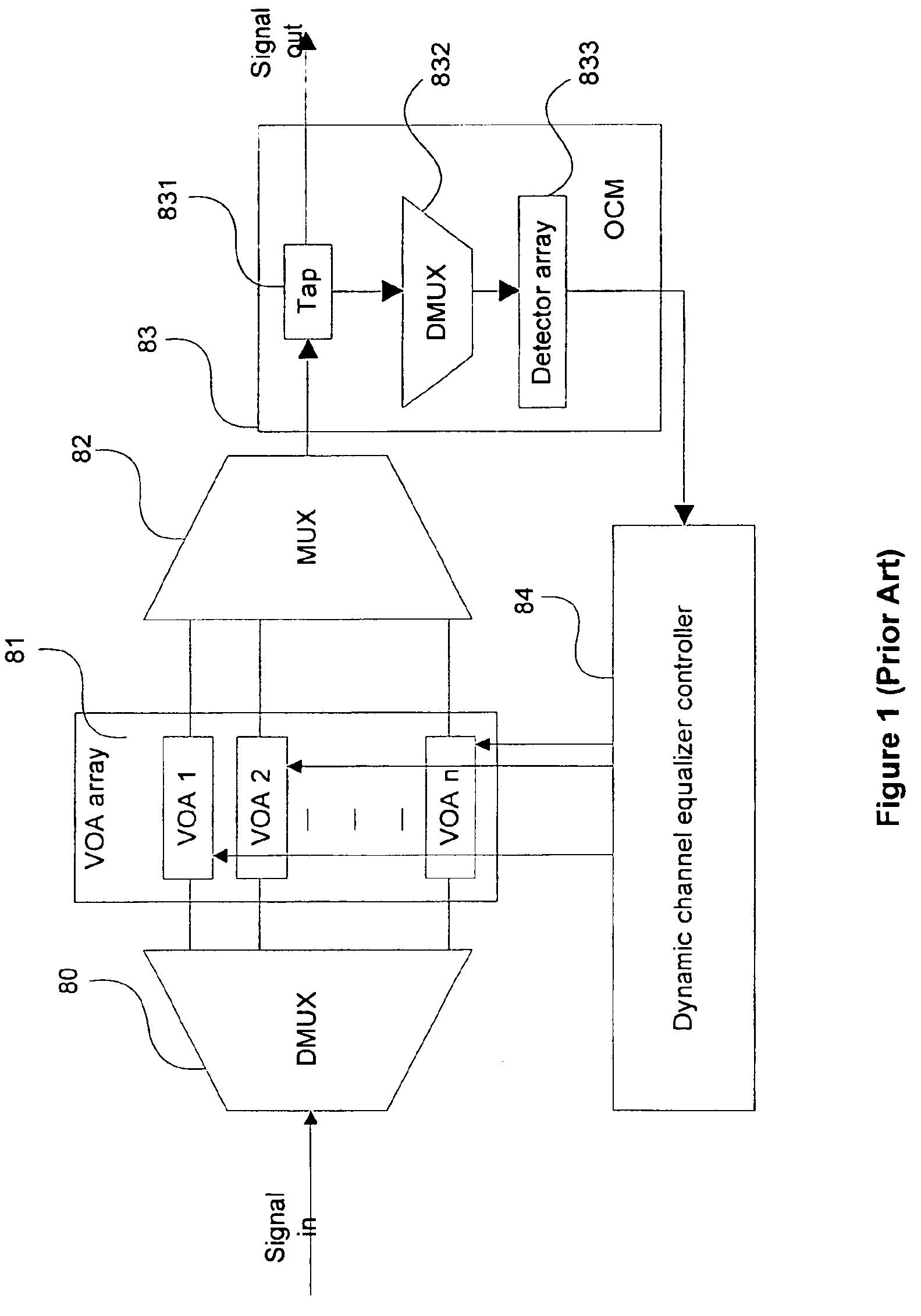
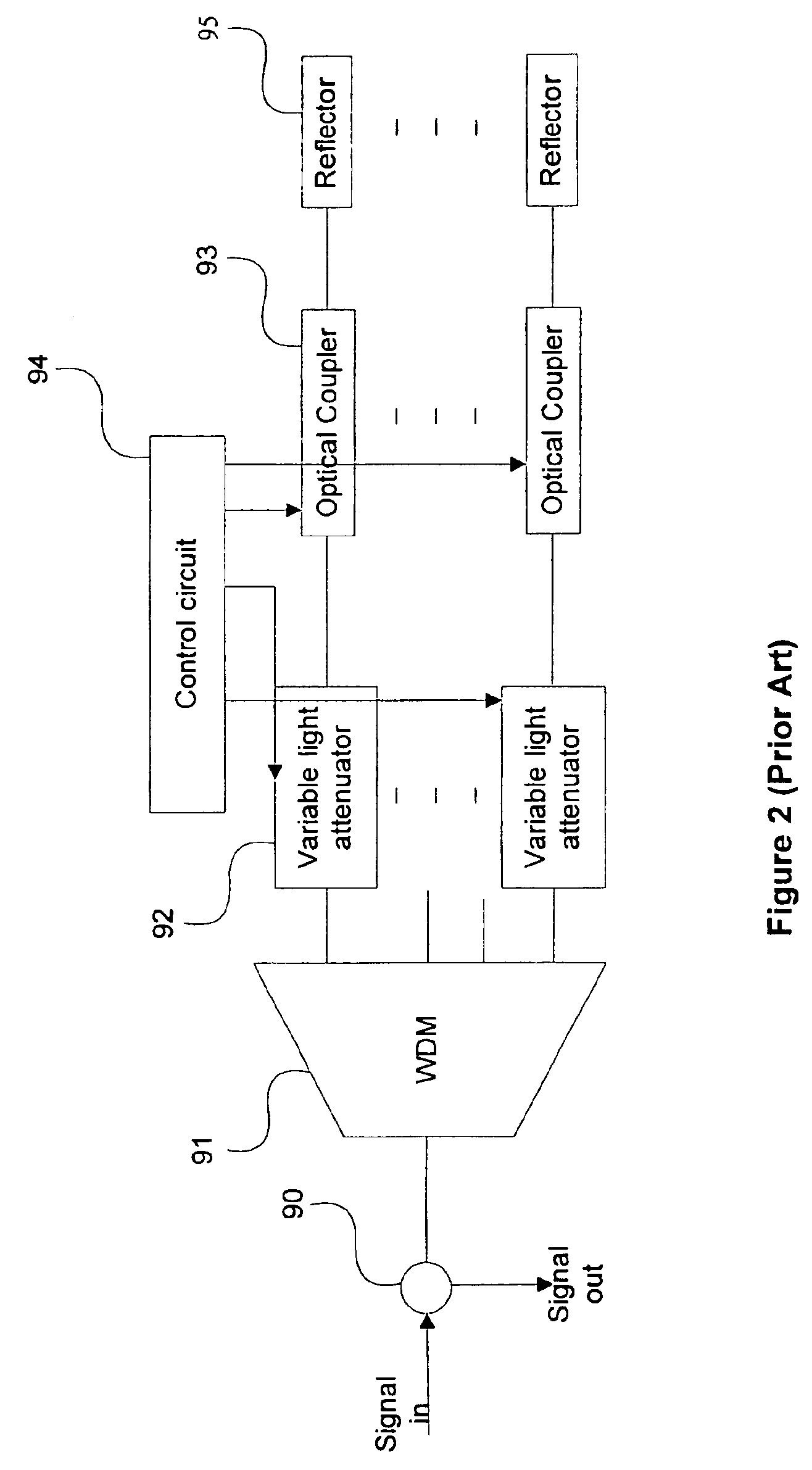
Compact hybrid integrated optical dynamic channel equalizer
InactiveUS6917747B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesDynamic channelMultiplexer
An integrated optical dynamic channel equalizer that can be employed to equalize the channel gain level in a WDM transmission line and monitor the optical channel performance. The device consists of a circulator, a dynamic gain equalizer chip and a controller. Due to the simplicity of the dynamic gain equalizer chip, which includes one 1×n multiplexer / demultiplexer, an n-channel variable optical attenuator array (VOA-n), a partially transparent dielectric reflective means and an n-channel detector array, the device is very compact and can be fabricated at low cost. By placing a quarter wave plate between the n-channel variable optical attenuator array and the partially transparent reflective means in the dynamic channel equalizer chip, the device can be rendered polarization insensitive.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Subchannel security at the optical layer
ActiveUS8705741B2Improve securityImprove network securitySecret communicationMultimode transmissionEngineeringOptical communication
The present invention includes various novel techniques, apparatus, and systems for optical WDM communications that involve dynamically modifying certain aspects of the WDM transmission (and corresponding receive) process at the optical (physical) layer to significantly enhance data / network security. These various dynamic modifications can be employed individually or in combination to provide even greater security depending upon the desired application and design tradeoffs. WDM transmission steps typically include encoding the client signals, mapping them to one or more subchannels within or across ITU channels, modulating them onto subcarrier frequencies, and multiplexing them together for optical transmission. By dynamically modifying one or more of these processing steps over time (in addition to any encryption of the underlying client signals), the current invention provides additional security at the physical (optical) layer of an optical network and thus greatly enhances overall network security.
Owner:VELLO SYST +1
Optical fiber
InactiveUS6853784B2Reduce transmission lossGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingLength waveTransmission loss
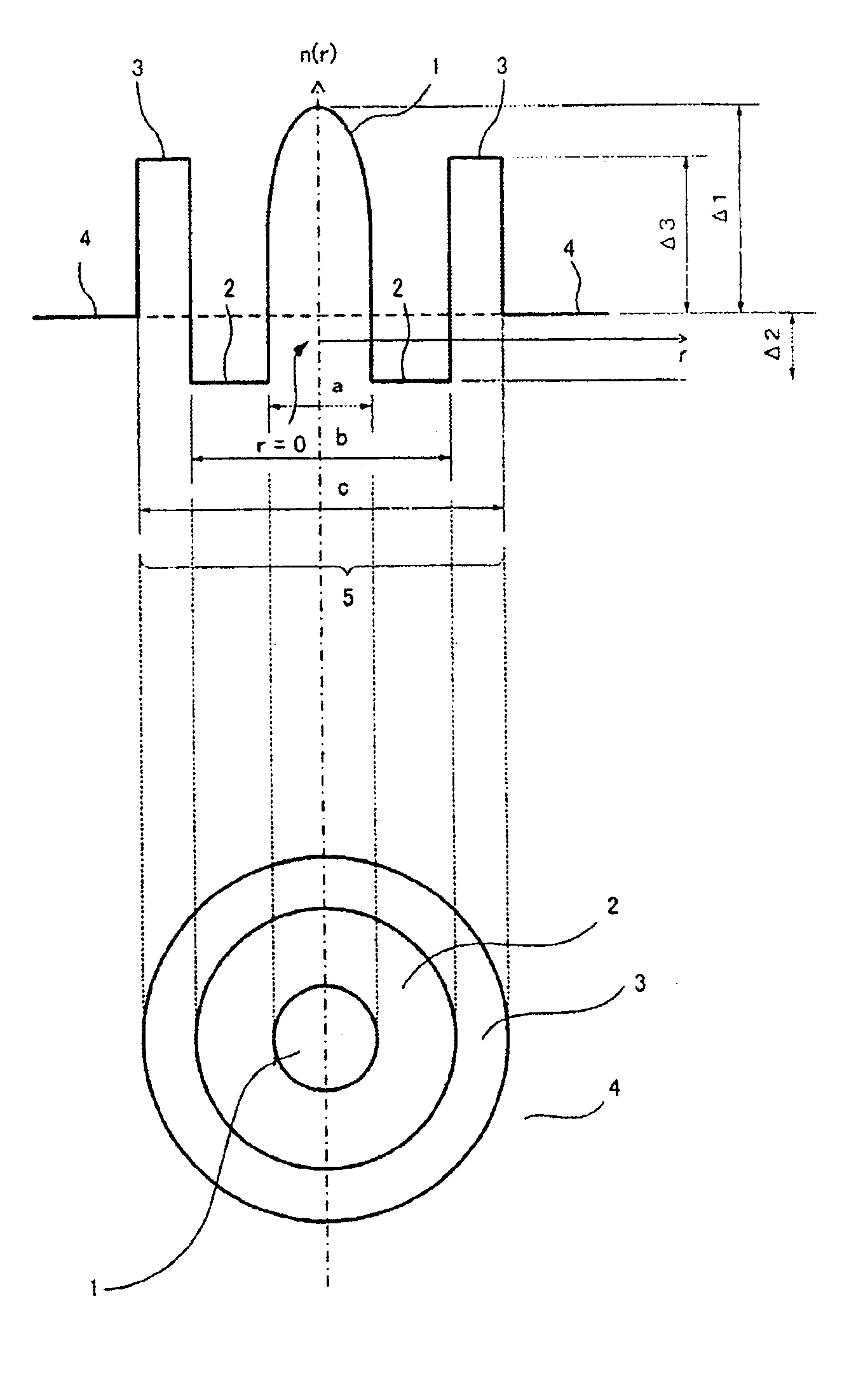
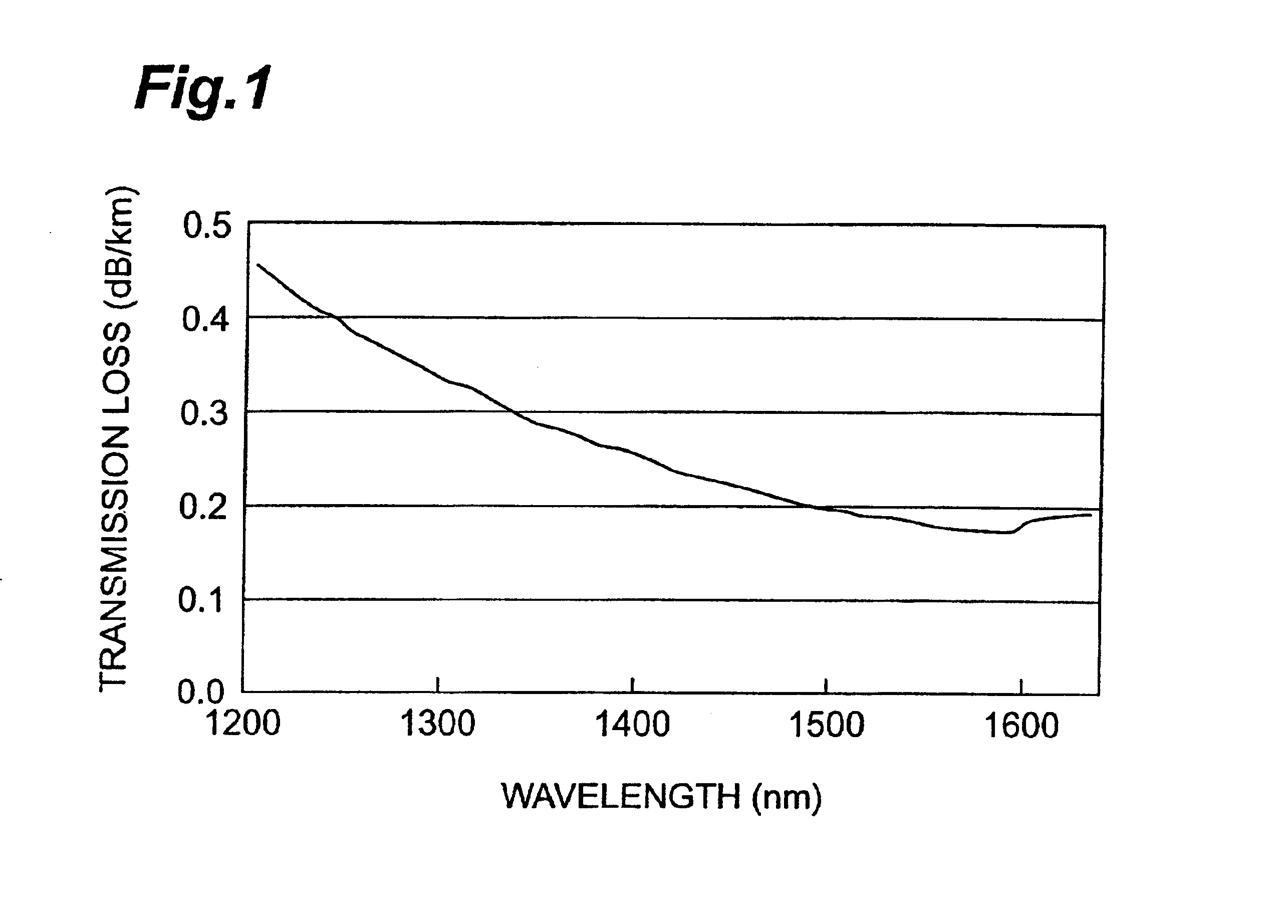
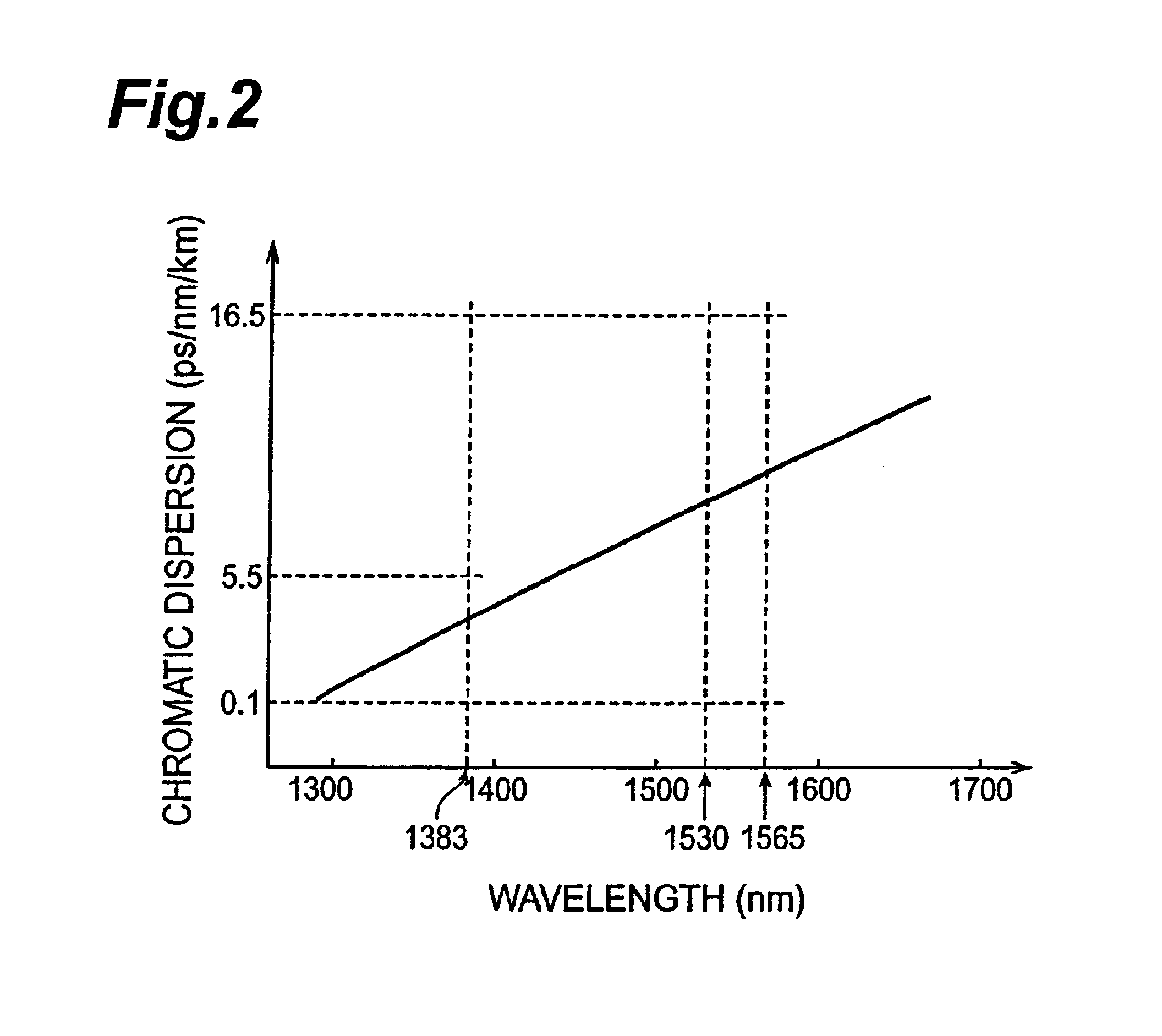
The present invention relates to an optical fiber comprising a structure enabling WDM transmissions by utilizing the whole wavelength range of 1300 nm to 1625 nm as a signal wavelength band. In the optical fiber according to the present invention, the transmission loss is 0.4 dB / km or less at a wavelength of 1310 nm, 0.4 dB / km or less at a wavelength of 1383 nm, and 0.3 dB / km or less at a wavelength of 1550 nm. The chromatic dispersion is 0.1 ps / nm / km or more but 5.5 ps / nm / km or less at a wavelength of 1383 nm, and 0.1 ps / nm / km or more but 16.5 ps / nm / km or less in the wavelength range of 1530 nm to 1565 nm. The cut off wavelength at a length of 22 m is 1300 nm or less, and the absolute value of dispersion slope in the wavelength range of 1300 nm to 1625 nm is 0.1 ps / nm2 / km or less.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
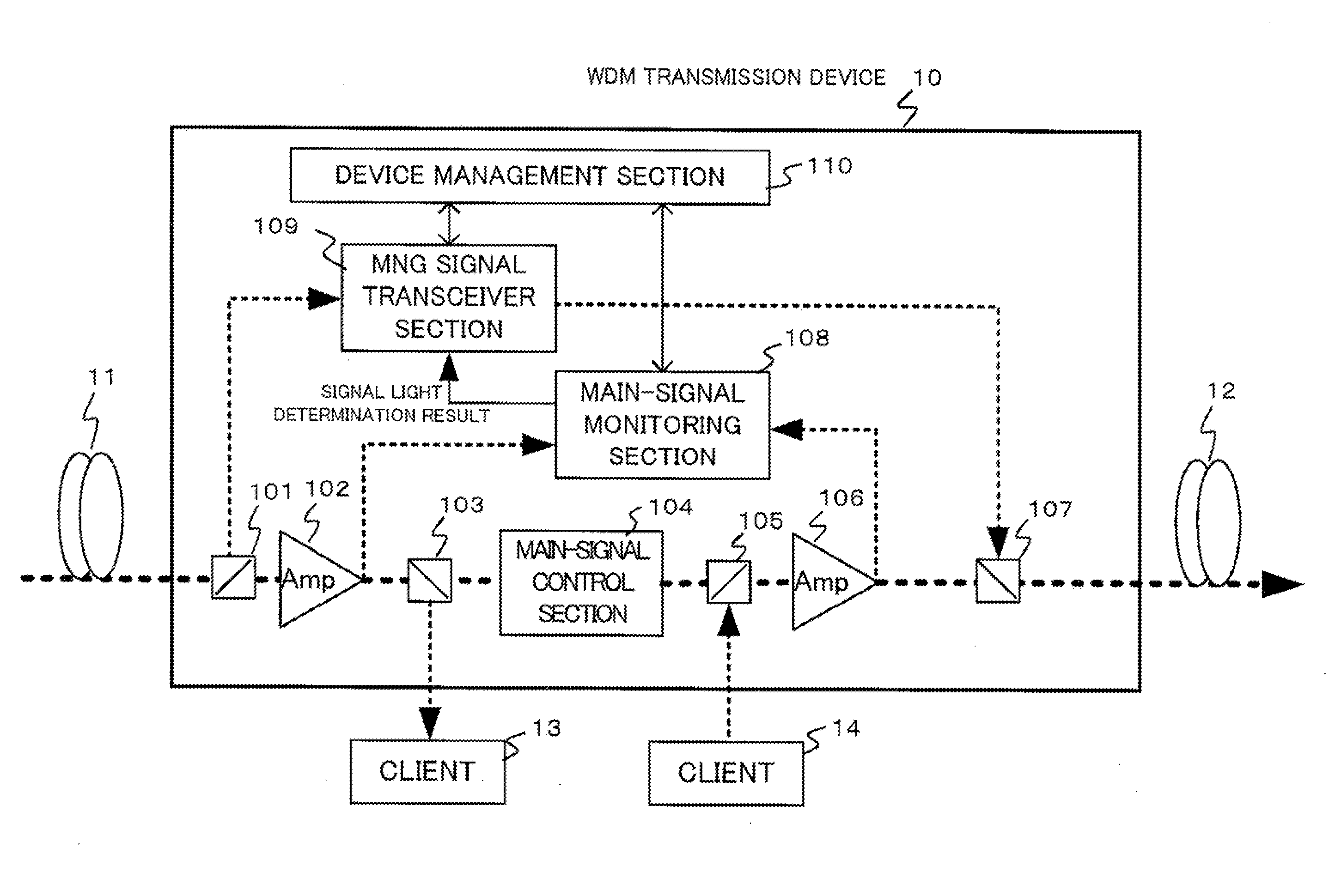
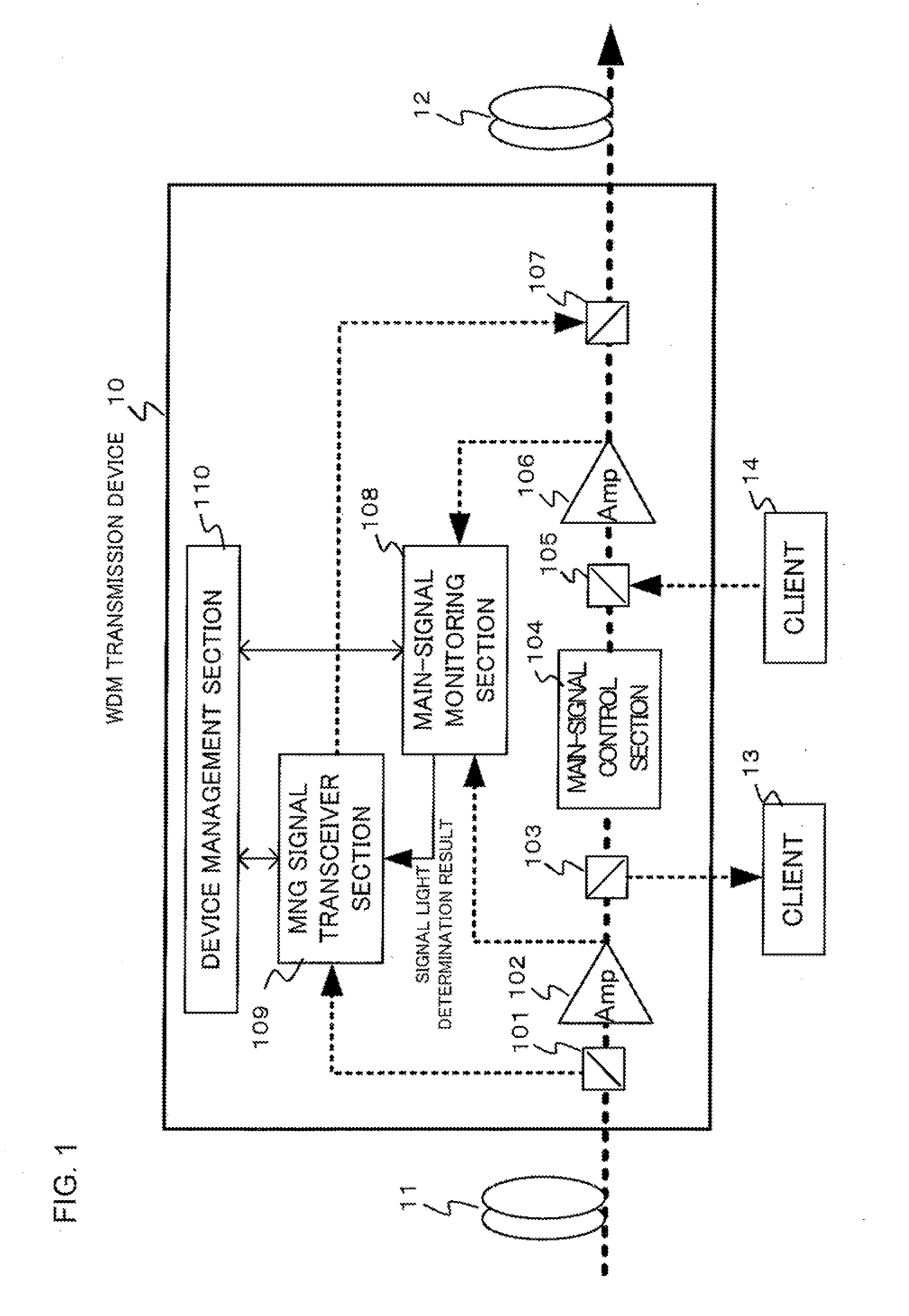
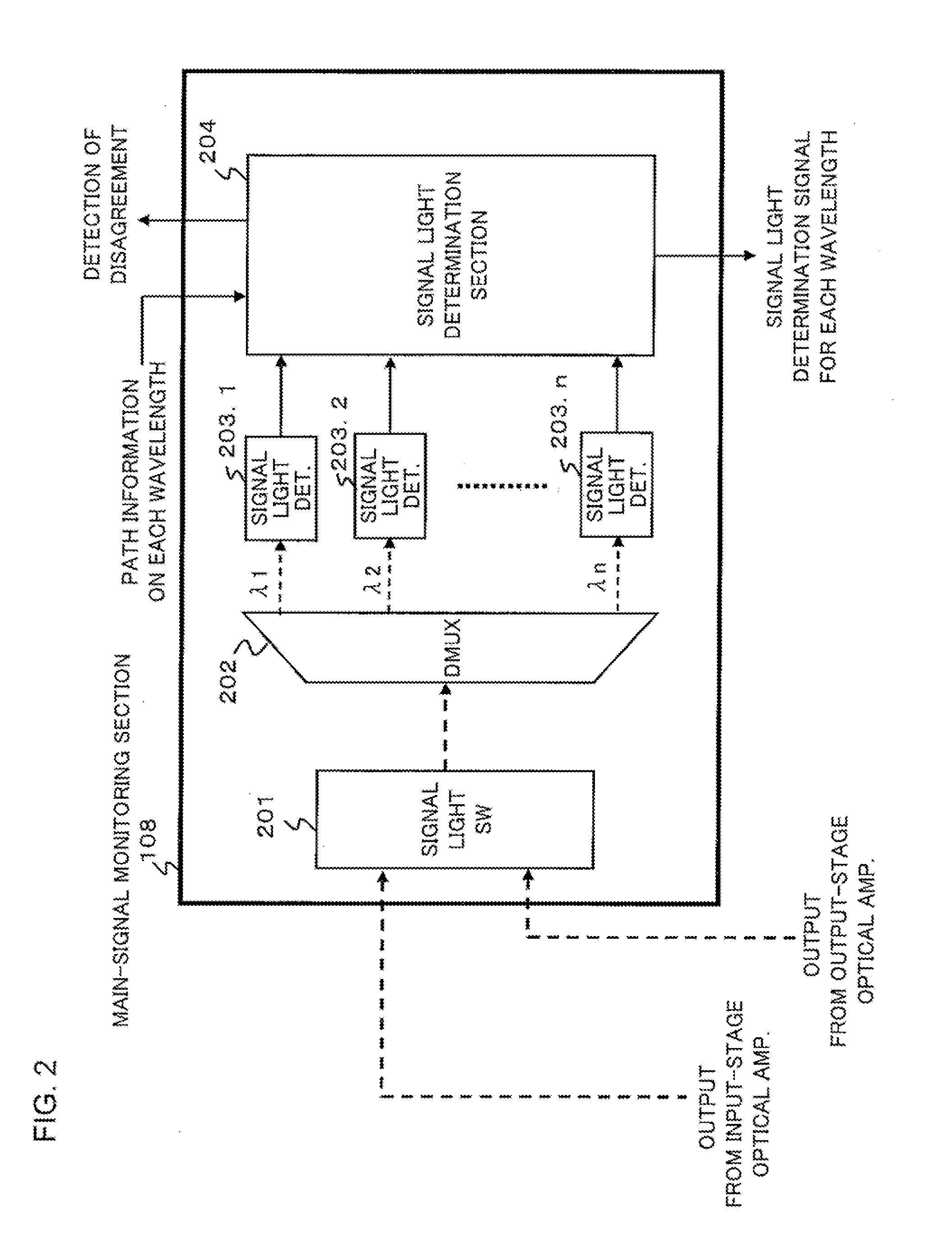
Method and device for monitoring WDM signal light
InactiveUS20110085798A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringSignal lightEngineering
A WDM signal light monitoring device includes a first monitor for monitoring input-side WDM main signal light and output-side WDM main signal light for each wavelength; and a second monitor for monitoring the first monitor by comparing a monitoring result received from an upstream WDM transmission device with a monitoring result of the first monitor, wherein the monitoring result of the first monitor is transmitted to a downstream WDM transmission device in the system.
Owner:NEC CORP
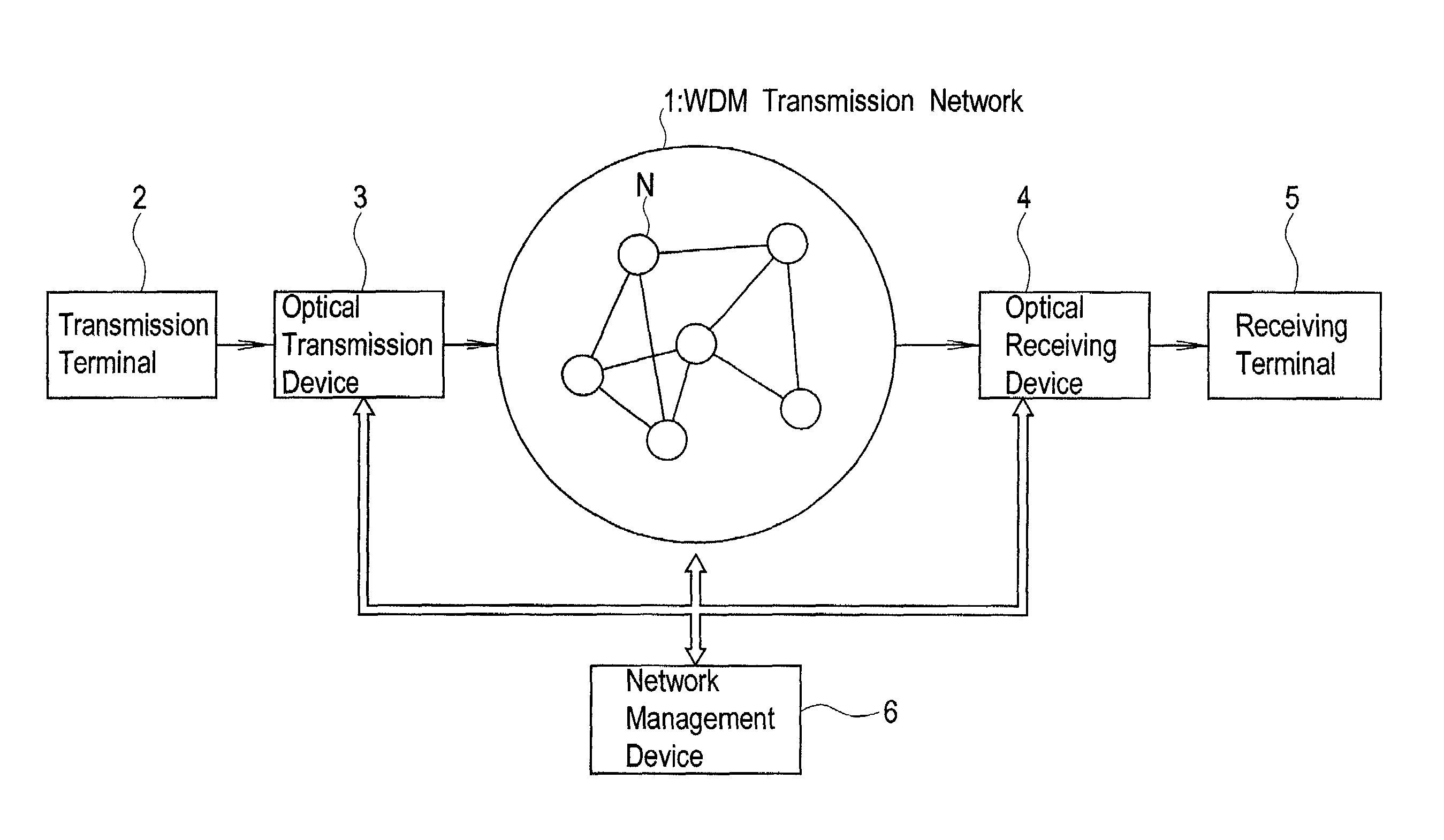
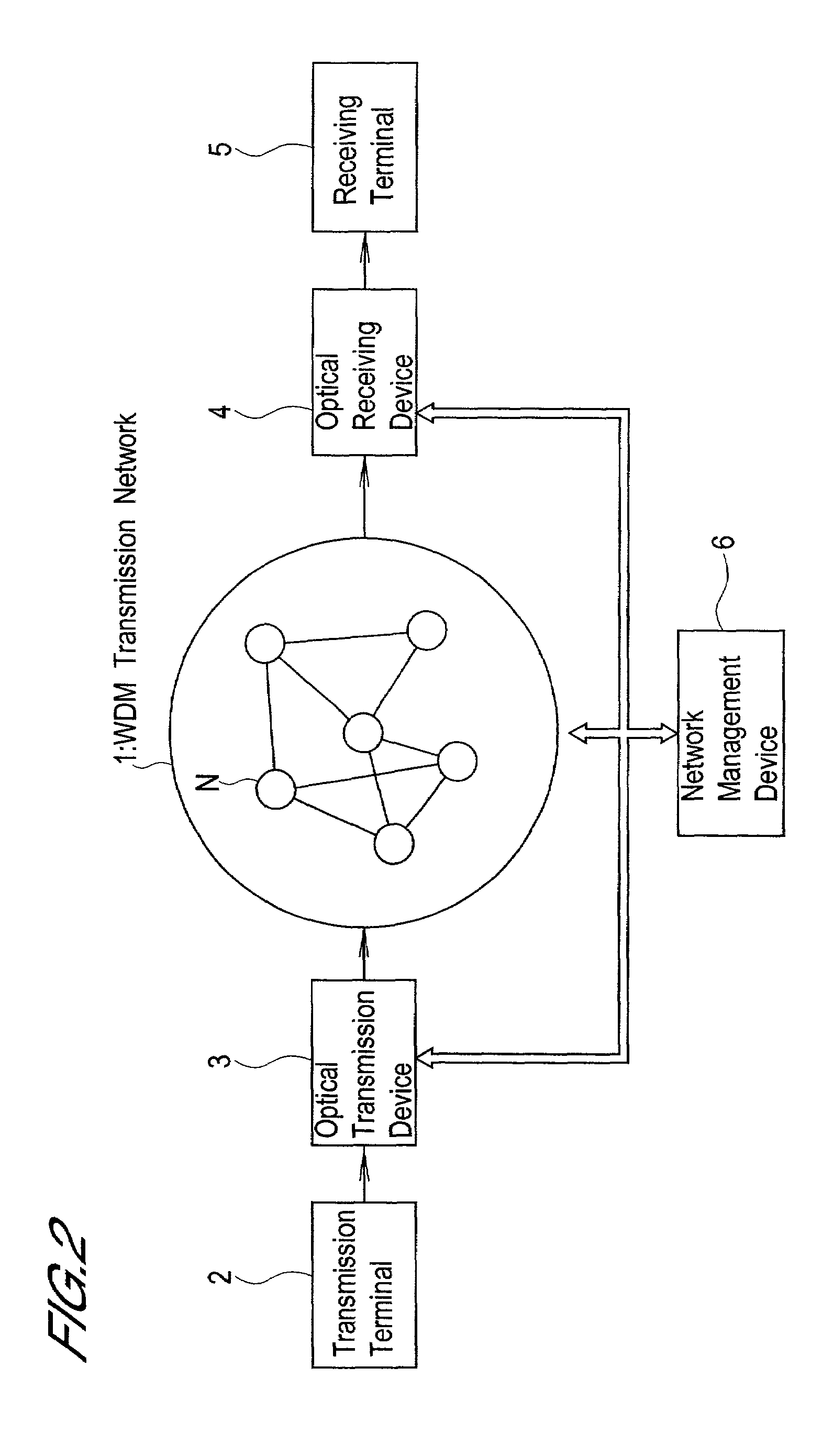
Wavelength division multiplex transmission system
InactiveUS7139482B2Satisfactory transmission characteristicEnhanced function for defect avoidanceRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsLength waveWdm transmission
There is provided a wavelength division multiplex transmission system with satisfactory transmission characteristics and extensive functions for avoidance of defects. Transmission signals to be transmitted by an optical transmission device are distributed among a plurality of wavelength components, converted into WDM signals, and sent to a WDM transmission network, and WDM signals from the WDM transmission network are restored to the transmission signals by an optical receiving device. This system includes a wavelength component-specific route setting device which sets routes for transmission on the WDM transmission network for each wavelength component.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
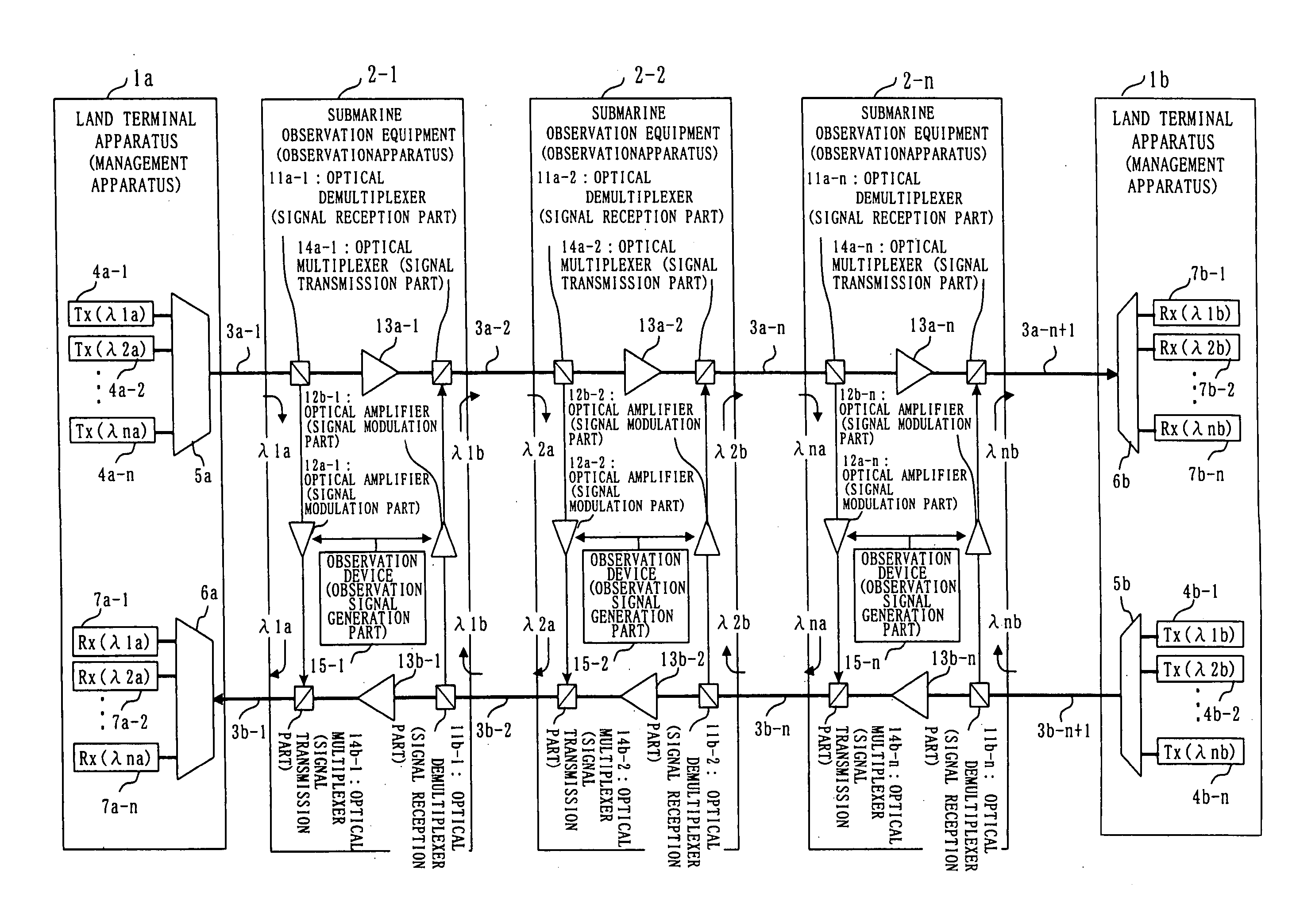
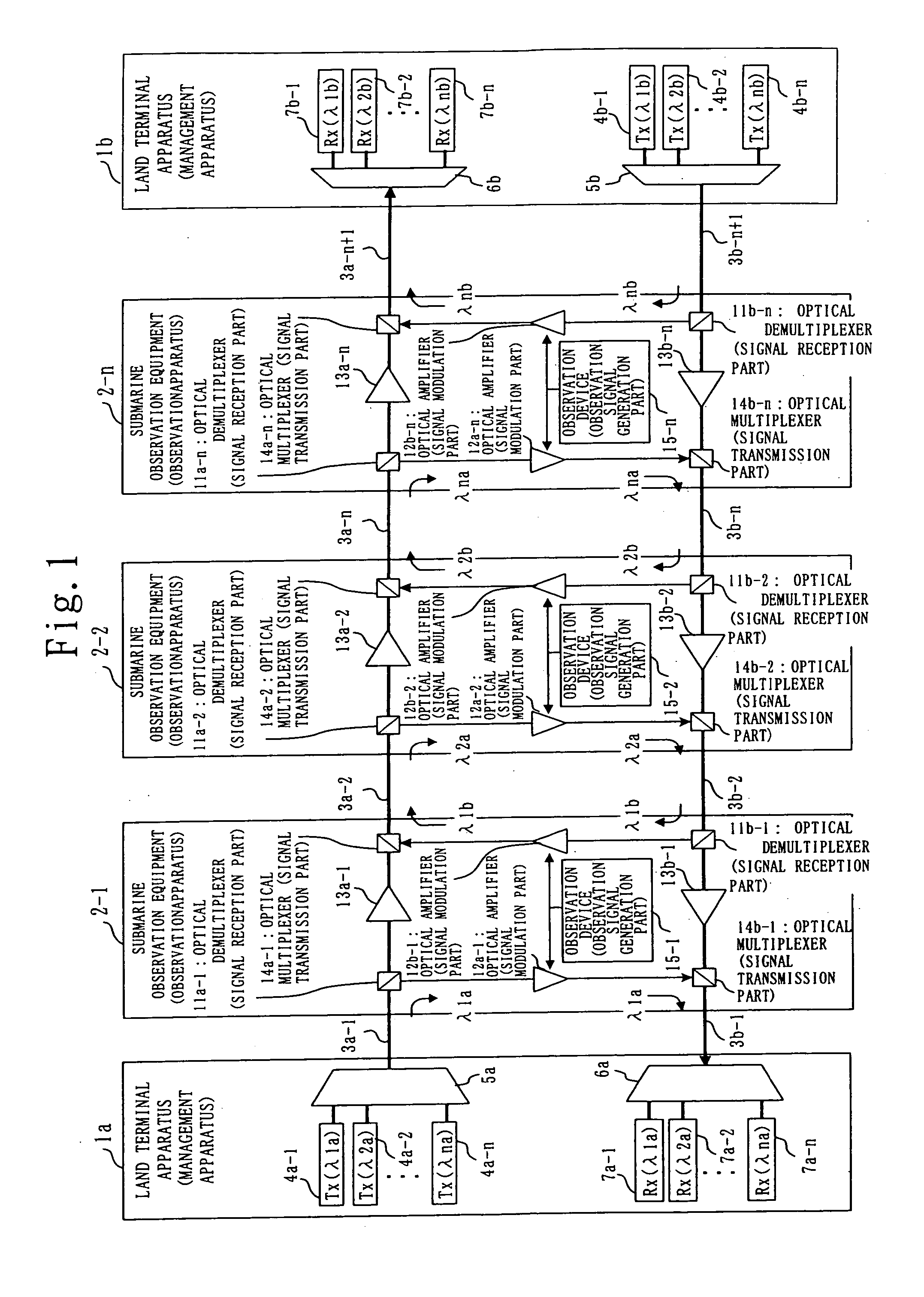
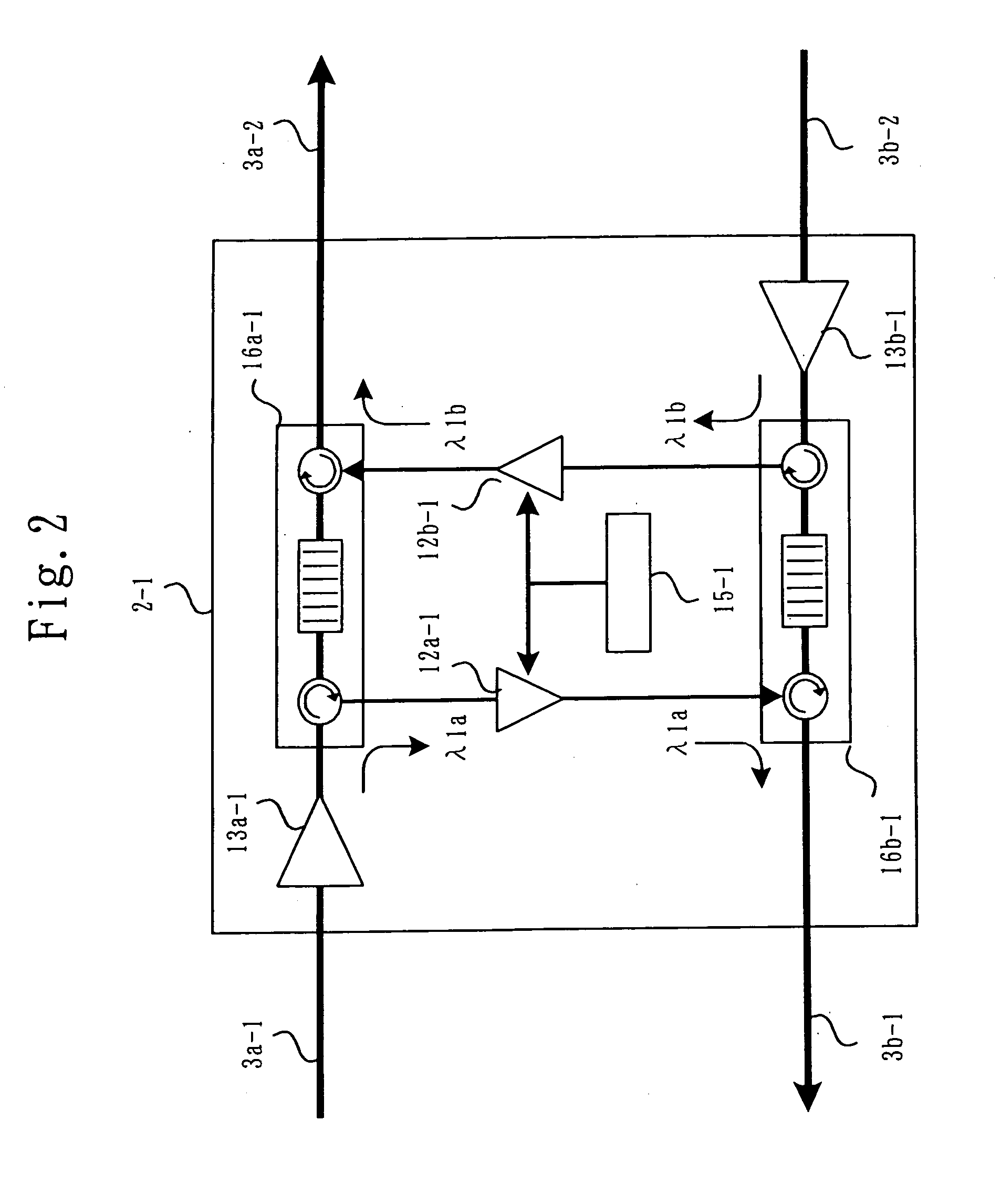
Observation apparatus and observation system
InactiveUS20050259264A1High extensibility and reliabilityReduce system costElectric signal transmission systemsNon-electrical signal transmission systemsOcean bottomCarrier signal
The present invention discloses a submarine observation system in which a plurality of carrier lights assigned to each submarine observation equipment is transmitted from a land terminal apparatus to an optical submarine cable (down-going) by using a WDM transmission. In the submarine observation equipment, only a prescribed carrier light is demultiplexed by an optical demultiplexer, an observation signal indicating an observation result is generated by an observation device, intensity of the carrier light demultiplexed by the optical demultiplexer is modulated by an optical amplifier based on an observation signal, and the modulated carrier light is multiplexed by an optical multiplexer. The multiplexed carrier light is output to the optical submarine cable (up-going) to be returned to the land terminal apparatus being the transmission station. The land terminal apparatus is able to obtain an observation signal of each observation point by separating carrier lights based on each wavelength and receiving a separated carrier light of each wavelength. Accordingly, the system can be structured with one optical fiber and can be extendable by increasing or decreasing carrier lights, and either one of the land terminal apparatuses can receive an observation signal even when the optical submarine cable is cut off.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
Flexible optimization of the signal-to-noise ratio for ultra dense coherent WDM systems
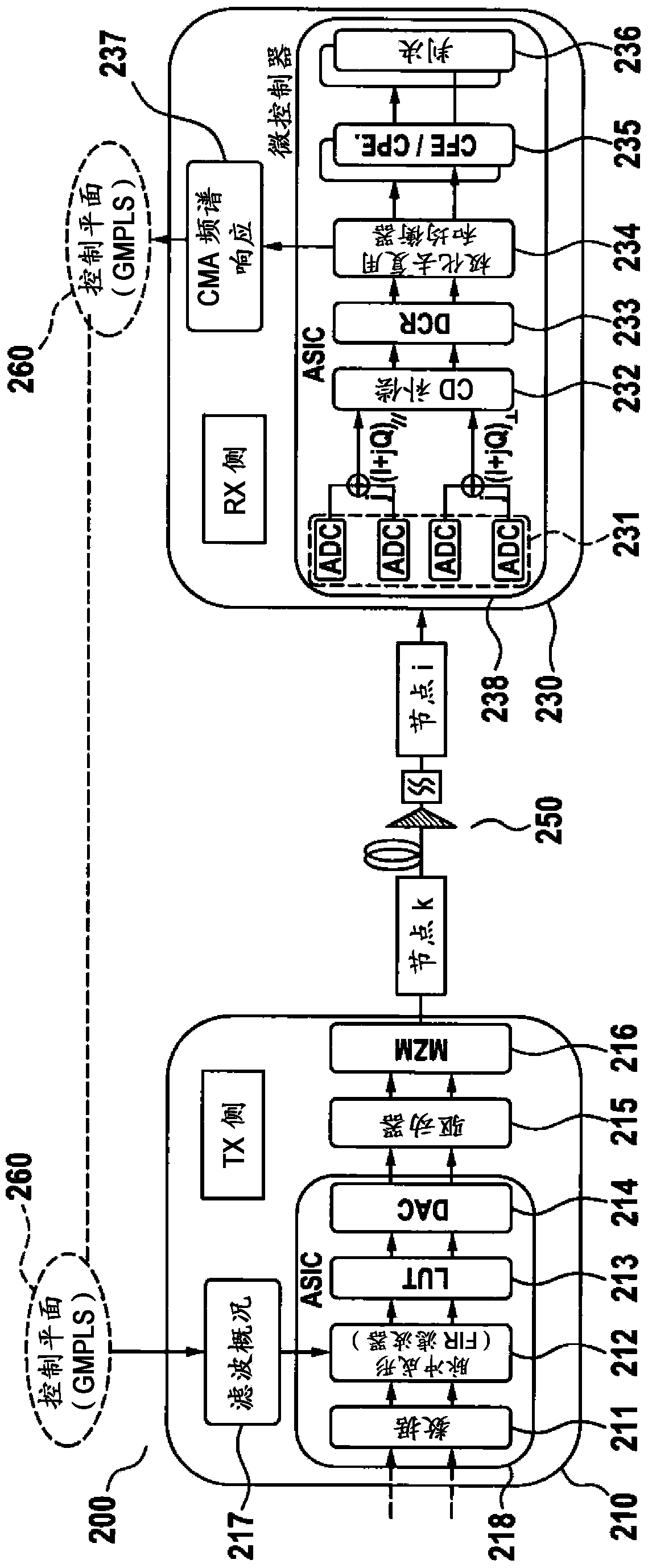
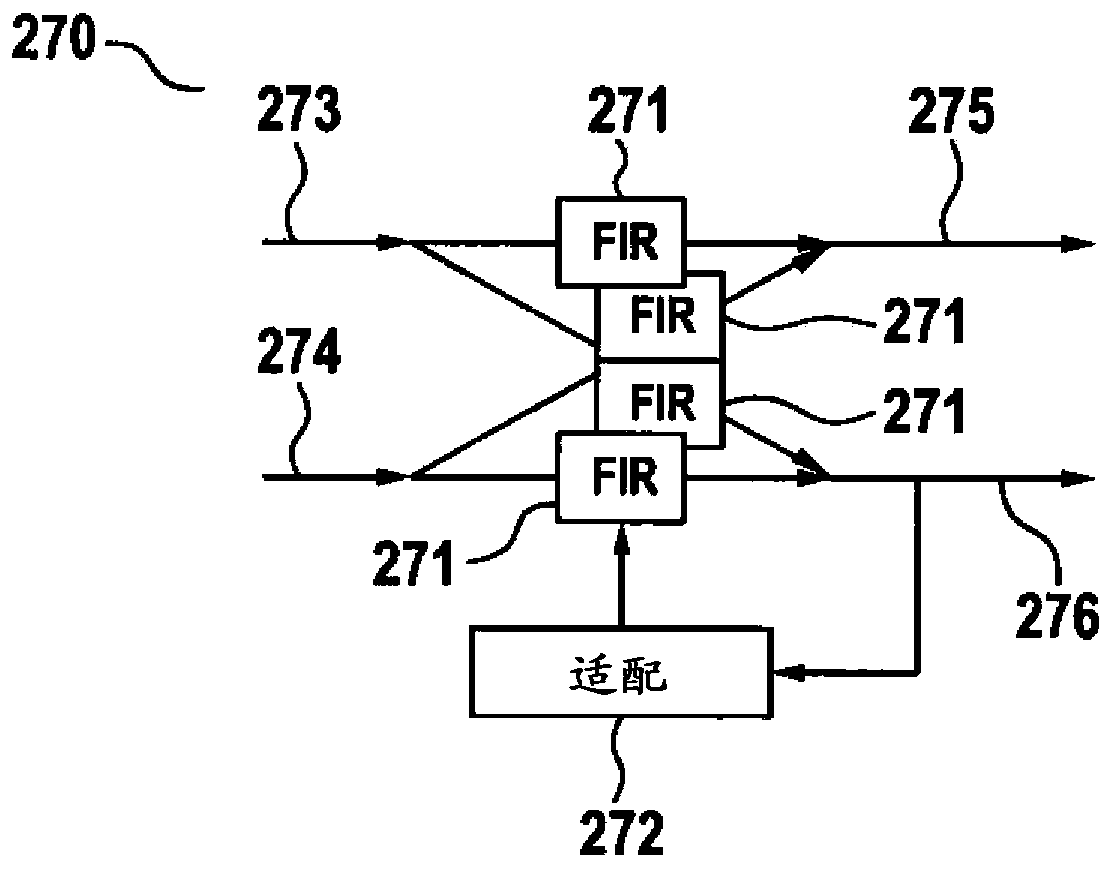
The present document relates to optical communication systems. In particular, the present document relates to high efficiency wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical communication systems. An optical transmitter (210) adapted to transmit an optical signal on an optical wavelength division multiplexed, referred to as WDM, transmission channel (111) to a corresponding optical receiver (230) is described. The optical transmitter (210) comprises a profiling unit (217) adapted to receive information regarding an equalization filter (270) adapted at the corresponding optical receiver (230), based on a first optical signal received from the optical transmitter (210); a pulse shaping filter unit (212) adapted to filter a sequence of data symbols (211) using a pulse shaping filter, thereby yielding a filtered sequence of data symbols (211); wherein a frequency response (404, 405) of the pulse shaping filter depends on the information regarding the equalization filter (270); and a digital-to-optical converter (214, 215 216) adapted to convert the filtered sequence of data symbols (211) into a second optical signal to be transmitted to the optical receiver (230).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com