Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5725 results about "Signal frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
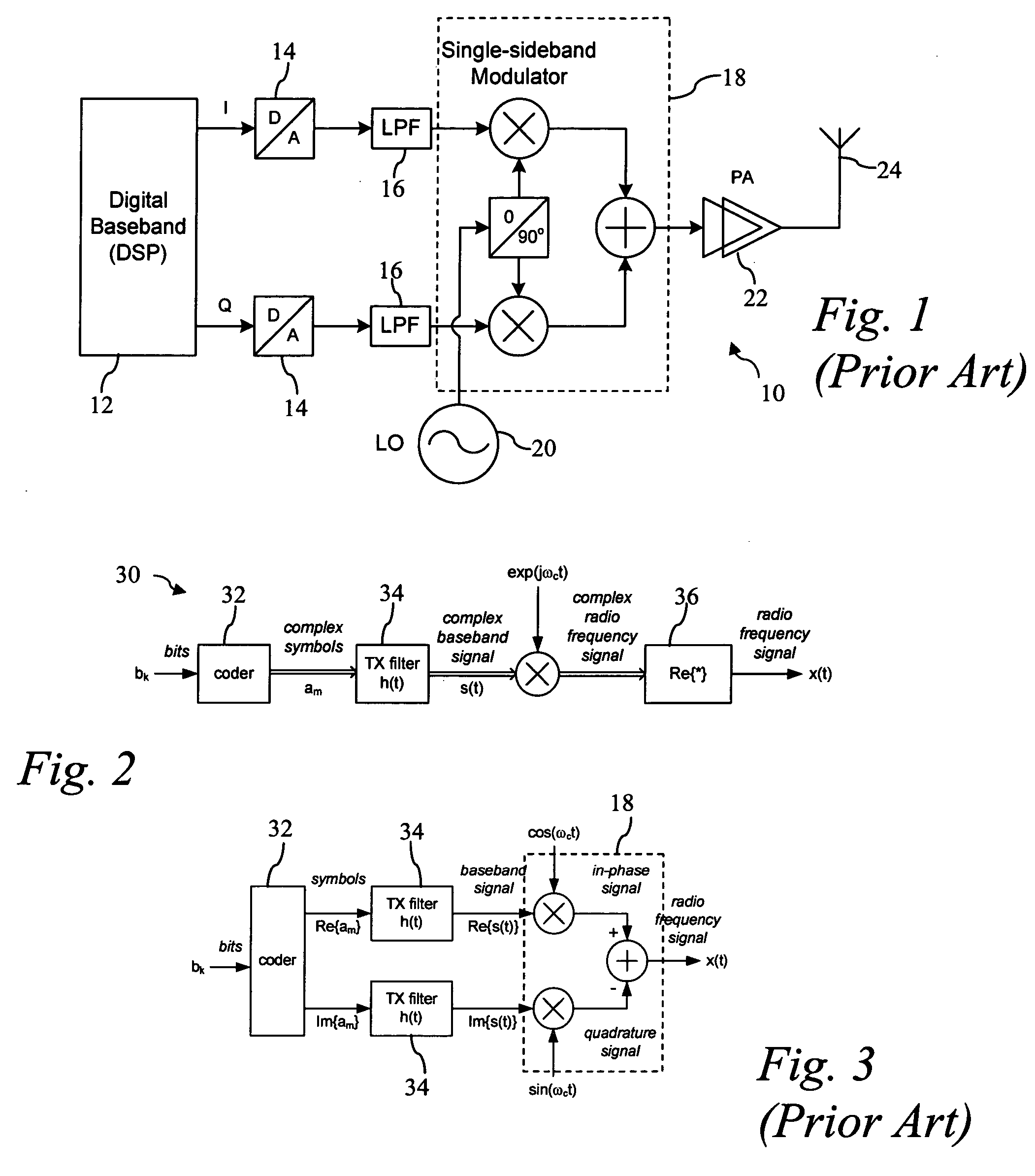
The test signal for frequency measurements is usually at a frequency of 1 MHz or higher, with 5 or 10 MHz being common. Frequency signals are usually sine waves, but can also be pulses or square waves.
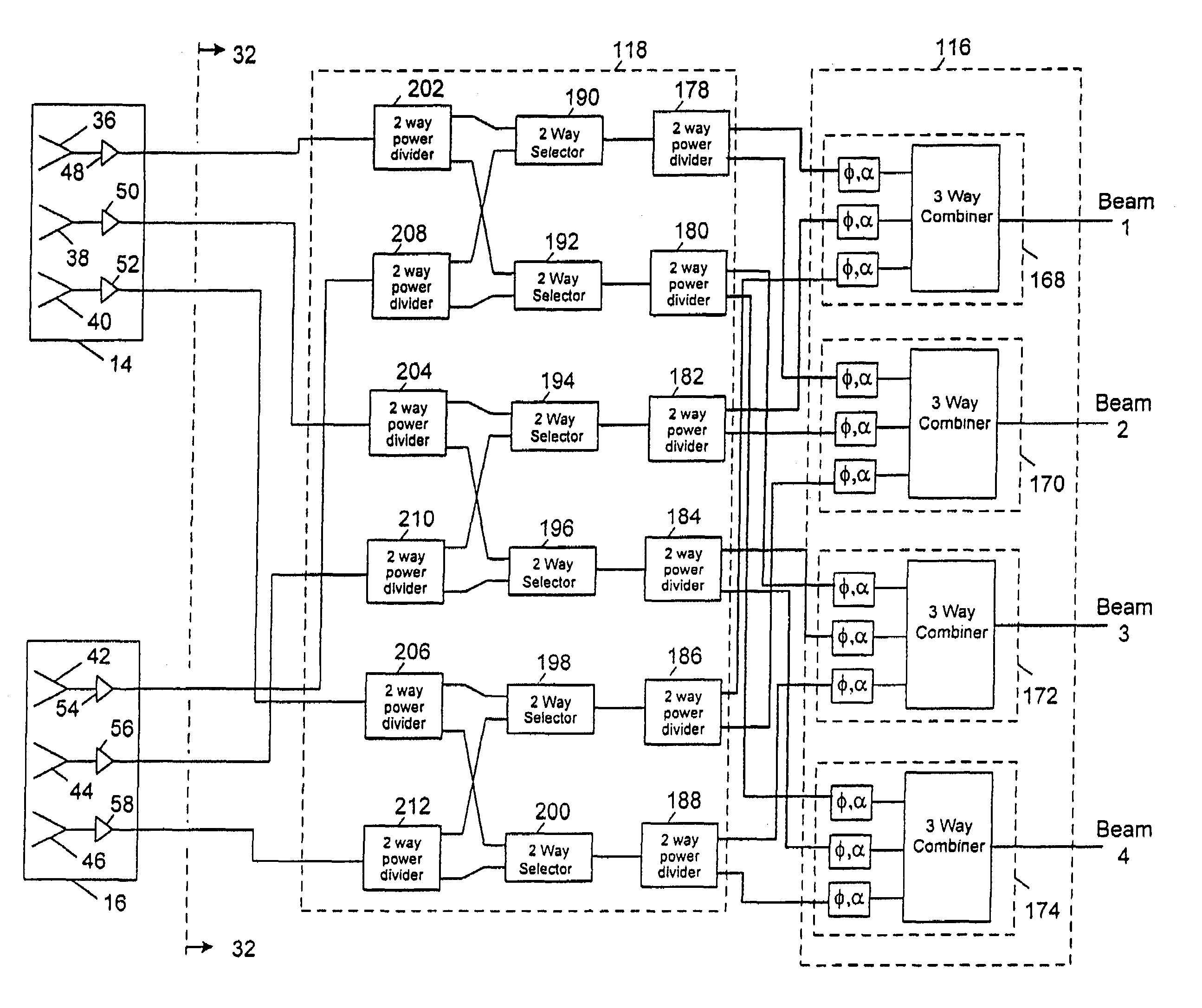
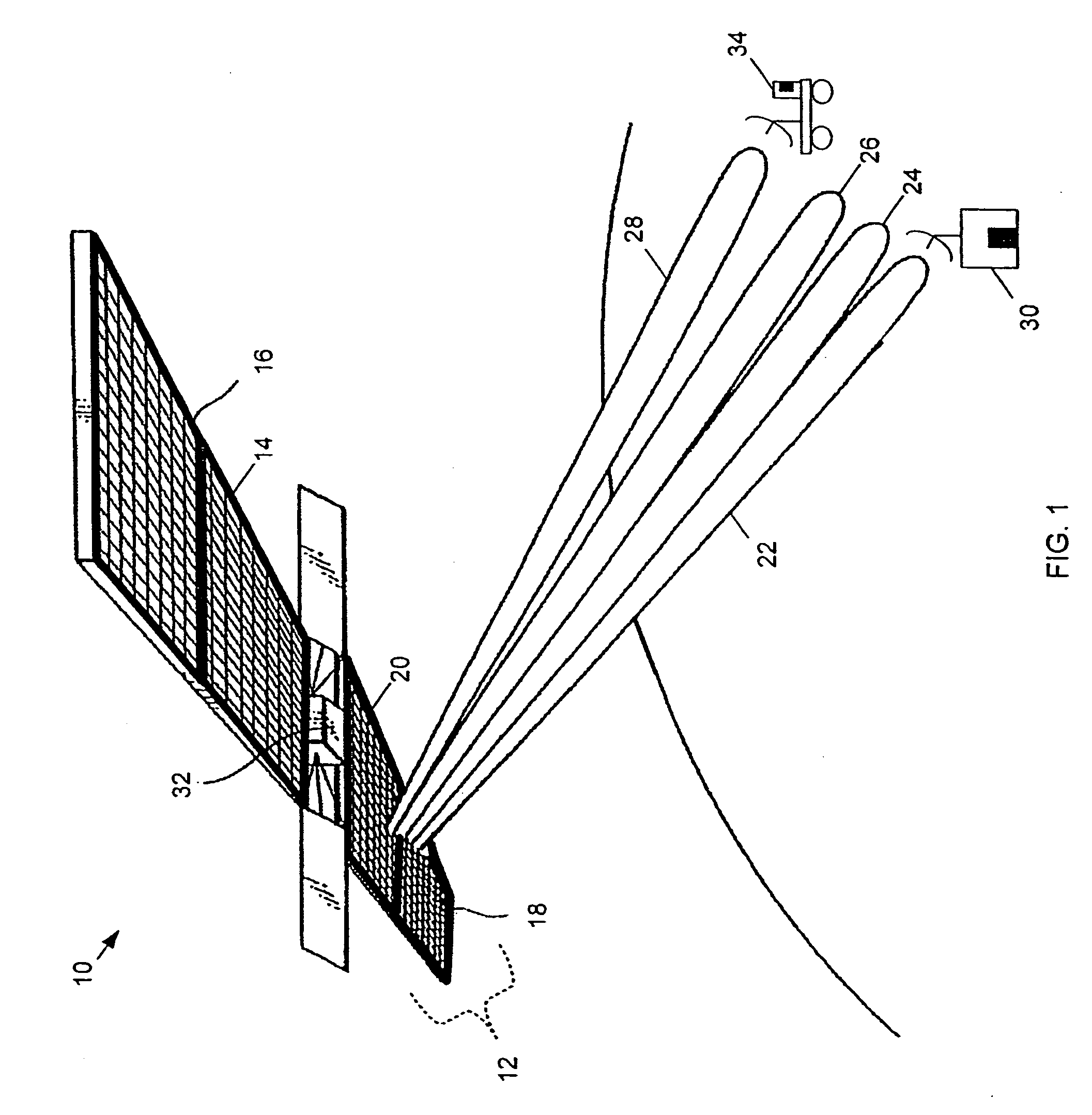
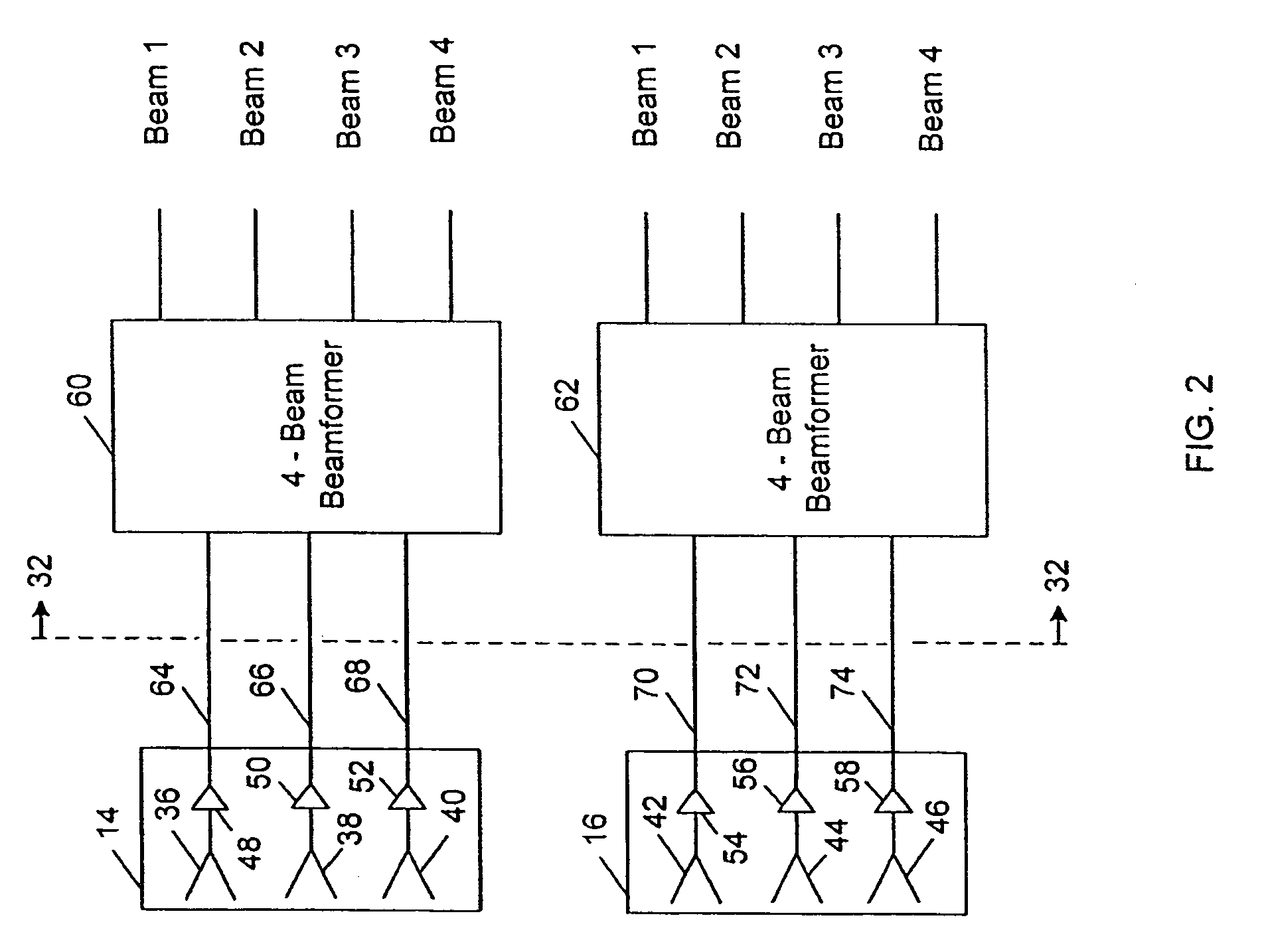
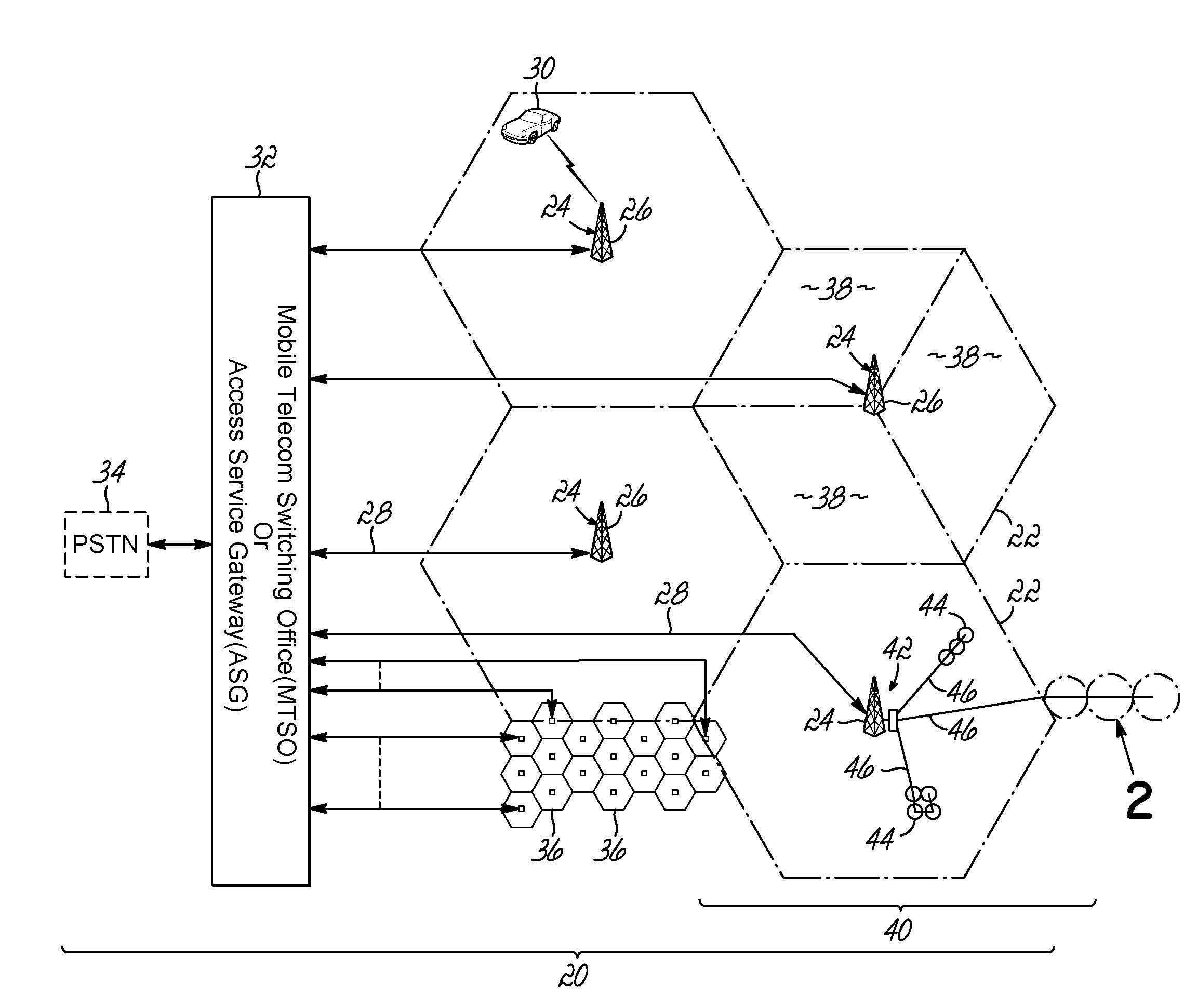
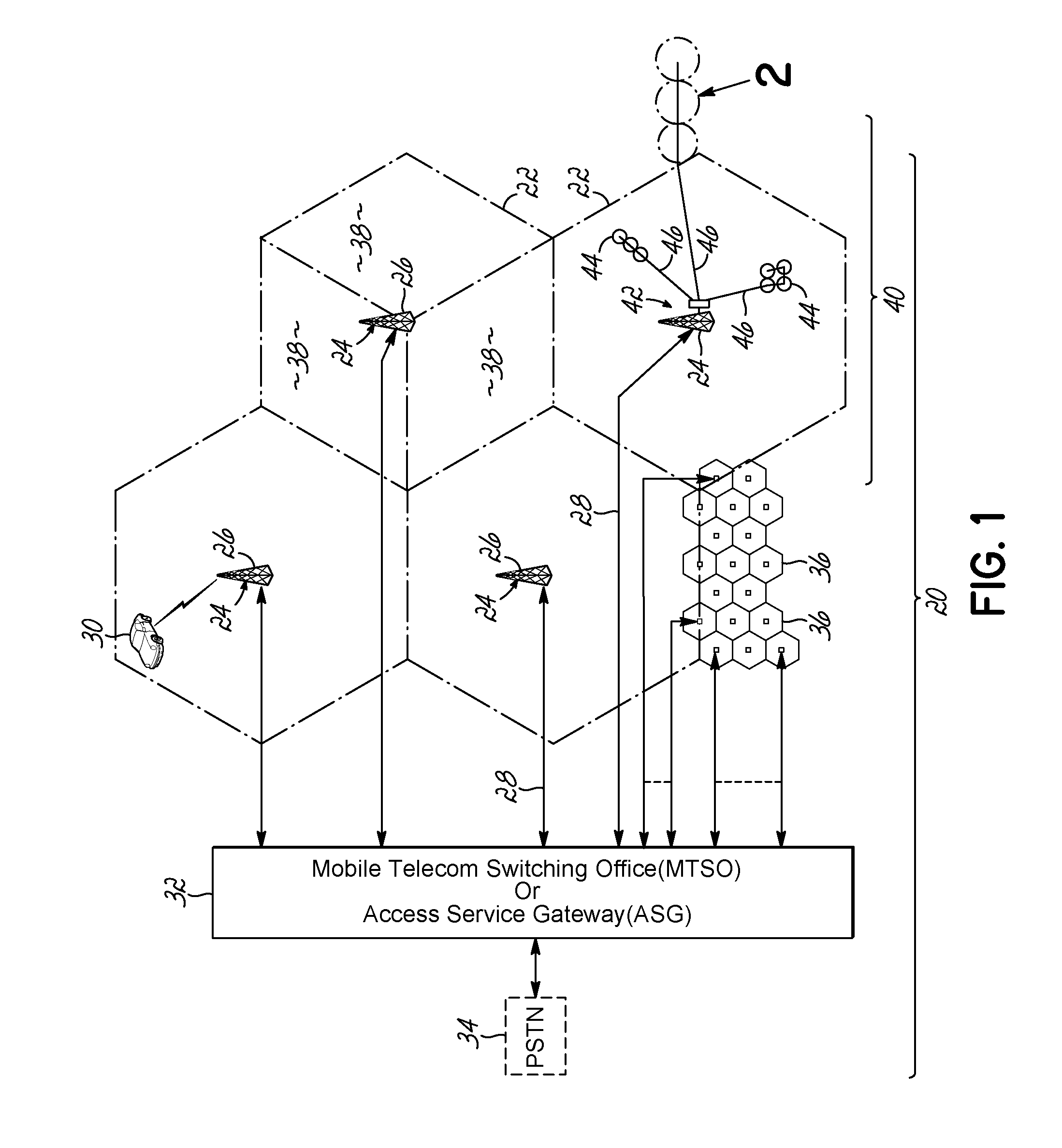
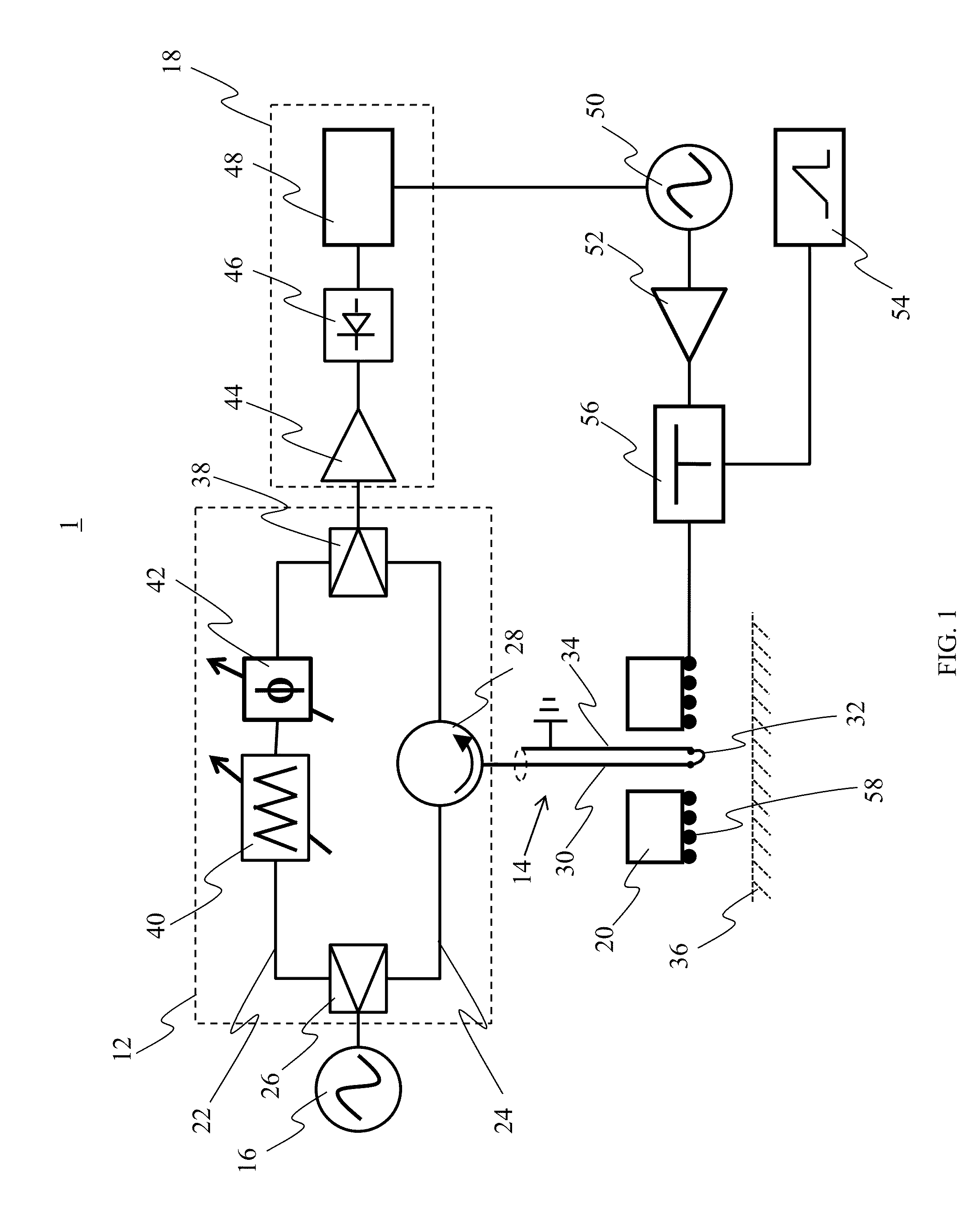
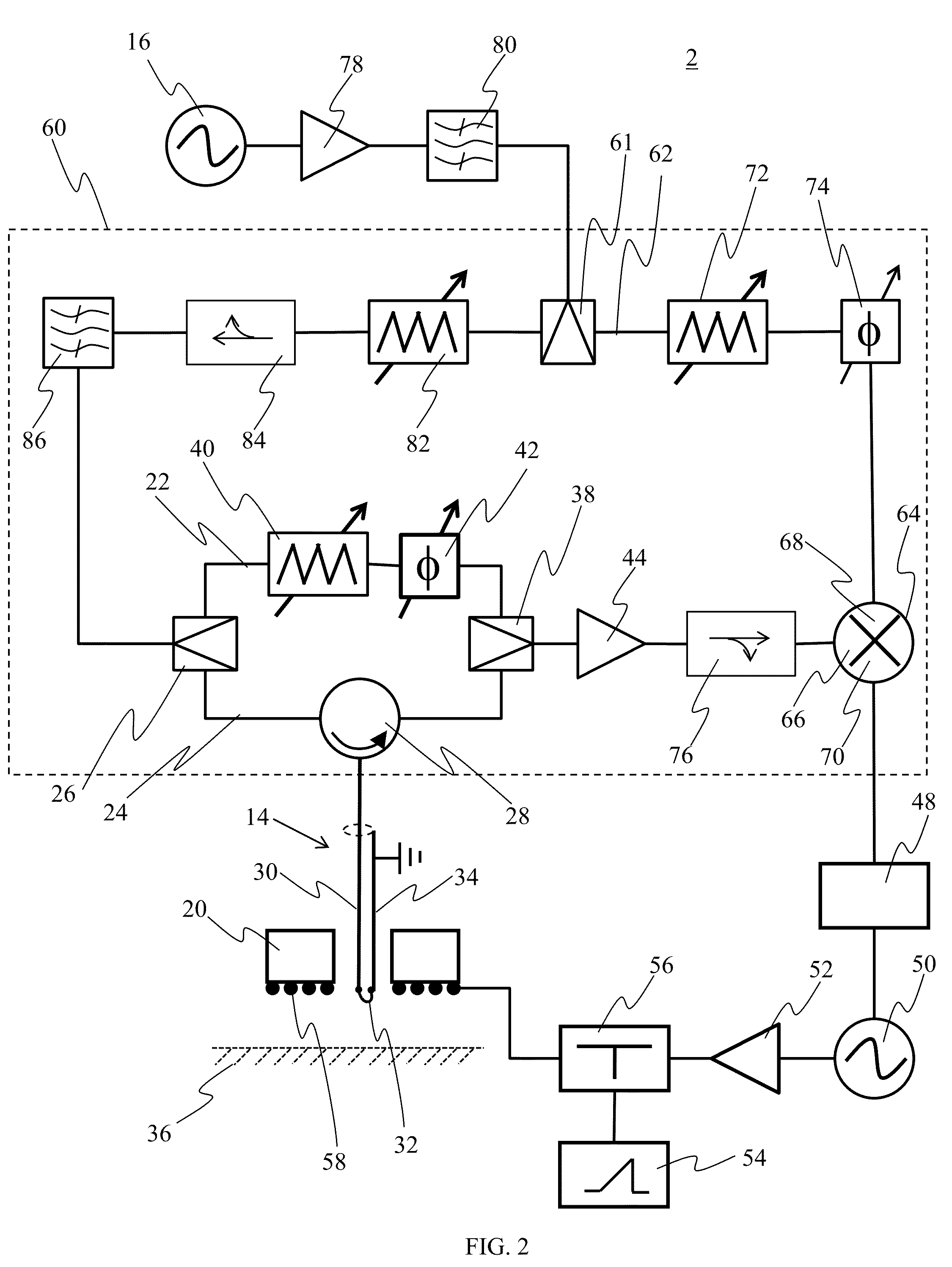
Shared phased array beamformer
A shared beamformer flexibly allocates beams among phased array antenna apertures of a satellite (or other type of platform). By sharing the beamformer among the apertures, if one aperture is not providing useful coverage (due to orientation, traffic volume, signal frequency, signal polarization, etc.), the beams may be reallocated to one or more other apertures that are providing useful coverage. To share the beamformer among the phased array antenna apertures, a selector network (e.g., one or more switches) is used to select which particular apertures are to send or receive signals.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
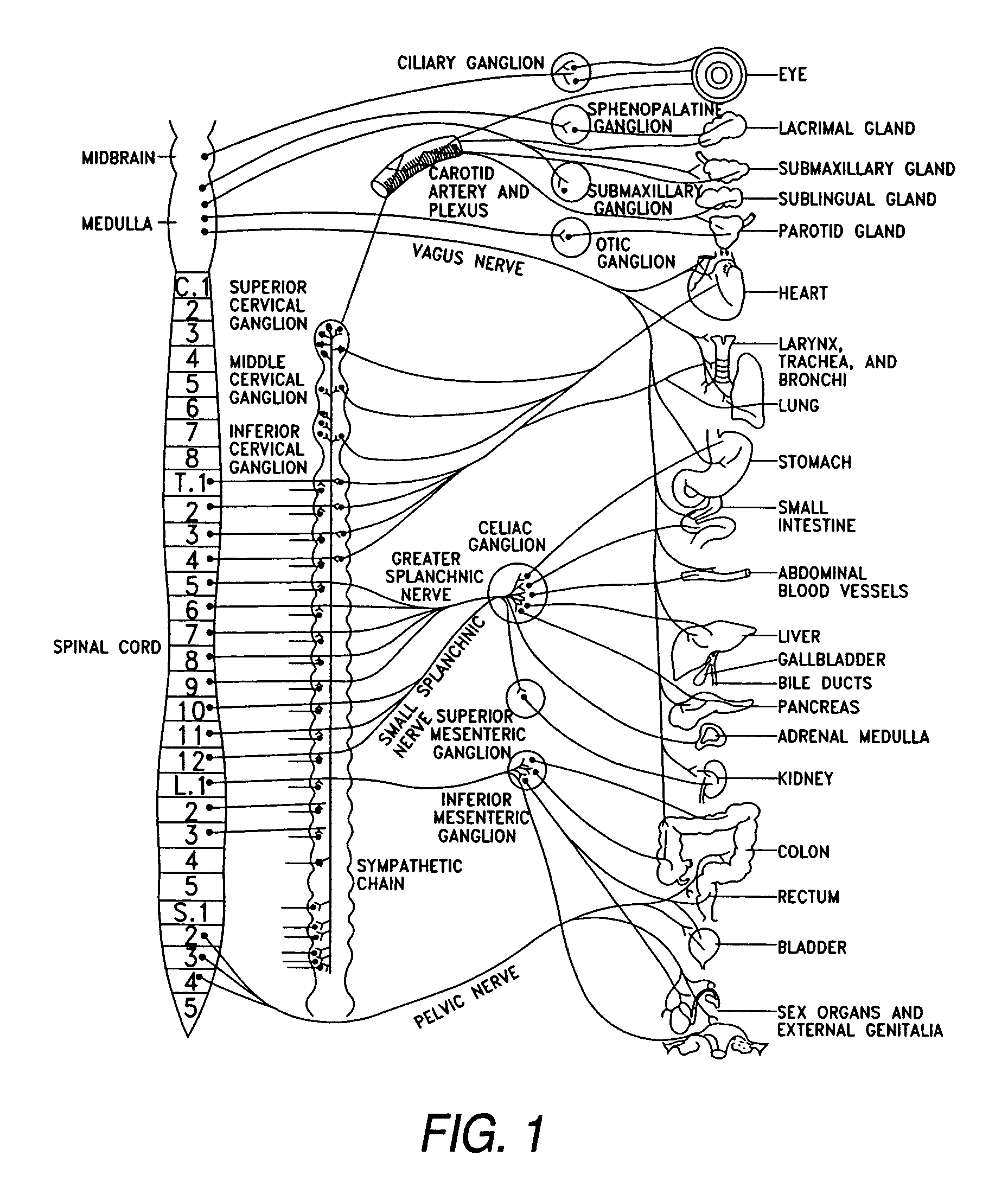
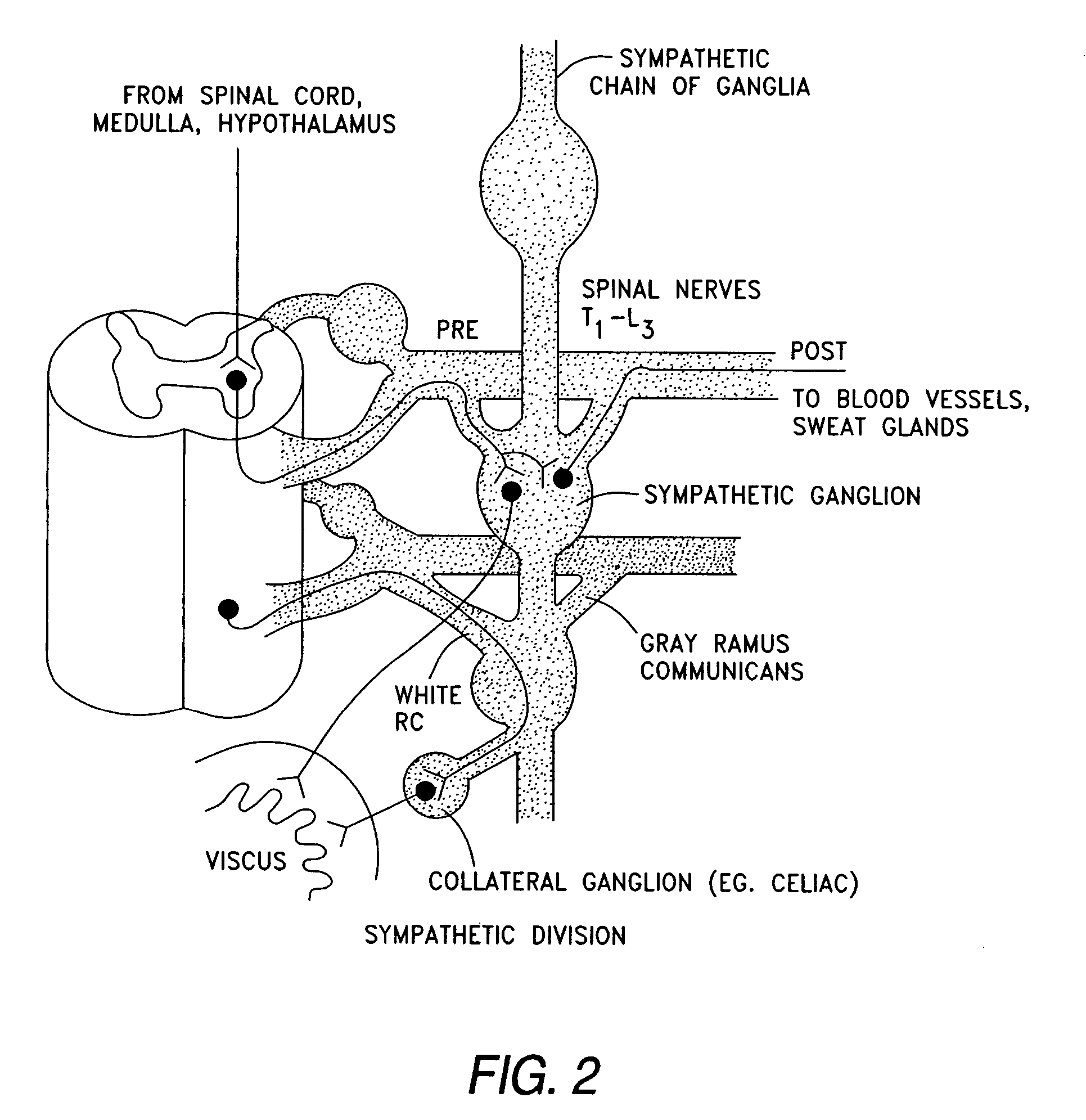
Dynamic nerve stimulation employing frequency modulation
InactiveUS7937145B2Reduce riskImplantable neurostimulatorsSensorsElectricitySacral nerve stimulation
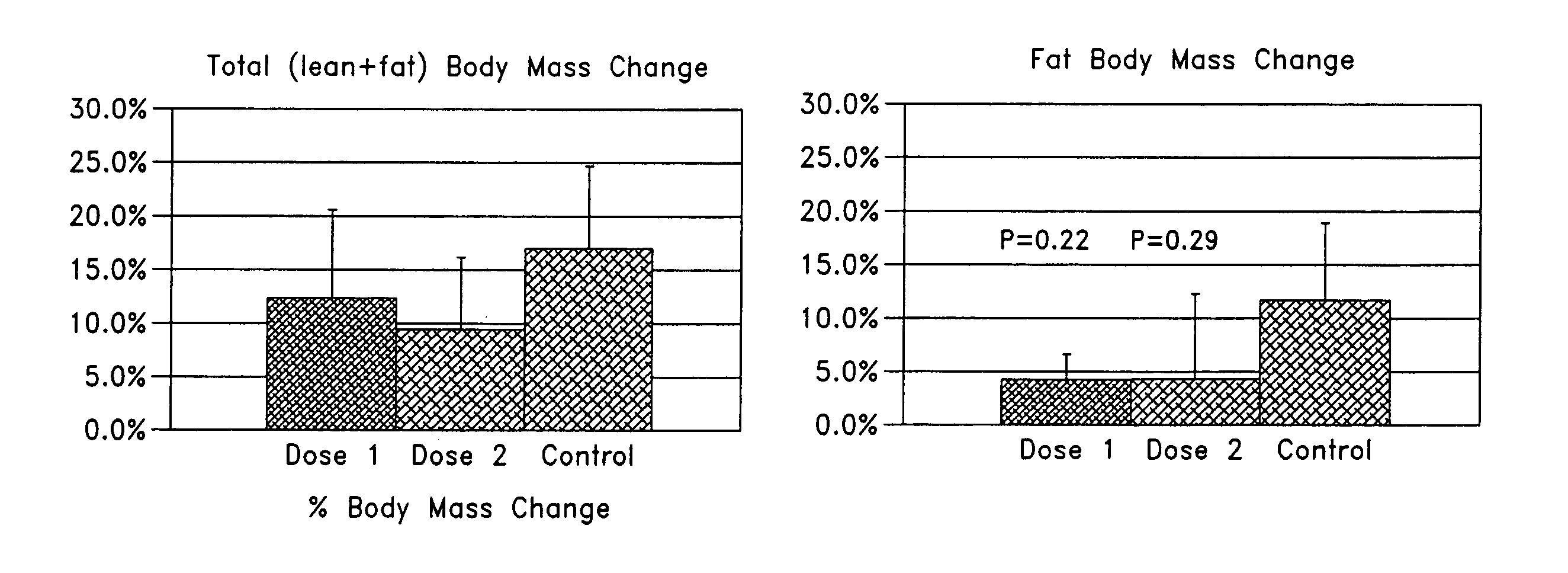
Described are apparatus and methods for electrically modulating a nerve in a mammal. An electrical signal that includes a signal intensity pattern and a signal frequency pattern is delivered to a nerve. The combination of the signal intensity pattern and the signal frequency pattern is effective to result in weight loss, fat loss, and / or lean-mass gain, in a mammal. In some embodiments the nerve is modulated in response to a physiological parameter. In some embodiments, the physiological parameter is measured by a sensor.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Method and apparatus for the manipulation of particles by means of dielectrophoresis
InactiveUS6942776B2Increase rangeAvoid the needElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentPlanar substrateEngineering
An apparatus and method for establishing closed dielectrophoretic potential cages and precise displacement thereof comprising a first array of selectively addressable electrodes, lying on a substantially planar substrate and facing toward a second array comprising one electrode. The arrays define the upper and lower bounds of a micro-chamber where particles are placed in liquid suspension. By applying in-phase and counter-phase periodic signals to electrodes, one or more independent potential cages are established which cause particles to be attracted to or repelled from cages according to signal frequency and the dielectric characteristics of the particles and suspending medium. By properly applying voltage signal patterns into arrays, cages may trap one or more particles, thus permitting them to levitate steadily and / or move. In the preferred embodiment, where one array is integrated on a semiconductor substrate, displacement of particles can be monitored by embedded sensors.
Owner:SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA +1
Dynamic nerve stimulation employing frequency modulation
InactiveUS20080033511A1Reduce riskEndoscopesImplantable neurostimulatorsElectricitySacral nerve stimulation
Described are apparatus and methods for electrically modulating a nerve in a mammal. An electrical signal that includes a signal intensity pattern and a signal frequency pattern is delivered to a nerve. The combination of the signal intensity pattern and the signal frequency pattern is effective to result in weight loss, fat loss, and / or lean-mass gain, in a mammal. In some embodiments the nerve is modulated in response to a physiological parameter. In some embodiments, the physiological parameter is measured by a sensor.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
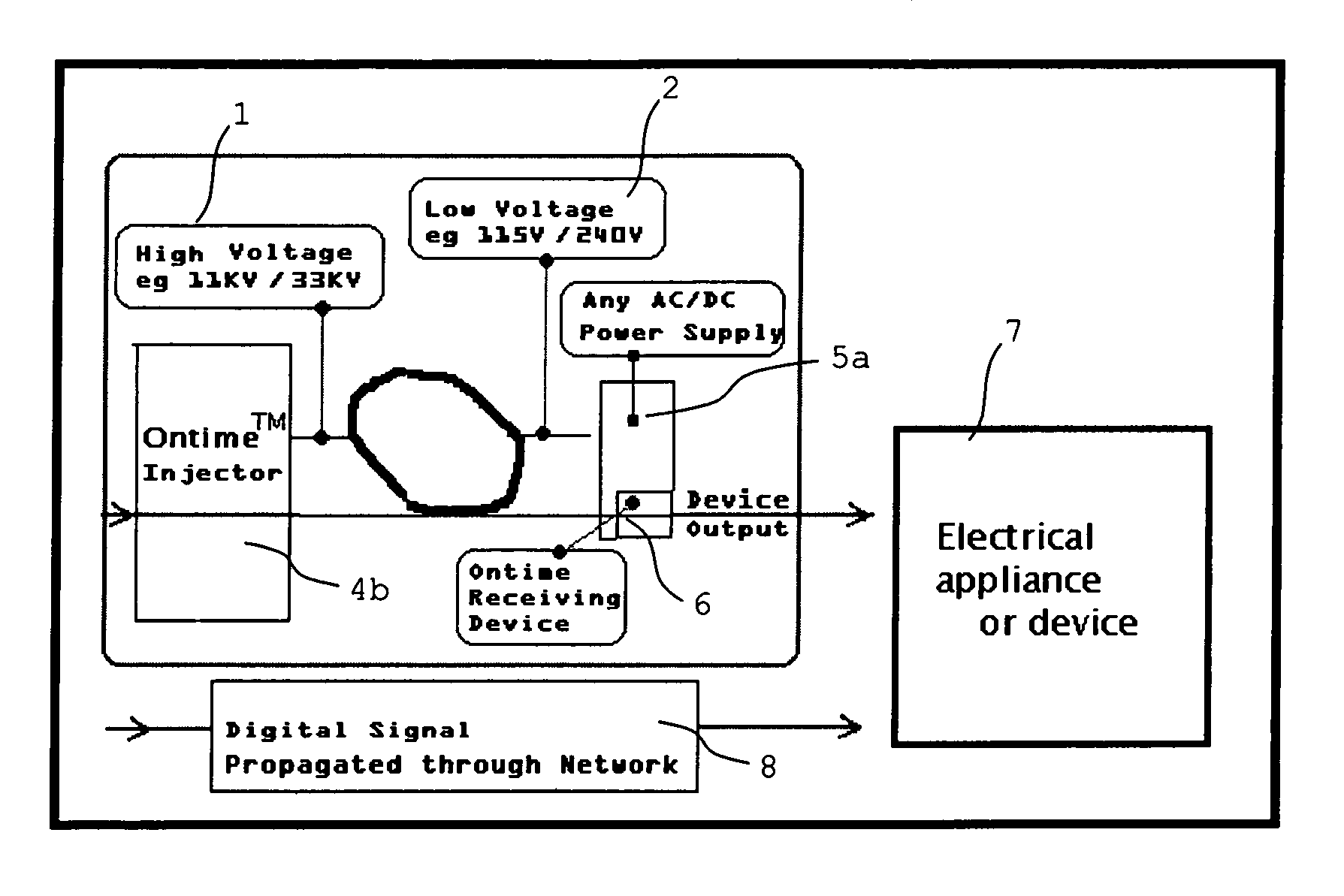
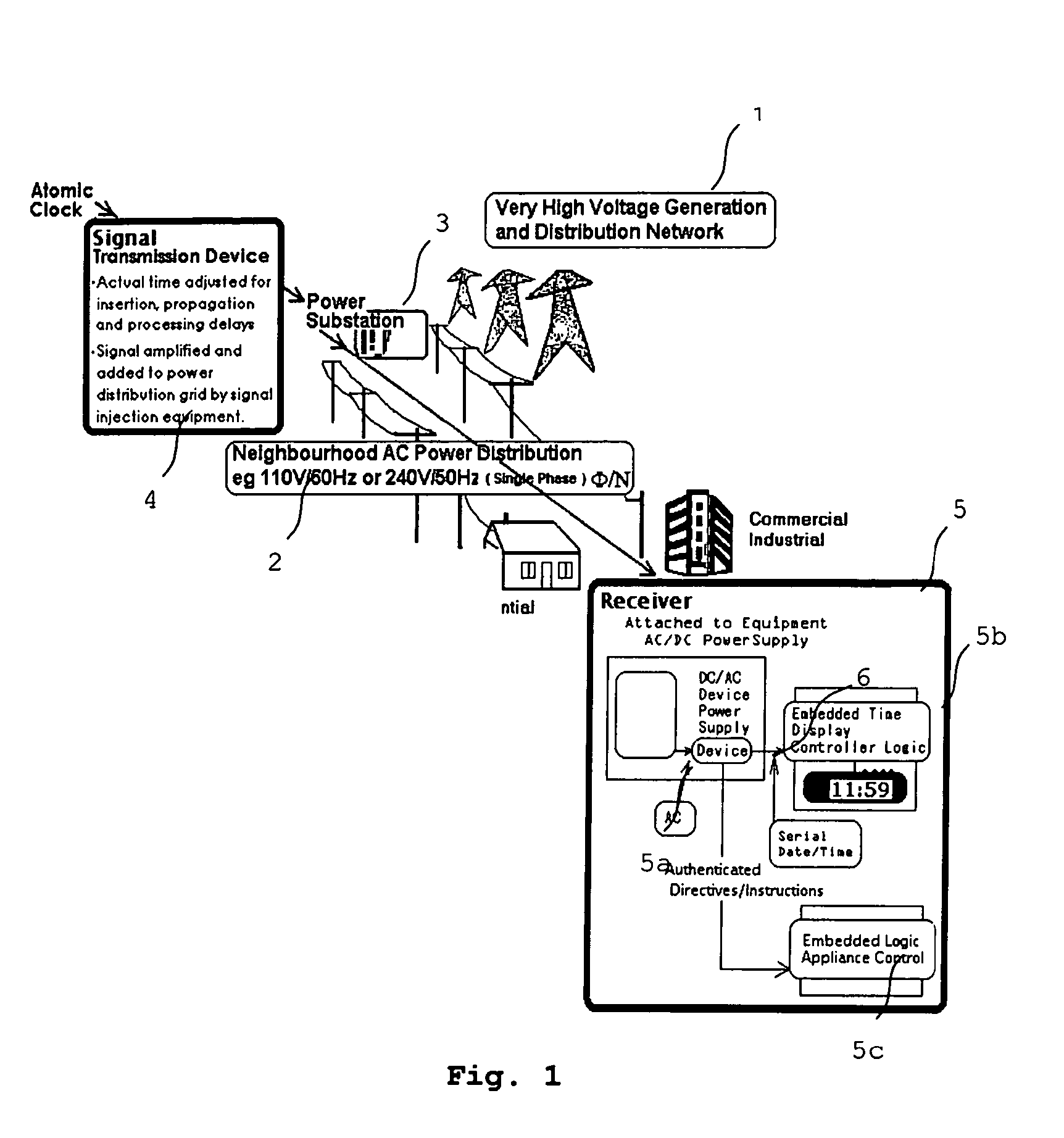
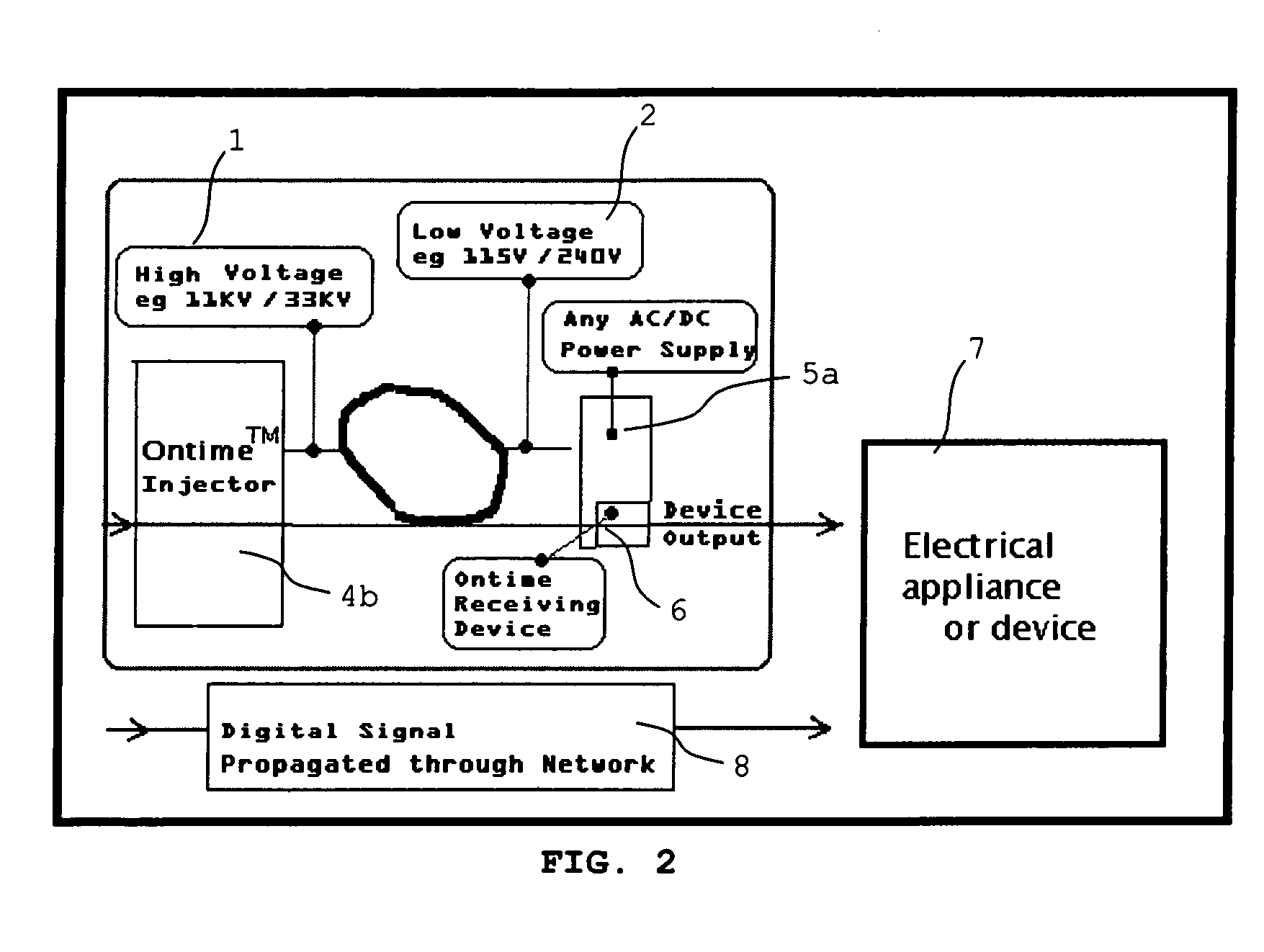
System and method for transmitting control information over an AC power network
Disclosed is a transmission system for transmitting digital information via a power supply network. In one embodiment, there is a transmission device which comprises a generator for generating a simulated digital wave-form carrying the digital information to be transmitted, and a high-voltage injector to inject the generated simulated digital wave-form carrying the digital information into the power supply network. A receiving device is also disclosed, which comprises an analog detector for detecting predetermined harmonic frequencies of a signal frequency, and a logic device to output a logic signal corresponding to the output of the analog detector as said digital information.
Owner:ADS ENTERPRISES NZ
Signal Transmission Method from a Local Network Node
ActiveUS20080069020A1Minimizes power neededImprove interference effectError prevention/detection by using return channelResonant long antennasElectricityData rate
A transmitter is provided having transmission methods that minimize the power needed to ensure reliable reception in a coverage area. In one aspect, data that requires re-transmission as acknowledged mode data is re-transmitted when the power level of the transmission link is higher than a pre-determined level set for reliable reception. The data rate of the re-transmitted data is set according to the difference in the actual power and the pre-determined level. In a second aspect, two transmitting antennae are used to transmit the same signals with a frequency off-set. The frequency off set can be used to determine the phase of the signals being received at the receiver, so that a phase off-set can be introduced to optimise the effect of interference at the receiver.
Owner:BISON PATENT LICENSING LLC
Method for identifying changes in signal frequencies emitted by a stylus interacting with a digitizer sensor
A method for dynamically updating at least one pre-defined value of a parameter used to identify at least one operational mode of an object for user interaction with a digitizer sensor during interaction with the digitizer sensor comprises detecting signal outputs from a plurality of sensing elements of a digitizer sensor during user interaction with the digitizer sensor; characterizing a pattern formed by the signal outputs from the plurality of sensing elements; identifying a pre-defined event associated with an operational mode of the object based on the pattern; determining a value of the parameter from the signal outputs in response to identification of the pre-defined event; and updating the pre-defined value used to identify the operational mode based on the value of the parameter determined from the identified event.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Universal digital framer architecture for transport of client signals of any client payload and format type
ActiveUS20050286521A1Reduce the required sizeReduce capacityError preventionTransmission systemsClient-sideByte
Client signals to be transported in a transmission network, particularly an optical transmission network, may have different payload envelope rates and are digitally mapped on the client egress side into first transport frames (also referred to as iDTF frames, or intra-node or internal digital transport frames), at the client side for intra-transport within terminal network elements (NEs) and further digitally mapped into second transport frames (also referred to as DTFs or digital transport frames) for inter-transport across the network or a link which, through byte stuffing carried out in the first transport frames so that they always have the same frame size. As a result, the system of framers provides for a DTF format to always have a uniformly universal frame rate throughout the network supporting any client signal frequency, whether a standard client payload or a proprietary client payload, as long as its rate is below payload envelope rate of the client signal. At the client signal ingress side, the signal are digitally demapped from the second transport frames (DTF format) into the first transport frames where the stuff bytes are removed and accordingly processed at an intermediate node element before further transport, or digitally demapped from the first transport frames (iDTF format) to reproduce or reassemble the client signal or signals comprising the client payload at the client payload envelope rate for reception at the client's equipment. Among various features disclosed, two predominate features are (1) a single channel or network rate for transport of all signals between network elements (NEs) and end terminal network elements and (2) the digitally wrapping of different types of payloads into N client side or first frames using stuff bytes to render each client side frame size equal to a predetermined value. Then the stuffed first frames are wrapped into line side or second frames for transport over the network at the same high speed line rate for all digitally wrapped client signals. The client side framers may be, for example, running at the lowest signal rate encountered, to digitally wrap then into parallel N client signals or digitally wrap a client signal multi-sected into N parts, where these two different client signals have different payload rates.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
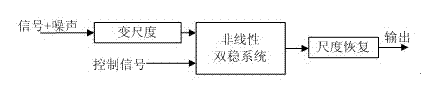
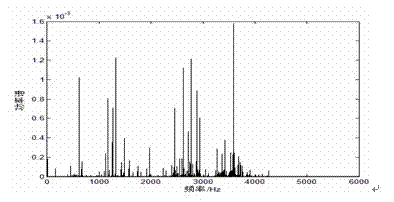
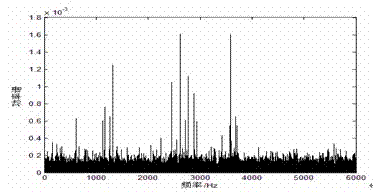
Bearing fault detection method based on manner of controlling stochastic resonance by external periodic signal
InactiveCN102226740AEnhanced spectral valueAccurate detectionMachine bearings testingControl signalEscape rate
The invention discloses a bearing fault detection method based on a manner of controlling stochastic resonance by an external periodic signal. According to the method provided in the invention, after a bearing fault signal is converted by a variable metric method, the converted signal is input in a bistable system; meanwhile, an external single frequency periodic signal is taken as a control signal to act directly on the system; contact barrier height of the bistable system and an escape rate of Kramers are changed by continuously adjusting an amplitude of the control signal. Therefore, stochastic resonance can be generated or increased artificially; a spectral value of an output power spectrum at the position of an input signal frequency can be effectively improved; and thus a characteristic signal of a bearing fault can be detected accurately at last. The detection method provided in the invention enables the effective control of the stochastic resonance to be realized, thereby providing a novel method for early detection of equipment faults.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Pre-acquisition frequency offset removal in a GPS receiver
InactiveUS6151353AReduce power consumptionShorten the timePower managementPosition fixationGps receiverLocal oscillator
A direct sequence spread spectrum receiver samples an incoming signal and stores the sample in memory. Prior to sampling and storage, the incoming signal is translated to an IF signal. Also prior to storage, the IF signal is corrected for a frequency offset signal. The frequency offset may be caused by many sources, Doppler shift or local oscillator error, for example. Once the signal is corrected for the frequency offset, the signal sample is stored in memory. The signal sample is read from memory as necessary to process the signal. Such a receiver is useful in global positioning satellite (GPS) signal processing where the incoming signal contains several satellite transmissions encoded with CDMA encoding.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cellular phone blocker
InactiveUS7123874B1Reduce usageElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageSignal frequencyFixed frequency
the invention shows a jamming device having a transmitting system that outputs a signal frequency modulated that inhibits a low power receiving antenna from receiving a fixed frequency such as a cellular telephone.The jamming device can function as a stand alone device or be incorporated into existing electrical systems whereby energizing said electrical system will cause said jammer to inhibit the use of low power radio transmission / reception devices such as cellular phones.
Owner:BRENNAN JOSEPH P
Apparatus and methods for network interface and spectrum management
Apparatus and methods for the management of radio frequency spectrum within a network such as a CATV network. In one aspect of the invention, an improved signal reflector apparatus adapted for use in the network is disclosed, the reflector circuit being designed to strongly reflect signal frequencies at the lower end of the CATV reverse band, and / or above the higher end of the forward band, while simultaneously allowing the rest of the reverse band and the entire forward band to pass freely through the device. This selective filtering of the spectrum allows control signals generated within a premises or private network to be directed (by reflection) to other devices within that network. A blocking element (e.g., amplifier) may also be used to provide control of the transmission and attenuation profile of the reflector apparatus. The passage of power signals such as DC or low frequency AC is also optionally provided.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
Radar apparatus and method of determining sign of velocity
ActiveUS20150185244A1Low costHigh sensitivityOptical rangefindersDevices using time traversedFrequency spectrumRadar
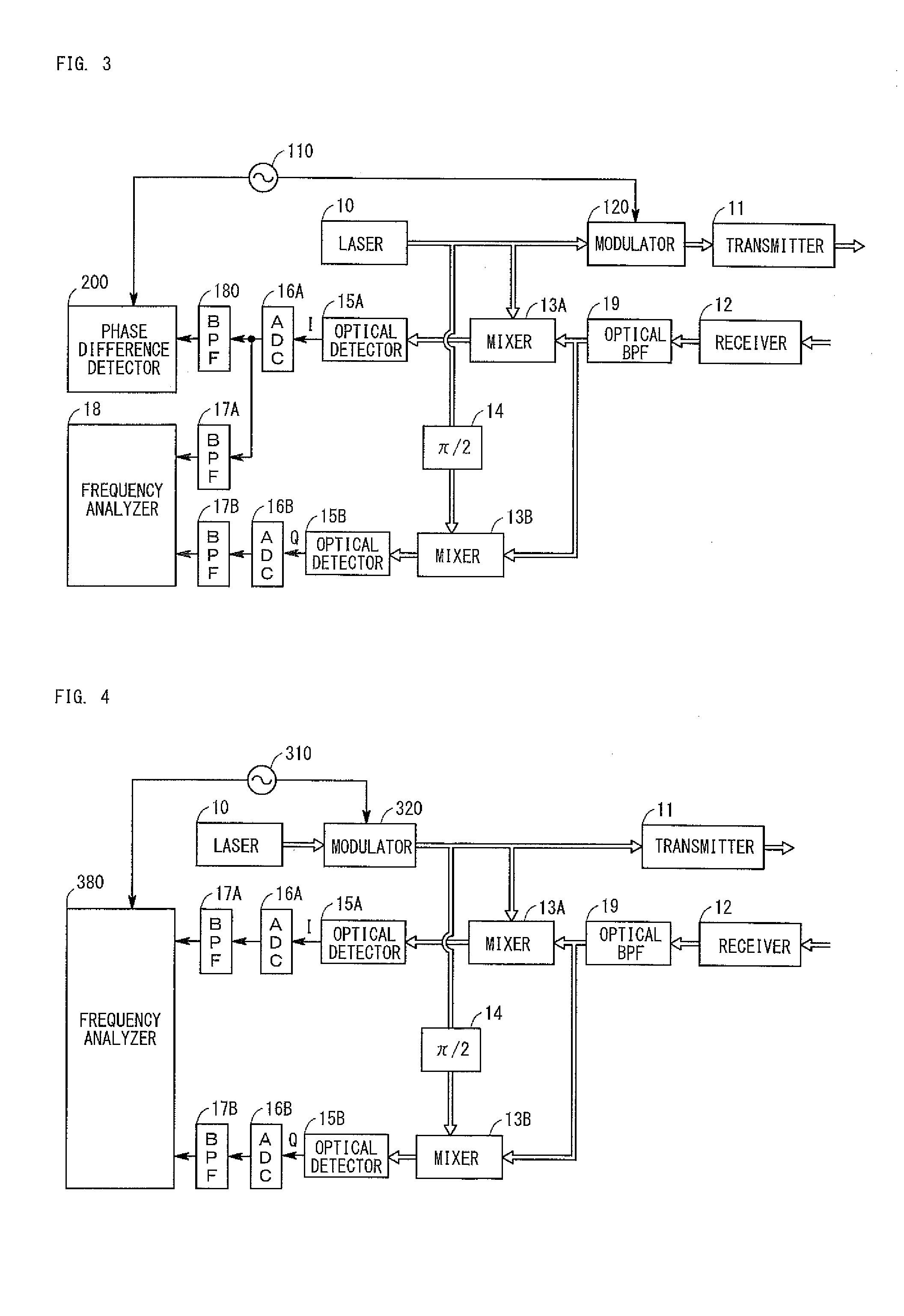
A radar apparatus which can simply determine the sign of velocity of an object is provided. Laser light reflected by the object undergoes quadrature optical heterodyne detection performed by mixers, optical detectors, and a π / 2 phase shifter, whereby I and Q component signals are output. A frequency analyzer performs FFT on a complex signal composed of the I component signal (real part) and the Q component signal (imaginary part) to thereby obtain its frequency spectrum. Since the frequency spectrum is calculated without being folded back even in a region where the frequency is negative, the sign of the Doppler frequency fd can be determined. When the Doppler frequency fd is positive, the sign of the velocity of the object is a direction toward the radar apparatus. When the Doppler frequency fd is negative, the sign of the velocity of the object is a direction away from the radar apparatus.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
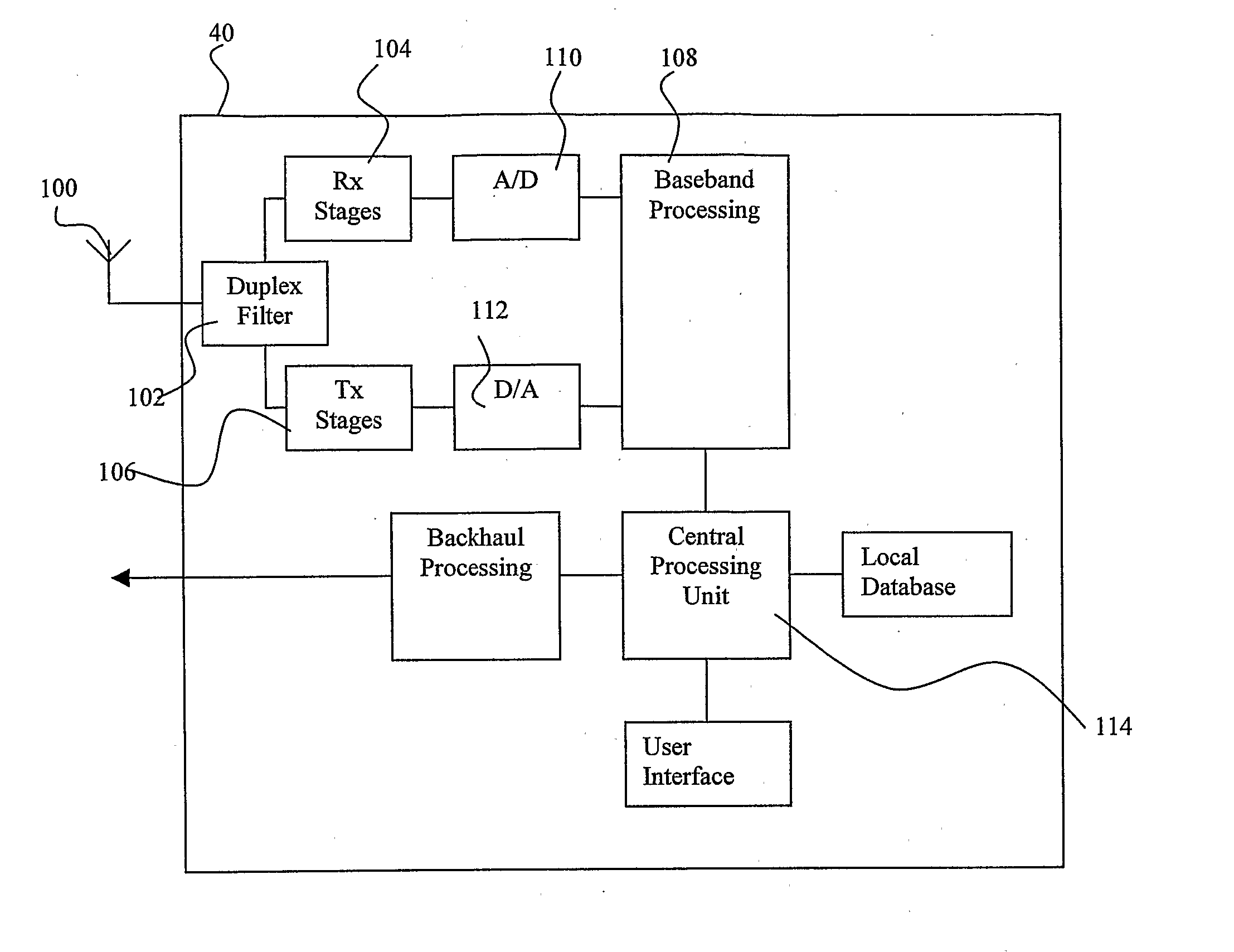
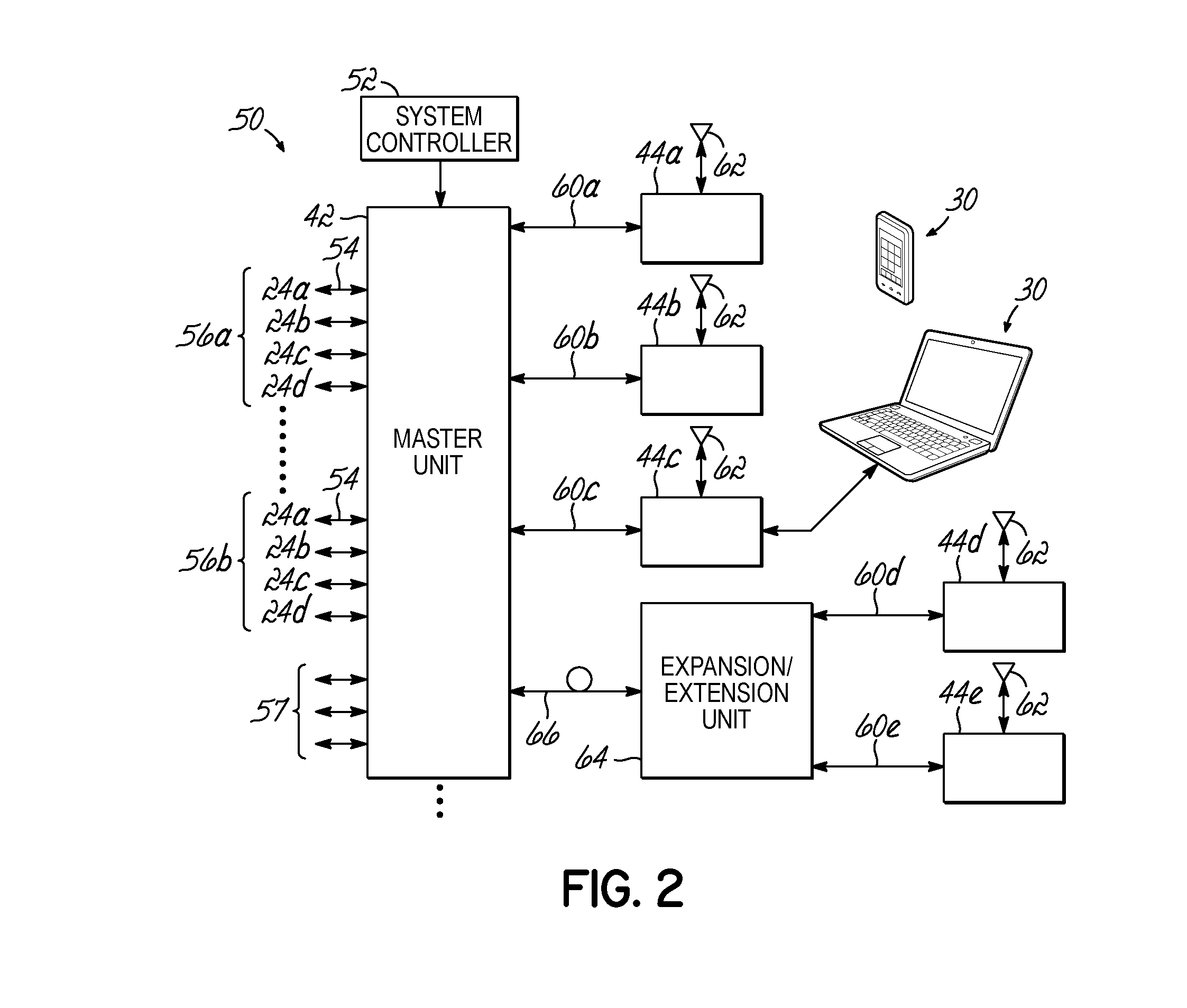
Synchronous transfer of streaming data in a distributed antenna system
Embodiments of the invention provide a method, distributed antenna system, and components that generate a jitter reduced clock signal from a serial encoded binary data stream transmitted over a communication medium. The method comprises receiving a modulated signal that includes the encoded binary data stream and extracting the encoded binary data stream. The method further comprises generating a recovered clock signal that is phase locked to the encoded binary data stream, generating an error signal based on a difference between a phase of the encoded binary data stream and the recovered clock signal, and integrating the error signal to generate a signal to control a voltage controlled oscillator. The method further comprises generating a stable recovered clock signal and producing at least one output clock by scaling the stable recovered clock signal frequency.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
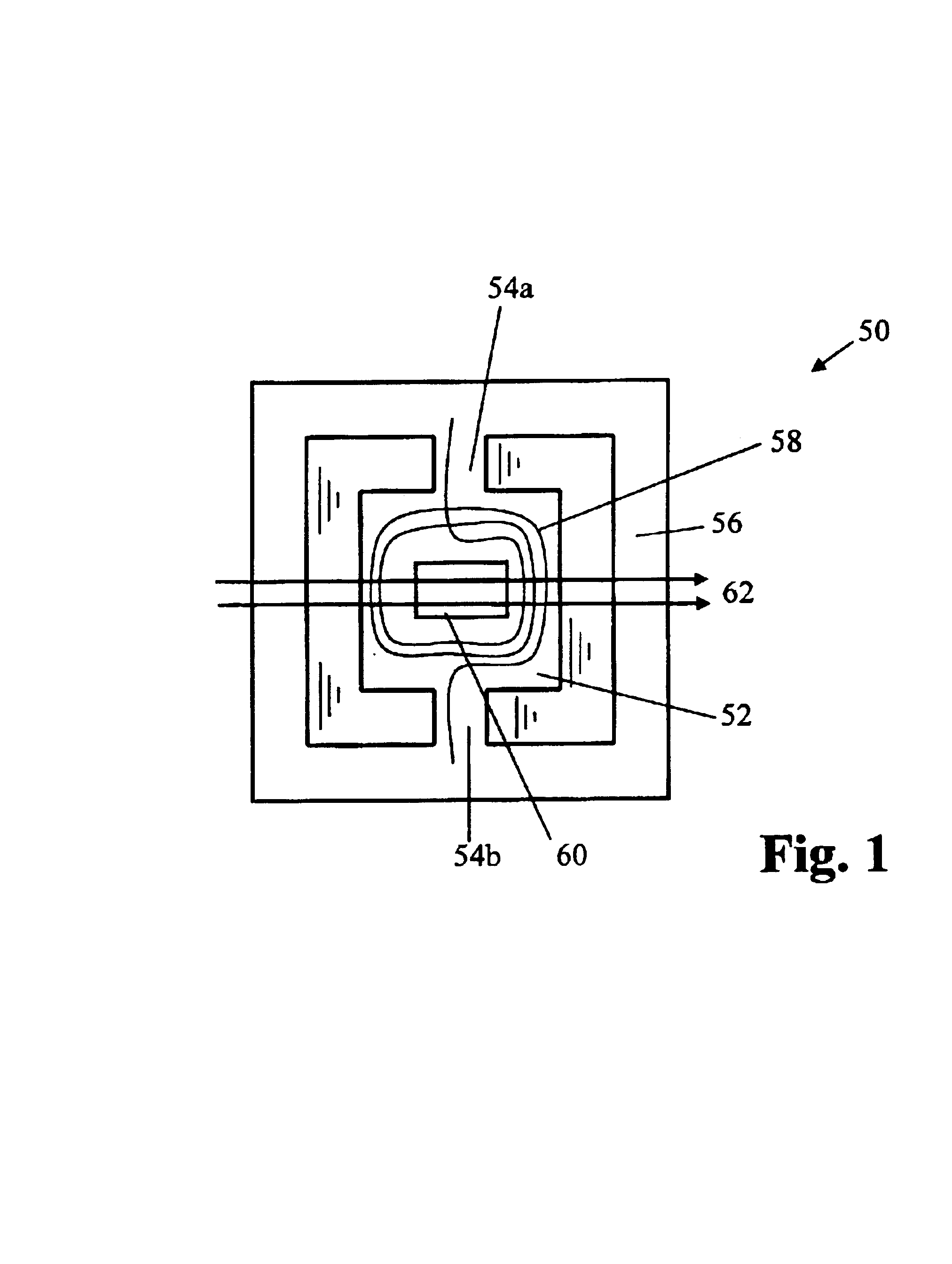
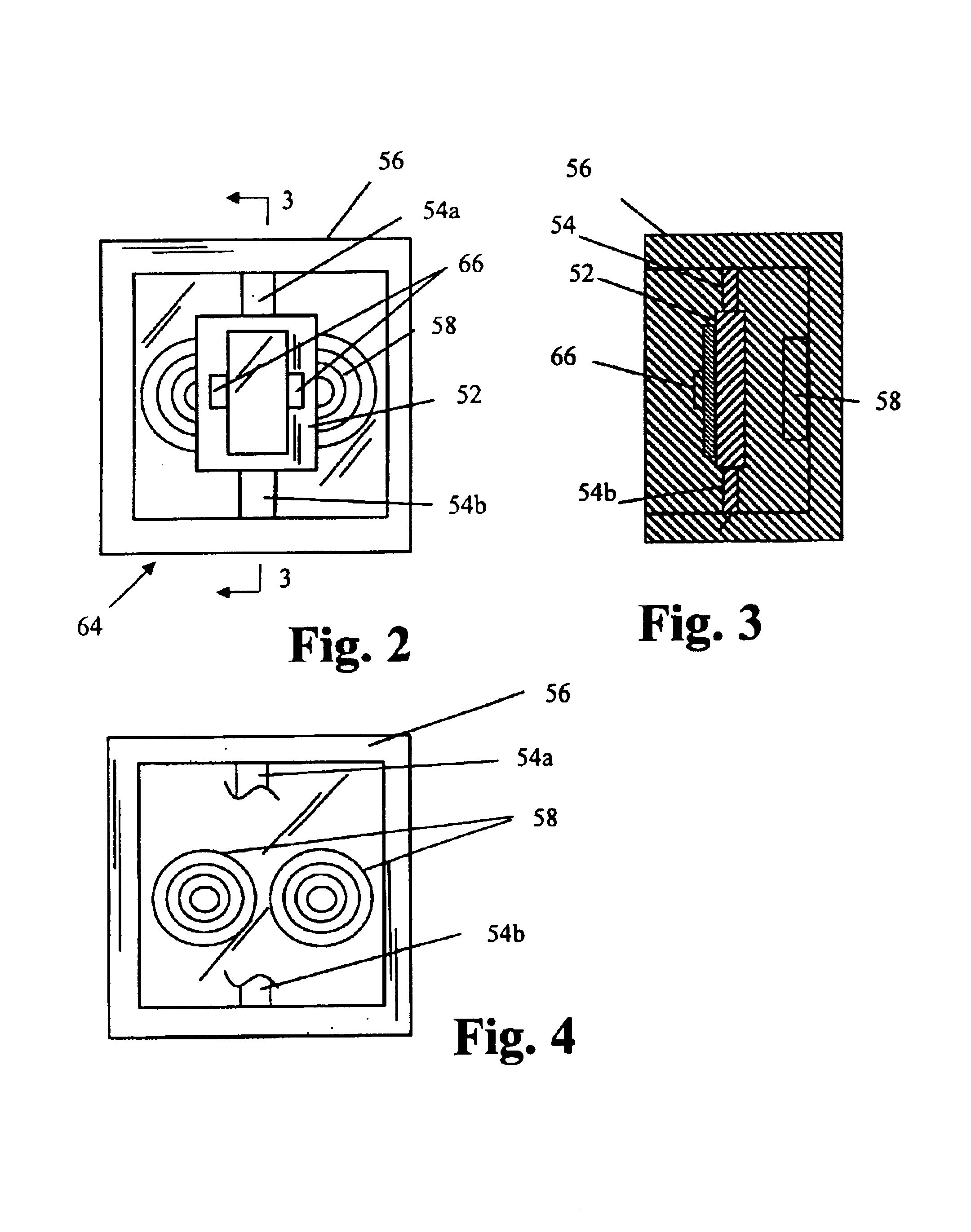
Electron spin resonance spectrometer and method for using same
ActiveUS20140210473A1Measurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceSignal frequencyNuclear magnetic resonance
An electron spin resonance spectrometer includes a bridge to transmit an excitation frequency and to receive a signal frequency; a probe electrically connected to the bridge and comprising: a first conductor in electrical communication with the bridge to transmit the signal frequency to the bridge; a shorting member electrically connected to the first conductor to transmit the excitation frequency to a sample, to produce the signal frequency, and to transmit the signal frequency to the first conductor; and a second conductor electrically connected to the shorting member; and a magnet disposed proximate to the probe.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
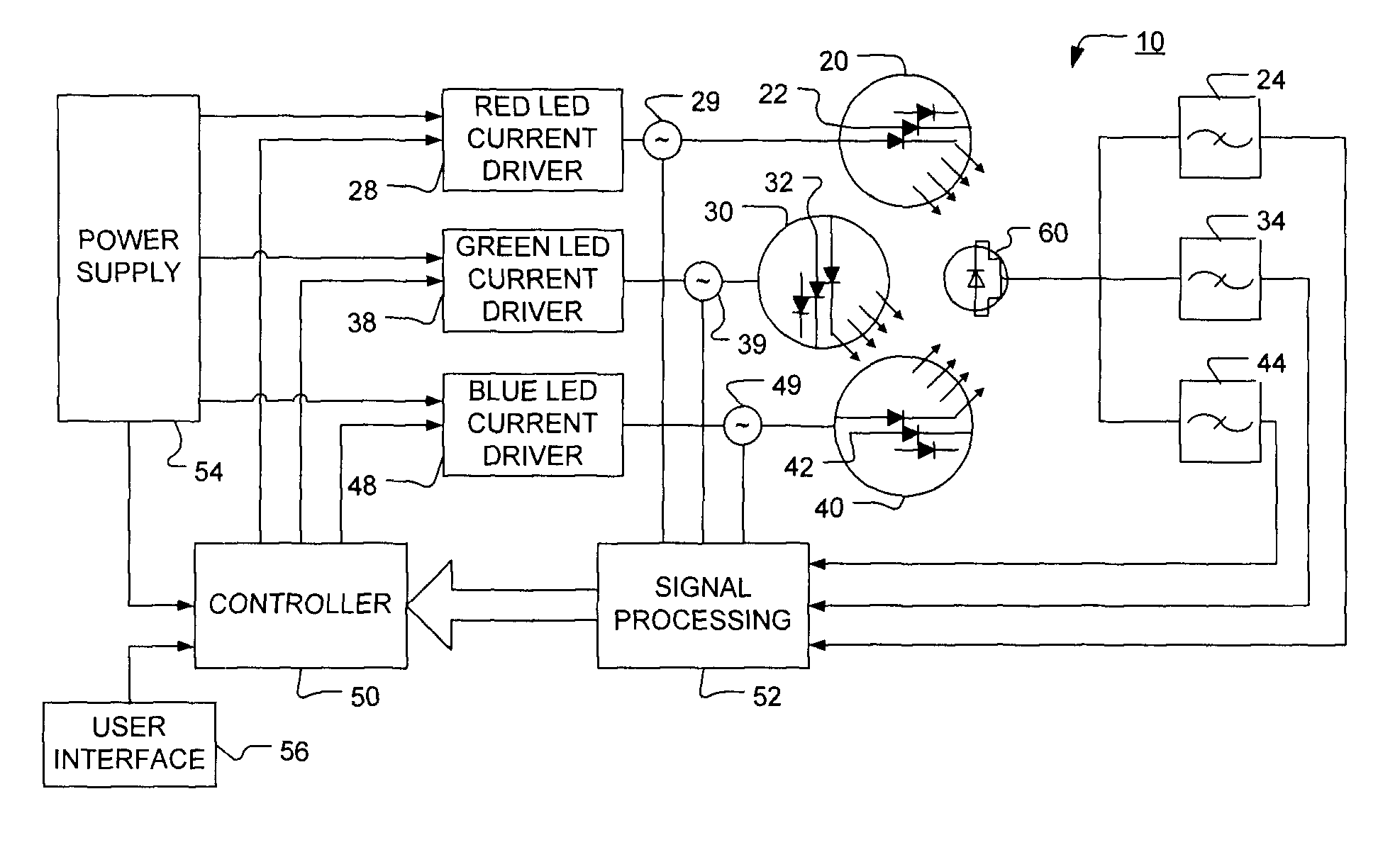
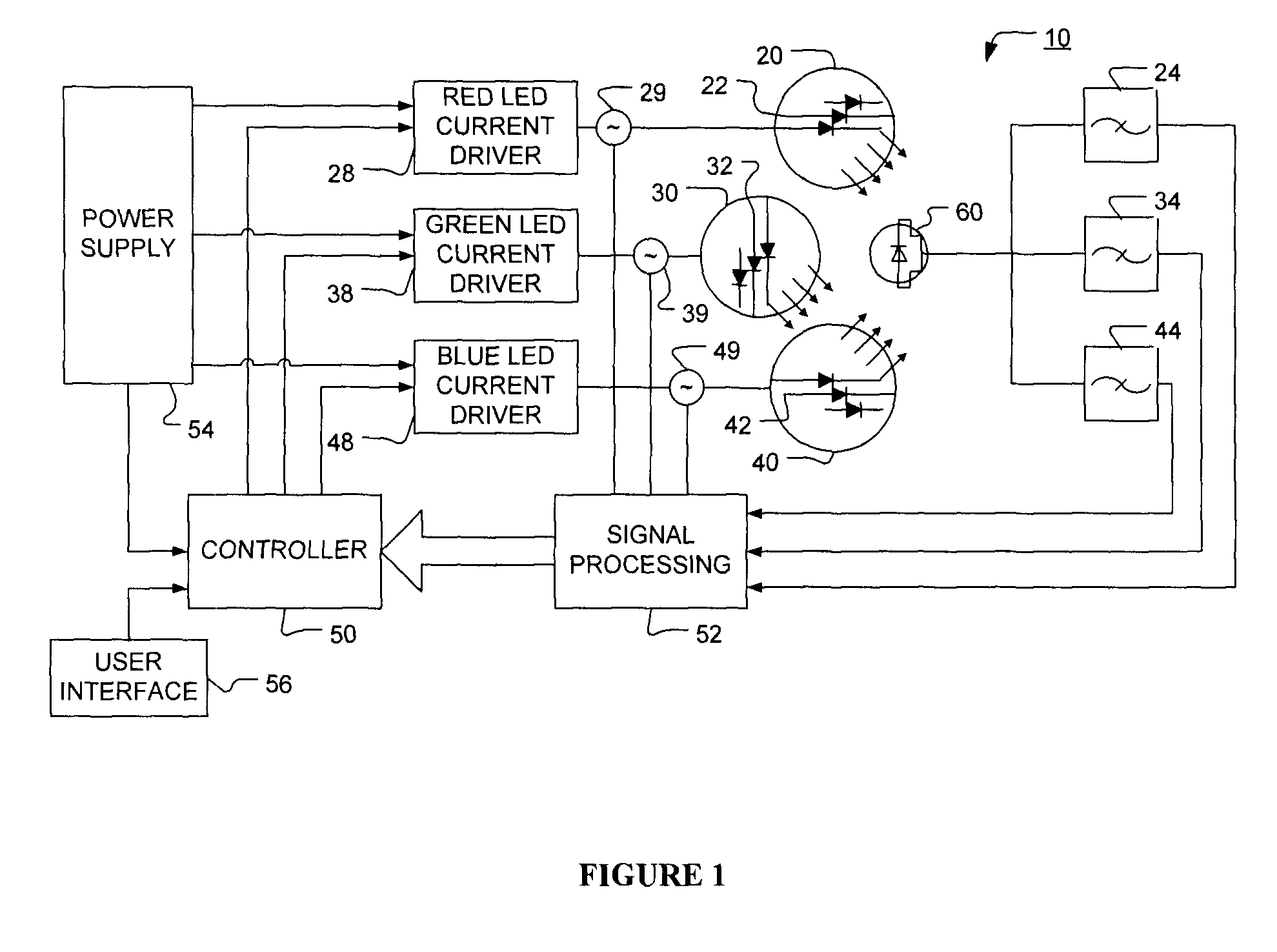
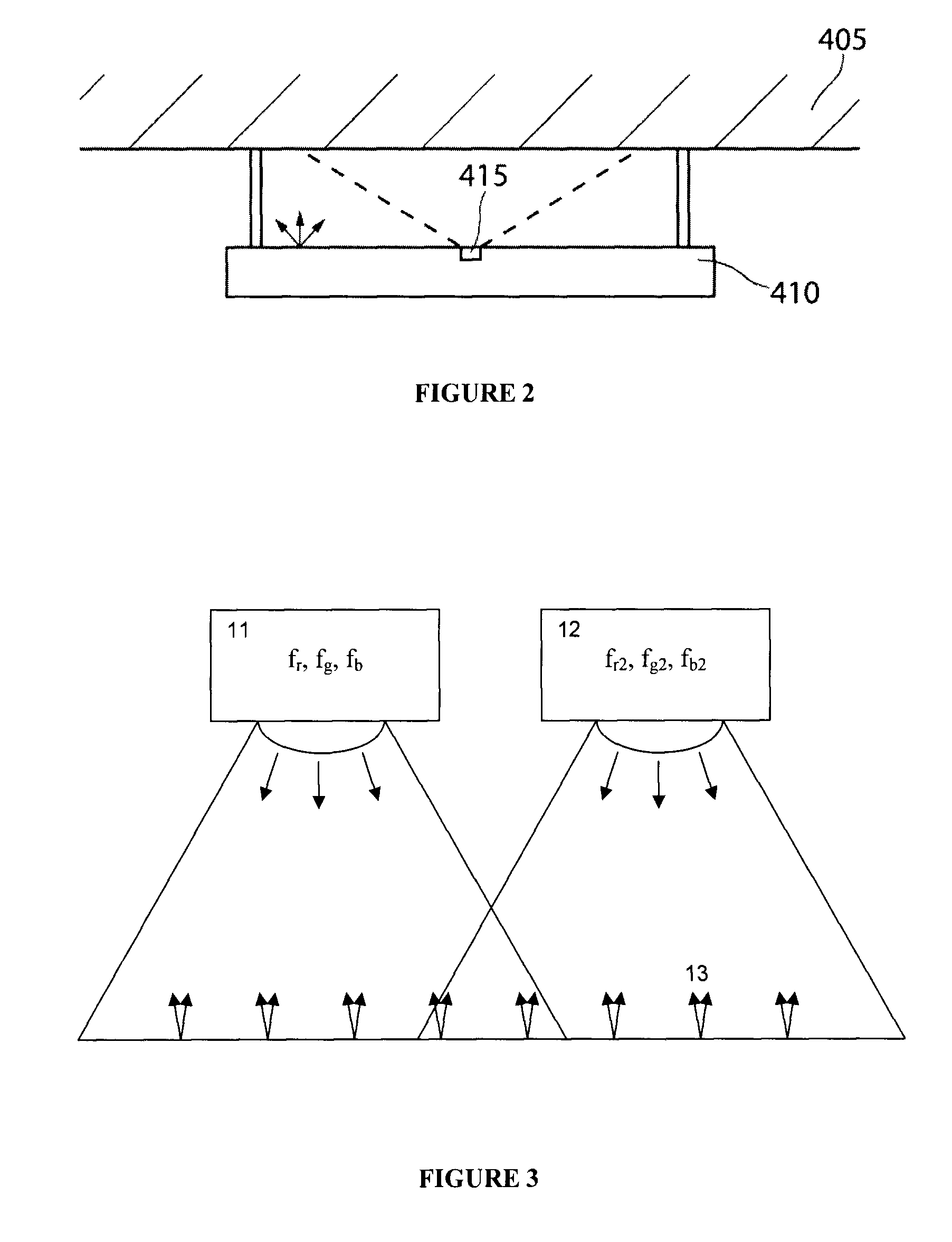
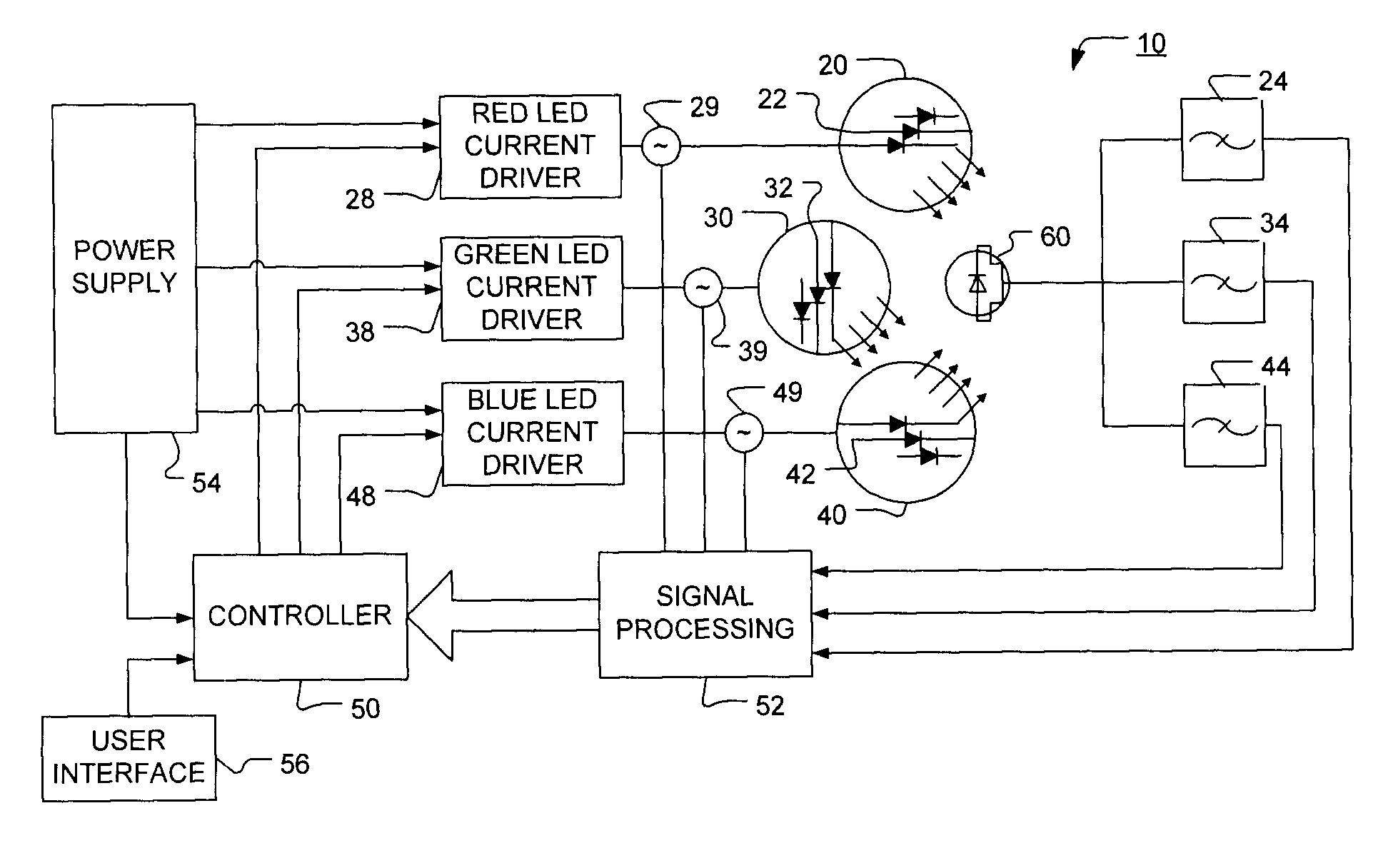
Method and apparatus for light intensity control
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for optical feedback control for an illumination device, wherein the control signal for each array of one or more light-emitting elements corresponding to a particular color, is independently configured using a modification signal whose frequency is different for each color. Electronic filters whose center frequencies are substantially equal to the modification signal frequencies of the drive currents for the light-emitting elements are used to discriminate between the radiant flux corresponding to each of the different colors of light-emitting elements, from a sample of the mixed radiant flux output collected by one or more optical sensors. The output of an individual electronic filter is substantially directly proportional to the radiant flux output of the light-emitting elements of the associated color, which together with the desired luminous flux and chromaticity of the output light, the controller can use to adjust the control signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Scanning with multiple oscillating scanners
InactiveUS6956597B2Easy to controlUniform speedInking apparatusOther printing apparatusEngineeringPhase adjustment
A method and device for managing and controlling a scanning system that incorporates multiple oscillating scanners is provided by the present invention. In accordance with the preferred embodiment, a resonant frequency is determined for each of the scanners. A drive signal for driving the oscillating scanners is generated based upon the determined resonant frequencies. An amplitude adjustment circuit determines the difference between the drive signal frequency and the resonant frequency of each oscillating scanner and adjusts the amplitude of the drive signal provided to that particular oscillating scanner such that scan amplitude of each oscillating scanner is approximately equal. The offset from the resonant frequency is also used to calculate a phase adjustment for the drive signal to insure that the oscillating scanners are operating in tandem.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
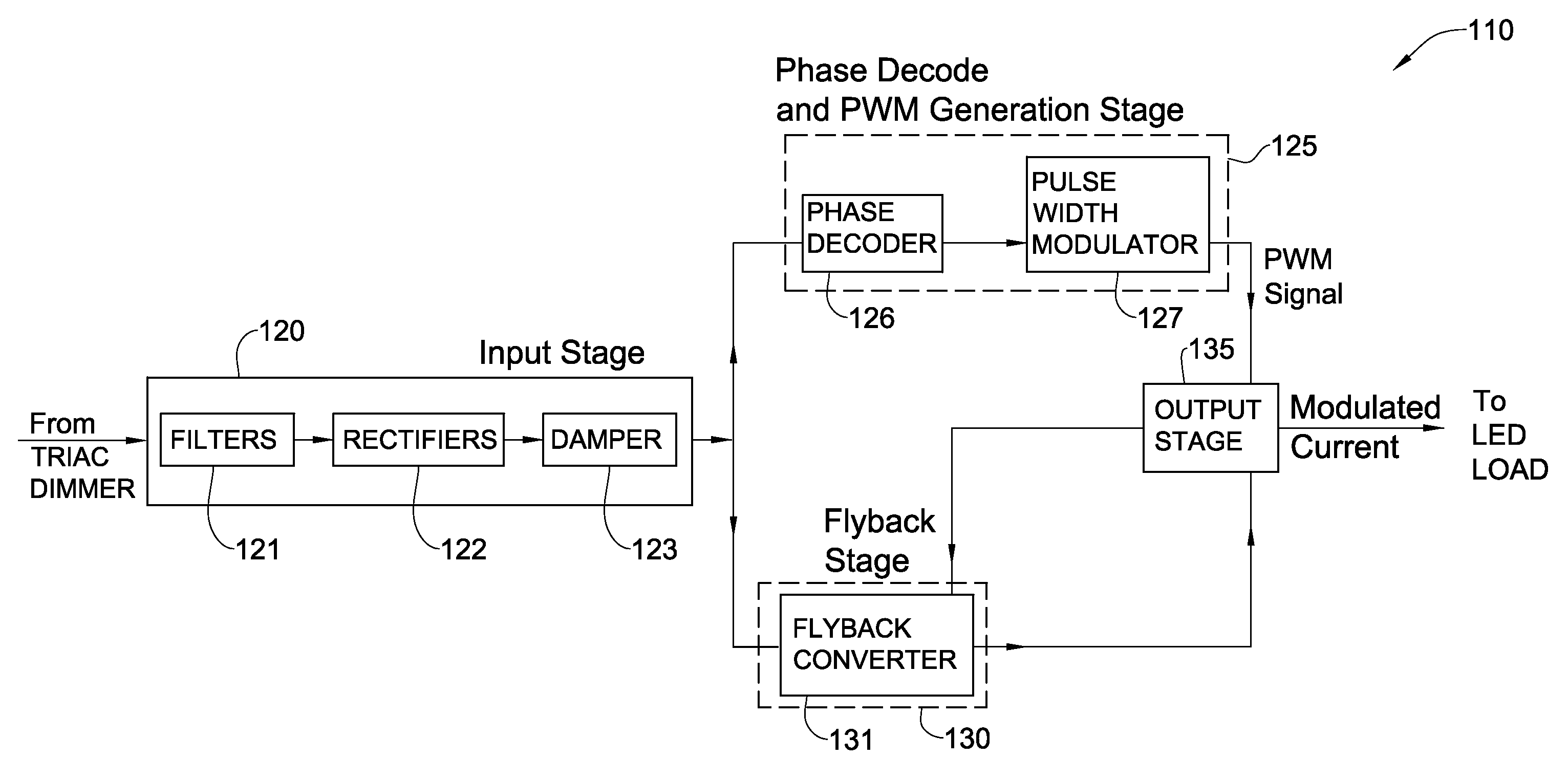
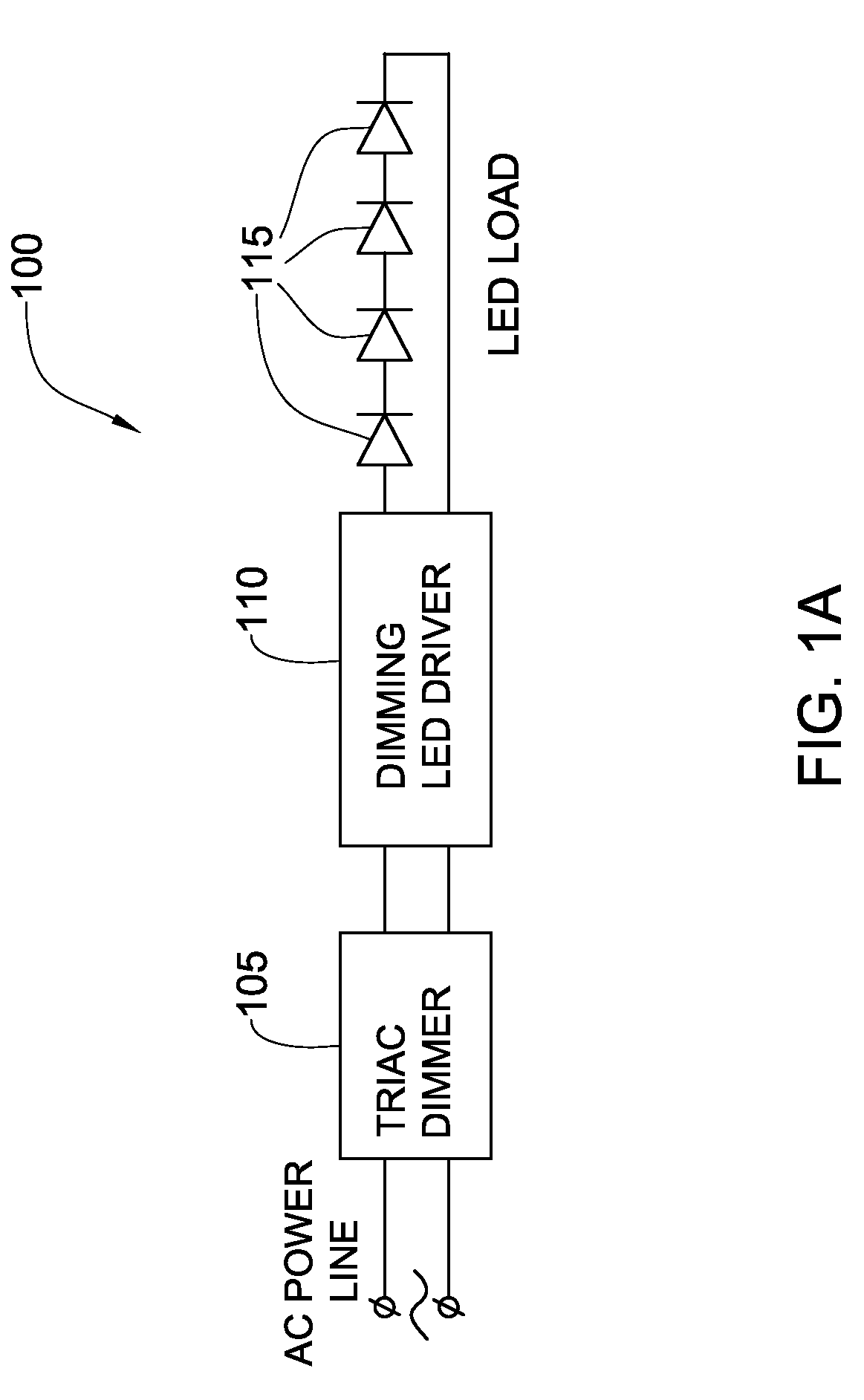
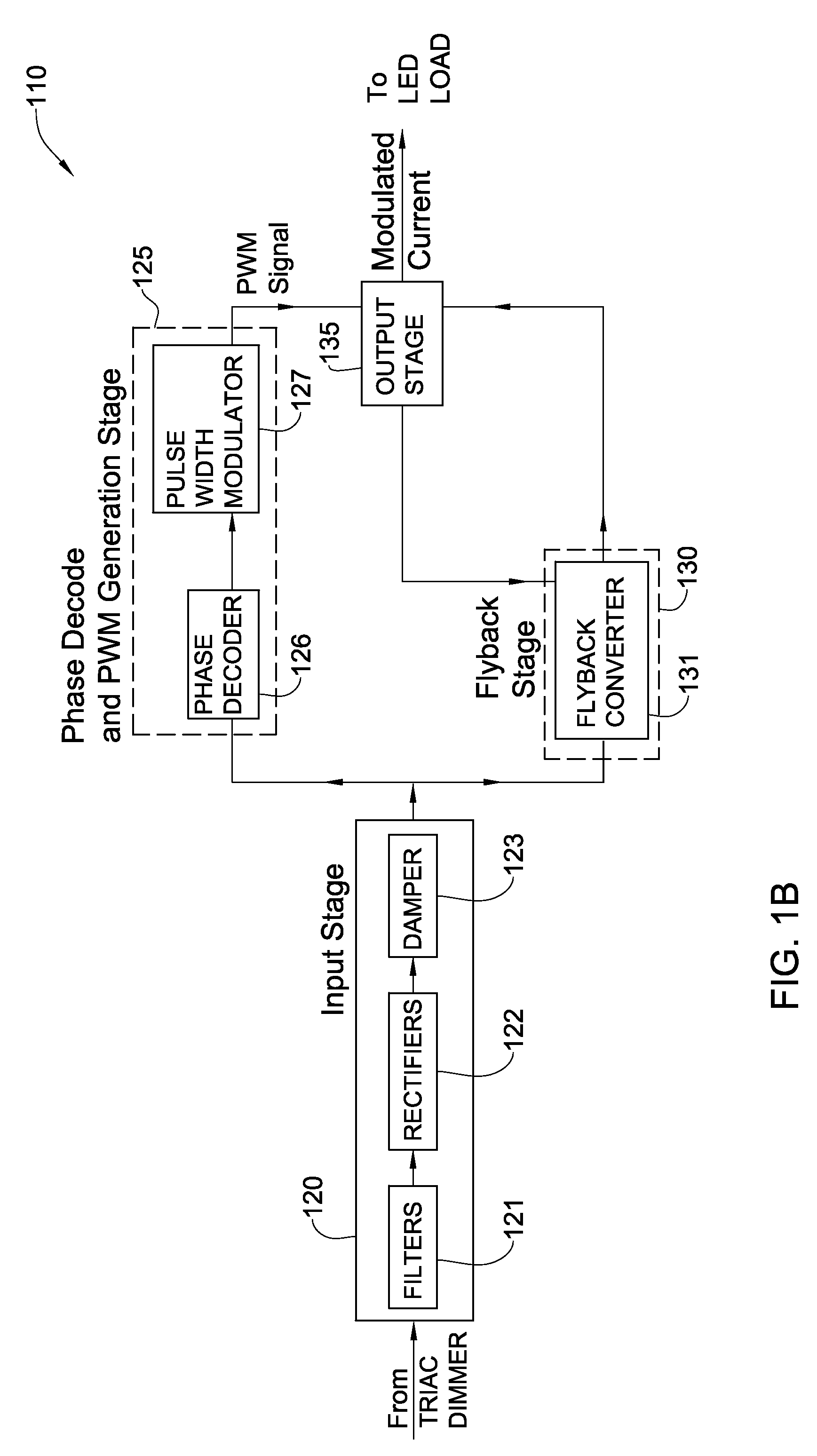
Phase controlled dimming LED driver system and method thereof
ActiveUS20100134038A1Guaranteed uptimeAchieve stable operationElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementDimmerEngineering
The present invention relates to providing an improved phase controlled dimming LED driver circuitry, system and a method thereof, which is configured to enable dimming intensity of light generated by a light source, said phase controlled dimming driver circuitry being connected to a phase control dimmer that provides to it a regulated alternating current (AC) signal, wherein said phase controlled dimming driver circuitry does not include a microprocessor and pulse width modulates its output current, provided to said light source, at a frequency unrelated to the AC signal frequency. Further, the phase controlled dimming driver circuitry applies amplitude modulation (AM) and pulse width modulation (PWM) substantially simultaneously to the output current provided to the light source.
Owner:SAVANT TECH LLC
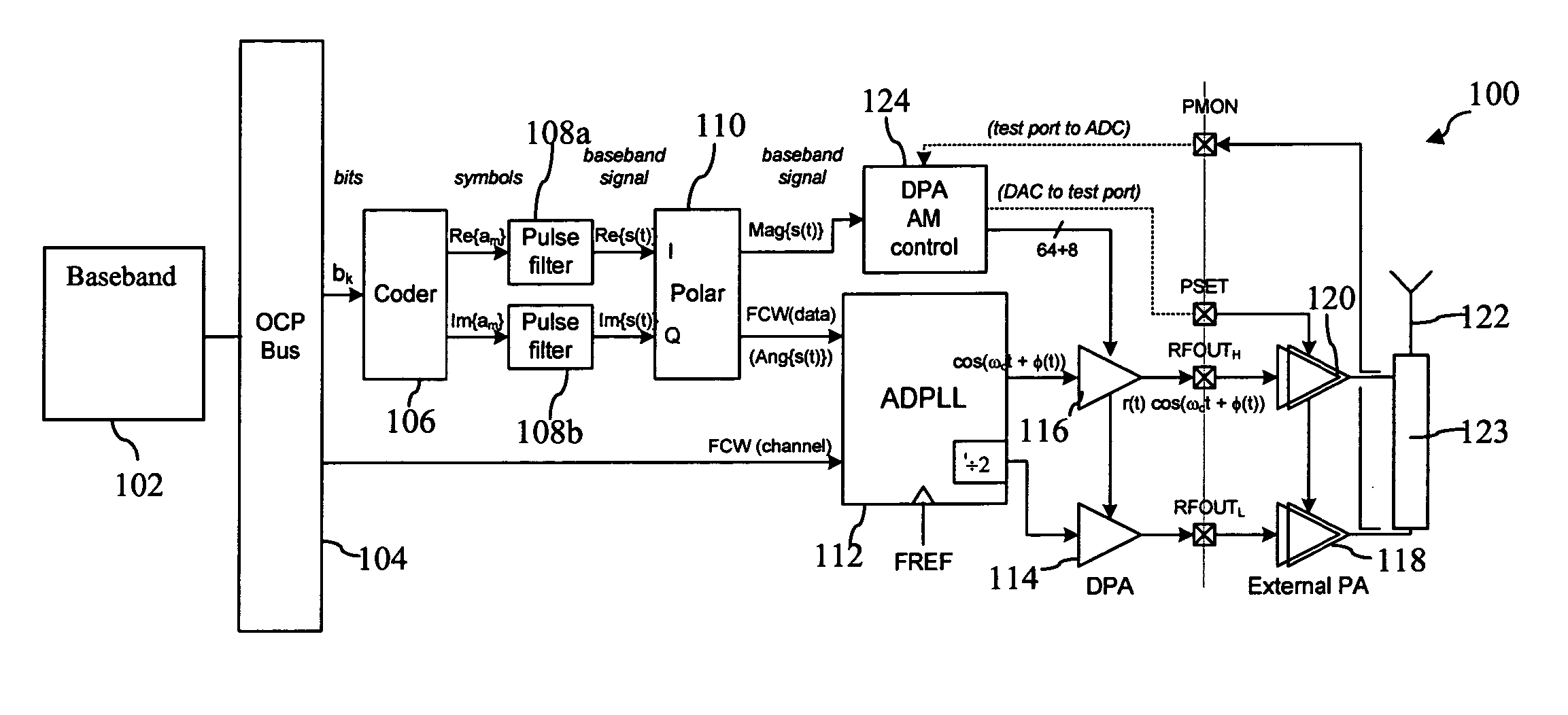
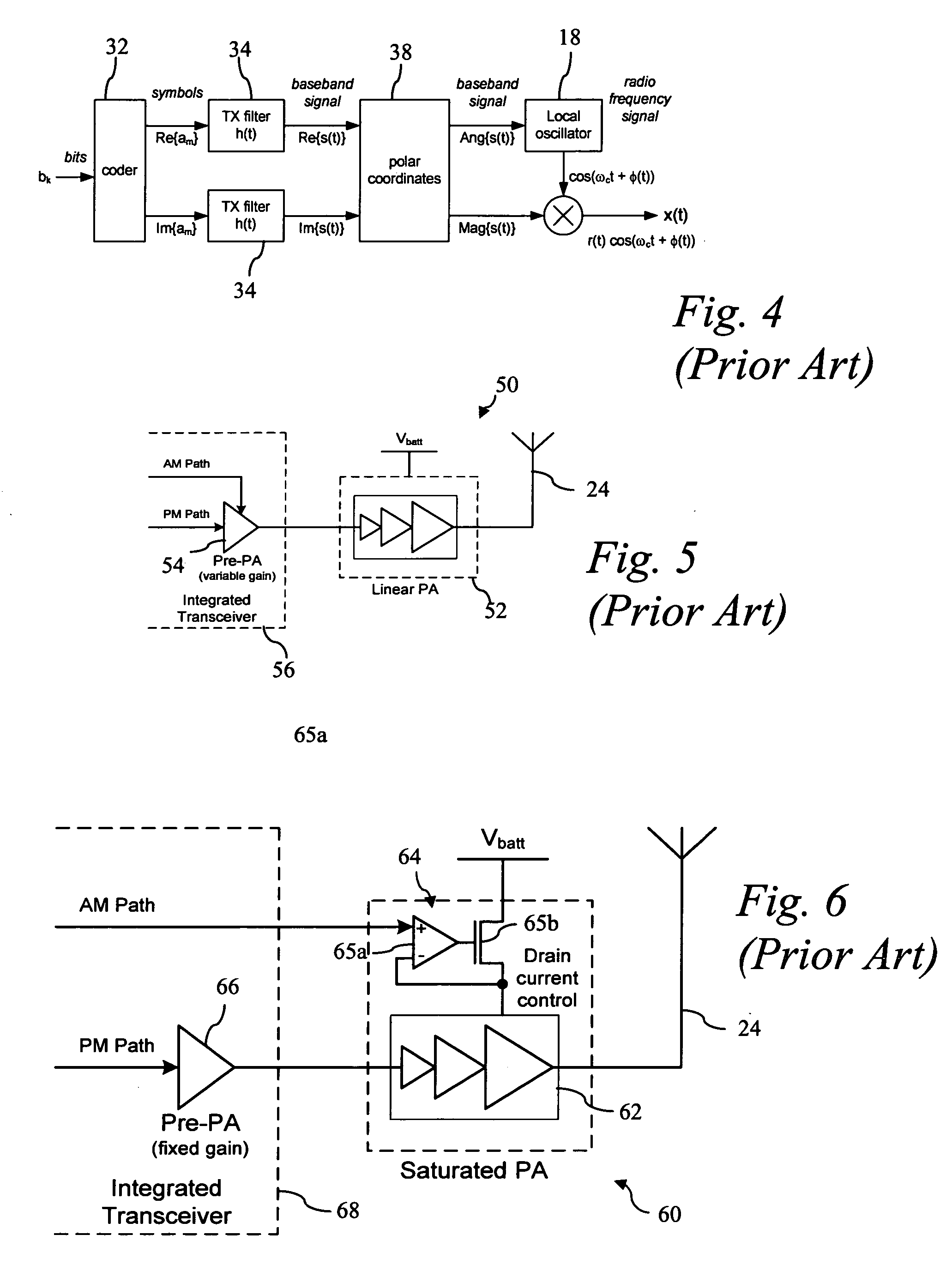
Digital amplitude modulation
ActiveUS20050271161A1Improve performanceLow costPower amplifiersModulation with suppressed carrierCarrier signalSignal frequency
A transmitter using quadrature modulation includes a rectangular to polar converter for converting data symbols into a polar form, where each polar symbol has a magnitude signal and an angle signal. Digital phase modulation circuitry includes an all digital PLL circuit for generating a phase modulated RF carrier signal responsive to the angle signal frequency control word (FCW) and a carrier frequency FCW. A digitally controlled amplifier for amplifying the phase modulated signal is controlled by a digital amplitude control circuitry for controlling the gain of the digitally controlled amplifier responsive to the magnitude signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
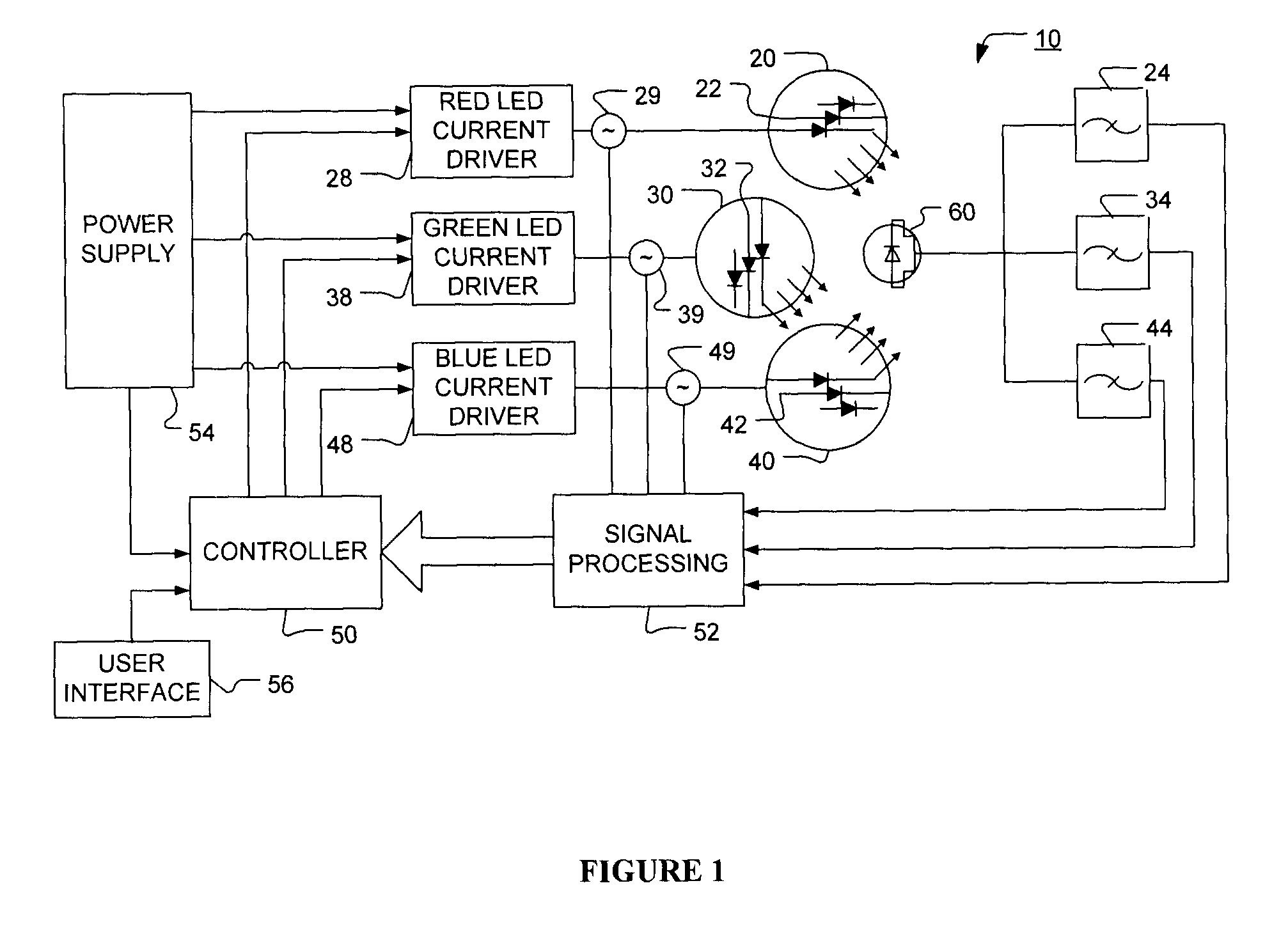
Method and apparatus for light intensity control
InactiveUS20090189530A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentControl signal
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for optical feedback control for an illumination device, wherein the control signal for each array of one or more light-emitting elements corresponding to a particular colour, is independently configured using a modification signal whose frequency is different for each colour. Electronic filters whose center frequencies are substantially equal to the modification signal frequencies of the drive currents for the light-emitting elements are used to discriminate between the radiant flux corresponding to each of the different colours of light-emitting elements, from a sample of the mixed radiant flux output collected by one or more optical sensors. The output of an individual electronic filter is substantially directly proportional to the radiant flux output of the light-emitting elements of the associated colour, which together with the desired luminous flux and chromaticity of the output light, the controller can use to adjust the control signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Synchronous transfer of streaming data in a distributed antenna system
Embodiments of the invention provide a method, distributed antenna system, and components that generate a jitter reduced clock signal from a serial encoded binary data stream transmitted over a communication medium. The method comprises receiving a modulated signal that includes the encoded binary data stream and extracting the encoded binary data stream. The method further comprises generating a recovered clock signal that is phase locked to the encoded binary data stream, generating an error signal based on a difference between a phase of the encoded binary data stream and the recovered clock signal, and integrating the error signal to generate a signal to control a voltage controlled oscillator. The method further comprises generating a stable recovered clock signal and producing at least one output clock by scaling the stable recovered clock signal frequency.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Wireless communication apparatus and receiving method
InactiveUS20080159442A1Single output arrangementsElectric pulse generatorAmplitude distortionTelecommunications
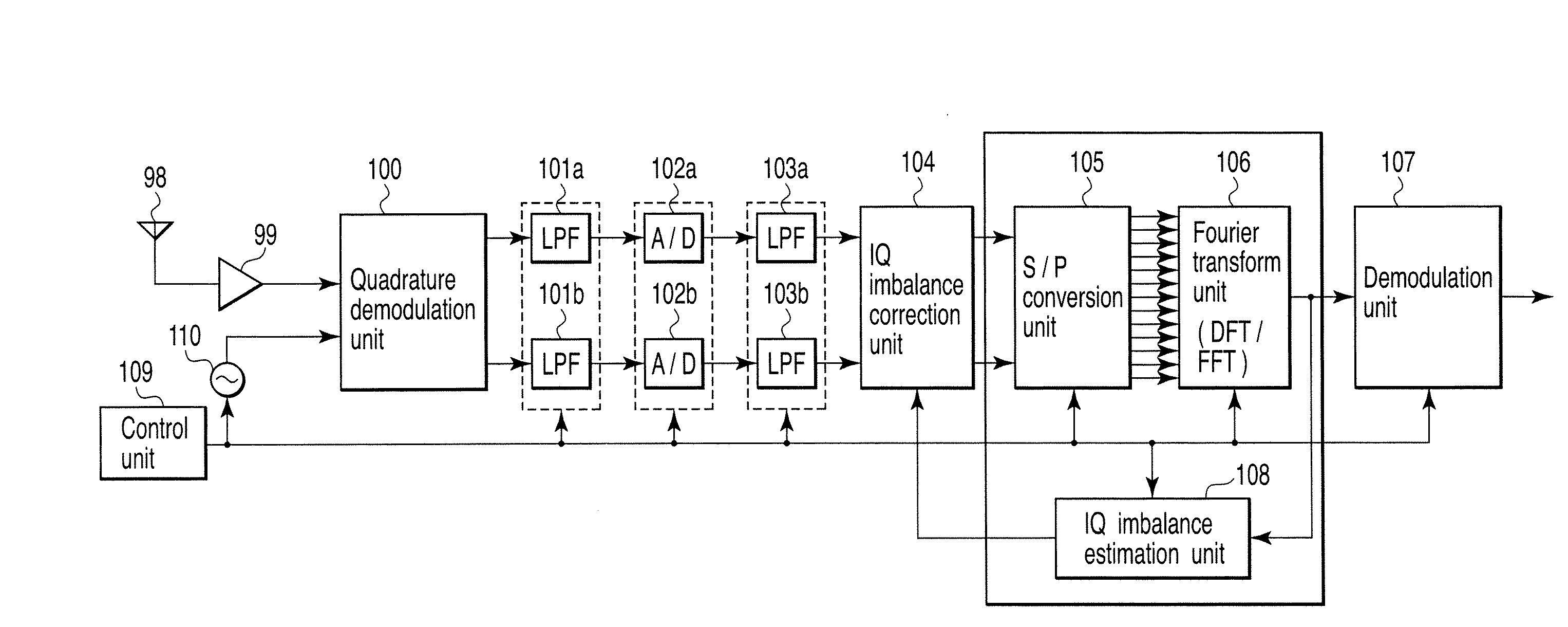
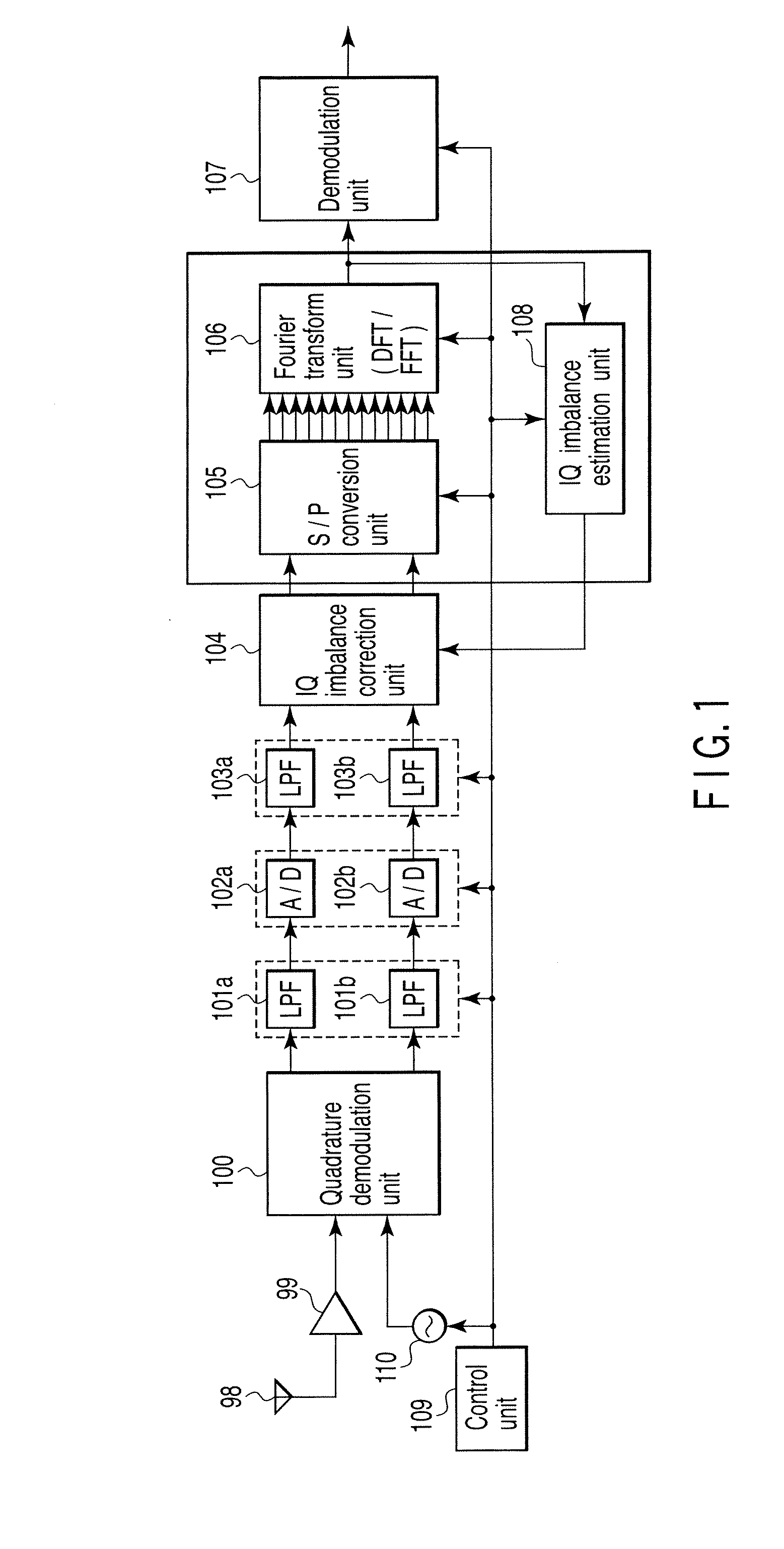
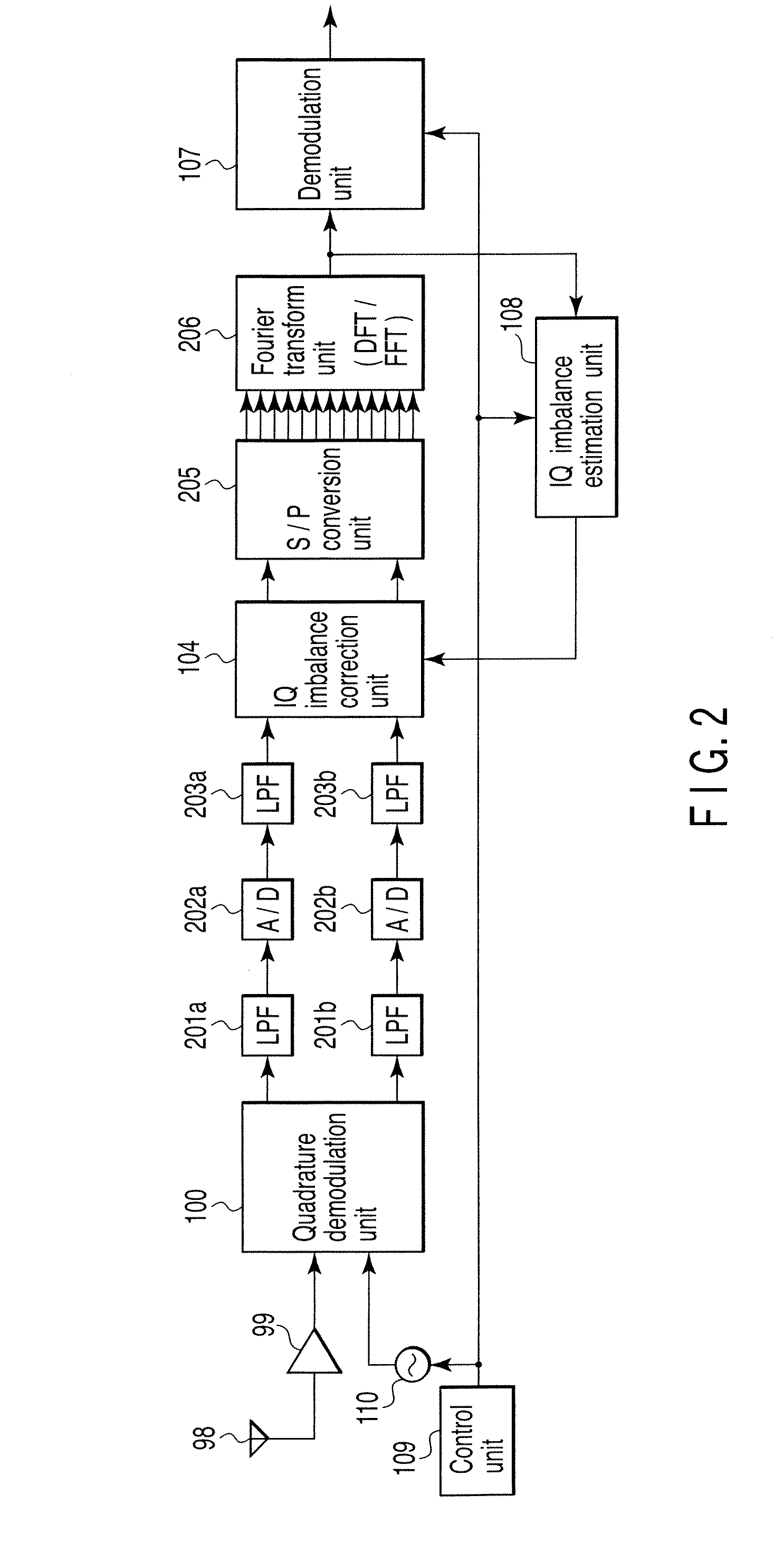
A wireless communication apparatus receives an quadrature modulated signal, generate a local signal having a frequency different from a center frequency of the quadrature modulated signal, performs quadrature demodulation on the quadrature modulated signal by using the local signal, to obtain an I channel signal and a Q channel signal, performs Fourier transform on the I channel signal and the Q channel signal, to obtain signals in a frequency domain, and calculates a first correction coefficient for correcting phase distortion and amplitude distortion caused by the quadrature demodulation by using pairs of signals among the signals, each of the pairs are located at symmetrical frequency positions with respect to the frequency of the local signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
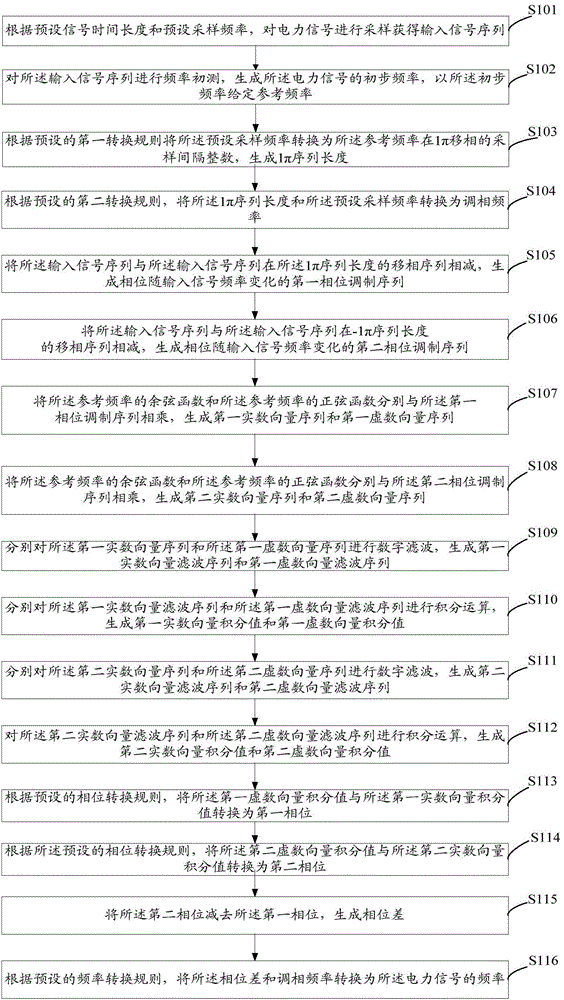
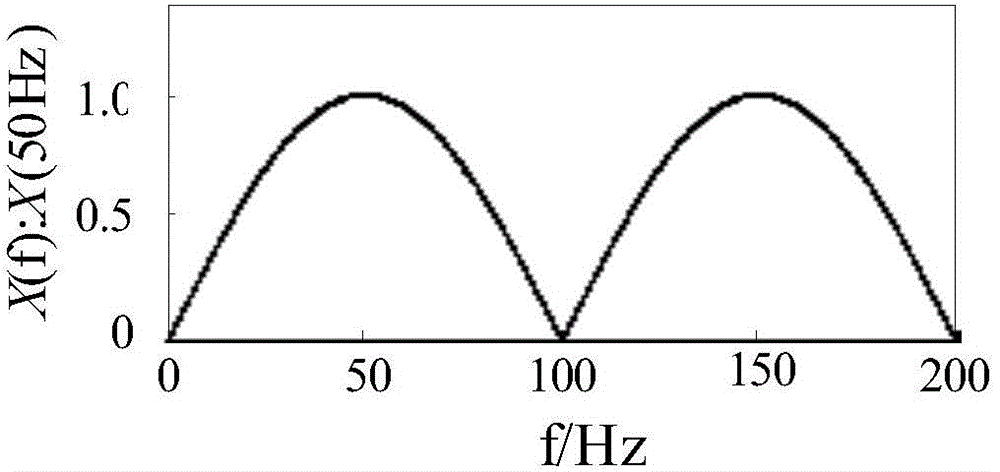
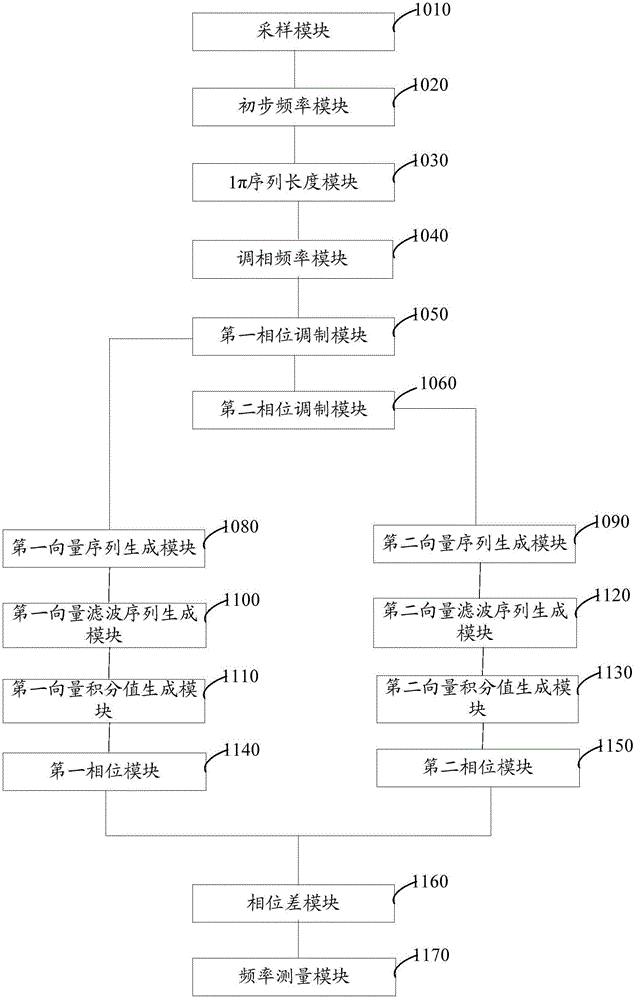
Power signal frequency detection method and system based on phase modulation
ActiveCN104635045AHigh precisionSuppression of aliasing interference componentsFrequency measurement arrangementPhase shiftedFrequency measurements
The invention discloses a power signal frequency detection method and a power signal frequency detection system based on phase modulation. The method comprises the steps: sampling a power signal according to preset signal time span and preset sampling frequency, so as to obtain an input signal sequence; measuring the frequency of the input signal sequence, so as to obtain the initial frequency of the power signal, and subtracting the input signal sequence and the plus or minus 1 Pi phase-shift sequence of the input signal sequence by using the initial frequency as reference frequency, so as to obtain two phase modulation sequences of which phases change along with the input signal frequency; respectively mixing, filtering and integrating the two phase modulation sequences, so as to obtain the phases of the two phase modulation phases for frequency measurement. By implementing the power signal frequency detection method and the power signal frequency detection system, frequency measurement results with higher accuracy can be obtained.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Film acoustically-coupled transformer with reverse C-axis piezoelectric material
ActiveUS20050093657A1Improved common mode rejection ratioIncreasing available choiceImpedence networksSolid-state devicesPlanar electrodeResonator
An embodiment of the acoustically-coupled transformer has first and second stacked bulk acoustic resonators (SBARs) each having a stacked pair of film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs) with an acoustic decoupler between the FBARs. Each FBAR has opposed planar electrodes with piezoelectric material between the electrodes. A first electrical circuit connects one FBARs of the first SBAR to one FBAR of the second SBAR, and a second electrical circuit connects the other FBAR of the first SBAR to the other FBAR of the second SBAR. The c-axis of the piezoelectric material of one of the FBARs is opposite in direction to the c-axes of the piezoelectric materials of the other three FBARs. This arrangement substantially reduces the amplitude of signal-frequency voltages across the acoustic decouplers and significantly improves the common mode rejection of the transformer. This arrangement also allows conductive acoustic decouplers to be used, increasing the available choice of acoustic decoupler materials.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
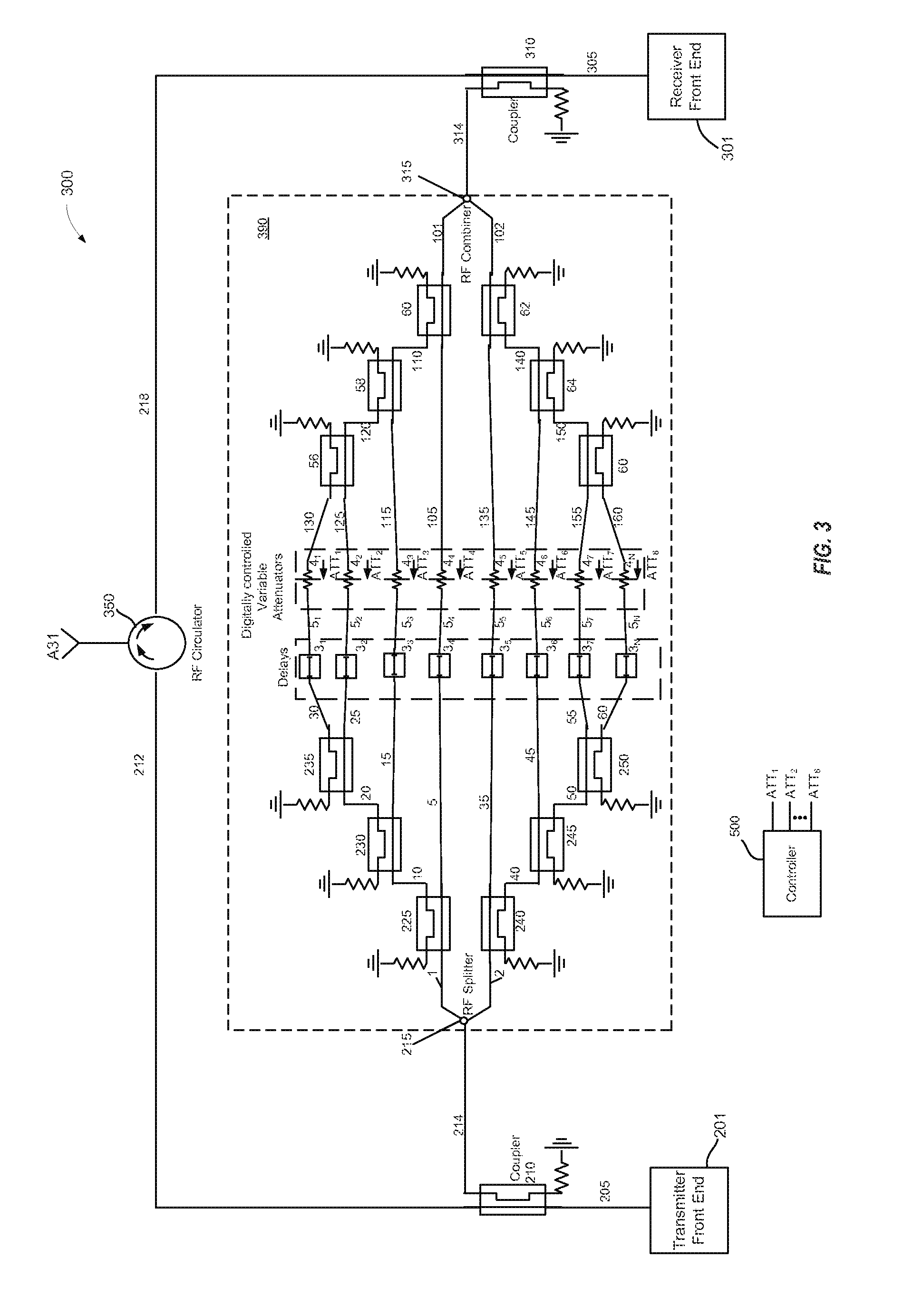
Tuning algorithm for multi-tap signal cancellation circuit
ActiveUS20140204808A1Easy to understandTransmission control/equalisingDuplex signal operationSelf interferenceUltrasound attenuation
A self-interference signal cancellation circuit includes a transmitter for transmitting a transmit signal, a plurality of signal paths, a controller, and a receiver for receiving a signal. Each signal path includes a delay element and a variable attenuator having attenuation levels set by the controller. A combiner generates an output signal by combining outputs of the signal paths. The circuit computes a matrix based on first and second output signals associated with first and second attenuation levels. The controller concurrently varies the attenuation level of each signal path so that a product of the matrix and the attenuation levels of the signal paths is substantially equal to the received signal. The circuit may iteratively compute the matrix using different transmit signal frequencies or with an FFT. The controller iteratively varies the attenuation level of the attenuators until a sum of the product and the received signal satisfies a predefined condition.
Owner:KUMU NETWORKS
Phase controlled oscillator circuit with input signal coupler
An oscillating signal in an oscillator is caused to phase shift toward the phase of an input signal coupled to the oscillating signal. The resonant frequency of the oscillator is about equal to an integer multiple of the frequency of the input signal. The input signal may be generated in a pulse generator to have an input pulse duration less than or equal to that of the oscillating signal. The oscillator circuit may be used as a filter to filter pulse width variations or to filter jitter from a reference clock. The oscillator circuit may also serve as a buffer by amplifying the input signal. Phase interpolation can be obtained by coupling at least one input signal with at least one oscillating signal.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
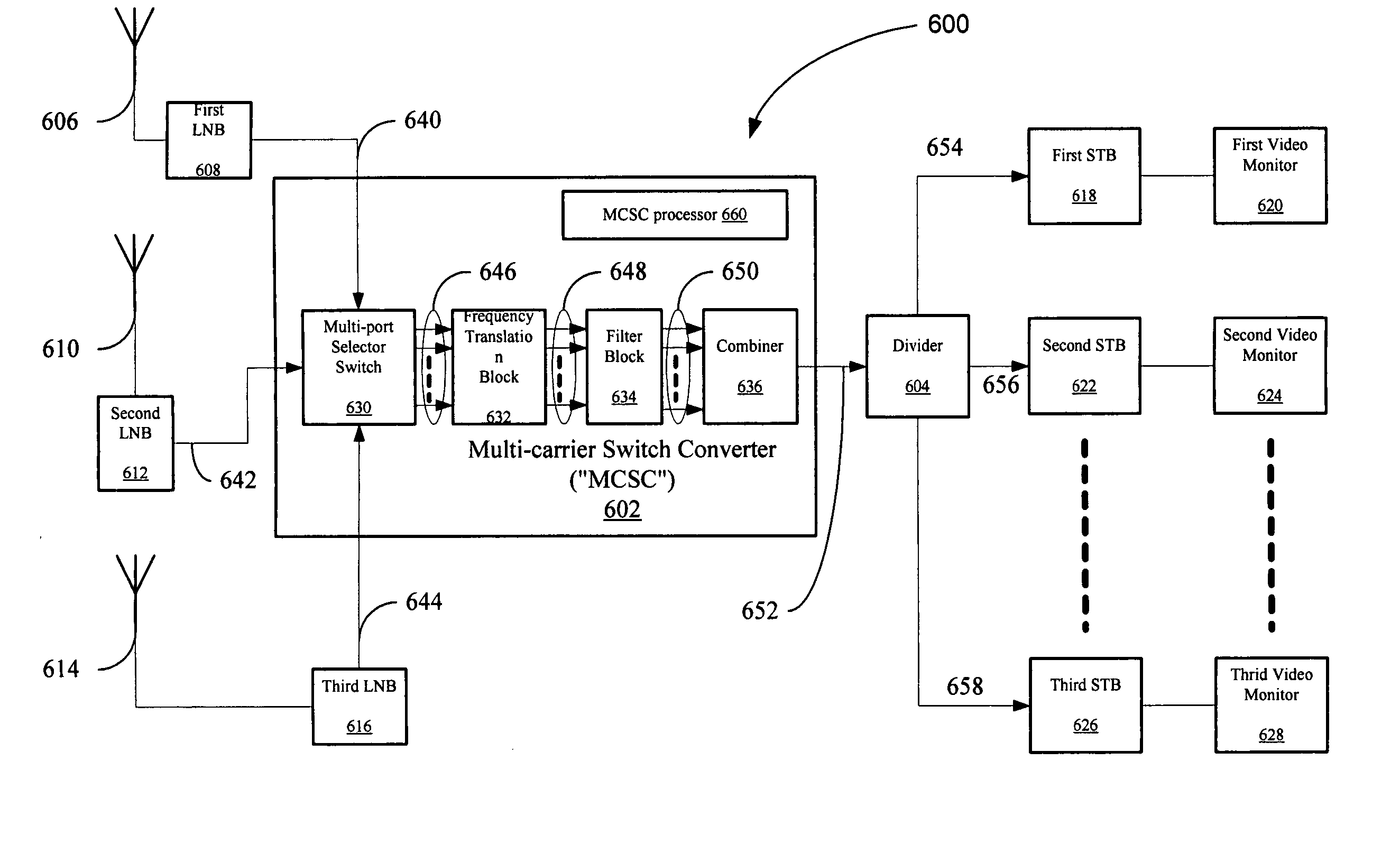
Satellite multi-choice switch system
ActiveUS20050193419A1Satellite broadcast receivingGHz frequency transmissionSatelliteSignal frequency
Owner:NXP BV
Systems and methods for providing an adjustable reference signal to RF circuitry
InactiveUS7035607B2Guaranteed interference effectReduce the impact of interferenceAutomatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayPulse automatic controlControl signalEngineering
Frequency modification circuitry may be employed as part of a crystal oscillator circuit to generate a reference signal with adjustable frequency. The frequency modification circuitry may be implemented as part of a crystal oscillator circuit that includes digitally controlled crystal oscillator (“DCXO”) circuitry and a crystal. The frequency modification circuitry may adjust the frequency of the reference signal in response to one or more frequency control signals. In one example, the frequency modification circuitry may include variable capacitors such as one or more continuously variable and / or discretely variable capacitors for providing coarse and / or fine adjustment of the reference signal frequency.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
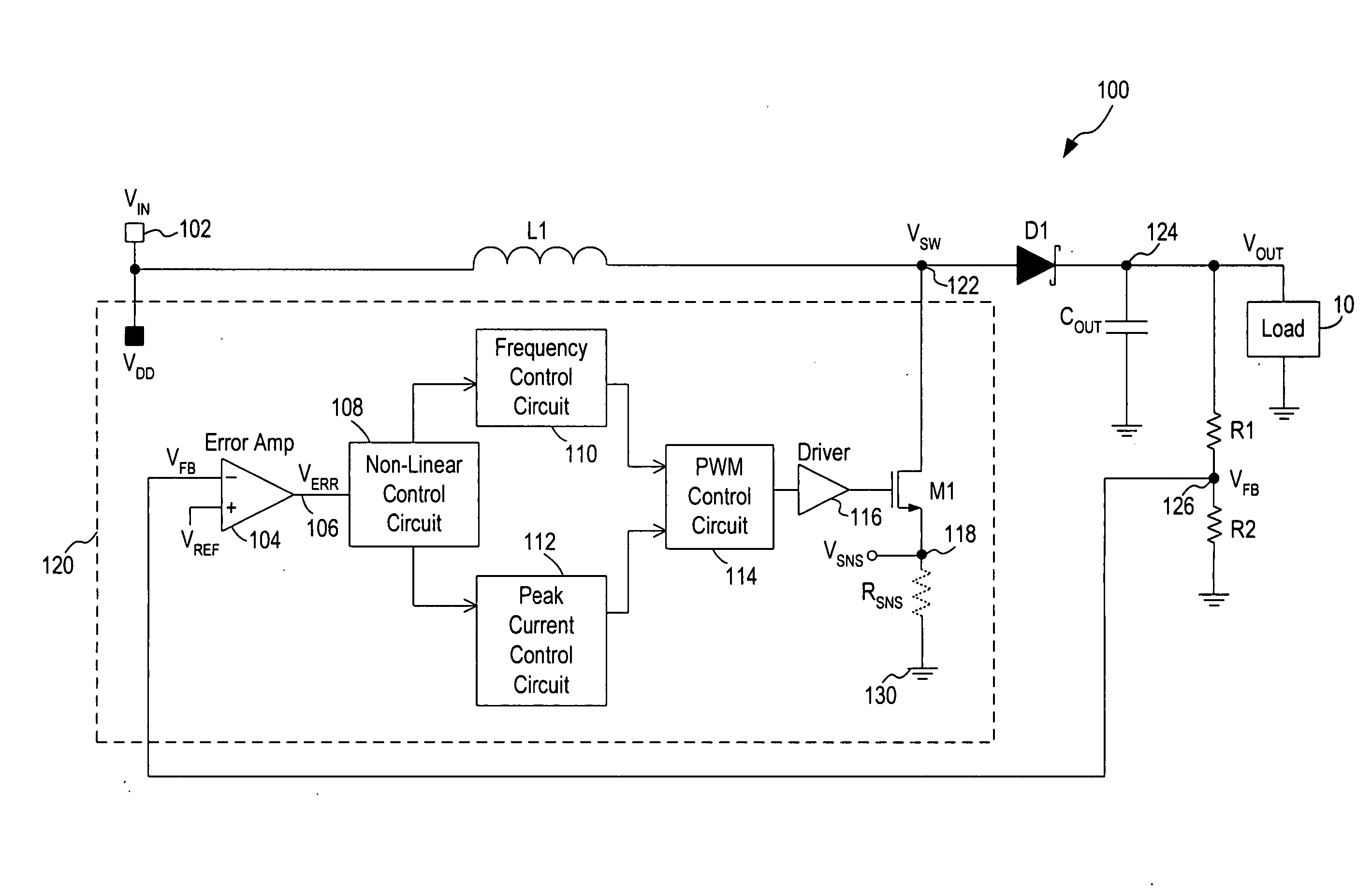
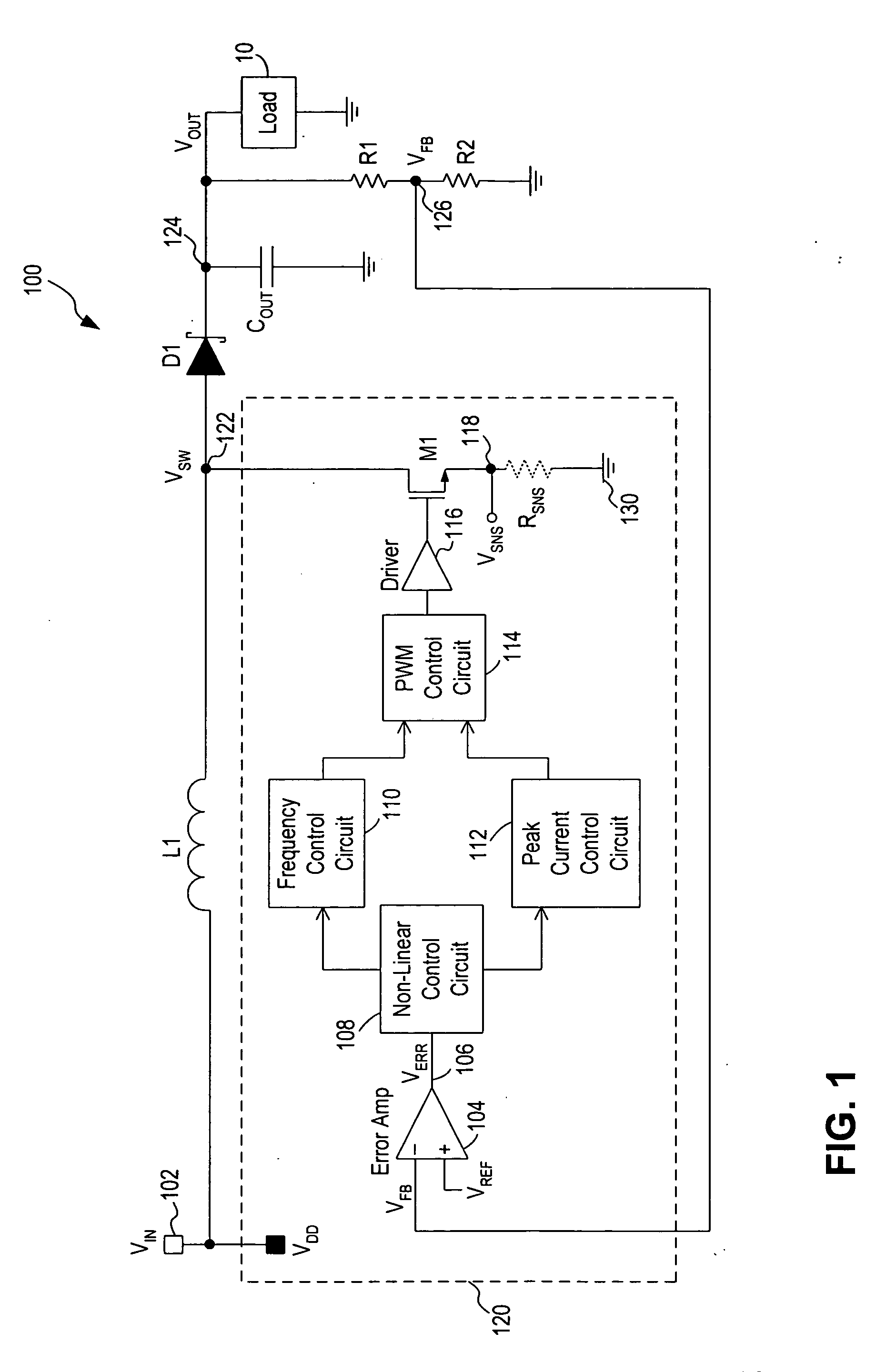
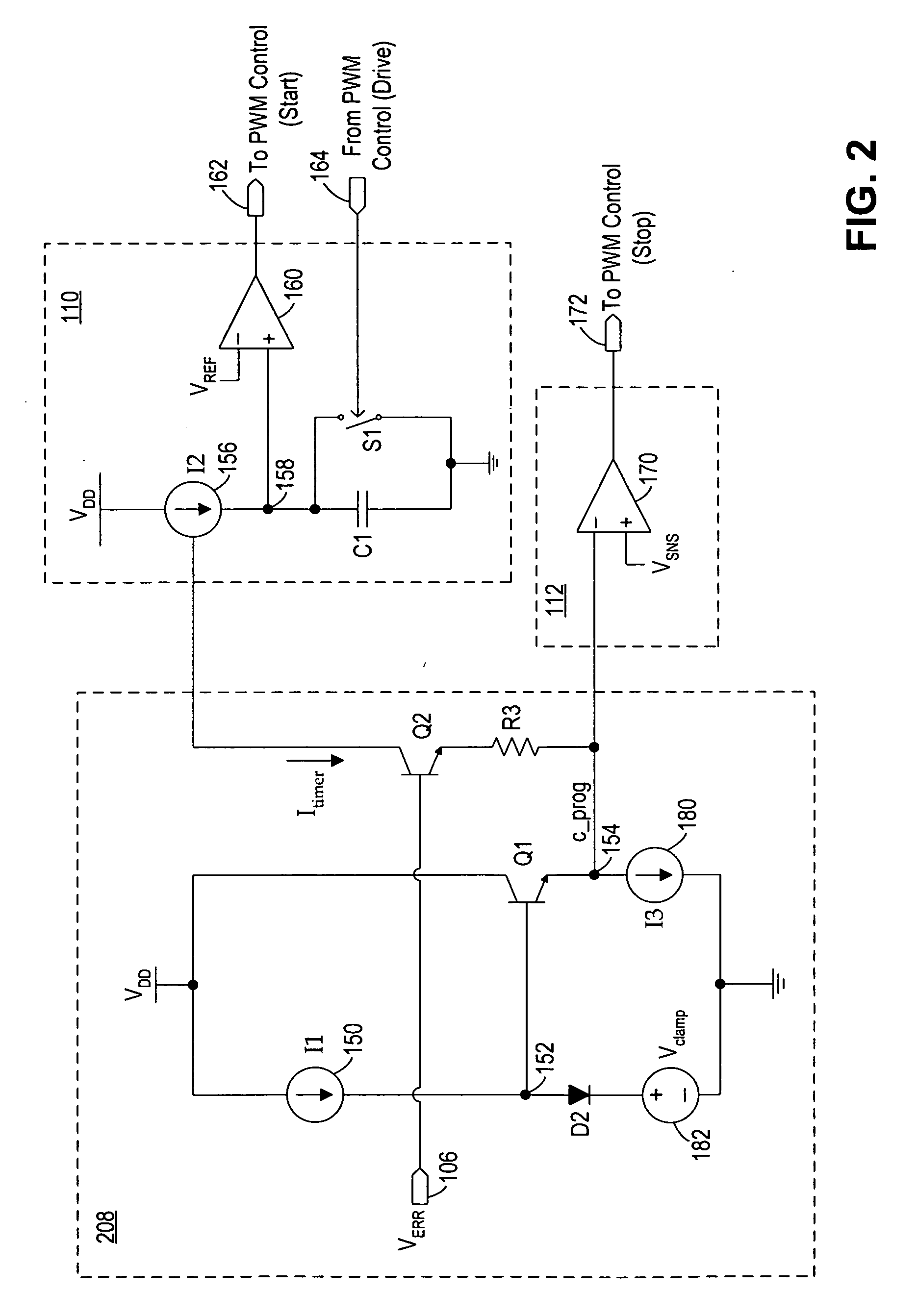
PFM and current controlled switching regulator
ActiveUS20070210772A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionLinear controlControl signal
A circuit and method for controlling a switching regulator utilize a combination of variable off-time control (or frequency control) and variable peak current control to achieve high efficiency at a wide range of load conditions. A non-linear control circuit receives an error voltage and generates a first control signal for controlling a frequency control circuit and a second control signal for controlling a peak current control circuit. The frequency control circuit and the peak current control circuit operate in conjunction over the entire range of load conditions with the frequency control dominates at light load (or low power) conditions and the variable peak current control dominates at moderate to heavy load (or high power) conditions. The switching regulator transitions smoothly between frequency control and peak current control with continous loop gain throughout the transition region.
Owner:MICREL
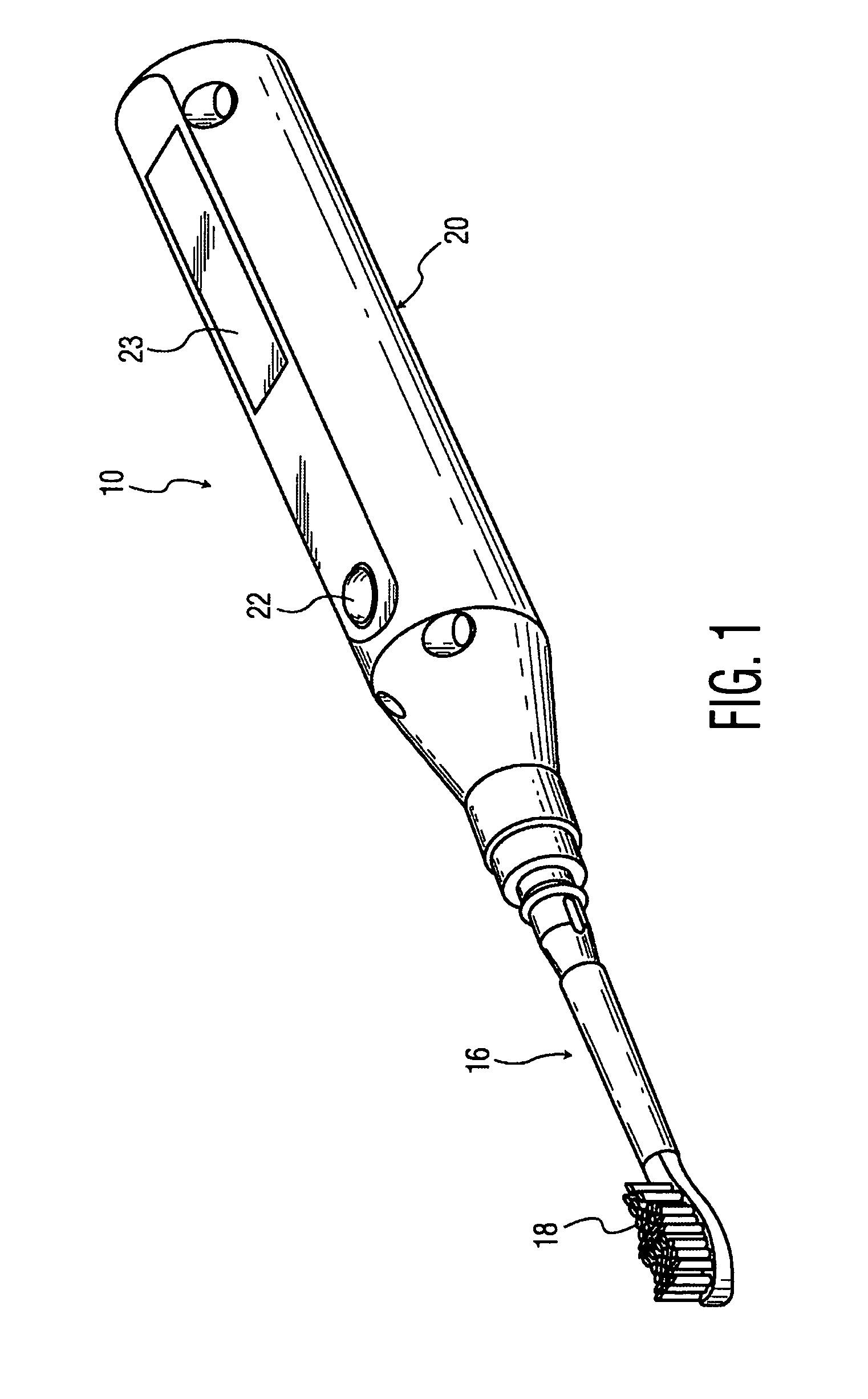
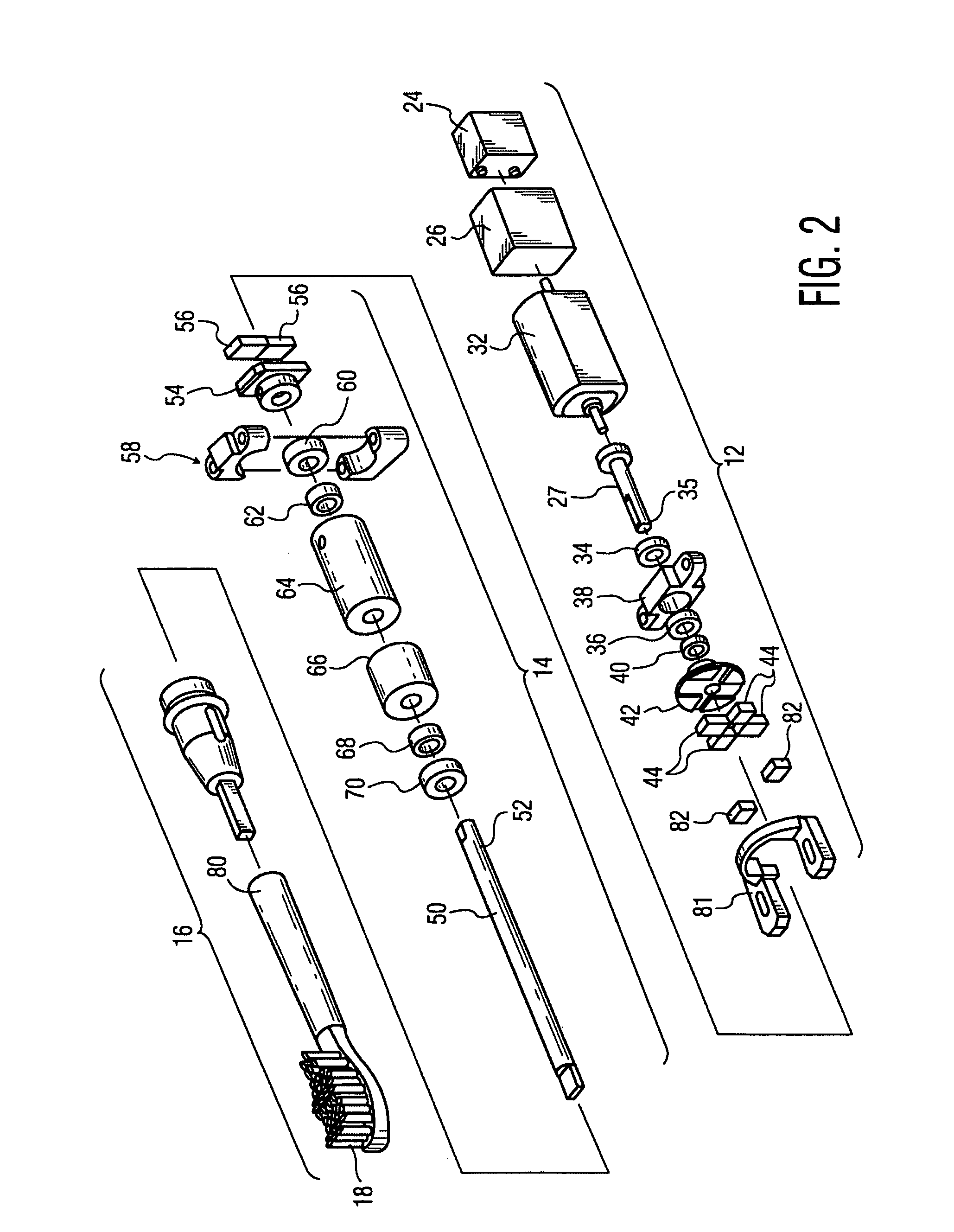
Reciprocating workpiece device with a drive system seeking the resonance of the driven system portion thereof
A workpiece system with a reciprocating motion which includes a motor assembly for producing an output drive signal with a periodic force pulse. The drive signal is coupled to a driven member assembly through a magnetic arrangement, wherein the driven member assembly has a workpiece mounted thereon with a return spring assembly. The driven member assembly has a resonant mechanical frequency. As the RPM of the motor increases from zero following startup, the drive signal frequency increases to the point very near resonance, where the energy from the drive signal is transferred into the reciprocating motion of the driven assembly, producing an effective amplitude of workpiece motion.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com