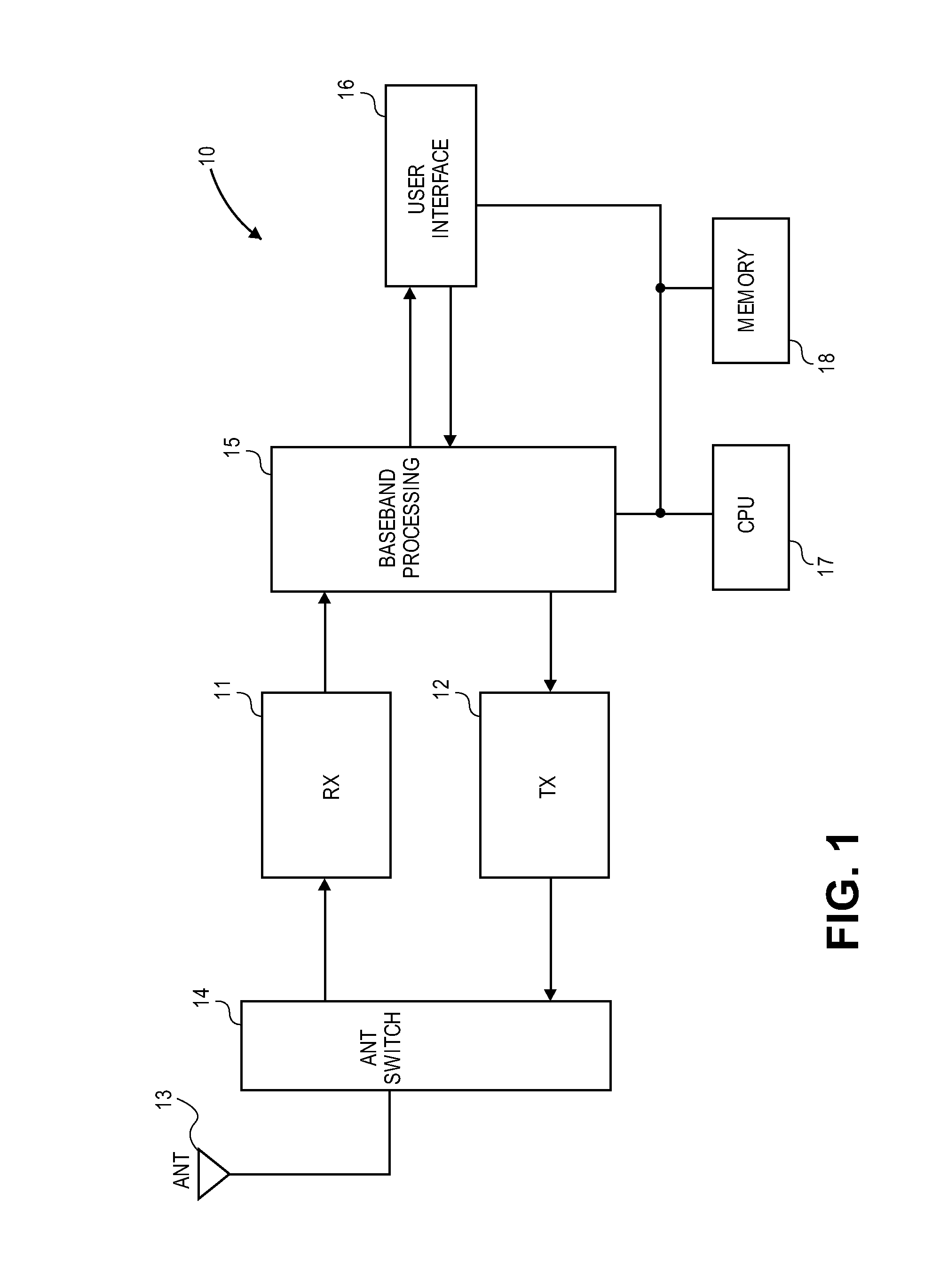
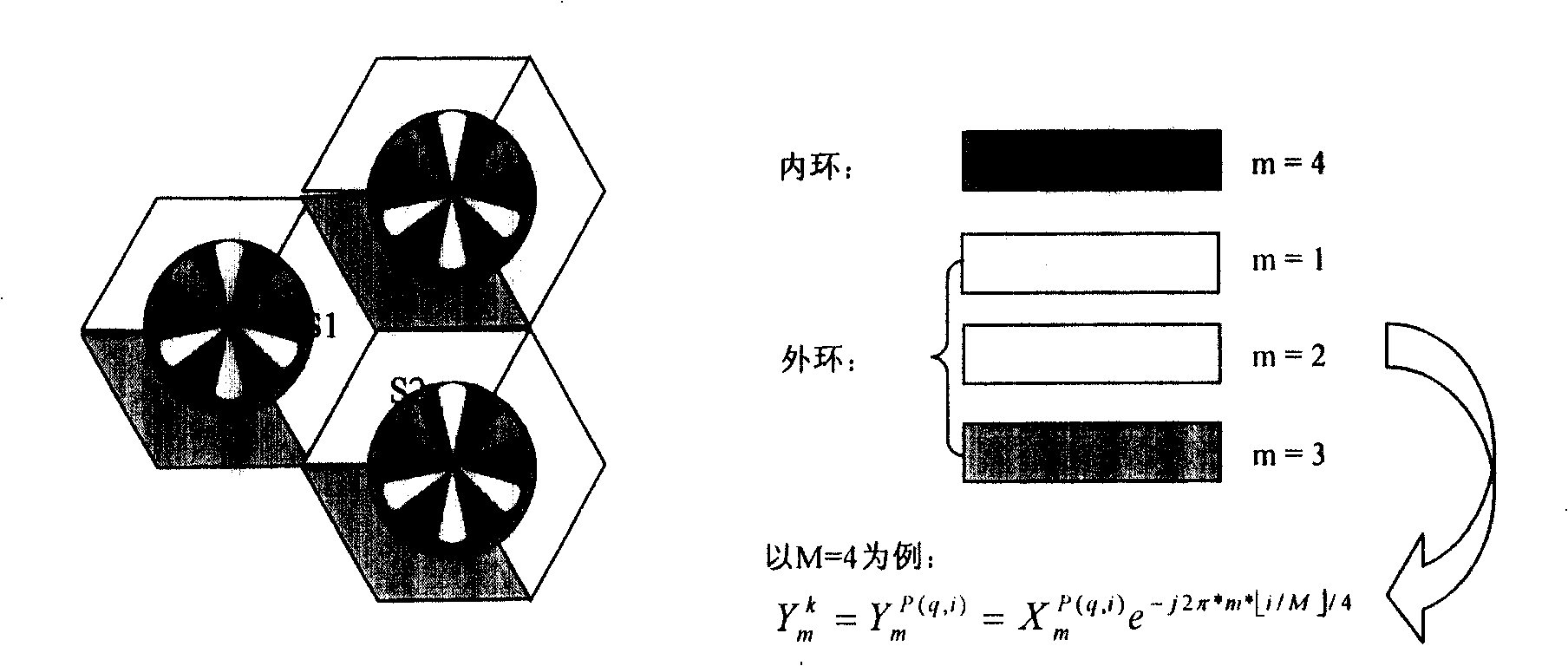
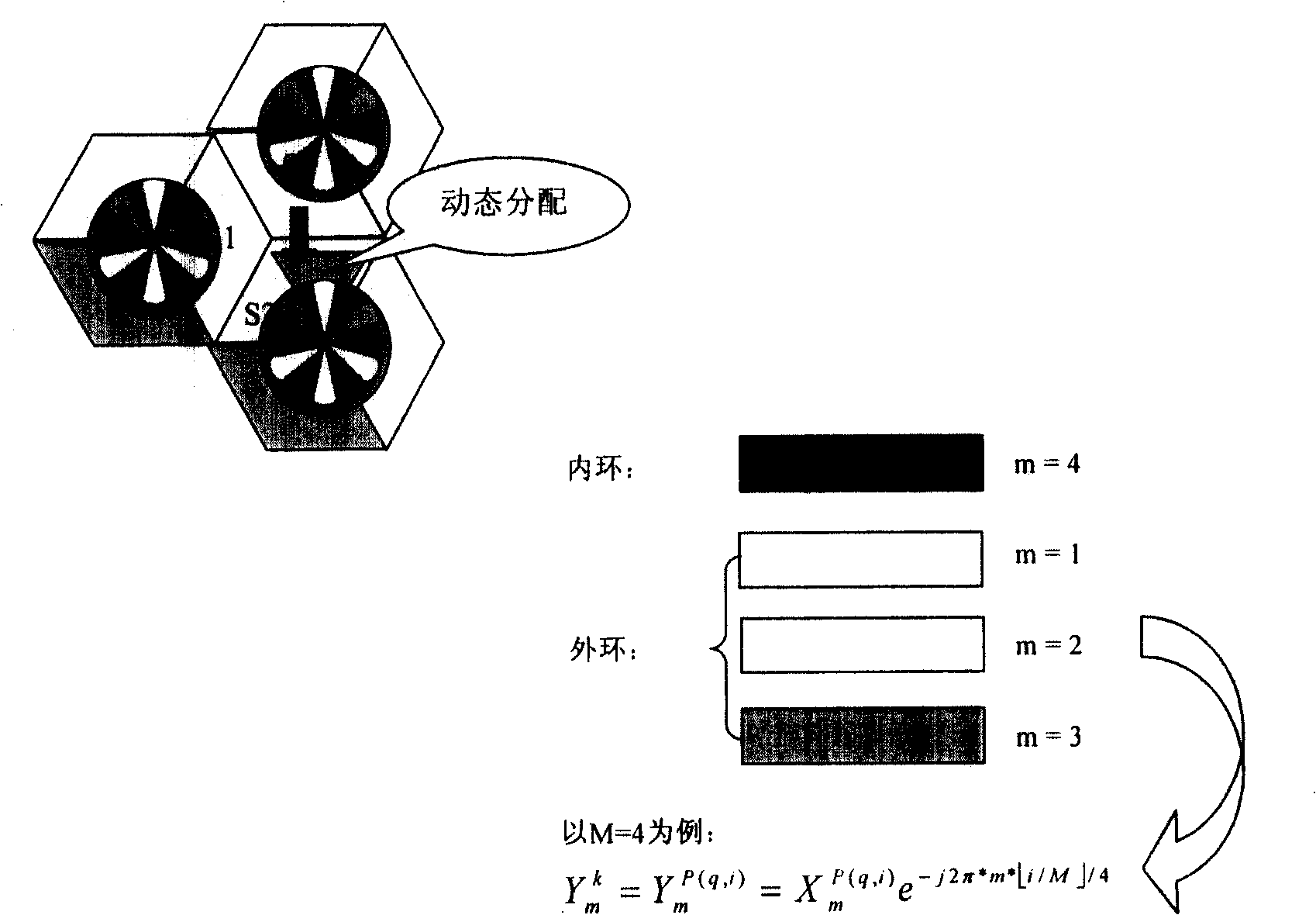
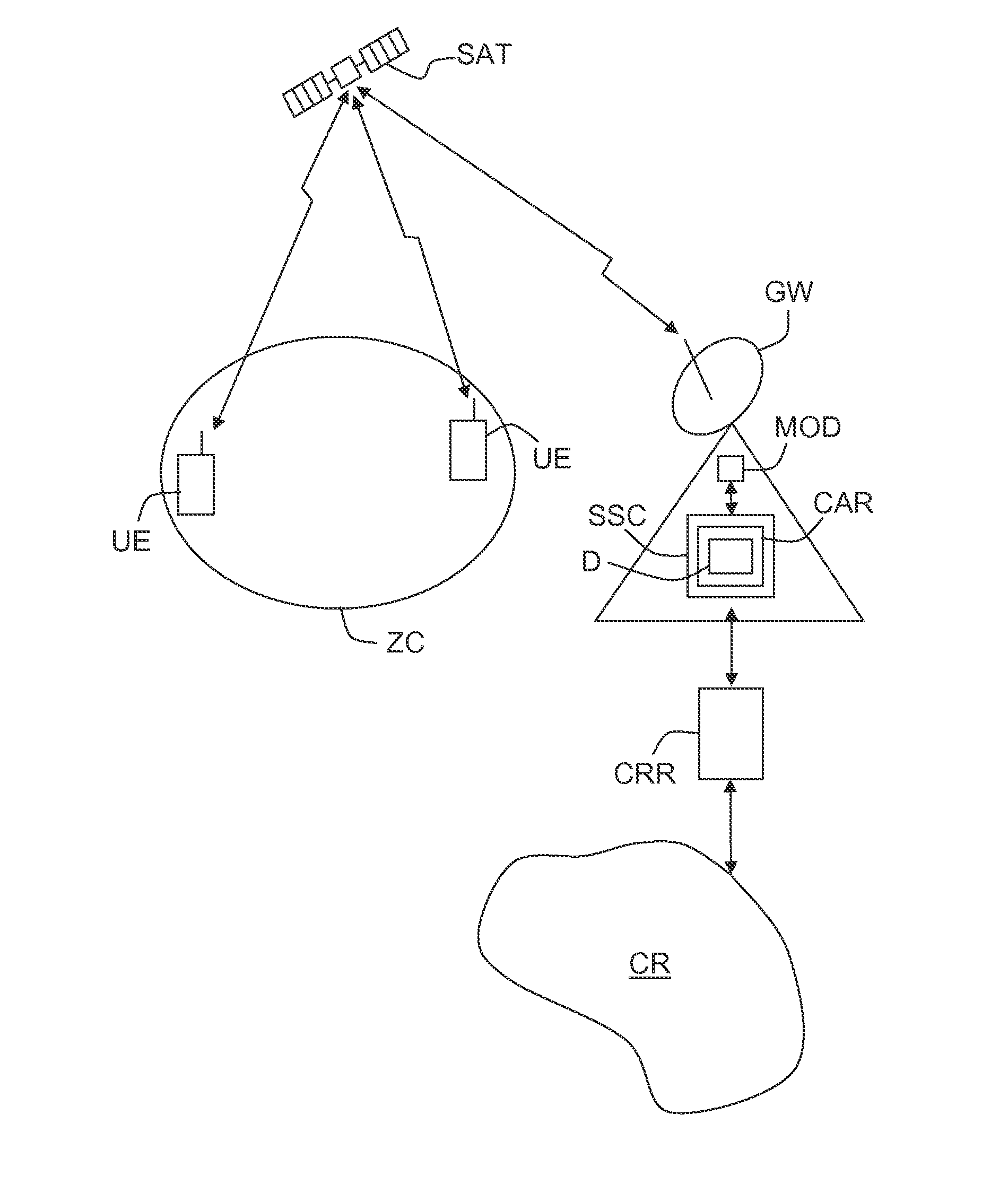
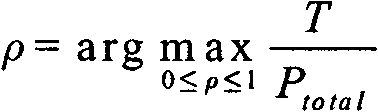Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117 results about "Frequency plan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
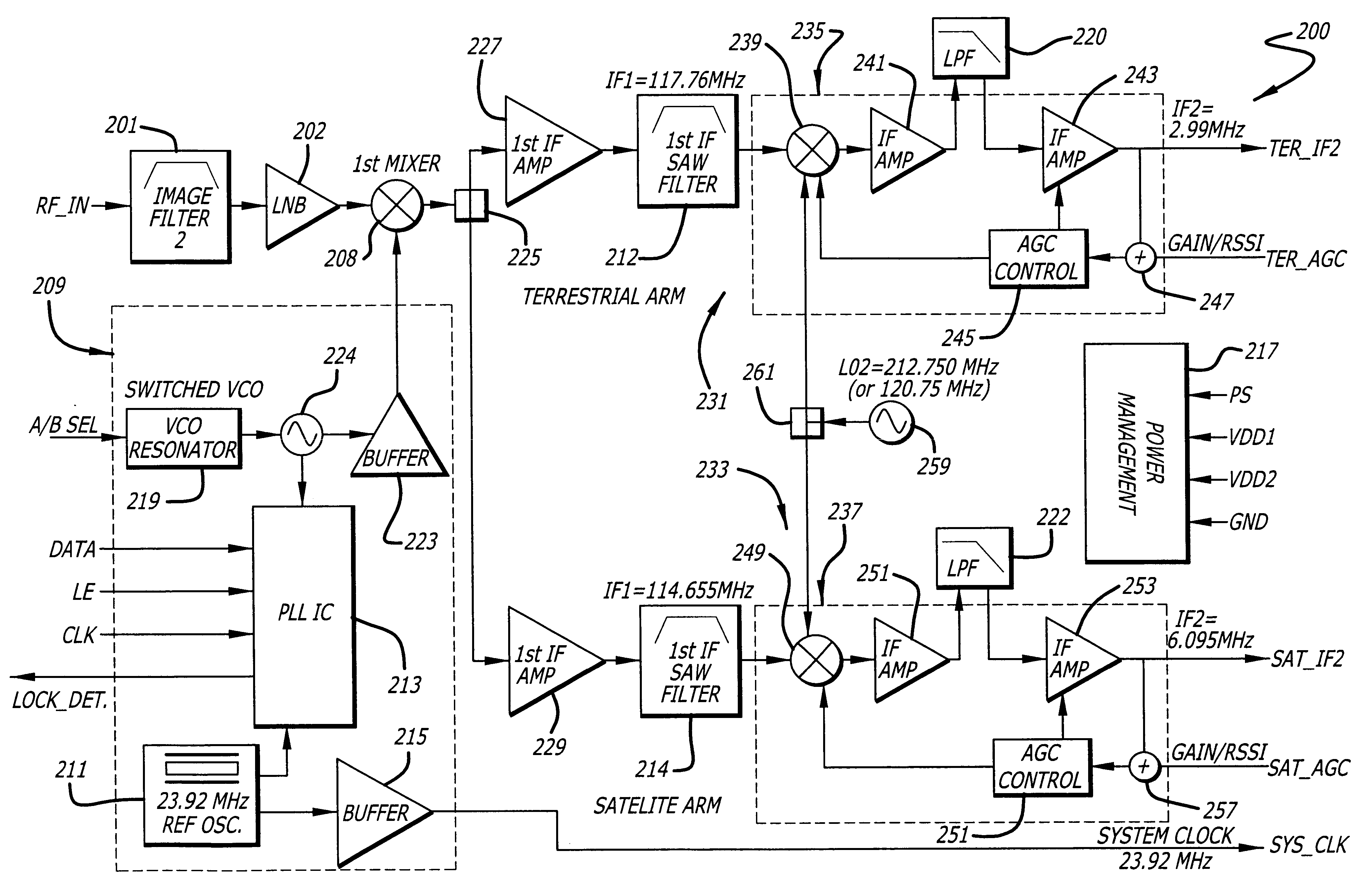
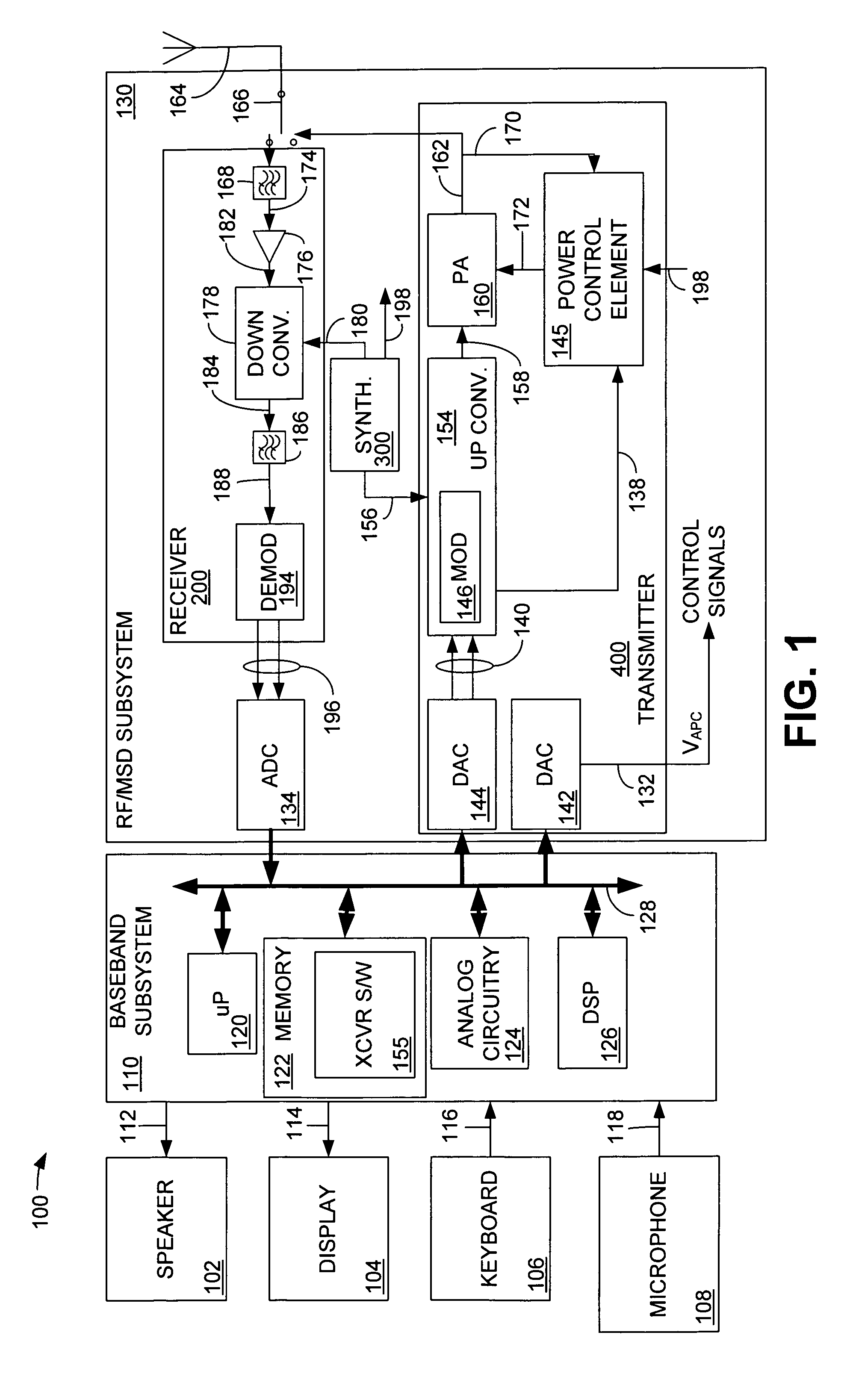
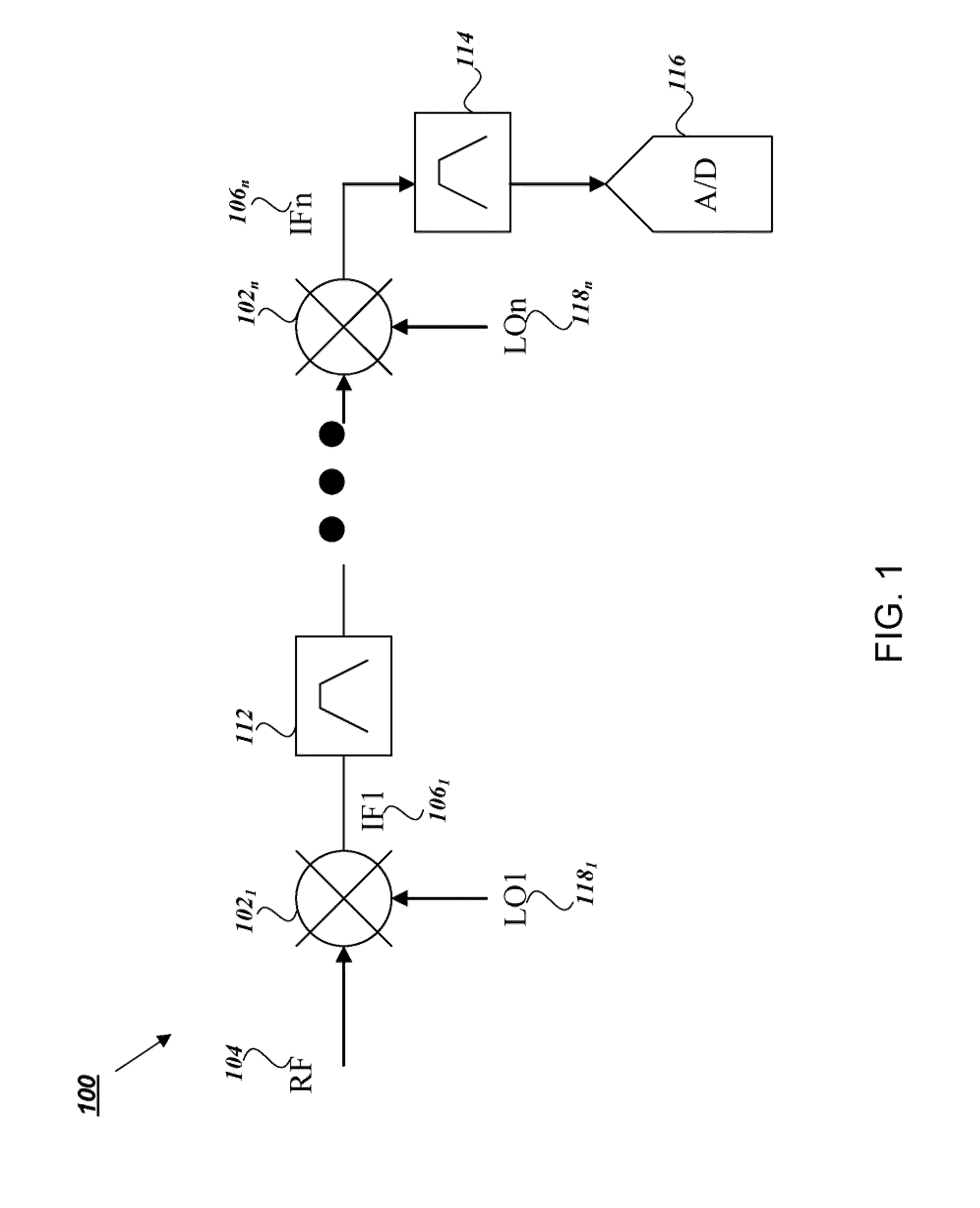
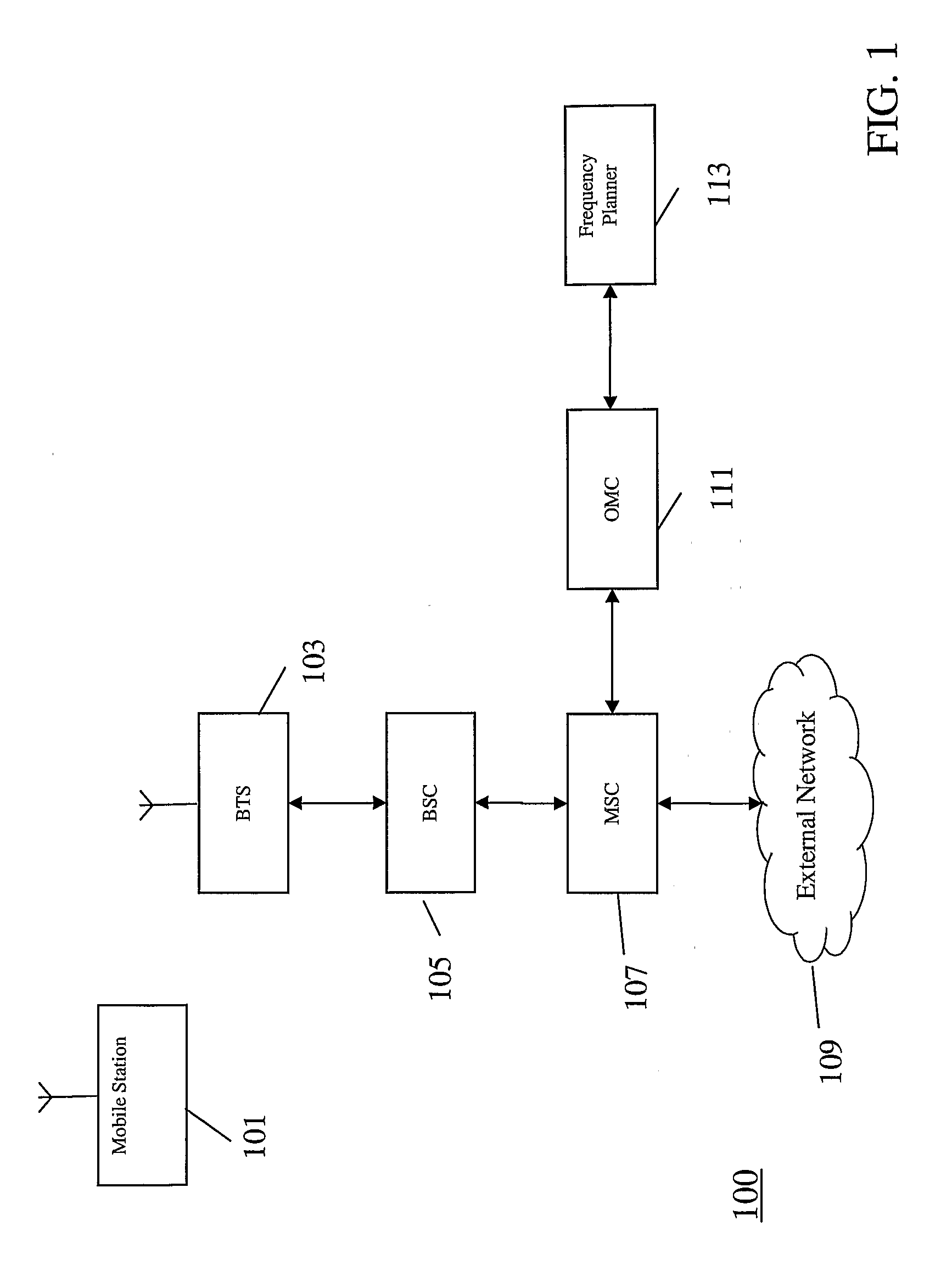
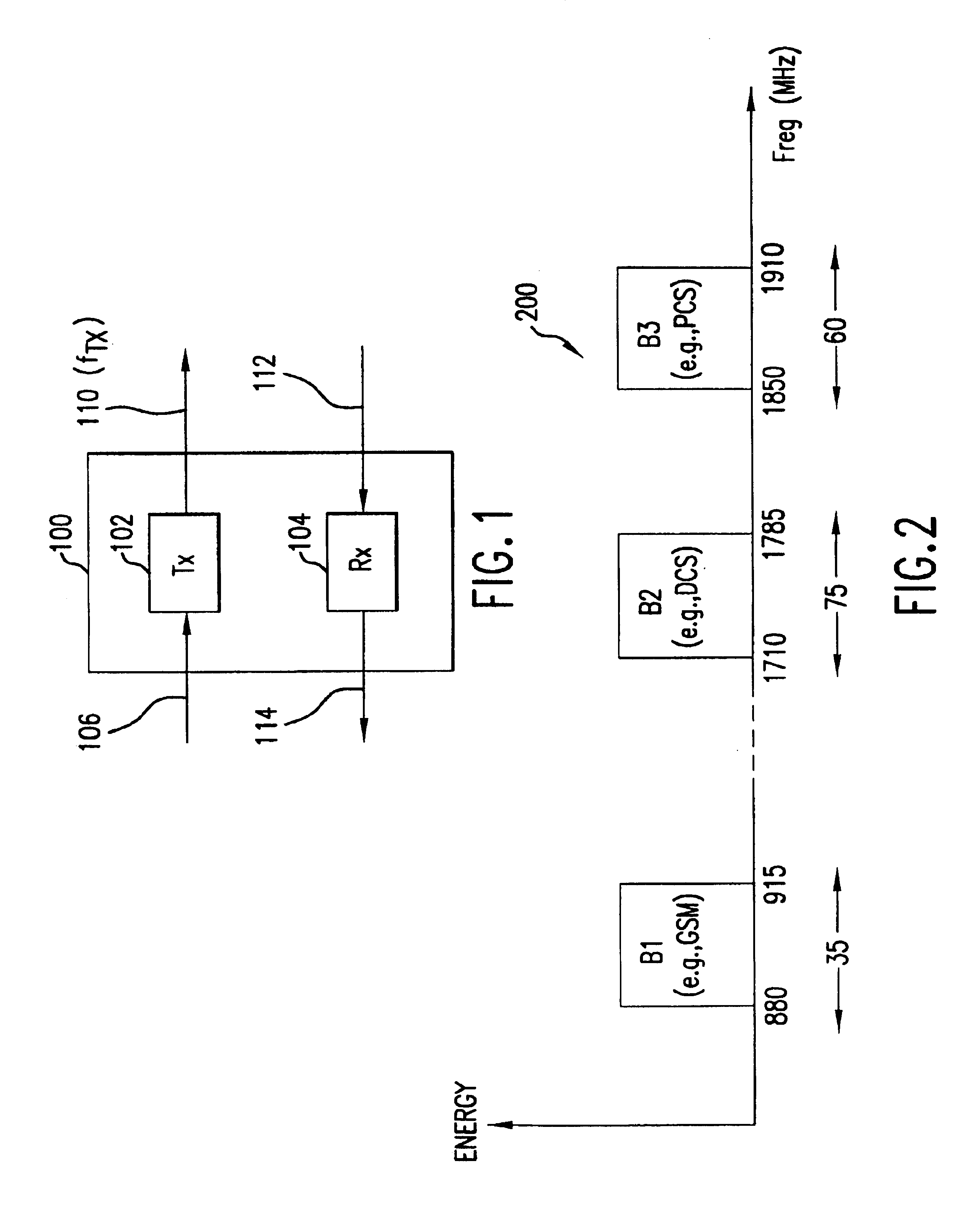
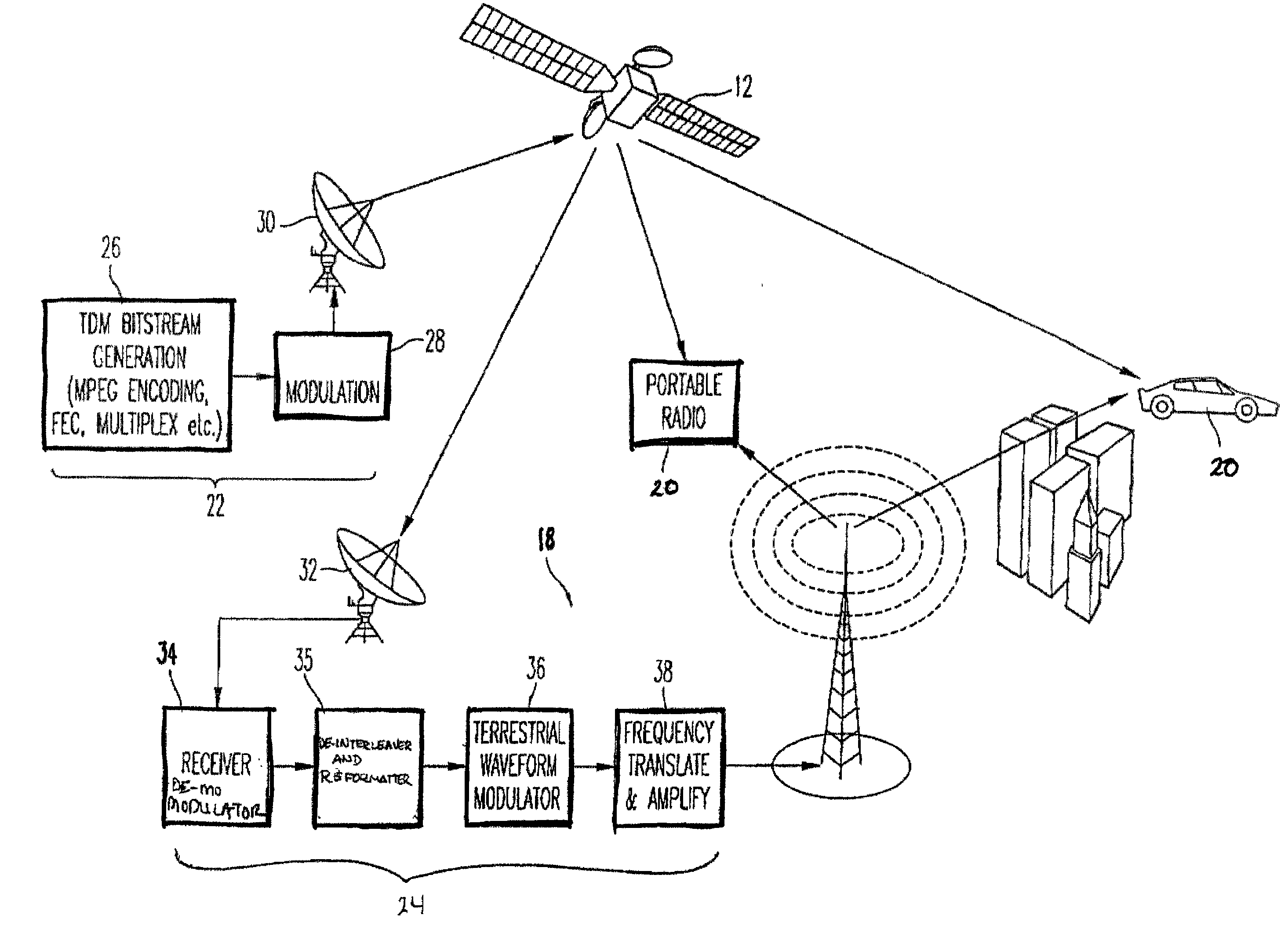
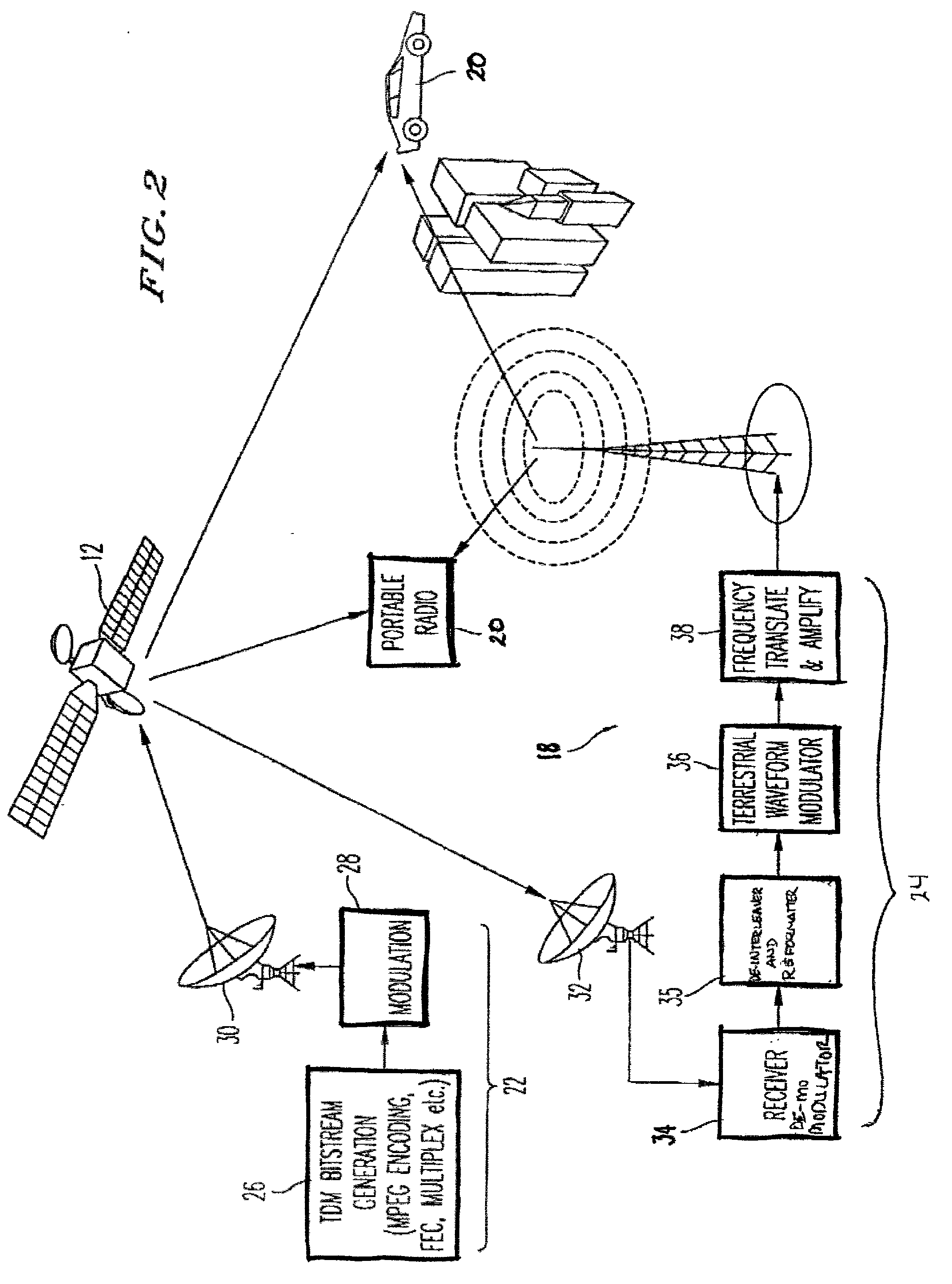
Satellite digital audio radio service tuner architecture for reception of satellite and terrestrial signals
InactiveUS6510317B1Broadcast transmission systemsRadio transmissionIntermediate frequencyRadio receiver
A satellite digital audio radio receiver system and method. The inventive receiver includes a circuit for down-converting a first ensemble in a received combined signal in a first mode of operation and for down-converting a second ensemble from the received combined signal in a second mode of operation. The first ensemble includes a first signal received from a first transmitter, a second signal received from a second transmitter, and a third signal received from a third transmitter. The second ensemble includes a second signal from the first transmitter, a second signal from the second transmitter, and a second signal from the third transmitter. A controller is included to selectively switch the circuit from the first mode to the second mode. The first ensemble comprises first, second and third frequency slots and the second ensemble comprises fourth, fifth, and sixth frequency slots. In the illustrative embodiment, the first and second transmitters are mounted on first and second satellites and the third transmitter is a terrestrial repeater. Both ensembles are transmitted in accordance with the XM frequency plan. The first ensemble is down-converted using low side injection and the second ensemble down-converted using high side injection. The inventive circuit includes a synthesized frequency source. The circuit further includes a first intermediate frequency down-conversion stage with a first mixer for mixing the received combined signals with the output of synthesized frequency source. The circuit further includes first and second surface acoustic wave filters for separating the first and second signals received from the third signals. The inventive circuit further includes a second intermediate frequency down-conversion stage having second and third mixers for mixing the outputs of the first and second filters, respectively, with the output of a local oscillator.
Owner:SIRIUS XM RADIO INC
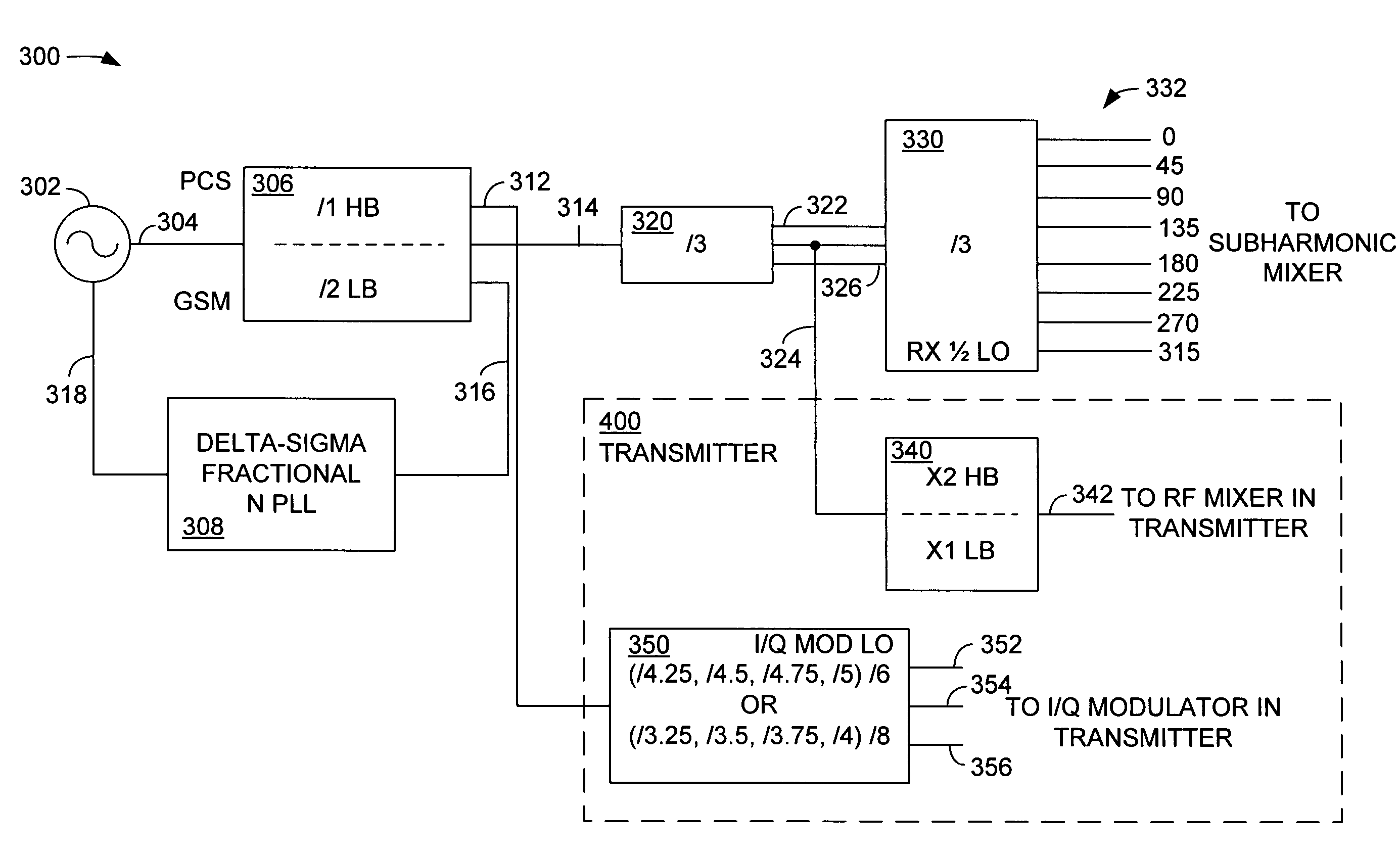
Single chip GSM/EDGE transceiver architecture with closed loop power control
InactiveUS7483678B2Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsClosed loopFrequency multiplier
Owner:INTEL CORP
CDMA frequency planning for fixed wireless application
InactiveUS6560459B1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency reuseCommunications system
The foregoing objects are achieved as is now described. A method for evaluating frequency plans for a CDMA based communication system having fixed base radio telephones is provided. The method begins by determining locations of a plurality of antennas. The plurality of antennas provide a coverage area for radio telephones. Then the method generates locations of radio telephones within the coverage area. Next, a distance from each radio telephone to the antennas is calculated. Then frequencies are allocated to the antennas. The resulting communication parameters between the radio telephones and the antennas are evaluated. Next, the coverage area which provides optimum power control to each radio telephone is determined. A frequency reuse factor is calculated to determine the efficiency of the allocated frequencies such that frequency allocation plans can be analyzed to determine efficient frequency planning.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
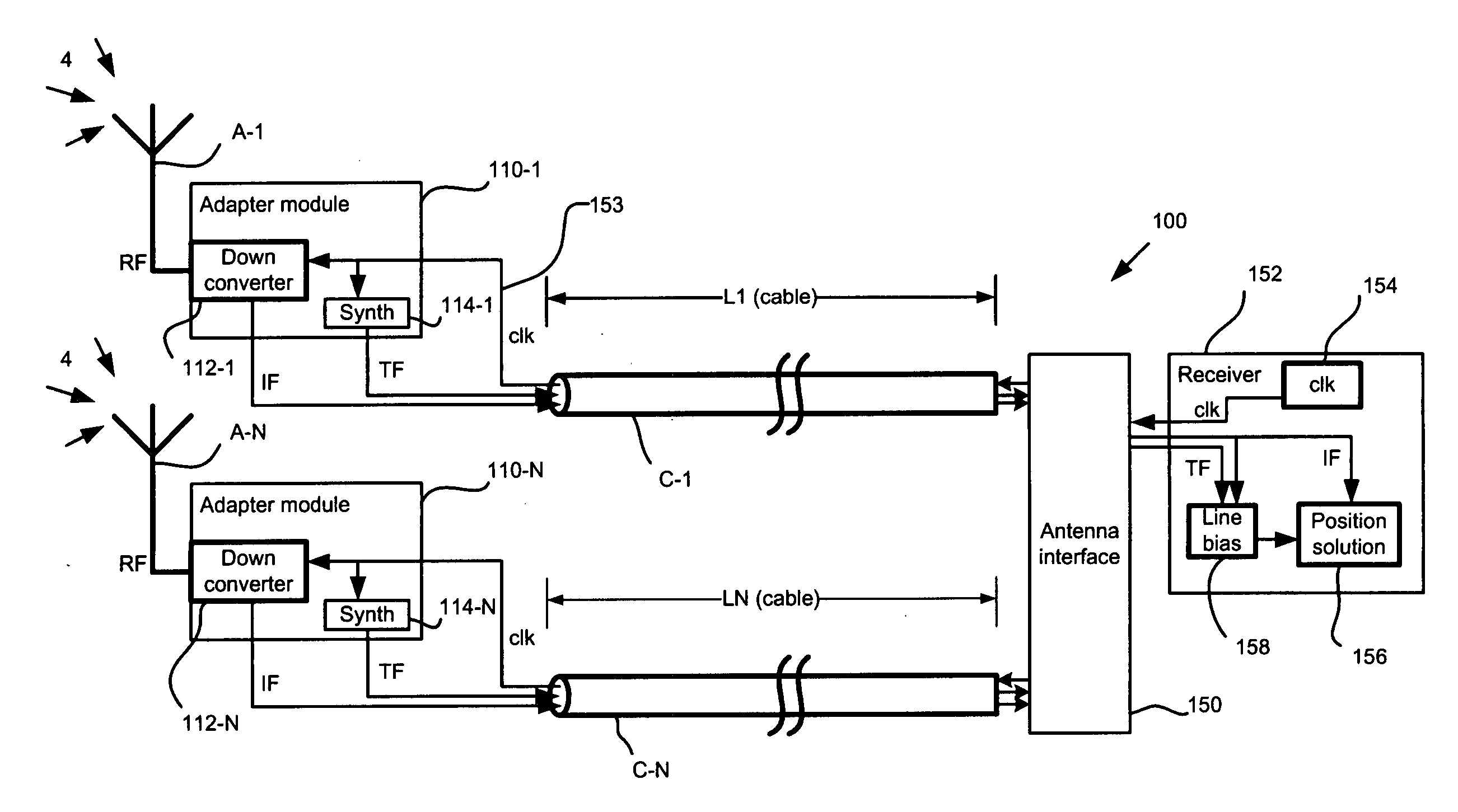
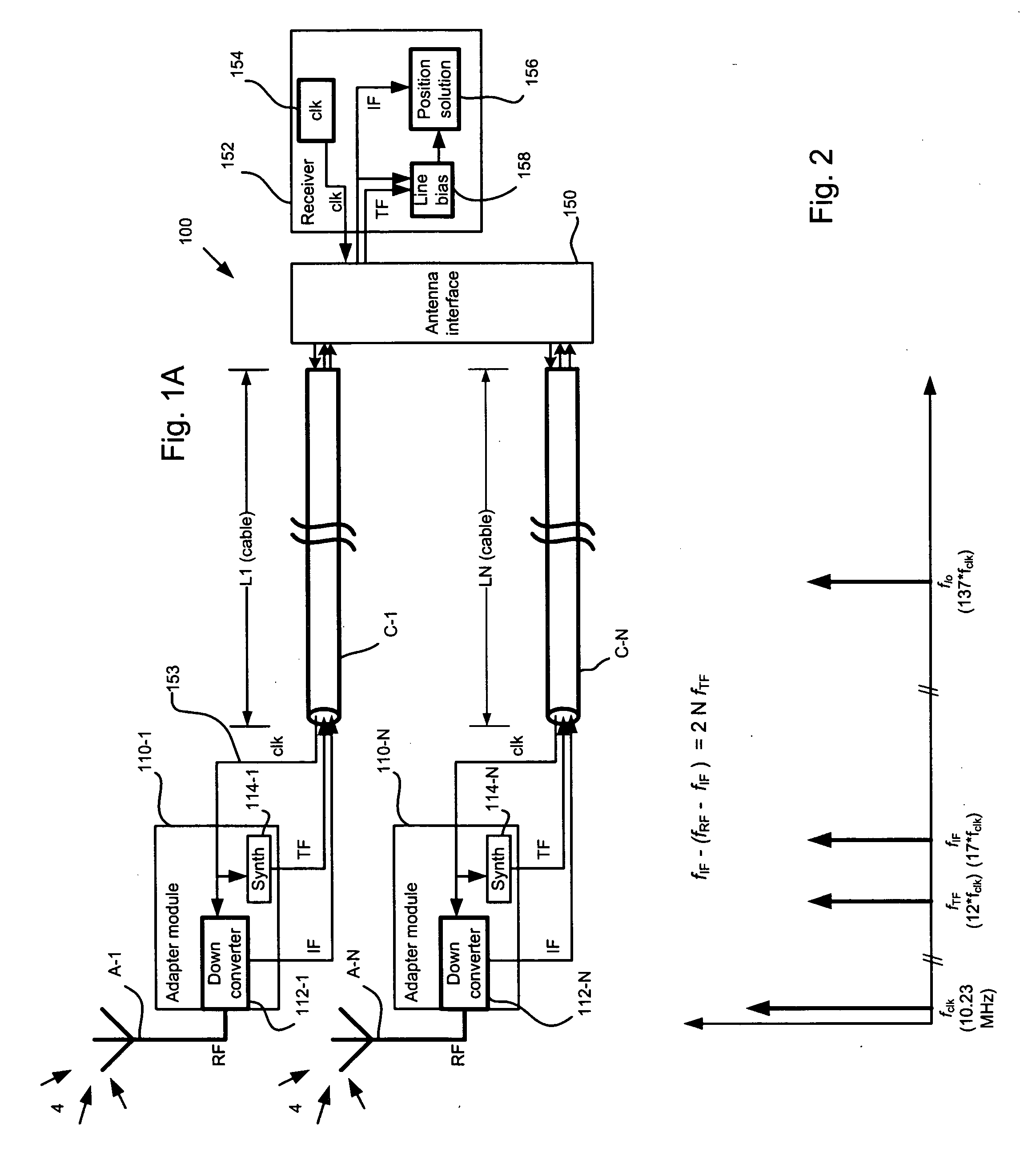
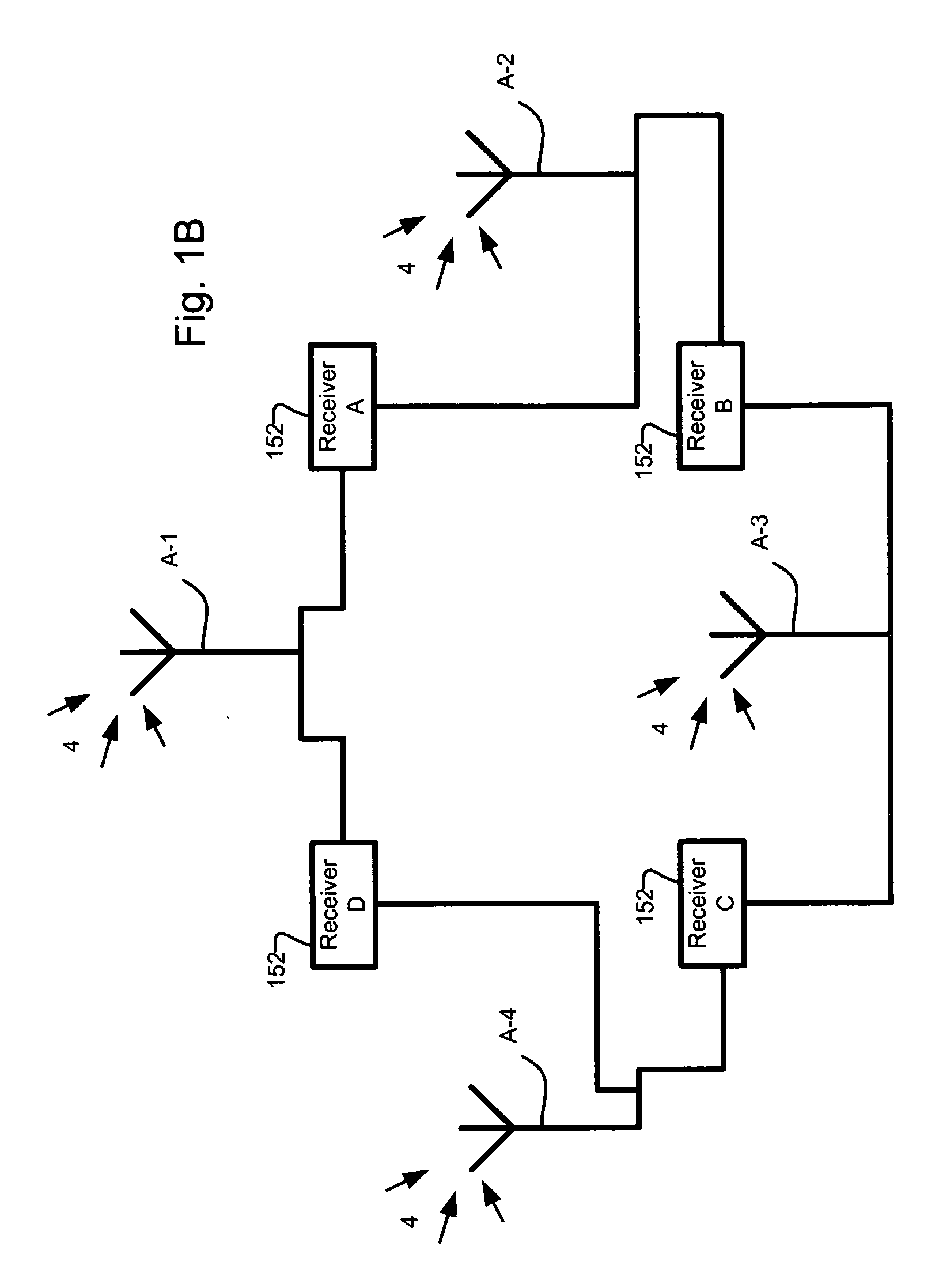
GNSS line bias measurement system and method
A number of solutions for deriving the line bias are disclosed. Some of these solutions utilize signal processing and judicious selection of the frequency plan used in the position detection systems to either enable the derivation of the line bias, or make the measurements insensitive to line bias. In other examples, the present invention utilizes measurement schemes for deriving the line bias and enabling a position detection system to process line bias information in order to find a position solution
Owner:NOVARIANT
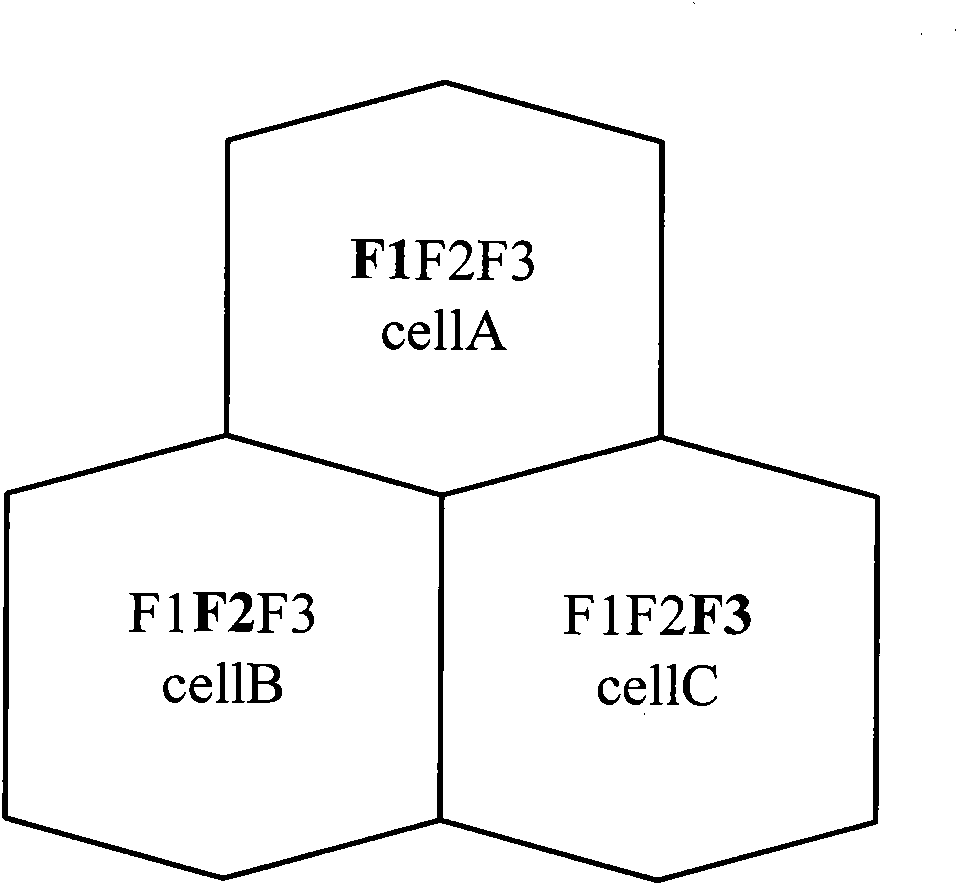
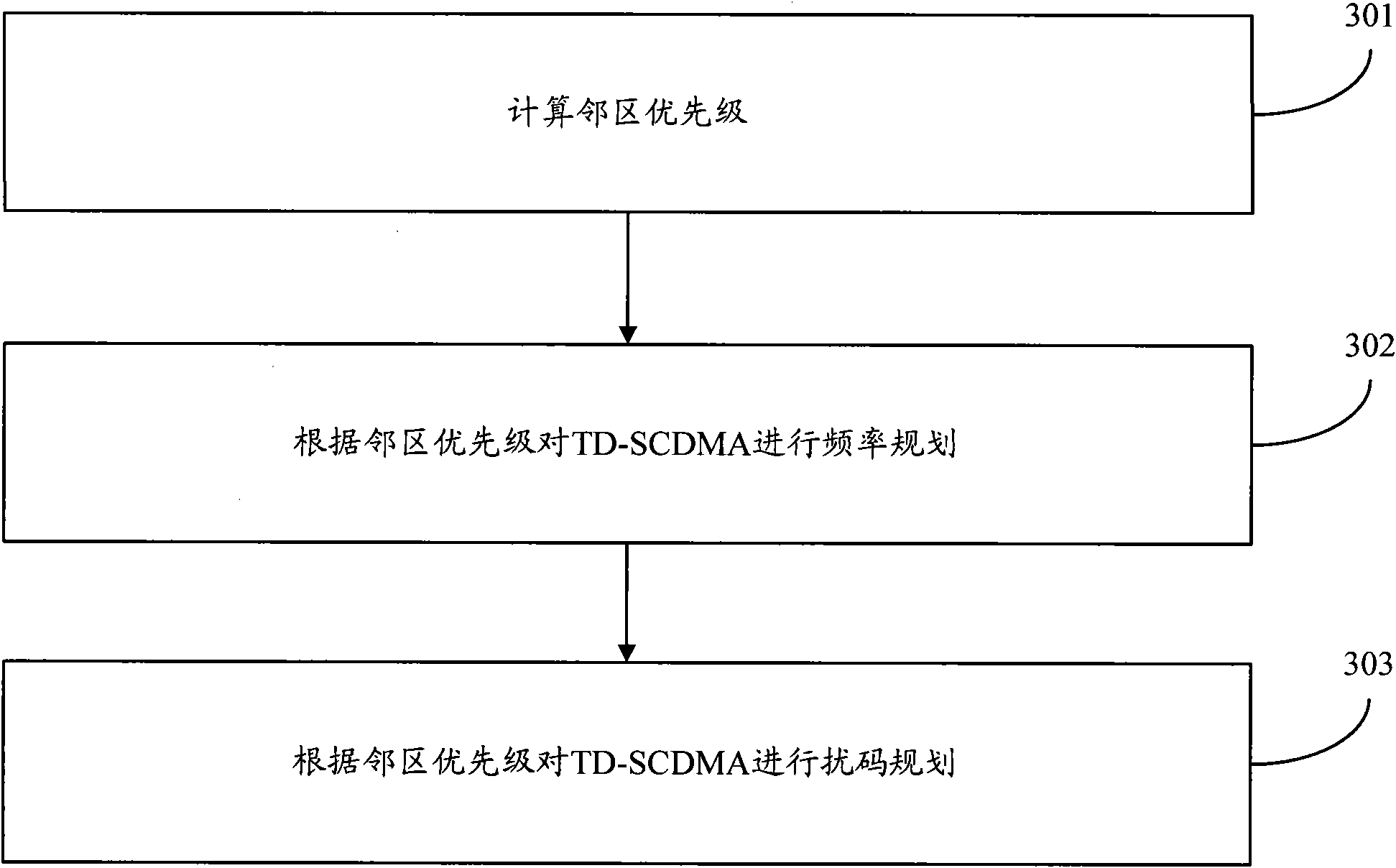
Frequency planning and scrambling code planning method and device based on adjacent zone priority level
ActiveCN102083075AMaximize utilizationImprove perceived qualityNetwork planningFactor baseResource utilization
The embodiment of the invention discloses a TD (time division) frequency planning and scrambling code planning method based on an adjacent zone priority level, comprising: an adjacent cell priority level is generated through a zone adjacent factor, a zone factor and a zone direction factor based on the base station zone attribute according to the system technical scheme; and a TD main carrier frequency is distributed according to the generated adjacent zone priority level to ensure the minimality of the frequency interferences among zones; and then, a system assigns base scrambling code blocks and scrambling codes according to the adjacent zone priority level and the frequency so as to ensure the average minimization of the mutual interference of the frequency scrambling code among zones. According to the embodiment of the invention, the calculation method of the adjacent zone priority level is more reasonable, and the setting and switching process of the adjacent zone relationship is more reasonable. Furthermore, co-frequency encounter phenomena among the adjacent zones are avoided by adopting the scheme, so that the mutual correlation of the scrambling codes among the adjacent zones is minimal, and the maximal frequency resource and scrambling code resource utilization and the minimum frequency and scrambling code interferences among zones are ensured. And the network performance indexes such as call completing rate are improved, and the client perception quality is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP JIANGSU
Single chip GSM/EDGE transceiver architecture with closed loop power control
InactiveUS20070072577A1Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsClosed loopFrequency multiplier
A single chip GSM / EDGE transceiver comprises a fully differential receive chain, a subharmonic mixer in the receive chain, the subharmonic mixer configured to receive a radio frequency (RF) input signal and a local oscillator (LO) signal that is phase-shifted by a nominal 45 degrees, and a synthesizer having a voltage controlled oscillator and having at least one frequency divider to generate desired transmit and receive LO signals. The transceiver also comprises a transmitter having a closed power control loop, and a harmonic rejection modulator, the use thereof made possible by a frequency plan designed to allow the synthesizer to develop the transmit and receive LO signals without a frequency multiplier.
Owner:INTEL CORP
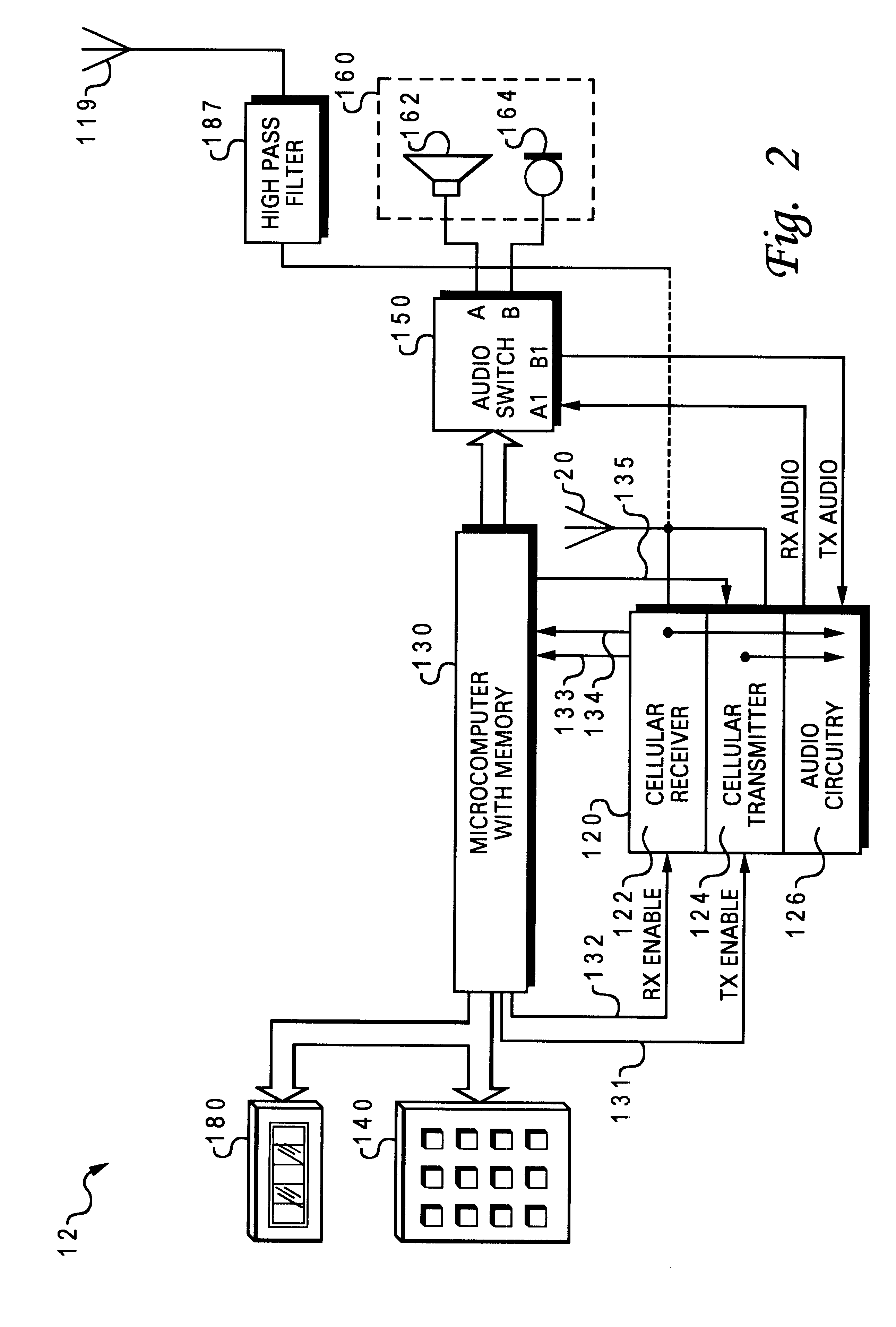
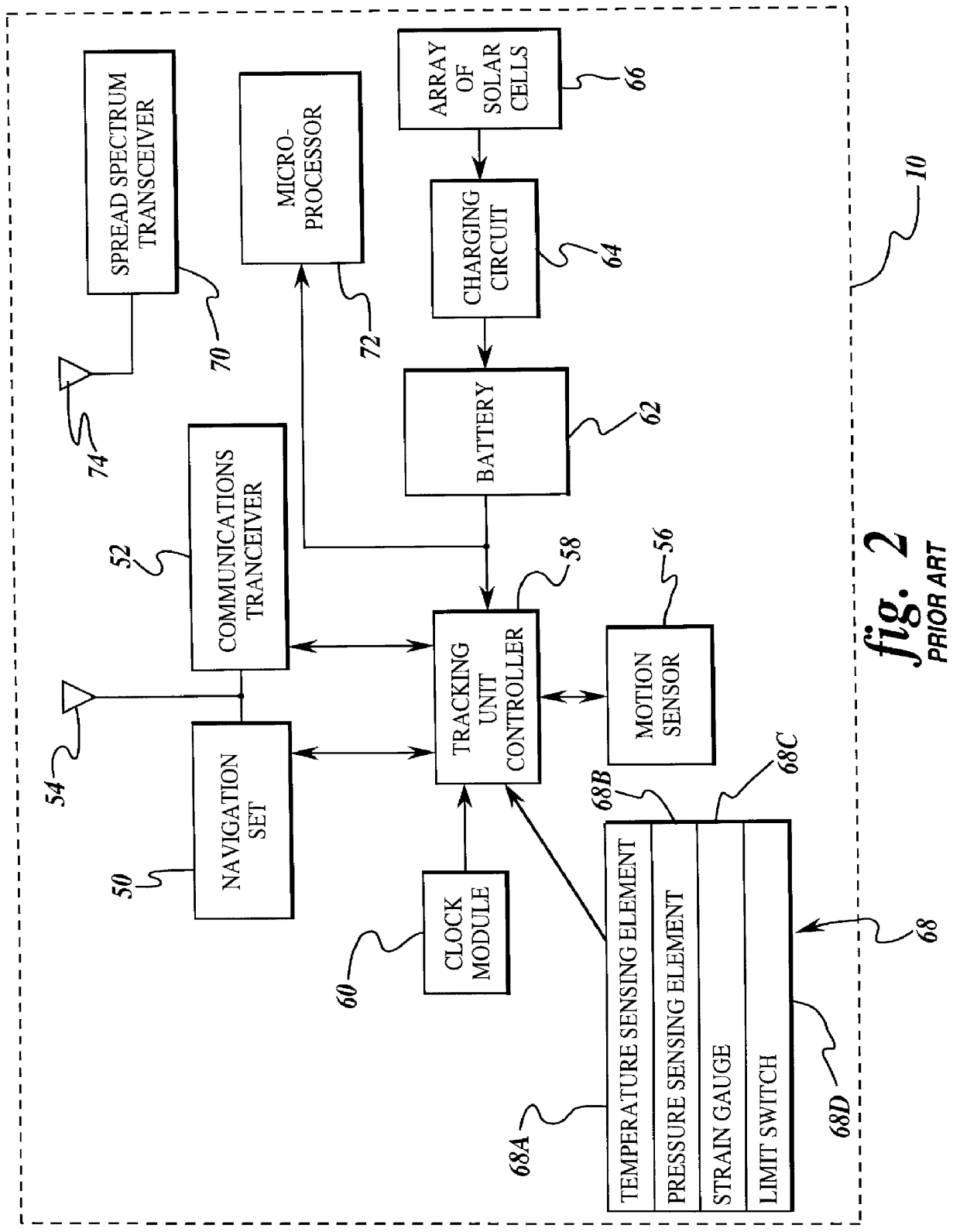
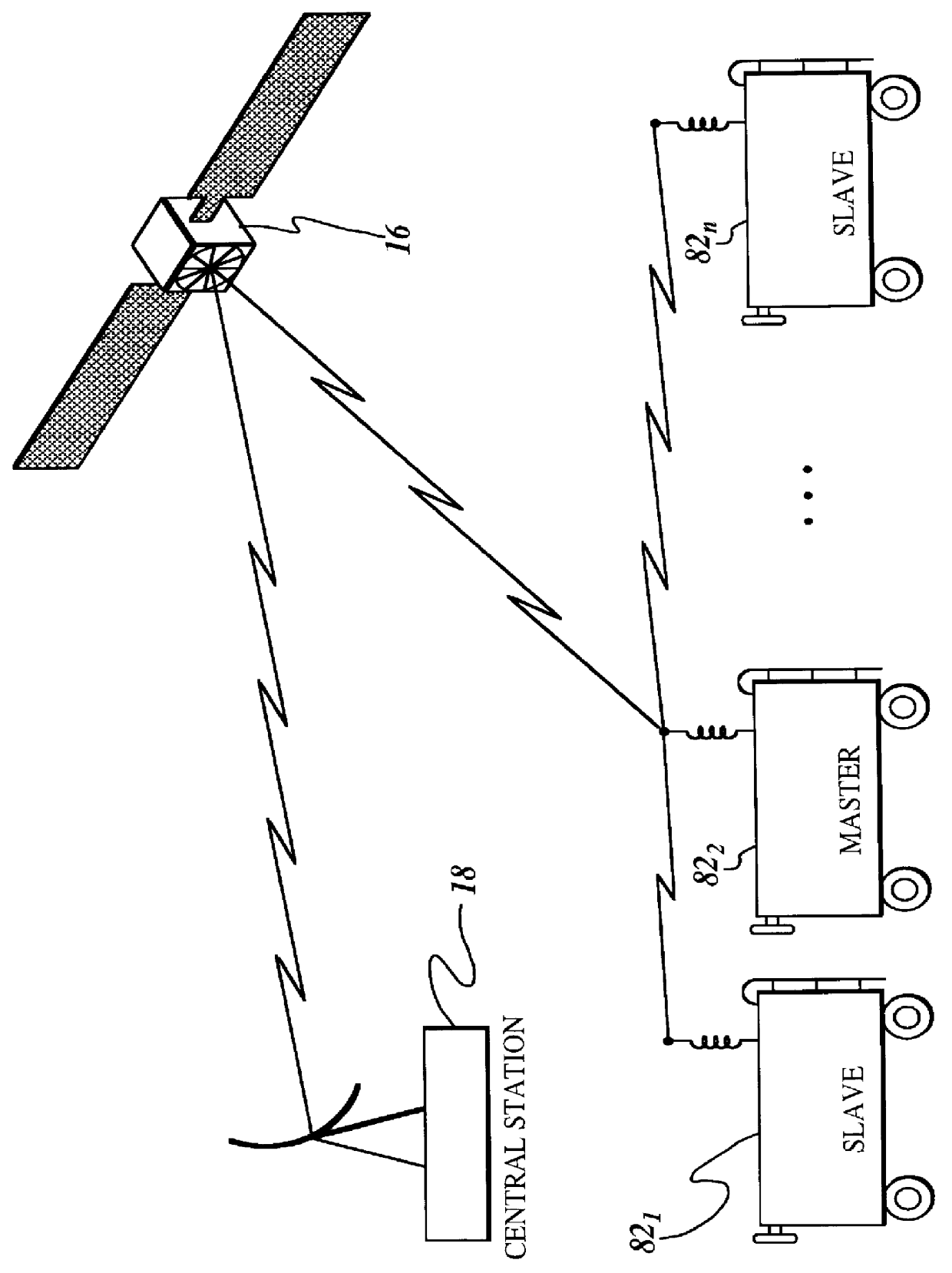
Inbound messaging transmission device and system for railcar asset tracking using high frequency signaling
InactiveUS6108524ASpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityTransmission protocolDiversity scheme
An asymmetrical (inbound only) high frequency communication system for asset tracking is made up of a message preparation and transmitter subsystem, a receiving subsystem, and a system monitoring subsystem. A transmission channel is selected randomly or pseudorandomly. Prior to each transmission, the transmitter performs a radiometric measurement of a selected channel. If the measurement exceeds a predetermined threshold, transmission in the selected channel is canceled and another channel is selected. The transmission protocol achieves frequency diversity by sequentially transmitting a message on a plurality of different channels. The receiving subsystem has a plurality of spatially separated receiver sites at various geographical points, thereby providing spatial diversity. The receiver sites are linked to a common processing center. Onboard the asset and collocated with the transmitter, a system monitoring subsystem records and stores parameters related to the message preparation and transmitter subsystem. These parameters are useful in assessing efficacy of transmission frequency planning algorithms and the transmission protocol.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
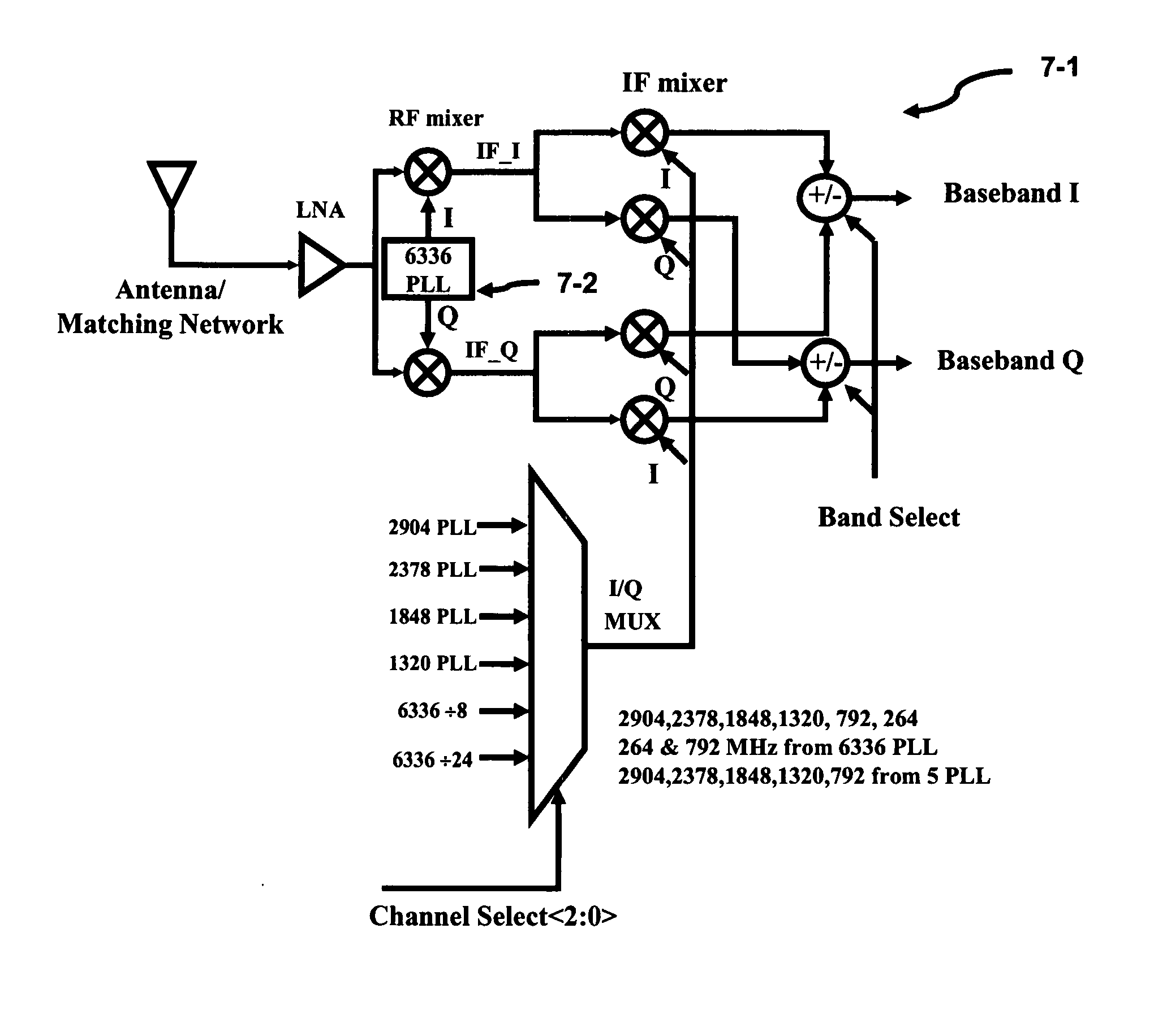
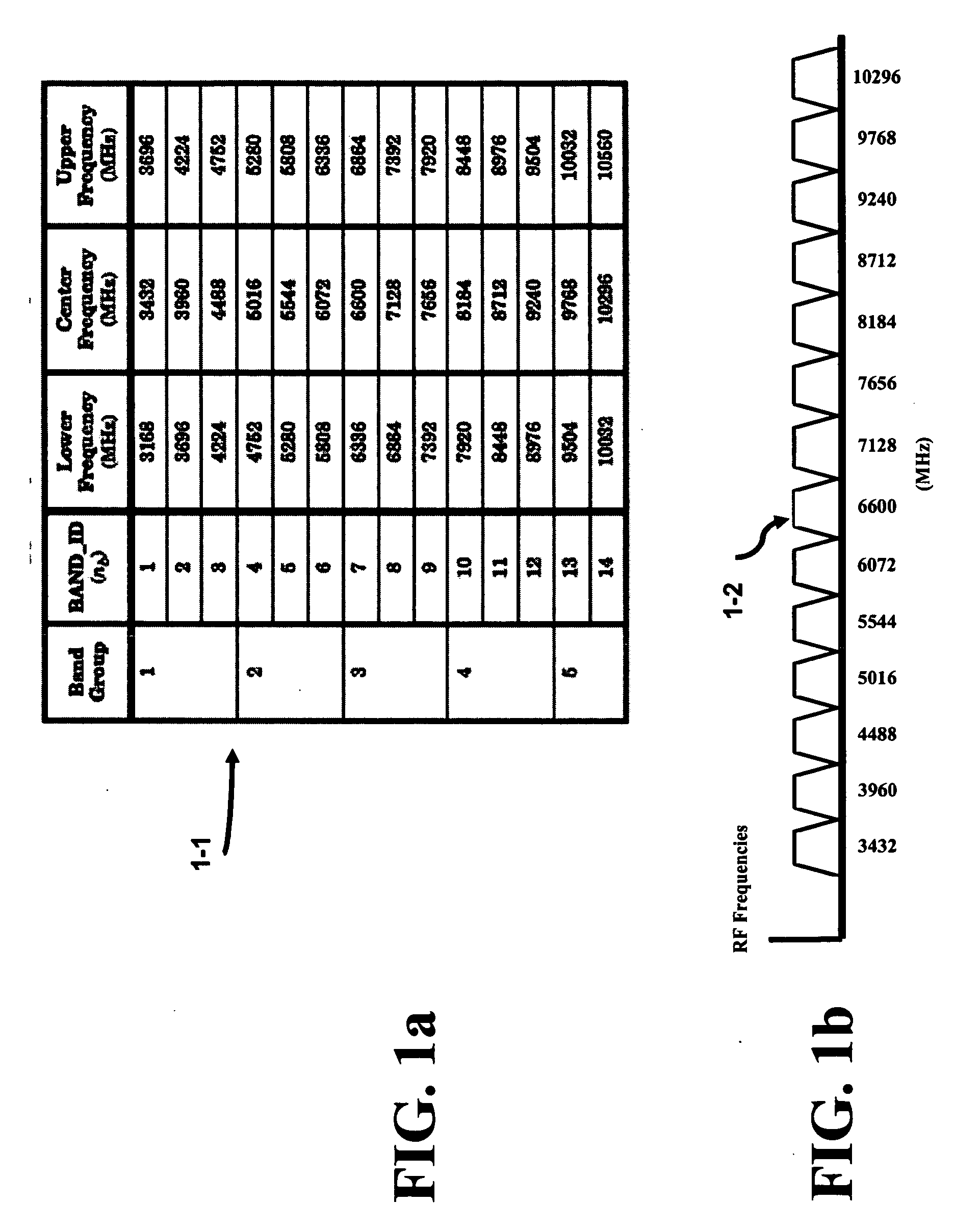
Method of frequency planning in an ultra wide band system
InactiveUS20070155350A1Simple technologyReduce in quantityAutomatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayModulation transferenceOperational systemOperating frequency
The present invention provides reduces the number of required synthesizers thereby reducing the area and power concerns to extract / insert a signal from / to a multi-channel communication system and is also known as frequency planning. The highest frequency of operation required for the synthesizers or oscillators is approximately the midpoint of the entire signal frequency range. Two superimposed Weaver architectures are used to form the architecture. The receiver extracts the baseband I and Q signals from the multi-channel communication system, while the transmitter upconverts the baseband I and Q signals to the multi-channel communication system. The Weaver architecture, depending on the select bit, can enhance the image signal and reduce the desired signal or the image signal can be reduced while the desired signal is enhanced. Because the image and signal components are symmetrically displaced from the RF LO, less IF LO frequencies or synthesizers are required to operate the system.
Owner:WINONICS RES
Frequency allocation in a radio system
InactiveUS20060105778A1Better utilisedRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationRadio channelFrequency plan
In a method of selecting a radio channel from a plurality of radio channels comprised in a frequency plan and assigning the selected radio channel to a mobile radio station in consideration of the current geographic location of the mobile radio station which is provided with memory means storing data representative of the frequency plan and of geographic locations in association with one another, the mobile radio station determines its current geographic location and dependent on its current geographic location bars the data of predetermined radio channels from the plurality of radio channels from being selected for use by the mobile radio station, and said mobile radio station selects one of the other radio channels the data of which are not barred within the memory and assigns same for use to at least itself.
Owner:WIEDERSPAHN FELIX
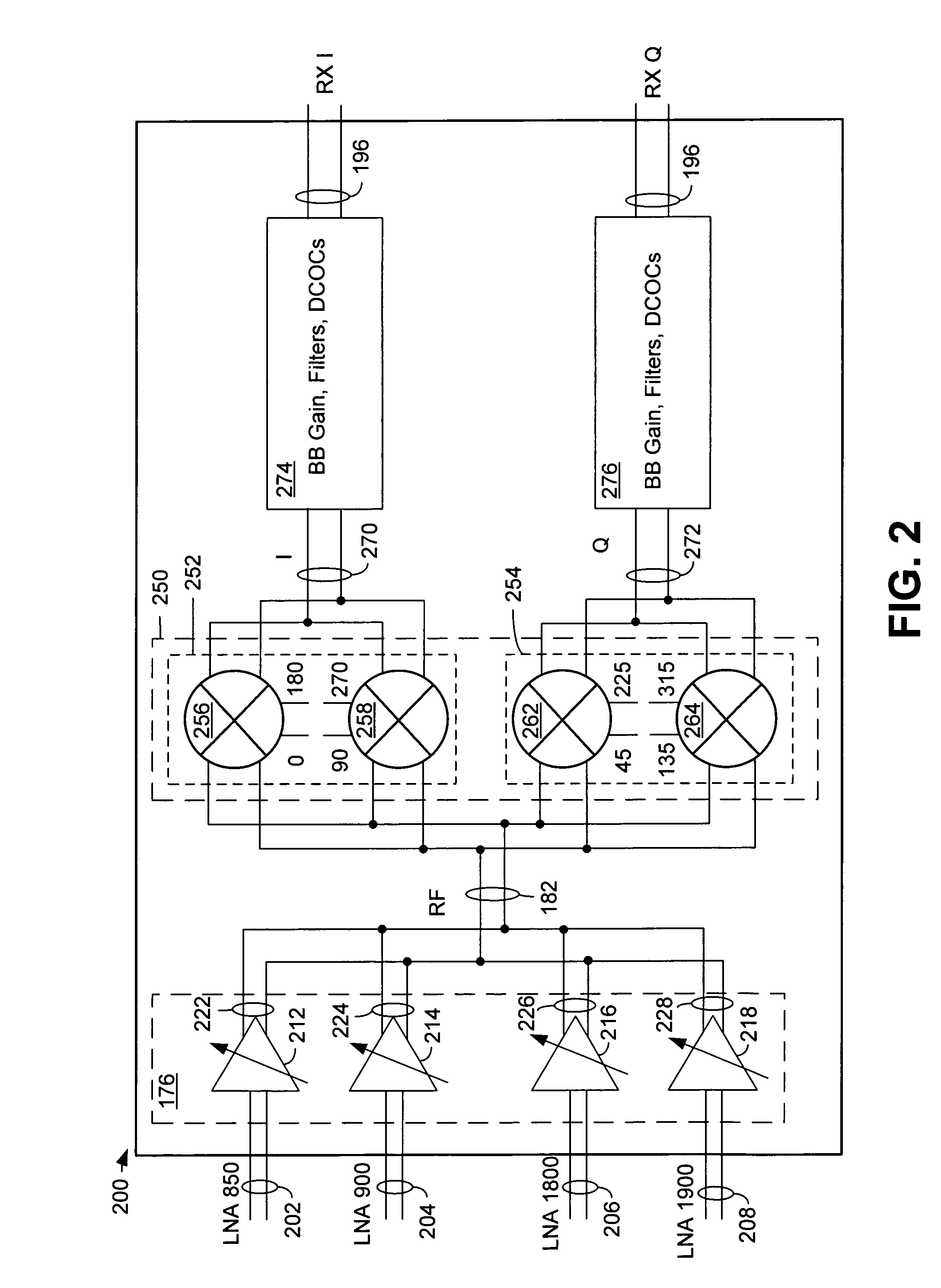
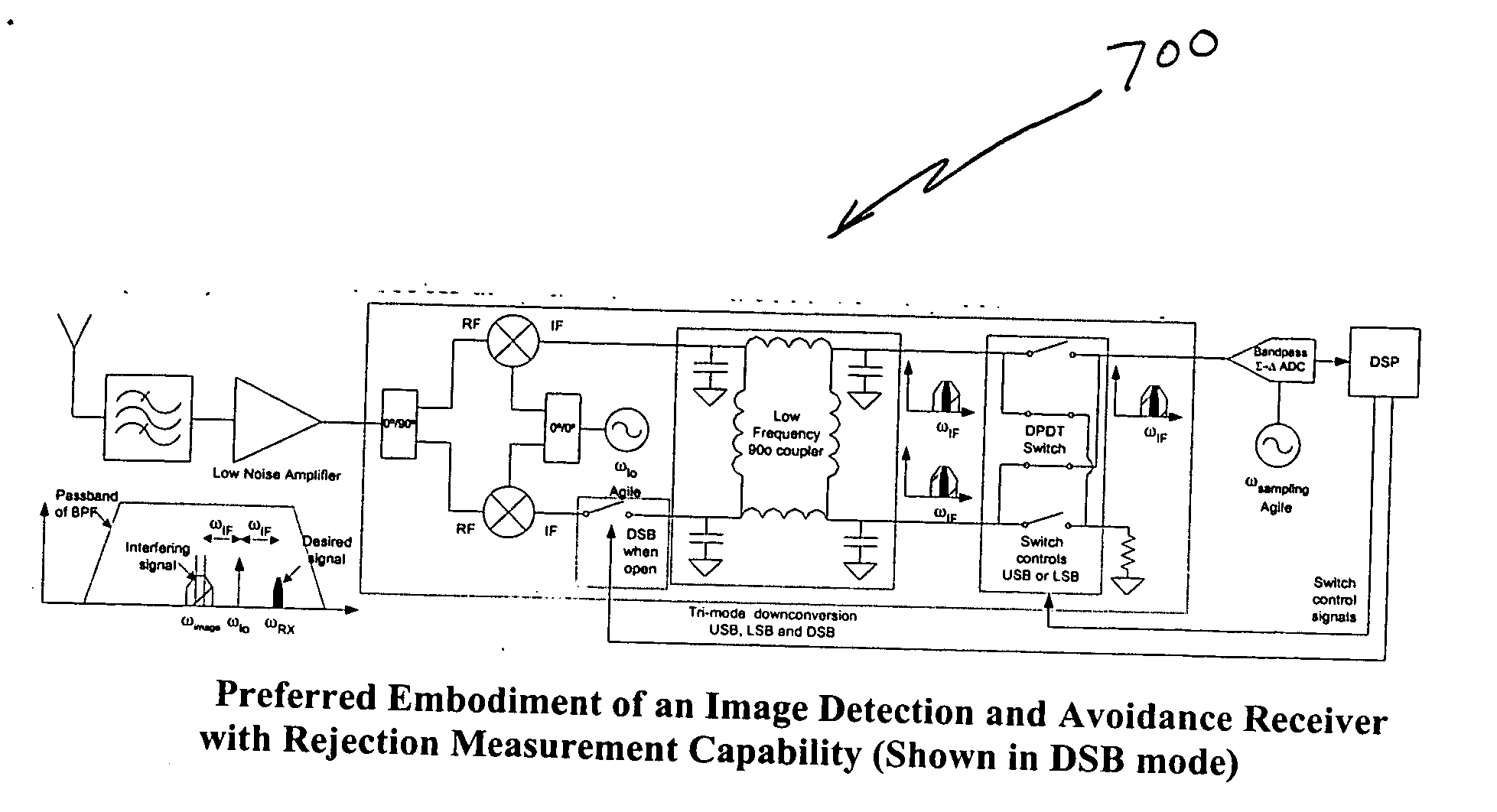
Very low intermediate frequency image rejection receiver with image interference detection and avoidance
InactiveUS20050143038A1Minimize powerReduce image noiseTransmissionFrequency mixerIntermediate frequency
A method and apparatus for minimizing image interference using a very low intermediate frequency image rejection receiver is disclosed. Image interference detection and avoidance by frequency plan adjustment within the very low intermediate frequency receiver image rejection receiver minimizes rejection requirements for an image reject mixer. Image rejection can be measured by switching between in-phase and out-of-phase image reject mixer output ports. Rejection may also be measured by creating a tri-mode image reject mixer. A set of linear equations allows rejection to be measured without requiring control of input signals and additional mixers.
Owner:2201028 ONTARIO
Base station and a method of operation therefor
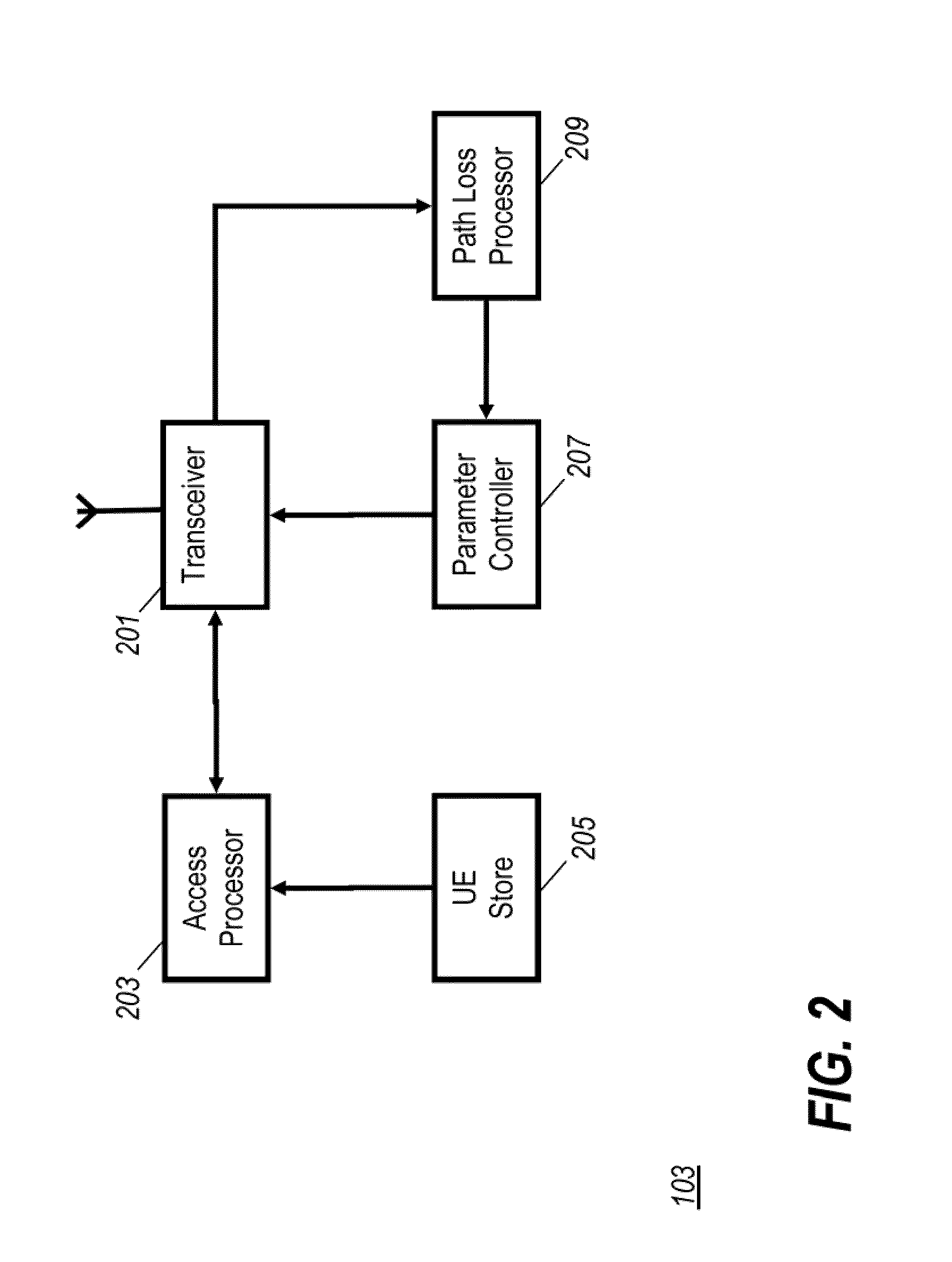
ActiveUS20100197306A1Improve performanceEasy to operateAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCellular communication systemsFrequency plan
A base station (103) for a cellular communication system comprises a user equipment store (205) which provides a user equipment subset which identifies at least one user equipment (107) associated with the base station. An access processor (203) restricts access to the base station (103) to the user equipments (107) that belong to the user equipment subset. A path loss processor (209) determines a path loss estimate indication from at least one neighbouring base station (101) to a cell supported by the base station (103). A parameter controller sets an operating parameter for the cell (105) in response to the path loss estimate indication. The invention may allow facilitated or improved introduction and / or configuration of restricted base stations supporting only specific user equipments. In many scenarios, a restricted base station may be configured depending on a path loss estimate such that improved performance may be achieved without any frequency planning for the base station.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
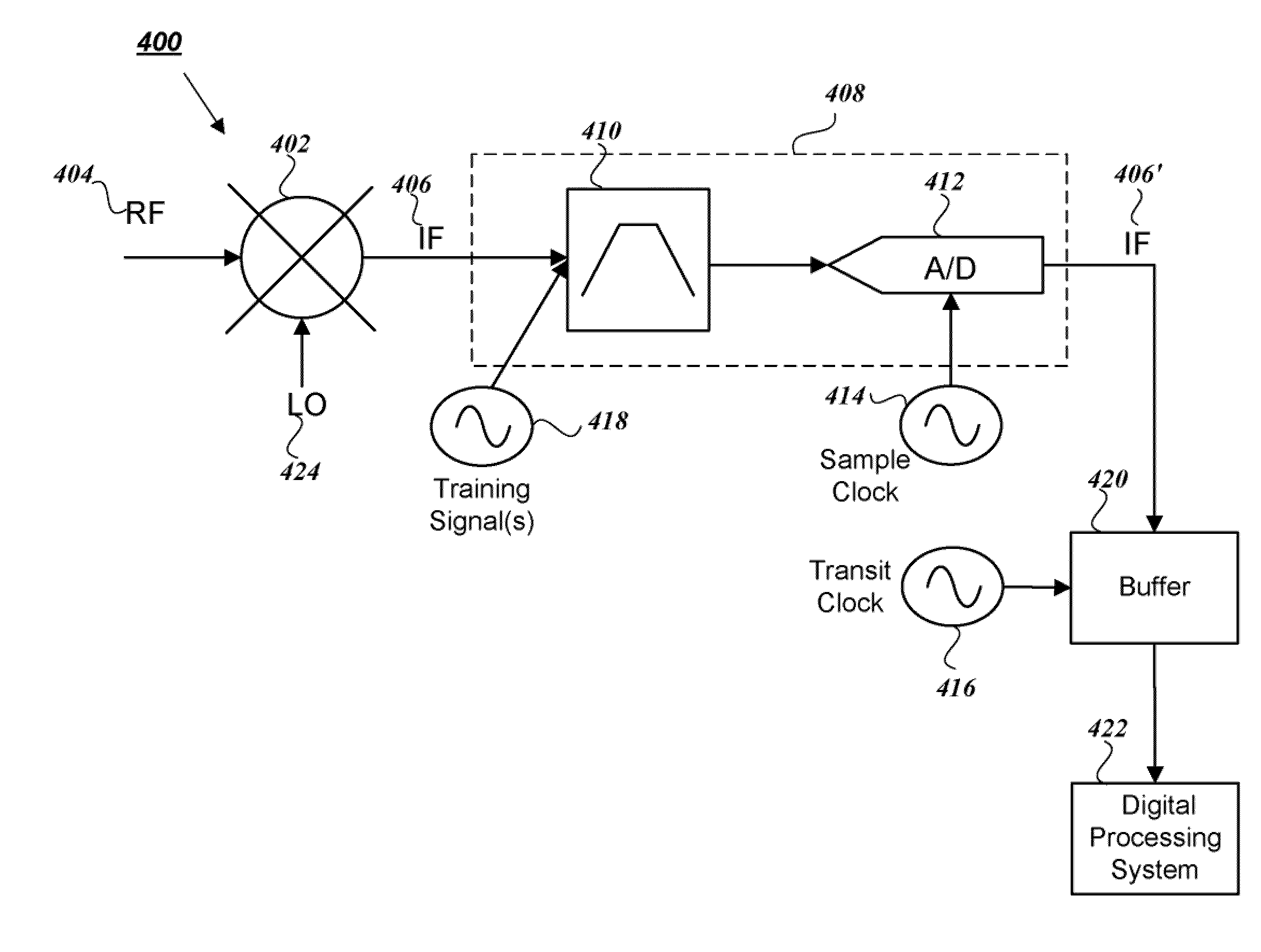
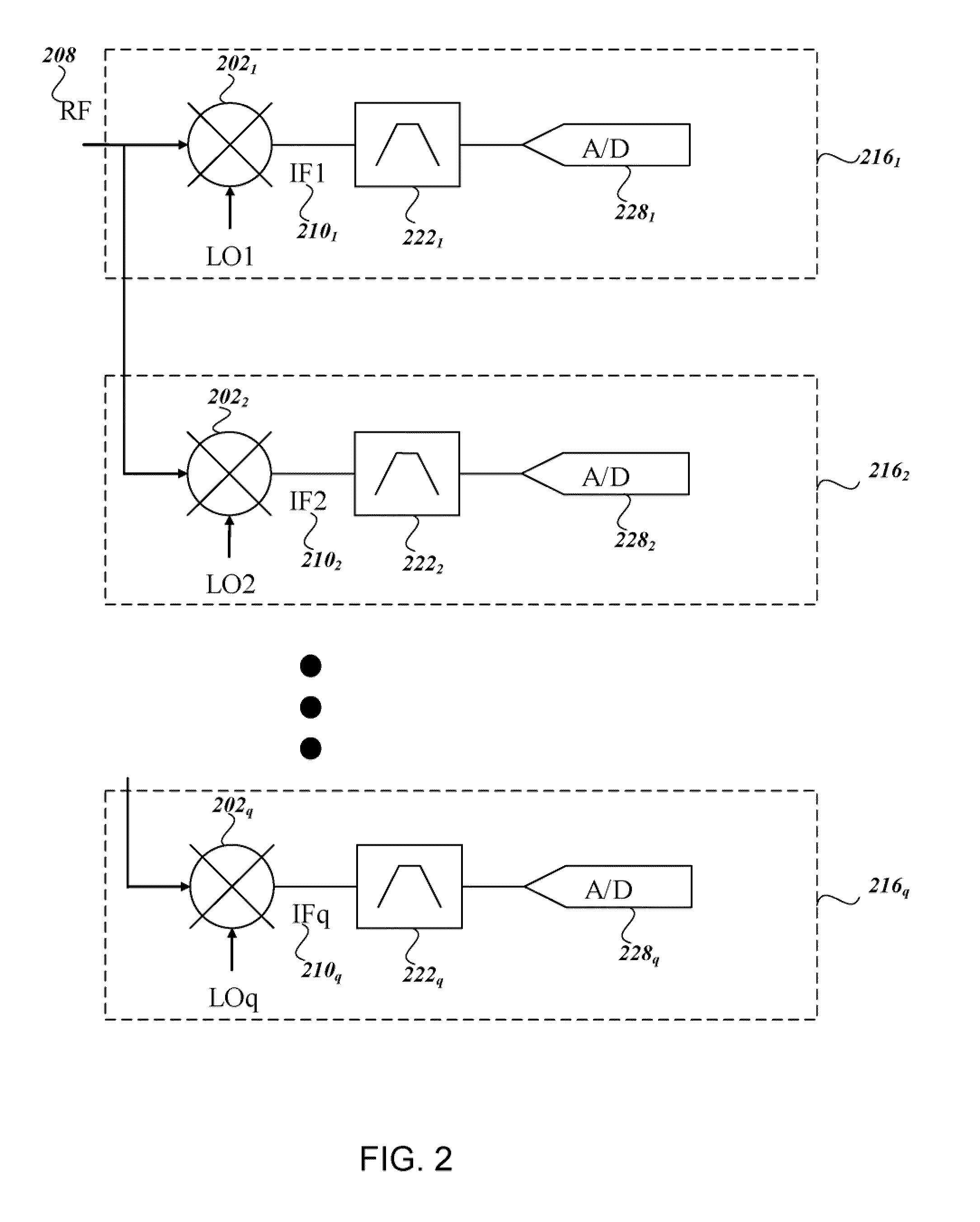
Dynamic spur avoidance for high speed receivers
ActiveUS8185078B2Minimal penalty to measurement speedInhibitory responseSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionIntermediate frequencyLocal oscillator
A system and method for implementing dynamic spur avoidance in a high speed receiver environment is provided. For a plurality of radio frequency (RF) input signal ranges, a range of intermediate frequency (IF) signals and a noise floor for each IF signal is determined. An identification of spurs that will affect the noise floor is also determined from a look up table for each range of the RF inputs. A frequency plan that sets local oscillator and constituent oscillator signals is selected such that the IF signals generated from the RF input will avoid lower order spurious responses of the identified spurs within the IF signal range.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
Dynamic spur avoidance for high speed receivers
ActiveUS20110098014A1Speed maximizationEliminate spurious responseSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionIntermediate frequencyLocal oscillator
A system and method for implementing dynamic spur avoidance in a high speed receiver environment is provided. For a plurality of radio frequency (RF) input signal ranges, a range of intermediate frequency (IF) signals and a noise floor for each IF signal is determined. An identification of spurs that will affect the noise floor is also determined from a look up table for each range of the RF inputs. A frequency plan that sets local oscillator and constituent oscillator signals is selected such that the IF signals generated from the RF input will avoid lower order spurious responses of the identified spurs within the IF signal range.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
Apparatus and Method for Frequency Planning for a Cellular Communication System
InactiveUS20080207210A1Improved frequency planningHigh frequencyRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningCommunications systemCarrier signal
The invention relates to frequency planning in a cellular communication system, such as a GSM cellular communication system. An apparatus for frequency planning comprises an interference matrix processor (201) which generates an interference matrix comprising interference relationships between different cells. For example, carrier to interference or interference penalty values for cell pairs can be determined. An interference matrix limiter (203) limits the number of interference relationships to a first number, N, of highest interference relationships for each cell. The first number N can be determined in response to the re-use pattern and number of frequencies available for the frequency plan. A frequency plan processor (205) then proceeds to perform a frequency planning using the interference matrix.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
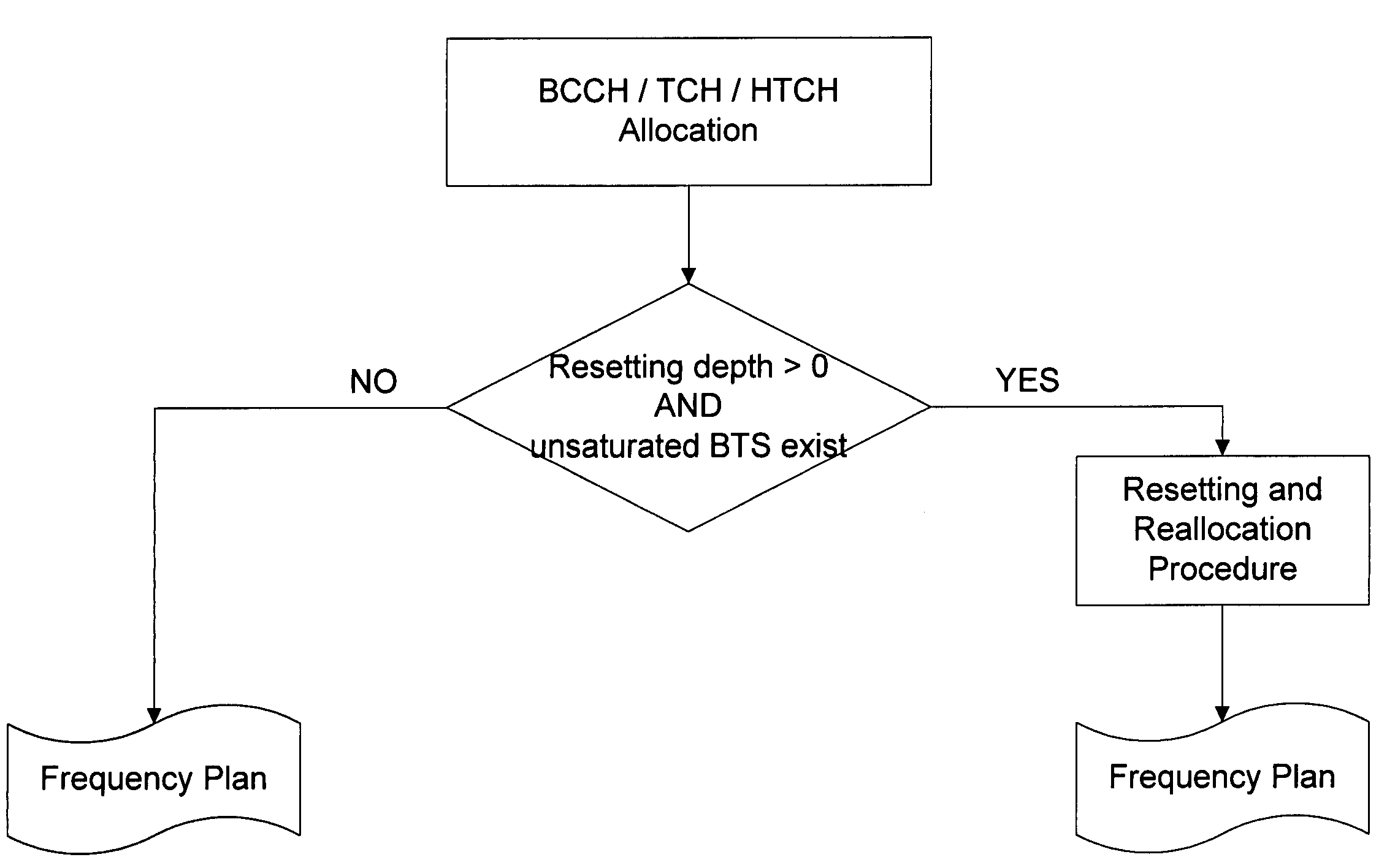
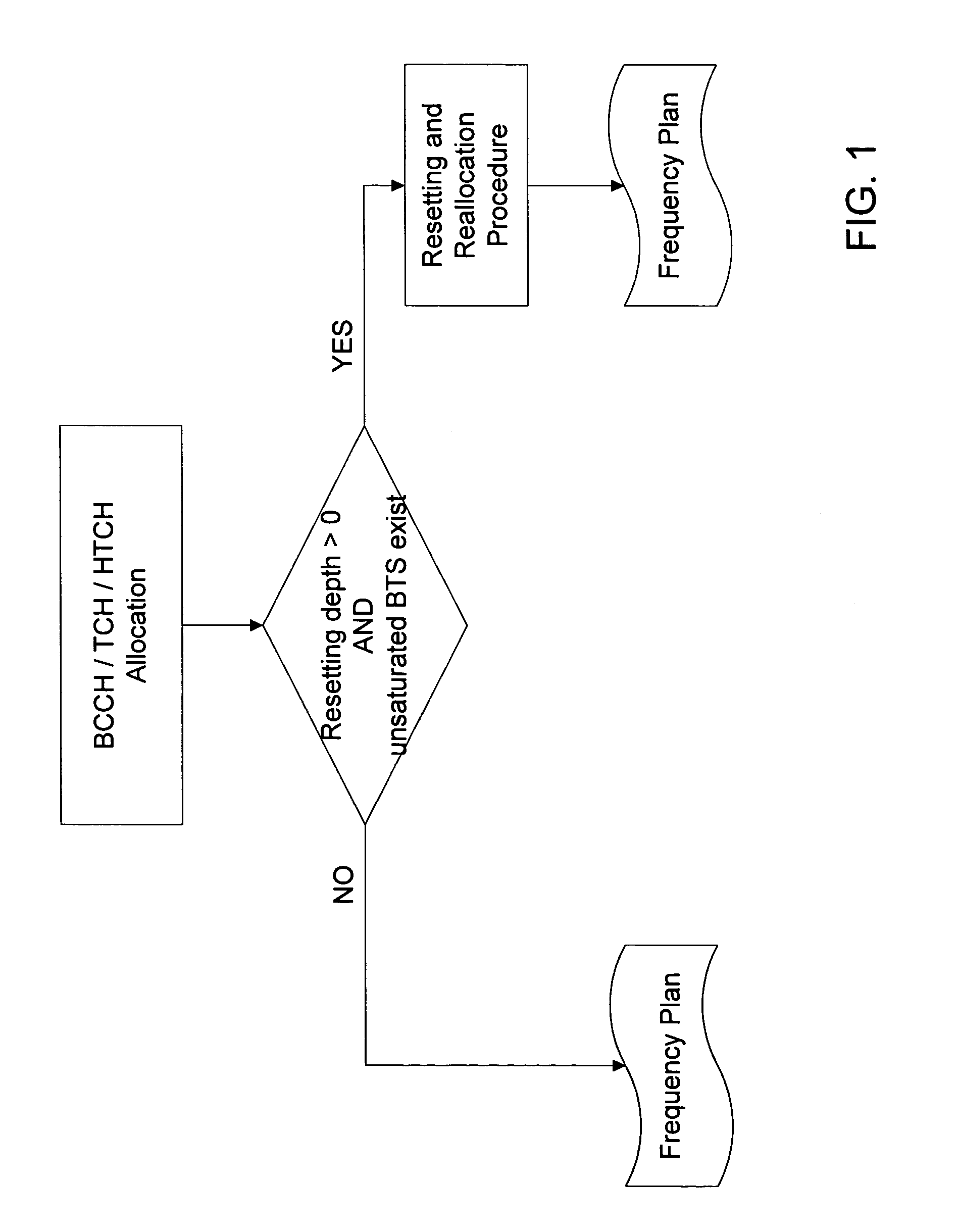
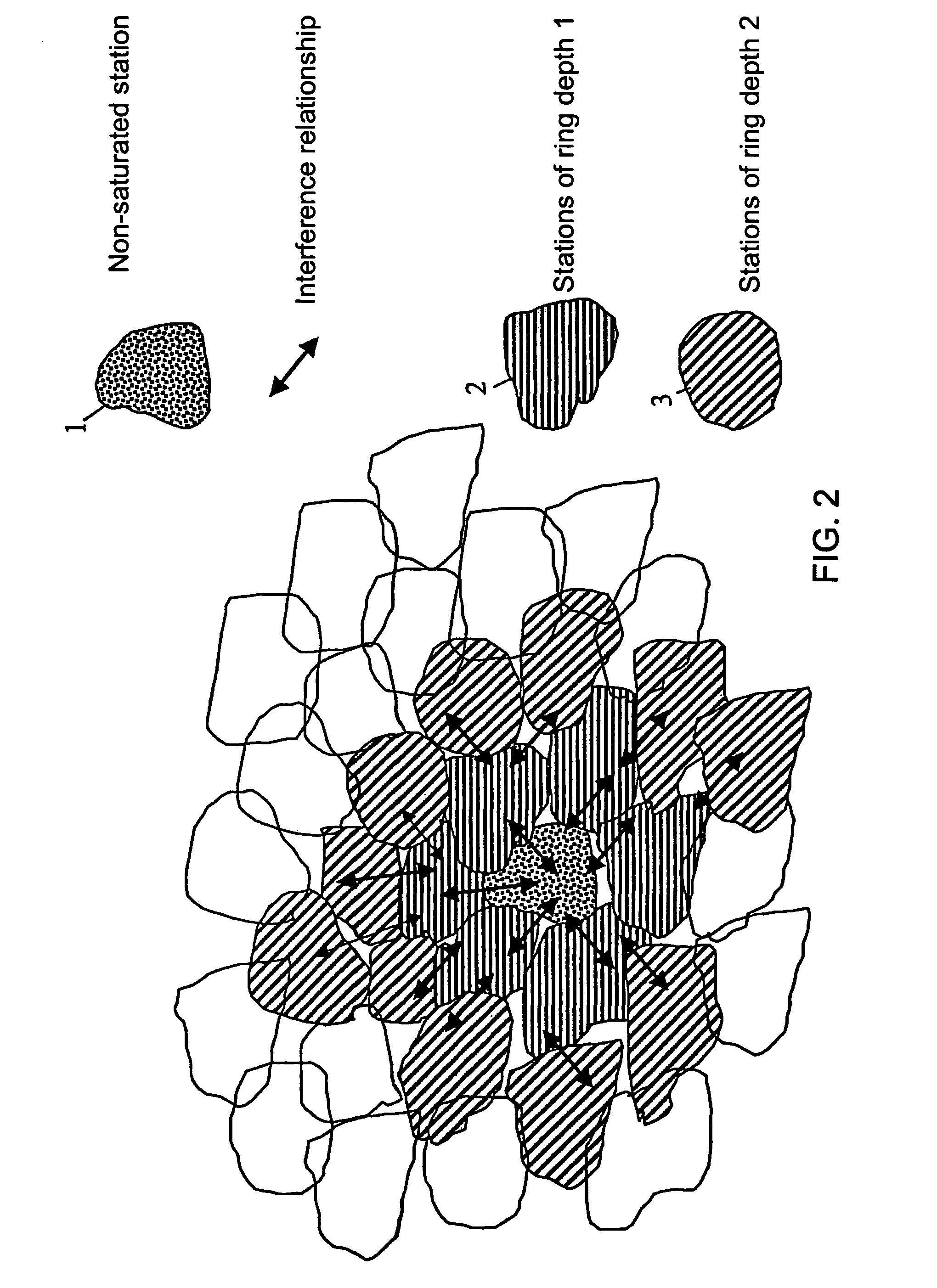
Method for assigning frequencies to base stations of a mobile telephone network
InactiveUS7133680B2Simple taskEliminate needNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelephone networkFrequency plan
The invention relates to a method for allocating frequencies to base stations in a mobile telephone network, especially a method for automatically resetting frequencies already allocated in the case of non-saturated base stations and re-allocating frequencies to said base stations. Firstly, frequencies are allocated to base stations using any known prior art method. In the case where no non-saturated base station is present, a complete frequency plan is obtained. However, if some base stations are not saturated, the inventive method is carried out: the current frequency allocation is reset and a new frequency allocation is carried out automatically. A parameter, the resetting extent parameter, is used to determine to which extent the resetting method is implemented.
Owner:T-MOBILE DEUTSCHLAND
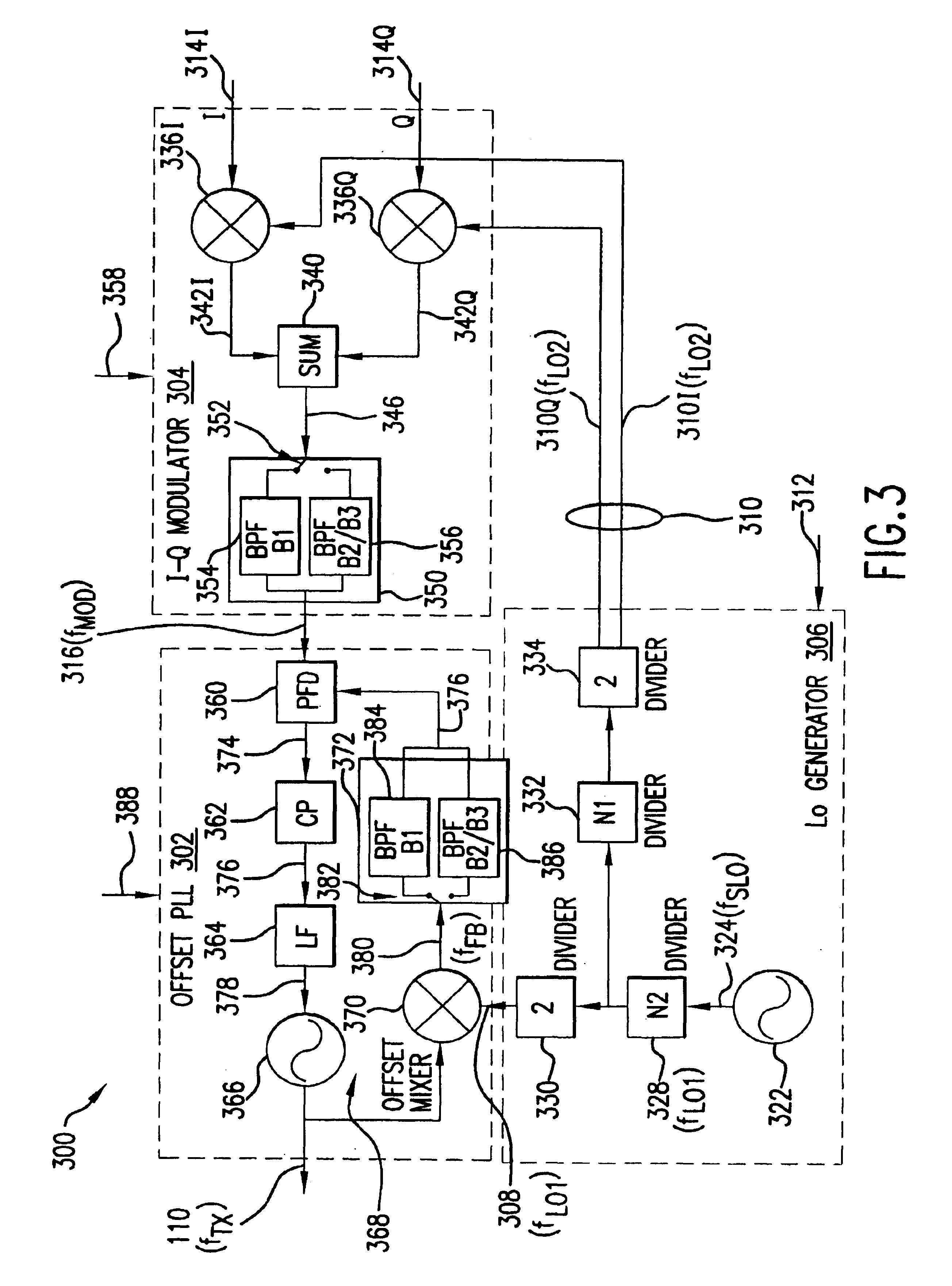
Transmitter method, apparatus, and frequency plan for minimizing spurious energy
InactiveUS6868261B2High frequencySmall sizeRadio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionLocal oscillatorEngineering
A translational-loop transmitter includes a local oscillator (LO) generator for generating first and second LO signals, a modulator for generating a modulated reference signal using the second LO signal, and an offset phase-locked-loop (PLL) for phase-locking an output signal to the reference signal, and for tuning the output signal in accordance with the first LO signal. The PLL includes an offset mixer in a feedback path of the PLL, and operates in accordance with a frequency plan that minimizes the effects of on- and off-channel spurs at the output of the offset mixer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
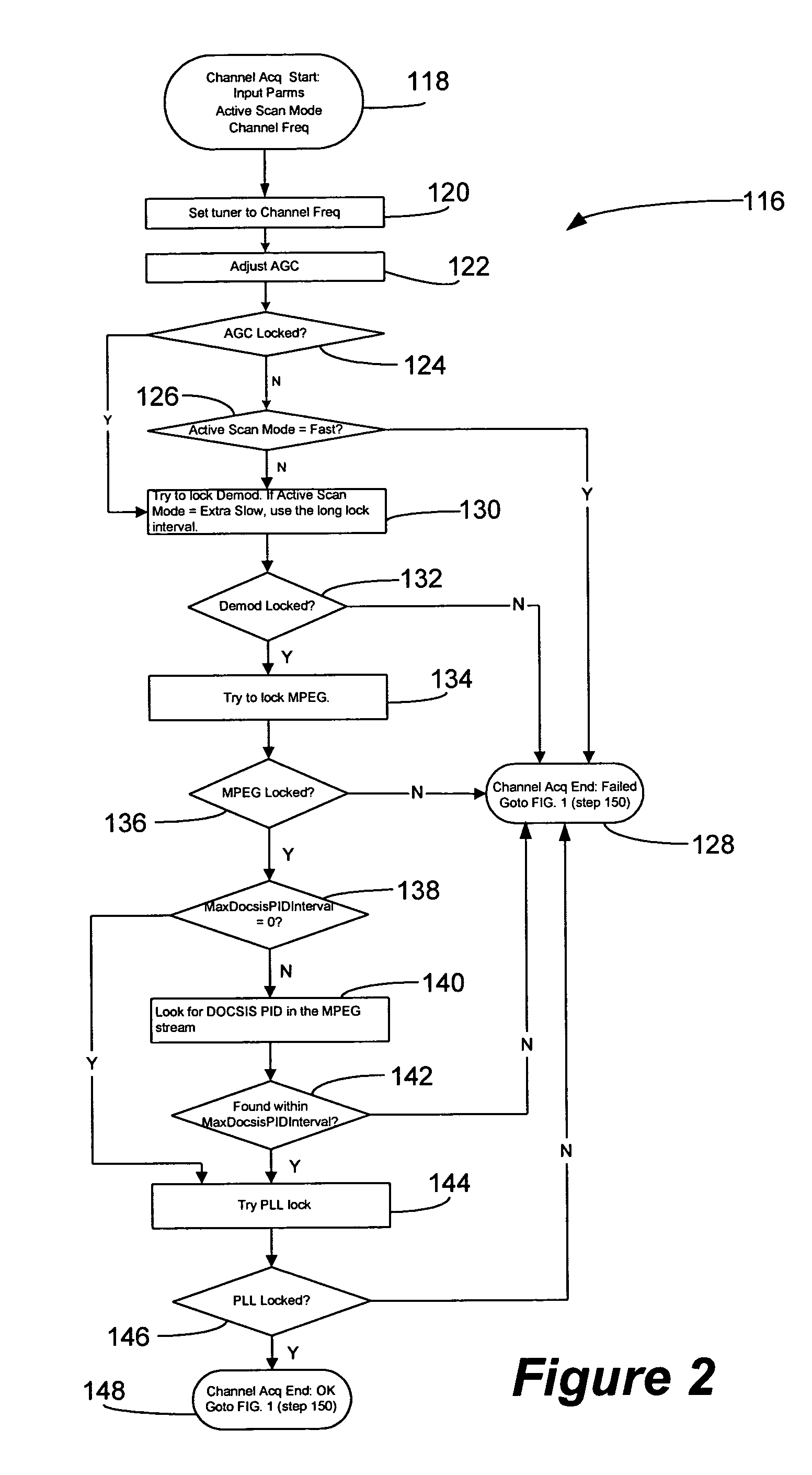
Fast channel scanning and acquisition system and method for cable modem applications
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Method, device and system for performing frequency planning in wireless Mesh returning network
InactiveCN101626575AEasy loadingReduce complexityRadio transmission for post communicationNetwork planningType frequencyFrequency spectrum
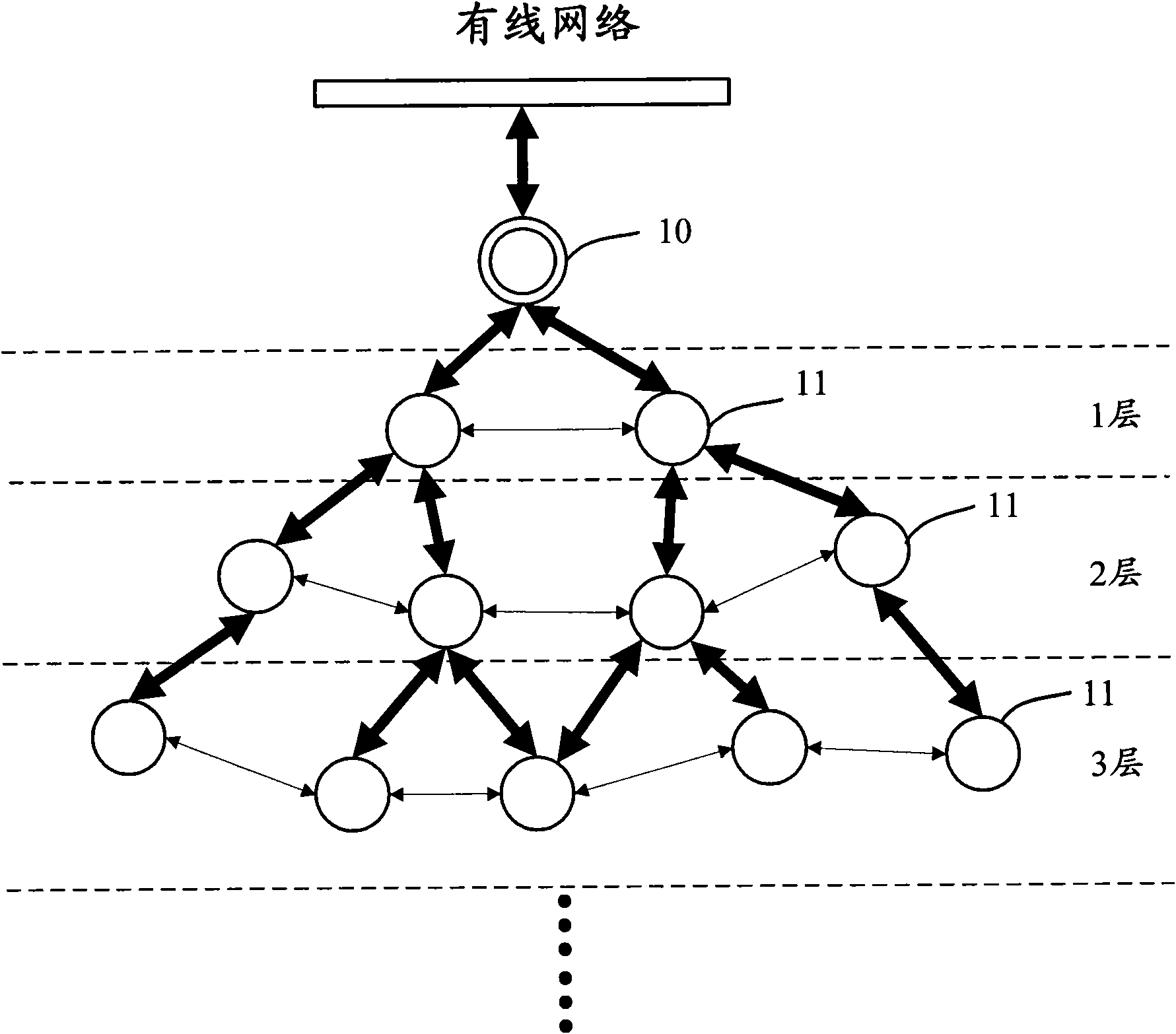
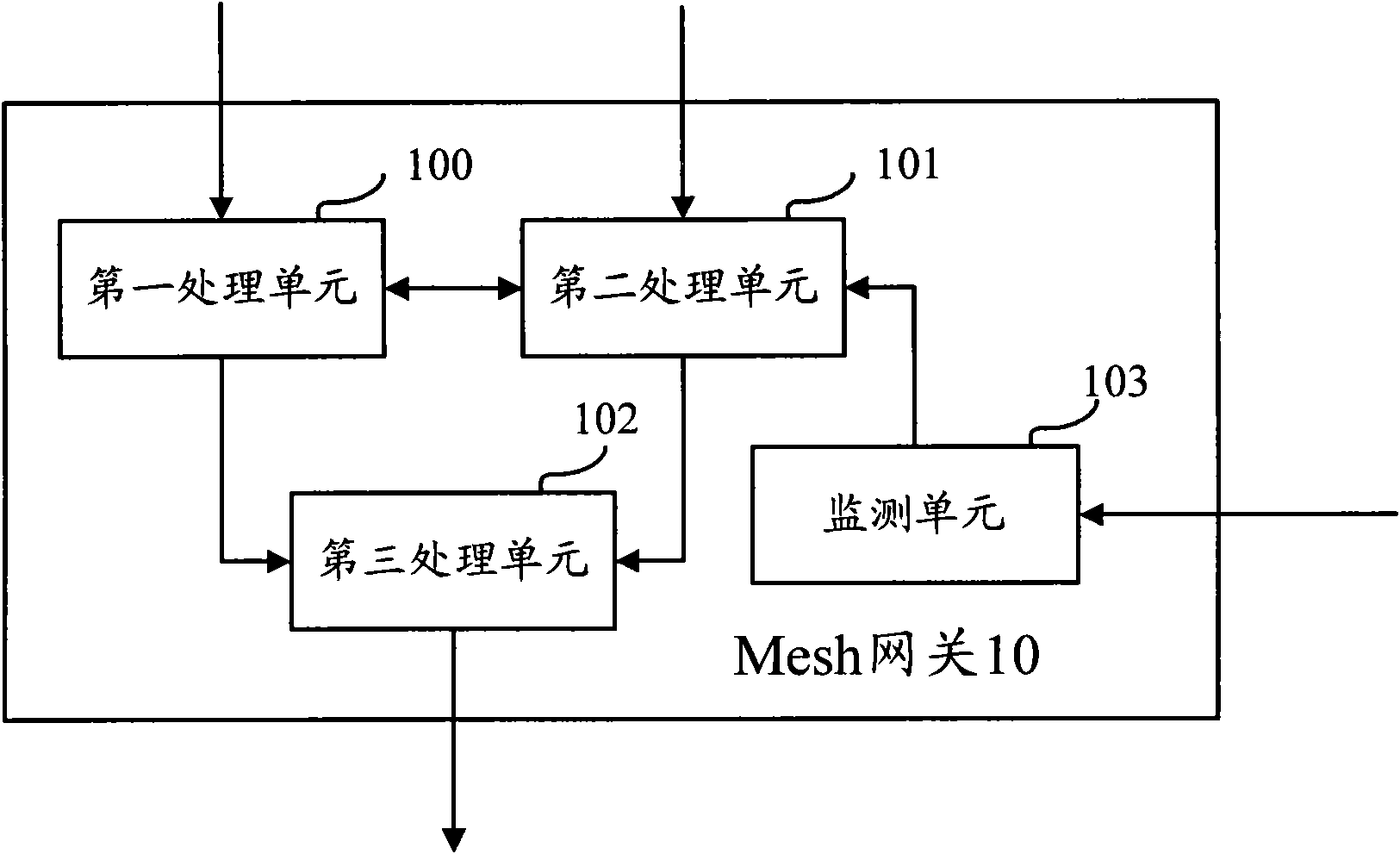
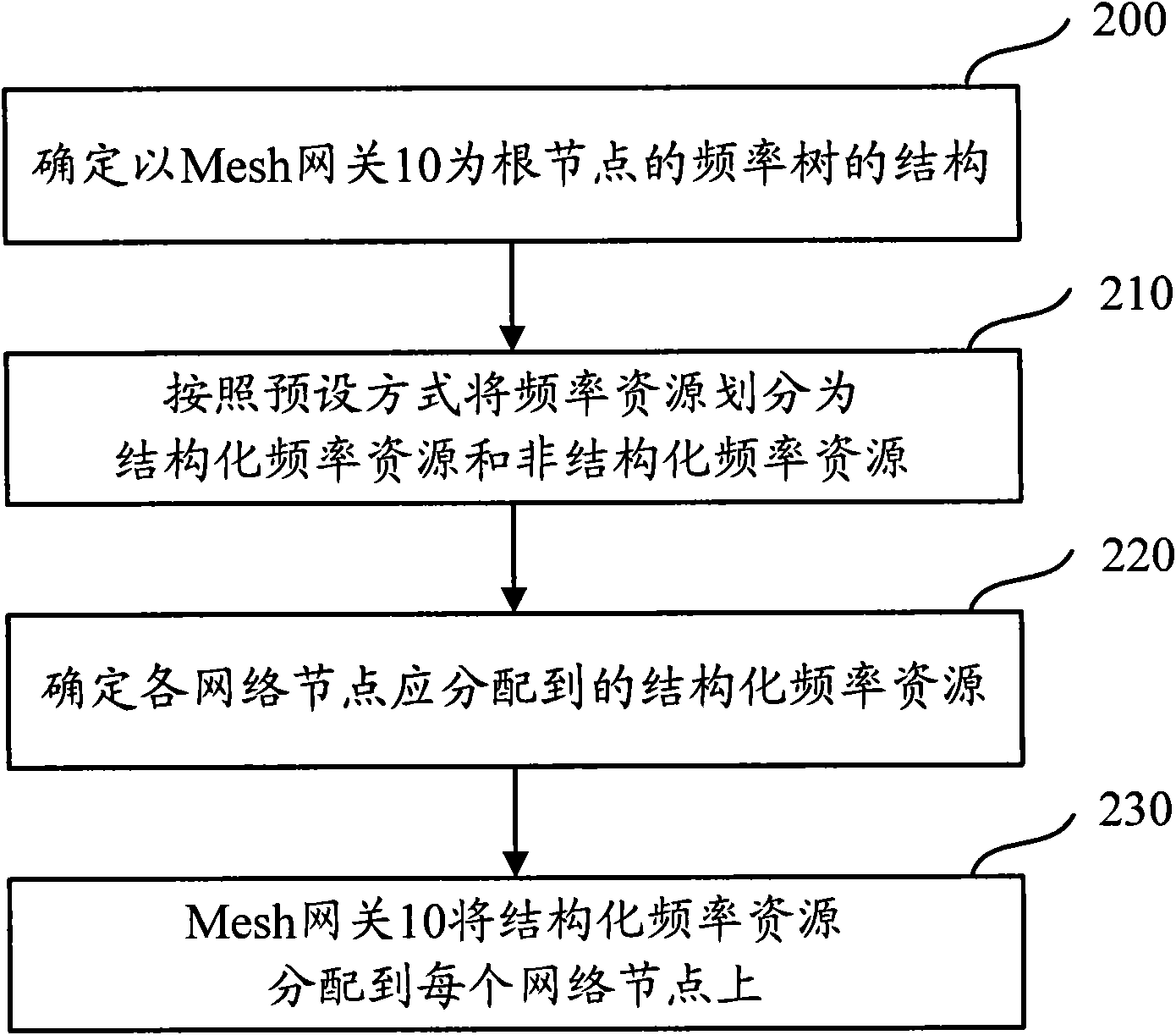
The invention discloses a method for performing frequency planning in a wireless Mesh returning network, which comprises the following steps: according to the traffic load reference gross in the wireless Mesh returning network, determining the total number of first type frequency blocks for performing fixed allocation in frequency resources, wherein the first type frequency blocks are used when performing communications between each network node and other network nodes having master-slave relations; according to the total number of the first type frequency blocks and the traffic load of each network node, determining the number of the first type frequency blocks required to be allocated to each network node; and according to the number of the first type frequency blocks required to be allocated to each network node, allocating corresponding number of the first type frequency blocks to each network node. Thus, the complexity of a frequency planning scheme is reduced effectively on the basis of ensuring the spectrum effectiveness, and the increase of network load is avoided. The invention simultaneously discloses a communication device and the wireless Mesh returning network.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Low cost interoperable satellite digital audio radio service (SDARS) receiver architecture
A system and method for simultaneously receiving first and second ensembles. The first ensemble includes a first signal from a first satellite, a first signal from a second satellite and a first signal from a terrestrial repeater. Likewise, the said second ensemble includes a second signal from the first satellite, a second signal from the second satellite and a second signal from the terrestrial repeater. The inventive receiver further includes a mechanism for selectively outputting signals transmitted within the first and second ensembles. In the illustrative embodiment, the first signal from the second satellite is identical to the first signal from the first satellite. Similarly, the first signal from the terrestrial repeater is identical to the first signal from the first satellite. In addition, a novel frequency plan is employed by which the carrier signal associated with the second satellite is disposed between the carrier signal associated with the first satellites and the carrier signal associated with the terrestrial repeater.
Owner:SIRIUS XM RADIO INC
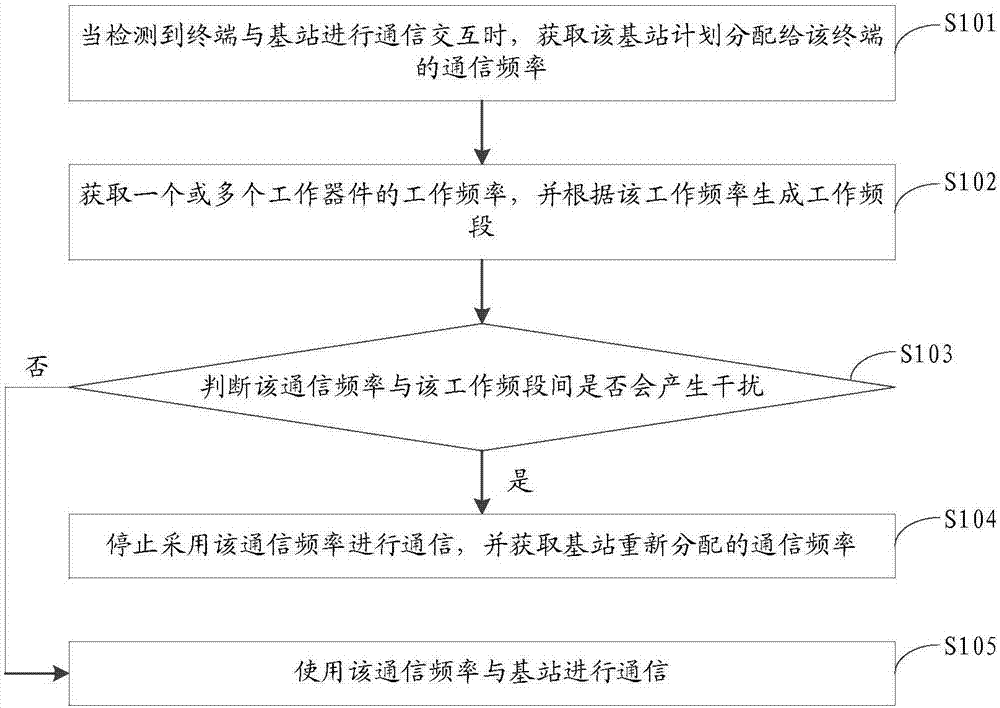
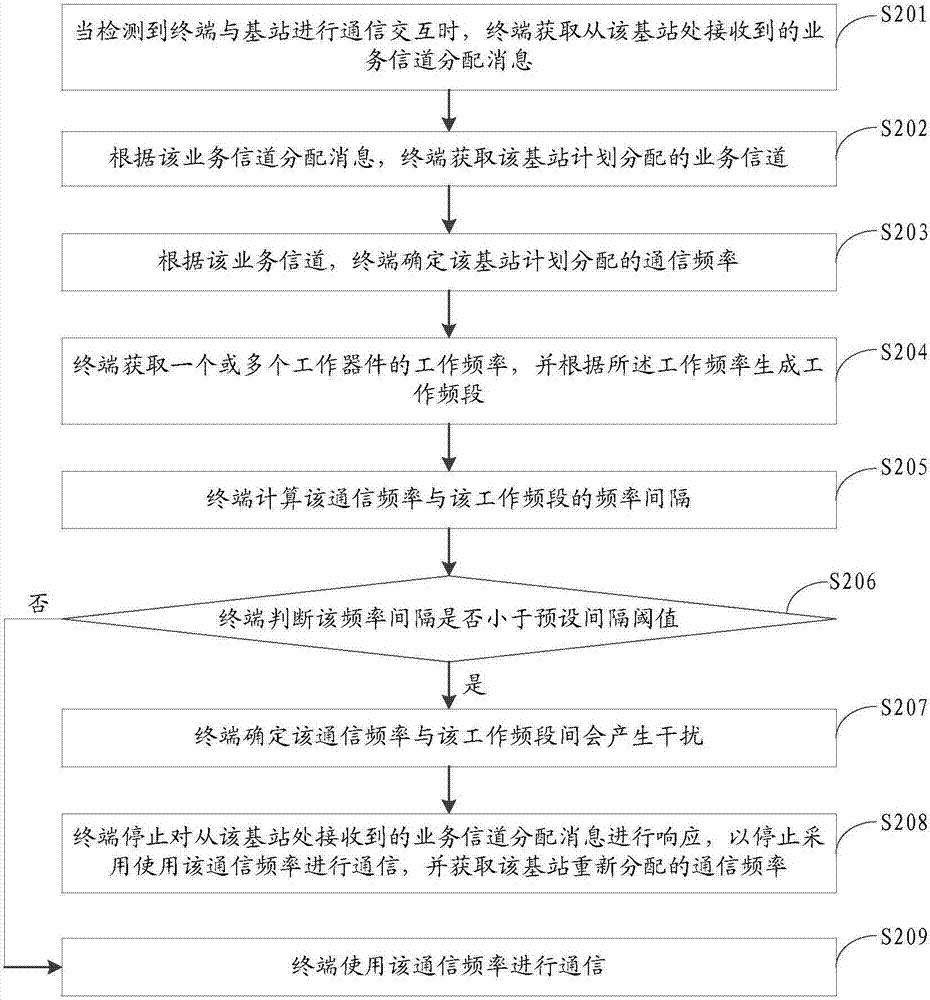
Method and apparatus for selecting communication frequency, storage medium and mobile terminal
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and apparatus for selecting communication frequency, a storage medium and a mobile terminal. The method for selecting the communication frequency comprises the following steps: when it is detected that the terminal performs communication interaction with a base station, obtaining the communication frequency planned to be allocated to the terminal by the base station; obtaining the working frequency of one or more working devices, and generating a working band according to the working frequency; judging whether the communication frequency and the working frequency generate interference; and it is judged that the communication frequency and the working frequency generate interference, stopping using the communication frequency to perform communication, and obtaining the communication frequency reallocated by the base station. By adoption of the method and apparatus disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, the interference between the terminal device and the radio frequency communication frequency can be effectively avoided.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Carrier resource planning method under carrier aggregation scene
InactiveCN103220719ASuppress co-channel interferenceReduce noise levelNetwork traffic/resource managementCarrier signalFrequency plan
The invention provides a carrier resource planning method under a carrier aggregation scene. The method comprises the following steps: setting a component carrier providing covering performance for each sector, and enabling the component carriers providing covering of adjacent sectors to have different frequencies; setting the main component carrier of edge users of each sector as the component carrier providing edge covering performance of the sector, configuring carrier aggregation for a central user of the sectors, and setting the component carrier providing edge covering as the main component carrier of the central user. The carrier resource planning method under the carrier aggregation scene can restrain same frequency interference among cells under a frequency planning scheme of multiple component carriers.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH
System and method for improved data transmission speed by fixing the lower corner frequency at a frequency above voice band in a symmetric DSL transmission system
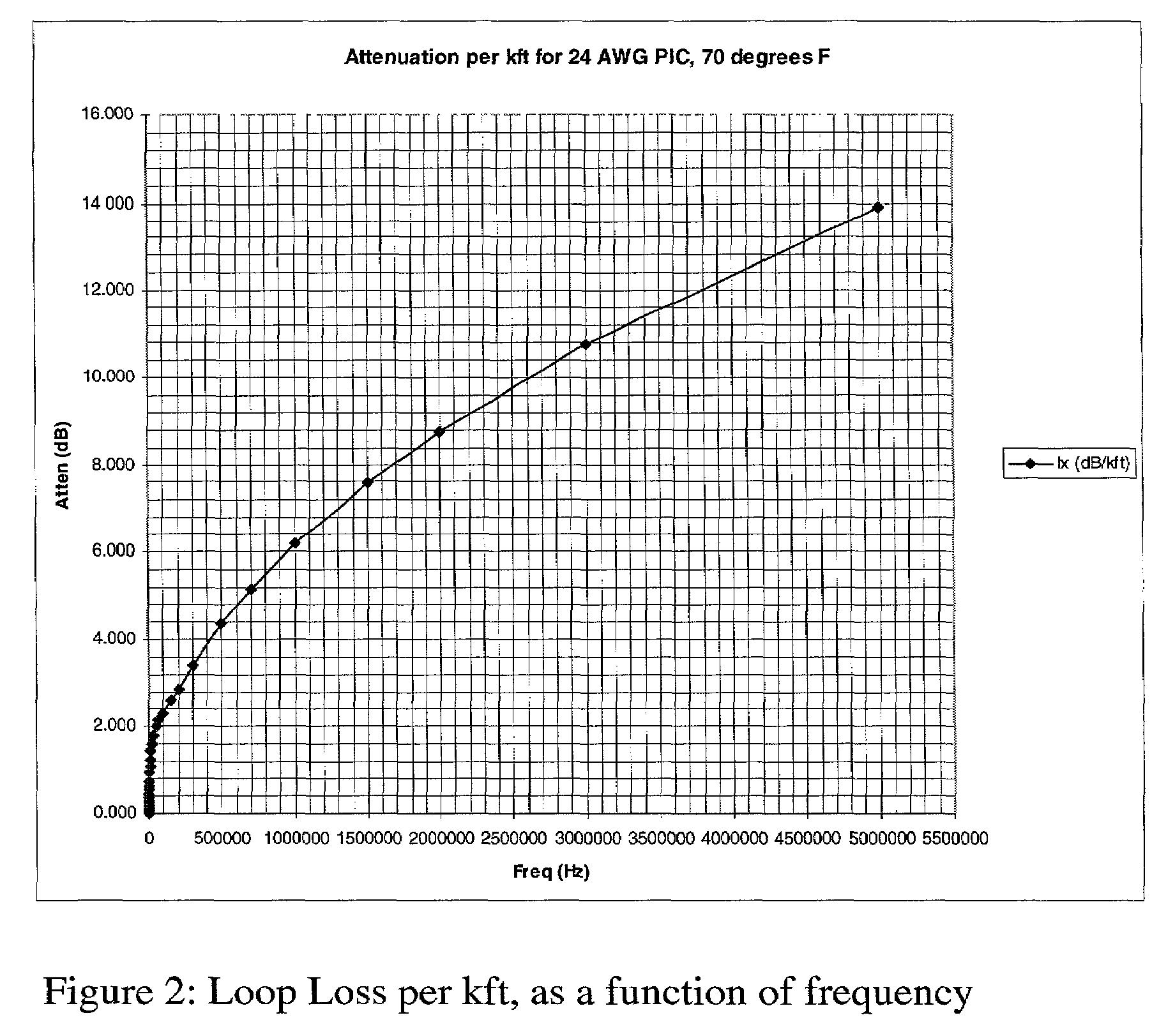
InactiveUS7430212B2Reduce crosstalkReduce lossTelephonic communicationTime-division multiplexModem deviceEngineering
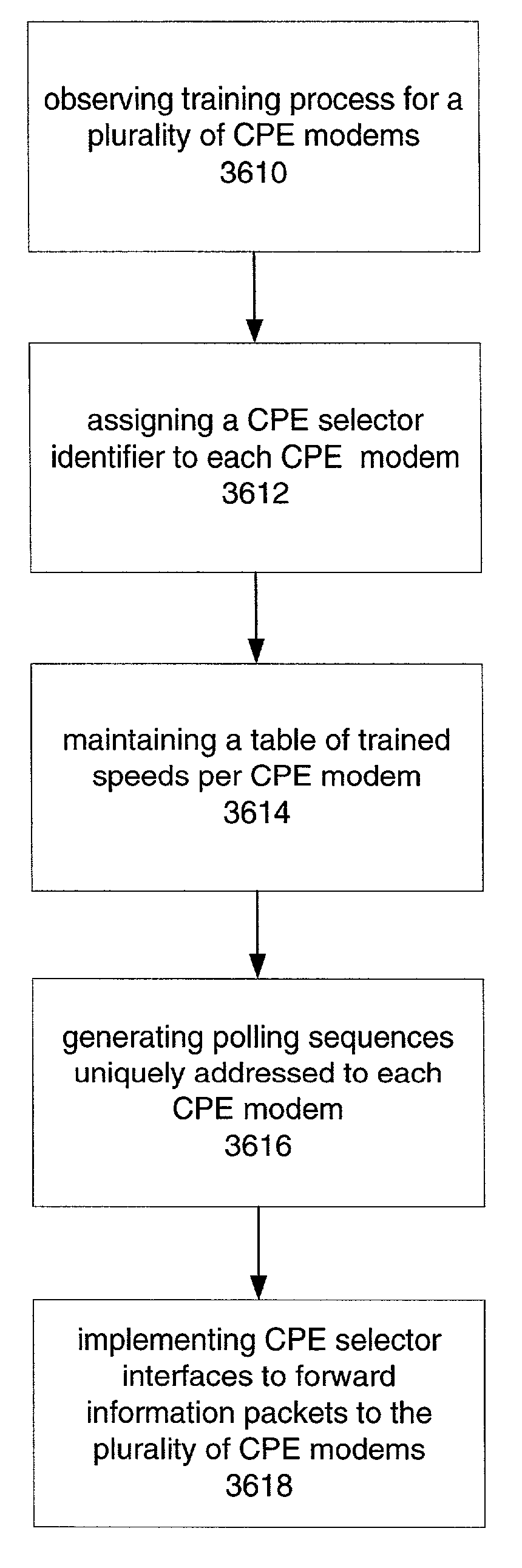
A system and method of the present invention improves data transmission speeds by fixing the lower corner frequency at a frequency above voice band in a symmetric DSL transmission system. By using a fixed lower corner frequency that is above the voiceband and increasing the upper corner frequency upward as the symbol rate increases, the communication equipment systems utilize symmetric frequency plans that incorporate the relatively low loss, low crosstalk spectrum range while still being able to operate on the same line as analog voice band. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to multiplexing a first modem for communicating information packets between the first modem and a plurality of second modems via a single two-wire (e.g. telephone subscriber) lines. The present invention provides a Multi-Access (MA) protocol that enables a single link to be utilized by more than one access device (e.g., a CPE Modem). The Multi-Access protocol of the present invention provides a means to connect to multiple endpoints on a single local loop. Each CPE Modem may communicate directly with a modem at a CO location thereby removing the need for expensive gateway devices and secondary in-building cabling to support multiple access points.
Owner:PARADYNE CORP
Method for agile region and band conscious frequency planning for wireless transceivers
InactiveUS20090213974A1Pulse automatic controlFrequency-modulated carrier systemsWireless transceiverLocal oscillator signal
A technique for agile region and band conscious frequency planning for wireless transceivers in which a comparison frequency is selected for generating a local oscillator signal. The comparison frequency (Fcomp) is selected for a frequency band of a particular communication standard or protocol, in order not to introduce harmonic components of the selected comparison frequency in a transmitted signal from the wireless device that generates spurious emissions restricted by the particular communication protocol or another protocol. The Fcomp selection may also take into consideration restrictive region-specific criteria for out-of band spurious emissions.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Frequency planning method and apparatus for multicarrier system
ActiveCN102223642AReduce distractionsReduce the impactHigh level techniquesNetwork planningFrequency spectrumMain channel
The embodiment of the invention brings forward a frequency planning method for a multicarrier system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining available frequency spectrum resources and determining an available bandwidth for networking and channel spacing; Selecting a frequency point set of a carrier wave based on the available bandwidth for networking and the channel spacing, wherein an occupied bandwidth of a main channel is larger than that of an auxiliary channel; and distributing the main channel and the auxiliary channel of the frequency point set of the carrier wave to corresponding sectors of a service area. The embodiment of the invention also provides a frequency planning apparatus for the multicarrier system. And the apparatus comprises a configuration module, an operation module and a distribution module. According to the method and the apparatus provided in the embodiment of the invention, interference of common channels is reduced by arranging different frequency point spacing of the main channel and the auxiliary channel; moreover, an influence of in-band adjacent-channel interference on down access is effectively reduced, and an effect of output power reduction caused by increase of in-band channel on a cell coverage area can be made up.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
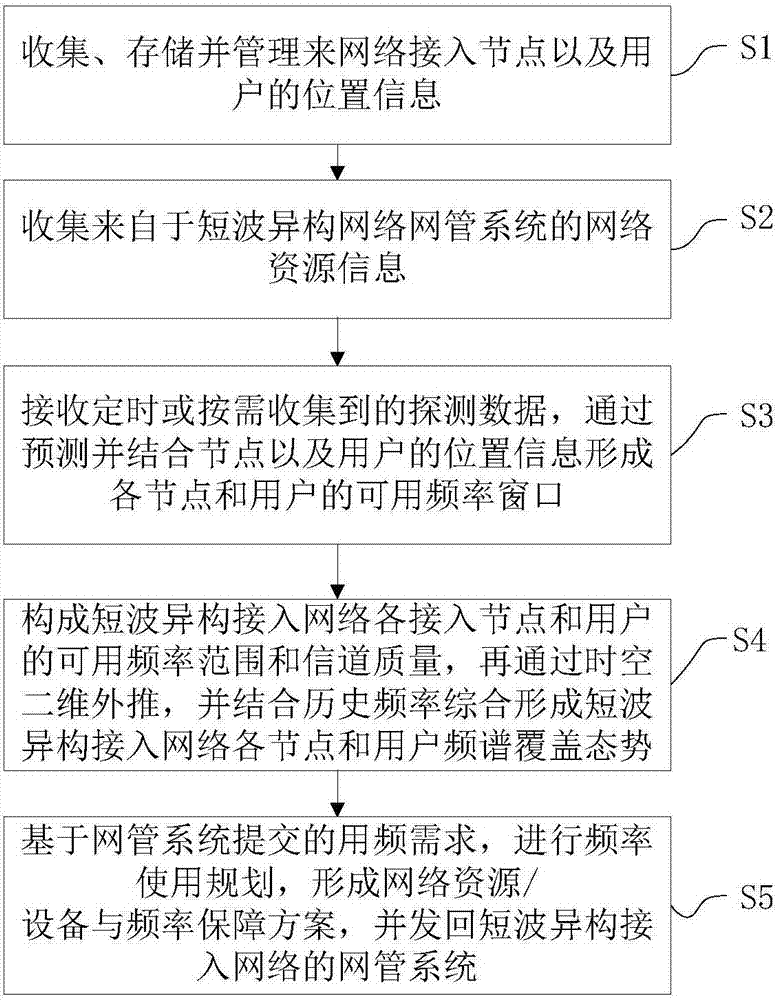
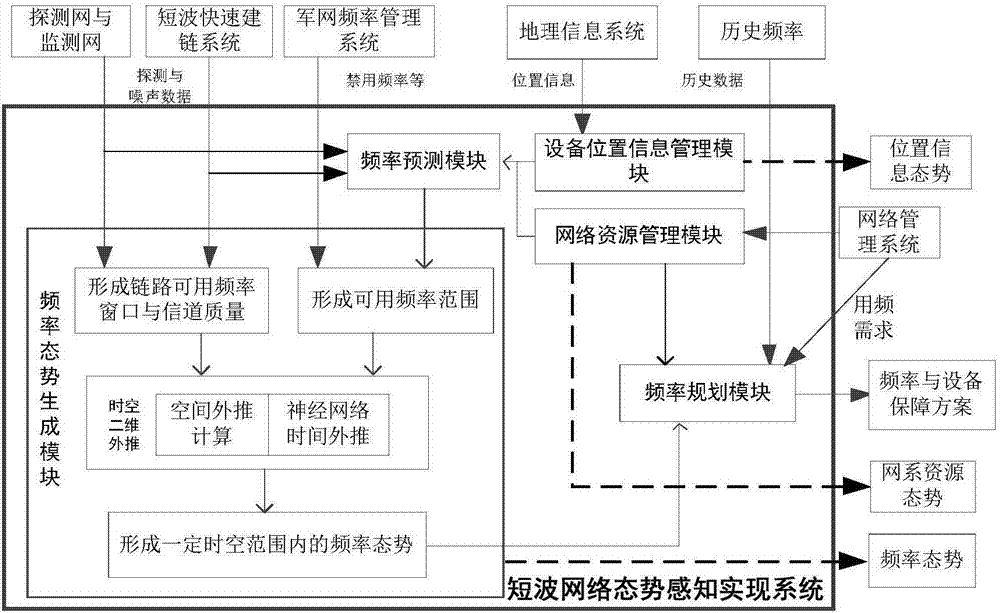
Short-wave network situation sensing implementation method and system
ActiveCN106878943APrecise frequency management serviceTransmission monitoringLocation information based serviceNetwork resource managementAccess route
The invention is suitable for the field of short-wave access communication networks. In an interconnection and intercommunication integrated short-wave heterogeneous access network, the invention provides a short-wave network situation sensing implementation method and system. The system comprises a network resource management module, an equipment position information management module, a frequency prediction module, a frequency situation generation module, and a frequency planning module. The system employs the network system resource data, geographic position data and frequency data, generates the coverage data of each node and user through the space-time correction, achieves the real-time sensing of the state of network resources, network coverage and the user position, achieves the real-time optimization of the access route of the user and the dynamic distribution of station resources, can provide precise frequency management service for the short-wave access communication network and short-wave users in different modes, and can provide decision support for the frequency utilization management and resource dispatching of the commanders at each level and the users during the emergency command communication.
Owner:中国人民解放军国防信息学院
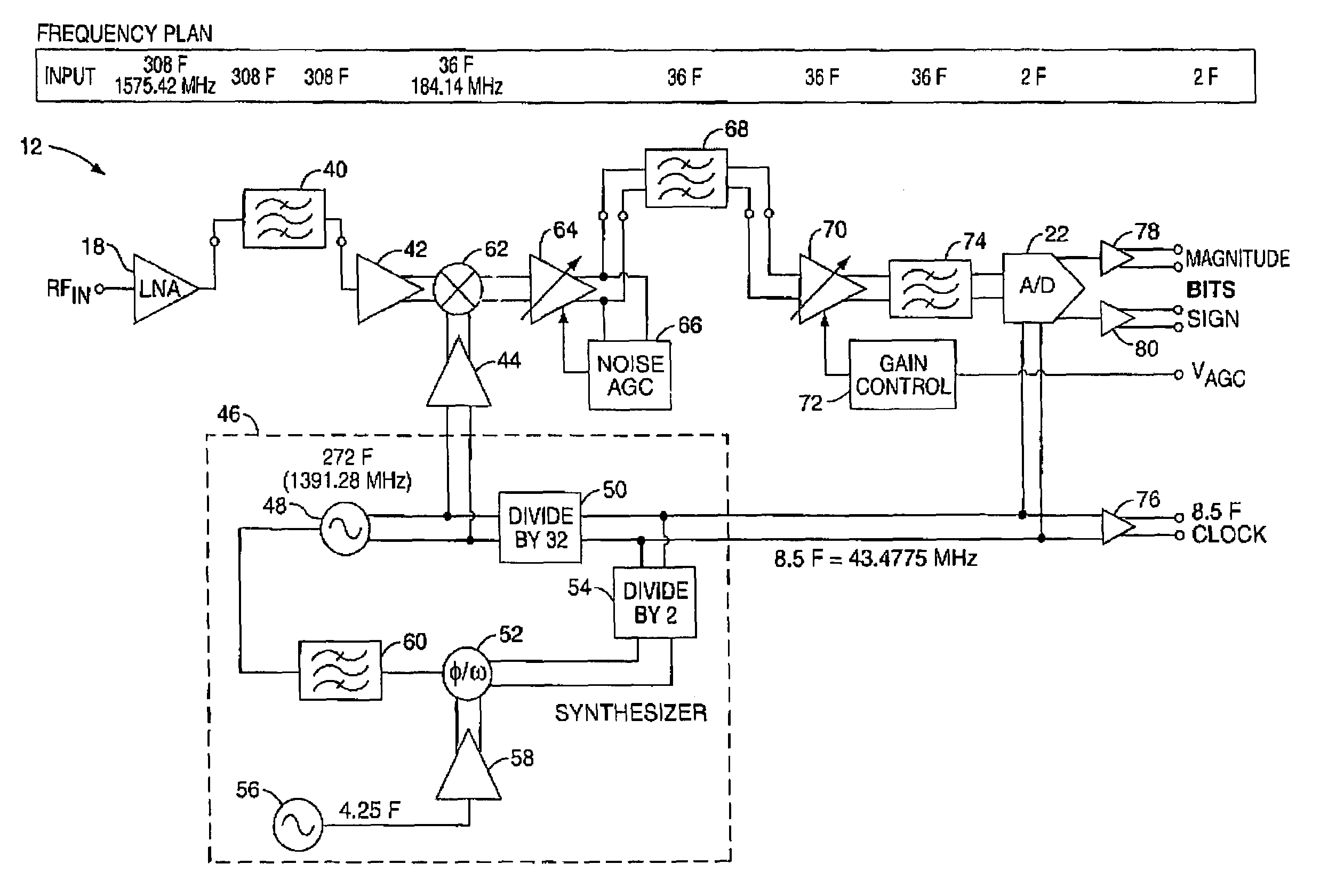
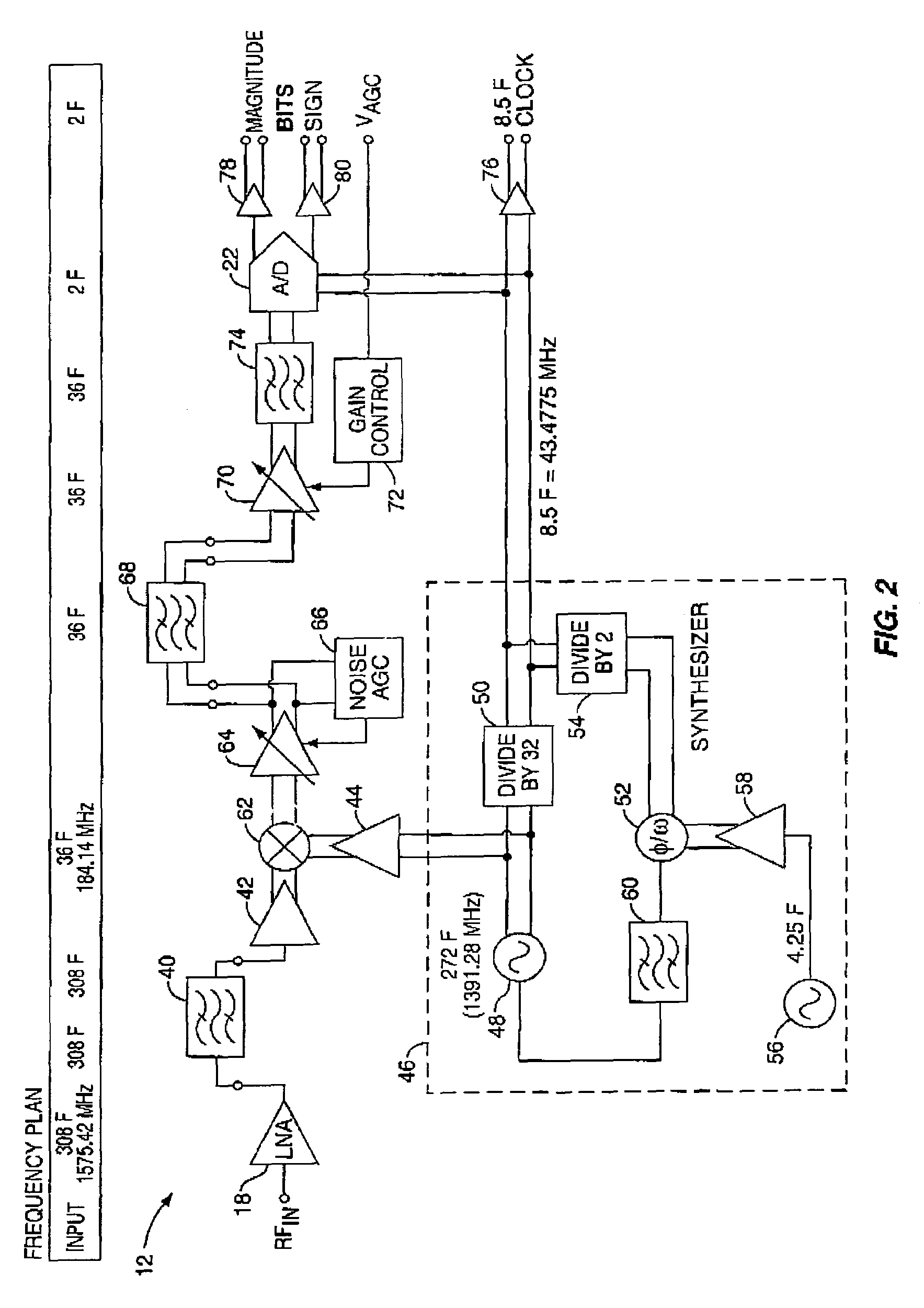
Frequency plan for GPS receiver
InactiveUS7197089B2Eliminate distractionsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsBeacon systemsIntermediate frequencyGps receiver
The present invention provides a GPS receiver having a unique frequency plan, thereby eliminating interference due to internally generated frequencies. In general, the GPS receiver has downconversion circuitry that uses a first synthesizer output signal with a center frequency of 272F to reduce the L1 (308F) or L2 (240F) GPS signal to an intermediate frequency signal. The intermediate frequency signal is then digitized by sampling circuitry wherein the sampling circuitry is driven by a second synthesizer output with a center frequency of 8.5F. The resultant digitized signal contains the GPS information carried in the received GPS signal and has a center frequency of 2F. By selecting 8.5F as the basic reference for all internally generated frequencies, where F is 5.115 MHz, all internally generated frequencies are interrelated by nature and no internal signals in the RF-to-baseband conversion can interfere with the received GPS signal within its information bandwidth.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for optimal frequency planning for an integrated communication system with multiple receivers
ActiveUS20090302966A1Current interference reductionTransmission monitoringCommunications systemEngineering
Methods and systems for optimal frequency planning for an integrated communication system with multiple receivers may include adjusting a center frequency of a low IF signal to reduce interference by a second order interference signal. The center frequency may be adjusted to avoid high power portions of the second order interference signal. The interference level corresponding to a center frequency may be determined by, for example, a SNR of the low IF signal, or by determining a BER for the low IF signal. The center frequency of the low IF signal may be dynamically adjusted to keep second order interference level at an acceptable level. Adjusting the center frequency of the low IF signal may also comprise keeping the low IF signal from being blocked by a DC component of the second order interference signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Resource allocation method in wireless communication
InactiveCN101247624AReduce complexityImprove SNRTransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMultiplexingCost effectiveness
The invention relates to a resource allocating method in the wireless communication, comprising the following steps: determining which region in the section the user belongs to; the system distributes the different subclass in sequence space to the different region of the section towards each section in the system. The invention makes the coverage area of the specified sequence different through the power control way, enhanced the noise-signal ratio, so as to enhance the spectrum effectiveness of the system. According to the method, wireless resources is dynamically distributed to different sections(or areola), which can enhance the spectrum effectiveness of the system greatly, realize that the coefficient of frequency multiplexing is one, and greatly reduce the complexity of the frequency planning when area deployment.
Owner:BEIJING SAMSUNG TELECOM R&D CENT +1
Method of dynamic allocation of shared resources in a time-frequency plan and associated device
ActiveUS20140112302A1Network traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
A method is provided of dynamic allocation of shared resources in a communication network, consisting in defining, in a time-frequency plan, a superframe of a given duration ΔT and a given spectral width Δf, made up of one or more frames, each defining a regular time-frequency grid, of which one square, referred to as a time-frequency unit, constitutes the smallest time and frequency interval allocable to a user of said network within said frame, said method consisting in reserving, on each carrier frequency of a frame, at least one block of a number K, greater than or equal to 1, of time-frequency units which can be dynamically allocated to a user for communication or for synchronization.
Owner:THALES SA +1
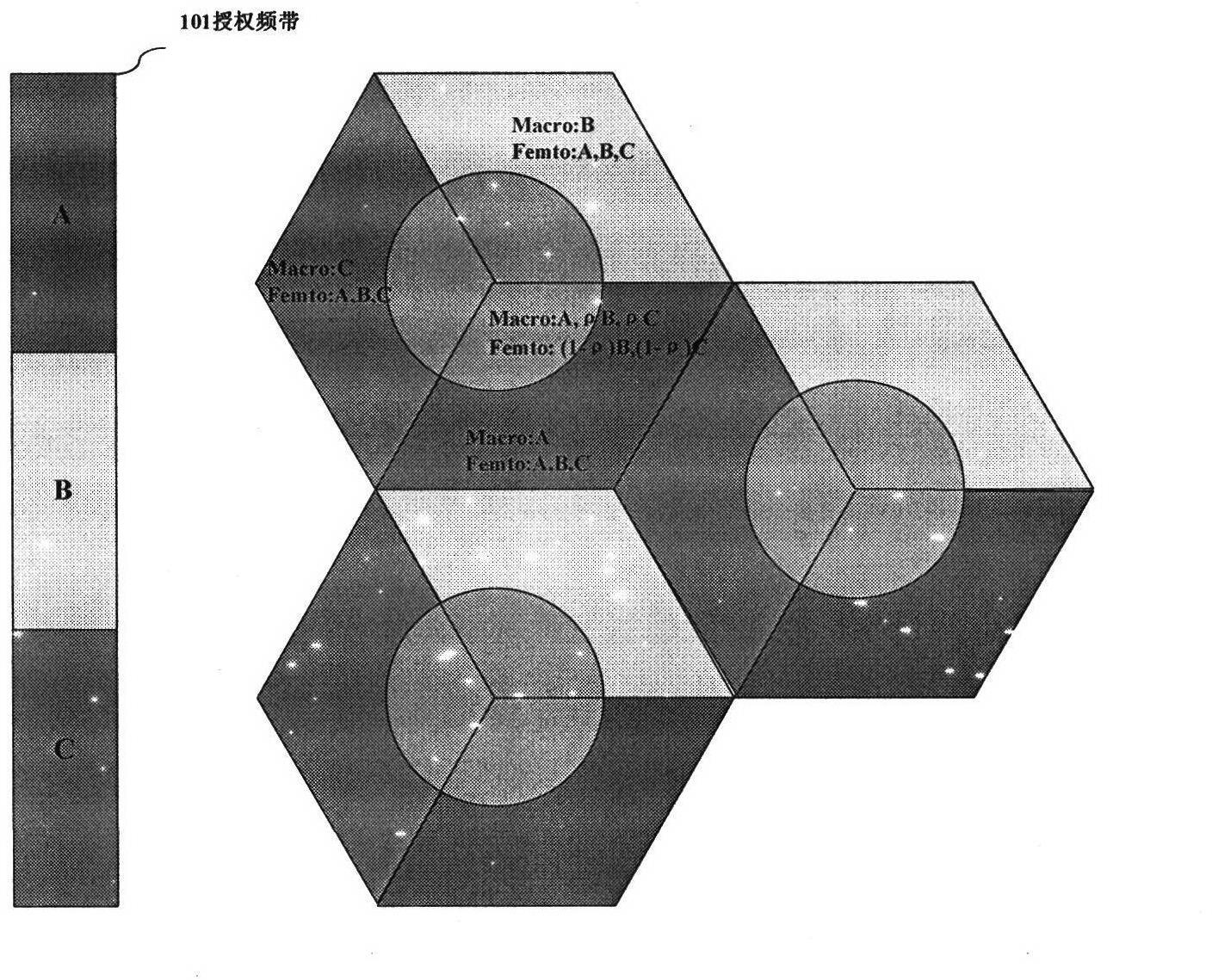
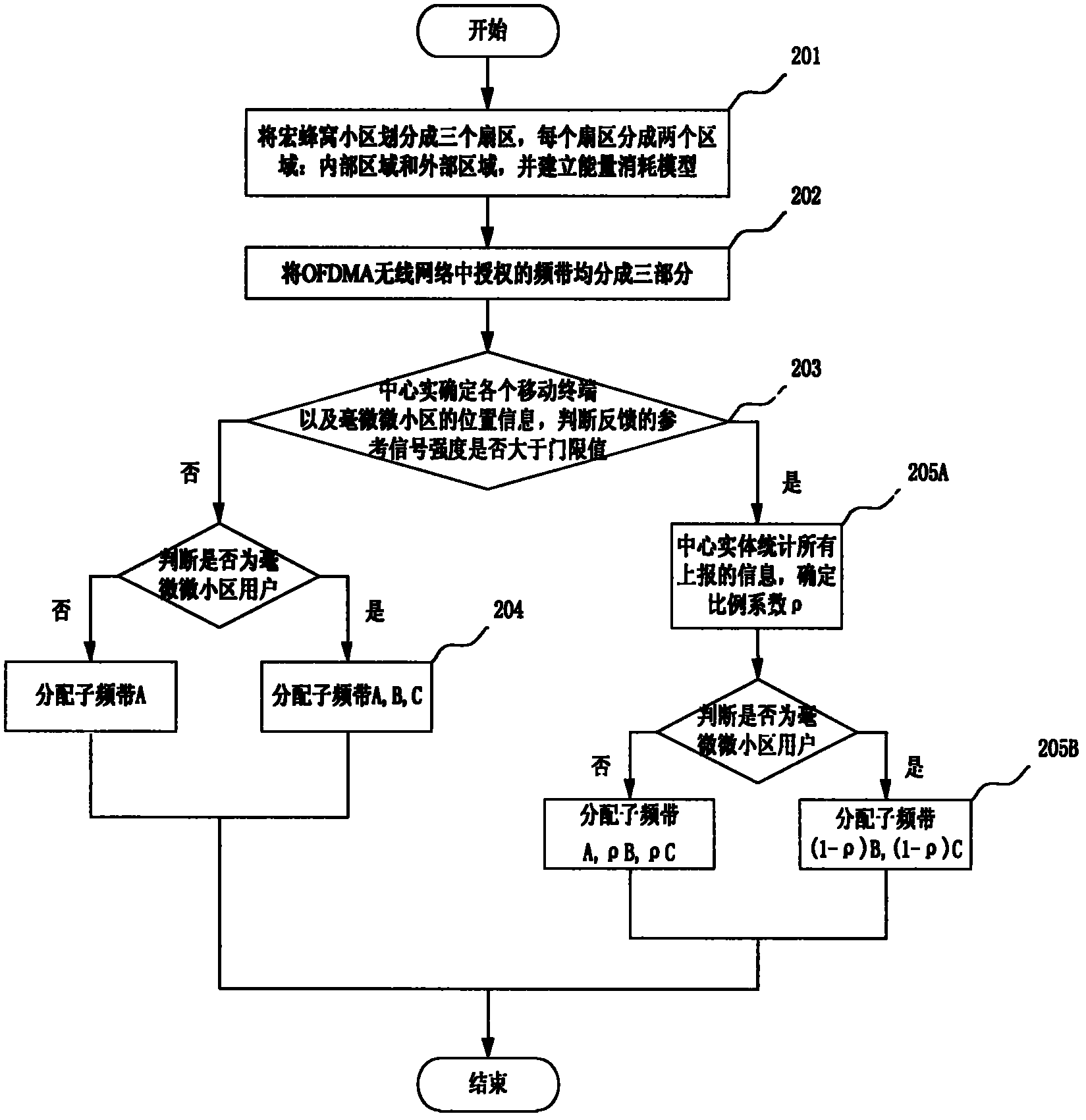
Energy-saving dynamic frequency spectrum planning method in femtocell network
InactiveCN102612046AReduce distractionsReduced probability of outageEnergy efficient ICTNetwork planningDynamic frequency planningQuality of service
The invention relates to an energy-saving dynamic frequency spectrum planning method in a femtocell network and provides an energy-saving dynamic frequency plan based on soft frequency reuse in a bilayer femtocell network, wherein an energy-consumption model of a downlink of a three-dimensional space femtocell bilayer network is established. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a soft frequency reuse scheme is adopted, interferences to macro cell users in a cell edge area are reduced, and the interruption rate of the edge users is reduced. Frequencies distributed to macro cell users and femtocell users in an internal area are orthogonal mutually, cross-layer interferences between a macro cell network layer and a femtocell network layer are avoided, the user distribution and business traffic distribution of the internal area and an external area of the macro cell are fully considered on the premise of guaranteeing QoS (Quality of Service) requirements of the users, the frequency spectra distributed to the macro cell users and the femtocell users are dynamically adjusted, the frequency spectrum utilization rate is increased, and thus, the energy utilization rate of the entire network is increased.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com