Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
225 results about "Radiometric measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiometric Level Measurement: The Measuring principle. The radiometric level measurement is based on a simple but very effective measuring principle. With the help of a rod source or a point source, a gamma ray field is generated, which radiates the vessel or container over the desired measuring range.
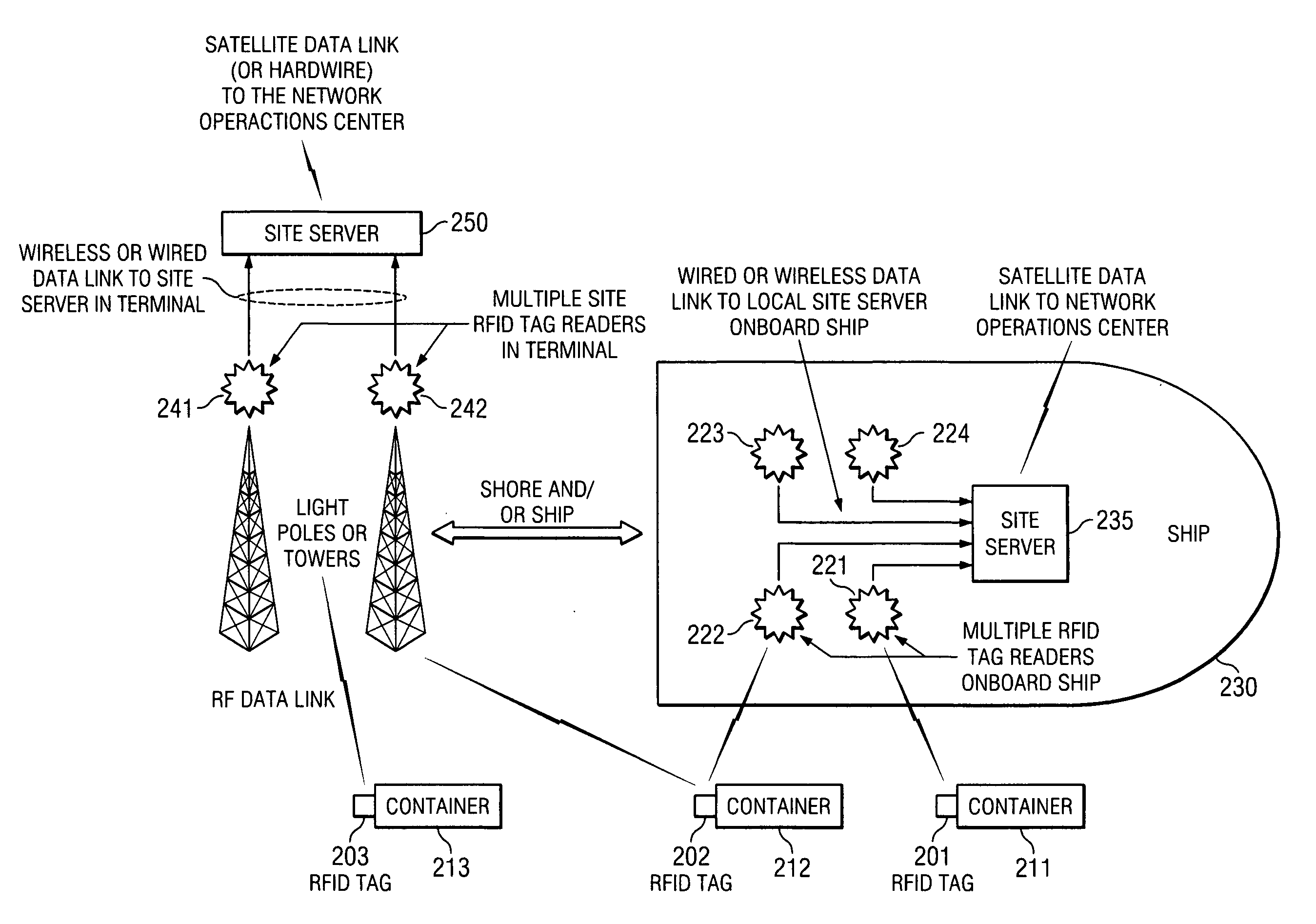
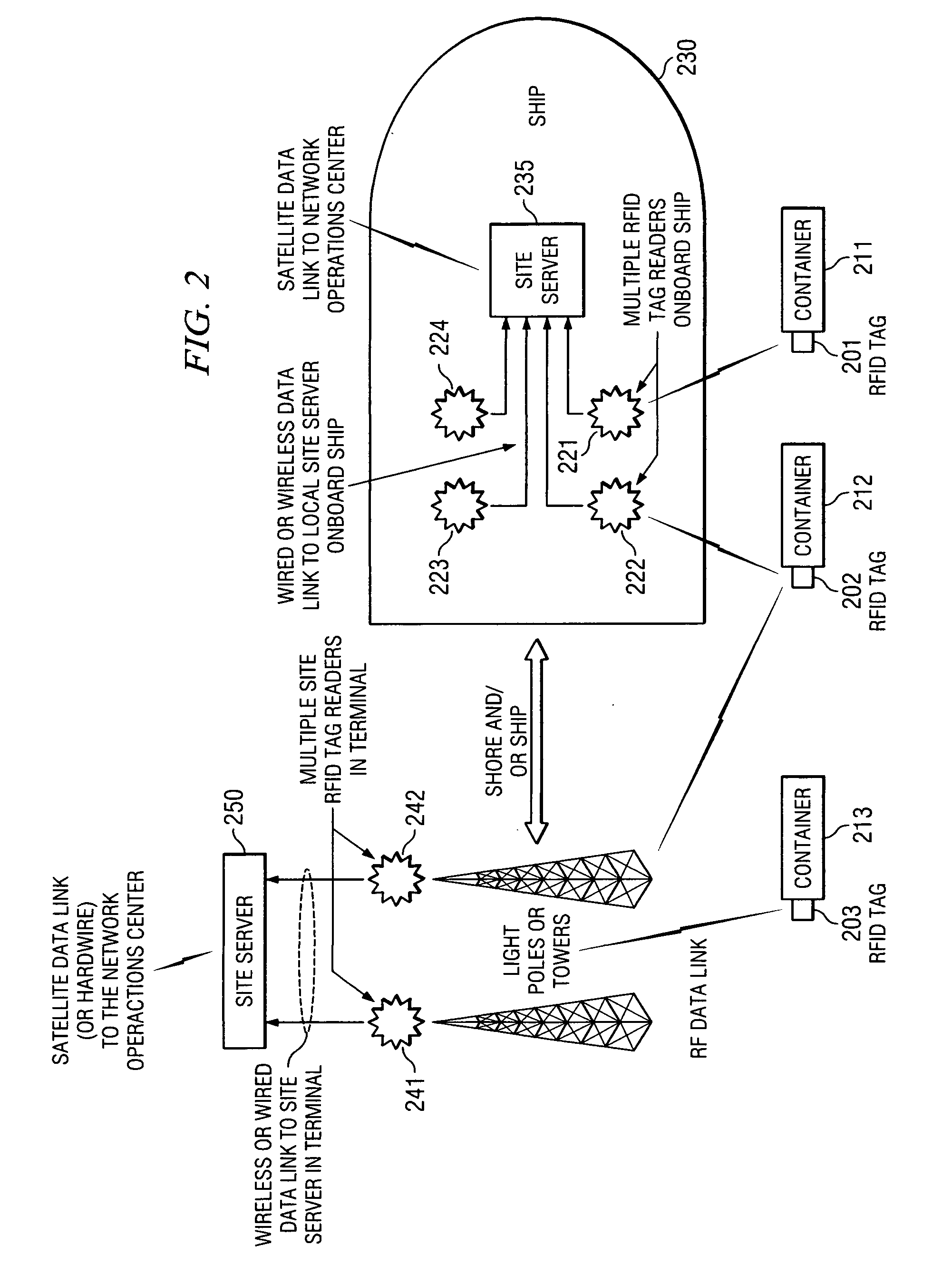
Space charge dosimeters for extremely low power measurements of radiation in shipping containers
InactiveUS20050248456A1Electric signal transmission systemsSolid-state devicesDosimeterRadiation sensor
Methods and apparatus are described for space charge dosimeters for extremely low power measurements of radiation in shipping containers. A method includes insitu polling a suite of passive integrating ionizing radiation sensors including reading-out dosimetric data from a first passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor and a second passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor, where the first passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor and the second passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor remain situated where the dosimetric data was integrated while reading-out. Another method includes arranging a plurality of ionizing radiation sensors in a spatially dispersed array; determining a relative position of each of the plurality of ionizing radiation sensors to define a volume of interest; collecting ionizing radiation data from at least a subset of the plurality of ionizing radiation sensors; and triggering an alarm condition when a dose level of an ionizing radiation source is calculated to exceed a threshold.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
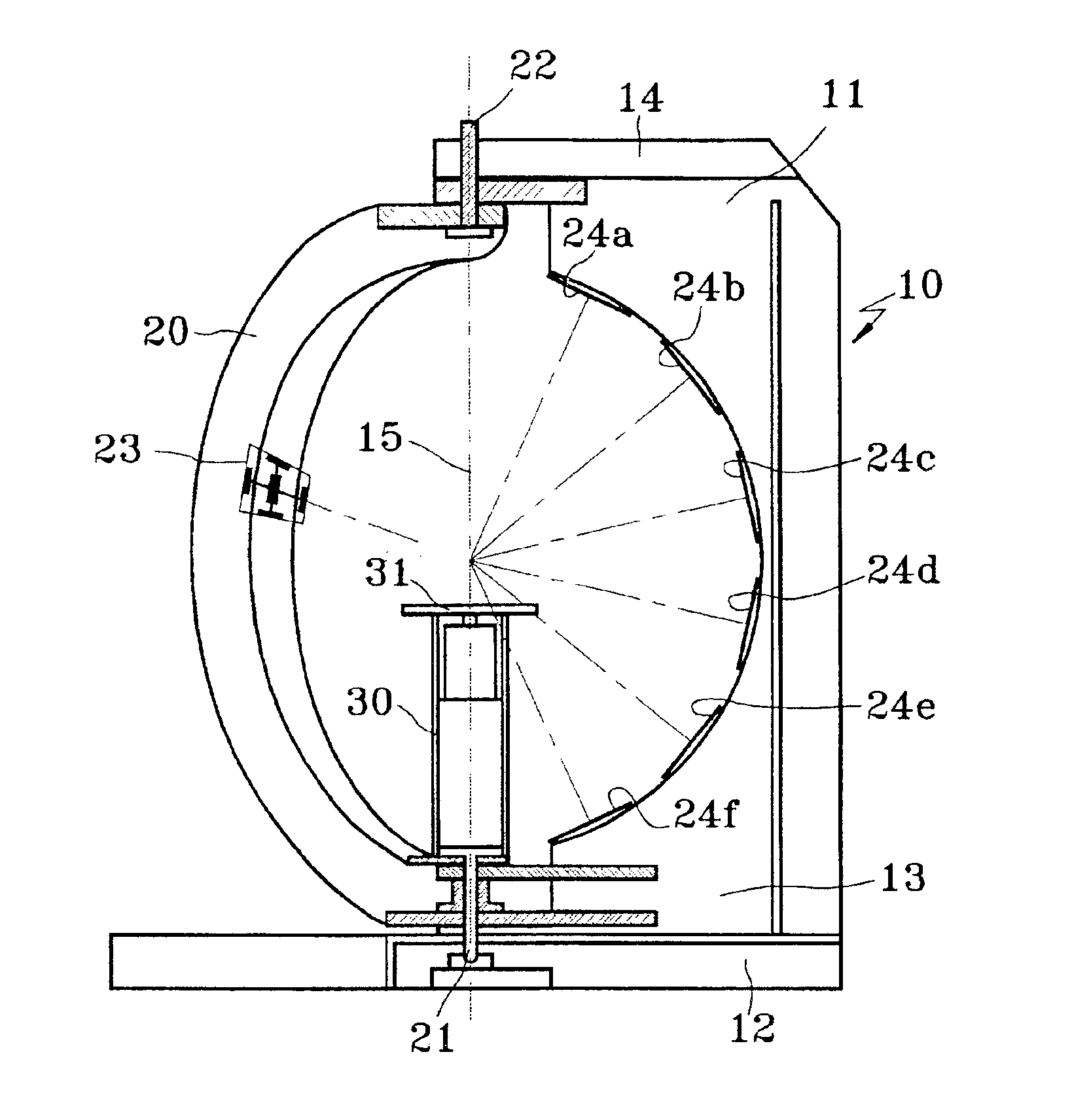
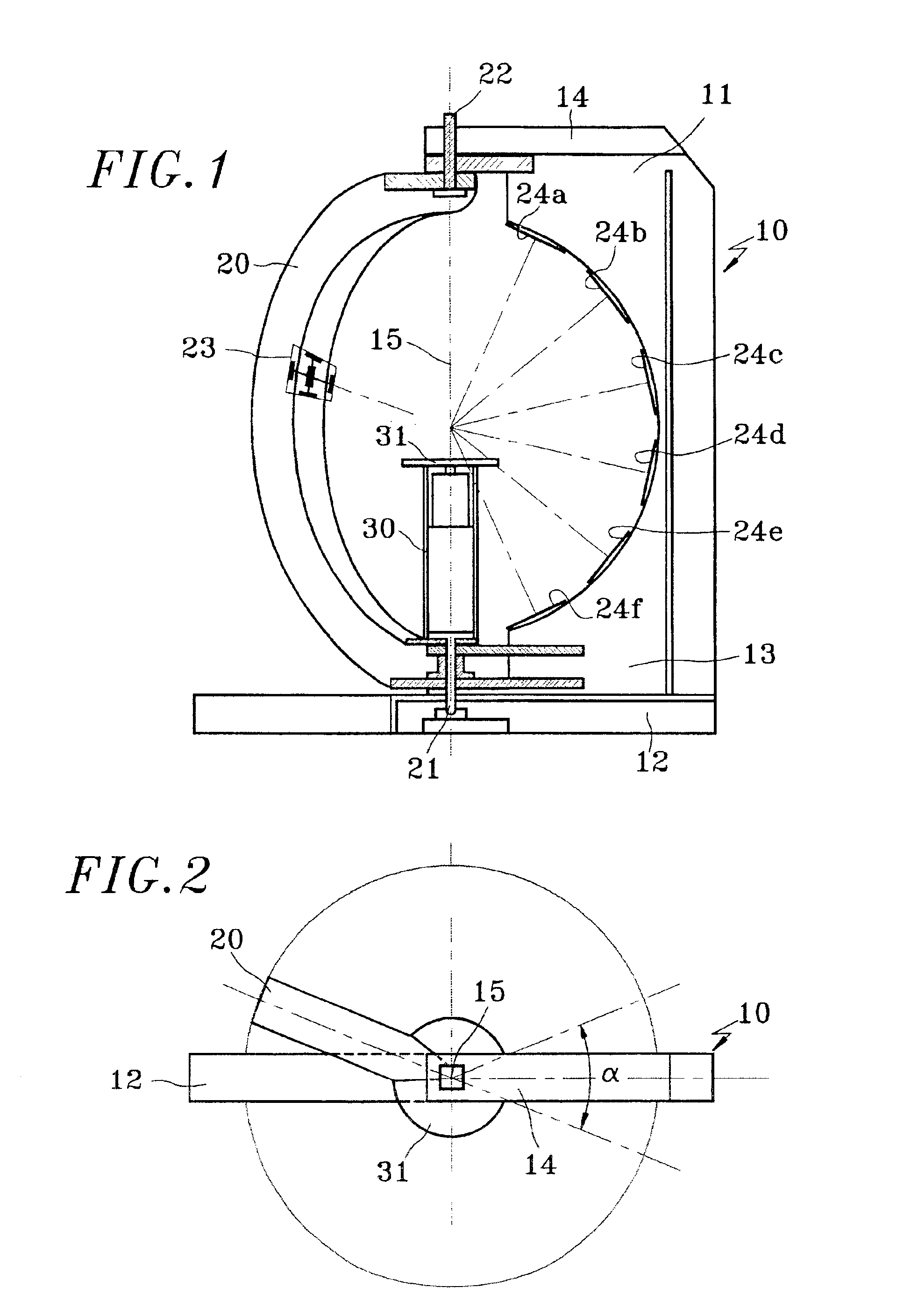
Panoramic video system with real-time distortion-free imaging
ActiveUS20060023105A1Minimizing software overheadHighly efficient regional transformationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsTime distortionGraphic card
A panoramic annular lens system (PAL), a unitary video camera and a PC-based software system that unwraps a 360° video image into a seamless, distortion free horizontal image image in real time. The PAL system of the preferred embodiment has a 360° horizontal field of view and a 90° vertical field of view in a 40 mm diameter compact package. The invention is not limited to any particular type of lens system. In fact, there are numerous lens systems for providing a 360° panoramic view. The video camera may be a CCD or CMOS based device having a pixel resolution of either 1280×1024 (high resolution) or 720×480 (NTSC). The unwrapping system is a radiometric ray tracing program carried out using a computer's graphics card capabilities to produce highly efficient regional transformation while minimizing software overhead. The result is real time, high resolution 30 fps conversion from a spherical distorted image to a flat panoramic image in Cartesian coordinates.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
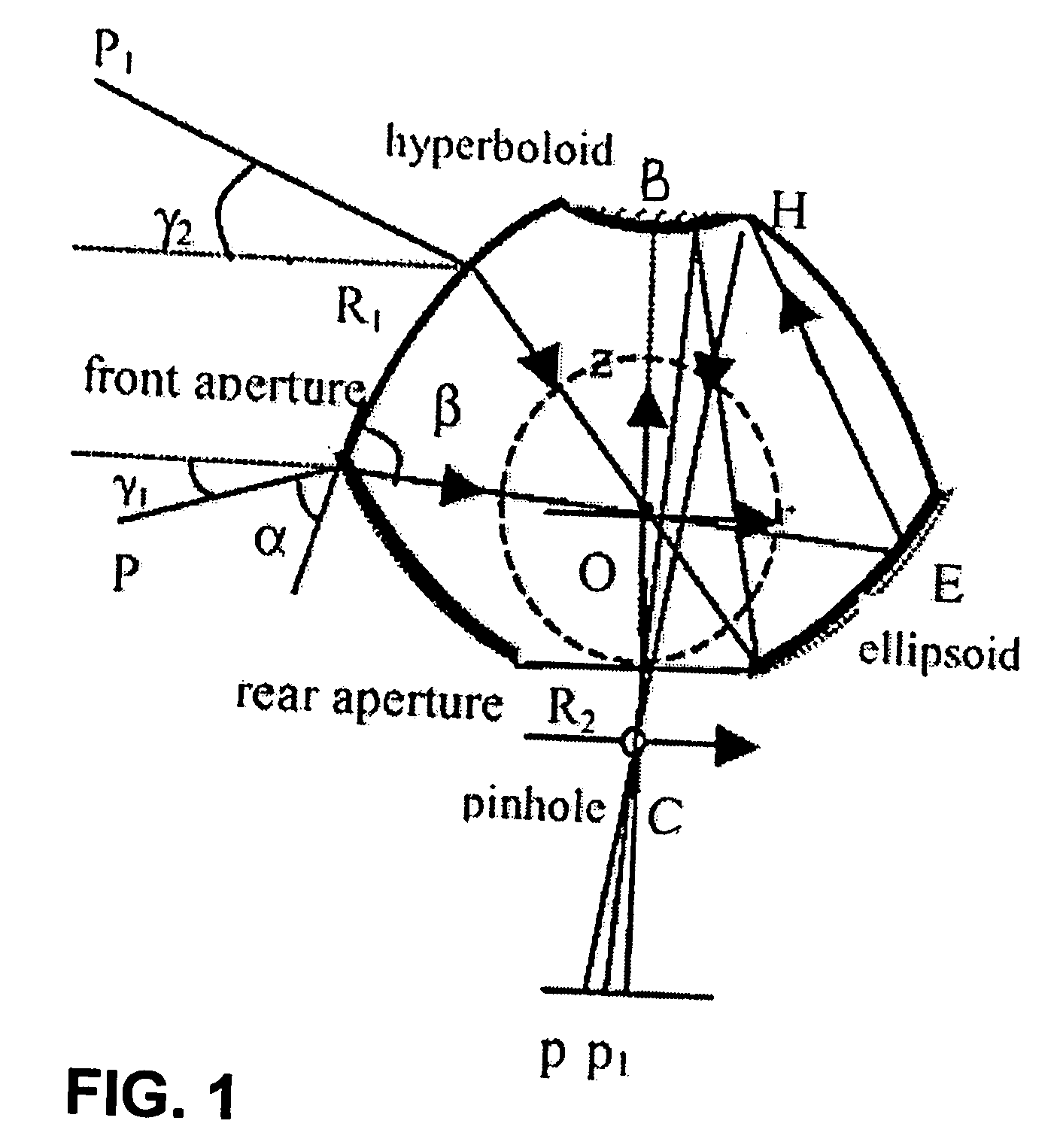
Portable radiometry and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6849849B1Protection elementEasy to installRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesParticulatesEngineering
An infrared (IR) camera and associated electronics including power are integrated into portable, self-contained, vision-enhancement apparatus useful in environments of dense air-borne particulate and thermal extremes such as encountered in fire fighting situations, in accordance with the invention. The IR camera is integral with a self-contained power supply so that the system is portable and requires no umbilical cord or other external connections. The camera includes an imager that is preferably an un-cooled focal plane array, and associated imaging, storing, processing and displaying electronics that are cooled in the extreme thermal environment using an integral plural phase heatsink.
Owner:TELEDYNE FLIR LLC
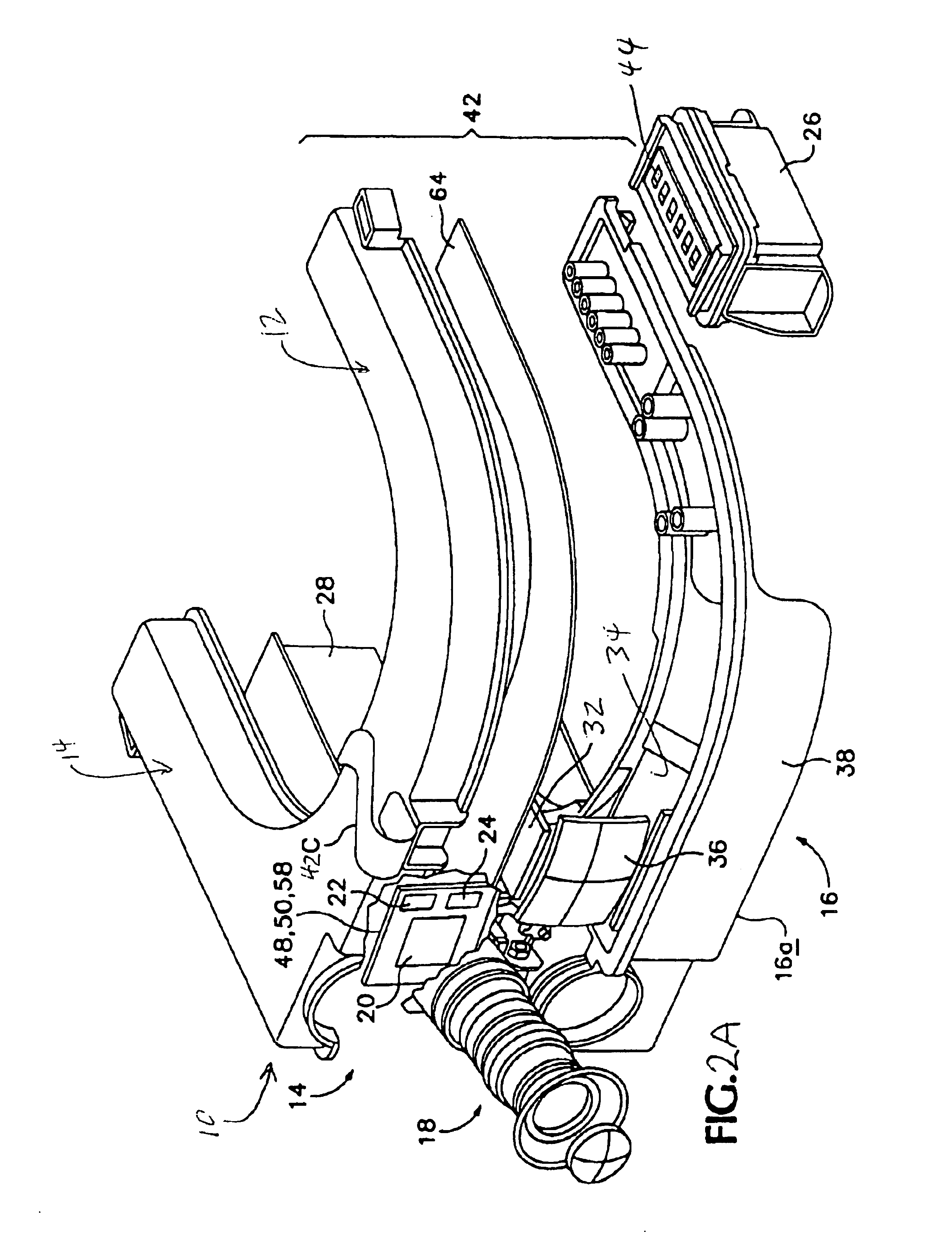
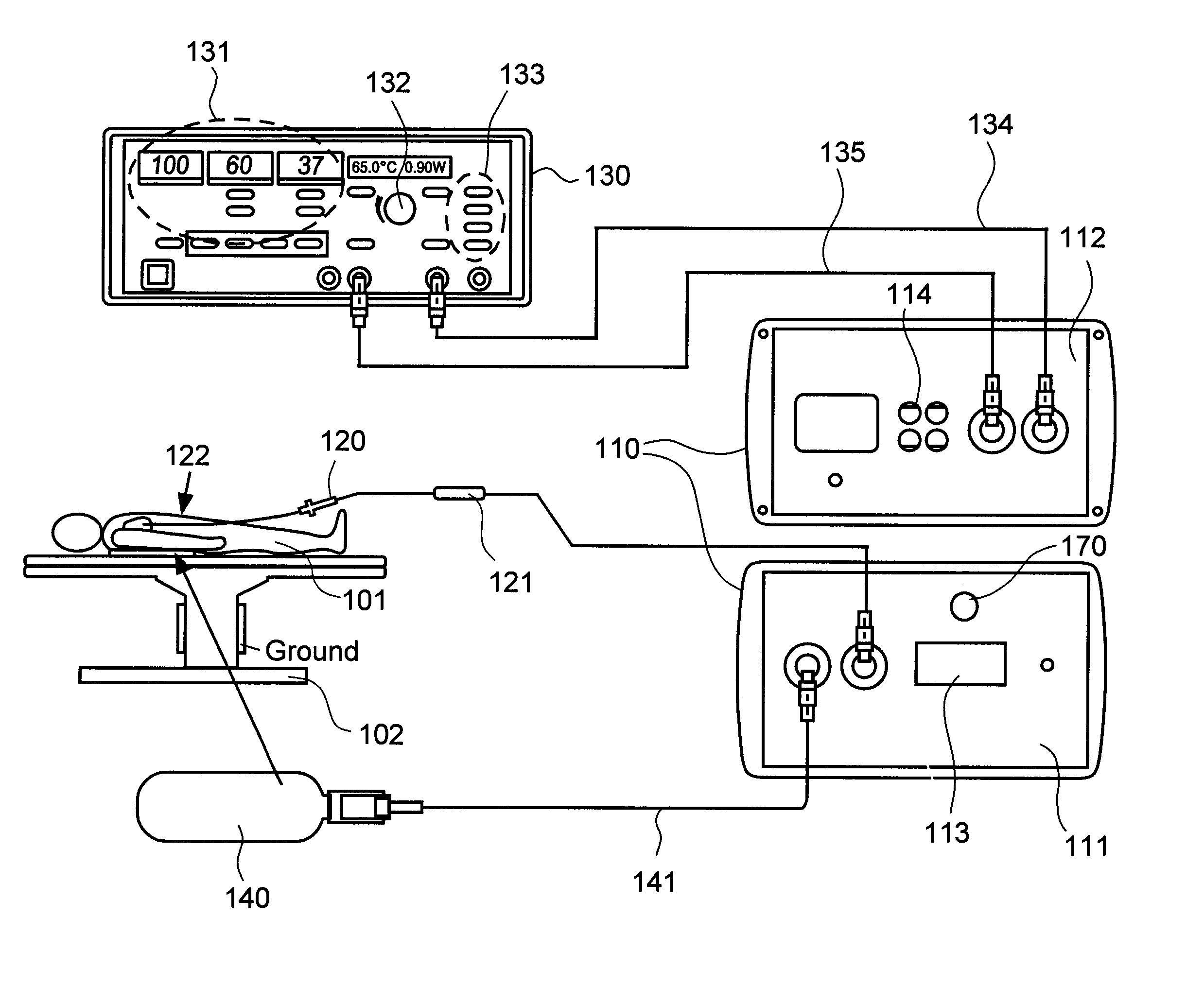
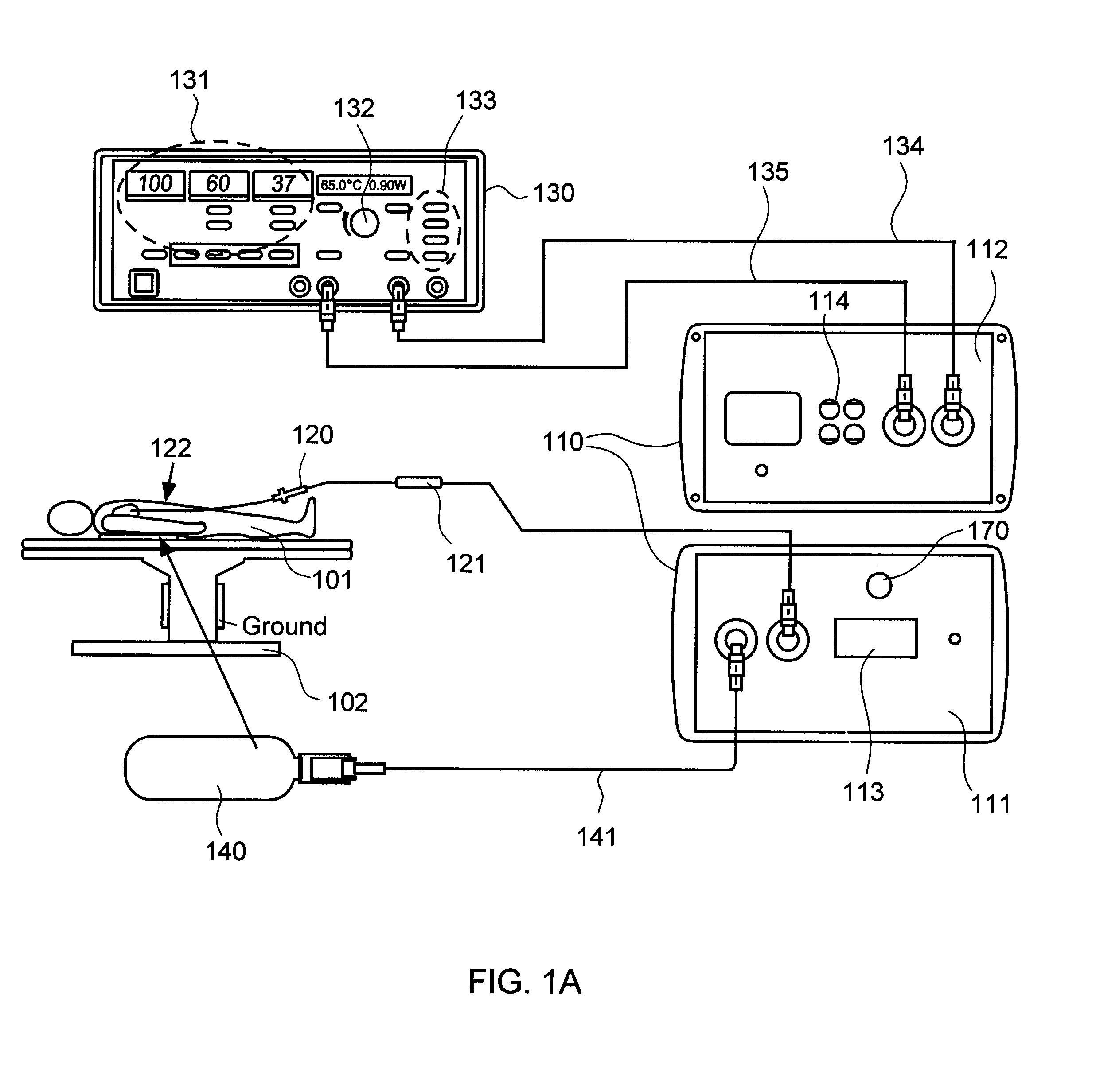
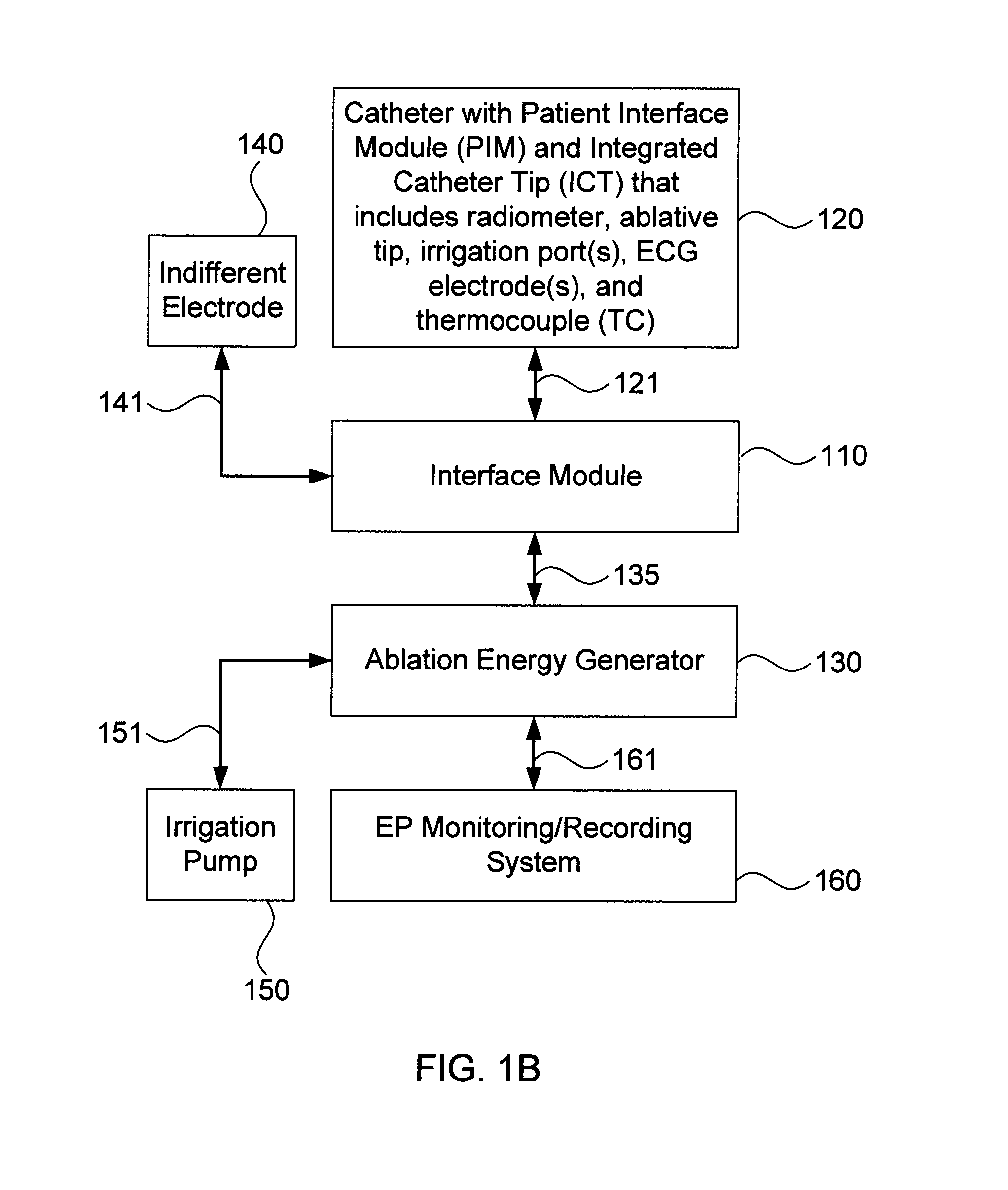
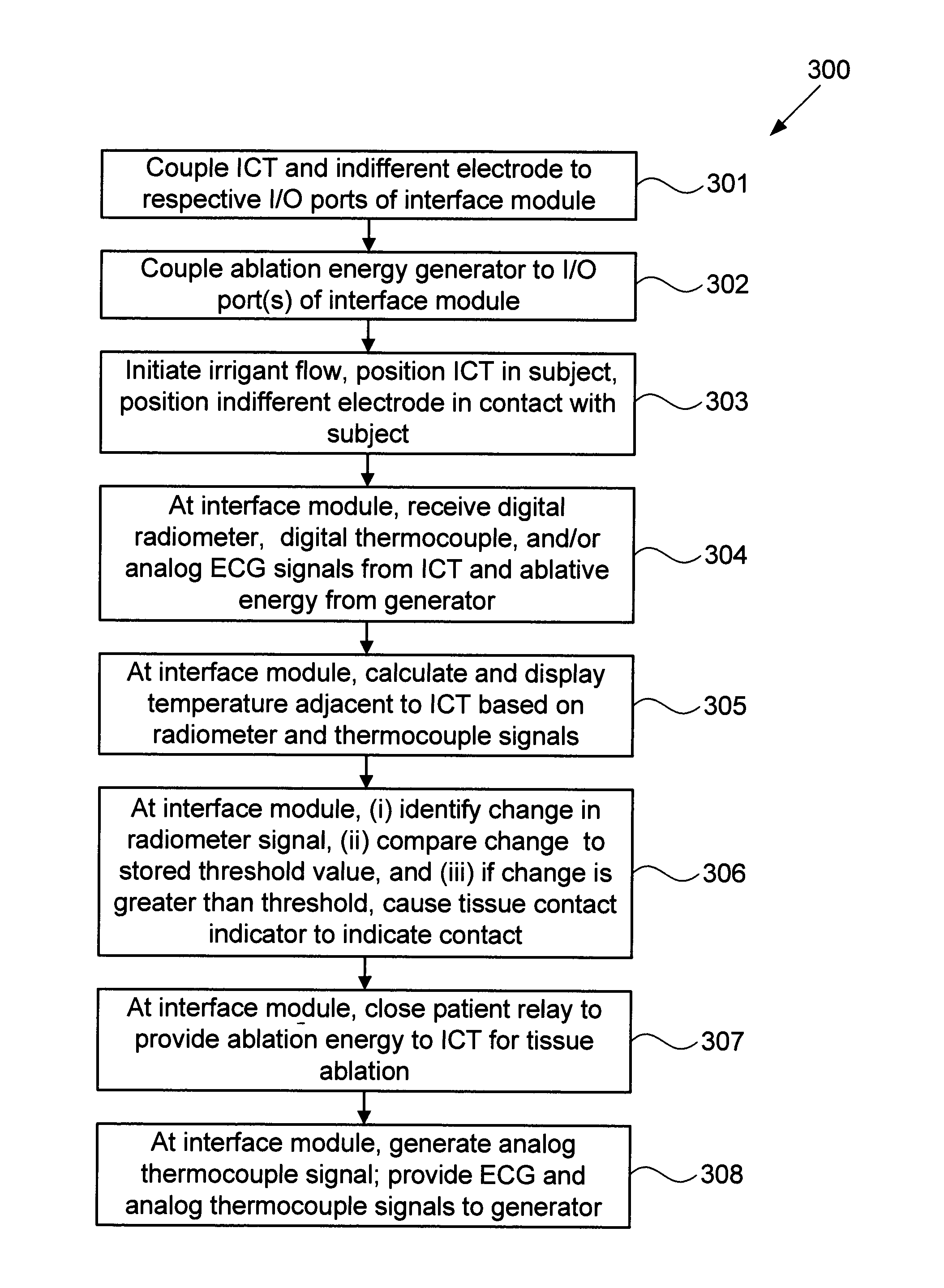
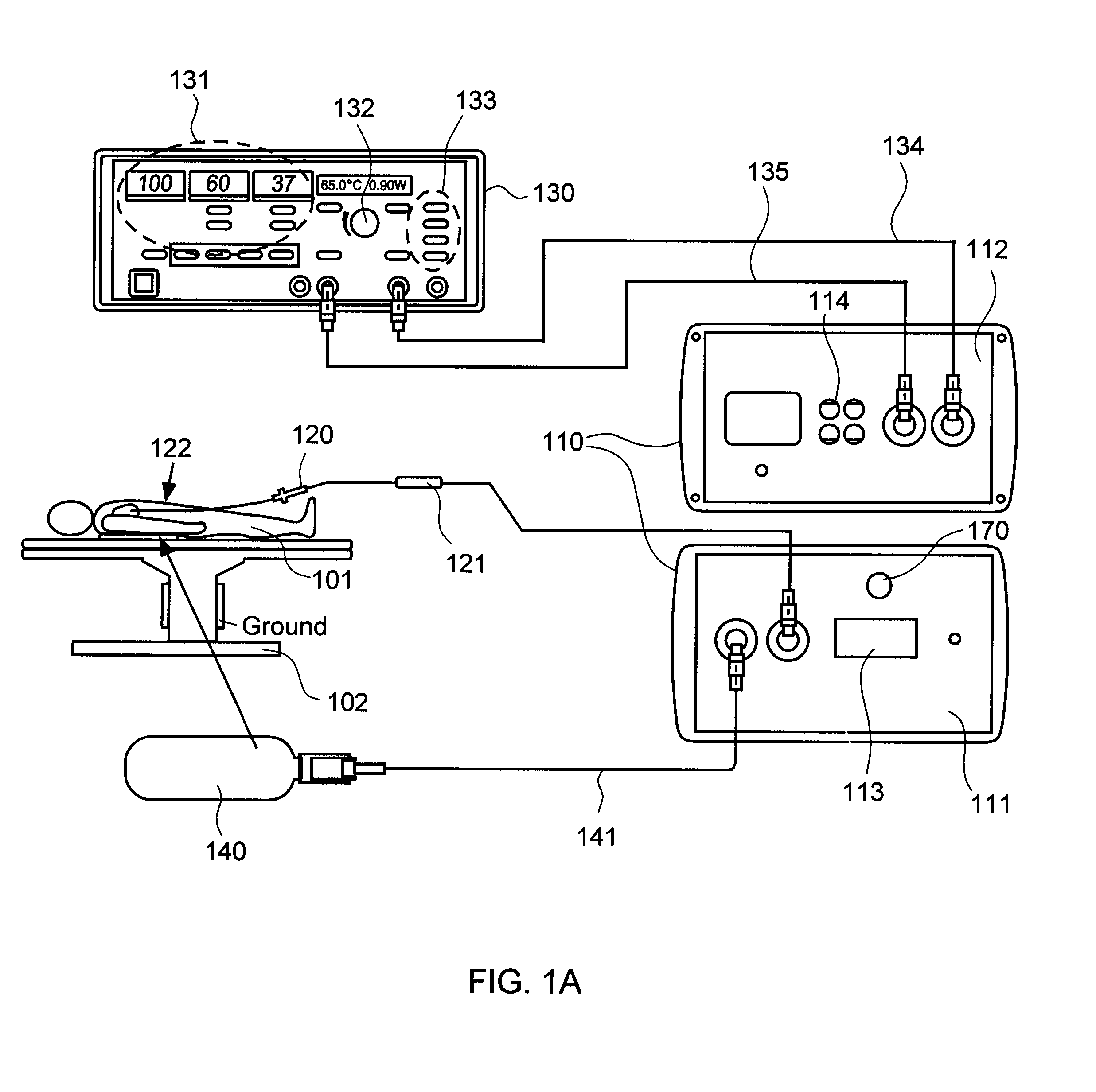
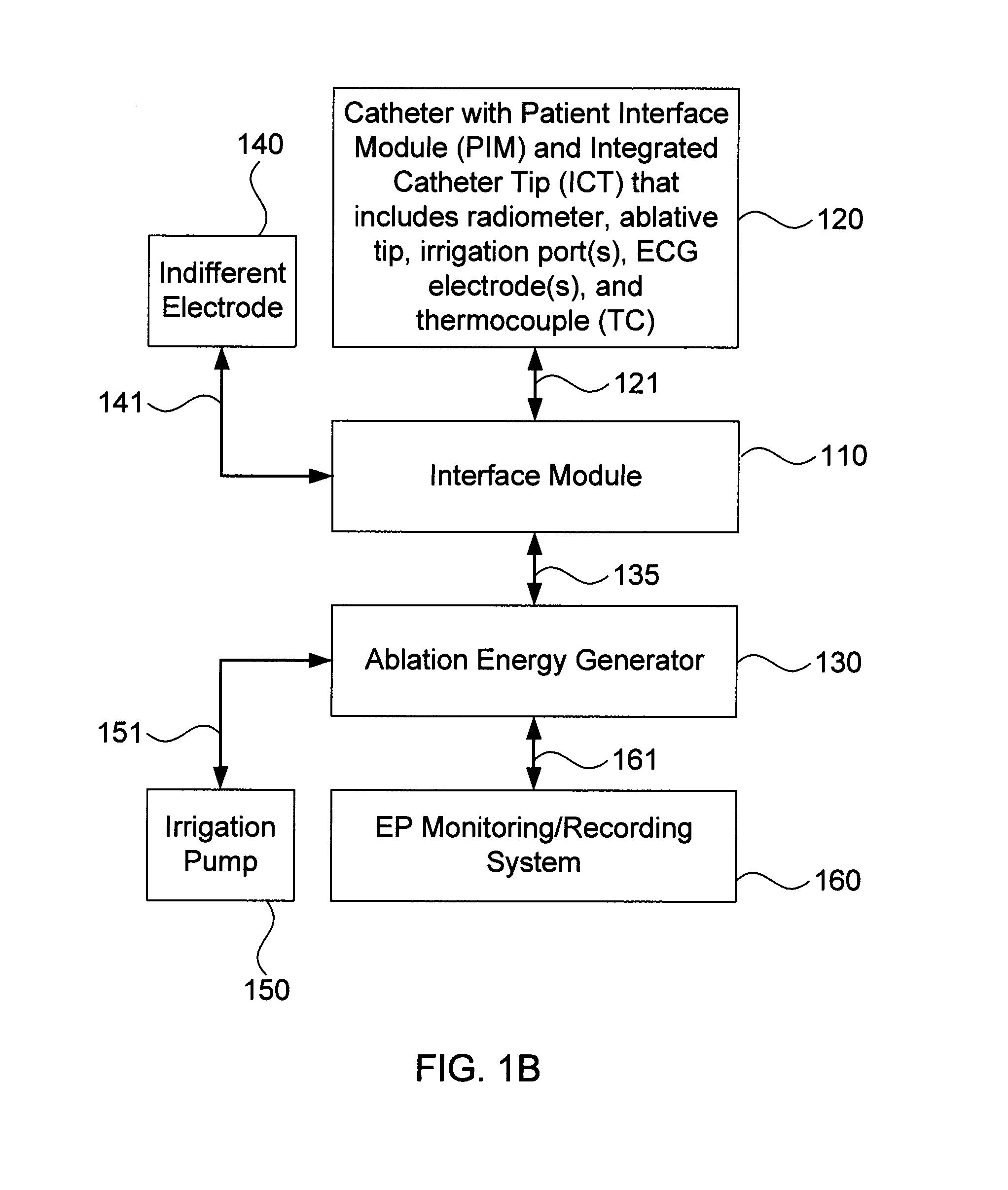
Systems and methods for radiometrically measuring temperature and detecting tissue contact prior to and during tissue ablation
ActiveUS20130324993A1Information can be usedProvide feedbackControlling energy of instrumentCatheterComputer moduleOutput device
The present invention provides systems and methods for radiometrically measuring temperature and detecting tissue contact during ablation. An interface module includes a first input / output (I / O) port for receiving radiometer and thermocouple signals from an integrated catheter tip (ICT) that includes a radiometer; a second I / O port for receiving ablative energy from an electrosurgical generator; a temperature display; a patient relay; a computer-readable medium storing radiometer and thermocouple parameters and instructions for causing the processor to: calculate a temperature adjacent to the ICT based on the radiometer and thermocouple signals and the parameters; causing the temperature display to display the calculated temperature; closing the patient relay to pass ablative energy from the second to the first I / O port; determining whether the ICT is in contact with tissue based on the radiometer signal. An output device indicates whether the ICT is determined to be in contact with the tissue.
Owner:ADVANCED CARDIAC THERAPEUTICS +1
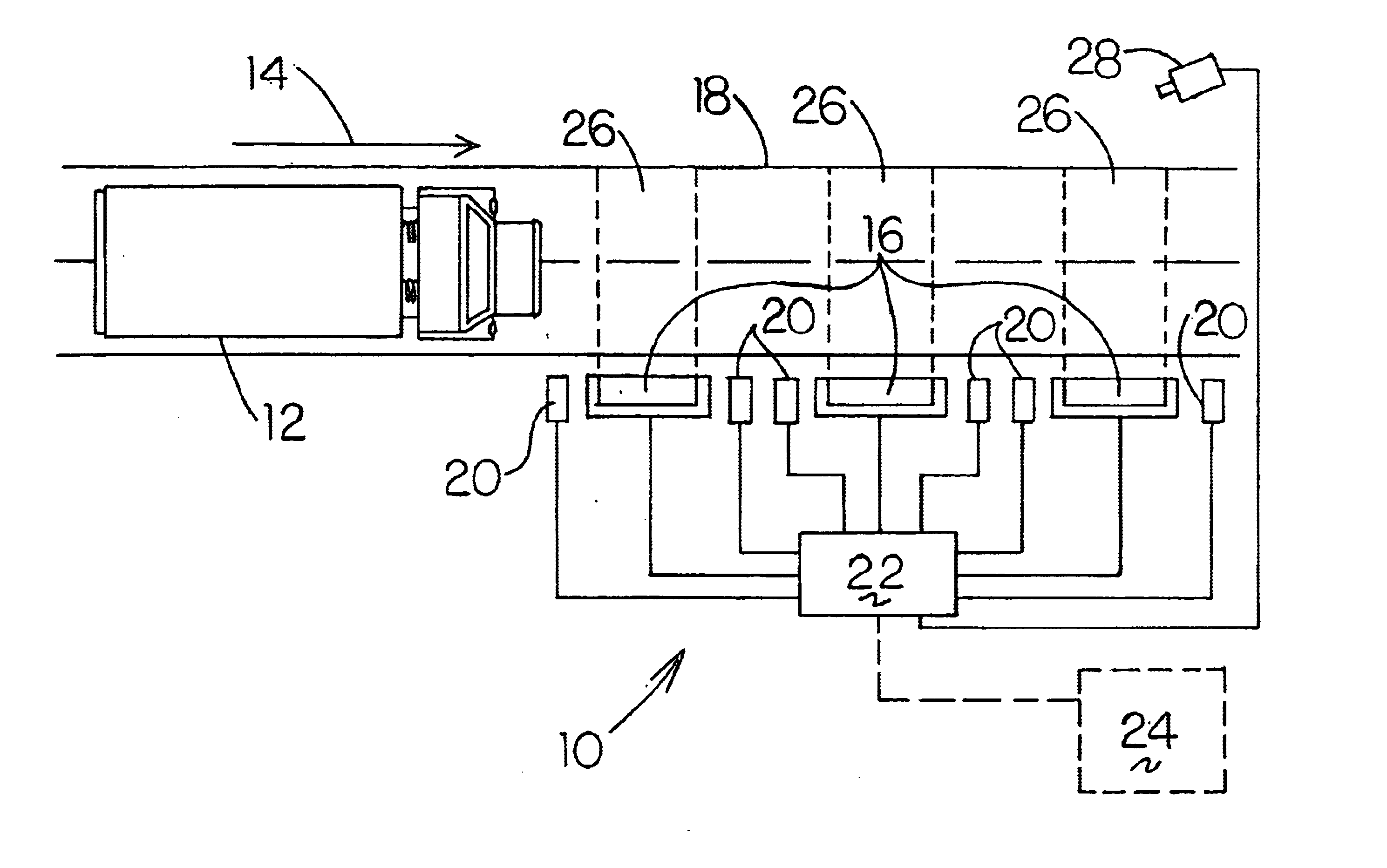
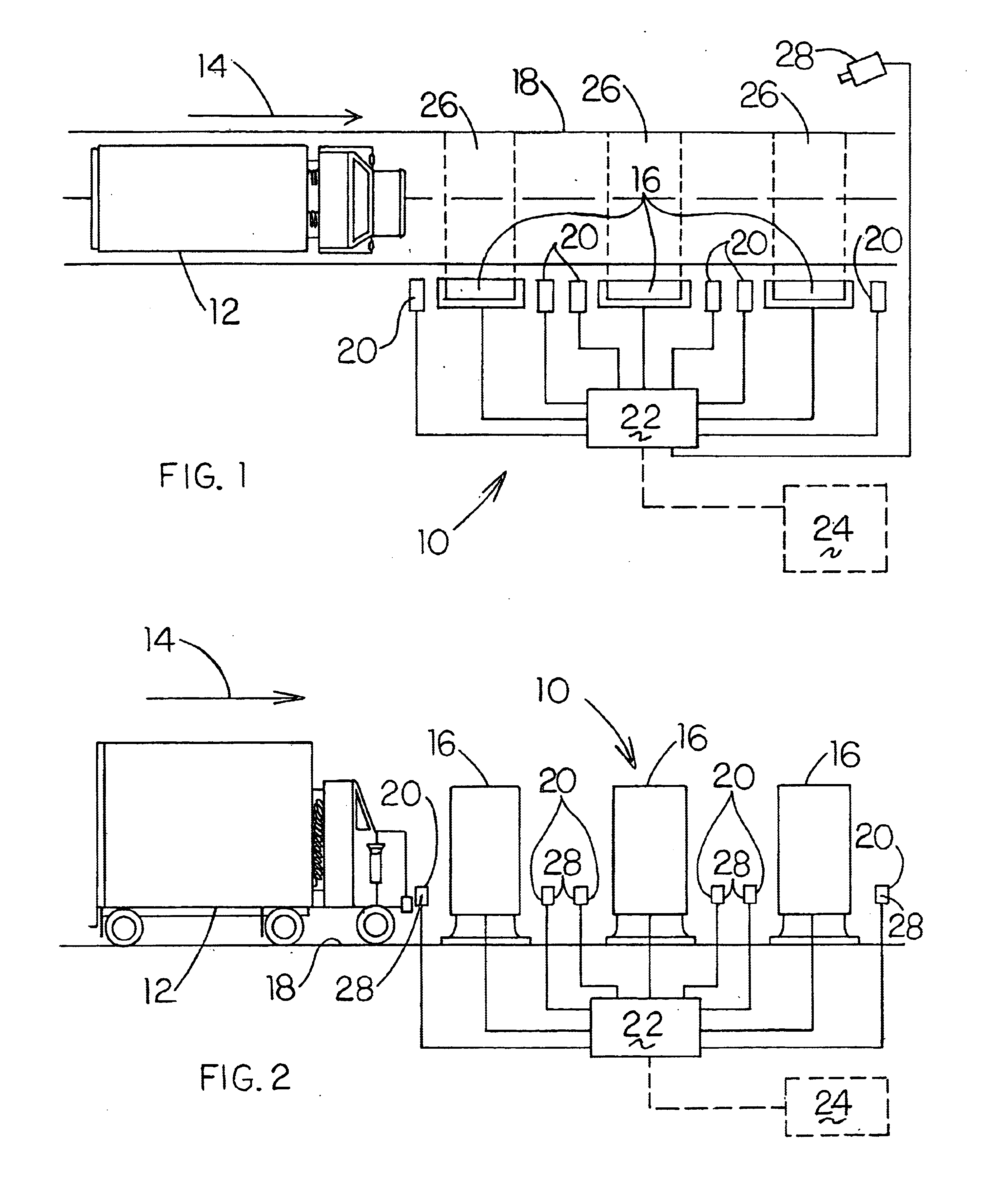
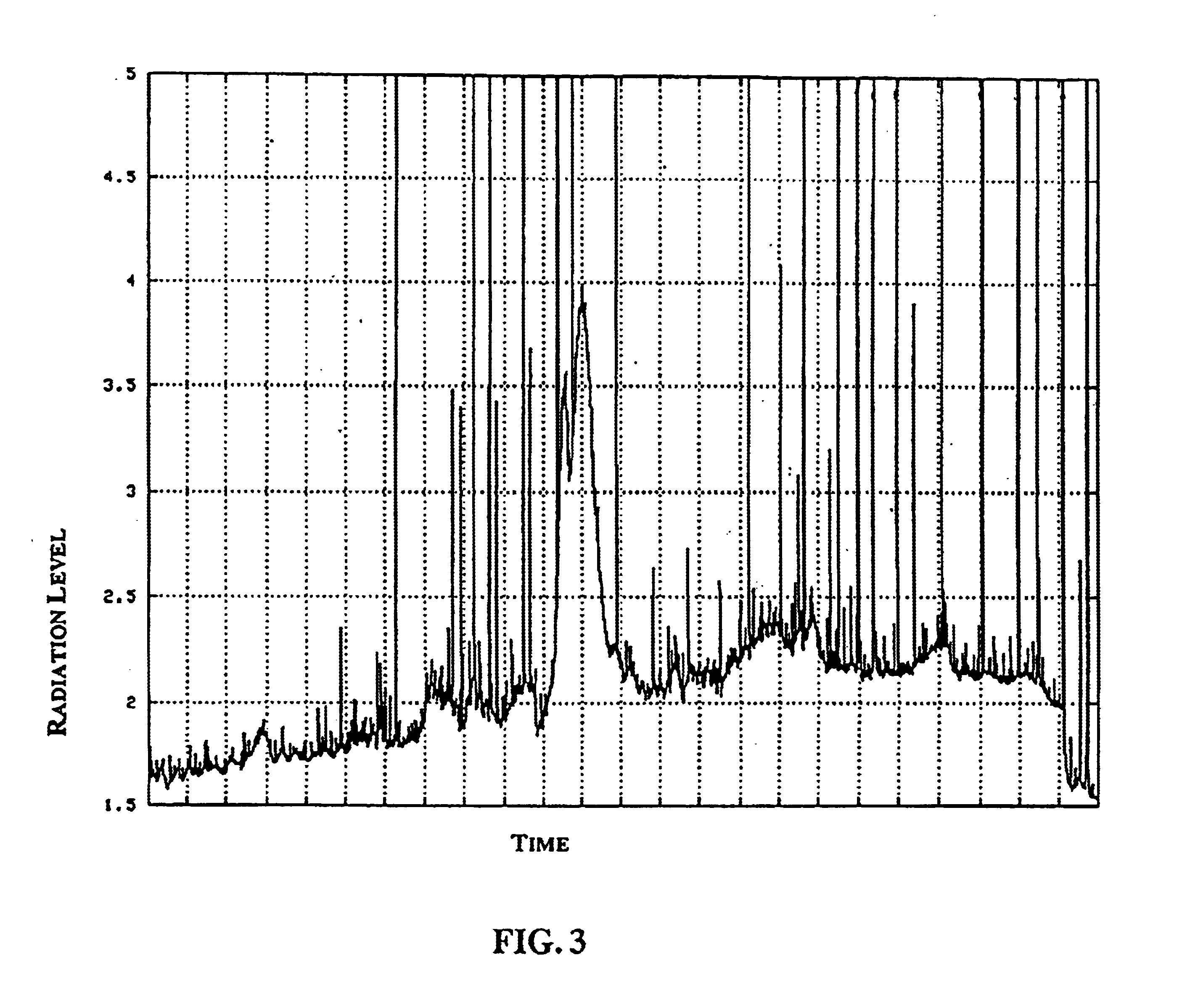
Method and apparatus for a radiation monitoring system
InactiveUS6727506B2High degree of sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsVehicle detectionCam
A radiation monitoring system for detecting levels of radiation emitted from moving objects traveling at a wide range of speeds, including the high speeds normally encountered with vehicles traveling on highways, interstates, thoroughfares, railroads and conveyors. At least two and preferably three ionizing radiation detectors are employed, spaced apart in series along the direction of travel of the moving object or vehicle. The object or vehicle is monitored for radioactivity and the results are transmitted and processed at a central location. The individual results from each detector for a particular object or vehicle are summed and averaged over the number of detectors used thereby clearly distinguishing the fluctuating background radiation detected at each detector from the consistent high levels of radiation detected from those moving objects or vehicles measured emitting radiation. The results are cooperatively linked by an identification system such as a web cam or other photographic device which obtains visual identification of the objects and vehicles emitting the abnormally high levels of radiation detected.
Owner:MALLETTE MALCOLM C
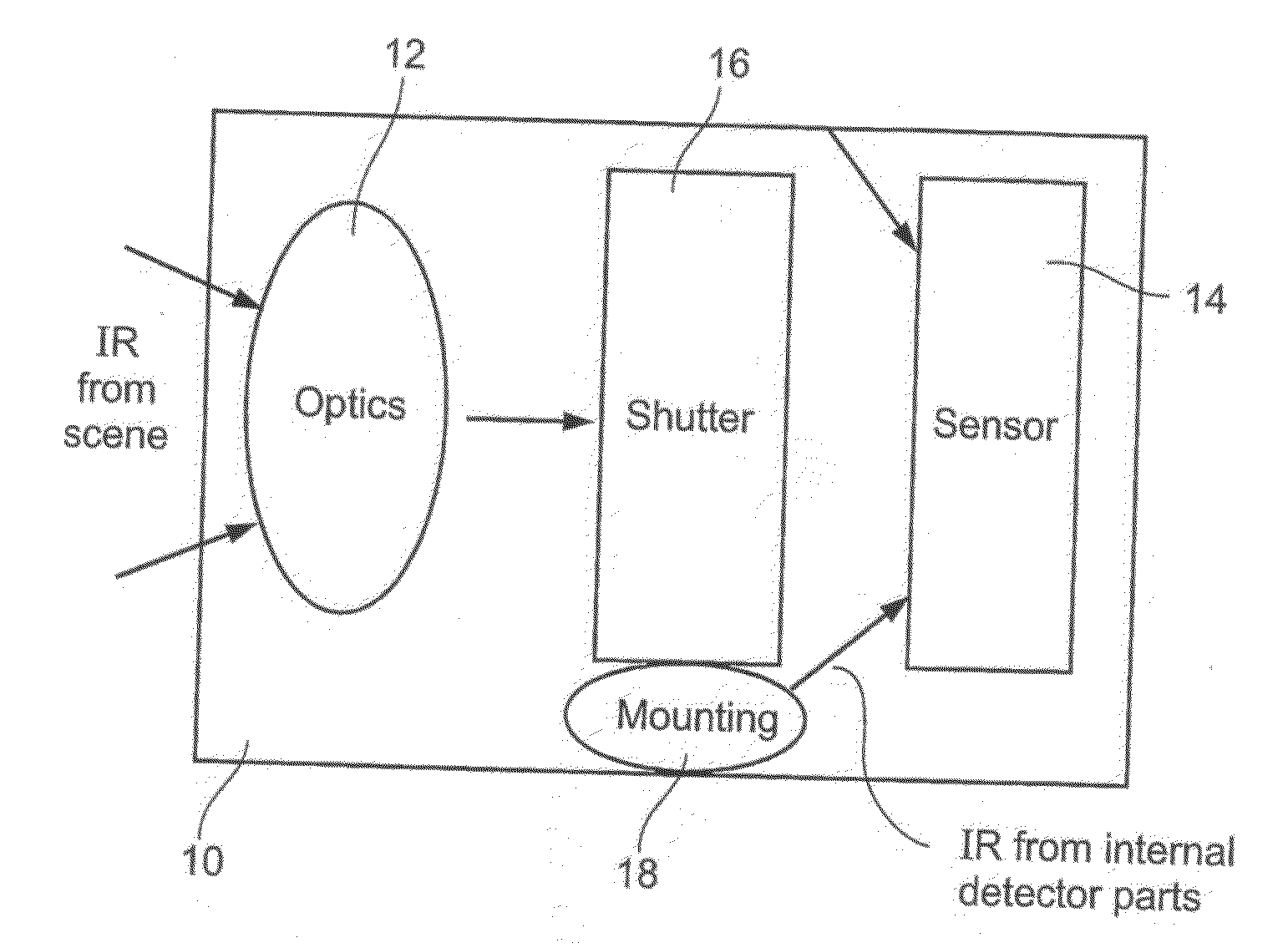
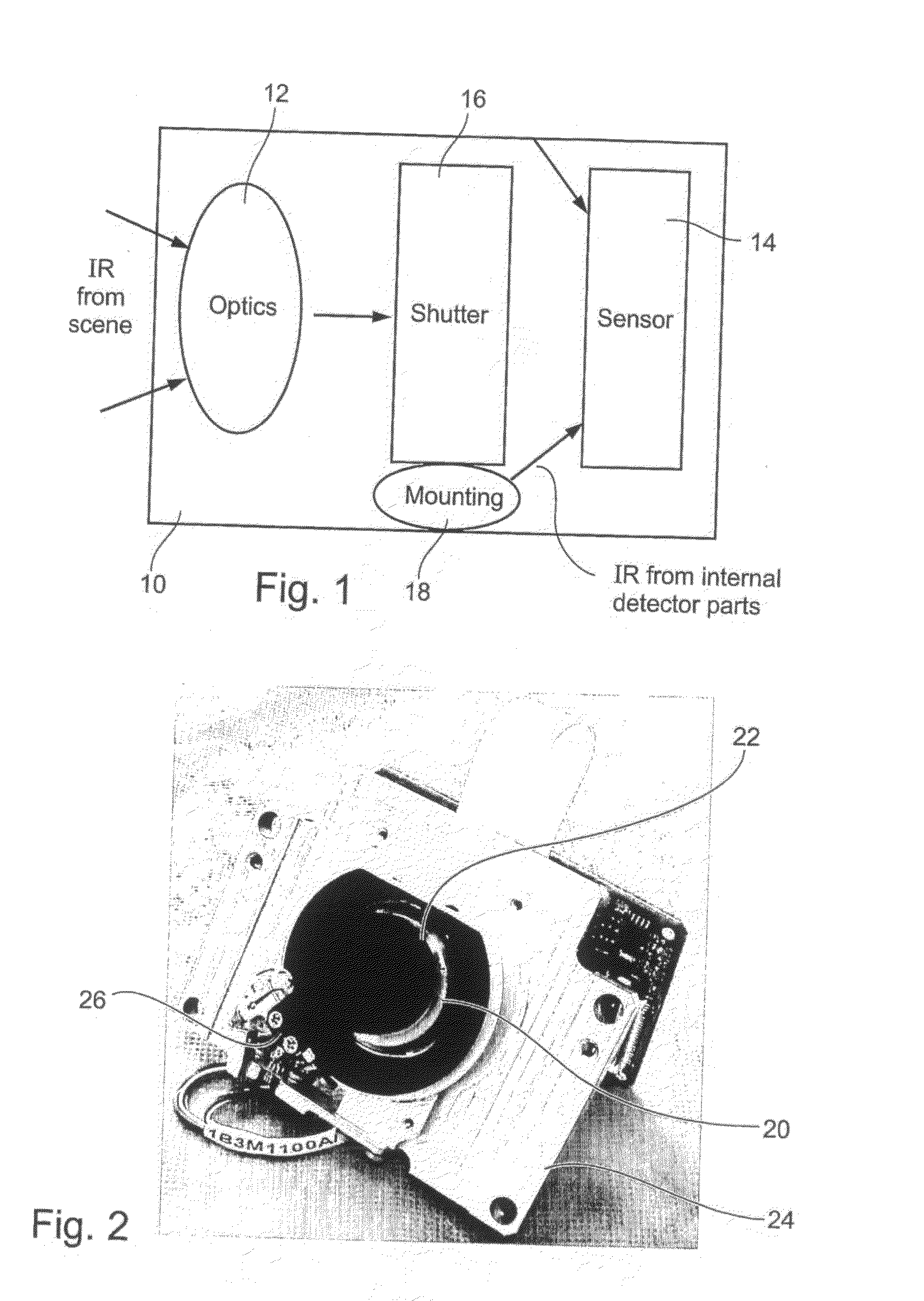
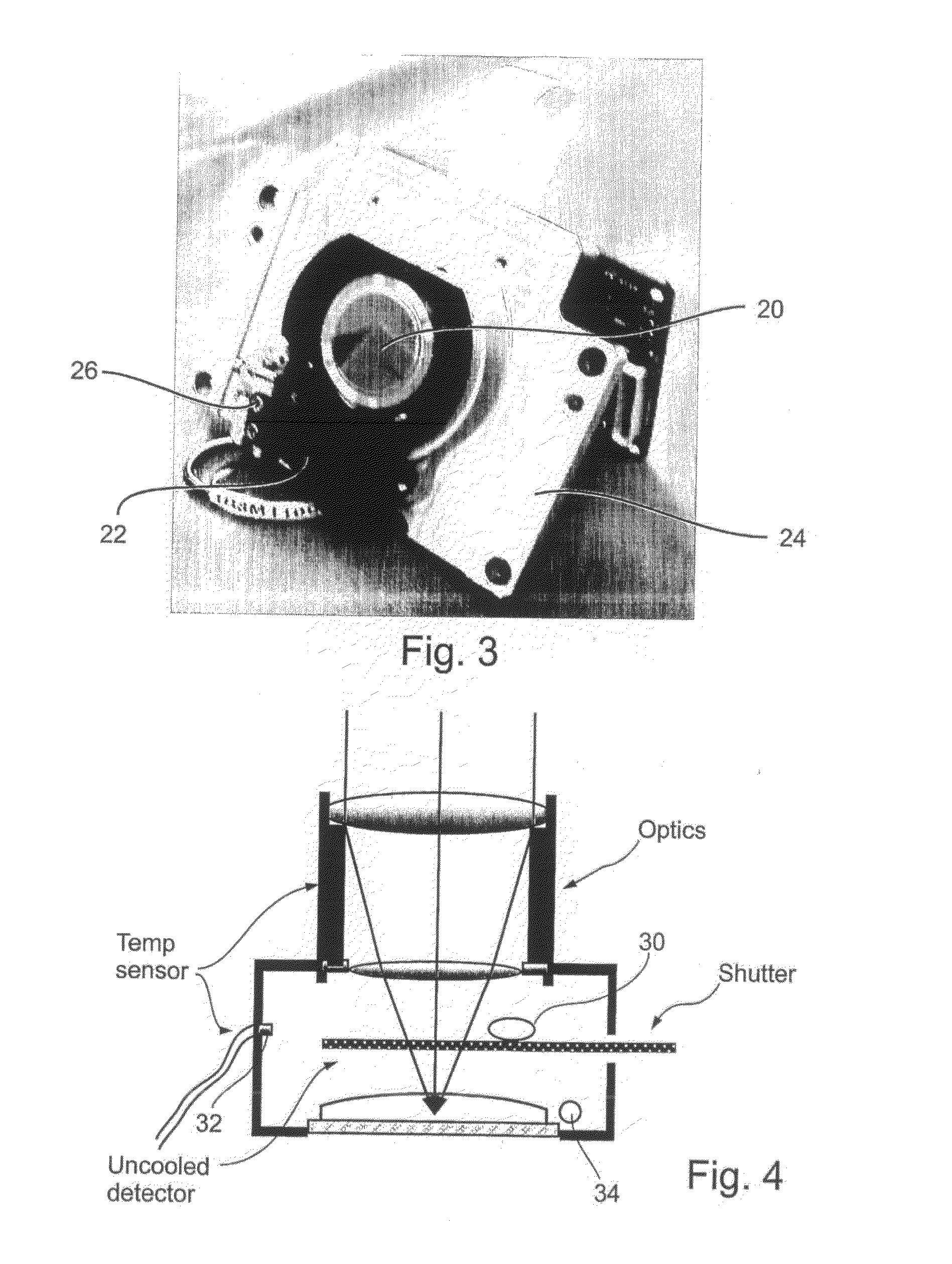
Radiometry Using an Uncooled Microbolometer Detector
InactiveUS20080210872A1Television system detailsRadiation pyrometryTemperature responseMicrobolometer
An infra-red imaging camera comprises focusing optics for gathering infra-red energy from an external scene, and an uncooled and unshielded detector arranged to detect infra red energy. Internal temperature sensing together with approximation of the temperature response of the camera provides a time varying calibration that allows the infra-red energy received at the detector to be used as a temperature measurement for objects in the camera's field of view.
Owner:OPGAL
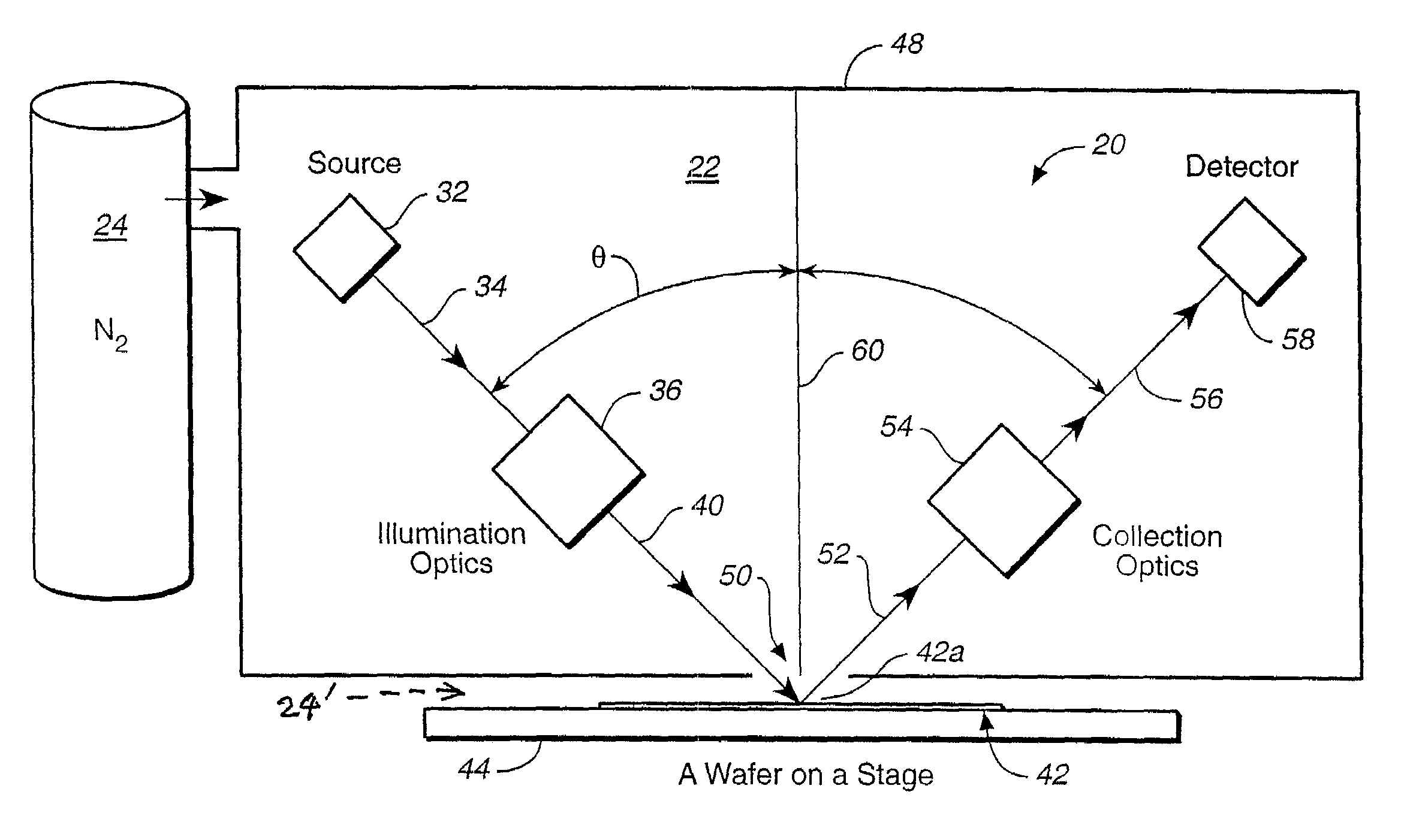
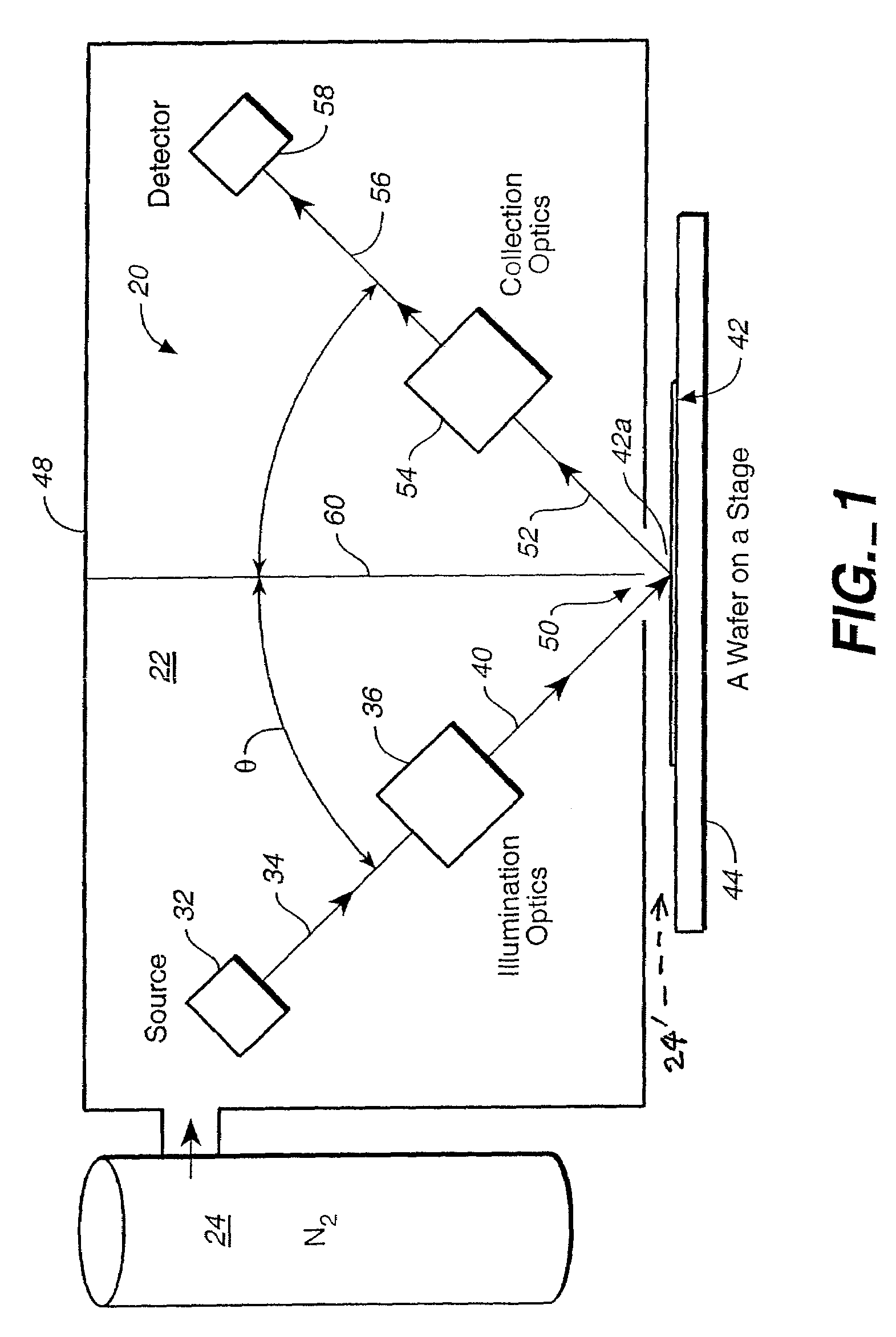
Optical system for measuring samples using short wavelength radiation
ActiveUS7369233B2Reduce decreaseImprove system throughputOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansUltrasound attenuationLength wave
In an optical system measuring sample characteristics, by reducing the amount of ambient absorbing gas or gases and moisture present in at least a portion of the illumination and detection paths experienced by vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) radiation used in the measurement process, the attenuation of such wavelength components can be reduced. Such reduction can be accomplished by a process without requiring the evacuation of all gases and moisture from the measurement system. In one embodiment, the reduction can be accomplished by displacing at least some of the absorbing gas(es) and moisture present in at least a portion of the measuring paths so as to reduce the attenuation of VUV radiation. In this manner, the sample does not need to be placed in a vacuum, thereby enhancing system throughput.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Thermoluminescence measurements and dosimetry with temperature control of the thermoluminescent element
ActiveUS20060043314A1Rapid responseEasy to optimizeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesTemperature controlDosimetry radiation
A thermoluminescence (TL) dosimetry (TLD) system comprises at least one TLD element that is controllably heated and which temperature is monitored in real time using an infrared (IR) radiometry subsystem that provides respective IR radiation inputs to a control subsystem. The control subsystem uses the inputs to effect the heating control. The TLD system further comprises a TL measuring subsystem for measuring TL emission data from each heated TLD element, the TL data used in obtaining a does curve indicative of the total radiation to which the TLD element has been exposed.
Owner:KATZIR ABRAHAM
Scanning apparatus
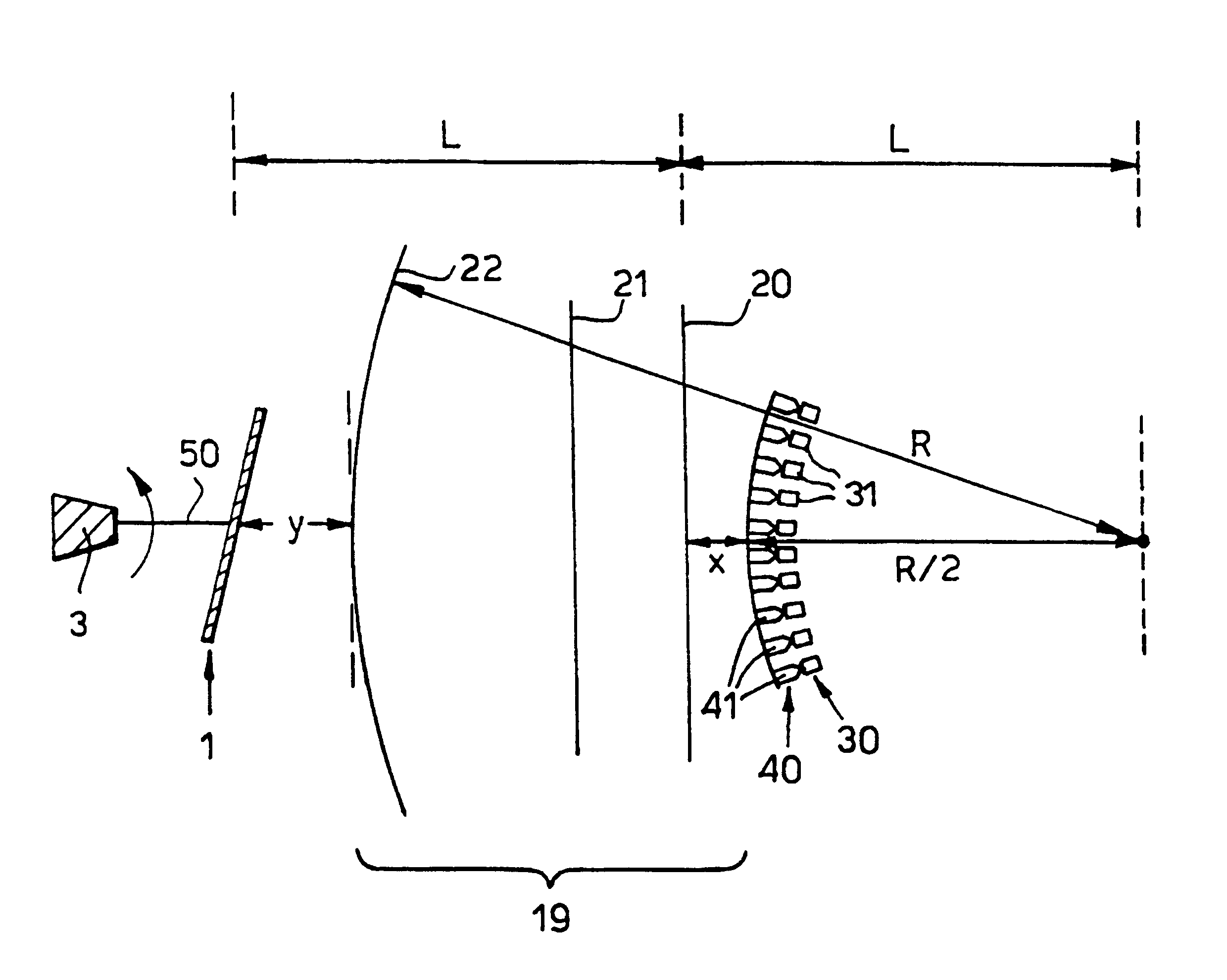
InactiveUS6587246B1Limited power requirementMinimum inertiaTelevision system detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRadarDetector array
Scanning apparatus which may be used in a real-time passive millimeter wavelength imaging system or in other radiometry systems. The apparatus scans input radiation from a scene and output radiation is transmitted to a receiver system, for example a millimeter wave imaging camera or a radar receiver. The apparatus comprises a rotatable reflective plate having an axis of rotation passing through the centre of its surface and a lens arrangement for selectively transmitting and focusing radiation having a particular direction of polarisation. The apparatus may also comprise a feed horn array comprising a plurality of feed horns, the feed horns forming part of a spherical surface having a radius of curvature substantially equal to R / 2 and being concentric with the third substantially spherical polarising element. The apparatus may further comprise a detector array comprising a plurality of detector elements. The detector array may form part of a millimeter wave imaging camera.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Space charge dosimeters for extremely low power measurements of radiation in shipping containers
Methods and apparatus are described for space charge dosimeters for extremely low power measurements of radiation in shipping containers. A method includes insitu polling a suite of passive integrating ionizing radiation sensors including reading-out dosimetric data from a first passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor and a second passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor, where the first passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor and the second passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor remain situated where the dosimetric data was integrated while reading-out. Another method includes arranging a plurality of ionizing radiation sensors in a spatially dispersed array; determining a relative position of each of the plurality of ionizing radiation sensors to define a volume of interest; collecting ionizing radiation data from at least a subset of the plurality of ionizing radiation sensors; and triggering an alarm condition when a dose level of an ionizing radiation source is calculated to exceed a threshold.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
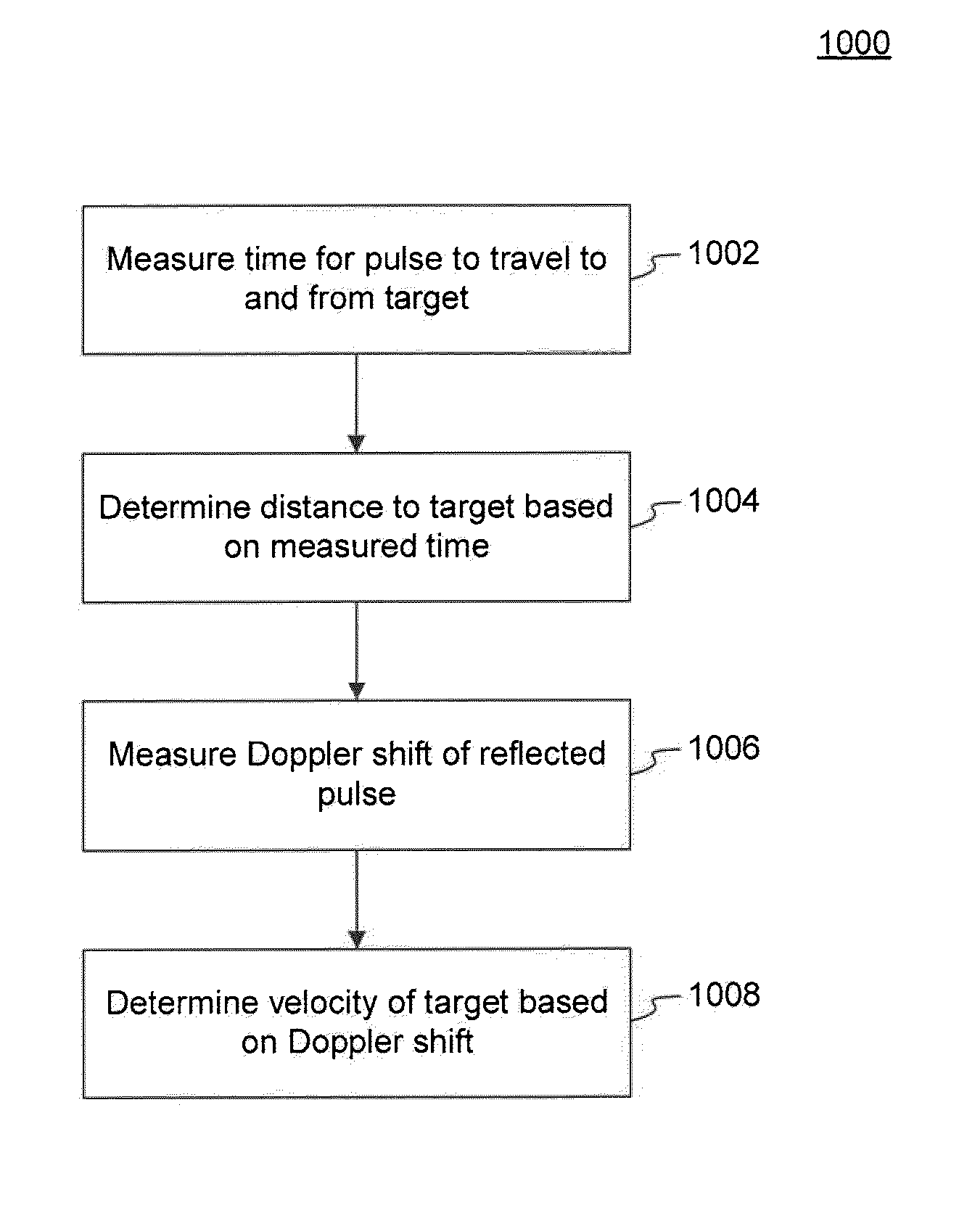
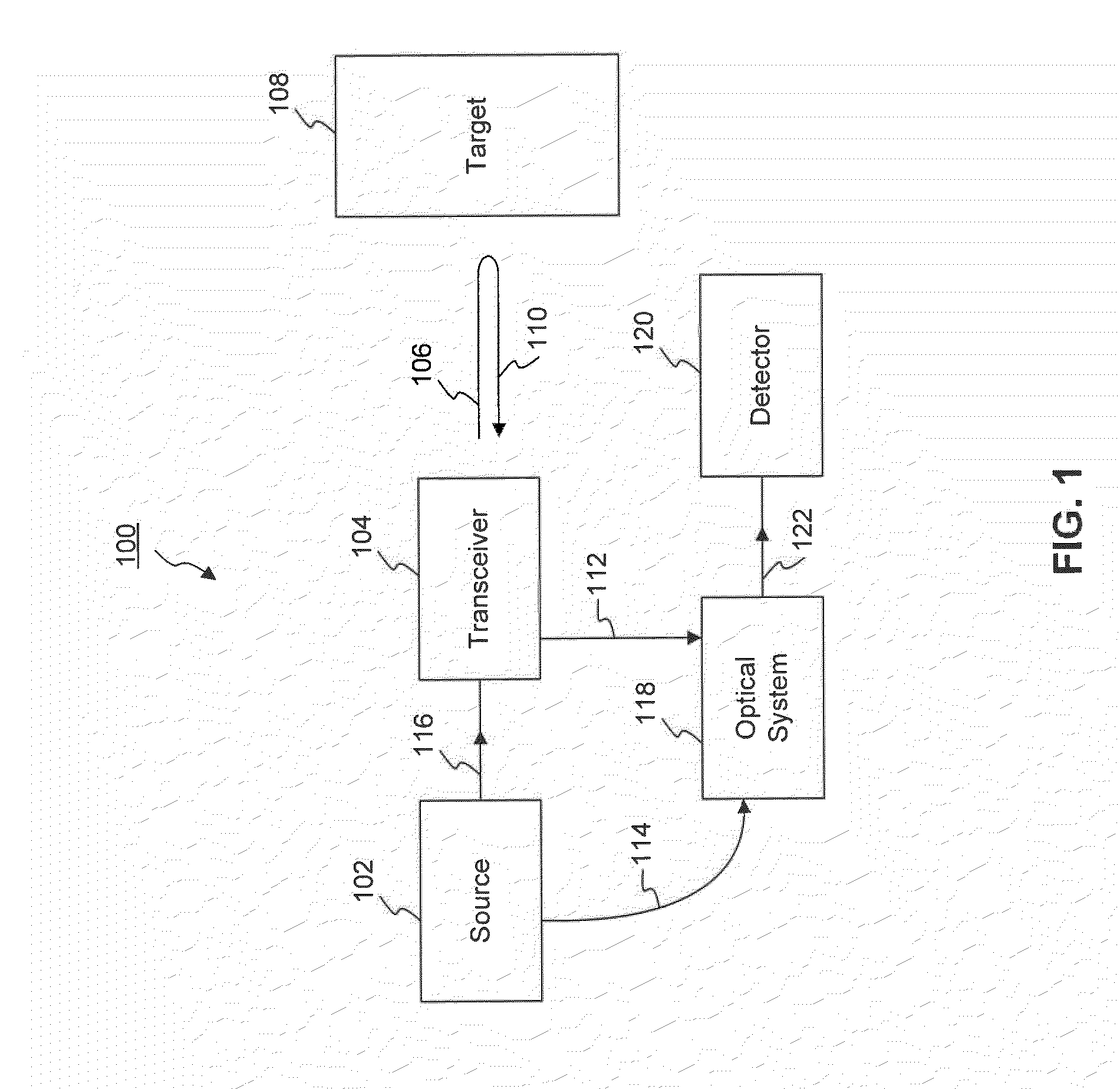
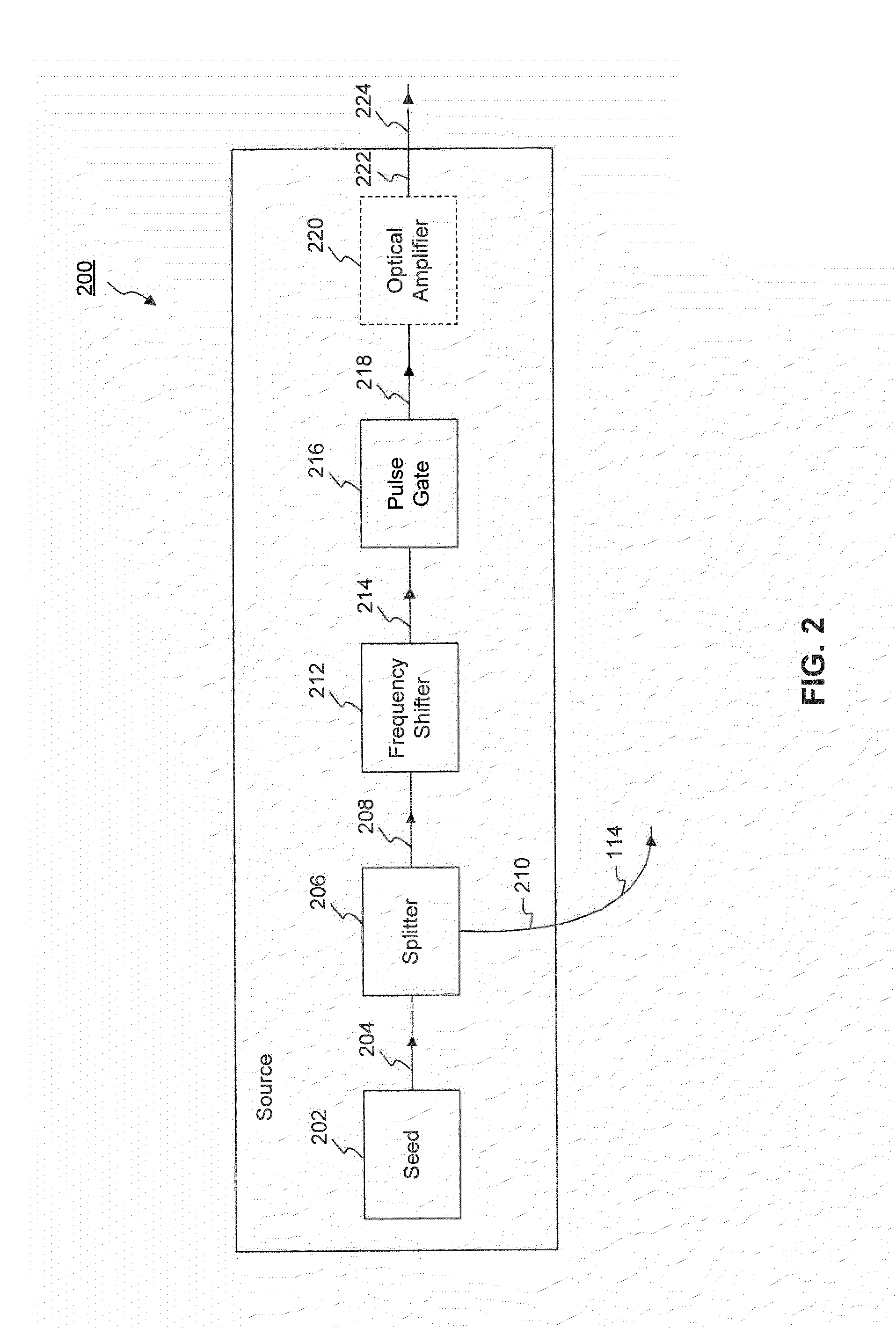
Method and Apparatus for a Pulsed Coherent Laser Range Finder
InactiveUS20110292371A1Improve accuracyMeasure can be takenOptical rangefindersDevices using optical meansLaser rangingTransceiver
Systems and methods are disclosed for measuring a distance, a velocity, etc., of a target using coherent laser radiation. In one example, a method is provided comprising measuring a time required for a light pulse to travel to and from a target, the light pulse reflecting from the target, and determining the distance to the target based on the measuring. The method also comprises measuring a Doppler shift of the reflected light pulse using an optical detection technique and determining the velocity of the target from the Doppler shift. In a further example, a system is disclosed comprising a transceiver, a coherent source, an optical system and a detector configured to measure the distance to the target based on a measured time for a light pulse to travel to and from the target. The system is also configured to determine the velocity of the target from a measured Doppler shift.
Owner:RD2 LLC
Method and device for near-field measuring of non-controlled radiation
InactiveUS6850851B1Method can be usedReduce measurementCurrent/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceShortest distanceAcoustics
An electric field emitted by an electronic equipment is measured by producing at least one radiation measurement in the radiating field of the equipment. Several sets of simultaneous near-field measurements, within a measuring surface located at a short distance from the equipment, are performed. The sets of performed measurements are processed by estimating the statistical properties of the radiated field at any point outside the measuring surface.
Owner:CHARTOLEAUX
Systems and methods for radiometrically measuring temperature and detecting tissue contact prior to and during tissue ablation
ActiveUS8954161B2Information can be usedProvide feedbackControlling energy of instrumentCatheterComputer moduleOutput device
The present invention provides systems and methods for radiometrically measuring temperature and detecting tissue contact during ablation. An interface module includes a first input / output (I / O) port for receiving radiometer and thermocouple signals from an integrated catheter tip (ICT) that includes a radiometer; a second I / O port for receiving ablative energy from an electrosurgical generator; a temperature display; a patient relay; a computer-readable medium storing radiometer and thermocouple parameters and instructions for causing the processor to: calculate a temperature adjacent to the ICT based on the radiometer and thermocouple signals and the parameters; causing the temperature display to display the calculated temperature; closing the patient relay to pass ablative energy from the second to the first I / O port; determining whether the ICT is in contact with tissue based on the radiometer signal. An output device indicates whether the ICT is determined to be in contact with the tissue.
Owner:ADVANCED CARDIAC THERAPEUTICS +1
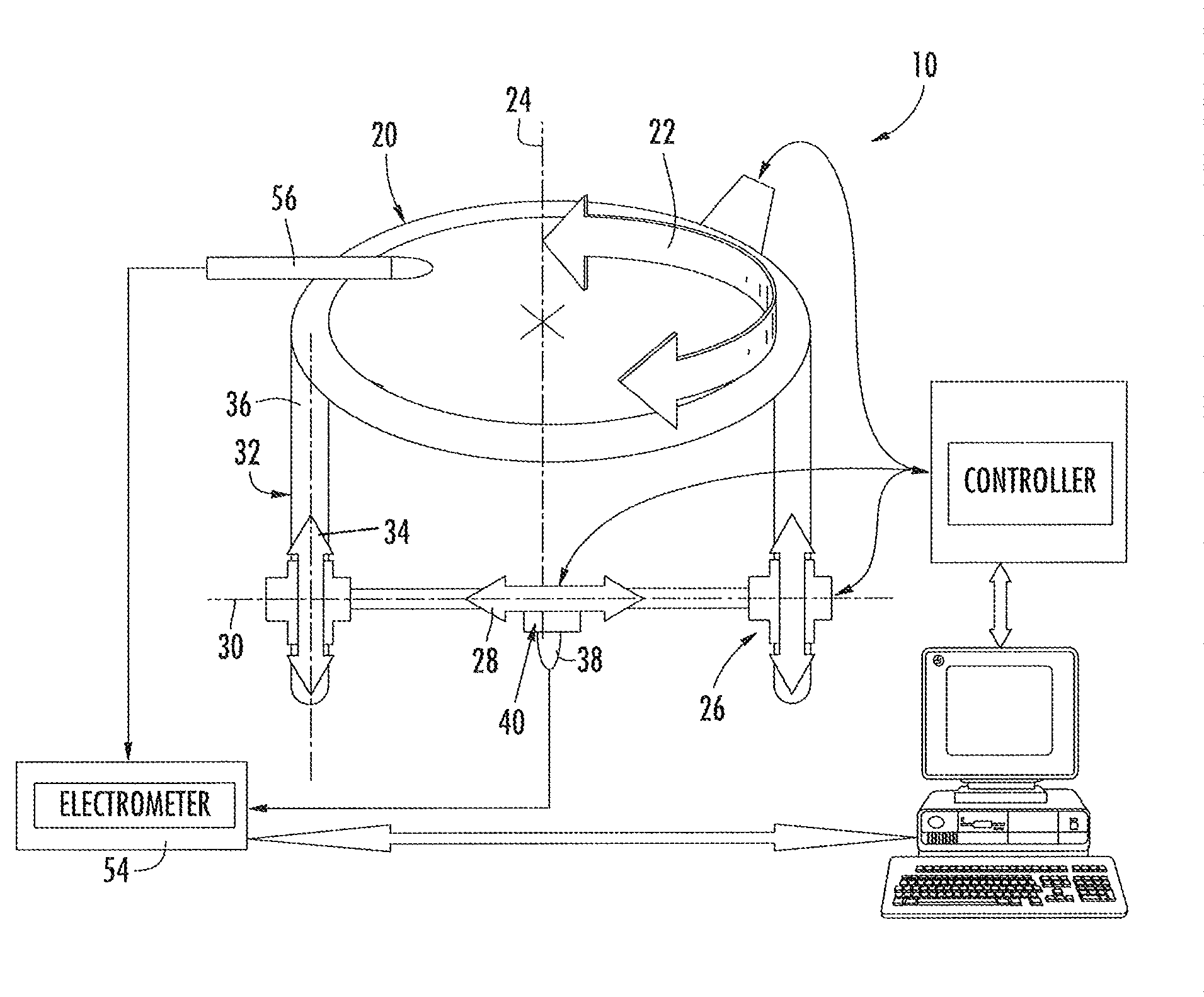
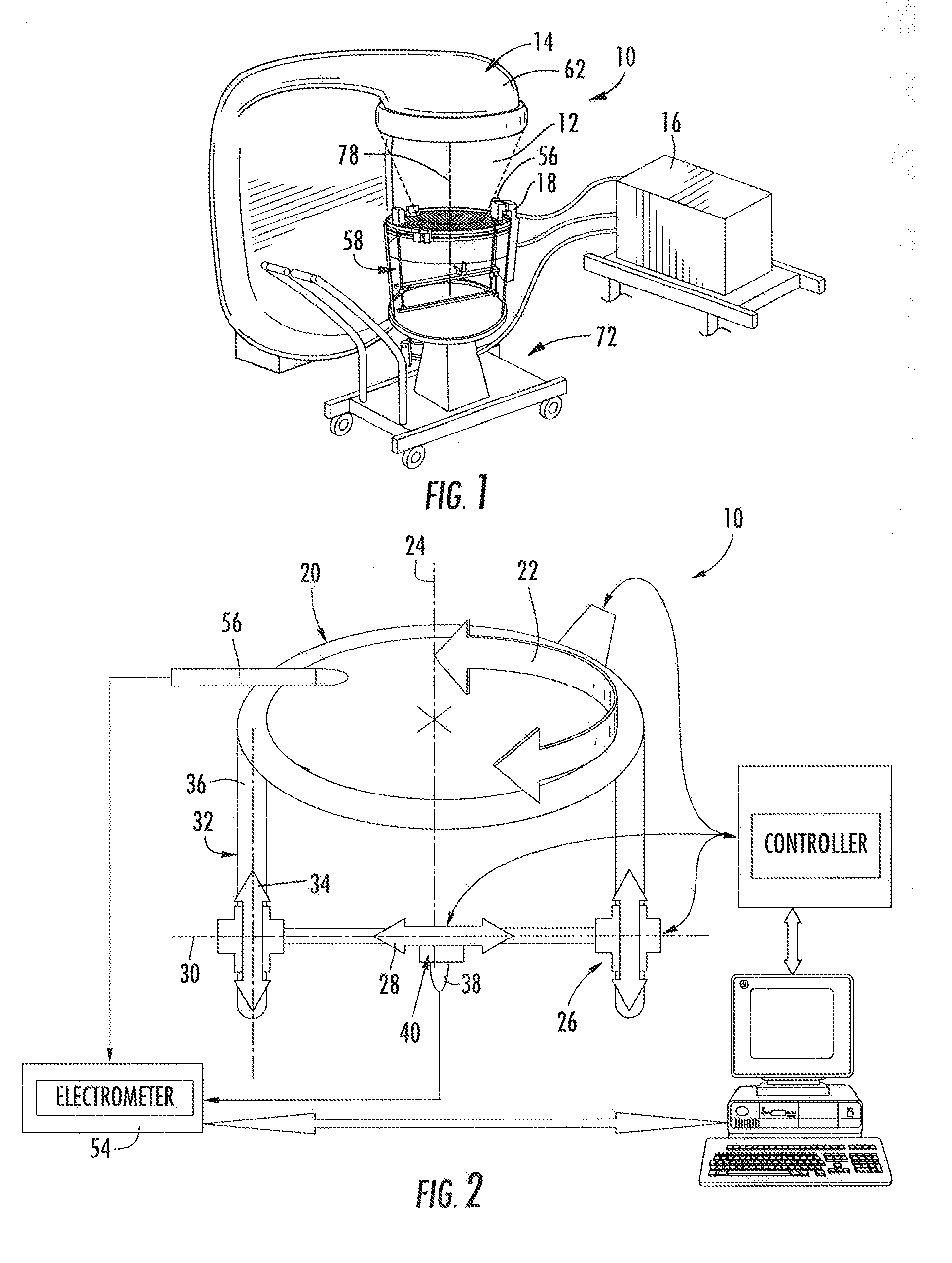
Multiple axes scanning system and method for measuring radiation from a radiation source
ActiveUS8321179B2Simple methodConfidenceTesting/calibration apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation fieldHorizontal and vertical
A three dimensional radiation measurement scanning system includes a circular drive operable with horizontal and vertical drives for moving a radiation detector through first, second and third orthogonal axes in a three dimensional scanning of the detector in a water tank. Motor are coupled to the drives and activated by a controller for providing the movement of the radiation detector which providing radiation field sensing signals for locations of the detector throughout the tank. A reference detector is fixed for comparing its radiation field measurements with those of the scanned radiation detector. An offset mount carries the radiation detector allowing it to be extended beyond the circular ring gear during horizontal movement of the radiation detector and thus position the radiation detector at wall surfaces of the water tank.
Owner:SUN NUCLEAR
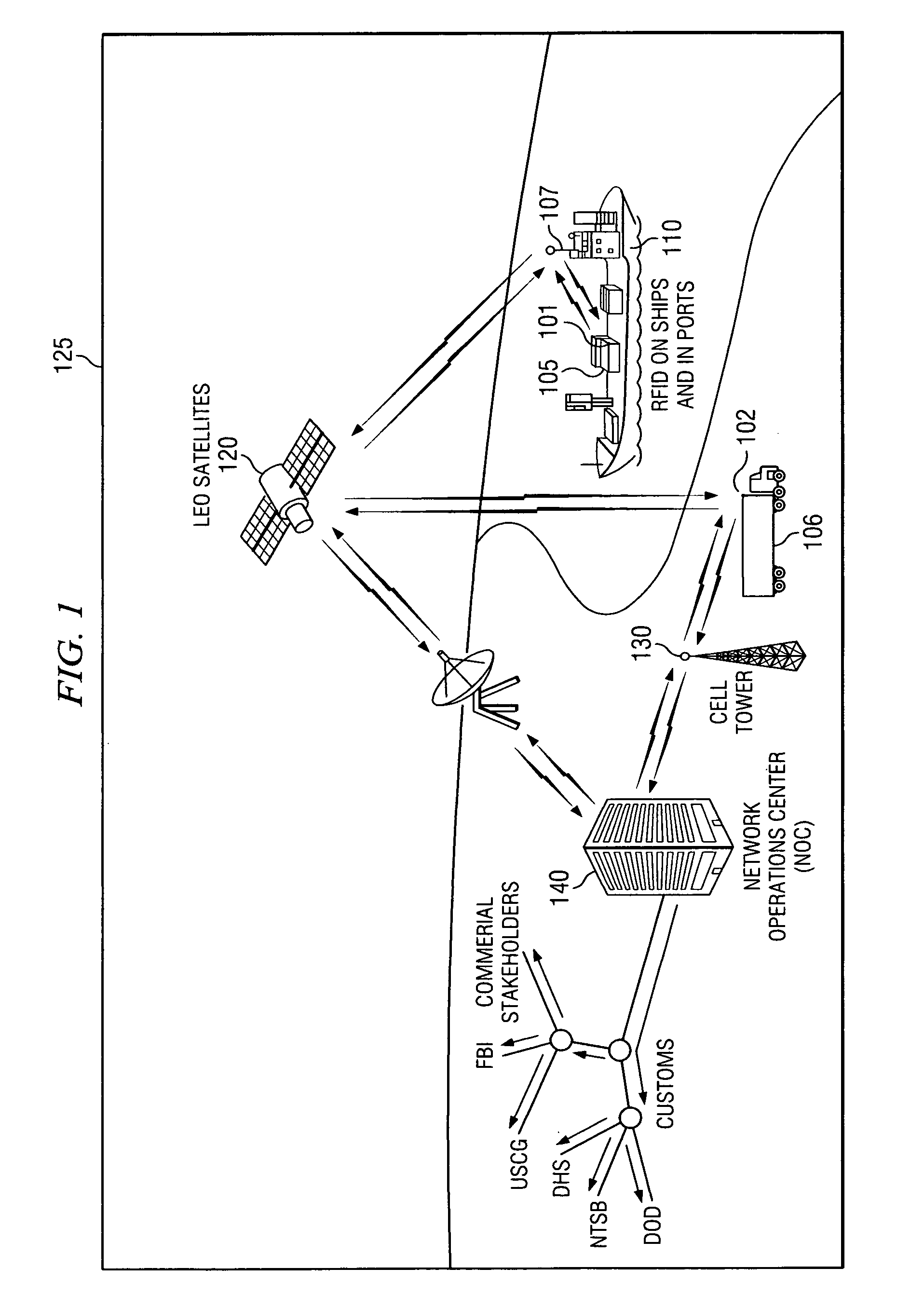
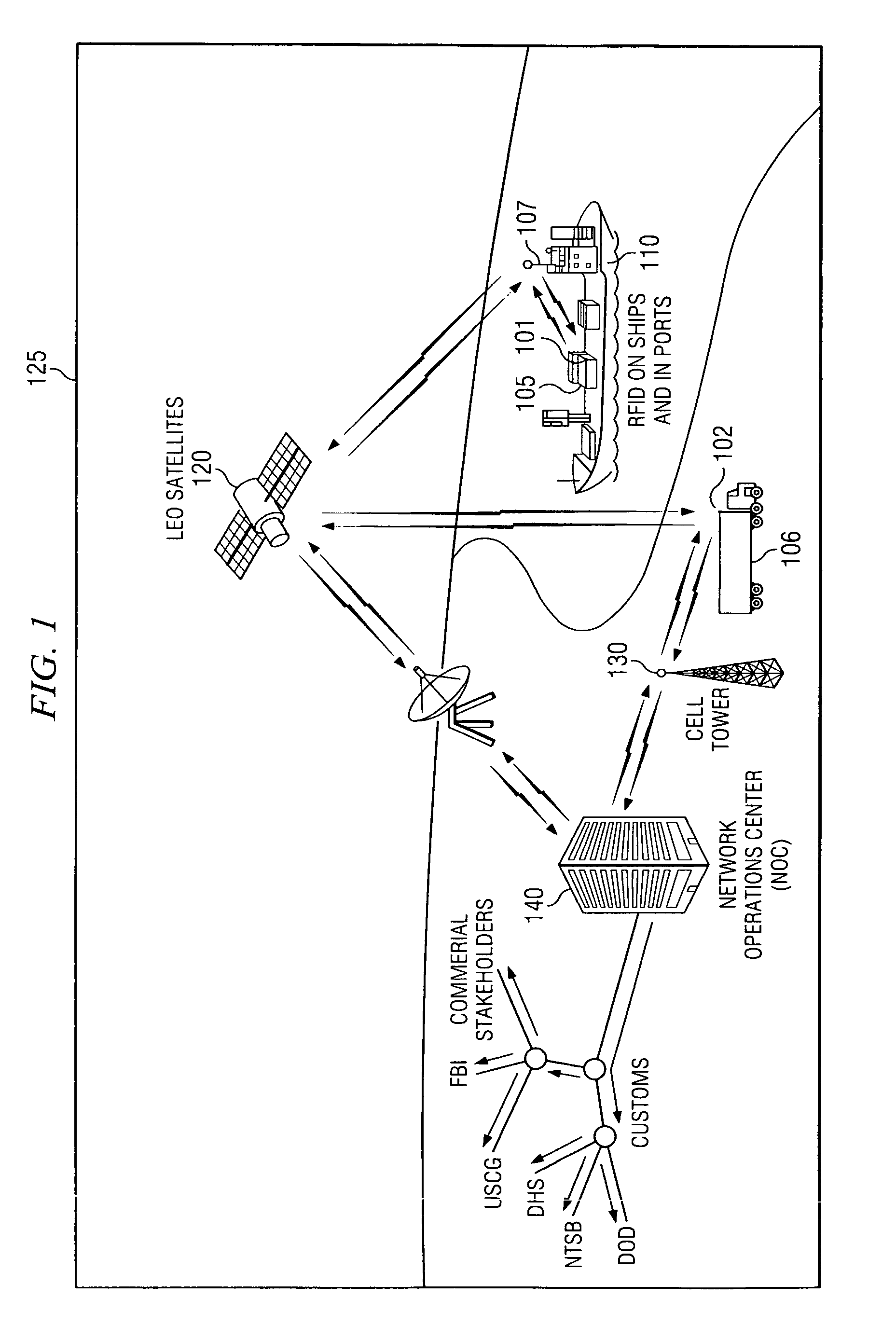
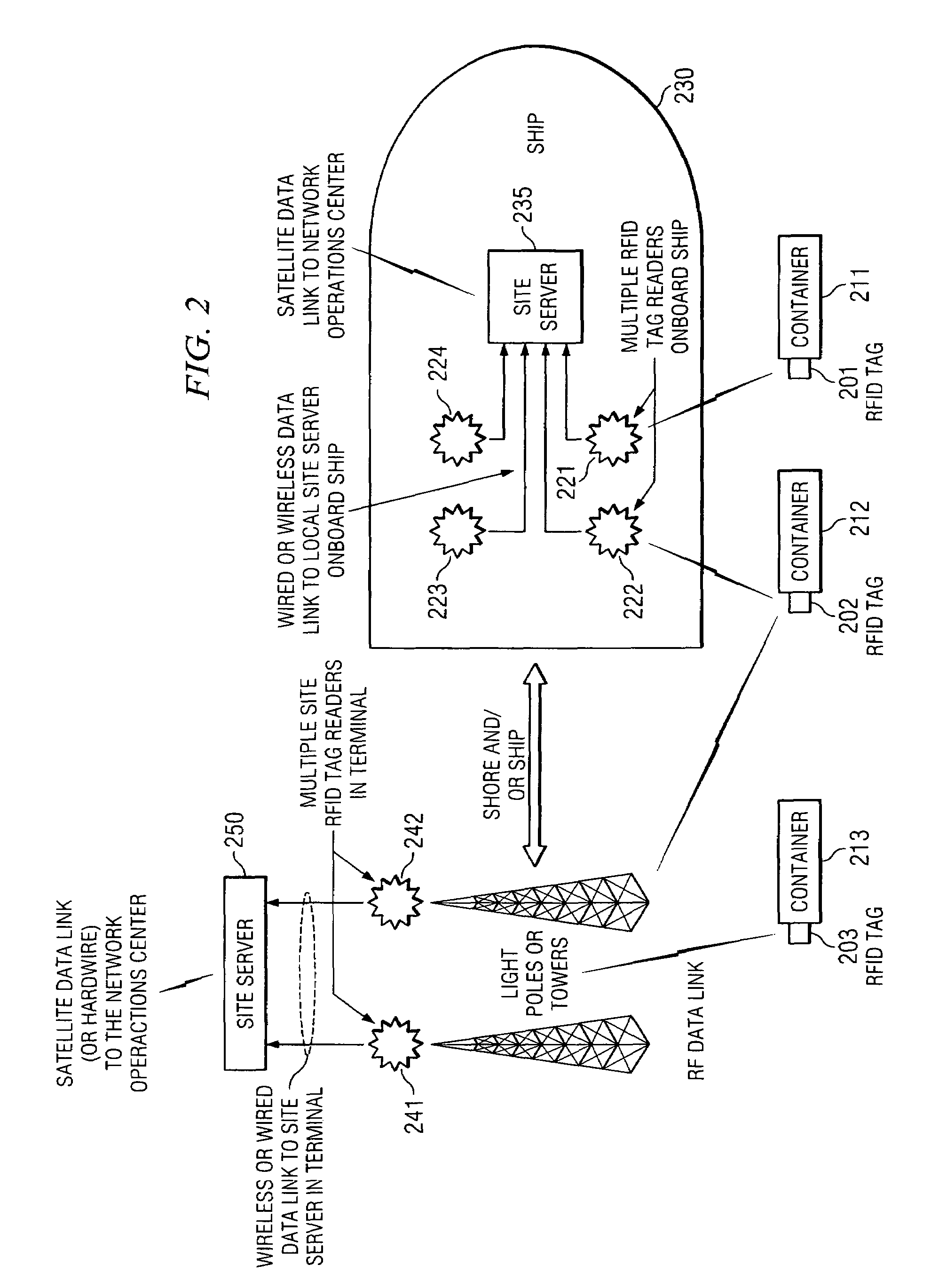
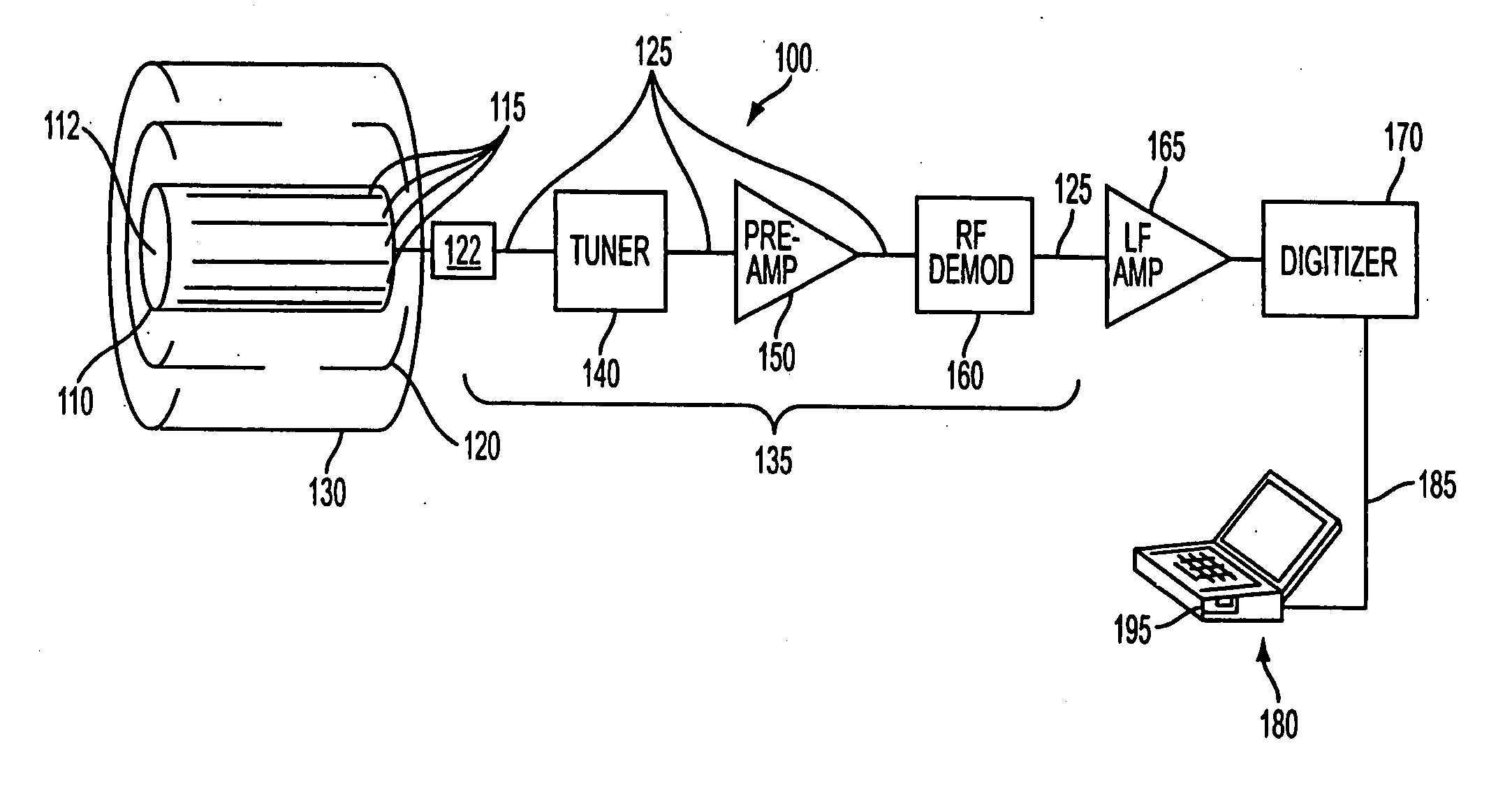
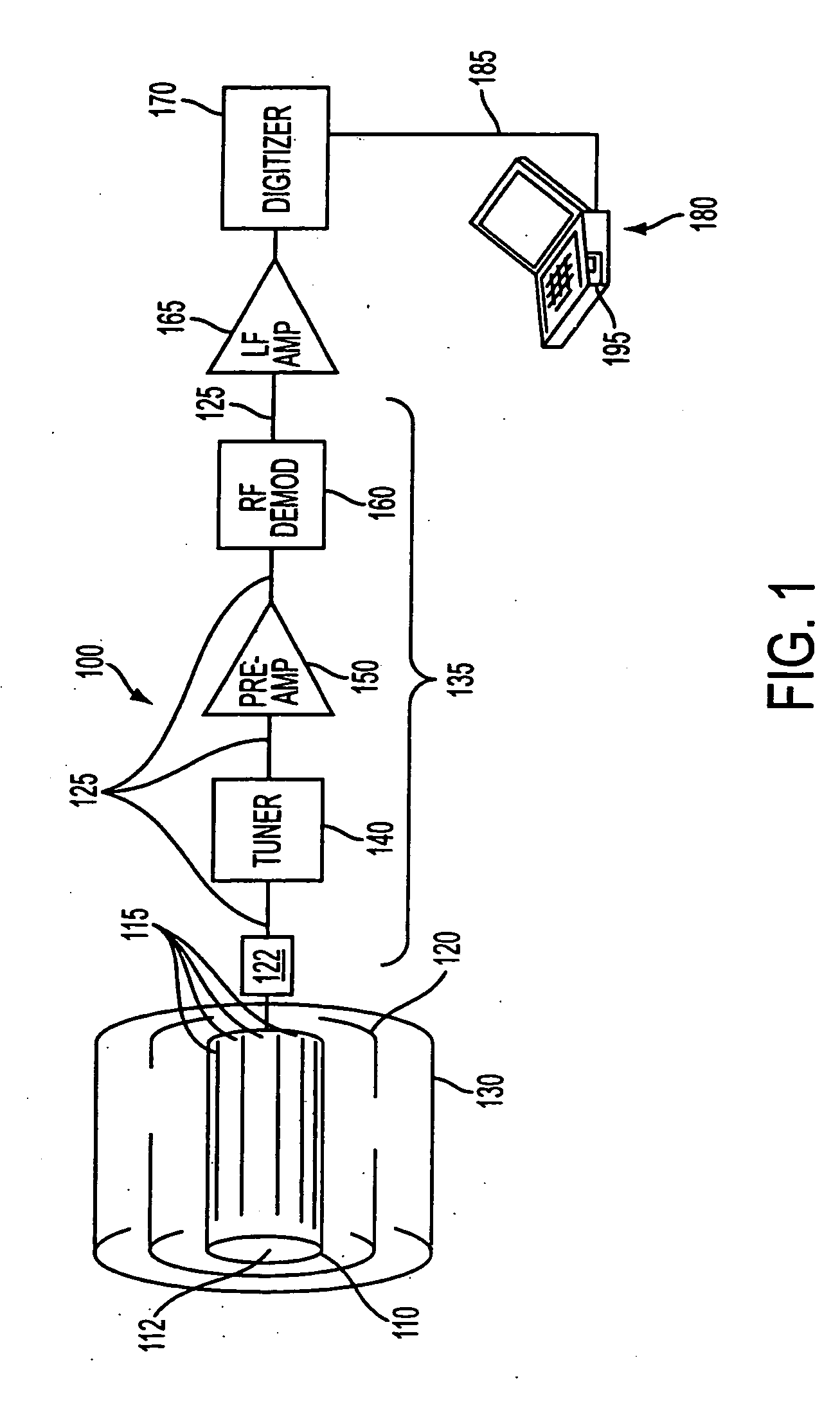
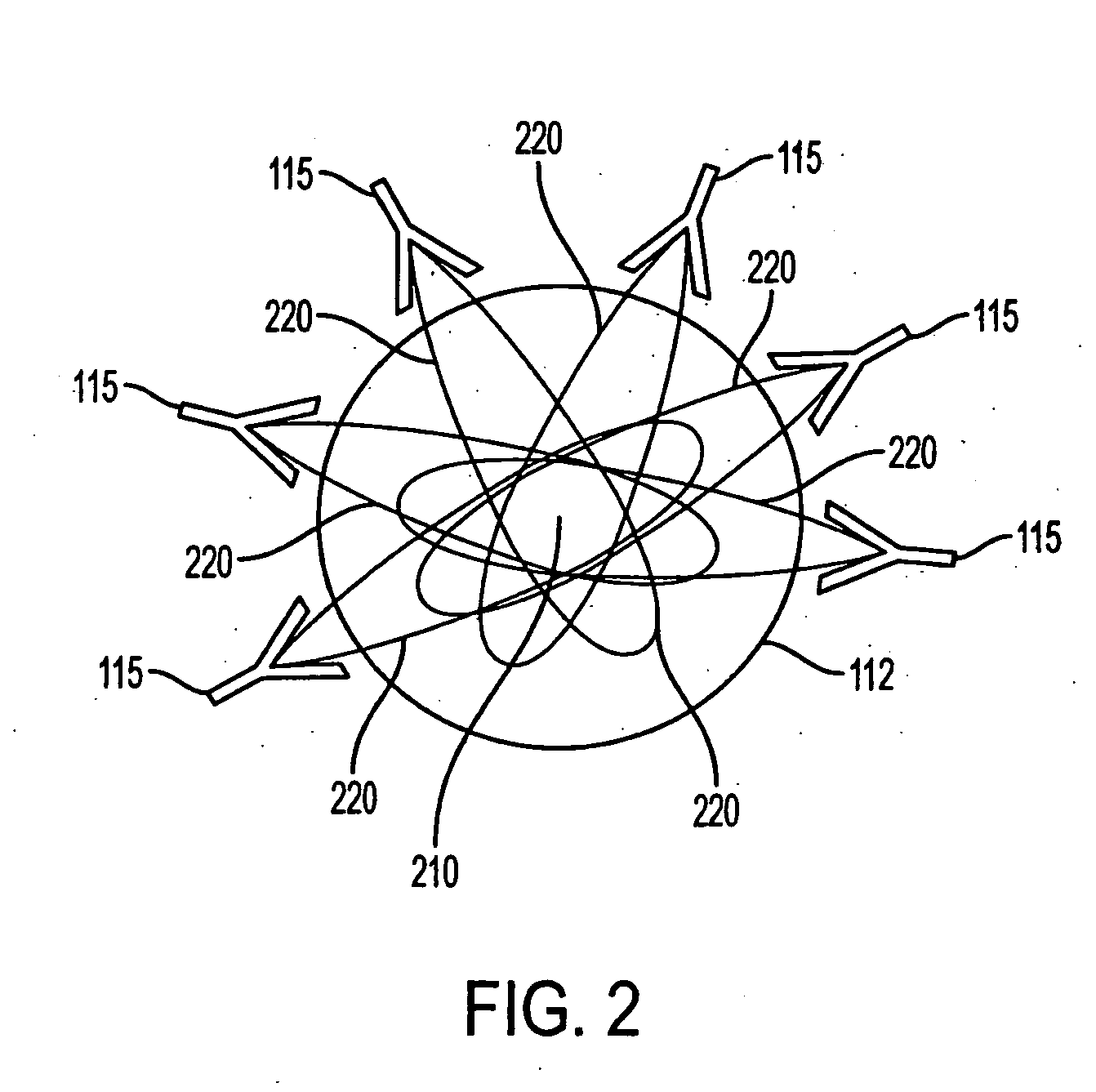
Inbound messaging transmission device and system for railcar asset tracking using high frequency signaling
InactiveUS6108524ASpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityTransmission protocolDiversity scheme
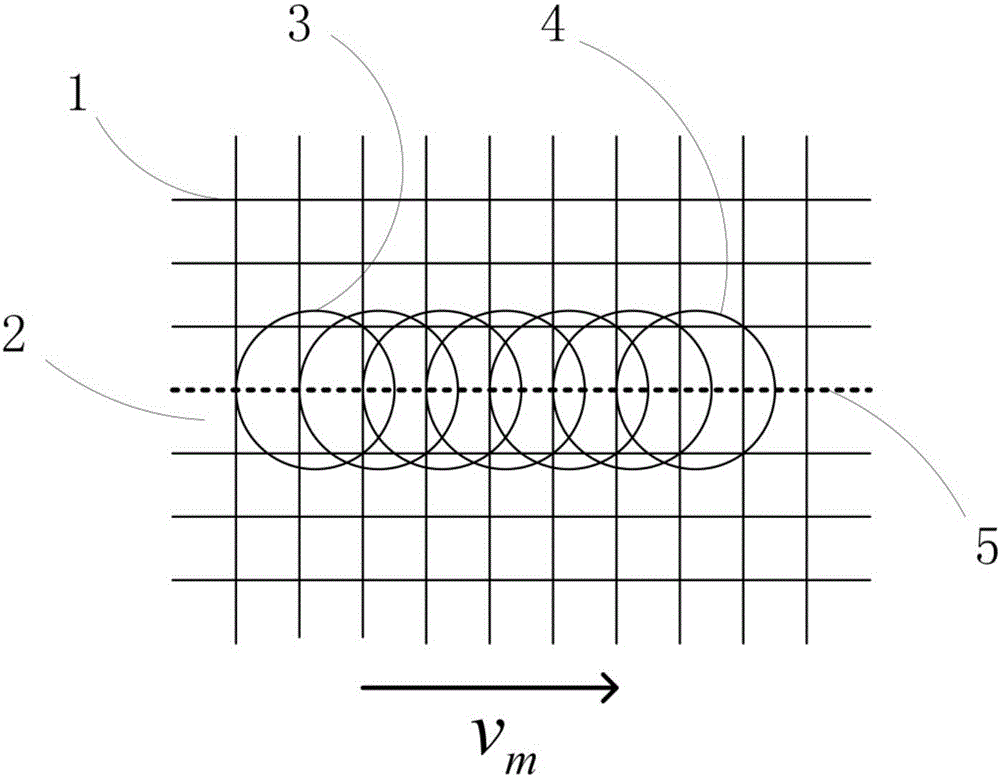
An asymmetrical (inbound only) high frequency communication system for asset tracking is made up of a message preparation and transmitter subsystem, a receiving subsystem, and a system monitoring subsystem. A transmission channel is selected randomly or pseudorandomly. Prior to each transmission, the transmitter performs a radiometric measurement of a selected channel. If the measurement exceeds a predetermined threshold, transmission in the selected channel is canceled and another channel is selected. The transmission protocol achieves frequency diversity by sequentially transmitting a message on a plurality of different channels. The receiving subsystem has a plurality of spatially separated receiver sites at various geographical points, thereby providing spatial diversity. The receiver sites are linked to a common processing center. Onboard the asset and collocated with the transmitter, a system monitoring subsystem records and stores parameters related to the message preparation and transmitter subsystem. These parameters are useful in assessing efficacy of transmission frequency planning algorithms and the transmission protocol.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
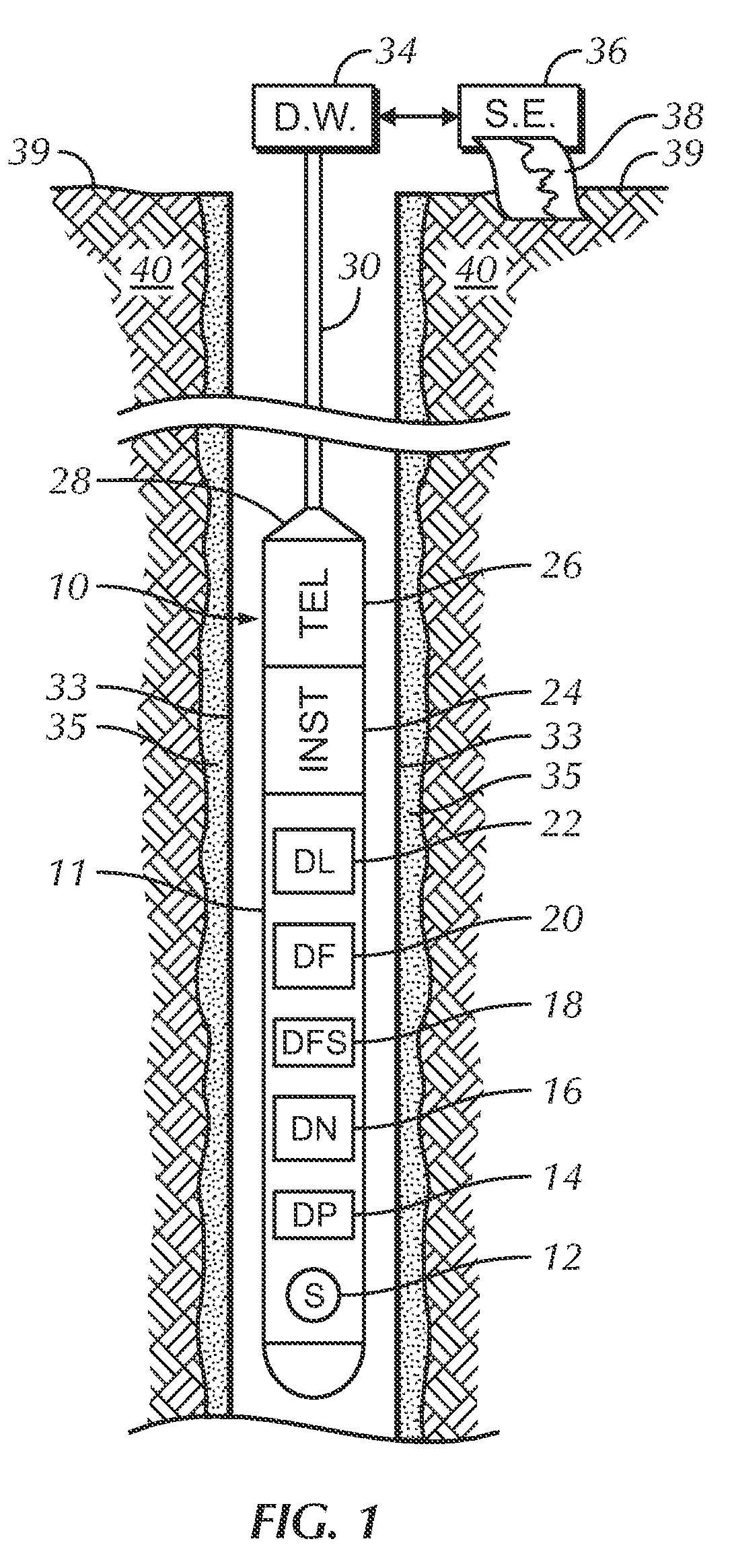
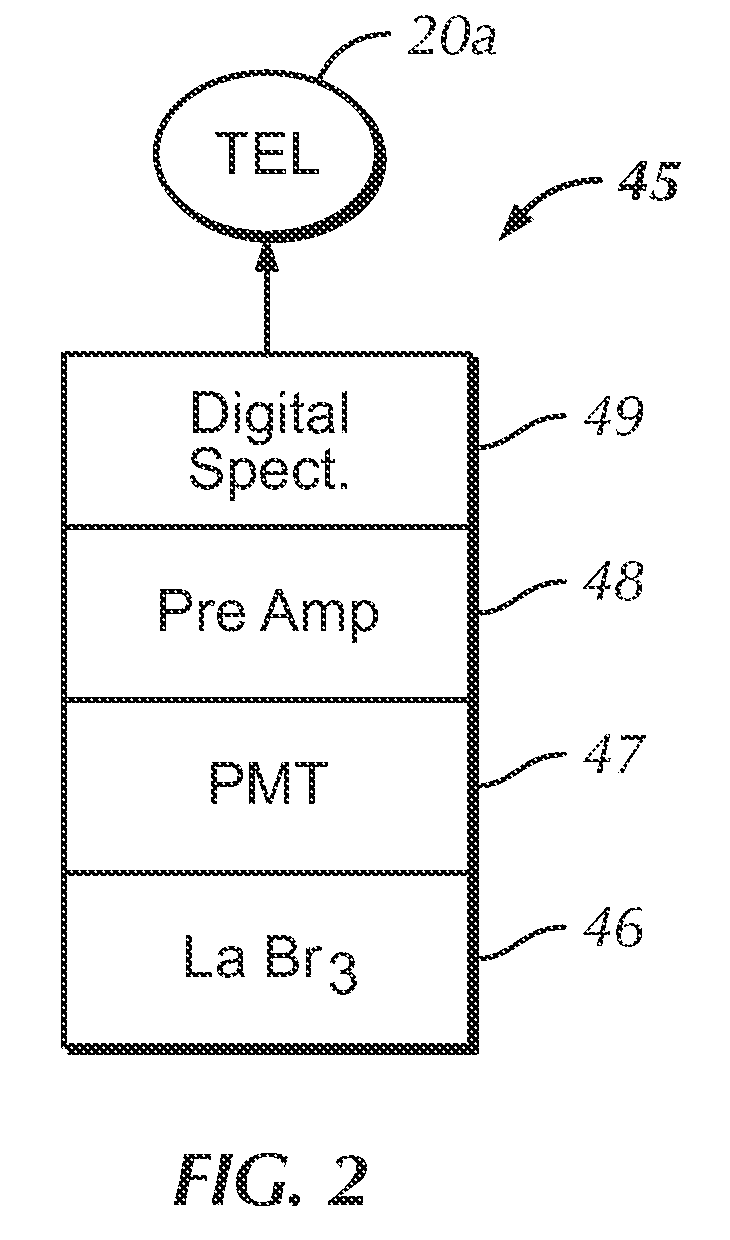
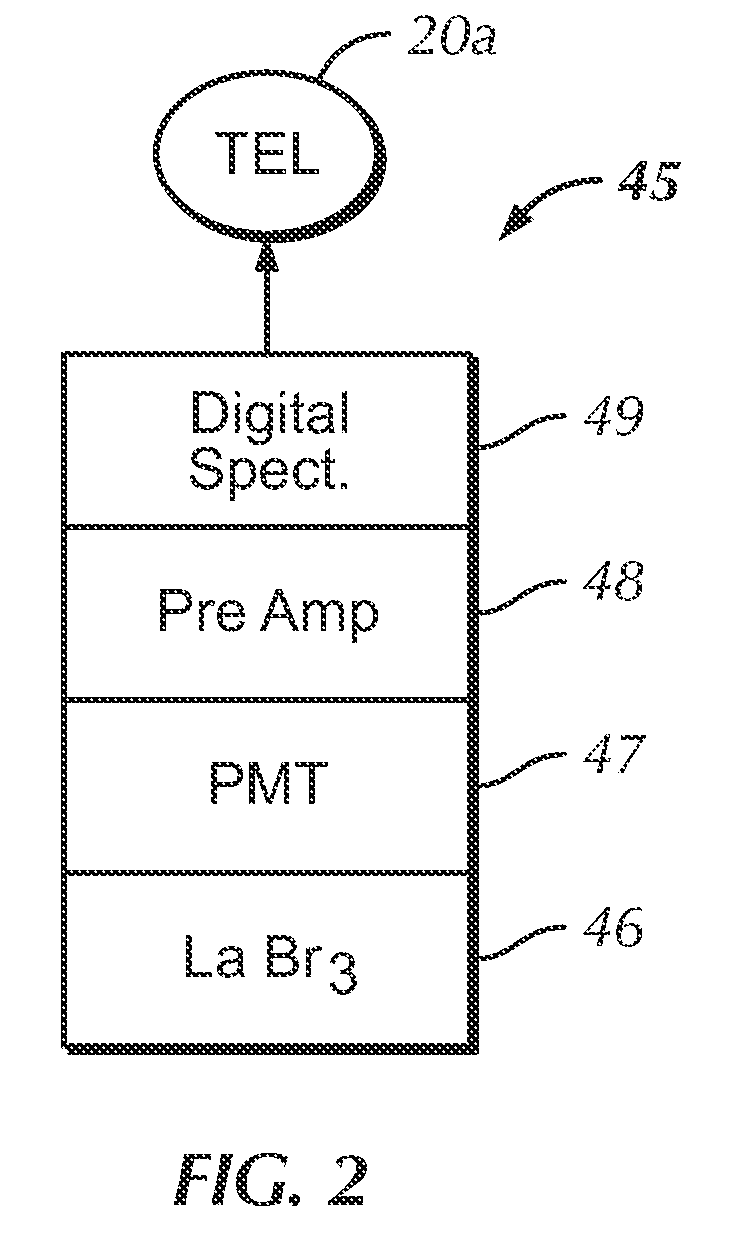
Borehole measurements using a fast and high energy resolution gamma ray detector assembly
ActiveUS7999220B2Energy optimizationFast emission timeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDead timePulse height
A gamma ray detector assembly for a borehole logging system that requires the measure of gamma radiation with optimized gamma ray energy resolution and with fast emission times required to obtain meaningful measurements in high radiation fields. The detector assembly comprises a lanthanum bromide (LaBr3) scintillation crystal and a digital spectrometer that cooperates with the crystal to maximize pulse processing throughput by digital filtering and digital pile-up inspection of the pulses. The detector assembly is capable of digital pulse measurement and digital pile-up inspection with dead-time less than 600 nanoseconds per event. Pulse height can be accurately measured (corrected for pile-up effects) for 2 pulses separated by as little as 150 nanoseconds. Although the invention is applicable to virtually any borehole logging methodology that uses the measure of gamma radiation in harsh borehole conditions, the invention is particularly applicable to carbon / oxygen logging.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
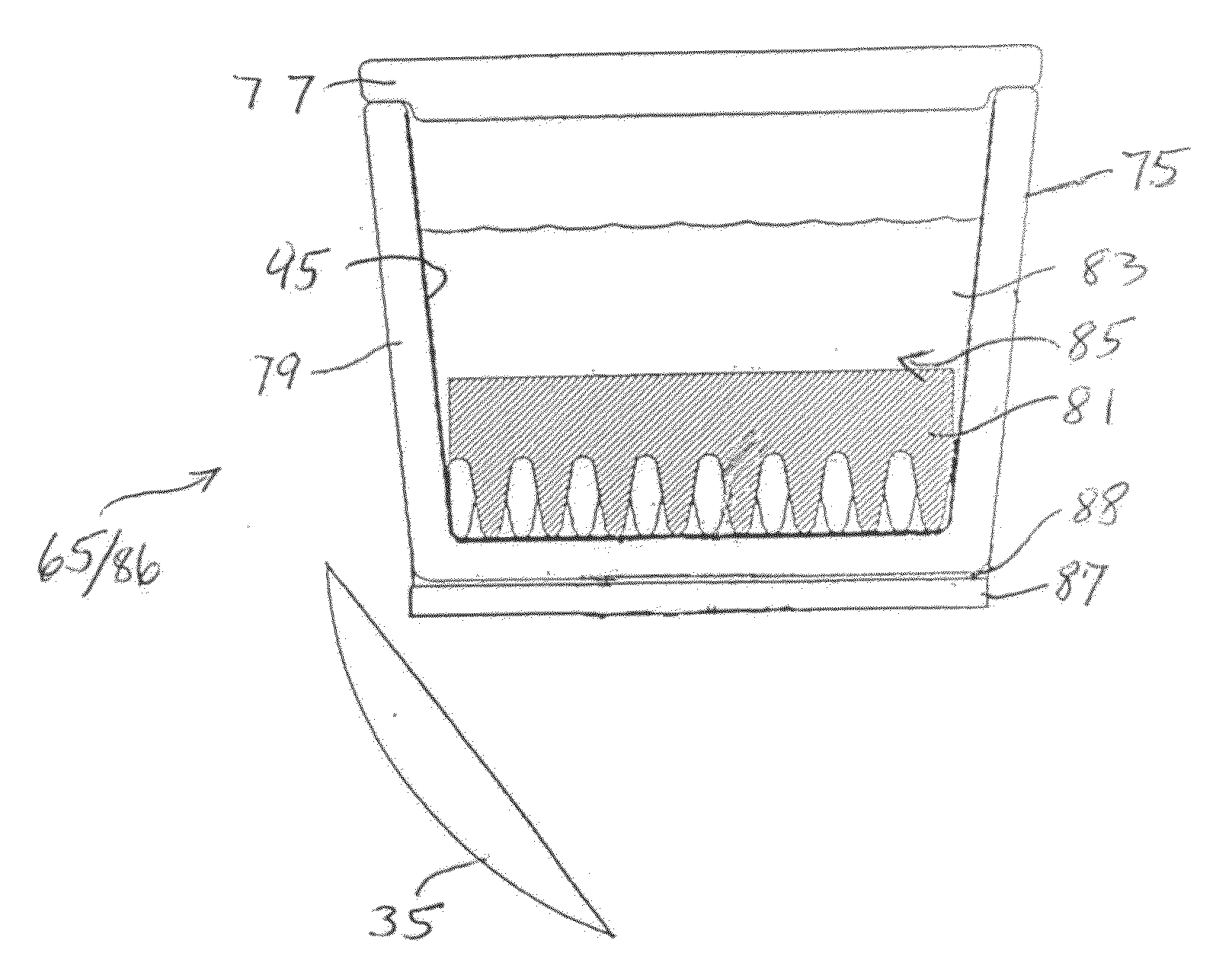
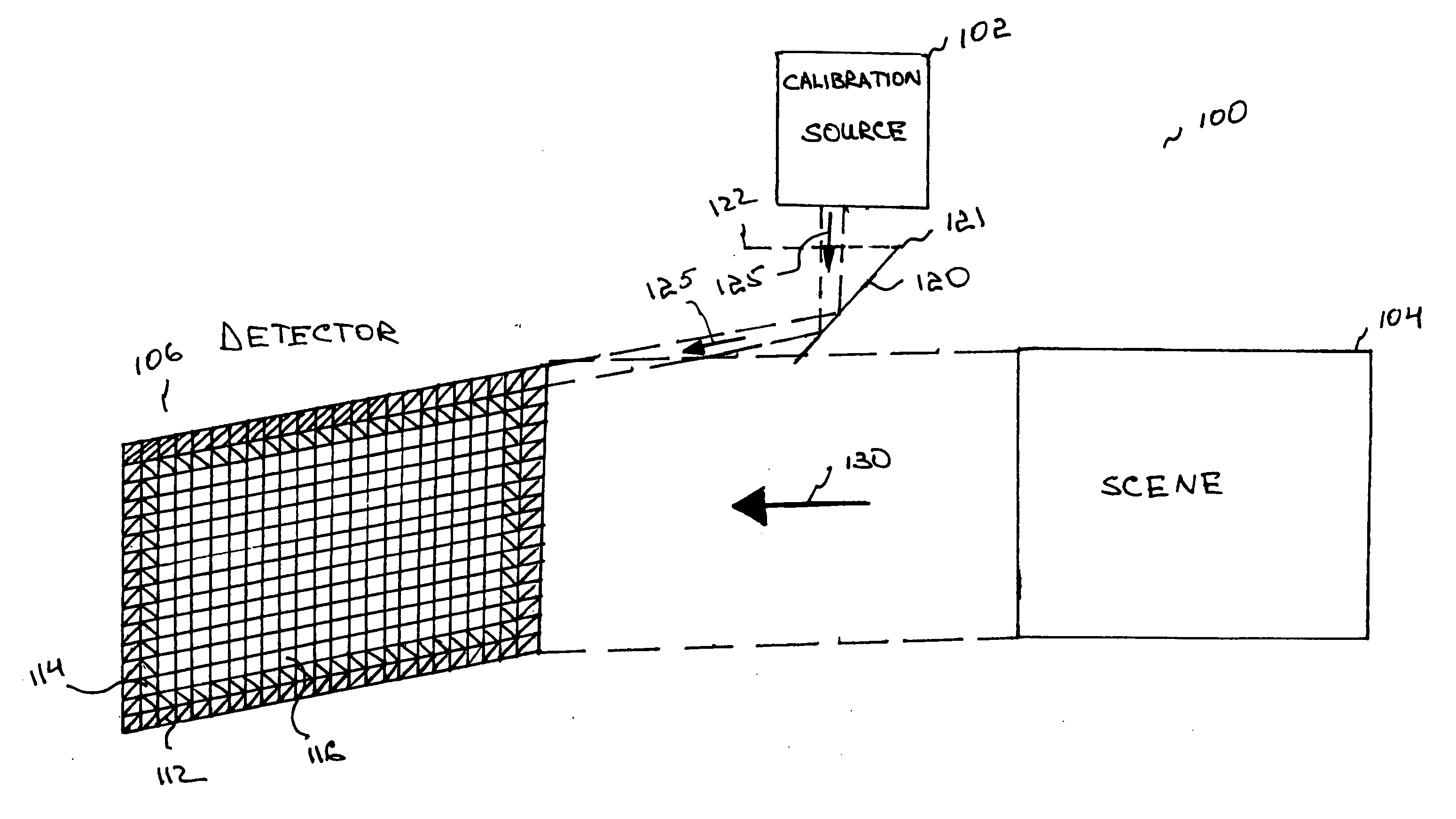
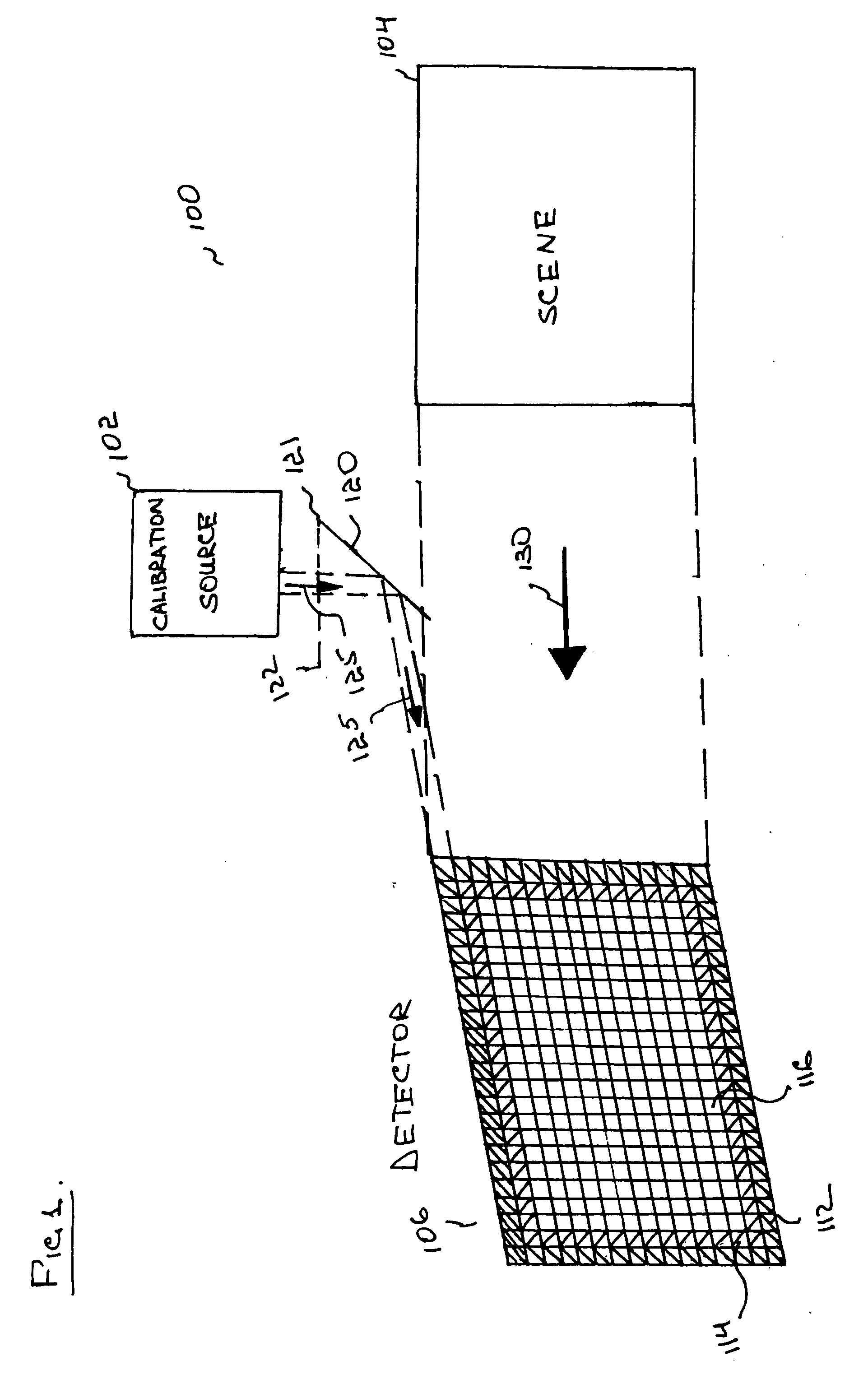
Uniform, non-disruptive, and radiometrically accurate calibration of infrared focal plane arrays using global scene motion
InactiveUS7132648B2Radiation pyrometryCalibration apparatusFocal Plane ArraysRadiometric measurement
A method of generating an image sequence that includes the steps of detecting scene irradiance using detectors in a focal plane array, generating an output image sequence for each of the detectors based on the detected irradiance, and correcting the output image sequence generated by a first subset of detectors in the focal plane array and the output image sequence generated by a second subset of detectors in the focal plane array using the correction provided to the first subset of detectors.
Owner:STC UNM
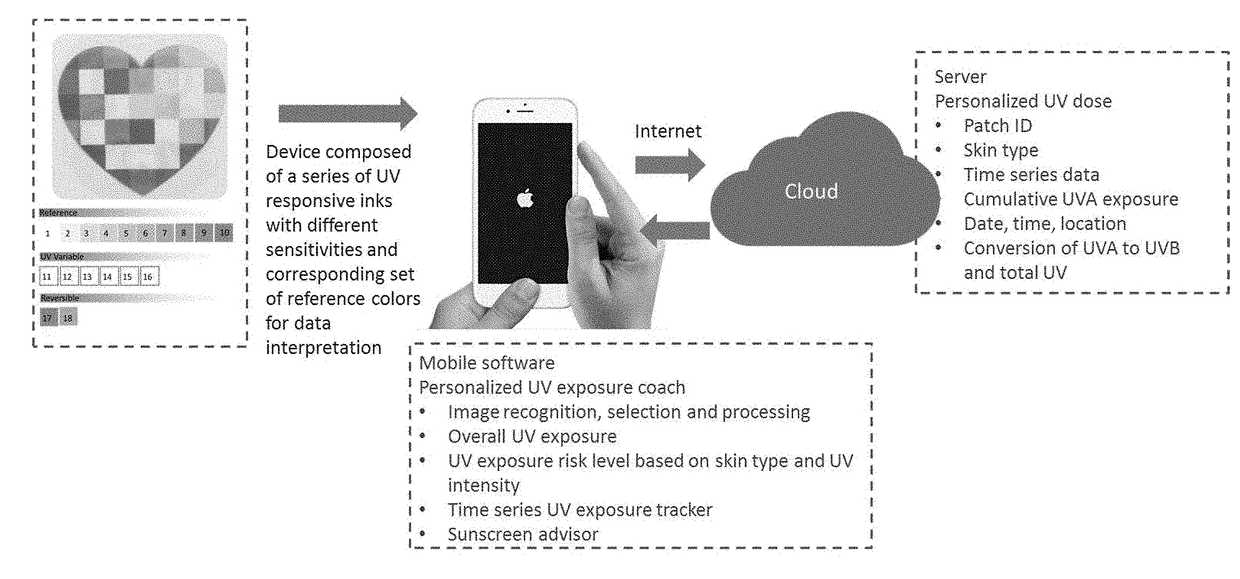
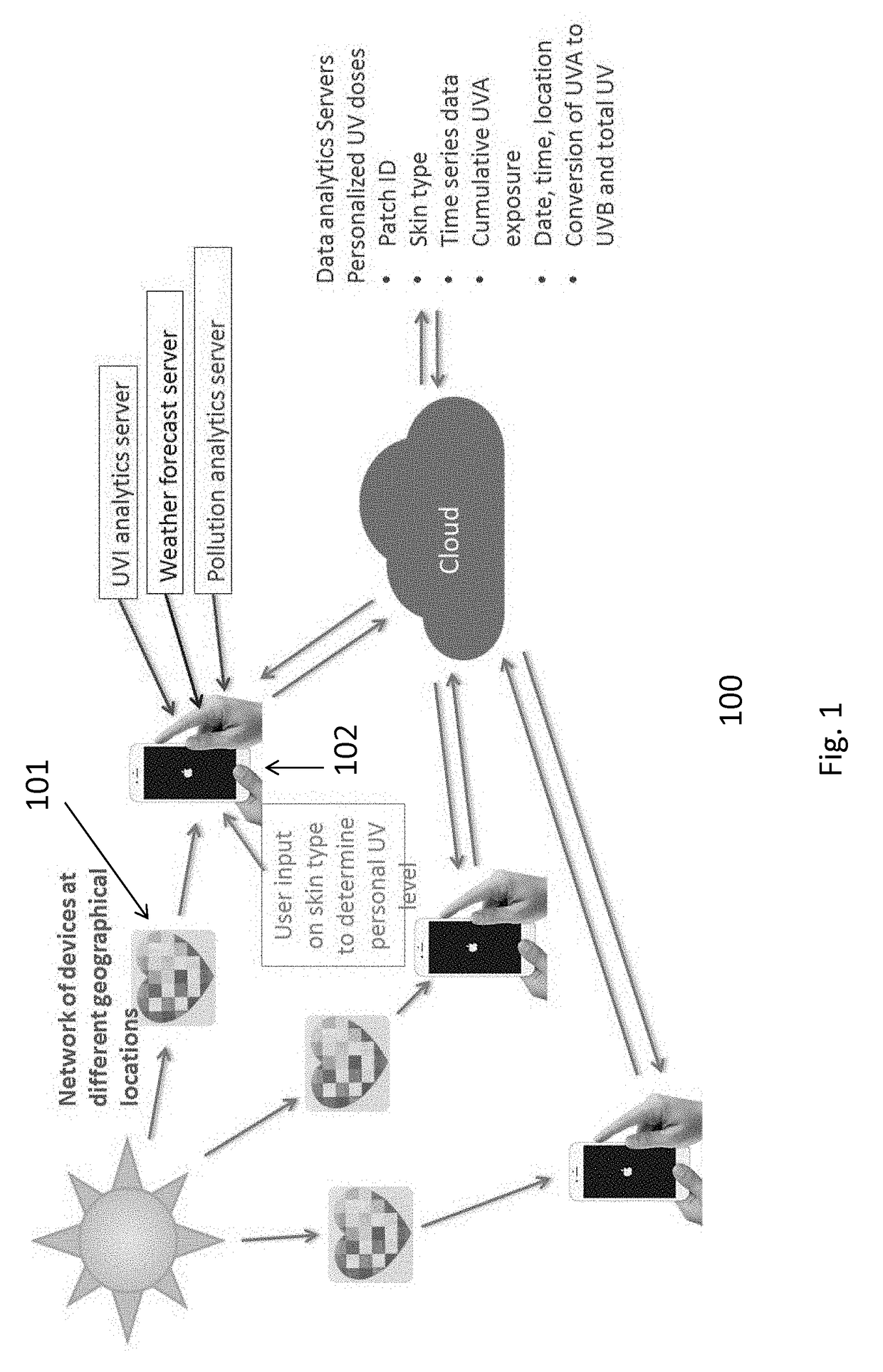
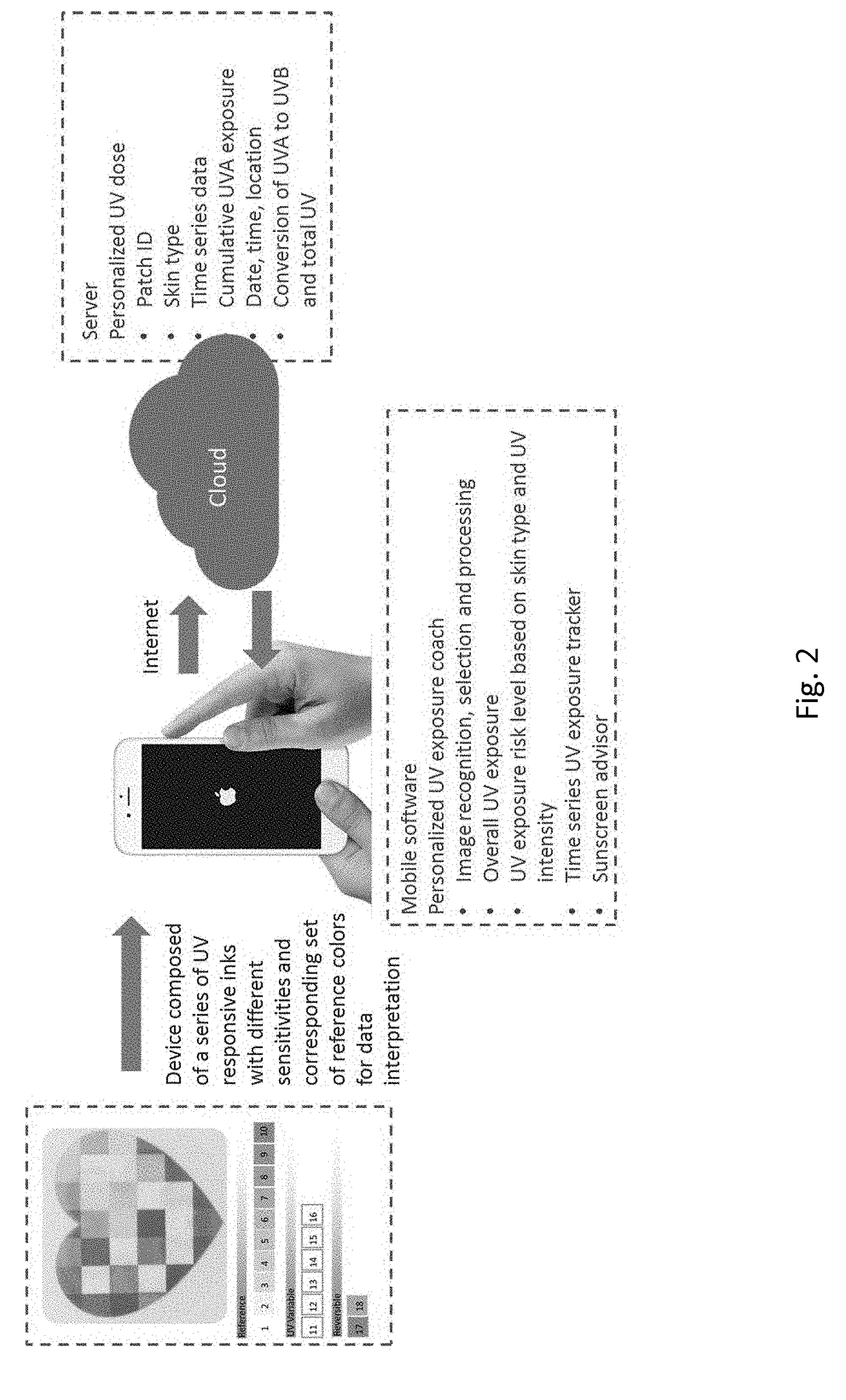
Device and system for personal UV exposure measurements
ActiveUS20170191866A1Photometry for measuring UV lightPhotometry for measuring solar lightRisk levelMeasurement device
A system is provided for determining personal ultra-violet (UV) radiation measurements, comprising: a measurement device configured to measure UV irradiation; and a terminal device configured to receive or capture an output of the measured UV irradiation from the measurement device and to determine a specific user's personal UV exposure risk level based on at least the measured sun irradiation and information of a skin type of the specific user. The measurement device configured to measure UV radiation exposure includes a surface that includes a plurality of different sections that each have a different sensitivity to UV radiation exposure, and each of the plurality of different sections are configured to display a different color in response to the UV radiation exposure.
Owner:LOREAL SA
High-precision surface source blackbody radiation source device applied under vacuum low temperature condition
ActiveCN107014494AEasy to control temperatureGuaranteed normal testRadiation pyrometryEmissivityBlack-body radiation
The invention relates to infrared radiation measurement and calibration technology field and especially relates to a high-precision surface source blackbody radiation source device capable of being applied under a vacuum low temperature condition. The device mainly comprises a blackbody radiation source main body module, a vacuum cabin, a control cable in the cabin, a through-wall air plug, a control cable outside the cabin, a refrigeration copper braid and a controller module. The blackbody radiation source main body module is placed in the vacuum cabin. The blackbody radiation source main body module is connected to an inner wall of the vacuum cabin through the refrigeration copper braid. The blackbody radiation source main body module is connected to the controller module successively through the control cable in the cabin, the through-wall air plug and the control cable outside the cabin. The device has advantages that a problem that effective emissivity, temperature uniformity and a wide temperature range can not be simultaneously satisfied in the prior art is effectively solved; and an application basis is provided for calibrating and testing infrared detection equipment and establishing a low temperature target performance test system under a vacuum environment.
Owner:BEIJING ZHENXING METROLOGY & TEST INST
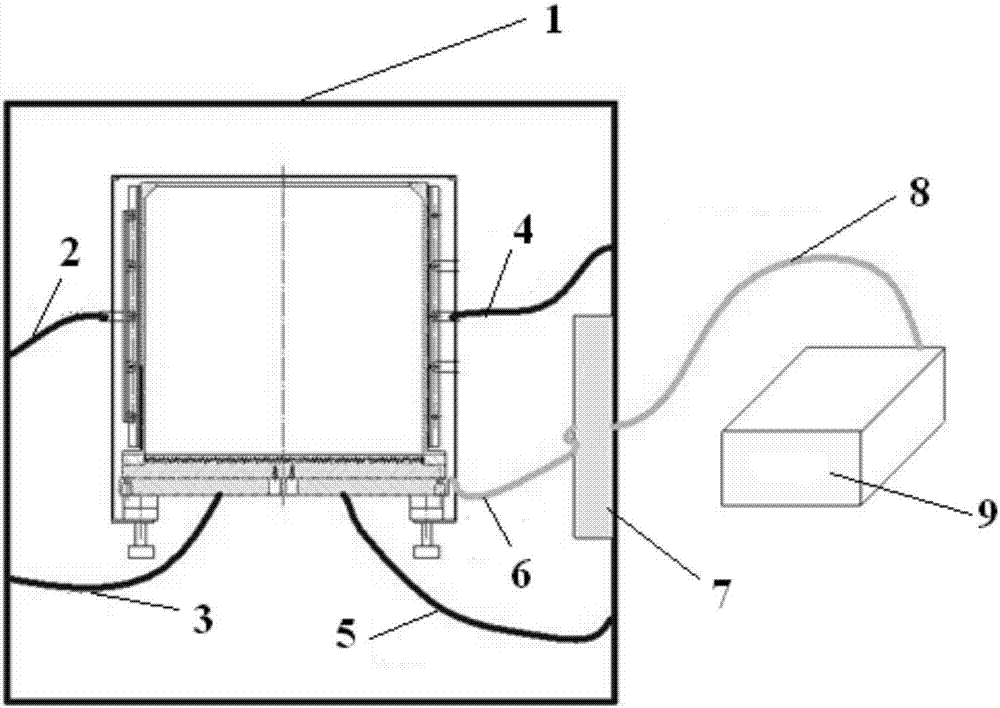
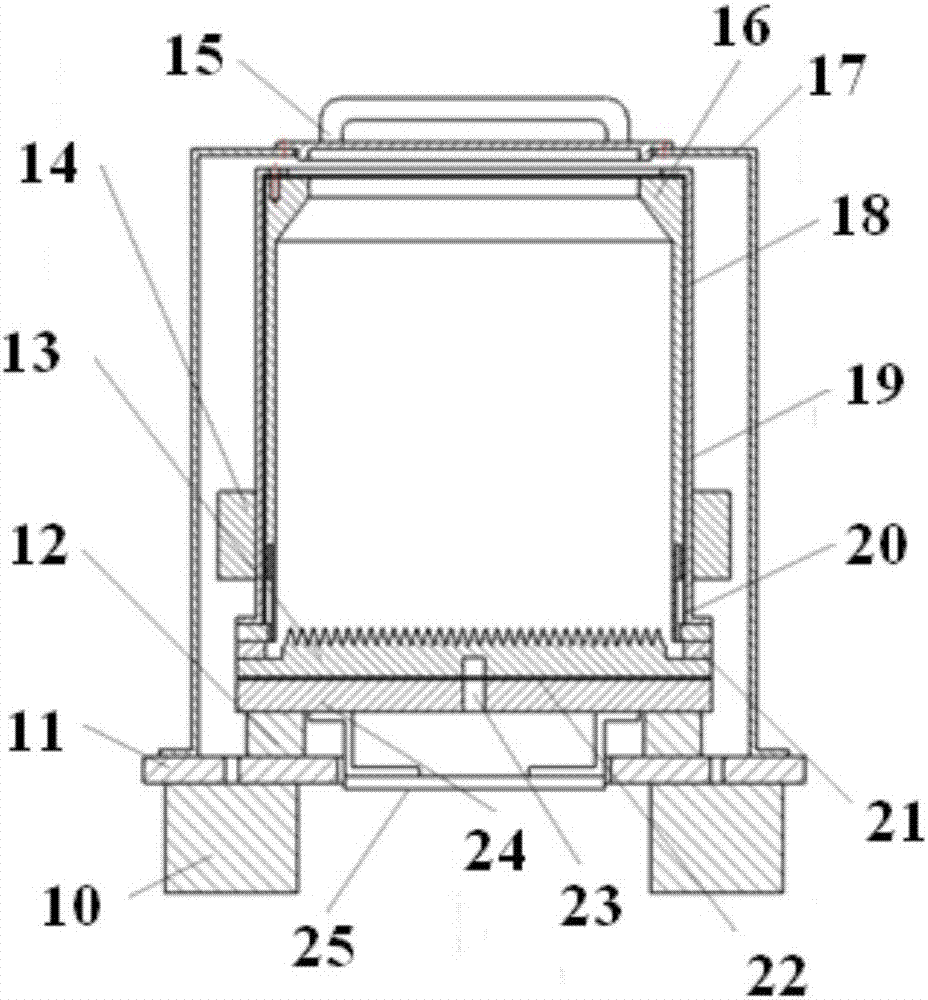
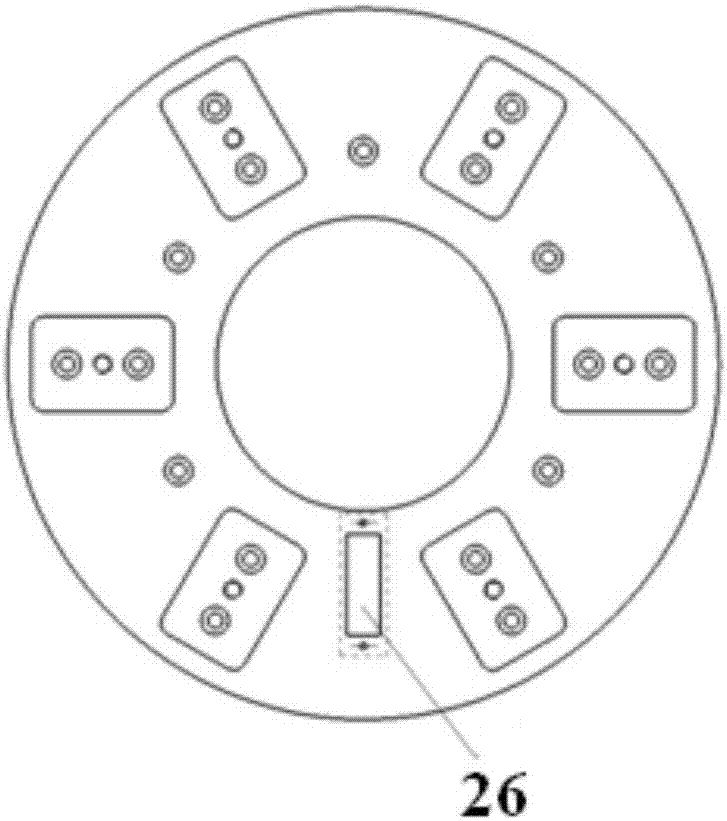
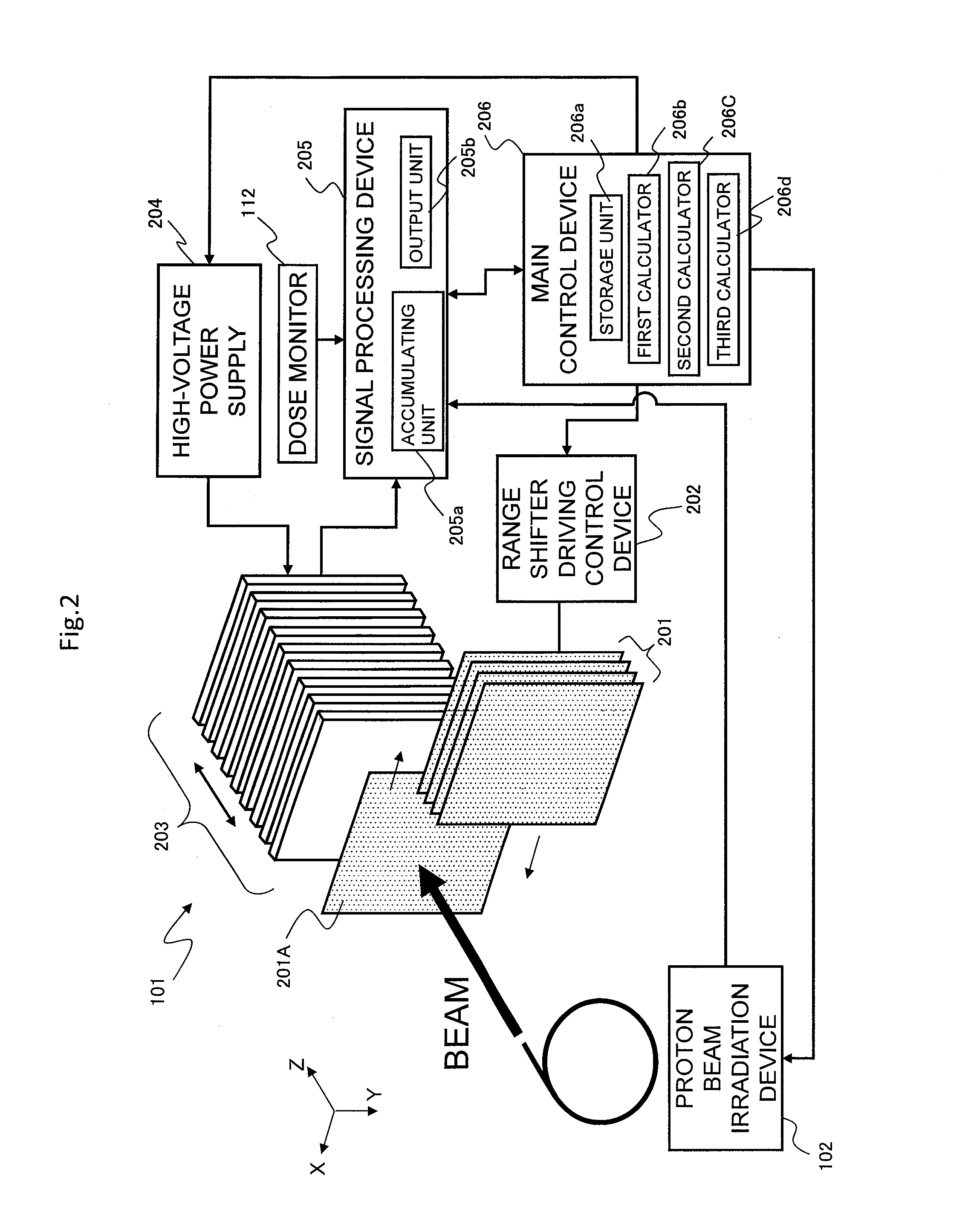
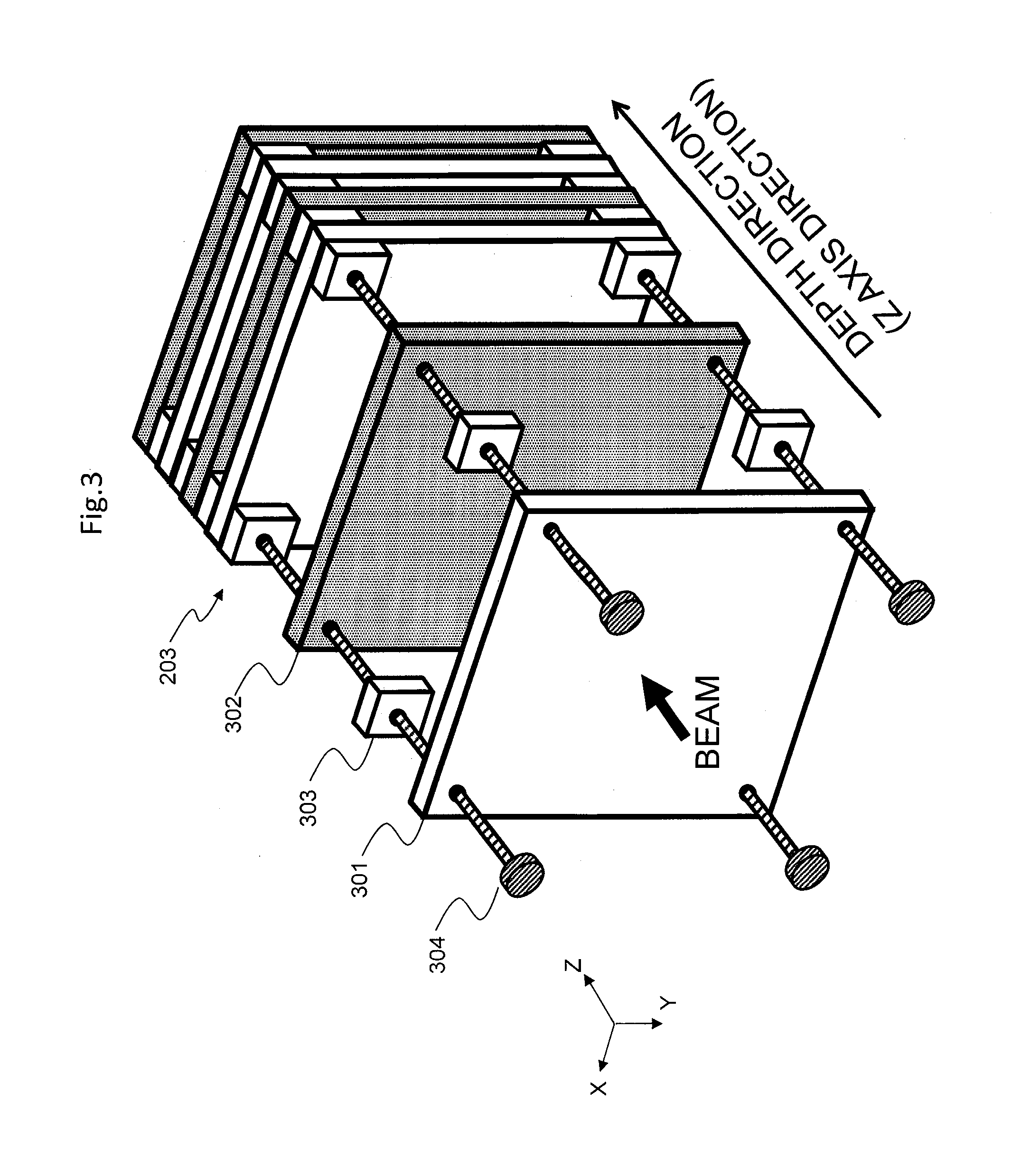
Radiation measuring device, particle beam therapy device provided with radiation measuring device, and method for calculating dose profile of particle beam
ActiveUS20150099918A1Improve accuracyReduce the differenceDosimetersElectrical measurementsDose profileBeam energy
A radiation measuring device having a plurality of sensors configured to generate charges in response to the radiation includes a signal processing device. The signal processing device uses an signal generated by a proton beam irradiation device upon changing of beam energy and causes accumulation values of charges output from the sensors to be separately stored in a main control device for each value of the energy. The main control device calculates depth dose profiles for values of the beam energy from the accumulation values stored in the main control device and representing the charges. The main control device calculates a range of the beam for each of the values of the beam energy from the depth dose profiles, corrects the depth dose profiles for the values of the beam energy using a correction coefficient that depends on the range and sums the corrected depth dose profiles.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
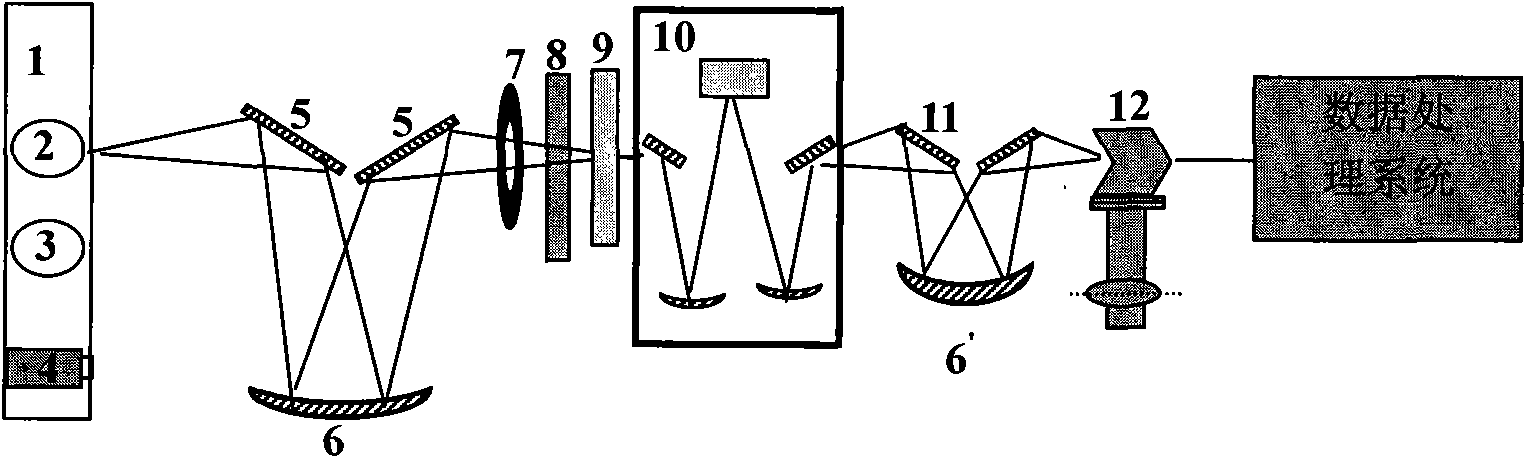
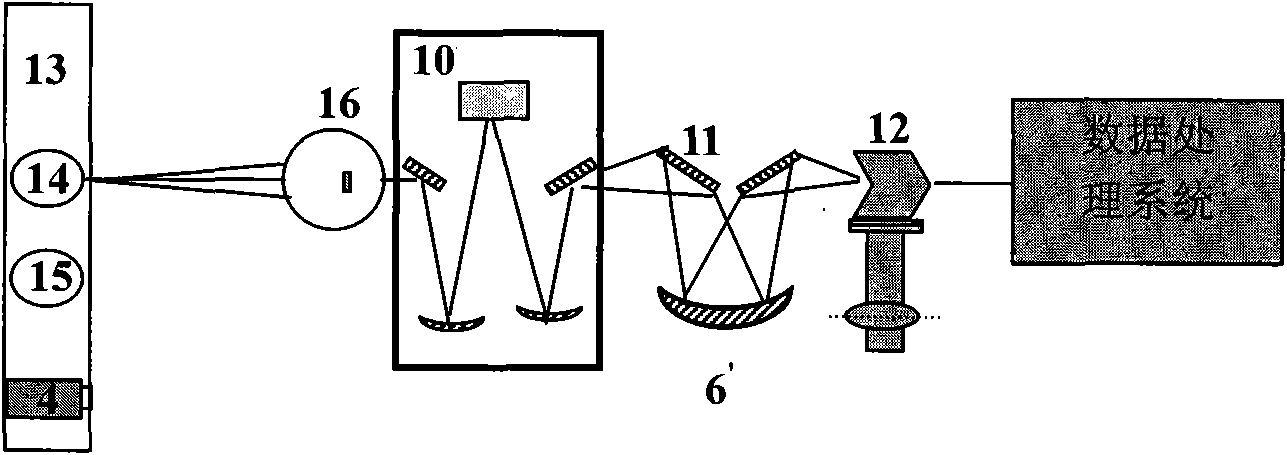
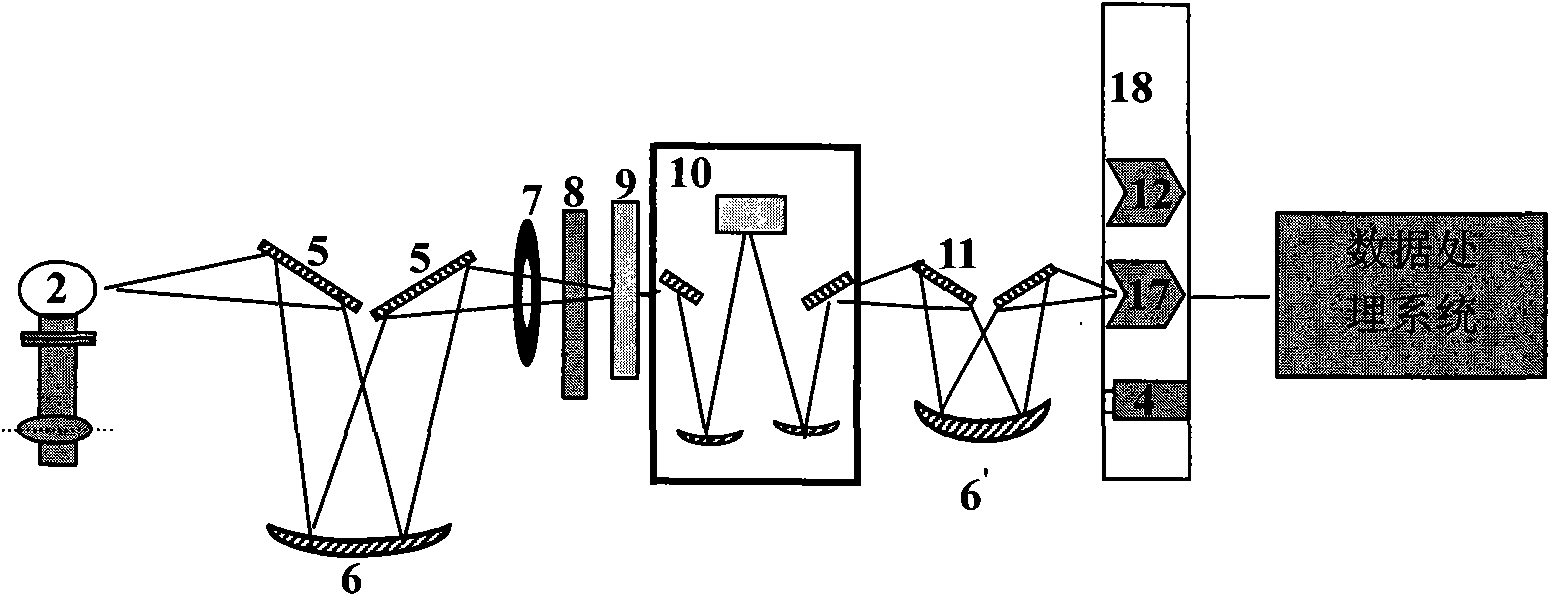
Ultraviolet radiation comprehensive test device
ActiveCN101915612AResource SharingLow costRadiation pyrometryPhotometrySpectral responsivityOptoelectronics
The invention discloses an ultraviolet radiation comprehensive test device and belongs to the field of optical tests and measurements. The device simplifies an input optical system, adds an integrating sphere and an ultraviolet irradiance standard lamp which is arranged on a second mobile platform, and correspondingly integrates the integrating sphere and an electronic shutter on a first mobile platform with the ultraviolet radiance standard lamp and a filtering component on the basis of a conventional spectral responsivity test device; the first mobile platform is in the same direction as a third mobile platform with an ultraviolet standard detector and is vertical to the second mobile platform; and all the standard lamps or the standard detector and lamps to be measured or detectors to be measured are cut into a measurement optical path under control of a data processing system so as to realize measurement and calibration of ultraviolet spectral radiance, spectral radiance illuminance and spectral responsivity. The device solves the problems of resource sharing and cost saving during ultraviolet radiation measurement, and has the characteristics of simple operation and high precision.
Owner:CHINA NORTH IND NO 205 RES INST
Highly accurate calibration of microwave radiometry devices
InactiveUS20140035779A1High precision calibrationEliminate reflectionsWave based measurement systemsThermometers using physical/chemical changesMicrowave radiometryWavelength
Systems and methods are disclosed for highly accurate calibration of microwave radiometry devices by defeating reflections from a cryogenic blackbody calibration target and, further, defeating a standing wave established between reflecting features at the device and at the blackbody calibration target. The preferred disclosed system includes adaptations for effective Brewster angle presentation of radiation emanating from the target to the radiometry device. Other embodiments are taught for substantially eliminating or randomizing the standing wave in both wavelength dependent and independent applications.
Owner:RADIOMETRICS CORP
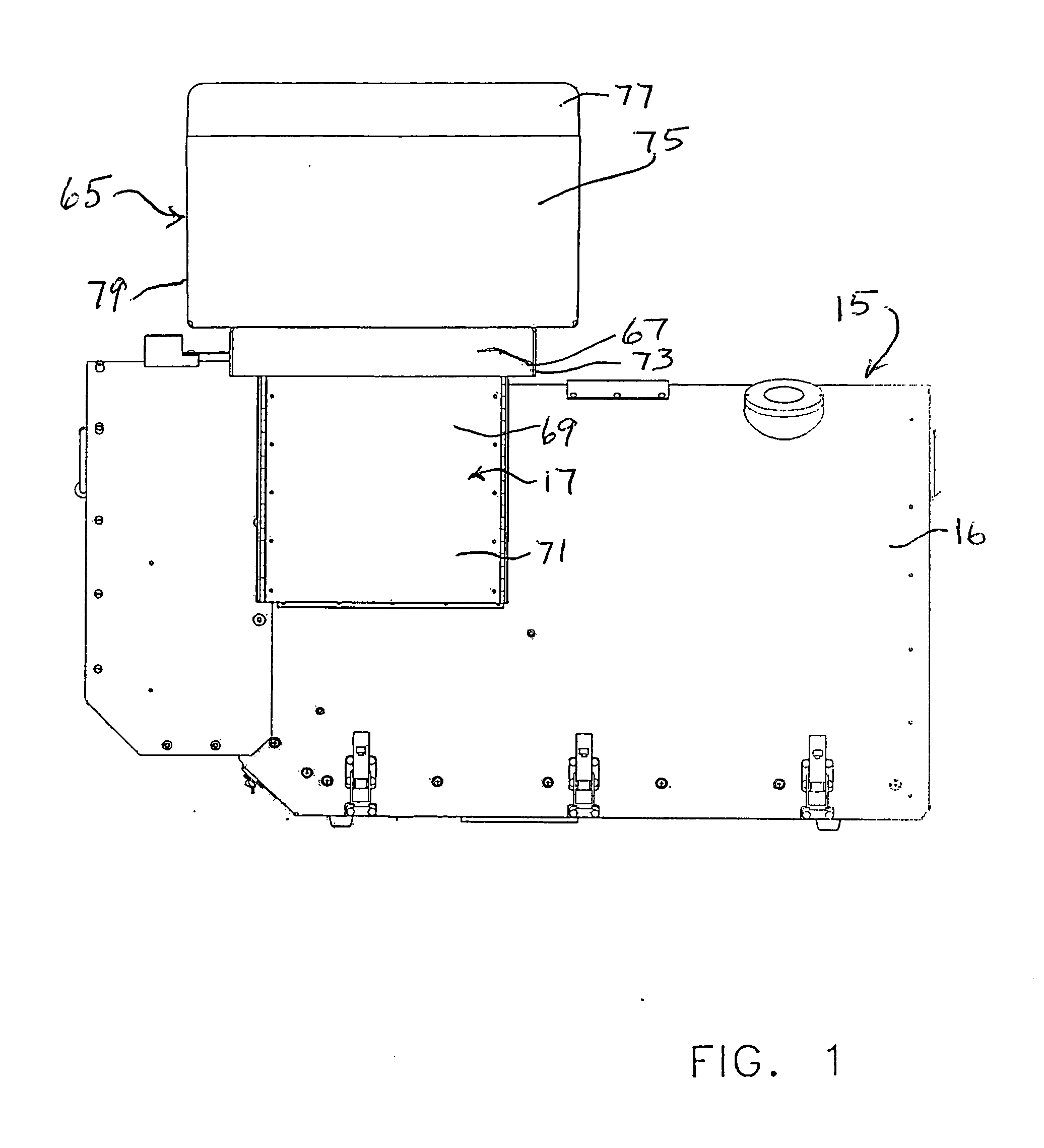
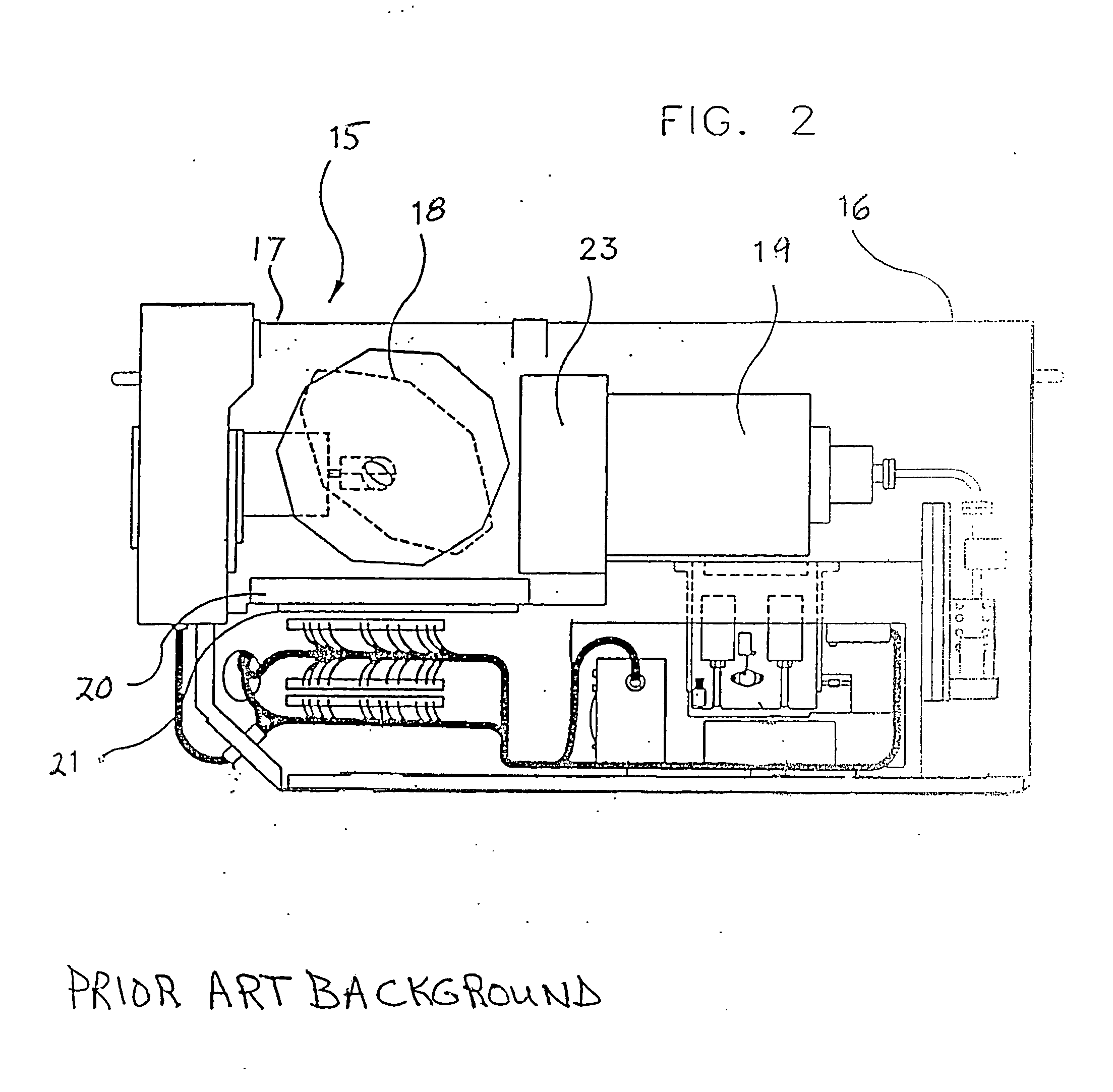
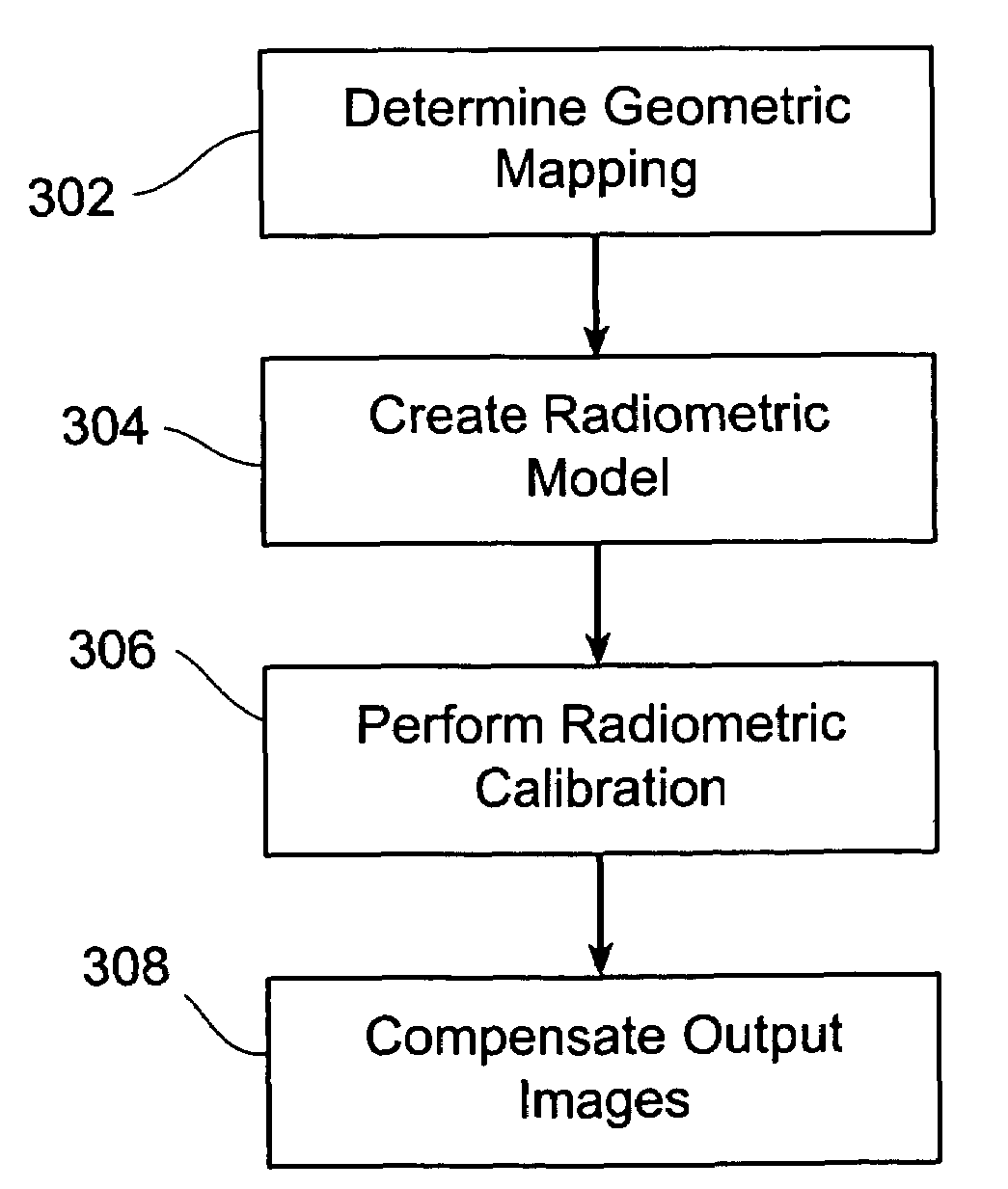
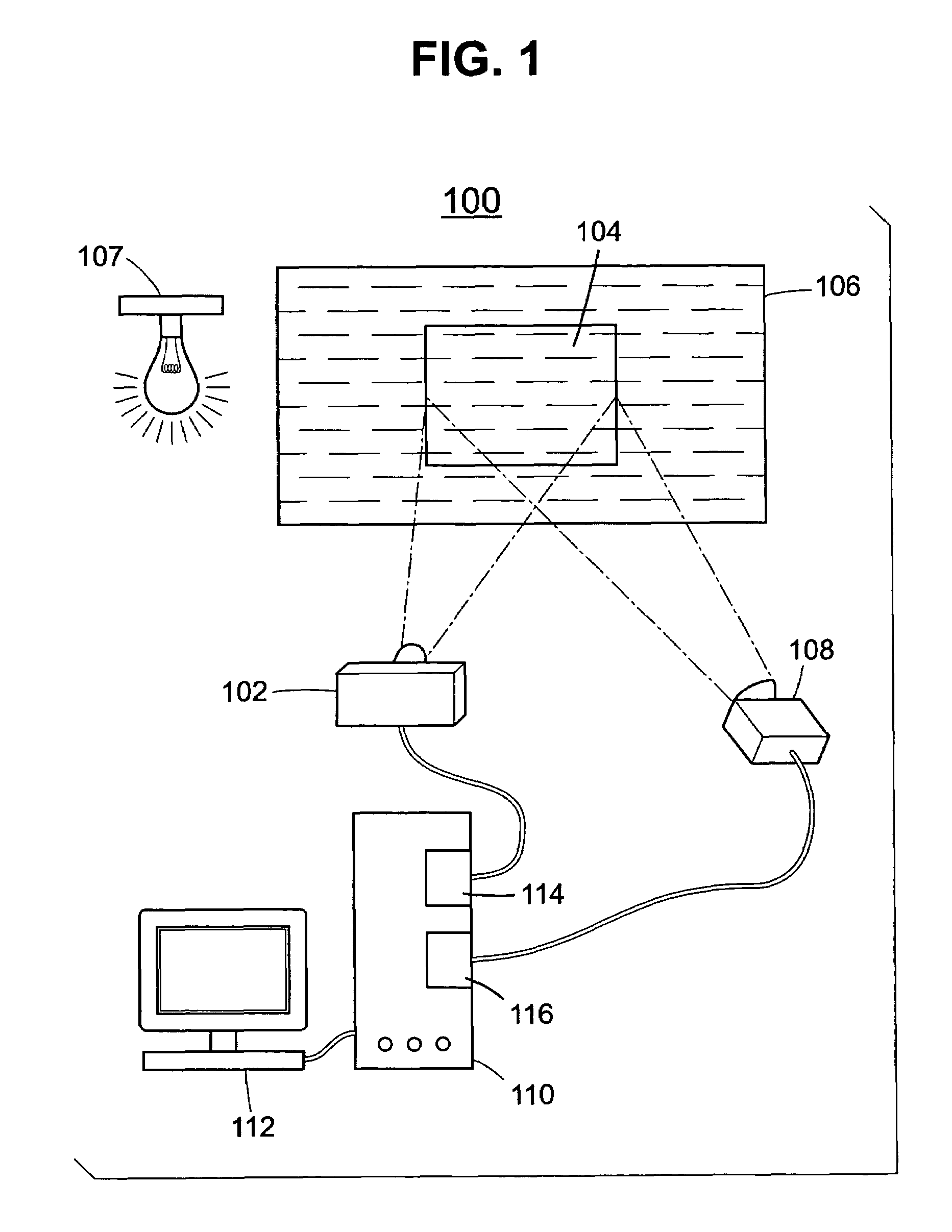
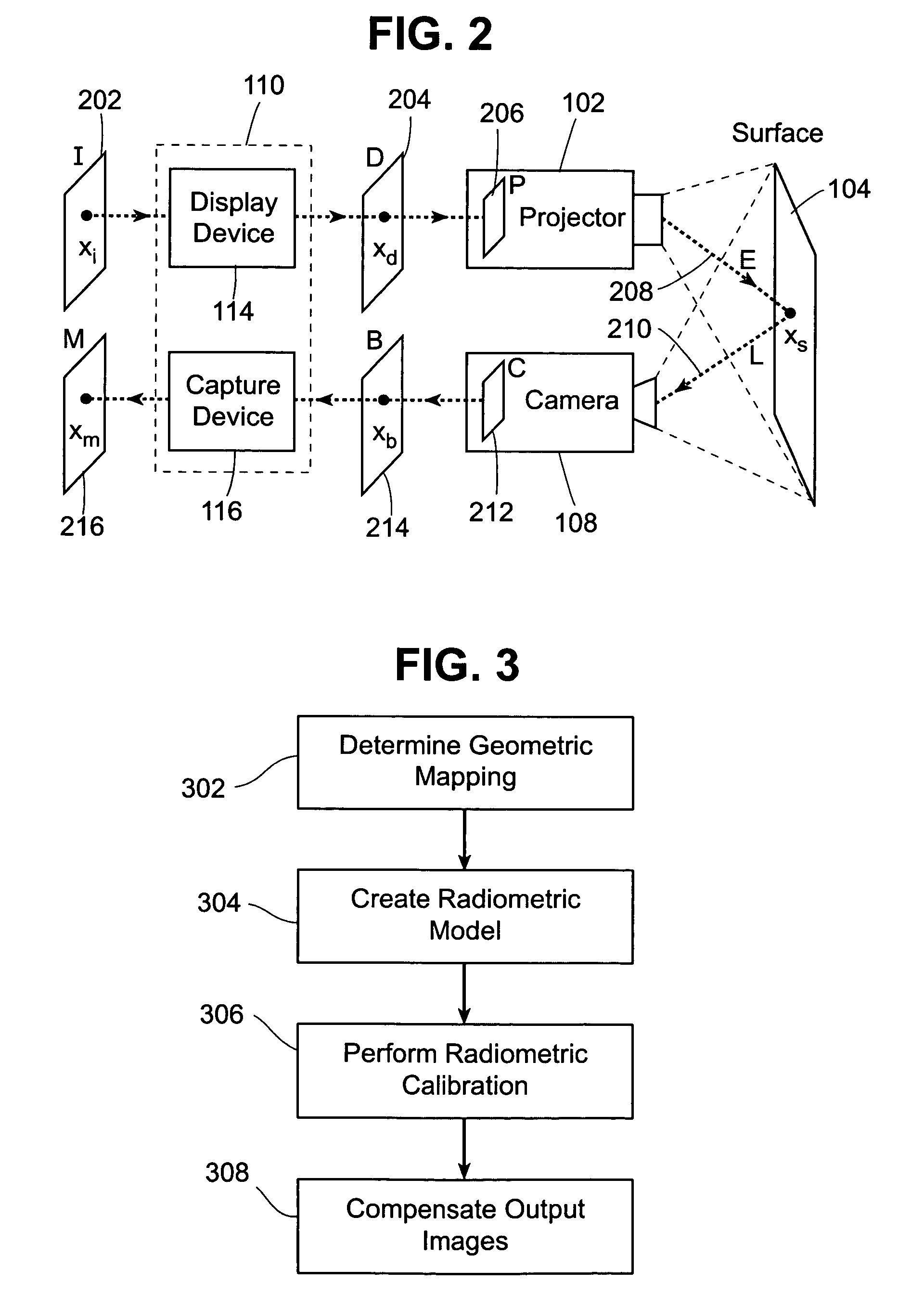
Methods and systems for compensating an image projected onto a surface having spatially varying photometric properties
ActiveUS7663640B2Guaranteed preservation qualityMaintain qualityGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsLuminositySpatial change
Methods and systems are provided for displaying images onto an arbitrary surface, using a projector, such that the quality of the images is preserved despite surface imperfections or color variations. Methods and systems are also provided for controlling the appearance of a projection surface. Various embodiments use a detailed radiometric model and a calibration method to determine the pixel values required to be projected by a projector in order for a camera to observe a desired image. Other embodiments use a compensation algorithm that uses a feedback approach to provide the desired image compensation. Geometric mapping may be used to establish a correspondence between points in the images to be displayed by the projector and the corresponding points in the images that are captured by the camera.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Display device measuring device simulating structure of human eyes and measuring method
ActiveCN105865755AData processing is accurateSpectrum investigationPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsMatching testSoftware system
The invention discloses a display device measuring device simulating the structure of human eyes and a measuring method. By means of an optical system and a software processing system, retinal imaging simulation and optical safe measurement are achieved. The optical system comprises one or two optical imaging devices, a light radiation measuring device and a dynamic measuring device. The software processing system comprises a human eye smooth tracking model, a subjective matching test model, a Photopic deviation model and other human eye visual models. A part of the optical system can finally generate images in human eye retinas by means of the optical imaging device of a simulation human eye structure and the software system simulating the human eye visual models. A light radiation measuring part of the optical system analyzes spectrum distribution needing light measurement through a photoelectric sensor array, and retinal damage can be accurately evaluated according to a retinal damage weight function curve. The measuring method simulating the structure of the human eyes is disclosed and can omnidirectionally evaluate color, brightness, motion blur and other characteristics of a display device in real time.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Borehole measurements using a fast and high energy resolution gamma ray detector assembly
ActiveUS20090296084A1Optimized gamma ray energy resolutionFast emission timeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDead timeScintillation crystals
A gamma ray detector assembly for a borehole logging system that requires the measure of gamma radiation with optimized gamma ray energy resolution and with fast emission times required to obtain meaningful measurements in high radiation fields. The detector assembly comprises a lanthanum bromide (LaBr3) scintillation crystal and a digital spectrometer that cooperates with the crystal to maximize pulse processing throughput by digital filtering and digital pile-up inspection of the pulses. The detector assembly is capable of digital pulse measurement and digital pile-up inspection with dead-time less than 600 nanoseconds per event. Pulse height can be accurately measured (corrected for pile-up effects) for 2 pulses separated by as little as 150 nanoseconds. Although the invention is applicable to virtually any borehole logging methodology that uses the measure of gamma radiation in harsh borehole conditions, the invention is particularly applicable to carbon / oxygen logging.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
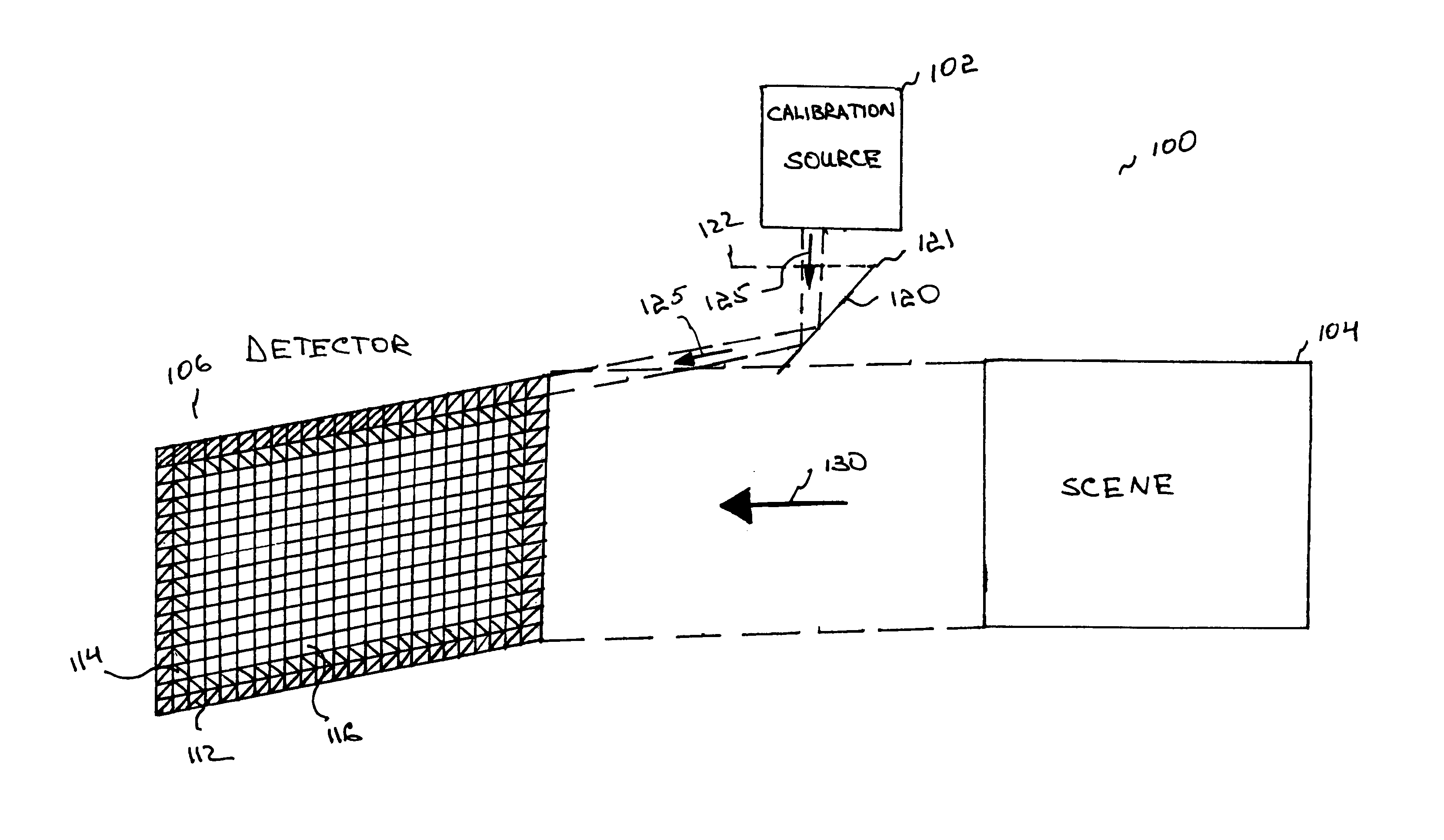
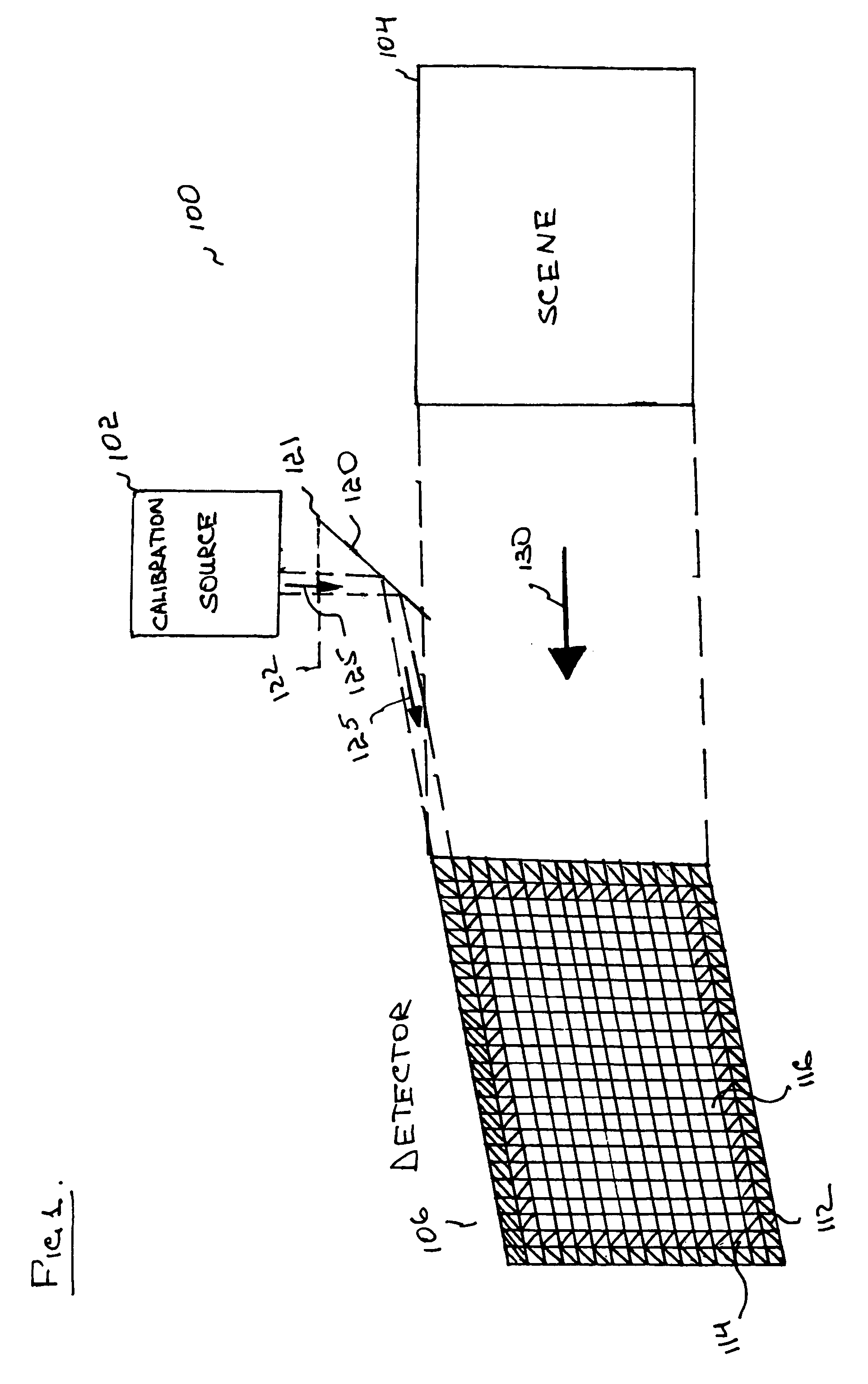
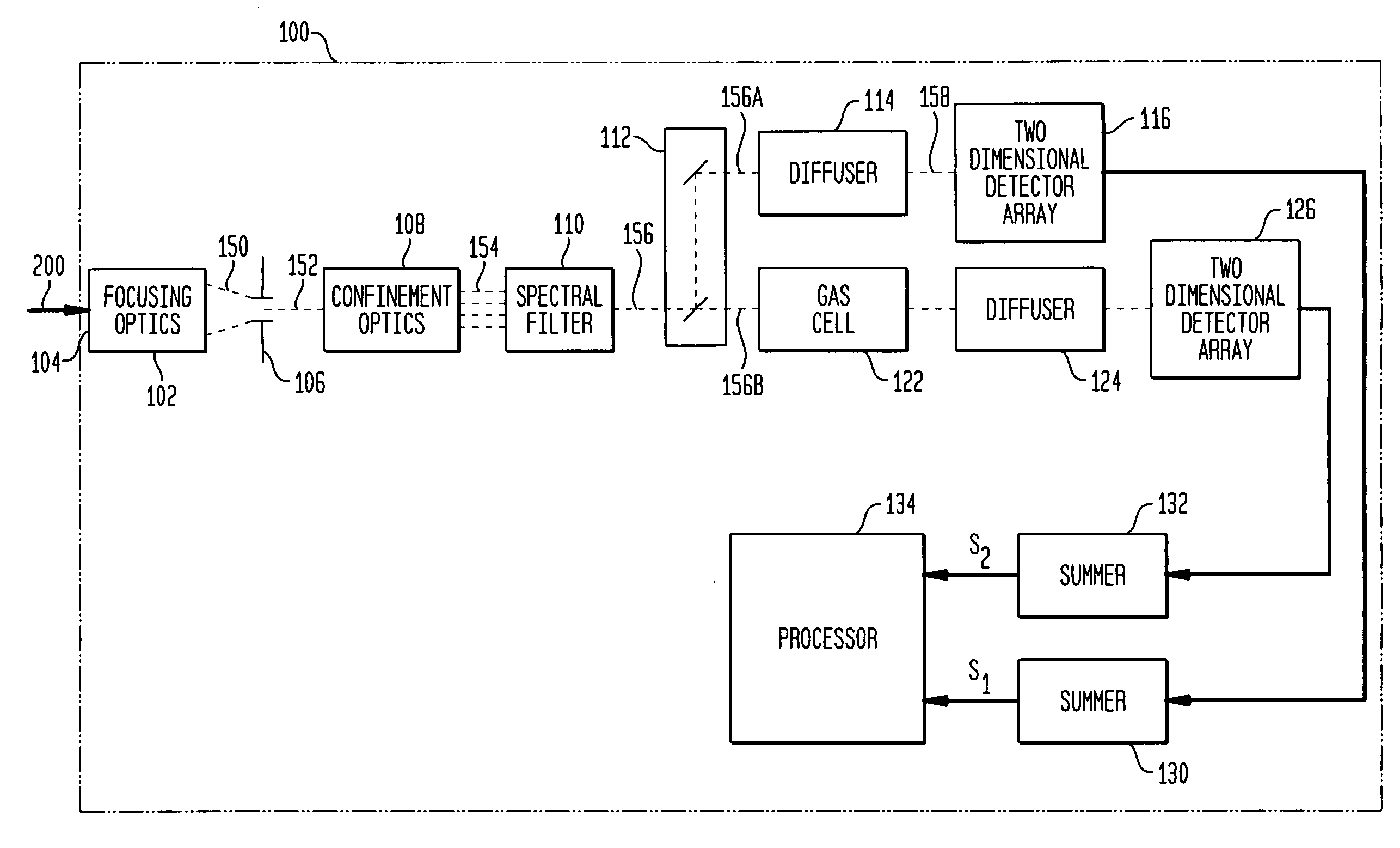
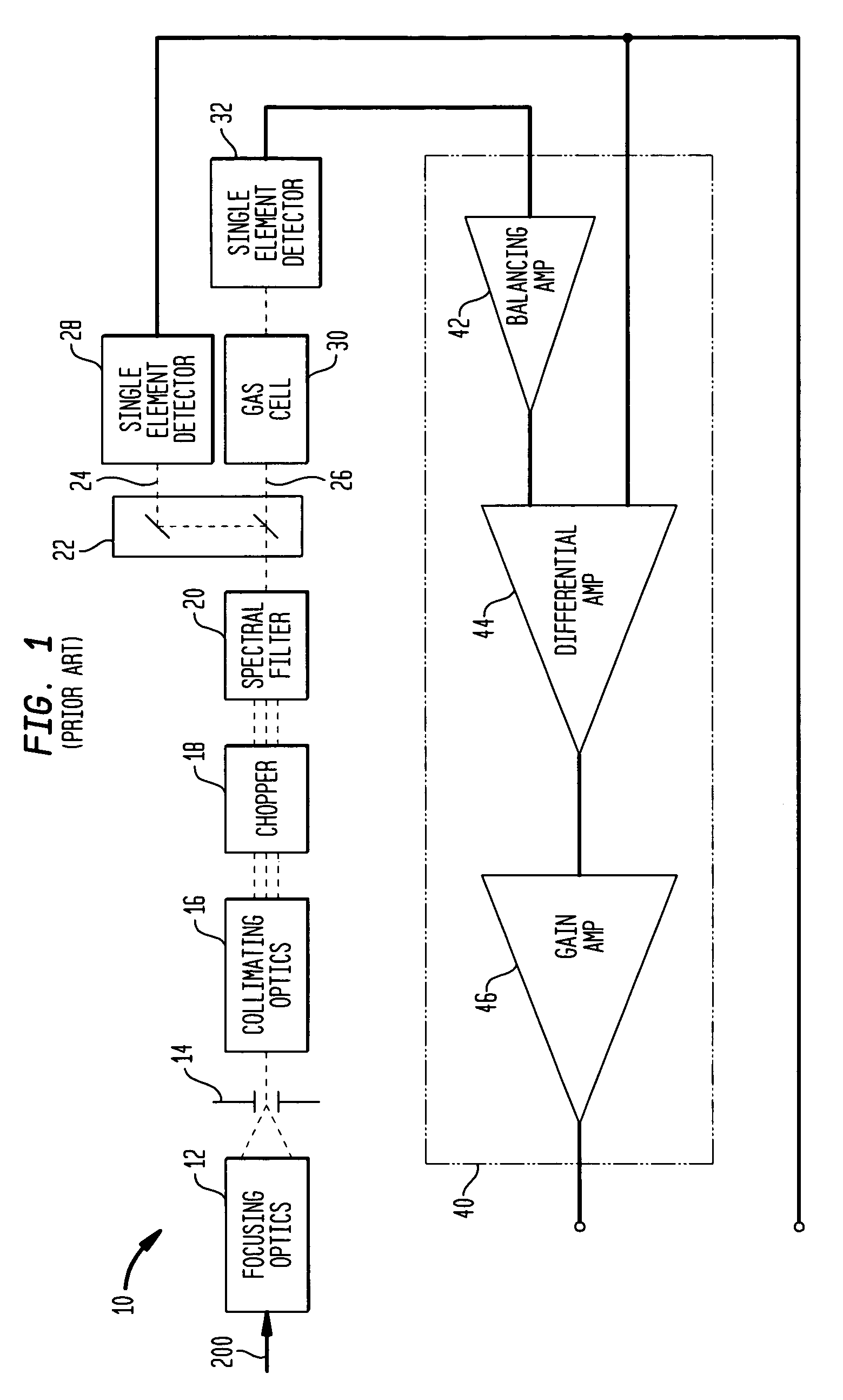
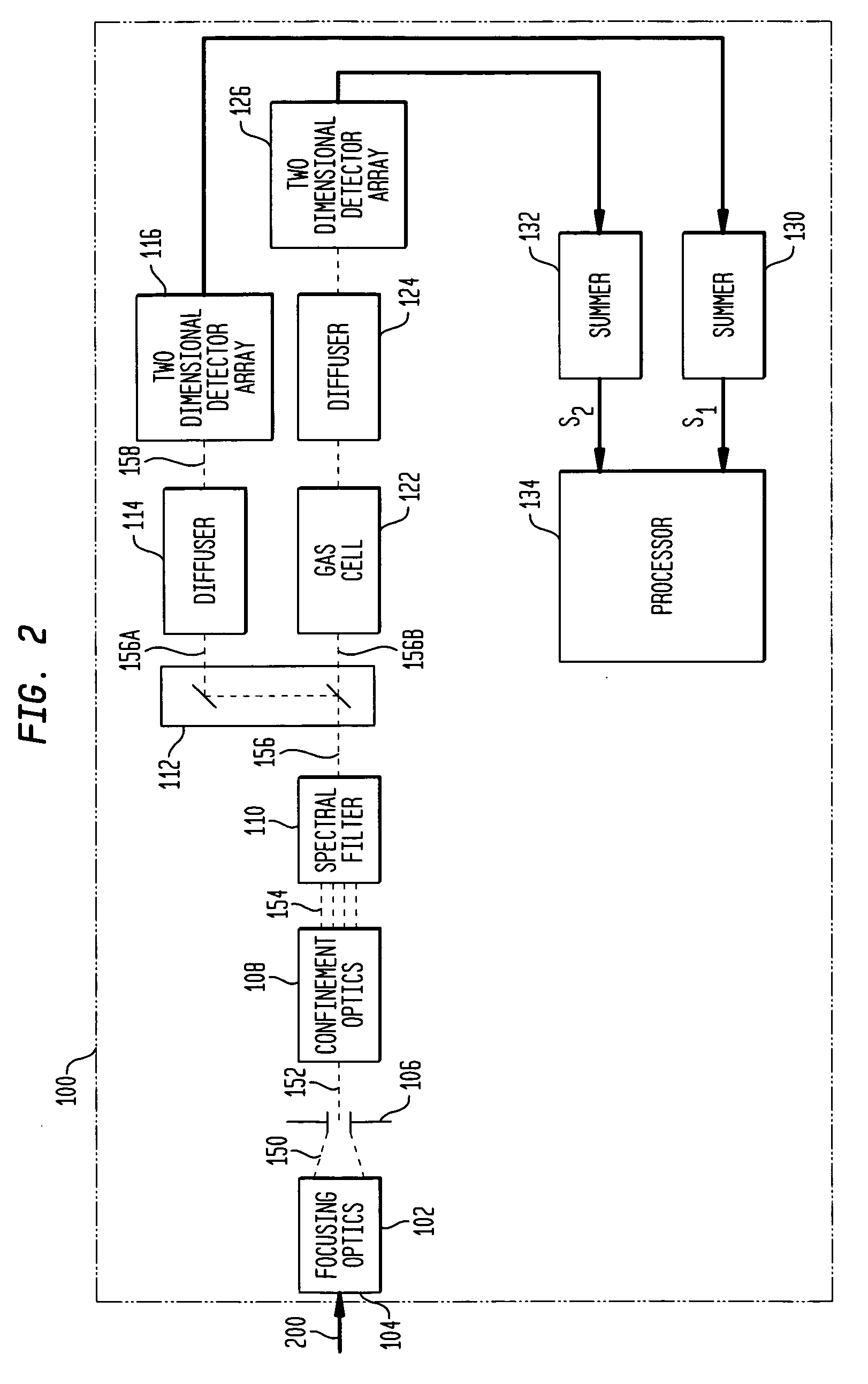
Internally-calibrated, two-detector gas filter correlation radiometry (GFCR) system
InactiveUS20080180677A1Accurate CalibrationEasy CalibrationRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral bandsField of view
An entrance aperture of a GFCR system receives light from a scene of interest. The light is focused to form an image at a focal plane. Light associated with a selected field-of-view of the image at the focal plane is then confined to a spectral band at which a gas of interest absorbs. The confined light is split into first and second paths. A calibrating light is selectively produced from within the optical train at the focal plane. A portion of the calibrating light traverses each of the first and second paths. A region that is substantially non-interfering with respect to the spectral band is disposed in the first path. A gas cell filled with the gas of interest is disposed in the second path. The light passed through the region and through the gas cell is independently detected and used to generate output signals indicative of the light so-detected. The output signals are processed with the output signals generated by the light from the selected field-of-view of the image being used to generate a measure of the gas of interest and the output signals generated by the portion of the calibrating light traversing the first and second paths being used to calibrate the GFCR system.
Owner:G & A TECHN SOFTWARE
Radiometric Approach to Temperature Monitoring Using a Magnetic Resonance Scanner
InactiveUS20070293753A1Accurate and absolute non-invasive thermal imagingEffective diagnosisBody temperature measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectromagnetic shieldingTemperature monitoring
Disclosed is a method and system for acquiring absolute temperature imagery using an MR scanner. The method involves using the RF coil as a passive antenna, and performing radiometric measurements of the noise variance of the target within the field of view of the RF coil. The noise variance corresponds to the absolute temperature of the volume within the field of view of the RF coil. The room of the MR scanner is used for electromagnetic shielding during the acquisition of radiometric data. This method may be performed with minimal or no add-ons to existing MR scanner hardware. Disclosed are a method for calibrating an MR scanner for radiometric temperature measurements, and a method for acquiring and generating thermal imagery with a calibrated MR scanner.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method and apparatus for measuring particle motion optically
InactiveUS20060152722A1Wide scattered signal bandwidthShort timeMaterial analysis by optical meansFluid speed measurementLight beamOptical measurements
A method and apparatus for measuring particle motion using electromagnetic radiation uses beams of radiation modulated with a distinct frequency and / or phase. A particle traversing these beams scatters a portion of the radiation. Scattered radiation, which retains its modulation information, is then detected, and a cross-correlation technique is used to quantify the particle's motion, for example, particle velocity.
Owner:NORTHBY JAN ARWOOD
Uniform, non-disruptive, and radiometrically accurate calibration of infrared focal plane arrays using global scene motion
A method of generating an image sequence that includes the steps of detecting scene irradiance using detectors in a focal plane array, generating an output image sequence for each of the detectors based on the detected irradiance, and correcting the output image sequence generated by a first subset of detectors in the focal plane array and the output image sequence generated by a second subset of detectors in the focal plane array using the correction provided to the first subset of detectors.
Owner:STC UNM
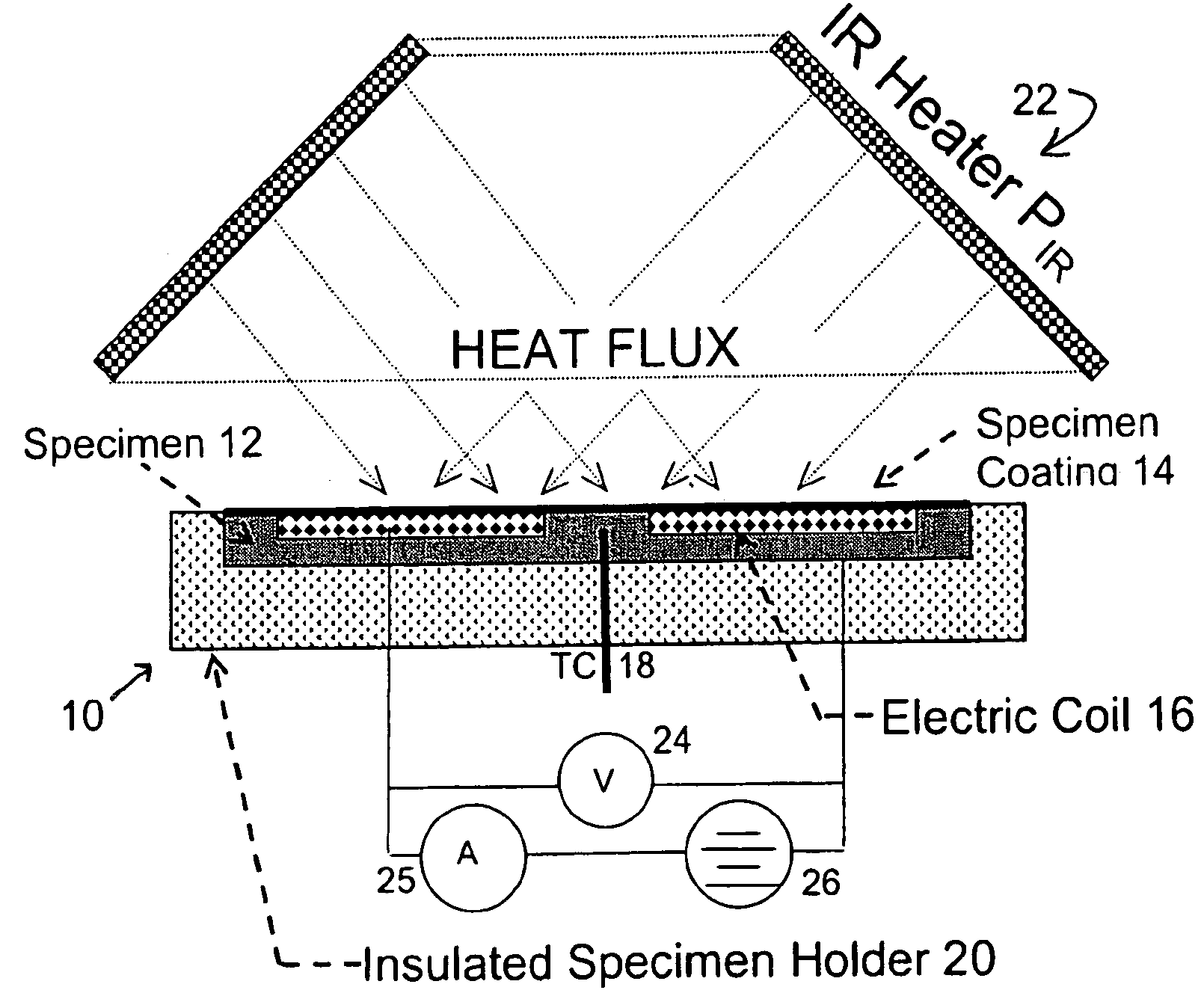
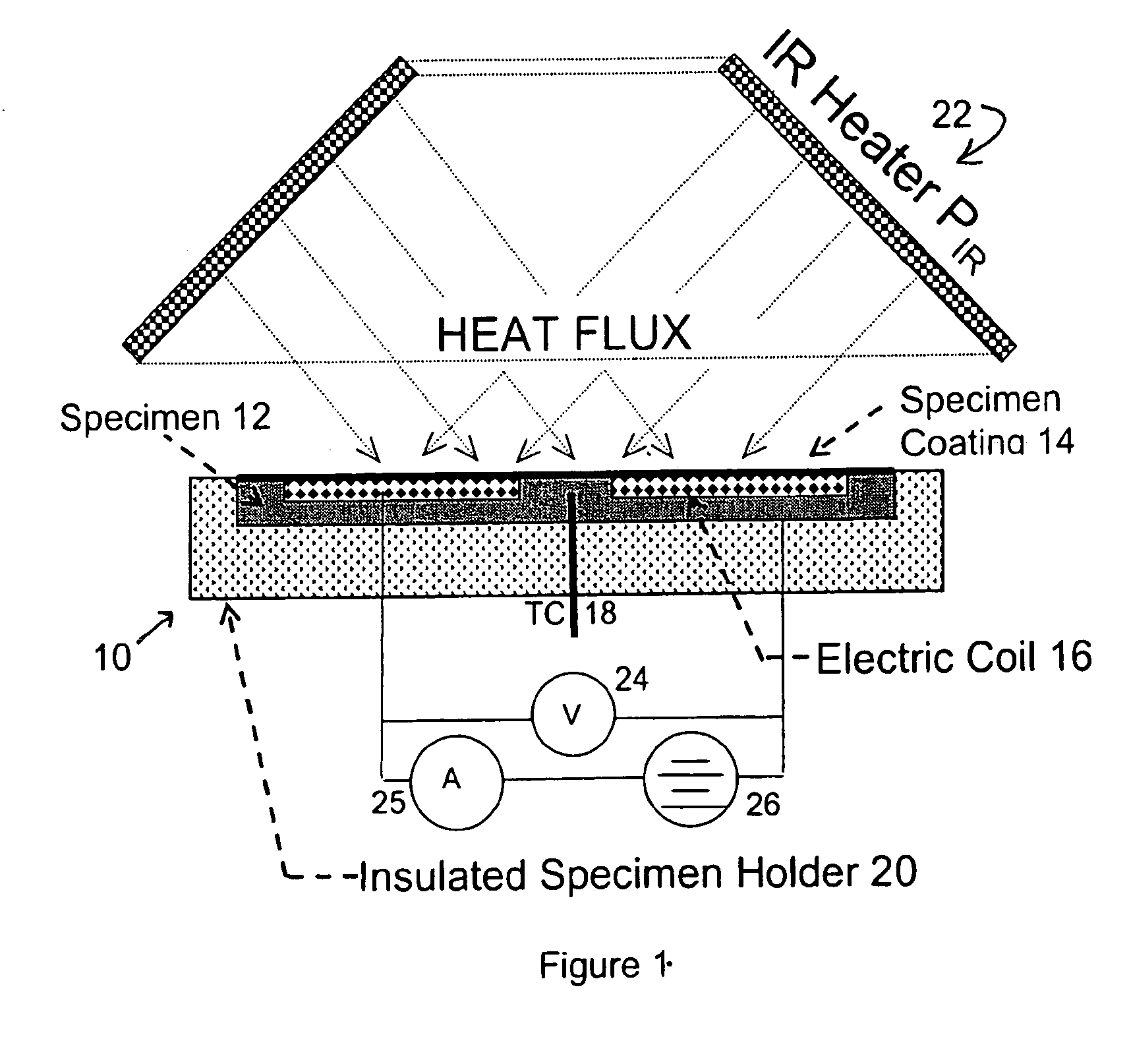
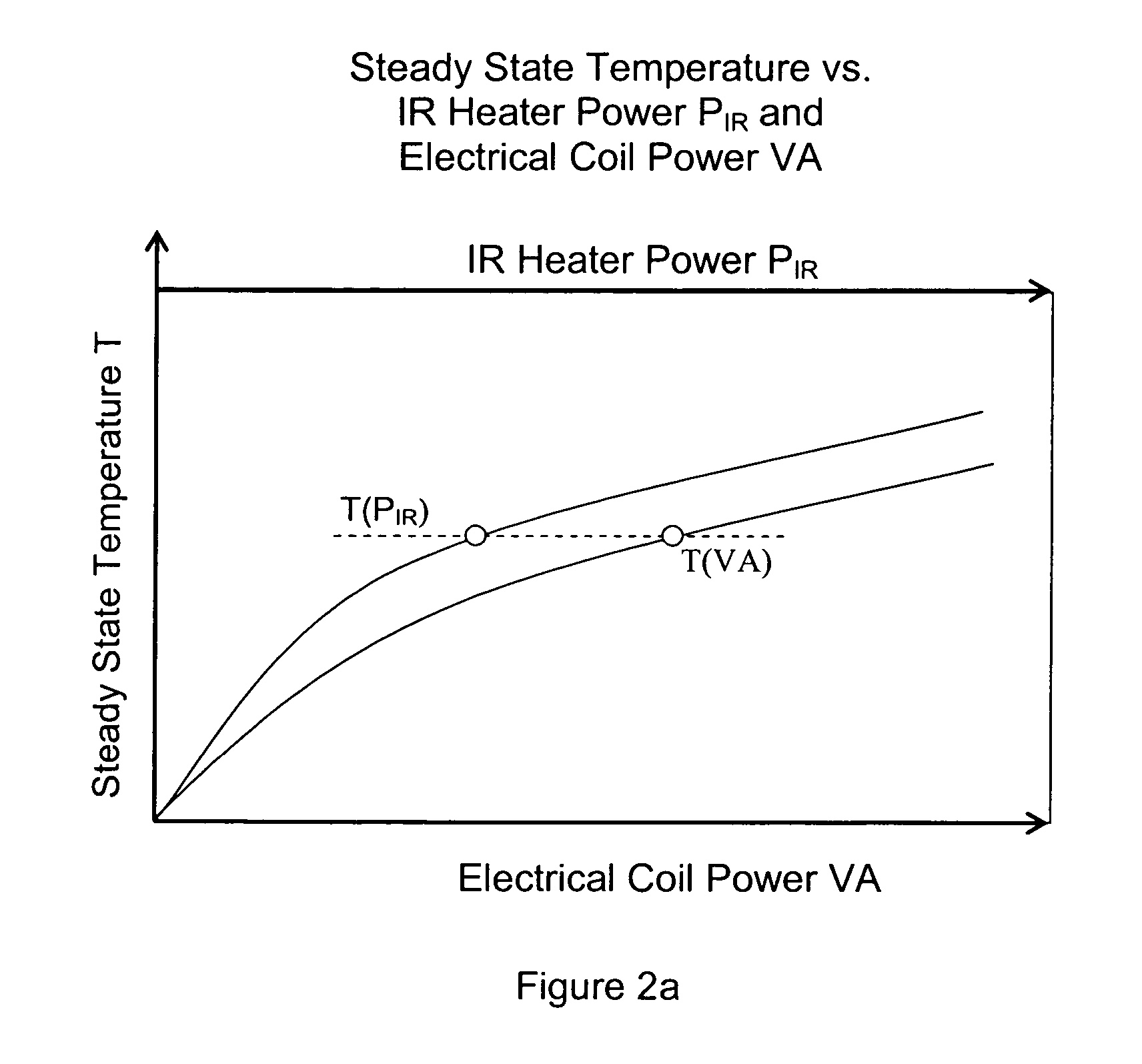
Device and method for measuring absorbed heat flux in a fire test apparatus
InactiveUS20050078732A1Overcomes possible measurement errorAccurate measurementMaterial thermal conductivityThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHeat fluxEngineering
A device for measuring the flux received by a specimen in fire test apparatuses has a copper disk or plate of the same dimensions and the same type of surface coating as a typical material specimen, an embedded heating coil and thermocouple, and an insulated sample holder similar to that used for a specimen. The transient response of the embedded thermocouple is measured for several different levels of imposed incident radiation without electrical heating and for several different known levels of electrical heating without any imposed radiation. The principle of Electrical Substitution Radiometry (ESR) is applied, and the transient responses to incident radiation and electrical heating under identical thermal conditions are compared to determine the amount of incident radiation that is actually absorbed by the device while it is being irradiated. The situations are kept thermally identical, thereby insuring that all effects due to heat losses (e.g. convection, radiation and conduction) are exactly the same.
Owner:FACTORY MUTUAL RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com