Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1220 results about "Graphic card" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
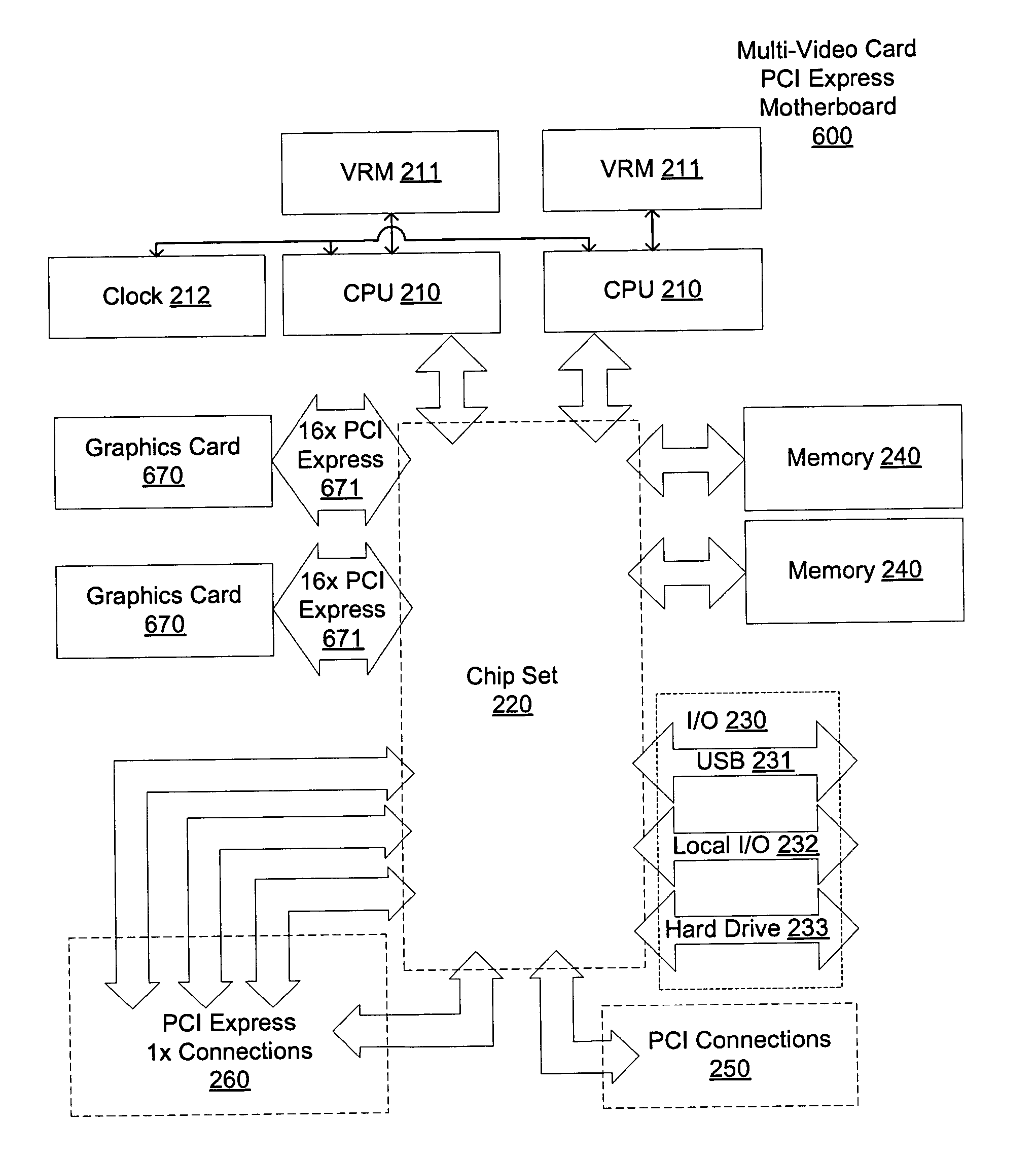
Motherboard for supporting multiple graphics cards
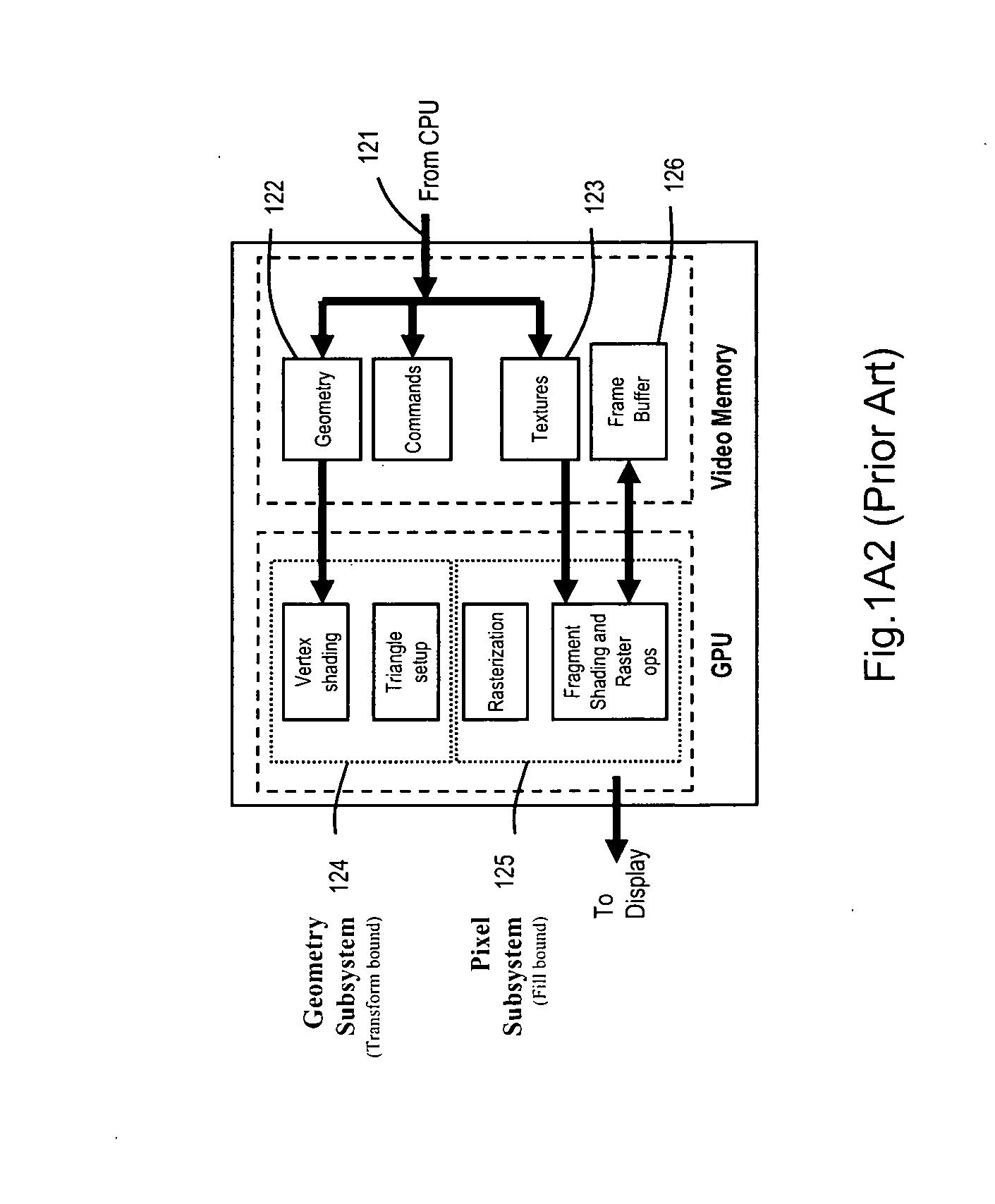
ActiveUS20050088445A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsScalable system
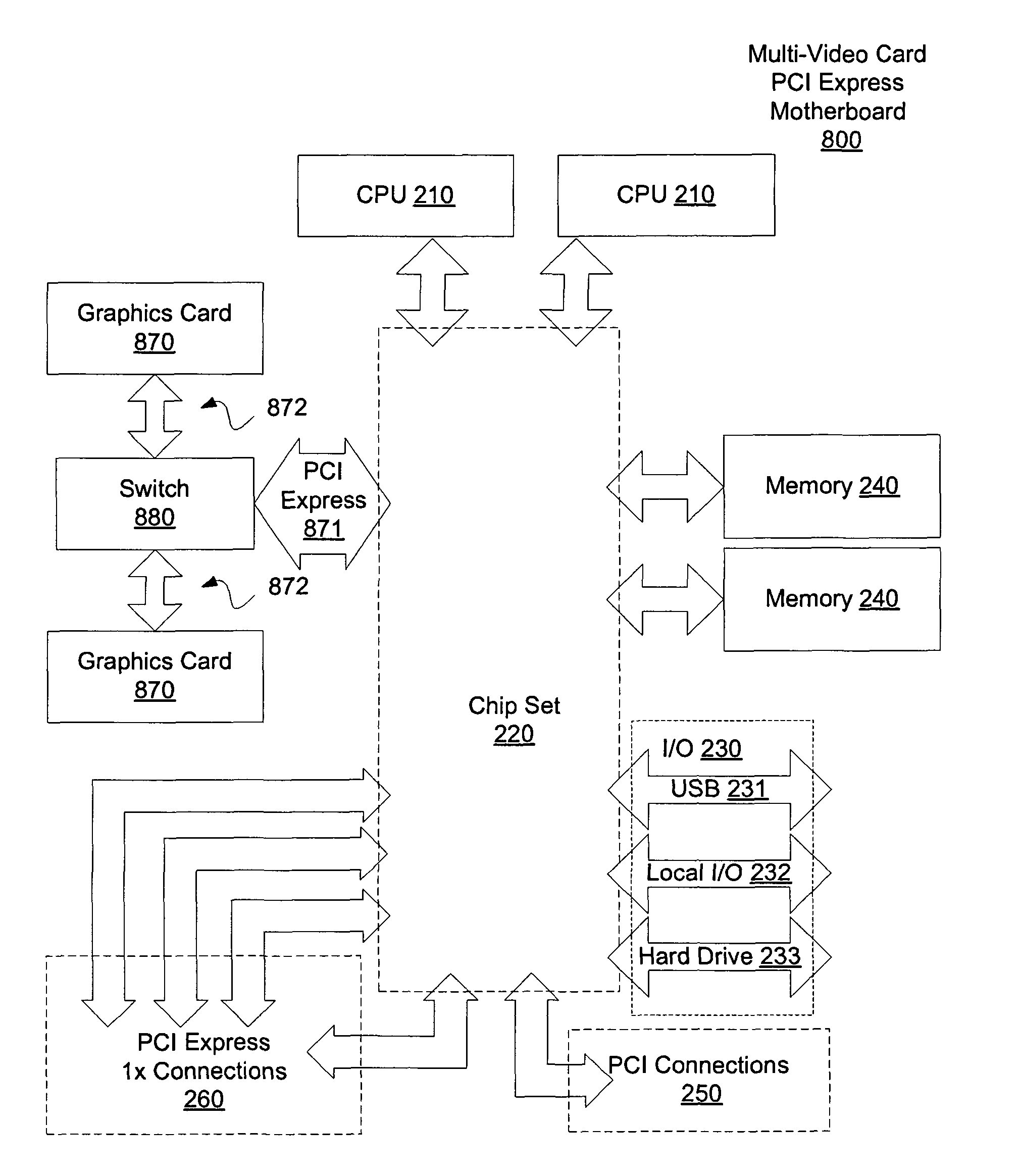
The present invention provides a motherboard that uses a high-speed, scalable system bus such as PCI Express® to support two or more high bandwidth graphics slots, each capable of supporting an off-the-shelf video controller. The lanes from the motherboard chipset may be directly routed to two or more graphics slots. For instance, the chipset may route (1) thirty-two lanes into two ×16 graphics slots; (2) twenty-four lanes into one ×16 graphics slot and one ×8 graphics slot (the ×8 slot using the same physical connector as a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes); or (3) sixteen lanes into two ×8 graphics slots (again, physically similar to a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes). Alternatively, a switch can convert sixteen lanes coming from the chipset root complex into two ×16 links that connect to two ×16 graphics slots. Each and every embodiment of the present invention is agnostic to a specific chipset.
Owner:DELL MARKETING
Panoramic video system with real-time distortion-free imaging
ActiveUS20060023105A1Minimizing software overheadHighly efficient regional transformationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsTime distortionGraphic card
A panoramic annular lens system (PAL), a unitary video camera and a PC-based software system that unwraps a 360° video image into a seamless, distortion free horizontal image image in real time. The PAL system of the preferred embodiment has a 360° horizontal field of view and a 90° vertical field of view in a 40 mm diameter compact package. The invention is not limited to any particular type of lens system. In fact, there are numerous lens systems for providing a 360° panoramic view. The video camera may be a CCD or CMOS based device having a pixel resolution of either 1280×1024 (high resolution) or 720×480 (NTSC). The unwrapping system is a radiometric ray tracing program carried out using a computer's graphics card capabilities to produce highly efficient regional transformation while minimizing software overhead. The result is real time, high resolution 30 fps conversion from a spherical distorted image to a flat panoramic image in Cartesian coordinates.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Daughter card approach to employing multiple graphics cards within a system
InactiveUS20050270298A1Low costMultiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingDigital dataGraphics
The invention provides, in one aspect, a digital data processor including a motherboard comprising a printed circuit board having disposed thereon (a) a central processing unit and one or more associated memories, and (b) a primary slot adapted to provide signal coupling compatible with the PCI-Express industry standard. The digital data processor further includes a graphics interface device that is mounted in the primary slot and that, as a consequence, is in mechanical and signal coupling with the motherboard. That graphics interface device, itself, has a plurality of further slots, each of which is adapted to provide signal coupling compatible with the PCI-Express industry standard.
Owner:MERCURY COMPUTER SYSTEMS INC
Ultrasound system and method for imaging and/or measuring displacement of moving tissue and fluid
ActiveUS20080086054A1Increase speedQuality improvementBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionGraphic cardSonification
A system and method for improved imaging is disclosed. An exemplary system provides a peripheral ultrasound system connected to a host computer with a plug-and-play interface such as a USB. An exemplary system utilizes a dedicated graphics processing unit such as a graphics card to analyze data obtained from a region of interest to produce an image on one or more output units for the user's viewing. Based on the image displayed on the output units, the user can determine the velocity of the moving tissue and fluid. The system of the present invention can be used to produce a Doppler color flow map or for power Doppler imaging.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
Panoramic video system with real-time distortion-free imaging
ActiveUS7336299B2Highly efficient regional transformationMinimize overheadImage enhancementTelevision system detailsTime distortionGraphic card
A panoramic annular lens system (PAL), a unitary video camera and a PC-based software system that unwraps a 360° video image into a seamless, distortion free horizontal image image in real time. The PAL system of the preferred embodiment has a 360° horizontal field of view and a 90° vertical field of view in a 40 mm diameter compact package. The invention is not limited to any particular type of lens system. In fact, there are numerous lens systems for providing a 360° panoramic view. The video camera may be a CCD or CMOS based device having a pixel resolution of either 1280×1024 (high resolution) or 720×480 (NTSC). The unwrapping system is a radiometric ray tracing program carried out using a computer's graphics card capabilities to produce highly efficient regional transformation while minimizing software overhead. The result is real time, high resolution 30 fps conversion from a spherical distorted image to a flat panoramic image in Cartesian coordinates.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
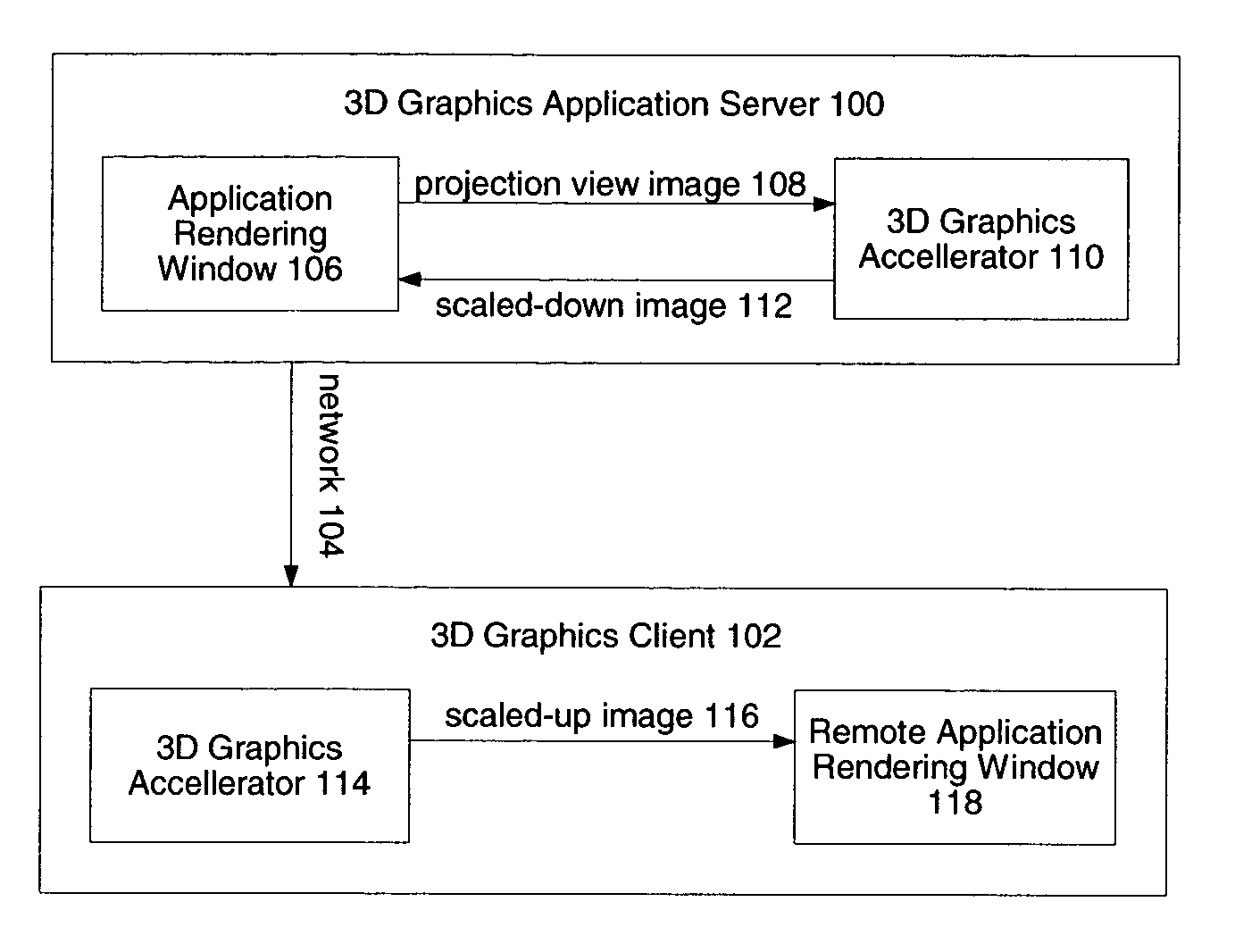
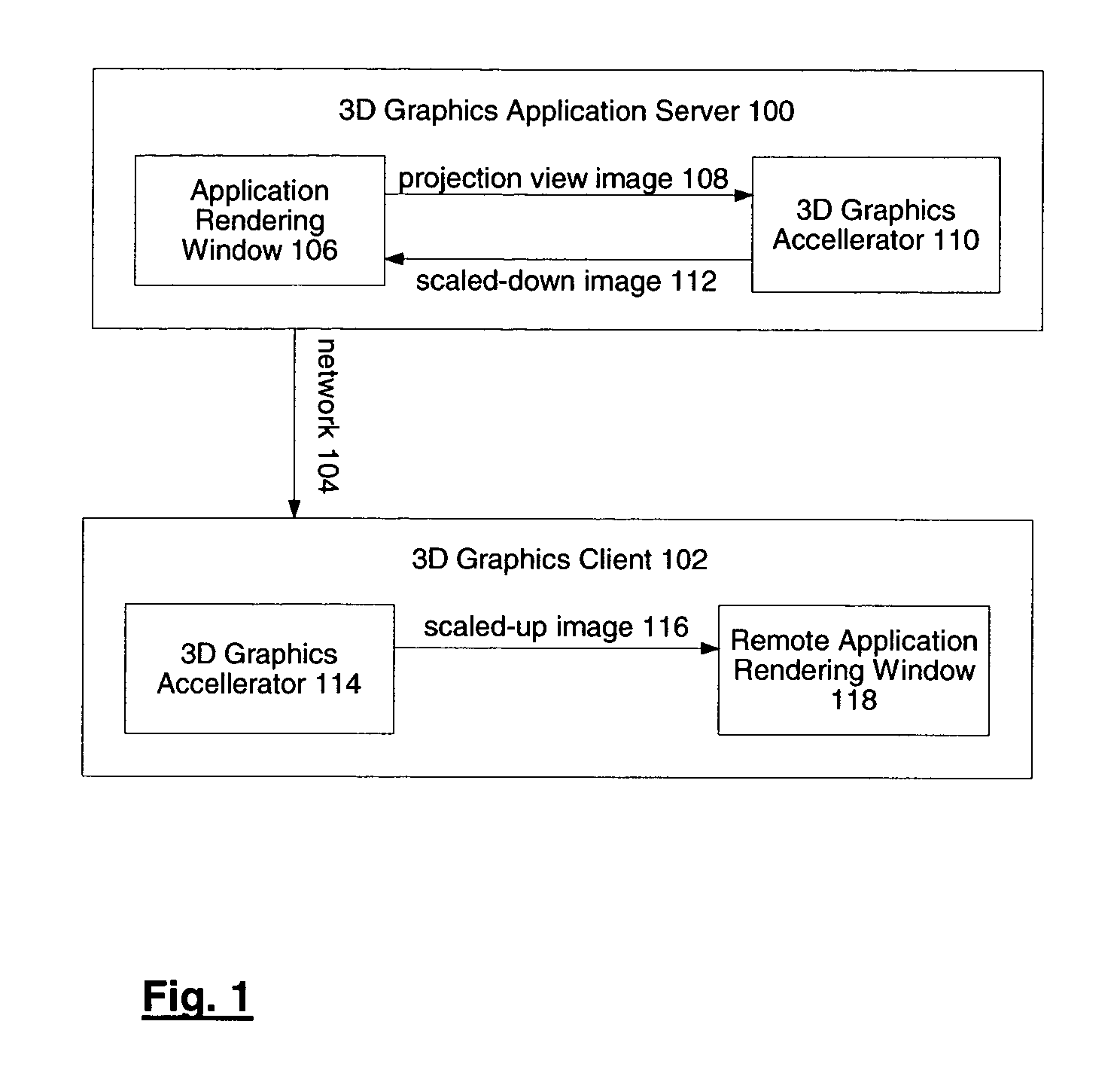
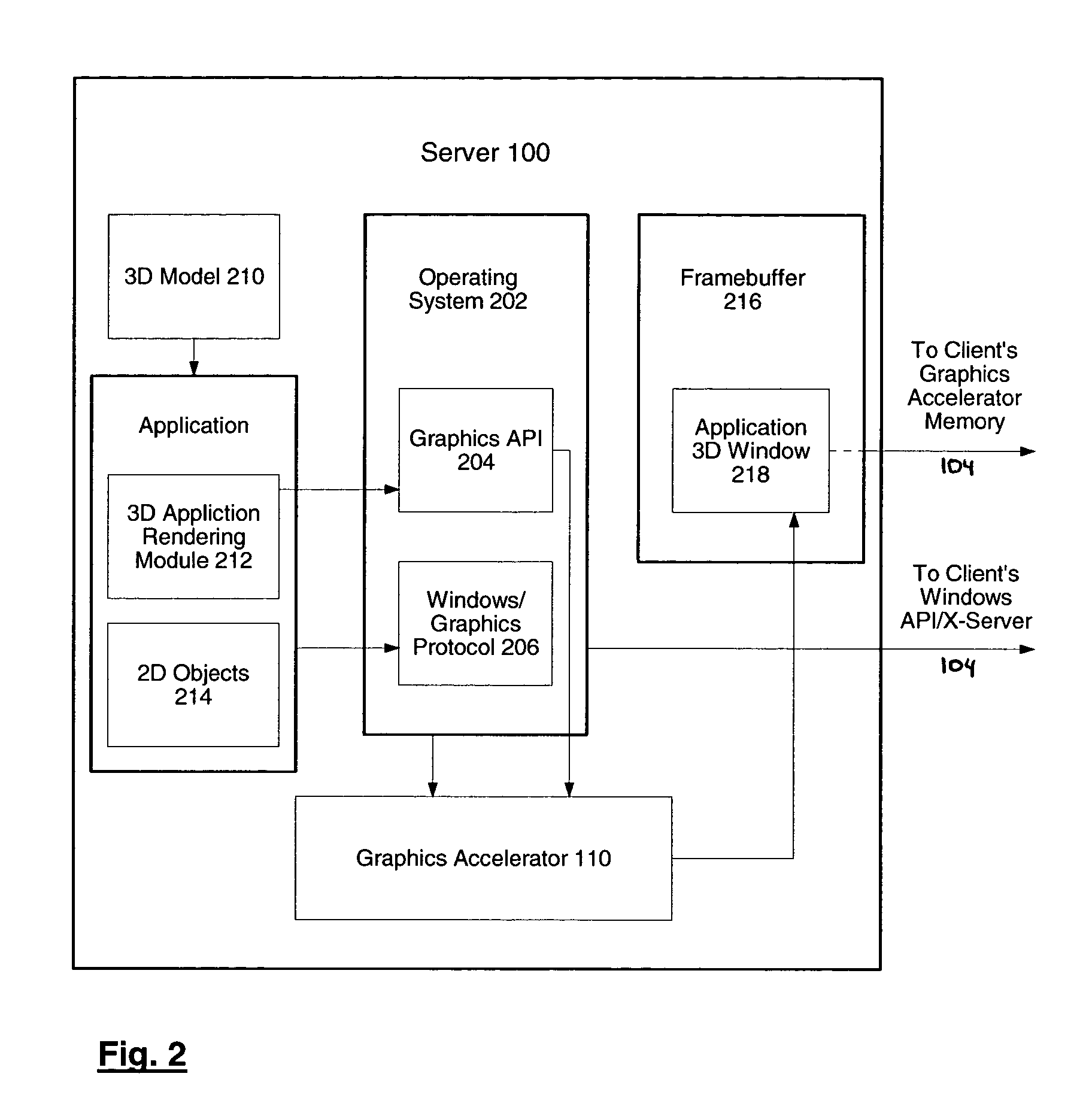
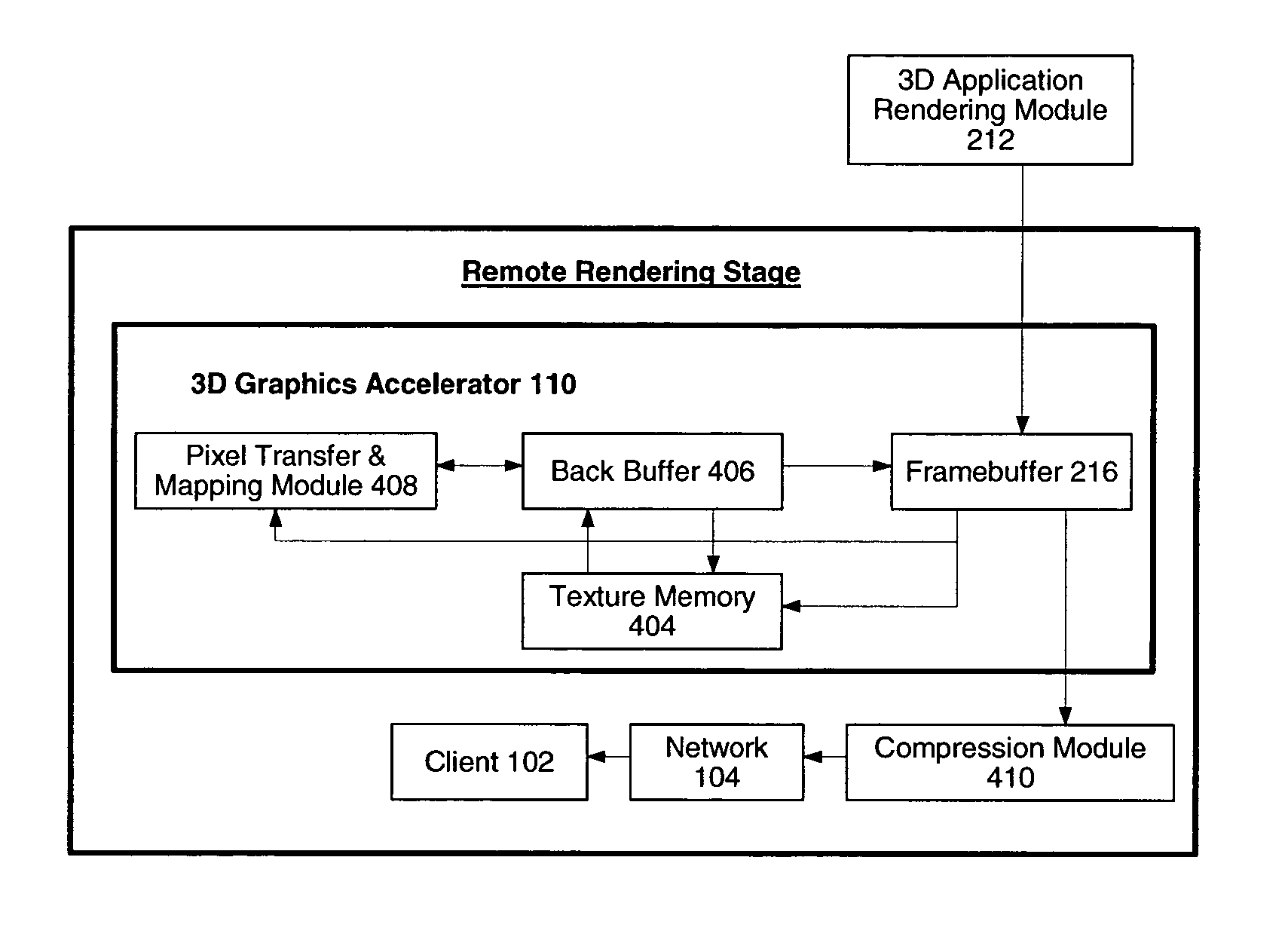
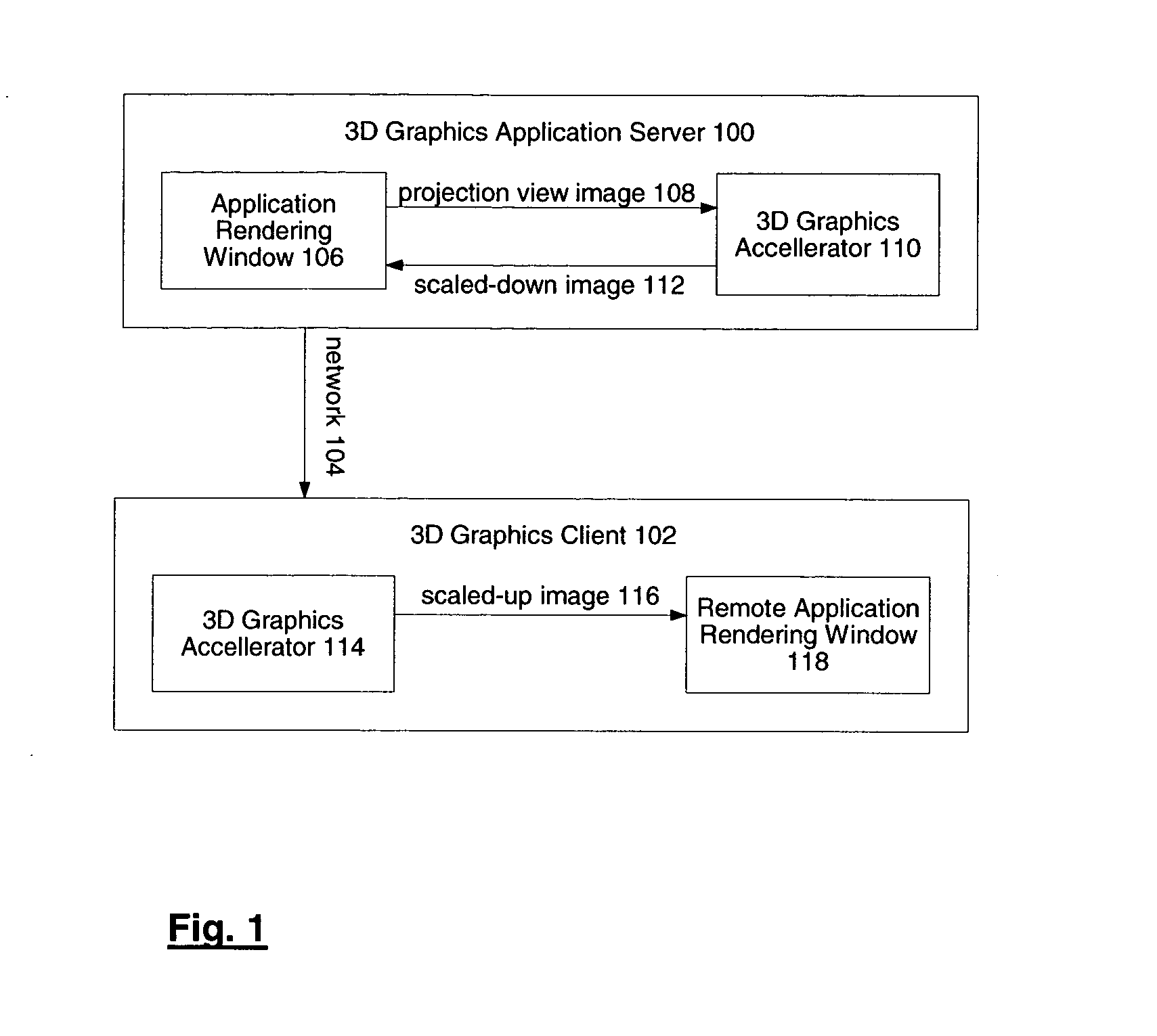
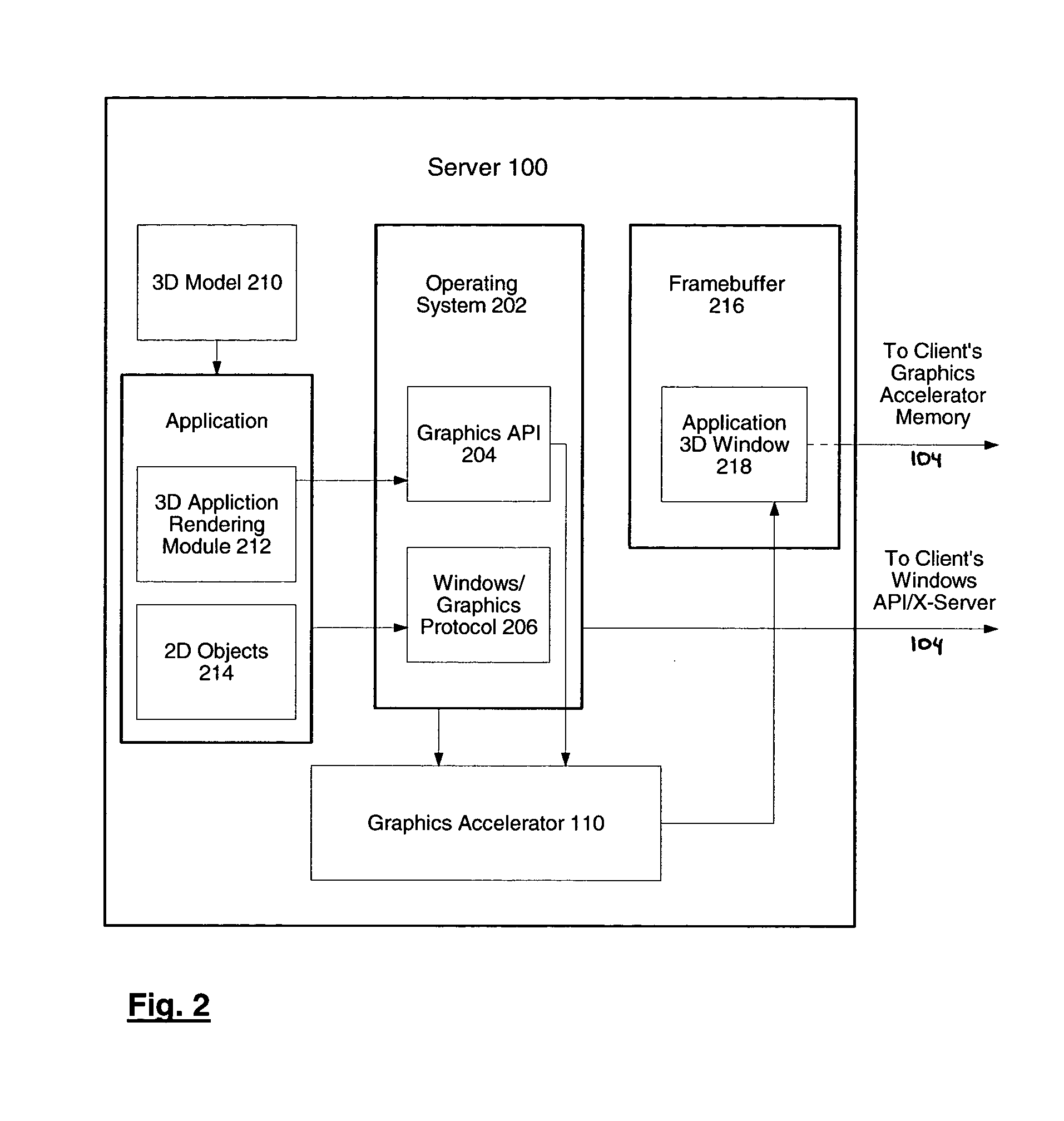
System and method for network transmission of graphical data through a distributed application
InactiveUS7076735B2Reduce network bandwidth requirementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsGraphic cardNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
Systems and methods for network transmission of three-dimensional graphical data are disclosed. A single graphical application instance can virtually and efficiently exist on multiple local or remote display systems by directly sharing its raw rendered framebuffer memory information among all local or remote graphics accelerators, thus avoiding the need to re-render any application information again on each node. An internal graphics card is used to scale the rendered data prior to transmission. This graphics scaling eliminates the need for data compression or image compression and achieves an adaptive, hardware-accelerated reduction in network bandwidth. Furthermore, since all memory and remote processing support tasks are performed within the graphics card, the CPU, system bus, and memory bandwidth remain available to the system and other applications.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
System and method for network transmission of graphical data through a distributed application
InactiveUS20050021656A1Reduce network bandwidth requirementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsGraphic card
Systems and methods for network transmission of three-dimensional graphical data are disclosed. A single graphical application instance can virtually and efficiently exist on multiple local or remote display systems by directly sharing its raw rendered framebuffer memory information among all local or remote graphics accelerators, thus avoiding the need to re-render any application information again on each node. An internal graphics card is used to scale the rendered data prior to transmission. This graphics scaling eliminates the need for data compression or image compression and achieves an adaptive, hardware-accelerated reduction in network bandwidth. Furthermore, since all memory and remote processing support tasks are performed within the graphics card, the CPU, system bus, and memory bandwidth remain available to the system and other applications.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
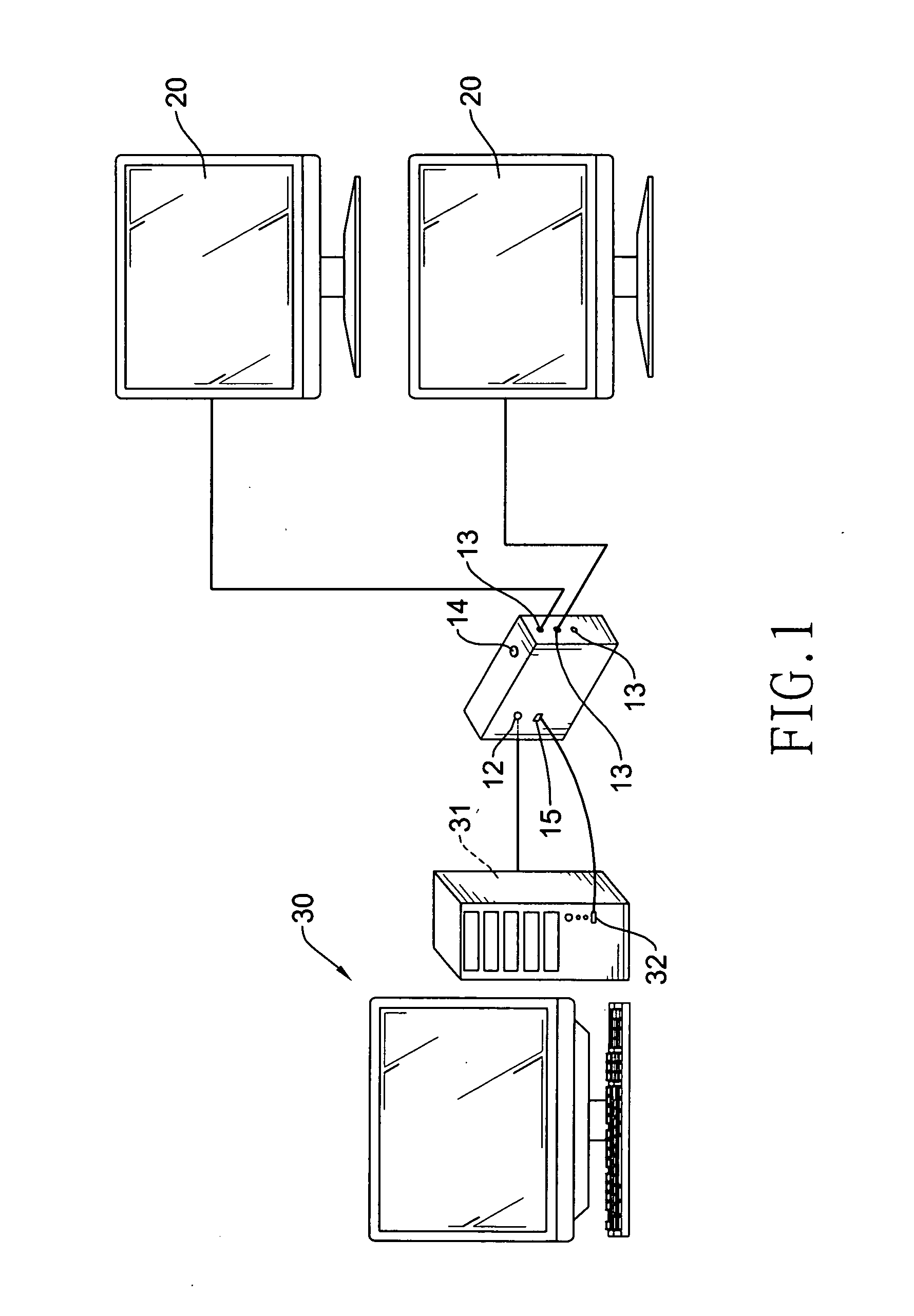
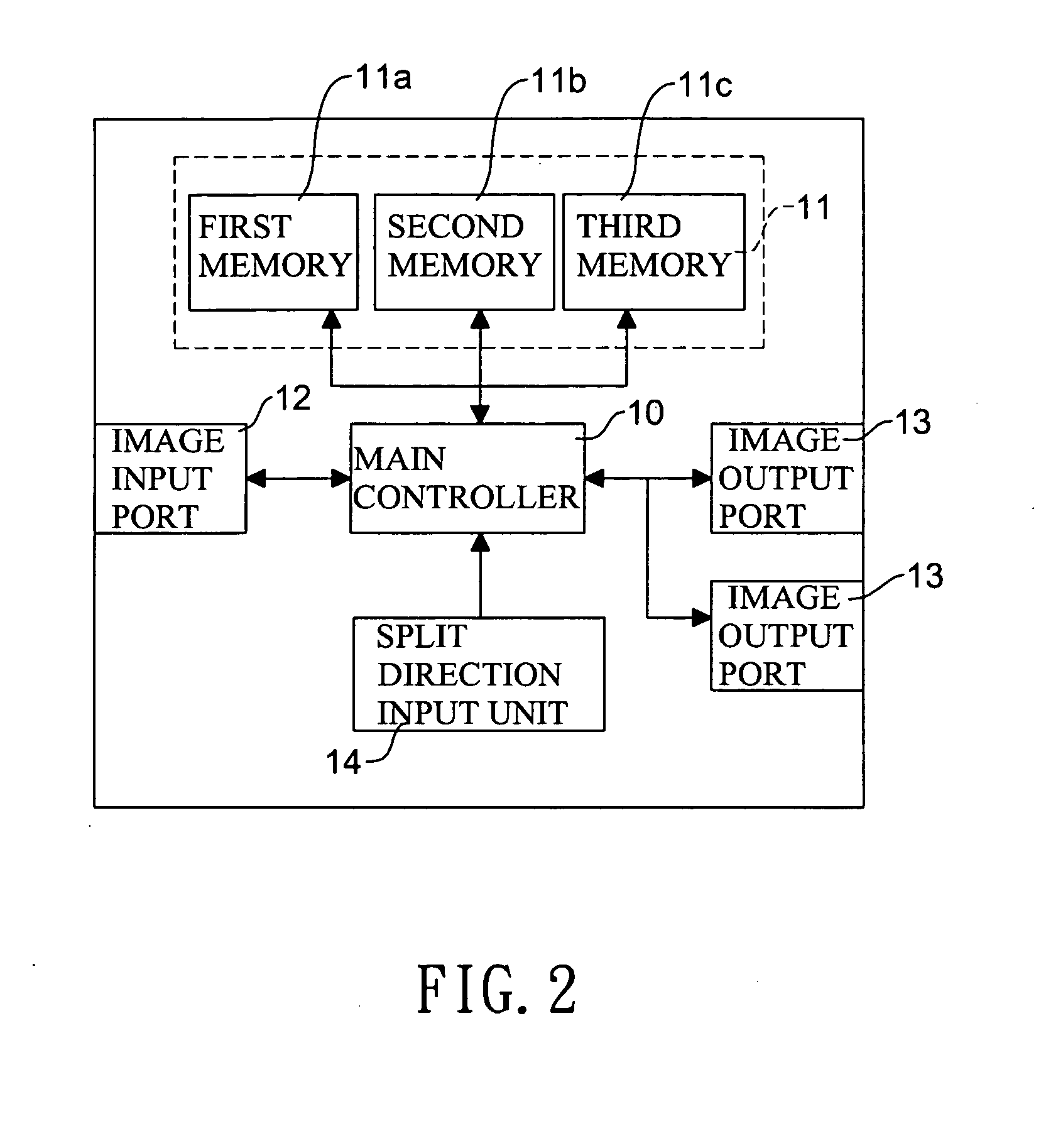
Automatic split-screen controller
InactiveUS20120050314A1Easy to operateCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphic card
An automatic split-screen controller has a main controller, an image input port connected to a graphics card and a plurality of image output ports connected to corresponding display devices. After detecting that the display devices and the graphics card are connected with the image input and output ports, the main controller executes an automatic frame dividing process to obtain a resolution in an EDID of each of the display devices, sum up the resolutions to store a total of the resolution in a dynamic EDID, divide image data received from the graphics card and complying with the total of the resolutions into a plurality of frames, and respectively output the frames to the corresponding image output ports. Accordingly, the present invention can automatically detect and drive a plurality of display devices to display image data with split screens.
Owner:PANAVIO TECH
System and Method for Displaying Computer Data in a Multi-Screen Display System
InactiveUS20080055189A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphic card
Described herein is a graphics apparatus for displaying video data on a display system having N monitors each containing a screen. The apparatus includes a central controller for receiving from a graphics card a video signal. The central controller divides at least a portion of the video signal into N video streams, each video stream sent to an associated one of the N monitors for producing images on the N screens.
Owner:WILK RAYMOND RICHARD +1
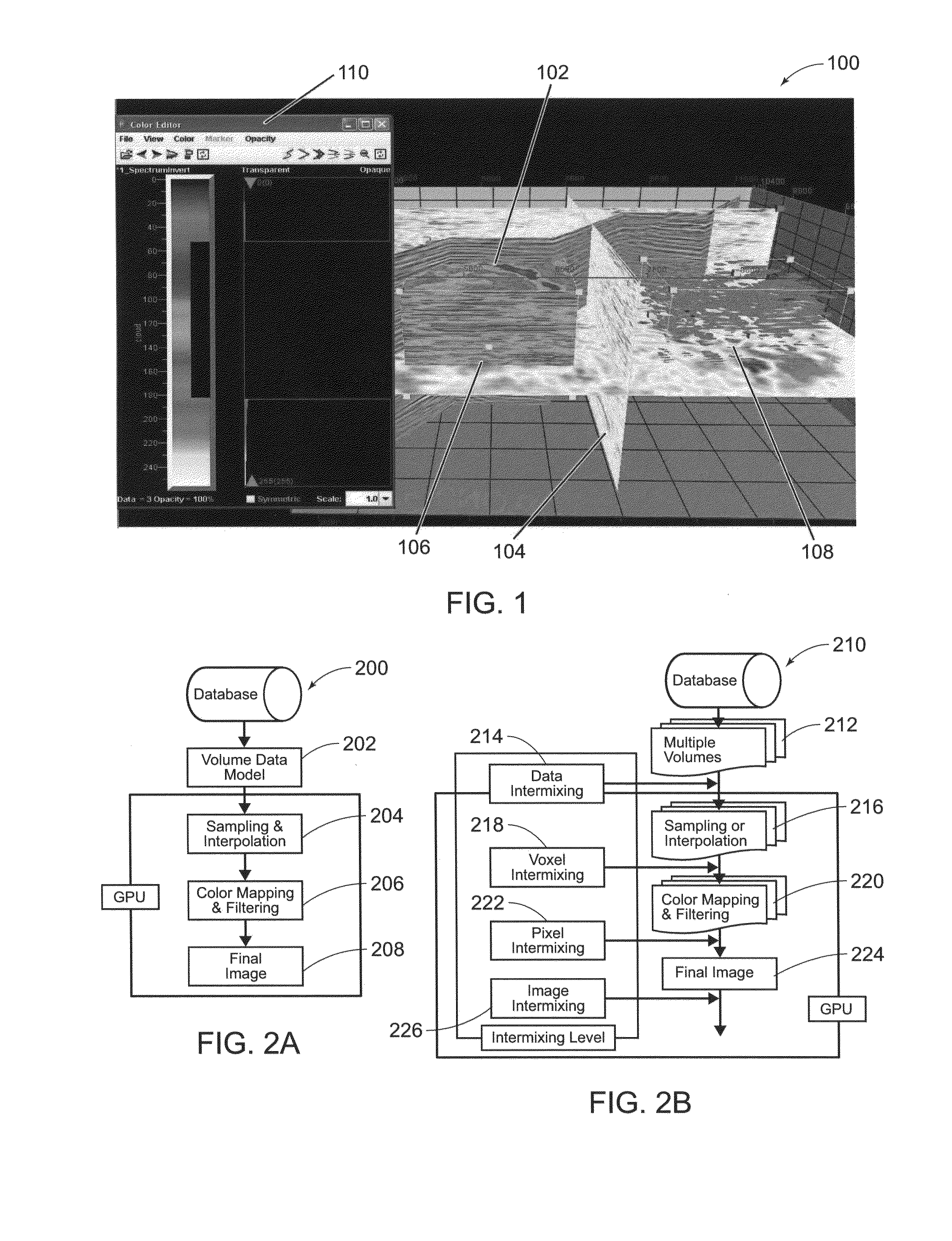
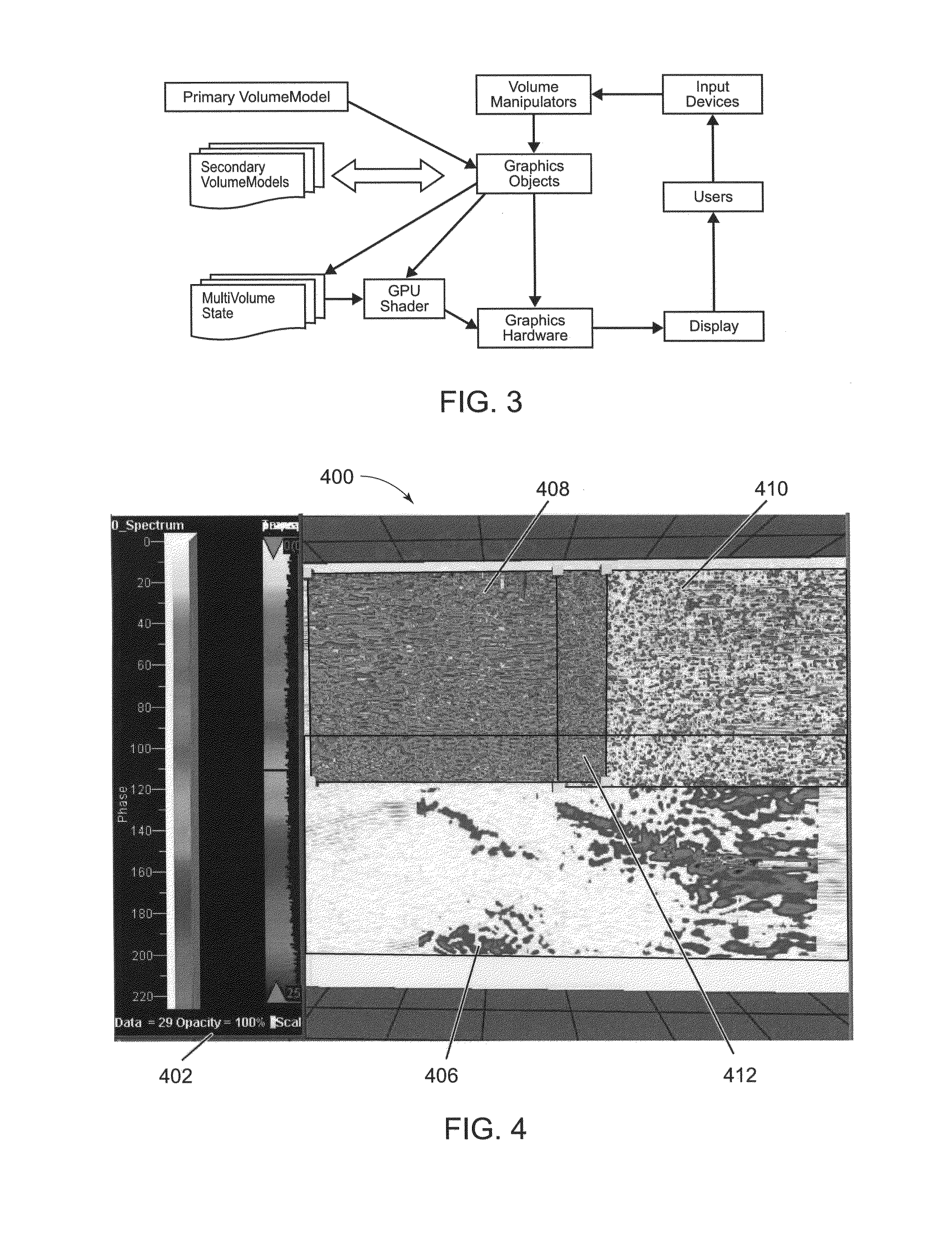
Systems and methods for visualizing multiple volumetric data sets in real time
ActiveUS20080165186A13D-image renderingDetails involving graphical user interfacePattern recognitionGraphics
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
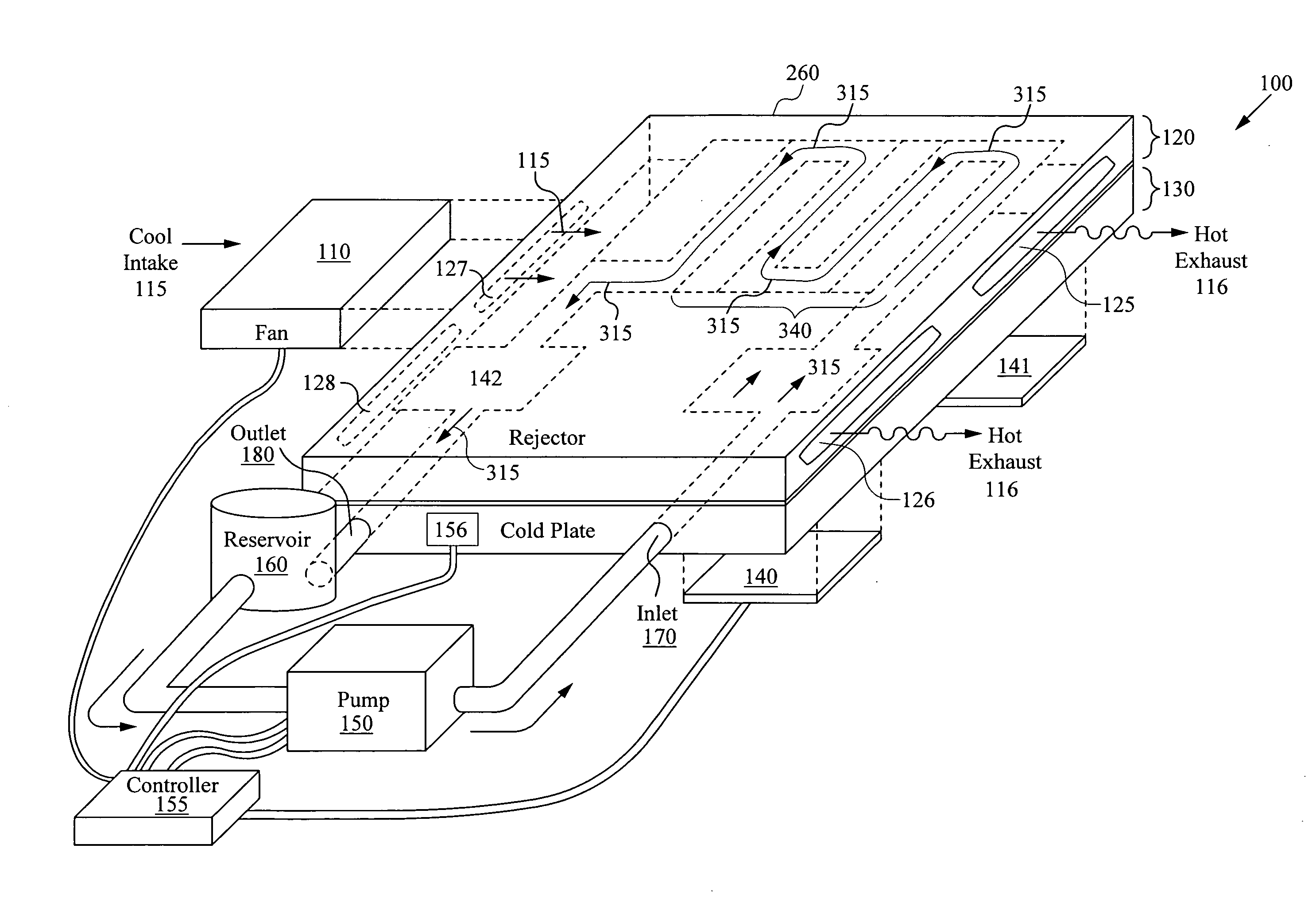
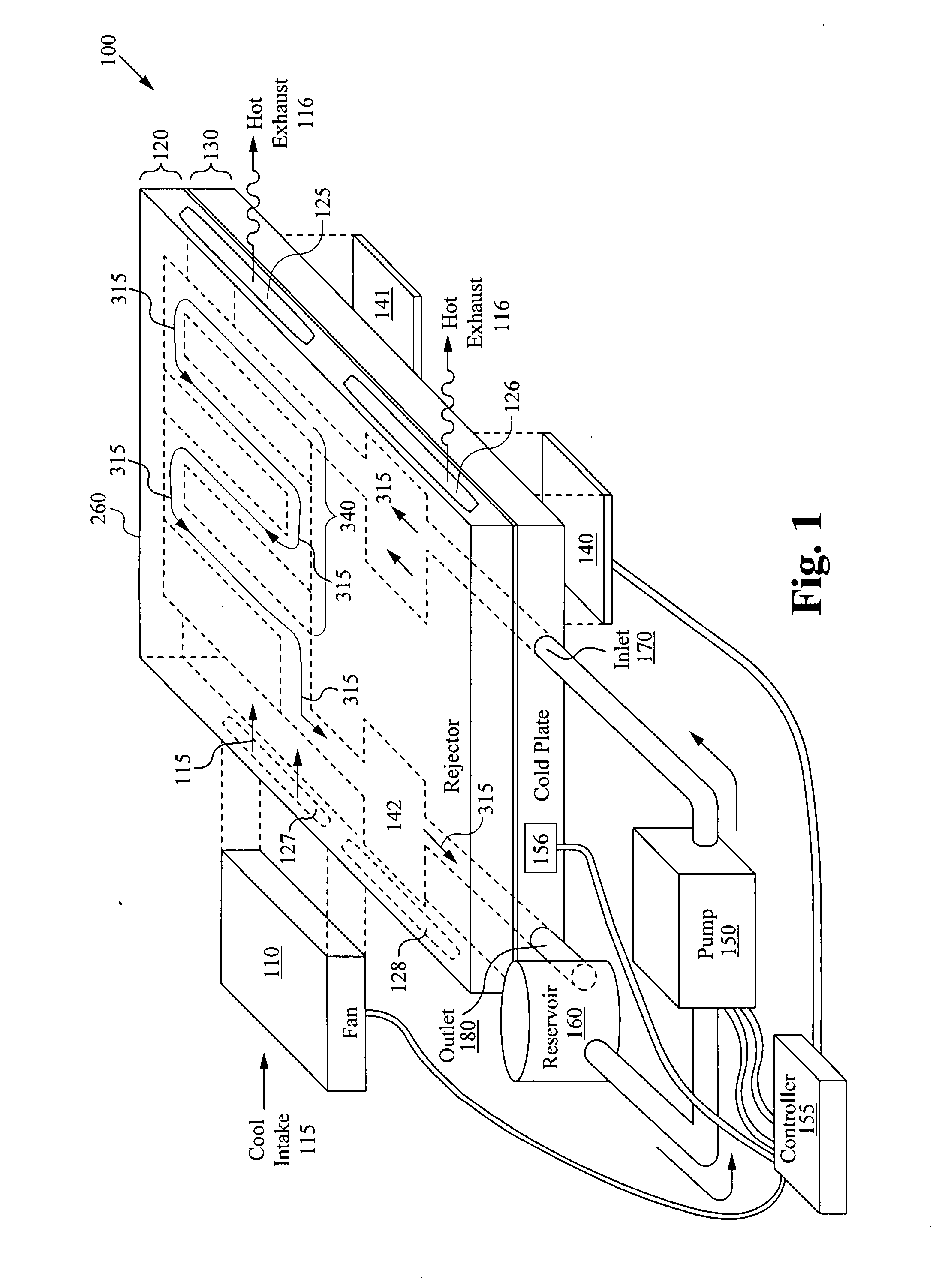
Integrated liquid to air conduction module
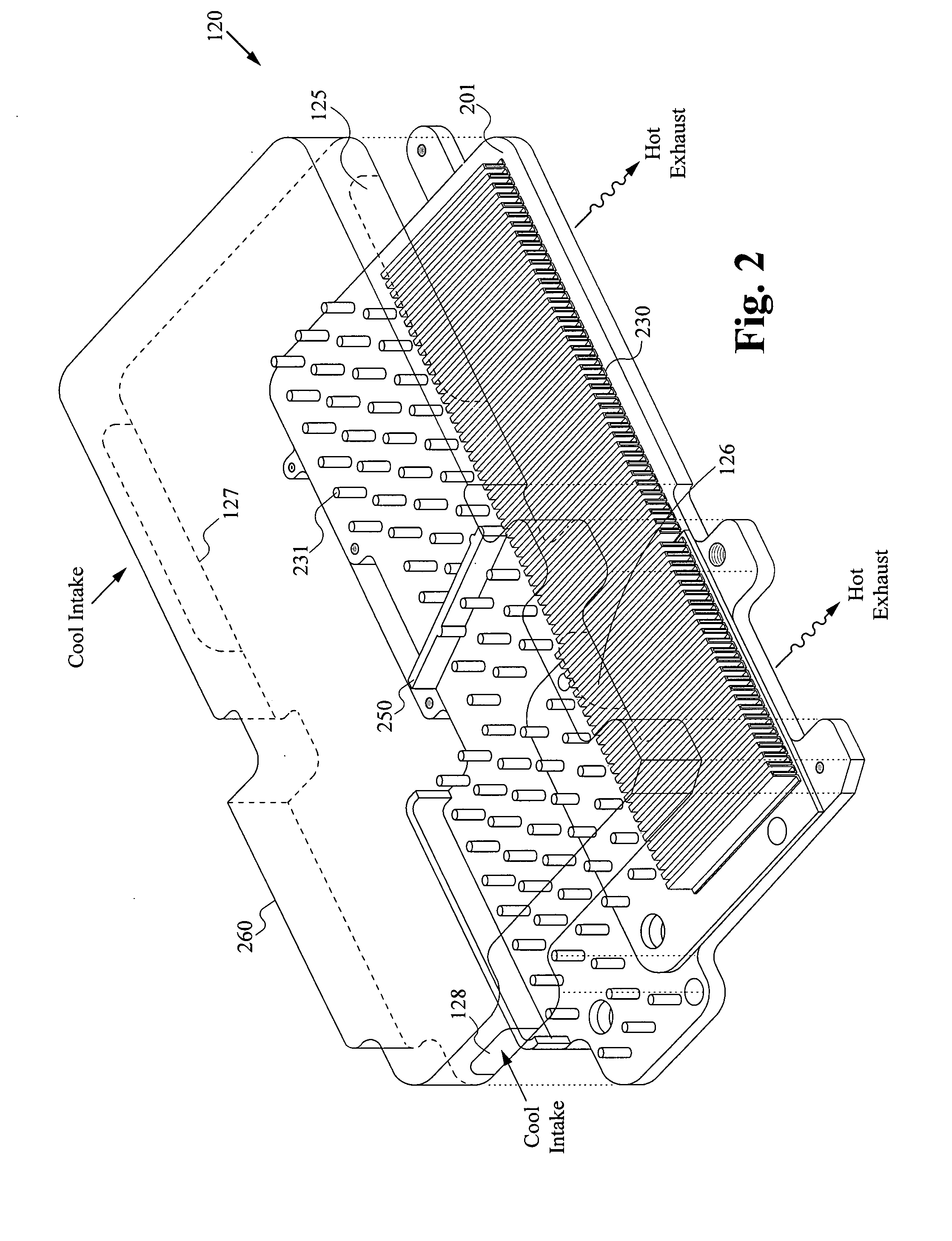
ActiveUS20070227708A1Increase the areaMaximizes timeSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsGraphic cardCounter flow
An integrated cooling system for cooling systems such as laptops or subsystems such as a graphics card is disclosed. An integrated cooling system includes a first layer having a contact area configured for coupling to a heat source, wherein the first layer has a fluid path passes adjacent to the contact area where the heat source is in thermal contact with first layer. Coupled to the first layer is a second layer to which a number of air fins are attached. The invention includes a pump that is connected to the fluid path forming a closed path for circulating a fluid through the first layer. Within the first layer, the fluid path will contain a plurality of fluid fins which control the flow of a fluid within the fluid path. Within the fluid path, a structure providing a double-counter flow adjacent to one or more electronic devices. Additionally the fluid path can include a microchannel plate structure. The system can include a includes a programmable controller connect the an air-mover, pump and temperature sensing device. A reservoir can be connected to the fluid path.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
Dummy scene roaming method and system based on spatial index cube panoramic video
InactiveCN101055494AQuality improvementImprove drawing speedInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphic card
A virtual scene roams method based on spatial index cube panoramic view video and a system thereof are disclosed. The system includes a motion control engine unit, a panoramic view video protract unit, a sound protract unit, a mapping unit and a text display unit, wherein the motion control engine unit is connected to an external input device and receives the spatial index cube panoramic view video signal input from external, the corresponding sound file of the roam paths, control map and text information. The invention executes fine model building for the virtual scene by existing three-dimensional tools, pre-protracts the required high quality image sequence, and compresses the panoramic view video data and improves the protracting speed by choosing the spatial index cube panoramic view video as input and using the compressing method supported by a three-dimension graphics card. The user can conveniently interact with the system by external instruments such as game handle; mouse and keyboard to obtain high quality roam experience.
Owner:上海虚拟谷数码科技有限公司
Motherboard for supporting multiple graphics cards
InactiveUS7782325B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsScalable systemGraphics
The invention provides a motherboard that uses a high-speed, scalable system bus such as PCI Express® to support two or more high bandwidth graphics slots. The lanes from the motherboard chipset may be directly routed to two or more graphics slots. For instance, the chipset may route (1) thirty-two lanes into two ×16 graphics slots; (2) twenty-four lanes into one ×16 graphics slot and one ×8 graphics slot (the ×8 slot using the same physical connector as a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes); or (3) sixteen lanes into two ×8 graphics slots (again, physically similar to a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes). Alternatively, a switch can convert sixteen lanes coming from the chipset root complex into two ×16 links that connect to two ×16 graphics slots. The system according to the invention is agnostic to a specific chipset.
Owner:DELL MARKETING
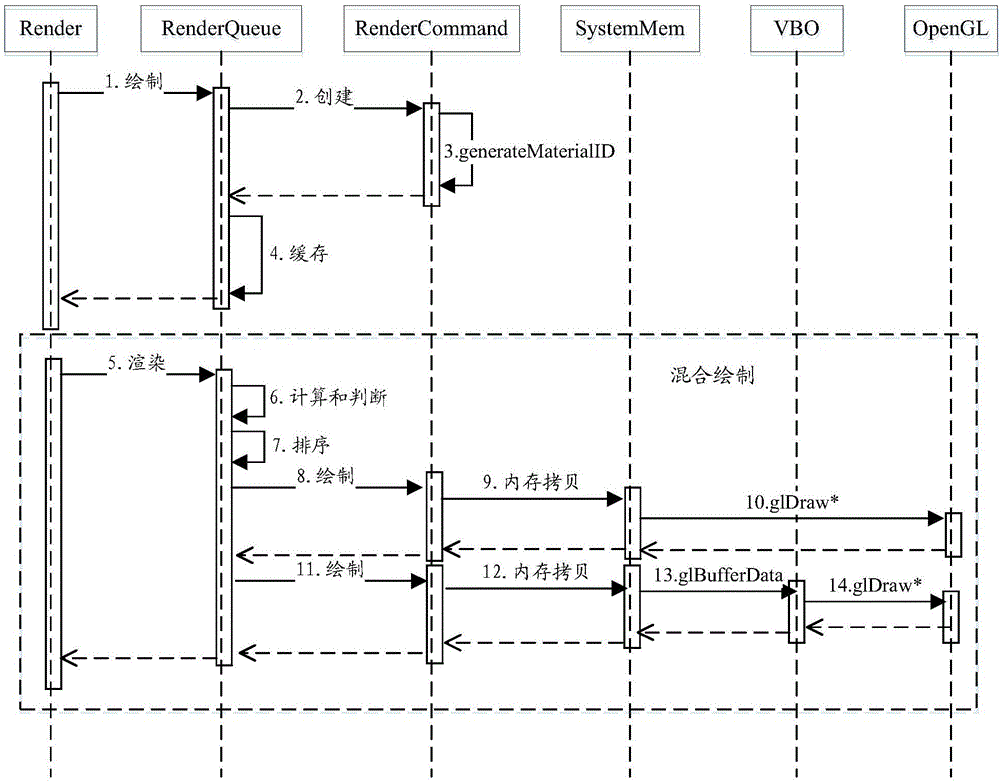
Rendering optimization method and device
ActiveCN106504185AReduce consumptionAvoid display effectsImage memory managementProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsGraphic card
The invention discloses a rendering optimization method and a device, wherein the display fluency of images is ensured and the frame-dropping phenomenon is avoided when the drawing and merging function is realized for a variety of types of mobile terminals. According to the method, the caching operation is conducted for a plurality of established rendering commands and vertex data associated with each rendering command. After that, the judgment and the analysis on the data volume of the vertex data, the GPU of a display card and a currently adopted operating system are conducted. If the data volume of the currently cached vertex data is smaller than or equal to a vertex data threshold, and / or the GPU belongs to a logic type set and the currently adopted operating system belongs to a system type set, at least two rendering commands among the plurality of rendering commands and having the same material identifier are merged. All merged rendering commands are then drawn. Finally, the vertex data associated with each rendering command are copied into a consecutive system memory and then are sent to a graphic rendering application program interface from the system memory.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Eye-tracking using a GPU
ActiveUS20110085139A1Easy to measureEasy extractionImage analysisAcquiring/recognising eyesGraphicsGraphic card
Provided is a method of determining a gaze point of an eye watching a visual display controllable by a display signal. The method comprises generating a display signal using a graphics card in order for the visual display to produce a screen pattern; receiving a signal encoding an image of the eye including a corneo-scleral reflection of the screen pattern; and determining, based on in part the geometry of said reflection, a gaze point of the eye, wherein said determining a gaze point includes utilising the graphics card as a parallel processor.The image of the eye may be received directly at the graphics card. The graphics card may extract image features in the eye images. Reference illuminators may be used, and the screen pattern may be interlaced with a distinctive reference pattern.Further provided are a gaze-tracking system and a personal computer system adapted to determine a gaze point of a viewer.
Owner:TOBII TECH AB
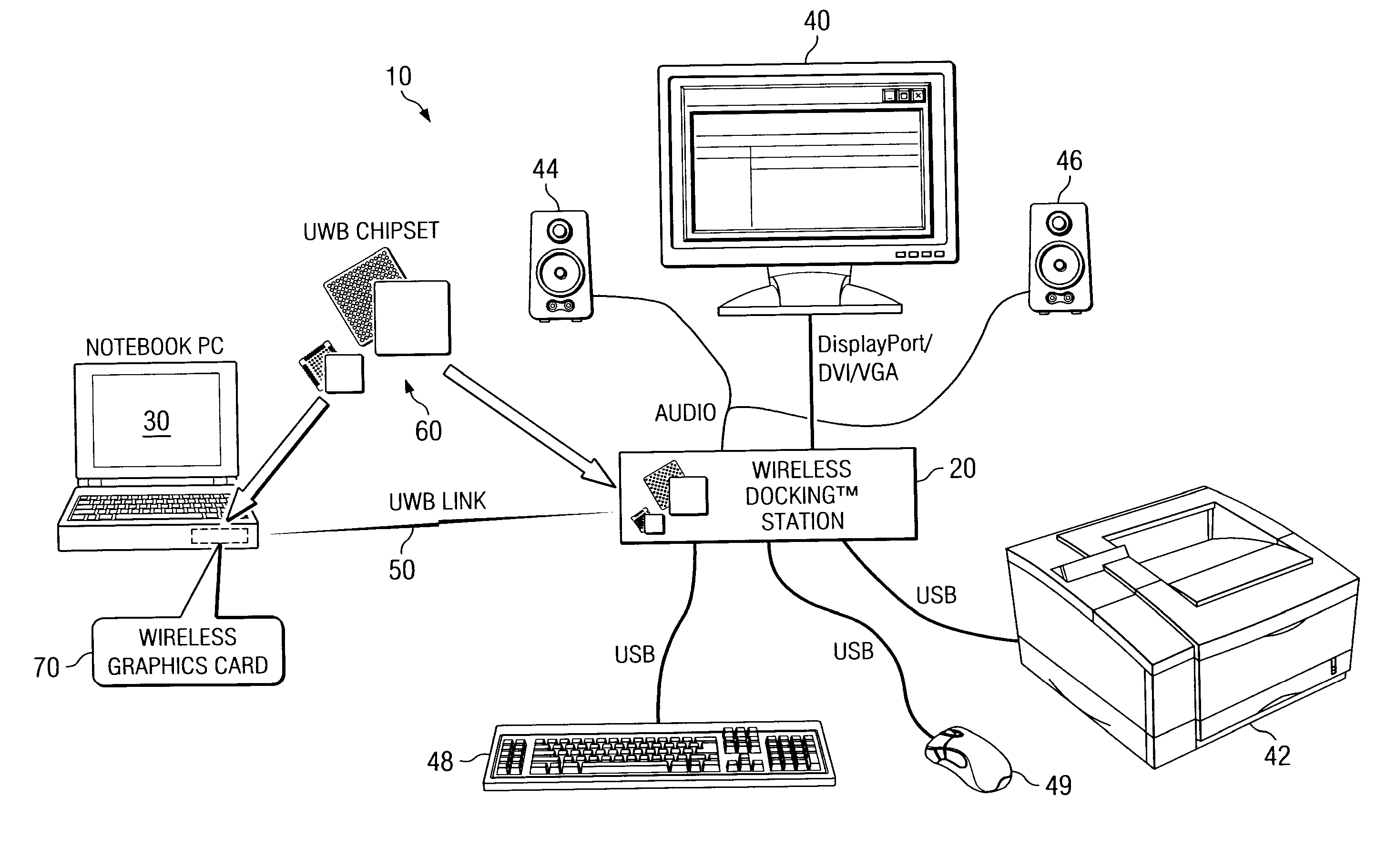
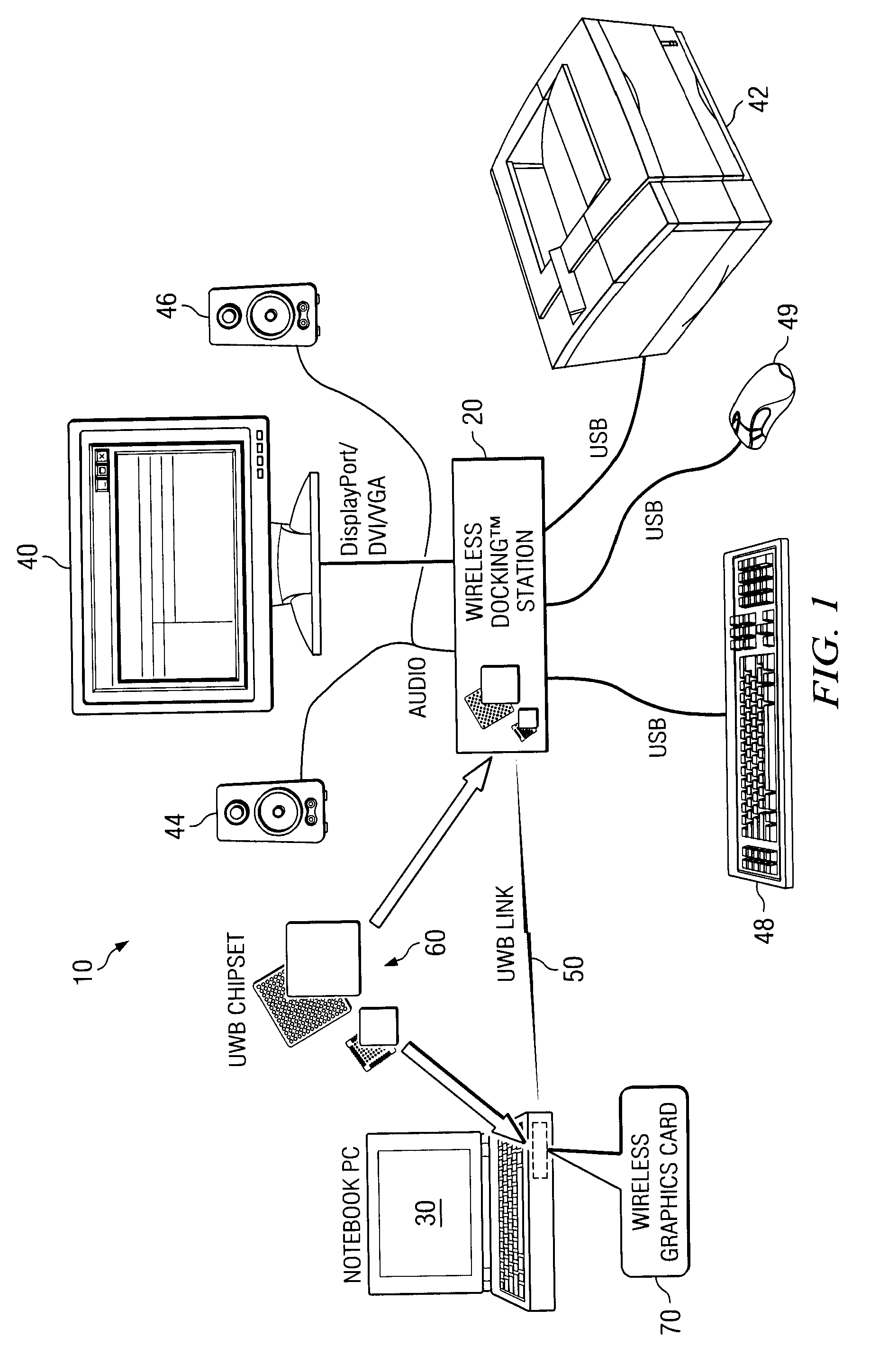
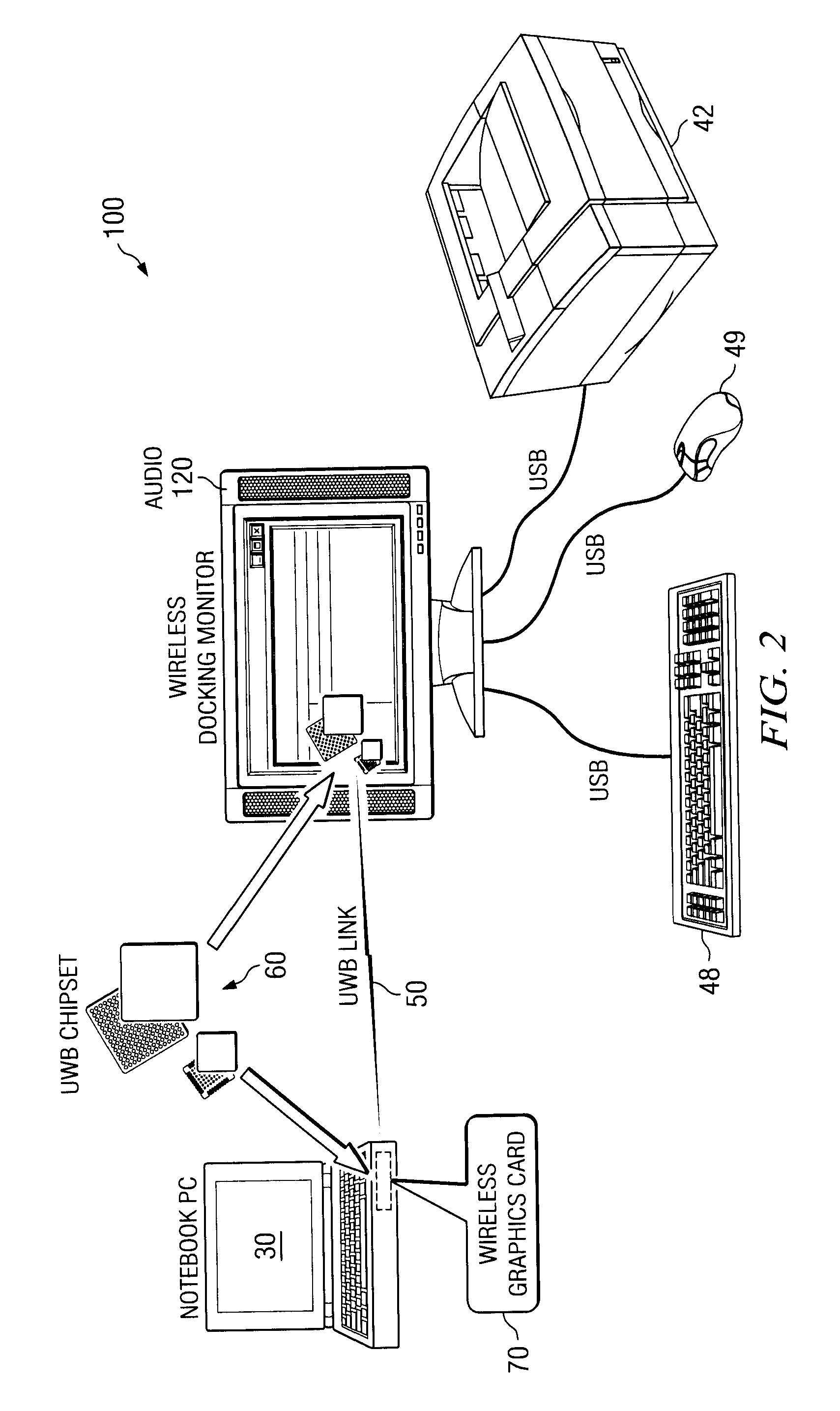
Wireless graphics card
A device is provided for use in a portable computer. The device includes a wireless graphics card that includes a connector for coupling to an expansion slot of the portable computer and for receiving a plurality of signals from the portable computer, the plurality of signals including video, audio, and data signals and an ultra wideband (UWB) chipset coupled to the connector for processing the plurality of signals and for generating an OFDM modulated signal that includes at least the video signal, where the OFDM modulated signal including the video signal is wirelessly transmitted over an UWB link to a monitor for display.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC +1
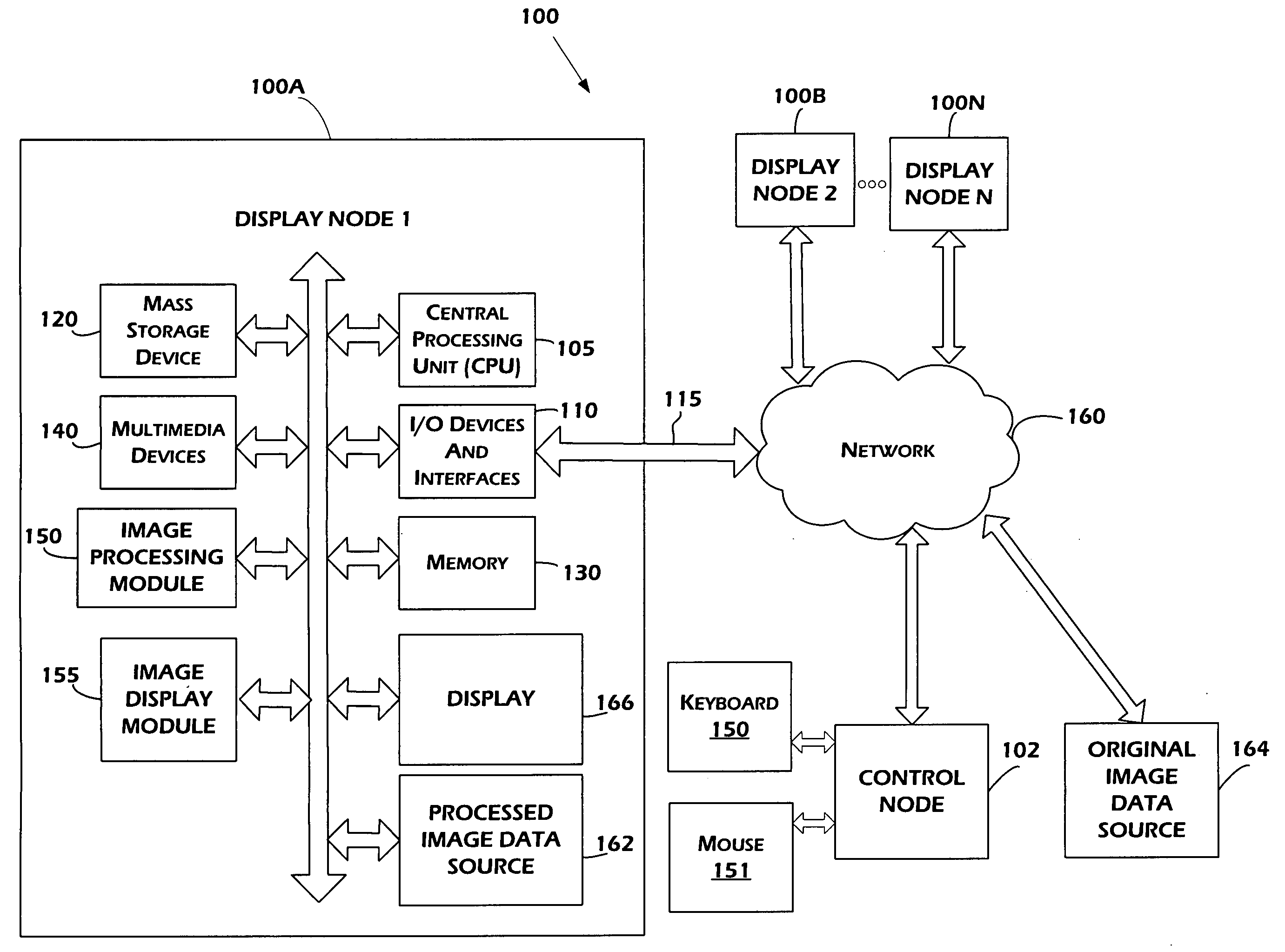
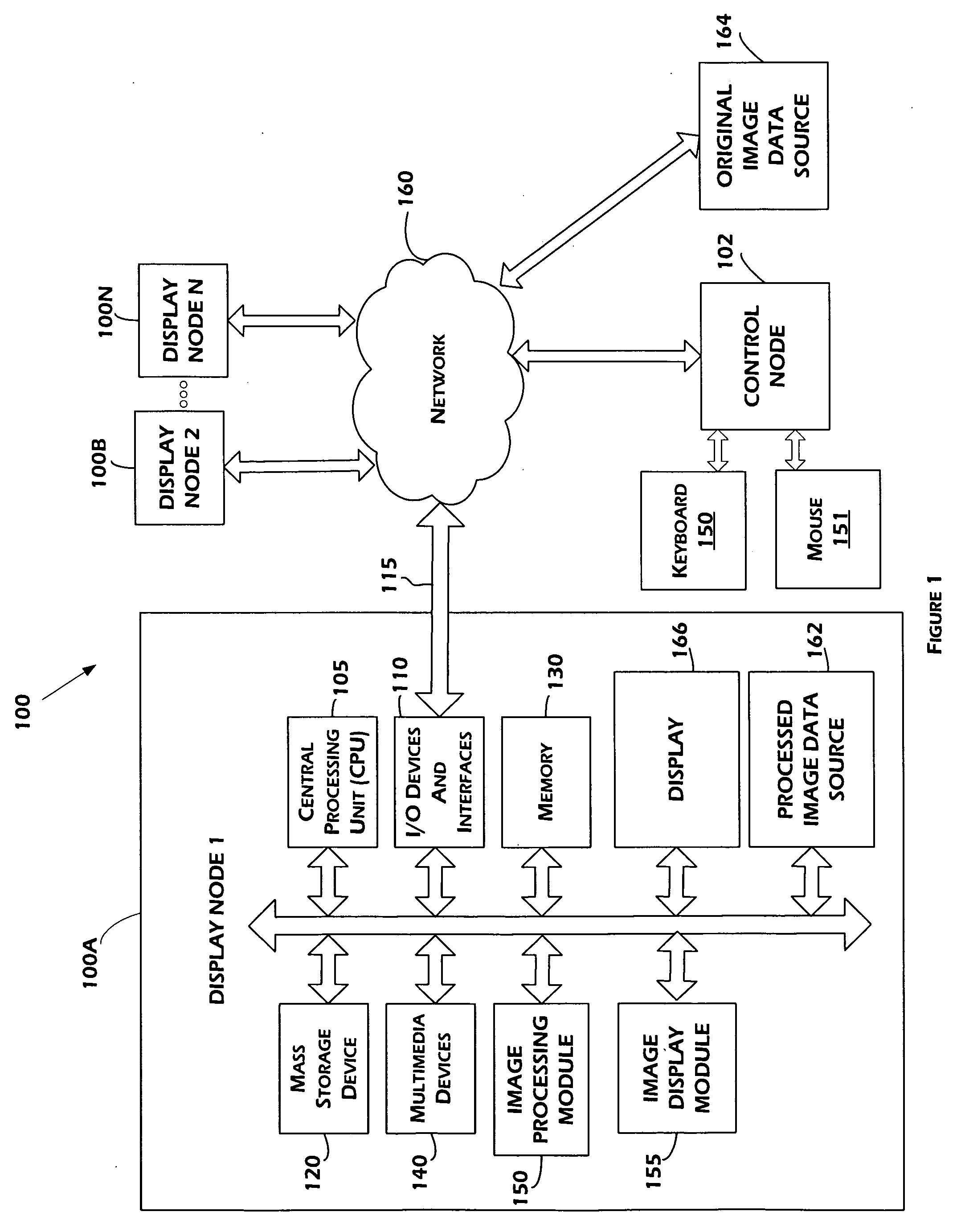
Systems, methods, and devices for dynamic management of data streams updating displays
ActiveUS20100045594A1Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsGraphicsData stream
Presented herein are methods, systems, devices, and computer-readable media for systems for dynamic management of data streams updating displays. Some of the embodiments herein generally relate to presenting video image data on an array of tiled display units, thereby allowing the display of much larger images than can be shown on a single display. Each display unit can include a video image display, a communication mechanism, such as a network interface card or wireless interface card, and a video image controller, such as a graphics card. Attached to the tiled display may be one or more user computers or other sources of video image data. A workstation may also be coupled to the tiled display and to the user computers. Each of the user computers can display data or images on the tiled display simultaneously. Since the tiled display is made up of multiple display units, the images from a single user computer may be on multiple, separate individual display units. The images from multiple user computers could also be shown on the same display unit and they may even overlap.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Three-dimension measuring system for dynamic object
The invention discloses a three-dimension measuring system for a dynamic object, which comprises a clock synchronous controller, a digital light processing (DLP) projector, two charge coupled device (CCD) cameras, an image acquisition card and a computer, wherein a color wheel for generating colorful images is removed from the DLP projector, included angles between optical mandrels of the CCD cameras and the optical mandrel of the DLP projector are both between 20 and 60 degrees, and the relative positions of the DLP projector and the CCD cameras are unchanged during measurement; the computer is a graphic card with a calculation-based uniform equipment framework; and the clock synchronous controller is connected with the DLP projector and the CCD cameras respectively, the DLP projector is connected with the computer, and the CCD cameras are connected with the computer through the graphic card respectively. The system has a most obvious characteristic of high measuring speed and can calculate and display the three-dimensional information of the dynamic object in real time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
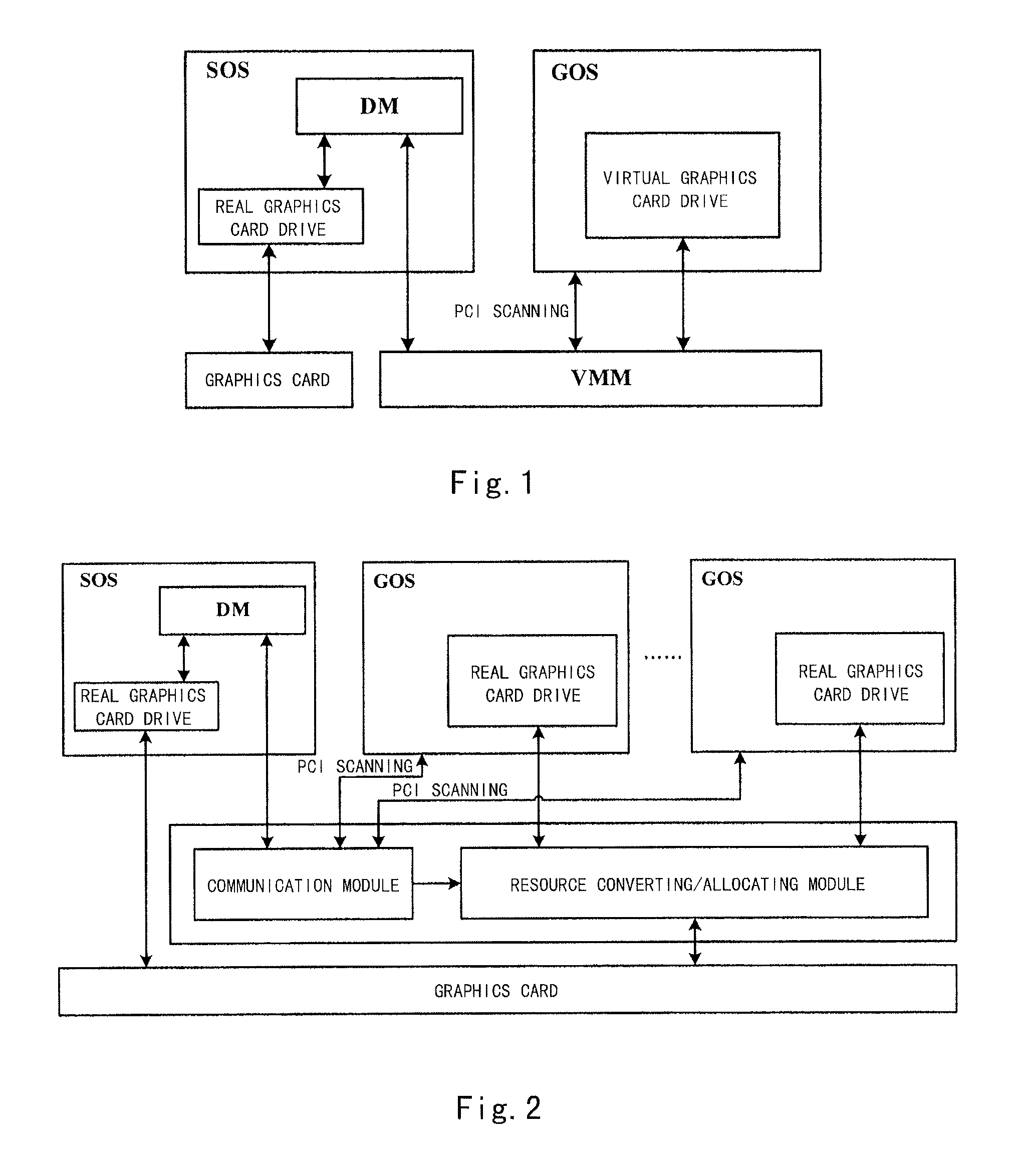
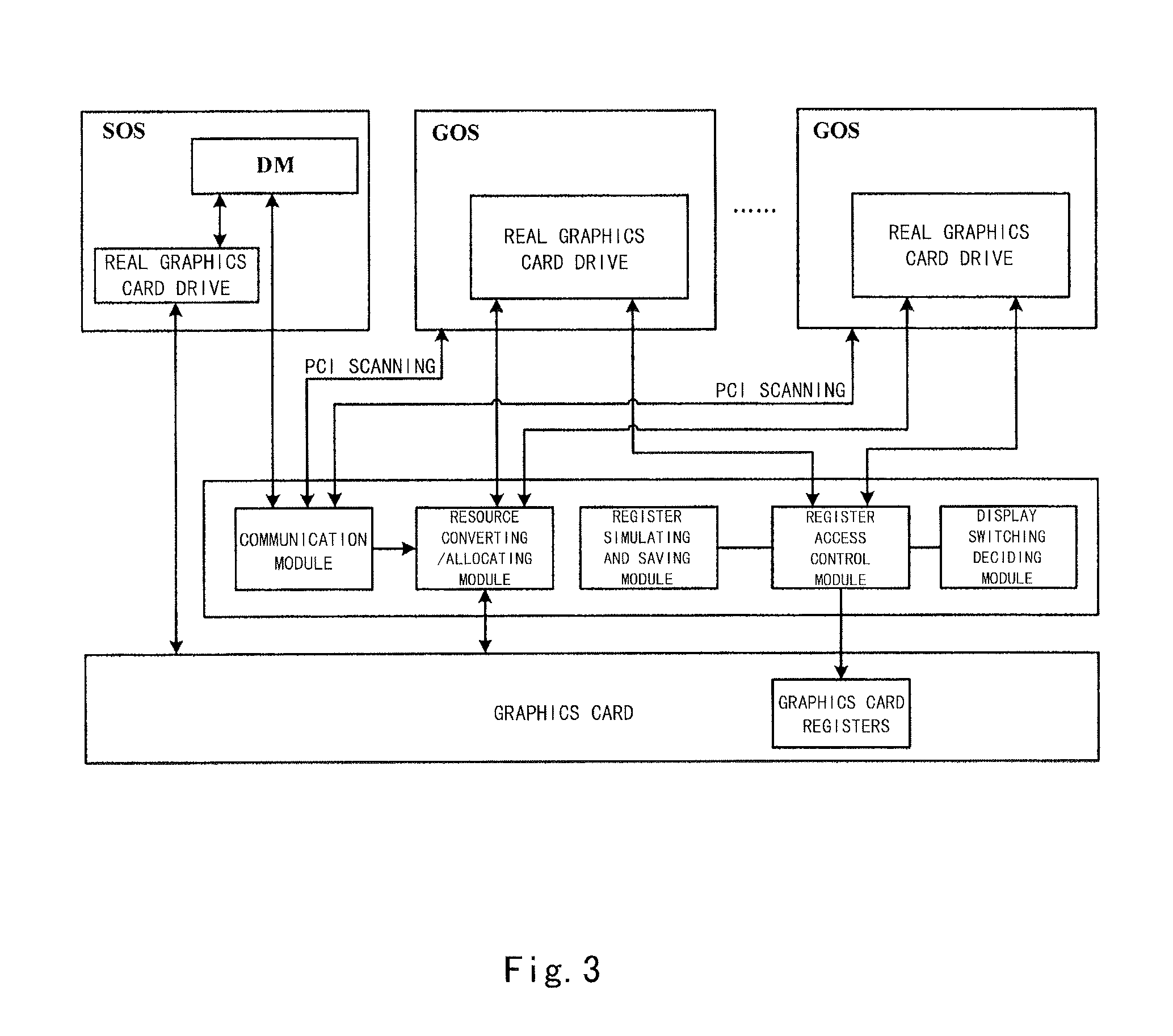
Method, apparatus and system for seamlessly sharing a graphics card amongst virtual machines
ActiveUS20080215770A1Confusing displayEfficient solutionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiprogramming arrangementsGraphic cardOperational system
The present invention provides a virtual machine system and a method of accessing a graphics card by the same, wherein, the virtual machine system includes a Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), a Service Operating System (SOS) and at least one Guest Operating System (GOS), and further includes a resource converting module for performing IO address converting on graphics card framebuffer accessing data from the GOS(s) or mapping MMIO(s) to physical MMIO(s) of a graphics card based on a resource converting table or resource converting tables, and sending the processed data to the graphics card; and a framebuffer allocating module for dividing a framebuffer resource of the graphics card into multiple blocks and allocating them respectively to the corresponding GOS(s). The resource converting table(s) records correspondences between a resource allocation for the graphics card by the SOS and a resource allocation or resource allocations for the graphics card by the GOS(s). The framebuffer MMIO resource(s) allocated to the graphics card by the GOS(s) is / are the framebuffer allocated to the GOS(s) by the framebuffer allocating module. The virtual machine system and the method according to the present invention are capable of accessing the real graphics card through the resource converting table(s), and also solve the problem of display confusion when multiple GOSs commonly access the real graphics card while being able to switch display.
Owner:LEGEND HOLDINGS +1
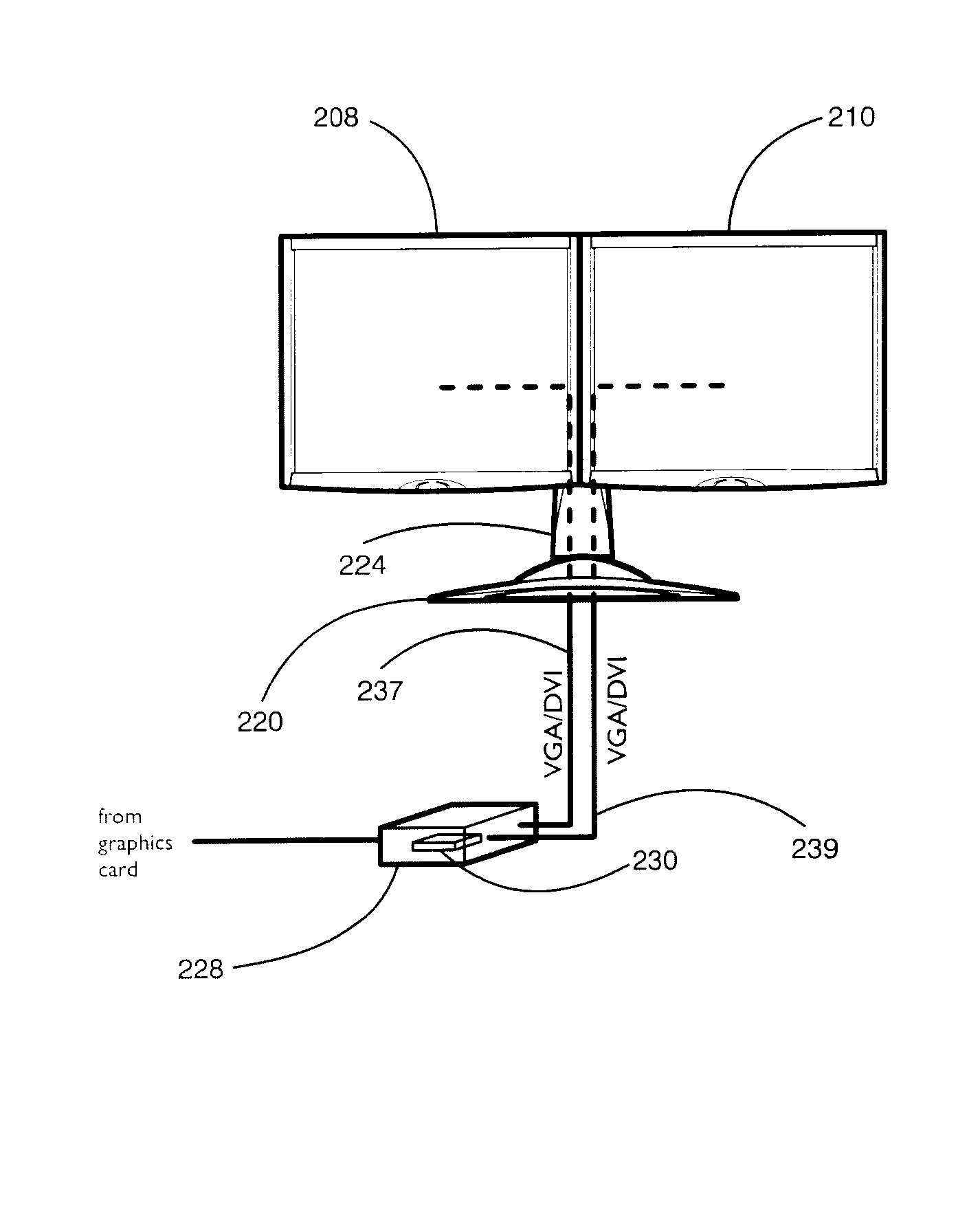
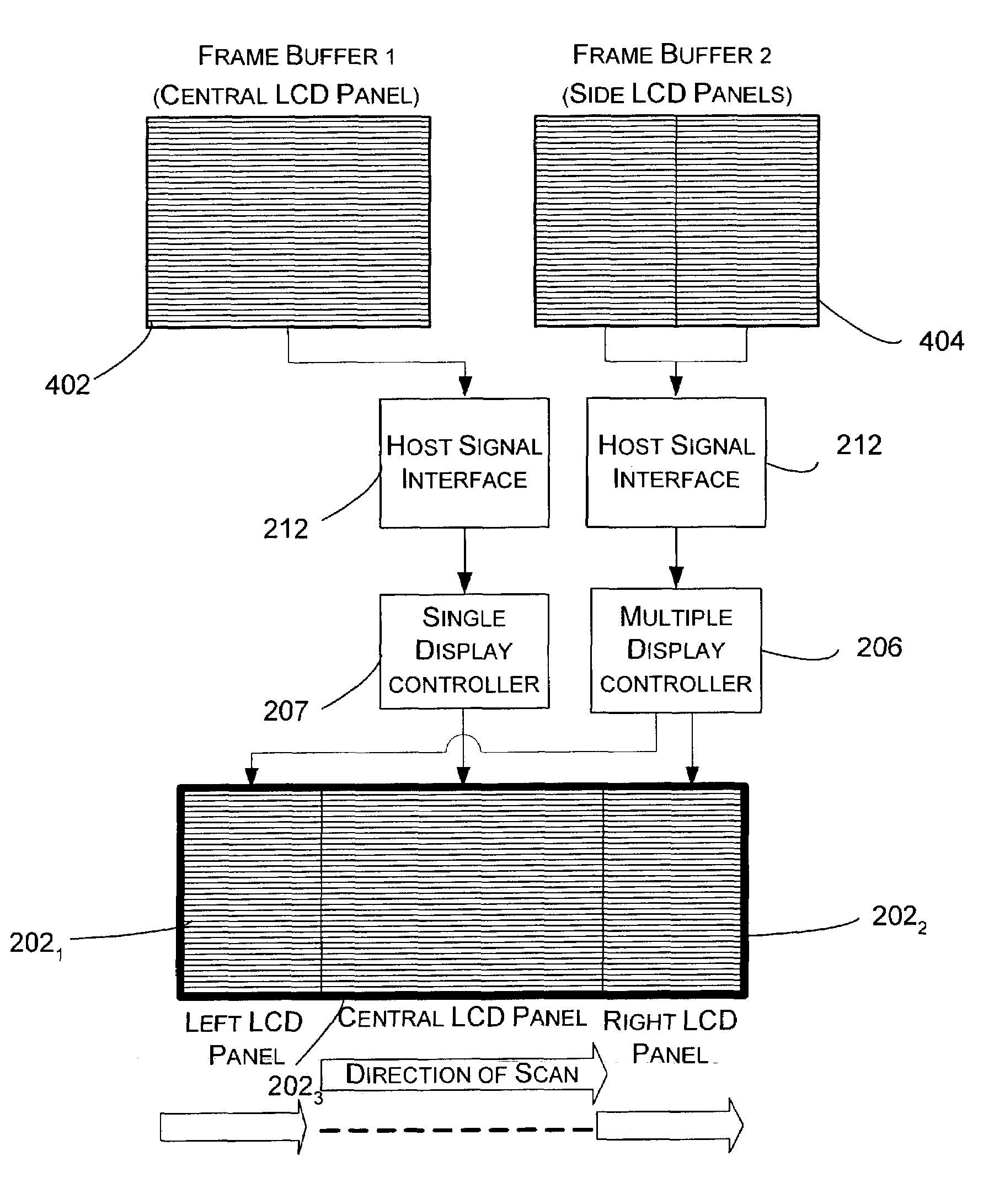
Multiple display monitor
InactiveUS7561116B2Avoid neck strainProduction cost of producing a multiple display monitor is lessDigital computer detailsImage memory managementGraphicsGraphic card
A monitor having multiple displays within the same housing. The displays may be, for example, separate LCD panels that are placed in close proximity to one another so as to give the appearance of a single, large display. At least two of the displays may be treated by a computer connected to the monitor as a single display. A display controller divides a single frame of information that is provided by a display adapter of the computer into display information for multiple displays. By using the multiple display controller, the multiple display monitor may have more displays or panels than the number of cables linking the monitor to a computer. The special display controller also does not require a graphics card for each display. A three panel or display monitor is provided in which a central, centered work area display is framed by two side panels or displays.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Computing system capable of parallelizing the operation graphics processing units (GPUs) supported on a CPU/GPU fusion-architecture chip and one or more external graphics cards, employing a software-implemented multi-mode parallel graphics rendering subsystem
InactiveUS20080094403A1Reduce loadKeep load balancedProgram controlArchitecture with multiple processing unitsComputer architectureGraphic card
A computing system capable of parallelizing the operation of multiple graphics processing units (GPUs) supported on external graphics cards, employing a multi-mode parallel graphics rendering subsystem. The computing system includes (i) CPU memory space for storing one or more graphics-based applications, (ii) a CPU / GPU fusion-architecture chip including one or more CPUs, one or more GPUs, a memory controller for controlling the CPU memory space, and an interconnect network, and (iii) an external graphics cards supporting multiple GPUs and being connected to the CPU / GPU fusion-architecture chip by way of a data communication interface. The computing system also includes (iv) an external graphics card supporting multiple GPUs and being connected to the CPU / GPU fusion-architecture chip by way of a data communication interface, (v) the multi-mode parallel graphics rendering subsystem supporting multiple modes of parallel operation, (vi) a plurality of graphic processing pipelines (GPPLs) implemented using the GPUs, and (vii) an automatic mode control module. During the run-time of the graphics-based application, the automatic mode control module automatically controls the mode of parallel operation of the multi-mode parallel graphics rendering subsystem so that the GPUs are driven in a parallelized manner.
Owner:LUCID INFORMATION TECH +1
Automated method and apparatus for vision registration of graphics areas operating from the unprinted side
ActiveUS20050247173A1Increase speedReduce the amount requiredBox making operationsPaper-makingGraphicsPoint registration
A method and apparatus are disclosed for performing finishing operations on at least one graphics area on a graphics sheet, the graphics sheet having a graphics side, an opposite process side, and reference features, the graphics side bearing the graphics area(s) and registration marks in predetermined positions with respect to the graphics area(s). The method comprises positioning the graphics sheet on a sheet-receiving surface, sensing from the graphics side the positions of the registration marks, determining the coordinates of the graphics area(s) with respect to the sheet-receiving surface as if viewable from the process side, and performing finishing operations on the process side of the graphics sheet based on such determination, whereby such process-side finishing operations compensate for variations of the graphics area(s).
Owner:ESKO GRAPHICS KONGSBERG
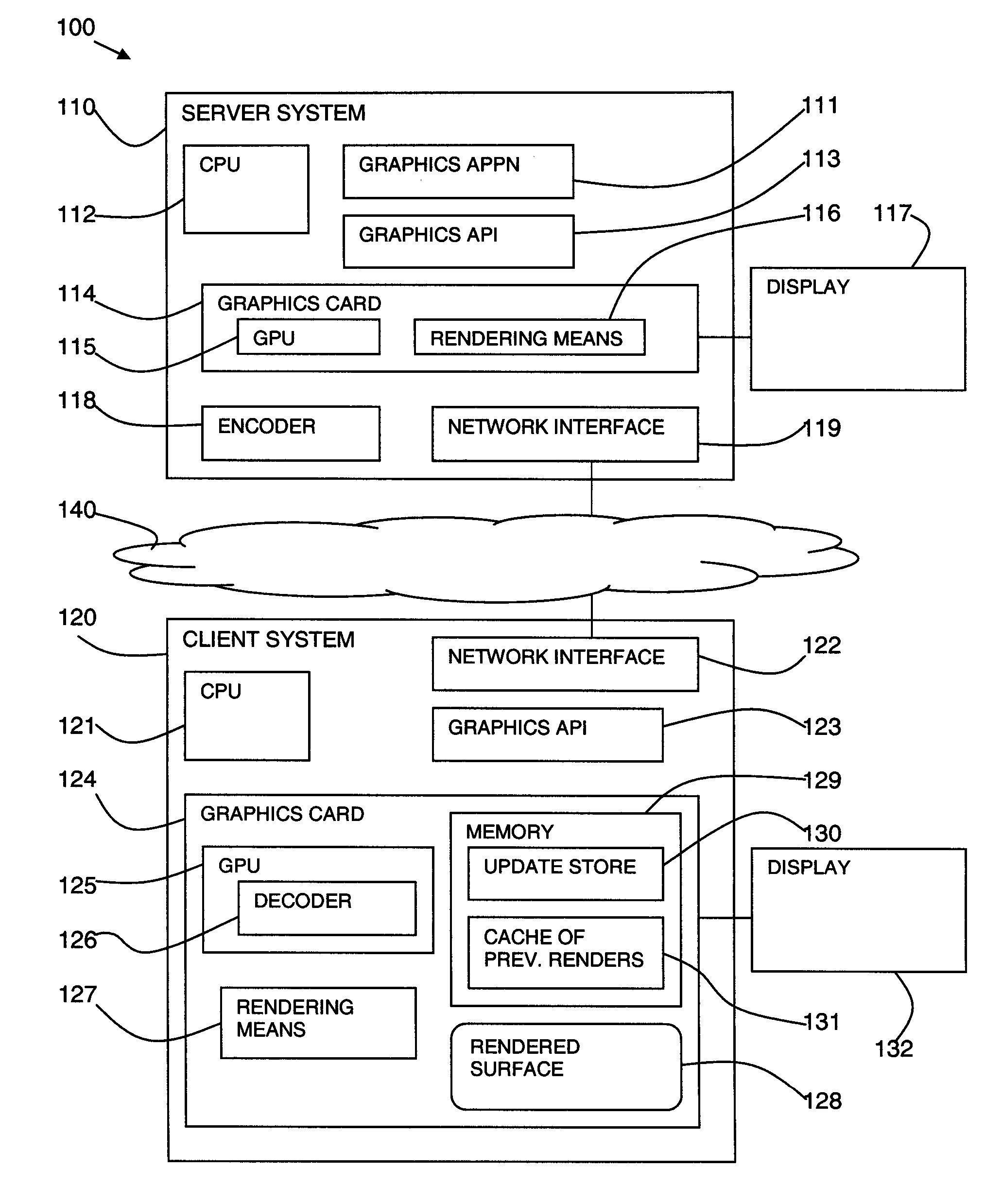
Method and System for Remote Visualization Client Acceleration
InactiveUS20100001995A1Optimize costly image decompressionStatic indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingGraphic cardClient-side
A method, system, and program product is disclosed for remote visualization in which a server window contents is displayed remotely at a client. The client creates a 3D rendering surface on a client graphics card to display a server window contents and receives update data from the server relating to the server window contents. The update data is uploaded to the client graphics card and the graphics processing unit (GPU) is used to decode the update data and render the update data to the 3D rendering surface. The graphical processing unit includes general purpose computing on graphics processing unit functionality to provide the decoding processing.
Owner:IBM CORP
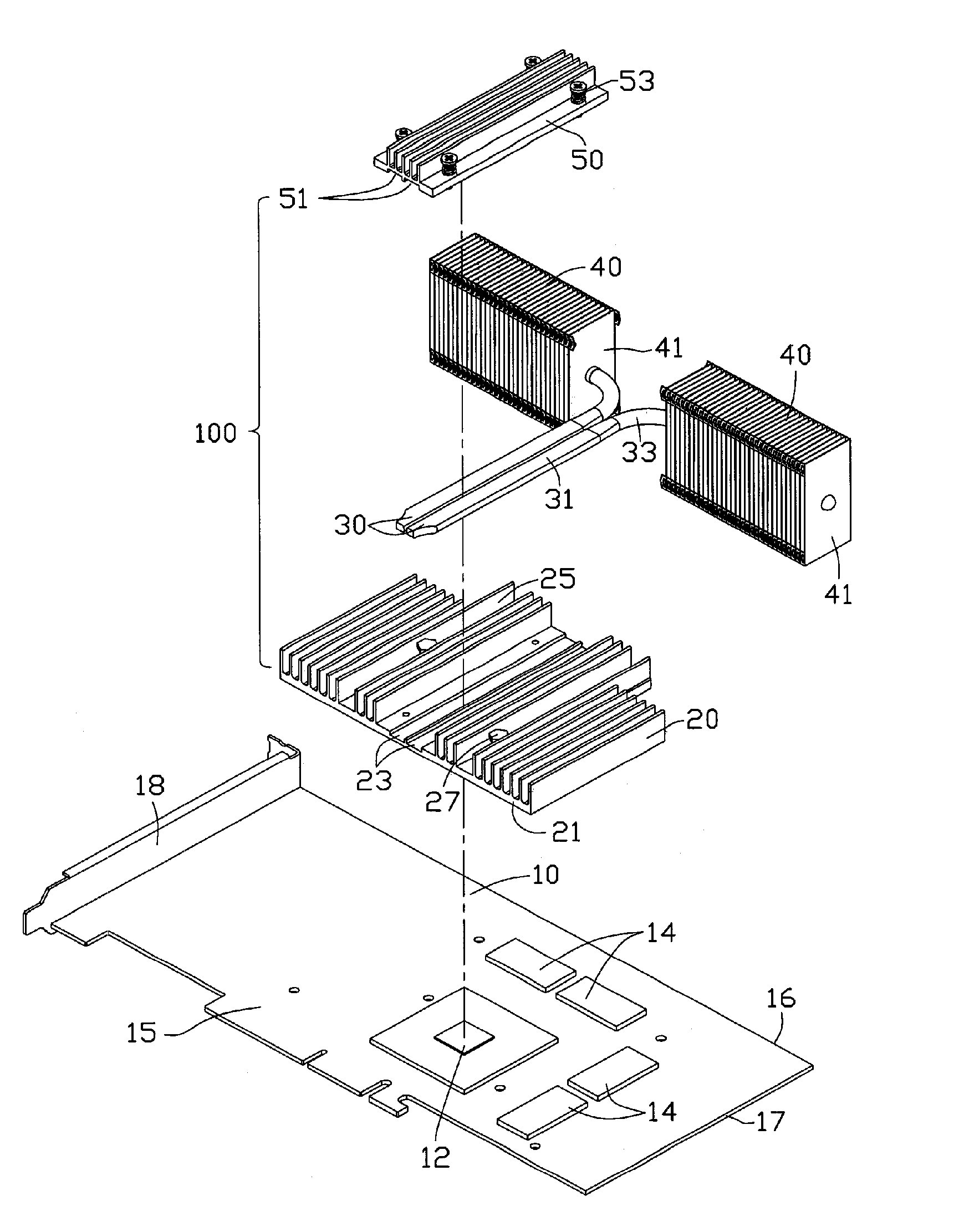
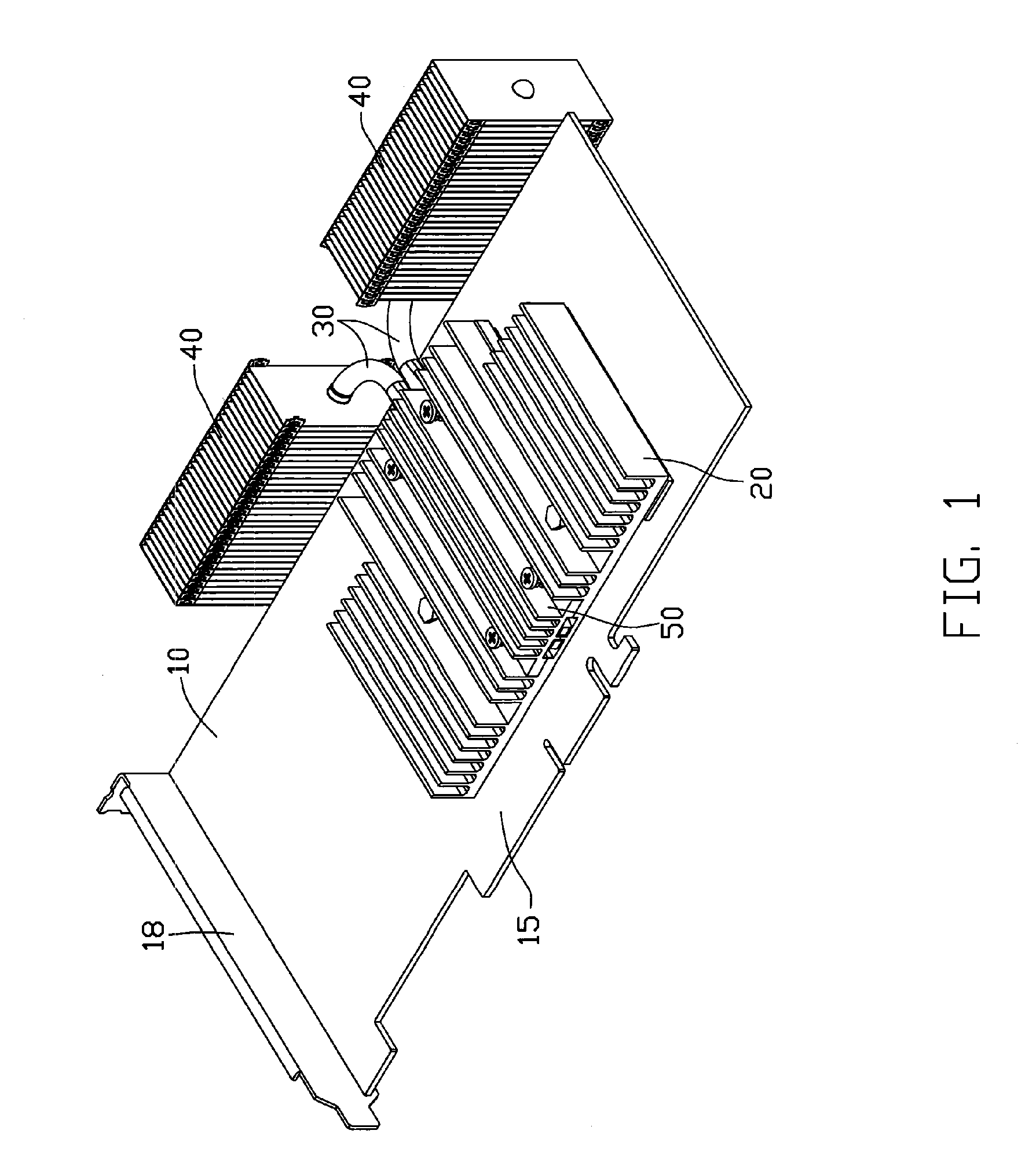
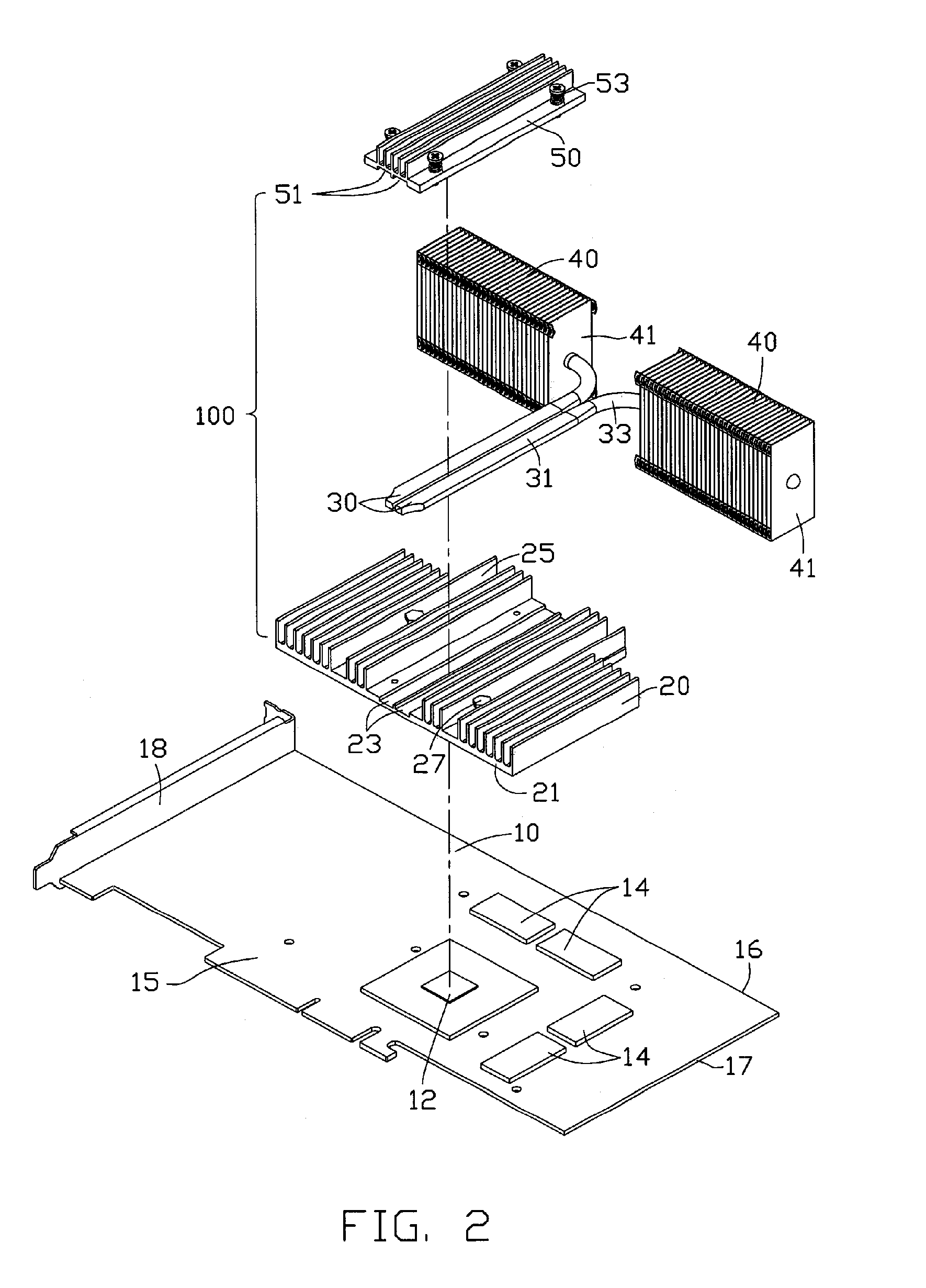
Heat dissipation device
InactiveUS7369412B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGraphic cardEngineering
A heat dissipation device used for dissipating heat from heat generating electronic components mounted on an interface card, which has a mounting bracket for being mounted to a computer case, includes a heat-absorbing member, a pair of heat pipes and a pair of heat-dissipating members. The heat-absorbing member is bound to the heat generating electronic components for absorbing heat generated by the electronic components. The heat-dissipating members are disposed within the computer case and located at one peripheral side edge of the graphics card. The heat-absorbing member and the heat-dissipating members are connected by the heat pipes so as to transfer the heat received by the heat-absorbing member to the heat-dissipating members for further dissipating.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD +1
Screen sharing and synchronous recording method based on IP network
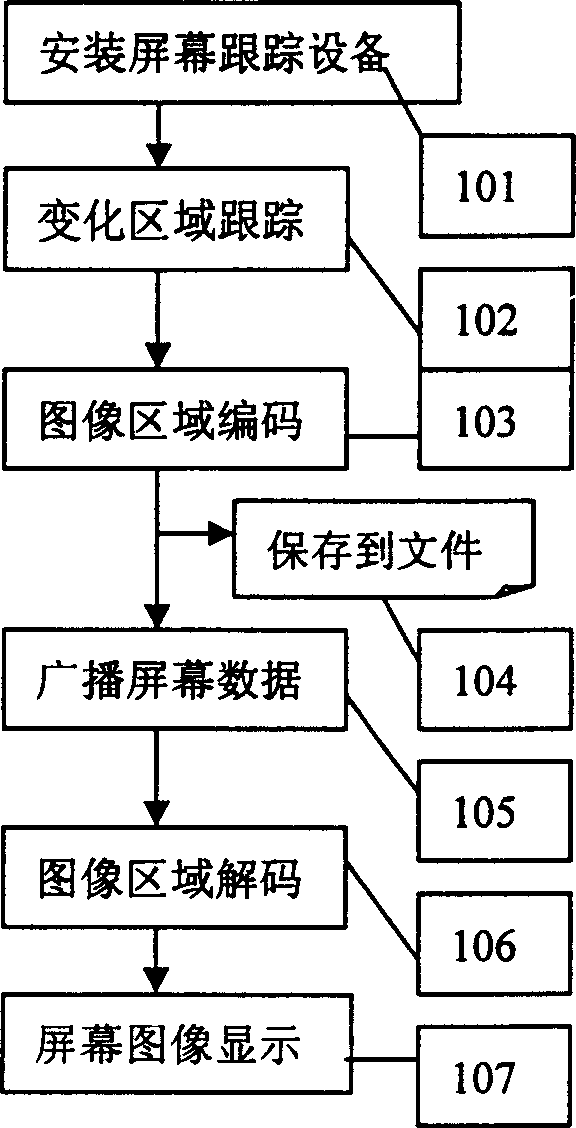
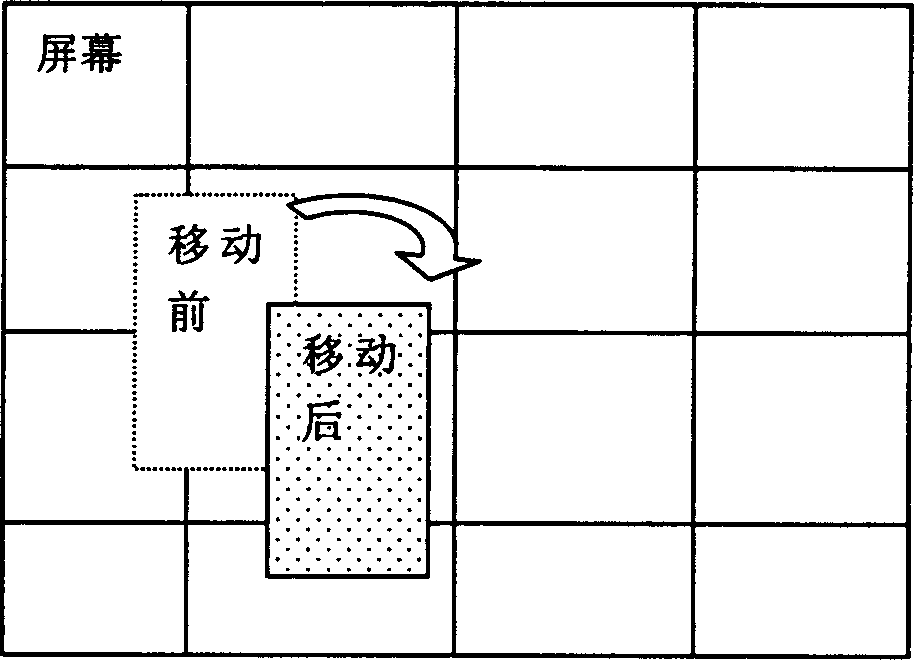
InactiveCN1455372AImprove image qualityImprove portabilityGeometric image transformationImage codingGraphic cardScreen sharing
Both the system information hooker and the API hooker are setup at same time and the screen image change area is traced. Based on the screen image change area, the changed screen image data are read fro the display card. The screen data are transmitted through two modes: unicast and multicast. The screen data are stored as the local file. The data received from IP network are decoded by using the reversed coding role. The decoded screen image is displayed on the pointed window. The invention makes general PC possible to run instructional software, meantime the screen image through network shared by other desktop can be synchronous recorded and stored as the local file. The invention possesses the features of good image quality, fast speed, easy of implementation and good portability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
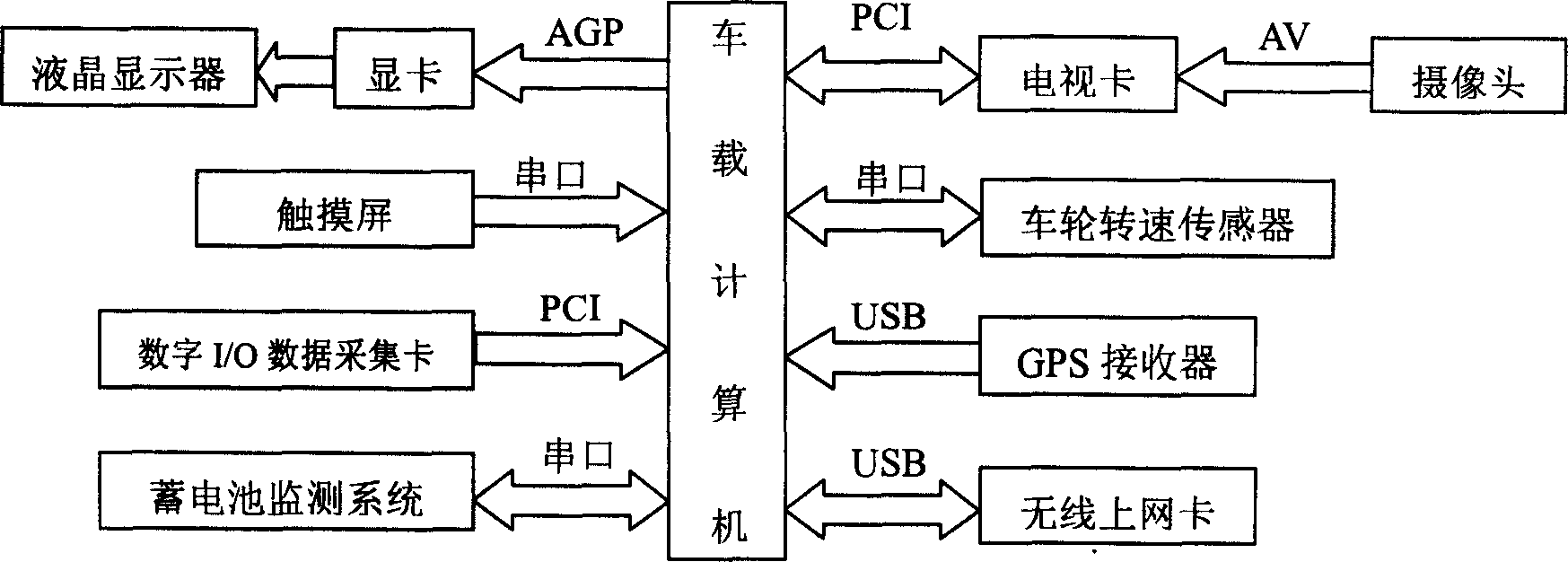
Composite automobile instrument and vehicle multifunction information platform based on virtual and digital technology
A virtual and digital technique-based combined meter board of car and the car-carried multifunctional information platform features that the LCD with display card, touch screen, digital I / O data acquisition card, wheel speed sensor, accumulator monitor system, TV card for cemera head, GPS receiver, and wireless network card are electrically connected to the car carried computer via different ports, slots, or interfaces.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
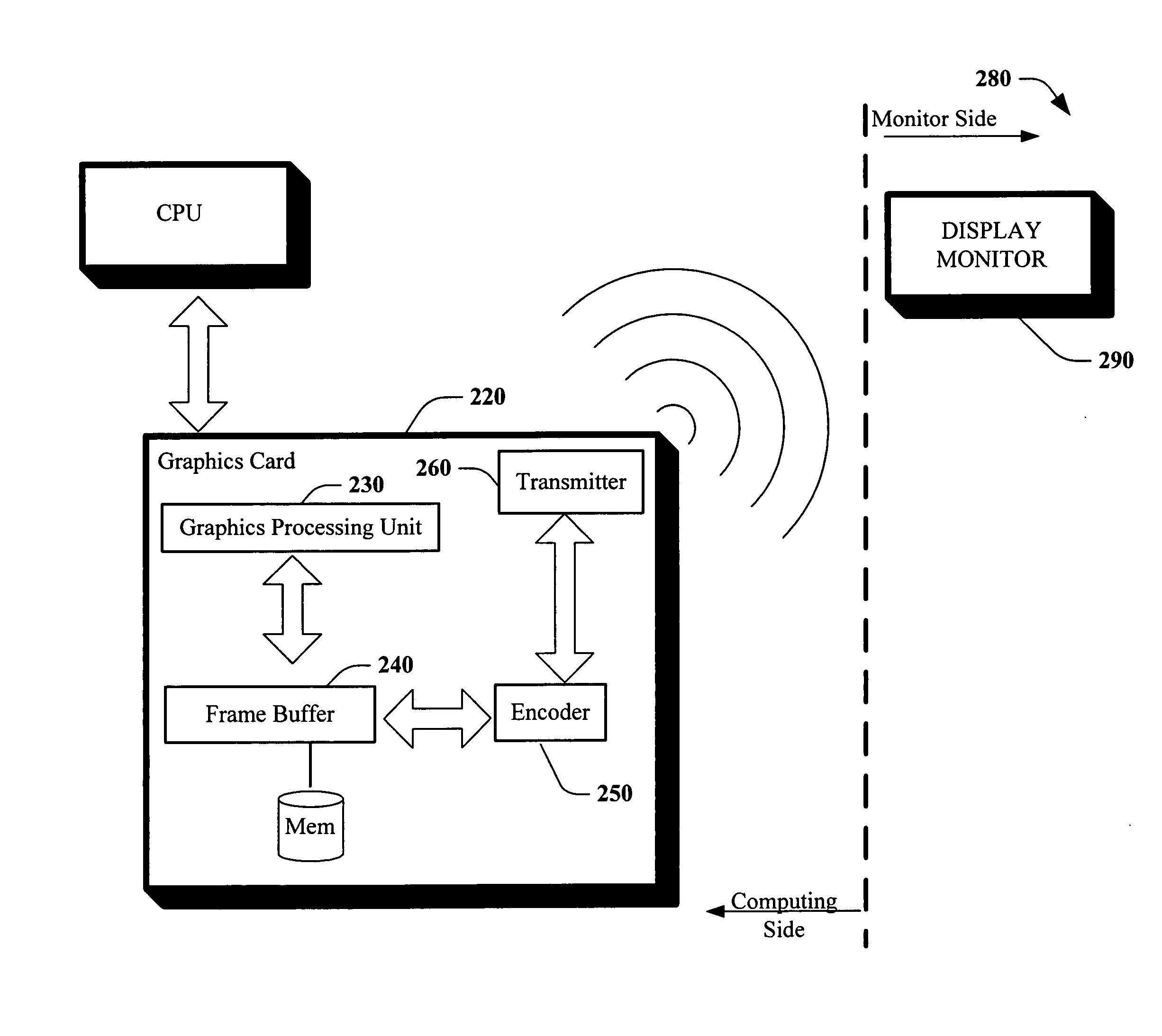
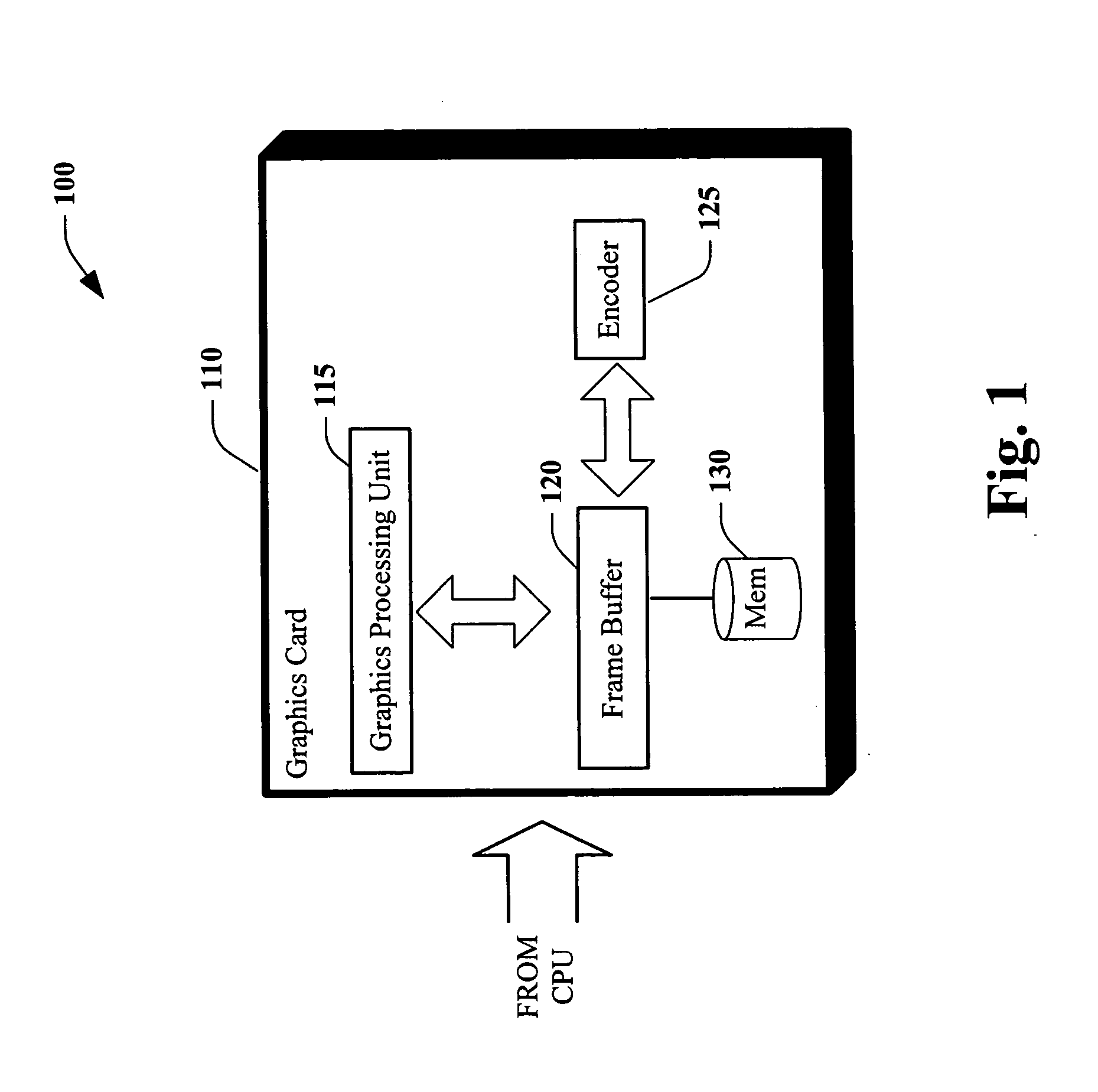
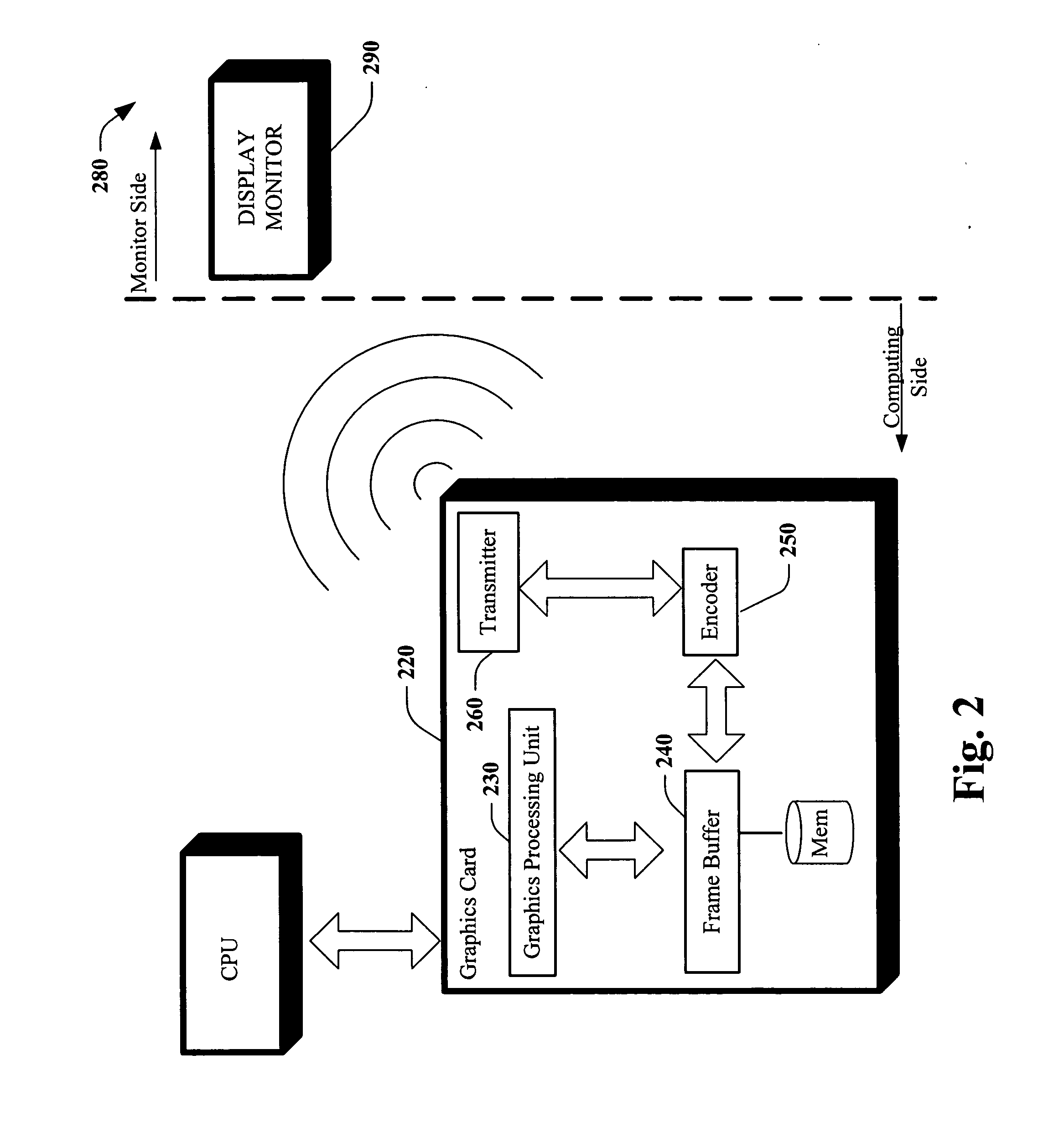
Method and apparatus for wireless display monitor
Systems and methods that facilitate wireless display via employing a frame buffer encoder and a wireless transmission as part of a graphics card of a computing device. The encoder can encode a scheme programmable in software to detect type of format the receiving monitor is capable of displaying. The wireless transmission can occur in a variety of formats; such as Ultra Wide Band (UWB), Internet Protocol (IP) data packets, and the like.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Free multi visul point polyprojecting 3D displaying system and method
InactiveCN1949166AEasy to watchWith auxiliary stereo display effectPrintersProjectorsVisual technologyViewpoints
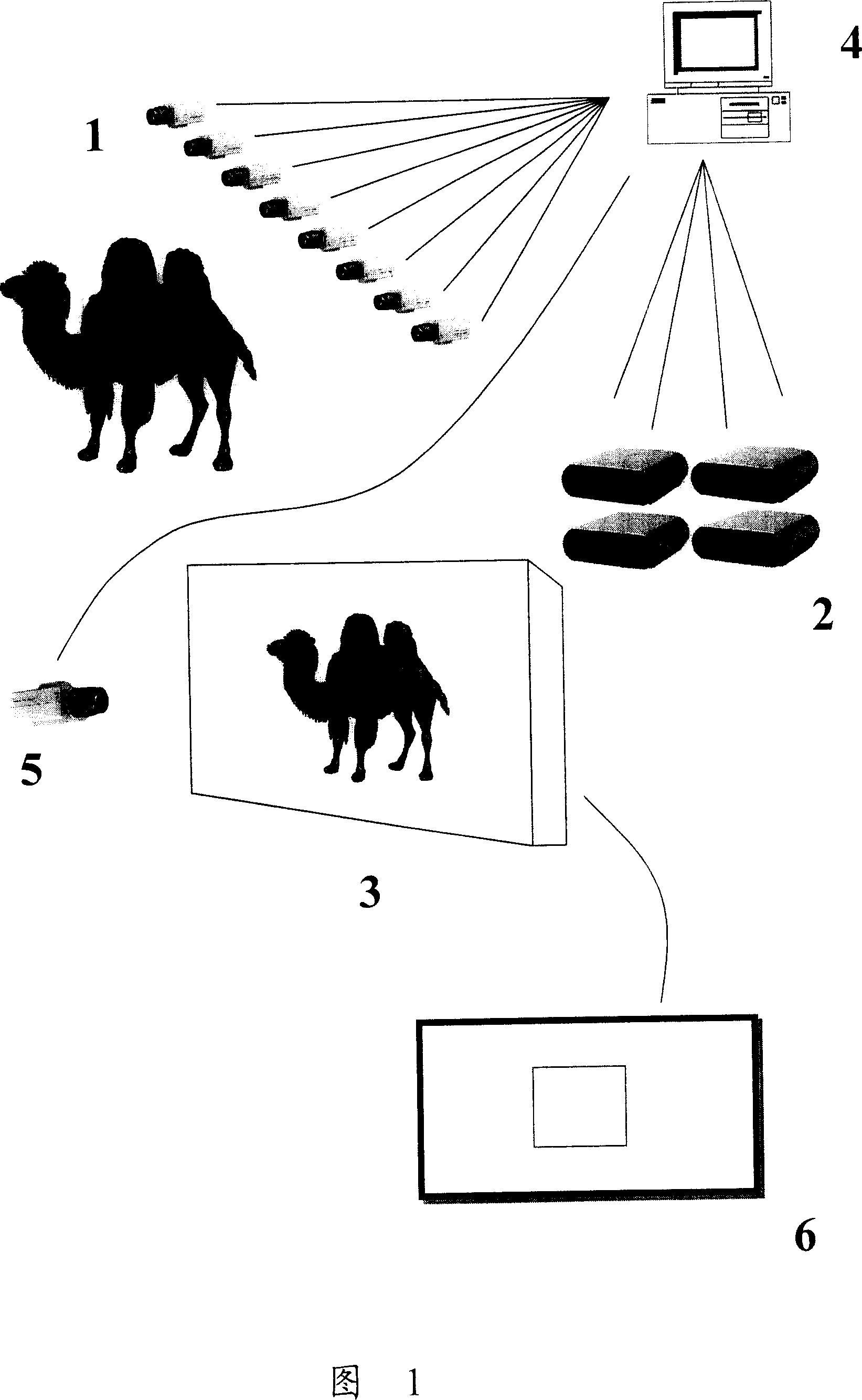
The invention relates to free multi-viewpoint multi-projection three-dimensional display system and method. The system includes one to five videotape color CCD video cameras, one calibration color CCD video camera, two to eight projectors, one large screen display terminal, one calibration plate, and the compute set multi-path synchronization image acquisition card by which it is connected with the video camera, and multi-path output display card by which it is connected with the projector. The method includes the steps that image source video frequency coding, projector calibration, stereo image mosaicking. The invention can realize large screen vivid three-dimensional multi-projection display based on computer vision technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
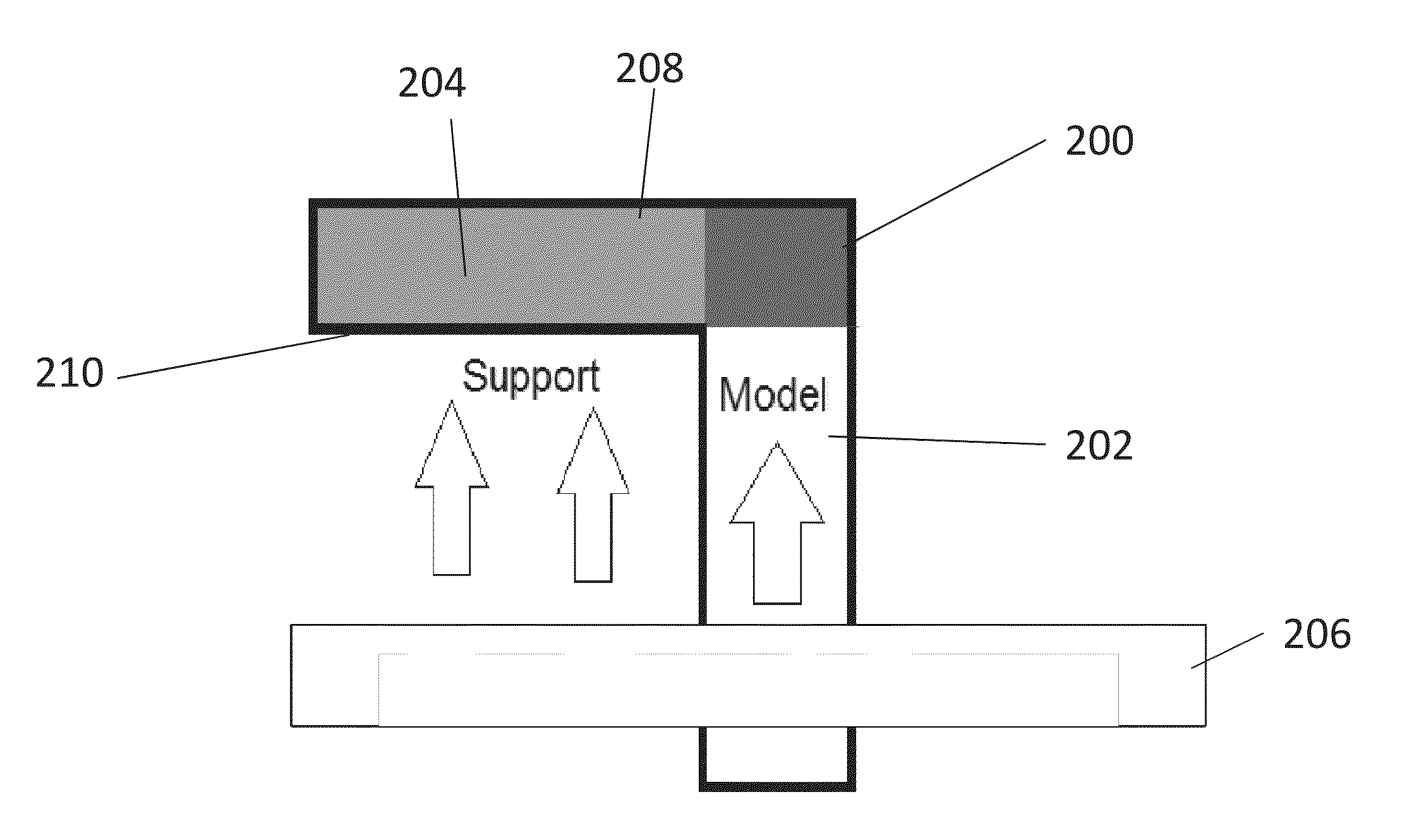
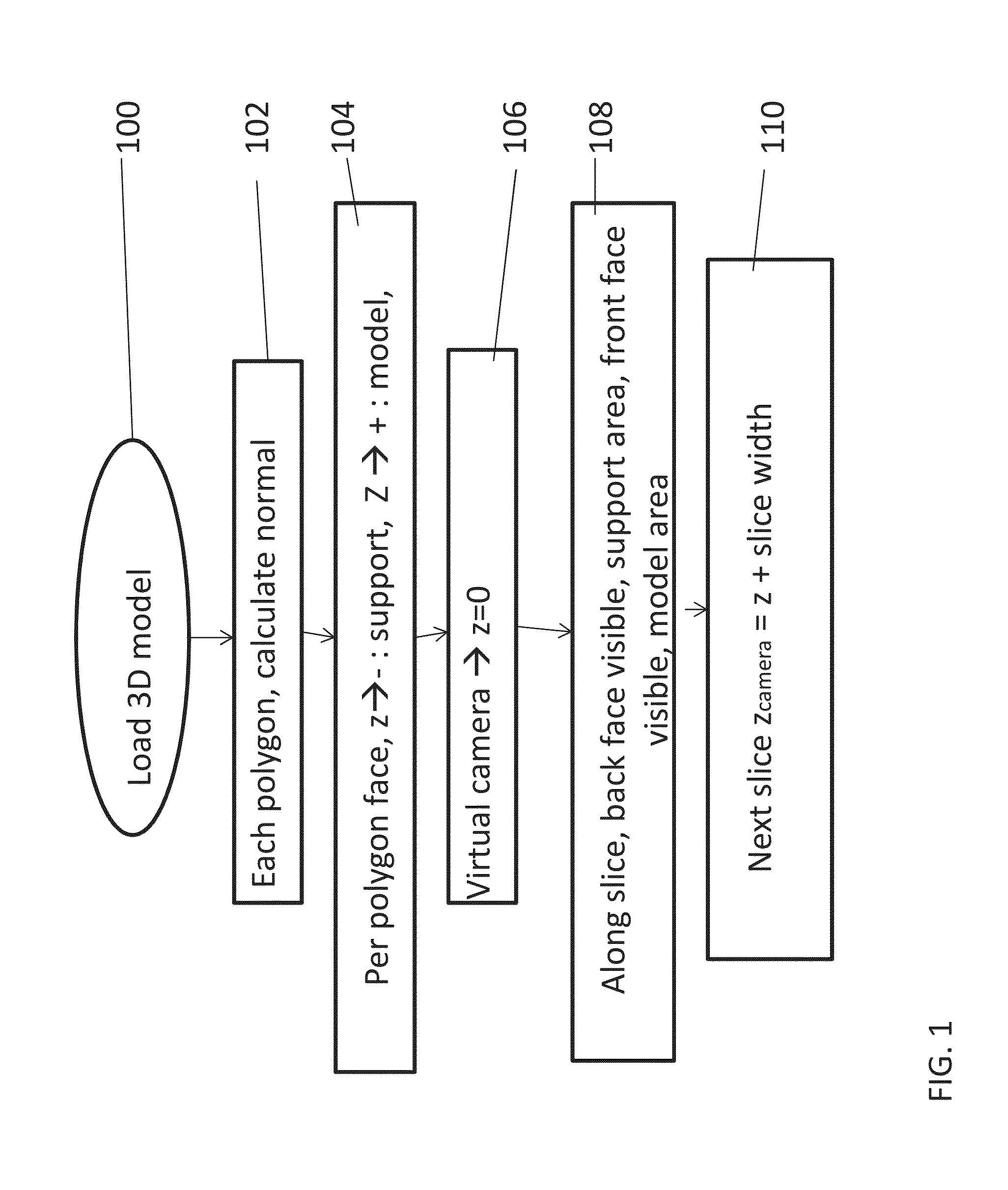
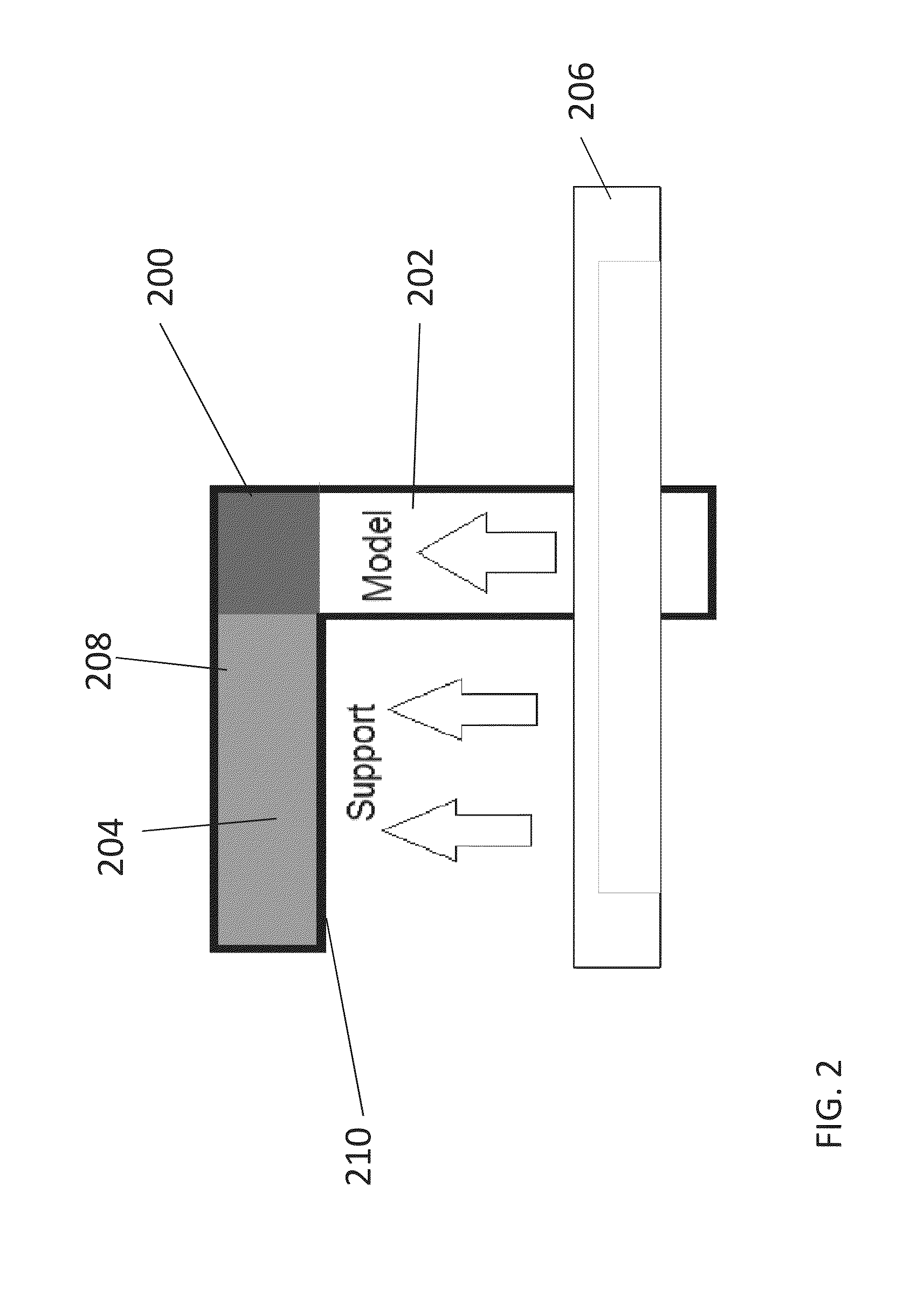
Slicing and/or texturing for three-dimensional printing
A method for slicing a three-dimensional model for printing of a corresponding object by a 3D printer, comprises: obtaining the envelope of the object as polygons, then for each region of a predefined work area within the slicing plane:identifying the closest polygon of said envelope that is positioned above said respective pixel; where no polygon is identified, then marking a corresponding region as a no-print region; if the direction vector of said closest above polygon has a positive component in the Z direction, then marking said corresponding region as a model region; and if the direction vector of said polygon has a negative component in the Z direction, then marking the region as a support region, and printing accordingly. An advantage of the above procedure is that the slicing, and in addition texture mapping, can be efficiently carried out on a graphics card or GPU.
Owner:STRATASYS LTD
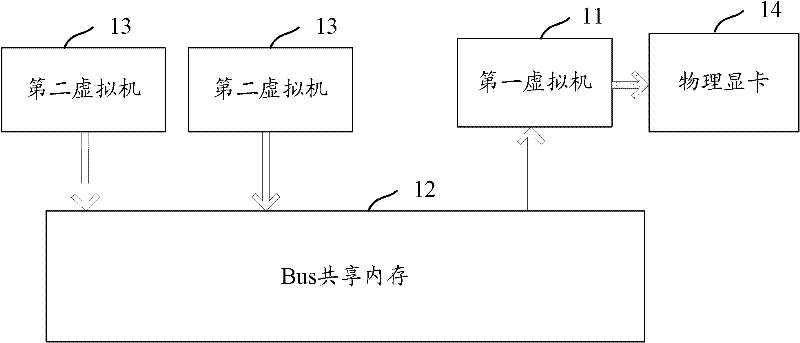
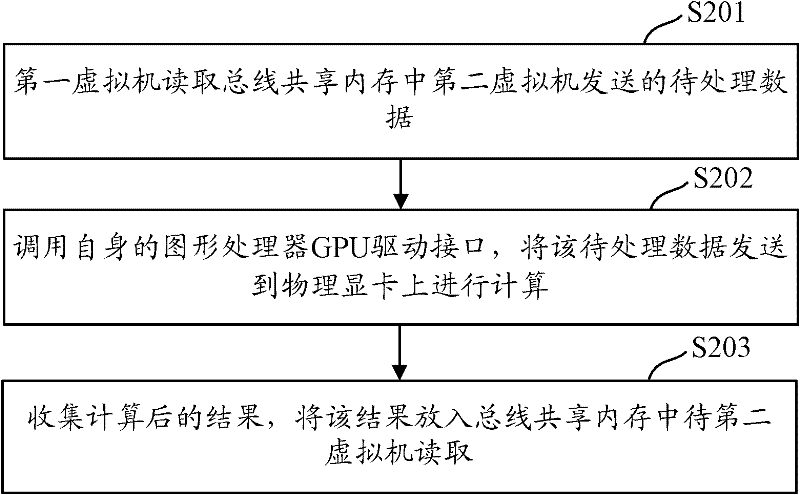
Implementation method, system and device for virtualization of universal graphic processor
ActiveCN102541618AImplement virtualizationProcessor architectures/configurationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationGeneral purposeGraphics
The invention discloses an implementation method, system and device for the virtualization of a GPGPU (General Purpose Graphics Processing Unit) to solve the problem that the virtualization of the GPGPU cannot be solved in the prior art. The implementation method comprises the following steps: a first virtual machine reads data to be processed in a shared memory of a bus, wherein the data to be processed is written by a second virtual machine; and the first virtual machine invokes a CPU (Central Processing Unit) driver interface, sends the data to be processed to a physical display card for calculation, collects calculated results, and inputs the results in the shared memory of the bus to be read by the second virtual machine. As the first virtual machine can visit the physical display card, and can realize information interaction with the second virtual machine, the virtualization of the GPGPU is realized.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com