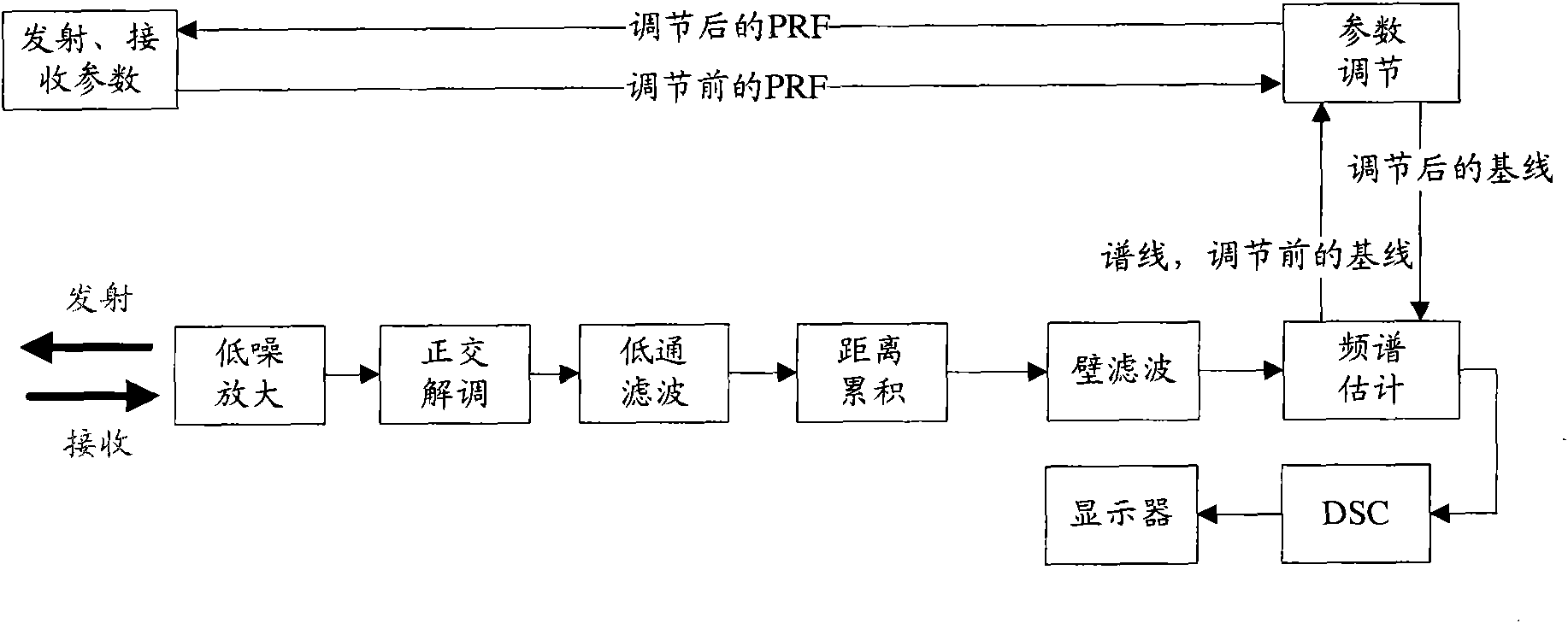
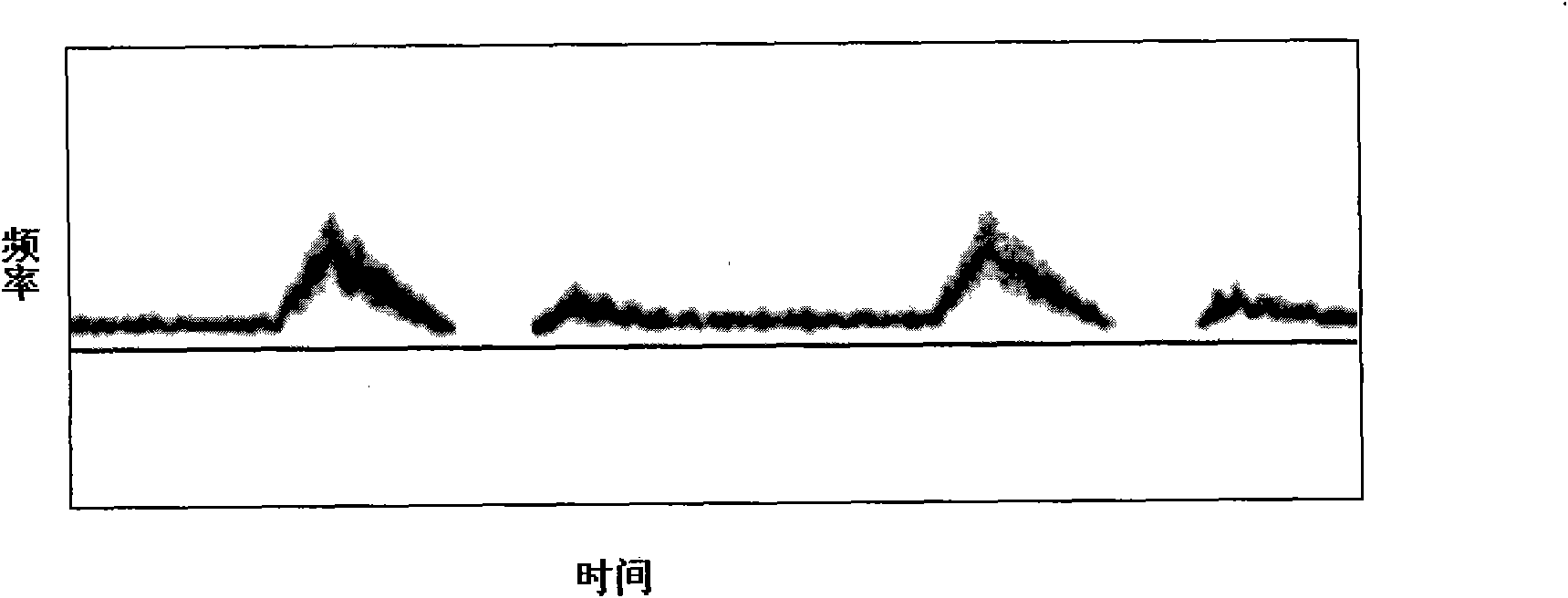
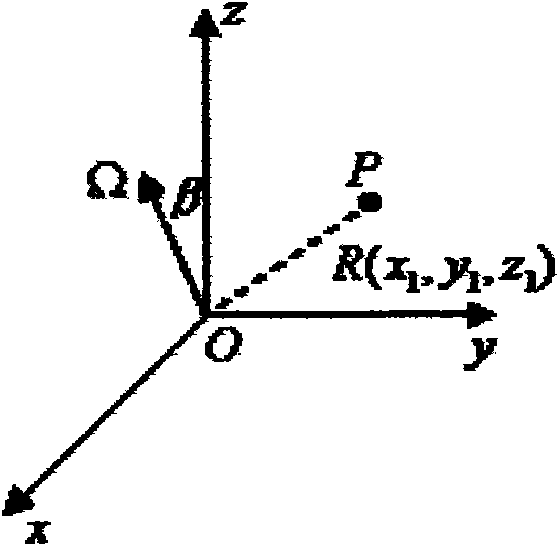Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
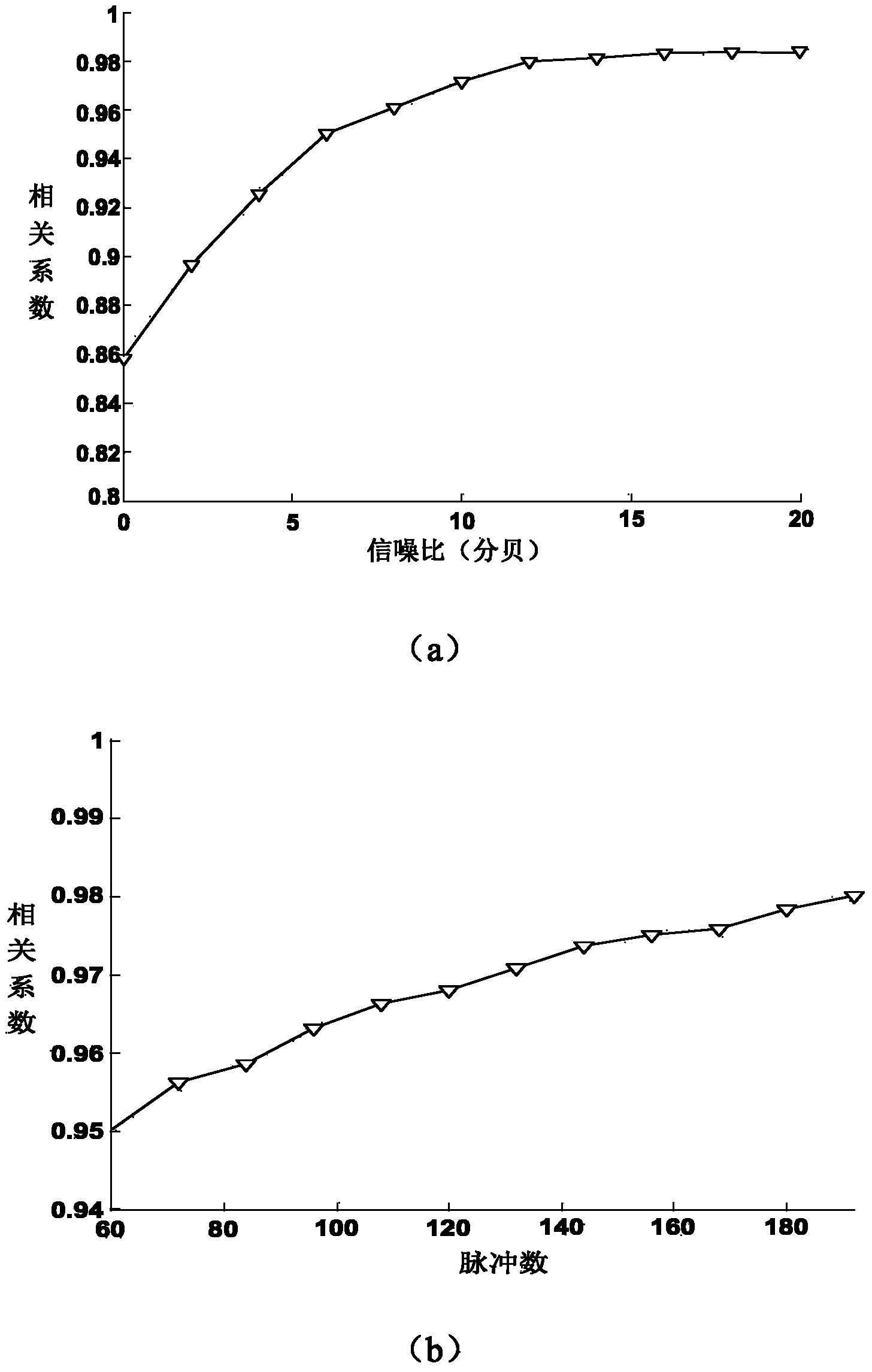
137 results about "Doppler imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inhomogeneous structures on stellar surfaces, i.e. temperature differences, chemical composition or magnetic fields, create characteristic distortions in the spectral lines due to the Doppler effect. These distortions will move across spectral line profiles due to the stellar rotation. The technique to reconstruct these structures on the stellar surface is called Doppler-imaging, often based on the Maximum Entropy image reconstruction to find the stellar image. This technique gives the smoothest and simplest image that is consistent with observations.
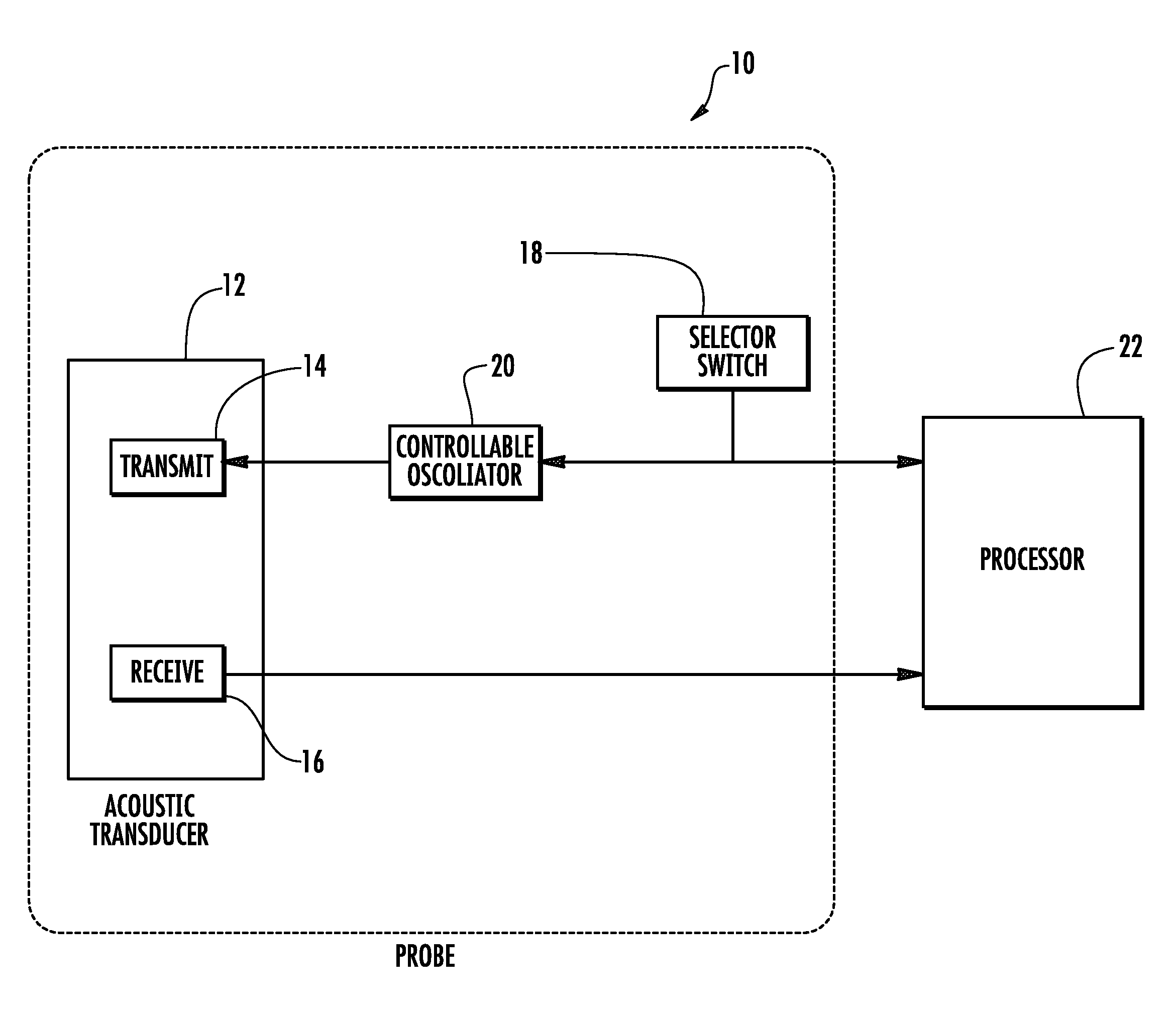
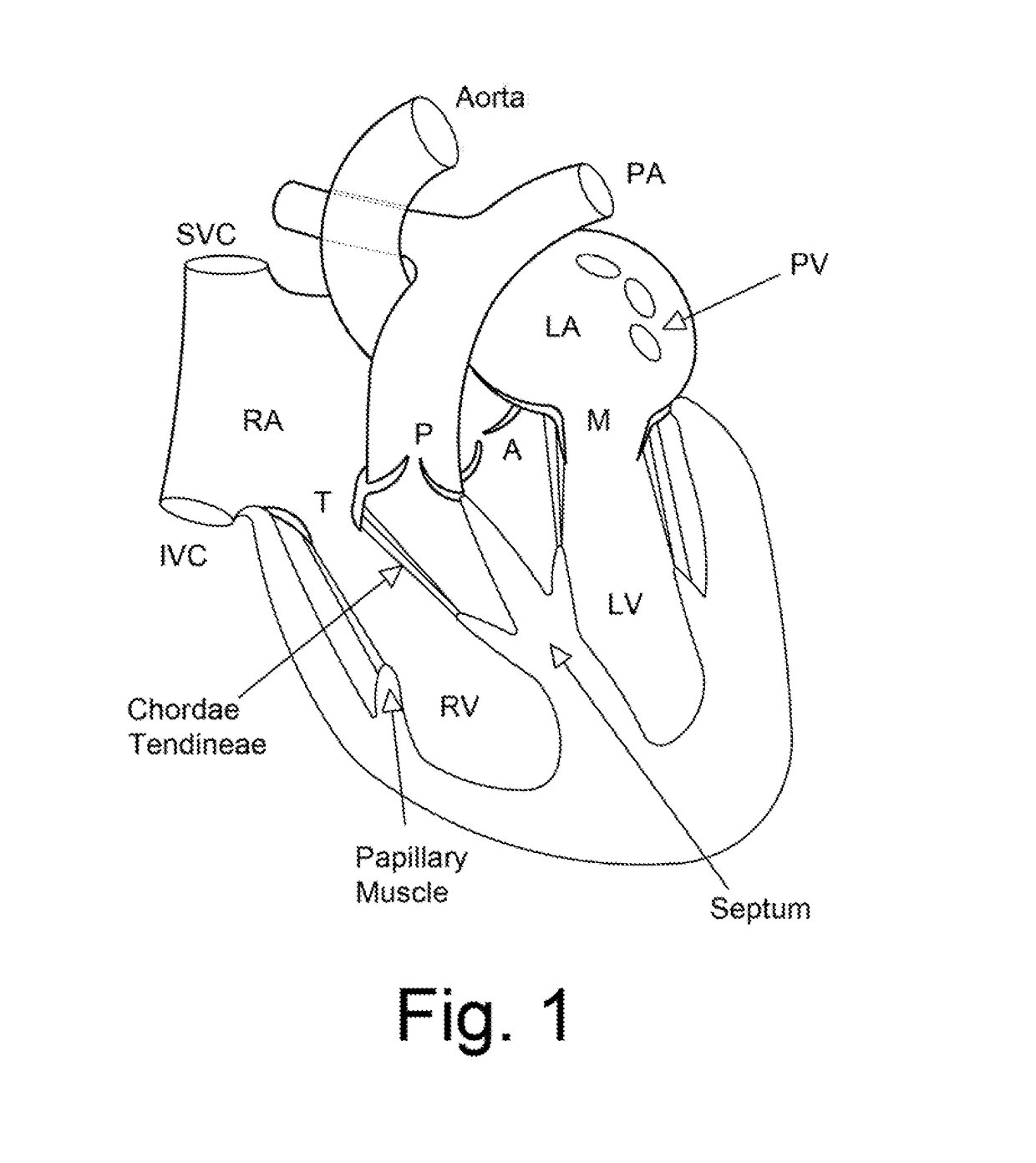
Methods and devices for providing acoustic hemostasis
InactiveUS6083159AEasy to aimReduce releaseChiropractic devicesEye exercisersInternal bleedingRadiology
Methods and apparatus for the remote coagulation of blood using high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) are provided. A remote hemostasis method comprises identifying a site of internal bleeding and focusing therapeutic ultrasound energy on the site, the energy being focused through an intervening tissue. An apparatus for producing remote hemostasis comprises a focused therapeutic ultrasound radiating surface and a sensor for identifying a site of internal bleeding, with a registration means coupled to the radiating surface and the sensor to bring a focal target and the bleeding site into alignment. The sensor generally comprises a Doppler imaging display. Hemostasis enhancing agents may be introduced to the site for actuation by the ultrasound energy.
Owner:THS INT
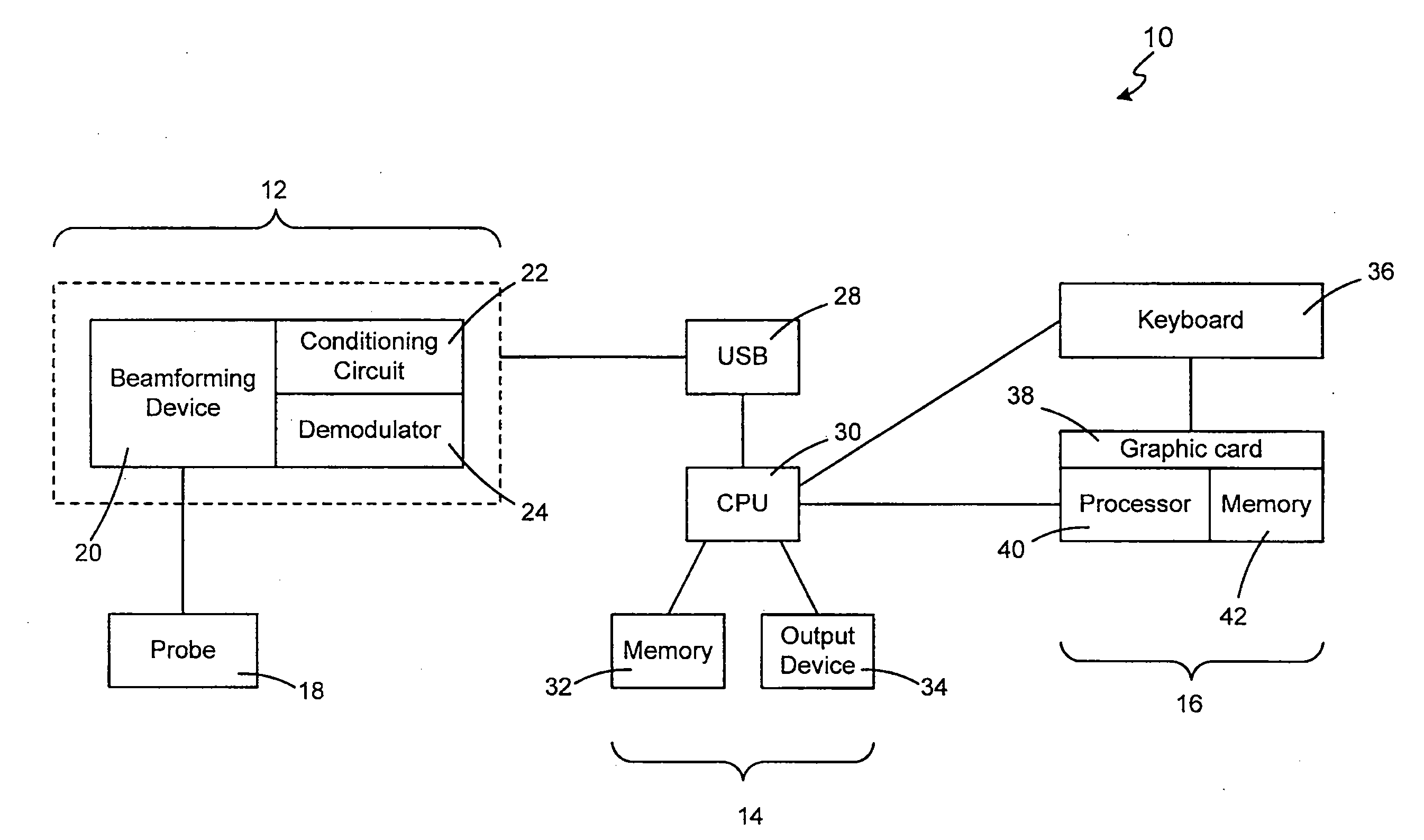
Ultrasound system and method for imaging and/or measuring displacement of moving tissue and fluid
ActiveUS20080086054A1Increase speedQuality improvementBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionGraphic cardSonification
A system and method for improved imaging is disclosed. An exemplary system provides a peripheral ultrasound system connected to a host computer with a plug-and-play interface such as a USB. An exemplary system utilizes a dedicated graphics processing unit such as a graphics card to analyze data obtained from a region of interest to produce an image on one or more output units for the user's viewing. Based on the image displayed on the output units, the user can determine the velocity of the moving tissue and fluid. The system of the present invention can be used to produce a Doppler color flow map or for power Doppler imaging.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
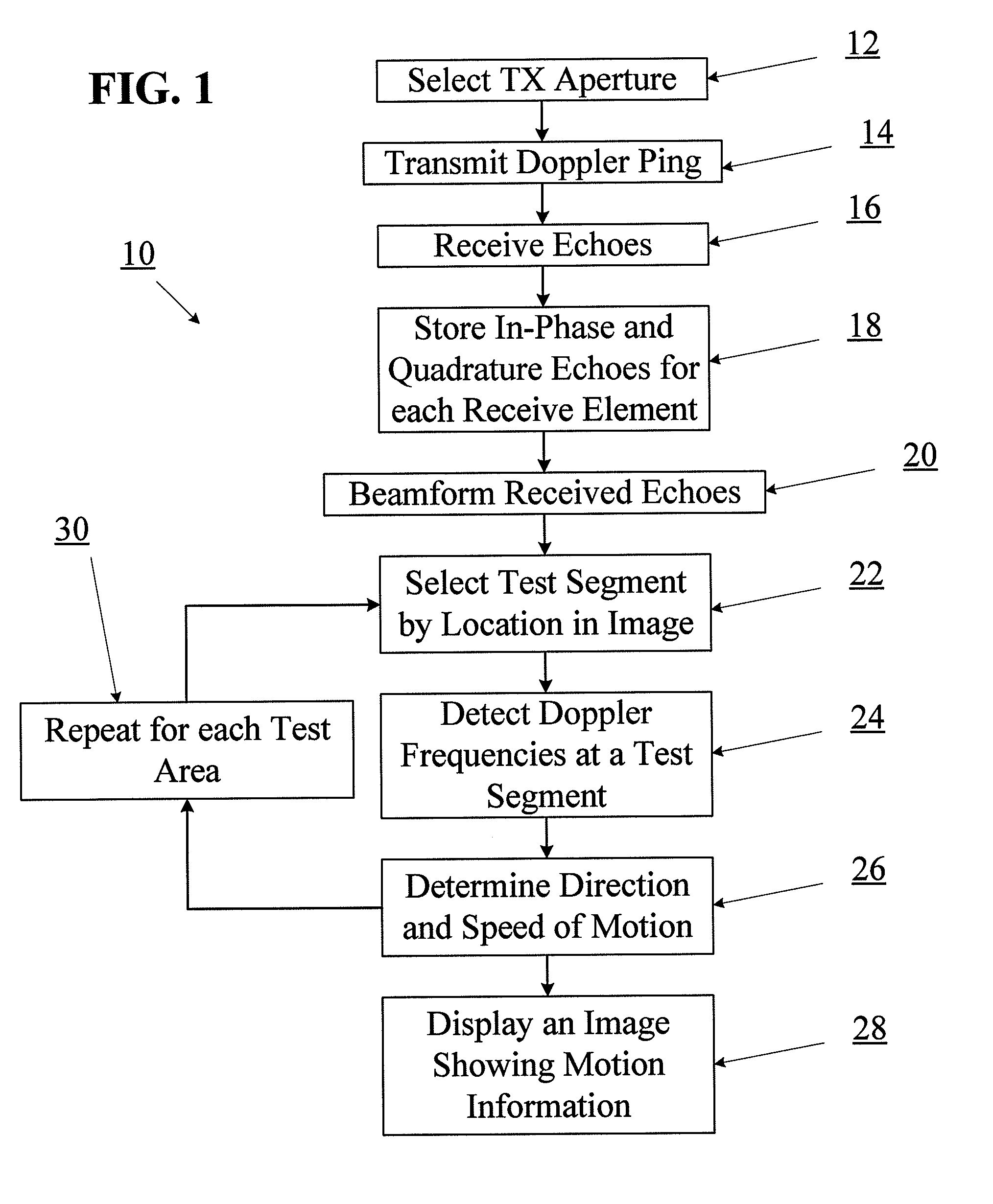
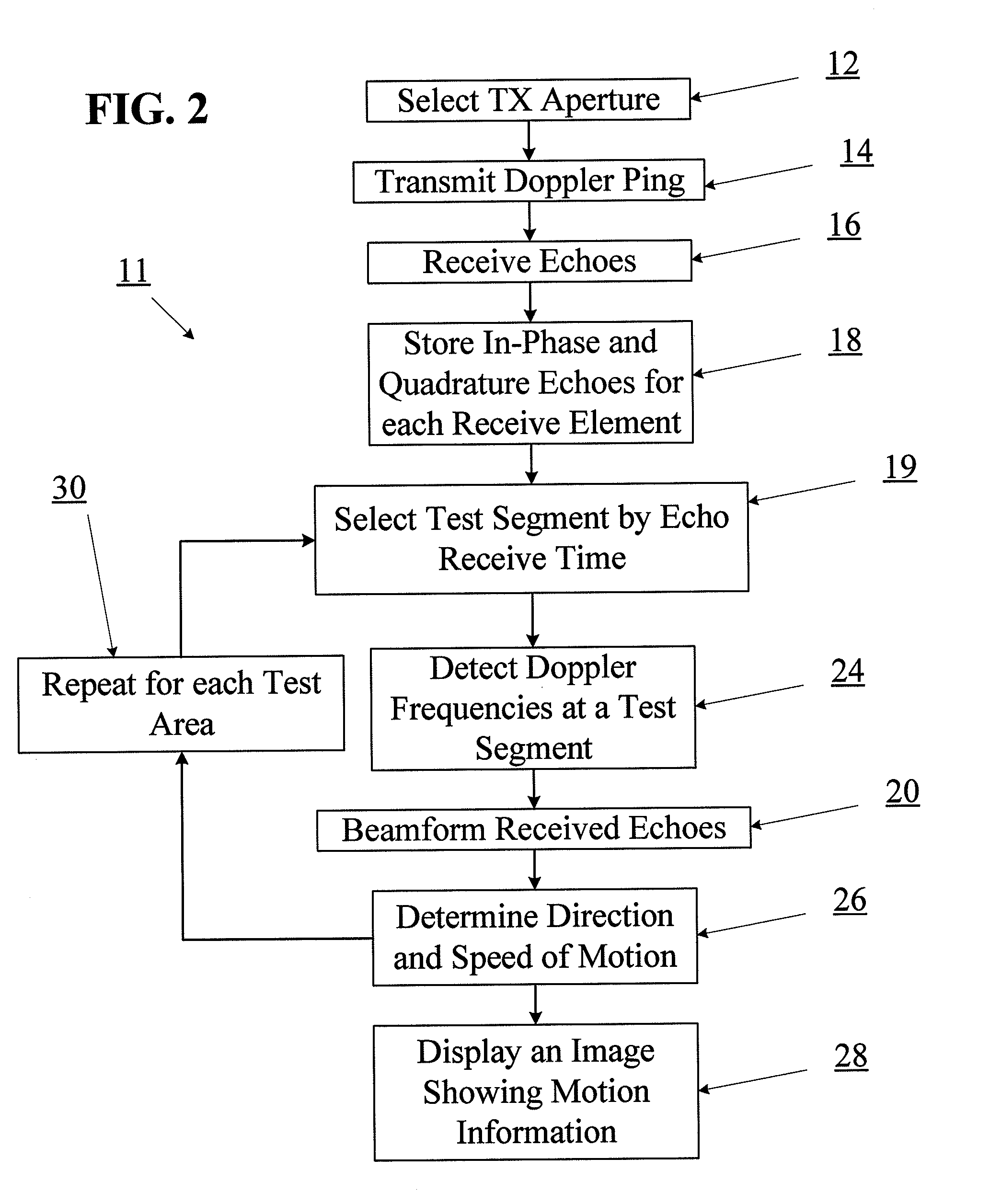
Motion detection using ping-based and multiple aperture doppler ultrasound
ActiveUS20130144166A1High resolutionOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDoppler Ultrasound ImagingSonification
A method of full-field or “ping-based” Doppler ultrasound imaging allows for detection of Doppler signals indicating moving reflectors at any point in an imaging field without the need to pre-define range gates. In various embodiments, such whole-field Doppler imaging methods may include transmitting a Doppler ping from a transmit aperture, receiving echoes of the Doppler ping with one or more separate receive apertures, detecting Doppler signals and determining the speed of moving reflectors. In some embodiments, the system also provides the ability to determine the direction of motion by solving a set of simultaneous equations based on echo data received by multiple receive apertures.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Wall motion analyzer
InactiveUS20050228276A1Used to determineOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterCardiac wallReference image
A system and method for real-time quantitative analysis of heart wall motion is provided. A Doppler imaging system is used to monitor the movement of a heart, or other organ. A B-mode reference image of the target organ is made and then a region-of-interest is defined through the use of a gate. Then pulsed wave spectral tissue Doppler data of the region-of-interest is formed and used to determine the velocity of a region of the target organ. The system may be used for determining appropriate biventricular pacemaker settings for patients suffering from heart disease.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
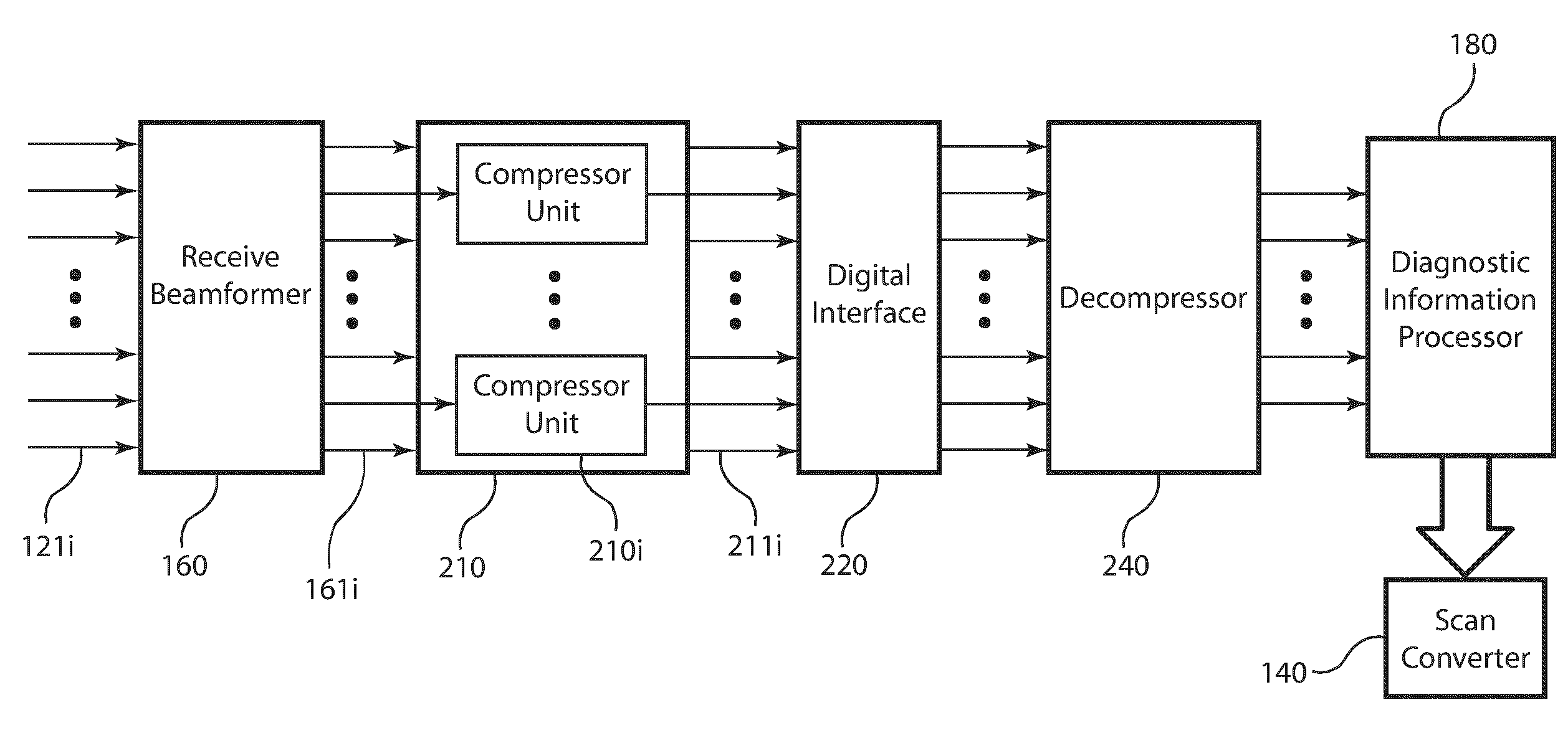
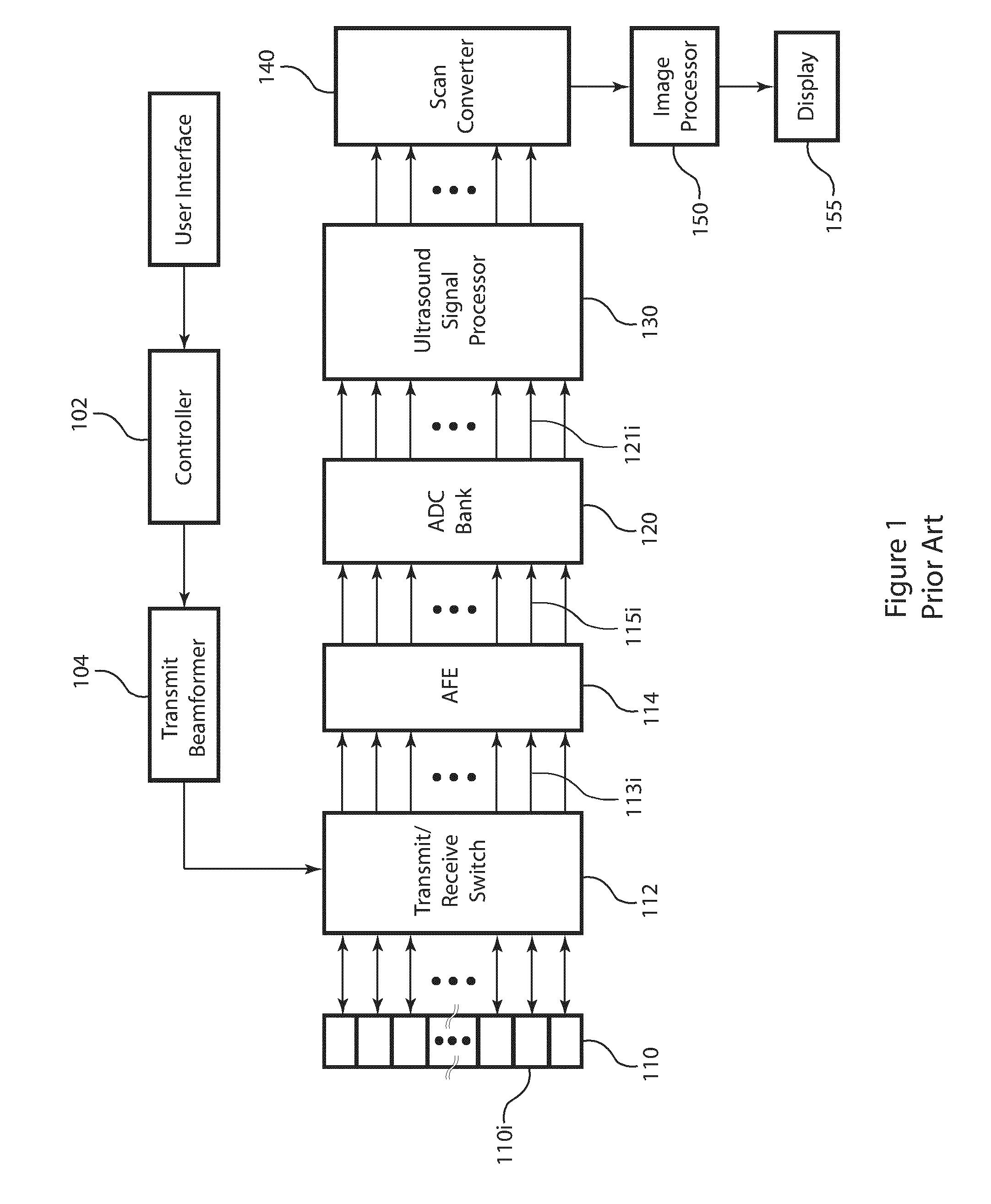
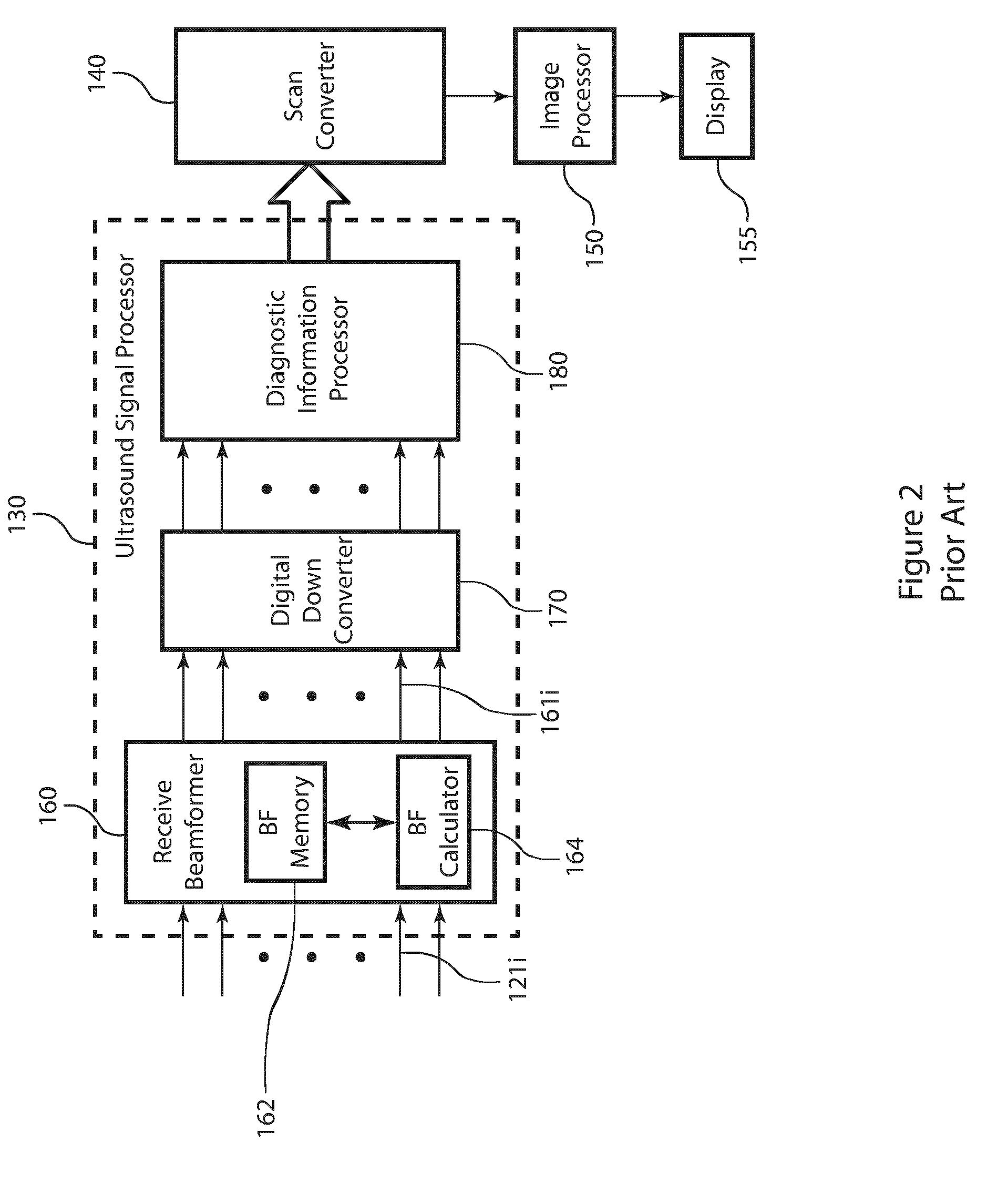
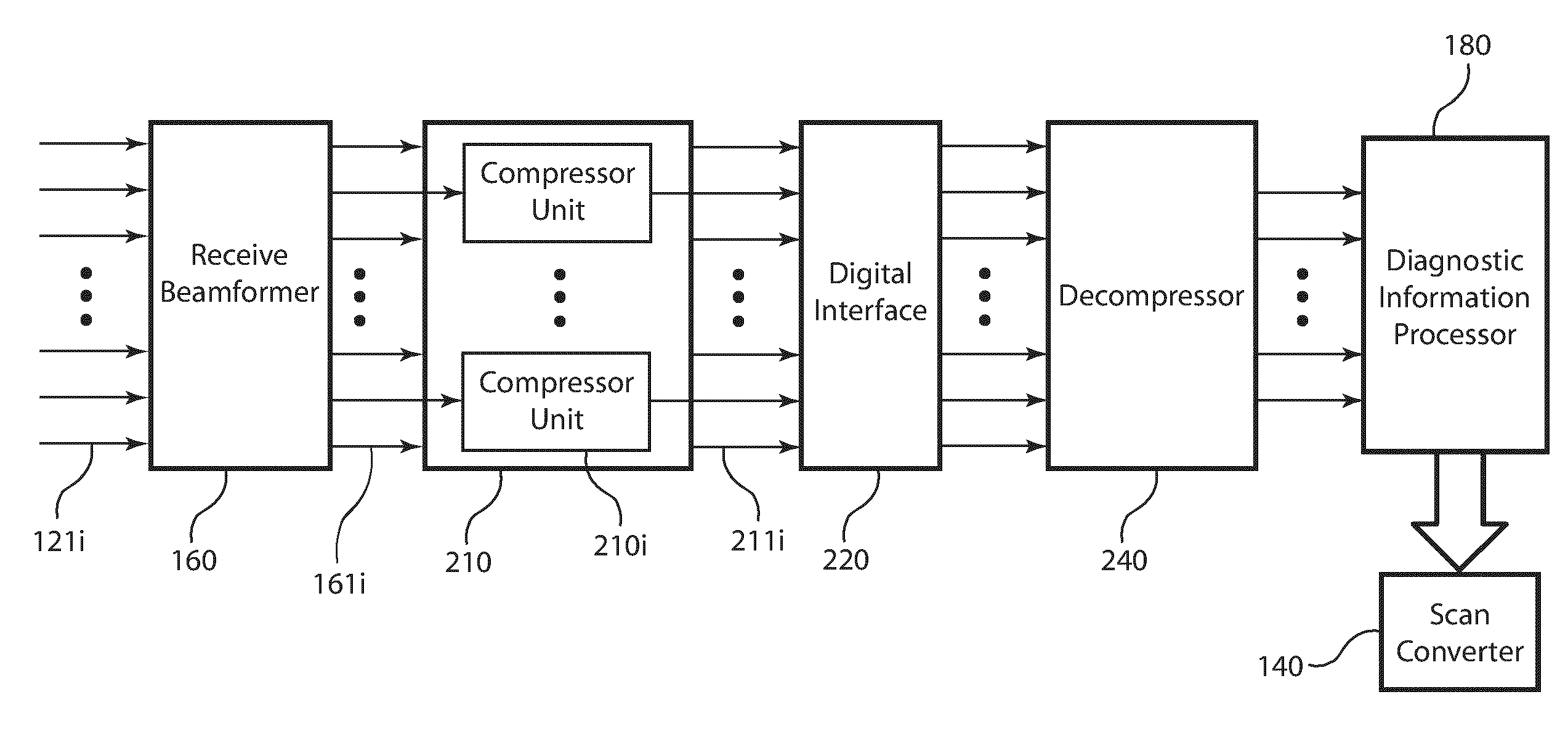
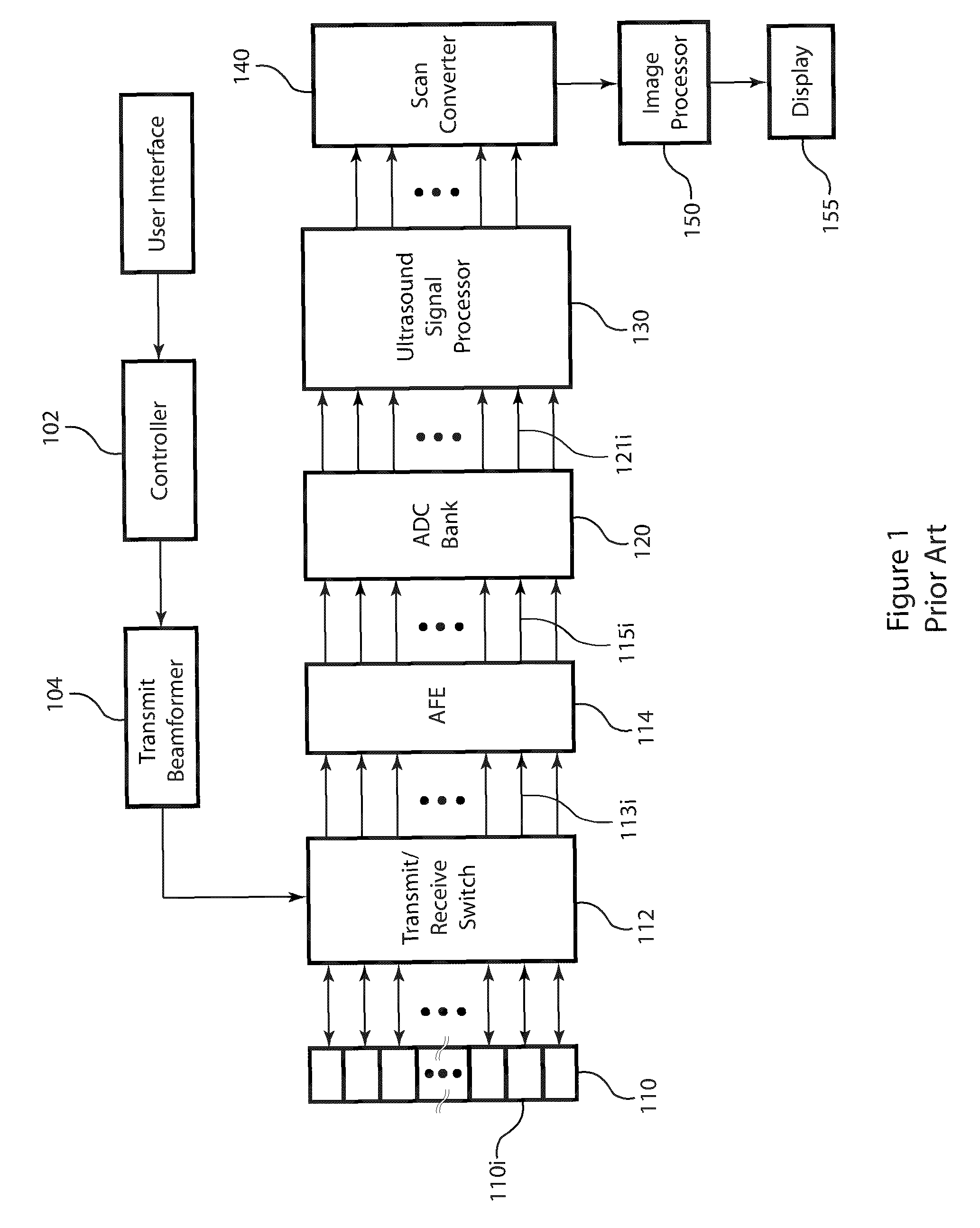
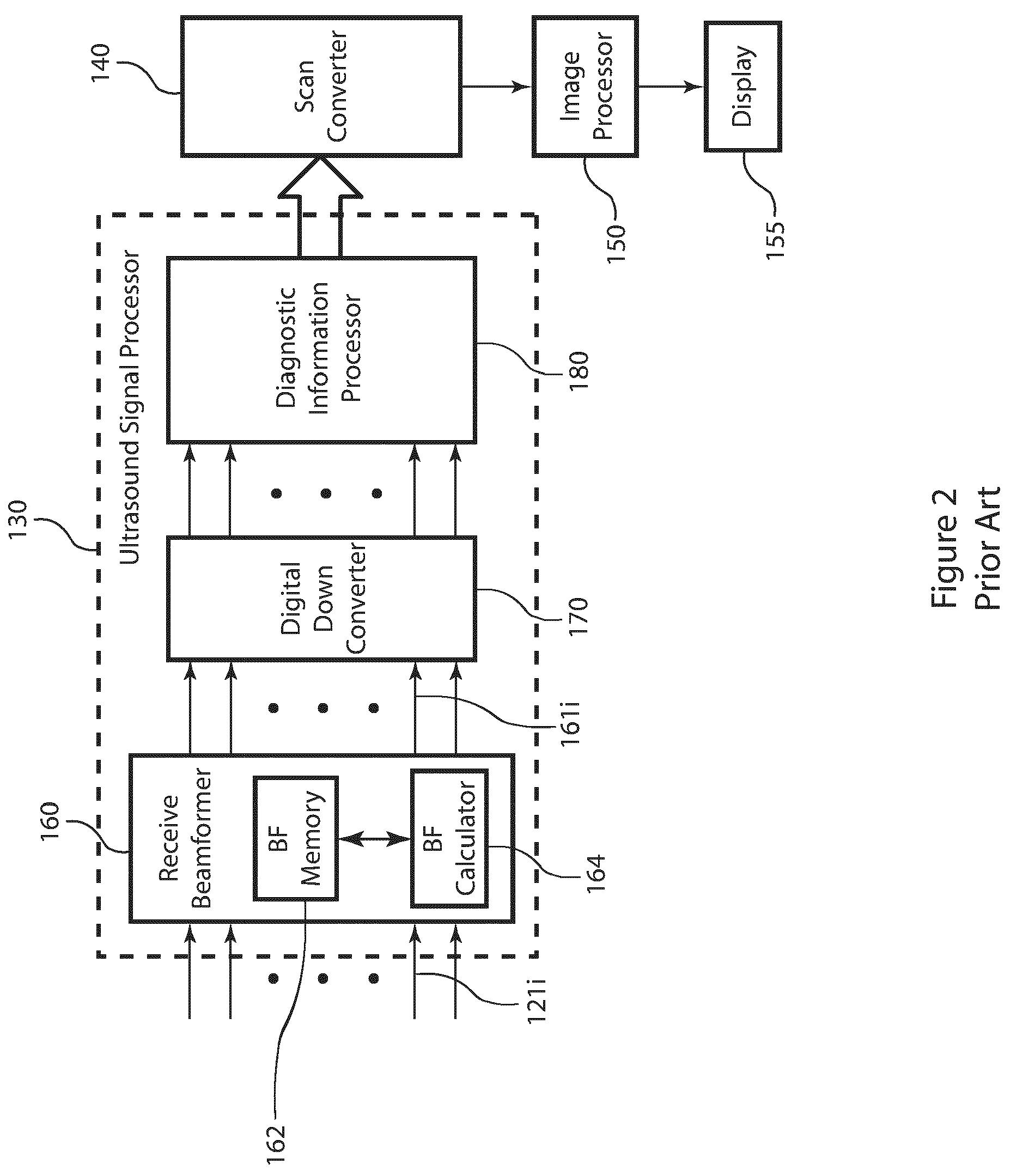
Post-beamforming compression in ultrasound systems
InactiveUS20100331689A1Efficient storageReduce storage capacityWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasound imagingScan conversion
In an ultrasound imaging system that applies a beamformer to received ultrasound signal samples to form one or more beams represented by arrays of beamformed samples, a method and an apparatus compress each array of beamformed samples independently of the other arrays to form compressed beams. A plurality of analog to digital converters sample multiple analog ultrasound signals produced by a transducer array to provide multiple streams of ultrasound signal samples to the beamformer. The compressed beams are transferred via a digital interface to a signal processor. At the signal processor, the compressed beams are decompressed to form decompressed beams. The signal processor further processes the decompressed beams for diagnostic imaging, such as for B-mode and Doppler imaging, and scan conversion to prepare the resulting ultrasound image for display. This abstract does not limit the scope of the invention as described in the claims.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
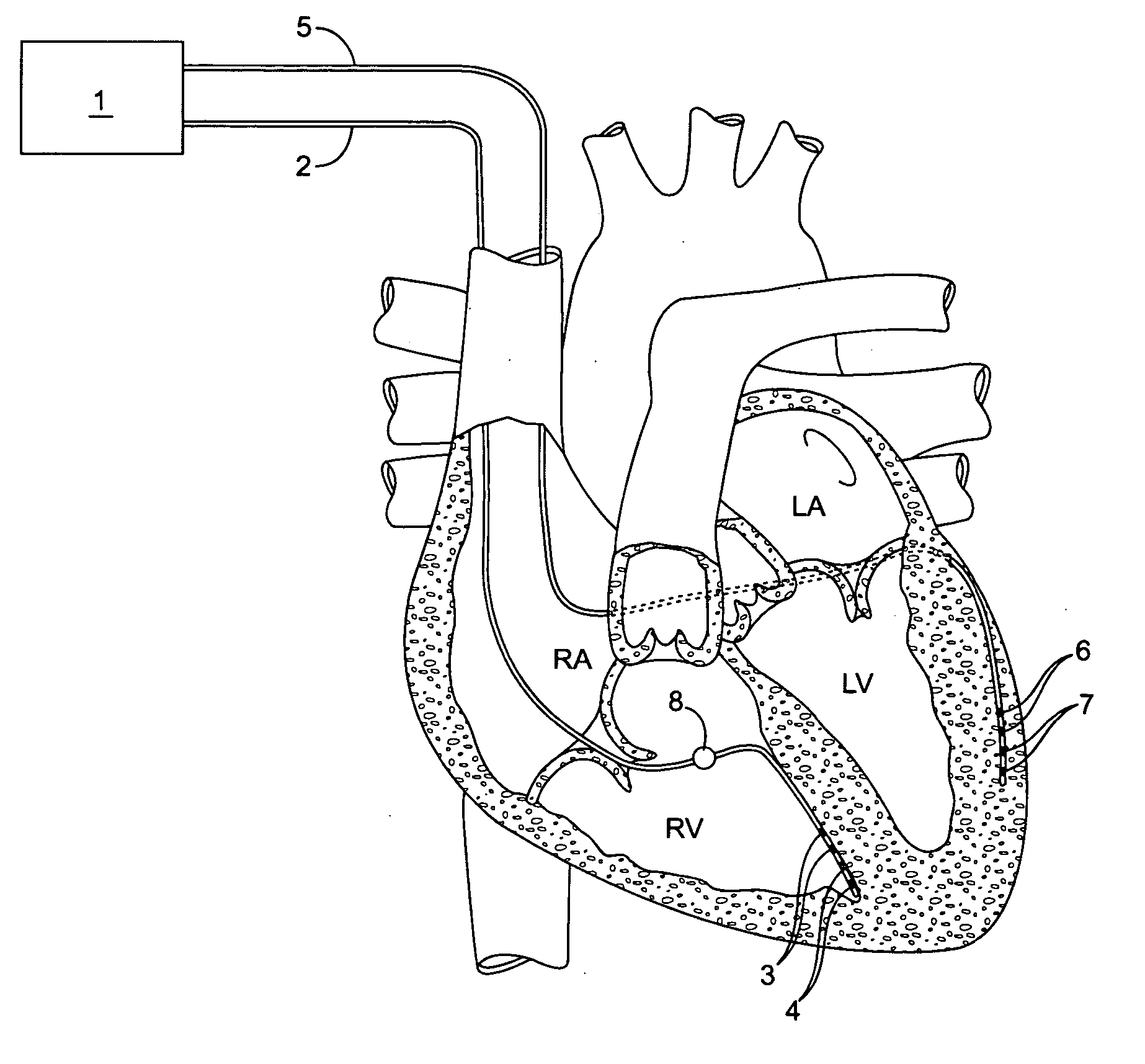
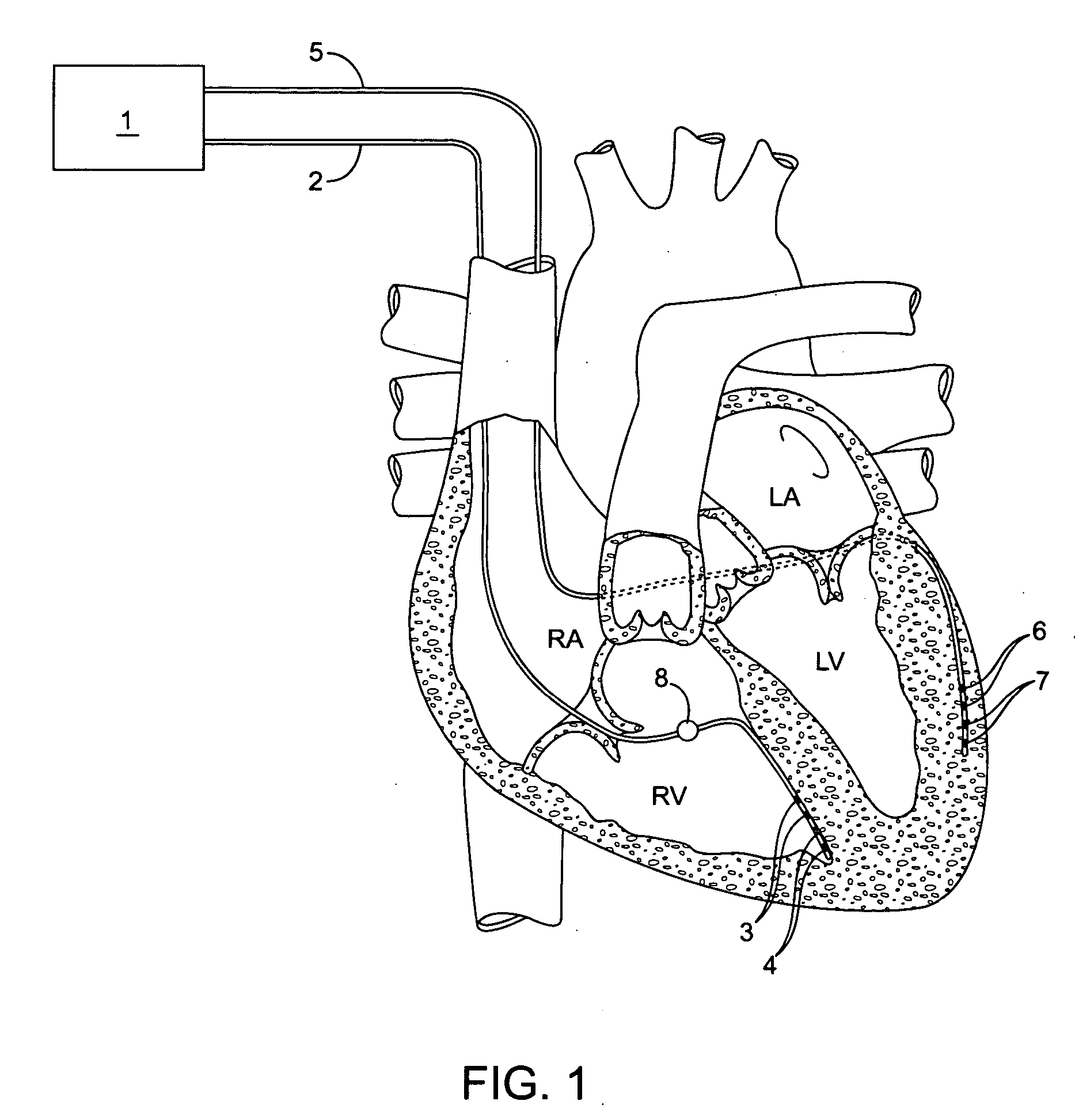
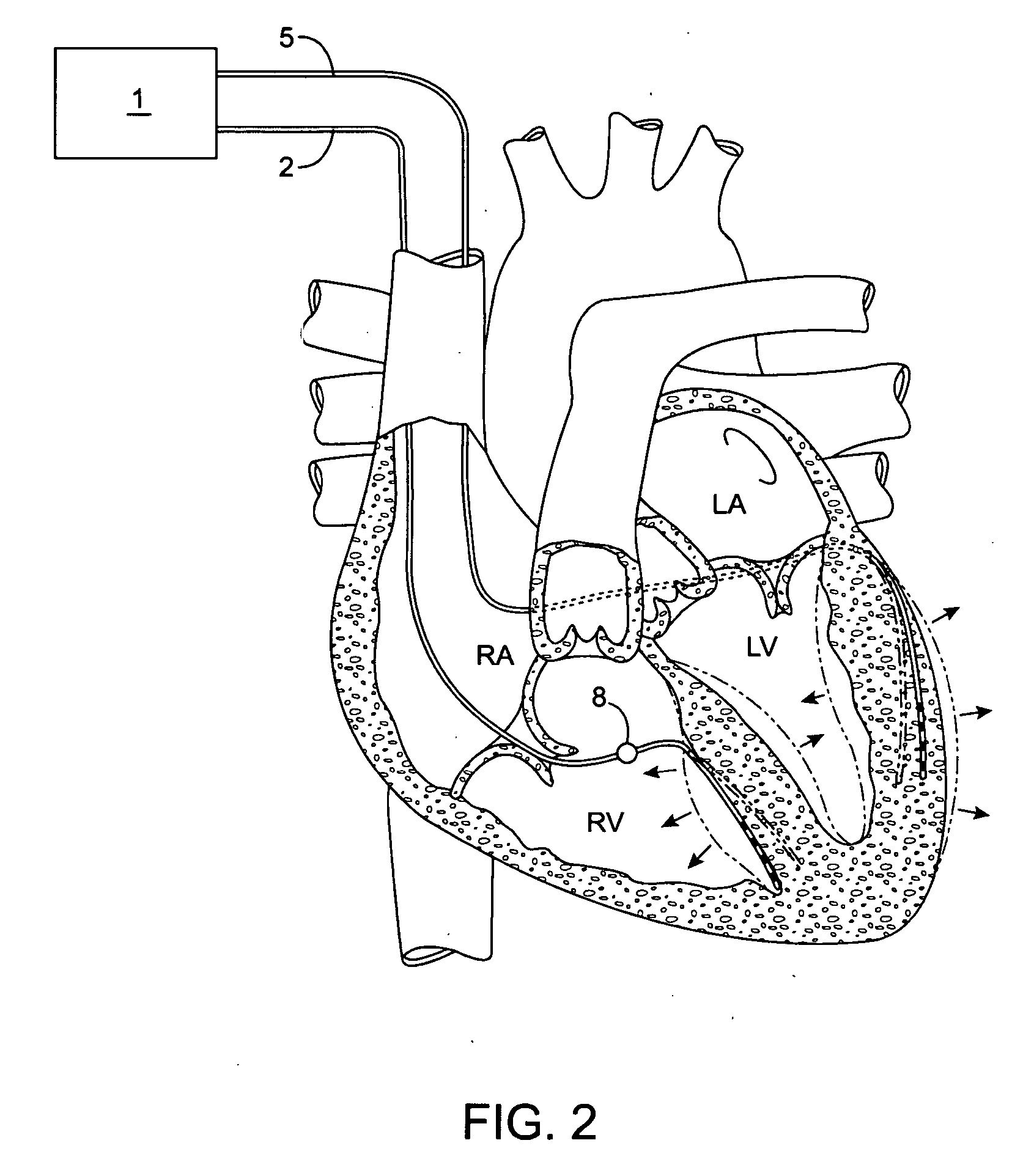
Implantable doppler tomography system
InactiveUS20060116581A1Beneficial to patientQuality improvementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyCardiac wallDoppler imaging
The inventive implantable Doppler tomography system allows, for the first time, the use of Doppler shift for purposes of tracking cardiac wall motion. The present inventive Doppler tomography system methods and devices provide a critical new tool in the physician's armamentarium which provides accurate, real time monitoring of the mechanical performance of the heart.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
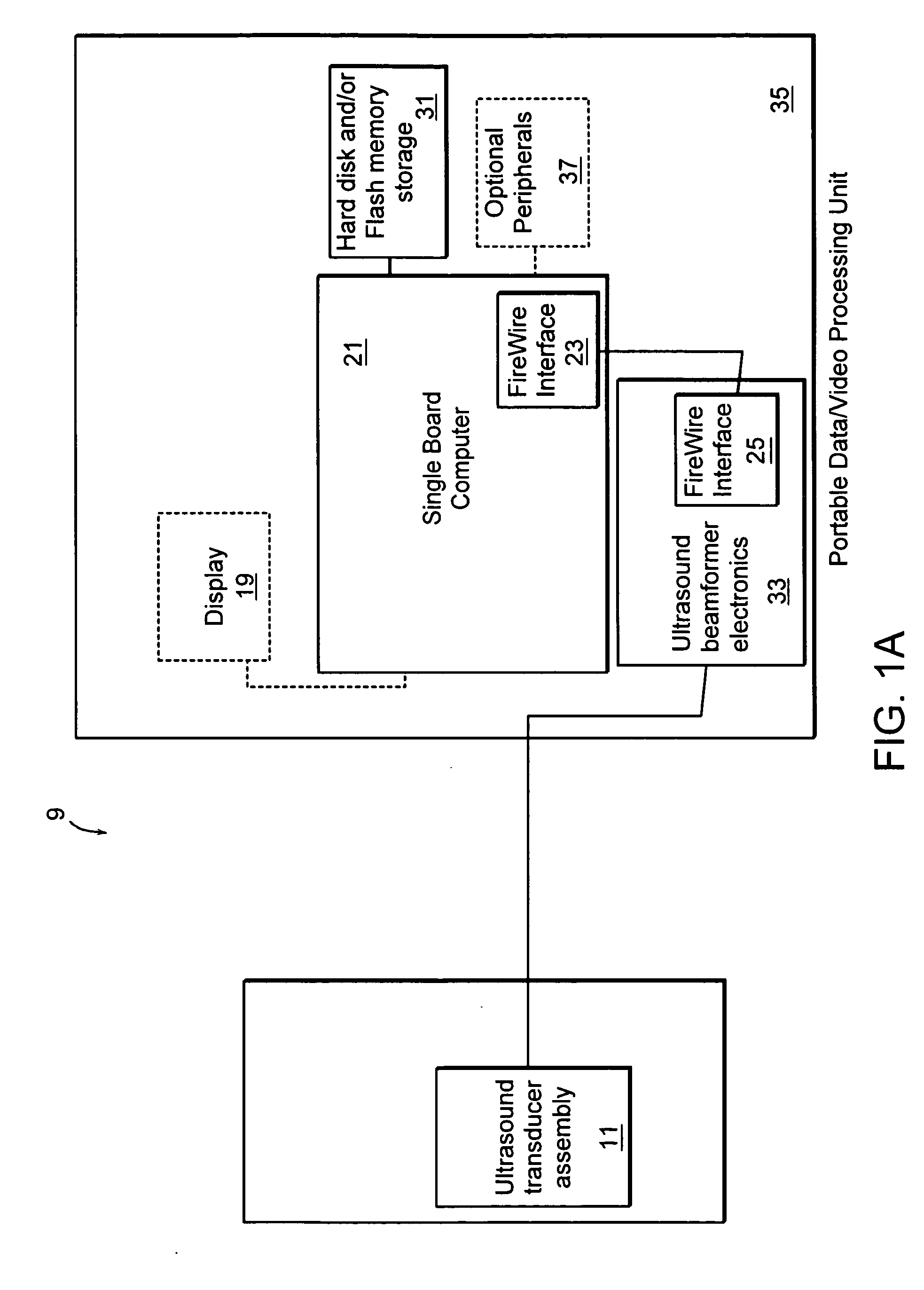
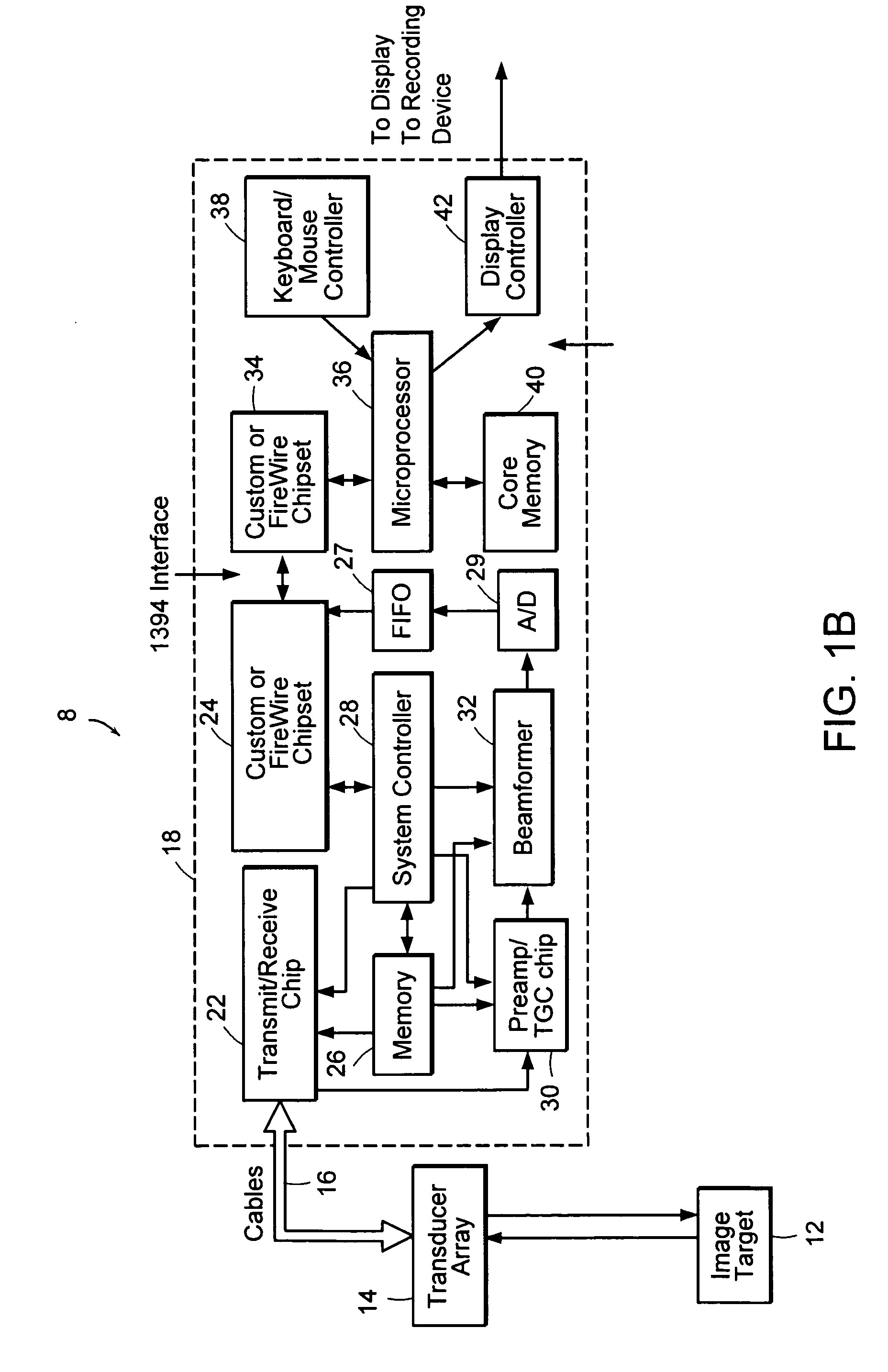
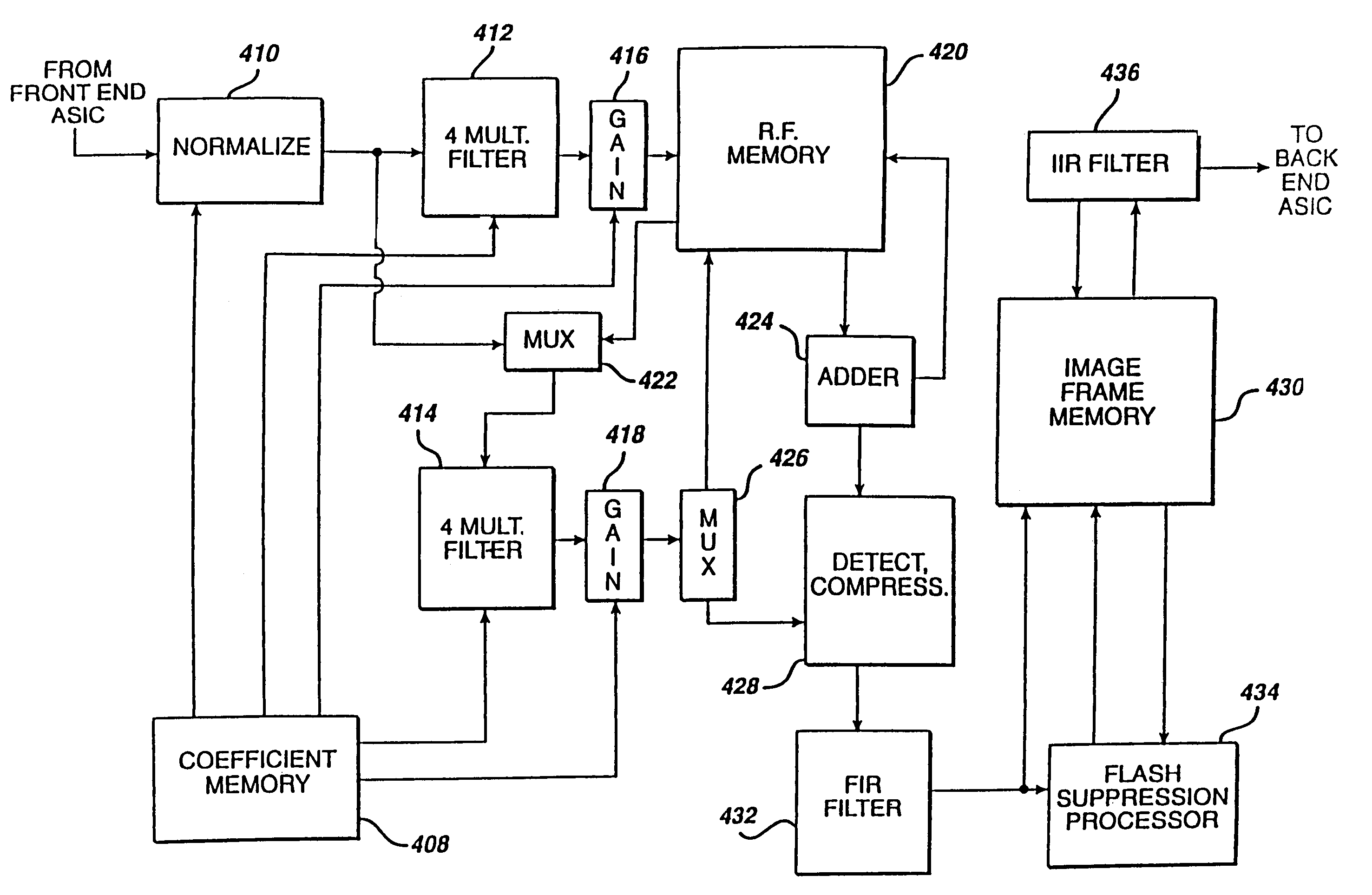
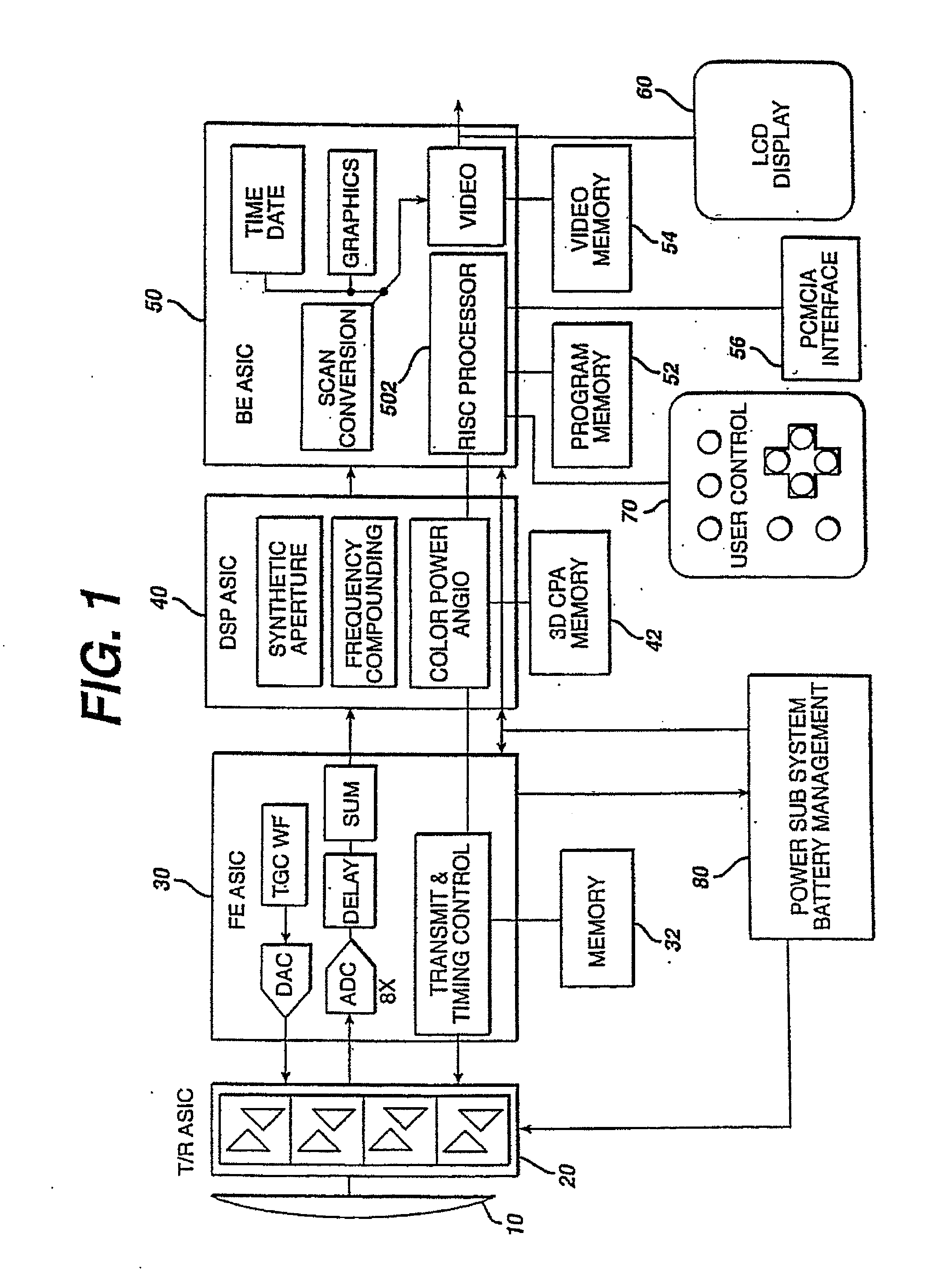
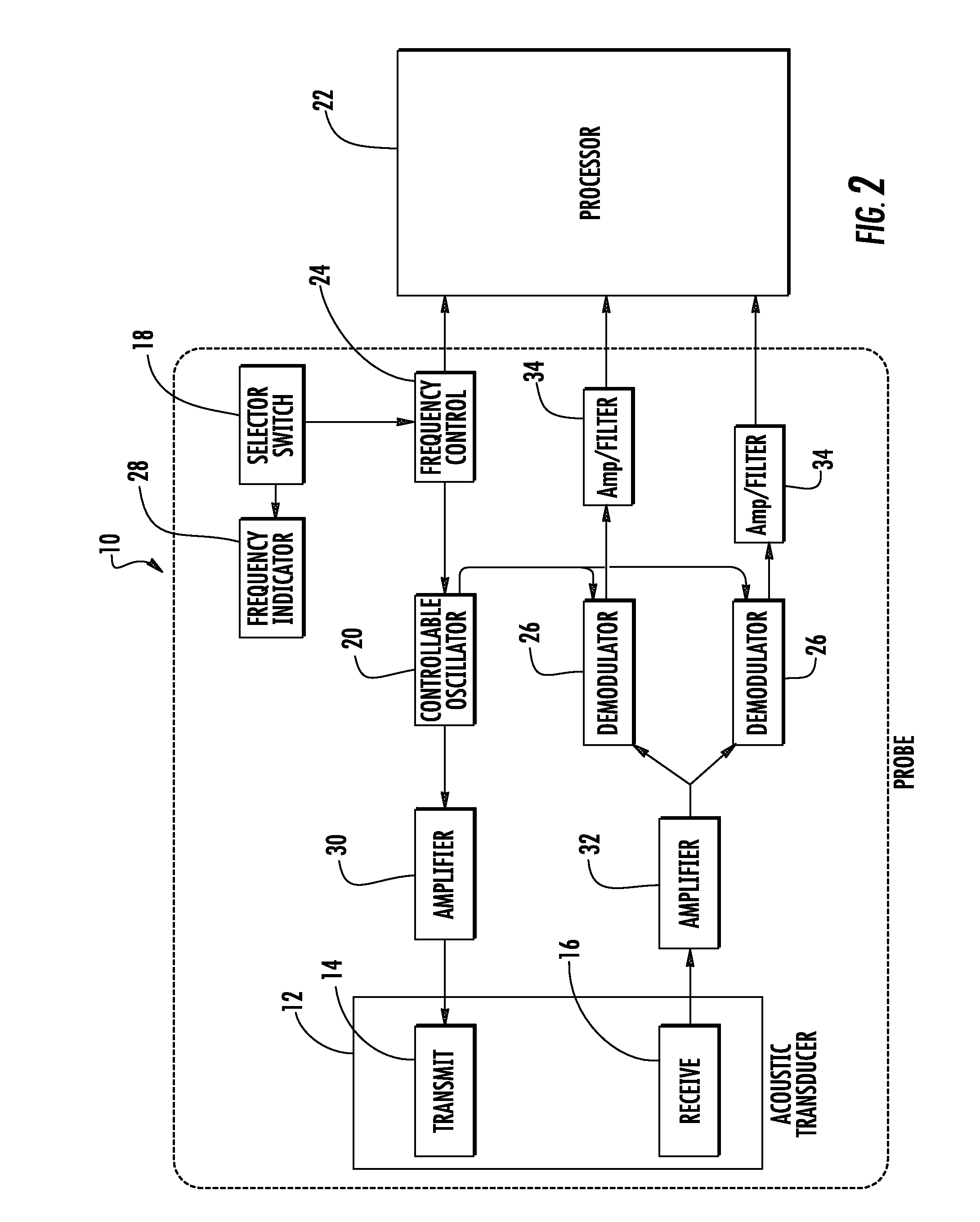
Ultrasonic signal processor for a hand held ultrasonic diagnostic instrument
InactiveUS7604596B2Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsDigital signal processingTransceiver
A hand held ultrasonic instrument is provided in a portable unit which performs both B mode and Doppler imaging. The instrument includes a transducer array mounted in a hand-held enclosure, with an integrated circuit transceiver connected to the elements of the array for the reception of echo signals. A digital signal processing circuit performs both B mode and Doppler signal processing such as filtering, detection and Doppler estimation, as well as advanced functions such as assembly of multiple zone focused scanlines, synthetic aperture formation, depth dependent filtering, speckle reduction, flash suppression, and frame averaging.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
Estimation and display for vector doppler imaging using plane wave transmissions
ActiveUS20140371594A1High precisionGood for observationBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionColor dopplerUltrasonic sensor
Vector Doppler Imaging (VDI) improves on conventional Color Doppler Imaging (CDI) by giving speed and direction of blood flow at each pixel of a display generated by a computing system. Multiple angles of Plane wave transmissions (PWT) via an ultrasound transducer conveniently give projected Doppler measurements over a wide field of view, providing enough angular diversity to identify velocity vectors in a short time window while capturing transitory flow dynamics. A fast, aliasing-resistant velocity vector estimator for PWT is presented, and VDI imaging of a carotid artery with a 5 MHz linear array is shown using a novel synthetic particle flow visualization method.
Owner:VERASONICS
Ultrasonic Signal Processor for a Hand Held Ultrasonic Diagnostic Instrument
InactiveUS20100121196A1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsDigital signal processingTransceiver
A hand held ultrasonic instrument is provided in a portable unit which performs both B mode and Doppler imaging. The instrument includes a transducer array mounted in a hand-held enclosure, with an integrated circuit transceiver connected to the elements of the array for the reception of echo signals. A digital signal processing circuit performs both B mode and Doppler signal processing such as filtering, detection and Doppler estimation, as well as advanced functions such as assembly of multiple zone focused scanlines, synthetic aperture formation, depth dependent filtering, speckle reduction, flash suppression, and frame averaging.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
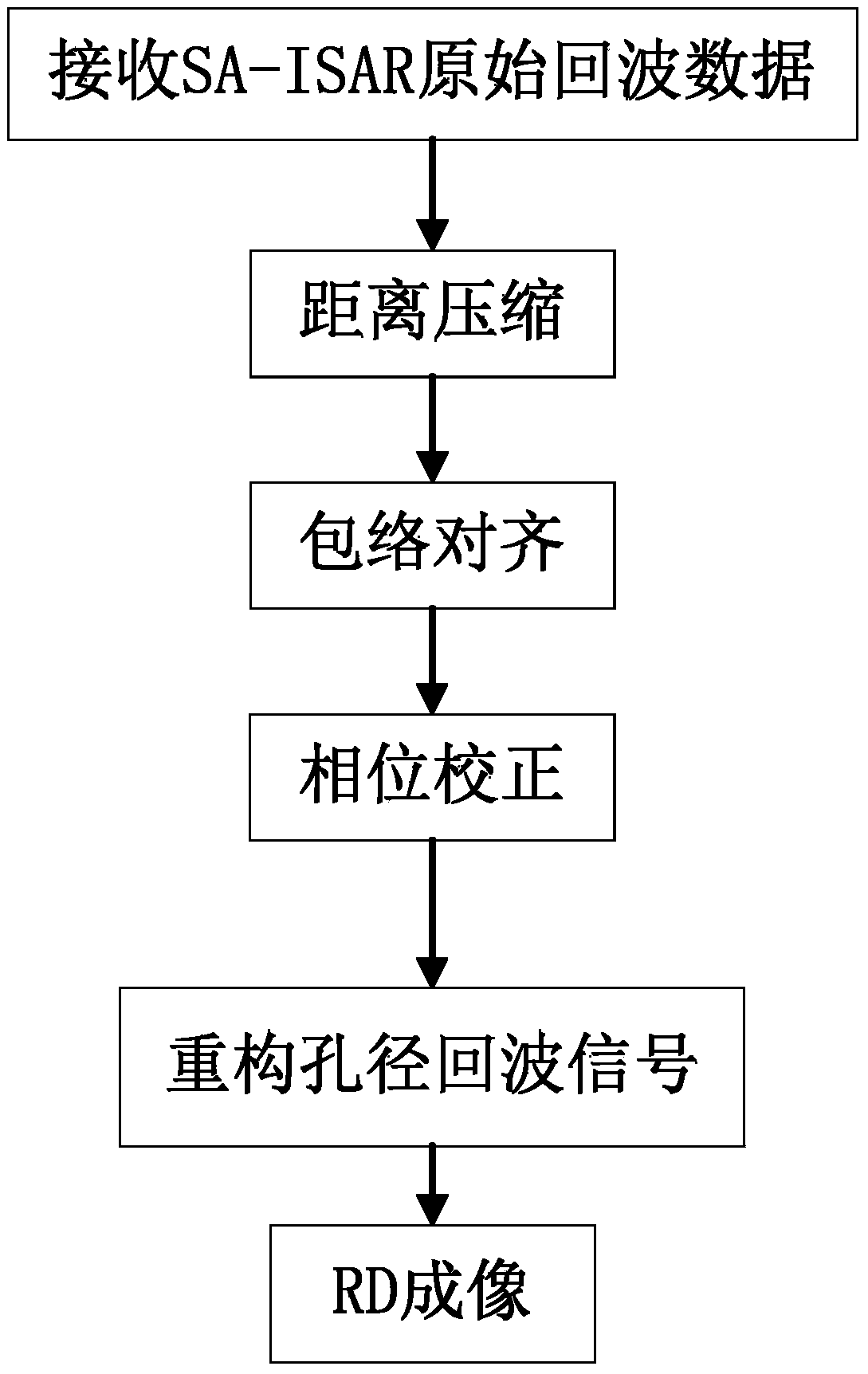
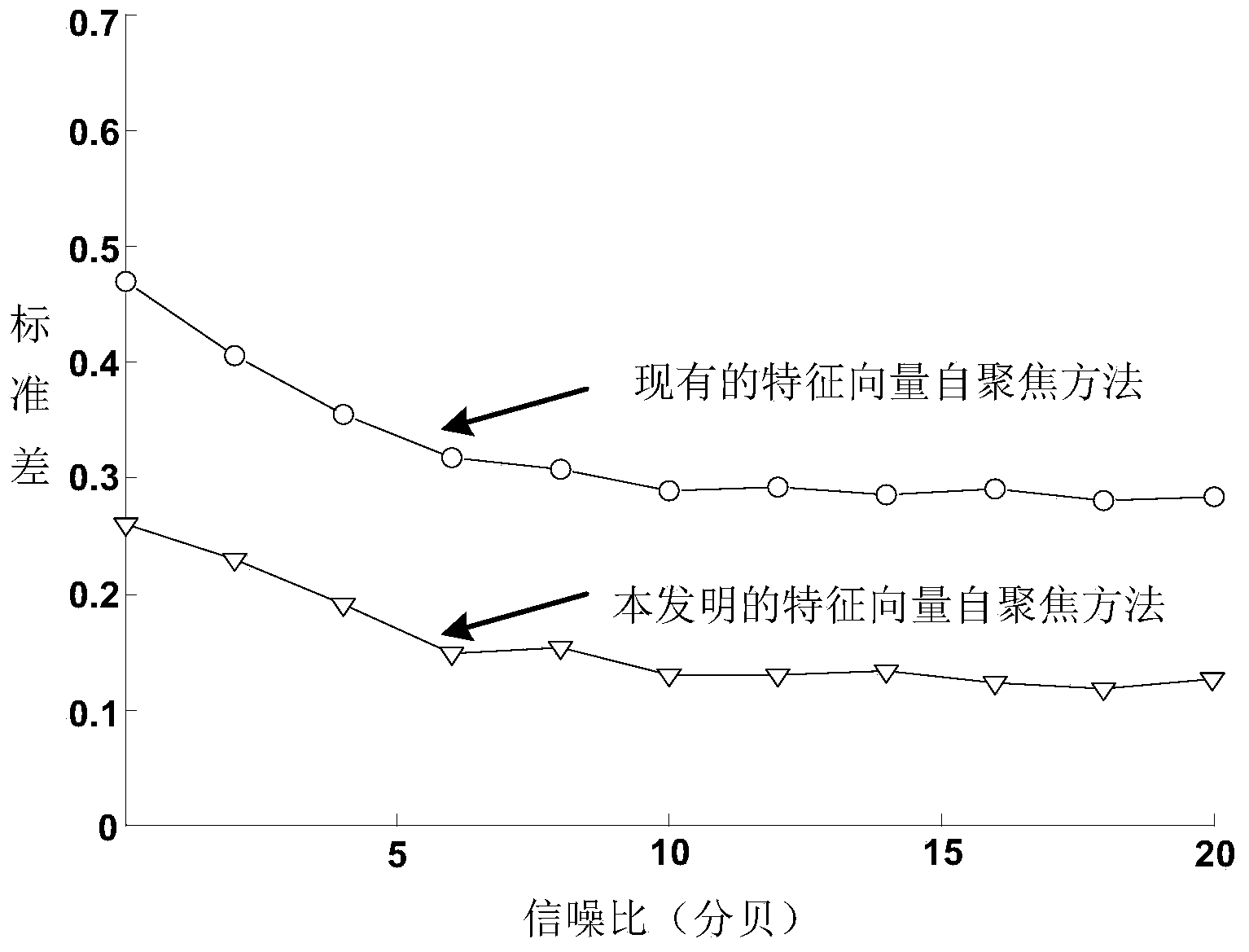
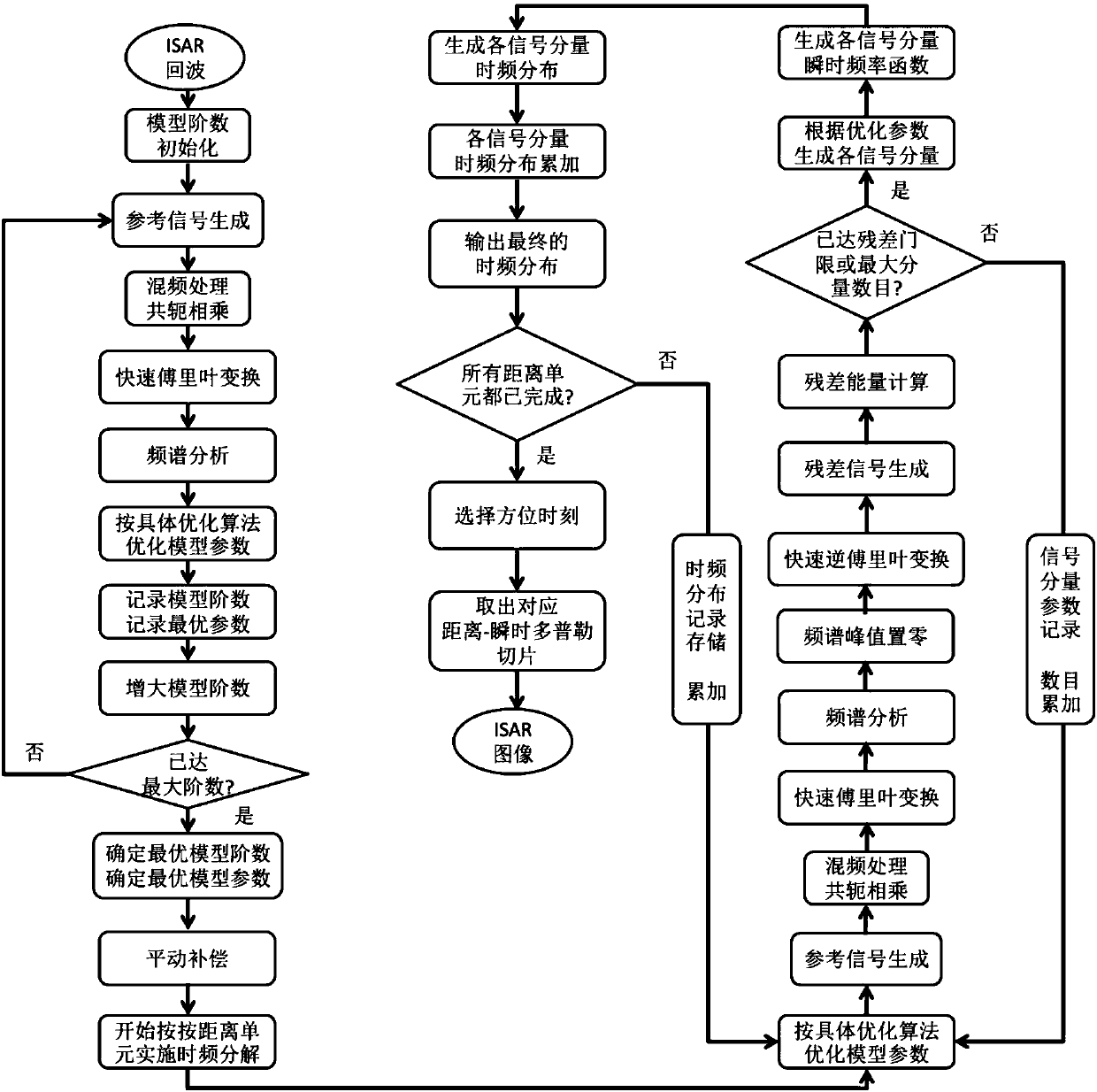
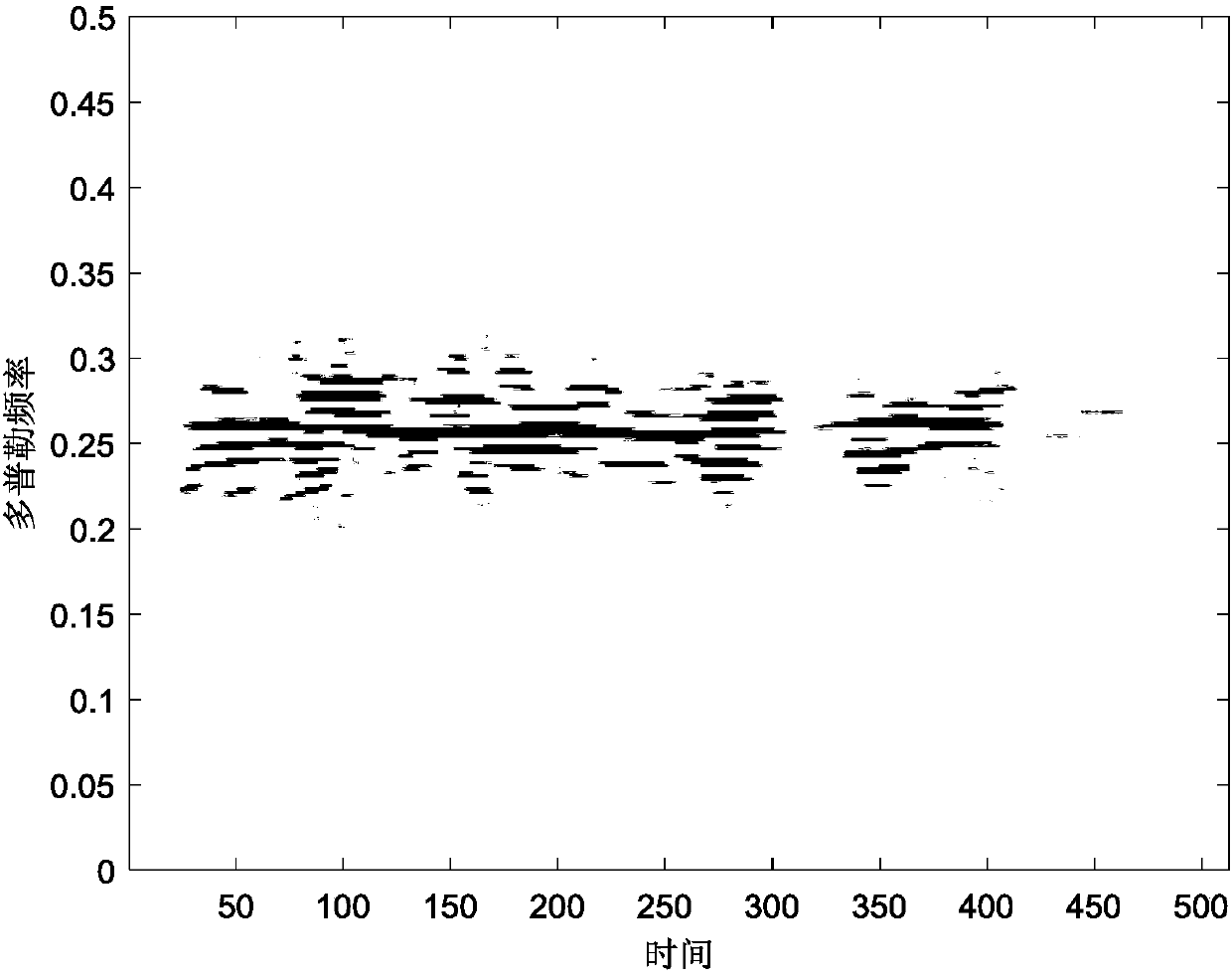
Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method for maneuvering targets on basis of sparse aperture
InactiveCN103901429AFocusOvercoming the drawbacks of phase compensation resultsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correctionImaging processing
The invention discloses an inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method for maneuvering targets on the basis of the sparse aperture. The inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method for the maneuvering targets on the basis of the sparse aperture comprises the implementation steps that (1) original echo data, with the sparse aperture, of an inverse synthetic aperture radar are received; (2) distance compression and envelope alignment processing are carried out; (3) phase correction is accurately carried out; (4) sparse aperture echo signals are reconstructed; (5) fast Fourier transform is carried out to achieve distance-Doppler imaging. According to the inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method for the maneuvering targets on the basis of the sparse aperture, accurate phase compensation and accurate data reconstruction can be carried out on ISAR imaging processing under the conditions of the maneuvering targets and the sparse aperture, and a more focused high-quality ISAR imaging result is obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Dual frequency doppler ultrasound probe
An ultrasonic Doppler probe is provided for use in connection with non-invasive Doppler imaging of fluid flow within the human body. The Doppler probe can be selectively operated at more than one frequency during the course of a Doppler imaging examination thereby enhancing the resolution of the image obtained while also increasing the effective depth of the image. The probe of the present invention employs piezo-electric materials for the formation of acoustic transmitting and receiving transducers that are positioned within the probe to allow the probe to be selectively operated at a number of different frequencies spanning no more than one octave in frequency range.
Owner:UNETIXS VASCULAR INC
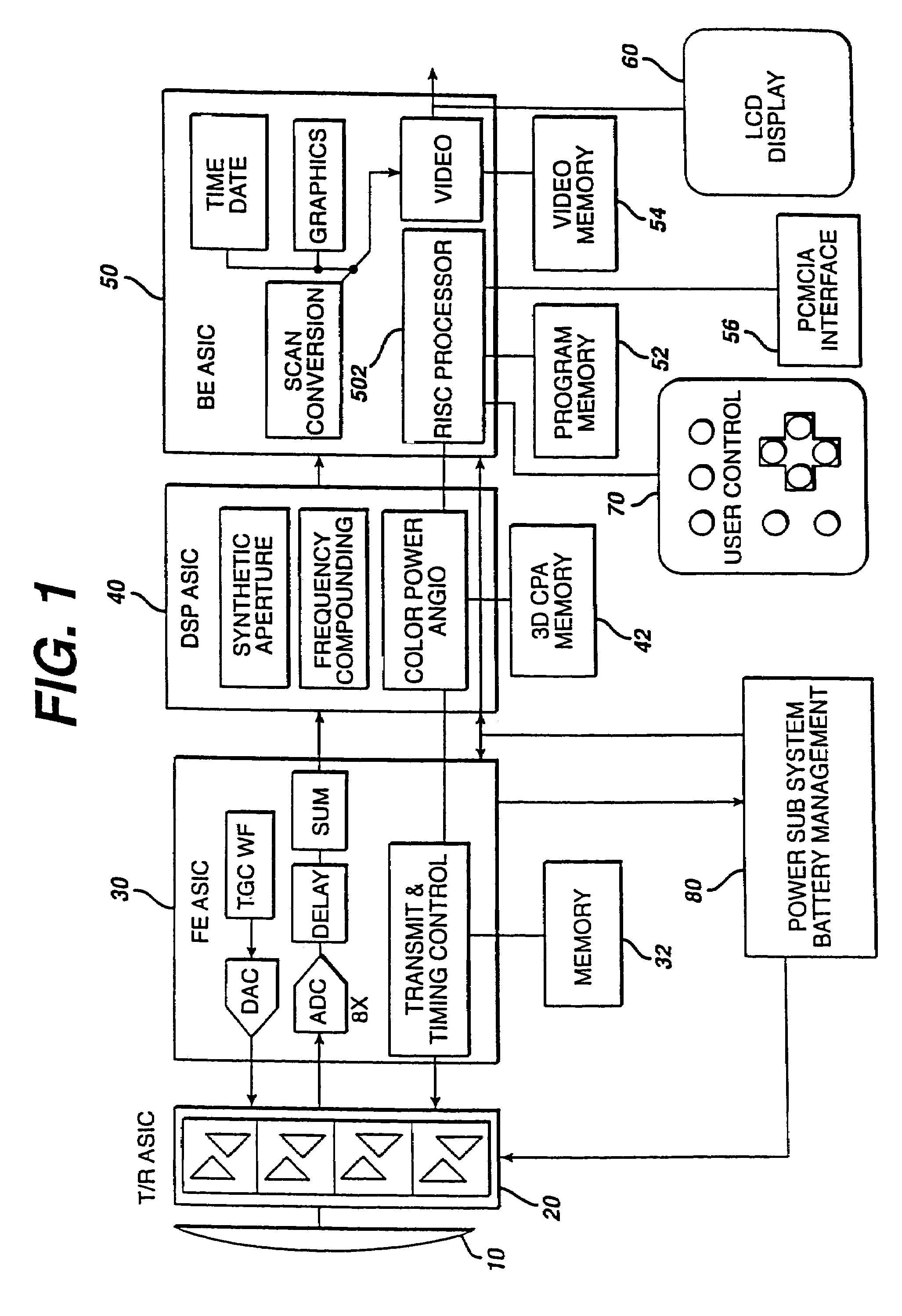
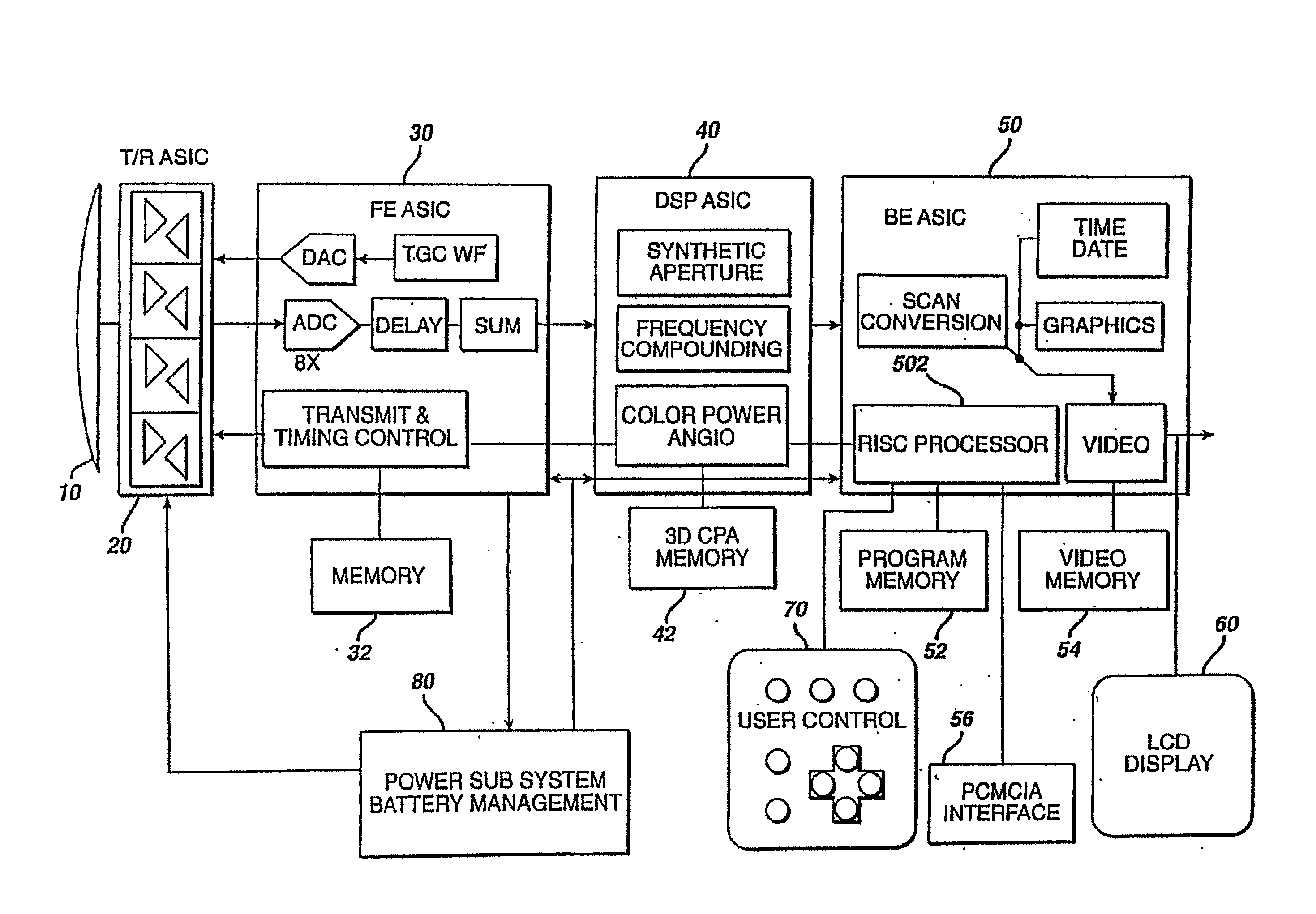
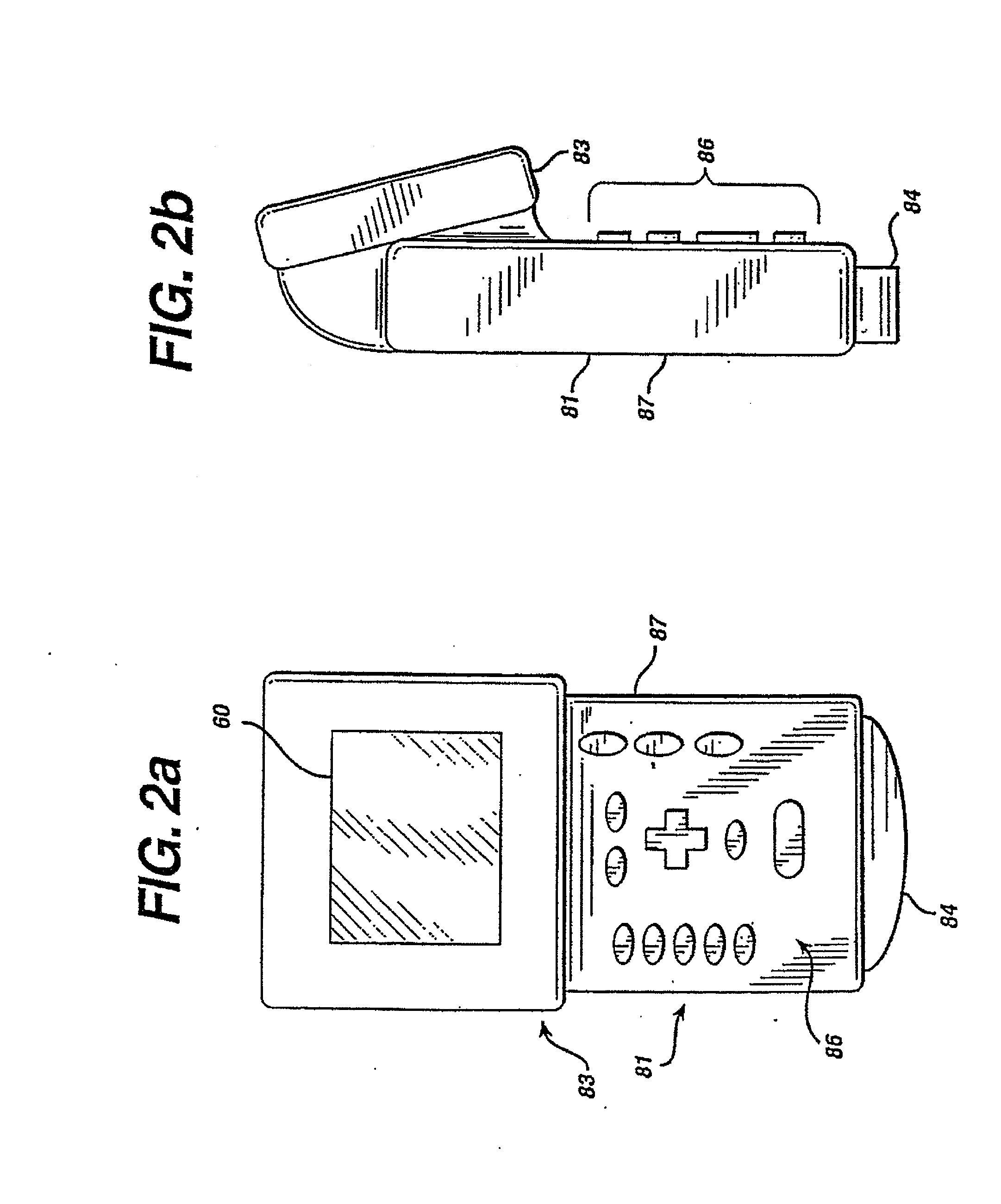
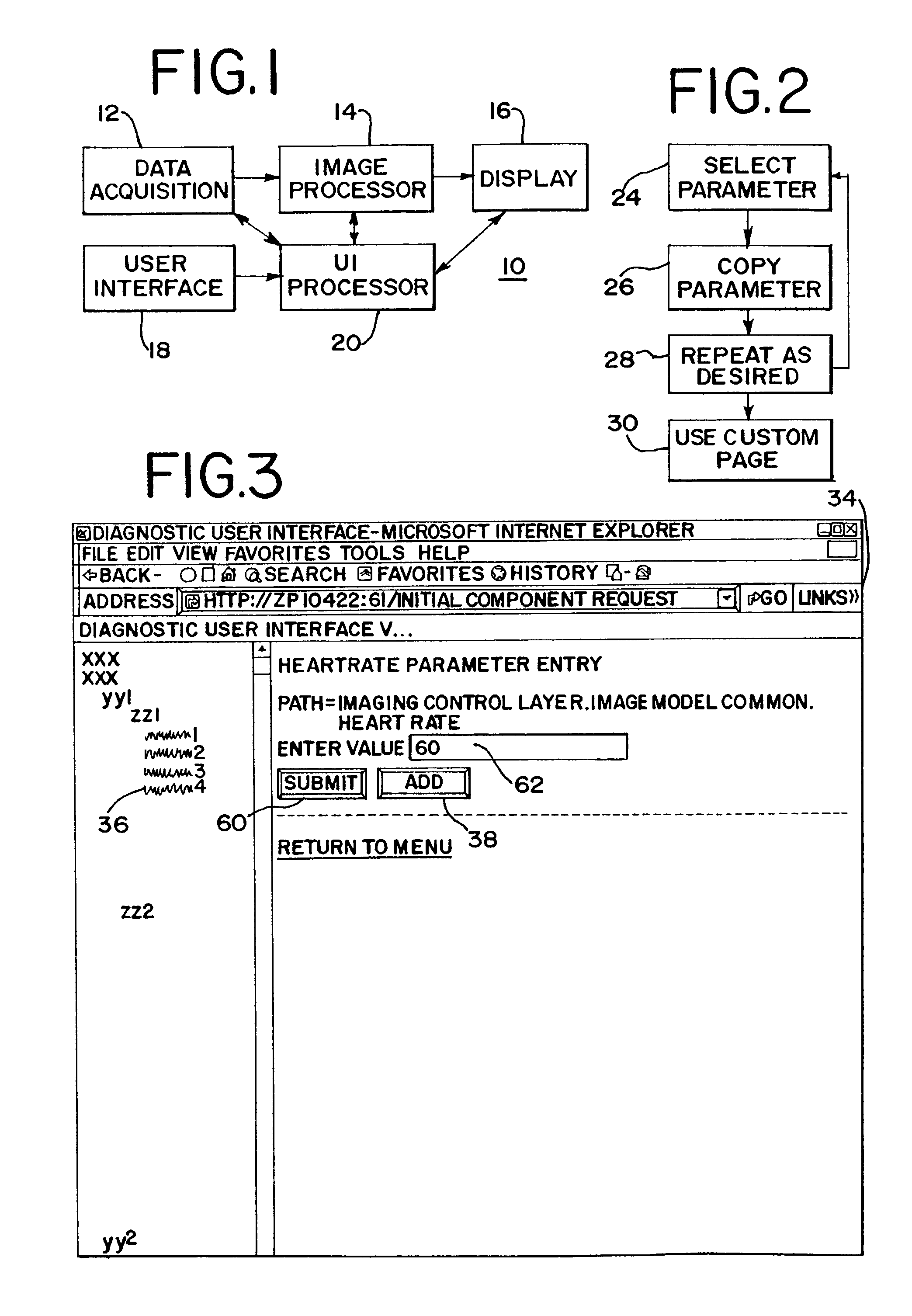
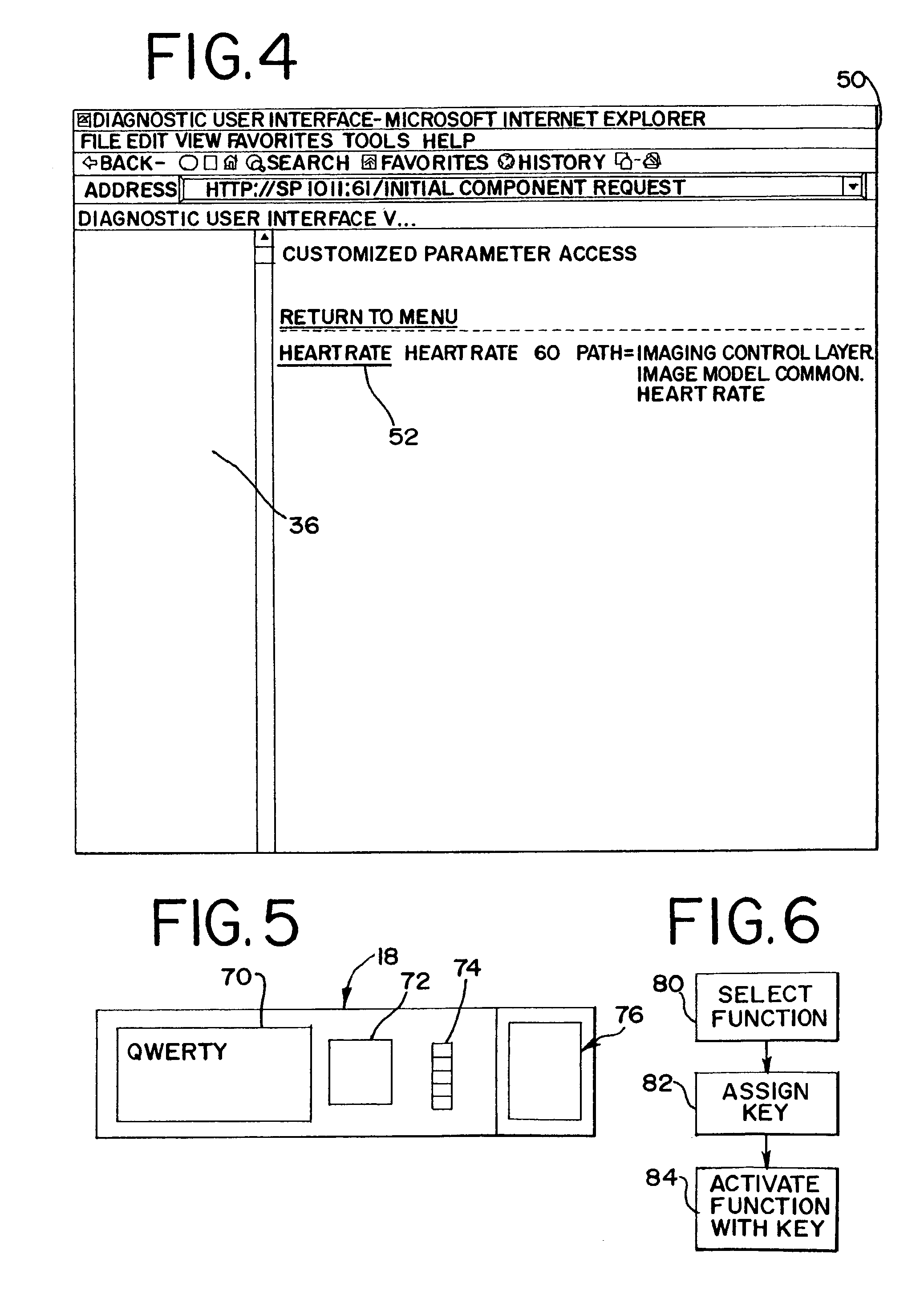
Medical imaging programmable custom user interface system and method
ActiveUS7904824B2Maximize easeImprove user efficiencyLocal control/monitoringCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceDoppler imaging
Methods and systems for a user to create a custom menu for medical imaging are provided. To maximize the ease of use and increase user efficiency, the user interface is tailored to a particular user or for a certain application. The user selects from various imaging parameters in a preprogrammed user interface displayed on a monitor or other display device. The selection is by collecting the desired items or by discarding undesired items. After selection, the desired items are displayed in a customized display state. This customized display state can be labeled and stored for later use. An assignable key is also provided. Imaging functions, such as a type of B-mode or Doppler imaging, are assigned to the key. Different or new functions may be later assigned to the key as the most used imaging functions change. Any customization may be different for different users of the same system, such as by saving the customization related to a log-on procedure.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
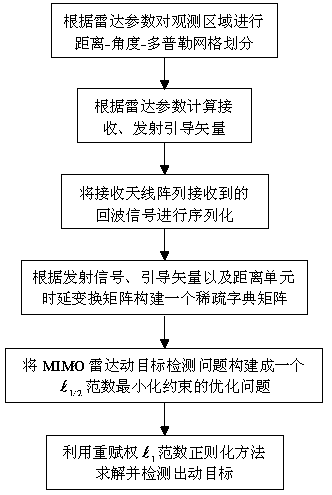
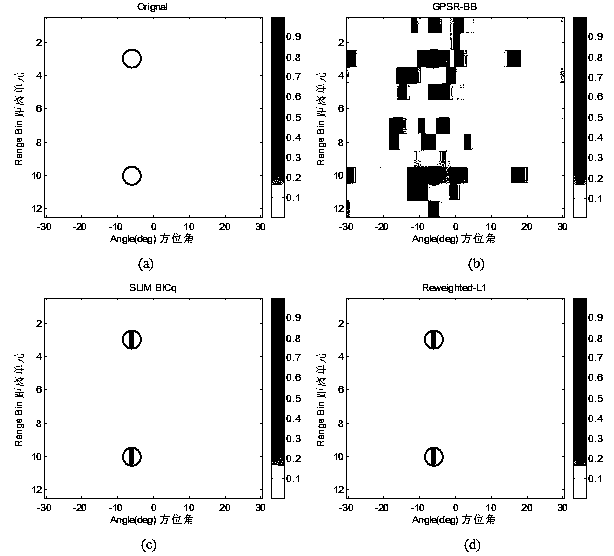
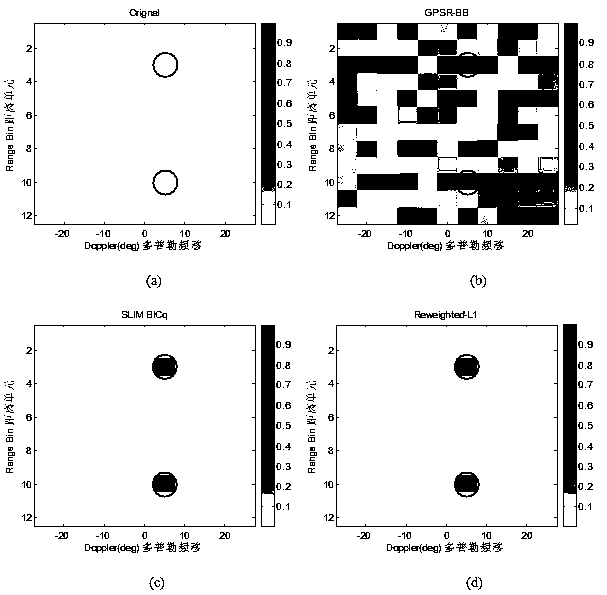
Non-convex optimization based MIMO radar moving object detection method
InactiveCN103744076AAccurate moving target detection resultsHigh resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar observationsImage resolution
The invention discloses a non-convex optimization based MIMO radar moving object detection method. The method comprises the following steps: according to radar parameters, performing distance-angle-Doppler grid dividing on an observation area; according to radar emission, the position of a receiving array, and radar observation area parameters, calculating emission and reception guiding vectors; according to emission signal waveforms, the guiding vectors and a distance unit time delay transformation matrix, constructing a sparse dictionary matrix; performing serialization on echo signals received by an antenna array; and according to an aforementioned model, constructing MIMO radar moving object detection to be an optimization problem of an L[1 / 2] norm minimizing constraint; and using a heavy weight determining L[1] norm regularization method to solve the optimization problem, obtaining distance-angle-Doppler imaging of a MIMO radar moving object, and detecting a moving object in the observation area. By using the method provided by the invention, a moving object detection result more accurate than a result by use of a convex optimization algorithm can be obtained, and the detection result is higher in resolution.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Simulation method of bistatic synthetic aperture radar sea wave direction spectrum
InactiveCN101697011AImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSea wavesWave parameter
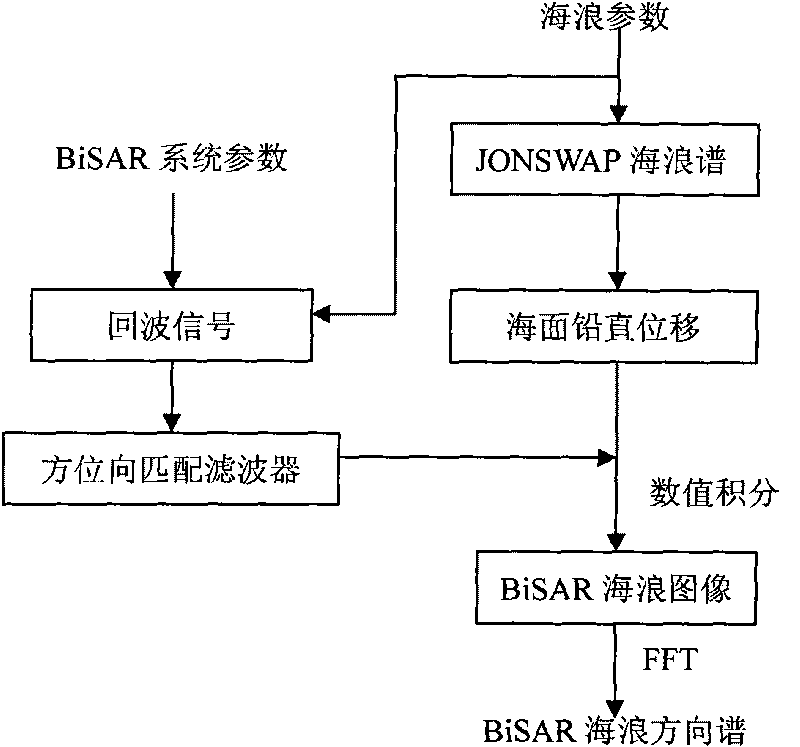
The invention discloses a simulation method of a bistatic synthetic aperture radar sea wave direction spectrum, which comprises the following steps of calculating a JONSWAP sea wave spectrum and a sea wave vertical displacement according to sea wave parameters; obtaining BiSAR echo signals comprising sea wave orbital velocity and accelerated velocity according to a radar wave modulation principle and BiSAR system parameters; carrying the matched filtering on the echo signals according to a BiSAR distance and Doppler imaging algorithm to obtain an analysis formula of a BiSAR sea wave image; working out the BiSAR sea wave image by adopting a numerical integration method; and at last, carrying out two-dimensional FFT operation on the BiSAR sea wave image to obtain the BiSAR sea wave direction spectrum. The BiSAR sea wave image can be worked out by adopting the numerical integration method without producing the echo signals and processing the image in a time domain, therefore, the invention has higher operation efficiency.
Owner:西安华瑞恒泰信息技术有限公司
Using Pulsed-Wave Ultrasonography For Determining an Aliasing-Free Radial Velocity Spectrum of Matter Moving in a Region
InactiveUS20080210016A1Readily implementableReadily integratableBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsPulse sequenceSolid matter
Using pulsed-wave (PW) ultrasonography for determining an aliasing-free radial velocity spectrum of matter moving in a region. Includes: transmitting into the region a plurality of pulse trains of sound waves at two or more different pulse repetition frequencies; spectrally analyzing each pulse train, for evaluating a Doppler frequency spectrum associated with each pulse train; combining frequency components of Doppler frequency spectrum of each pulse train, for obtaining aliasing-free instantaneous Doppler frequency spectrum for the region; using Doppler effect for translating aliasing-free frequency spectrum to aliasing-free radial velocity spectrum. Implementable using pulsed-wave Doppler (PWD), color flow Doppler (CFD), tissue Doppler imaging (TDI), or pulsed-wave (PW) ultrasonography. Applicable to liquid or / and solid forms of matter, moving in a two- or three-dimensional region. Matter is any substance or material, composed of organics or / and inorganics, which is part of a non-living object, or, part of a human or animal subject.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Synthesis method and device for digitalization ultrasonic beam with adjustable receiver aperture
ActiveCN101209211AChange the maximum number of aperturesBlood flow measurement devicesAcoustic wave reradiationSonificationUltrasonic beam
The invention discloses an adjustable receiving aperture digital ultrasonic beam synthesis method and a device, which relates to the medical ultrasonic field; the invention supports the synthesis of a single or a plurality of ultrasonic beam synthesis, can be combined with the different application occasions, and can change the maximum number of the receiving aperture and the position of the receiving aperture on a probe flexibly. When in observation of a static tissue structure, a transmitter scans the same physical position twice, and the number of the receiving aperture at the moment is twice the number of the physical channels, which can significantly improve the image quality. When in observation of a high-speed moving tissue or in Doppler imaging of the blood flow, the transmitter scans the same physical position once only, the center of the receiving aperture is near a emission line or coincided with the emission line, and the frame rate at the moment can be doubled. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that: the invention applies the single ultrasonic beam or multiple ultrasonic beams to support and receive the ultrasonic echo of the receiving aperture at an arbitrary position. The invention can also change the maximum number of the aperture and leads the center of the aperture to be near or coincided with the emission line; the results of ultrasonic beam synthesis can still be obtained without the synthesis of the aperture, and the frame rate under the same scanning depth can be doubled as the earlier applied patent.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
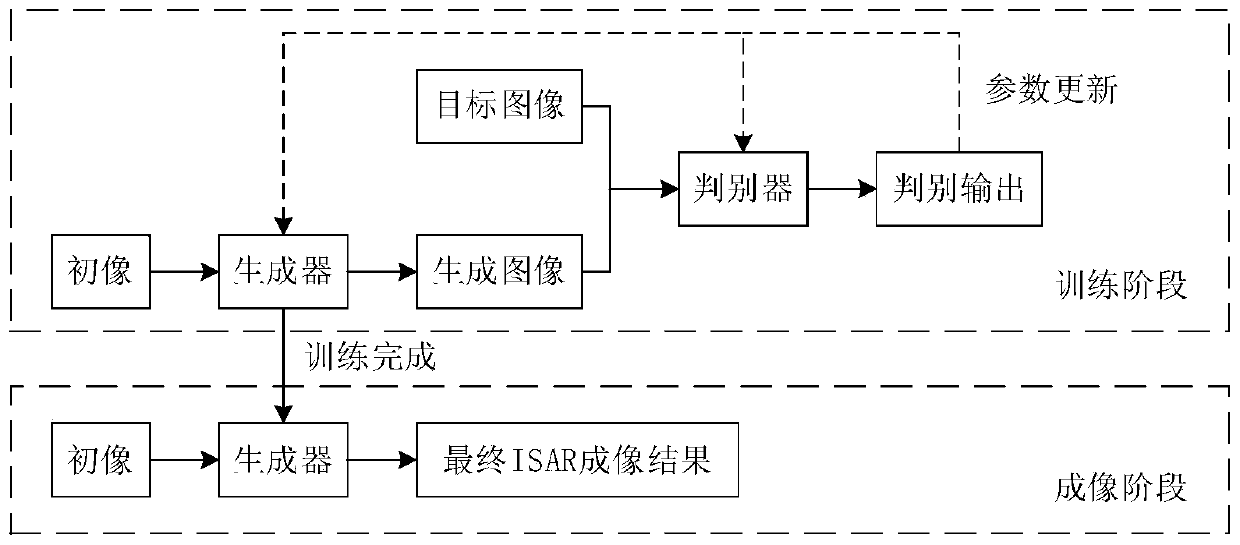
Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on generative adversarial network
ActiveCN111077523AReduce lossesAvoid vanishing gradientsNeural learning methodsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionSynthetic aperture radar
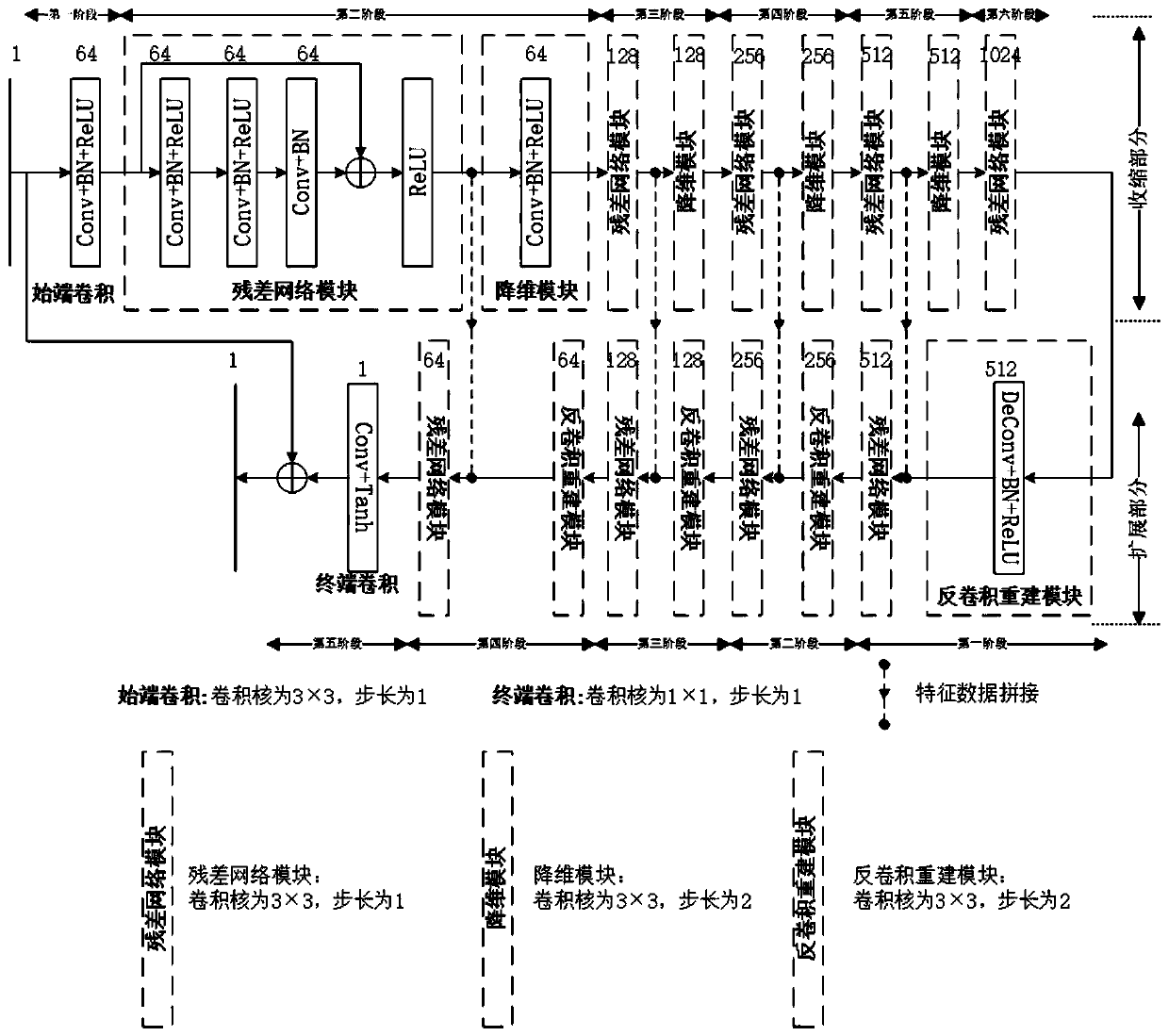
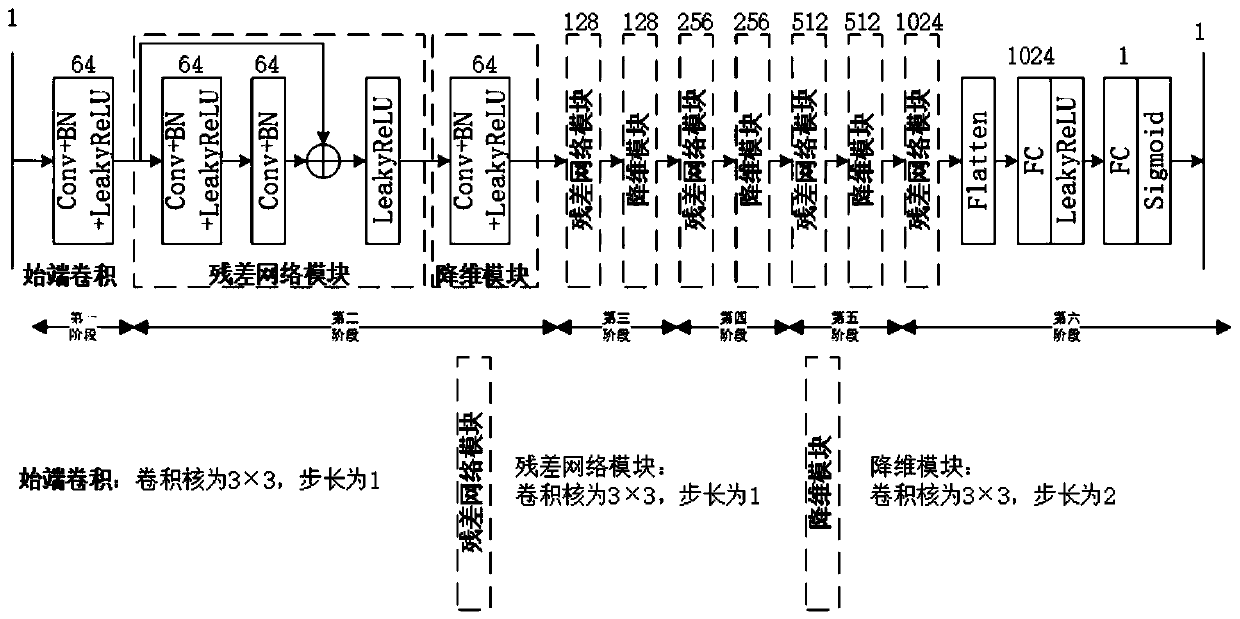
The invention discloses an inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on a generative adversarial network. A generative adversarial network (GAN) is composed of a generator network and a discriminator network. The generator network uses a convolution layer and a residual network module to extract feature representation and maintain low-dimensional feature information, and uses a deconvolution layer to reconstruct an ISAR target image. And the discriminator network extracts feature information from an ISAR image output by the generator network by using the convolutional layer, thereby realizing authenticity discrimination of the ISAR image. And at the network training stage, all layers of parameters of the generator network and the discriminator network are updated by using the training error output by the discriminator network. And the trained generator network is separated from the GAN and is used for under-sampling ISAR data imaging. At the imaging stage, a low-quality target image obtained by under-sampling ISAR target echo data through a distance-Doppler RD method is input into the generator network, and correspondingly, a high-quality ISAR target image is output. The imaging quality and the calculation efficiency of the method are superior to those of a traditional distance Doppler imaging method and a compressed sensing imaging result.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Combined B-mode / tissue doppler approach for improved cardiac motion estimation in echocardiographic images
ActiveUS9629615B1Promote resultsImprove smoothnessImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationMotion field
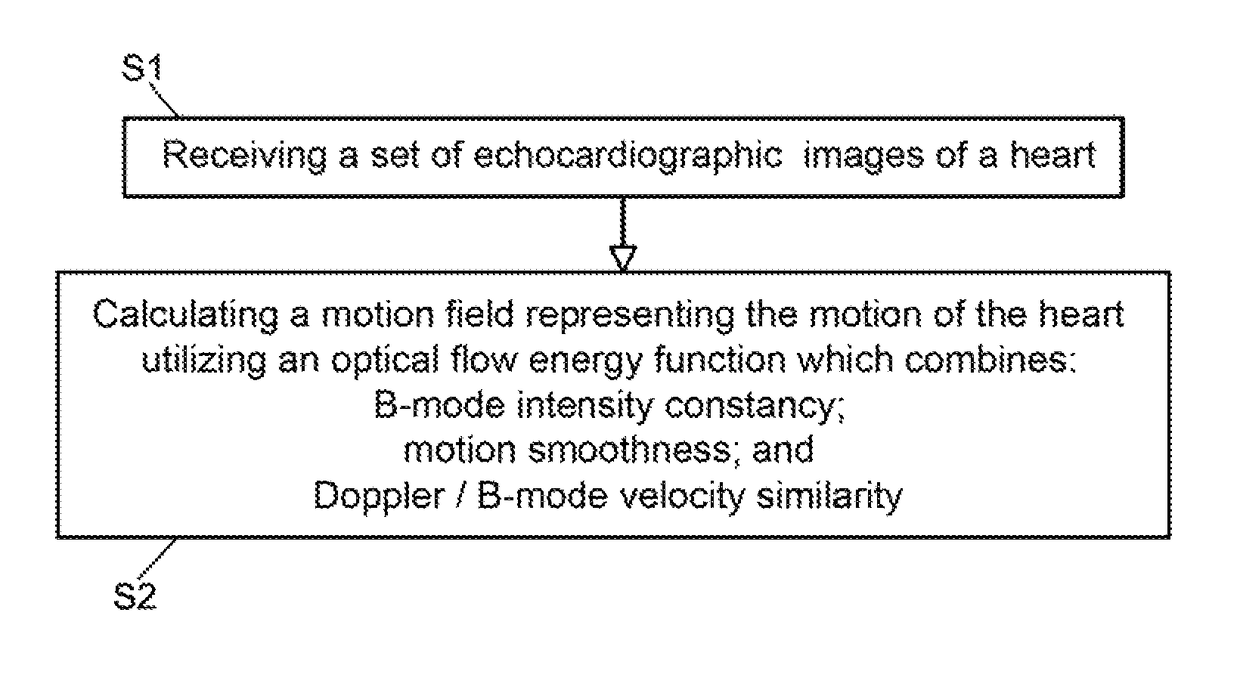
A method for cardiac motion estimation includes: receiving a set of echocardiographic images of a heart, the echocardiographic images including B-mode ultrasonic images and Tissue Doppler Imaging (TDI) images; and calculating, by the image processing machine, a motion field representing the motion of the heart using the B-mode ultrasonic images and applying a velocity constraint from the TDI images. A system for cardiac motion estimation, includes: an imaging device configured to acquire a set of echocardiographic images of a heart, the echocardiographic images including B-mode ultrasonic images and TDI images; a data storage device in communication with the imaging device and configured to store the set of echocardiographic images; an image processing machine in communication with the data storage device and configured to calculate a motion field representing the motion of the heart using the B-mode ultrasonic images and applying a velocity constraint from the TDI images.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
High-precision moving target imaging and recognition method based on multi-target tracking
ActiveCN108957453AResolve offsetRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti target trackingMotion parameter
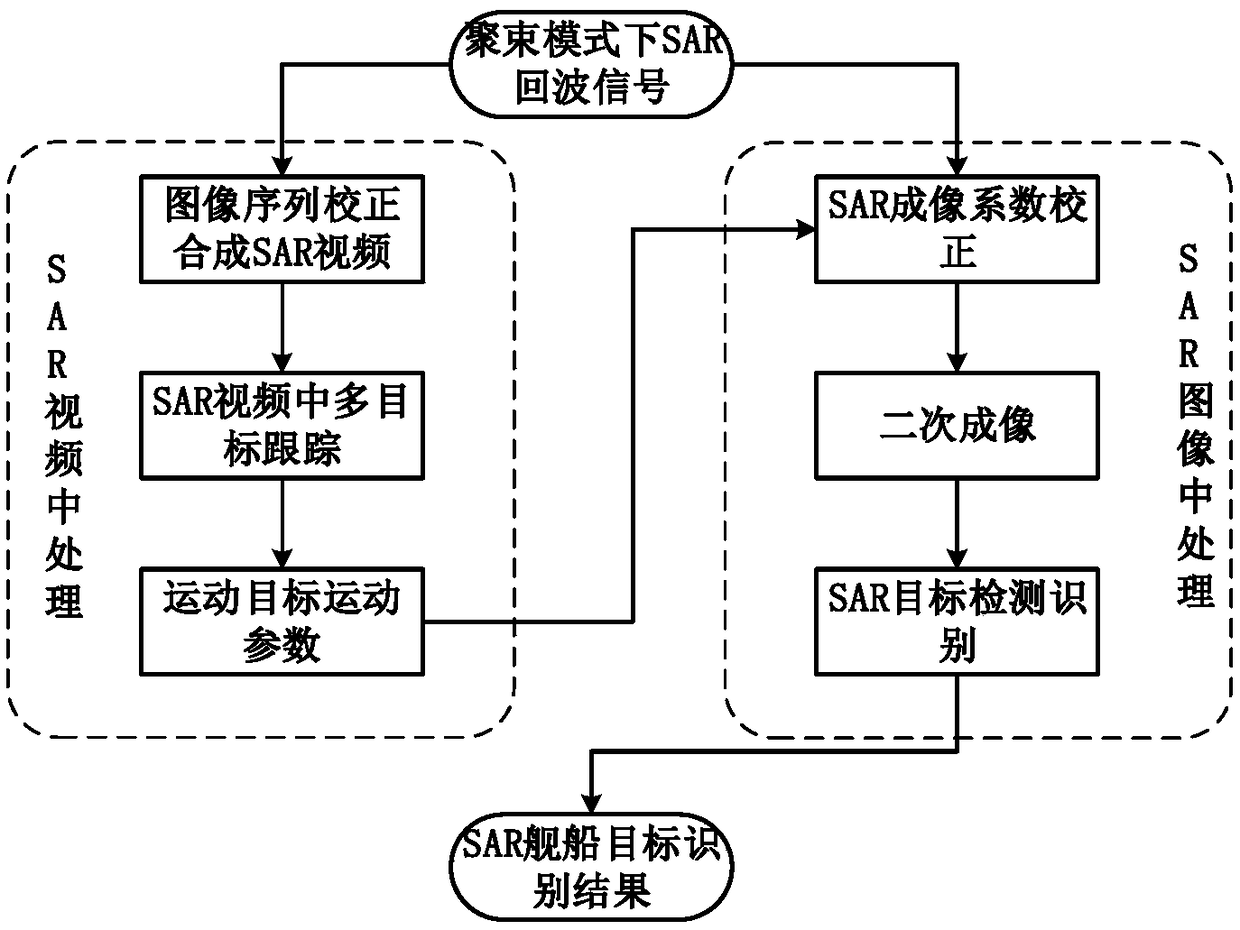
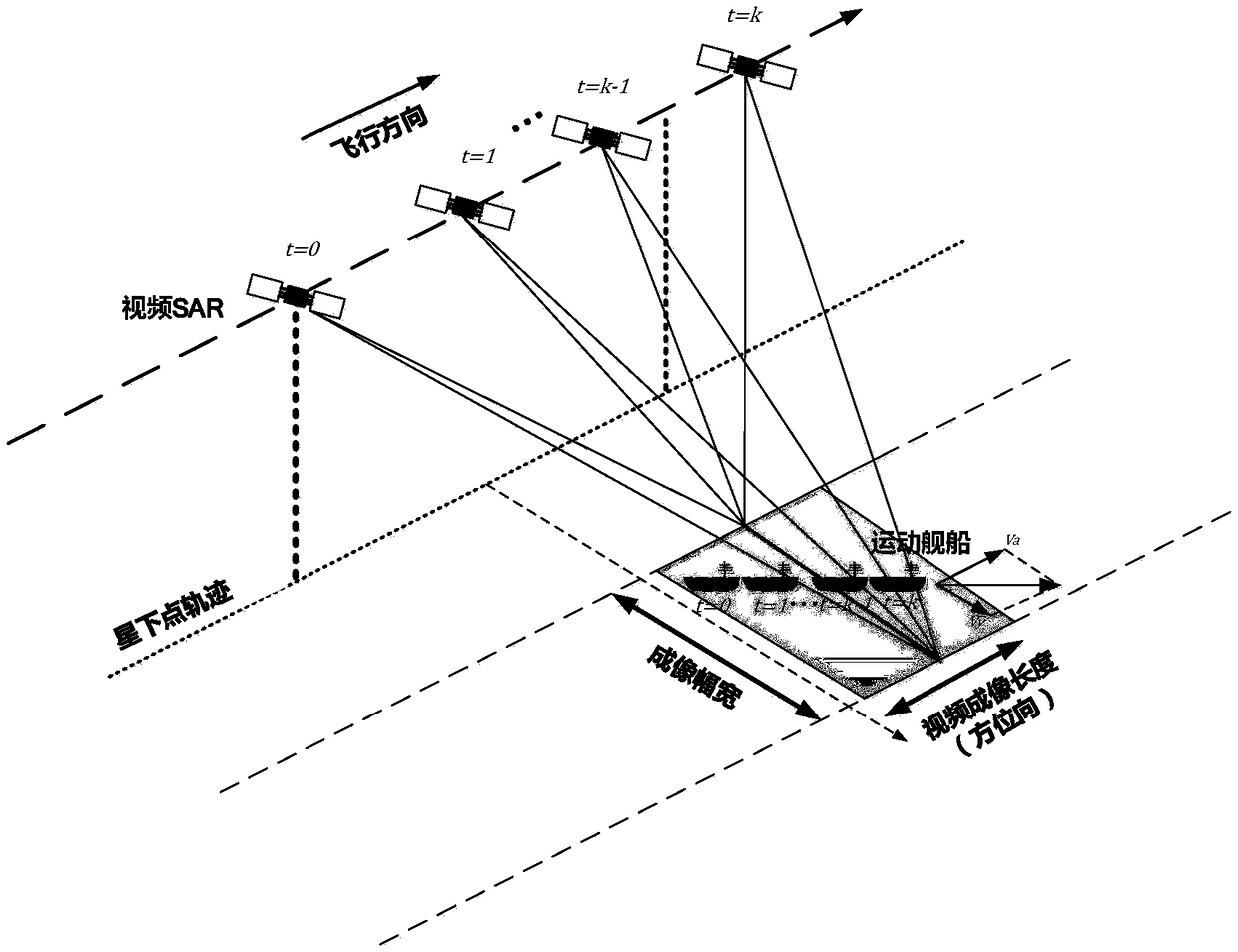
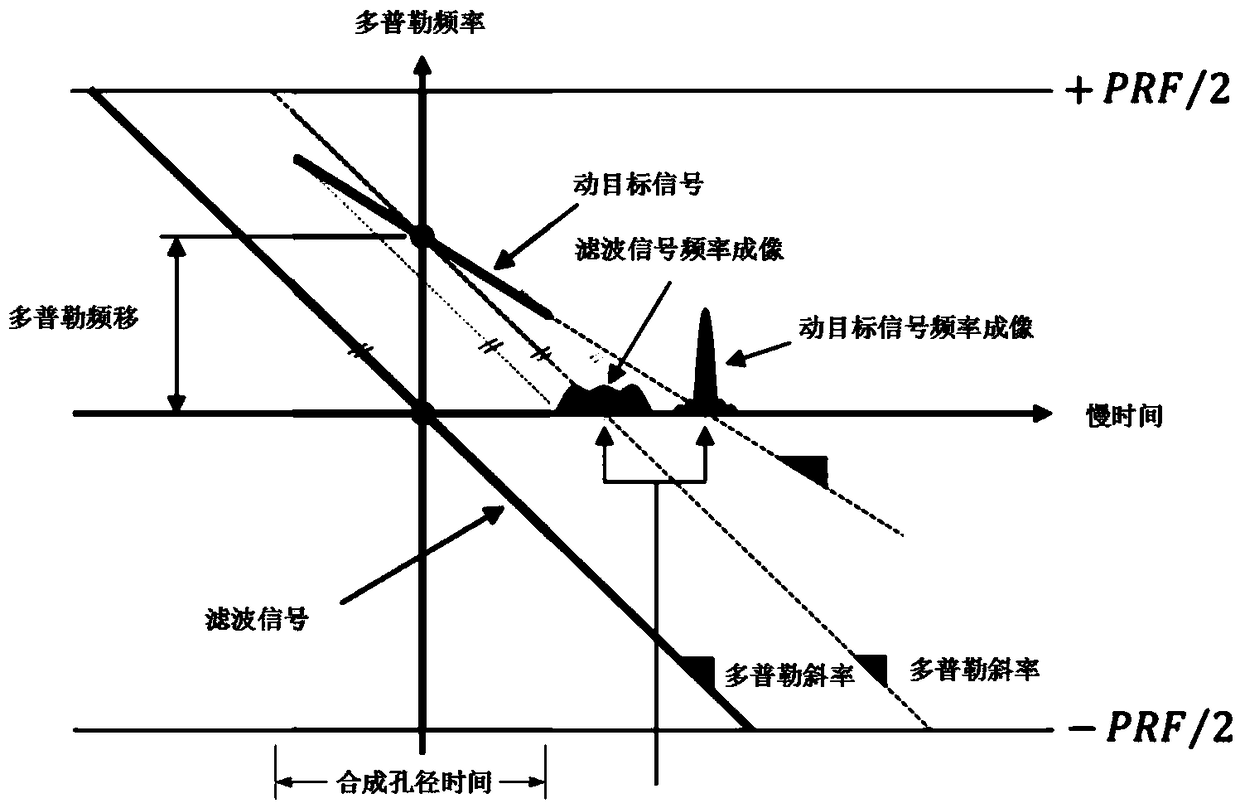
The invention discloses a high-precision moving target imaging and recognition method based on target tracking. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a SAR video by an SAR platform working in a bunching mode; using the Probability Hypothesis Density multi-target tracking method to perform tracking, and estimating motion parameters of moving targets; using the acquired motion parameters of the moving targets to correct a Doppler imaging coefficient, and acquiring SAR images that are accurately imaged after defocusing and displacement; and detecting and recognizing the moving targets in the acquired accurate SAR images. The technical effects of the method are that the motion parameters of the moving targets in the SAR video can be acquired through the multi-target tracking method in the video, the Doppler imaging coefficient and the problems of defocusing and offsetting in the images are corrected according to the acquired motion parameters of the moving targets so as to obtain high-precision images; and a support is provided for high-precision recognition.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Method for tracking features of ultrasound pattern and system thereof
ActiveCN101926657AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesColor dopplerDoppler velocity
The invention discloses a method for tracking features of an ultrasound pattern and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: setting an initial region of features of interest; calculating the regional gray-scale similarity to obtain a regional gray-scale similarity parameter; reading Doppler velocity information in the region of features of interest, and establishing a constraint condition; and constructing a similarity measurement by combining the regional gray-scale similarity parameter and the constraint condition, and calculating the extreme value of the similarity measurement to obtain the position of a tracked track point. By combining the features of color Doppler tissue imaging, the invention effectively improves the accuracy and the robustness of tracking of the region of features.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Ultrasonic color Doppler image post-processing method
ActiveCN105590315AShorten speedOutliers that reduce varianceImage enhancementImage analysisColor dopplerProcess module
The invention provides an ultrasonic color Doppler image post-processing method, which comprises the following steps of 1) setting a blood parameter estimation module in an ultrasonic color Doppler imaging system; 2) correspondingly receiving a blood flow variance signal and a blood flow velocity signal by a blood flow signal processing module; 3) setting a parameter pre-processing module in the ultrasonic color Doppler imaging system; 4) comparing and judging whether a signal is a blood flow signal or not by the parameter pre-processing module; 5) setting a spatial processing module for processing an image. Based on the above method, the generation of anomalous points is lowered maximally.
Owner:南京云石医疗科技有限公司
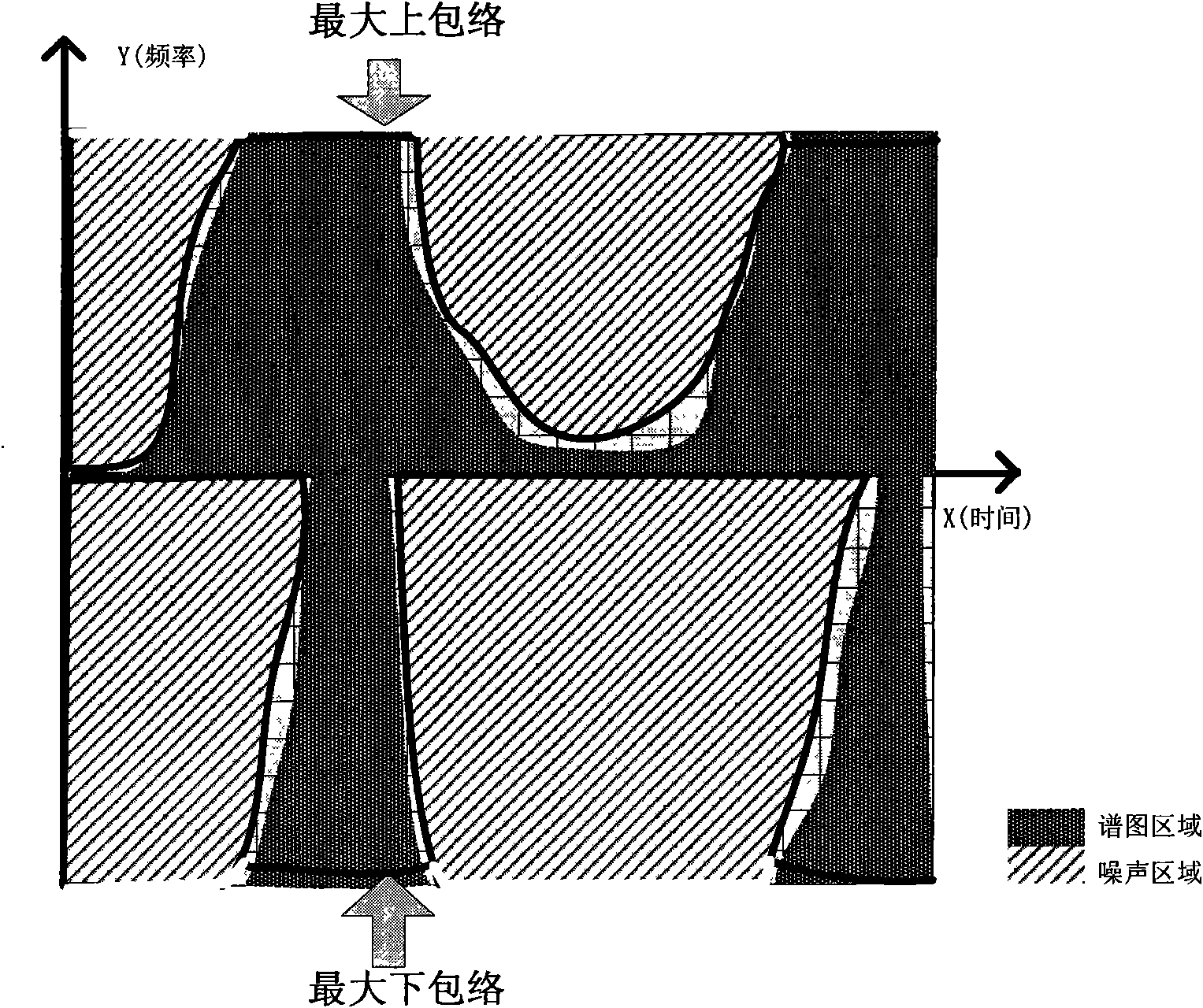
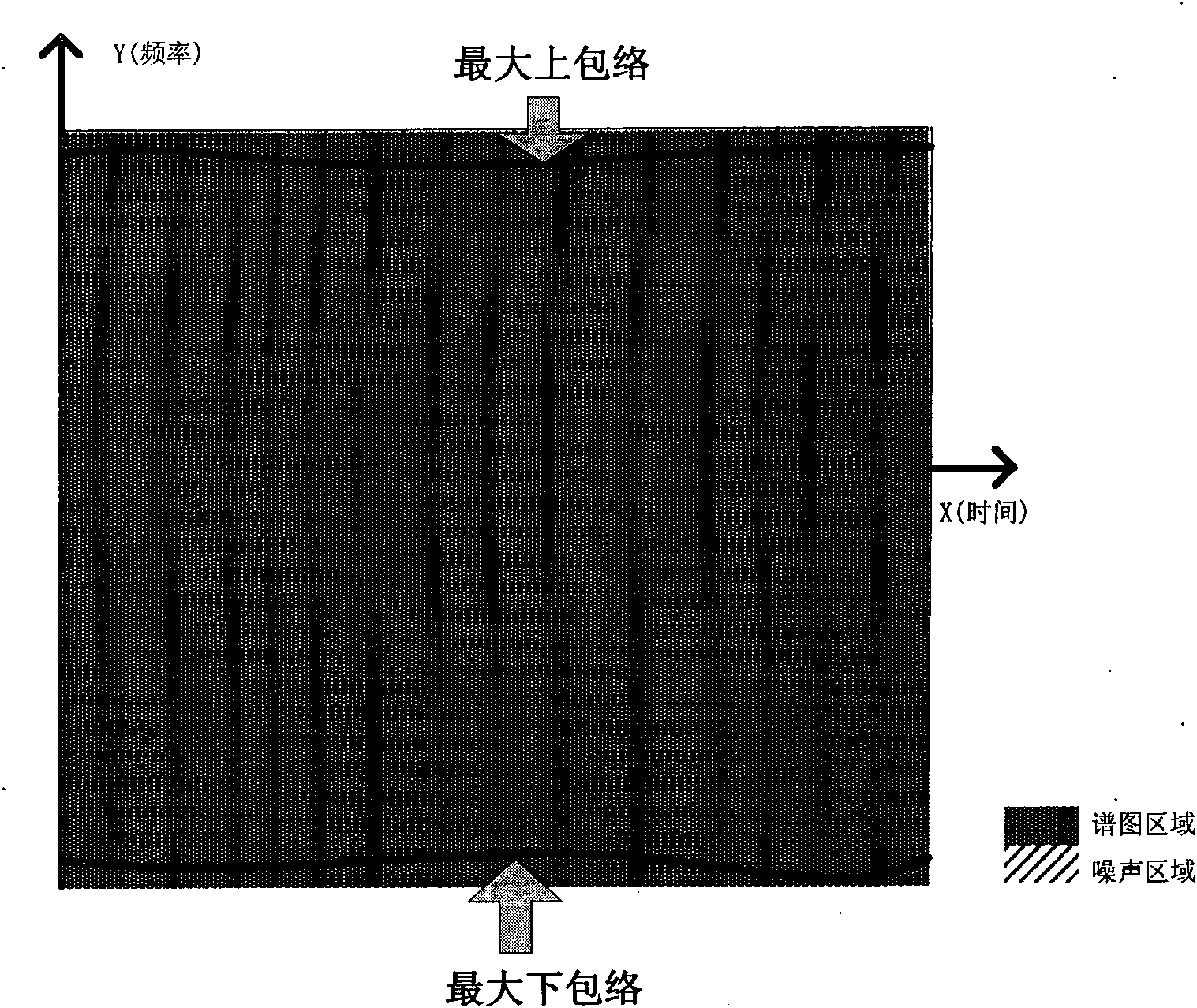
Automatic aliasing judgment and Doppler imaging adjusting method and ultrasonic system thereof
ActiveCN101897596AImprove accuracyAvoid misjudgmentBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsVeinDoppler imaging
The invention discloses an automatic aliasing judgment and Doppler imaging adjusting method and an ultrasonic system thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a Doppler spectrogram; comparing strong and weak parameters of the whole field signals of the spectrogram with a threshold value and judging whether the spectrogram performs vein aliasing for multiple times or not; according to the characteristics of the spectrogram area signals, judging whether the spectrogram performs artery aliasing for multiple times or not; and if the vein aliasing judgment result and the artery aliasing judgment result perform aliasing for multiple times, judging that the Doppler spectrogram does not perform aliasing for multiple times. In the method, the influence of spectrogram forms on the judgment is taken into full consideration, so the aliasing judgment of a vein spectrogram is added, the probability of erroneous judgment is reduced, and the accuracy of the aliasing judgment is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
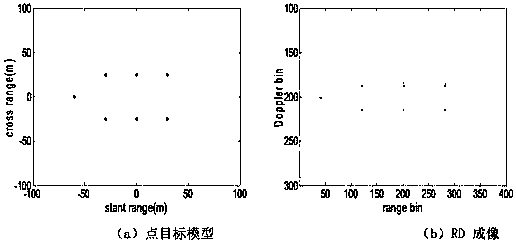
Ship target ISAR imaging method based on fractional Fourier transform
ActiveCN108107430AAccurate estimateEliminate couplingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime delaysFourier transform on finite groups
The invention provides a ship target ISAR imaging method based on fractional Fourier transform. The ship target ISAR imaging method comprises the steps of: acquiring a radar echo signal of a scattering point of a ship target in each distance unit; modeling the acquired radar echo signals in the distance units into multi-component secondary frequency modulation signals through pulse compression andmotion compensation; determining estimated parameters of scattering point echo signals in the distance units according to the secondary frequency modulation signals; updating radar echo signals in the distance units by adopting the estimated parameters of the scattering point echo signals in the distance units; and acquiring an ISAR image of a ship target by utilizing the updated radar echo signals. The ship target ISAR imaging method adopts a symmetrical correlation function, fractional Fourier transform and multi-product processing for the radar echo signals in sequence, avoids the couplingof time and time delay, estimates a quadratic term phase coefficient and a cubic term phase coefficient with high precision, adopts a range-instantaneous-Doppler imaging technology combining with parameter estimation, and obtains a high-quality and high-precision ISAR image of a moving target.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Estimation and display for vector doppler imaging using plane wave transmissions
ActiveUS9192359B2Simplifies vector velocity computationEasy to operateBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionColor dopplerUltrasonic sensor
Vector Doppler Imaging (VDI) improves on conventional Color Doppler Imaging (CDI) by giving speed and direction of blood flow at each pixel of a display generated by a computing system. Multiple angles of Plane wave transmissions (PWT) via an ultrasound transducer conveniently give projected Doppler measurements over a wide field of view, providing enough angular diversity to identify velocity vectors in a short time window while capturing transitory flow dynamics. A fast, aliasing-resistant velocity vector estimator for PWT is presented, and VDI imaging of a carotid artery with a 5 MHz linear array is shown using a novel synthetic particle flow visualization method.
Owner:VERASONICS
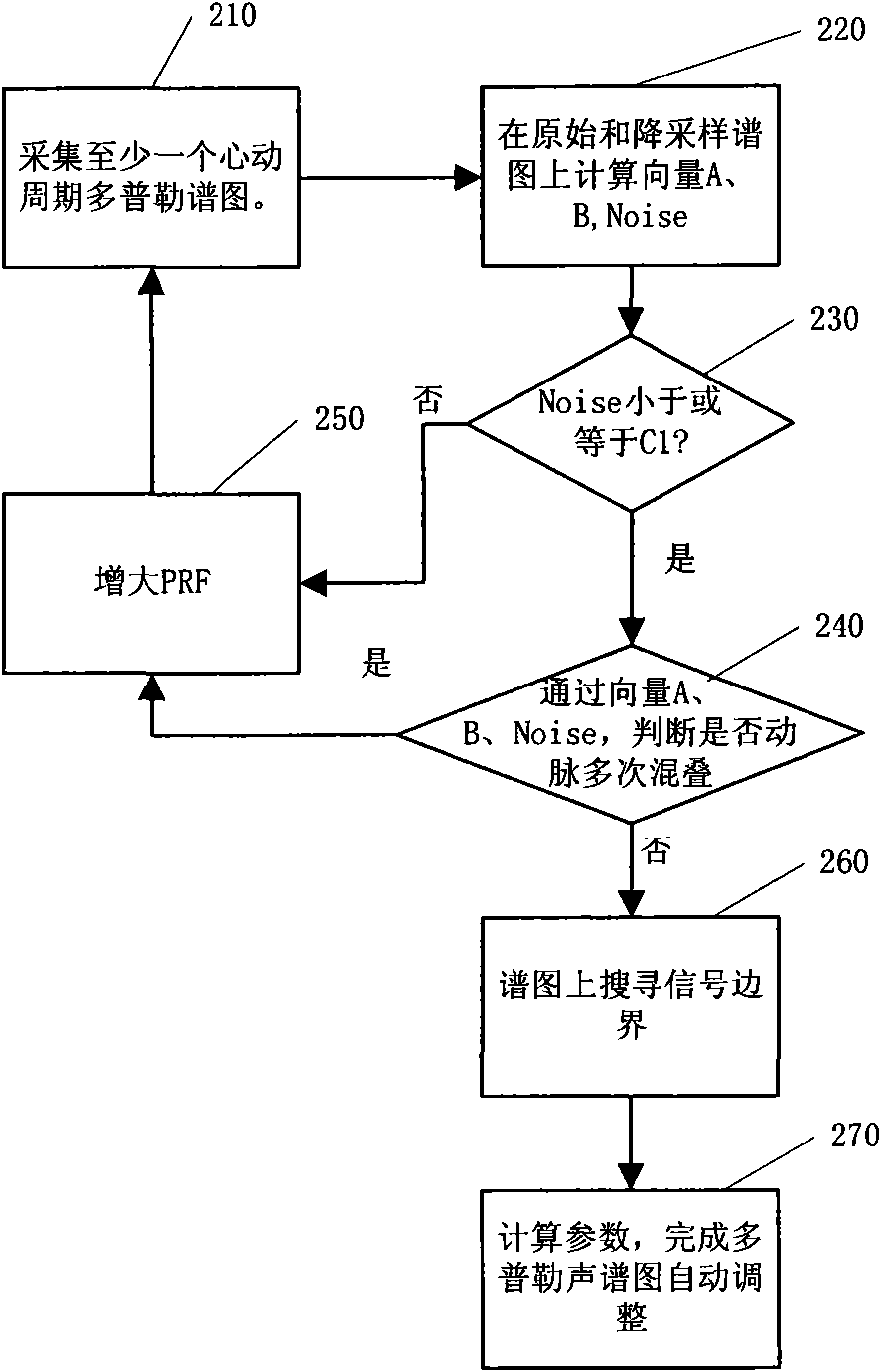
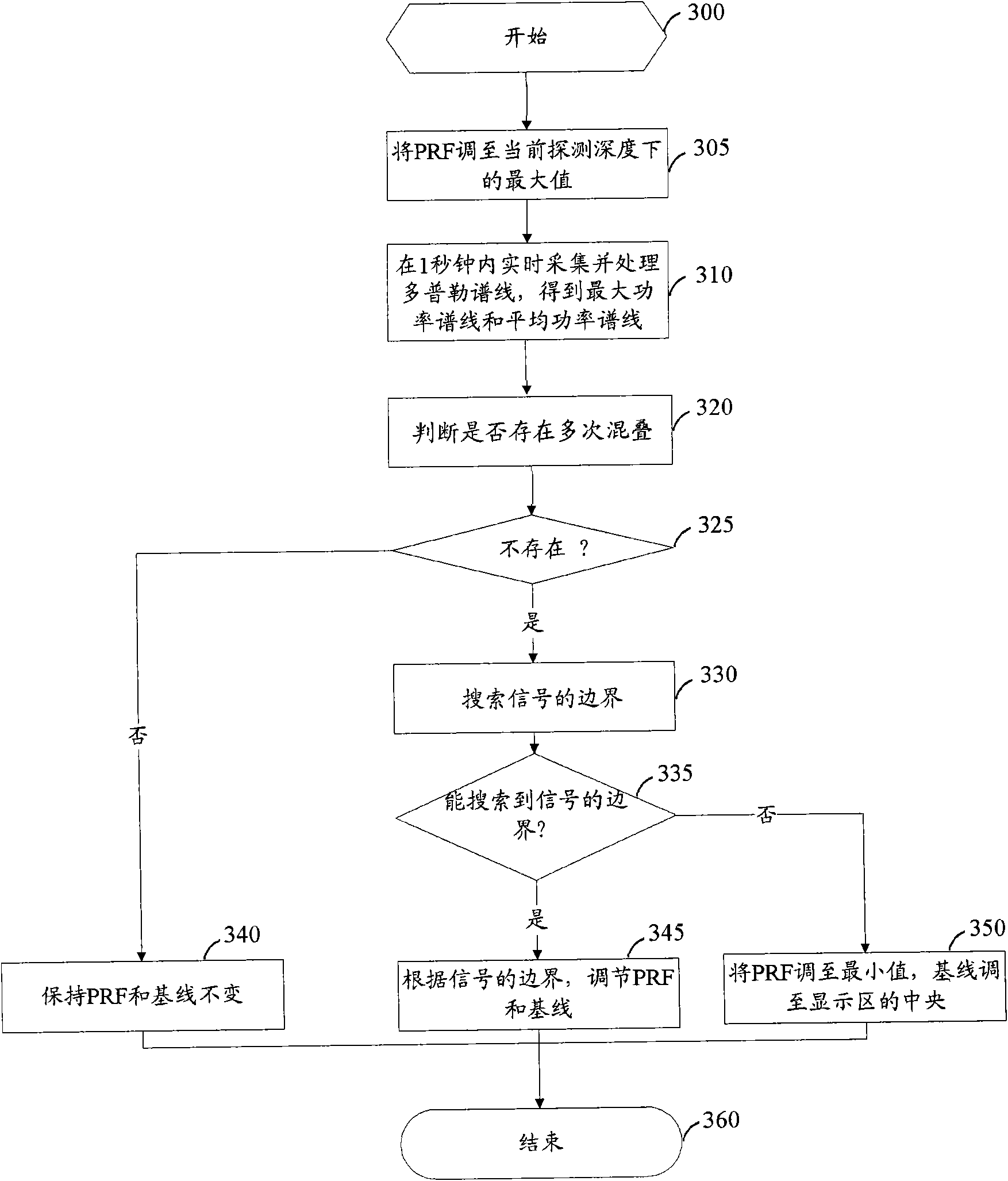
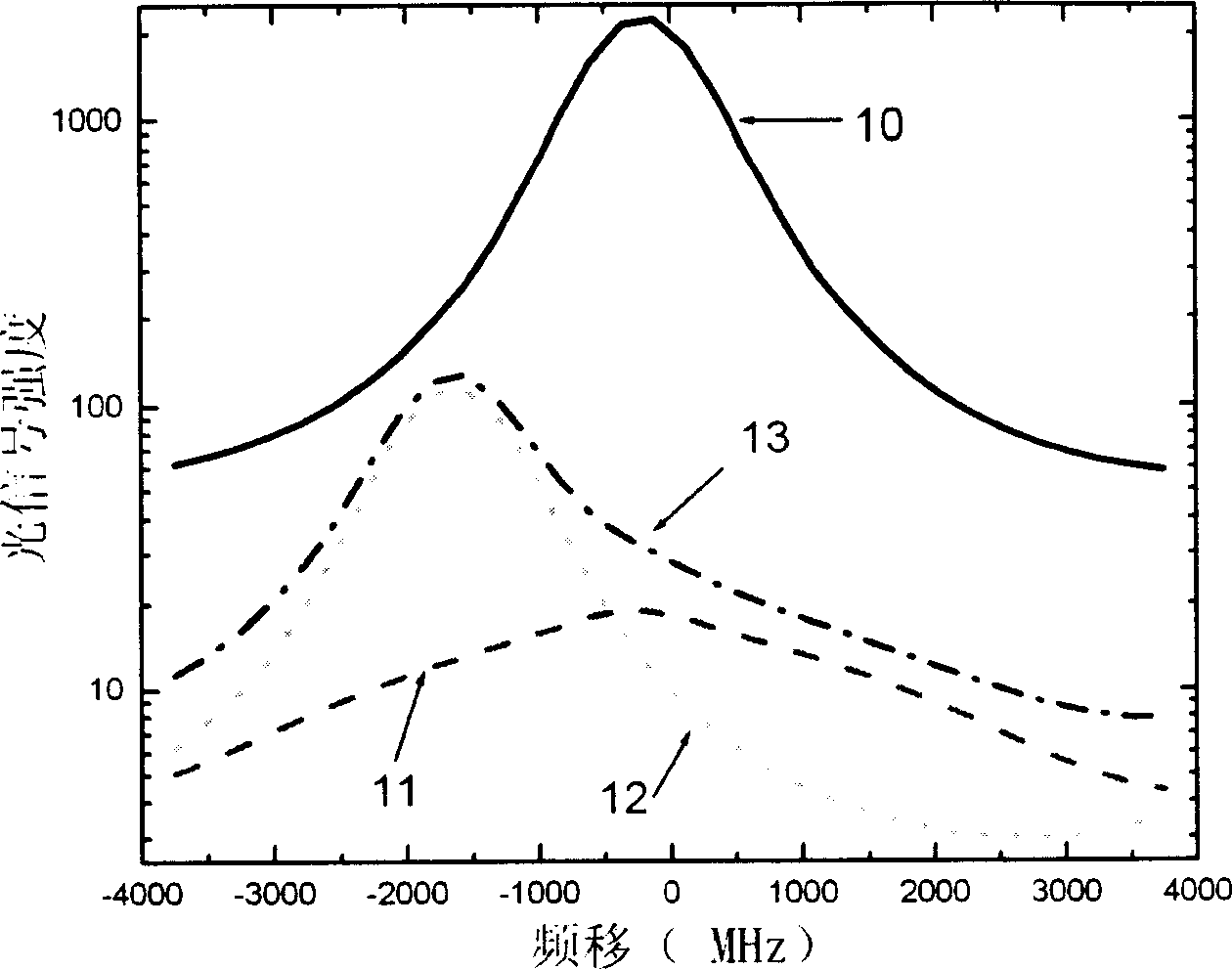
Method and device for automatically optimizing Doppler imaging parameters
ActiveCN101647715ALarge storage capacityAchieve automatic optimizationBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsDoppler imagingComputer vision
The invention provides a method and a device for automatically optimizing Doppler imaging parameters. The method comprises: an acquiring step used for acquiring at least two characteristic spectral lines under a predetermined pulse repetition frequency; a storage step used for storing the at least two characteristic spectral lines; and an optimizing step used for optimizing at least one of the Doppler imaging parameters based on the stored at least two characteristic spectral lines and a predetermined noise average power. In the predetermined time, the acquiring step acquires the at least twocharacteristic spectral lines by acquiring Doppler spectral lines under the predetermined pulse repetition frequency in real time and processing the acquired Doppler spectral lines in real time without storage. Compared with the prior art, the method and the device realize automatic optimization of the Doppler imaging parameters only by storing and processing the two characteristic spectral linesand the predetermined noise average power, thereby having the advantages of few occupied resource, low complexity and good stability.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Laser detecting device for concealed flying object
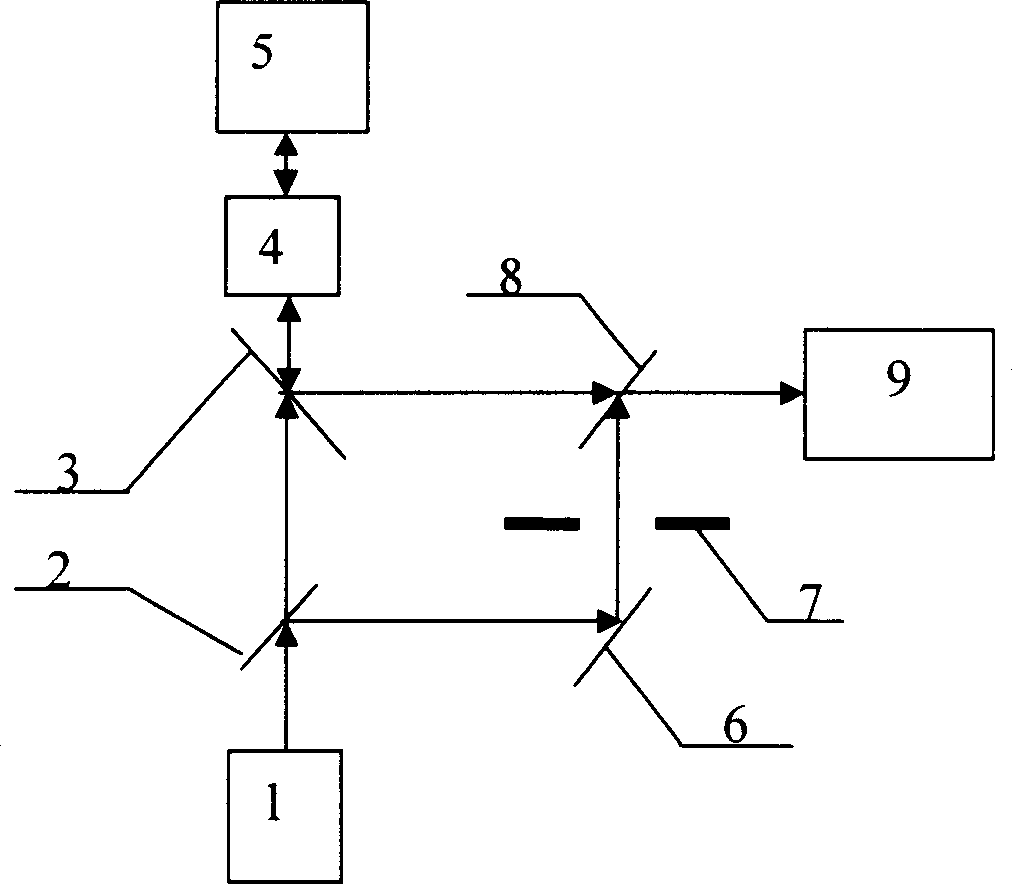
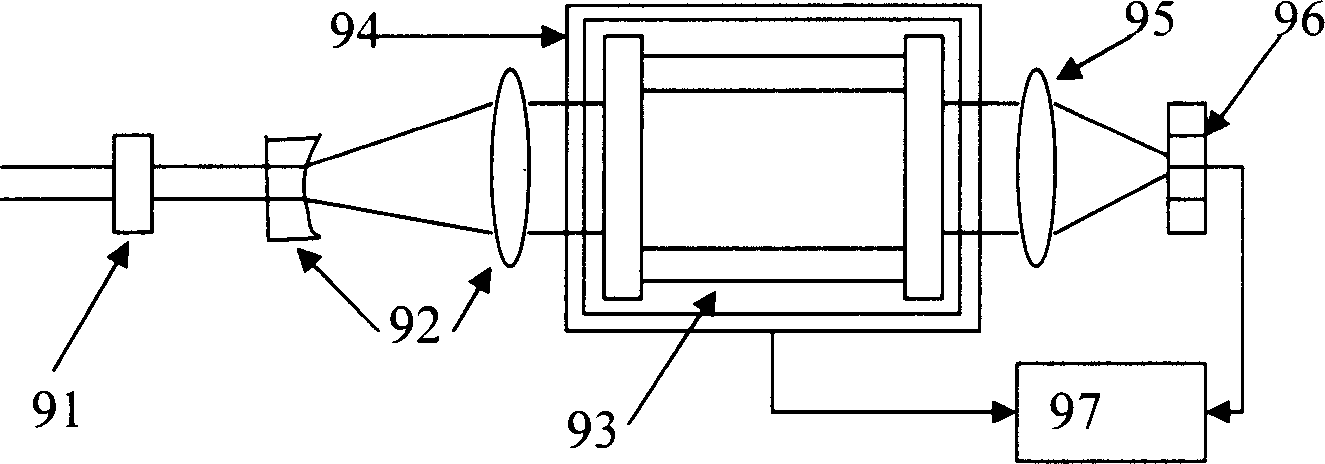
InactiveCN1828332AMake up for the lack of detection abilityImprove anti-electromagnetic interference performanceElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splitterOptical axis
The device comprises: a laser, a first / second spectroscope, a polarization beam-splitter piece, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a telescope, a full-reflection mirror on reflection beam of the first spectroscope, a switch, and an optical Doppler imaging detector on the output light direction of second spectroscope. Wherein, arranging the first spectroscope and beam-splitter piece both as 45Deg, 1 / 4 wave plate and telescope on the OA of output beam of the laser in turn; arranging with 45Deg the second spectroscope on the cross point of switch light path and reflection light path of laser echo of beam-slitter piece. This invention can determine the position, height, velocity and direction.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
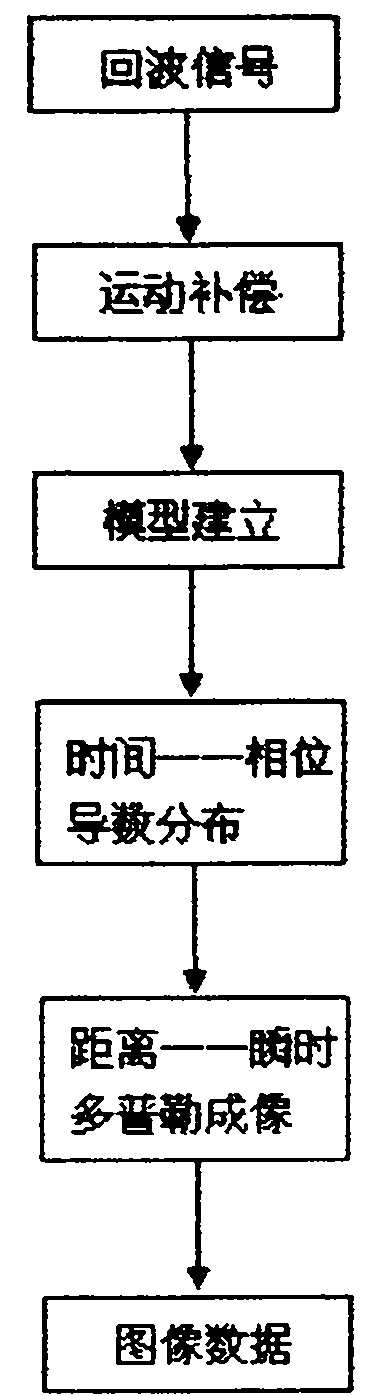
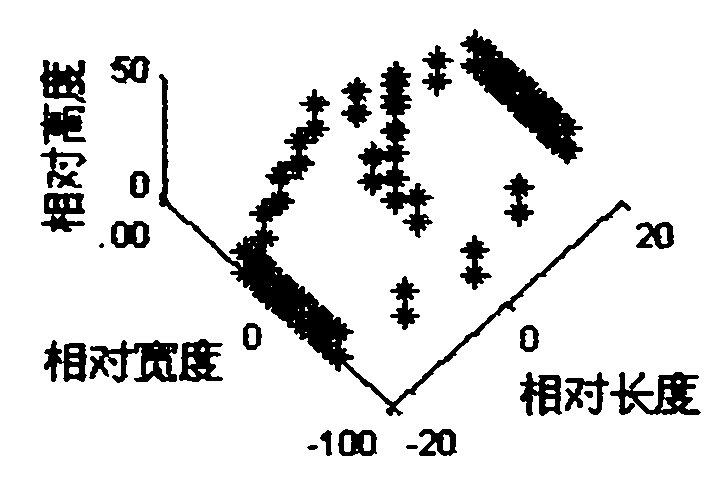
Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on time-phase derivative distribution
InactiveCN102012510AClear goalsReduce computationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionProduct typeObject motion
The invention discloses an inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on time-phase derivative distribution. Under the situation of very complicated object motion, the Doppler frequency of echo signals of scatter points is time-varying, and an image obtained by using a traditional distance-Doppler imaging method is vague at the moment so that an object is difficult to identify. In the invention, the echo signals of the scatter points are described to be multi-component quartic-phase signals, and a parameter evaluation method based on the time-phase derivative distribution is proposed in specific to the situation of single-component signals; and a parameter evaluation method in which product type time-phase derivative distribution is adopted and a clean technology is combined, is proposed in specific to the situation of multi-component signals. Finally, a transient image with a clear object is obtained by combining a distance-transient Doppler imaging method.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Post-beamforming compression in ultrasound systems
InactiveUS8317706B2Efficient storageReduce storage capacityWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasound imagingSonification
Owner:ALTERA CORP
ISAR (Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar) imaging method for complex moving target
ActiveCN107843894AExcellent time-frequency joint resolutionOvercome the defect of cross term in non-single componentRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDecompositionSynthetic aperture radar
The invention provides an ISAR (Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar) imaging method for a complex moving target. Through polynomial phase optimization estimation on each dominant scatterer distance unitecho signal after translational compensation and polynomial phase signal time frequency decomposition, each signal component obtained by decomposition is a single component only corresponding to one frequency point at any time, the defect that cross terms exist in a non-signal component corresponding to multiple frequency points at one time in the traditional time frequency transform is overcome,each dominant scatterer distance unit echo signal has no any cross term interference and building of time frequency distribution with good time frequency joint resolution is realized finally, and range-instantaneous Doppler imaging is thus obtained. The principle is simple, the operation is convenient, bad influences of cross term interference in the classical time frequency analysis method and losses of the time frequency joint resolution are overcome effectively, the quality and the benefits of nonstationary polynomial phase signal time frequency analysis are effectively enhanced, and a target image with good quality and good resolution is obtained.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Full-aperture imaging method for multi-channel wave beam-pointing synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
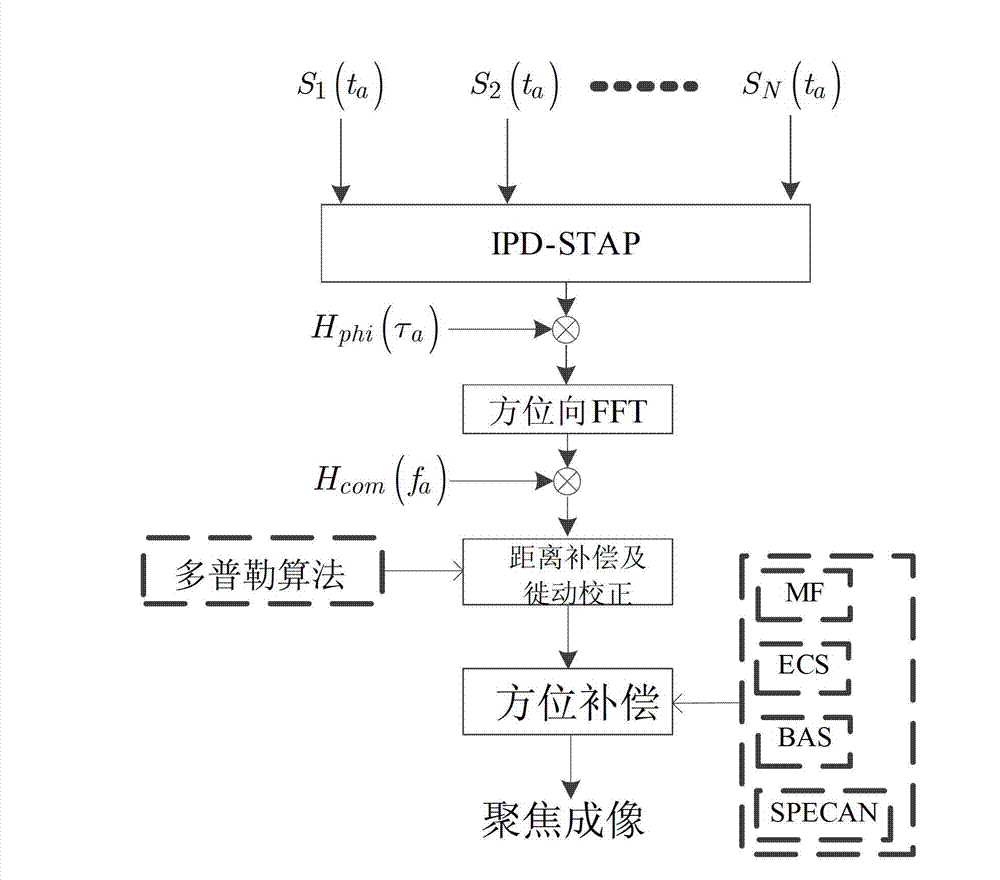
ActiveCN102928839AOvercoming the problem of low azimuth resolutionHigh azimuth resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarImaging processing
The invention discloses a full-aperture imaging method for multi-channel wave beam-pointing synthetic aperture radar (SAR), and mainly solves the problem of low imaging resolution in a wide scene. The full-aperture imaging method comprises the following implementation processes of: (1) receiving original SAR echo signals in a full-aperture way in a one-transmitting multi-receiving channel mode; (2) performing azimuth bandwidth compressing processing and wave beam compressing processing on the echo signals; (3) recovering and reconstructing the compressed echo signals by a Doppler space-time adaptive post-processing method; (4) transforming the recovered and reconstructed echo signals into a two-dimensional frequency domain; and (5) performing distance migration correction and pulse compression on the echo signals in the two-dimensional frequency domain by utilizing a Doppler imaging algorithm to realize imaging. According to the method, the azimuth resolution is improved by utilizing the wave beam-pointing SAR; the problem that the bandwidth of the wave beam-pointing SAR is over-wide is solved by compressing a wave beam domain and an angle domain; simultaneously, an imaging processing flow is simplified; the imaging processing efficiency is improved; and the method can be used in the SAR imaging of a space-borne platform under the requirements of wide scene and high resolution.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com