Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
193 results about "Scan conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
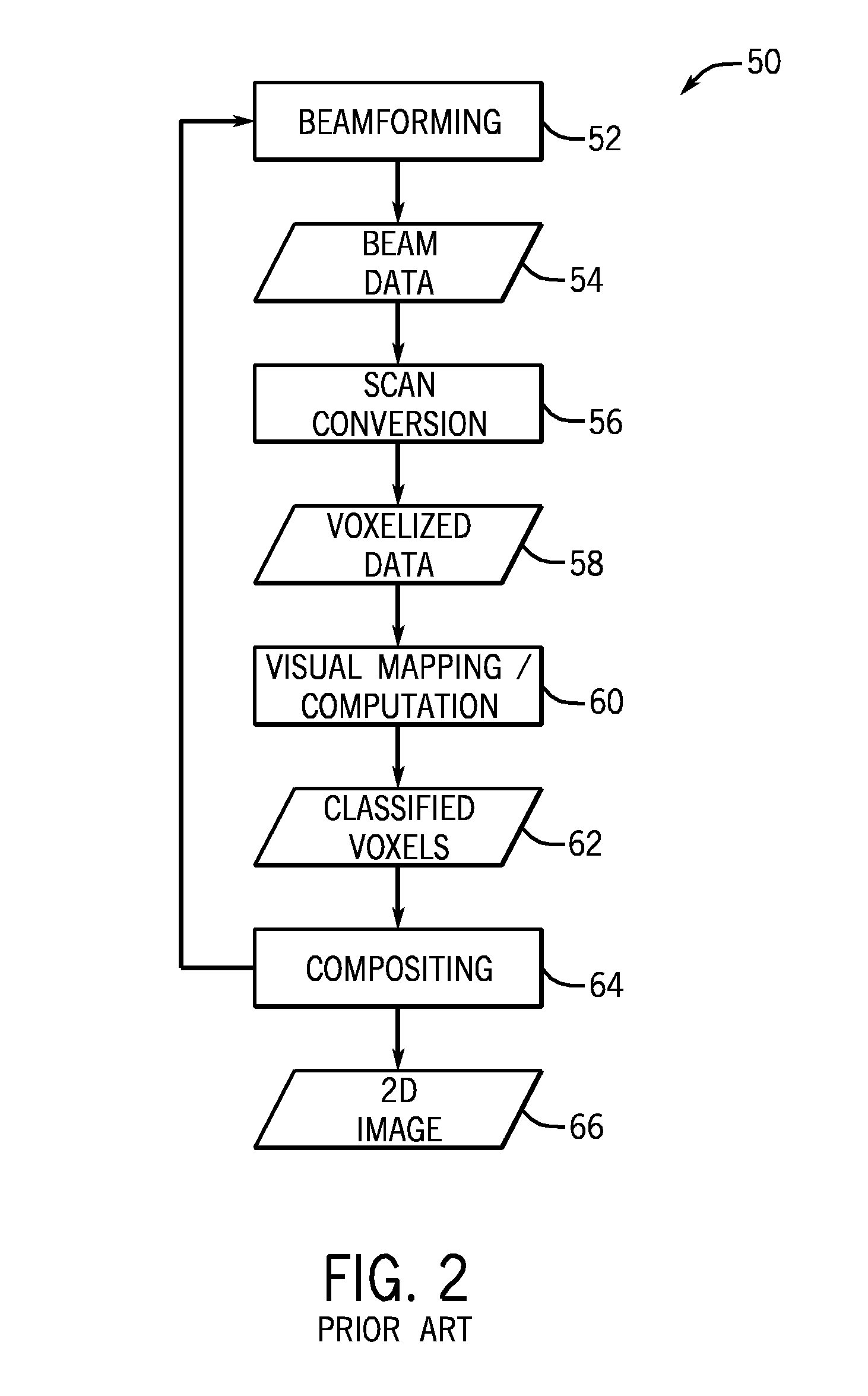
The process of representing continuous graphics objects as a collection of discrete pixels is called scan conversion. Scan conversion or scan converting rate is a video processing technique for changing the vertical / horizontal scan frequency of video signal for different purposes and applications. The device which performs this conversion is called a scan converter.
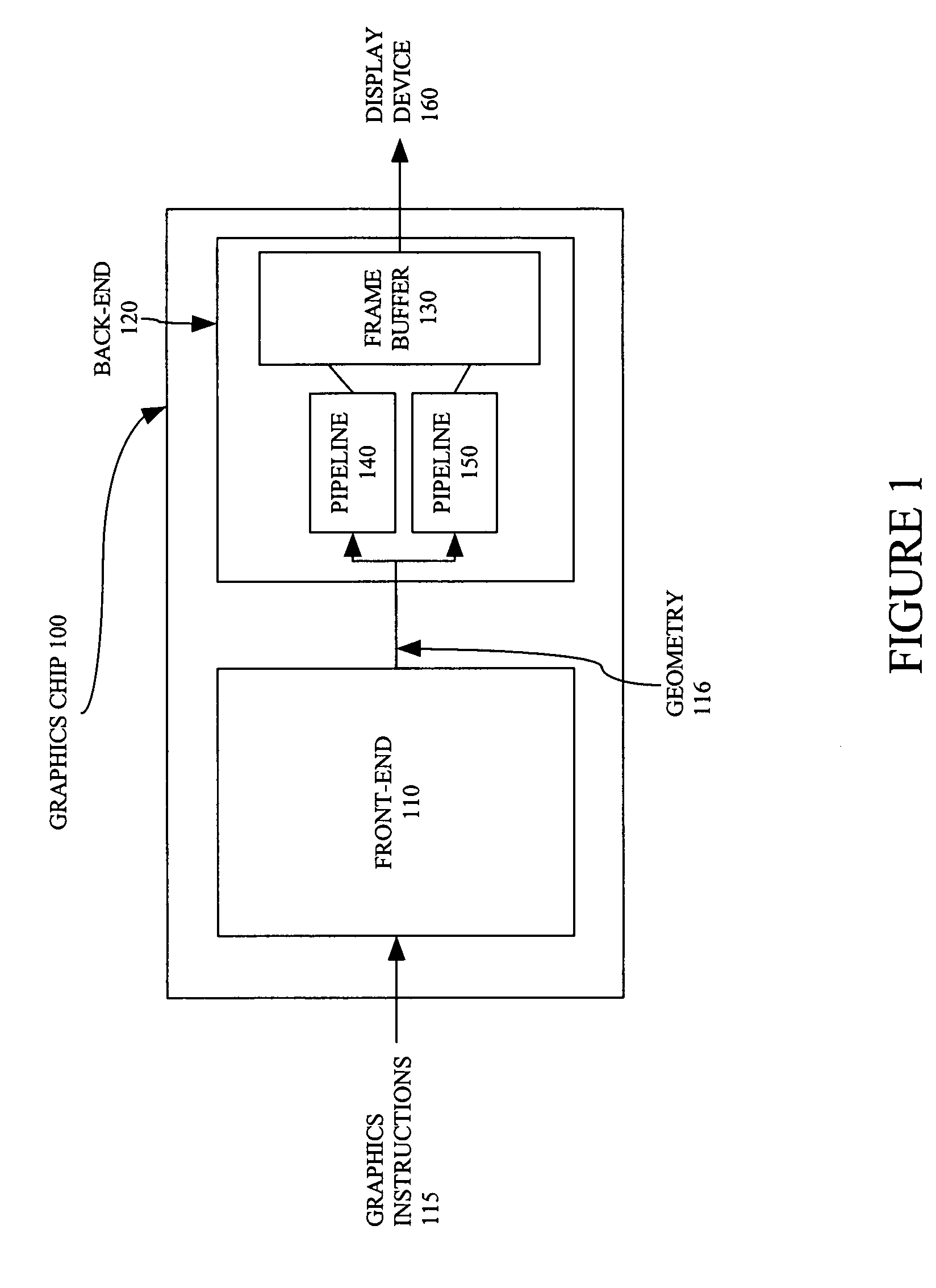
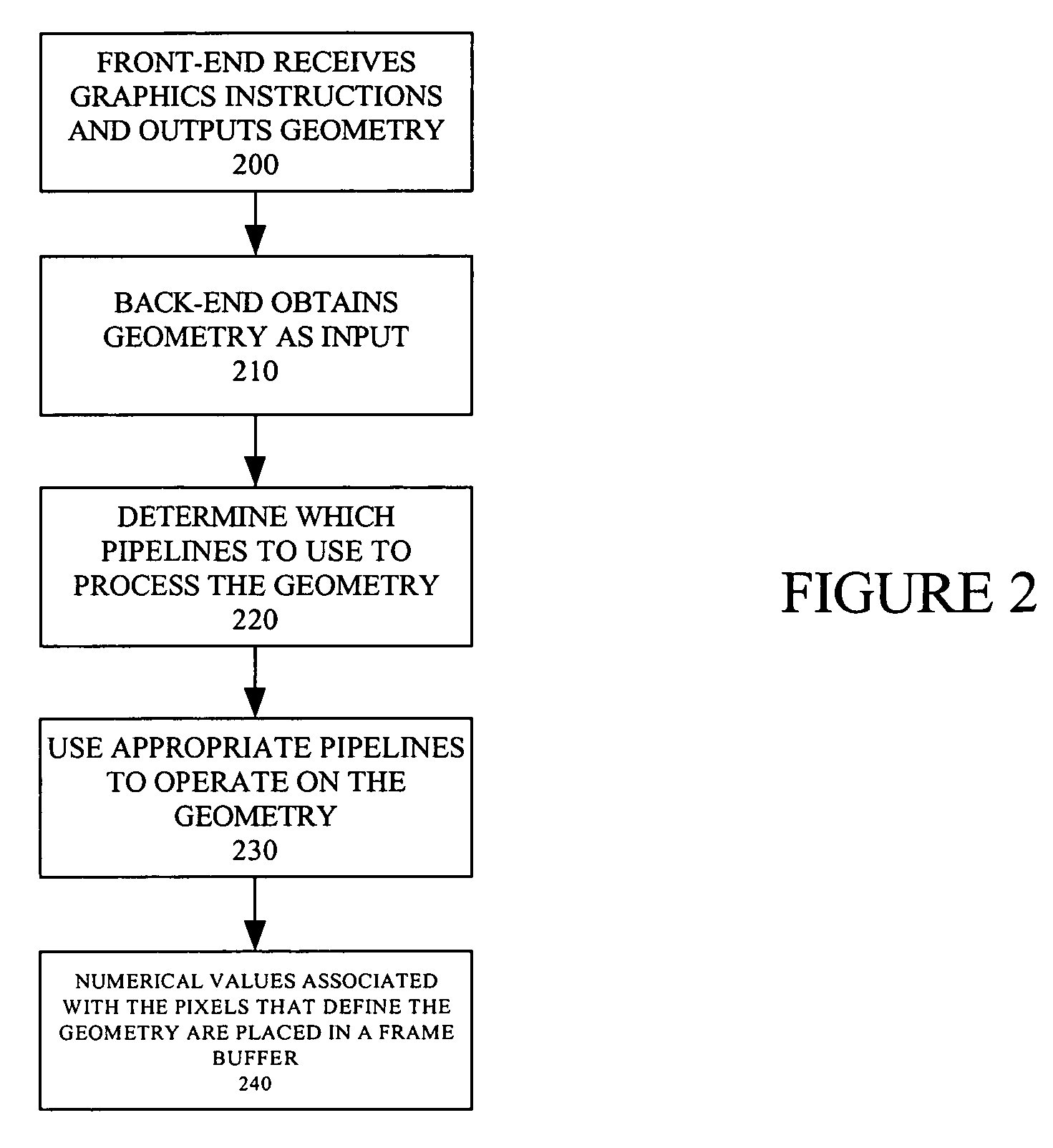
Rendering pipeline
InactiveUS7170515B1EfficientlyReduce memory bandwidth3D-image rendering3D modellingComputational scienceVisibility
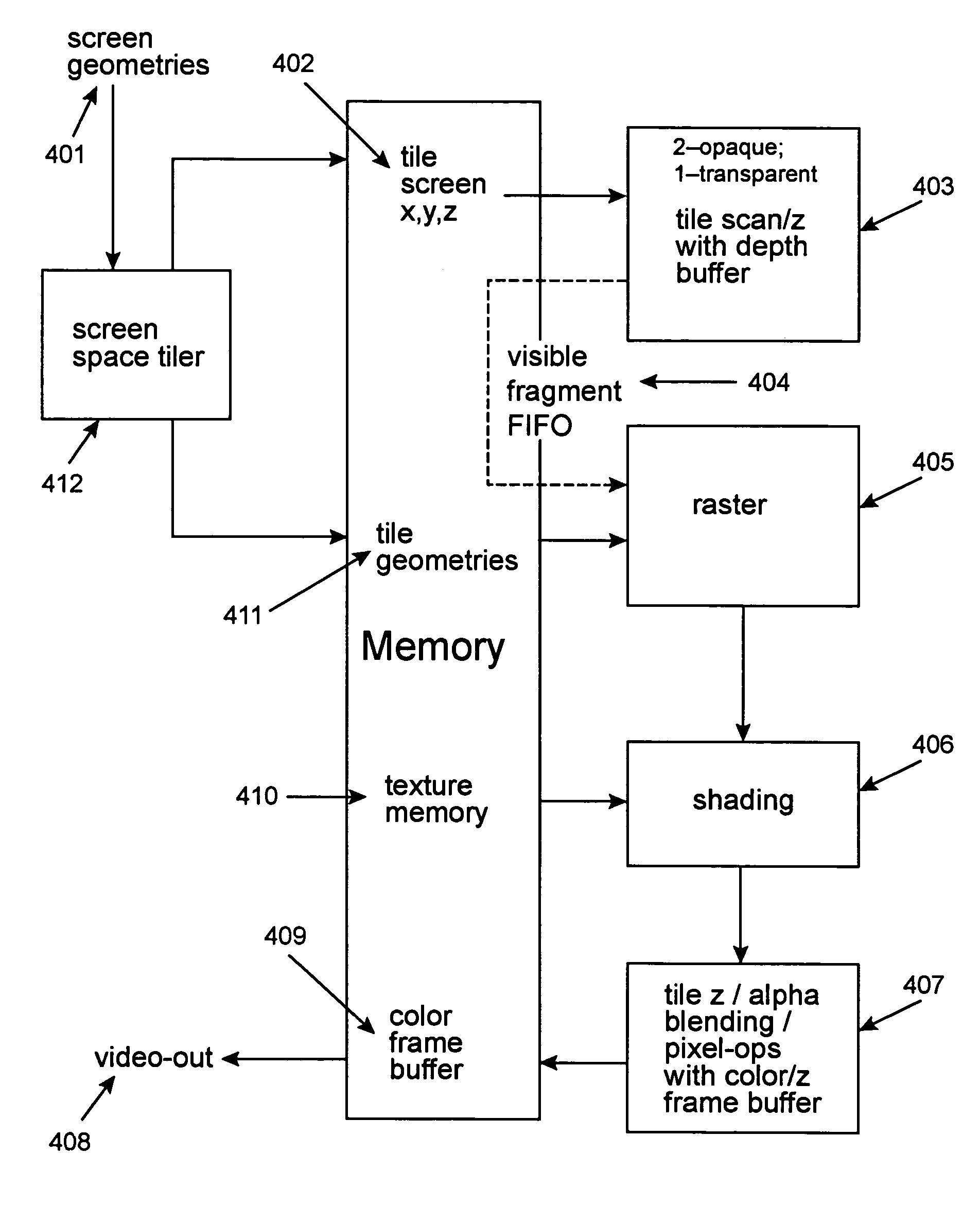
A rendering pipeline system for a computer environment uses screen space tiling (SST) to eliminate the memory bandwidth bottleneck due to frame buffer access and performs screen space tiling efficiently, while avoiding the breaking up of primitives. The system also reduces the buffering size required by SST. High quality, full-scene anti-aliasing is easily achieved because only the on-chip multi-sample memory corresponding to a single tile of the screen is needed. The invention uses a double-z scheme that decouples the scan conversion / depth-buffer processing from the more general rasterization and shading processing through a scan / z engine. The scan / z engine externally appears as a fragment generator but internally resolves visibility and allows the rest of the rendering pipeline to perform setup for only visible primitives and shade only visible fragments. The resulting reduced raster / shading requirements can lead to reduced hardware costs because one can process all parameters with generic parameter computing units instead of with dedicated parameter computing units. The invention processes both opaque and transparent geometries.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method and apparatus for transforming polygon data to voxel data for general purpose applications
InactiveUS6867774B1Efficient conversionHigh resolution3D-image rendering3D modellingGeneral purposeScan conversion
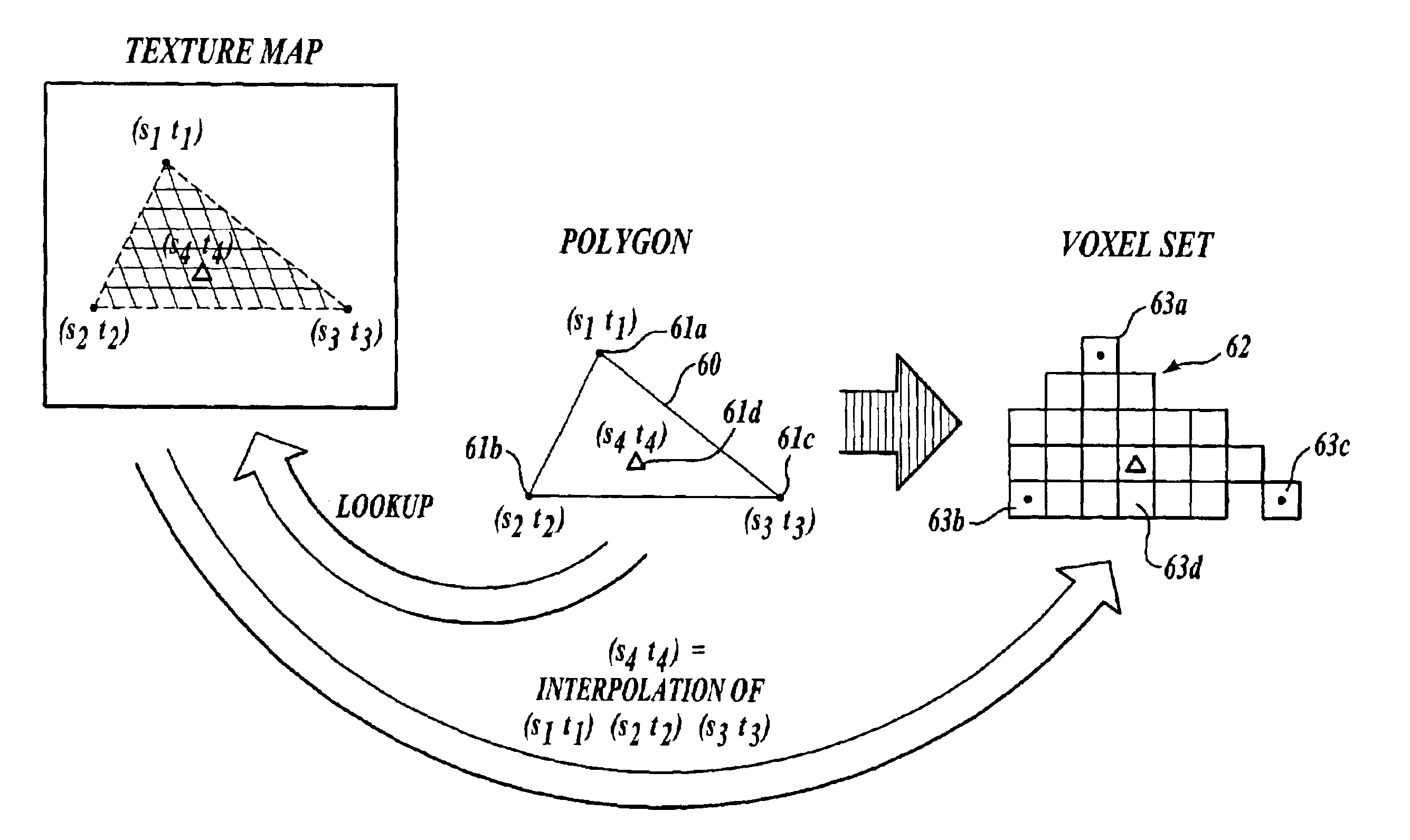
A method and apparatus are provided for transforming 3D geometric data, such as polygon data (16) formed of polygons (18), into volumetric data (14) formed of voxels (12). According to the method, 3D geometric data to be converted to voxel data are acquired, and the resolution of a final voxel grid to be produced is obtained (e.g., user-defined). Then, each geometric unit (e.g., a polygon) in the 3D geometric data is mapped (or scan converted) to an imaginary voxel grid having a higher resolution than the resolution of the final voxel grid. Next, with respect to the geometric units that are mapped to the imaginary voxels in the imaginary voxel grid dividing one final (actual) voxel into smaller sub-volumes, a weighted average of the attribute values (color, normal, intensity, etc.) is obtained. The weighted average is stored as the attribute value of the final voxel.
Owner:MCLOUD TECH USA INC
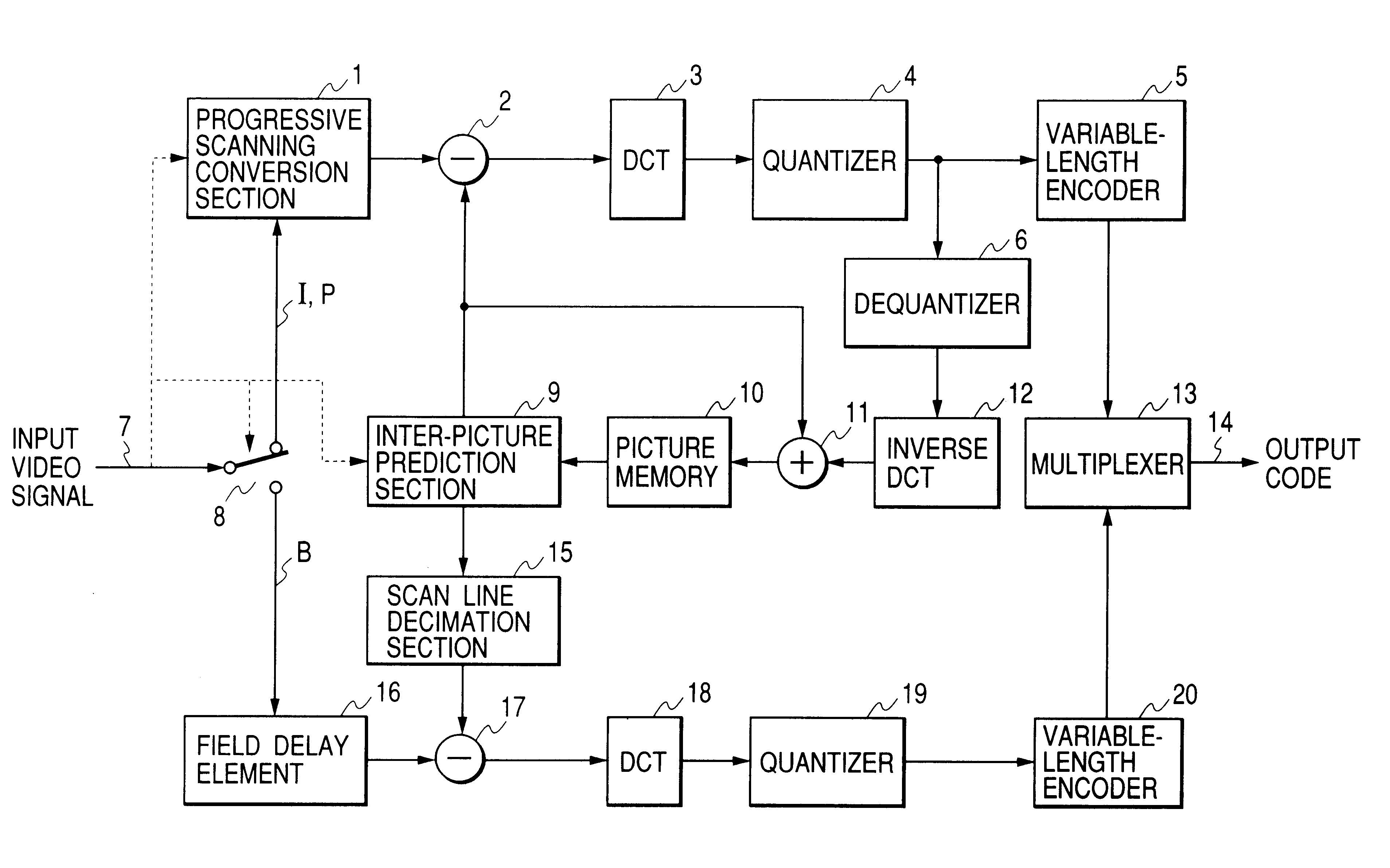
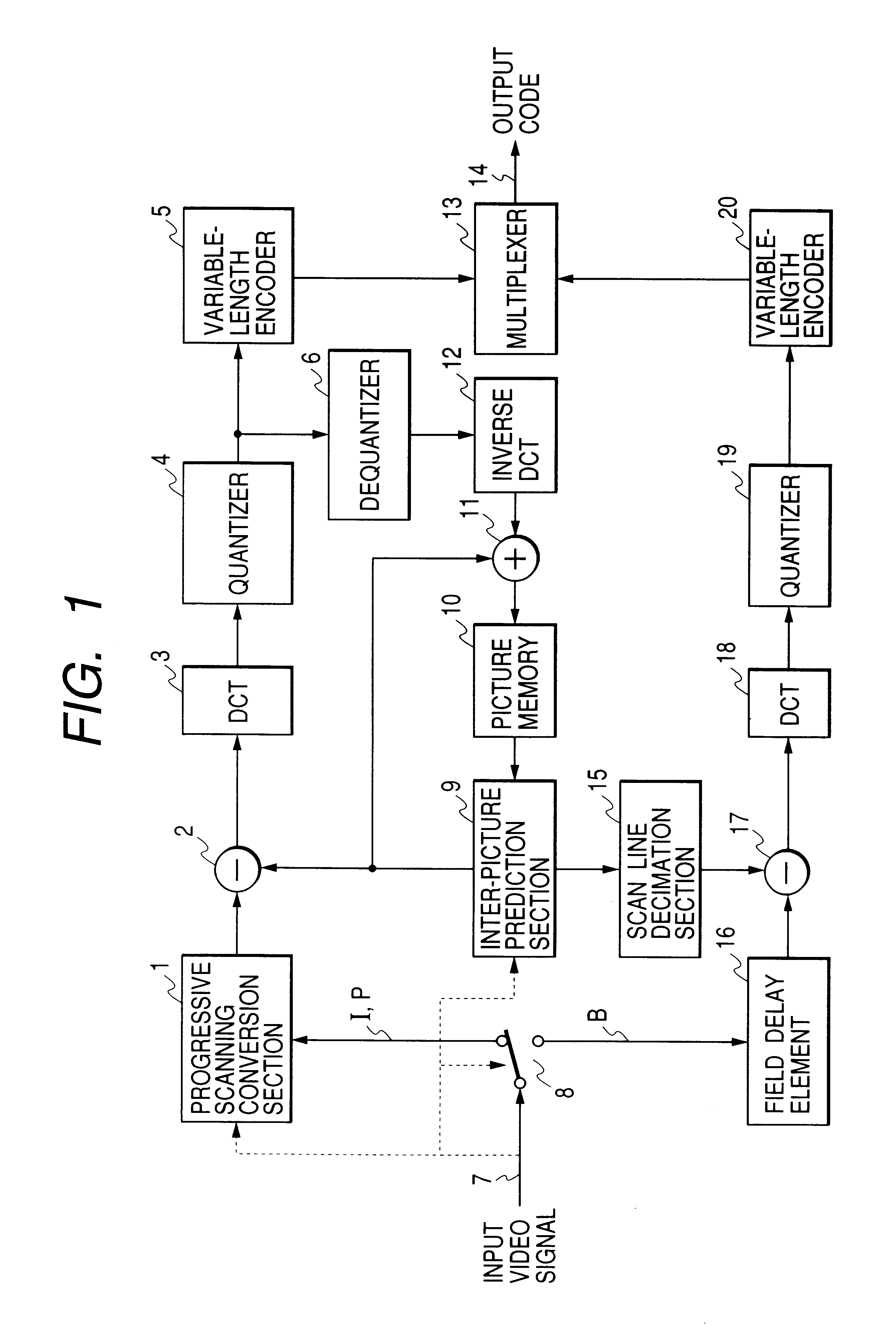
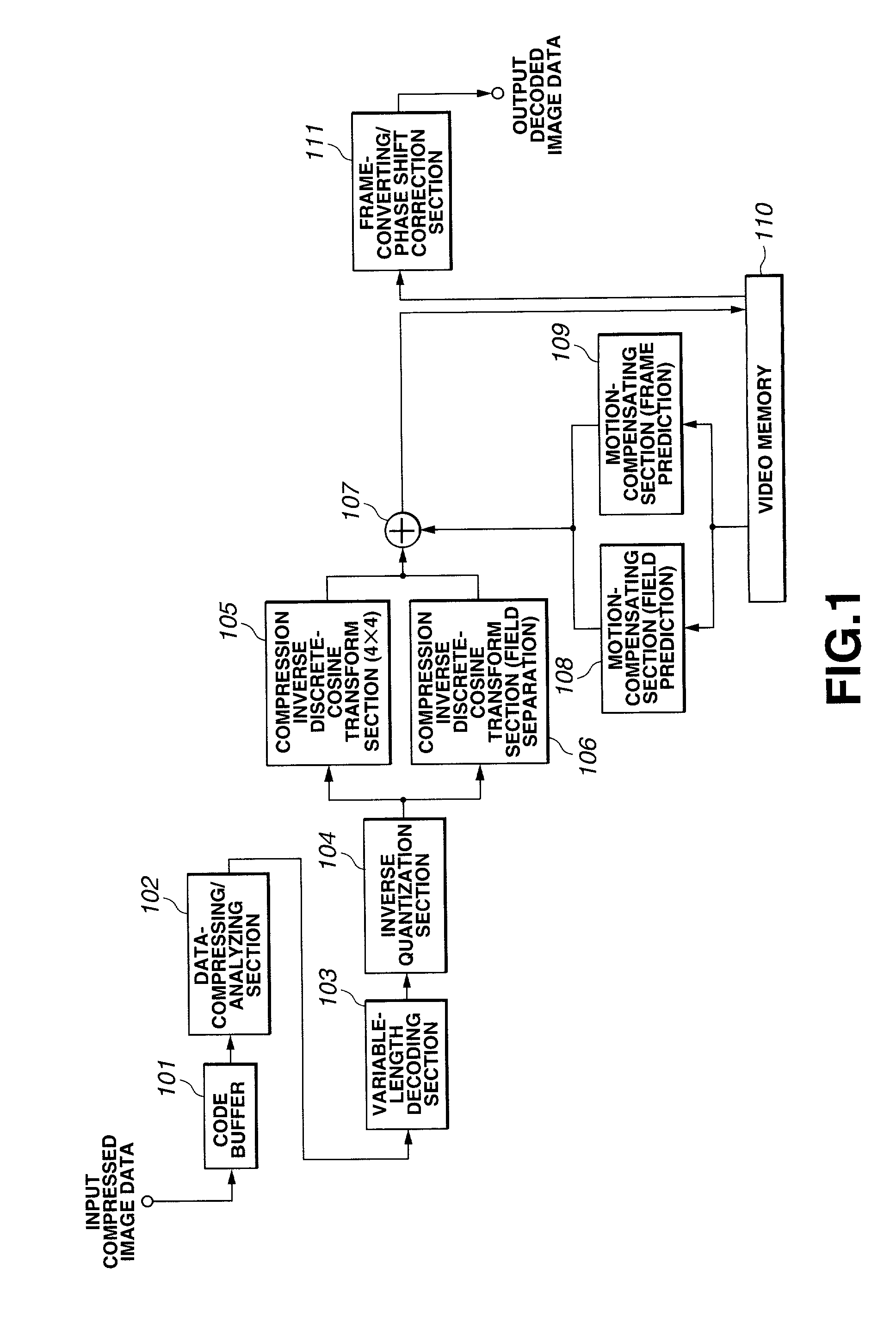
Interplaced video signal encoding and decoding method, and encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus utilizing the method, providing high efficiency of encoding by conversion of periodically selected fields to progressive scan frames which function as reference frames for predictive encoding
InactiveUS6188725B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesScan conversionInterlaced video
An encoding apparatus includes a selector for periodically selecting fields of an interlaced video signal to be converted to respective progressive scanning frames, by a scanning converter which doubles the number of scanning lines per field. The apparatus encodes these frames by intra-frame encoding or unidirectional predictive encoding using preceding ones of the frames, and encodes the remaining fields of the video signal by bidirectional prediction using preceding and succeeding ones of the progressive scanning frames for reference. The resultant code can be decoded by an inverse process to recover the interlaced video signal, or each decoded field can be converted to a progressive scanning frame to thereby enable output of a progressive scanning video signal. Enhanced accuracy of motion prediction for inter-frame encoding can thereby be achieved, and generation of encoded aliasing components suppressed, since all reference pictures are progressive scanning frames rather than pairs of fields constituting interlaced scanning frames.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Antialiased imaging with improved pixel supersampling
An image processing system is described that receives polygonal image data at the direction of a processor and develops antialiased image data for display on a raster scanned display. In particular, the image system includes a scan convertor for converting the polygonal image data into pixel data, which includes pixel screen coordinates and at least one color value for each polygon covered pixel of the pixel data and a supersample coverage mask indicating an extent of polygon coverage within each polygon covered pixel. The image system also includes a raster system having at least one image processor for receiving the pixel data for each pixel, for developing a region mask based on the supersample coverage mask, and for storing the color value in association with the region mask as anitialiased display data in an image memory in communication with the image processor based on the pixel screen coordinates. The region mask indicates one or more, geographical regions of supersamples within each pixel covered by one or more polygons and indicates a color value stored in the image memory to be assigned to the supersamples in a region. This requires only a single color value for supersamples within a region of a covered pixel to be stored in the image memory. The image system can also be configured to develop and store Z-values, alpha values, stencil values, and texture values for each pixel for storage in the image memory in association with the region mask.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Parallel pipeline graphics system
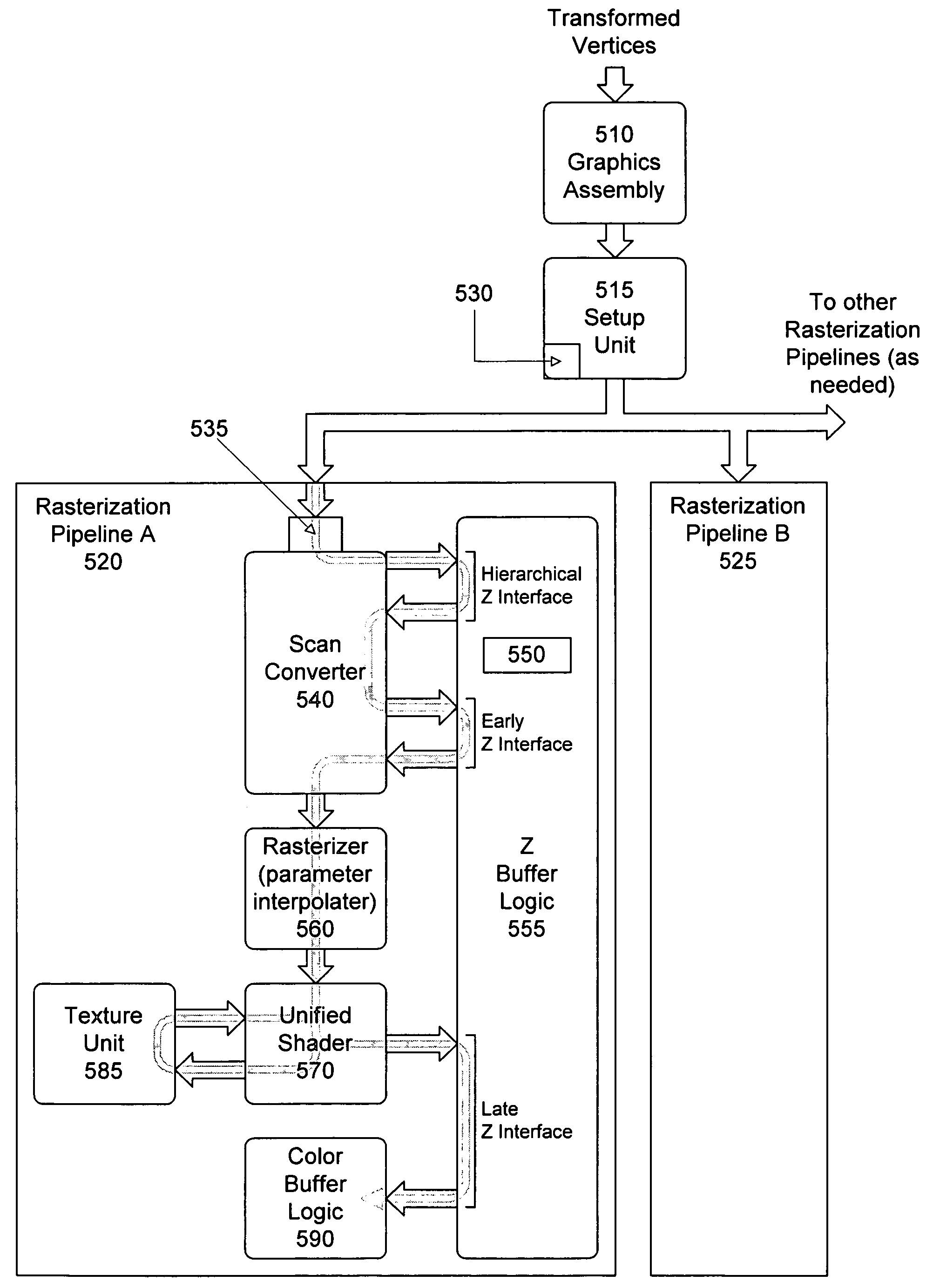
ActiveUS7633506B1Precise definitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationComputational scienceScan conversion
The present invention relates to a parallel pipeline graphics system. The parallel pipeline graphics system includes a back-end configured to receive primitives and combinations of primitives (i.e., geometry) and process the geometry to produce values to place in a frame buffer for rendering on screen. Unlike prior single pipeline implementation, some embodiments use two or four parallel pipelines, though other configurations having 2^n pipelines may be used. When geometry data is sent to the back-end, it is divided up and provided to one of the parallel pipelines. Each pipeline is a component of a raster back-end, where the display screen is divided into tiles and a defined portion of the screen is sent through a pipeline that owns that portion of the screen's tiles. In one embodiment, each pipeline comprises a scan converter, a hierarchical-Z unit, a z buffer logic, a rasterizer, a shader, and a color buffer logic.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
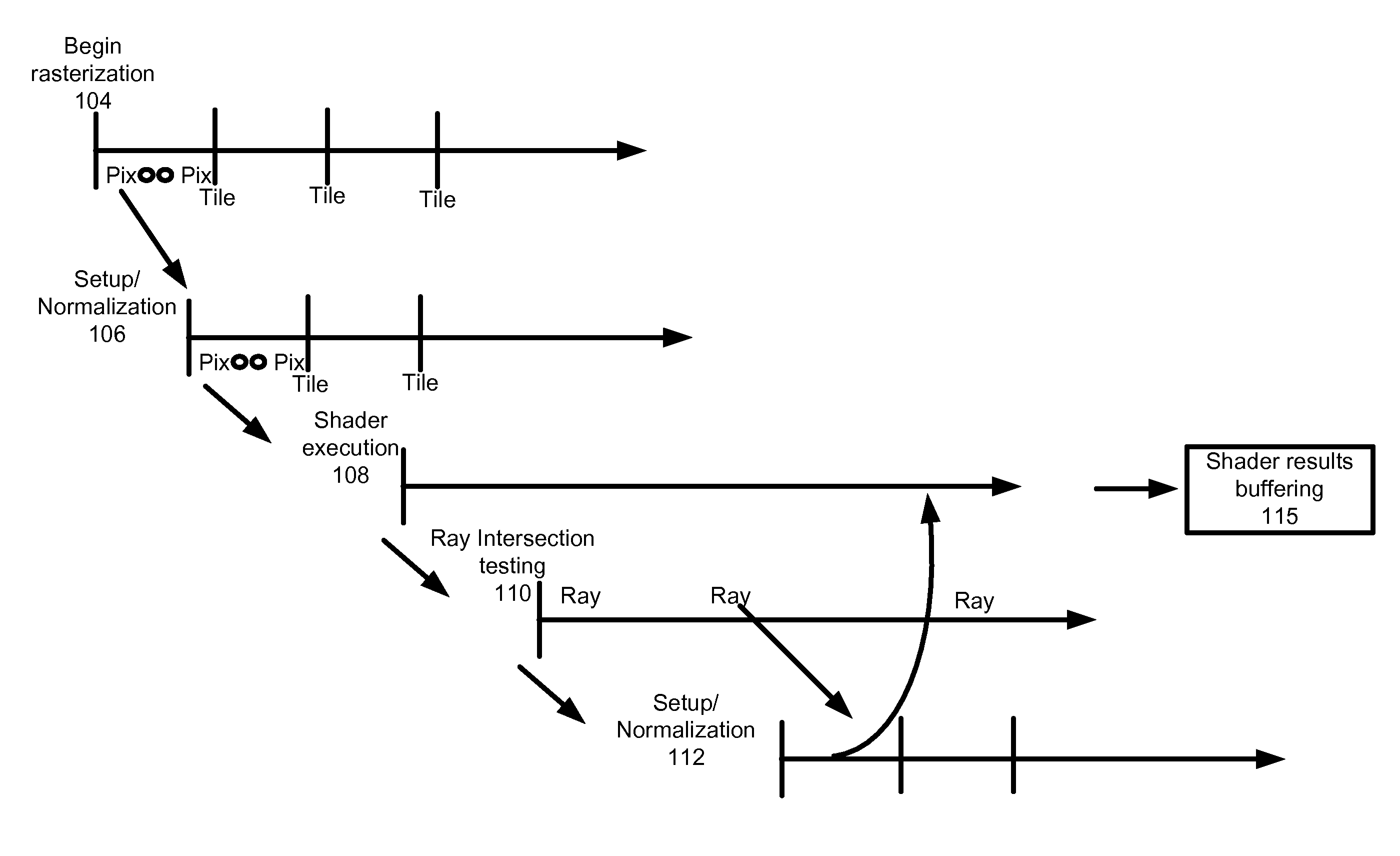
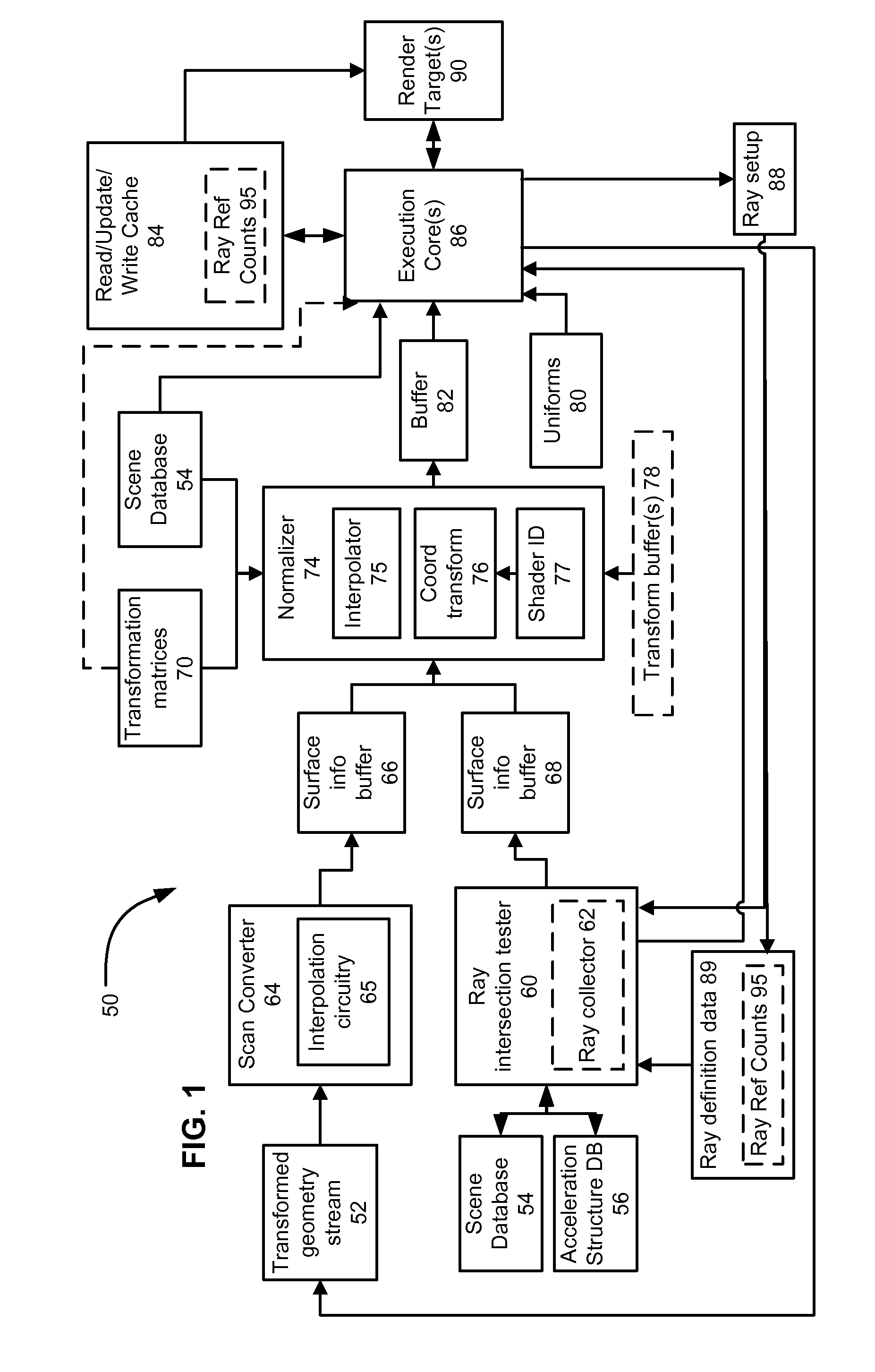
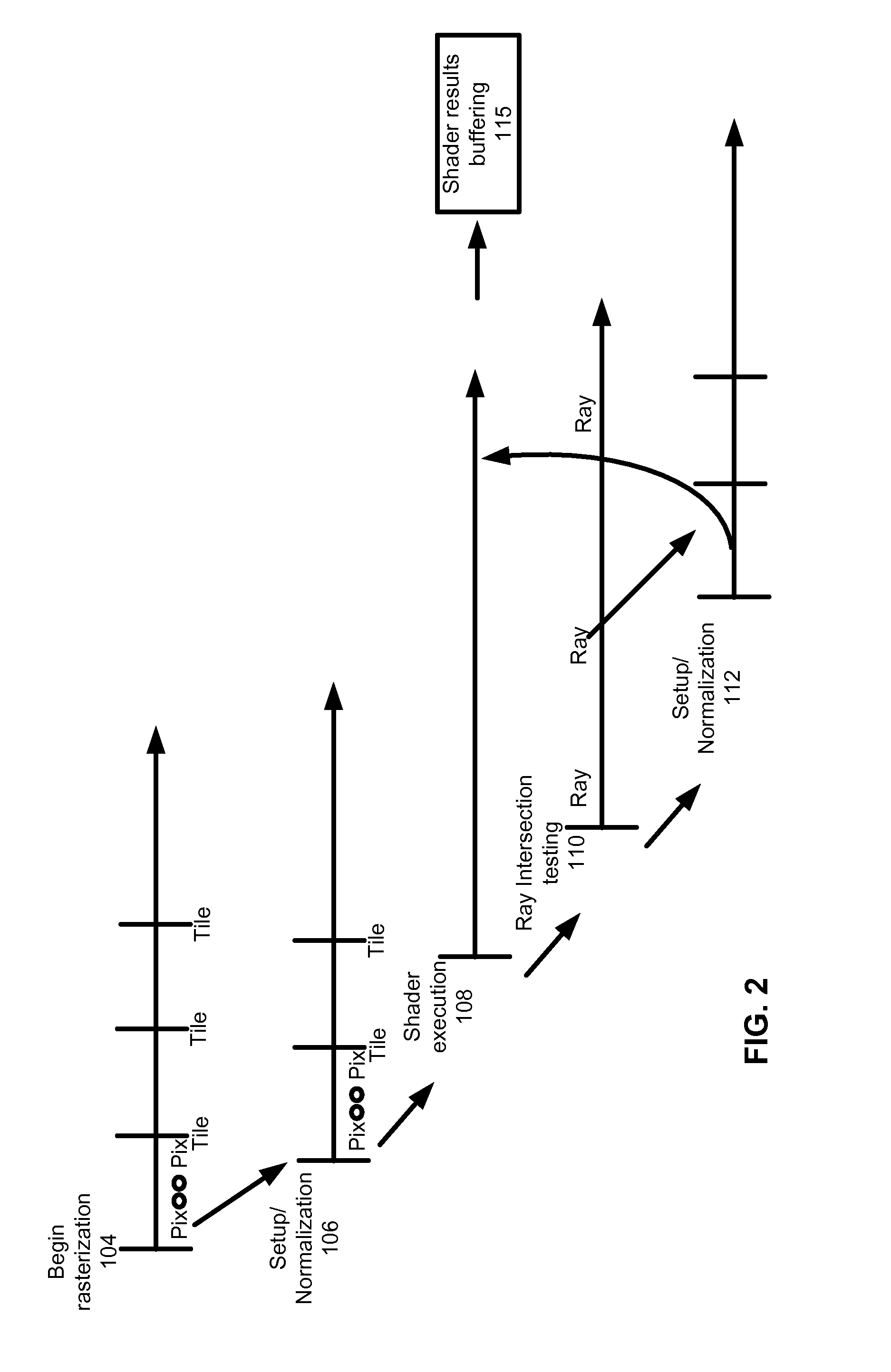
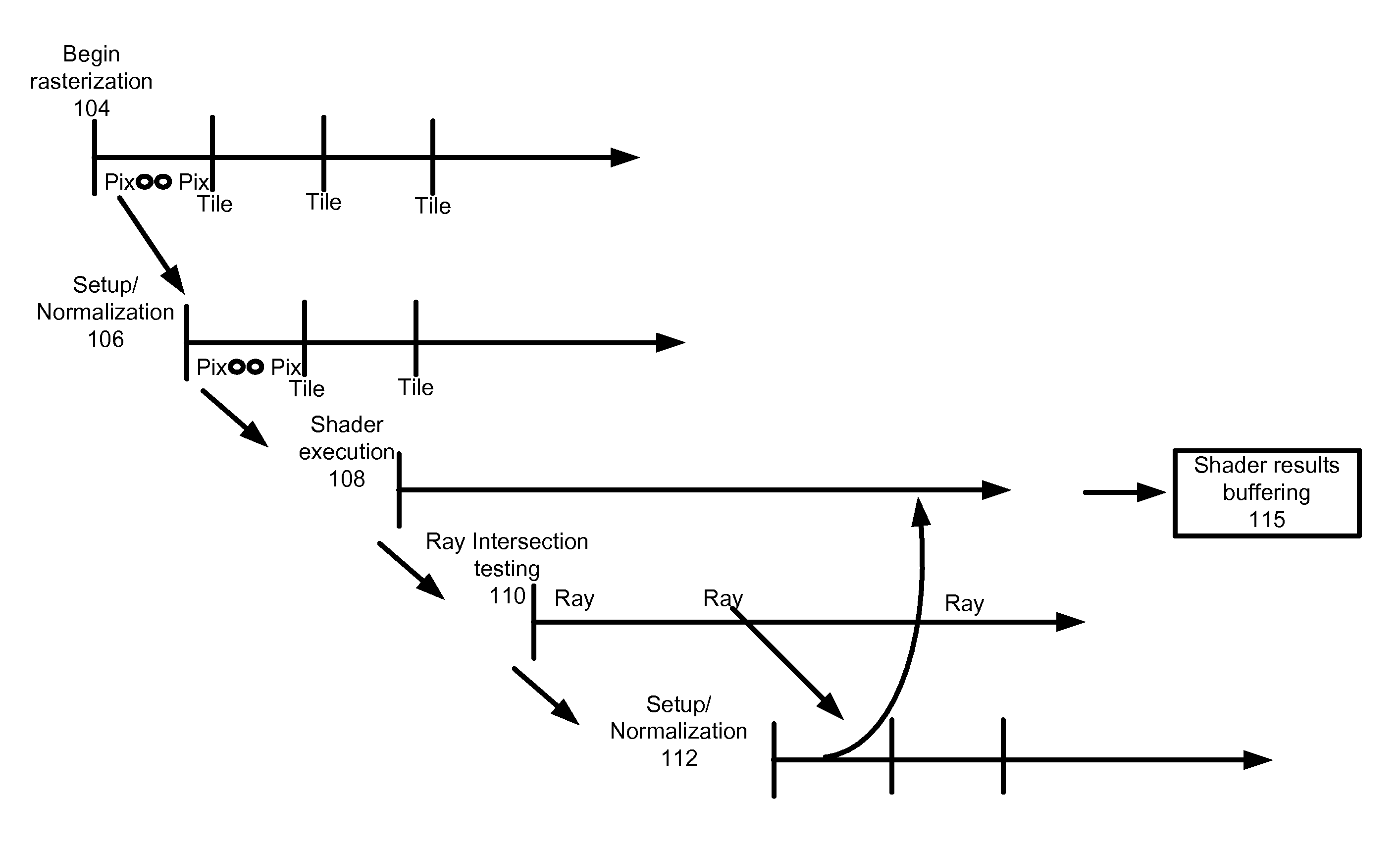
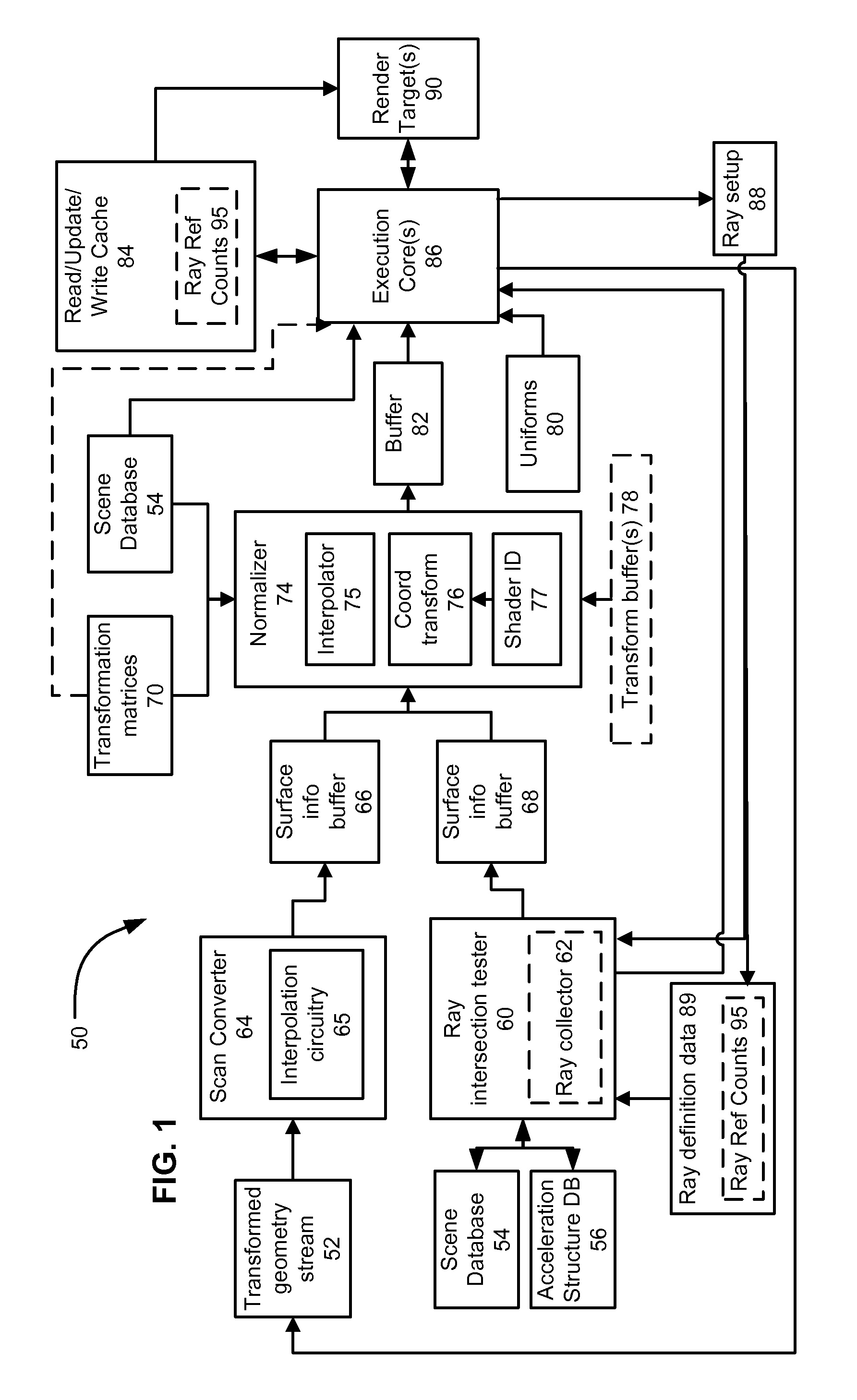
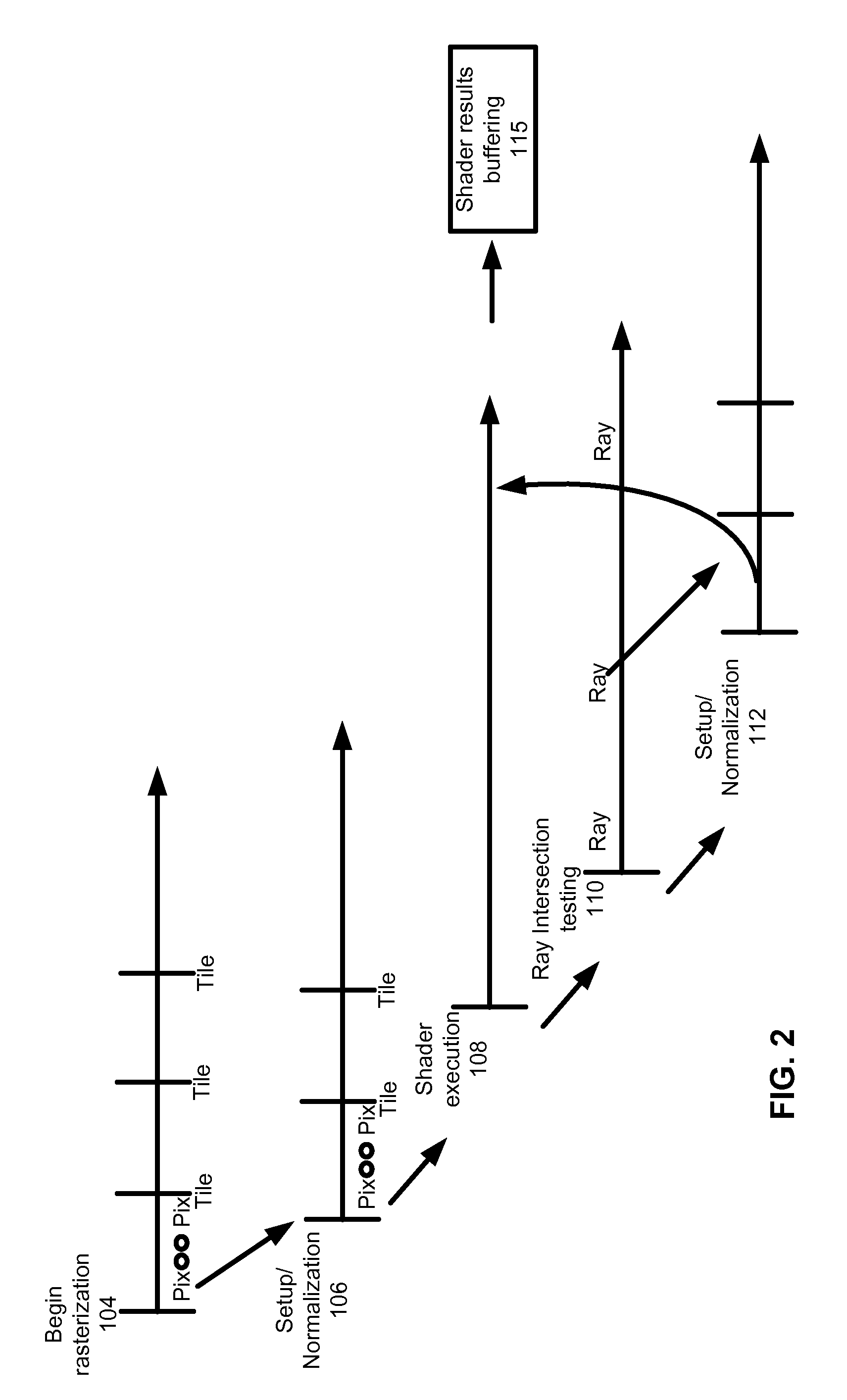
Unified rasterization and ray tracing rendering environments
A graphics processor architecture provides for scan conversion and ray tracing approaches to visible surface determination as concurrent and separate processes. Surfaces can be identified for shading by scan conversion and ray tracing. Data produced by each can be normalized, so that instances of shaders, being executed on a unified shading computation resource, can shade surfaces originating from both ray tracing and rasterization. Such resource also may execute geometry shaders. The shaders can emit rays to be tested for intersection by the ray tracing process. Such shaders can complete, without waiting for those emitted rays to complete. Where scan conversion operates on tiles of 2-D screen pixels, the ray tracing can be tile aware, and controlled to prioritize testing of rays based on scan conversion status. Ray population can be controlled by feedback to any of scan conversion, and shading.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
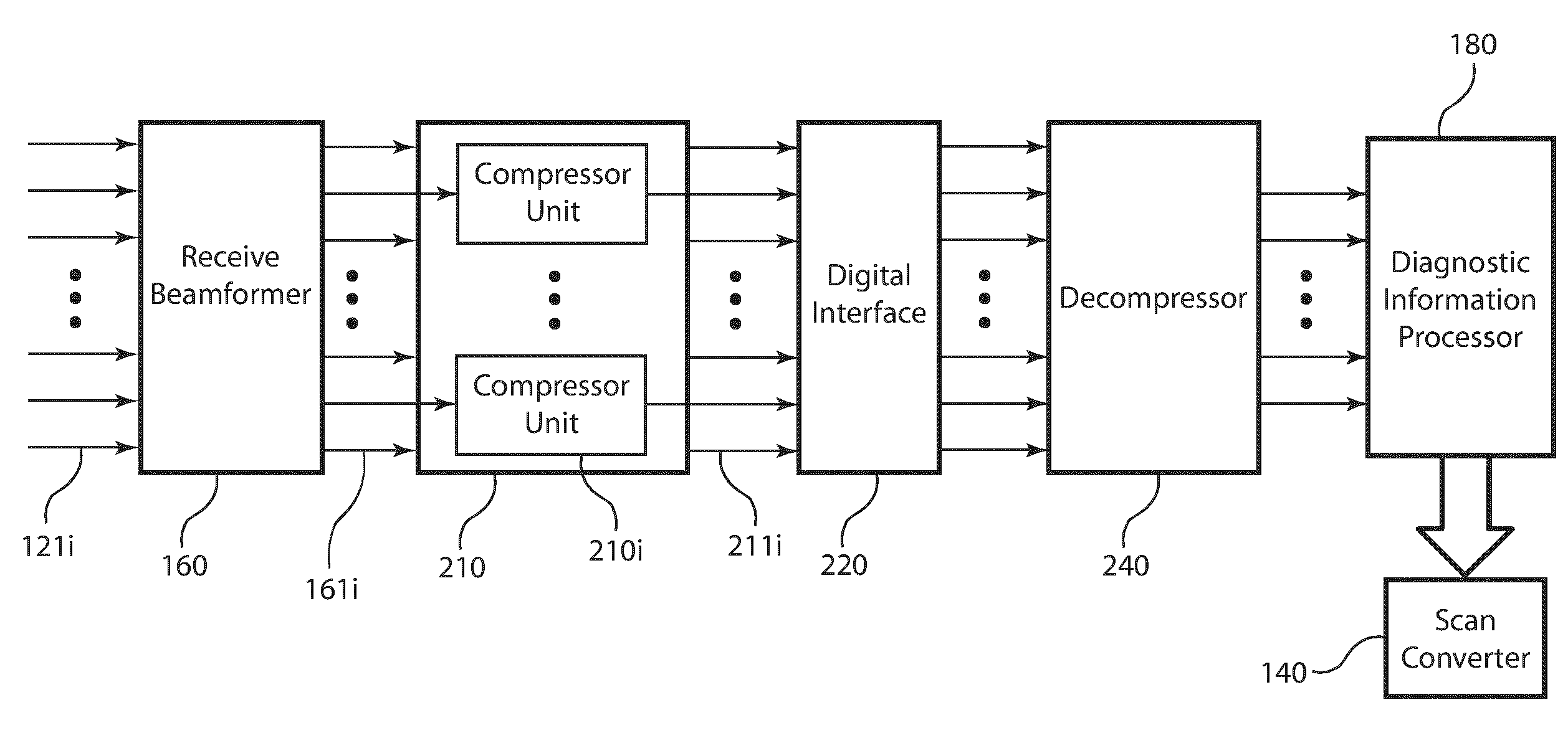
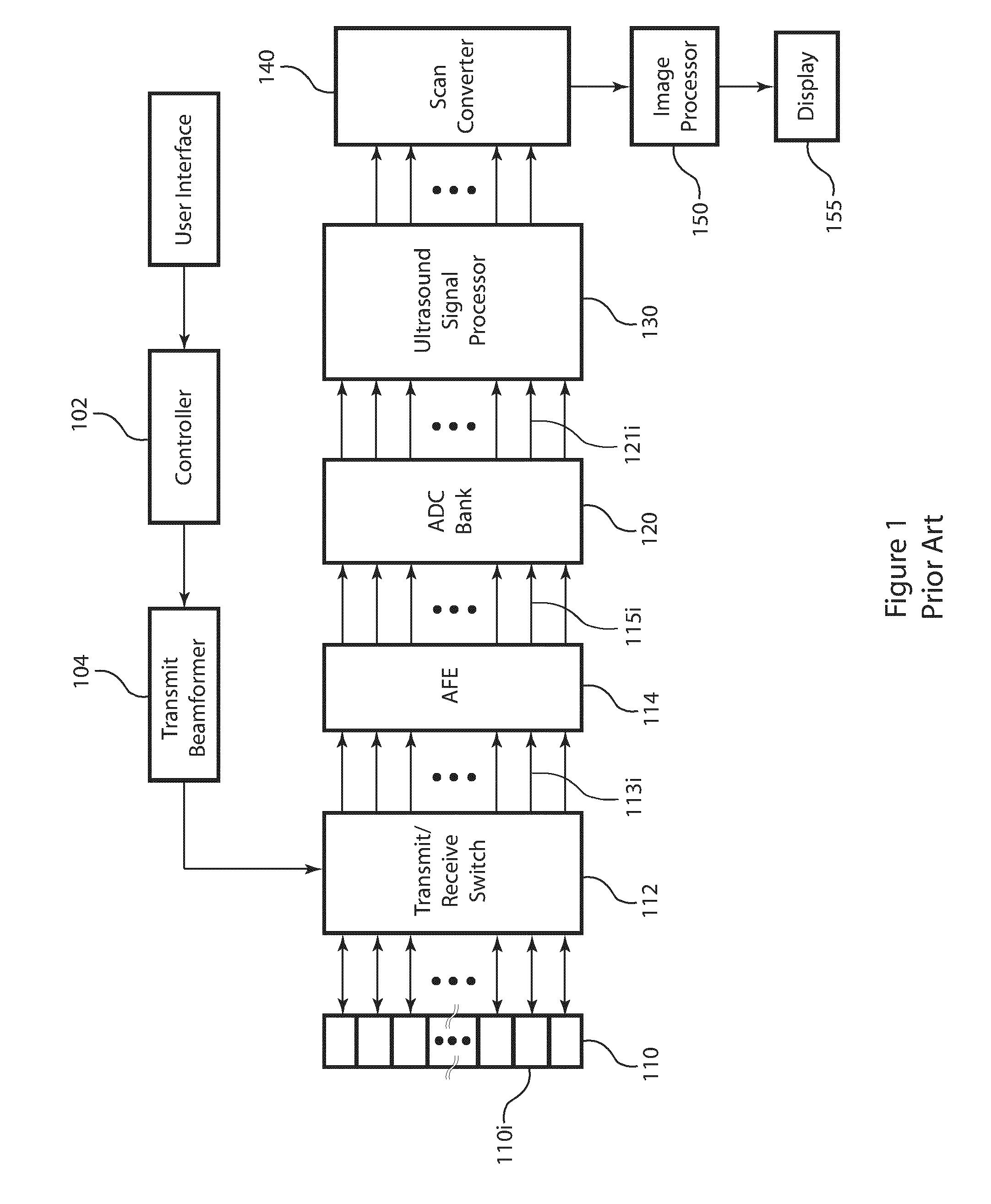
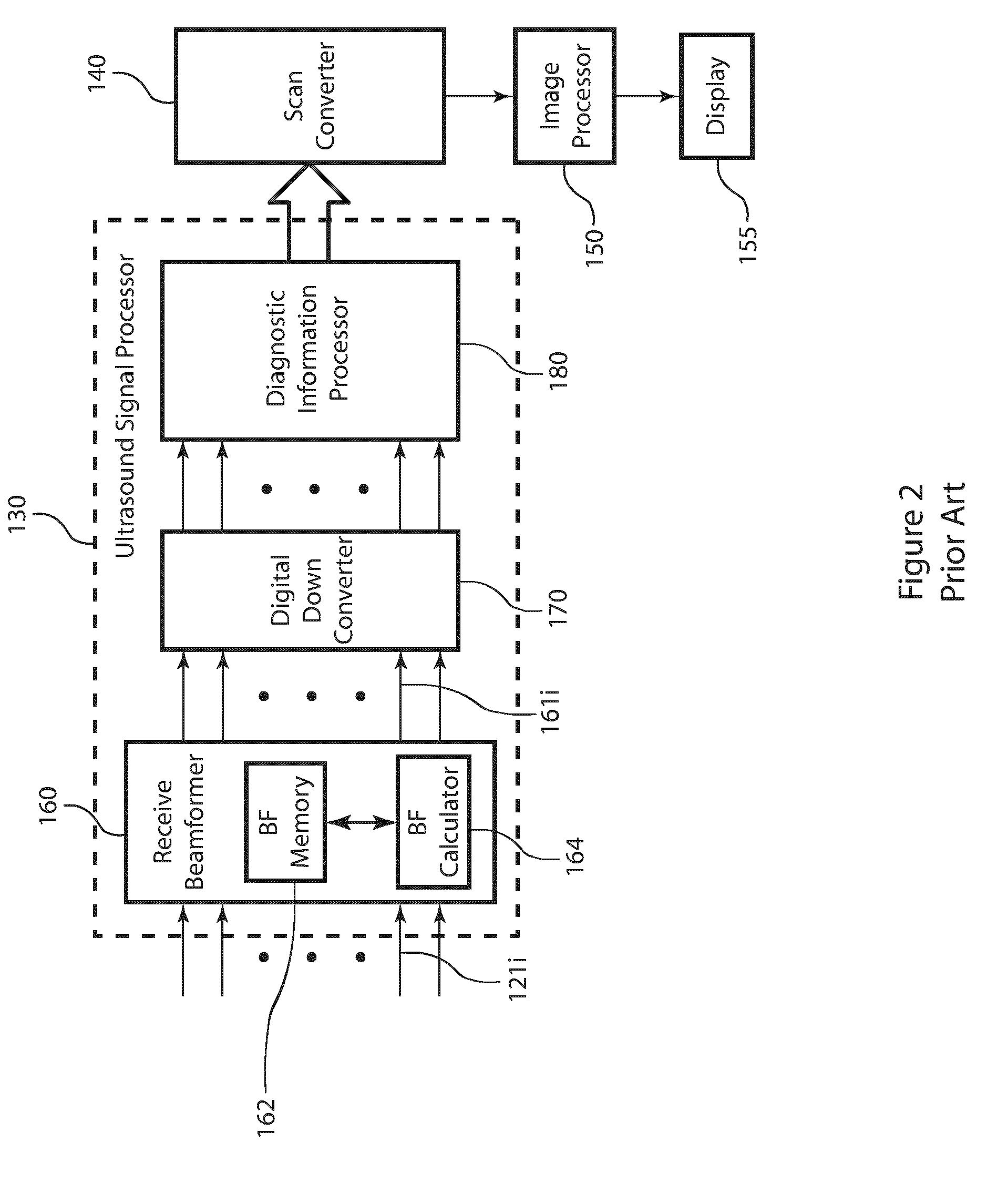
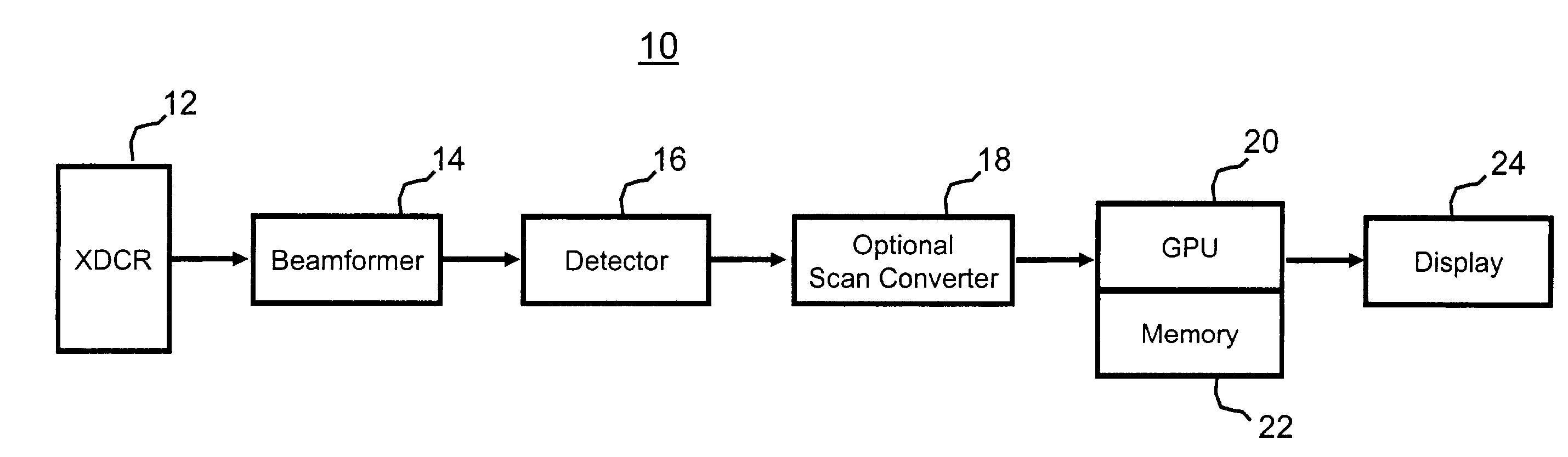
Post-beamforming compression in ultrasound systems
InactiveUS20100331689A1Efficient storageReduce storage capacityWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasound imagingScan conversion
In an ultrasound imaging system that applies a beamformer to received ultrasound signal samples to form one or more beams represented by arrays of beamformed samples, a method and an apparatus compress each array of beamformed samples independently of the other arrays to form compressed beams. A plurality of analog to digital converters sample multiple analog ultrasound signals produced by a transducer array to provide multiple streams of ultrasound signal samples to the beamformer. The compressed beams are transferred via a digital interface to a signal processor. At the signal processor, the compressed beams are decompressed to form decompressed beams. The signal processor further processes the decompressed beams for diagnostic imaging, such as for B-mode and Doppler imaging, and scan conversion to prepare the resulting ultrasound image for display. This abstract does not limit the scope of the invention as described in the claims.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Volume rendering in the acoustic grid methods and systems for ultrasound diagnostic imaging
InactiveUS6852081B2Amount is reduced and eliminatedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryData setSonification
Methods and systems for volume rendering three-dimensional ultrasound data sets in an acoustic grid using a graphics processing unit are provided. For example, commercially available graphic accelerators cards using 3D texturing may provide 256×, 256×128 8 bit volumes at 25 volumes per second or better for generating a display of 512×512 pixels using ultrasound data. By rendering from data at least in part in an acoustic grid, the amount of scan conversion processing is reduced or eliminated prior to the rendering.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
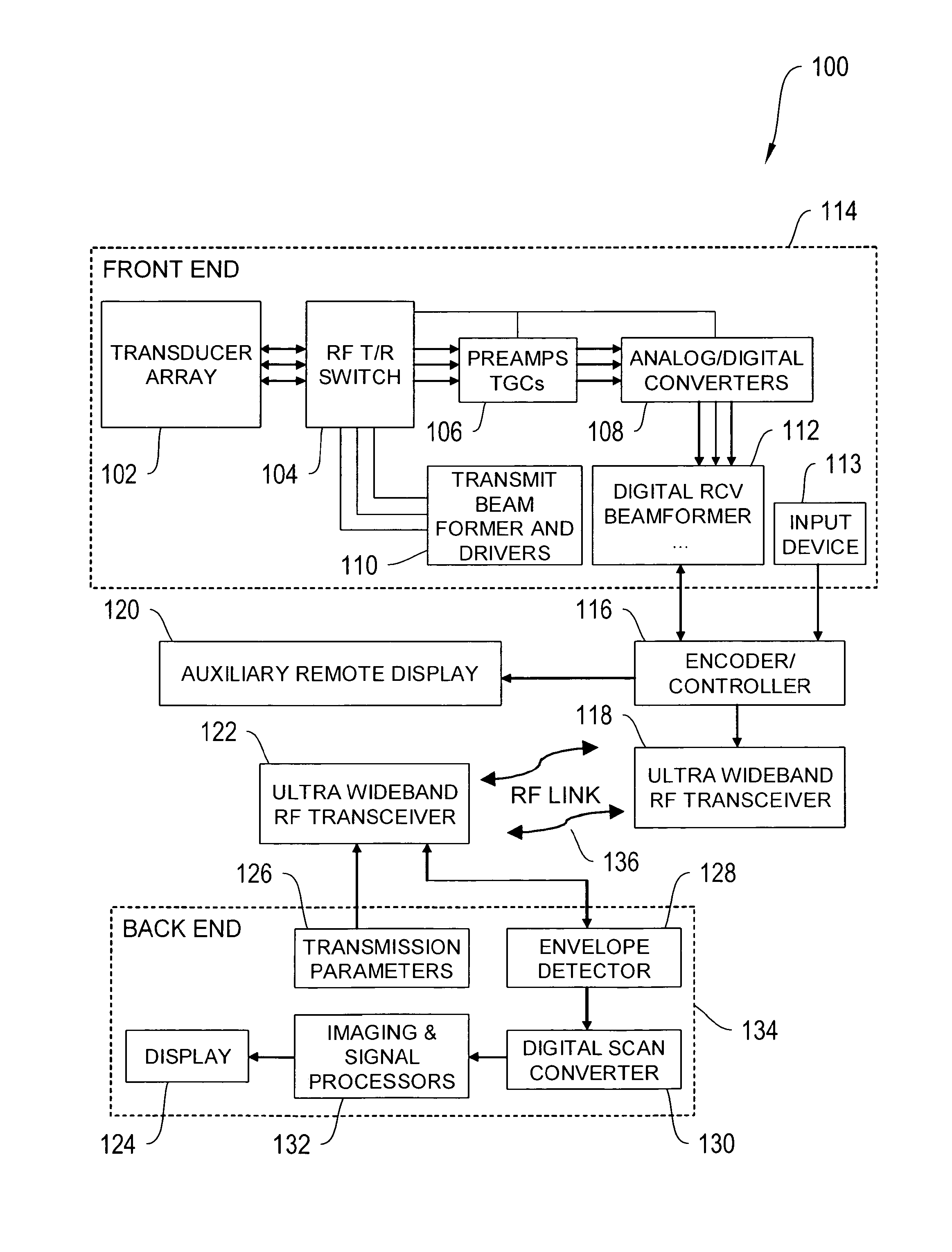
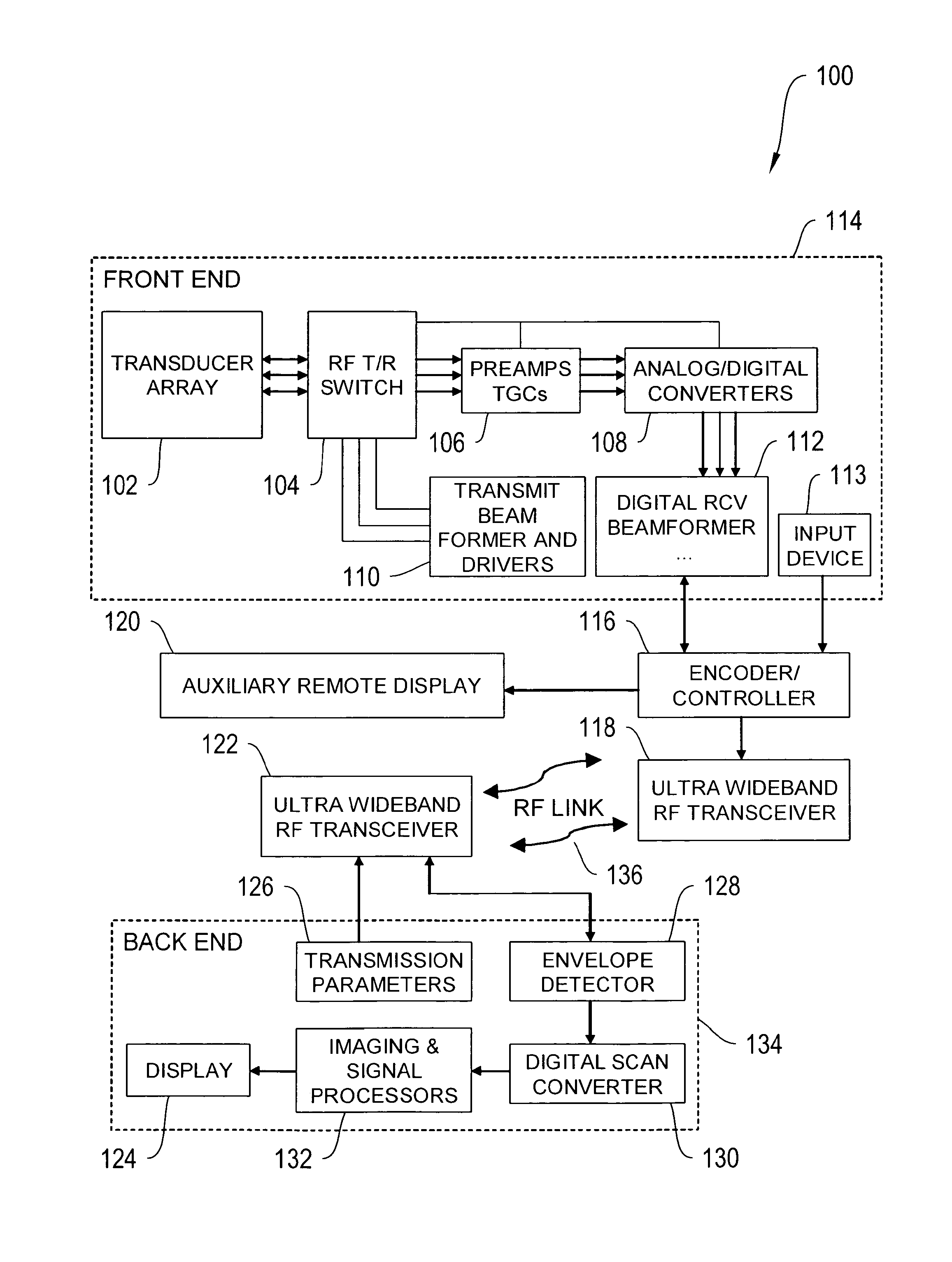
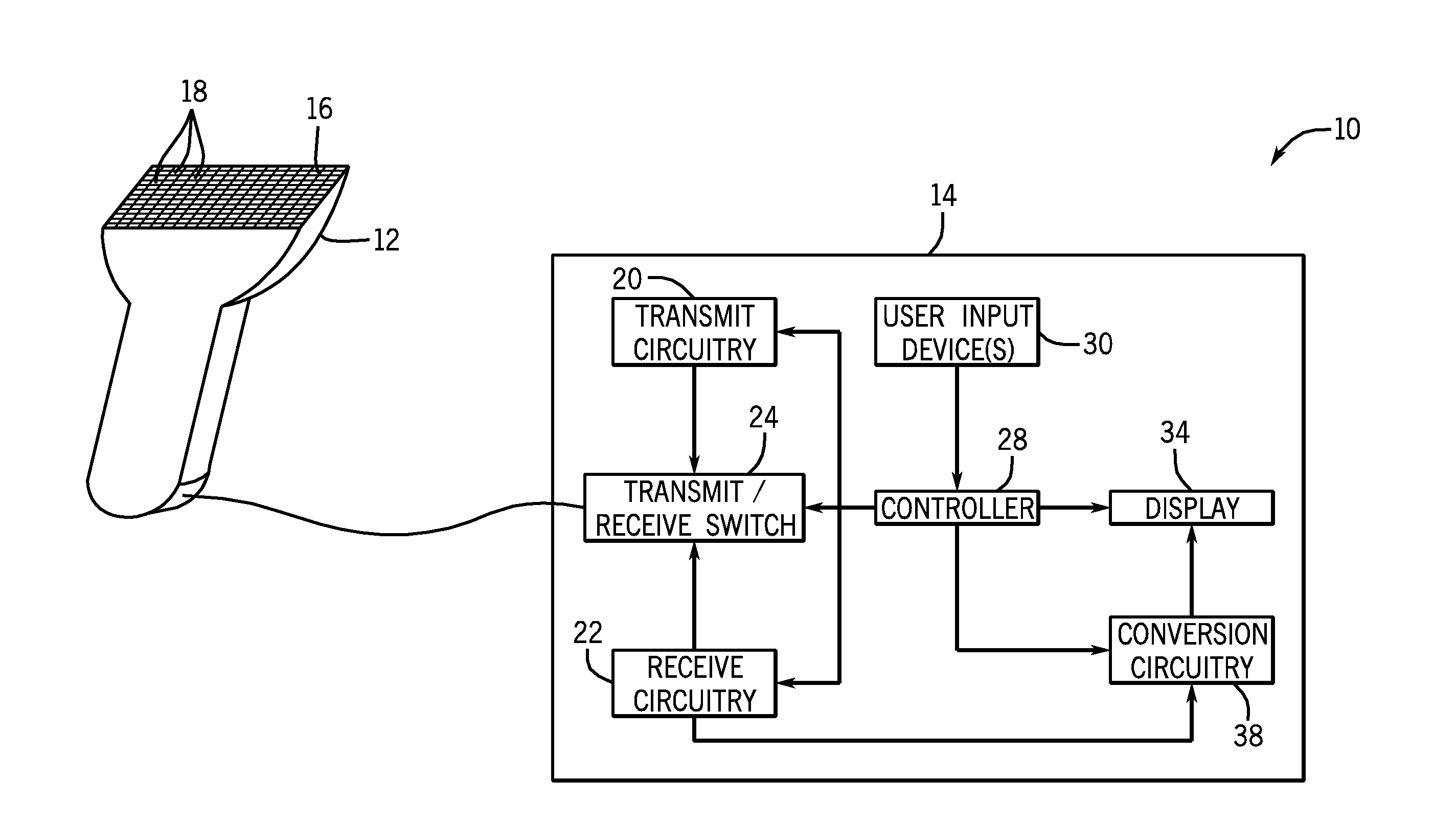
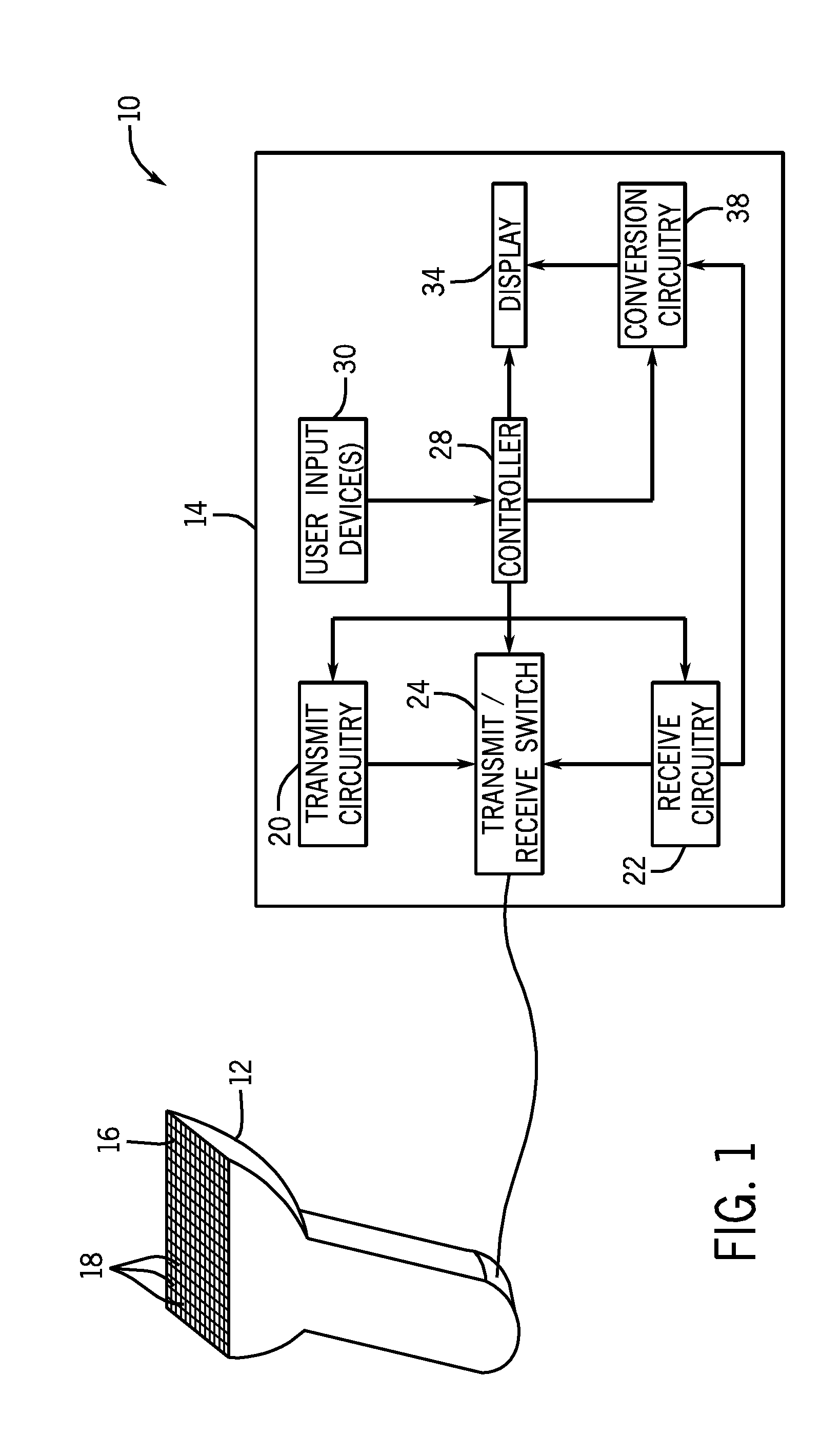
Wireless ultrasound transducer using ultrawideband
InactiveUS20100298711A1Eliminate useEliminate needTelemedicineInfrasonic diagnosticsTransceiverUltrasonic sensor
Ultrasound imaging systems and methods are described that include a cableless front end having a UltraWideBand transceiver and a beamformer that transmit ultrasound data to a back end physically separated from the front end, with the back end having a UltraWideBand transceiver for receiving ultrasound data from the front end UltraWideBand transceiver via a peer-to-peer communication protocol. The back end unit can also receive and transmit commands to and from the front end unit to select an image mode and has a signal processor and scan converter that can convert ultrasound data into image data for display. An input device in the front end allows the operator to selectively display ultrasound data or patient data on an auxiliary worn display or the nearest local display.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
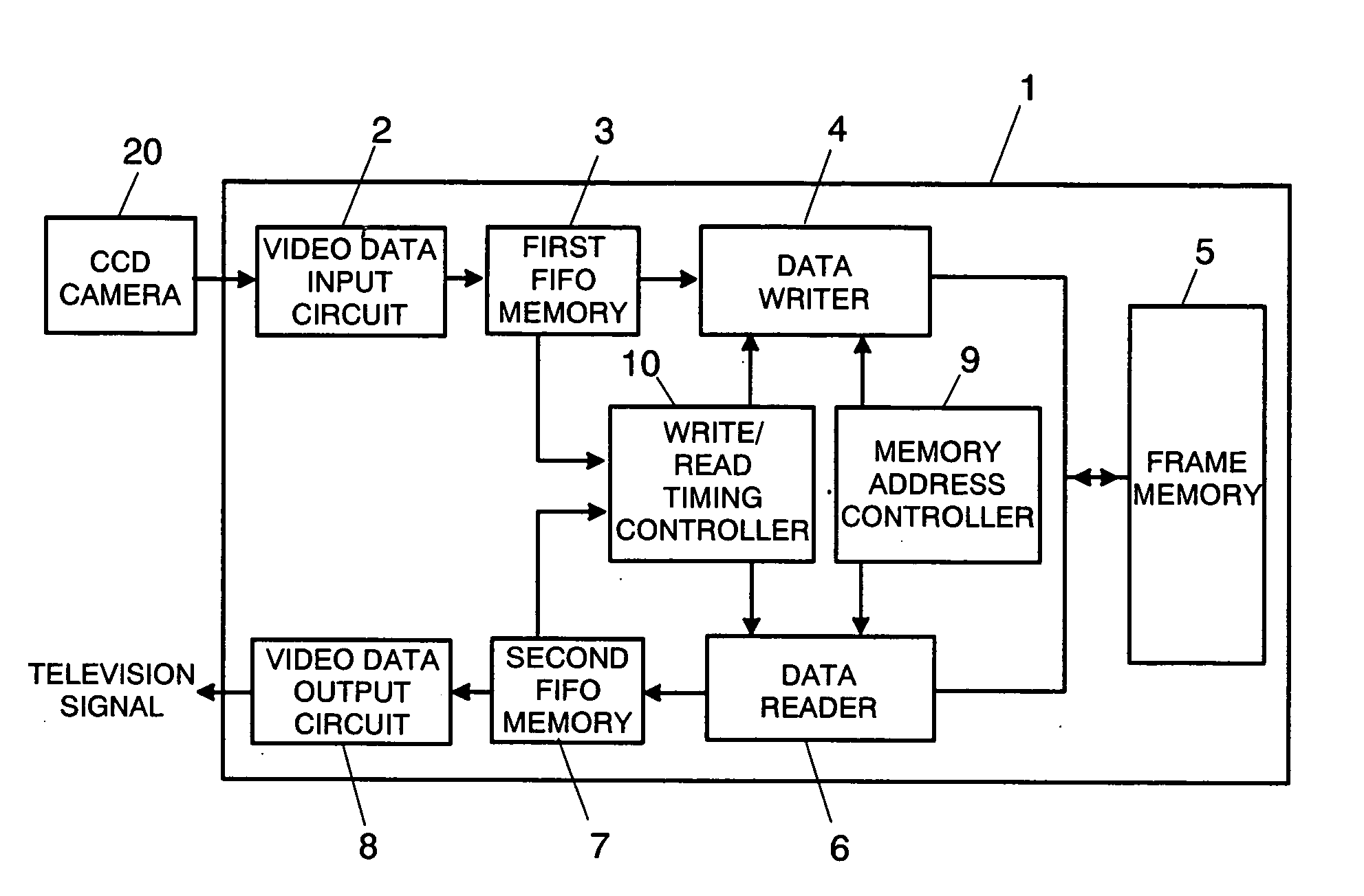
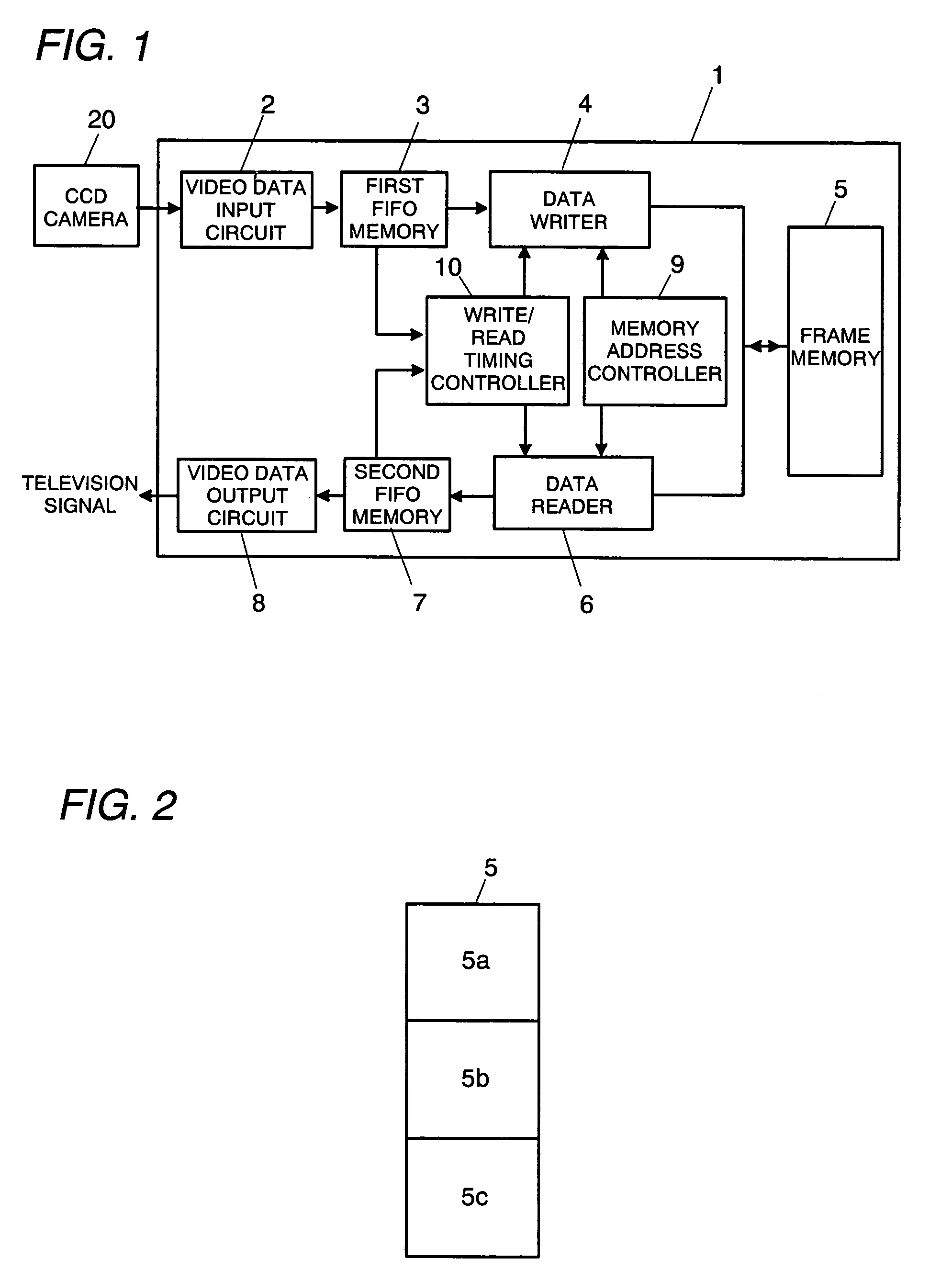
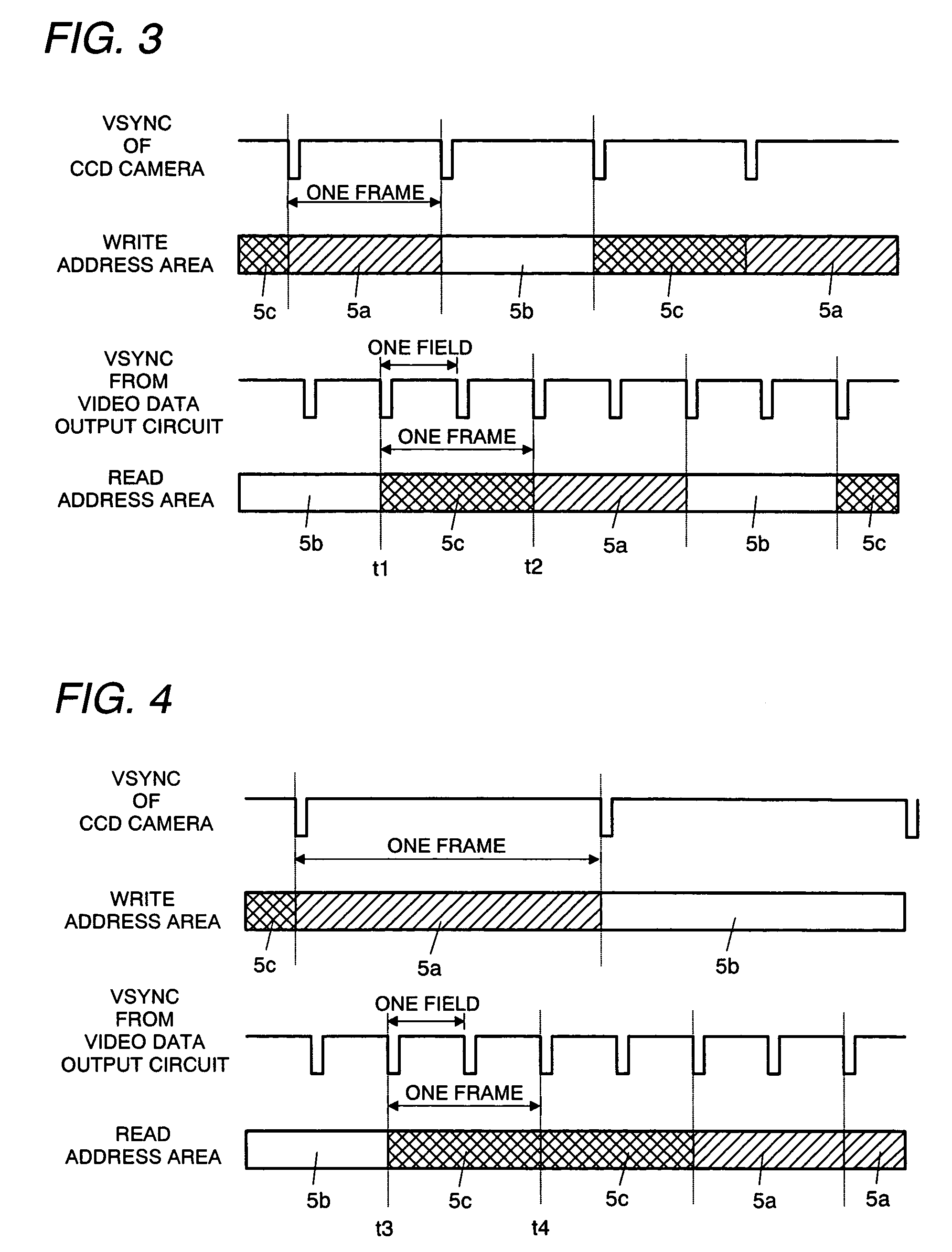
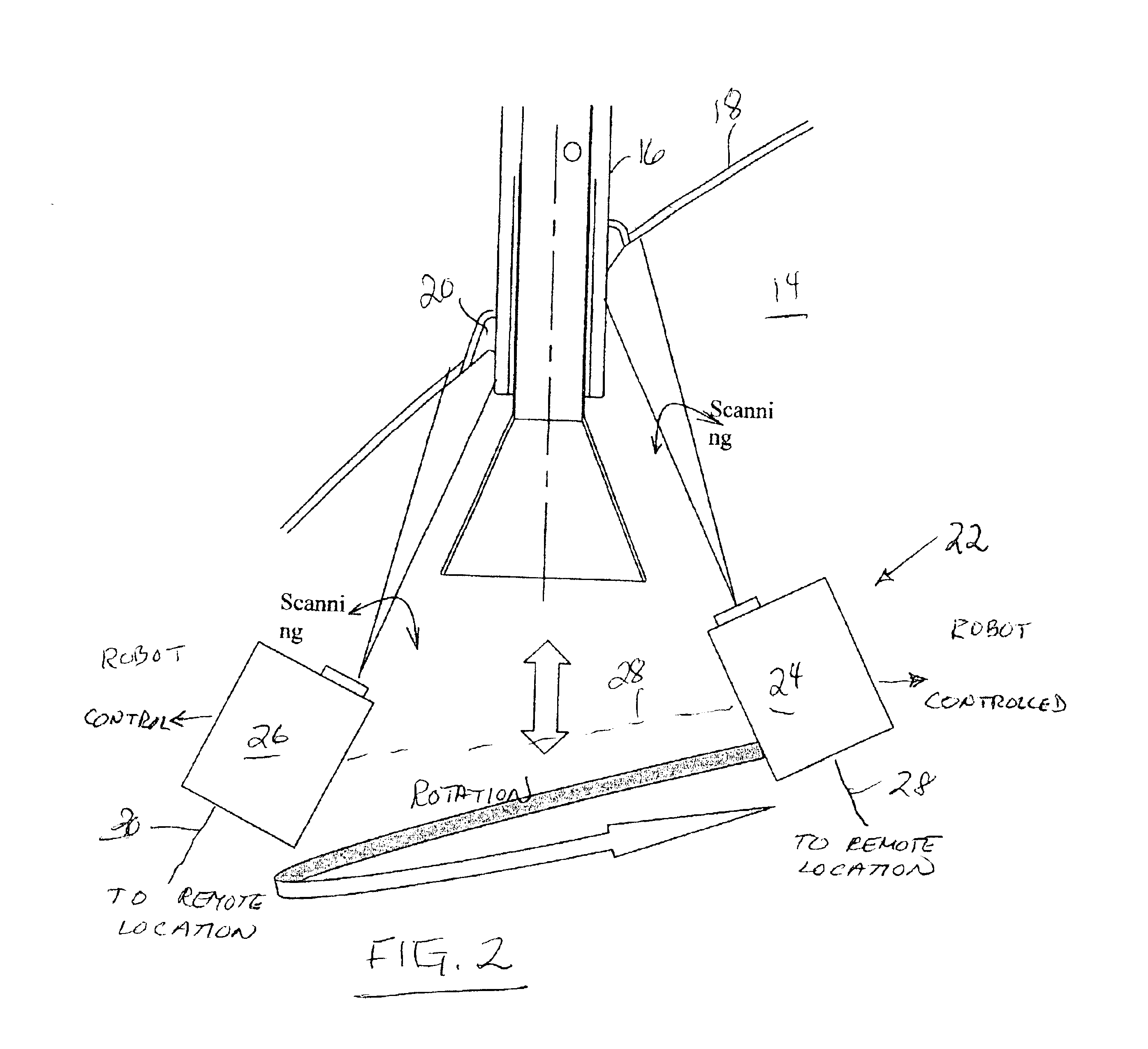
Scan converter
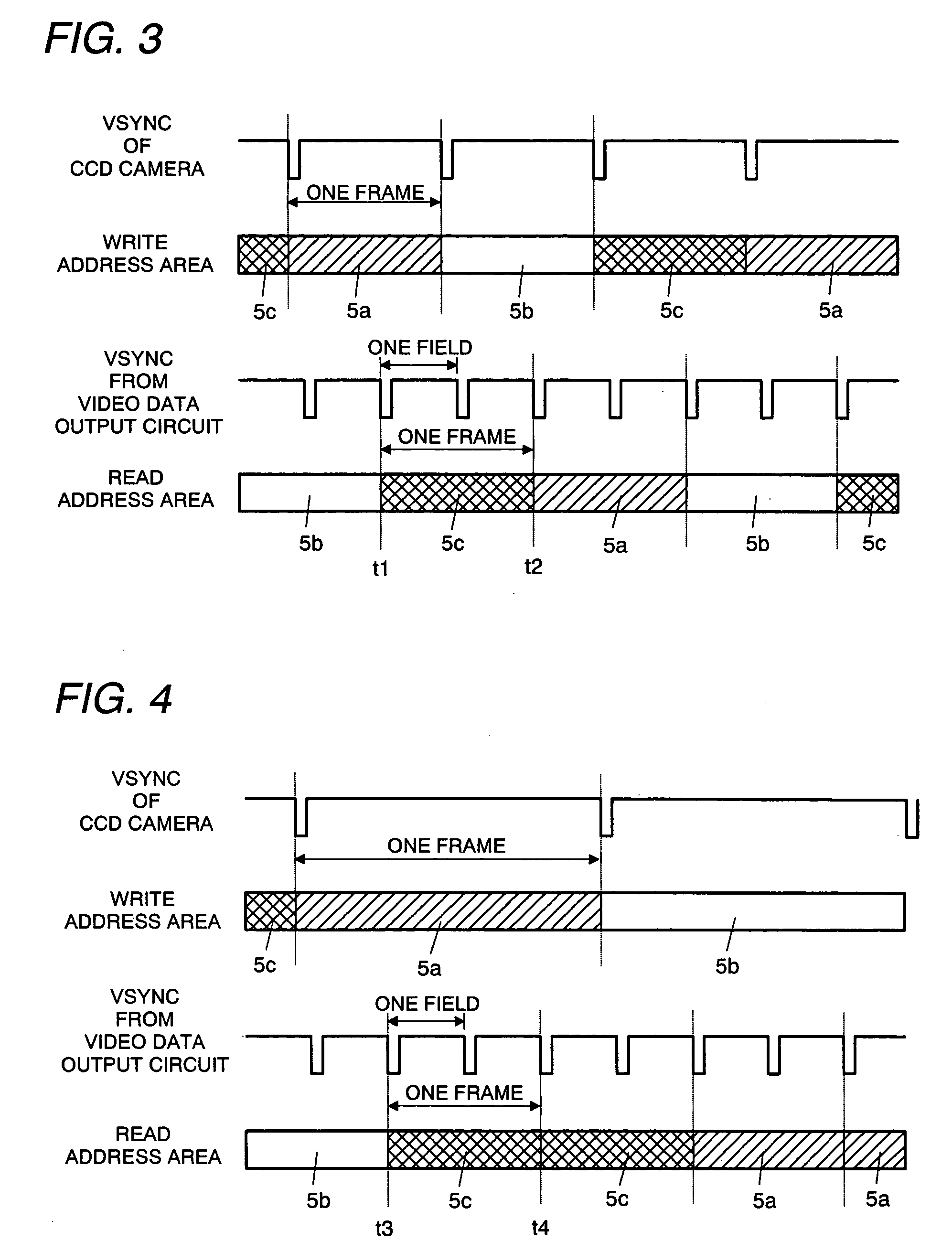
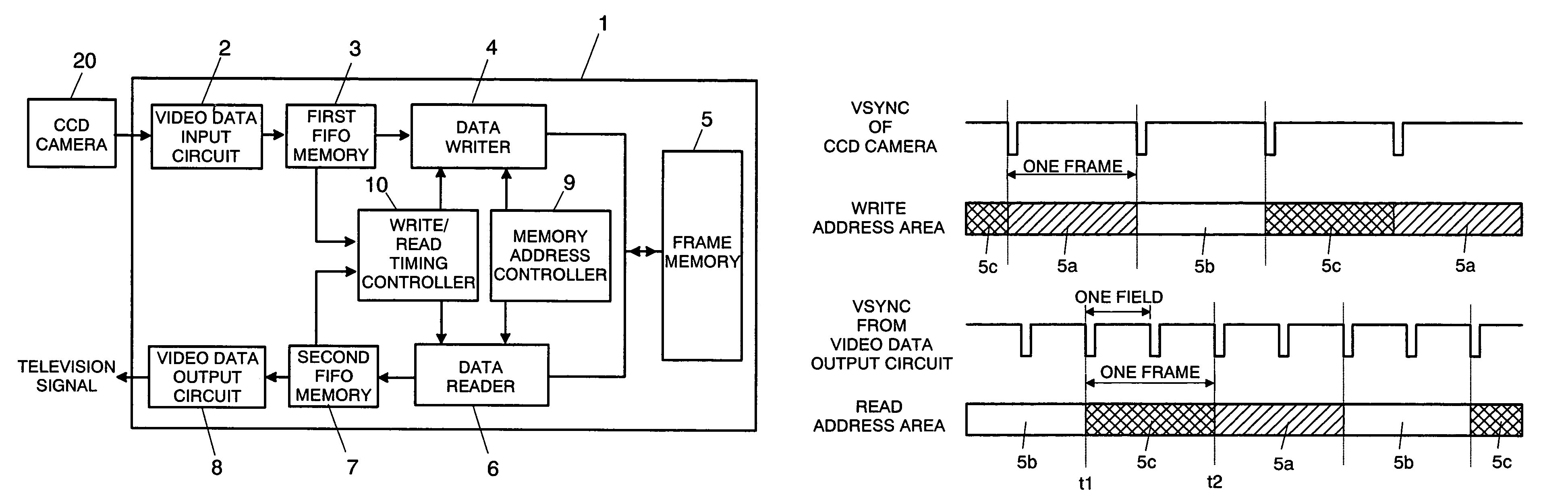
InactiveUS20050264691A1Reduce data storage capacityReduce dataTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsScan conversionData input
The scan converter comprises first and second memories 3, 7, a frame. memory 5 having a write period and a read period, a video data input circuit 2 for writing data at a first transfer rate into the memory 3, a video data output circuit 8 for outputting the data from the memory 7 at a third transfer rate. The transfer rate between the memories 3, 7 and the memory 5 is twice as fast as the first or third transfer rate, whichever is faster, and the memories 3 has data storage capacities greater than an amount of the data to be written into the memory 5 in each write period, and the memories 7 has data storage capacities greater than an amount of the data to be read from the memory 5 in each read period.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus and method for processing ultrasonic signal
InactiveUS6878113B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationAnalog-to-digital converter
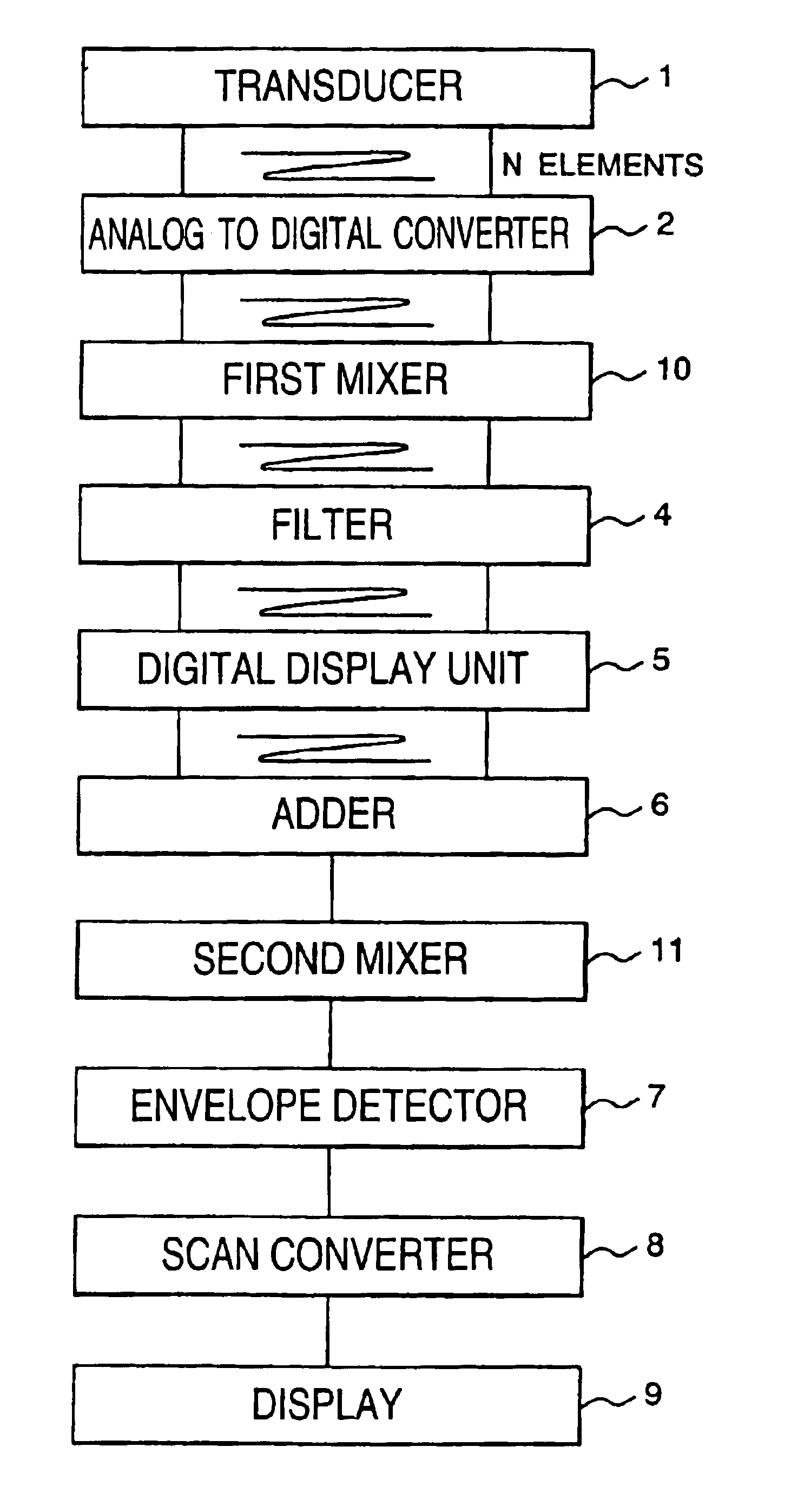
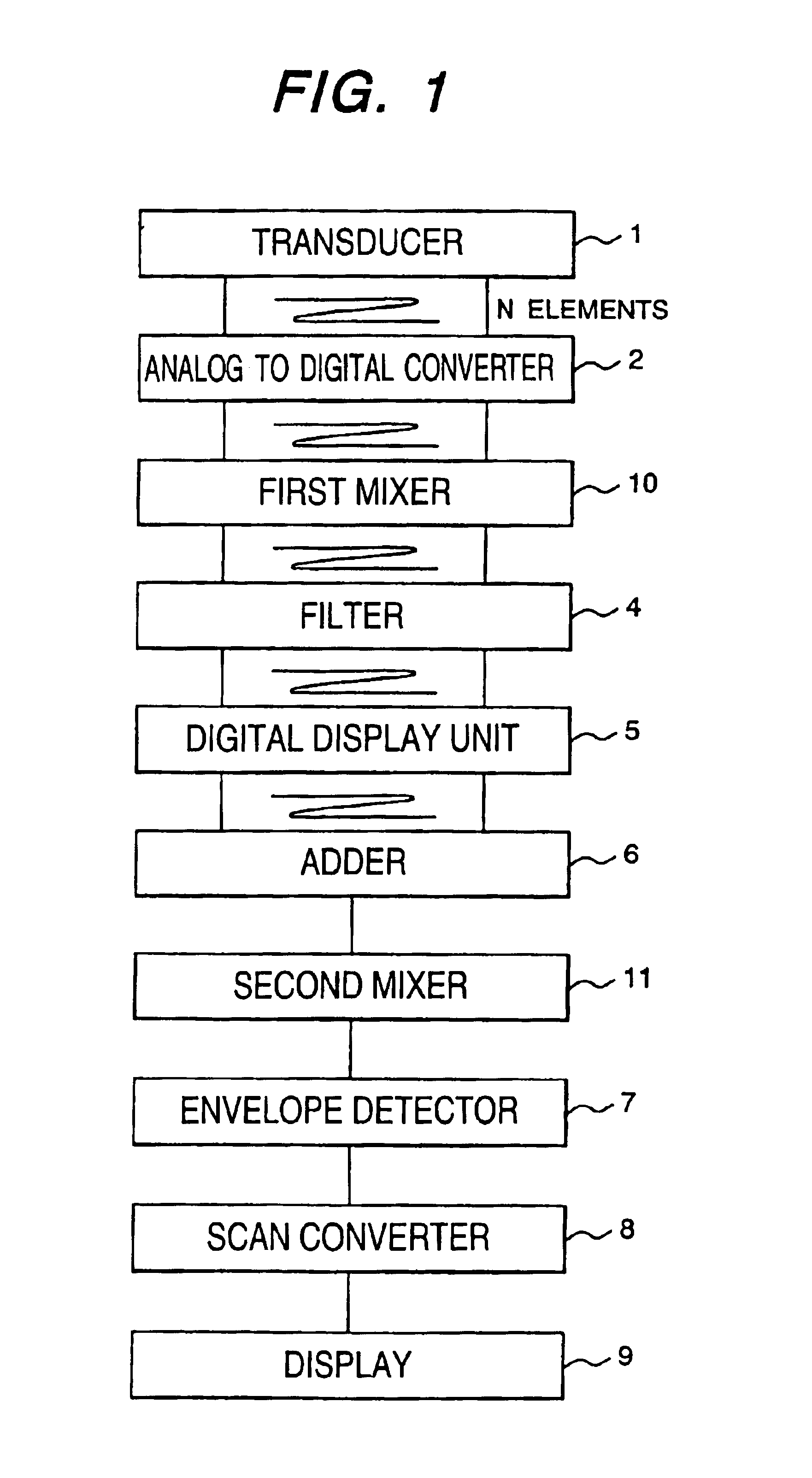
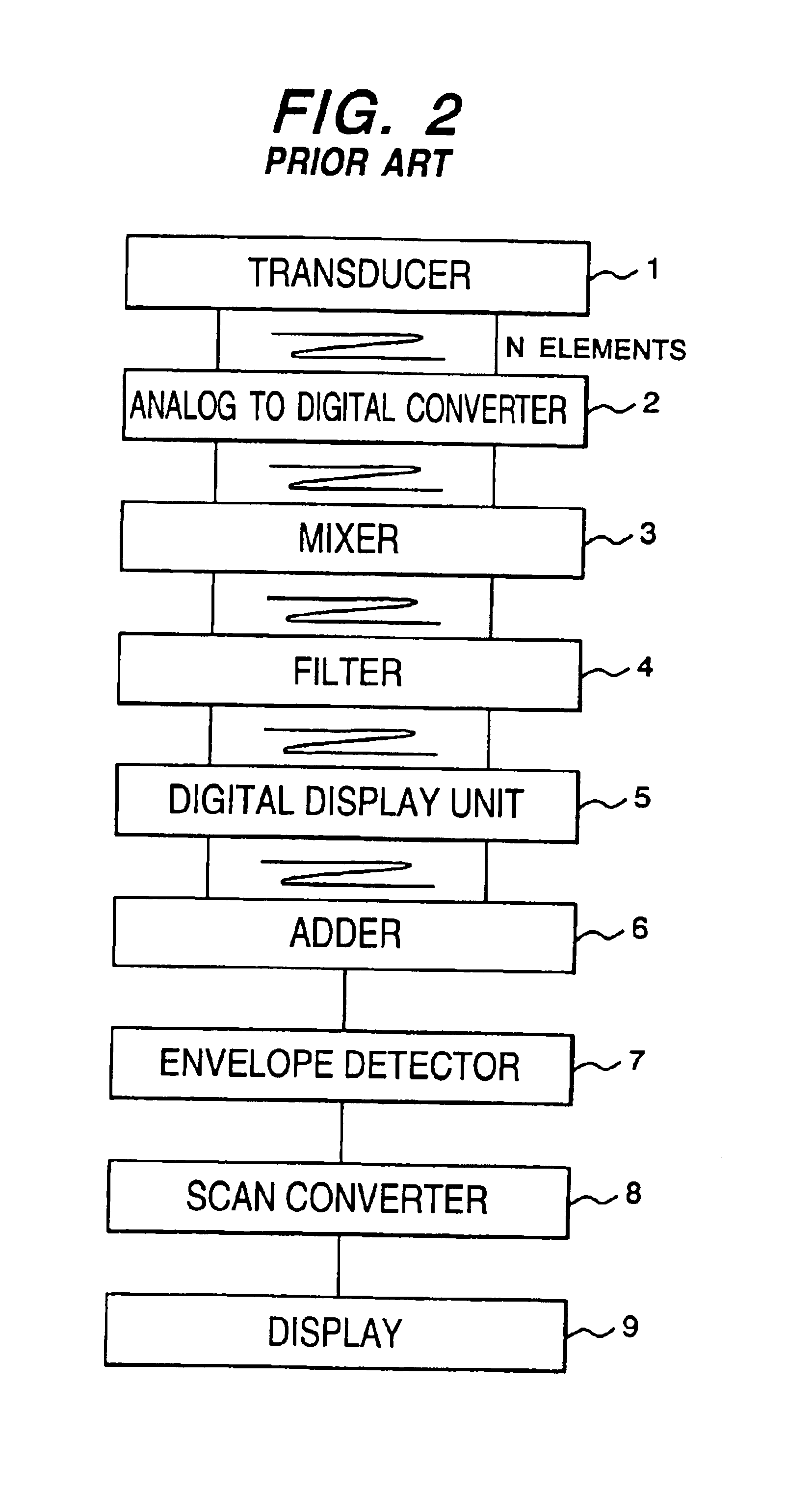
An ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus acquires images different in a frequency. The invention is composed of a transducer including plural elements for sending an ultrasonic wave and receiving the reflected ultrasonic wave, analog to digital converters that digitize plural received signals, first mixers that respectively multiply a signal from the converter and a first digital reference signal, first filters that respectively extract a signal having a predetermined center frequency from a signal from each first mixer, digital delay units that respectively delay a signal from each first filter, an adder that adds plural signals from the digital delay units, and a second mixer that multiplies a signal from the adder and a second digital reference signal. An envelope detector detects a signal from the second mixer, and a scan converter converts a signal from the detector to a picture signal for display, so the pass band of the filter is not required to be changed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
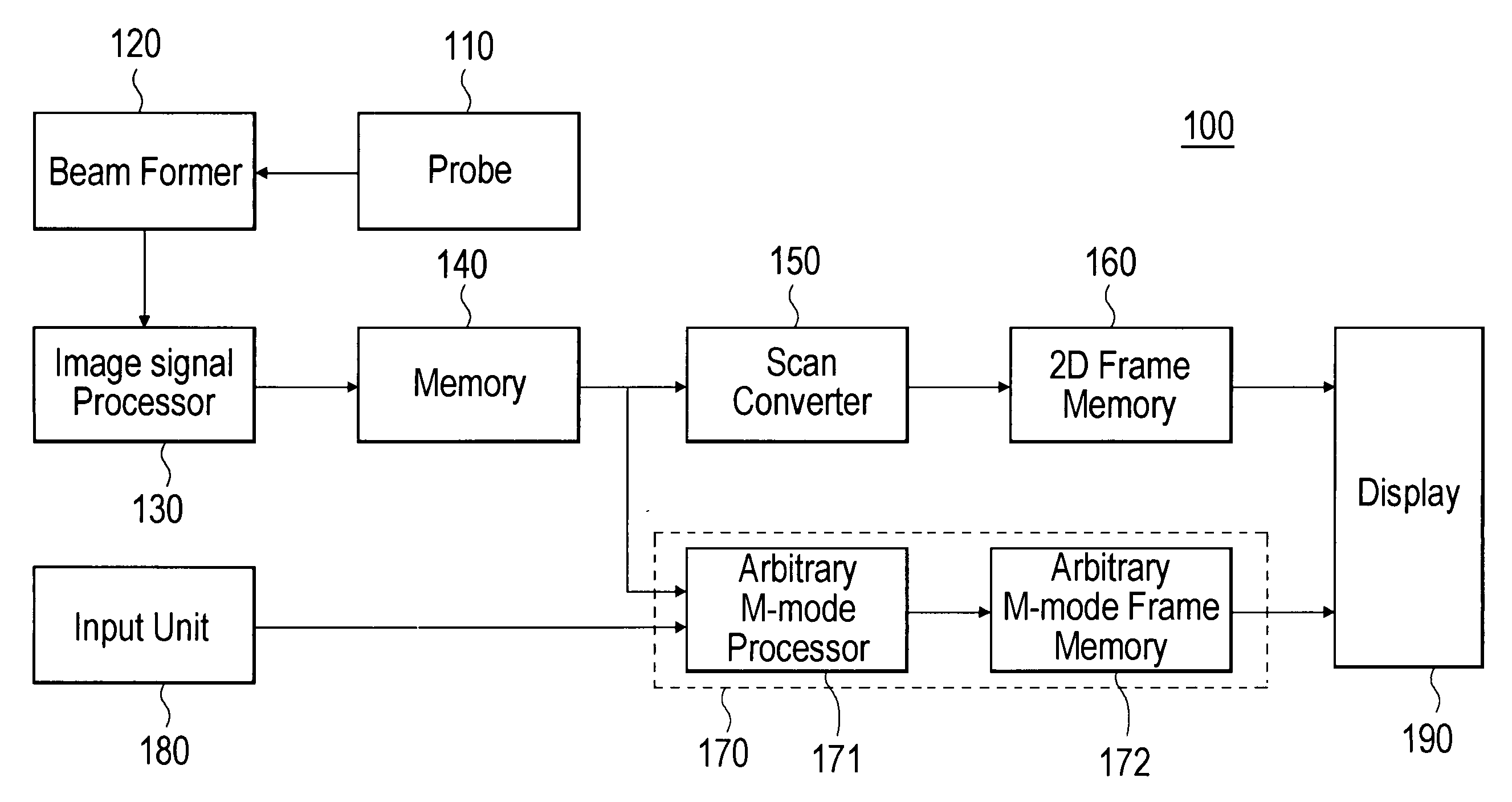
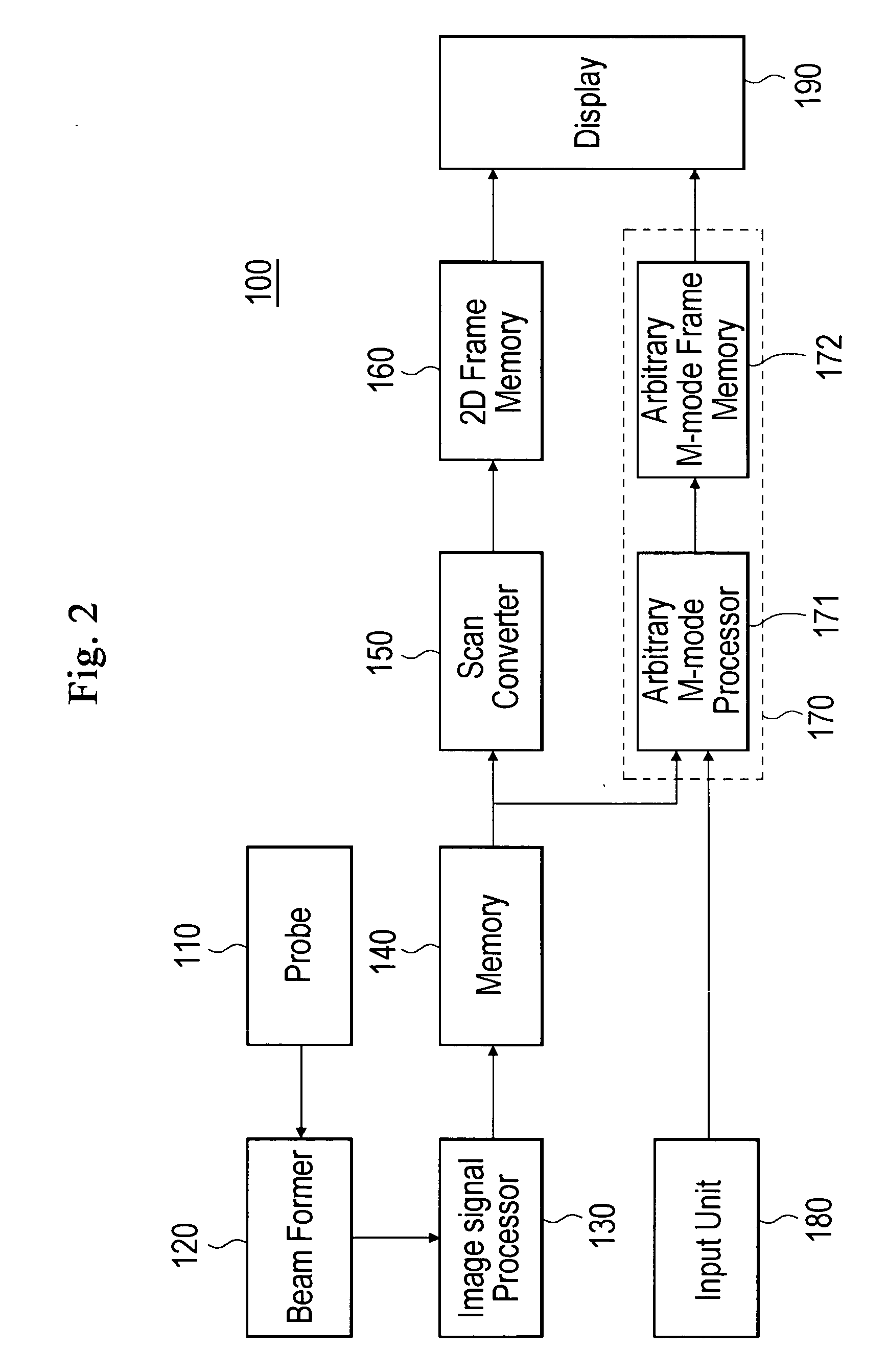
Ultrasound diagnostic system and method of forming arbitrary M-mode images
InactiveUS20060173327A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPipe supportsSonificationScan conversion
The present invention relates to an ultrasound diagnostic system and a method of forming arbitrary M-mode ultrasound images. The ultrasound diagnostic system includes: a probe for transmitting ultrasound signals toward a desired part of a target object and receiving the ultrasound signals reflected from the desired part; a scan converter for converting an ultrasound image data into a B-mode image data, the ultrasound image data being obtained based on the ultrasound signal received from the probe; an input unit for receiving an arbitrary M-mode scan line set by a user; an arbitrary M-mode processor for generating an arbitrary M-mode image data corresponding to the arbitrary M-mode scan line; and a display unit for displaying at least one of the B-mode image data, the M-mode image data and the arbitrary M-mode scan line. In accordance with the present invention, the biological information of the target object can be observed and diagnosed from an arbitrary direction and path, regardless of the direction of the ultrasound signals. Additionally, the arbitrary M-mode image, which is more similar to the real image, can be provided for the user by generating the arbitrary M-mode images corresponding to the arbitrary M-mode scan line by using ultrasound image data before scan-conversion.
Owner:MEDISON CO LTD
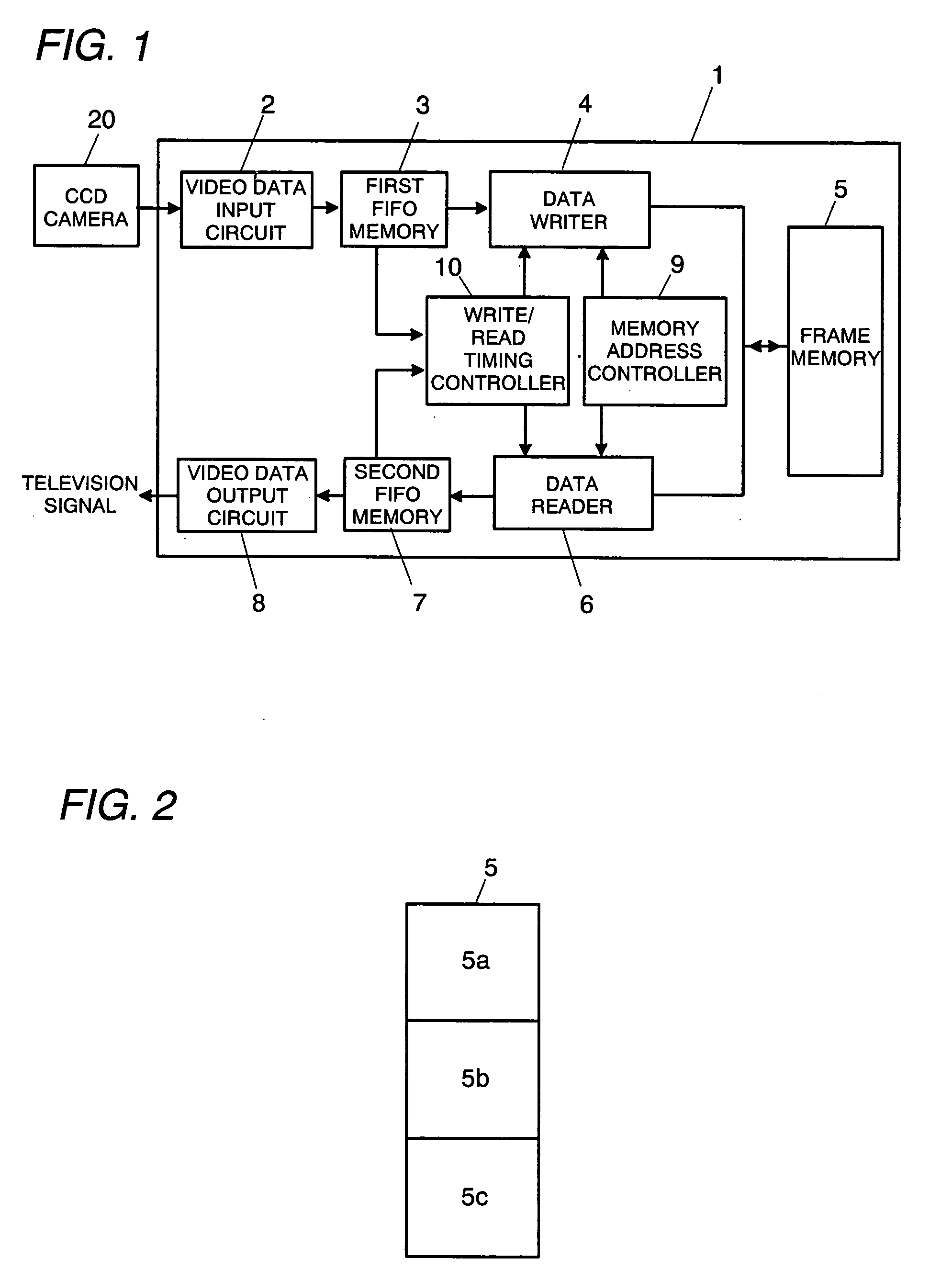
Scan converter
InactiveUS7349027B2Reduce data storage capacityReduce dataTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsScan conversionData input
The scan converter comprises first and second memories 3, 7, a frame memory 5; having a write period and a read period, a video data input circuit 2 for writing data at a first transfer rate into the memory 3, a video data output circuit 8 for outputting the data from the memory 7 at a third transfer rate. The transfer rate between the memories 3, 7 and the memory 5 is twice as fast as the first or third transfer rate, whichever is faster, and the memories 3 has data storage capacities greater than an amount of the data to be written into the memory 5 in each write period, and the memories 7 has data storage capacities greater than an amount of the data to be read from the memory 5 in each read period.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Volume rendering in the acoustic grid methods and systems for ultrasound diagnostic imaging
InactiveUS20040181151A1Amount is reduced and eliminatedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryData setSonification
Methods and systems for volume rendering three-dimensional ultrasound data sets in an acoustic grid using a graphics processing unit are provided. For example, commercially available graphic accelerators cards using 3D texturing may provide 256x, 256x128 8 bit volumes at 25 volumes per second or better for generating a display of 512x512 pixels using ultrasound data. By rendering from data at least in part in an acoustic grid, the amount of scan conversion processing is reduced or eliminated prior to the rendering.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
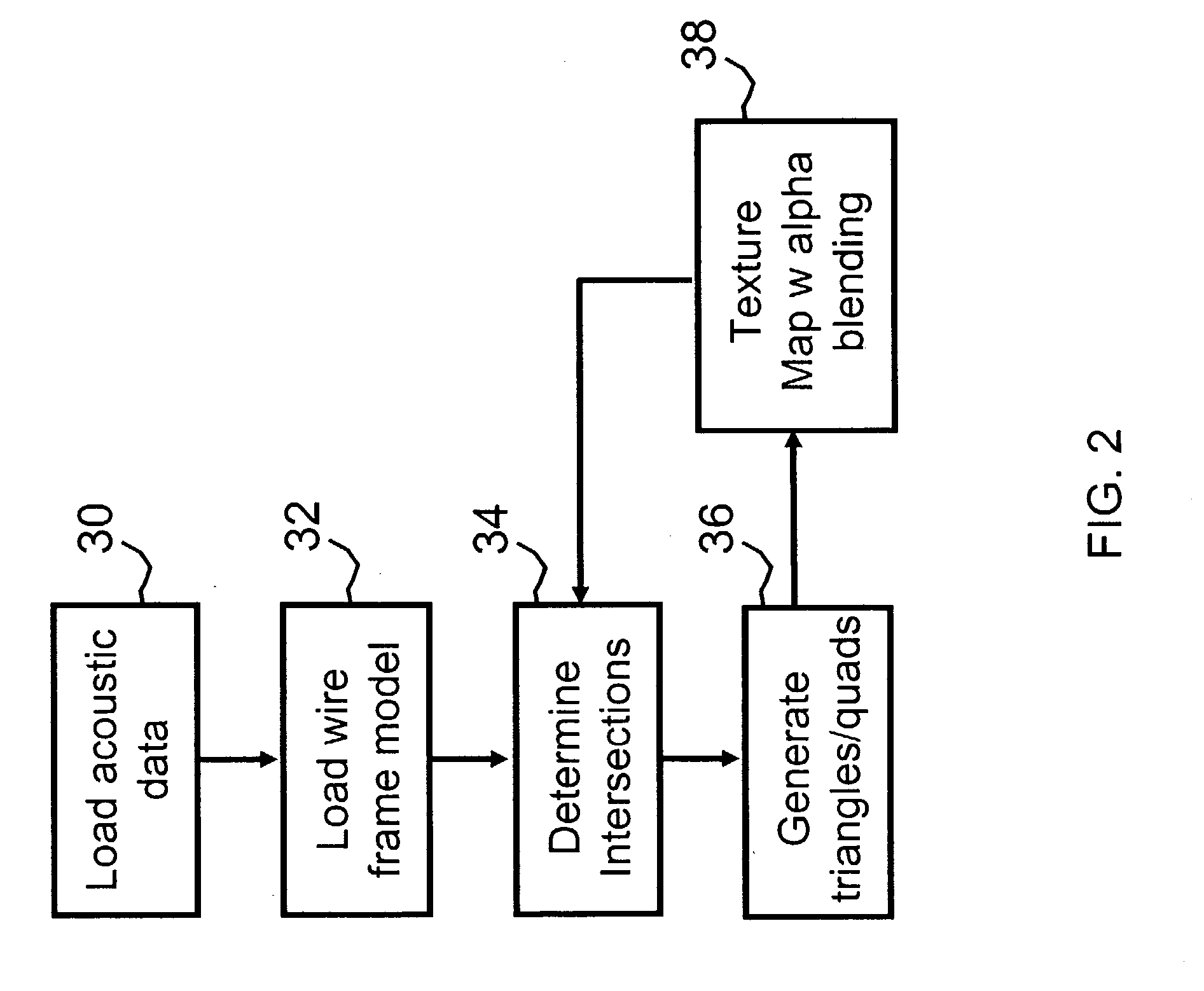
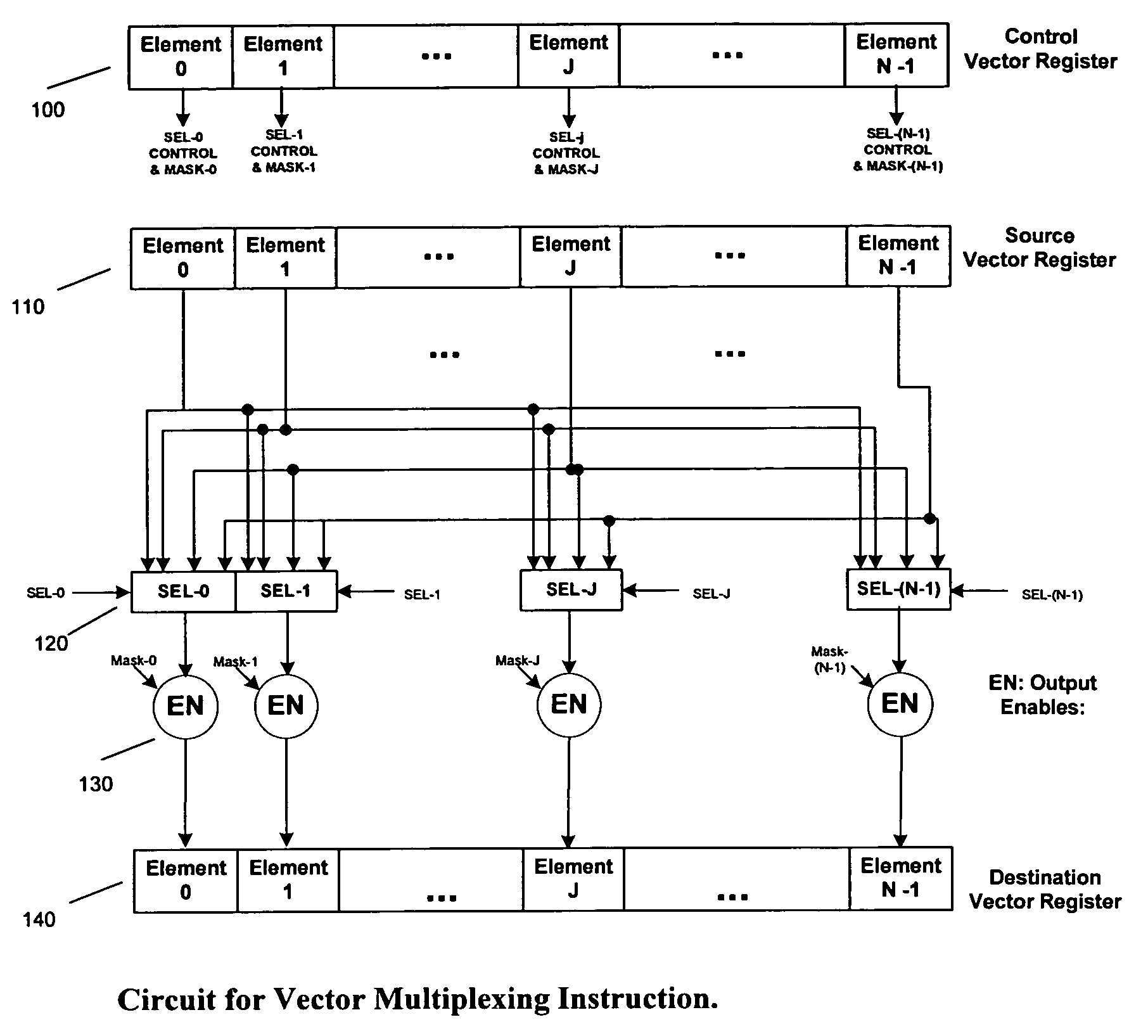
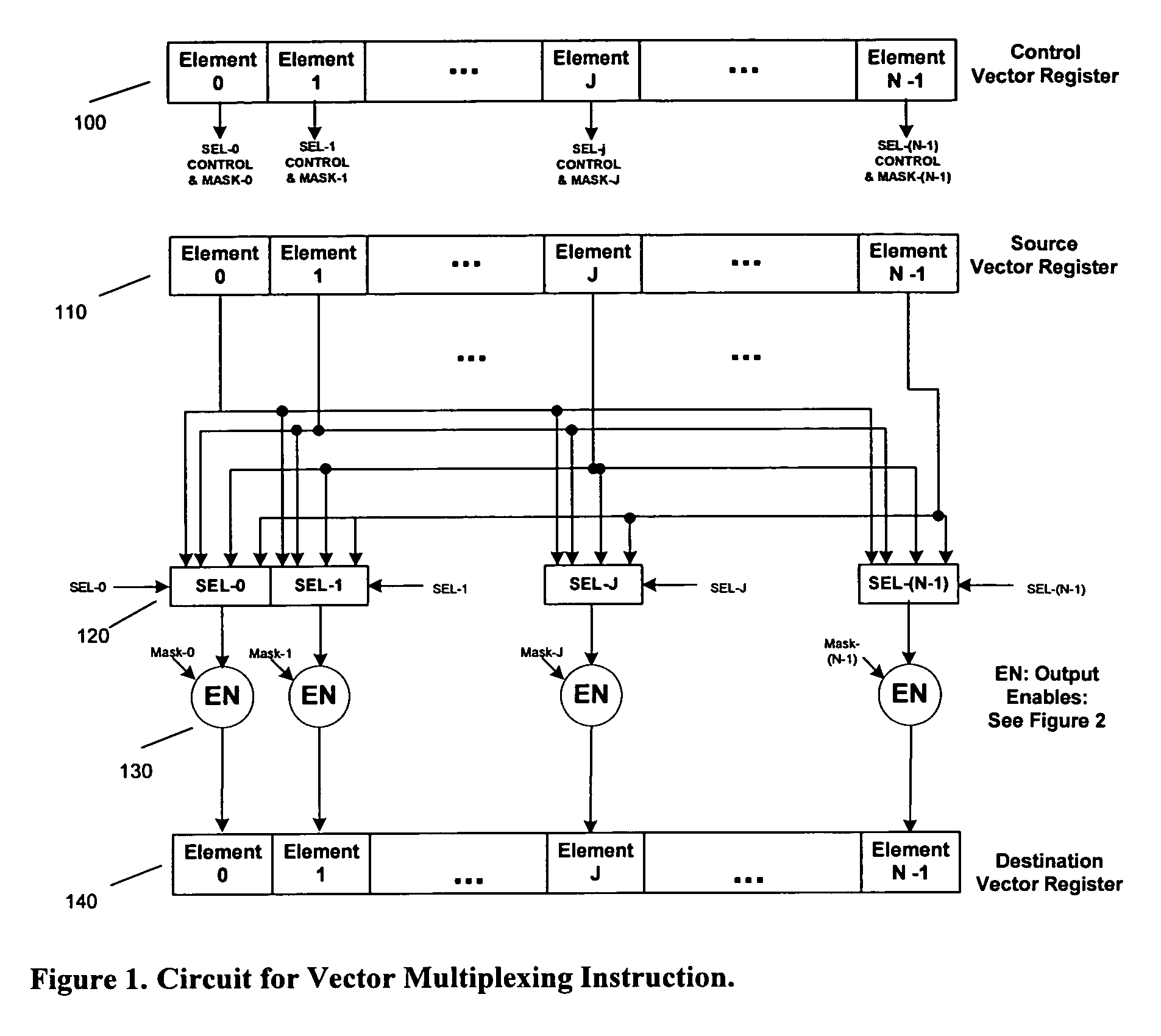
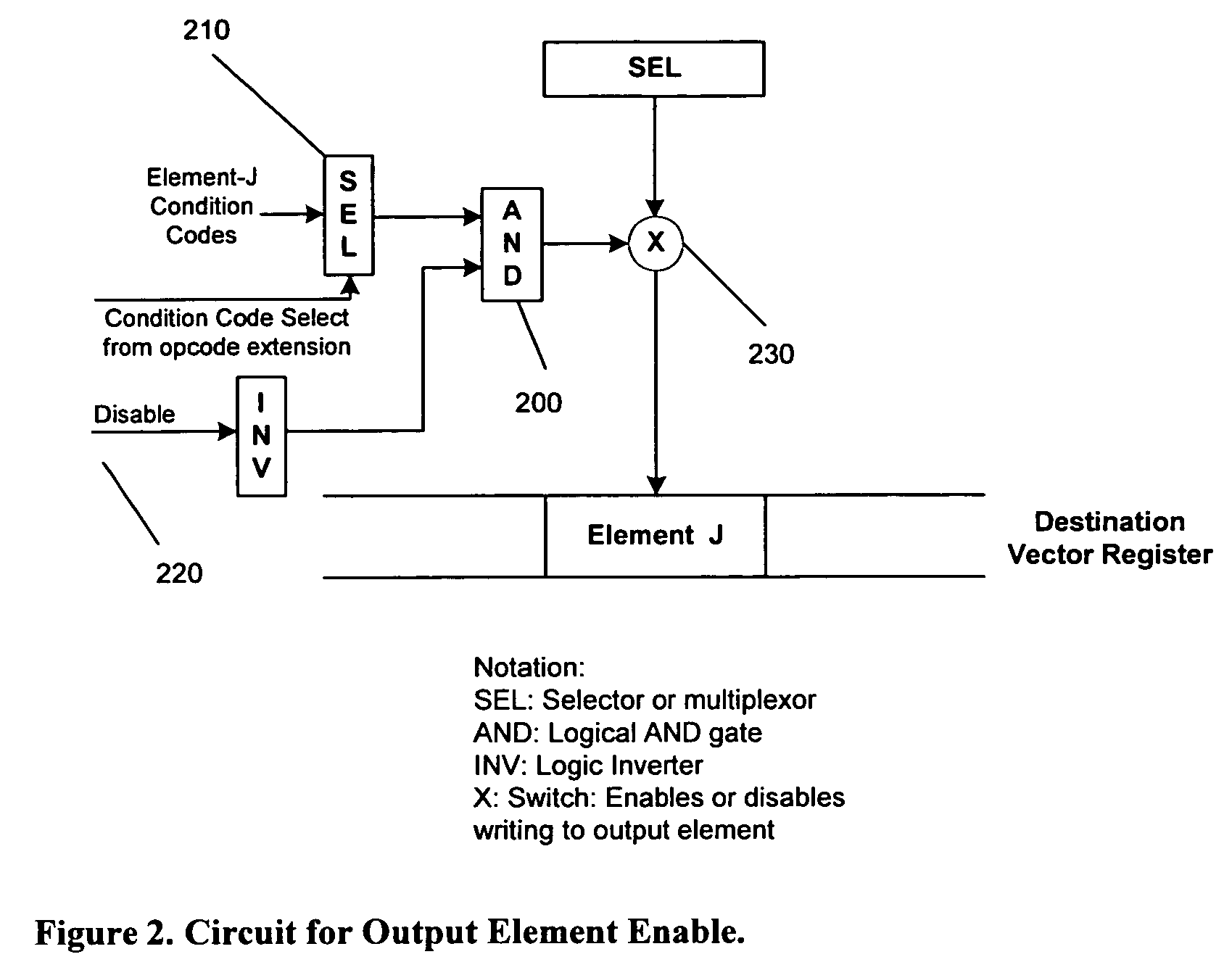
Fast and flexible scan conversion and matrix transpose in a SIMD processor
InactiveUS6963341B1Efficient and flexibleQuick implementationProgram controlArchitecture with single central processing unitPresent methodScan conversion
The present invention provides efficient ways to implement scan conversion and matrix transpose operations using vector multiplex operations in a SIMD processor. The present method provides a very fast and flexible way to implement different scan conversions, such as zigzag conversion, and matrix transpose for 2×2, 4×4, 8×8 blocks commonly used by all video compression and decompression algorithms.
Owner:MIMAR TIBET
Unified rasterization and ray tracing rendering environments
A graphics processor architecture provides for scan conversion and ray tracing approaches to visible surface determination as concurrent and separate processes. Surfaces can be identified for shading by scan conversion and ray tracing. Data produced by each can be normalized, so that instances of shaders, being executed on a unified shading computation resource, can shade surfaces originating from both ray tracing and rasterization. Such resource also may execute geometry shaders. The shaders can emit rays to be tested for intersection by the ray tracing process. Such shaders can complete, without waiting for those emitted rays to complete. Where scan conversion operates on tiles of 2-D screen pixels, the ray tracing can be tile aware, and controlled to prioritize testing of rays based on scan conversion status. Ray population can be controlled by feedback to any of scan conversion, and shading.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
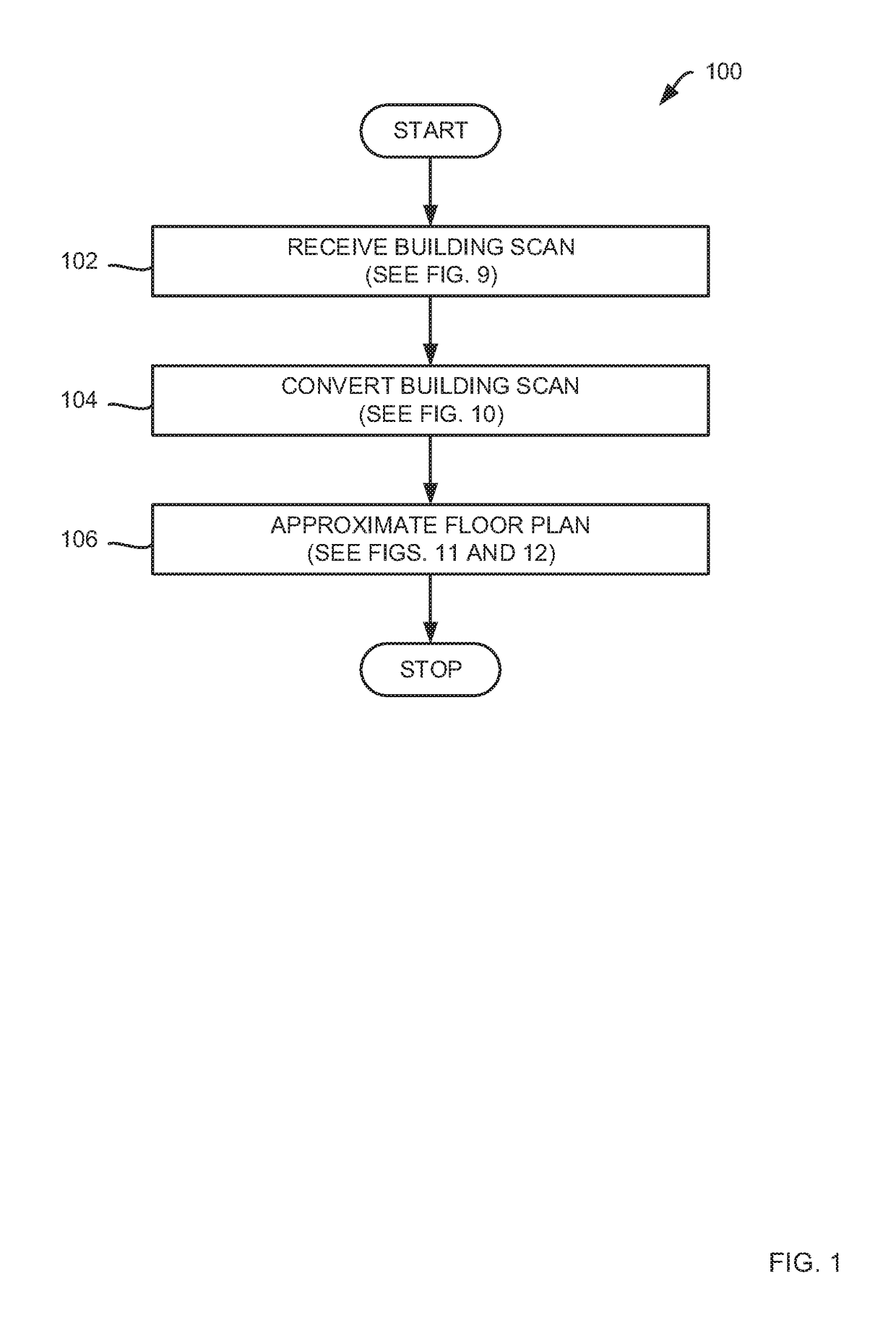
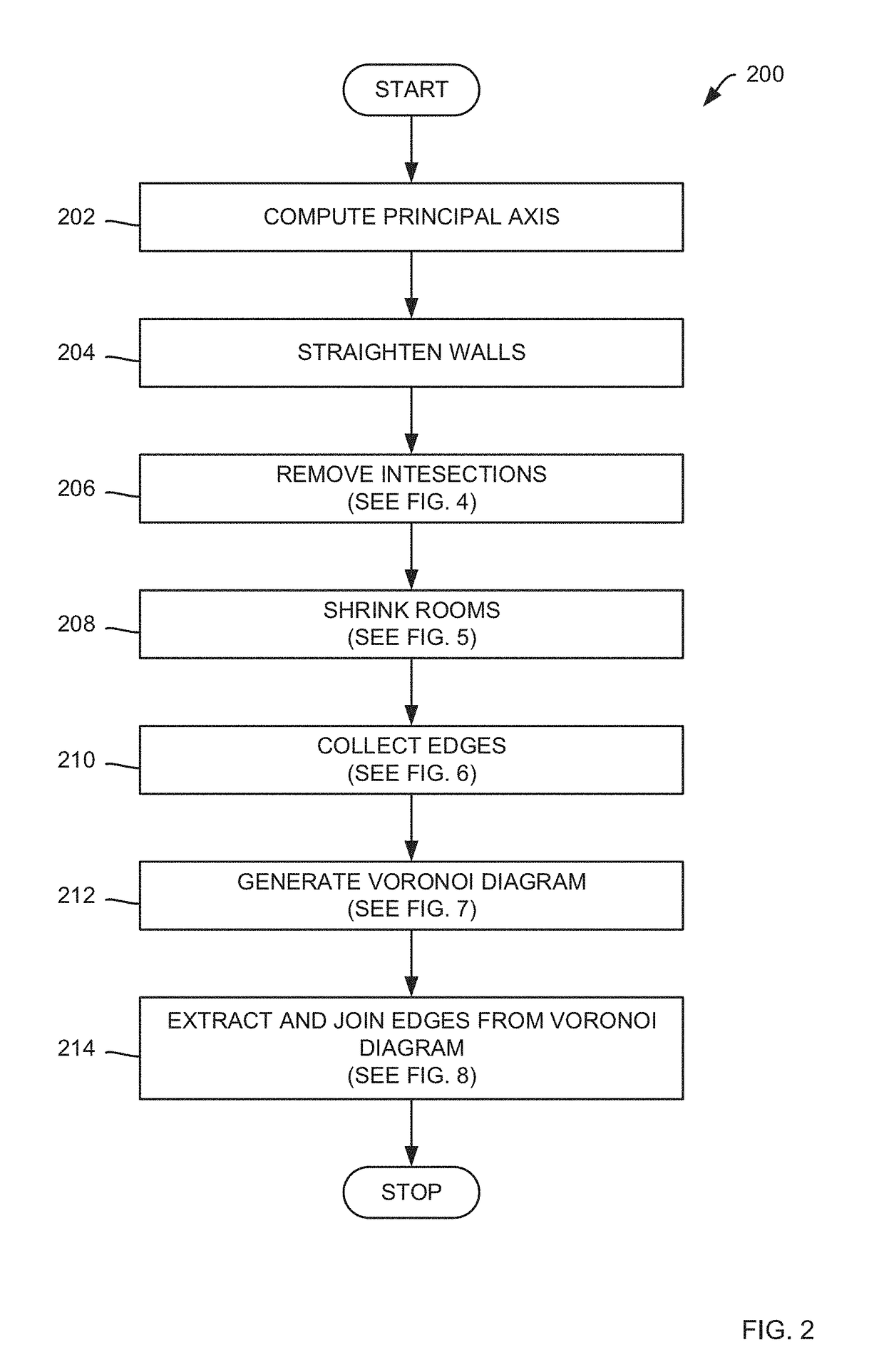
Methods for generating a floor plan from a building scan
Methods for generating a floor plan from a building scan of a building using an electronic computing device are presented, the method including: causing the electronic computing device to receive the building scan; converting the building scan to a floor plan; and refining the floor plan to approximate the building. In some embodiments, the causing the electronic computing device to receive the building scan further includes: extracting information from an input file to obtain a representation of a number of rooms and walls corresponding with the building scan, where the information is selected from the group consisting of: a set of vertices, a set of triangles, and a set of rooms.
Owner:HILTI AG
Modular apparatus for diagnostic ultrasound
A modular diagnostic ultrasound apparatus is provided comprising a core unit, system electronics and an I / O port. The core unit comprises a housing and a system electronics package within the housing. The system electronics has one or more concatenated filters, including a front end transmit / receive circuit, a processor, a back end circuit for scan conversion, a system clock and a programmable system memory device. There is at least one I / O port connected to the front end and the back end of the system electronics package and extending through the core unit housing wherein all system data processing information is transmitted or received through the I / O port.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
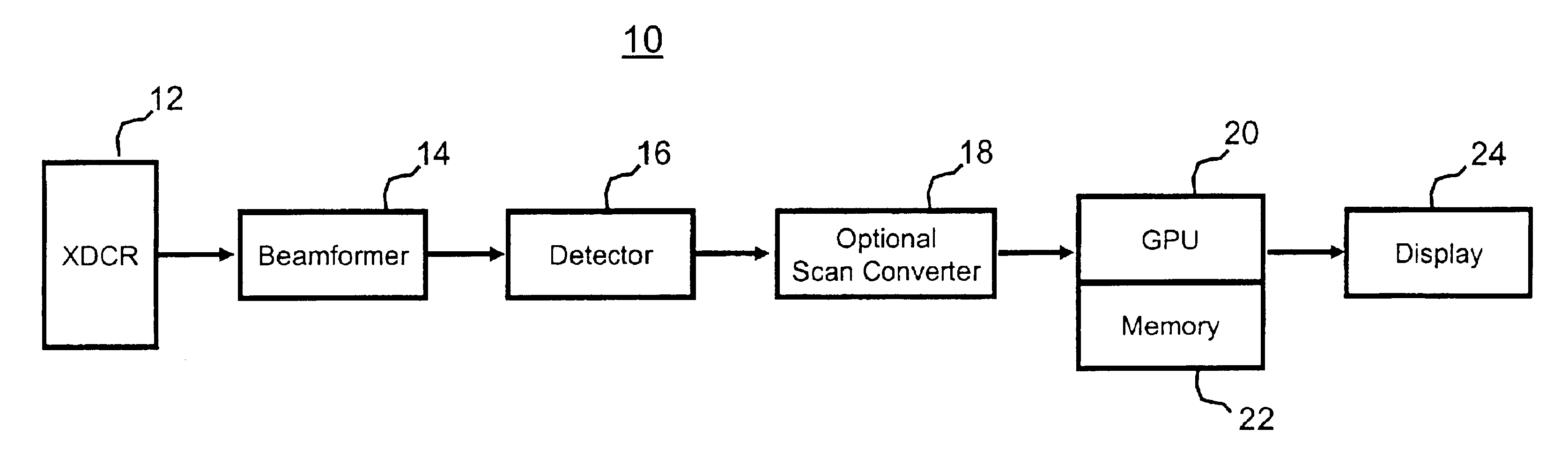
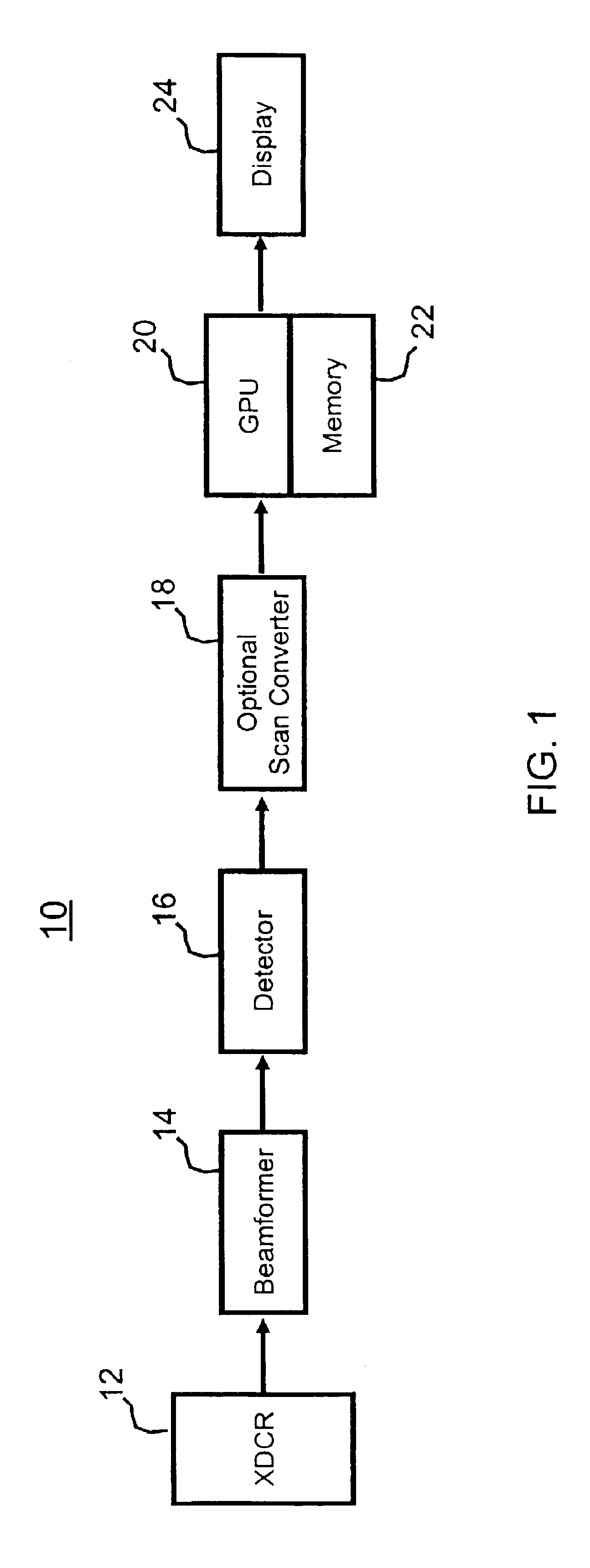
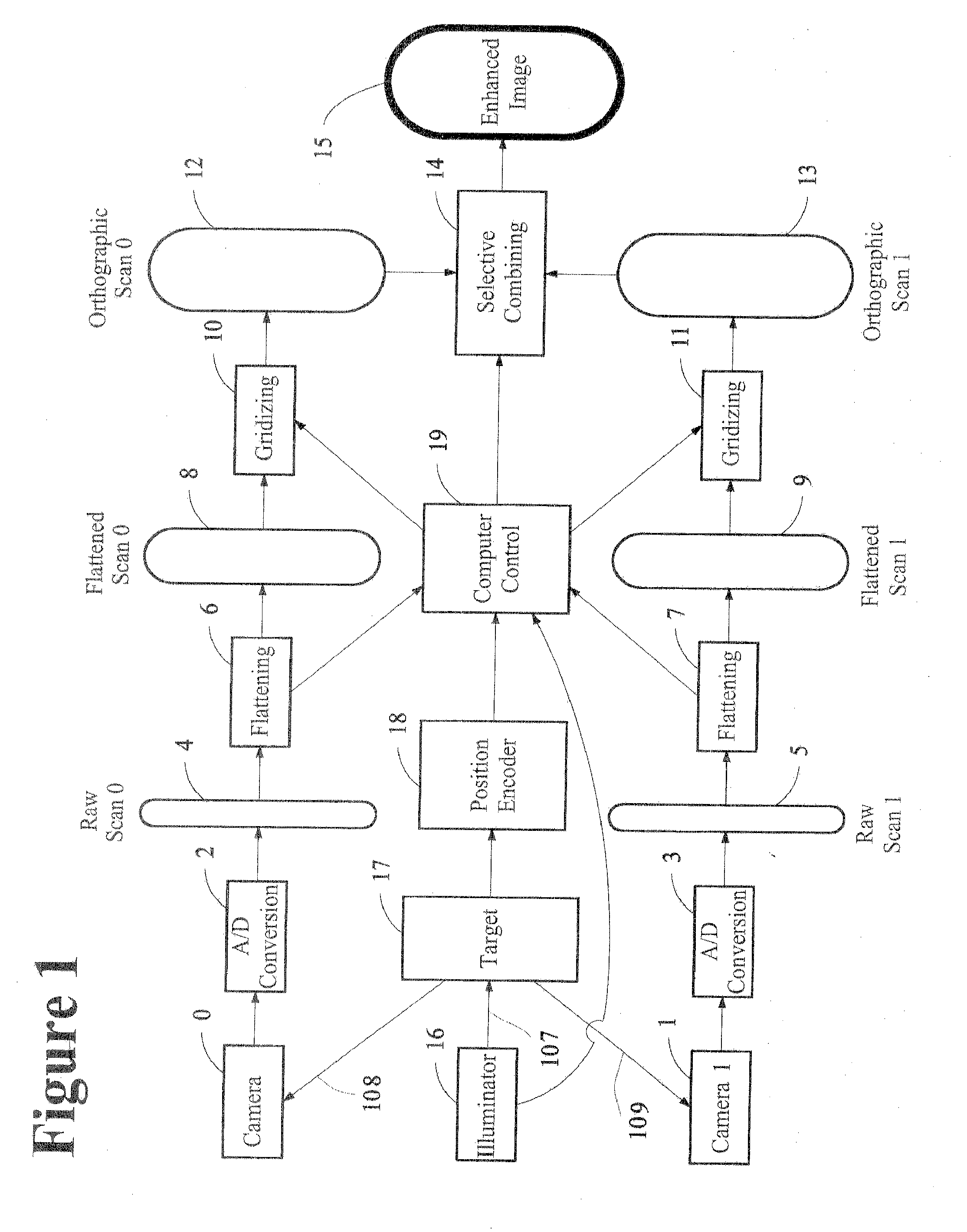
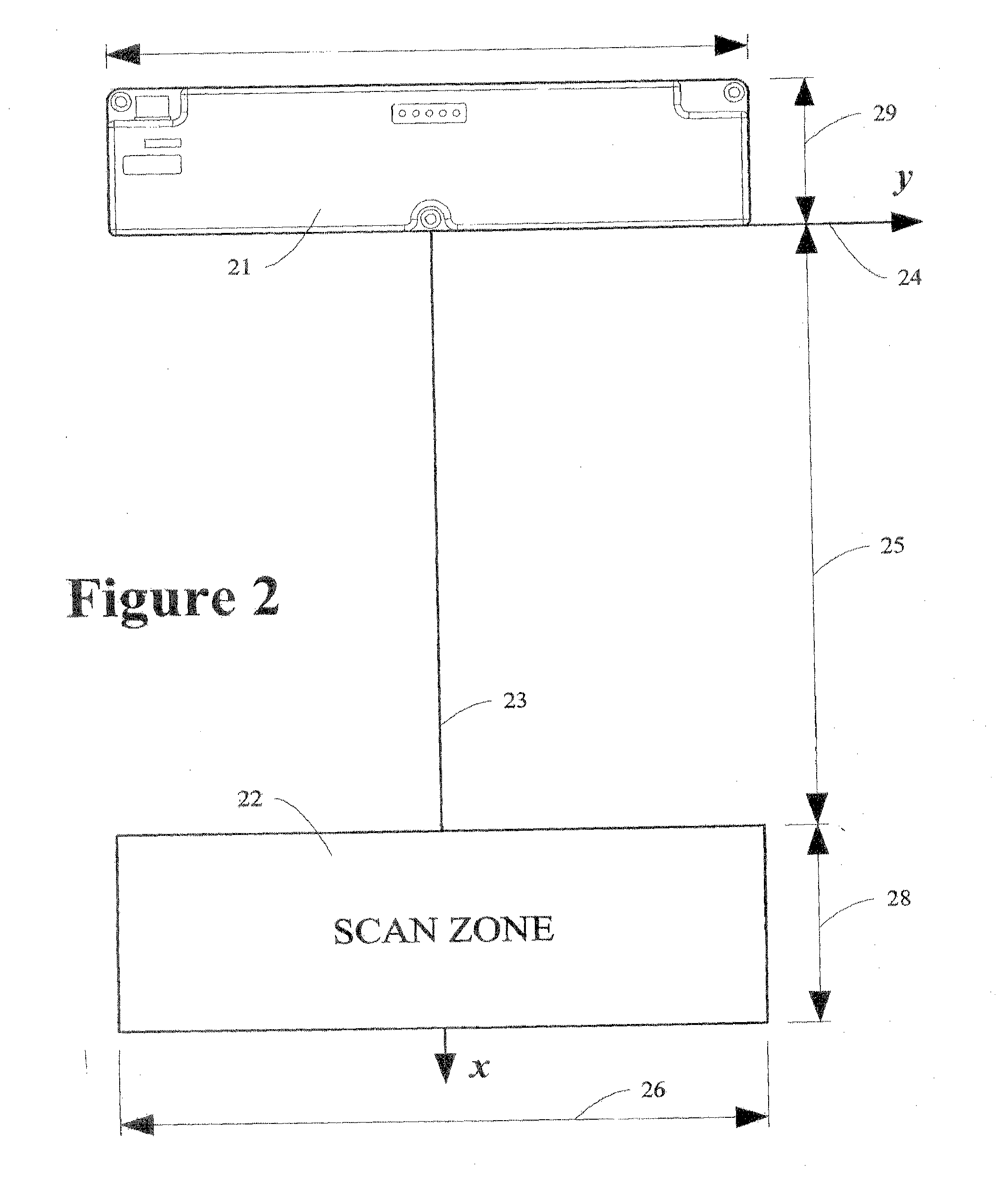
Enhanced imaging method and apparatus
ActiveUS20120218437A1Quality improvementAccurate areaImage enhancementTelevision system detailsParallaxScan conversion
This invention provides accurate, high quality images for the identification of the surface characteristics of an object, that may be used as an input to suitable industrial process. It involves acquiring a first raw scan of a portion of a target object across a scan line in a scan zone with a first camera and simultaneously acquiring a second raw scan of the same portion of the target object across the scan line in the scan zone with a second camera. The raw scans are converted to digital and then processed with flattening coefficients derived from measurements of variations in illumination. The first and second cameras sets of flattened image data are then gridized to compensate for parallax, make them orthographic sets of image data that can be compared on a pixel-by-pixel basis with a known or measured geometric profile of the target. A selection of enhanced pixel value for a surface coordinate can then be made, based on both sets of data. The obscuring of surface features by specular reflection can thus be effectively eliminated.
Owner:HERMARY OPTO ELECTRONICS
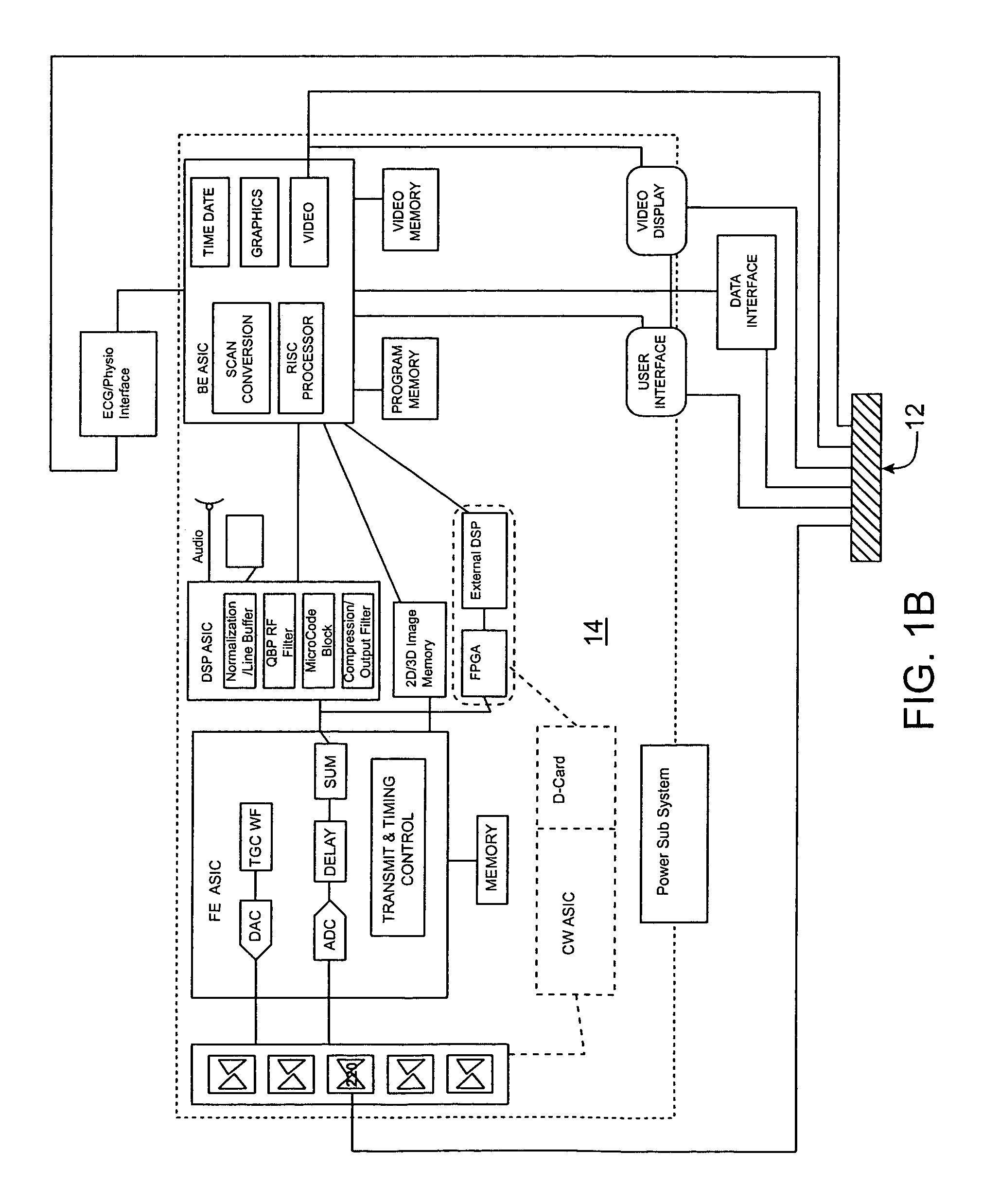
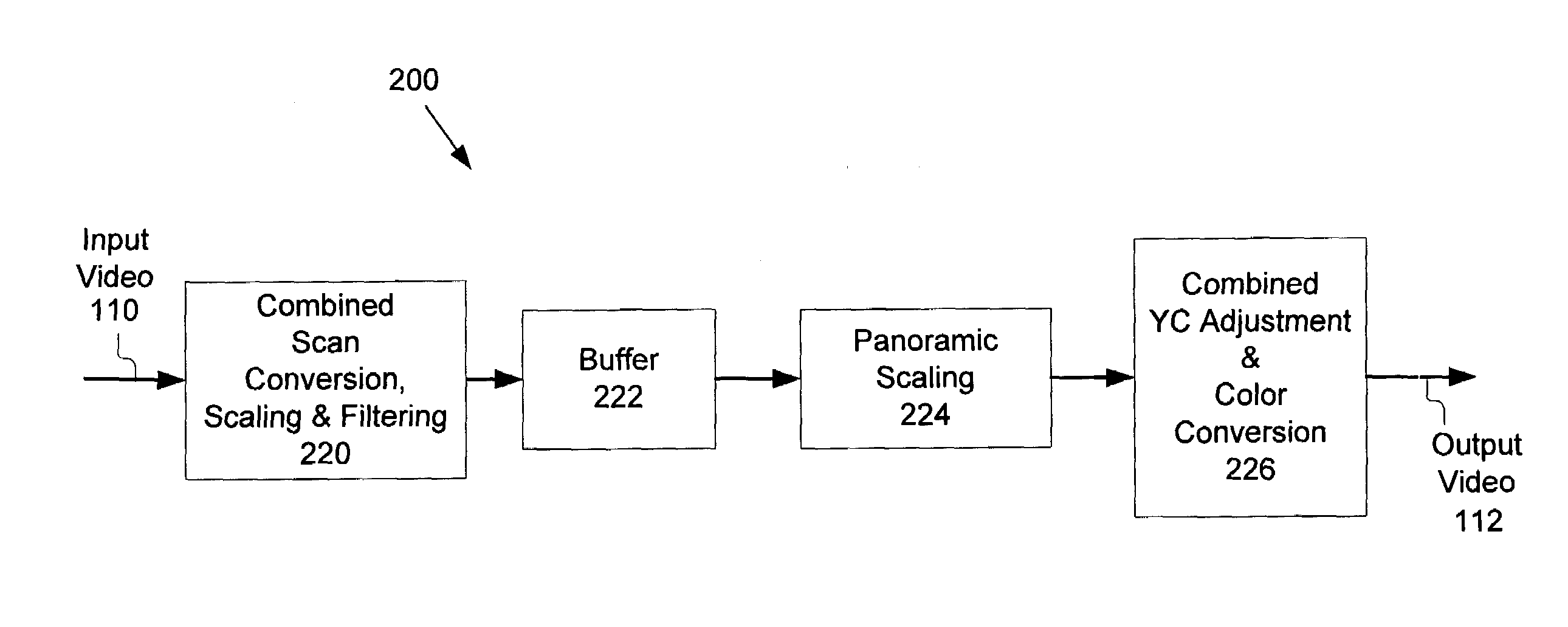
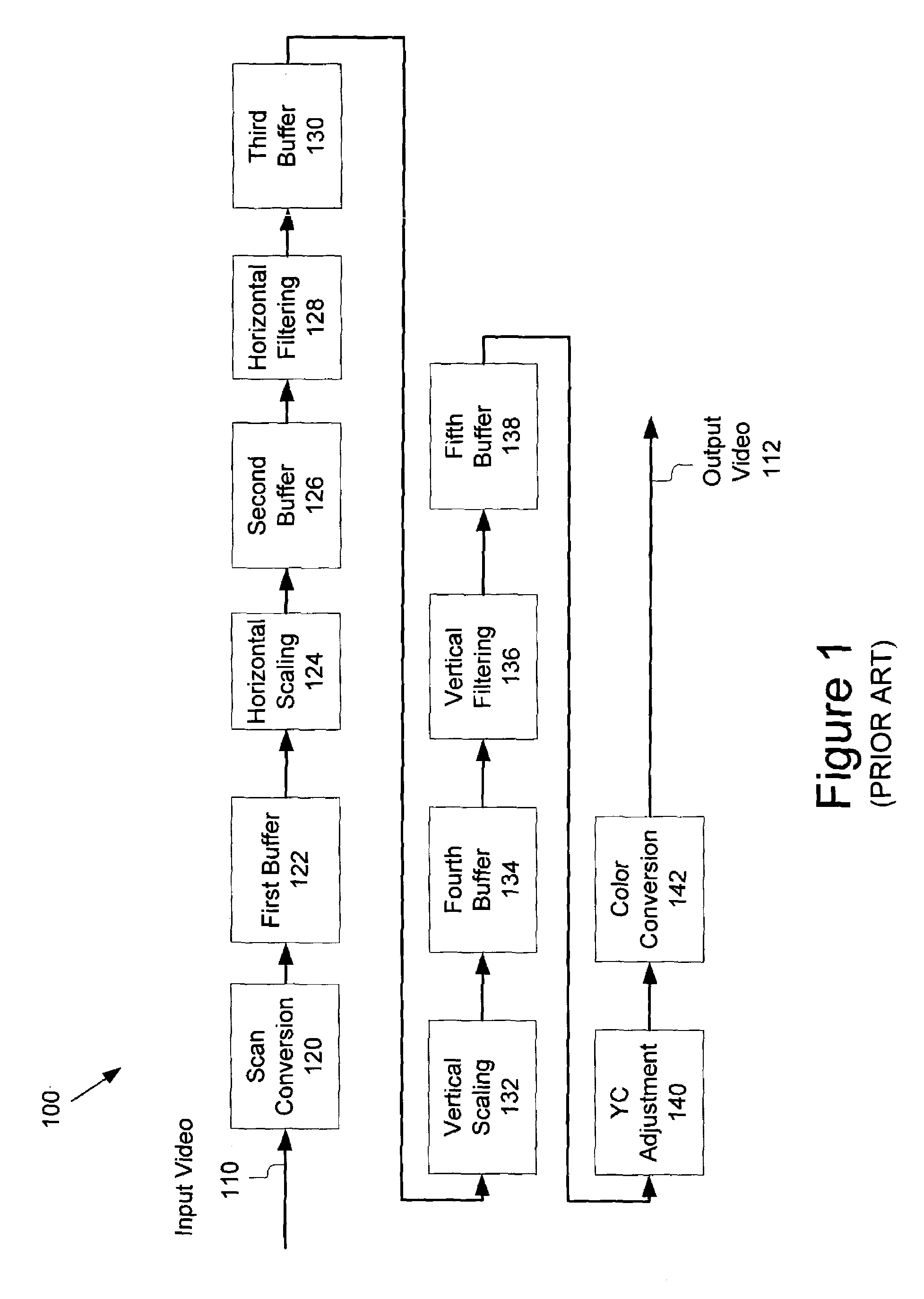
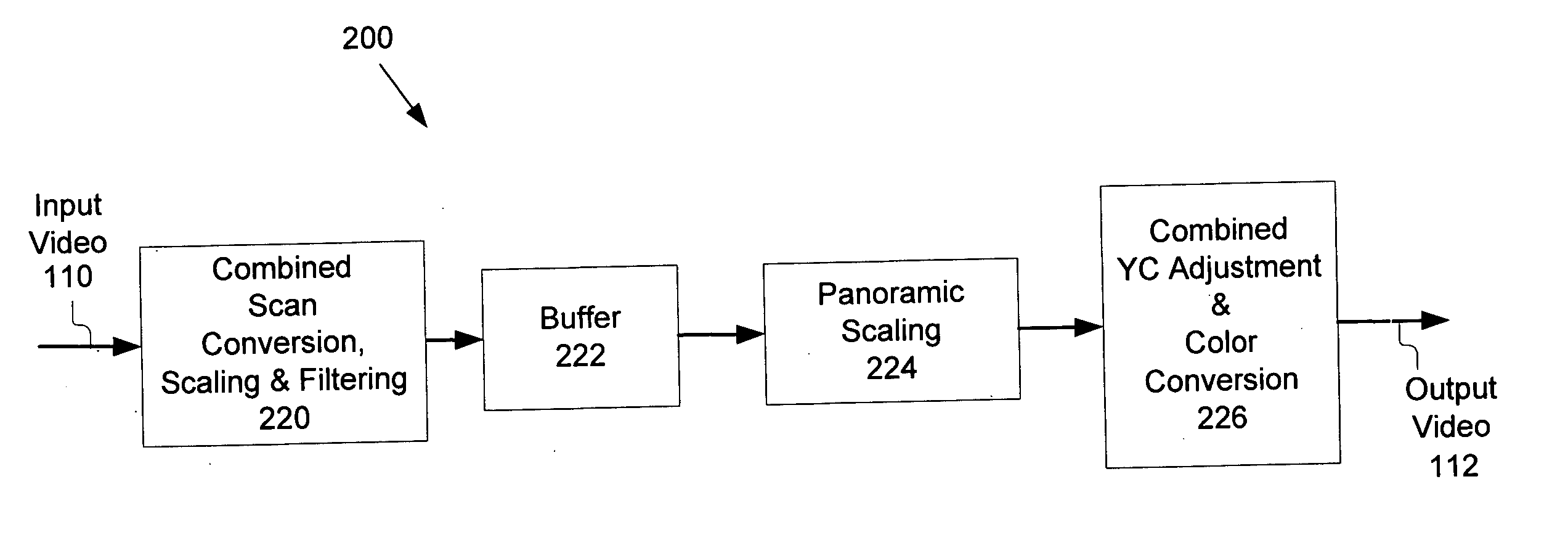
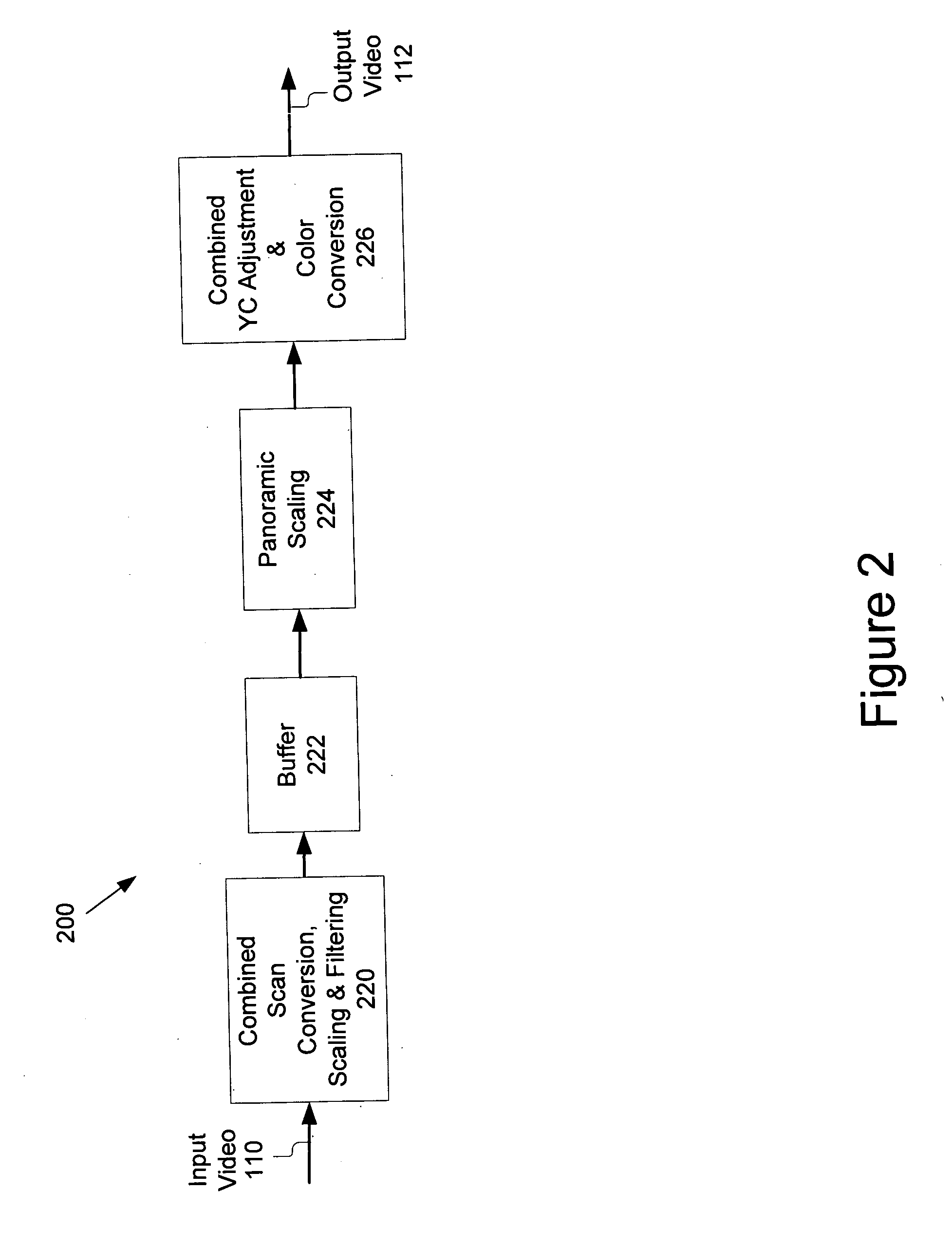
Method and system for scaling, filtering, scan conversion, panoramic scaling, YC adjustment, and color conversion in a display controller
InactiveUS7411628B2Reduce distortionRaise the ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer hardwareColor transformation
Owner:MICRONAS
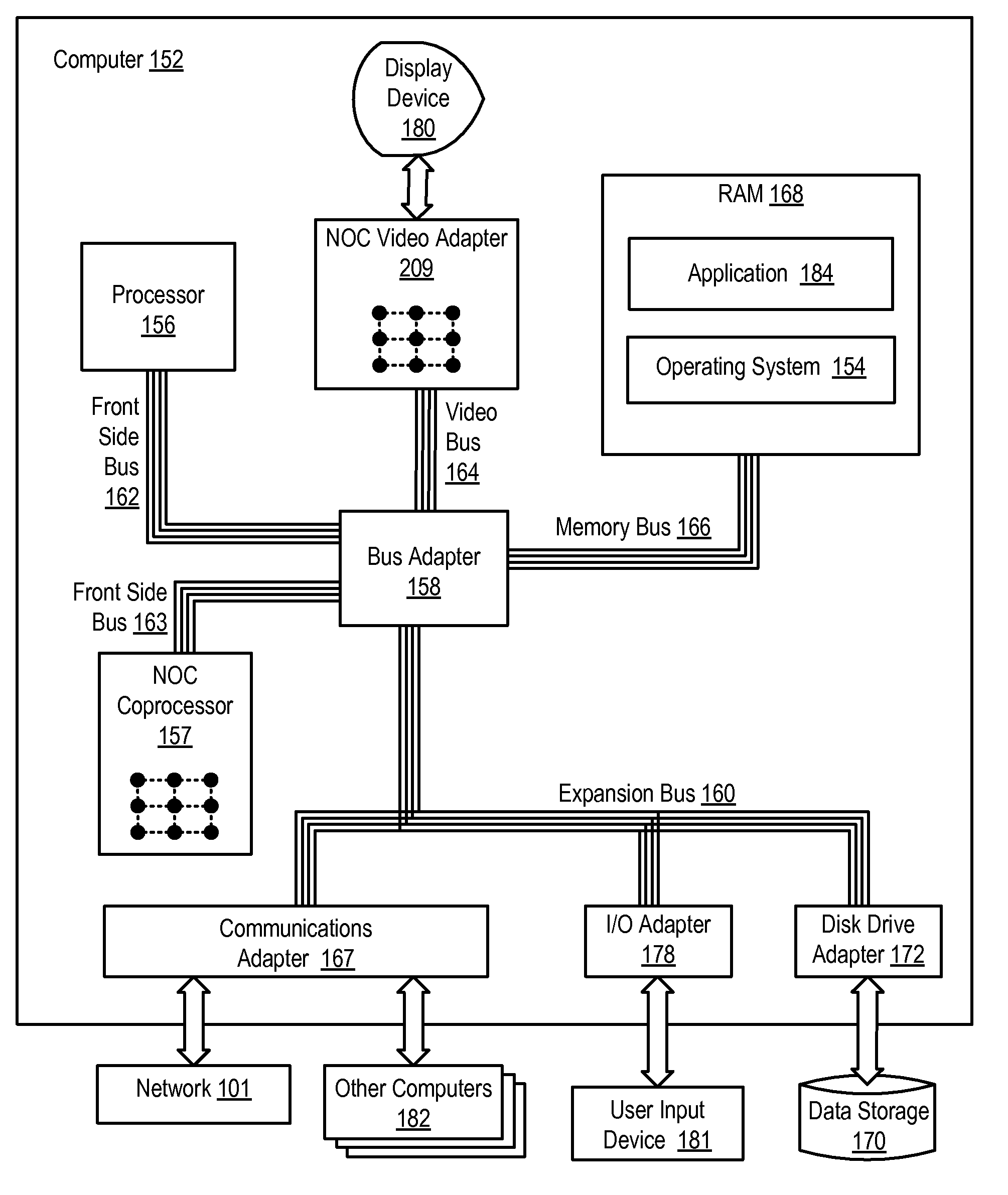
Graphics Rendering On A Network On Chip
InactiveUS20090201302A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsScan conversion
Graphics rendering on a network on chip (‘NOC’) including receiving, in the geometry processor, a representation of an object to be rendered; converting, by the geometry processor, the representation of the object to two dimensional primitives; sending, by the geometry processor, the primitives to the plurality of scan converters; converting, by the scan converters, the primitives to fragments, each fragment comprising one or more portions of a pixel; for each fragment: selecting, by the scan converter for the fragment in dependence upon sorting rules, a pixel processor to process the fragment; sending, by the scan converter to the pixel processor, the fragment; and processing, by the pixel processor, the fragment to produce pixels for an image.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wireless audio-video conversion transmitting-receiving system and method thereof
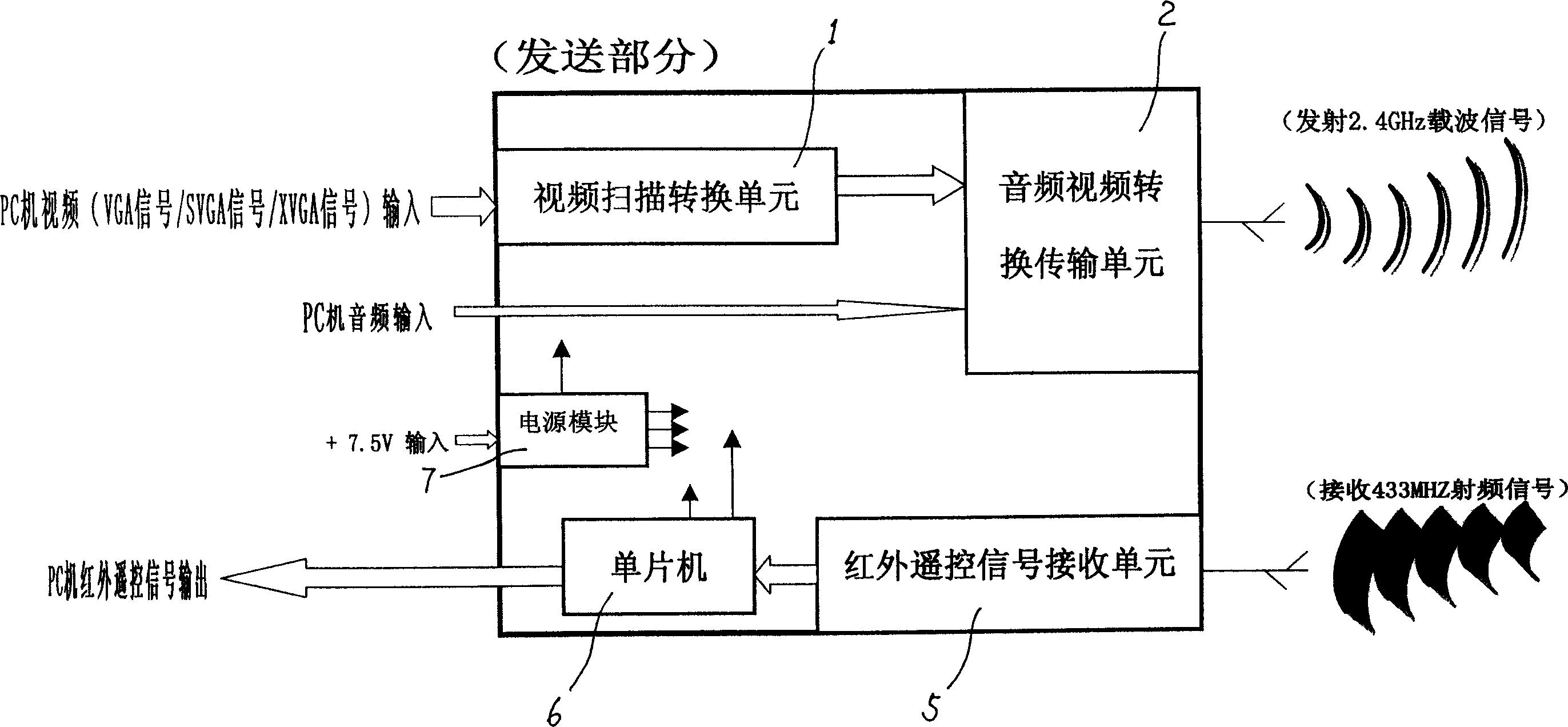
InactiveCN1607780AImplement wireless network connectionNon-electrical signal transmission systemsData switching by path configurationMicrocontrollerFrequency spectrum
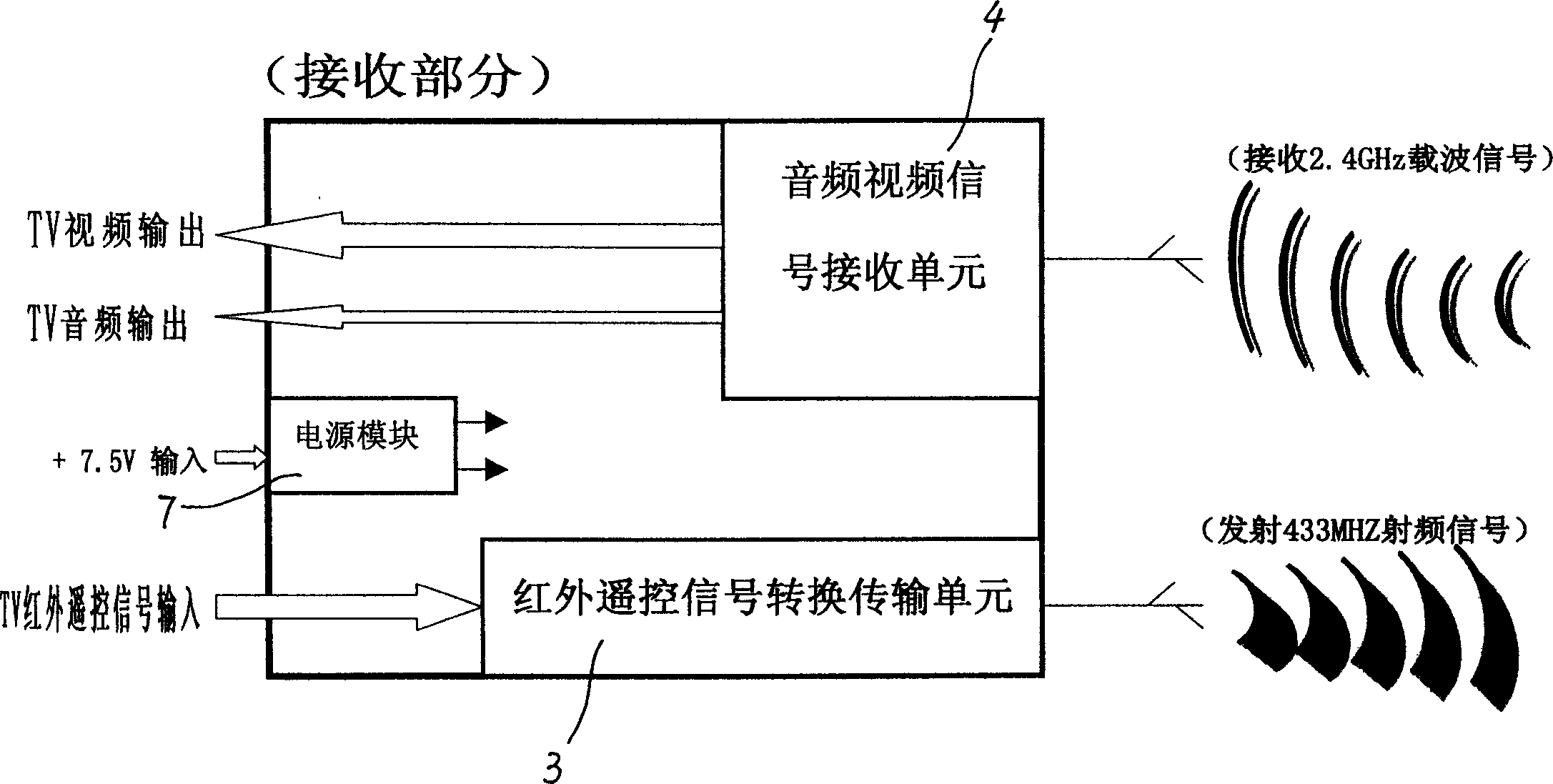
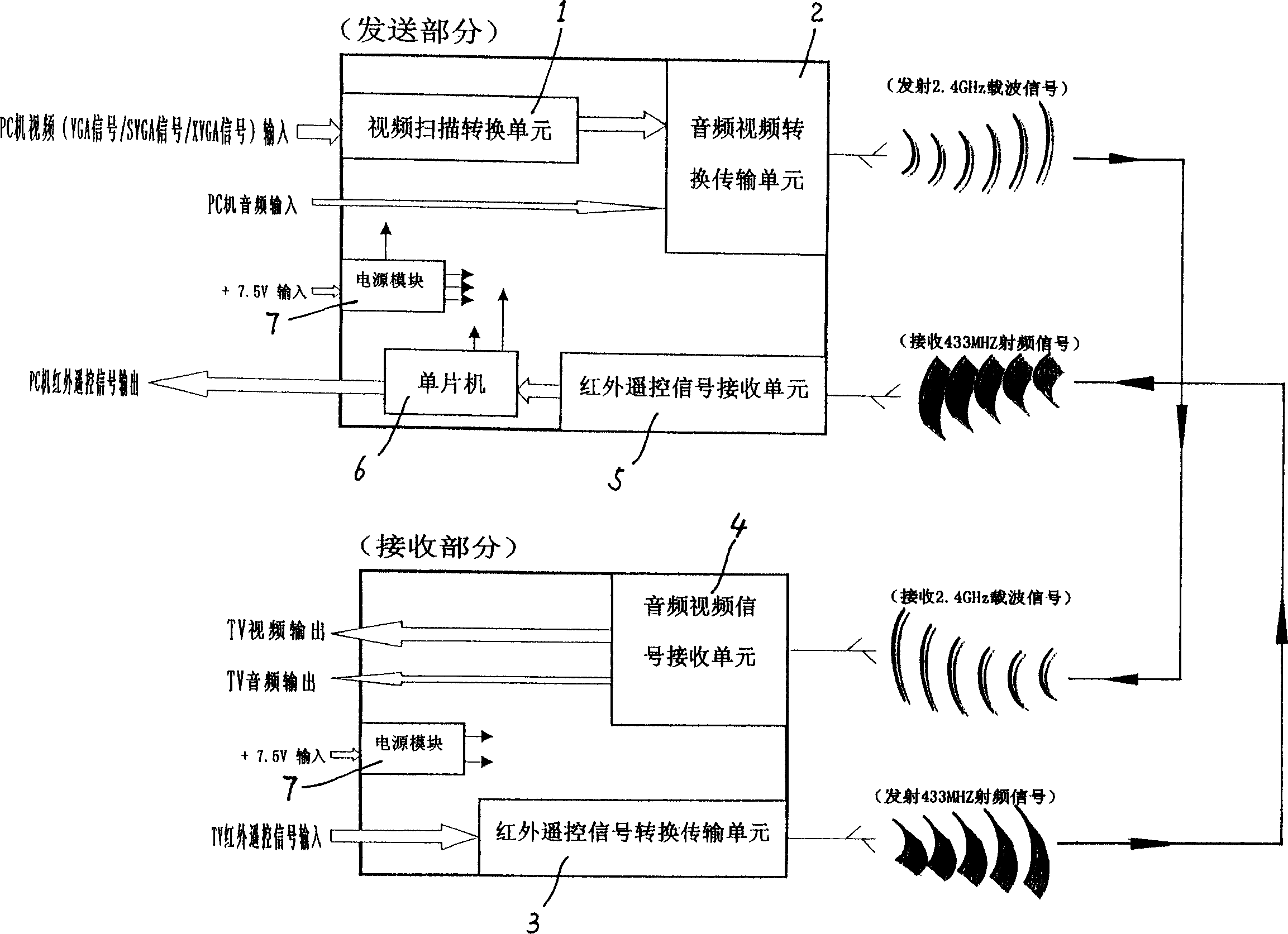
This invention discloses a wireless audio / video transforming emit and receive system and a method for converting video / audio signals and infrared remote signals on PC devices with audio / video output to their signals and related control signals operated on TV devices with video / audio input, including: a video scan conversion unit and a step, an audio / video conversion transferring unit and a step, an infrared remote control signal conversion and transferring unit and a step, an audio / video signal receive unit and step, an infrared remote control signal receiving unit and step, mainly utilizing a video scanning conversion unit, 2.4 GHz antenna direct sequence expansion spectrum transmission technology, 433 MHz RF wireless infrared remote signal transmission technology and mono-chip processor and a supply module to realize the wireless connection.
Owner:SHANGHAI FULLBAND TECH
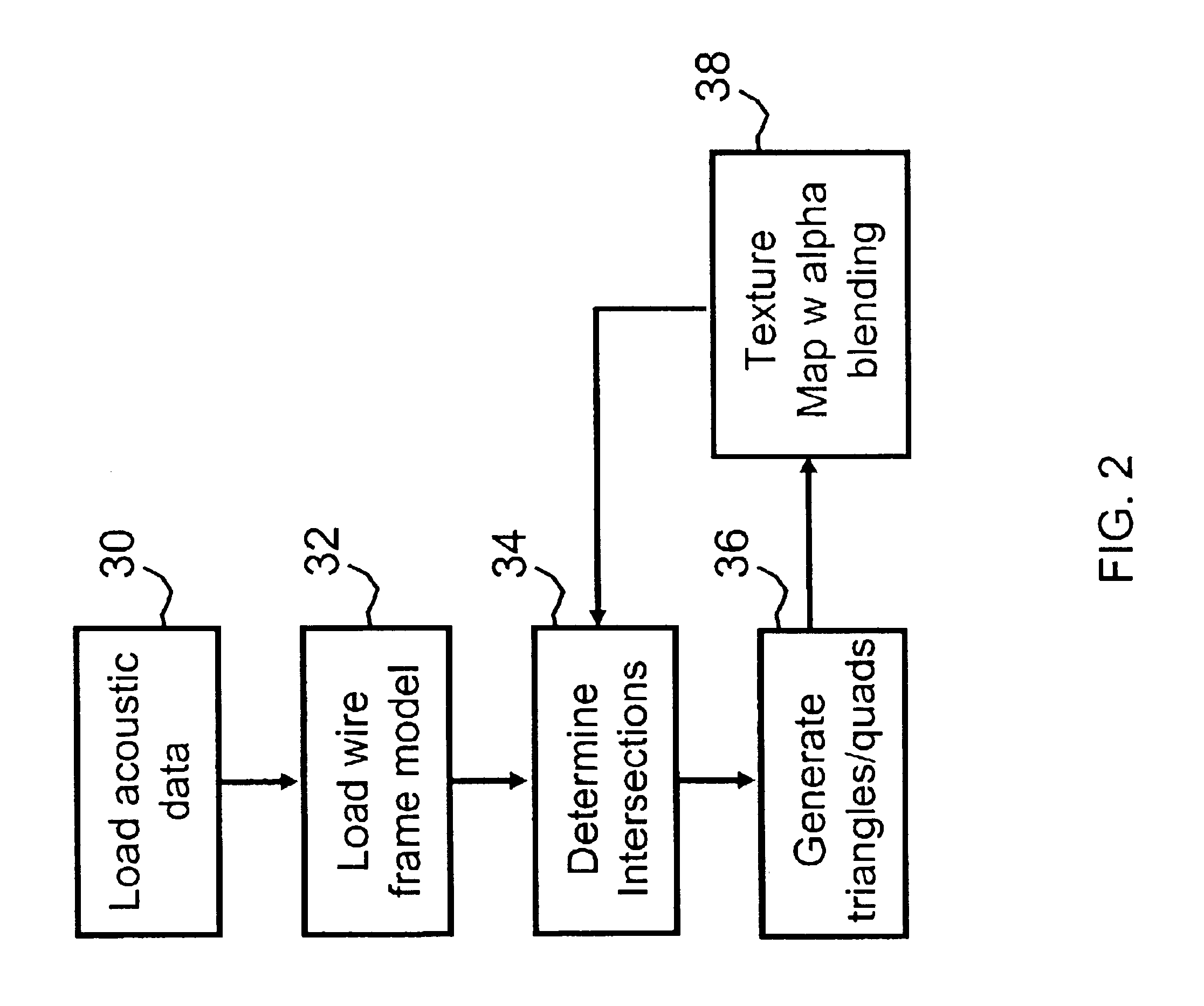
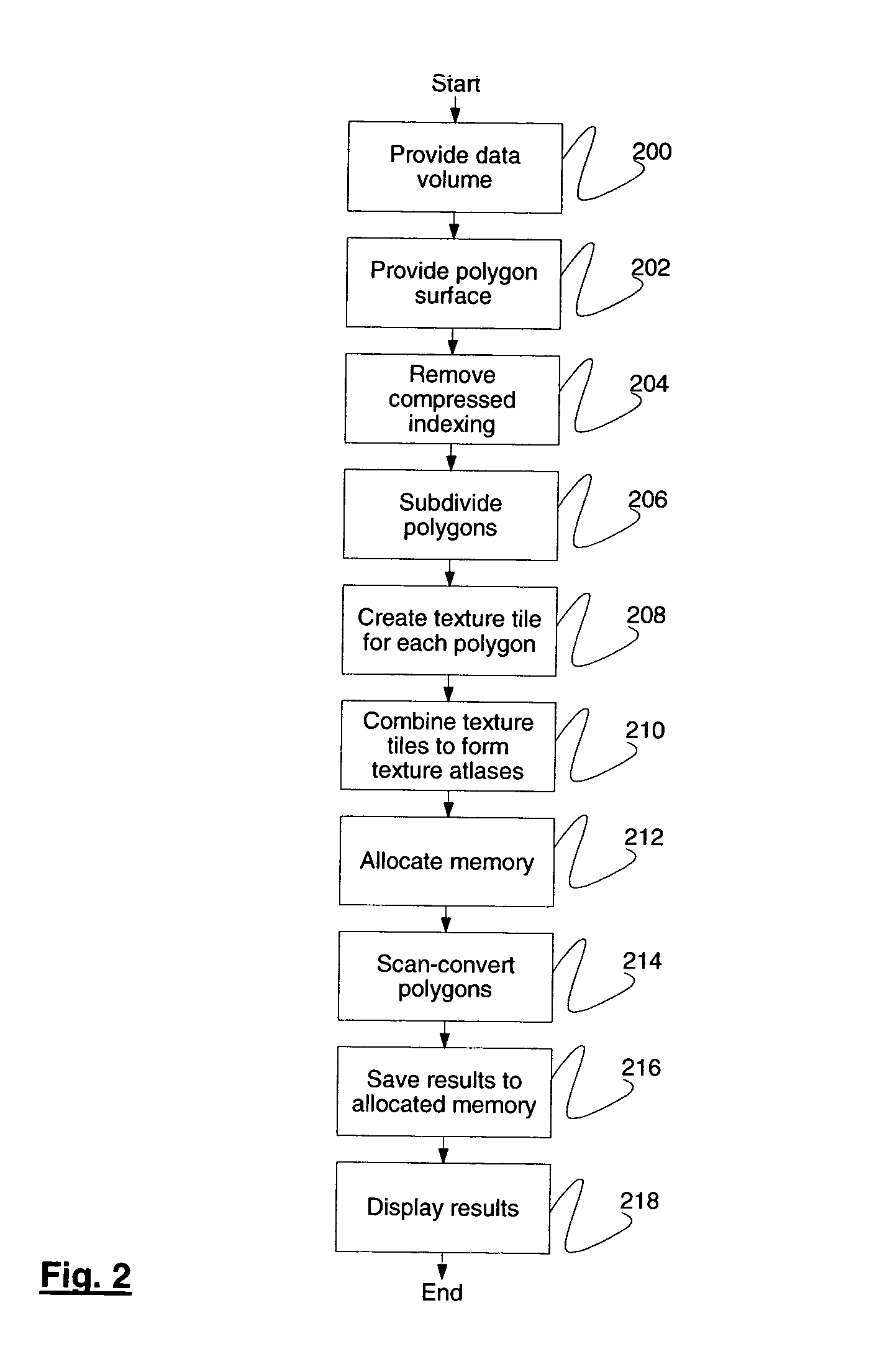
System and method for applying accurate three-dimensional volume textures to arbitrary triangulated surfaces
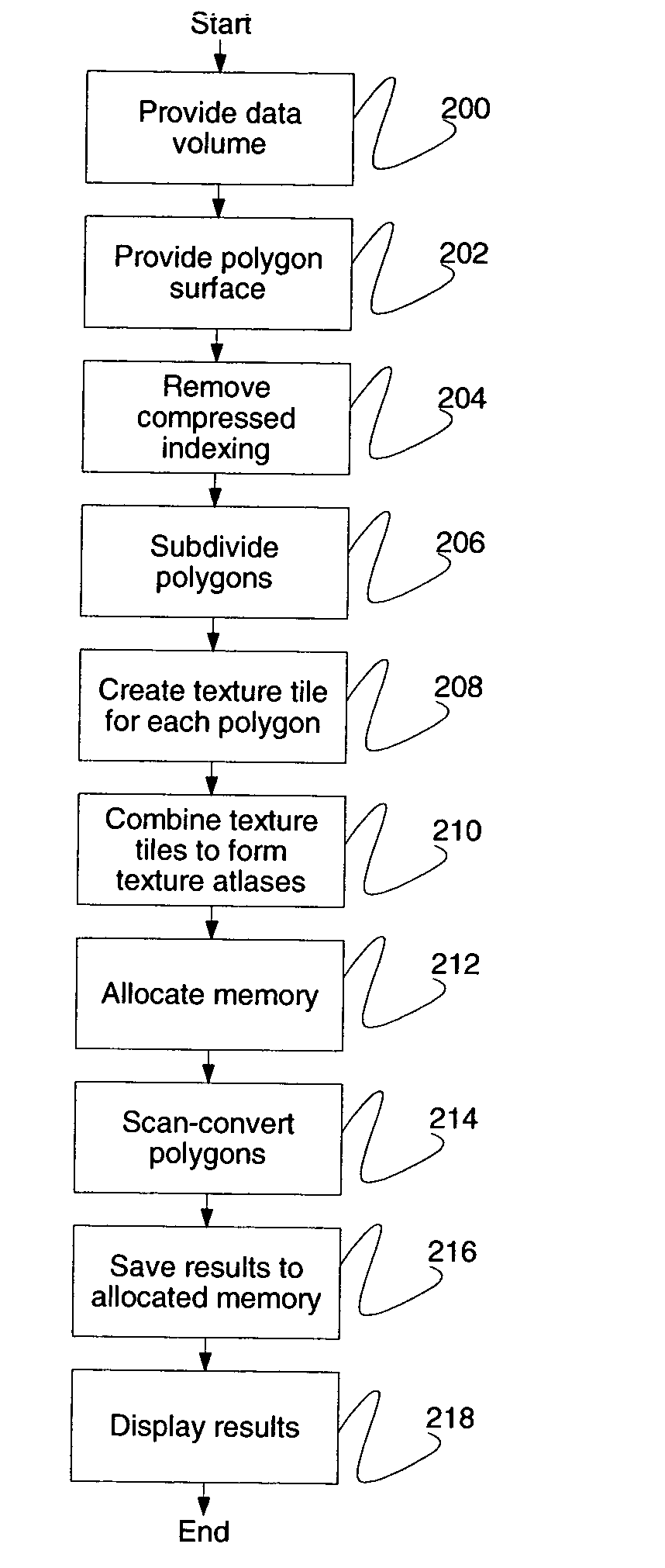
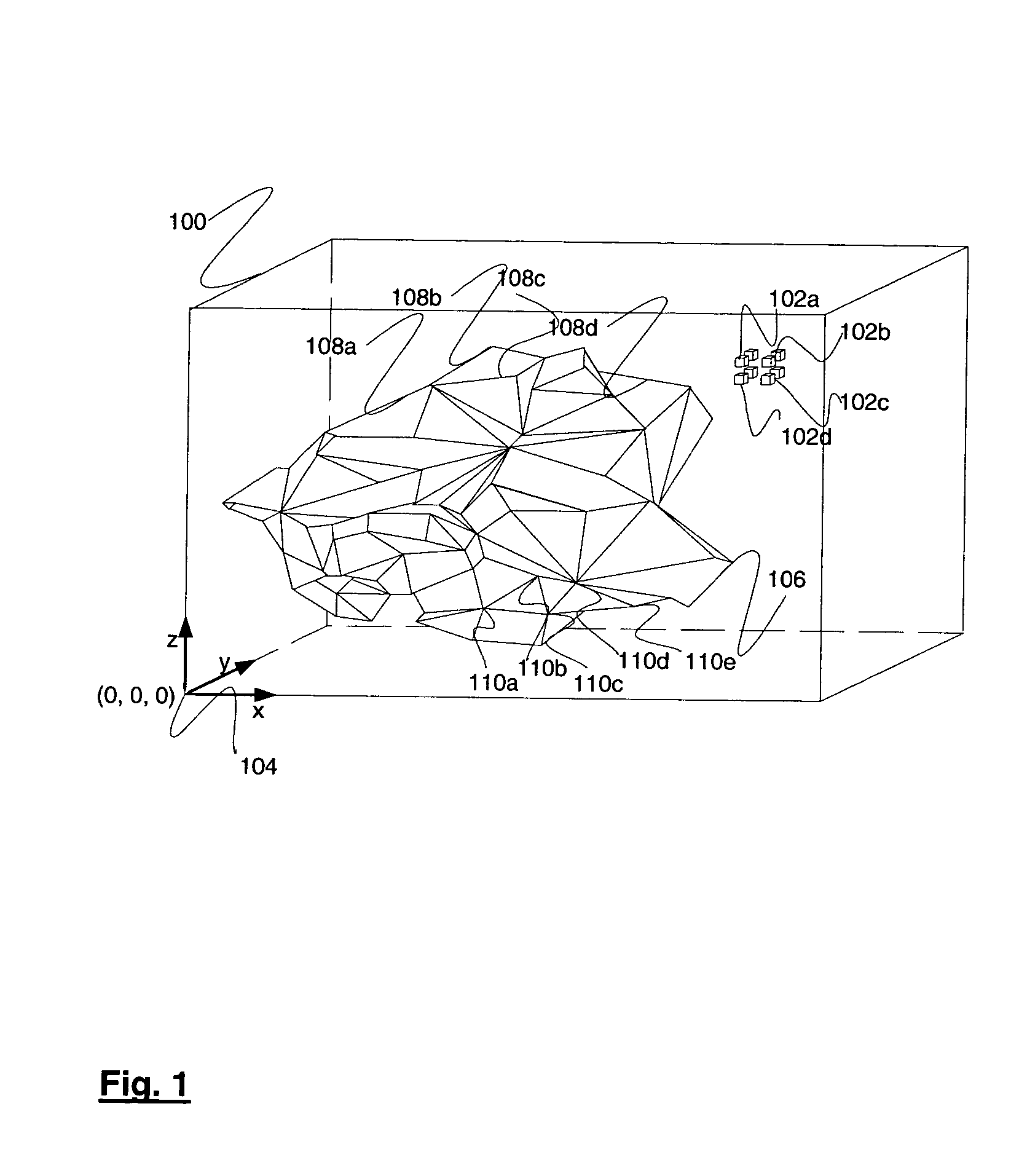
Systems and methods for displaying volume data on an arbitrary three-dimensional polygonal surface are disclosed. For each polygon in the polygonal surface, a two-dimensional texture tile is created and these texture tiles are combined to form texture atlases. Each texture atlas is allocated a specific amount of memory in a texture cache. Each polygon in the polygonal surface may be scan-converted and the resulting texels may be placed in the texture cache. Voxels that do not intersect any polygon in the polygonal surface may not be scan-converted. This method may result in reduced use of texture cache.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
Method for self-adaptation ultrasonic imaging of spatio-temporally smoothed coherence factor type
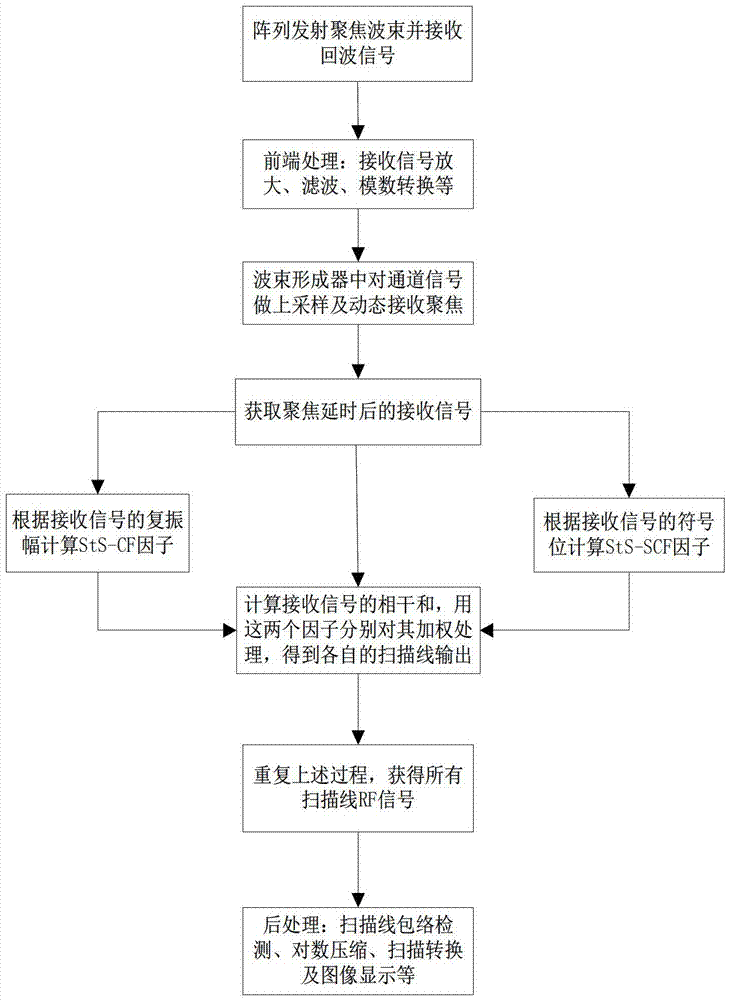
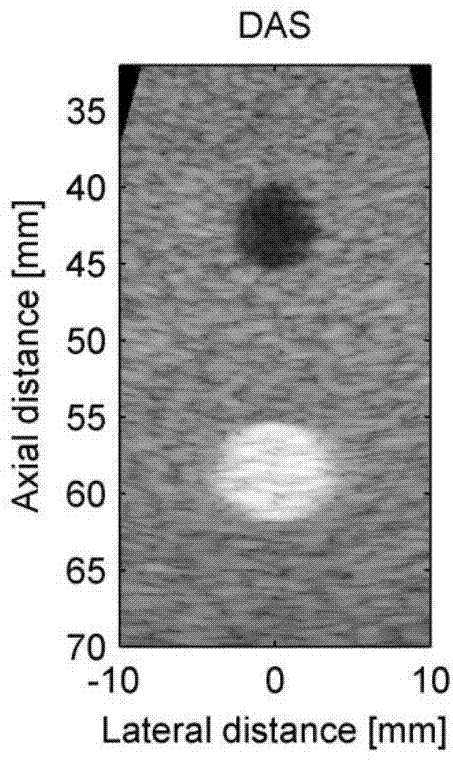
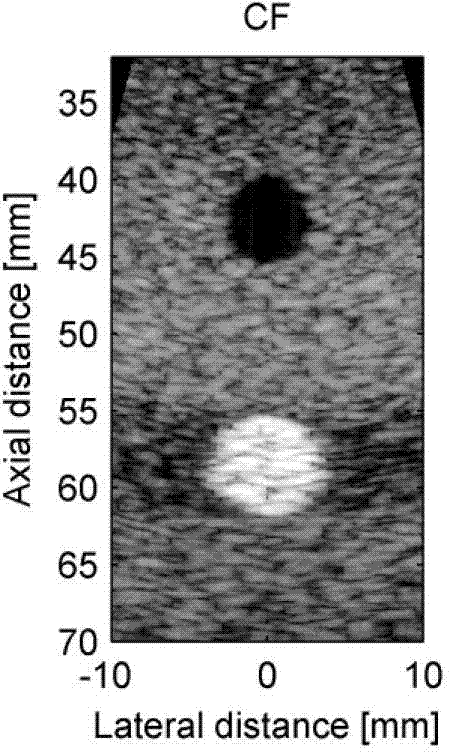
ActiveCN103536316AIncrease contrastReduce noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsComputation complexitySonification
The invention discloses a method for self-adaptation ultrasonic imaging of a spatio-temporally smoothed coherence factor type. The method comprises the following steps that (1) beam forming preprocessing is conducted; (2) beam forming processing is conducted, wherein beam forming processing comprises the steps that delayed focusing is conducted on each channel received signal, a coherence factor value of the spatio-temporally smoothed coherence factor type is calculated according to the channel received signal after delayed processing, and weighted processing is conducted on the coherence sum of the received signals through coherence factors so that beams of each scanning line can be obtained and output; (3) beam forming post-processing is conducted, wherein beam forming post-processing comprises the steps that envelope detection, logarithm compression, scanning conversion and display are conducted on the scanning lines. According to the method for self-adaptation ultrasonic imaging of the spatio-temporally smoothed coherence factor type, side lobe can be restrained, sound disorder is reduced, the contrast ratio of an image is improved, an artifact is remarkably eliminated, the imaging quality is improved, the calculation complexity is low, and the method is easy to achieve in hardware.
Owner:维视医学影像有限公司
Modular apparatus for diagnostic ultrasound
A modular diagnostic ultrasound apparatus is provided comprising a core unit, system electronics and an I / O port. The core unit comprises a housing and a system electronics package within the housing. The system electronics has one or more concatenated filters, including a front end transmit / receive circuit, a processor, a back end circuit for scan conversion, a system clock and a programmable system memory device. There is at least one I / O port connected to the front end and the back end of the system electronics package and extending through the core unit housing wherein all system data processing information is transmitted or received through the I / O port.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
Remote examination of reactor nozzle J-groove welds
InactiveUS6856662B2Easy to understandMinimize difficultyNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringGraphicsScan conversion
A combined laser and infra red sensing camera is located beneath the reactor head in the vicinity of the closure head tube welds by manipulating known robotic device handling the laser which is used to heat a line along the surface thereby generating a thermal wave that propagates over the one to two square inch test area where the increased thermal resistance of cracks and anomalies makes the surface temperature profile gradient greater at a crack or anomaly. An IR camera captures the test area image of interest as the thermal wave propagates across the target inspection area and the image is processed and enhanced to show cracks and other anomalies as a sharp drop in the thermal scan at the point of the crack using known Photo Thermal NDE technology to convert the scan into a pictorial representation of the scanned surface clearly showing any cracks therein. This process is repeated sequentially until the entire circumference of the weld is scanned.
Owner:FRAMATOME ANP RICHLAND
Ultrasound imaging with ray casting and software-based image reconstruction
ActiveUS20110270086A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionSonificationData set
Systems and methods are presented for increasing the frame rate of real-time 3D ultrasound imaging. In one embodiment, the frame rate for generating a pseudo-shaded 2D projection image may be increased by controlling the image reconstruction process. Rather than beamforming, scan converting, and interpolating a 3D voxelized data set of an entire scanned volume, only samples required for generating the 2D projection image may be reconstructed. The element data measured from each transducer array element may be combined to directly reconstruct those 3D image samples required by the volume rendering algorithm to generate the 2D projection image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
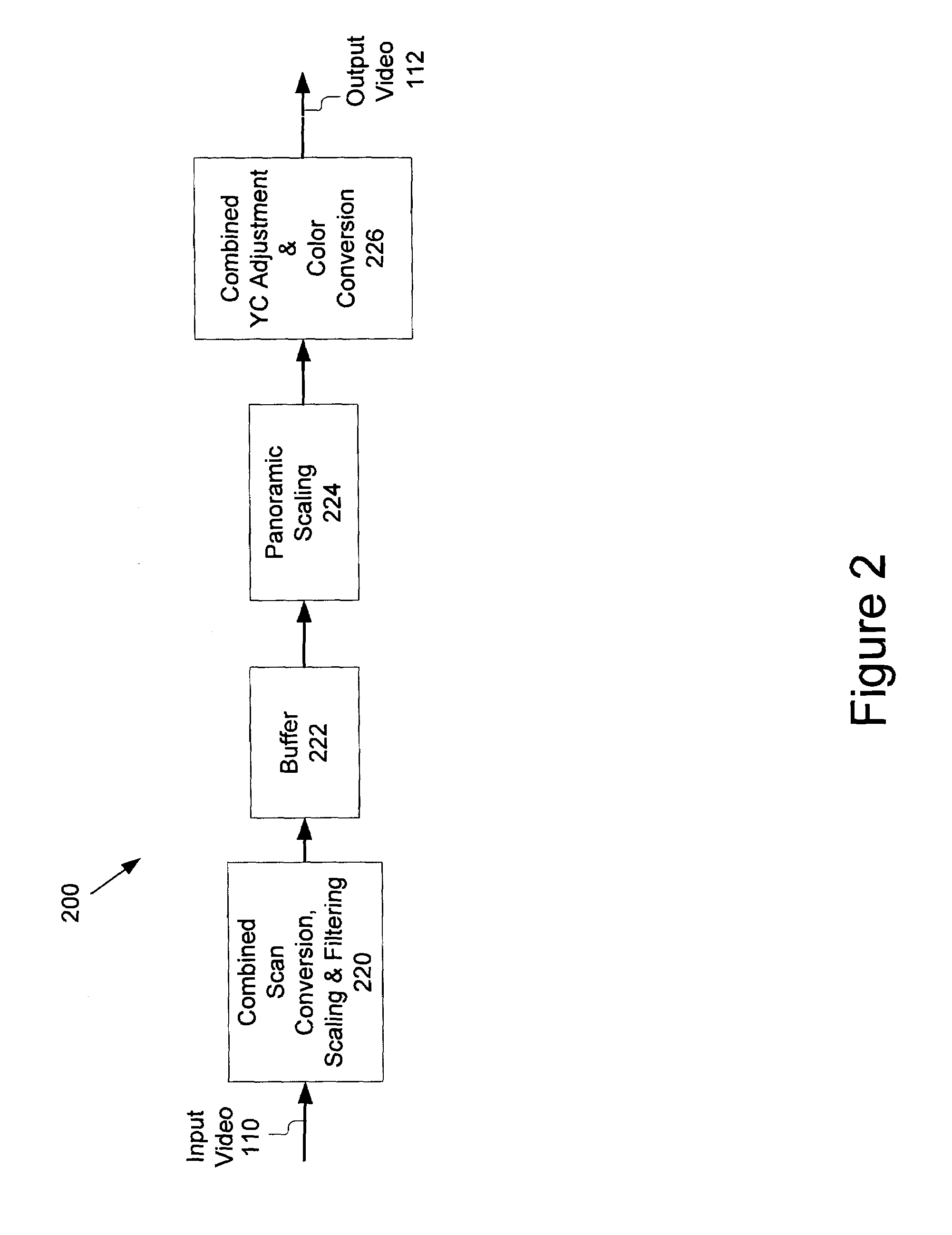
Method and system for scaling, filtering, scan conversion, panoramic scaling, YC adjustment, and color conversion in a display controller
InactiveUS20050248590A1Small sizeReduced Power RequirementsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer hardwareScan conversion
Techniques for performing panoramic scaling are disclosed that reduce visible distortion in a panoramic image. Further, techniques for performing combined YC adjustment and color conversion are disclosed that reduce the size and power requirements of video manipulation hardware by reducing the number of logic gates and memory buffers required when YC adjustment and color conversion are implemented as separate operations.
Owner:MICRONAS
Apparatus and method for converting image data
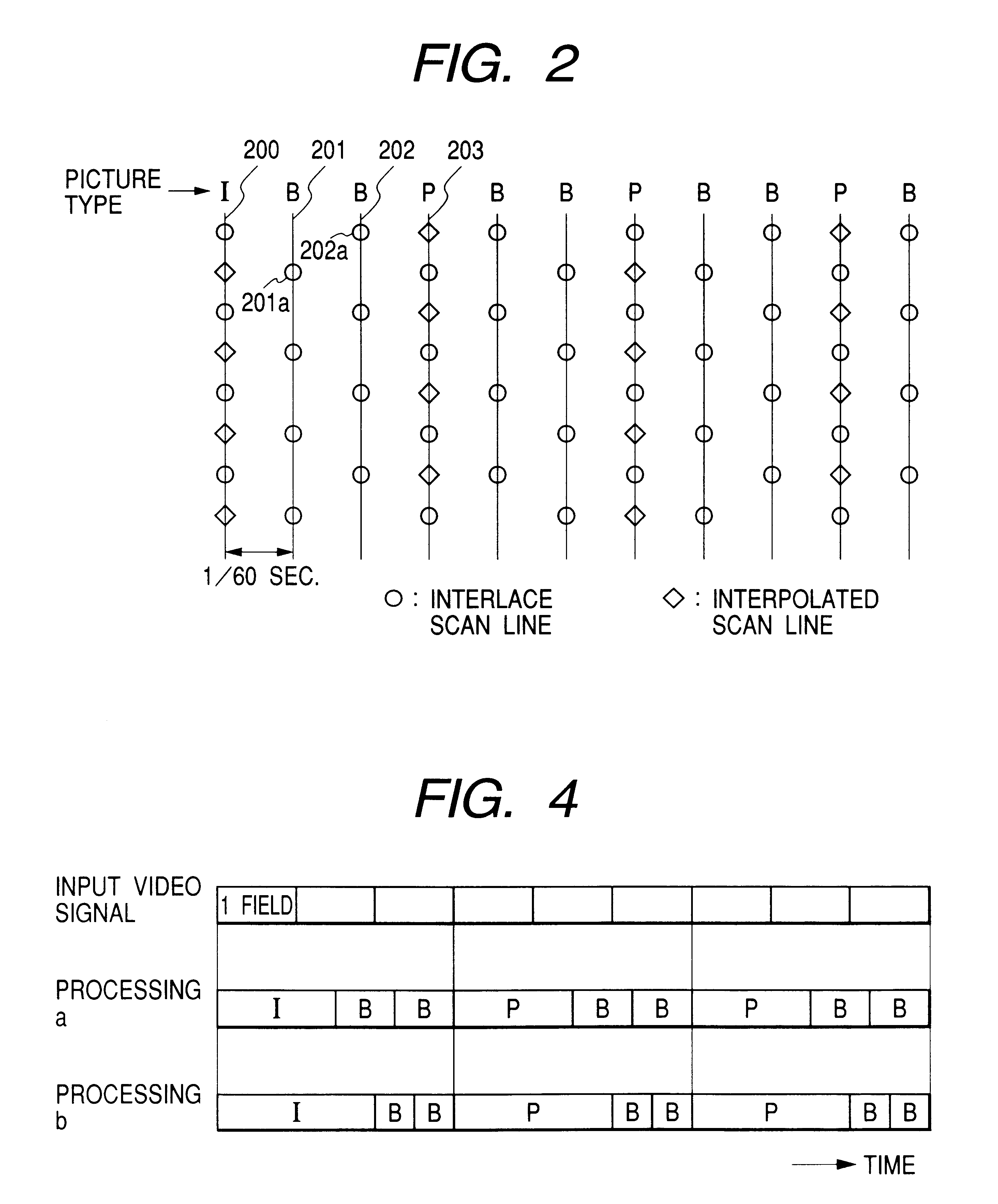
InactiveUS7088775B2Low costSolve large capacityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesScan conversionImage type
An image data converting apparatus comprising an MPEG2-image data decoding section 19, a scan-converting section 20, an MPEG4-image encoding section 21, and a picture-type determining section 18. The MPEG2-image data decoding section 19 decodes input MPEG2-image compressed data in both the vertical direction and the horizontal direction by using only lower, fourth-order coefficients. The scan-converting section 20 converts interlaced-scan pixel data to sequential-scan pixel data. The MPEG4-image encoding section 21 generates MPEG4-image compressed data from the sequential-scan pixel signals. The sections 19, 20 and 21 are connected in series. The picture-type determining section 18 is connected to the input of the MPEG2-image data decoding section 19. The section 18 determines the picture type of each frame data contained in the interlaced-scan MPEG4-picture compressed data, outputs only the frame data about I / P pictures, discards the frame data about B pictures, thereby converting the frame rate.
Owner:SONY CORP
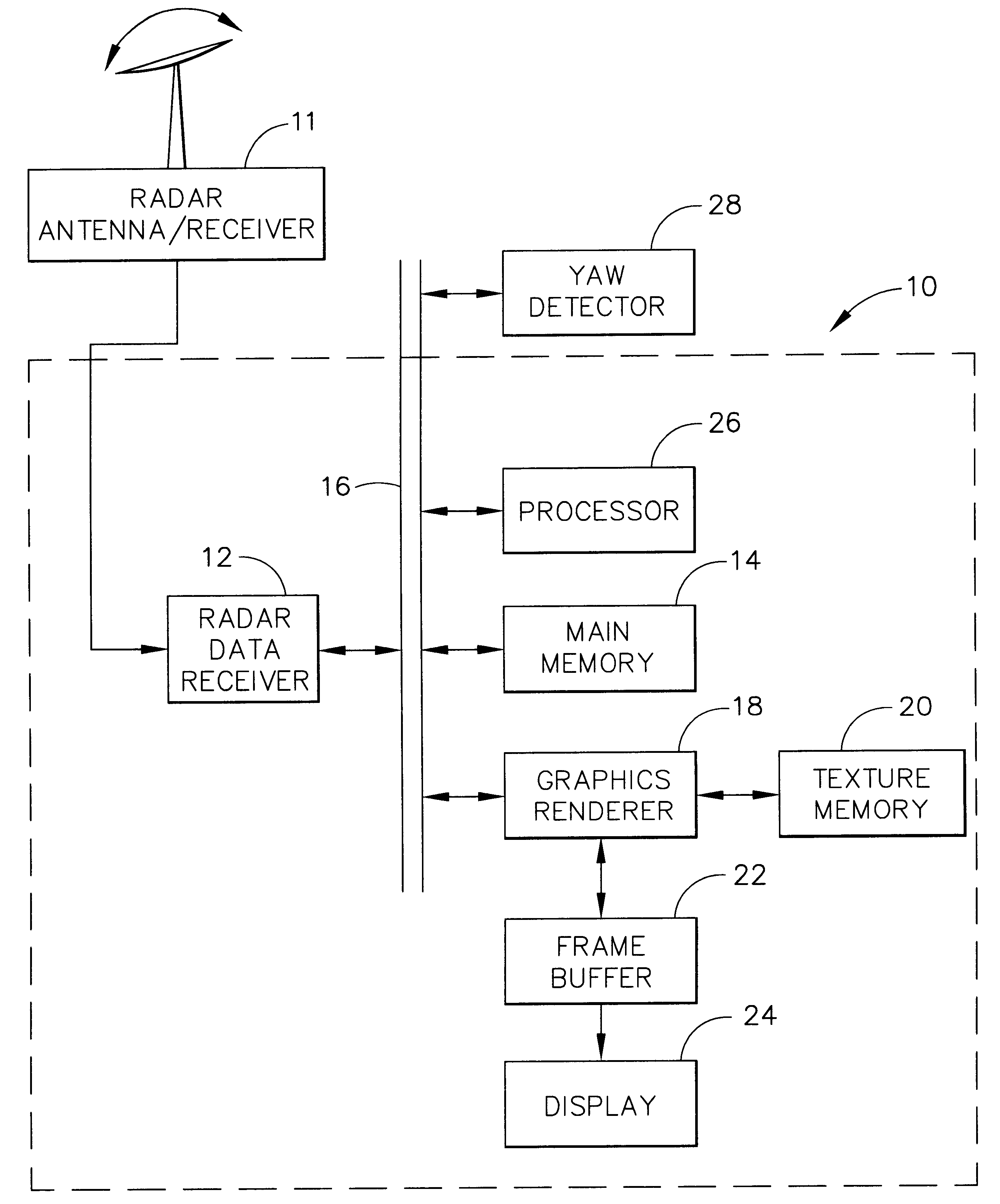
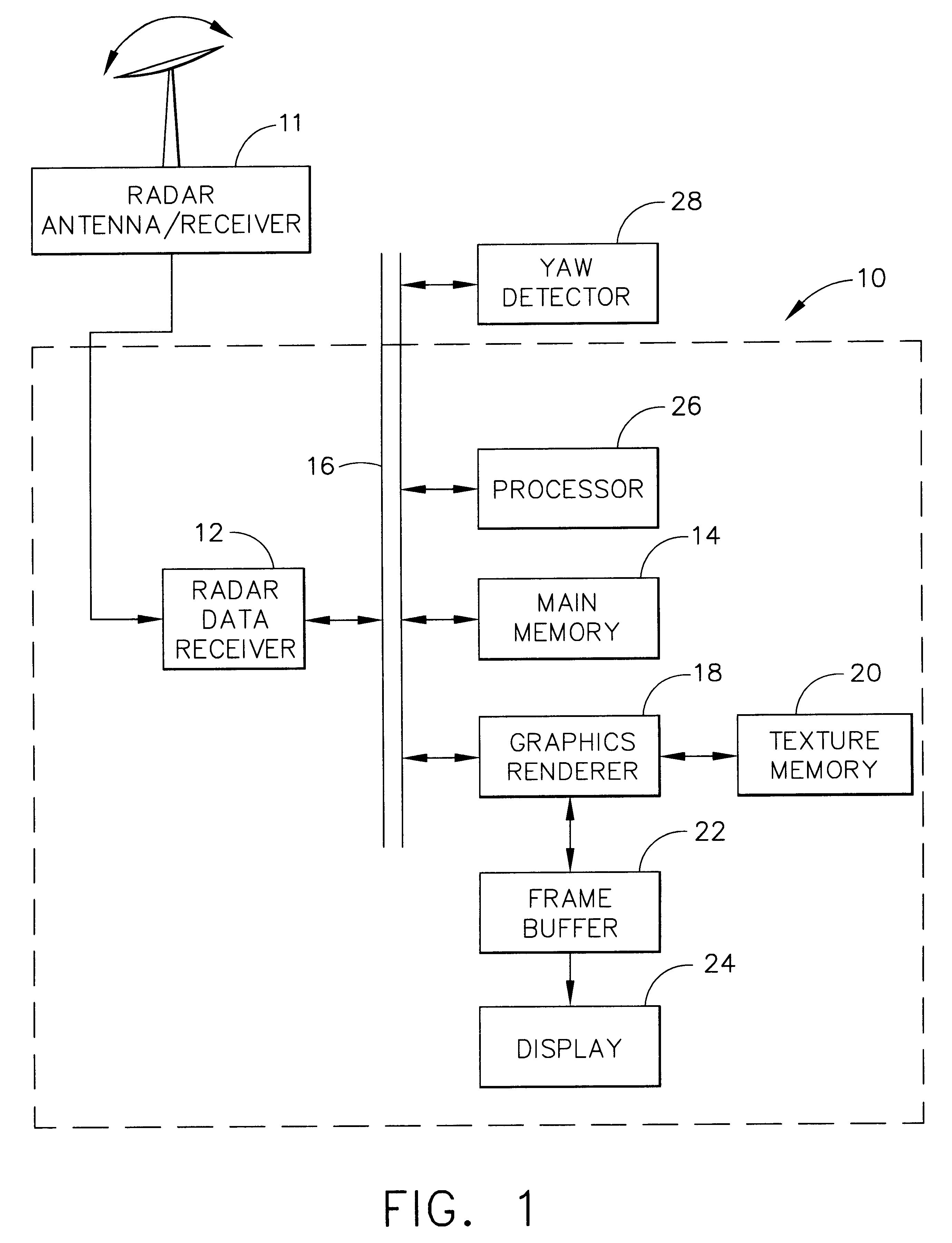
Use of texture memory for WX scan conversion
A radar display system (10) according to the present invention generates textured radar display data by utilizing a direct memory access receiver (12) to receive radially scanned radar data, to convert the radially scanned radar data into range bin data sets, and to store the range bin data sets. A graphics renderer (18) stores the set of range bin data sets in a texture memory (20) as a plurality of rectangular textures, and bit maps the rectangular textures to a series of display triangles in a frame buffer (22). The graphics renderer (18) colors the display triangles in accordance with the rectangular textures by performing a bi-linear interpolation of the color and warps the display triangles in accordance with the size of a display (24).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com