Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
598results about How to "Minimize overhead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
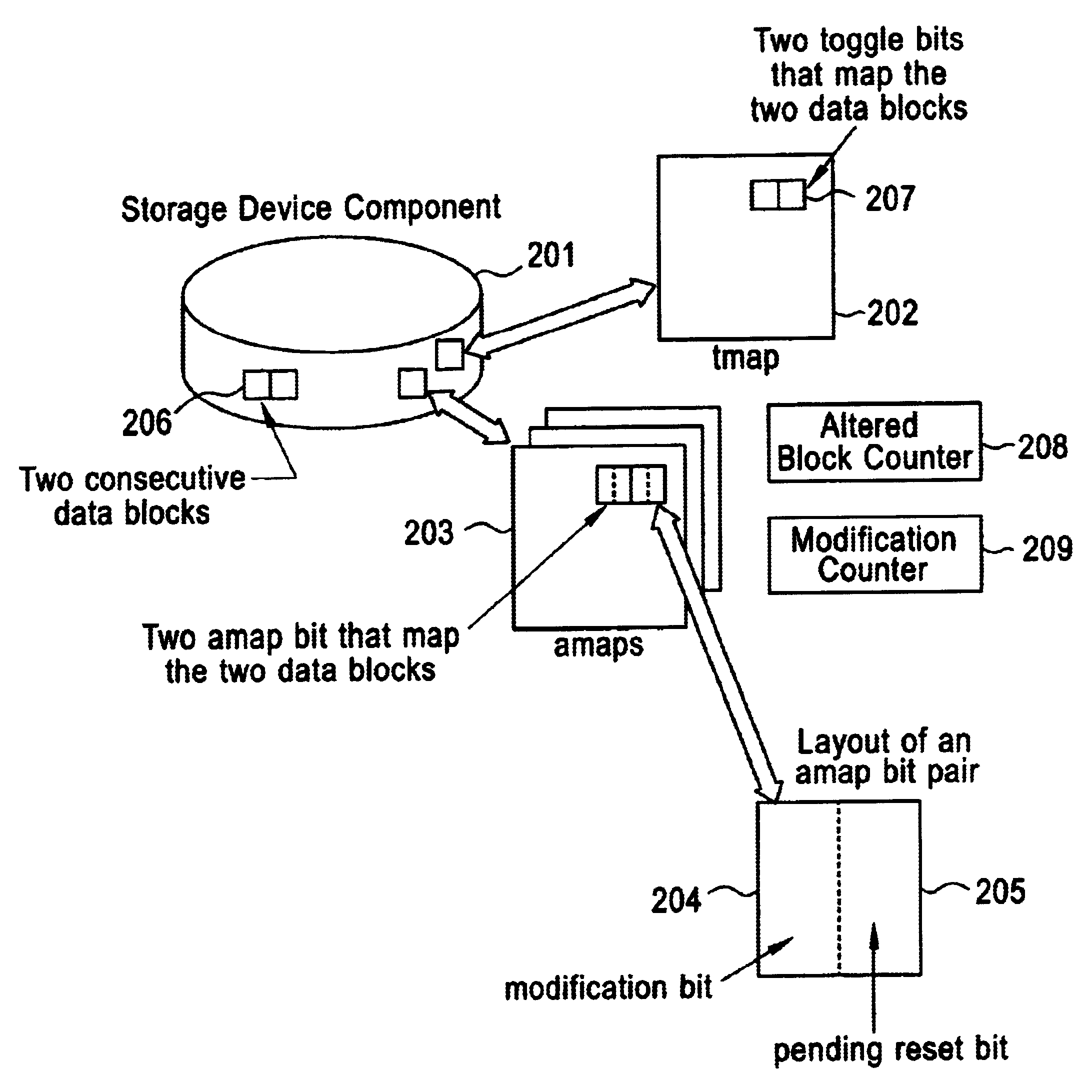
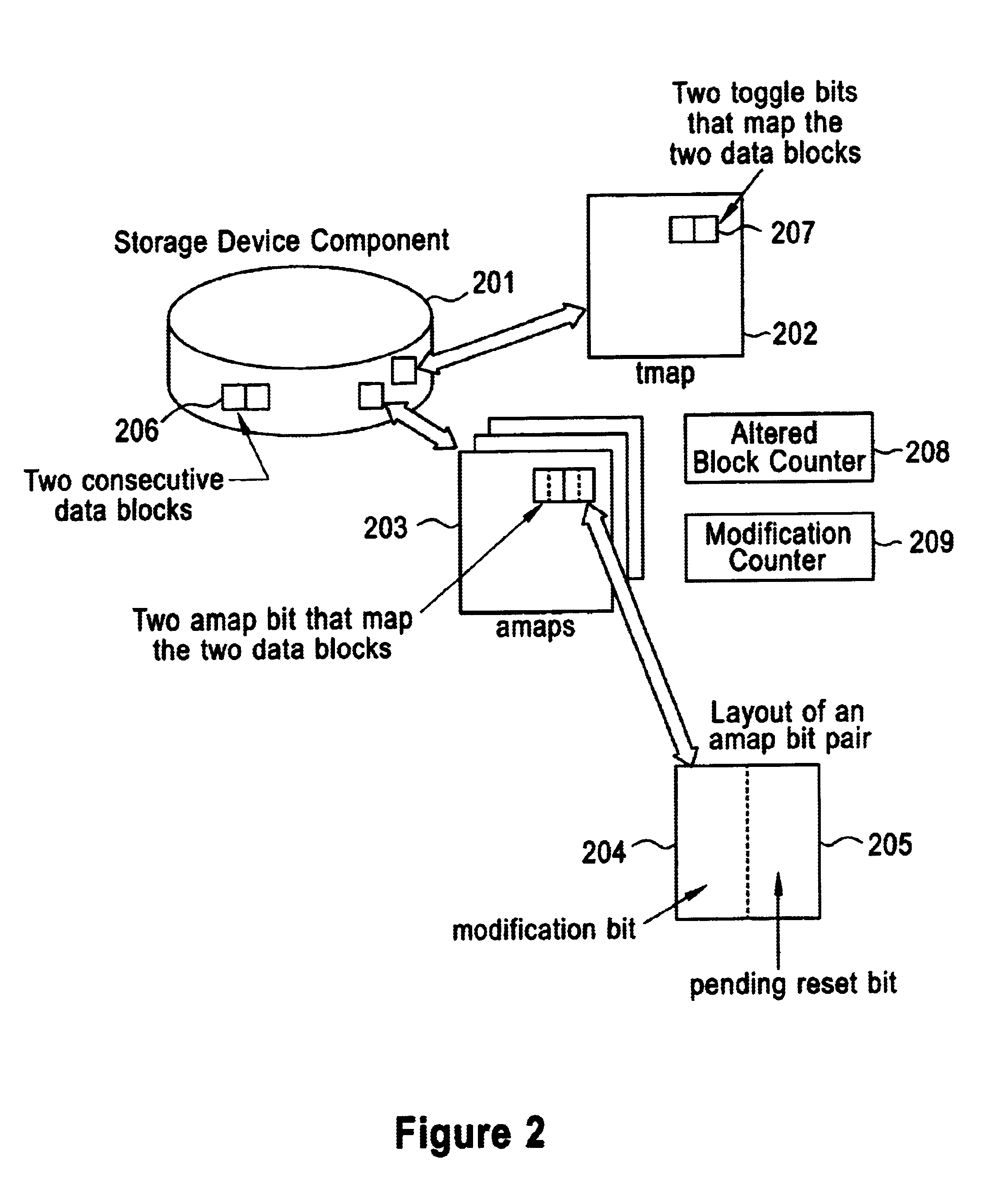
Method and system for providing consistent data modification information to clients in a storage system
InactiveUS6952758B2Minimize overheadRapid data replicationData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersClient-sideData store
A data storage system and method for providing consistent data to multiple clients based on data modification information as existing data is updated and new data is written to the system. The information indicates the modification status of each data block and identifies which data blocks have been modified during a certain time interval. The clients may query and update the modification information by submitting requests through a request processor. The data modification information includes an Altered Block Map that indicates block modification status and a Toggle Block Map that identifies which blocks have been modified. The system further includes a Modification Counter a Pending Reset Counter for improved recognition and handling of the modified data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Knowledge Discovery Agent System and Method
ActiveUS20070203693A1Maximizes rangeFacilitate communicationWeb data indexingNatural language data processingUnstructured dataConditional probability
A system and method for processing information in unstructured or structured form, comprising a computer running in a distributed network with one or more data agents. Associations of natural language artifacts may be learned from natural language artifacts in unstructured data sources, and semantic and syntactic relationships may be learned in structured data sources, using grouping based on a criteria of shared features that are dynamically determined without the use of a priori classifications, by employing conditional probability constraints.
Owner:DIGITAL REASONING SYST
Asynchronous unconscious retrieval in a network of information appliances
InactiveUS7305381B1Optimize networkGathering informationDigital data processing detailsMarketingRelevant informationApplication software
A method, system, and computer program product for asynchronous unconscious retrieval retrieves and presents information to end users without requiring the end users to explicitly request the information. The invention automatically and asynchronously formulates queries and presents relevant information to end users within the context of existing applications, so as to minimize the effort, overhead, and context shifts associated with conventional conscious retrieval.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method and apparatus for parallel data preparation and processing of integrated circuit graphical design data
InactiveUS7434185B2Improve scalabilityIncrease loadDetecting faulty computer hardwareOriginals for photomechanical treatmentGraphicsComputer architecture
A method for implementing an ORC process to facilitate physical verification of an integrated circuit (IC) graphical design. The method includes partitioning the IC graphical design data into files by a host machine such that the files correspond to regions of interest or partitions with defined margins, dispersing the partitioned data files to available cpus within the network, processing of each job by the cpu receiving the file, wherein artifacts arising from bisection of partitioning margins during the partitioning, including cut-induced false errors, are detected and removed, and the shape-altering effects of such artifact errors are minimized and transmitting the results of processing at each cpu to the host machine for aggregate processing.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Virtual peripheral hub device and system
ActiveUS20110205965A1Improve privacyRapid and efficient deploymentVolume/mass flow measurementSubstation remote connection/disconnectionTransceiverStore and forward
Methods and devices provide a virtual peripheral hub and services enabling remote access to peripherals commonly connected to personal computers in a manner that simplifies device networking. A virtual peripheral hub device may include a processor and wireless communication transceivers configured to connect to cellular and / or WiFi networks to access a remote server, and wired and / or wireless local networks for connecting to peripheral devices. The virtual peripheral hub device may plug into a power source (e.g., a wall socket or cigarette lighter), connect to a peripheral device, and be configured to enable any computer attached to a local area network or the Internet to use or access the peripheral device. An associated server-based service enables discovery of the virtual peripheral hub device and connected peripherals. The associated server-based server may provide the drivers for various peripherals, store and forward data, and provide remote access to the various peripherals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Knowledge discovery agent system and method
ActiveUS7249117B2Facilitate communicationMaximizes rangeChaos modelsNon-linear system modelsUnstructured dataConditional probability
A system and method for processing information in unstructured or structured form, comprising a computer running in a distributed network with one or more data agents. Associations of natural language artifacts may be learned from natural language artifacts in unstructured data sources, and semantic and syntactic relationships may be learned in structured data sources, using grouping based on a criteria of shared features that are dynamically determined without the use of a priori classifications, by employing conditional probability constraints.
Owner:DIGITAL REASONING SYST
Collaborative team crawling:Large scale information gathering over the internet
InactiveUS6182085B1Reduce processing overheadEfficient accessDrawing from basic elementsData processing applicationsTree (data structure)Workload
A distributed collection of web-crawlers to gather information over a large portion of the cyberspace. These crawlers share the overall crawling through a cyberspace partition scheme. They also collaborate with each other through load balancing to maximally utilize the computing resources of each of the crawlers. The invention takes advantage of the hierarchical nature of the cyberspace namespace and uses the syntactic components of the URL structure as the main vehicle for dividing and assigning crawling workload to individual crawler. The partition scheme is completely distributed in which each crawler makes the partitioning decision based on its own crawling status and a globally replicated partition tree data structure.
Owner:IBM CORP
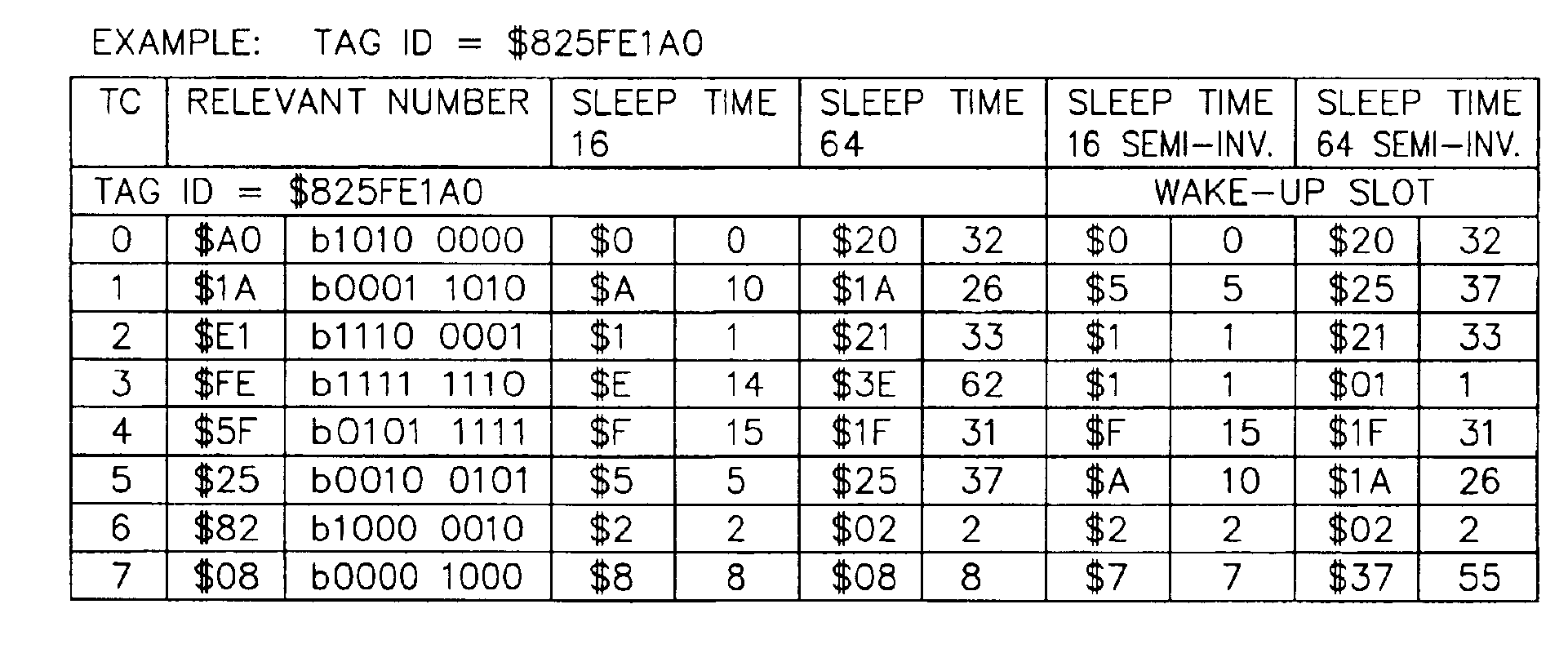
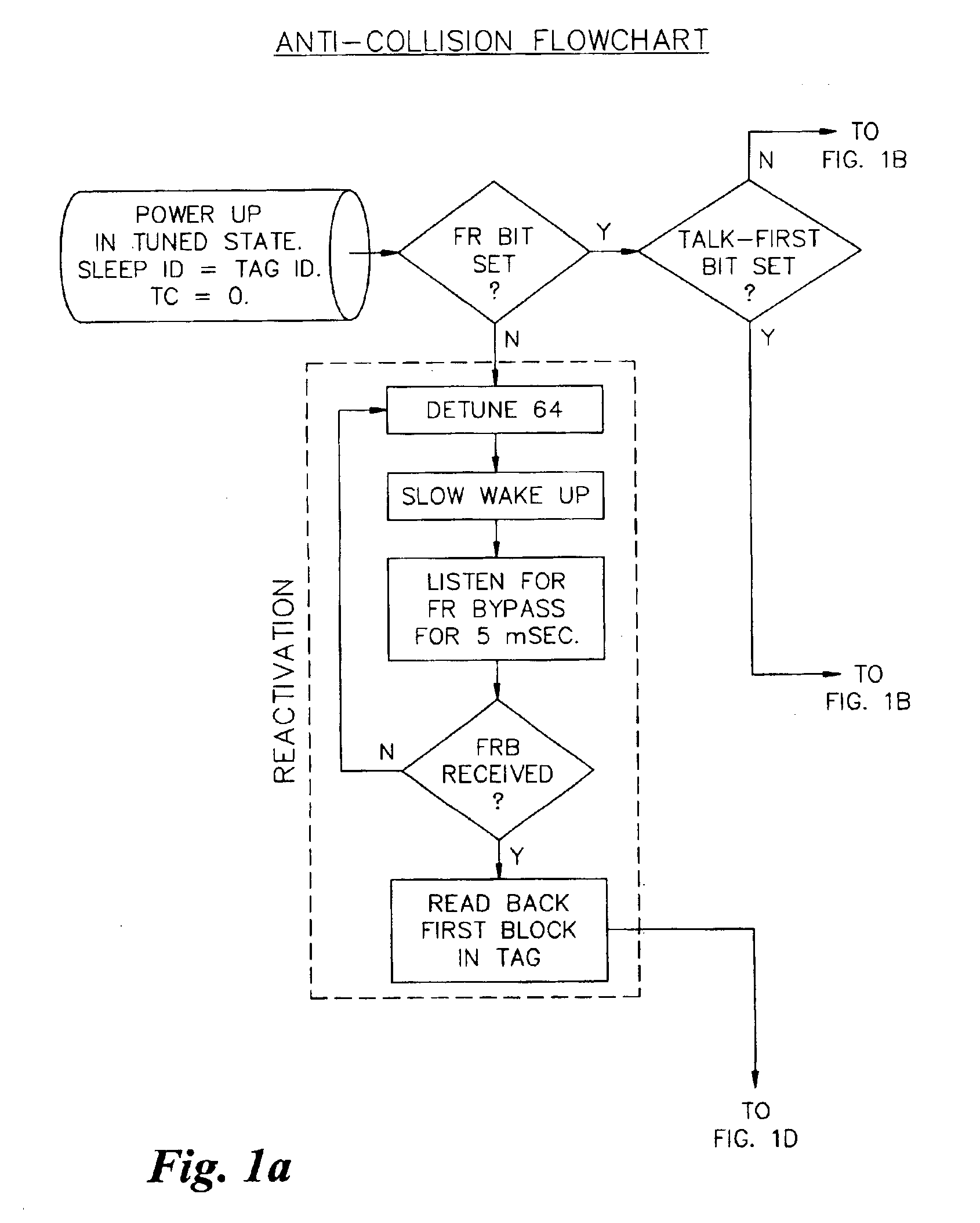
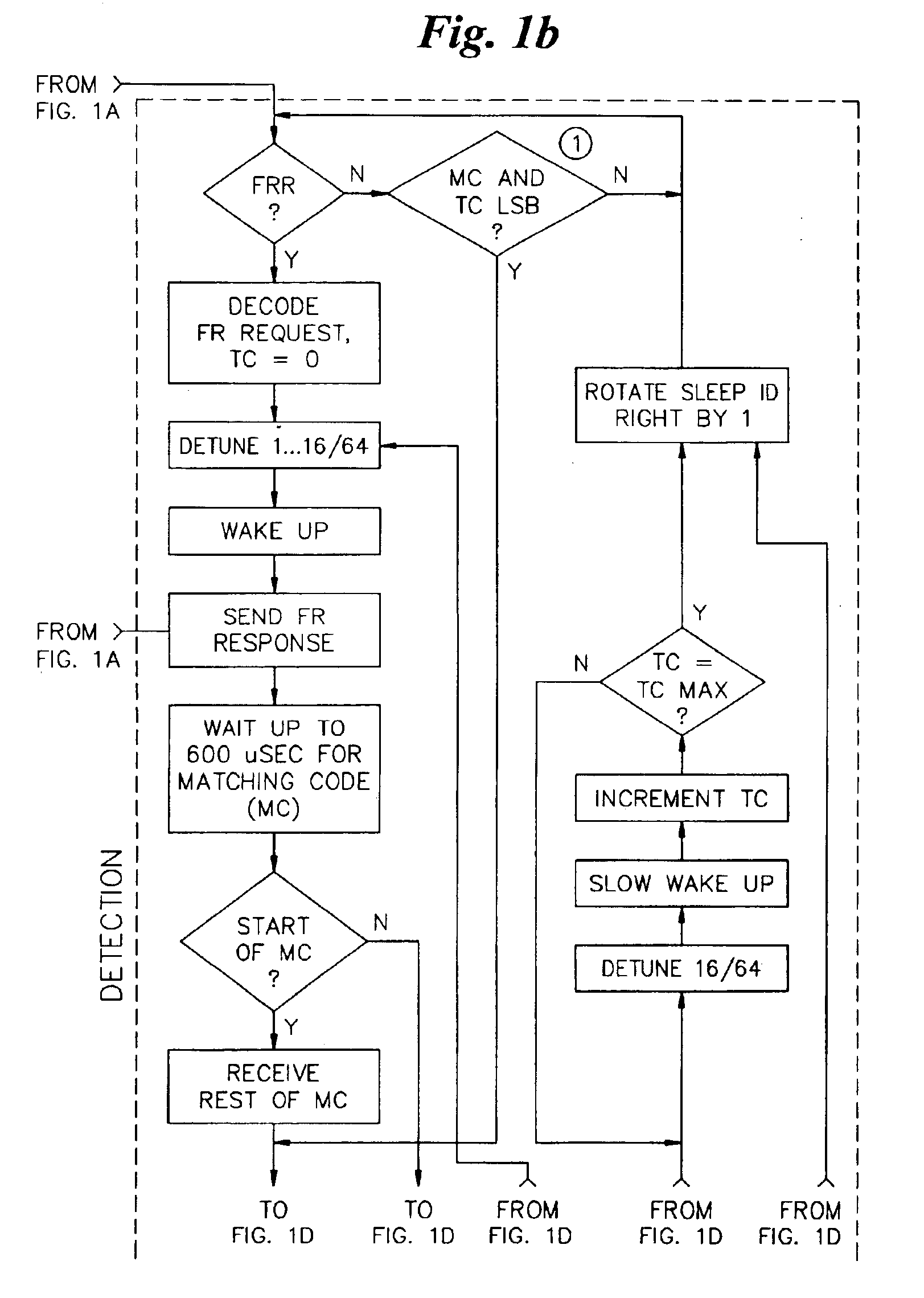
Anticollision protocol with fast read request and additional schemes for reading multiple transponders in an RFID system
InactiveUS6963270B1Fast readMinimize overheadTransmission systemsMemory record carrier reading problemsData rateCommunication control
Arbitration of multiple transponders, such as RFID tags, occurs in an interrogation field. The arbitration process is custom-tailored for individual applications, under software control, by the transponder reader or tag reader. Different wake-up slots are calculated for each tag during successive transmission cycles based upon the tag ID and the transmission cycle number. The tag reader may send a special fast read command to the tag which includes a read request and communications control parameters including the number of time slots for transponder communications, the number of transmissions that an individual transponder is allowed to issue, and the data rate at which the reader communicates to the transponder. The tag reader may also send a special command to a tag to read its data and cause the tag to become decoupled from the environment. Additional schemes are provided to halve the number of active tags in each transmission cycle and to selectively inactivate designated groupings of tag, thereby improving discrimination of the tags in the interrogation field. The tags may be selectively placed in either a tag-talk-first mode or a reader-talk-first mode.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC +2
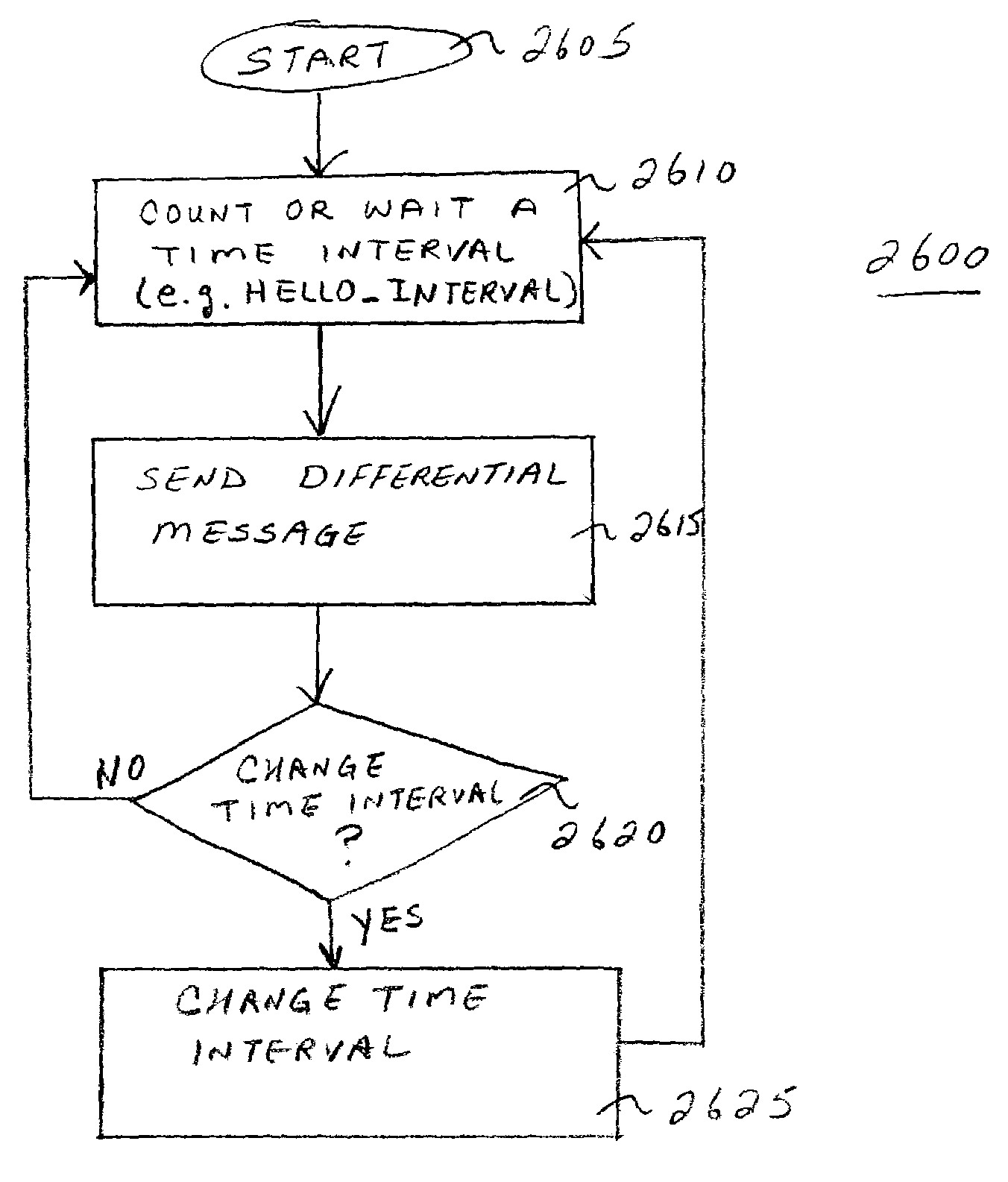
Method and apparatus for disseminating topology information and for discovering new neighboring nodes
InactiveUS7327683B2Improve robustnessMinimize overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsTopology informationLink-state routing protocol
A proactive link-state routing protocol designed for mobile ad-hoc networks is disclosed, which provides hop-by-hop routing along shortest paths to each destination. Each node running the present protocol will compute a source tree (providing paths to all reachable nodes) based on partial topology information stored in its topology table. To minimize overhead, each node reports only “part” of its source tree to neighbors. The present invention employs a combination of periodic and differential updates to keep all neighbors informed of the reportable part of its source tree. The present invention performs neighbor discovery using “differential” HELLO messages that report only “changes” in the status of neighbors. This results in HELLO messages that are much smaller than those of other link-state routing protocols.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
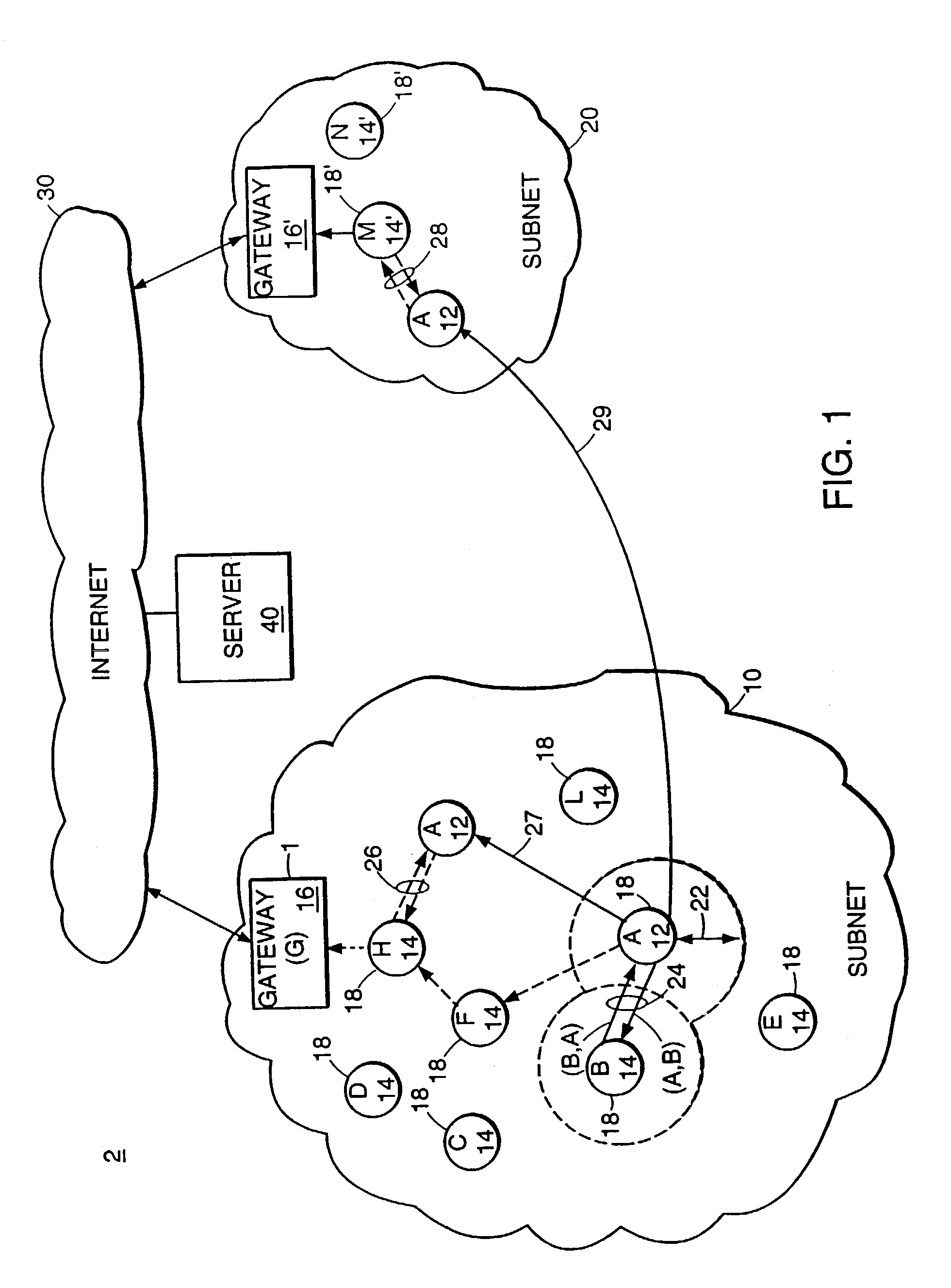
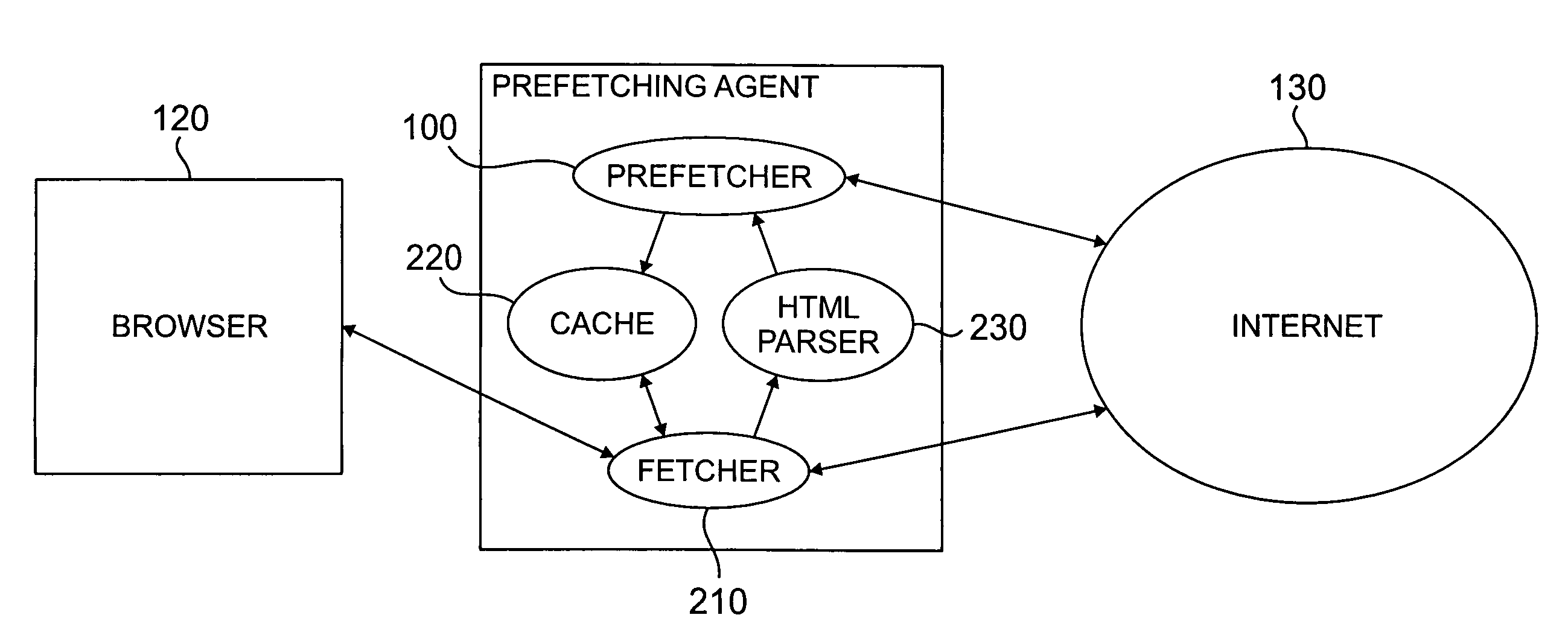
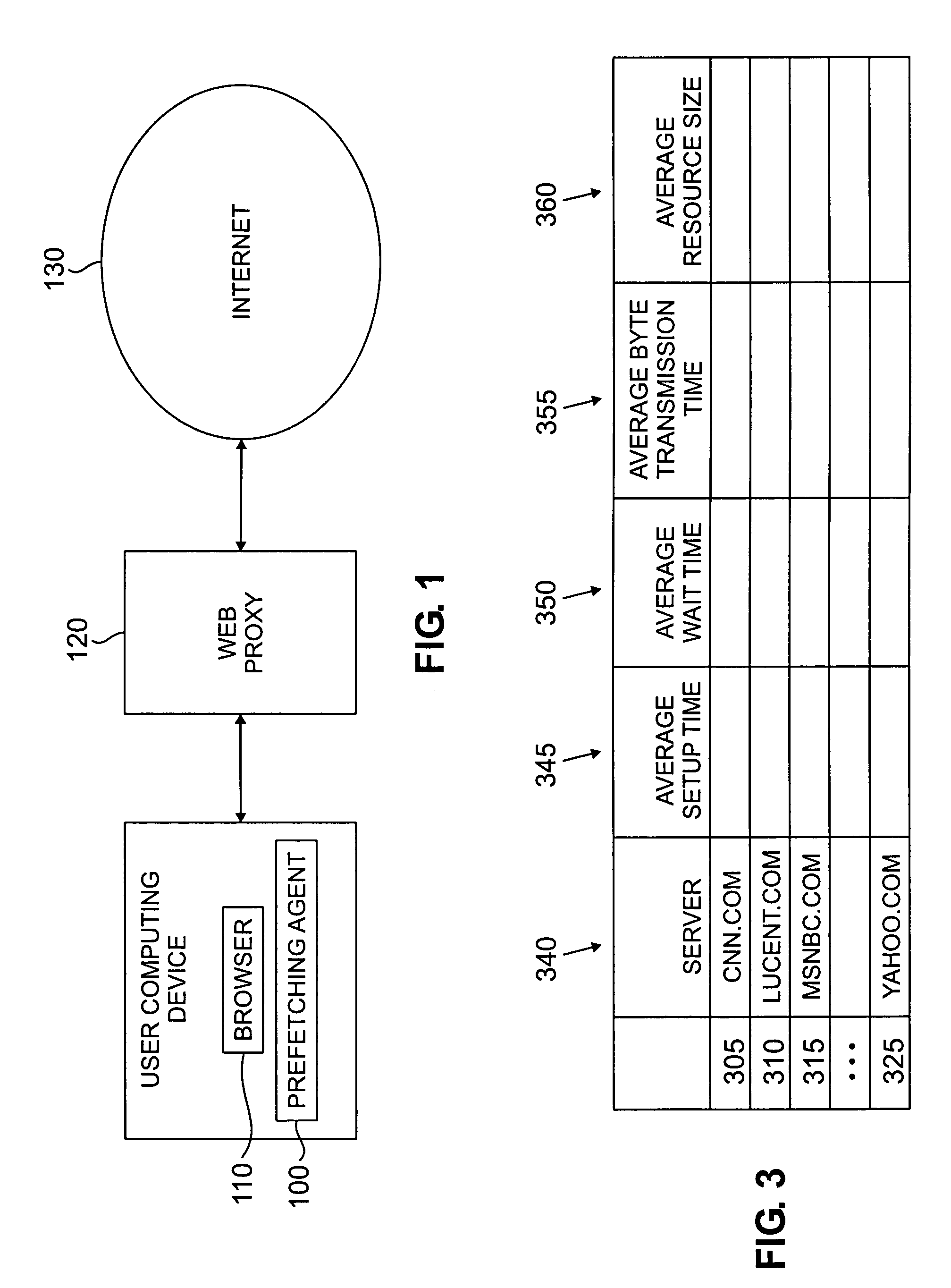
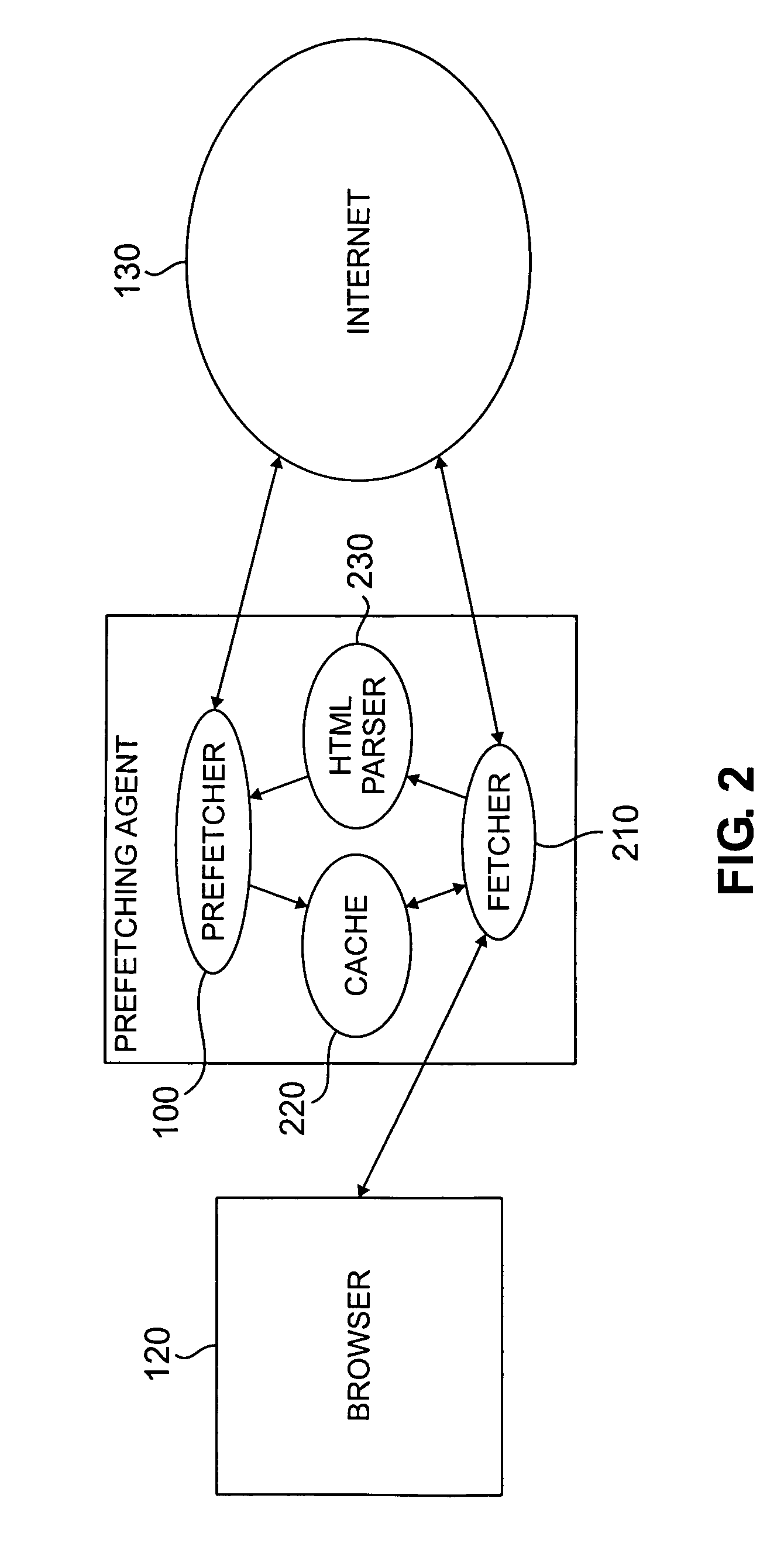
Method and apparatus for prefetching internet resources based on estimated round trip time
InactiveUS6993591B1Shorten access timeMinimizing networkData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsHyperlinkTTEthernet
A method and apparatus are disclosed for prefetching Internet resources based on the estimated round trip time of the resources. Whenever a user clicks on an embedded hyperlink, the prefetching strategy aims to ensure that the corresponding document has been prefetched or can be fetched very quickly from its origin server. Web access time as perceived by the user is reduced, while also minimizing the network, server and local resource overhead due to prefetching. The estimated round trip time is obtained or approximated for all referenced documents. The “round trip” time or access time of a resource is the time interval between the sending of the first byte of an HTTP request for the resource until the last byte of the server response has arrived at the requesting Web client. Documents with the longest access times are prefetched first and prefetching generally continues until the estimated round trip time falls below a predefined threshold. An HTTP HEAD request may be used to determine the estimated round trip time of a Web resource. The prefetching agent can be configured to prevent prefetching of those documents that are quickly fetchable, dynamically generated or non-HTTP based resources, or those documents whose size exceed a certain limit, to minimize the network, server and local resource overhead due to prefetching. The thresholds applied to the list of documents to be prefetched can be dynamically adjusted by the agent, based on changing network and server conditions.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
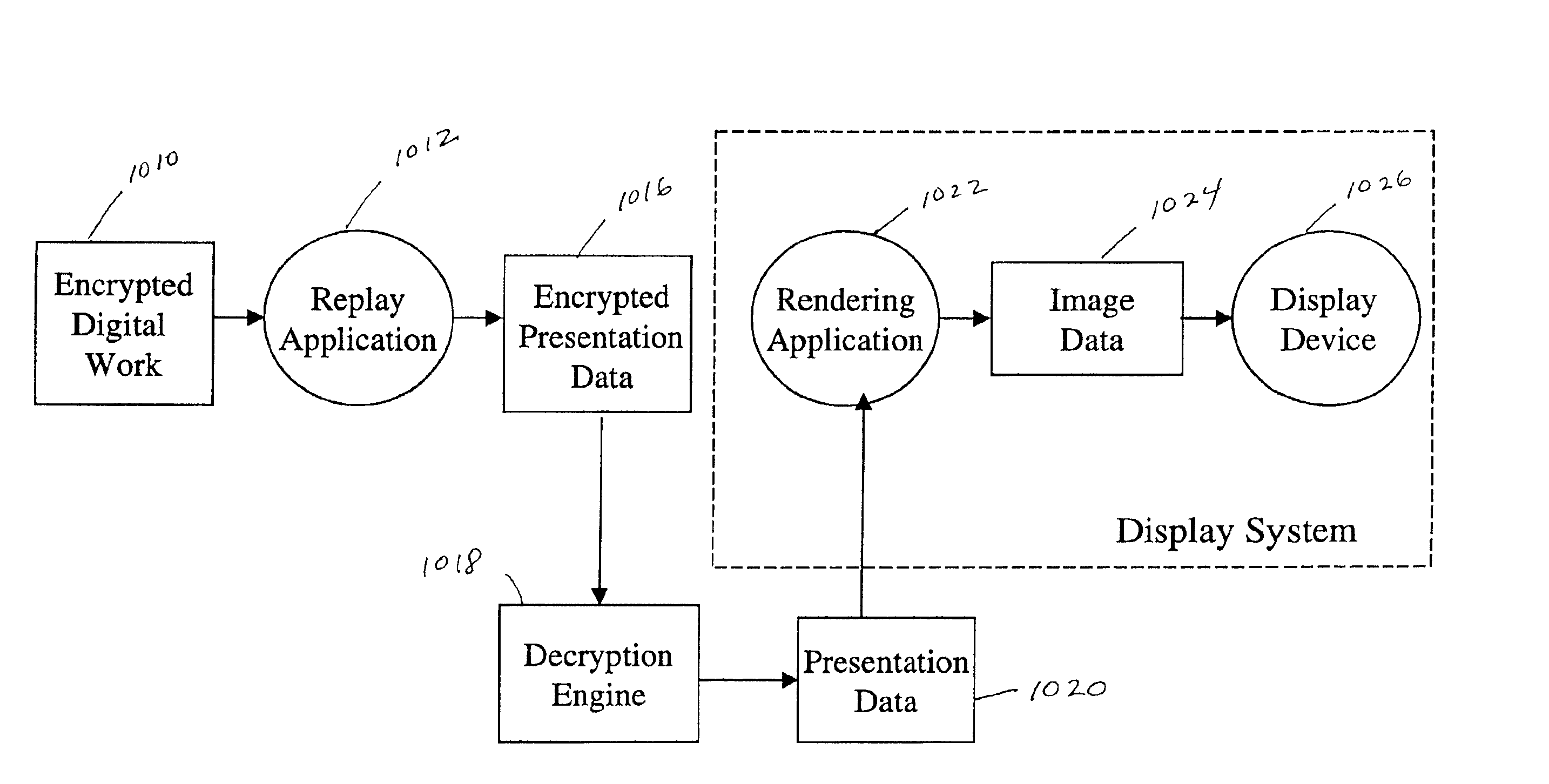
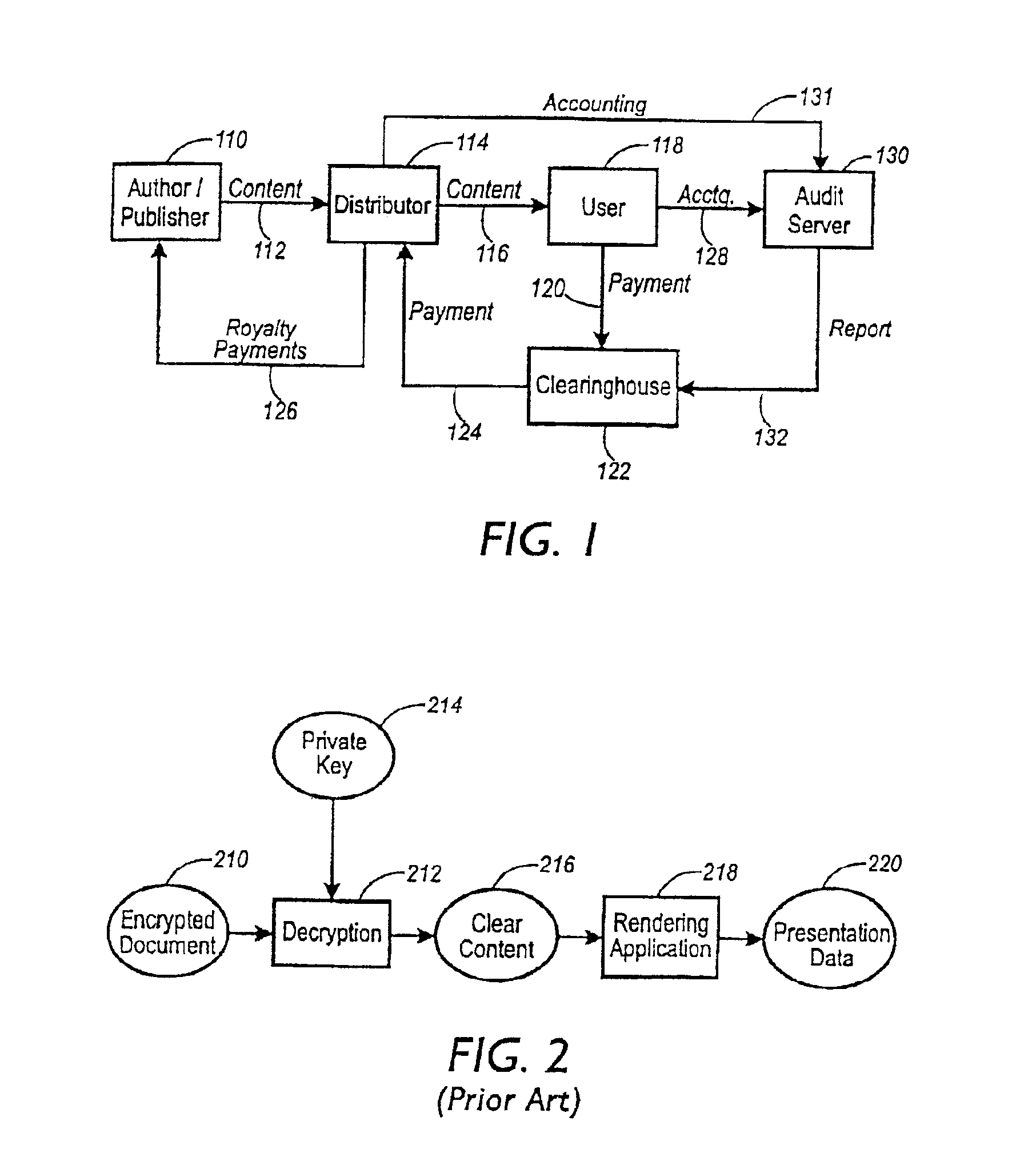
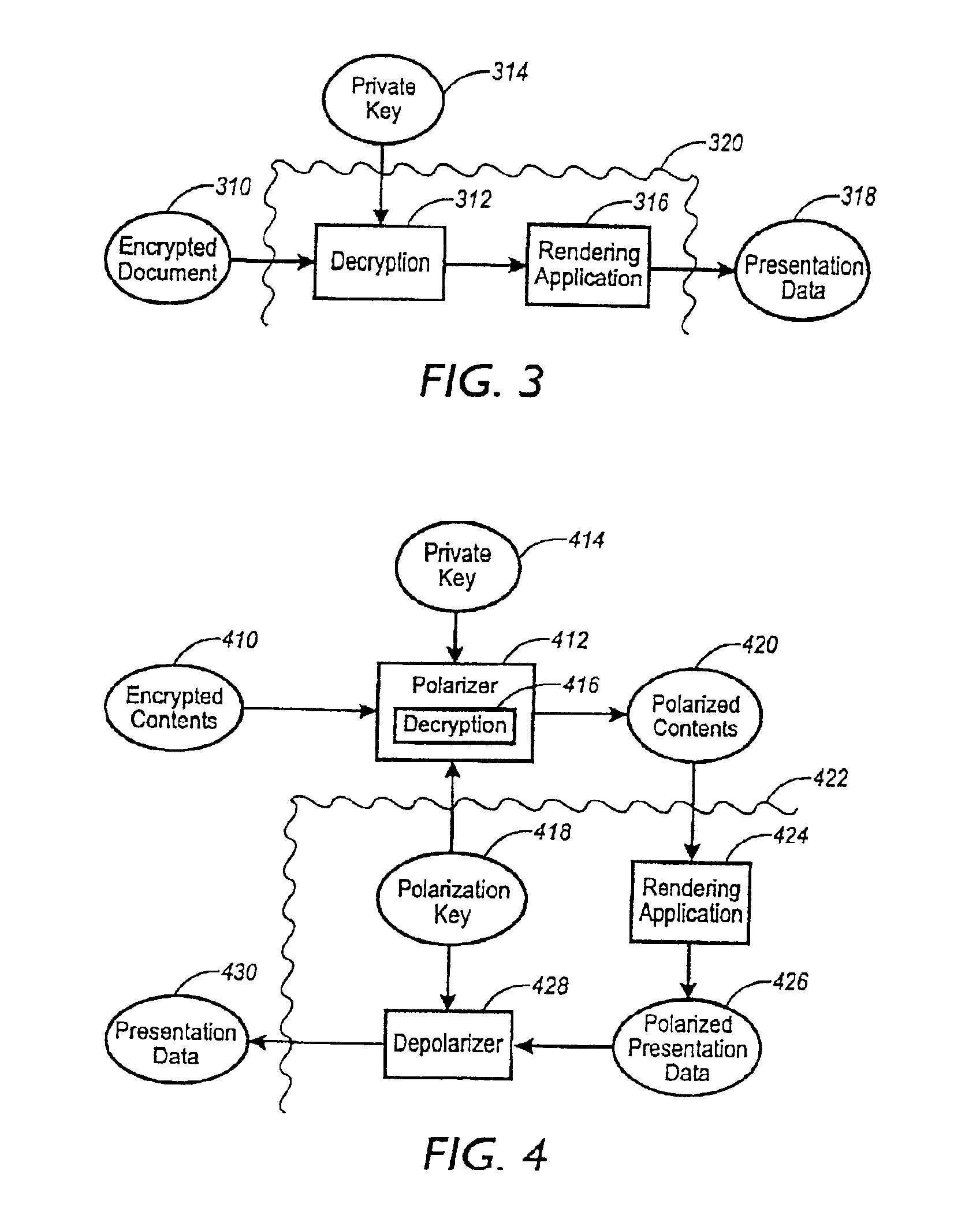
System and method for protection of digital works
InactiveUS6885748B1Improve performanceMinimize overheadTelevision system detailsMultiple keys/algorithms usageApplication softwareEncryption
A method of protecting a digital work uses a format preserving encryption scheme to encrypt the digital work. This enables any native replay application or rendering application to transform an encrypted digital work into encrypted presentation data. The originator's digital content is protected in its original form by not being decrypted. This method enables the rendering or replay application to process the encrypted document into encrypted presentation data without decrypting it first. Encrypted presentation data is then decrypted just before it is displayed to the user. An additive encryption scheme is a particular type of encryption scheme which preserves formatting of a digital work.
Owner:CONTENTGUARD HLDG
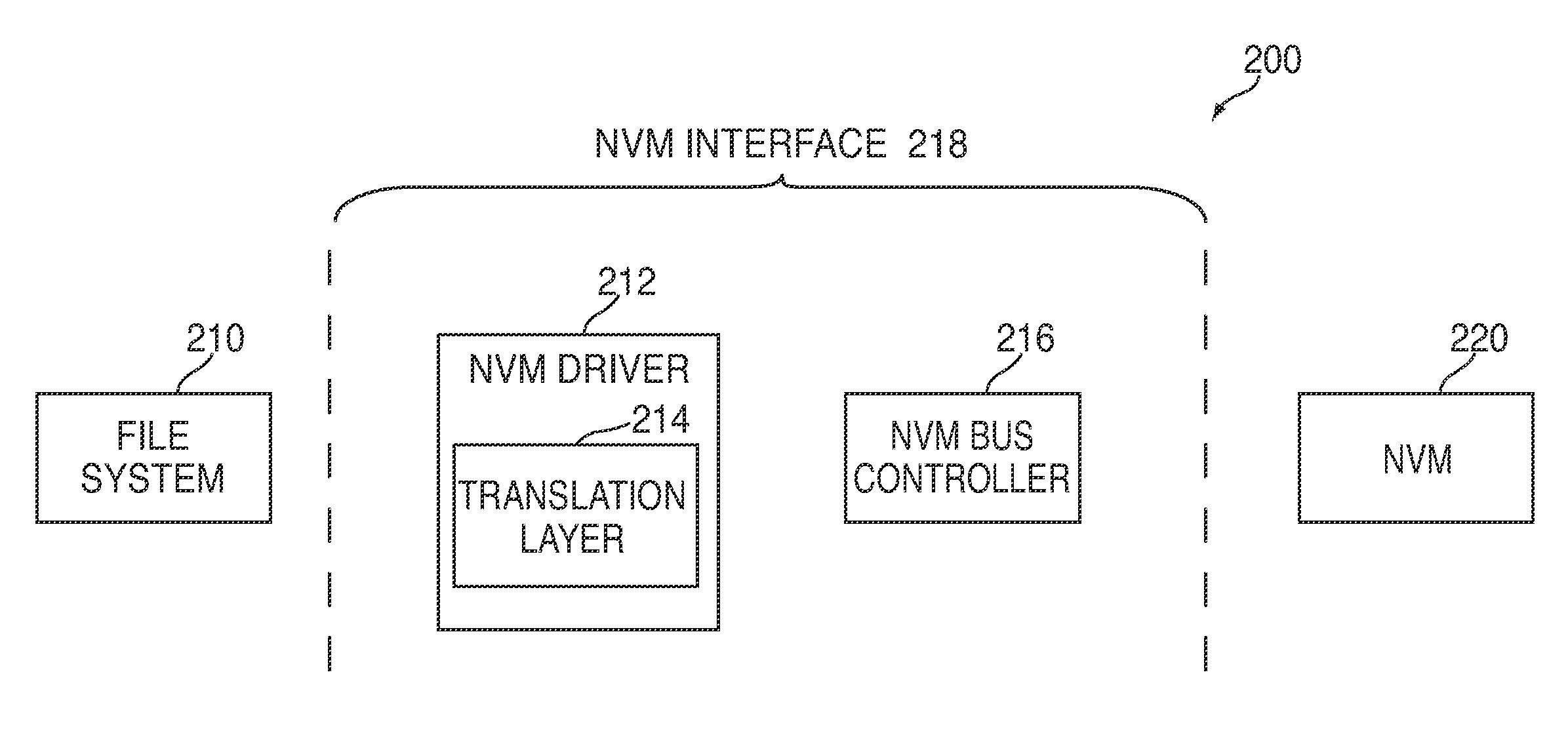
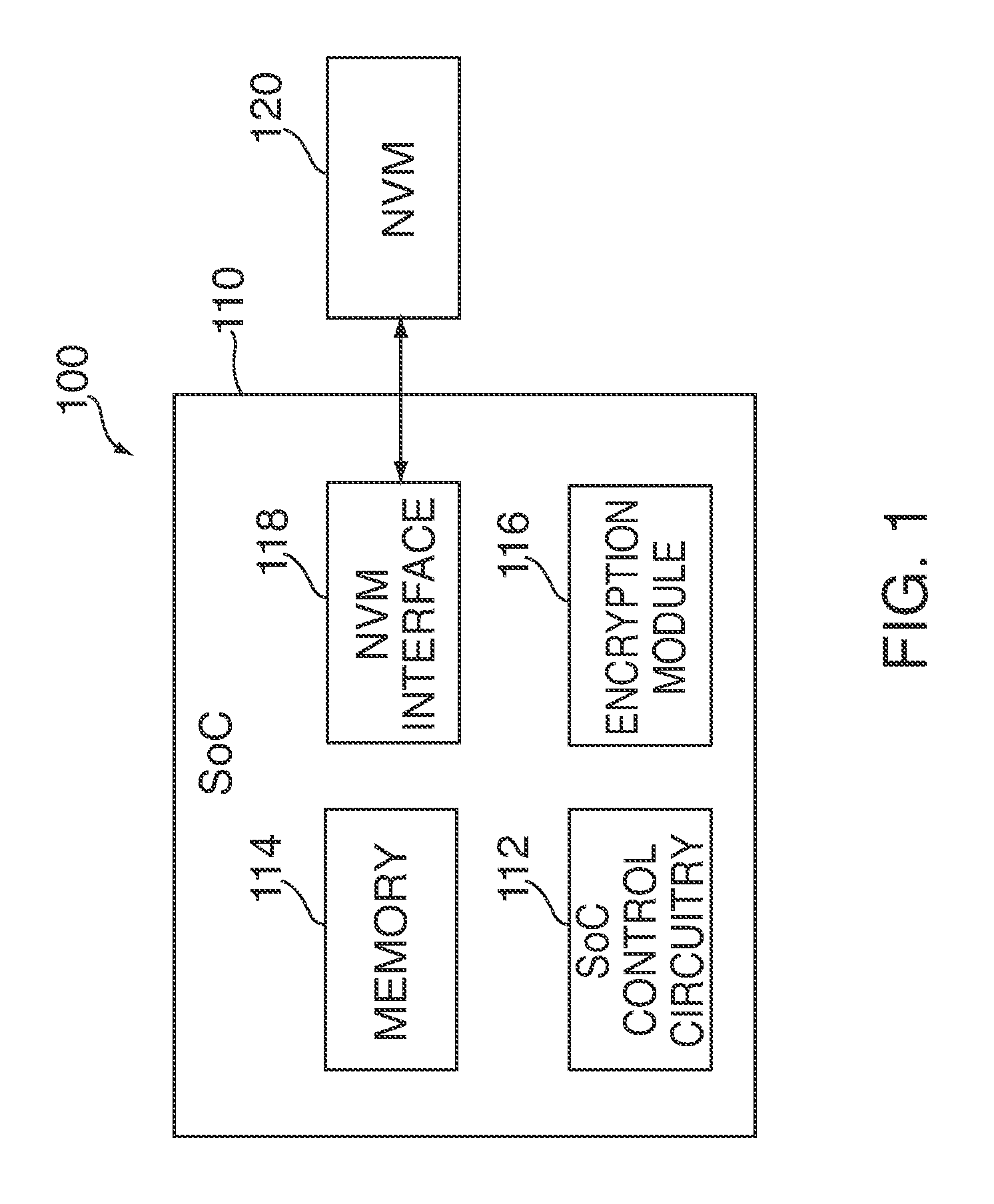
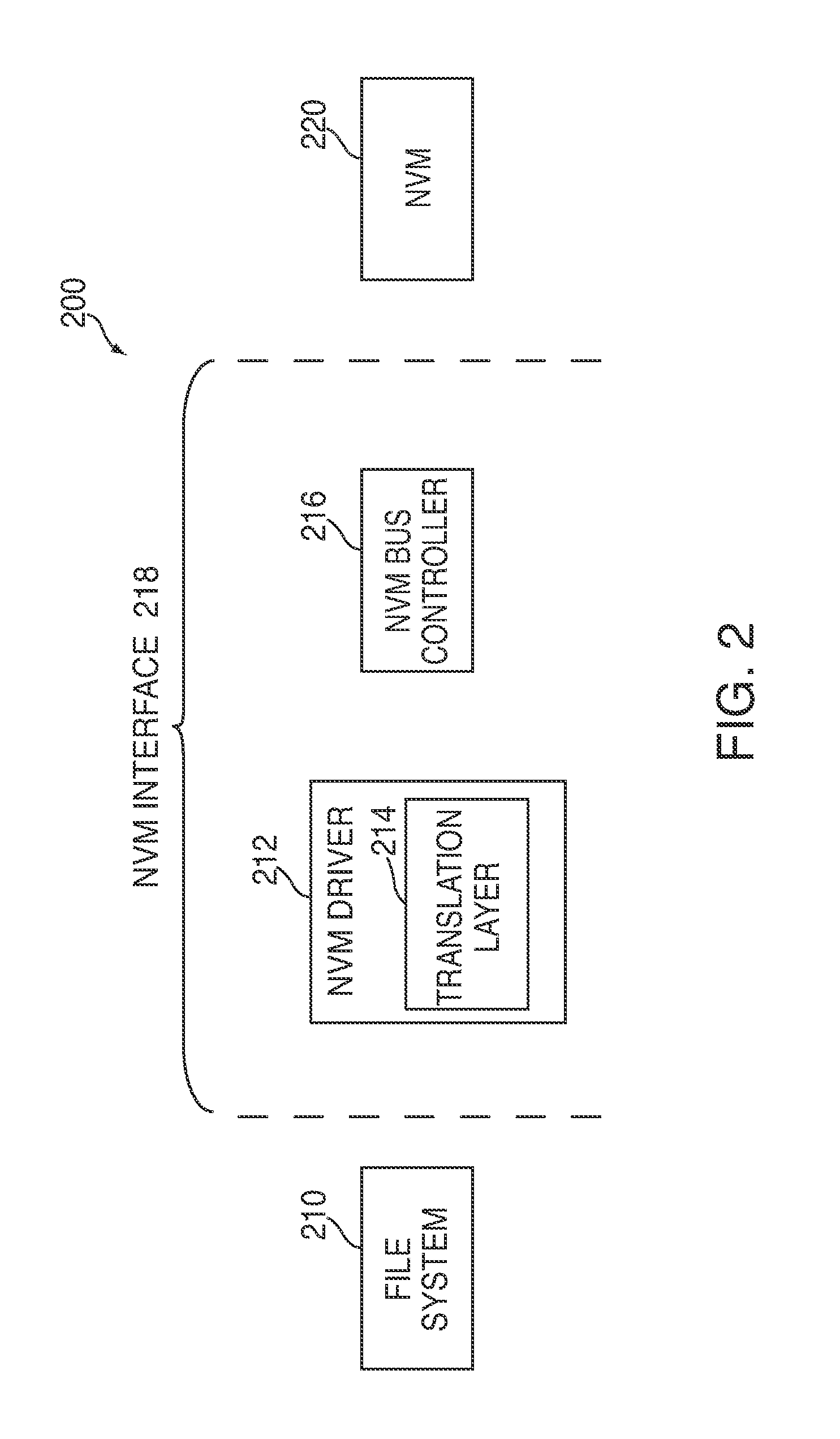
Efficient buffering for a system having non-volatile memory
InactiveUS20120221767A1Effective bufferImprove system performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTFile systemHeuristic
Systems and methods are disclosed for efficient buffering for a system having non-volatile memory (“NVM”). In some embodiments, a control circuitry of a system can use heuristics to determine whether to perform buffering of one or more write commands received from a file system. In other embodiments, the control circuitry can minimize read energy and buffering overhead by efficiently re-ordering write commands in a queue along page-aligned boundaries of a buffer. In further embodiments, the control circuitry can optimally combine write commands from a buffer with write commands from a queue. After combining the commands, the control circuitry can dispatch the commands in a single transaction.
Owner:APPLE INC
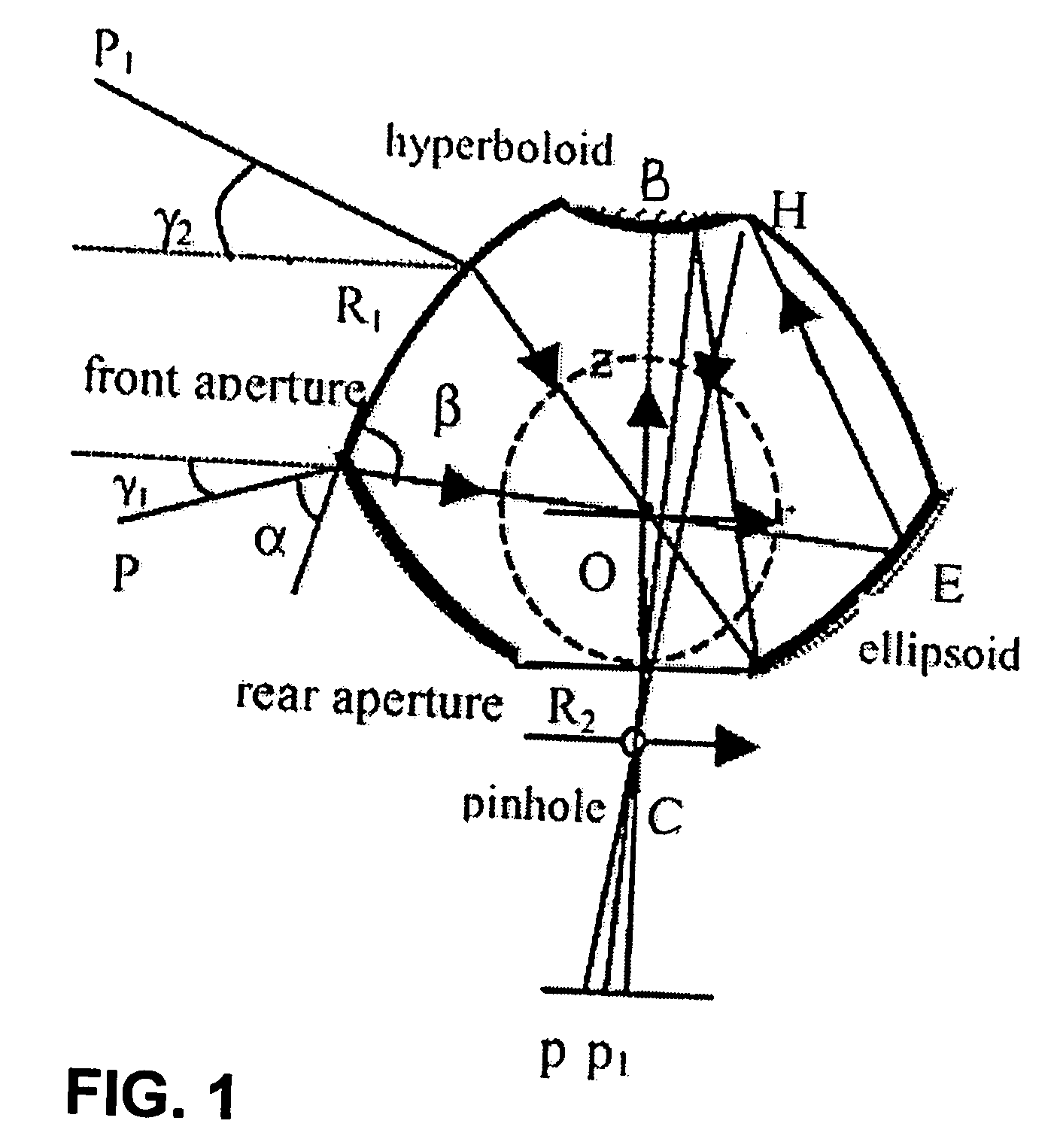
Panoramic video system with real-time distortion-free imaging
ActiveUS20060023105A1Minimizing software overheadHighly efficient regional transformationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsTime distortionGraphic card
A panoramic annular lens system (PAL), a unitary video camera and a PC-based software system that unwraps a 360° video image into a seamless, distortion free horizontal image image in real time. The PAL system of the preferred embodiment has a 360° horizontal field of view and a 90° vertical field of view in a 40 mm diameter compact package. The invention is not limited to any particular type of lens system. In fact, there are numerous lens systems for providing a 360° panoramic view. The video camera may be a CCD or CMOS based device having a pixel resolution of either 1280×1024 (high resolution) or 720×480 (NTSC). The unwrapping system is a radiometric ray tracing program carried out using a computer's graphics card capabilities to produce highly efficient regional transformation while minimizing software overhead. The result is real time, high resolution 30 fps conversion from a spherical distorted image to a flat panoramic image in Cartesian coordinates.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
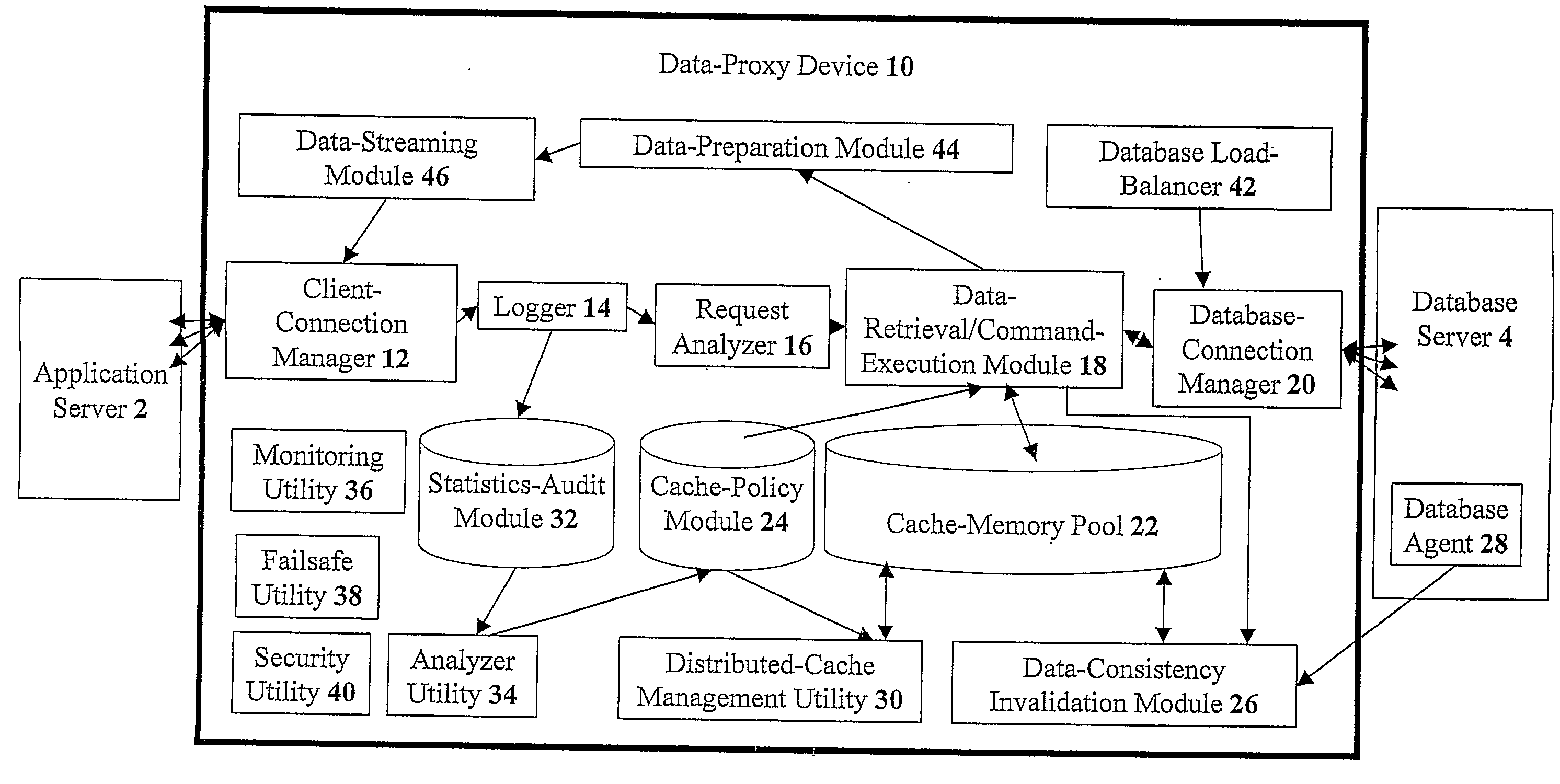
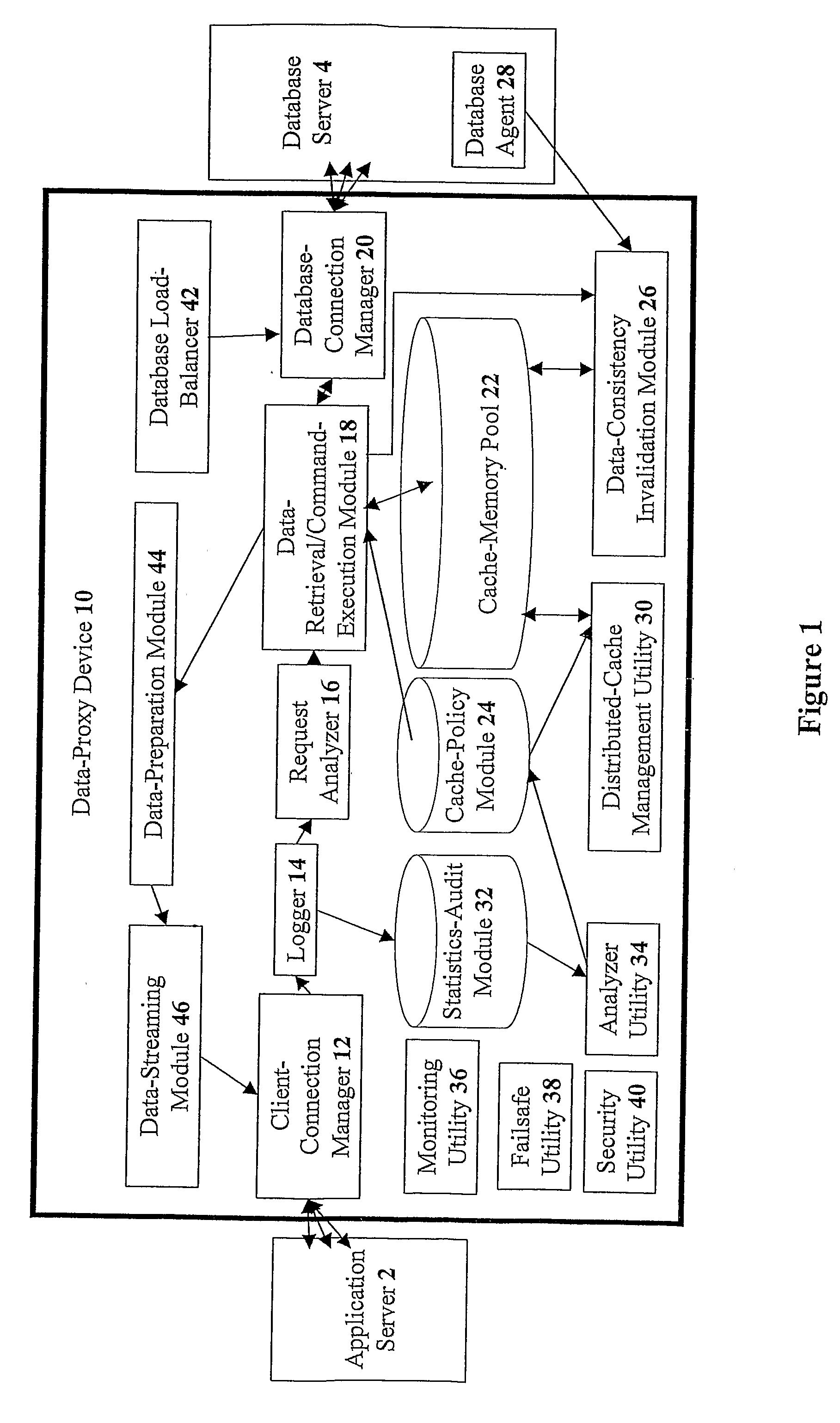
Devices for providing distributable middleware data proxy between application servers and database servers
InactiveUS20100174939A1Shorten the timeSave resourcesDigital data information retrievalResource allocationClient dataTerm memory
The present invention discloses devices Including a transparent client-connection manager for exchanging client data between an application server and the device: a request analyzer for analyzing query requests from at least one application server; a data-retrieval / command-execution module for executing query requests; a database connection manager for exchanging database data between at least one database server and the device: a cache-memory pool for storing data items from at least one database server: a cache-policy module for determining cache criteria for storing the data Items In the cache-memory pool; and a data-consistency invalidation module for determining invalidated data Items based on invalidation criteria for removing from the cache-memory pool. The cache-memory pool Is configured to utilize memory modules residing in data proxy devices and distributed cache management utility, enabling the memory capacity to be used as a cluster to balance workloads.
Owner:DCF TECH
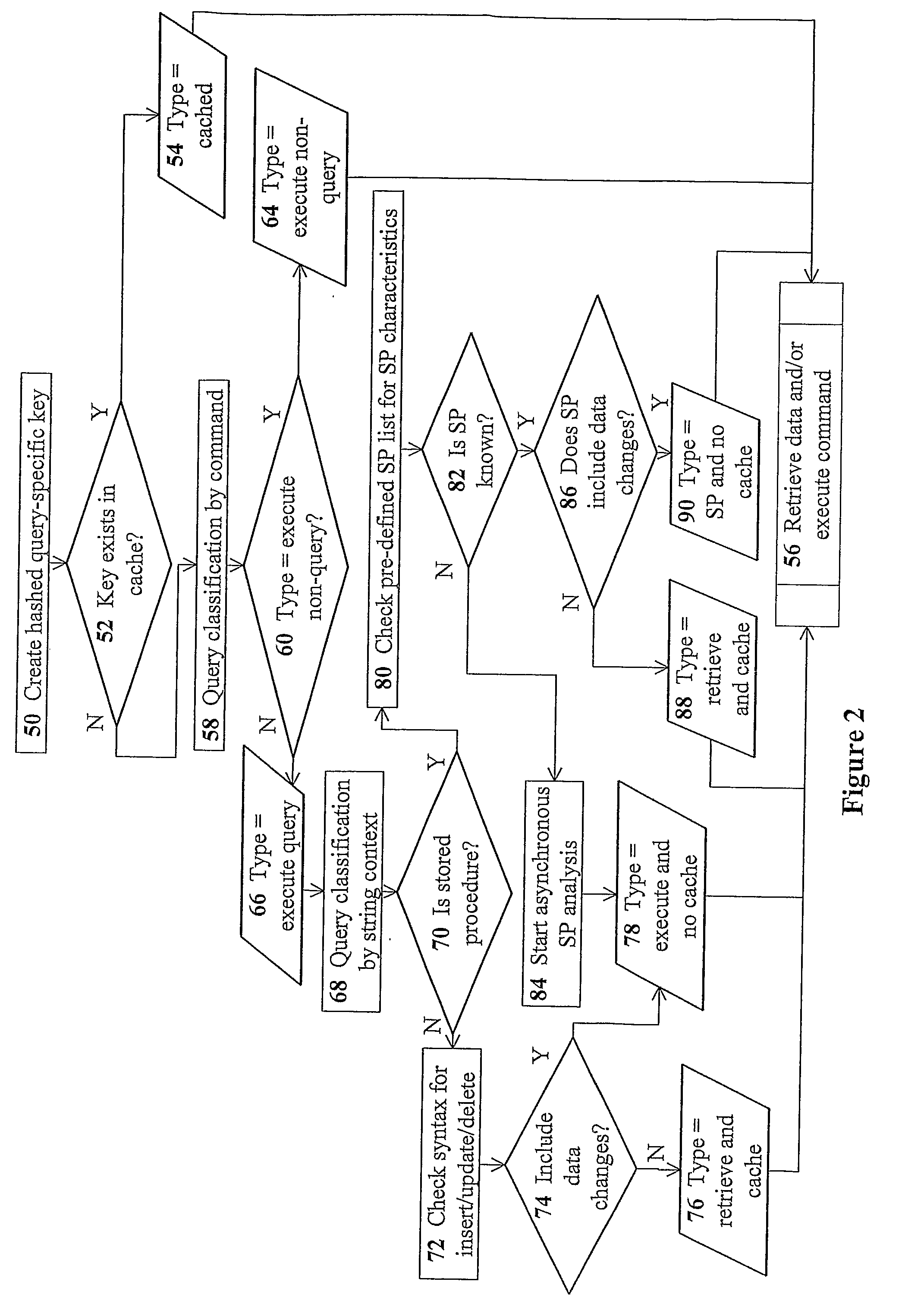
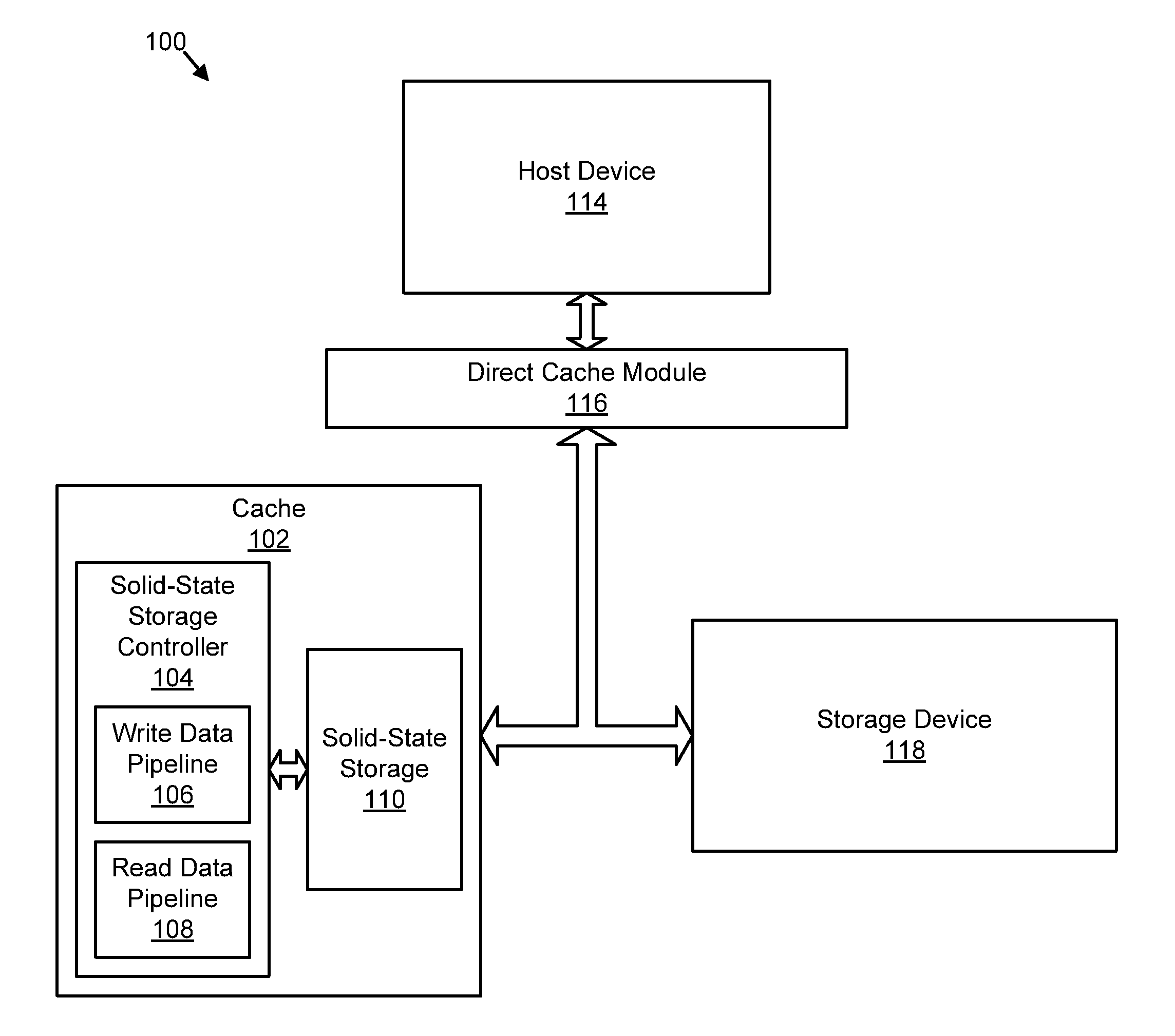
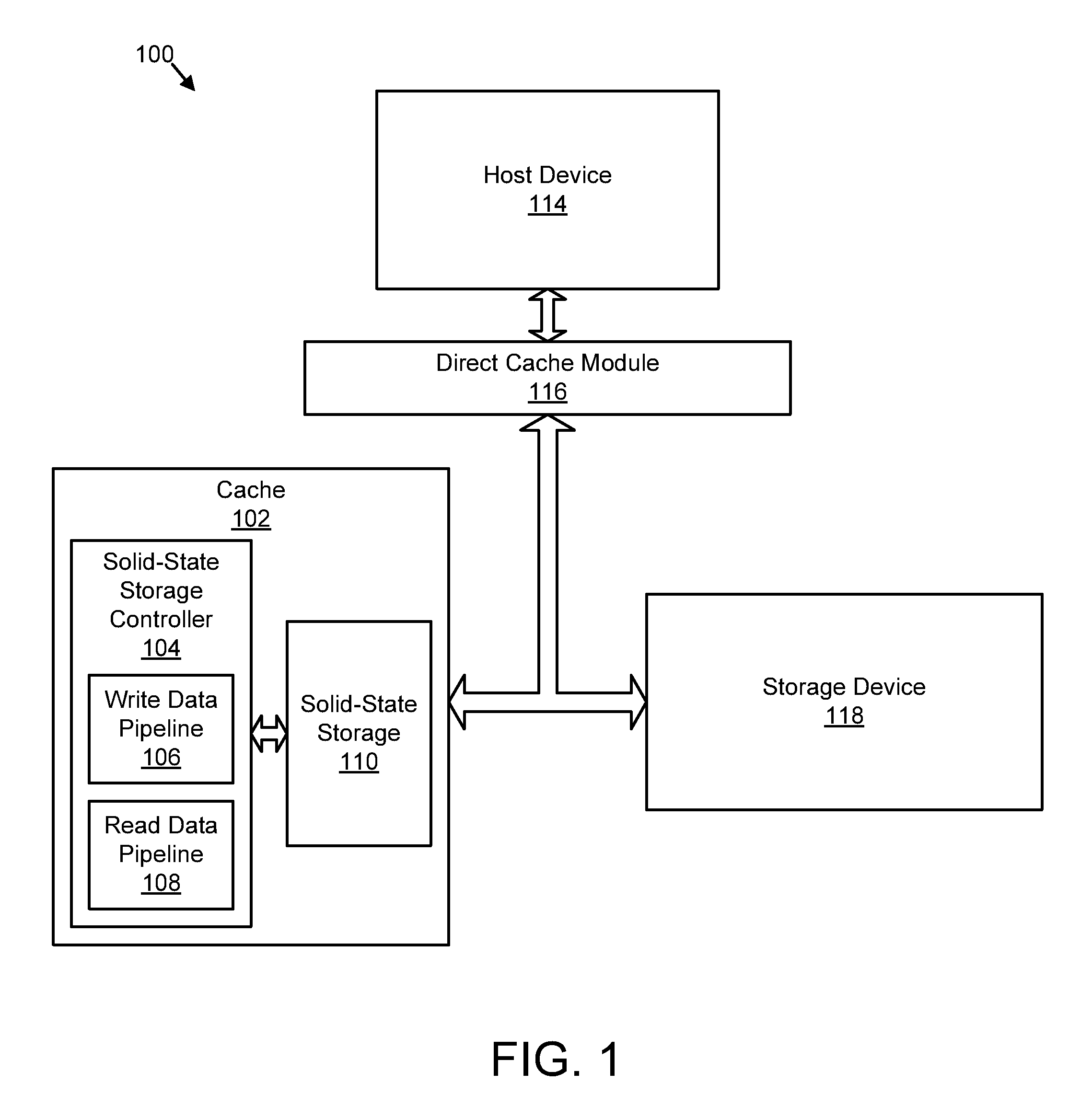
Apparatus, system, and method for caching data
ActiveUS20120210041A1Effective cachingMinimize cache collisionMemory architecture accessing/allocationServersSolid-state storageLogical block addressing
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for caching data. A storage request module detects an input / output (“I / O”) request for a storage device cached by solid-state storage media of a cache. A direct mapping module references a single mapping structure to determine that the cache comprises data of the I / O request. The single mapping structure maps each logical block address of the storage device directly to a logical block address of the cache. The single mapping structure maintains a fully associative relationship between logical block addresses of the storage device and physical storage addresses on the solid-state storage media. A cache fulfillment module satisfies the I / O request using the cache in response to the direct mapping module determining that the cache comprises at least one data block of the I / O request.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
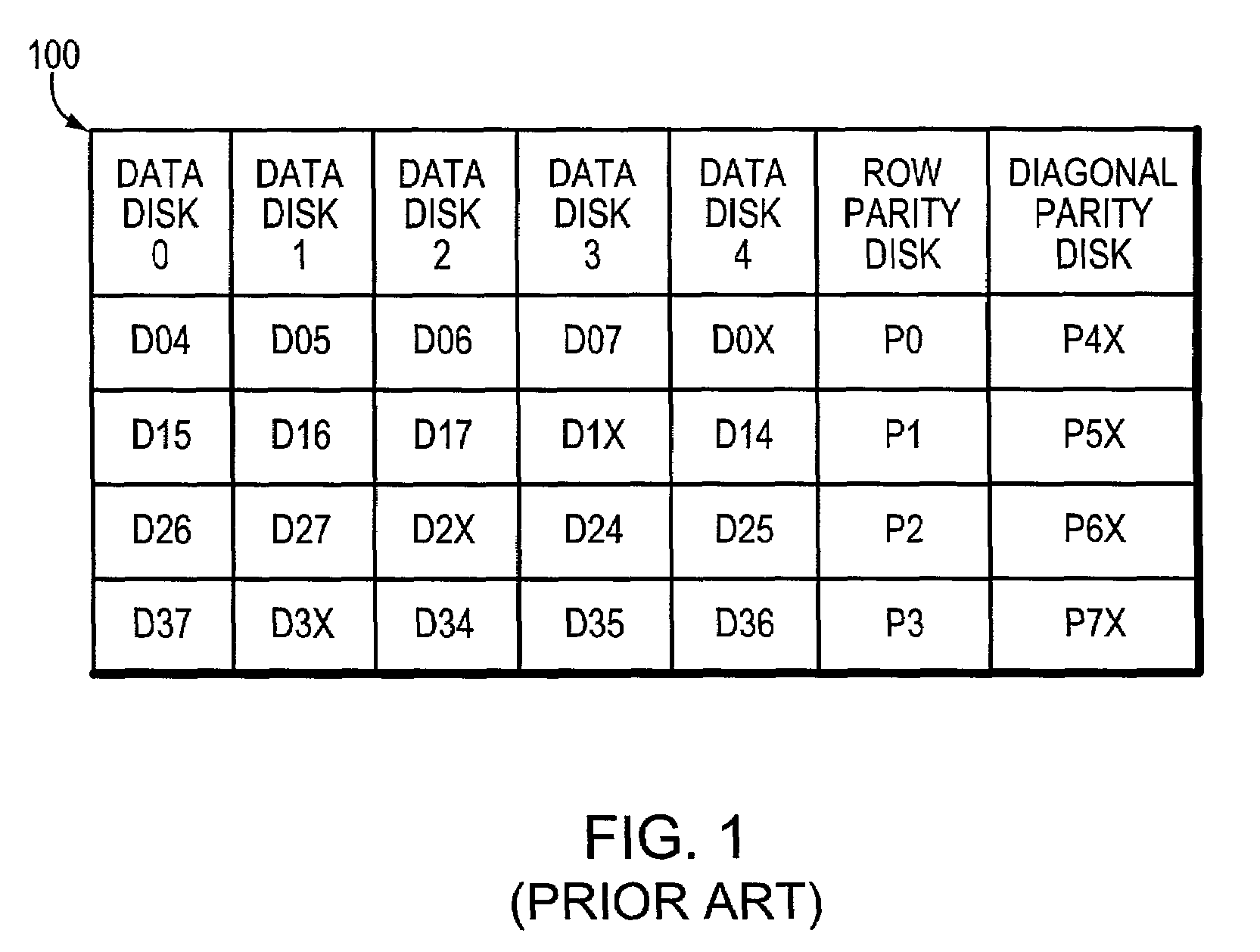
Row-diagonal parity technique for enabling efficient recovery from double failures in a storage array
ActiveUS6993701B2Reduce overheadEffective recoveryInput/output to record carriersStatic storageTheoretical computer scienceDouble fault
A “row-diagonal” (R-D) parity technique reduces overhead of computing diagonal parity for a storage array adapted to enable efficient recovery from the concurrent failure of two storage devices in the array. The diagonal parity is computed along diagonal parity sets that collectively span all data disks and a row parity disk of the array. The parity for all of the diagonal parity sets except one is stored on the diagonal parity disk. The R-D parity technique provides a uniform stripe depth and an optimal amount of parity information.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
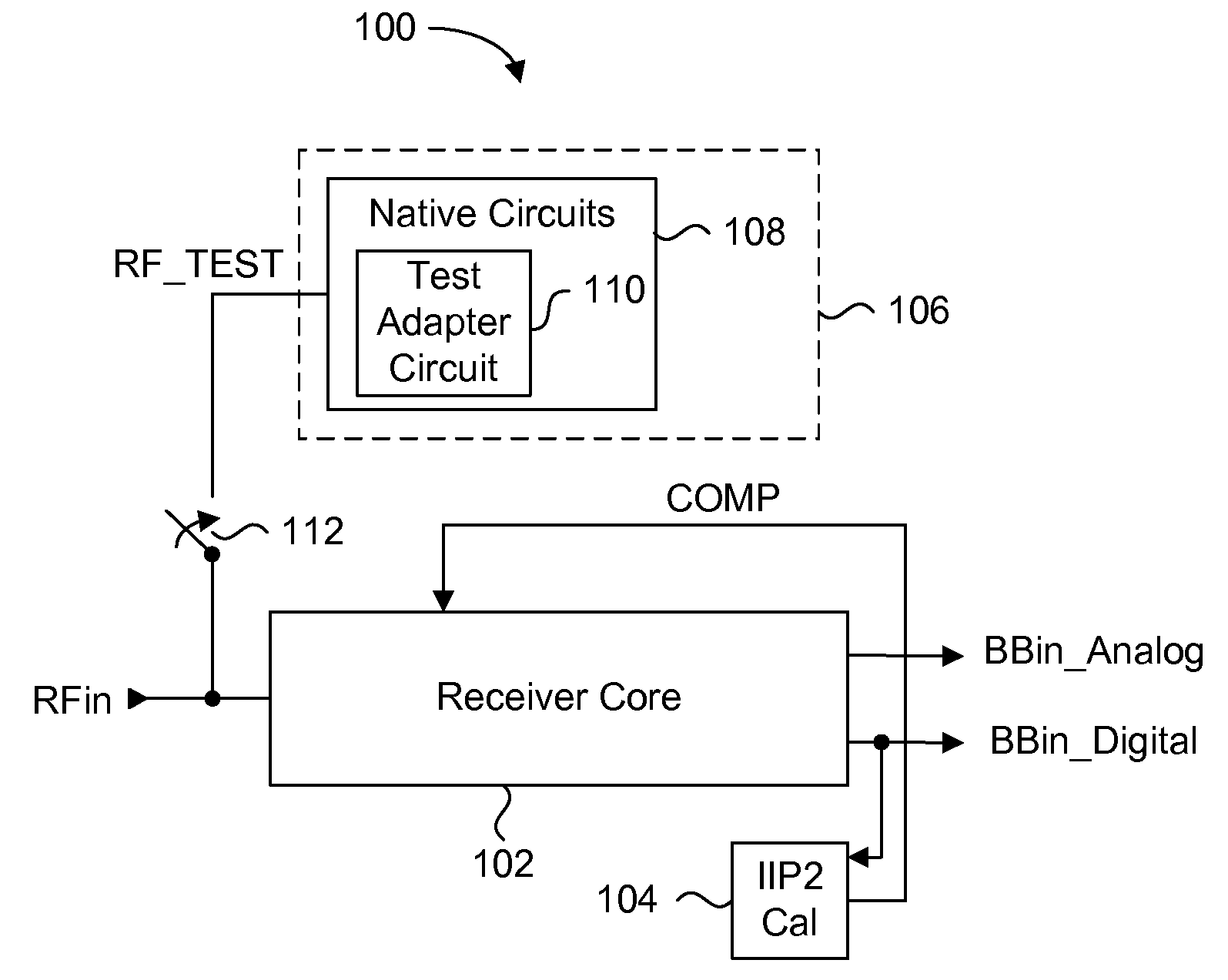
Automatic iip2 calibration architecture
ActiveUS20080182537A1Minimize circuit overheadEasing testing requirementReceivers monitoringDemodulationWireless transceiverEngineering
An integrated automatic IIP2 calibration architecture for wireless transceivers is disclosed. The architecture enables a wireless transceiver to generate a test radio frequency (RF) signal having a second order tone with minimal additional circuitry. In particular, the test RF signal is generated using a combination of native transceiver circuits and test adaptor circuits. Native transceiver circuits are those circuits implemented on the transceiver chip for executing native transceiver functions during normal operation, which can be used for generating the test (RF) signal. Test adaptor circuits are added to the transceiver chip, more specifically to the native circuits, for enabling the native circuits to generate the test RF signal in a self-test mode of operation. Circuits for implementing a particular IIP2 minimizing scheme can be included on the transceiver chip for automatic IIP2 calibration during the self-test mode of operation.
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
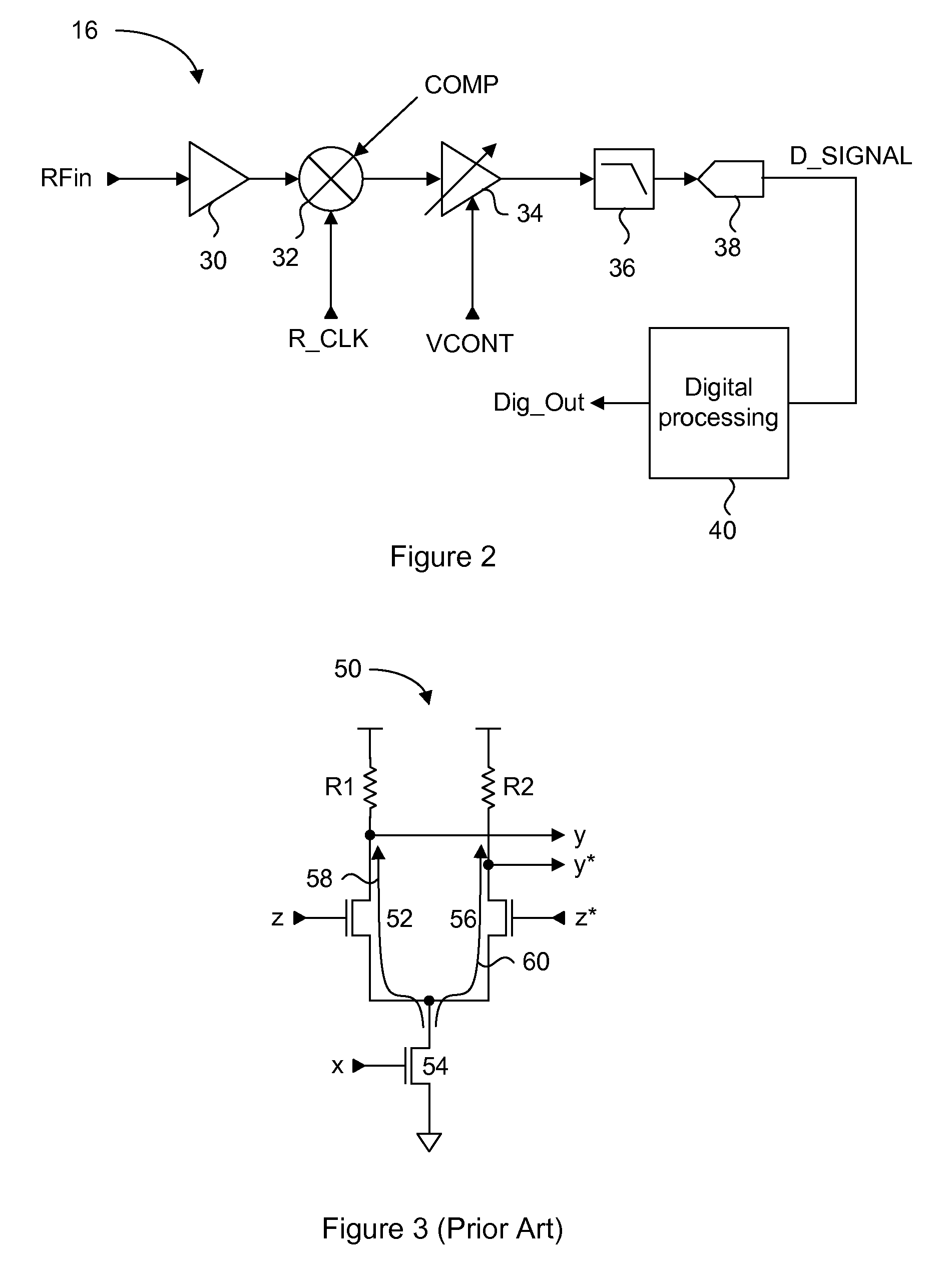
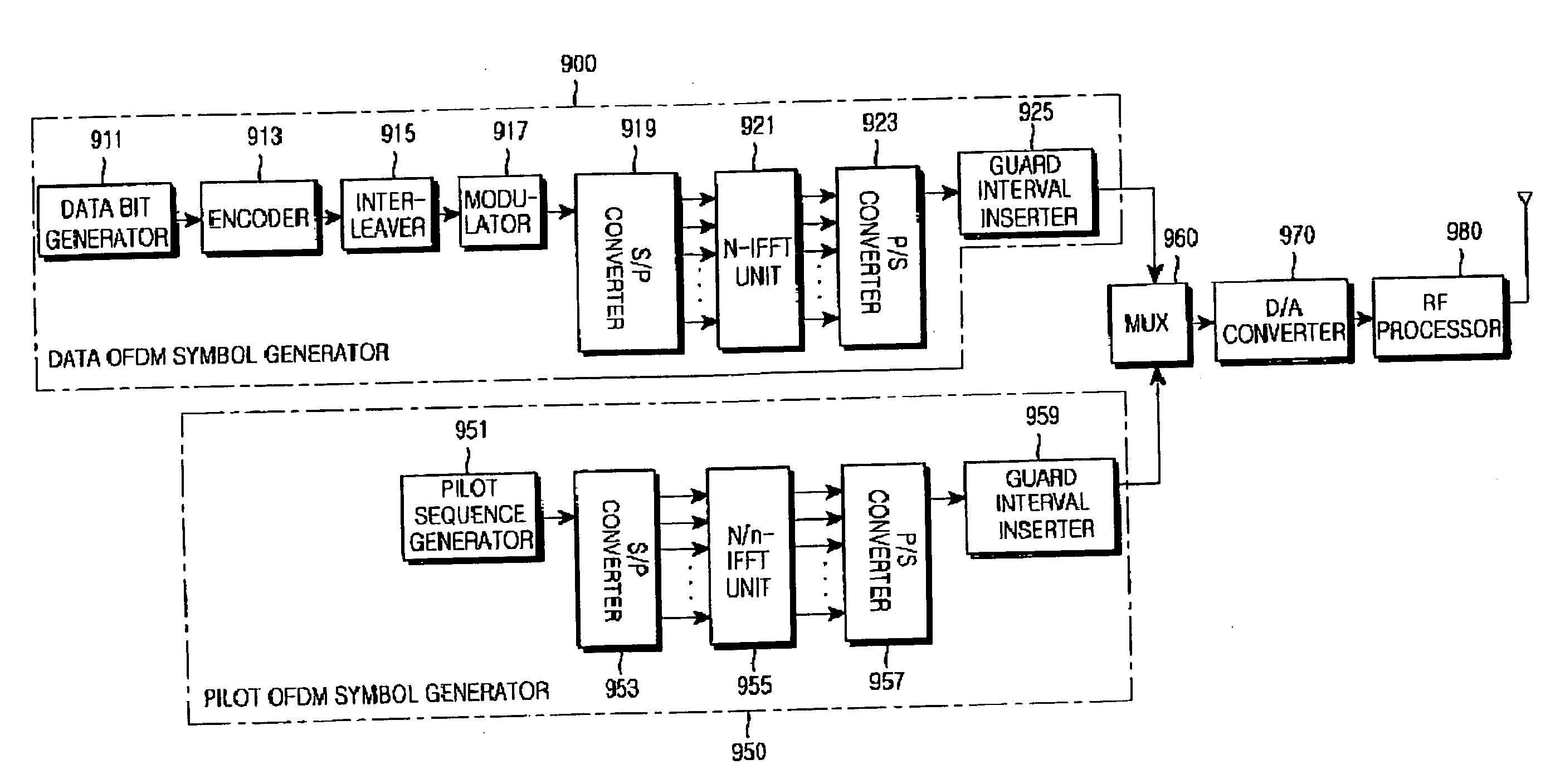
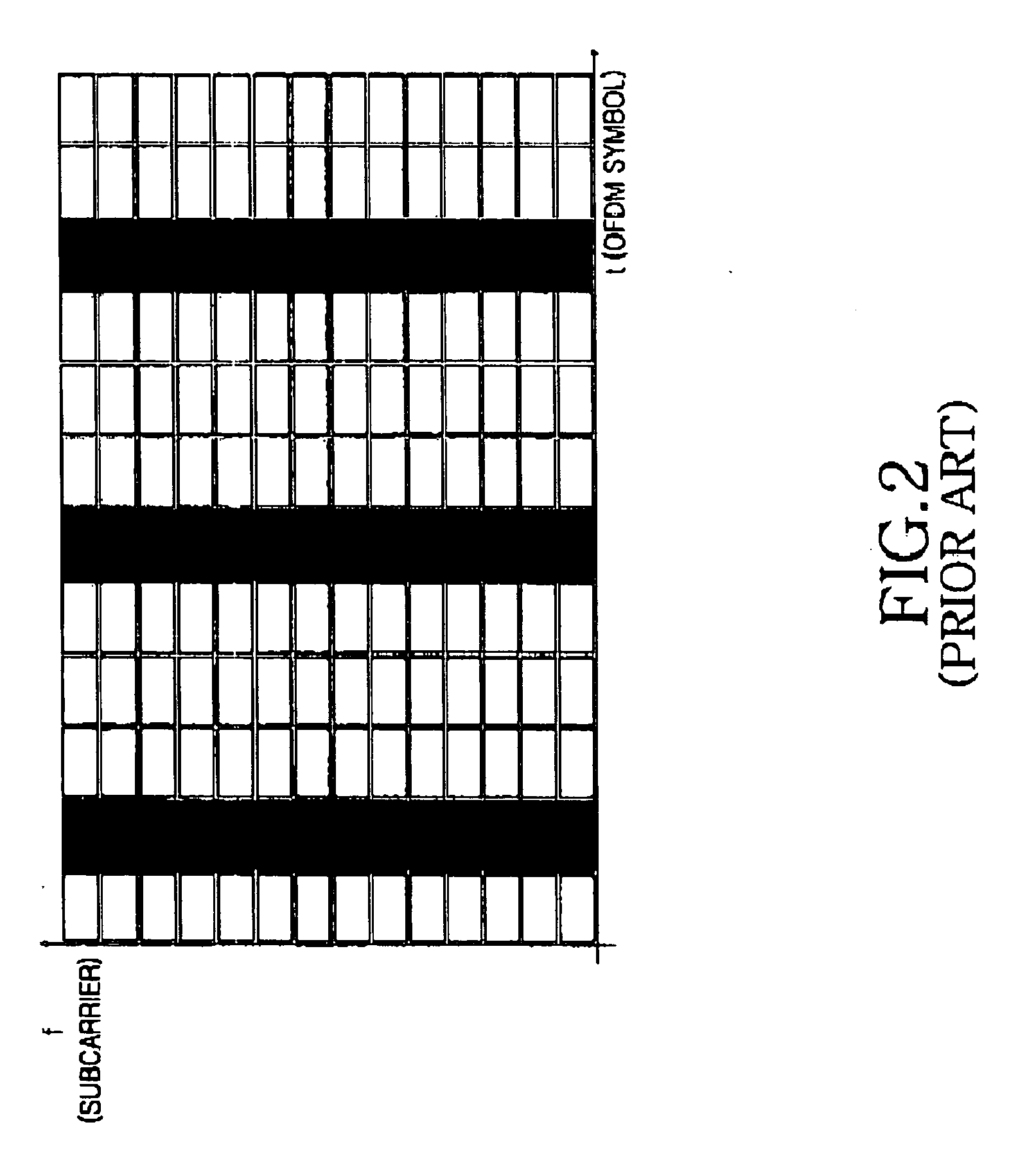
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving pilot signals in an OFDM communication system
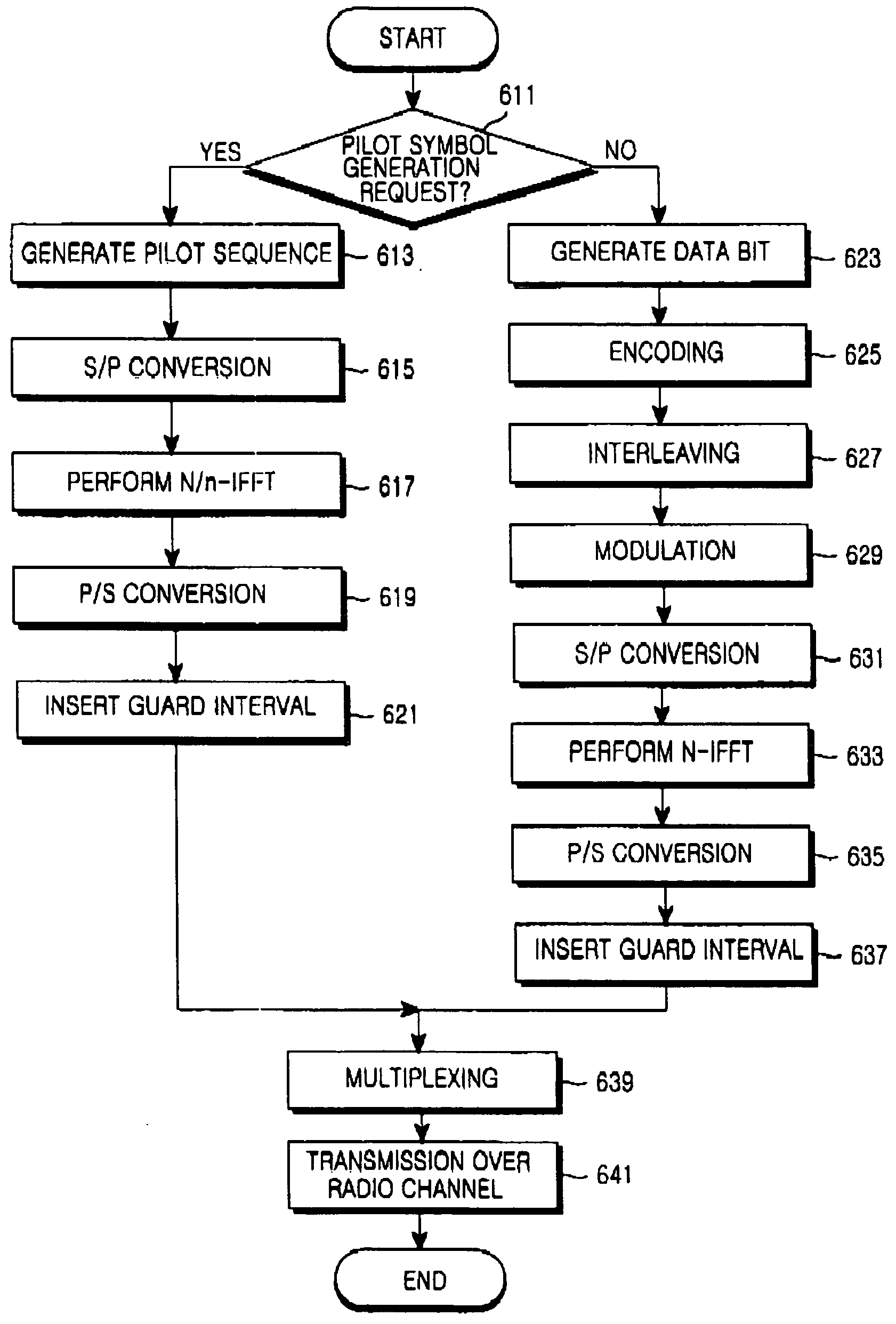
InactiveUS20050094550A1Maximizing a carrier to interference noise ratioMinimize overheadTransmission path divisionMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformCommunications system
A radio communication system divides an entire frequency band into a plurality of subcarrier bands, forms a symbol with signals on the subcarrier bands, forms a frame with a plurality of symbols, transmits a pilot signal within symbols in a predetermined position of the frame, and transmits a data signal within symbols other than the symbols for transmitting the pilot signal. A transmitter allocates subcarriers through which the reference signal is transmitted, wherein the subcarriers are allocated to have an exclusive relation with subcarriers through which reference signals of other transmitters are transmitted, generates the pilot signal, performs an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) on the pilot signal by applying an IFFT size which is less than or equal to an IFFT size applied to the data signal, and transmits the IFFT-processed reference signal to a receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Database store for a virtual heap
InactiveUS6957237B1Meet constraintsEnsure consistencyData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationApplication programming interfaceApplication software
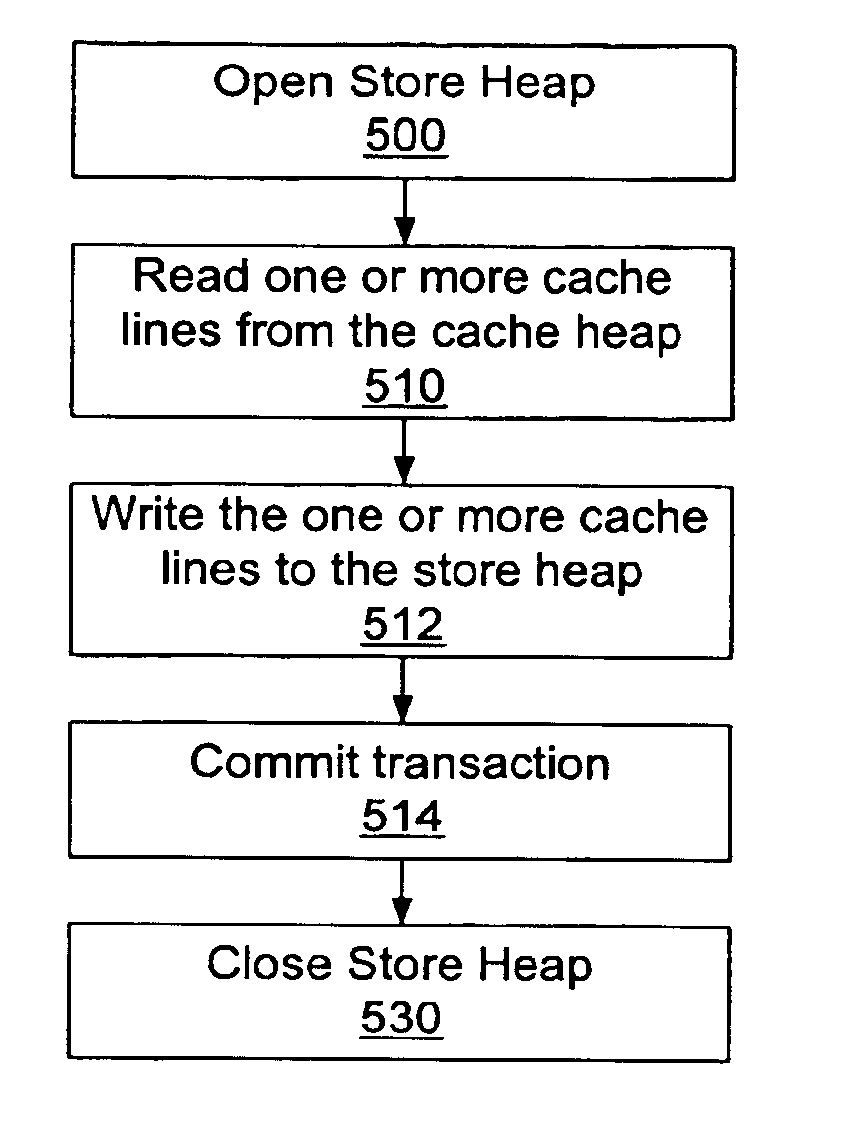
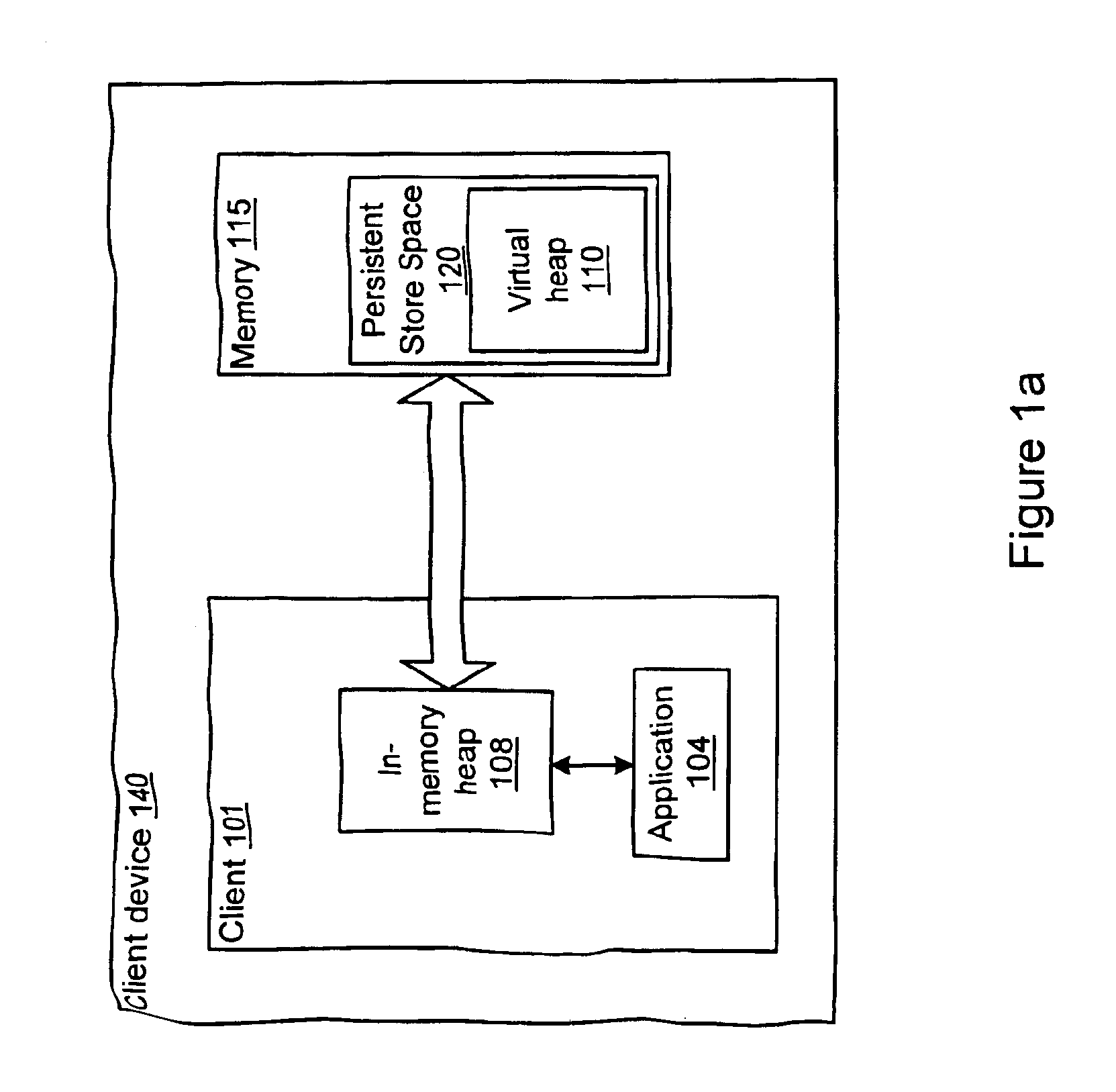
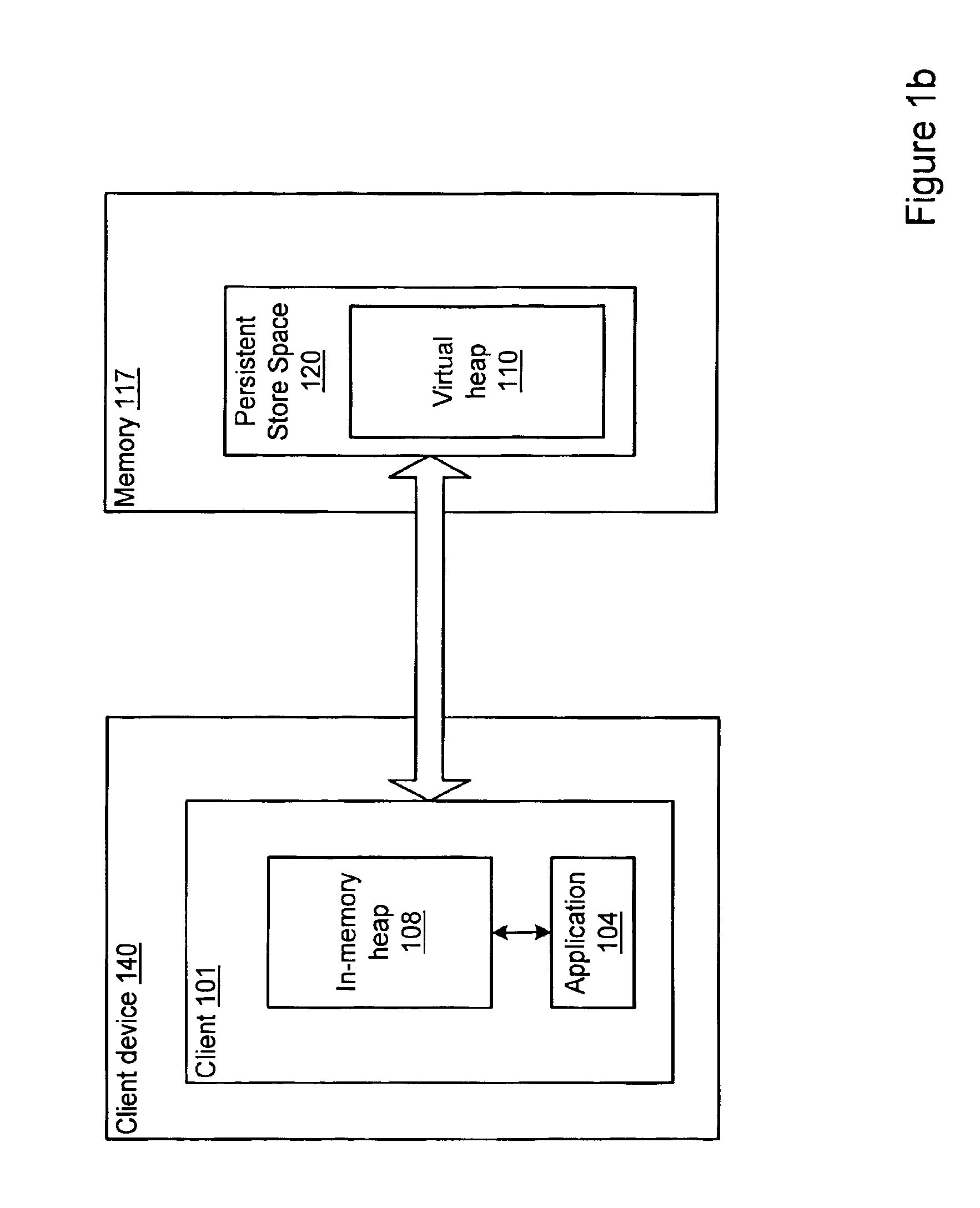
A database store method and system for a virtual persistent heap may include an Application Programming Interface (API) that provides a mechanism to cache portions of the virtual heap into an in-memory heap for use by an application. The virtual heap may be stored in a persistent store that may include one or more virtual persistent heaps, with one virtual persistent heap for each application running in the virtual machine. Each virtual persistent heap may be subdivided into cache lines. The store API may provide atomicity on the store transaction to substantially guarantee the consistency of the information stored in the database. The database store API provides several calls to manage the virtual persistent heap in the store. The calls may include, but are not limited to: opening the store, closing the store, atomic read transaction, atomic write transaction, and atomic delete transaction.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Routing of protocol data units within a communication network
InactiveUS7471669B1Reduce calculationMinimises routing information overheadData switching by path configurationProtocol data unitBroadcast communication network
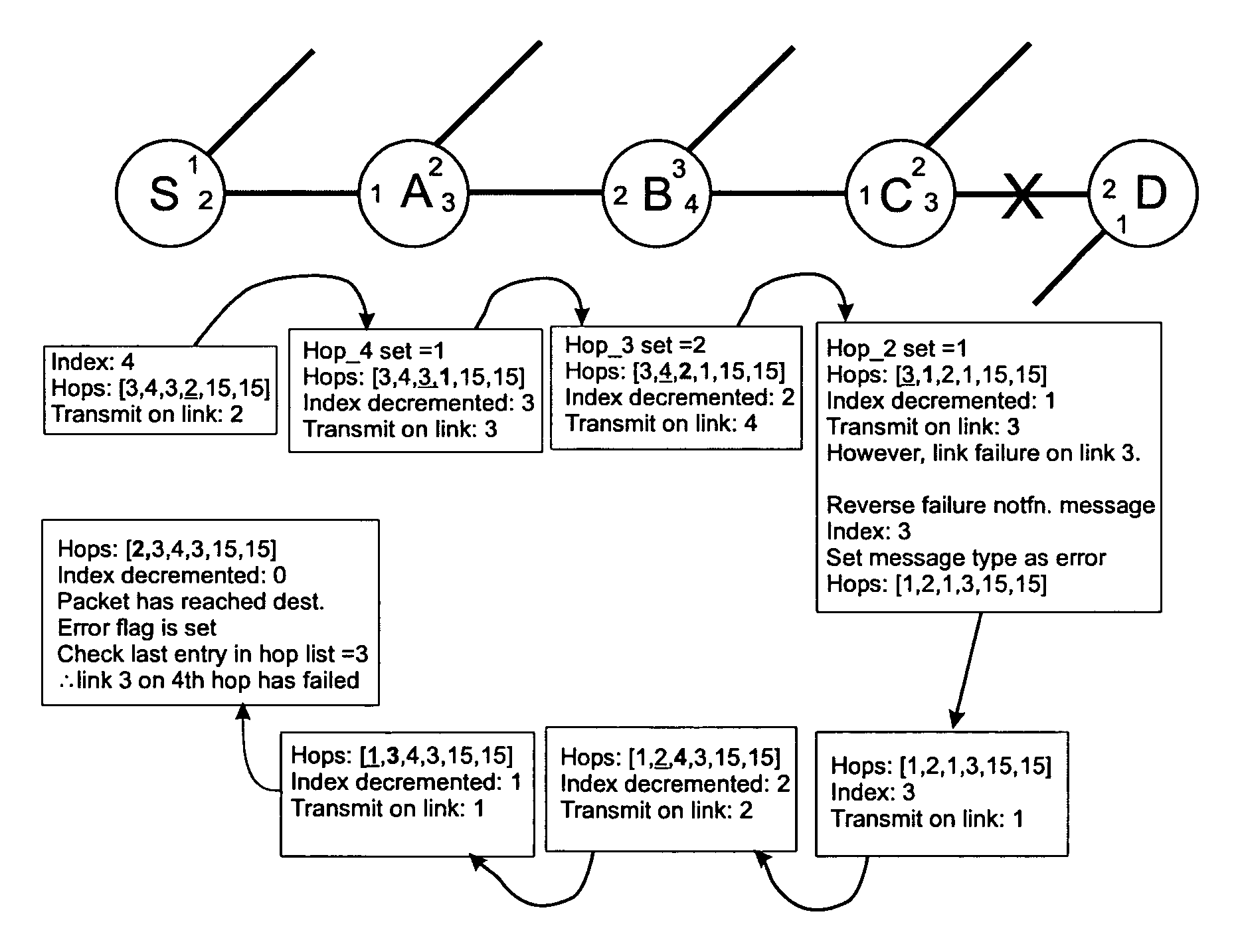
A protocol data unit is routed along a path between a first node and a second node within a communication network. The protocol data unit carries routing information which specifies the path in the form of a list of identifiers of the links to be followed towards the second node. At each intermediate node, the link identifier for the link just traversed with a link identifier for the corresponding link in the reverse direction towards the first node. At any point along the path the protocol data unit carries information which allows it to be carried towards the second node, or to follow a reverse path towards the first node. This reverse path can be used to report a fault to the first node.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
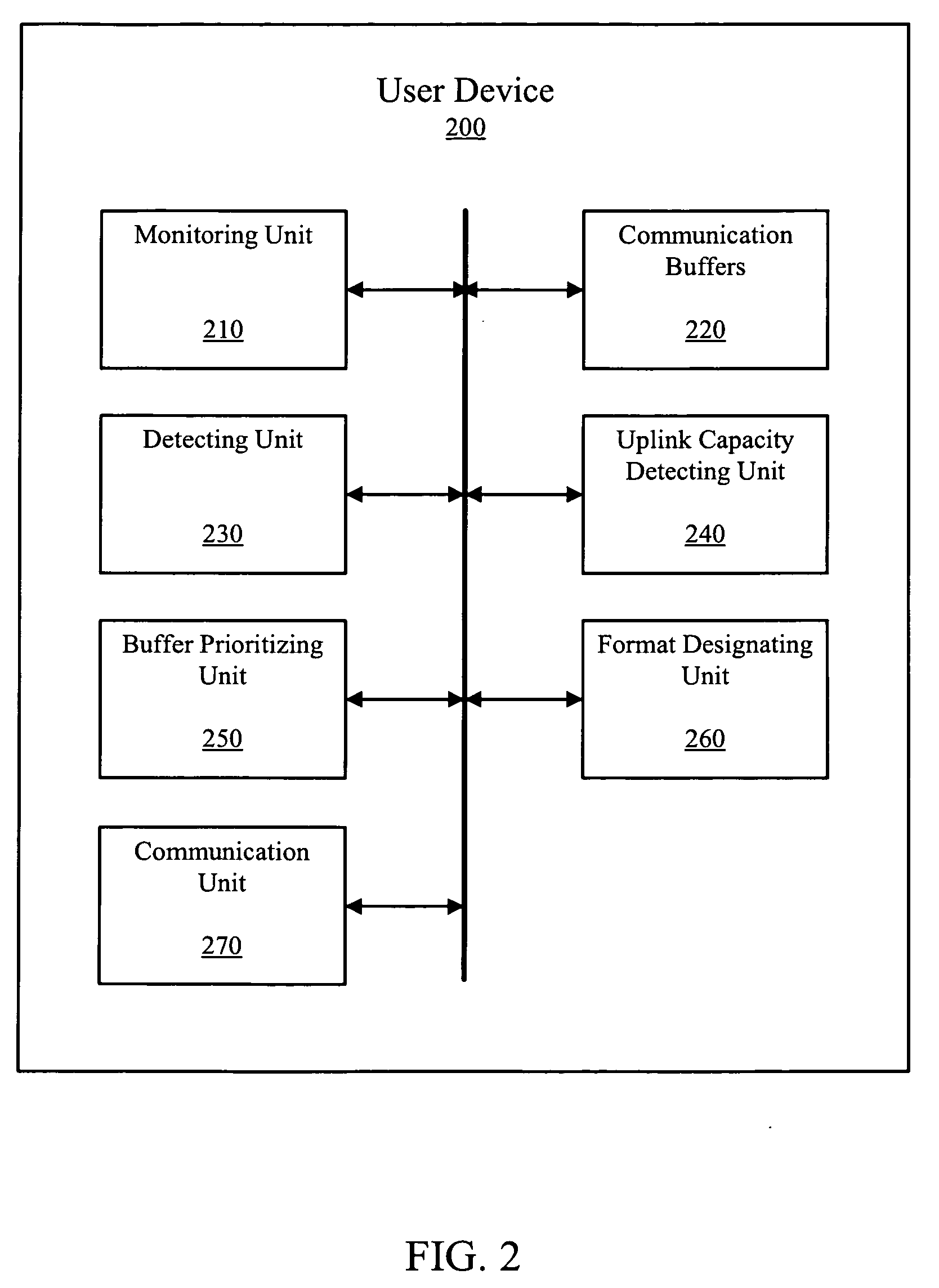
Buffer status reporting apparatus, system, and method
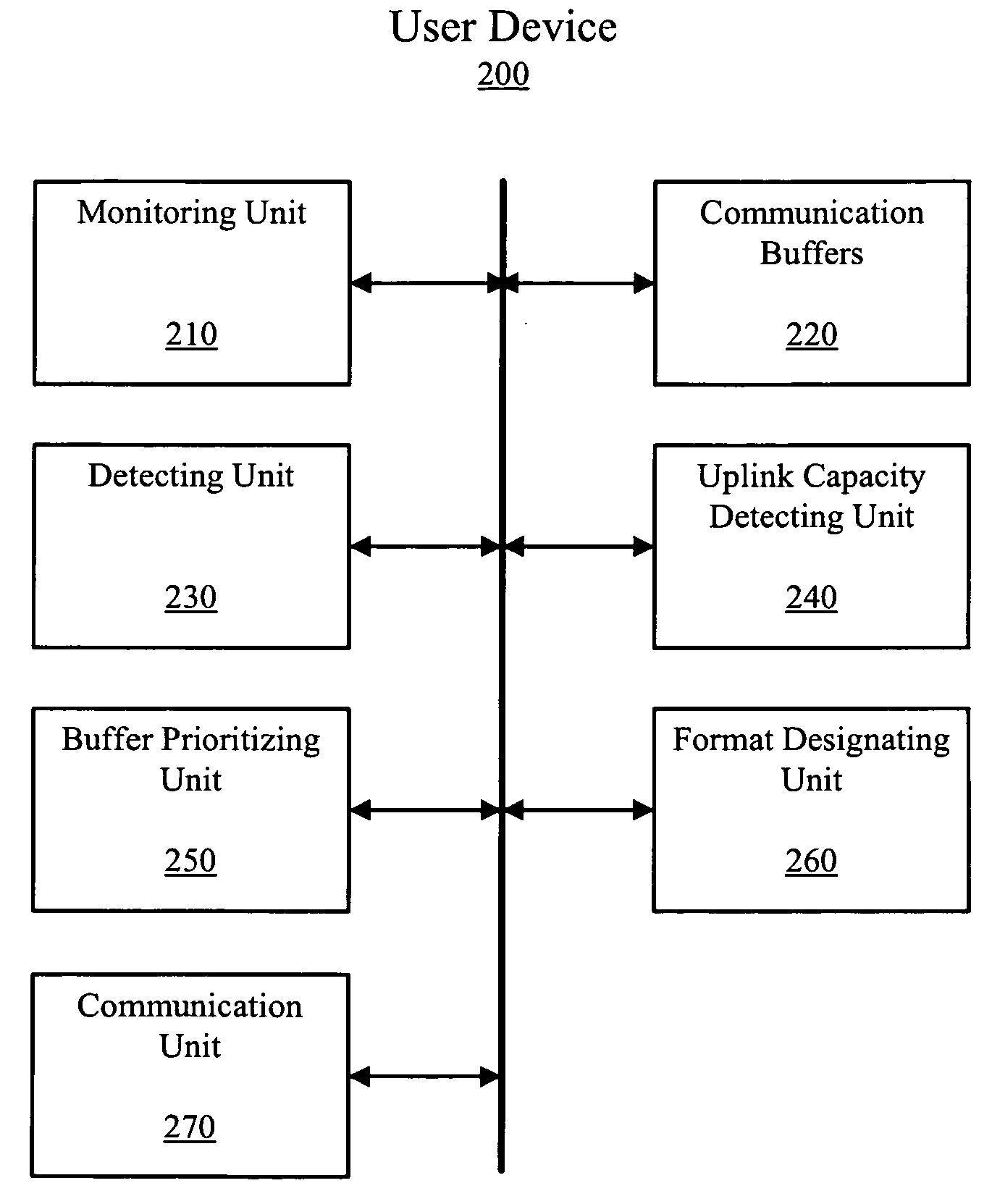
ActiveUS20090125650A1Minimize buffer status reporting overheadMinimize overheadError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementUser equipmentStatus report
An apparatus, system and method for increasing buffer status reporting efficiency and adapting buffer status reporting according to uplink capacity. User equipment is configured a monitor a usage of a plurality of buffers, detect one of a plurality of pre-selected conditions corresponding to at least one of the plurality of buffers, designate one of a plurality of buffer status reporting formats depending on the pre-selected condition detected, communicate a buffer status report to a network device in accordance with the buffer status reporting format designated. The buffer status reporting format is configured to minimize buffer status reporting overhead created by the communicating of the buffer status report.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
System and method for manipulating and managing computer archive files
InactiveUS6879988B2Easy to carryQuick and easy management and manipulationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDrag and dropResource management
A computer program for managing and manipulating archive zip files of a computer. The program includes a system and method for opening, creating, modifying, and extracting zip archive files. The program is fully integrated into Microsoft Windows Explorer and is accessed via Explorer menus, toolbars, and / or drag and drop operations. An important feature of the program is the archive manager which may be used to open a zip file, create a new zip file, extract zip files, modify zip files, etc. The program is integrated into Microsoft Windows Explorer using the shell name space extension application program interface developed by Microsoft.
Owner:PKWARE
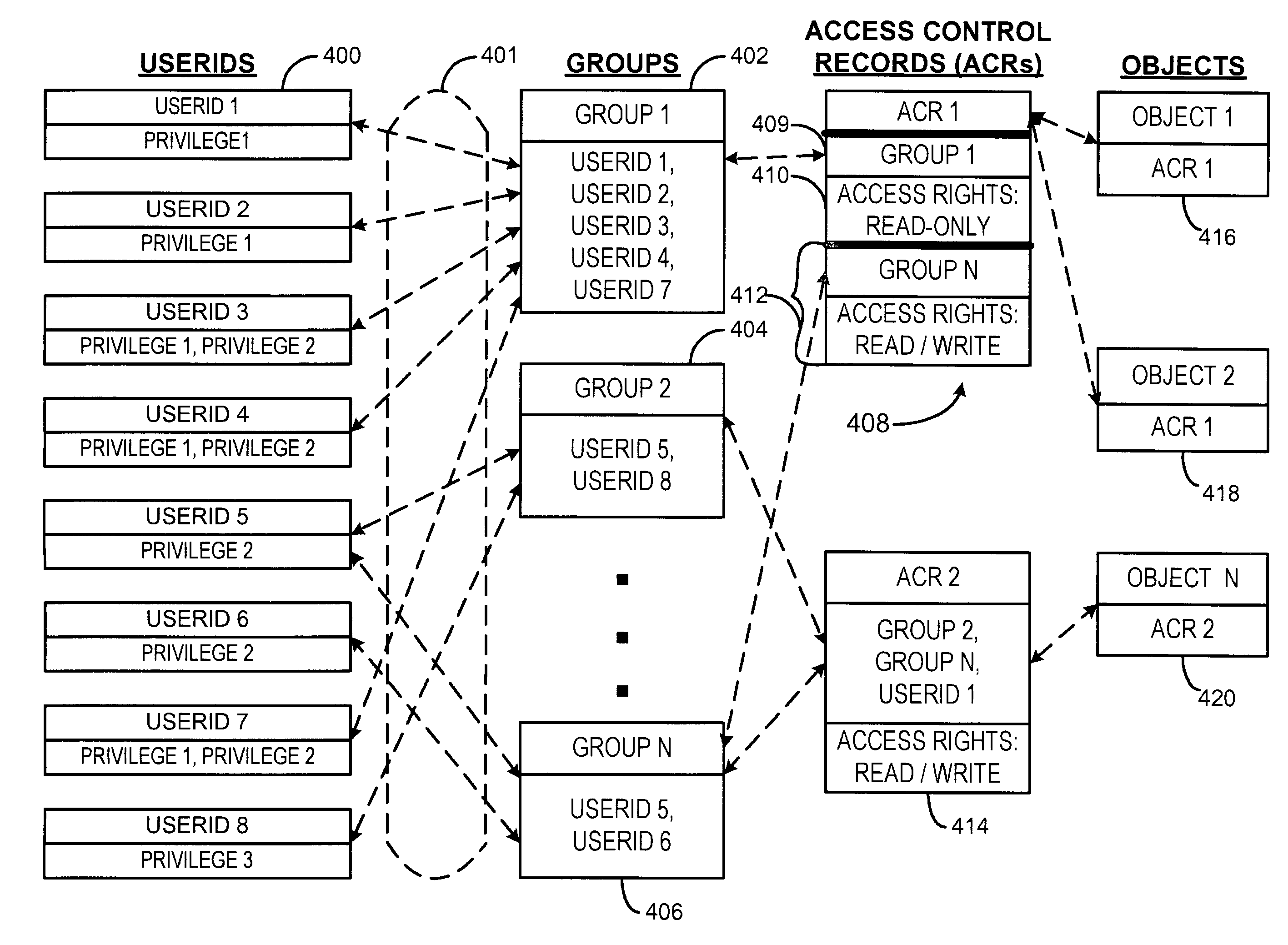
System and method for managing access rights and privileges in a data processing system
ActiveUS7219234B1Reduce numberMinimize in sizeDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser groupManagement system
Owner:UNISYS CORP
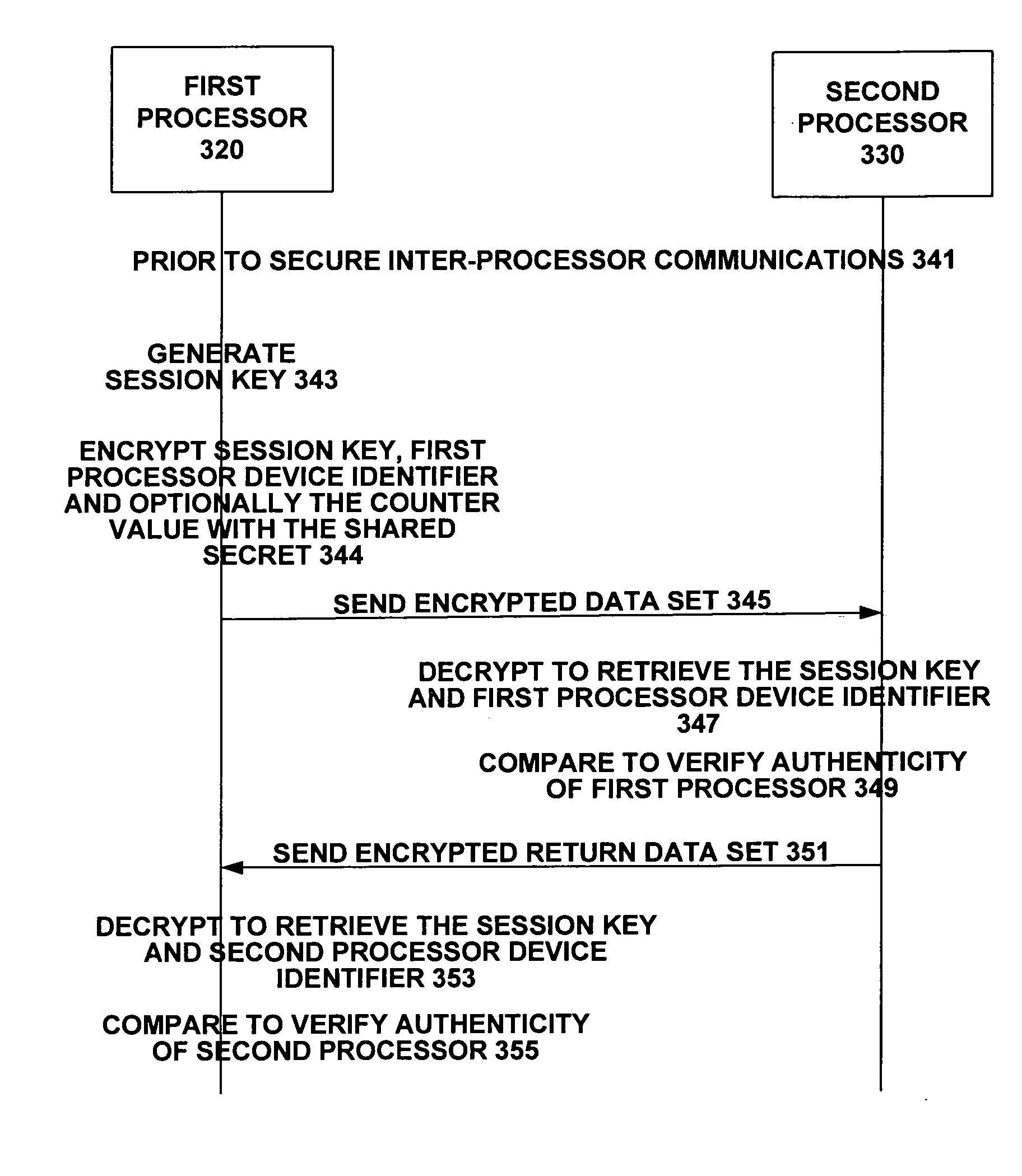
Method and apparatus for secure inter-processor communications
InactiveUS20060288209A1Considerable overheadMinimize overheadUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareInterprocessor communication
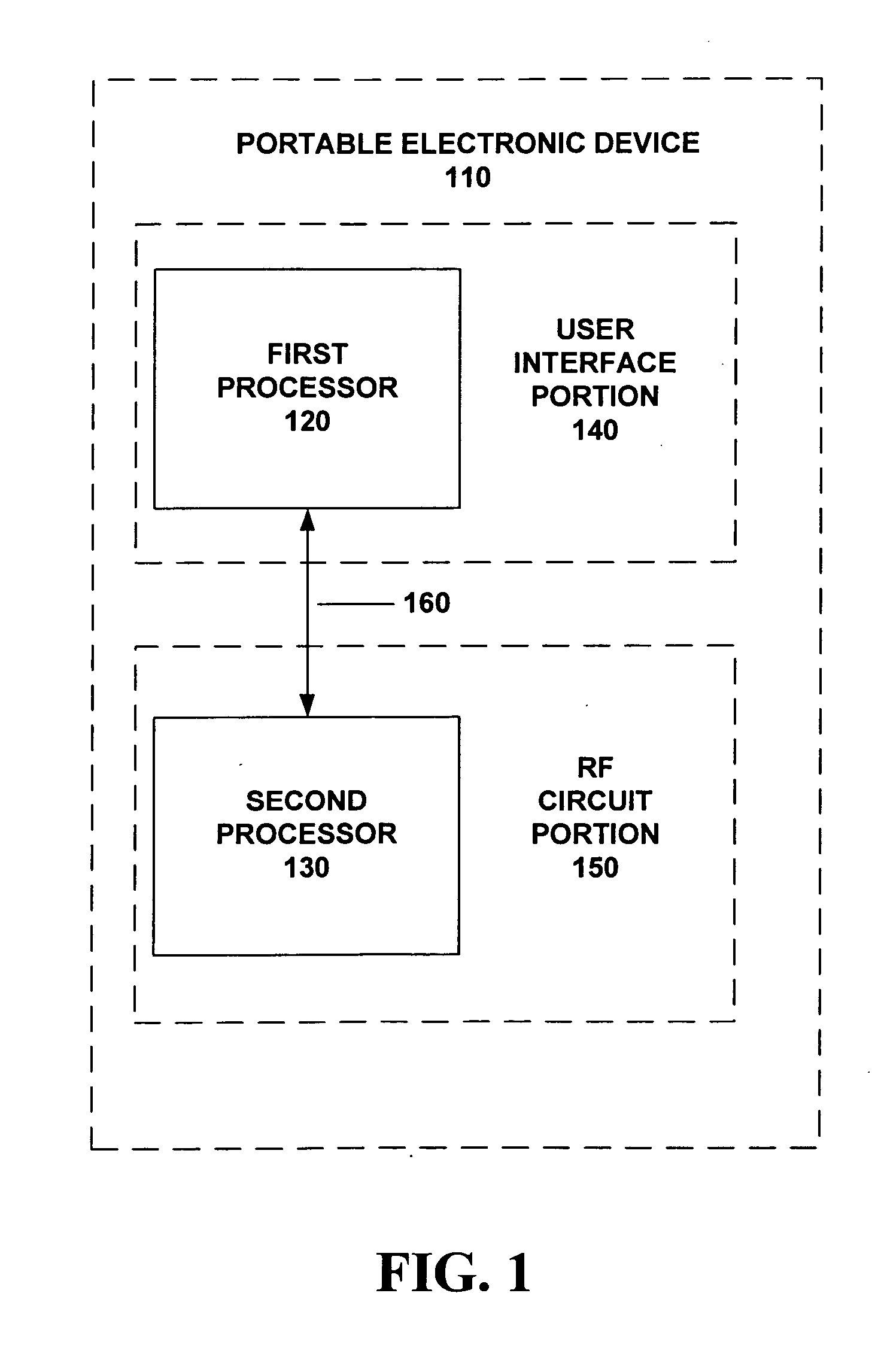
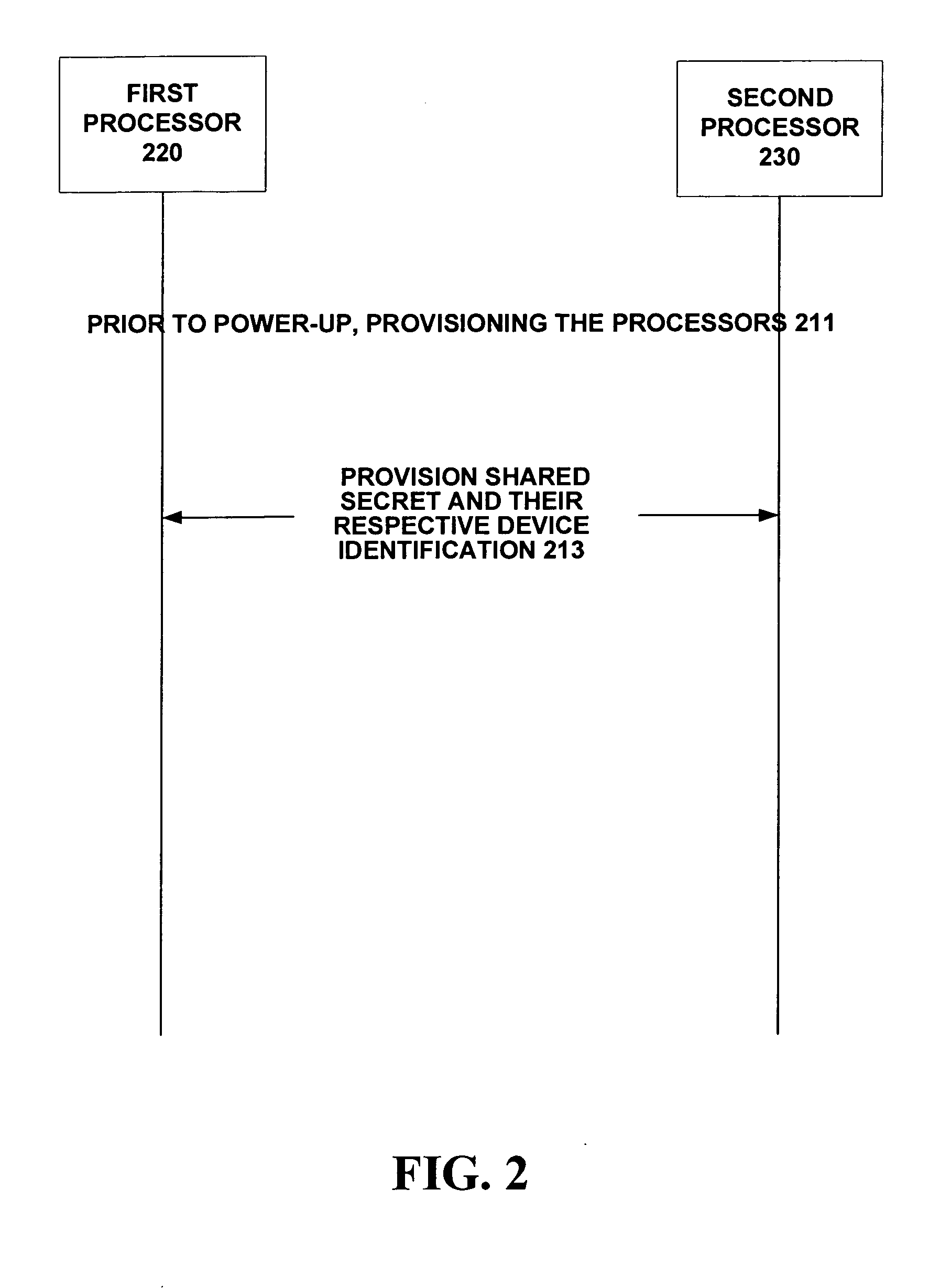
A portable electronic device (110) is capable of secure inter-processor communications (160) between processors (120, 130). The processors have unique and unalterable device identifiers used to encrypt session key data using shared secrets. A first processor device identifier is encrypted by a first processor (120) and decrypted by a second processor (130) and compared against a known device identifier to verify authenticity. Then the second processor (130) likewise encrypts and the first processor (120) likewise decrypts and likewise compares device identity to verify authenticity.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving pilot signals in an OFDM communication system
InactiveUS20050099939A1Minimize overheadMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexFast Fourier transformCommunications system
A radio communication system divides an entire frequency band into a plurality of subcarrier bands, forms a symbol from signals on the subcarrier bands, forms a frame from a plurality of symbols, transmits a pilot signal within symbols in a predetermined position of the frame, and transmits a data signal within symbols other than the symbols for transmitting the pilot signal. A transmitter generates the pilot signal, performs an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) on the pilot signal by applying an IFFT size which is less than an IFFT size applied to the data signal, and transmits the IFFT-processed reference signal to a receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Enhanced association for access points
ActiveUS8126145B1Reduce the possibilitySmall rangeData switching by path configurationSecret communicationClient-sideHandshake
The invention relates to a method for associating a client with an access point using a security protocol. The method may include initiating a handshake and exchanging operational information between the access point and the client, establishing an encrypted operational key if the operational information is validated and entering an operational phase using the operational key and an unique service set identifier if valid.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Panoramic video system with real-time distortion-free imaging
ActiveUS7336299B2Highly efficient regional transformationMinimize overheadImage enhancementTelevision system detailsTime distortionGraphic card
A panoramic annular lens system (PAL), a unitary video camera and a PC-based software system that unwraps a 360° video image into a seamless, distortion free horizontal image image in real time. The PAL system of the preferred embodiment has a 360° horizontal field of view and a 90° vertical field of view in a 40 mm diameter compact package. The invention is not limited to any particular type of lens system. In fact, there are numerous lens systems for providing a 360° panoramic view. The video camera may be a CCD or CMOS based device having a pixel resolution of either 1280×1024 (high resolution) or 720×480 (NTSC). The unwrapping system is a radiometric ray tracing program carried out using a computer's graphics card capabilities to produce highly efficient regional transformation while minimizing software overhead. The result is real time, high resolution 30 fps conversion from a spherical distorted image to a flat panoramic image in Cartesian coordinates.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Computer method and system for concurrency control using dynamic serialization ordering
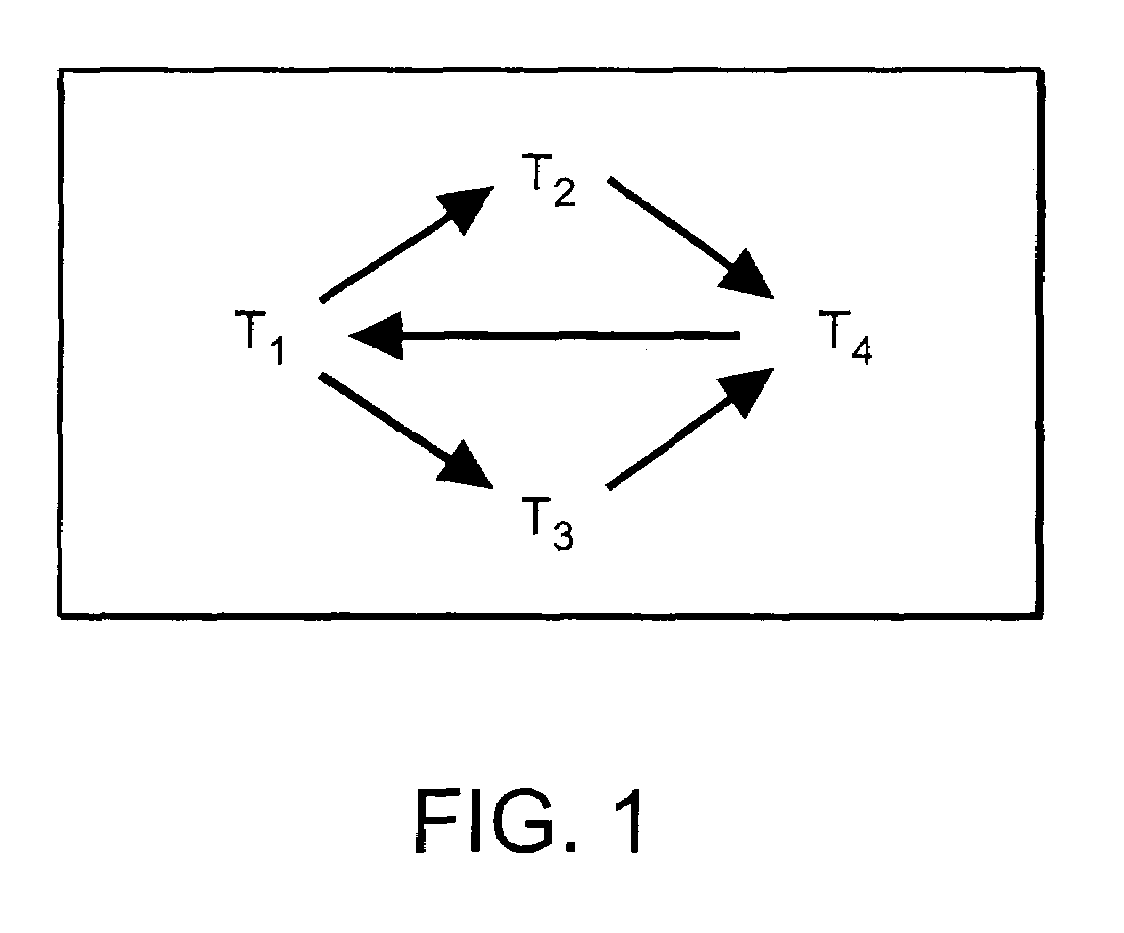
InactiveUS7089253B2Well throughputGood throughputDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsSerializationSerializability
A mechanism controls concurrency among database transactions through the use of serial ordering relations. The ordering relations are computed dynamically in response to patterns of use. An embodiment of the present invention serializes a transaction that accesses a resource before a transaction that modifies the resource, even if the accessor starts after the modifier starts or commits after the modifier commits. A method of concurrency control for a database transaction in a distributed database system stores an intended use of a database system resource by the database transaction in a serialization graph. A serialization ordering is asserted between the database transaction and other database transactions based on the intended use of the database system resource by the database transaction. The serialization ordering is then communicated to a node in the distributed database system that needs to know the serialization ordering to perform concurrency control. Cycles in the serialization graph are detected based on the asserted serialization order and in order to break such cycles and ensure transaction serializability a database transaction is identified that is a member of a cycle in the serialization graph.
Owner:IBM CORP
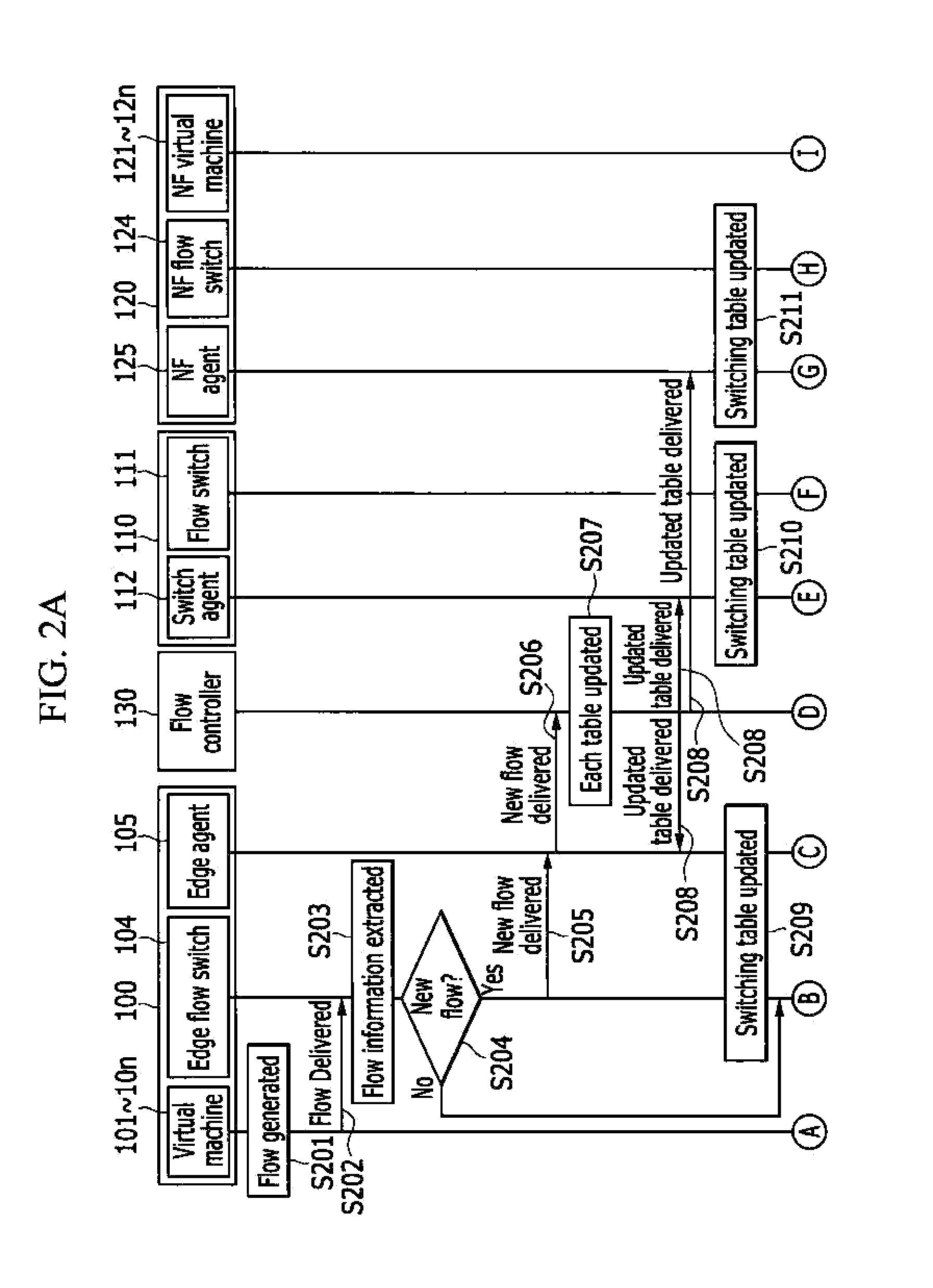
Network function virtualization method and apparatus using the same
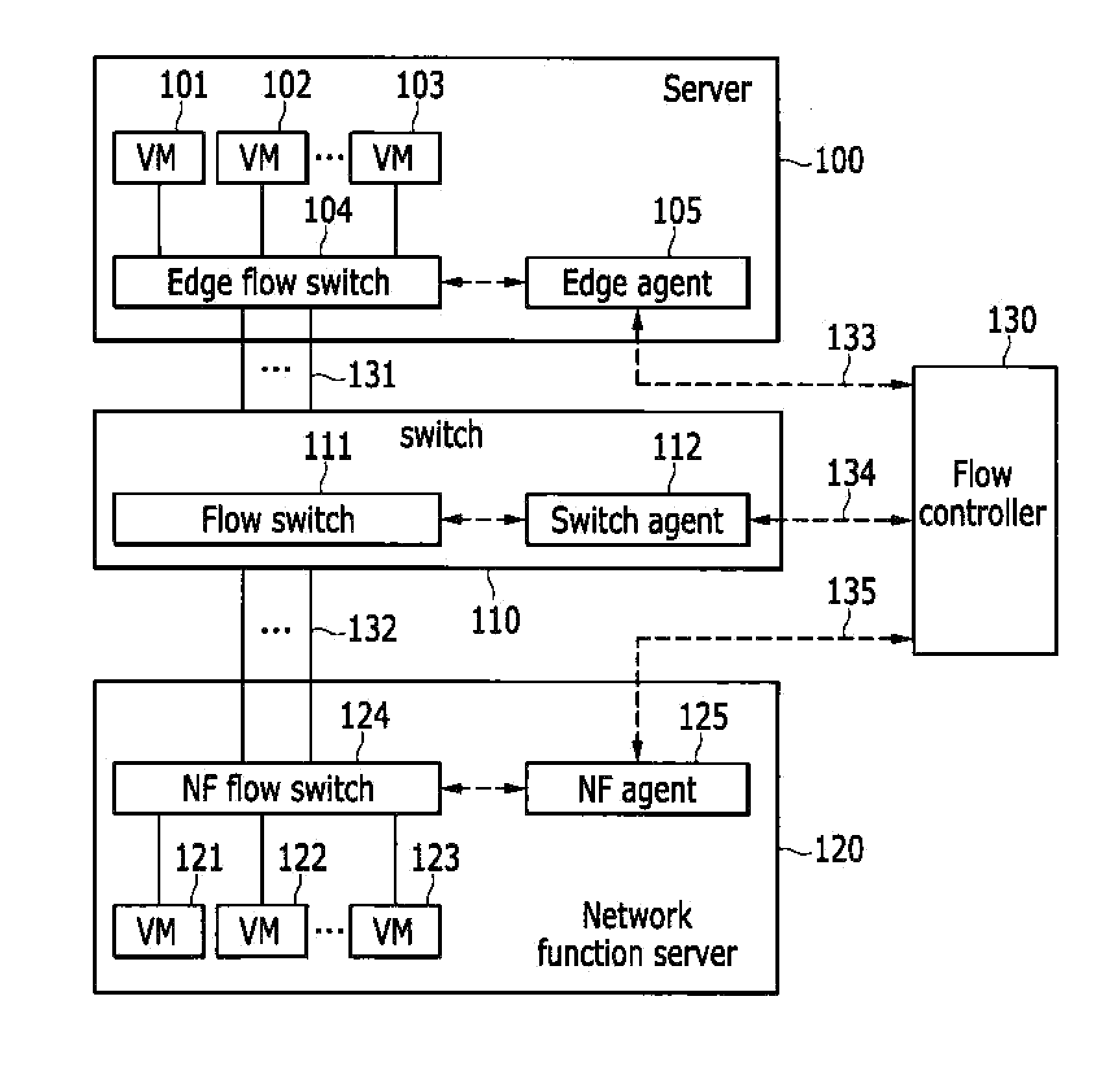
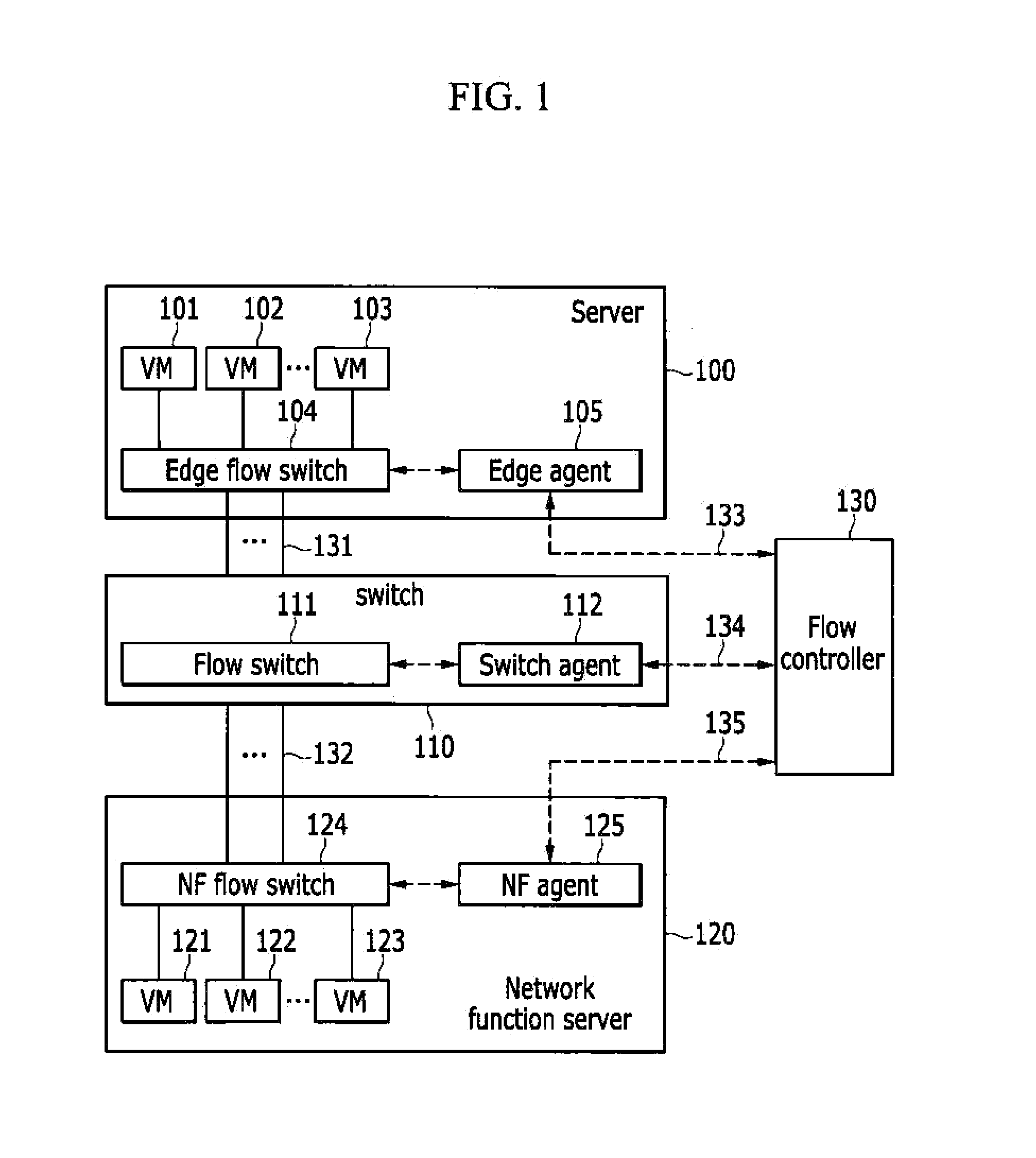
InactiveUS20140376555A1Performance of was minimizedMinimize delayData switching by path configurationVirtualizationDistributed computing
A network function virtualization device includes at least one network function virtual machine; and a network function flow switch configured to receive flows and to switch the flows to the at least one network function virtual machine, and a network functions virtualization method for applying the virtualized network function to the flows.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
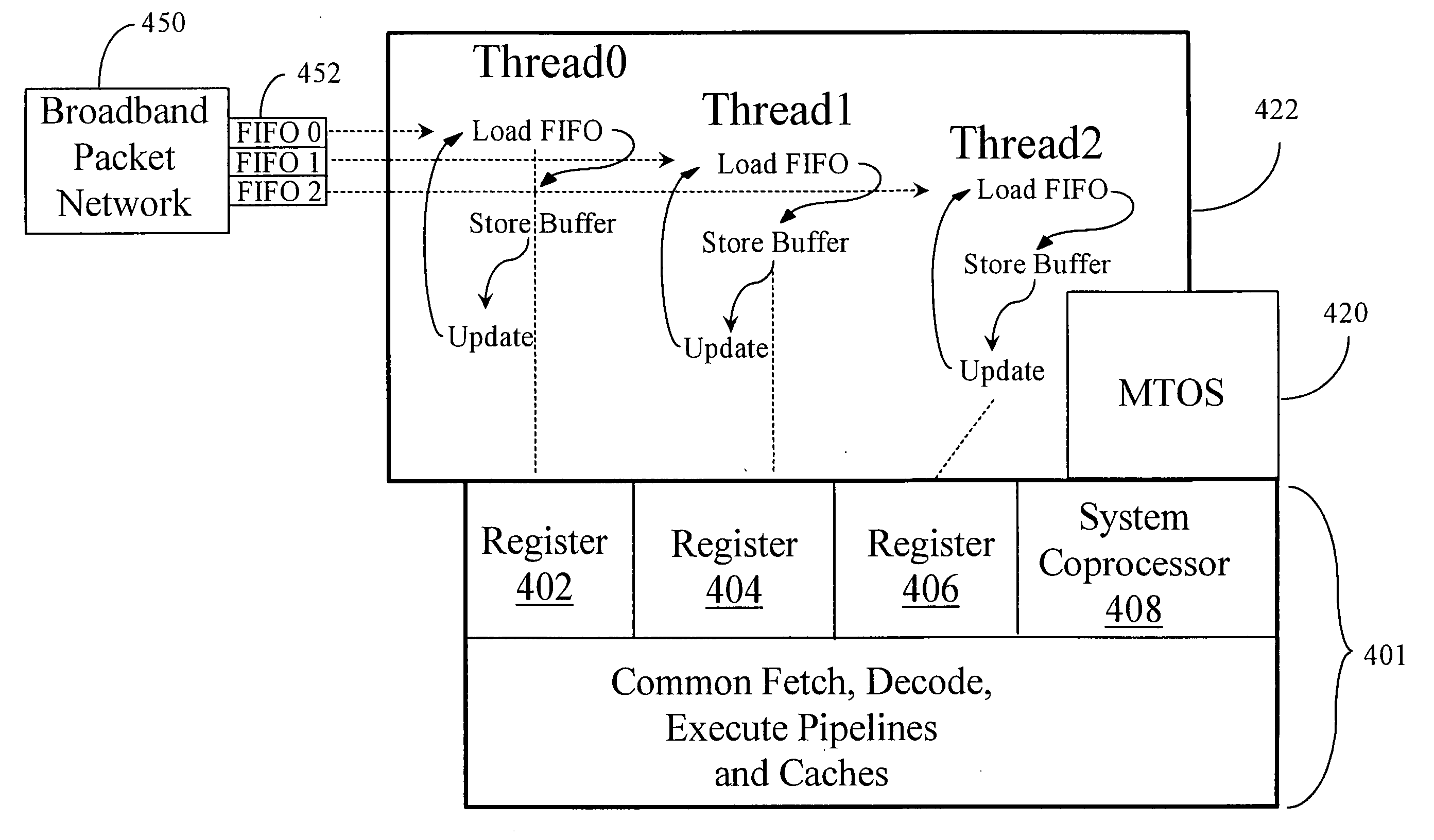
Integrated mechanism for suspension and deallocation of computational threads of execution in a processor
InactiveUS20050050305A1Minimize overheadMinimal overheadProgram initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringProgram ThreadComputer science
A mechanism for processing in a processor enabled to support and execute multiple program threads includes a parameter for scheduling a program thread and an instruction disposed within the program thread and enabled to access the parameter. When the parameter equals a first value the instruction, when issued by a program thread, reschedules the program thread in accordance with one or more conditions encoded within the parameter.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com