Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6039 results about "Limiter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, a limiter is a circuit that allows signals below a specified input power or level to pass unaffected while attenuating (lowering) the peaks of stronger signals that exceed this threshold. Limiting is a type of dynamic range compression. Clipping is an extreme version of limiting.
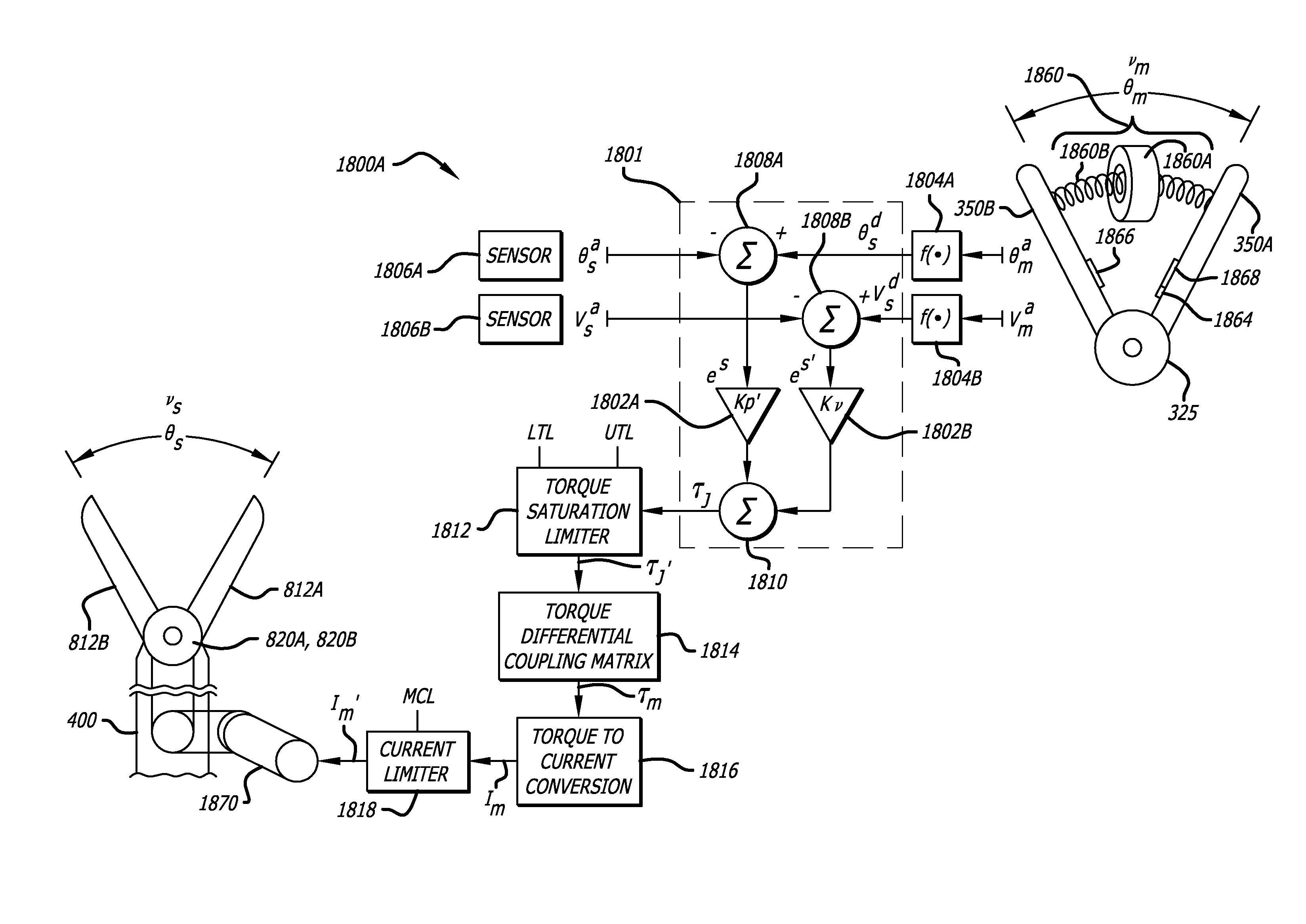
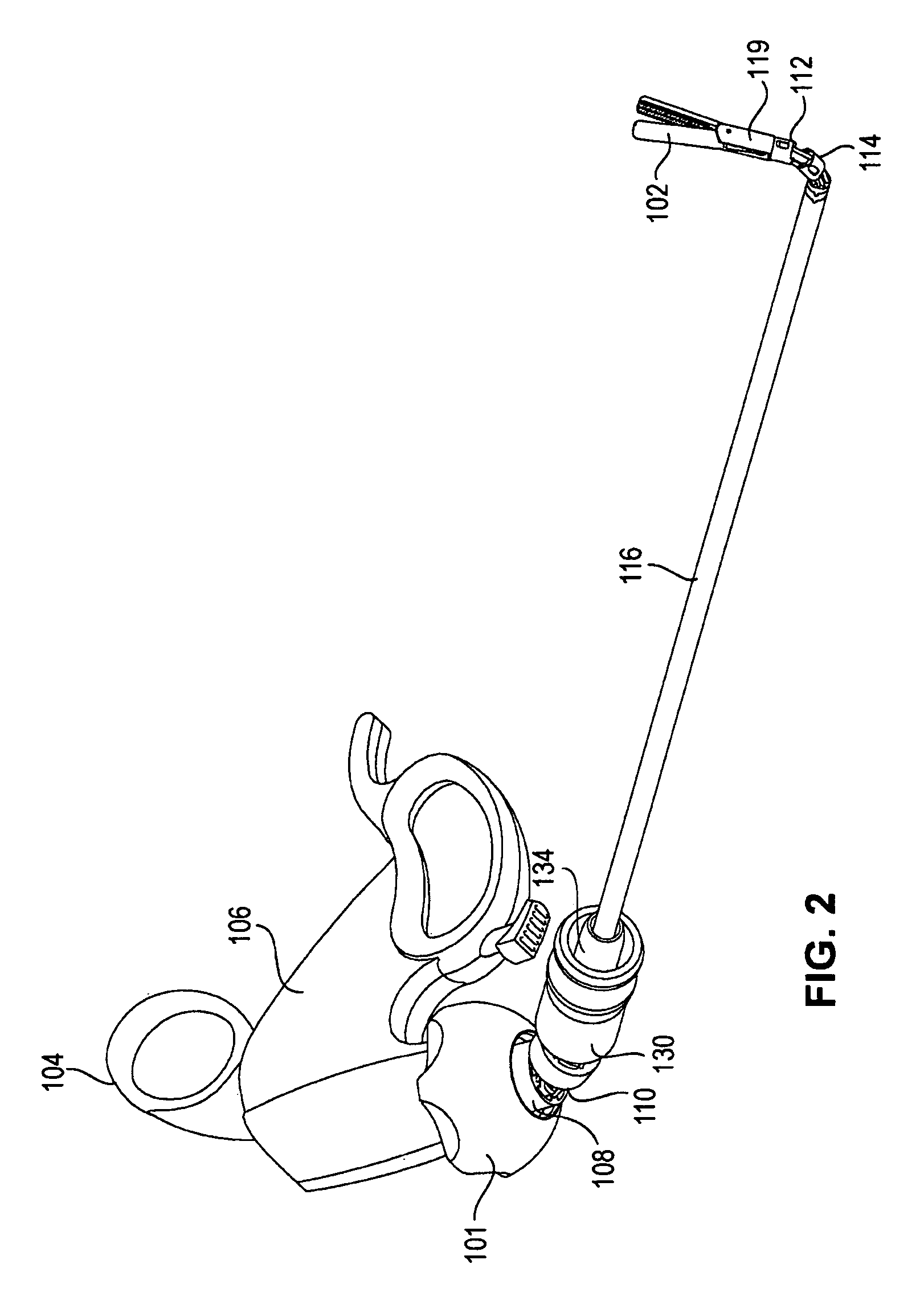
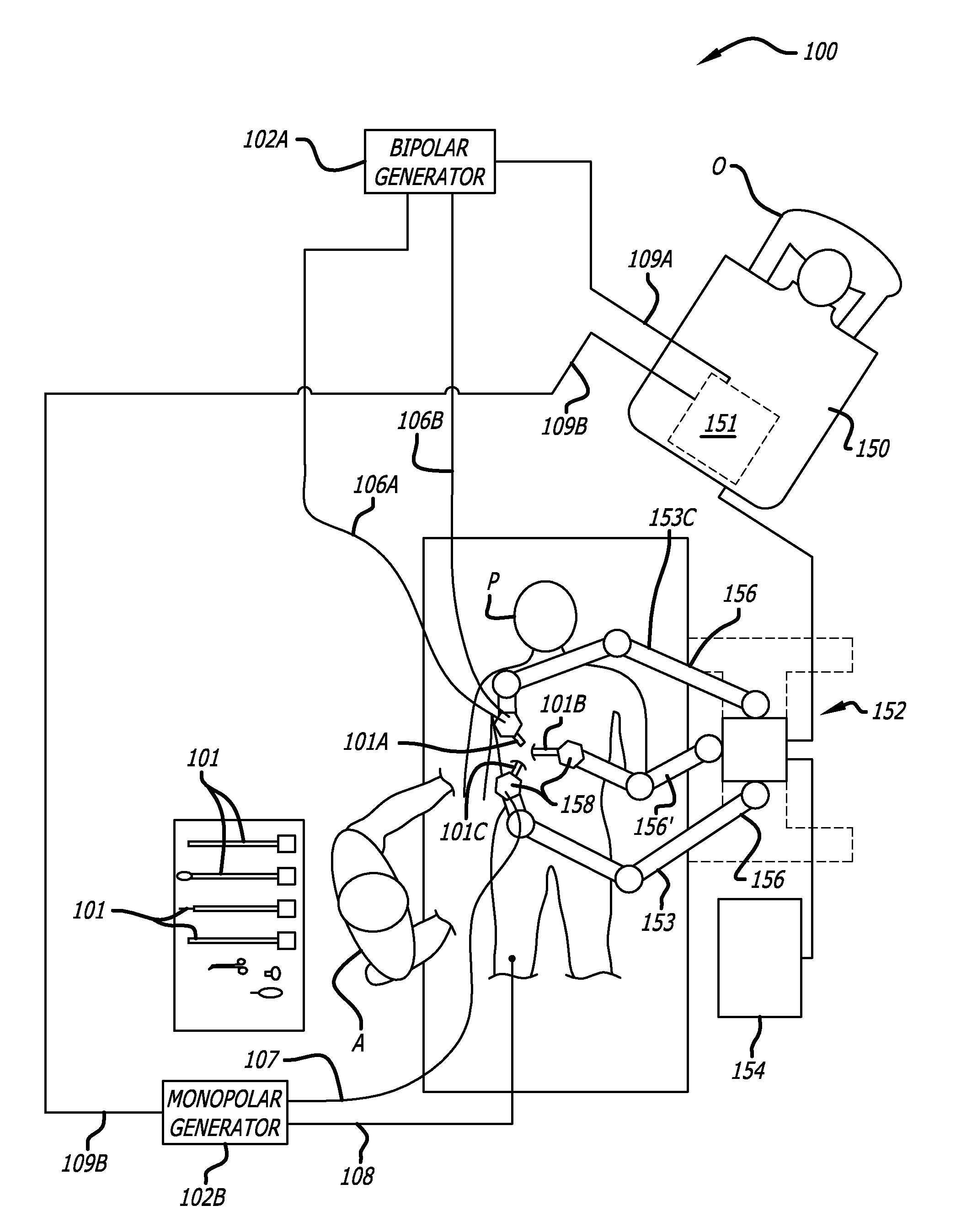
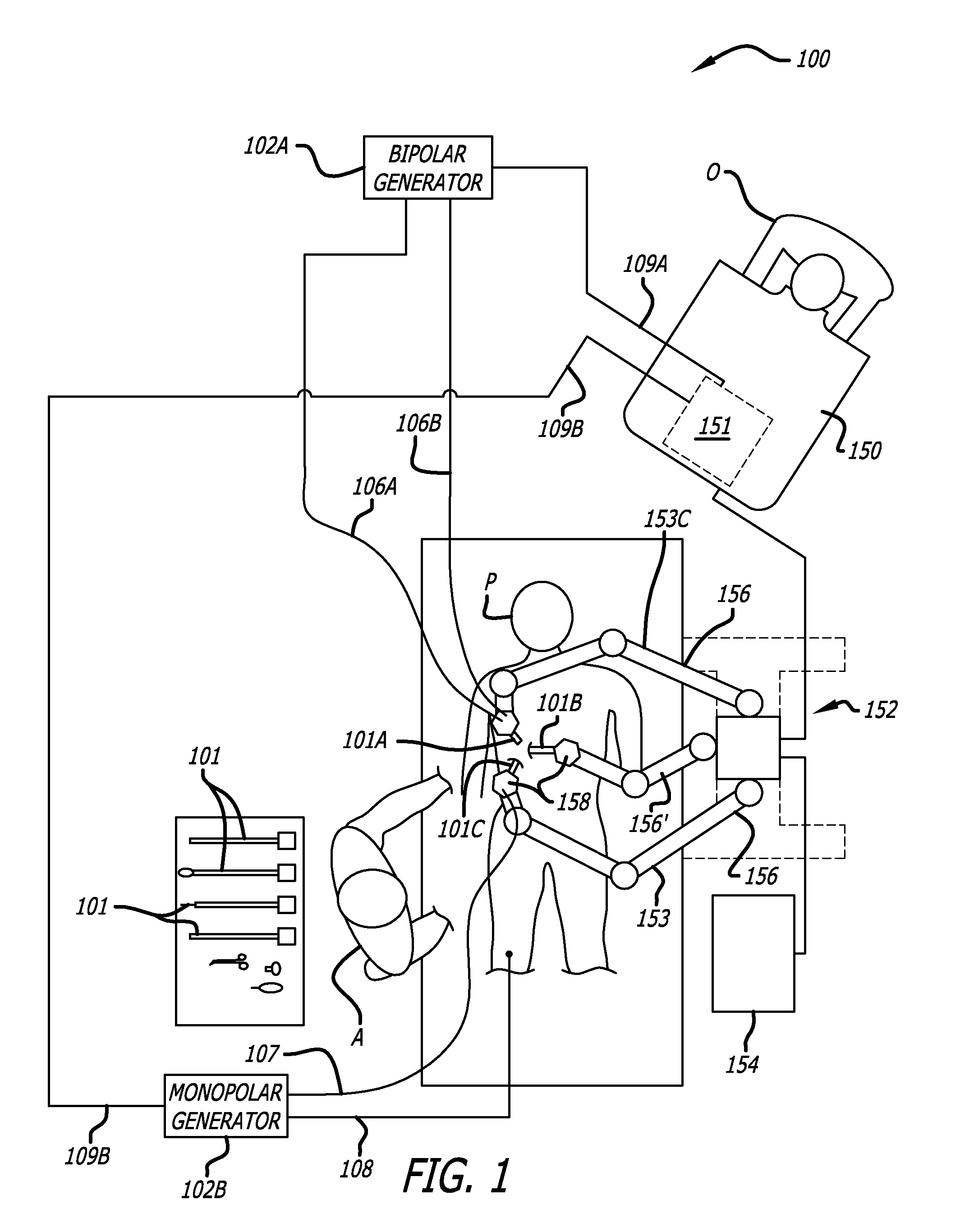
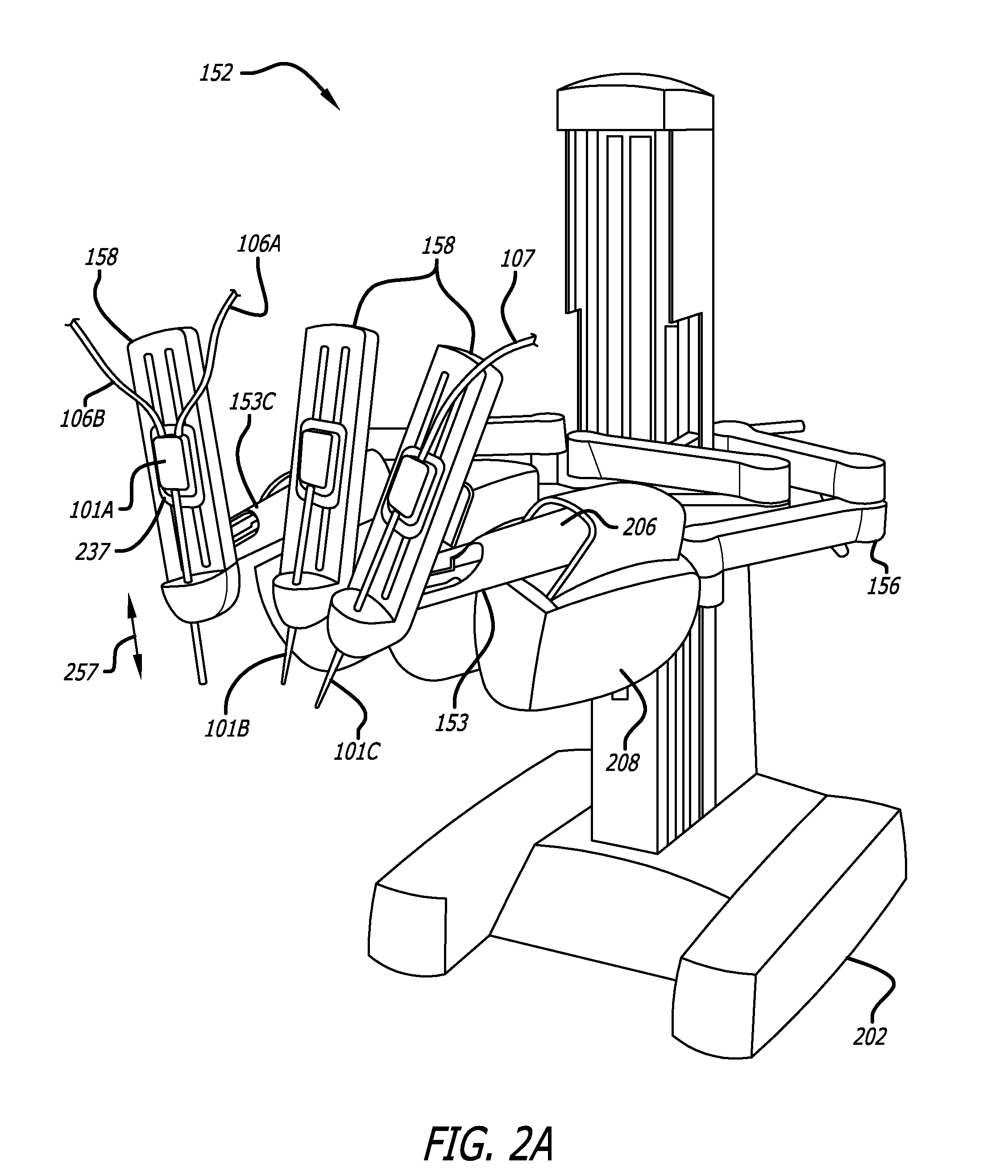
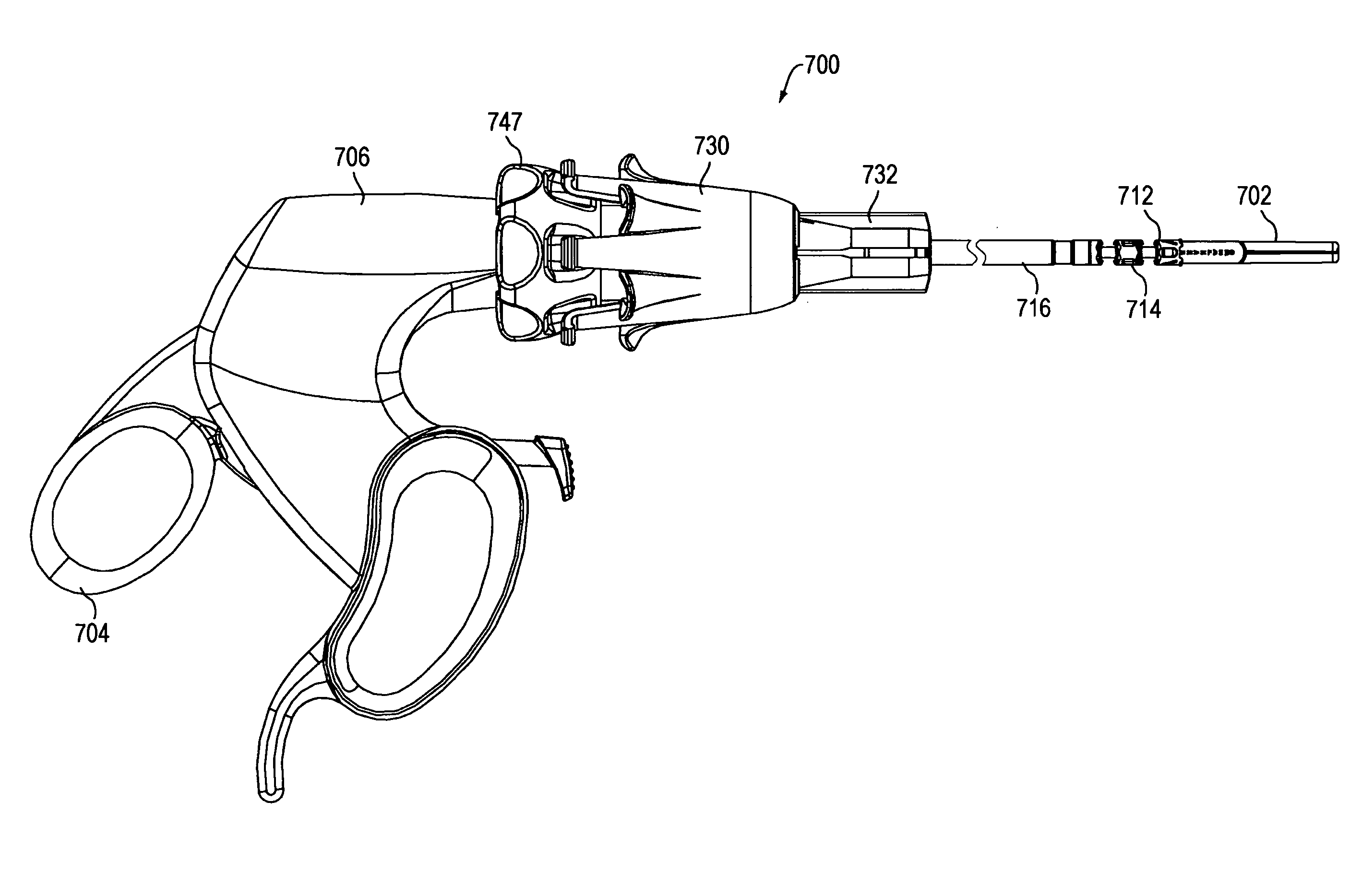
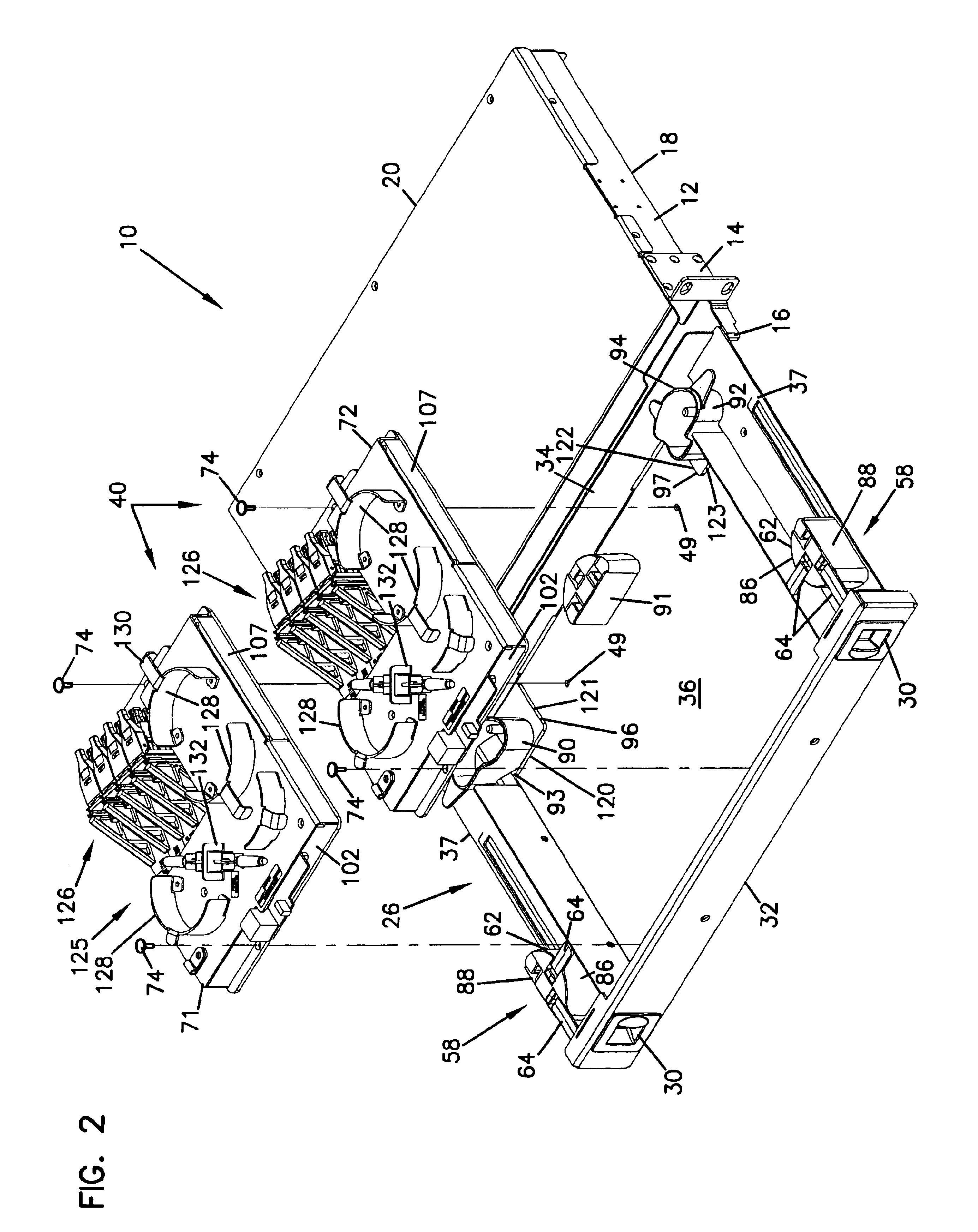
Maximum torque driving of robotic surgical tools in robotic surgical systems
ActiveUS9002518B2Programme-controlled manipulatorMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMaximum torqueMotor drive
In one embodiment of the invention, a control system for a robotic surgical instrument is provided including a torque saturation limiter, a torque to current converter coupled to the torque saturation limiter, and a motor coupled to the torque to current converter. The torque saturation limiter receives a desired torque signal for one or more end effectors and limits the desired torque to a range between an upper torque limit and a lower torque limit generating a bounded torque signal. The torque to current converter transforms a torque signal into a current signal. The motor drives an end effector of one or more end effectors to the bounded torque signal in response to the first current signal.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
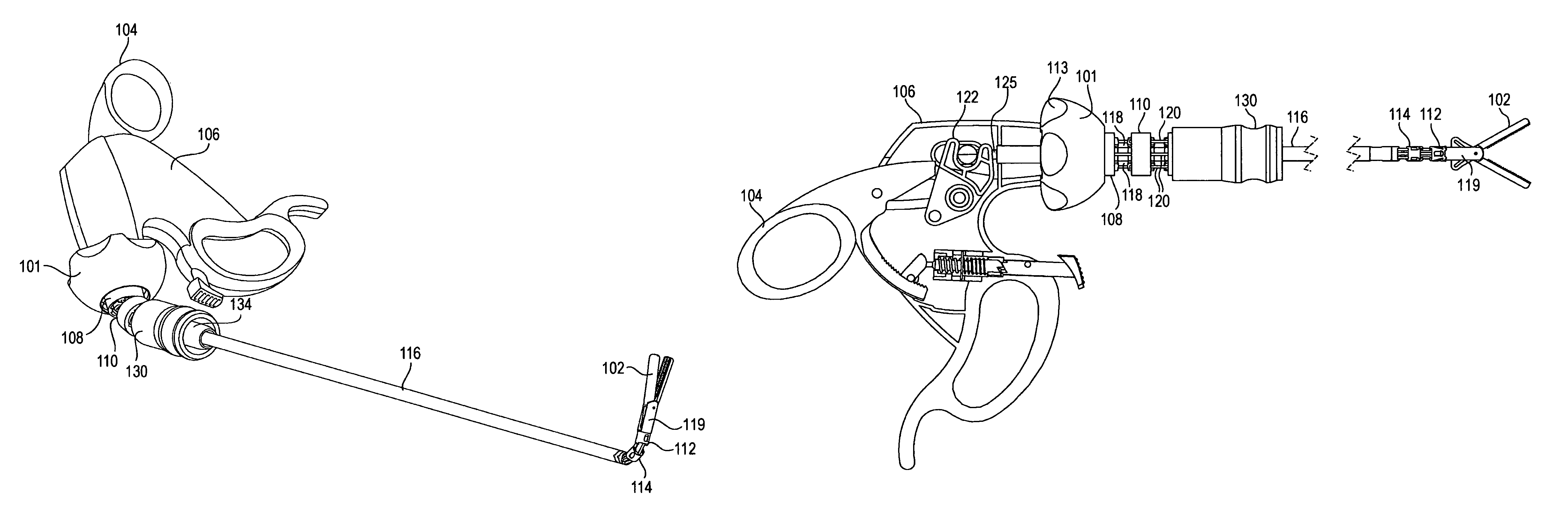
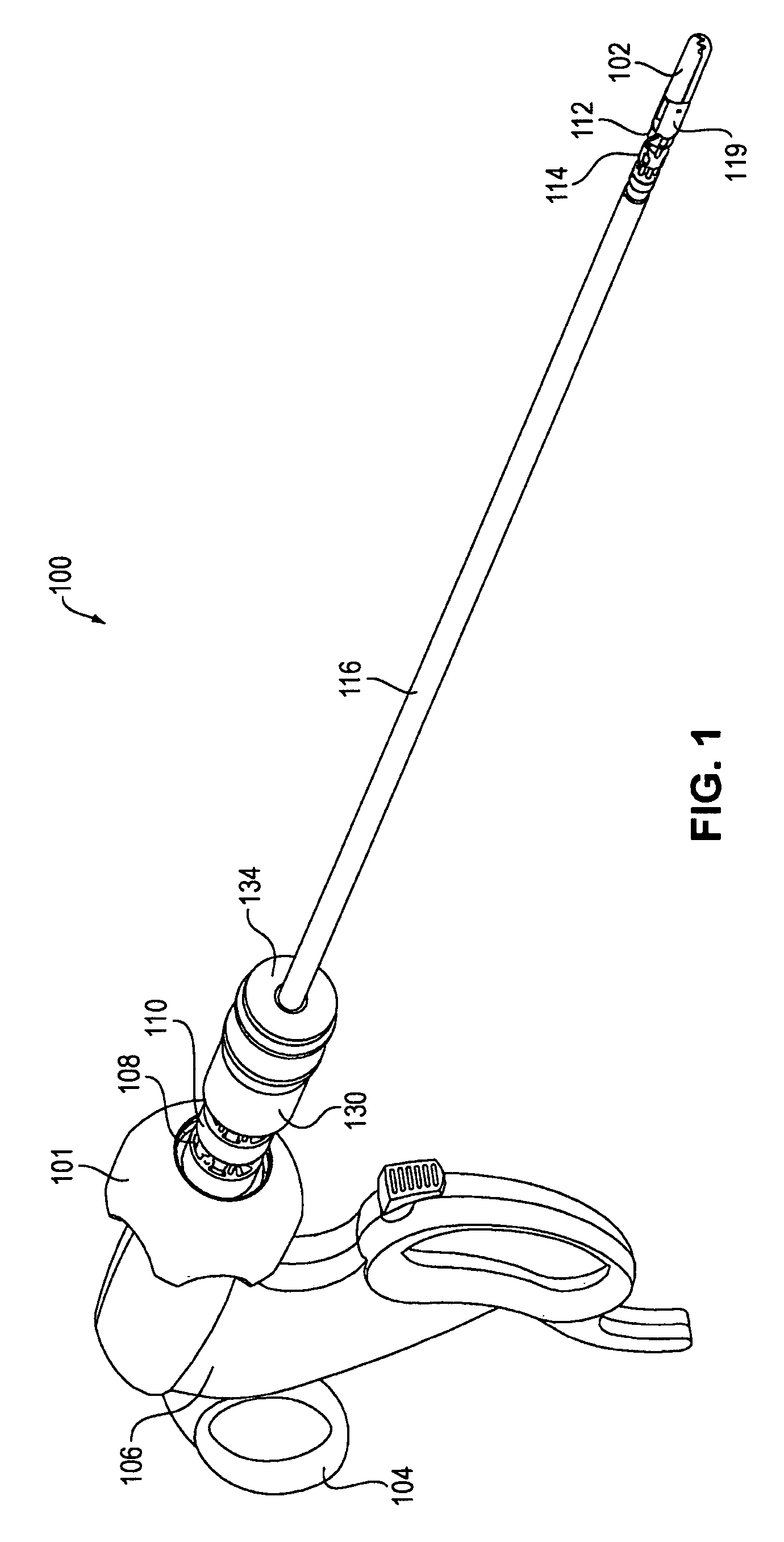
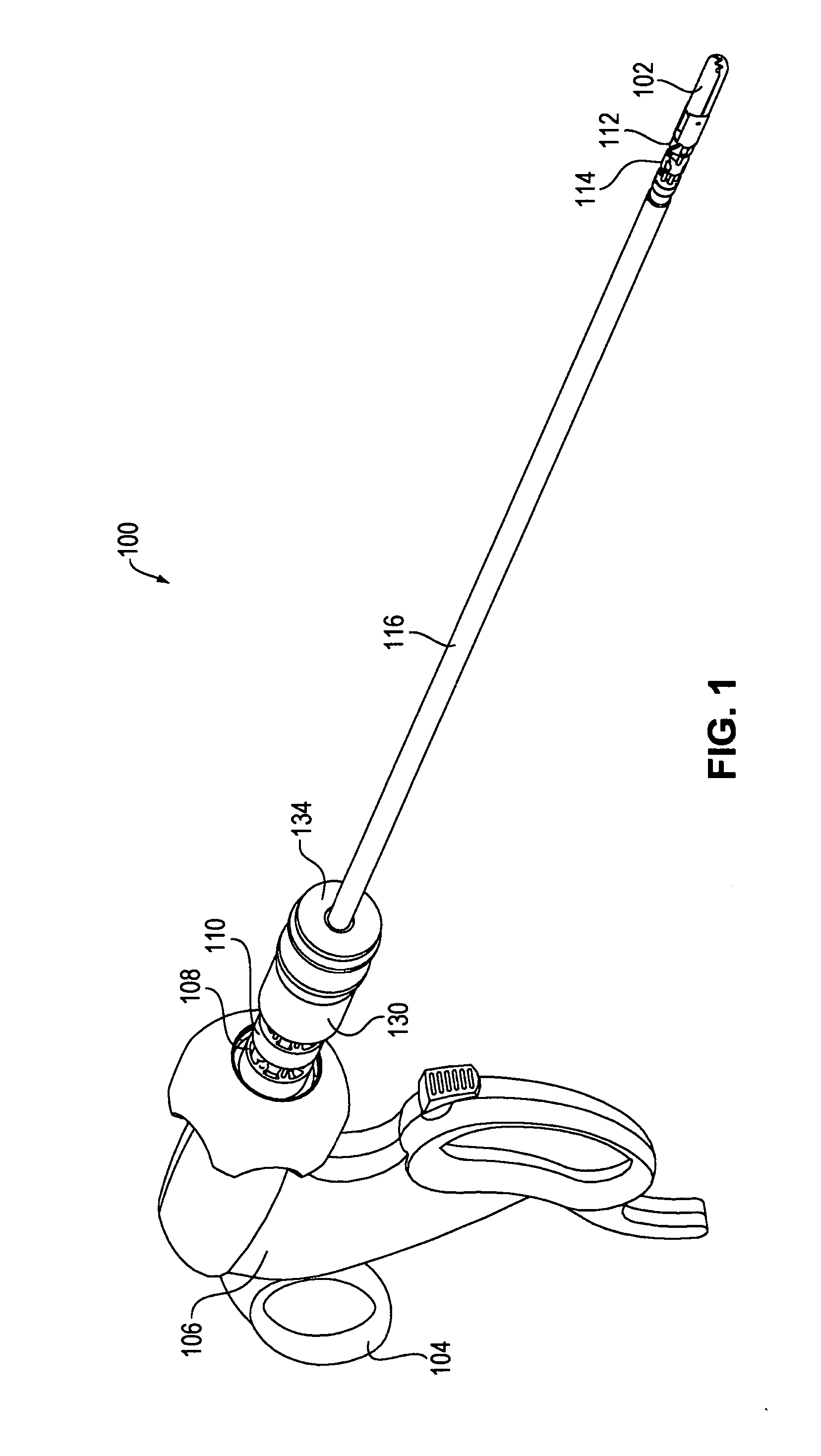
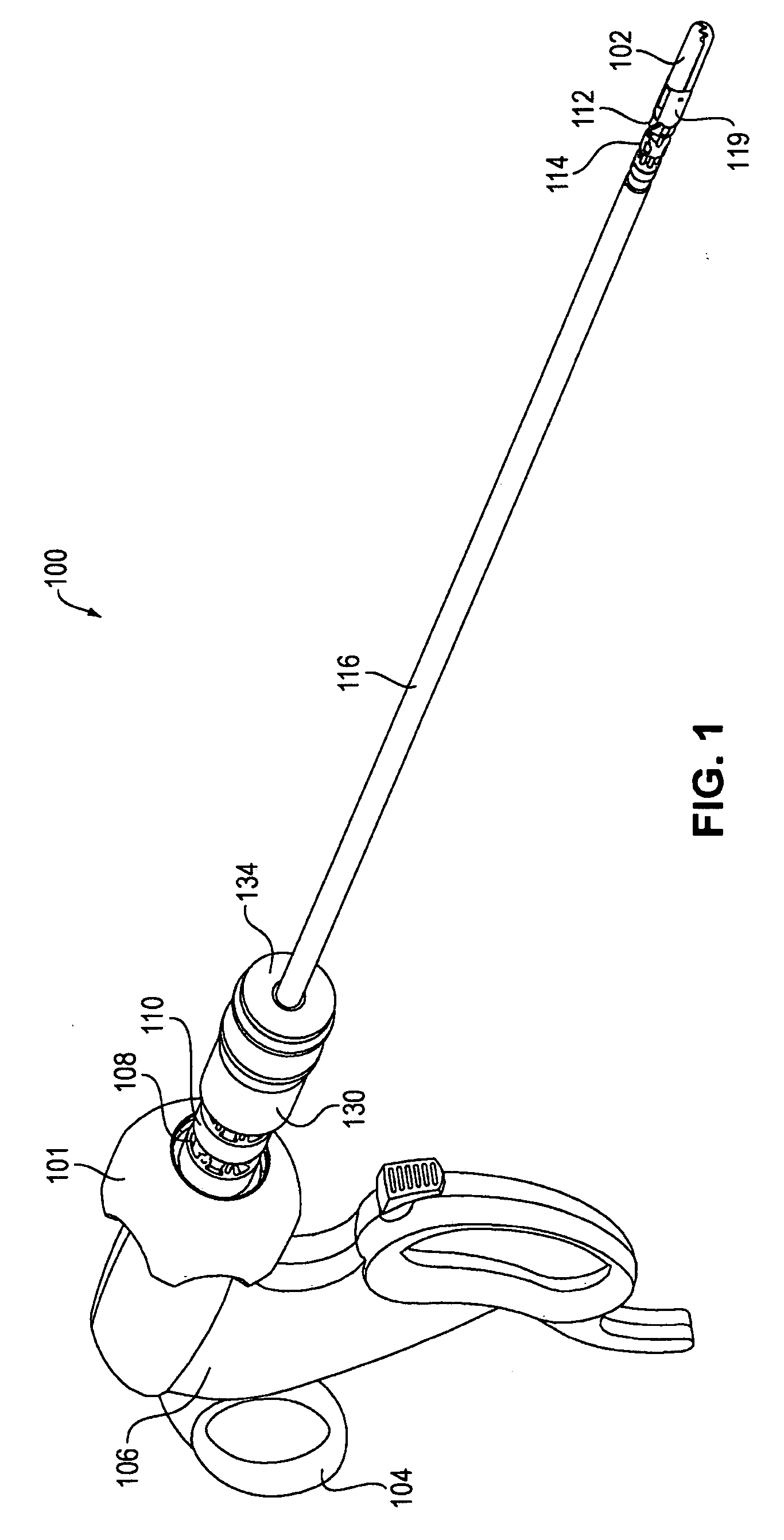
Tool with rotation lock
The invention provides surgical or diagnostic tools and associated methods that offer improved user control for operating remotely within regions of the body. These tools include a proximally-located actuator for the operation of a distal end effector, as well as proximally-located actuators for articulational and rotational movements of the end effector. Control mechanisms and methods refine operator control of end effector actuation and of these articulational and rotational movements. A rotation lock provides for enablement and disablement of rotatability of the end effector. The tool may also include other features. A multi-state ratchet for end effector actuation provides enablement-disablement options with tactile feedback. A force limiter mechanism protects the end effector and manipulated objects from the harm of potentially excessive force applied by the operator. An articulation lock allows the fixing and releasing of both neutral and articulated configurations of the tool and of consequent placement of the end effector.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Maximum torque driving of robotic surgical tools in robotic surgical systems
ActiveUS20080046122A1Improve the level ofProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLower limitMaximum torque
In one embodiment of the invention, a control system for a robotic surgical instrument is provided including a torque saturation limiter, a torque to current converter coupled to the torque saturation limiter, and a motor coupled to the torque to current converter. The torque saturation limiter receives a desired torque signal for one or more end effectors and limits the desired torque to a range between an upper torque limit and a lower torque limit generating a bounded torque signal. The torque to current converter transforms a torque signal into a current signal. The motor drives an end effector of one or more end effectors to the bounded torque signal in response to the first current signal.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
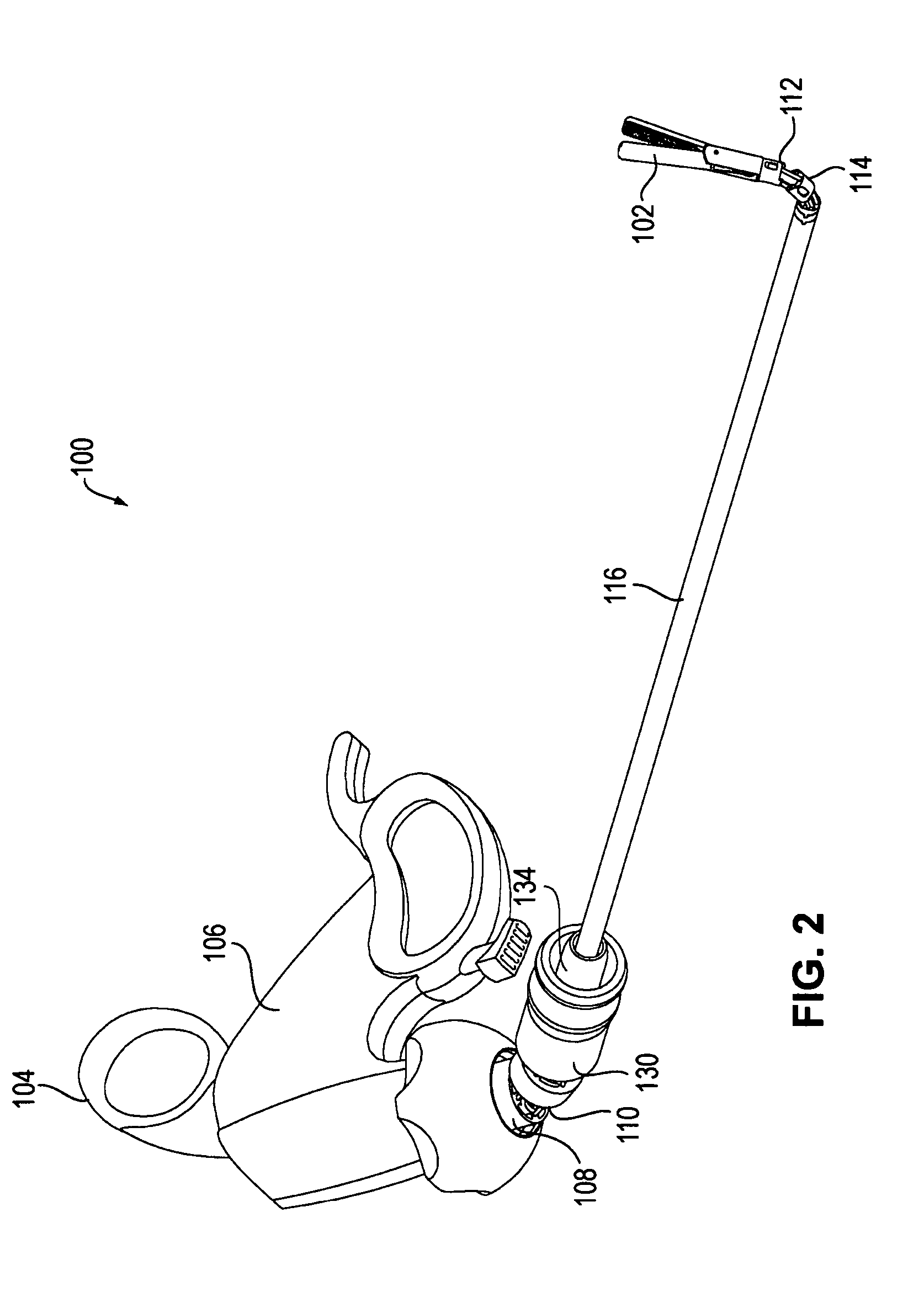
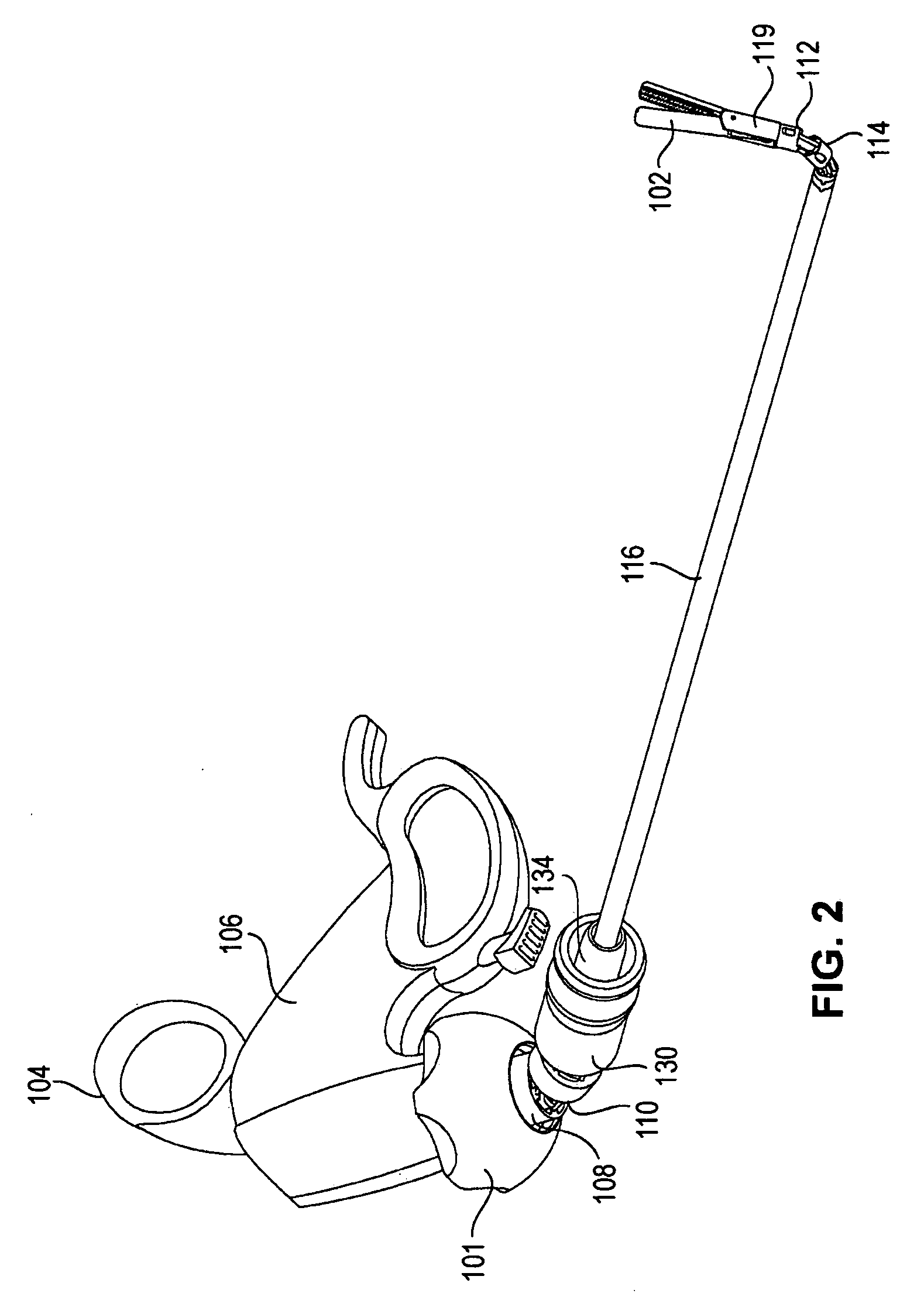
Tool with articulation lock
ActiveUS8100824B2Increase frictionMovement is blocked and preventedEndoscopesSubstation equipmentEngineeringActuator
The invention provides surgical or diagnostic tools and associated methods that offer user control for operating remotely within regions of the body. These tools include a proximally-located actuator for the operation of a distal end effector, as well as proximally-located actuators for articulational and rotational movements of the end effector. Control mechanisms and methods refine operator control of end effector actuation and of these articulational and rotational movements. An articulation lock allows the fixing and releasing of both neutral and articulated configurations of the tool and of consequent placement of the end effector. The tool may also include other features. A multi-state ratchet for end effector actuation provides enablement-disablement options with tactile feedback. A force limiter mechanism protects the end effector and manipulated objects from the harm of potentially excessive force applied by the operator. A rotation lock provides for enablement and disablement of rotatability of the end effector.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Tool with rotation lock
The invention provides surgical or diagnostic tools and associated methods that offer improved user control for operating remotely within regions of the body. These tools include a proximally-located actuator for the operation of a distal end effector, as well as proximally-located actuators for articulational and rotational movements of the end effector. Control mechanisms and methods refine operator control of end effector actuation and of these articulational and rotational movements. A rotation lock provides for enablement and disablement of rotatability of the end effector. The tool may also include other features. A multi-state ratchet for end effector actuation provides enablement-disablement options with tactile feedback. A force limiter mechanism protects the end effector and manipulated objects from the harm of potentially excessive force applied by the operator. An articulation lock allows the fixing and releasing of both neutral and articulated configurations of the tool and of consequent placement of the end effector.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
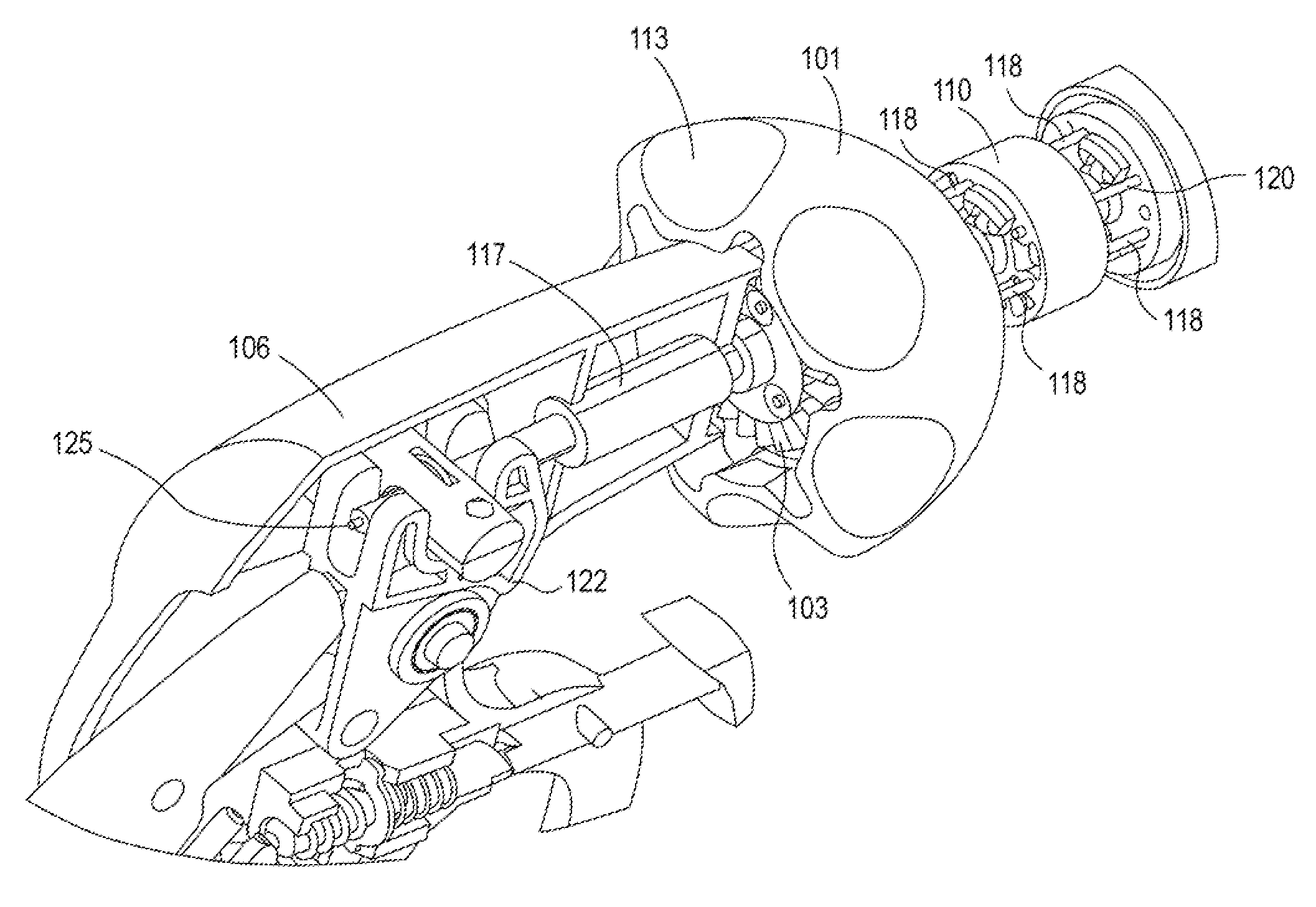
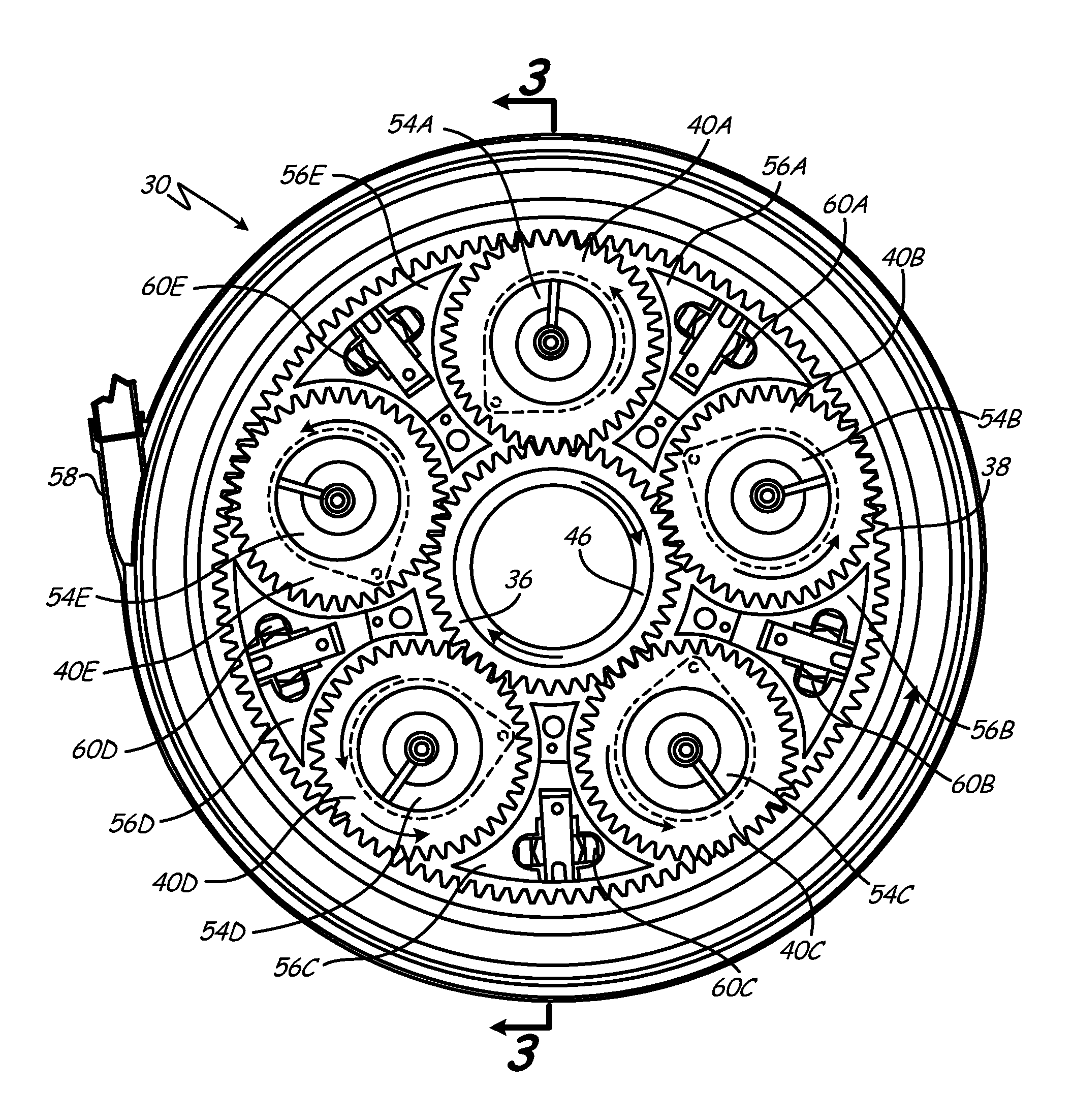
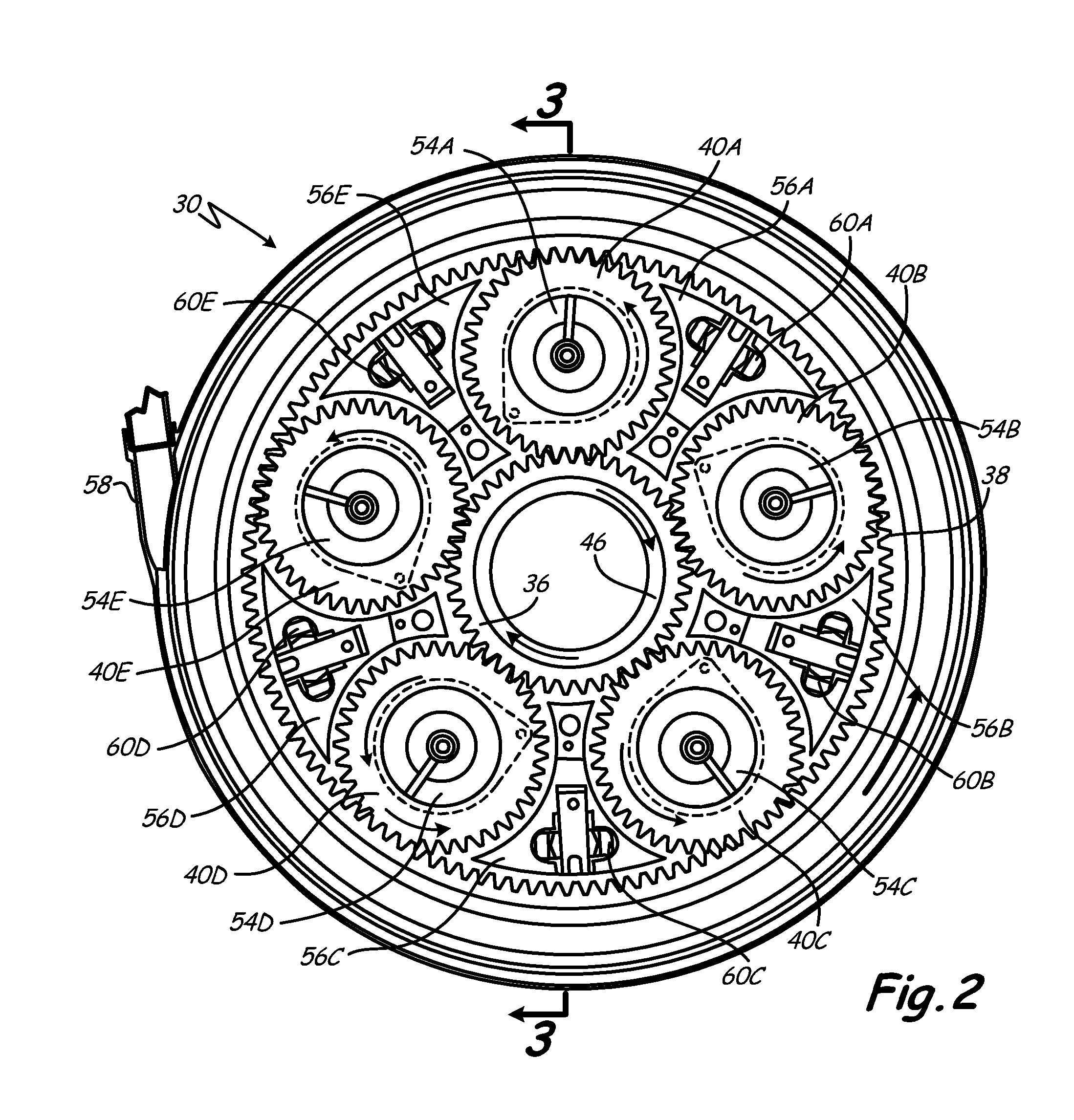
Coupling system for a star gear train in a gas turbine engine
A star gear train for use in a gas turbine engine includes a sun gear, a ring gear, a plurality of star gears and a coupling system. The sun gear is rotatable by a shaft. The ring gear is secured to a ring gear shaft. Each of the plurality of star gears is rotatably mounted in a star carrier and meshes with the sun gear and the ring gear. The coupling system comprises a sun gear flexible coupling, a carrier flexible coupling and a deflection limiter. The sun gear flexible coupling connects the sun gear to the shaft. The carrier flexible coupling connects the carrier to a non-rotating mechanical ground. The deflection limiter is connected to the star carrier to limit excessive radial and circumferential displacement of the star gear train.
Owner:RTX CORP
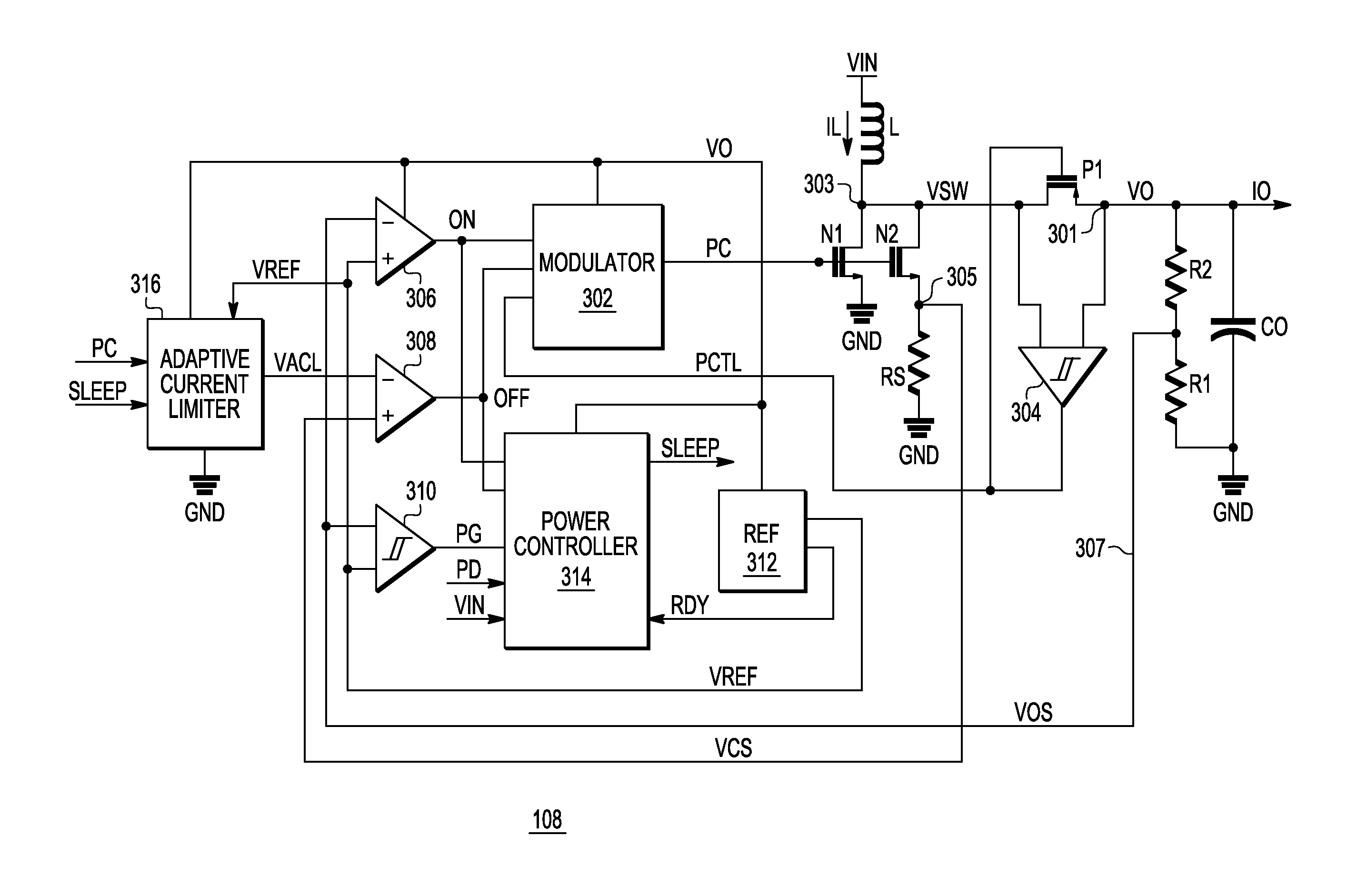
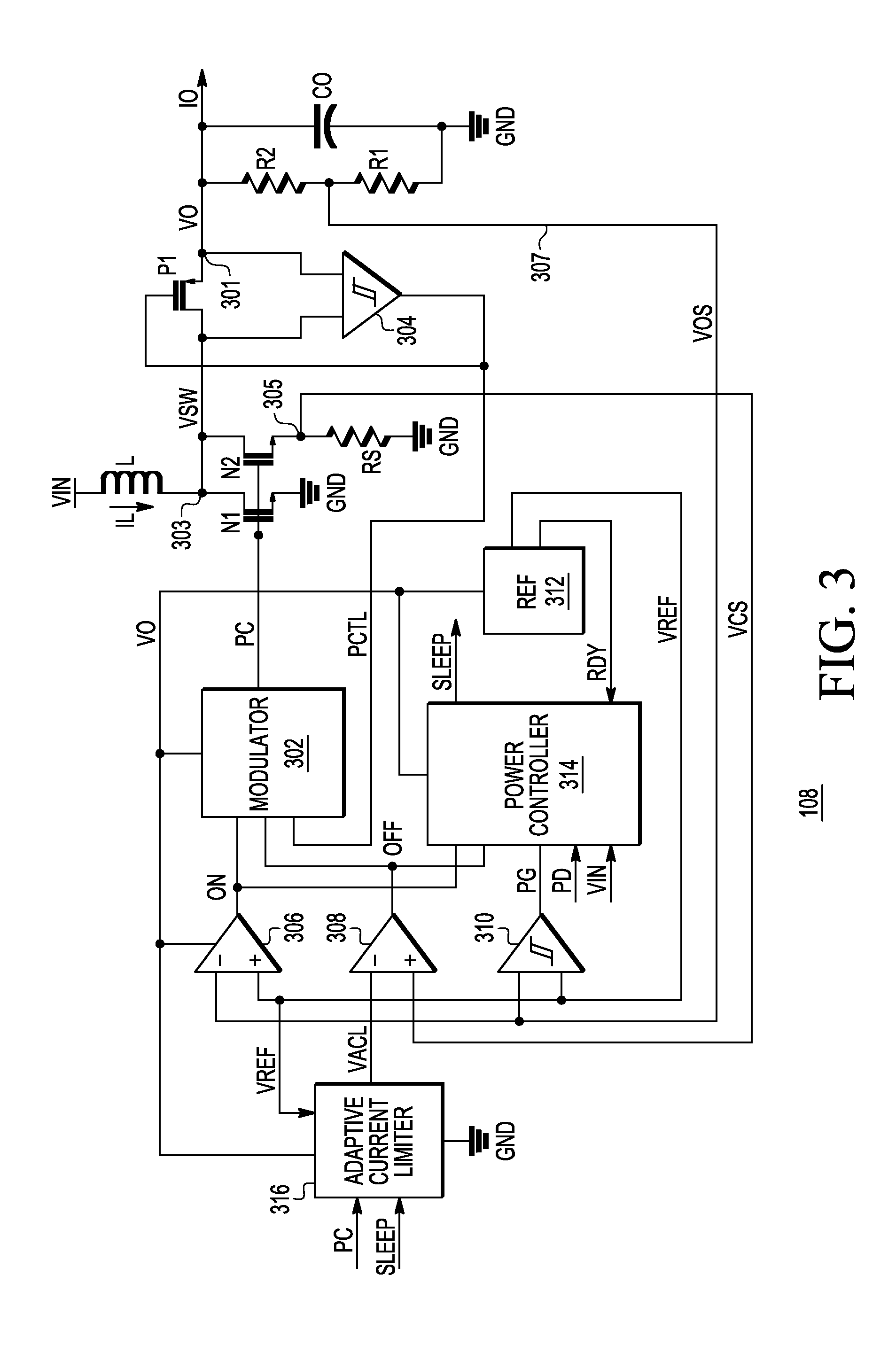
System and method for adaptive current limit of a switching regulator
ActiveUS9099922B2Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalReference current
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
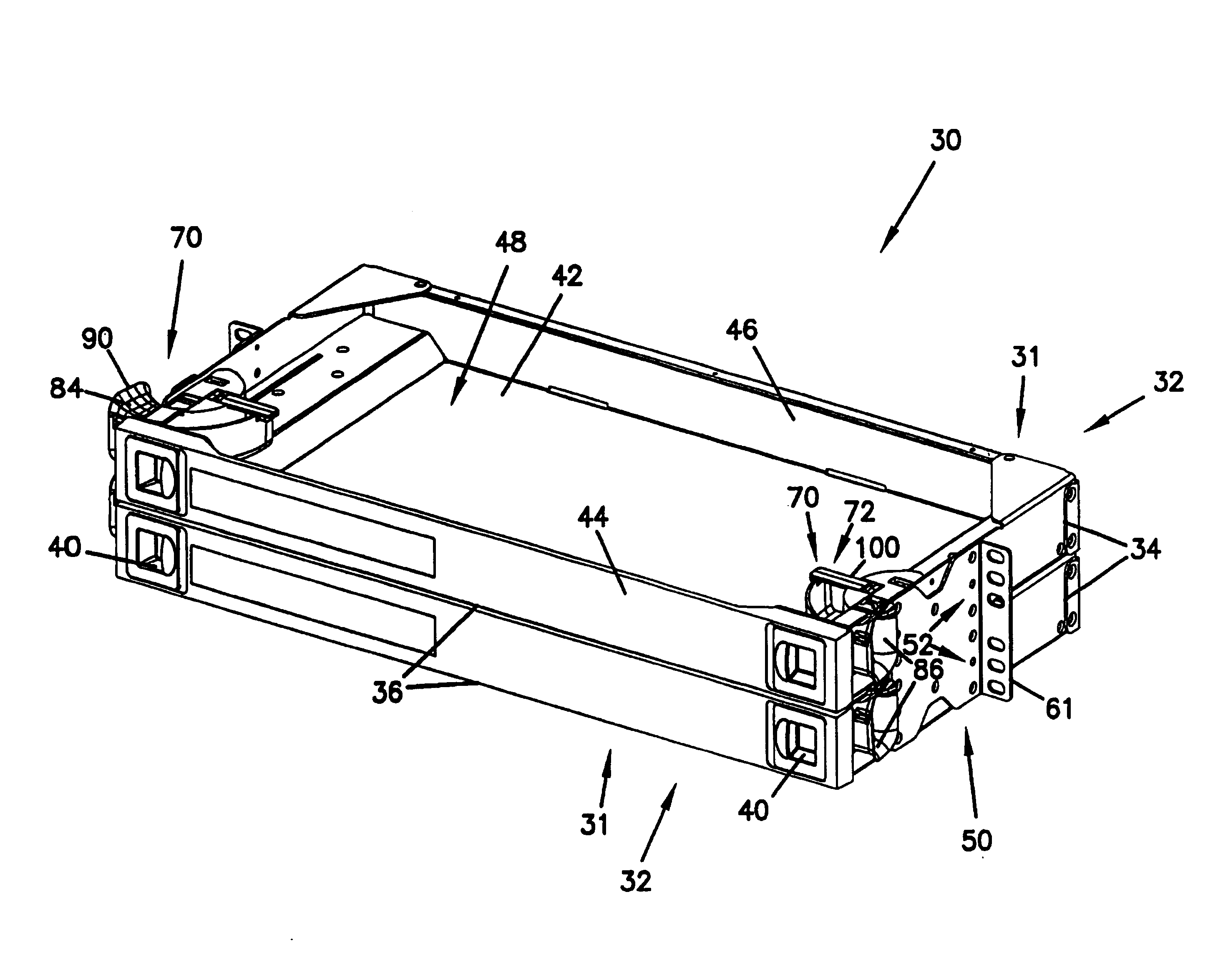
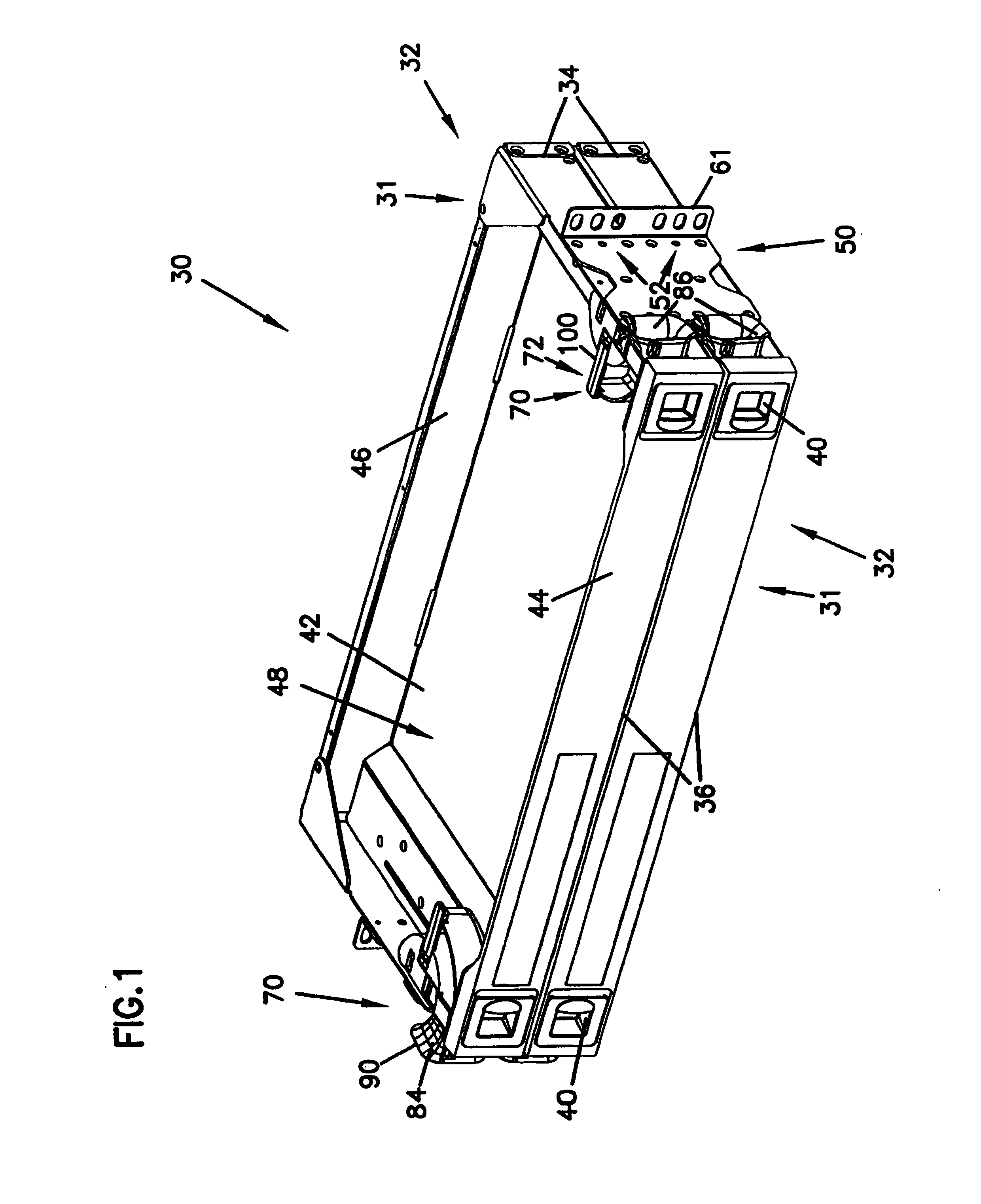
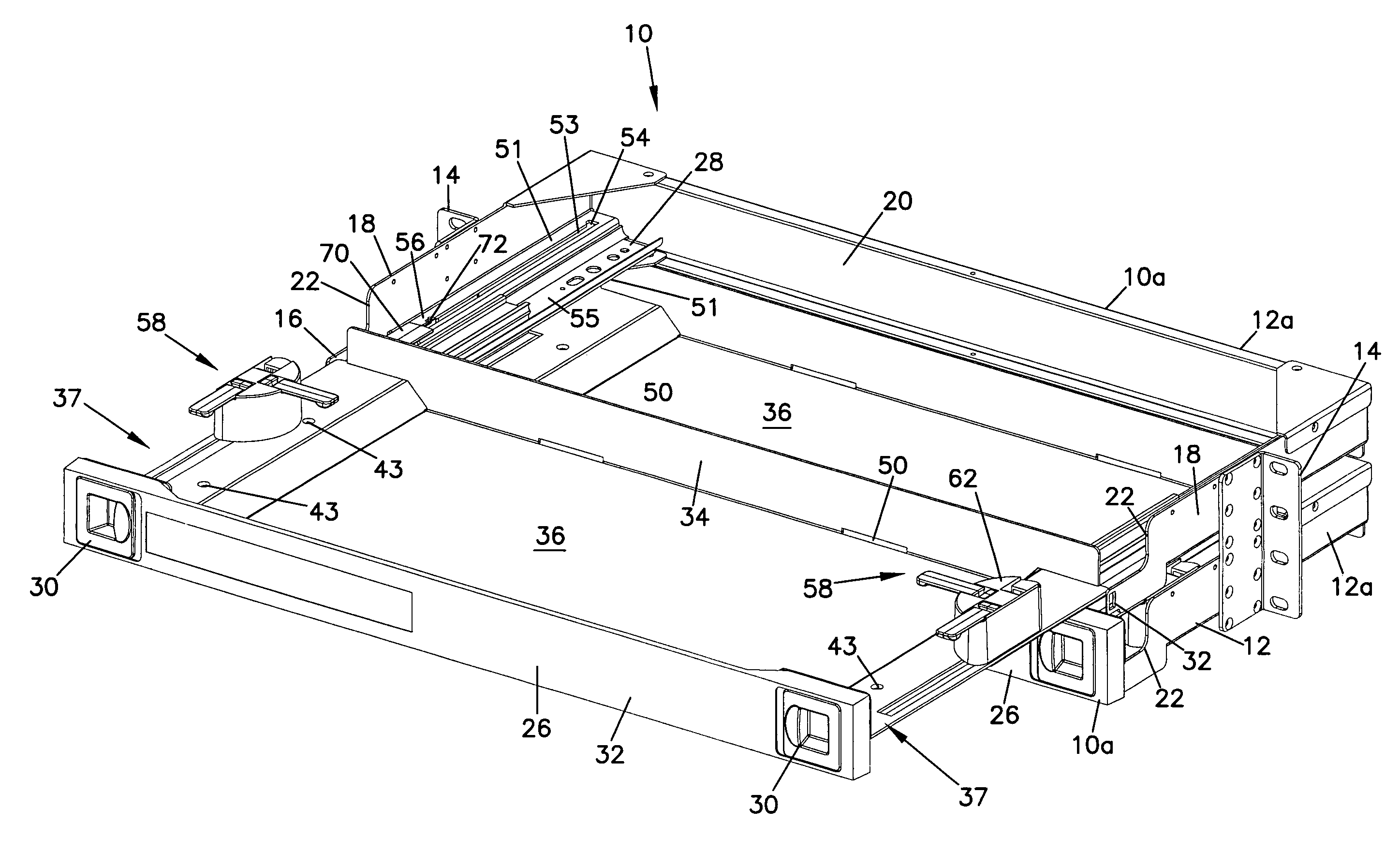
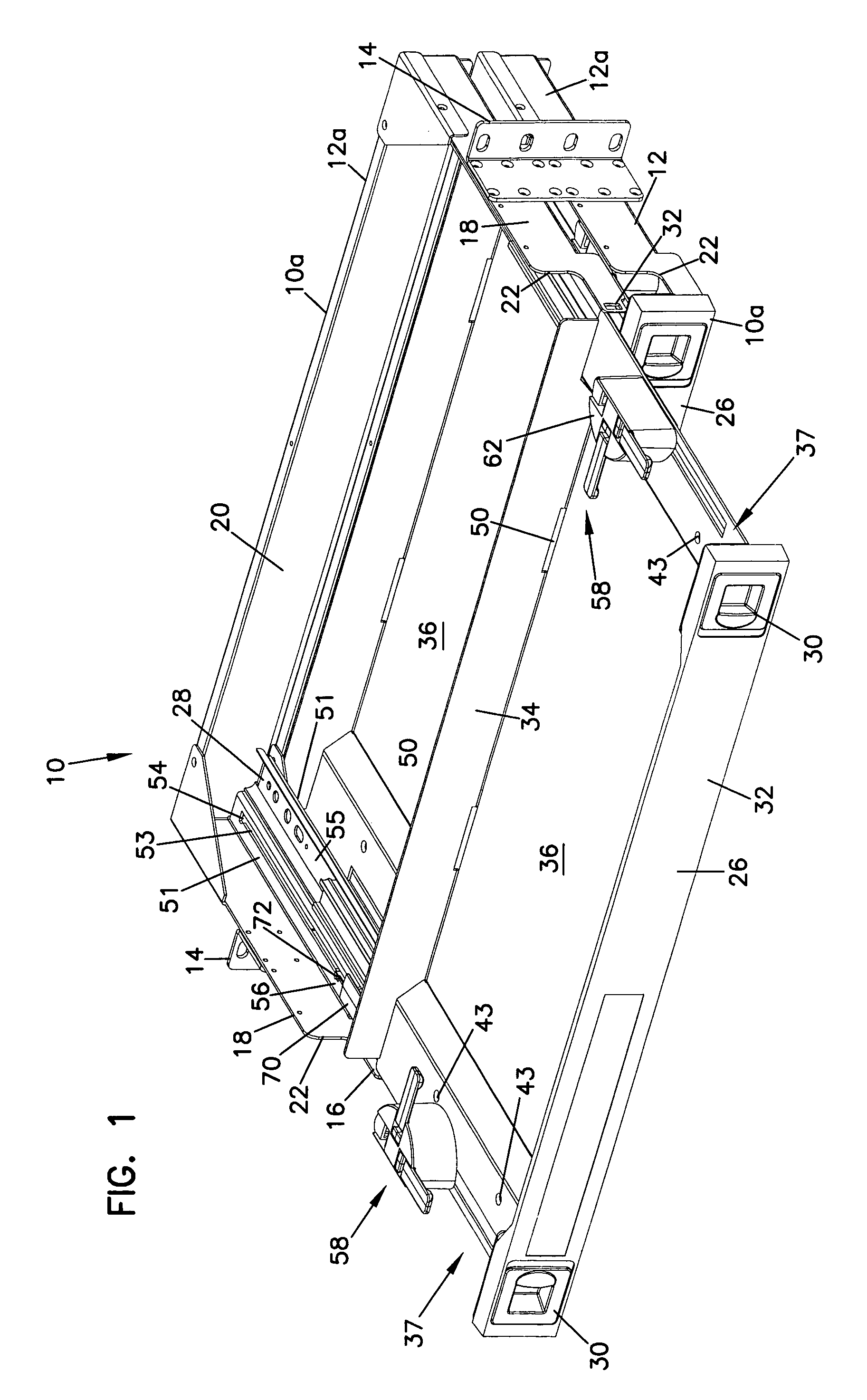
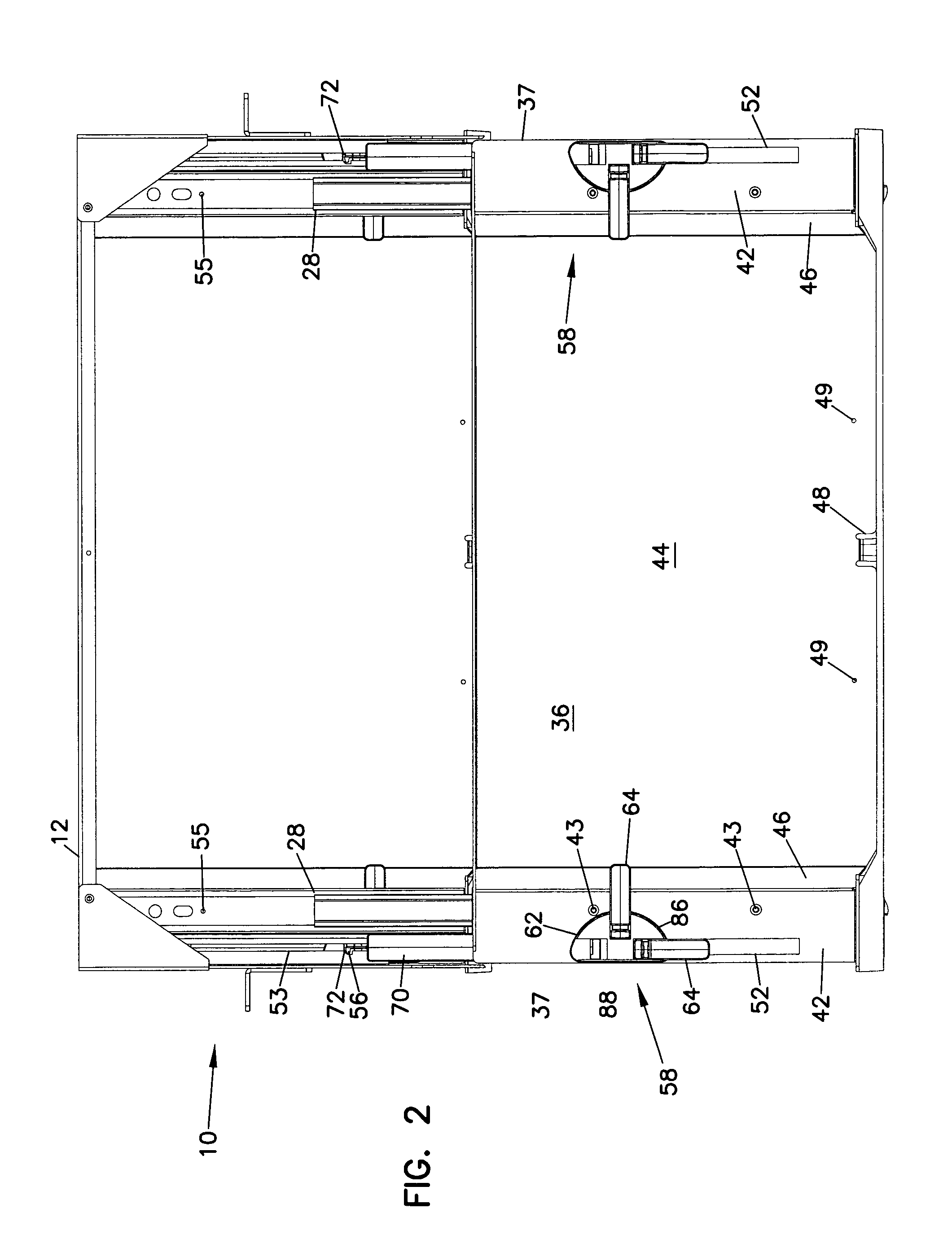
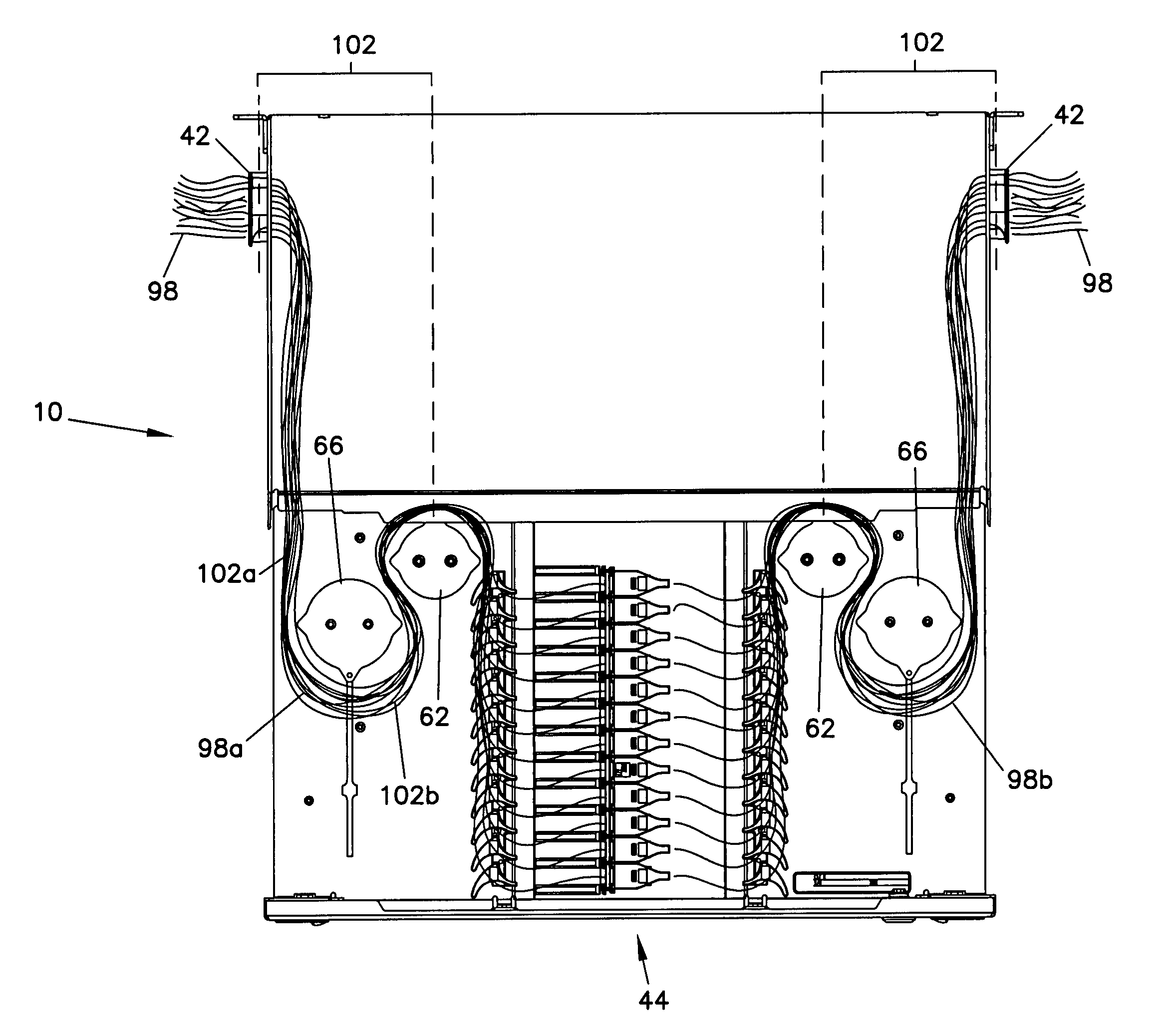
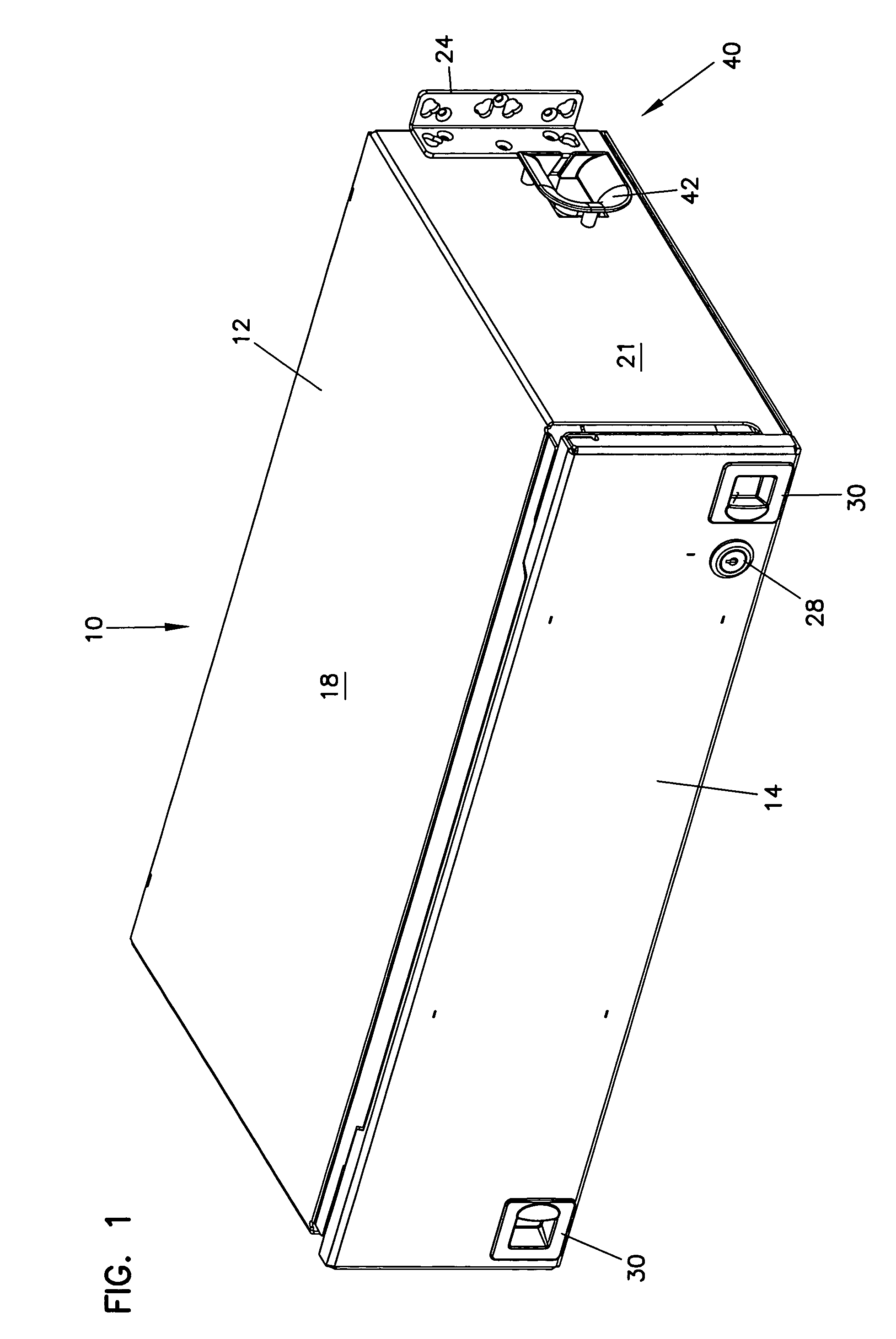
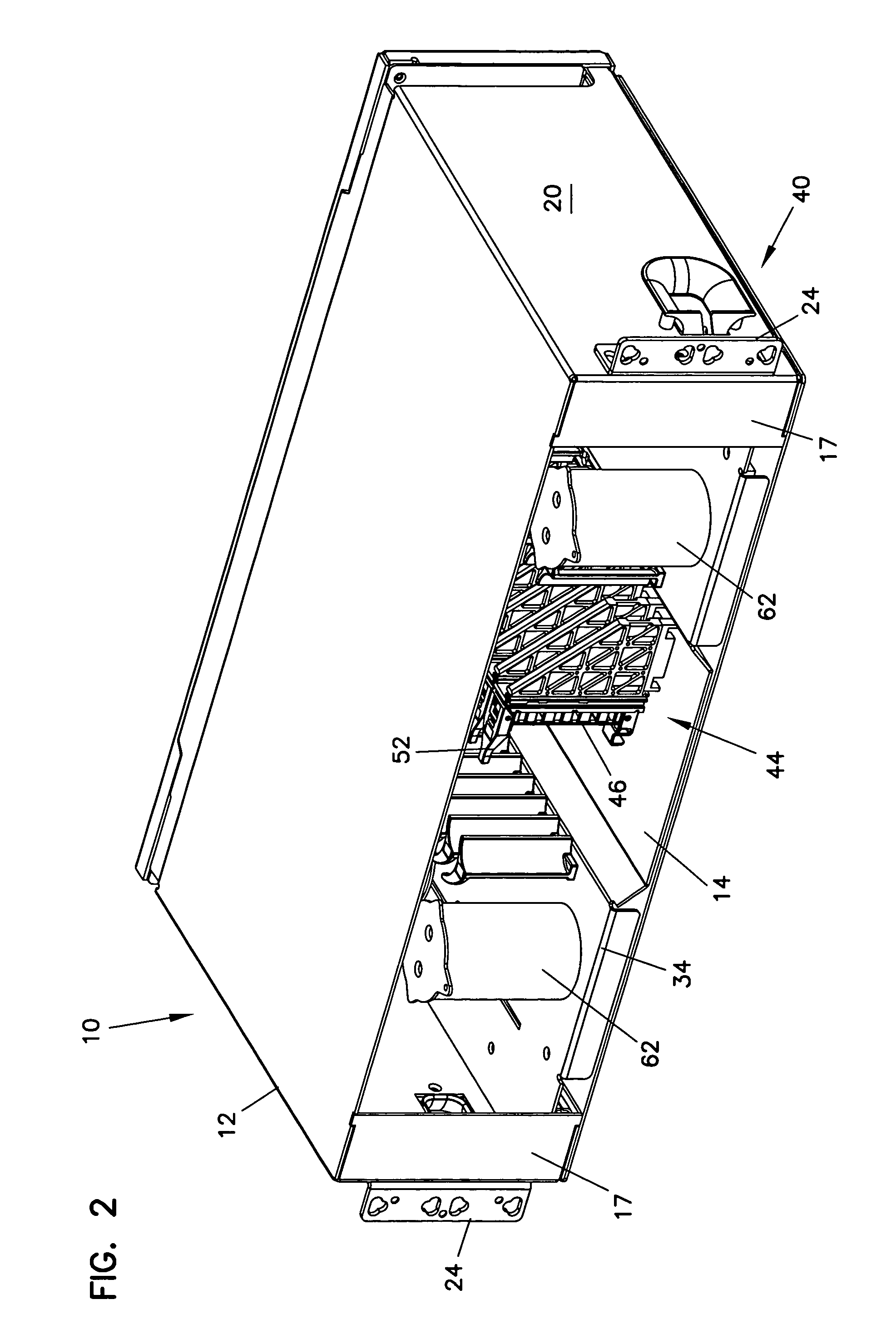
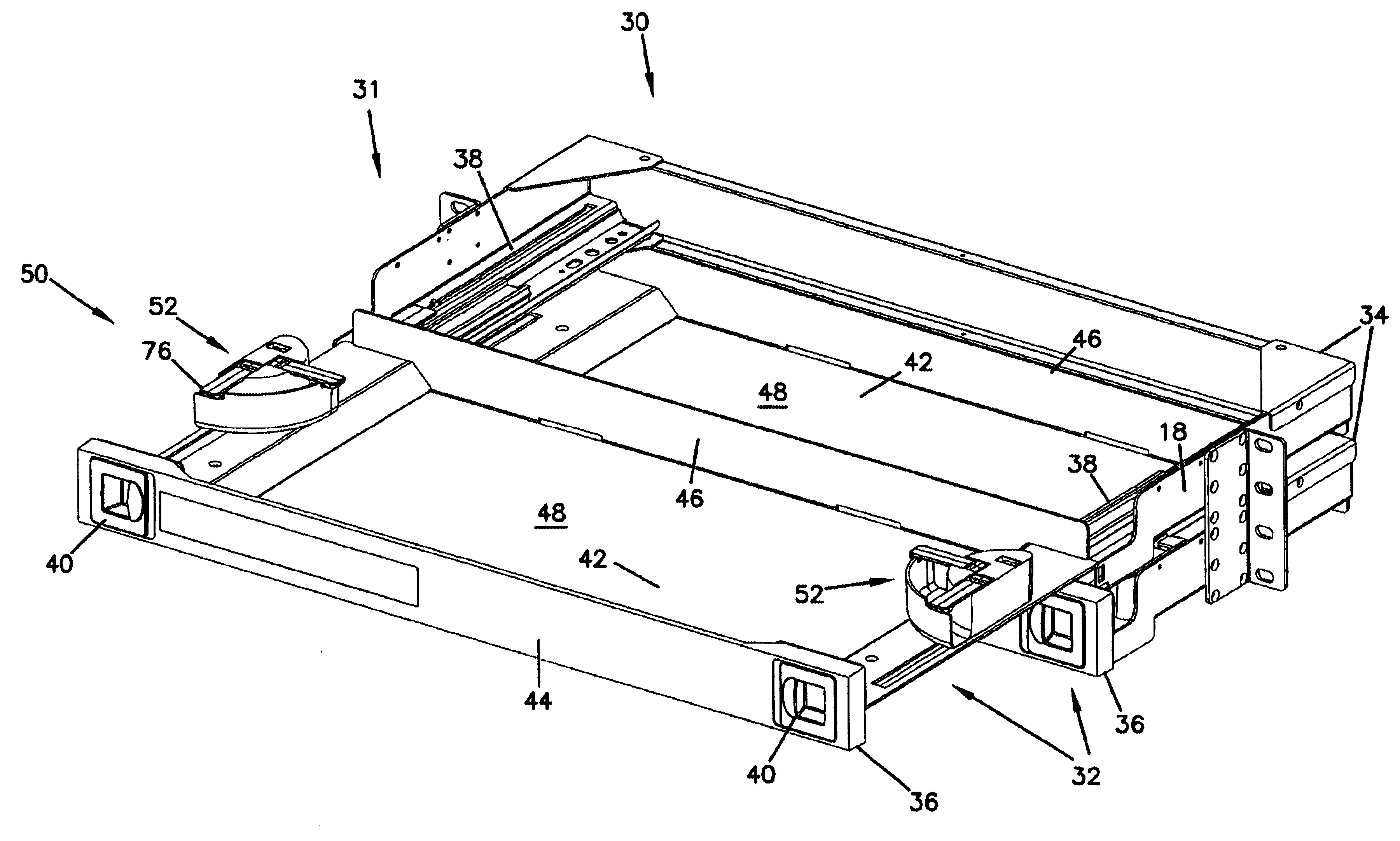
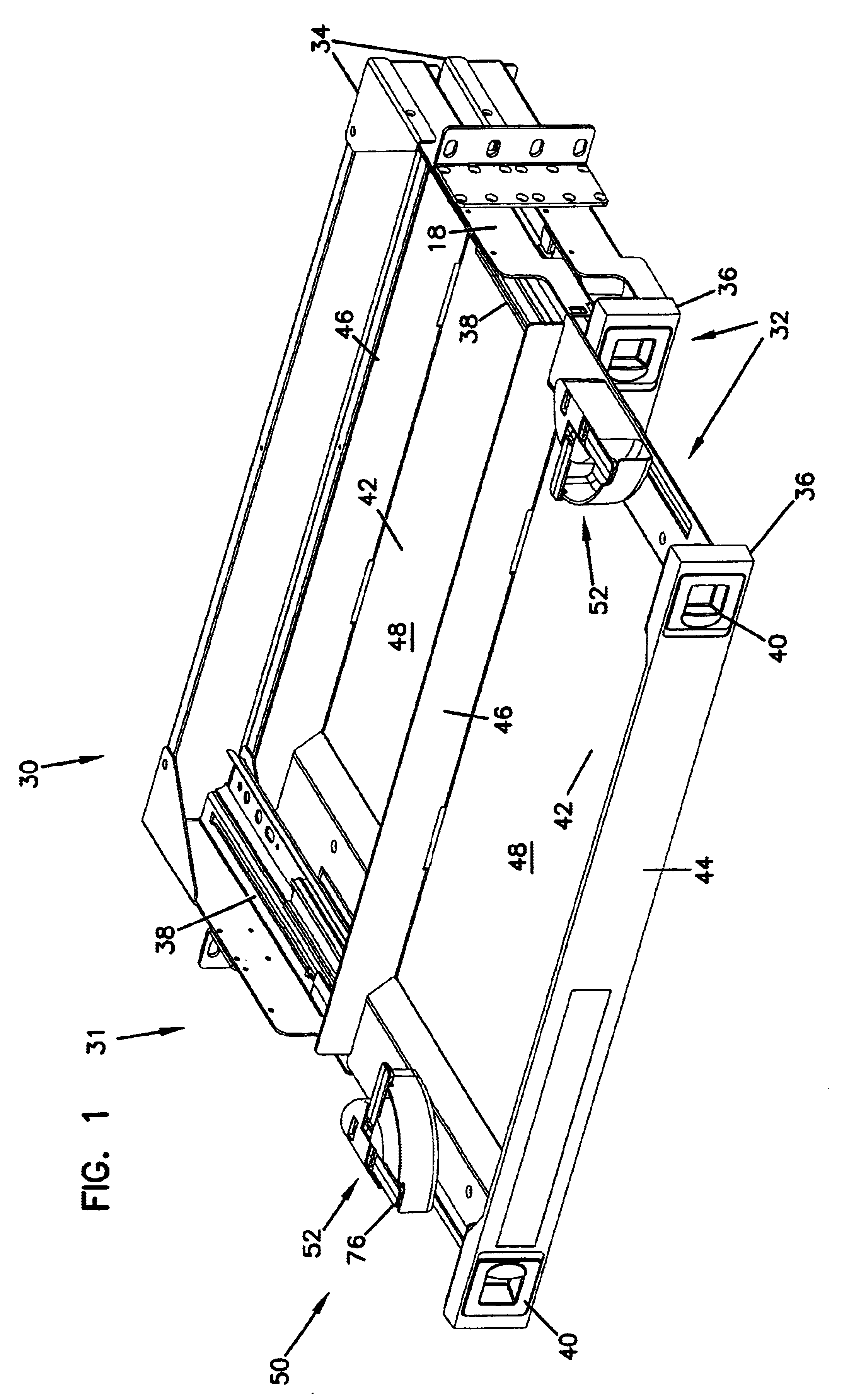
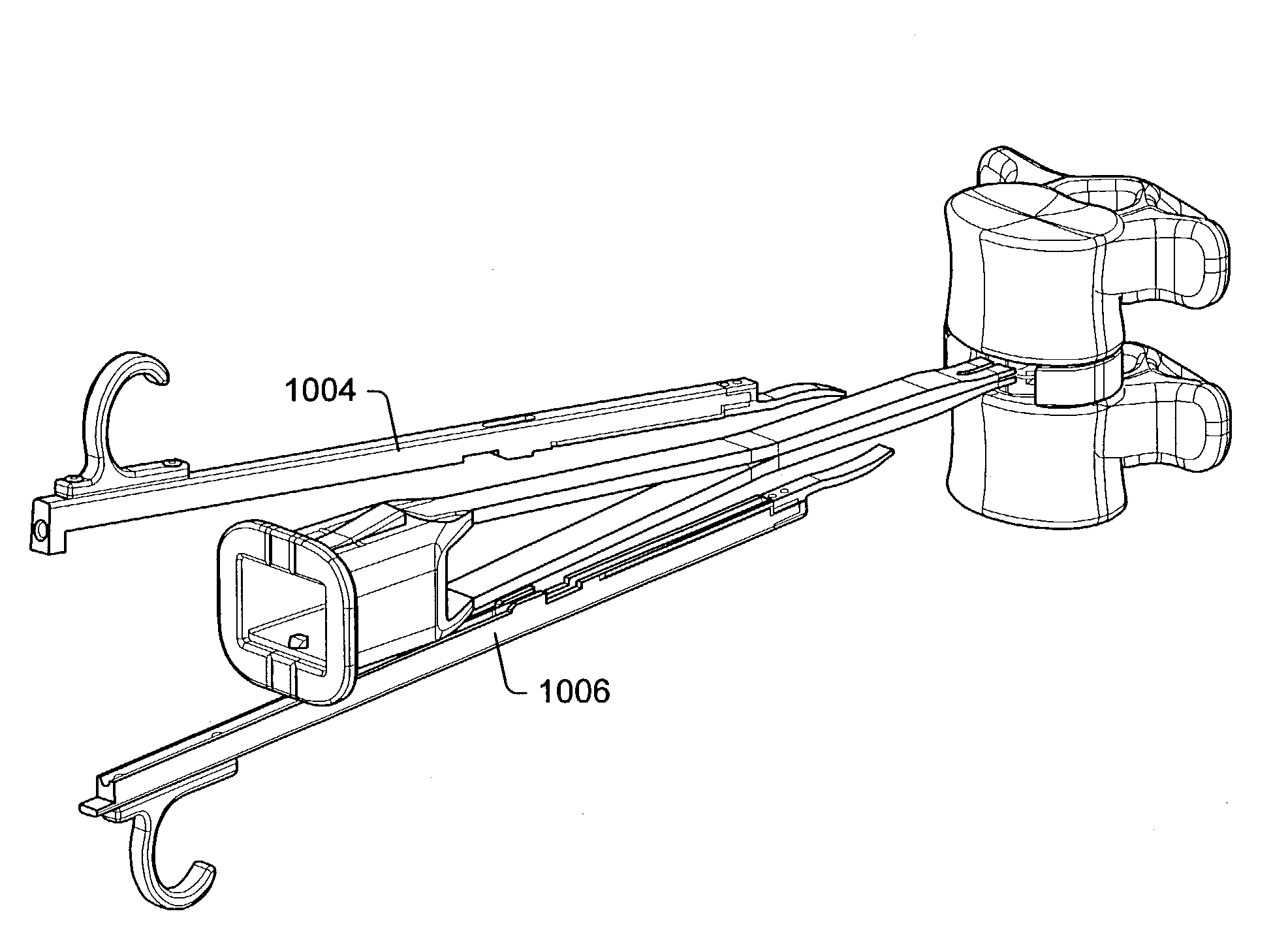
Cable management panel with sliding drawer and methods
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Cable management panel with sliding drawer
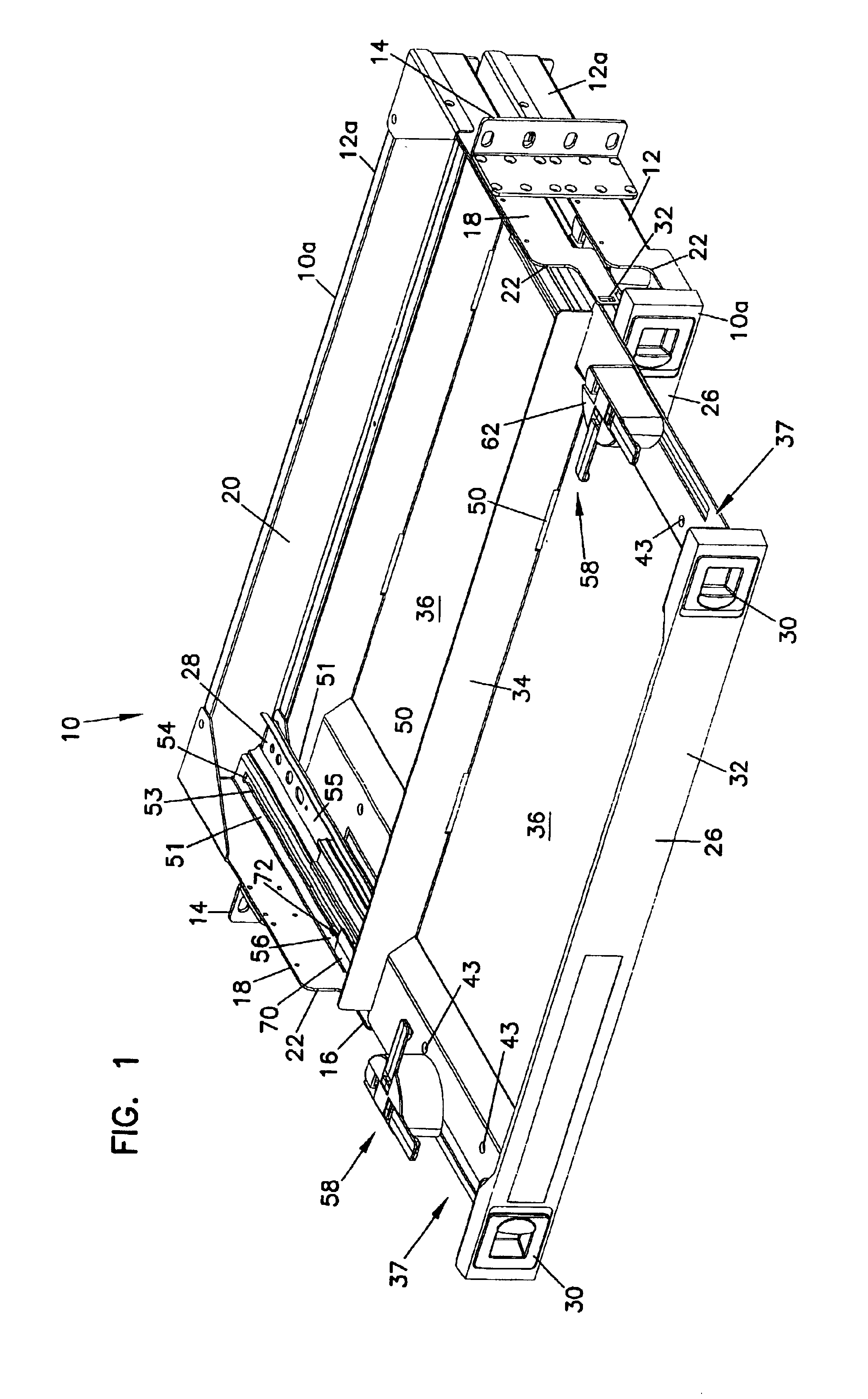
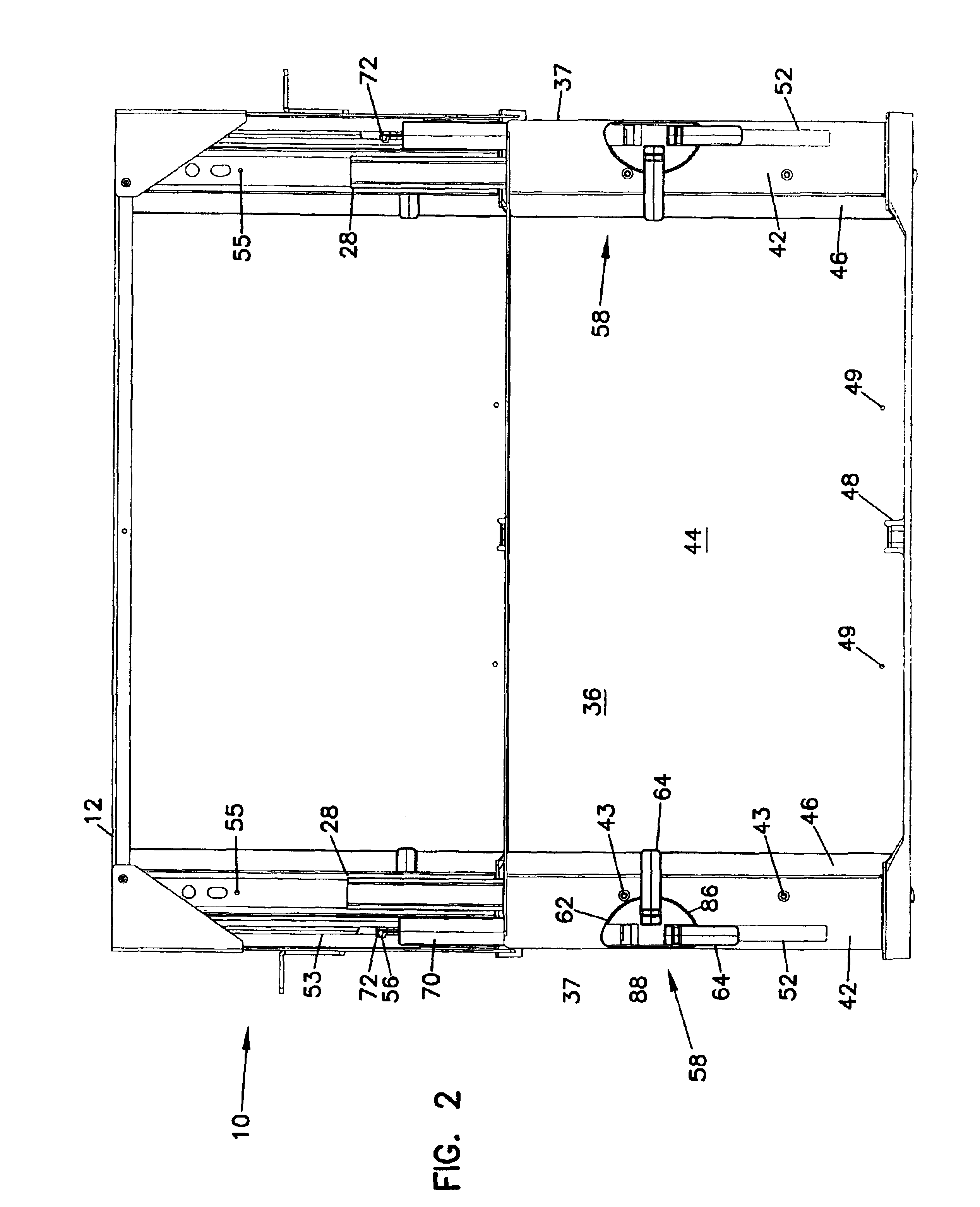
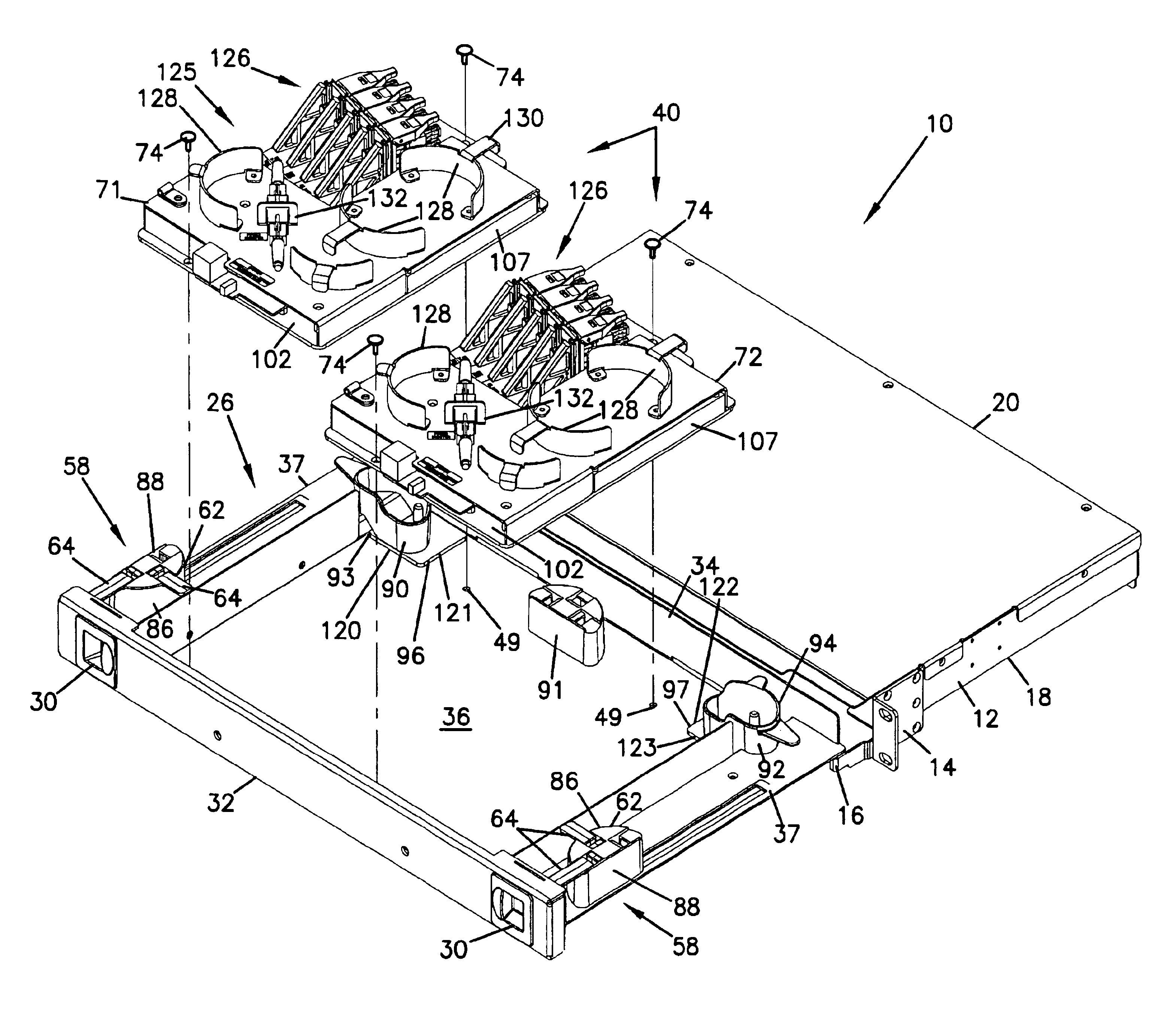
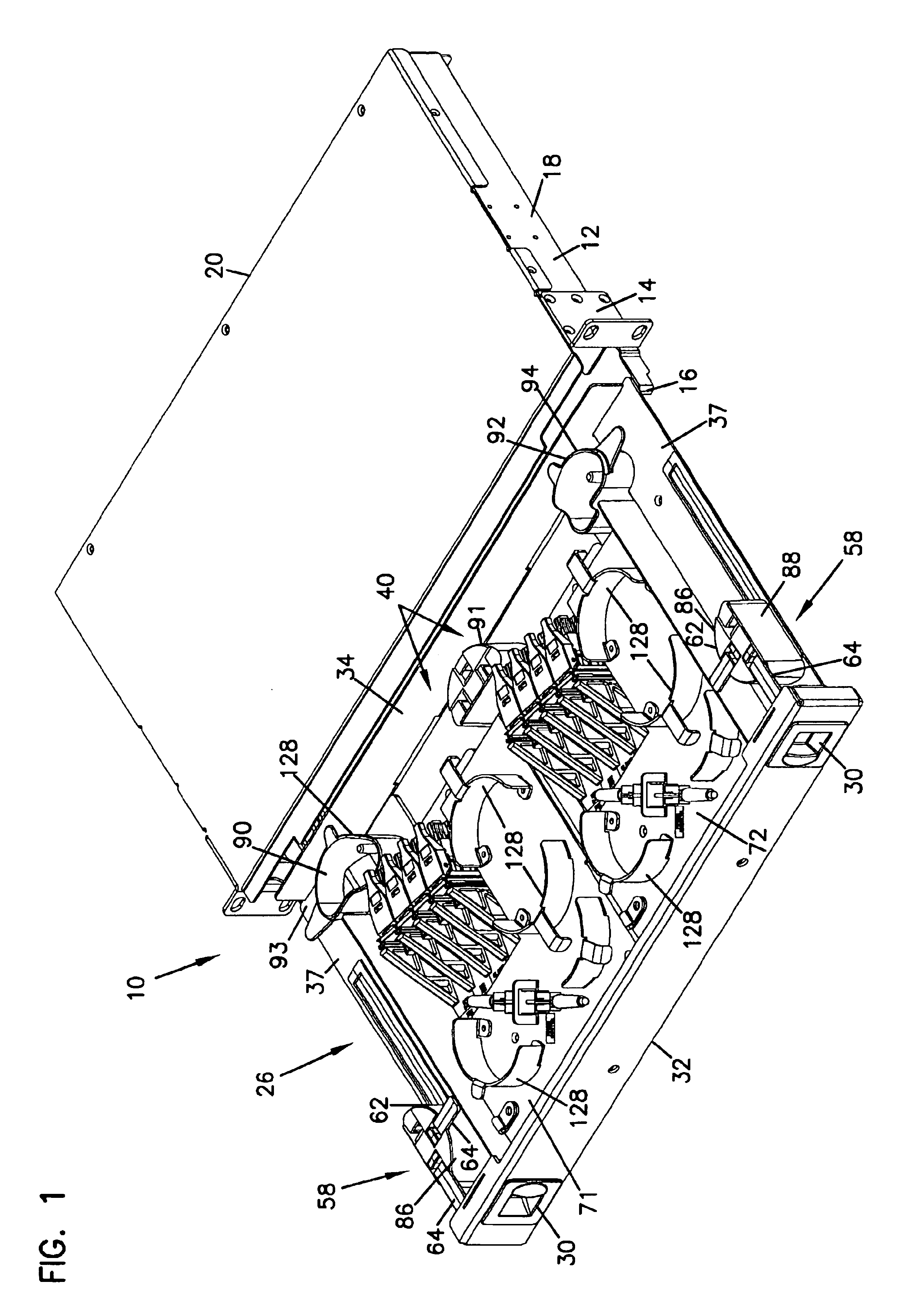
An optical fiber cable management panel is provided with slideable drawers and structure within the drawers for cable management and / or connection to other devices. Tray inserts drop into the drawers to provide the appropriate management and connection devices. A movable take-up mechanism manages the cable entering and exiting the drawers at side openings. Stackable pivoting storage trays on the tray insert include a detent arrangement for holding each tray in a pivoted access position. The tray inserts further include a front key, and a back tab mounting arrangement for mounting the tray inserts to the drawers, and side radius limiters including notches for extending over raised portions of the drawer. The take-up mechanism includes a U-shaped trough section and cable retention tabs. A control mechanism is provided for controlling movement of the take-up mechanism relative to the drawer.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Cable management panel with sliding drawer
An optical fiber cable management panel includes at least one slideable drawer and structure within the drawer for cable management and / or connection to other devices. At least two tray inserts drop into the drawers to provide the appropriate management and connection devices. Each of the drop-in plates includes fastener structure to accommodate removable securement of the drop-in plates to the drawer. The drop-in plates accommodate selected fiber management components thereon. The fiber management components can include radius limiters, adapters, or LEDs. A method of providing fiber management components in a cable management panel includes operably mounting at least two drop-in trays in a drawer, each of the drop-in trays including a fiber management component.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Dose setting limiter
InactiveUS6524280B2Easy to manufactureImprove gripOther blood circulation devicesInfusion syringesMedicineBiomedical engineering
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
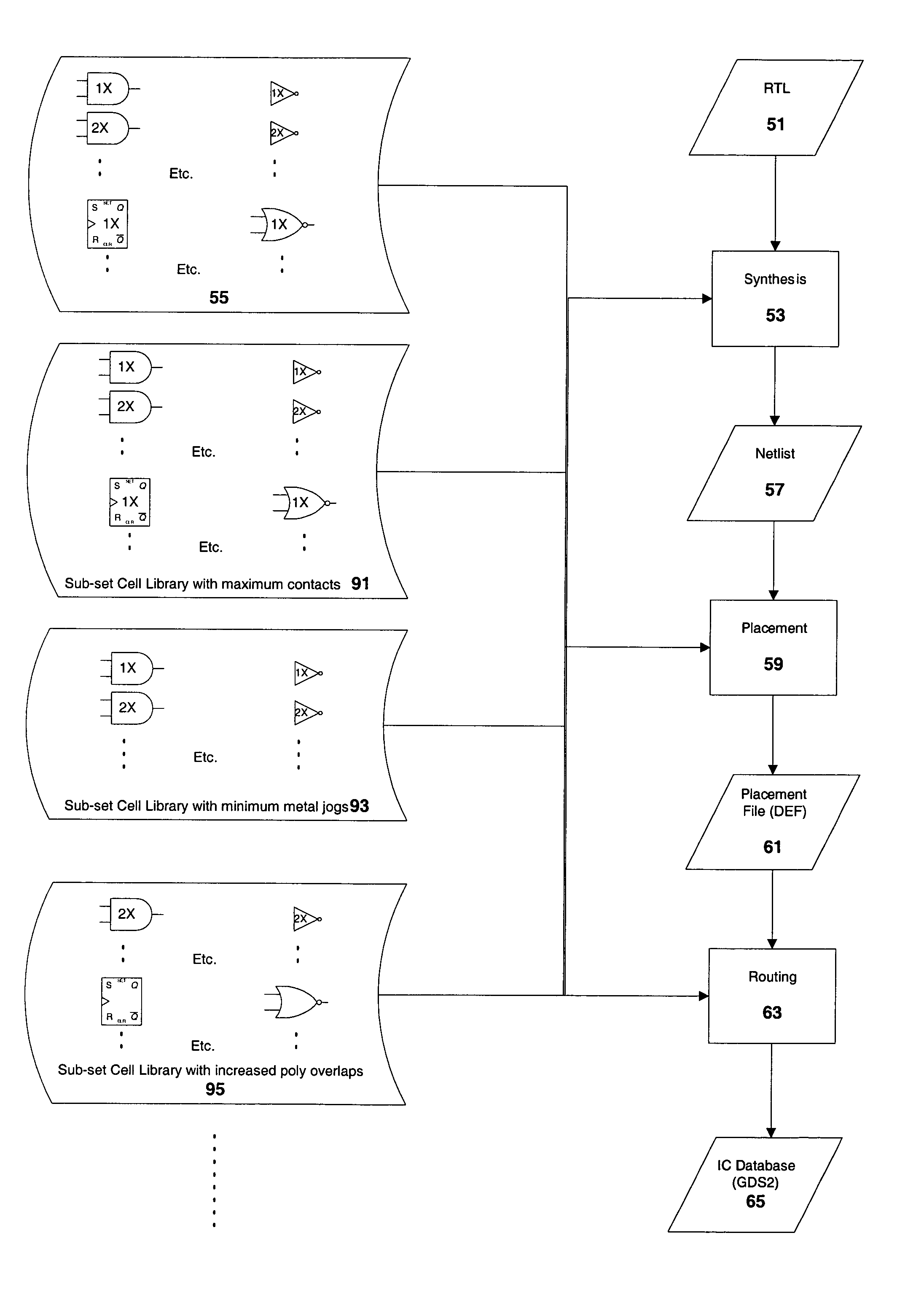
Yield maximization in the manufacture of integrated circuits
InactiveUS6957402B2Increase productionHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer-aidedEngineering
A method and apparatus for improving the manufacturability of Integrated Circuits (ICs) formed on semiconductor dies is described. A plurality of different designs for some or all of the standard cells are made available to the circuit designer. Each different design may address a different problem associated with different manufacturing processes or a different design related yield limiter. Each of the design variants is characterized indicating its relative ease of manufacture, or it's yield sensitivity to certain IC design factors. The designer, typically with assistance from computer aided tools, can then select the standard cell variant for each of the cell used in the IC design that best addresses his or her design constraints. In other embodiments, variant versions of I / O cells and memory cells could also be created and made available to the designer in a similar fashion.
Owner:ARM INC
Cable management panel with sliding drawer
An optical fiber cable management panel is provided with slideable drawers and structure within the drawers for cable management and / or connection to other devices. Tray inserts drop into the drawers to provide the appropriate management and connection devices. A movable take-up mechanism manages the cable entering and exiting the drawers at side openings. Stackable pivoting storage trays on the tray insert include a detent arrangement for holding each tray in a pivoted access position. The tray inserts further include a front key, and a back tab mounting arrangement for mounting the tray inserts to the drawers, and side radius limiters including notches for extending over raised portions of the drawer. The take-up mechanism includes a U-shaped trough section and cable retention tabs. A control mechanism is provided for controlling movement of the take-up mechanism relative to the drawer.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
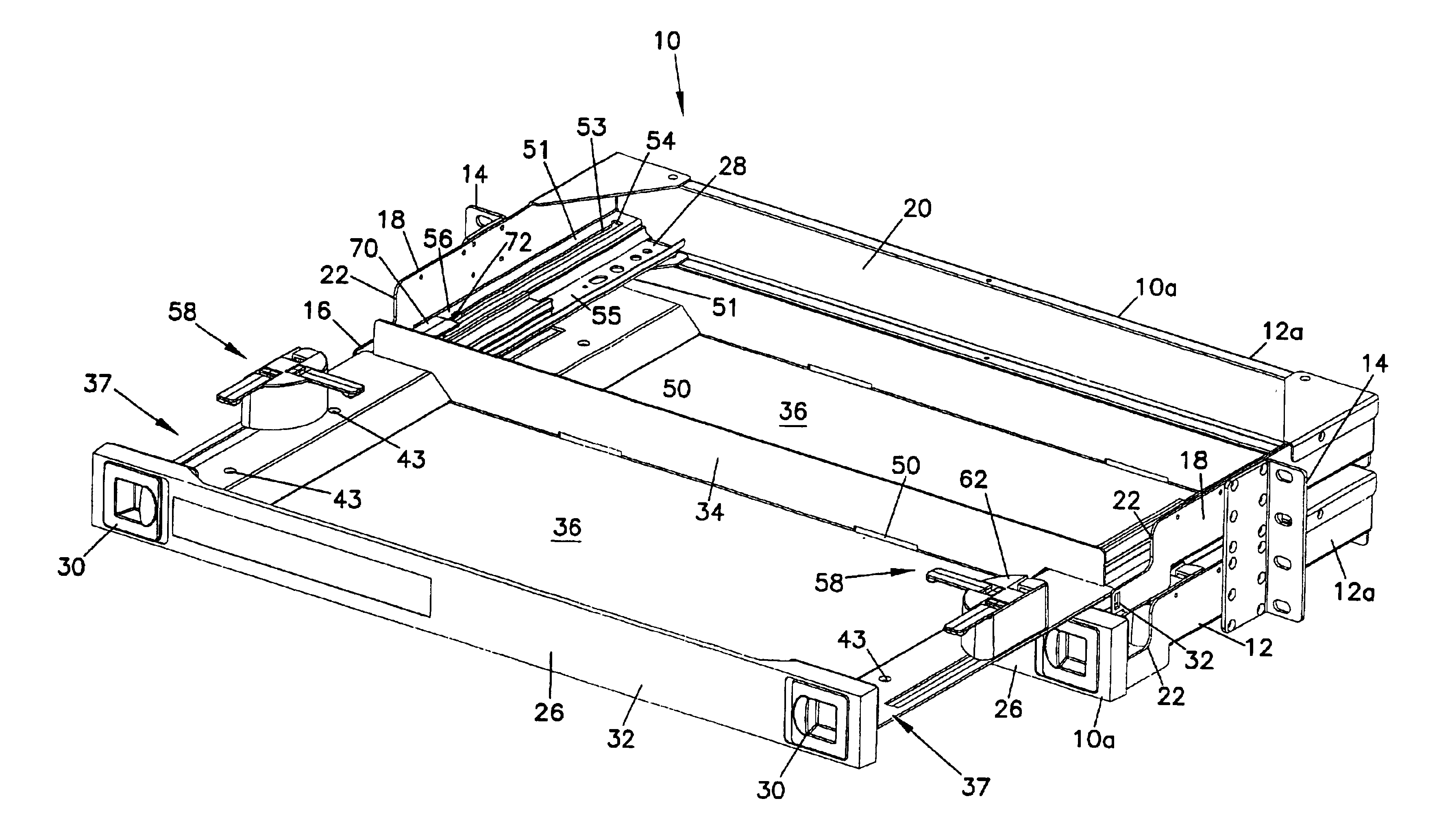
Cable management panel with sliding drawer and methods
ActiveUS6944383B1Cladded optical fibreElectric connection structural associationsTelecommunications cableEngineering
A cable management panel for telecommunications cables. A chassis holds a slideable drawer. The drawer includes cable terminations or splices. The drawer further includes a radius limiter which moves with synchronized movement with movement of the drawer. Cables enter the chassis through a side wall, such as located adjacent the rear of the chassis. The radius limiter manages a slack loop of cable disposed within the chassis.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
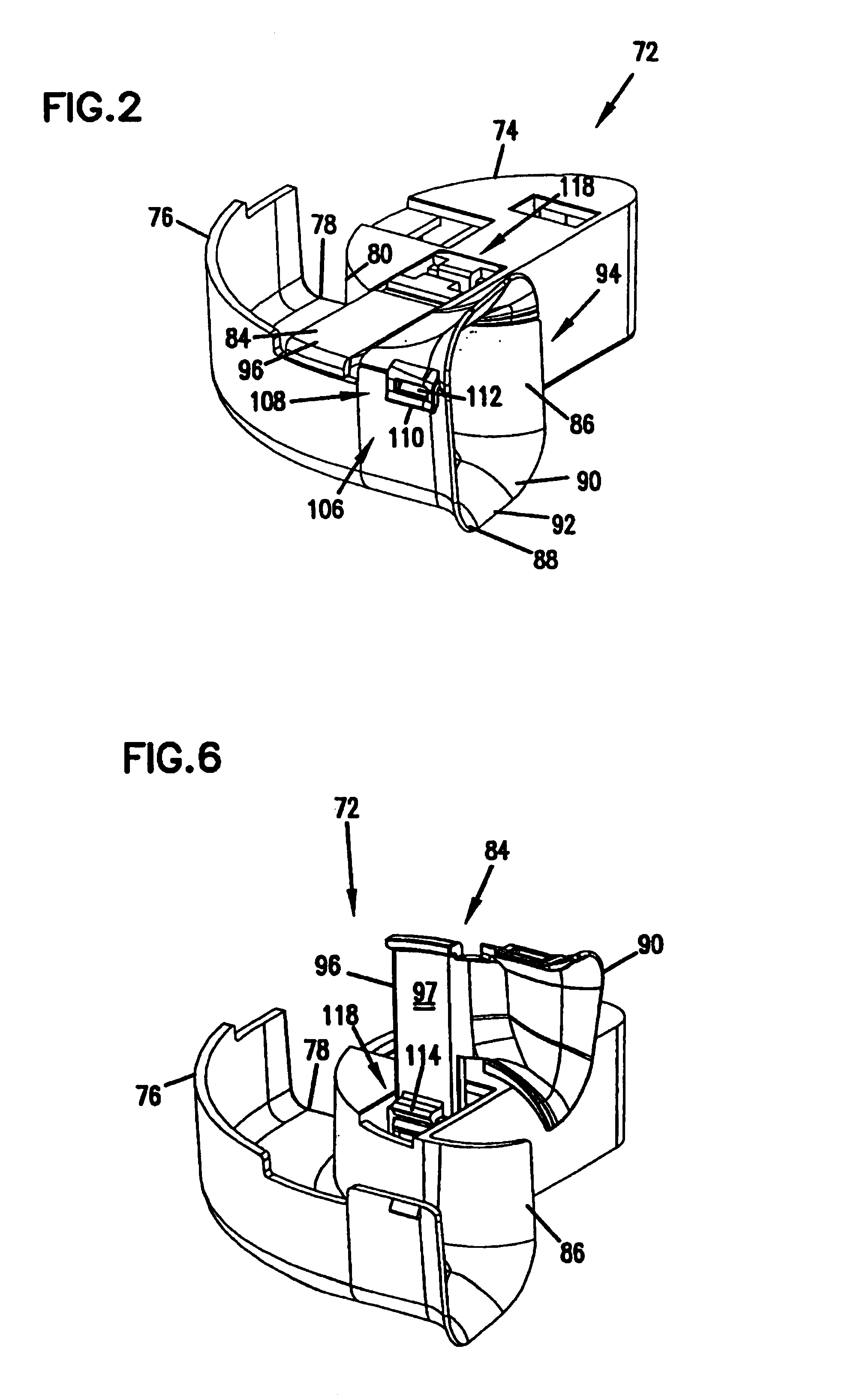
Rotating radius limiter for cable management panel and methods
A rotating radius limiter for an optical fiber cable management panel is provided. The radius limiter includes a radius limiter structure and a bracket that permit relative motion between the structure and the bracket. The structure and bracket are mounted to a sliding cable management panel. The radius limiter structure includes a curved wall, an opening for receiving cables and a trough section for retaining cables about a radius portion.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
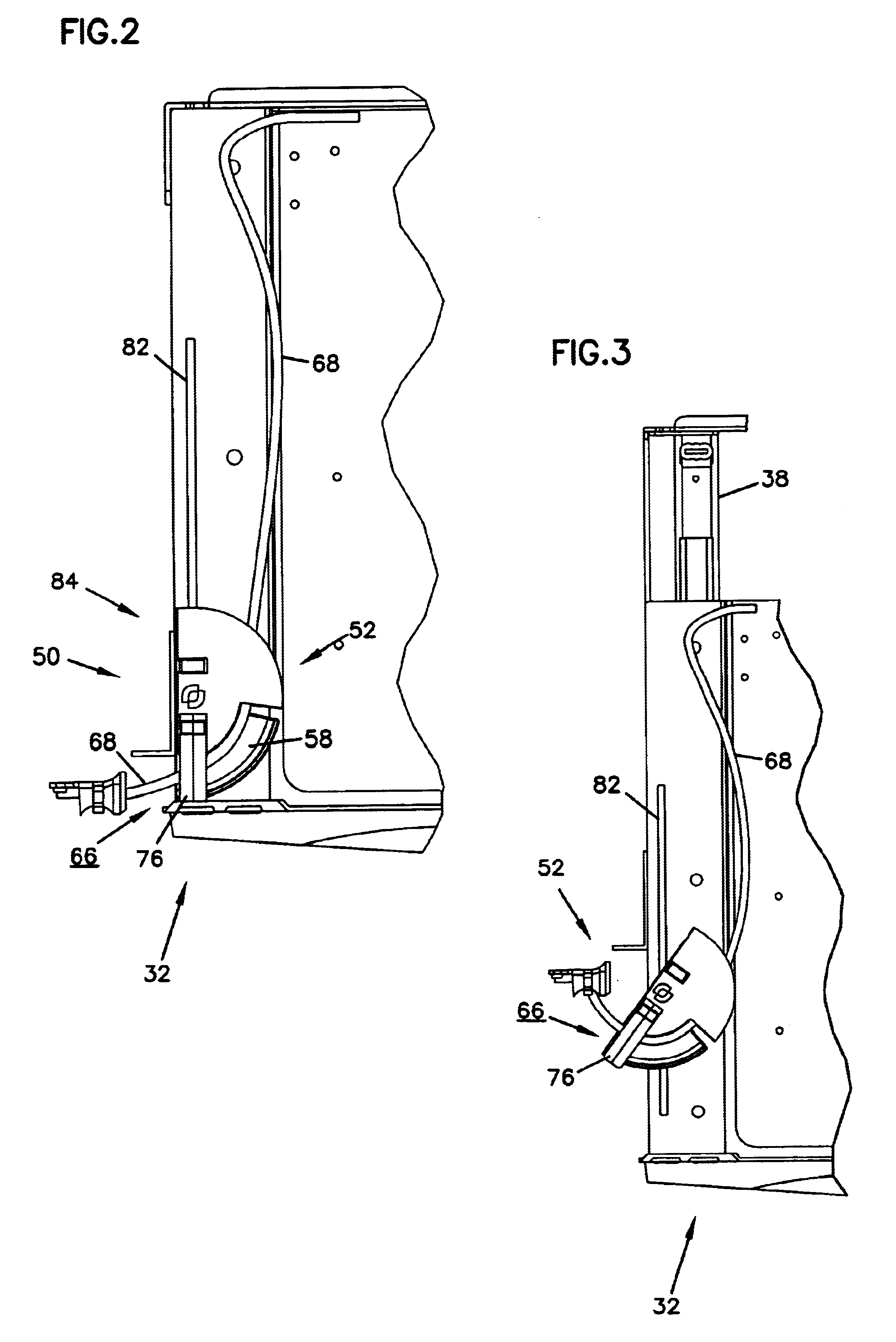
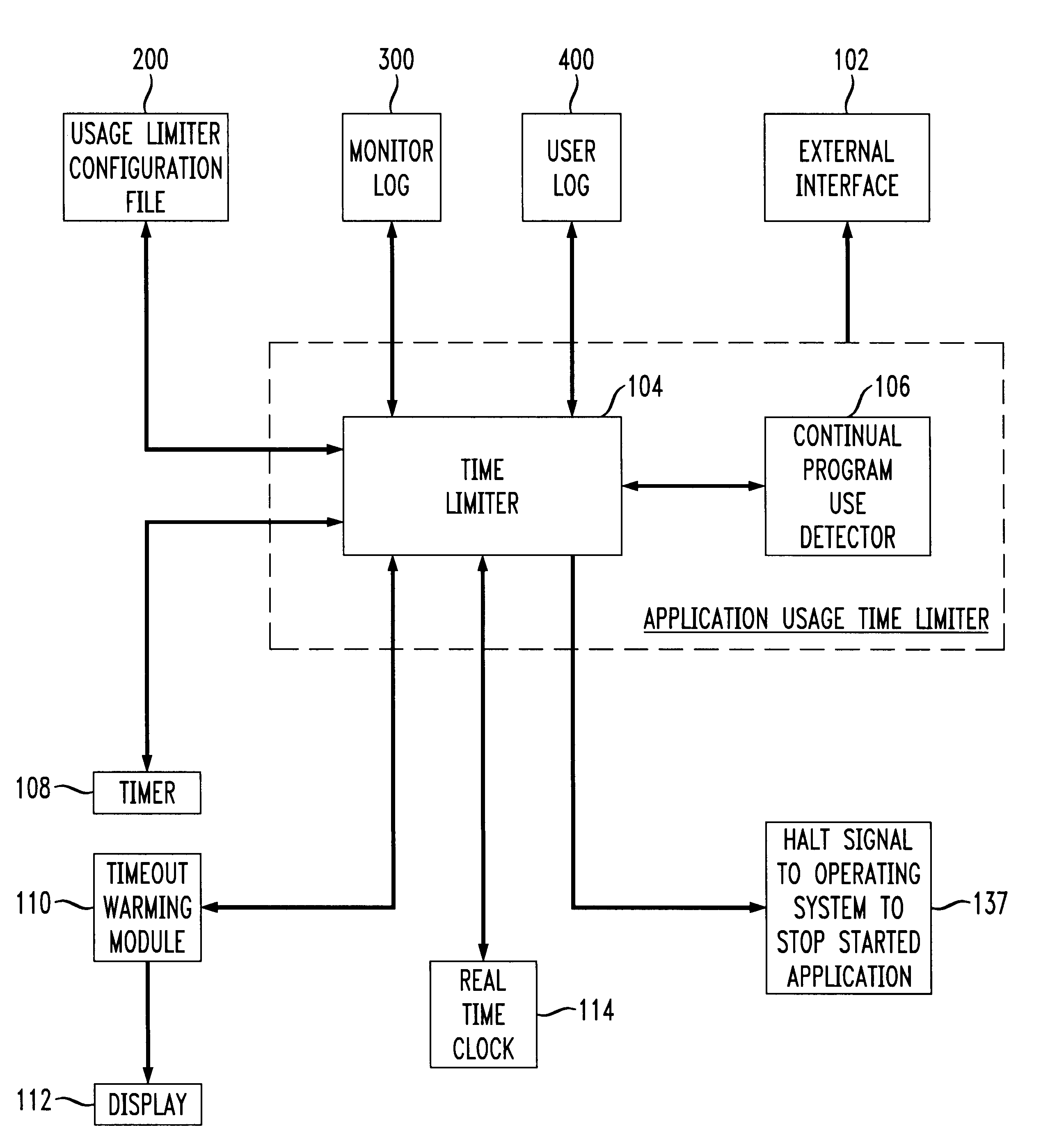
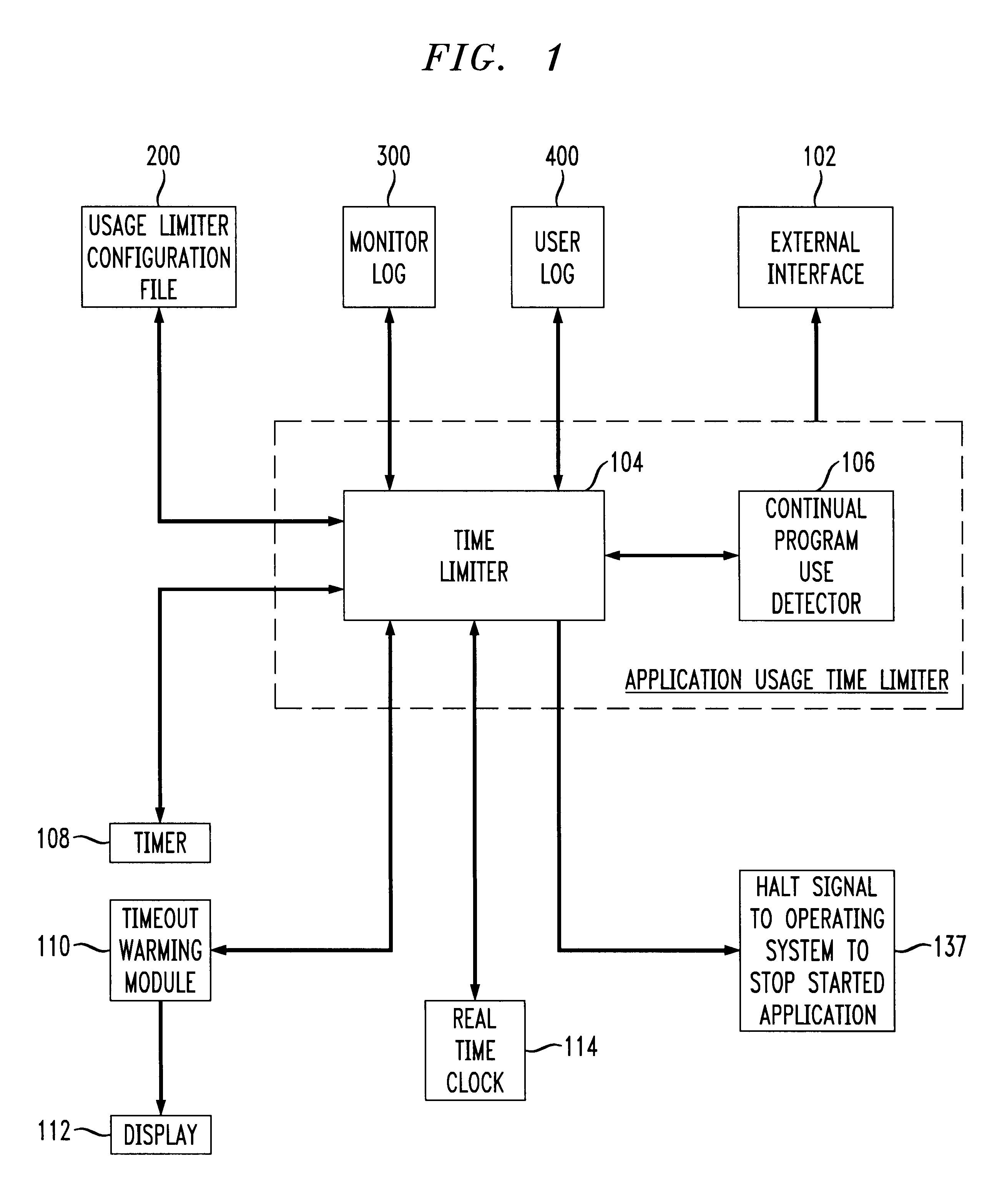
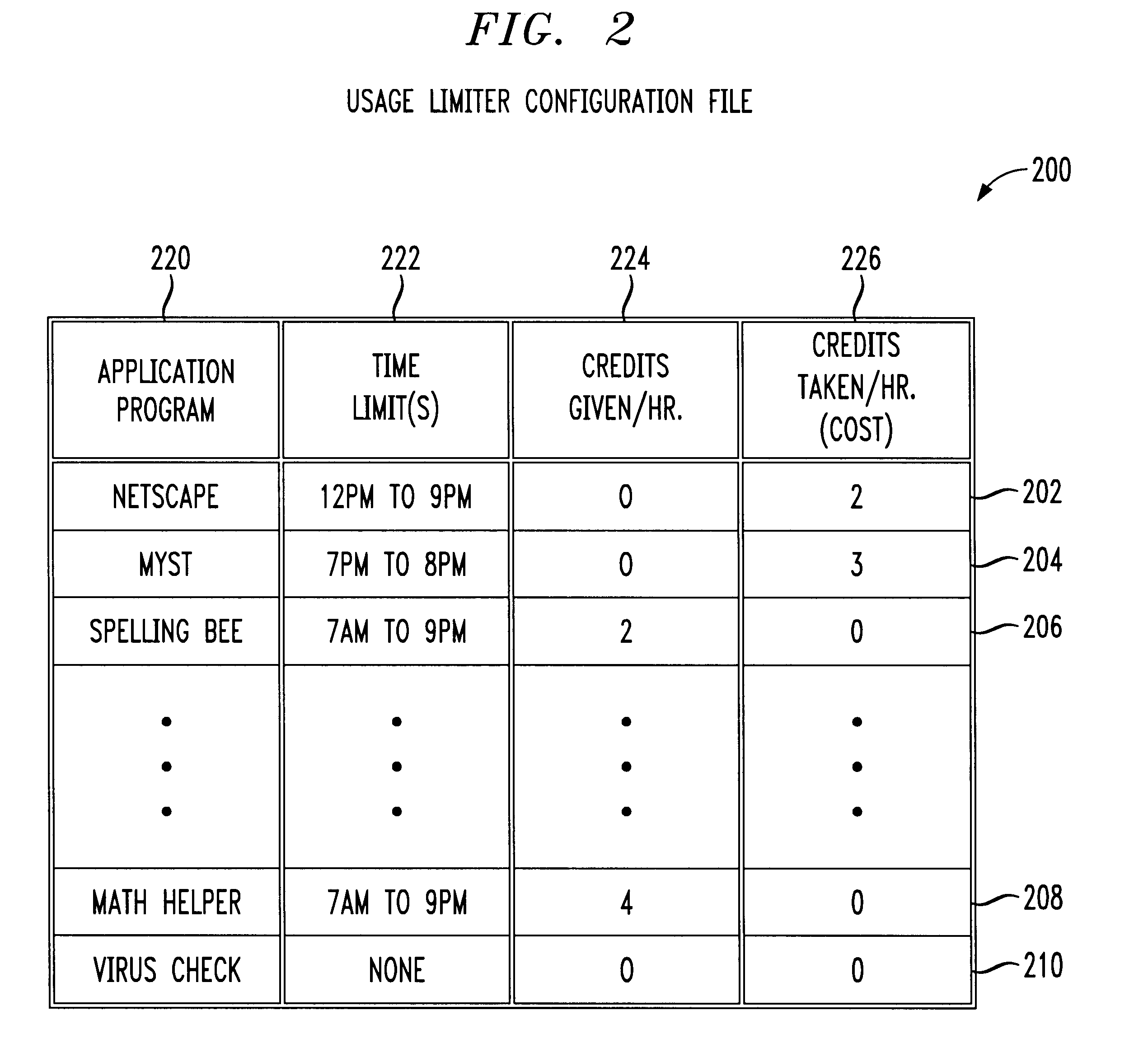
Application usage time limiter
An application usage time limiter monitors certain pre-configured application programs when opened or otherwise executed on a computer (e.g. a PC). The application usage time limiter is itself a program running either as a front end to various selected programs for monitoring, or as a separate program running in a time-sharing operating system environment. Pre-configurable options in a usage limiter configuration file or other memory area are set to limit real time ranges that particular application programs on a particular computer can be started and run, and a limit to a length of time that a specific program (or category of programs-an be operated given a number of available credits for a current user. The user is given credits at a pre-configured rate per hour of usage of an application program designated in the usage limiter configuration file as being beneficial, and the user gives back (or looses) credits at a pre-configured rate per hour of usage for use of programs designated as non-beneficial. Preferably, continued usage of beneficial programs is detected, e.g., by keystrokes. Application programs selected for monitoring in the usage limiter configuration file can be identified on an application by application basis, as a specific category of applications identifiable when the particular application is started, or as being stored in a specific directory (e.g., folder in a Windows(TM) operating system). A credit-giving (i.e., beneficial program) must be run by a particular user to earn credits before a credit-taking (i.e., non-beneficial program) can be run by that user. Up front credits may be provided to a particular user in a user log.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
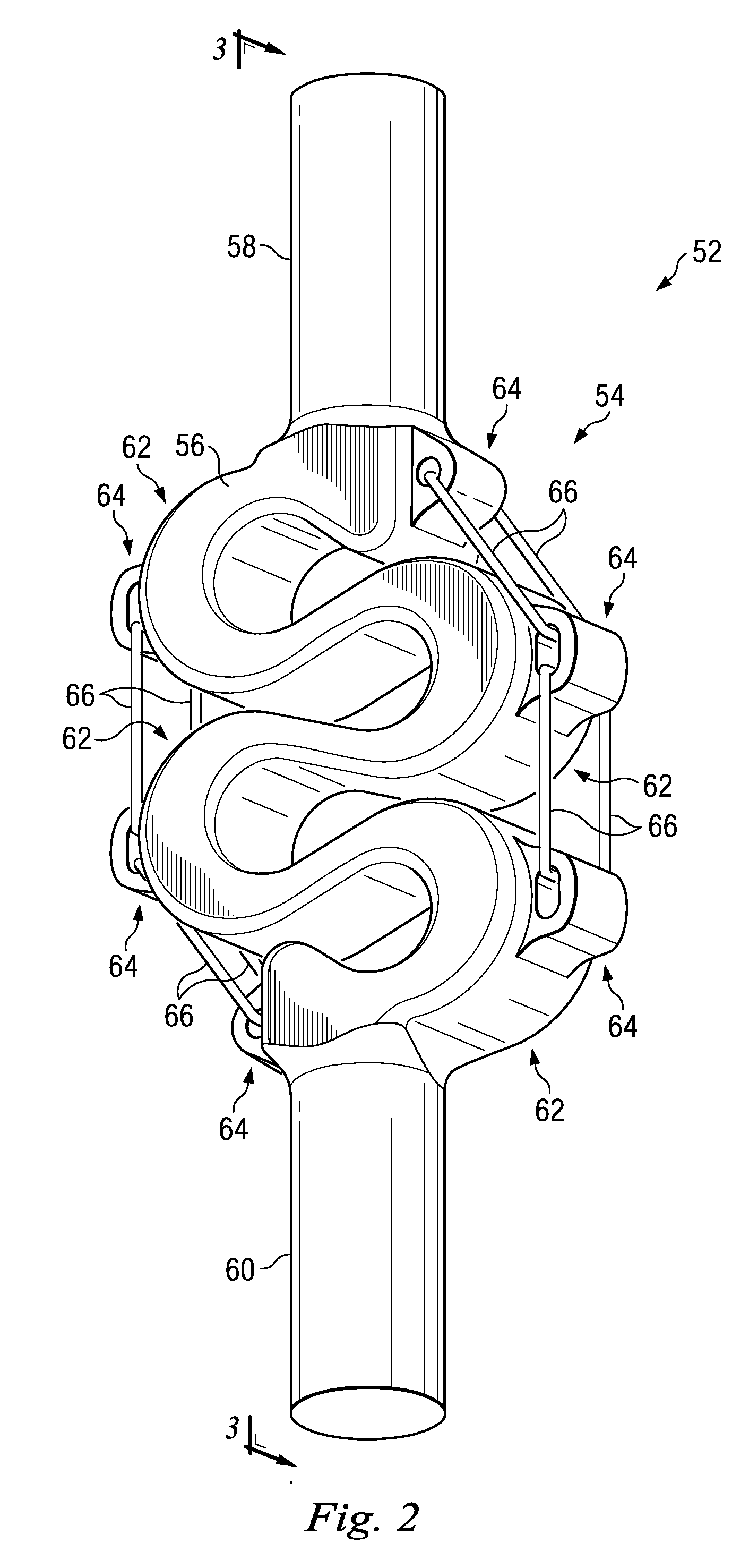
Spinal implant including a compressible connector
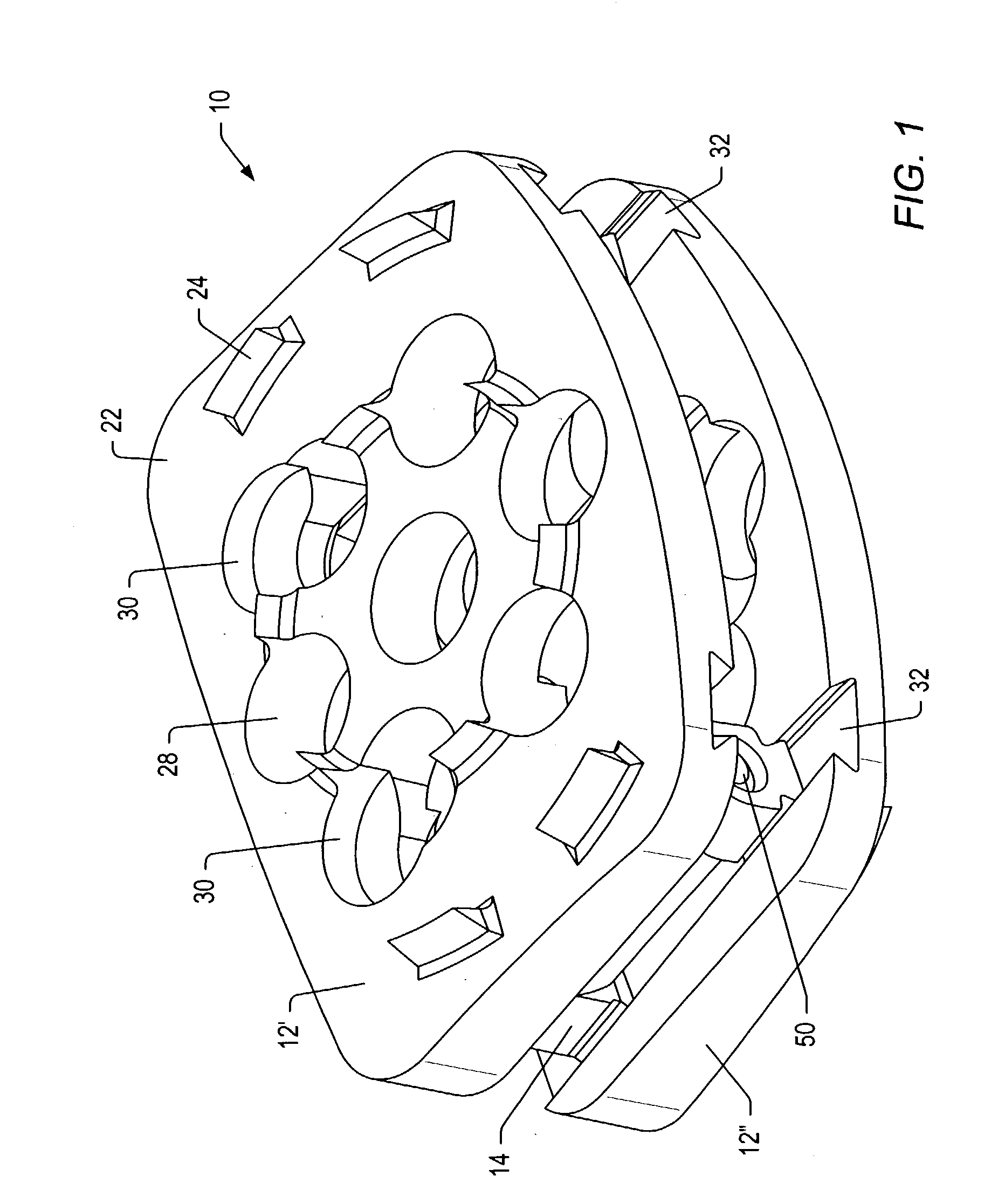
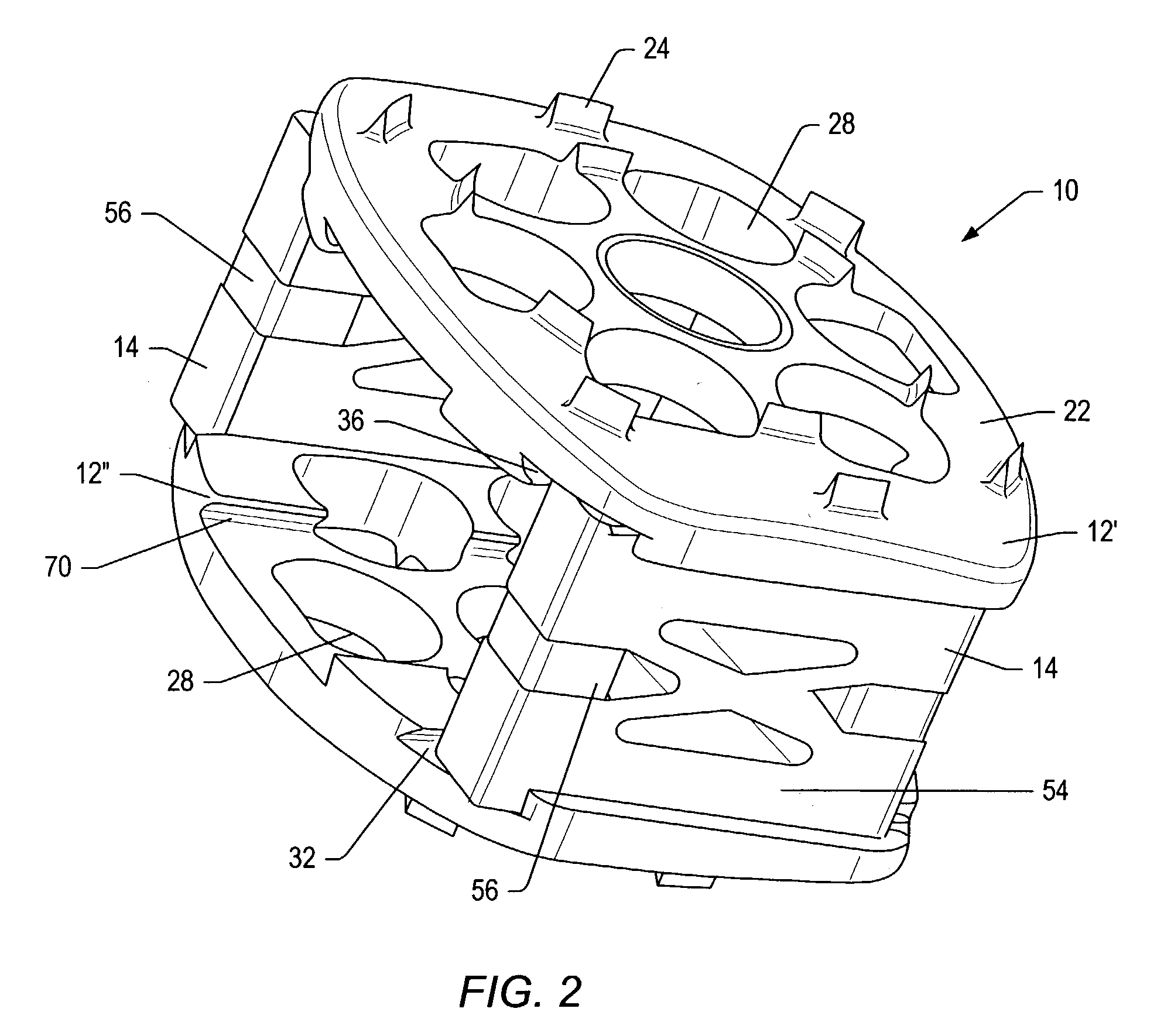
An implant may be formed in a disc space during a spinal fusion procedure. The implant may include implant members and connectors. The connectors may include sections with removed material that allow for some flexibility of the connectors. The connectors may include limiters that limit the amount of flexibility of the connectors. The ability of the connectors to flex may allow stress to be applied to bone growth material positioned in the implant. Stress may promote desirable bone growth.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Artificial total lumbar disc for unilateral safe and simple posterior placement in the lumbar spine, and removable bifunctional screw which drives vertical sliding expansile plate expansion, and interplate widening, and angled traction spikes
A total artificial expansile disc and a method for posterior insertion between a pair of vertebral endplates are disclosed. The total artificial expansile disc includes at least one pair of substantially parallel plates that move apart along a first axis, in order to occupy a space defined by the vertebral endplates. In another embodiment, each of substantially parallel plates includes a first plate and a second sliding plate. An expansion device or tool is used to move the substantially parallel pair of plates apart along the first axis. A core is disposed between the pair of plates, and the core permits the vertebral endplates to move relative to one another. A ball limiter or ball extender prevents the core from being extruded from between the substantially parallel plates.
Owner:MOSKOWITZ FAMILY LLC
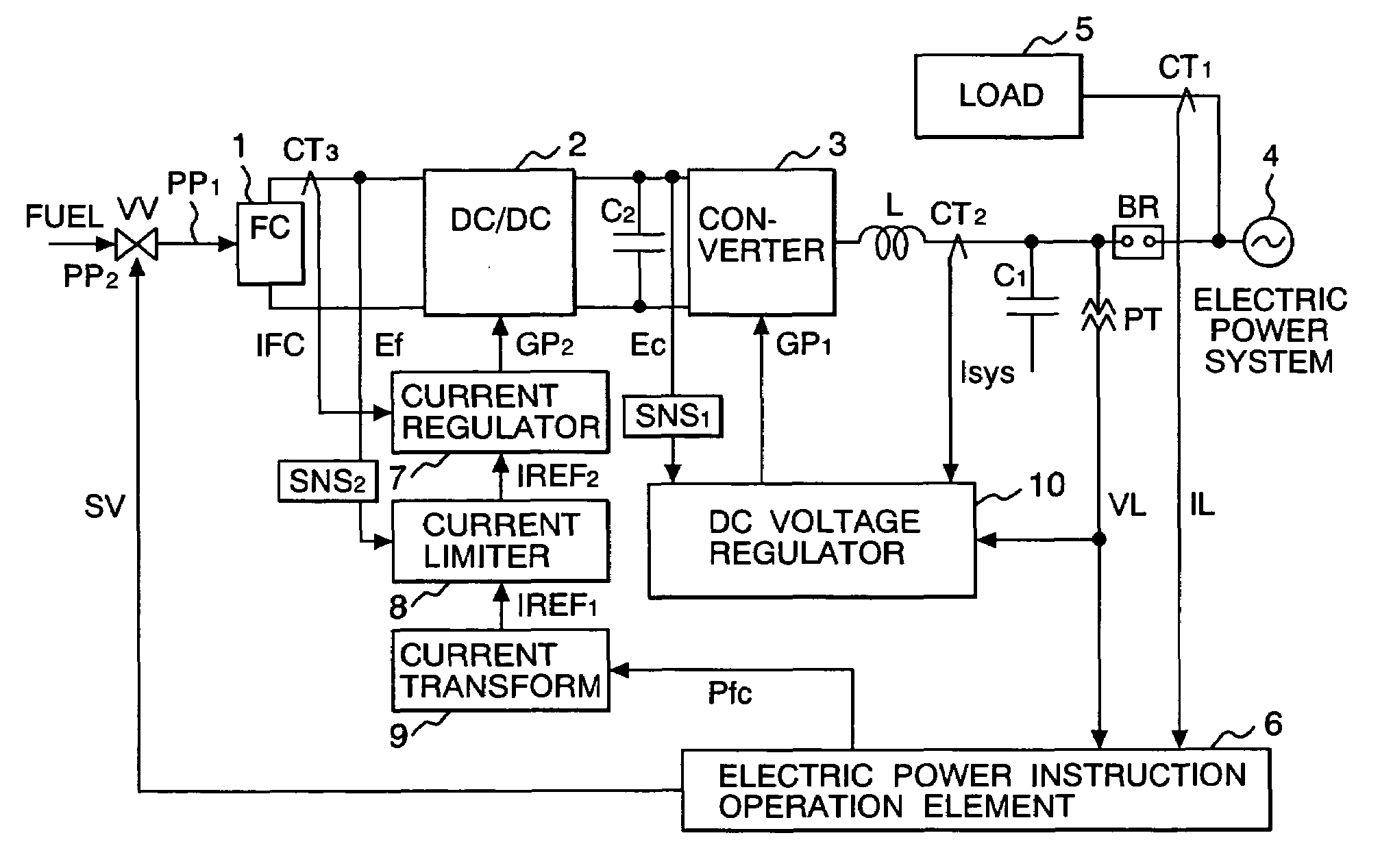
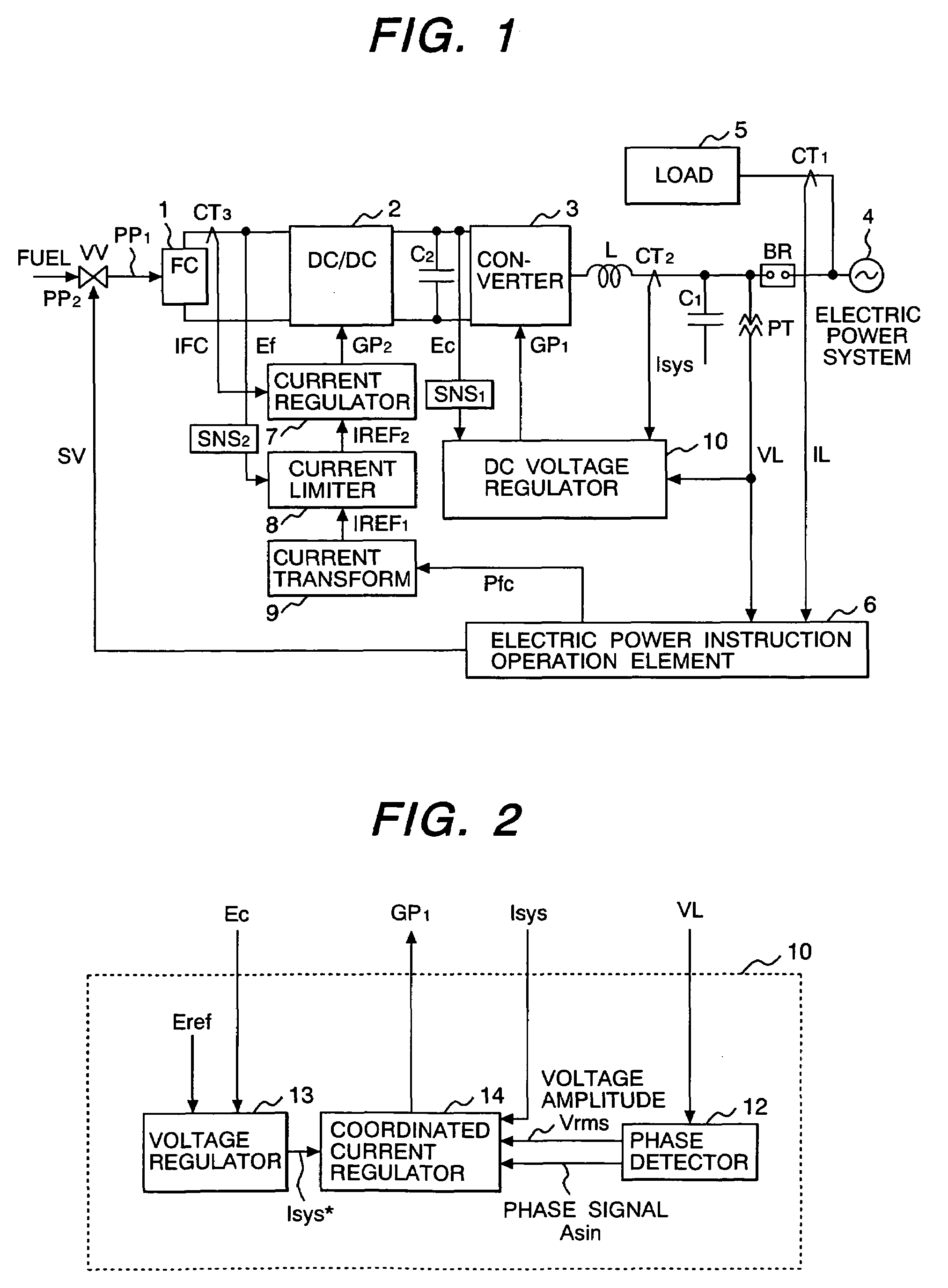
Fuel cell system and control method
ActiveUS7064967B2Dc network circuit arrangementsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFuel cellsVoltage drop
A battery voltage Ef of a fuel cell 1 is detected, and a current instruction value which transformed an electric power instruction value Pfc of the fuel cell is reduced at falling-down of the voltage Ef. A current limiter 8 makes the current instruction value a limit value at the time of the falling-down of Ef, and reduces the limit value according to the fall of Ef. For example, current instruction value is restricted so as to begin to reduce battery current IFC at voltage drop alarm level (first threshold value), and become zero at voltage drop protection level (second threshold value).
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
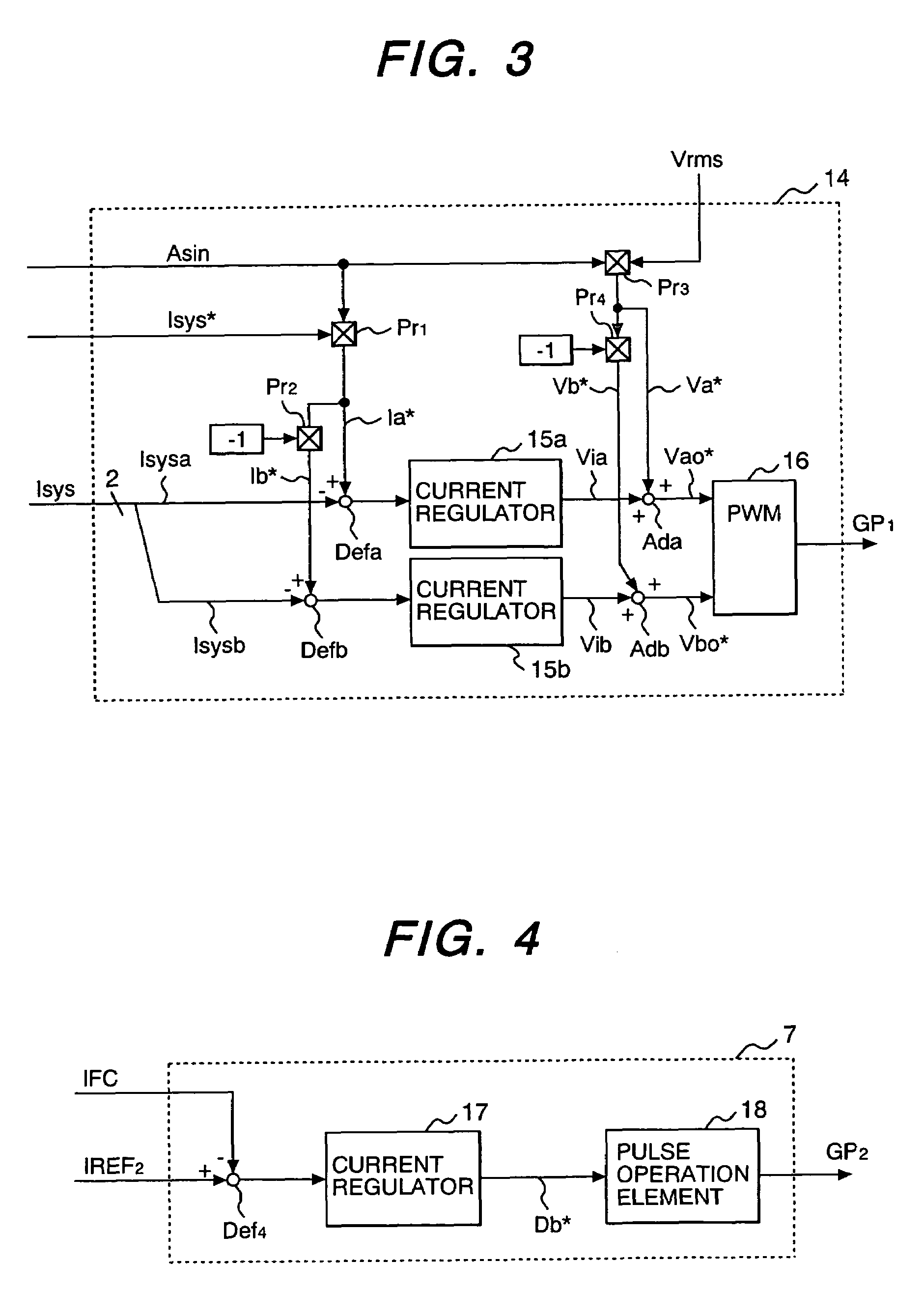
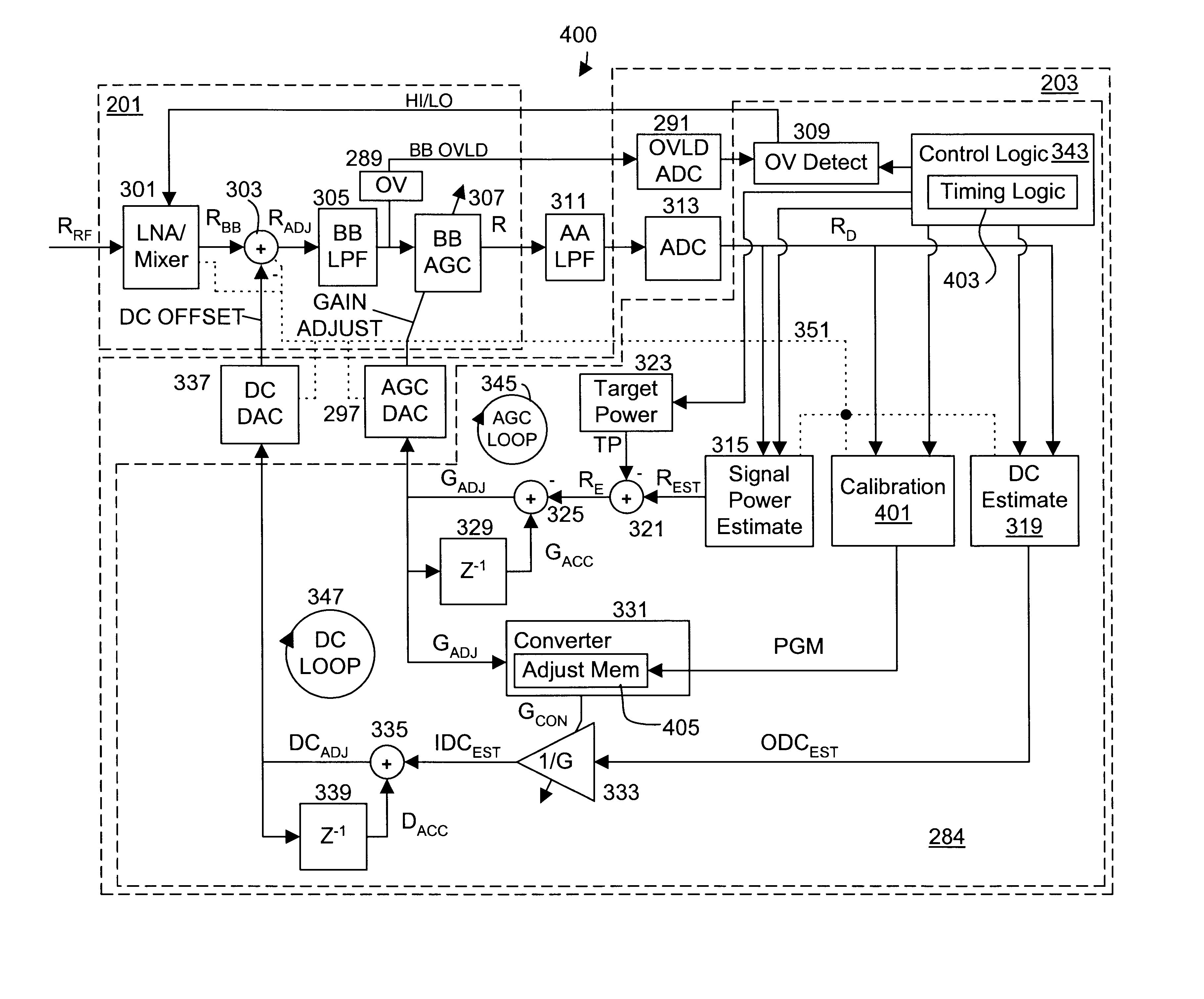
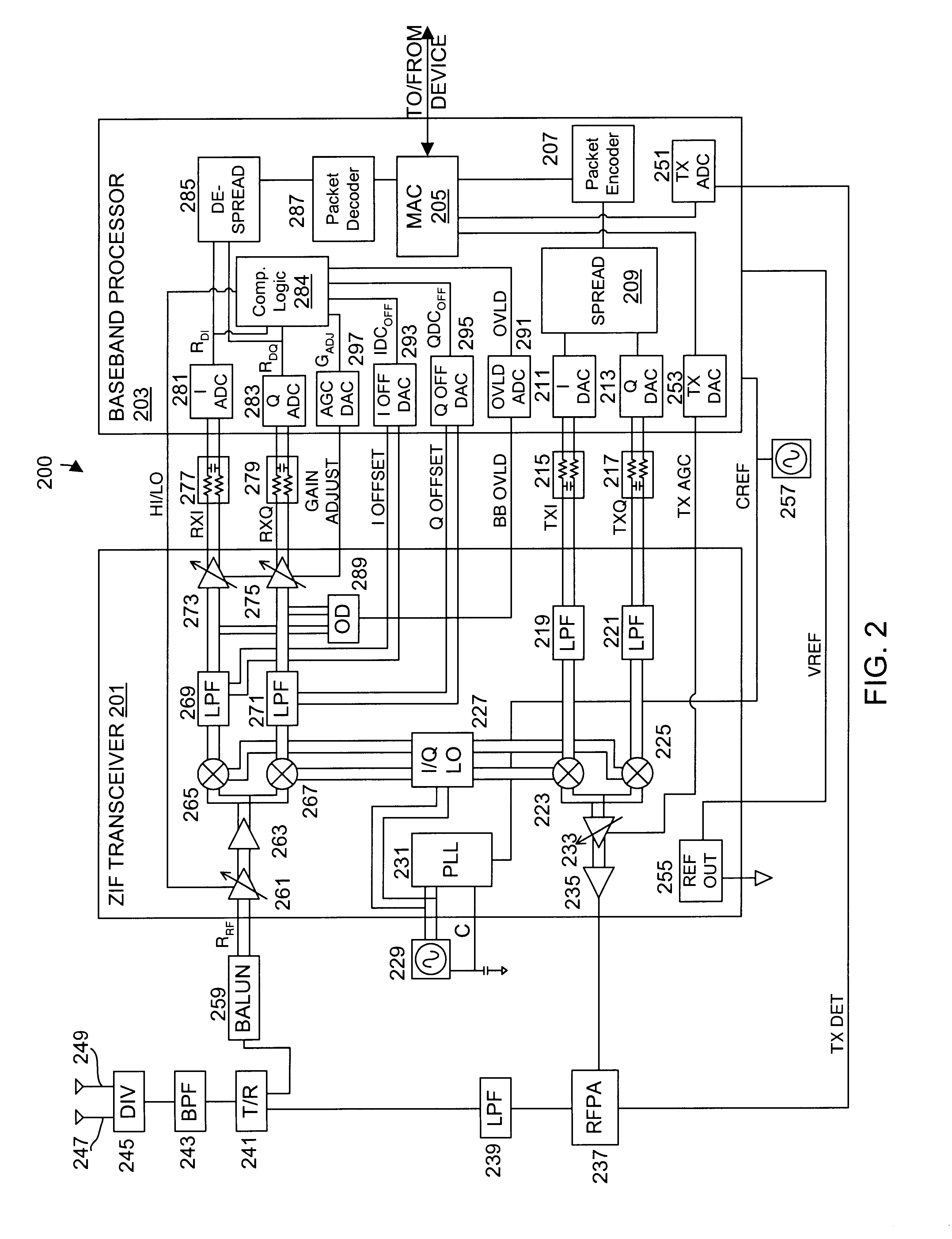
Calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
InactiveUS6735422B1Low costMaximum performancePulse automatic controlGain controlTransceiverAudio power amplifier
A calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency (ZIF) architecture. The device includes a ZIF transceiver and a baseband processor, which further includes a calibrator that periodically performs a calibration procedure. The baseband processor includes gain control logic, DC control logic, a gain converter and the calibrator. The gain converter converts gain between the gain control logic and the DC control logic. The calibrator programs the gain converter with values determined during the calibration procedure. The gain converter may be a lookup table that stores gain conversion values based on measured gain of a baseband gain amplifier of the ZIF transceiver. The gain control logic may further include a gain adjust limiter that limits change of a gain adjust signal during operation based on a maximum limit or on one or more gain change limits. A second lookup table stores a plurality of DC adjust values, which are added during operation to further reduce DC offset. The calibration procedure includes sampling an output signal for each gain step of the baseband amplifier at two predetermined range values and corresponding DC offsets using successive approximation. The data is used to calculate gain, DC offset and DC differential values, which are used to determine the conversion values programmed into the lookup tables or the gain adjust limiter.
Owner:M RED INC
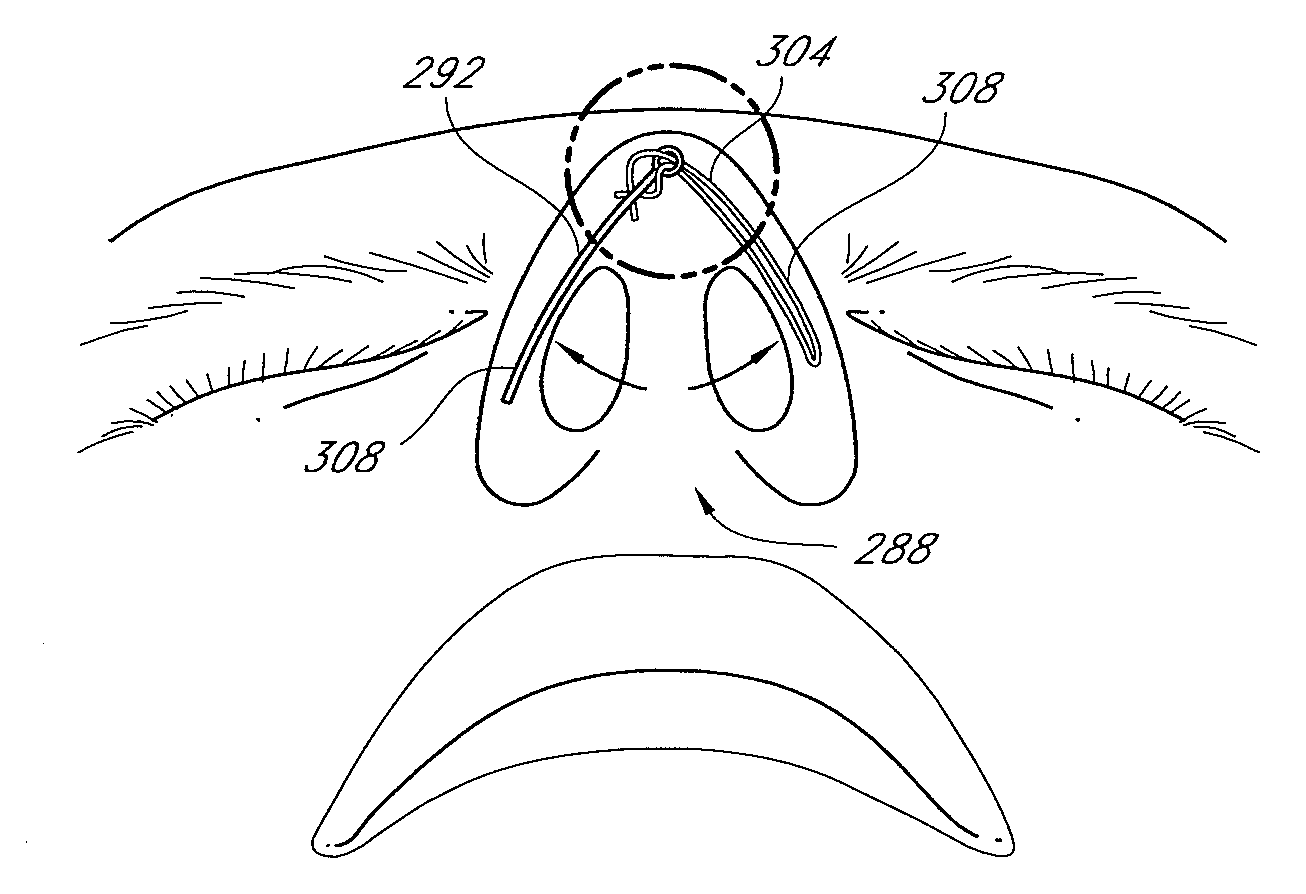
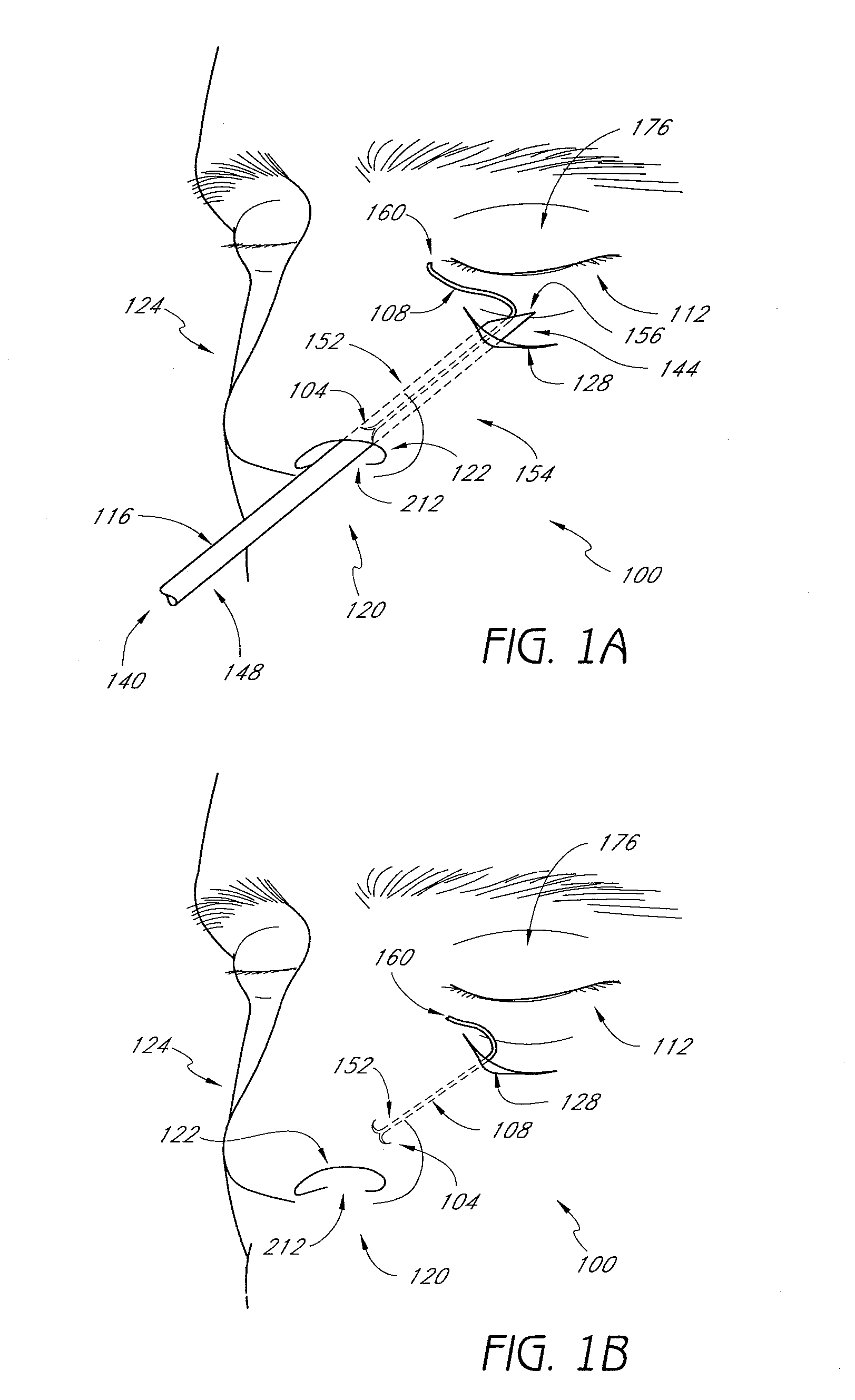
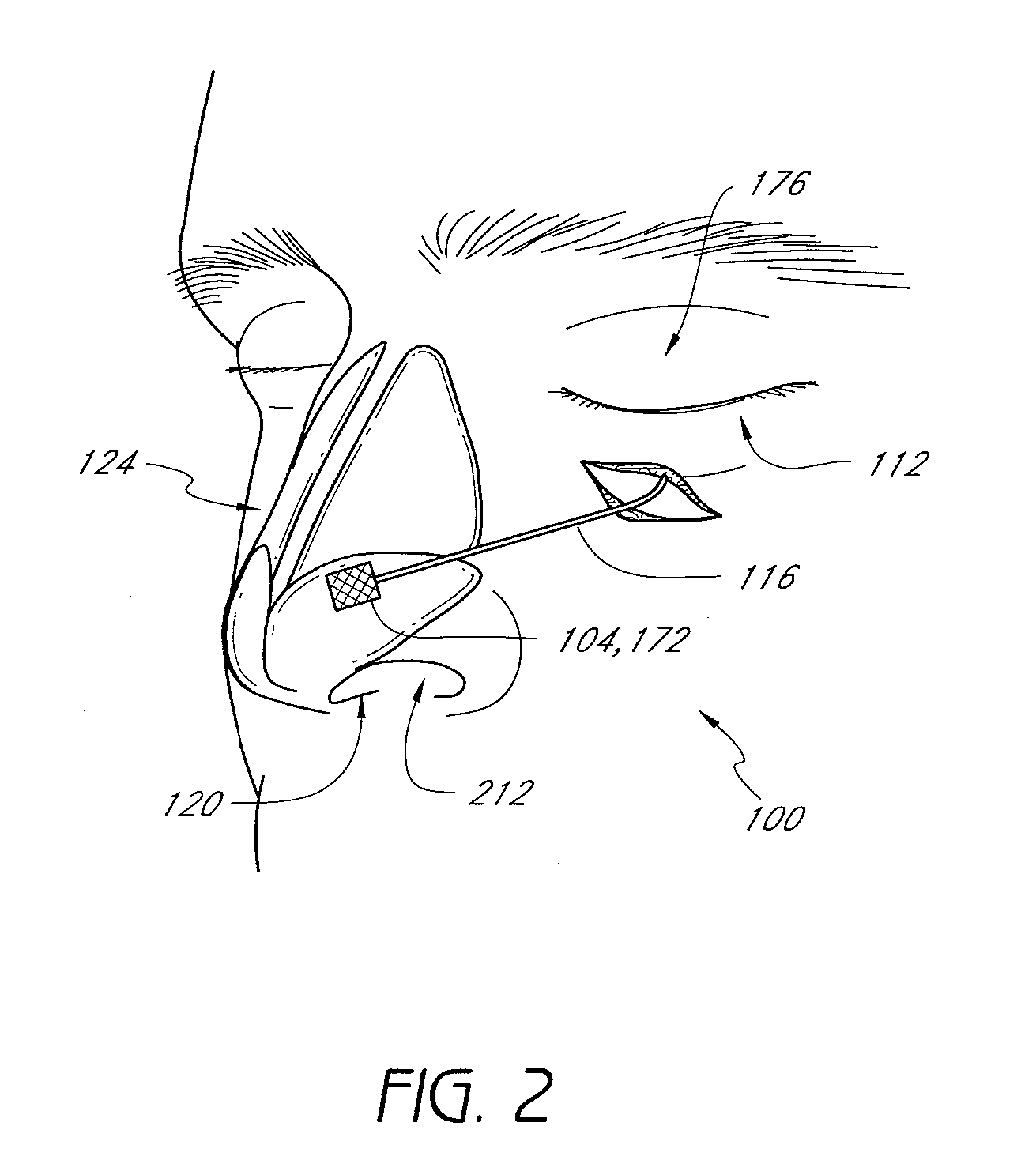
Methods and devices for rhinoplasty and treating internal valve stenosis
ActiveUS20080027480A1Increase the cross-sectional areaIncrease exposureSuture equipmentsNose implantsNasal cavityMitral valve stenosis
Methods and devices for rhinoplasty and treating nasal valve stenosis are disclosed herein. The nasal valve acts as a flow-limiter and can contribute to airway obstruction if resistance within the nasal valve is excessive. In one embodiment, a system for treating nasal valve stenosis includes a first elongate implant and a second elongate implant configured to support the nasal valves when implanted. The implants can be coupled together by connecting elements, such as eyelets, tethers, complementary socket joints, and button-rivet supports.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
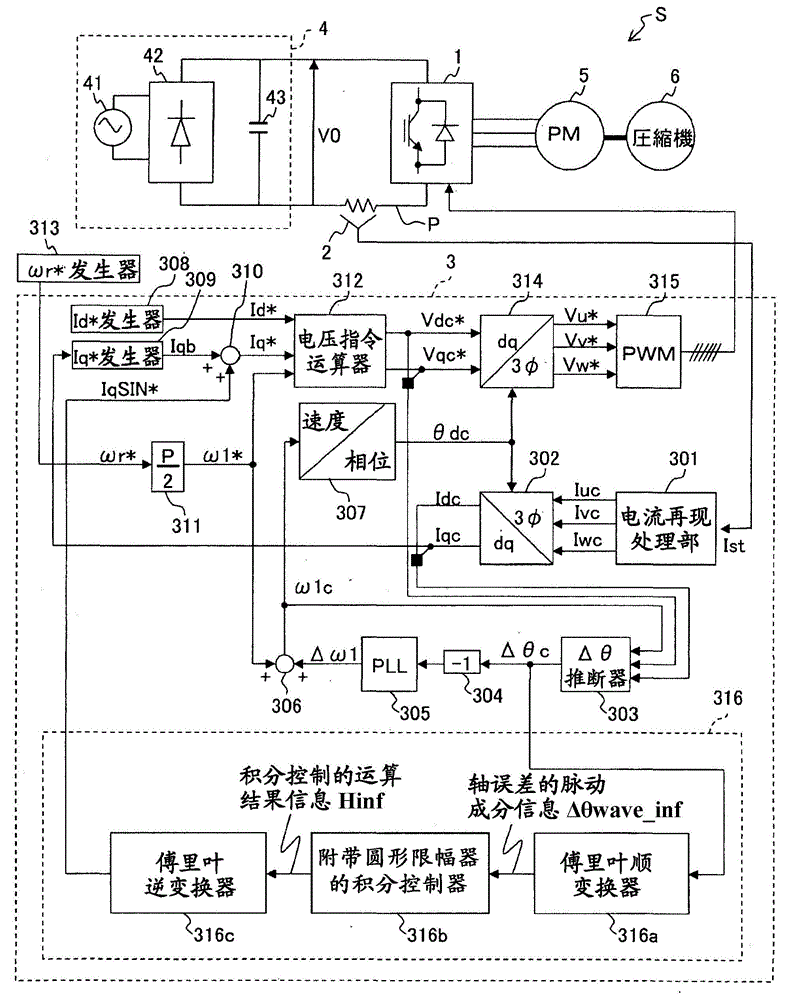
Motor control device
ActiveCN104038127ASuppression of pulsating torqueVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlCurrent sensorIntegral controller
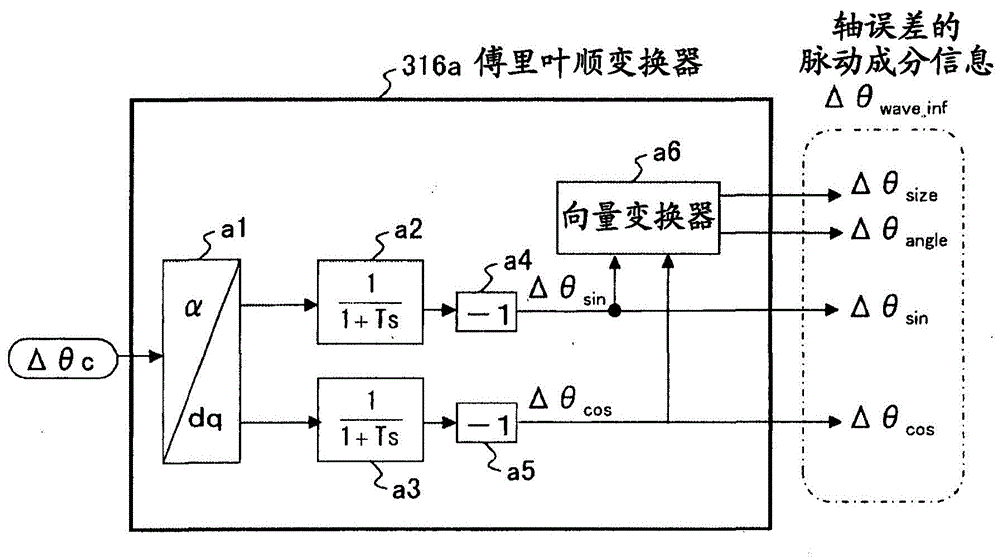
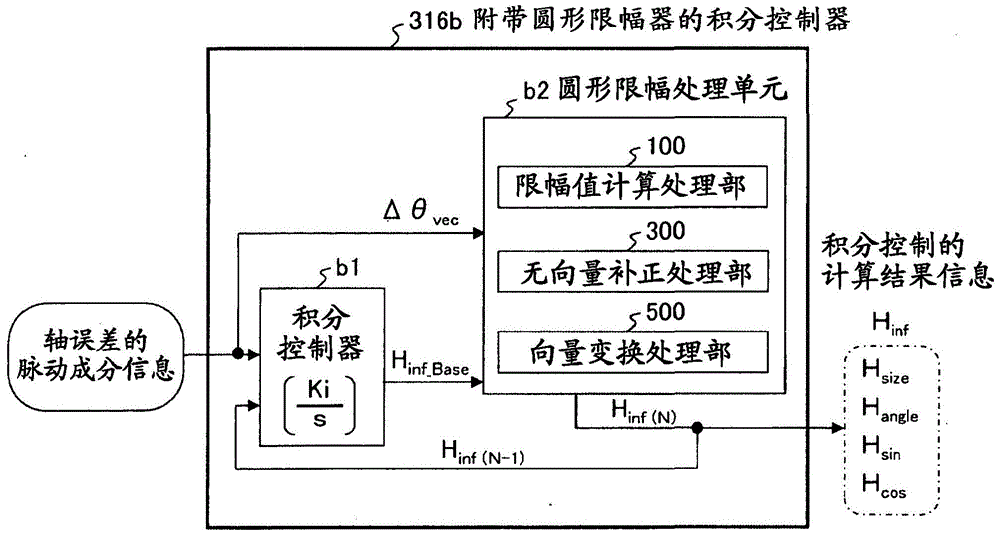
A motor control device capable of suitably inhibiting the pulsating torque of an alternating-current motor is provided. The motor control device comprises an axis error inference machine (30) which infers an axis error based on a current value of an inverter, detected by a current sensor (2); a Fourier rectification machine (316a) which extracts an axis error vector from the time-base changes of the axis error; an integral control machine (316b) additionally provided with a circular amplitude limiter, which is used to calculate a correction current vector for offsetting the pulsating torque, wherein a circle with a set amplitude limiting value serving as the radius is used as the base for limiting the movement of the correction current vector, and the integral control machine (316b) additionally provided with the circular amplitude limiter performs the circular amplitude limiting for limiting the movement of the correction current vector so as to enable the deflection angle of the correction current vector to be close to the deflection angle of the axis error vector.
Owner:HITACHI JOHNSON CONTROLS AIR CONDITIONING INC
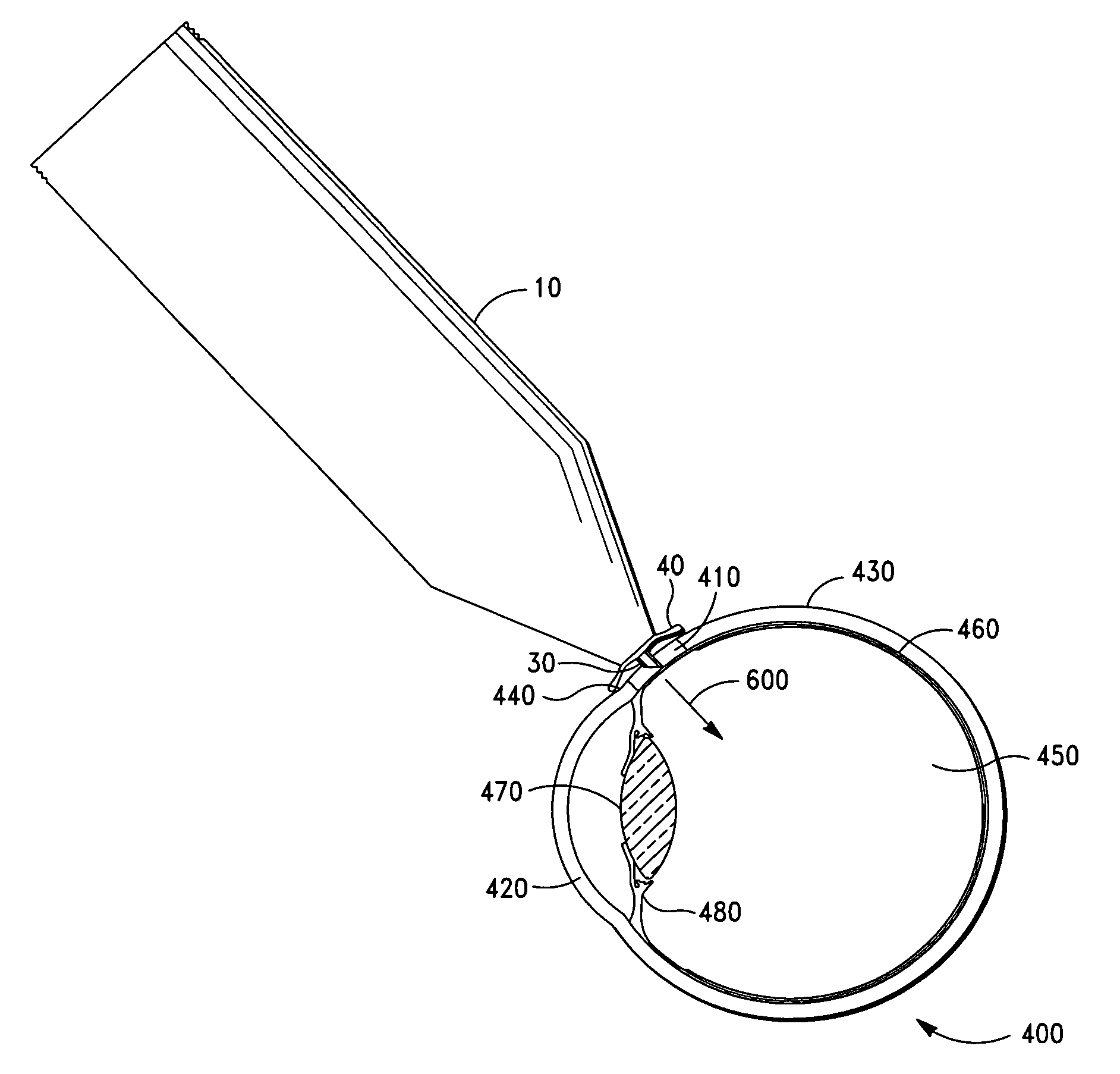
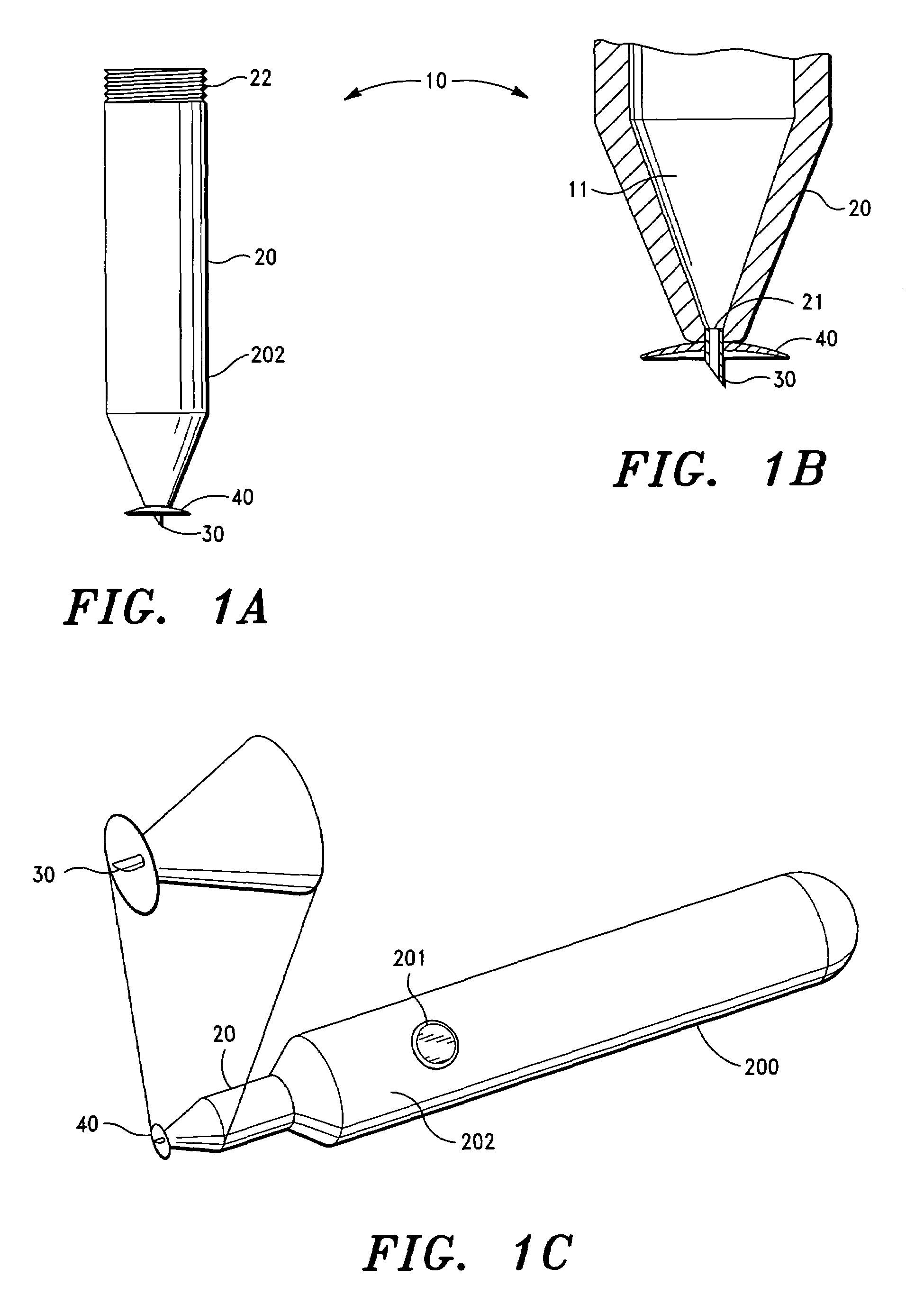
Intravitreal injection device, system and method
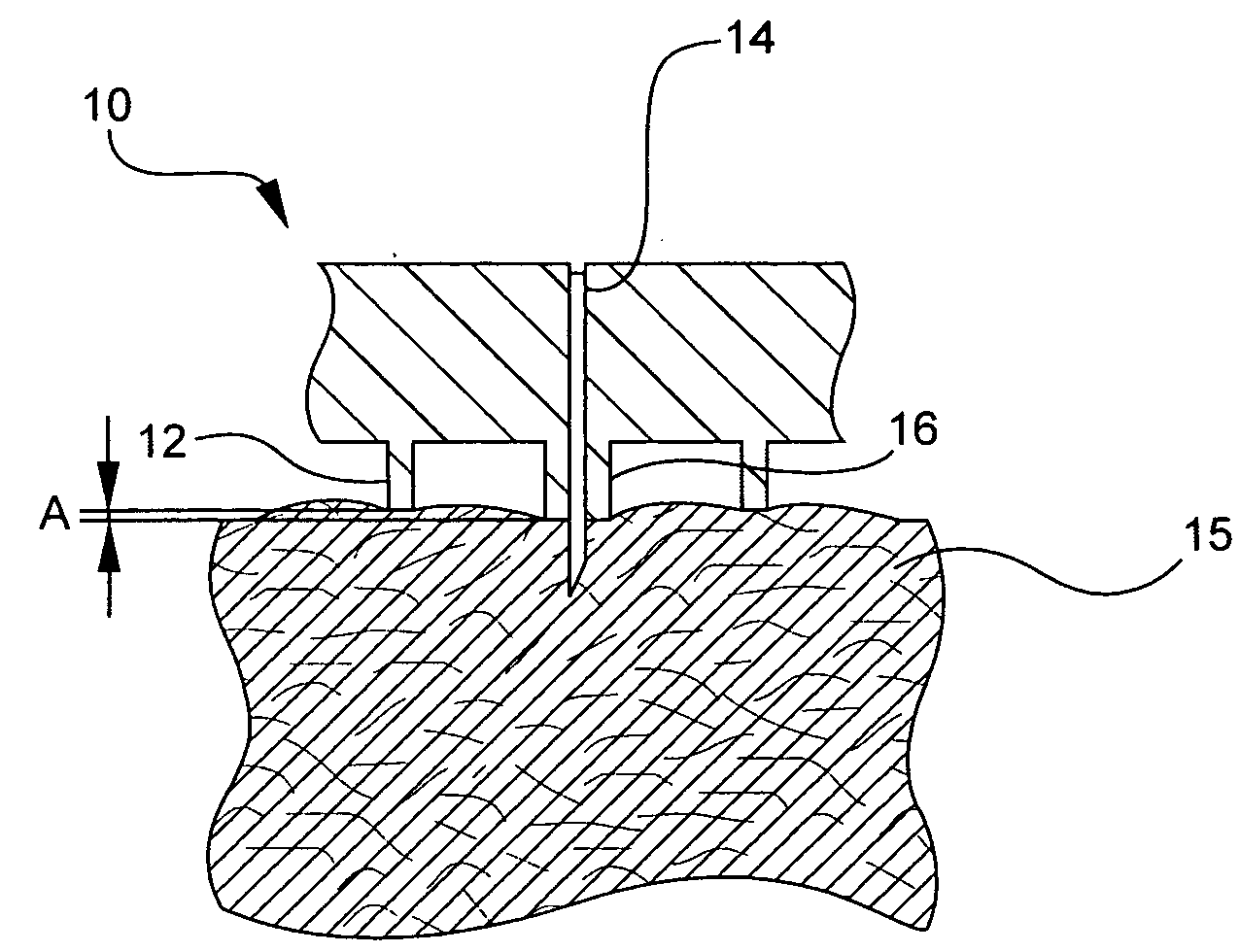
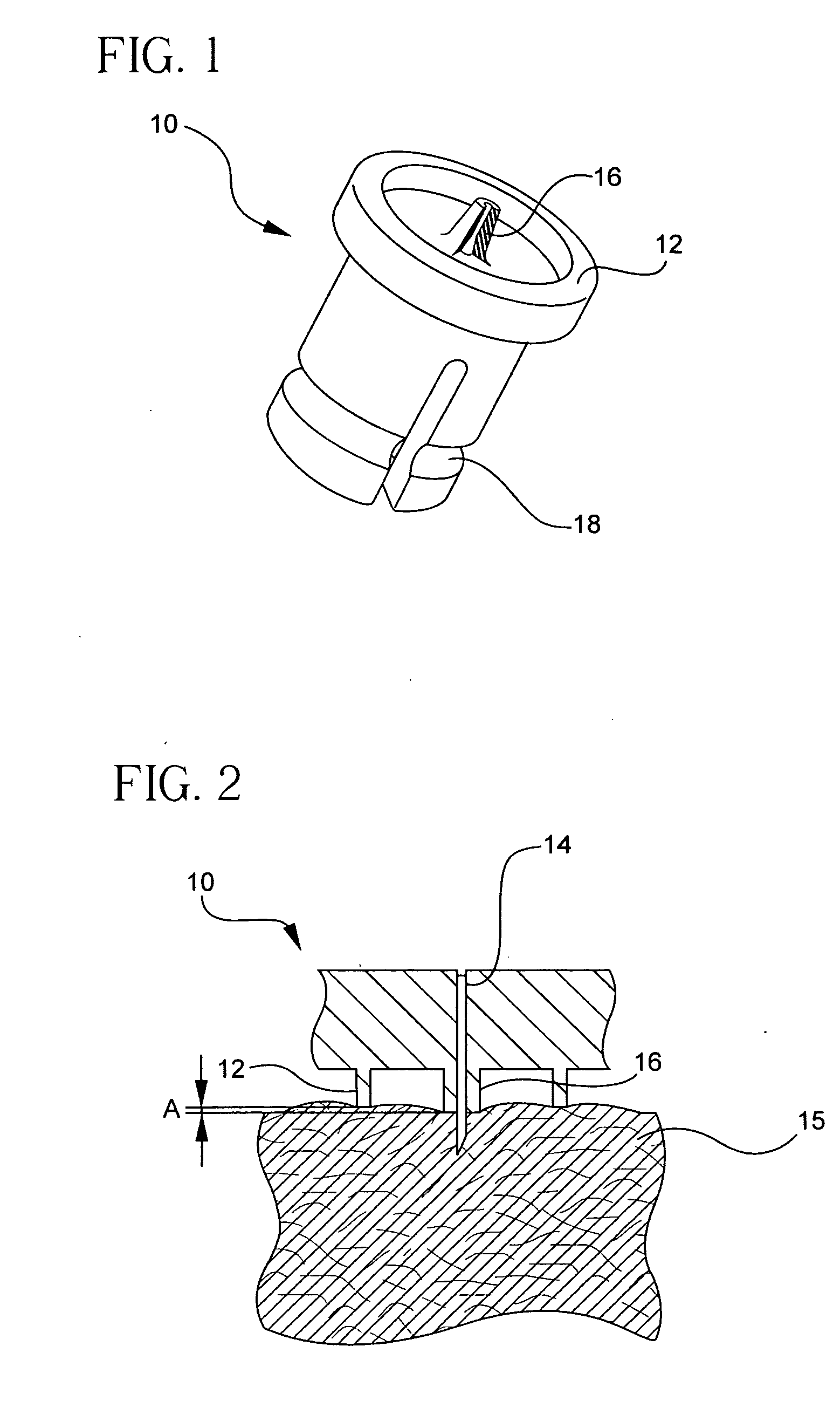
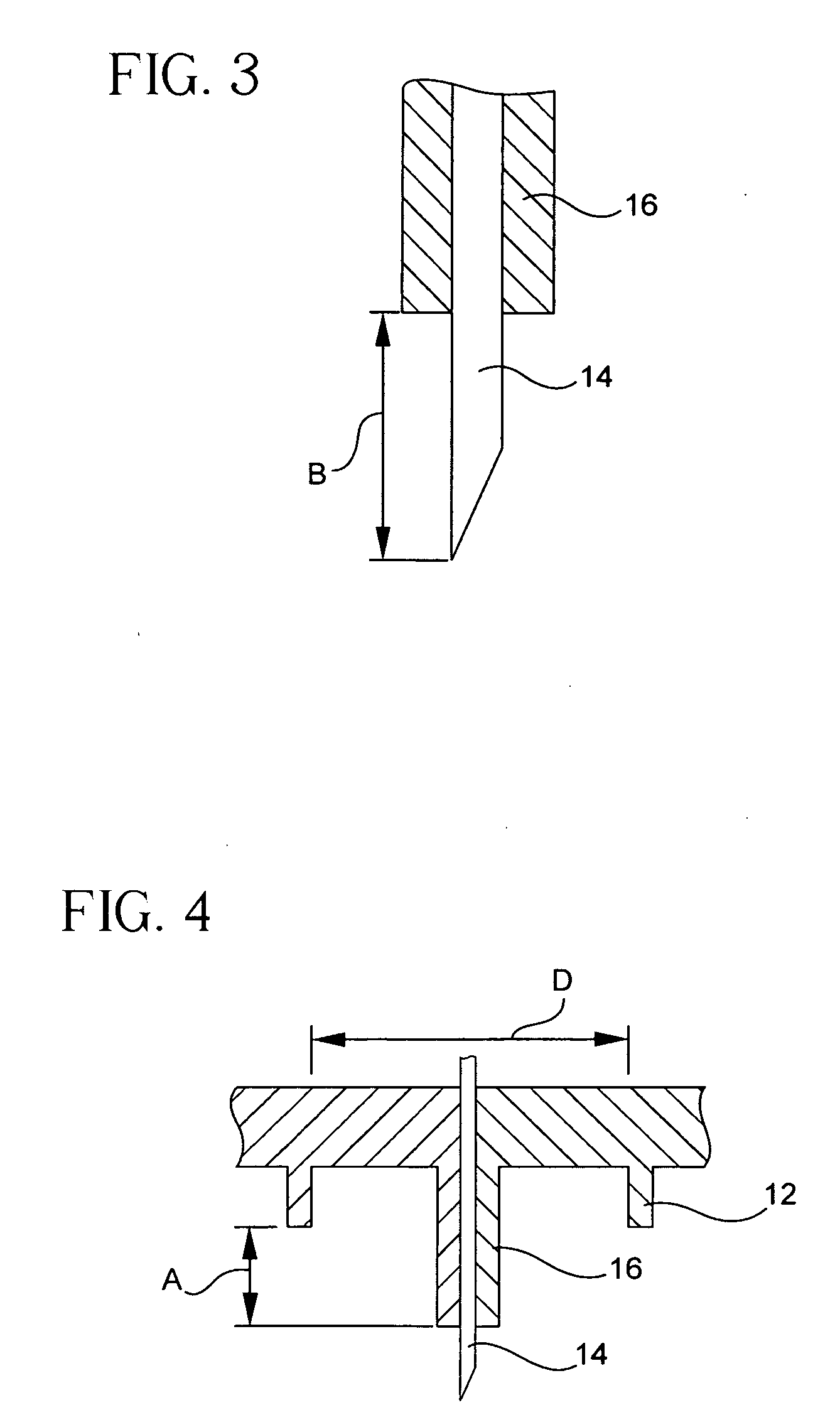
An intravitreal injection device for administering a pharmacological agent formulation to an intravitreal compartment of an eye, comprising (i) a nozzle member having an internal formulation chamber that is adapted to receive and contain the pharmacological agent formulation therein, (ii) a microneedle having a first end that is in communication with the nozzle member and a second ejection end, (iii) and piercing depth limiter means for limiting the penetration depth of the microneedle into the eye, the microneedle piercing depth limiter means including guide means for positioning the limiter means and guiding the microneedle.
Owner:KMG PHARMA
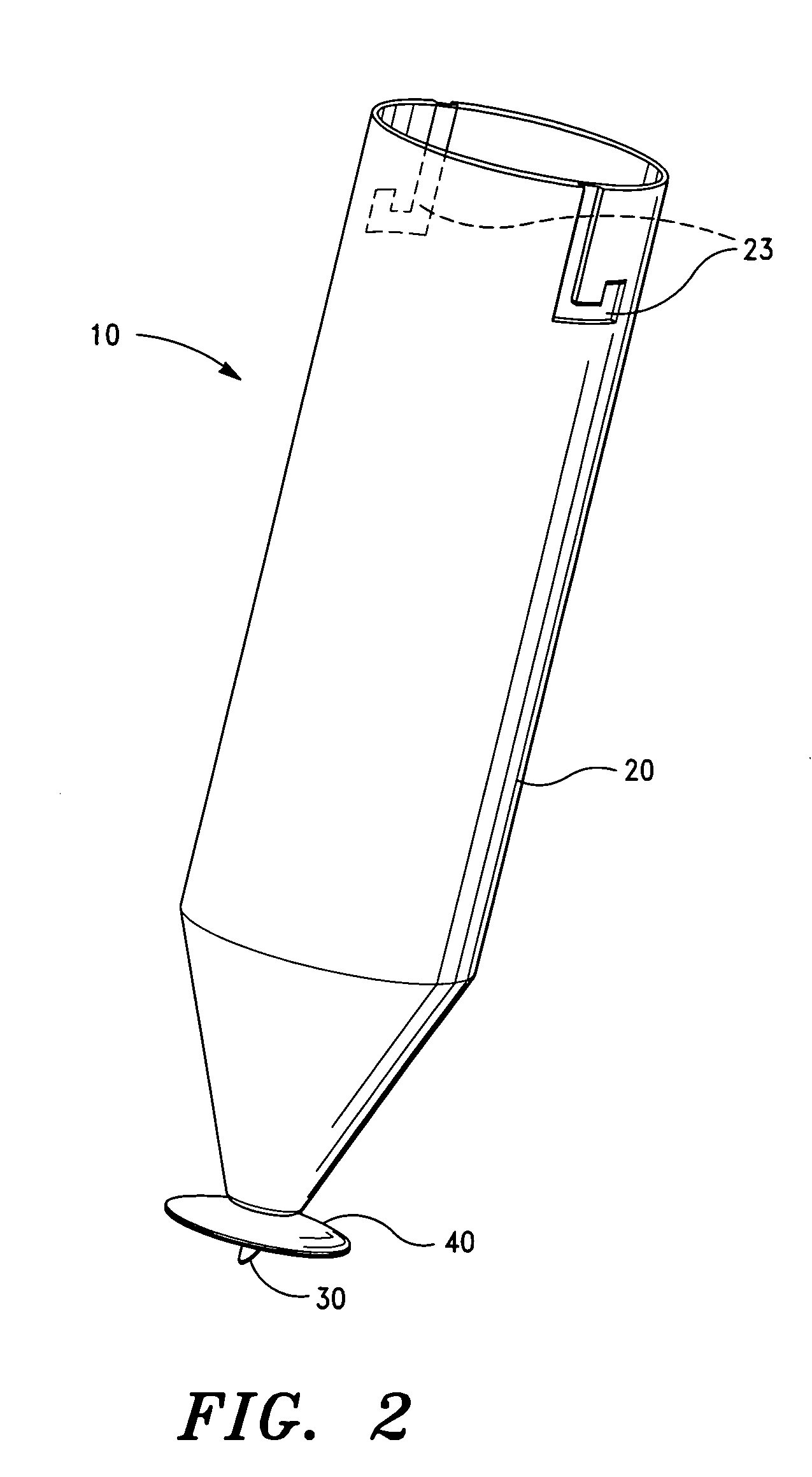
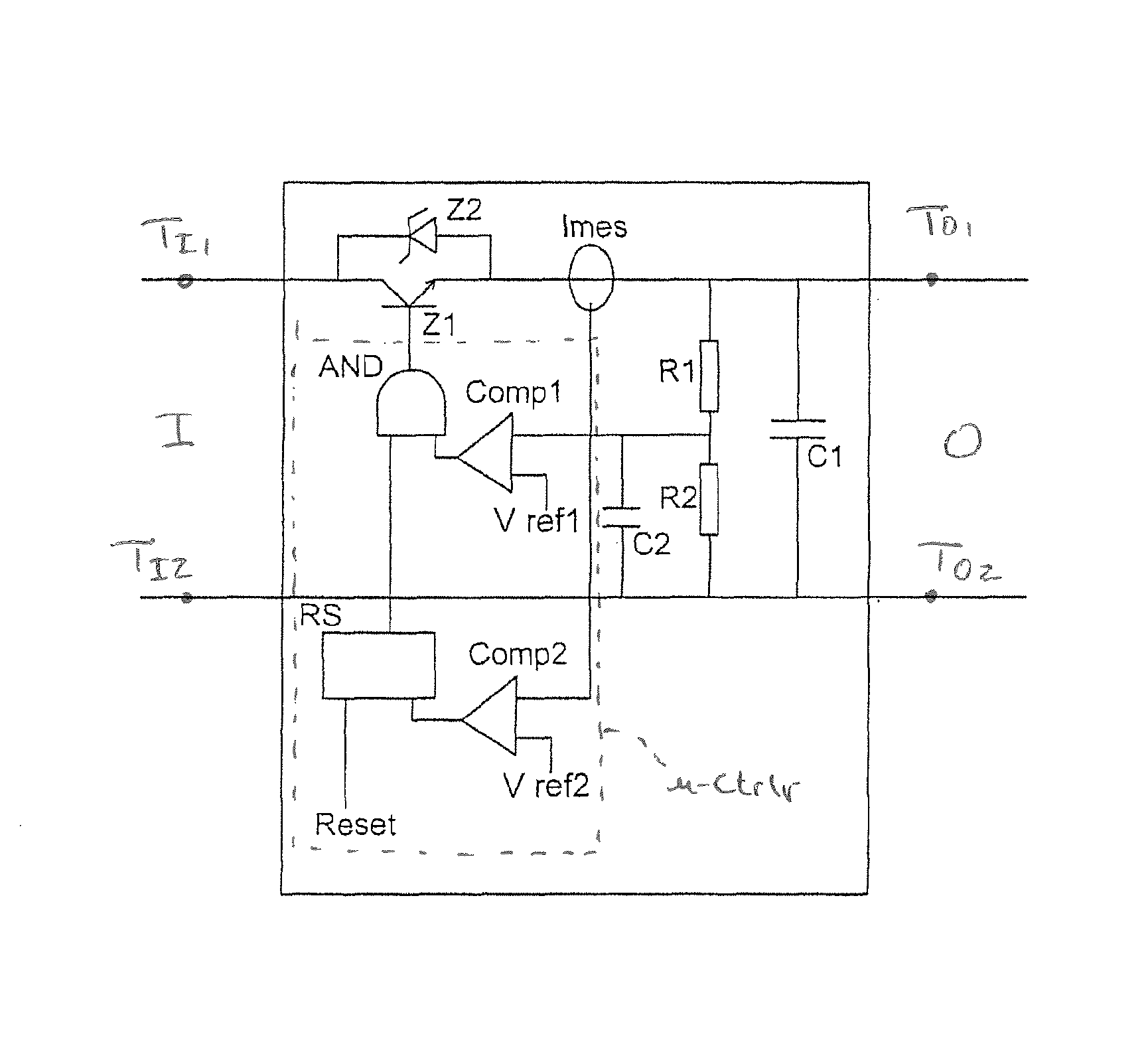
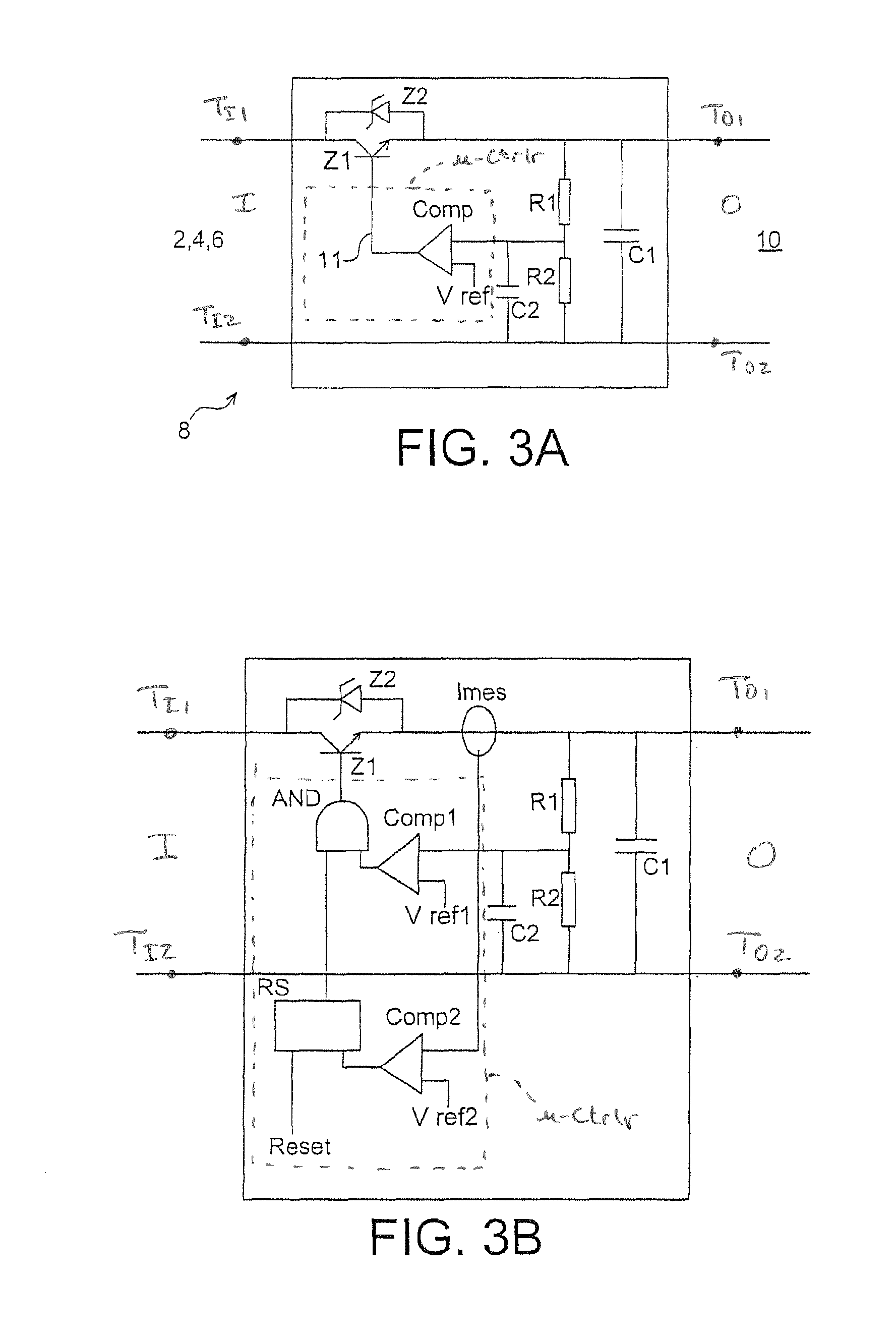
Voltage limiter and protection of a photovoltaic module
ActiveUS8570017B2Arrangements responsive to excess currentPhotovoltaic energy generationElectronic switchVoltage reference
A voltage limiter device of an assembly of photovoltaic modules, including: (a) means (Z1) forming an electronic switch for a current of said assembly; (b) comparison means (Comp, R1, R2, C2) for comparing a voltage at the output of the limiter with a reference voltage value (Vref); and (c) means for controlling the means forming an electronic switch, depending on the result of the comparison carried out by the comparison means.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
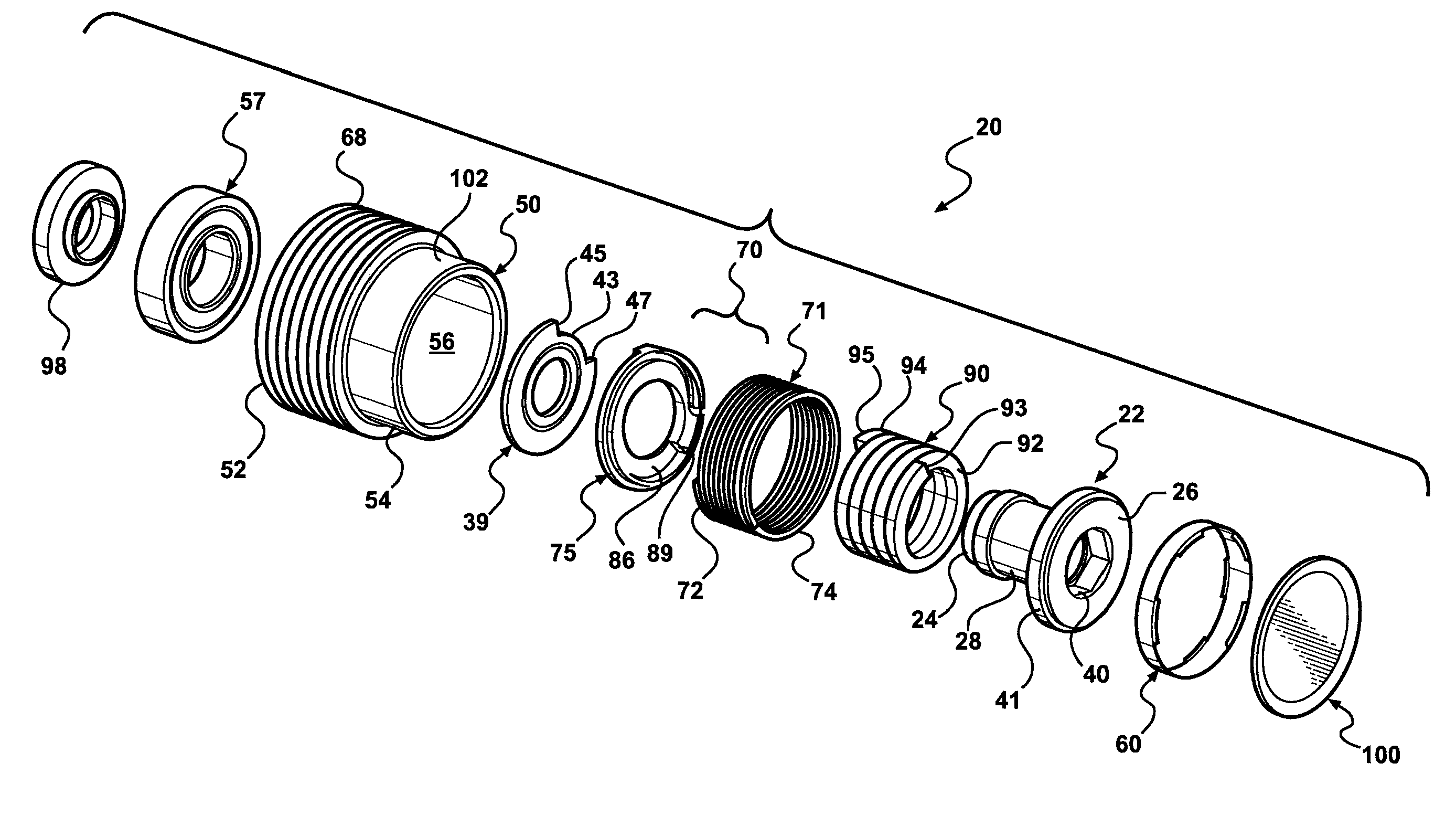
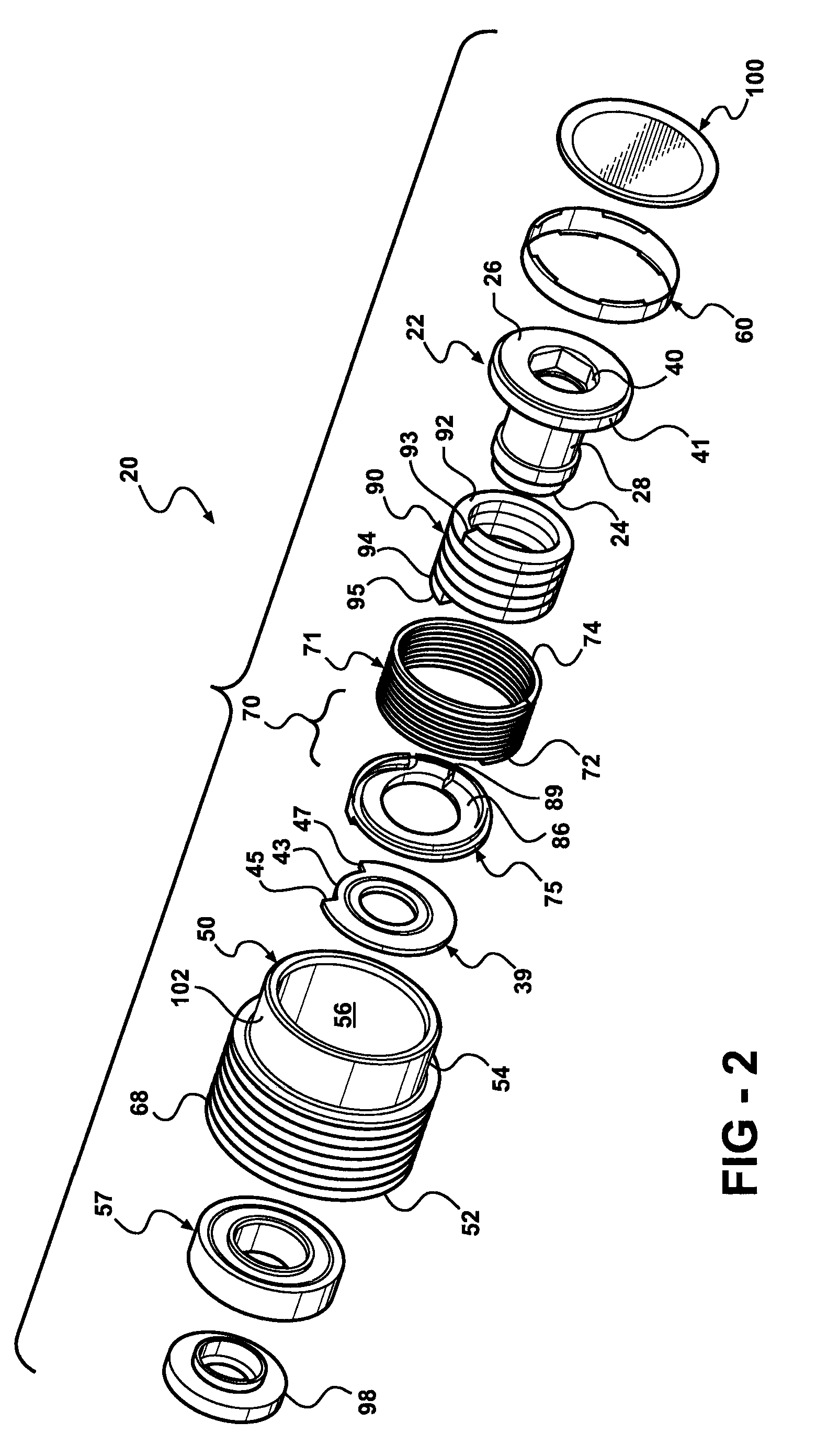
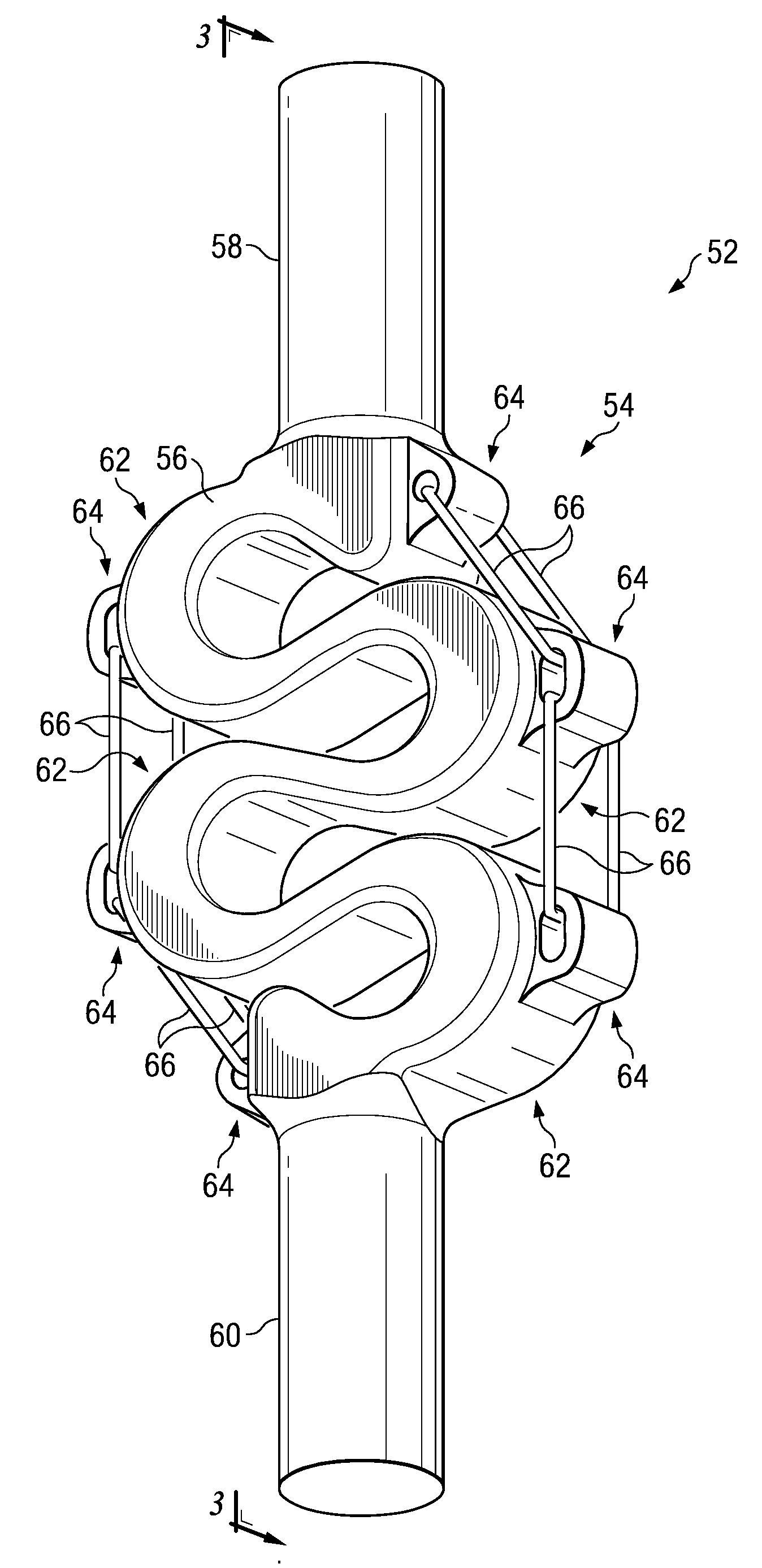
Spring travel limiter for overrunning alternator decoupler
ActiveUS7712592B2Prevent movementPrevent rotationYielding couplingSlip couplingSerpentine beltAlternator
A decoupler assembly for transferring rotary movement between an engine driven shaft and a serpentine belt. The decoupler includes a hub configured to be assembled to the shaft. The hub has a helical first slot formed therein. A pulley is rotatably coupled to the hub. A carrier is mounted on the hub and includes a helical second slot formed therein, as well as an anti-ramp up boss formed thereon. A thrust plate is fixed to the hub and has a slot formed therein. A torsion spring is compressed between a hub end retained in the helical first slot and a carrier end retained in the helical second slot for transferring torque between the hub and carrier. The anti-ramp up boss travels within the slot formed in the thrust plate for limiting rotation between the carrier and thrust plate and preventing rotation of the torsion spring relative to the hub and carrier.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
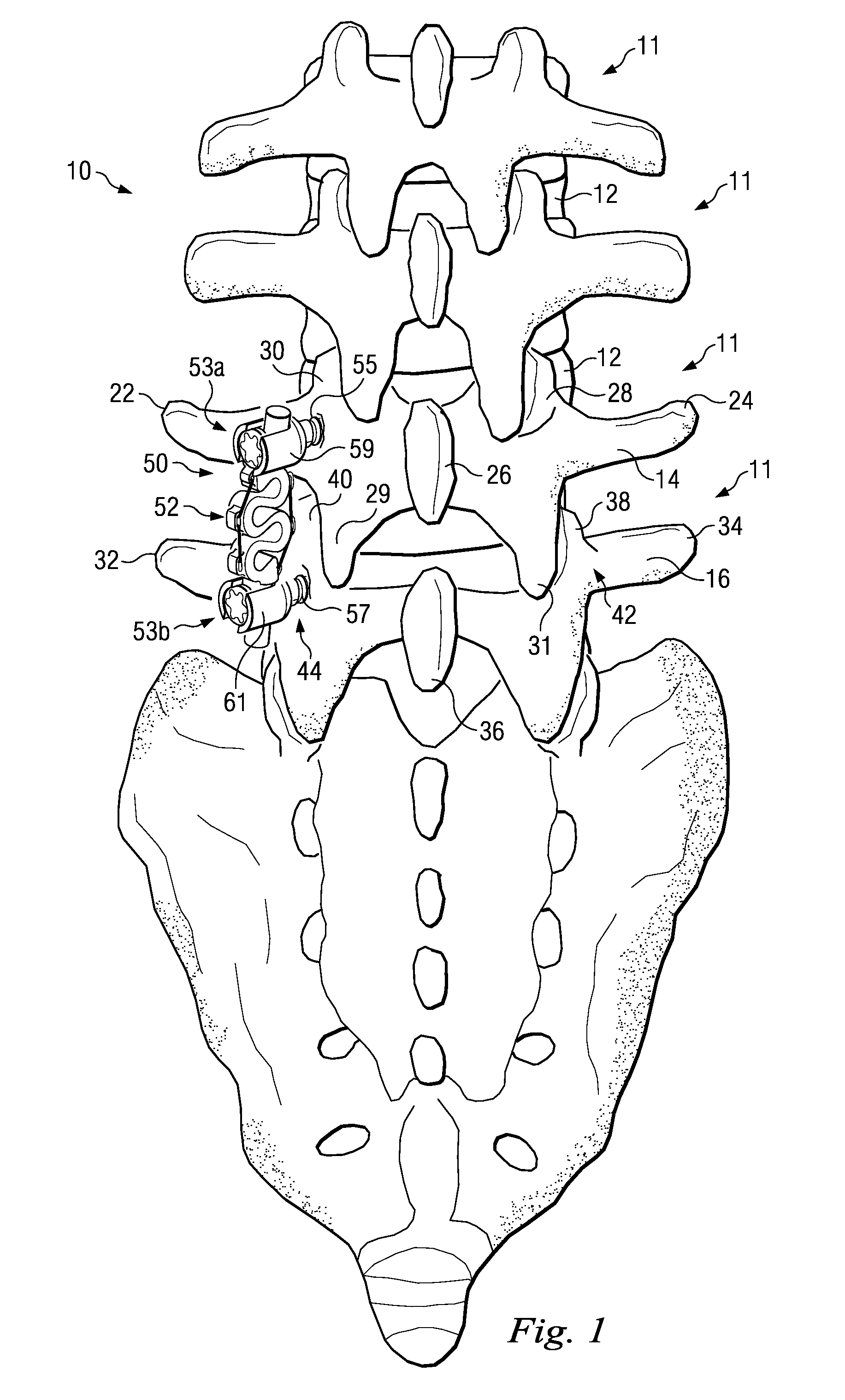
Vertebral Stabilizer
ActiveUS20080234736A1Improve the immunitySmooth motionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringStress shielding
A bio-compatible stabilization system includes one or more inserters and a connector for traversing a space between one or more bony structures. The stabilization system is designed to reduce or eliminate stress shielding effects while functioning as a tension band. The connector includes an extendable member and an over-extension limiter that limits extension of the extendable member.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHODEPIC
Card delivery shoe and methods of fabricating the card delivery shoe
A playing card delivery shoe for a casino table card game and method of fabricating such shoe. The shoe has an adjustable limiter and removable protective cover. The position of the card feed limiter sets a gap size of an opening though which cards pass. The card feed limiter may have openings therein through which a card reading sensor can be accessed. The card reading sensor can be accessed without substantial disassembly of the shoe. The removable protective cover provides a protective shield for the card reading sensor.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
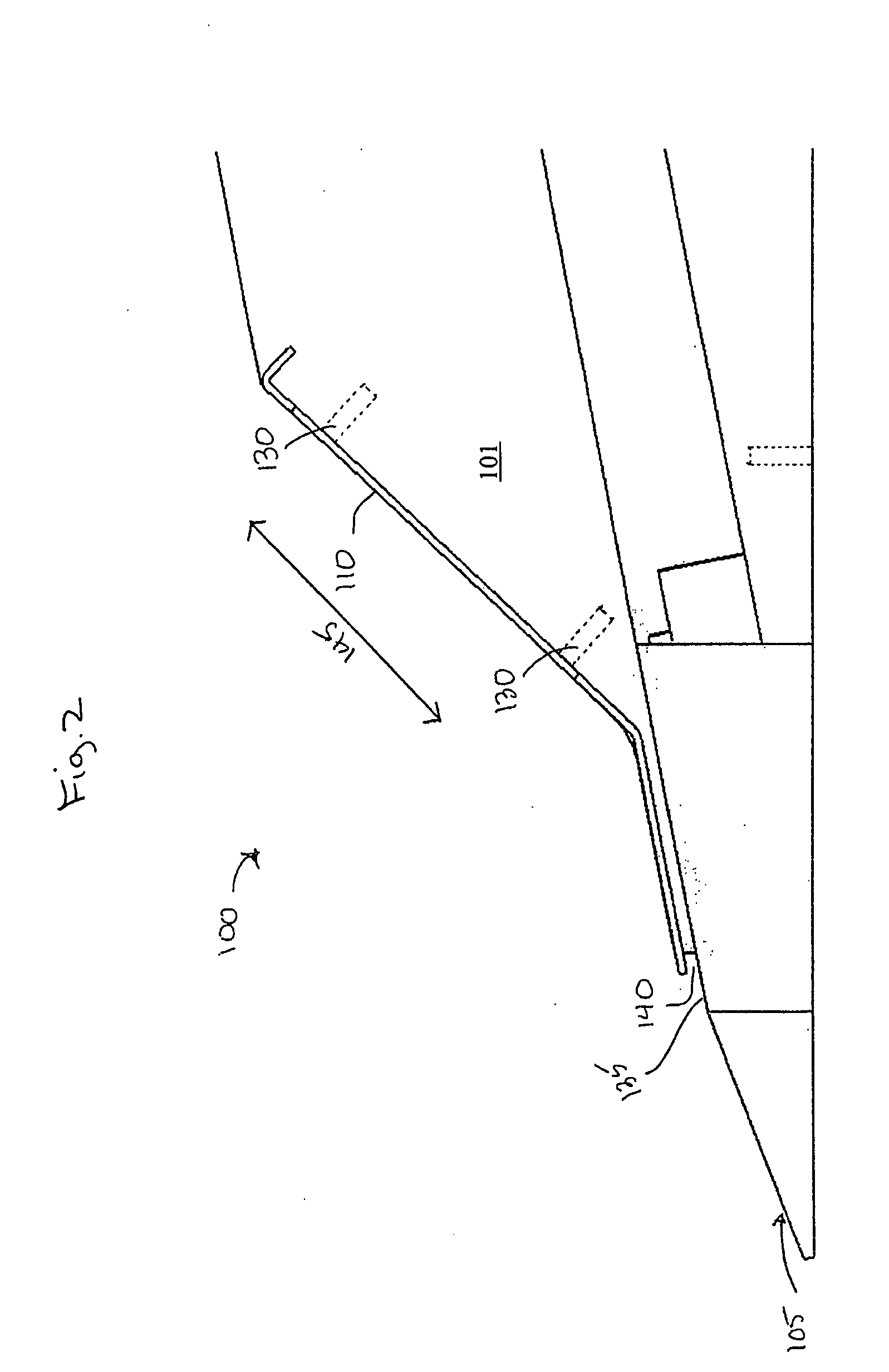
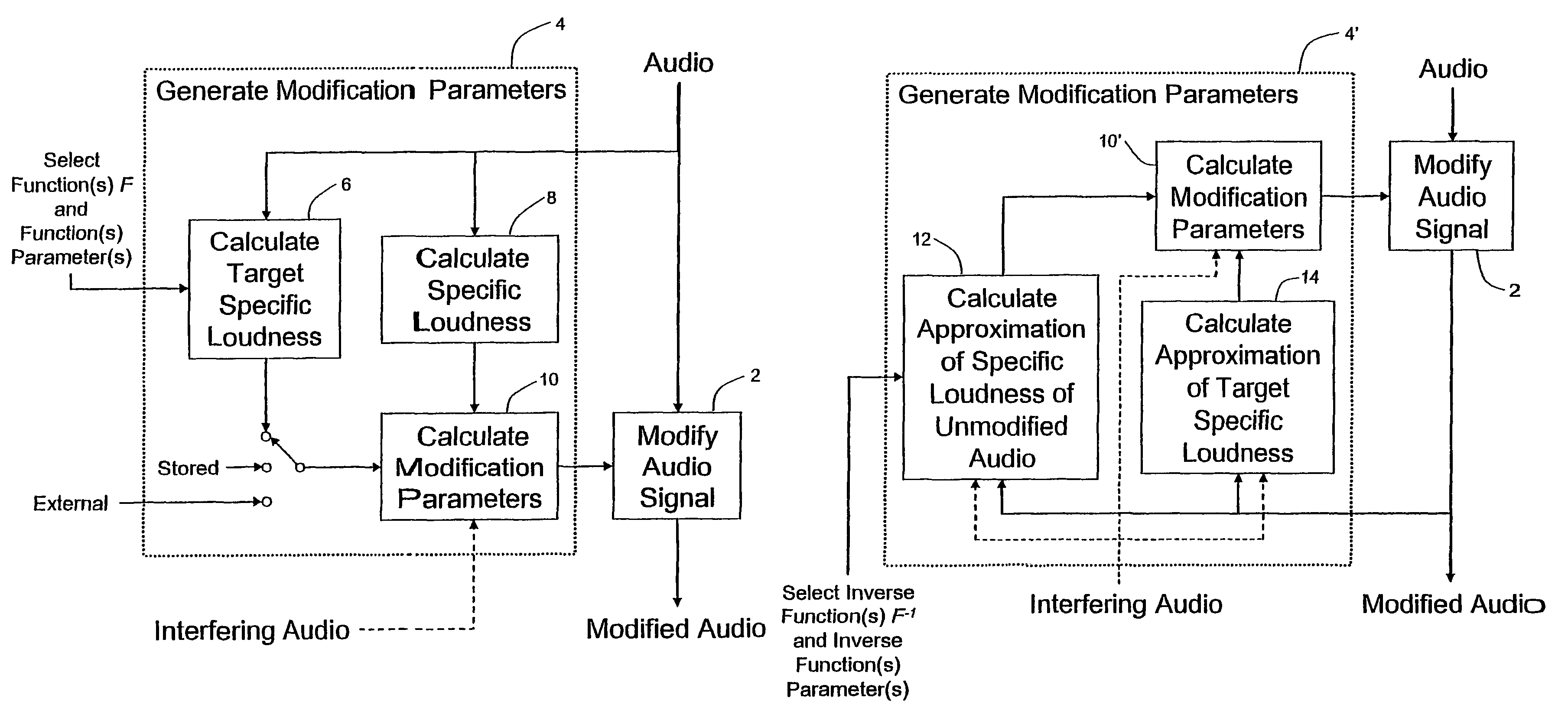
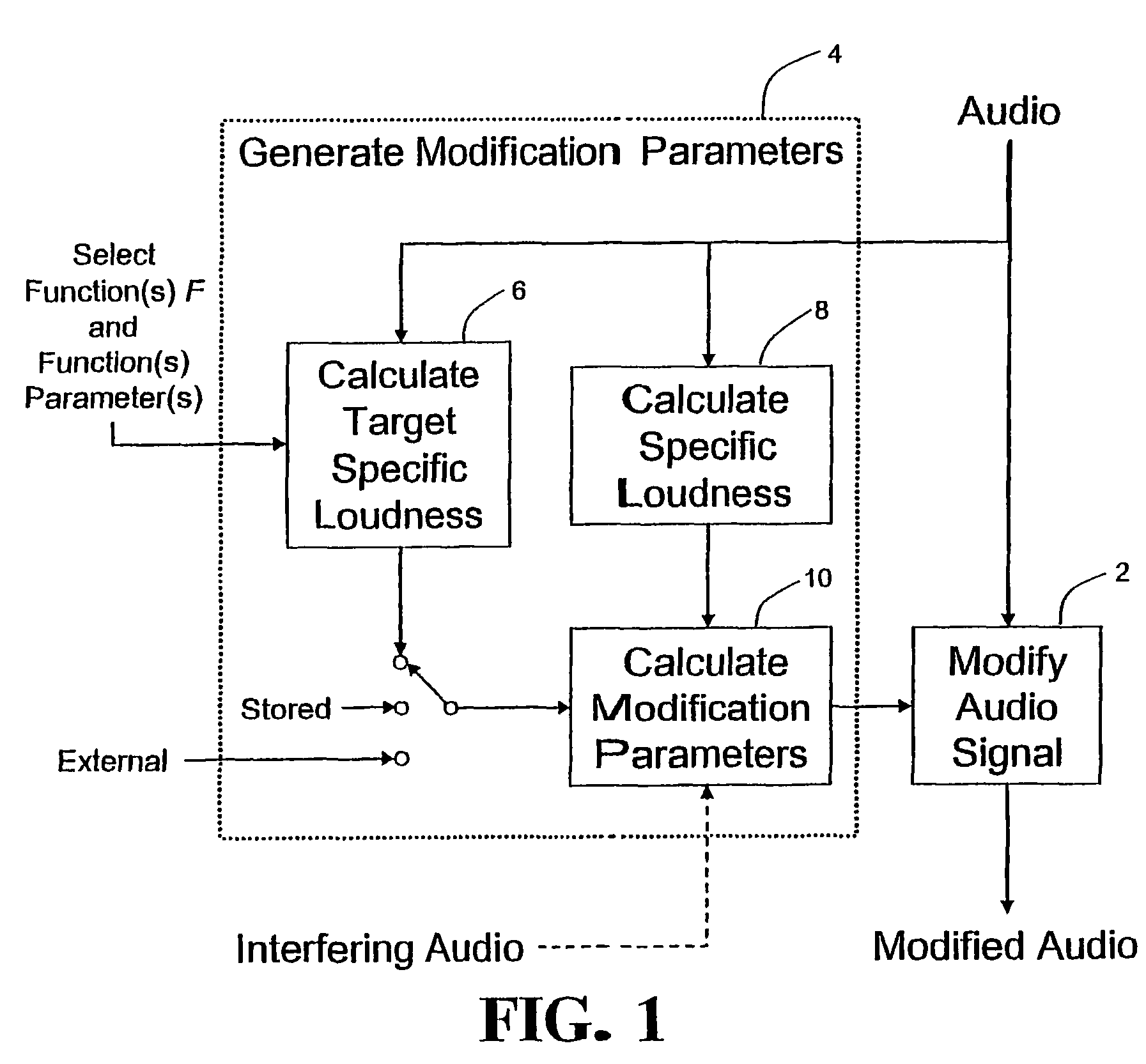
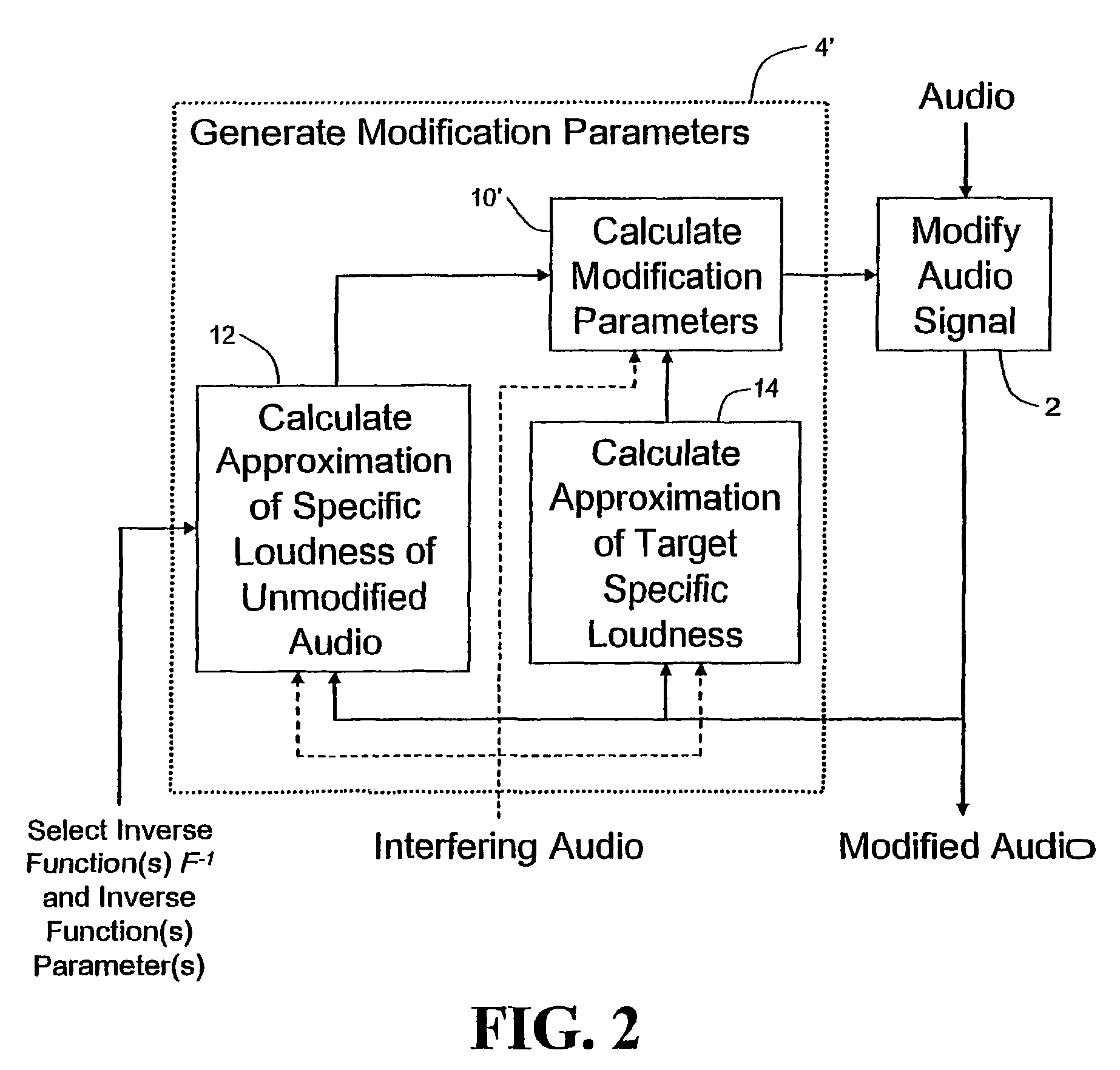
Calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness and/or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal
ActiveUS8090120B2Reduce the differenceReduce impactGain controlSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumEqualization
The invention relates to the measurement and control of the perceived sound loudness and / or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal. An audio signal is modified in response to calculations performed at least in part in the perceptual (psychoacoustic) loudness domain. The invention is useful, for example, in one or more of: loudness-compensating volume control, automatic gain control, dynamic range control (including, for example, limiters, compressors, expanders, etc.), dynamic equalization, and compensating for background noise interference in an audio playback environment. The invention includes not only methods but also corresponding computer programs and apparatus.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Intradermal delivery device
ActiveUS20070118077A1Minimal leakageReduce pressureCatheterInfusion needlesProportional controlInsertion depth
A system and method is provided for an injectable substance delivery device comprising a limiter, shoulder or post, that controls how deep the needle is inserted into the tissue. The limiter is sized in proportions that control the maximum insertion depth of the needle into the tissue without excessively restricting the complete insertion of the needle. The system and method further comprises an normalization or stabilizer ring that prevents distortion of the tissue in the vicinity of the infusion, so that the needle length is the major determining factor as to how deep the infusion is delivered.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
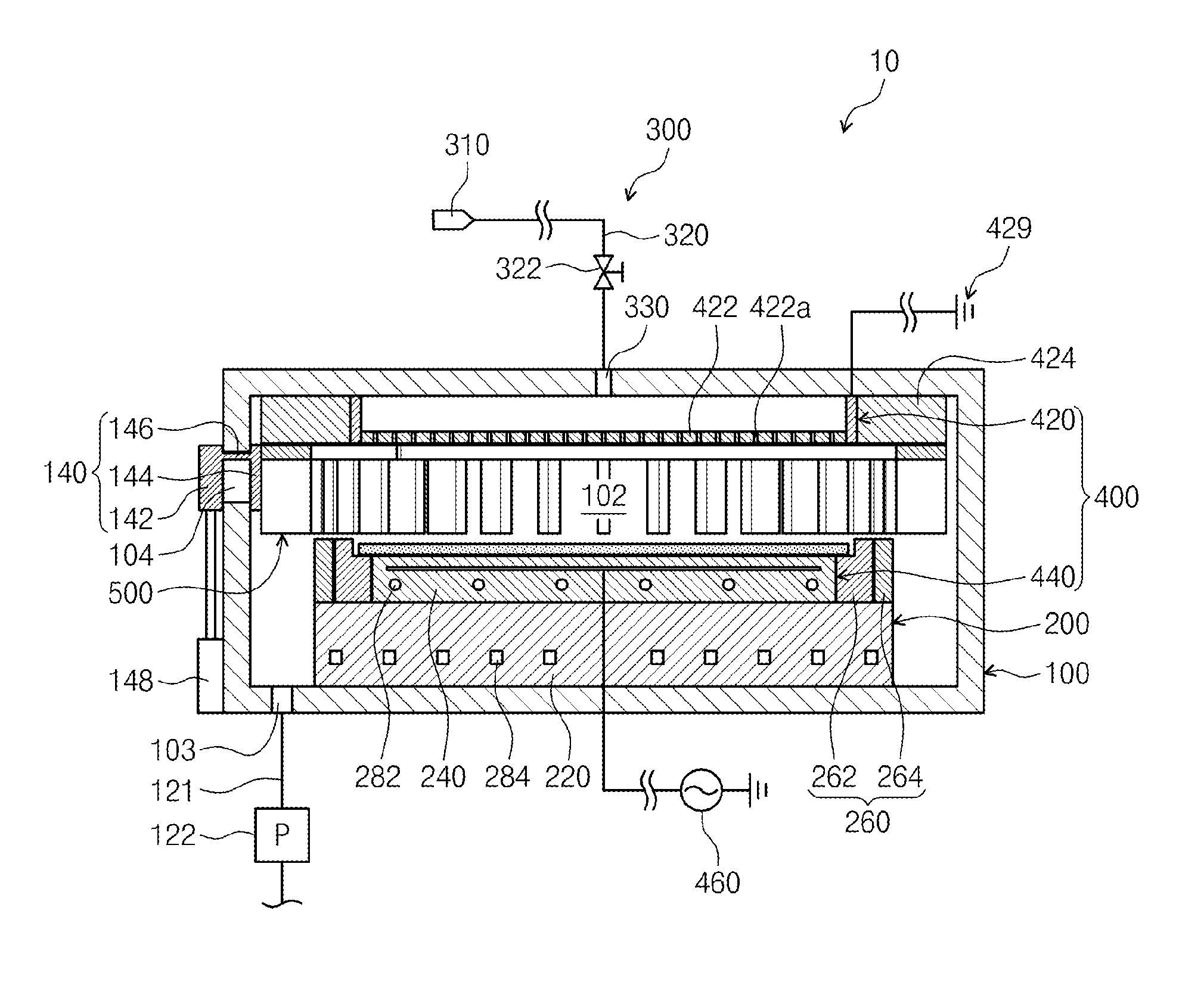
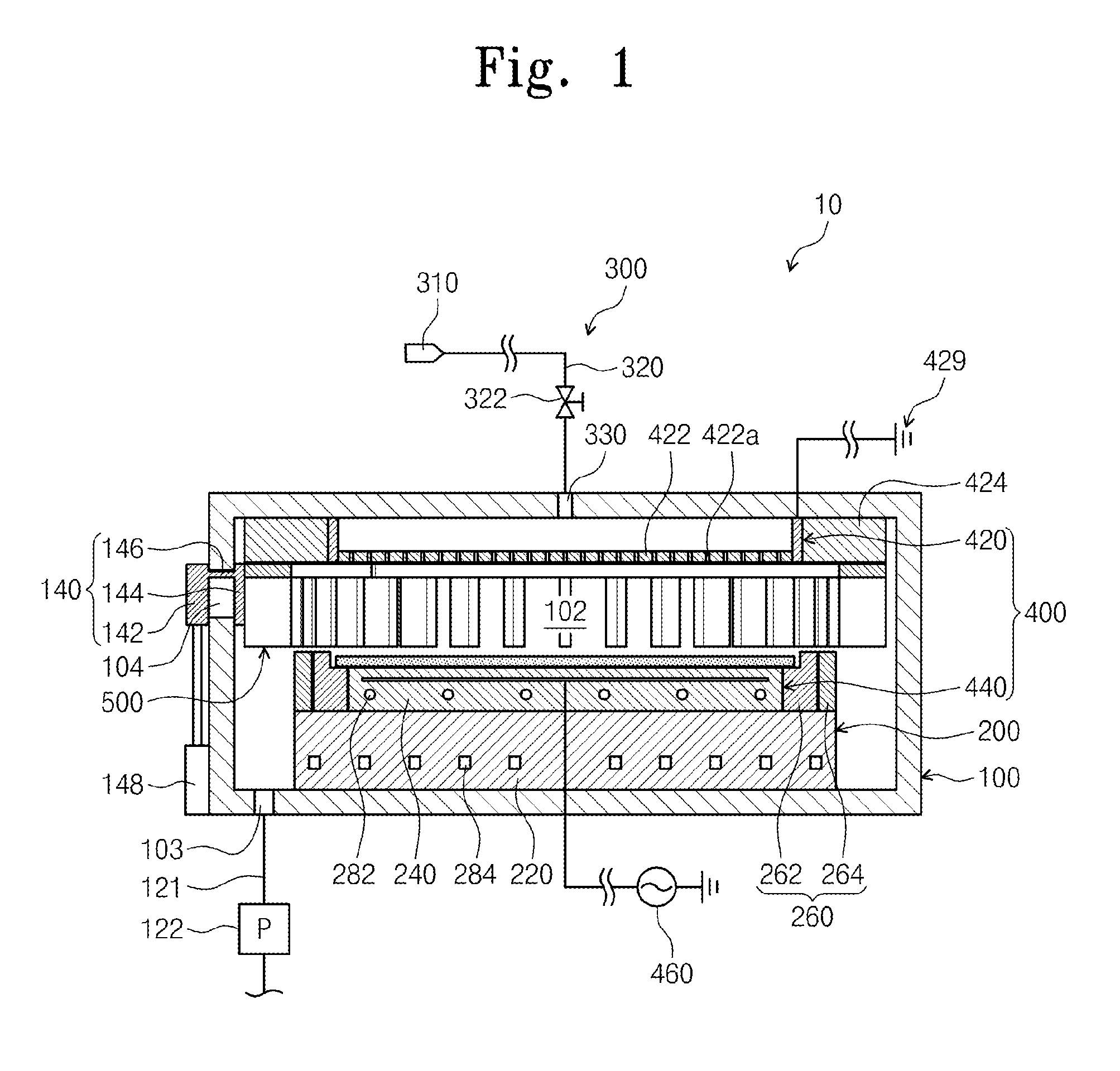
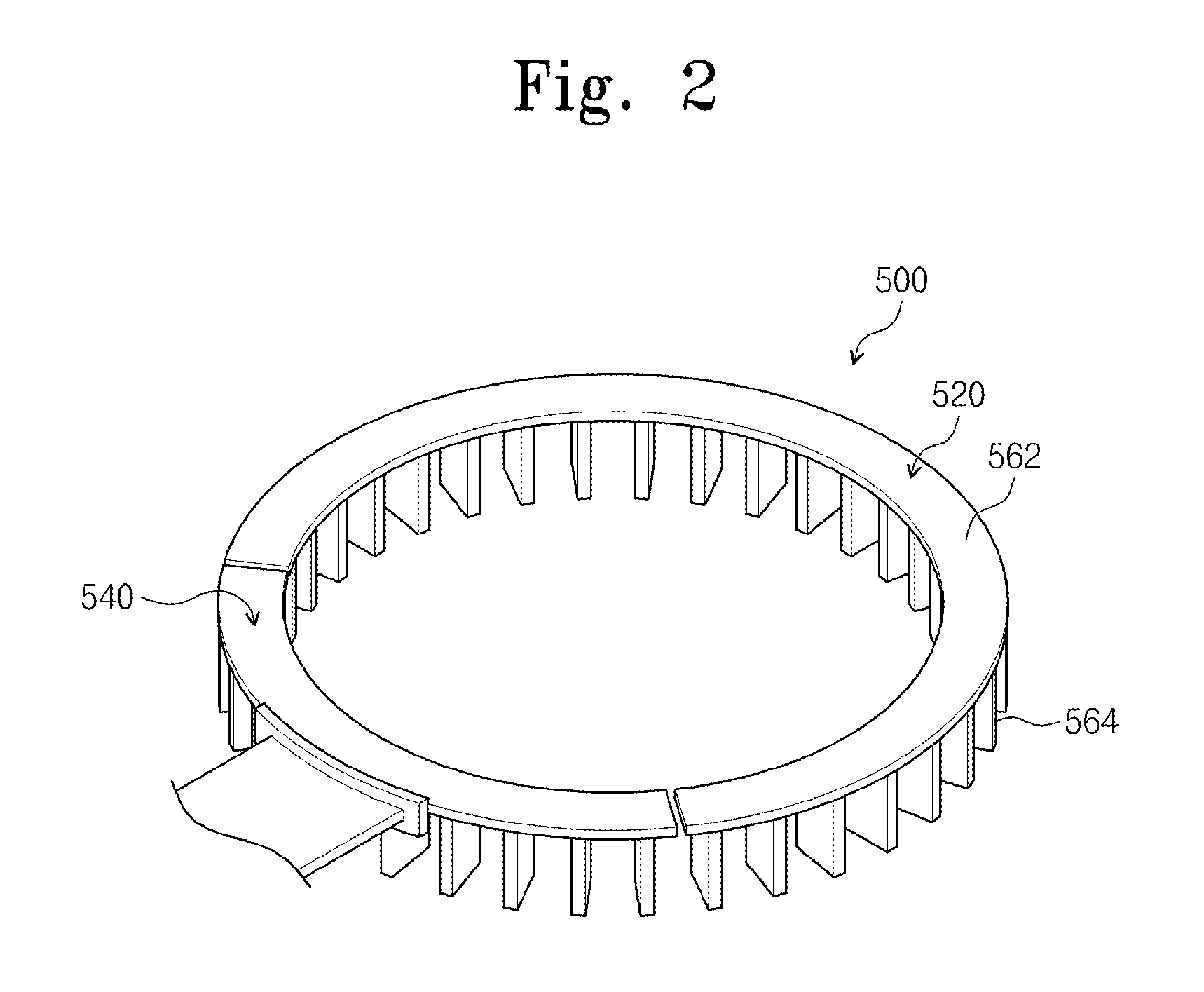
Plasma boundary limiter unit and apparatus for treating substrate
ActiveUS20130220550A1Prevent leakageLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesEngineeringLimiter
Provided is an apparatus for treating a substrate. The apparatus comprises a plasma boundary limiter unit disposed within a process chamber to surround a discharge space defined above a support unit. The plasma boundary limiter unit comprises a plurality of plates disposed along a circumference of the discharge space, and the plurality of plates are spaced apart from each other along the circumference of the discharge space so that a gas within the discharge space flows to the outside of the discharge space through passages provided between the adjacent plates.
Owner:SEMES CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com