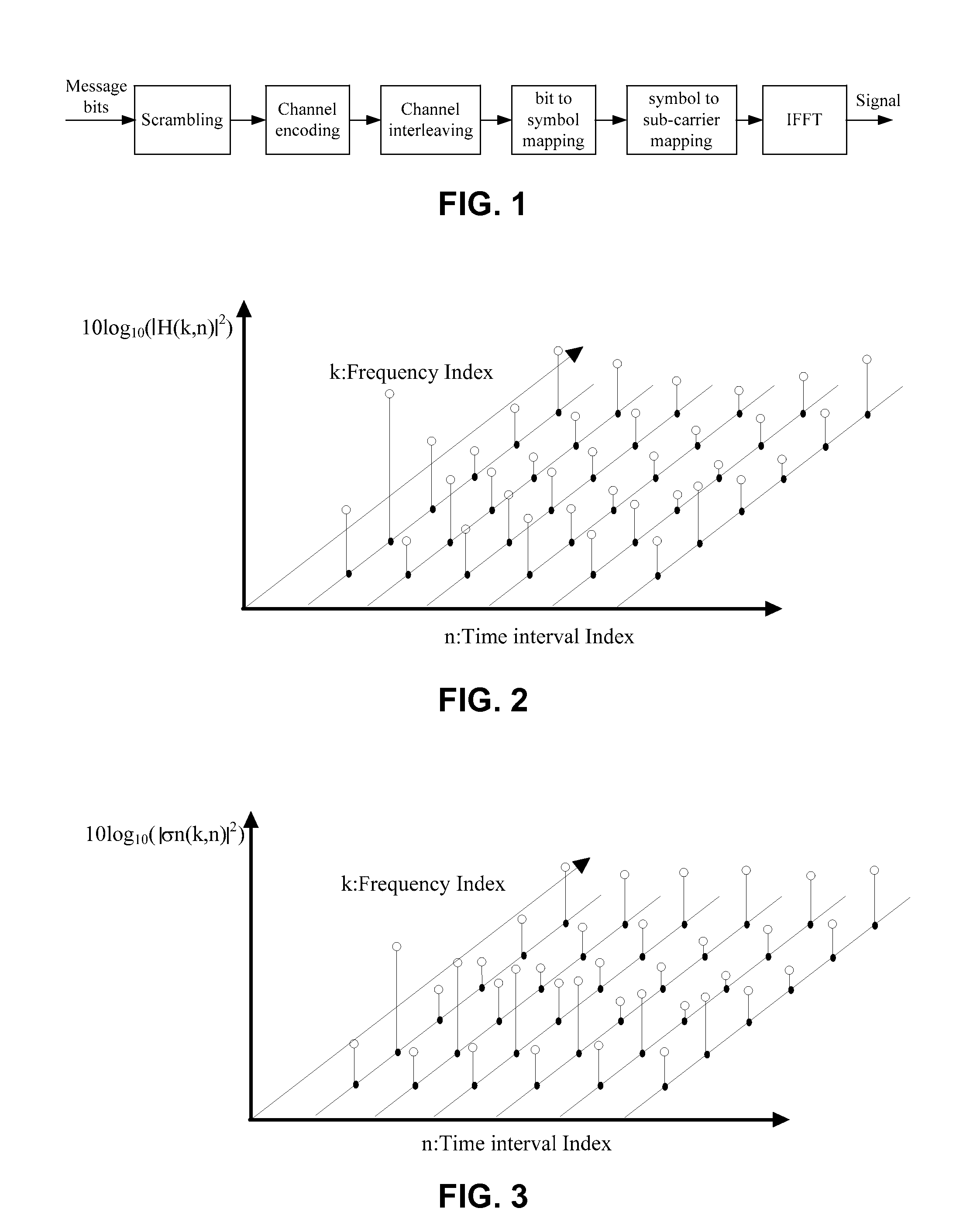
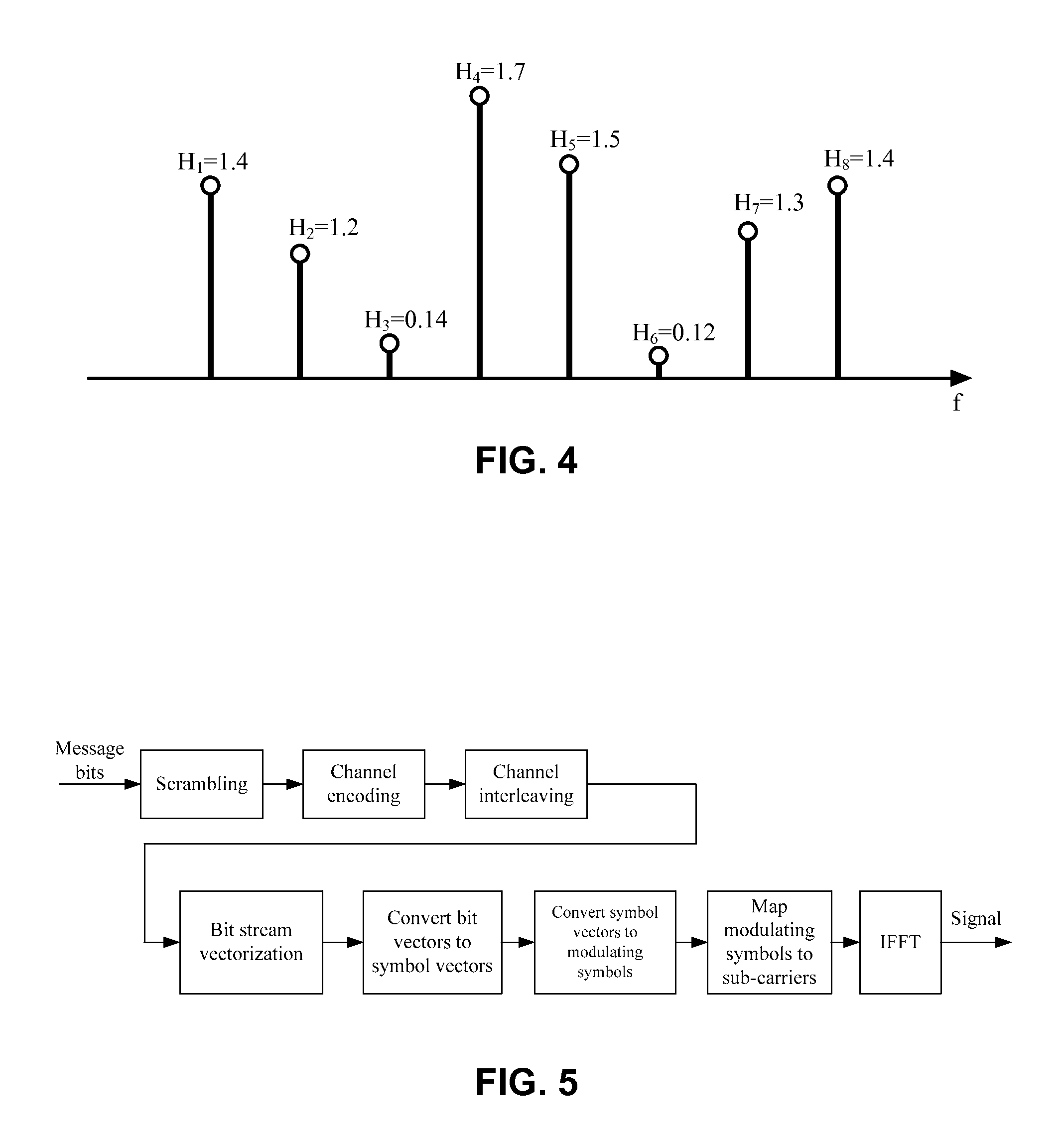
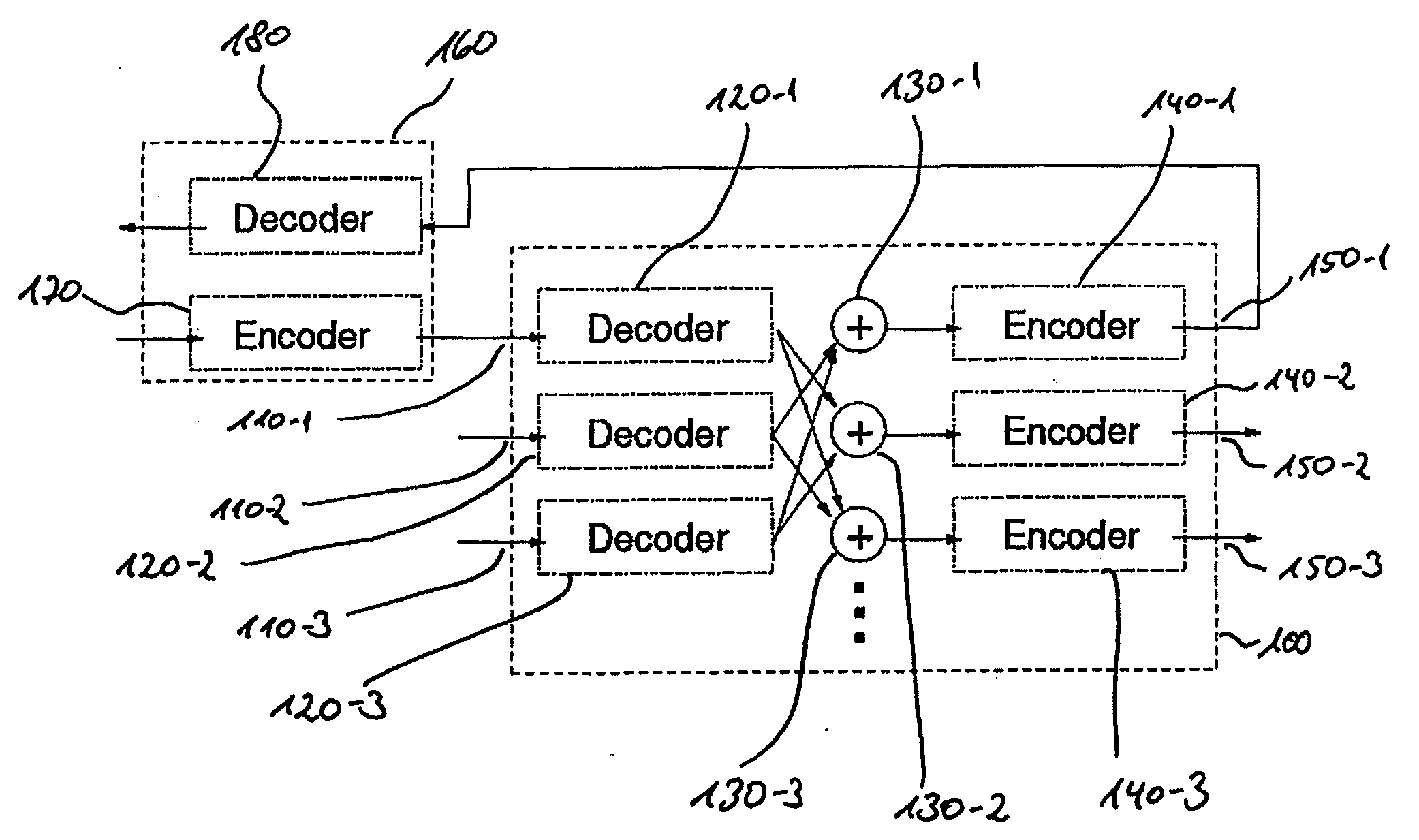
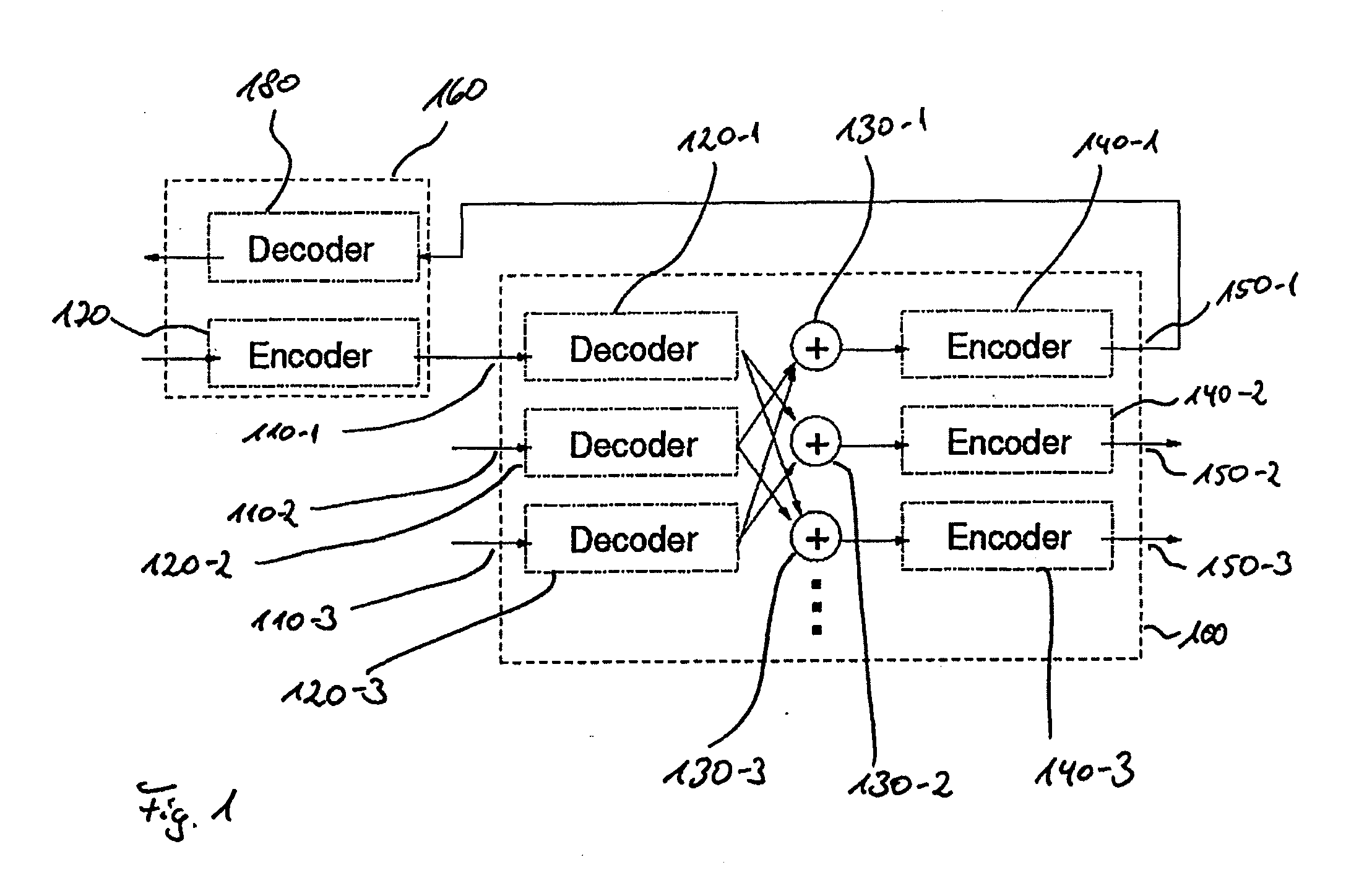
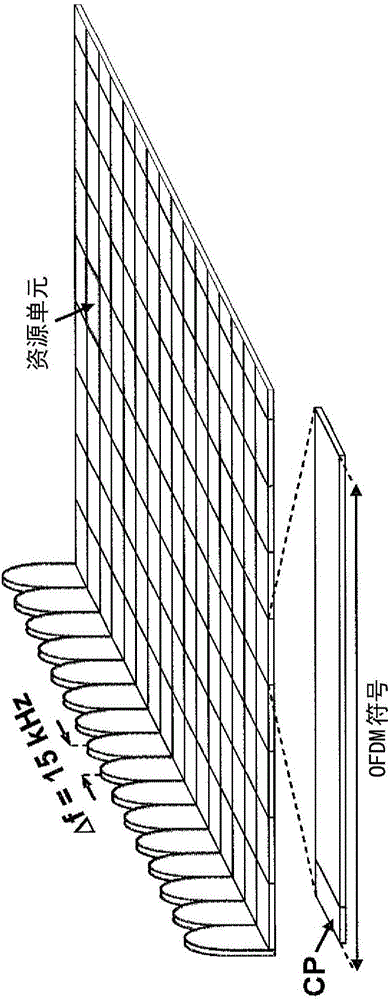
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
147 results about "Frequency grid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A frequency grid is a table of all the central frequencies (and corresponding wavelengths) of channels allowed in a communications system. The most common frequency grid used for fiber-optic communication is that used for channel spacing in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) at wavelengths around 1550 nm and defined by ITU-T G.694.1. The grid is defined relative to 193.1 THz and extends from 191.7 THz to 196.1 THz with 100 GHz spacing. While defined in frequency, the grid is often expressed in terms of wavelength, in which case it covers the wavelength range of 1528.77 nm to 1563.86 nm with approximately a 0.8 nm channel spacing.
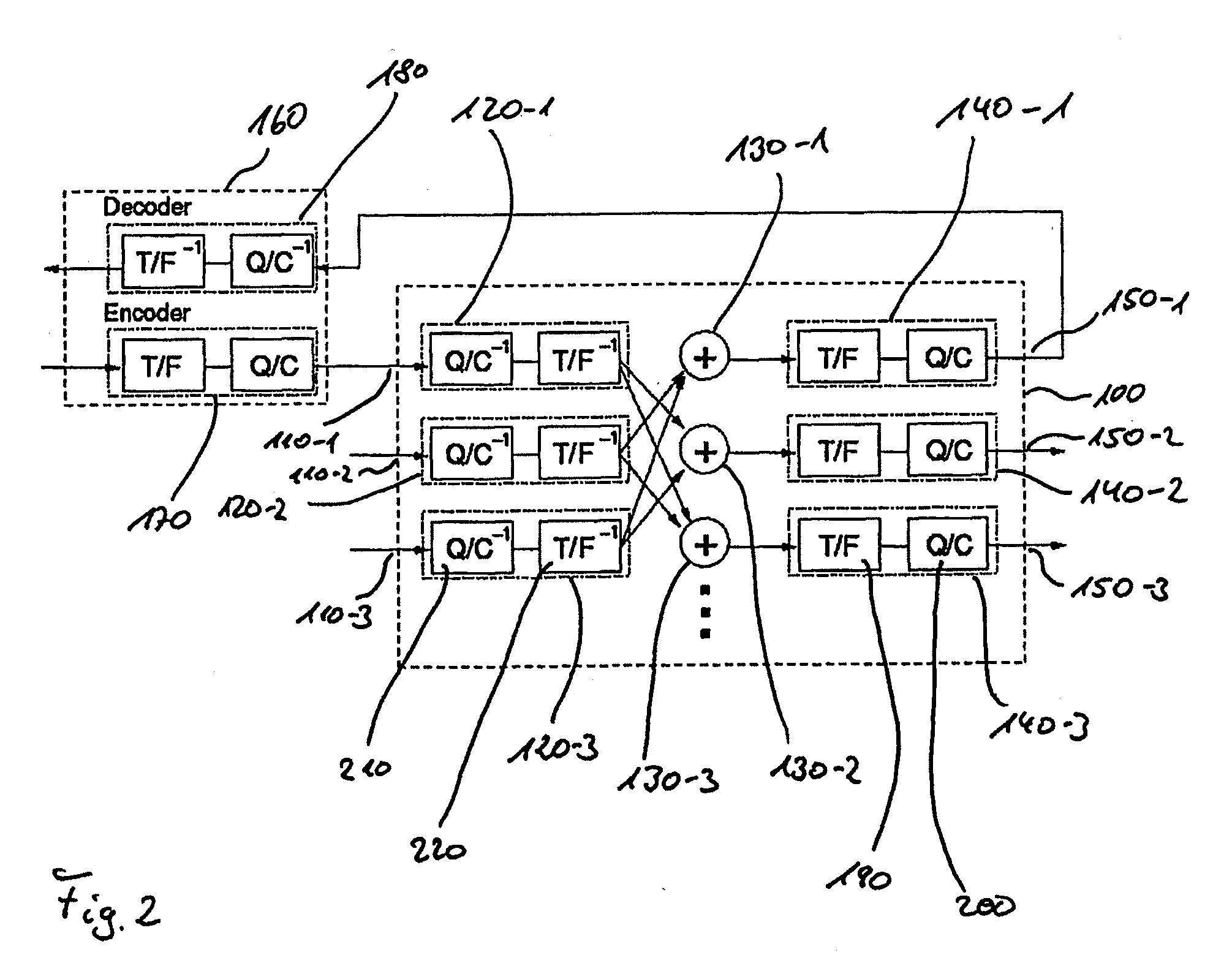
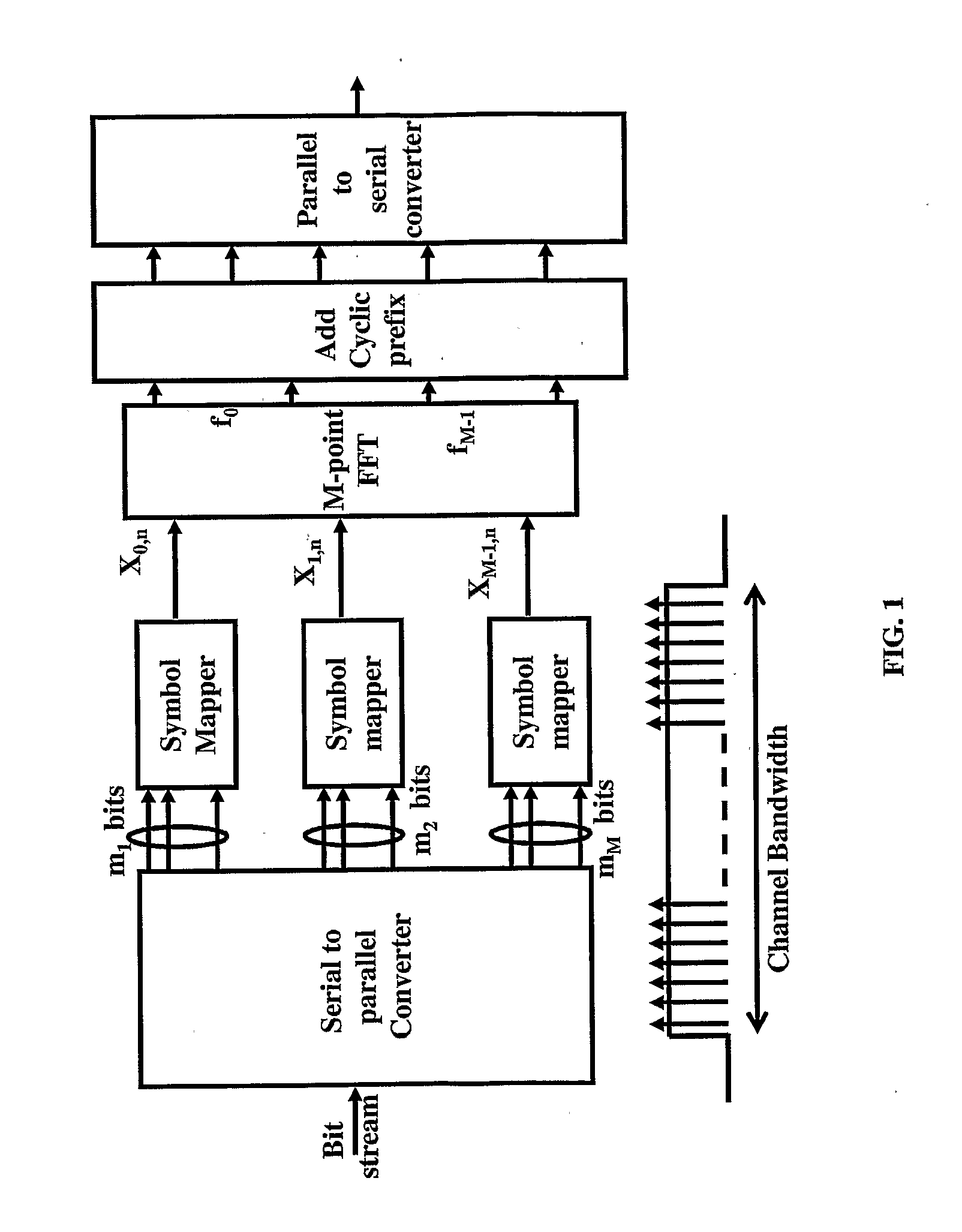
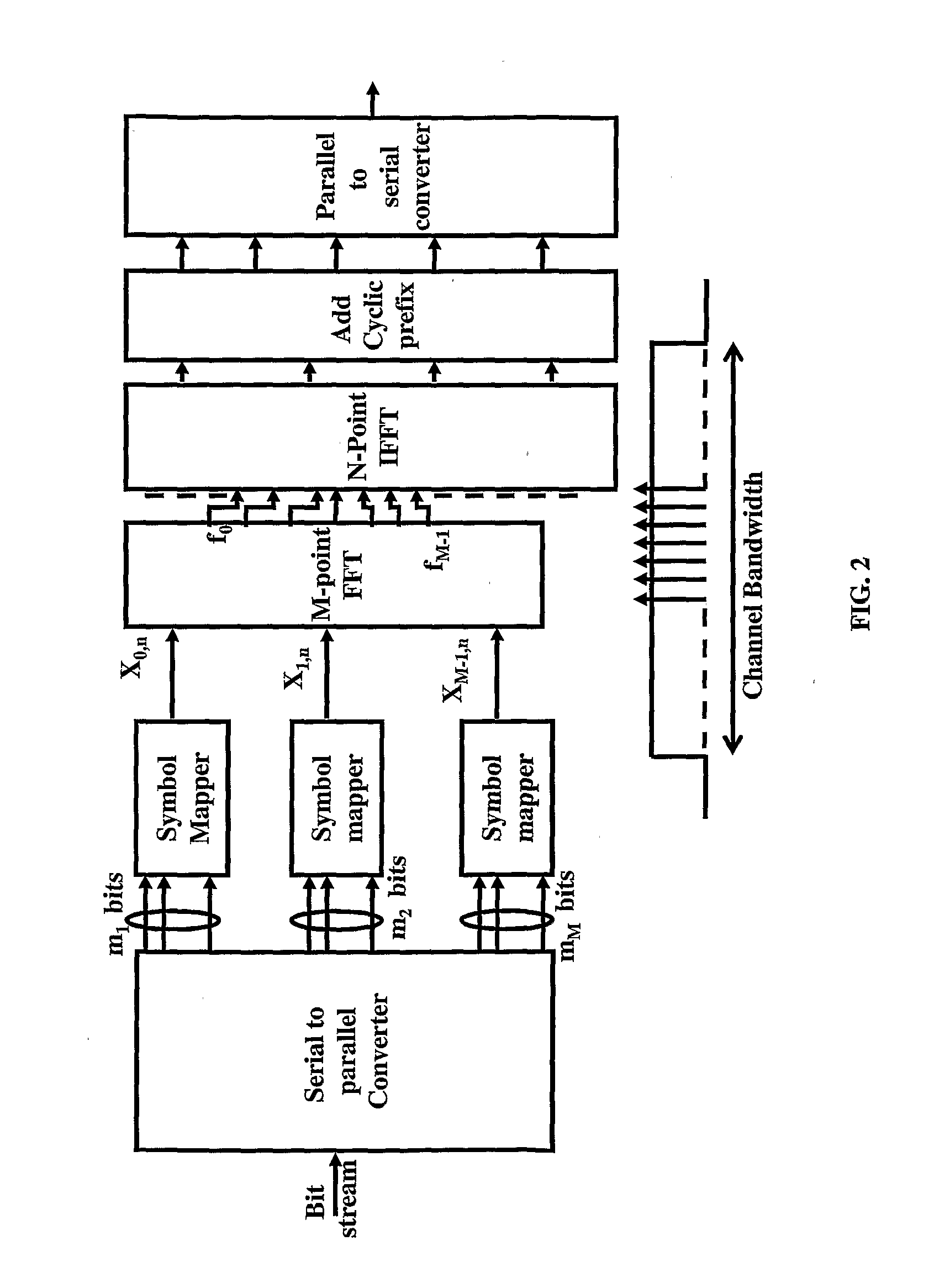
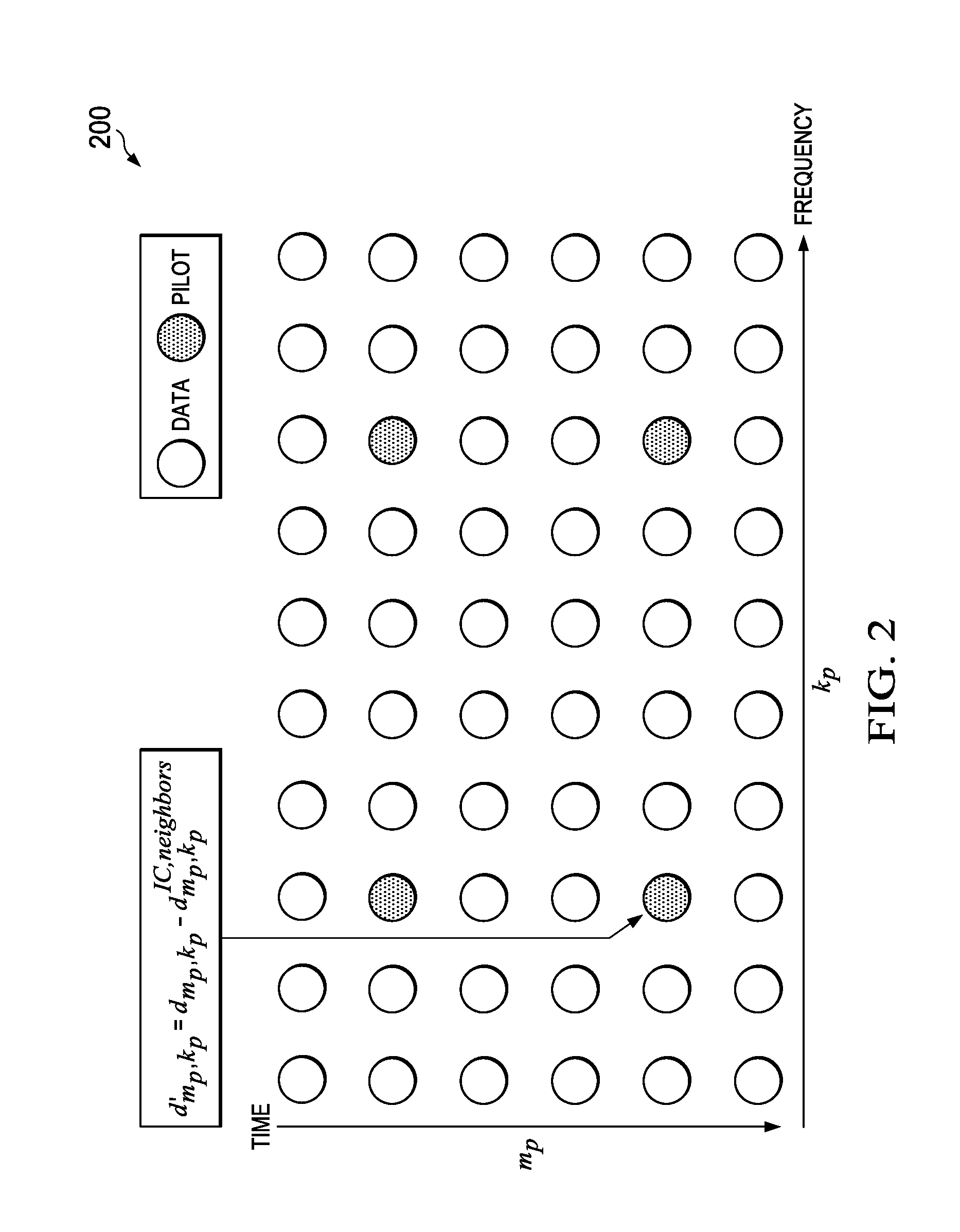
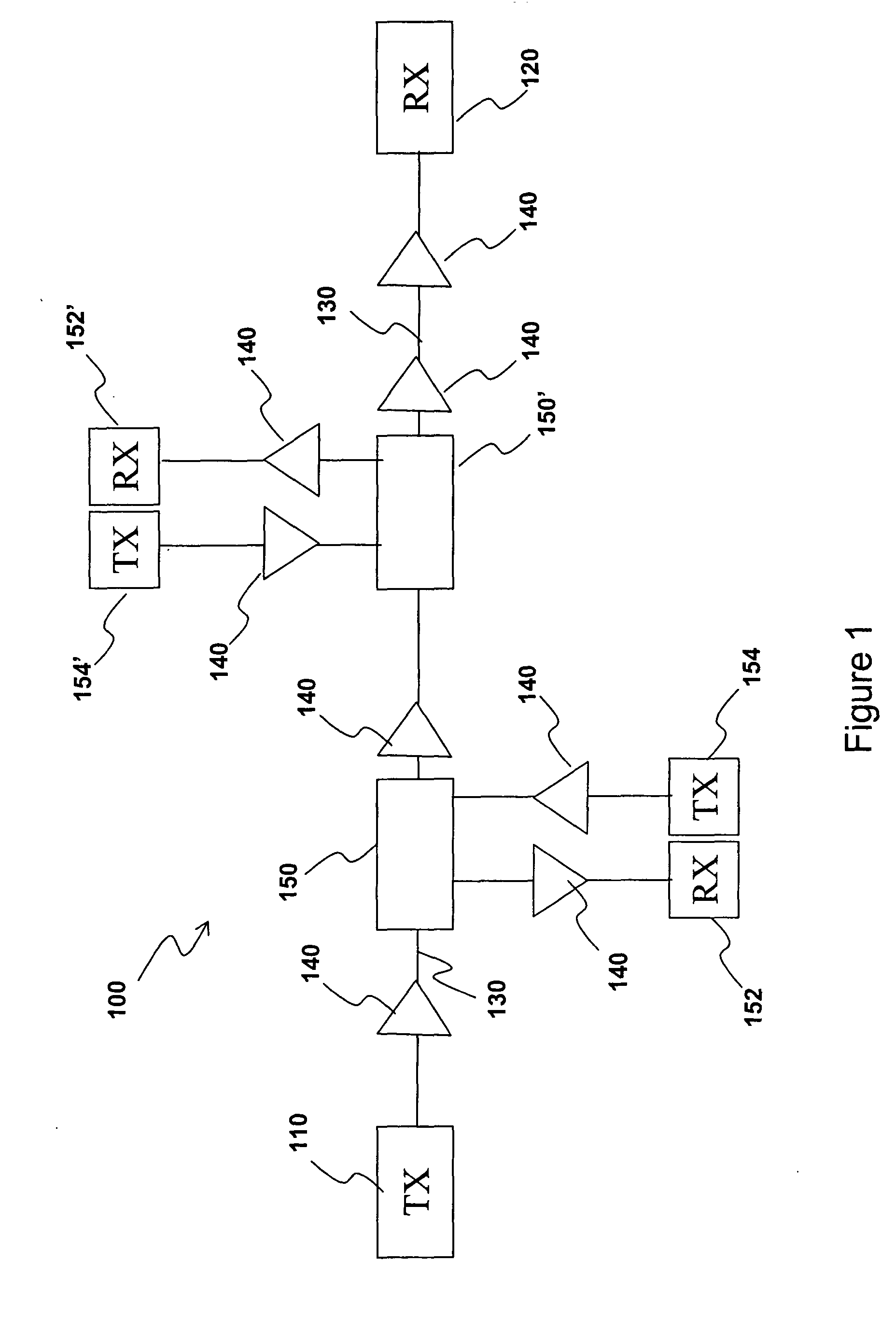
Pilot use in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing based spread spectrum multiple access systems
InactiveUS6954481B1Easy to useRadio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsSystem parametersSpread spectrum
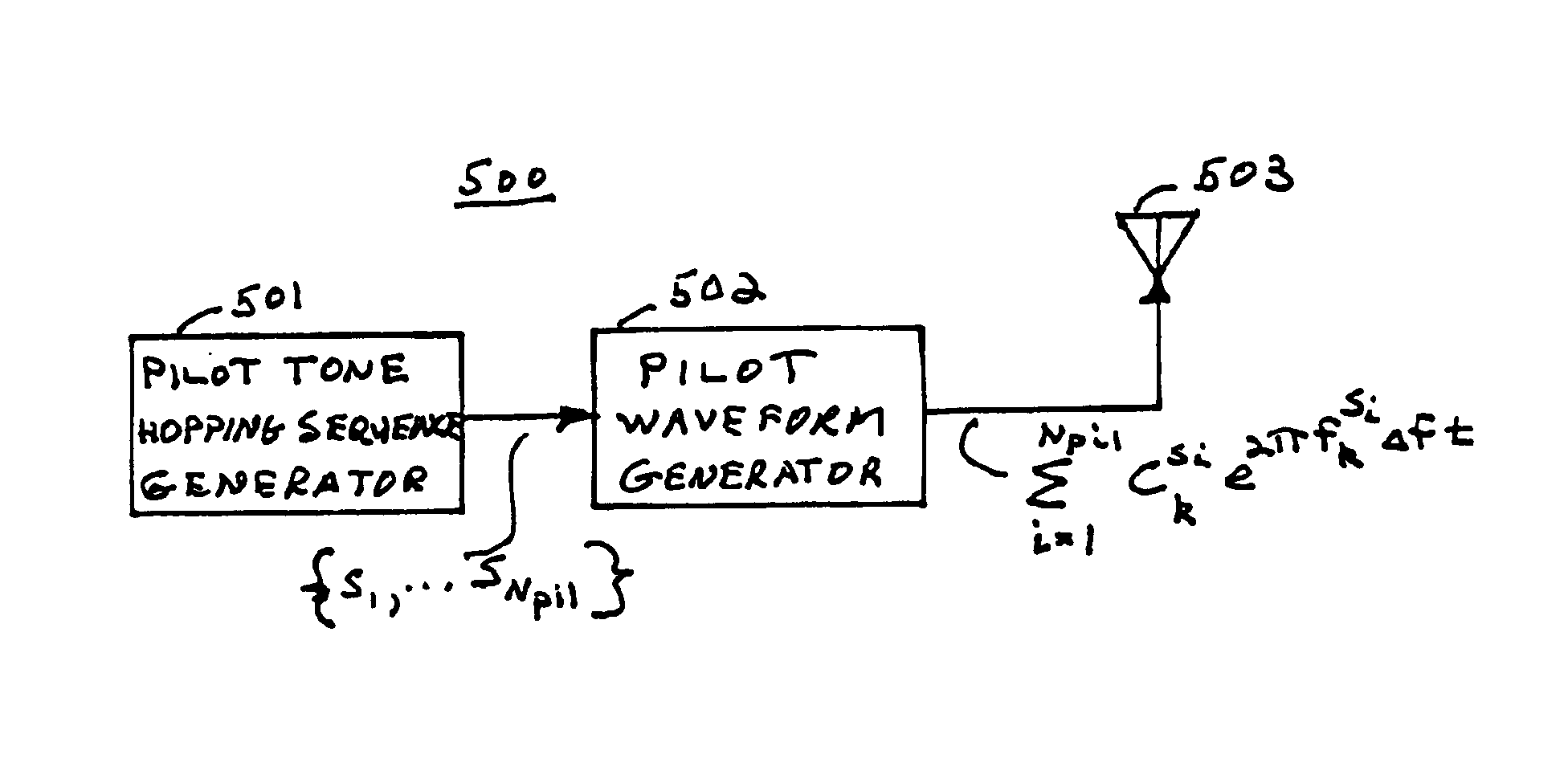
Base station identification and downlink synchronization are realized by employing pilots including known symbols transmitted at prescribed frequency tones in individual ones of prescribed time intervals. Specifically, the symbols used in the pilots are uniquely located in a time-frequency grid, where the locations are specified by periodic pilot tone hopping sequences. In a specific embodiment of the invention, a period of a pilot tone hopping sequence is constructed by starting with a Latin-square based hopping sequence, truncating it over time, and possibly offsetting and permuting it over frequency. Particular examples of pilot tone hopping sequences are parallel slope hopping sequences in which the periodicity of the sequences is chosen to be a prime number of symbol time intervals. In another embodiment of the invention, a notion of phantom pilots is employed to facilitate use of various system parameters while accommodating the above noted pilot tone hopping sequences.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Signal transmission method and apparatus used in OFDMA wireless communication system
InactiveUS8289914B2Improve signal transmission stabilityImprove interferenceTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationLoading factorCommunications system
Embodiments of the present invention provide a signal transmission method and apparatus used in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) wireless communication system, to enhance stability of signal transmission and resist time-frequency dispersion. The signal transmission method used in the OFDMA wireless communication system provided by an embodiment of the invention includes: converting an L×1 symbol vector into an N×1 modulating signal vector according to a loading factor fed back by a receiving party, in which value of N is known, both L and N are natural numbers larger than one, N is larger than or equal to L, the loading factor is a ratio of L and N; mapping the N×1 modulating signal vector into N time-frequency grids; and converting the N time-frequency grids into a signal waveform and sending the signal waveform to the receiving party.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
Apparatus for Mixing a Plurality of Input Data Streams
An apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention for mixing a first frame of a first input data stream and a second frame of a second input data stream has a processing unit adapted to generate an output frame, wherein the output frame has output spectral data describing a lower part of an output spectrum up to an output cross-over frequency, and wherein the output frame further has output SBR-data describing a higher part of the output spectrum above the output cross-over frequency by way of energy-related values in an output time / frequency grid resolution. The processing unit is further adapted such that the output spectral data corresponding to frequencies below a minimum value of cross-over frequencies of the first frame, the second frame and the output cross-over frequency is generated in a spectral domain and the output SBR-data corresponding to frequencies above a maximum value of cross-over frequencies of the first and second frames and the output cross-over frequency is processed in a SBR-domain.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
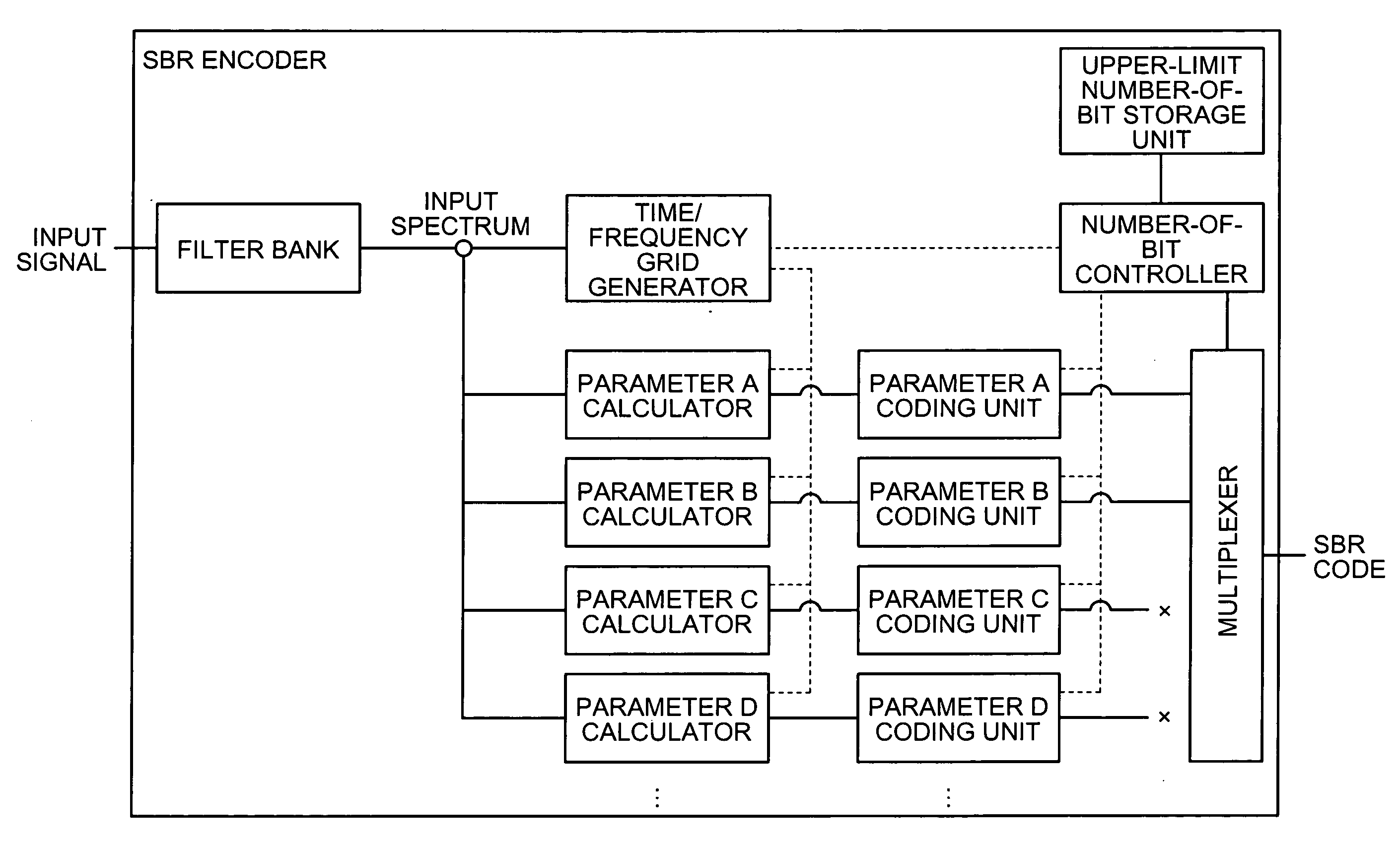
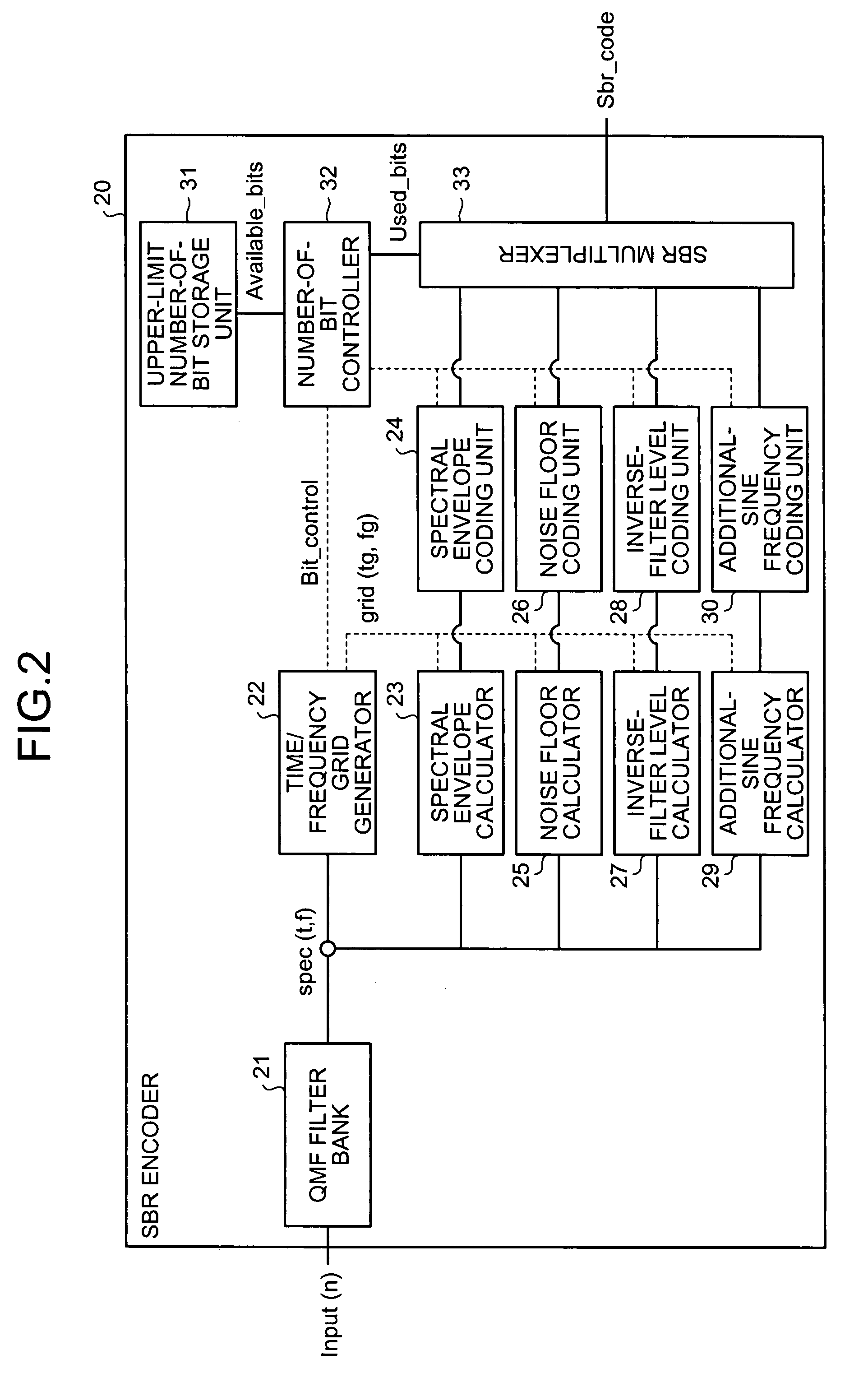
SBR encoder with high frequency parameter bit estimating and limiting
An SBR encoder includes a filter bank that receives an input signal, a time / frequency grid generator that controls a number of bits of various parameters, a parameter calculator that calculates various parameters, a parameter coding unit that encodes the parameters, an upper-limit number-of-bit storage unit that stores an upper limit of the number of bit of encoded data of high-frequency component finally generated in a high-pass encoding process, and a number-of-bit controller. The number-of-bit controller controls the high-pass encoding process by preferentially encoding a parameter having a large influence to sound quality and not encoding a parameter having a small influence to the sound quality relative to a plurality of parameters, so that the number of bits of the encoded data of high-frequency component finally generated in the high-pass encoding process becomes equal to or less than the upper limit to be stored in the upper-limit number-of-bit storage unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
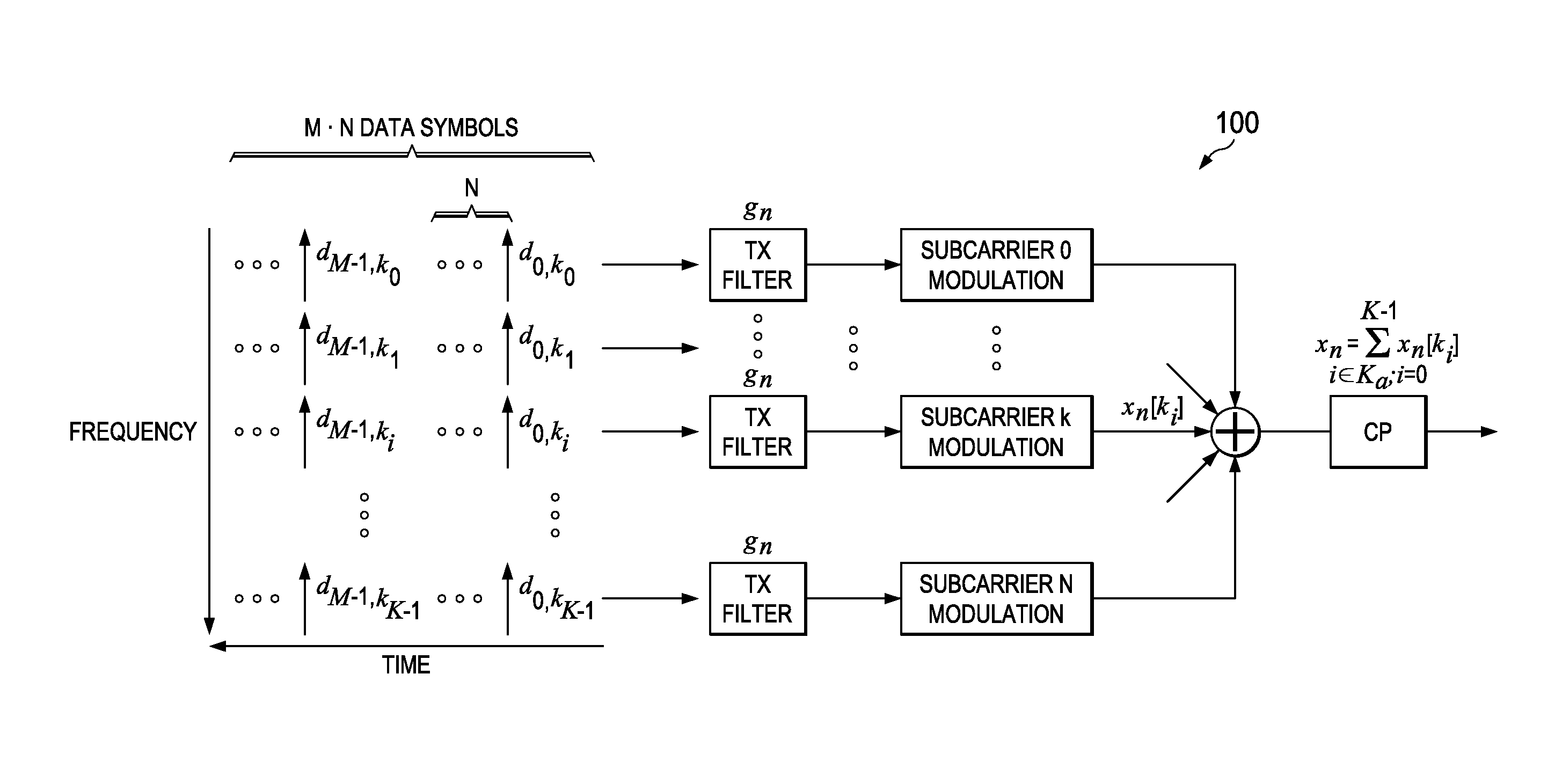
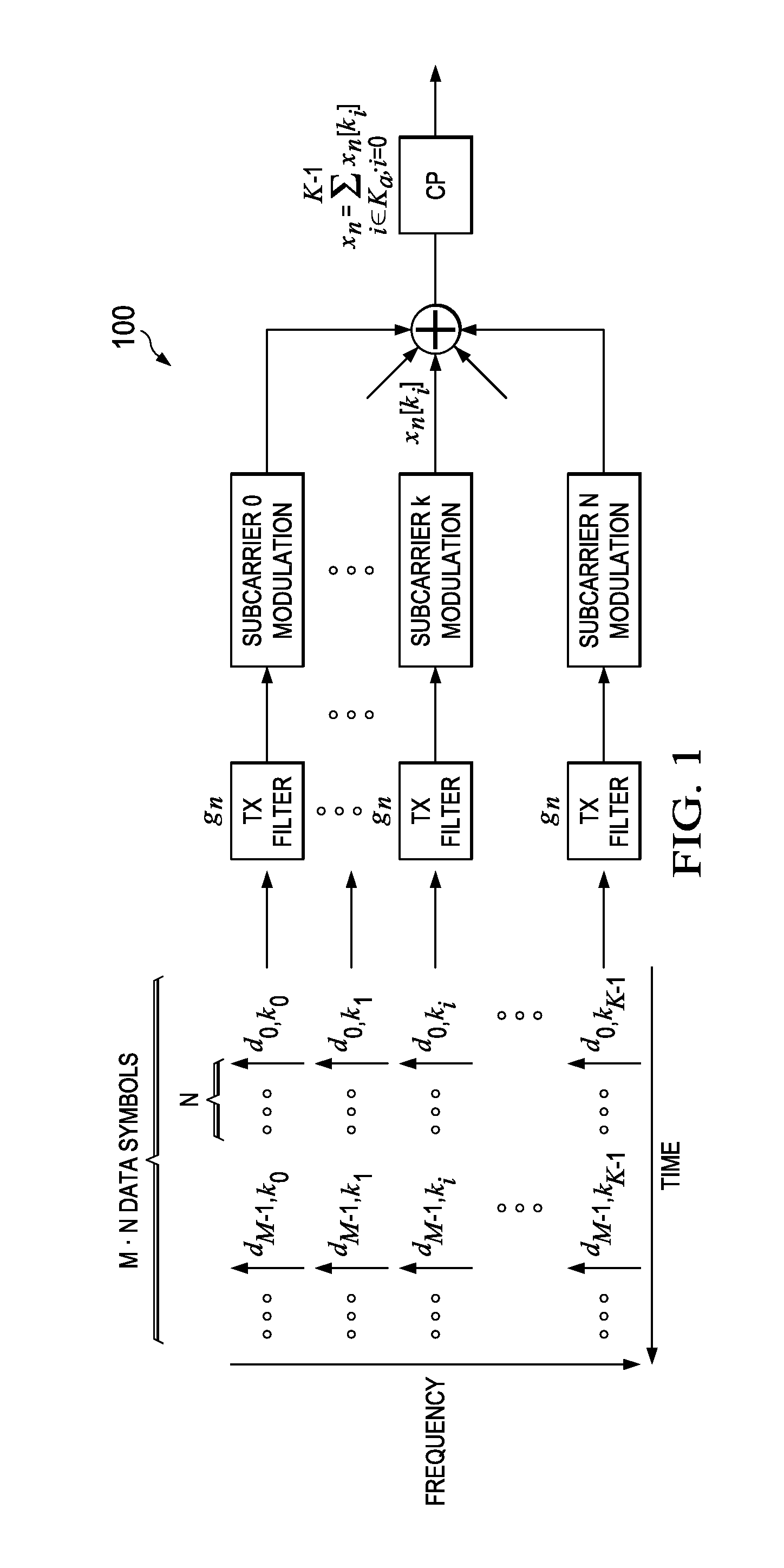
Precoding for single transmission streams in multiple antenna systems
Precoding for multiple transmission streams in multiple antenna systems. Disclosed herein is a general method that transmits signal from multiple antennas using a one / two dimensional precoder. This precoder is fixed in a given resource block (RB) or slot, which is composed of P subcarriers and Q OFDM symbols (where the values for P and Q are greater than or equal to 1). The precoder in each resource block may take same or different values, which span the two dimensional time-frequency grid. The precoder is chosen as a function of either logical frequency index or physical frequency index of the RB.
Owner:CENT OF EXCELLENCE & WIRELESS TECH
Precoding for Multiple Transmission Streams in Multiple Antenna Systems
Precoding for multiple transmission streams in multiple antenna systems. Embodiments herein disclose a general method that transmits signal from multiple antennas using a one / two dimensional precoder followed by STBC / SFBC or SM encoder. This precoder is fixed in a given resource block (RB) or slot, which is composed of P subcarriers and Q OFDM symbols (where the values for P and Q are greater than or 5 equal to 1). The precoder in each resource block may take same or different values, which span the two dimensional time-frequency grid. The precoder is chosen as a function of either logical frequency index or physical frequency index of the RB.
Owner:CENT OF EXCELLENCE & WIRELESS TECH
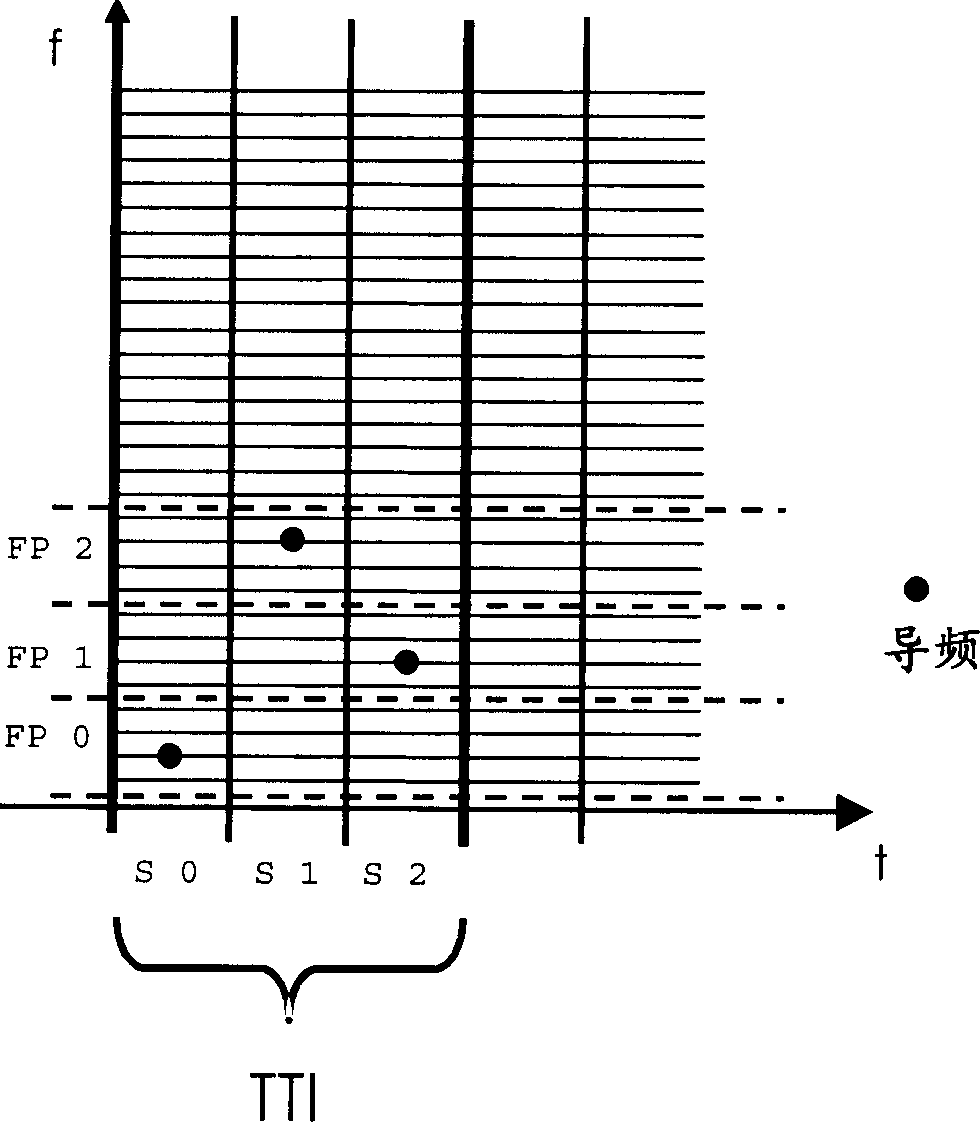
A method for OFDM data transmission, a base transceiver station, a base station controller, a mobile terminal and a mobile network therefor
InactiveCN1829373ATransmission path divisionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData transmissionMobile Web
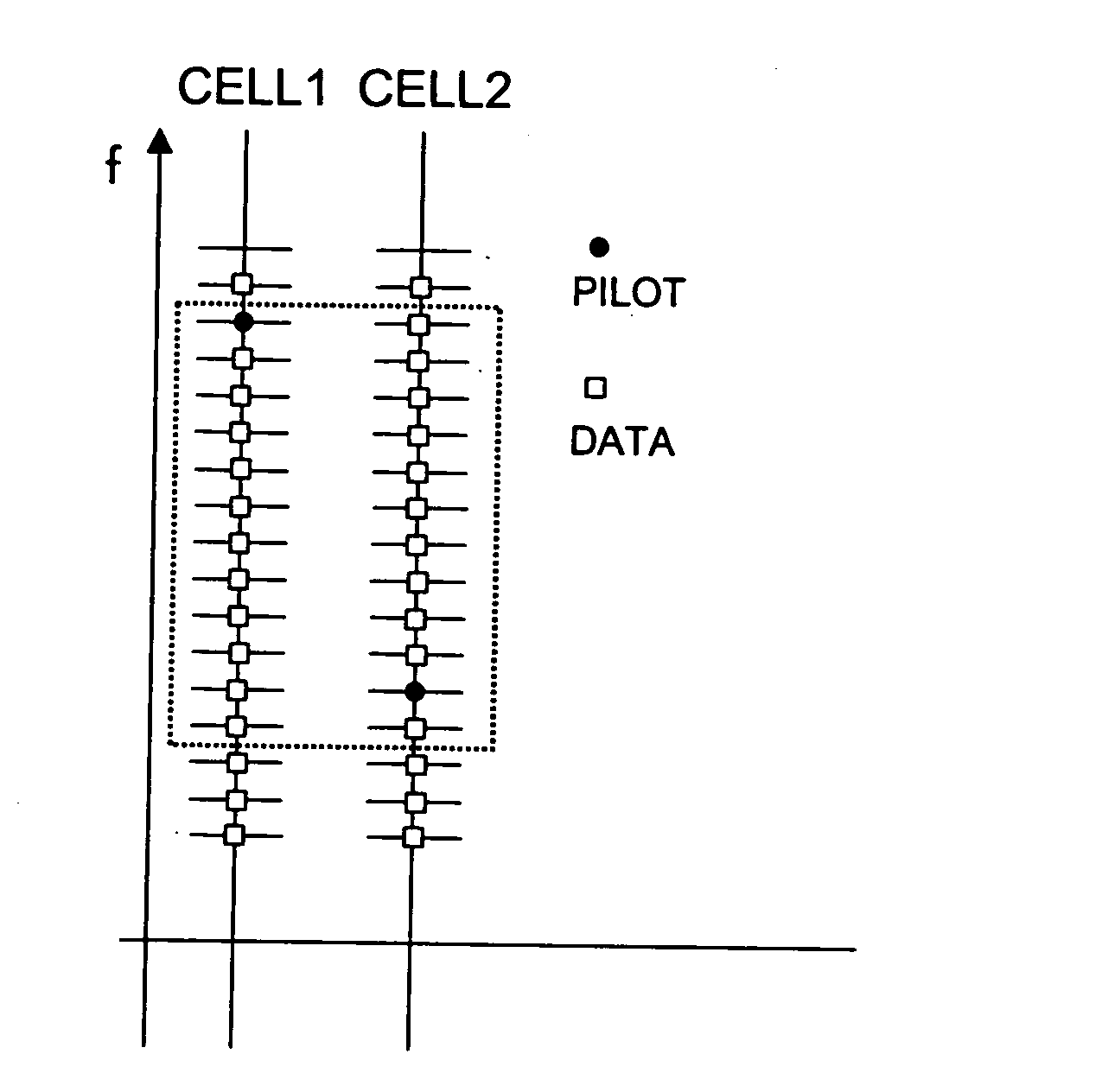
The invention concerns a method for OFDM data transmission in a single-frequency multi-cell mobile network from and to mobile terminals (MT) with channel estimation by means of pilots (PILOT) of a pilot subgrid in an OFDM time-frequency grid, whereby the positions of the pilot subgrids of different cells of the mobile network are randomly or pseudo-randomly distributed, a base transceiver station, a base station controller, a mobile terminal and a mobile network therefor.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Encoder, method of encoding, and computer-readable recording medium
An SBR encoder includes a filter bank that receives an input signal, a time / frequency grid generator that controls a number of bits of various parameters, a parameter calculator that calculates various parameters, a parameter coding unit that encodes the parameters, a multiplexer that multiplexes encoded data, an upper-limit number-of-bit storage unit that stores an upper limit of the number of bit of encoded data of high-frequency component finally generated in a high-pass encoding process, and a number-of-bit controller. The number-of-bit controller controls the high-pass encoding process by preferentially encoding a parameter having a large influence to sound quality and not encoding a parameter having a small influence to the sound quality relative to a plurality of parameters, so that the number of bits of the encoded data of high-frequency component finally generated in the high-pass encoding process becomes equal to or less than the upper limit to be stored in the upper-limit number-of-bit storage unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
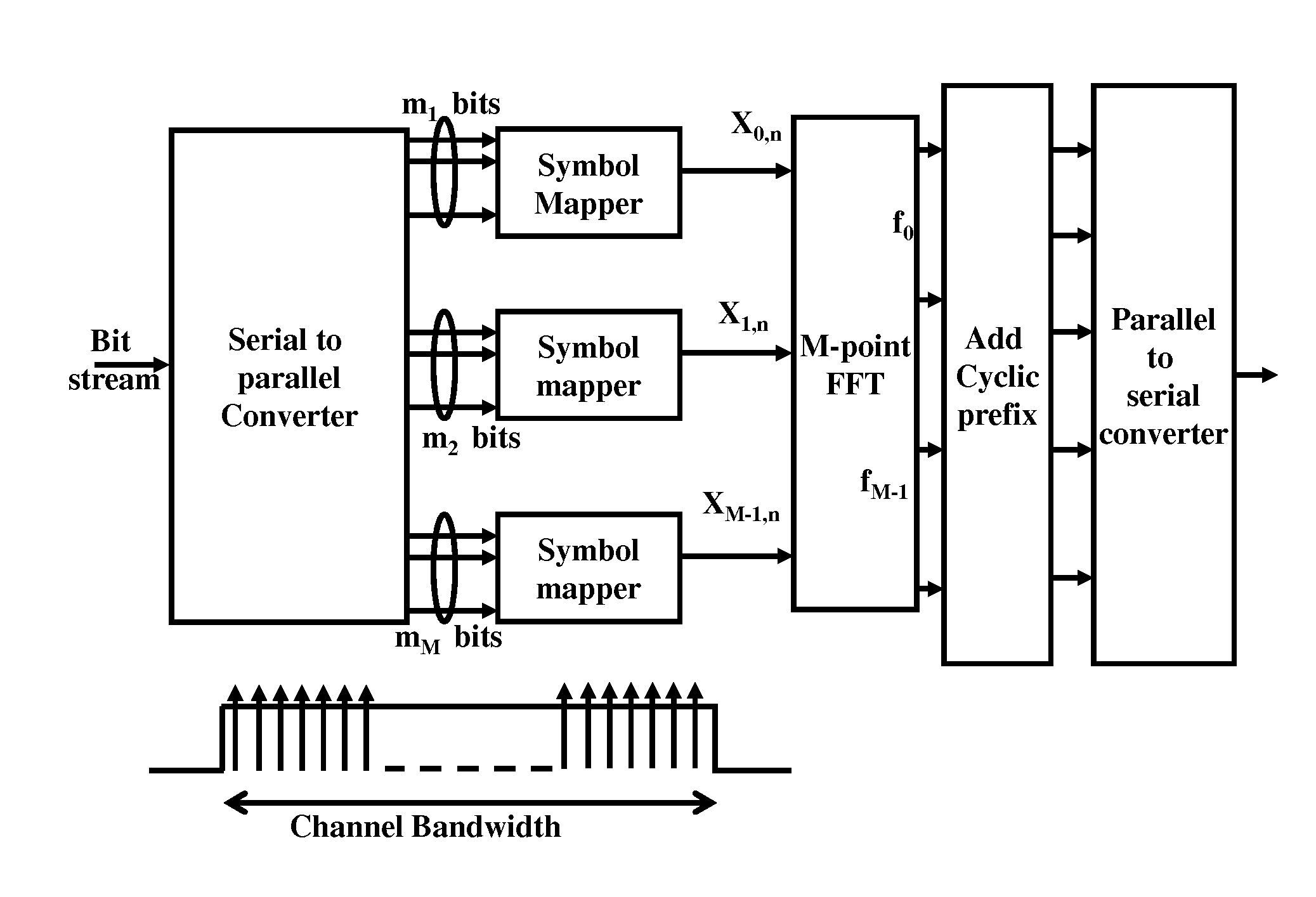
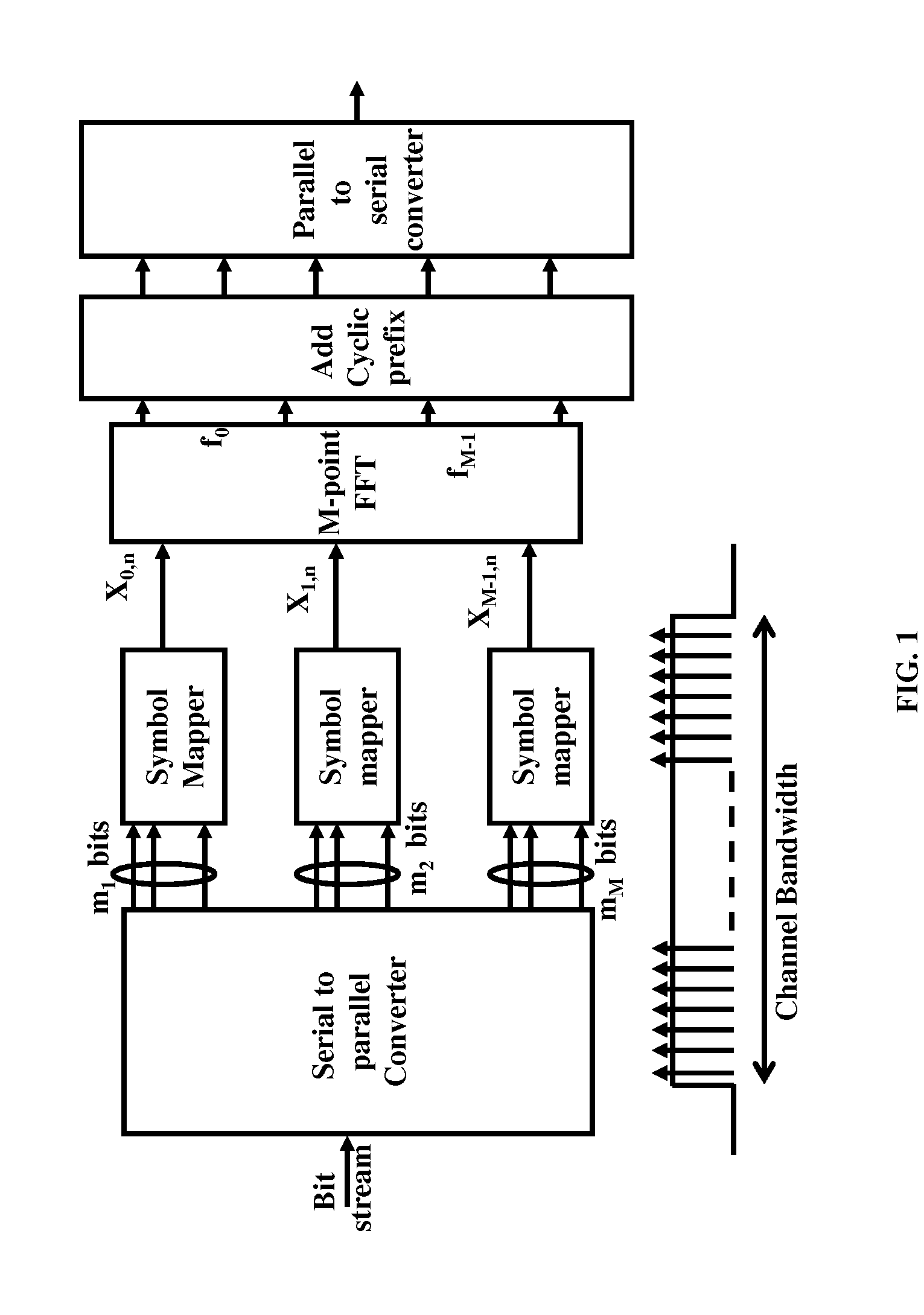
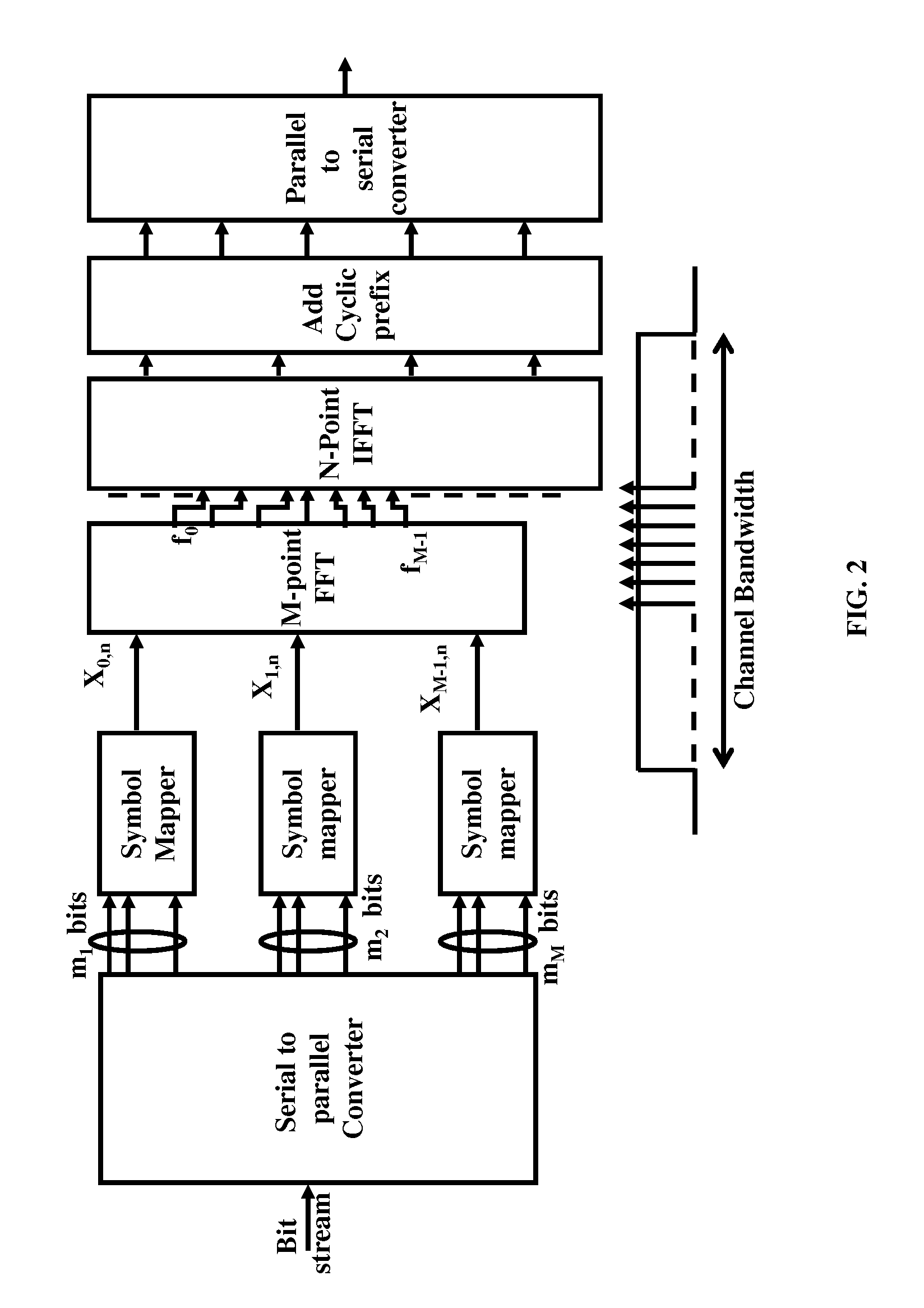
System and Method for Channel Estimation for Generalized Frequency Division Multiplexing (GFDM)
ActiveUS20150071242A1Channel estimationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTelecommunicationsEngineering
Embodiments are provided for pre-cancelling signal interference in Generalized Frequency Division Multiplexing (GFDM). Signal interference is pre-cancelled, at a transmitter, so that clean pilots are observed at a receiver and hence used for channel estimation. Using a Pilot-Interference Cancellation (Pilot-IC) method, interference is pre-cancelled at only pilot symbols. Alternatively, interference is simultaneously pre-cancelled at all symbols using a Transmitter IC (Tx-IC) method. The embodiments also include scattering the pilots over frequency and time resources to estimate channels which are frequency selective and time-variant. The channel estimates at the receiver are then used for single-tap channel equalization at time-frequency grid data points, where no assumption of time-invariant channels is required.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
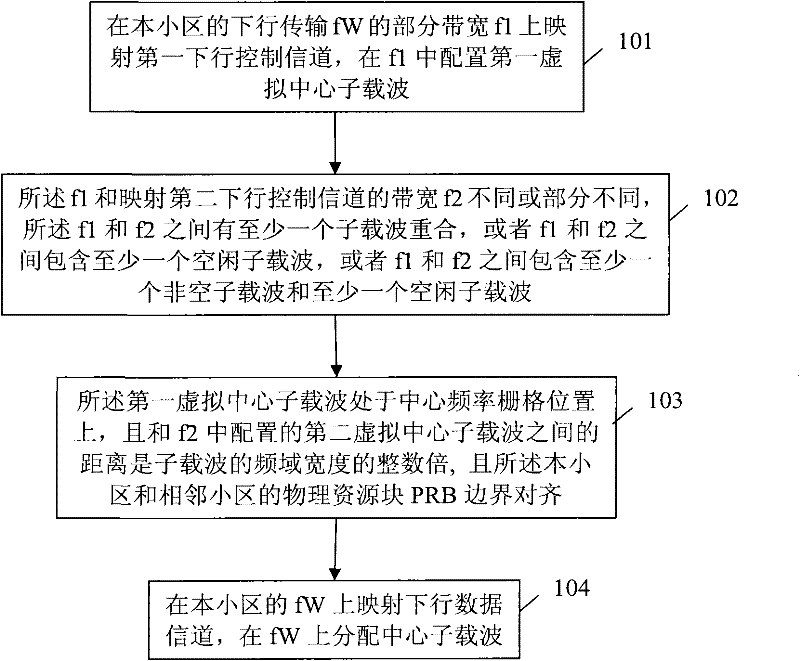
Central subcarrier configuring method and device
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
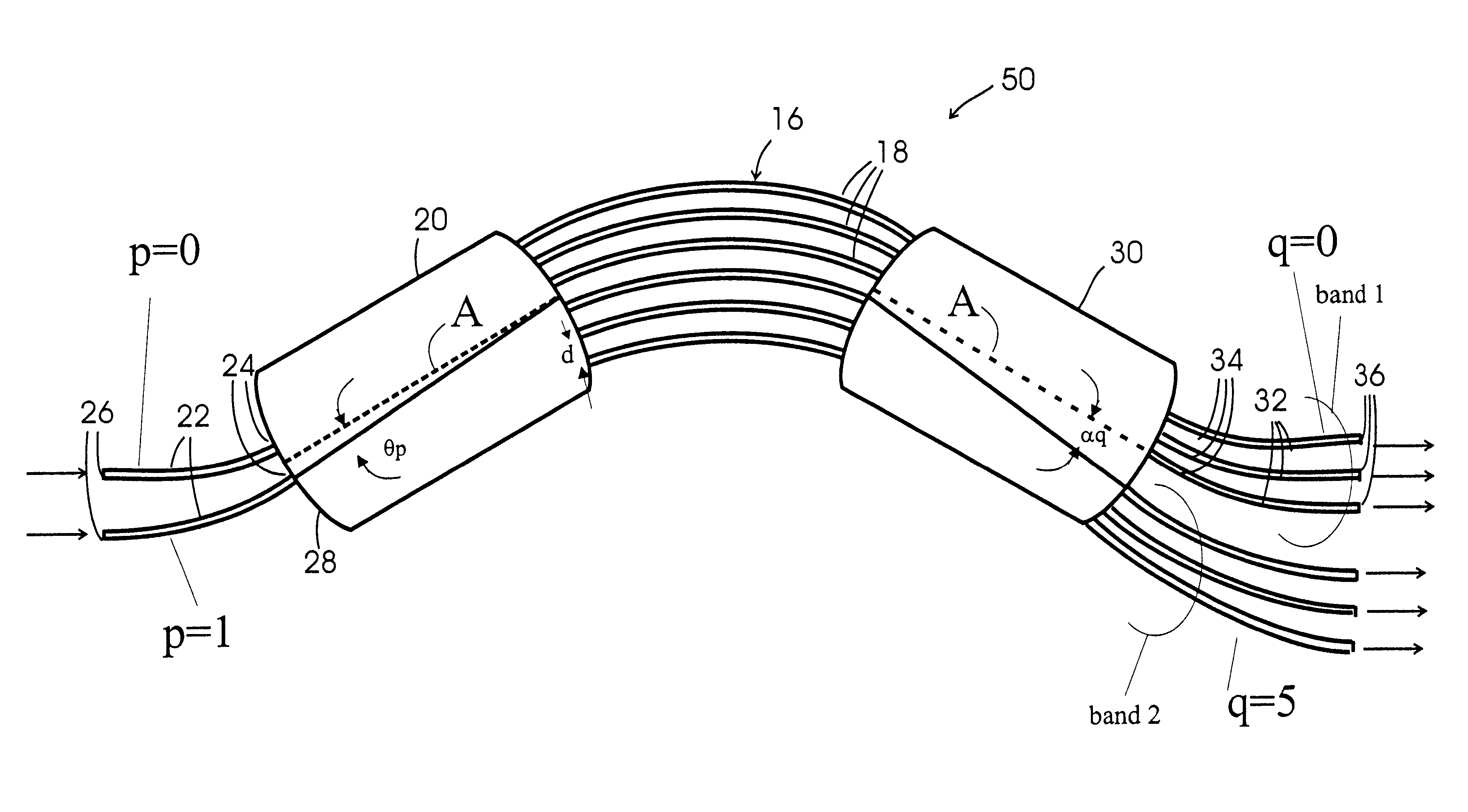
Multi-band arrayed waveguide grating
An arrayed waveguide grating router (AWGR) comprises sets of output waveguides for a number of bands. Angular separation of adjacent output waveguides is relatively small for adjacent output waveguides. within a band and significantly larger for adjacent output waveguides belonging to different bands. In specific embodiments the output waveguides are arranged into at least two bands, each band comprising at least two adjacent waveguides. Each band is used in conjunction with an input waveguide specific to the particular band. AWGRs according to the invention may be made so that the passbands from a plurality of output waveguides fall on a wavelength grid or a frequency grid. Dummy waveguides may be included for ease of fabrication.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
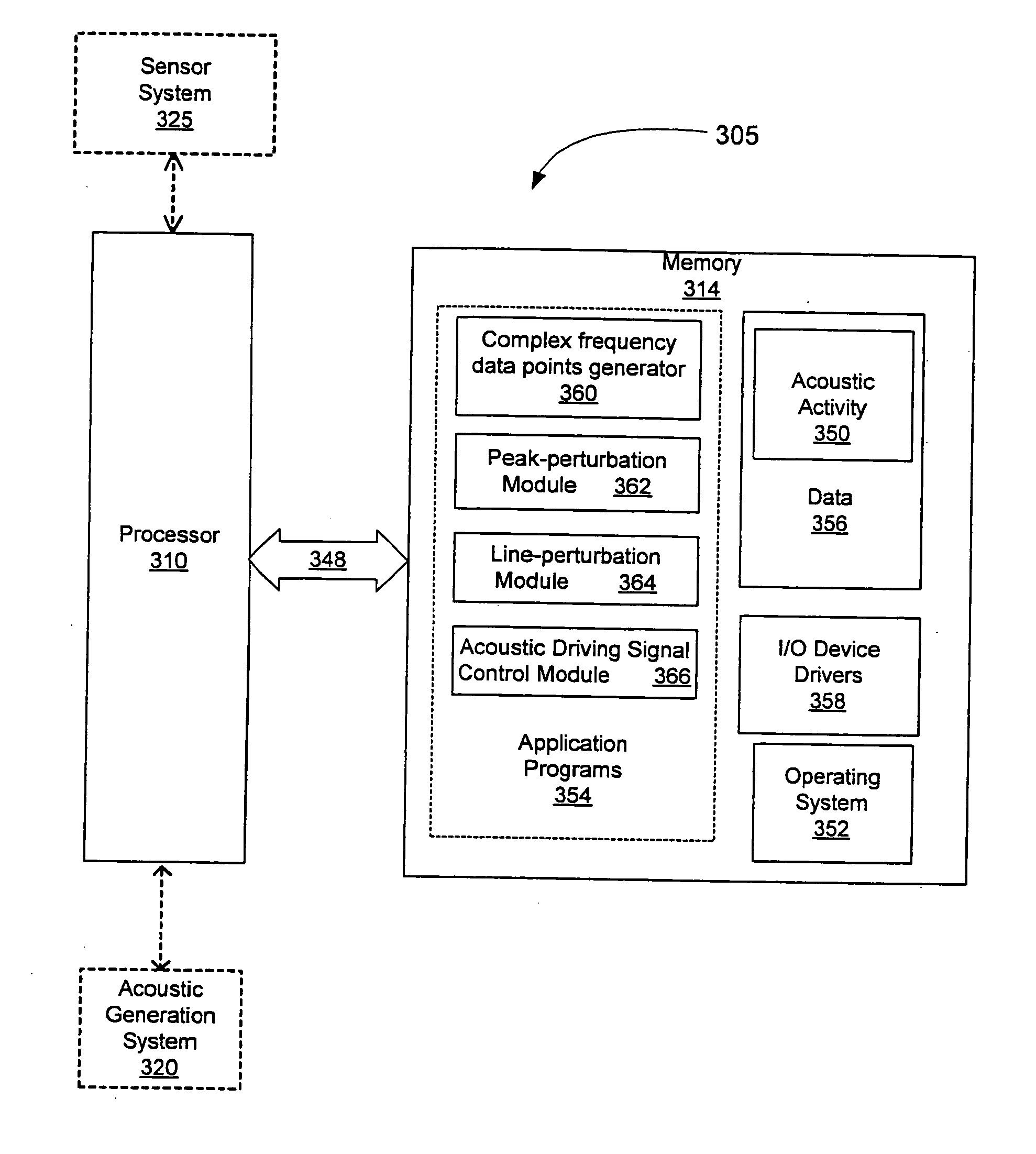
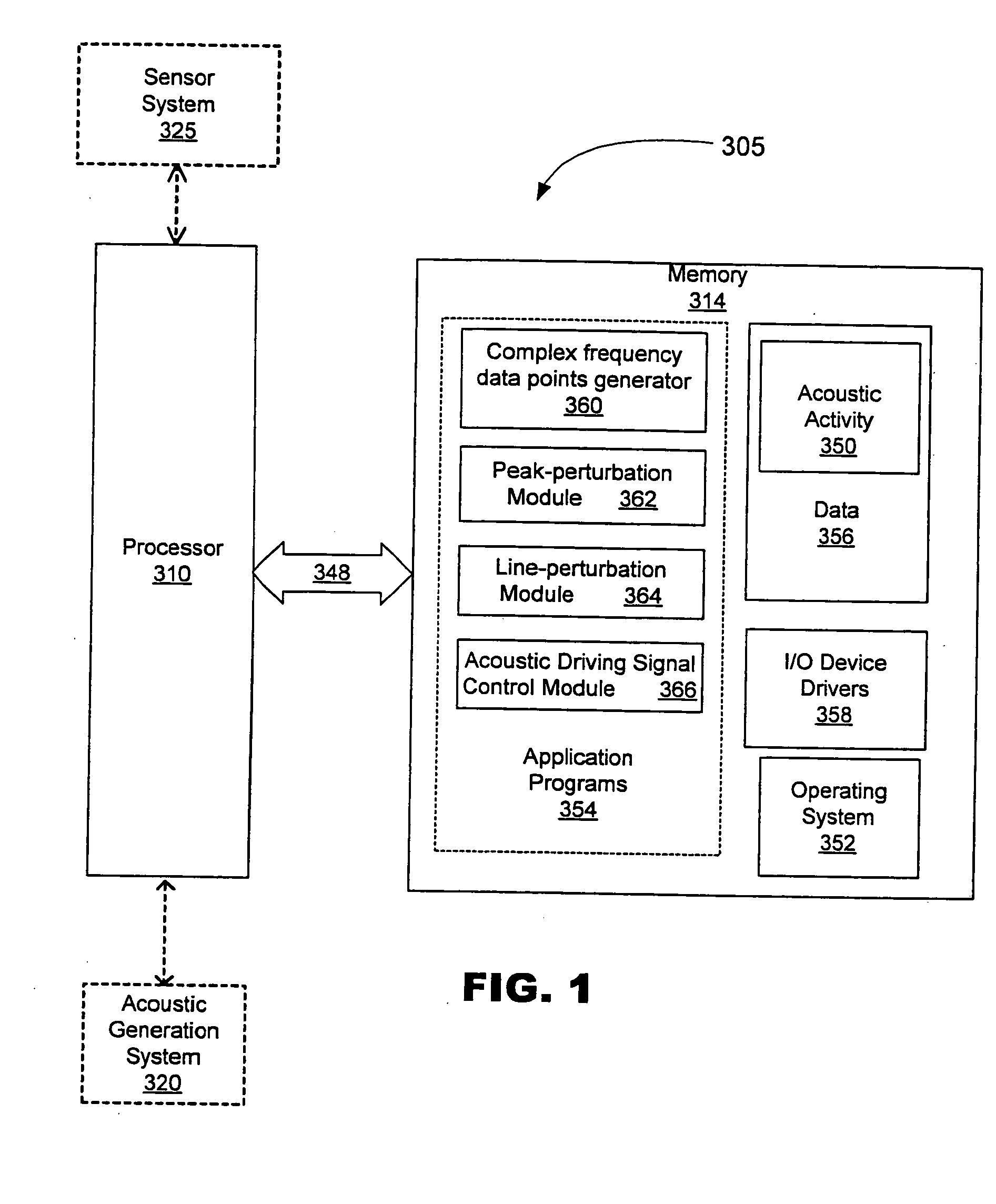
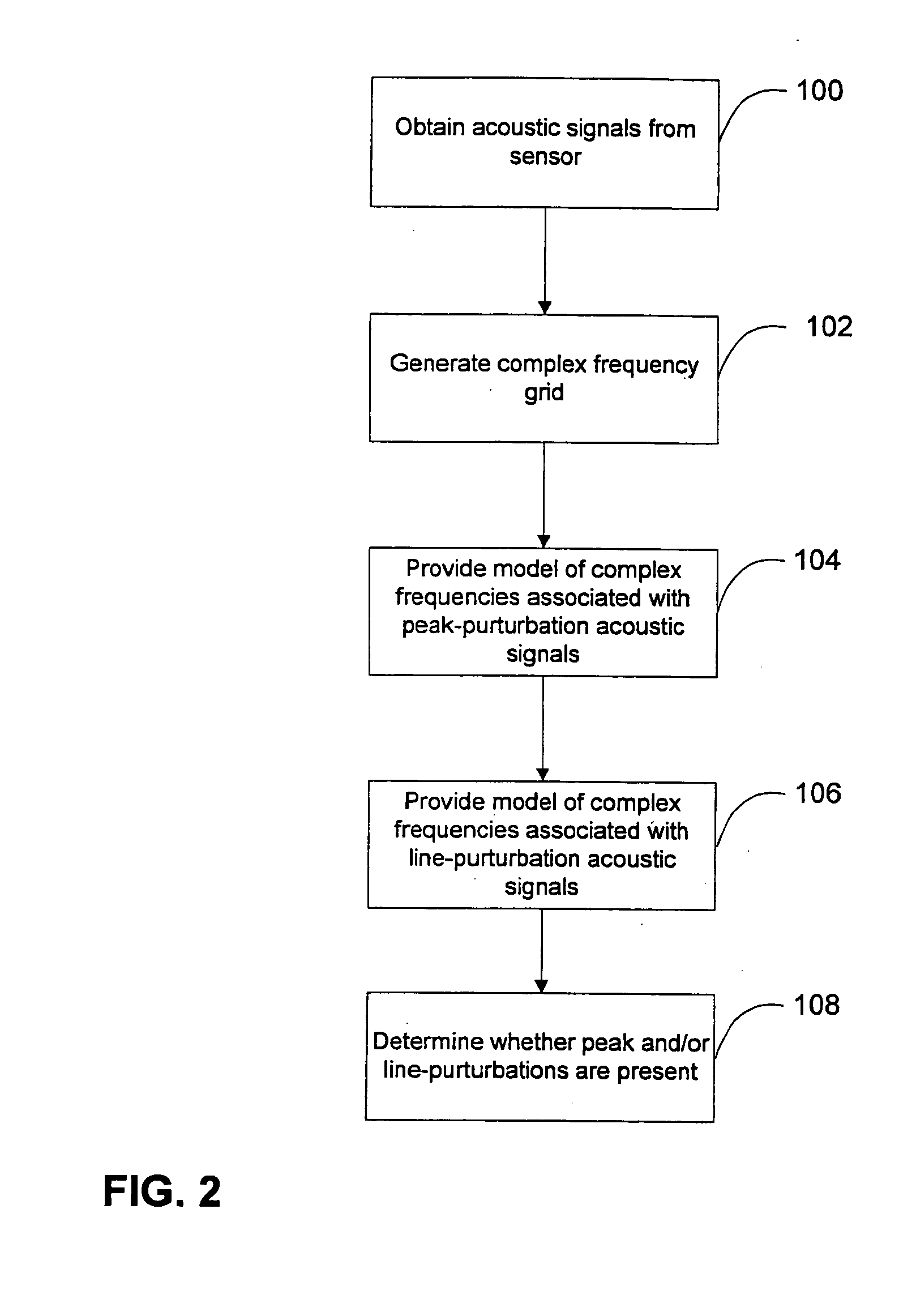
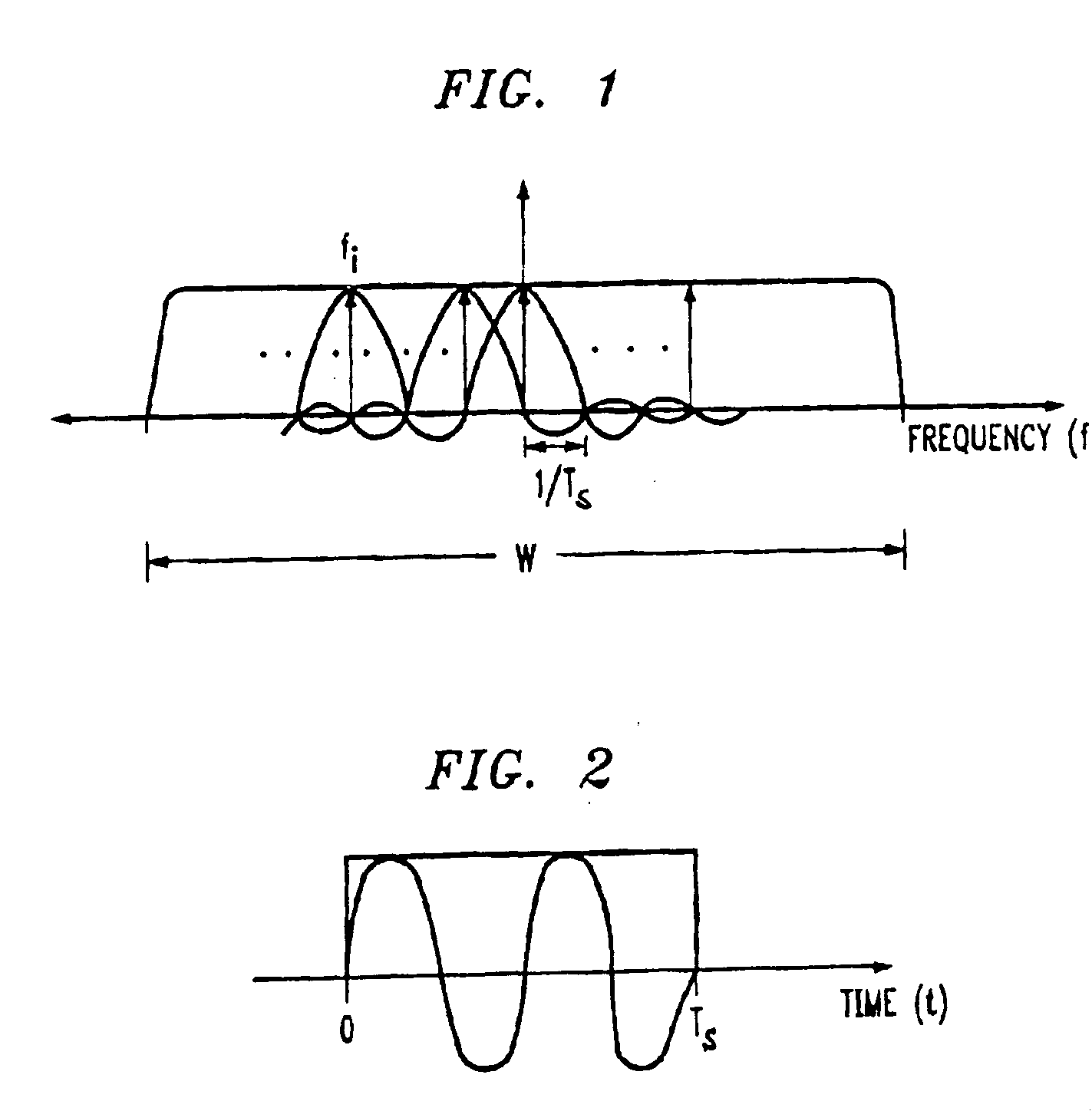
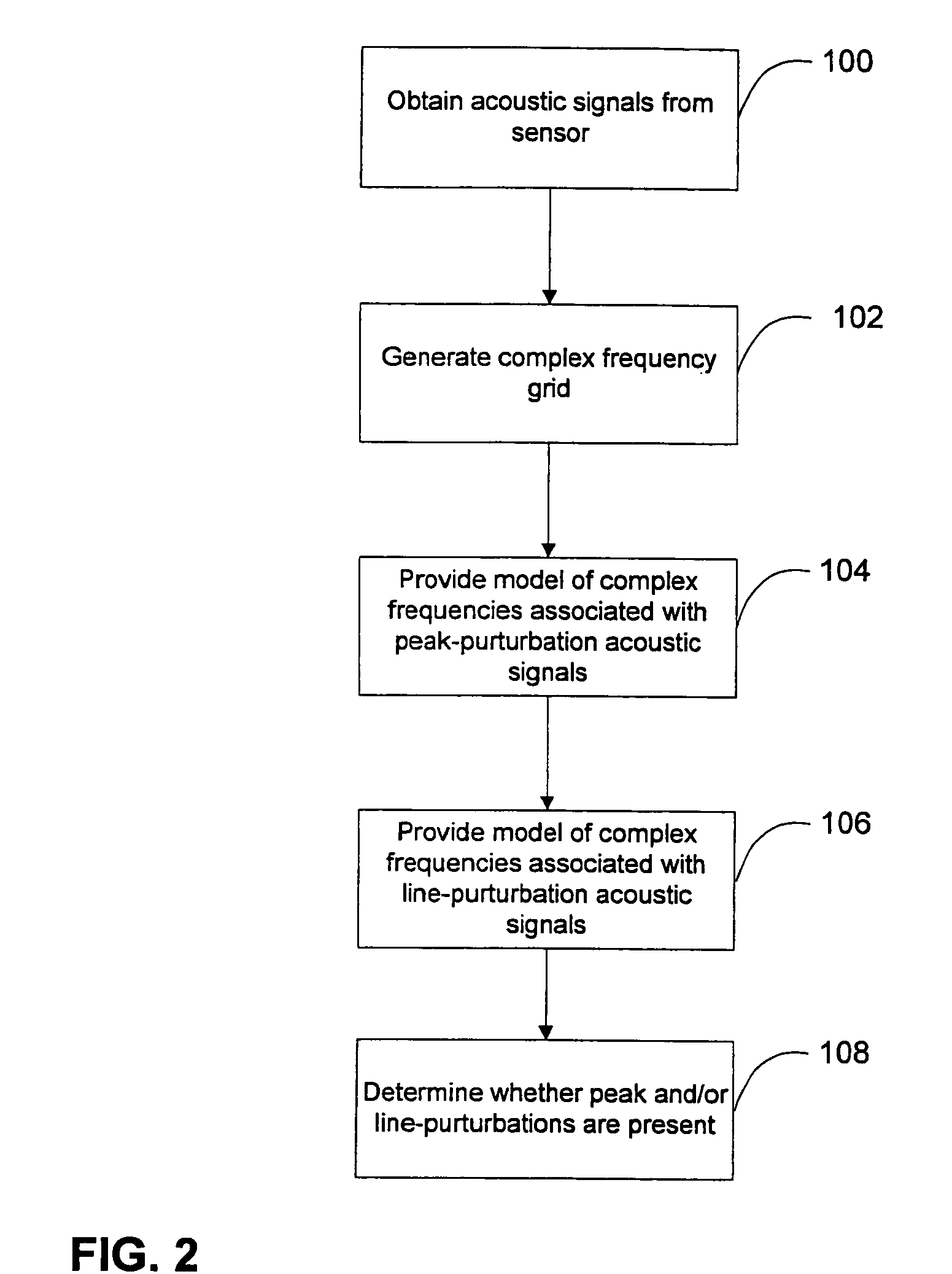
Methods, systems, and computer program products for analyzing cardiovascular sounds using eigen functions
Non-invasive methods for detecting arterial disease in vivo include obtaining acoustic signals from a sensor held on an external body region proximate an artery. A complex frequency grid of frequencies and associated lifetimes of the obtained acoustic signals is generated. A predictive model of complex frequencies associated with peak-perturbation acoustic signals attributed to boundary perturbations in vivo that occur with early stage arterial disease is provided. A predictive model of complex frequencies associated with line-perturbation acoustic signals attributed to boundary perturbations in vivo that occur with later stage arterial disease and thickening of arterial junctions is also provided. It is determined whether peak and / or line-perturbation acoustic signals of the predictive models are present to detect whether the subject has arterial disease.
Owner:EAST CAROLINA UNIVERISTY
Tunable optical filter
ActiveUS20090263142A1Small sizeWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumRetroreflector
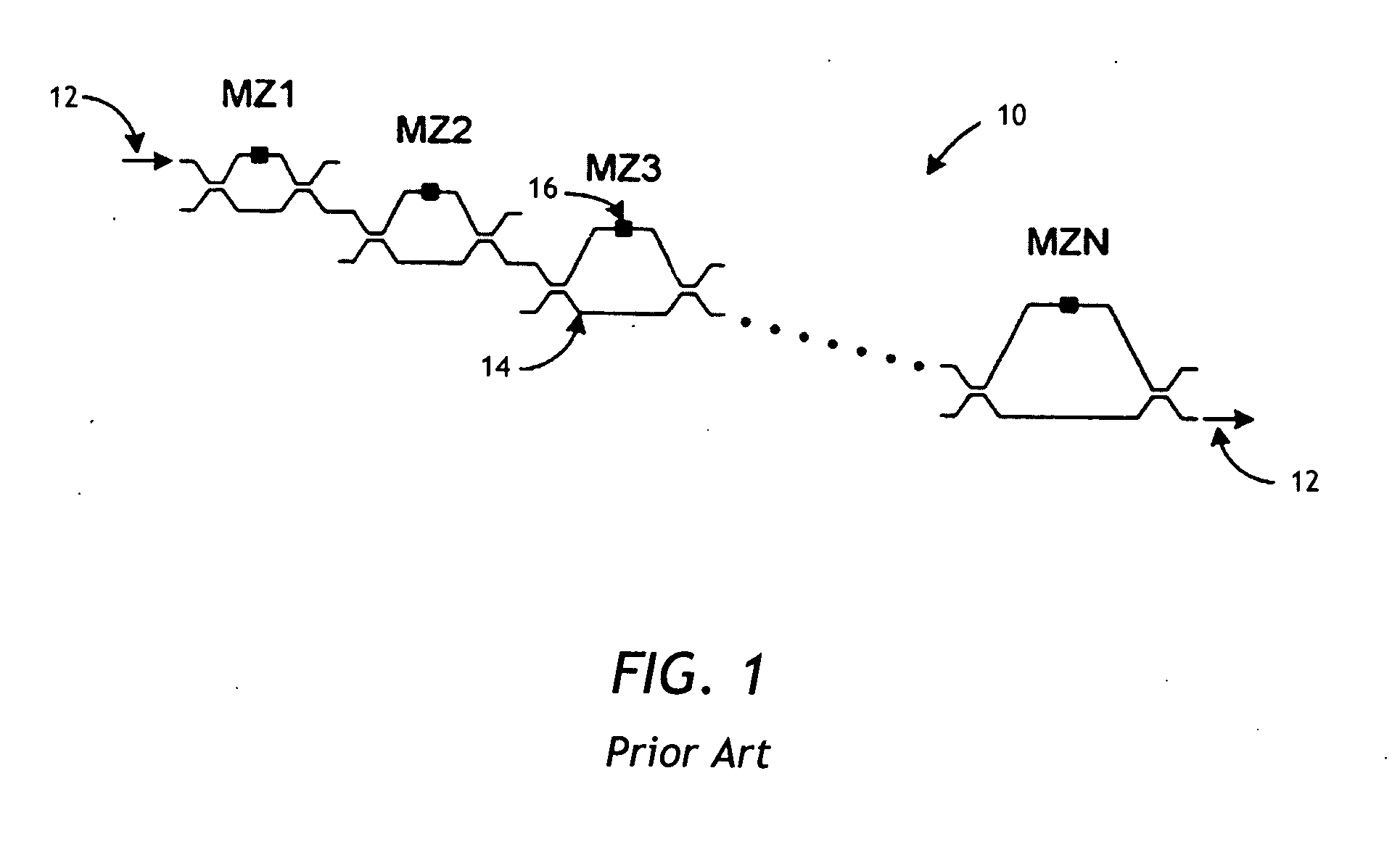
A tunable PLC optical filter having sequentially connected thermally tunable Mach-Zehnder (MZ) interferometers is described. The MZ interferometers, having free spectral ranges matching ITU frequency grid spacing, are tuned so as to have a common passband centered on the frequency of the signal being selected, while having at least one of the stopbands centered on any other ITU frequency. Any other optical channel that may be present at any other ITU frequency is suppressed as a result. The PLC chip, including a zero-dispersion lattice-filter interleaver stage, a switchable fine-resolution stage and, or a retroreflector for double passing the filter, is packaged into a hot-pluggable XFP transceiver package. A compensation heater is used to keep constant the amount of heat applied to the PLC chip inside the XFP package, so as to lessen temperature variations upon tuning of the PLC optical filter.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Pilot use in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing based spread spectrum multiple access systems
InactiveUS20060002452A1Radio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsSystem parametersSpread spectrum
Owner:QUALCOMM INC +1
Methods, systems, and computer program products for analyzing cardiovascular sounds using eigen functions
Non-invasive methods for detecting arterial disease in vivo include obtaining acoustic signals from a sensor held on an external body region proximate an artery. A complex frequency grid of frequencies and associated lifetimes of the obtained acoustic signals is generated. A predictive model of complex frequencies associated with peak-perturbation acoustic signals attributed to boundary perturbations in vivo that occur with early stage arterial disease is provided. A predictive model of complex frequencies associated with line-perturbation acoustic signals attributed to boundary perturbations in vivo that occur with later stage arterial disease and thickening of arterial junctions is also provided. It is determined whether peak and / or line-perturbation acoustic signals of the predictive models are present to detect whether the subject has arterial disease.
Owner:EAST CAROLINA UNIVERISTY
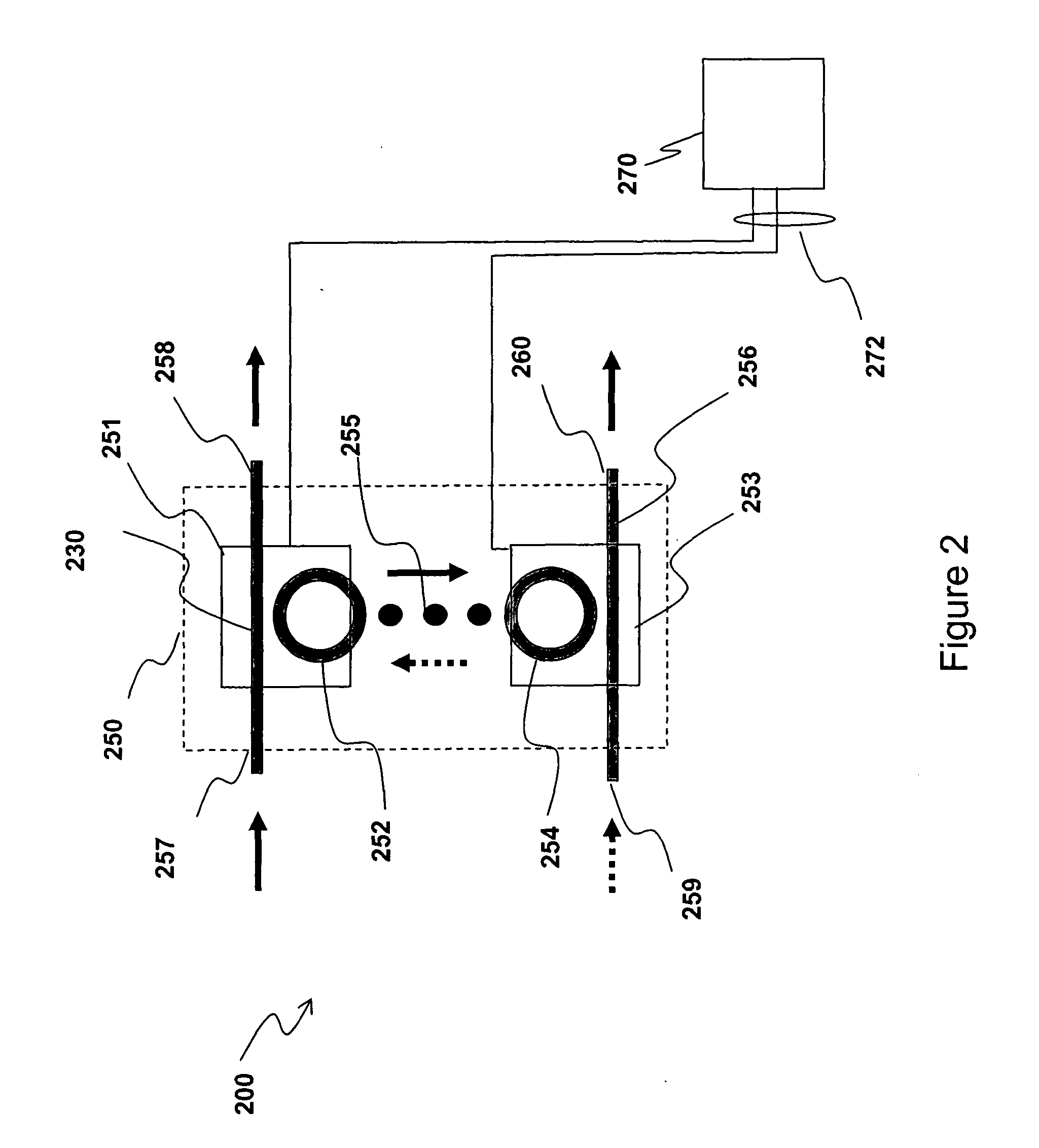
Method and device for hitless tunable optical filtering
ActiveUS20100183312A1Reduces alterationFast broadbandWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical frequenciesResonance
The method for filtering an optical signal comprising a plurality of channels lying on a grid of optical frequencies equally spaced by a frequency spacing and occupying an optical bandwidth, comprises: a) operating an optical filter comprising a plurality of resonators each having a respective free spectral range, wherein a first resonator of the plurality is optically coupled to the optical signal and the remaining resonators are optically coupled in series to the first resonator, so that a respective resonance of each one of the plurality of resonators falls within a first frequency band having bandwidth less than or equal to 15 GHz; b) operating the optical filter so as to obtain a separation between any resonance of at least one resonator falling within the optical bandwidth with respect to a resonance of at least another different resonator nearest to the any resonance, the separation being greater than or equal to 150 GHz and no more than 1 THz; c) tuning all the resonators of the optical filter so as to move all respective resonances of the resonators by a respective frequency interval greater than the frequency spacing while maintaining a distance between the any resonance of the at least one resonator with respect to the nearest resonance of the at least another different resonator not less than 150 GHz and no more than 1 THz; and d) operating the optical filter so that a further respective resonance of each one of the plurality of resonators falls within a second frequency band, different from the first frequency band, having bandwidth less than or equal to 15 GHz. A corresponding device for filtering an optical signal is disclosed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method for distributing data on an OFDM time-frequency grid allowing for coordination of interferences and adaptive subcarrier frequency allocation, a base transceiver station, a base station controller and a mobile network therefor
The invention concerns a method for distributing data on an OFDM time-frequency grid for data transmission from and to mobile terminals in a mobile network allowing for coordination of interferences between different cells of the mobile network and adaptive subcarrier frequency allocation to mobile terminals, whereby subcarrier frequencies of the OFDM time-frequency grid are gathered in frequency patterns, the frequency patterns are constructed to accommodate the use of pilot subgrids, a set of frequency patterns is changed in a pilot compatible manner between frequency diverse and frequency selective frequency patterns, and said frequency patterns are allocated to mobile terminals for data transmission , a base transceiver station, a base station controller and a mobile network therefor.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Phase response calibration method of nonlinear vector network analyzer based on fine frequency grid calibration
InactiveCN102087346AAchieving Phase AlignmentPhase calibration with high frequency resolutionResistance/reactance/impedencePhase responseImage resolution
The invention relates to a nonlinear vector network analyzer calibration method, in particular relating to a phase response calibration method of a nonlinear vector network analyzer based on fine frequency grid calibration. The method provided by the invention can be used for the problem that the existing phase response calibration method of a nonlinear network analyzer has low phase calibration frequency resolution. The method comprises: constructing an amplitude modulation signal xAM(t); constructing a fine frequency grid on both sides of a carrier frequency fc; calibrating the phase of a square law detector by use of the fine frequency grid to obtain the phase transmission standard of the fine frequency grid; and carrying out fine frequency phase calibration of the nonlinear vector network analyzer by use of the phase transmission standard of the fine frequency grid. The method is applicable to the phase calibration of the nonlinear vector network analyzer.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Group-based resource element mapping for radio transmission of data
ActiveCN105917610ATransmission path divisionInter user/terminal allocationTime domainResource element
For transmitting data over a radio interface using subframes with a plurality of resource elements organized in a time-frequency grid, at least two groups of resource elements are determined from the resource elements of one of the subframes. Each group covers multiple consecutive resource elements in the time domain and is distinct from the at least one other group in the frequency domain. Data symbols of a sequence are consecutively mapped to the resource elements of one of the groups. If a data symbol is mapped to each resource element of the group, the next data symbols of the sequence are consecutively mapped to the resource elements of a further one of the groups.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
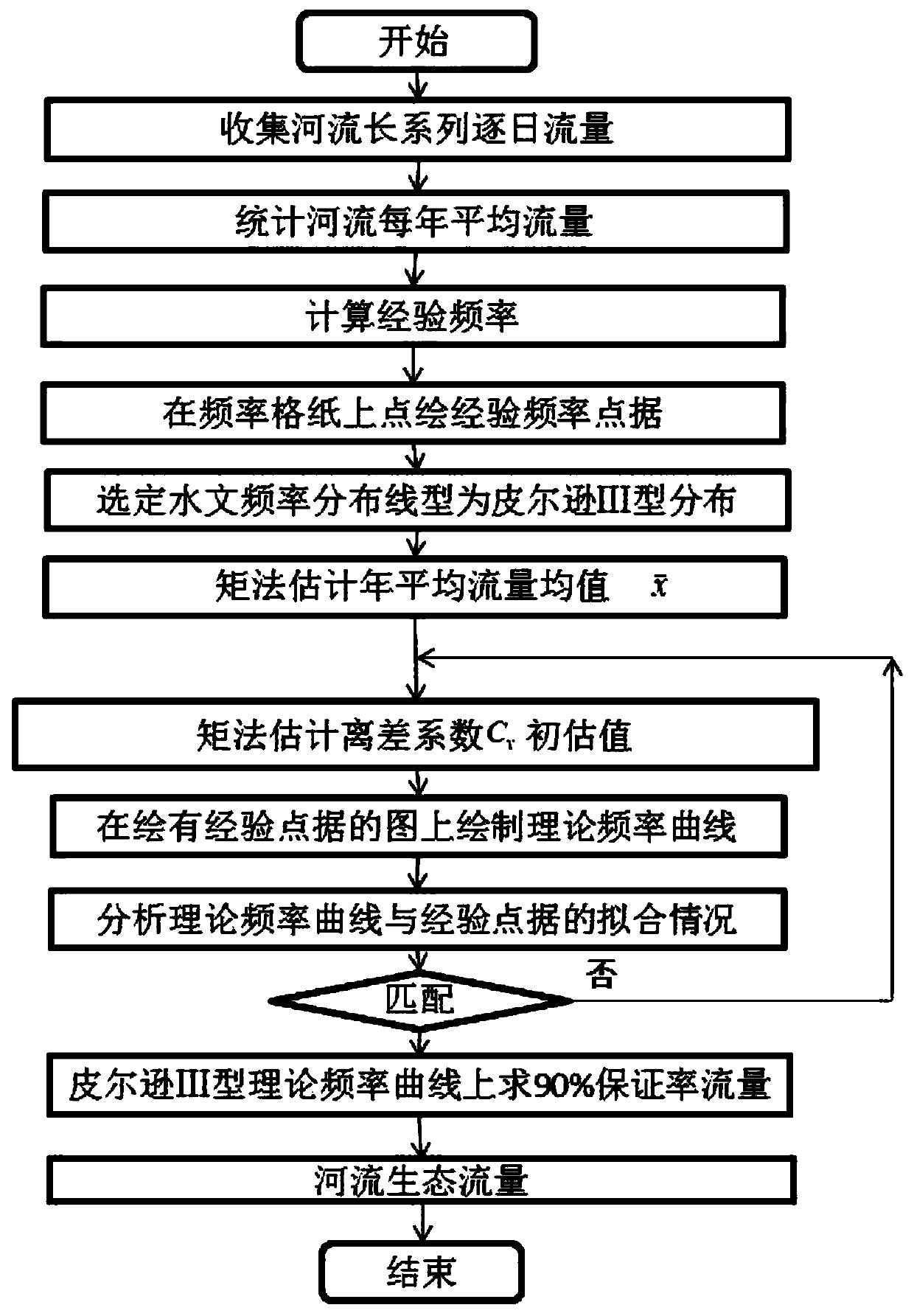
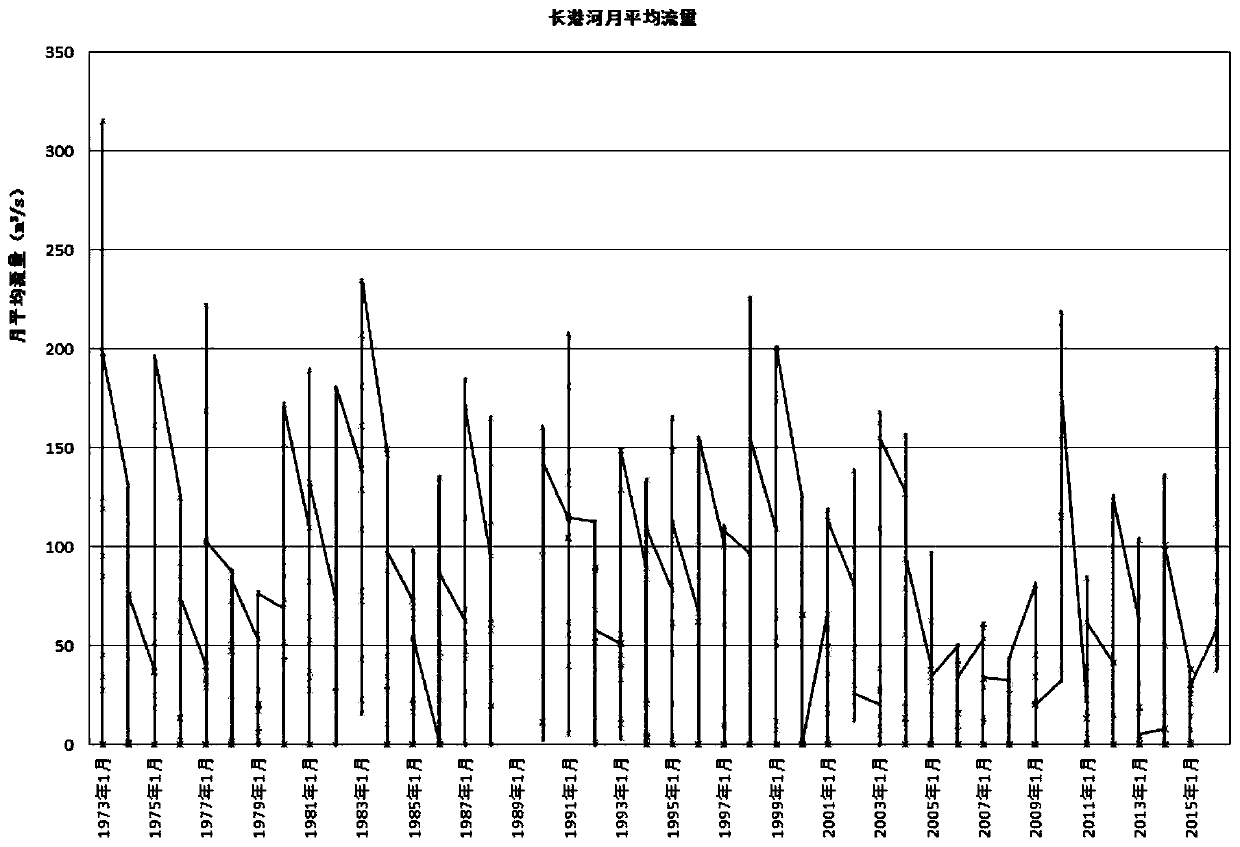
River ecological flow calculation method
InactiveCN110580327ARaw data and river flow data are completeComplete informationComplex mathematical operationsData seriesMeasurement point
The invention discloses a river ecological flow calculation method. The method comprises the steps of collecting long-series day-by-day flow data of a river hydrological survey station, counting annual average flow, arranging the annual average flow as a data series according to a descending order no matter what the annual sequence is, calculating an experience frequency greater than or equal to the corresponding annual average flow in the series, and plotting an experience frequency point data graph on frequency grid paper; selecting a hydrological frequency distribution line type as PearsonIII type distribution; estimating initial estimation values of an average flow mean value and a deviation coefficient by using a moment method, calculating flow values corresponding to different accumulated frequencies, drawing a Pearson III-type theoretical frequency curve, judging a fitting condition of the Pearson III-type theoretical frequency curve and experience point data, and if the Pearson III-type theoretical frequency curve is matched with the experience point data, taking a parameter corresponding to the curve as an estimation value of an overall parameter; and finally, solving a flow value of 90% guarantee rate on the Pearson III-type theoretical frequency curve, namely the river ecological flow. The lower end or the upper end of the empirical frequency curve can be extended,and the defect of no actual measurement point data is overcome.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
User signal transmitting and receiving method, apparatus and system in ofdma system
InactiveUS20100296385A1Reduce various interferenceImprove performanceTransmission path divisionSecret communicationTime domainCarrier signal
This invention provides a user signal transmitting method in an OFDMA system, where all the time-frequency grids of each timeslot are divided into sub-channels, each sub-channel comprises Nf sub-carriers overlapping in time, Nf≧4, and in each sub-channel, a maximum value of a frequency interval between adjacent sub-carriers is no less than three times of a minimum value thereof; and when a user message is sent, comprising: generating a modulating signal; allocating a time-frequency grid set which is a union set of sub-channel, where the sub-channel's quantity is determined by the user message's size, and the sub-channel's time-frequency position is selected according to a rule; and mapping the modulating signal to the time-frequency grid set to generate a frequency-domain signal; performing IFFT on the frequency-domain signal to generate a time-domain signal for transmission. This invention also provides a corresponding user signal receiving method, user signal transmitting and receiving apparatus and access system.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
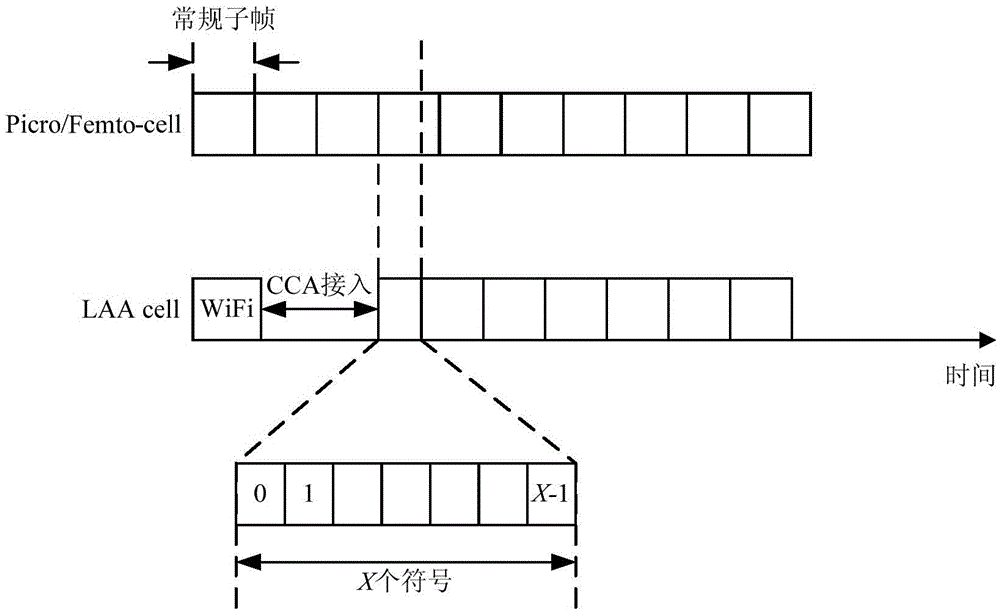
Downlink transmission method and system for unauthorized spectrum
InactiveCN106851827AImprove throughputGuaranteed normal transmissionWireless communicationCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a downlink transmission method and system for an unauthorized spectrum. The downlink transmission method comprises the following steps: sequentially performing symbol division from one end of each of partial subframes according to the number of symbols of the partial subframes; calculating the sizes of schedulable resource blocks of the partial subframes according to the number of the symbols and the sizes of pre-allocated resource blocks; calculating the time-frequency grid of downlink transmission according to the sizes of the schedulable resource blocks and the number of the symbols; and mapping the PDSCH resource and downlink reference signals to the time-frequency grid to perform downlink transmission according to a preset mapping rule, wherein the mapping positions of the PDSCH resource and the downlink reference signals are not overlapped. By adopting the downlink transmission method and system disclosed by the invention, the technical problem of effectively performing downlink transmission on the partial subframes can be solved, and the throughput of communication systems can be increased.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
Signal Transmission Method and Apparatus for OFDMA Wireless Communication System
InactiveUS20100208676A1Improve signal transmission stabilityImprove interferenceTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationLoading factorCommunications system
Embodiments of the present invention provide a signal transmission method and apparatus used in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) wireless communication system, to enhance stability of signal transmission and resist time-frequency dispersion. The signal transmission method used in the OFDMA wireless communication system provided by an embodiment of the invention includes: converting an L×1 symbol vector into an N×1 modulating signal vector according to a loading factor fed back by a receiving party, in which value of N is known, both L and N are natural numbers larger than one, N is larger than or equal to L, the loading factor is a ratio of L and N; mapping the N×1 modulating signal vector into N time-frequency grids; and converting the N time-frequency grids into a signal waveform and sending the signal waveform to the receiving party.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
Method and device for hitless tunable optical filtering
ActiveUS20100196014A1Reduces alterationLow-costWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesPhysicsFrequency band
The method for filtering an optical signal comprising a plurality of channels lying on a grid of optical frequencies equally spaced by a frequency spacing and occupying an optical bandwidth, comprises: a) operating an optical filter comprising a plurality of resonators, wherein a first resonator of the plurality is optically coupled to the optical signal and the remaining resonators are optically coupled in series to the first resonator, so that a respective resonance of each one of the plurality of resonators falls within a first frequency band having bandwidth less than or equal to 15 GHz; b) operating the optical filter so as to obtain a separation between said respective resonance of at least one resonator with respect to said respective resonance of at least another different resonator, the separation being greater than or equal to 25 GHz; c) operating the optical filter so that said respective resonance of each one of the plurality of resonators falls within a second frequency band, different from the first frequency band, having bandwidth less than or equal to 15 GHz, wherein during the procedure from step a) to step c), at least one among said respective resonance of the at least one resonator and said respective resonance of the at least another different resonator is moved also outside a frequency region spanning between, and including, the first and the second frequency band. A corresponding device for filtering an optical signal is disclosed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Tunable optical filter
ActiveUS8340523B2Small sizeWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionRetroreflectorMaterials science
A tunable PLC optical filter having sequentially connected thermally tunable Mach-Zehnder (MZ) interferometers is described. The MZ interferometers, having free spectral ranges matching ITU frequency grid spacing, are tuned so as to have a common passband centered on the frequency of the signal being selected, while having at least one of the stopbands centered on any other ITU frequency. Any other optical channel that may be present at any other ITU frequency is suppressed as a result. The PLC chip, including a zero-dispersion lattice-filter interleaver stage, a switchable fine-resolution stage and, or a retroreflector for double passing the filter, is packaged into a hot-pluggable XFP transceiver package. A compensation heater is used to keep constant the amount of heat applied to the PLC chip inside the XFP package, so as to lessen temperature variations upon tuning of the PLC optical filter.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
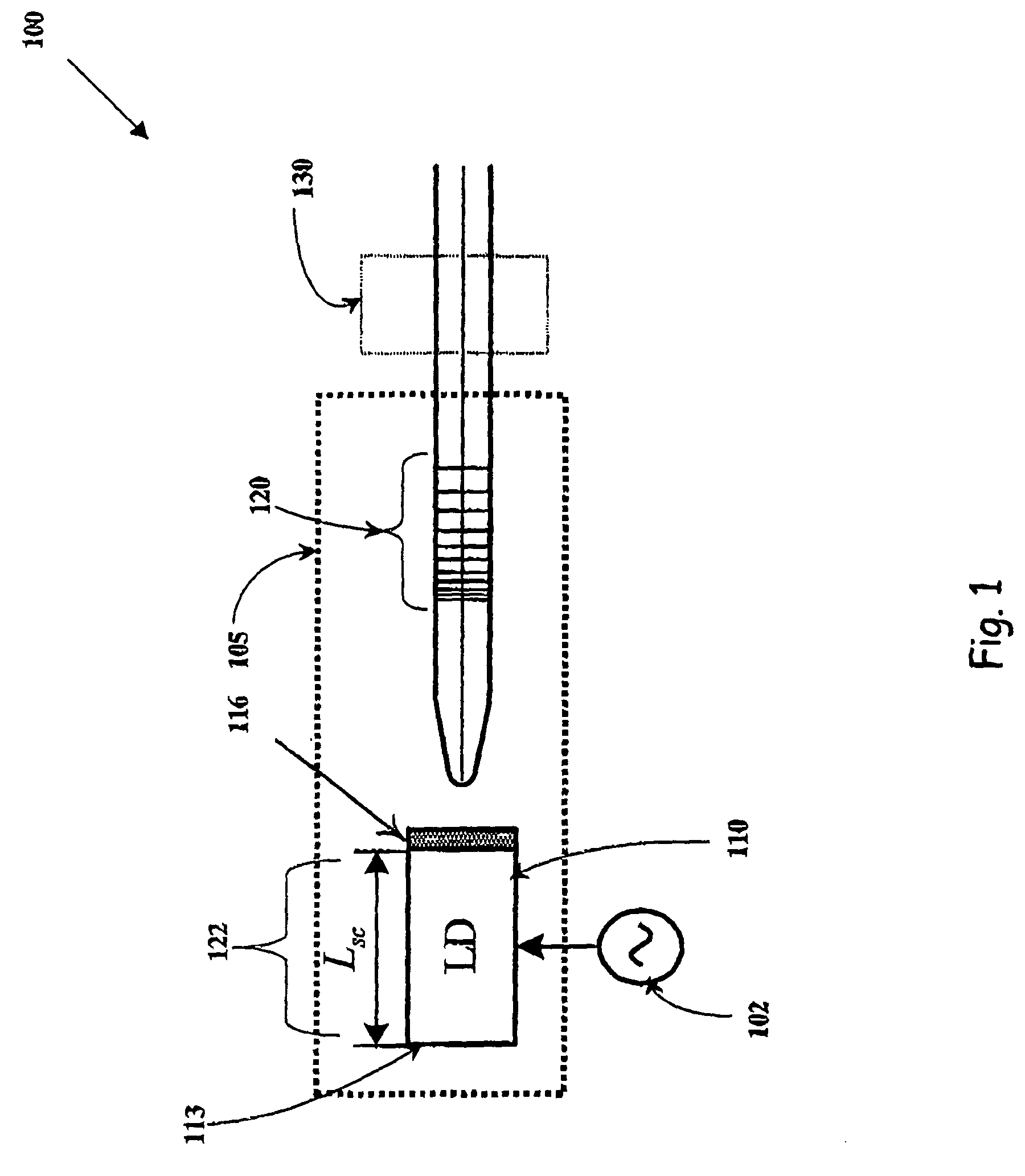
Tunable laser with a fixed and stable wavelength grid especially useful for WDM in fiber optic communication systems
InactiveUS7046704B2Efficient modulationAccurate placementLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionFrequency stabilizationOptical frequencies
A wavelength tunable mode-locked laser system including a complex laser cavity comprising a broadband reflective mirror at one end and a wavelength chirped selective mirror at the other end. The system further includes a gain element and a low finesse Fabry-Perot etalon element inside the laser cavity. The gain element may be a semiconductor laser chip, with a broadband high reflection coating at one end and a partially reflecting coating at its other end. The gain element has a well-defined length, such that its longitudinal modes match a required optical frequency grid. The system also includes an active modulation element applied externally on said complex laser cavity to provide mode-locking of a specific cavity length among said defined predetermined cavity lengths, such that all possible optical frequencies emitted by the laser system are stabilized to the linear grid dictated by the Fabry-Perot longitudinal modes, that could be in accordance with the International Telecommunications Union Standards.
Owner:MRV COMM LTD 50
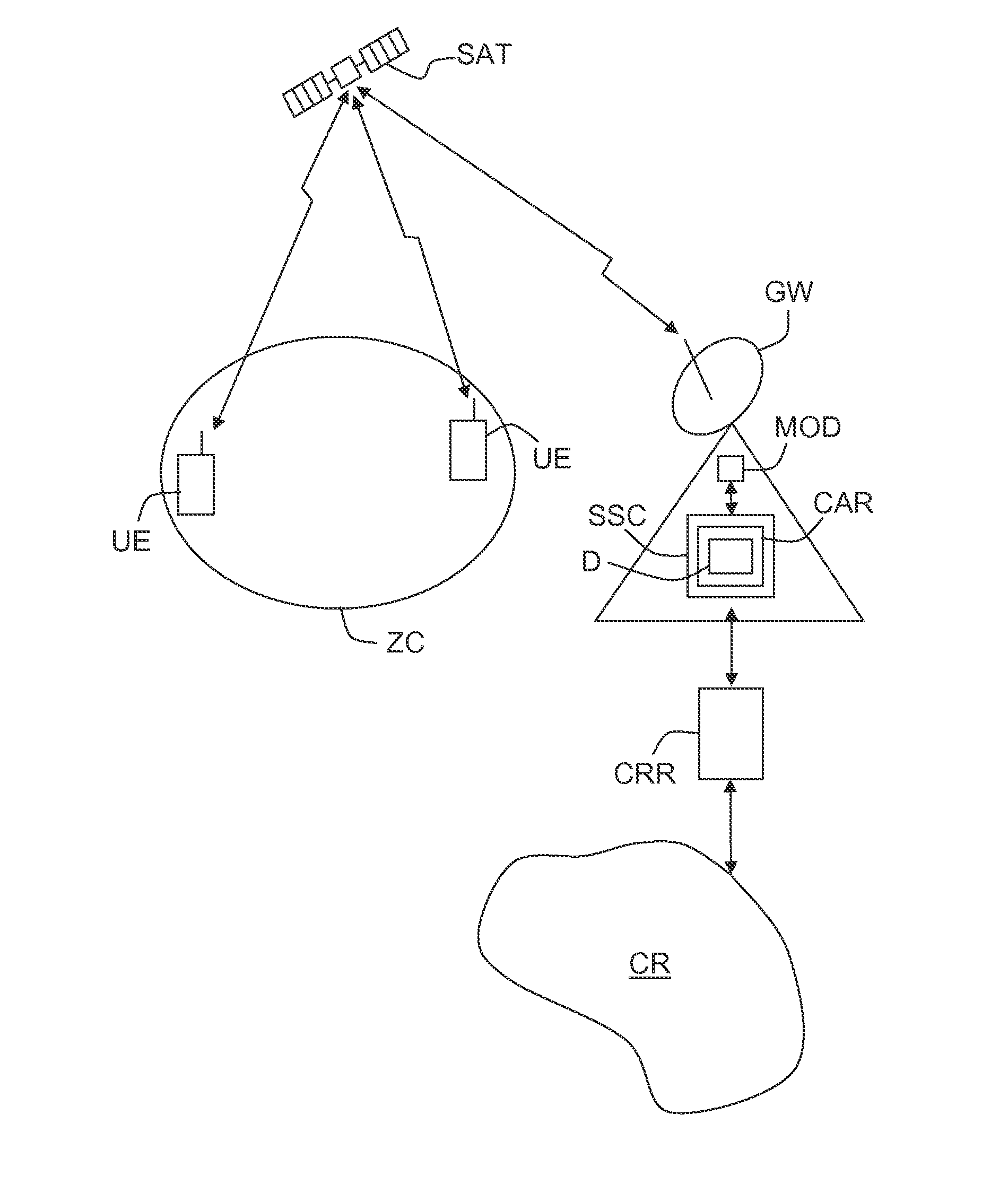
Method of dynamic allocation of shared resources in a time-frequency plan and associated device
ActiveUS20140112302A1Network traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
A method is provided of dynamic allocation of shared resources in a communication network, consisting in defining, in a time-frequency plan, a superframe of a given duration ΔT and a given spectral width Δf, made up of one or more frames, each defining a regular time-frequency grid, of which one square, referred to as a time-frequency unit, constitutes the smallest time and frequency interval allocable to a user of said network within said frame, said method consisting in reserving, on each carrier frequency of a frame, at least one block of a number K, greater than or equal to 1, of time-frequency units which can be dynamically allocated to a user for communication or for synchronization.
Owner:THALES SA +1
Flat-top tunable filter
InactiveUS20140293393A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsNon symmetricCenter frequency
A tunable PLC optical filter having sequentially connected thermally tunable Mach-Zehnder (MZ) interferometers is described. The cascade of MZ interferometers, each having a free spectral ranges matching ITU frequency grid spacing, are tuned so as to have a common passband centered on the frequency of the signal being selected, while having at least one of the stopbands centered on any other ITU frequency. Any other optical channel that may be present at any other ITU frequency is suppressed as a result. Another MZ interferometer in series with the cascade of interferometers including an asymmetric or variable coupler, is tuned to have low transmission at the center frequency of the selected optical channel.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Method and device for sequencing frequency points of LTE (Long Term Evolution) system
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and device for sequencing frequency points of an LTE (Long Term Evolution) system, relating to the field of communication and being capable of realizing the rapid sequencing of the frequency points of the LET system and increasing sequencing accuracy. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of: acquiring filter data of preset frequency bands; determining bandwidth enabling signs of the frequency bands corresponding to the filter data, and merging the frequency bands corresponding to the filter data according to the bandwidth enabling signs to obtain a merged frequency band, wherein the bandwidth enabling signs are true or false; acquiring signal power at each frequency grid inside the frequency bands corresponding to the filter data; calculating a power window specific value at each frequency point inside the merged bandwidth according to the merged frequency band and the signal power at the frequency grids; and sequencing the frequency points according to the magnitudes of the power window specific values correspondingly. The embodiment of the invention is mainly applied in a process for sequencing the frequency points of the LTE system.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
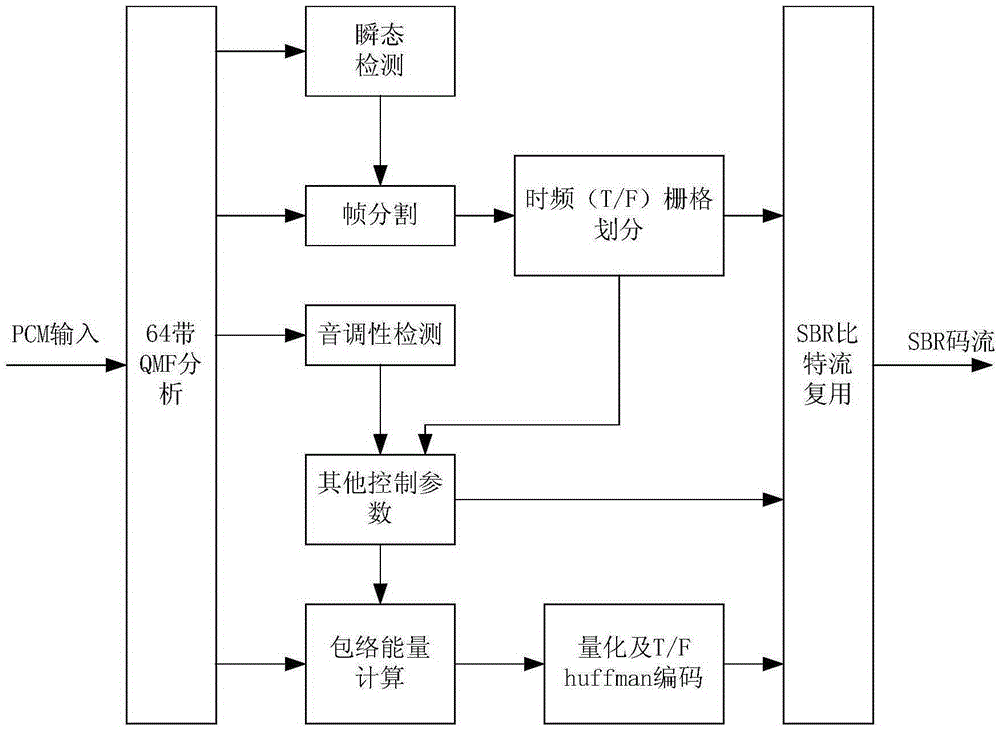
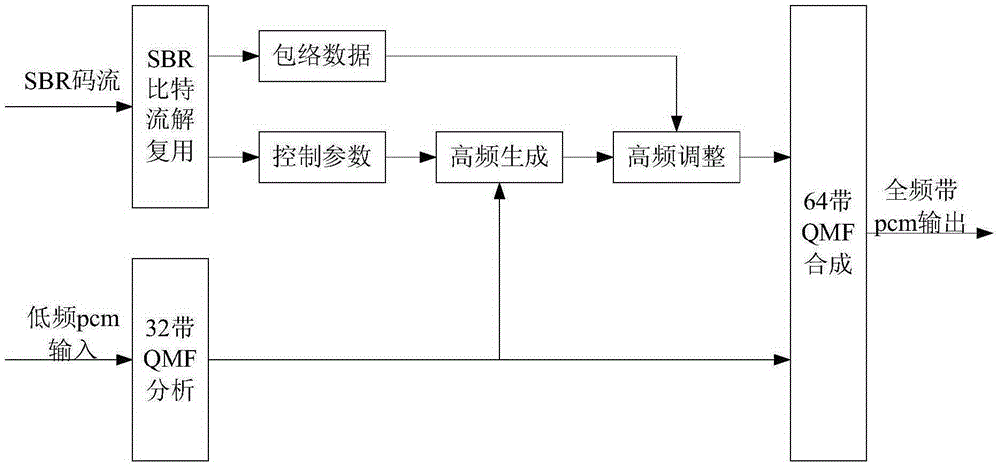
Bandwidth extension coding and decoding method and apparatus
ActiveCN105280190AImprove coding efficiencyImprove sound qualitySpeech analysisSound qualityPerceptual coding
The invention relates to a bandwidth extension coding and decoding method and apparatus. The combination of adaptive multiresolution filtering and adaptive time-frequency grid structure and a plurality of linear prediction encoding high-frequency details generates two key technologies, so that the high-frequency part encoding efficiency of digital audio signals and the sound quality of high-frequency part signals can be obviously improved, the low-frequency part of the digital audio signals can still be encoded by means of the traditional perceptual audio coding (for example DRA), and the encoding technology with high subjective sound quality at low bit rate and medium bit rate is realized. In another aspect, an enhancement tool is added on the basis of a current high-quality perceptual coding algorithm such as the DRA, in this way, the downward compatibility with the traditional perceptual coding DRA or other algorithms can be guaranteed. A digital audio encoding and decoding device based on the bandwidth extension coding and decoding method and apparatus can be applied to the fields of satellite HDTV sound accompaniment processing and high-quality audio broadcasting.
Owner:广东广晟研究开发院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com