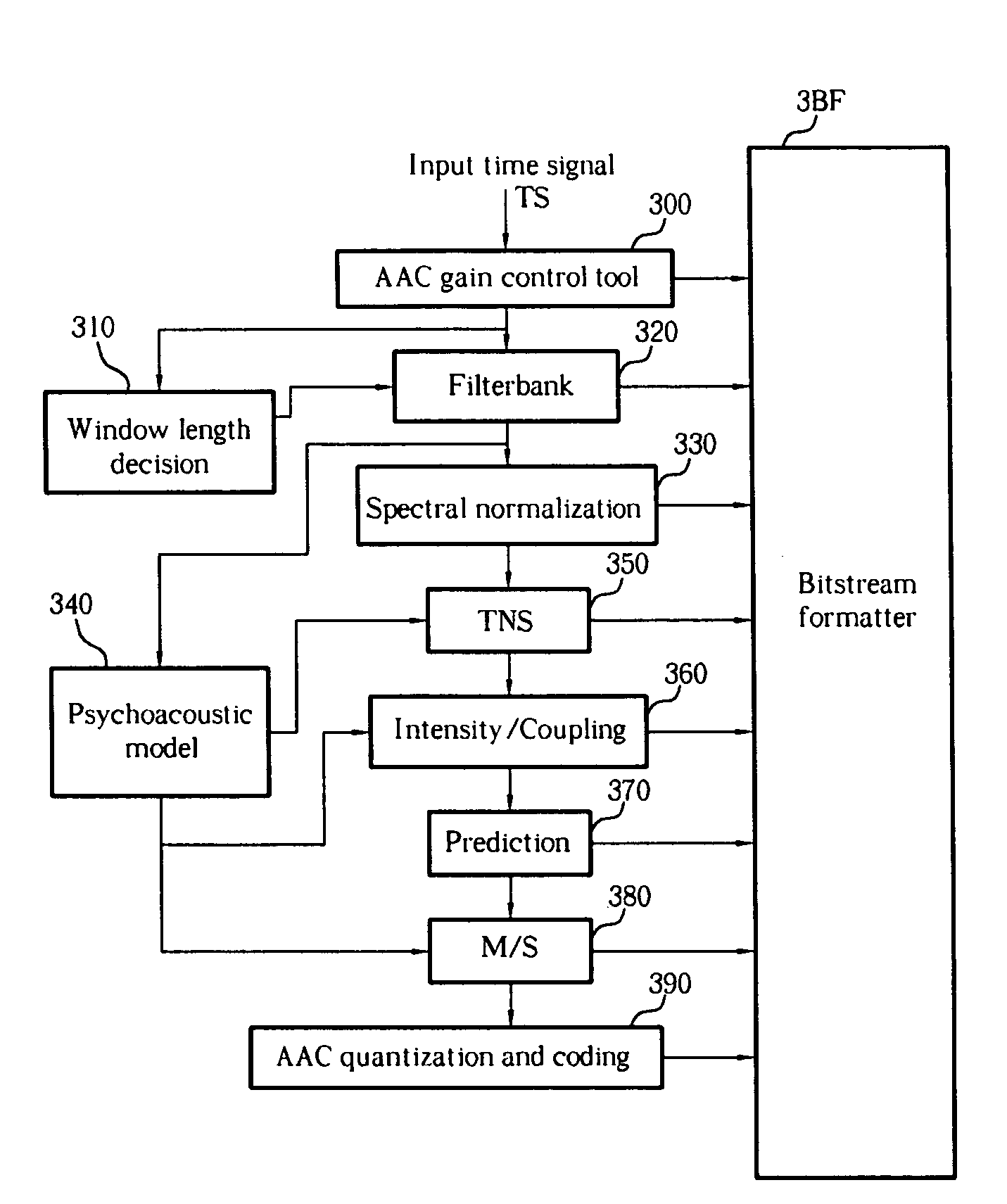
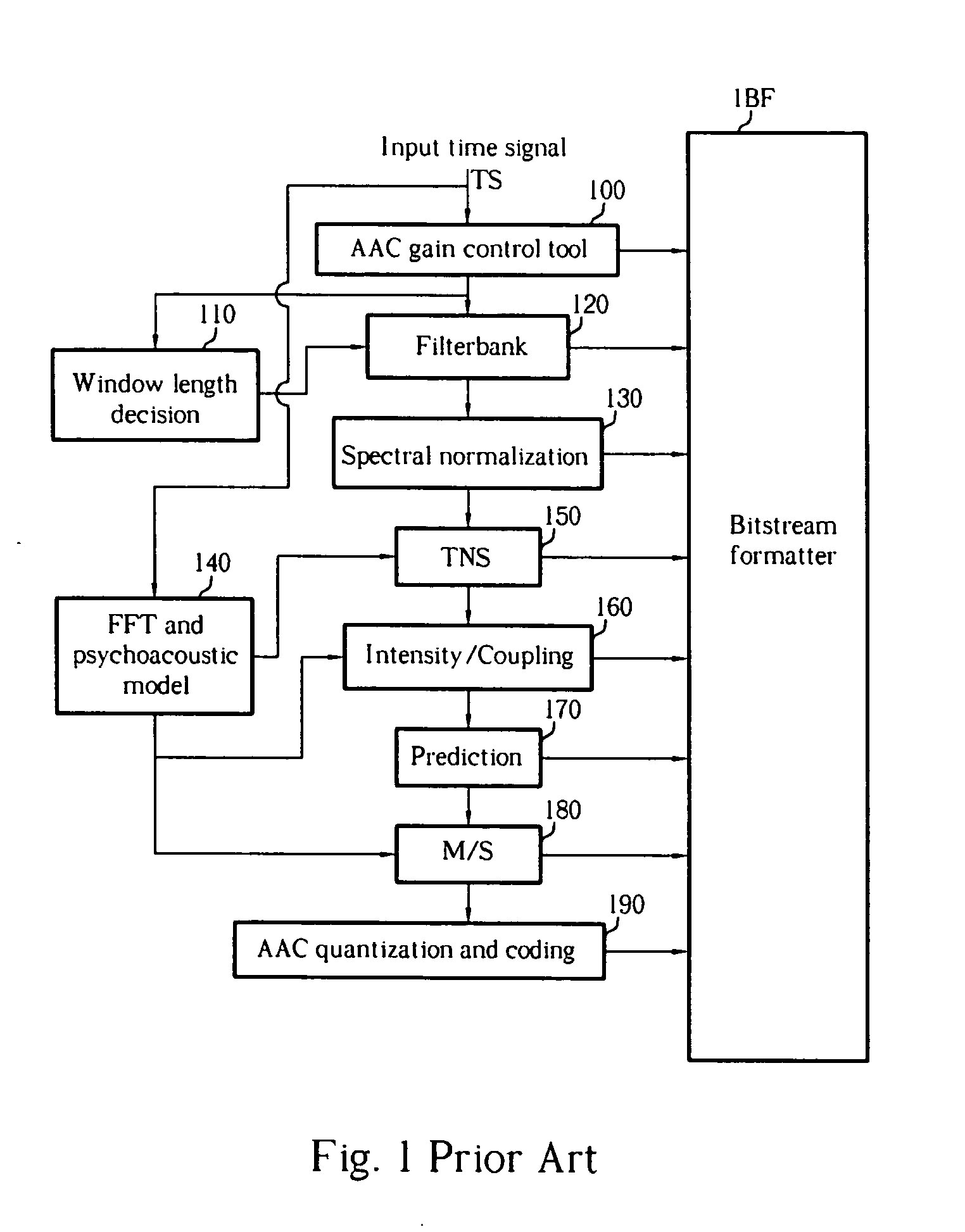
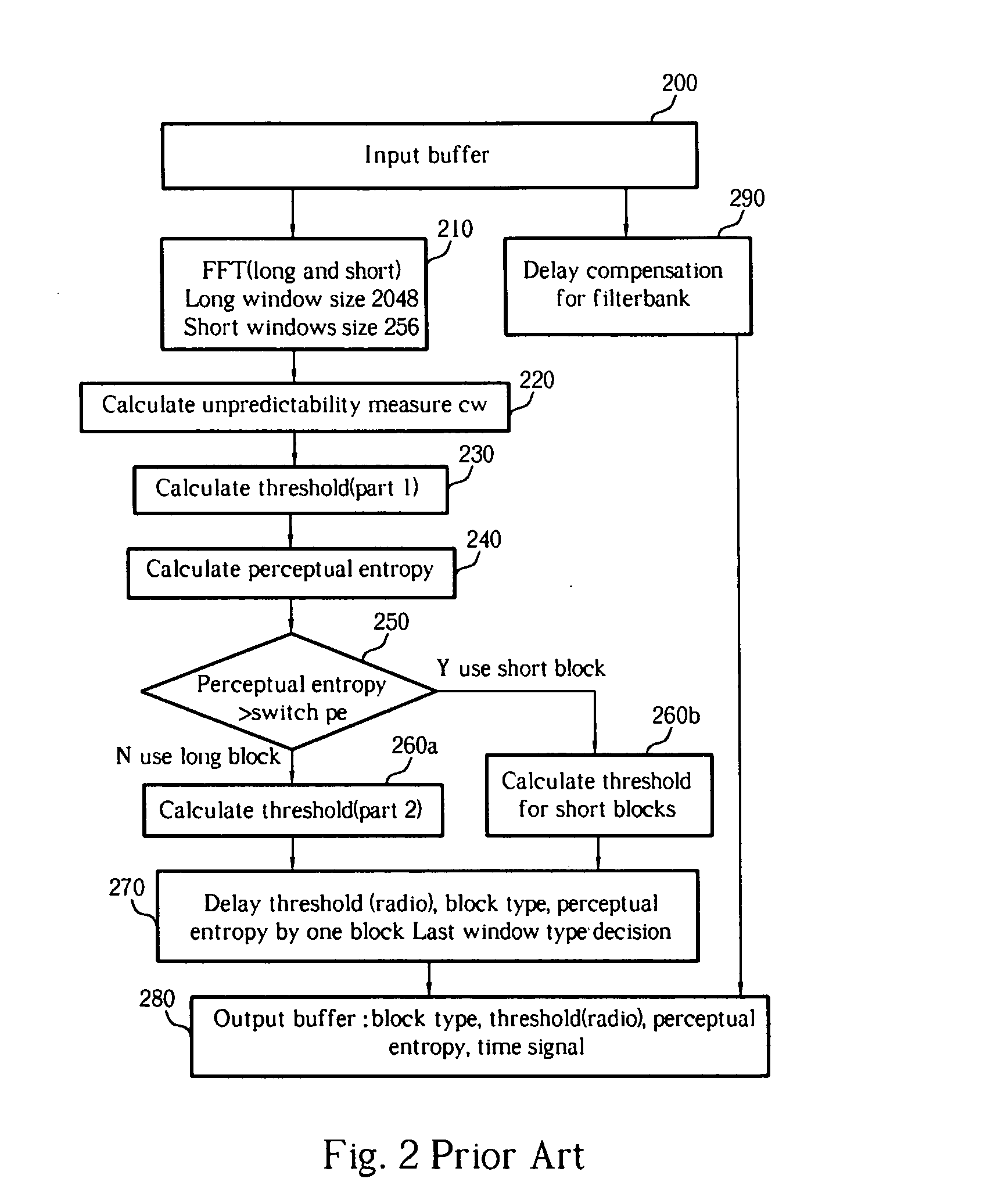
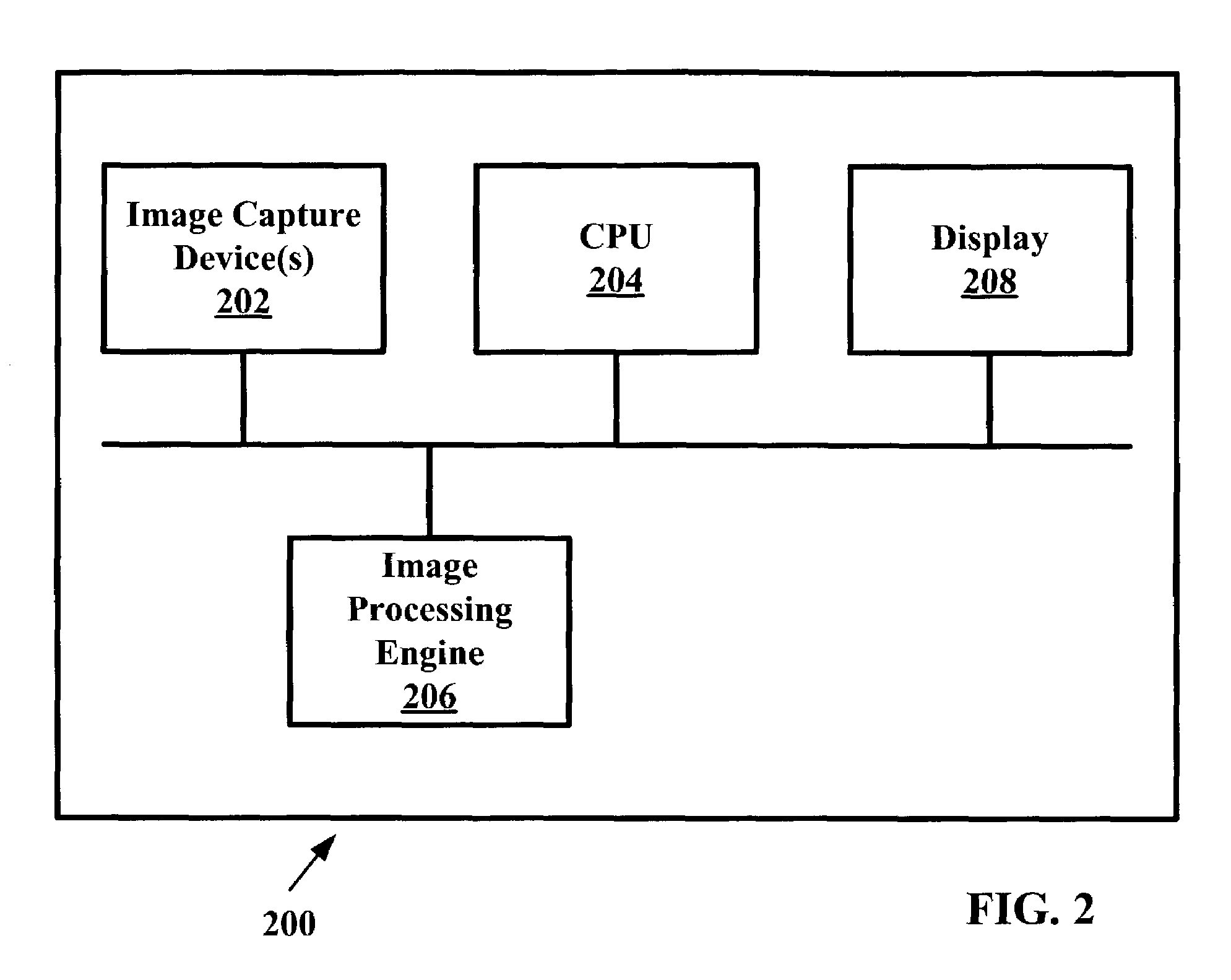
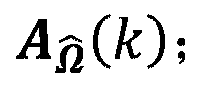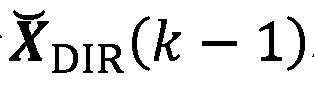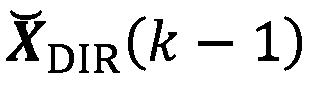Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Perceptual coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
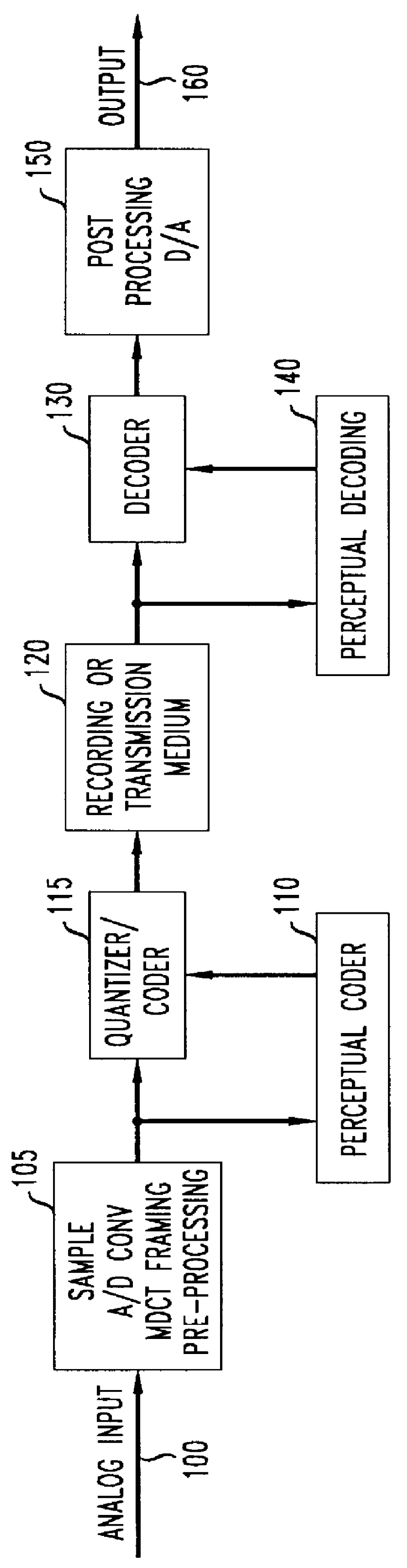
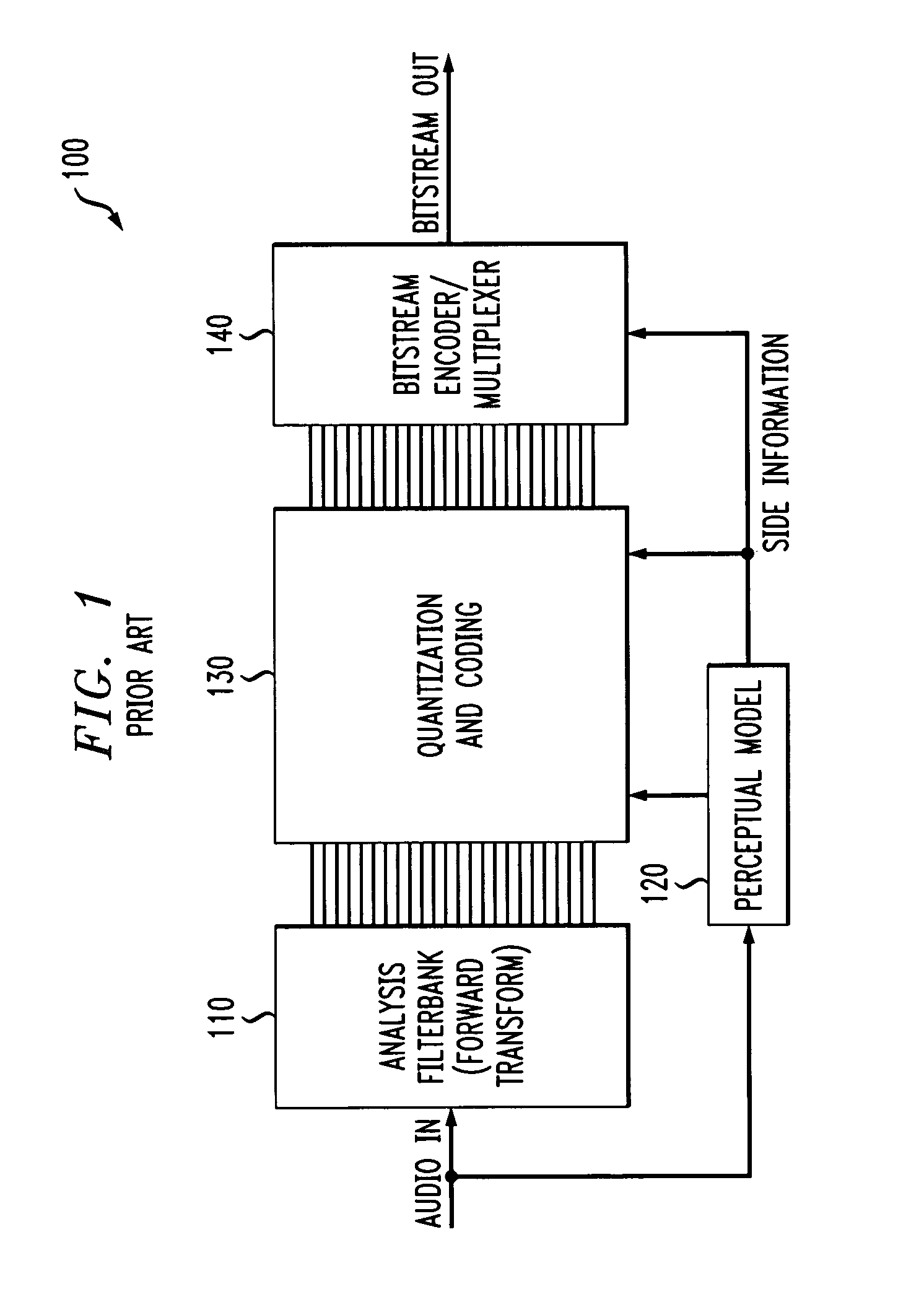
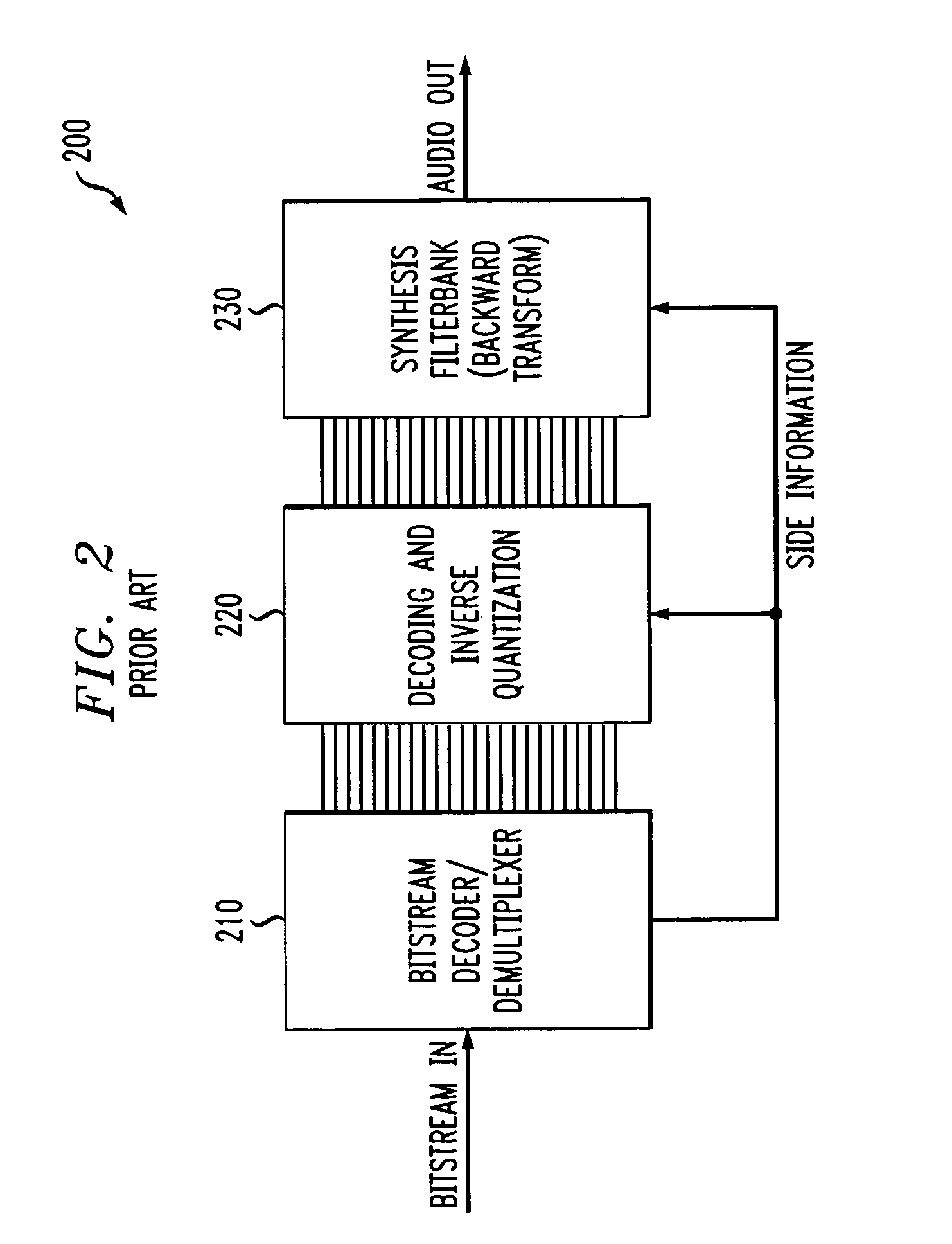
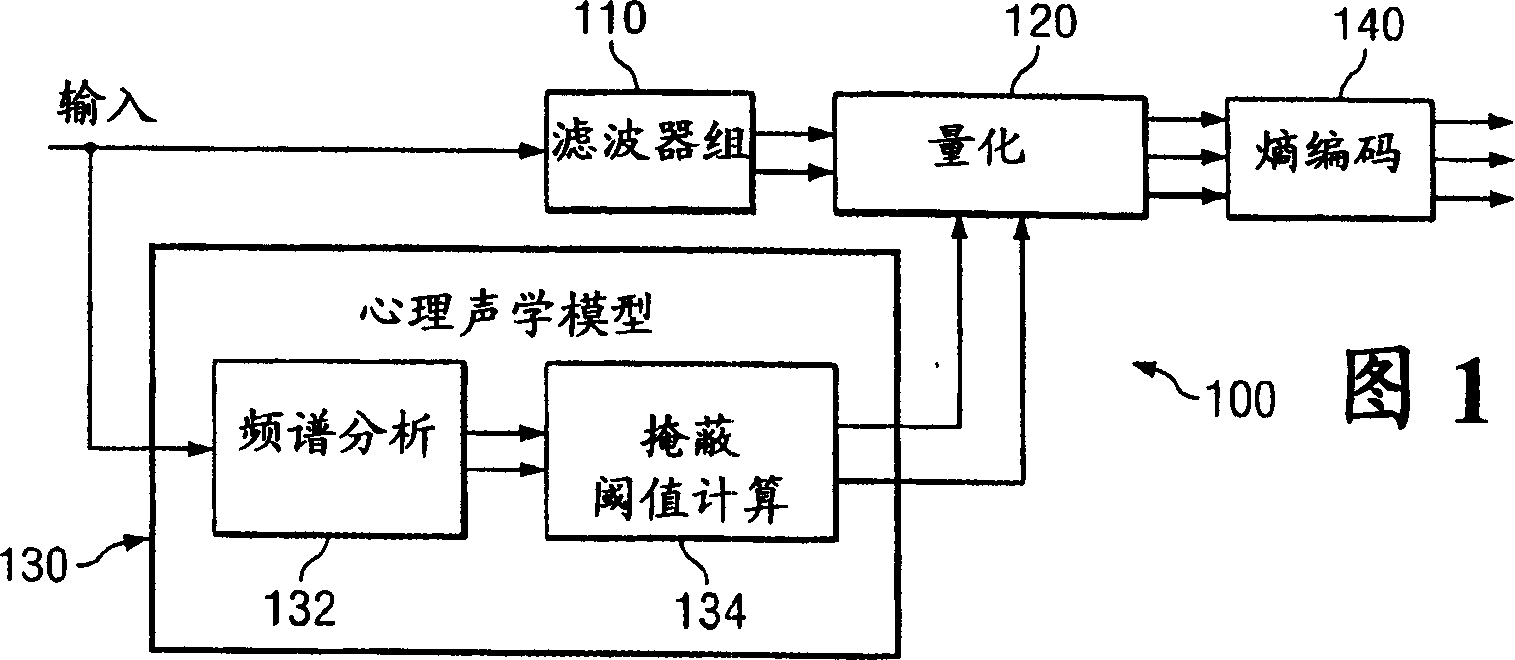
In digital audio perceptual coding is a coding method used to reduce the amount of data needed to produce high-quality sound. Perceptual coding takes advantage of the human ear, screening out a certain amount of sound that is perceived as noise.
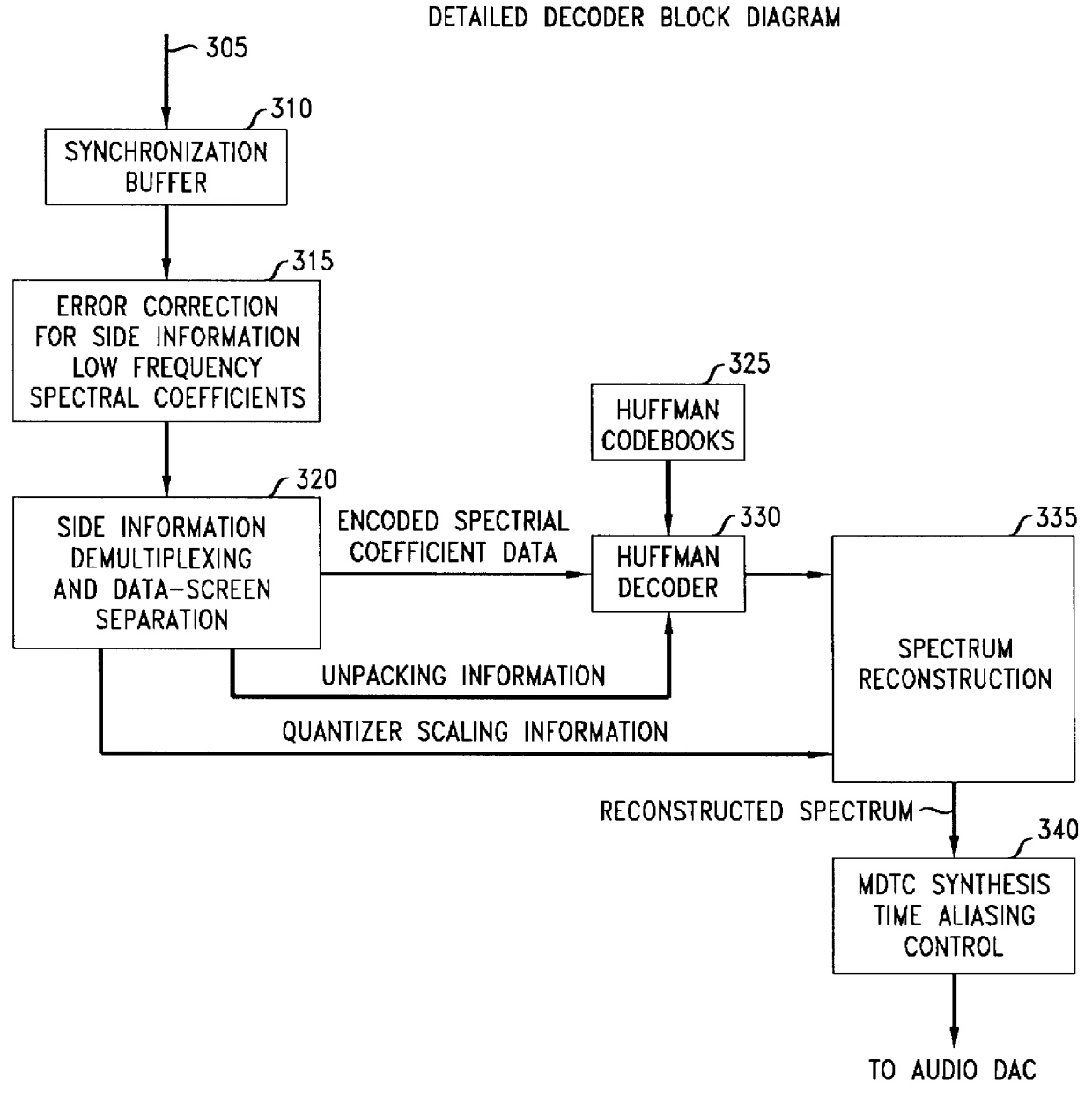
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20070238415A1Reduce bit demandValid encodingSpeech analysisRadio transmissionMulti bandBandwidth extension
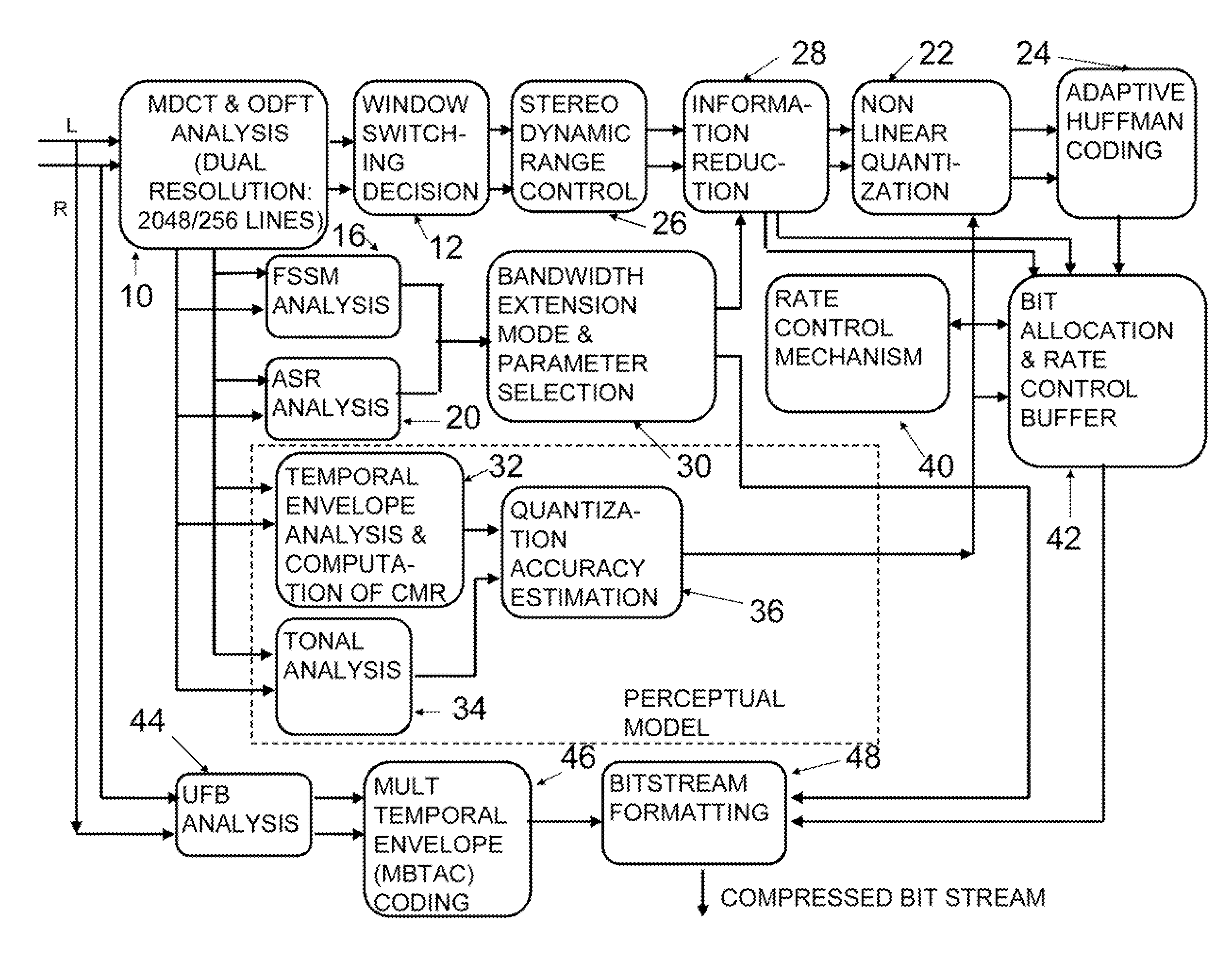
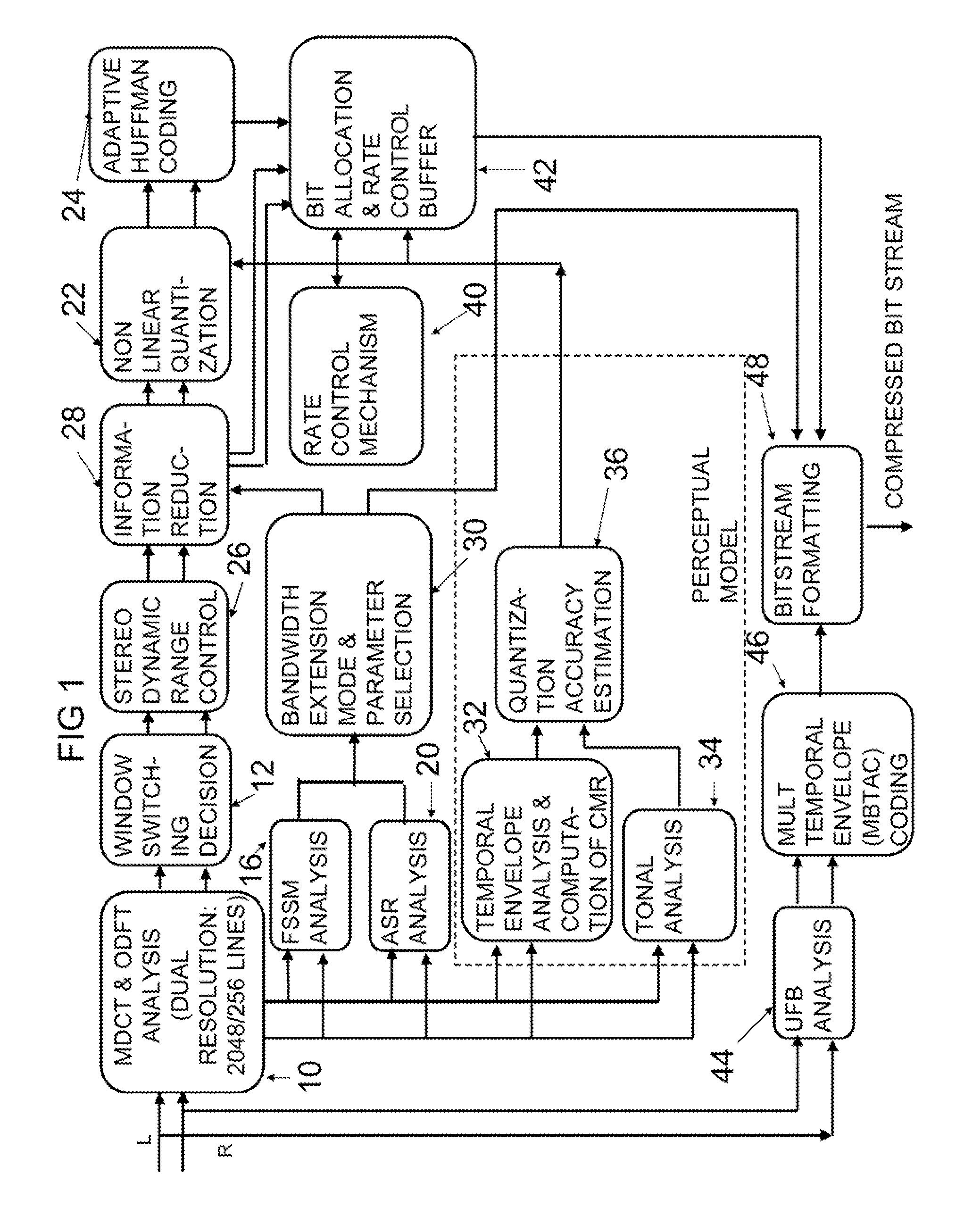
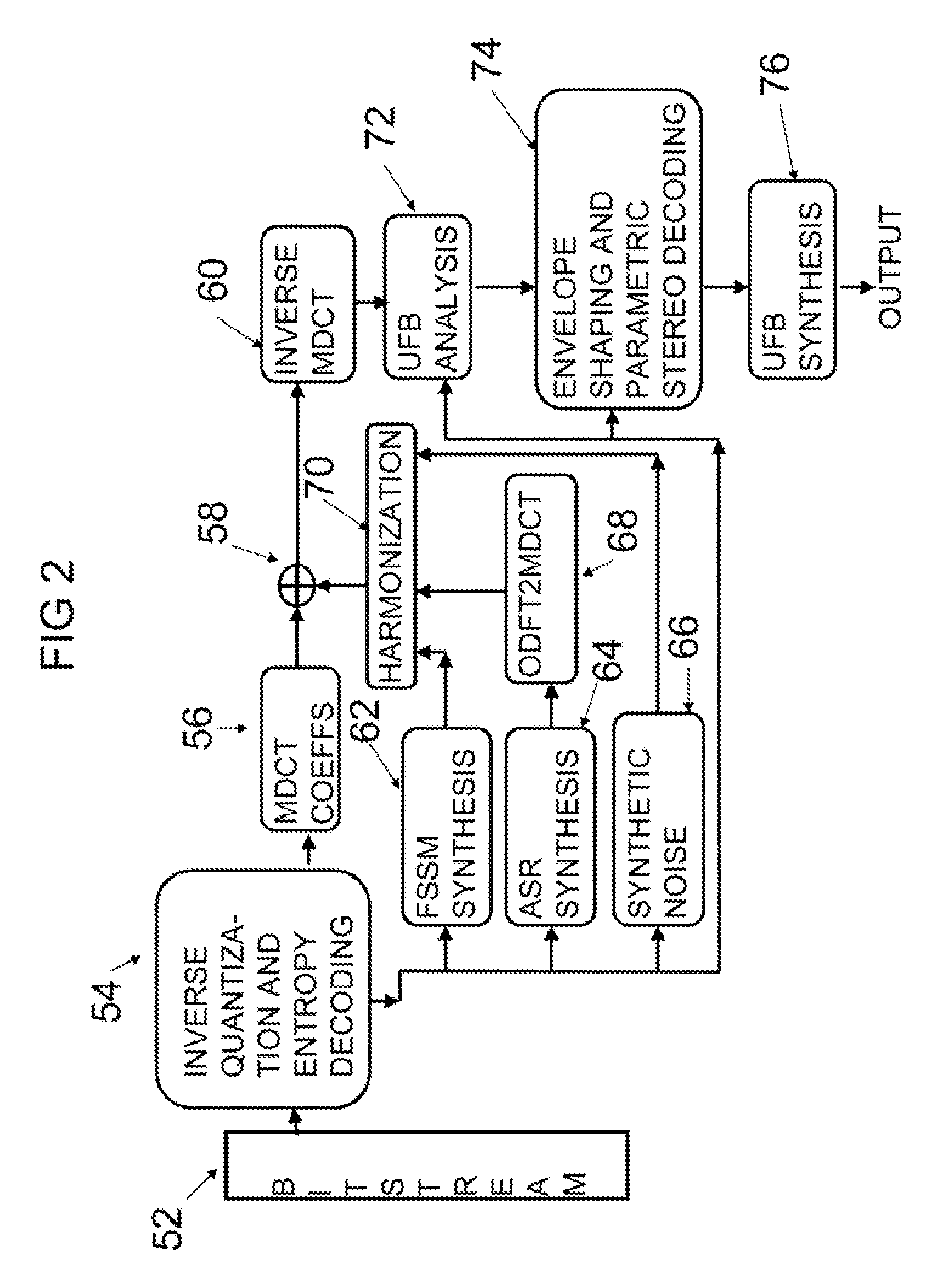
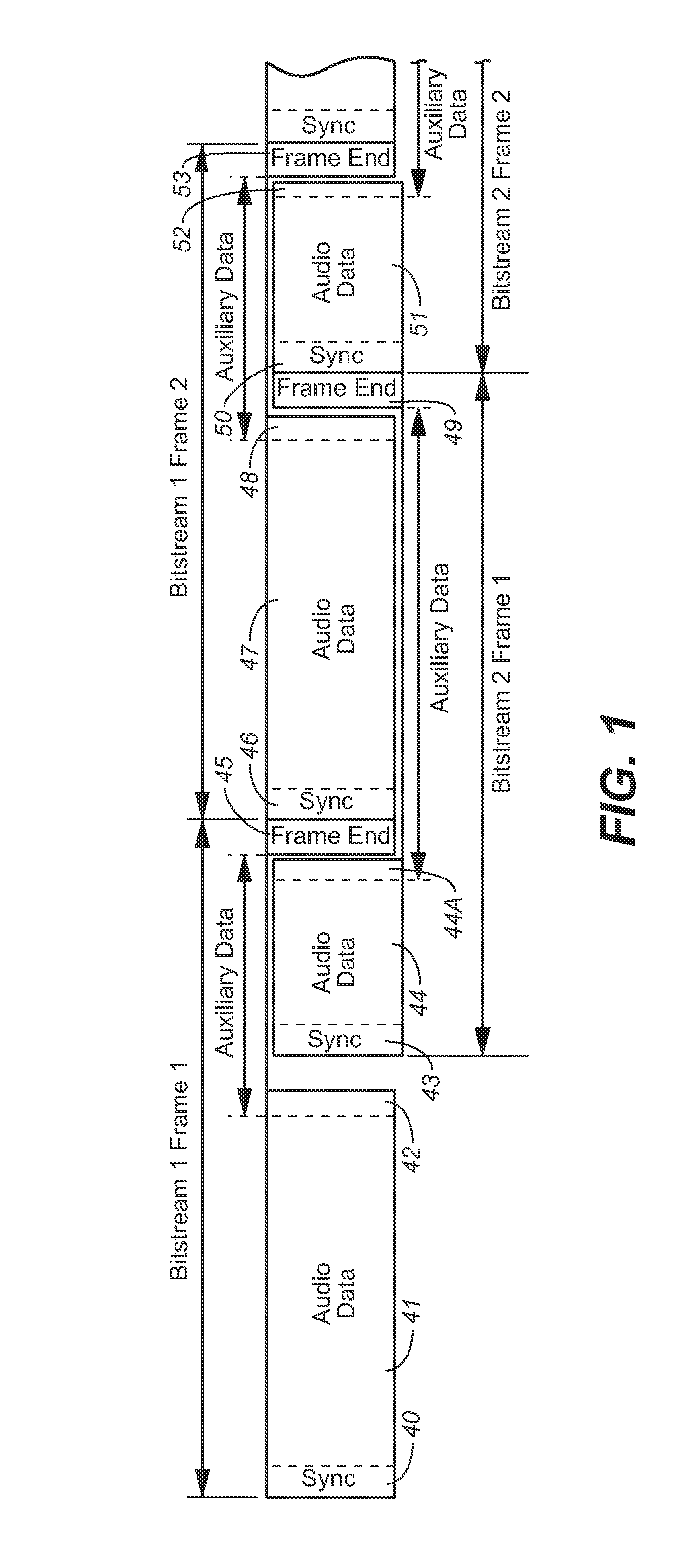
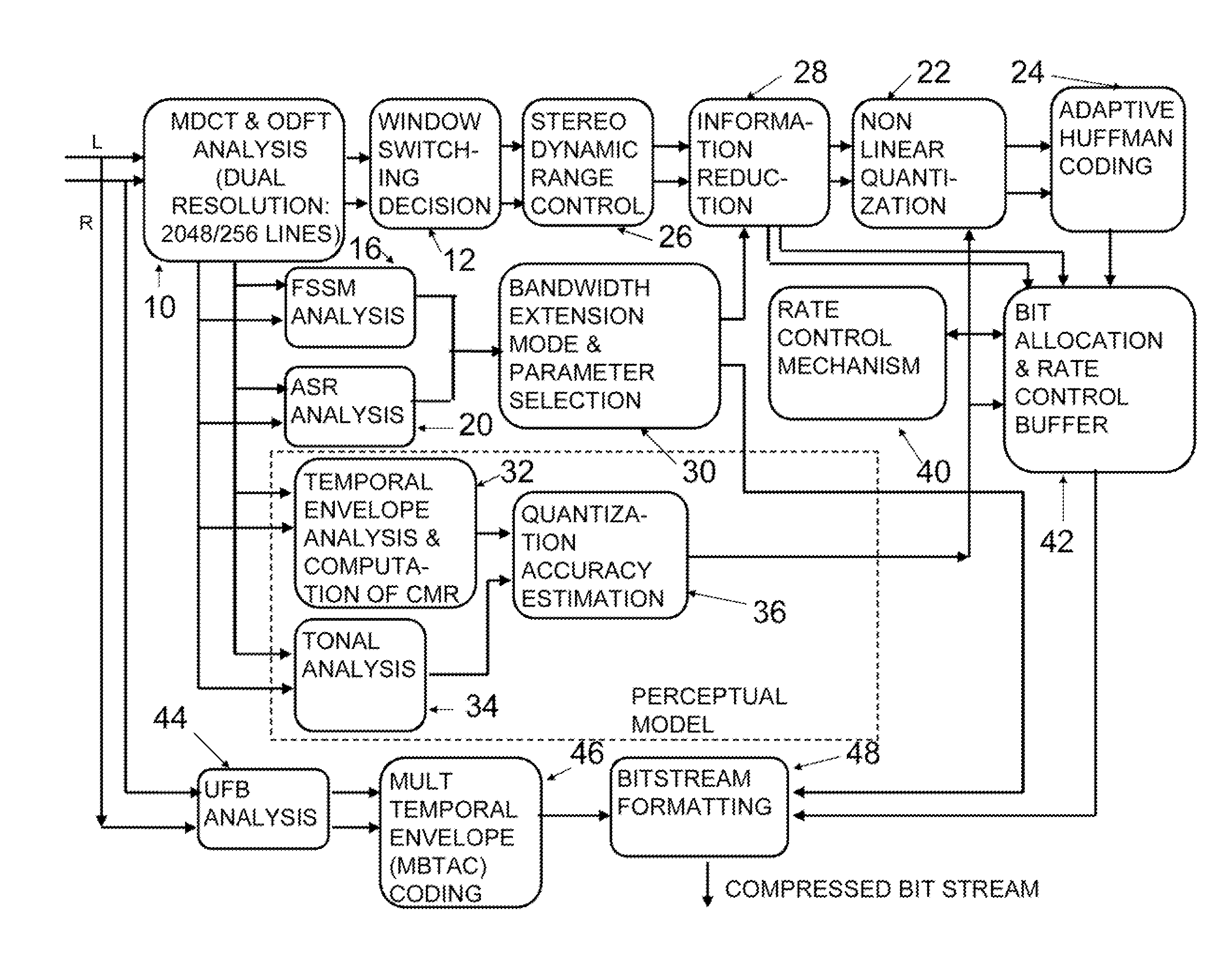
A novel bandwidth extension technique allows information to be encoded and decoded using a fractal self similarity model or an accurate spectral replacement model, or both. Also a multi-band temporal amplitude coding technique, useful as an enhancement to any coding / decoding technique, helps with accurate reconstruction of the temporal envelope and employs a utility filterbank. A perceptual coder using a comodulation masking release model, operating typically with more conventional perceptual coders, makes the perceptual model more accurate and hence increases the efficiency of the overall perceptual coder.
Owner:AUDIO TECH & CODECS
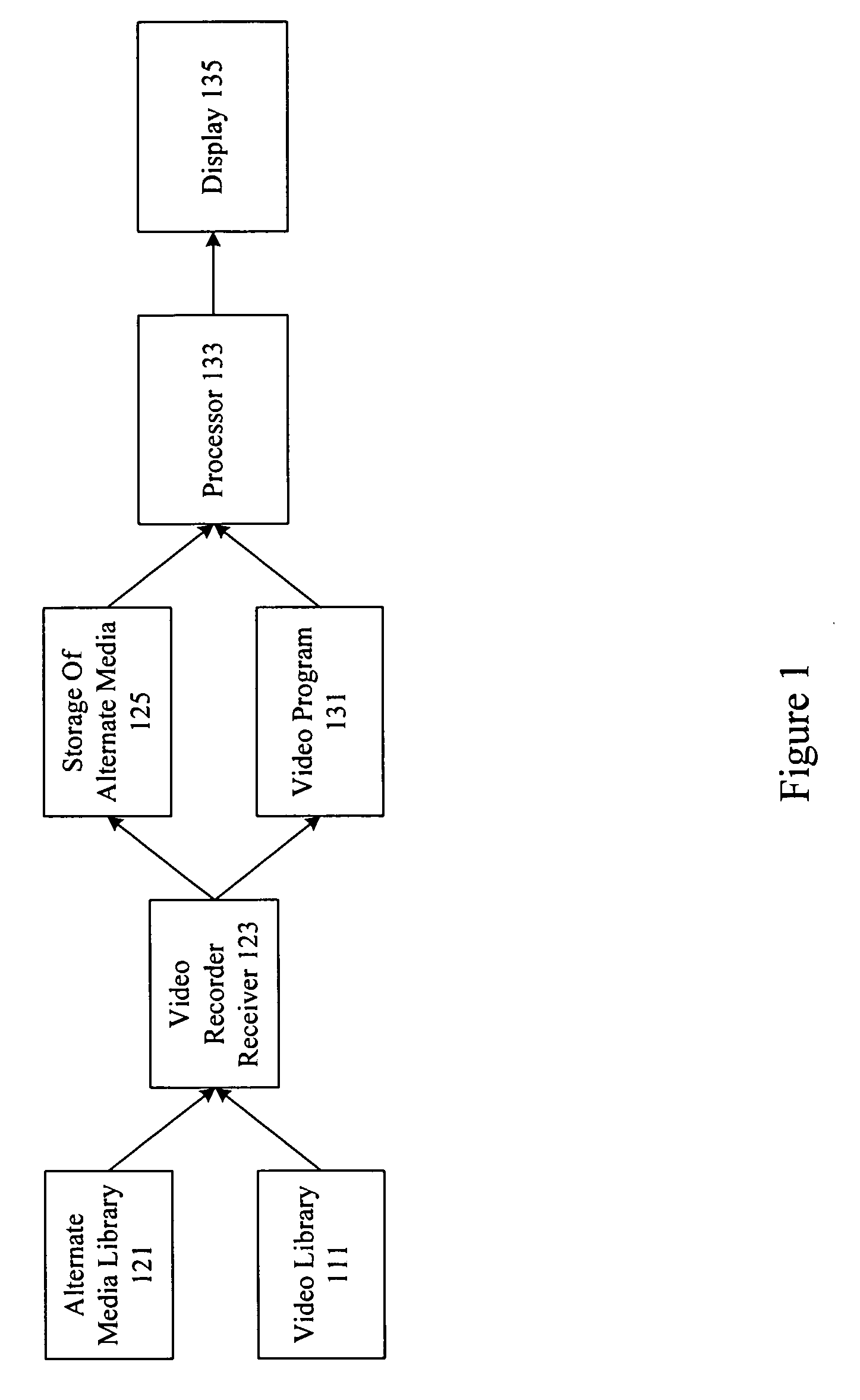
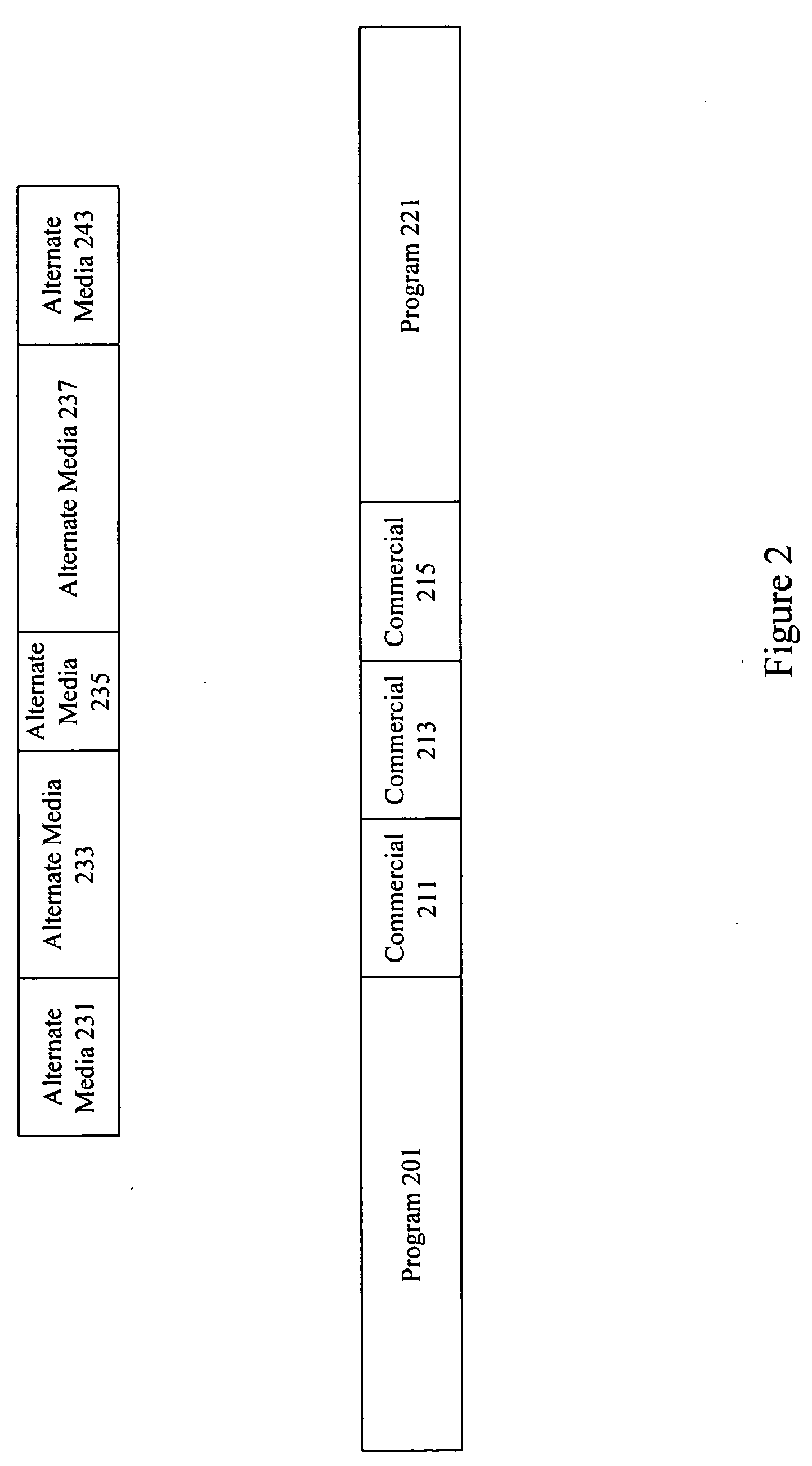
Methods and apparatus for providing alternate media for video decoders
ActiveUS20100186032A1Television system detailsUsing non-detectable carrier informationDigital videoComputerized system
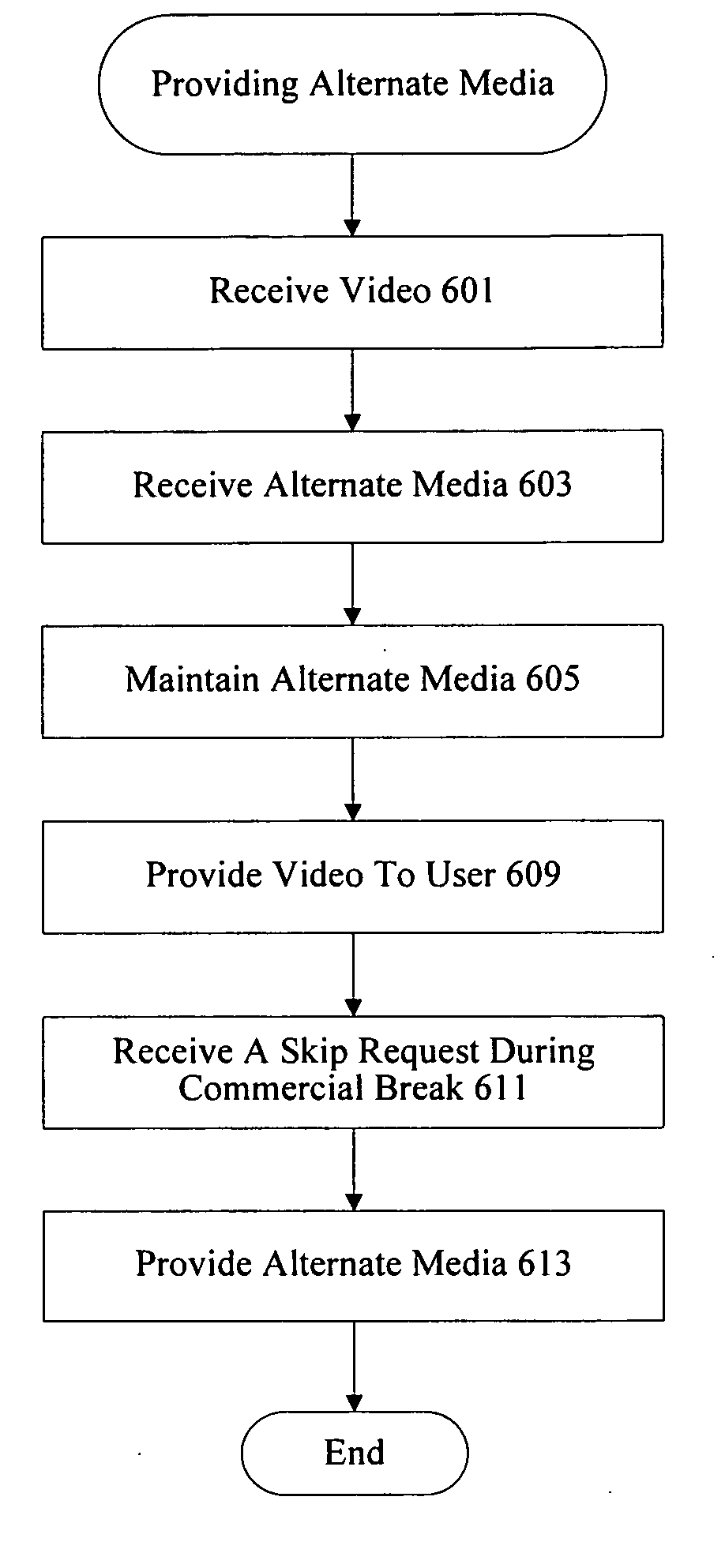
A system provides programming and advertising to a video decoder such as a digital video recorder, computer system, software or hardware player, etc. When a user makes a request to skip a commercial by issuing a command such as 30 second skip forward, alternate media is provided. In some examples, an image advertisement is provided for a predetermined period of time either during the commercial break or when regular programming resumes. In other examples, a substitute commercial is shown. The substitute commercial may be shortened or compressed. The alternate media may be perceptually encoded in a video stream, hidden in a video stream, or provided in a separate stream. In some examples, survey based and neuro-response based data is used to evaluate and select alternate media for particular programming.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
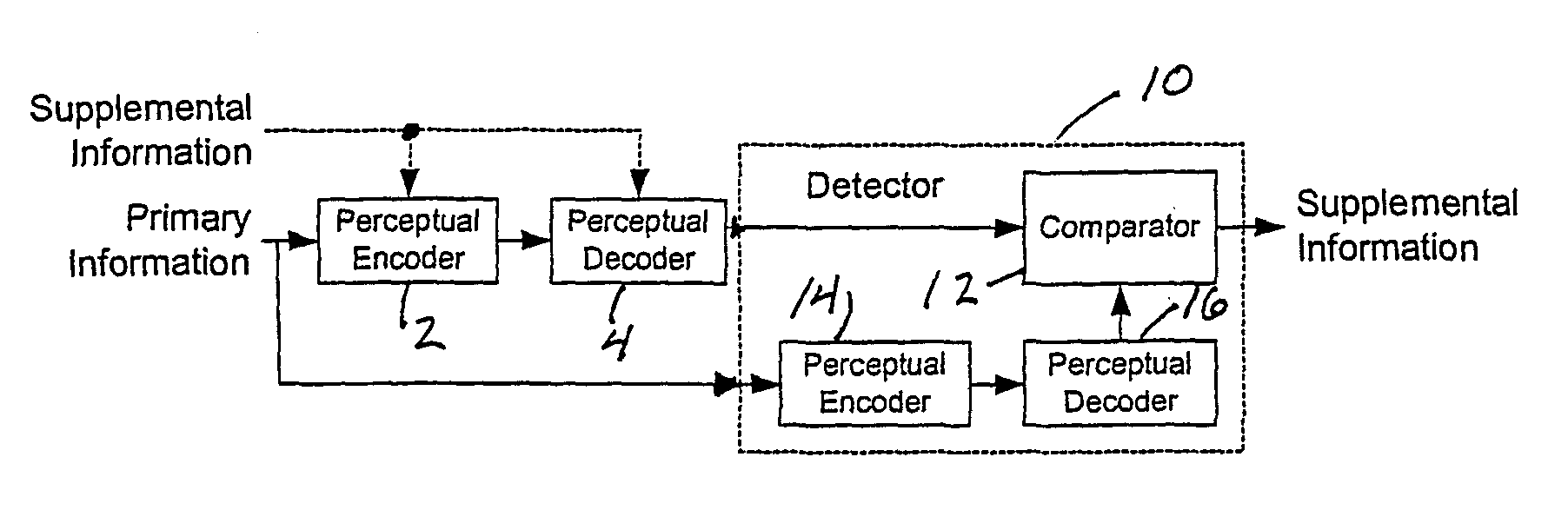
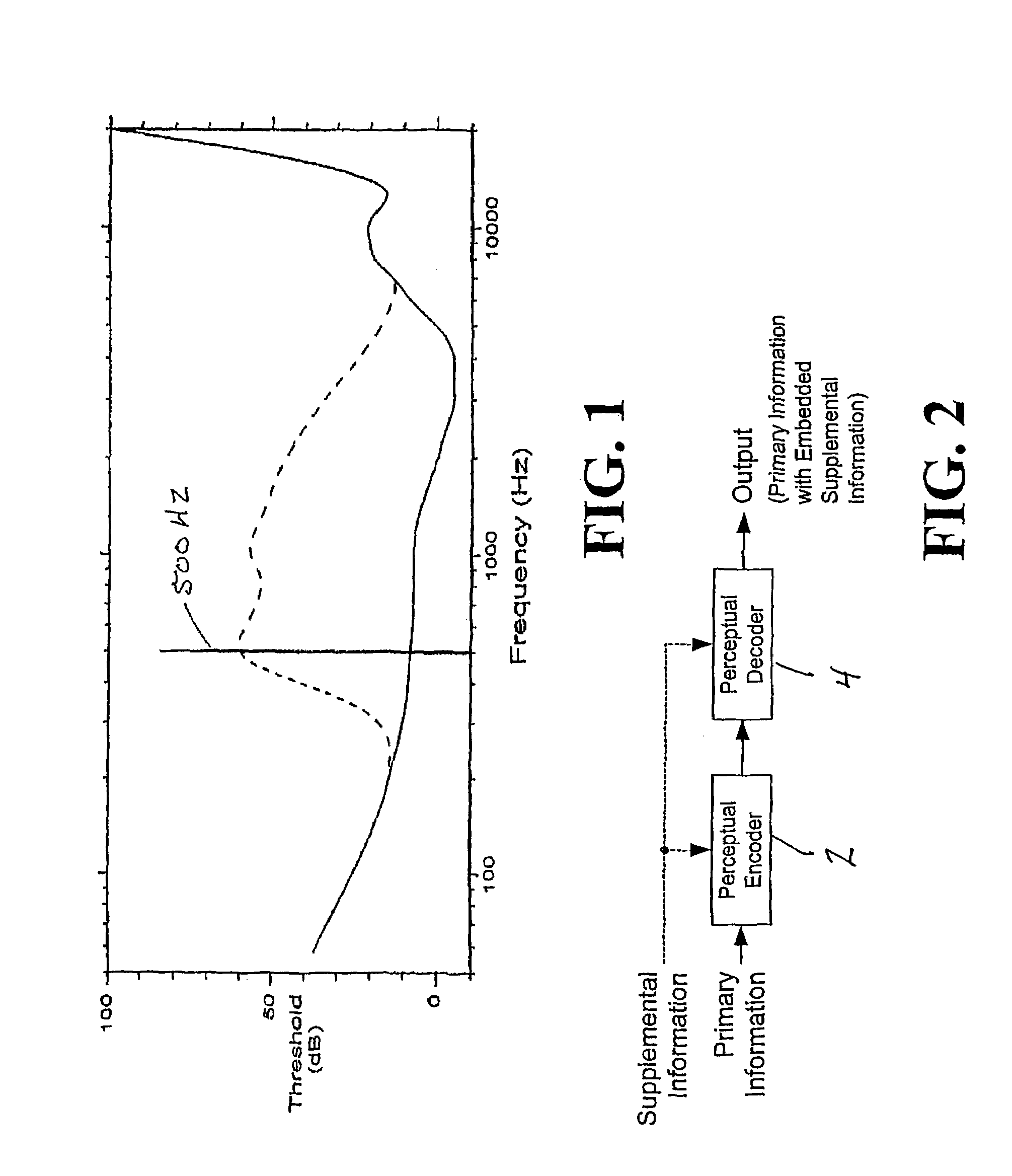
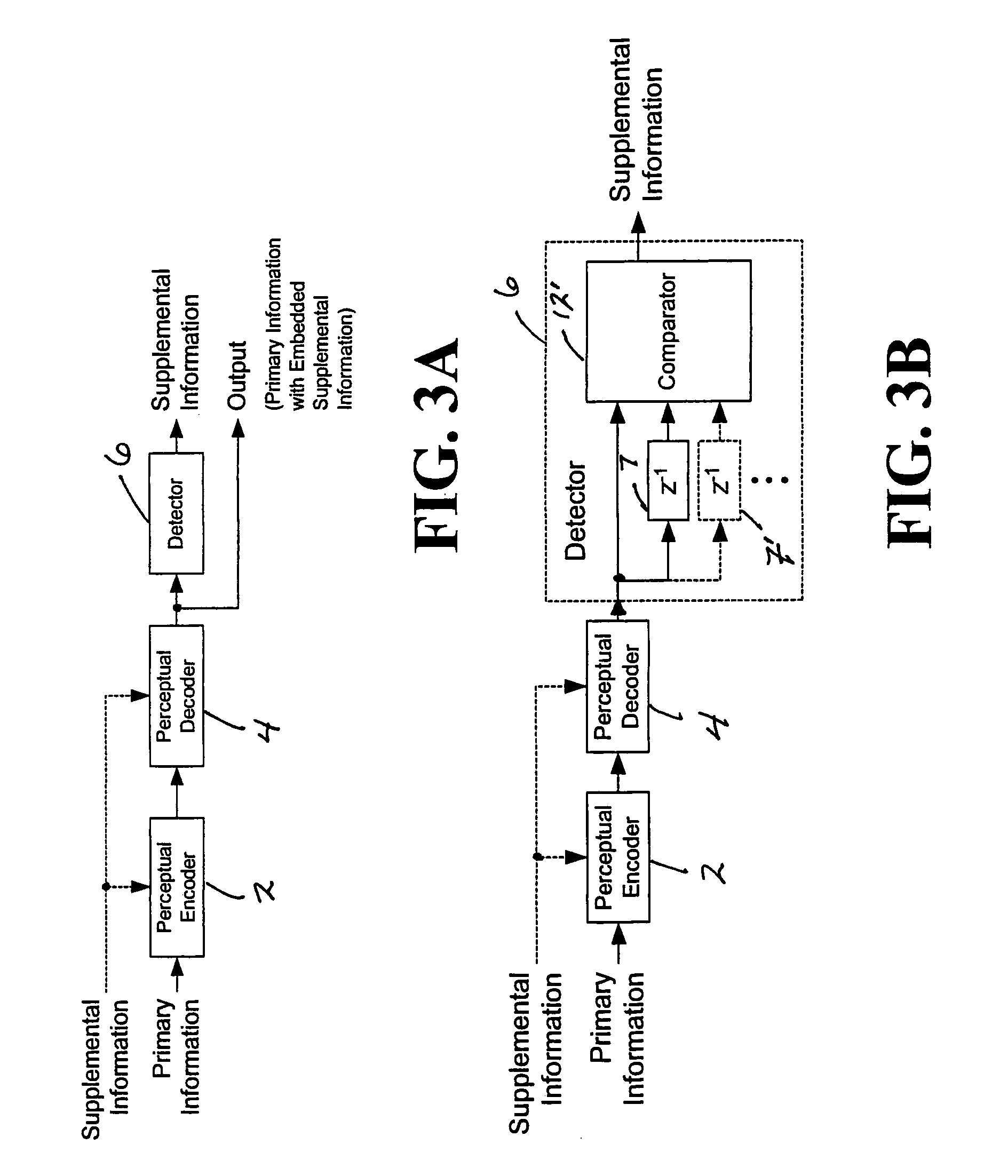
Modulating one or more parameters of an audio or video perceptual coding system in response to supplemental information
ActiveUS7395211B2Maximized strengthPerceptibility is minimizedTelevision system detailsSpeech analysisComputer architecturePerceptual coding
A method of modifying the operation of the encoder function and / or the decoder function of a perceptual coding system in accordance with supplemental information, such as a watermark, so that the supplemental information may be detectable in the output of the decoder function. One or more parameters are modulated in the encoder function and / or the decoder function in response to the supplemental information.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Perceptual coding of audio signals
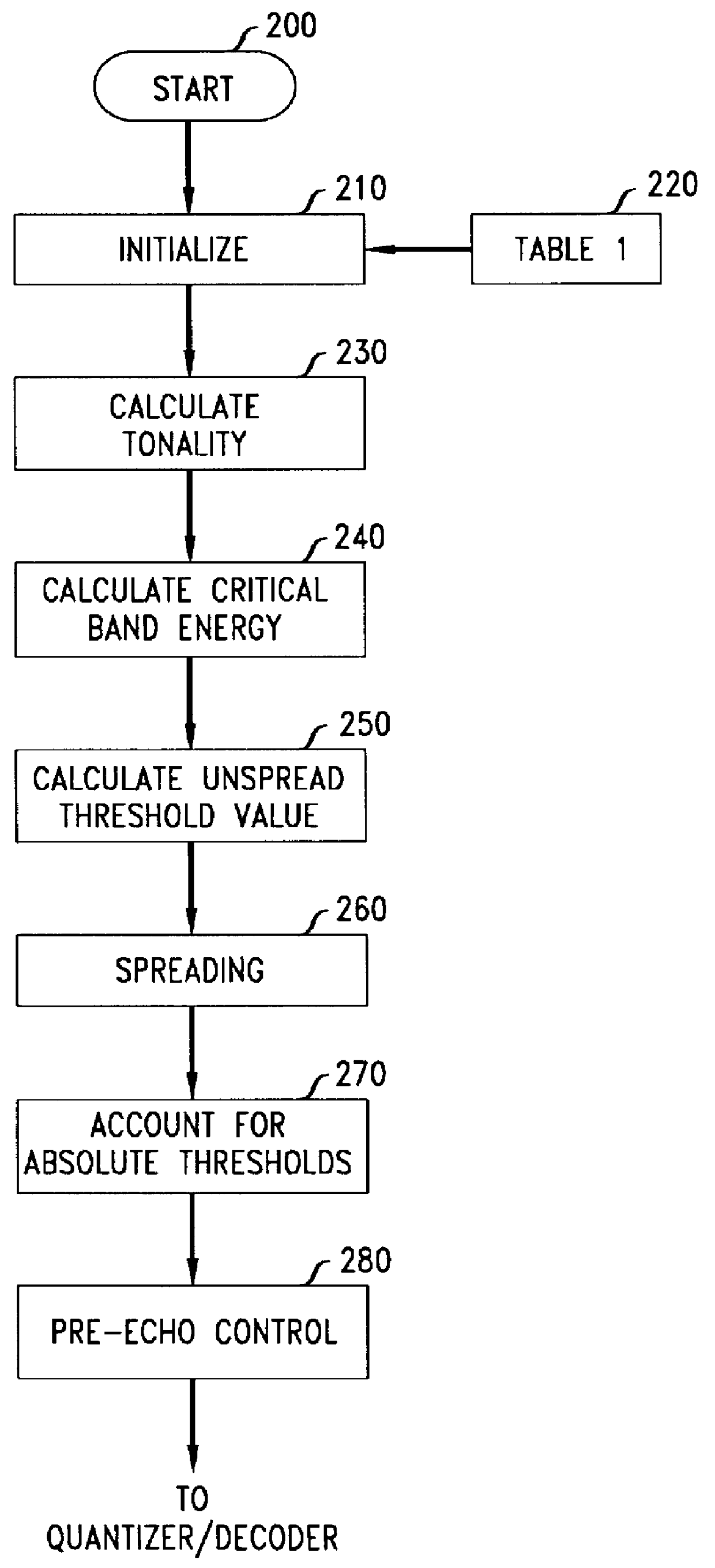
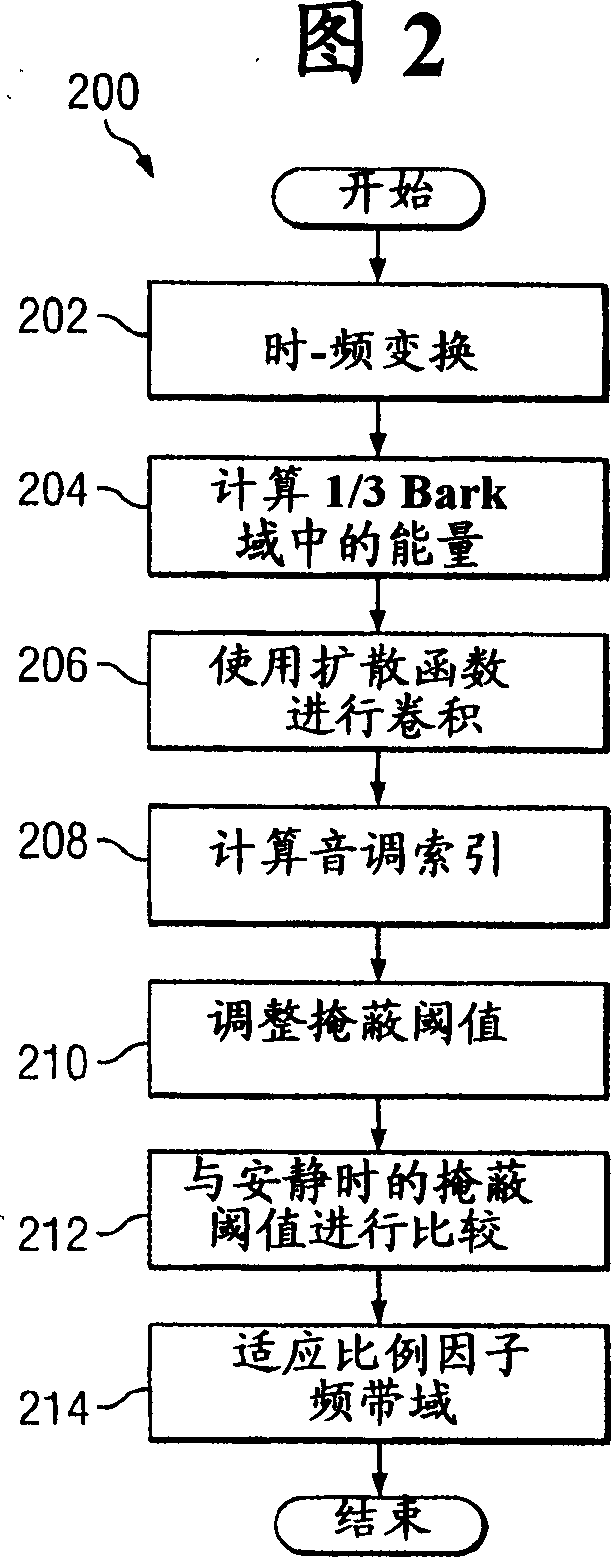
A method is disclosed for determining estimates of the perceived noise masking level of audio signals as a function of frequency. By developing a randomness metric related to the euclidian distance between (i) actual frequency components amplitude and phase for each block of sampled values of the signal and (ii) predicted values for these components based on values in prior blocks, it is possible to form a tonality index which provides more detailed information useful in forming the noise masking function. Application of these techniques is illustrated in a coding and decoding context for audio recording or transmission. The noise spectrum is shaped based on a noise threshold and a tonality measure for each critical frequency-band (bark).
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
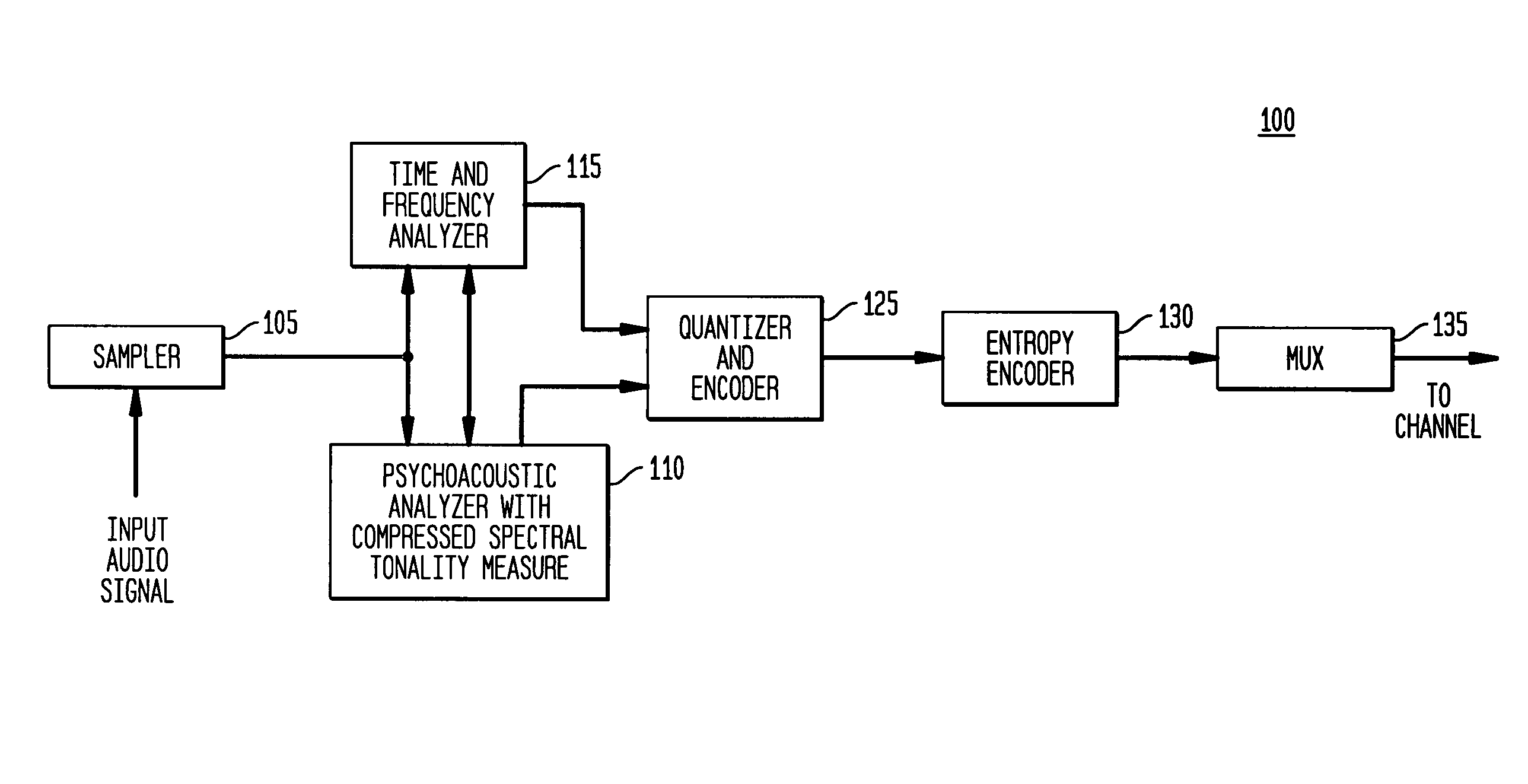
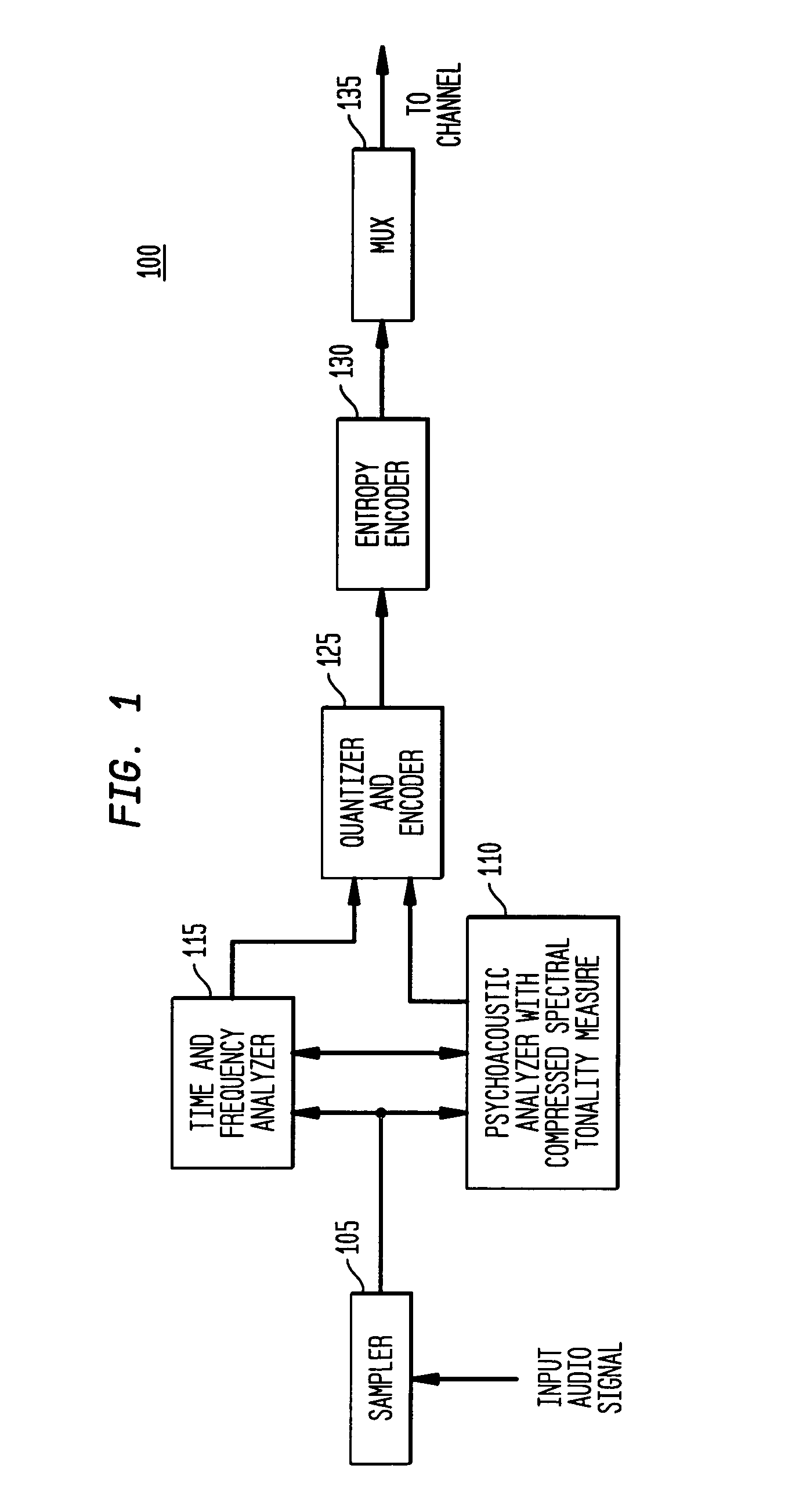
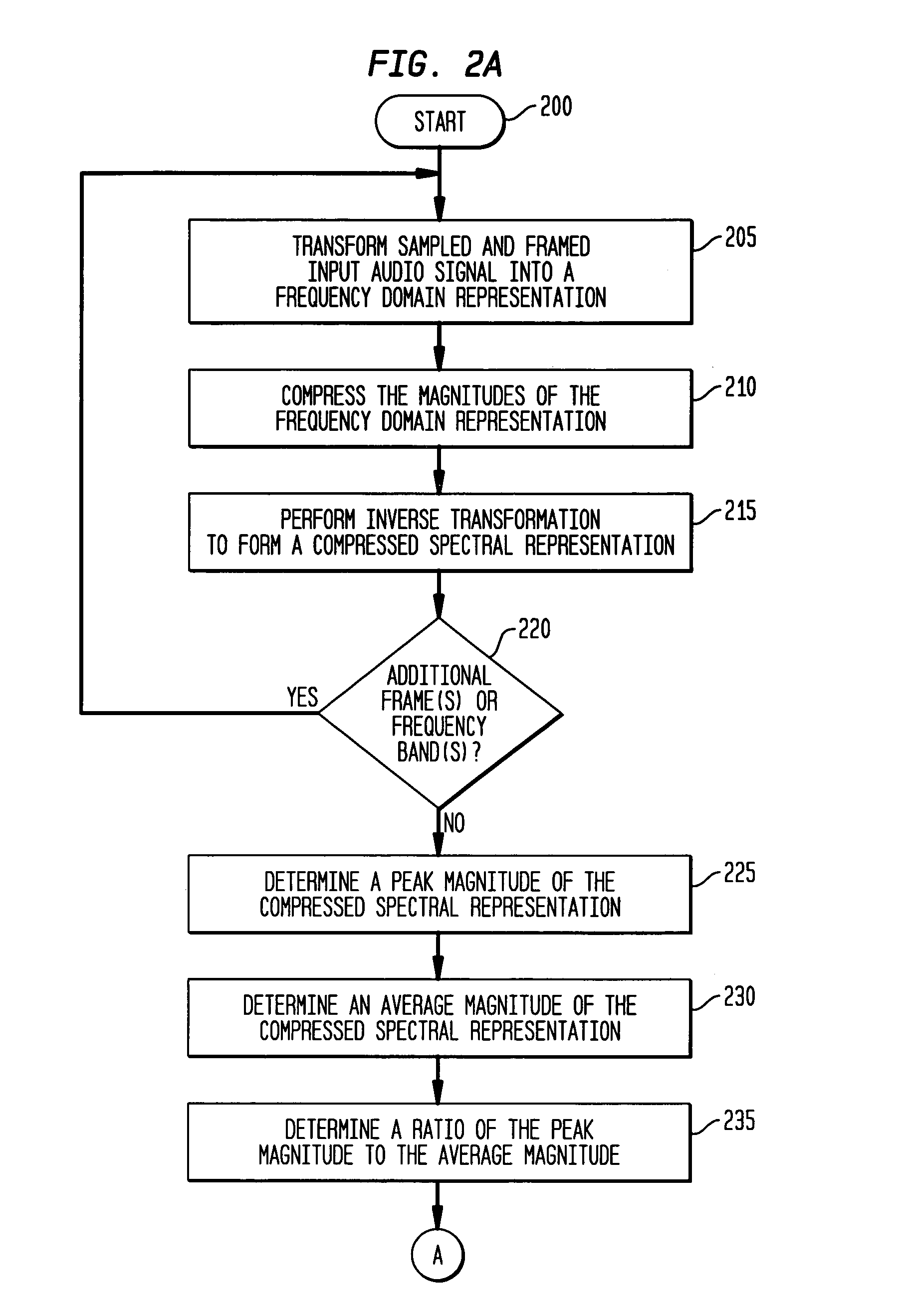
Tonal analysis for perceptual audio coding using a compressed spectral representation
The present invention provides an apparatus, method and tangible medium storing instructions for determining tonality of an input audio signal, for selection of corresponding masked thresholds for use in perceptual audio coding. In the various embodiments, the input audio signal is sampled and transformed using a compressed spectral operation to form a compressed spectral representation, such as a cepstral representation. A peak magnitude and an average magnitude of the compressed spectral representation are determined. Depending upon the ratio of peak-to-average magnitudes, a masked threshold is selected having a corresponding degree of tonality, and is used to determine a plurality of quantization levels and a plurality of bit allocations to perceptually encode the input audio signal with a distortion spectrum beneath a level of just noticeable distortion (JND). The invention also includes other methods and variations for selecting substantially tone-like or substantially noise-like masked thresholds for perceptual encoding of the input audio signal.
Owner:MUCH SHELIST FREED DENENBERG ARNENT & RUBENSTEIN P C +1
System and method for dynamic perceptual coding of macroblocks in a video frame
InactiveUS7162096B1Increasing bandwidth required to carry videoImprove video qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Perceptual coding
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
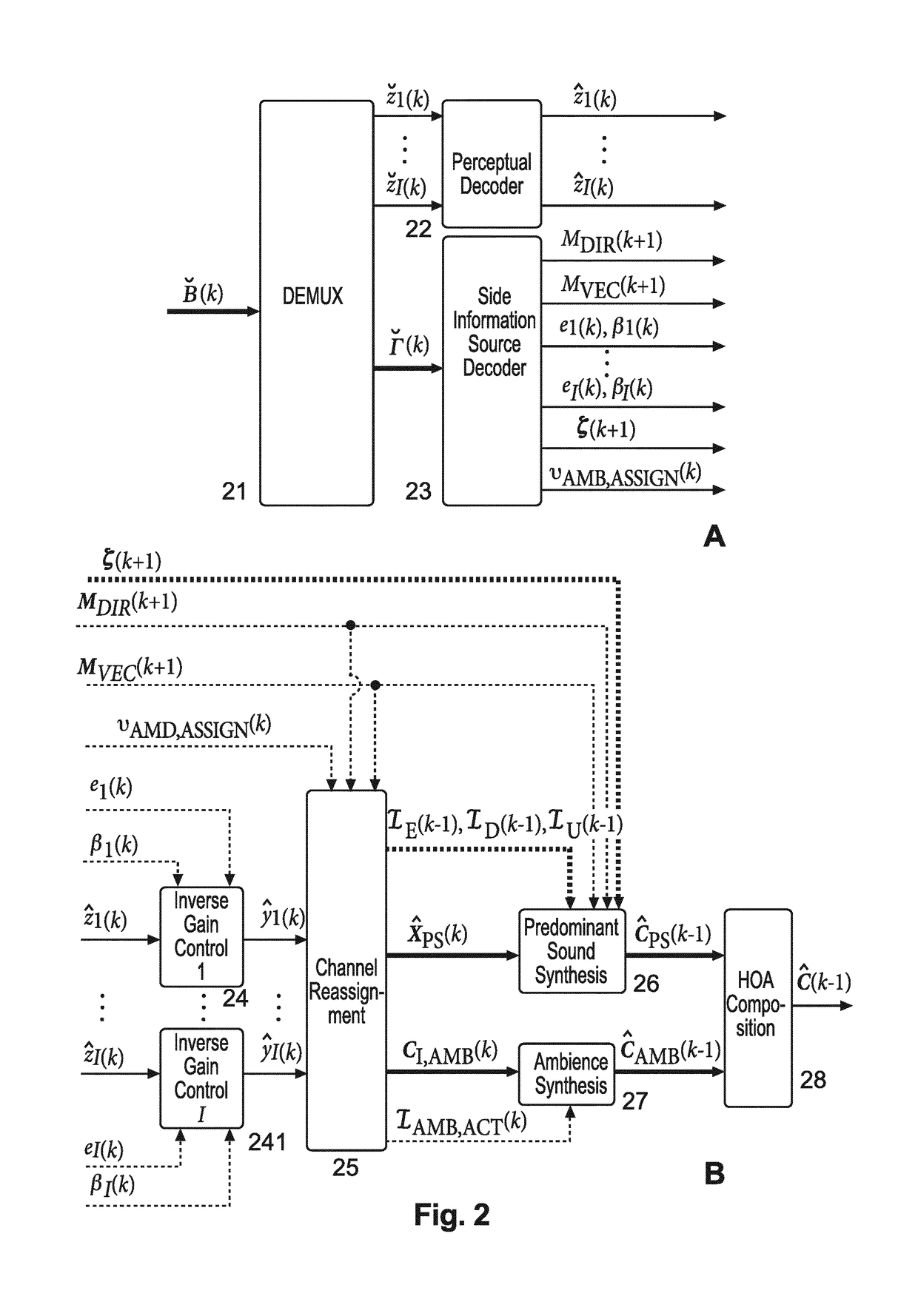
Method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing a higher order ambisonics signal representation
ActiveCN104285390AImprove spatial resolutionBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisTime domainHigh spatial resolution
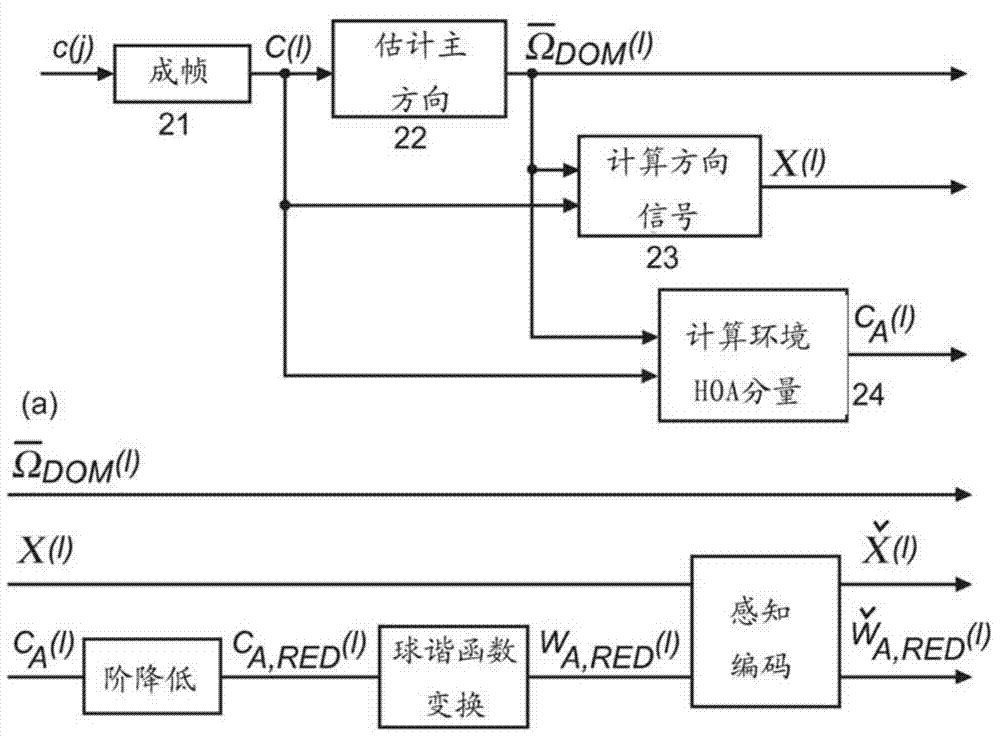
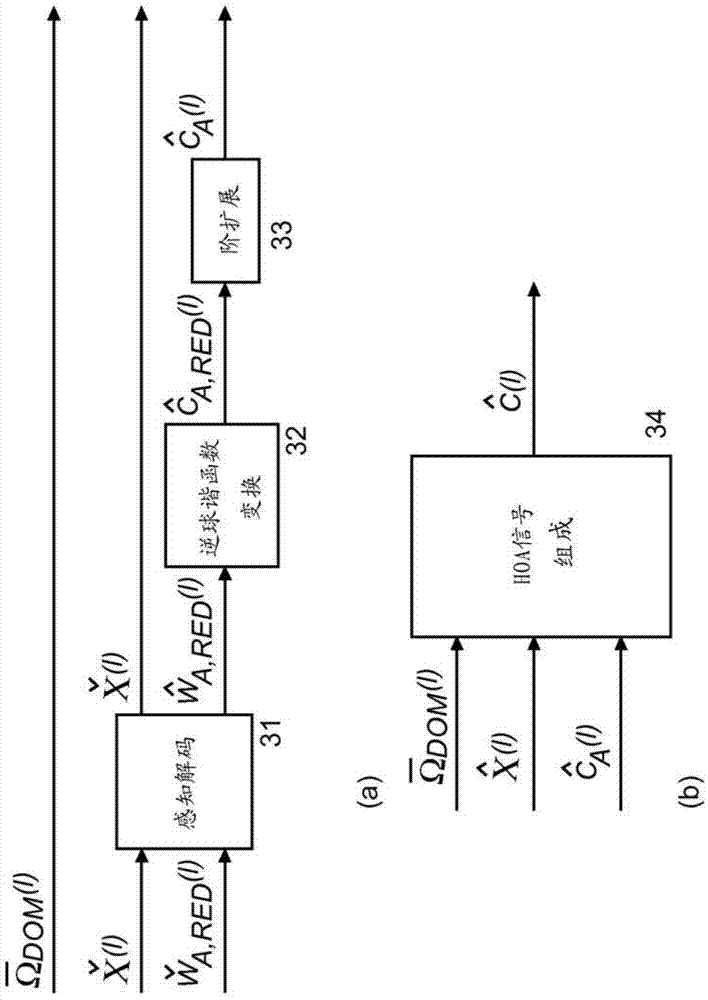
Higher Order Ambisonics (HOA) represents a complete sound field in the vicinity of a sweet spot, independent of loudspeaker set-up. The high spatial resolution requires a high number of HOA coefficients. In the invention, dominant sound directions are estimated and the HOA signal representation is decomposed into dominant directional signals in time domain and related direction information, and an ambient component in HOA domain, followed by compression of the ambient component by reducing its order. The reduced-order ambient component is transformed to the spatial domain, and is perceptually coded together with the directional signals. At receiver side, the encoded directional signals and the order-reduced encoded ambient component are perceptually decompressed, the perceptually decompressed ambient signals are transformed to an HOA domain representation of reduced order, followed by order extension. The total HOA representation is re-composed from the directional signals, the corresponding direction information, and the original-order ambient HOA component.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
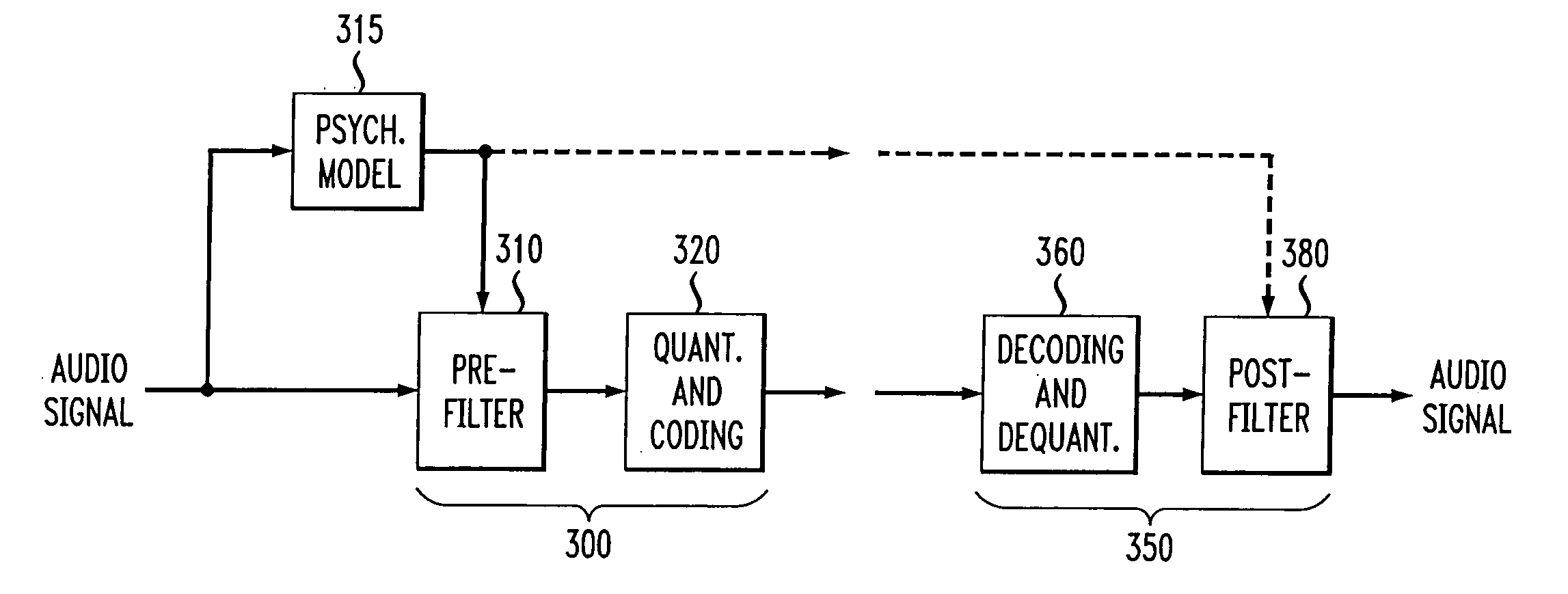
Perceptual coding of image signals using separated irrelevancy reduction and redundancy reduction
InactiveUS20060147124A1Guaranteed normal transmissionConserving transmitted bitsSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumTemporal resolution
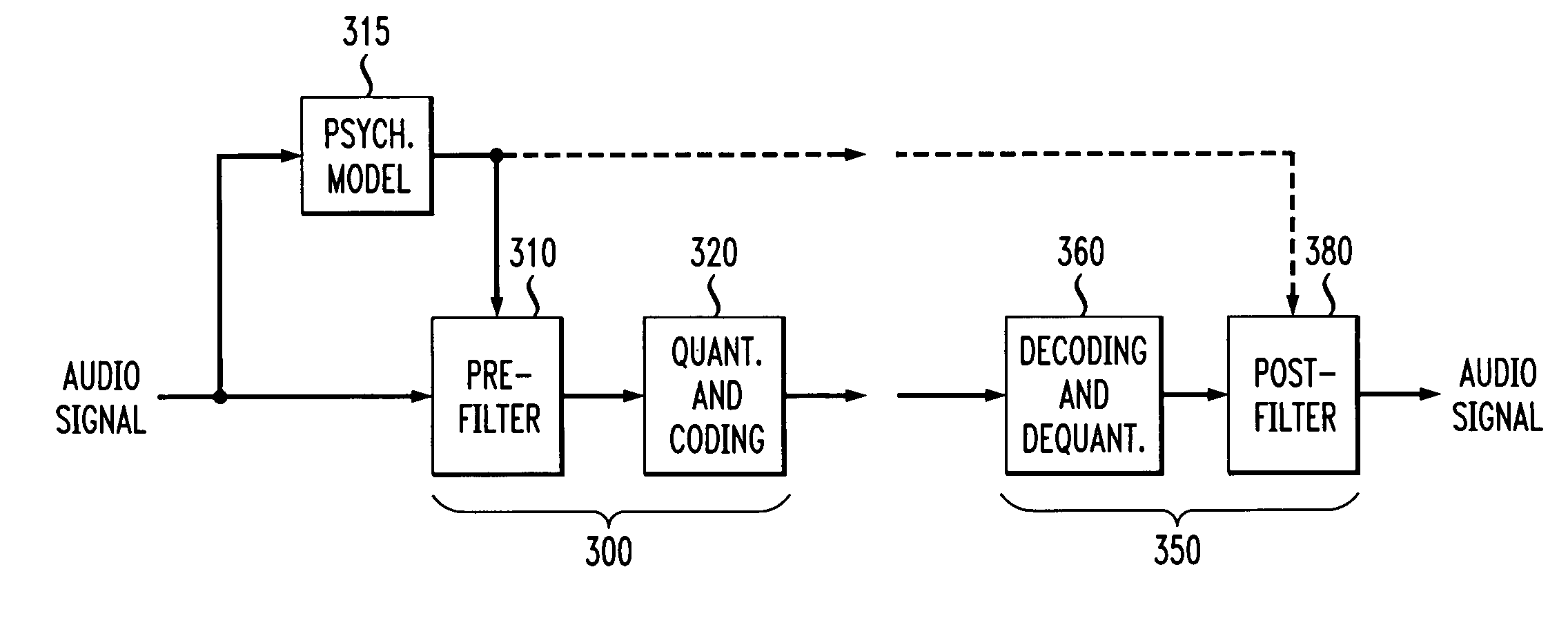
A perceptual coder is disclosed for encoding image signals, such as speech or music, with different spectral and temporal resolutions for redundancy reduction and irrelevancy reduction. The image signal is initially spectrally shaped using a prefilter. The prefilter output samples are thereafter quantized and coded to minimize the mean square error (MSE) across the spectrum. The disclosed perceptual image coder can use fixed quantizer step-sizes, since spectral shaping is performed by the pre-filter prior to quantization and coding. The disclosed pre-filter and post-filter support the appropriate frequency dependent temporal and spectral resolution for irrelevancy reduction. A filter structure based on a frequency-warping technique is used that allows filter design based on a non-linear frequency scale. The characteristics of the pre-filter may be adapted to the masked thresholds, using techniques known from speech coding, where linear-predictive coefficient (LPC) filter parameters are used to model the spectral envelope of the speech signal. Likewise, the filter coefficients may be efficiently transmitted to the decoder for use by the post-filter using well-established techniques from speech coding, such as an LSP (line spectral pairs) representation, temporal interpolation, or vector quantization.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
Audio encoding method and system for generating a unified bitstream decodable by decoders implementing different decoding protocols
ActiveUS20140358554A1Eliminate needImprove efficiencySpeech analysisComputer hardwareComputer architecture
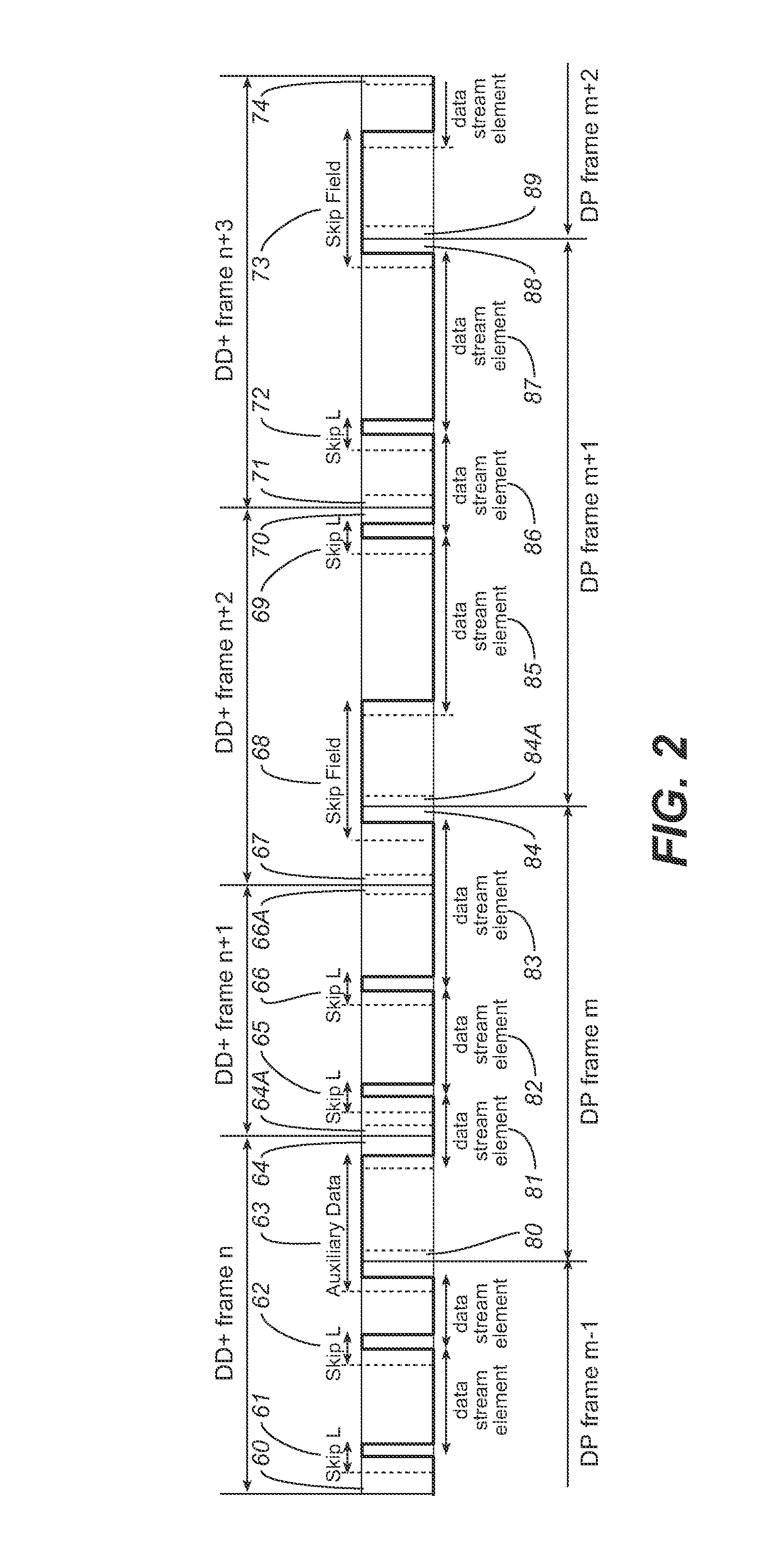
In a class of embodiments, an audio encoding system (typically, a perceptual encoding system that is configured to generate a single (“unified”) bitstream that is compatible with (i.e., decodable by) a first decoder configured to decode audio data encoded in accordance with a first encoding protocol (e.g., the multichannel Dolby Digital Plus, or DD+, protocol) and a second decoder configured to decode audio data encoded in accordance with a second encoding protocol (e.g., the stereo AAC, HE AAC v1, or HE AAC v2 protocol). The unified bitstream can include both encoded data (e.g., bursts of data) decodable by the first decoder (and ignored by the second decoder) and encoded data (e.g., other bursts of data) decodable by the second decoder (and ignored by the first decoder). In effect, the second encoding format is hidden within the unified bitstream when the bitstream is decoded by the first decoder, and the first encoding format is hidden within the unified bitstream when the bitstream is decoded by the second decoder. The format of the unified bitstream generated in accordance with the invention may eliminate the need for transcoding elements throughout an entire media chain and / or ecosystem. Other aspects of the invention are an encoding method performed by any embodiment of the inventive encoder, a decoding method performed by any embodiment of the inventive decoder, and a computer readable medium (e.g., disc) which stores code for implementing any embodiment of the inventive method.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP +1
Method and apparatus for audio encoding and decoding using wideband psychoacoustic modeling and bandwidth extension
ActiveUS7953605B2High frequency resolutionAccurate reconstructionSpeech analysisRadio transmissionMulti bandBandwidth extension
Owner:AUDIO TECH & CODECS
Perceptual coding of audio signals using separated irrelevancy reduction and redundancy reduction
InactiveUS7110953B1Conserving transmitted bitsGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumTemporal resolution
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
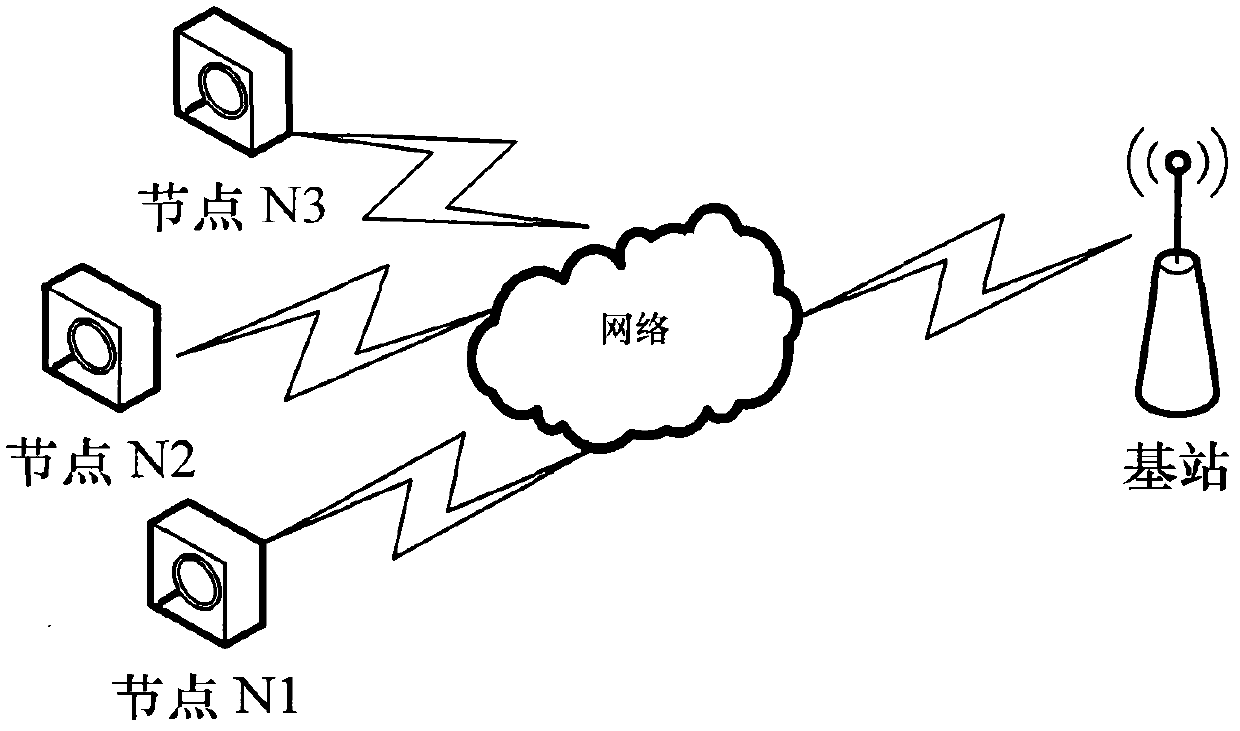
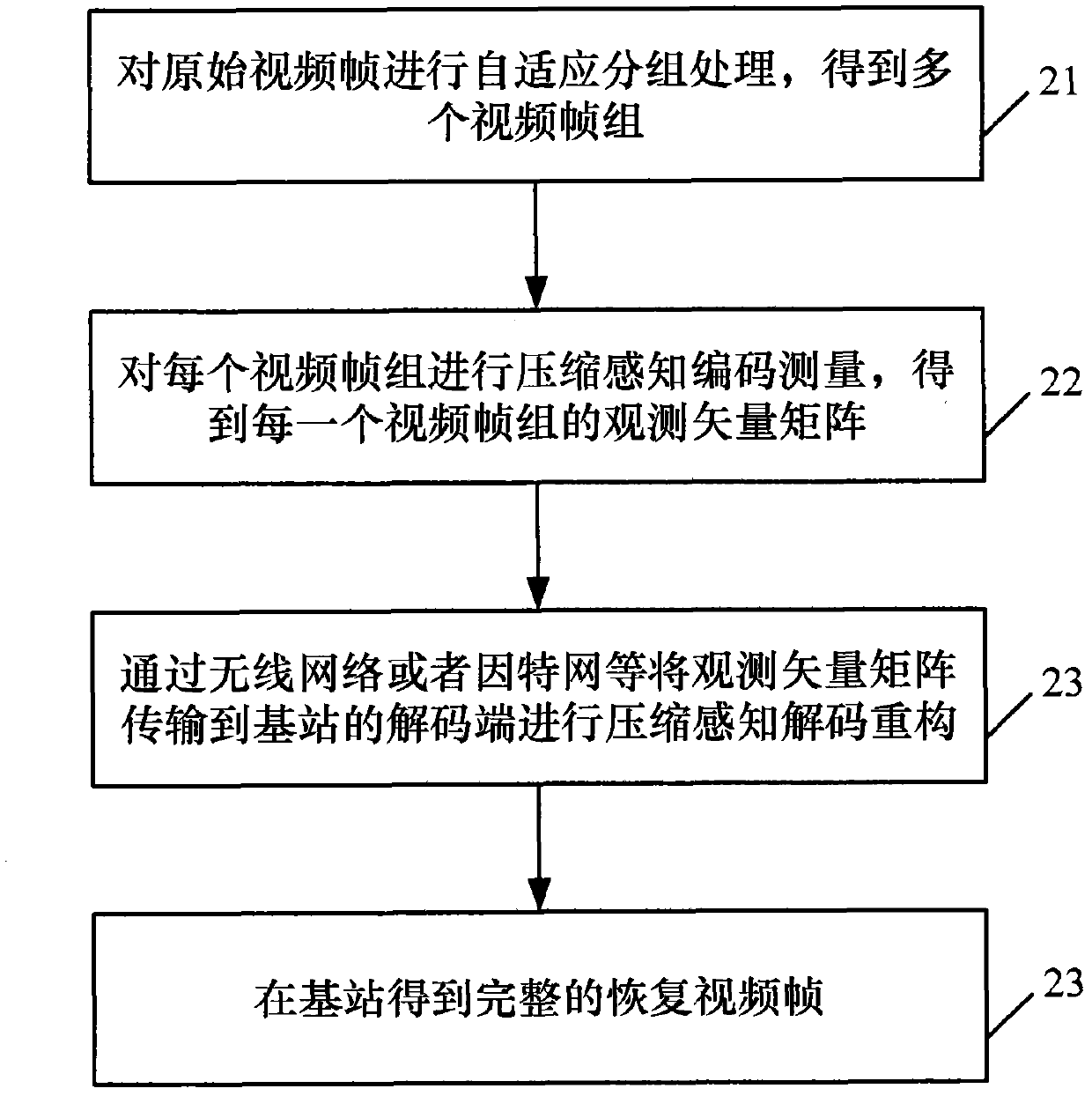
Compressive perceptual coding and decoding method and system in video sensor network
InactiveCN102630011AKeep properlyIncrease diversityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsPattern recognition
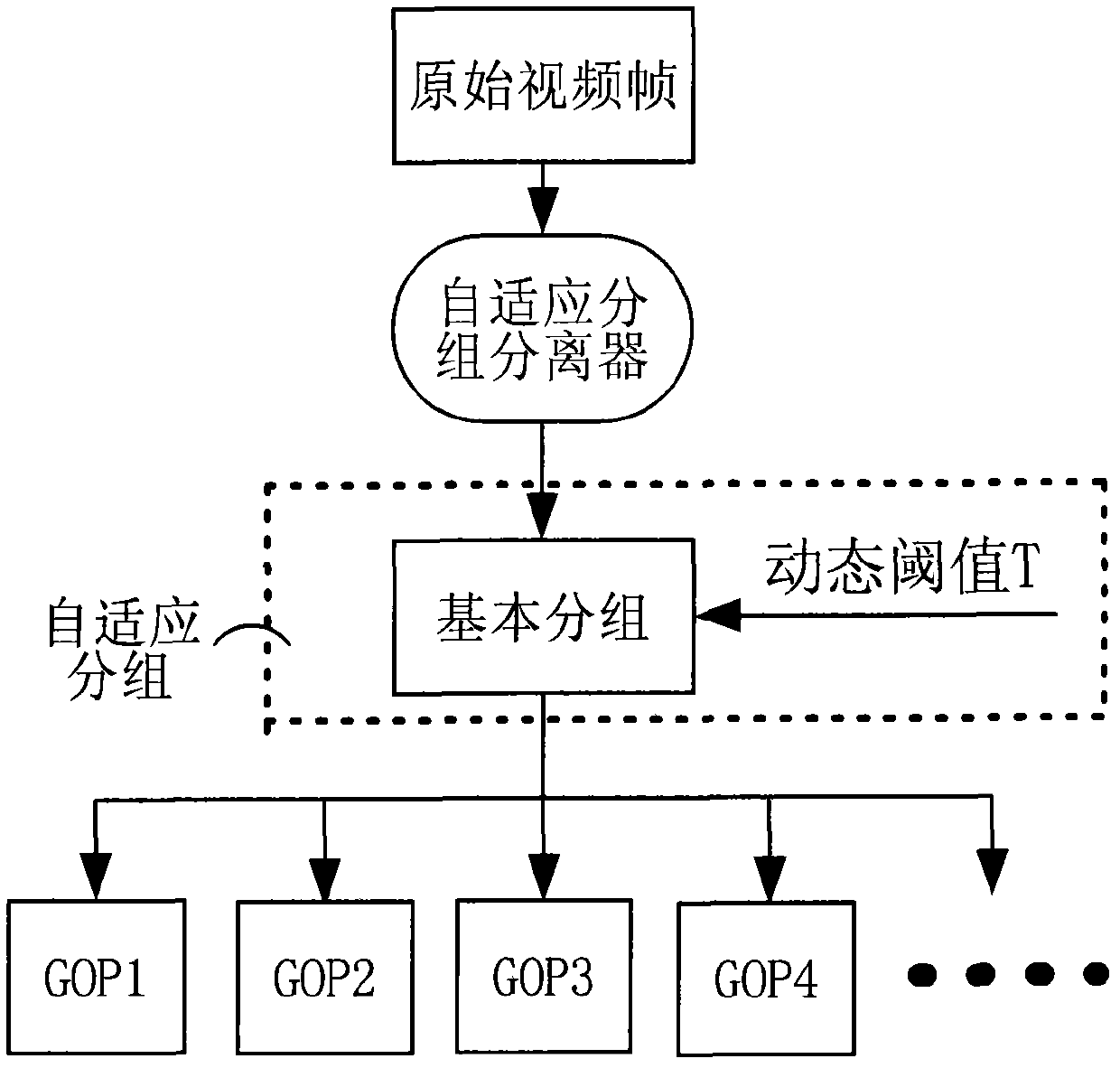
The invention discloses a compressive perceptual coding and decoding method and a system in a video sensor network, which can achieve high compression ratio and have a good reconstruction effect simultaneously. The method comprises the steps of performing a self-adaptation grouping for original video frames, performing compression perceptual coding measuring for the video frames acquired through the grouping, obtaining an observation vector matrix of each of video frame groups, and performing compressive perceptual decoding reconstruction for the observation vector matrix. Combining a compressive perceptual technique, the method and the system perform measuring, so that reconstruction performance is improved greatly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
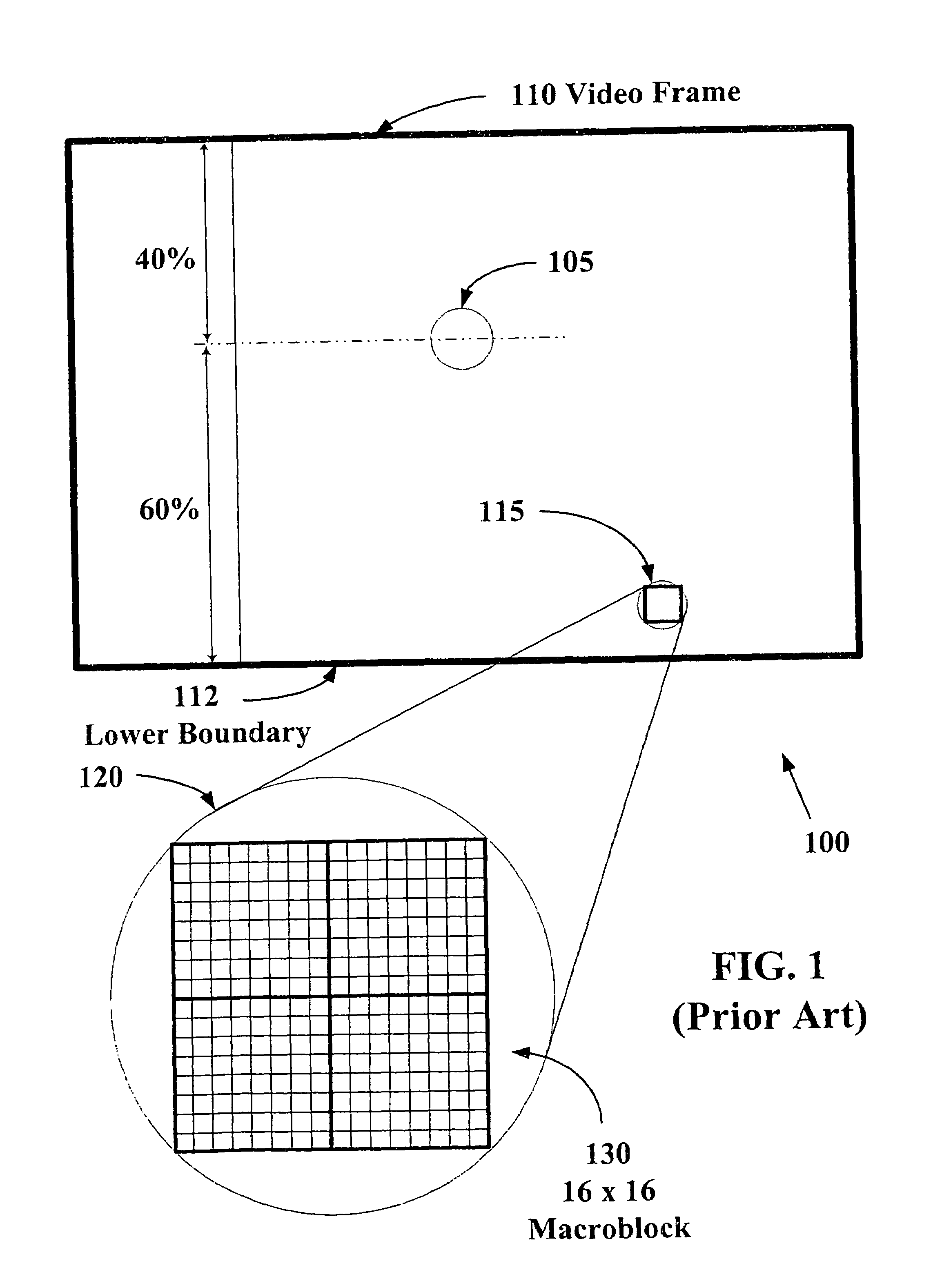
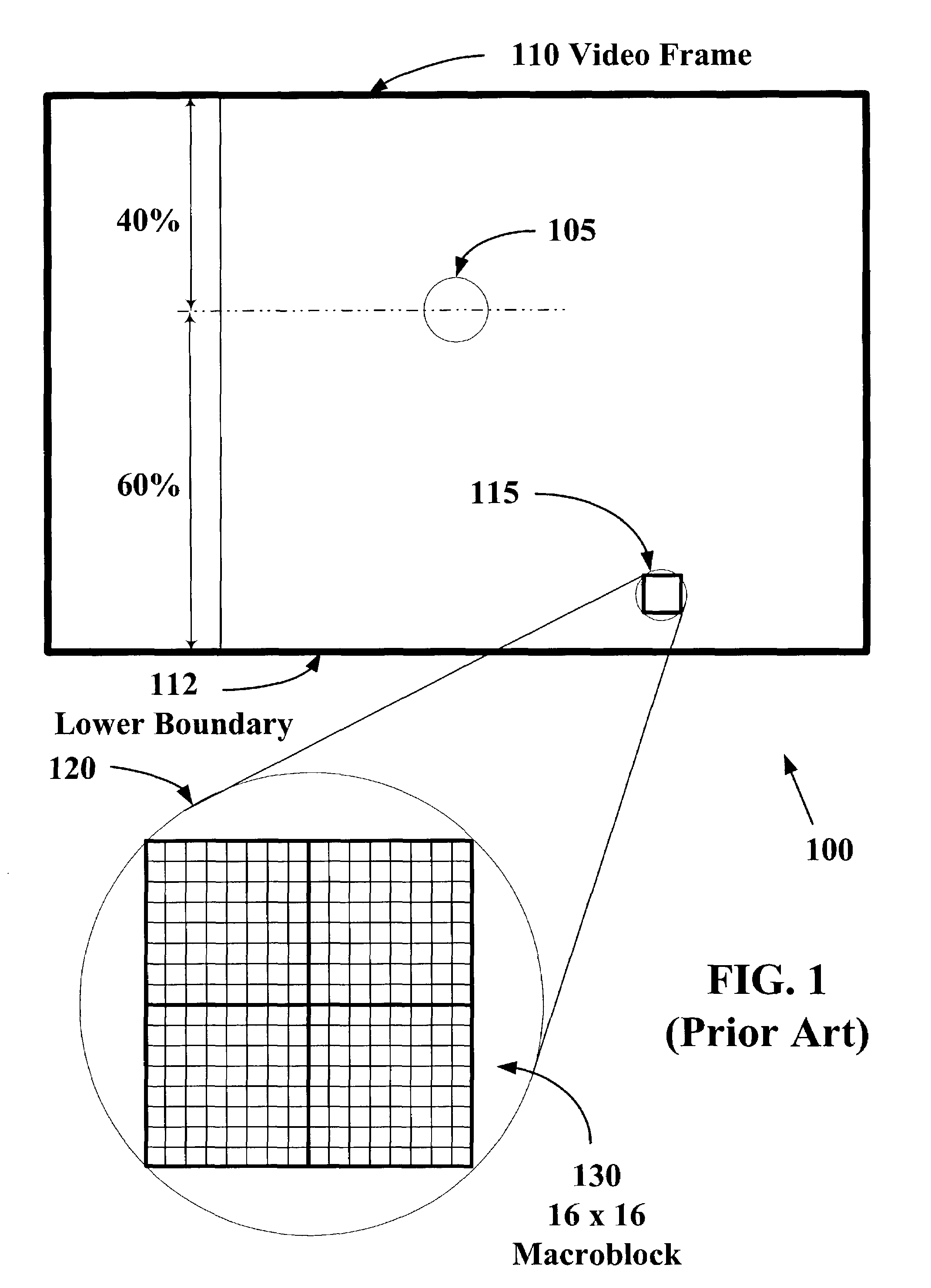
System and method for static perceptual coding of macroblocks in a video frame
InactiveUS6864909B1Increased subjective video qualityIncreasing bandwidth required to carry videoTwo-way working systemsDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Video quality
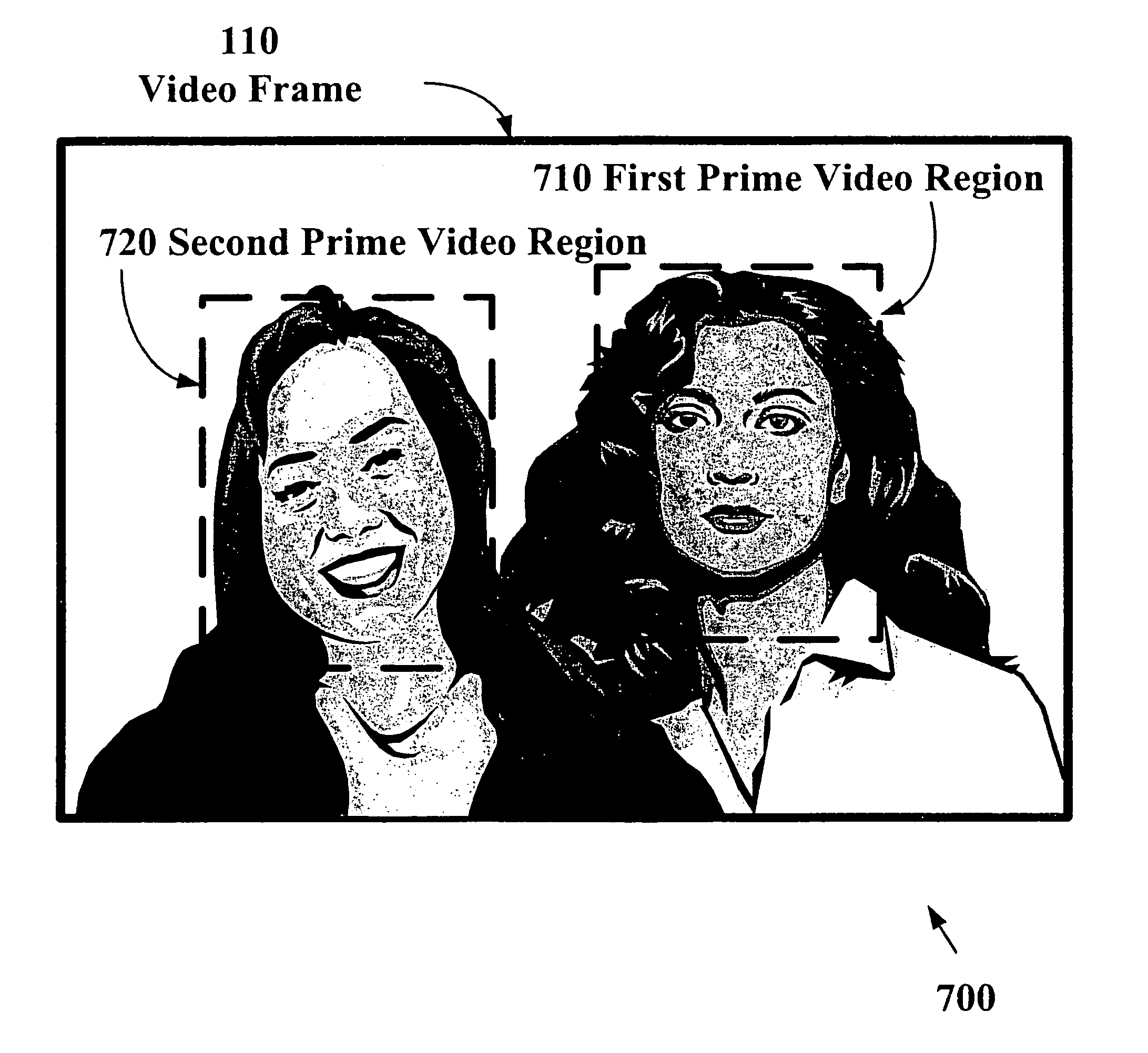
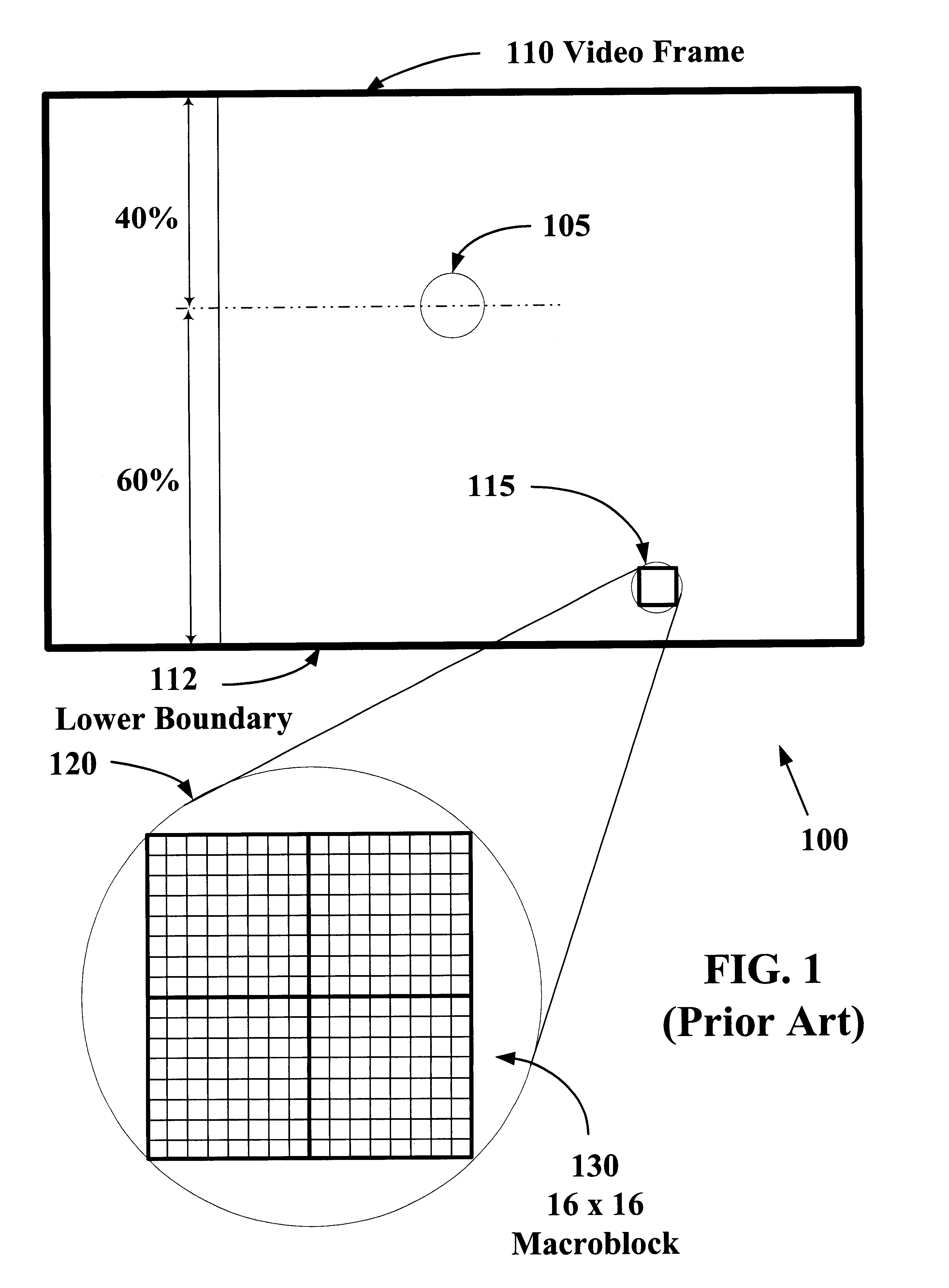
The present invention allows video images with improved subjective quality to be transmitted without a concomitant increase in a total number of bits transmitted per frame. Quantization parameters are applied to coefficients of macroblocks within a given video frame. A lower value of quantization parameter is applied near a central region of a video frame. This central region is referred to as a prime video region. Applying a lower quantization parameter to the prime video region has the effect of increasing the bit density within that area thereby improving the video quality. Outside of the prime video region, the bit density is progressively decreased on a macroblock-by-macroblock basis so as to have a zero or near-zero net-gain in bit density over the entire video frame.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Perceptual coding of audio signals by spectrum uncertainty
InactiveUS20080004873A1Reduce computational overheadAccurately measure masking effectSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSpectral flatness
A method for digital encoding of an audio stream in which the psychoacoustic modeling bases its computations upon an MDCT for the intensity and a spectral flatness measurement that replaces the phase data for the unpredictability measurement. This dramatically reduces computational overhead while also providing an improvement in objectively measured quality of the encoder output. This also allows for determination of tonal attacks to compute masking effects.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
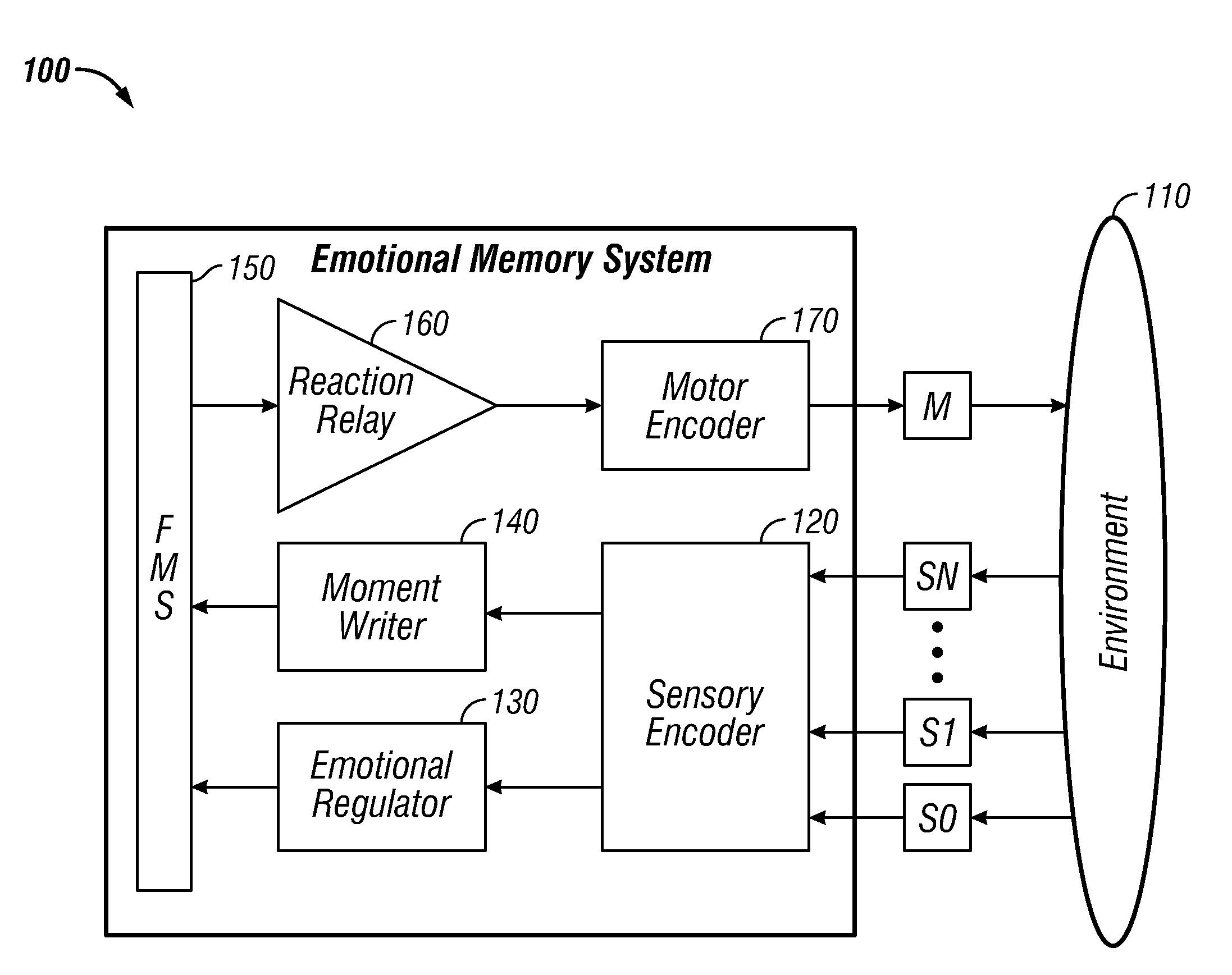
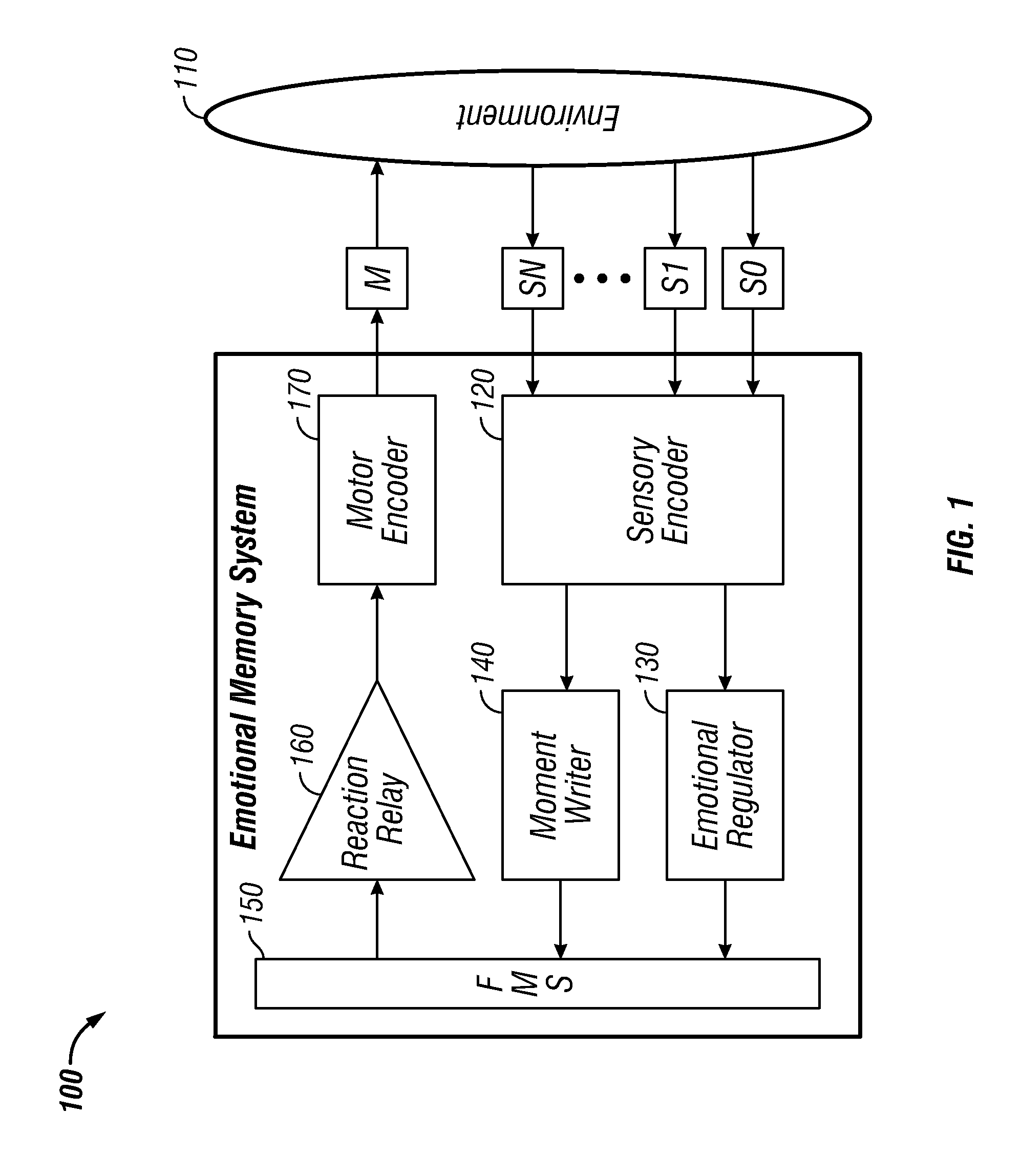
Watershed memory systems and methods
An emotional memory control system and method for generating behavior. A sensory encoder provides a condensed encoding of a current circumstance received from an external environment. A memory associated with a regulator recognizes the encoding and activates one or more emotional springs according to a predefined set of instructions. The activated emotional springs can then transmit signals to at least one moment on a fractal moment sheet incorporated with a timeline for each channel in order to form one or more watersheds. An activation magnitude can be calculated for each moment and transmitted to a reaction relay. A synaptic link can then form between the moment and a motor encoder, thereby linking a specific moment with a specific action state.
Owner:KNOWM TECH
Method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing higher order ambisonics representation for sound field
ActiveCN104854655AEliminate shortcomingsBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisSound sourcesOrder reduction
The invention improves HOA sound field representation compression. The HOA representation is analysed for the presence of dominant sound sources and their directions are estimated. Then the HOA representation is decomposed into a number of dominant directional signals and a residual component. This residual component is transformed into the discrete spatial domain in order to obtain general plane wave functions at uniform sampling directions, which are predicted from the dominant directional signals. Finally, the prediction error is transformed back to the HOA domain and represents the residual ambient HOA component for which an order reduction is performed, followed by perceptual encoding of the dominant directional signals and the residual component.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
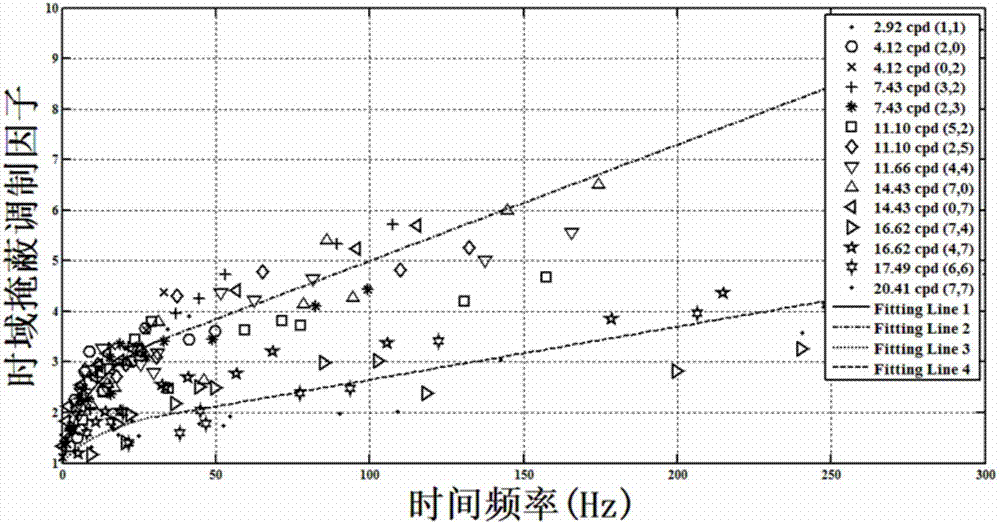
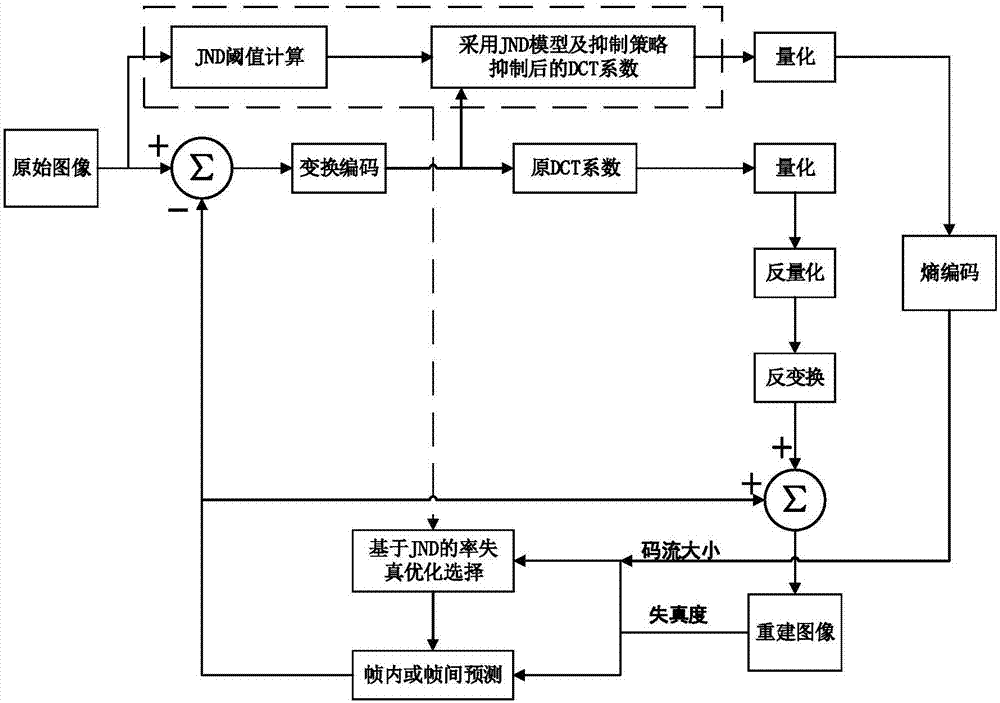
Visual perceptual coding method based on multi-domain JND (Just Noticeable Difference) model
ActiveCN107241607ARemove Perceptual RedundancyImprove subjective qualityDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionInformation processing
The invention discloses a visual perceptual coding method based on a multi-domain JND (Just Noticeable Difference) model and relates to video information processing. The method comprises the following steps: respectively calculating a space-domain basic JND threshold value, a luminance masking modulation factor, a contrast masking modulation factor and a time domain masking modulation factor of each transformation coefficient in a DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) block by utilizing a time-space-domain multi-domain JND model so as to obtain the time-space-domain multi-domain JND threshold value of each transformation coefficient; introducing a block perception-based distortion probability evaluative criteria in the transform coding process, and searching a correction factor of each coefficient relative to the JND threshold value through an adaptive searching algorithm so as to obtain a transformation coefficient suppression value; and finally, subtracting the original transformation coefficient from the most appropriate suppression value obtained through corresponding calculation, and taking the coefficient as a novel coefficient to be put at an entropy coding stage. According to the coded suppression strategy of the multi-domain JND model and the block perception-based distortion probability, the coding rate can be effectively reduced on the premise of guaranteeing certain subjective quality, and the compression ratio of the current coding standard is further improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
System and method for dynamic perceptual coding of macroblocks in a video frame
ActiveUS6987889B1Improves perceived video qualityIncreasing bandwidth required to carry videoCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Perceptual coding
The present invention allows higher quality video images to be transmitted without a concomitant increase in a total number of video data bits transmitted per frame. Quantization parameters are applied to coefficients of macroblocks within a given video frame. A lower value of the quantization parameter is applied near a central region of a video frame. This central region is referred to as a prime video region. Applying the lower quantization parameter to the prime video region has the effect of increasing the video data bit density within that area. Outside of the prime video region, the video data bit density per macroblock is decreased so as to have a zero net-gain in bit density over the entire video frame. Furthermore, there may be a plurality of prime video regions where quantization parameters are dynamically coded. In this case, the value of the quantization parameter will increase or decrease within a given prime video region based on a relative importance of a particular prime video region. Consequently, a quantization parameter matrix may vary depending on the video scene.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Multichannel sound signal coding and decoding method and device
ActiveCN105336333AReduce Statistical RedundancyGood estimateSpeech analysisMultichannel codeVocal tract
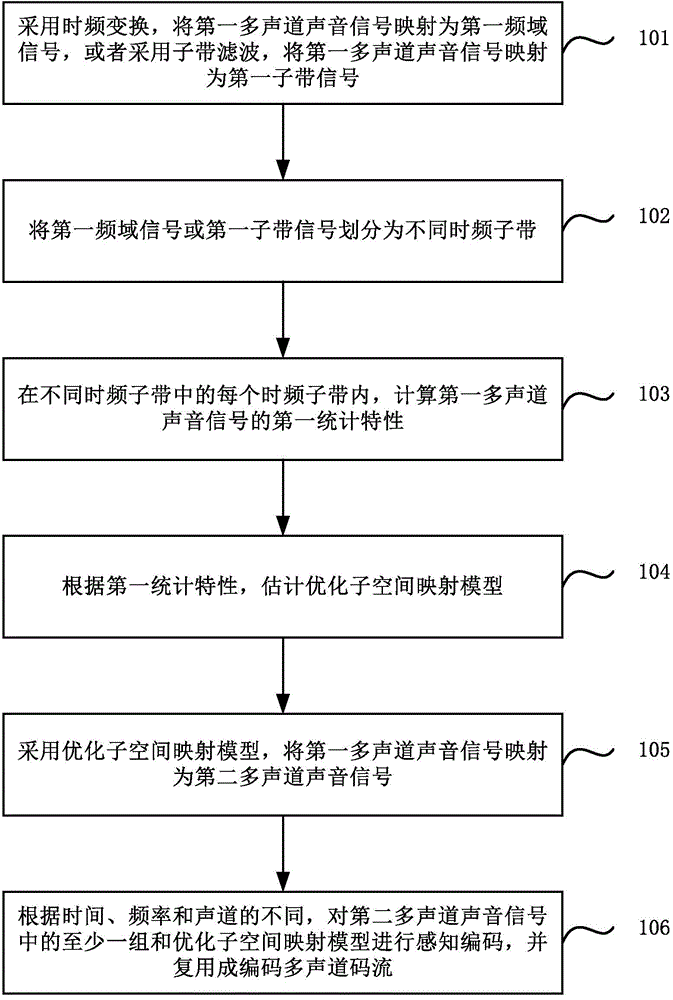
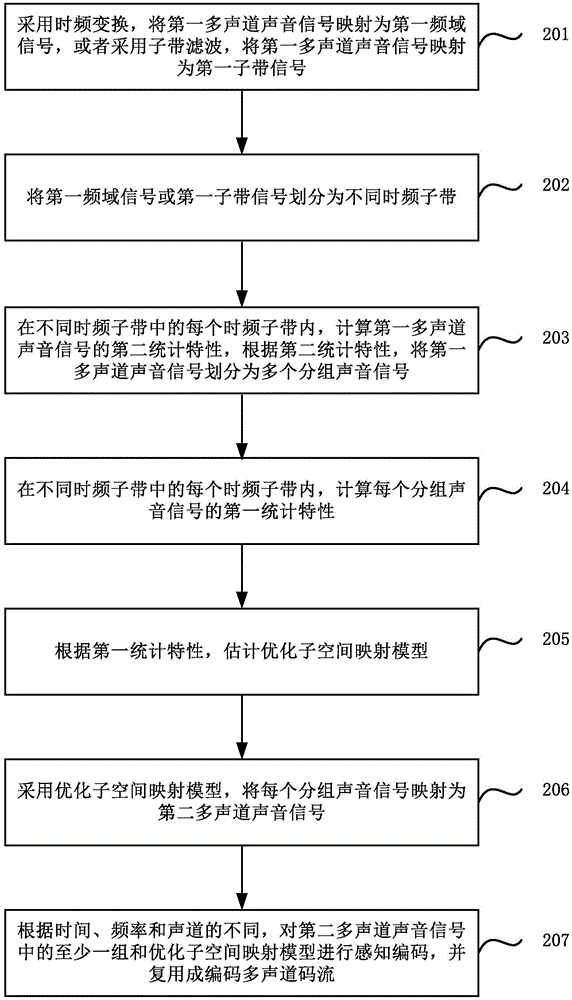
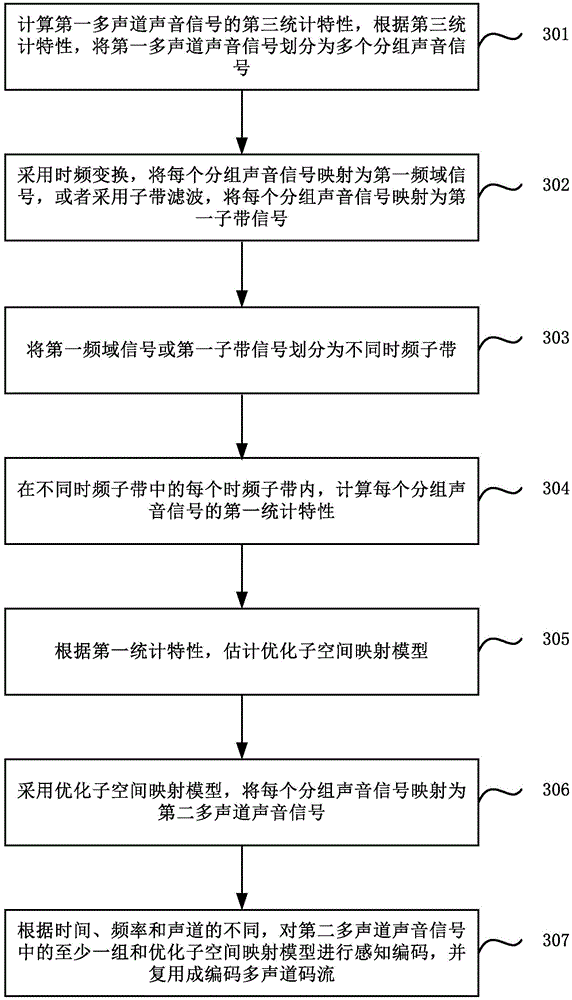
The invention relates to a multichannel sound signal coding and decoding method and device. The coding method includes: adopting time-frequency transformation to map first multichannel sound signals to be first frequency domain signals, or adopting sub-band filtering to map the first multichannel sound signals to be first sub-band signals; dividing the first frequency domain signals or the first sub-band signals into different time-frequency sub-bands; in each time-frequency sub-band, calculating first statistical characteristics of the first multichannel sound signals; according to the first statistical characteristics, estimating an optimized sub-space mapping model; adopting the optimized sub-space mapping model to map the first multichannel sound signals to be second multichannel sound signals; according to time, frequency and sound channels, performing perceptual coding on at least one group of the second multichannel sound signals and the optimized sub-space mapping model to acquire coded multichannel code stream. In a word, the coding method selects mapping models in a self-adaptive manner, and higher coding efficiency and coding quality can be realized.
Owner:BEJING ANGEL VOICE DIGITAL TECH
Bandwidth extension coding and decoding method and apparatus
ActiveCN105280190AImprove coding efficiencyImprove sound qualitySpeech analysisSound qualityPerceptual coding
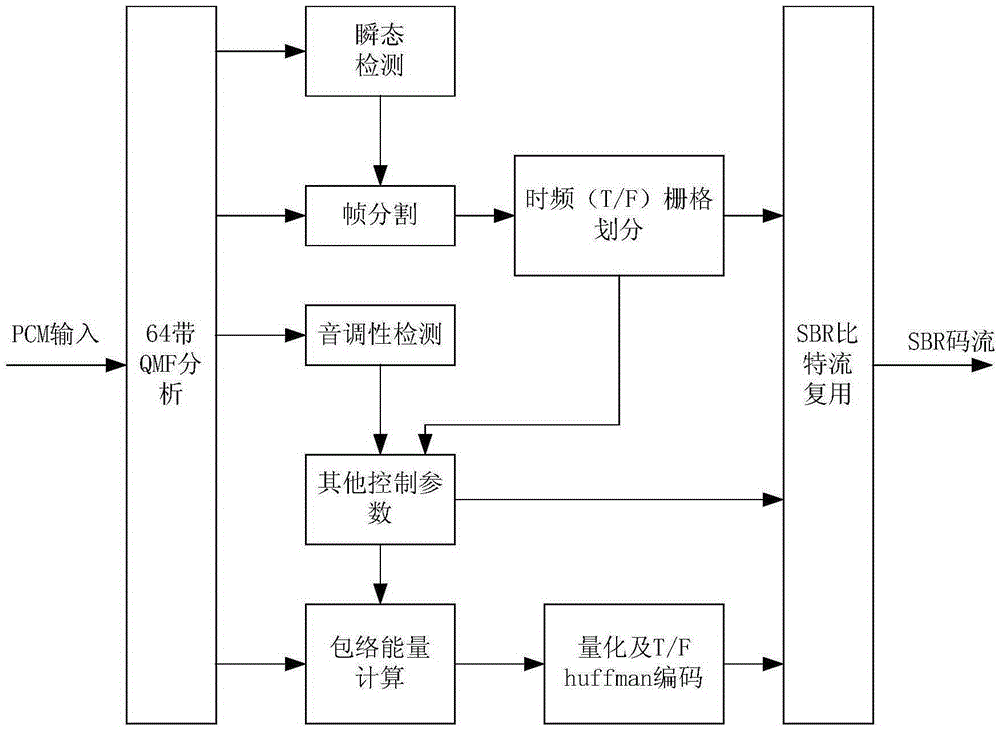
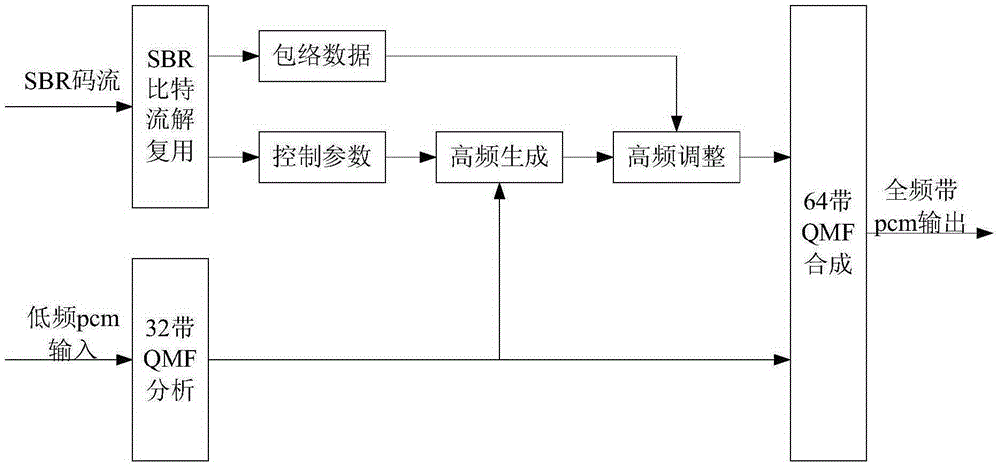
The invention relates to a bandwidth extension coding and decoding method and apparatus. The combination of adaptive multiresolution filtering and adaptive time-frequency grid structure and a plurality of linear prediction encoding high-frequency details generates two key technologies, so that the high-frequency part encoding efficiency of digital audio signals and the sound quality of high-frequency part signals can be obviously improved, the low-frequency part of the digital audio signals can still be encoded by means of the traditional perceptual audio coding (for example DRA), and the encoding technology with high subjective sound quality at low bit rate and medium bit rate is realized. In another aspect, an enhancement tool is added on the basis of a current high-quality perceptual coding algorithm such as the DRA, in this way, the downward compatibility with the traditional perceptual coding DRA or other algorithms can be guaranteed. A digital audio encoding and decoding device based on the bandwidth extension coding and decoding method and apparatus can be applied to the fields of satellite HDTV sound accompaniment processing and high-quality audio broadcasting.
Owner:广东广晟研究开发院有限公司
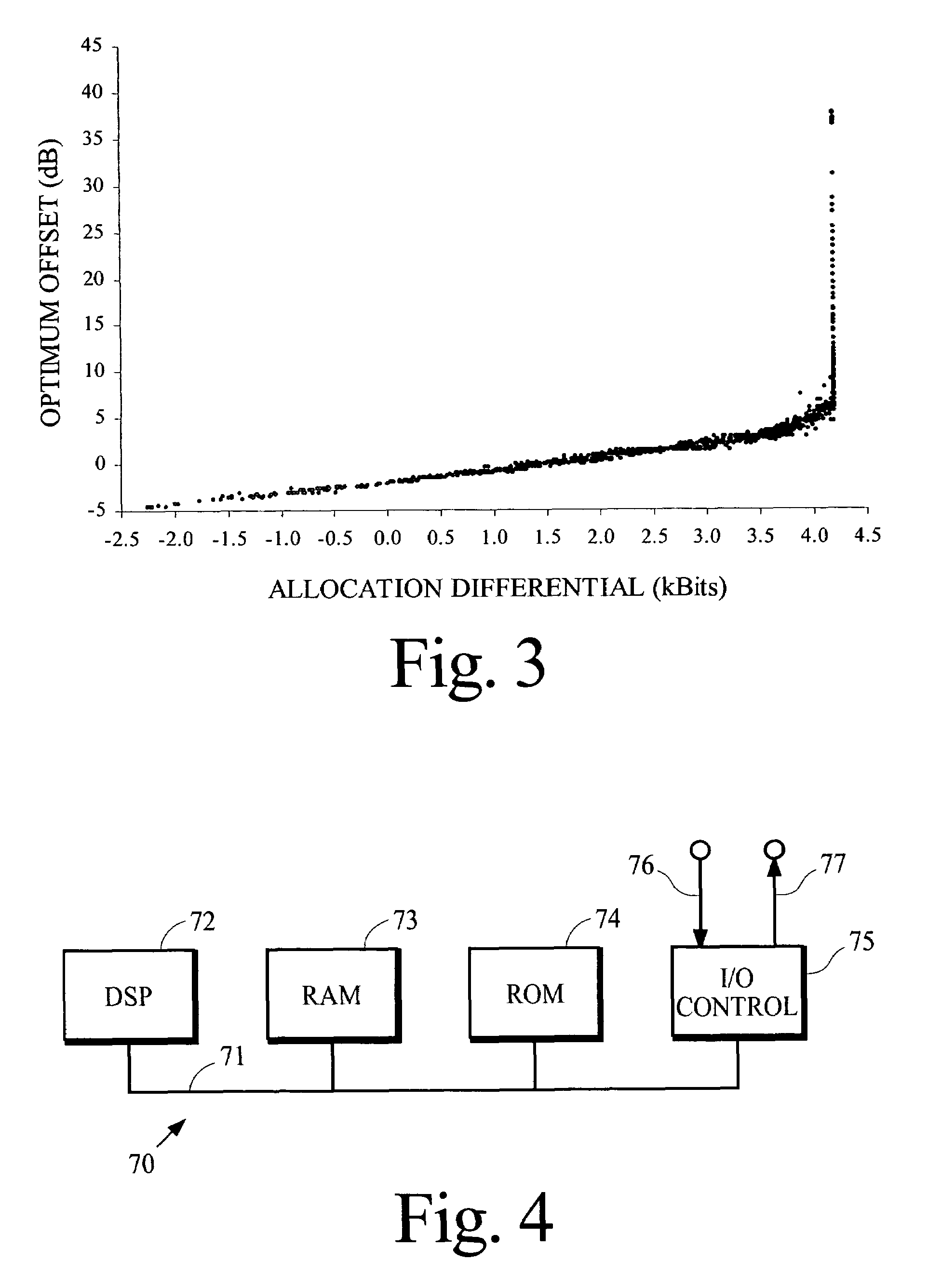
Reduced computational complexity of bit allocation for perceptual coding
InactiveUS7406412B2Increase valueEfficient implementationSpeech analysisComputation complexityFrequency spectrum
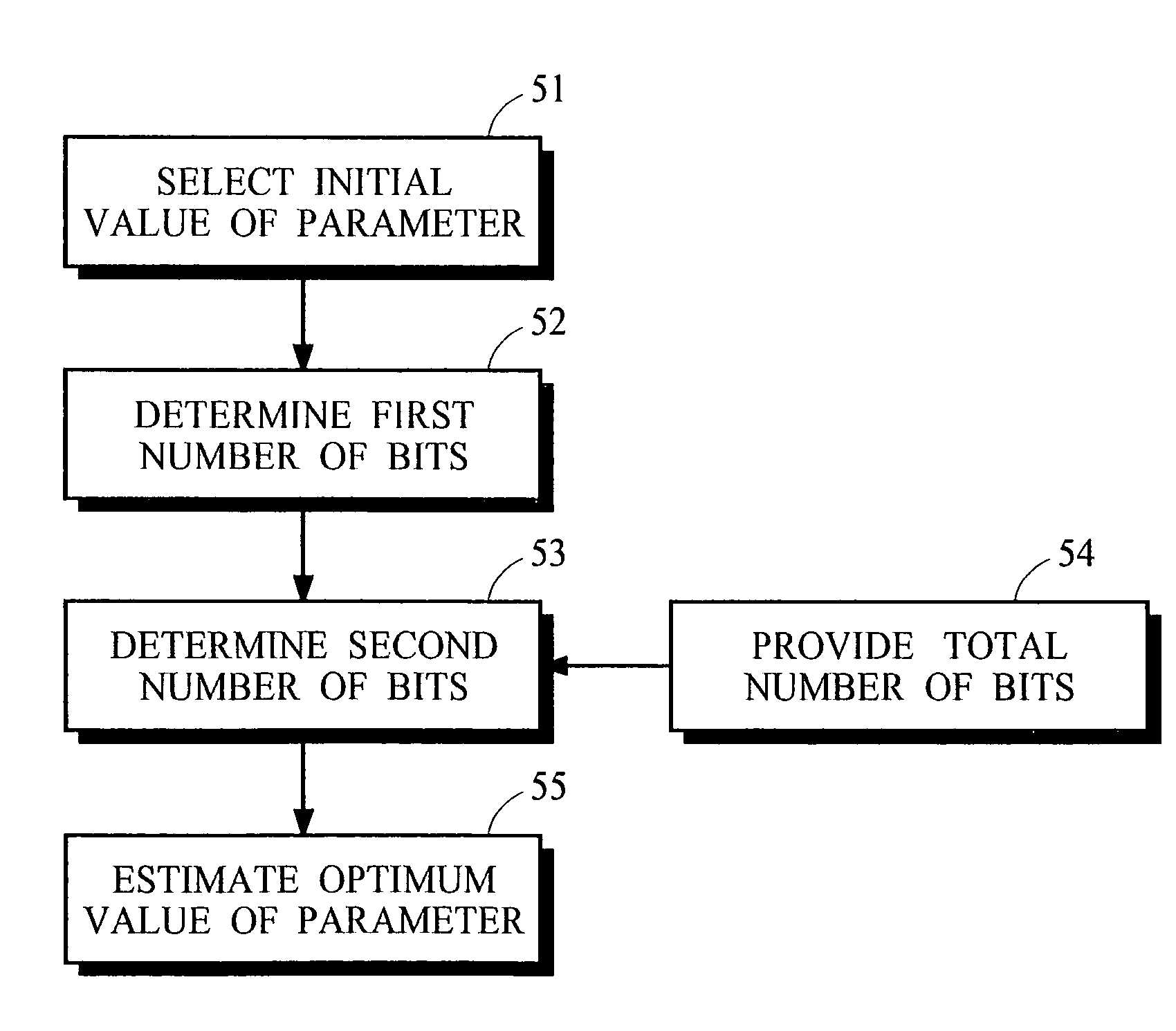
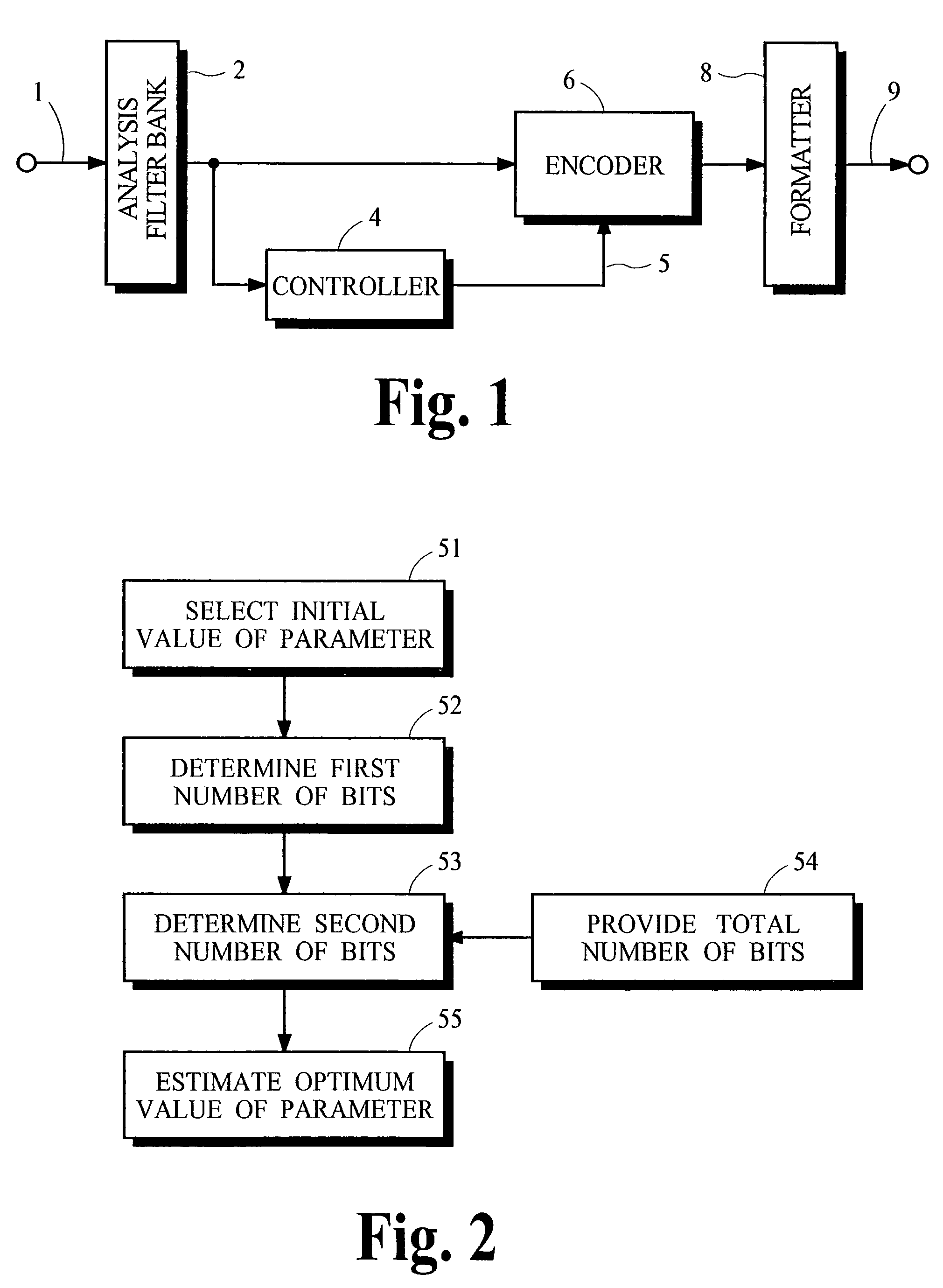
A process that allocates bits for quantizing spectral components in a perceptual coding system is performed more efficiently by obtaining an accurate estimate of the optimal value for one or more coding parameters that are used in the bit allocation process. In one implementation for a perceptual audio coding system, an accurate estimate of an offset from a calculated psychoacoustic masking curve is derived by selecting an initial value for the offset, calculating the number of bits that would be allocated if the initial offset were used for coding, and estimating the optimum value of the offset from a difference between this calculated number and the number of bits that are actually available for allocation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
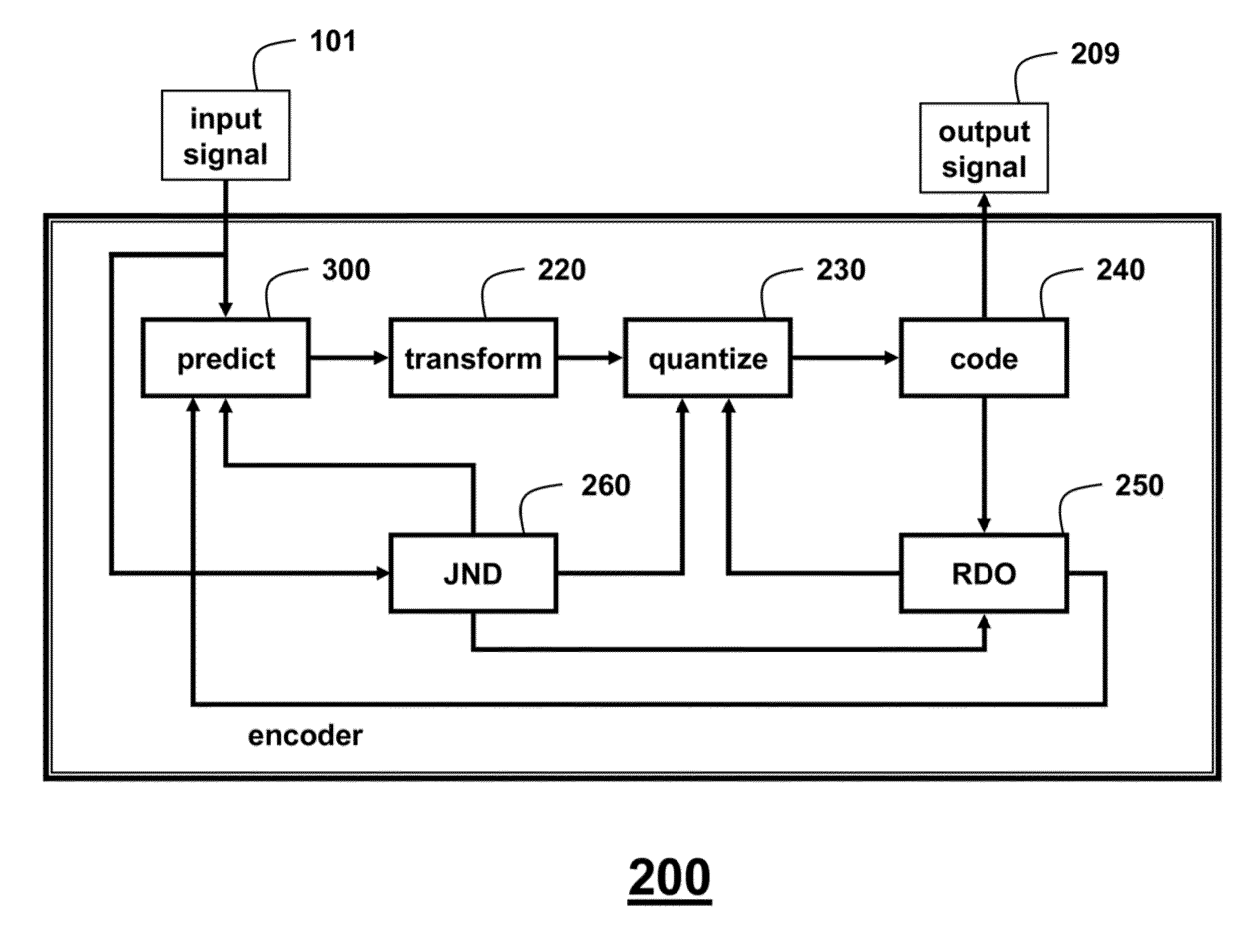
Perceptually coding images and videos
Blocks in pixel images are template matched to select candidate blocks and weights according to a structural similarity and a perceptual distortion of the blocks. The perceptual distortion is a function of a just-noticeable-distortion (JND). A filter outputs a prediction residual between the block and the candidate blocks. The prediction residual is transformed and quantized to produce a quantized prediction residual using the JND. The matching and quantizing is optimized jointly using the perceptual distortion. Then, the quantized prediction residual and the weights are entropy encoded into a bit-stream for later decoding.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
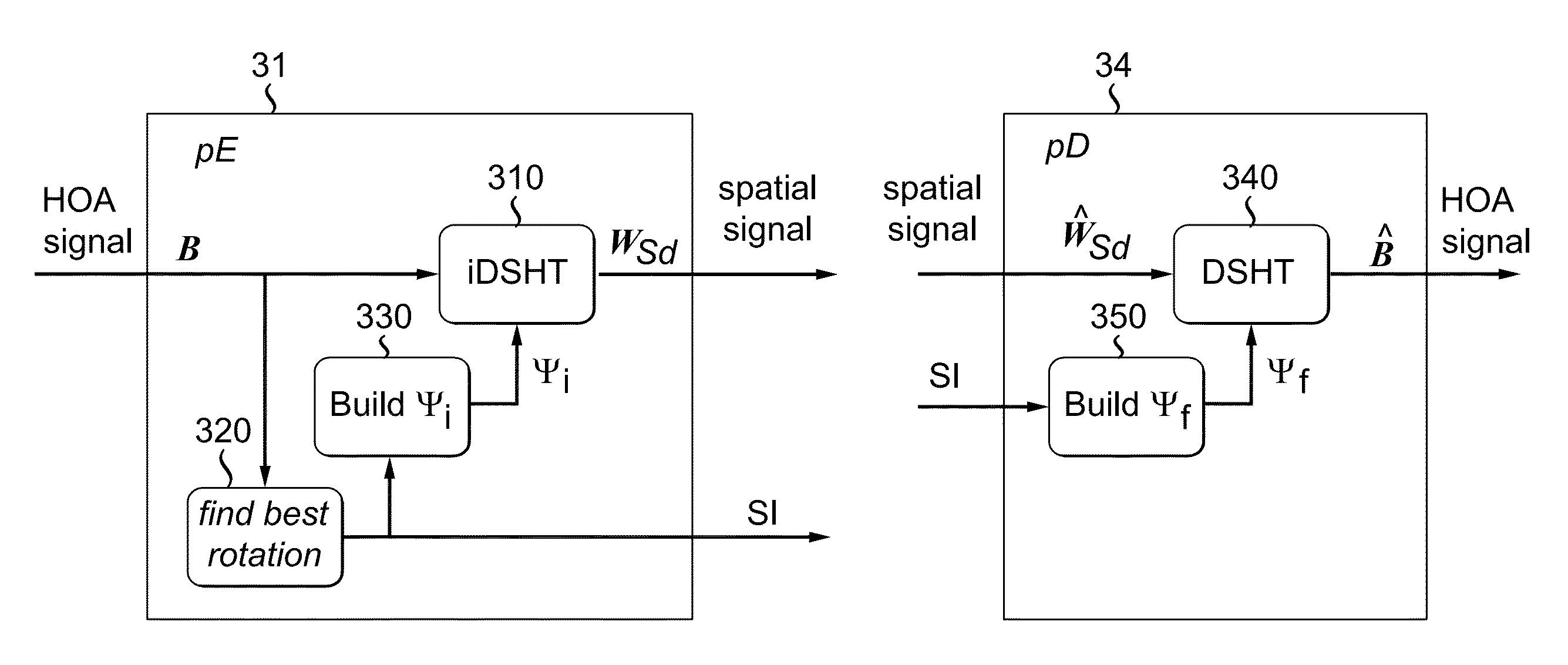
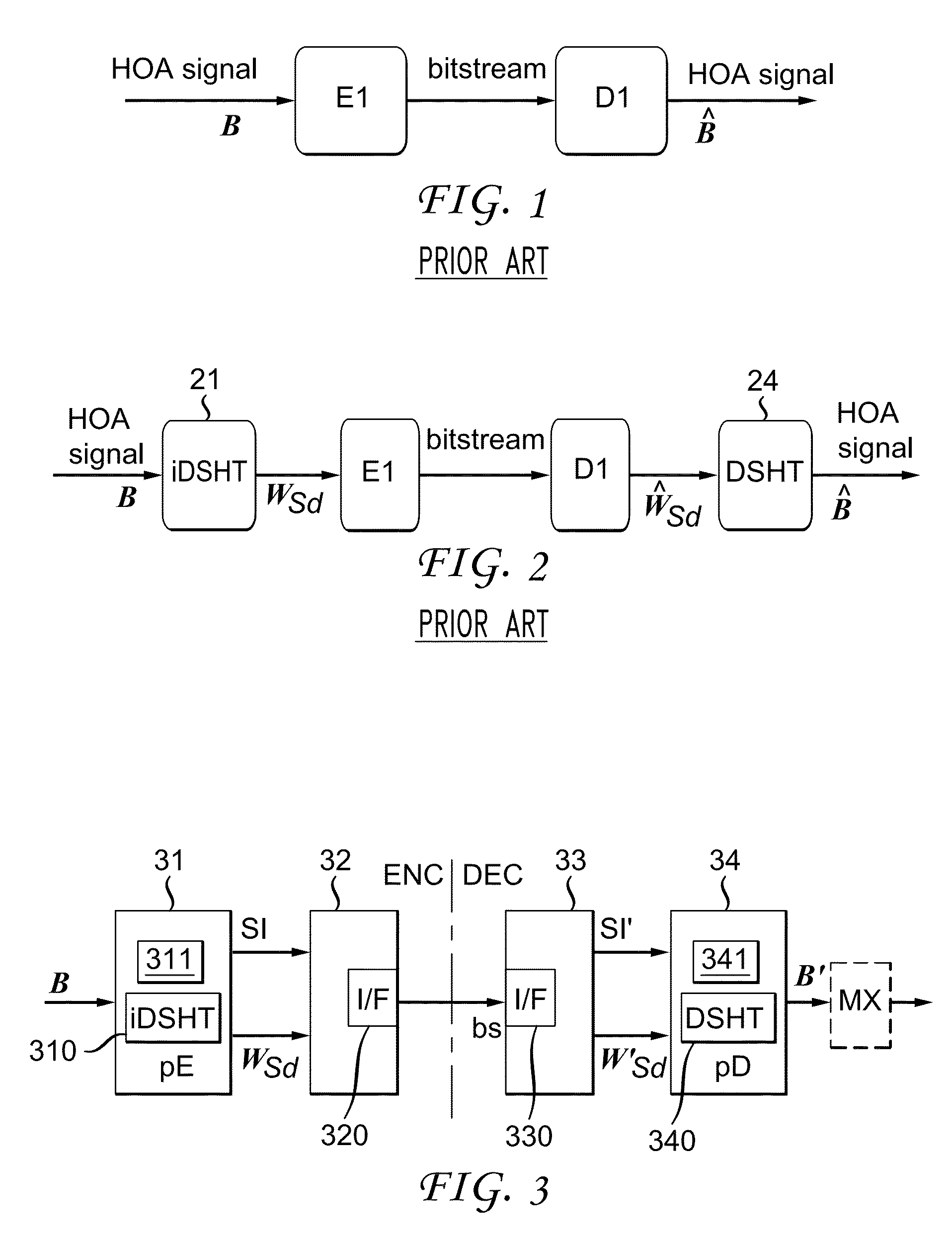
Method and apparatus for encoding multi-channel HOA audio signals for noise reduction, and method and apparatus for decoding multi-channel HOA audio signals for noise reduction
ActiveUS9460728B2Minimize impactReduce the amount requiredSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsVocal tractNoise reduction
A method for encoding multi-channel HOA audio signals for noise reduction comprises steps of decorrelating the channels using an inverse adaptive DSHT, the inverse adaptive DSHT comprising a rotation operation and an inverse DSHT, with the rotation operation rotating the spatial sampling grid of the iDSHT, perceptually encoding each of the decorrelated channels, encoding rotation information, the rotation information comprising parameters defining said rotation operation, and transmitting or storing the perceptually encoded audio channels and the encoded rotation information.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Video perception coding method and device
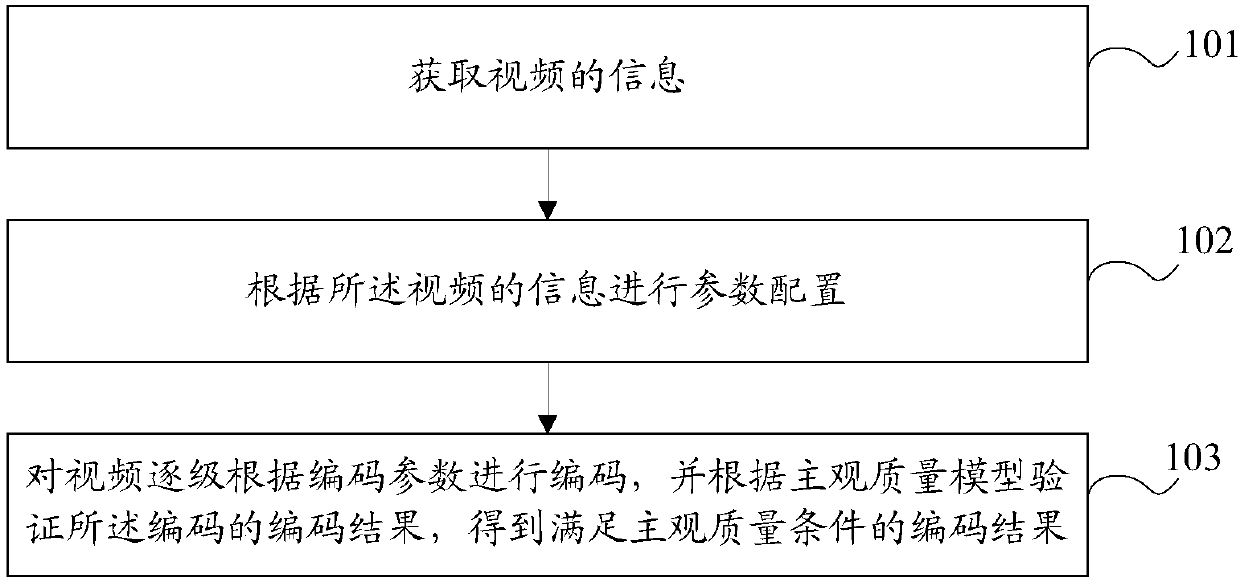
ActiveCN107820084AImprove transcoding efficiencySatisfy subjective coding quality requirementsDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureTranscoding
The invention discloses a video perception coding method and device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring video information; initializing parameter configuration; selecting a hierarchyand an object thereof to be coded currently; and coding the object, verifying a coding result of the coding based on a subjective quality model of the hierarchy, and selecting the coding result. The video perception coding method provided by the invention not only can strictly satisfy the subjective coding quality requirements of users at each hierarchy, but also can achieve a better coding efficiency at each level, so that the overall coding efficiency is better, and a greater video compression and video transcoding efficiency can be achieved on the premise of guaranteeing that there is no subjective loss or subjective loss of a given degree.
Owner:BEIJING KINGSOFT CLOUD NETWORK TECH CO LTD +1
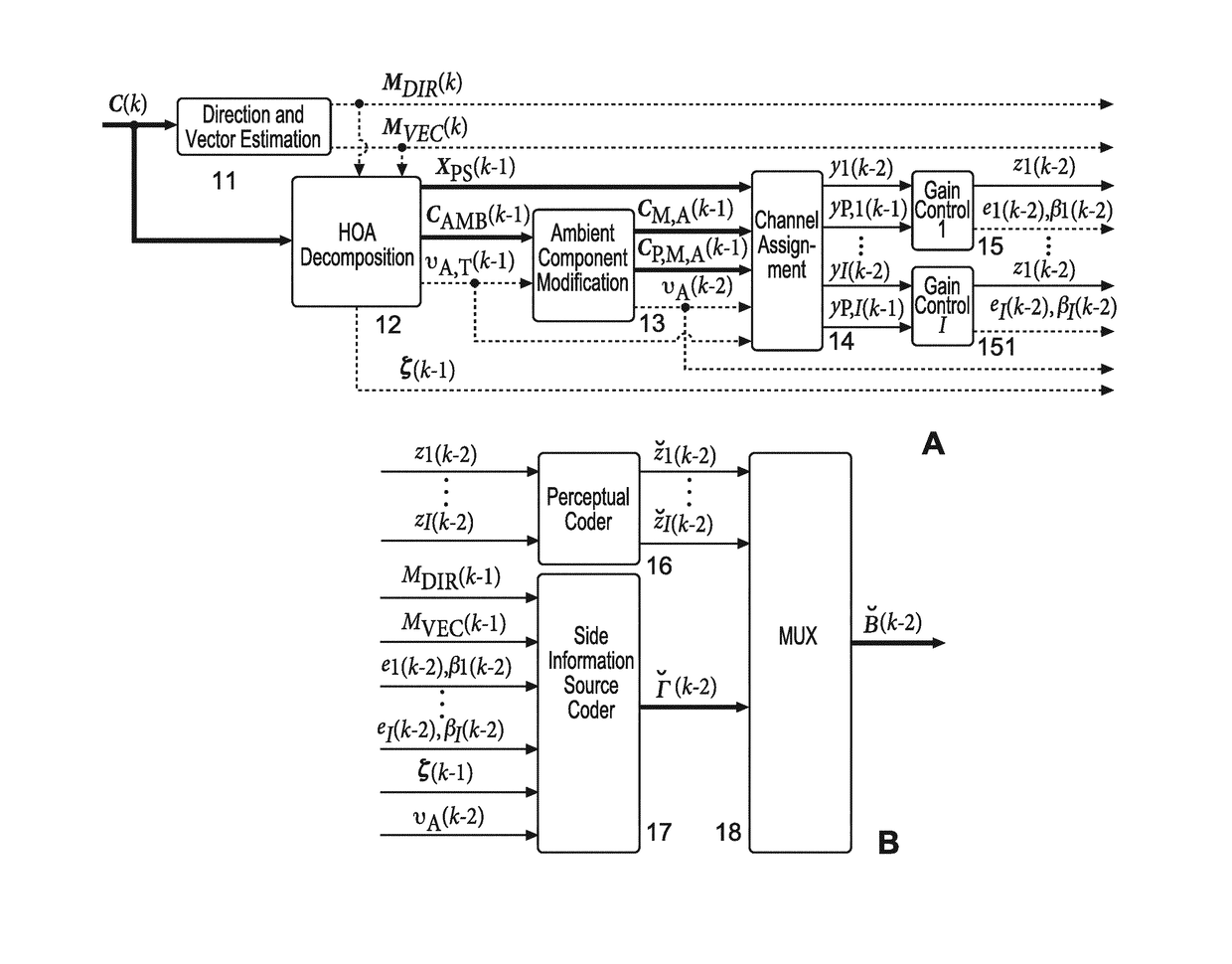
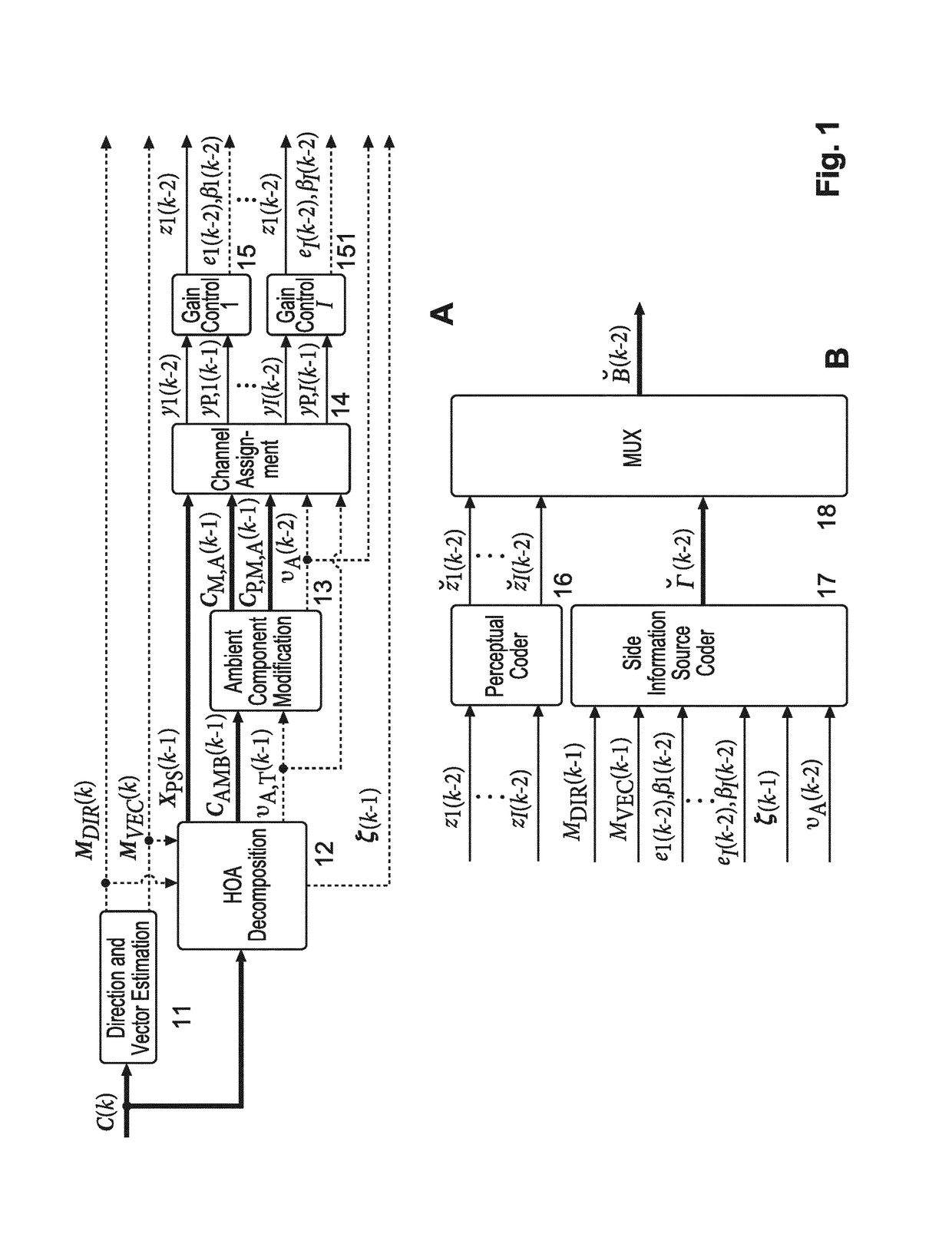
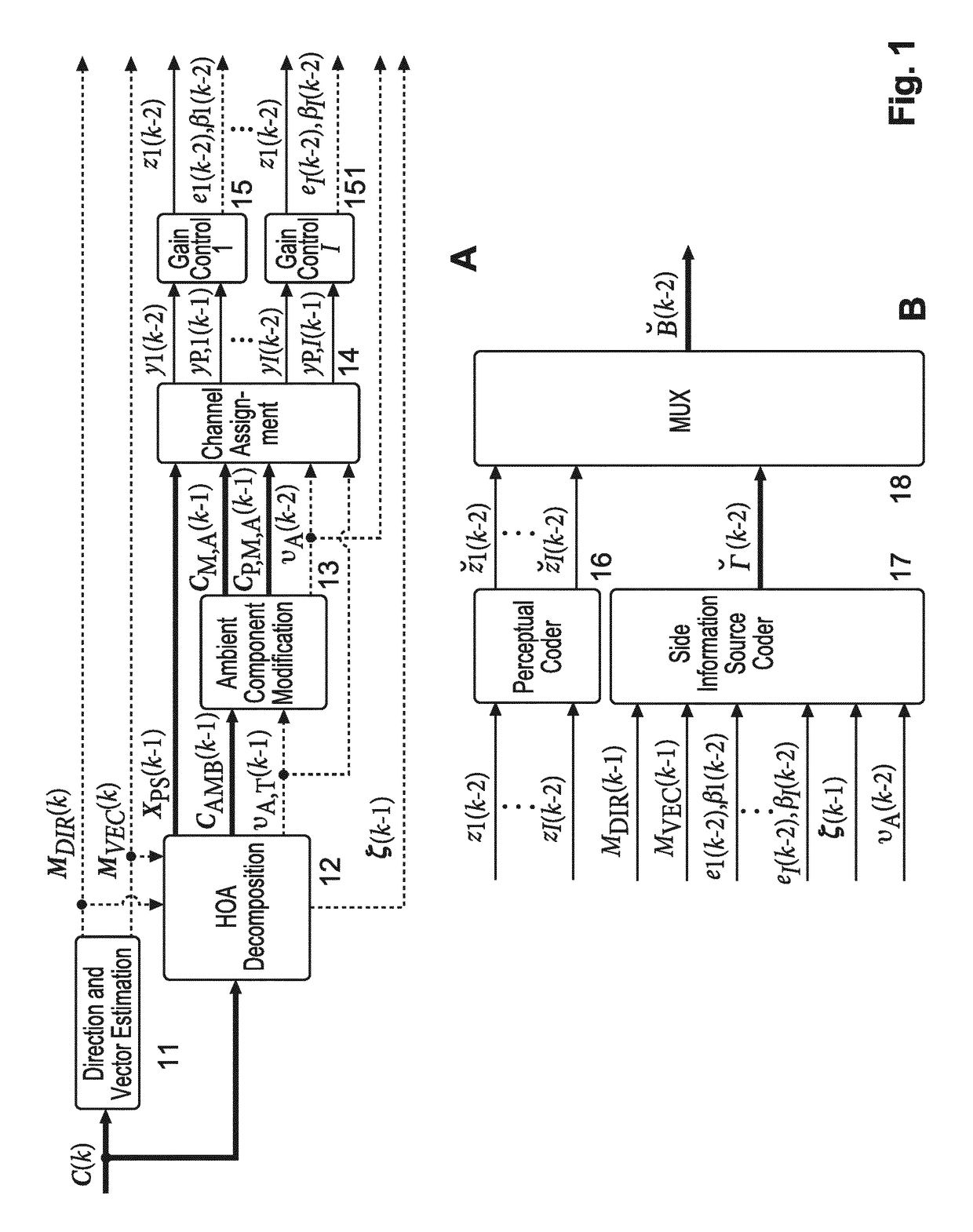
Coded HOA data frame representation that includes non-differential gain values associated with channel signals of specific ones of the dataframes of an HOA data frame representation
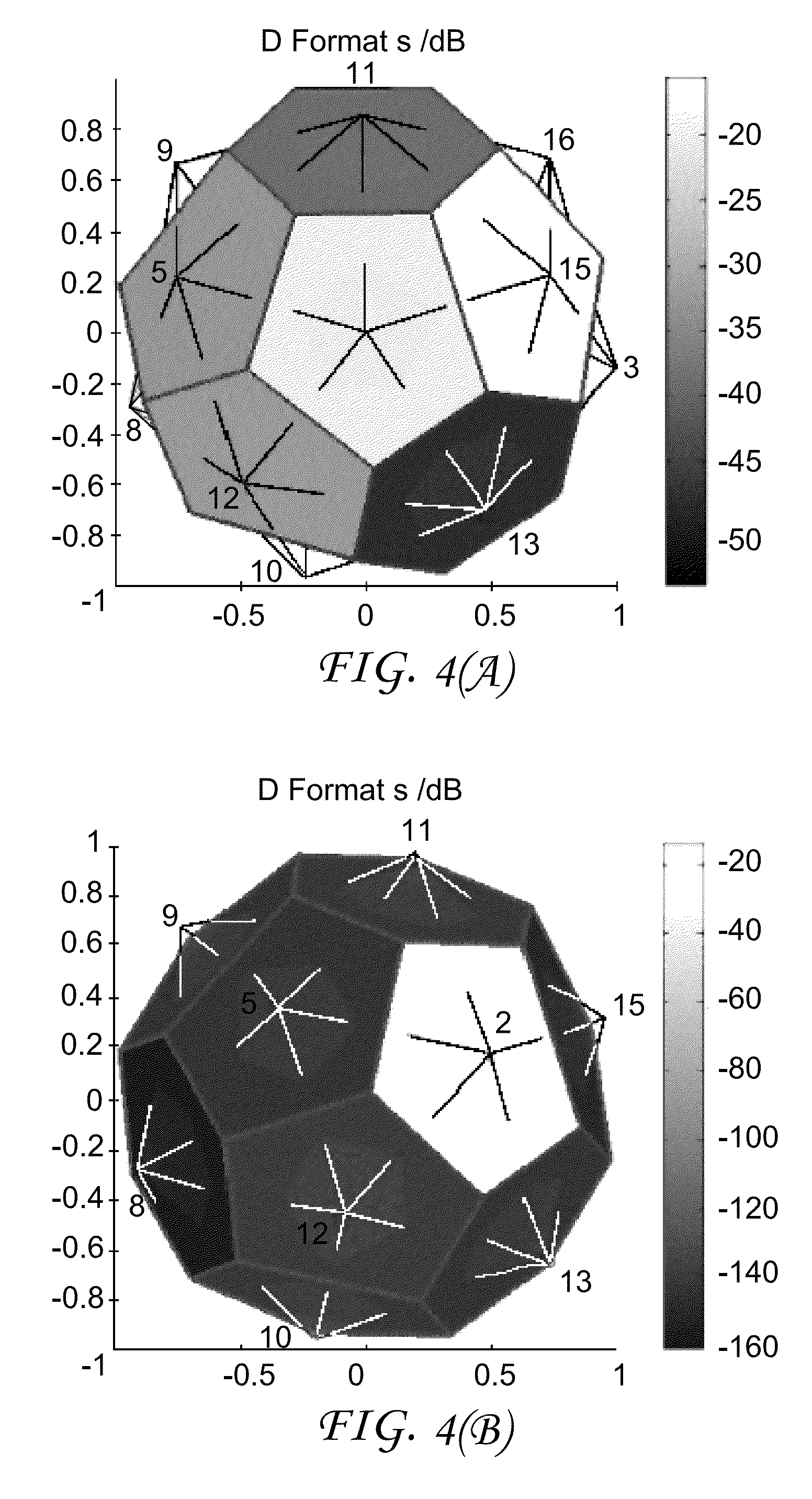
When compressing an HOA data frame representation, a gain control (15, 151) is applied for each channel signal before it is perceptually encoded (16). The gain values are transferred in a differential manner as side information. However, for starting decoding of such streamed compressed HOA data frame representation absolute gain values are required, which should be coded with a minimum number of bits. For determining such lowest integer number (βe) of bits the HOA data frame representation (C(k)) is rendered in spatial domain to virtual loudspeaker signals lying on a unit sphere, followed by normalization of the HOA data frame representation (C(k)). Then the lowest integer number of bits is set to (AA).βe=⌈log2(⌈log2(KMAX·O)⌉+1)⌉(AA)
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
System and method for stereo perceptual audio coding using adaptive masking threshold
A method for stereo audio perceptual encoding of an input signal includes masking threshold estimation and bit allocation. The masking threshold estimation and bit allocation are performed once every two encoding processes. Another method for stereo audio perceptual encoding of an input signal includes performing a time-to-frequency transformation, performing a quantization, performing a bitstream formatting to produce an output stream, and performing a psychoacoustics analysis. The psychoacoustics analysis includes masking threshold estimation on a first of every two successive frames of the input signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
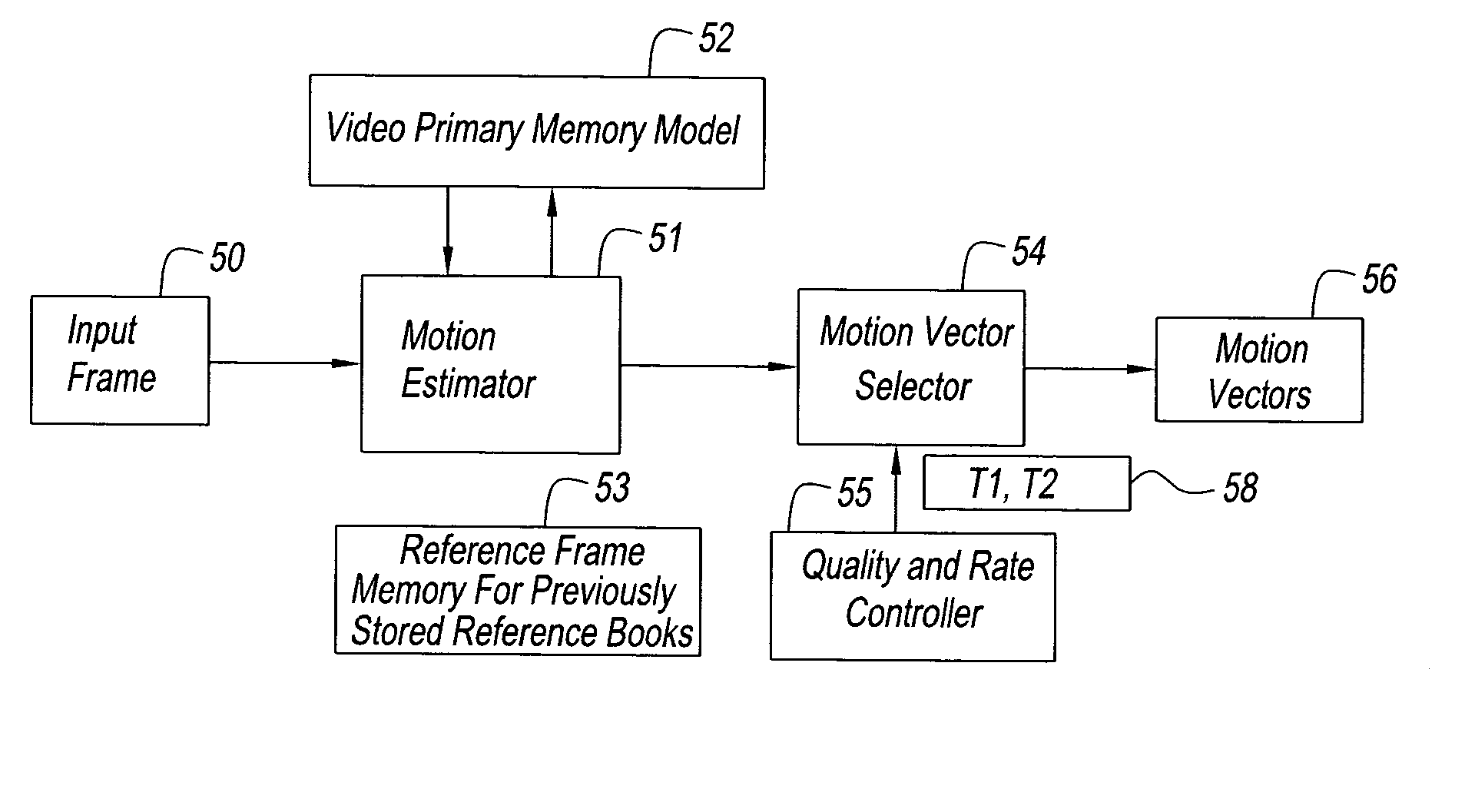
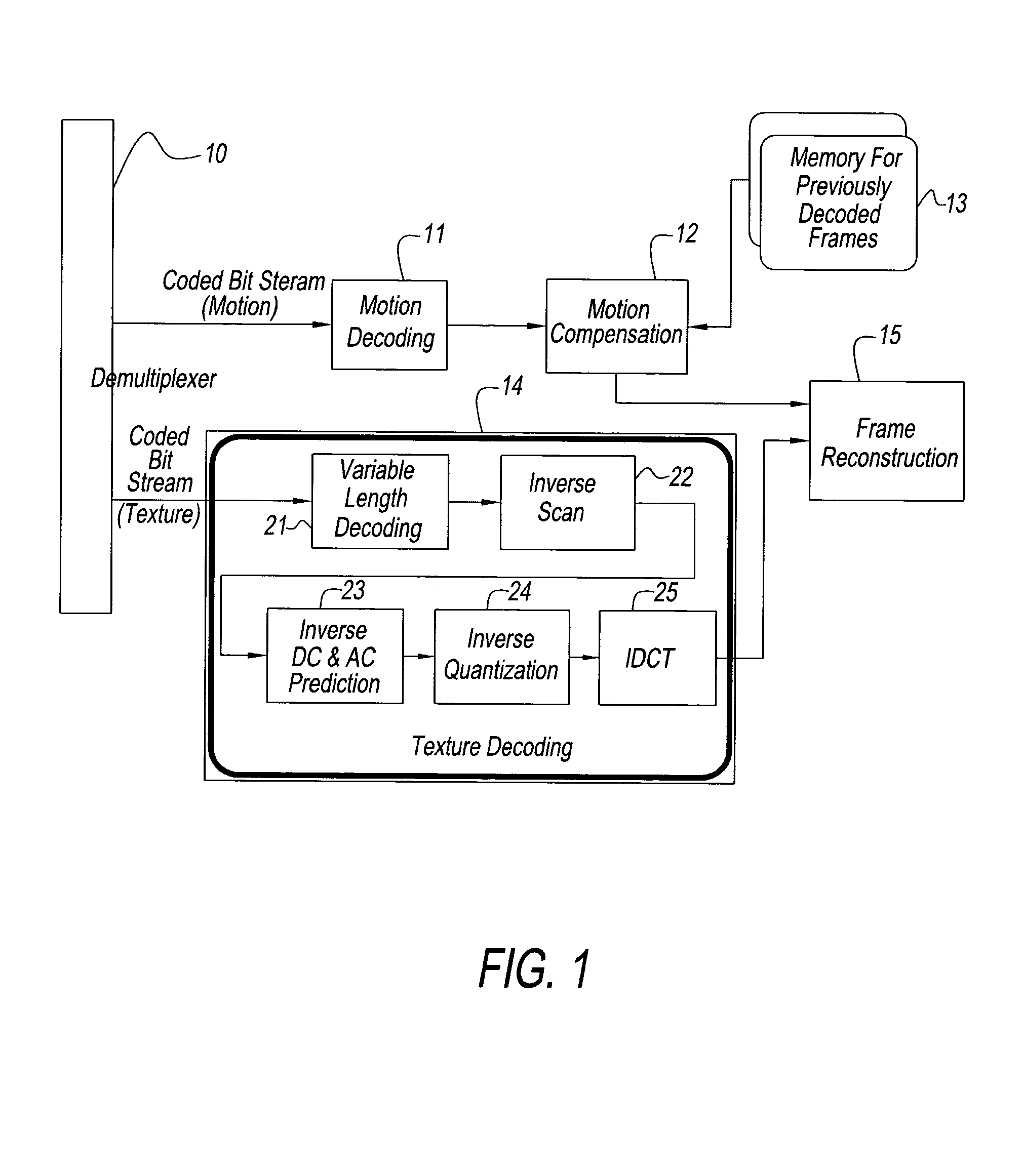
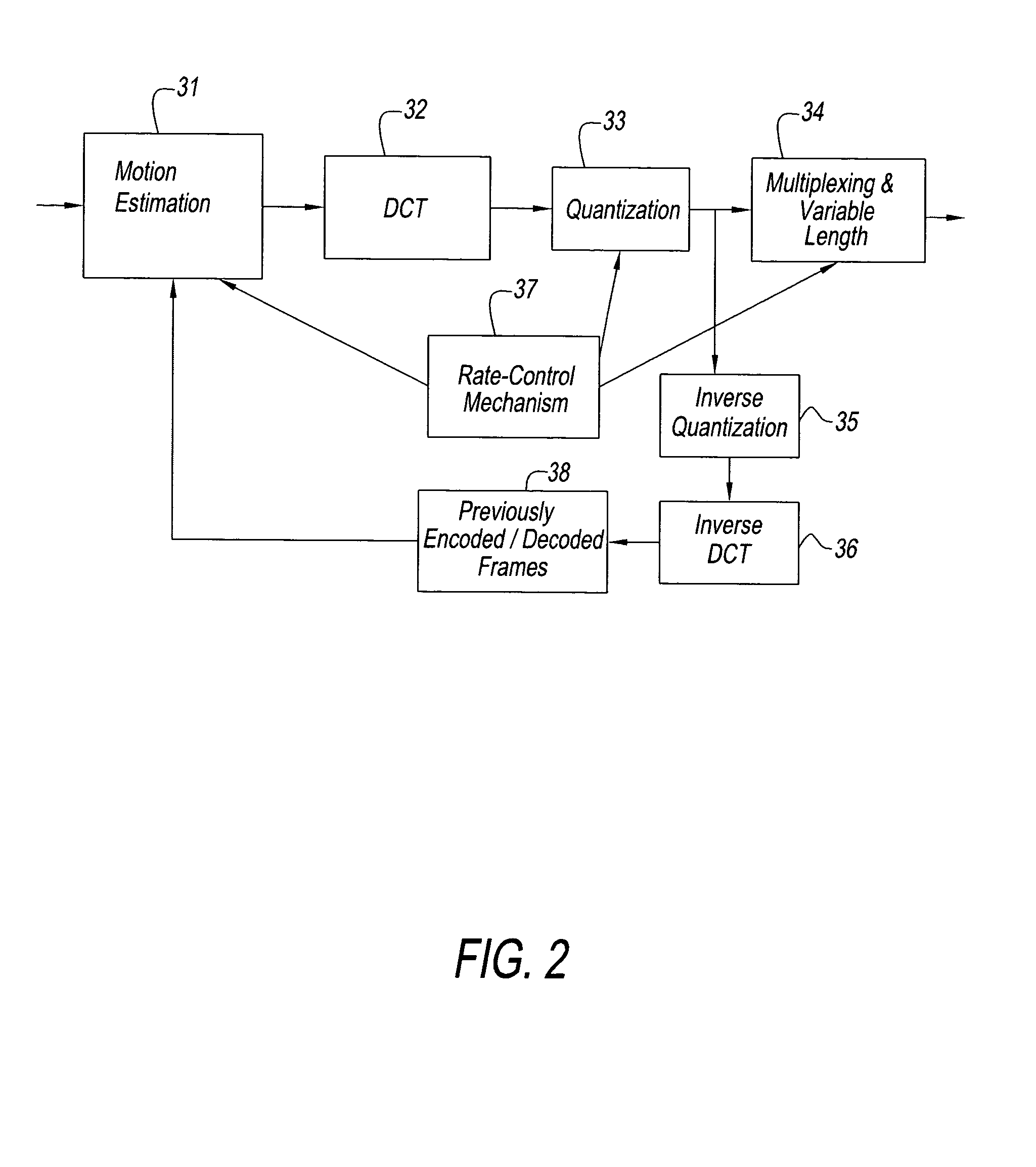
Power-aware on-chip memory management for video coding algorithms
ActiveUS20050018909A1Reduce trafficImprove real-time performanceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingTheoretical computer science
A decoding power aware encoding method for generating a predictively encoded data stream, in which predictions, that result in a reduction in the amount of data transferred from the secondary memory to primary memory during the decoding process, are favored, said method for favoring certain predictions comprising: a model for transfer of data from secondary memory to primary memory in the decoding process; a scheme for weighting the relative merits of favoring a certain prediction and the associated loss in compression gain; and based on said weighting scheme, choosing a particular prediction from the candidates allowed by the compression scheme.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Method and apparatus for determining for the compression of an HOA data frame representation a lowest integer number of bits required for representing non-differential gain values
When compressing an HOA data frame representation, a gain control (15, 151) is applied for each channel signal before it is perceptually encoded (16). The gain values are transferred in a differential manner as side information. However, for starting decoding of such streamed compressed HOA data frame representation absolute gain values are required, which should be coded with a minimum number of bits. For determining such lowest integer number (βe) of bits the HOA data frame representation (C(k)) is rendered in spatial domain to virtual loudspeaker signals lying on a unit sphere, followed by normalization of the HOA data frame representation (C(k)). Then the lowest integer number of bits is set to: (AA).
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Linear predictive coding of an audio signal
InactiveCN101460998AImprove encoding qualityReduce complexitySpeech analysisSelf correlationData rate
An apparatus for linear predictive coding of an audio signal comprises a segmentation processor (201) which generates signal segments for the audio signal. An autocorrelation processor (401) for generates a first autocorrelation sequence for each signal segment and a modification processor (403) generates a second autocorrelation sequence for each signal segment by modifying the first autocorrelation sequence in response to at least one psychoacoustic characteristic. A prediction coefficient processor (405) determines linear predictive coding coefficients for each signal segment in response to the second autocorrelation sequence. The invention allows a low complexity linear encoding which takes into account psychoacoustic considerations thereby allowing an improved perceived coding quality for a given data rate.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
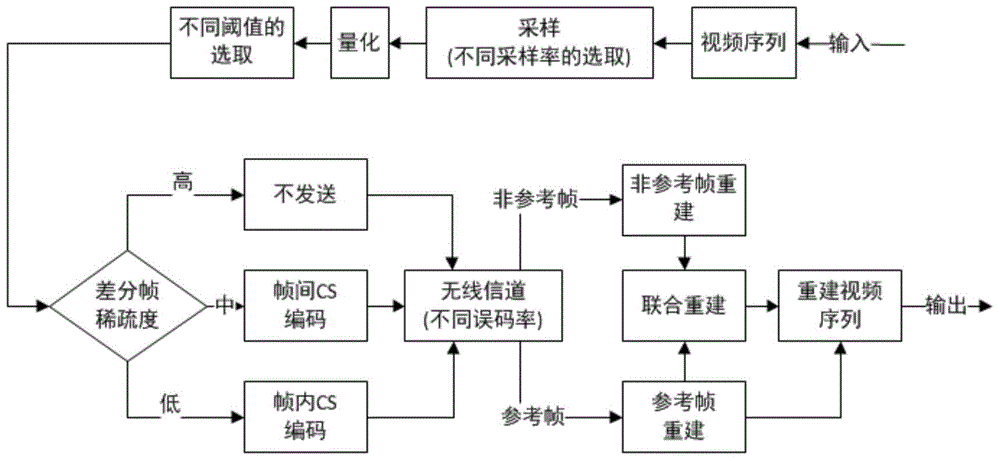
CS (compressed sensing) distributed type based video coding transmission method in WMSN (wireless multimedia sensor network)
ActiveCN104796718AEfficient use ofReduce occupancyDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
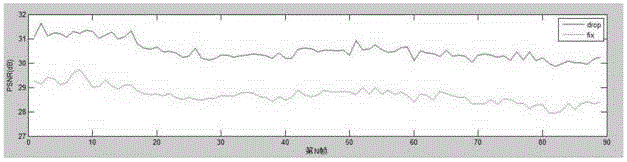
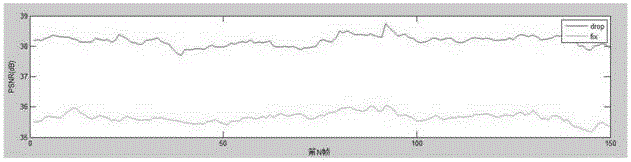
The invention provides a CS (compressed sensing) distributed type based video coding transmission method in a WMSN (wireless multimedia sensor network). The method includes: performing self-adaptive GOP (group of pictures) selection and self-adaptive sampling rate selection under different channel BER (basic encoding rules) environments; on the basis of perceptual coding compression, realizing data size compression through difference frame coding; performing threshold judgment on points of a difference frame, performing zero setting on pixel points within the threshold, and retaining points outside the threshold. Compared with an existing transmission strategy algorithm, the video coding transmission method has the advantages that utilization of the channel bandwidth is better, reconstruction quality in video reconstruction is higher, and peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) of a restored image is higher than that with the original algorithm. Meanwhile, the transmission strategy is smaller in occupation of the transmission bandwidth as compared with the existing algorithm.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com