Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116 results about "Critical frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
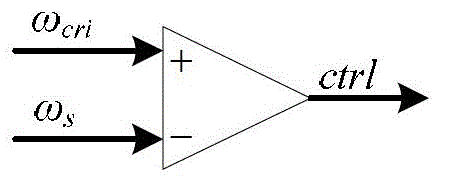
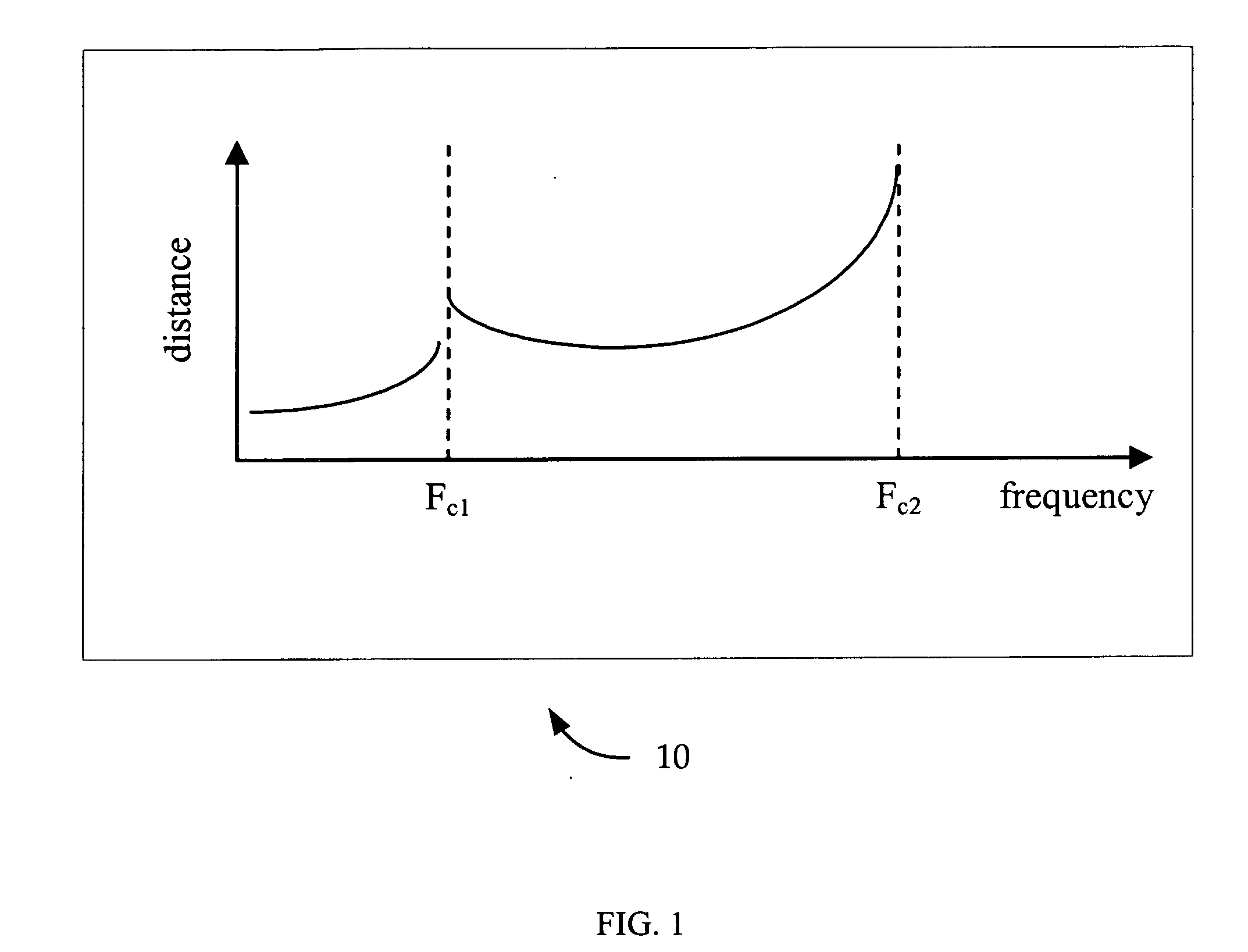
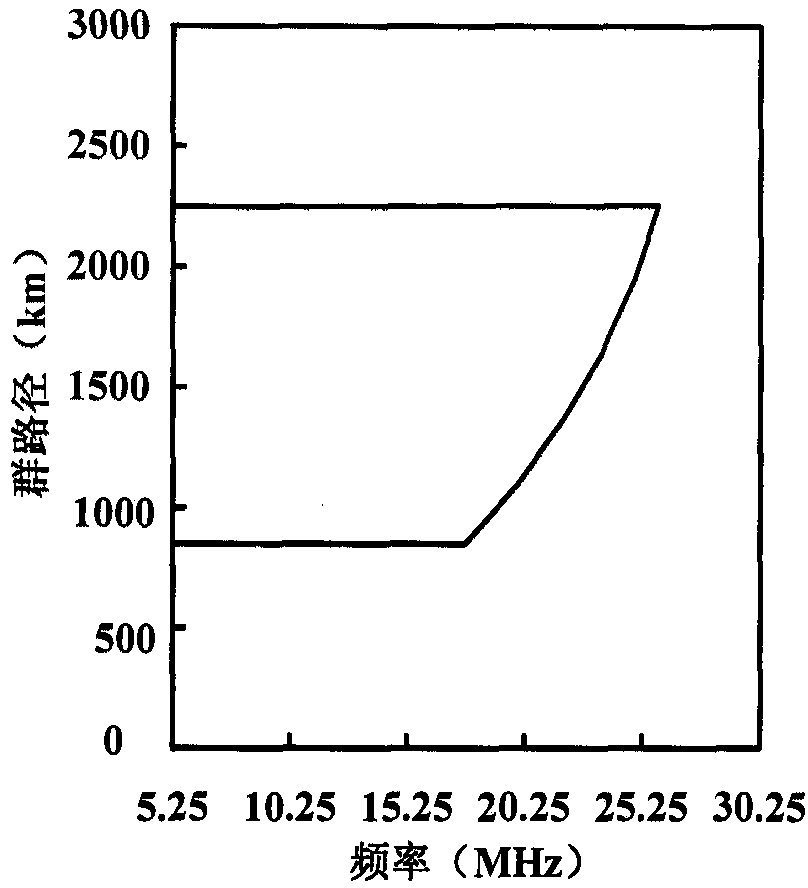
In telecommunication, the term critical frequency has the following meanings: In radio propagation by way of the ionosphere, the limiting frequency at or below which a wave component is reflected by, and above which it penetrates through, an ionospheric layer. At near vertical incidence, the limiting frequency at or below which incidence, the wave component is reflected by, and above which it penetrates through, an ionospheric layer. Critical Frequency changes with time of day, atmospheric conditions and angle of fire of the radio waves by antenna. The existence of the critical frequency is the result of electron limitation, i.e., the inadequacy of the existing number of free electrons to support reflection at higher frequencies. In signal processing the critical frequency it is also another name for the Nyquist frequency. Critical frequency is the highest magnitude of frequency above which the waves penetrates the ionosphere and below which the waves are reflected back from the ionosphere. It is denoted by "fc". Its value is not fixed and it depends upon electron density of ionosphere. It is given by: fc=9√Nmax Nmax is maximum electron density.
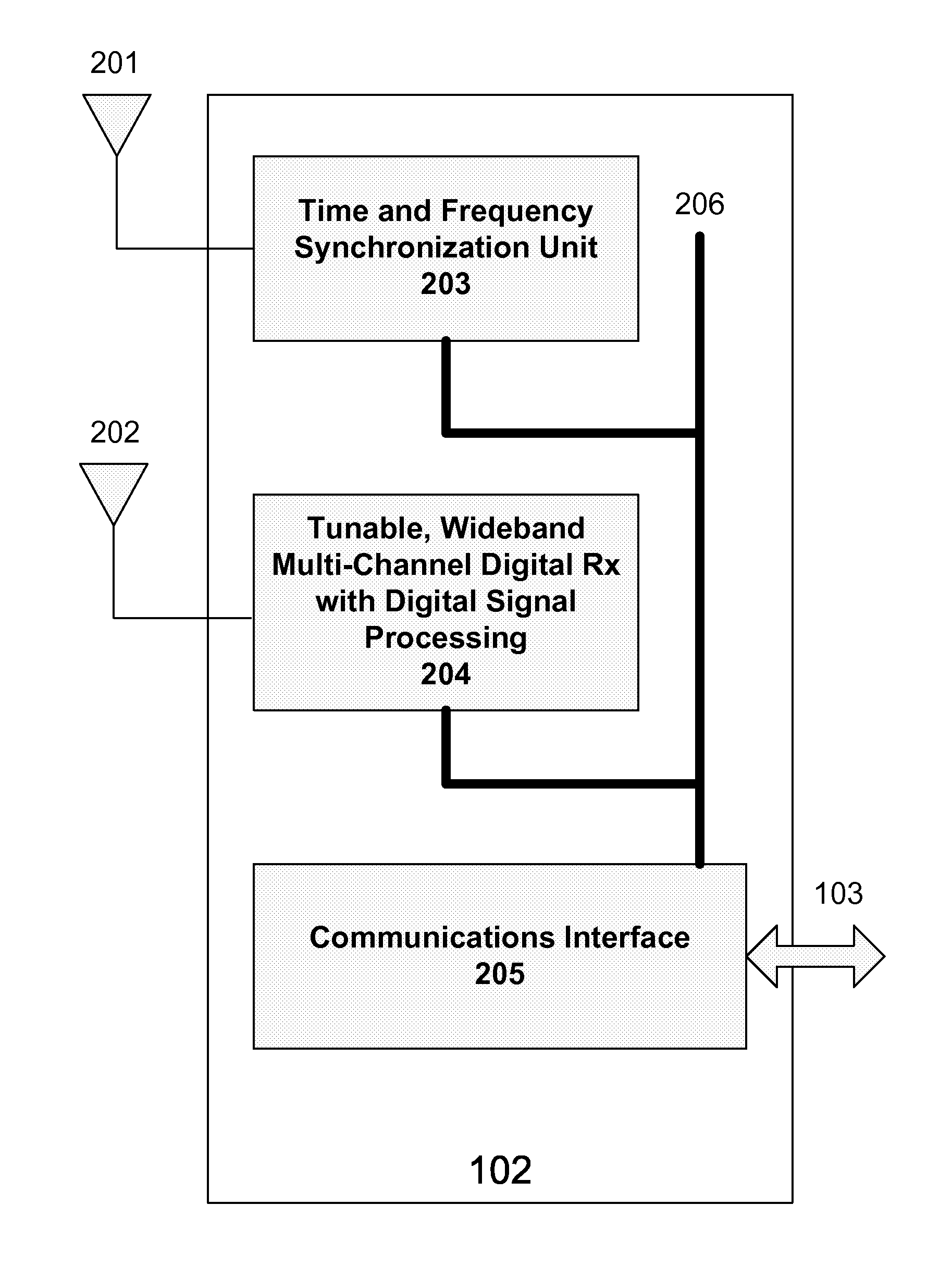
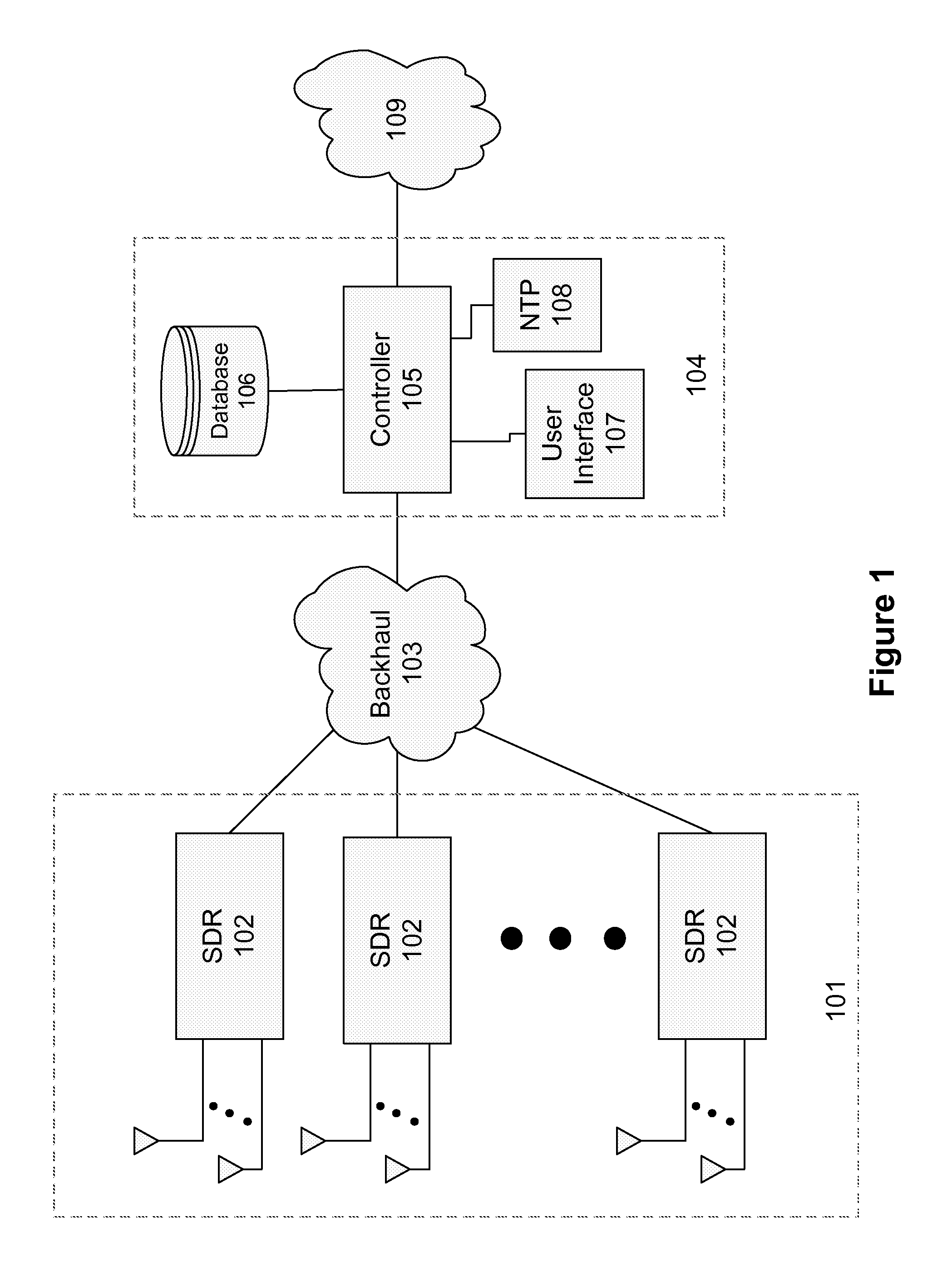
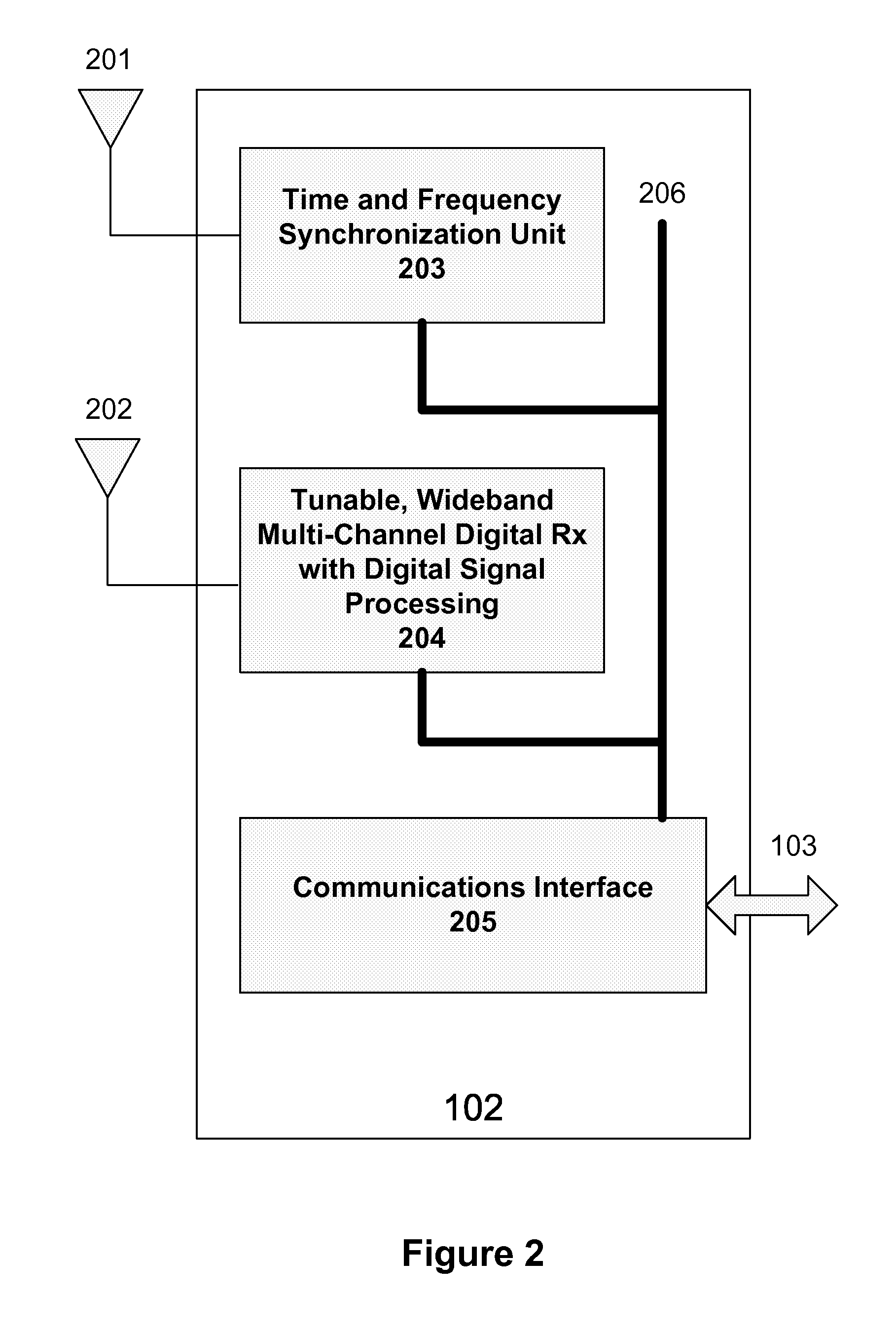
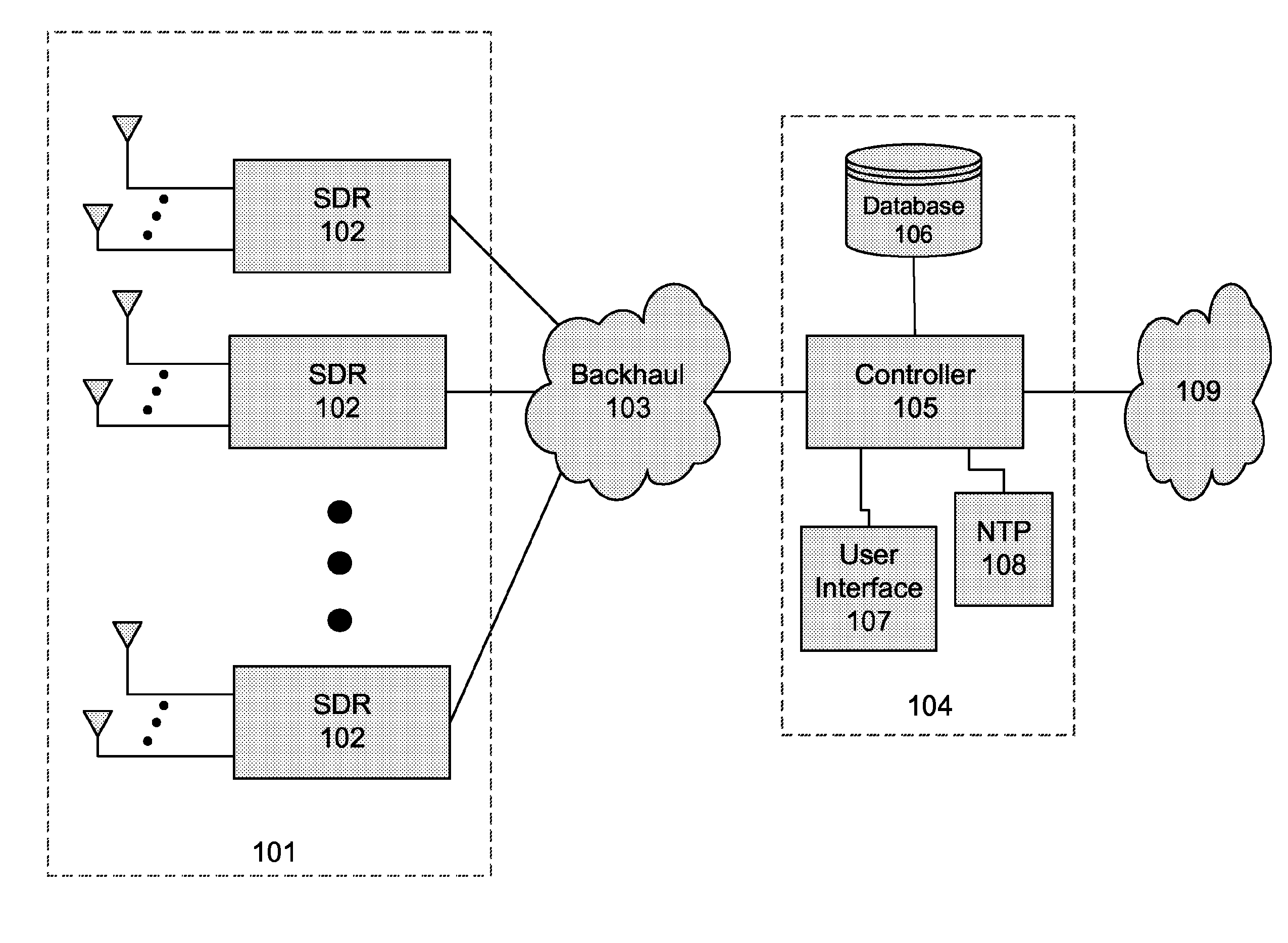
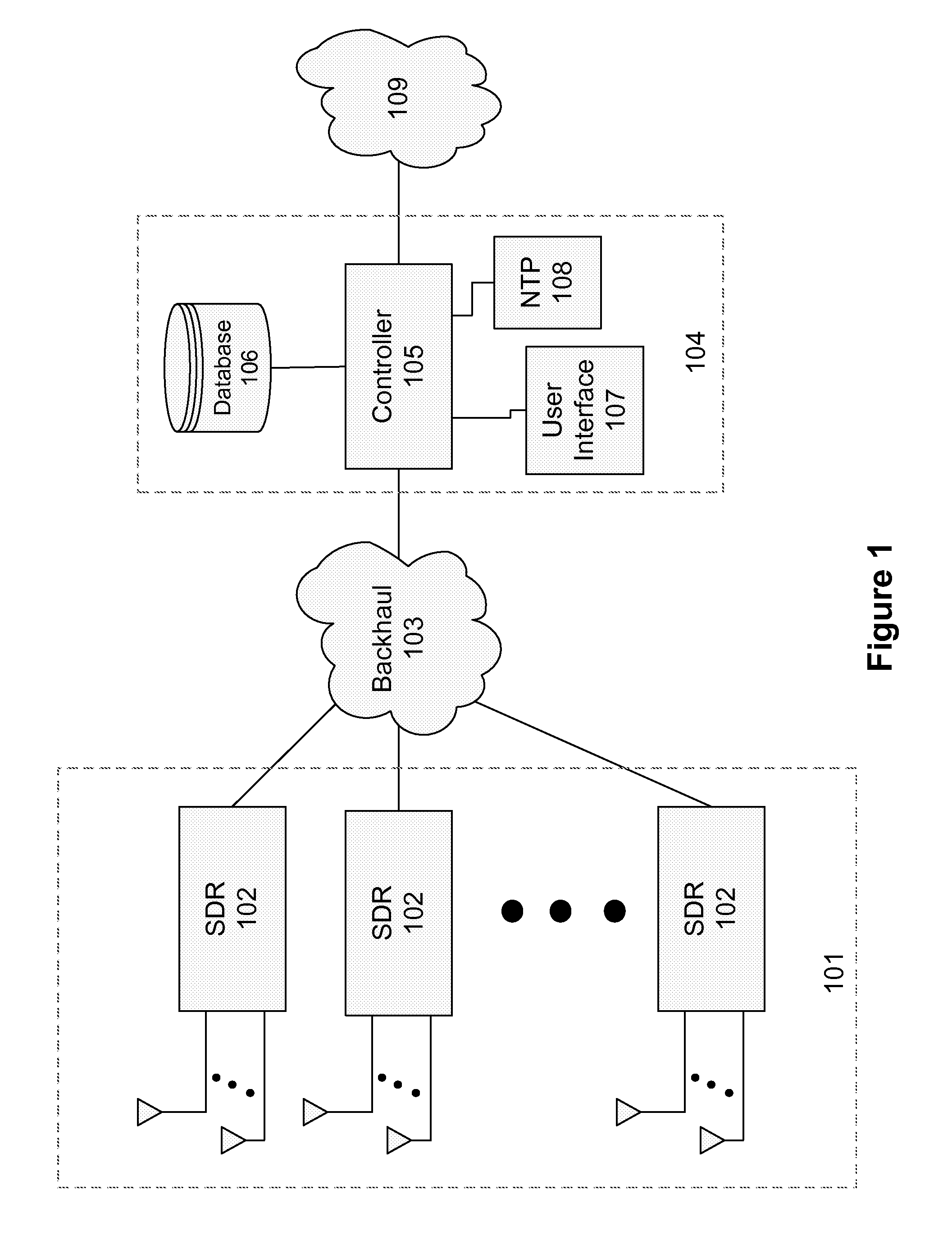
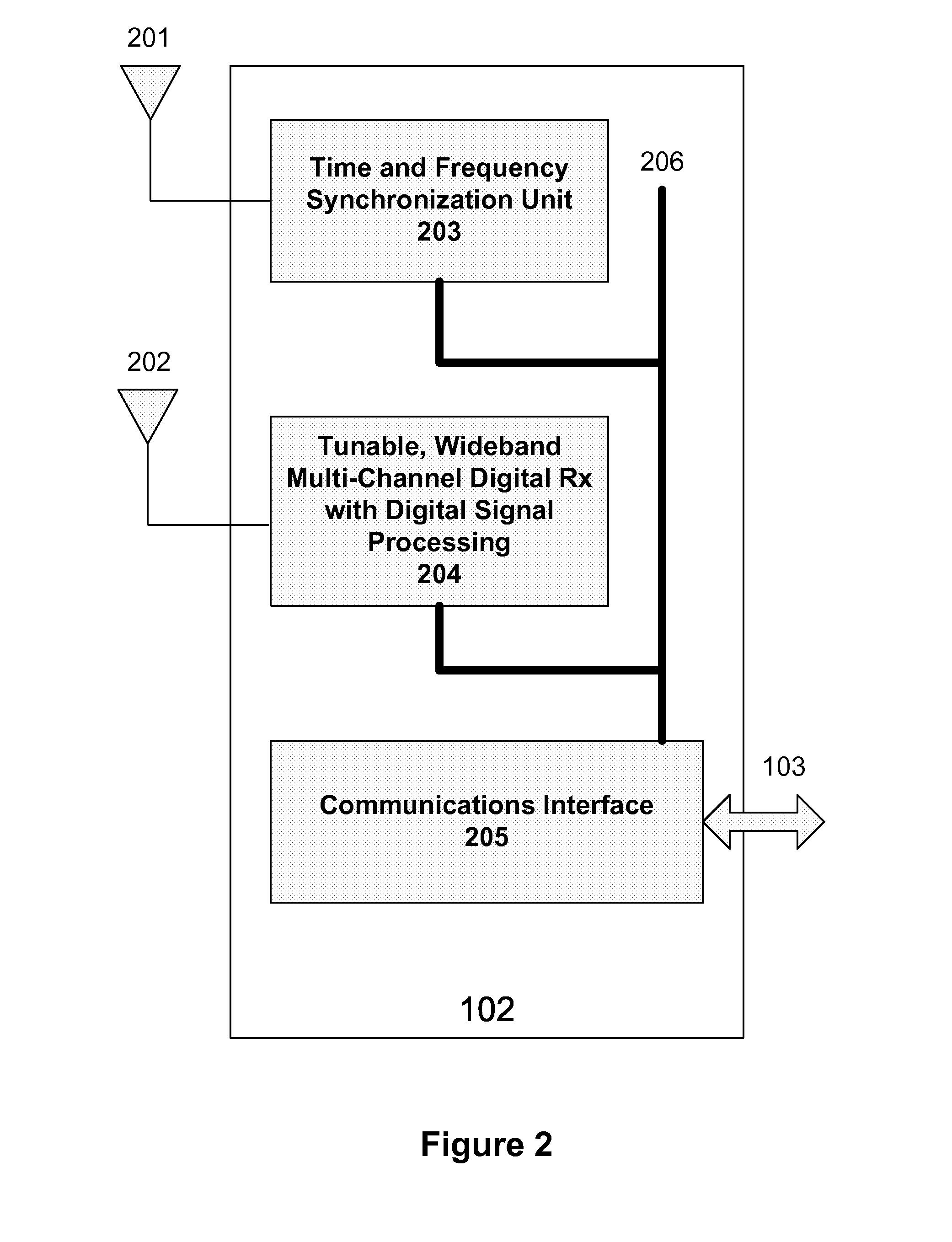
Interference detection, characterization and location in a wireless communications or broadcast system
ActiveUS20120032854A1Direction finders using radio wavesNetwork traffic/resource managementSoftware define radioTransmitted power
A Wide Area Sensor Network (WASN) is disclosed that utilizes wideband software defined radios (SDRs) to monitor RF energy over a wide frequency range, detect when critical frequencies are being jammed or otherwise interfered with, and locate the source of the interference so that the interference can be eliminated. The WASN may use one or more geolocation techniques In addition, the WASN may detect and locate unauthorized transmitters as well as estimate the transmitted power of authorized transmitters to assure they are not transmitting more power than authorized.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
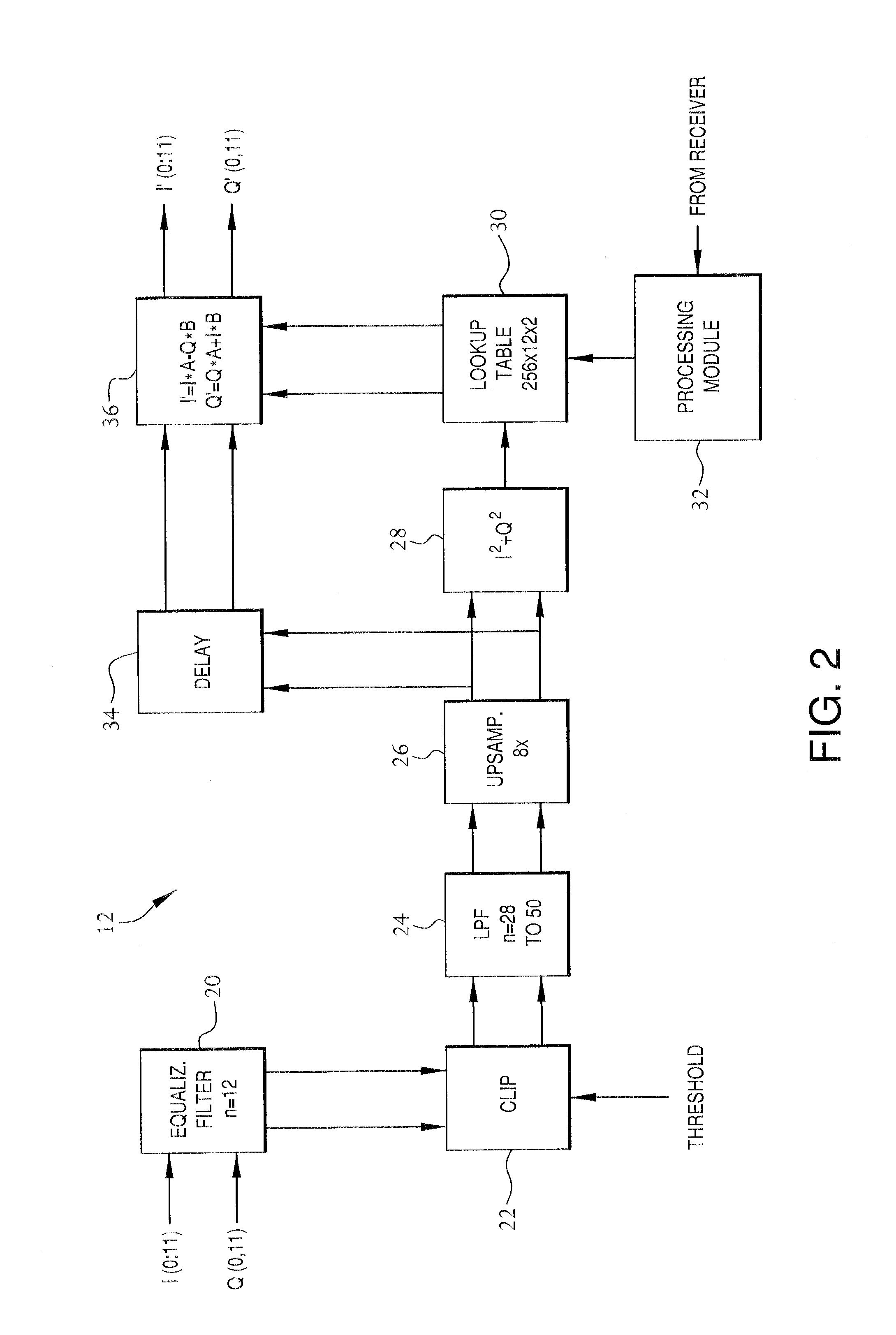
Frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion for reducing spurious emissions in communication networks
InactiveUS7248642B1Spurious emission can be reducedEmission reductionModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationPhase differenceSpurious emission
A frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion technique is applied to an input signal in order to reduce spurious emissions resulting from subsequent amplification of the signal. In preferred embodiments, the frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion of the present invention is implemented in combination with the (frequency-independent) magnitude and phase pre-distortion technique described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 395,490 (“the '490 application”), where one or more frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion signals are either advanced or delayed relative to the main pre-distorted signal generated in accordance with the '490 application. Each frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion signal is preferably based on a 180° phase difference between a pair of (critical) frequencies located outside (e.g., one on each side) of the signal channel. The magnitude of the frequency difference between the pair of critical frequencies dictates the magnitude of the desired advancement or delay in time of the frequency-dependent pre-distortion signal relative to the main pre-distorted signal. Embodiments of the present invention may be implemented in either the baseband domain or the RF domain. Implementations may also be based on look-up tables that are adaptively updated to ensure optimal performance over time.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Method for operating offshore wind turbine plants based on the frequency of their towers
A method for operating a wind power plant which is provided with a device for regulating the speed of a rotor of the wind power plant. The method includes the steps of: determining the critical frequency of the respective turbine and / or turbine components, determining the speed range of the rotor in which the entire turbine and / or individual turbine components are excited in the vicinity of their critical frequencies and operation of the wind turbine plant only below and above the critical range; the latter being traversed rapidly.
Owner:MULTIBRID
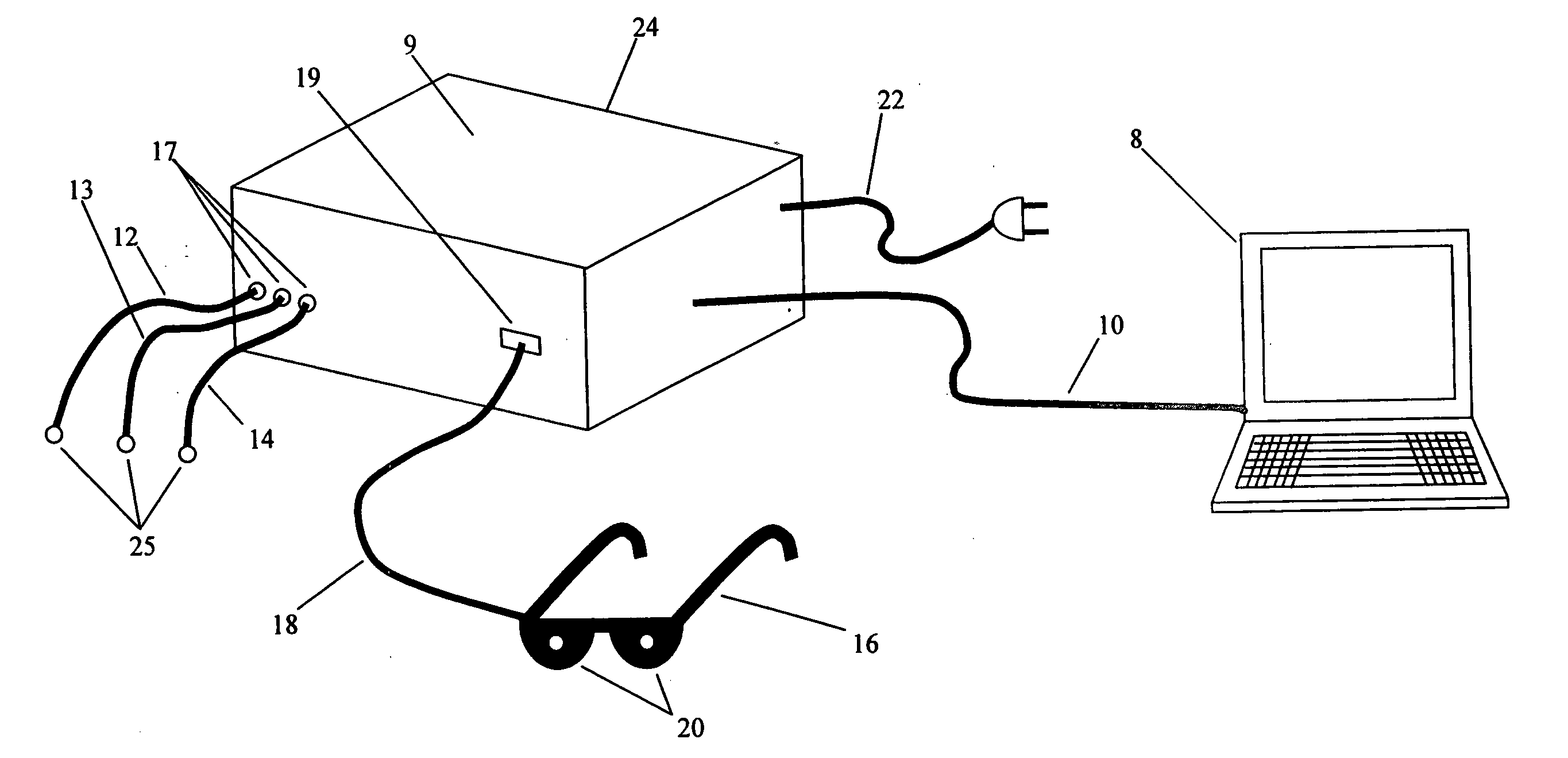
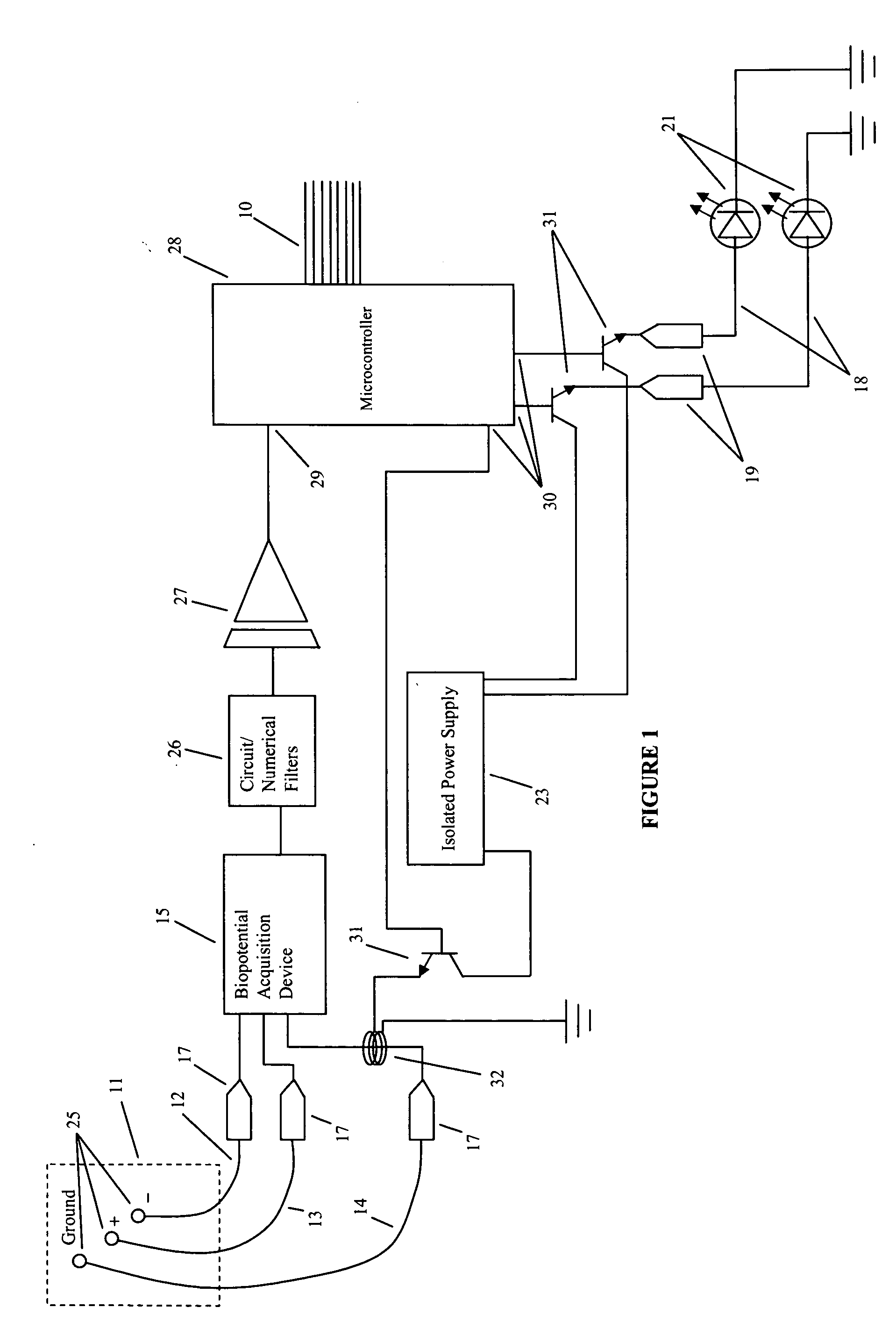
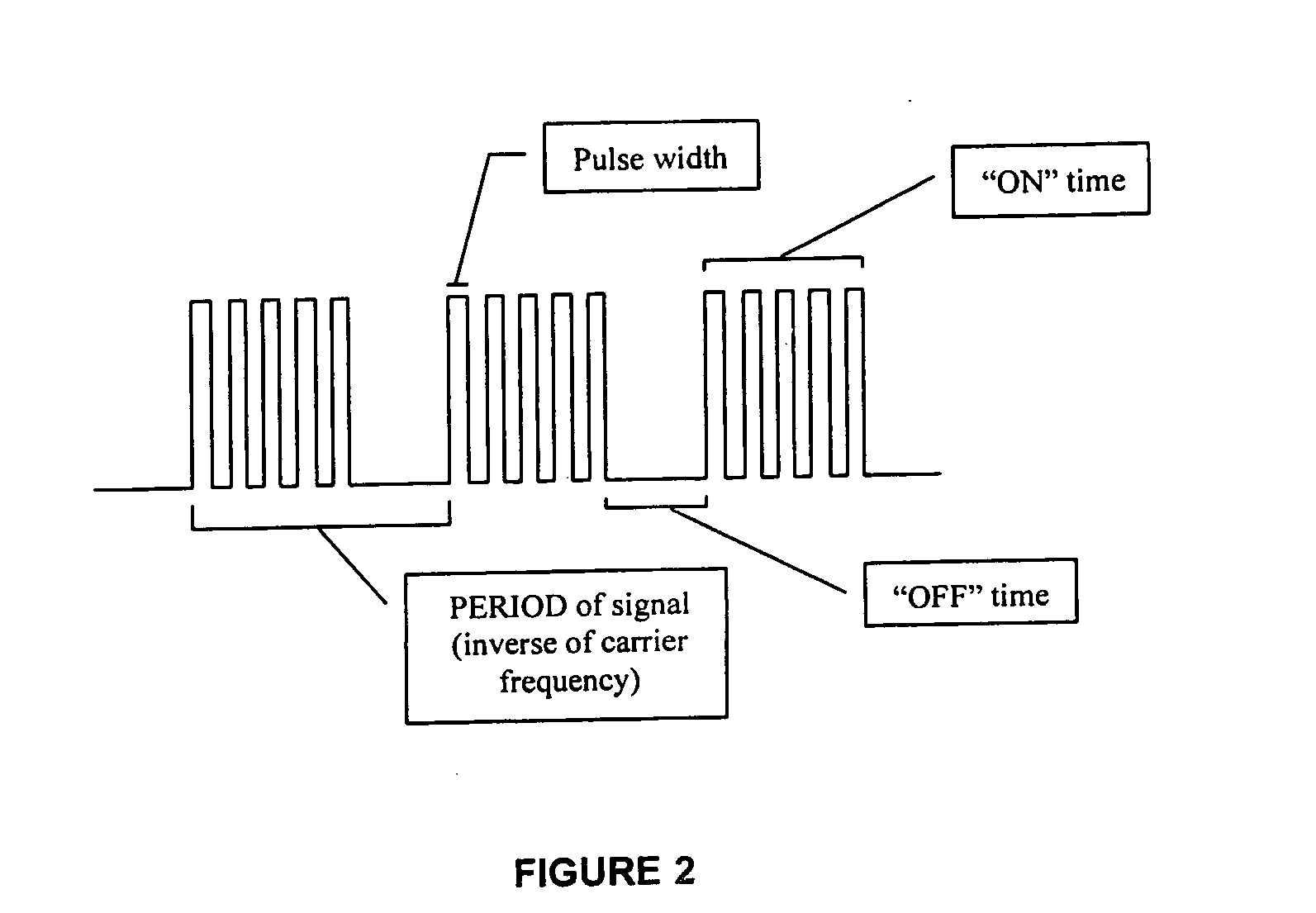
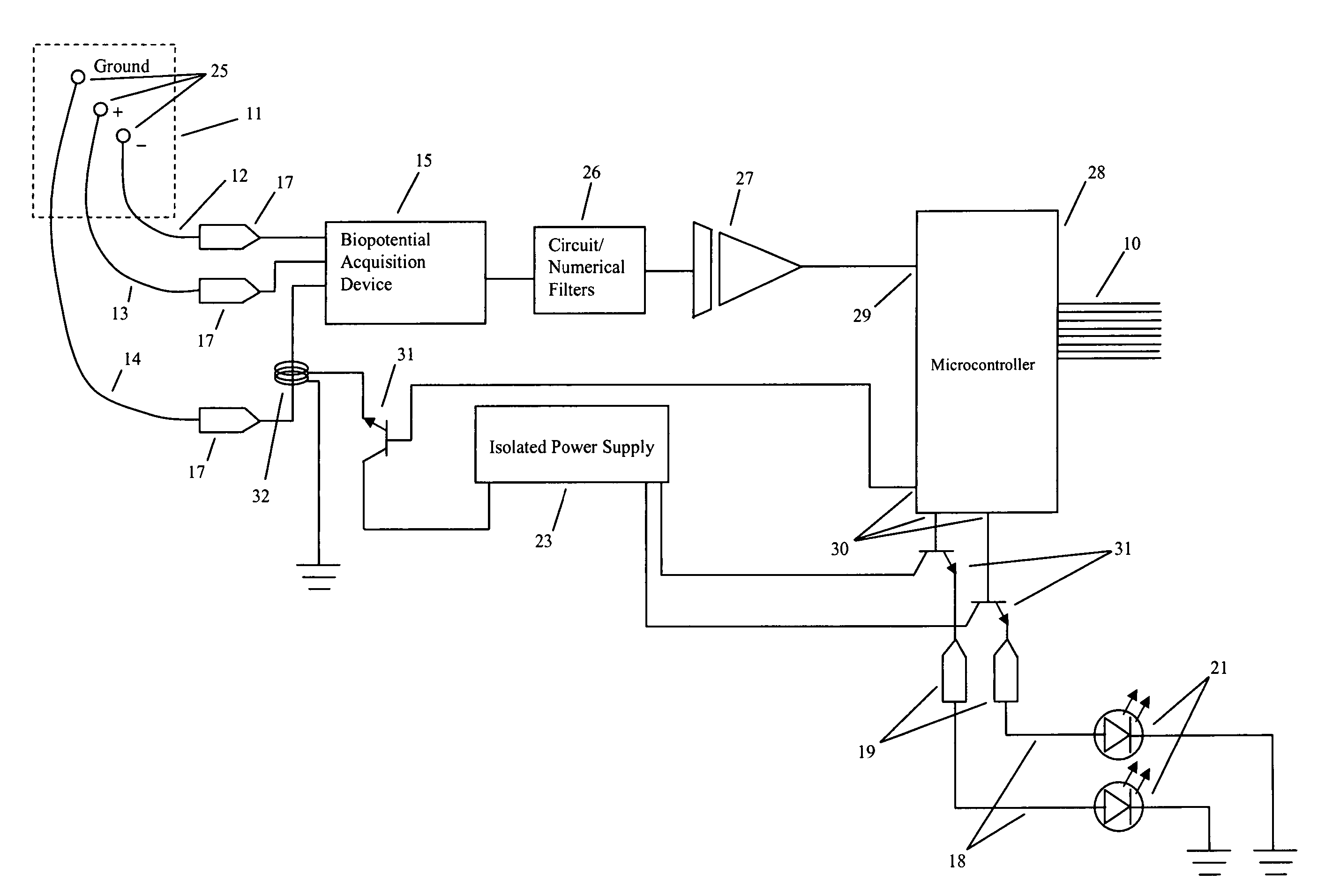
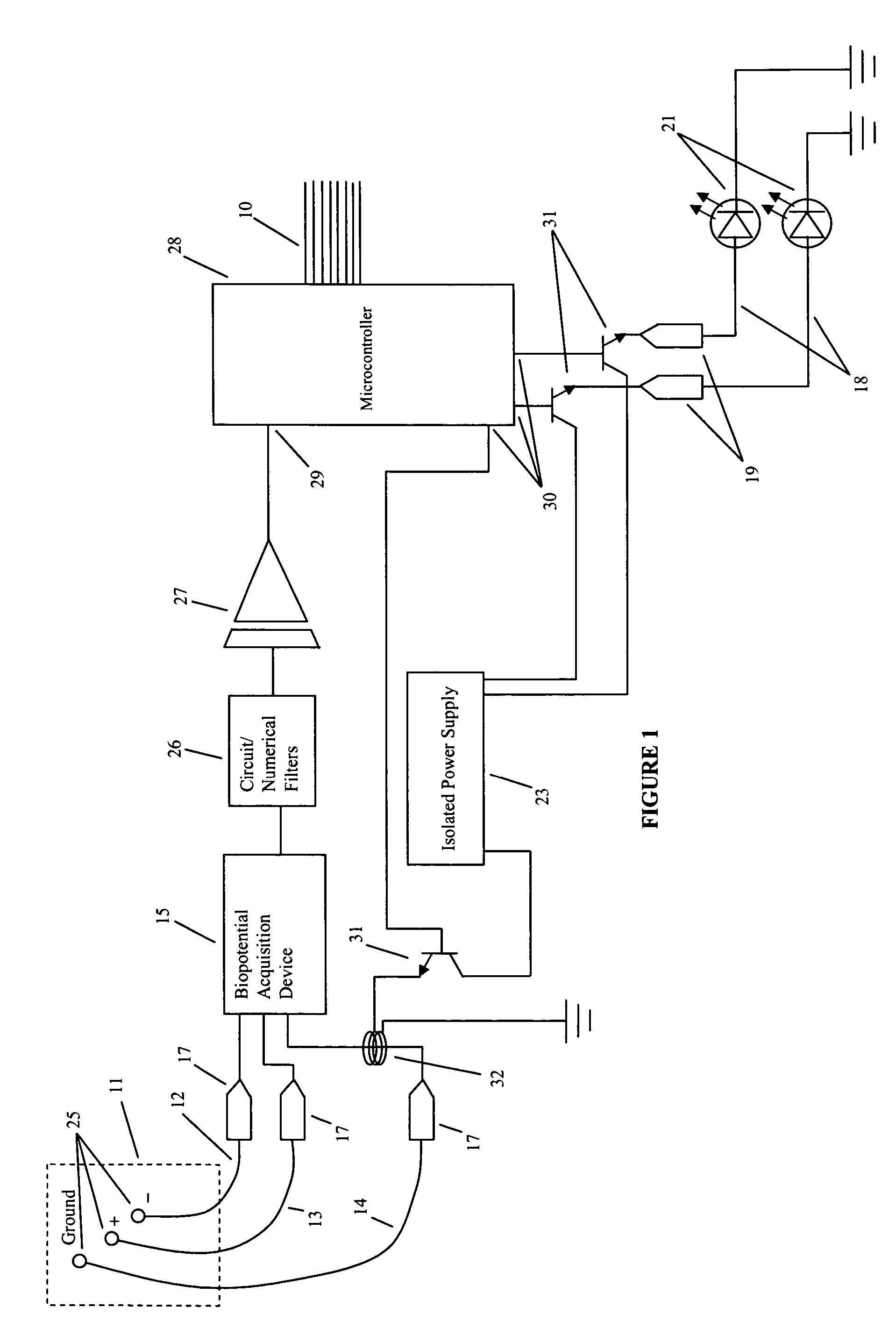
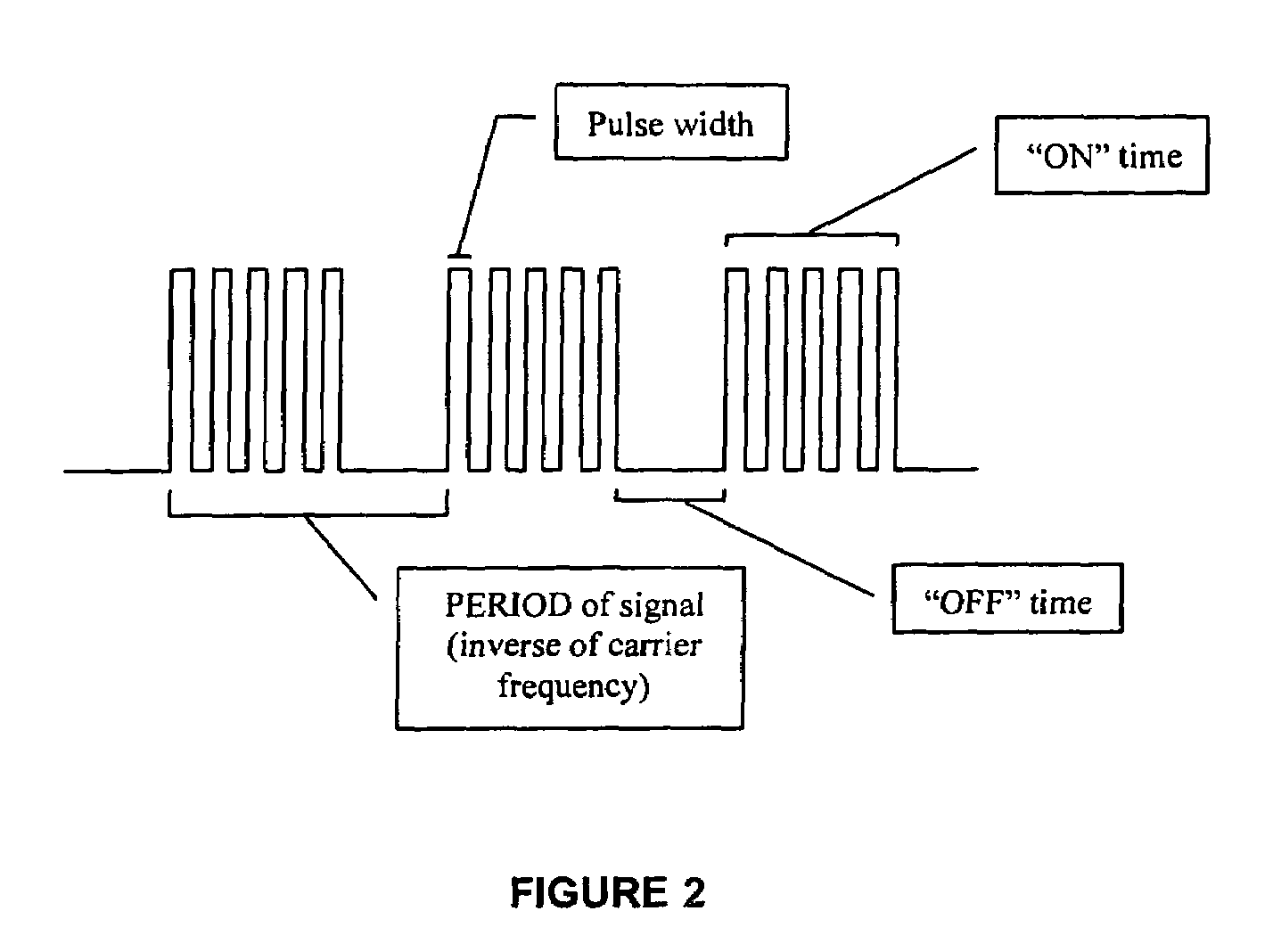
Method and apparatus for utilizing amplitude-modulated pulse-width modulation signals for neurostimulation and treatment of neurological disorders using electrical stimulation
InactiveUS20060258950A1Good effectEliminating conscious patient perceptionElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyStatistical analysisCarrier signal
A computing device-controlled system is described for the generation of amplitude-modulated pulse-width modulation (AMPWM) signals for use in treating neurological dysfunction via cranial neurostimulation, where the AMPWM signal is specifically designed to minimize the electrical impedance of the tissues of the head. A low-frequency carrier signal is determined for the AMPWM signal by measuring EEG activity at a reference site or sites, generally corresponding with the location of suspected brain dysfunction. Carrier signal frequency is variably related to critical frequency components of the EEG power spectral density, determined from statistical analysis of amplitudes and variability, and dynamically changed as a function of time to prevent entrainment. The AMPWM signal is presented to a subject via a plurality of neurostimulation delivery modes for therapeutic use.
Owner:HARGROVE JEFFREY B
Sound perception using frequency transposition by moving the envelope
ActiveUS20110249843A1Facilitate cognitionImprove sound qualityHearing aids signal processingTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsSound perceptionSound quality
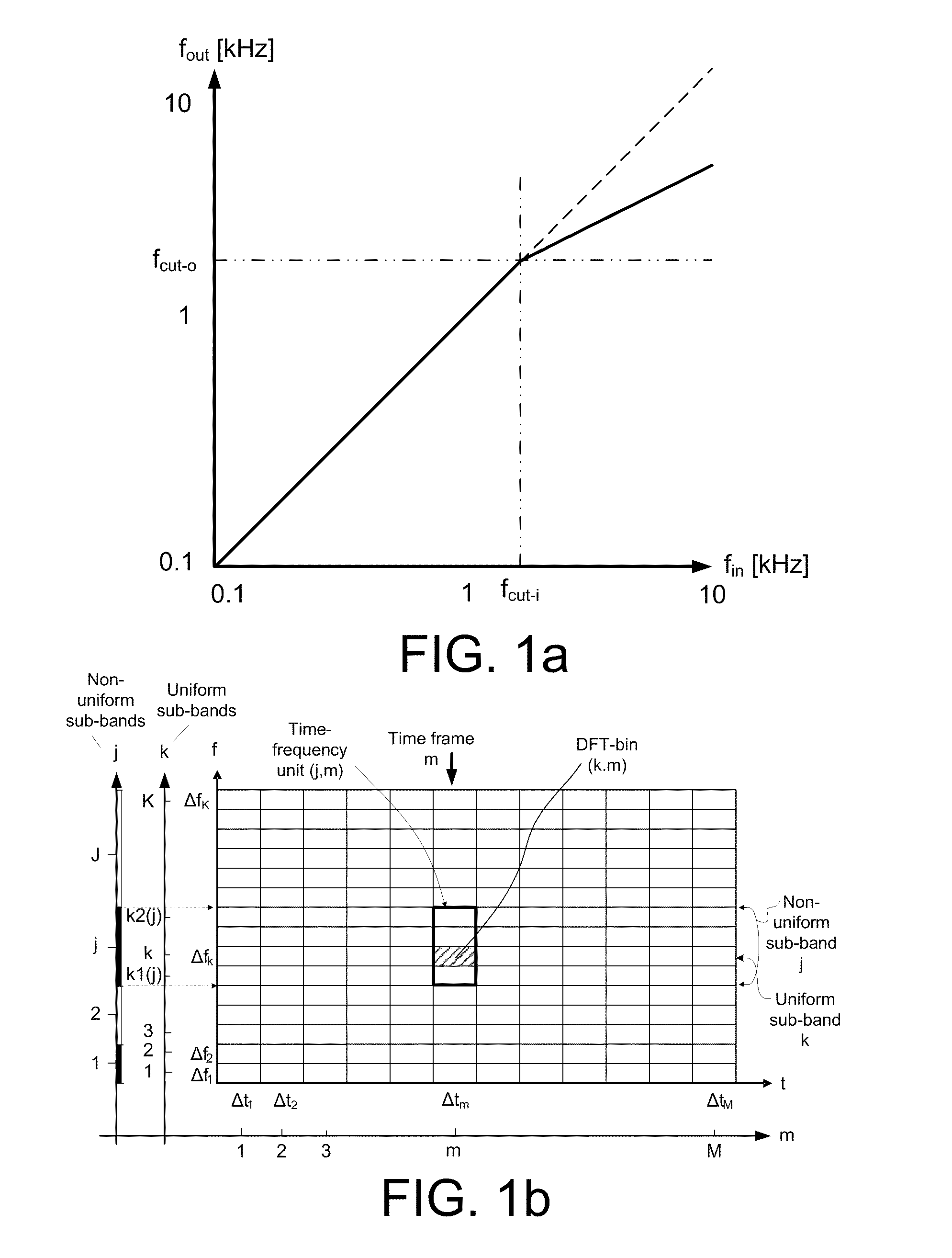
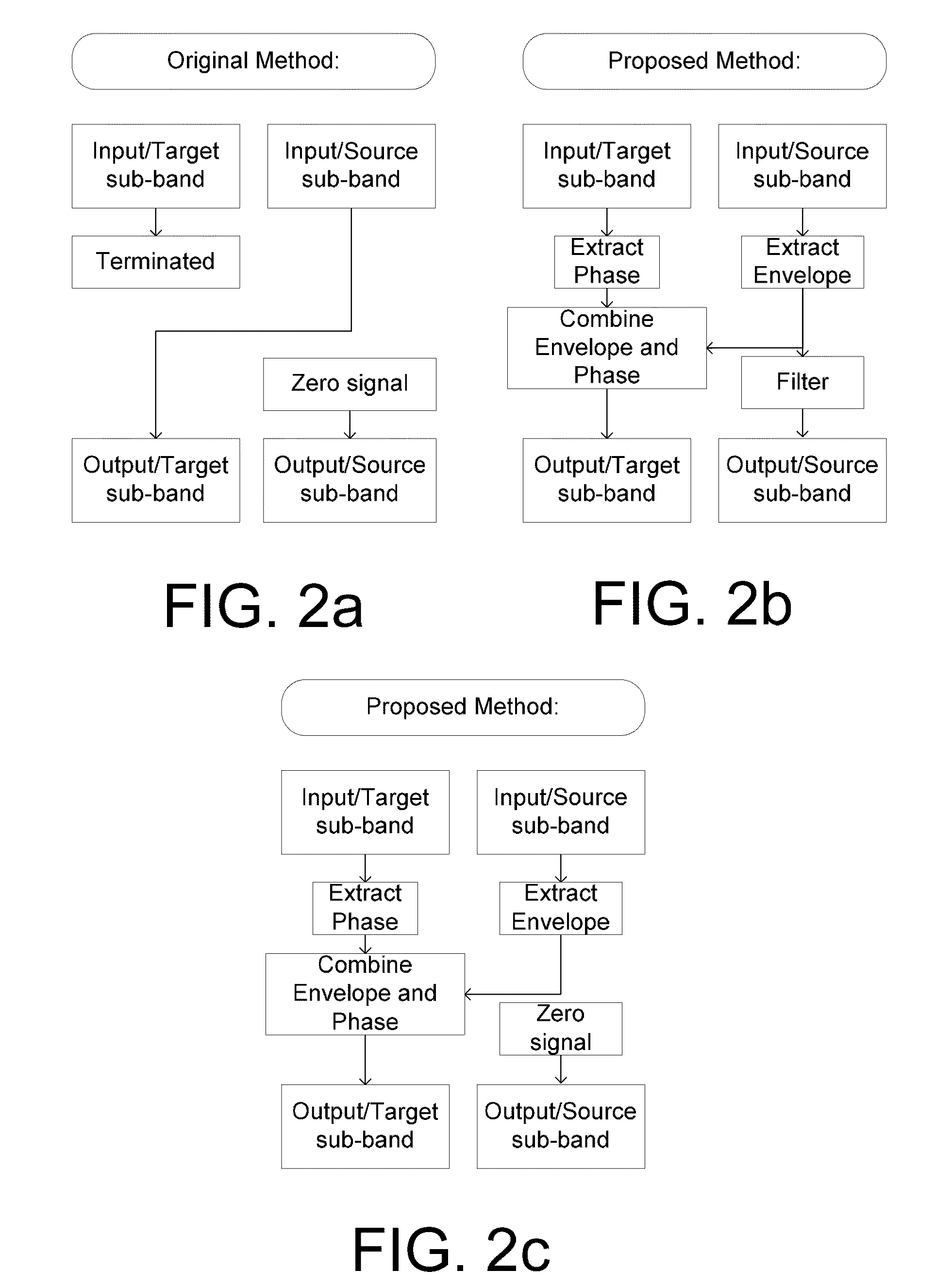
The application relates to a method of improving a user's perception of an input sound. The application further relates to an audio processing device and to its use. The object of the present application is to increase the sound quality of a sound signal as perceived by a user, e.g. a hearing impaired user. The method comprises a) Defining a critical frequency fcrit between a low frequency range and a high frequency range; b) Analyzing an input sound in a number of frequency bands below and above said critical frequency; c) Defining a cut-off frequency fcut below said critical frequency fcrit; d) Identifying a source frequency band above said cut-off frequency fcut; e) Extracting the envelope of said source band; f) Identifying a corresponding target band below said critical frequency fcrit; g) Extracting the phase of said target band; h) Combining the envelope of said source band with the phase of said target band. This has the advantage of increasing the sound quality, and the potential to further improve speech intelligibility in frequency transposition, e.g. frequency lowering systems. The invention may e.g. be used in communication devices, such as telephones, or listening devices, e.g. hearing instruments, headsets, head phones, active ear protection devices or combinations thereof.
Owner:OTICON
Perceptual coding of audio signals
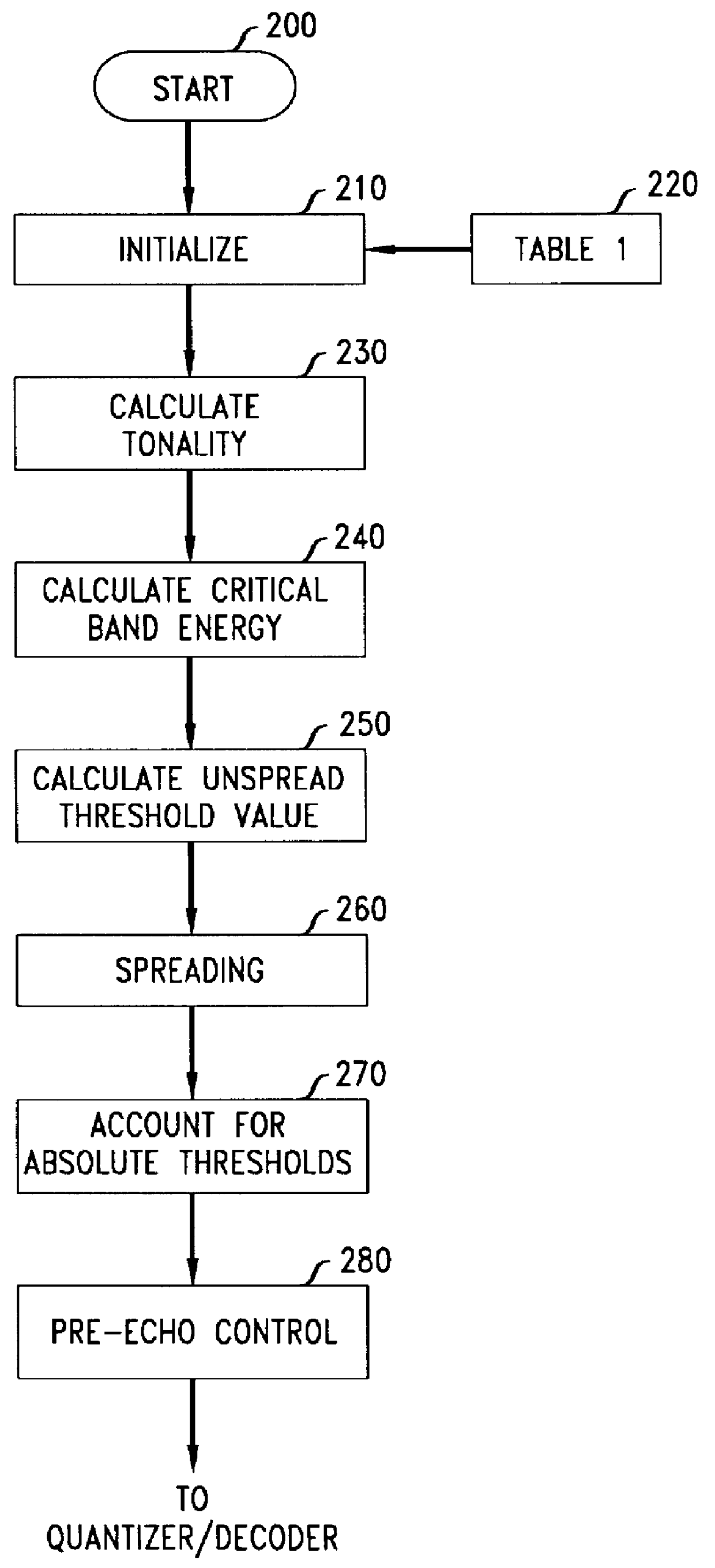
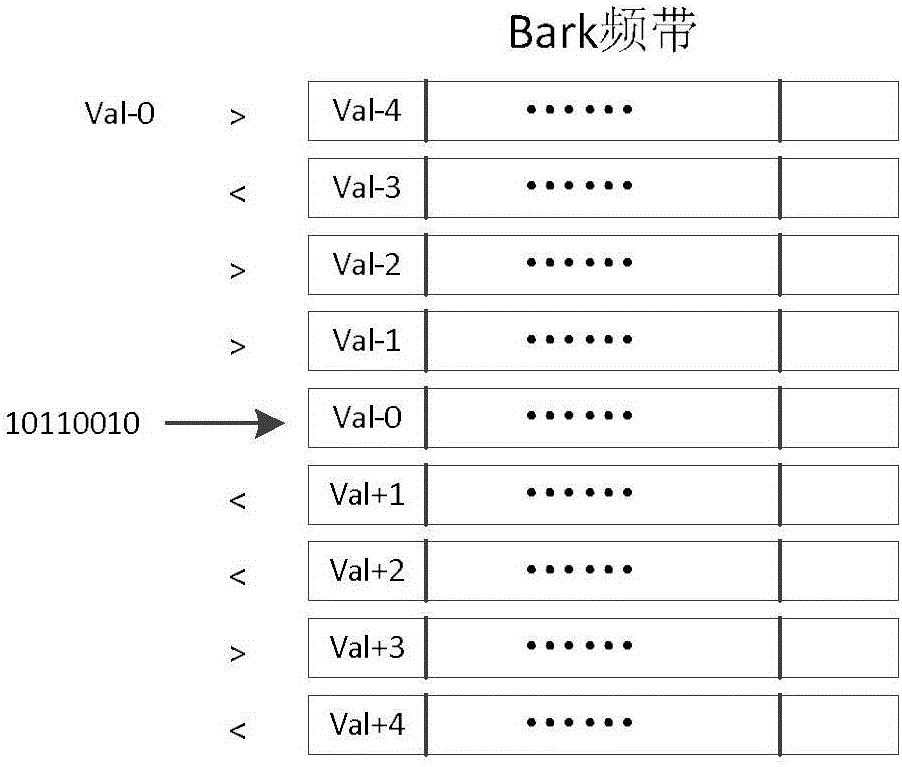
A method is disclosed for determining estimates of the perceived noise masking level of audio signals as a function of frequency. By developing a randomness metric related to the euclidian distance between (i) actual frequency components amplitude and phase for each block of sampled values of the signal and (ii) predicted values for these components based on values in prior blocks, it is possible to form a tonality index which provides more detailed information useful in forming the noise masking function. Application of these techniques is illustrated in a coding and decoding context for audio recording or transmission. The noise spectrum is shaped based on a noise threshold and a tonality measure for each critical frequency-band (bark).
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
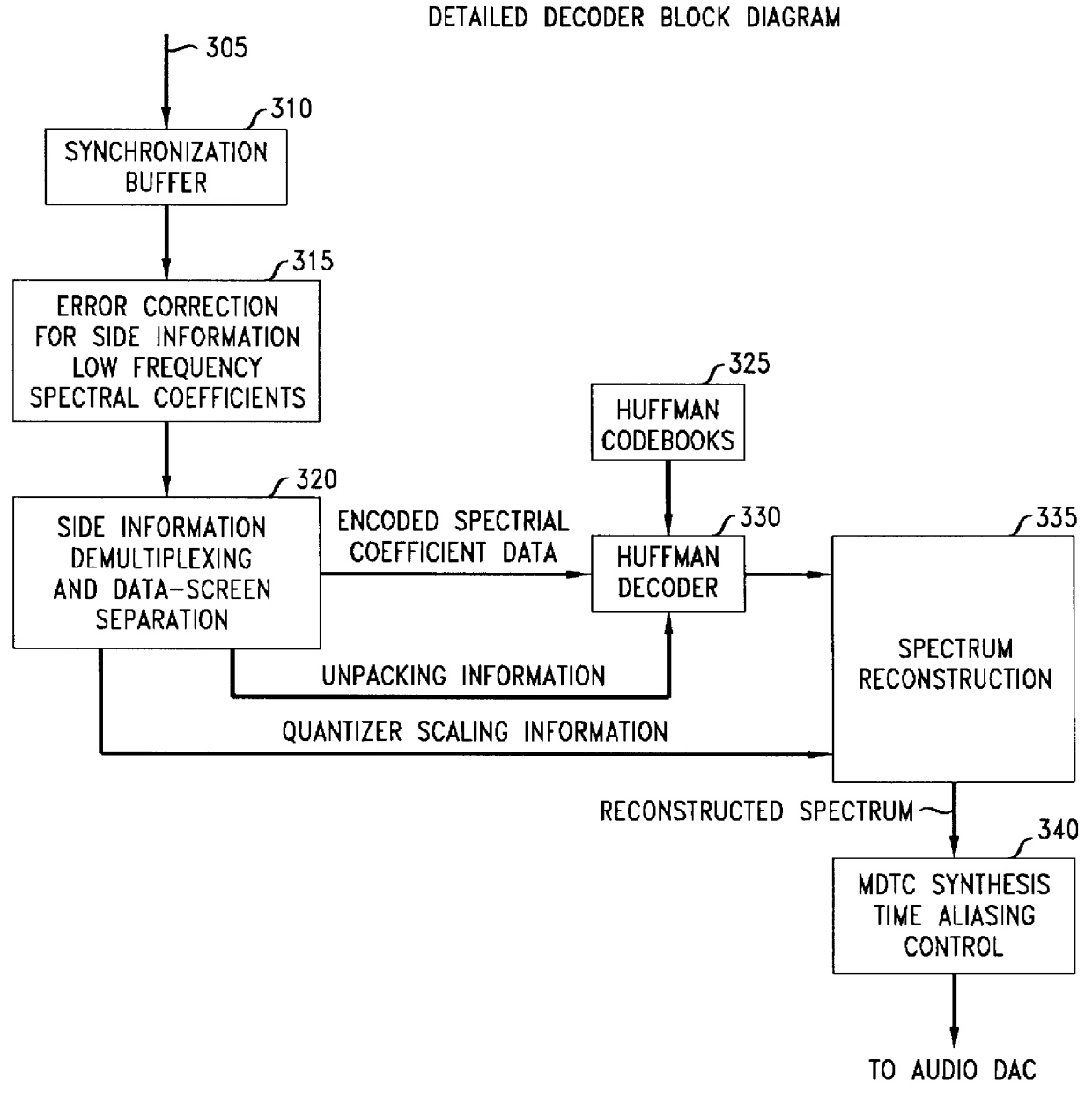
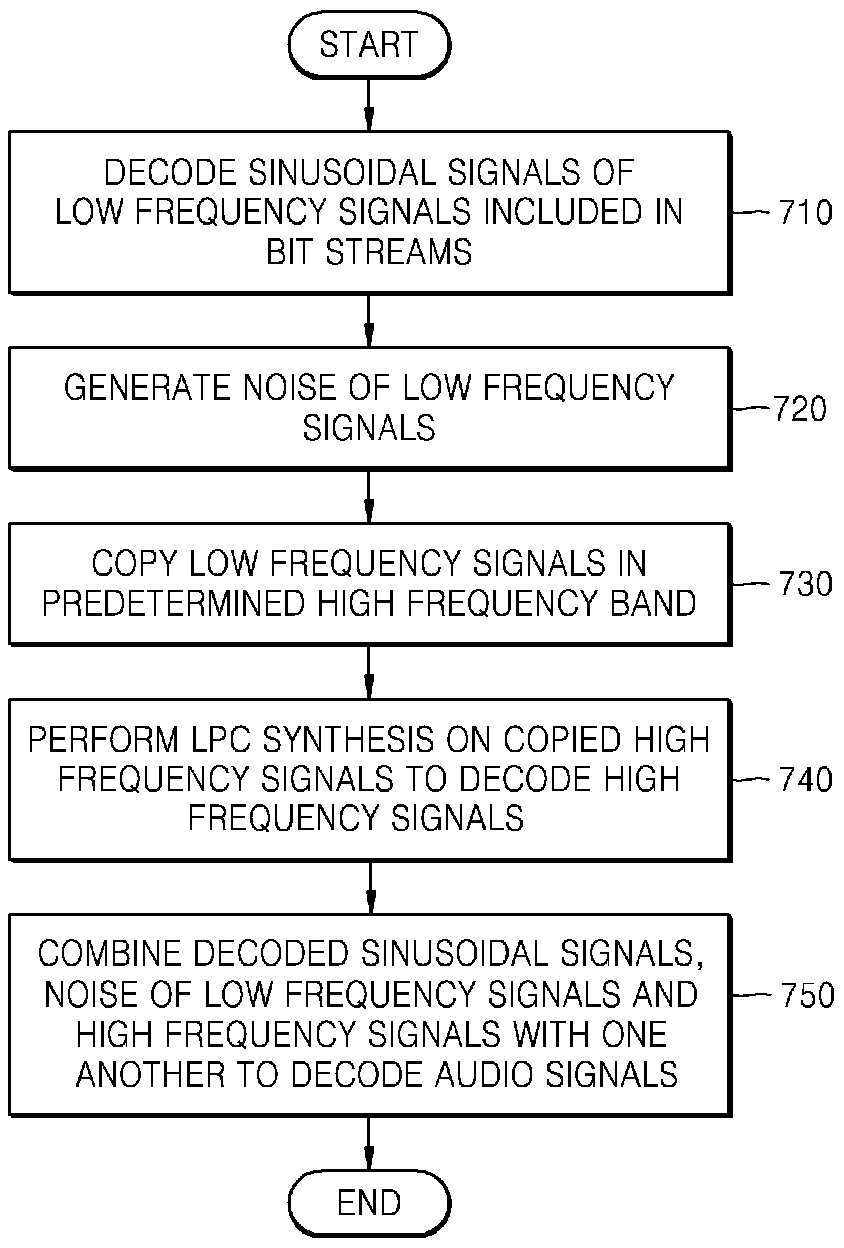
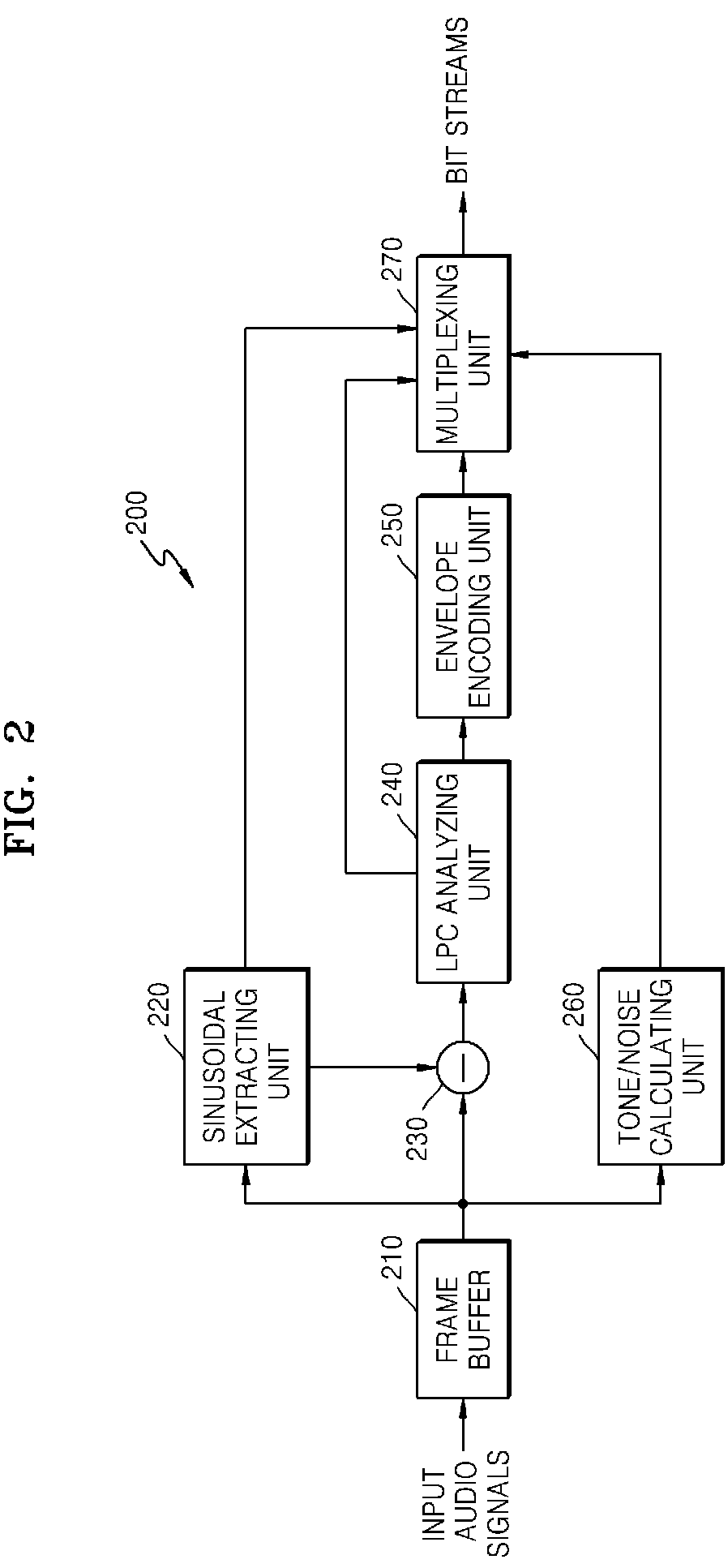
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding audio signals
InactiveUS20090192789A1Big lossEfficient encoding/decodingSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingLinearity
Provided are a method and apparatus for effectively encoding / decoding remaining difference signals excluding sinusoidal components, from input audio signals. In the method and apparatus for encoding audio signals, sinusoidal analysis is performed on low frequency signals of less than a predetermined critical frequency in order to extract sinusoidal signals and then, an encoding operation is performed on the remaining difference signals excluding the sinusoidal signals, from input audio signals, by using linear prediction coding (LPC) analysis.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and Method for Enhancing a Decoded Tonal Sound Signal
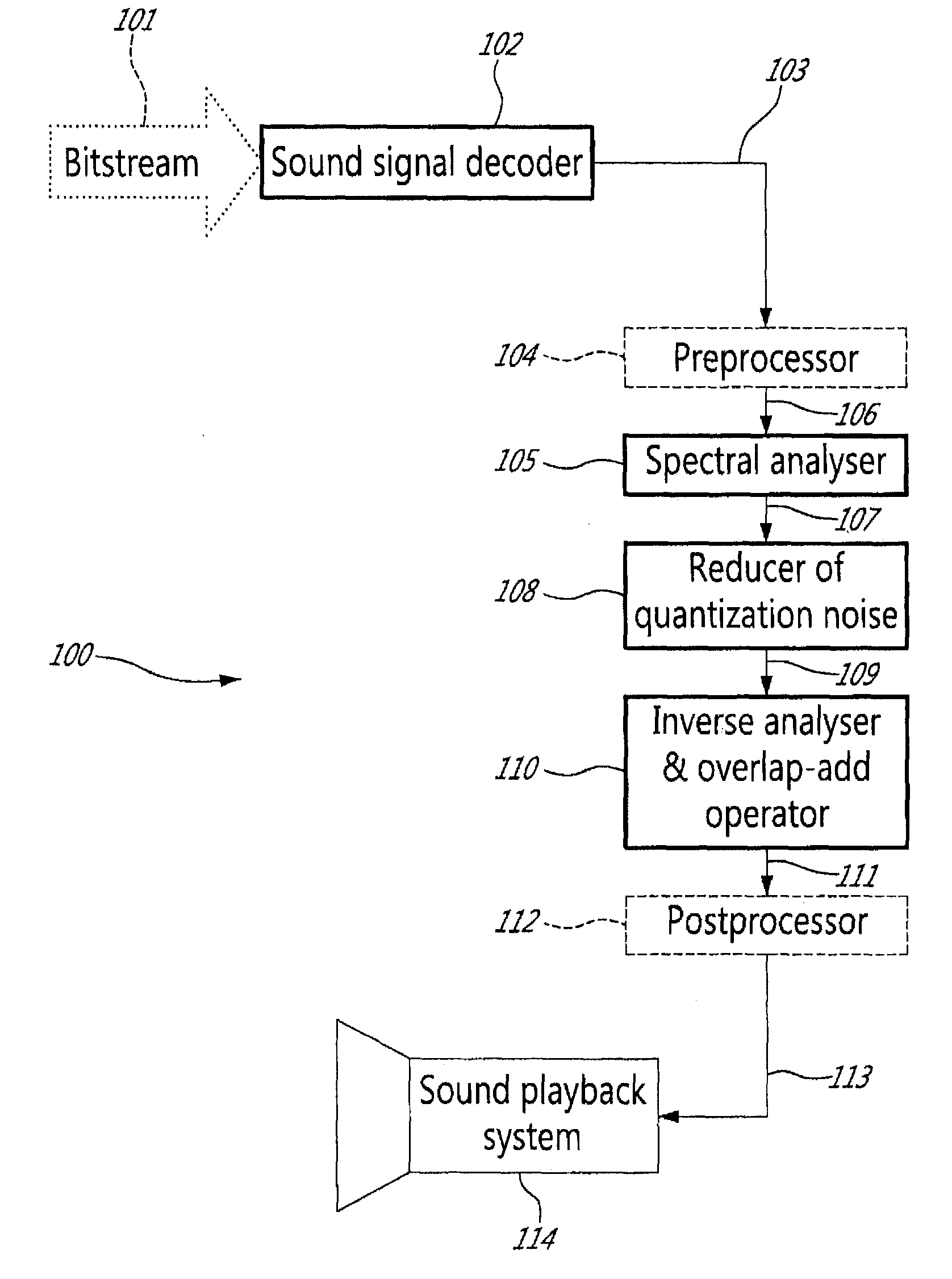
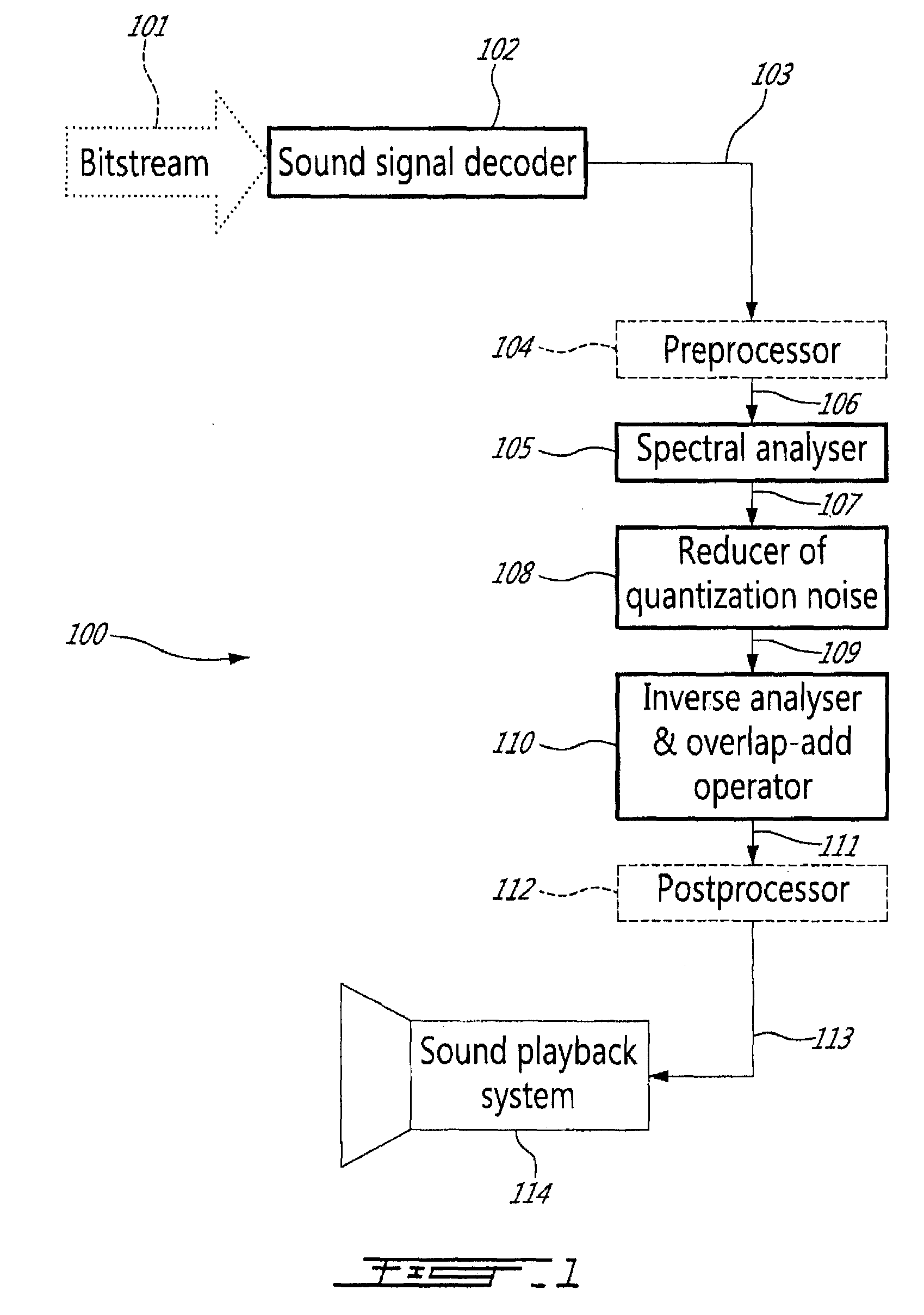
ActiveUS20110046947A1Enhanced signalReduce quantization noiseSpeech analysisTransmission noise suppressionFrequency spectrumSpectrum analyzer
A system and method for enhancing a tonal sound signal decoded by a decoder of a speech-specific codec in response to a received coded bit stream, in which a spectral analyser is responsive to the decoded tonal sound signal to produce spectral parameters representative of the decoded tonal sound signal. A quantization noise in low-energy spectral regions of the decoded tonal sound signal is reduced in response to the spectral parameters produced by the spectral analyser. The spectral analyser divides a spectrum resulting from spectral analysis into a set of critical frequency bands each comprising a number of frequency bins, and the reducer of quantization noise comprises a noise attenuator that scales the spectrum of the decoded tonal sound signal per critical frequency band, per frequency bin, or per both critical frequency band and frequency bin.
Owner:VOICEAGE EVS LLC
Method of controlling running of modularized multi-level converter in low frequency model
InactiveCN103337977ASimplified generation methodVersatilityAc-dc conversionDifferential coefficientModel selection
The invention relates to a method of controlling running of a modularized multi-level converter in a low frequency model, which belongs to the technical field of controlling multi-level power electronic converters. The method comprises the following steps: setting high frequency common mode voltage and high frequency ring current both required to be superimposed, revising a switching function of a submodule and bridge arm current, obtaining an expression of capacitance voltage differential coefficient of the submodule according to volt-ampere characteristics of capacitance of the submodule, and in order to allow the capacitance voltage of the submodule to only have high-frequency component, assuming high frequency common mode voltage is known to obtain a expression of the high frequency circular current; comparing a running frequency with a critical frequency to obtain frequency model selection signals, combining an energy control and a circular current control of a phase unit of the modularized multi-level converter, determining whether the high frequency common mode voltage and the high frequency circular current are required to be superimposed to an original instruction or not according to the frequency model selection signals, and generating voltage required to be superimposed in the bridge arm of the phase unit of the high frequency circular current by controlling. The method is easy to realize and strong in universality, and provides reference for low frequency application of the modularized multi-level converter.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Interference detection, characterization and location in a wireless communications or broadcast system
ActiveUS8138975B2Direction finders using radio wavesNetwork traffic/resource managementWide areaPositional Technique
A Wide Area Sensor Network (WASN) is disclosed that utilizes wideband software defined radios (SDRs) to monitor RF energy over a wide frequency range, detect when critical frequencies are being jammed or otherwise interfered with, and locate the source of the interference so that the interference can be eliminated. The WASN may use one or more geolocation techniques In addition, the WASN may detect and locate unauthorized transmitters as well as estimate the transmitted power of authorized transmitters to assure they are not transmitting more power than authorized.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
Method and apparatus for utilizing amplitude-modulated pulse-width modulation signals for neurostimulation and treatment of neurological disorders using electrical stimulation
InactiveUS7715910B2Eliminating conscious patient perceptionGood effectElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyStatistical analysisCarrier signal
A computing device-controlled system is described for the generation of amplitude-modulated pulse-width modulation (AMPWM) signals for use in treating neurological dysfunction via cranial neurostimulation, where the AMPWM signal is specifically designed to minimize the electrical impedance of the tissues of the head. A low-frequency carrier signal is determined for the AMPWM signal by measuring EEG activity at a reference site or sites, generally corresponding with the location of suspected brain dysfunction. Carrier signal frequency is variably related to critical frequency components of the EEG power spectral density, determined from statistical analysis of amplitudes and variability, and dynamically changed as a function of time to prevent entrainment. The AMPWM signal is presented to a subject via a plurality of neurostimulation delivery modes for therapeutic use.
Owner:HARGROVE JEFFREY B
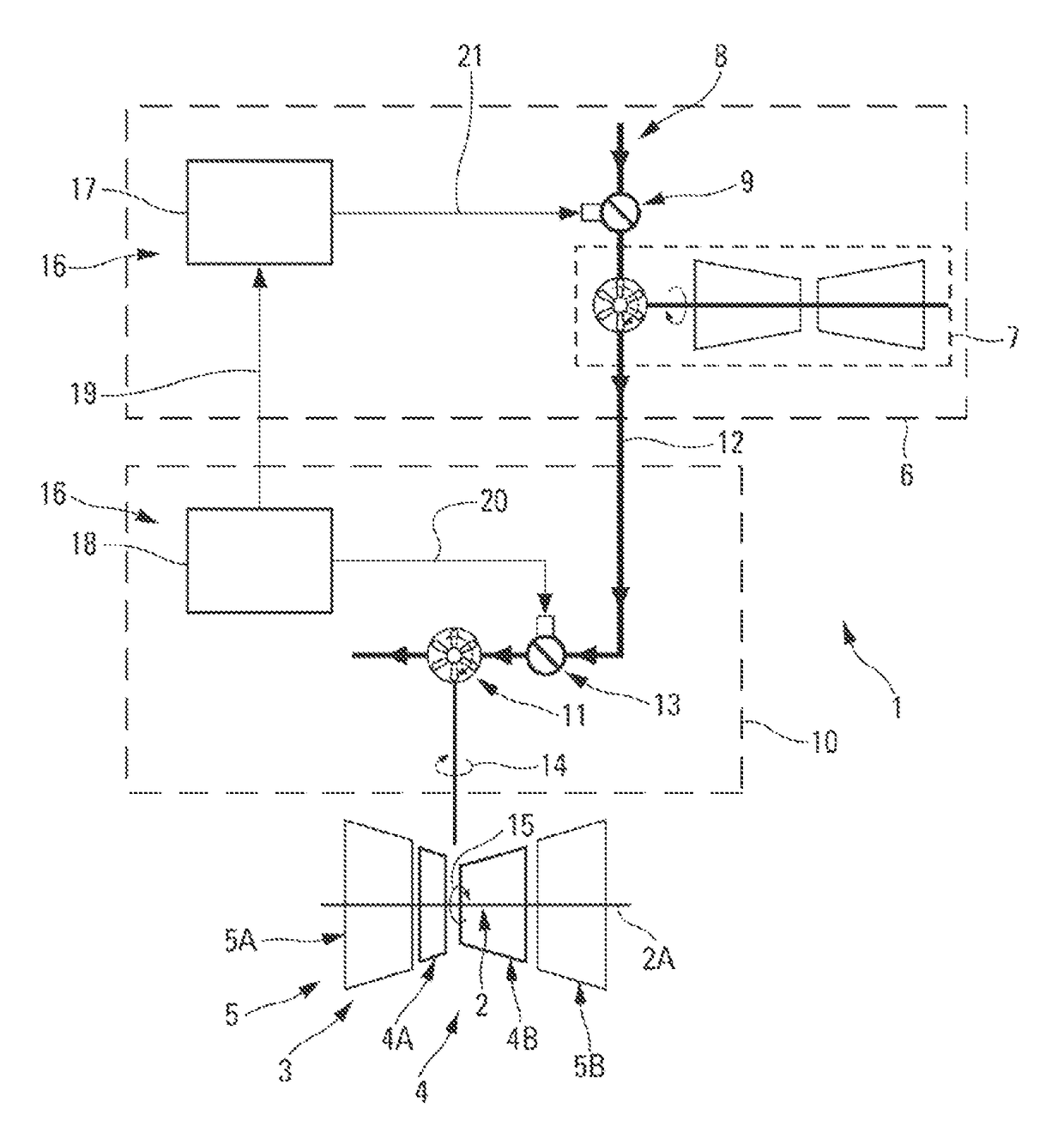
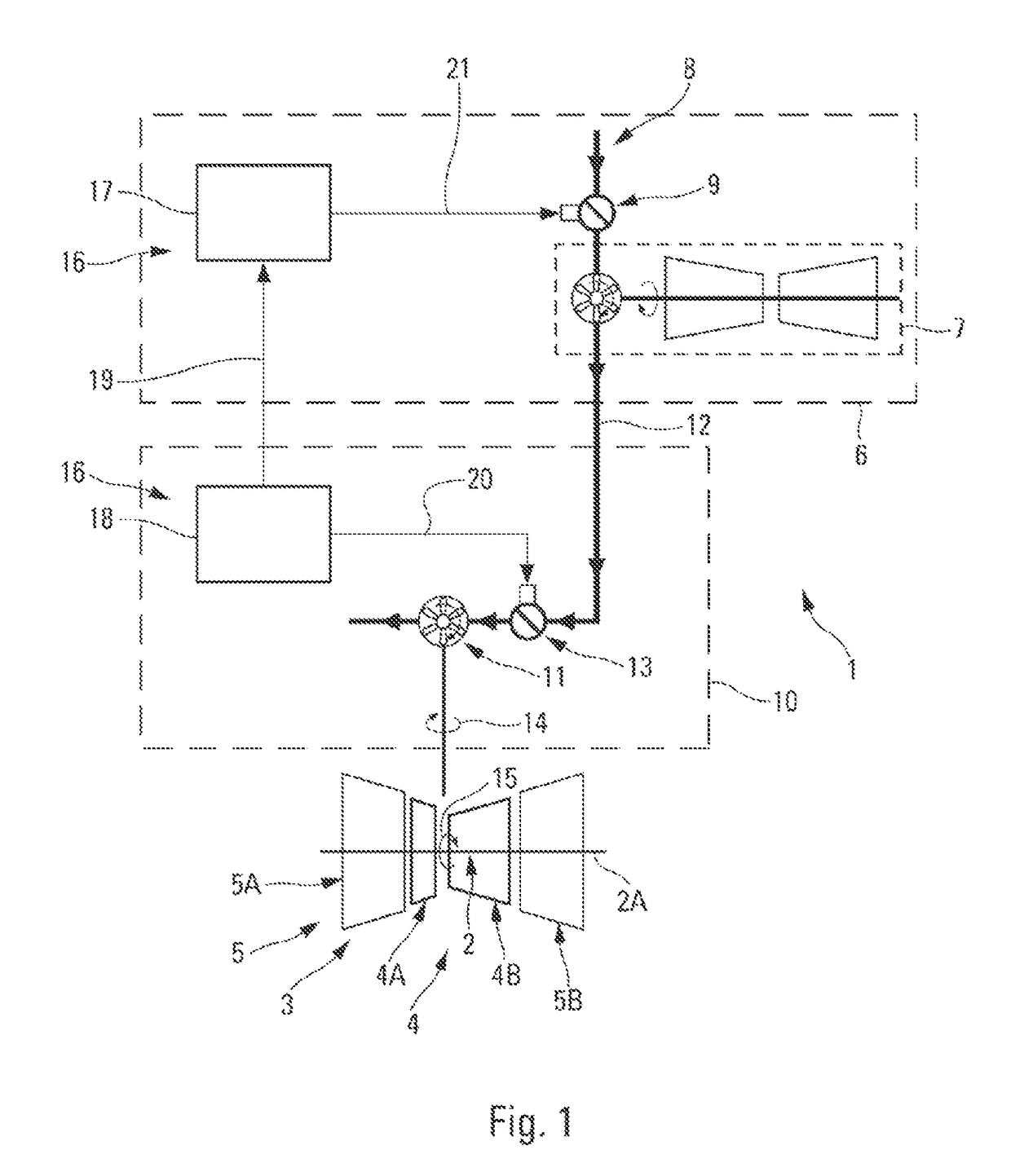
Method and system for starting up an aircraft turbomachine
A start-up system including a control system controlling a partial opening of an air intake valve of a start-up turbine during a first phase of the start-up. The start-up turbine is capable of turning a rotor of the turbomachine for the purpose of the start-up, so as to prevent the rotor from encountering critical frequencies of the turbomachine.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS) +1
Generator set multivariable system identification method based on normal operating data
InactiveCN103760768AOvercoming Non-LinearityImprove anti-interference abilityAdaptive controlTransfer function matrixFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a generator set multivariable system identification method based on normal operating data. The method comprises the steps that the step response test is carried out on a generator set multivariable system running normally to obtain input and output signals of loops of the generator set multivariable system, the signal decomposition and the spectral analysis are carried out to obtain the maximum critical frequency of all the loops of the generator set multivariable system, the frequency characteristics of the generator set multivariable system on a plurality of frequency points are calculated according to the maximum critical frequency, and a transfer function matrix model of the generator set multivariable system is established according to the frequency characteristics. According to the technical scheme, the identification process of the strongly-coupled generator set multivariable system is divided into the identification processes of a plurality of single-input and single-output systems, the frequency characteristics of the system in the important frequency bands are determined through the step response test carried out when the systems run normally under the normal running state of the generator set multivariable system, the identification process is simple, the anti-interference capability is high, and the identification precision is high.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
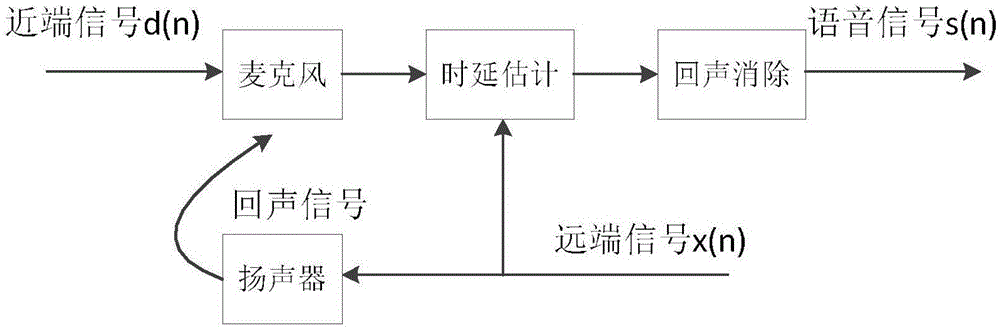
Speech signal time delay estimation method and system used for echo cancellation
ActiveCN105872275AQuality improvementSimple calculationTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsDecompositionProximal point
The invention discloses a speech signal time delay estimation method and system used for echo cancellation. The method comprises the following steps of respectively obtaining a far-end signal and a near-end signal of a voice signal received by a microphone in a call and generating a corresponding far-end frequency domain signal and a corresponding near-end frequency domain signal; adopting a critical band based on the auditory masking effect to respectively carry out sub-band decomposition in the frequency band on the far-end frequency domain signal and the near-end frequency domain signal and obtaining a power spectrum of each critical frequency point of the far-end frequency domain signal and a power spectrum of each critical frequency point of the near-end frequency domain signal; respectively extracting local binary features of the power spectrum of each critical frequency point of the far-end frequency domain signal and the power spectrum of each critical frequency point of the near-end frequency domain signal, respectively matching and generating and outputting a time delay estimation result. According to the method and the system, the correlation between the far-end signal and the near-end signal is counted based on the auditory masking effect, the computation is simple, and the accurate time delay estimation can be obtained to bring great convenience for echo cancellation.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
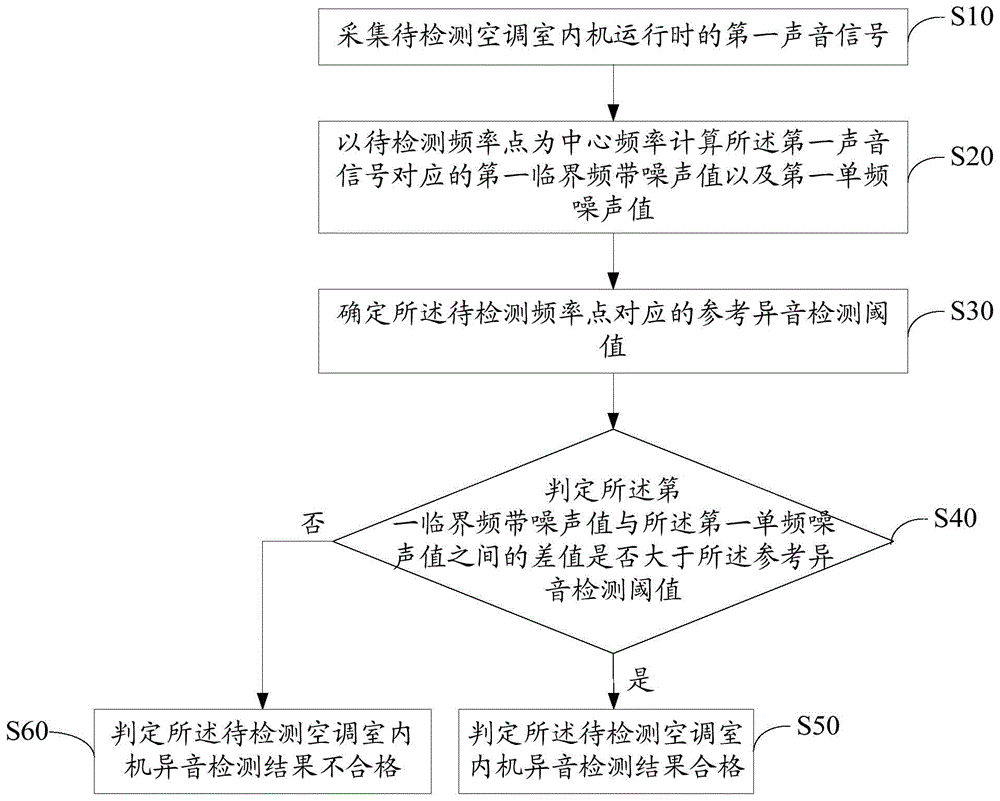
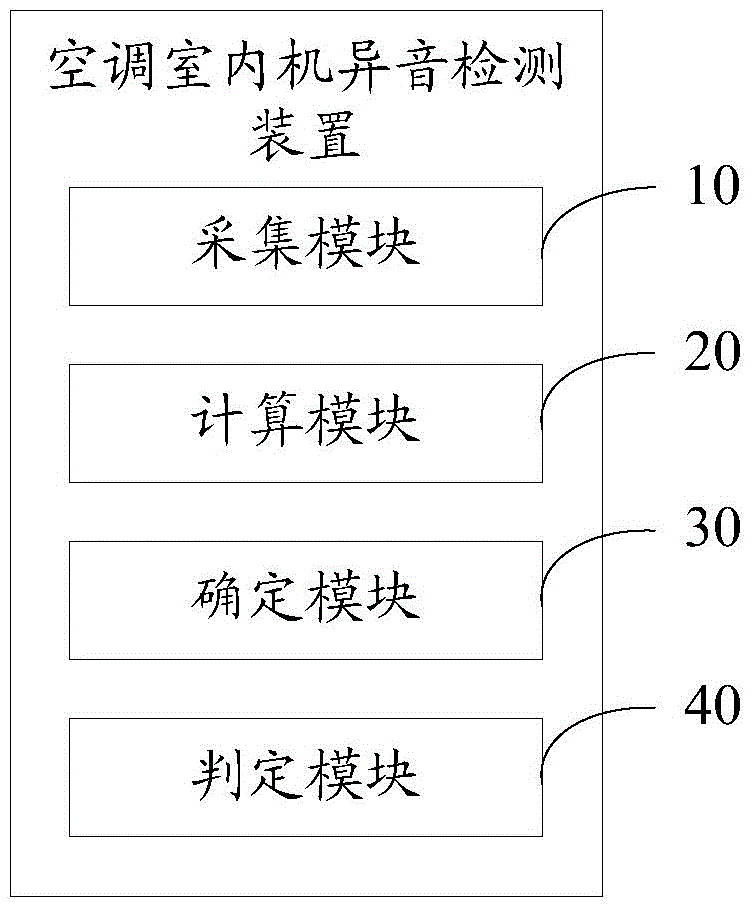
Method and device for detecting abnormal sound of air-conditioning indoor set
ActiveCN105698919AUnified evaluation criteriaReduce labor costsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound detectionAir conditioning
The invention discloses a method for detecting the abnormal sound of an air-conditioning indoor set, and the method comprises the steps: collecting a first sound signal of a to-be-detected air-conditioning indoor set during operation; taking a to-be-detected frequency point as the central frequency, and calculating a first critical frequency band noise value and a first single-frequency noise value, which are corresponding to a first sound signal; determining a reference abnormal sound detection threshold value corresponding to the to-be-detected frequency point; determining that the abnormal detection result of the to-be-detected air-conditioning indoor set is qualified when the difference between the first critical frequency band noise value and the first single-frequency noise value is greater than the reference abnormal sound detection threshold value, or else, determining that the abnormal detection result of the to-be-detected air-conditioning indoor set is not qualified. The invention discloses a device for detecting the abnormal sound of the air-conditioning indoor set. During the detection of abnormal sound, an evaluator does not participate each time, and just needs to detect the abnormal sound according to the abnormal sound detection threshold value, thereby effectively unifying the evaluation standard of abnormal sound detection and reducing the manpower cost.
Owner:HANDAN MIDEA REFRIGERATION EQUIP
Stimulating galvanic or slow AC current for therapeutic physiological effects
InactiveUS20070203534A1Efficient deliveryReduce stimulationElectrotherapyPreventing injuryCarbon particle
Basically, the present invention is directed to a new and improved system for the therapeutic use of currents which includes conducting direct electrical current through the skin of a body being treated, and periodically reversing the electrical current and conducting the current through the skin in the opposite direction, to effectively deliver very low frequency AC current, substantially in the critical range of approximately 0.0027 Hz to 20 Hz. It has been discovered that, within this substantially critical frequency window between approximately six minutes per full cycle and approximately ten cycles per second, a dramatic cancellation of skin damaging ions takes place. At frequencies higher than approximately 20 Hz, the effect is to diminish its DC-like blood stimulation. At frequencies lower than approximately 0.0027 Hz, the risk of skin injury increases substantially. It is well known that the positive electrode unfortunately produces skin damaging hydrochloric acid. Likewise, the negative electrode unfortunately also produces skin damaging sodium hydroxide. However, within the aforementioned frequency range of the present invention, either polarity stimulates blood circulation, but also cancels the undesired skin damaging ions with the reverse portion of the electrical cycle. The reason for neutralization of the harsh injury producing chemicals, i.e., hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, is that both of these chemicals require a finite period of time on the skin to cause damage. Hence, these damaging chemicals are made to cancel each other before damage takes place, by critical frequency selection, in accordance with the invention, of the AC driving signal. Therefore, optimization of a long sought electrotherapeutic device with reduced side effects has been achieved. Another use of the safe AC currents cited above and / or a DC signal with charged membranes preventing injury is its application to wound healing. The conductive electrodes for these devices may take either of two forms, i.e., one may be non-metallic carbon-filled silicone or, preferably of powdered carbon particles. A second form may be a metallic electrode preferably of aluminum, copper, zinc and / or magnesium as examples of metallic electrodes but not necessarily limited to these metals. These metals are preferably in powdered form and contained within a porous membrane with a small opening to attach a conductive lead to a battery source. Still other applications of the innovative use in electrotherapy of charged membranes and / or powdered metal electrodes is its use for drug delivery and diagnostic purposes. For instance, a membrane enclosed stainless steel powdered negative electrode may be used in the pickup probe for glucose detection. Charged membranes would surround the probe as an intervenor between skin and the electrode.
Owner:TAPPER ROBERT
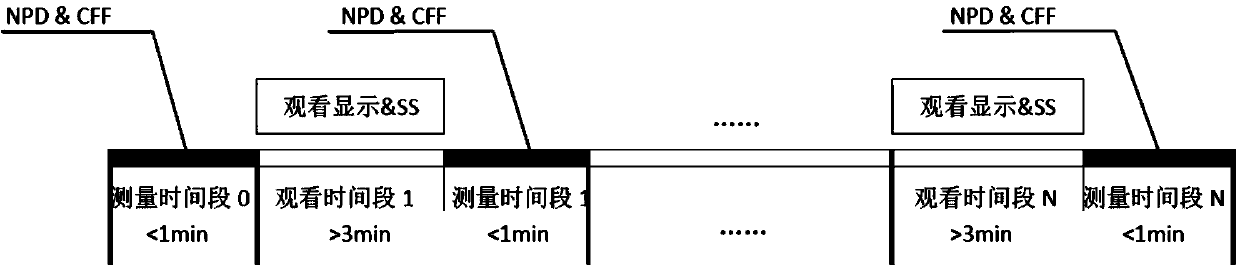
Three-dimensional display asthenopia detection system and method
ActiveCN103796010AImprove reliabilityImprove stabilityTelevision systemsSteroscopic systemsSimulationEye straining
The invention discloses a three-dimensional display asthenopia detection system and method. The three-dimensional display asthenopia detection system comprises three-dimensional display equipment, flicker fusion critical frequency (CFF) measuring equipment, near point distance (NPD) measuring equipment and a data processing unit, wherein the CFF measuring equipment is used for collecting a CFF when a user watches three-dimensional display and transmitting the CFF to the data processing unit, the NPD measuring equipment is used for collecting a NPD when the user watches the three-dimensional display and transmitting the NPD to the data processing unit, the data processing unit comprises a three-dimensional asthenopia prediction model, and the three-dimensional asthenopia prediction model predicates the three-dimensional asthenopia of the user according to the input CFF and the NPD. The three-dimensional display asthenopia detection system and method can rapidly detect the asthenopia degree caused by three-dimensional display, and can be used for evaluating three-dimensional display equipment and content and guiding equipment to produce and manufacture comfortable three-dimensional resources and the like.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
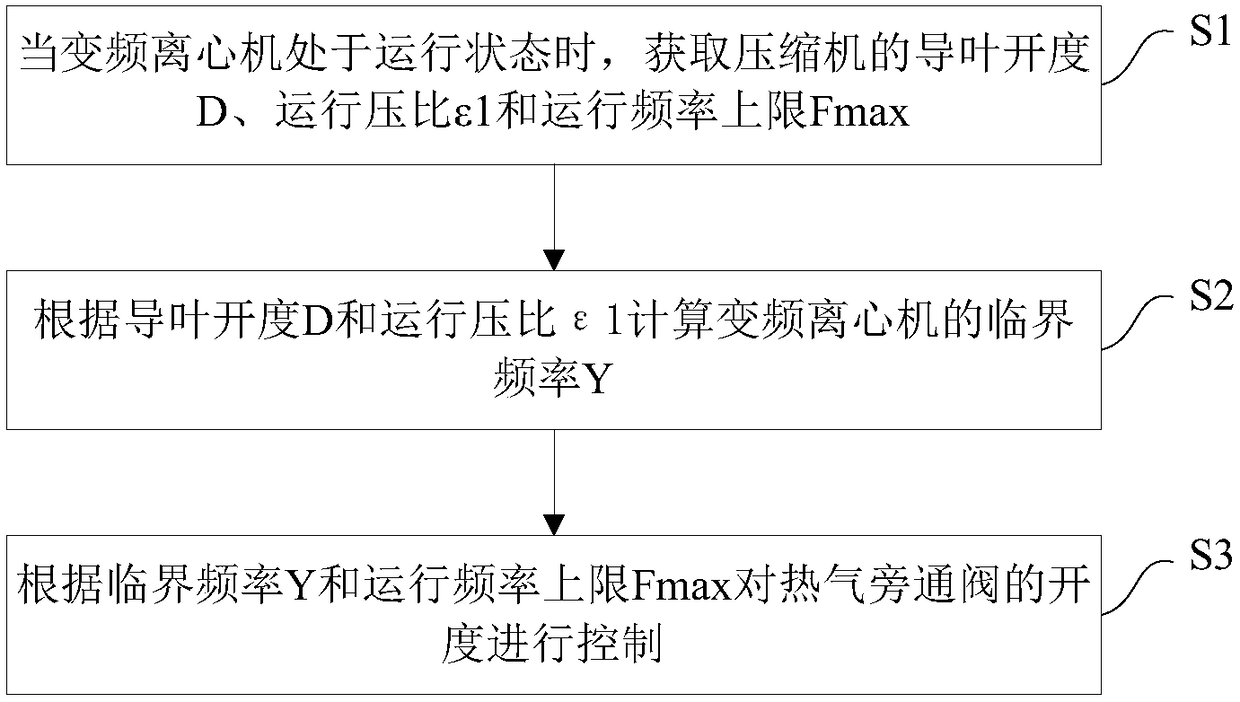
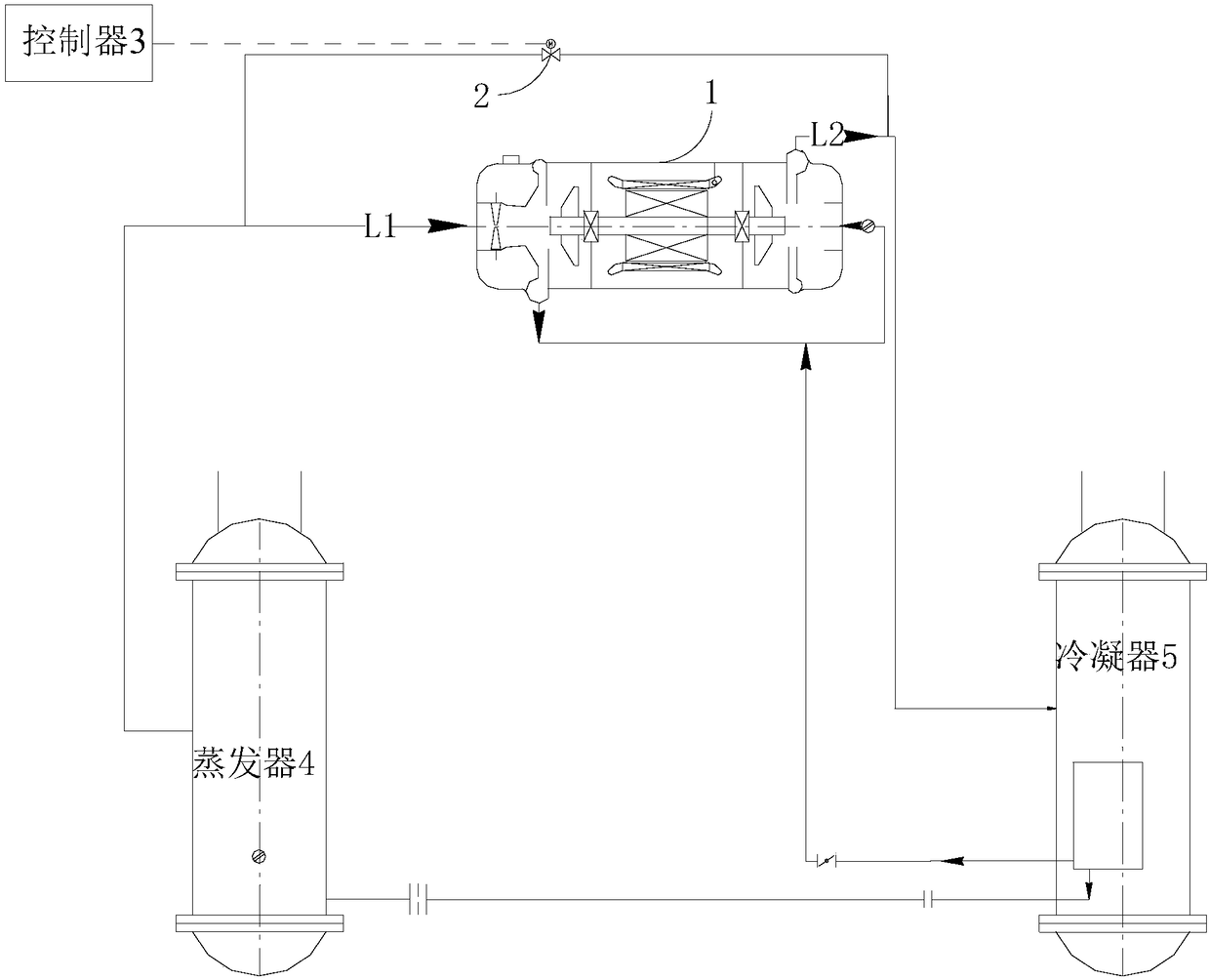
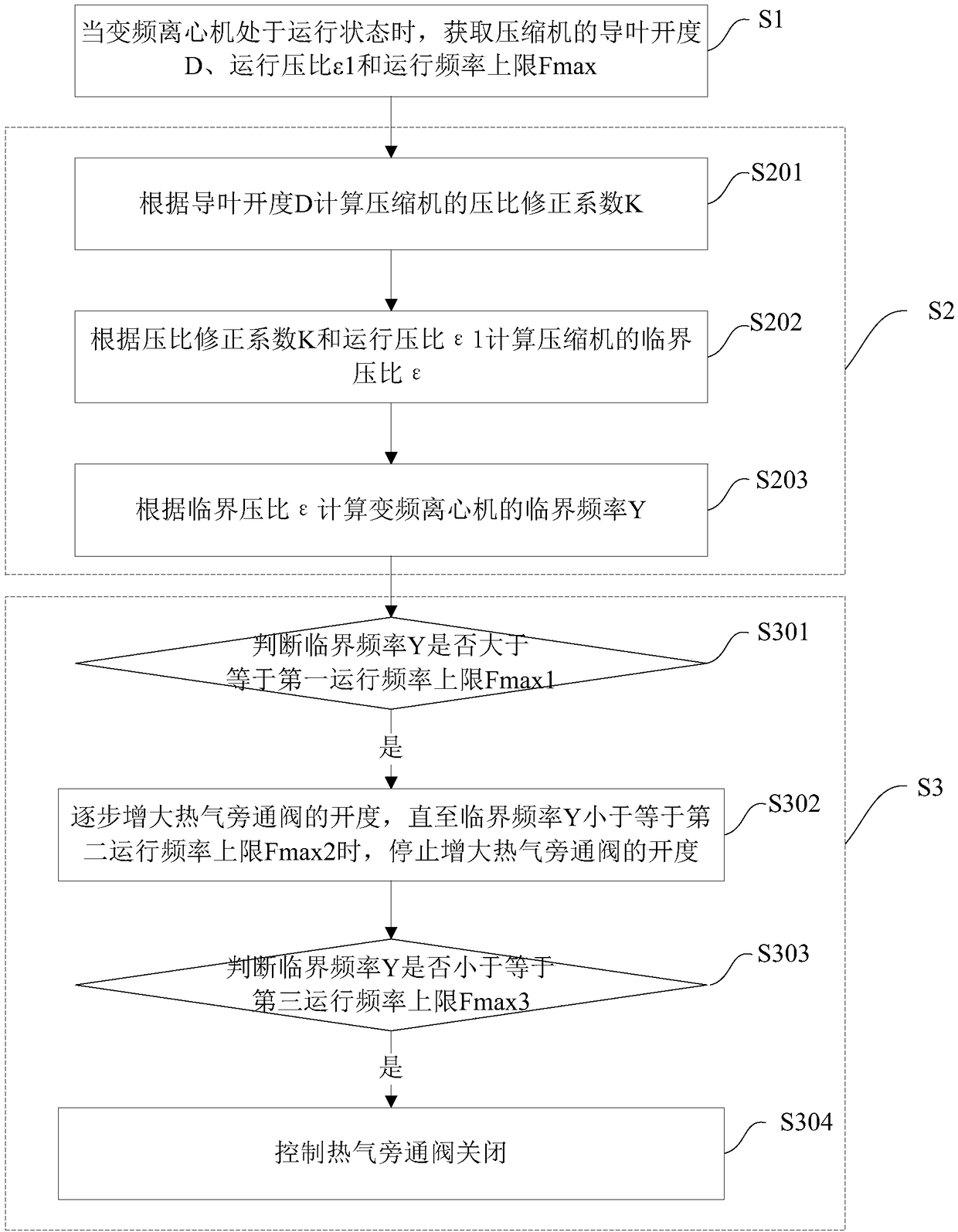
Variable frequency centrifuge and control method of hot gas bypass valve in variable frequency centrifuge
ActiveCN108131871AImprove reliabilityNo surgeMechanical apparatusFluid circulation arrangementControl theoryOperating frequency
The invention discloses a variable frequency centrifuge and a control method of a hot gas bypass valve in the variable frequency centrifuge. The variable frequency centrifuge includes a compressor, and the hot gas bypass valve is disposed between an air suction pipe and an air exhaust pipe of the compressor. The method comprises the following steps of when the variable frequency centrifuge is in an operating state, obtaining a guide vane opening degree, an operating pressure ratio and the upper limit of the operating frequency of the compressor, wherein the operating pressure ratio is a ratioof an air exhaust absolute pressure value to an air suction absolute pressure value of the compressor; calculating the critical frequency of the variable frequency centrifuge according to the guide vane opening degree and the operating pressure ratio; controlling the opening degree of the hot gas bypass valve according to the critical frequency and the upper limit of the operating frequency. By controlling the opening degree of the hot gas bypass valve, the variable frequency centrifuge can safely operate with a small load under high ambient temperature and large pressure ratio, and at the same time, the compressor surging phenomenon does not occur under small load operation, so that the operation reliability of the variable frequency centrifuge is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING MIDEA GENERAL REFRIGERATING EQUIP
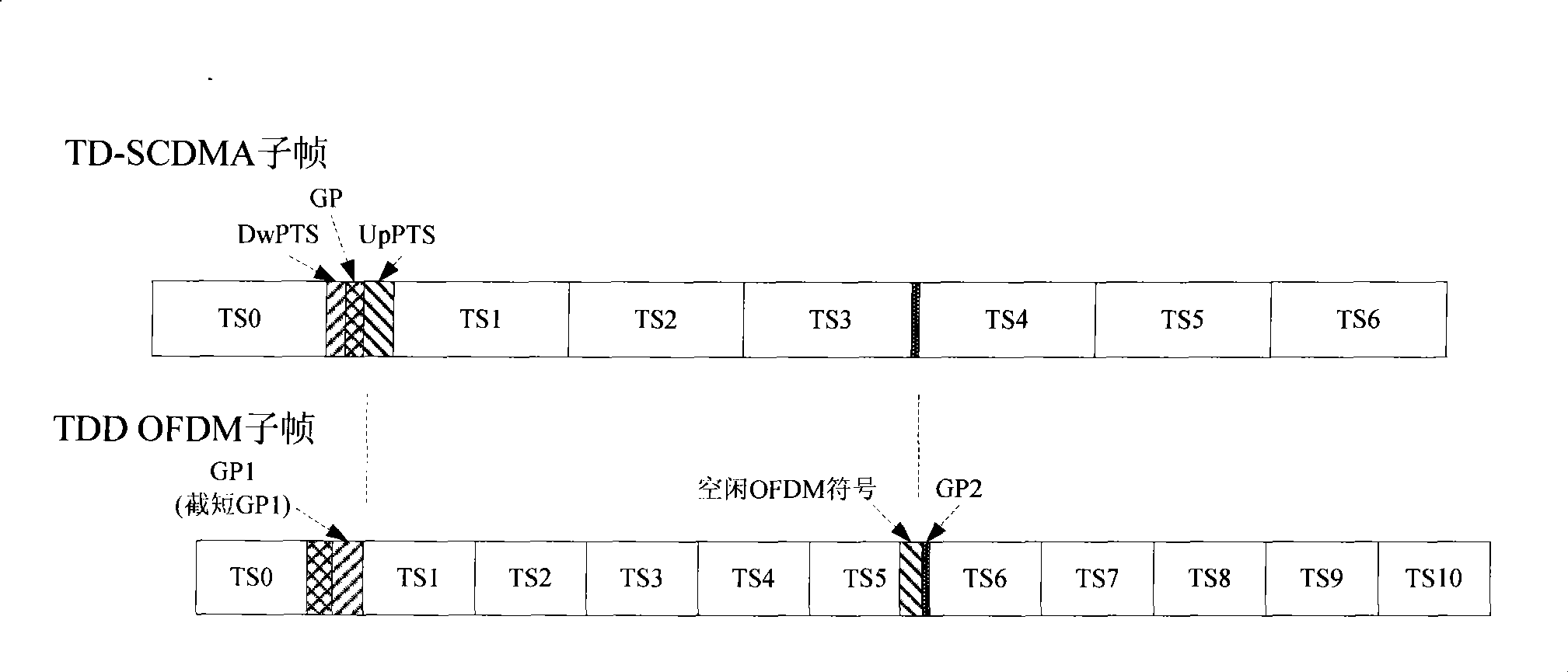
Method for implementing critical frequency coexist between two different communication systems and physical layer frame structure
InactiveCN101374011AIncrease profitEliminate mutual interferenceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationTD-SCDMAWireless transmission
The invention discloses a wireless communication method of a TDD OFDM wireless communication system, and a physical layer frame structure for realizing the communication method. During conducing wireless transmission, each sub-frame in the physical layer frame sends a downlink service control message by using a regular time slot, receives uplink service by using one or more regular time slots after pausing for a period of time, and sends downlink service by using one or more regular time slots after pausing for a period of time. Considering the adjacent frequency coexistence problem of the TDD OFDM system and the TD-SCDMA system, the sub-frame conducts mutual switching between the uplink and the downlink during pausing periods, so as to ensure alignment of the same type of uplink and downlink switching points in the two communication systems, including the alignment of downlink / uplink switching points and the alignment of uplink / downlink switching points. The inventive method conducts wireless service transmission by using the alignment of the uplink and downlink switching points, thereby eliminating intersystem interference and improving the utilization ratio of system resources.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Wave stringer for controlling acoustic noise and shock vibration in a storage device
InactiveUS6947252B2Weaken energyUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionFluid-dynamic spacing of headsHard disc driveLongitudinal wave
A hard disk drive that includes a wave stringer. The wave stringer can attenuate energy which propagates through a base plate of the disk drive. The wave stringer may be designed by initially analyzing propagation patterns of both acoustic and shock waves applied to the drive. The wave stringer is then designed, constructed and assembled to the disk drive to attenuate critical frequencies at weak points of the disk drive. The wave stringer may have a plurality of ribs designed to vary the mechanical impedance of the drive to attenuate the propagated energy.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for improving the tuning of a radio receiver and a radio receiver
InactiveUS6125267AQuick and easy mannerAccurate frequencyPulse automatic controlElectrial characteristics varying frequency controlOptimal tuningRadio receiver design
In order to tune a radio receiver (10) to an optimal tuning frequency it is found the critical frequency closest to the current tuning frequency (60) at which the radio receiver loses the locking to the clock frequency of the received signal, and, if necessary (62), the tuning frequency is corrected away from the critical frequency found. The control block (13) of the radio receiver comprises means for adjusting the tuning of the reception part (11) in response to the information (17) indicating whether the locking to the clock frequency is on. The search for the critical frequency may be performed in on or two stages and alternately on both sides of the current tuning frequency or first on one side and then on the other.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Apparatus for relay based multiple point process frequency response estimation and control tuning
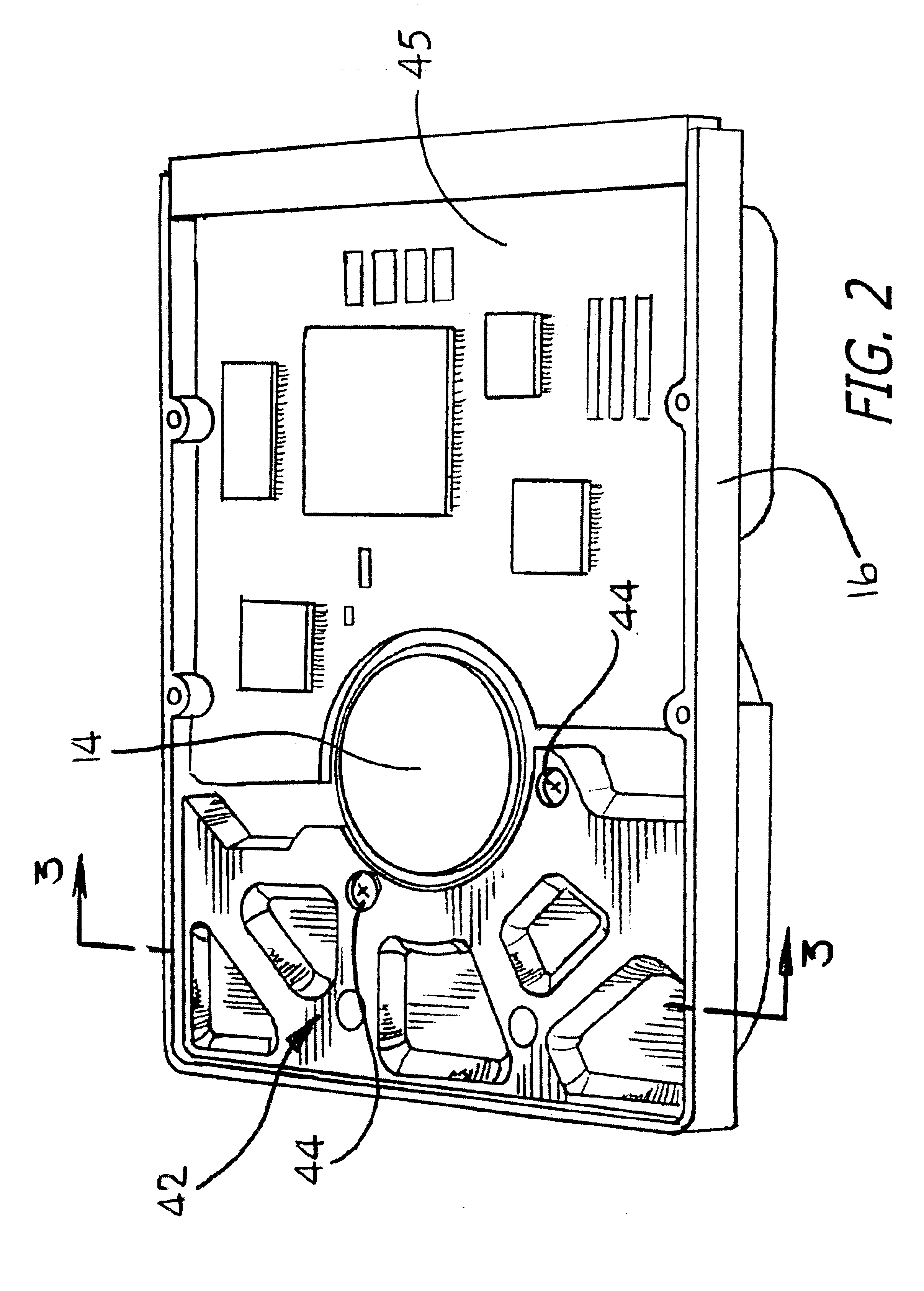
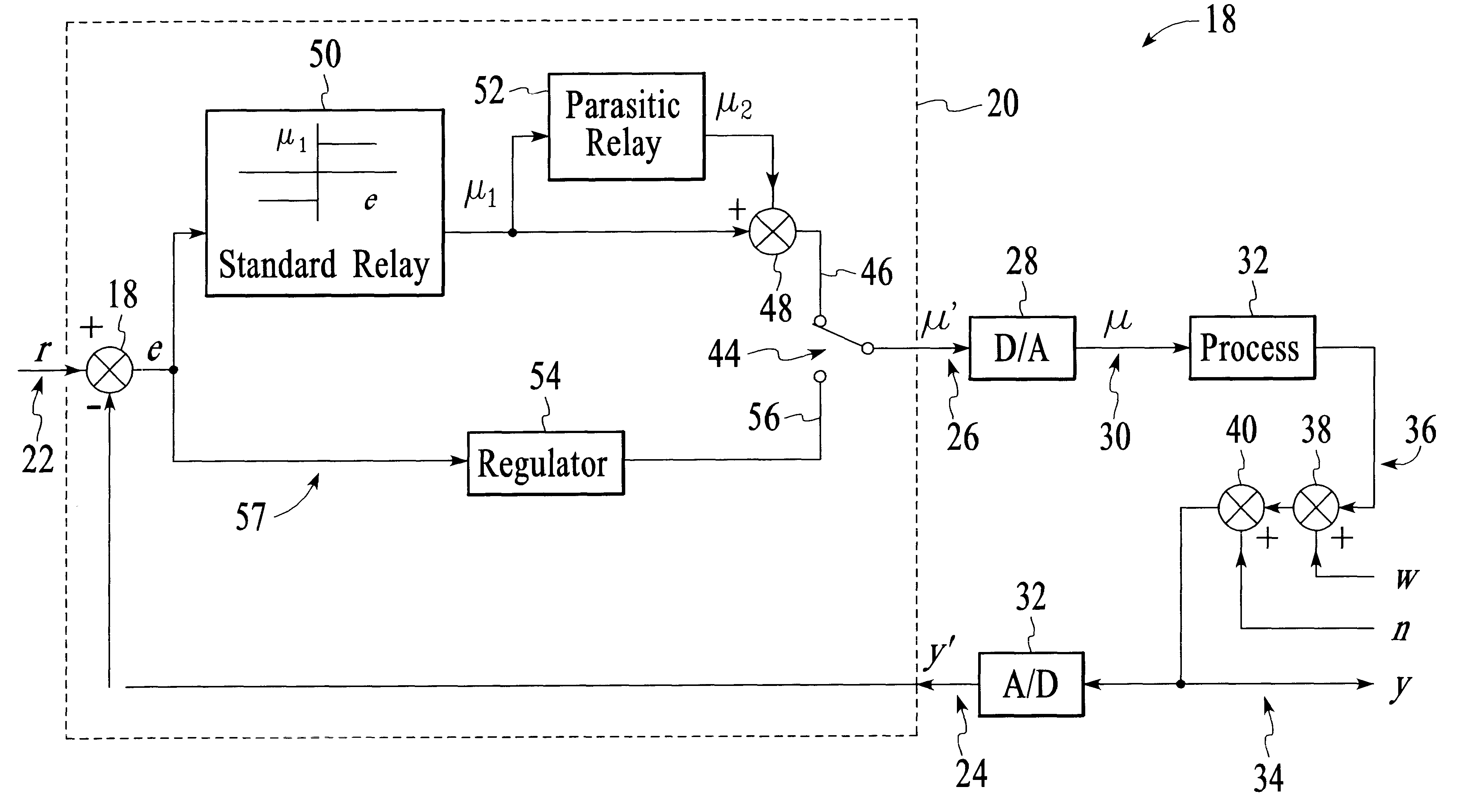
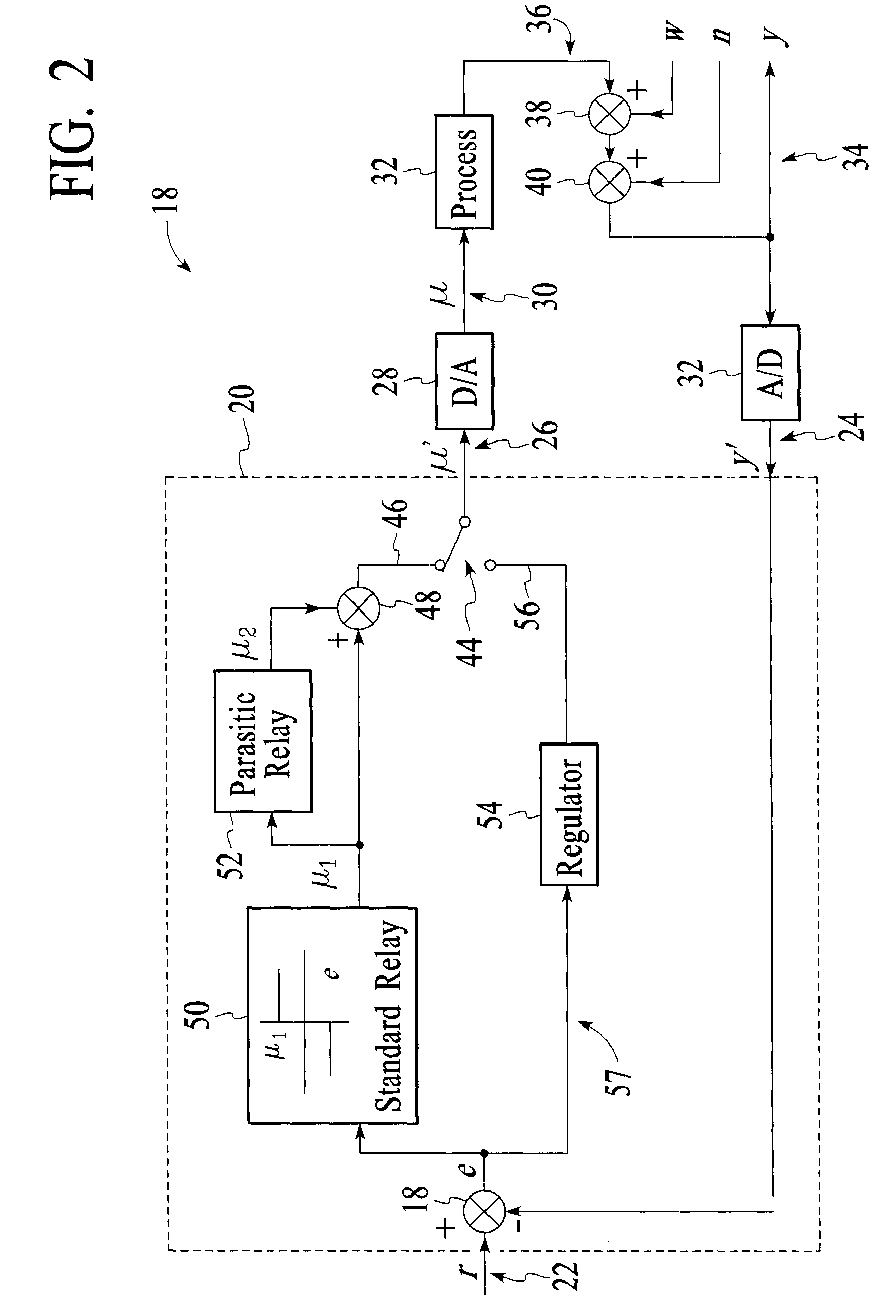
InactiveUS6438431B1Accurate identificationImproved and uniform responseElectric testing/monitoringAdaptive controlDigital analog converterMultiple point
Briefly, a preferred embodiment of the present invention includes an apparatus for tuning a regulator in a process controller. The digitized output from a standard relay and a parasitic relay are fed through digital to analog converter providing signals at 0.5omegac, omegac and 1.5omegac to the process, where omegac is the process critical frequency. The apparatus records the digitized relay output u' and the digitized process output y' until stationary oscillations are reached. The outputs u' and y' are then used to calculate the process frequency response at 0.50omegac, omegac and 1.5omegac. This data is then used to design the regulator, the output of which is converted to analog form and inputted to control the process.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
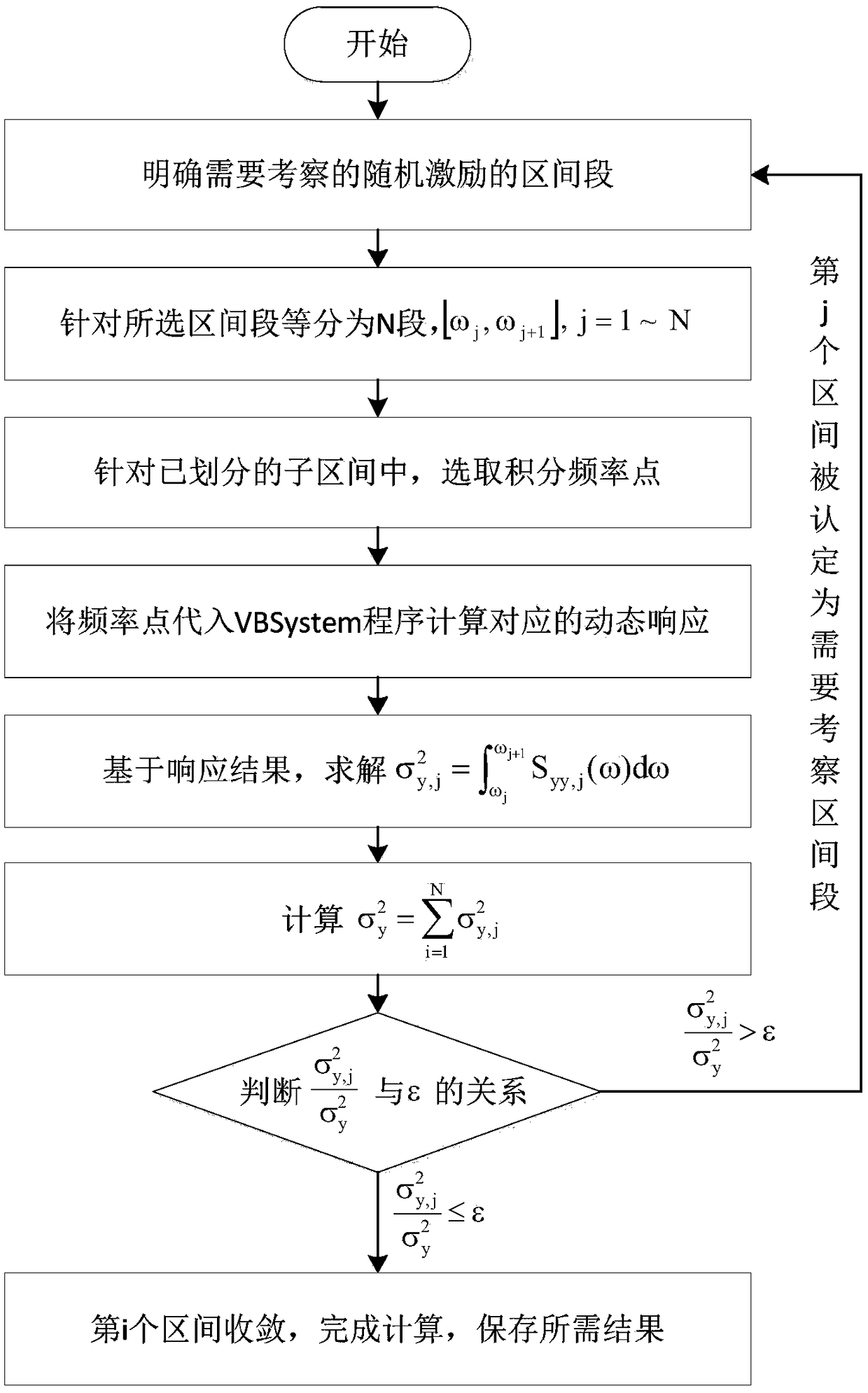
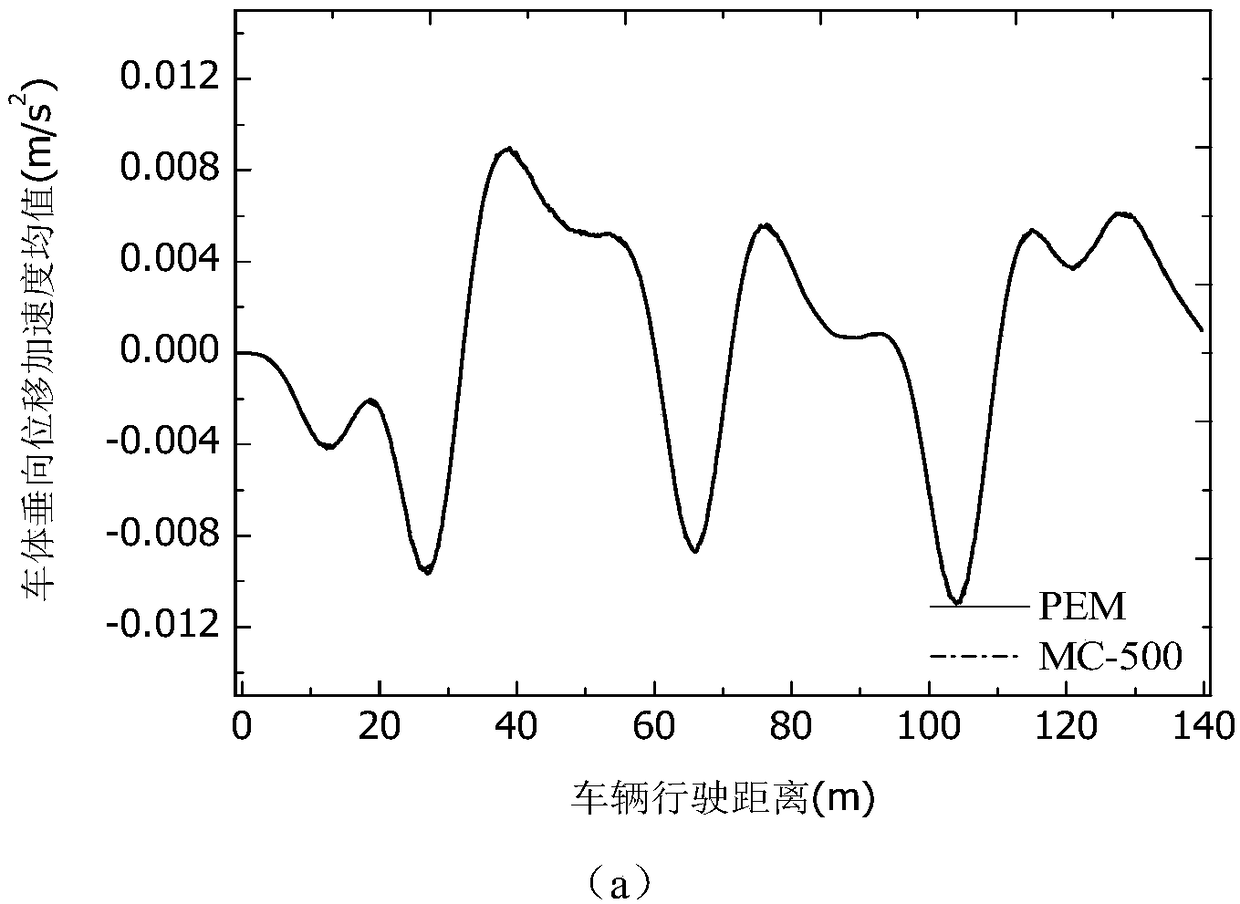
Analysis method for efficiently solving bridge vibration random characteristics of high-speed train
InactiveCN109459129AReduce computing costImprove computing efficiencySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVibration testingCoupling systemSelf adaptive
The invention discloses an analysis method for efficiently solving bridge vibration random characteristics of a high-speed train. A virtual excitation algorithm is combined with a self-adaptive Gaussian integration technology, a frequency interval section with the key influence of random excitation on a coupling system is identified in a self-adaptive mode, and a critical frequency interval section is intelligently refined or a non-critical frequency interval is roughly drawn or abandoned; corresponding frequency points are found on the basis of the frequency interval section after intelligentprocessing and substituted into vehicle-bridge system coupling vibration for calculation; on the basis of dynamic responses obtained by all the frequency points, calculation results with the statistical property and the random characteristics are obtained through Gaussian integration, and the calculation results are verified through a Monte Carlo method. According to the analysis method, the calculation cost is effectively reduced, and the calculation efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
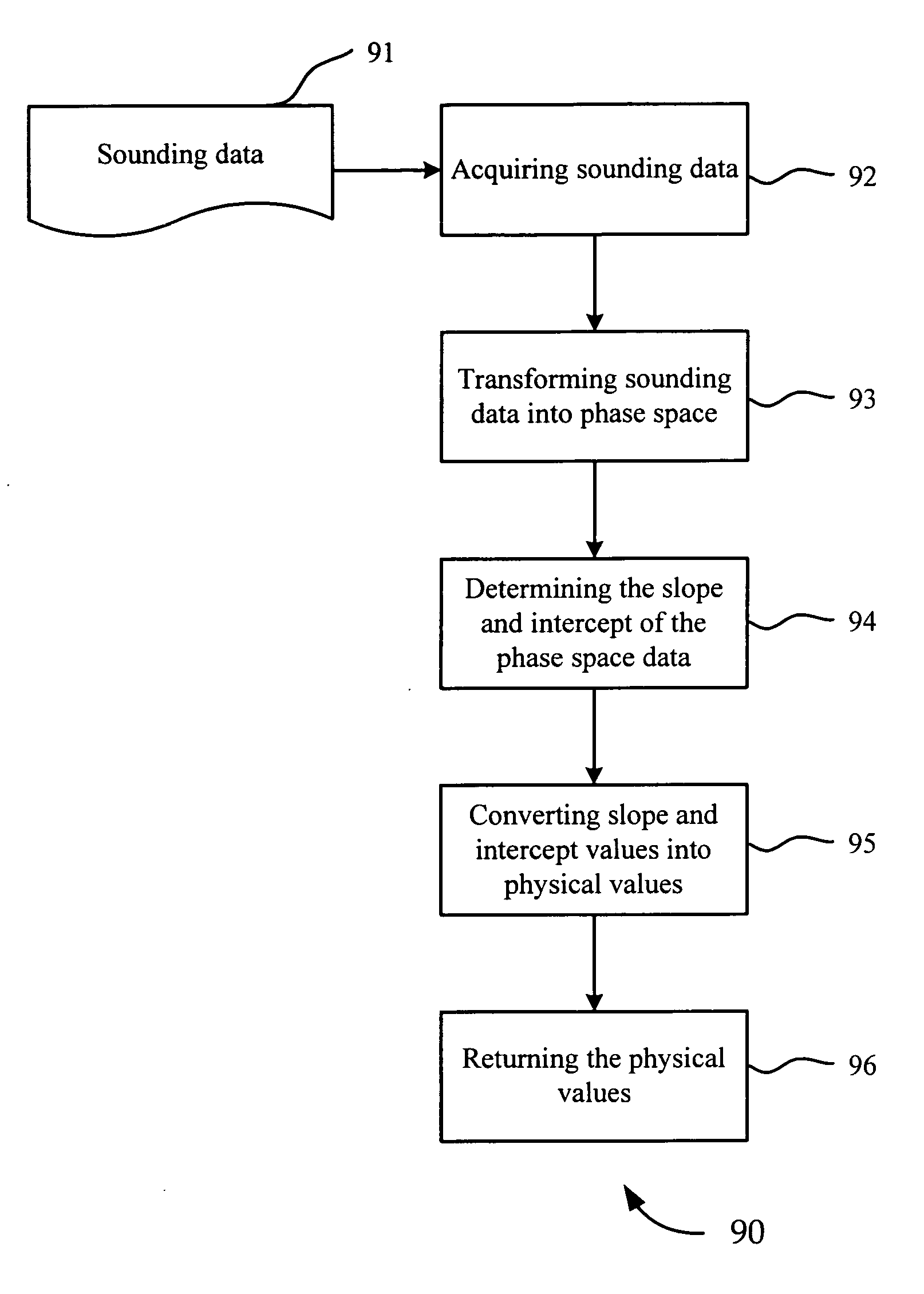
Sounding transformation and recognition
InactiveUS20080143571A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsIonogramPhase space
A method for scaling and converting sounding data into physical properties of a scanned medium is disclosed. In one embodiment, sounding data is received and transformed into phase space, where the phase space transformation linearizes the sounding data. The slope and intercept of the phase space data is determined and then converted into physical parameters. The physical parameters are then returned. In a more specific embodiment, the critical frequency is returned for an ionogram.
Owner:SPACE ENVIRONMENT CORP
A Method of Inverting es Layer Parameters Based on Backscattered Ionogram
InactiveCN106134481BMeet engineering needsSpecial data processing applicationsHorizontal distributionLeading edge
The present invention provides a method for inverting Es layer parameters based on backscattered ionograms, which includes the following steps: Step A: using the established Es layer model to invert the Es layer parameters according to the measured backscattered ionograms' steep front information QPS parameters include the critical frequency, peak height, and half-thickness of Es; Step B: Calculate the elevation angle corresponding to the flat leading and trailing edges of the backscatter ionogram according to the determined QPS parameters to determine the area where Es exists. The present invention uses the inferred Es parameters to synthesize the front and rear edges of the backscattered ionization map Es, which can well conform to the measured Es front and back edges, and can better obtain the vertical distribution and horizontal distribution of the electron concentration in the ES layer, overcoming the traditional definition that considers the electron concentration alone The lack of vertical distribution or spatial distribution of electron concentration can better meet engineering needs.
Owner:THE 22ND RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
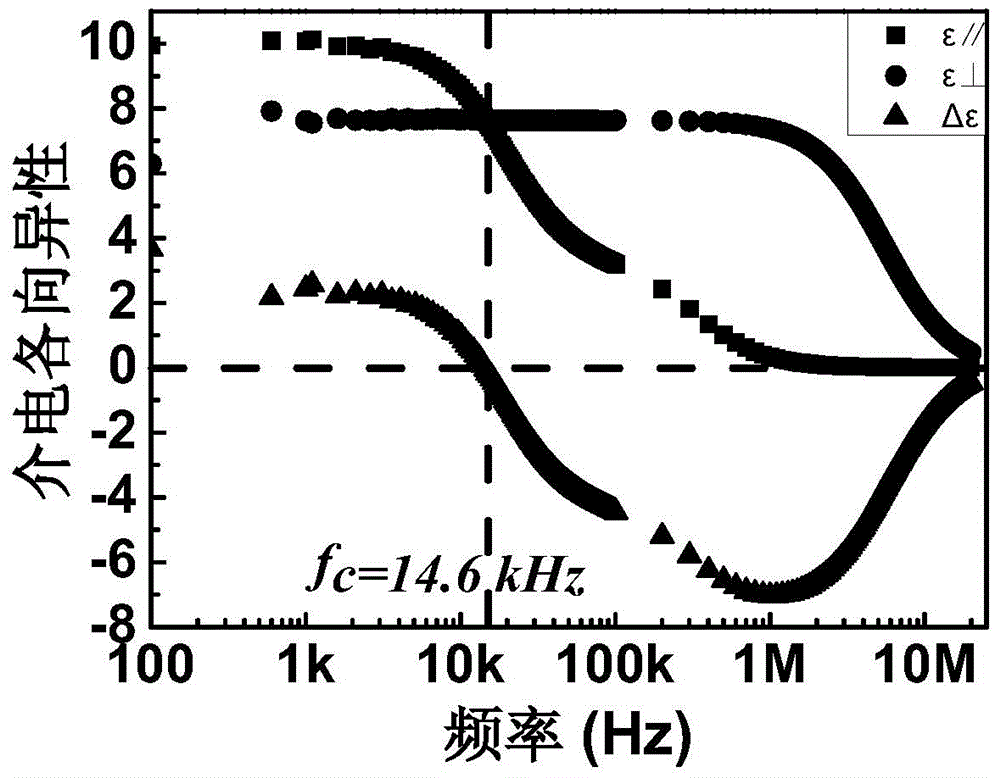
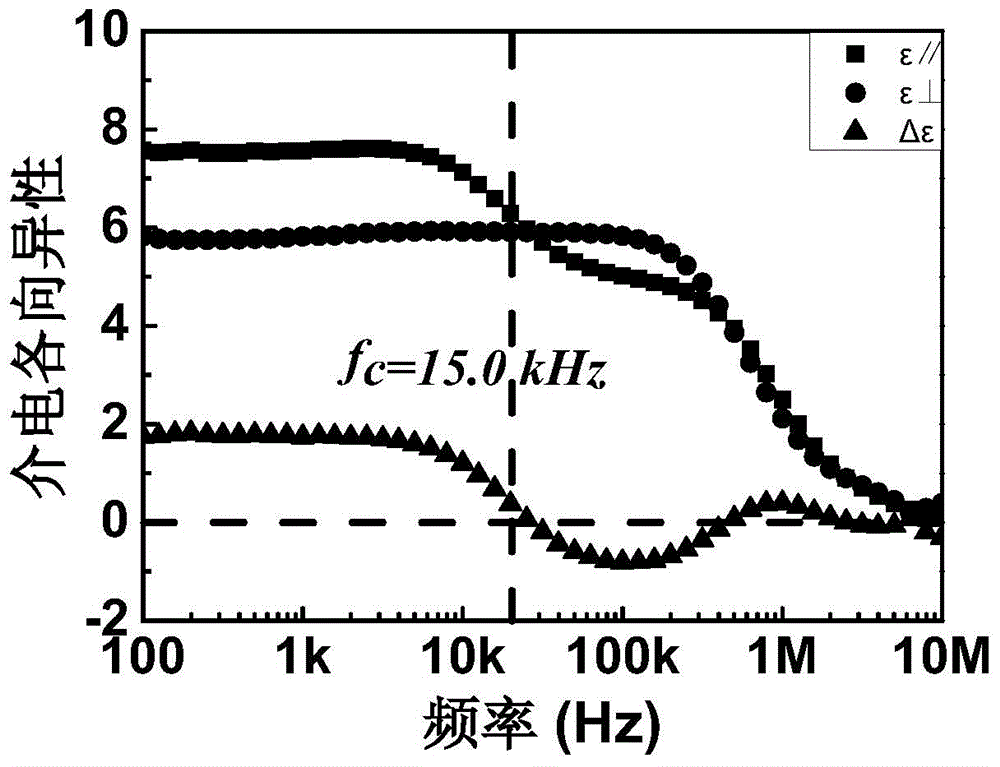
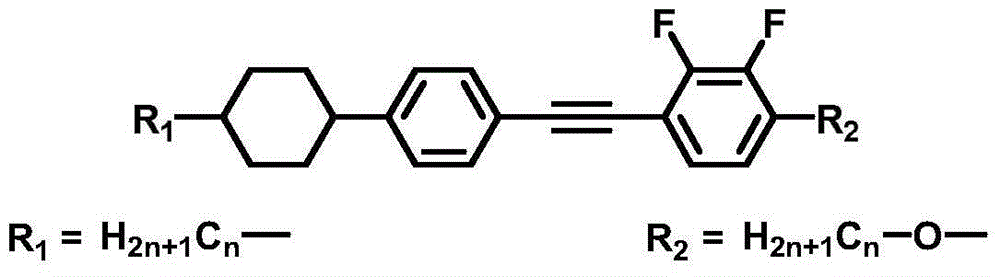
Double-frequency liquid crystal material having low critical frequency
ActiveCN104130782ALow critical frequencyWide liquid crystal phase temperatureLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsLiquid crystallineBenzene
The invention discloses a double-frequency liquid crystal material having low critical frequency. The double-frequency liquid crystal material comprises 20.0-25.0% of an ingredient A, 20.0-25.0% of an ingredient B, 17.5-22.5% of an ingredient C, 7.5-12.5% of an ingredient D, 7.5-12.5% of an ingredient E, 5.0-10.0% of an ingredient F and 5.0-10.0% of an ingredient G, and the above material are melt and mixed. The ingredient A comprises a series of derivatives having cyclohexylfluorodiphenylacetylene skeleton structures, the ingredient B comprises a series of derivatives having fluorodiphenylacetylene skeleton structures, the ingredient C comprises a series of derivatives having cyclohexylbenzene ring skeleton structures, the ingredient D comprises a series of derivatives having diphenylacetylene skeleton structures, the ingredient E comprises a series of derivatives having three-ring monoester lateral fluoro-group-containing cyano-terminated skeleton structures, and the ingredient F comprises a series of derivatives having three-ring diester lateral dicyano-containing skeleton structures. The double-frequency liquid crystal material has low critical frequency, wide liquid crystalline phase temperature and low viscosity and can be used for preparation of a double-frequency driven liquid crystal device having low work voltage and fast response rate.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Drilling mud pump punch speed and stroke frequency measuring equipment and method thereof
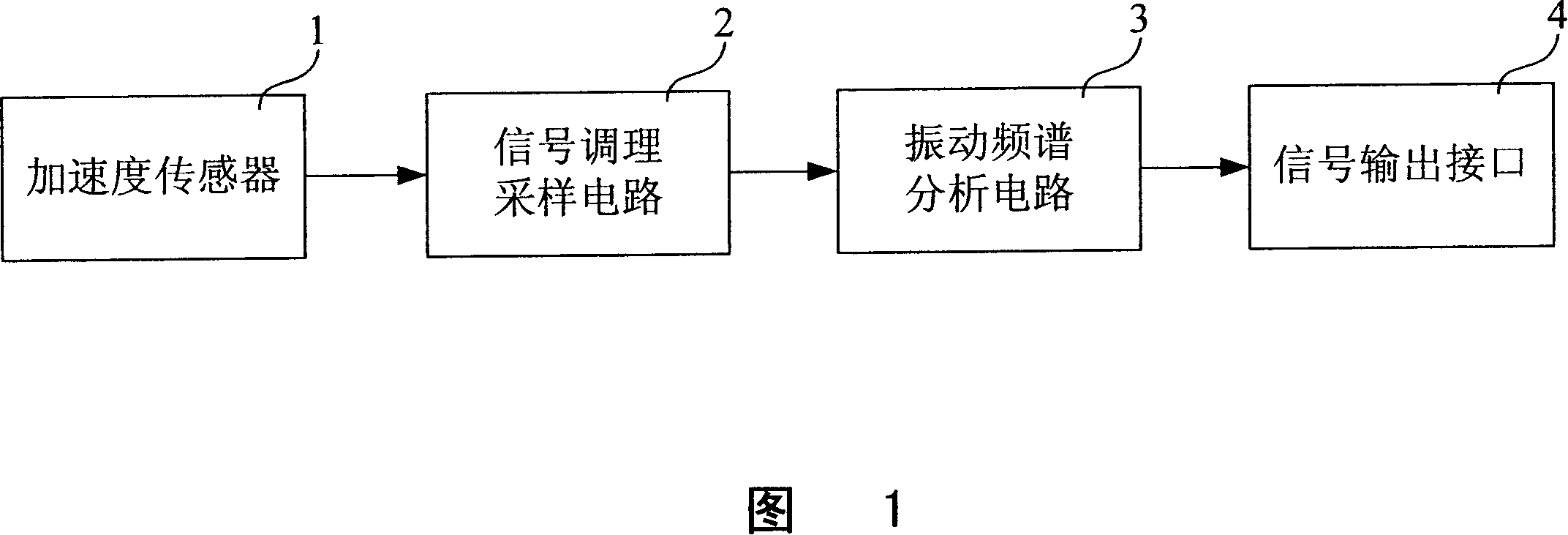
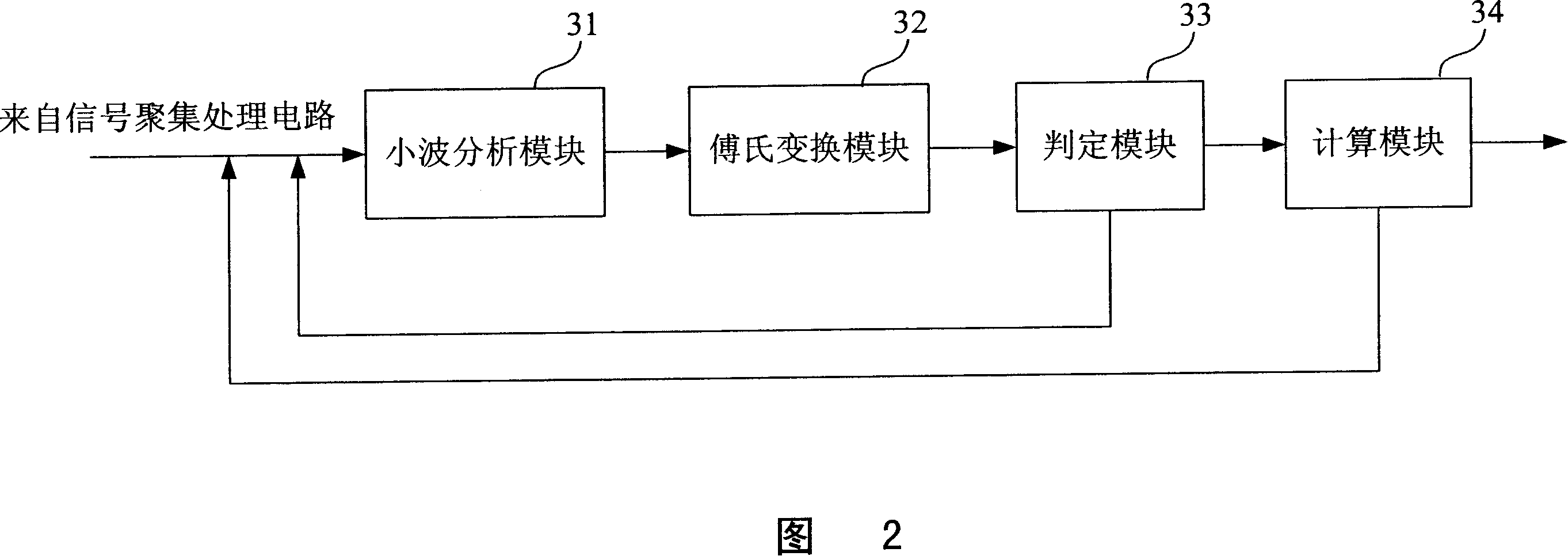
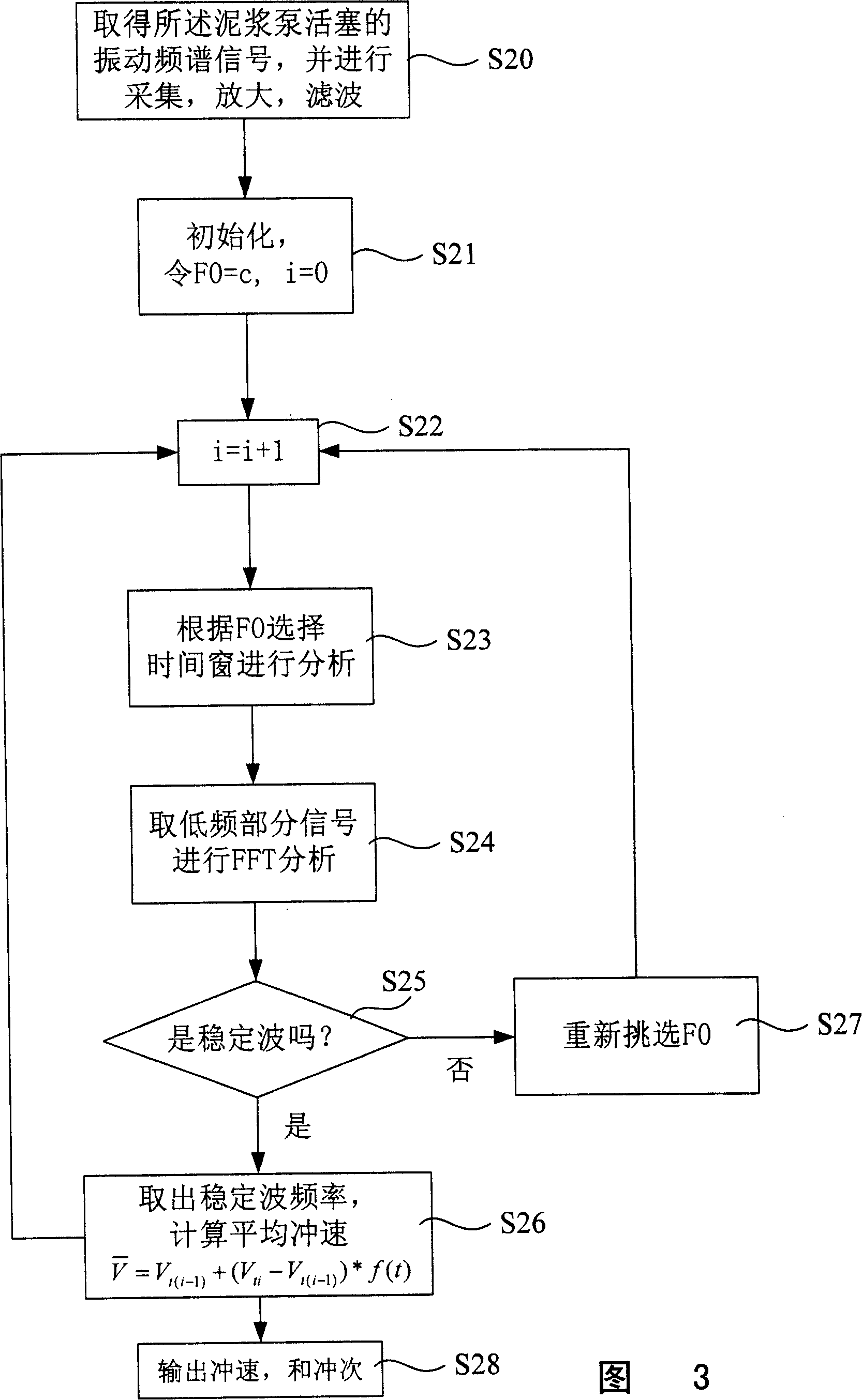
InactiveCN101139986ALower quality requirementsGood repeatabilityPump testingPositive-displacement liquid enginesFrequency spectrumPiston
The invention discloses a measuring device for impulse speed and impulse times in well-drilling mud pumps, and comprises: An acceleration transducer, a signal acquisition and process circuit, a vibration frequency spectrum ananysis circuit, a signal output interface, and a final output for average impulse speed. The invention also discloses a measuring method for impulse speed and impulse times of the well-drilling mud pumps; the measuring device is characterized by the following composition: Measure vibration frequency spectrum signals of a mud pump piston, and perform acquisition, amplification and filtering for the vibration frequency spectrum signals; provide a critical frequency spectrum point; select a time window according to the critical frequency points, and perform wavelet ananysis, and maintain low-frequency signals from the ananysis; conver the low-frequency signals from time domain to frequency domain; determine whether the low-frequency domain signals are steady waves; if yes, take the frequency and calculate to gain the average impulse speed, and then, calculate impulse times in accordance with the average impulse speed and corresponding time segments; then, go back to Step III; if the low-frequency domain signals are not steady waves, re-select a critical frequency spectrum point before returning to Step III; and after that, output the impulse times and average impulse speed that are received.
Owner:SHANGHAI GASOLINEEUM & CHEM EQUIP +2
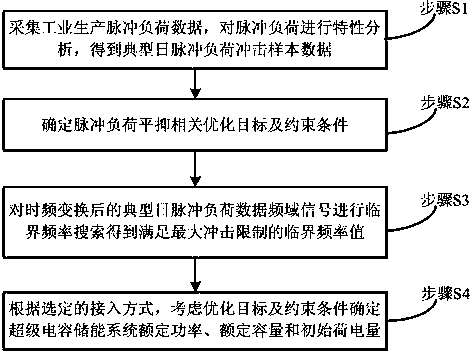
Super-capacitor configuration method adaptive to pulse load power fluctuation stabilization
ActiveCN104333025AAc network load balancingPower oscillations reduction/preventionPulse loadCapacitance
The invention relates to a super-capacitor configuration method adaptive to pulse load power fluctuation stabilization. The super-capacitor configuration method includes firstly acquiring industrial production pulse load data, and analyzing the characteristics of the pulse load to obtain typical daily pulse load impact sample data; secondly, determining relevant optimization goals and constraints of the pulse load stabilization; subjecting typical daily pulse load data frequency domain signals after time-frequency conversion to critical frequency search to obtain the critical frequency of the maximum impact limit; finally, considering the optimization goals and the constraints to determine the rated power, the rated capacity and the initial load capacity of an energy storage system of a super-capacitor. By configuring energy storage to alleviate the impact of the pulse load of the industrial production on the power grid, theoretical basis can be provided for the energy storage configuration of the super-capacitor of the pulse load.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Pile foundation dynamic stability analysis and calculation method under action of wave load
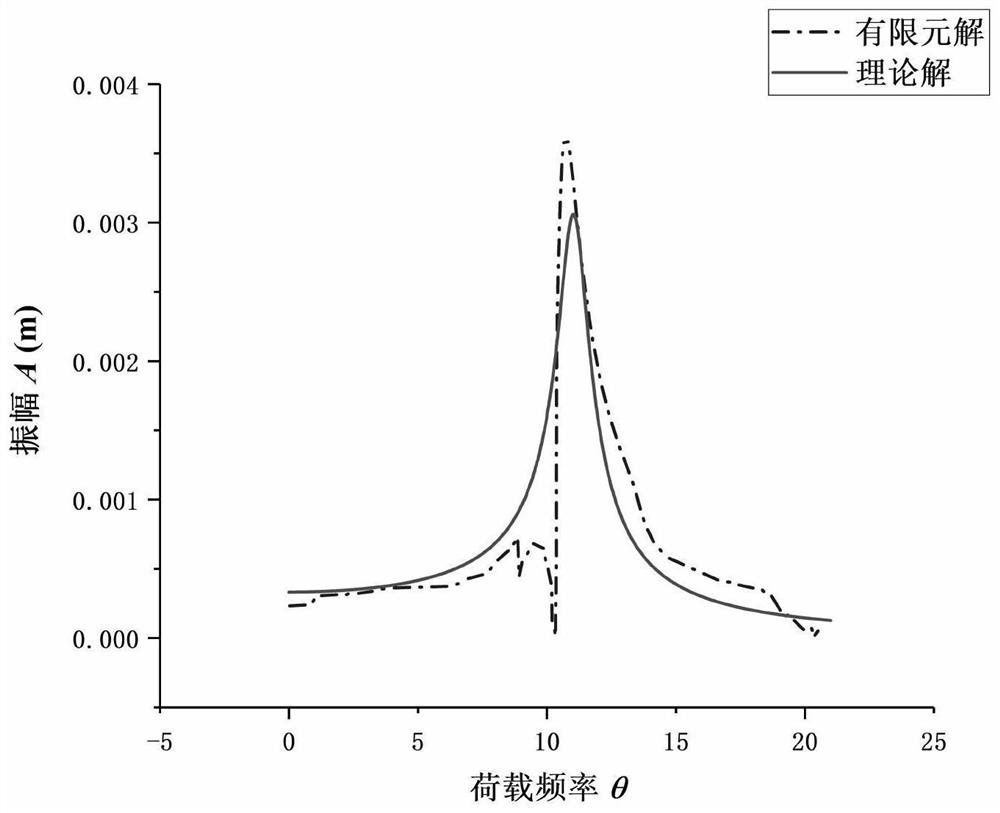
ActiveCN112287574AImprove stabilityRaise the resonance frequencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationClassical mechanicsEngineering
The invention discloses a pile foundation dynamic stability analysis and calculation method under the action of a wave load, which comprises the following steps: sorting to obtain a Mathieu equation in a non-homogeneous form, and solving to obtain a critical frequency and an unstable load of parameter resonance; verifying the correctness of theoretical derivation by comparing an analytical solution with a calculation result of finite element simulation. Calculation result analysis shows that the pile top load P0 and the pile body water entry depth have great influence on the instability load,but the instability load is also influenced by the resonance frequency; the influence of the pile side soil body resistance coefficient m on the parameter resonance frequency is maximum, the instability frequency of parameter resonance is rapidly increased along with the increase of m, the stability of the pile body can be effectively improved, and the relative influence of the pile body mass M and the soil body shearing rigidity G on the instability frequency of the pile body is small and cannot be ignored; influences of factors such as pile diameter, wavelength and wave height on amplitude are different and can be adjusted according to specific engineering practice, so that the stability of a pile body is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Wideband floating wire antenna using a double negative meta-material
InactiveUS7429957B1Improve performanceAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSubaqueous/subterranean adaptionWave structureDouble negative
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com