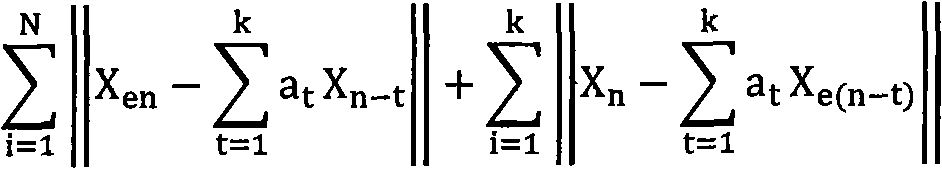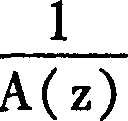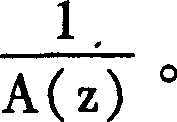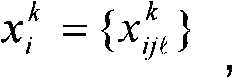Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Linear prediction coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Linear predictive coding (LPC) is a widely used technique in audio signal processing, especially in speech signal processing. It has found particular use in voice signal compression, allowing for very high compression rates.
Multi-mode audio signal decoder, multi-mode audio signal encoder, methods and computer program using a linear-prediction-coding based noise shaping
ActiveUS20120245947A1Without inacceptable artifactEasy transitionSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingFrequency spectrum
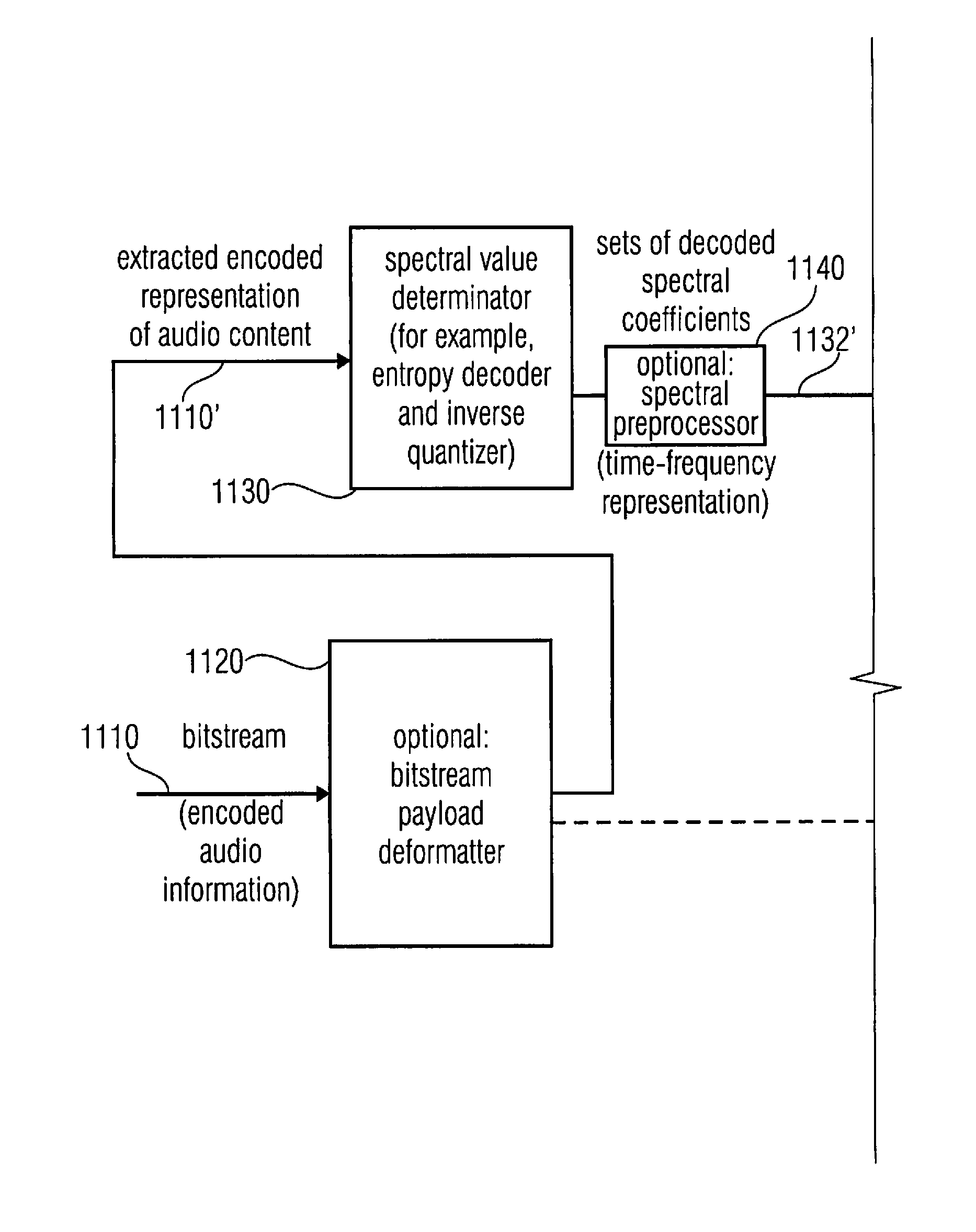
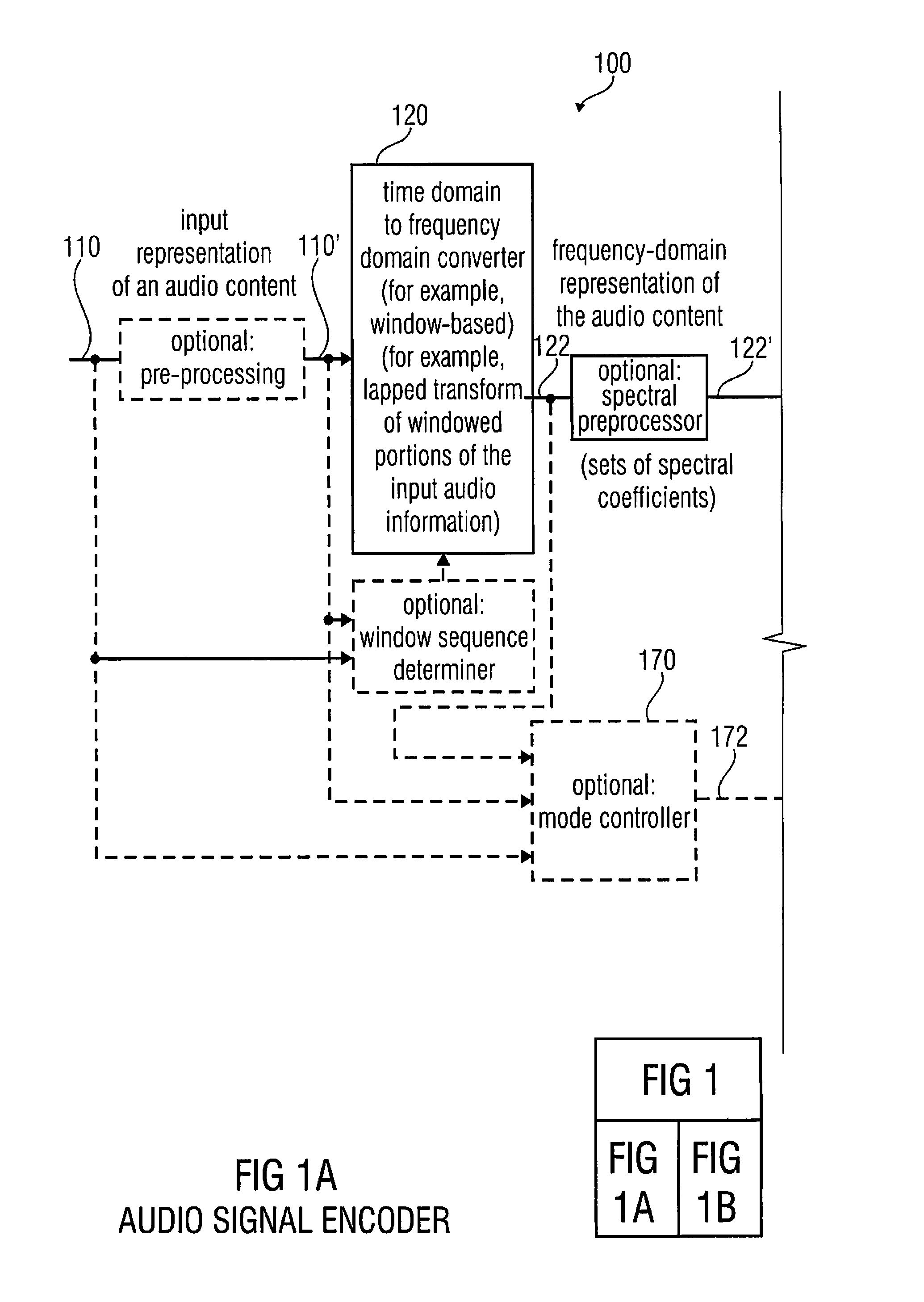
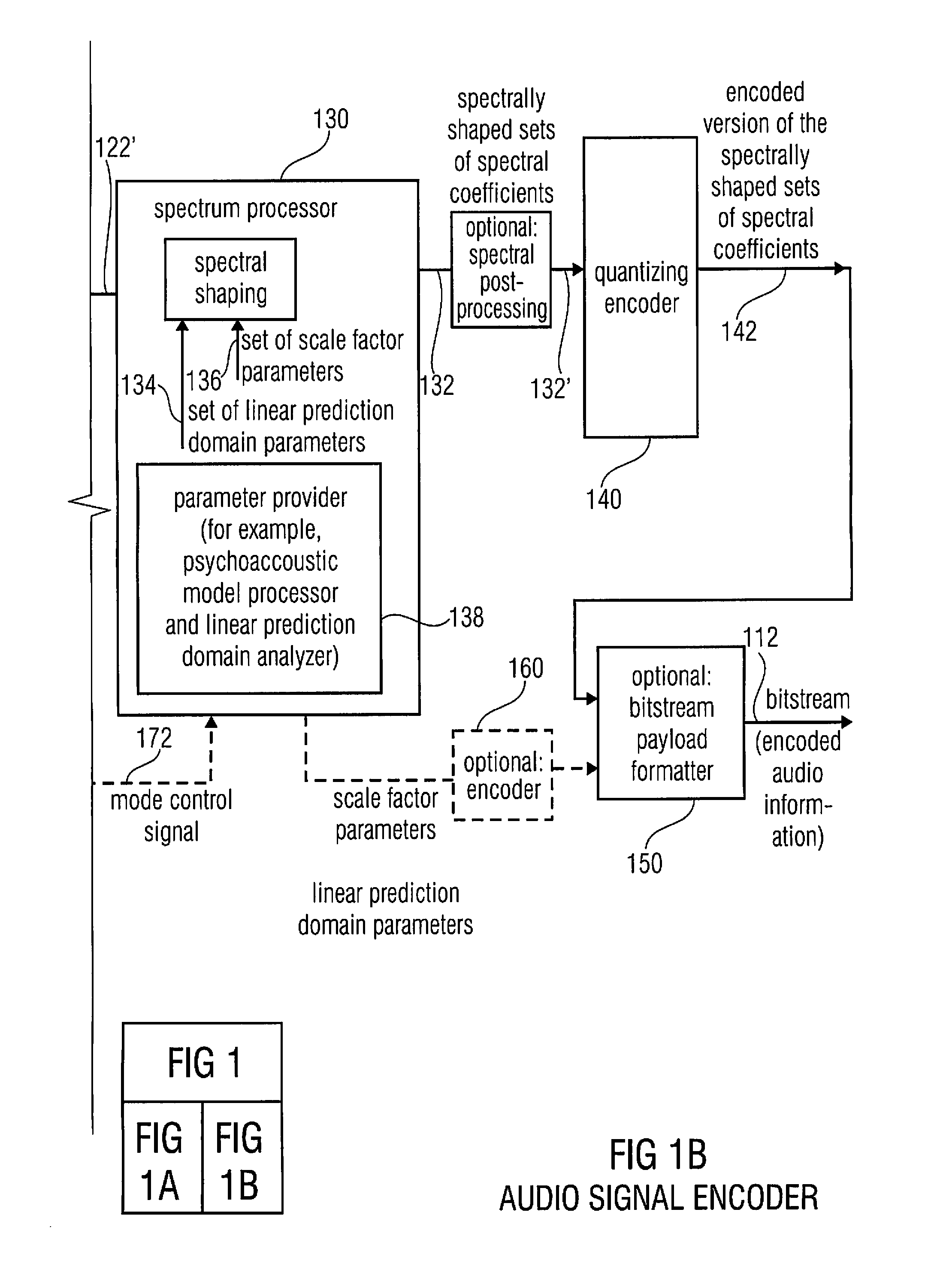
A multi-mode audio signal decoder has a spectral value determinator to obtain sets of decoded spectral coefficients for a plurality of portions of an audio content and a spectrum processor configured to apply a spectral shaping to a set of spectral coefficients in dependence on a set of linear-prediction-domain parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a linear-prediction mode, and in dependence on a set of scale factor parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a frequency-domain mode. The audio signal decoder has a frequency-domain-to-time-domain converter configured to obtain a time-domain audio representation on the basis of a spectrally-shaped set of decoded spectral coefficients for a portion of the audio content encoded in the linear-prediction mode and for a portion of the audio content encoded in the frequency domain mode. An audio signal encoder is also described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding audio signals
InactiveUS20090192789A1Big lossEfficient encoding/decodingSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingLinearity
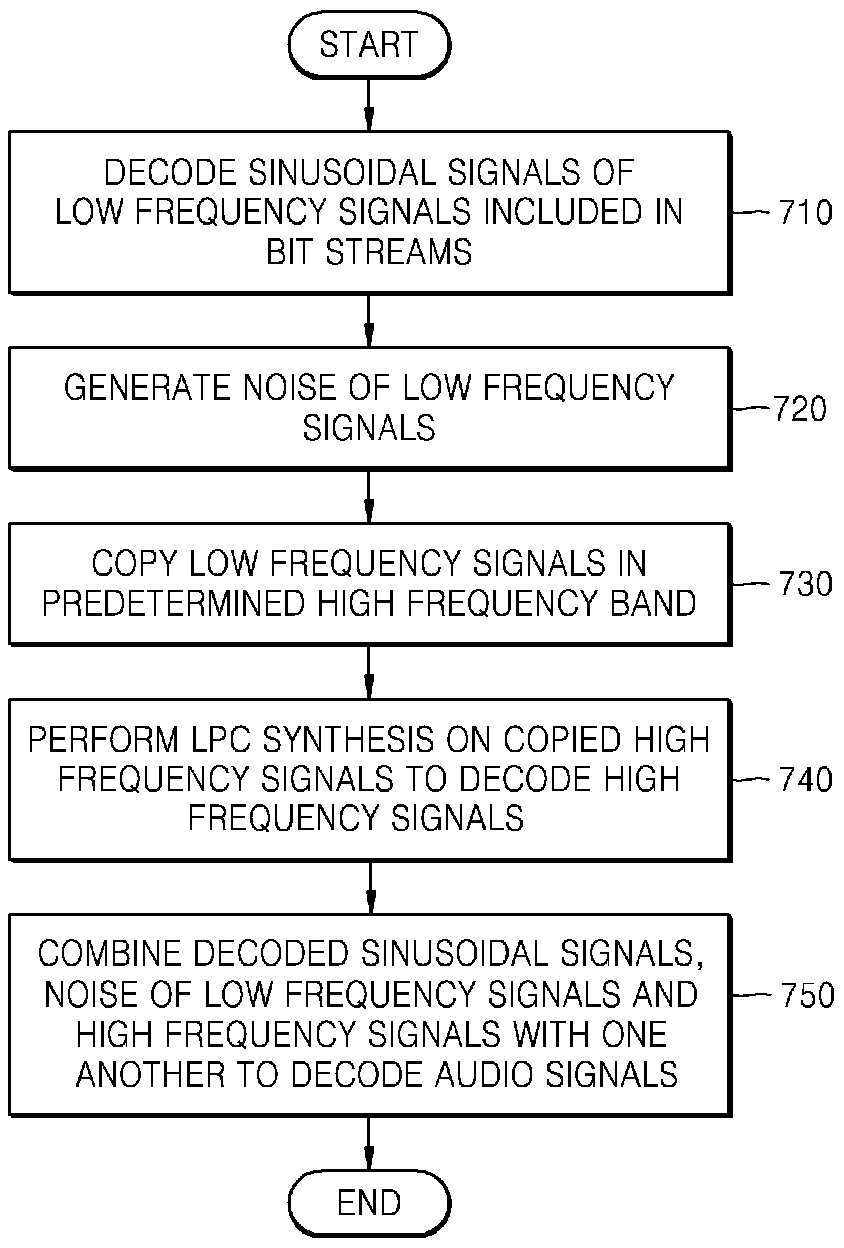
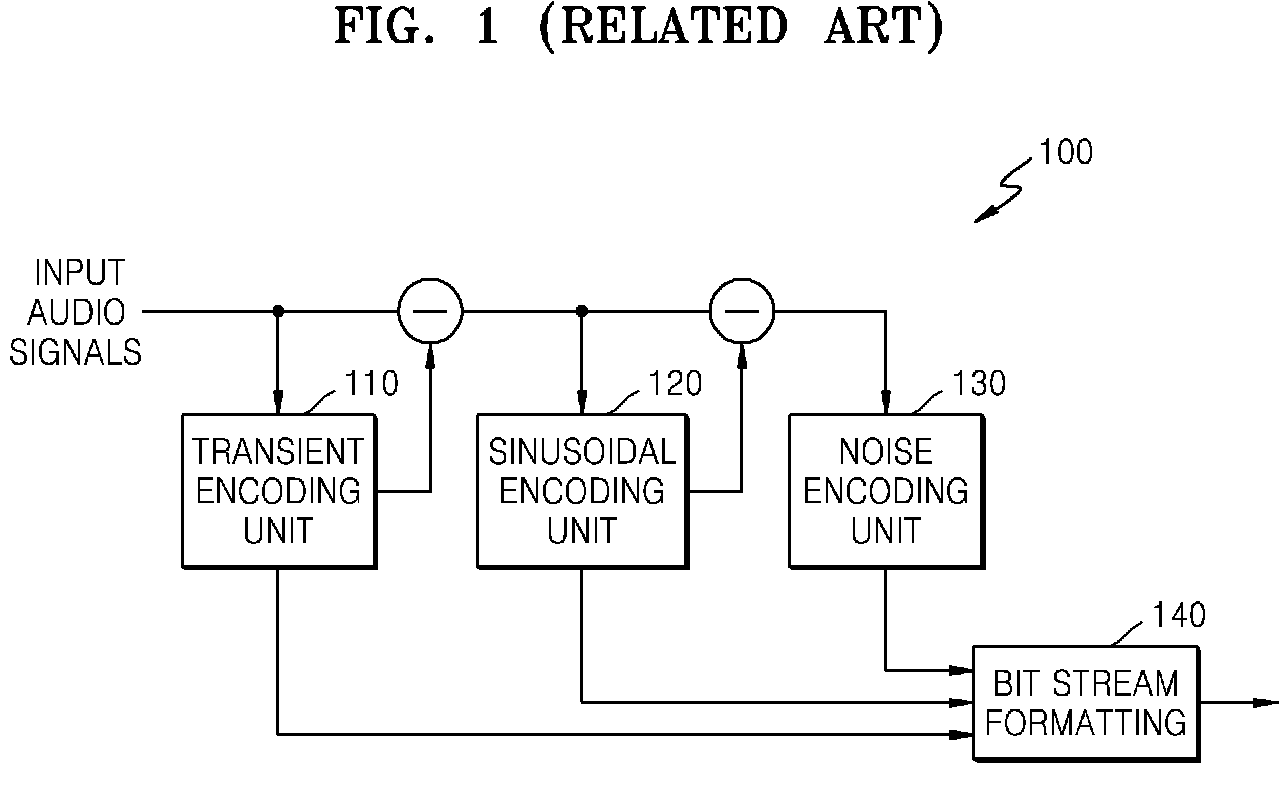
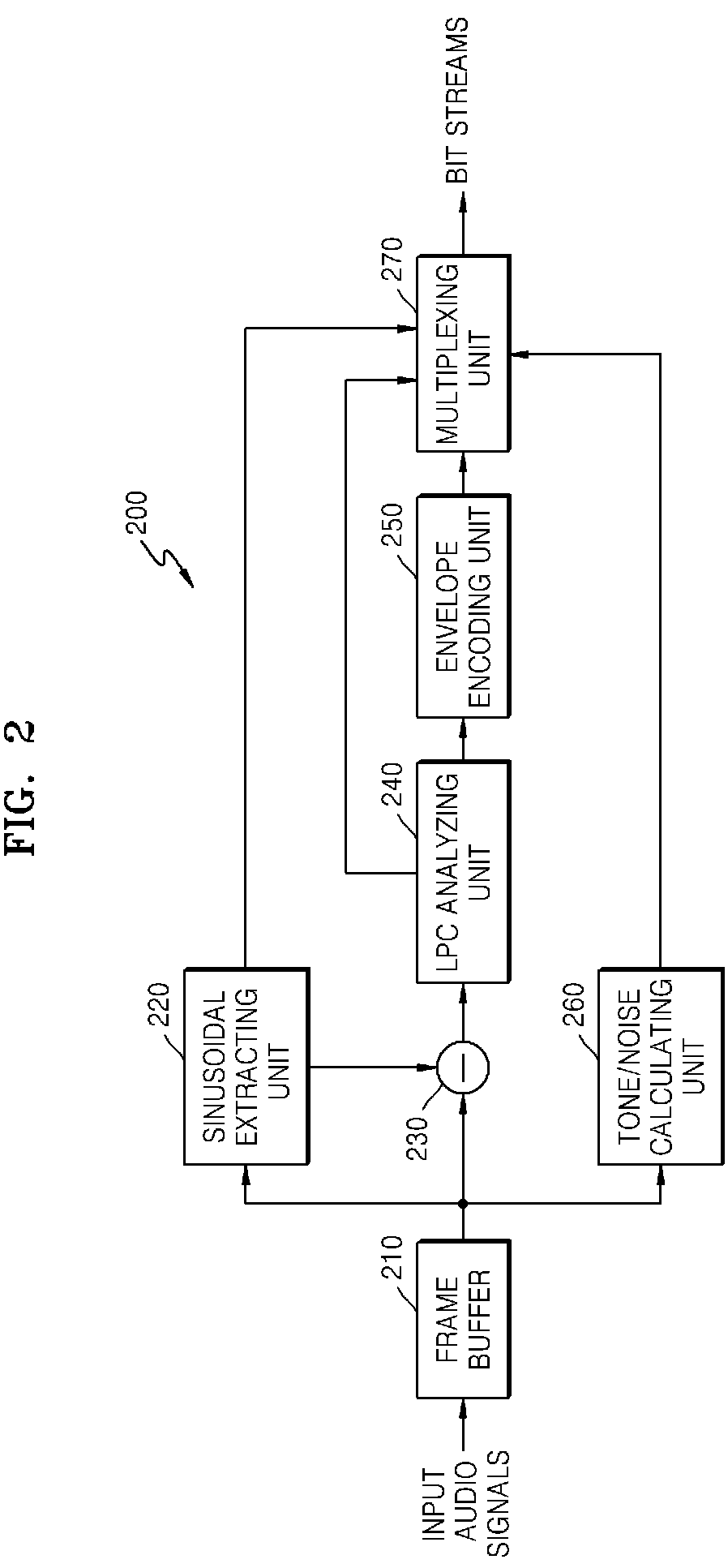
Provided are a method and apparatus for effectively encoding / decoding remaining difference signals excluding sinusoidal components, from input audio signals. In the method and apparatus for encoding audio signals, sinusoidal analysis is performed on low frequency signals of less than a predetermined critical frequency in order to extract sinusoidal signals and then, an encoding operation is performed on the remaining difference signals excluding the sinusoidal signals, from input audio signals, by using linear prediction coding (LPC) analysis.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
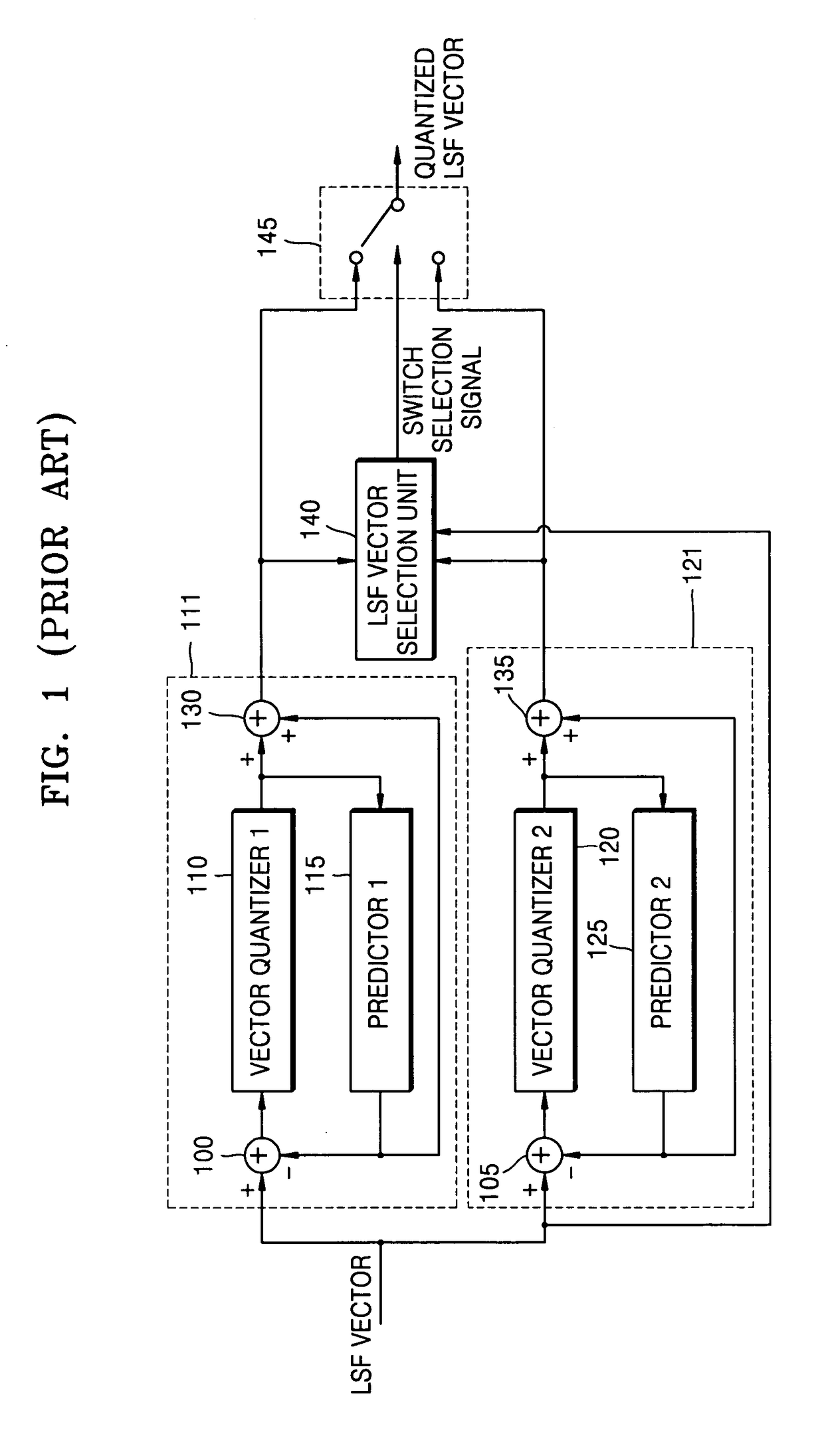
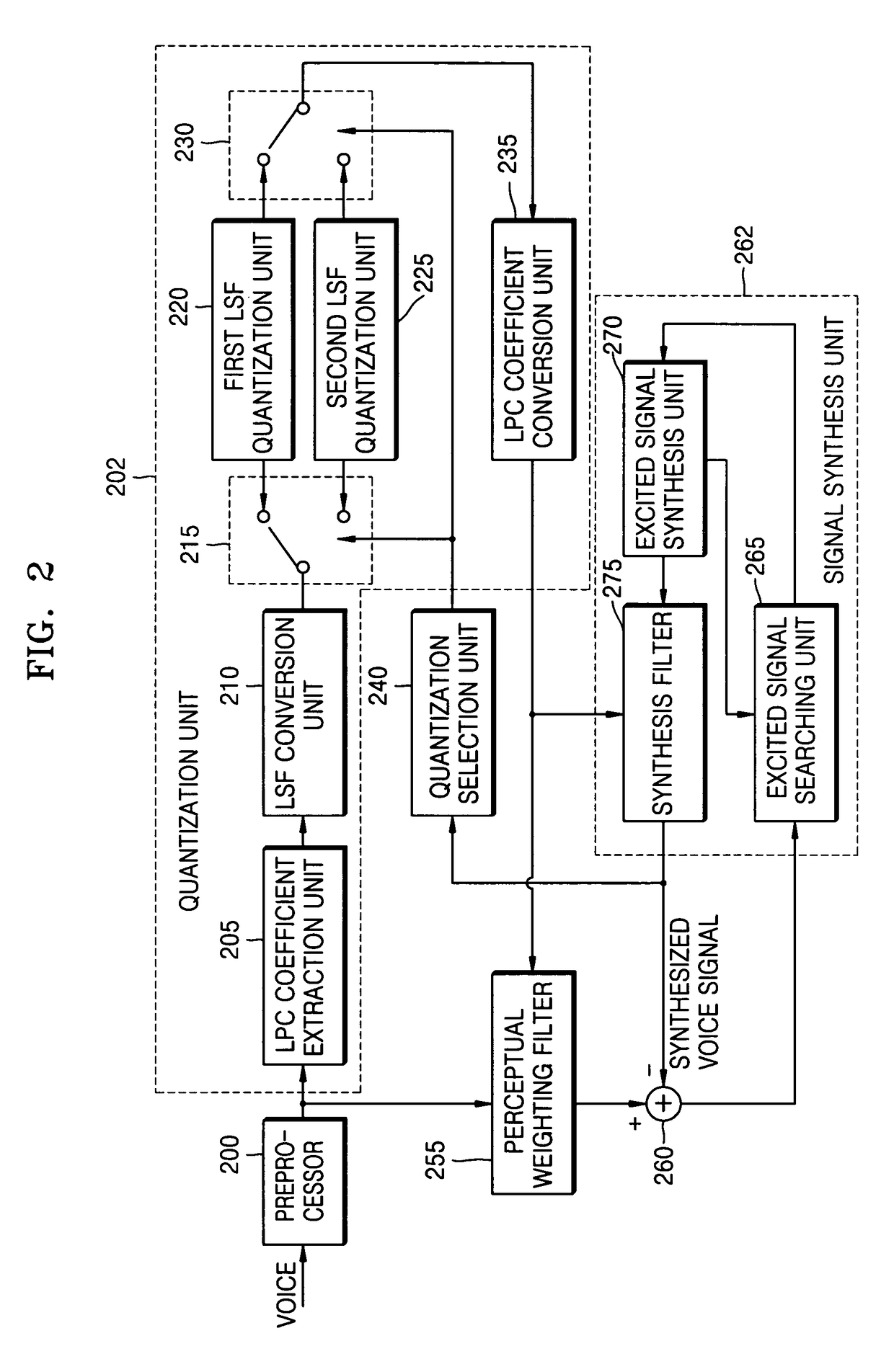
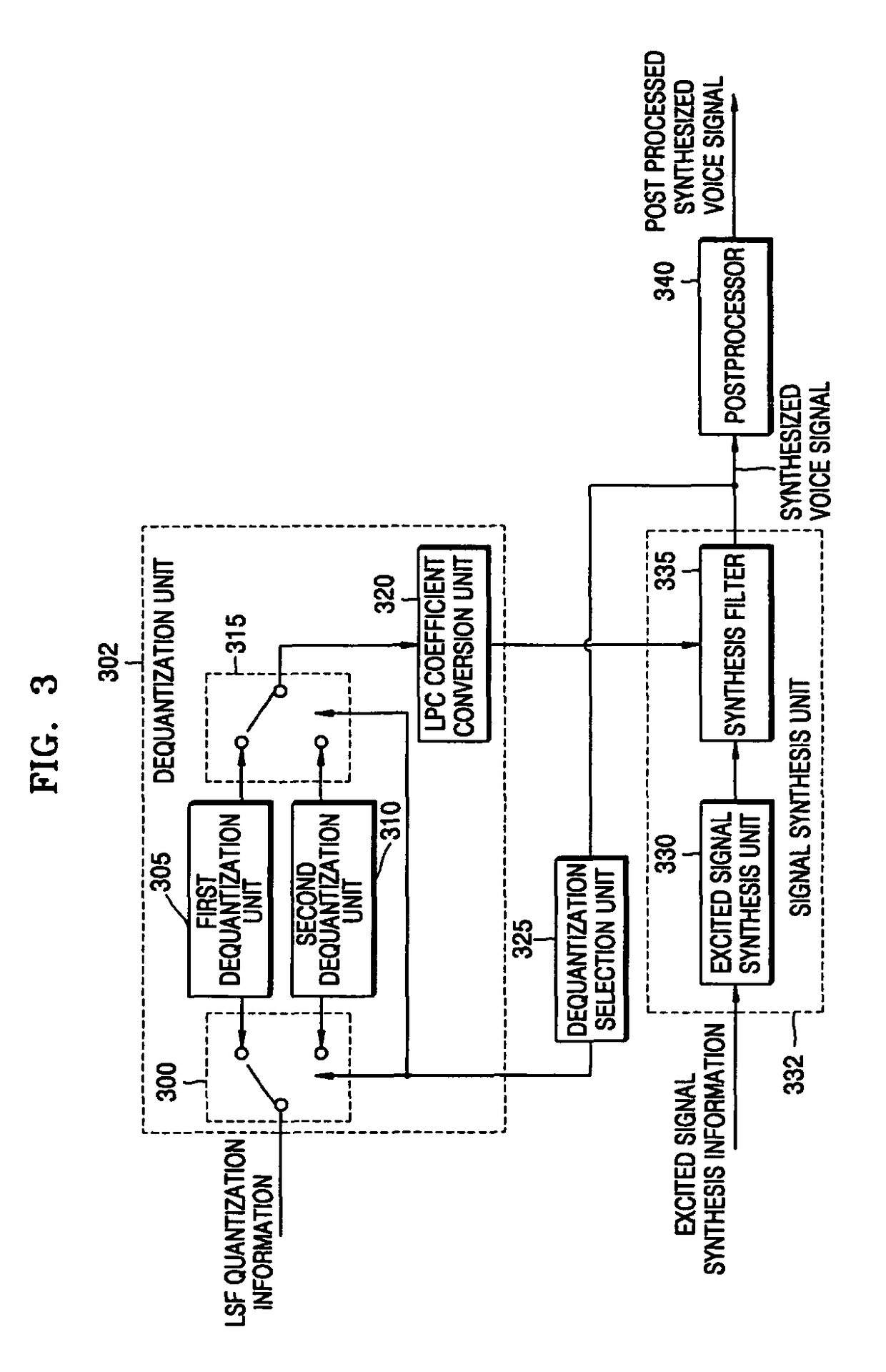
Apparatus and method of encoding/decoding voice for selecting quantization/dequantization using characteristics of synthesized voice
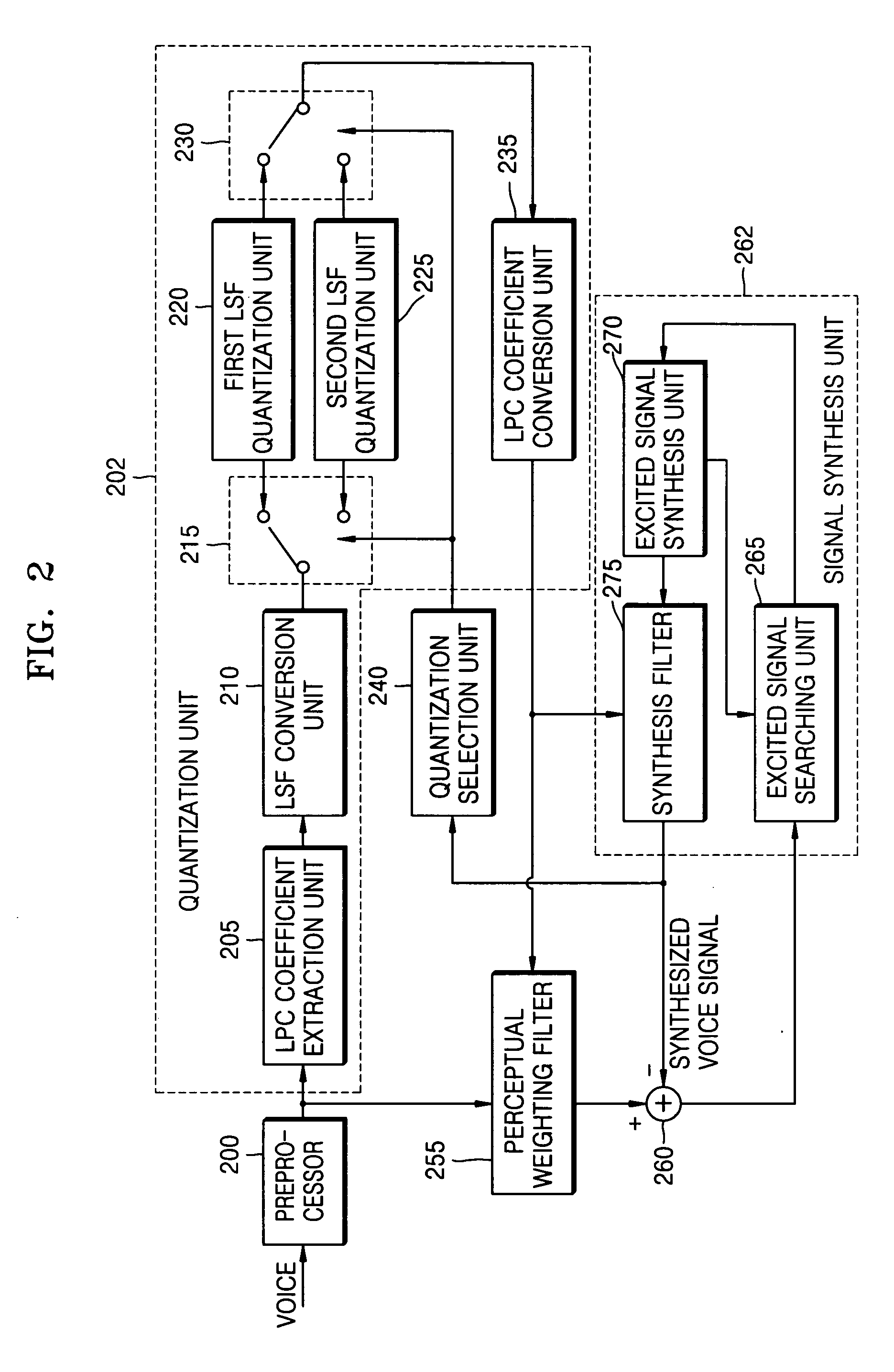
InactiveUS20060074643A1Modulated-carrier systemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDecoding methodsLinear prediction coding
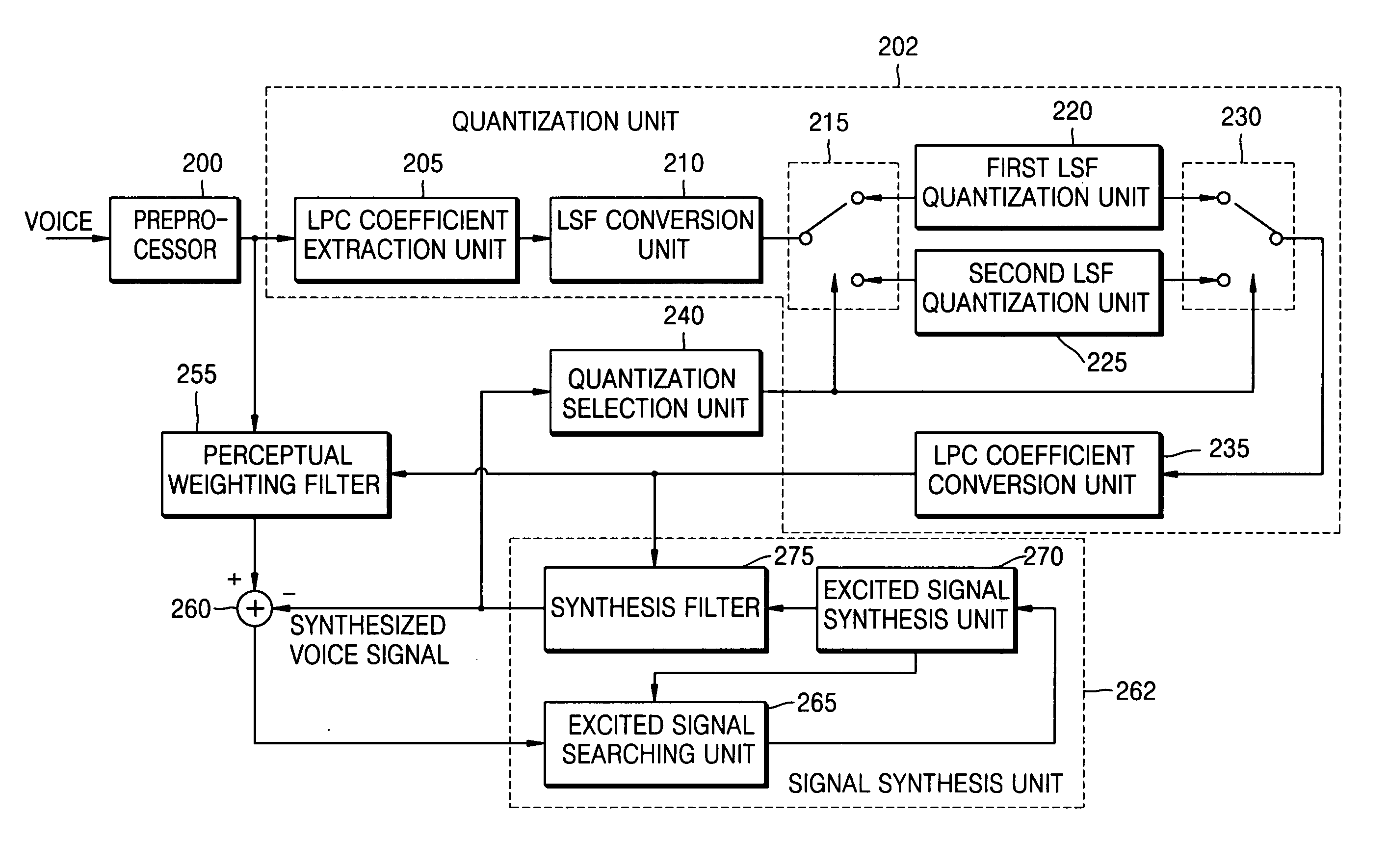
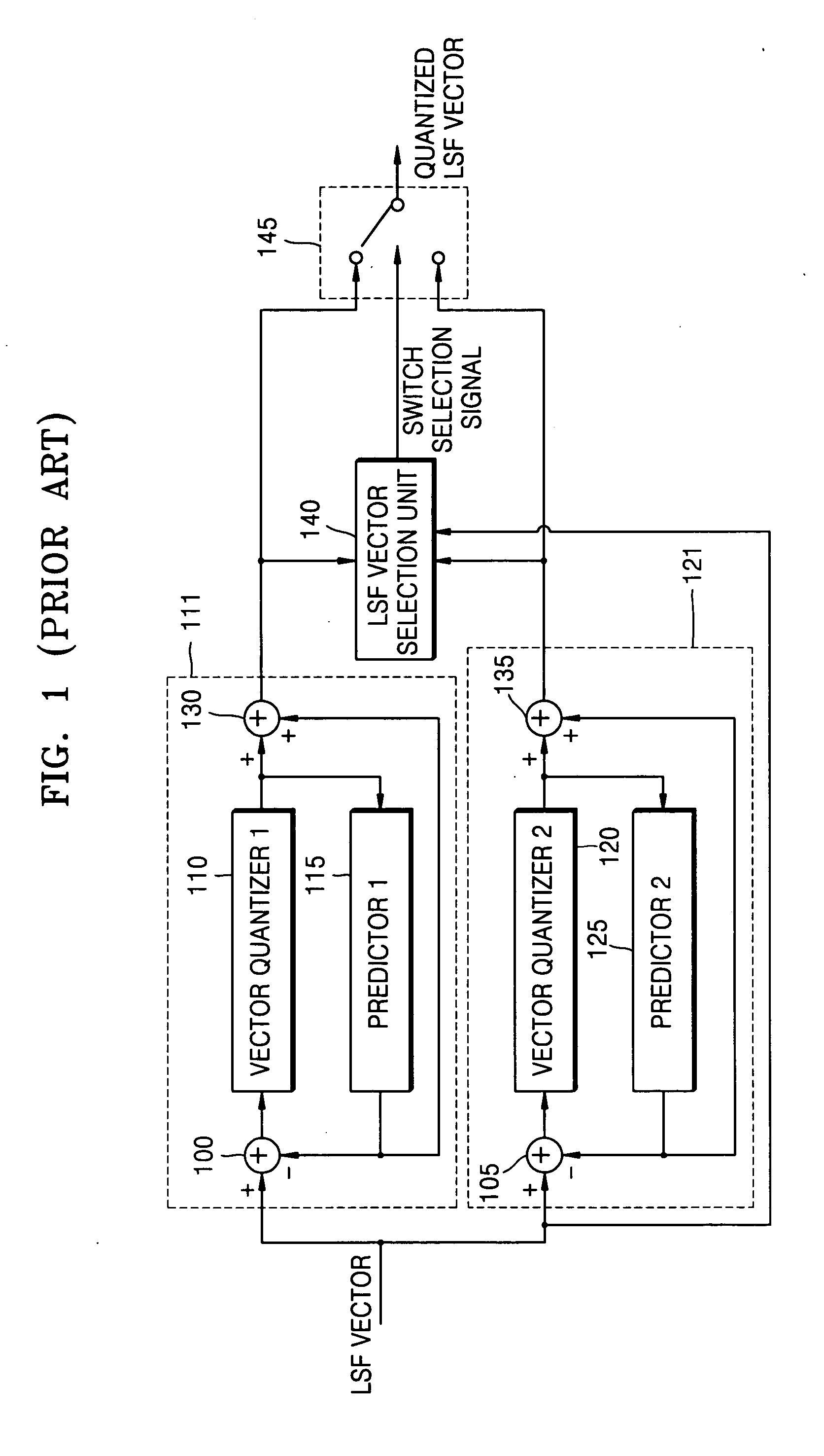
A voice encoding / decoding method and apparatus. A voice encoder includes: a quantization selection unit generating a quantization selection signal; and a quantization unit extracting a linear prediction coding (LPC) coefficient from an input signal, converting the extracted LPC coefficient into a line spectral frequency (LSF), quantizing the LSF with a first LSF quantization unit or a second LSF quantization unit based on the quantization selection signal, and converting the quantized LSF into a quantized LPC coefficient. The the quantization selection signal selects the first LSF quantization unit or second LSF quantization unit based on characteristics of a synthesized voice signal in previous frames of the input signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Bit rate scalable speech coding and decoding apparatus and method
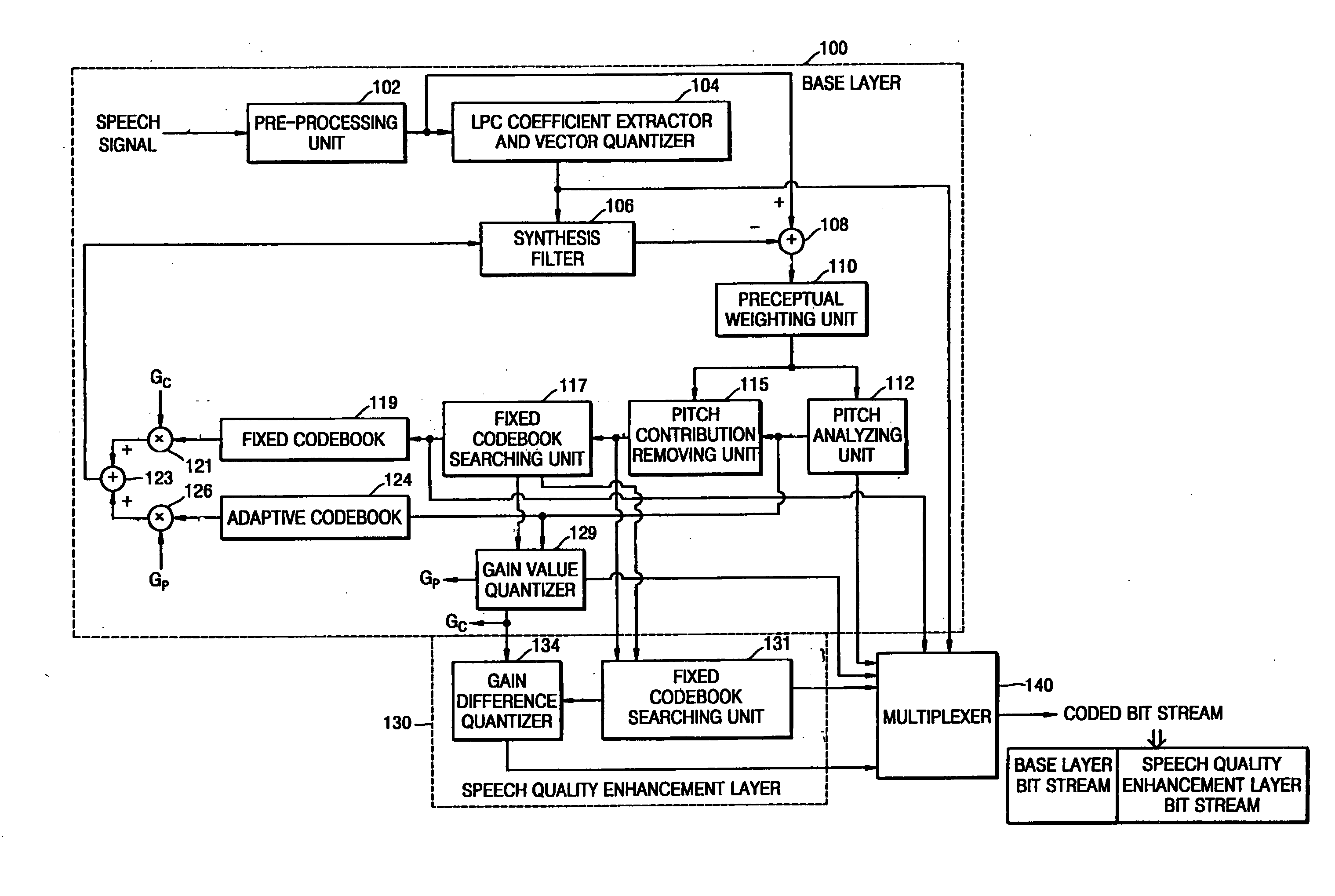
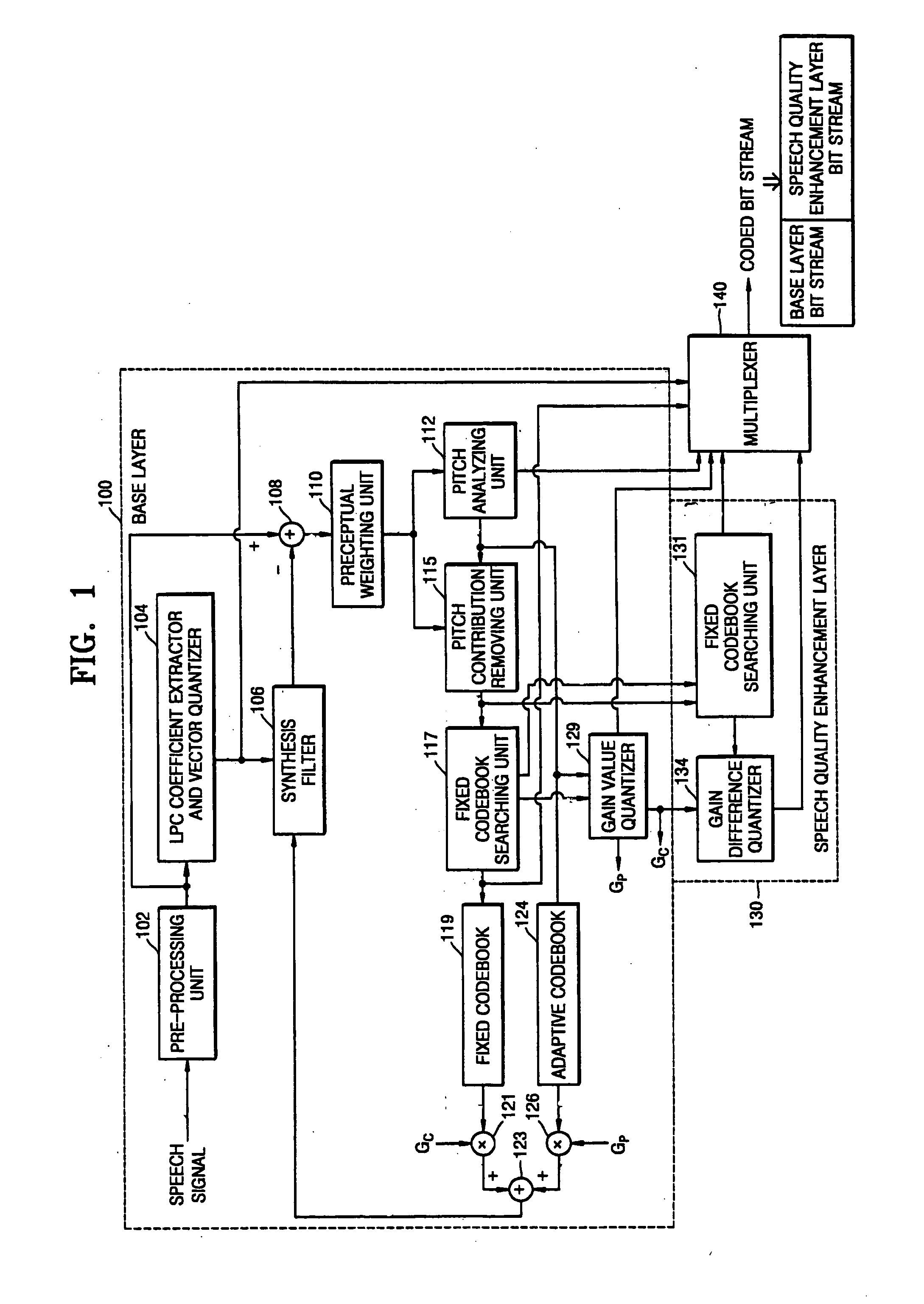
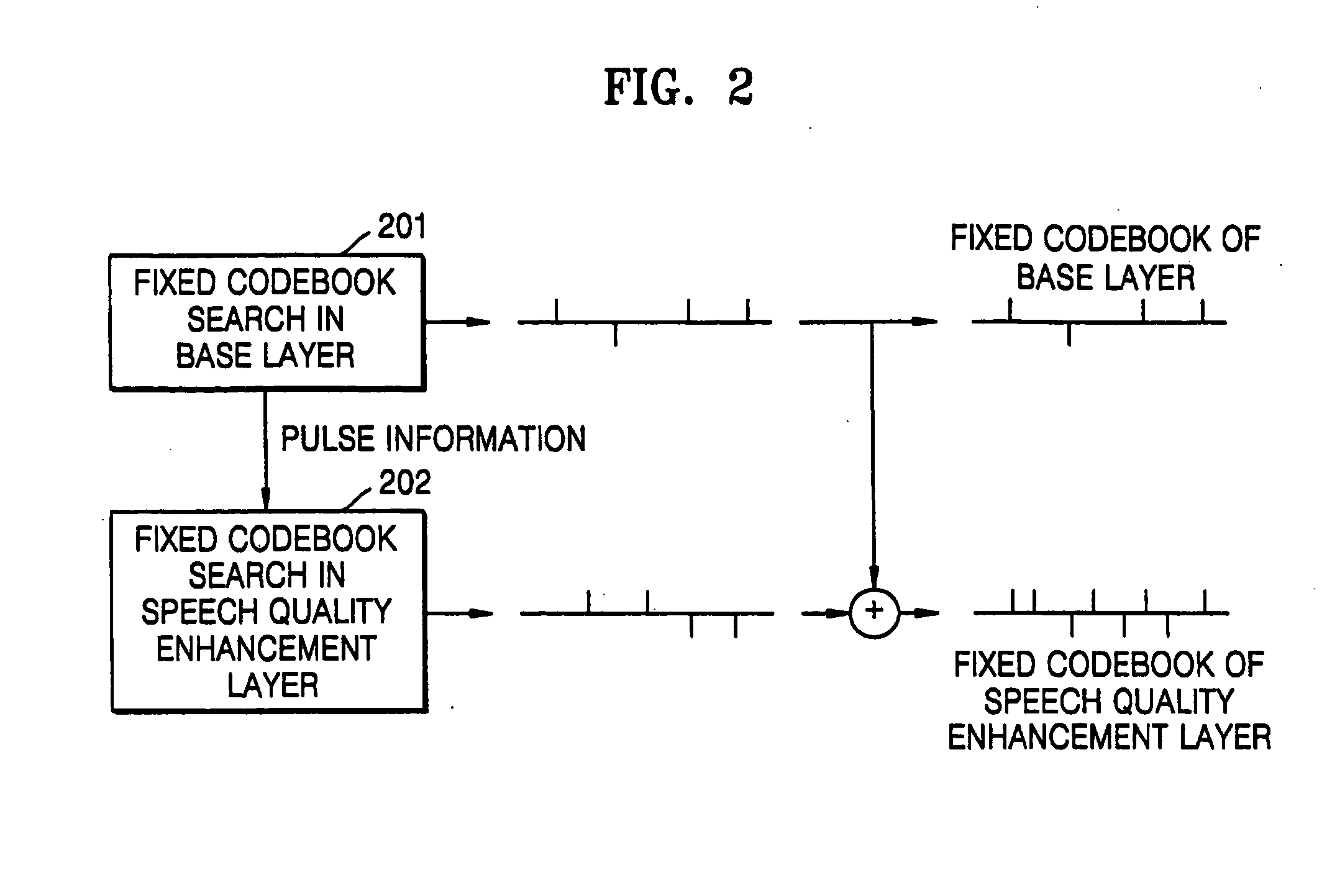
InactiveUS20050010404A1Reduce in quantitySpeech analysisCode conversionLinear prediction codingTarget signal
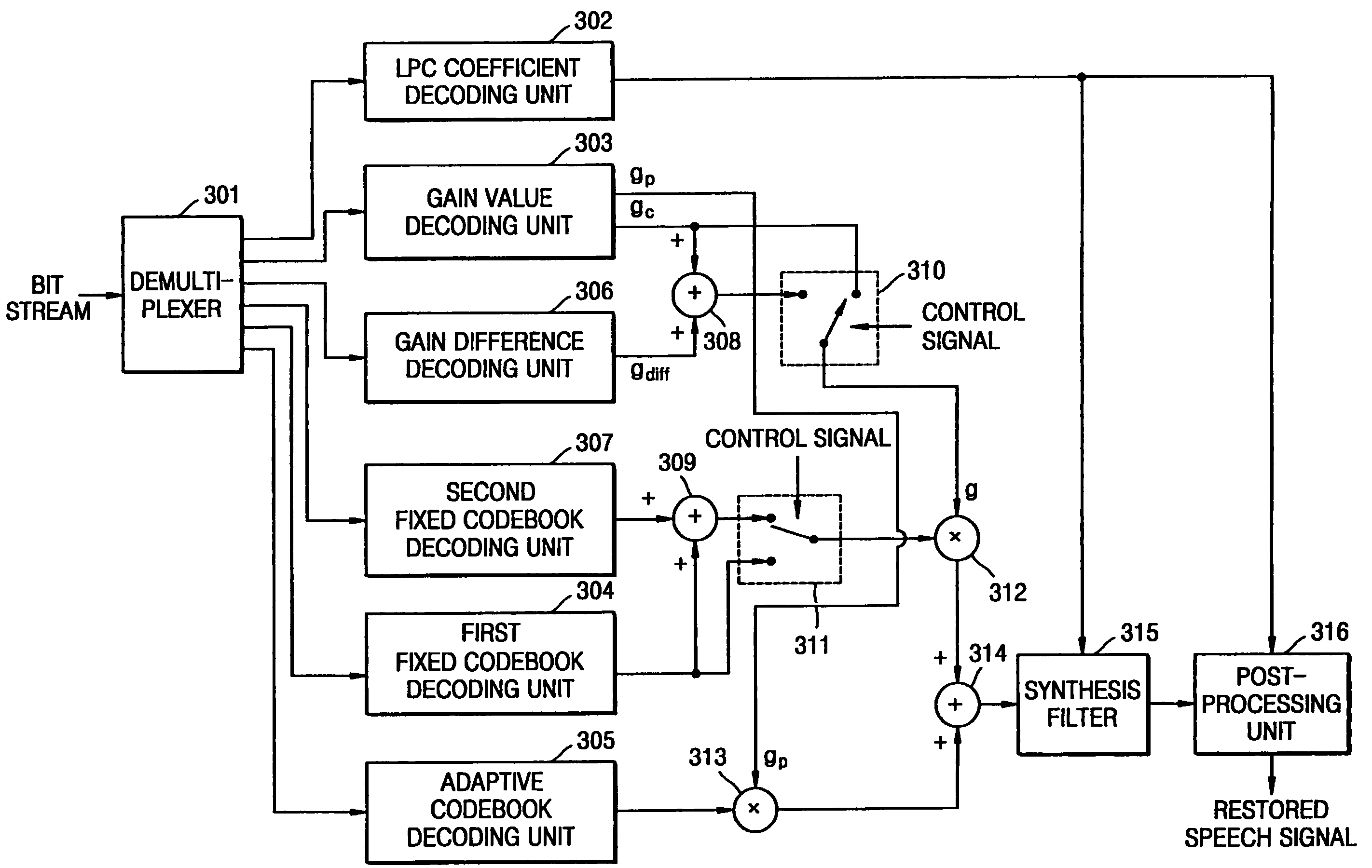
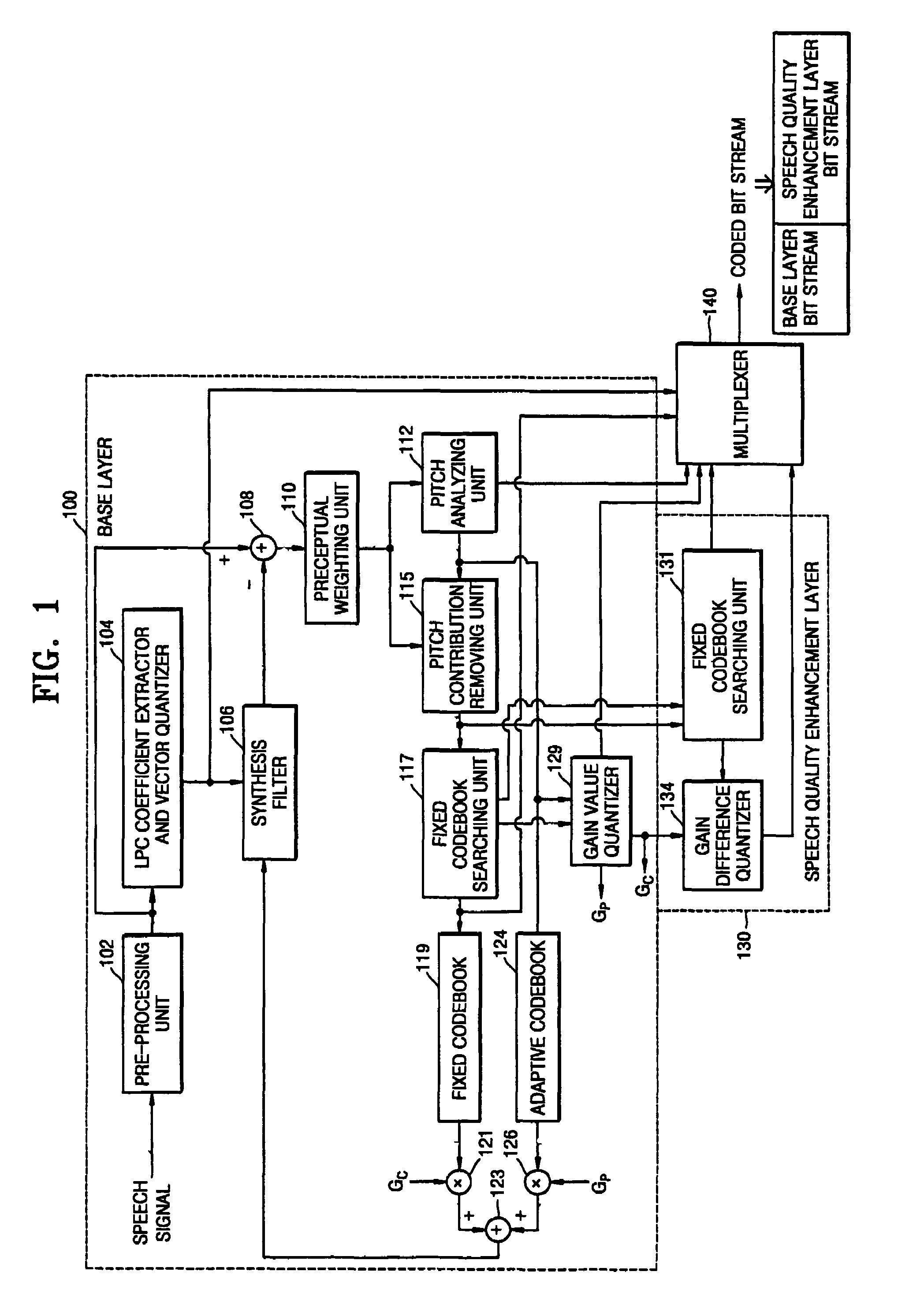
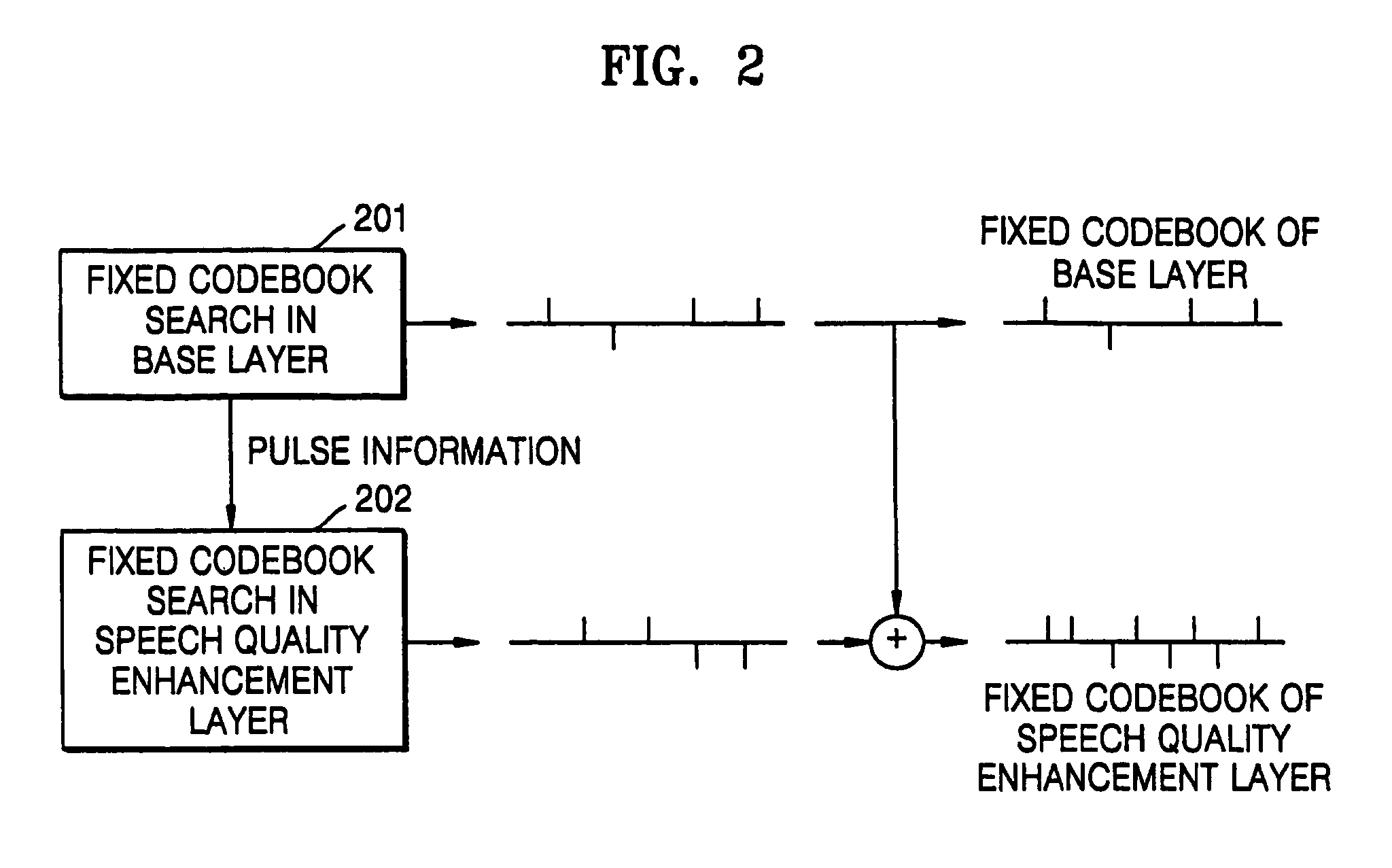
A coding apparatus including a base layer, a speech quality enhancement layer, and a multiplexer. The base layer filters an input speech signal using linear prediction coding and generates an excitation signal corresponding to the filtered speech signal through a fixed codebook search and an adaptive codebook search. The speech quality enhancement layer searches a fixed codebook using parameters obtained through the fixed codebook search in the base layer, or searches the fixed codebook using a target signal, which is obtained by removing a contribution of a fixed codebook of the base layer and a signal which is obtained by synthesizing and filtering a previous fixed codebook of the speech quality enhancement layer from a target signal for the fixed codebook search of the base layer. The multiplexer multiplexes signals generated by the base layer and the at least one speech quality enhancement layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
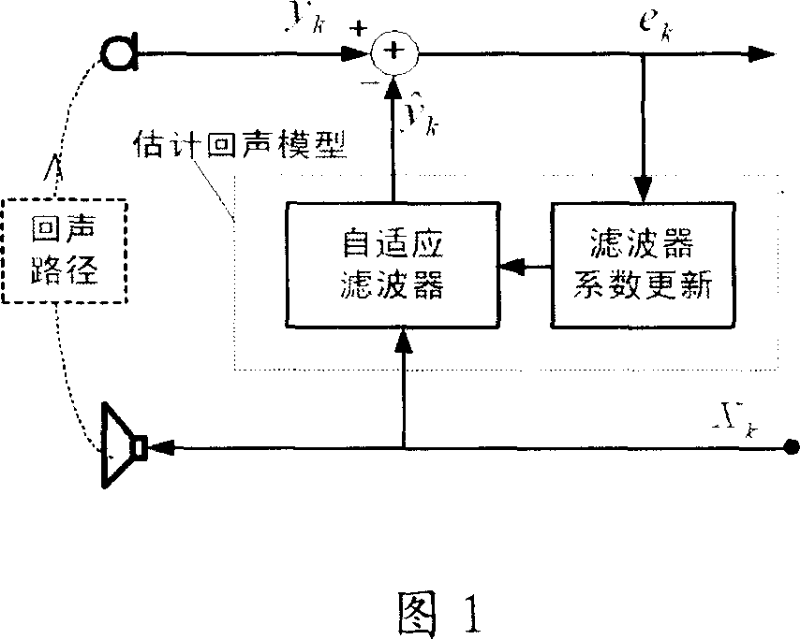
Echo eliminator and echo cancellation method
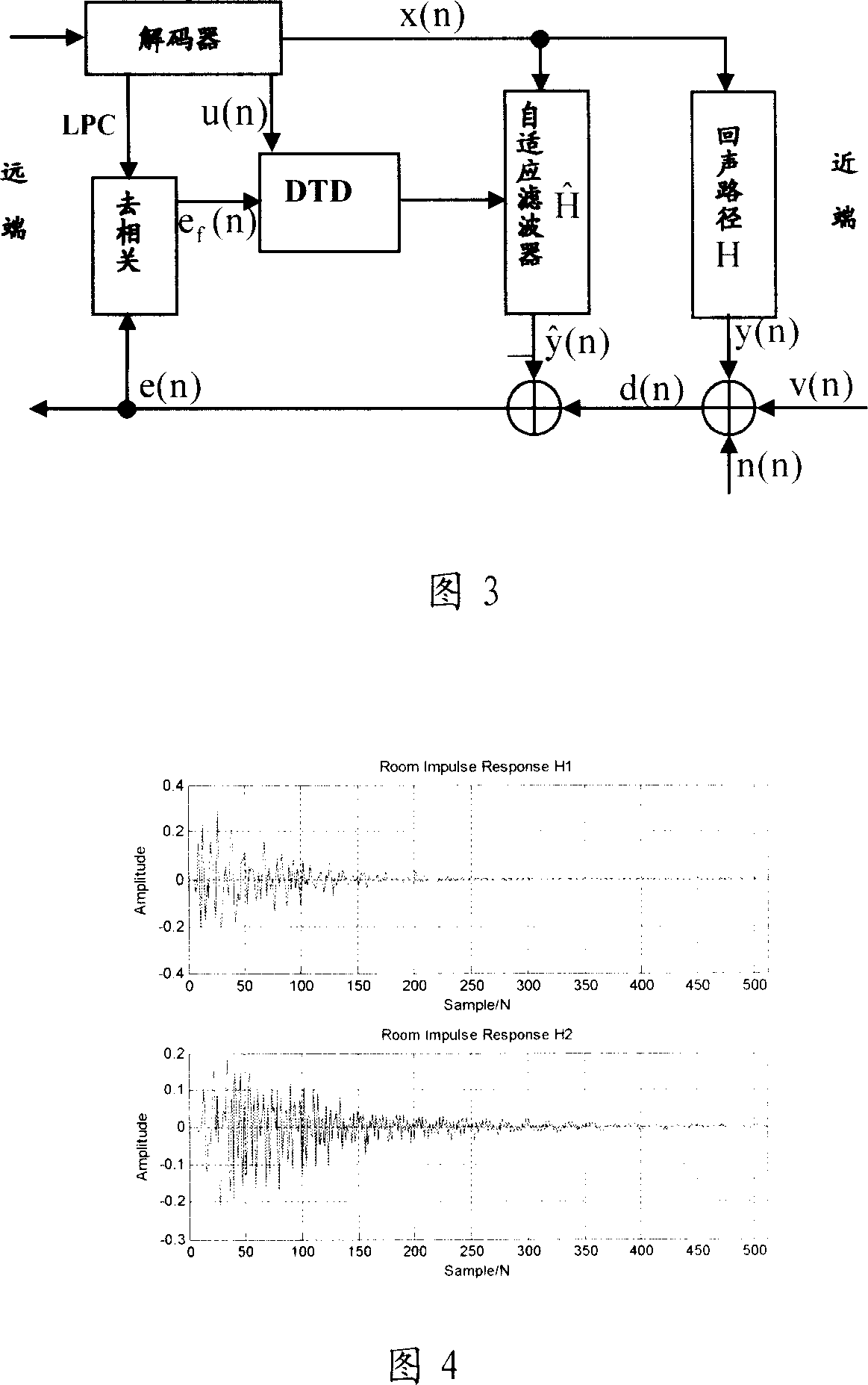
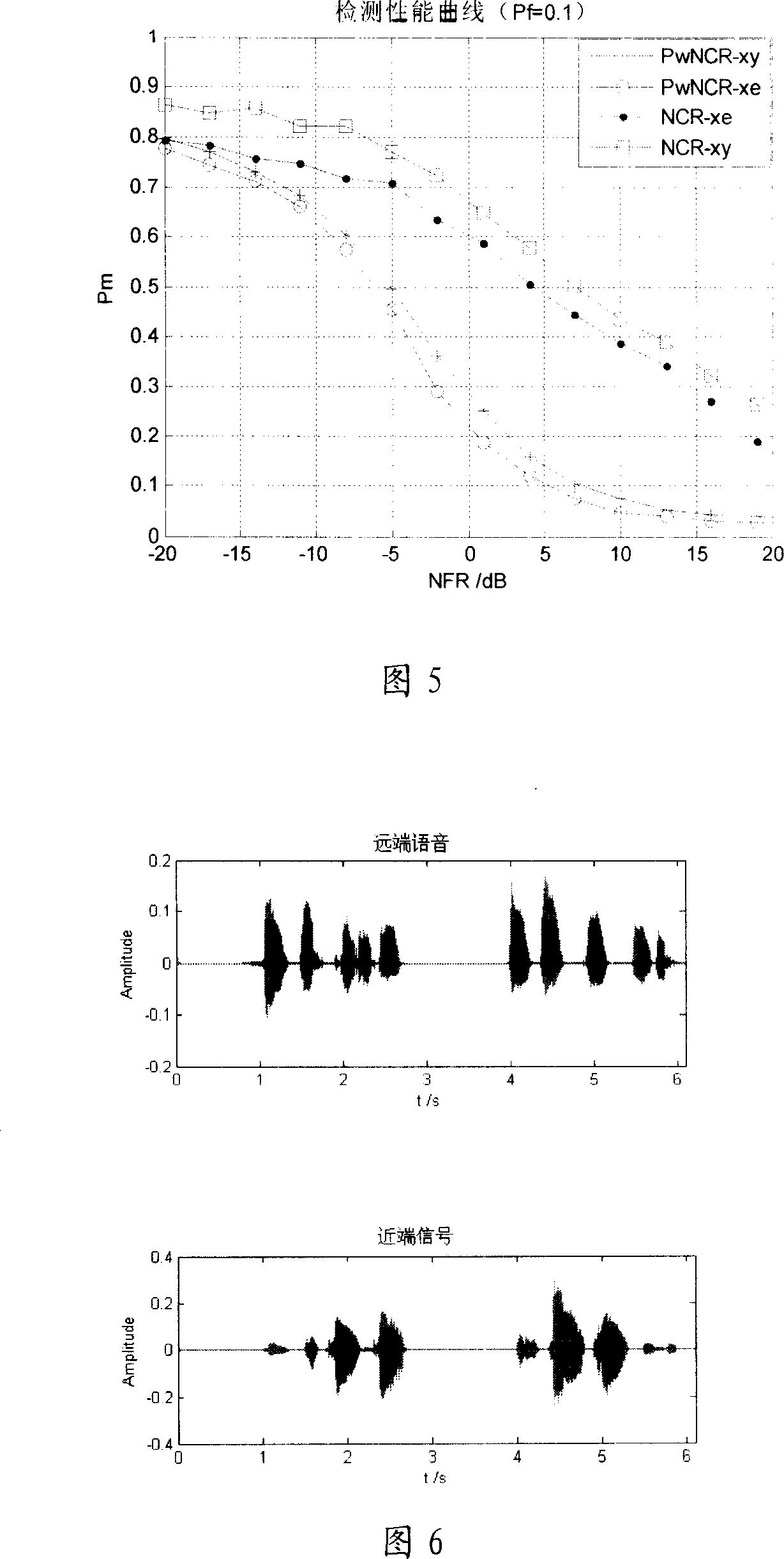
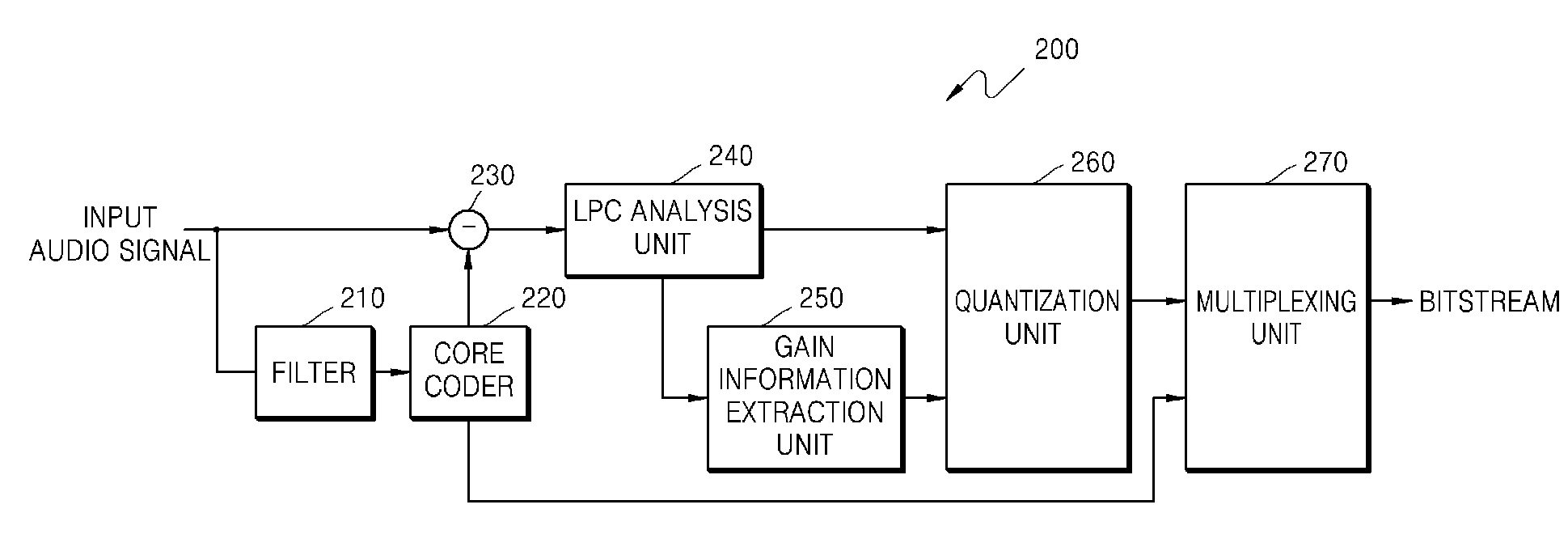
InactiveCN101043560ASmall amount of calculationFast convergenceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingData stream
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
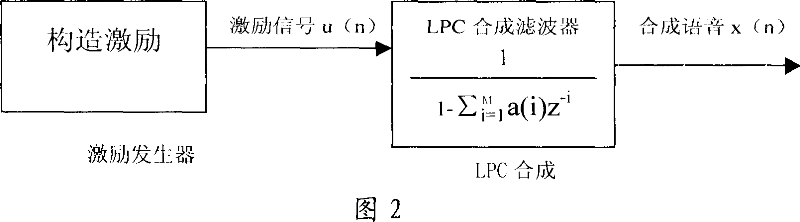
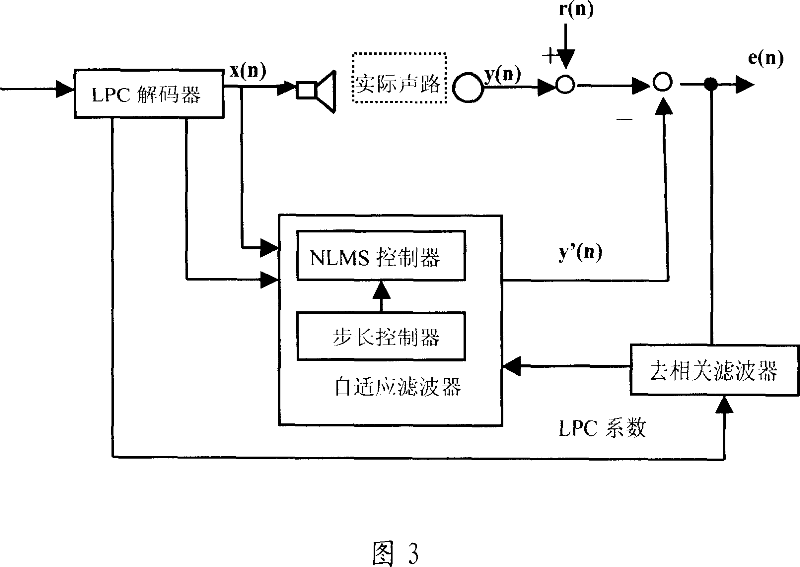
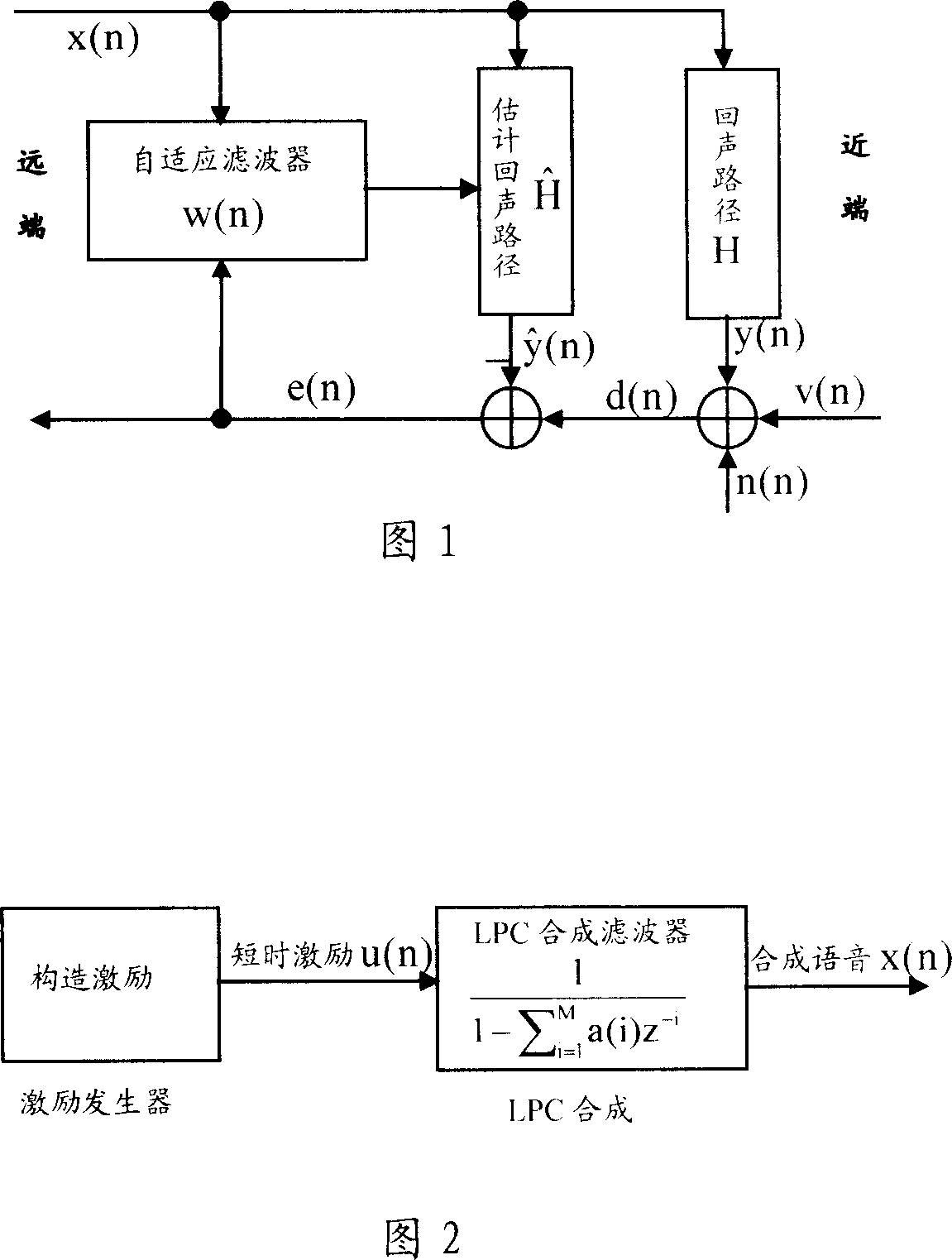
Method for eliminating echo in echo eliminator and its dual end communication detection system
InactiveCN101106405AReduce computational complexityEcho effect reductionLine-transmissionAdaptive filterLinear prediction coding
The invention relates to an echo canceller, an echo cancellation method and the double-end talking detection system thereof, wherein, the echo canceller decodes a data stream from the network end into a far-end voice signal and extracts a short-time excitation signal as well as a linear prediction coding coefficient by utilizing a linear prediction decoder. Based on the linear prediction coding coefficient, the echo canceller carries out a decorrelation process to a residual signal by a decorrelation filter, and executes a normalized cross correlation process to the short-time excitation signal and the decorrelation residual signal by utilizing the double-end talking detector to generate the normalized cross correlation detection variable, hence, the echo canceller detects the existence of the double-end talking and then further controls the renewal of the self-adaptive filter. The invention is capable of detecting the existence of the double-end talking by the decorrelation process as well as the normalized cross correlation process to the far-end voice signal and the residual signal, thus obviously decreasing the calculation complexity of the double-end talking detection and the storage space consumption.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
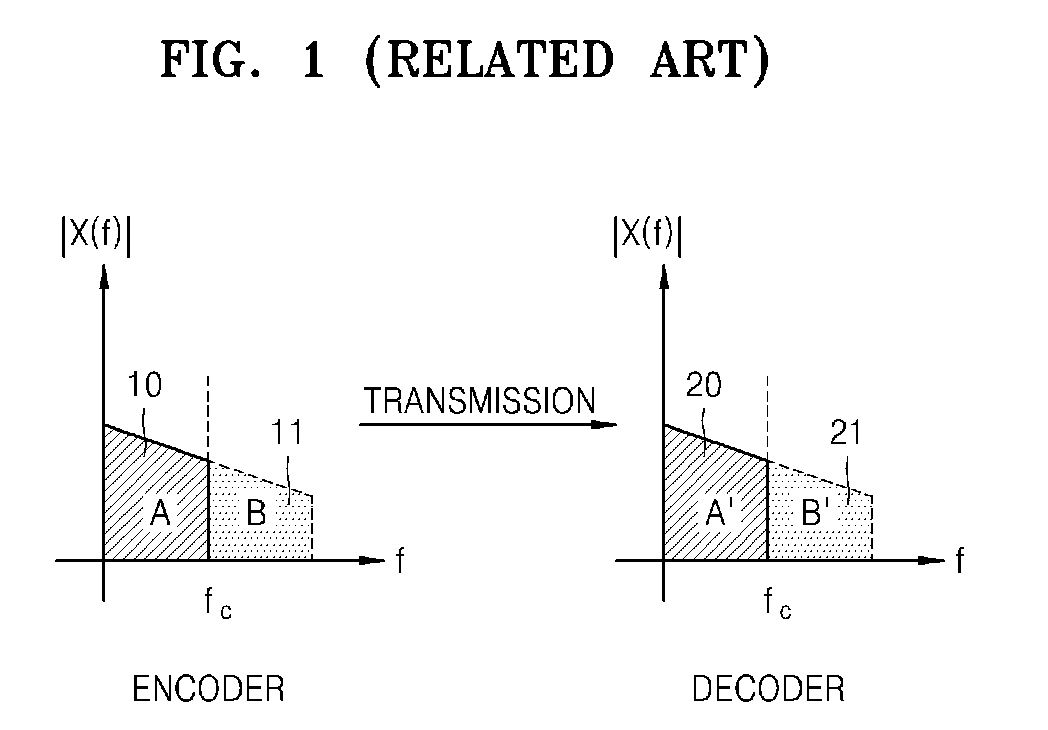
Methods and apparatuses for encoding and decoding audio signal
InactiveUS20090192792A1Efficient decodingEfficient encodingSpeech recognitionLinear prediction codingSound quality
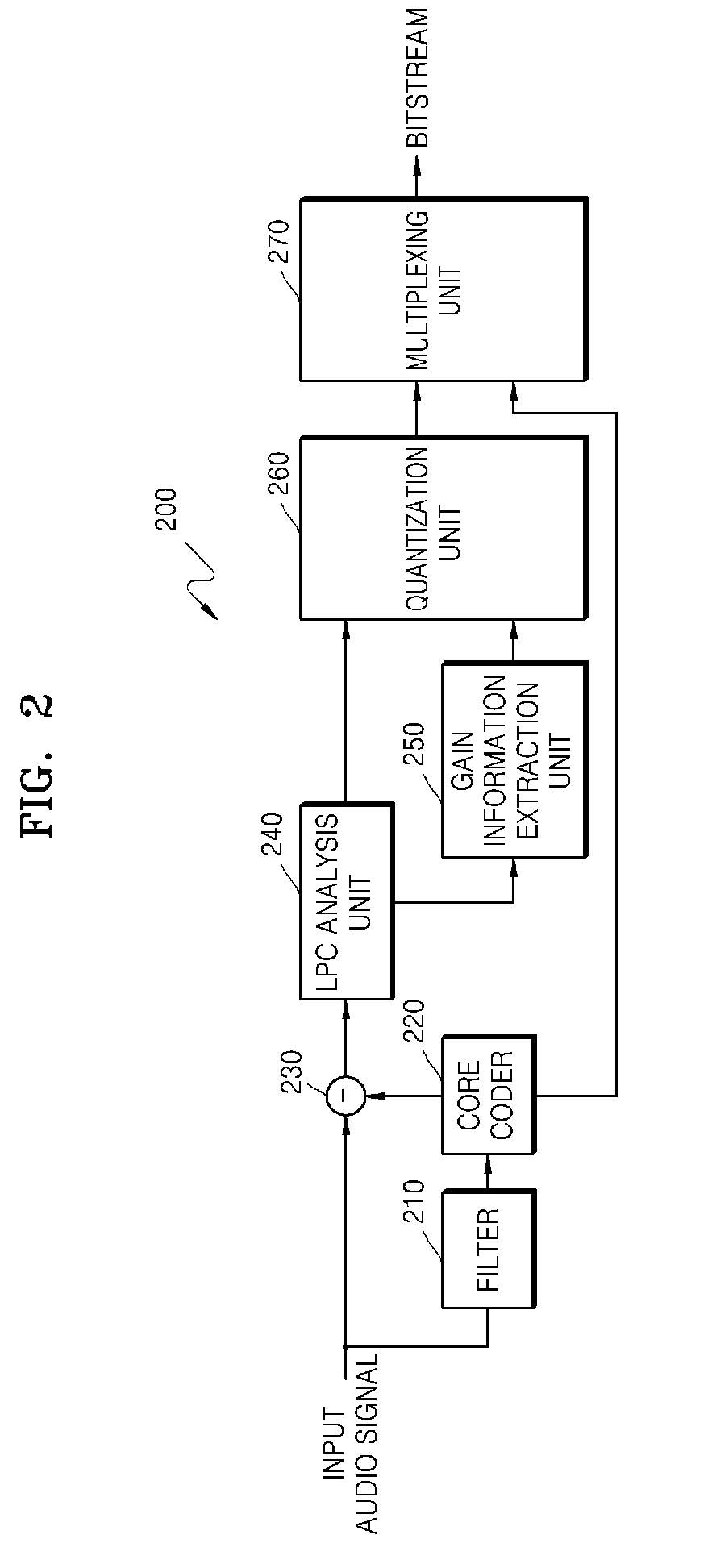
Provided are methods and apparatuses for more efficiently encoding and decoding a high frequency band signal which is from an audio signal and which is greater than a predetermined threshold frequency. The method and apparatus for encoding the audio signal encodes a linear prediction coding (LPC) coefficient and gain information of a residual signal, which are generated by performing LPC analysis, thereby encoding a high frequency signal so as to have enhanced sound quality, while using less bits.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and an apparatus for processing a signal
ActiveUS20100070272A1Improve efficiencySpeech analysisTime-division multiplexLinear prediction codingFrequency spectrum
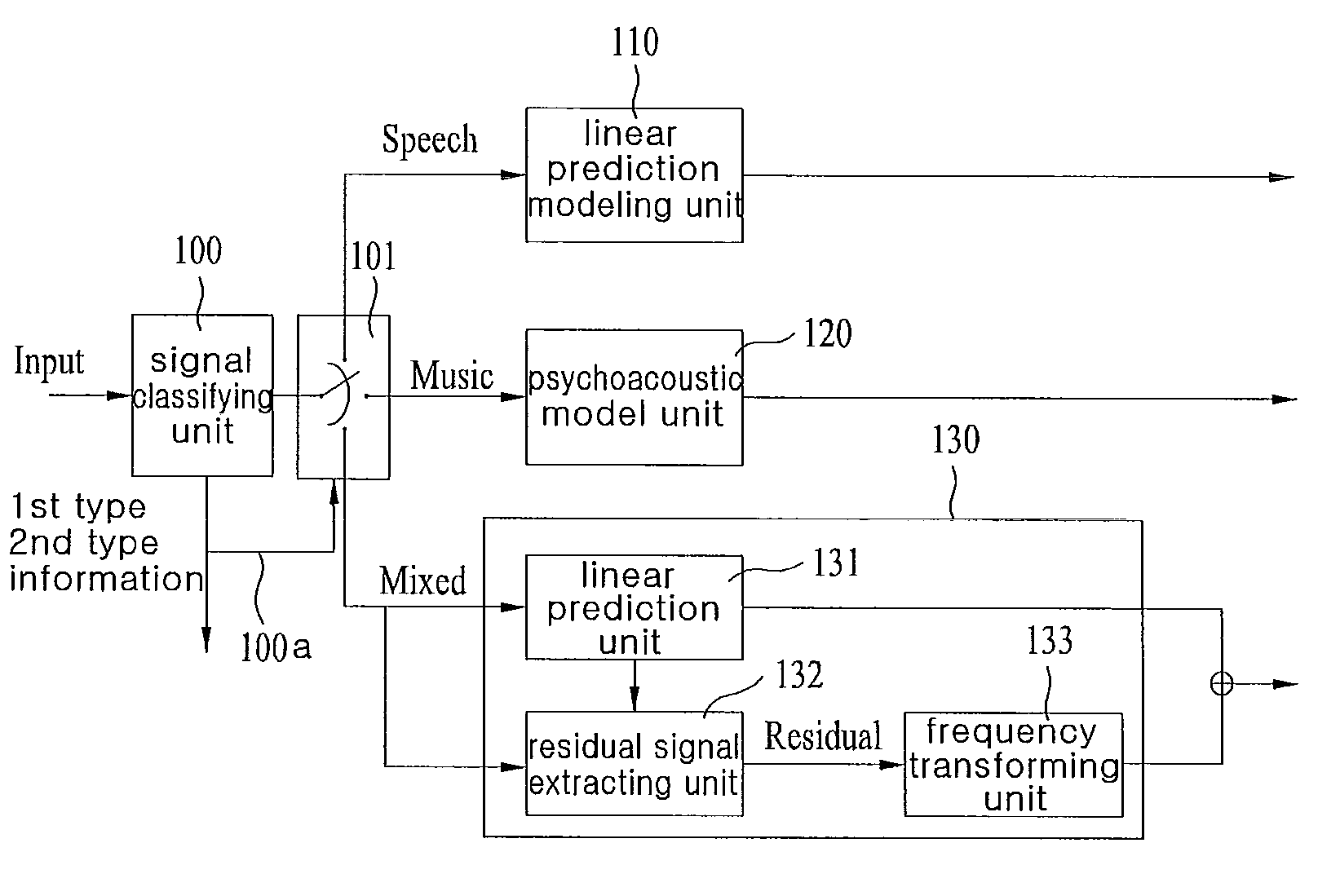
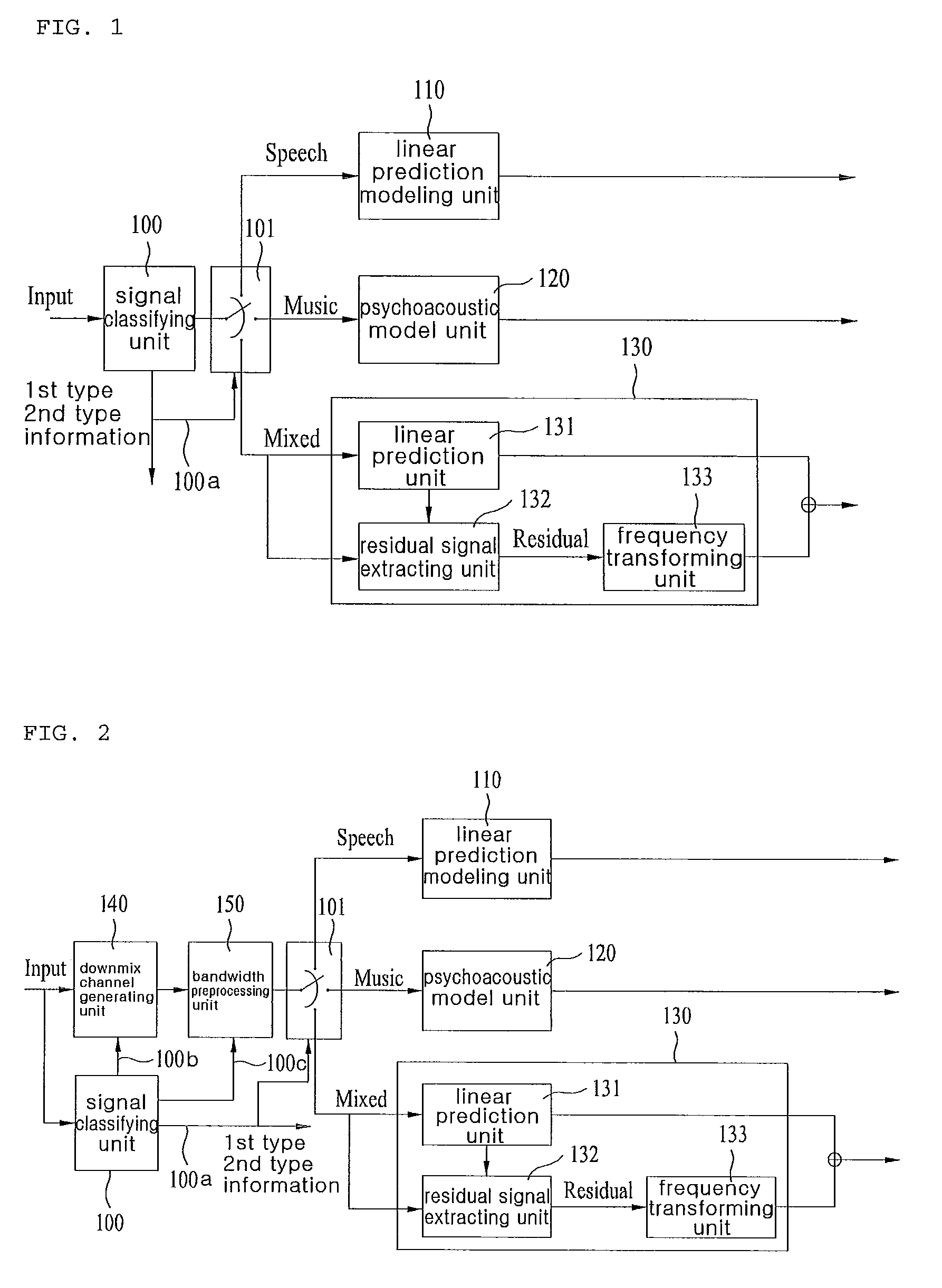
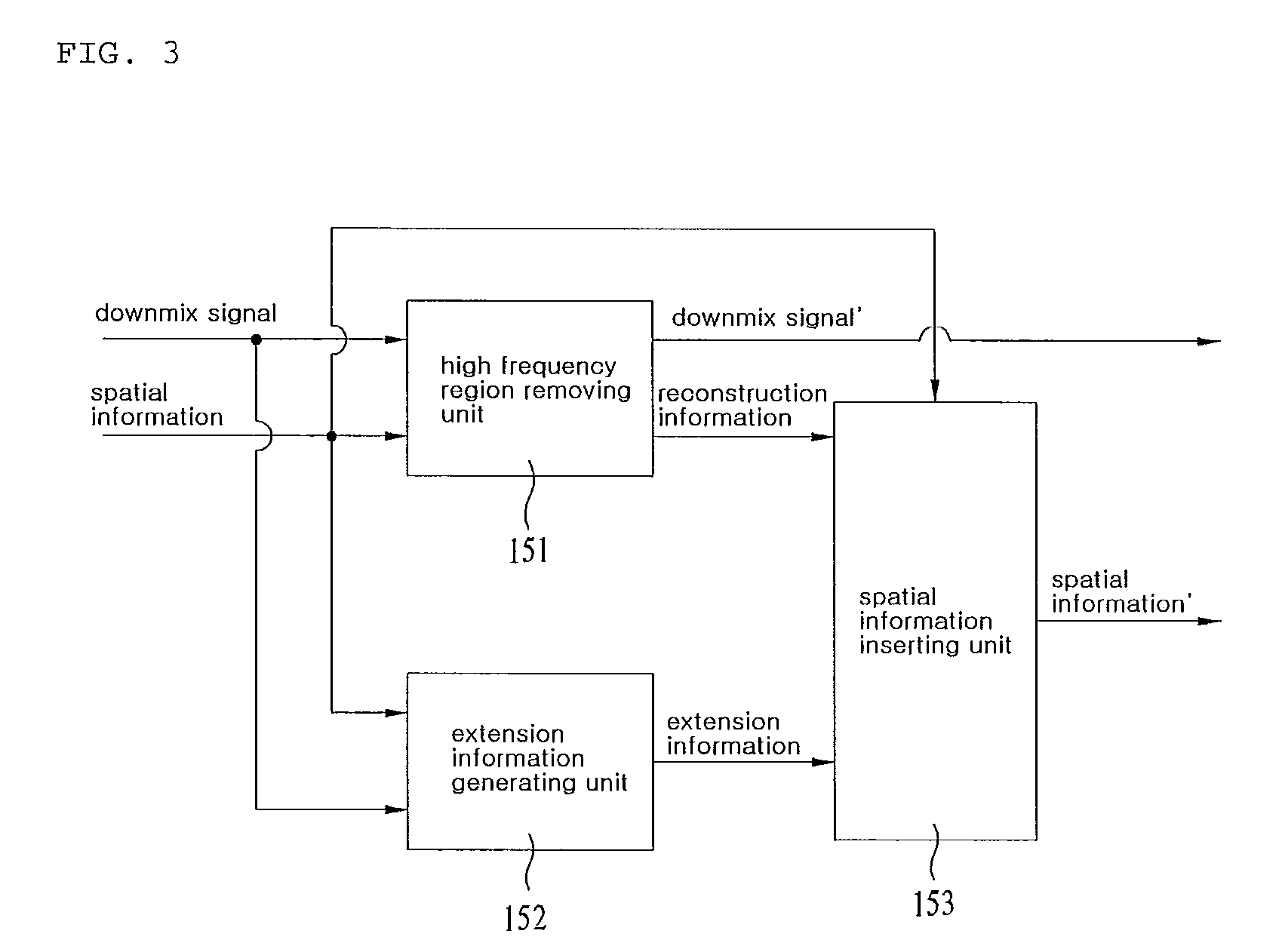
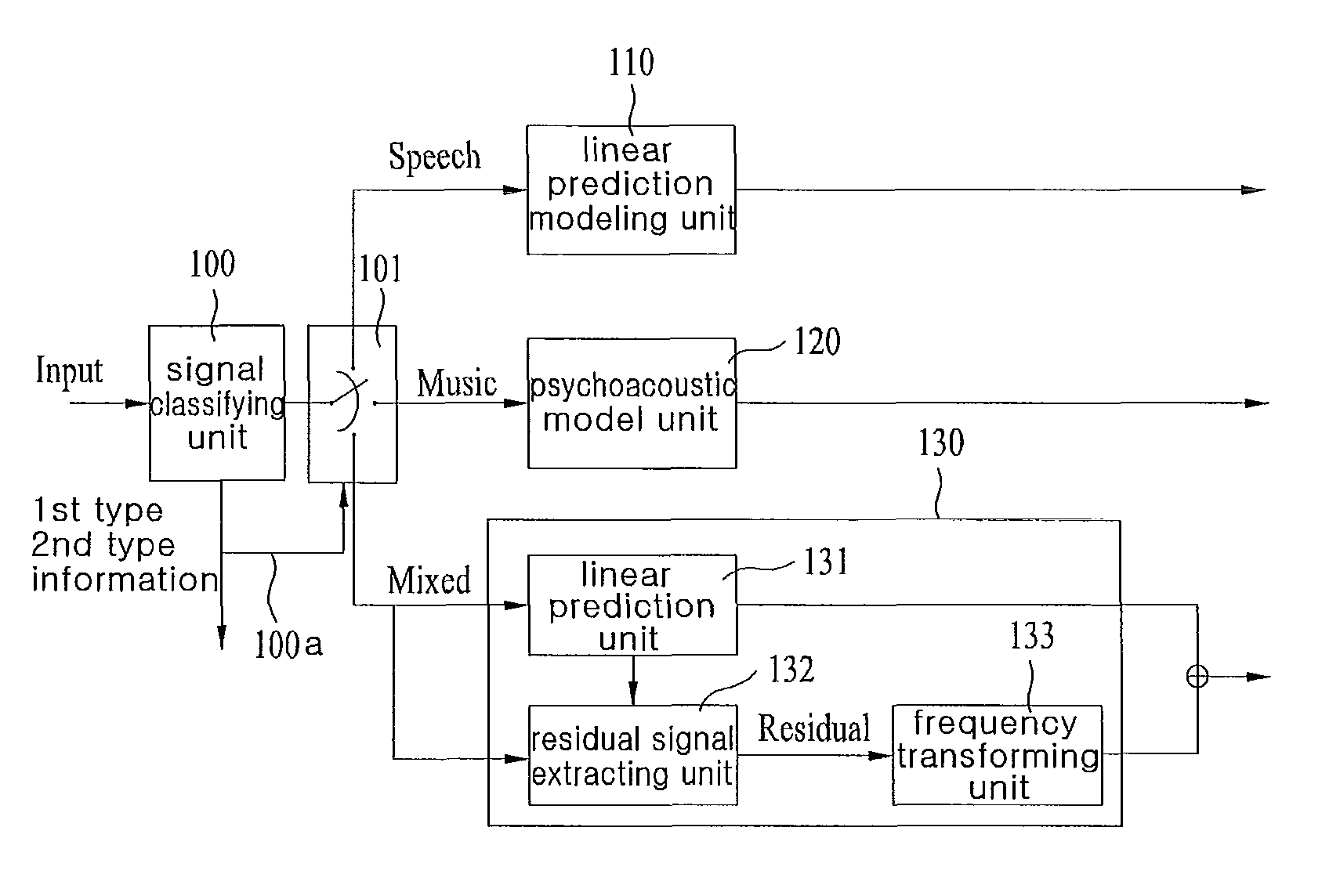
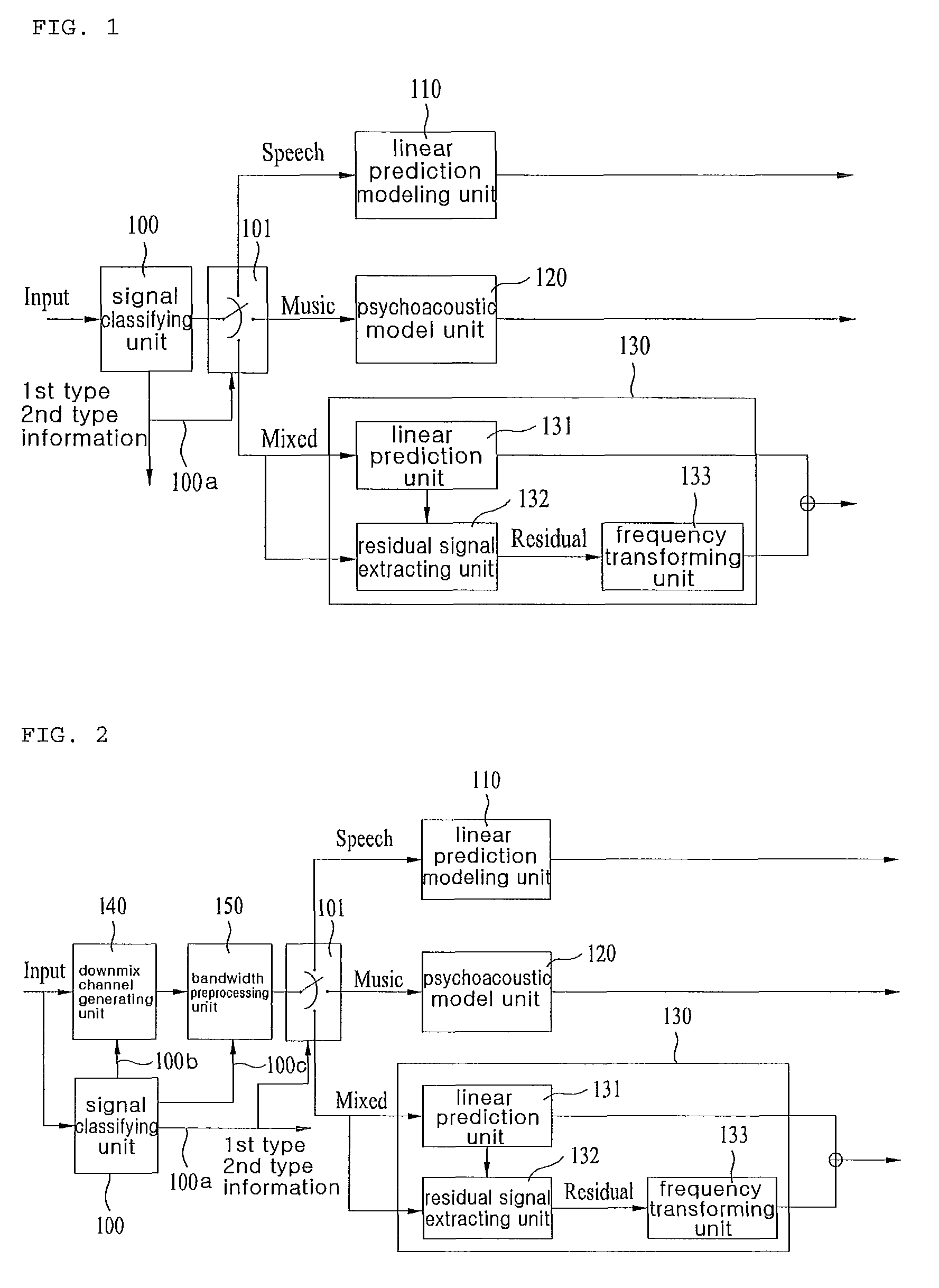
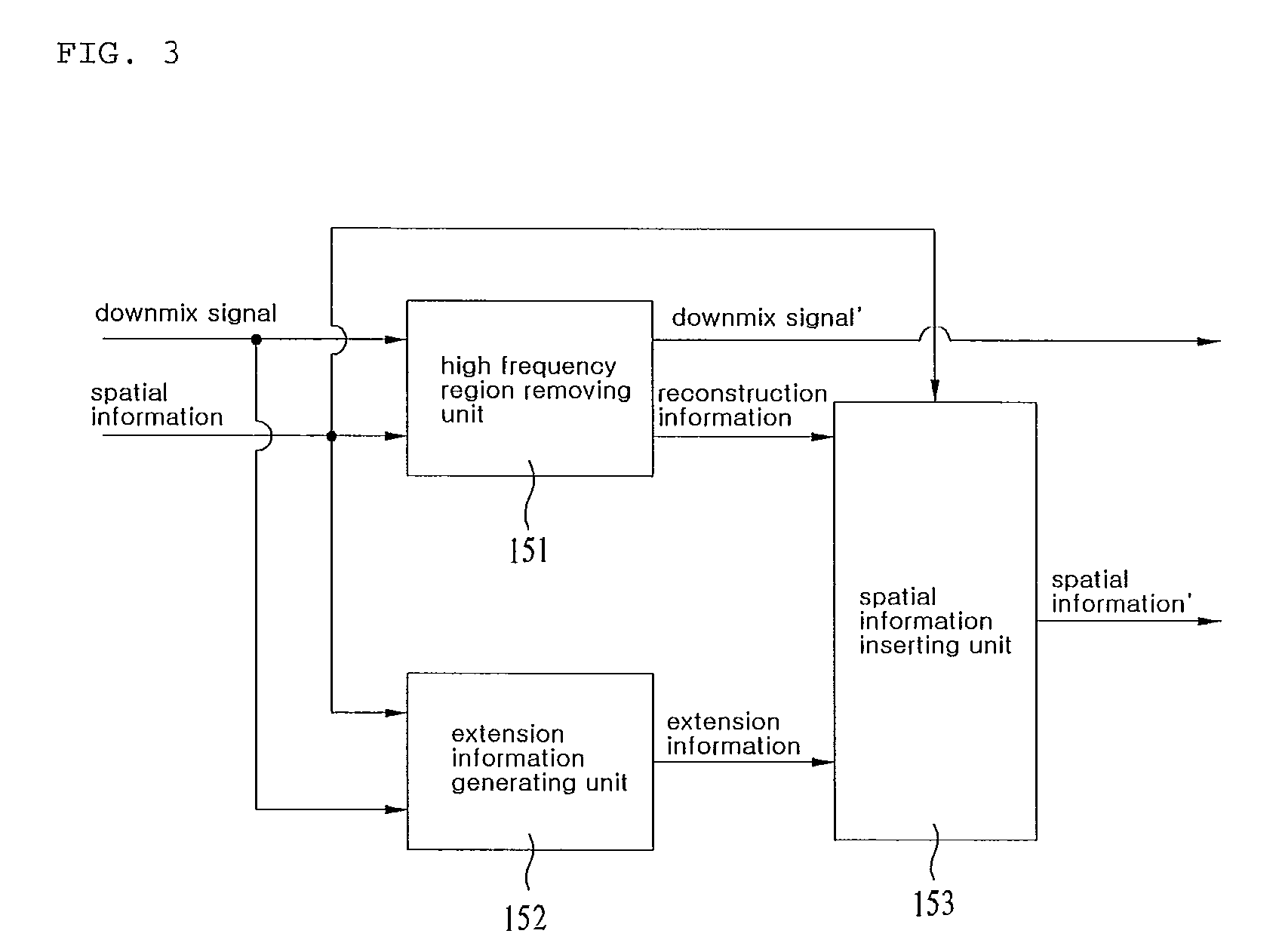
An apparatus for processing an encoded signal and method thereof are disclosed, by which an audio signal can be compressed and reconstructed in higher efficiency. An audio signal processing method includes the steps of identifying whether a coding type of the audio signal is a music signal coding type using first type information, if the coding type of the audio signal is not the music signal coding type, identifying whether the coding type of the audio signal is a speech signal coding type or a mixed signal coding type using second type information, if the coding type of the audio signal is the mixed signal coding type, extracting spectral data and a linear predictive coefficient from the audio signal, generating a residual signal for linear prediction by performing inverse frequency conversion on the spectral data, reconstructing the audio signal by performing linear prediction coding on the linear predictive coefficient and the residual signal, and reconstructing a high frequency region signal using an extension base signal corresponding to a partial region of the reconstructed audio signal and band extension information. Accordingly, various kinds of audio signals can be encoded / decoded in higher efficiency.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Audio coding and decoding apparatuses and methods, and recording mediums storing the methods
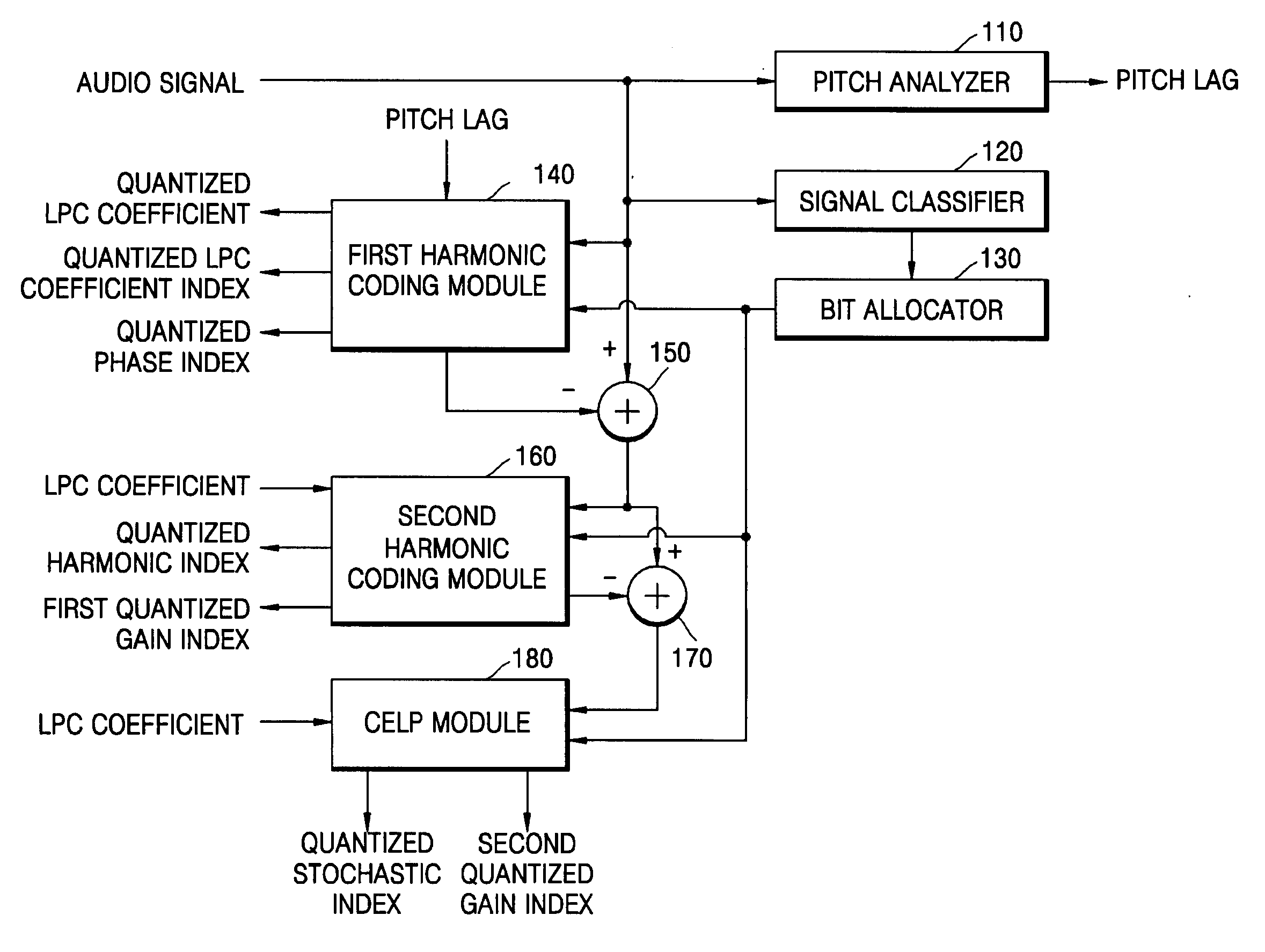
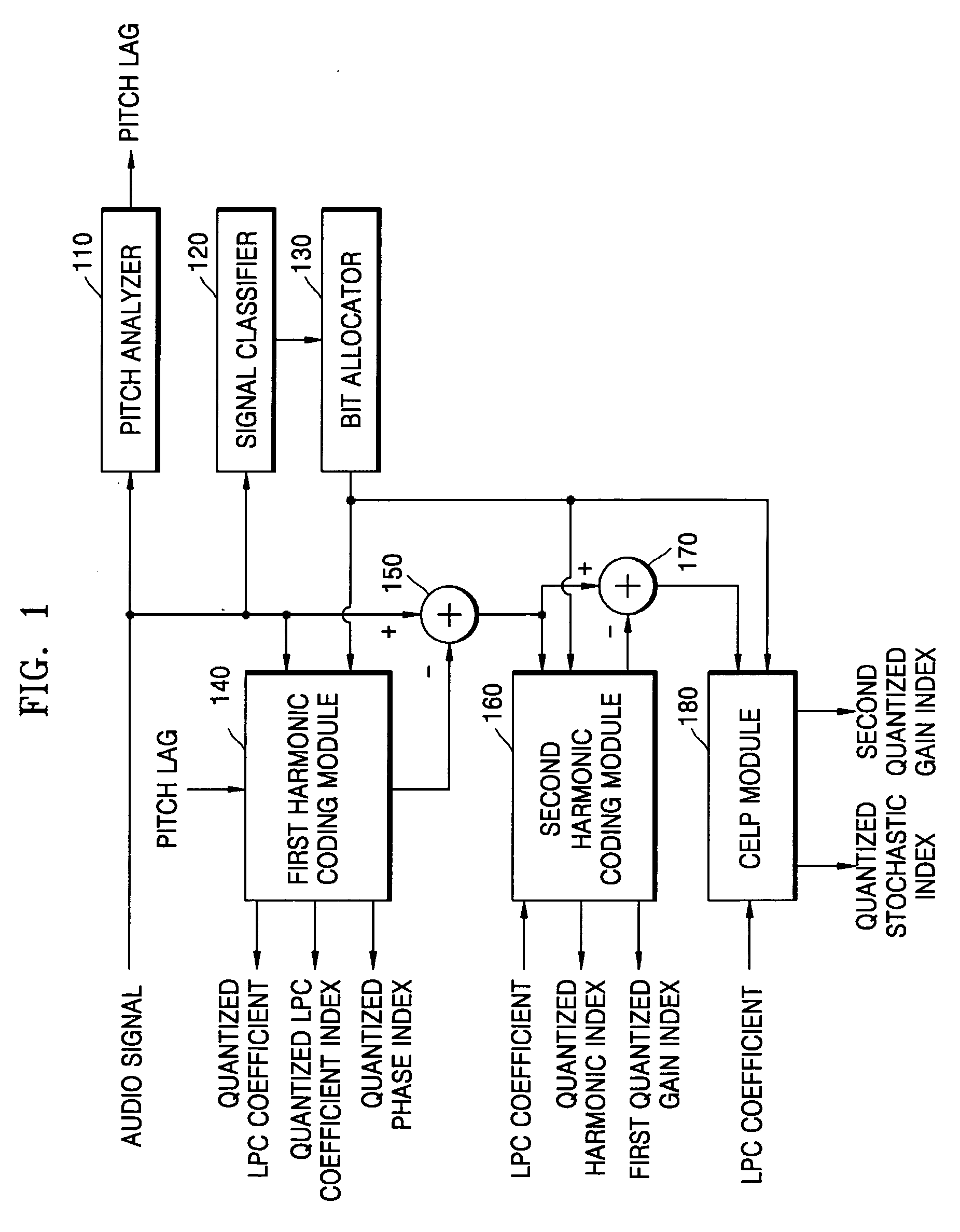
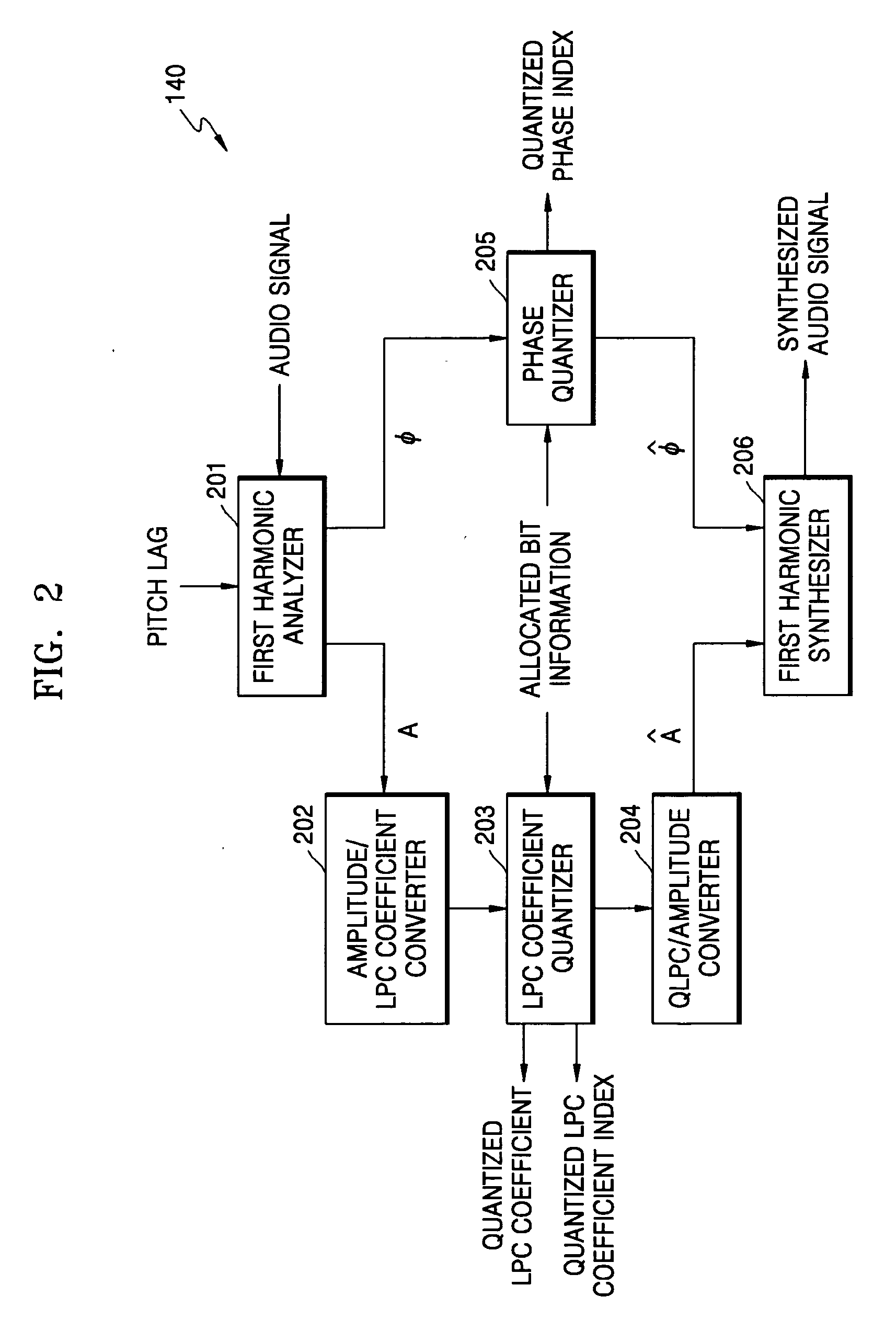
Audio coding and decoding apparatuses and methods that can optimize the quality of an audio signal including harmonics, and recording mediums storing the methods. An audio coding apparatus includes: a first harmonic coding module performing first harmonic coding on an input audio signal using a pitch lag of the input audio signal and producing a quantized linear prediction coding coefficient; a first detector detecting a first difference audio signal from a difference between an audio signal output from the first harmonic coding module and the input audio signal; a second harmonic coding module performing harmonic coding on the first difference audio signal using the quantized linear prediction coding coefficient and a previous harmonic coding result; a second detector detecting a second difference audio signal obtained from a difference between an audio signal output from the second harmonic coding module and the first difference audio signal; and a code excited linear prediction (CELP) module CELP coding the second difference audio signal using the quantized linear prediction coding coefficient obtained from the first harmonic coding module.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
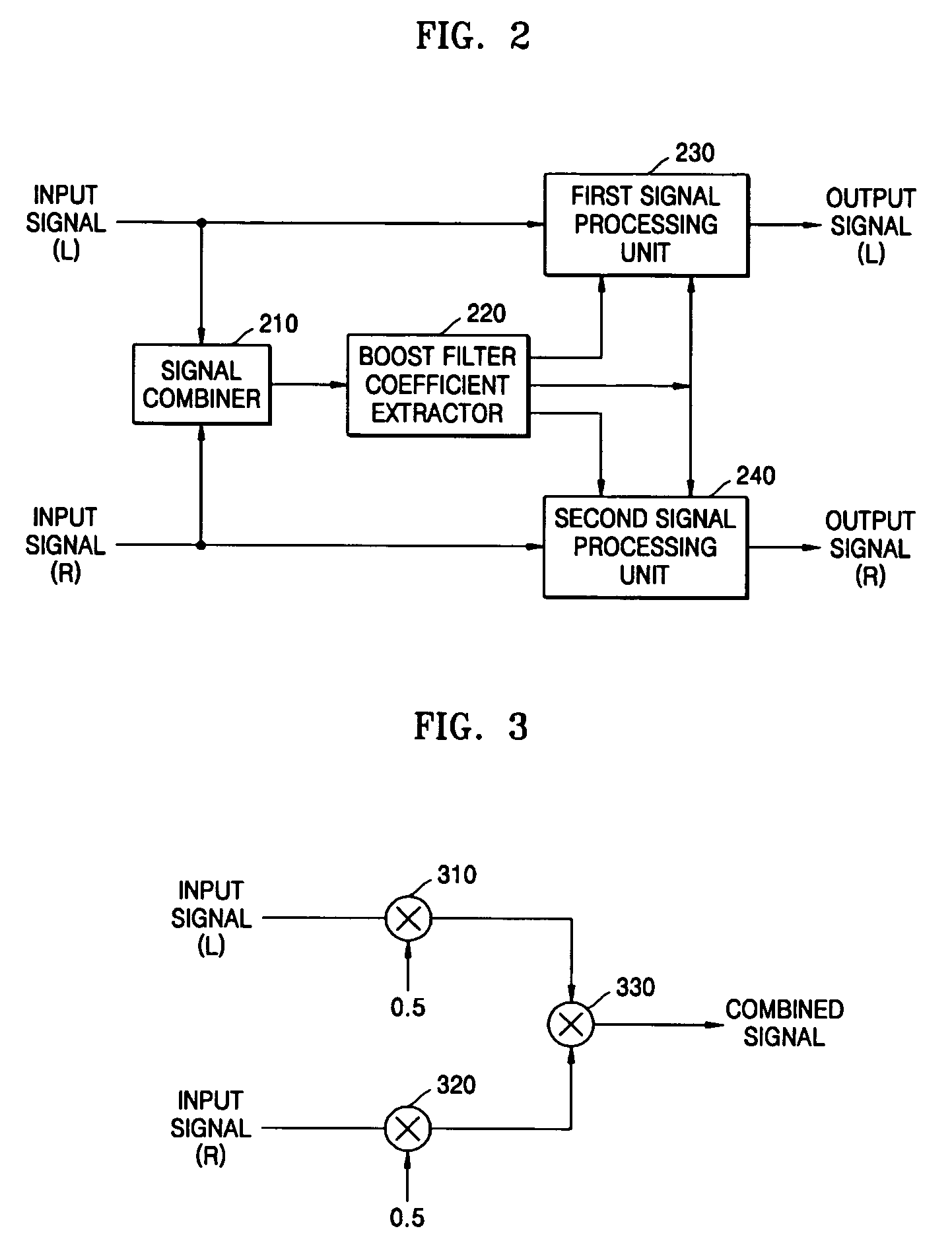
Method of and apparatus for enhancing dialog using formants
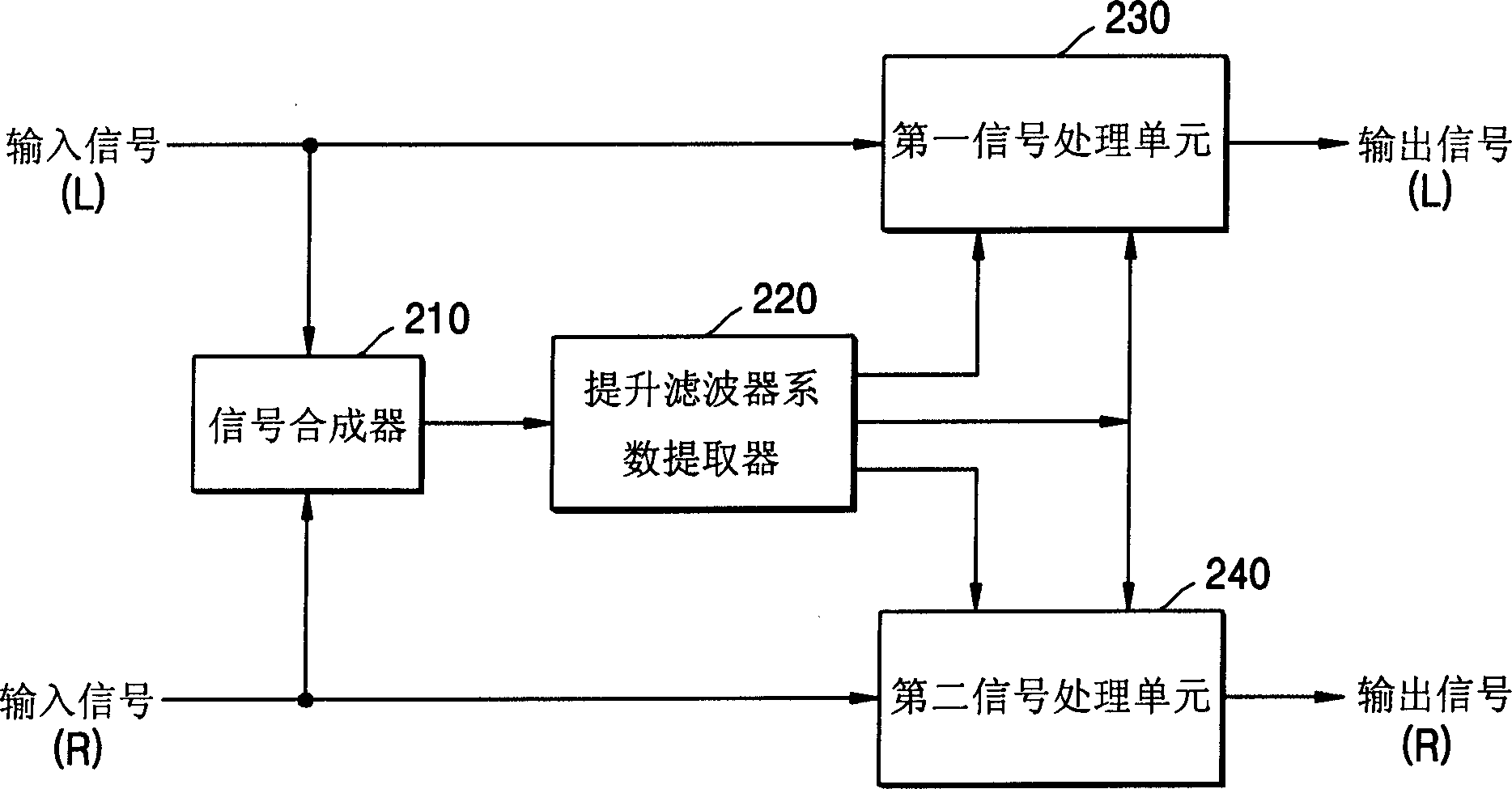
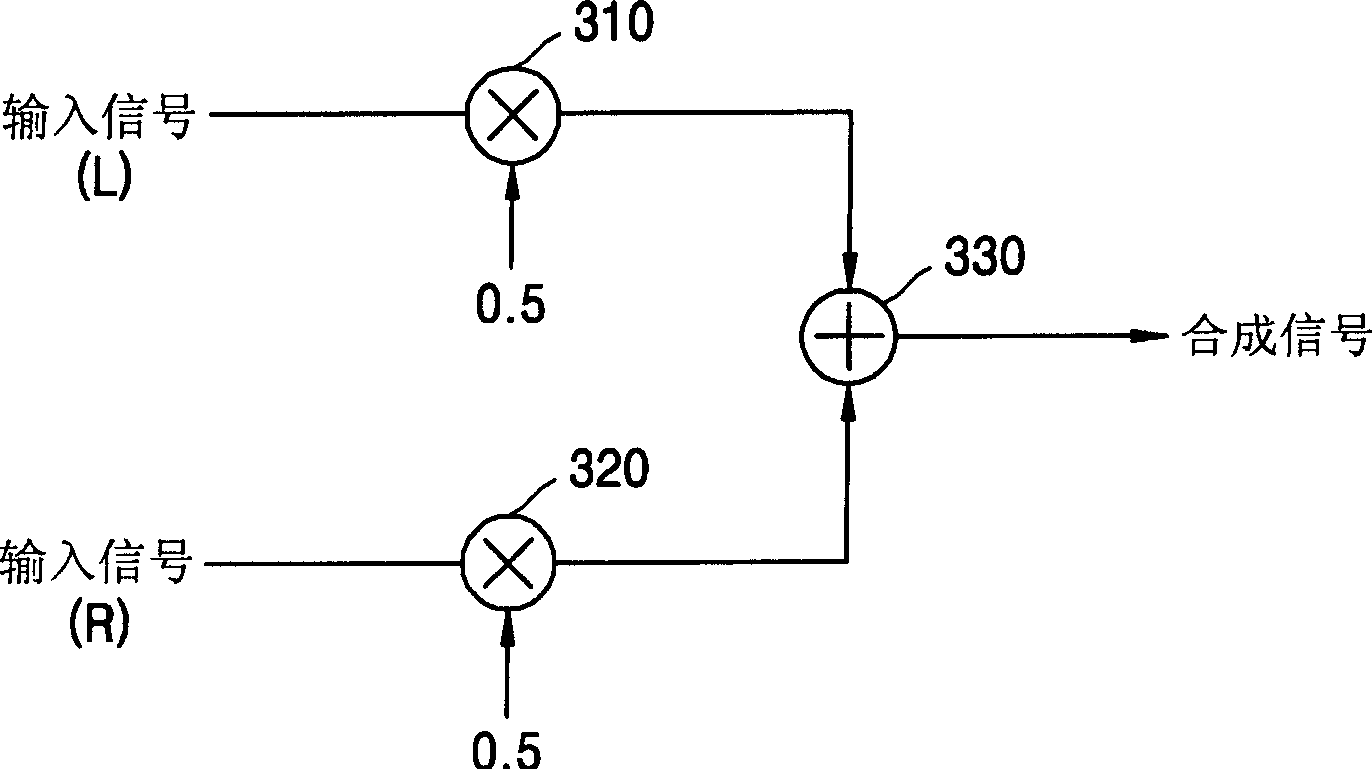
A dialog enhancement method and device for enhancing the formant of the dialog area without changing the voice area, comprising: calculating line spectral pair (LSP) coefficients based on linear predictive coding (LPC) from an input signal; determining based on the calculated LSP coefficients Whether there is a speech region in the input signal; and extracting formants from LSP coefficients according to whether there is a speech region, and lifting the formants.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Bit rate scalable speech coding and decoding apparatus and method
InactiveUS7702504B2Reduce in quantitySpeech analysisCode conversionLinear prediction codingTarget signal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrocardiogram signal lossless compression method based on PT conversion and linear prediction combination
InactiveCN101669819AMaintain integrityKeep properlyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLinear prediction codingLossless compression
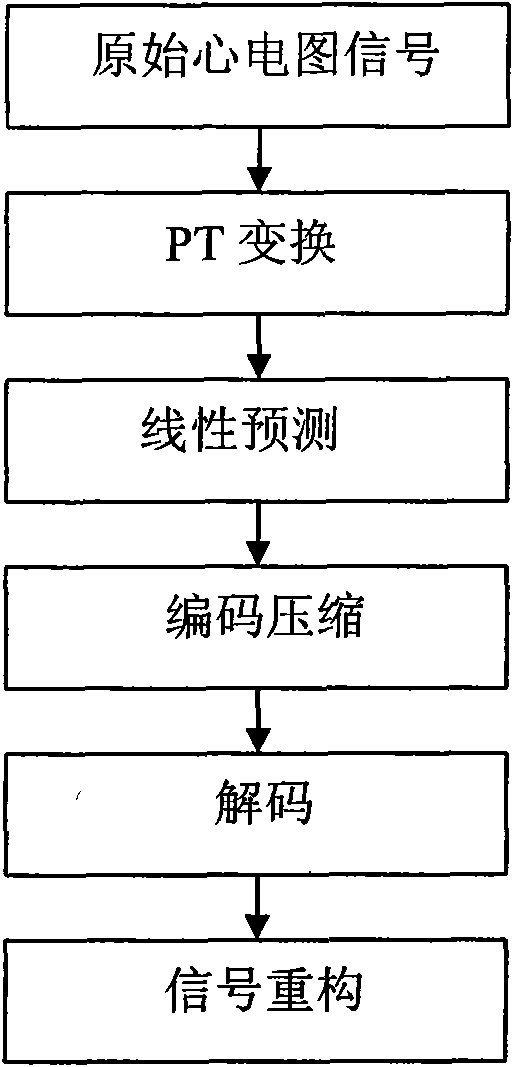
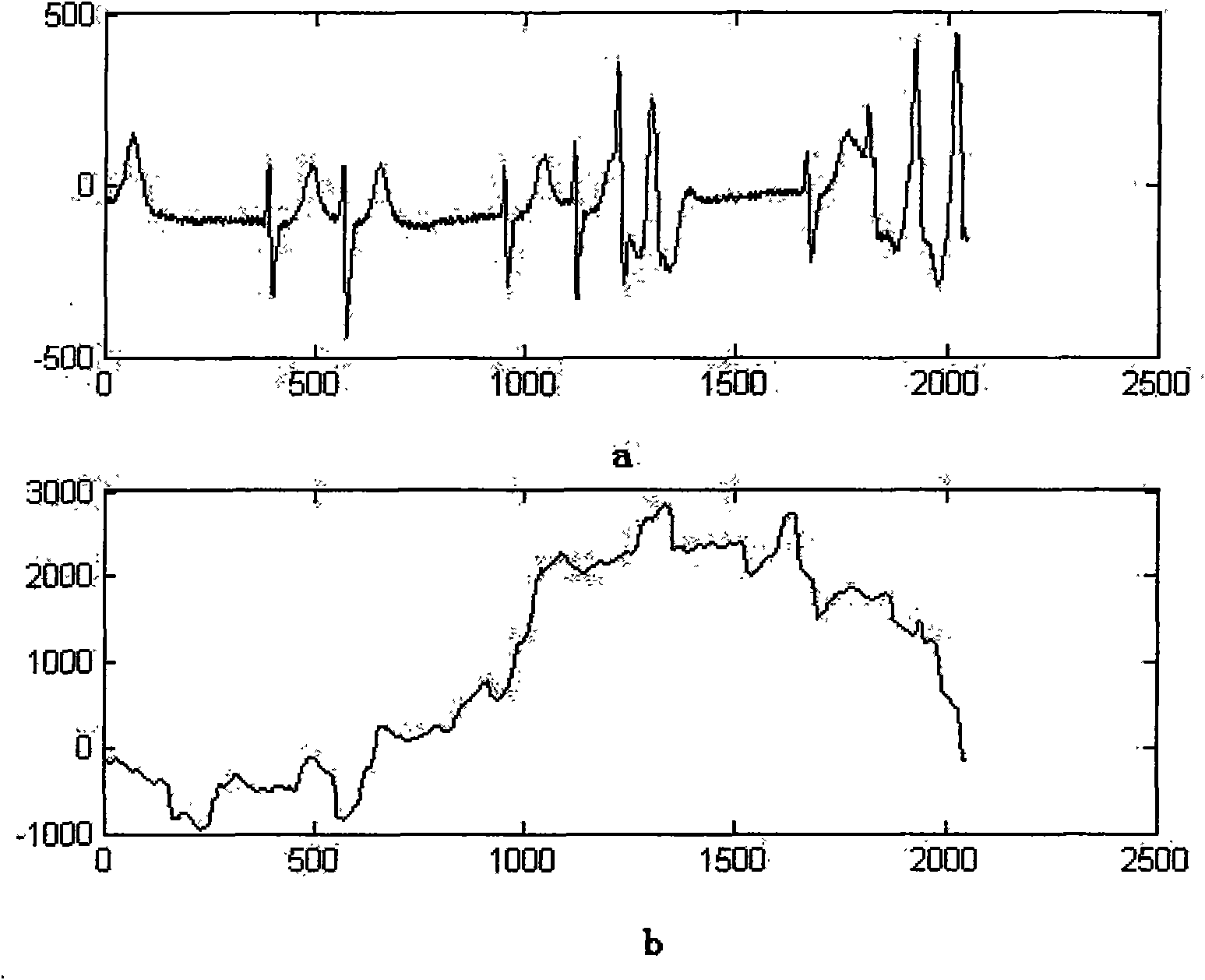
The invention discloses an electrocardiogram signal lossless compression method based on PT conversion and linear prediction combination, belonging to the technical field of data processing. The method comprises the following compression processes: carrying out PT conversion on an original electrocardiogram signal; subtracting a converted original signal value and an estimated value to obtain a residual error signal of the whole electrocardiogram signal; carrying out self-adaption variable grade RICE coding on the residual error signal to output a coding bit stream and finishing the lossless compression on the electrocardiogram signal; decoding the compressed bit stream; reconstructing the signal and finishing decompression. The lossless compression method ensures the information completion and accuracy of the compressed electrocardiogram signal and can be used for transmitting and storing the electrocardiogram signal.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Changable rate vocoder
InactiveCN1381956AError-proneRobustAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLinear prediction codingAcoustics
An apparatus for masking frame errors comprising memory means for storing at least one previous frame of data and for providing said at least one previous frame of data in response to a frame error signal; and masking means for receiving said frame error signal and for generating a masking signal in accordance with at least one previous frame of data and a predetermined error masking format.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
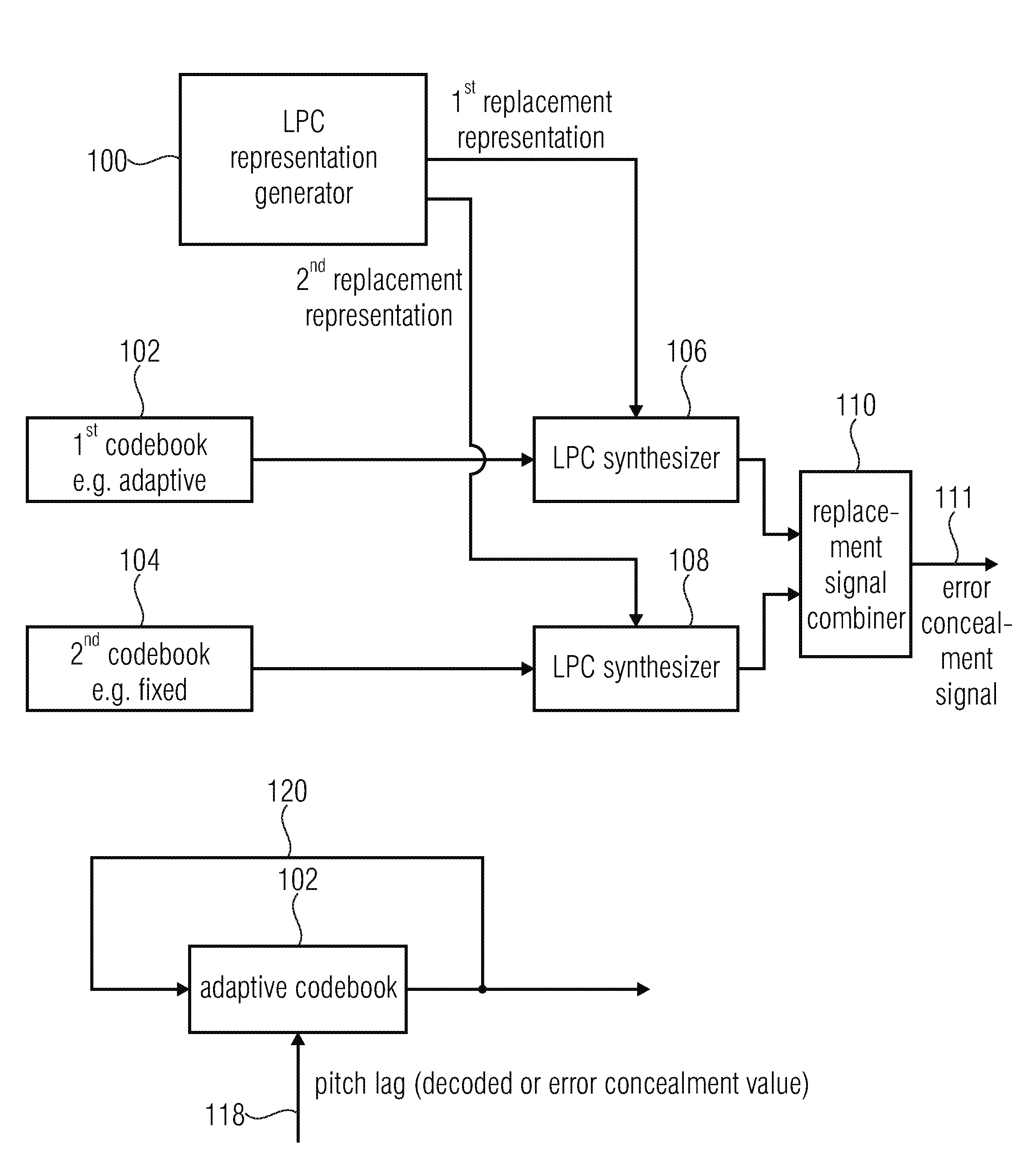
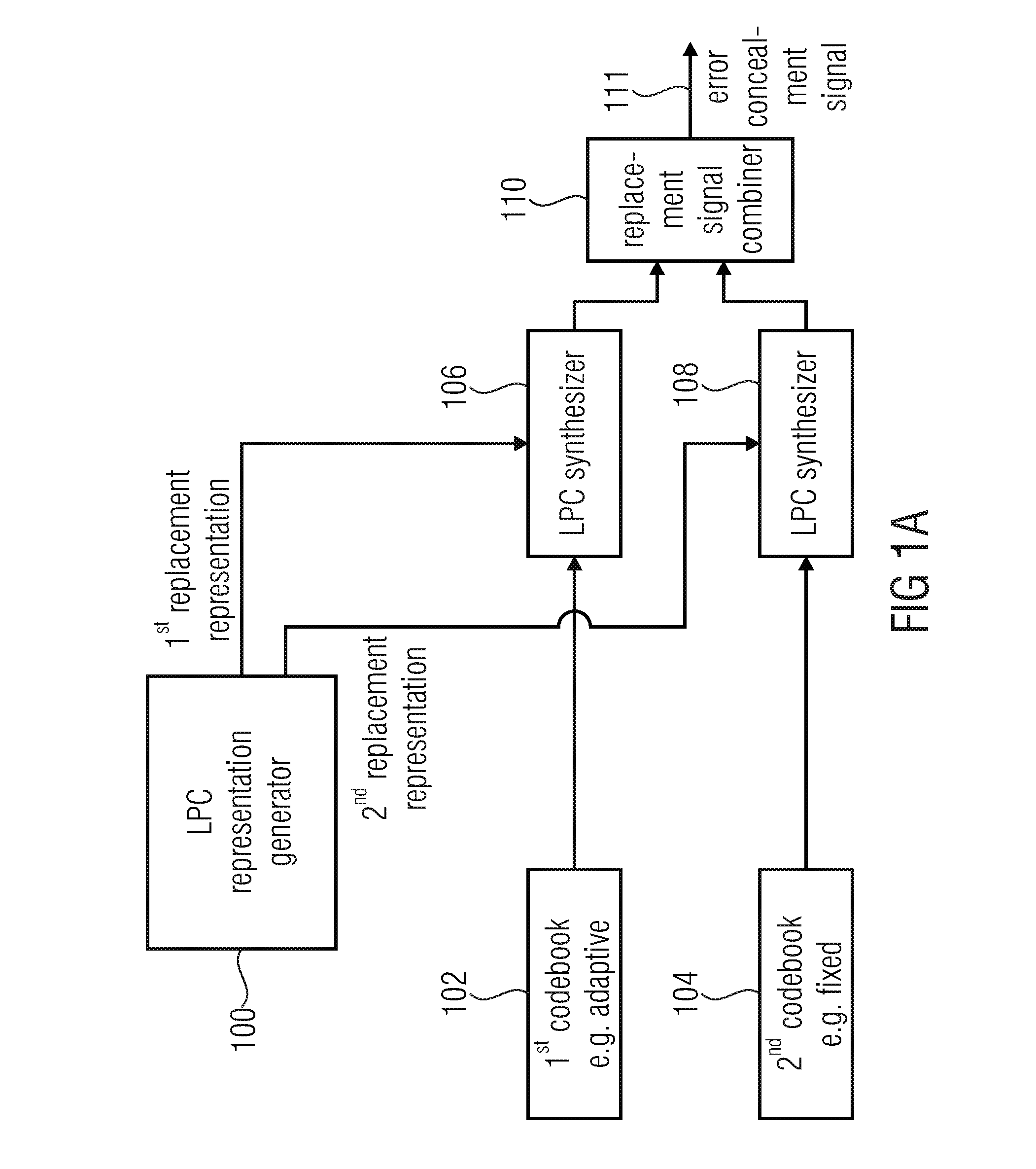
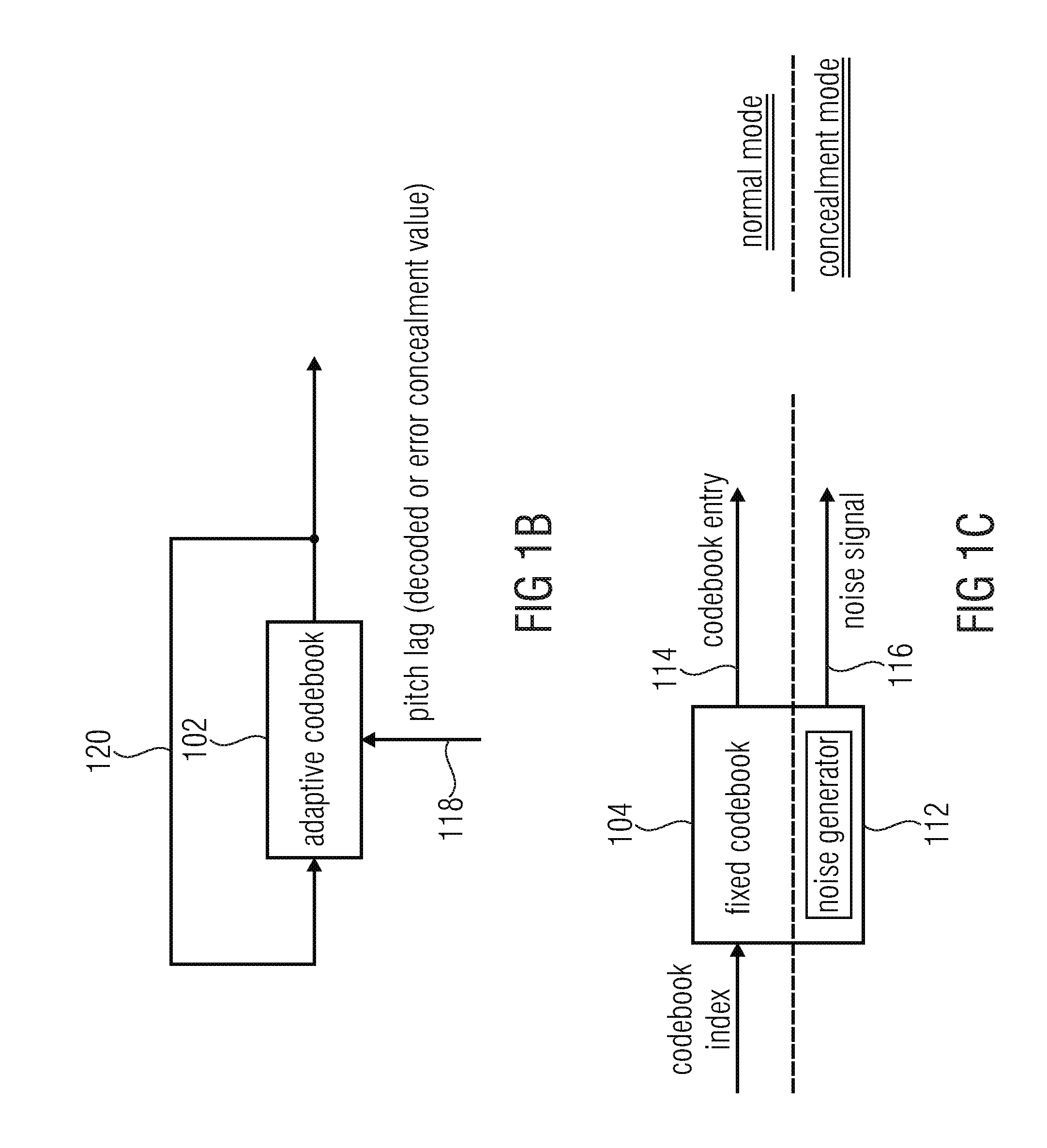
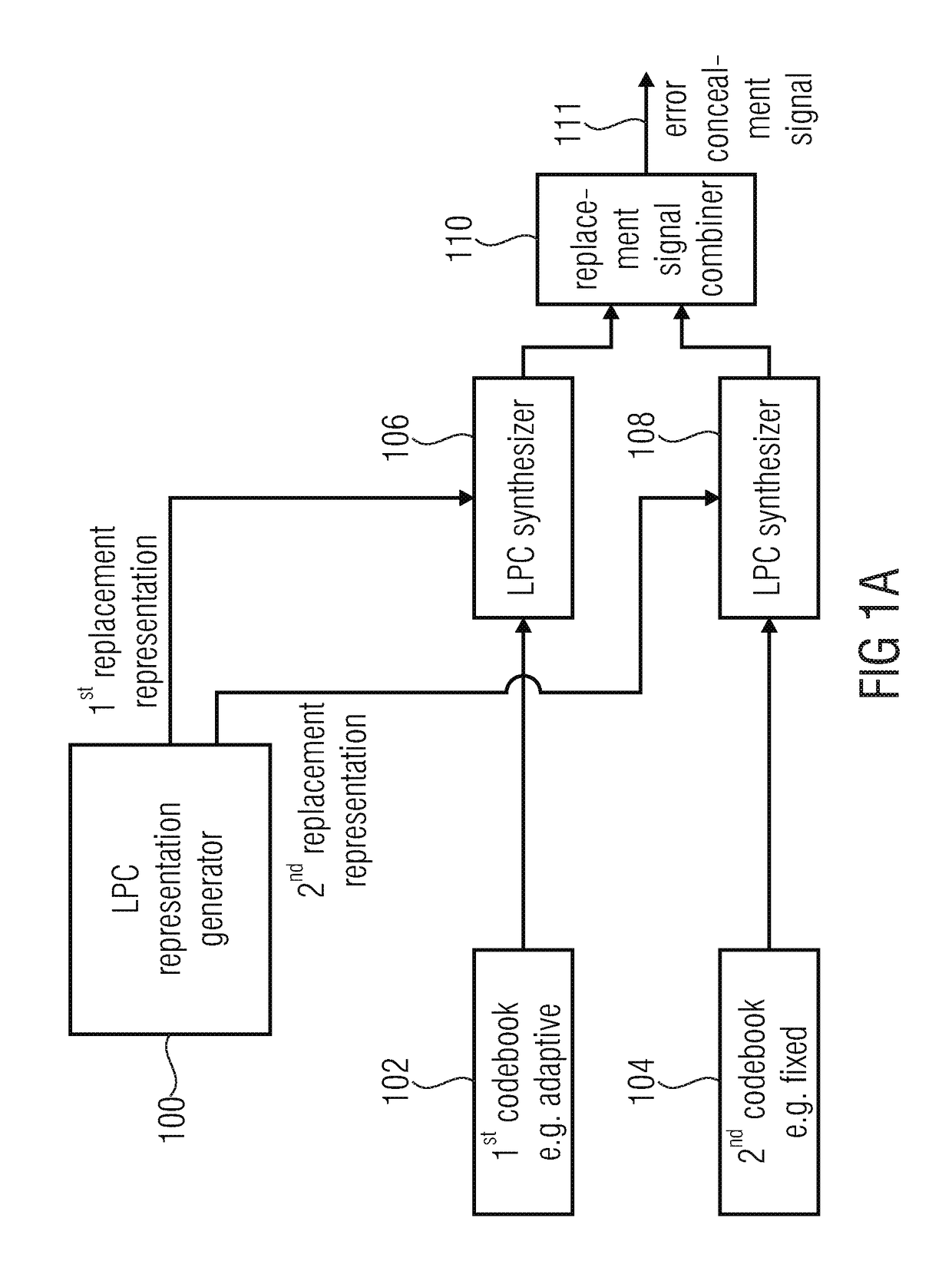
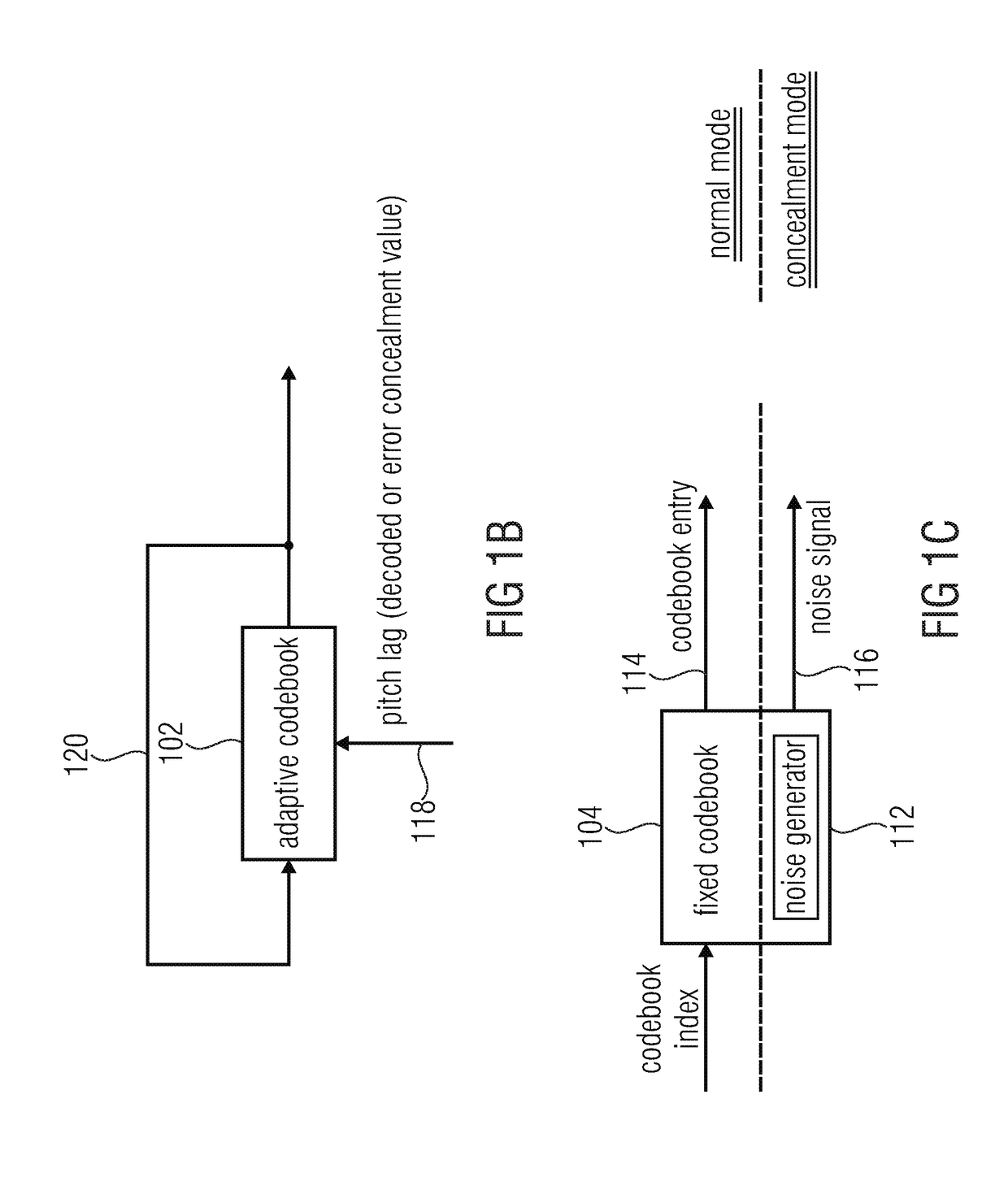
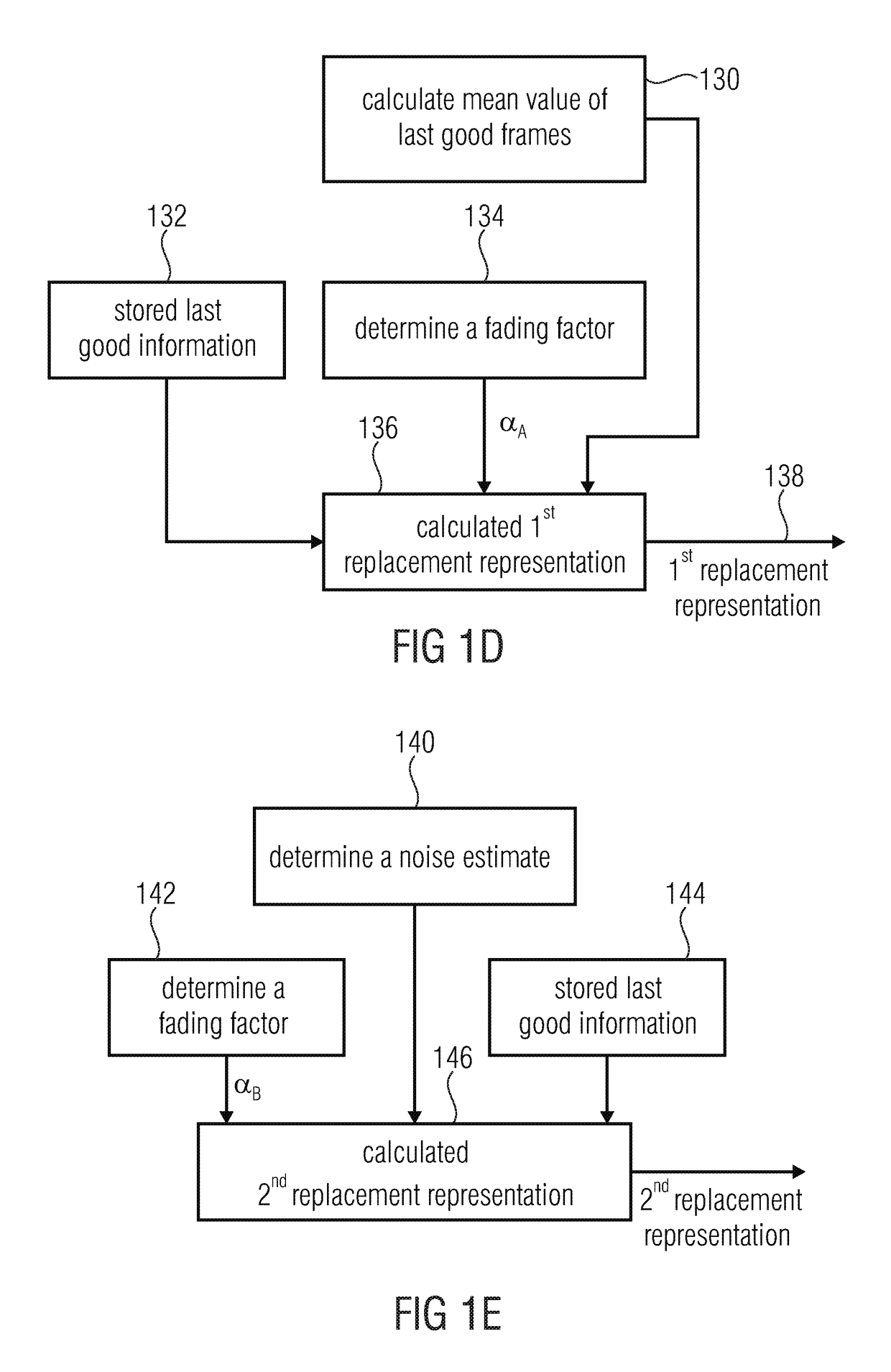
Apparatus and method for generating an error concealment signal using individual replacement LPC representations for individual codebook information
An apparatus for generating an error concealment signal includes an LPC (linear prediction coding) representation generator for generating a first replacement LPC representation and a different second replacement LPC representation; an LPC synthesizer for filtering a first codebook information using the first replacement representation to obtain a first replacement signal and for filtering a different second codebook information using the second replacement LPC representation to obtain a second replacement signal; and a replacement signal combiner for combining the first replacement signal and the second replacement signal to obtain the error concealment signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
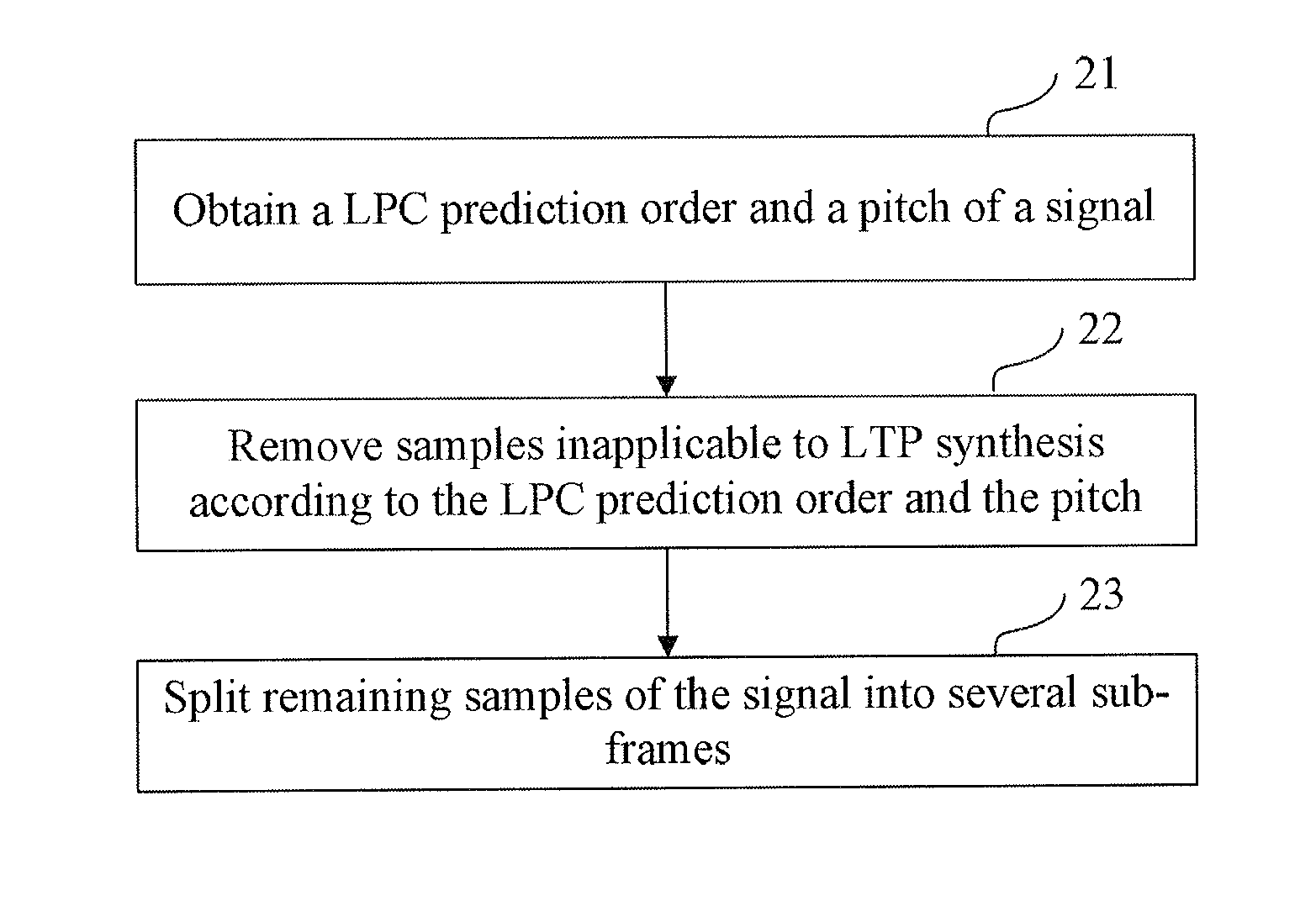
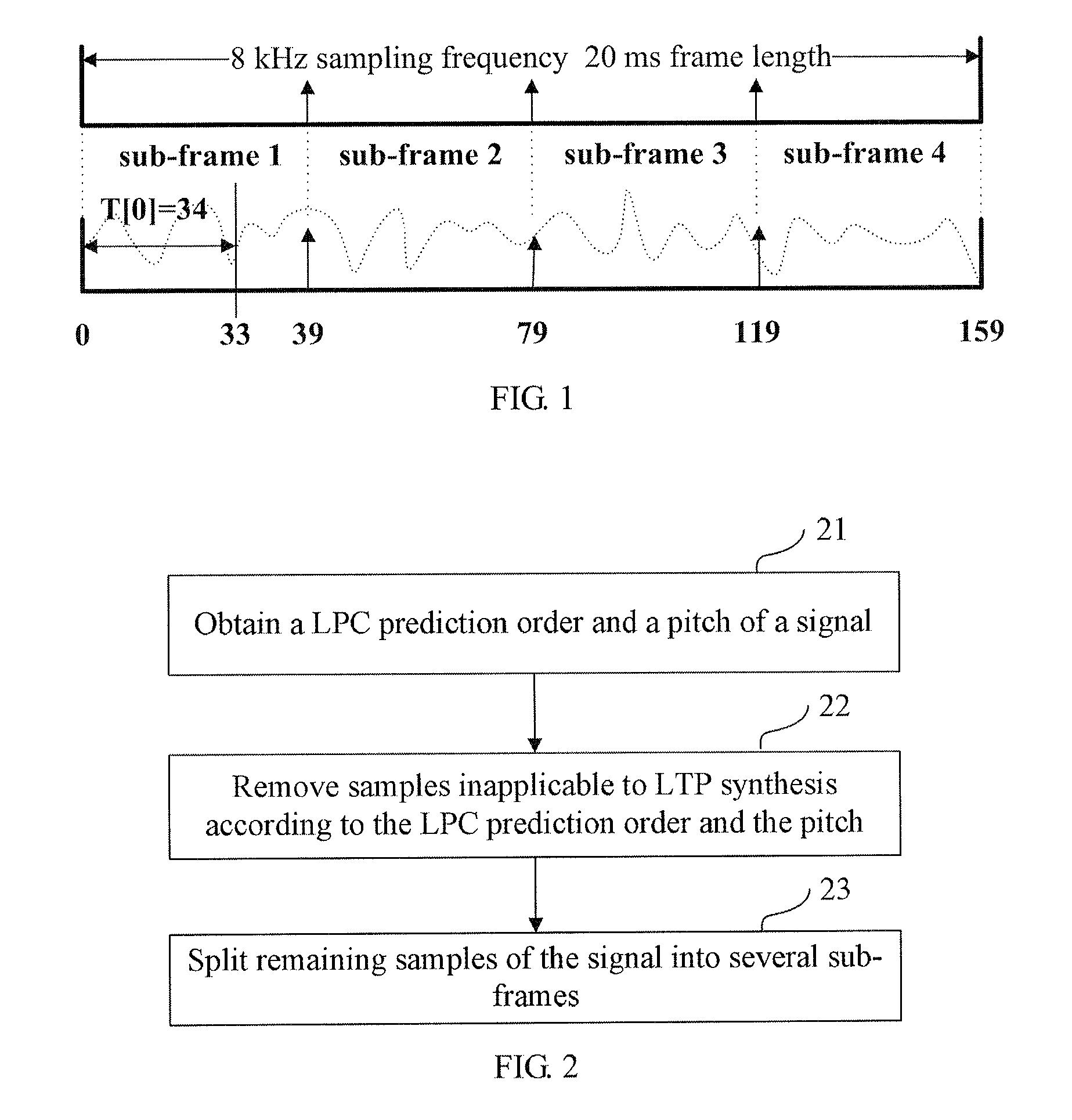
Framing method and apparatus
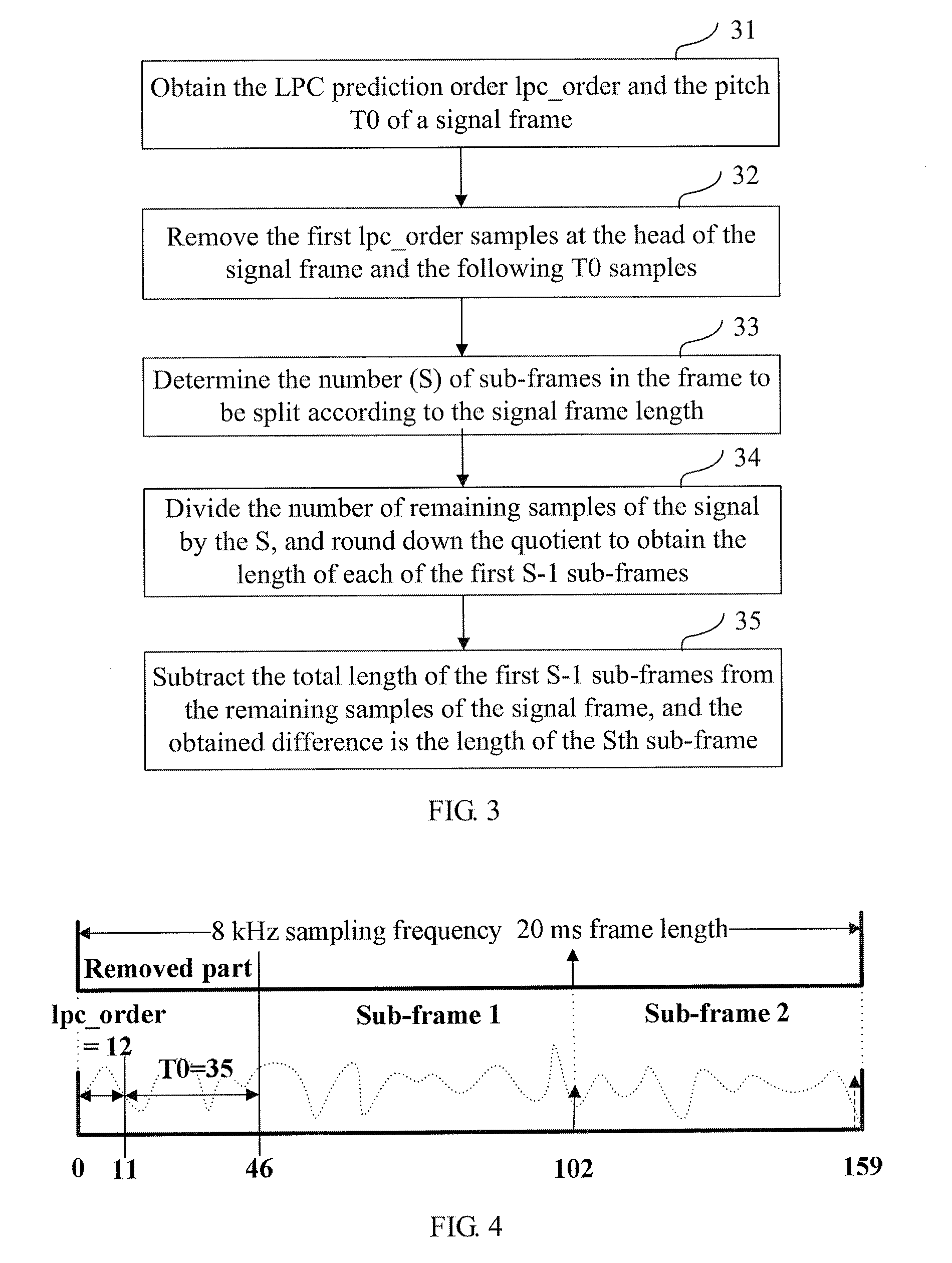
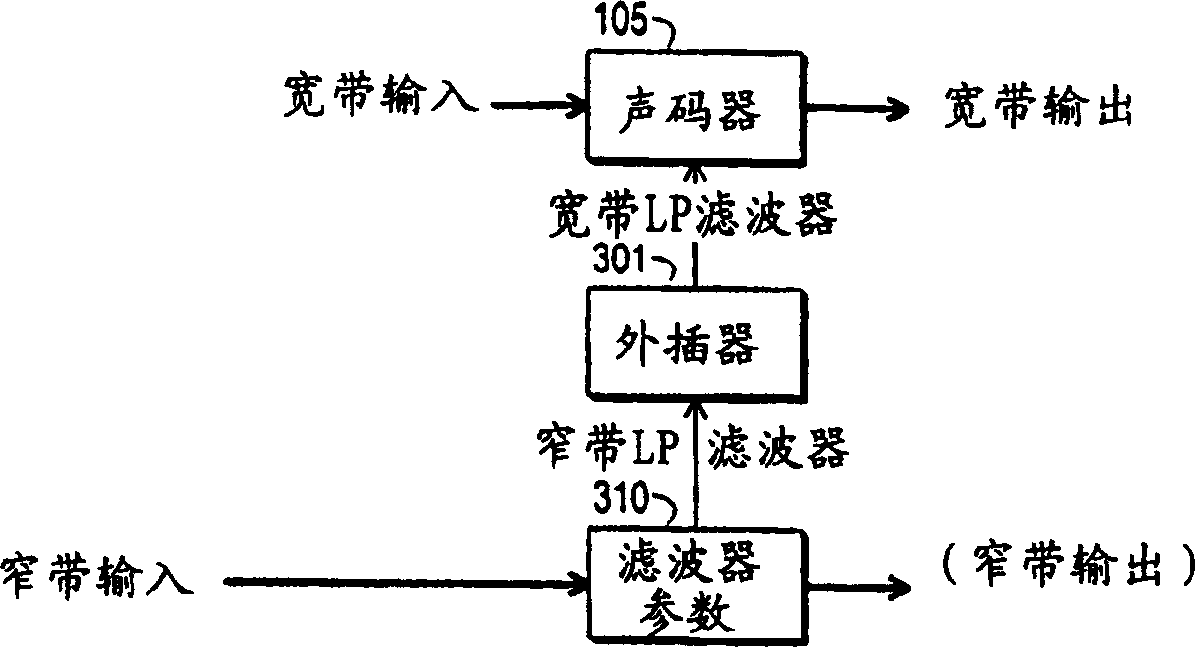
A framing method and apparatus are disclosed to overcome inconsistency of gains between sub-frames caused by simple average framing in the prior art. The method includes: obtaining the Linear Prediction Coding (LPC) order and the pitch of the signal; removing the samples inapplicable to Long-Term Prediction (LTP) synthesis according to the LPC prediction order and the pitch; and splitting the remaining samples of the signal into several sub-frames. The technical solution under the present invention is applicable to the multimedia speech coding field.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
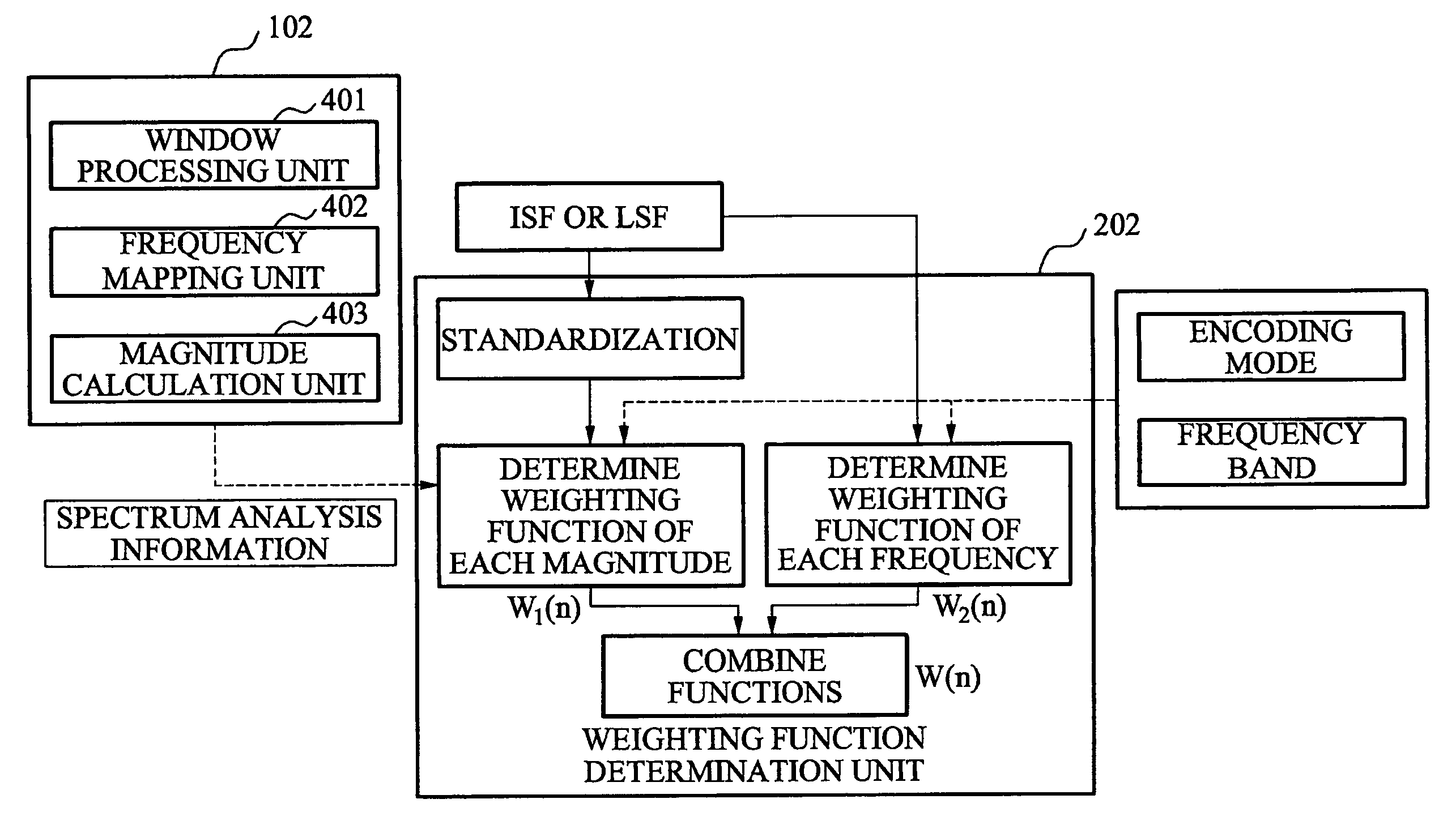
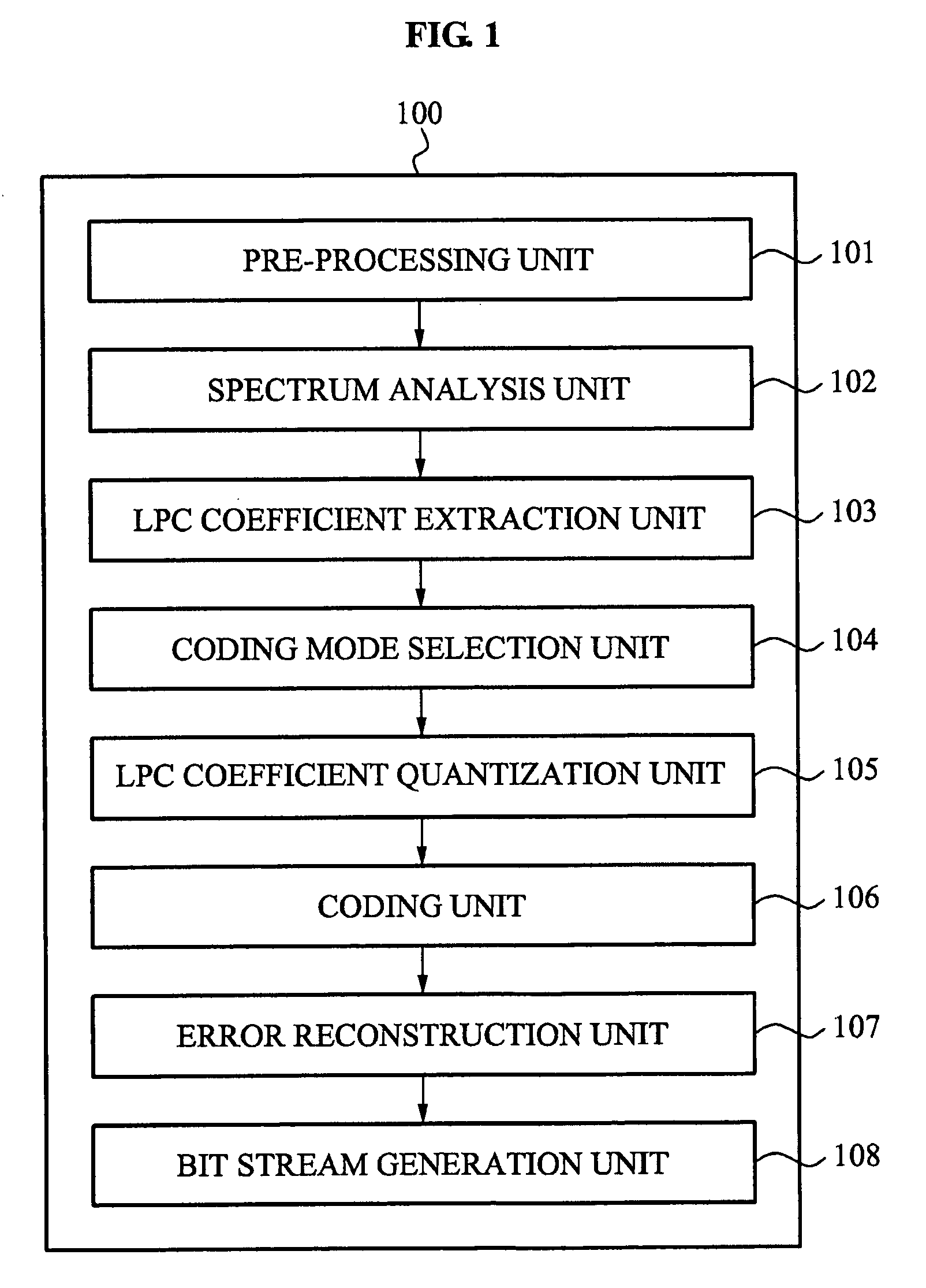
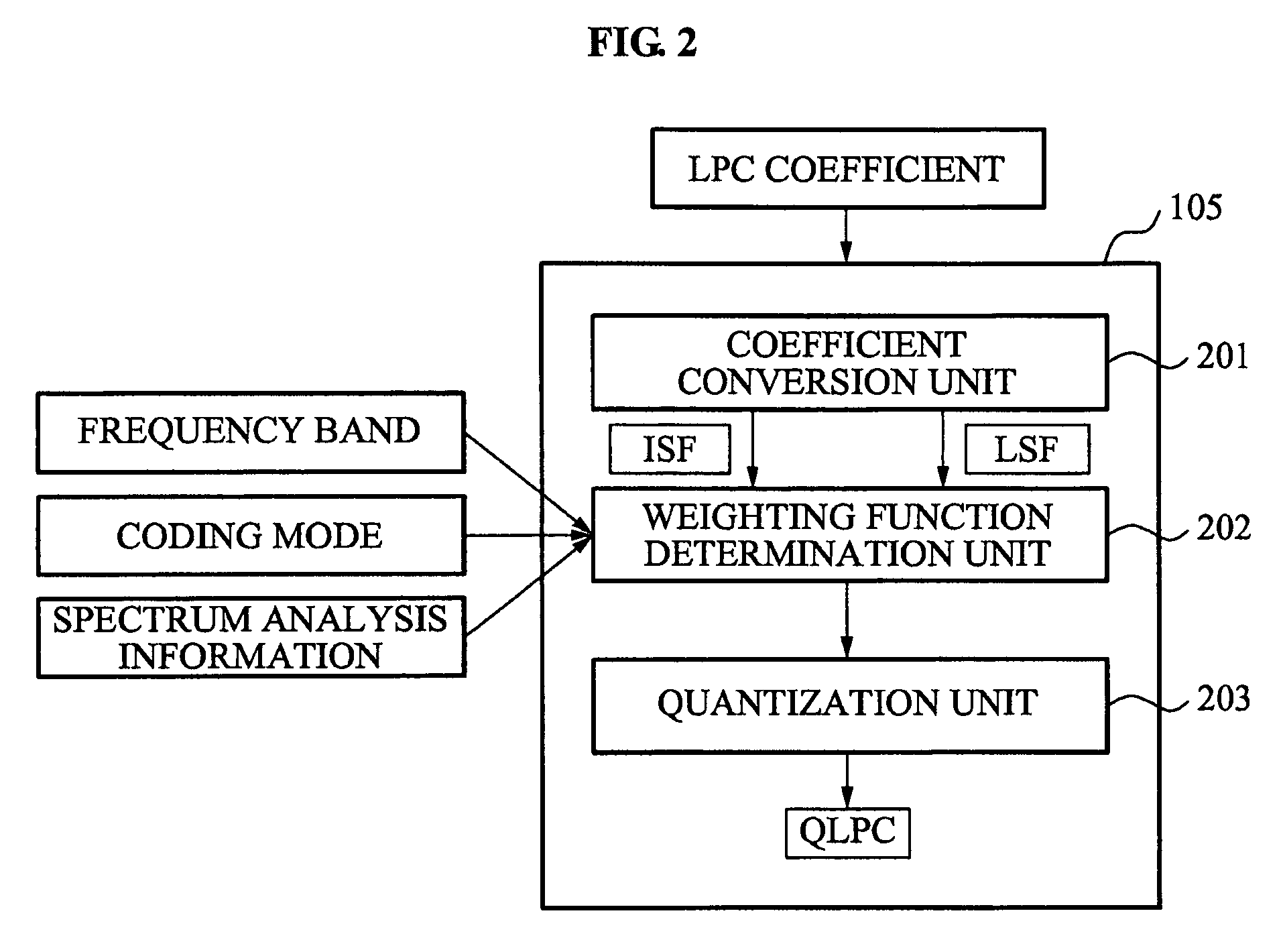
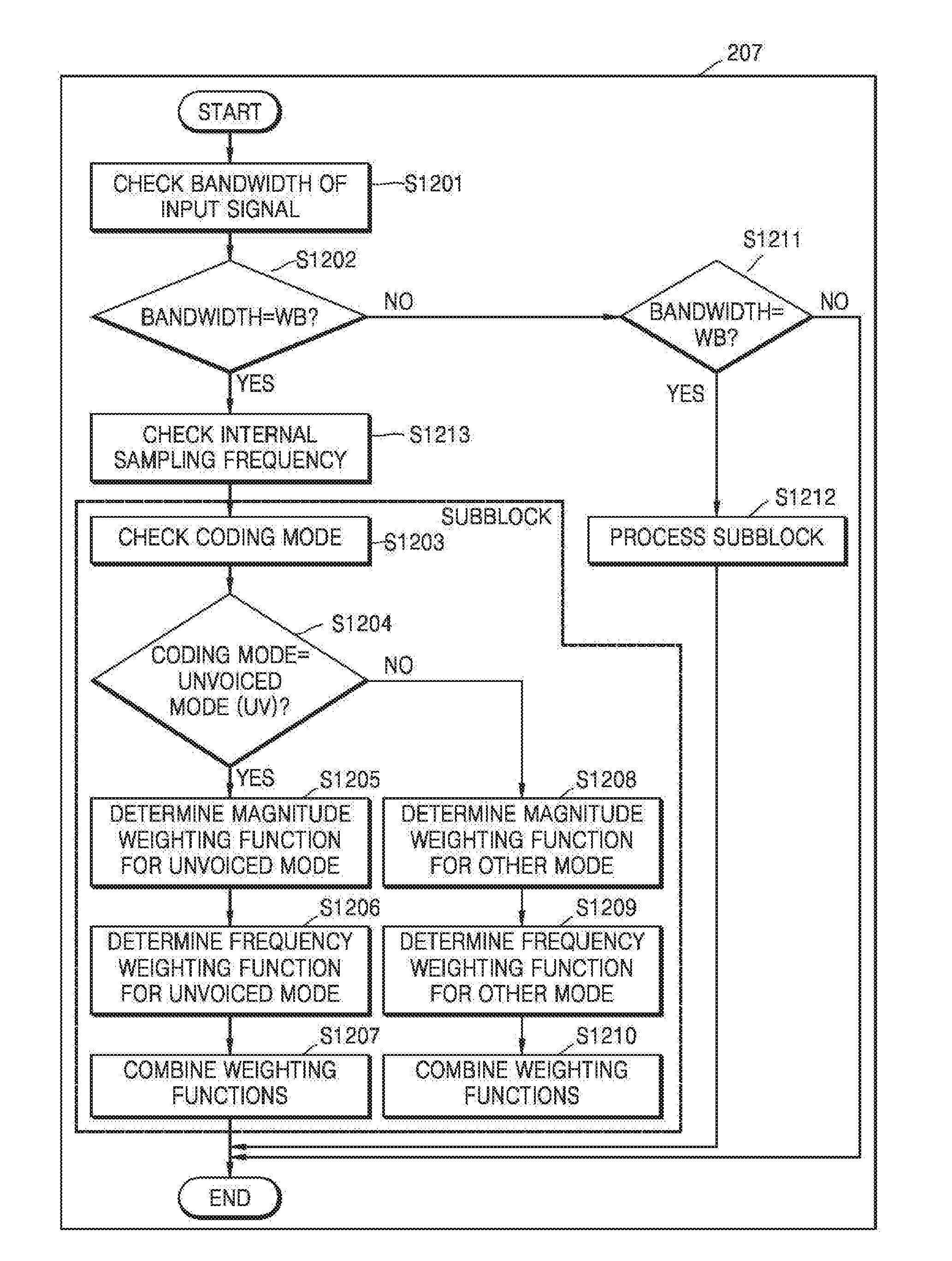
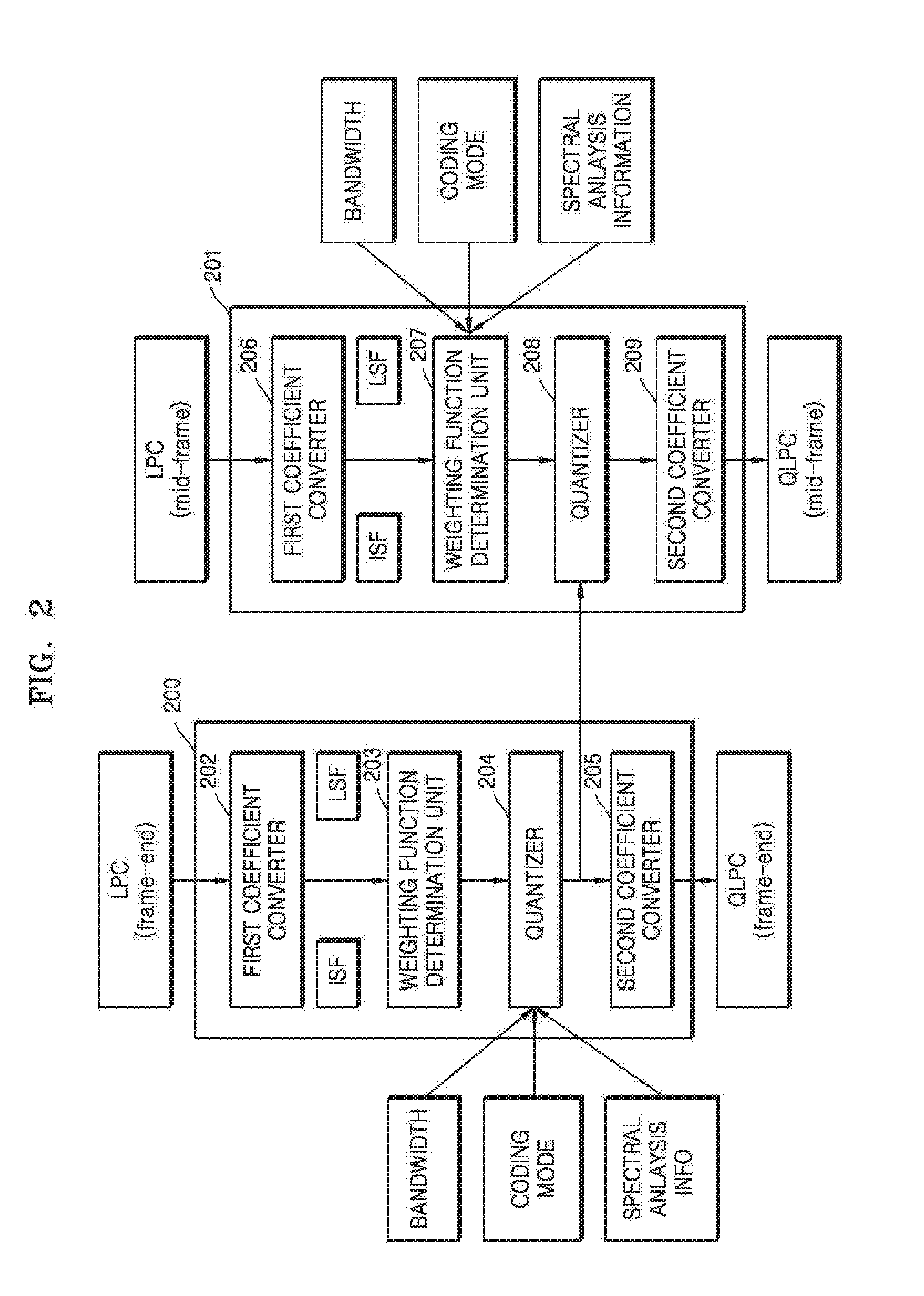
Apparatus and method determining weighting function for linear prediction coding coefficients quantization
ActiveUS9236059B2Improve Quantization EfficiencyQuality improvementSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingLinear prediction
An apparatus determining a weighting function for line prediction coding coefficients quantization converts a linear prediction coding (LPC) coefficient of an input signal into one of a line spectral frequency (LSF) coefficient and an immitance spectral frequency (ISF) coefficient and determines a weighting function associated with one of an importance of the ISF coefficient and importance of the LSF coefficient using one of the converted ISF coefficient and the converted LSF coefficient.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for generating an error concealment signal using individual replacement LPC representations for individual codebook information
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method of and apparatus for enhancing dialog using formants
InactiveUS20050114119A1Enhance only dialogSpeech recognitionLinear prediction codingFrequency spectrum
A dialog enhancing method and apparatus to boost formants of dialog zones without changing sound zones includes calculating line spectrum pair (LSP) coefficients based on linear prediction coding (LPC) from an input signal, determining whether voice zones exist in the input signal on the basis of the calculated LSP coefficients, and extracting formants from the LSP coefficients according to whether the voice zones exist, and boosting the formants.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
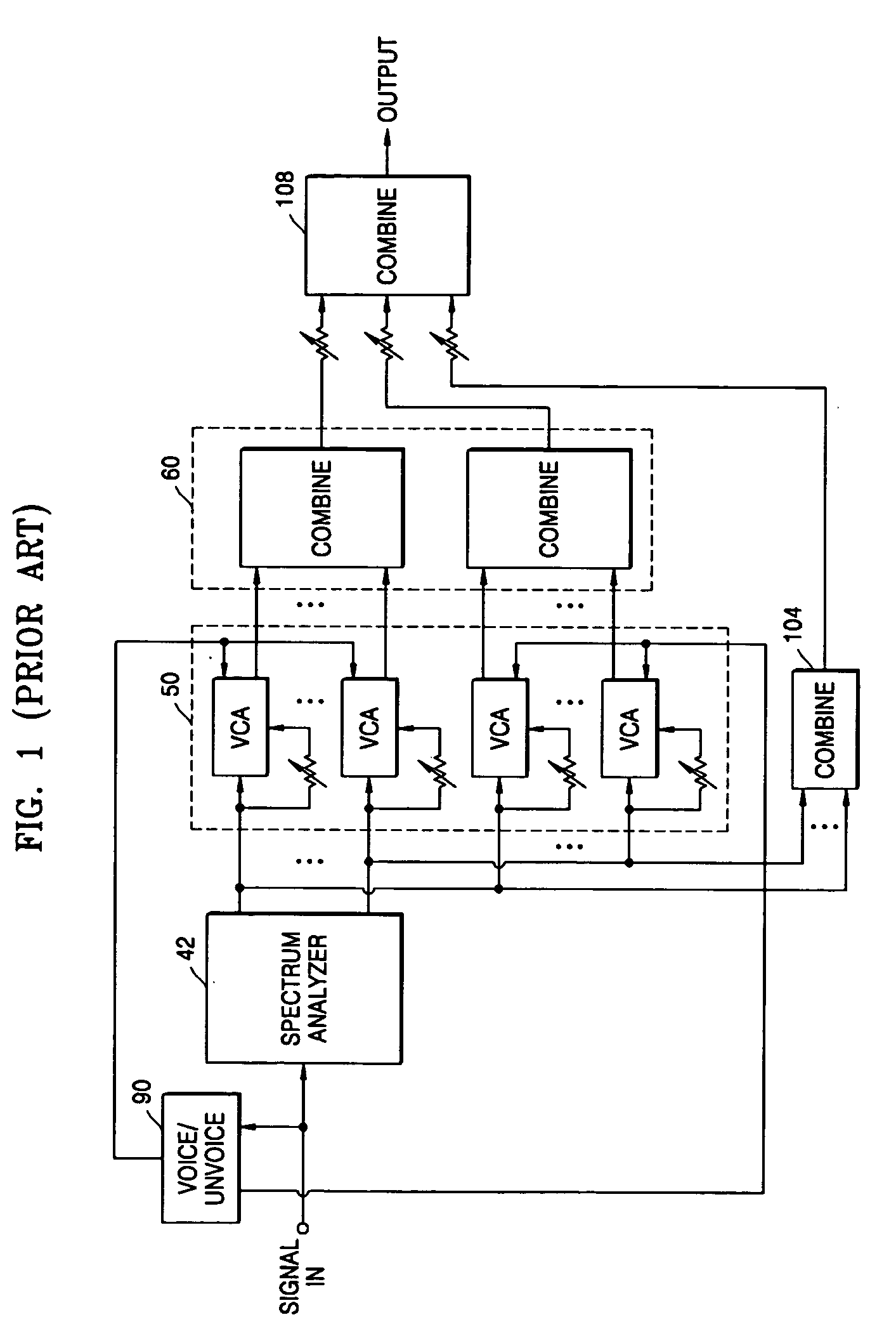
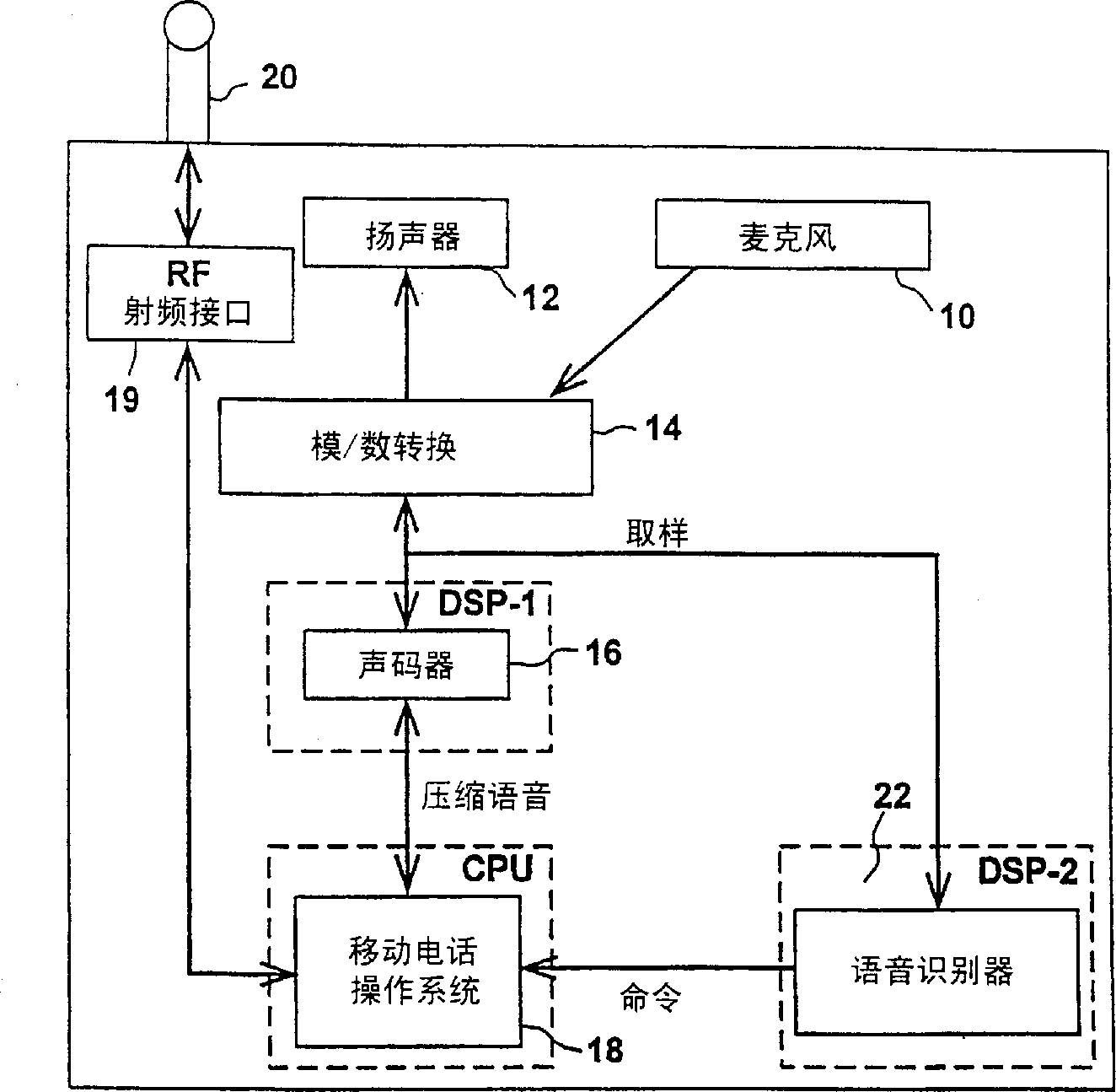
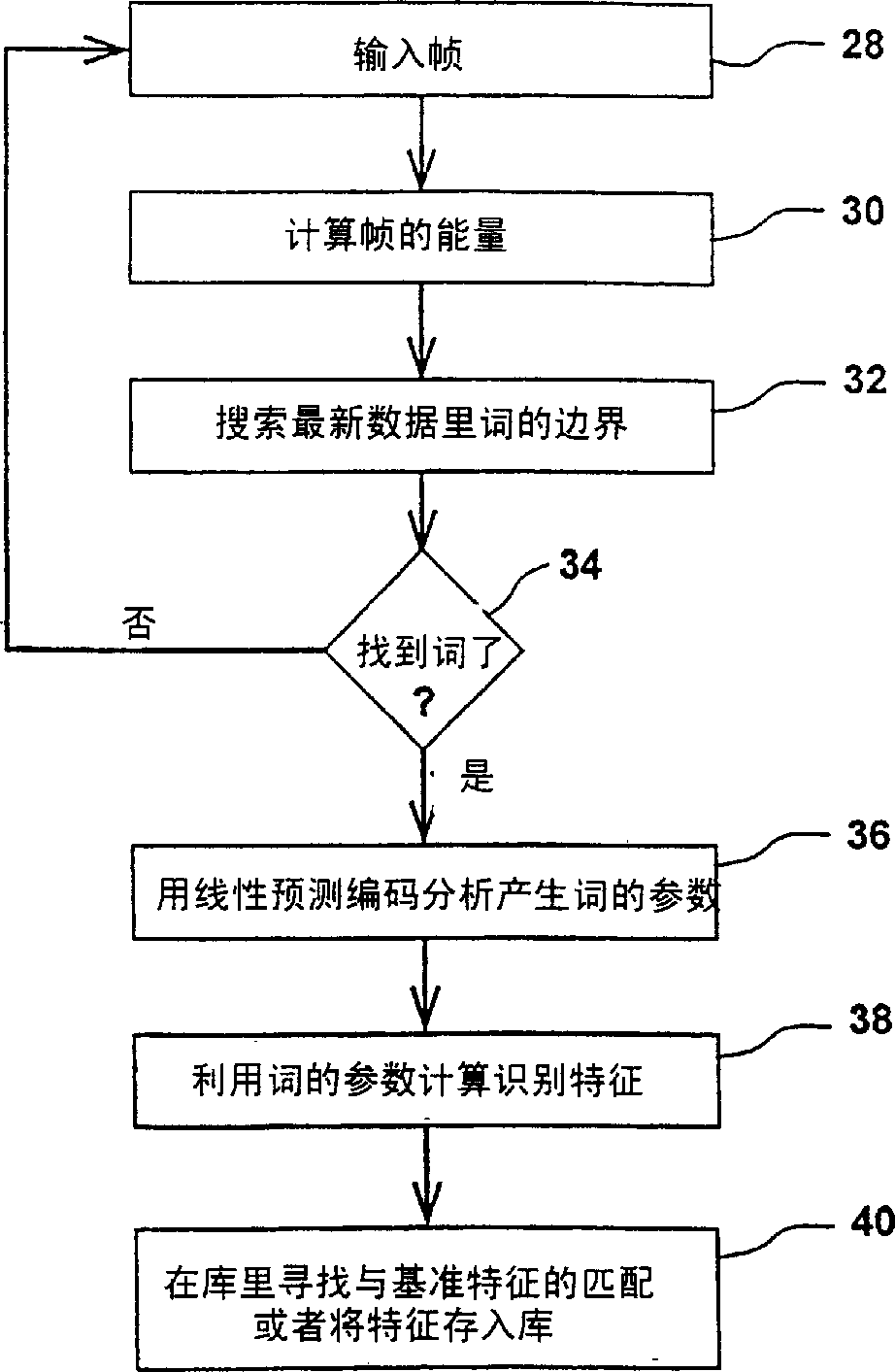
Vocoder-based voice recognizer
InactiveCN1273662ASmall amount of calculationSpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisLinear prediction codingSpeech identification
A vocoder based voice recognizer recognizes a spoken word using linear prediction coding based vocoder data without completely reconstructing the voice data. The recognizer generates at least one energy estimate per frame of the vocoder data (60) and searches for word boundaries in the vocoder data (64) using the associated energy estimates. If a word is found (66), the linear prediction coding word parameters are extracted (68) from the vocoder data associated with the word and recognition features are calculated (70) from the extracted linear prediction coding word parameters. Finally, the recognition features are matched with previously stored recognition features of other words (40), thereby recognizing the spoken word.
Owner:ART ADVANCED RECOGNITION TECH
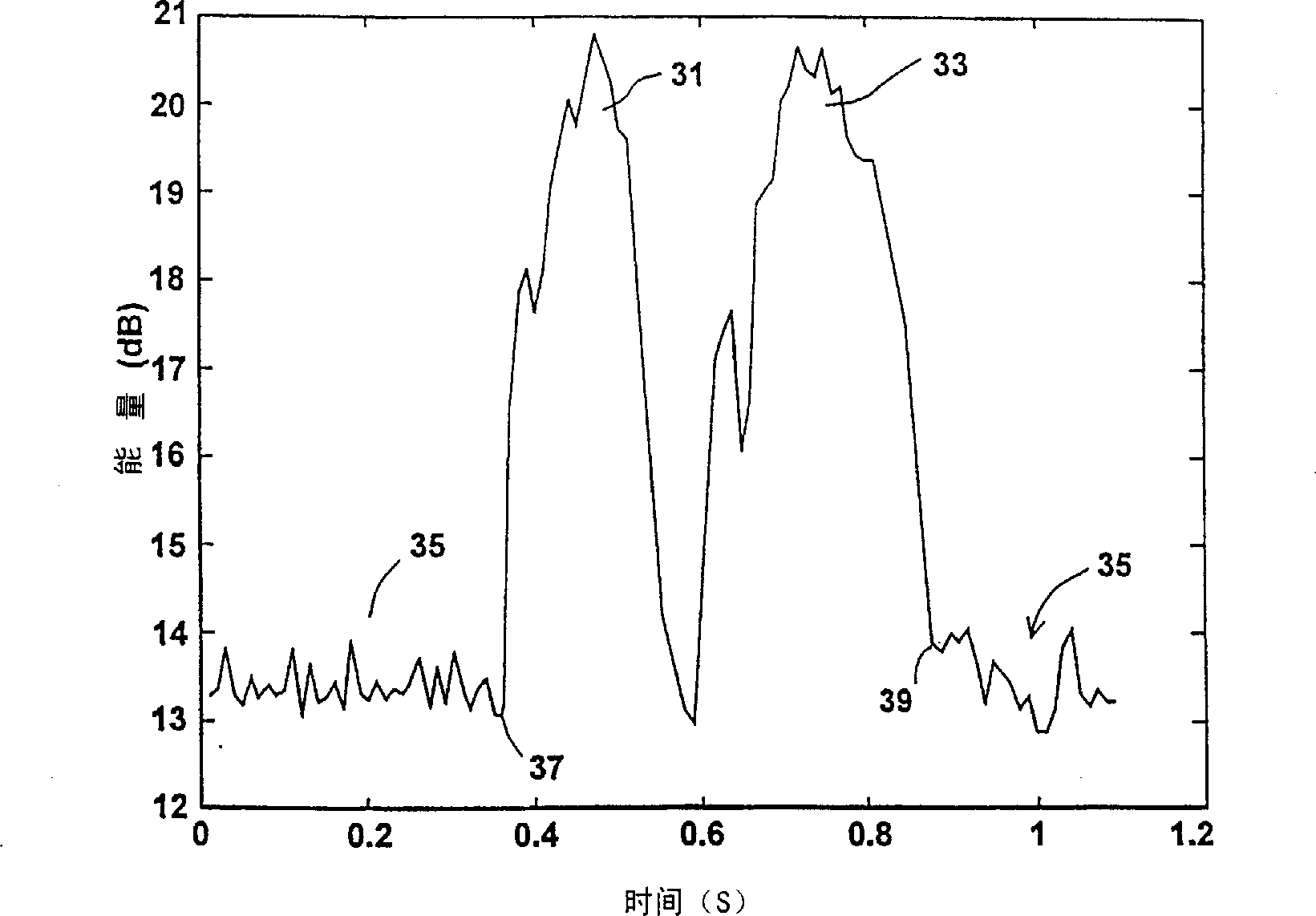
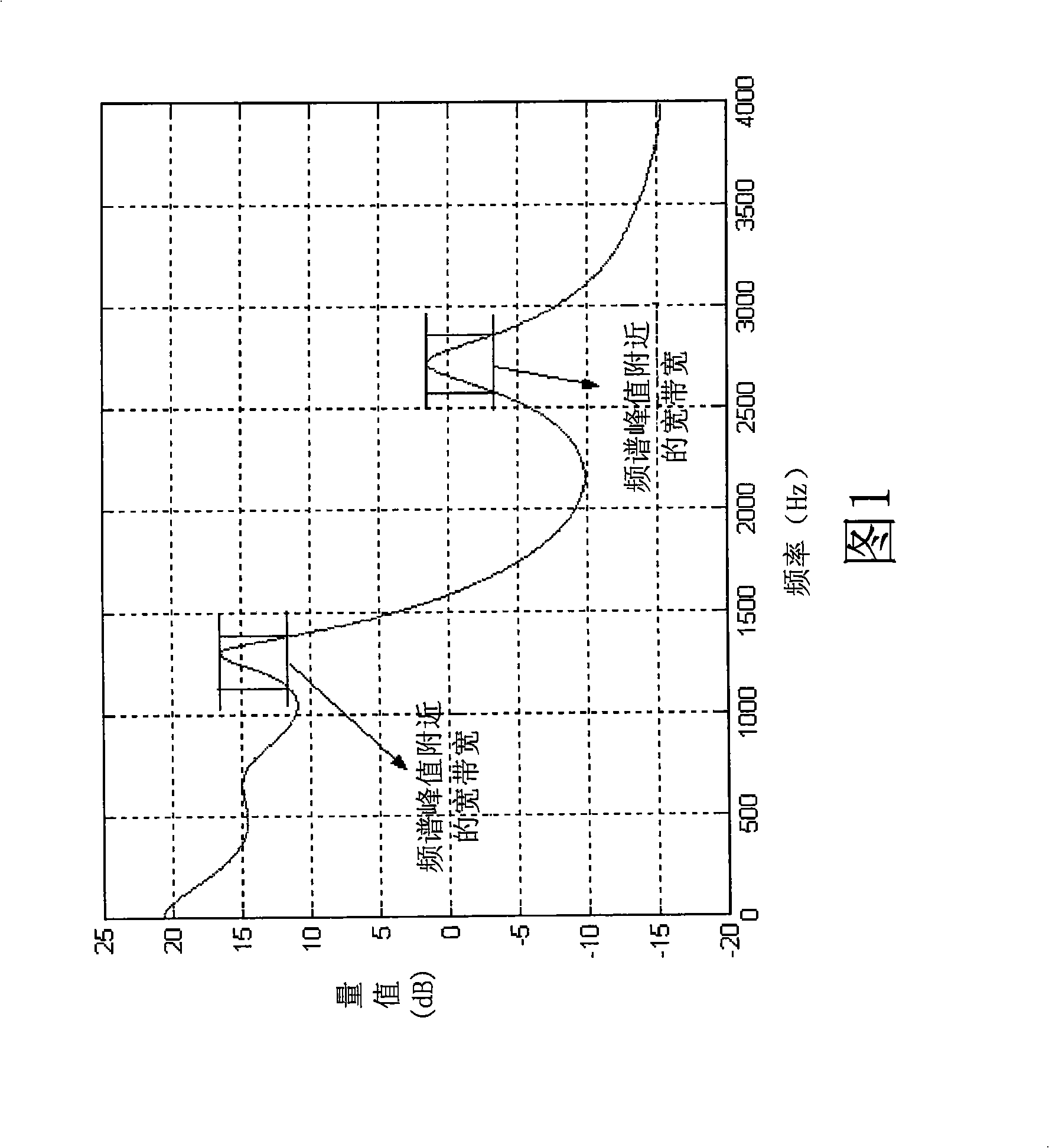
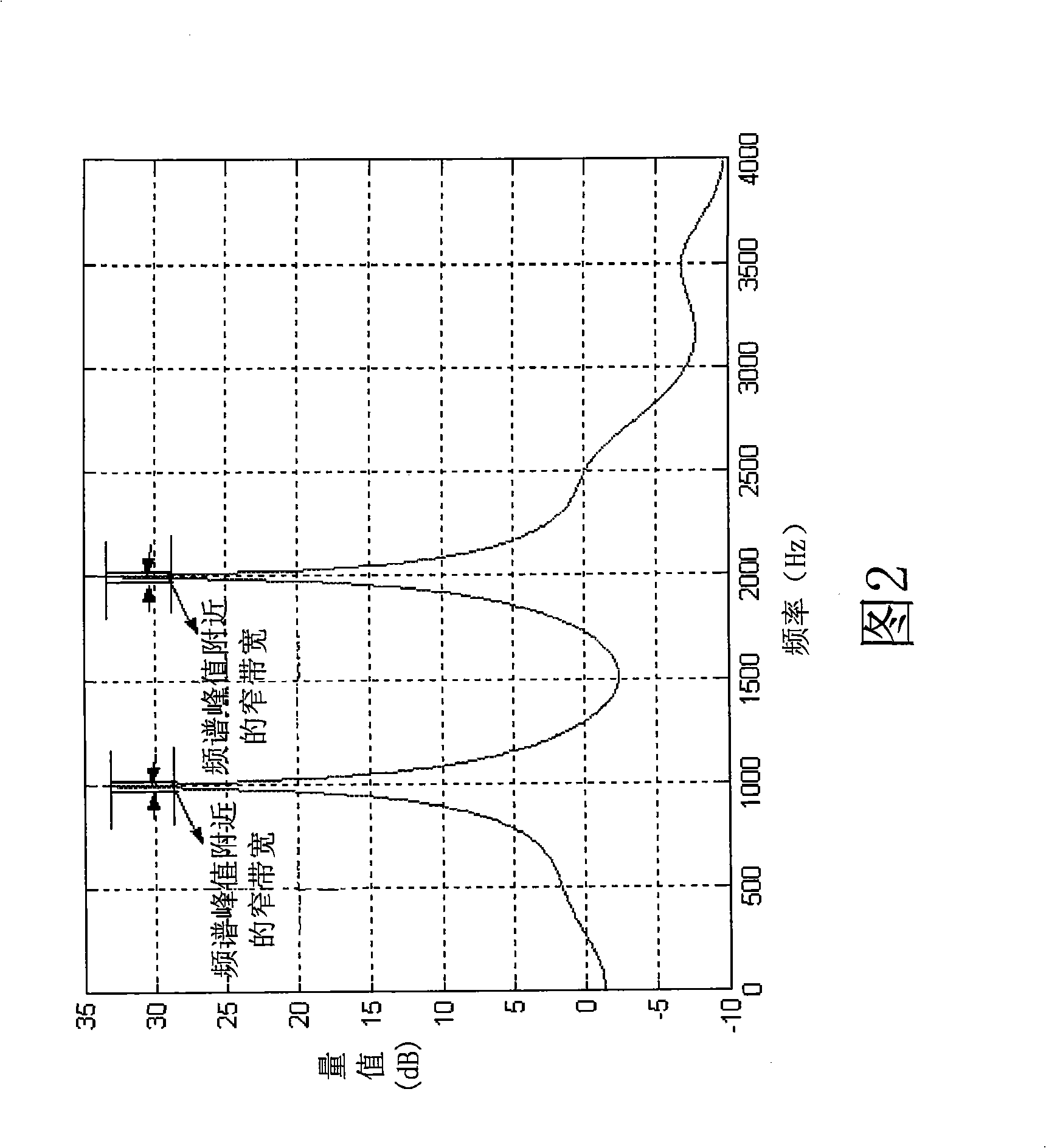
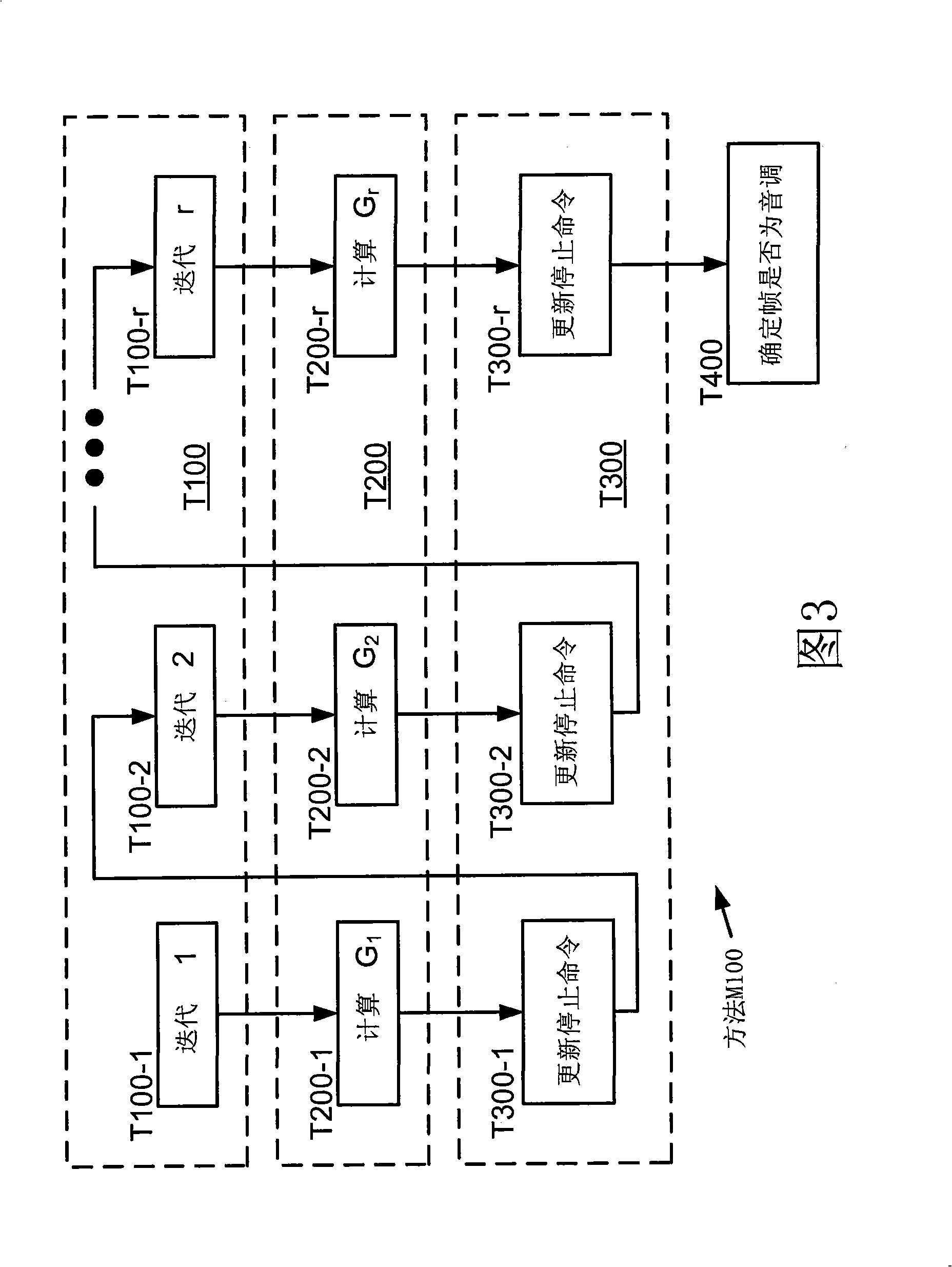
Systems, methods, and apparatus for detection of tonal components
Systems, methods, and apparatus for the detection of signals having spectral peaks with narrow bandwidth are described herein. The range of described configurations includes implementations that perform such detection using parameters of a linear prediction coding (LPC) analysis scheme.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and an apparatus for processing a signal
ActiveUS8135585B2Improve efficiencySpeech analysisTime-division multiplexFrequency spectrumLinear prediction coding
An apparatus and method for processing an encoded signal are discussed. The method includes: if a coding type of an audio signal is a mixed signal coding type, extracting spectral data and a linear predictive coefficient from the audio signal; generating a residual signal for the linear prediction by performing an inverse frequency conversion on the spectral data; reconstructing the audio signal by performing a linear prediction coding on the linear predictive coefficient and the residual signal; and reconstructing a high frequency region signal using an extension base signal corresponding to a partial region of the reconstructed audio signal and band extension information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Linear predication analysis method, device and system
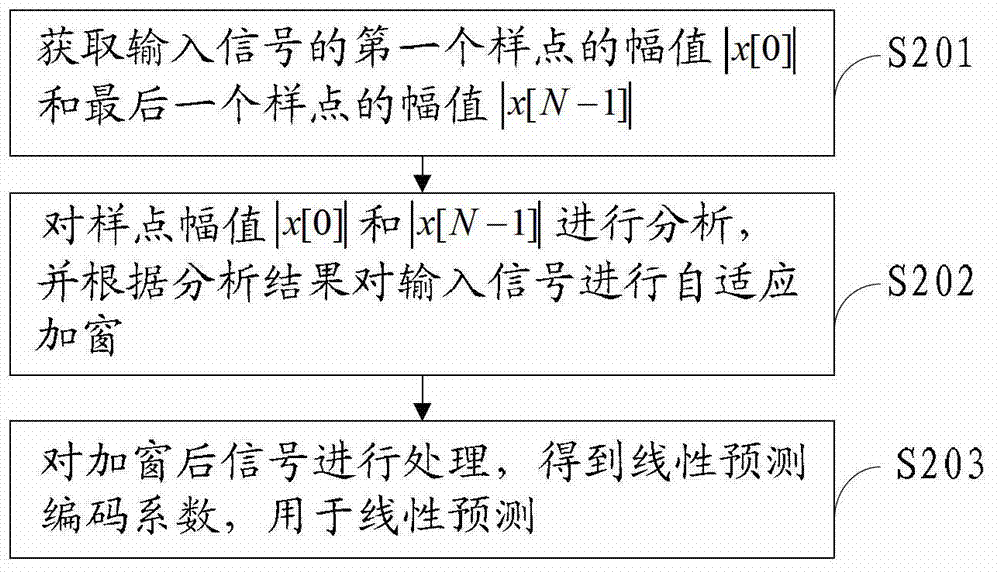
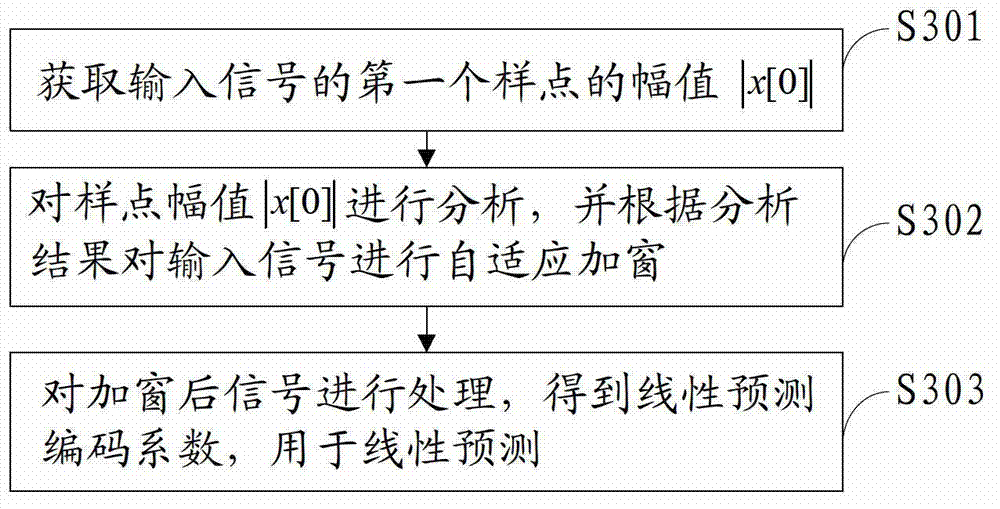
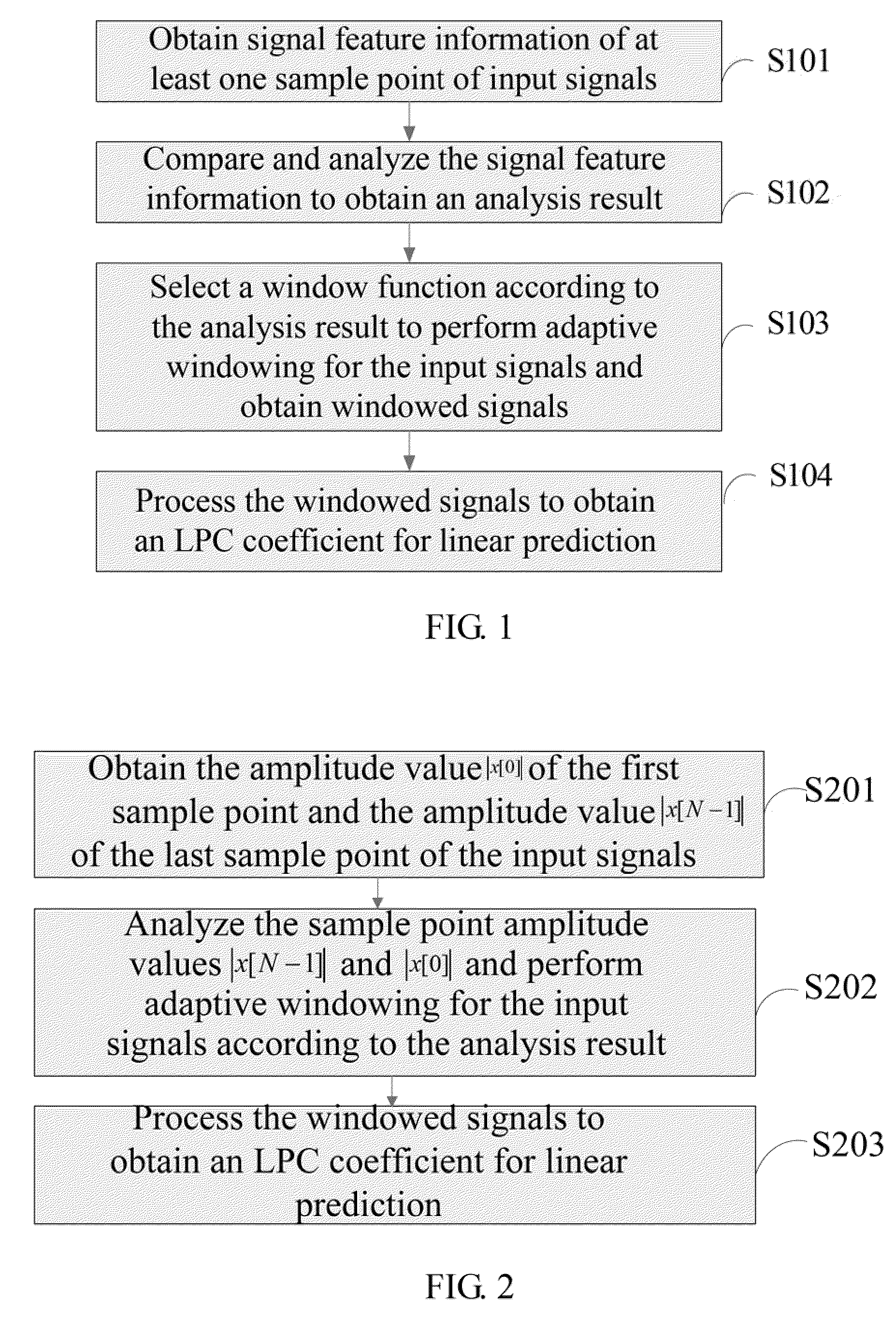
ActiveCN102930871AReduce coding complexityImprove predictive performanceSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingPredicting performance
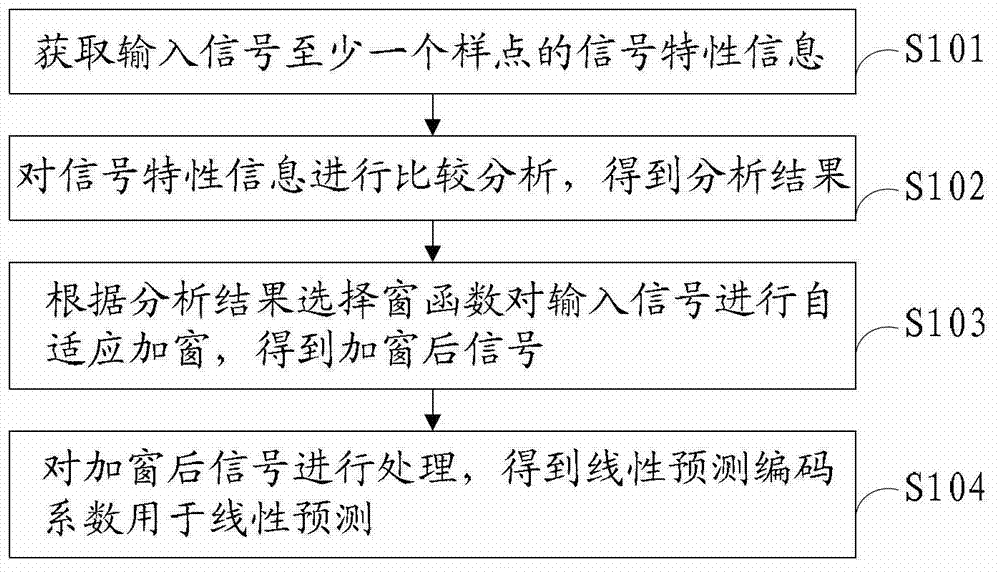
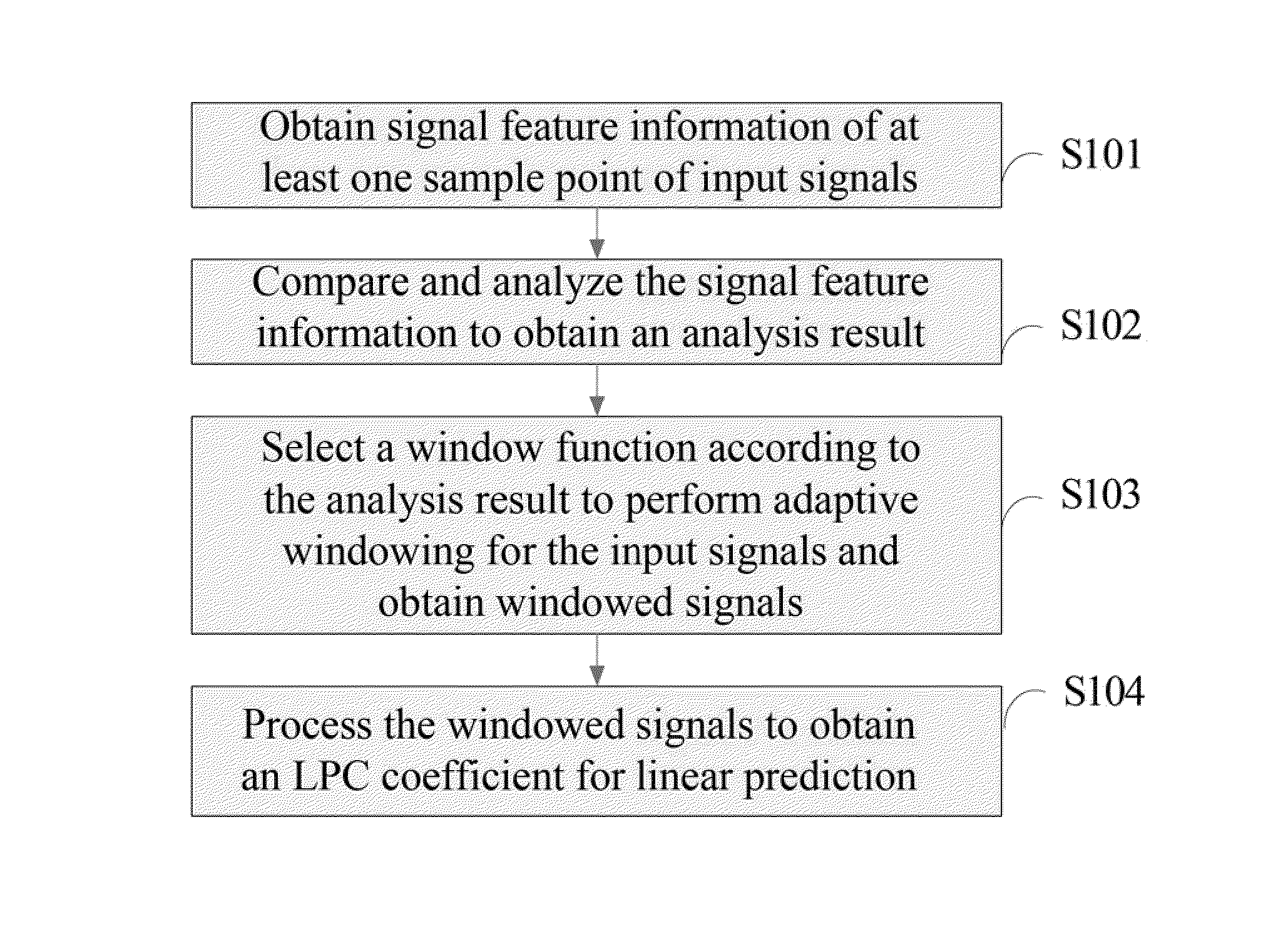
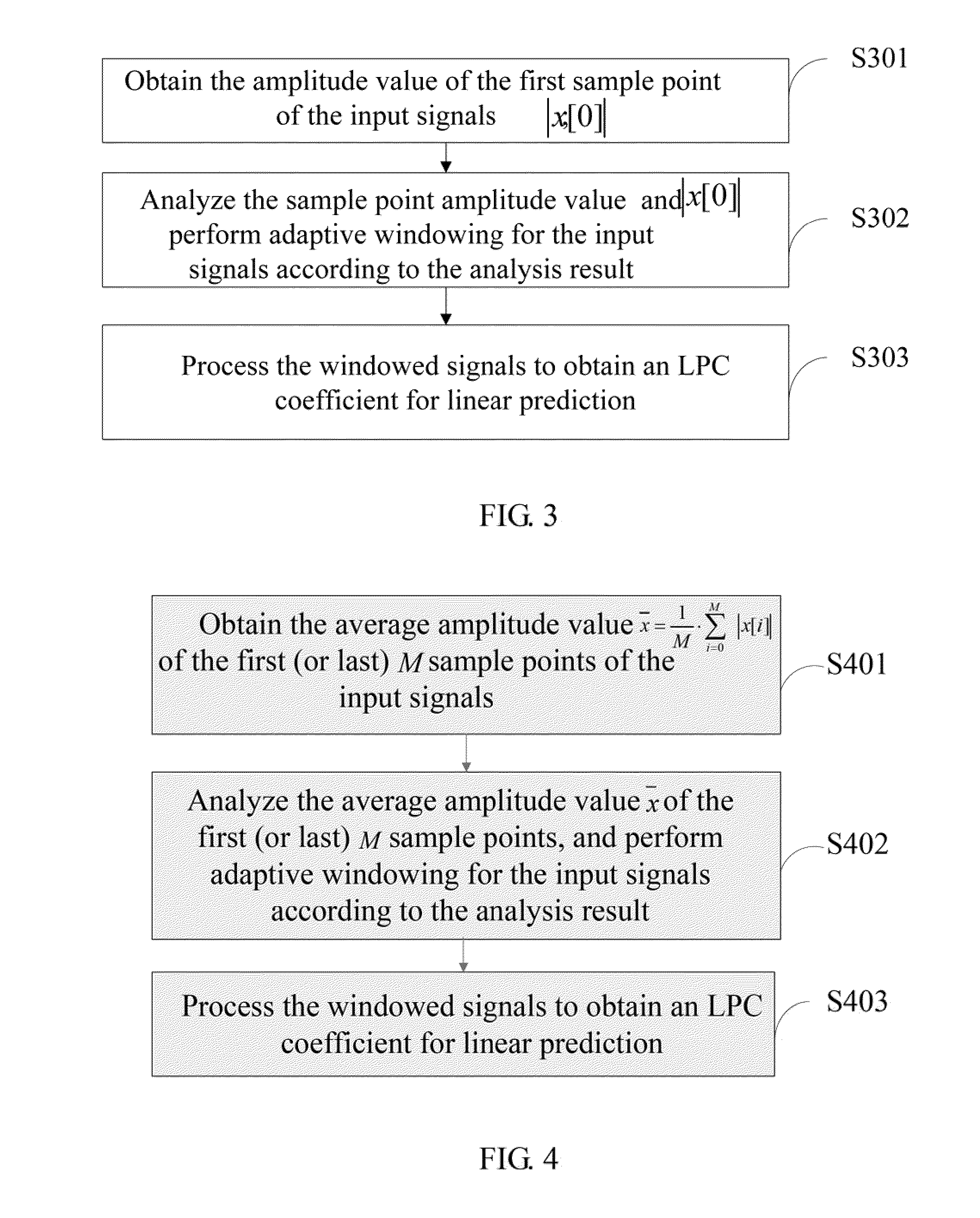
The invention discloses a linear prediction analysis method, device and system and relates to the field of communication. According to the linear prediction analysis method, device and system, the predicting performance of a linear prediction code can be improved and the complexity of analysis operation is low. The solution is as follows: the linear prediction analysis method comprises the following steps: acquiring signal characteristic information of at least one sample point of an input signal; carrying out comparative analysis on the signal characteristic information to obtain an analysis result; selecting a window function according to the analysis result for self-adaptively windowing the input signal to obtain a windowed signal; and processing the windowed signal to obtain a linear prediction coding coefficient for linear prediction. The linear prediction analysis method, device and system disclosed by the invention are used for linear predication coding.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method, apparatus and system for linear prediction coding analysis
ActiveUS8812307B2Predictive performanceEasy to operateSpeech analysisCode conversionLinear prediction codingSelf adaptive
The present invention relates to communication technologies and discloses a method, an apparatus and a system for Linear Prediction Coding (LPC) analysis to improve LPC prediction performance and simplify analysis operation. The method includes: obtaining signal feature information of at least one sample point of input signals; comparing and analyzing the signal feature information to obtain an analysis result; selecting a window function according to the analysis result to perform adaptive windowing for the input signals and obtain windowed signals; and processing the windowed signals to obtain an LPC coefficient for linear prediction. The embodiments of the present invention are applicable to LPC.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for changing voice by means of speech tone modification on basis of derivative glottal flow models
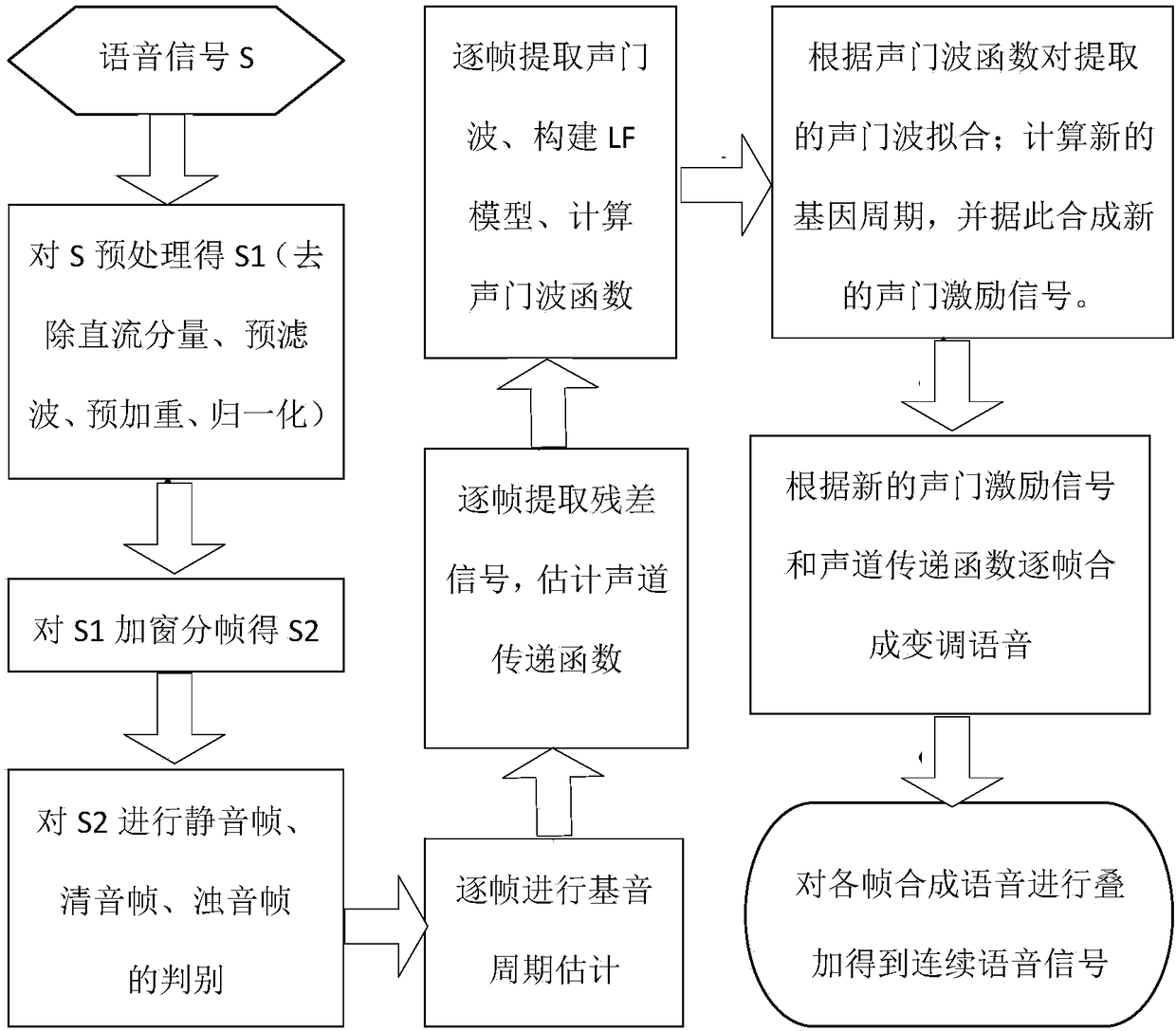
ActiveCN108281150AQuality improvementAccurate estimateSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingGlottis
The invention discloses a method for changing voice by means of speech tone modification on the basis of derivative glottal flow models. The method has the advantages that tone-modified speech can besynthesized by the aid of linear prediction coding technology and derivative glottal flow combined processes, residual signals can be obtained from speech signals by the aid of LPC (linear predictioncoding) inverse filters, are first-order difference of glottal signals, and are simulated by LF models in detail to obtain high-quality glottal excitation signals, and accordingly high-quality tone-modified speech can be synthesized; the method is simple, effective and speedy and has extensive practical value, and voice sources can be flexibly controlled by te / tc and tp / tc.
Owner:上海泰亿格康复医疗科技股份有限公司
Speech decoder and method for decoding speech
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Weight function determination device and method for quantizing linear prediction coding coefficient
ActiveUS20160336018A1Improve Quantization EfficiencyQuality improvementSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingAlgorithm
A weighting function determination method includes obtaining a line spectral frequency (LSF) coefficient or an immitance spectral frequency (ISF) coefficient from a linear predictive coding (LPC) coefficient of an input signal and determining a weighting function by combining a first weighting function based on spectral analysis information and a second weighting function based on position information of the LSF coefficient or the ISF coefficient.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Residual coding method of linear prediction coding coefficient based on collaborative quantization, and computing device for performing the method
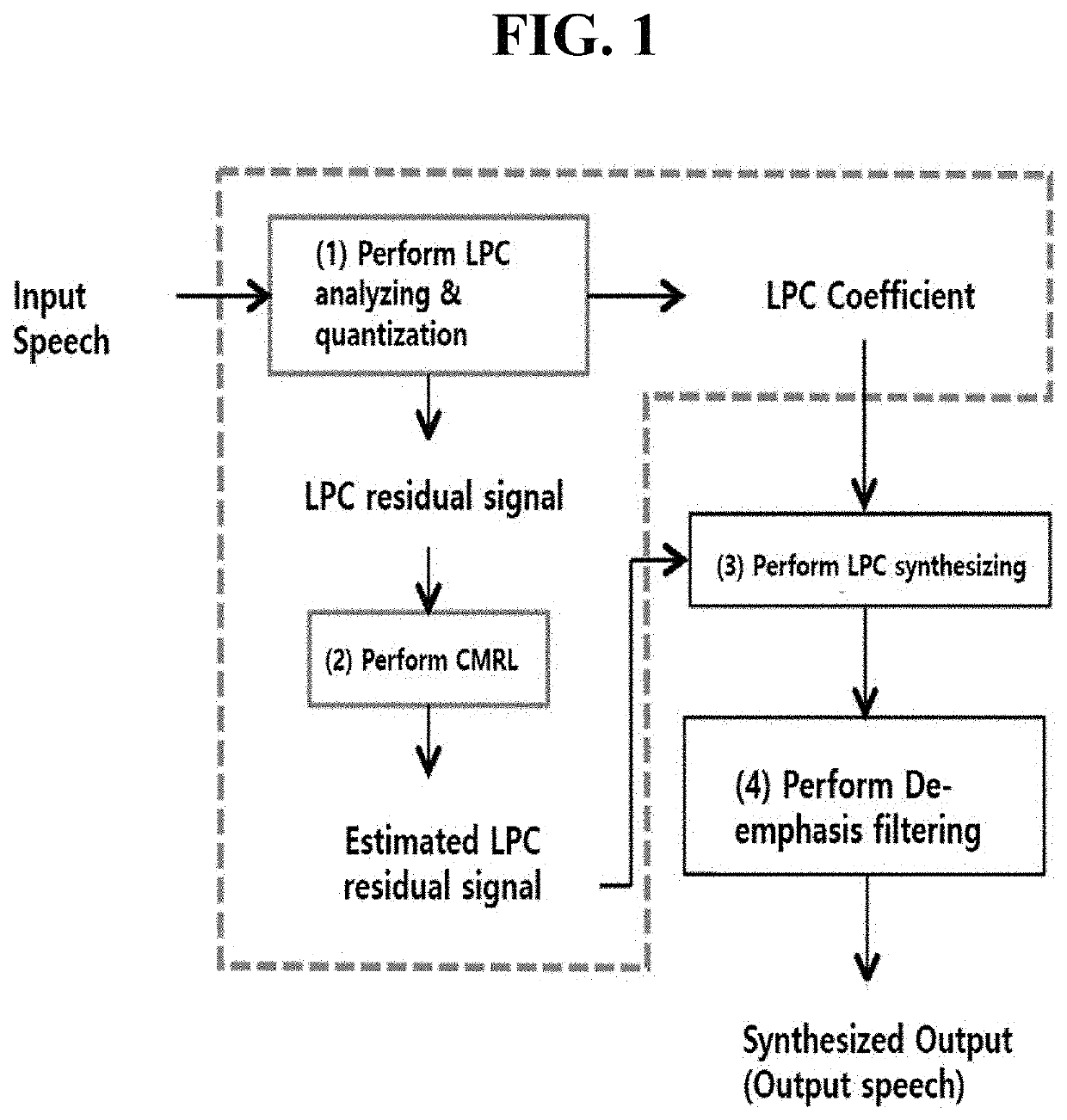
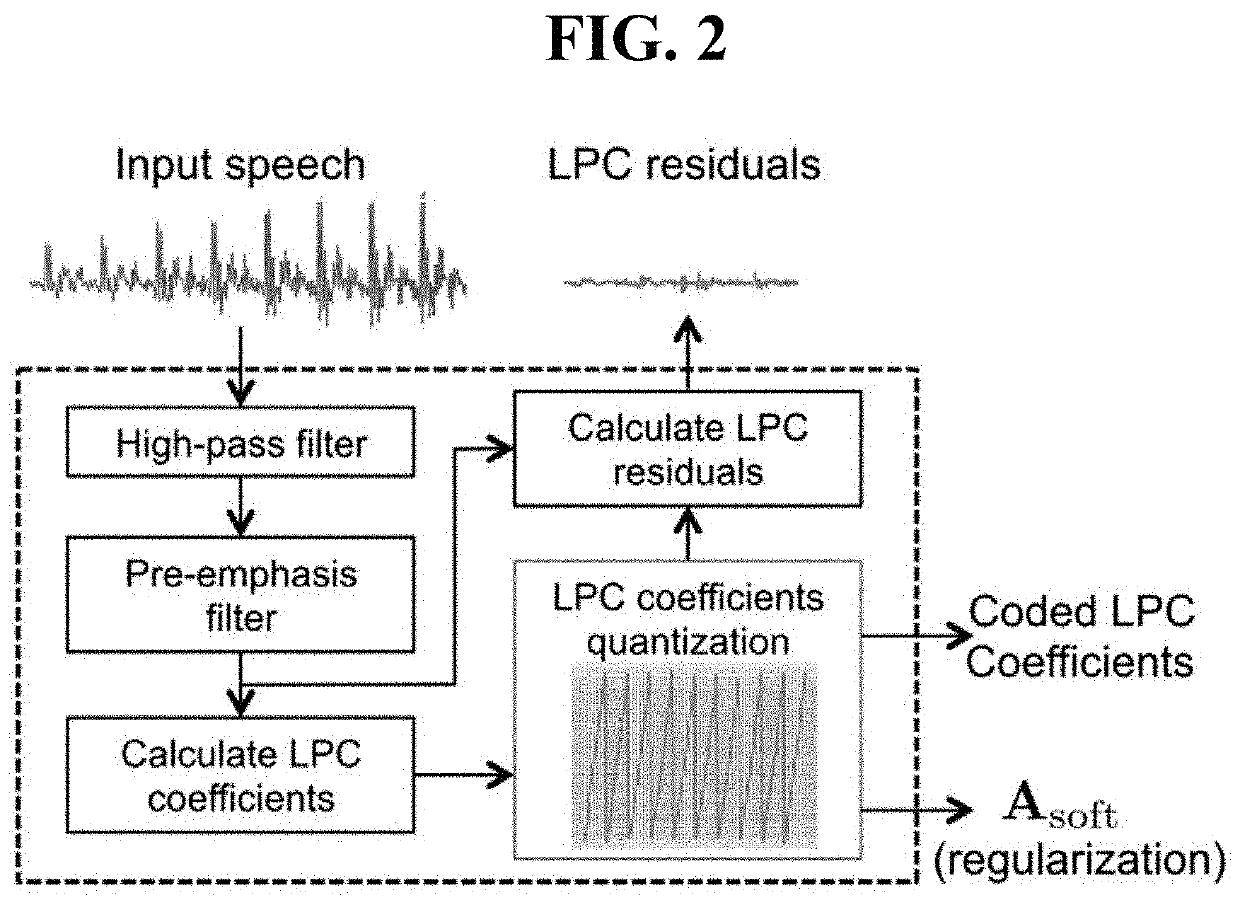
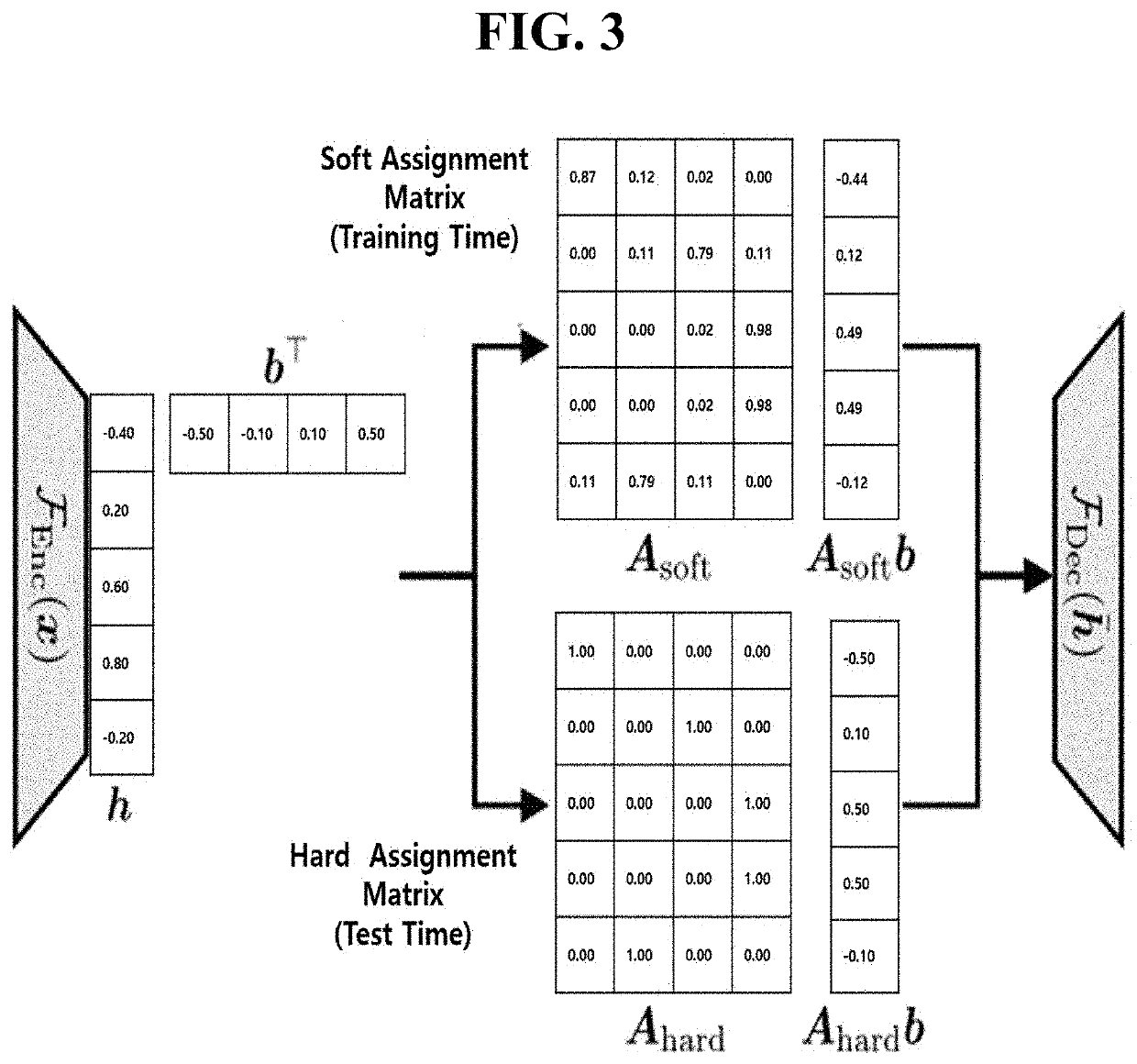
Disclosed are a method for coding a residual signal of LPC coefficients based on collaborative quantization and a computing device for performing the method. The residual signal coding method includes: generating encoded LPC coefficients and LPC residual signals by performing LPC analysis and quantization on an input speech; Determining a predicted LPC residual signal by applying the LPC residual signal to cross module residual learning; Performing LPC synthesis using the coded LPC coefficients and the predicted LPC residual signal; It may include the step of determining an output speech that is a synthesized output according to a result of performing the LPC synthesis.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Method, apparatus and system for linear prediction coding analysis
ActiveUS20110320195A1Increased complexityPredictive performanceSpeech analysisCode conversionLinear prediction codingLinear prediction
The present invention relates to communication technologies and discloses a method, an apparatus and a system for Linear Prediction Coding (LPC) analysis to improve LPC prediction performance and simplify analysis operation. The method includes: obtaining signal feature information of at least one sample point of input signals; comparing and analyzing the signal feature information to obtain an analysis result; selecting a window function according to the analysis result to perform adaptive windowing for the input signals and obtain windowed signals; and processing the windowed signals to obtain an LPC coefficient for linear prediction. The embodiments of the present invention are applicable to LPC.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
National language single tone recognizing system capable of wide application
InactiveCN101339765AAchieve timely recognitionTimely identificationSpeech recognitionLinear prediction codingFrequency spectrum
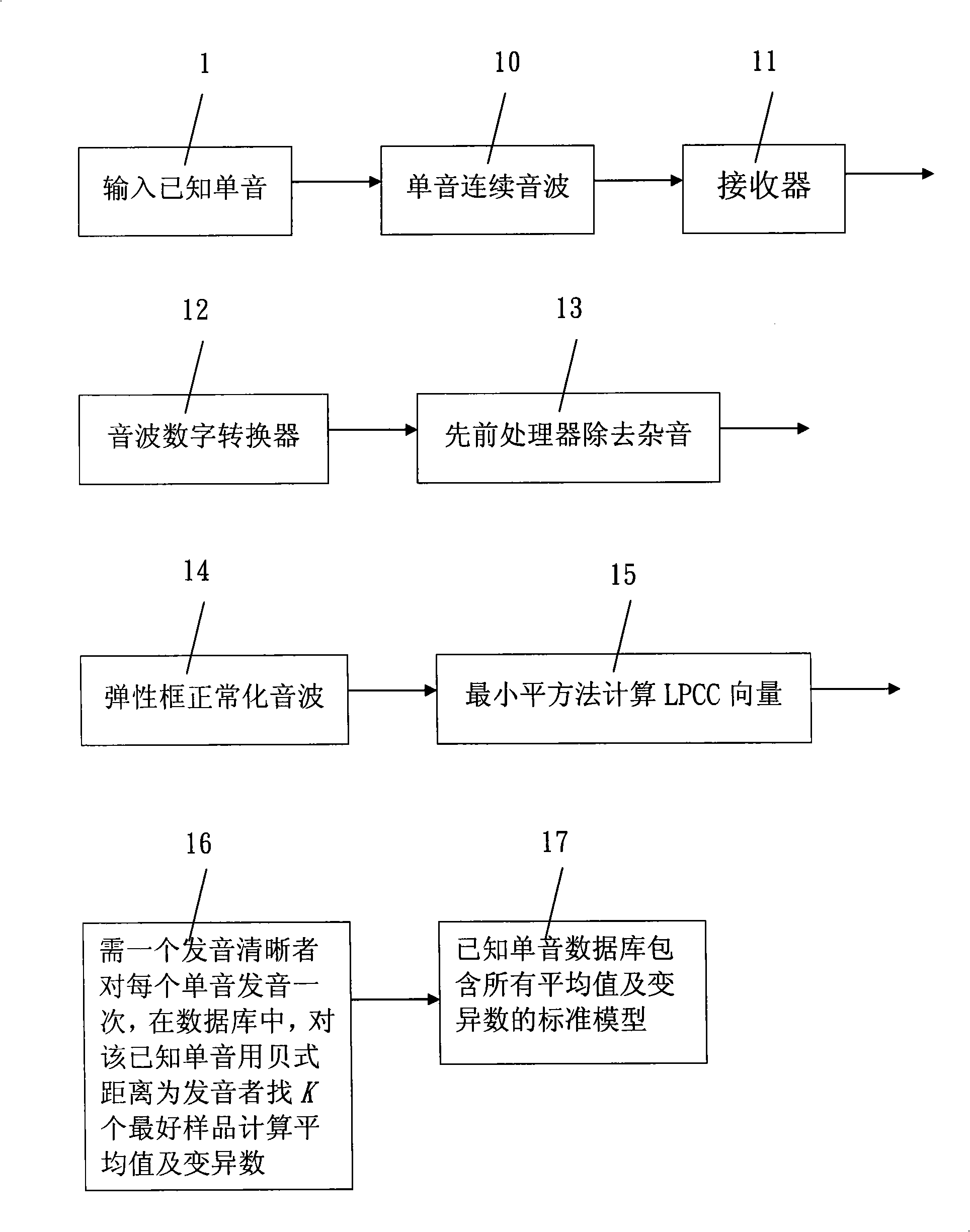
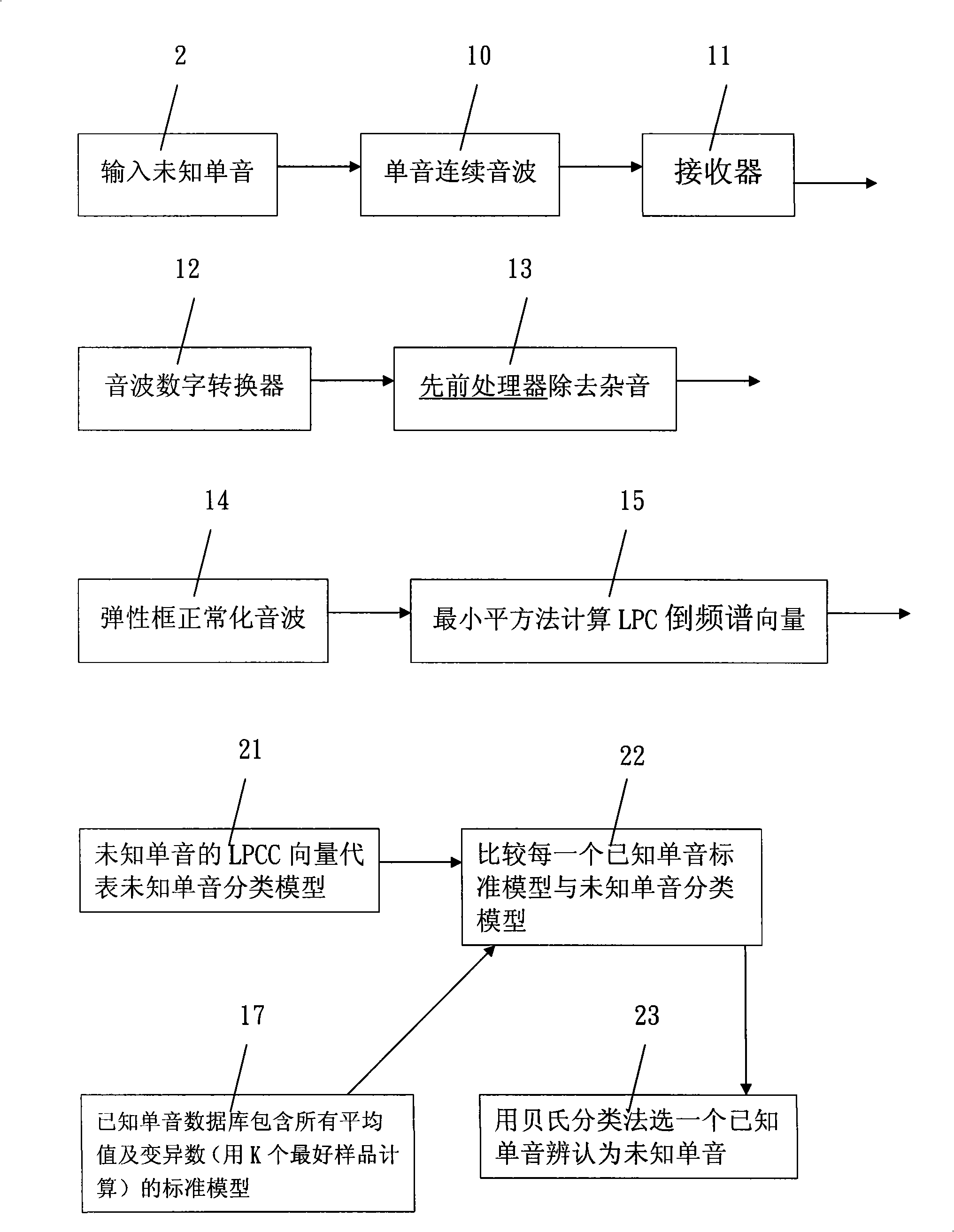
The invention relates to a widely applicable mother tongue monosyllable identification system which comprises a previous processor, a characteristic matrix method in which the known monosyllable sound wave normalization is consistent with the selected size, wherein, an elastic frame is adopted to normalize the sound wave and transfer the sound wave into linear prediction coding cepstrum characteristic matrixes in equal size and the same known monosyllable sound wave is transferred into matrixes with the same characteristics; to each known monosyllable, K best samples are chosen; and the K best samples of one known monosyllable characteristic matrix are transferred into a standard model and stored in a database. The standard model comprises the mean value and the variance number of the K best samples of the known monosyllable characteristic matrix; the unknown monosyllable sound wave is normalized and transferred into a characteristic matrix which has the same size with the known standard model, includes the linear prediction coding ceptrum inside, and is called as an unknown monosyllable classifying model; the unknown monosyllable classifying model are compared with all the known monosyllable standard model in the database to find a known monosyllable, which has the smallest distance with the unknown monosyllable and is identified as an unknown monosyllable.
Owner:黎自奋 +2
Apparatus and method of encoding/decoding voice for selecting quantization/dequantization using characteristics of synthesized voice
InactiveUS8473284B2Modulated-carrier systemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDecoding methodsLinear prediction coding
A voice encoding / decoding method and apparatus. A voice encoder includes: a quantization selection unit generating a quantization selection signal; and a quantization unit extracting a linear prediction coding (LPC) coefficient from an input signal, converting the extracted LPC coefficient into a line spectral frequency (LSF), quantizing the LSF with a first LSF quantization unit or a second LSF quantization unit based on the quantization selection signal, and converting the quantized LSF into a quantized LPC coefficient. The quantization selection signal selects the first LSF quantization unit or second LSF quantization unit based on characteristics of a synthesized voice signal in previous frames of the input signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com