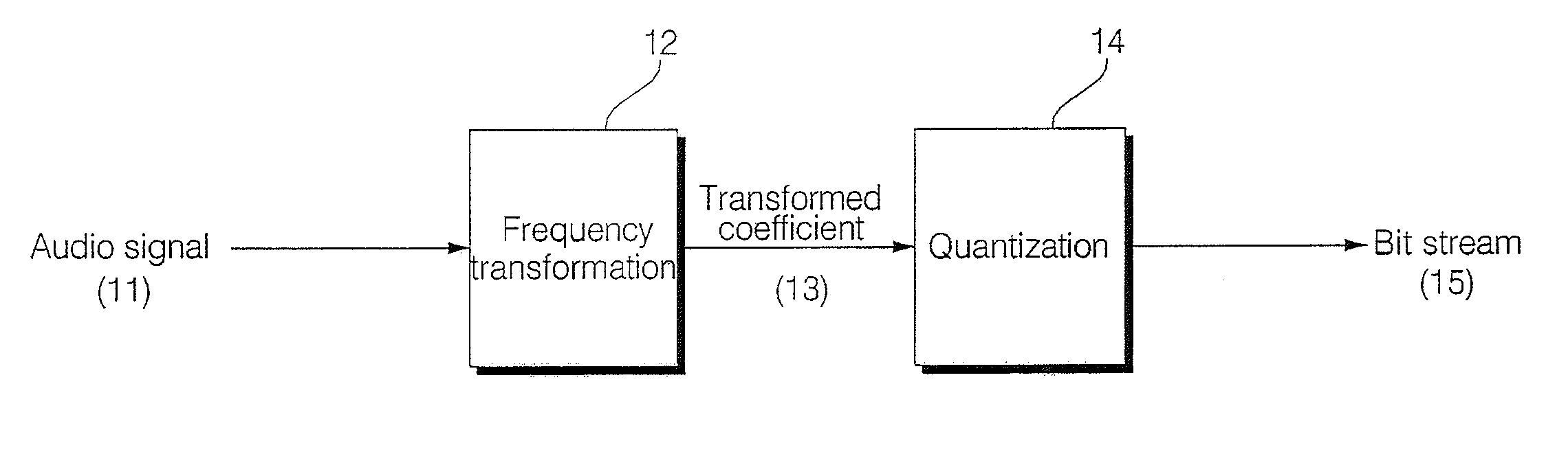
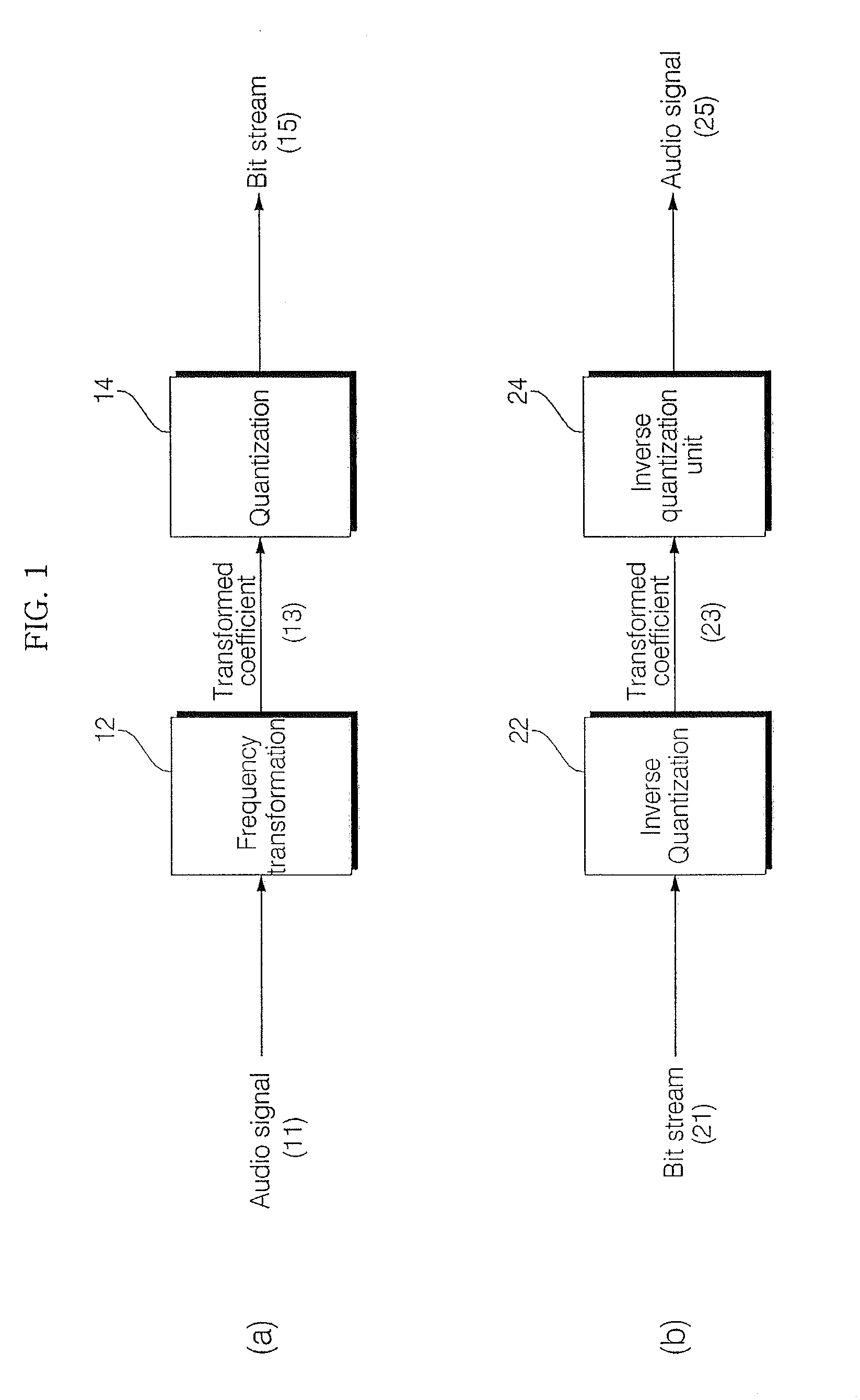
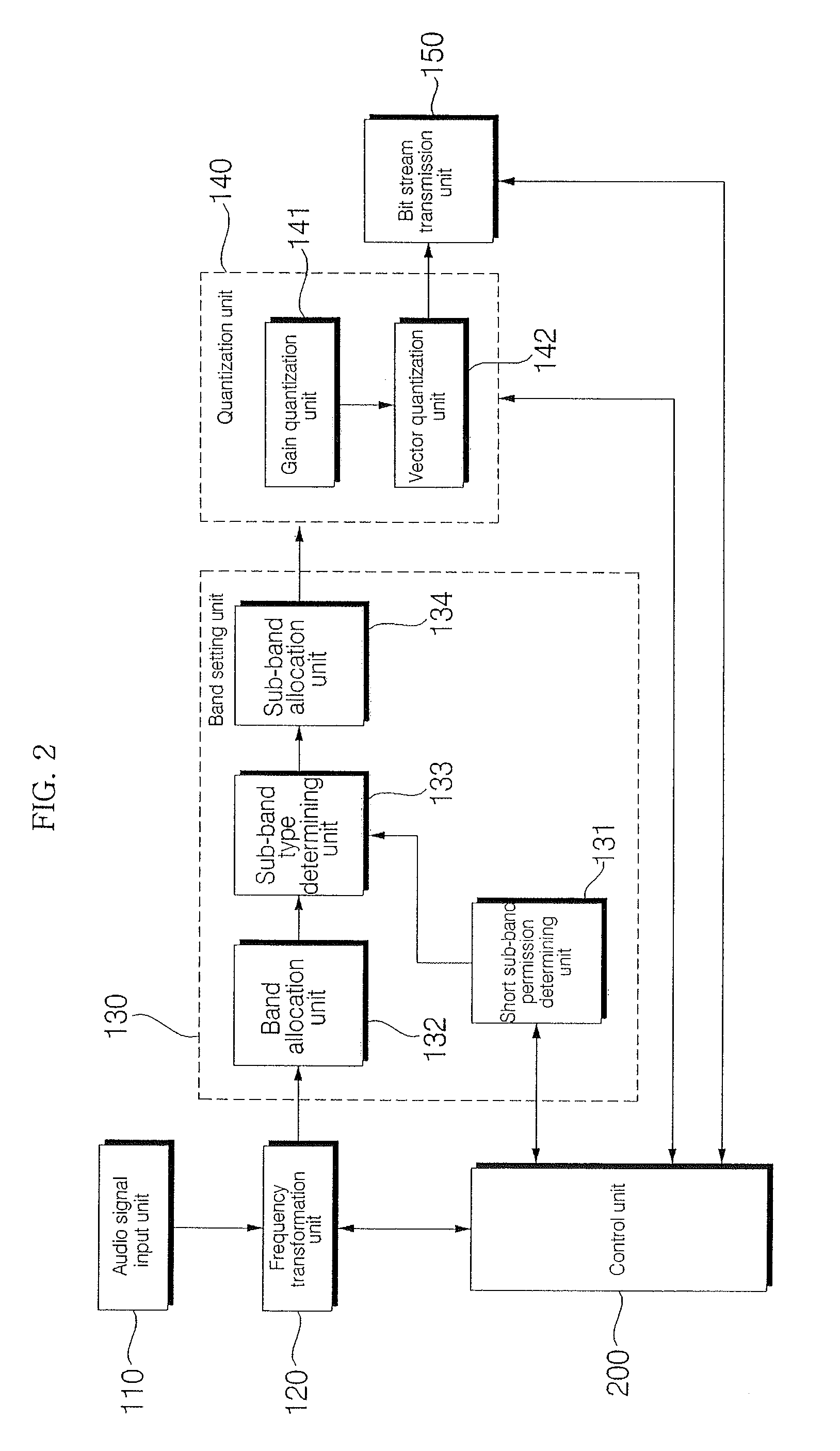
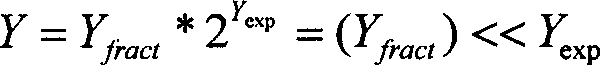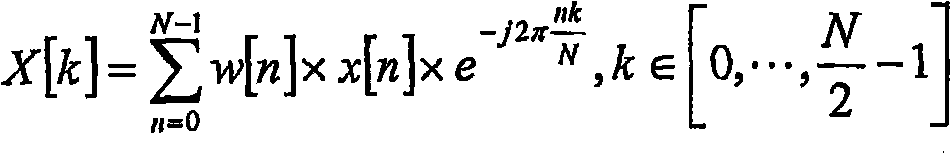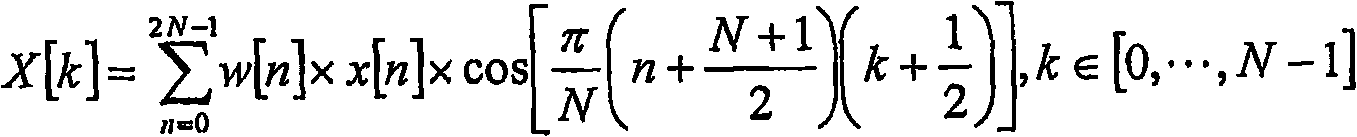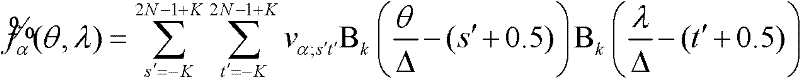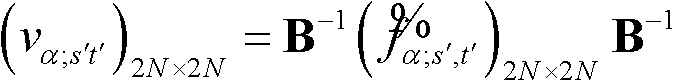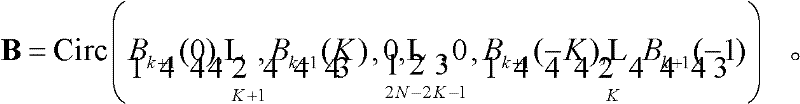Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117 results about "Spectral coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
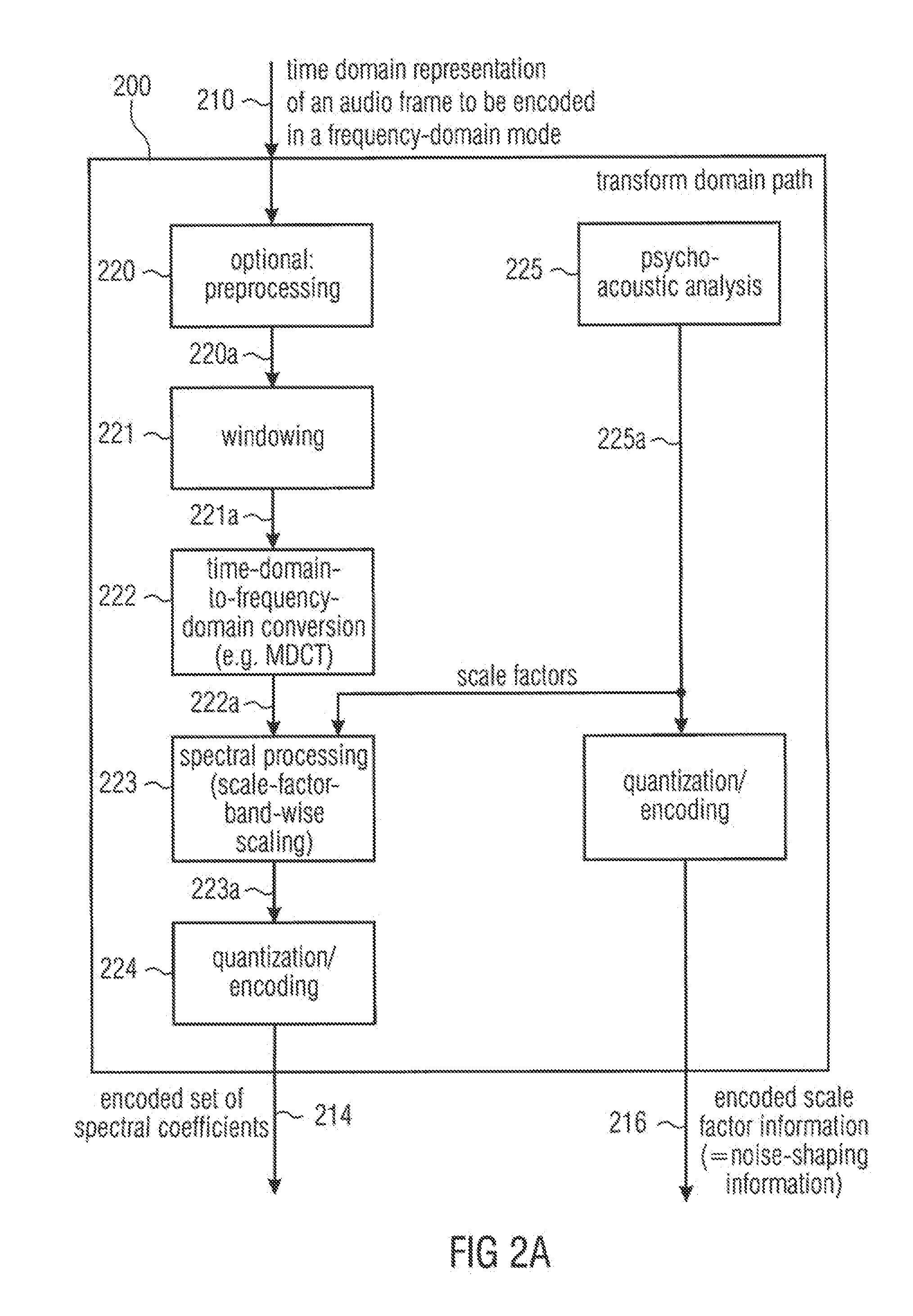
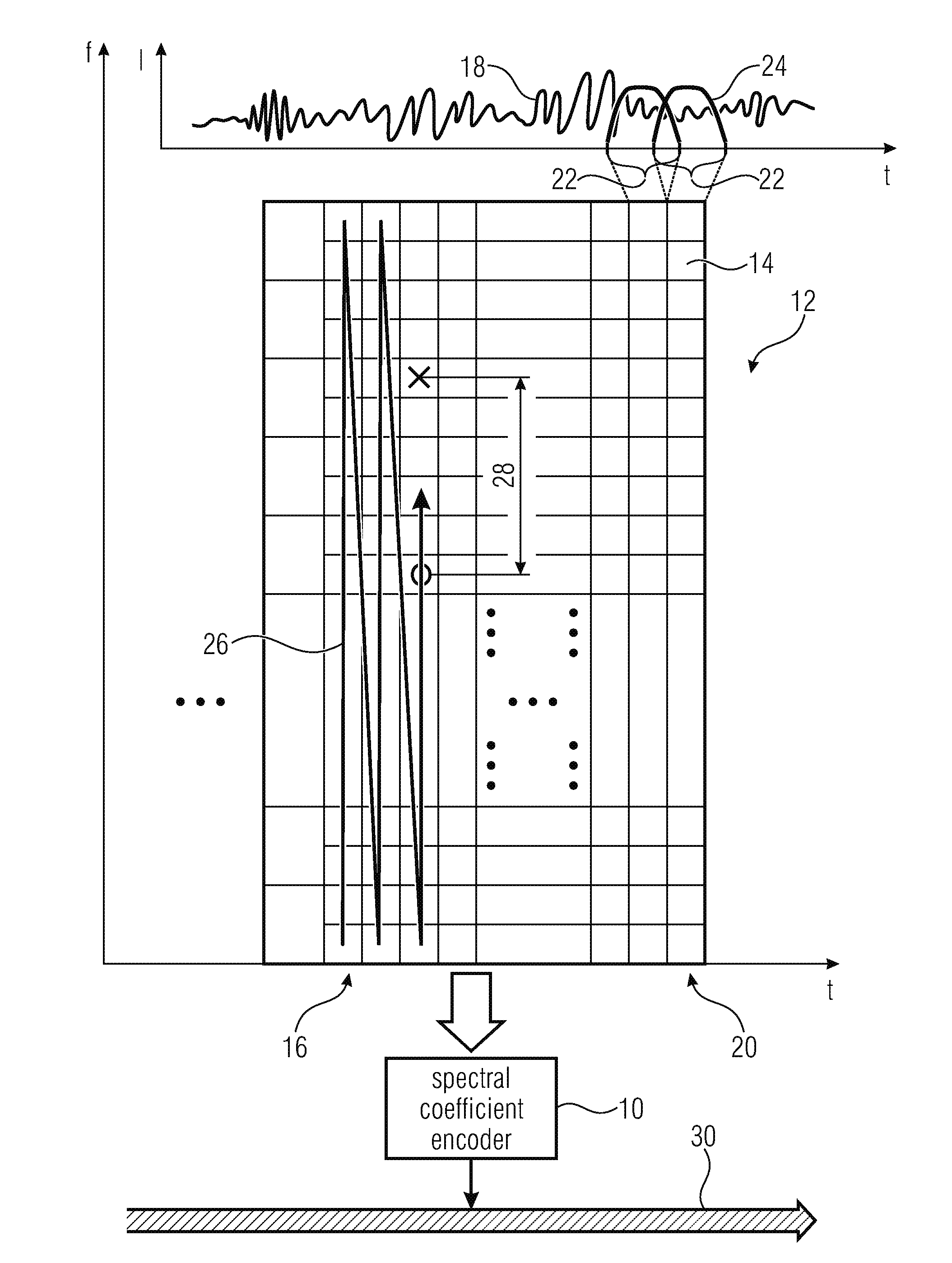
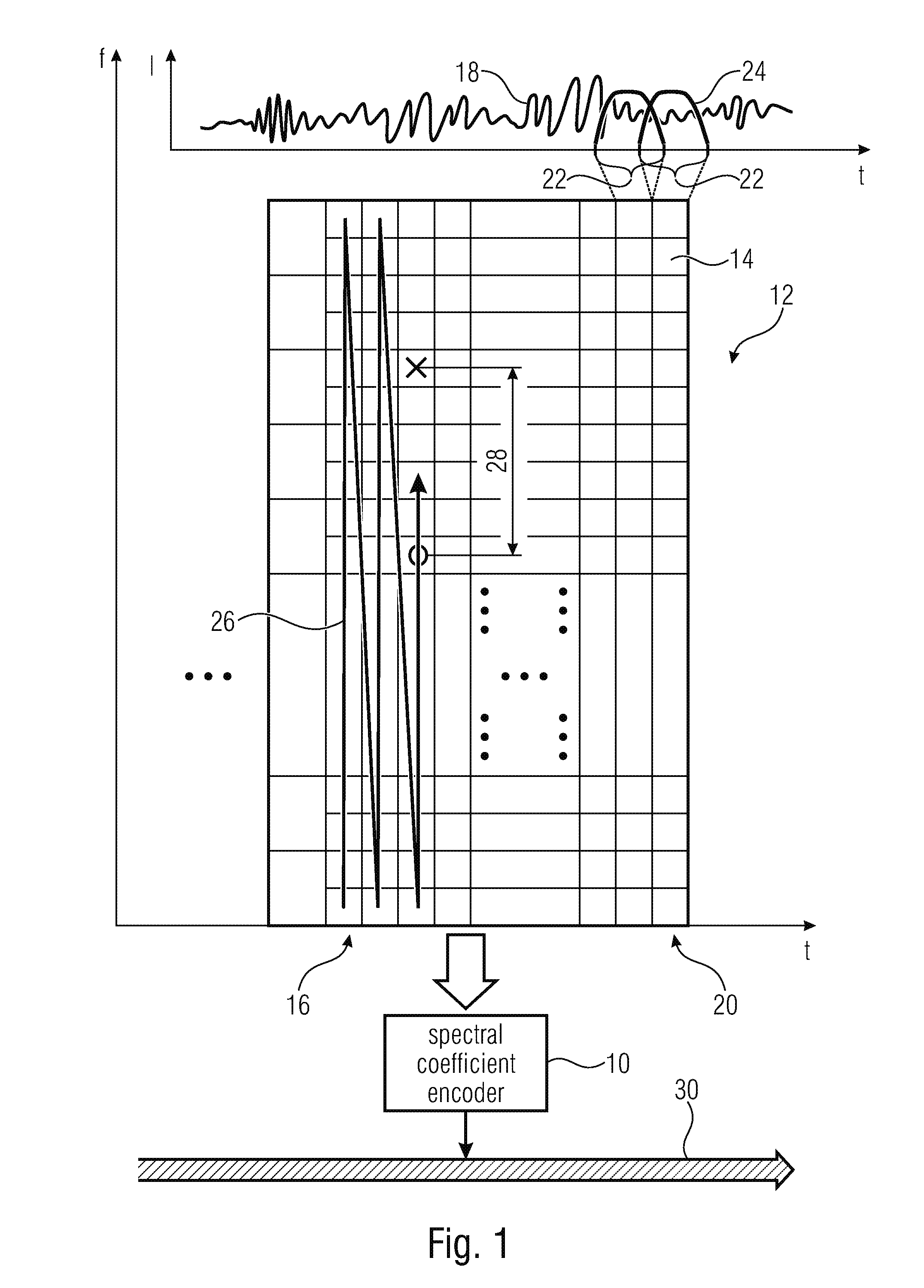
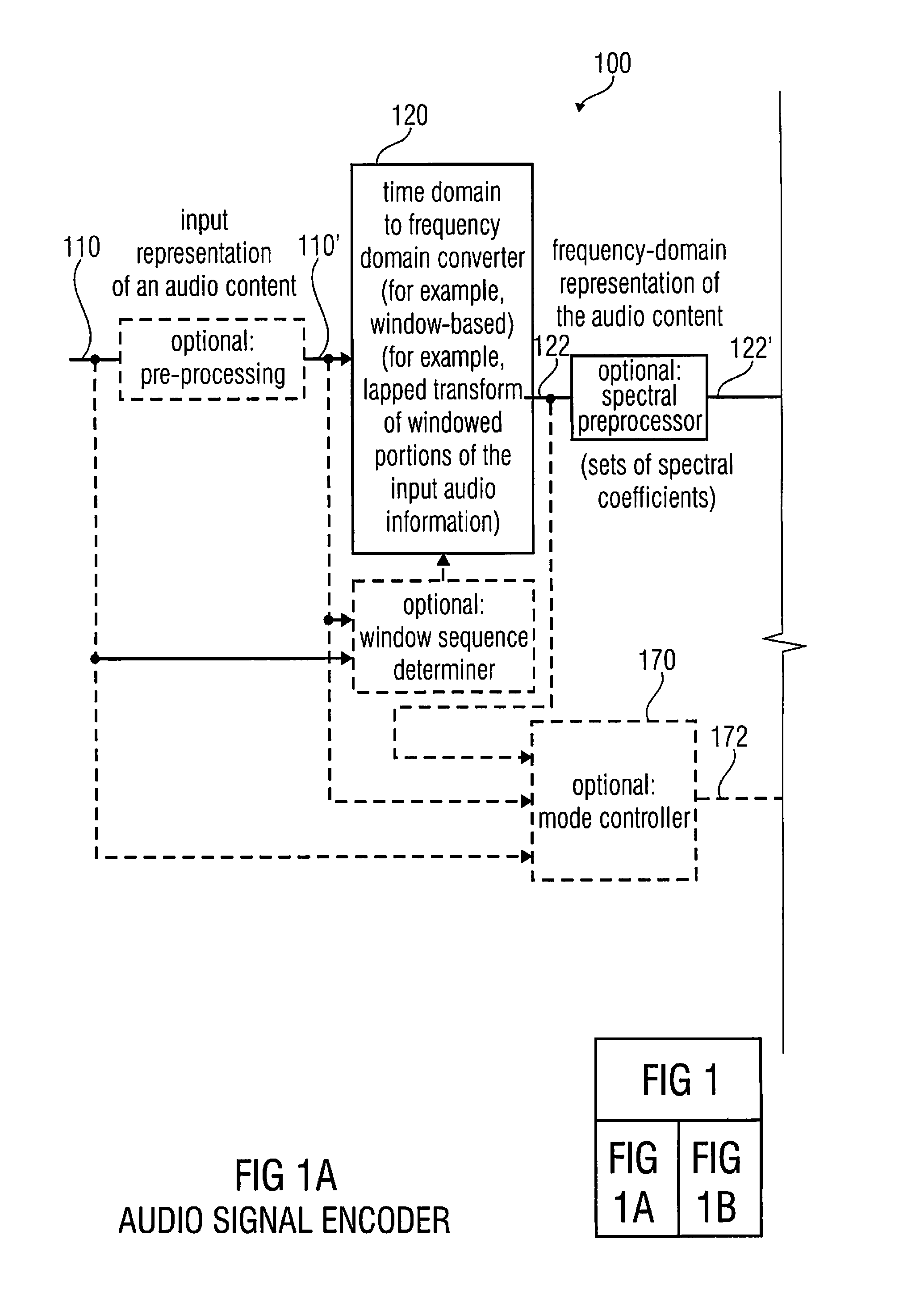
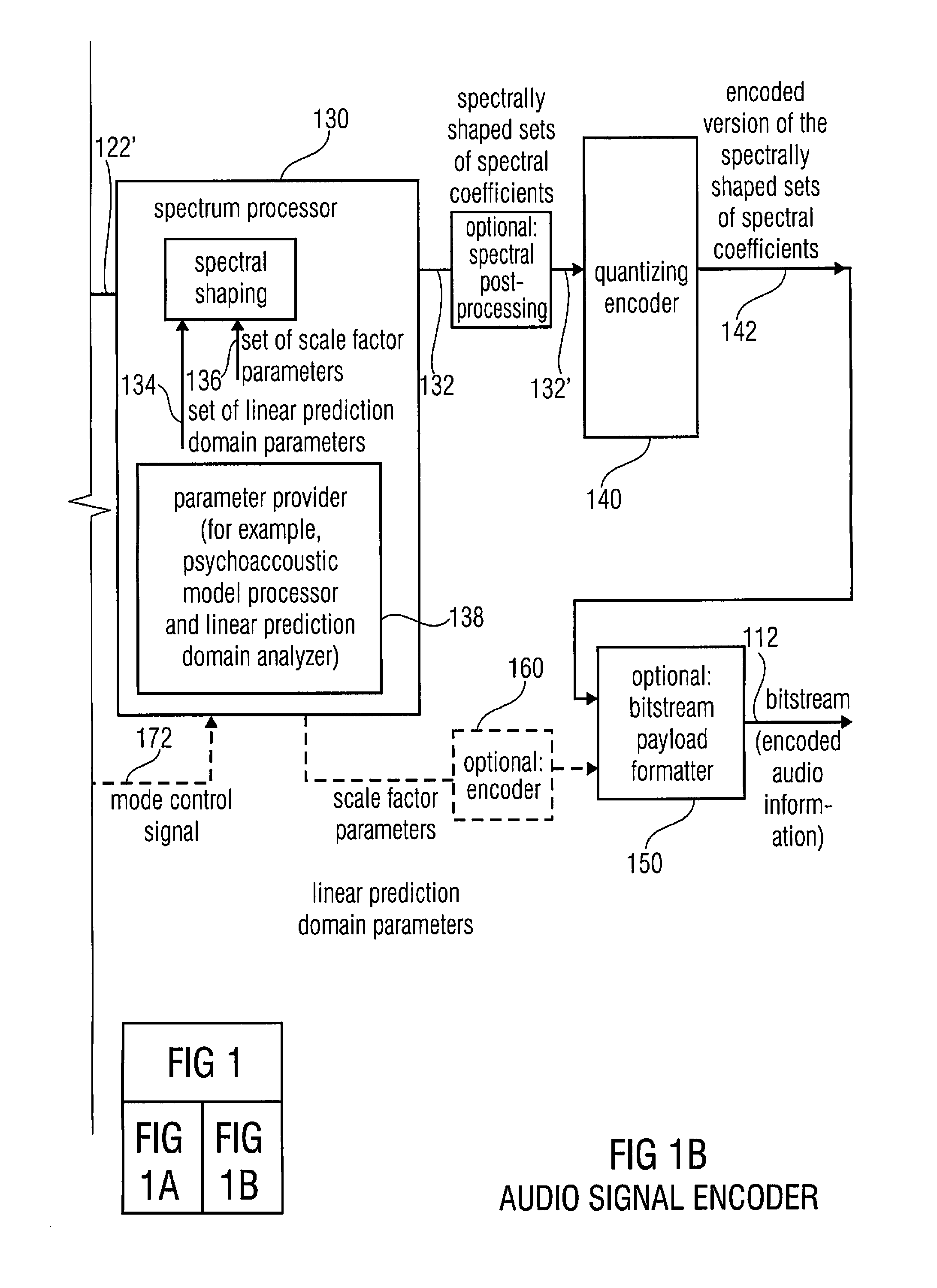
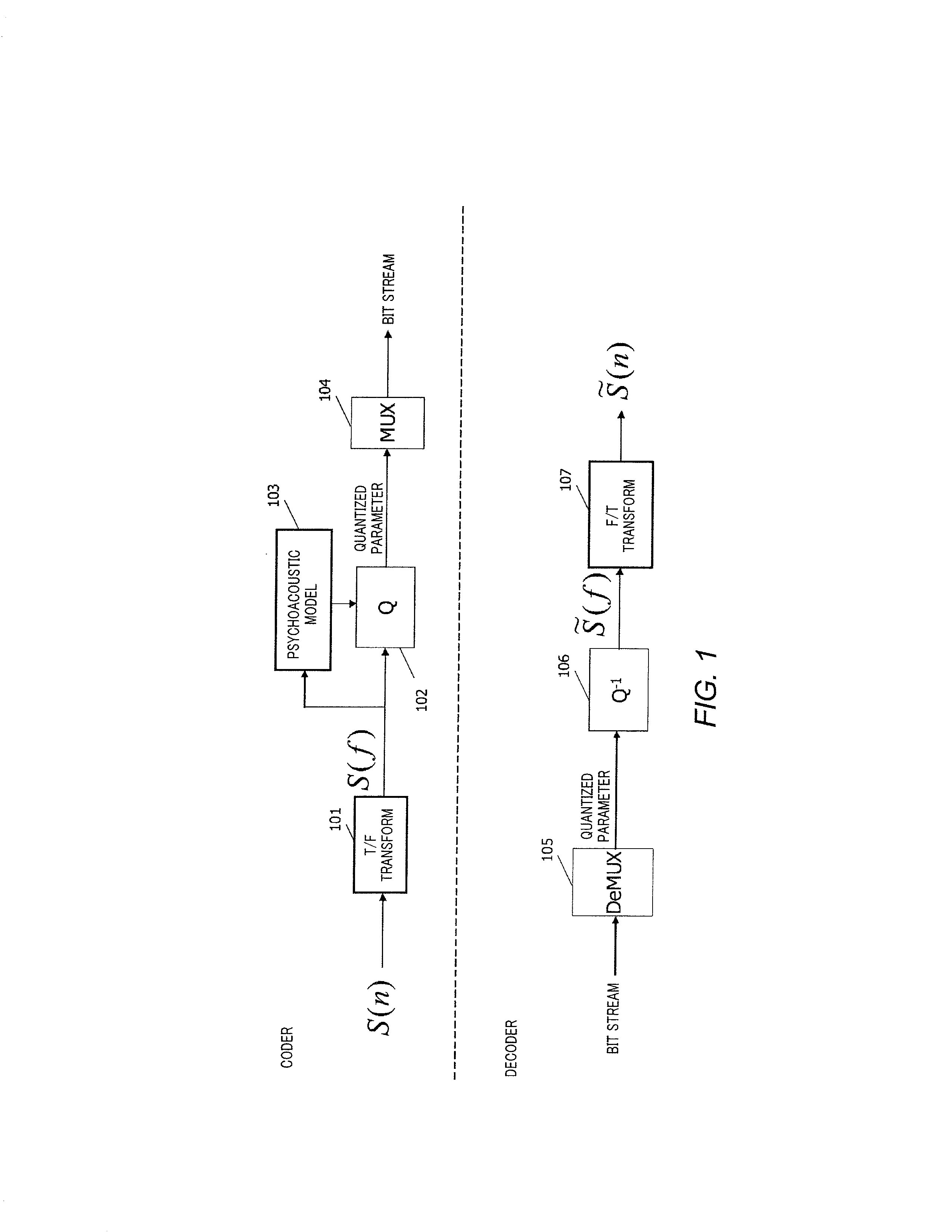
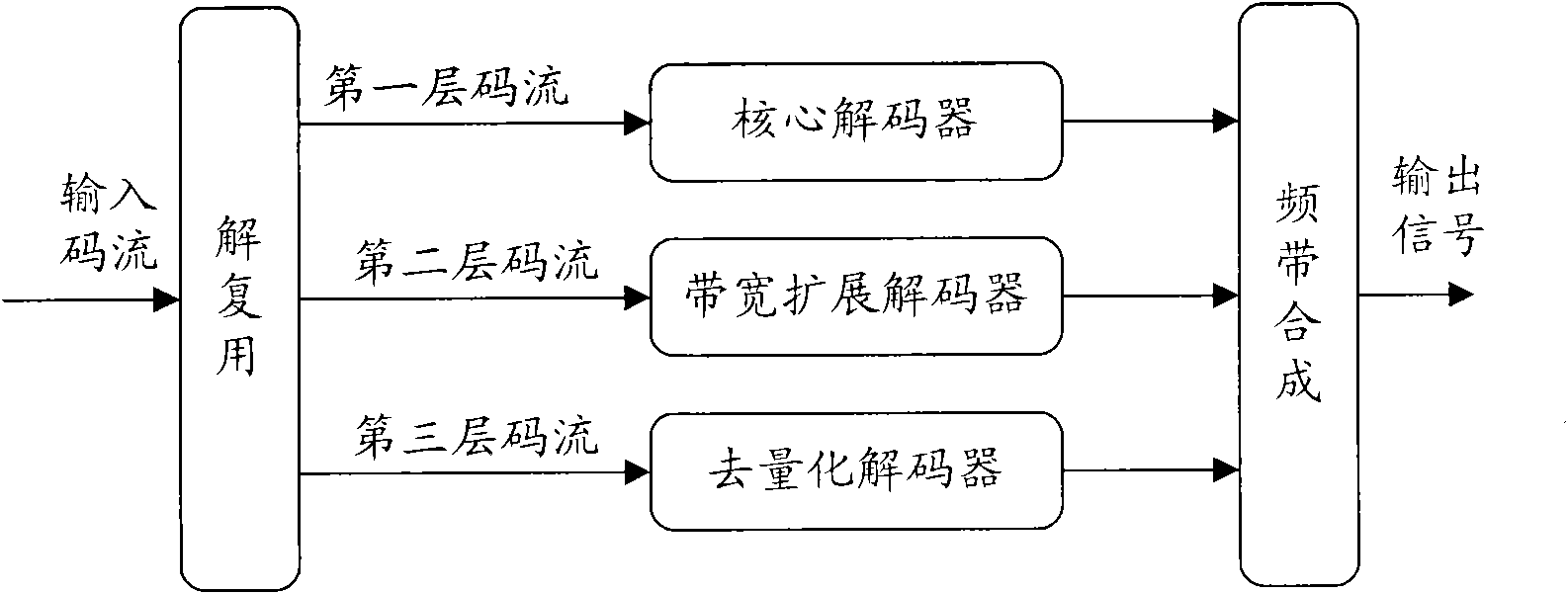
Multi-mode audio signal decoder, multi-mode audio signal encoder, methods and computer program using a linear-prediction-coding based noise shaping
ActiveUS20120245947A1Without inacceptable artifactEasy transitionSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingFrequency spectrum
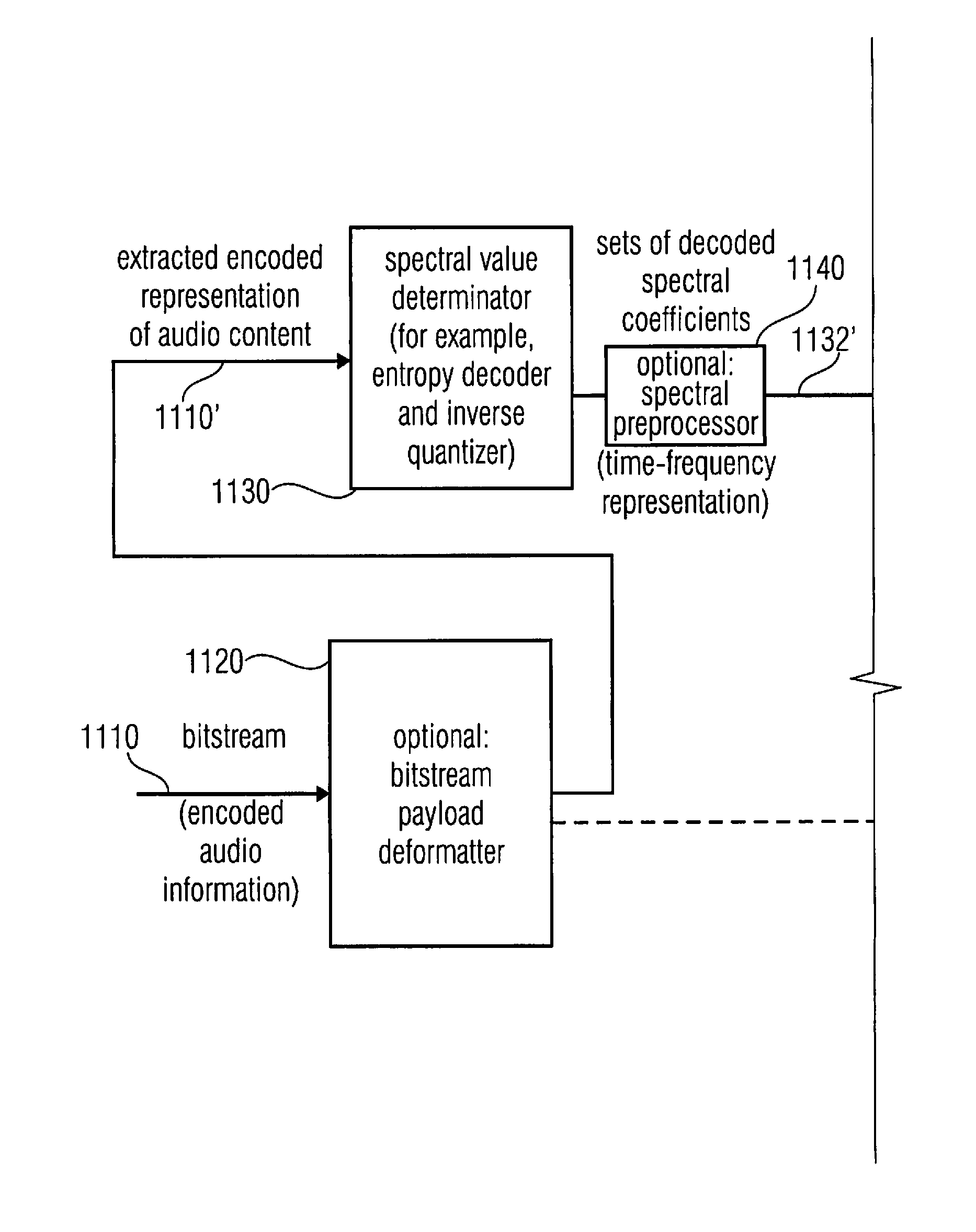
A multi-mode audio signal decoder has a spectral value determinator to obtain sets of decoded spectral coefficients for a plurality of portions of an audio content and a spectrum processor configured to apply a spectral shaping to a set of spectral coefficients in dependence on a set of linear-prediction-domain parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a linear-prediction mode, and in dependence on a set of scale factor parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a frequency-domain mode. The audio signal decoder has a frequency-domain-to-time-domain converter configured to obtain a time-domain audio representation on the basis of a spectrally-shaped set of decoded spectral coefficients for a portion of the audio content encoded in the linear-prediction mode and for a portion of the audio content encoded in the frequency domain mode. An audio signal encoder is also described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
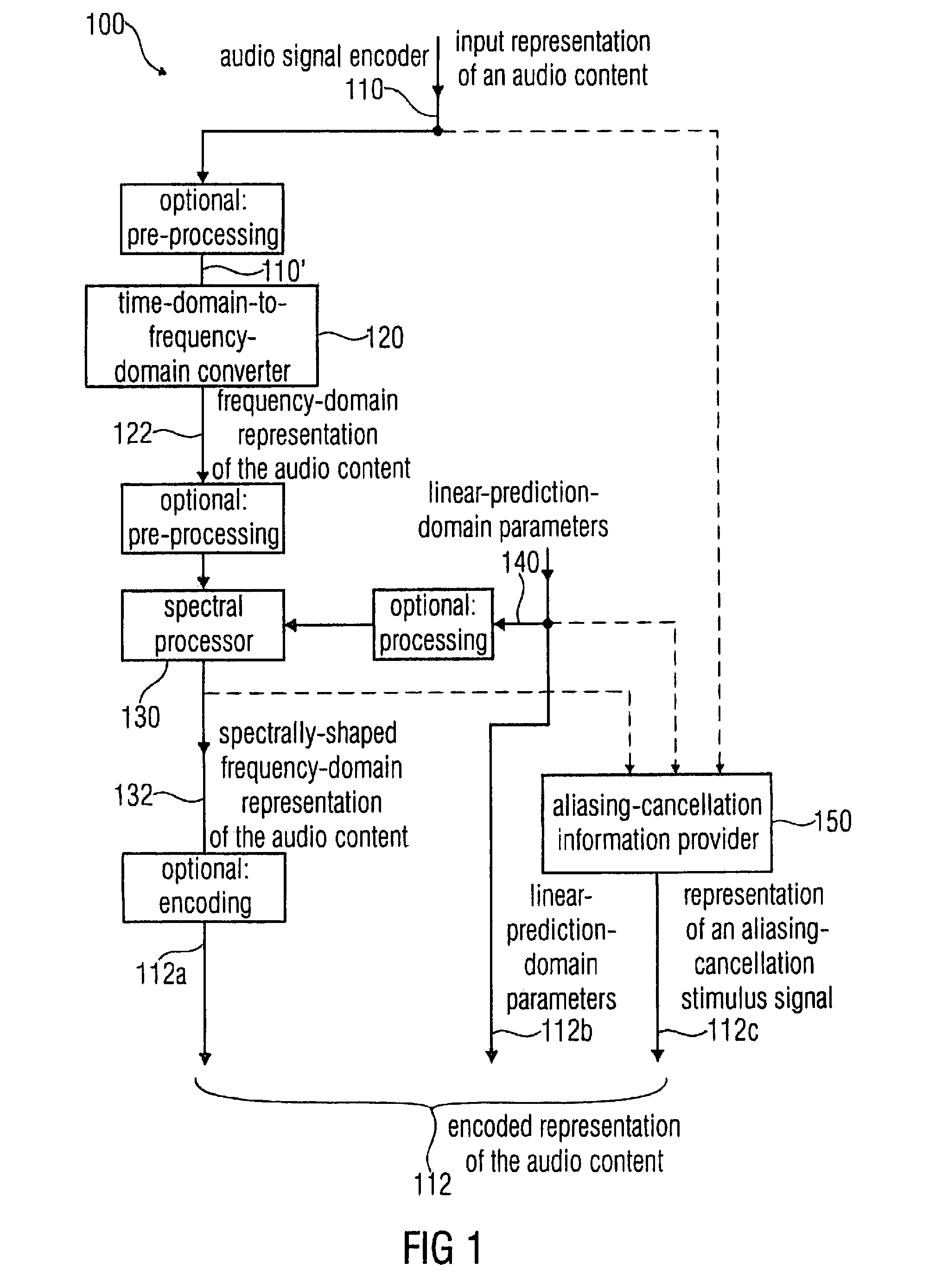
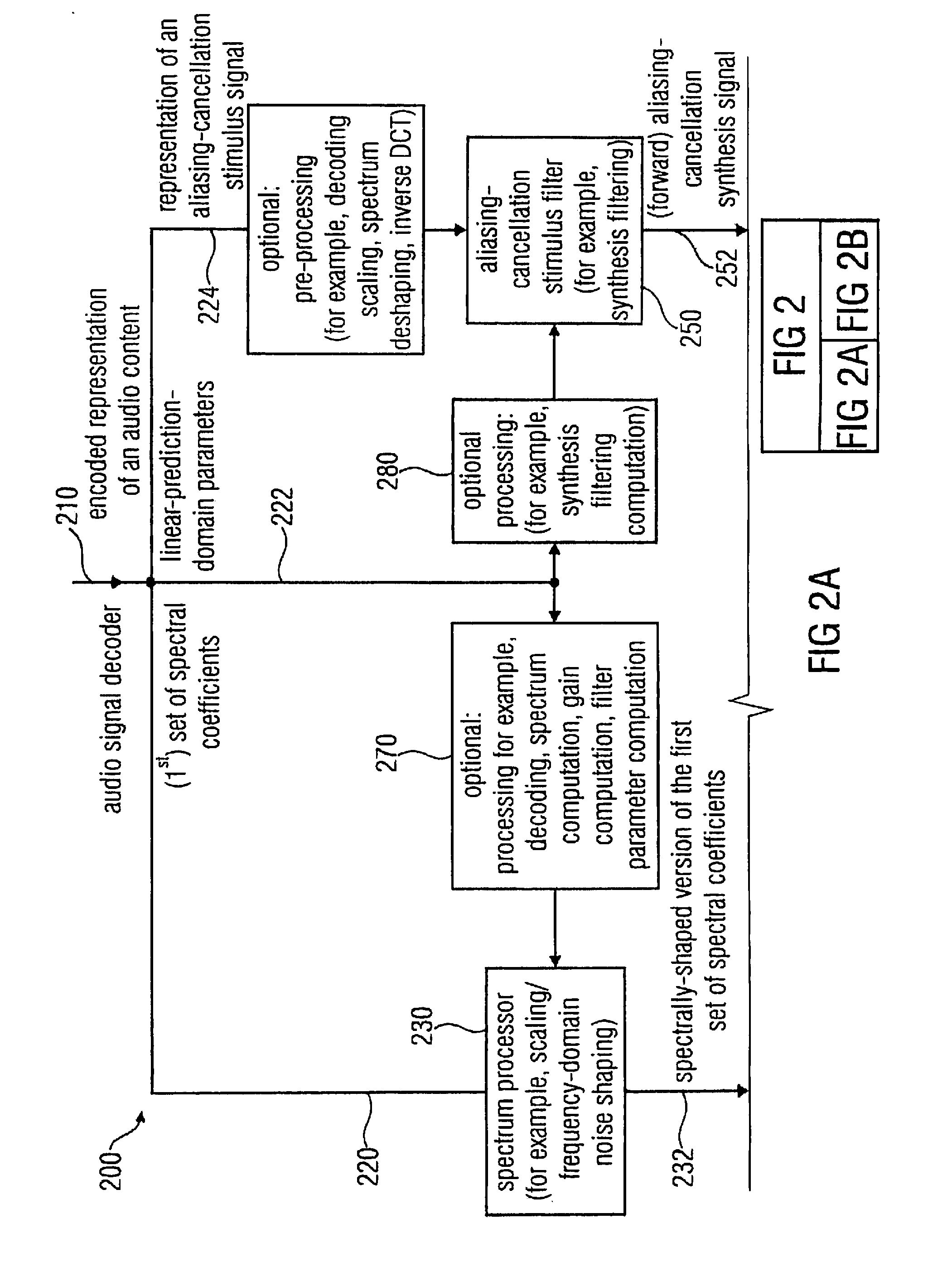
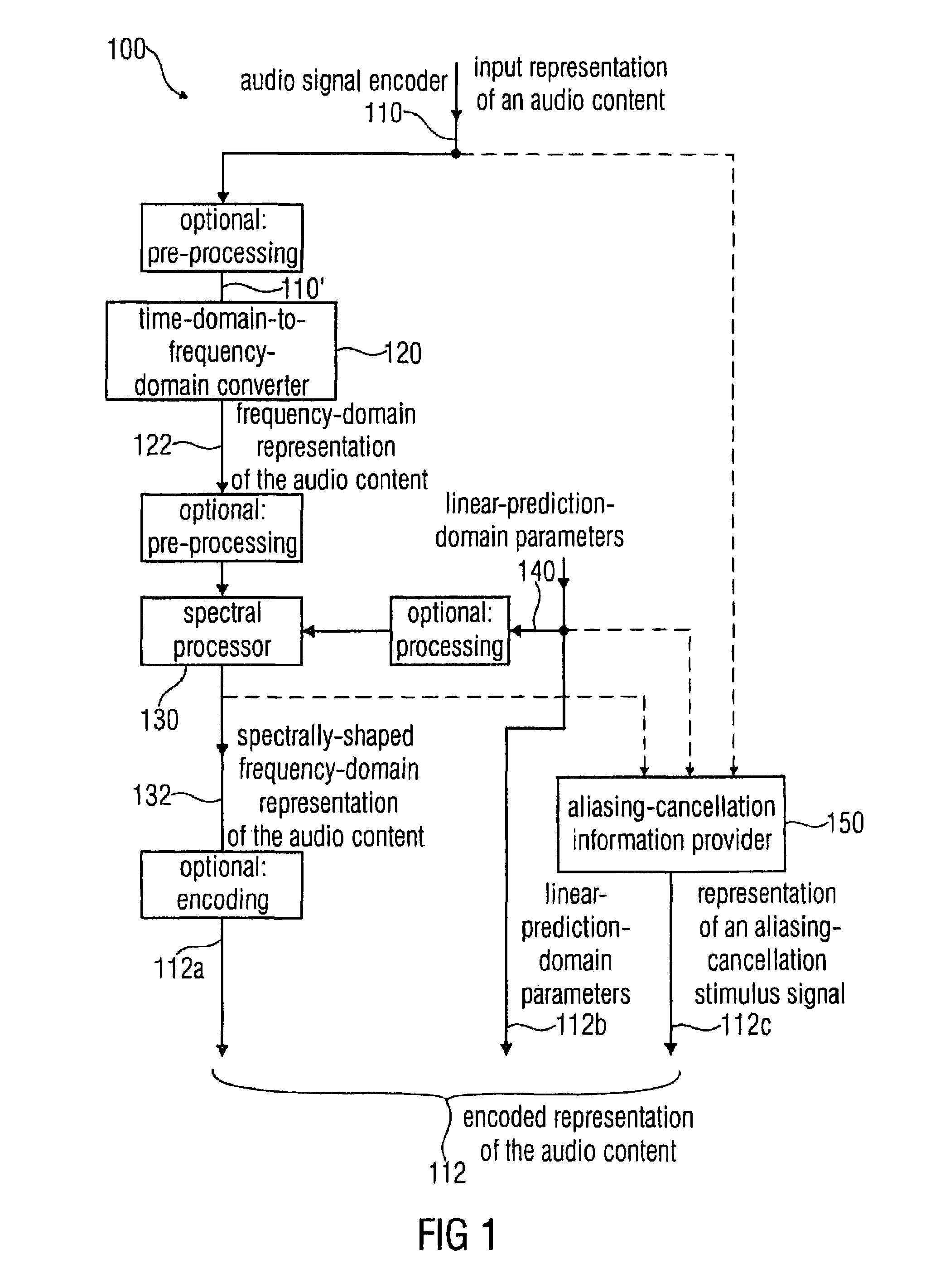
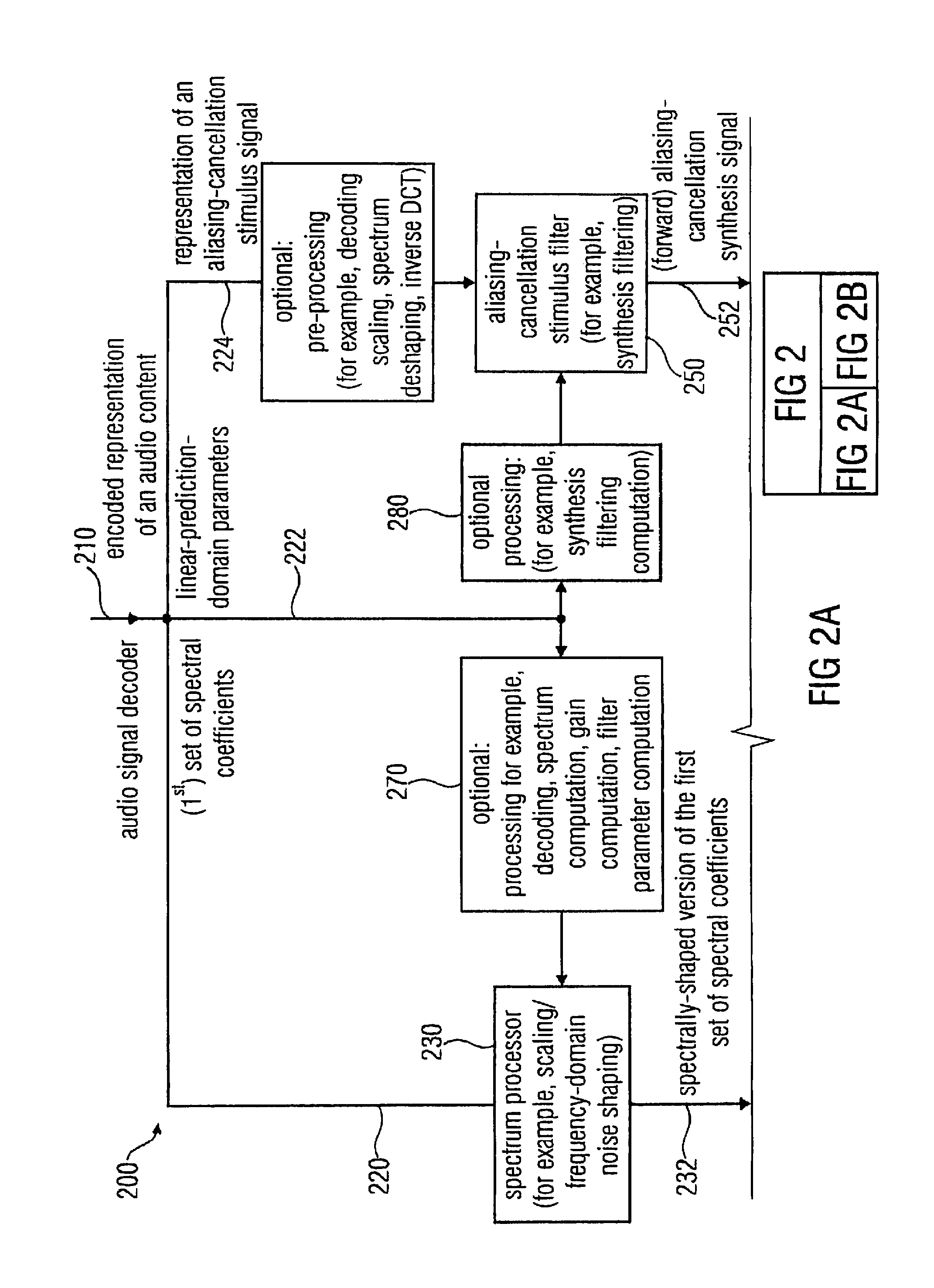
Audio signal encoder, audio signal decoder, method for encoding or decoding an audio signal using an aliasing-cancellation
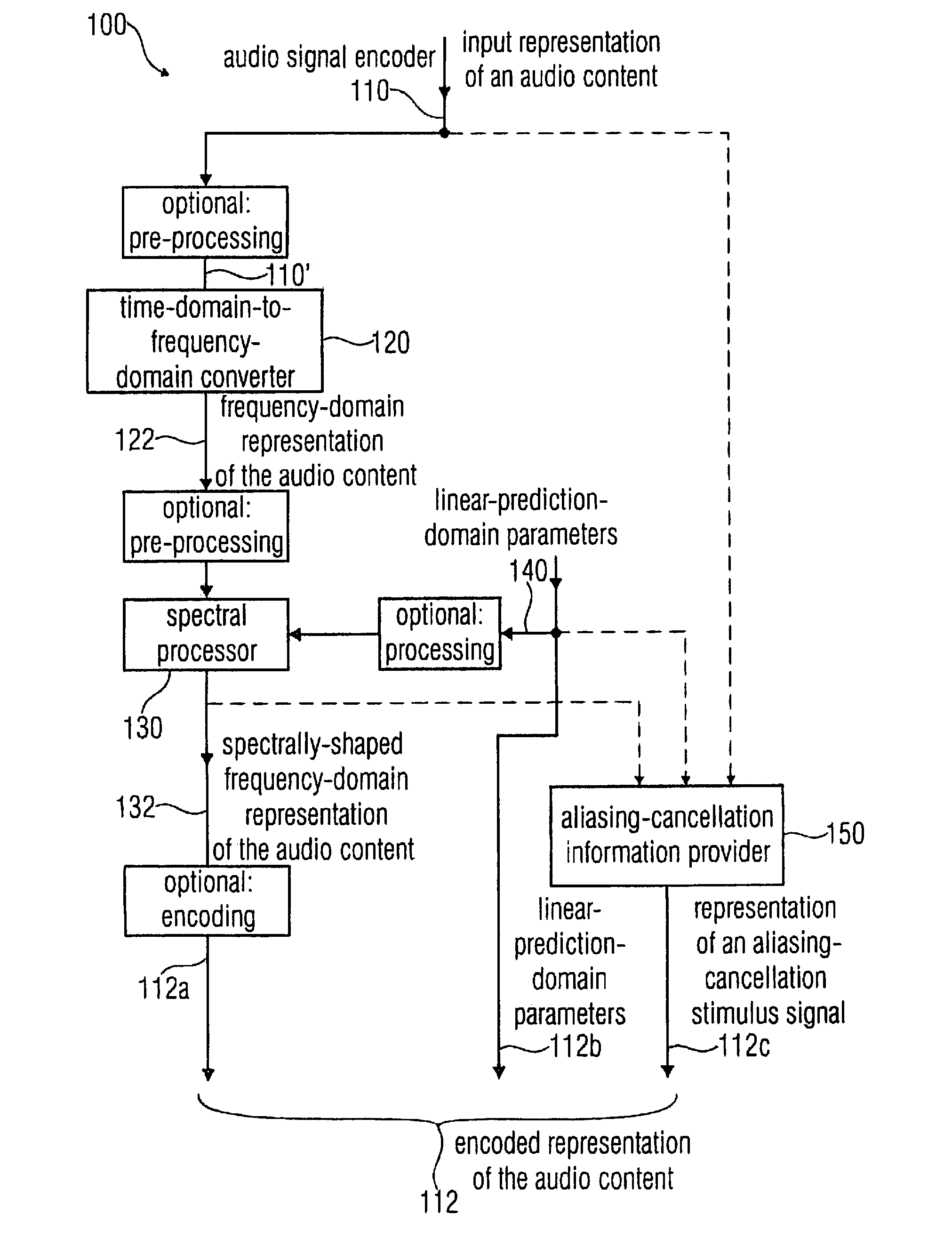
An audio signal decoder includes a transform domain path configured to obtain a time-domain representation of a portion of an audio content on the basis of a first set of spectral coefficients, a representation of an aliasing-cancellation stimulus signal and a plurality of linear-prediction-domain parameters. The transform domain path applies a spectrum shaping to the first set of spectral coefficients to obtain a spectrally-shaped version thereof. The transform domain path obtains a time-domain representation of the audio content on the basis of the spectrally-shaped version of the first set of spectral coefficients. The transform domain path includes an aliasing-cancellation stimulus filter to filter the aliasing-cancellation stimulus signal in dependence on at least a subset of the linear-prediction-domain parameters. The transform domain path also includes a combiner configured to combine the time-domain representation of the audio content with an aliasing-cancellation synthesis signal to obtain an aliasing reduced time-domain signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +3
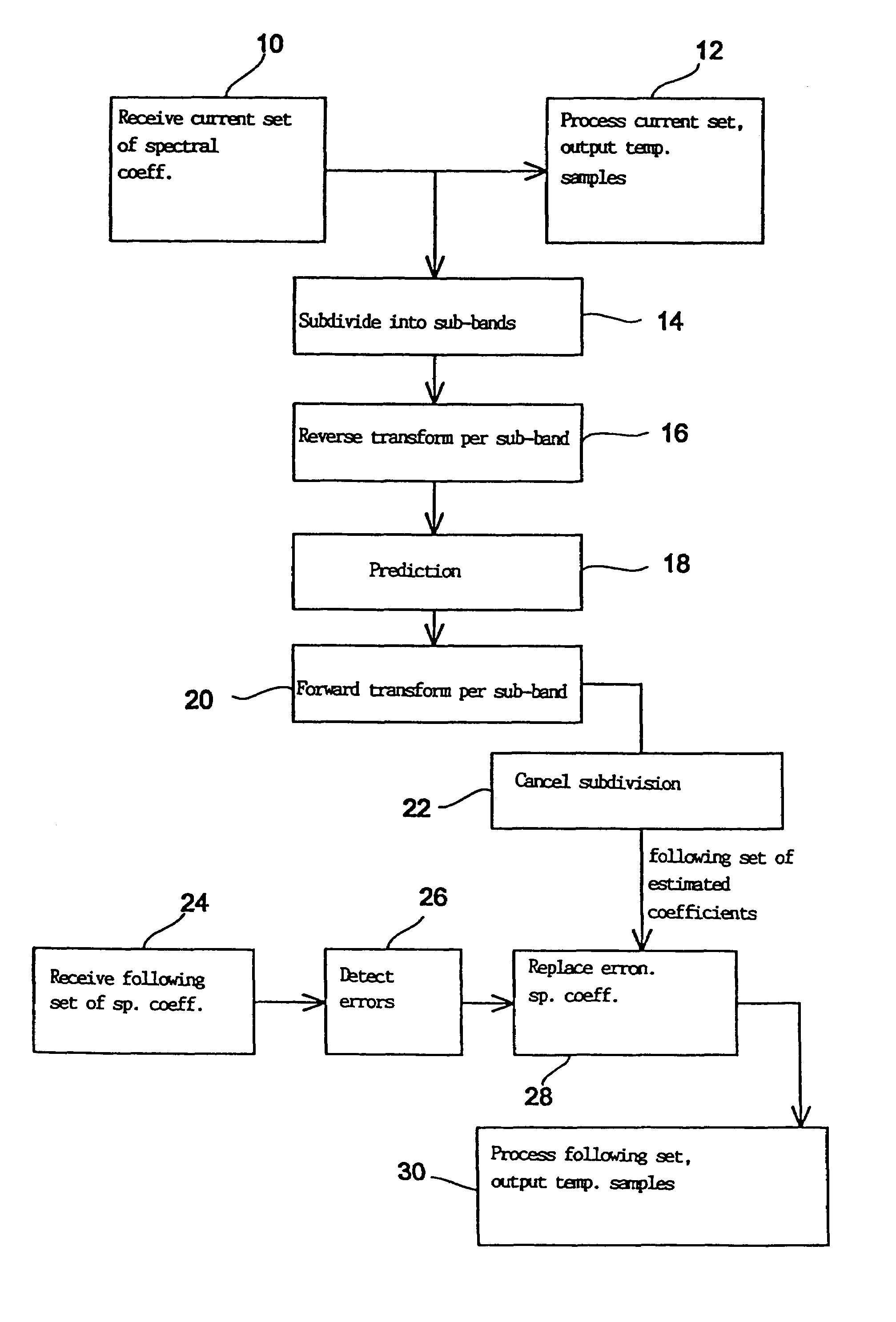
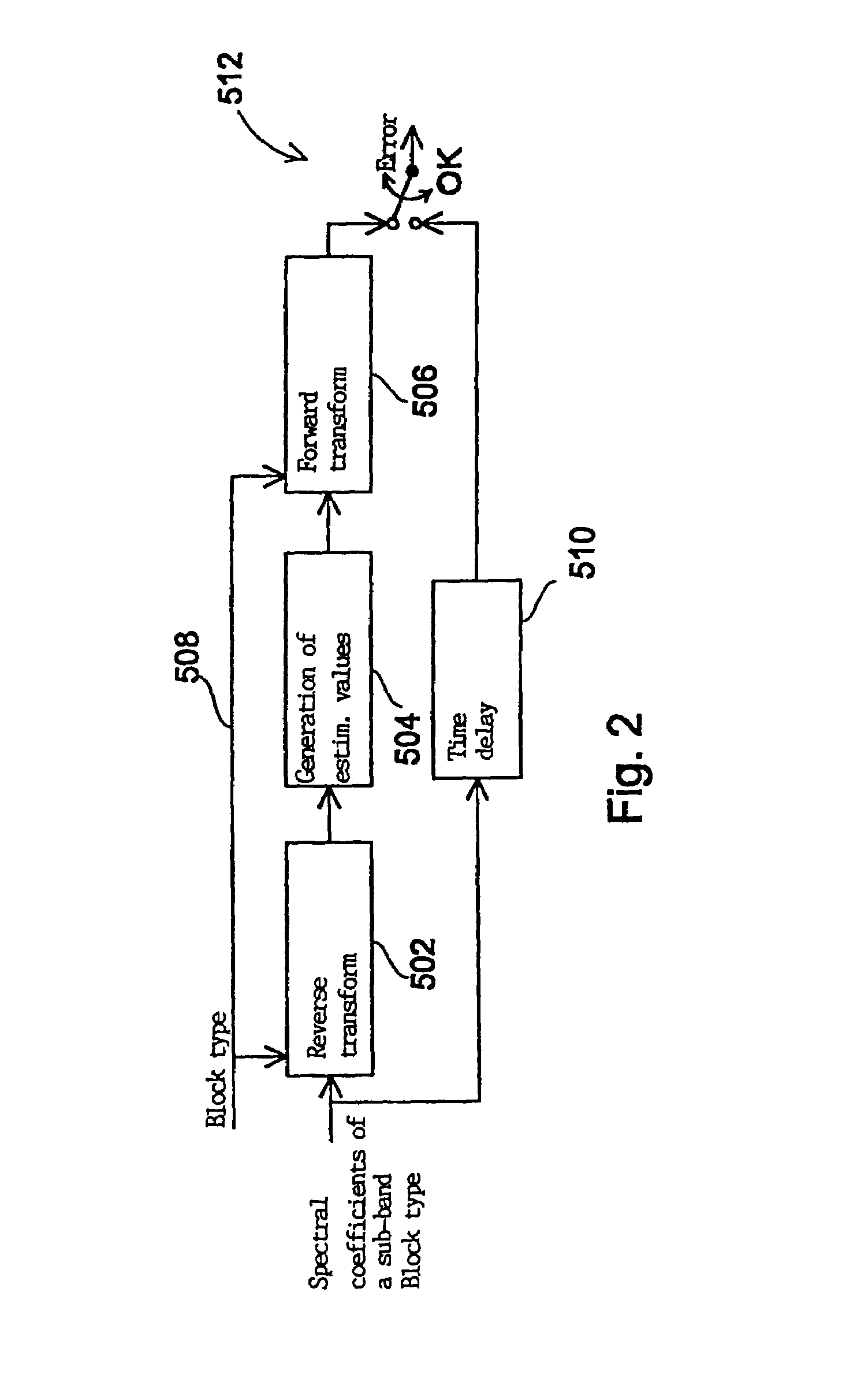
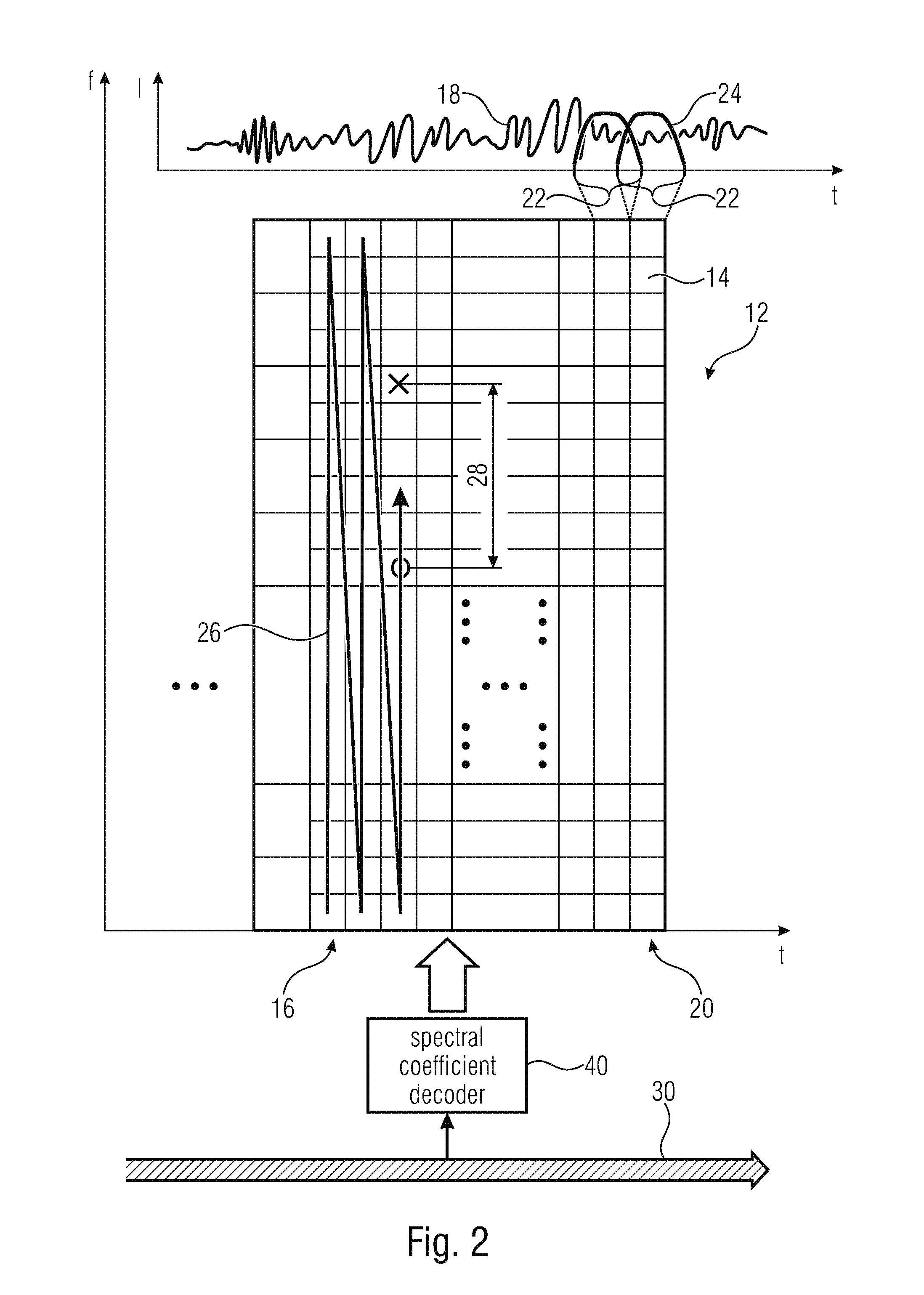
Method and device for error concealment in an encoded audio-signal and method and device for decoding an encoded audio signal
InactiveUS7003448B1Precise and flexible error concealmentEffort controlCode conversionSpeech synthesisFrequency spectrumError concealment
In a method for concealing an error in an encoded audio signal a set of spectral coefficients is subdivided into at least two sub-bands (14), whereupon the sub-bands are subjected to a re-verse transform (16). A specific prediction is performed (18) for each quasi time signal of a sub-band to obtain an estimated temporal representation for a sub-band of a set of spectral coefficients following the current set. A forward transform (20) of the time signal of each sub-band provides estimated spectral coefficients which can be used (28) instead of erroneous spectral coefficients of a following set of spectral coefficients, e.g. in order to conceal transmission errors. Transforming at the sub-band level provides independence from transform characteristics such as block length, window type and MDCT algorithm while at the same time preserving spectral processing for error concealment. Thus the spectral characteristics of audio signals can also be taken into account during error concealment.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
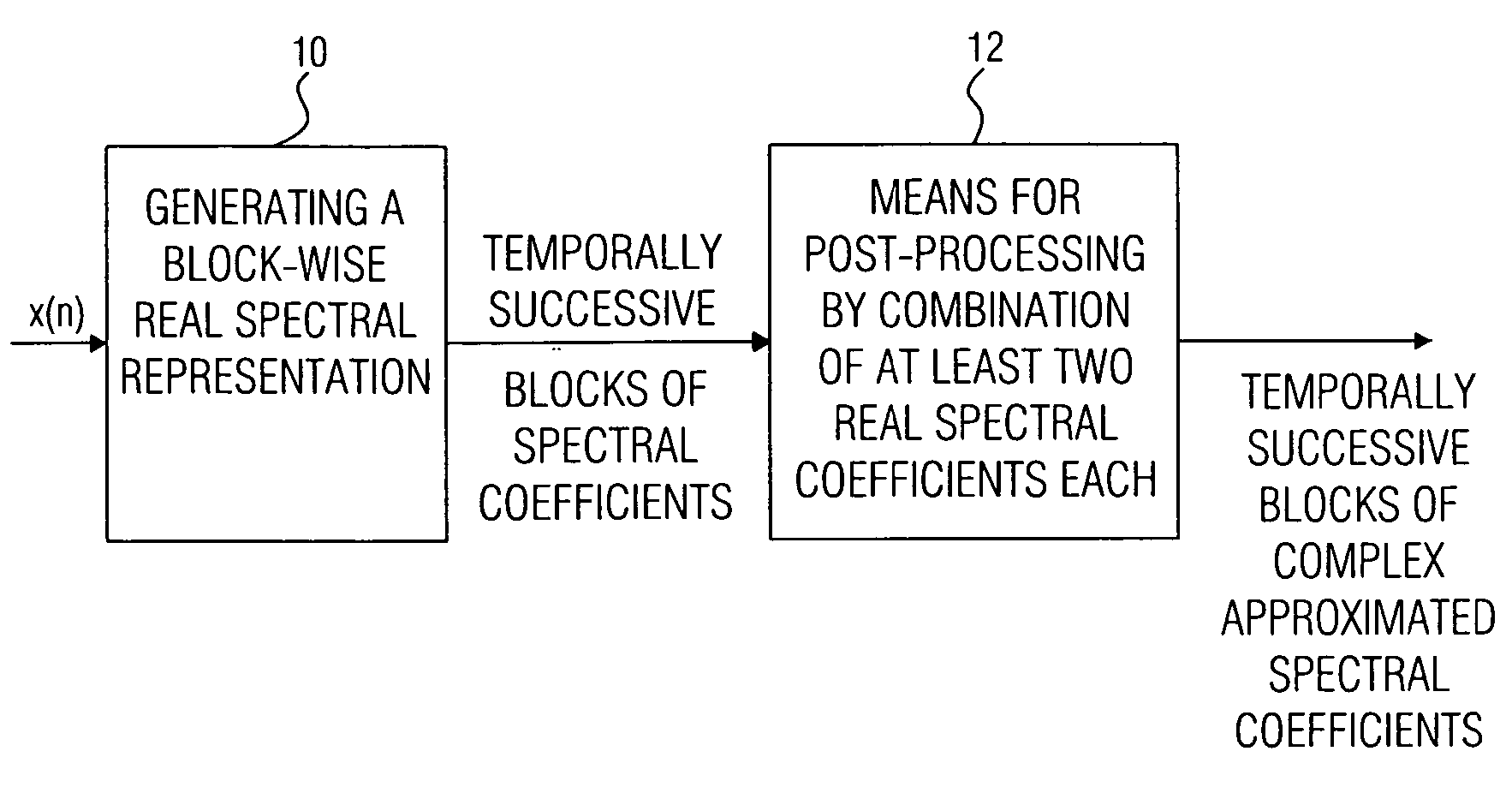
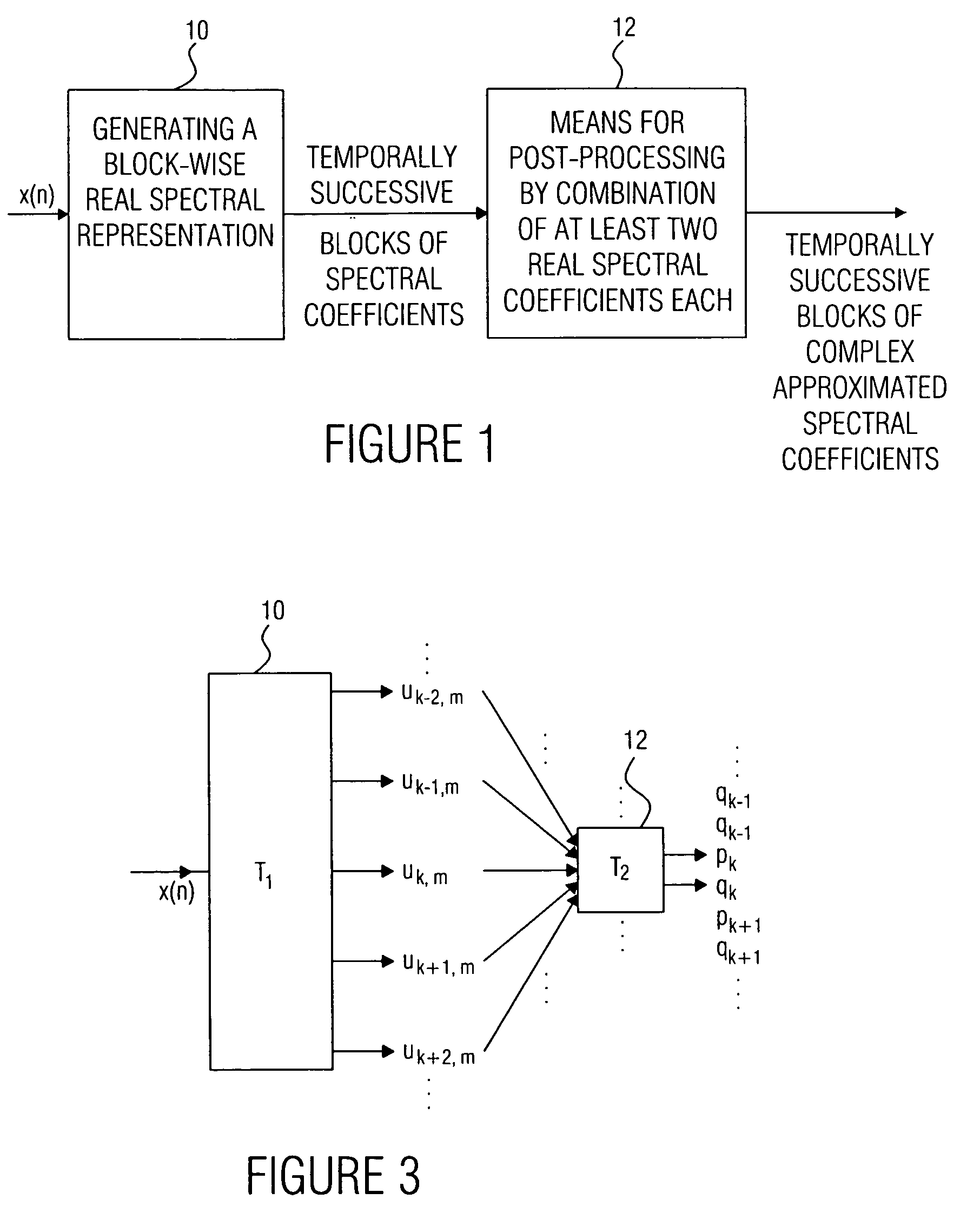
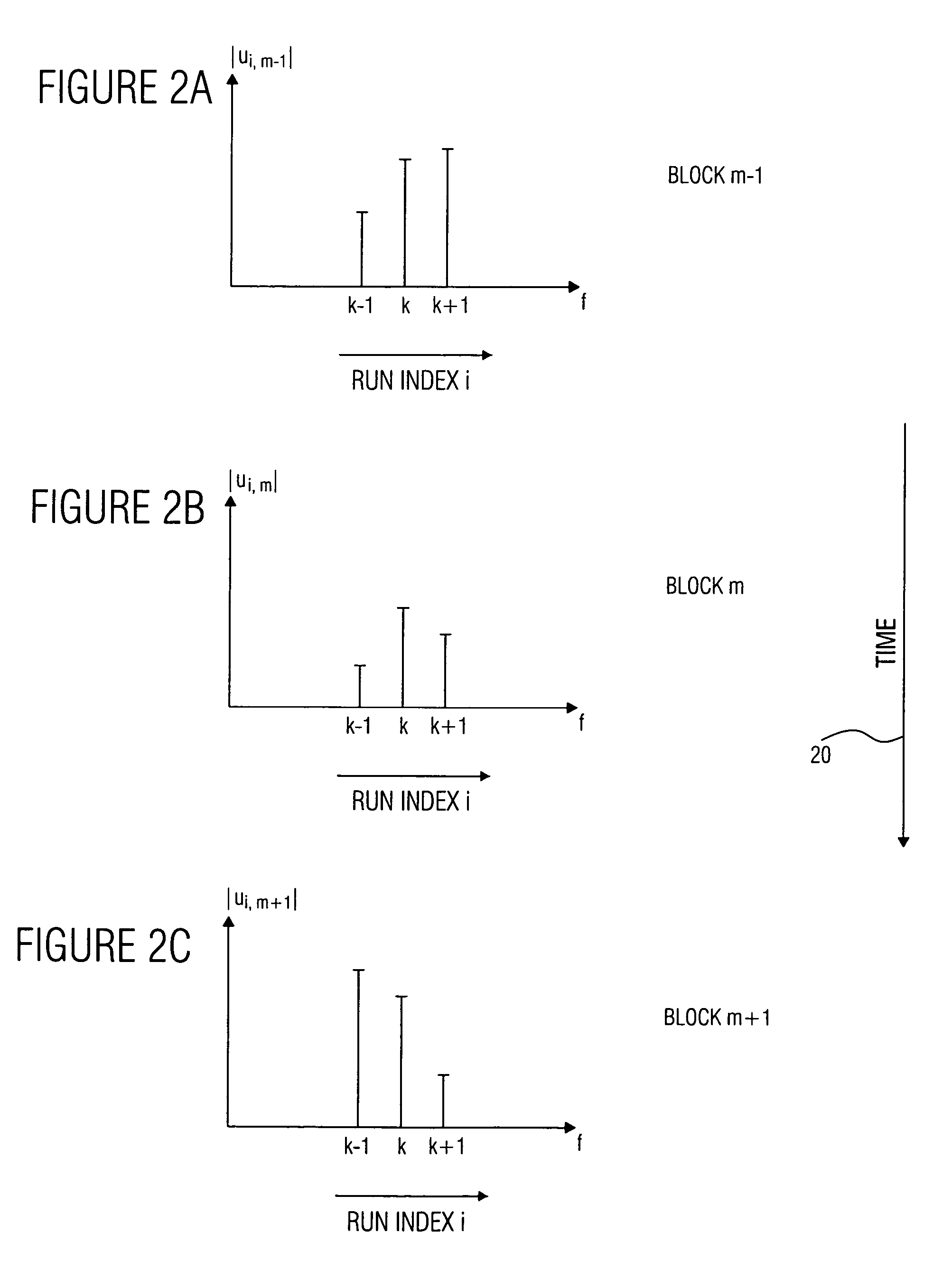
Device and method for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal
ActiveUS20050197831A1Improve approximationSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumPost processor
A filter bank device for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal includes a generator for generating a block-wise real spectral representation, which, for example, implements an MDCT, to obtain temporally successive blocks of real spectral coefficients. The output values of this spectral conversion device are fed to a post-processor for post-processing the block-wise real spectral representation to obtain an approximated complex spectral representation having successive blocks, each block having a set of complex approximated spectral coefficients, wherein a complex approximated spectral coefficient can be represented by a first partial spectral coefficient and by a second partial spectral coefficient, wherein at least one of the first and second partial spectral coefficients is determined by combining at least two real spectral coefficients. A good approximation for a complex spectral representation of the discrete-time signal is obtained by combining two real spectral coefficients, preferably by a weighted linear combination, wherein additionally more degrees of freedom for optimizing the entire system are available.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
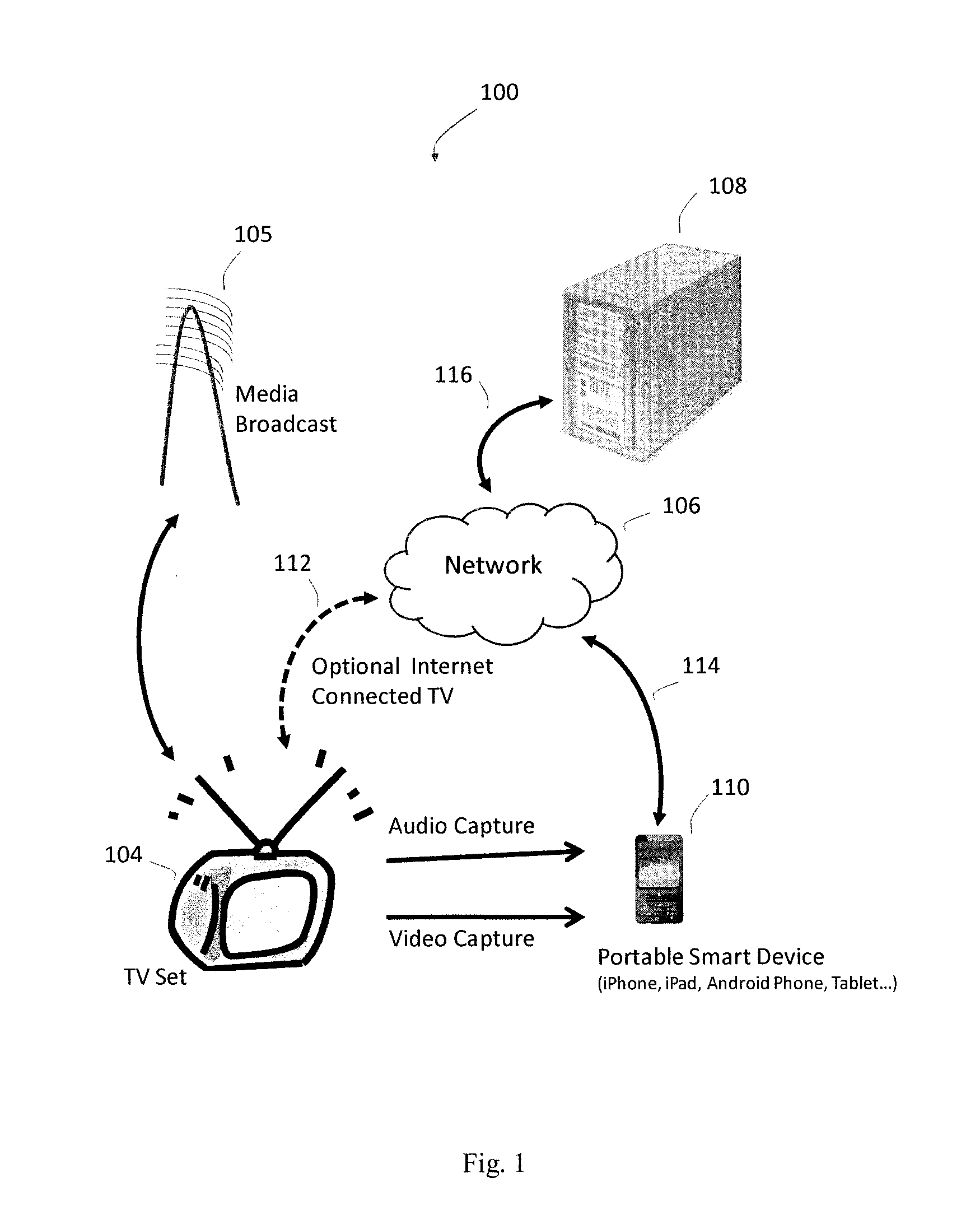
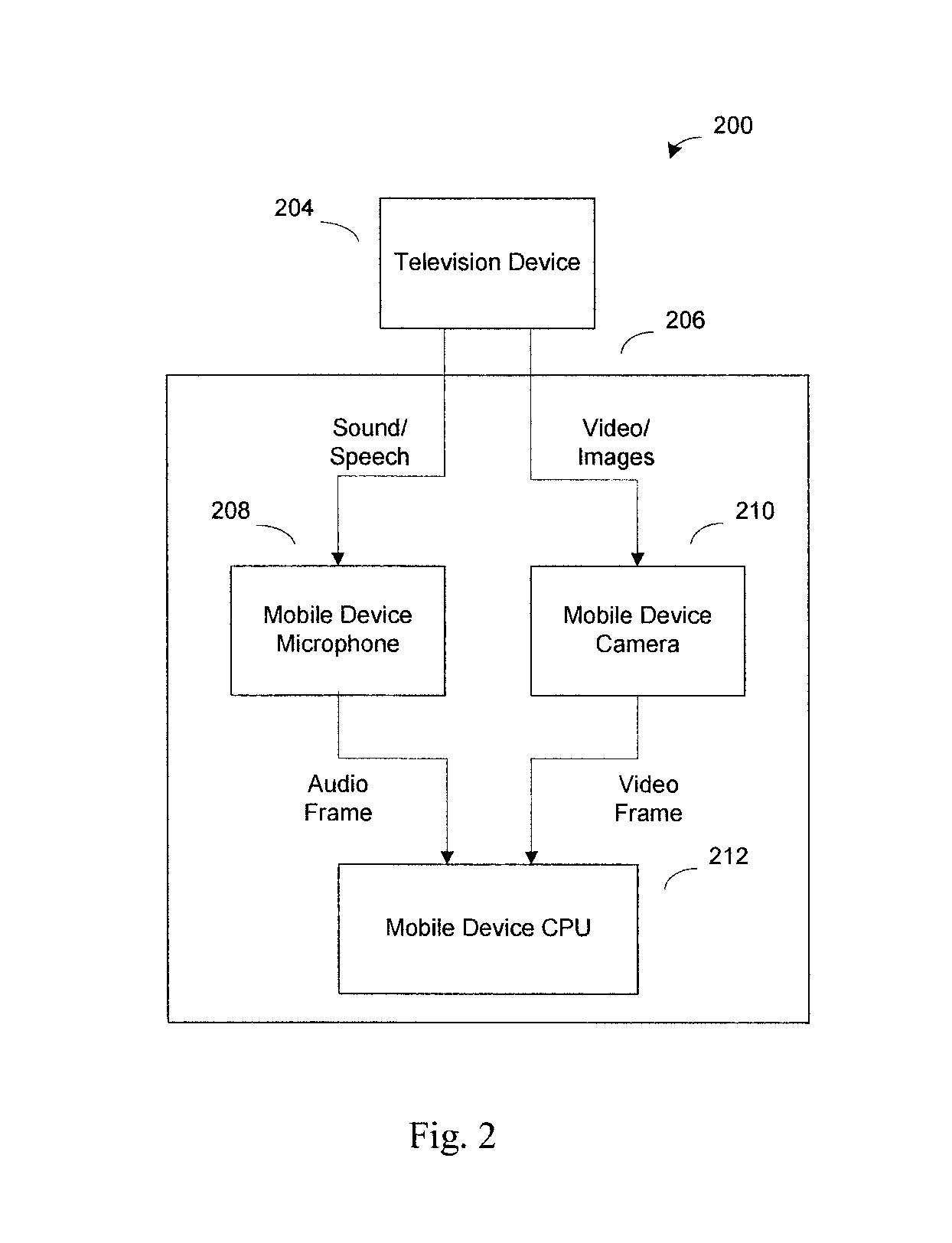
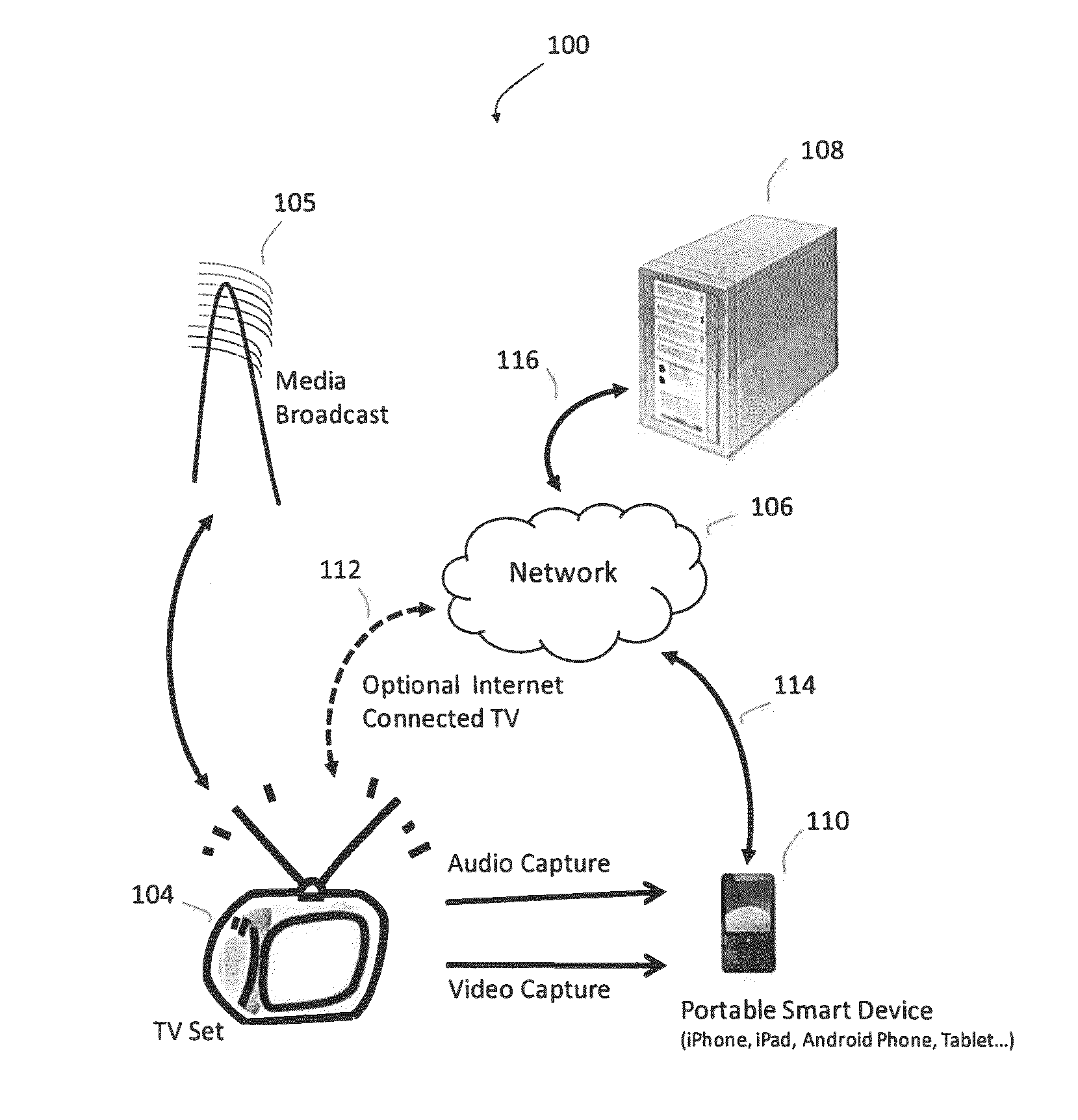
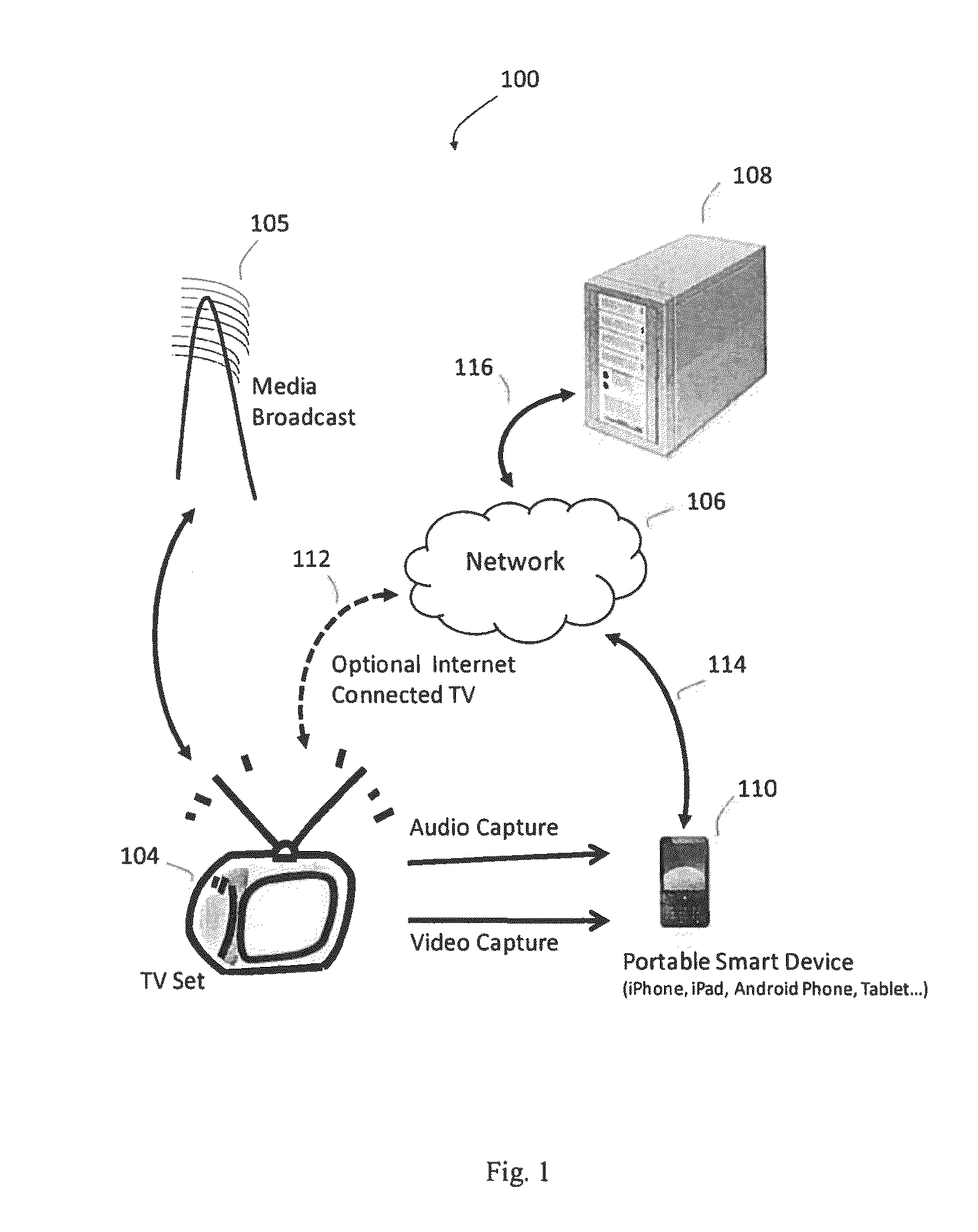
Media content identification on mobile devices
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
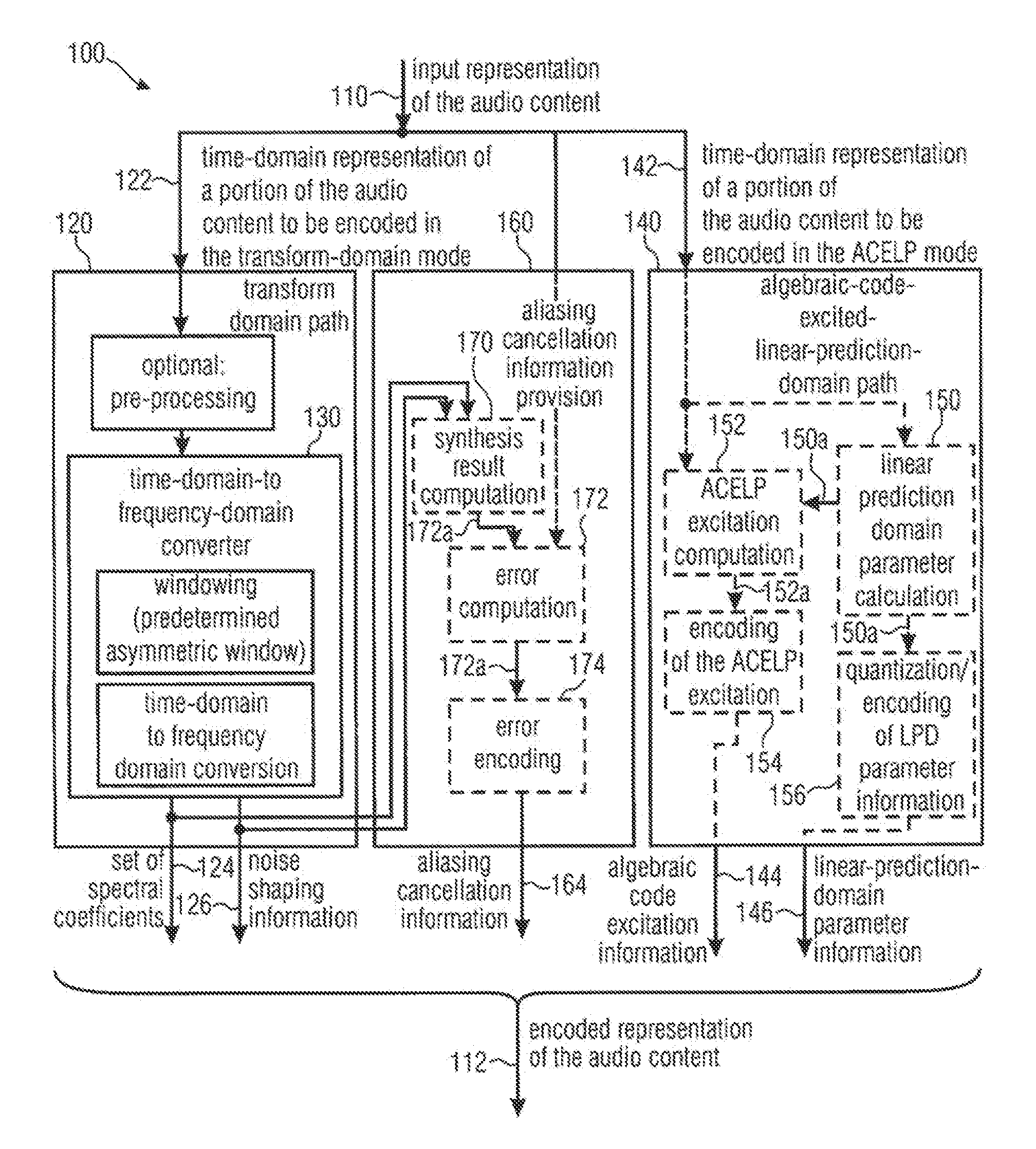
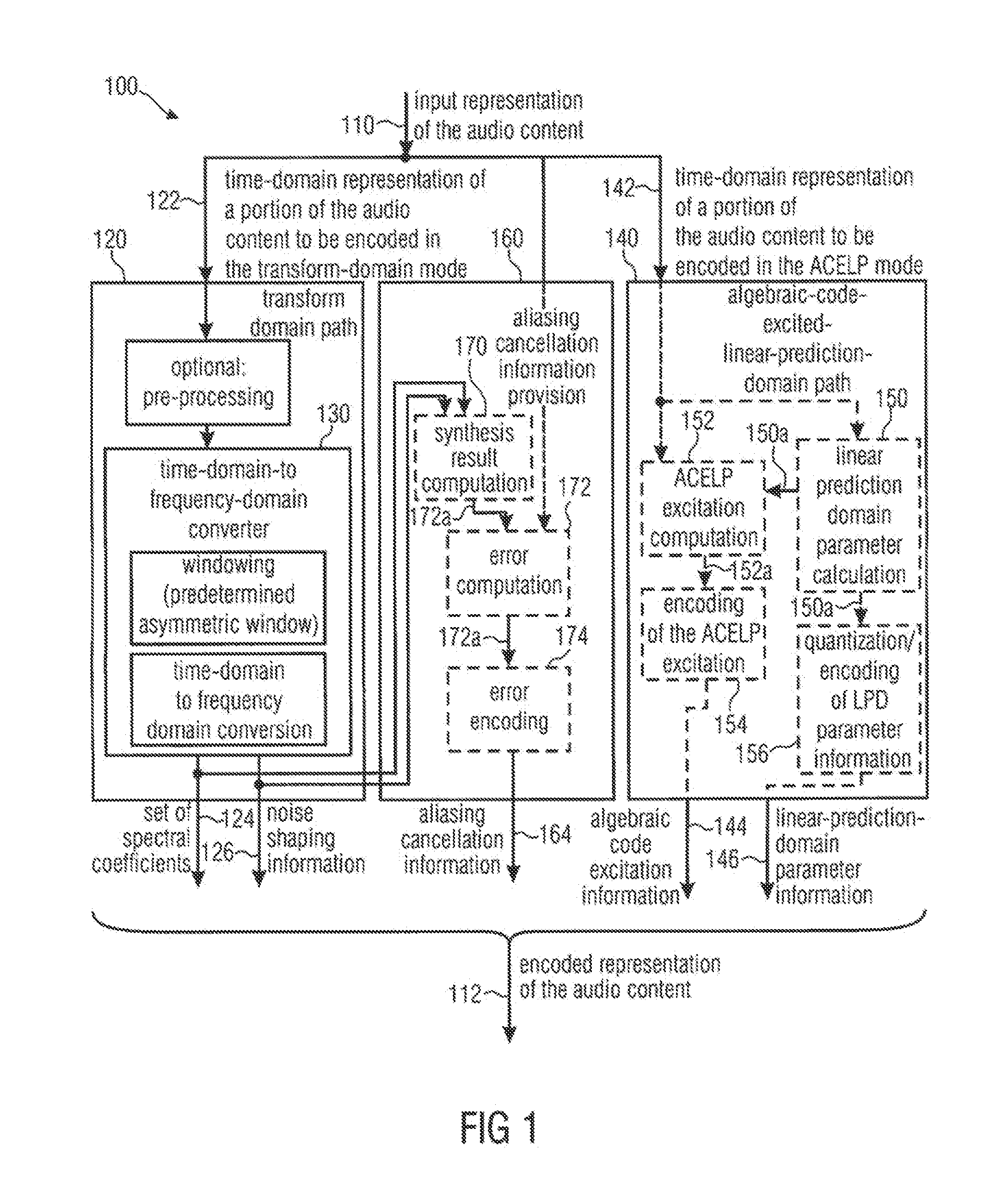
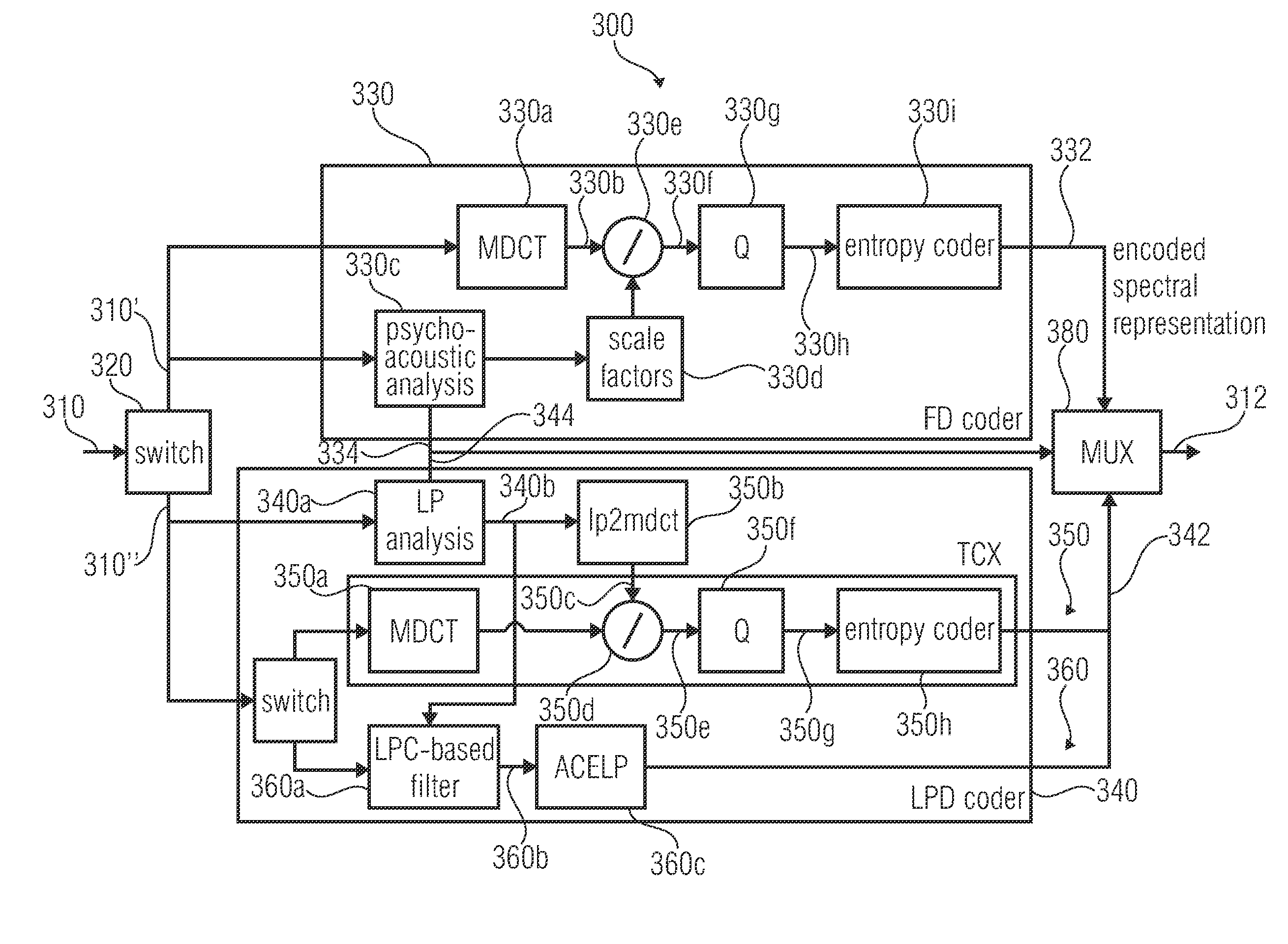
Audio signal encoder, audio signal decoder, method for providing an encoded representation of an audio content, method for providing a decoded representation of an audio content and computer program for use in low delay applications
ActiveUS20120265541A1Reduces and cancel aliasing artifactImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumNoise shaping
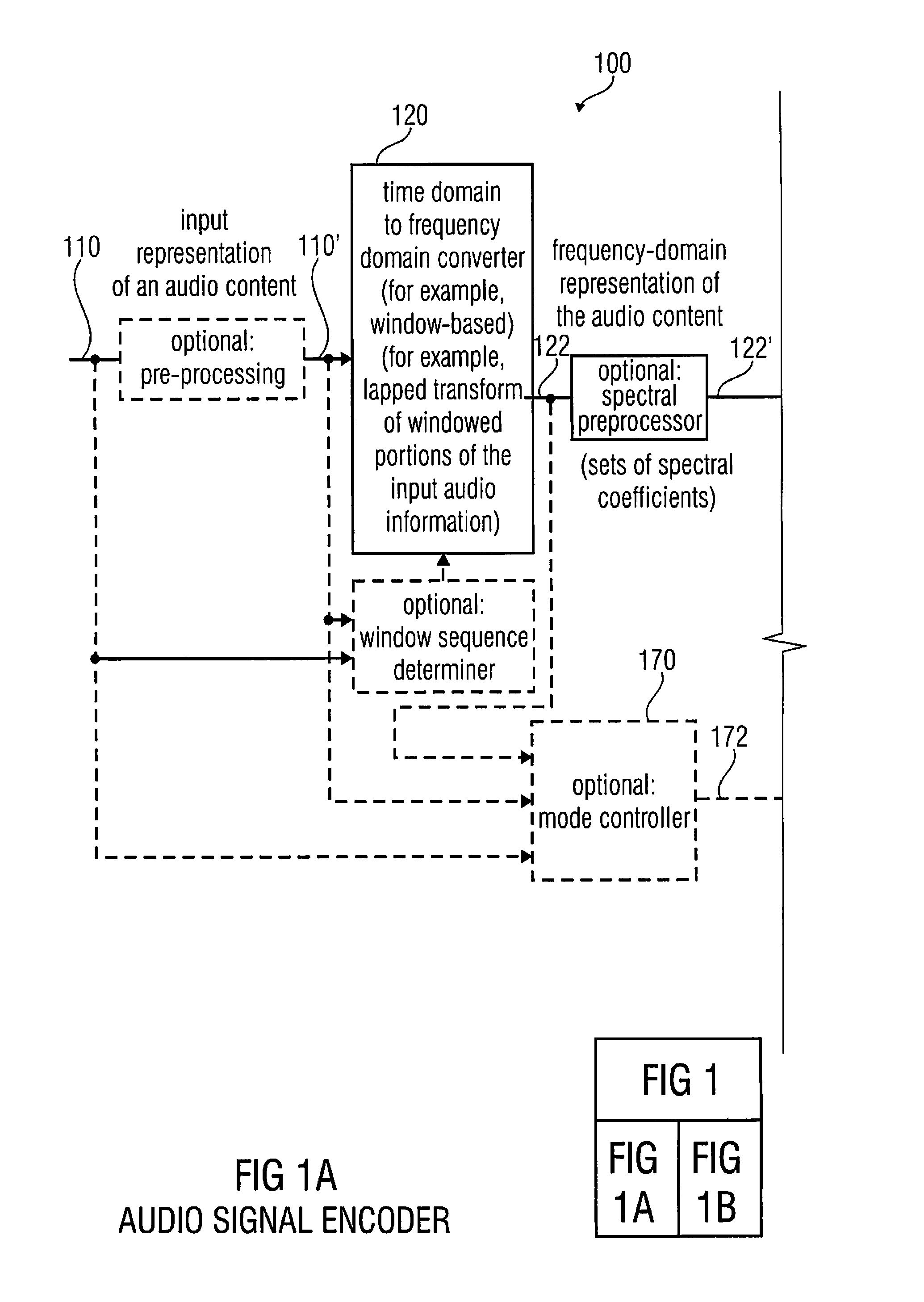
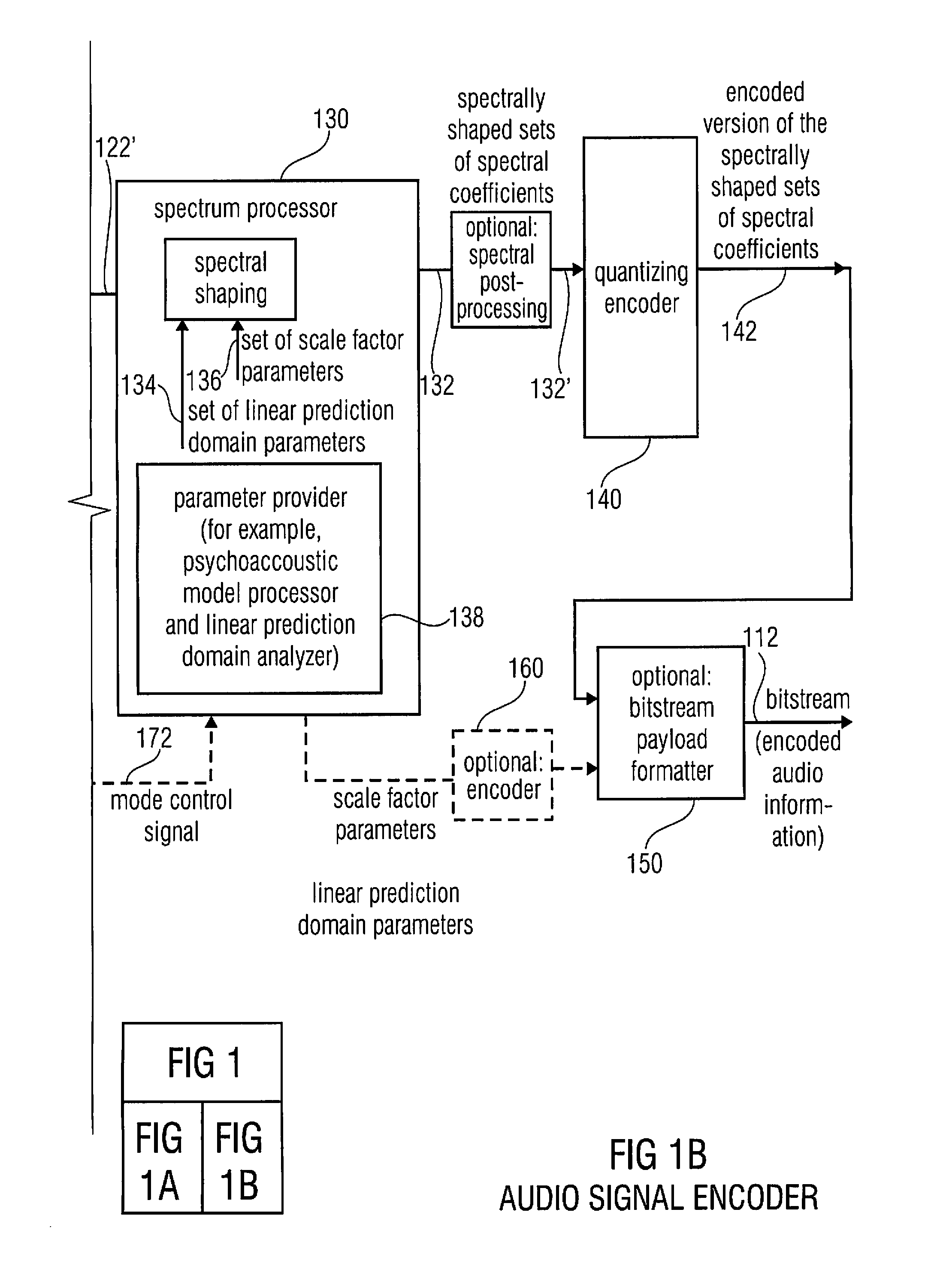
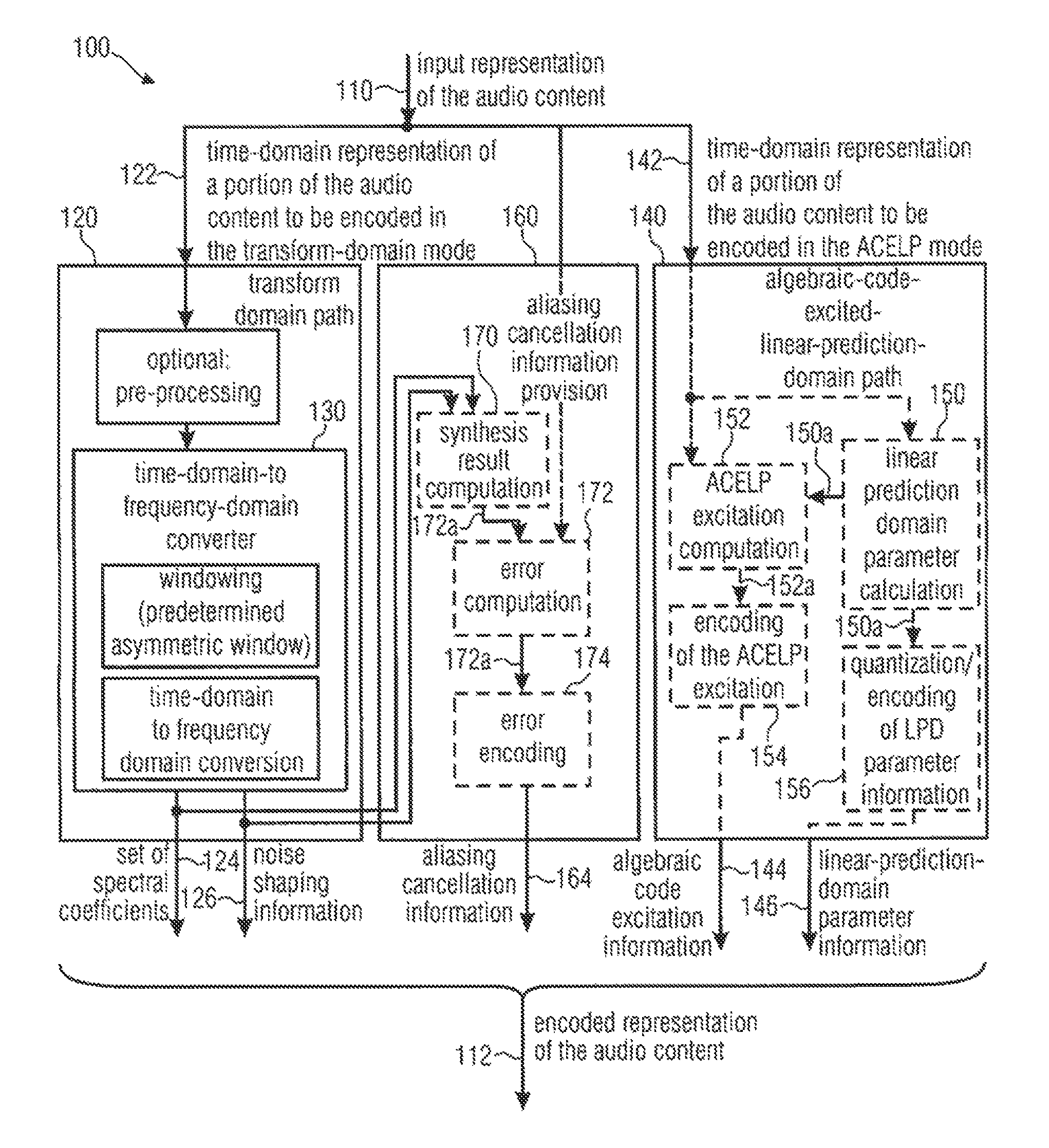
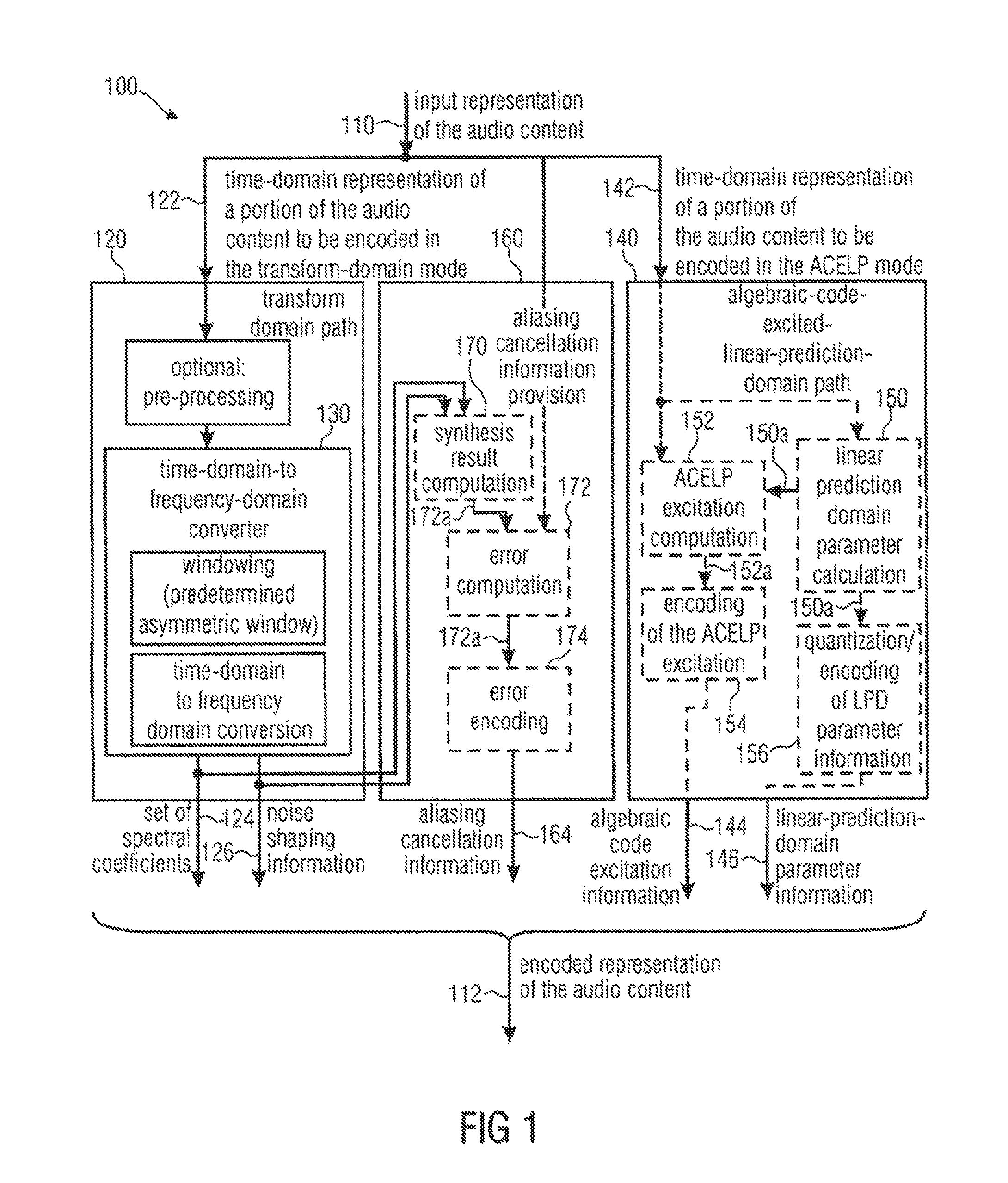
An audio signal encoder includes a transform-domain path which obtains spectral coefficients and noise-shaping information on the basis of a portion of the audio content, and which windows a time-domain representation of the audio content and applies a time-domain-to-frequency-domain conversion. The audio signal decoder includes a CELP path to obtain a code-excitation information and a LPD parameter information. A converter applies a predetermined asymmetric analysis window in both if a current portion is followed by a subsequent portion to be encoded in the transform-domain mode or in the CELP mode. Aliasing cancellation information is selectively provided in the later case.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
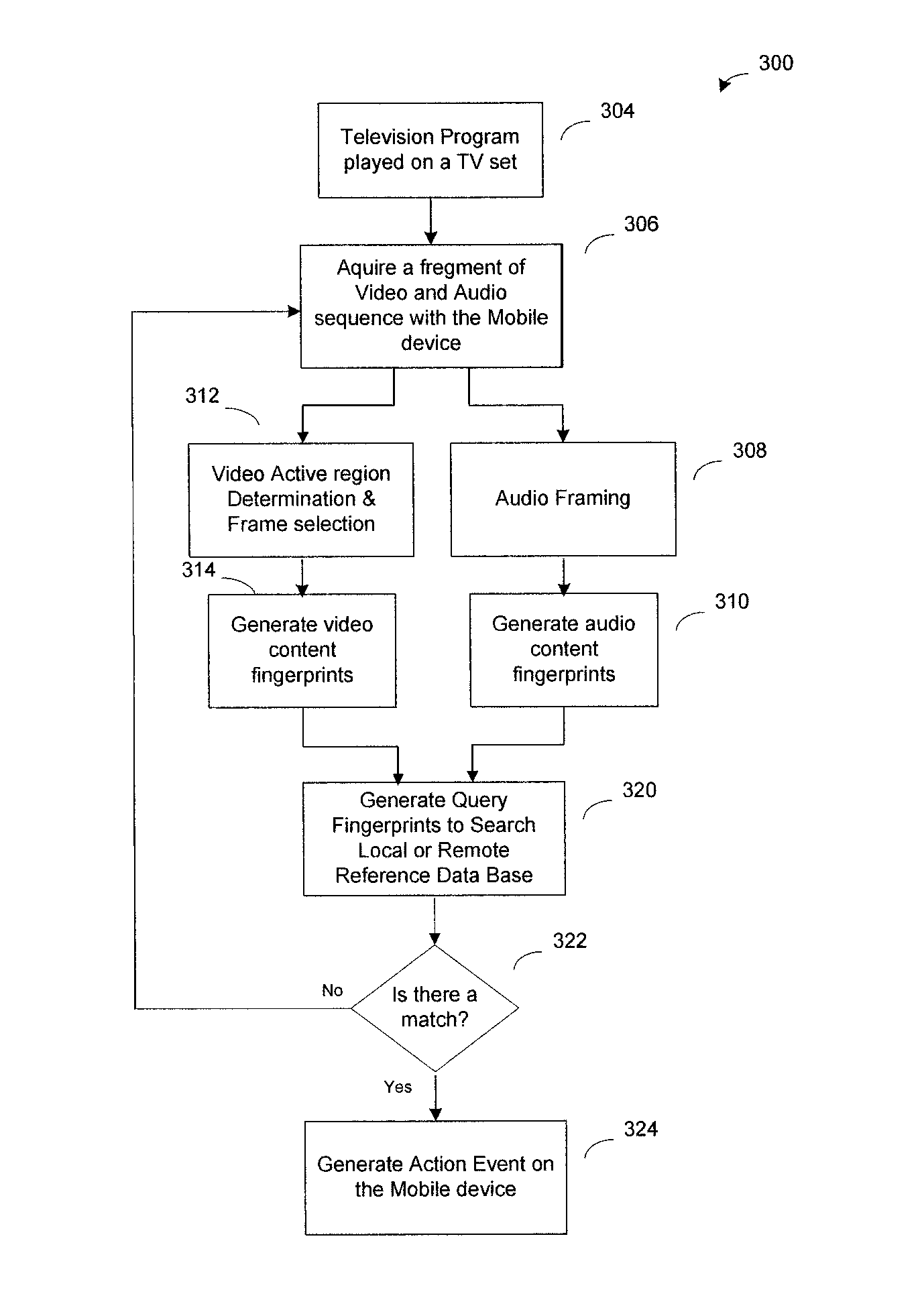
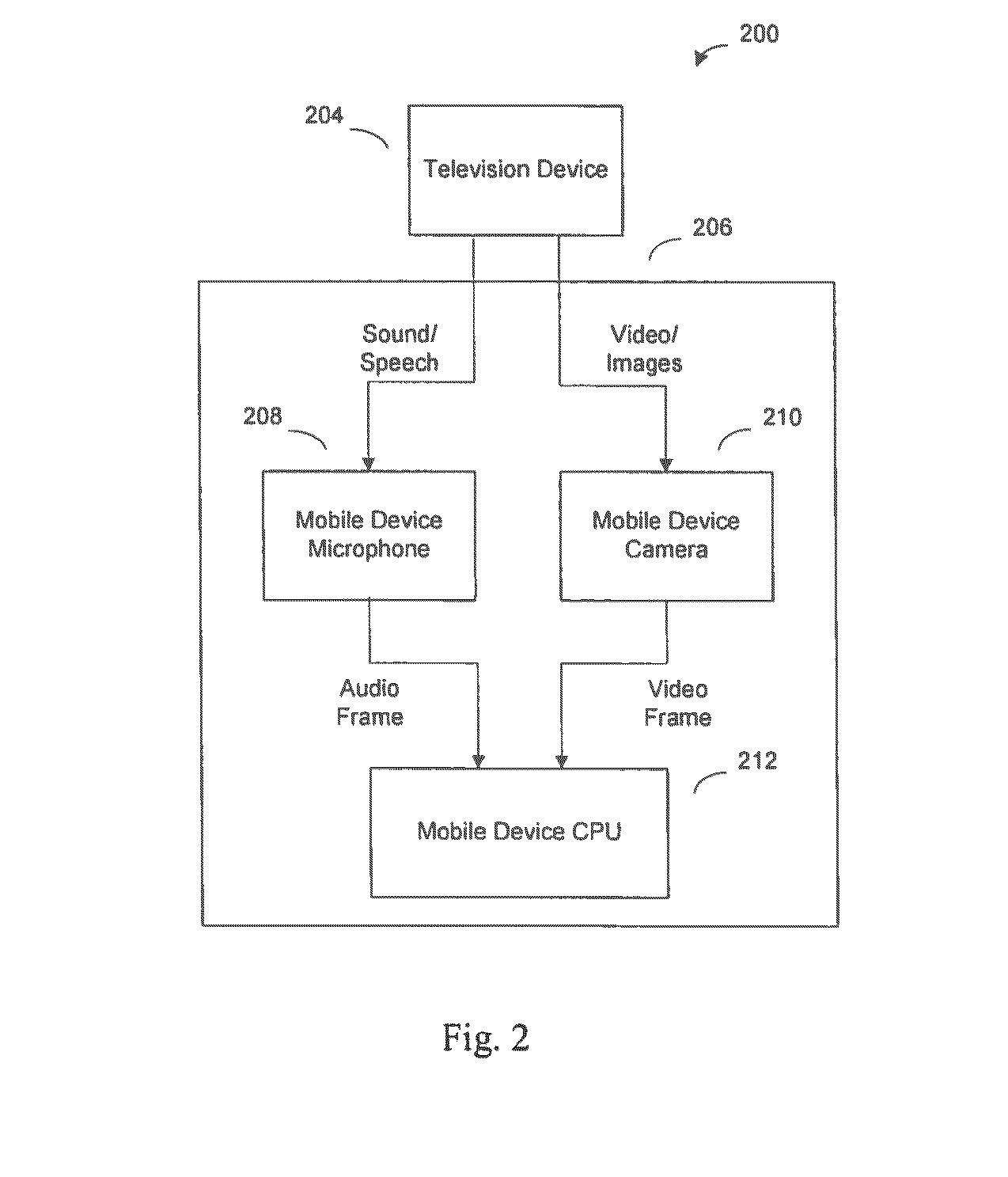
Media Content Identification on Mobile Devices
ActiveUS20160249093A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsSelective content distributionAudio signalMicrophone
A mobile device responds in real time to media content presented on a media device, such as a television. The mobile device captures temporal fragments of audio-video content on its microphone, camera, or both and generates corresponding audio-video query fingerprints. The query fingerprints are transmitted to a search server located remotely or used with a search function on the mobile device for content search and identification. Audio features are extracted and audio signal global onset detection is used for input audio frame alignment. Additional audio feature signatures are generated from local audio frame onsets, audio frame frequency domain entropy, and maximum change in the spectral coefficients. Video frames are analyzed to find a television screen in the frames, and a detected active television quadrilateral is used to generate video fingerprints to be combined with audio fingerprints for more reliable content identification.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
Voice sensitive information detecting and filtering method based on unspecified people
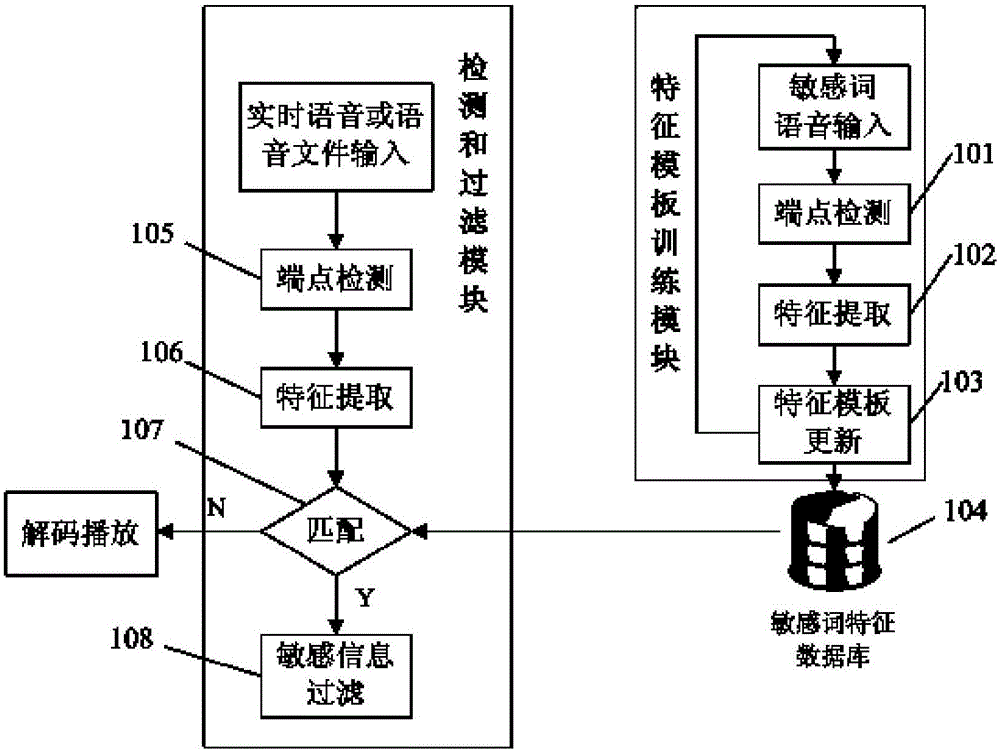
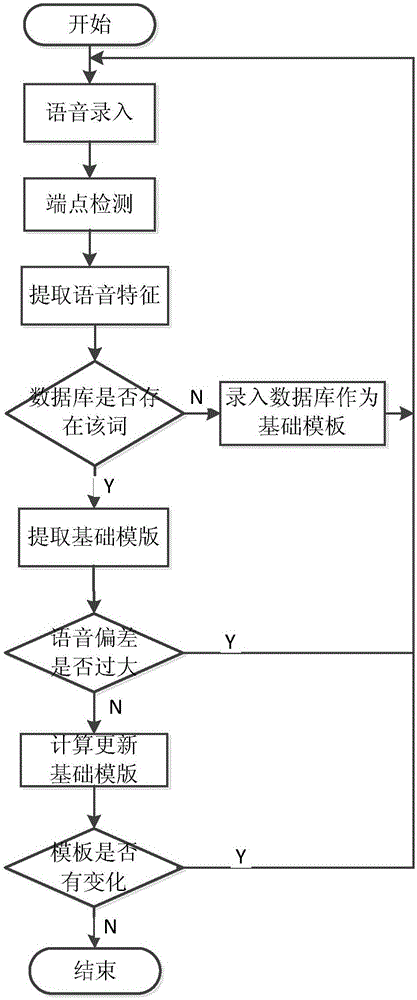
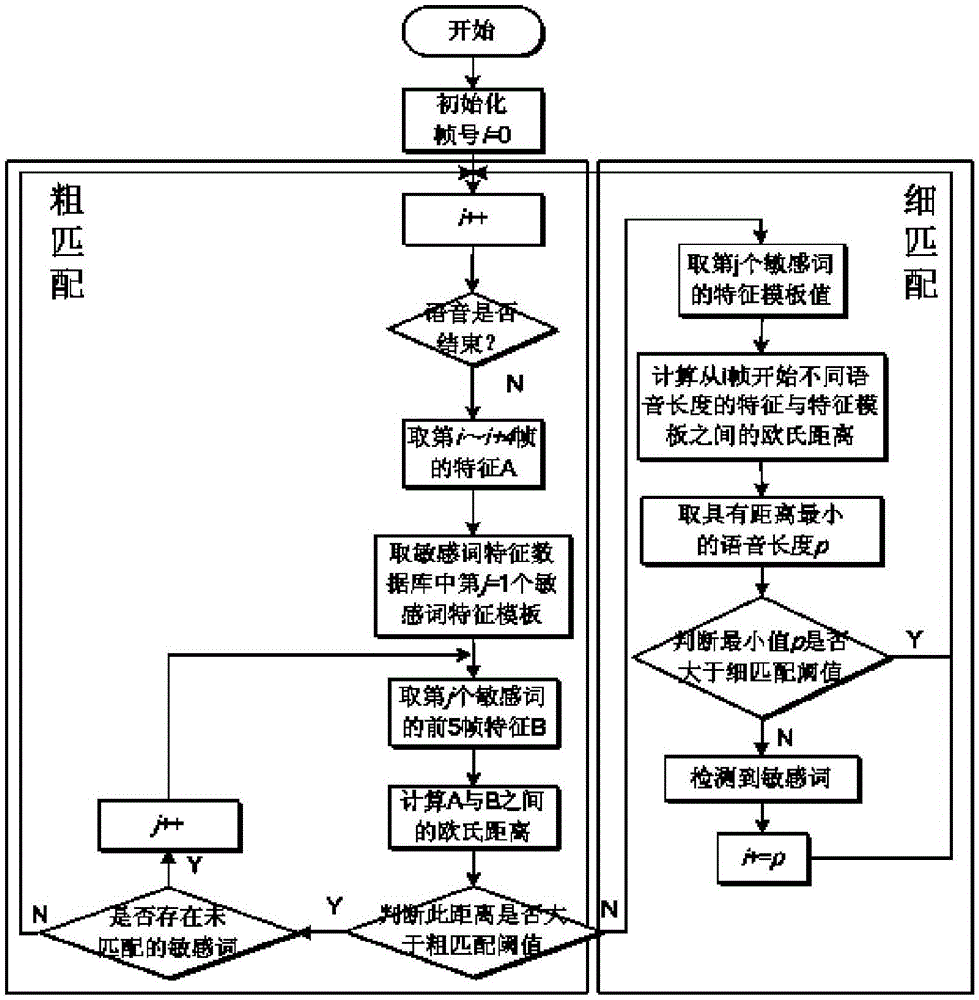
InactiveCN105006230AImprove accuracyGuaranteed accuracySpeech recognitionPattern recognitionDouble threshold
The invention discloses a voice sensitive information detecting and filtering method based on unspecified people. The method is capable of detecting and filtering real-time voices and voice files. The method includes the steps: carrying out end point detection for an original voice through an improved double threshold end point detection algorithm, extracting the Mel frequency inverted spectral coefficient characteristic of the voice, training an appropriate voice characteristic template through a self-learning time warping algorithm, and storing the template in a database; and then performing end point detection for the original voice through the improved double threshold end point detection algorithm, extracting the MFCC characteristic, comparing the extracted voice characteristic with the template in the sensitive word characteristic template database by combining rough matching with fine matching, detecting sensitive words input to the voice, and filtering the detected sensitive words.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for computing nonlinear function in inverse quantization formula
InactiveCN1741394ASmall amount of calculationHigh precisionSpeech analysisCode conversionCount distributionComputer science
A method for calculating nonlinear function in counter quantization formula includes counting distribution probability of quantized spectral coefficient in code stream , calculating nonlinear function with table looking - up method in scope that occurrence probability of quantized spectral coefficient is relatively concentrated , using polynomial approximation to calculate nonlinear function is scope that occurrence probability of spectral coefficient is not relatively concentrated.
Owner:GUANGDONG VIMICRO
Perceptually improved enhancement of encoded acoustic signals
InactiveUS6654716B2Improve sound qualityLarge coefficientSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumSound sources
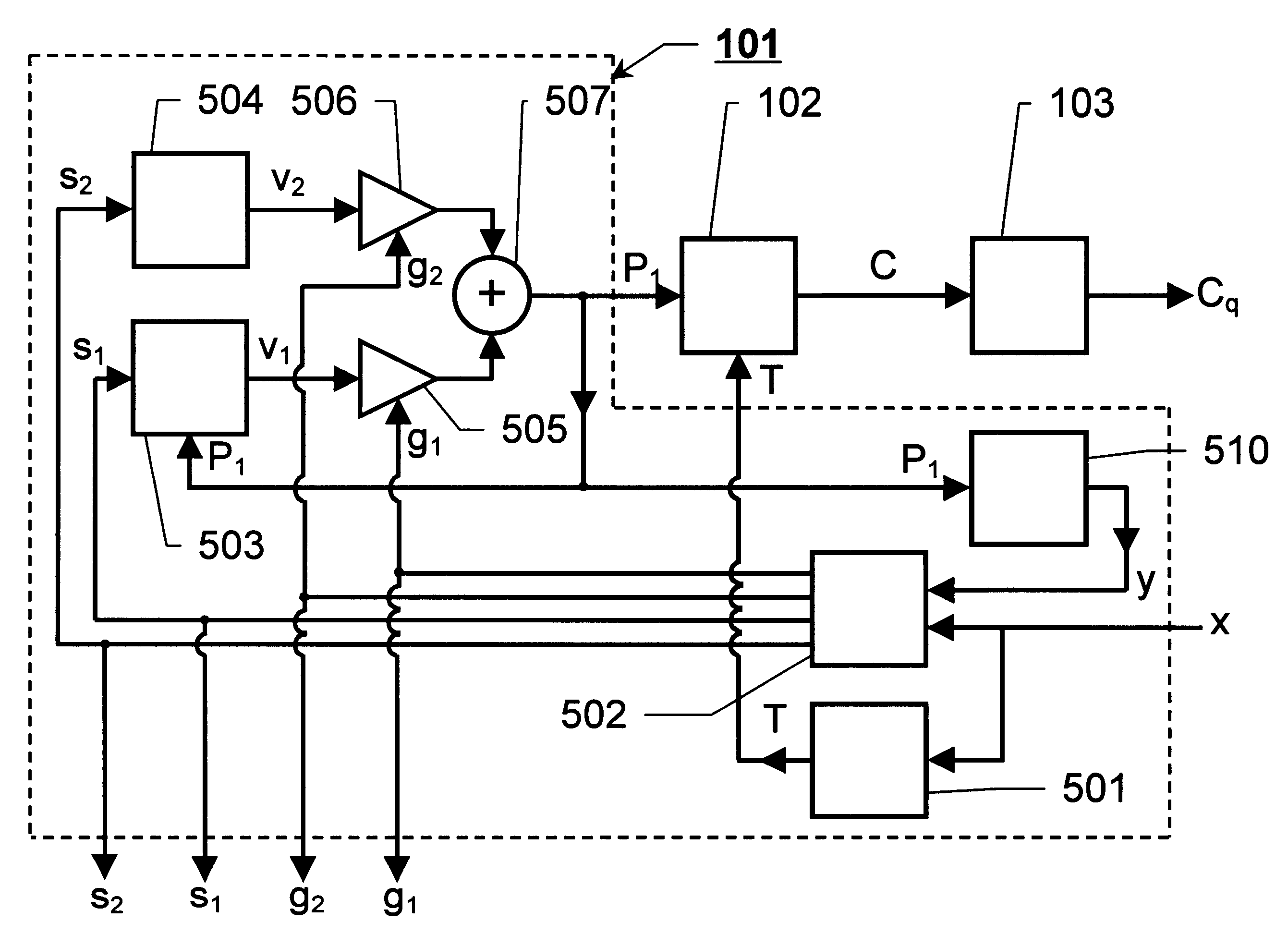
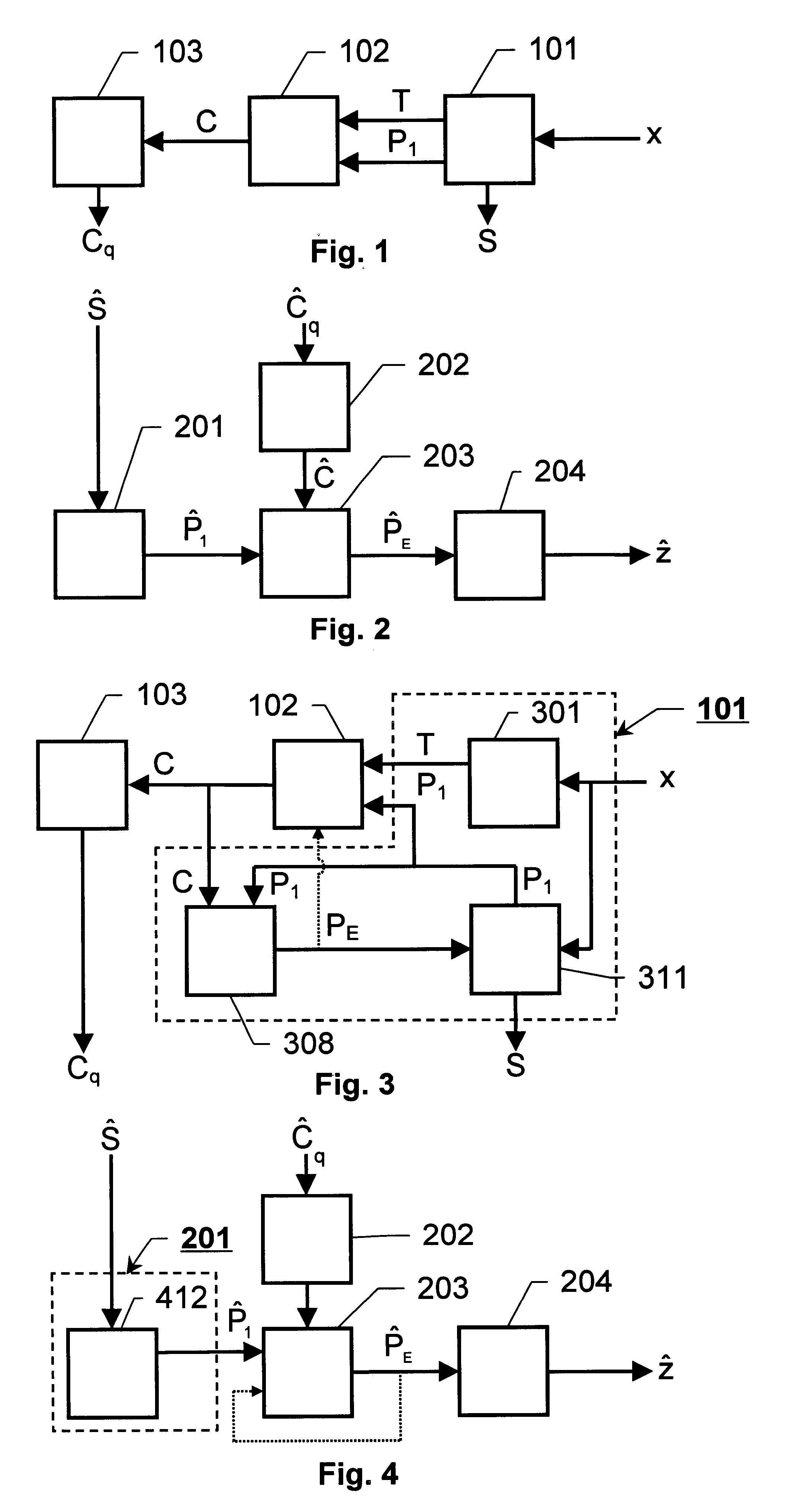
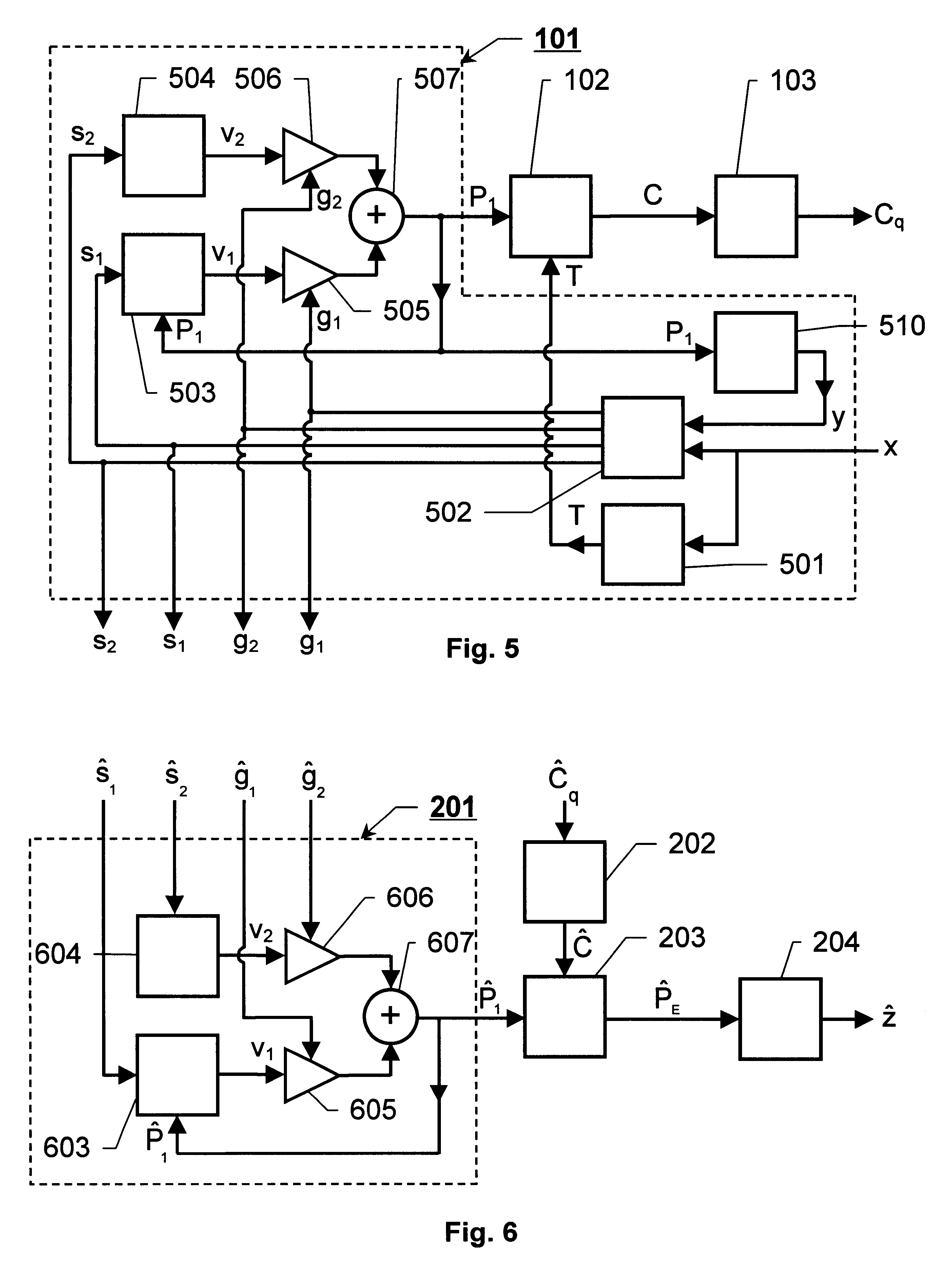
The invention relates to encoding of broadband and narrowband acoustic source signals (x) such that the perceived sound quality of corresponding reconstructed signals is improved in comparison to the known solutions. An enhancement estimation unit (102), operating in serial or in parallel with the regular encoding / decoding means (101), perceptually enhances a reconstructed acoustic source signal by utilization of an enhancement spectrum (C) comprising a larger number of spectral coefficients than the number of sample values in corresponding frames of the signals carrying the basic encoded representation of the acoustic source signal. The thus extended block length of the enhancement spectrum frame provides a basis for accomplishing the desired improvement of the perceived sound quality.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Coding of spectral coefficients of a spectrum of an audio signal
ActiveUS20160307576A1Enhancing entropy coding efficiencyImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumHarmonic
A coding efficiency of coding spectral coefficients of a spectrum of an audio signal is increased by en / decoding a currently to be en / decoded spectral coefficient by entropy en / decoding and, in doing so, performing the entropy en / decoding depending, in a context-adaptive manner, on a previously en / decoded spectral coefficient, while adjusting a relative spectral distance between the previously en / decoded spectral coefficient and the currently en / decoded spectral coefficient depending on an information concerning a shape of the spectrum. The information concerning the shape of the spectrum may have a measure of a pitch or periodicity of the audio signal, a measure of an inter-harmonic distance of the audio signal's spectrum and / or relative locations of formants and / or valleys of a spectral envelope of the spectrum, and on the basis of this knowledge, the spectral neighborhood which is exploited in order to form the context of the currently to be en / decoded spectral coefficients may be adapted to the thus determined shape of the spectrum, thereby enhancing the entropy coding efficiency.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Multi-mode audio encoder and audio decoder with spectral shaping in a linear prediction mode and in a frequency-domain mode
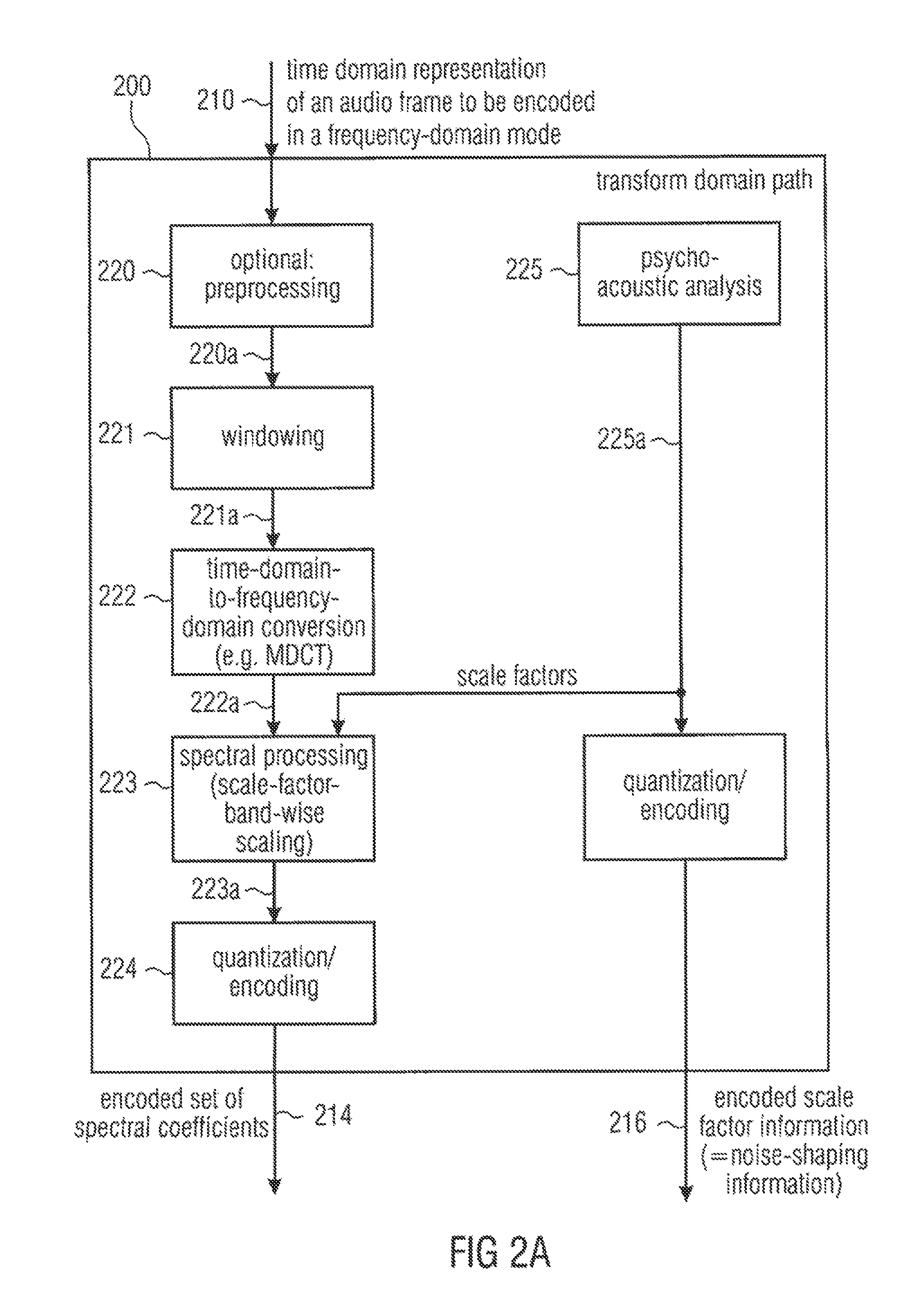
ActiveUS8744863B2Without inacceptable artifactEasy transitionSpeech analysisTime domainFrequency spectrum
A multi-mode audio signal decoder has a spectral value determinator to obtain sets of decoded spectral coefficients for a plurality of portions of an audio content and a spectrum processor configured to apply a spectral shaping to a set of spectral coefficients in dependence on a set of linear-prediction-domain parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a linear-prediction mode, and in dependence on a set of scale factor parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a frequency-domain mode. The audio signal decoder has a frequency-domain-to-time-domain converter configured to obtain a time-domain audio representation on the basis of a spectrally-shaped set of decoded spectral coefficients for a portion of the audio content encoded in the linear-prediction mode and for a portion of the audio content encoded in the frequency domain mode. An audio signal encoder is also described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and device for noise filling
A method for perceptual spectral decoding comprises decoding of spectral coefficients recovered from a binary flux into decoded spectral coefficients of an initial set of spectral coefficients. The initial set of spectral coefficients are spectrum filled. The spectrum filling comprises noise filling of spectral holes by setting spectral coefficients in the initial set of spectral coefficients not being decoded from the binary flux equal to elements derived from the decoded spectral coefficients. The set of reconstructed spectral coefficients of a frequency domain formed by the spectrum filling is converted into an audio signal of a time domain. A perceptual spectral decoder comprises a noise filler, operating according to the method for perceptual spectral decoding.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
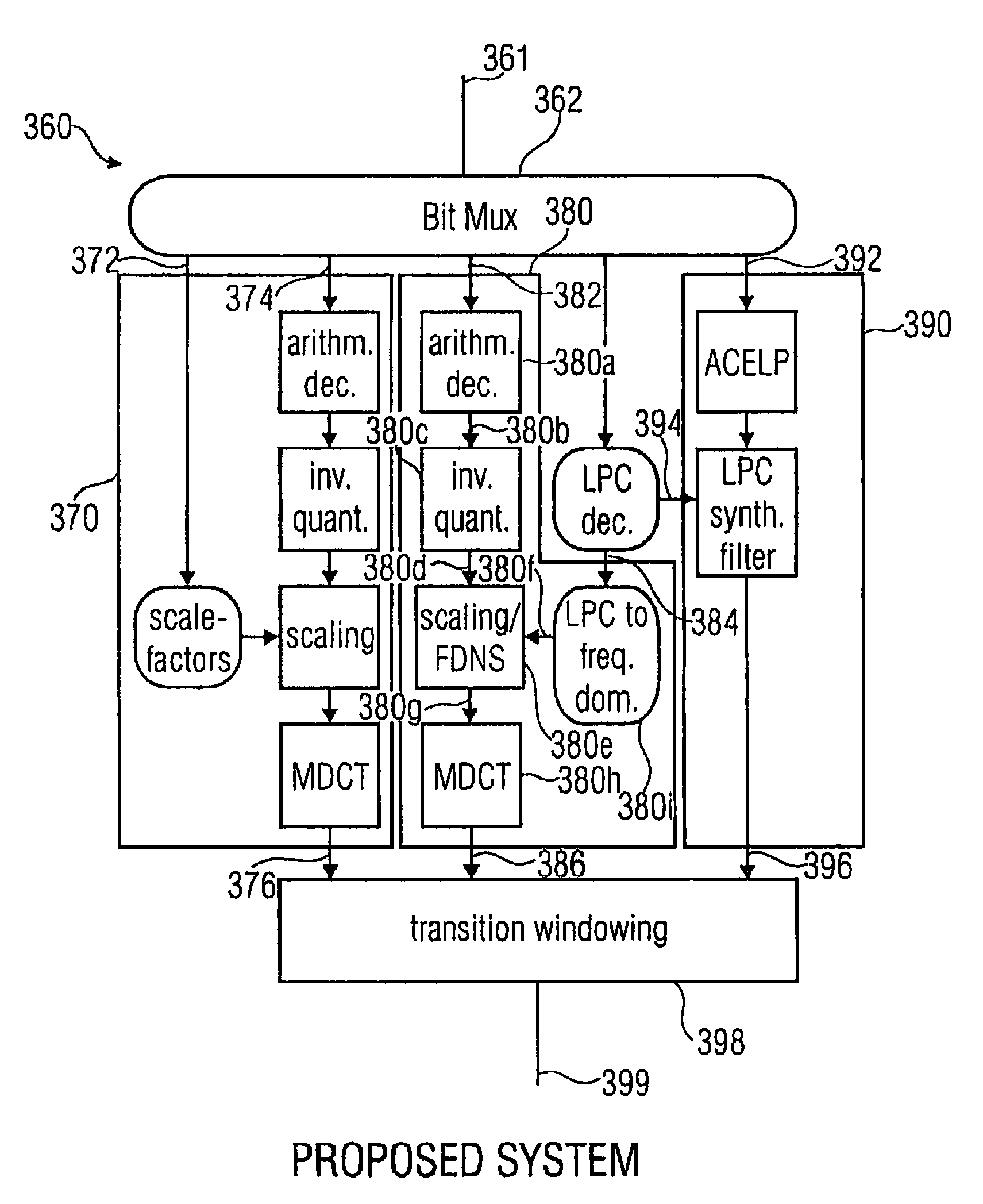
Audio signal encoder/decoder for use in low delay applications, selectively providing aliasing cancellation information while selectively switching between transform coding and celp coding of frames
ActiveUS8630862B2Improve coding efficiencyImprove the level ofSpeech analysisTime domainFrequency spectrum
An audio signal encoder includes a transform-domain path which obtains spectral coefficients and noise-shaping information on the basis of a portion of the audio content, and which windows a time-domain representation of the audio content and applies a time-domain-to-frequency-domain conversion. The audio signal decoder includes a CELP path to obtain a code-excitation information and a LPC parameter information. A converter applies a predetermined asymmetric analysis window in both if a current portion is followed by a subsequent portion to be encoded in the transform-domain mode or in the CELP mode. Aliasing cancellation information is selectively provided in the latter case.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Apparatus and method for processing a multi-channel signal
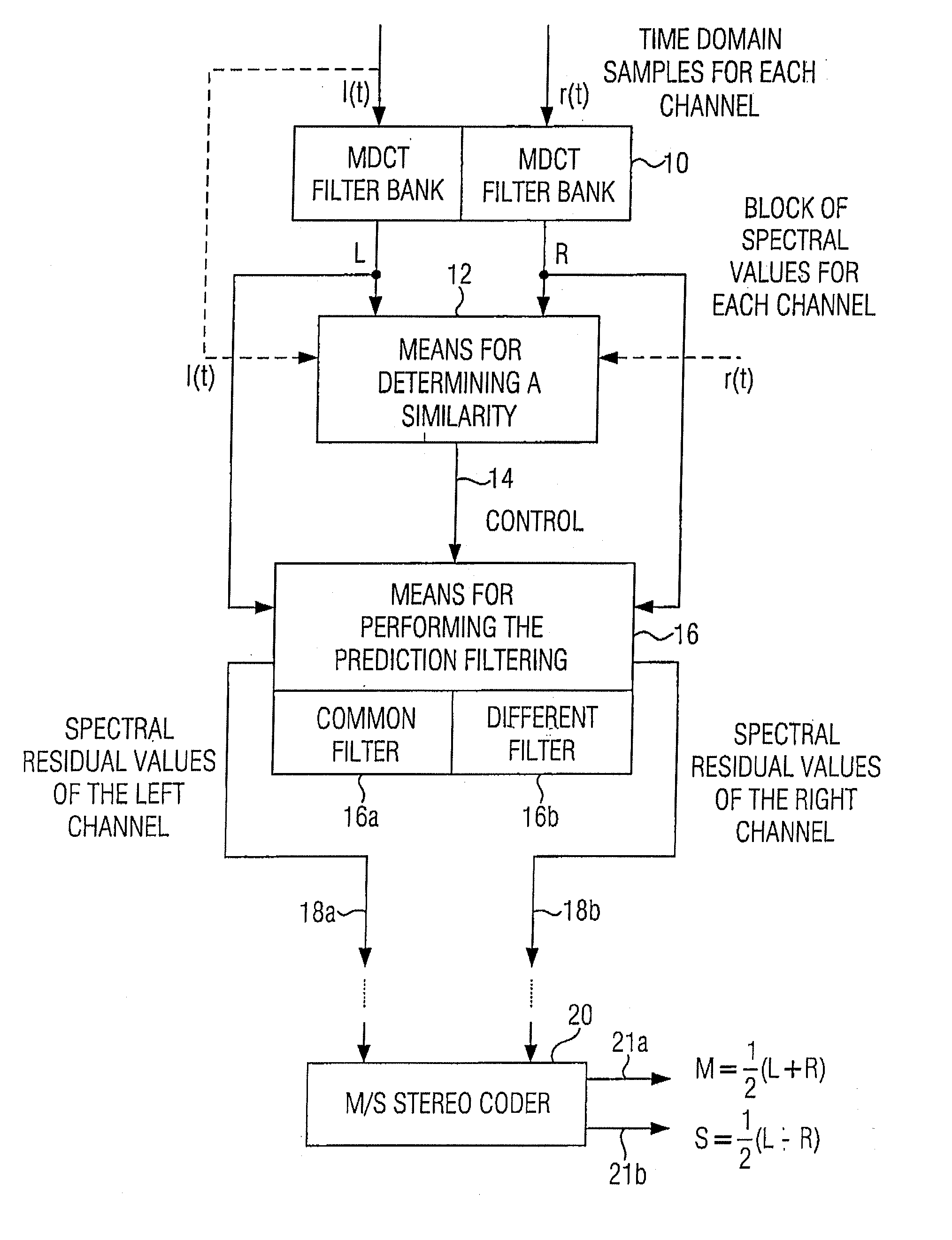
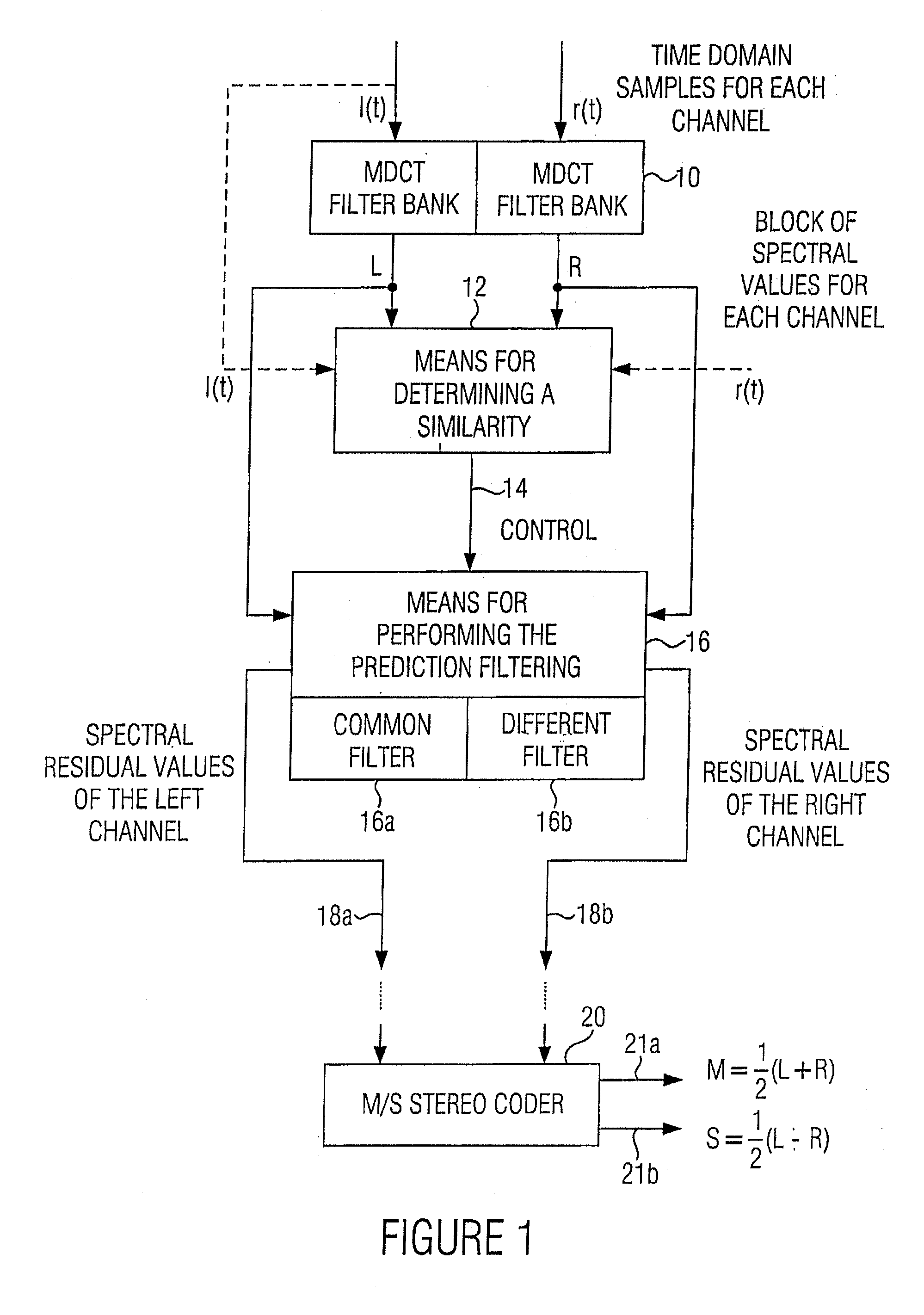
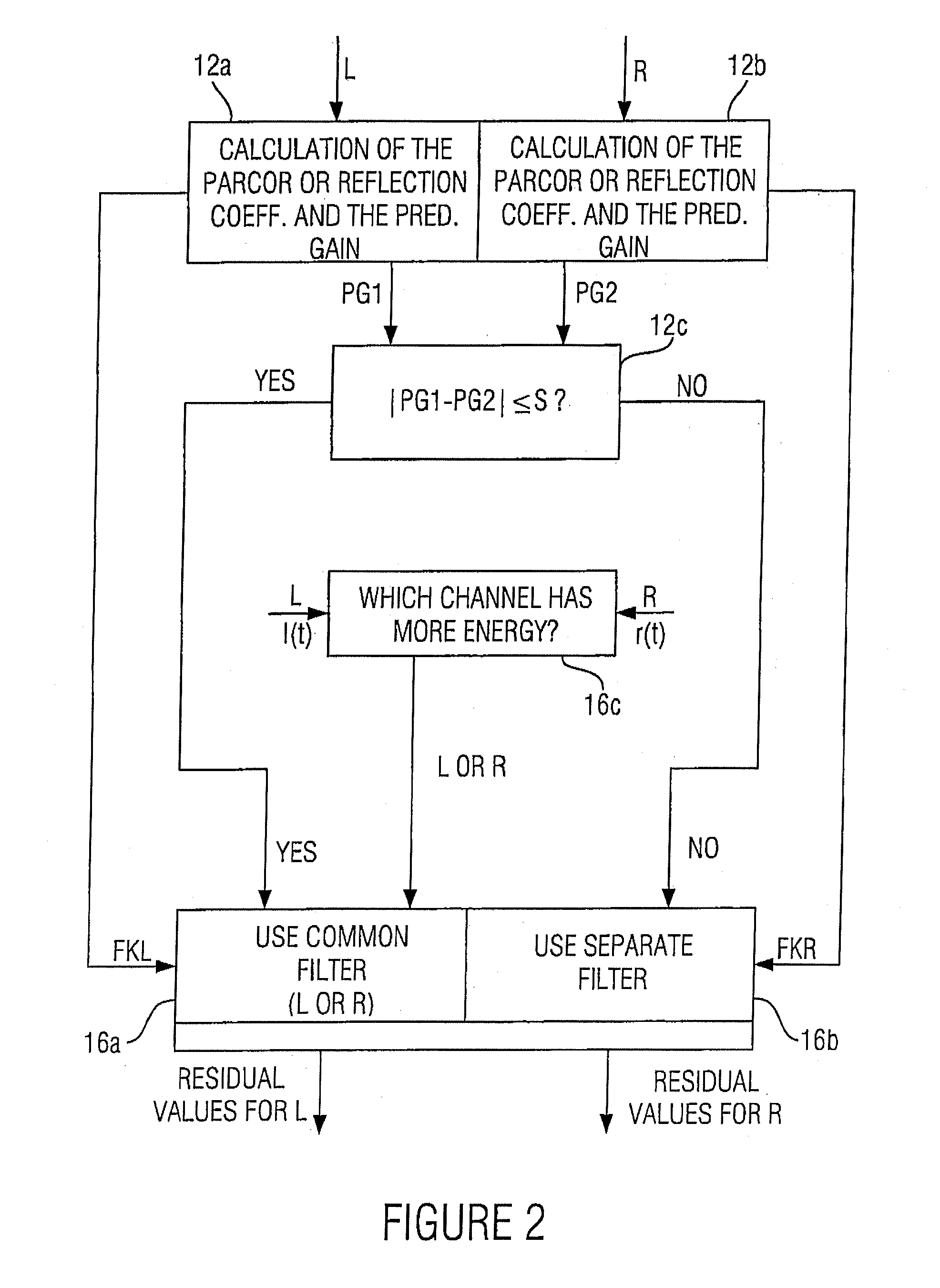
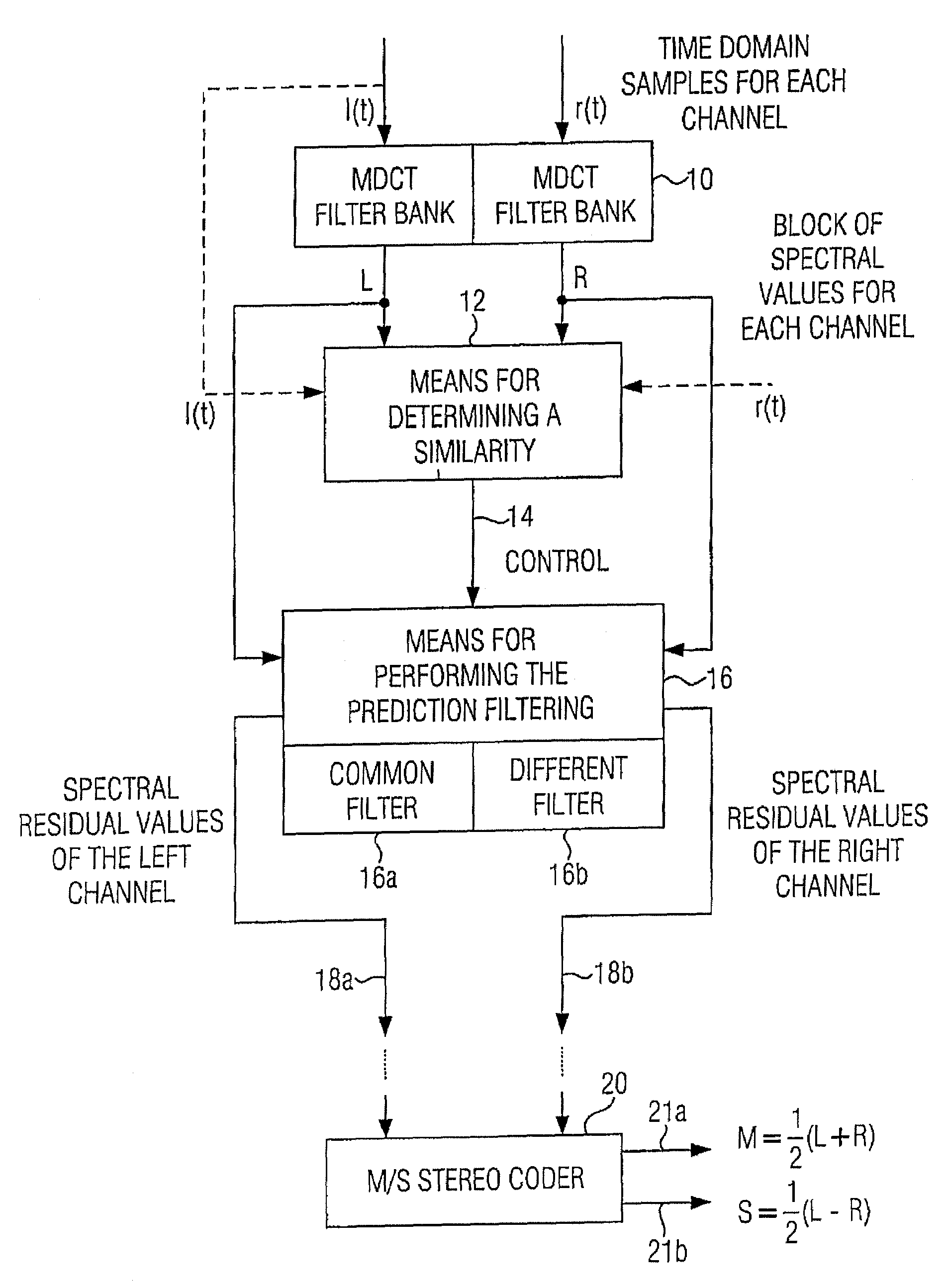
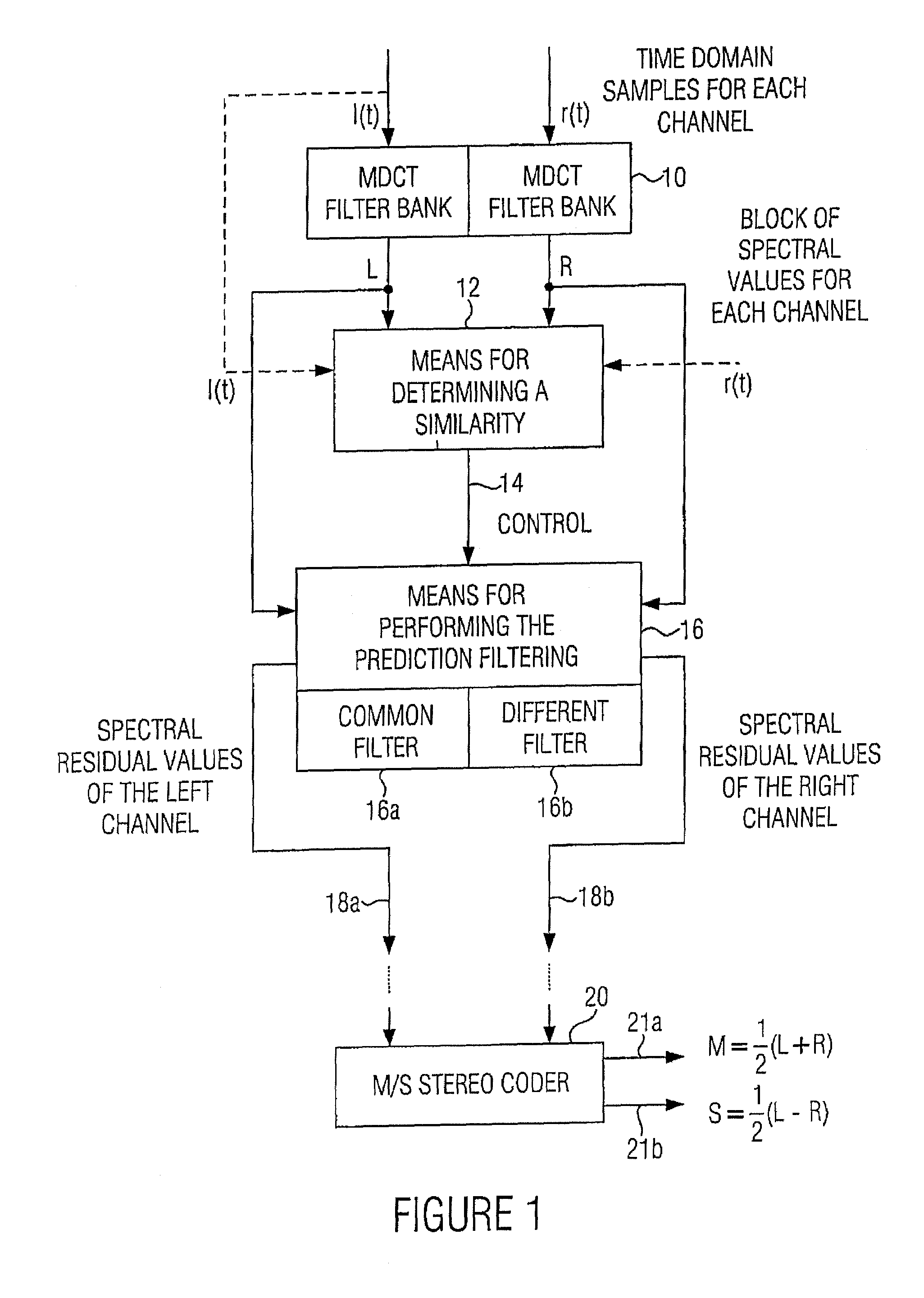
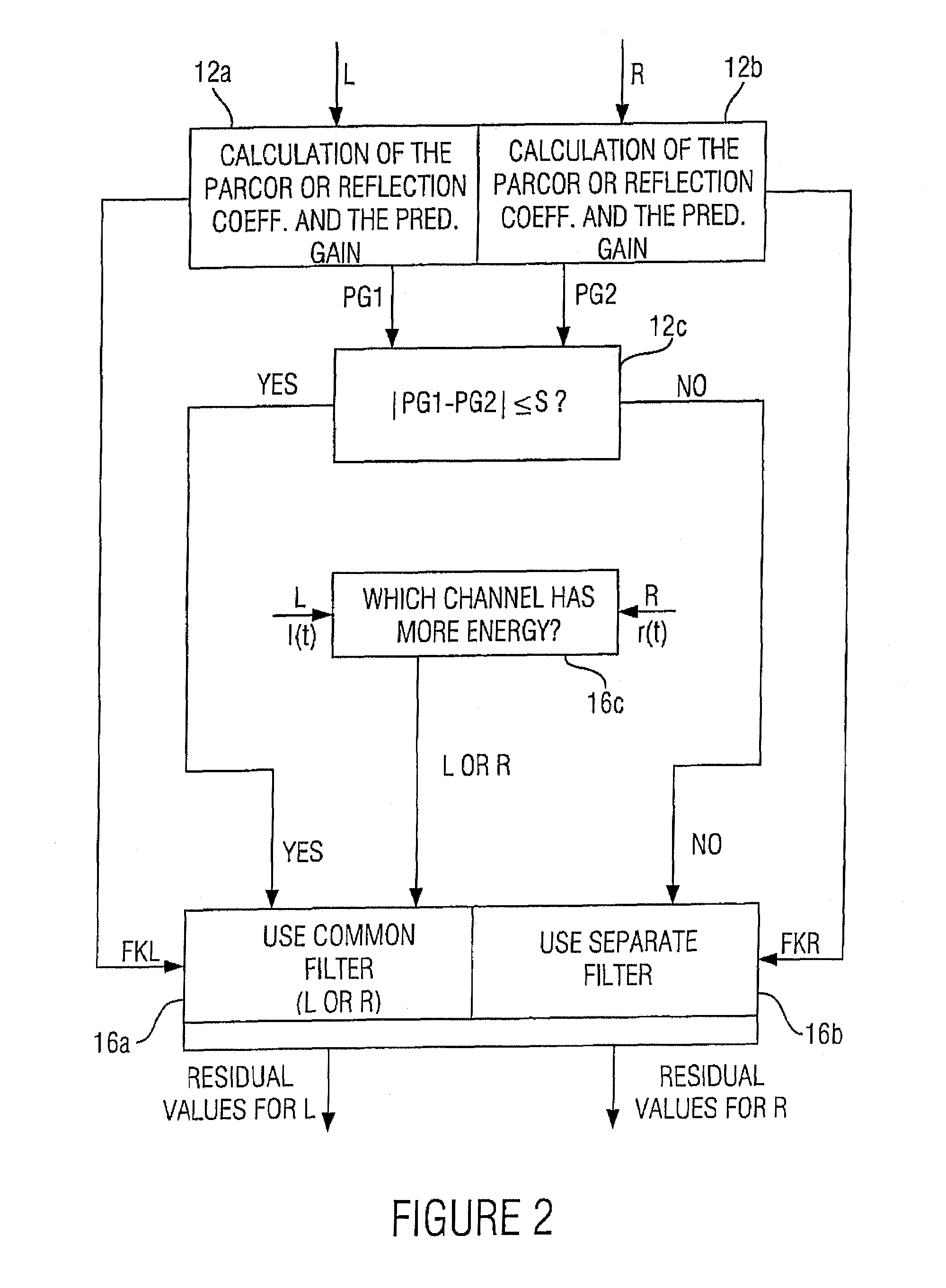
ActiveUS20070033056A1Small loss in prediction gainEasy to compressSpeech analysisPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
An apparatus for processing a multi-channel signal includes a means for determining a similarity between a first one of two channels and a second one of the two channels. Furthermore, a means for performing a prediction filtering of the spectral coefficients is provided, which is formed to perform a prediction filtering with only a single prediction filter for both channels in case of high similarity between the first and the second channel, and to perform a prediction filtering with two separate prediction filters in case of a dissimilarity between the first and the second channel. With this, an introduction of stereo artifacts and a deterioration of the coding gain in stereo coding techniques are avoided.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Audio signal encoder, audio signal decoder, method for encoding or decoding an audio signal using an aliasing-cancellation
ActiveUS8484038B2Improve audio qualityModerate level of overheadSpeech analysisTime domainFrequency spectrum
An audio signal decoder includes a transform domain path configured to obtain a time-domain representation of a portion of an audio content on the basis of a first set of spectral coefficients, a representation of an aliasing-cancellation stimulus signal and a plurality of linear-prediction-domain parameters. The transform domain path applies a spectrum shaping to the first set of spectral coefficients to obtain a spectrally-shaped version thereof. The transform domain path obtains a time-domain representation of the audio content on the basis of the spectrally-shaped version of the first set of spectral coefficients. The transform domain path includes an aliasing-cancellation stimulus filter to filter the aliasing-cancellation stimulus signal in dependence on at least a subset of the linear-prediction-domain parameters. The transform domain path also includes a combiner configured to combine the time-domain representation of the audio content with an aliasing-cancellation synthesis signal to obtain an aliasing reduced time-domain signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +3
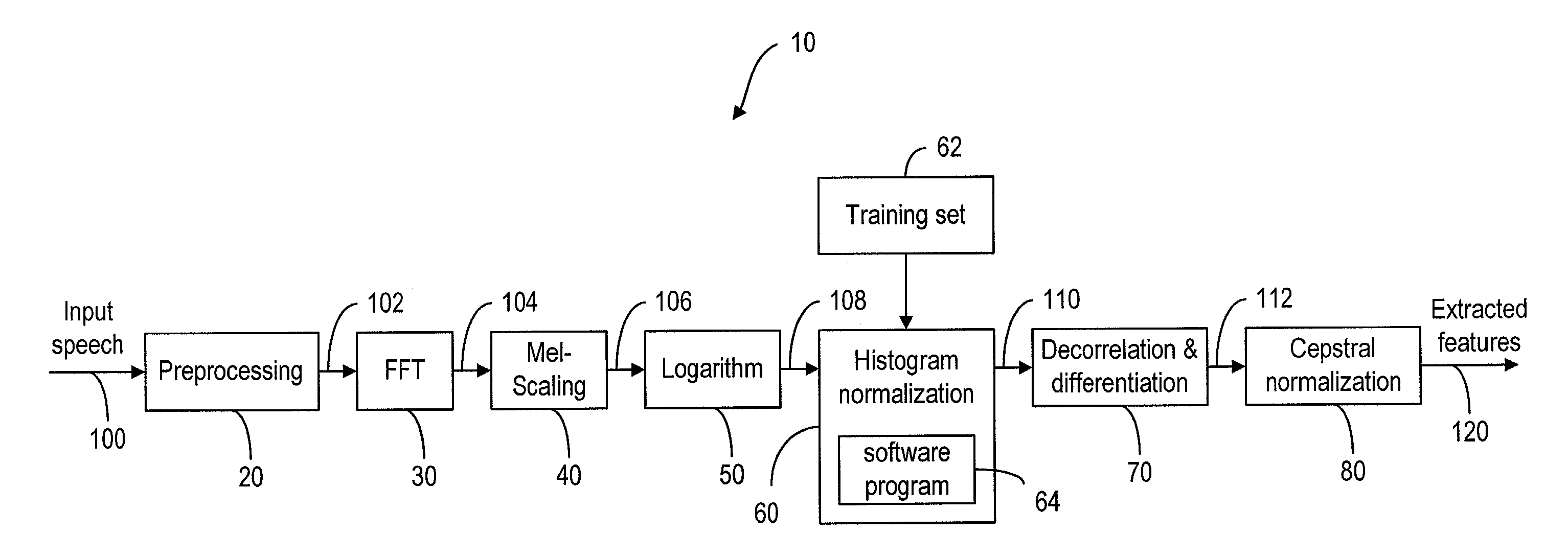
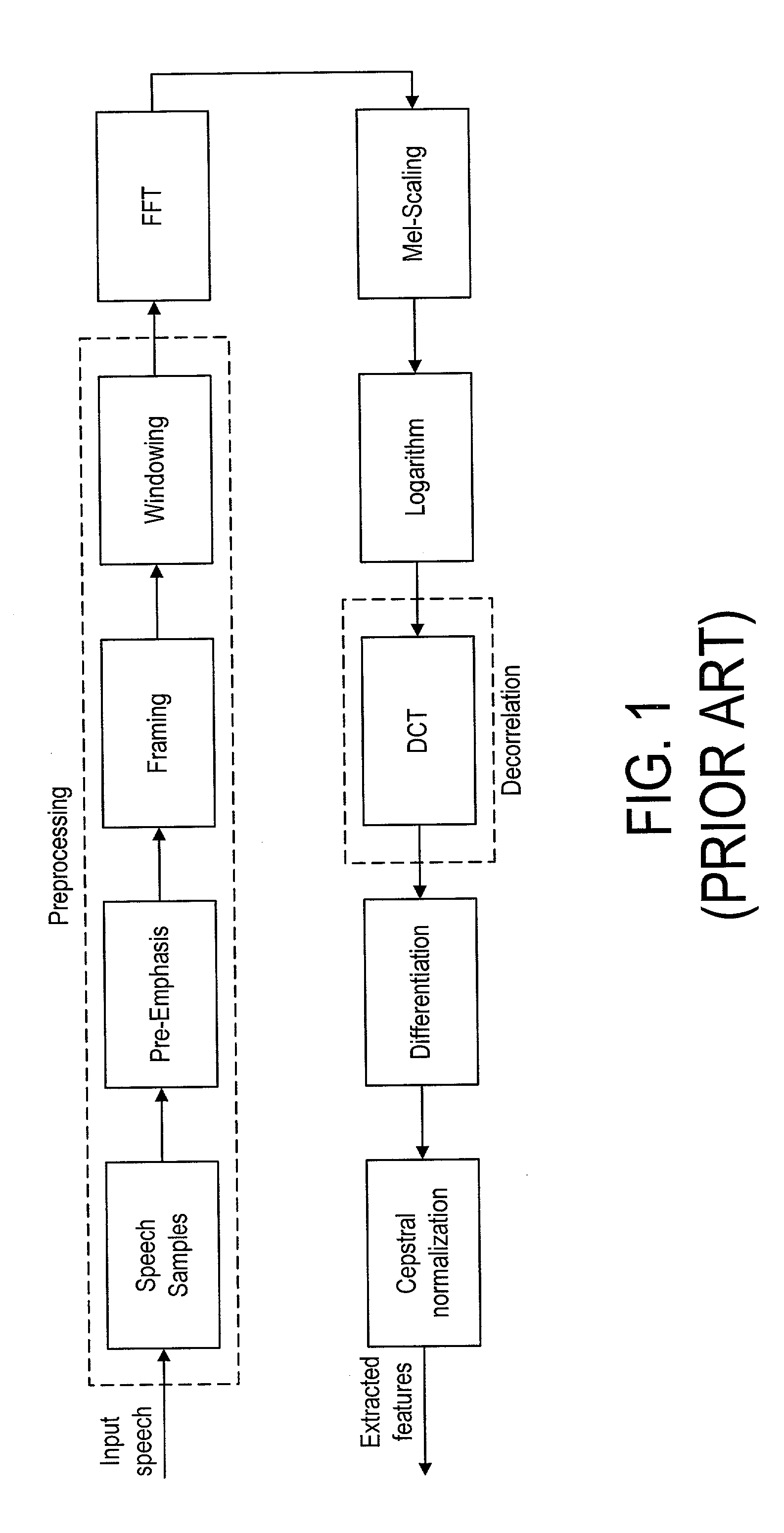
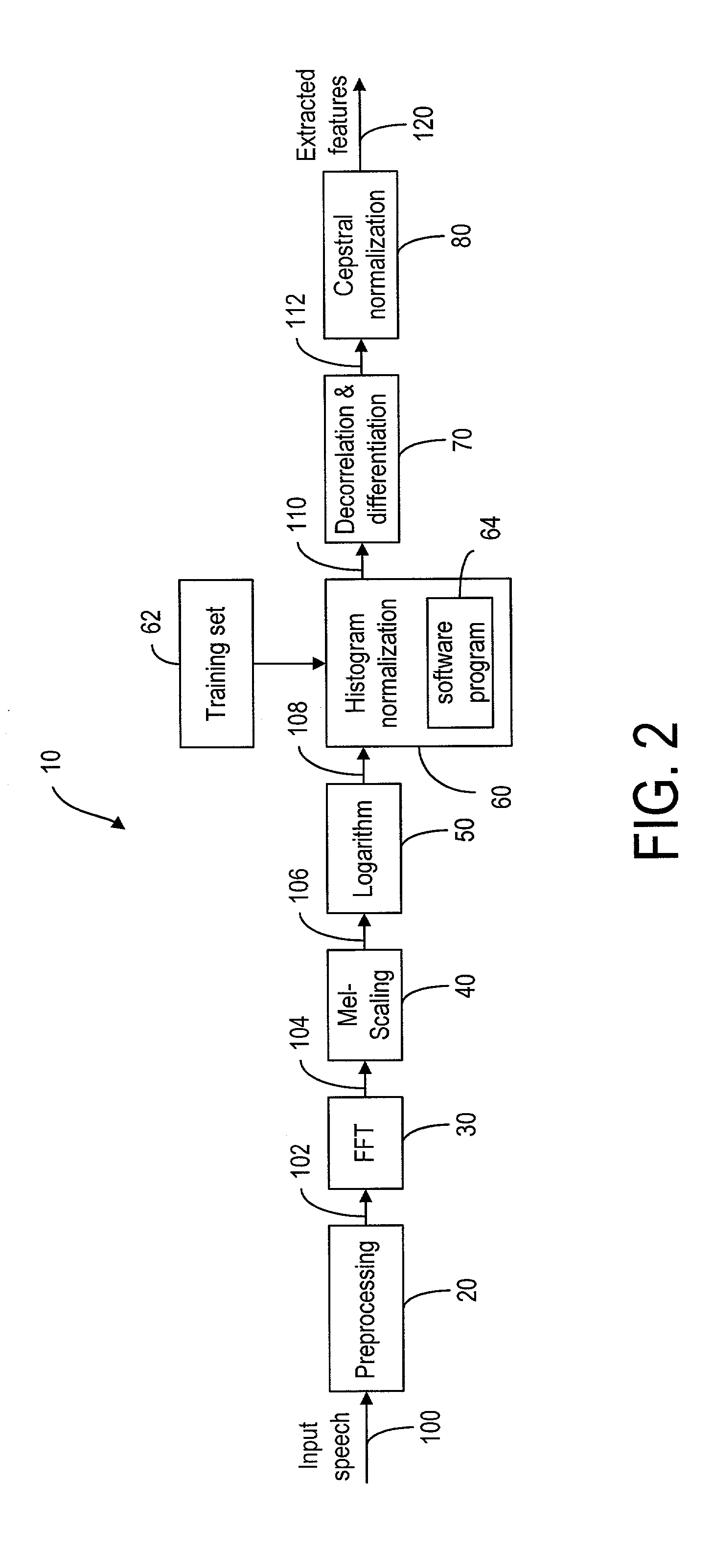
On-line parametric histogram normalization for noise robust speech recognition
A method for improving noise robustness in speech recognition, wherein a front-end is used for extracting speech feature from an input speech and for providing a plurality of scaled spectral coefficients. The histogram of the scaled spectral coefficients is normalized to the histogram of a training set using Gaussian approximations. The normalized spectral coefficients are then converted into a set of cepstrum coefficients by a decorrelation module and further subjected to ceptral domain feature-vector normalization.
Owner:RPX CORP
Apparatus and method for processing a multi-channel signal
An apparatus for processing a multi-channel signal includes a means for determining a similarity between a first one of two channels and a second one of the two channels. Furthermore, a means for performing a prediction filtering of the spectral coefficients is provided, which is formed to perform a prediction filtering with only a single prediction filter for both channels in case of high similarity between the first and the second channel, and to perform a prediction filtering with two separate prediction filters in case of a dissimilarity between the first and the second channel. With this, an introduction of stereo artifacts and a deterioration of the coding gain in stereo coding techniques are avoided.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Low-complexity spectral analysis/synthesis using selectable time resolution
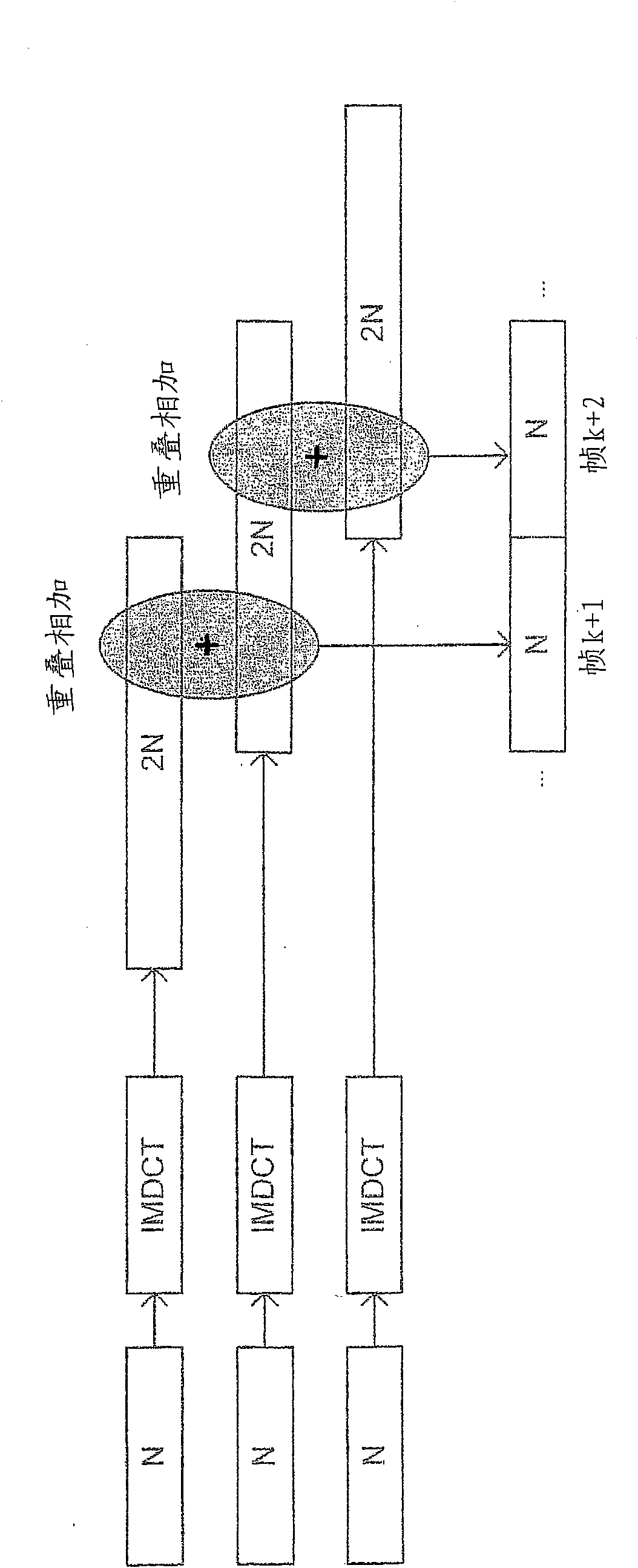
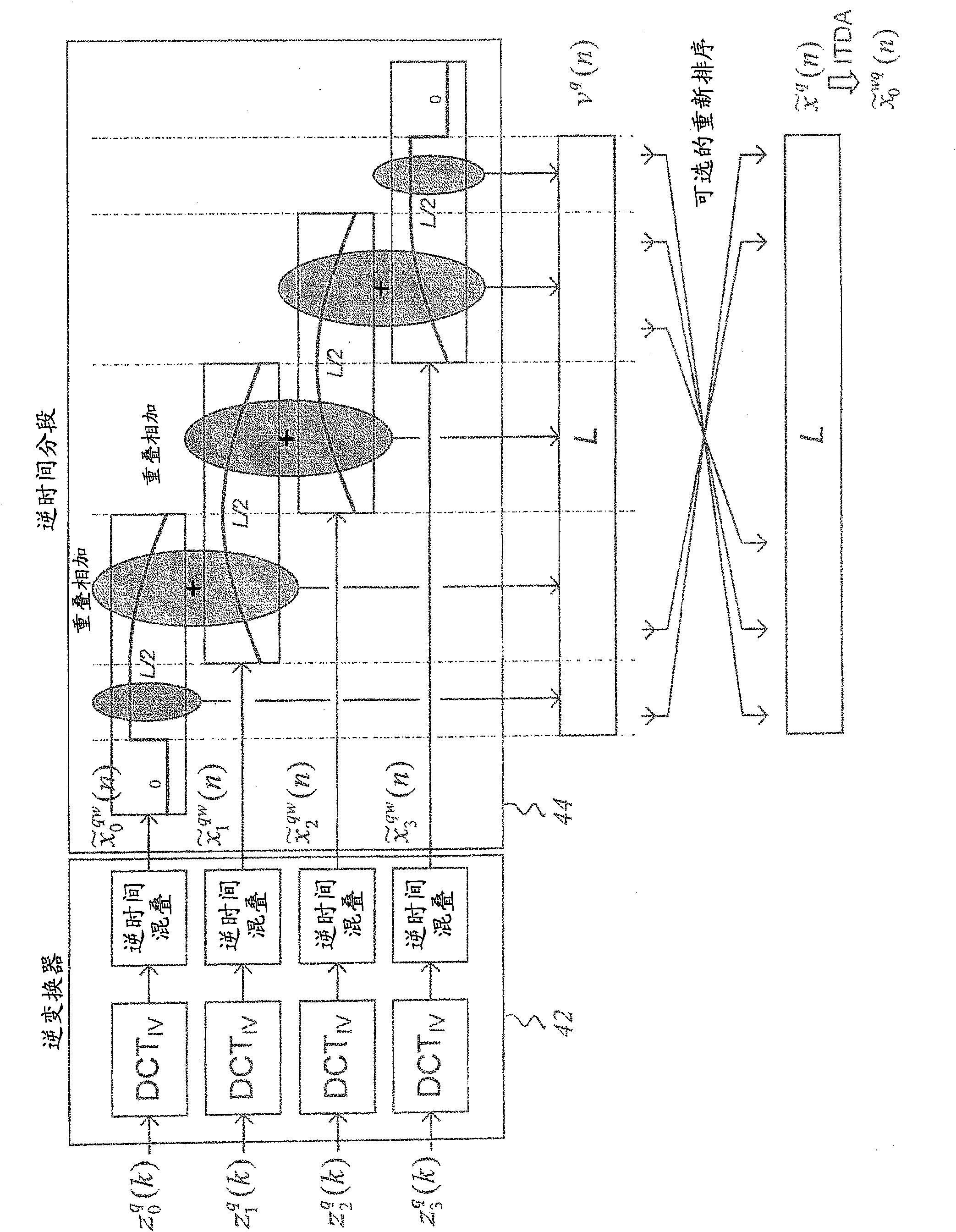
The signal processing is based on the c oncept of using a time-domain aliased (12, TDA) frame as a basis for time segmen tation (14) and spectral analysis (16), performing segmentation in time based on the time-domain aliased frame and performing spectral analysis based on the resulting time segments. The time resolution of the overall segmented time-to-frequenc y transform can thus be changed by simply adapting the time segmentation to ob tain a suitable number of time segments based on which spectral analysis is applied. The overall set of spectral coefficients, obtained for all the segments, provides a selectable time-frequency tiling of the original signal frame.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
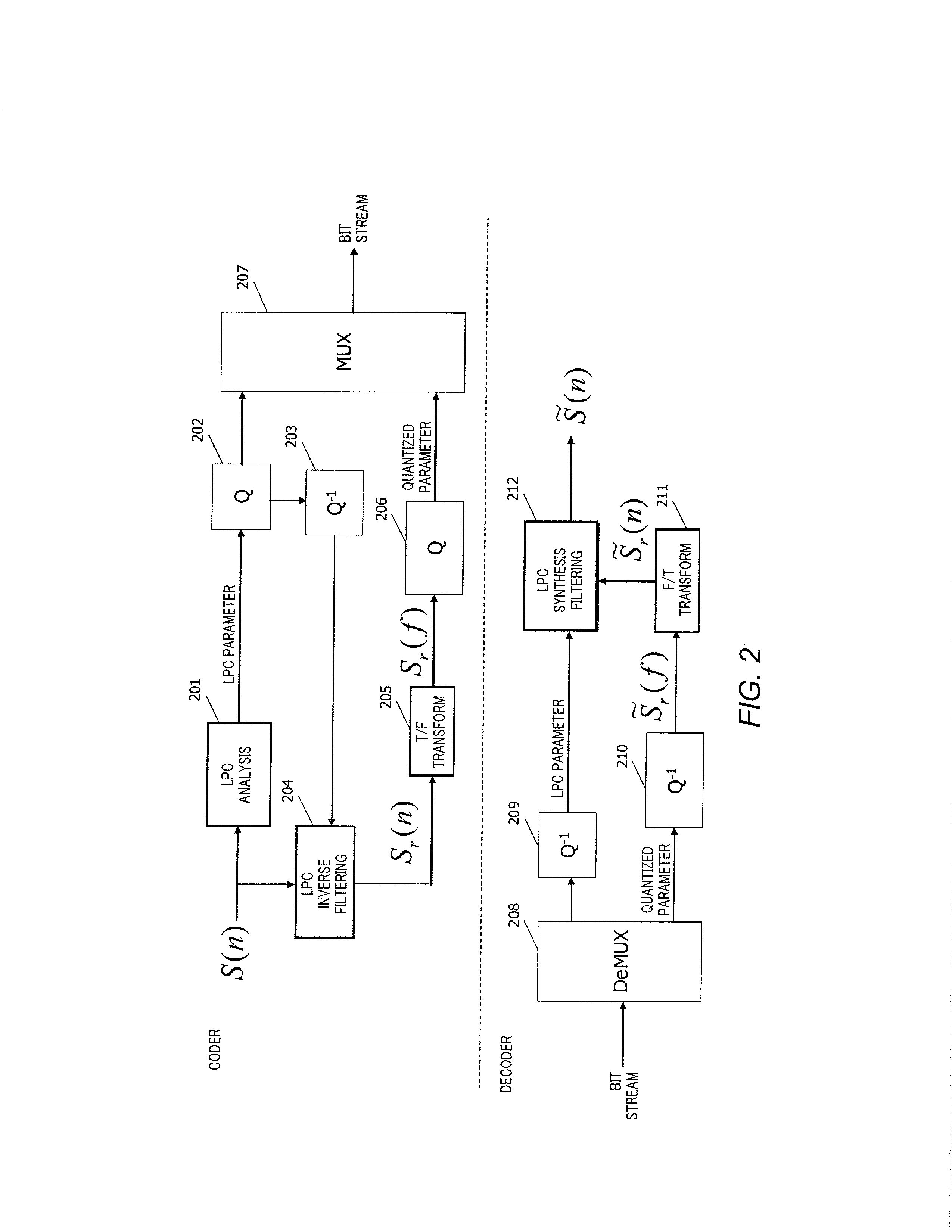
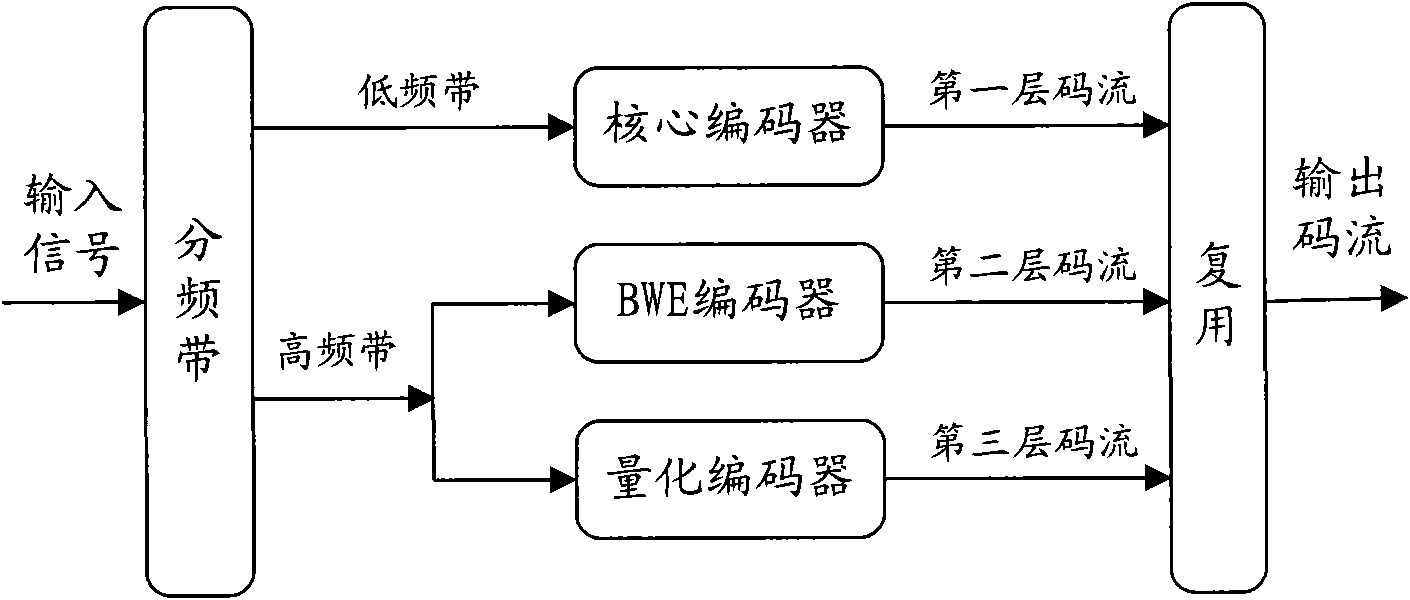
Audio encoding device and audio decoding device
InactiveUS20130173275A1Mitigate degradation of sound qualityReduce degradationSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumTransform coding
Provided is an audio encoding device that can suppress degradation of audio quality. Spectral coefficients of synthesized signal from CELP core layer are utilized to fulfill spectral gaps in error signal spectrum coefficients from a transform coding layer. By both spectral coefficients, decoded signal spectral coefficients are generated. The decoded signal spectral coefficients and the input signal spectral coefficients are divided into a plurality of sub bands. In each sub band, the energy of the input signal spectral coefficient corresponding to a zero decoded error signal spectral coefficient is calculated, and the energy of the decoded signal spectral coefficient corresponding to the zero decoding error signal spectral coefficient is calculated, and their energy ratio is calculated and is quantized and transmitted.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
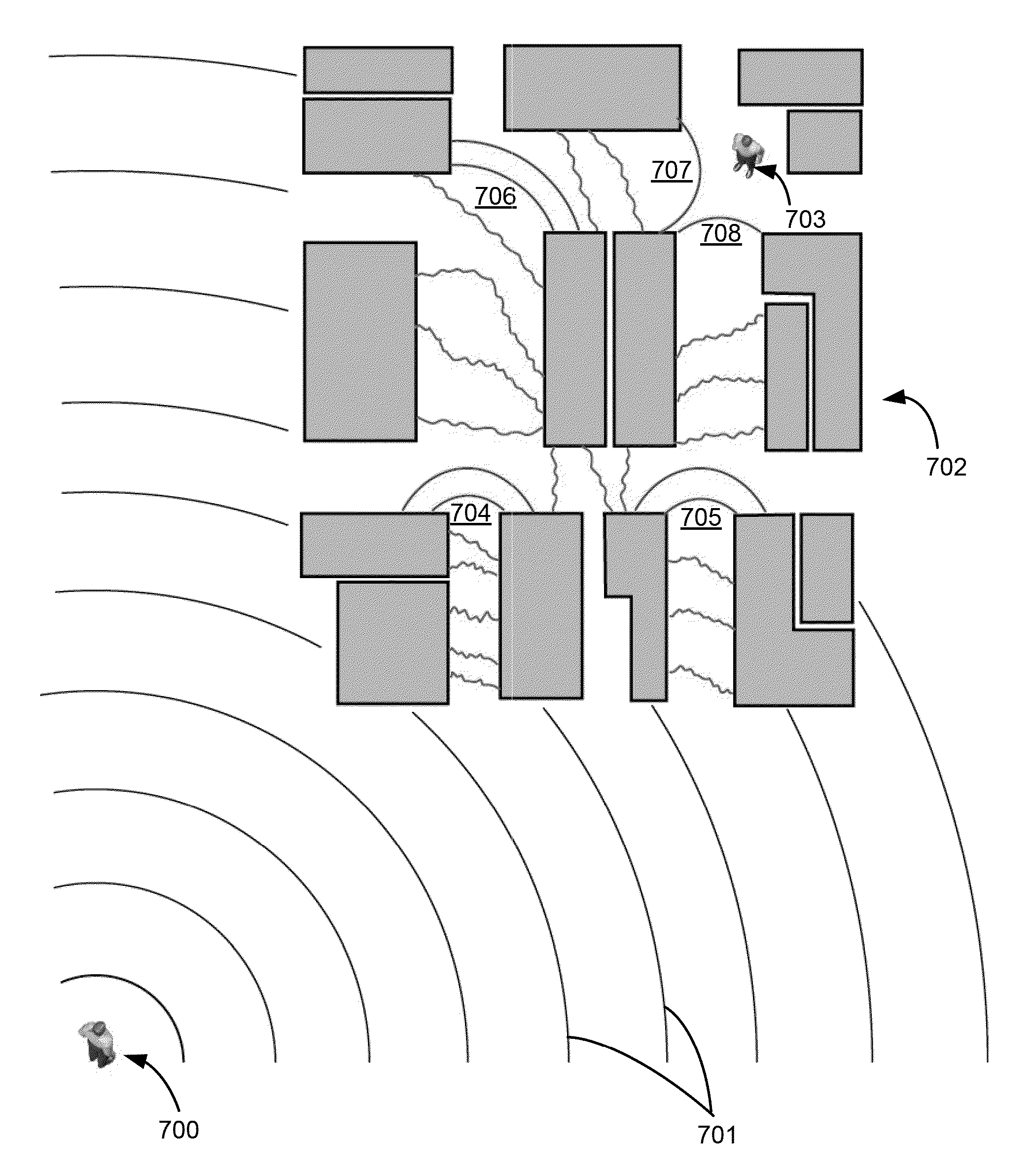
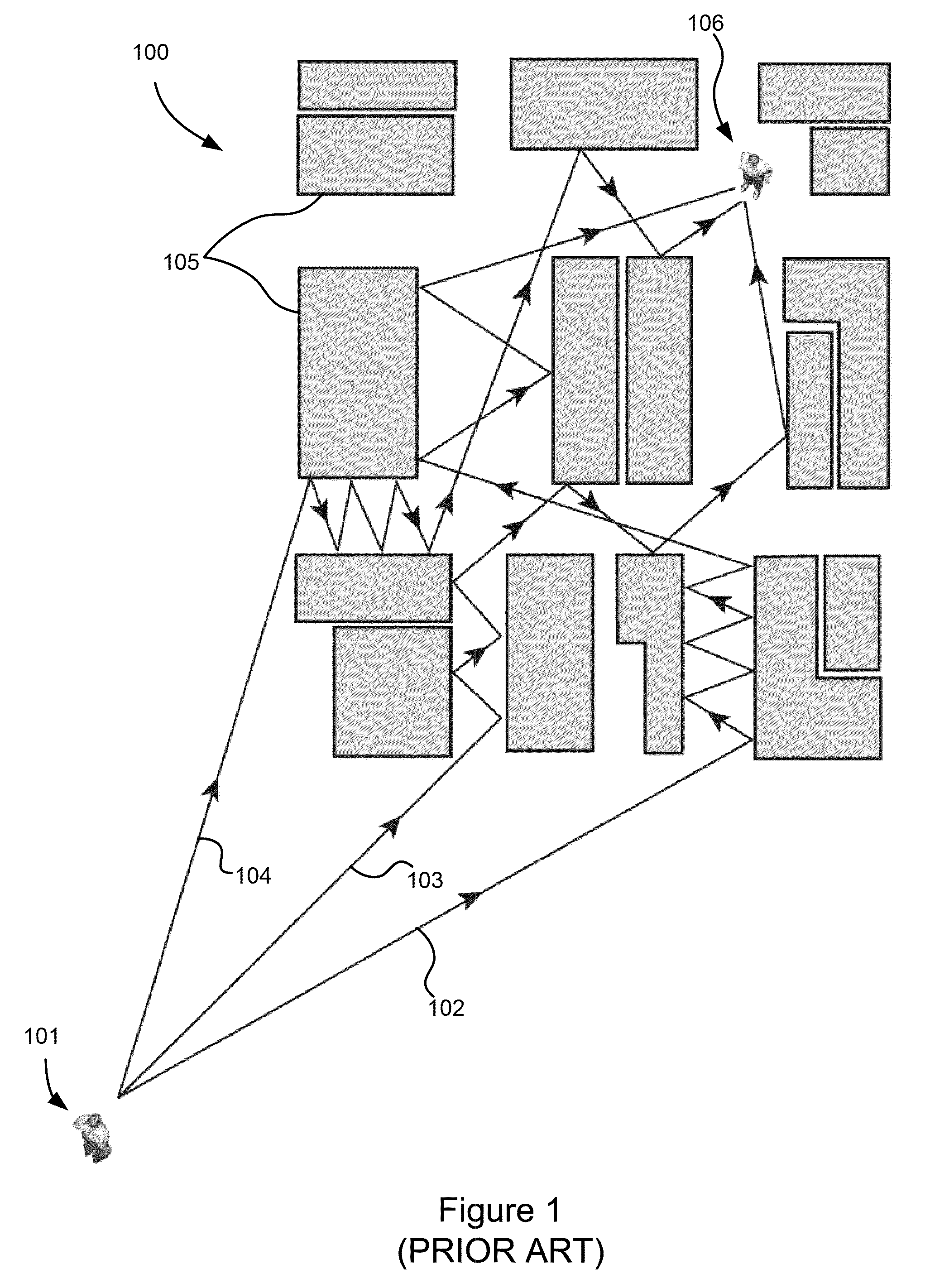
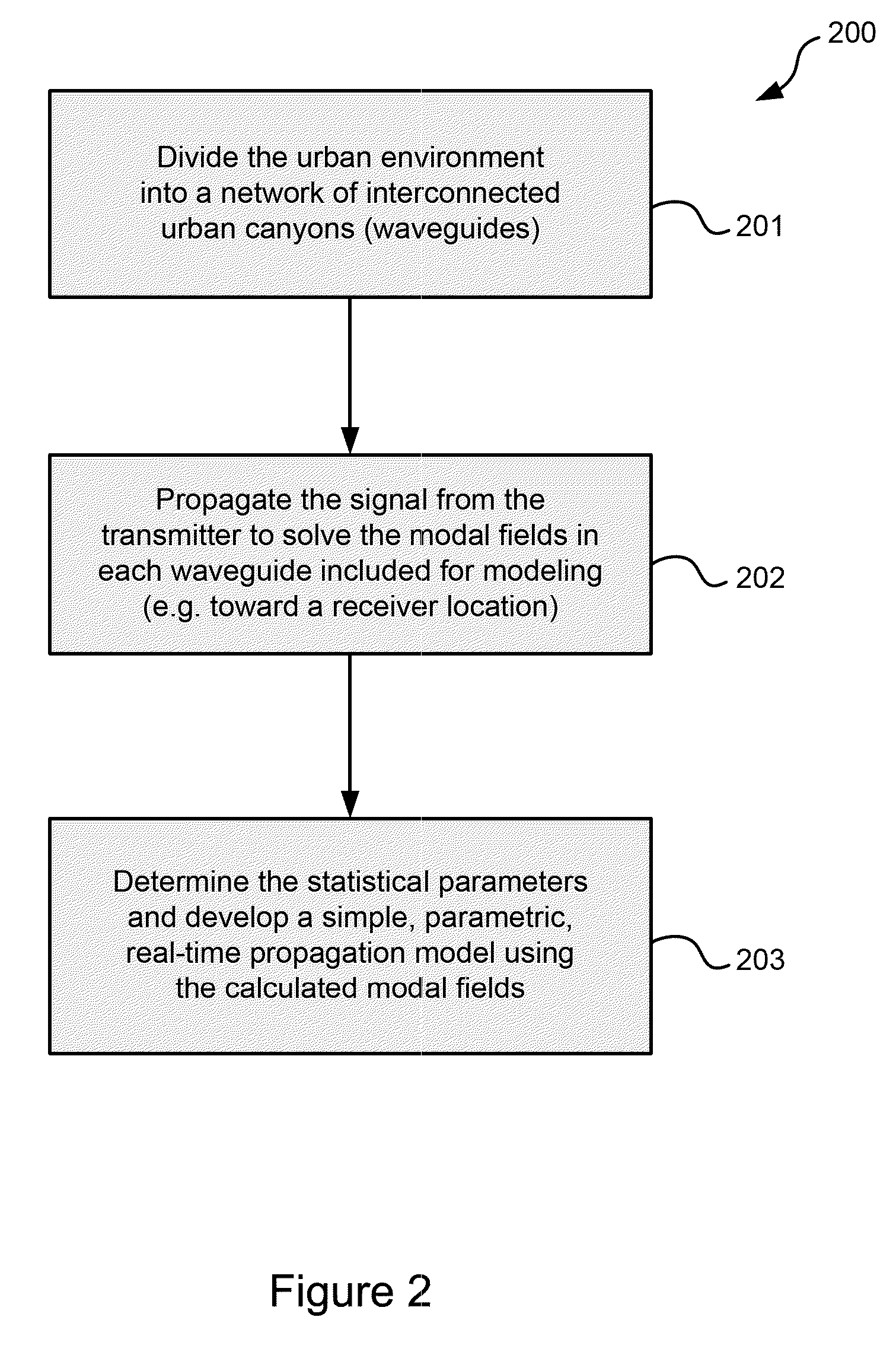
Physics-based statistical model and simulation method of RF propagation in urban environments
InactiveUS7796983B2Accurate acquisitionSimulate the realTransmission monitoringNetwork planningFrequency spectrumCanyon
A physics-based statistical model and simulation / modeling method and system of electromagnetic wave propagation (wireless communication) in urban environments. In particular, the model is a computationally efficient close-formed parametric model of RF propagation in an urban environment which is extracted from a physics-based statistical wireless channel simulation method and system. The simulation divides the complex urban environment into a network of interconnected urban canyon waveguides which can be analyzed individually; calculates spectral coefficients of modal fields in the waveguides excited by the propagation using a database of statistical impedance boundary conditions which incorporates the complexity of building walls in the propagation model; determines statistical parameters of the calculated modal fields; and determines a parametric propagation model based on the statistical parameters of the calculated modal fields from which predictions of communications capability may be made.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Perceptually improved enhancement of encoded acoustic signals
InactiveUS20020049583A1Improve sound qualityLarge coefficientSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumSound sources
The invention relates to encoding of broadband and narrowband acoustic source signals (x) such that the perceived sound quality of corresponding reconstructed signals is improved in comparison to the known solutions. An enhancement estimation unit (102), operating in serial or in parallel with the regular encoding / decoding means (101), perceptually enhances a reconstructed acoustic source signal by utilisation of an enhancement spectrum (C) comprising a larger number of spectral coefficients than the number of sample values in corresponding frames of the signals carrying the basic encoded representation of the acoustic source signal. The thus extended block length of the enhancement spectrum frame provides a basis for accomplishing the desired improvement of the perceived sound quality.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
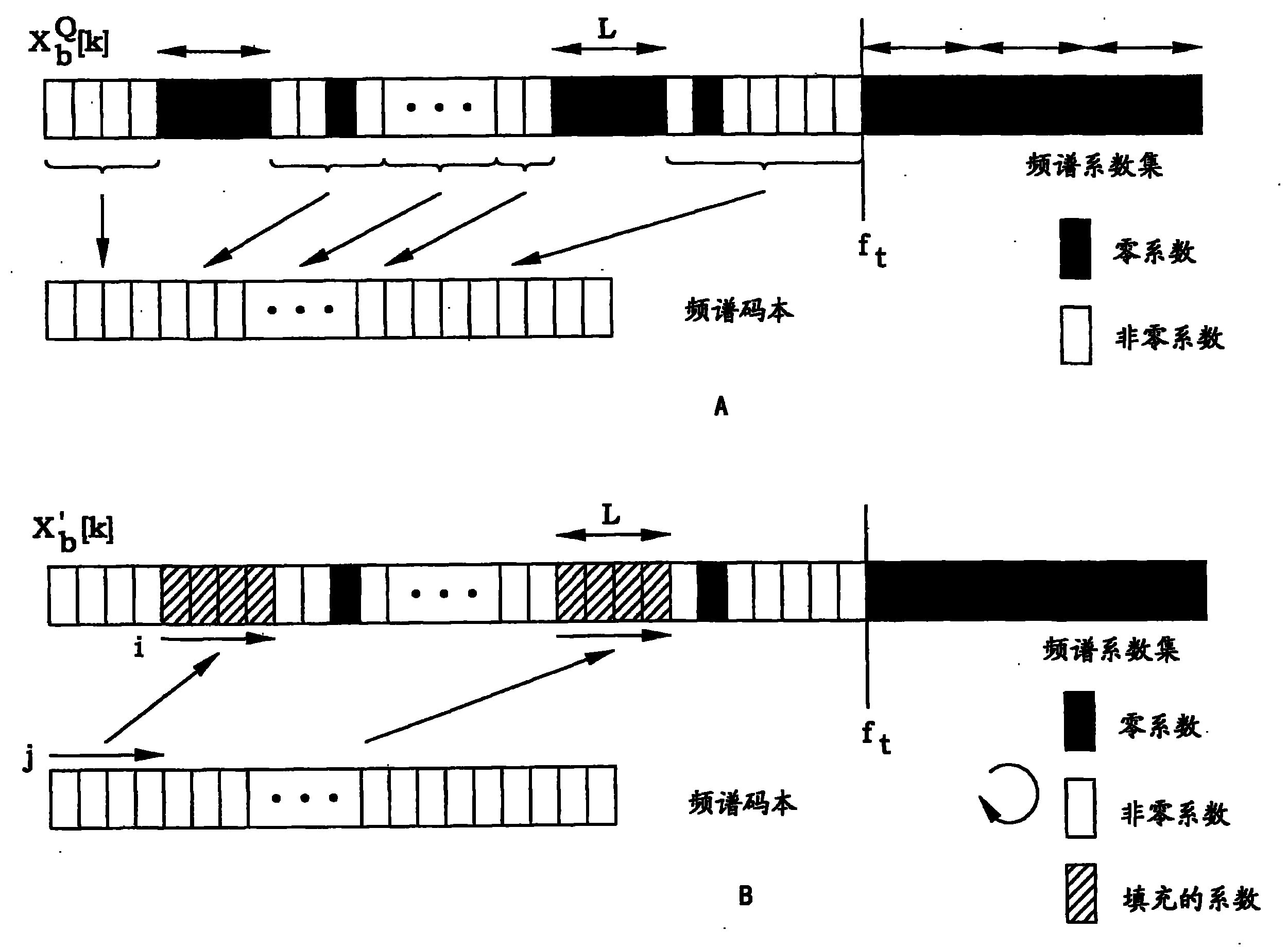
Method and apparatus for adaptive sub-band allocation of spectral coefficients
InactiveUS20100161320A1Improve signal qualityEffective distributionSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSound quality
An apparatus and method for adaptive sub-band allocation of spectral coefficients are disclosed. The sizes of sub-bands are determined according to the distribution of spectral coefficients transformed from an input speech / audio signal to perform more elaborate quantization in units of sub-bands. Thus, quantization noise of the spectral coefficients is reduced, and sound quality in a frequency region is enhanced, thereby improving the quality of the signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
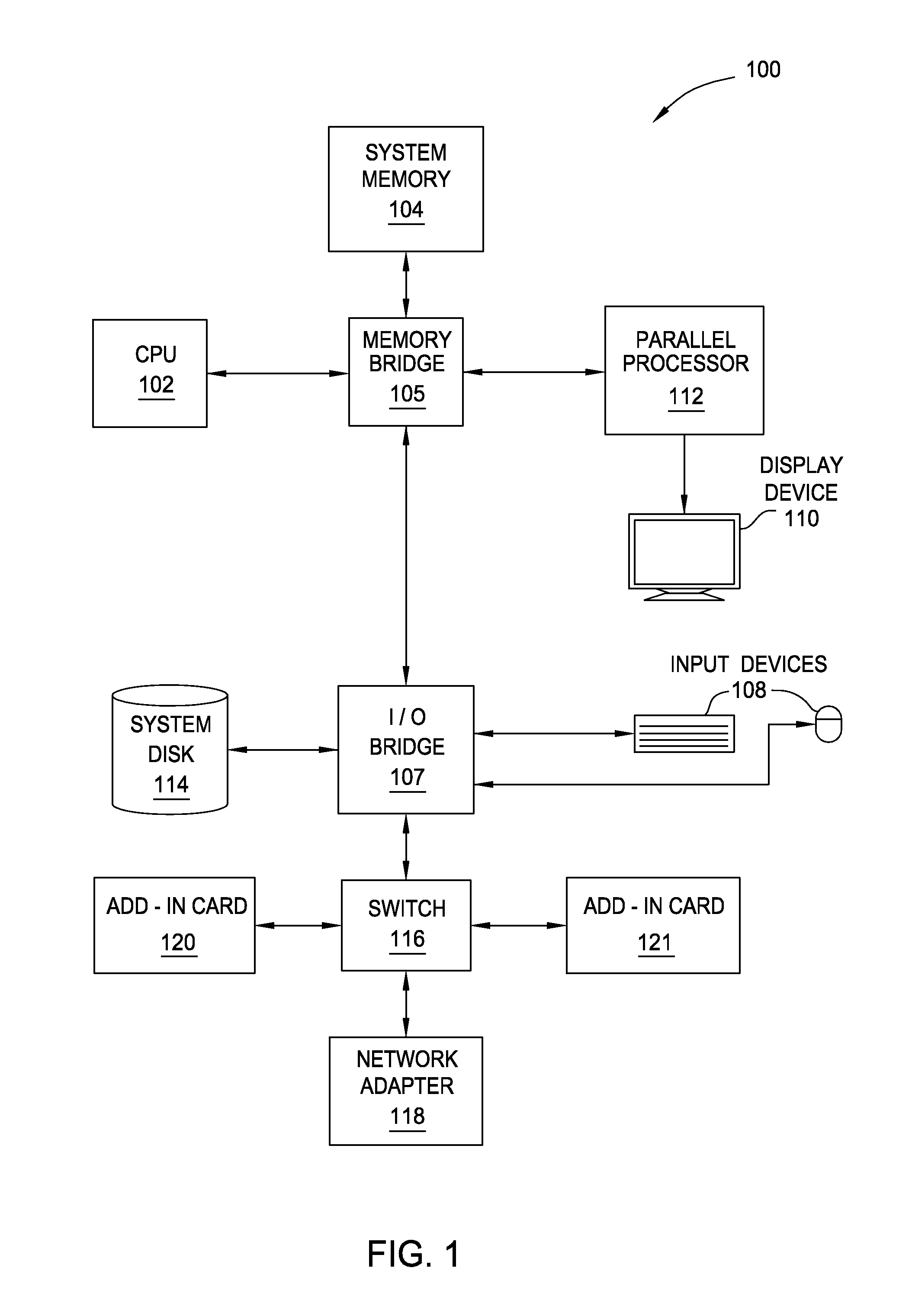
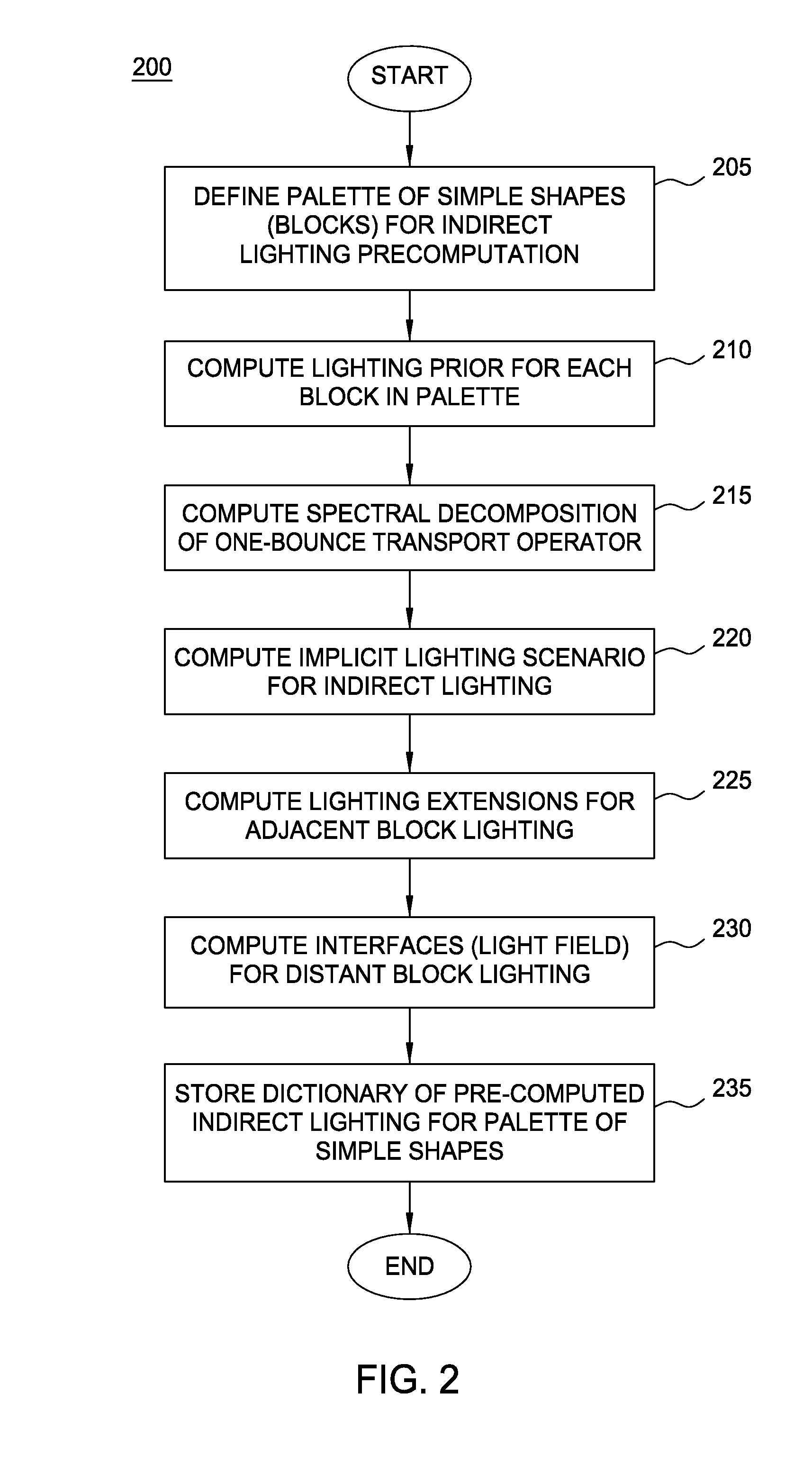
Modular radiance transfer
Modular radiance transfer pre-computes a spectral decomposition of a one bounce transport operator for each of a set of shapes and replaces a scene dependent direct-to-indirect transfer lighting computation with an art-directable mapping step. Modular radiance transfer provides an approach for rendering an approximate indirect lighting which requires small amounts of data, can be used to model very large (or even random scenes), and propagates much of the indirect lighting using a small number of spectral coefficients, so that rendering scales well to large scenes.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
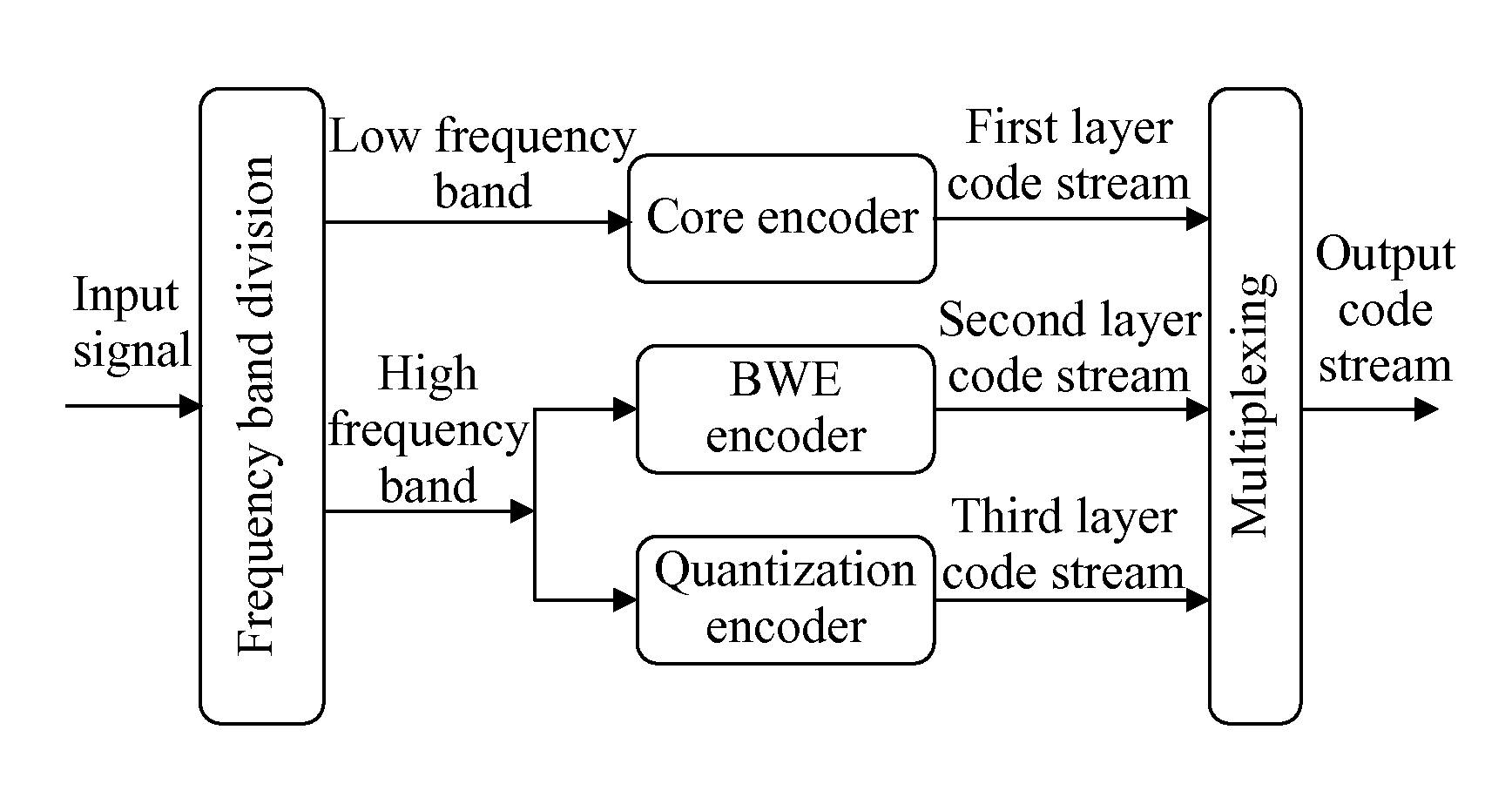
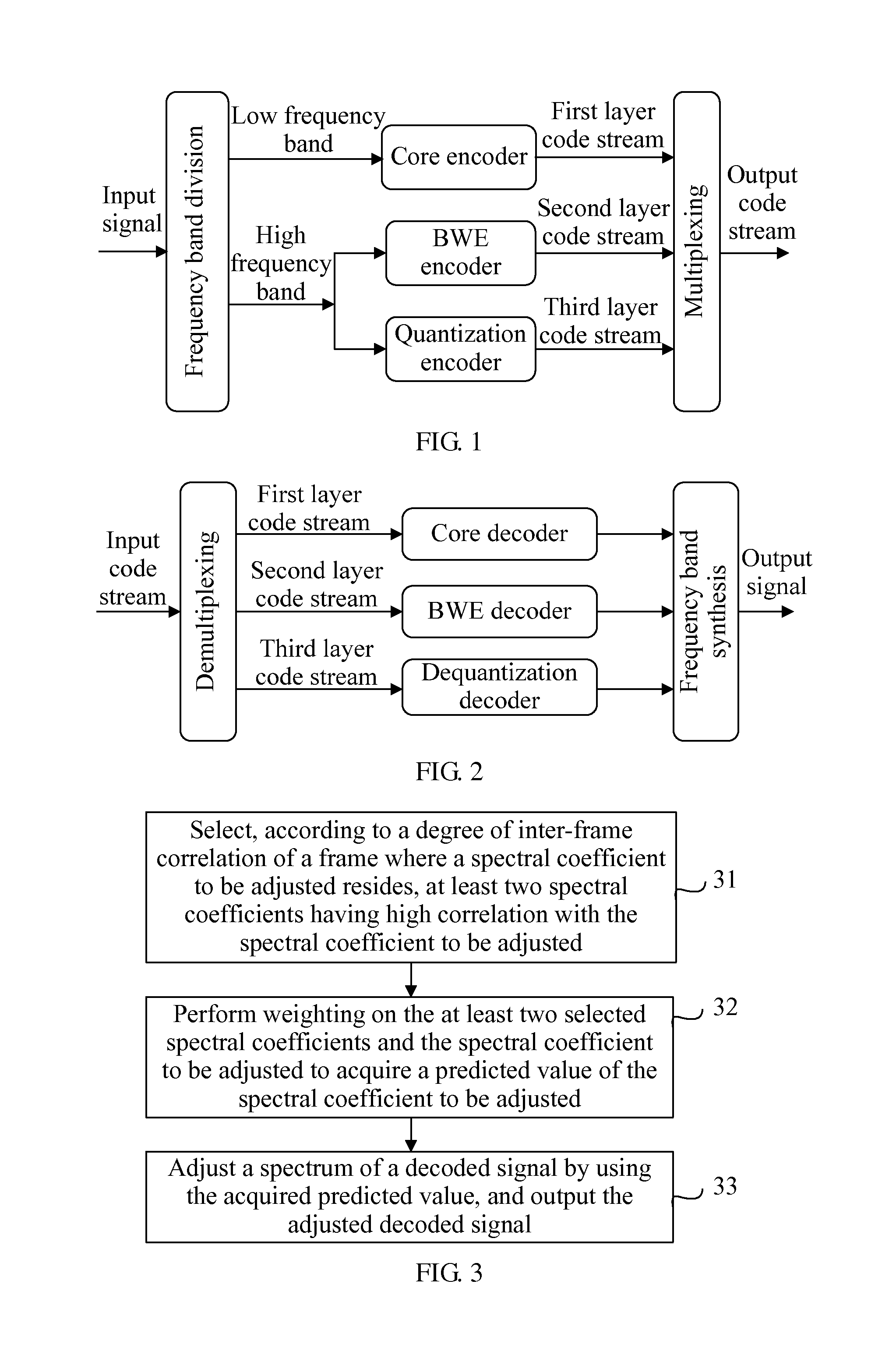
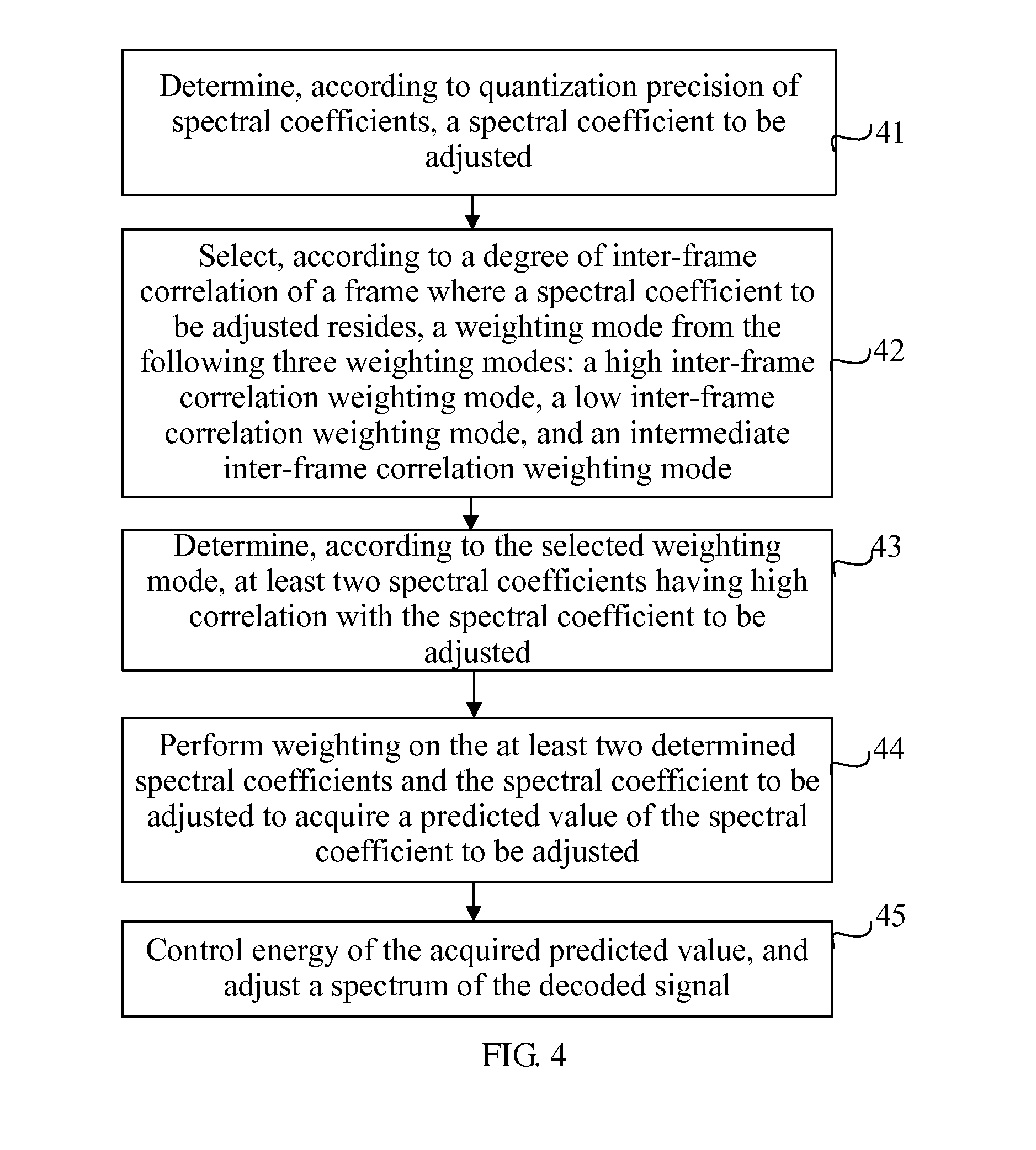
Signal de-noising method, signal de-noising apparatus, and audio decoding system
In the field of audio encoding / decoding technologies, a signal de-noising method is provided. The method includes: selecting, according to a degree of inter-frame correlation of a frame where a spectral coefficient to be adjusted resides, at least two spectral coefficients having high correlation with the spectral coefficient to be adjusted; performing weighting on the at least two selected spectral coefficients and the spectral coefficient to be adjusted to acquire a predicted value of the spectral coefficient to be adjusted; and adjusting a spectrum of a decoded signal by using the acquired predicted value, and outputting the adjusted decoded signal. A signal de-noising apparatus corresponding to the signal de-noising method and an audio decoding system using the signal de-noising apparatus are also provided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and device for arithmetic encoding or arithmetic decoding
ActiveUS20120195375A1Non uniformColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNormal densityFrequency spectrum
The invention proposes a method and a device for arithmetic encoding of a current spectral coefficient using preceding spectral coefficients. Said preceding spectral coefficients are already encoded and both, said preceding and current spectral coefficients, are comprised in one or more quantized spectra resulting from quantizing time-frequency—transform of video, audio or speech signal sample values. Said method comprises processing the preceding spectral coefficients, using the processed preceding spectral coefficients for determining a context class being one of at least two different context classes, using the determined context class and a mapping from the at least two different context classes to at least two different probability density functions for determining the probability density function, and arithmetic encoding the current spectral coefficient based on the determined probability density function wherein processing the preceding spectral coefficients comprises non-uniformly quantizing absolutes of the preceding spectral coefficients for use in determining of the context class.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and device for local spectral analysis of an ultrasonic signal
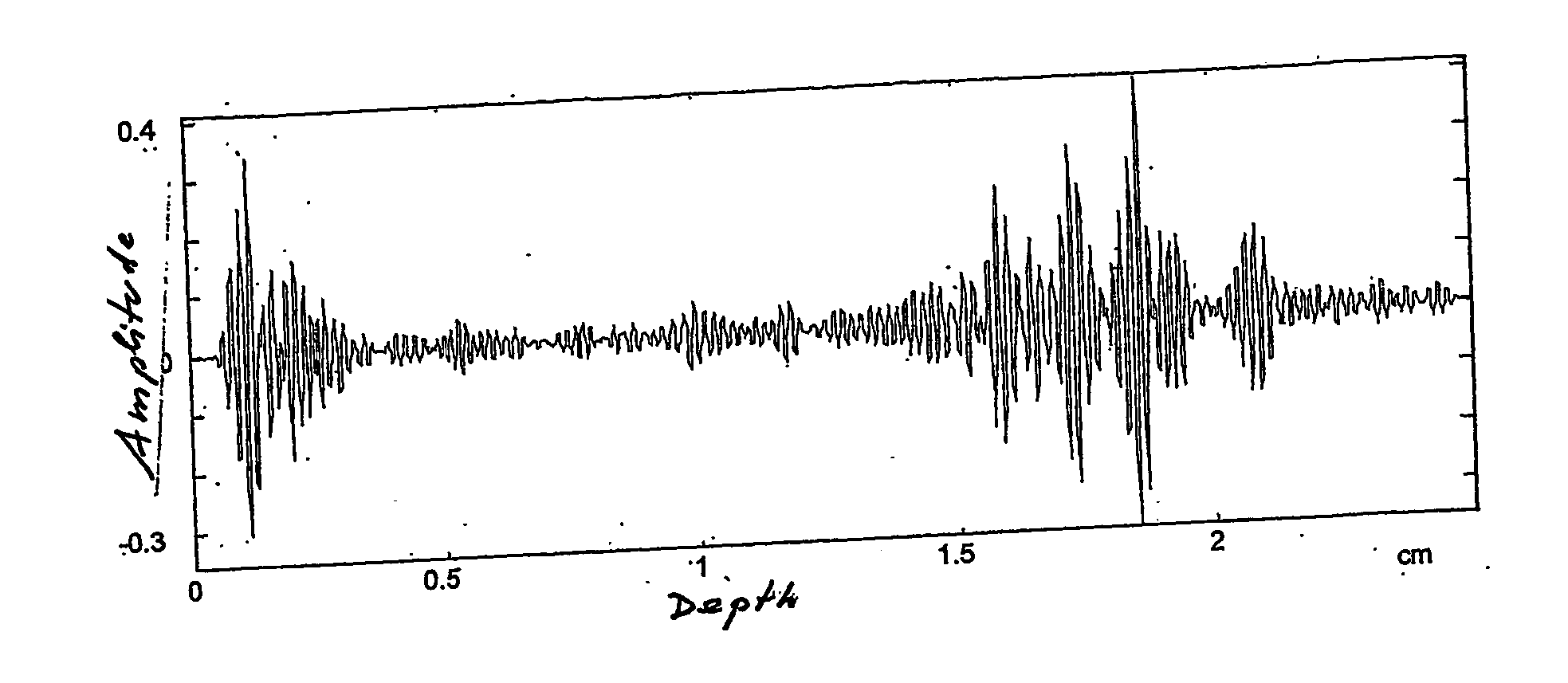
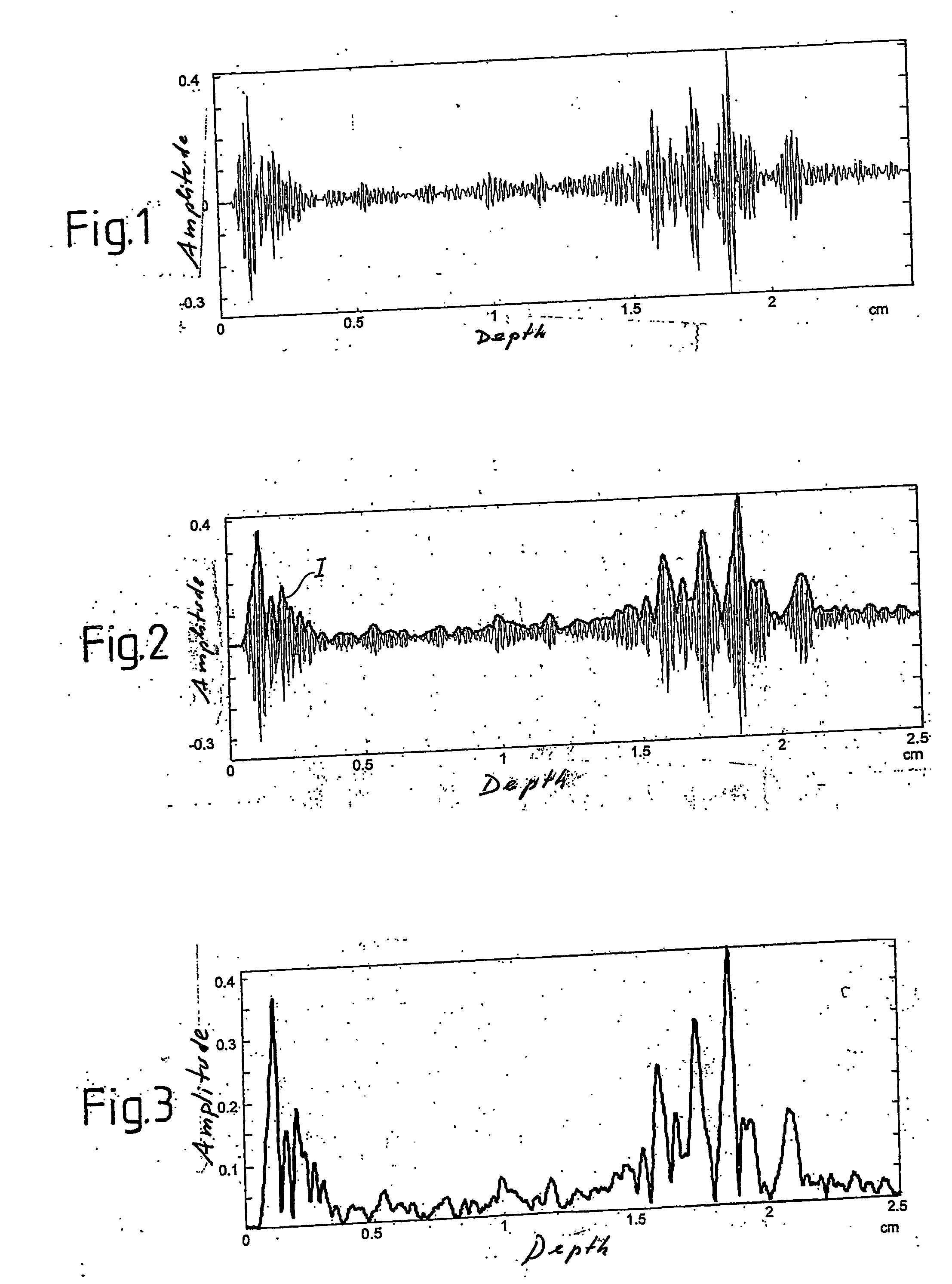
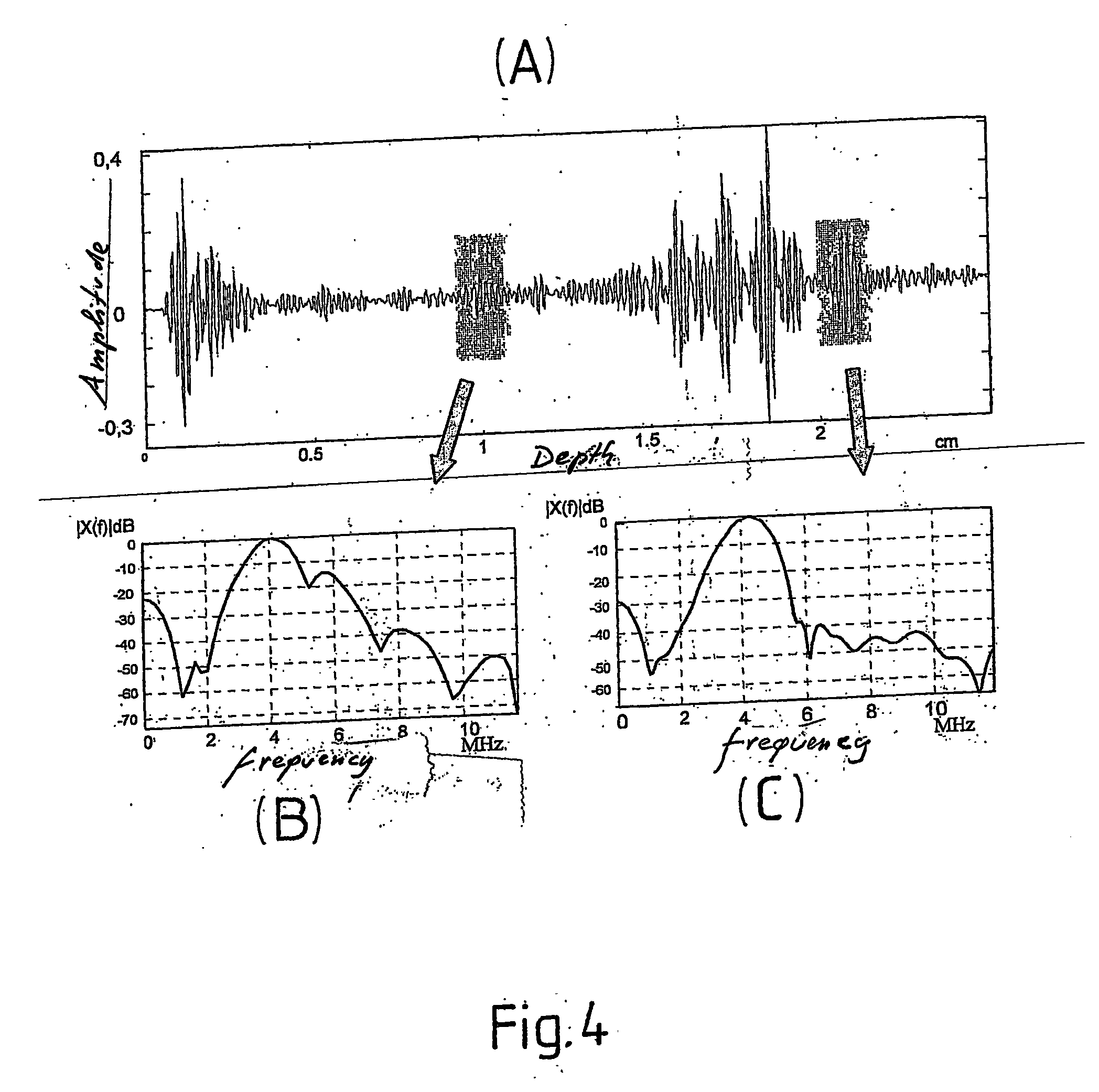
InactiveUS20060277998A1Great and precise informationEasy to useVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFrequency spectrumSonification
The method decomposes the radio frequency signal into sub-bands by filtering, for example with a time-frequency transform. From the coefficients acquired through decomposition a matrix of spectral coefficients is obtained, from which local estimators are obtained, constituted in particular by the coefficients of the interpolating polynomials. The statistical distribution of the local estimators is evaluated in windows overlaid on the ultrasound frame. The conformation of the distribution histograms of the spectral coefficients provides a parameter which, combined with the local estimators, provides weighted local estimators, which contain spectral information useful in the identification of specific structures in the organ subjected to ultrasound analysis.
Owner:ACTIS ACTIVE SENSORS +1
Signal denoising method and device and audio decoding system
The embodiment of the invention discloses a signal denoising method, a signal denoising device and an audio decoding system, which belong to the technical field of audio coding and decoding. The method provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises: selecting at least two spectral coefficients which have high relevance to a spectral coefficient to be adjusted according to the inter-frame relevance of the frame of the spectral coefficient to be adjusted; performing weighting by using the selected at least two spectral coefficients and the spectral coefficient to be adjusted and acquiring a predicted value of the spectral coefficient to be adjusted; and performing the spectral adjustment of a decoded signal by using the acquired predicted value and outputting an adjusted decoded signal. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a signal denoising device and an audio decoding system. Through the embodiment of the invention, the noises generated in frequency synthesis after decoding are reduced, and the auditory effect is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Bluetooth audio howling detection suppression method and device, medium and Bluetooth equipment
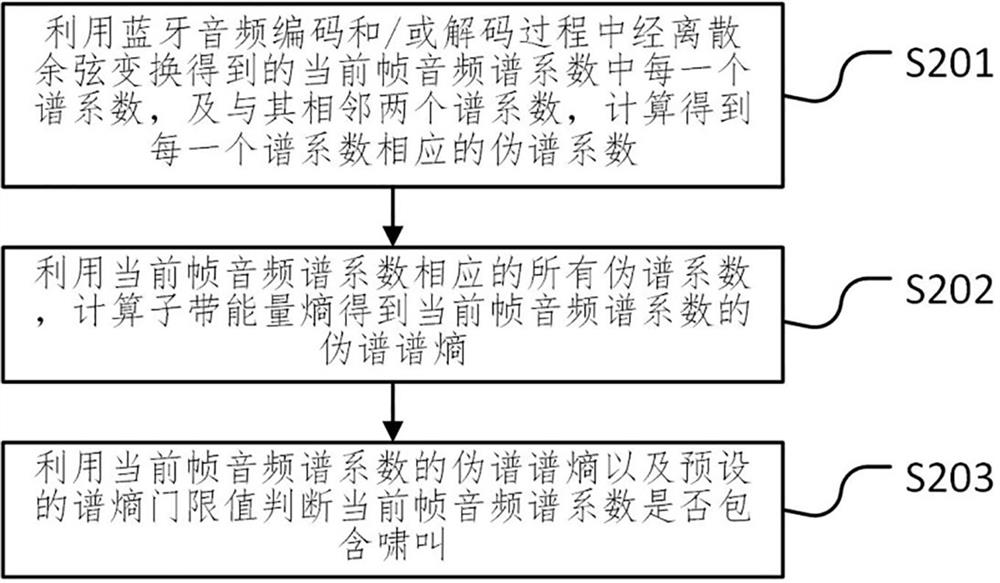
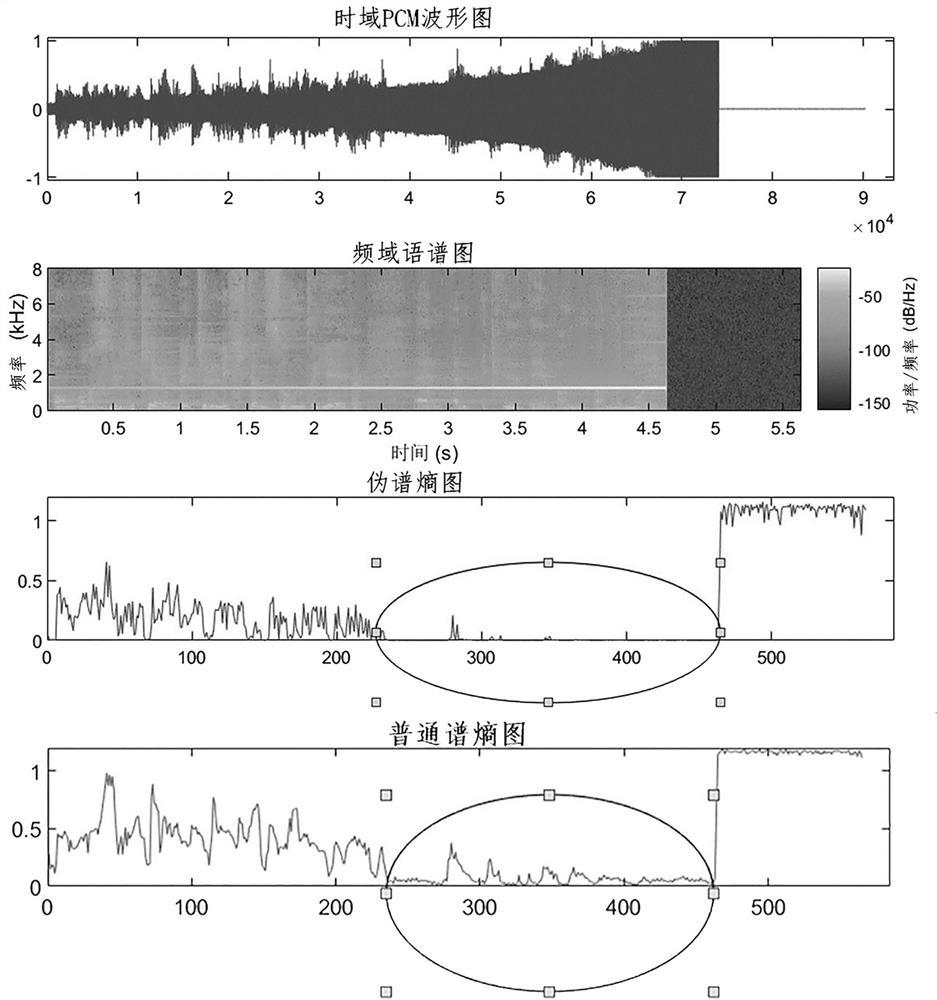
ActiveCN113724725AImprove detection accuracyAvoid Time-Frequency TransformationSpeech analysisDiscrete cosine transformDelay
The invention discloses a Bluetooth audio howling detection suppression method and device, a medium and Bluetooth equipment and belongs to the technical field of audio coding and decoding. The method comprises the following steps of calculating to obtain a pseudo-spectral coefficient corresponding to each spectral coefficient by using each spectral coefficient in current frame audio spectral coefficients obtained through discrete cosine transform in a Bluetooth audio coding and / or decoding process and two spectral coefficients adjacent to the spectral coefficient; calculating a sub-band energy entropy by using all pseudo-spectral coefficients corresponding to the current frame audio spectral coefficient to obtain a pseudo-spectral entropy of the current frame audio spectral coefficient; and judging whether the current frame audio spectrum coefficient contains howling or not by using the pseudo spectrum entropy of the current frame audio spectrum coefficient and a preset spectrum entropy threshold value. The howling detection method and device can avoid time-frequency transformation required by howling detection in the prior art, save the operand and reduce the system time delay.
Owner:BEIJING BAIRUI INTERNET TECH CO LTD
Ring surface harmonic-analysis method on basis of satellite gravity gradient observation data
InactiveCN102567627AHigh precisionHigh Efficiency Self-Consistent TuningComplex mathematical operationsRegular gridObservation data
The invention relates to a ring surface harmonic-analysis method on the basis of satellite gravity gradient observation data, which includes the following steps: preprocessing the satellite gravity gradient observation data, integrally reducing the satellite gravity gradient observation data to the same spherical surface and performing gridding process on the same to obtain regular grid average value; mapping the grid value on the spherical surface to the ring surface by means of mapping relation of the spherical surface to the ring surface, and obtaining circular regular grid value; perform spline analysis on the gravity gradient data on the ring surface, converting the regular grid average value on the ring surface into continuous spline approximating function; performing two-dimensional Fourier analysis on the gravity gradient on the ring surface, and converting spline approximation to determine Fourier coefficient; and computing the two-dimensional Fourier spectral coefficient of the ring surface into harmonic expansion coefficient. High-accuracy and high-efficiency self-consistency harmonic analysis of the satellite gravity gradient observation data is realized, the error caused by inaccuracy and the like of smoothing factors in existing harmonic analysis is overcome, and the ring surface harmonic-analysis method has the advantages of high computing speed and accuracy.
Owner:THE CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY 92859 TROOPS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com