Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86results about How to "Few artifact" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microplate with fewer peripheral artifacts
InactiveUS20080095673A1Few artifactReduce impactAnalysis using chemical indicatorsLaboratory glasswaresMedicineMicro plate
The current invention relates to an improved microplate. The microplate is characterized by modified quadrilateral edges, which bring less artificially induced inaccuracies in peripheral wells, especially in corner wells. Preferably, the microplate possesses a bottom that is elongated to cover the non-experimental slots. The microplate might further comprise sham wells.
Owner:XU LIN
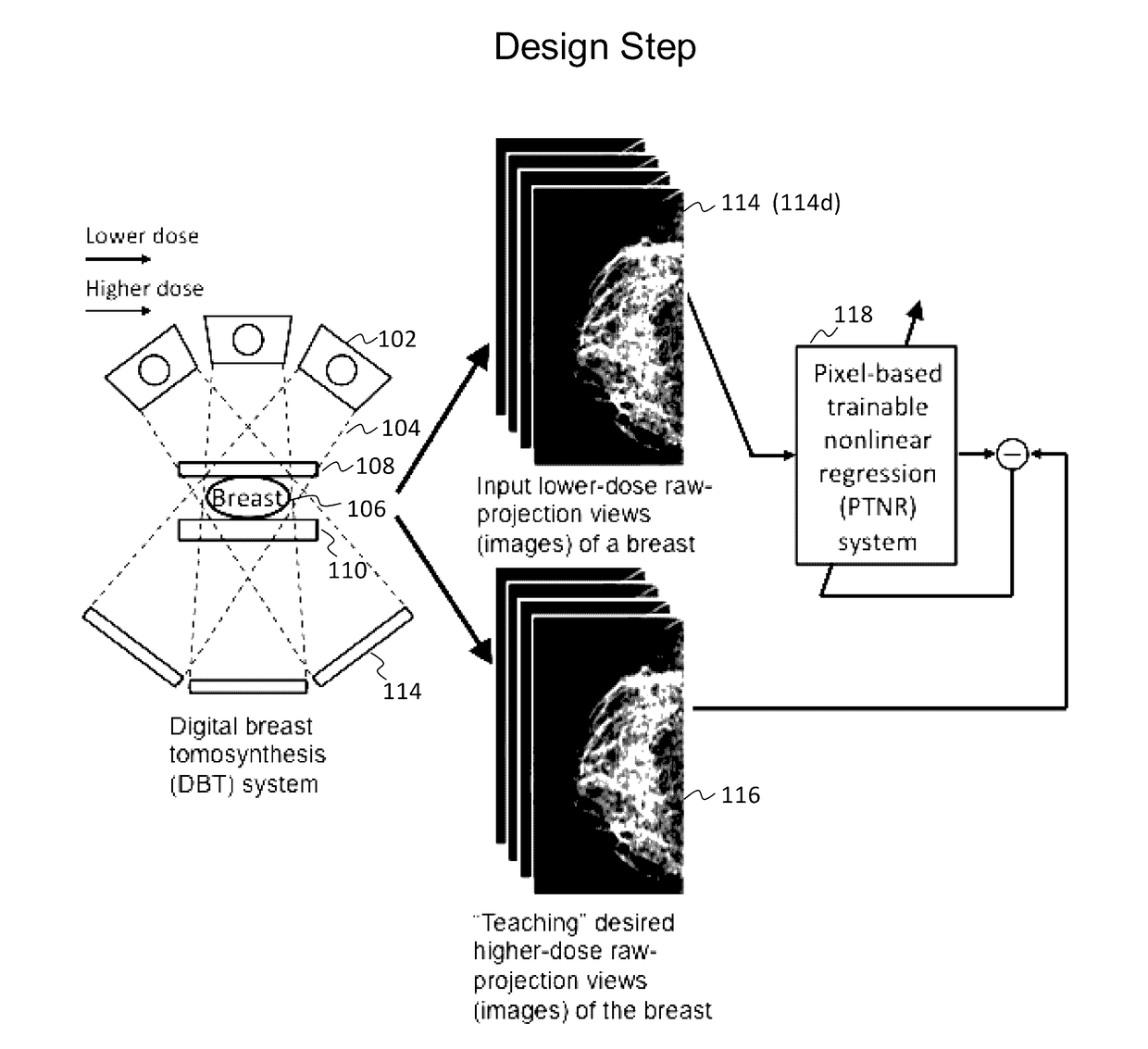
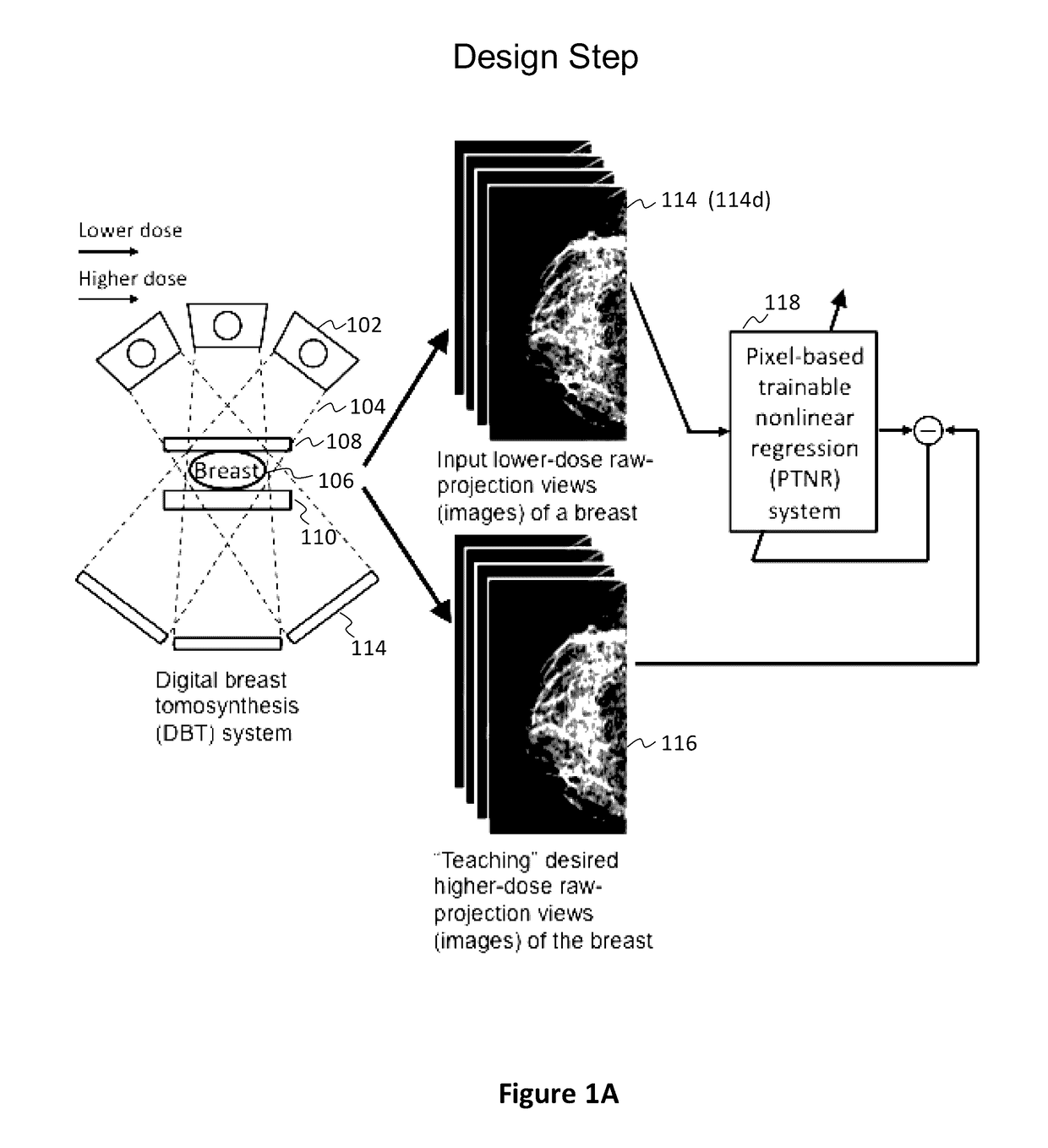
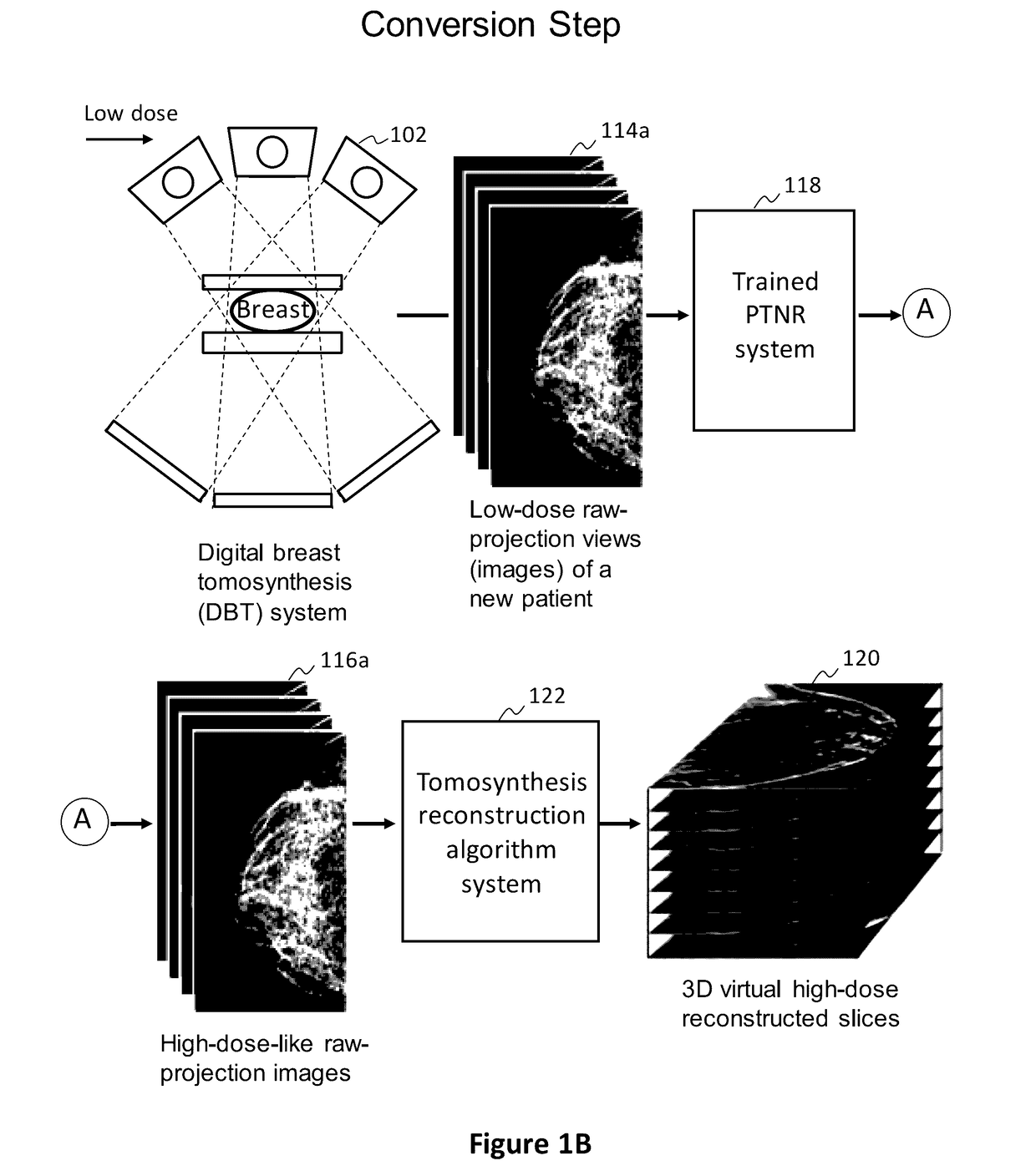
Converting low-dose to higher dose 3D tomosynthesis images through machine-learning processes
ActiveUS20170071562A1Quality improvementReduce noiseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisImaging quality
A method and system for converting low-dose tomosynthesis projection images or reconstructed slices images with noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like tomosynthesis reconstructed slices, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme called a pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input raw projection views (images) of a breast acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of raw projection views (images together with corresponding desired x-ray radiation dose raw projection views (images) (higher-dose). Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose raw projection images to high-dose-like raw projection images. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose raw projection images anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) raw projection images is entered, the trained PTNR outputs a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it outputs high-dose-like raw projection images where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. Then, from the “high-dose-like” projection views (images), “high-dose-like” 3D tomosynthesis slices are reconstructed by using a tomosynthesis reconstruction algorithm. With the “virtual high-dose” tomosynthesis reconstruction slices, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
Acoustic holography
ActiveUS20110120222A1Quality improvementReduce artifactsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidWavenumberFrequency domain
A method of performing near- field acoustic holography comprises the following steps. Establishing (102) acoustic data representing a set of near-field acoustic holography measurements at a first set of positions. Extrapolating (204) acoustic data using a model-based extrapolation to obtain extrapolated acoustic data relating to a plurality of positions outside the aperture. Applying a spatial frequency transform to the padded acoustic data to obtain data in a spatial frequency domain. Propagating (110) the Fourier transformed acoustic data. Applying (112) a regularization in a wavenumber domain. Performing (114) an inverse spatial frequency transform.
Owner:STICHTING VOOR DE TECH WETENSCHAPPEN +1
Method for Weighted Overlap-Add
ActiveUS20080275580A1Effectively mitigatedFew artifactDigital data processing detailsSpeech analysisComputer scienceA-weighting
A method for generating an output sequence of samples in response to a first and a second subsequence of samples, the method comprising—applying a weighted overlap-add procedure to the first and second subsequences so as to generate the output sequence of samples, —optimizing a weighting function involved in the weighted overlap-add procedure in response to a measure of matching between the output sequence of samples and one or more target sequences of samples.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
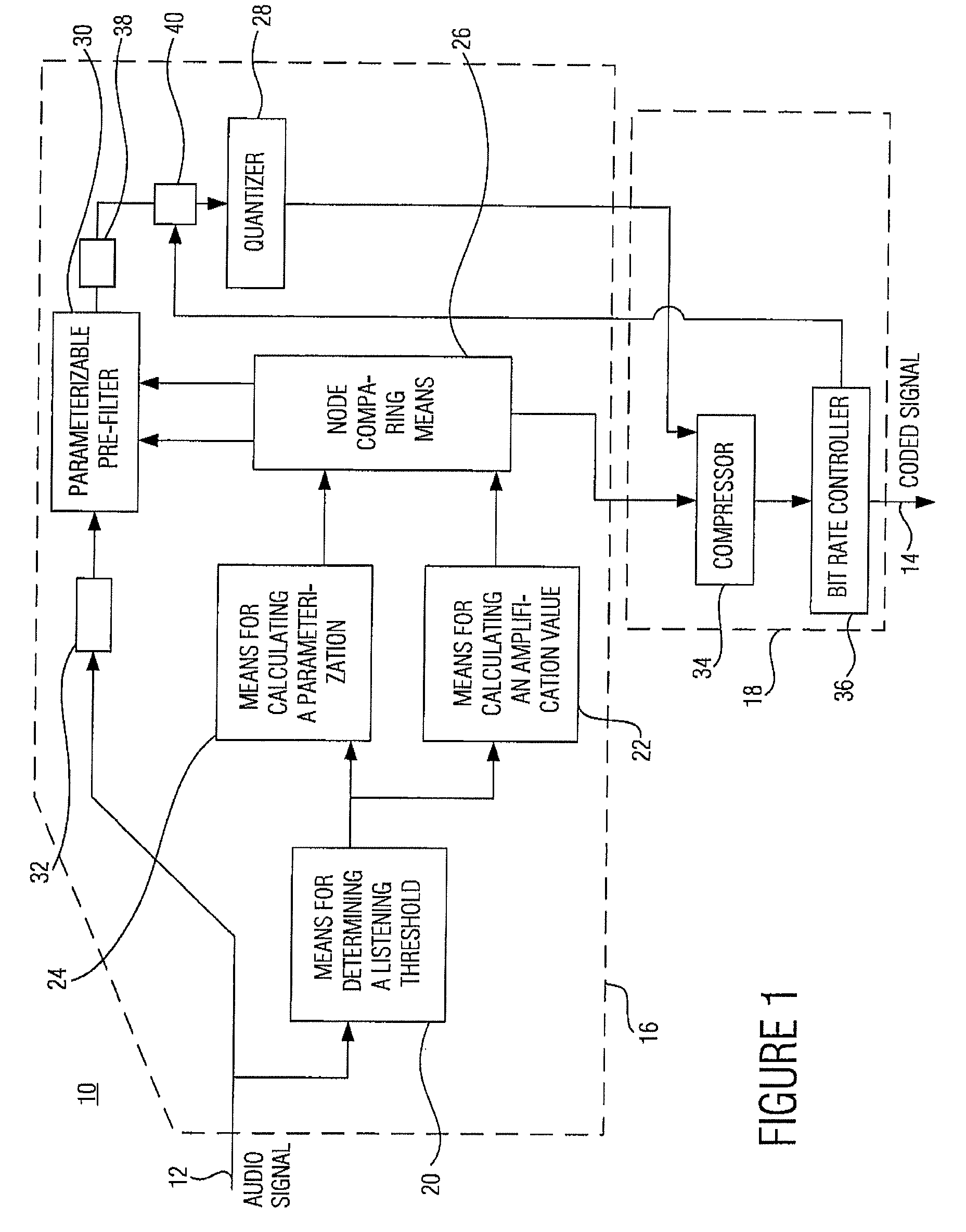
Audio coding
ActiveUS20070016403A1Many solutionsFew artifactSpeech analysisCode conversionConstant frequencyMasking threshold
The central idea of the present invention is that the prior procedure, namely interpolation relative to the filter coefficients and the amplification value, for obtaining interpolated values for the intermediate audio values starting from the nodes has to be dismissed. Coding containing less audible artifacts can be obtained by not interpolating the amplification value, but rather taking the power limit derived from the masking threshold, preferably as the area below the square of the magnitude of the masking threshold, for each node, i.e. for each parameterization to be transferred, and then performing the interpolation between these power limits of neighboring nodes, such as, for example, a linear interpolation. On both the coder and the decoder side, an amplification value can then be calculated from the intermediate power limit determined such that the quantizing noise caused by quantization, which has a constant frequency before post-filtering on the decoder side, is below the power limit or corresponds thereto after post-filtering.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Auxiliary data for artifacts - aware view synthesis
ActiveUS20170188002A1Reduce artifactsLarge discontinuityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processingData packMissing data
Original or compressed Auxiliary Data, including possibly major depth discontinuities in the form of shape images, partial occlusion data, associated tuned and control parameters, and depth information of the original video(s), are used to facilitate the interactive display and generation of new views (view synthesis) of conventional 2D, stereo, and multi-view videos in conventional 2D, 3D (stereo) and multi-view or autostereoscopic displays with reduced artifacts. The partial or full occlusion data includes image, depth and opacity data of possibly partially occluded areas to facilitate the reduction of artifacts in the synthesized view. An efficient method is used for extracting objects at partially occluded regions as defined by the auxiliary data from the texture videos to facilitate view synthesis with reduced artifacts. Further, a method for updating the image background and the depth values uses the auxiliary data after extraction of each object to reduce the artifacts due to limited performance of online inpainting of missing data or holes during view synthesis.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Method for Concatenating Frames in Communication System
InactiveUS20080154584A1Effective limitFew artifactSpeech analysisData switching by path configurationCommunications systemPhase filter
A method for concatenating a first frame of samples and a subsequent second frame of samples, the method comprising applying a phase filter adapted to minimizing a discontinuity at a boundary between the first and second frames of samples.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
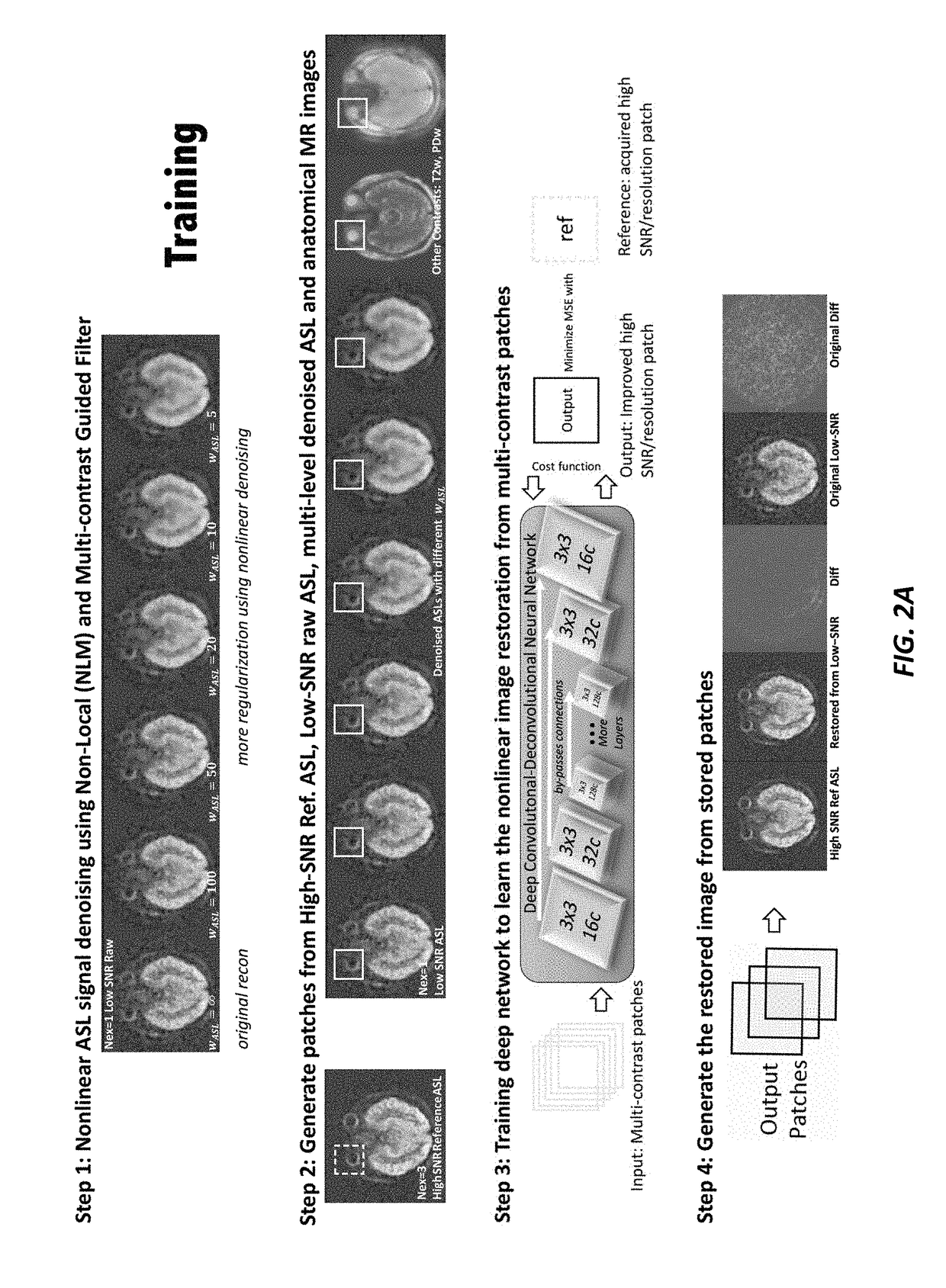
Quality of Medical Images Using Multi-Contrast and Deep Learning
ActiveUS20180286037A1Reduced imaging timeImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisNetwork modelModel parameters
A method of improving diagnostic and functional imaging is provided by obtaining at least two input images of a subject, using a medical imager, where each input image includes a different contrast, generating a plurality of copies of the input images using non-local mean (NLM) filtering, using an appropriately programmed computer, where each input image copy of the subject includes different spatial characteristics, obtaining at least one reference image of the subject, using the medical imager, where the reference image includes imaging characteristics that are different form the input images of the subject, training a deep network model, using data augmentation on the appropriately programmed computer, to adaptively tune model parameters to approximate the reference image from an initial set of the input and reference images, with the goal of outputting an improved quality image of other sets of low SNR low resolution images, for analysis by a physician.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and system for data hiding and authentication via halftoning and coordinate projection
ActiveUS20020171853A1Improve fidelityImprove performanceImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersComputer graphics (images)Computer science
Owner:TWITTER INC
Method for sharpening a digital image without amplifying noise
A method of sharpening a digital image having image pixels according to its material content, includes the steps of: generating a subject matter belief map corresponding spatially to the image pixels, having belief values indicating the likelihood that respective image pixels are representative of a particular subject matter, generating a noisy pixel belief map corresponding spatially to the image pixels having belief values indicating the likelihood that the modulation about respective pixels are due to system noise; generating gain map from the subject matter belief map and the noisy pixel belief map having values that indicate the degree of sharpening to be applied to the image pixels; and using the gain map to sharpen the image.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
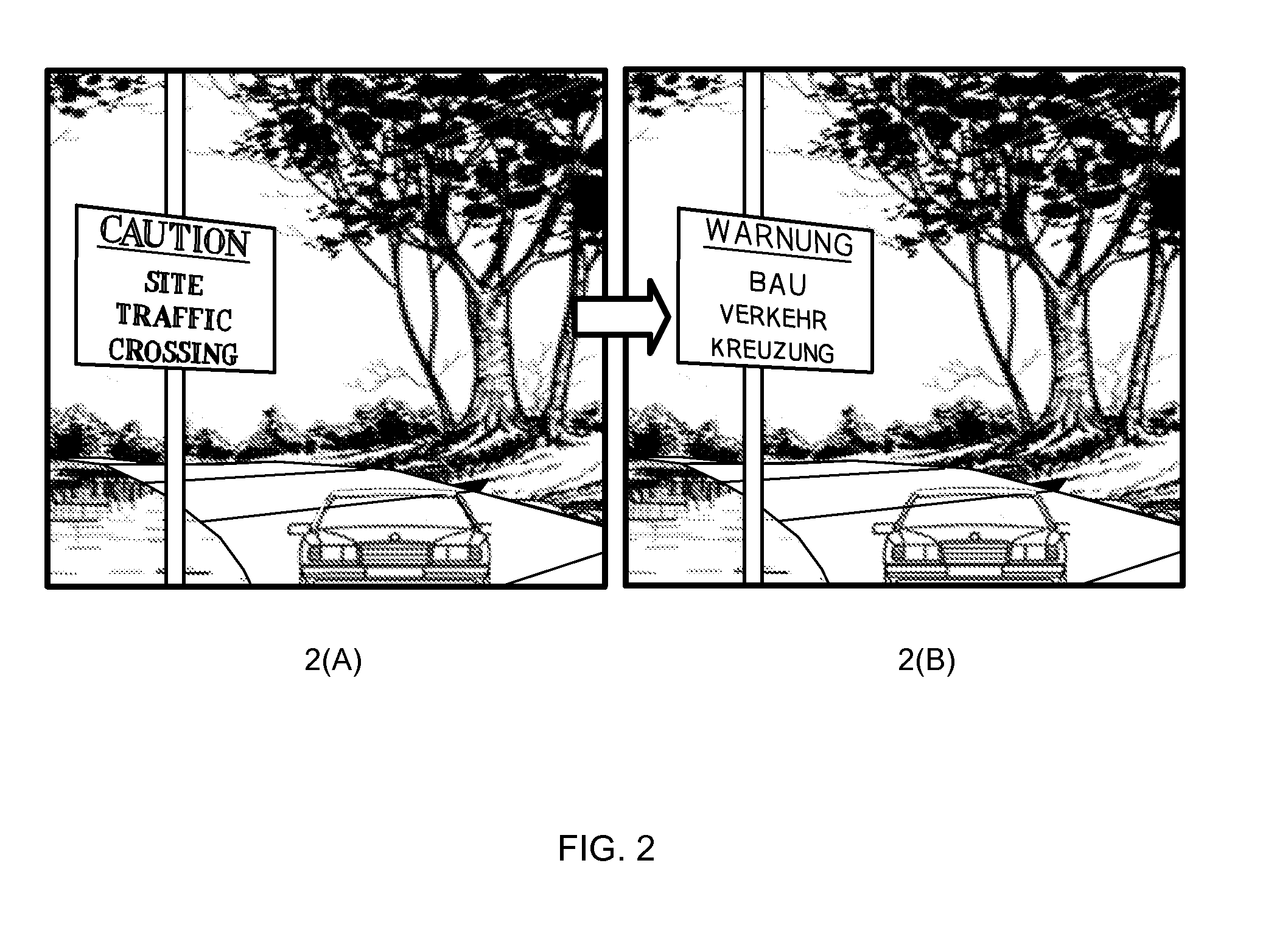
Efficient blending methods for ar applications
ActiveUS20130004068A1Low costReduce artifactsNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsMobile deviceBackground image
The use of optical character recognition (OCR) in mobile devices is becoming prevalent with the increasing use of mobile devices. One important application for OCR in mobile devices is recognizing and translating the text to a language understandable by the user. Techniques are provided for replacing symbols in an image, while reducing the artifacts as a result of re-rendering of the background image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
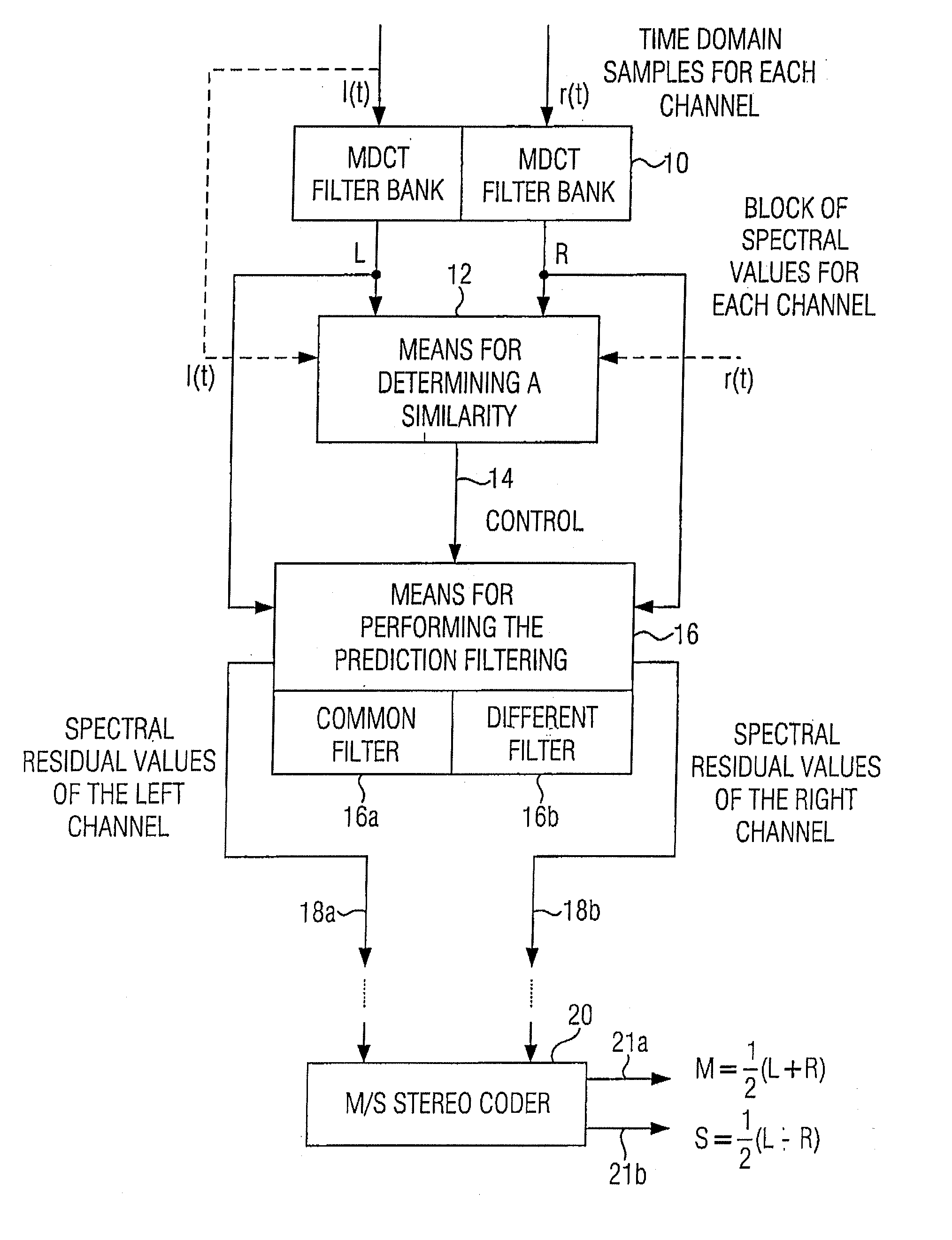
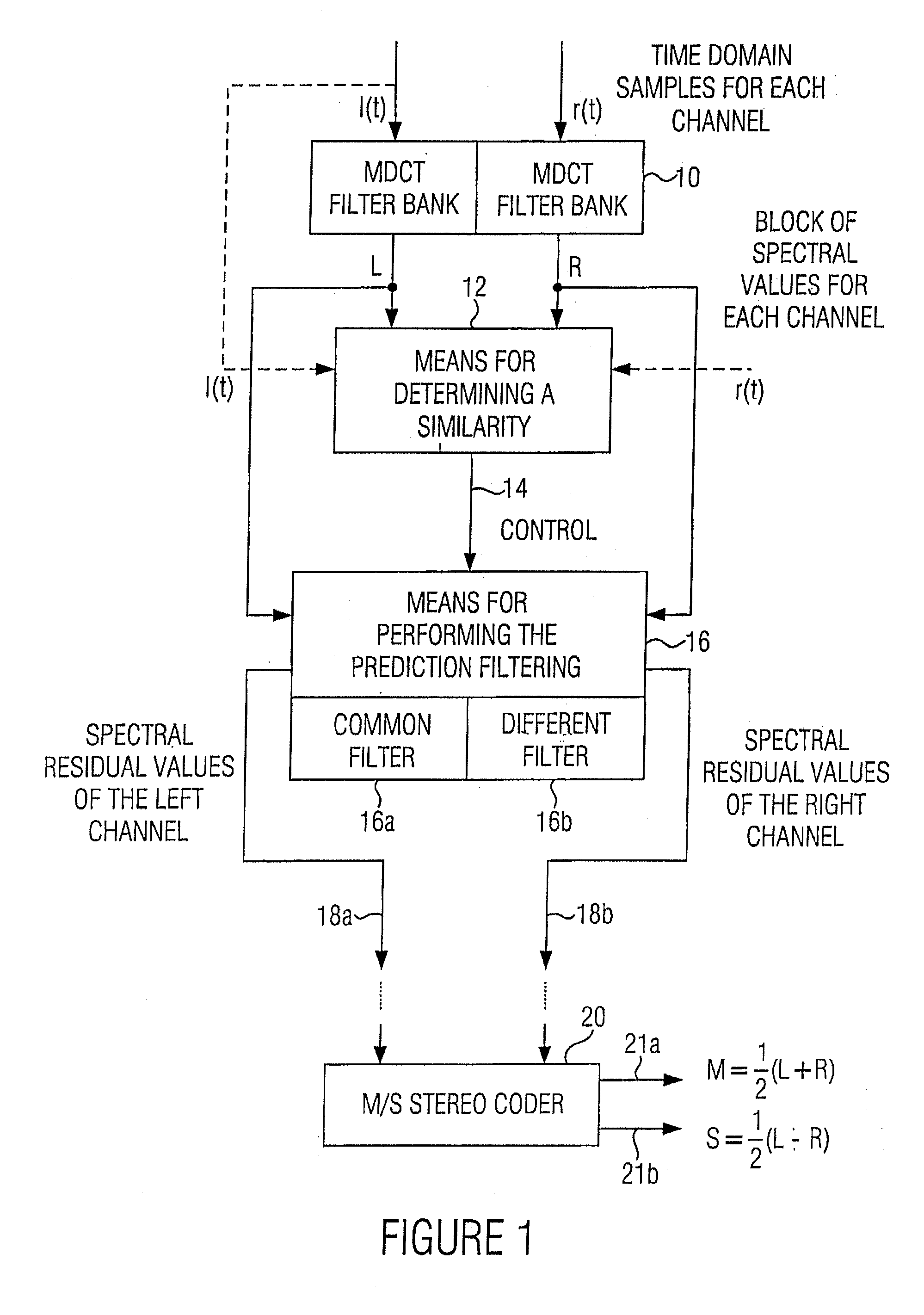
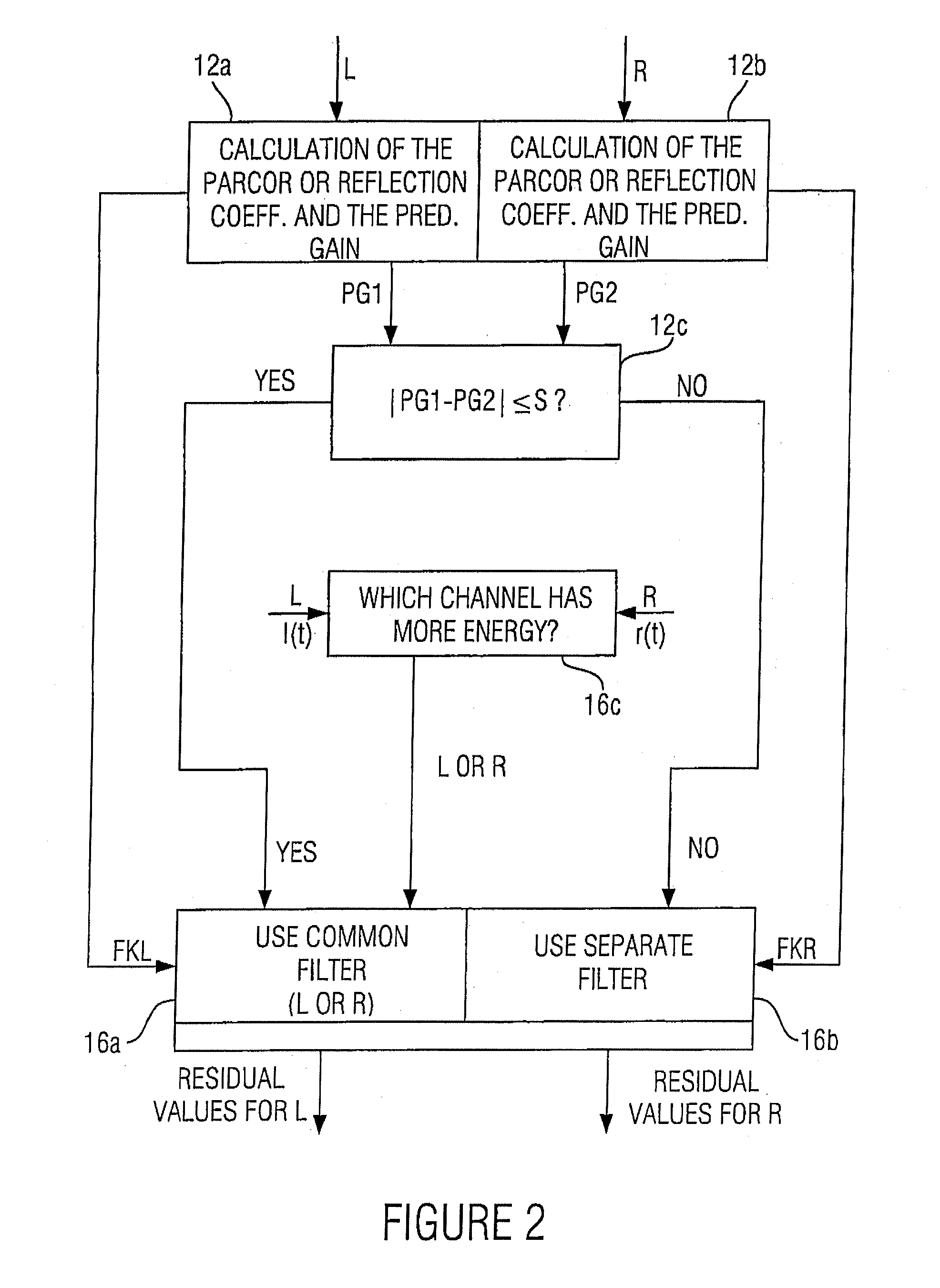
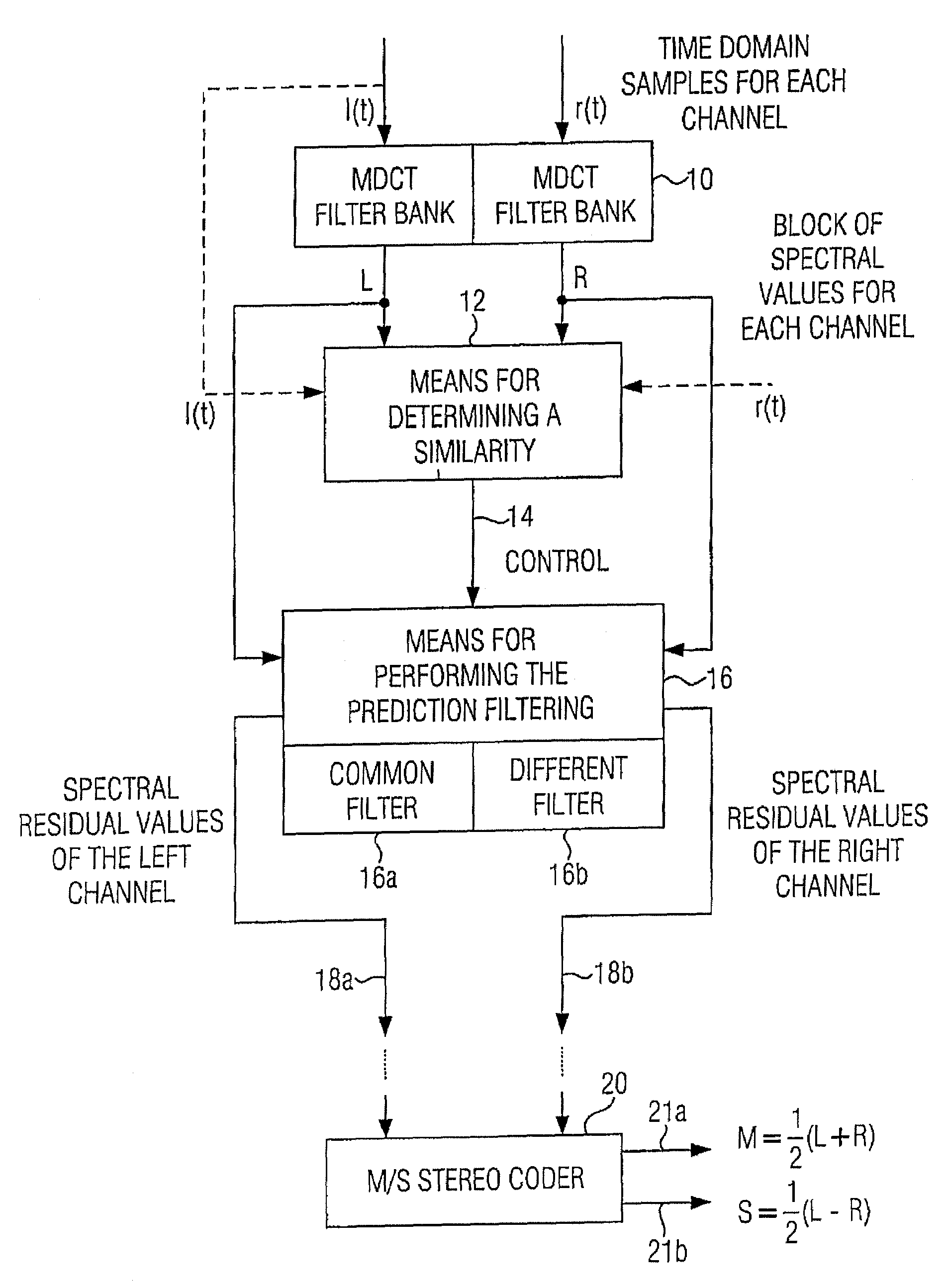
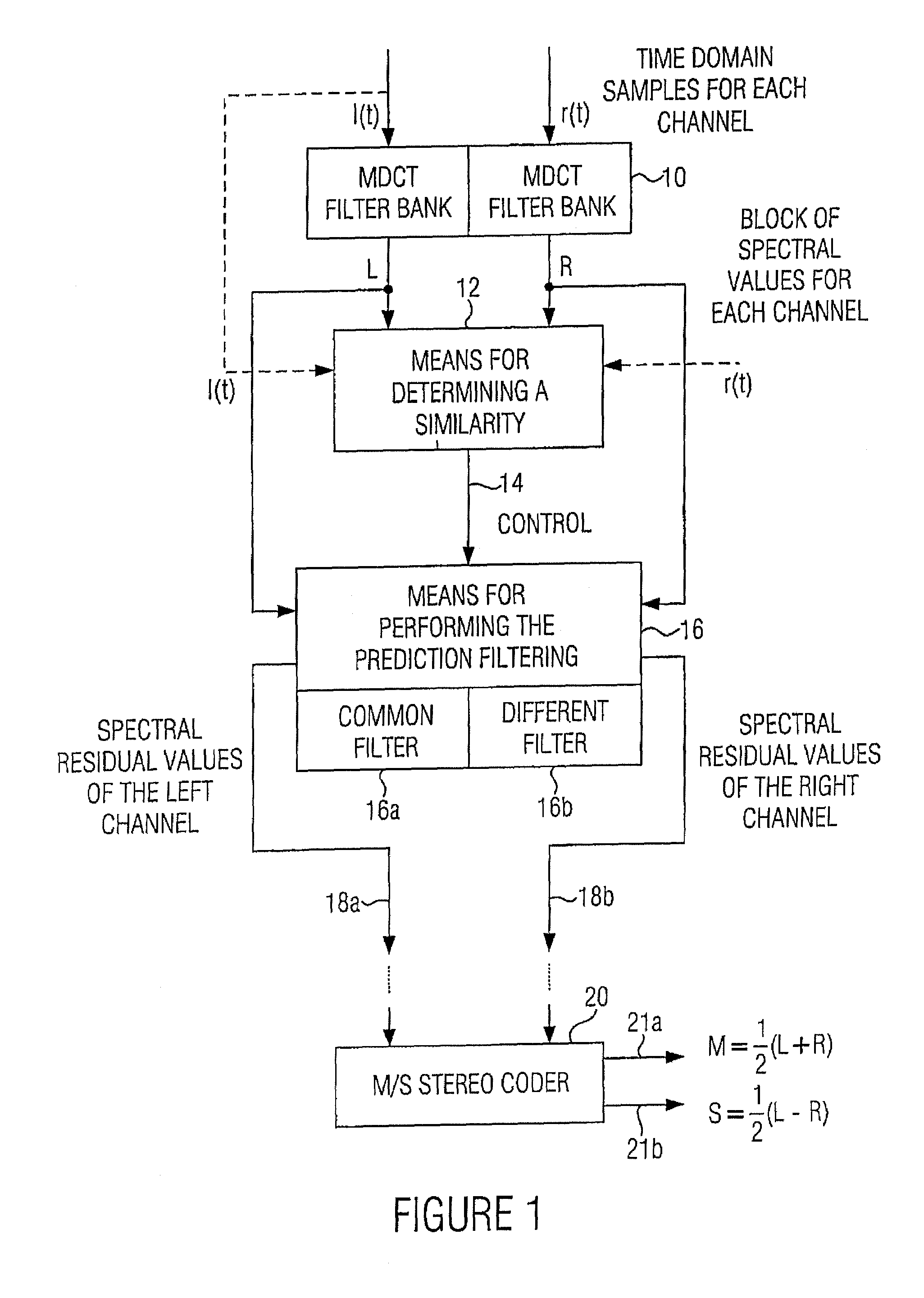
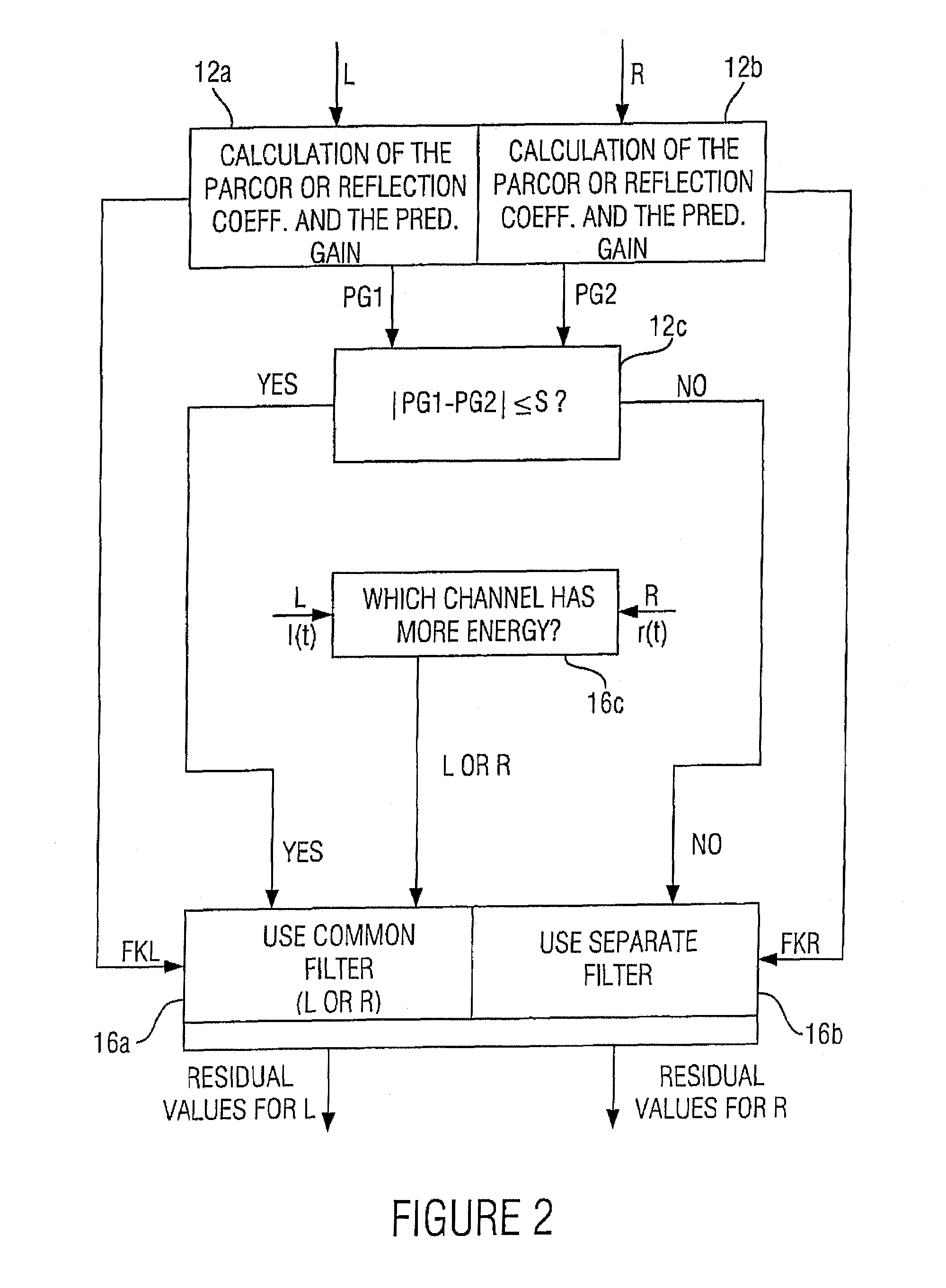
Apparatus and method for processing a multi-channel signal
ActiveUS20070033056A1Small loss in prediction gainEasy to compressSpeech analysisPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
An apparatus for processing a multi-channel signal includes a means for determining a similarity between a first one of two channels and a second one of the two channels. Furthermore, a means for performing a prediction filtering of the spectral coefficients is provided, which is formed to perform a prediction filtering with only a single prediction filter for both channels in case of high similarity between the first and the second channel, and to perform a prediction filtering with two separate prediction filters in case of a dissimilarity between the first and the second channel. With this, an introduction of stereo artifacts and a deterioration of the coding gain in stereo coding techniques are avoided.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for Generating Bone Mask
ActiveUS20120121147A1Few artifactClear picture qualityImage enhancementImage analysisData setTomography
The present invention discloses a method for generating a bone mask. The method comprises the following steps: performing a noncontrast computed tomography scan on a subject in axial mode to get a first data set; after the subject injected with a contrast medium, performing a postcontrast computer tomography angiography scanning on the subject in helical mode to get a second data set; reconstructing the two mentioned data set to acquire a first reconstruction image and a second reconstruction image respectively; resampling the first reconstruction image based on the second reconstruction image by using a computer to get a third reconstruction image; and thresholding values of data which are greater than or equal to a scheduled Hounsfield unit in the third reconstruction image to get a bone mask.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Detection values correction apparatus
ActiveUS20100189376A1Few artifactReduces scatter artifactImage enhancementImage analysisProjection imageComputer science
The present invention relates to a detection values correction apparatus for correcting detection values of a projection image of a multi-energy imaging system. A scatter contribution providing unit provides scatter contributions for different intensities, different energies and different locations on the detection surface of the detection values. A scatter contributions combining unit combines scatter contributions for correcting a detection value, wherein the combined scatter contributions represent the contribution of the scatter, which is caused by radiation of the other detection values of the projection image, to the detection value to be corrected and wherein the scatter contributions are combined under consideration of the intensity, energy and location on the detection surface of the other detection values. A correction unit scatter corrects the detection value of the projection image by using the combined scatter contributions.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Apparatus and method for processing a multi-channel signal
An apparatus for processing a multi-channel signal includes a means for determining a similarity between a first one of two channels and a second one of the two channels. Furthermore, a means for performing a prediction filtering of the spectral coefficients is provided, which is formed to perform a prediction filtering with only a single prediction filter for both channels in case of high similarity between the first and the second channel, and to perform a prediction filtering with two separate prediction filters in case of a dissimilarity between the first and the second channel. With this, an introduction of stereo artifacts and a deterioration of the coding gain in stereo coding techniques are avoided.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and apparatus for video object segmentation
ActiveUS20120294530A1Improve compression efficiencyFew artifactImage enhancementImage analysisSpacetimeNormalized correlation
Methods and apparatus for video object segmentation are provided, suitable for use in a super-resolution system. The method comprises alignment of frames of a video sequence, pixel alignment to generate initial foreground masks using a similarity metric, consensus filtering to generate an intermediate foreground mask, and refinement of the mask using spatio-temporal information from the video sequence. In various embodiments, the similarity metric is computed using a sum of squared differences approach, a correlation, or a modified normalized correlation metric. Soft thresholding of the similarity metric is also used in one embodiment of the present principles. Weighting factors are also applied to certain critical frames in the consensus filtering stage in one embodiment using the present principles.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Focally aligned CT detector
InactiveUS20070086565A1Less prone to artifactOvercomes drawbackMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLight emissionX-ray
A focally aligned scintillator is constructed such that its scintillator walls are sloped so as to be angularly aligned with an x-ray source. The scintillator has a planar x-ray reception surface and a planar light emission surface, and a plurality of sidewalls connecting the planar x-ray reception surface and the planar light emission surface. The sidewalls extend non-perpendicularly between the planar x-ray reception surface and the planar light emission surface.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for picking up auditory evoked potentials
InactiveUS20020095194A1Reduce measurement errorGood reproducibilityElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyDifferential amplifierAuditory system
The present invention relates to a device for picking up biological electrical signals, and more precisely auditory evoked potentials generated by acoustic and / or electrical and / or mechanical stimulation of the cochlea, or of a portion of the auditory system in man or animal. The device for measuring or picking up auditory evoked potentials is surgically implantable in the temporo-occipital area and comprises at least two extracochlear pickup electrodes connected to the inputs of a differential amplifier.
Owner:NEURELEC FIFTY PERCENT INTEREST
Fractal-dithering technique for image display
InactiveUS7206001B1Rapid ditheringFew artifactCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPattern recognitionDeterministic method
Rapid dithering of an RGB image from a higher order to a lower order number of bits is provided while introducing fewer undesirable artifacts than are visible in conventional dithering technology. A compact, deterministic method enables the elimination of banding, for example as is seen in 24-bit monitors when viewing color images with greater color depth. A fractal dithering engine selects a threshold matrix appropriate for an input stream, and using the threshold matrix, dithers images of the input stream to output images having a lower order number of color bits. In one embodiment, the threshold matrix is obtained by traversing 2-by-2 sub-regions of an N-by-N matrix according to a traversal pattern, and then applying a reverse binary function to the values in the original matrix to yield the threshold matrix. The threshold matrix preferably tessellates the pixel plane, subject to certain constraints.
Owner:APPLE INC
Magnetic resonance imaging with motion correction suing pre-pulses and navigators
ActiveUS20170038449A1Improve efficiencyHigh resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImage contrastResonance
The present invention provides a method for magnetic resonance (MR) imaging of a region of interest (142) of a subject of interest (120) under application of a scanning sequence (200) comprising at least one pre-pulse (202, 204) and multiple readouts (206), whereby the multiple readouts (206) are performed after the at least one pre-pulse (202, 204) with different configurations causing different image contrasts, comprising the steps of performing a preparation phase comprising applying at least one scanning sequence (200) to provide a set of reference readouts (206) using the different configurations, and generating a set of navigator images (210) with one navigator image (210) of the region of interest (142) for each configuration of the reference readouts (206), performing an examination phase comprising applying at least one scanning sequence (200), whereby at least one image (212) of the region of interest (142) is generated for each scanning sequence (200), determining motion of the subject of interest (120) by comparing at least one image (212) of the scanning sequence of the examination phase to the navigator image (210) having the same configuration as the compared image (212), performing motion correction of the at least one image (212) based on the determined motion of the subject of interest (120) of the at least one image (212), and providing an MR scan (214) of the region of interest (142) of the subject of interest (120) based on the images (212) after performing motion correction. The invention also provides a MR imaging system (110) adapted to perform the above method and a software package for upgrading a MR imaging system (110), whereby the software package contains instructions for controlling the MR imaging system (110) according to the above method.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Magnetic resonance system, operating method and control device to generate t2-weighted images using a pulse sequence with very short echo times
InactiveUS20130169273A1Suppressed quickly and wellSuppressed quickly and effectivelyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsProton magnetic resonanceResonance
In a method to control a magnetic resonance system to generate magnetic resonance exposures of an examination subject, a first magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse with a pulse length of at most 50 μs is initially emitted in a volume region of the examination subject. At least one second magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse, whose phase is essentially rotated by 180° relative to the first magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse, with a pulse length of at most 50 μs, is emitted in the same volume region of the examination subject in a predetermined time interval immediately after the first magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse. An acquisition of raw data from the volume region of the examination subject then takes place. Furthermore, a control device for operating a magnetic resonance system as well as a magnetic resonance system with such a control device to implement such a method, are described.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Computed tomography apparatus and program
ActiveUS7006591B2Improve accuracyHigh approximation precisionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationThree dimensional ctData set
A computed tomography apparatus includes a two-dimensional data acquisition system which acquires projection data of a radiographic region within a subject using a multirow detector, and a hybrid image reconstruction system which reconstructs an image of the radiographic region on the basis of both the projection data and additional data calculated from the projection data. The hybrid image reconstruction system functionally includes a unit for calculating an additional intermediate beam data set, a unit for executing hybrid reconstruction of an oblique section, and a unit for generating a parallel section group. Owing to the construction, there are provided an image reconstruction method which is practicable and which affords a high precision, and a three-dimensional CT system which has the functions of the image reconstruction method.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Cardiac computed tomography methods and systems using fast exact/quasi-exact filtered back projection algorithms
InactiveUS8483351B2Accurate and reliable processAccurate imagingReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTemporal resolutionCardiac computed tomography
The present invention provides systems, methods, and devices for improved computed tomography (CT). More specifically, the present invention includes methods for improved cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) resolution using improved filtered back projection (FBP) algorithms, which can be used for cardiac tomography and across other tomographic modalities. Embodiments provide methods, systems, and devices for reconstructing an image from projection data provided by a computed tomography scanner using the algorithms disclosed herein to generate an image with improved temporal resolution.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Tube alignment functionality for mobile radiography systems
ActiveUS20160183909A1Quantity minimizationPrecise alignmentRadiation beam directing meansX-raySpatial configuration
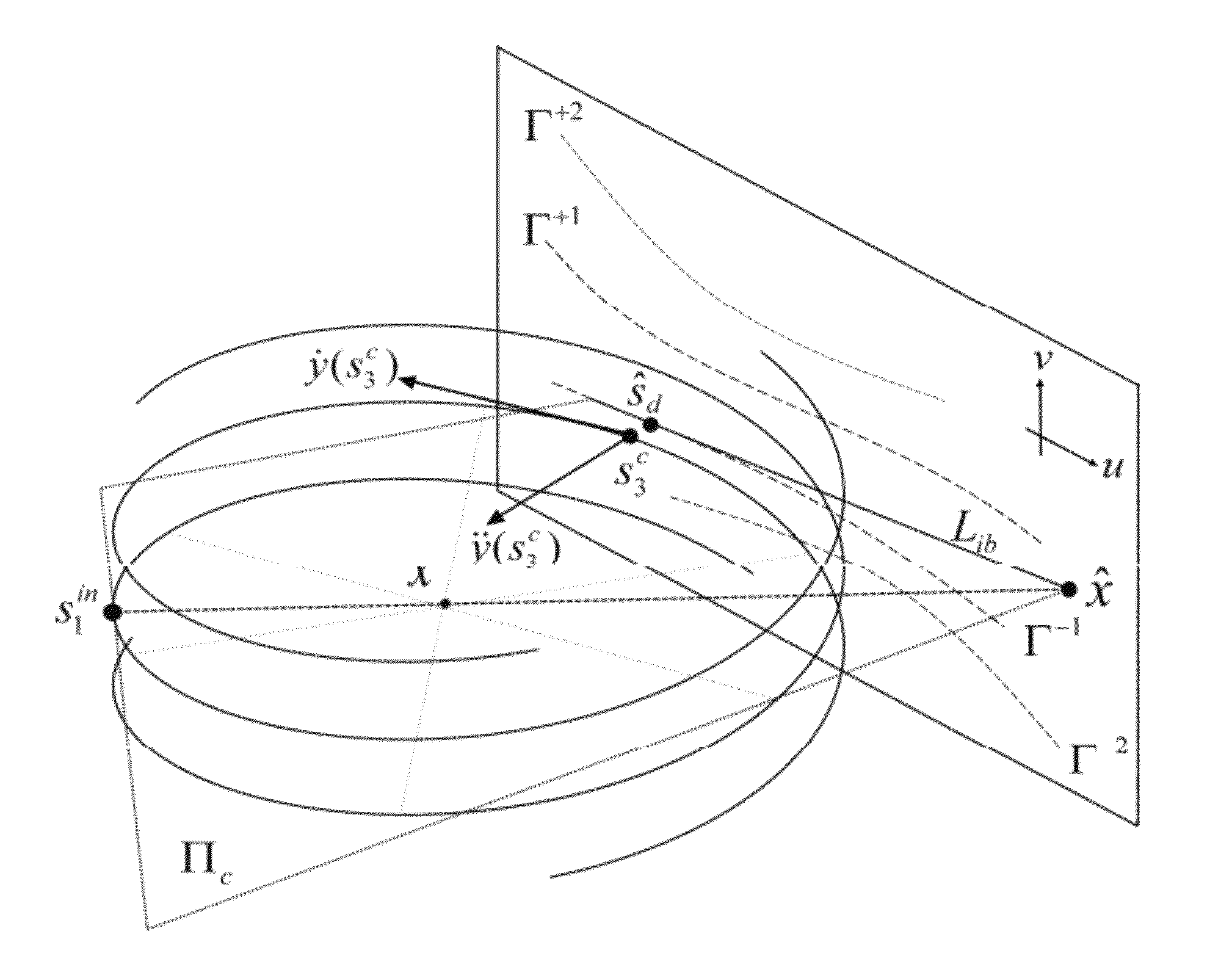
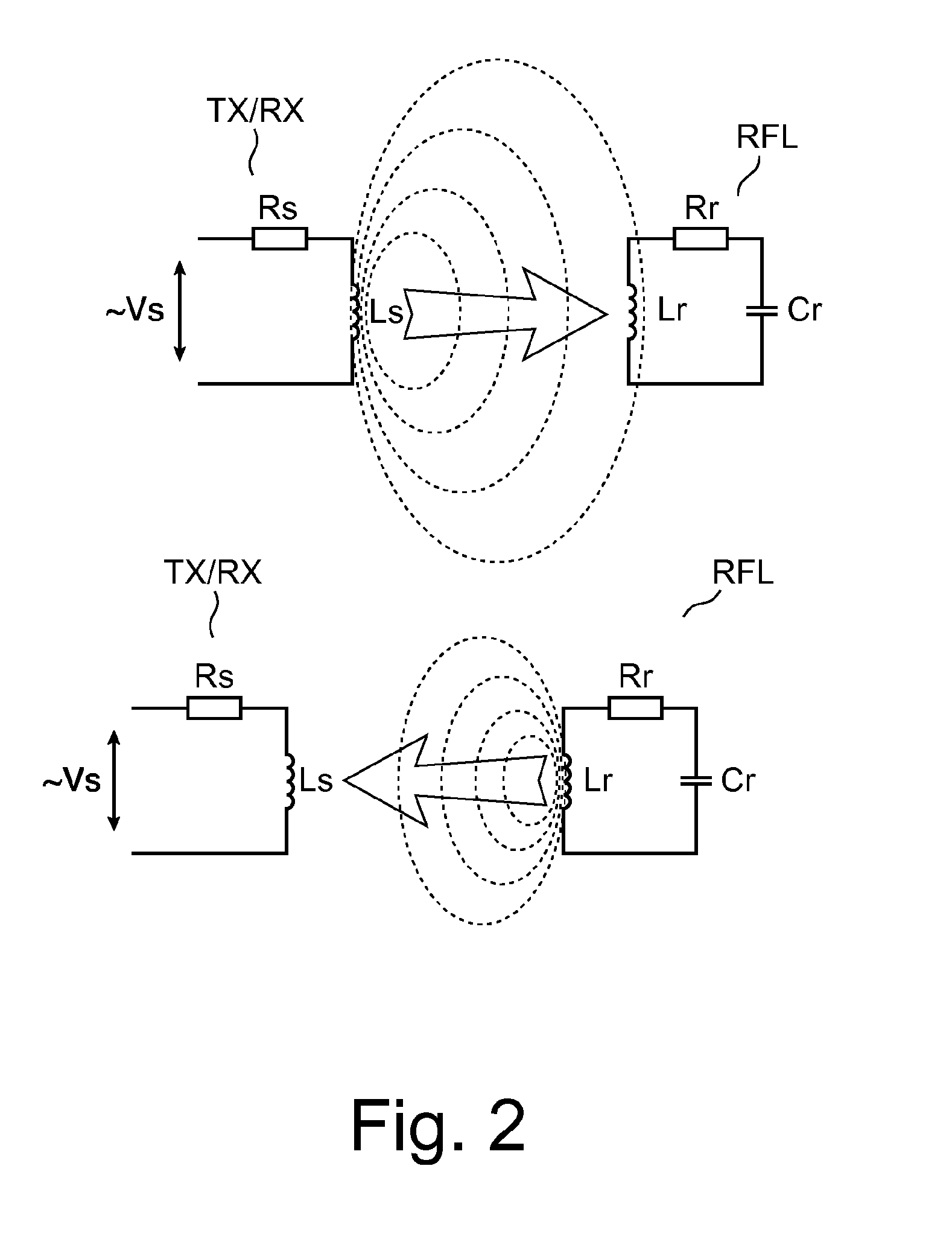
An X-ray imager having a navigation-aid subsystem including one or more transmitters (TX), one or more receivers (RX) and one or more reflectors (RFL). A radio signal is transmitted by transmitter(TX), is then reflected off reflector RFL and is then received at receiver (RX). The received signal is then resolved into positional correction information that can be used to guide a motion of the imager's tube (S) and or detector (D) to position and / or align the tube (S) and / or detector (D) relative to each other in a desired spatial configuration to ensure optimal imaging results. The imager may be a mobile imaging system with the detector (D) portable.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
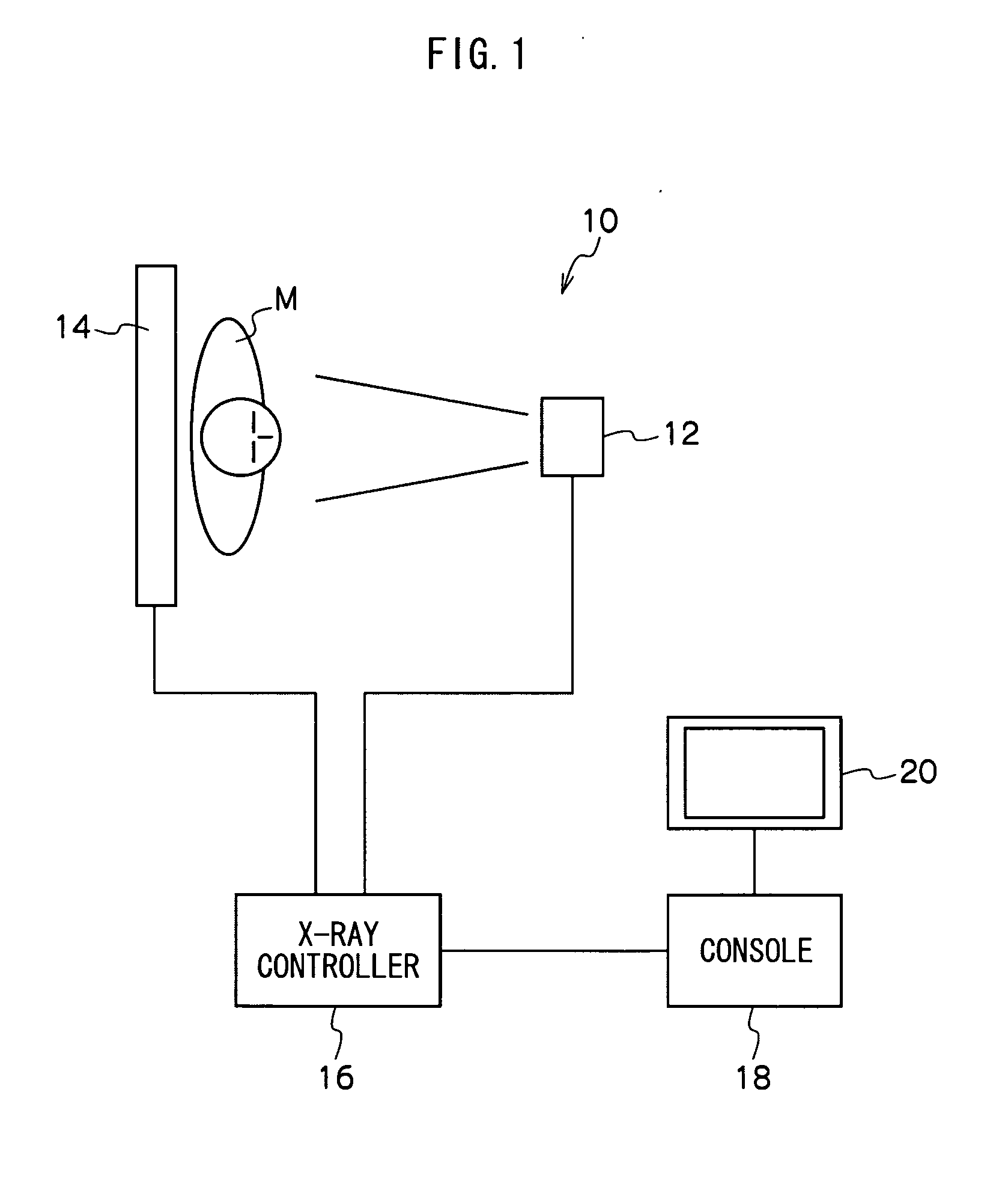
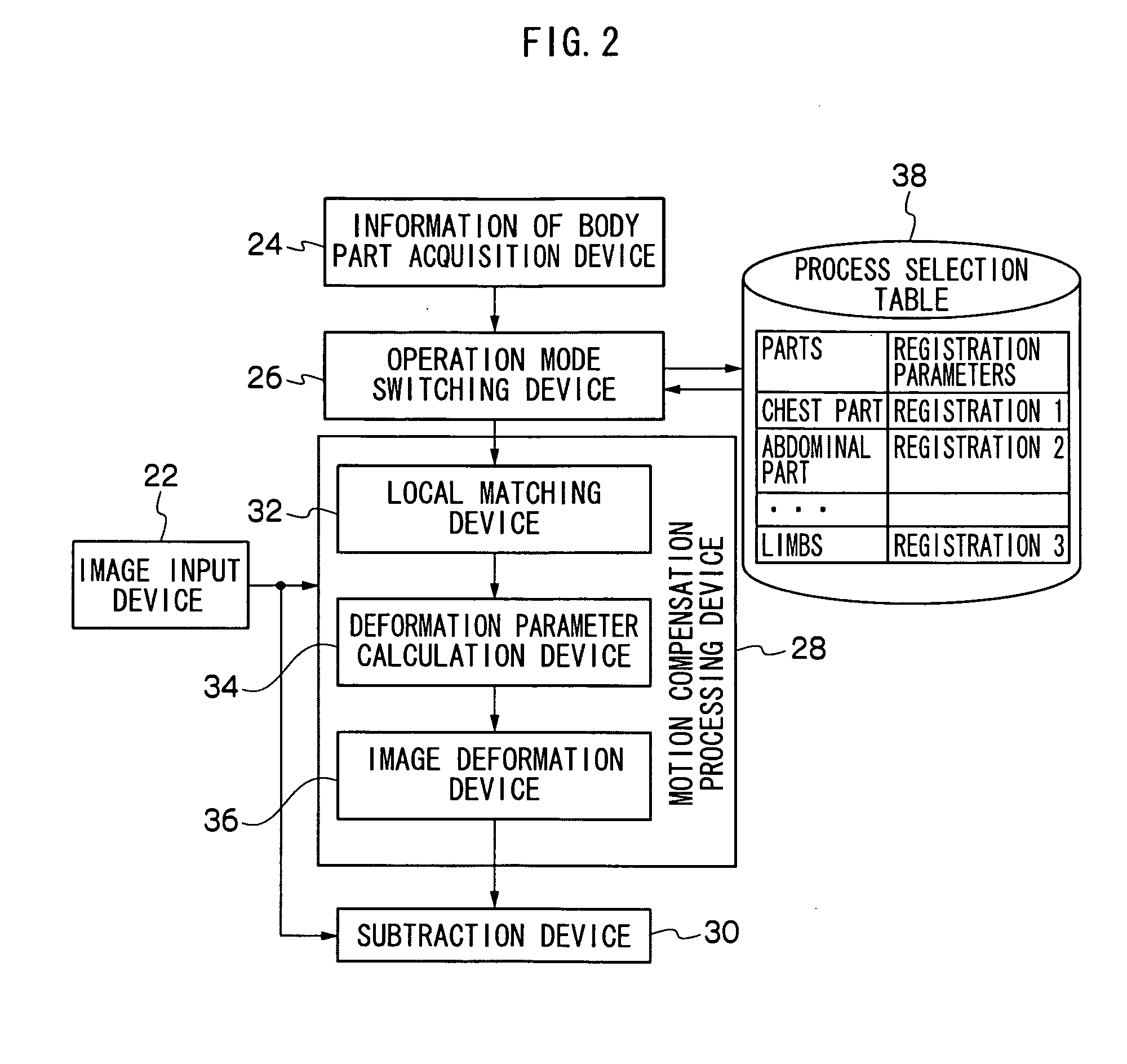
Energy substraction method and apparatus
ActiveUS20090285361A1Less motion artifactFew artifactImage enhancementImage analysisOperation modeRadiation rays
The energy subtraction apparatus of the present invention comprises an image input device which inputs two or more different kinds of radiographic images having been taken by irradiating a subject with radiation rays with different radiation qualities, an information of body part acquisition device which designates a information of body part, a motion compensation processing device which performs a registration process by compensating for shift between corresponding points between the two or more different kinds of radiographic images due to movement of the subject, a subtraction device which performs an energy subtraction process on the two or more different kinds of radiographic images, and an operation mode switching device which switches an operation mode of the registration process at the motion compensation processing device depending on the information of body part.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Acoustic holography
ActiveUS8701491B2Quality improvementEasy to fillAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidComputer scienceWavenumber
A method of performing near-field acoustic holography comprises the following steps. Establishing (102) acoustic data representing a set of near-field acoustic holography measurements at a first set of positions. Extrapolating (204) acoustic data using a model-based extrapolation to obtain extrapolated acoustic data relating to a plurality of positions outside the aperture. Applying (108) a spatial frequency transform to the padded acoustic data to obtain data in a spatial frequency domain. Propagating (110) the Fourier transformed acoustic data. Applying (112) a regularization in a wavenumber domain. Performing (114) an inverse spatial frequency transform.
Owner:STICHTING VOOR DE TECH WETENSCHAPPEN +1
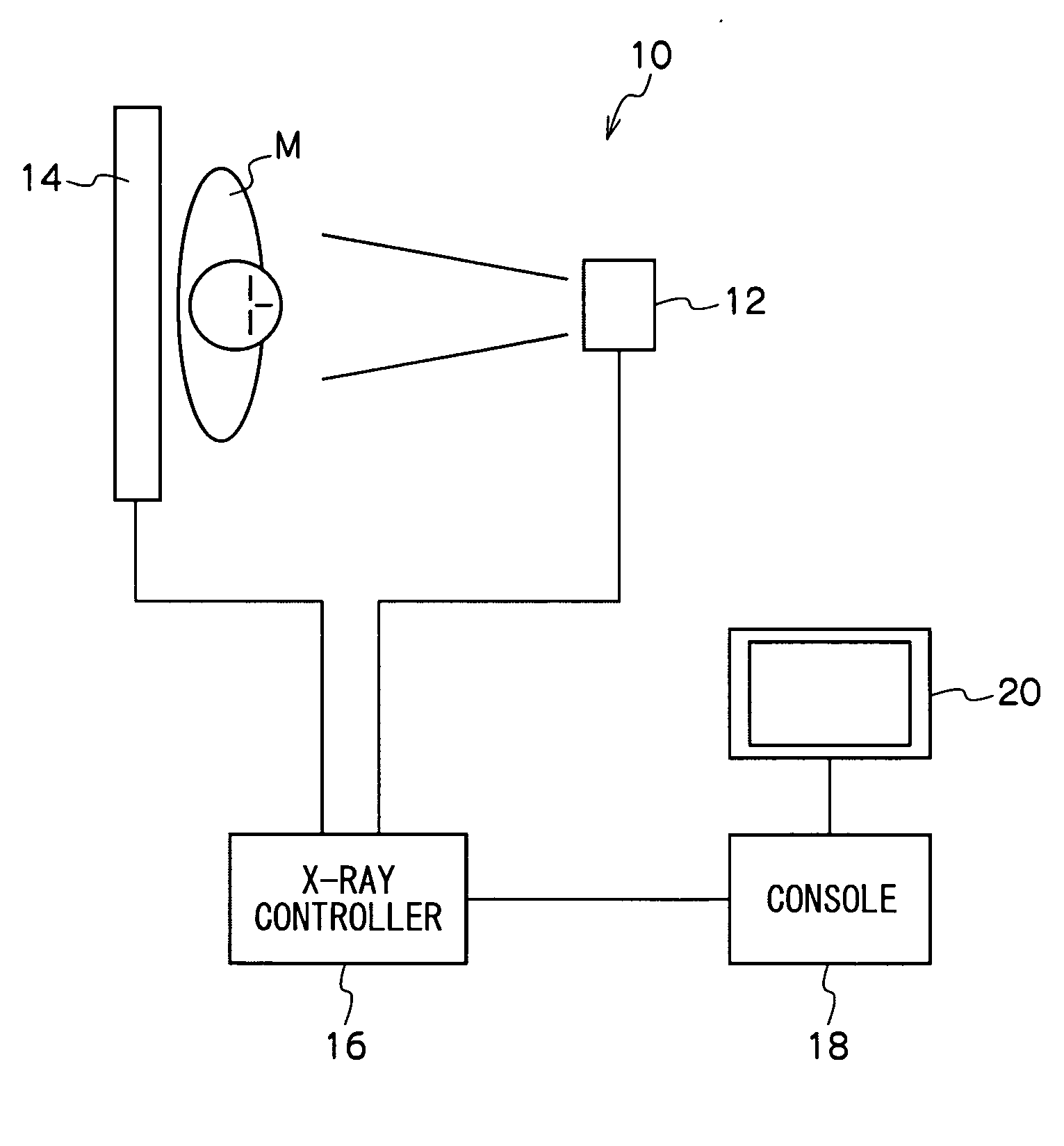
Imaging apparatus, imaging system, and method for controlling imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20120075600A1Reducing exposure preparation periodShorten the overall cycleExposure controlPhotographic printingImaging equipmentImaging data
An imaging apparatus includes a detector in which a plurality of pixels are arranged in a matrix; each pixel includes a conversion element that converts radiation or light into an electric charge. The detector performs an exposure imaging operation for outputting exposure image data, a correction imaging operation for outputting correction image data, and a correction imaging preparation operation including an initialization operation for initializing the conversion element between the exposure imaging operation and the correction imaging operation. A correction unit corrects the exposure image data using the correction image data; and a control unit controls the operation of the detector so that the detector performs the initialization operation based on an amount of variation in offset of the conversion element at the time of transitioning from an exposure imaging preparation operation to the exposure imaging operation.
Owner:CANON KK
Anti-p40 Antibodies Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20160009795A1Strong specificityCleaner stainingImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingAntibodyCancer
The present invention is related to the anti-p40 antibodies, kits, cocktails, and use of anti-p40 antibodies for detection of cancer.
Owner:BIOCARE MEDICAL
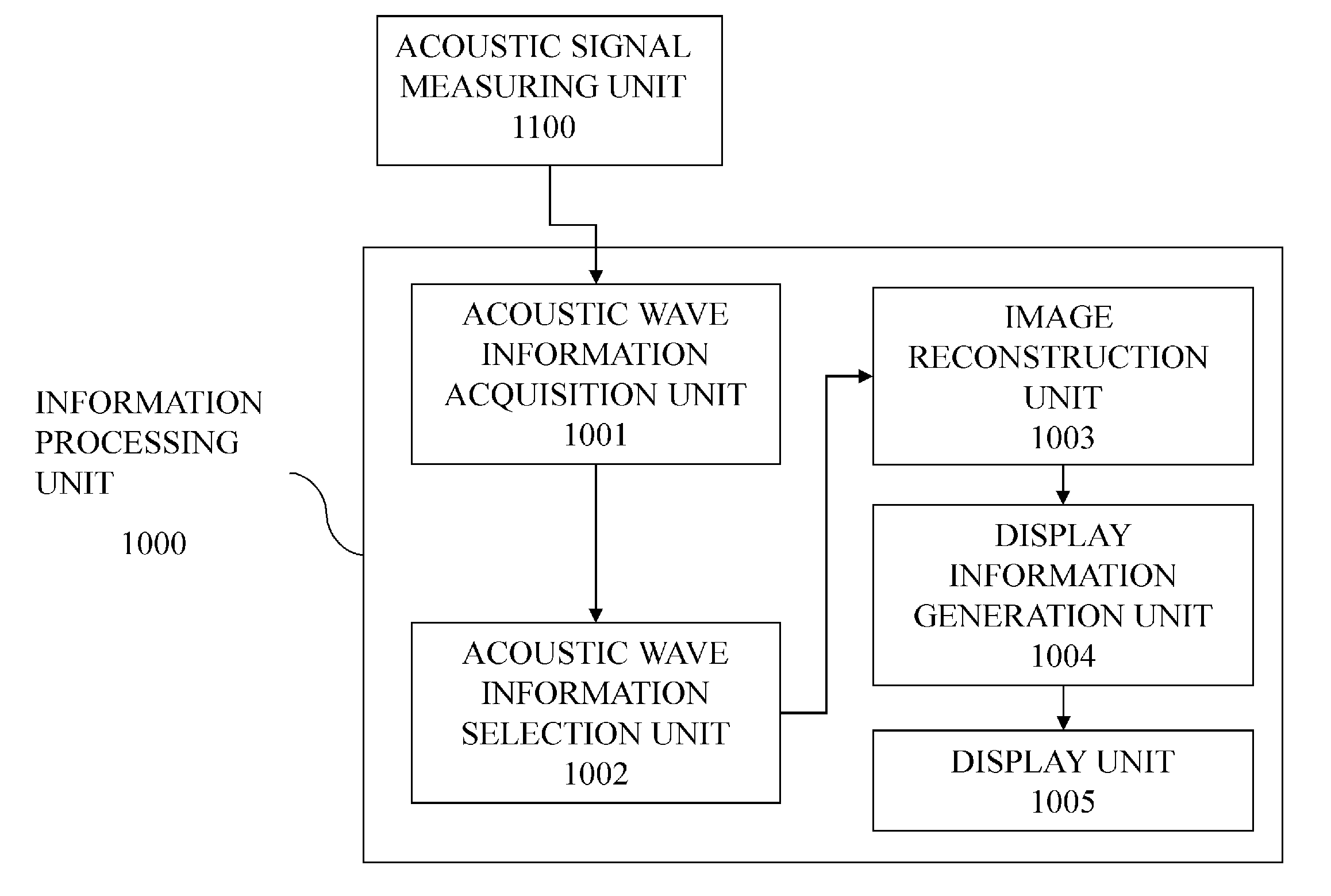
Image information acquiring apparatus, image information acquiring method and image information acquiring program
ActiveUS20130114859A1Few artifactAcoustic sensorsCharacter and pattern recognitionAcoustic waveSignal generator
An image information acquiring apparatus of the present invention includes an acoustic wave detector having, disposed on a reception surface thereof, a plurality of elements that detect acoustic waves generated by an object corresponding to a reconstruction area; an acoustic signal generator that generates acoustic signals that are used in image reconstruction, from the detected acoustic waves; an element selector that selects elements that are used in image reconstruction; and a reconstructor that performs image reconstruction of a point of interest using acoustic signals based on the acoustic waves detected by the selected elements, the image information acquiring apparatus being configured such that, for each selected element, there exists another selected element located at a symmetrical position with respect to a point at which the reception surface is intersected by a perpendicular line drawn from the point of interest to the reception surface.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods for improved single photon emission computed tomography using exact and stable region of interest reconstructions
InactiveUS8952333B2Accurate and reliable processAccurate imagingReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTemporal resolution
The present invention provides systems, methods, and devices for improved computed tomography (CT) and, more specifically, to methods for improved single photon computed tomography (SPECT) using exact and stable region of interest (ROI) reconstructions. This technology can be extended across all tomographic modalities. Embodiments provide a method and a system for reconstructing an image from projection data provided by a single photon emission computed tomography scanner comprising: identifying a region of interest in an object; defining an attenuation coefficient and object boundary; computing the generalized Hilbert transform of the data through the defined region of interest and a known subregion; and reconstructing the image with improved temporal resolution at lower radiation doses, wherein the reconstructing comprises performing a reconstruction method that yields an exact and stable reconstruction. Embodiments also provide a method and a system for reconstructing an image from projection data provided by a single photon emission computed tomography scanner comprising: identifying a region of interest in an object; defining an attenuation coefficient and object boundary; and reconstructing the images by minimizing the high order total variation while minimizing the data discrepancy.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com